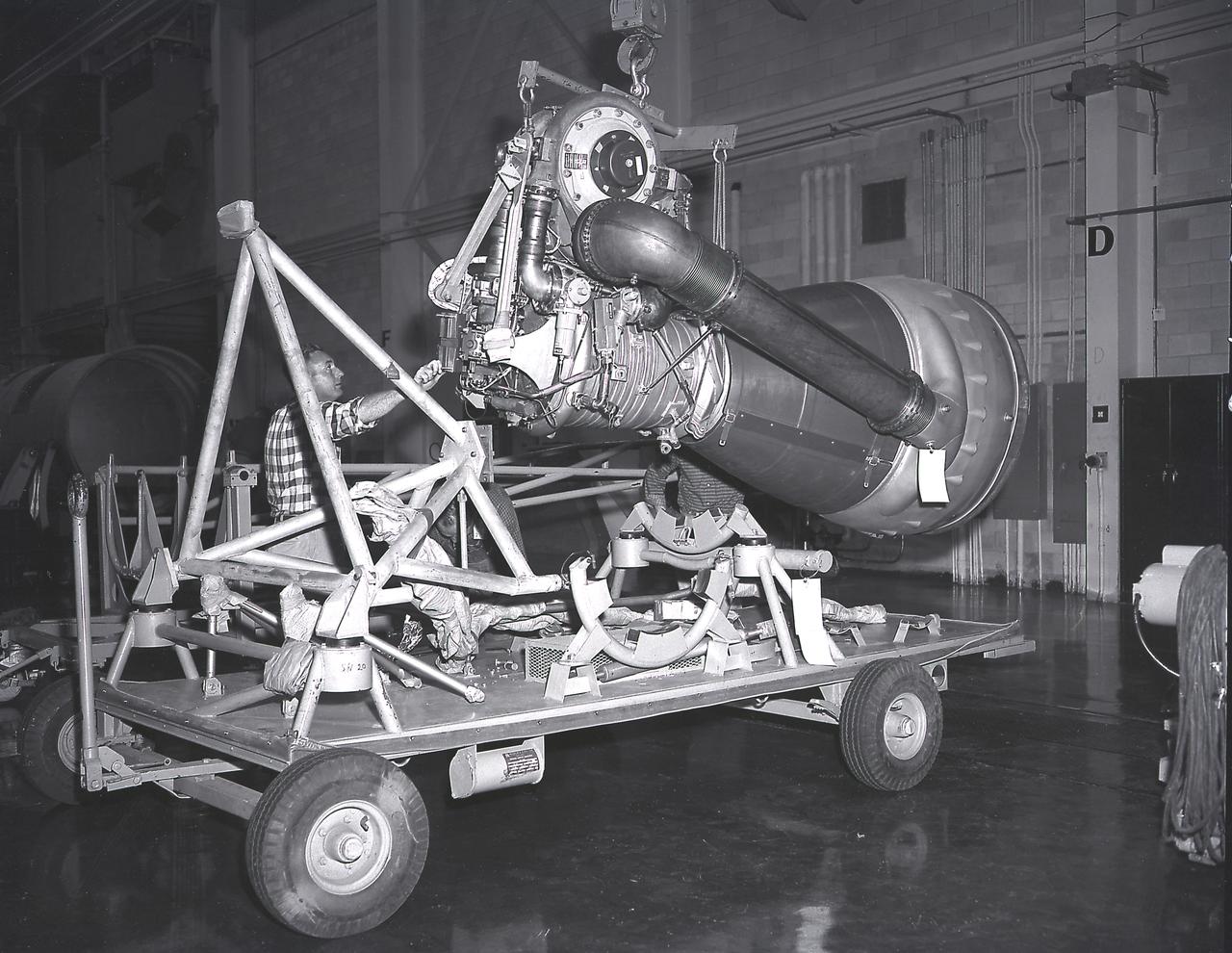
Alignment of the H-1 engine performed in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA ), building 4708, in February 1960. A cluster of eight H-1 engines were used to thrust the first stage of the Saturn I launch vehicle. The H-1 engine was developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
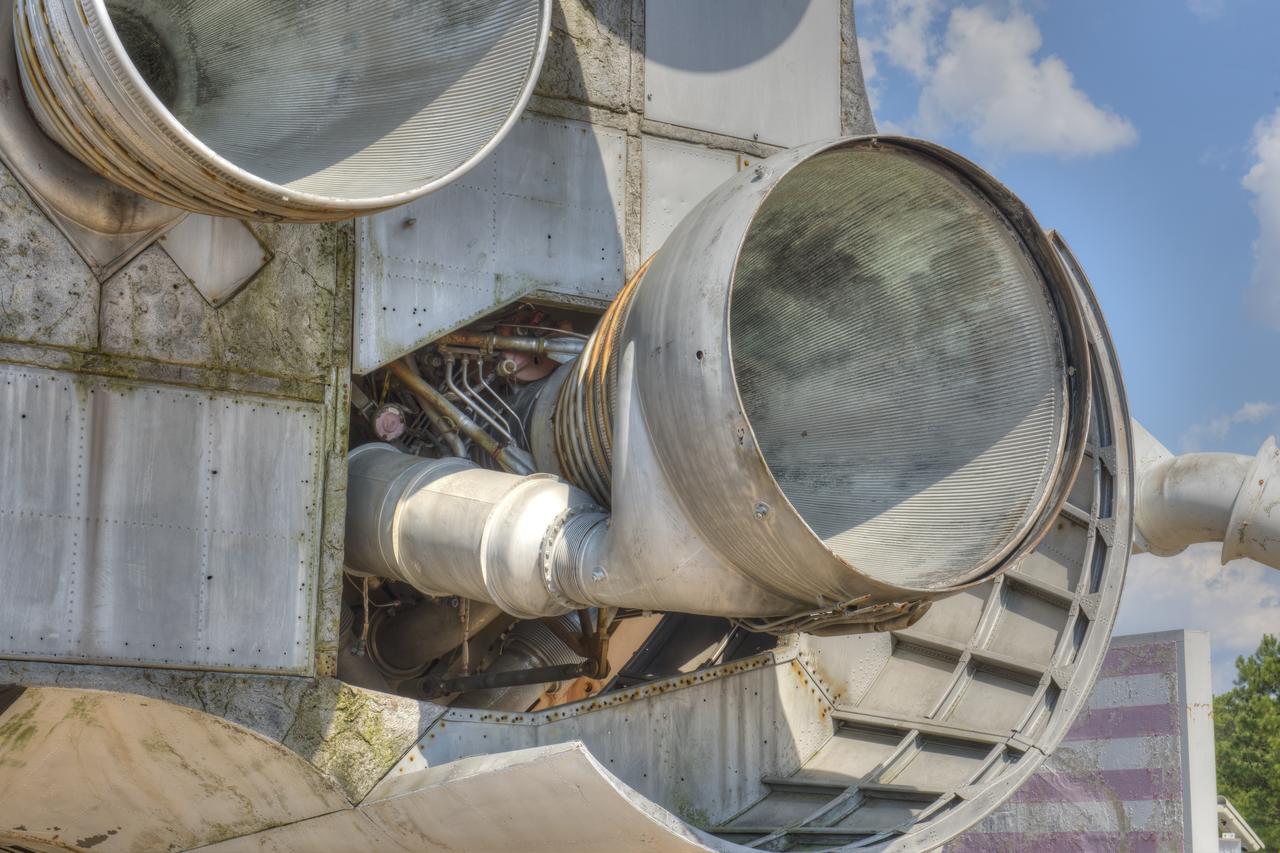

CLOSE-UP OF H-1 ENGINE INSTALLED ON SATURN S-1B STAGE (SA-T) NEAR PROPULSION AND STRUCTURAL TEST FACILITY (BUILDING 4572) AT THE GEORGE C. MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER.
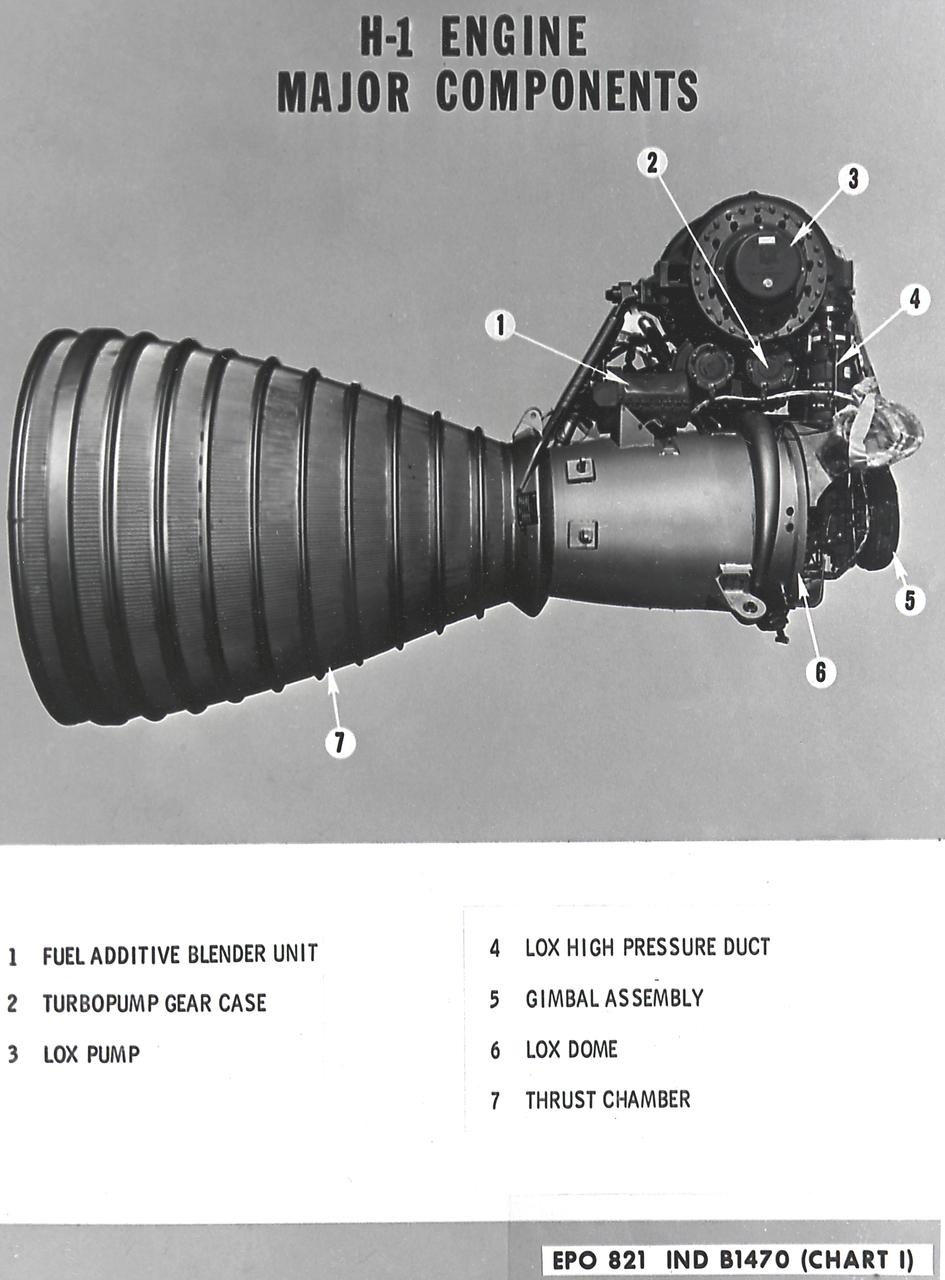
H-1 Engine major components with callouts (chart 1): The H-1 engine was used in a cluster of eight on the the first stage of Saturn I (S-I stage) and Saturn IB (S-IB stage). The engines were arranged in a double pattern: four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern and each outer engine was gimbaled. Each H-1 engine had a thrust of 188,000 pounds for a combined thrust of over 1,500,000 pounds.
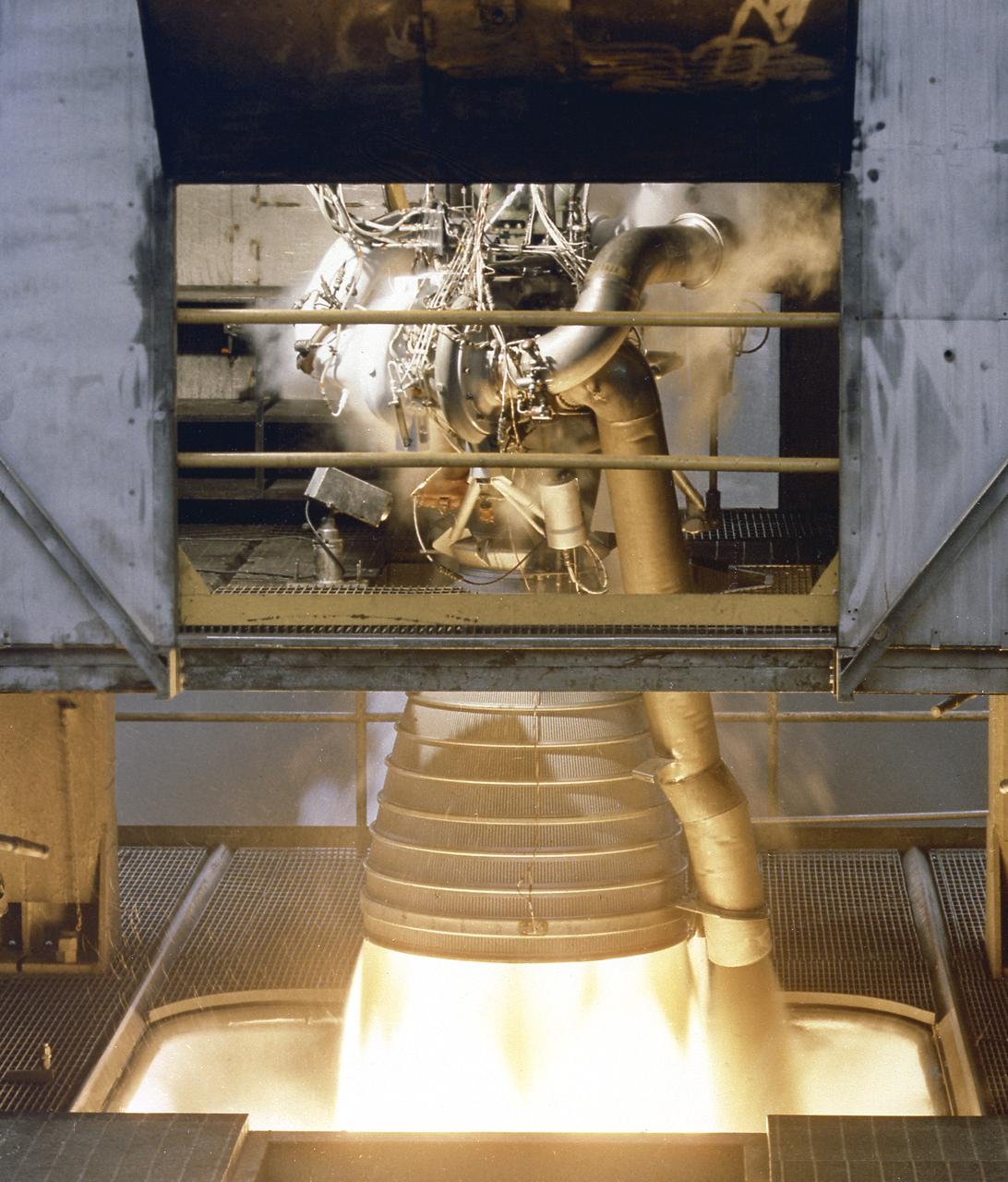
A close-up image of the single H-1 engine was test-fired at Canoga Park, California. Initial development of testing for the H-1 engine took place in the engineering facilities at Rocketdyne's main plant in Canoga Park, California.

In this photograph, the single H-1 engine was test-fired at Canoga Park, California. Initial development of testing for the H-1 engine took place in the engineering facilities at Rocketdyne's main plant in Canoga Park, California.
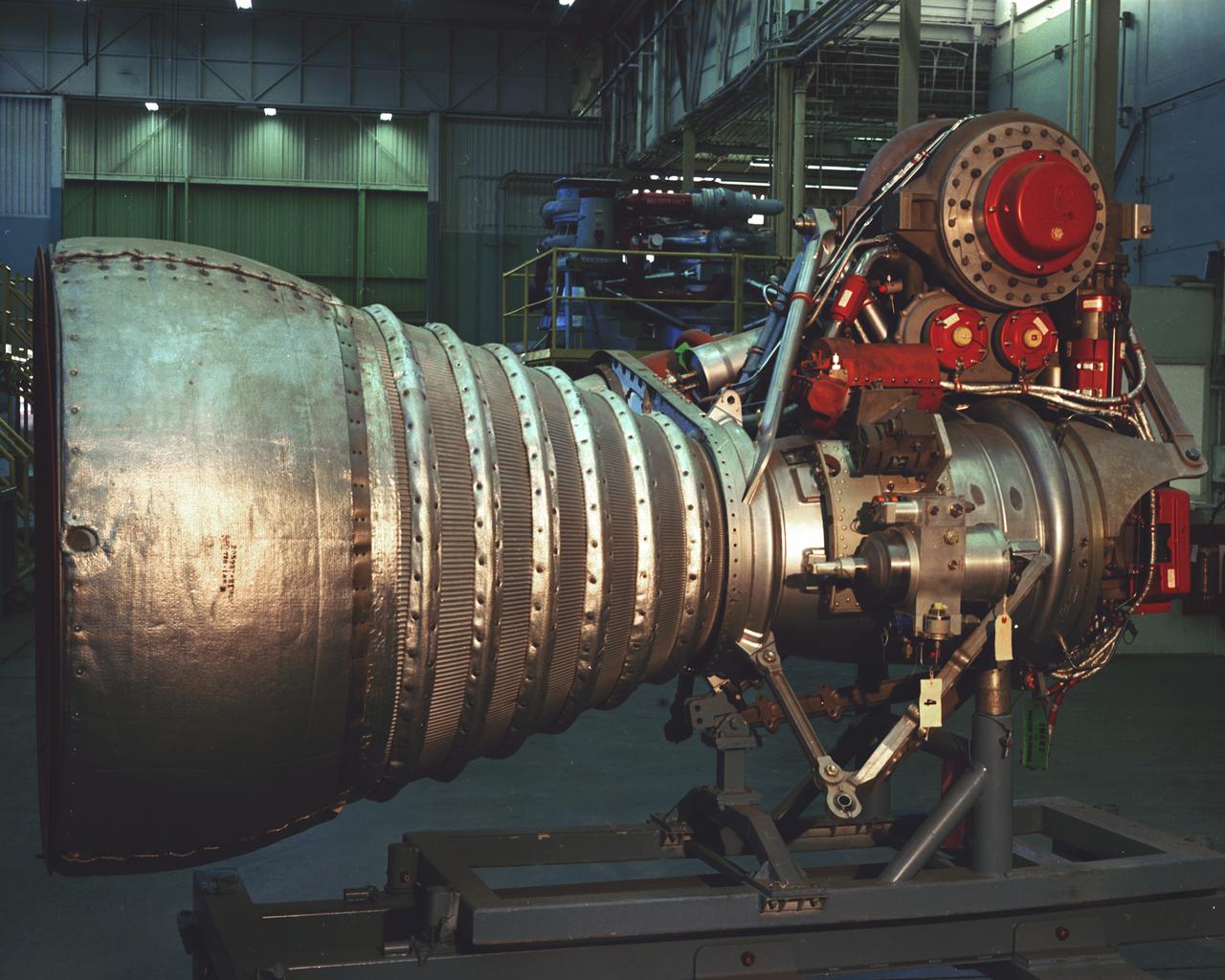
A cluster of eight H-1 engines were used to thrust the first stage of Saturn I (S-I stage) and Saturn IB (S-IB stage). The engines were arranged in a double pattern. Four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern and each outer engine was gimbaled. Each H-1 engine, fueled with liquid oxygen (LOX) and kerosene (RP-1), initially had a thrust of 188,000 pounds each for a combined thrust of over 1,500,000 pounds. Later, the H-1 engine was upgraded to 205,000 pounds of thrust and a combined total thrust of 1,650,000 pounds for the Saturn IB program. This photo depicts a single modified H-1 engine. The H-1 engine was developed under the direction of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
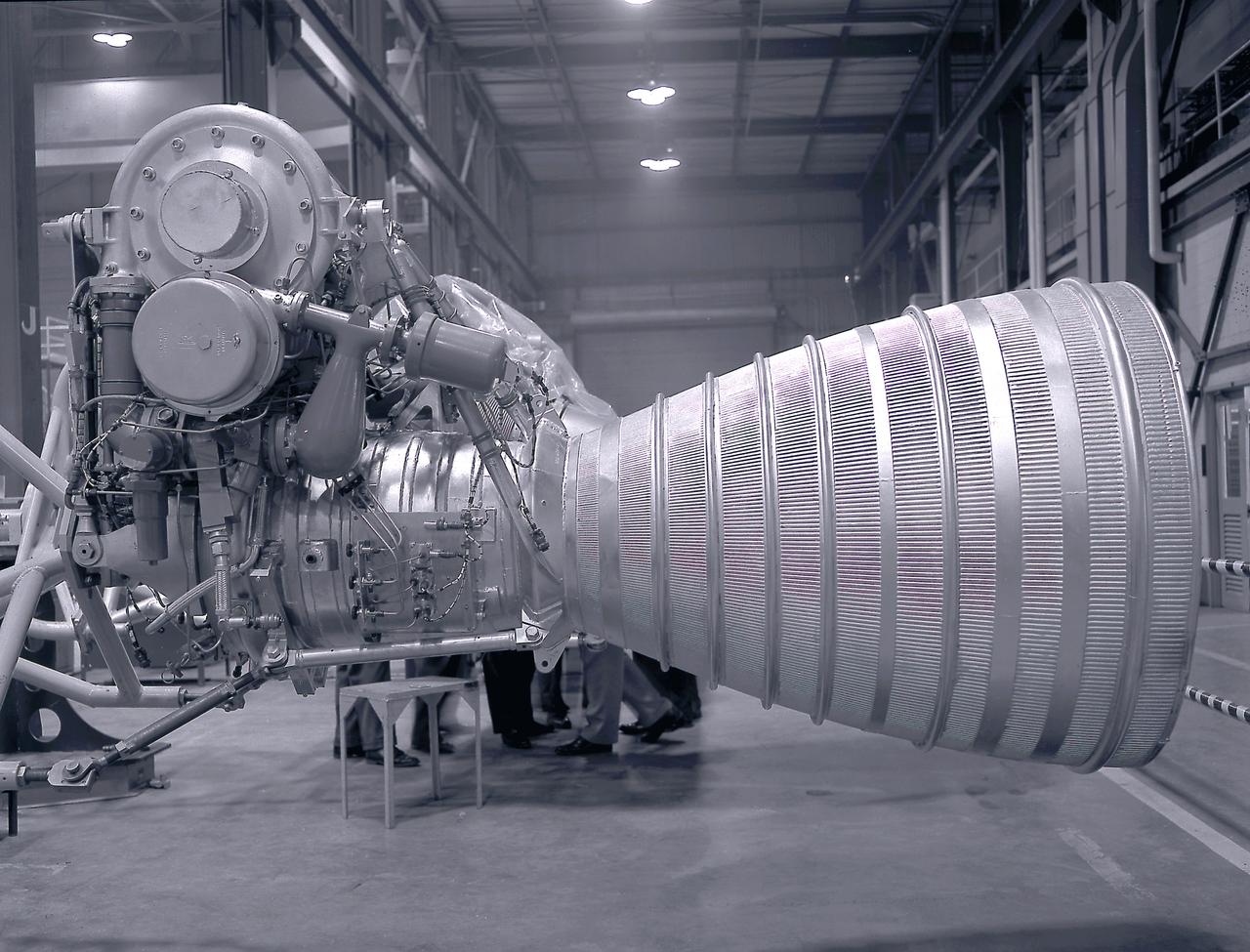
A Cluster of eight H-1 engines were used to thrust the first stage of Saturn I (S-I stage) and Saturn IB (S-IB stage). The engines were arranged in a double pattern. Four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern and each outer engine was gimbaled. The H-1 engine, fueled with liquid oxygen (LOX) and kerosene (RP-1), had a thrust of 188,000 pound each for a combined thrust of over 1,500,000 pounds. Each H-1 engine was developed under the direction of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
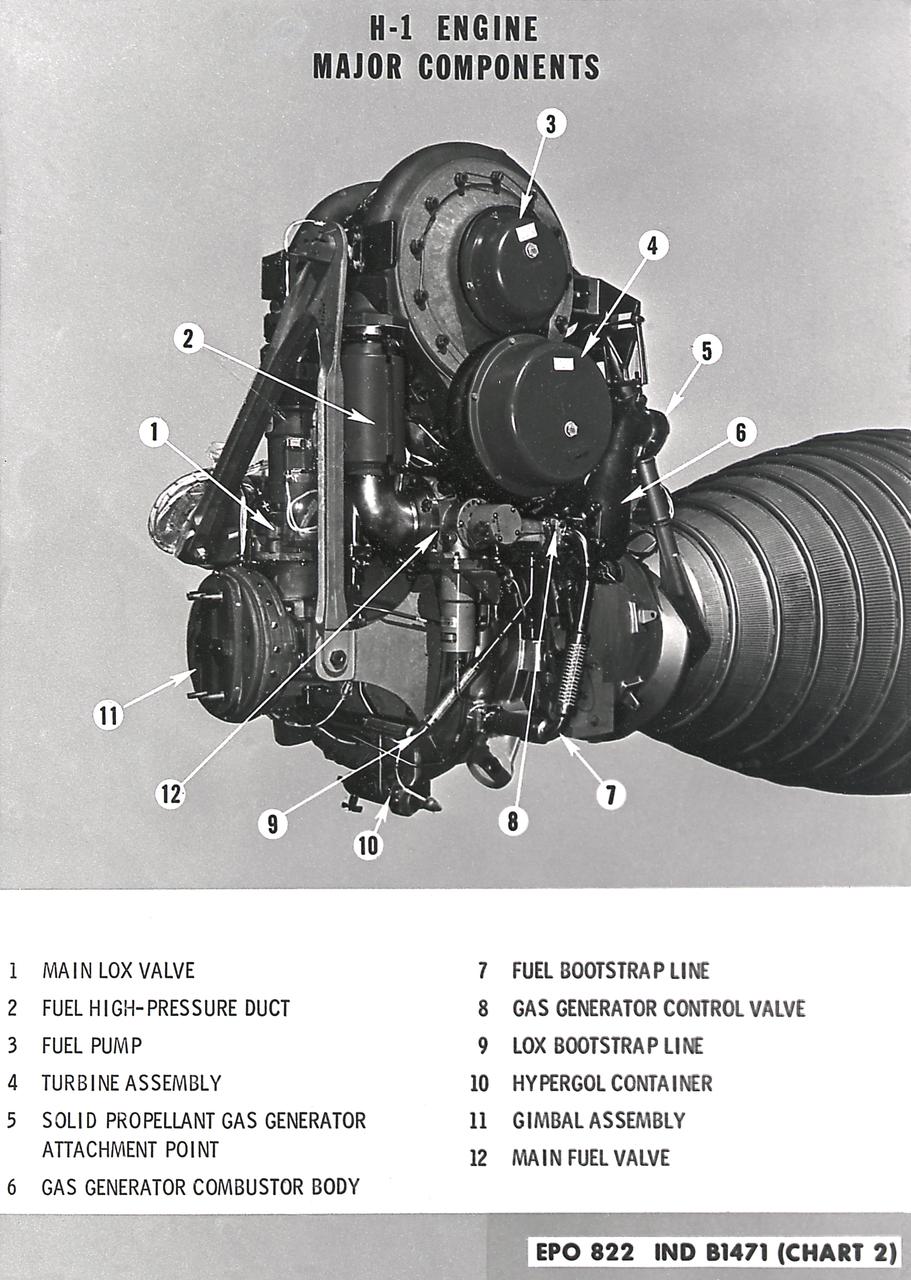
H-1 engine major components with callouts (chart 1). The H-1 engine was used in a cluster of eight on the the first stage of Saturn I (S-I stage) and Saturn IB (S-IB stage). The engines were arranged in a double pattern: four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern and each outer engine was gimbaled. Each H-1 engine had a thrust of 188,000 pounds for a combined thrust of over 1,500,000 pounds.
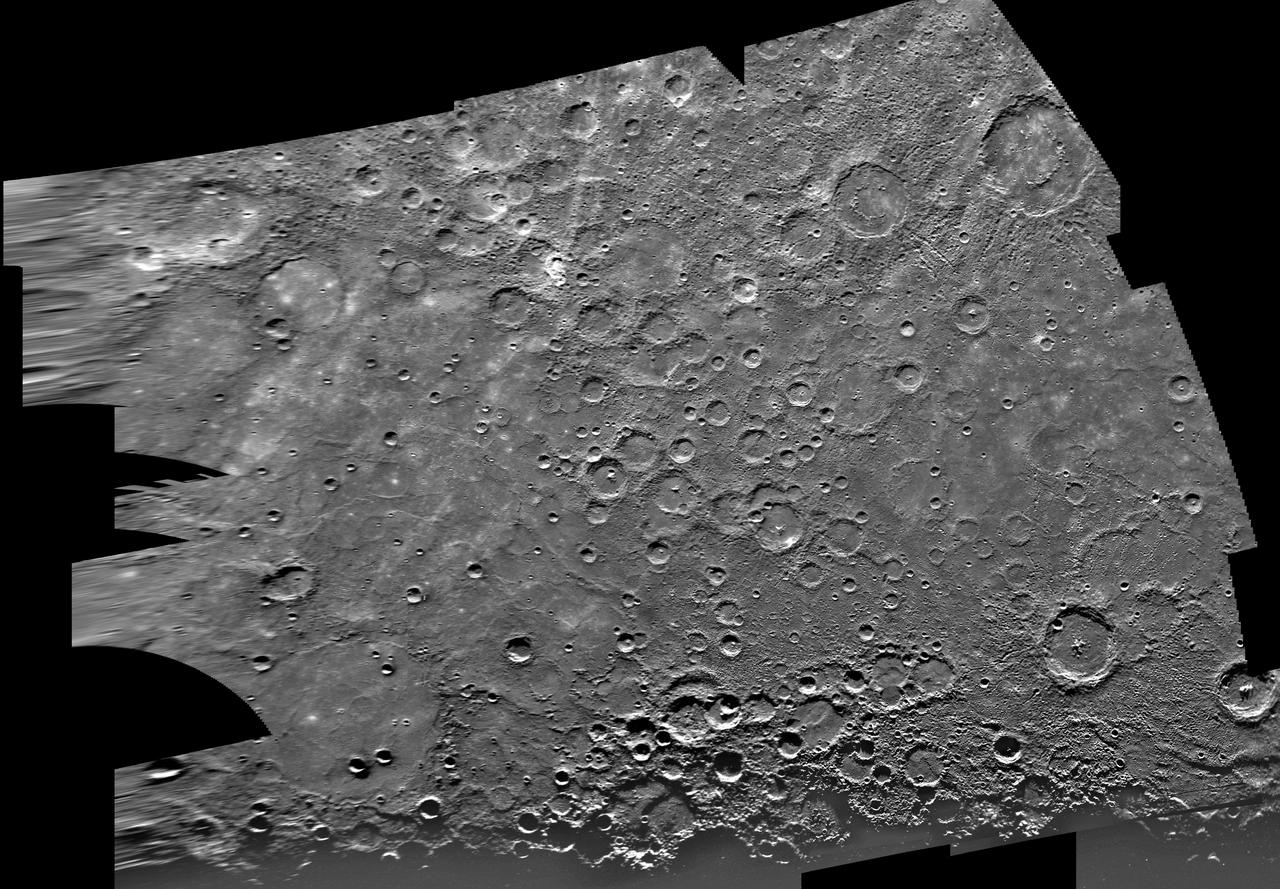

This image, from NASA Mariner 10 spacecraft which launched in 1974, is of the Borealis area H-1, located in Mercury northern hemisphere. The north pole is visible at the top of the image.
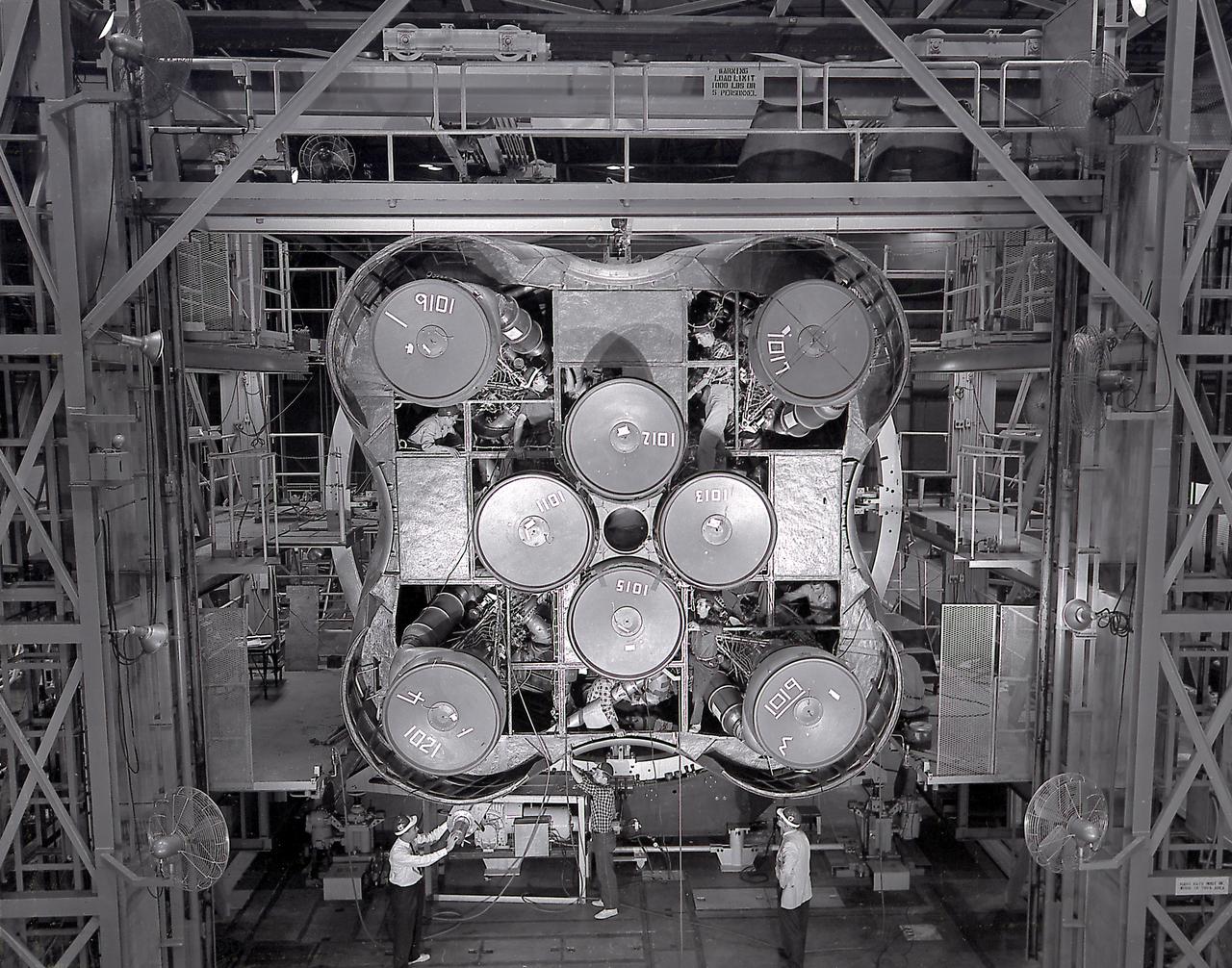
The Saturn I S-I stage with eight H-1 engines, located in Marshall Space Flight Center building 4705, showing the positioning of eight H-1 engines. The Saturn I S-I stage had eight H-1 engines clustered, using liquid oxygen/kerosene-1 (LOX/RP-1) propellants capable of producing a total of 1,500,000 pounds of thrust.

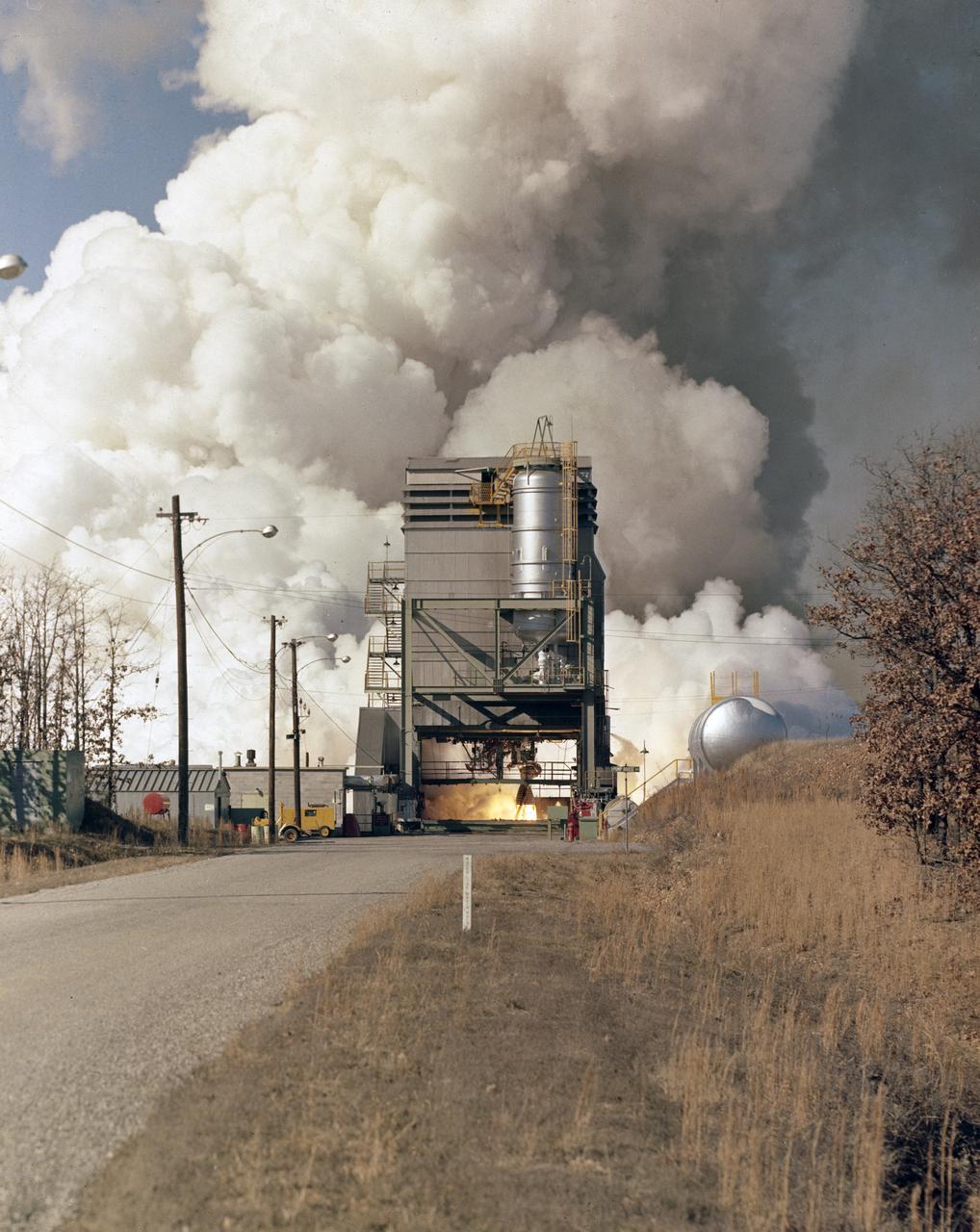
This image depicts a firing of a single H-1 engine at the Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC’s) Power Plant test stand. This 1950s test stand, inherited from the Army, was used to test fire engines until the Test Area was completed in the latter 1960s. The H-1 engine was the workhorse of the first Saturn launch vehicles and used in the Saturn I, Block 1 and II, and in the Saturn IB. The eight H-1 engines were attached to a thrust frame on the vehicle’s aft end in two different ways. Four engines are rigidly attached to the inboard position and canted at a three degree angle to the long axis of the booster. The other four engines, mounted in the outboard position, are canted at six degrees.

This drawing clearly shows the comparative sizes of the rocket engines used to launch the Saturn vehicles. The RL-10 and the H-1 engines were used to launch the Saturn I rockets. The J-2 engine was used on the second stage of Saturn IB and the second and third stages of Saturn V. The F-1 engine was used on the first stage of the Saturn V.
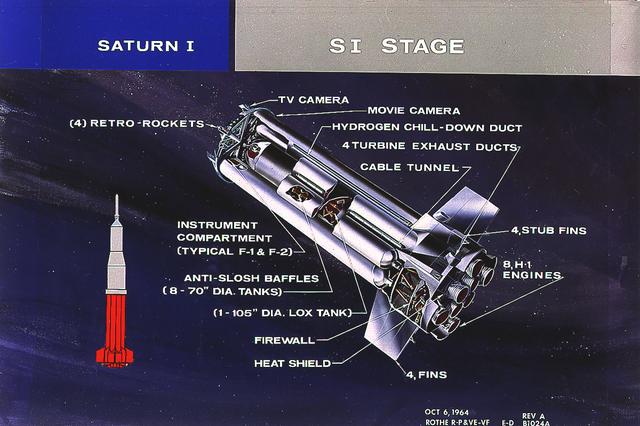
This cutaway illustrates the S-I stage, the first stage of the Saturn I vehicle developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The stage was propelled by a cluster of eight H-1 engines, capable of producing 1,500,000 pounds of thrust.
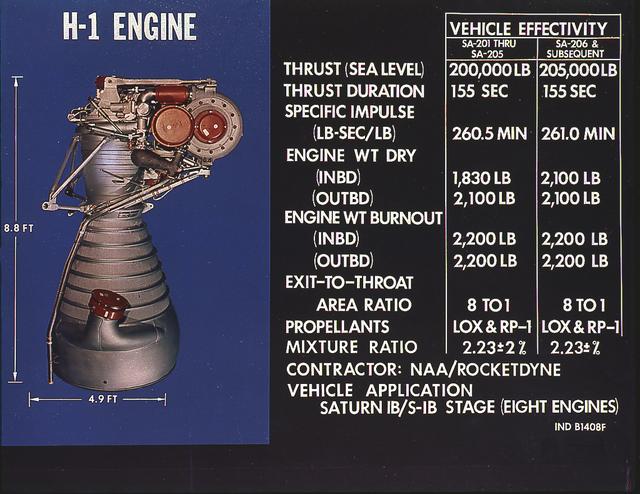
H-1 engine characteristics: The H-1 engine was developed under the management of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The cluster of eight H-1 engines was used to power the first stage of the Saturn I (S-I stage) and Saturn IB (S-IVB stage) launch vehicles, and produced 188,00 pounds of thrust, a combined thrust of 1,500,000 pounds, later uprated to 205,000 pounds of thrust and a combined total thrust of 1,650,000 pounds for the Saturn IB program.

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the birthplace of the United States' rocket program. In the early 1960s, most of the rocket development and testing were done at the MSFC. Pictured is an example of what the test engineers would have seen from the pillbox as eight H-1 engines for the first stage of the Saturn I rocket were test fired.
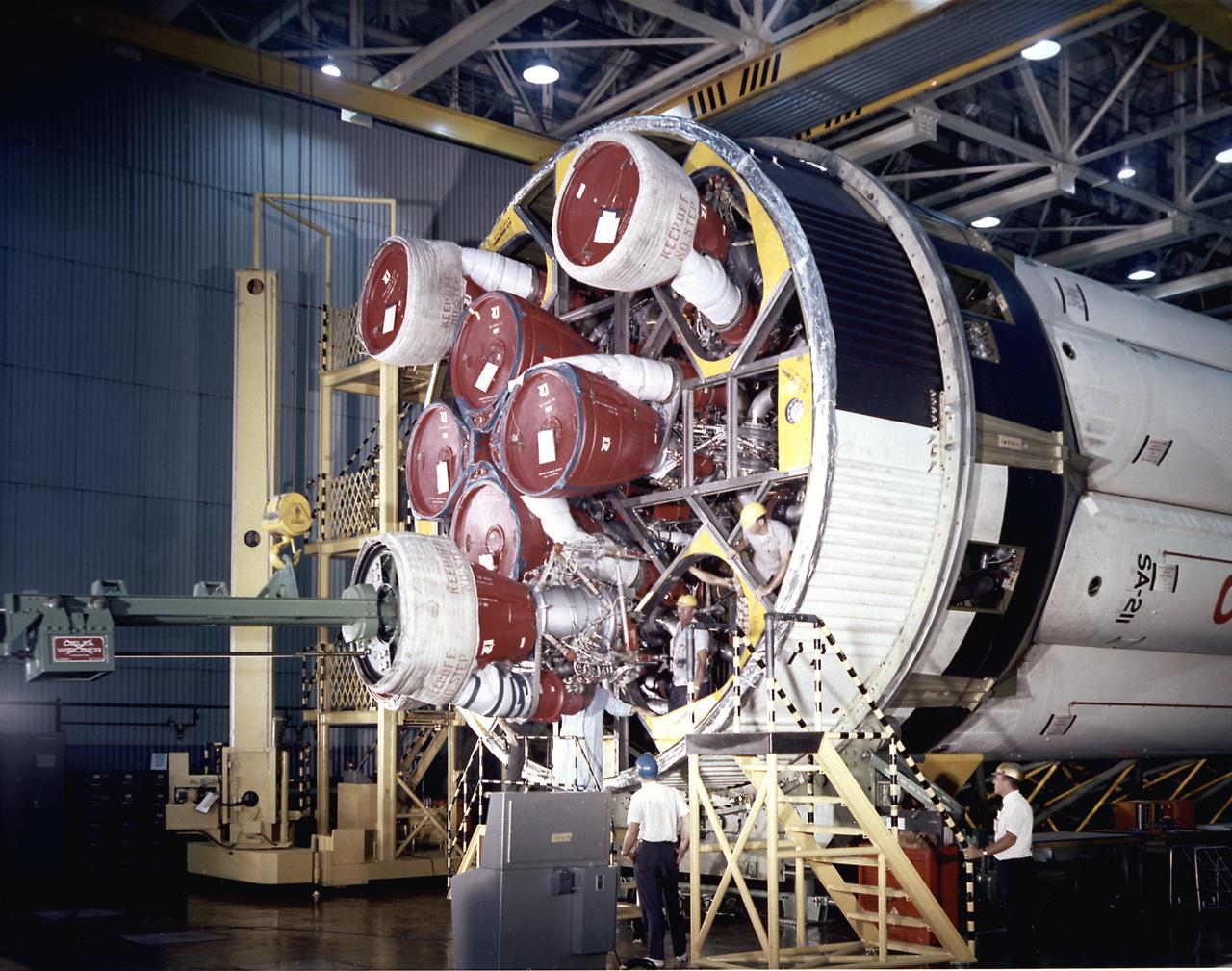
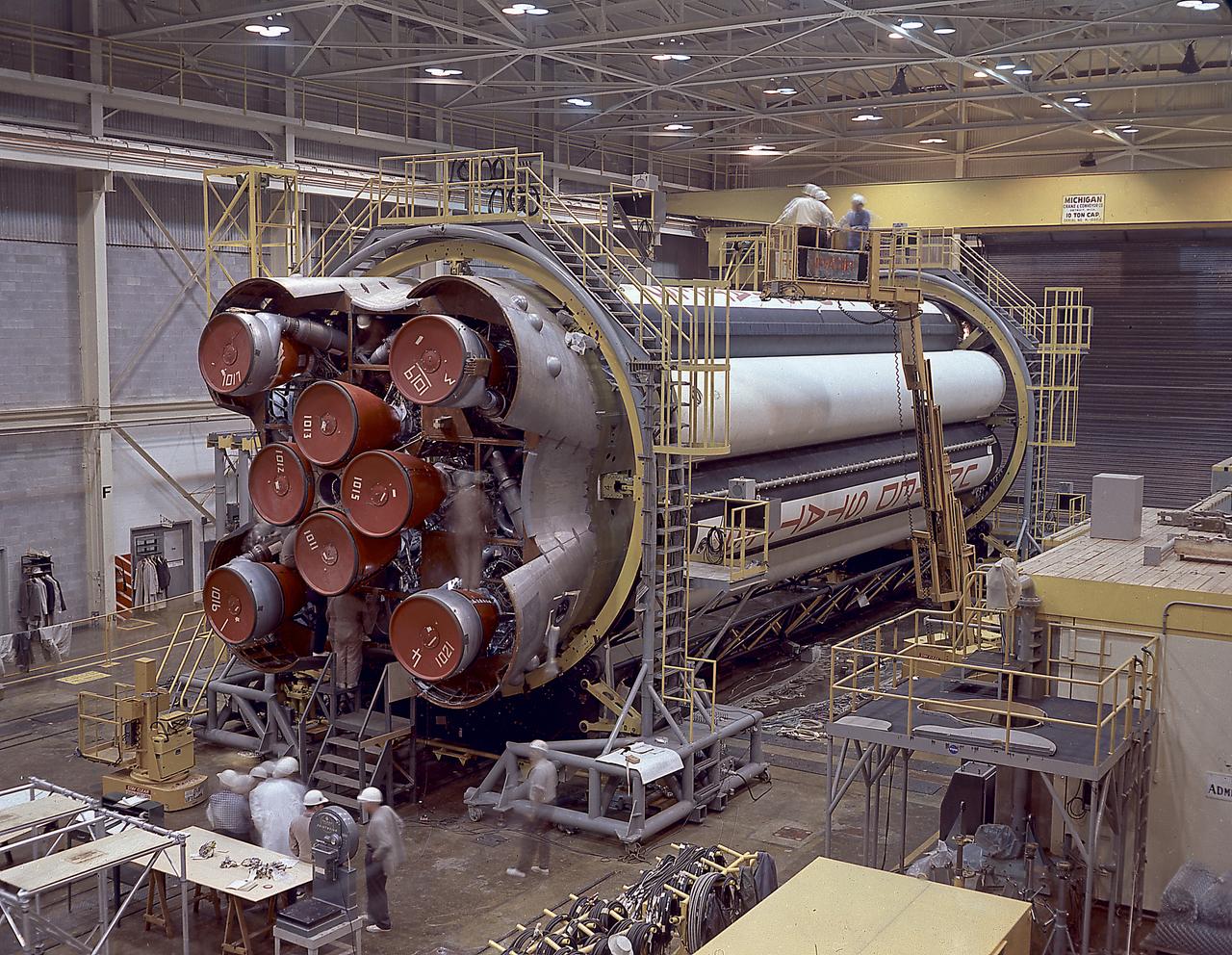
Workers at the Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans, Louisiana install the H-1 engines into the S-IB stage, the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Chrysler Corporation at MAF, the 90,000-pound booster utilized eight H-1 engines to produce a combined thrust of 1,600,000 pounds.
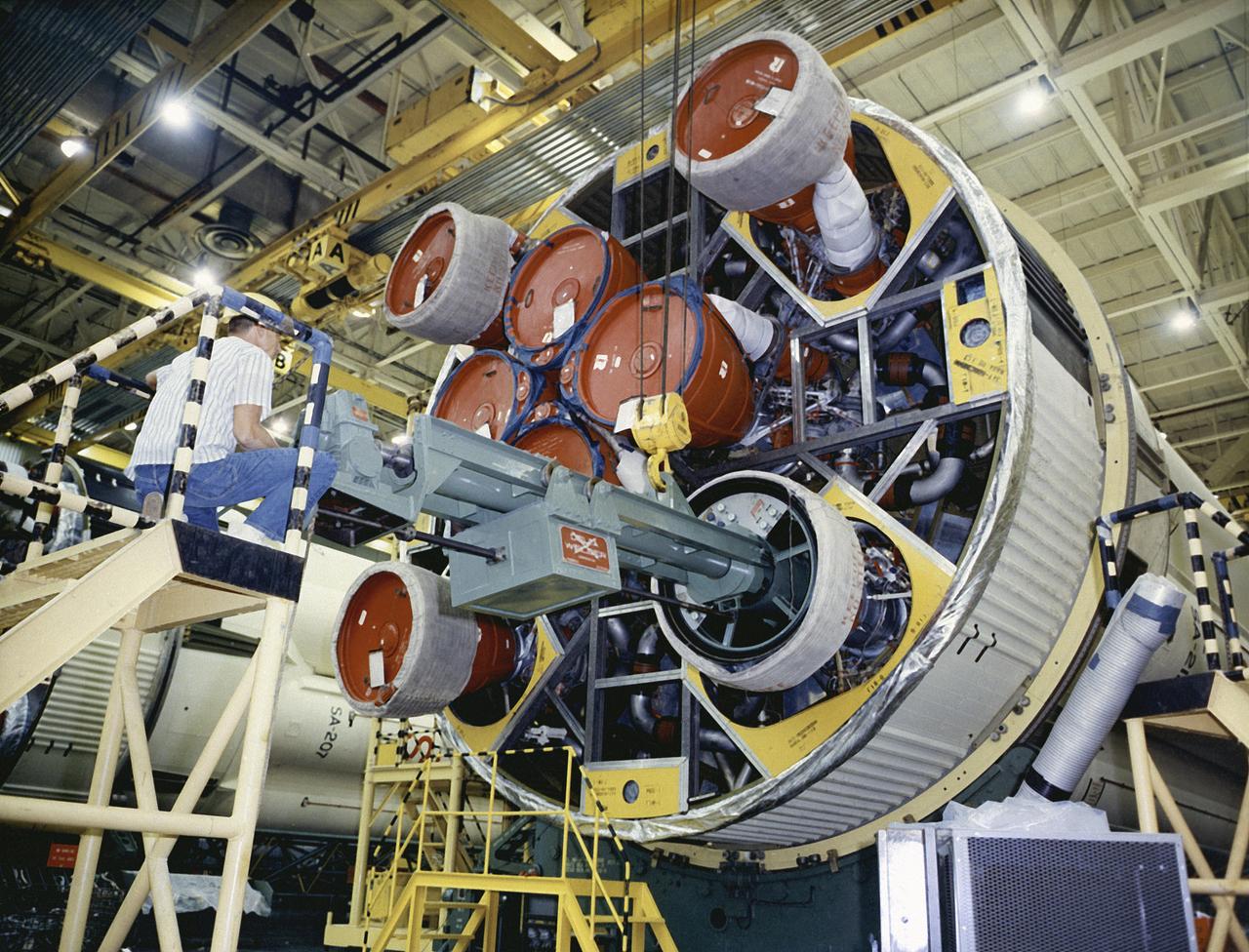
Workers at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) near New Orleans, Louisiana, install the last engine on the S-IB stage. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and built by the Chrysler Corporation at MAF, the S-IB stage utilized eight H-1 engines to produce a combined thrust of 1,600,000 pounds.

The Saturn 1B S-IB (first) stage being prepared for shipment at Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF), near New Orleans, Louisiana. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Chrysler Corporation at MAF, the S-IB stage utilized the eight H-1 engines and each produced 200,000 pounds of thrust, a combined thrust of 1,600,000 pounds.
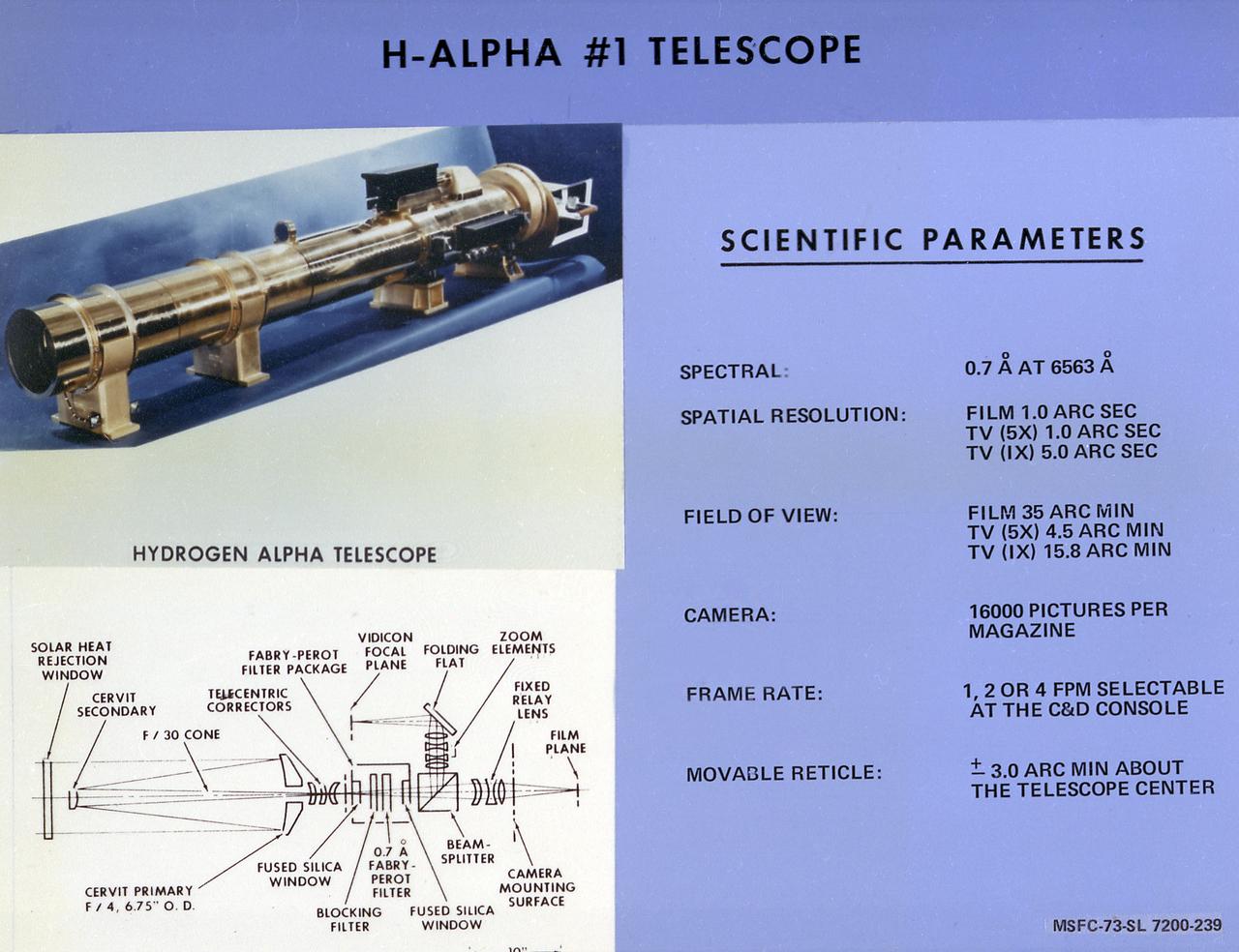
This chart describes the Hydrogen-Alpha (H-Alpha) #1 Telescope, one of eight major solar study facilities on the Skylab Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM). There were two H-Alpha telescopes on the ATM that were used primarily to point the ATM and keep a continuous photographic record during the solar observation periods. Both telescopes gave the Skylab astronauts a real-time picture of the Sun in the red light of the H-Alpha spectrum through a closed-circuit television. The H-Alpha #1 Telescope provided simultaneous photographic and ultraviolet (UV) pictures, while the #2 Telescope operated only in the TV mode. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for development of the H-Alpha Telescopes.

Mission Control Center (MCC) activities during Day-1 of the STS-9 mission with Flight Director Jay H. Greene and Lt. Gen. James A. Abrahamson. 1. Lt. General James A. Abrahamson 2. Jay H. Green 3. MOCR JSC, Houston, TX
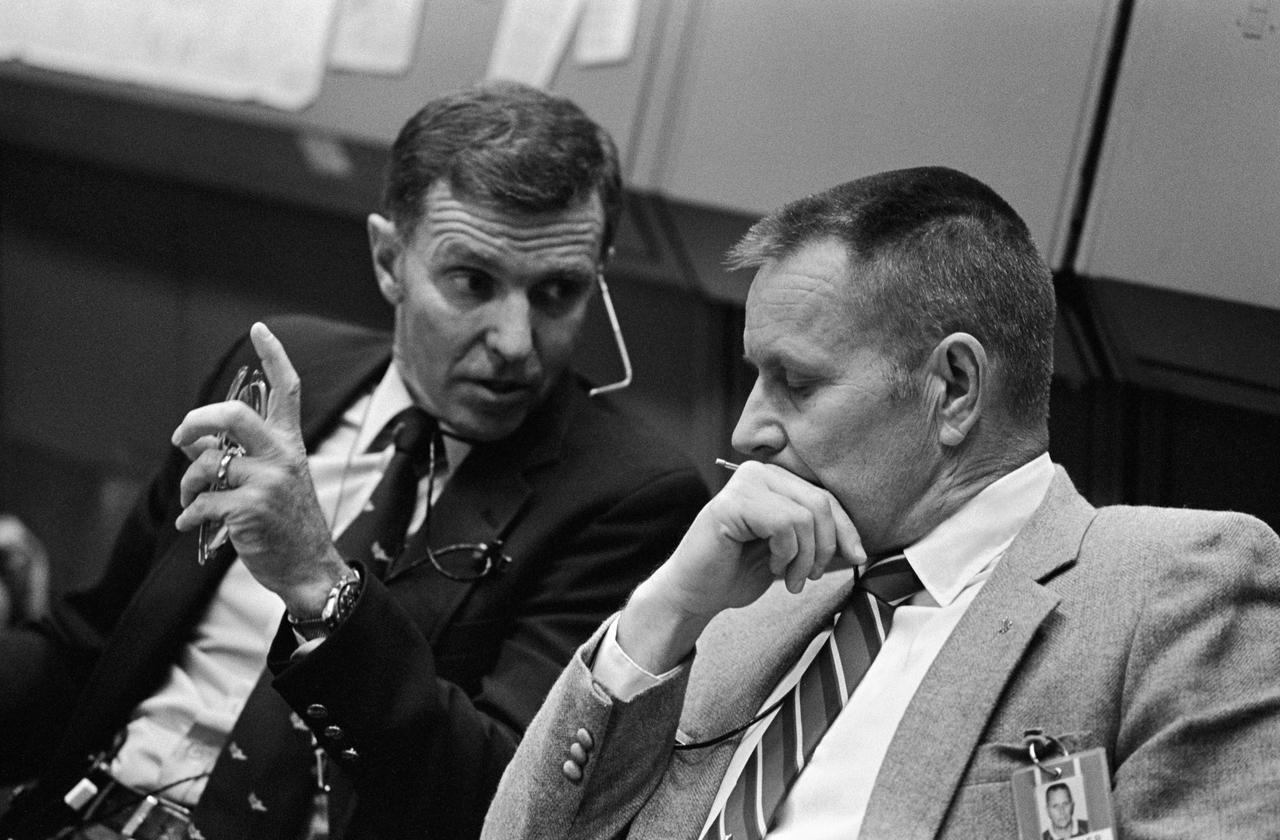

Mission Control Center (MCC) activities during Day-1 of the STS-9 mission with Flight Director Jay H. Greene and Lt. Gen. James A. Abrahamson. 1. Lt. General James A. Abrahamson 2. Jay H. Green 3. MOCR JSC, Houston, TX
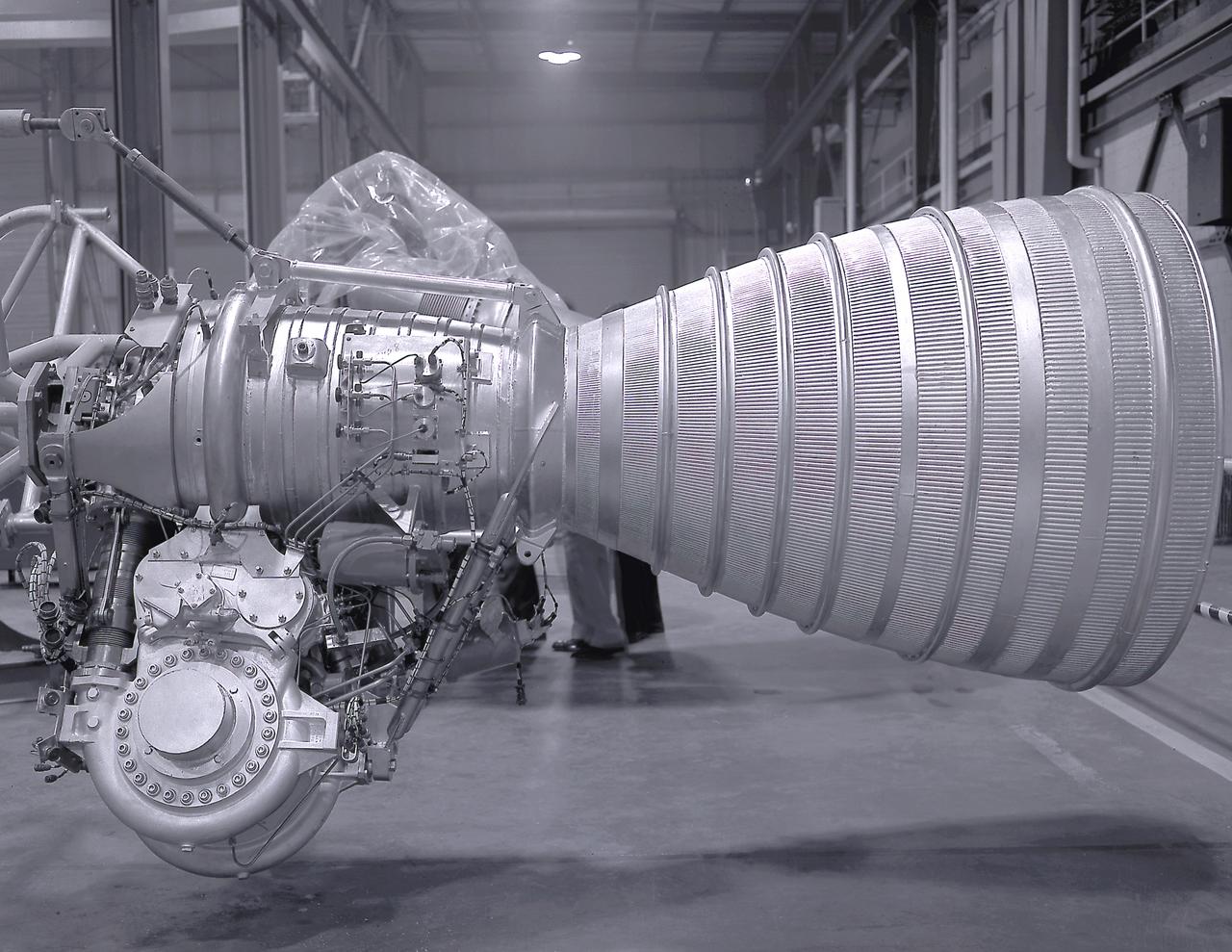
A Cluster of eight H-1 engines were used to thrust the first stage of Saturn I (S-I stage) and Saturn IB (S-IB stage). The engines were arranged in a double pattern. Four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern and each outer engine was gimbaled. Each H-1 engine, fueled with liquid oxygen (LOX) and kerosene (RP-1), had a thrust of 188,000 pound each for a combined thrust of over 1,500,000 pounds. The H-1 engine was developed under the direction of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
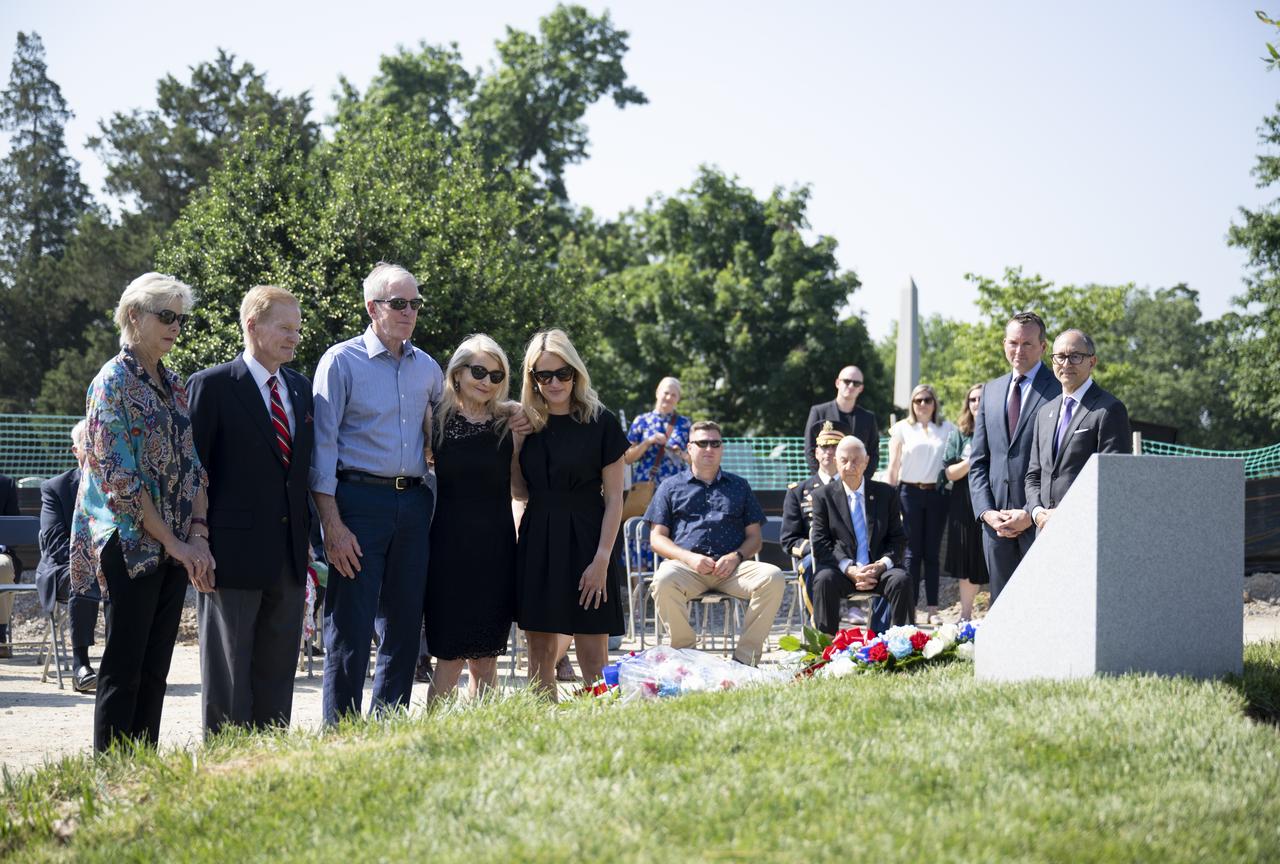

Family members of Apollo 1 astronaut Edward H. White II are joined by NASA Administrator Bill Nelson as they place flowers at the Apollo 1 monument during its dedication at Arlington National Cemetery, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Family members of Apollo 1 astronaut Edward H. White II are joined by NASA Administrator Bill Nelson as they place flowers at the Apollo 1 monument during its dedication at Arlington National Cemetery, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
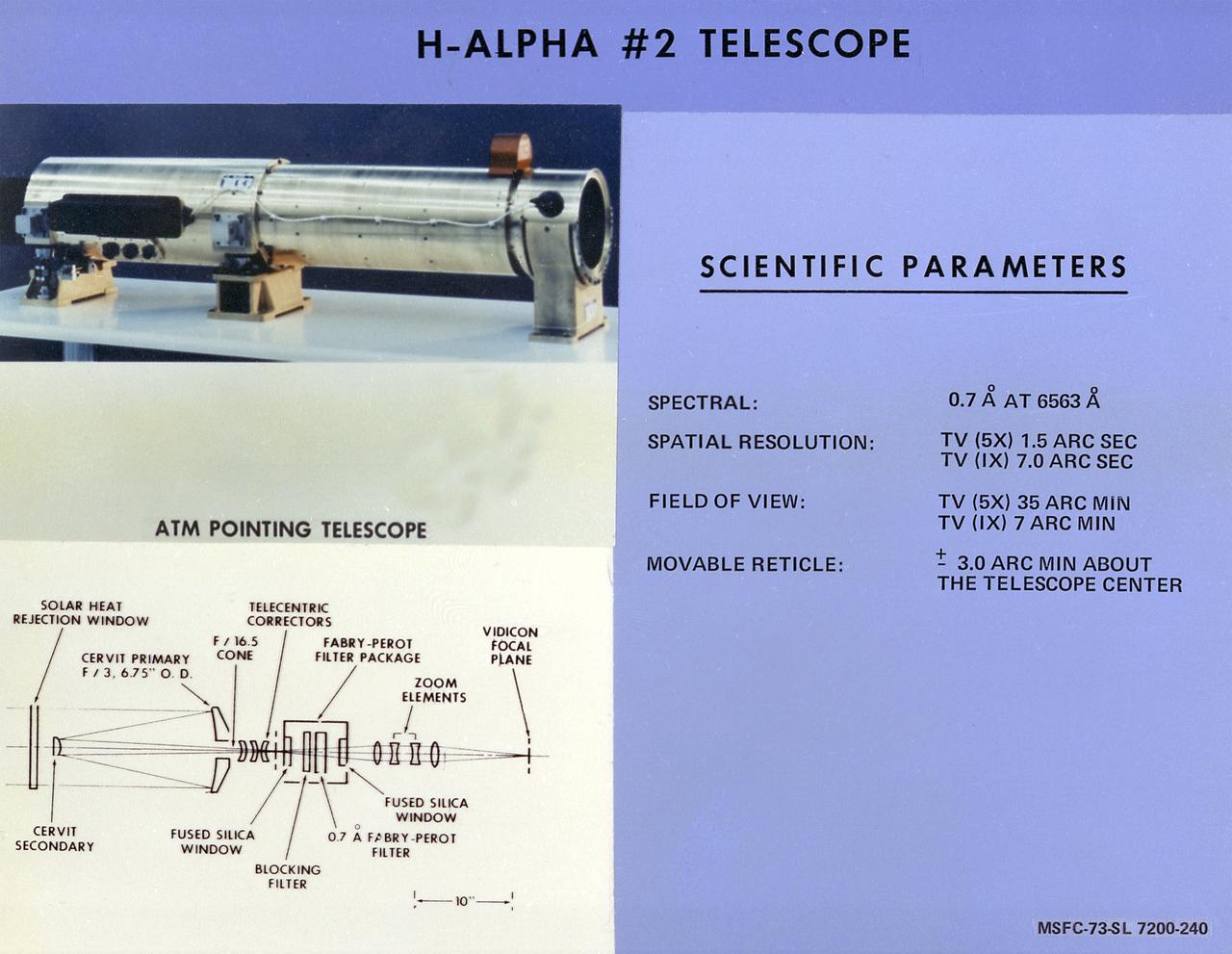
This chart describes the Hydrogen-Alpha (H-Alpha) #2 Telescope, one of eight major solar study facilities on the Skylab Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM). There were two H-Alpha telescopes on the ATM that were used primarily to point the ATM and keep a continuous photographic record during solar observation periods. Both telescopes gave the Skylab astronauts a real-time picture of the Sun in the red light of the H-Alpha spectrum through a closed-circuit television. The H-Alpha #1 telescope provided simultaneous photographic and ultraviolet (UV) pictures, while the #2 telescope operated only in the TV mode. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for development of the H-Alpha Telescopes.

S81-30479 (April 1981) --- Astronauts John W. Young, second from left, and Robert L. Crippen, left, discuss photography from their recent STS-1 mission with astronauts Joe H. Engle, right, and Richard H. Truly during a post-mission debriefing session. Engle and Truly were backup crewmen for STS-1 and they have been named as prime crew members for STS-2, scheduled for a Sept. 30, 1981 liftoff. Photo credit: NASA
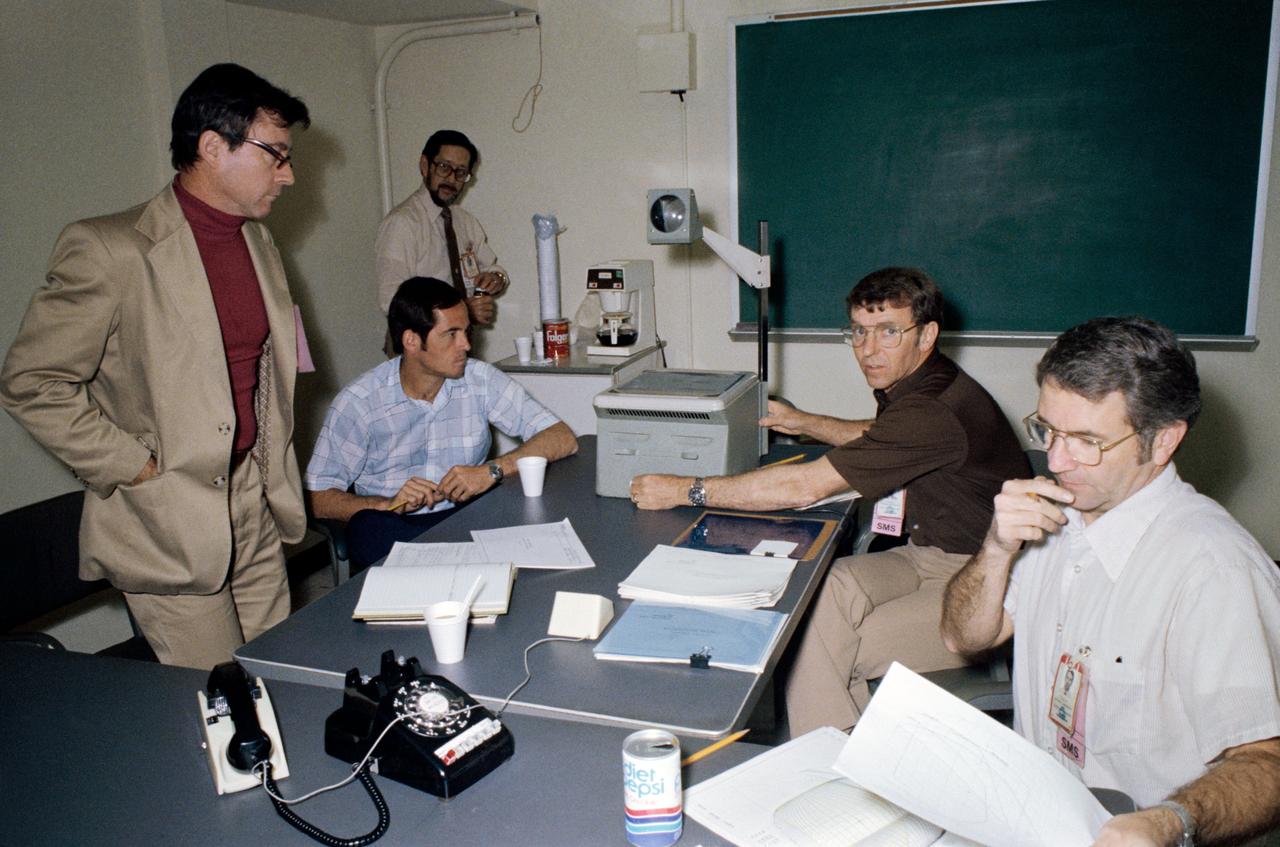

S81-29620 (6 April 1981) --- Prime and backup crew members for STS-1 take part in a briefing with engineers located in another building at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC) and with Rockwell International representatives in California via telephone. Astronauts John W. Young, left, and Robert L. Crippen, second from left, are STS-1 prime crewmen. Backup crewmen are astronauts Joe H. Engle, second from right, and Richard H. Truly. Photo credit: NASA
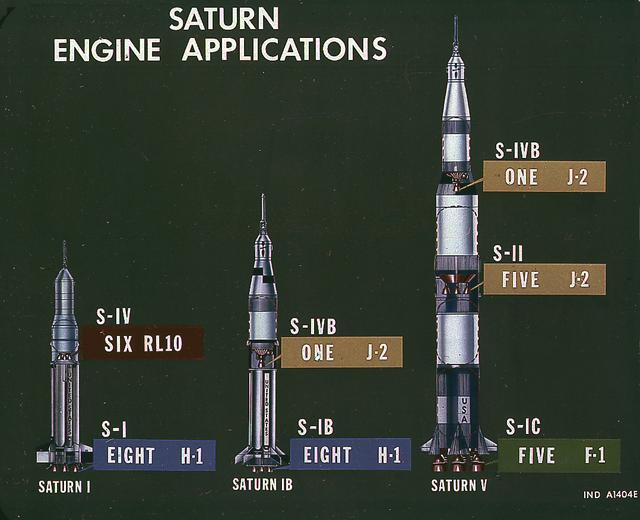
This image illustrates the basic differences between the three Saturn launch vehicles developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The Saturn I, consisted of two stages, the S-I (eight H-1 engines) and the S-IV (six RL-10 engines). The Saturn IB (center) also consisted of two stages, the S-IB (eight H-1 engines) and the S-IVB (one J-2 engine). The Saturn V consisted of three stages, the S-IC (five F-1 engines), the S-II (five J-2 engines), and the S-IVB (one J-2 engine).
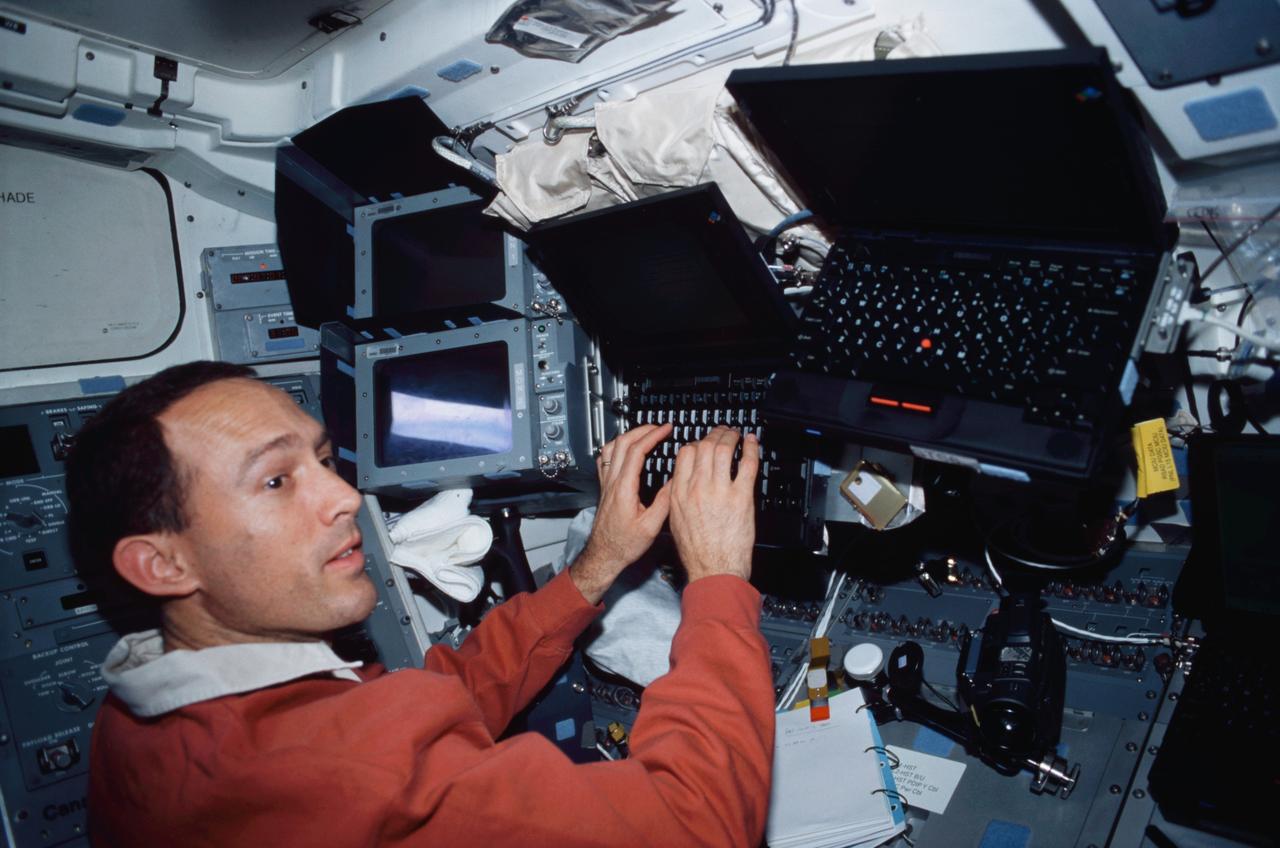

STS109-406-026 (1-12 March 2002) --- Astronaut James H. Newman, STS-109 mission specialist, works with Payload and General Support Computers (PGSC) on the mid deck of the Space Shuttle Columbia.
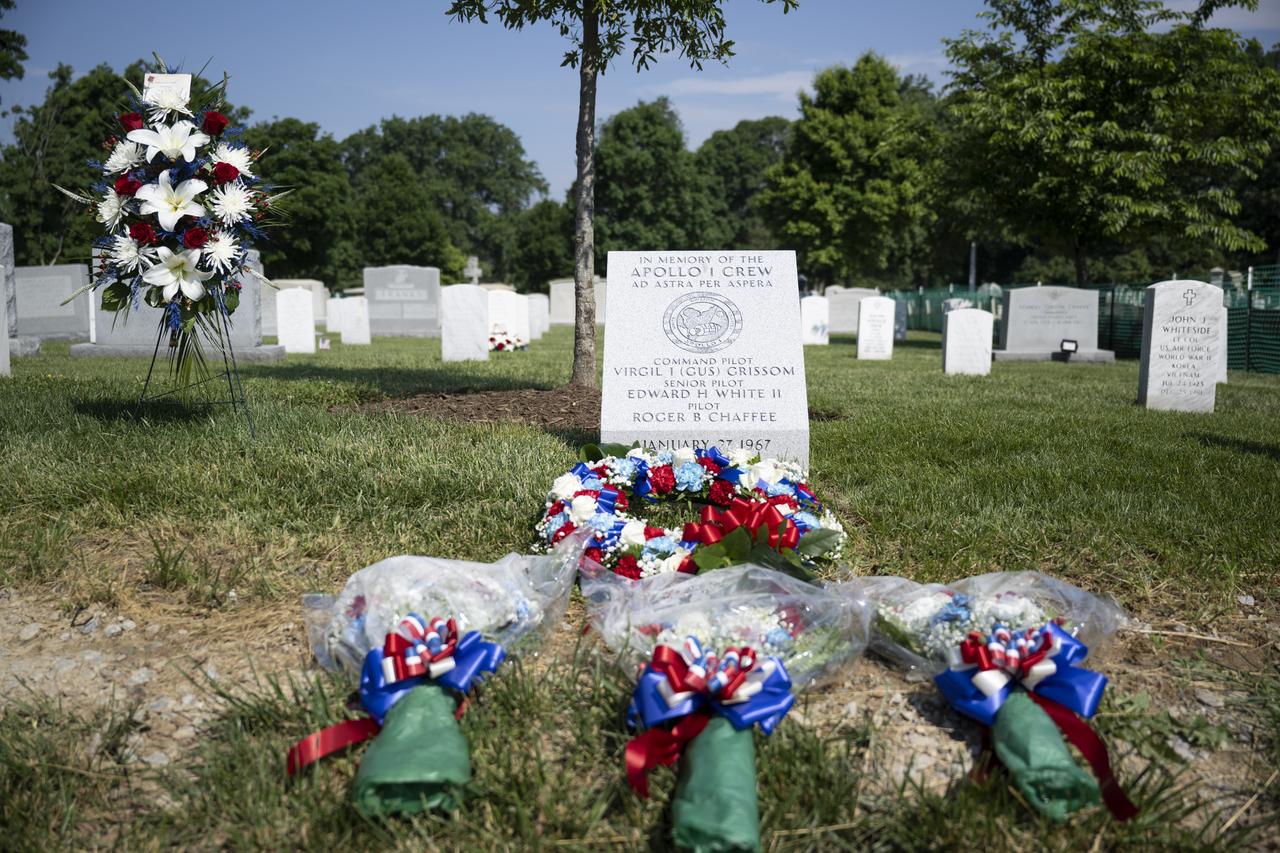

The Apollo 1 monument at Arlington National Cemetery is seen following its dedication, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
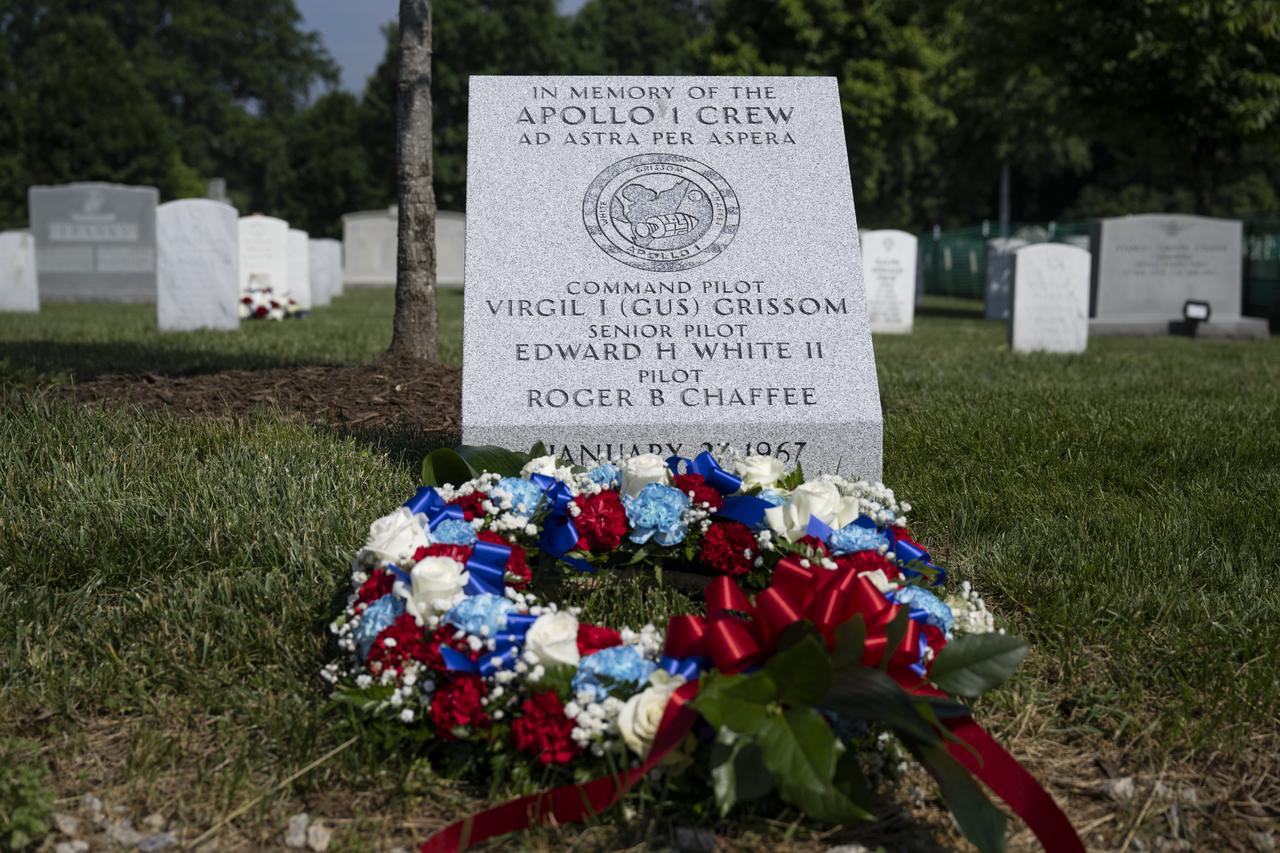

The Apollo 1 monument is seen at Arlington National Cemetery, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
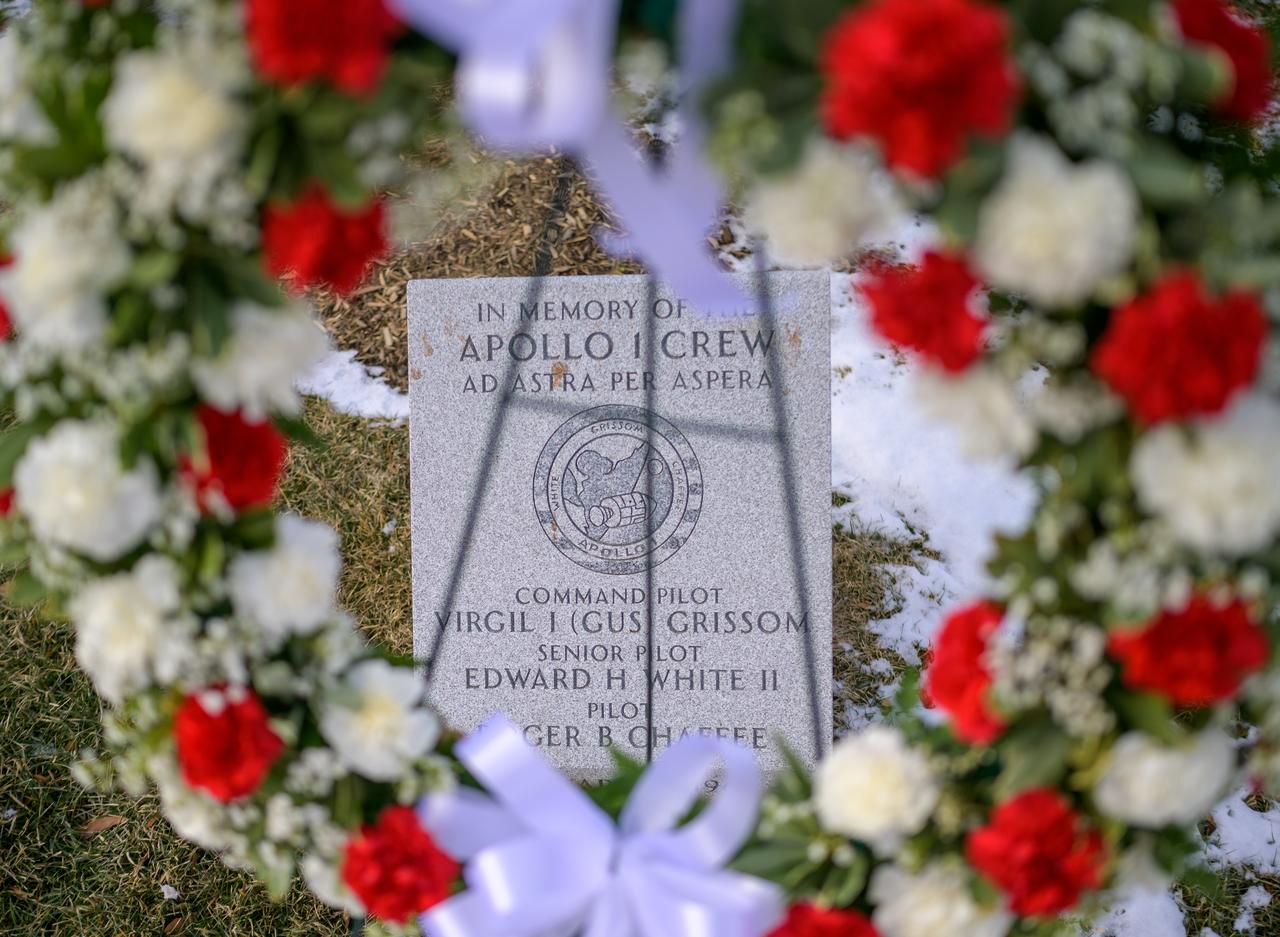

A wreath is left at the Apollo 1 monument as part of NASA's Day of Remembrance, Thursday, Jan. 23, 2025, at Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
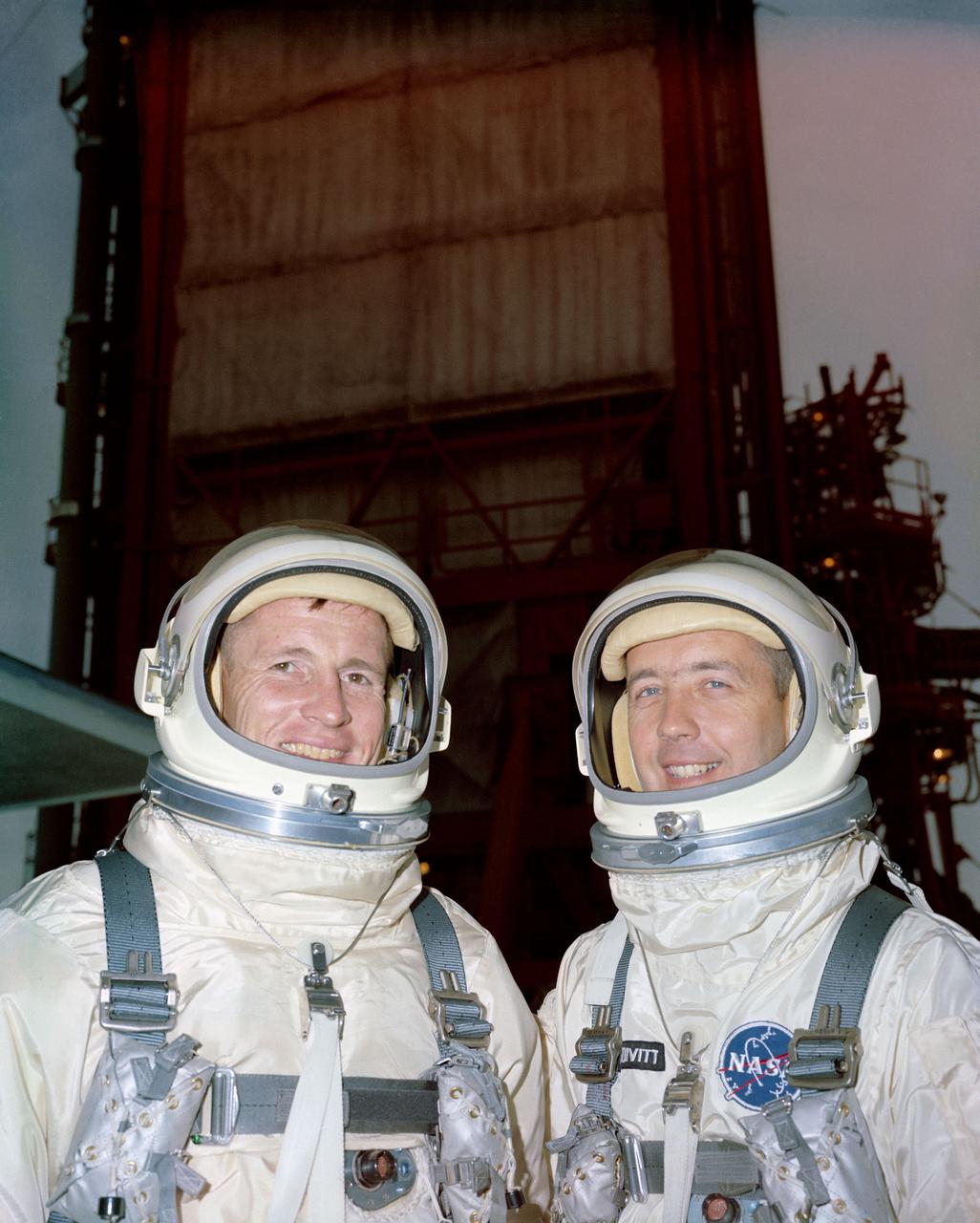

S65-19528 (1 June 1965) --- Astronauts Edward H. White II (left), Gemini-Titan 4 pilot; and James A. McDivitt, command pilot. EDITOR?S NOTE: Astronaut White died in the Apollo 1/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy on Jan. 27, 1967.
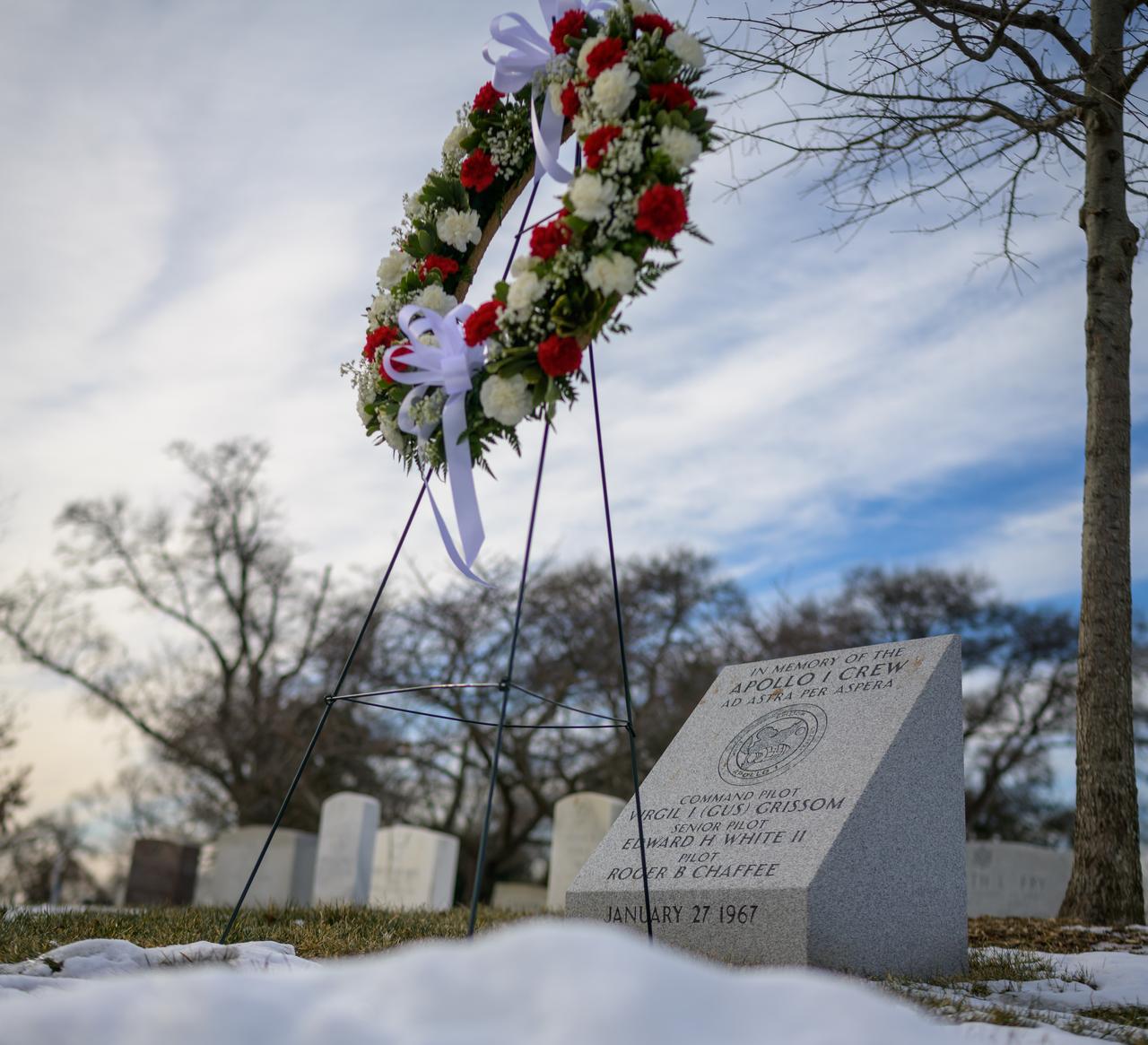

A wreath is left at the Apollo 1 monument as part of NASA's Day of Remembrance, Thursday, Jan. 23, 2025, at Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
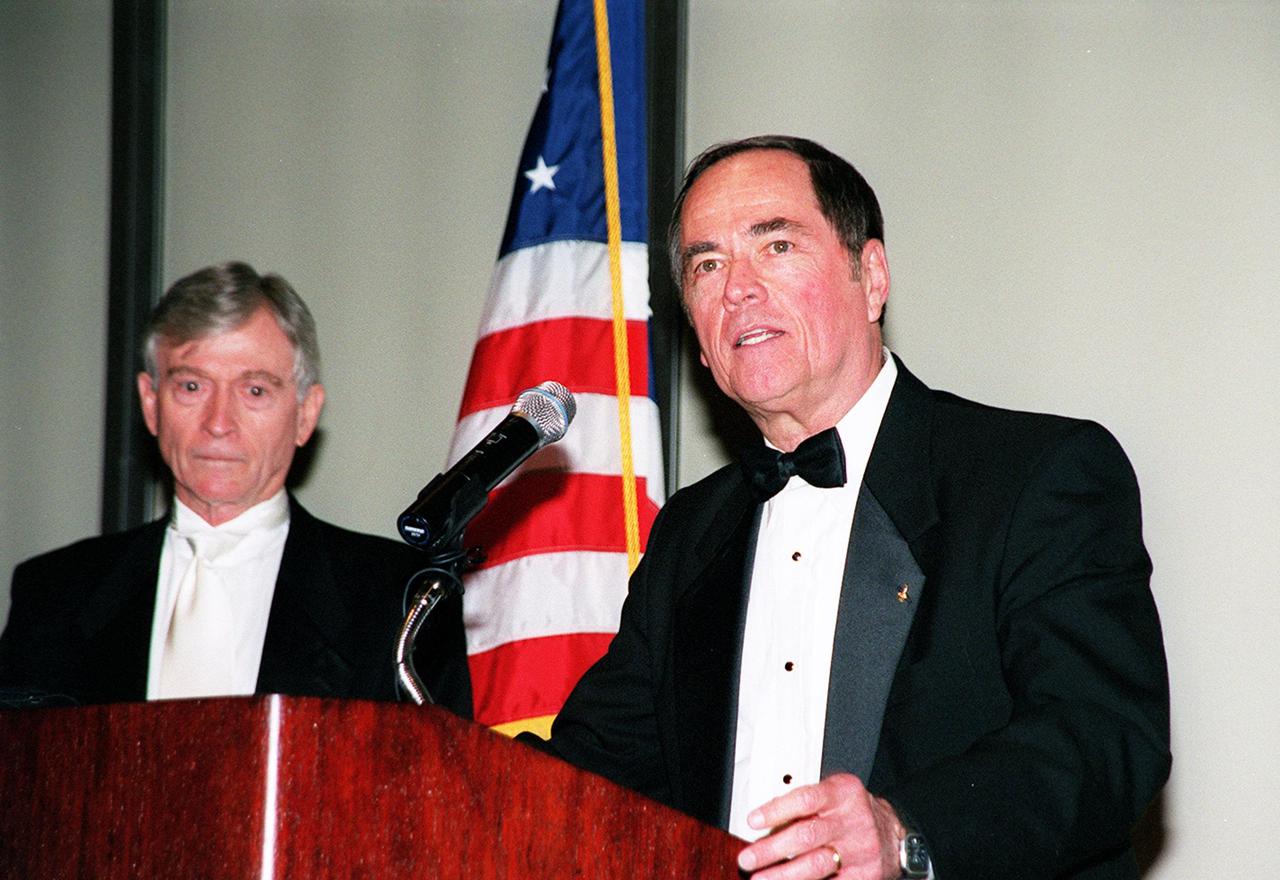

The 12th annual Dr. Kurt H. Debus Award Dinner included as speakers the first Shuttle crew from STS-1, John Young (left) and Robert Crippen (right). At the dinner, Center Director Roy Bridges received the 2001 Dr. Kurt H. Debus Award honoring his progressive, visionary leadership and contributions to space technology and exploration. The Florida Committee of the National Space Club presented the award. The Debus Award was first given in 1980. Created to recognize significant achievements and contributions made in Florida to the American aerospace effort, the award is named for the KSC’s first Director, Dr. Kurt H. Debus
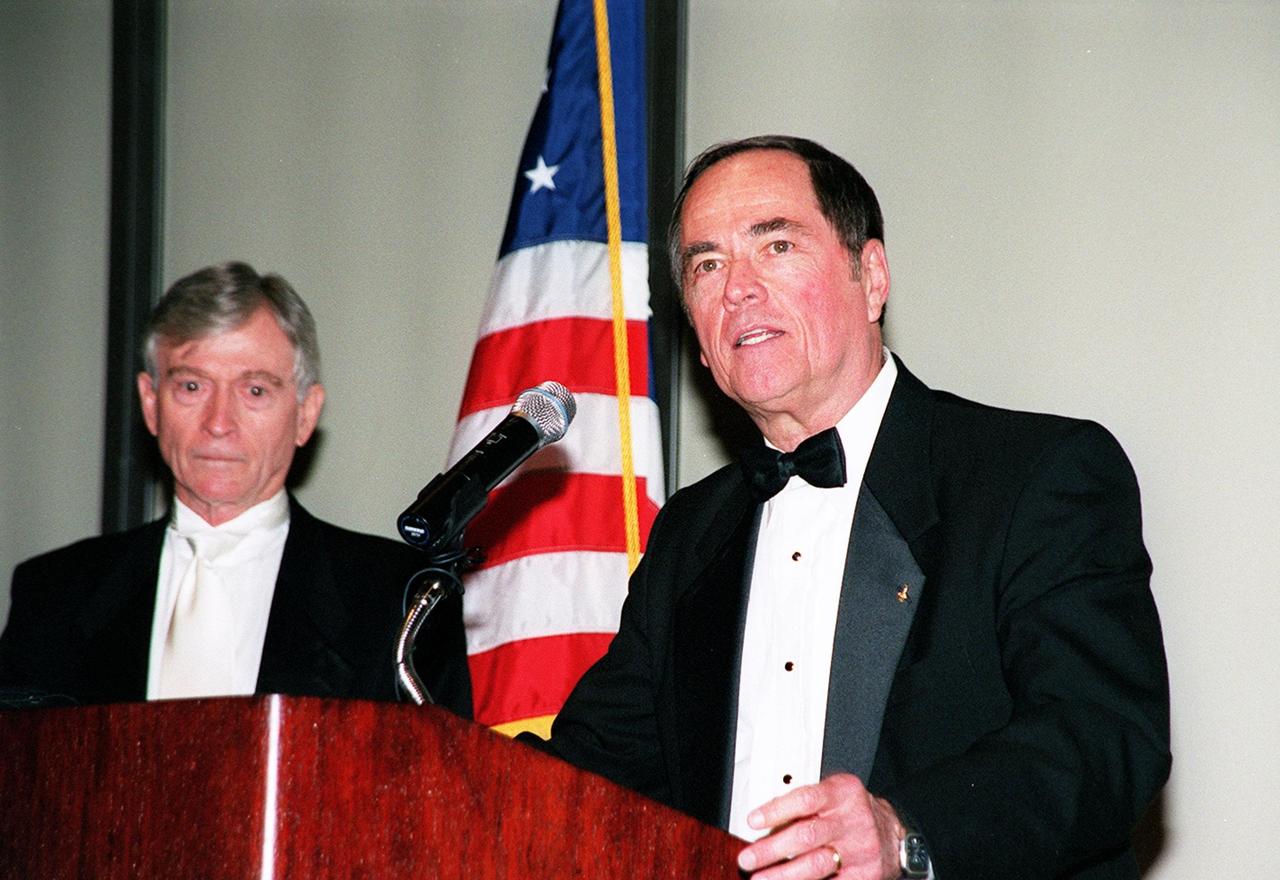

The 12th annual Dr. Kurt H. Debus Award Dinner included as speakers the first Shuttle crew from STS-1, John Young (left) and Robert Crippen (right). At the dinner, Center Director Roy Bridges received the 2001 Dr. Kurt H. Debus Award honoring his progressive, visionary leadership and contributions to space technology and exploration. The Florida Committee of the National Space Club presented the award. The Debus Award was first given in 1980. Created to recognize significant achievements and contributions made in Florida to the American aerospace effort, the award is named for the KSC’s first Director, Dr. Kurt H. Debus
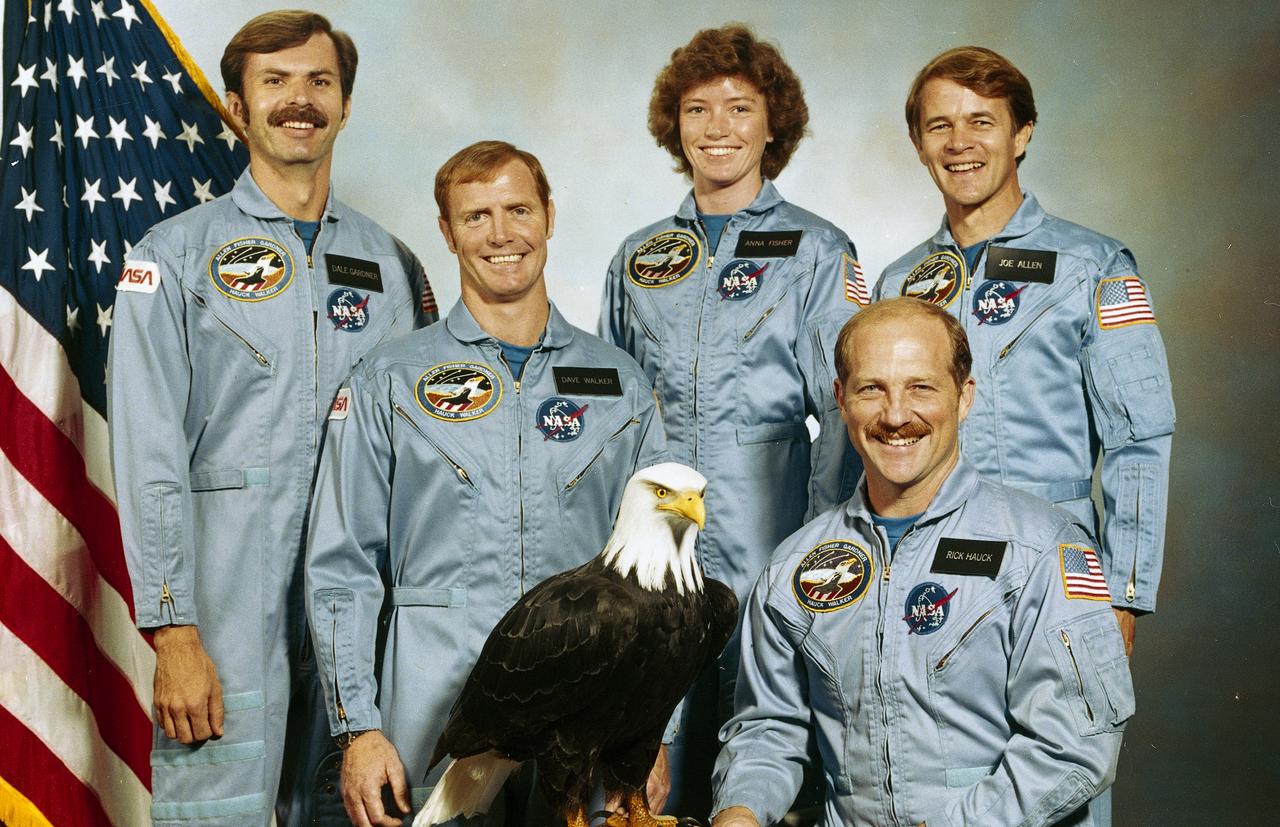

The crew assigned to the STS-51A mission included Frederick H. Hauck, commander,who is seated to the right. Standing, left to right, are Dale A. Gardner, mission specialist; David M. Walker, pilot; and mission specialists Anna L. Fisher, and Joseph P. Allen. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on November 8, 1984 at 7:15:00 am (EST), the STS-51A mission deployed the Canadian communications satellite TELLESAT-H (ANIK), and the defense communications satellite SYCOM IV-1 (also known as LEASAT-1). In addition, 2 malfunctioning satellites were retrieved: the PALAPA-B2 and the WESTAR-VI.

S81-29618 (6 April 1981) --- STS-1 prime and backup astronaut crew members look at visuals during a coordinated teleconference with engineers. Seated at the table in a briefing room at NASA's Johnson Space Center are, clockwise from the left, George W.S. Abbey, Director of Flight Operations, John W. Young, Robert L. Crippen, Joe H. Engle and Richard H. Truly. Young and Crippen are prime crewmen preparing to man the Columbia later this week for the flight of STS-1. Rockwell International engineers in California as well as JSC engineers participated in this telecon. Photo credit: NASA
The photograph shows the completed Saturn 1 S-1 stage (booster) during the checkout in the Marshall Space Flight Center, building 4705, January 23, 1961. The Saturn I S-I stage had eight H-1 engines clustered, using liquid oxygen/kerosene-1 (LOX/RP-1) propellants capable of producing a total of 1,500,000 pounds of thrust.

The completely assembled Saturn 1 S-1 stage is being ready for checkout in the Marshall Space Flight Center, building 4705, January 18, 1961. The Saturn I S-I stage had eight H-1 engines clustered, using liquid oxygen/kerosene-1 (LOX/RP-1) propellants capable of producing a total of 1,500,000 pounds of thrust.
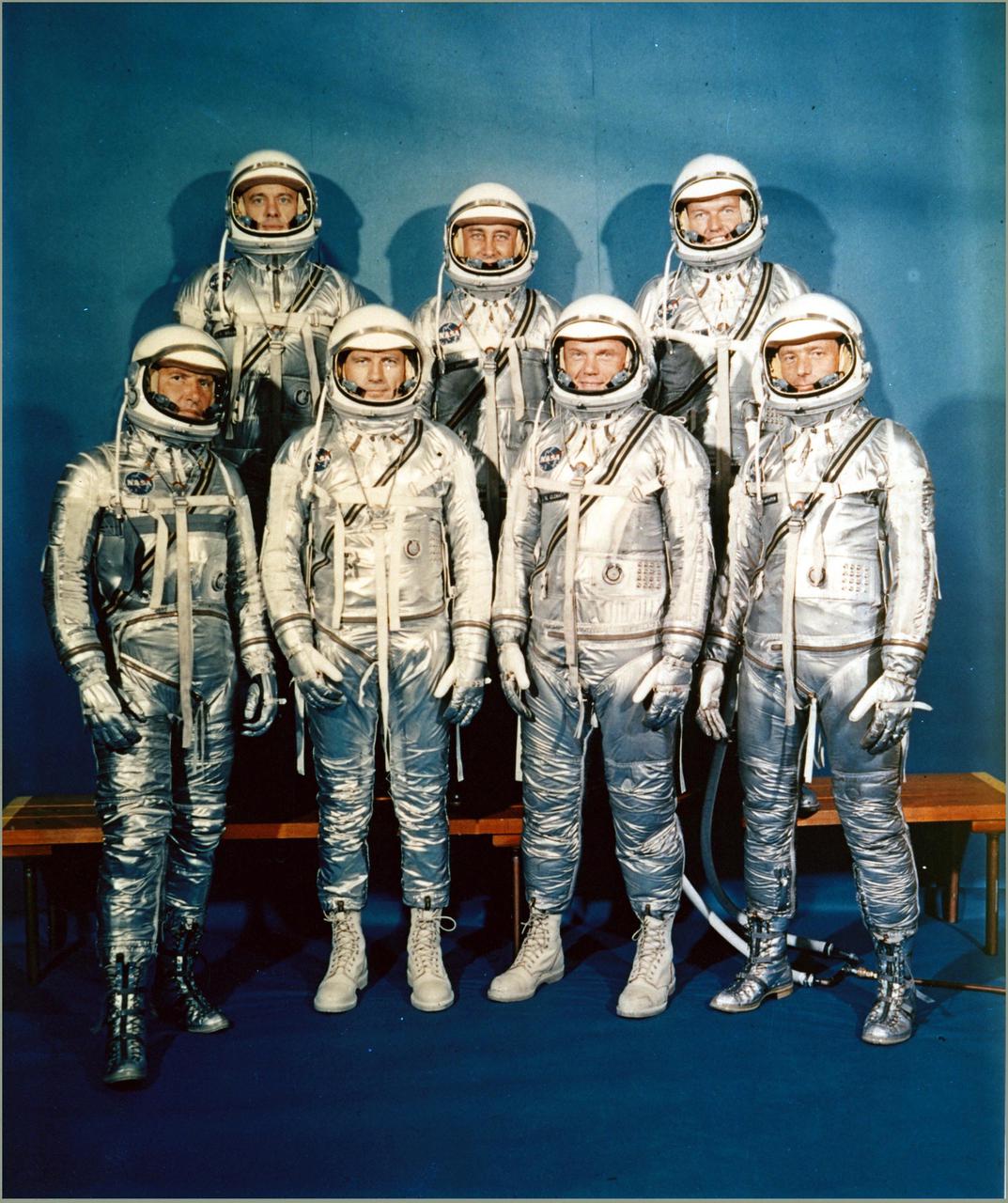

MANNED SPACECRAFT CENTER, HOUSTON, TX. -- FIRST ASTRONAUT TEAM -- Project Mercury Astronauts, whose selection was announced on April 9, 1959, only six months after the National Aeronautics and Space Administration was formally established on Oct. 1, 1958, included: front row, left to right, Walter H. Schirra Jr., Donald K. Slayton, John H. Glenn Jr., and Scott Carpenter back row, Alan B. Shepard Jr., Virgil I. 'Gus' Grissom, and L. Gordon Cooper.

The STS-36 crew portrait features 5 astronauts who served in the 6th Department of Defense (DOD) mission. Posed near the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery are (left to right) Pierre J. Thuot, mission specialist 3; John H. Caster, pilot; John H. Creighton, commander; Richard M. (Mike) Mullane, mission specialist 1; and David. C. Hilmers, mission specialist 2. The crew launched aboard Atlantis on February 28, 1990 at 2:50:22am (EST).
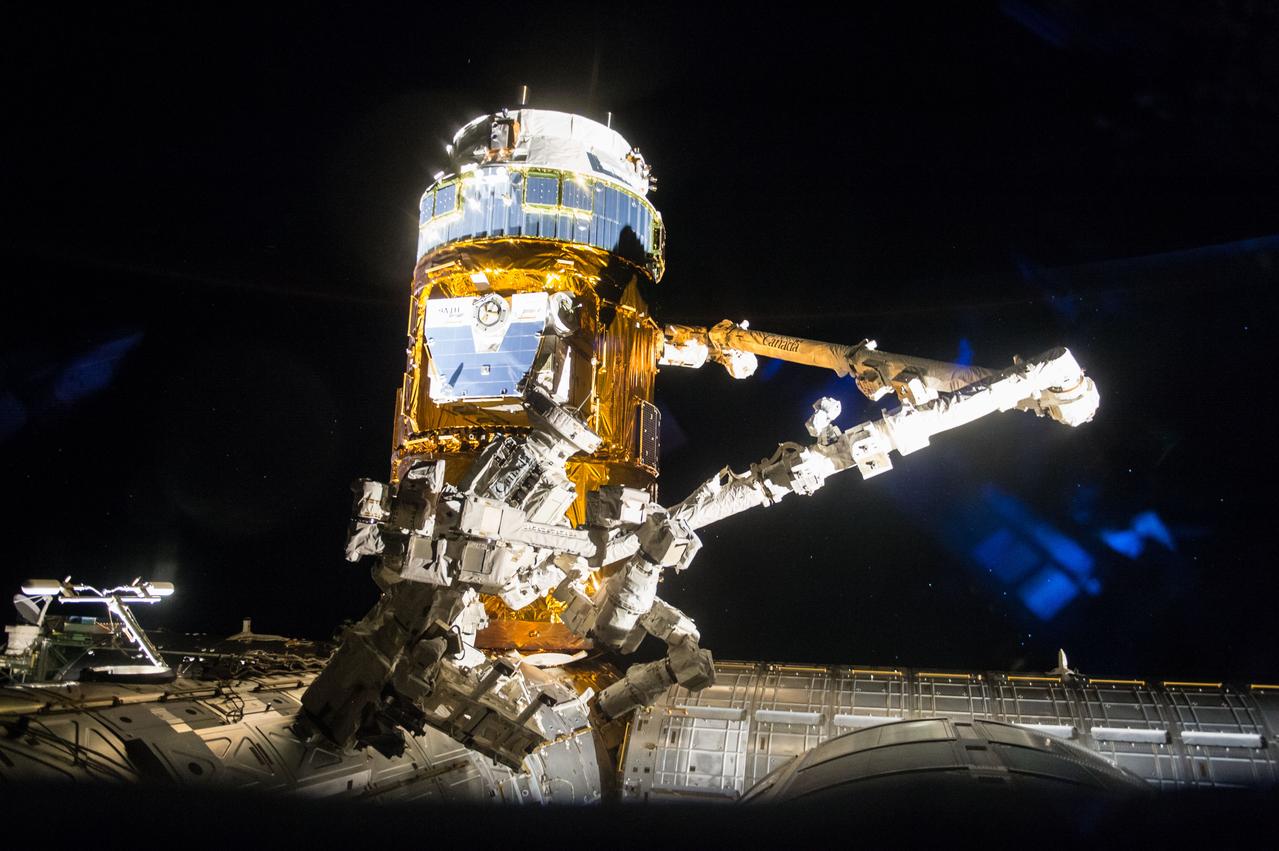

iss050e036114 (1/27/2017) --- A view of H2 Transfer Vehicle (HTV) 6 at dawn. HTV-6, is the sixth flight of the H-II Transfer Vehicle, an unmanned cargo spacecraft launched to resupply the International Space Station. It was launched at 13:26:47 UTC on 9 December 2016 aboard H-IIB launch vehicle from Tanegashima Space Center.
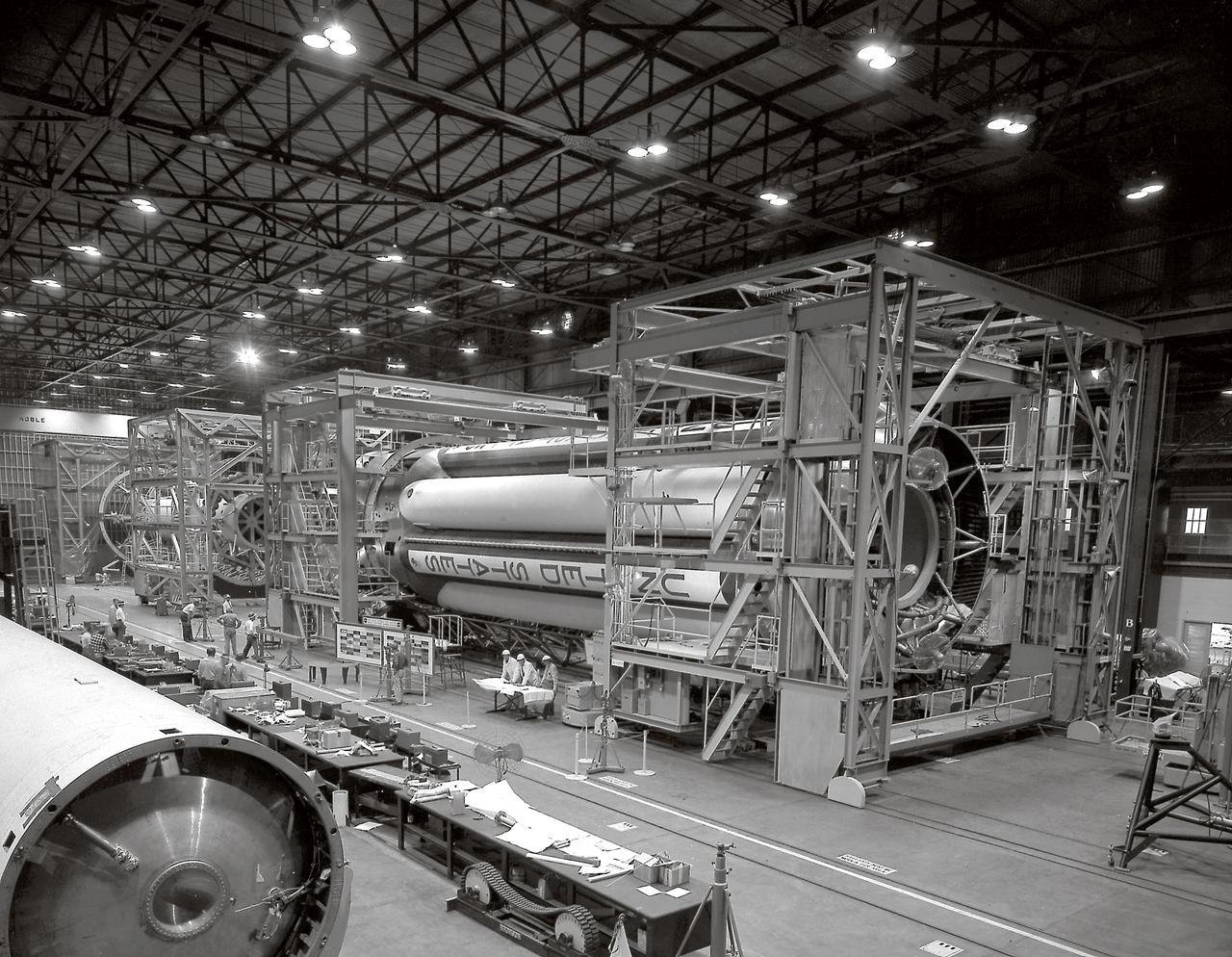

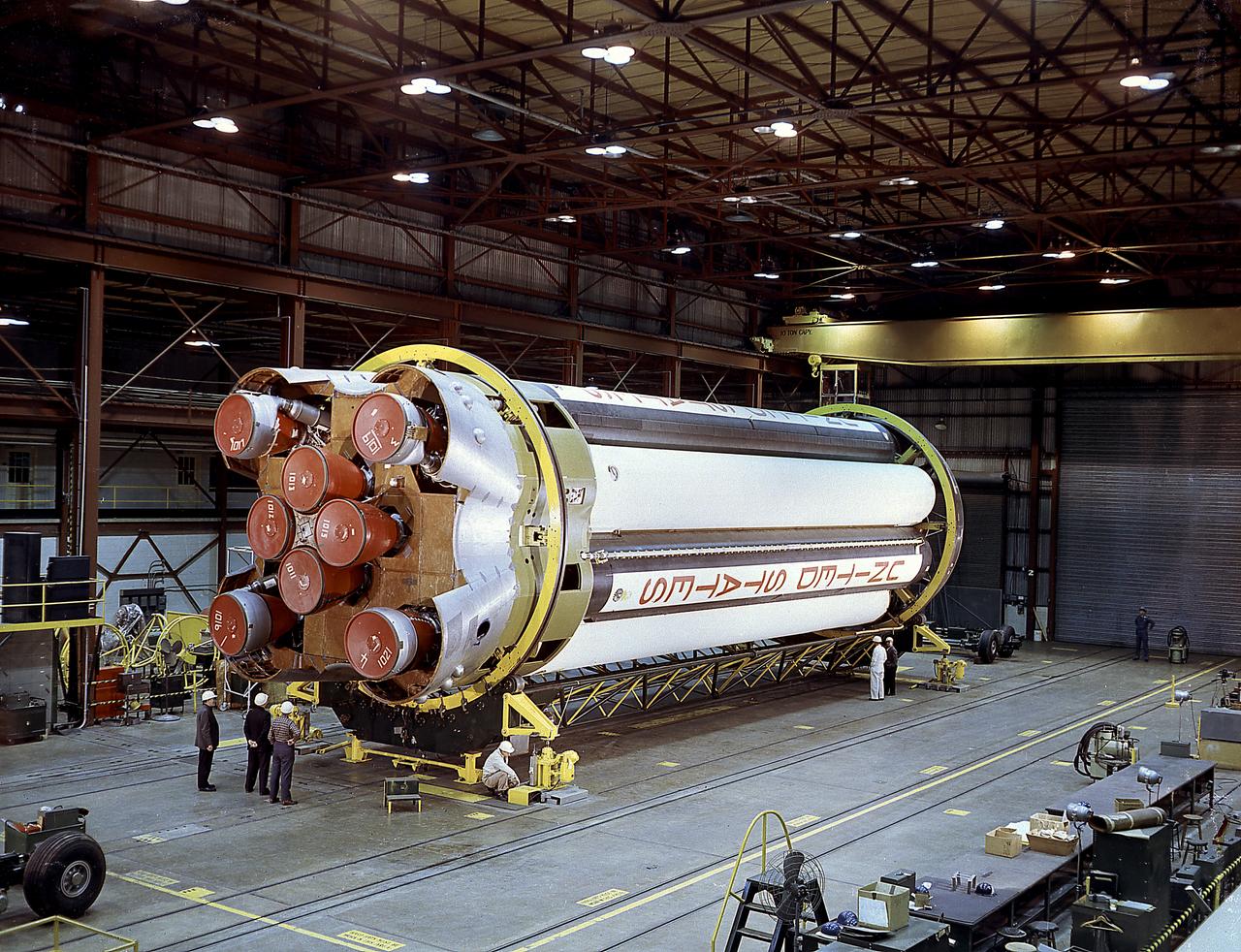
The S-I stages for the Saturn I (SA-1 at right and SA-2 at left) are being assembled at the Marshall Space Flight Center, building 4705. The Saturn I S-I stage had eight H-1 engines clustered, using liquid oxygen/kerosene-1 (LOX/RP-1) propellants capable of producing a total of 1,500,000 pounds of thrust.
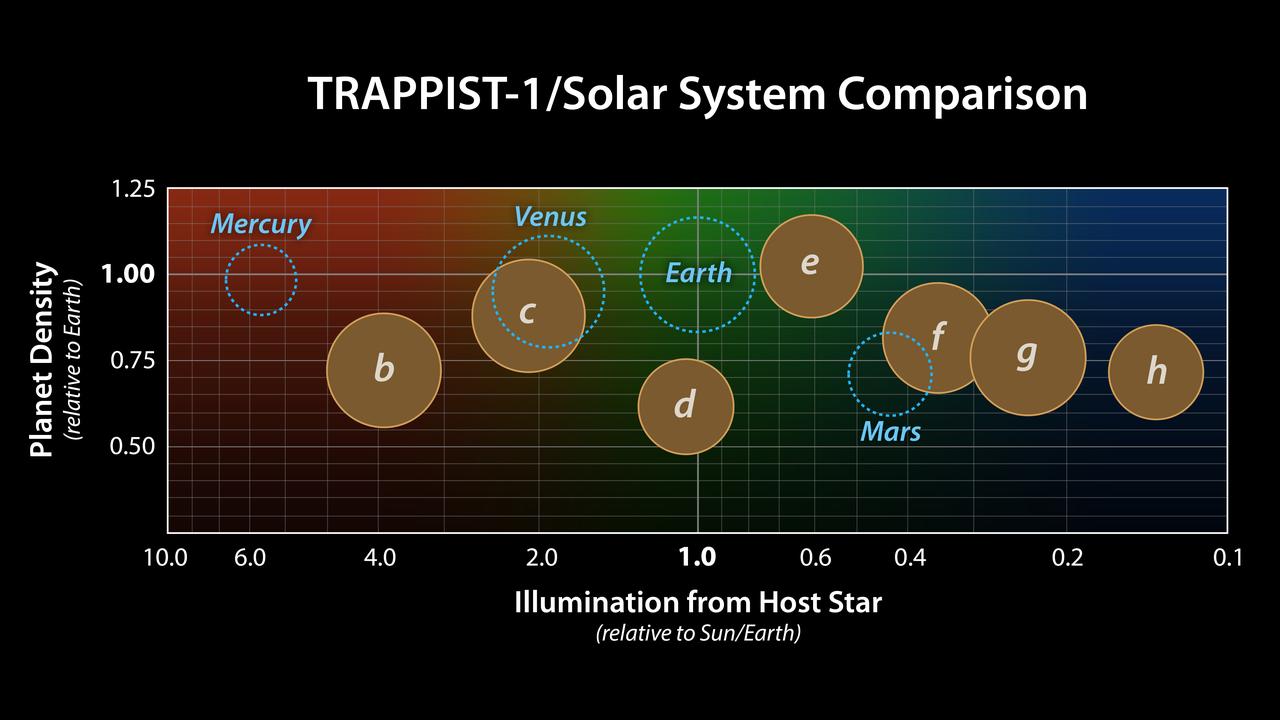
This graph presents known properties of the seven TRAPPIST-1 exoplanets (labeled b through h), showing how they stack up to the inner rocky worlds in our own solar system. The horizontal axis shows the level of illumination that each planet receives from its host star. TRAPPIST-1 is a mere 9 percent the mass of our Sun, and its temperature is much cooler. But because the TRAPPIST-1 planets orbit so closely to their star, they receive comparable levels of light and heat to Earth and its neighboring planets. The vertical axis shows the densities of the planets. Density, calculated based on a planet's mass and volume, is the first important step in understanding a planet's composition. The plot shows that the TRAPPIST-1 planet densities range from being similar to Earth and Venus at the upper end, down to values comparable to Mars at the lower end. The relative sizes of the planets are indicated by the circles. The masses and densities of the TRAPPIST-1 planets were determined by careful measurements of slight variations in the timings of their orbits using extensive observations made by NASA's Spitzer and Kepler space telescopes, in combination with data from Hubble and a number of ground-based telescopes. These measurements are the most precise to date for any system of exoplanets. By comparing these measurements with theoretical models of how planets form and evolve, researchers have determined that they are all rocky in overall composition. Estimates suggest the lower-density planets could have large quantities of water -- as much as 5 percent by mass for TRAPPIST-1d. Earth, in comparison, has only about 0.02 percent of its mass in the form of water. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22095
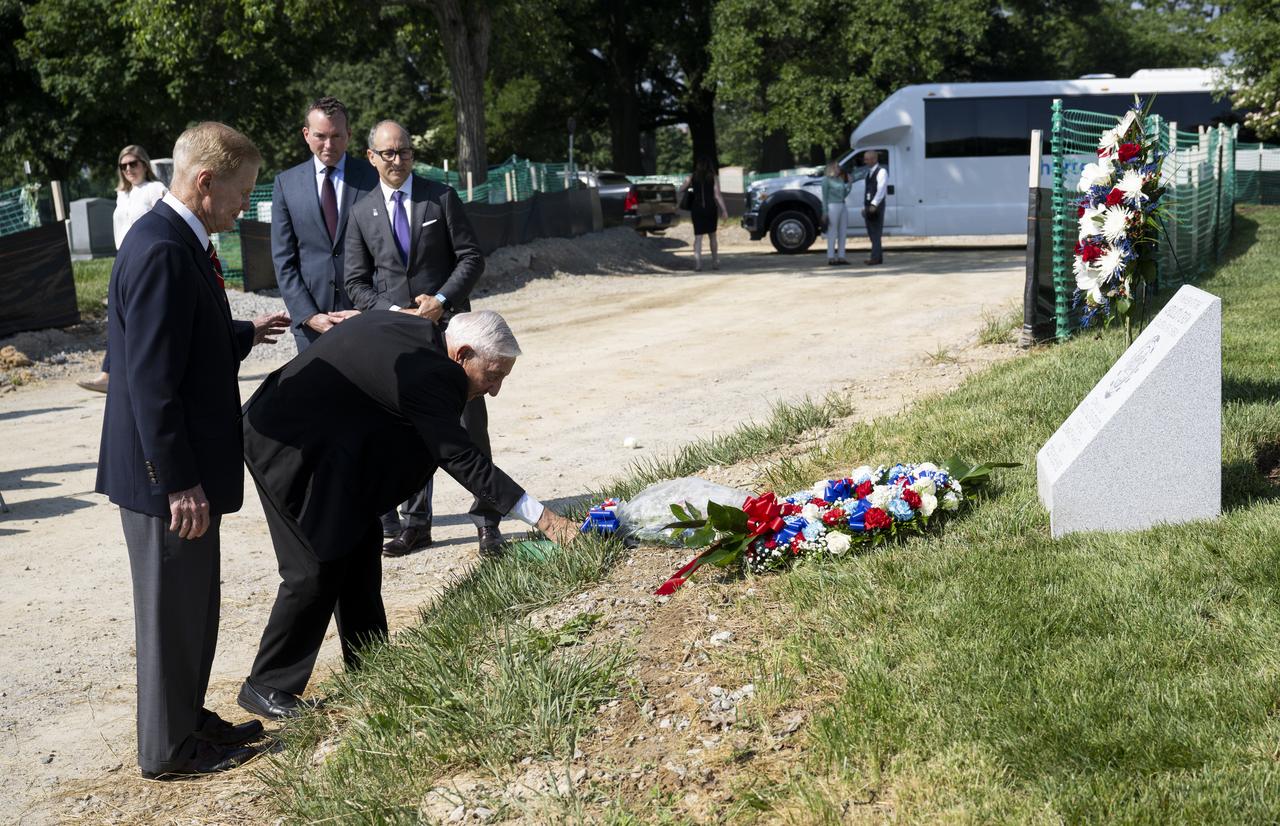

Lowell Grissom, brother of Apollo 1 astronaut Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, is joined by NASA Administrator Bill Nelson as he places flowers at the Apollo 1 monument during its dedication at Arlington National Cemetery, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
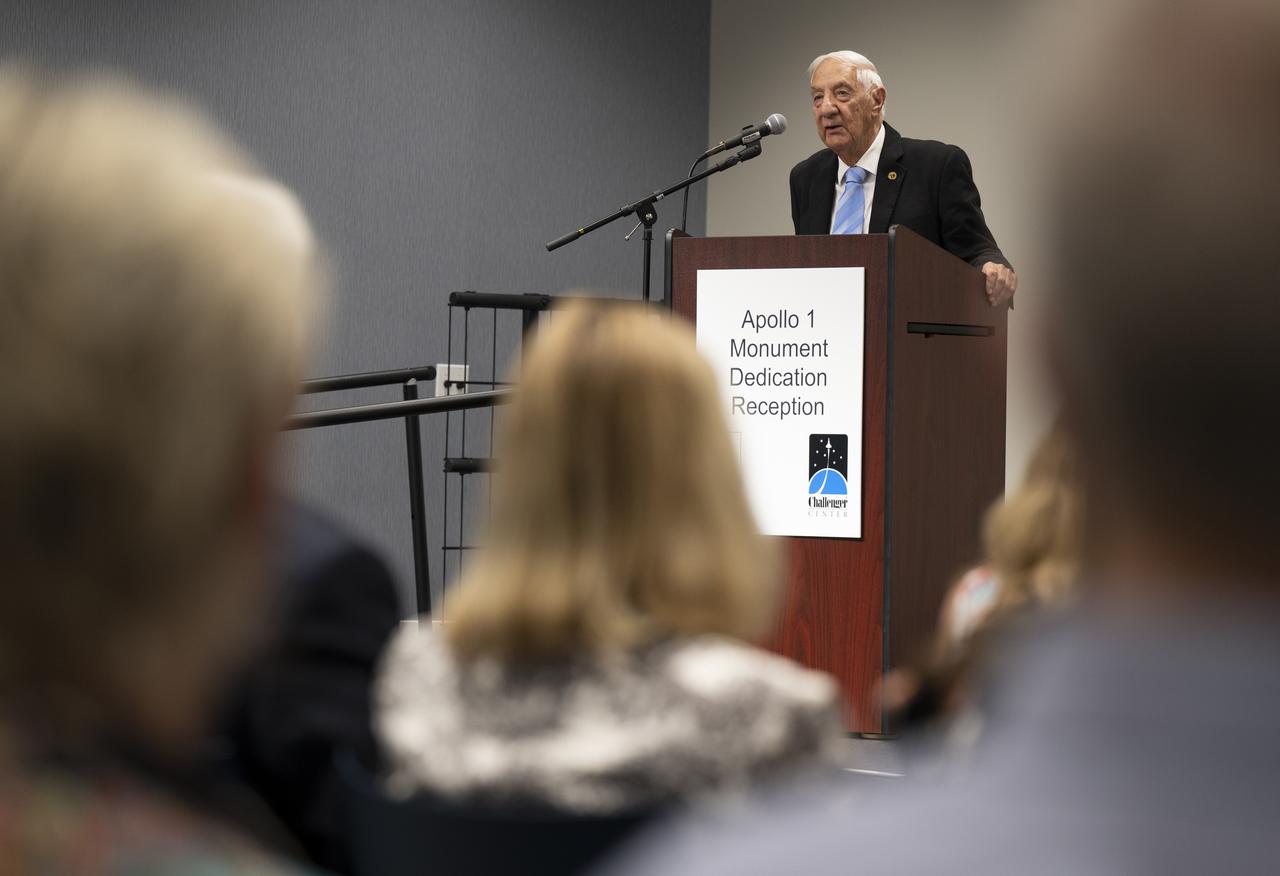

Lowell Grissom, brother of Apollo 1 astronaut Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, delivers remarks at a reception following the dedication of the Apollo 1 monument, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in the Reception Hall of the Military Women’s Memorial at Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - John H. Young is the commander for the STS-1 mission of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia. The STS-1 mission, known as a shuttle systems test flight, will seek to demonstrate safe launch into orbit and safe return of the orbiter and crew and verify the combined performance of the entire shuttle vehicle -- orbiter, solid rocket boosters and external tank. STS-1 will be launched from Pad A at the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 no earlier than March 1981.
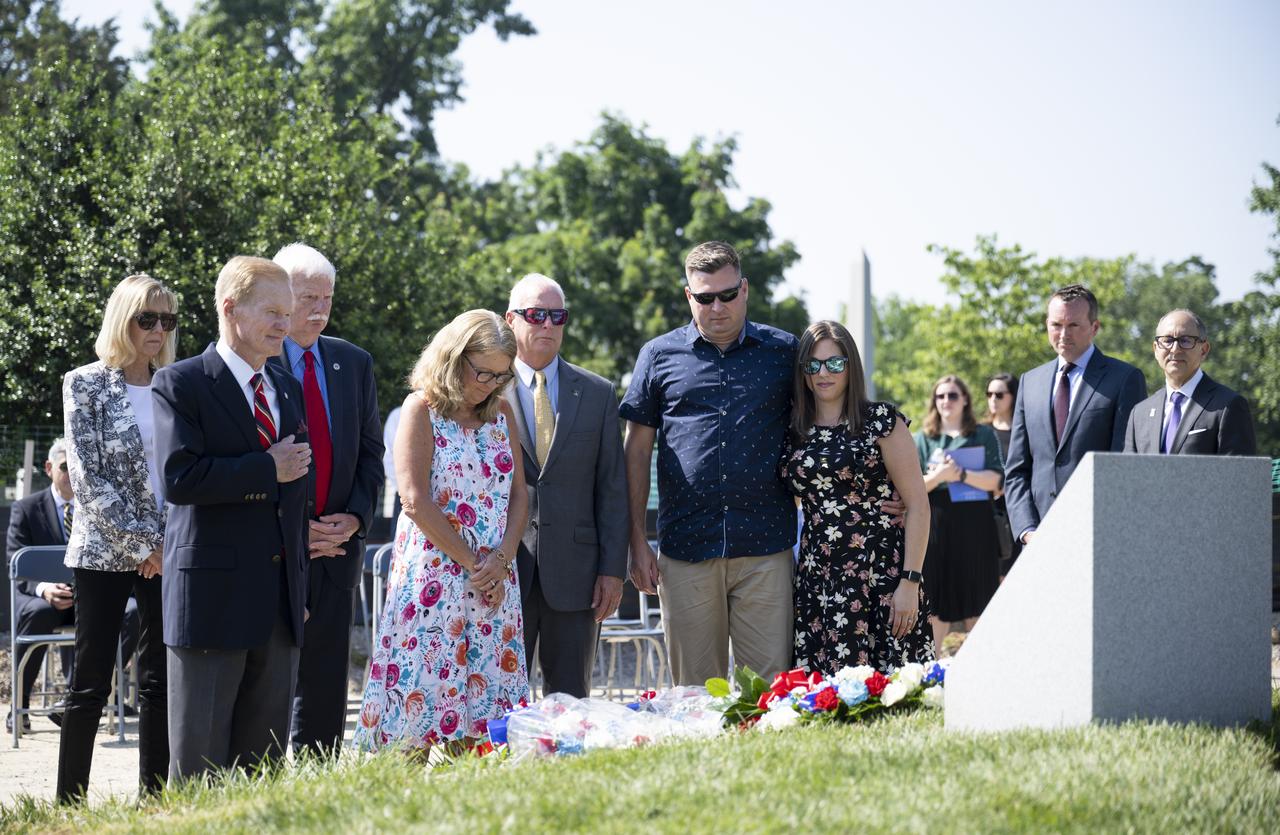

Family members of Apollo 1 astronaut Roger B. Chaffee are joined by NASA Administrator Bill Nelson as they place flowers at the Apollo 1 Monument during its dedication at Arlington National Cemetery, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Sheryl Chaffee, daughter of Apollo 1 astronaut Roger B. Chaffee, delivers remarks at a reception following the dedication of the Apollo 1 monument, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in the Reception Hall of the Military Women’s Memorial at Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
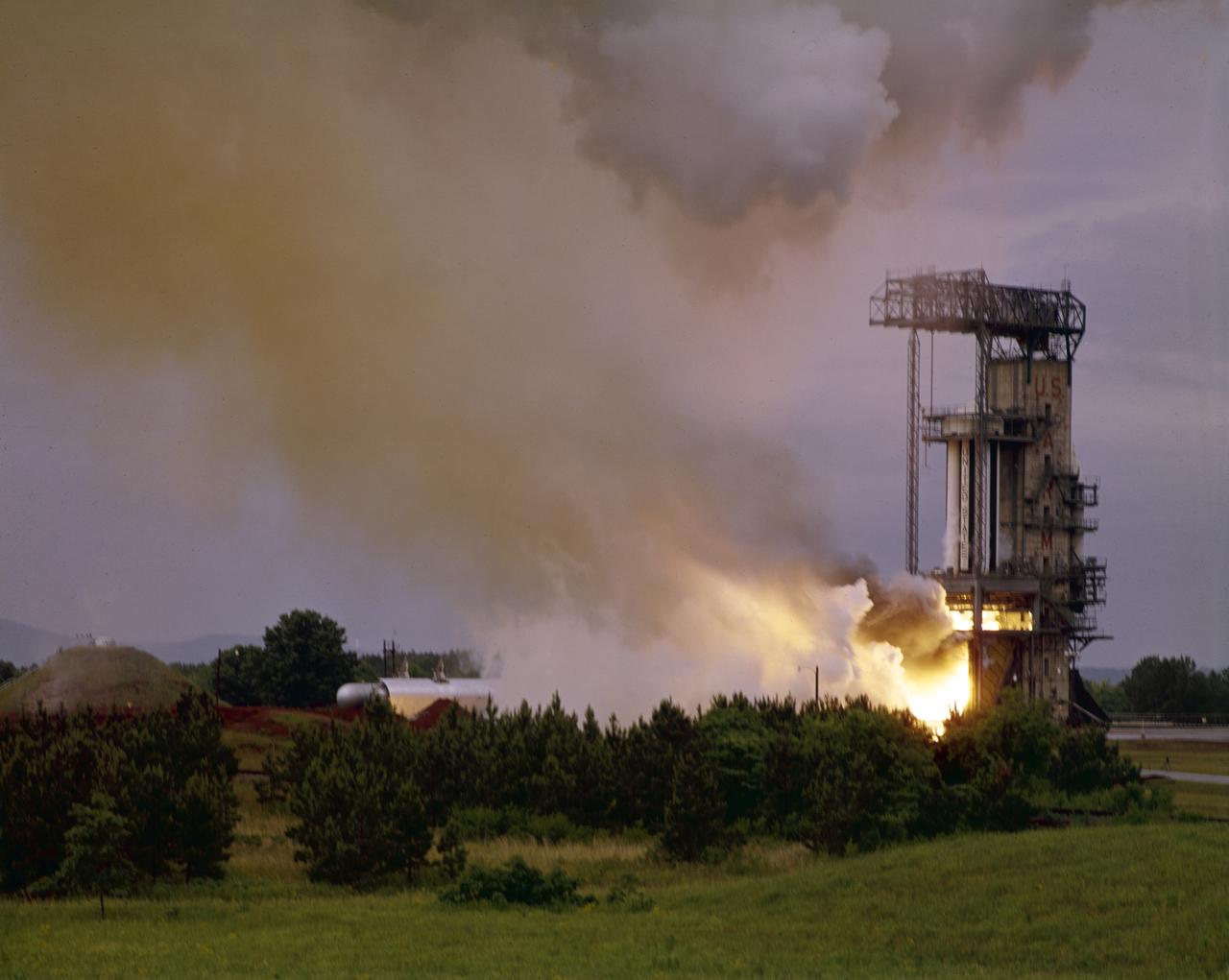

Pictured is one of the earliest testing of the Saturn I S-I (first) stage, with a cluster of eight H-1 engines, at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). It was a part of the test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept. MSFC was responsible for designing and development the Saturn launch vehicles.
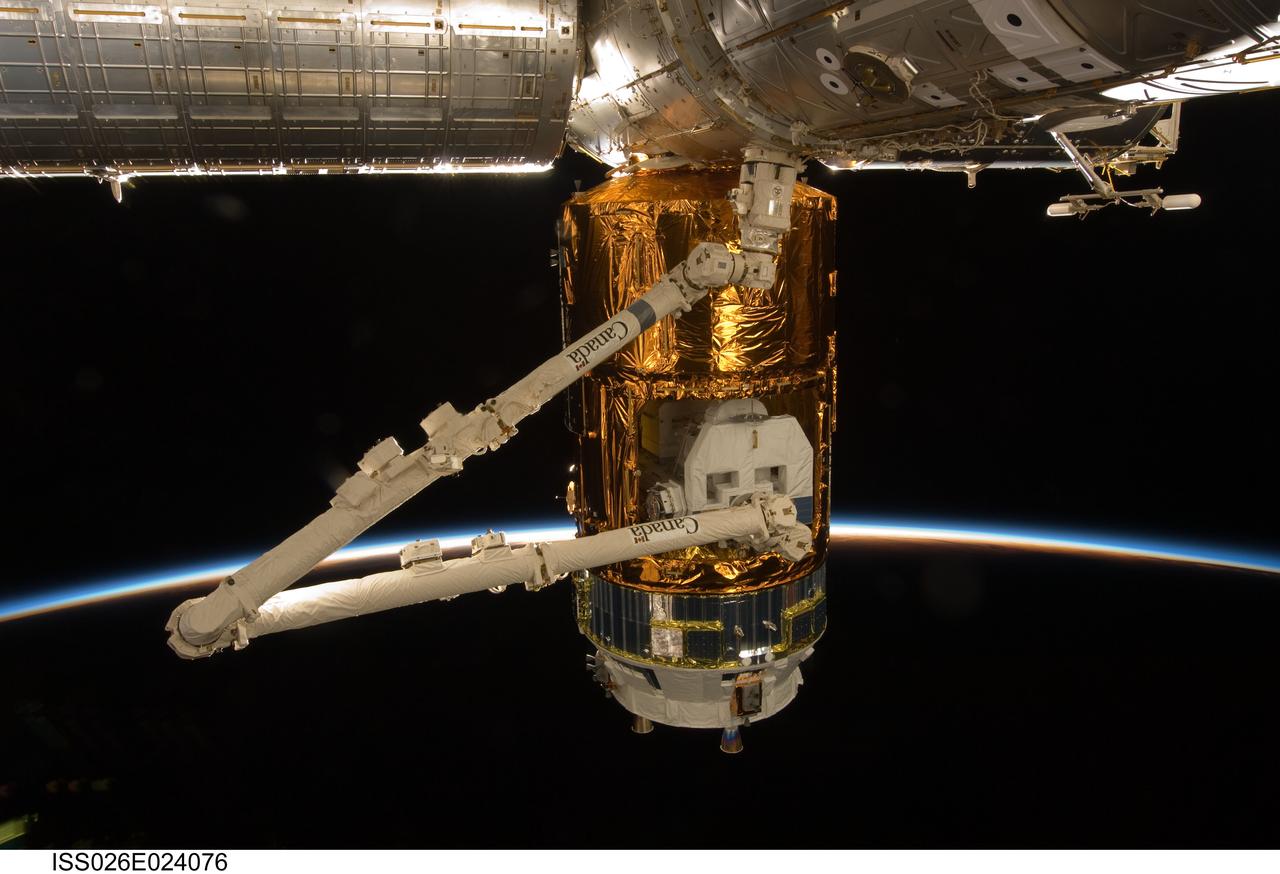

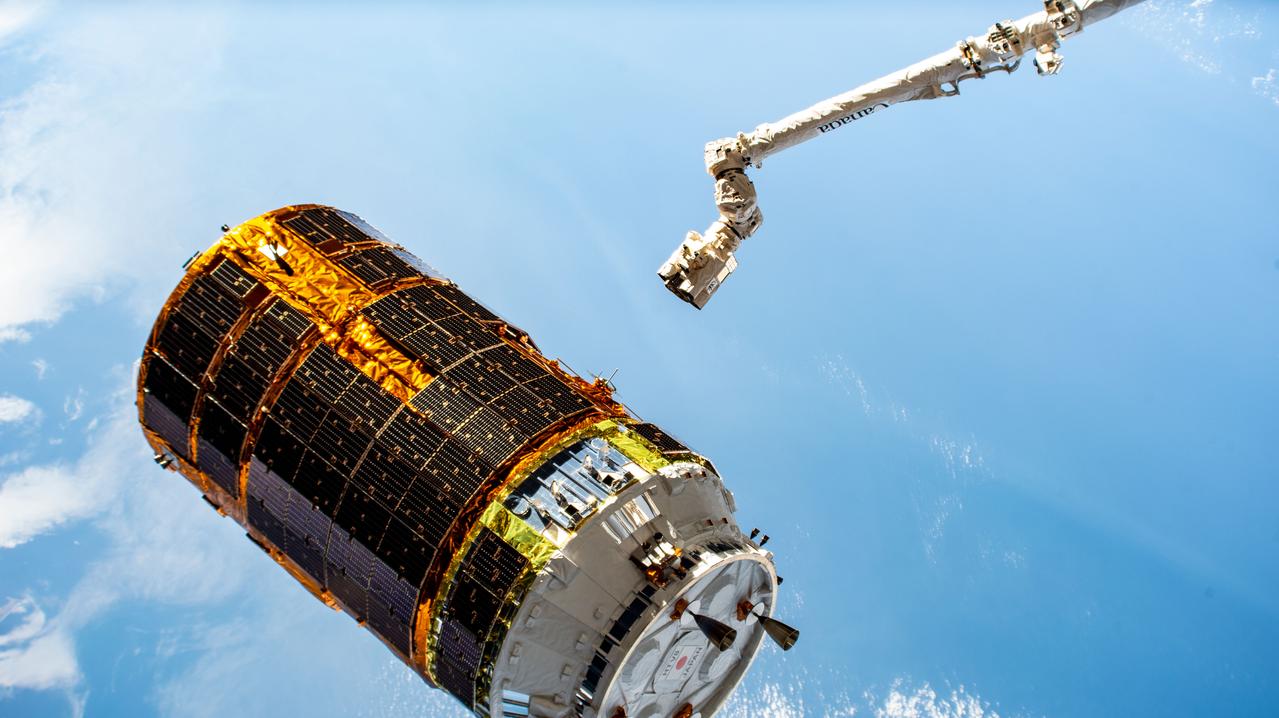
ISS026-E-024076 (1 Feb. 2011) --- The Japanese Kounotori2 H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV2), docked to the Earth-facing port of the Harmony node and in the grapple of the Candarm2, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 26 crew member on the International Space Station. The thin line of Earth's atmosphere and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene.
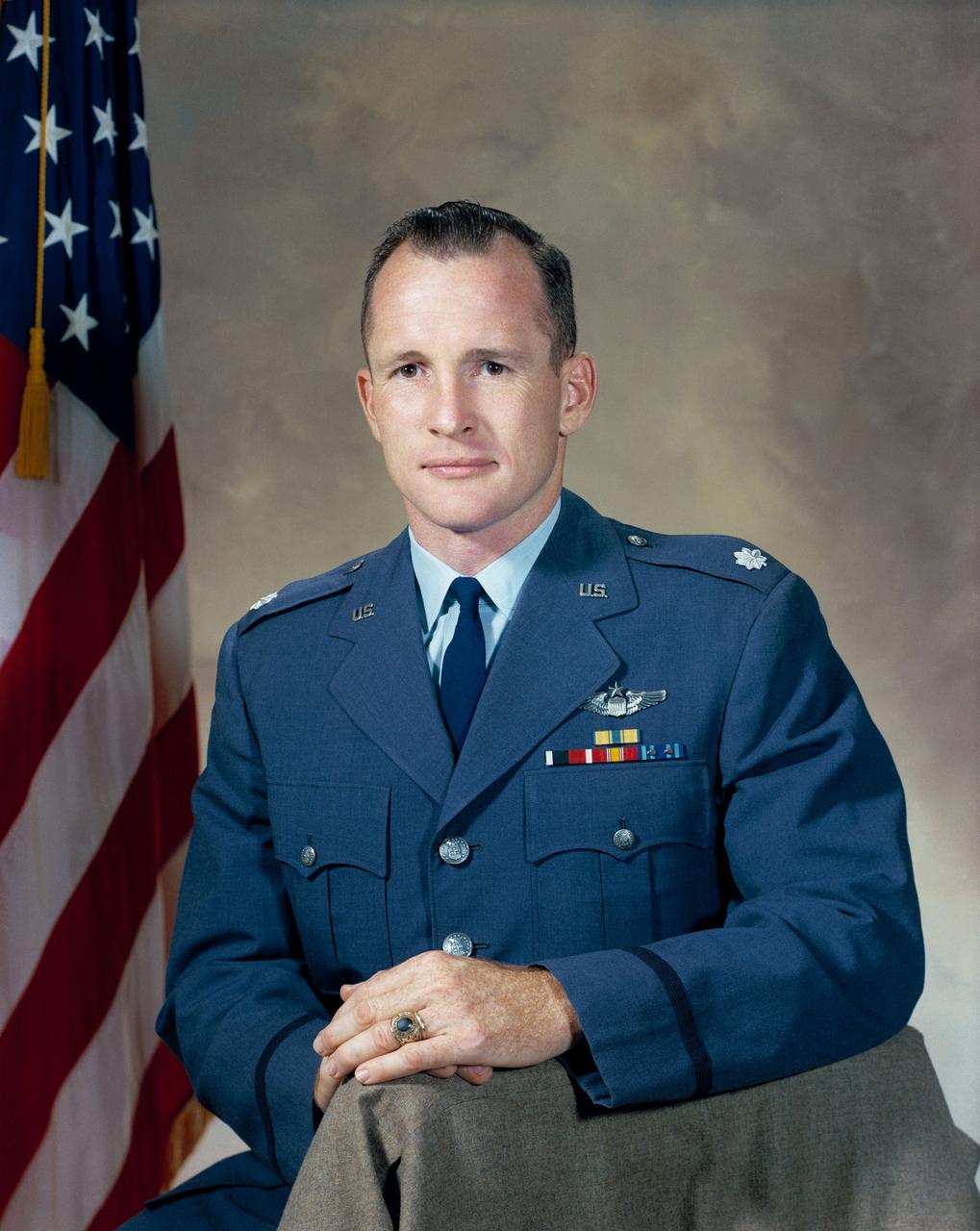

S66-35219 (1966) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II (United States Air Force Lieutenant Colonel), Gemini 4 pilot. Editor's Note: Since this portrait was taken astronaut White lost his life on Jan. 27, 1967, in the Apollo 1/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy, KSC, Florida.

S79-30367/69: Exterior views of 747 Shuttle Aircraft. S79-30360/66: ASCAN Don Williams during H Reflex Studies and Hamilton-Standard Tool Belt and Suit Cooling System Tests. 1. AIRCRAFT - 747 2. SHUTTLE - TESTS. S79-30360 thru S79-30369
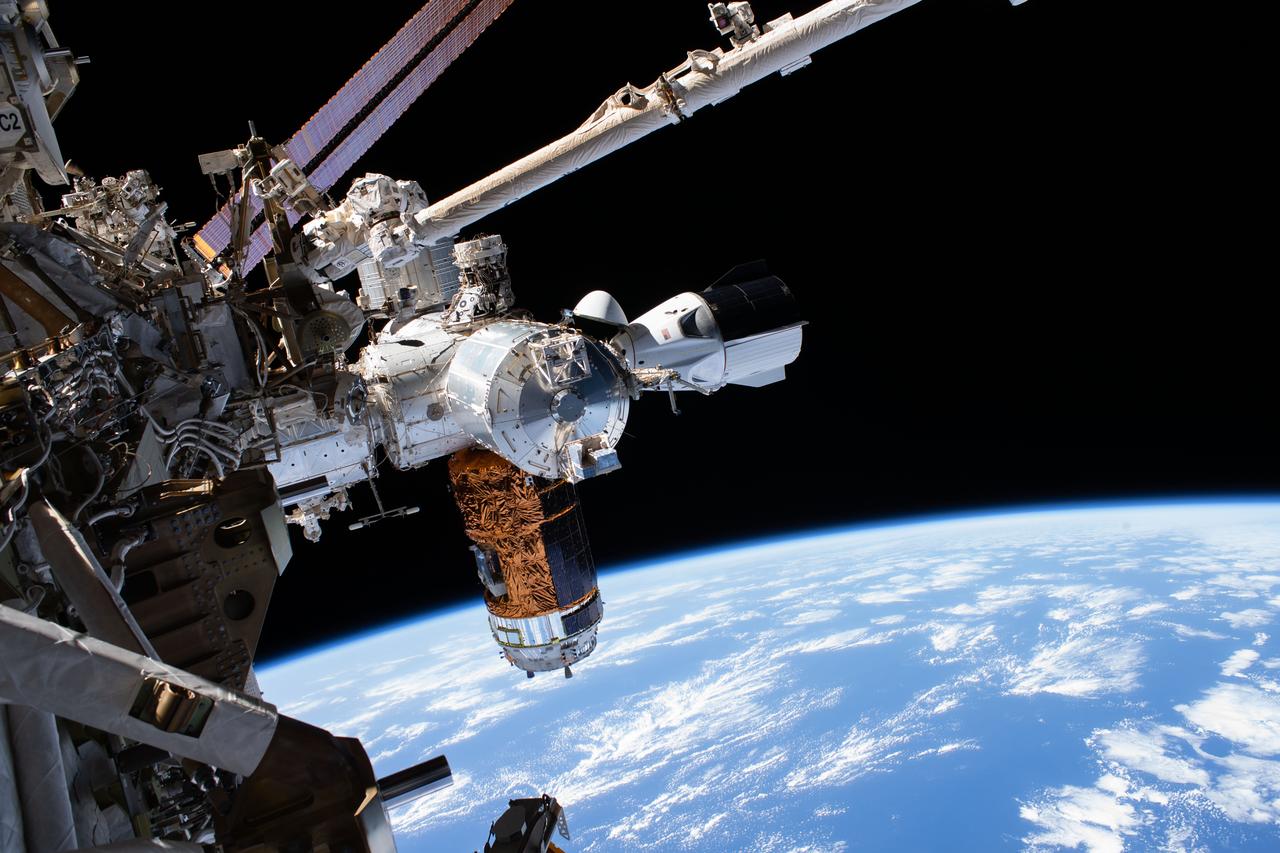

iss063e034054 (July 1, 2020) --- The SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Japanese H-II Transfer Vehicle-9 resupply ship and Europe's Columbus laboratory module figure prominently in this photograph taken during a spacewalk with astronauts Bob Behnken and Chris Cassidy. All three are attached to the U.S. Harmony module with the International Docking Adapter on top.

S79-30367/69: Exterior views of 747 Shuttle Aircraft. S79-30360/66: ASCAN Don Williams during H Reflex Studies and Hamilton-Standard Tool Belt and Suit Cooling System Tests. 1. AIRCRAFT - 747 2. SHUTTLE - TESTS. S79-30360 thru S79-30369

iss061e026343 (Nov. 1, 2019) --- Japan's H-II Transfer Vehicle-8 (HTV-8) is pictured moments after being released from the grips of the Canadarm2 robotic arm after completing a 34-day cargo mission attached to the International Space Station's Harmony module.
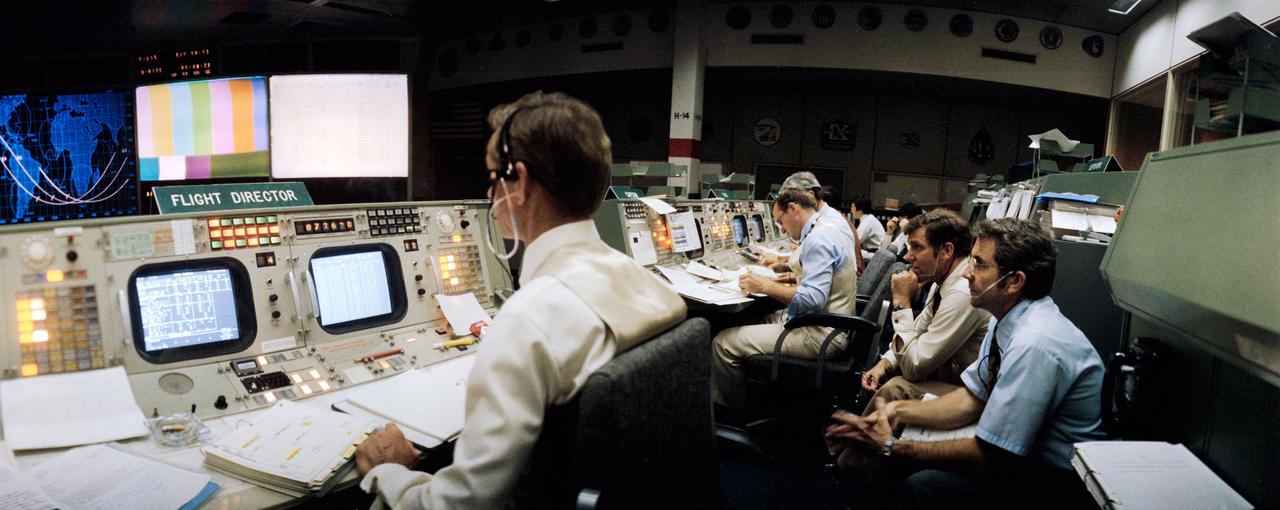

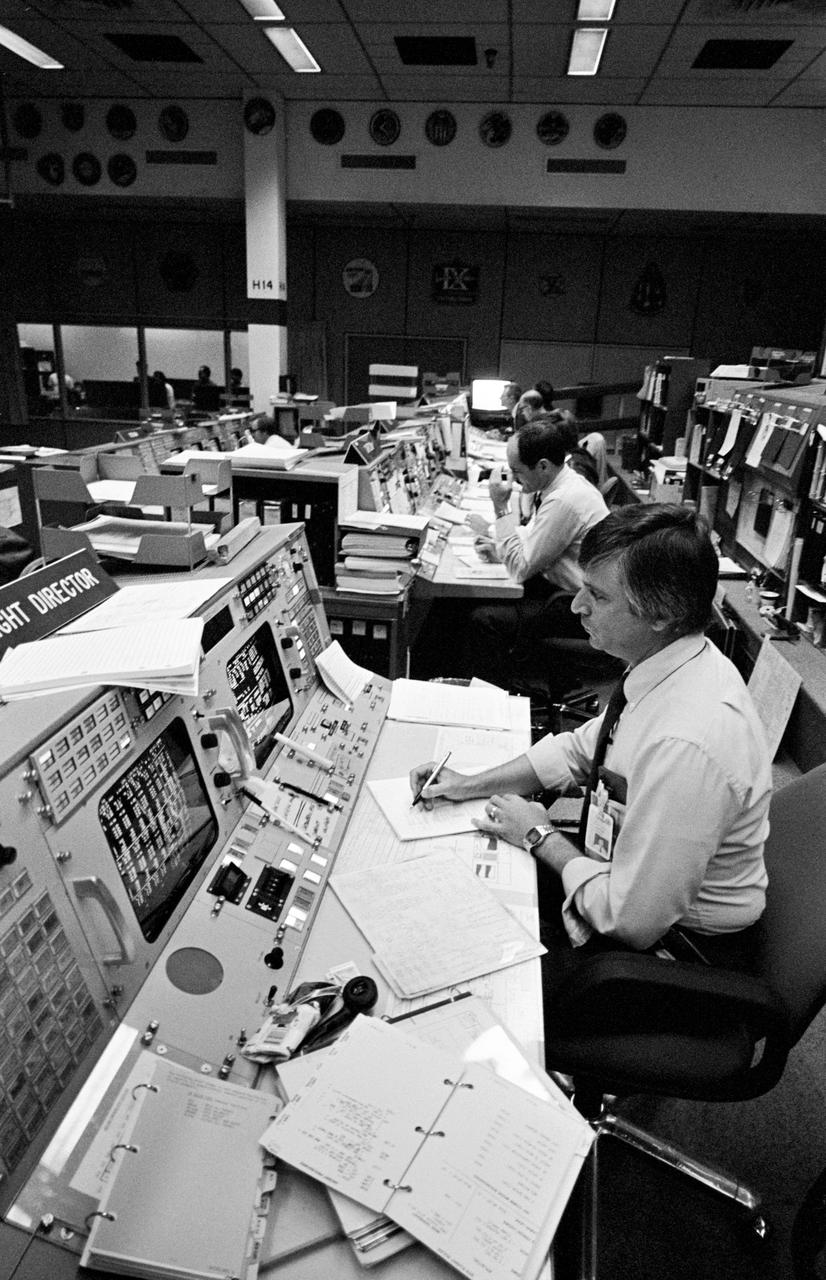
S81-30386 (14 April 1981) --- Flight director Charles R. Lewis, left, studies a chart display on his console?s monitor in the mission operations control room (MOCR) in the Johnson Space Center?s Mission Control Center. The photograph was taken just prior to a TV transmission on day two of STS-1, with a special wide-angle lens. Astronauts Joe H. Engle (second from right) and Richard H. Truly, right, are backup commander and pilot, respectively, for NASA?s first space shuttle orbital test mission. Astronaut James F. Buchli, spacecraft communicator, is at right center. Photo credit: NASA

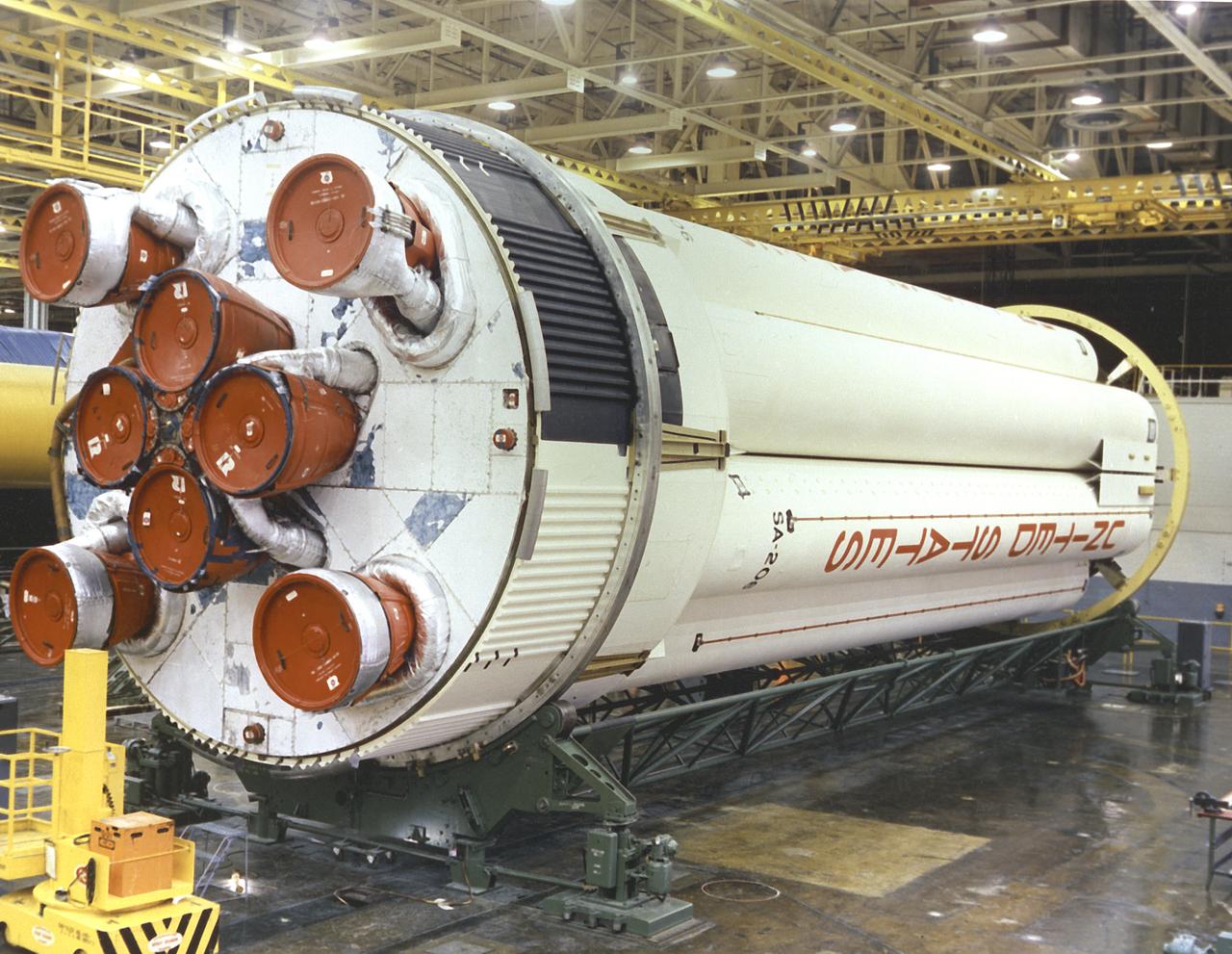
S-IB-1, the first flight version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage (S-IB stage), sat in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Saturn IB static test stand on March 15, 1965. Developed by the MSFC and built by the Chrysler Corporation at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) in New Orleans, Louisiana, the 90,000-pound booster utilized eight H-1 engines to produce a combined thrust of 1,600,000 pounds.
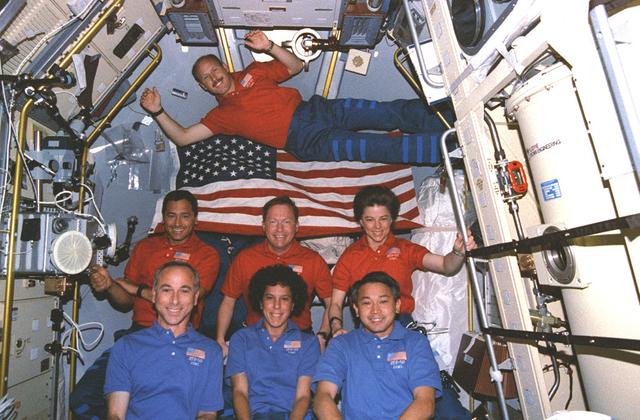

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-50) crewmembers rally around the American flag in the United States Microgravity Laboratory-1 (USML-1). Pictured are (from top, left to right) pilot Kerneth D. Bowersox; payload specialist Lawrence J. Delucas; commander Richard N. Richards; payload commander Bonnie J. Dunbar; mission specialists Carl J. Meade and Ellen S. Baker; and payload specialist Eugene H. Trinh.

The Marshall Space Flight Center's first Saturn I vehicle, SA-1, lifts off from Cape Canaveral, Florida, on October 27, 1961. This early configuration, Saturn I Block I, 162 feet tall and weighing 460 tons, consisted of the eight H-1 engines S-I stage and the dummy second stage (S-IV stage).
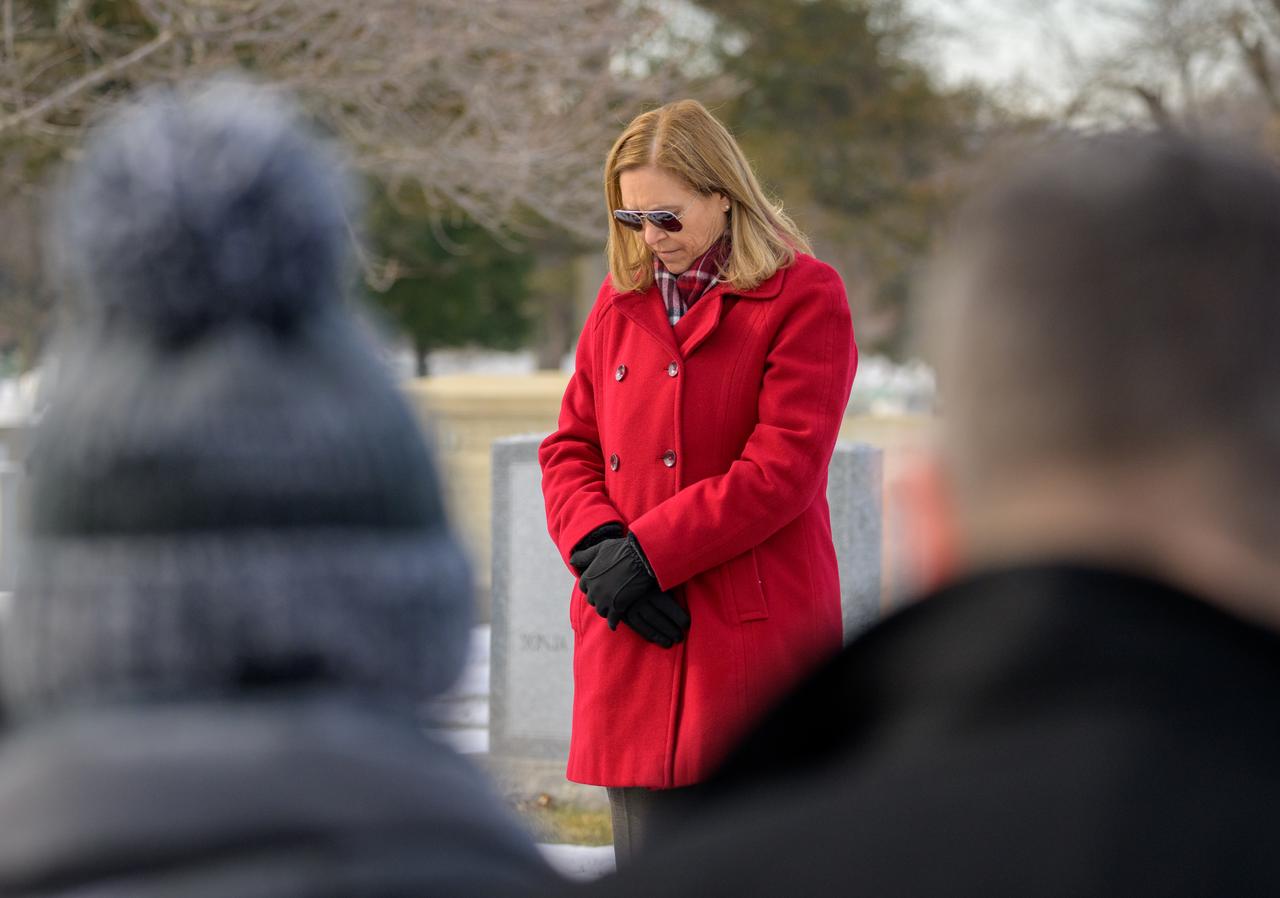

NASA acting Administrator Janet Petro leads guests to a moment of silence at the Apollo 1 monument as part of NASA's Day of Remembrance, Thursday, Jan. 23, 2025, at Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Lance Bush, President and CEO of the Challenge Center, delivers remarks at a reception following the dedication of the Apollo 1 monument, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in the Reception Hall of the Military Women’s Memorial at Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
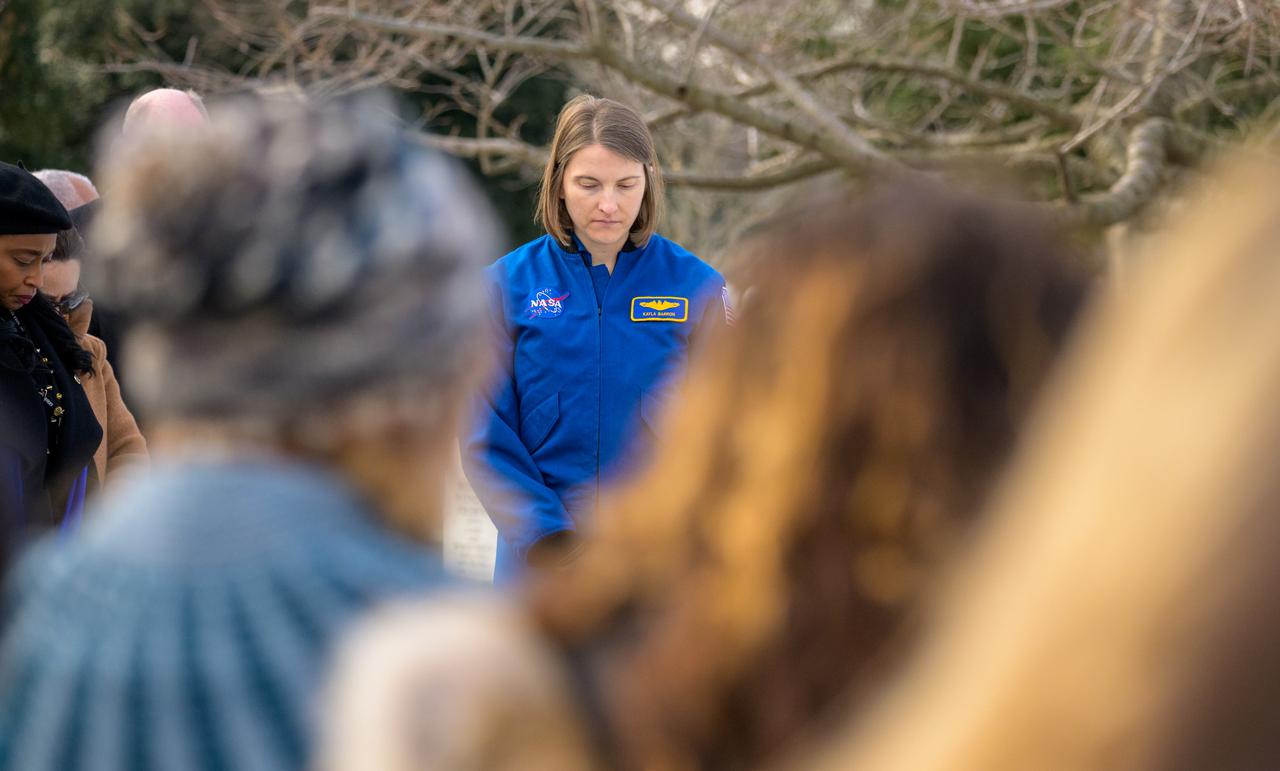

NASA Astronaut Kayla Barron is seen during a moment of silence at the Apollo 1 monument as part of NASA's Day of Remembrance, Thursday, Jan. 23, 2025, at Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
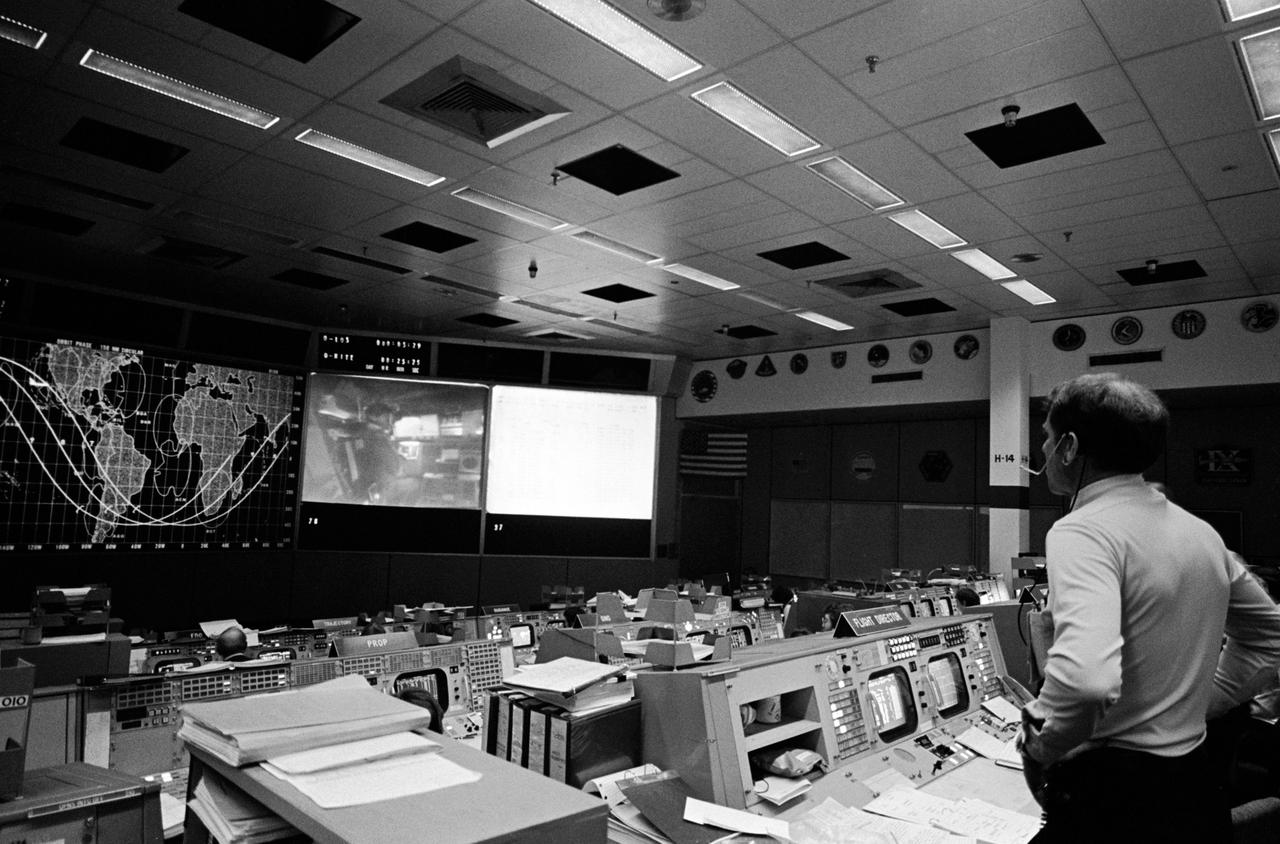

S81-30216 (12 April 1981) --- Astronaut Joe H. Engle, backup crew commander for STS-1, watches a large screen in the mission operations control room of the Johnson Space Center?s Mission Control Center during the STS-1 flight?s prime crew commander?s status report. Astronaut John W. Young, commander, can be seen in the image at left center, which is displayed via rear screen projector. Photo credit: NASA
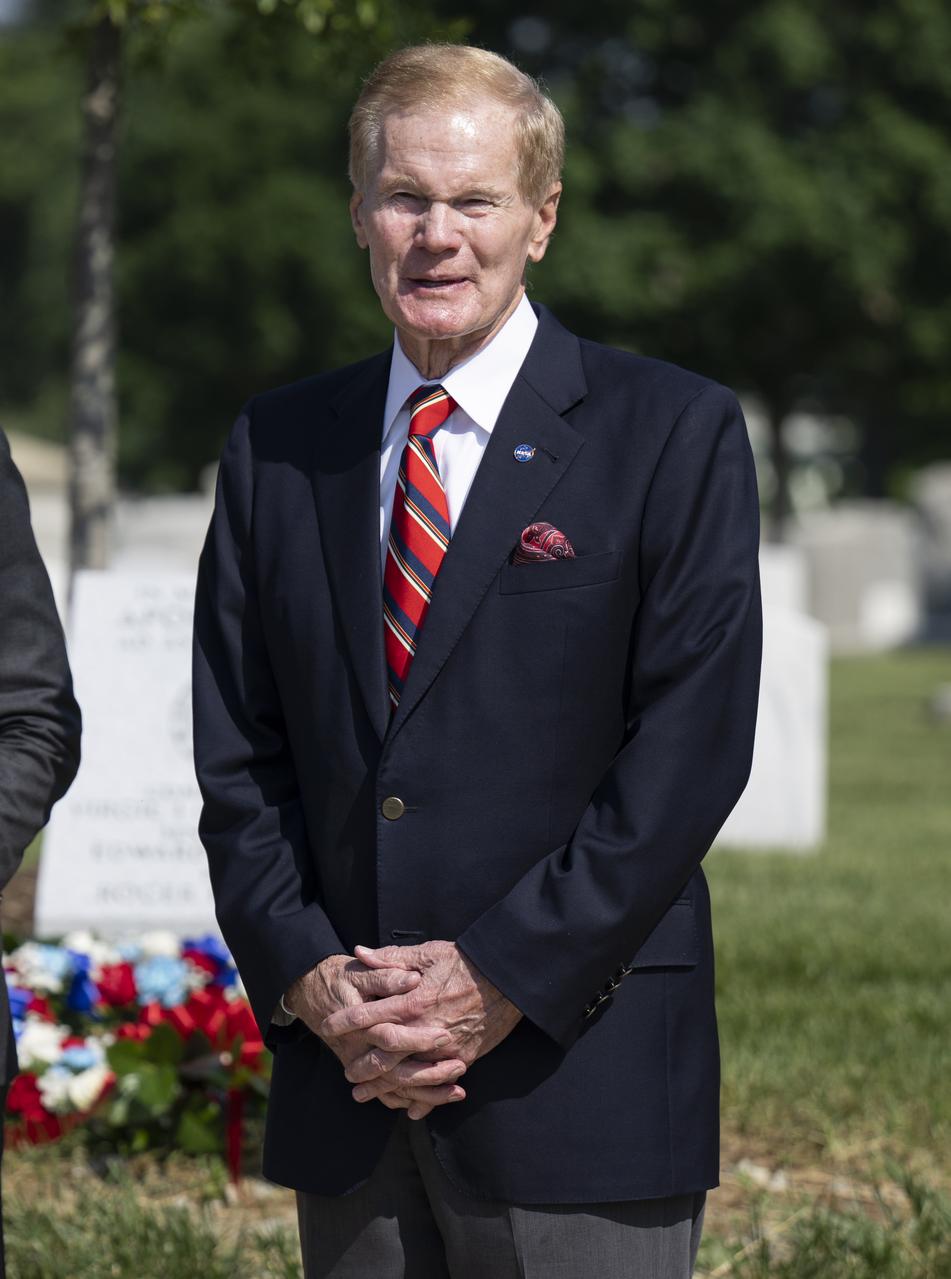

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson delivers remarks at the dedication of the Apollo 1 monument at Arlington National Cemetery, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
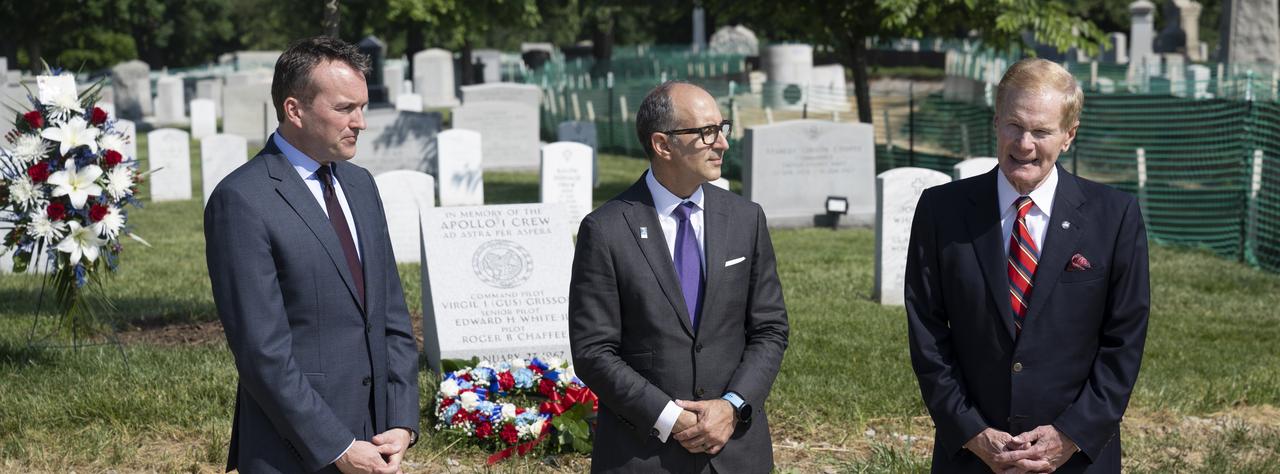

Eric Fanning, AIA President and CEO, left, Lance Bush, President and CEO of the Challenge Center, center, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, are seen as they deliver remarks during the dedication of the Apollo 1 monument at Arlington National Cemetery, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
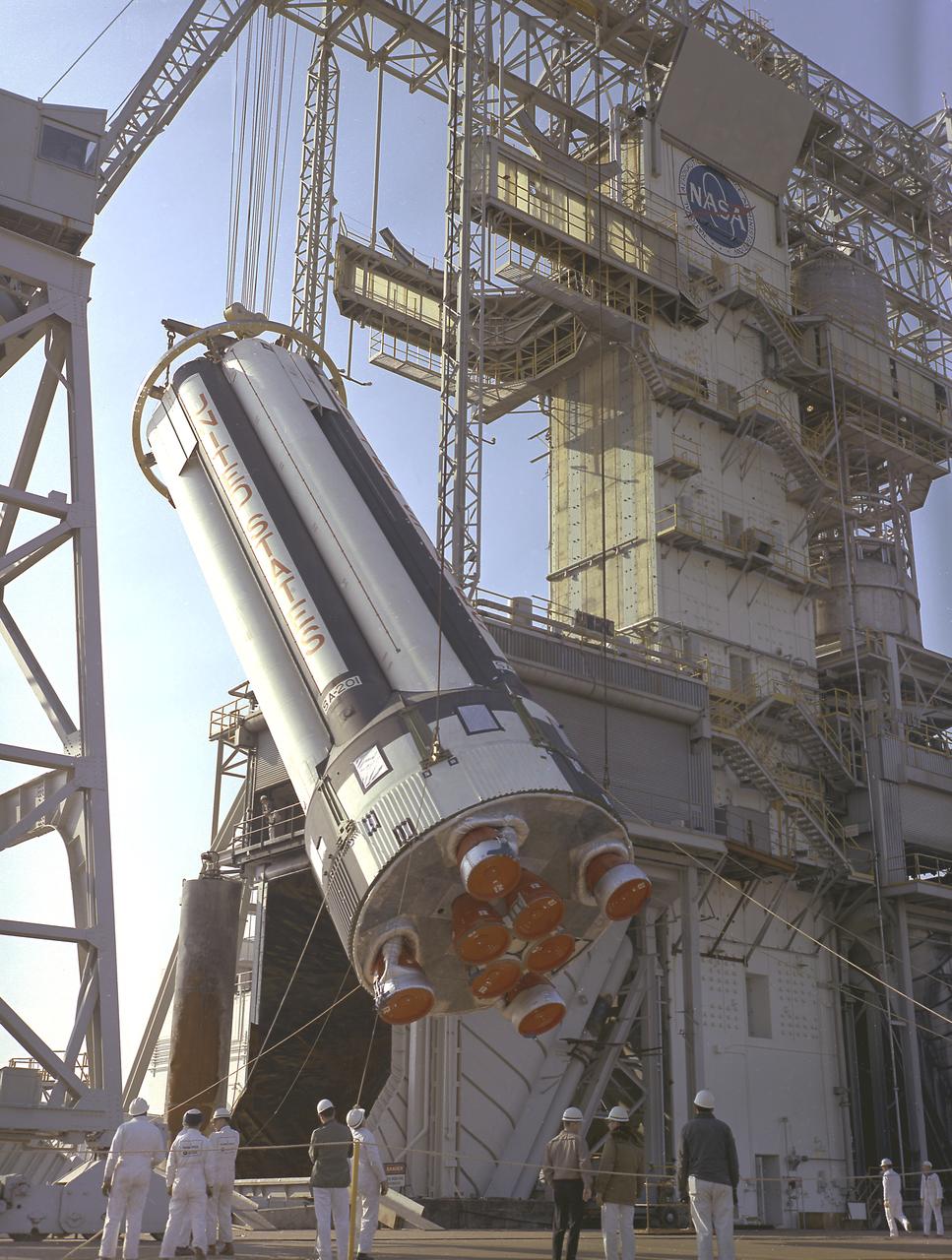

Workers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) hoist S-IB-1, the first flight version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage (S-IB stage), into the Saturn IB static test stand on March 15, 1965. Developed by the MSFC and built by the Chrysler Corporation at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) in New Orleans, Louisiana, the 90,000-pound booster utilized eight H-1 engines to produce a combined thrust of 1,600,000 pounds.
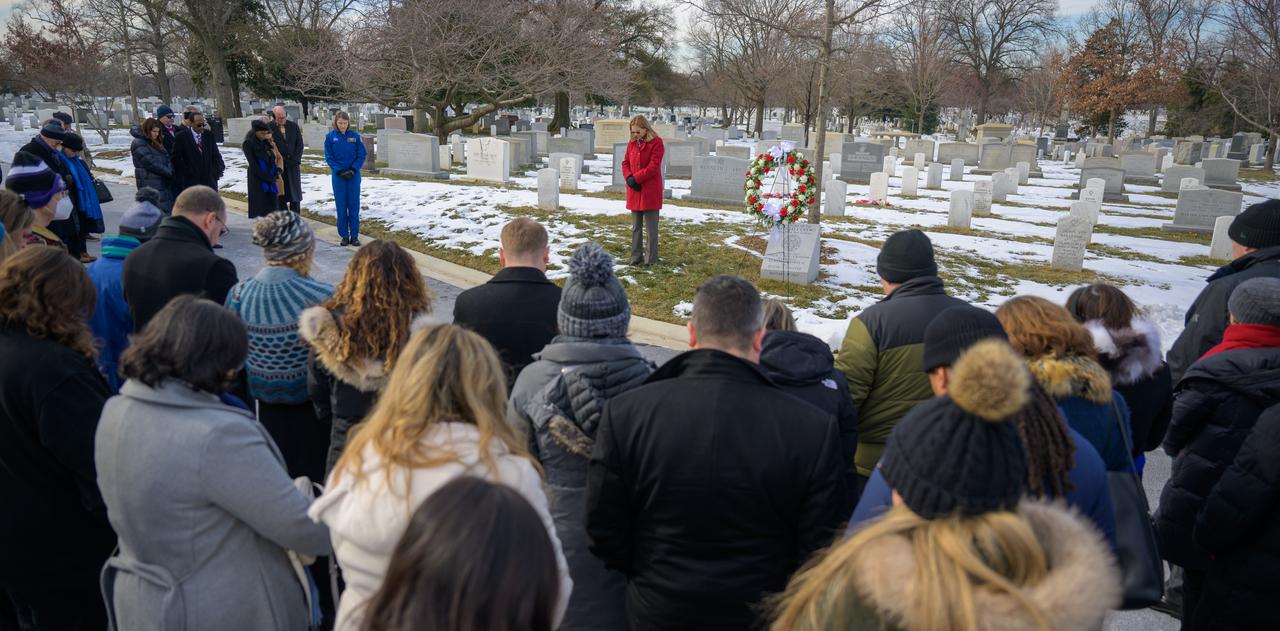

NASA acting Administrator Janet Petro leads guests to a moment of silence at the Apollo 1 monument as part of NASA's Day of Remembrance, Thursday, Jan. 23, 2025, at Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
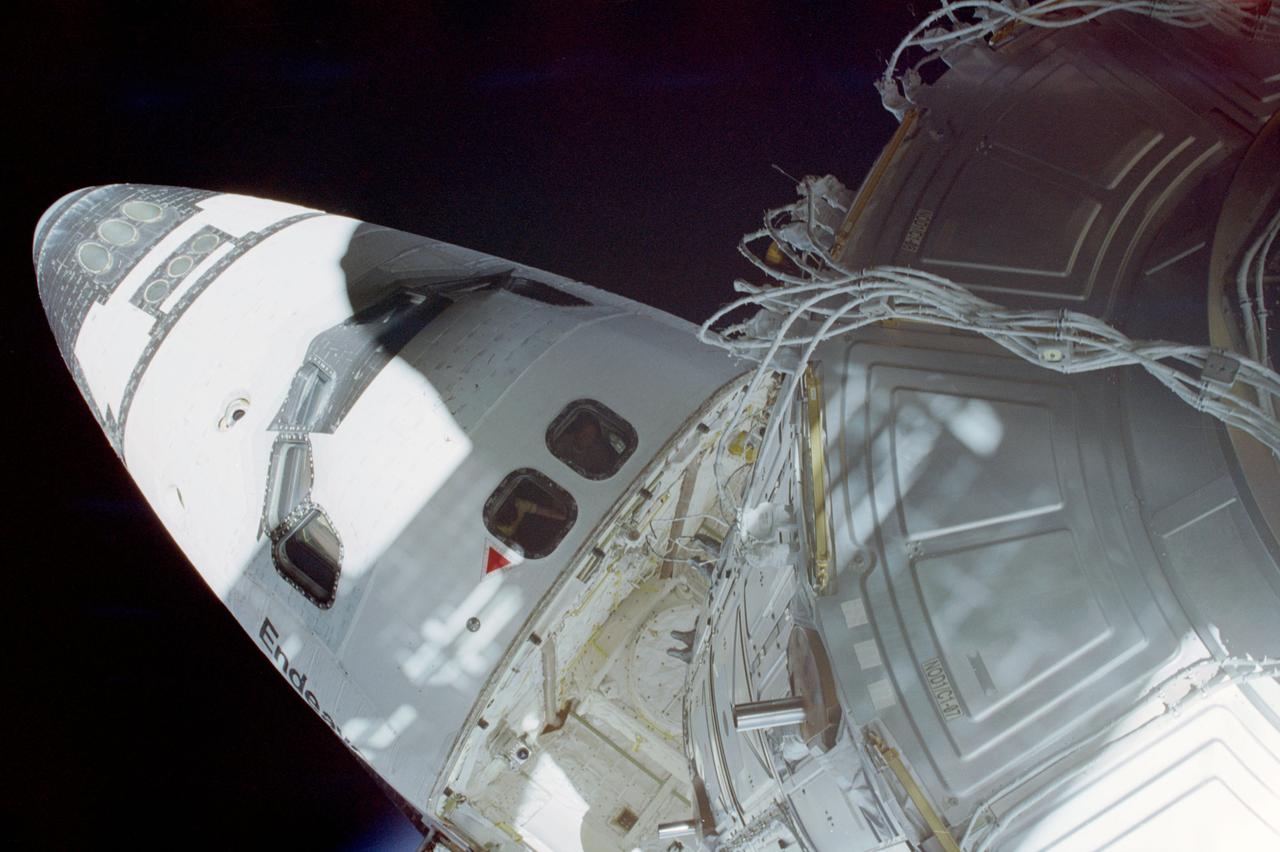

STS088-344-016 (4-15 Dec. 1998) --- This scene photographed from the top of Node 1 shows the nose of the Space Shuttle Endeavour, during one of three Extravehicular Activities (EVA) by astronaut Jerry L. Ross and James H. Newman (both out of frame). The EVA was part of the overall effort to ready for release the recently-joined Russian-built Zarya Module (FGB) and the United States-built Unity (Node 1) Module.
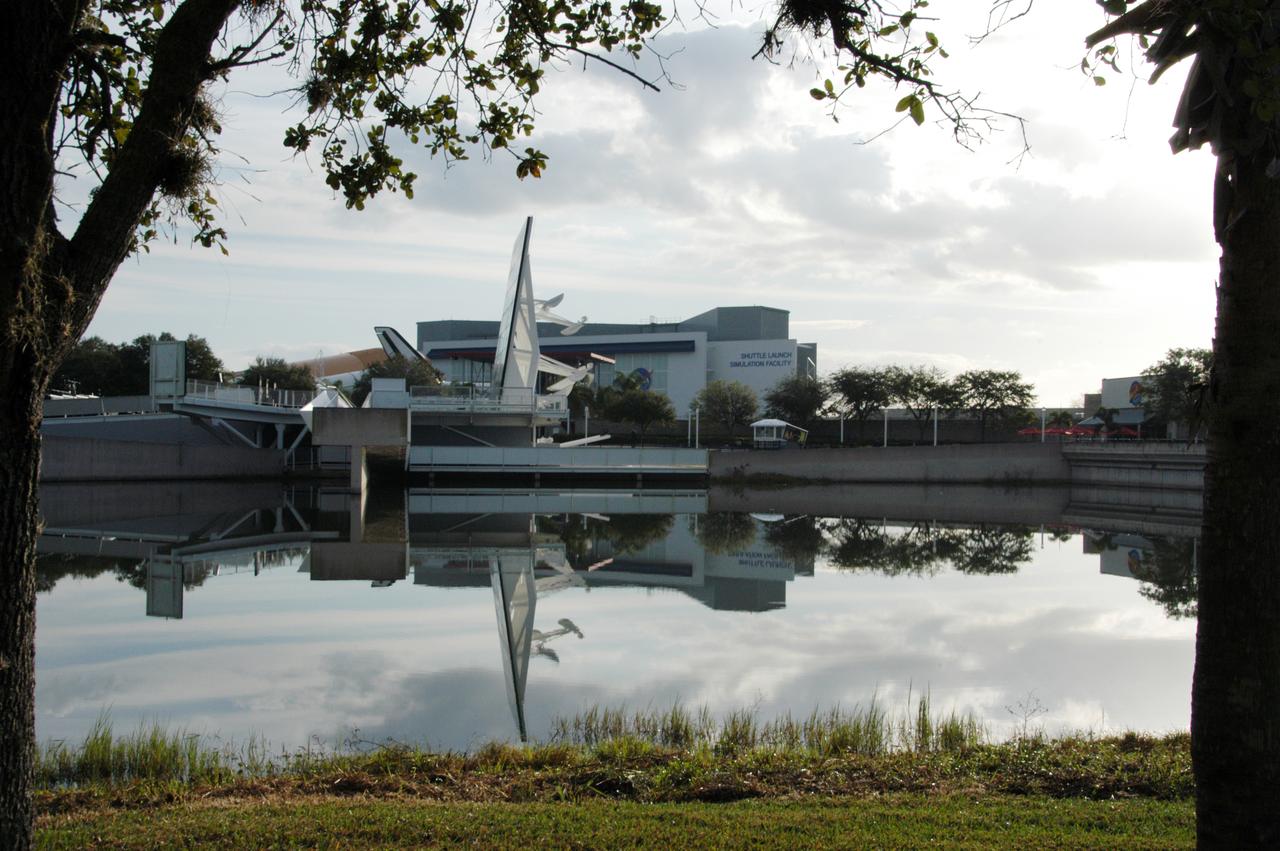

The Space Mirror Memorial, seen in profile, is reflected in the nearby lake at the KSC Visitor Complex. The memorial is the scene of a ceremony being held in remembrance of the astronauts lost in the Apollo 1 fire: Virgil "Gus" Grissom, Edward H. White II and Roger B. Chaffee. The mirror was designated as a national memorial by Congress and President George Bush in 1991 to honor fallen astronauts. Their names are emblazoned on the monument's 42-1/2-foot-high by 50-foot-wide black granite surface as if to be projected into the heavens.
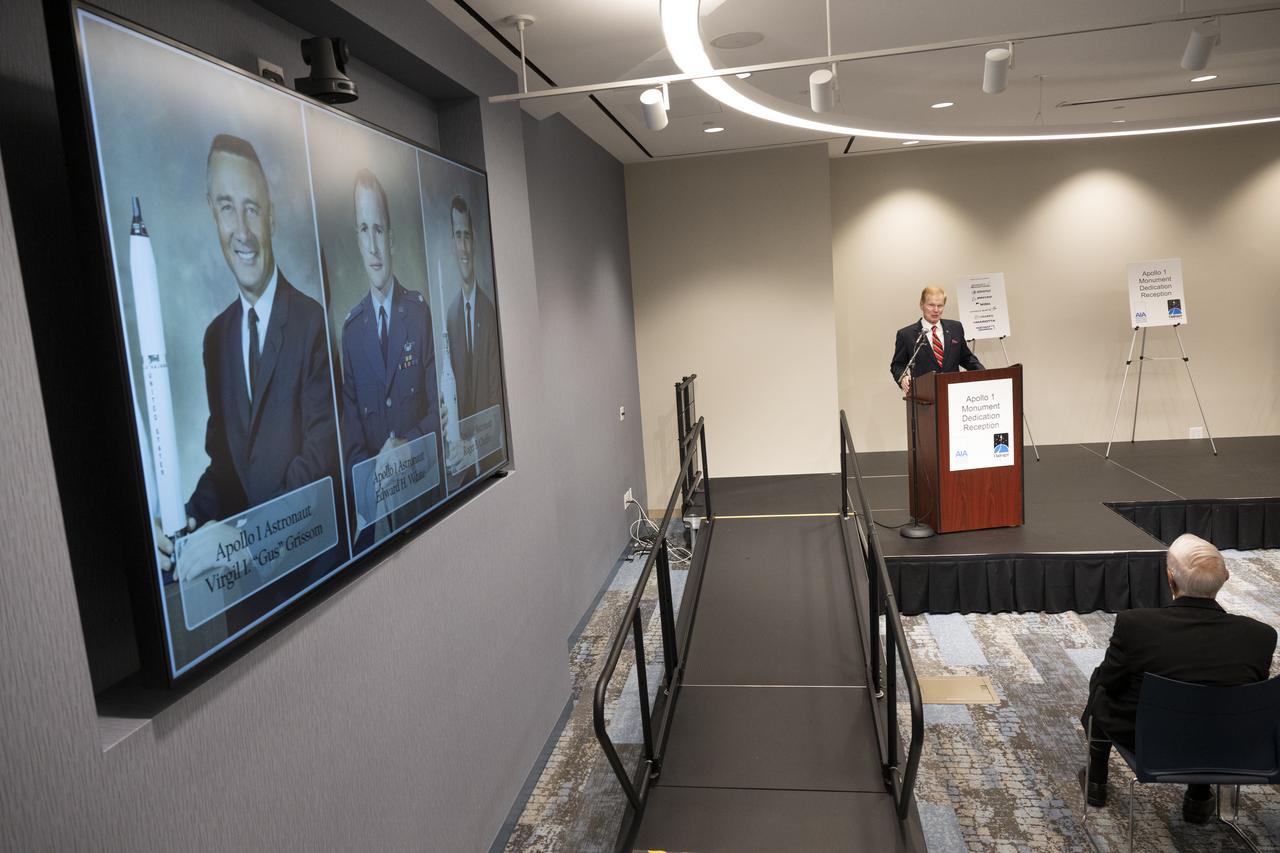

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson delivers remarks at a reception following the dedication of the Apollo 1 monument, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in the Reception Hall of the Military Women’s Memorial at Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
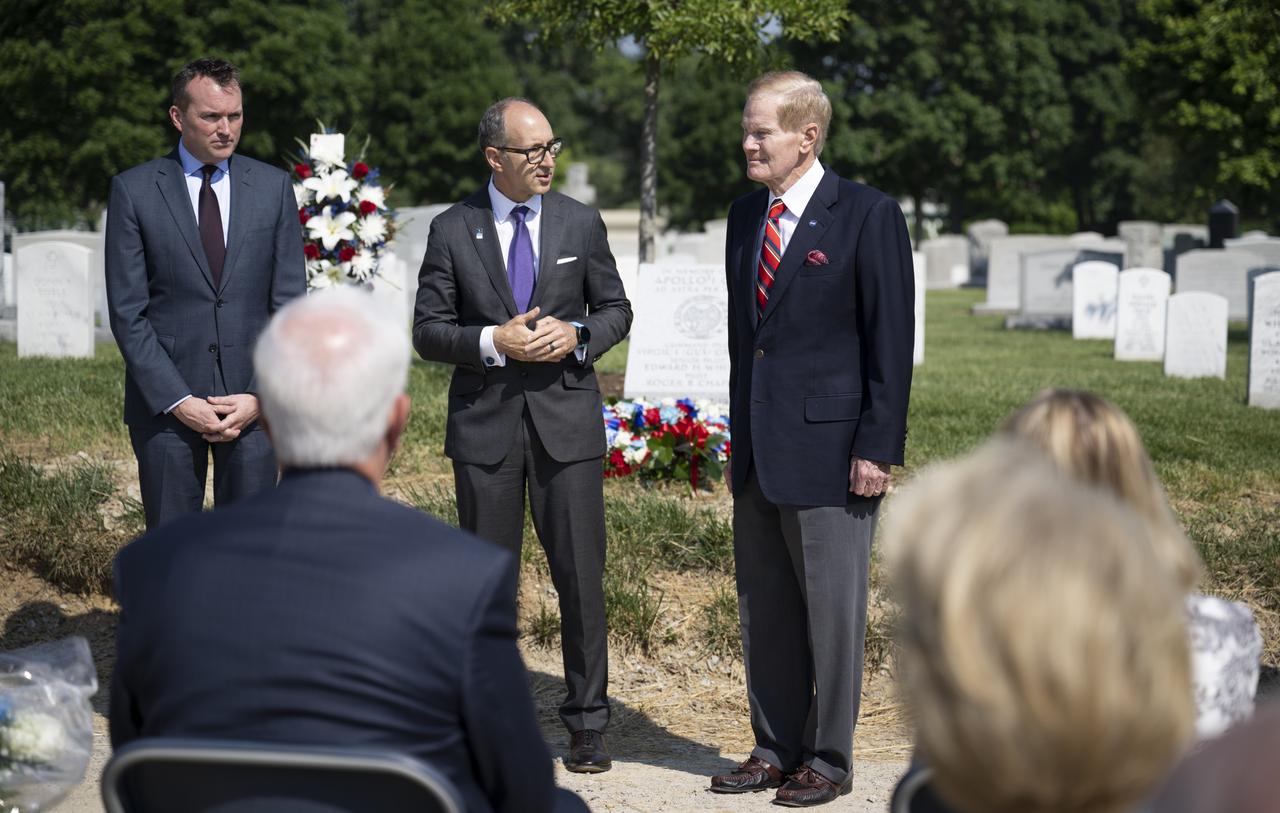

Eric Fanning, AIA President and CEO, left, Lance Bush, President and CEO of the Challenge Center, center, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, left, are seen as they deliver remarks during the dedication of the Apollo 1 monument at Arlington National Cemetery, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
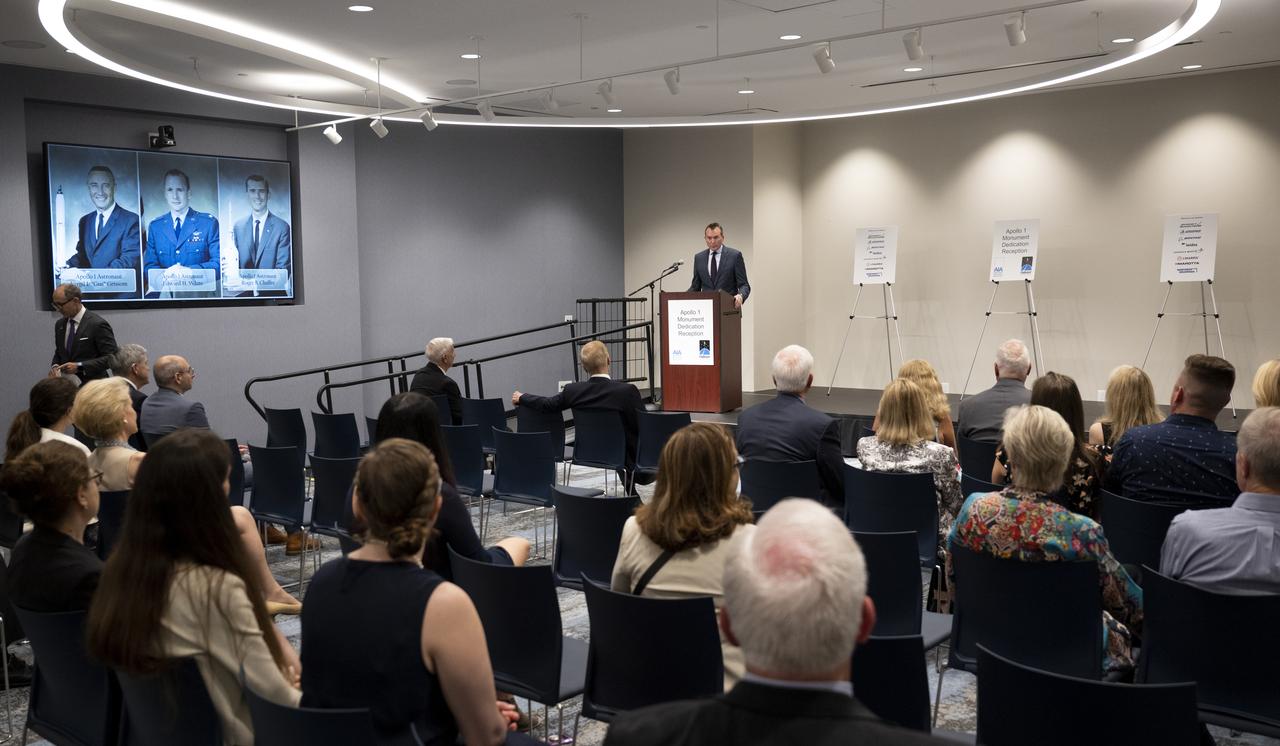

Eric Fanning, AIA President and CEO, delivers remarks at a reception following the dedication of the Apollo 1 monument, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in the Reception Hall of the Military Women’s Memorial at Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
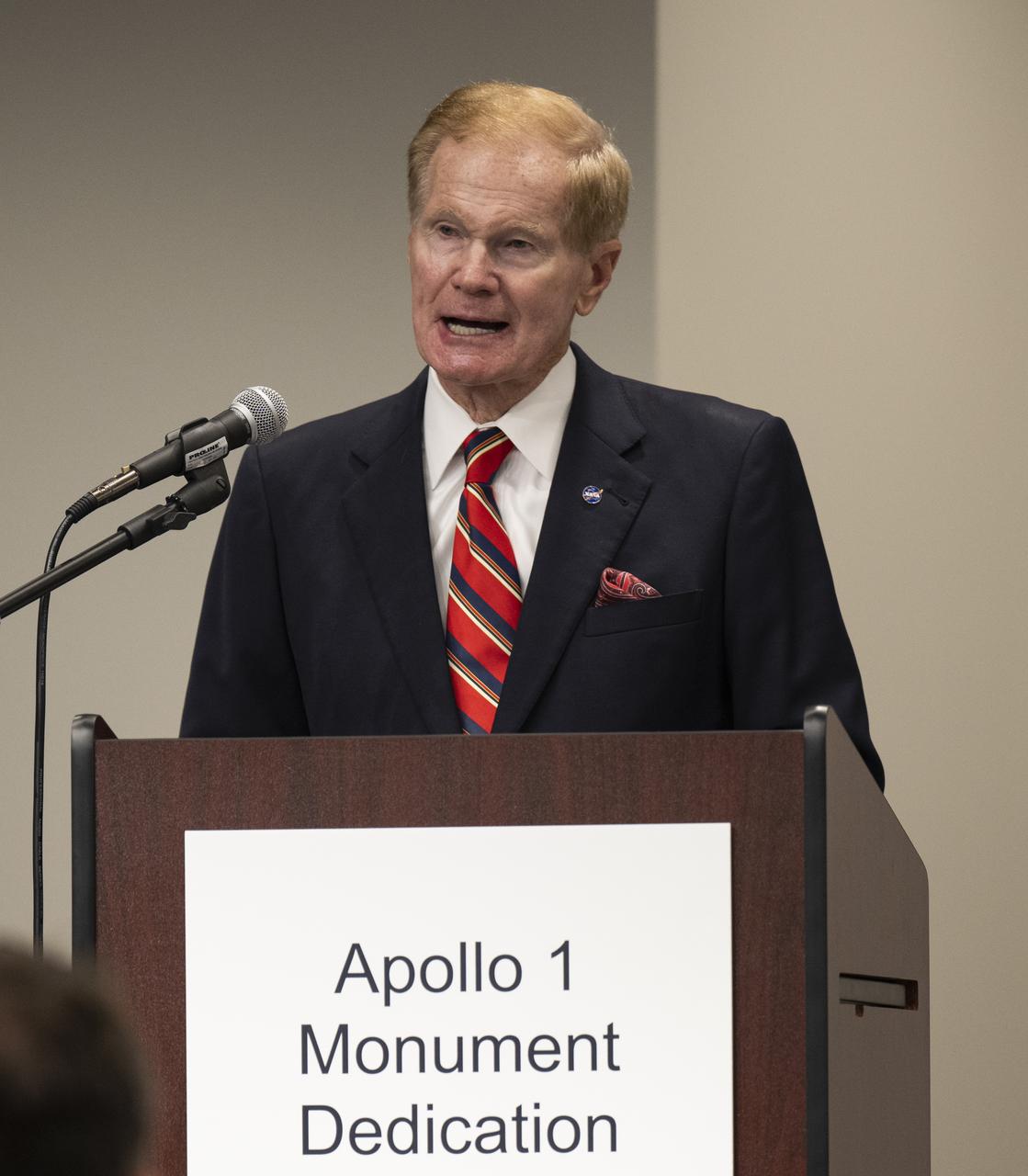

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson delivers remarks at a reception following the dedication of the Apollo 1 monument, Thursday, June 2, 2022, in the Reception Hall of the Military Women’s Memorial at Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington, Va. The monument honors and memorializes the Apollo 1 crew of Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
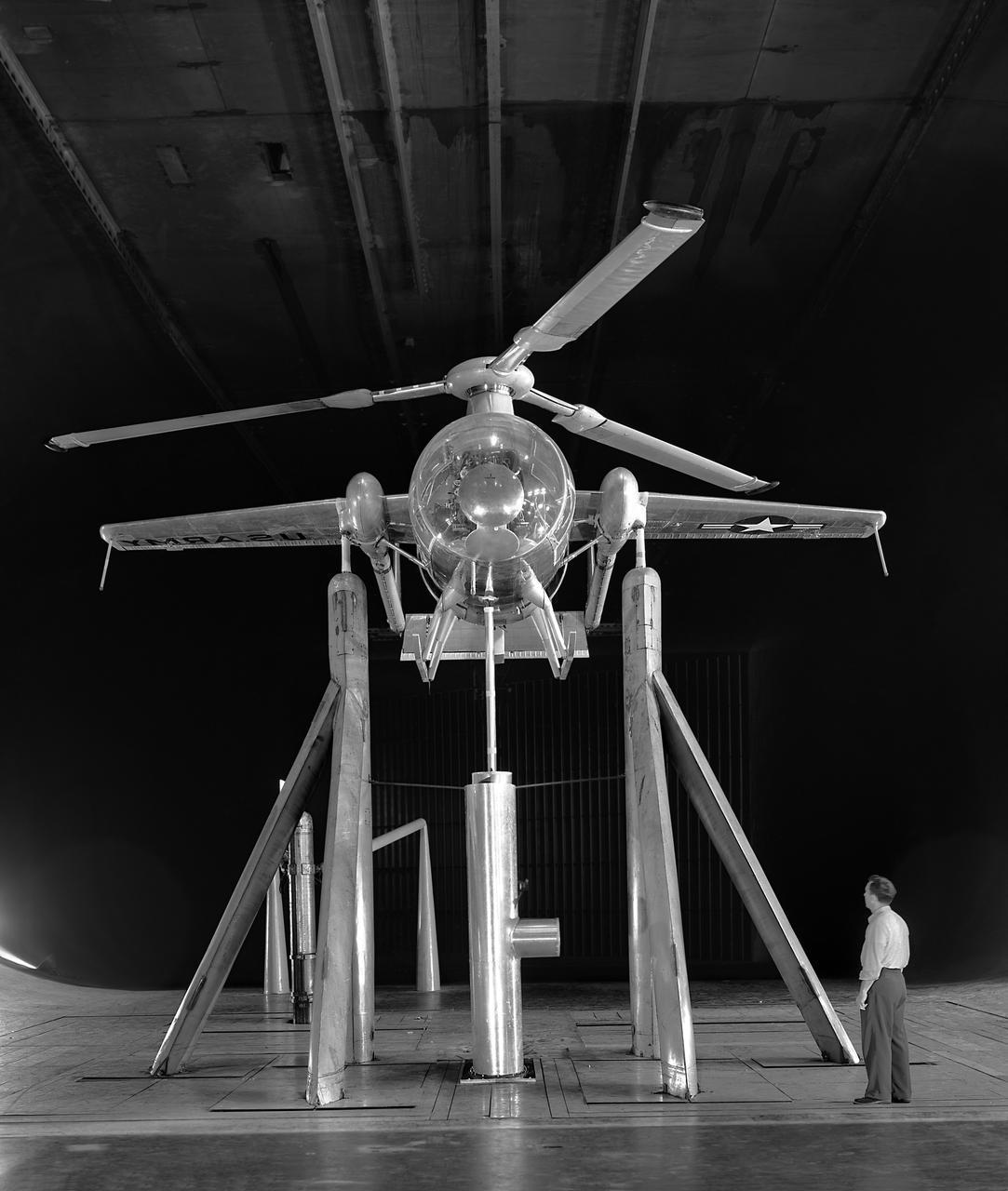

Foreword, front view of McDonnell Model XV-1 Convertiplane in the Ames 40x80 Foot Wind Tunnel. The McDonnell XV-1 was an experimental compound gyroplane developed for a joint research program between the United States Air Force and the United States Army to explore technologies to develop an aircraft that could take off and land like a helicopter but fly at faster airspeeds, similar to a conventional airplane. The XV-1 would reach a speed of 200 mph (322 km/h), faster than any previous rotorcraft, but the program was terminated due to the tip-jet noise and complexity of the technology which gave only a modest gain in performance.
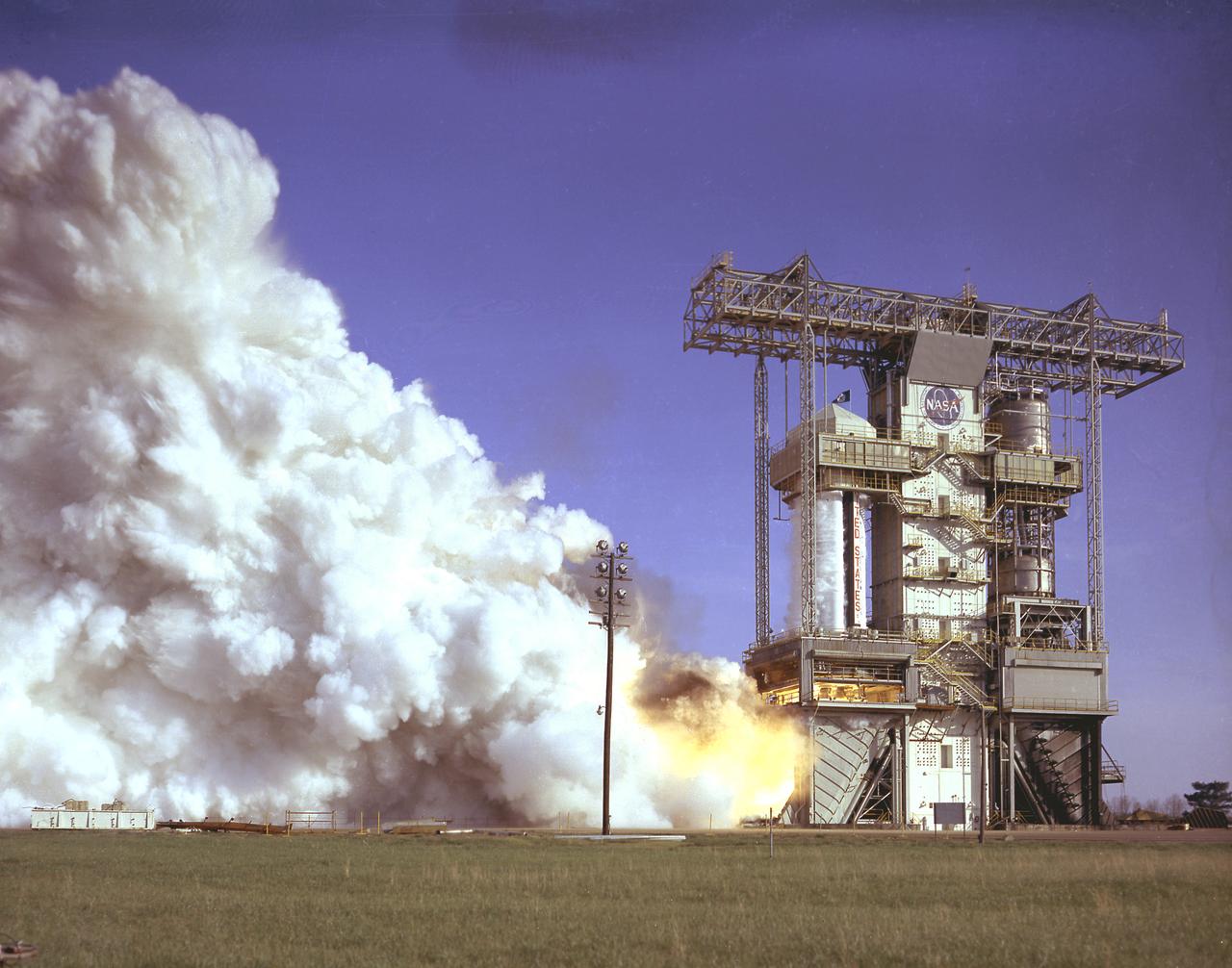

S-IB-1, the first flight version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage (S-IB stage), undergoes a full-duration static firing in Saturn IB static test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) on April 13, 1965. Developed by the MSFC and built by the Chrysler Corporation at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) in New Orleans, Louisiana, the 90,000-pound booster utilized eight H-1 engines to produce a combined thrust of 1,600,000 pounds. Between April 1965 and July 1968, MSFC performed thirty-two static tests on twelve different S-IB stages.
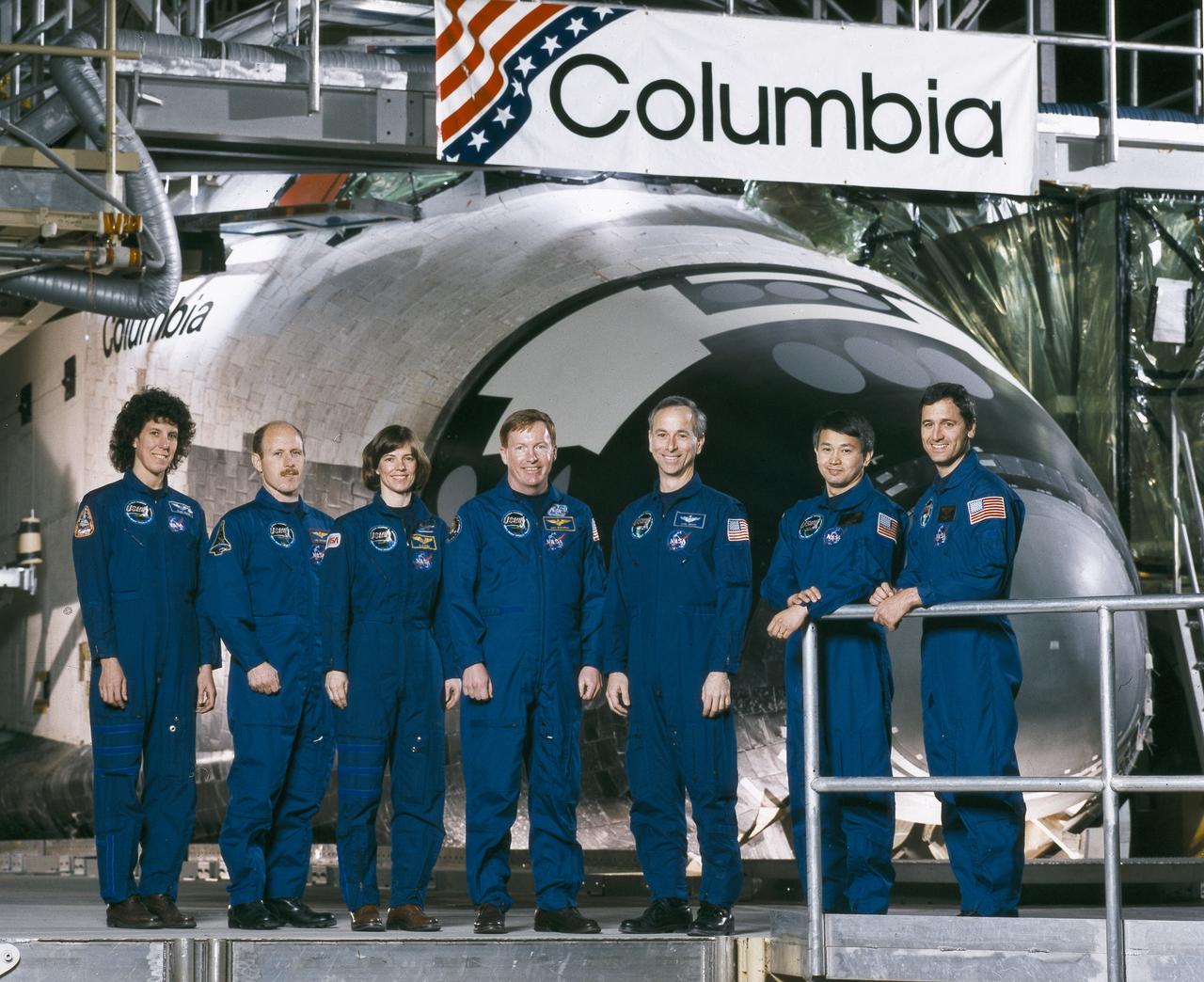

The STS-50 crew portrait includes (from left to right): Ellen S. Baker, mission specialist; Kenneth D. Bowersox, pilot; Bonnie J. Dunbar, payload commander; Richard N. Richards, commander; Carl J. Meade, mission specialist; Eugene H. Trinh, payload specialist; and Lawrence J. DeLucas, payload specialist. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on June 25, 1992 at 12:12:23 pm (EDT), the primary payload for the mission was the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory-1 (USML-1) featuring a pressurized Spacelab module.
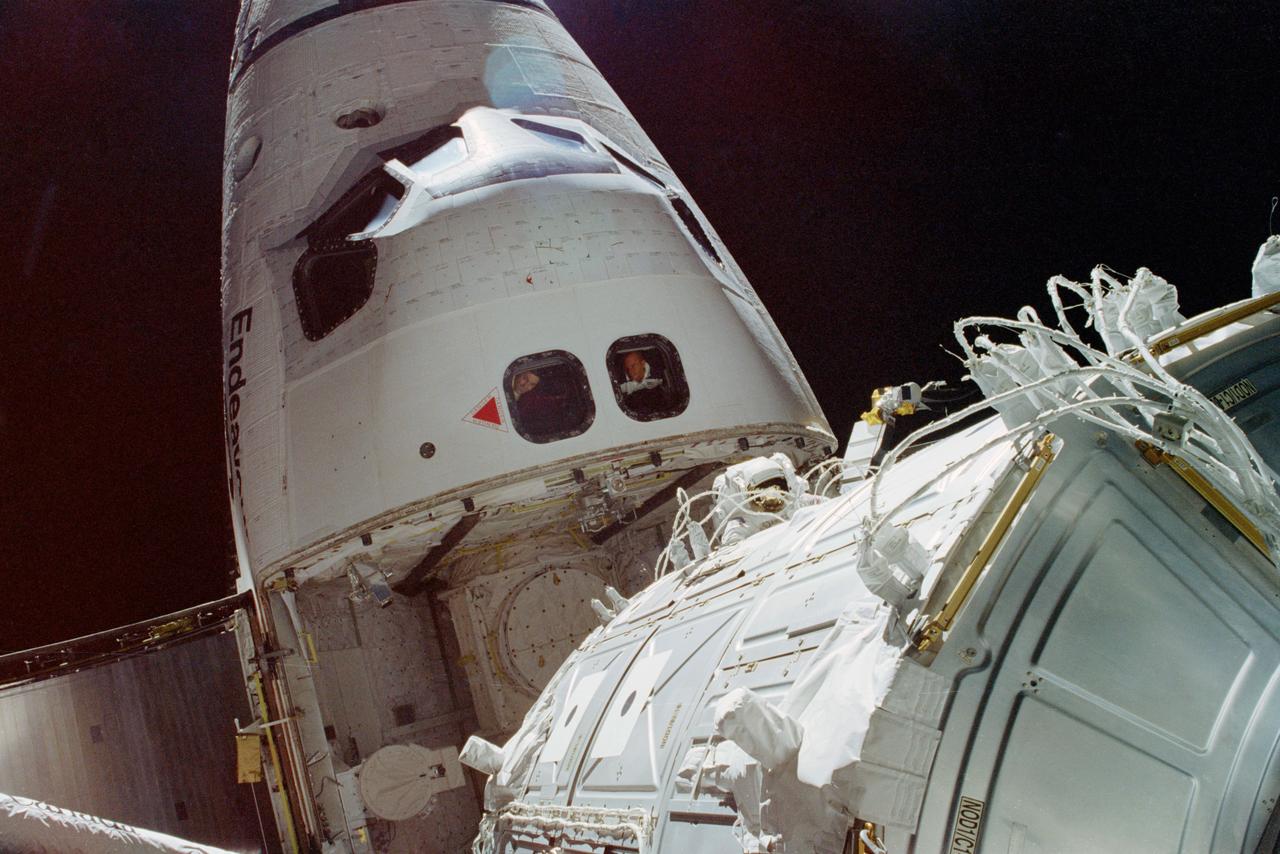

STS088-352-034 (4-15 Dec. 1998) --- This scene photographed from the top of Node 1 shows the nose of the Space Shuttle Endeavour, during one of three space walks. Astronaut James H. Newman, mission specialist (frame center), was joined by astronaut Jerry L. Ross, mission specialist (out of frame), for the extravehicular activity (EVA) to ready for release the recently-joined Russian-built Zarya Module (FGB) and the United States-built Unity (Node 1) Module. Fellow crew members Robert D. Cabana, commander (left window), and Frederick W. ?Rick? Sturckow, pilot, observe the EVA through aft flight deck overhead windows at left center.
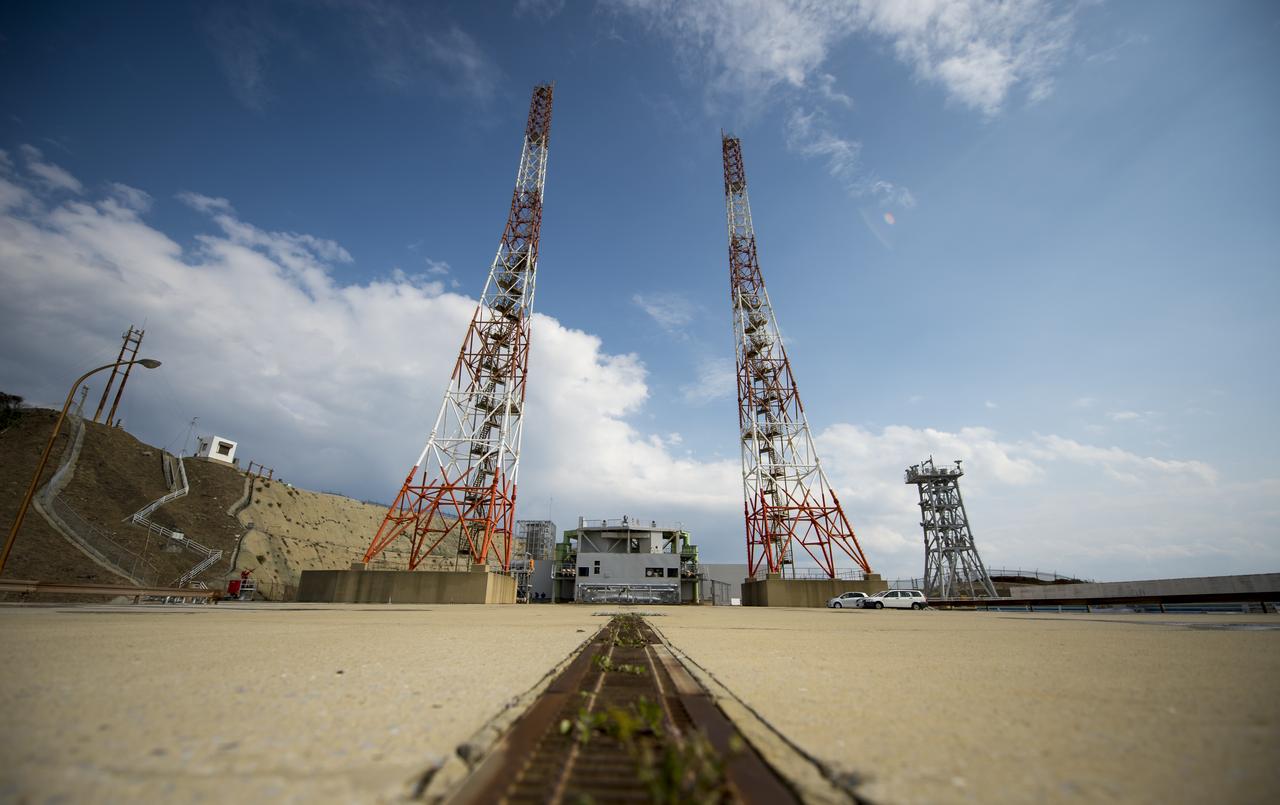

Launch pad 1 is seen at the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Monday, Feb. 24, 2014 in Tanegashima, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from pad 1 on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
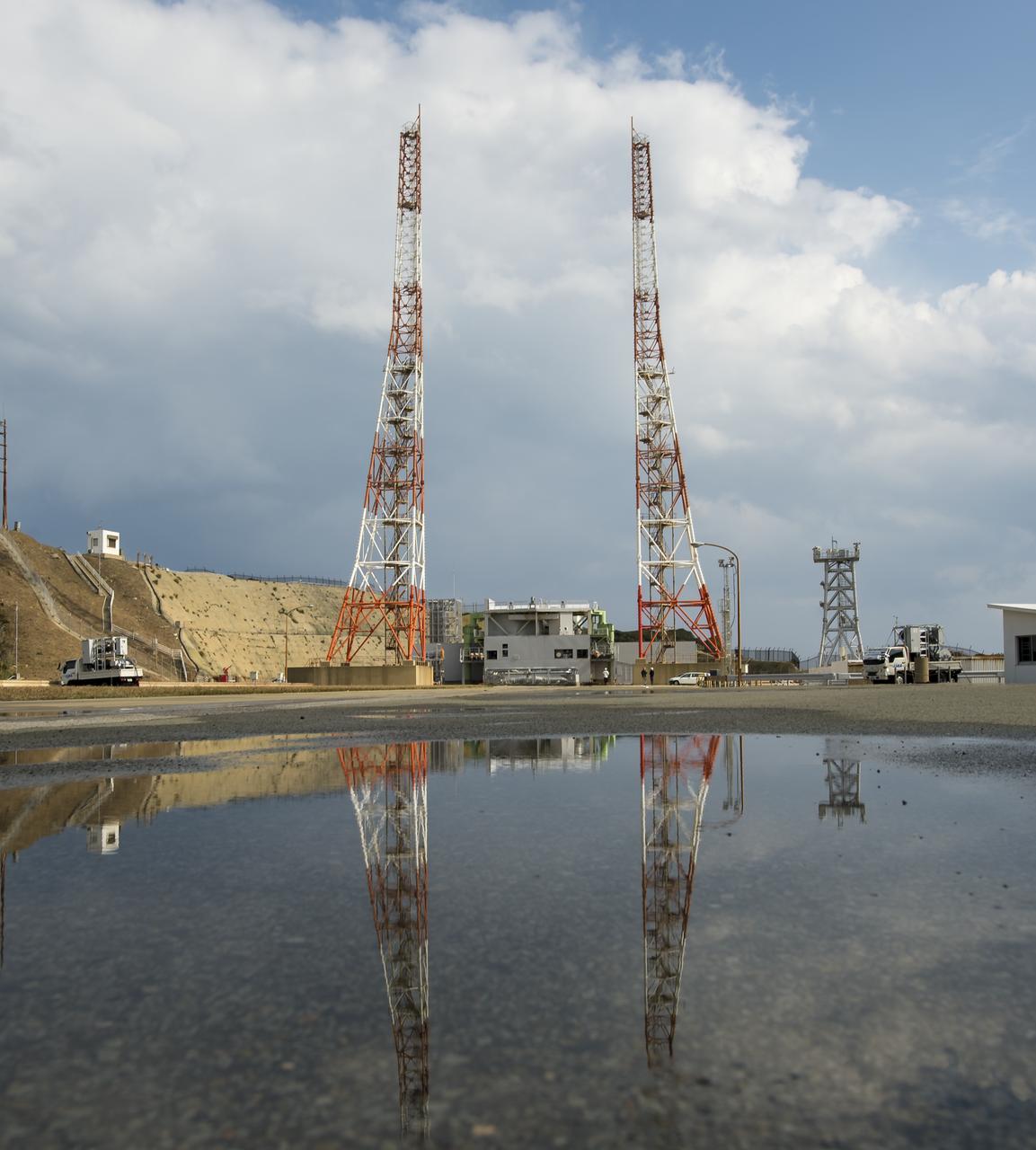

Launch pad 1 is seen at the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Monday, Feb. 24, 2014 in Tanegashima, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from pad 1 on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
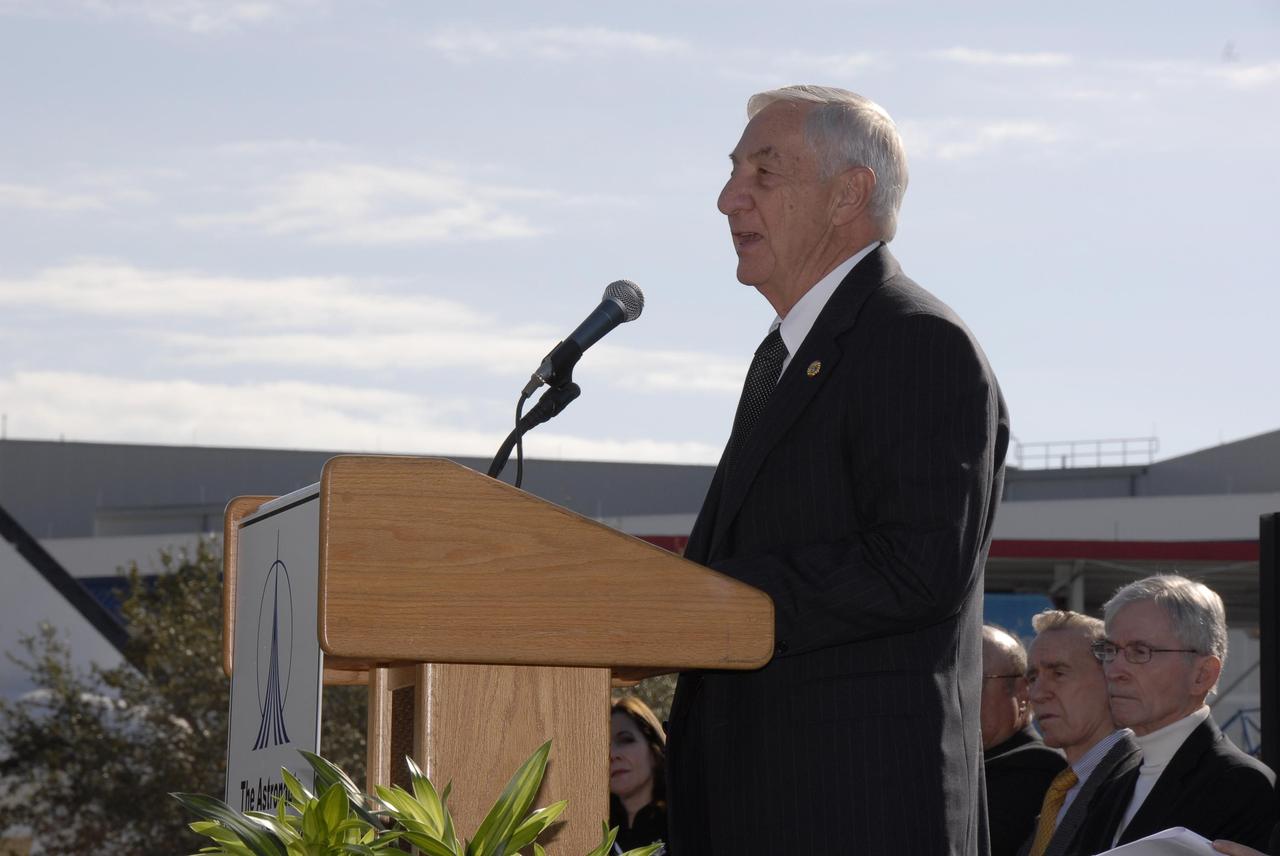

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Lowell Grissom addresses guests attending a ceremony at the KSC Visitor Complex held in remembrance of the astronauts lost in the Apollo 1 fire: Virgil "Gus" Grissom, Edward H. White II and Roger B. Chaffee. Grissom is the brother of Gus Grissom. Members of the Apollo 1 families, along with KSC Director Bill Parsons, Associate Administrator for Space Operations William Gerstenmaier, President of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation Stephen Feldman, Chairman of the Board of Directors of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation William Potter and former astronaut John Young (seen at lower right), attended the ceremony. Photo credit:NASA/Kim Shiflett
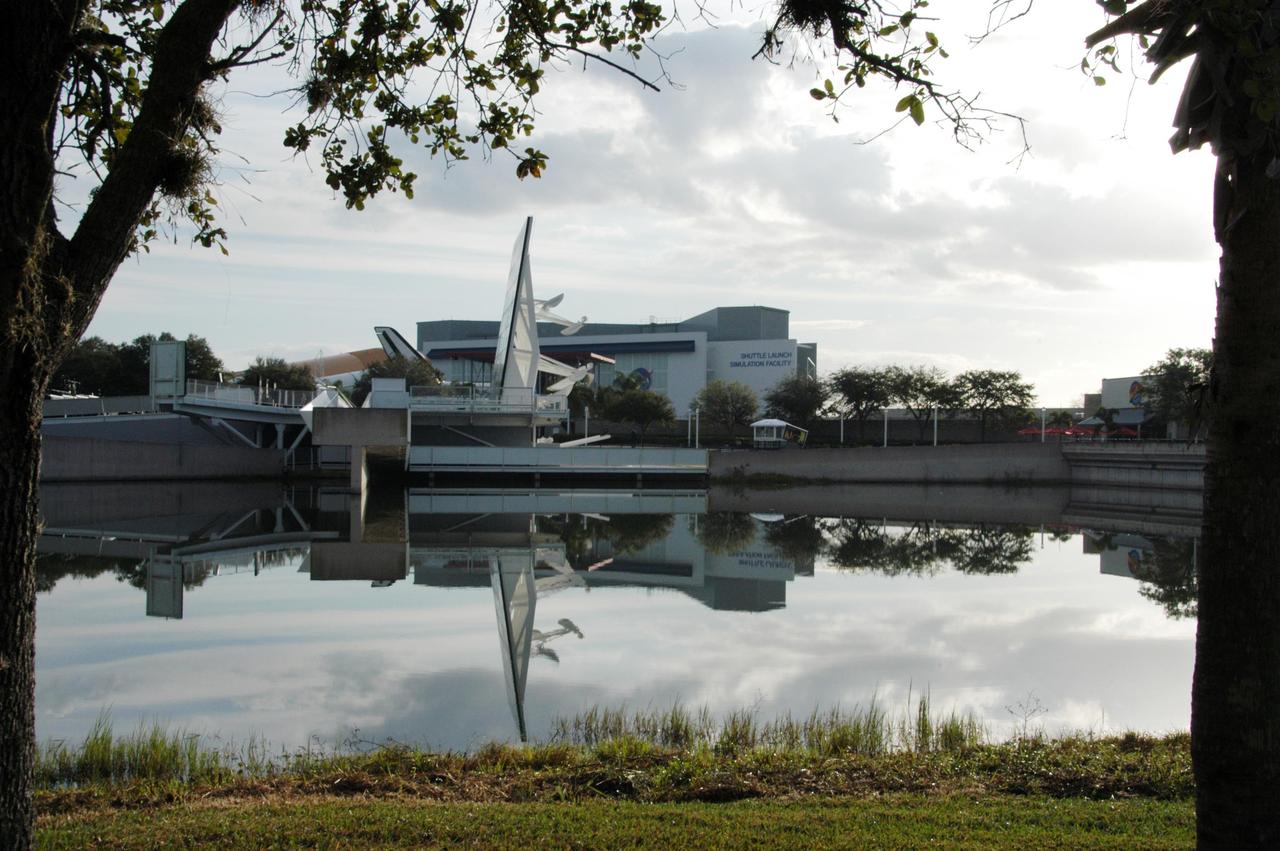

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Mirror Memorial, seen in profile, is reflected in the nearby lake at the KSC Visitor Complex. The memorial is the scene of a ceremony being held in remembrance of the astronauts lost in the Apollo 1 fire: Virgil "Gus" Grissom, Edward H. White II and Roger B. Chaffee. The mirror was designated as a national memorial by Congress and President George Bush in 1991 to honor fallen astronauts. Their names are emblazoned on the monument's 42-1/2-foot-high by 50-foot-wide black granite surface as if to be projected into the heavens. Photo credit:NASA/George Shelton
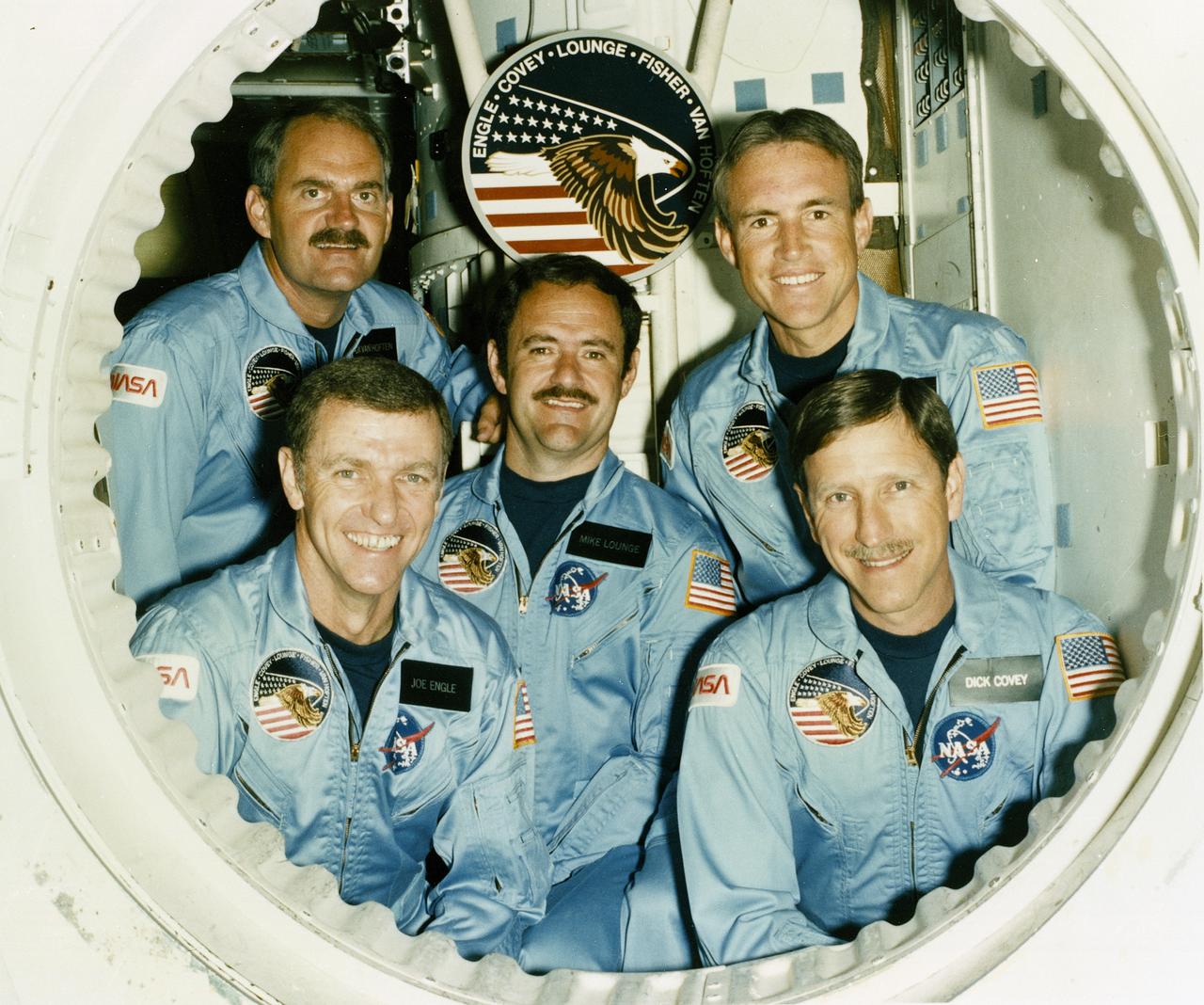

The crew assigned to the STS-51I mission included (front row left to right) Joe H. Engle, commander; and Richard O. Covey, pilot. In the center is John M. (Mike) Lounge, mission specialist. On the back row, from left to right, are mission specialists James D. van Hoften, and William F. Fisher. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on August 27, 1985 at 6:58:01 am (EDT), the STS-51I mission’s primary payloads were three communication satellites: the ASC-1 for the American Satellite Company; the AUSSAT-1, an Australian communications satellite; and the SYNCOM-IV-4, the synchronous communications satellite.
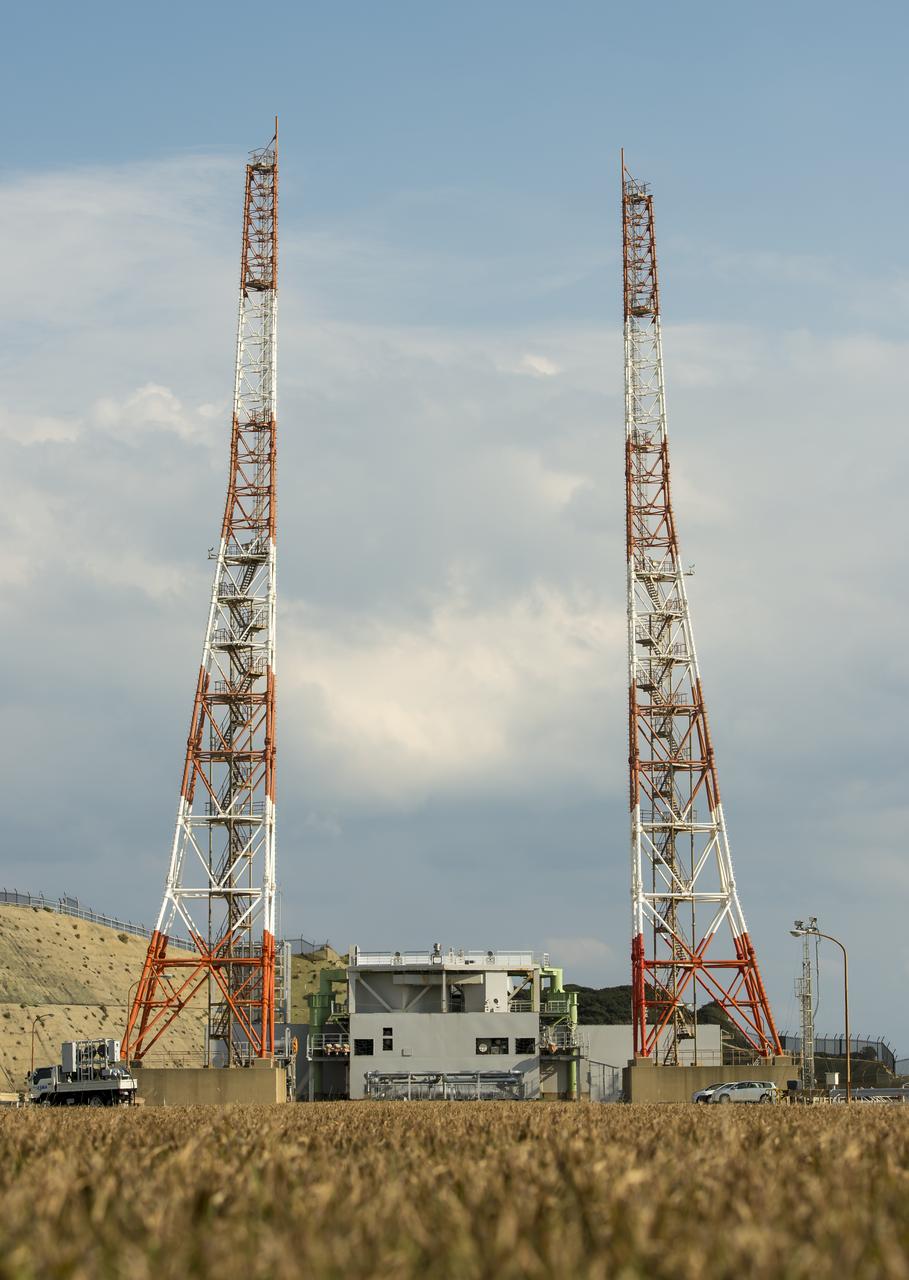

Launch pad 1 is seen at the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Monday, Feb. 24, 2014 in Tanegashima, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from pad 1 on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Launch pad 1 is seen at the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) on Monday, Feb. 24, 2014 in Tanegashima, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from pad 1 on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

S63-00562 (February 1963) --- Portrait of astronaut groups 1 and 2. The original seven Mercury astronauts selected by NASA in April 1959, are seated (left to right): L. Gordon Cooper Jr., Virgil I. Grissom, M. Scott Carpenter, Water M. Schirra Jr., John H. Glenn Jr., Alan B. Shepard Jr., and Donald K. Slayton. The second group of NASA astronauts, which were named in September 1962, are standing (left to right): Edward H. White II, James A. McDivitt, John W. Young, Elliot M. See Jr., Charles Conrad Jr., Frank Borman, Neil A. Armstrong, Thomas P. Stafford, and James A. Lovell Jr. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
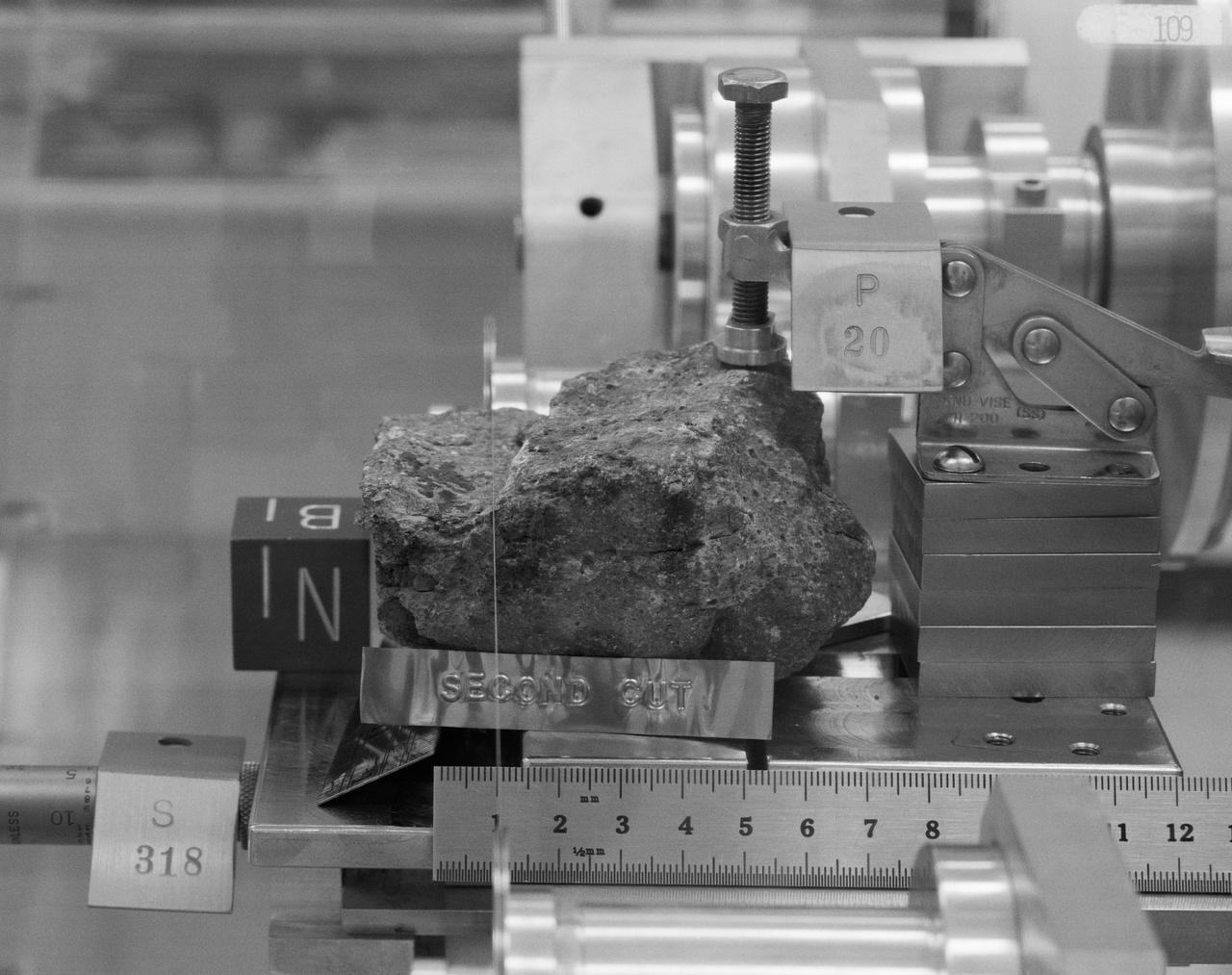

Generic: 14318. Mission: Apollo 14. Station: H. Landmark: NORTH BOULDER FIELD. BagNumber: Bag 1038. OriginalWeight: 600.2. SuperClass: Breccia. SubClass: Regolith. Category: ROCK. Classifications: VMB. Description: Vitric Matrix Breccia. Ipidesc: Breccia sample 14318 was collected from the regolith near the south end of North Boulder Field at Station H during the second EVA. It was returned in weigh bag 1038. Sample 14318 is one of the specimens chosen for study by the Imbrium Consortium, who received 14318,0. A complete set of matched thin sections, across the entire specimen was made by the Consortium (1976); This sample is a very coherent, gray, polymict breccia consisting of light gray clasts in a medium gray matrix. Classification 1: BRECCIA.
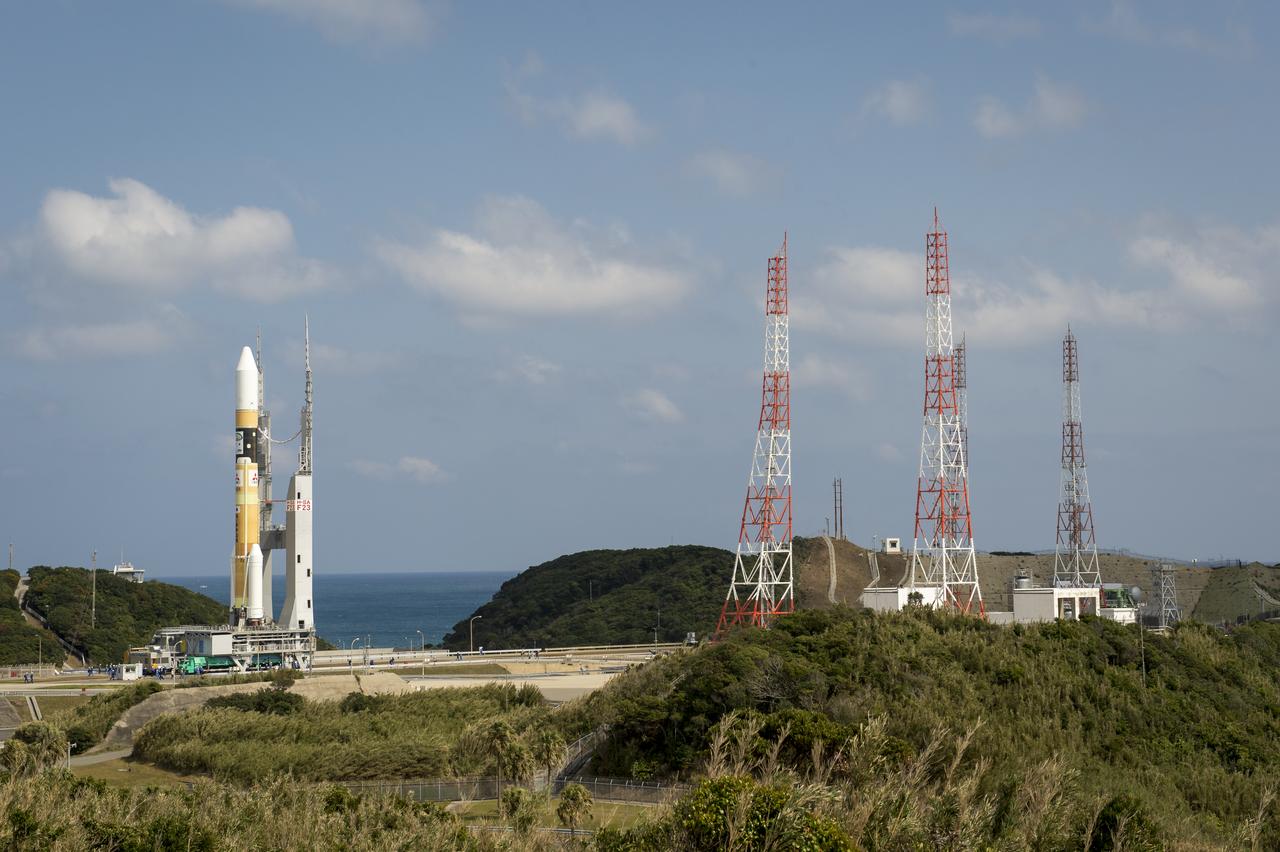

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

STS088-318-023 (4-15 December 1998) --- This photograph taken out the window of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour shows the two astronaut spacewalkers, during one of three extravehicular activity (EVA) sessions, readying the recently-connected Russian-built FGB Module (Zarya) and the United States-built Unity Module (Node 1). The two EVA astronauts are mission specialists James H. Newman (right)and Jerry L. Ross (lower left with red stripe on suit).
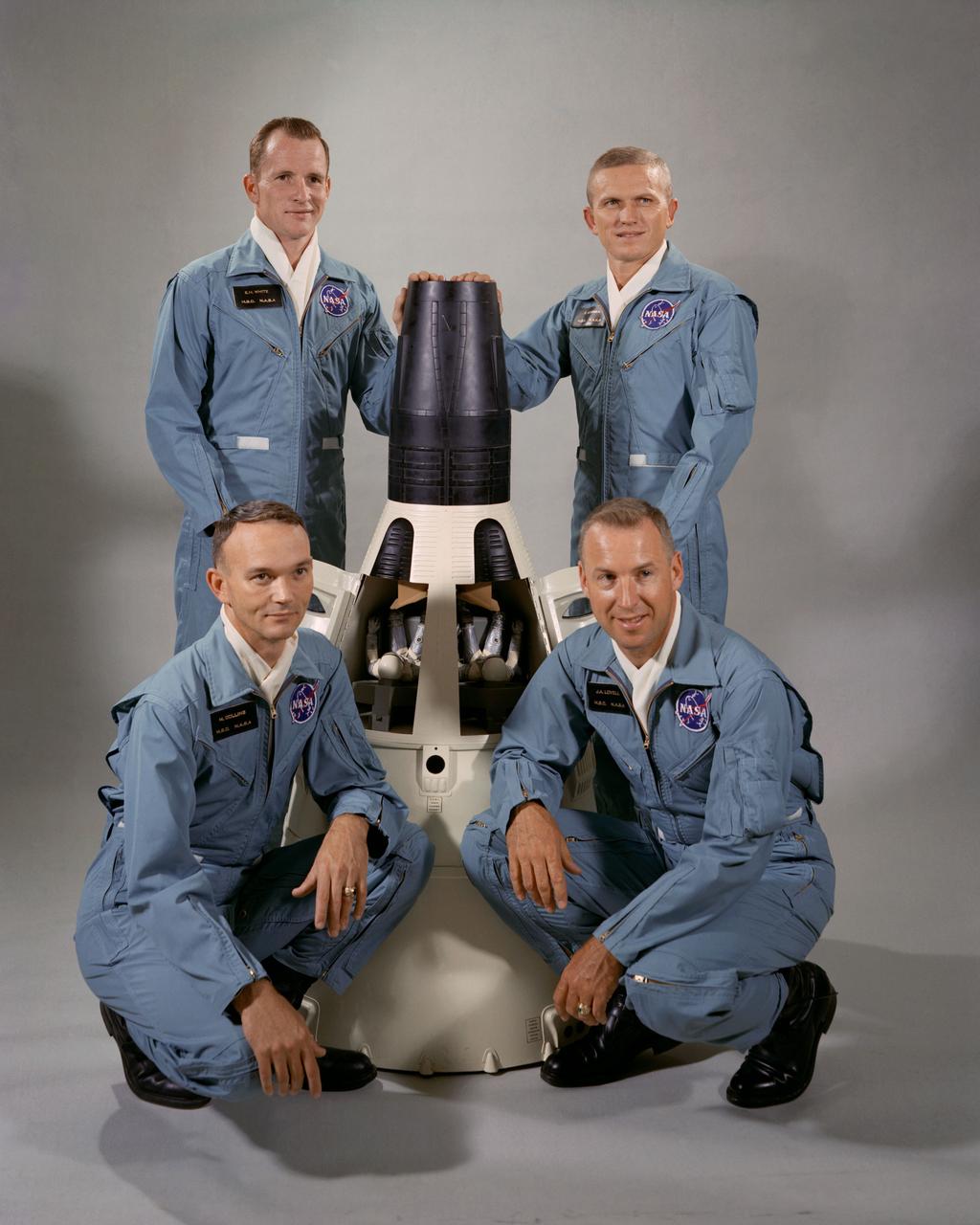

S65-41828 (September 1965) --- Portrait of the Gemini-7 prime and backup crew members around a model of the Gemini-7 spacecraft. The prime crew members for the Gemini-Titan 7 (GT-7) are astronauts Frank Borman (standing right), command pilot, and James A. Lovell Jr. (kneeling right), pilot. Astronauts Michael Collins (kneeling left), pilot, and Edward H. White II (standing left), command pilot, were named as GT-7 backup crew members on July 1, 1965. Photo credit: NASA
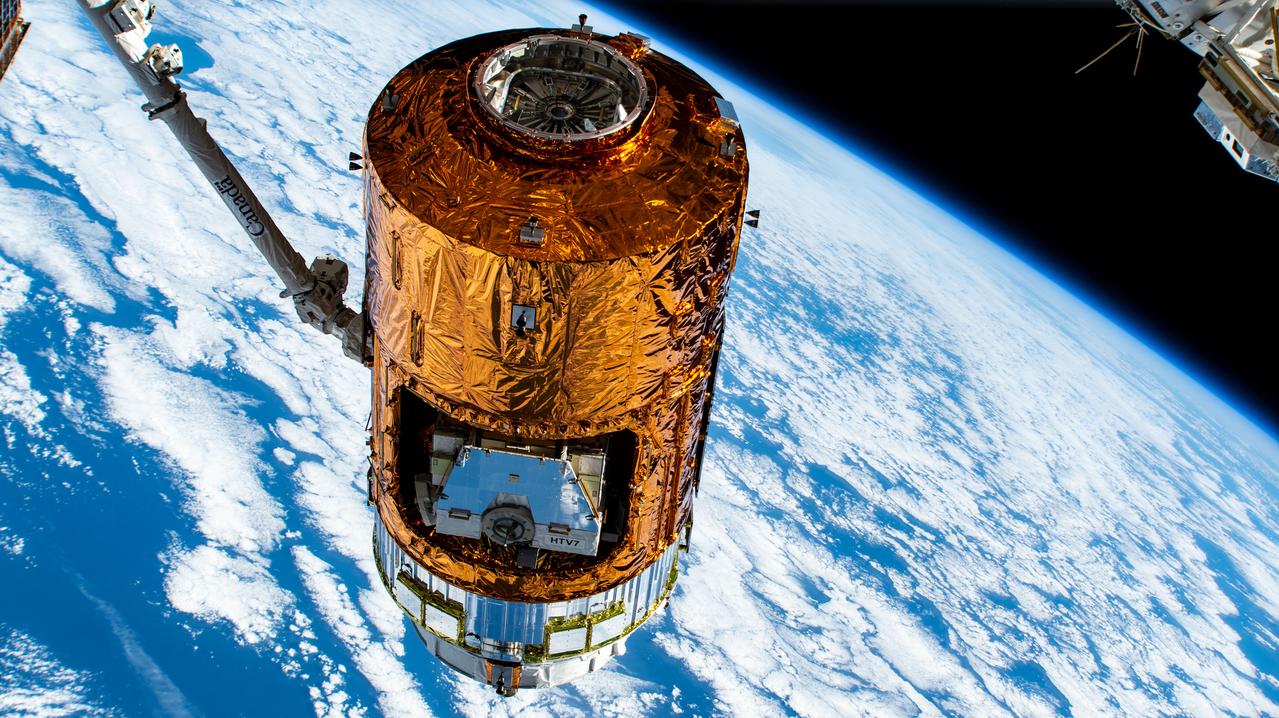

iss061e026343 (Nov. 1, 2019) --- Japan's H-II Transfer Vehicle-8 (HTV-8) is pictured in the grips of the Canadarm2 robotic arm after ground controllers remotely detached the HTV-8 from the International Space Station's Harmony module. NASA astronauts Christina Koch and Jessica Meir would command the Canadarm2 to release the HTV-8 after a 34 day cargo mission at the orbiting lab.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The first flight of Challenger on mission STS-6. The primary payload is the first Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-1. The mission also is using the first lightweight external tank and lightweight solid rocket booster casings. The crew comprises Commander Paul J. Weitz, Pilot Karol J. Bobko, and Mission Specialists Donald H. Peterson and F. Story Musgrave.

A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is seen as it rolls out to launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
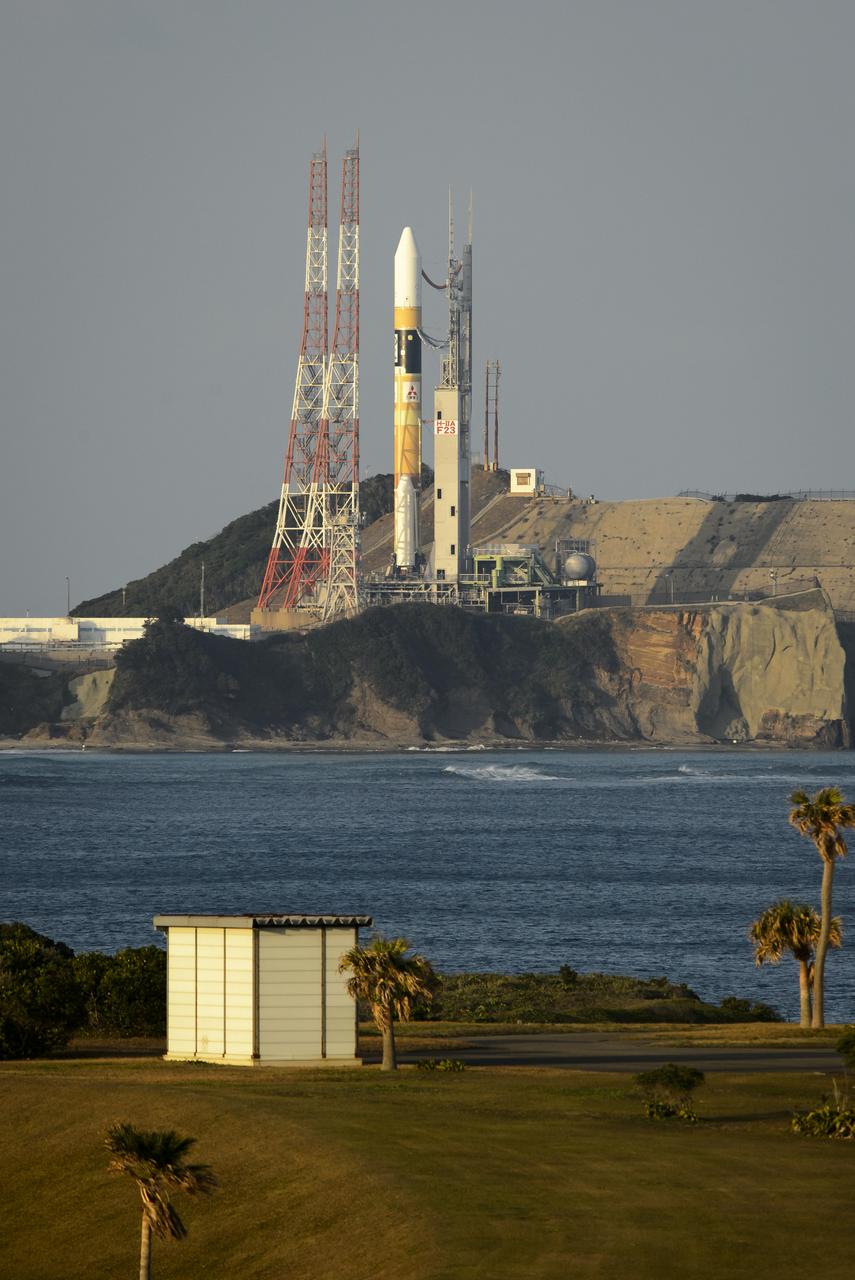

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Thursday, Feb. 27, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
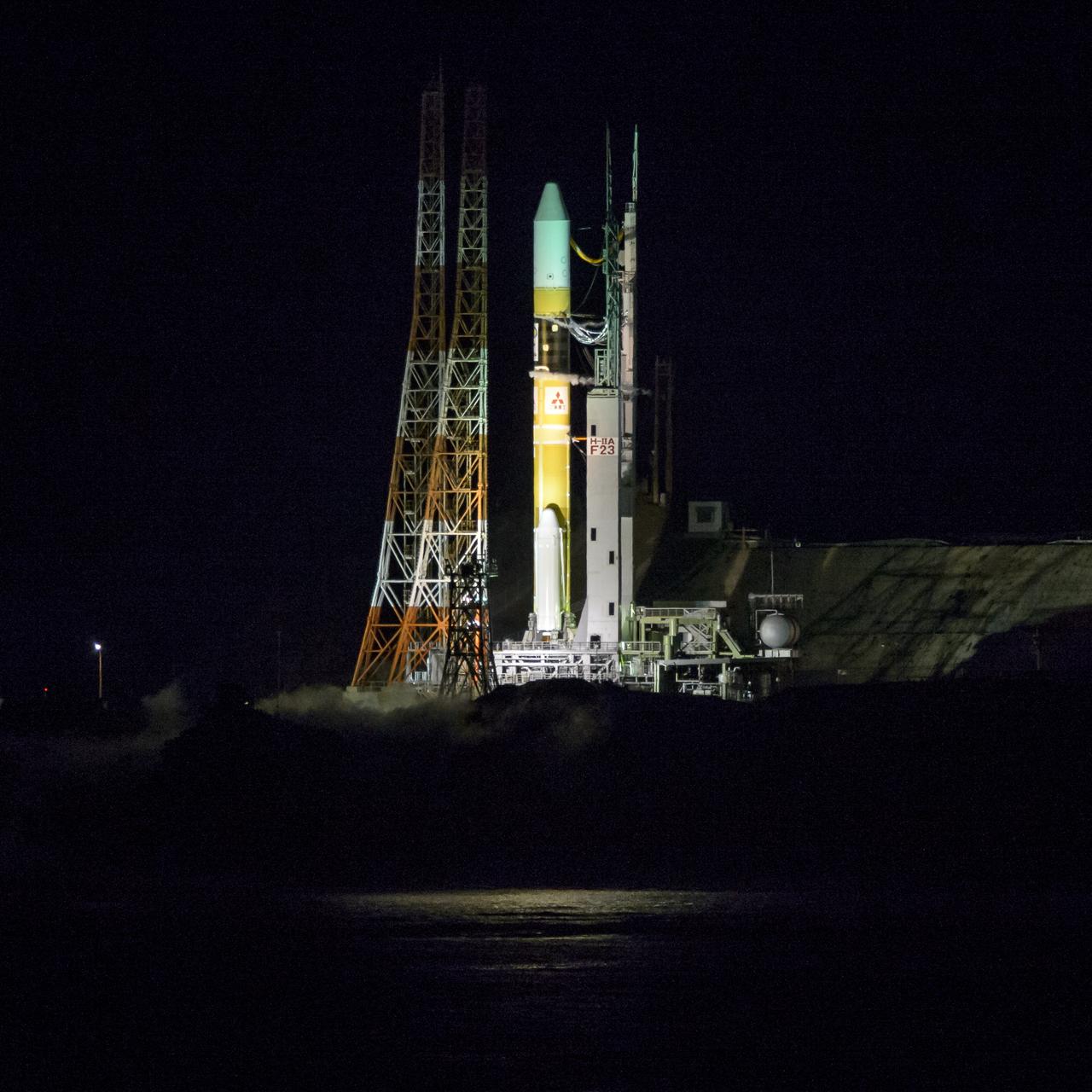

A Japanese H-IIA rocket with the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory onboard, is seen on launch pad 1 of the Tanegashima Space Center, Friday, Feb. 28, 2014, Tanegashima, Japan. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
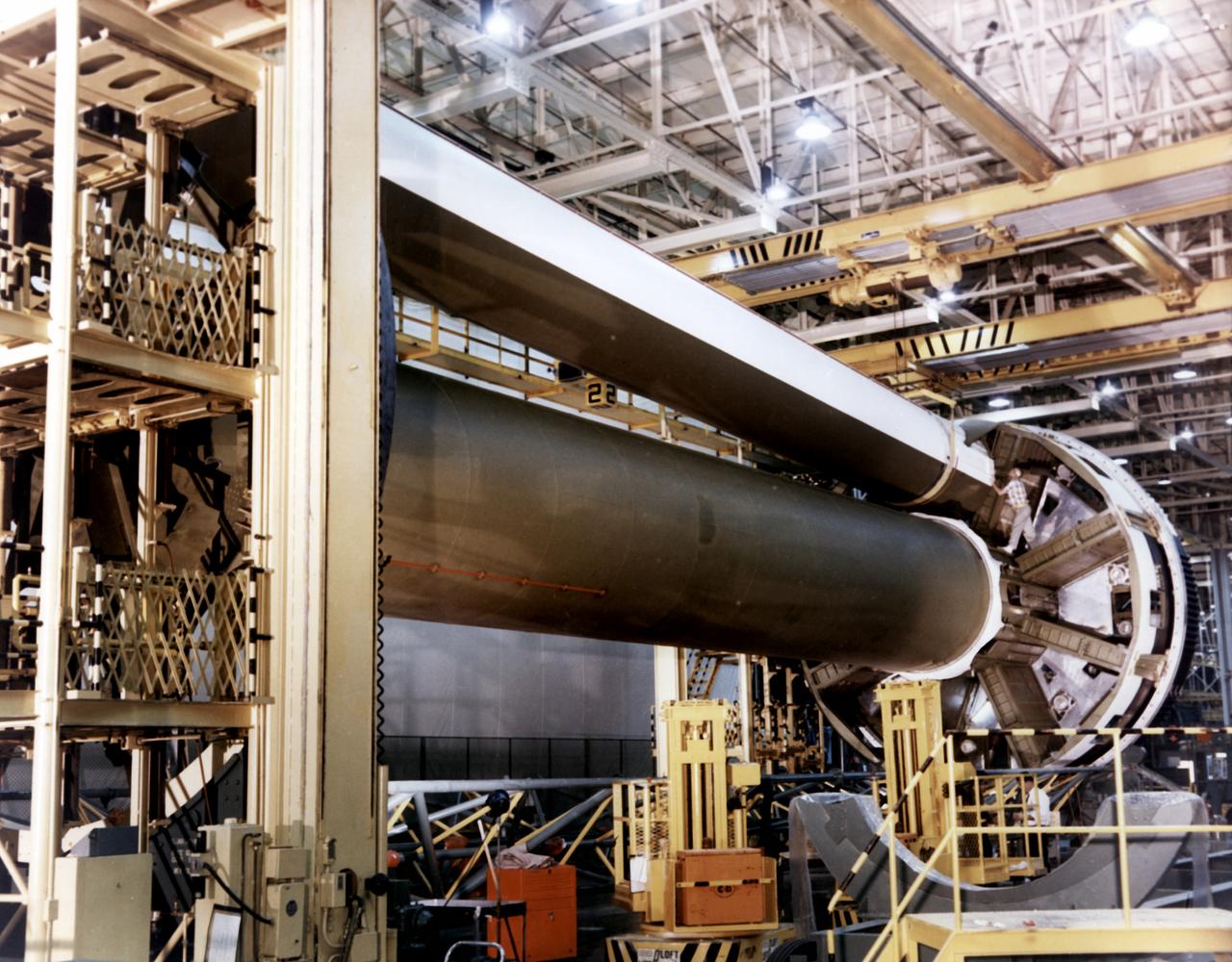

In the clustering procedure, an initial assembly step for the Saturn IB launch vehicle's S-IB (first) stage, workers at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) near New Orleans, Louisiana, place the first of eight outboard fuel tanks atop the central liquid-oxygen tank. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Chrysler Corporation at Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF), the S-IB utilized eight H-1 engines and each produced 200,000 pounds of thrust, a combined thrust of 1,600,000 pounds.
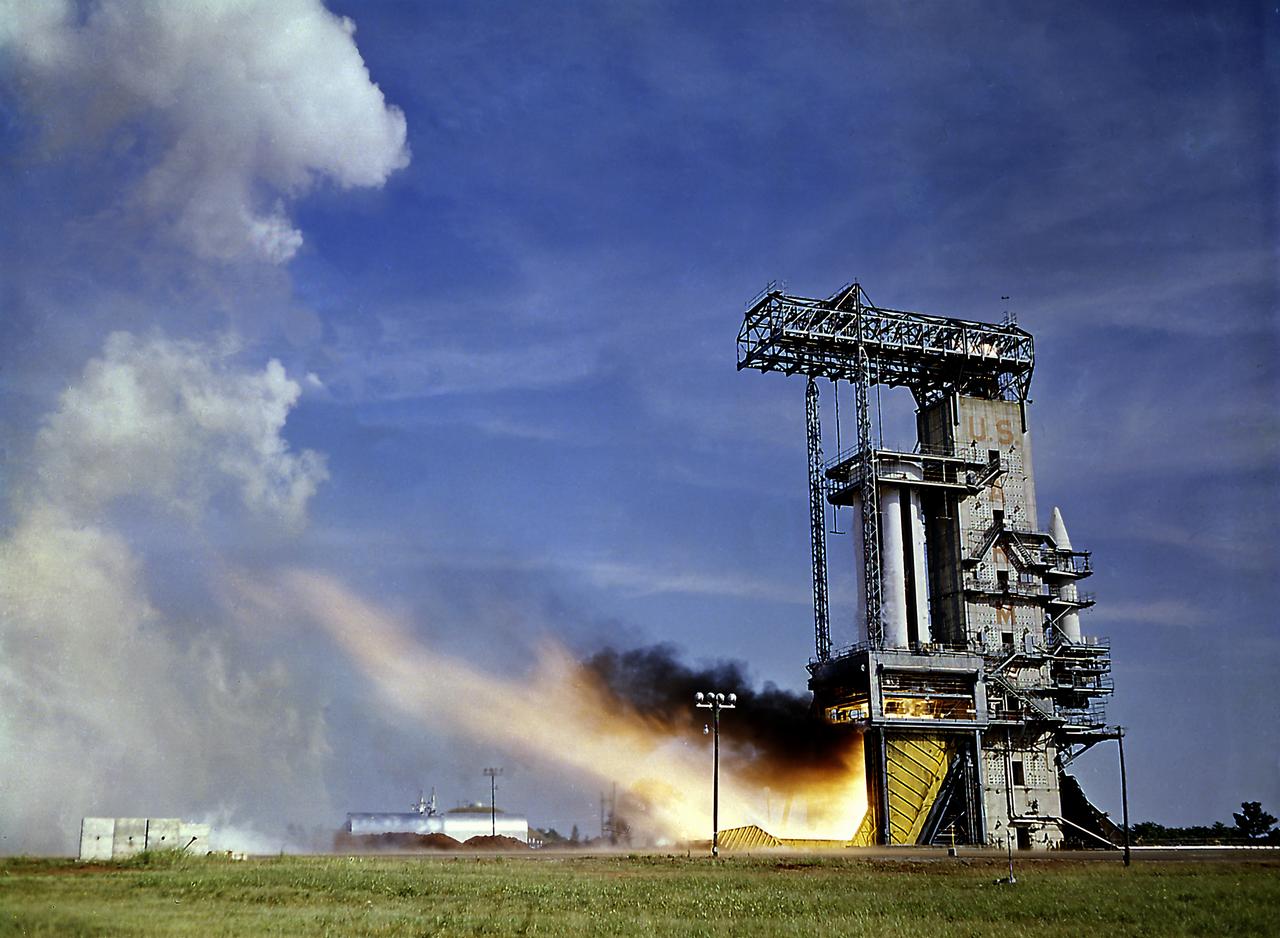

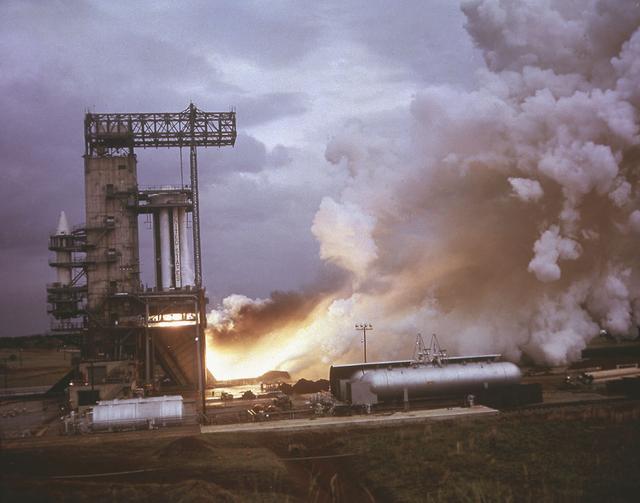
The Saturn Project was approved on January 18, 1960 as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept was well underway. A series of static tests of the Saturn I booster (S-I stage) began June 3, 1960 at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This photograph depicts the Saturn I S-I stage equipped with eight H-1 engines, being successfully test-fired for the duration of 121 seconds on June 15, 1960.
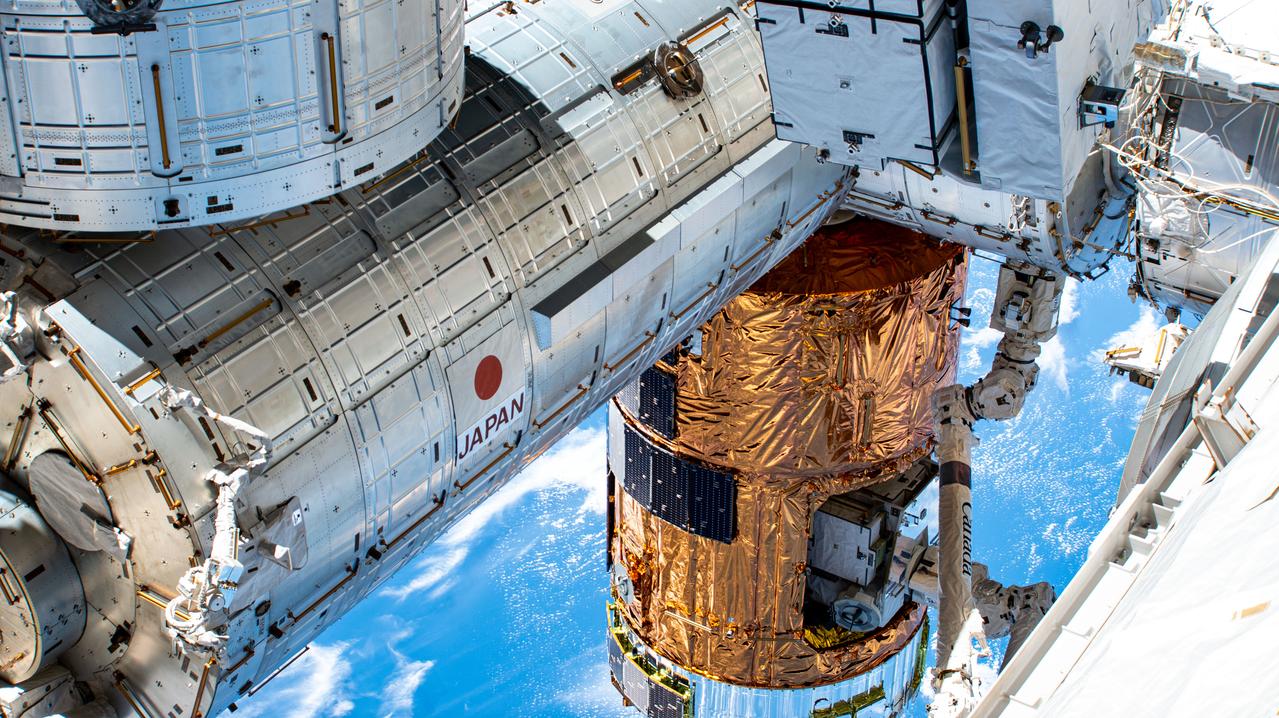

iss063e022443 (June 1, 2020) --- This oblique view from the port side of the International Space Station's truss structure shows JAXA's (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency's (CSA) contribution to the orbiting lab. Included in this photograph is a major portion of the Kibo laboratory module, the H-II Transfer Vehicle-9 (HTV-9) resupply ship and the Canadarm2 robotic arm.
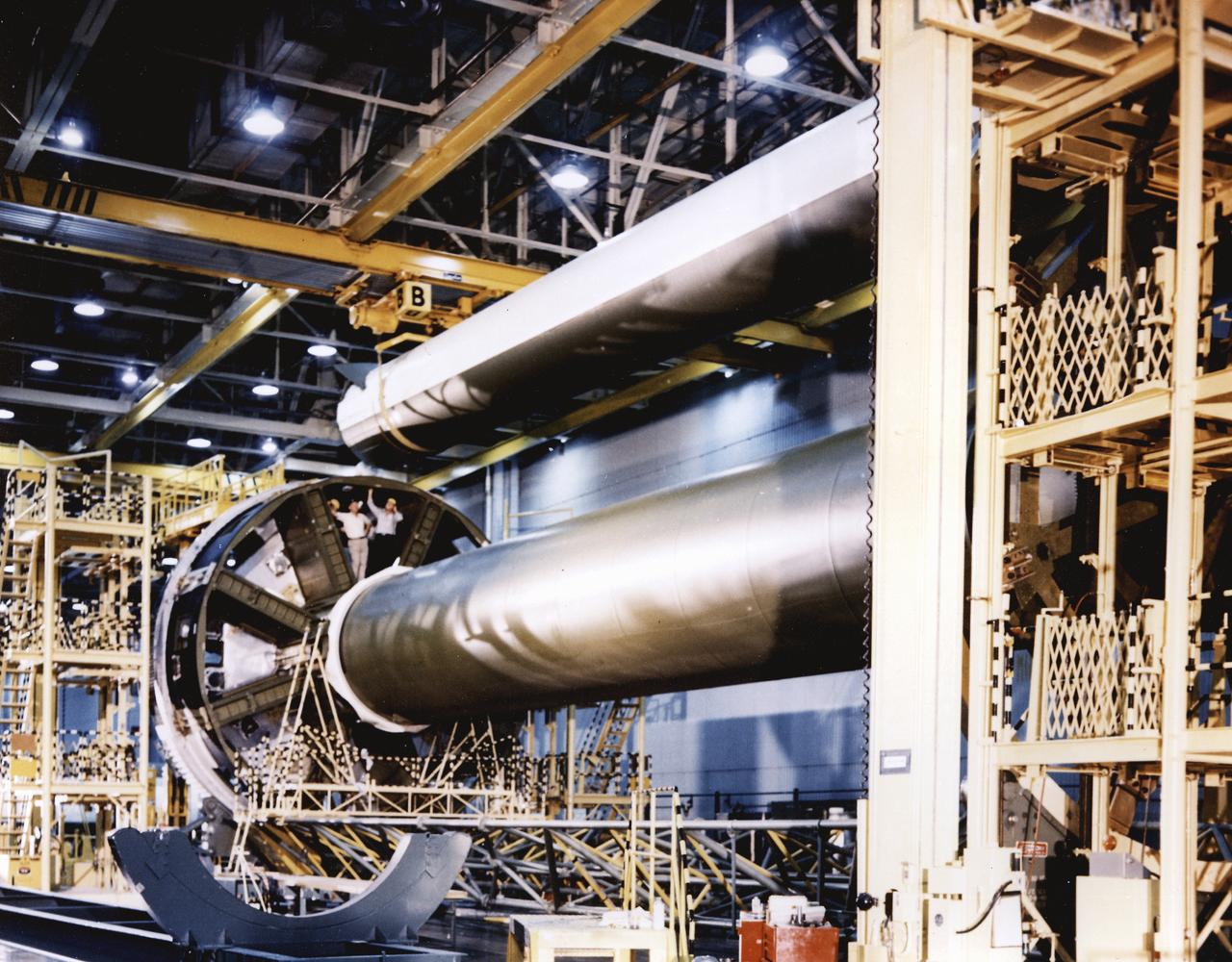

In the clustering procedure, an initial assembly step for the first stage (S-IB stage) of the Saturn IB launch vehicle, workers at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) near New Orleans, Louisiana, place the first of eight outboard fuel tanks next to the central liquid-oxygen tank of the S-IB stage. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and built by the Chrysler Corporation at MAF, the S-IB stage utilized eight H-1 engines to produce a combined thrust of 1,600,000 pounds.