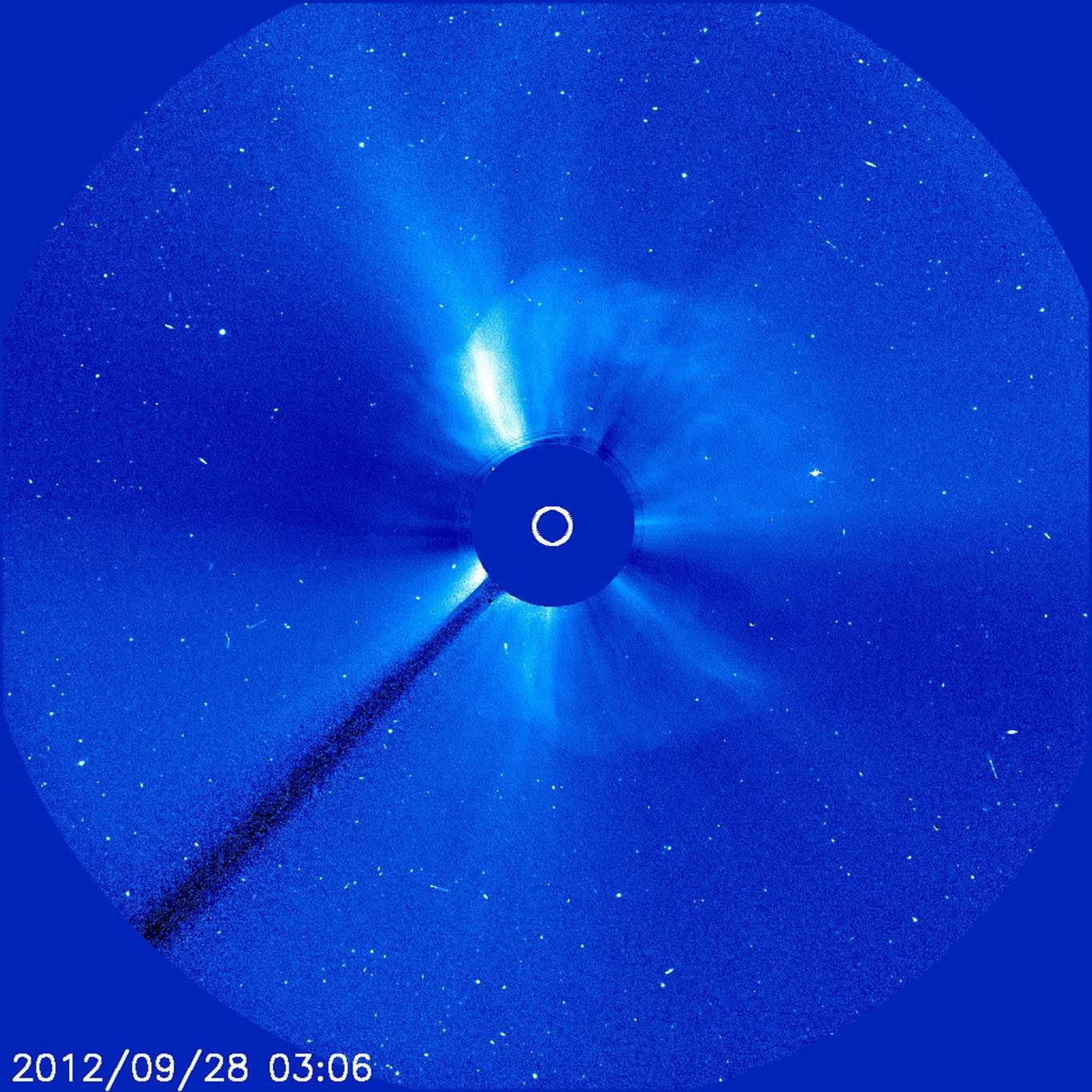
A giant cloud appears to expand outward from the sun in all directions in this image from Sept. 28, 2012, which is called a halo CME. This kind of image occurs when a CME moves toward Earth – as here – or directly away from it. Credit: ESA/NASA/SOHO CME WEEK: What To See in CME Images Two main types of explosions occur on the sun: solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Unlike the energy and x-rays produced in a solar flare – which can reach Earth at the speed of light in eight minutes – coronal mass ejections are giant, expanding clouds of solar material that take one to three days to reach Earth. Once at Earth, these ejections, also called CMEs, can impact satellites in space or interfere with radio communications. During CME WEEK from Sept. 22 to 26, 2014, we explore different aspects of these giant eruptions that surge out from the star we live with. When a coronal mass ejection blasts off the sun, scientists rely on instruments called coronagraphs to track their progress. Coronagraphs block out the bright light of the sun, so that the much fainter material in the solar atmosphere -- including CMEs -- can be seen in the surrounding space. CMEs appear in these images as expanding shells of material from the sun's atmosphere -- sometimes a core of colder, solar material (called a filament) from near the sun's surface moves in the center. But mapping out such three-dimensional components from a two-dimensional image isn't easy. Watch the slideshow to find out how scientists interpret what they see in CME pictures. The images in the slideshow are from the three sets of coronagraphs NASA currently has in space. One is on the joint European Space Agency and NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO. SOHO launched in 1995, and sits between Earth and the sun about a million miles away from Earth. The other two coronagraphs are on the two spacecraft of the NASA Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, mission, which launched in 2006. The two STEREO spacecraft are both currently viewing the far side of the sun. Together these instruments help scientists create a three-dimensional model of any CME as its journey unfolds through interplanetary space. Such information can show why a given characteristic of a CME close to the sun might lead to a given effect near Earth, or any other planet in the solar system...<b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
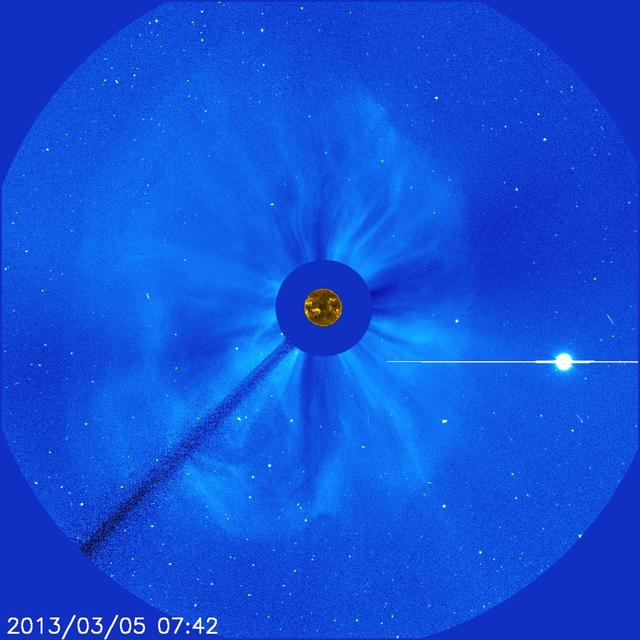
There's no way to tell from this SOHO image whether the halo CME on March 5, 2013, originated from the front or far of the sun. But the STEREO spacecraft were watching the sun from the sides and showed it was from the far side. The bright planet is Venus. Credit: NASA/SOHO CME WEEK: What To See in CME Images Two main types of explosions occur on the sun: solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Unlike the energy and x-rays produced in a solar flare – which can reach Earth at the speed of light in eight minutes – coronal mass ejections are giant, expanding clouds of solar material that take one to three days to reach Earth. Once at Earth, these ejections, also called CMEs, can impact satellites in space or interfere with radio communications. During CME WEEK from Sept. 22 to 26, 2014, we explore different aspects of these giant eruptions that surge out from the star we live with. When a coronal mass ejection blasts off the sun, scientists rely on instruments called coronagraphs to track their progress. Coronagraphs block out the bright light of the sun, so that the much fainter material in the solar atmosphere -- including CMEs -- can be seen in the surrounding space. CMEs appear in these images as expanding shells of material from the sun's atmosphere -- sometimes a core of colder, solar material (called a filament) from near the sun's surface moves in the center. But mapping out such three-dimensional components from a two-dimensional image isn't easy. Watch the slideshow to find out how scientists interpret what they see in CME pictures. The images in the slideshow are from the three sets of coronagraphs NASA currently has in space. One is on the joint European Space Agency and NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO. SOHO launched in 1995, and sits between Earth and the sun about a million miles away from Earth. The other two coronagraphs are on the two spacecraft of the NASA Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, mission, which launched in 2006. The two STEREO spacecraft are both currently viewing the far side of the sun. Together these instruments help scientists create a three-dimensional model of any CME as its journey unfolds through interplanetary space. Such information can show why a given characteristic of a CME close to the sun might lead to a given effect near Earth, or any other planet in the solar system...<b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
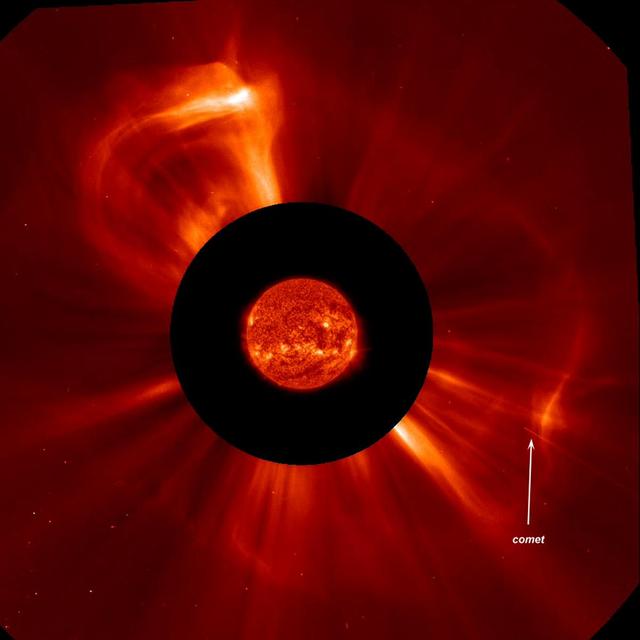
A small comet was streaking towards the Sun when the Sun blew out a "halo" coronal mass ejection (CME) Aug. 19-20, 2013). The CME originated from the far side of the Sun and did not have any interaction with the comet. The comet, only perhaps 30 meters across, was not seen after it went out of view, likely disintegrated by the heat and radiation from the Sun. We call this a "full halo" CME since the front edge of the CME is expanding in all directions around the Sun like a halo. The images were taken by SOHO's coronagraphs in which a disk (red) blocks the Sun and some of the area around it so we can see faint structures beyond that. Here we superimposed the Sun from NASA's SDO. The movie covers about five hours of activity and can be seen here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/9601034896/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/9601034896/</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/SOHO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

STEREO witnessed the March 5, 2013, CME from the side of the sun – Earth is far to the left of this picture. While the SOHO images show a halo CME, STEREO shows the CME clearly moving away from Earth. Credit: NASA/STEREO --- CME WEEK: What To See in CME Images Two main types of explosions occur on the sun: solar flares and coronal mass ejections. Unlike the energy and x-rays produced in a solar flare – which can reach Earth at the speed of light in eight minutes – coronal mass ejections are giant, expanding clouds of solar material that take one to three days to reach Earth. Once at Earth, these ejections, also called CMEs, can impact satellites in space or interfere with radio communications. During CME WEEK from Sept. 22 to 26, 2014, we explore different aspects of these giant eruptions that surge out from the star we live with. When a coronal mass ejection blasts off the sun, scientists rely on instruments called coronagraphs to track their progress. Coronagraphs block out the bright light of the sun, so that the much fainter material in the solar atmosphere -- including CMEs -- can be seen in the surrounding space. CMEs appear in these images as expanding shells of material from the sun's atmosphere -- sometimes a core of colder, solar material (called a filament) from near the sun's surface moves in the center. But mapping out such three-dimensional components from a two-dimensional image isn't easy. Watch the slideshow to find out how scientists interpret what they see in CME pictures. The images in the slideshow are from the three sets of coronagraphs NASA currently has in space. One is on the joint European Space Agency and NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO. SOHO launched in 1995, and sits between Earth and the sun about a million miles away from Earth. The other two coronagraphs are on the two spacecraft of the NASA Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, mission, which launched in 2006. The two STEREO spacecraft are both currently viewing the far side of the sun. Together these instruments help scientists create a three-dimensional model of any CME as its journey unfolds through interplanetary space. Such information can show why a given characteristic of a CME close to the sun might lead to a given effect near Earth, or any other planet in the solar system. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
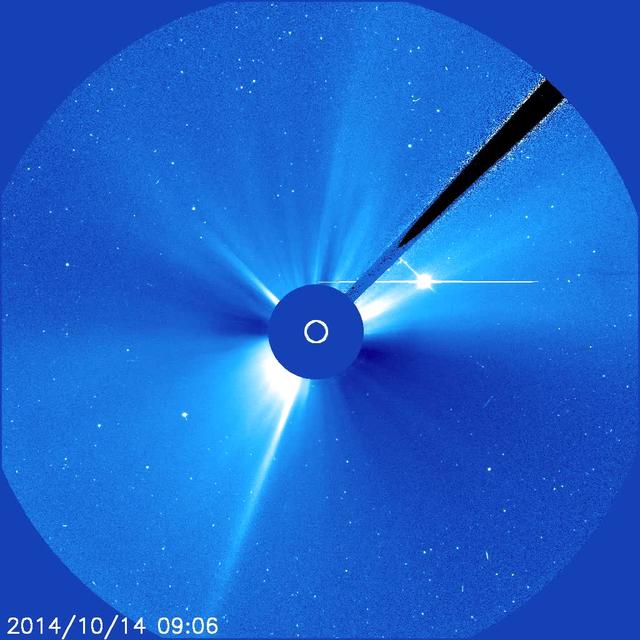

The Sun blew out a powerful coronal mass ejection (CME) from just around the edge of the Sun (Oct. 14, 2014). The particle cloud expanded around all the Sun in a rough circle, hence the name 'halo' CME. This event was also associated with a fairly strong flare. The active region that was the source of these events is just rotating into view. Then, we can better observe its size and structure. The bright object to the right and just above the Sun is Venus now on the far side of the Sun. Credit: NASA/ESA/SOHO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
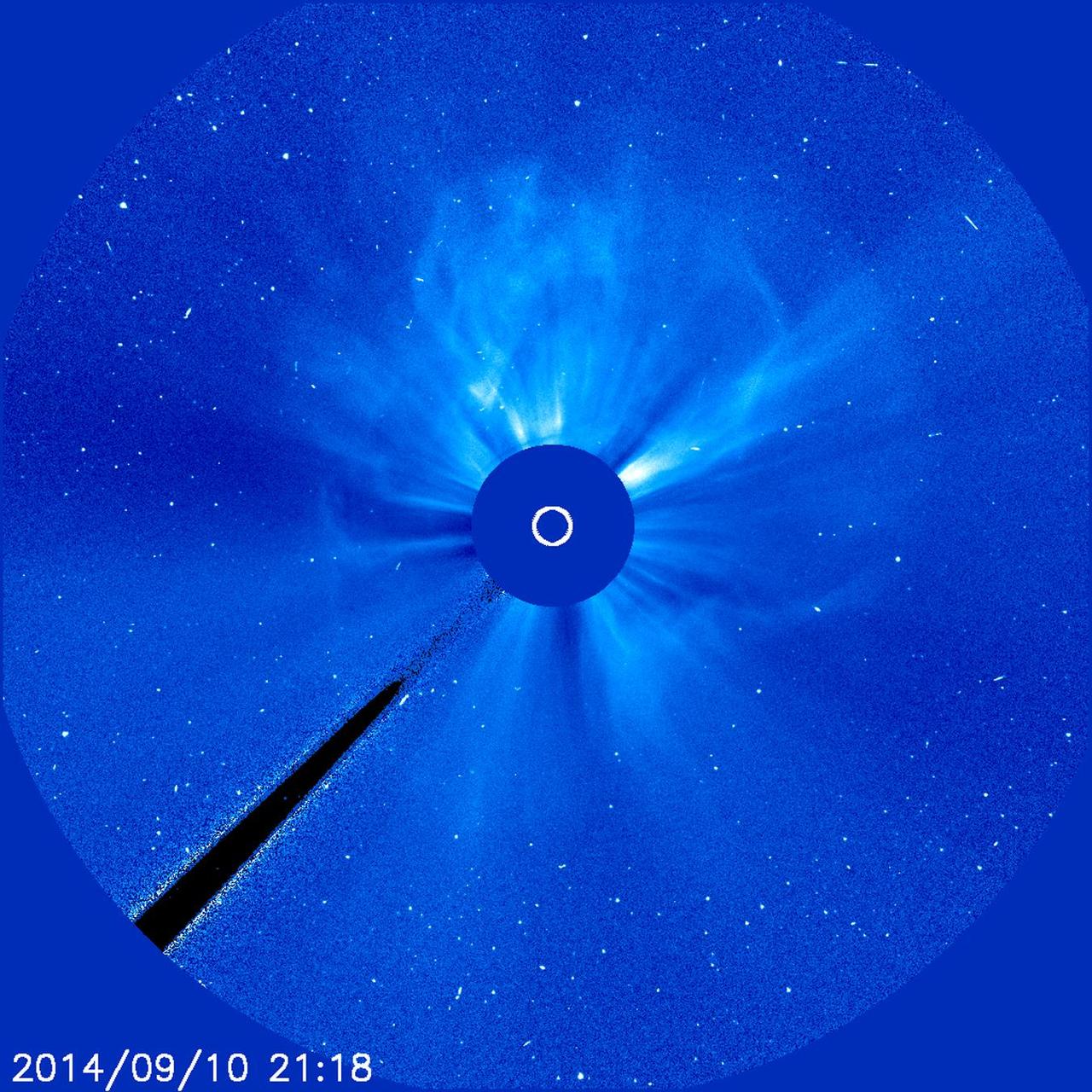
An active region just about squarely facing Earth erupted with an X 1.6 flare (largest class) as well as a coronal mass ejection (CME) on Sept. 10-11, 2014. This event featured both a long flare decay time and a storm of electrically charged, energetic particles. The particles can be seen as bright white specks scattering across the frames. The coronagraph movie shows the cloud of particles expanding in all directions as if it were creating a halo around the Sun. Data shows that the CME was heading towards Earth that could generate strong aurora displays several days later. In coronagraph images the Sun (represented by the small white circle in the center) is blocked by an occulting disk so that we can observe faint features in the corona and beyond. Credit: NASA/ESA/Goddard/SOHO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>