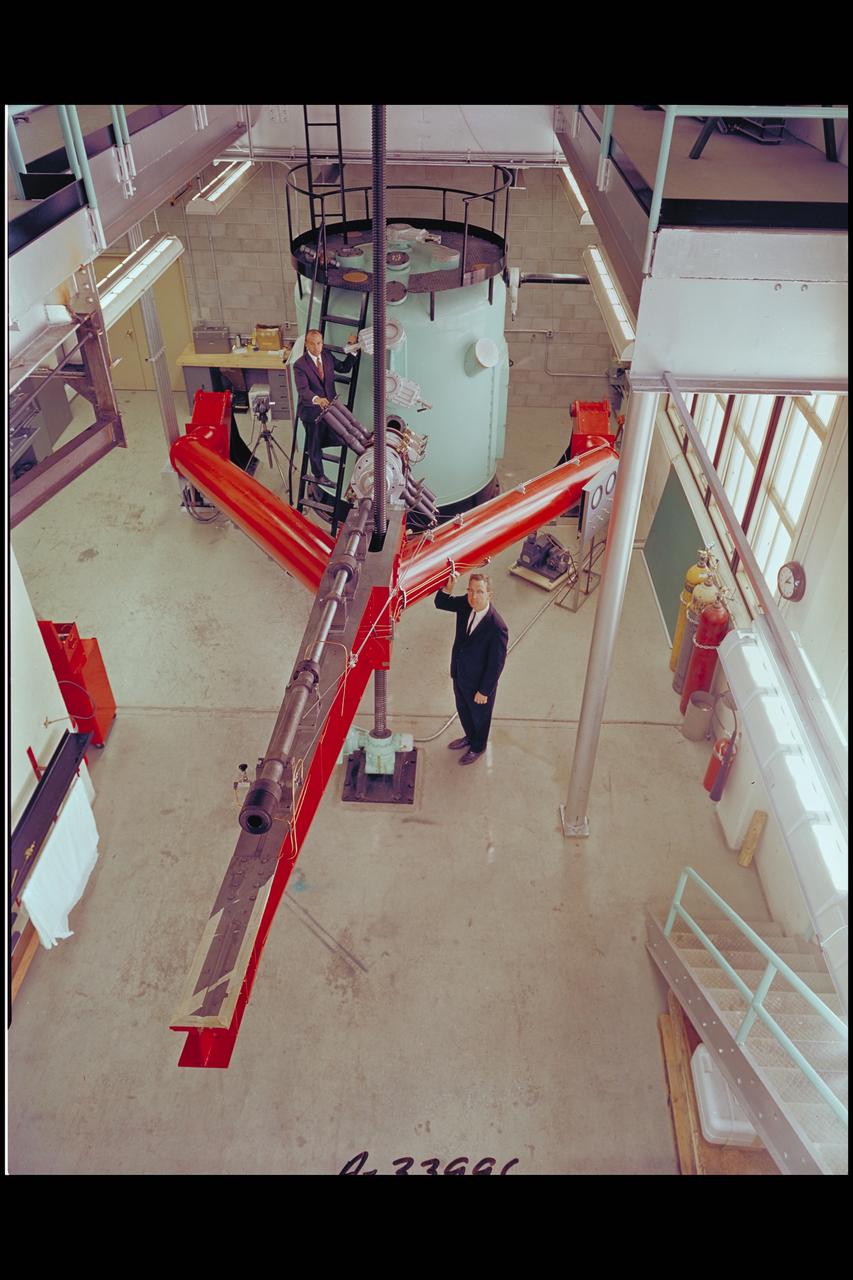

30 calibabor Vertical Gun Range in horizontal loading position. Dr. William Quaide and Donald Gault of Ames planetology branch used this gun range to study the formation of impact craters on the Moon. N-204A Verticle Gun is used to simulate the physics and mechanics of planetaryimpact cratering phenomena.
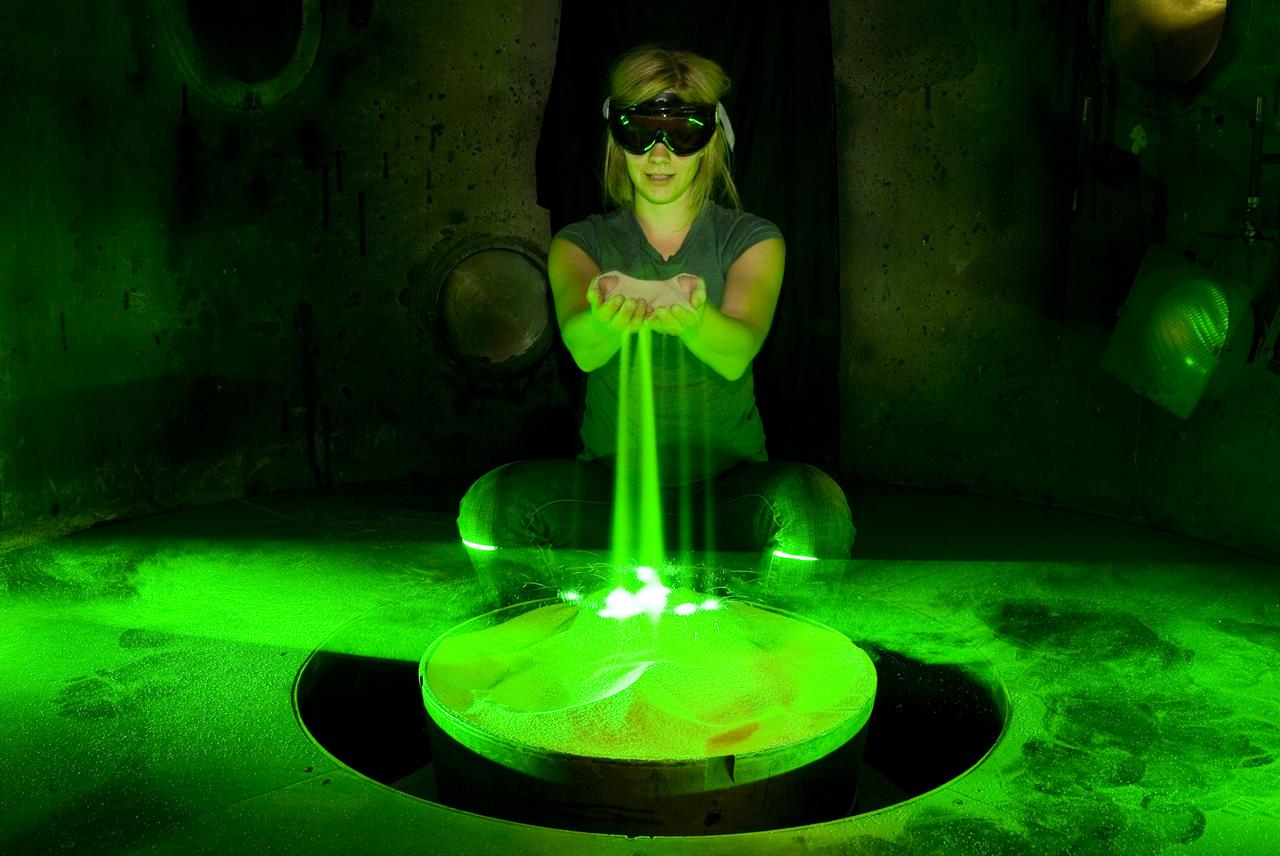

Laura Kushner in test chamber preparing for testing PCI sysem by dropping sand to check laser sheet to be used in study at AVGR (Ames Vertical Gun Range)
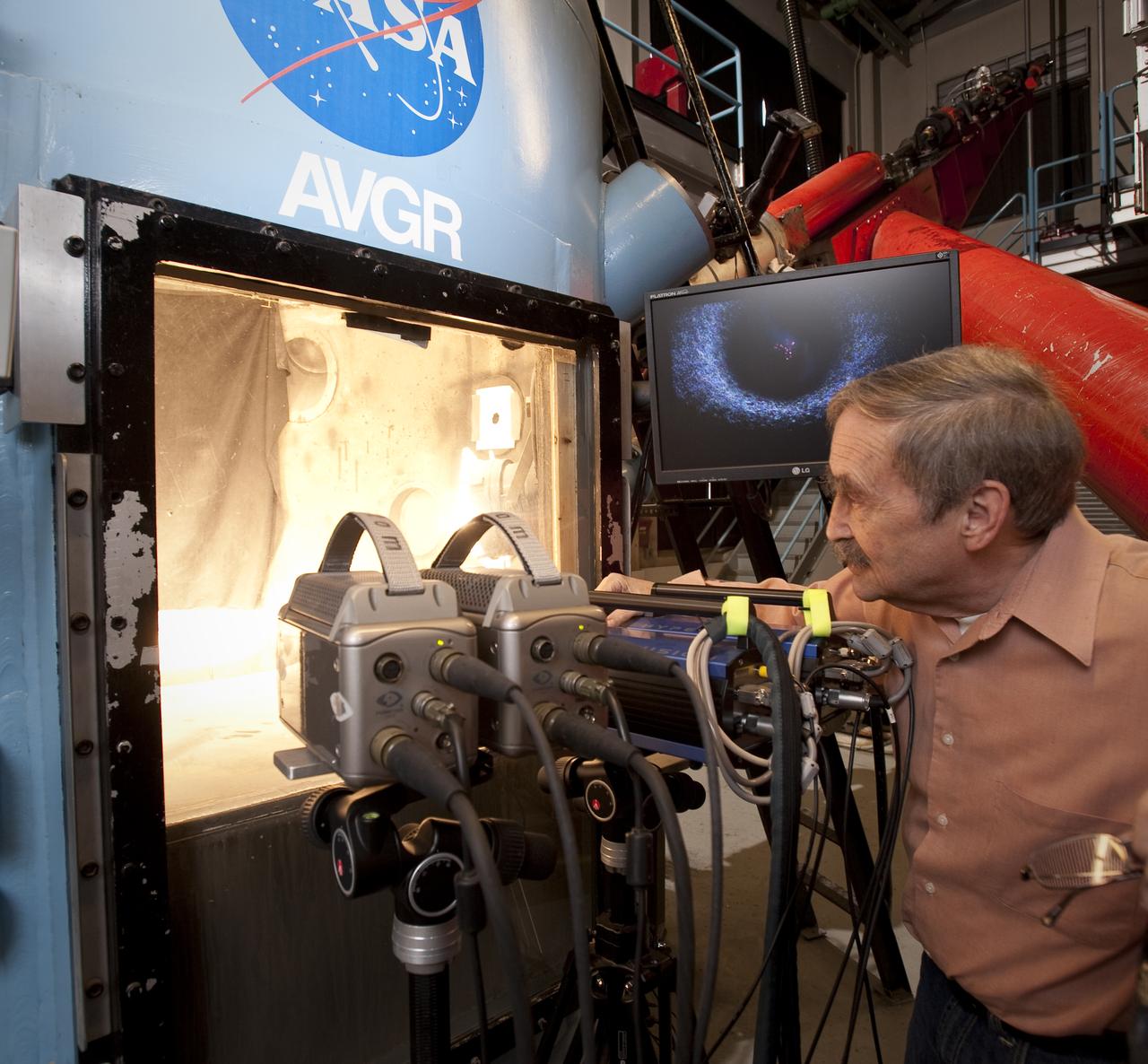

Dr. Peter Schultz, Brown University at NASA Ames Vertical Gun Range Facility during running of tests simulating LCROSS impact debris in preparaton for the real thing on October 9, 2009 when LCROSS impact the Moon southpole in search of hidden water.
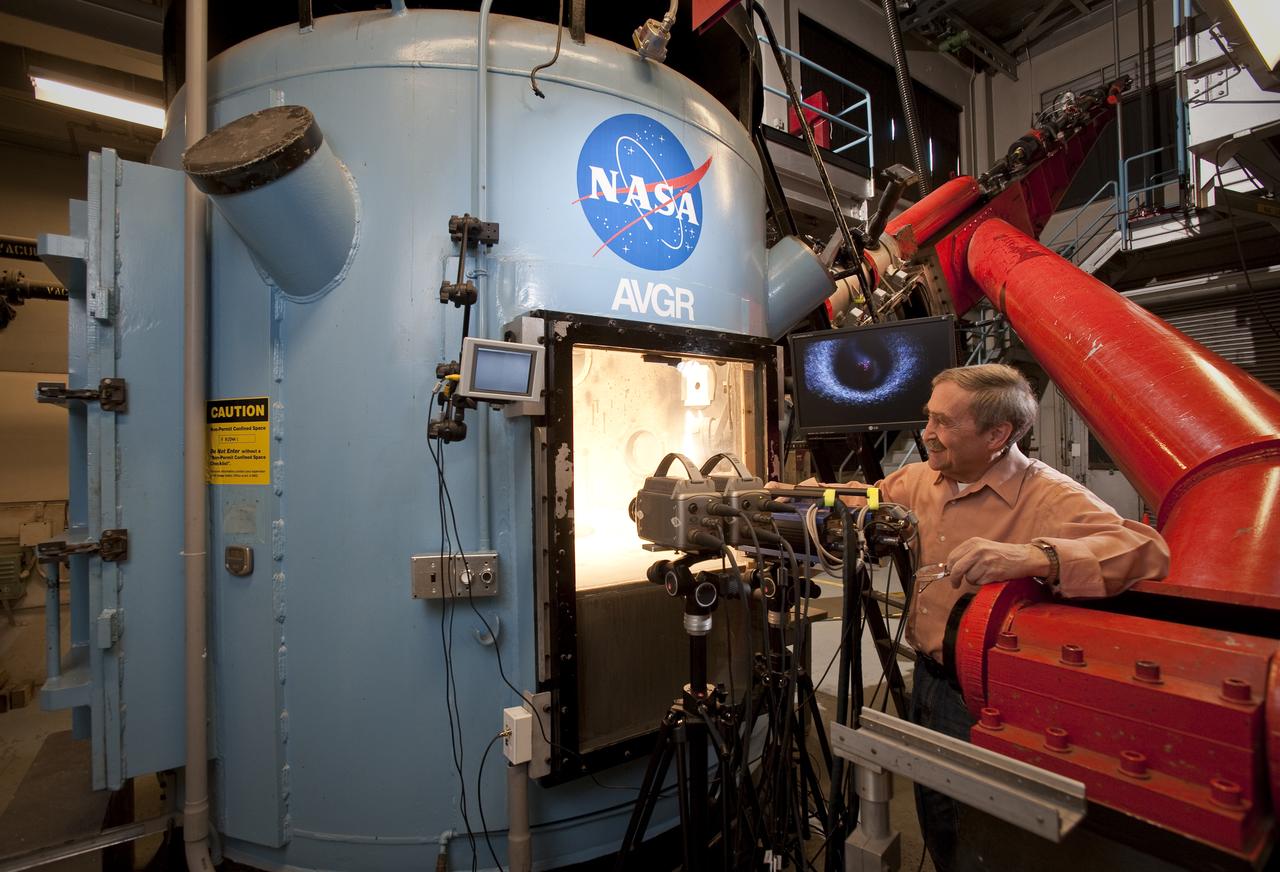

Dr. Peter Schultz, Brown University at NASA Ames Vertical Gun Range Facility during running of tests simulating LCROSS impact debris in preparaton for the real thing on October 9, 2009 when LCROSS impact the Moon southpole in search of hidden water.

Dr. Peter Schultz, Brown University at NASA Ames Vertical Gun Range Facility during running of tests simulating LCROSS impact debris in preparaton for the real thing on October 9, 2009 when LCROSS impact the Moon southpole in search of hidden water.
Thomas N. Canning, Hypersonic Free-Flight Branch Chief, holds model that is fired down range in gun. Hypersonic Free-Flight Gun.

.50 Cal Gun Range: Hypervelocity Impact Test; 6.8 km/s

Taking a break from his duties at the Ames Vertical Gun Range to look up at the eclipse over Ames Research Center in Mountain View Adam Parrish not only views but wears, on his forehead, the image of the 2017 Solar eclipse at 09:20:56 on August 21, 2017.

Taking a break from their duties at the Ames Vertical Gun Range to look up at the eclipse over Ames Research Center in Mountain View are from left to right are Alfredo "Freddie" Perez, Chuck Cornelison, Don Bowling, Adam Parish

Ames holds a Media Day at the Hypervelocity Free Flight facility where Ames is conducting high-speed tests of small models of the agency's new Orion CEV to learn about stability during flight. The hypervelocity test facility uses a gun to shoot Orion models between 0.5 and l.5 inches (1.25 - 3.75 centimeters in diameter. The facility can conduct experiments with speeds up to 19,000 miles per hour (30,400 kilometers per hour) - NBC Channel 11 Technology/Business reporter Scott Budman at the gun range (w/C Acosta in bkgrd)
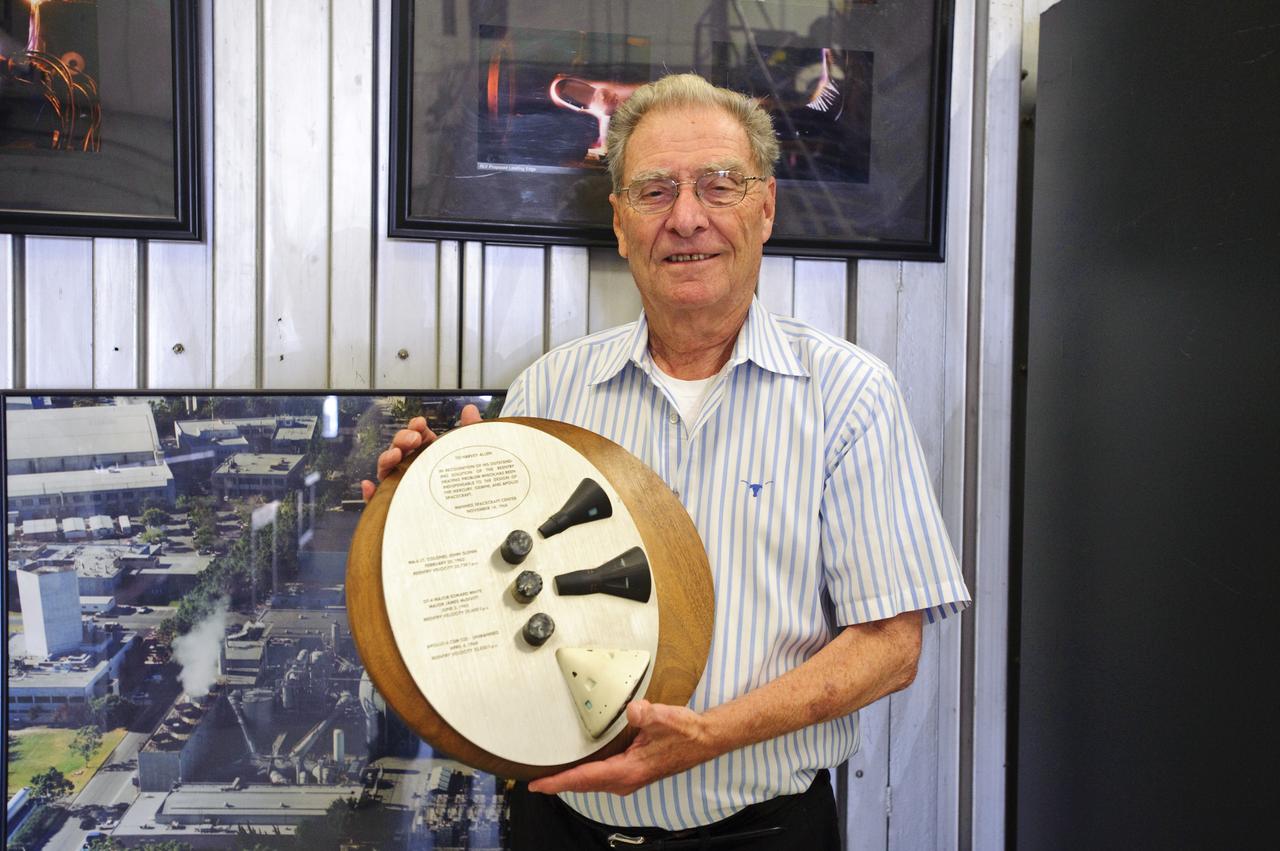

John W. 'Jack Boyd holds a plaque presented to Harvey Allen in recognition of his outstanding solution of the reentry heating problem which has been indispensable to the design of the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo spacecraft (Manned Spacecraft Center, November 14, 1968) Plaque contains samples of tested materials and models of spacecraft.
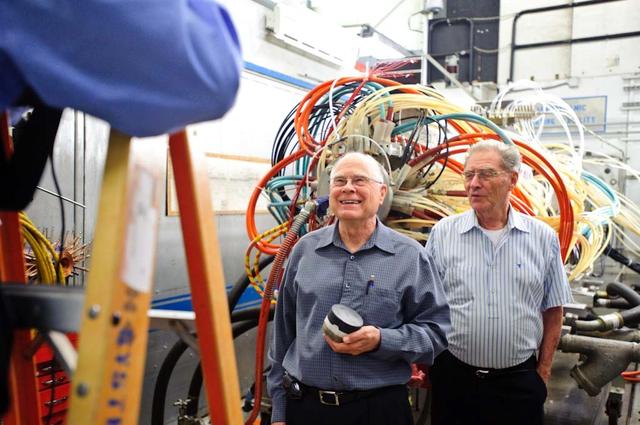

Dr William 'Bill' Borucki, NASA Ames Scientist on the Kepler Mission and John W. 'Jack' Boyd, NASA Ames Historian at the Ames Arc Jet Complex, Aerodynamic Heating Facility talking with a Mercury News photographer about the Kepler Mission and the 40th Anniversary of the Apollo 11 Mission.
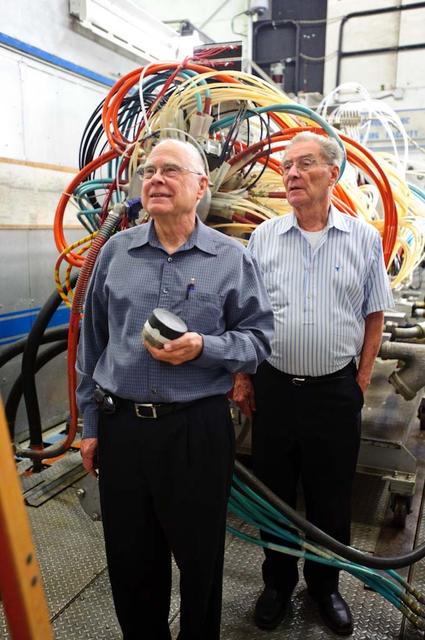

Dr William 'Bill' Borucki, NASA Ames Scientist on the Kepler Mission and John W. 'Jack' Boyd, NASA Ames Historian at the Ames Arc Jet Complex, Aerodynamic Heating Facility talking with a Mercury News photographer about the Kepler Mission and the 40th Anniversary of the Apollo 11 Mission.
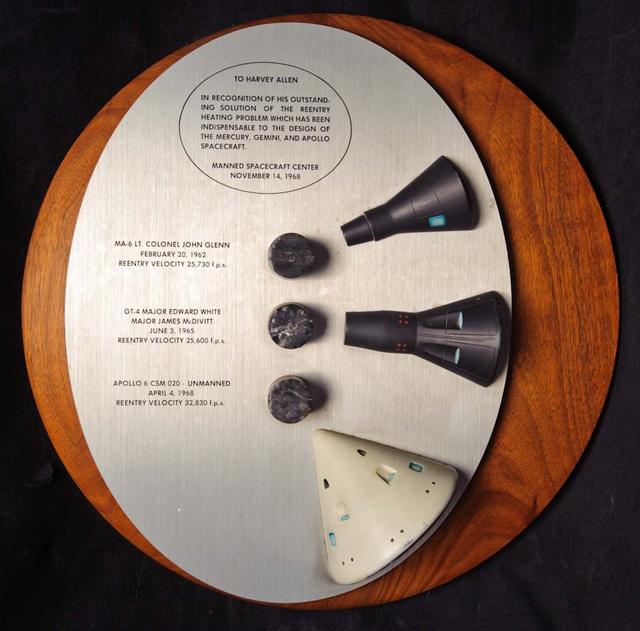

A plaque presented to Harvey Allen in recognition of his outstanding solution of the reentry heating problem which has been indispensable to the design of the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo spacecraft (Manned Spacecraft Center, November 14, 1968) Plaque contains samples of tested materials and models of spacecraft.
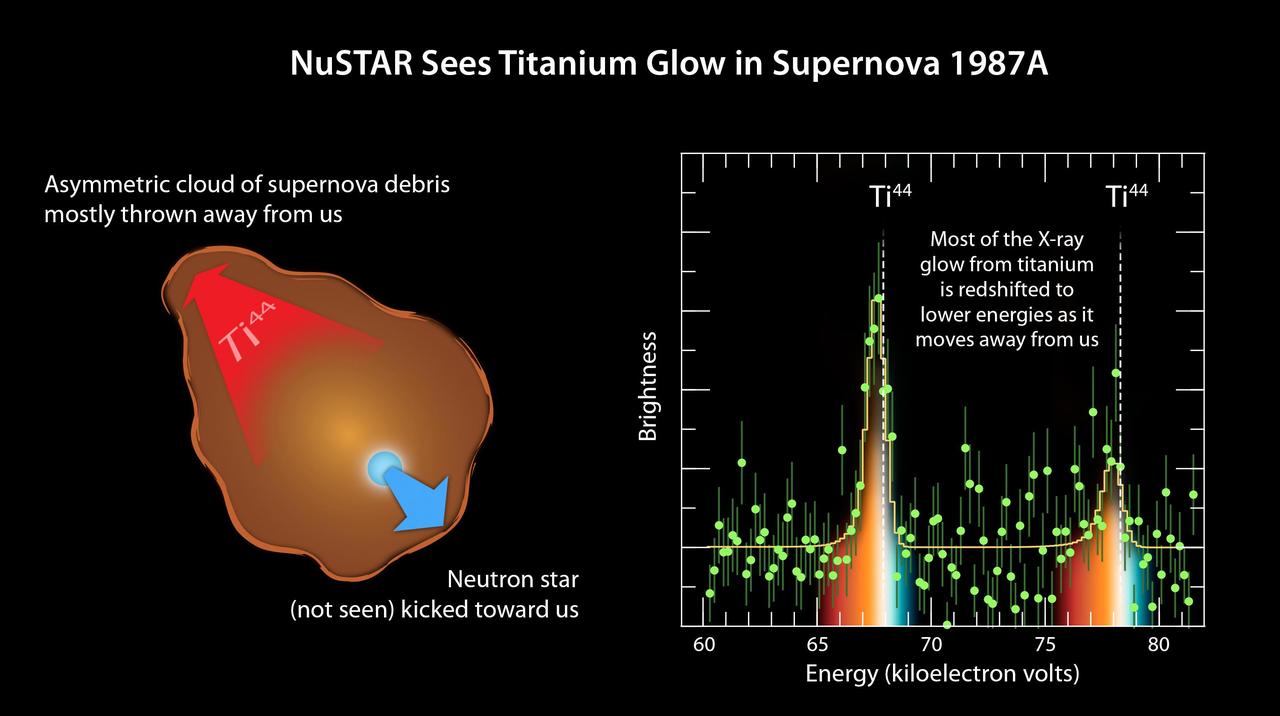
The plot of data from NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR (right), amounts to a "smoking gun" of evidence in the mystery of how massive stars explode. The observations indicate that supernovae belonging to a class called Type II or core-collapse blast apart in a lopsided fashion, with the core of the star hurtling in one direction, and the ejected material mostly expanding the other way (see diagram in Figure 1). NuSTAR made the most precise measurements yet of a radioactive element, called titanium-44, in the supernova remnant called 1987A. NuSTAR sees high-energy X-rays, as shown here in the plot ranging from 60 to more than 80 kiloelectron volts. The spectral signature of titanium-44 is apparent as the two tall peaks. The white line shows where one would expect to see these spectral signatures if the titanium were not moving. The fact that the spectral peaks have shifted to lower energies indicates that the titanium has "redshifted," and is moving way from us. This is similar to what happens to a train's whistle as the train leaves the station. The whistle's sound shifts to lower frequencies. NuSTAR's detection of redshifted titanium reveals that the bulk of material ejected in the 1987A supernova is flying way from us at a velocity of 1.6 million miles per hour (2.6 million kilometers per hour). Had the explosion been spherical in nature, the titanium would have been seen flying uniformly in all directions. This is proof that this explosion occurred in an asymmetrical fashion. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19335