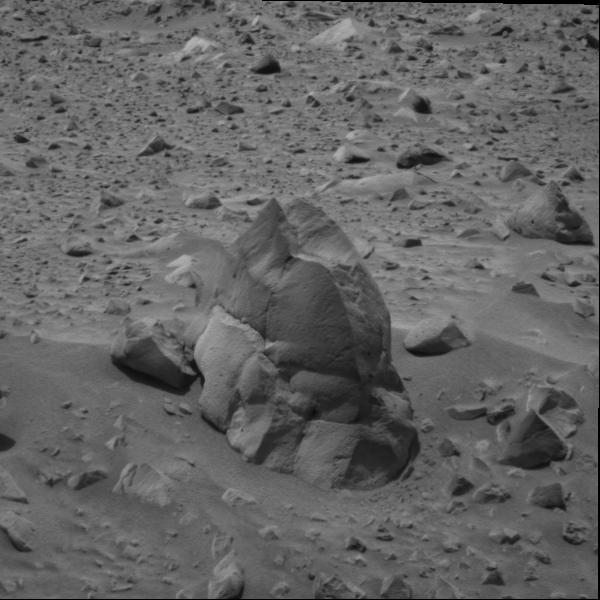

Heading for Humphrey

Heading for the Hills

Heading for the Hills

Spirit Heads Toward History
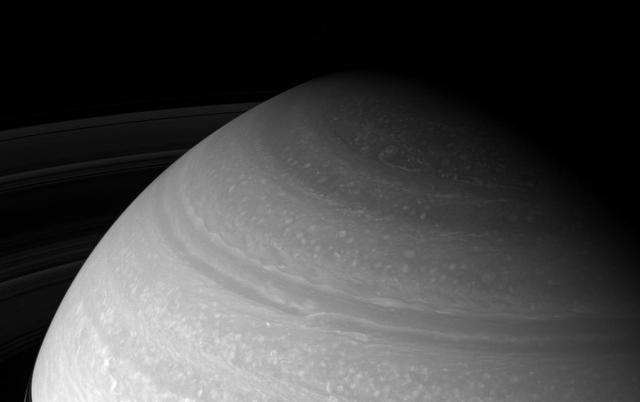

Over Your Head
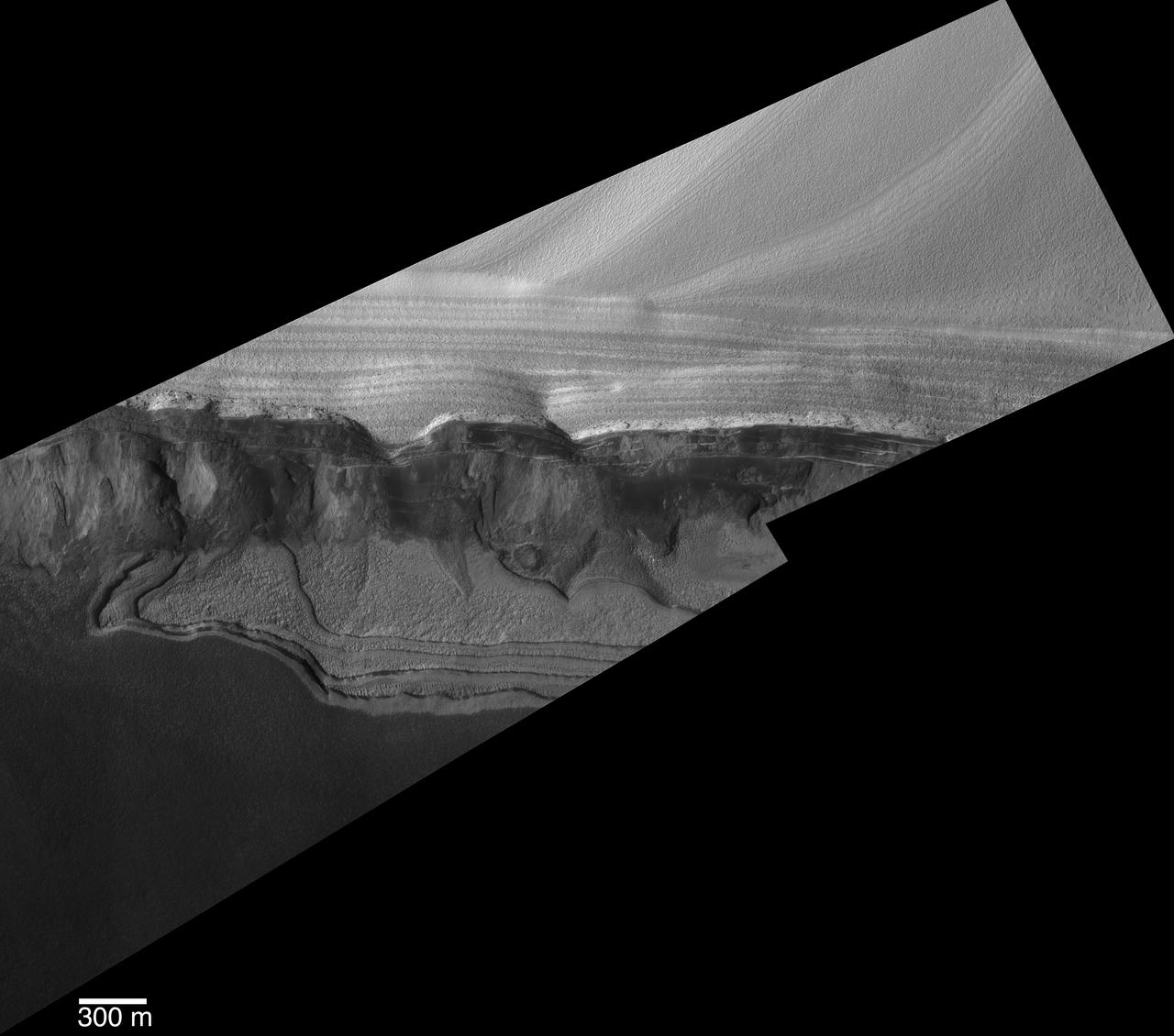

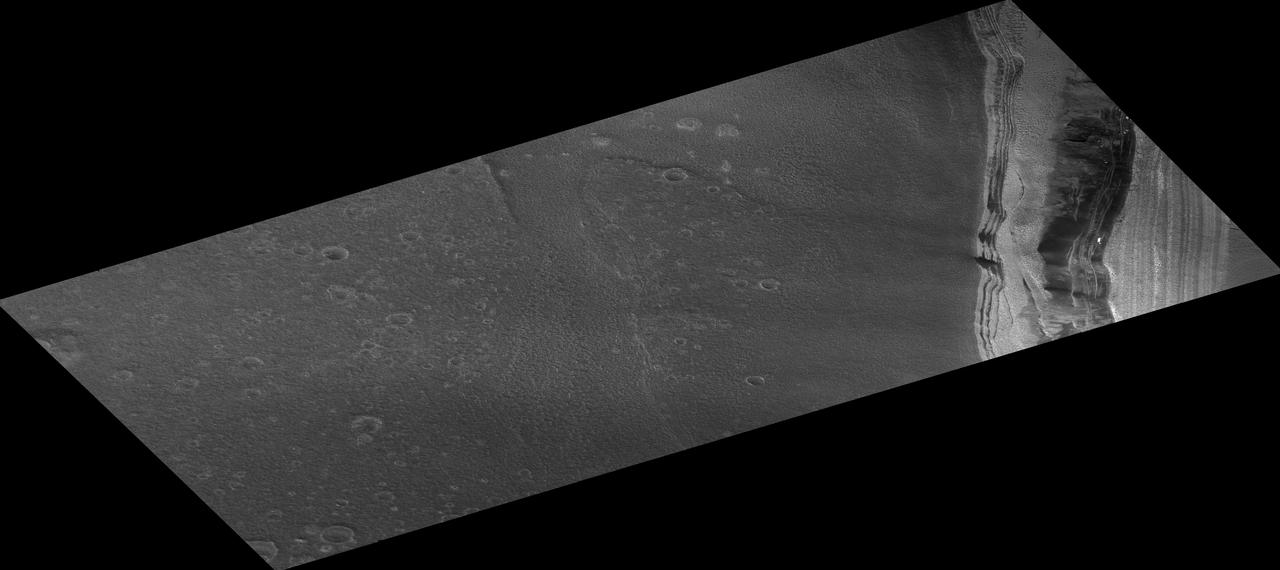
Scarp at Head of Chasma Boreale

Heading South on Erebus Highway
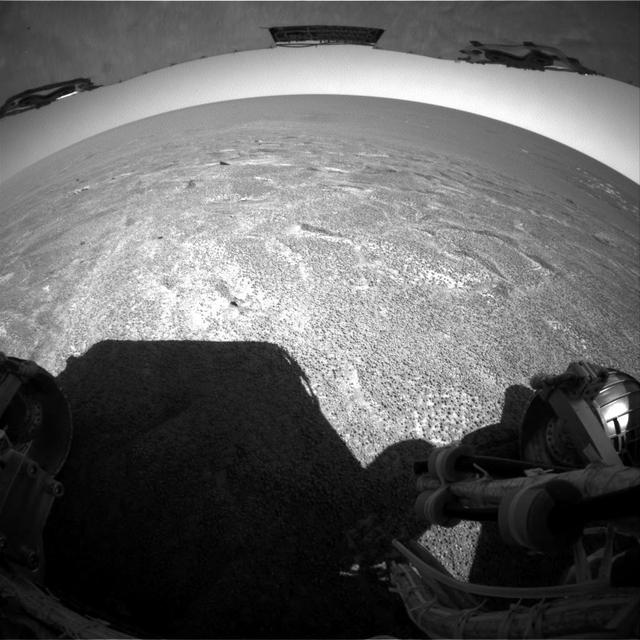

Out of Endurance, Heading South
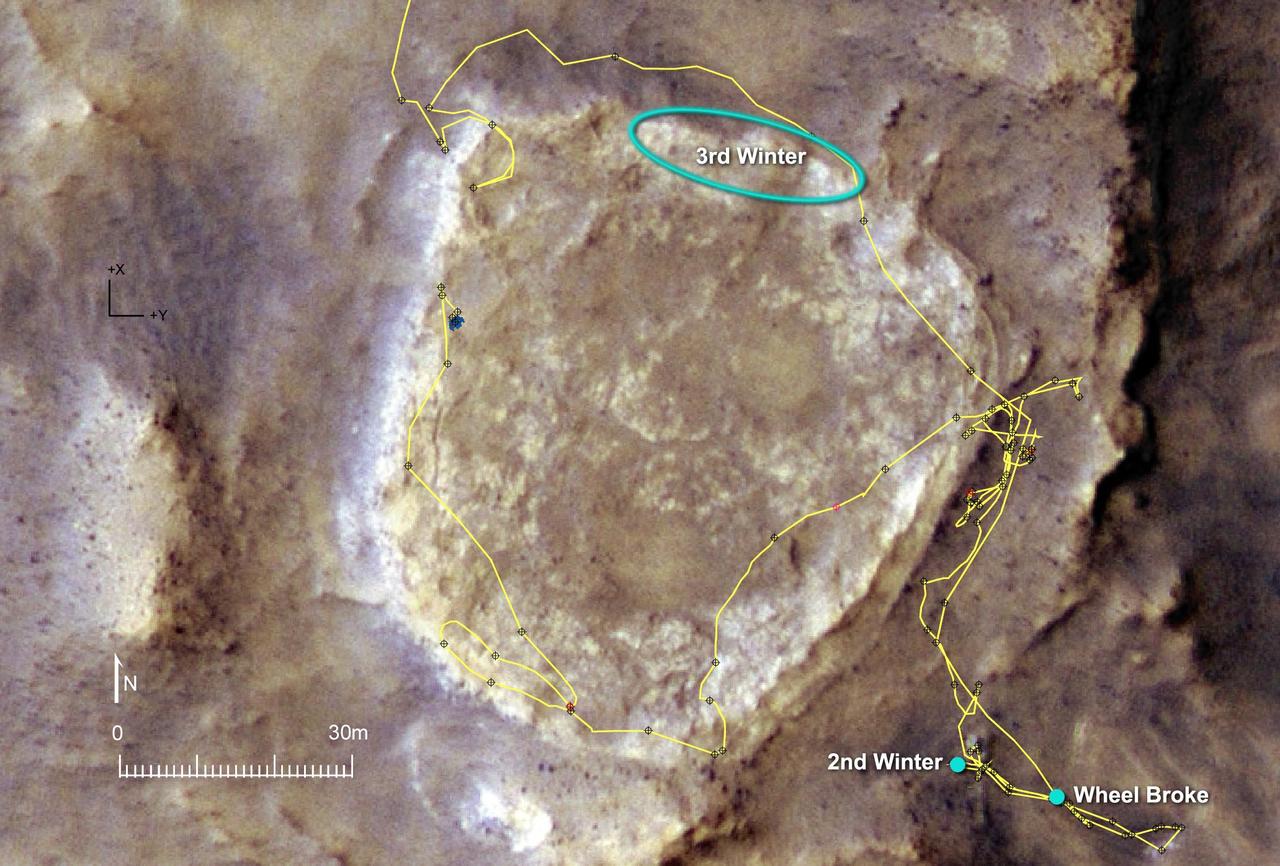
Heading for Next Winter Haven
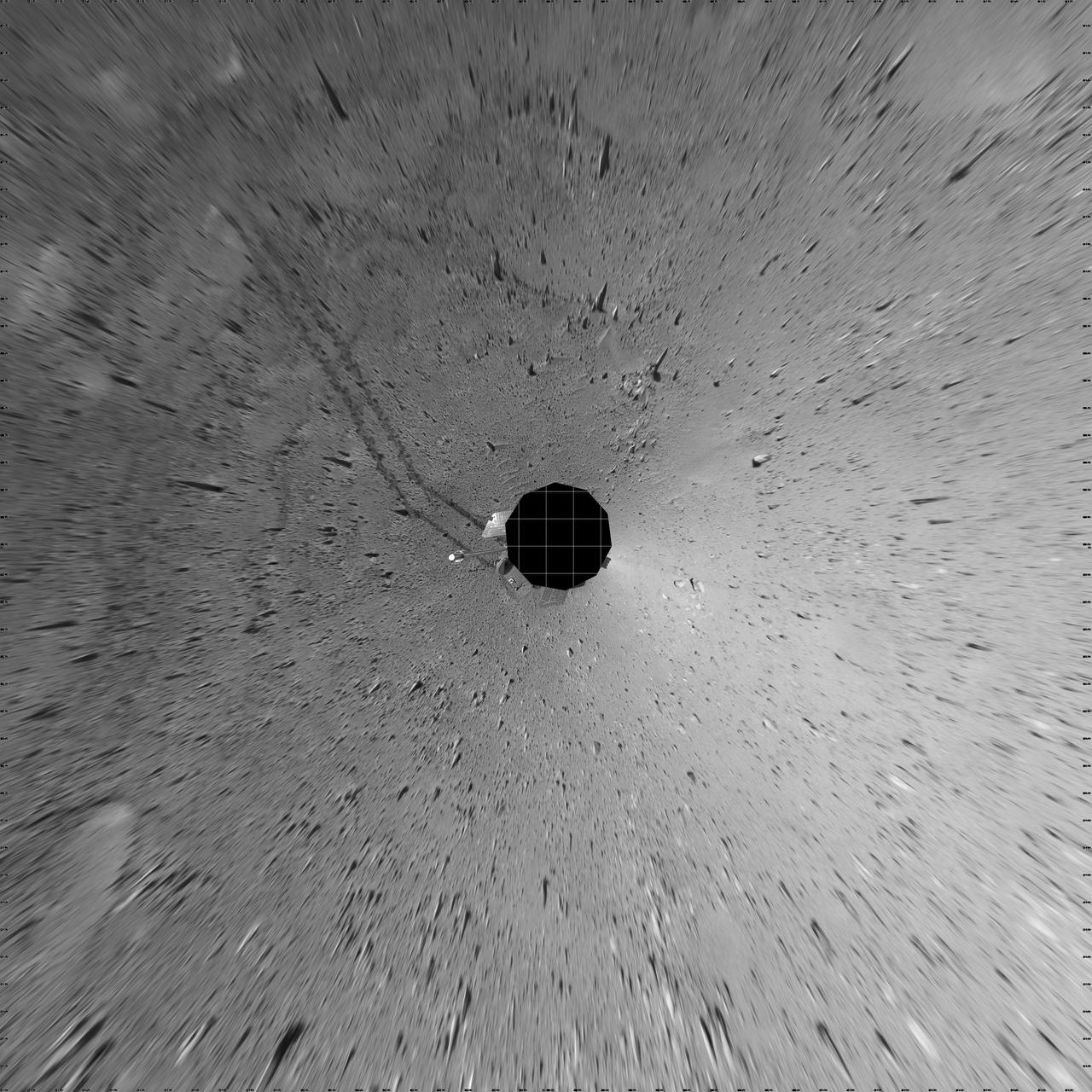

Spirit Heads Toward History vertical

Spirit Heads Toward History polar
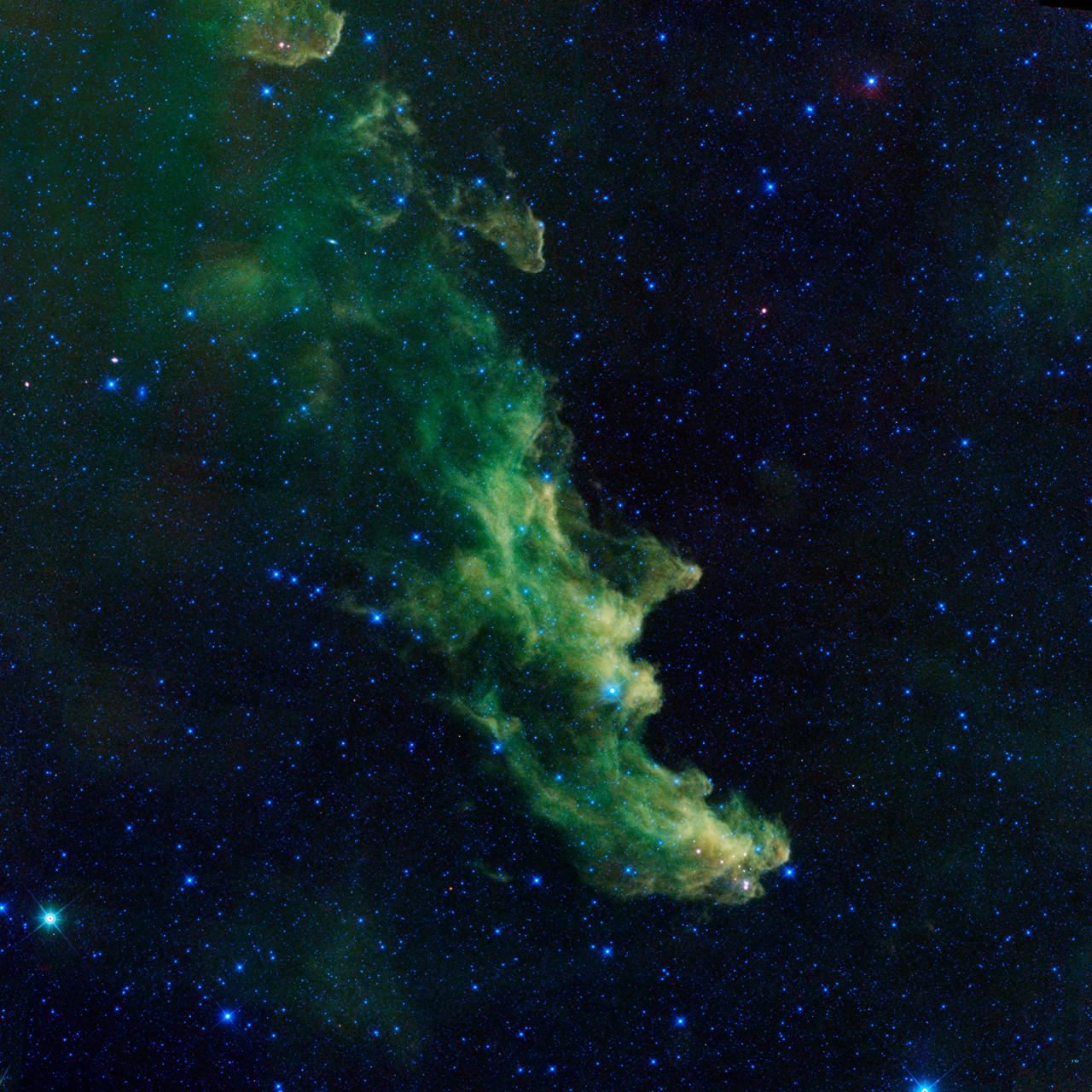

A witch appears to be screaming out into space in this new image from NASA's Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE. The infrared portrait shows the Witch Head nebula, named after its resemblance to the profile of a wicked witch. Astronomers say the billowy clouds of the nebula, where baby stars are brewing, are being lit up by massive stars. Dust in the cloud is being hit with starlight, causing it to glow with infrared light, which was picked up by WISE's detectors. The Witch Head nebula is estimated to be hundreds of light-years away in the Orion constellation, just off the famous hunter's knee. WISE was recently "awakened" to hunt for asteroids in a program called NEOWISE. The reactivation came after the spacecraft was put into hibernation in 2011, when it completed two full scans of the sky, as planned. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Spirit Heads Toward History left eye

Head of Chasma Boreale Near Mars North Pole

Spirit Heads Toward History right eye

Looking like a colorful holiday card, a new image from NASA Hubble Space Telescope reveals a vibrant green and red nebula far from Earth.
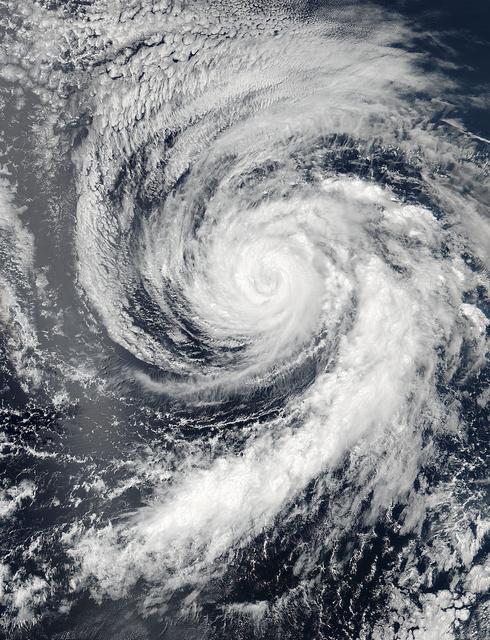

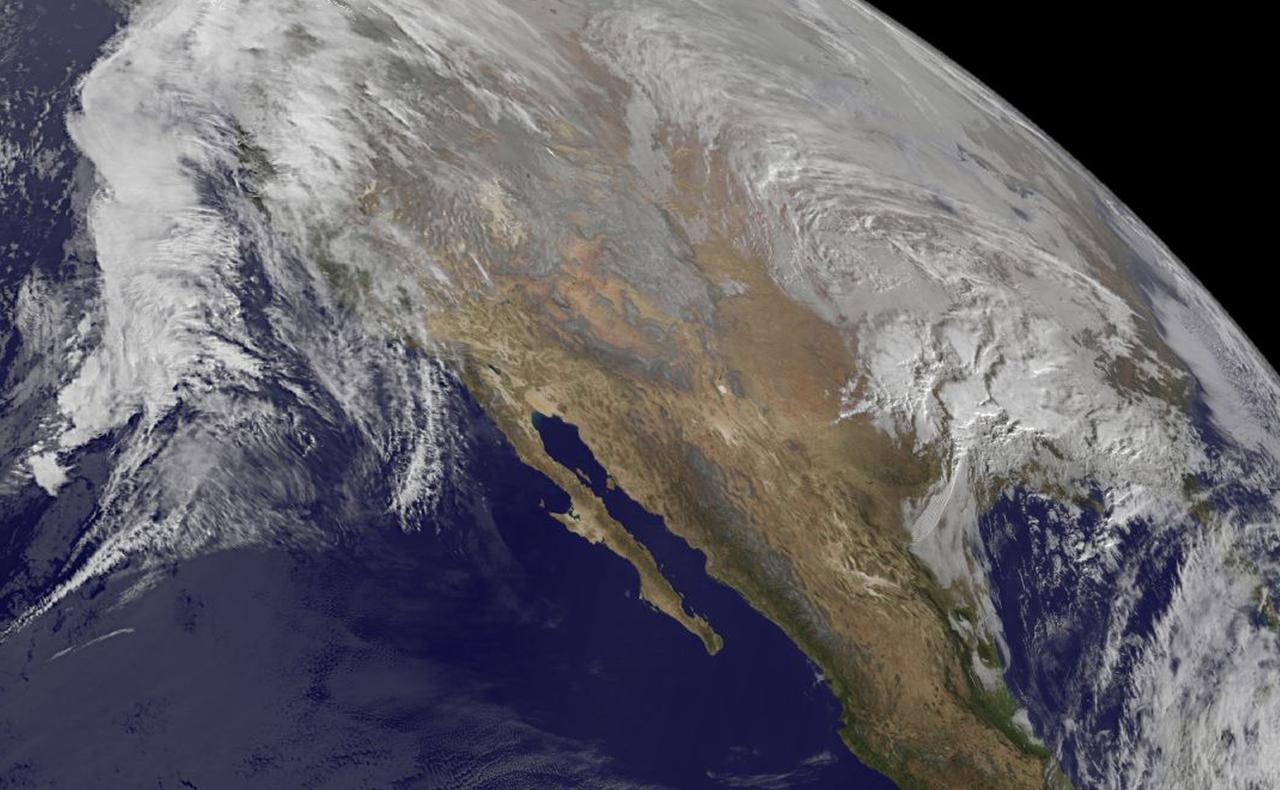
Hurricane Celia is currently in the Eastern Pacific Ocean, but once it passes west of 140 degrees west longitude, warnings on the system will be issued by NOAA's Central Pacific Hurricane Center. On July 11 at 22:05 UTC (6:05 p.m. EDT) the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard NASA-NOAA-DOD's Suomi NPP satellite captured a visible light image of Hurricane Celia that showed a cloud-filled eye with powerful bands of thunderstorms wrapping around the low level center. The VIIRS image also showed a large band of thunderstorms that extended to the south, wrapping into the storms' eastern quadrant. At 5 a.m. EDT (0900 UTC) on July 12 the center of Hurricane Celia was located near 16.2 north latitude and 127.9 west longitude. That's about 1,260 miles (2,025 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California, Mexico. It was moving to the west-northwest at 10 mph (17 kph) and NOAA's National Hurricane Center (NHC) expects Celia to turn toward the northwest later today, with this motion continuing Tuesday night and Wednesday. Maximum sustained winds were near 100 mph (155 kph). NHC forecasts weakening over the next two days and Celia could weaken to a tropical storm on Wednesday. Read more: NASA Sees Hurricane Celia Headed for Central Pacific Credit: NASA/Goddard/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The Collector Head Of Viking Lander 1 Surface Sampler http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00395

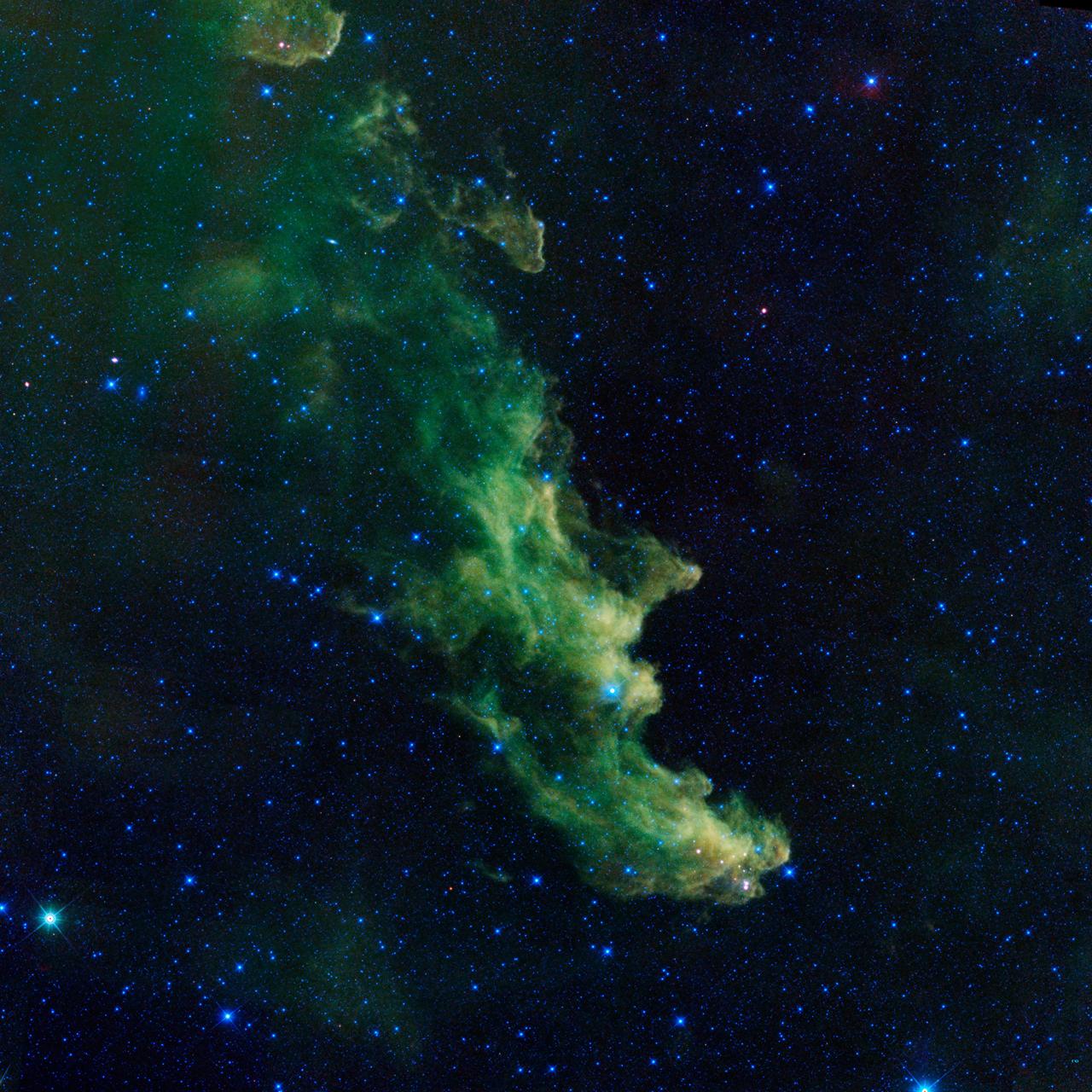
A witch appears to be screaming out into space in this new image from NASA's Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE. The infrared portrait shows the Witch Head nebula, named after its resemblance to the profile of a wicked witch. Astronomers say the billowy clouds of the nebula, where baby stars are brewing, are being lit up by massive stars. Dust in the cloud is being hit with starlight, causing it to glow with infrared light, which was picked up by WISE's detectors. The Witch Head nebula is estimated to be hundreds of light-years away in the Orion constellation, just off the famous hunter's knee. WISE was recently "awakened" to hunt for asteroids in a program called NEOWISE. The reactivation came after the spacecraft was put into hibernation in 2011, when it completed two full scans of the sky, as planned. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech NASA image use policy. ( http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html ) NASA Goddard Space Flight Center ( http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html ) enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. Follow us on Twitter ( http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix ) Like us on Facebook ( http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd ) Find us on Instagram ( http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid )
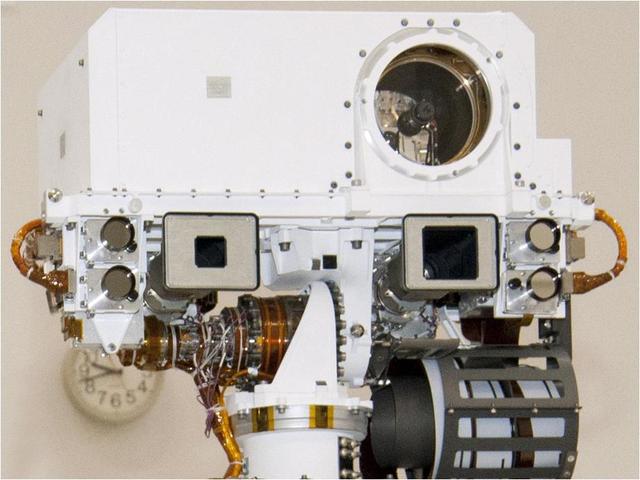
This view of the head of the remote sensing mast on the Mars Science Laboratory mission rover, Curiosity, shows seven of the 17 cameras on the rover.
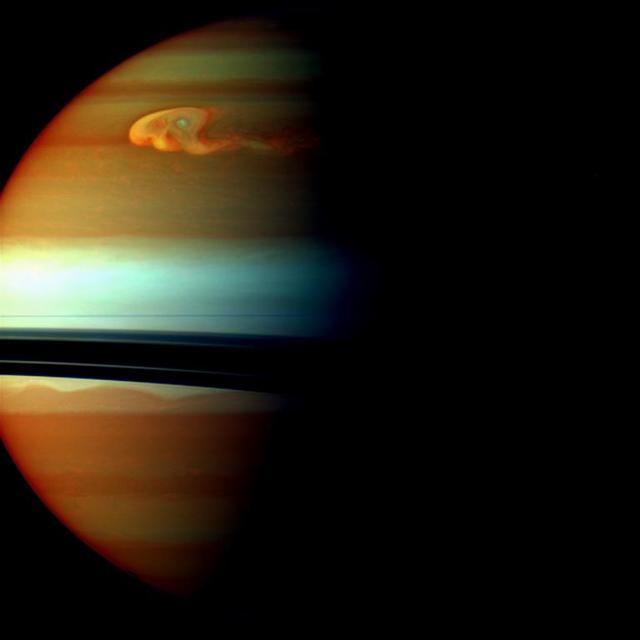

The head of Saturn huge northern storm is well established in this view captured early in the storm development by NASA Cassini spacecraft in late 2010.
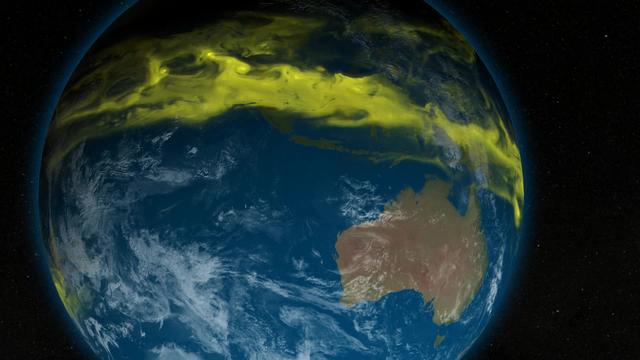
Caption: This is a conceptual animation showing ozone-depleting chemicals moving from the equator to the poles. The chemicals become trapped by the winds of the polar vortex, a ring of fast moving air that circles the South Pole. Watch full video: <a href="https://youtu.be/7n2km69jZu8" rel="nofollow">youtu.be/7n2km69jZu8</a> -- The next three decades will see an end of the era of big ozone holes. In a new study, scientists from NASA Goddard Space Flight Center say that the ozone hole will be consistently smaller than 12 million square miles by the year 2040. Ozone-depleting chemicals in the atmosphere cause an ozone hole to form over Antarctica during the winter months in the Southern Hemisphere. Since the Montreal Protocol agreement in 1987, emissions have been regulated and chemical levels have been declining. However, the ozone hole has still remained bigger than 12 million square miles since the early 1990s, with exact sizes varying from year to year. The size of the ozone hole varies due to both temperature and levels of ozone-depleting chemicals in the atmosphere. In order to get a more accurate picture of the future size of the ozone hole, scientists used NASA’s AURA satellite to determine how much the levels of these chemicals in the atmosphere varied each year. With this new knowledge, scientists can confidently say that the ozone hole will be consistently smaller than 12 million square miles by the year 2040. Scientists will continue to use satellites to monitor the recovery of the ozone hole and they hope to see its full recovery by the end of the century. Research: Inorganic chlorine variability in the Antarctic vortex and implications for ozone recovery. Journal: Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, December 18, 2014. Link to paper: <a href="http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2014JD022295/abstract" rel="nofollow">onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2014JD022295/abstract</a>.

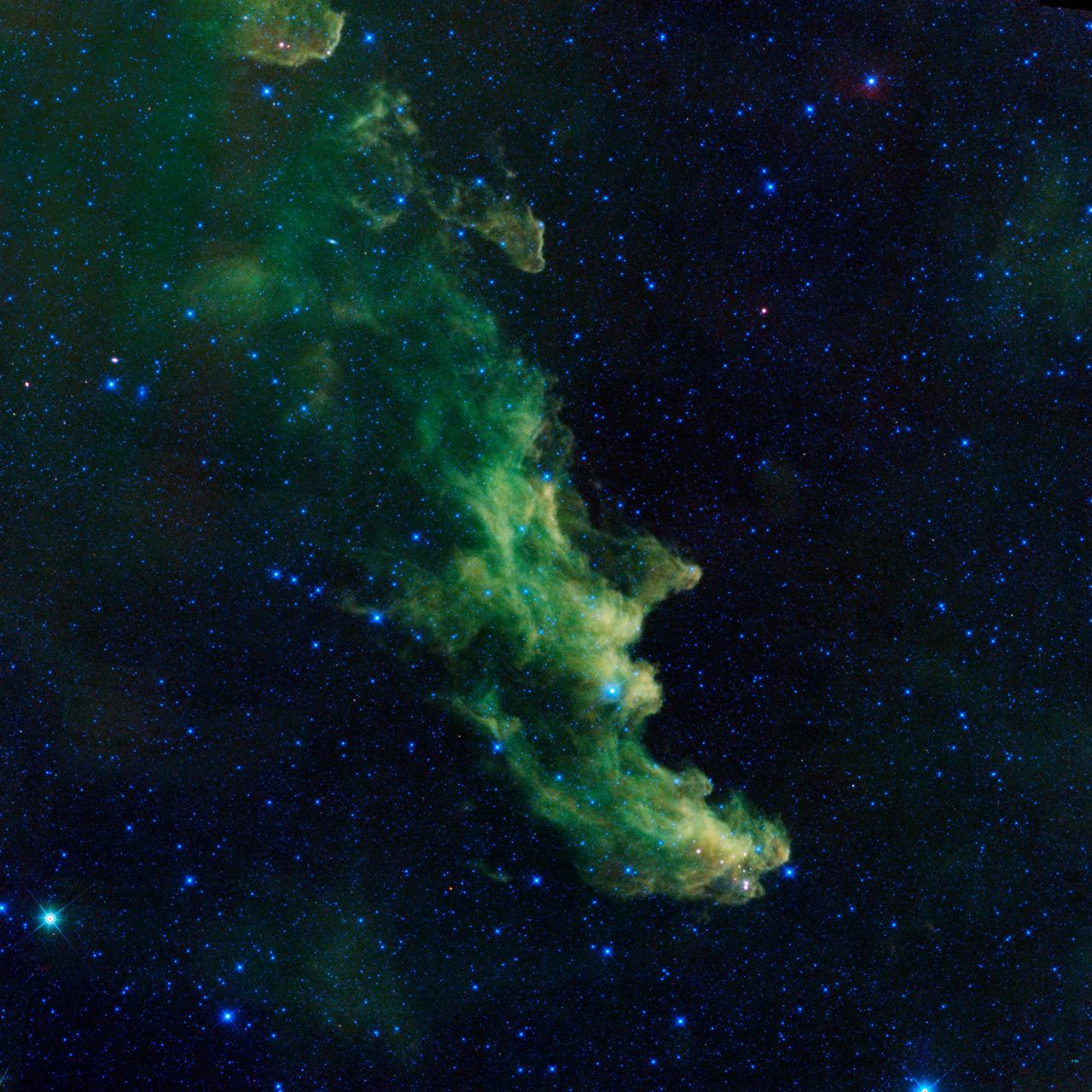
An infrared portrait of the Witch Head nebula from NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, shows billowy clouds where new stars are brewing.
NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, shows a giant nebula around Lambda Orionis, inflating Orion head to huge proportions.

Dr. Walther Pelzer, Head of the German Space Agency, German Aerospace Center (DLR) gives remarks in a Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Volodymyr Taftai, Head of Agency, State Space Agency of Ukraine (SSAU) gives remarks in a Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Opportunity used its Pancam to record this view of the rise in the foreground, called Nobbys Head. This view is centered toward the south-southeast, with Opportunity next destination, Solander Point, toward the right edge of the view.
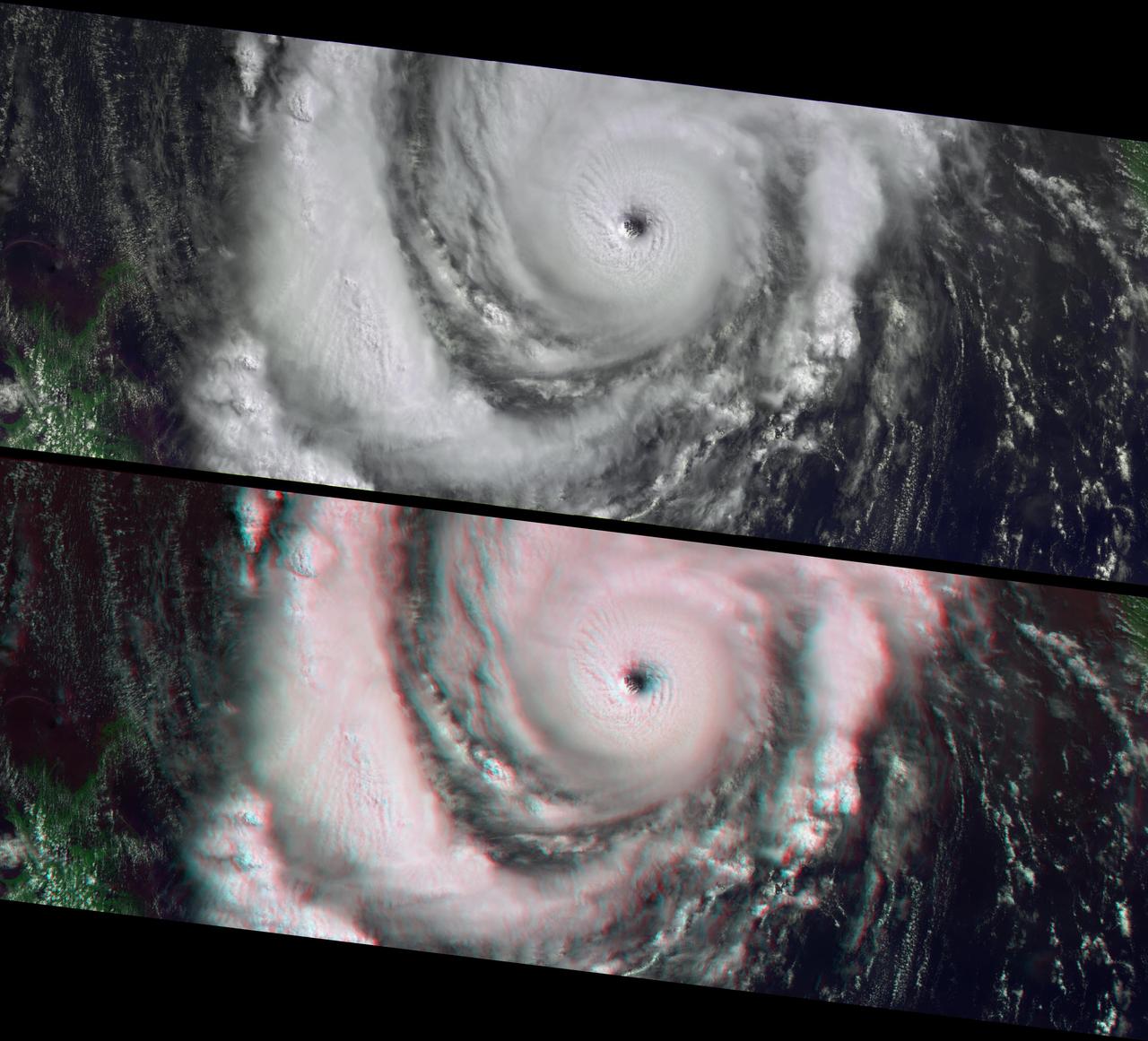
This anaglyph from the MISR instrument aboard NASA Terra spacecraft shows Hurricane Lili headed for Louisiana on October 2, 2002. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
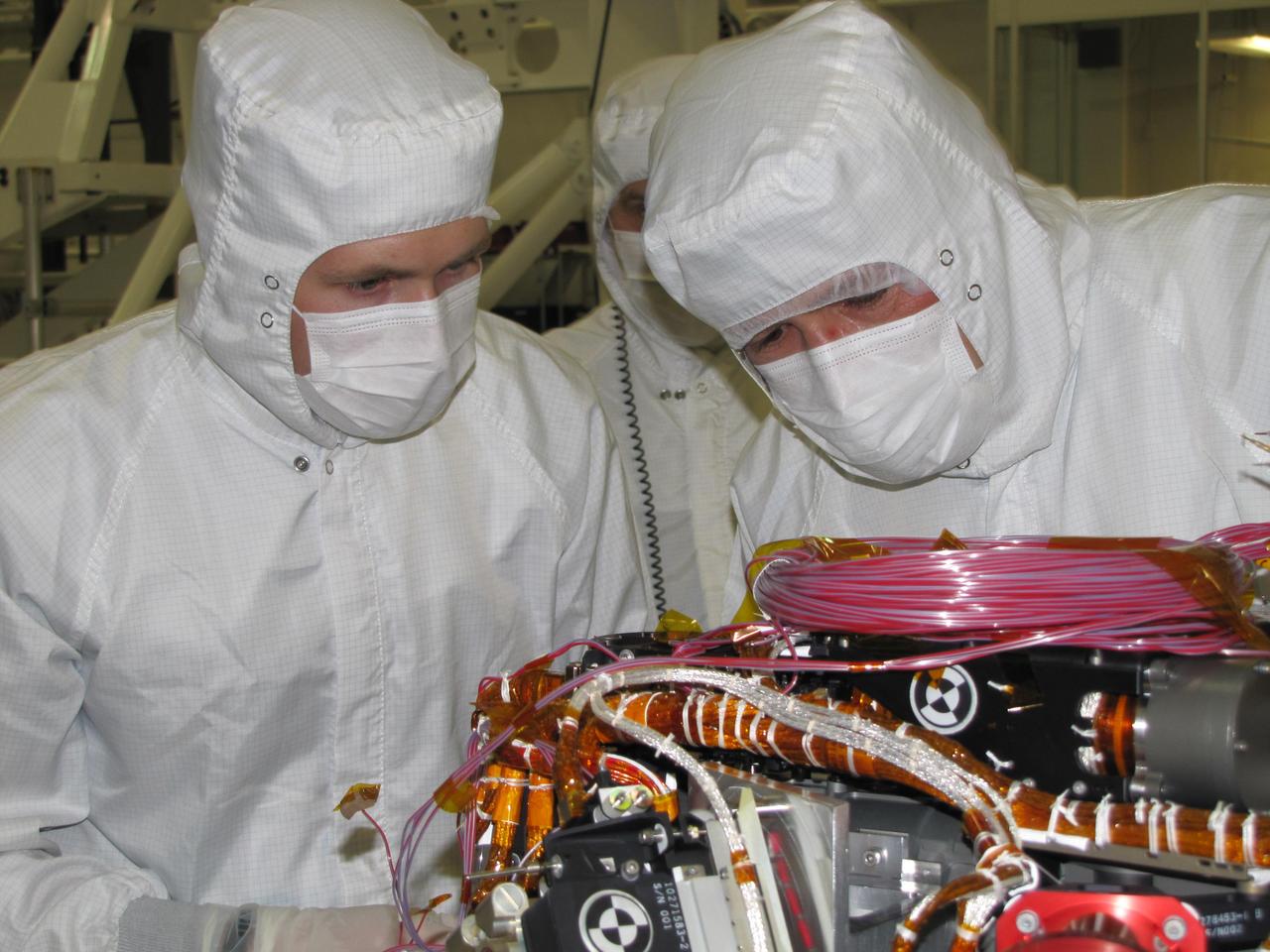

Grad student Nicholas Boyd left and Principal Investigator Ralf Gellert, both of the University of Guelph, Ontario, Canada, prepare for the installation of the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer sensor head during testing at NASA JPL.
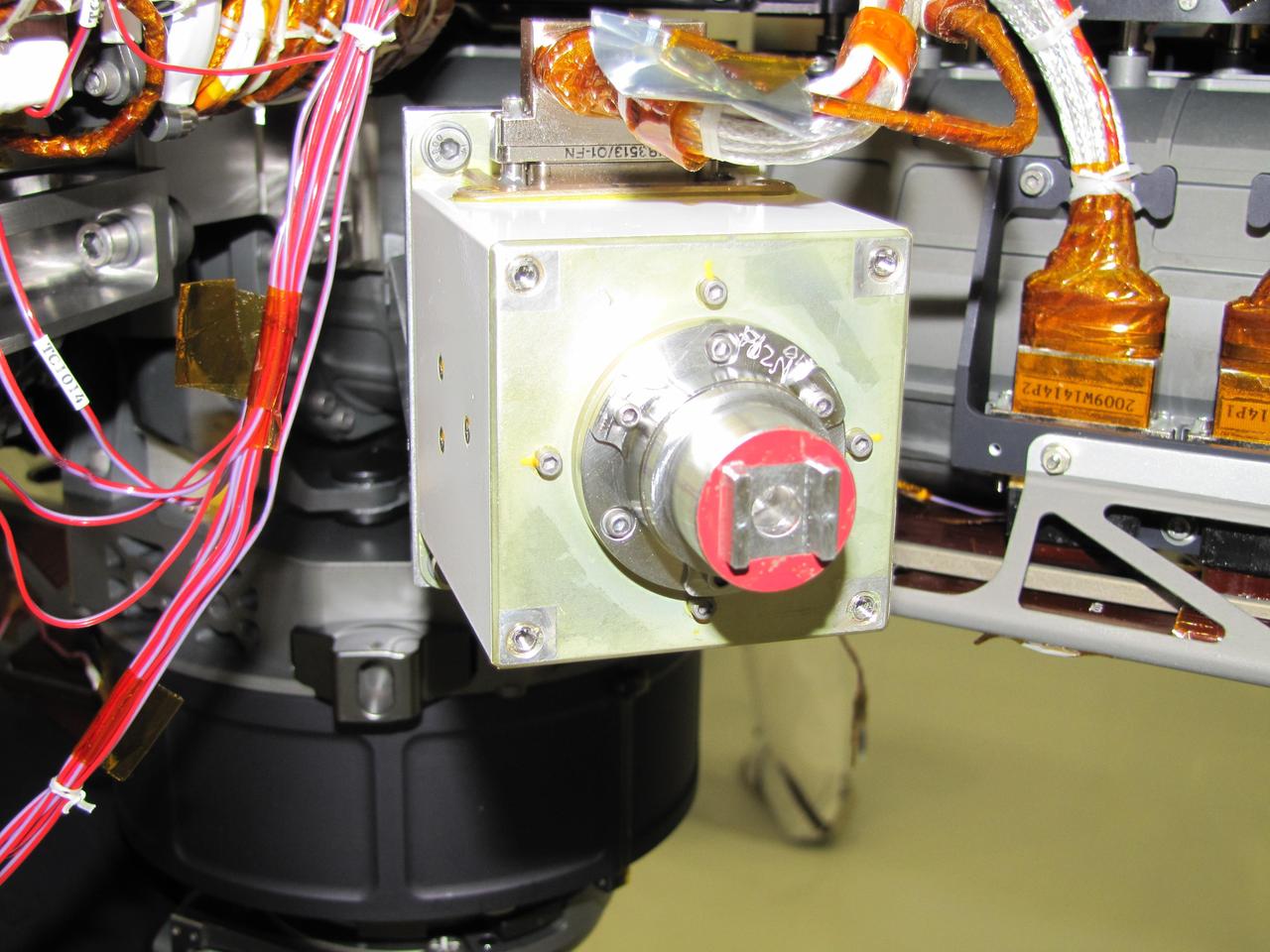

The sensor head on the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer instrument was installed during testing at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The instrument is part of NASA Curiosity rover.
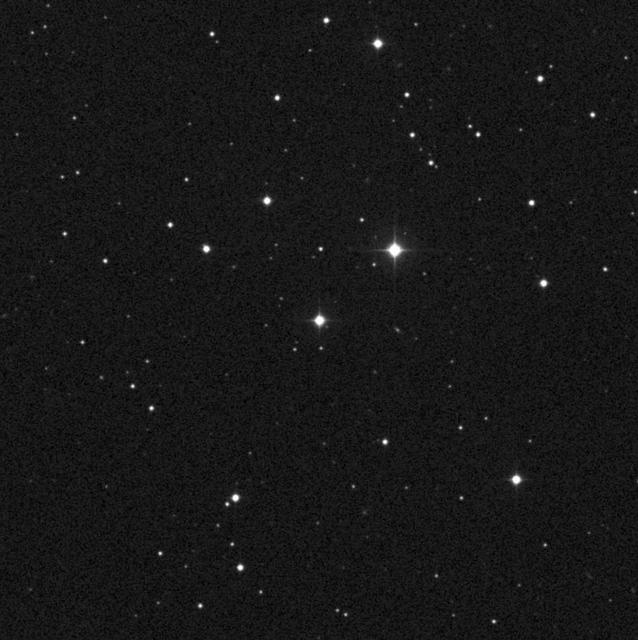

The image taken by the Oschin Schmidt Telescope, shows the star AC +79 3888, also known as Gliese 445. NASA Voyager 1 spacecraft, which is on a trajectory out of our solar system, is headed toward an encounter with AC +79 3888 circled in red.
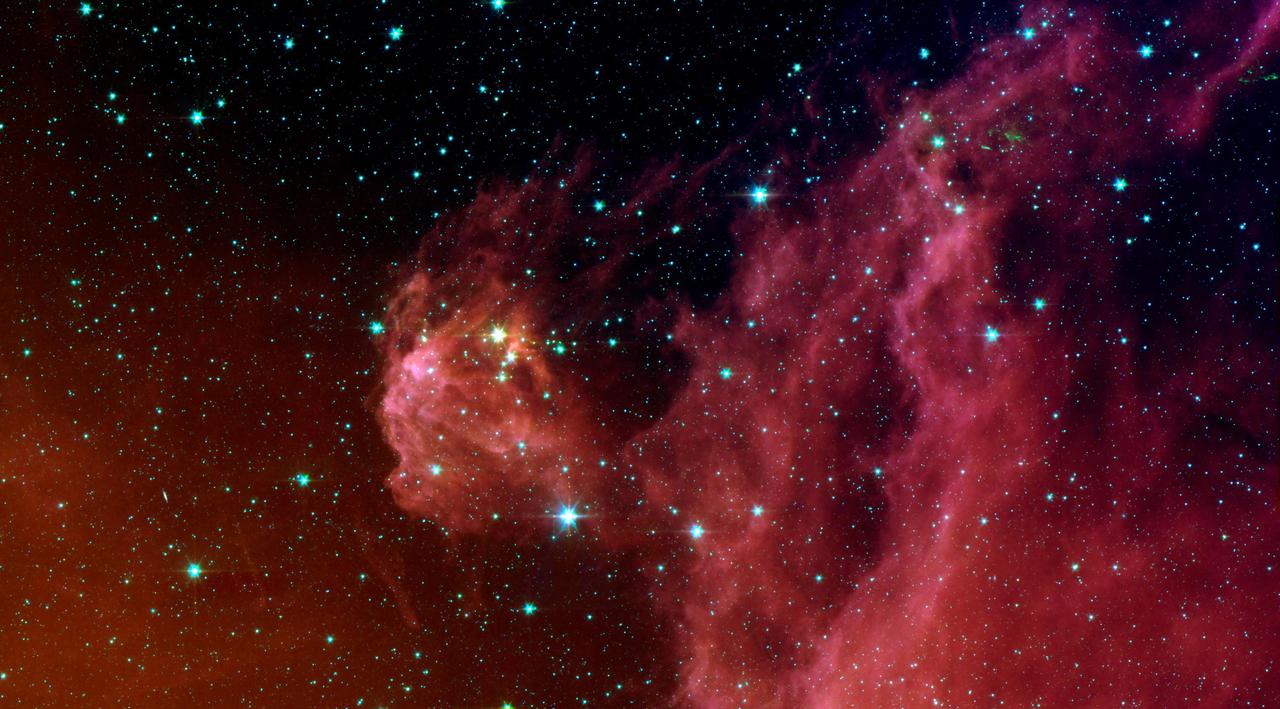

This image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows infant stars "hatching" in the head of the hunter constellation, Orion. Astronomers suspect that shockwaves from a supernova explosion in Orion's head, nearly three million years ago, may have initiated this newfound birth . The region featured in this Spitzer image is called Barnard 30. It is located approximately 1,300 light-years away and sits on the right side of Orion's "head," just north of the massive star Lambda Orionis. Wisps of red in the cloud are organic molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. These molecules are formed anytime carbon-based materials are burned incompletely. On Earth, they can be found in the sooty exhaust from automobile and airplane engines. They also coat the grills where charcoal-broiled meats are cooked. This image shows infrared light captured by Spitzer's infrared array camera. Light with wavelengths of 8 and 5.8 microns (red and orange) comes mainly from dust that has been heated by starlight. Light of 4.5 microns (green) shows hot gas and dust; and light of 3.6 microns (blue) is from starlight. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA09412

Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Dr. Walther Pelzer, Executive Board Member and Head of the German Space Agency at the German Aerospace Center (DLR) speaks in a Heads of Agency panel during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity recorded this 3D view of a rise called Nobbys Head during a stop on a multi-week southward drive between two raised segments of the west rim of Endeavour Crater.

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson gives remarks in a Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
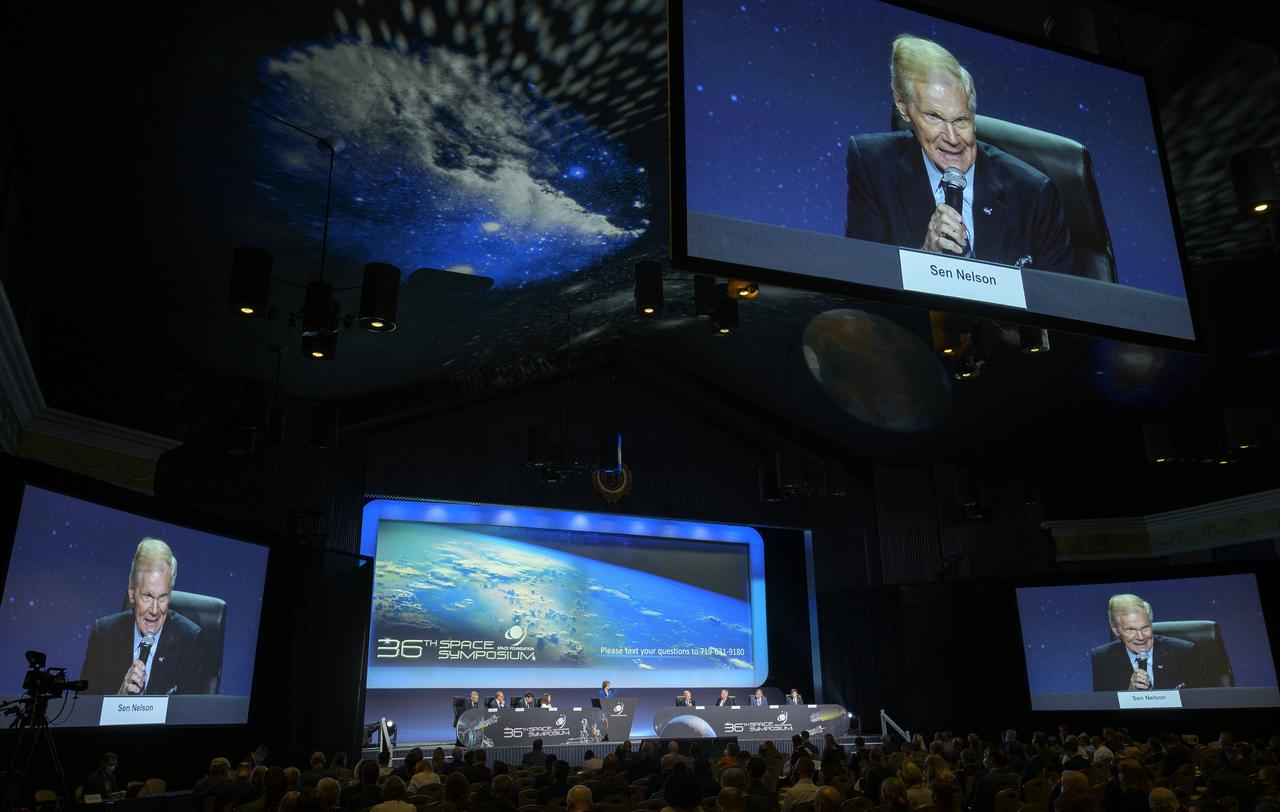

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson gives remarks in a Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
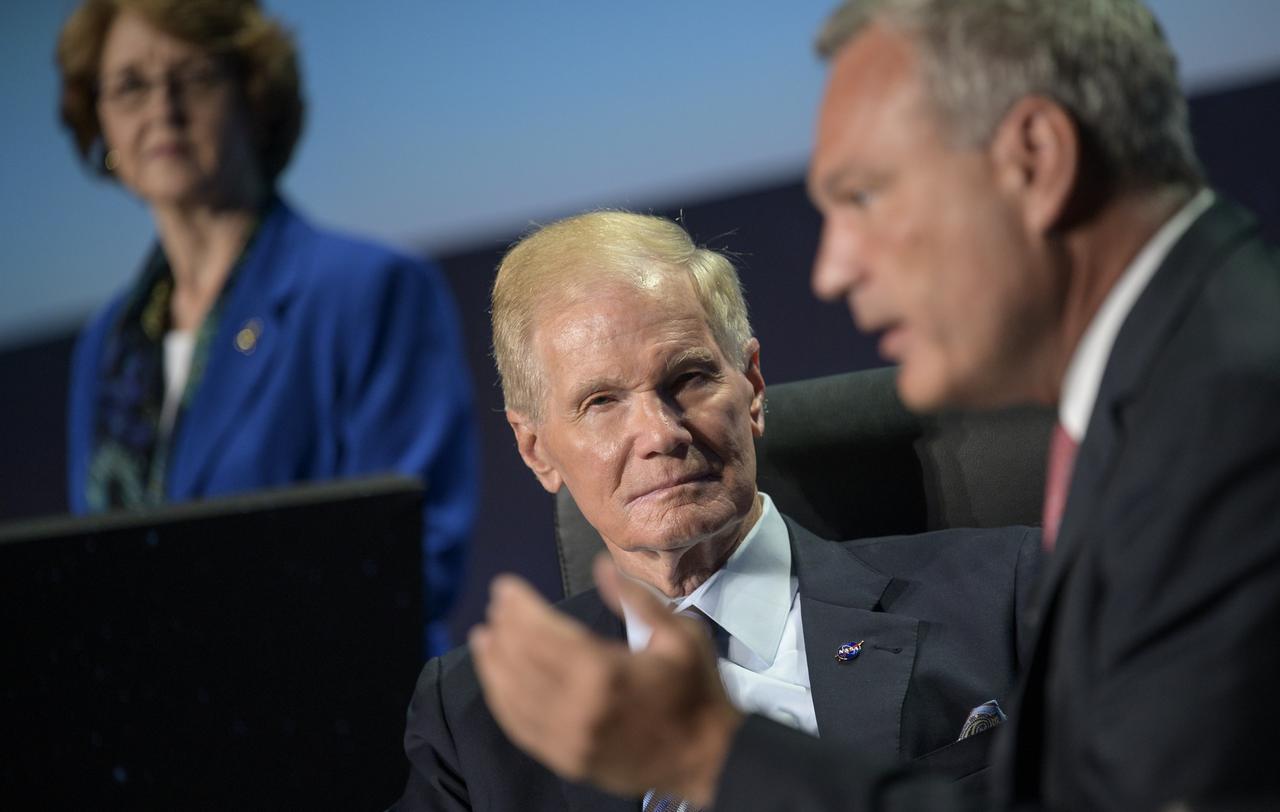

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson listens in a Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
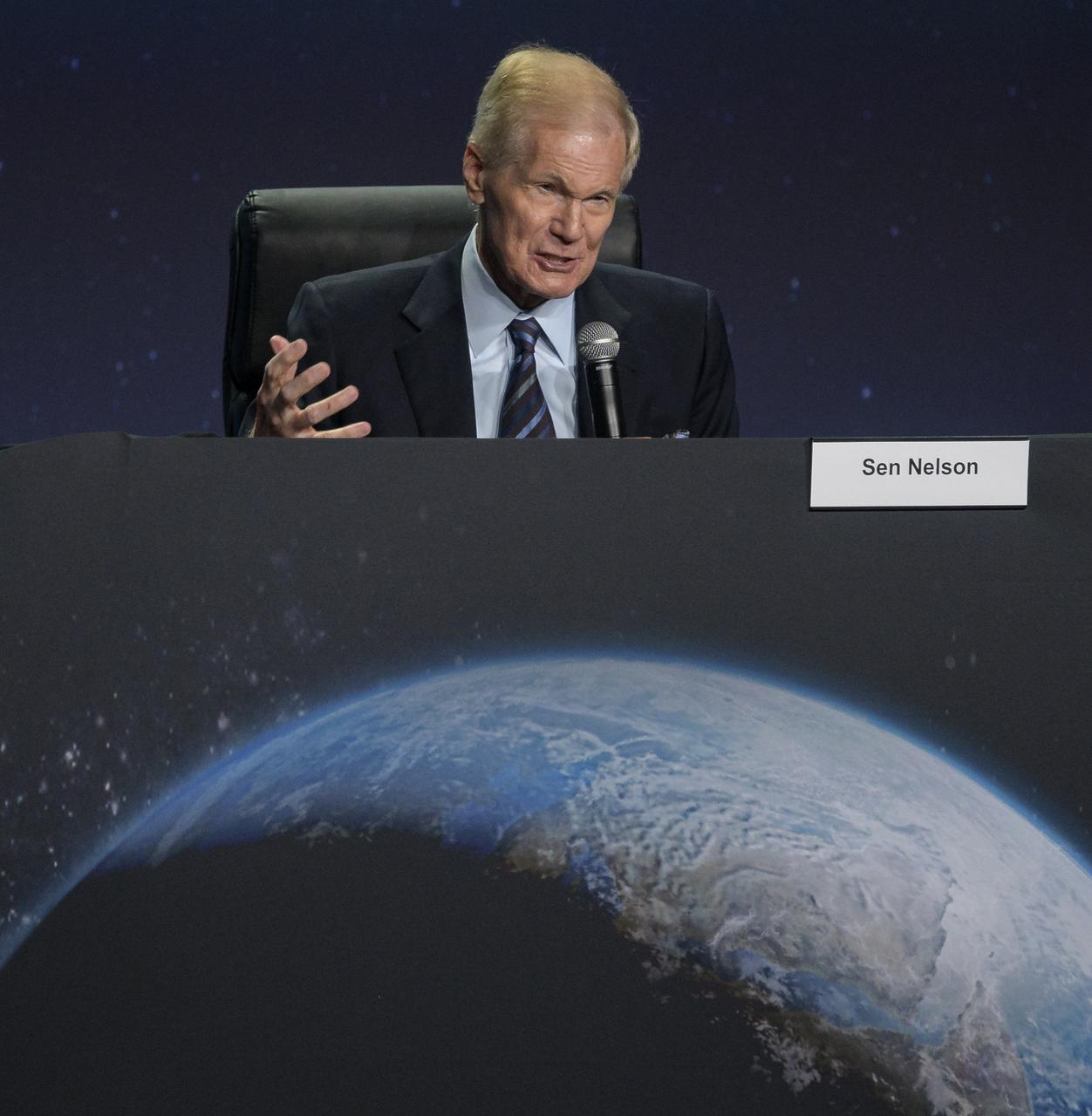

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson gives remarks in a Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
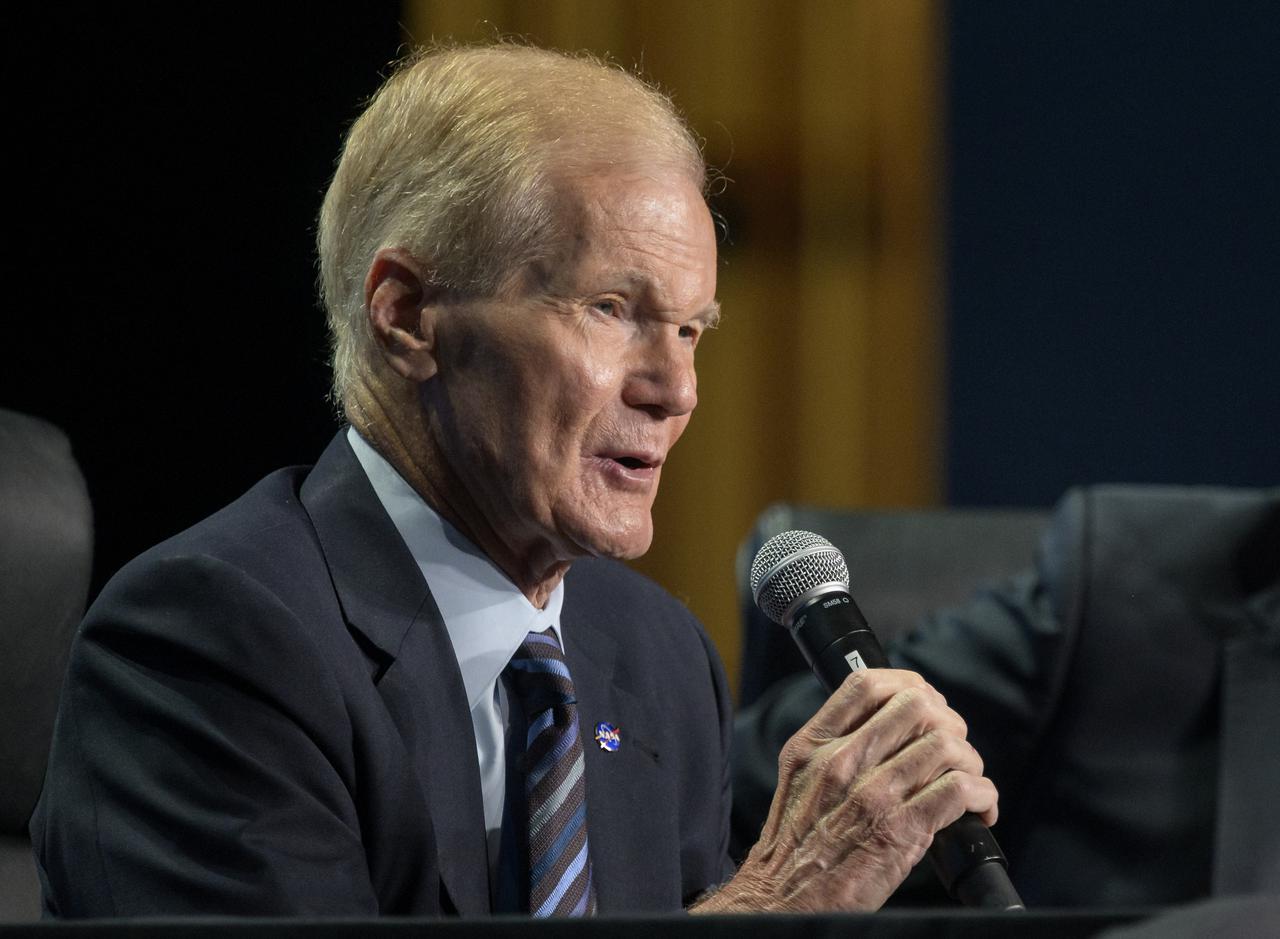

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson gives remarks in a Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
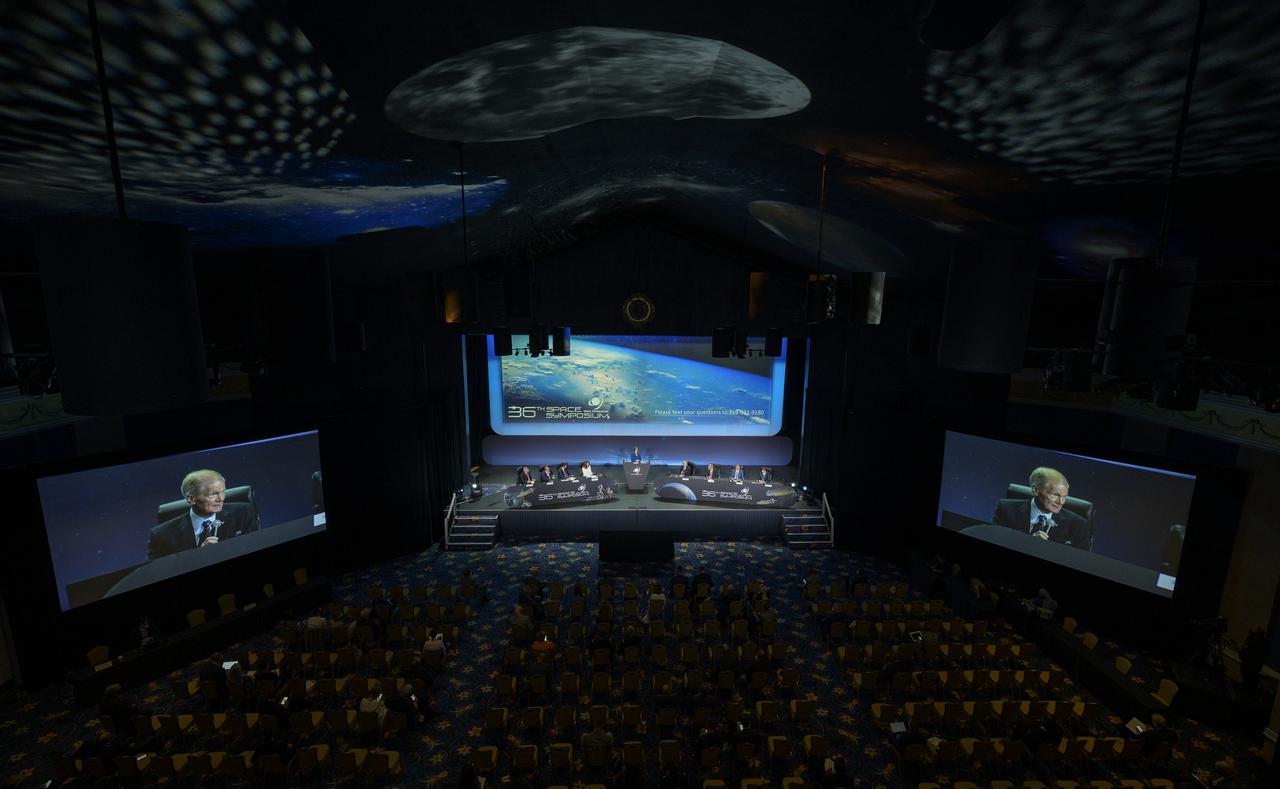

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson gives remarks in a Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

This satellite imagery from Jan. 21 at 10:00 a.m. EST shows the large winter storm over near the Gulf coast and another storm approaching the Pacific coast. Credits: NASA/NOAA GOES Project <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows infant stars "hatching" in the head of the hunter constellation, Orion. Astronomers suspect that shockwaves from a supernova explosion in Orion's head, nearly three million years ago, may have initiated this newfound birth. The region featured in this Spitzer image is called Barnard 30. It is located approximately 1,300 light-years away and sits on the right side of Orion's "head," just north of the massive star Lambda Orionis. Wisps of green in the cloud are organic molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. These molecules are formed anytime carbon-based materials are burned incompletely. On Earth, they can be found in the sooty exhaust from automobile and airplane engines. They also coat the grills where charcoal-broiled meats are cooked. Tints of orange-red in the cloud are dust particles warmed by the newly forming stars. The reddish-pink dots at the top of the cloud are very young stars embedded in a cocoon of cosmic gas and dust. Blue spots throughout the image are background Milky Way along this line of sight. This composite includes data from Spitzer's infrared array camera instrument, and multiband imaging photometer instrument. Light at 4.5 microns is shown as blue, 8.0 microns is green, and 24 microns is red. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA09411
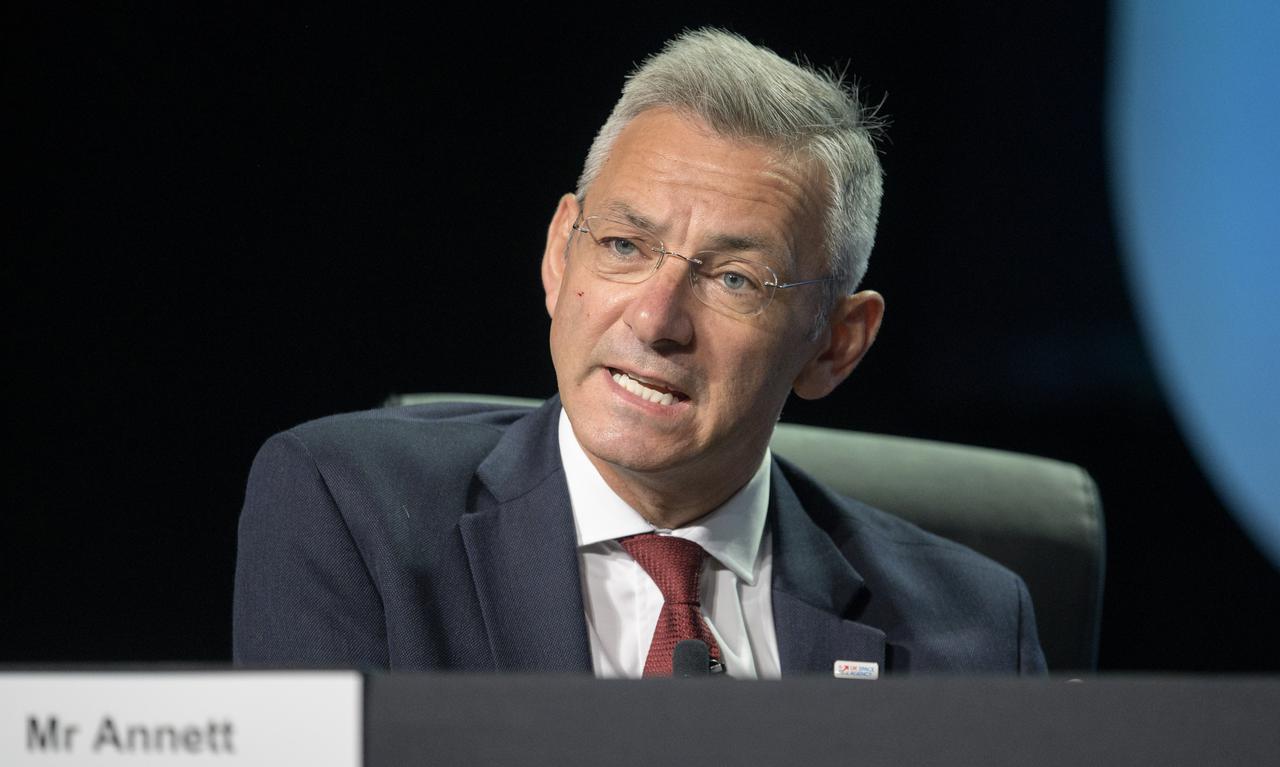

Ian Annett, Acting CEO for Programme Delivery, UK Space Agency (UKSA) gives remarks in a Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
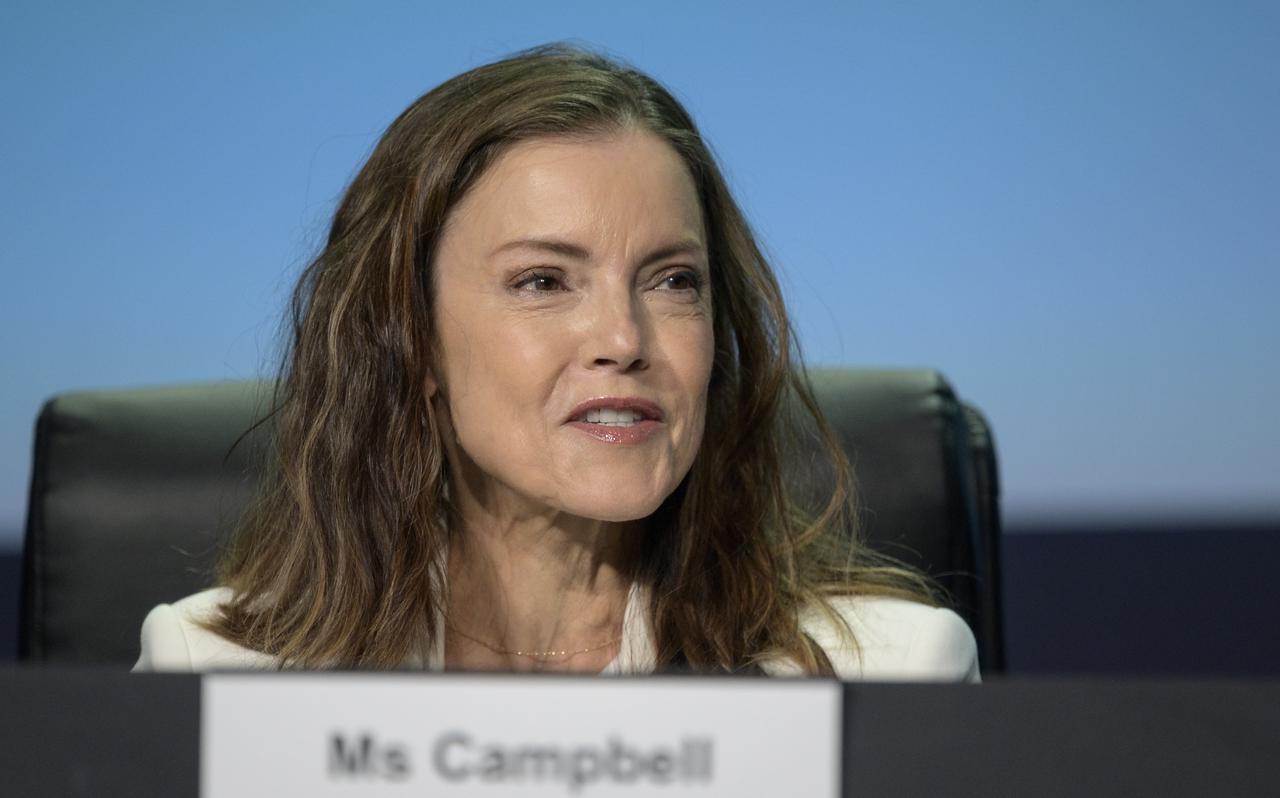

Lisa Campbell, President, Canadian Space Agency (CSA) gives remarks in a Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
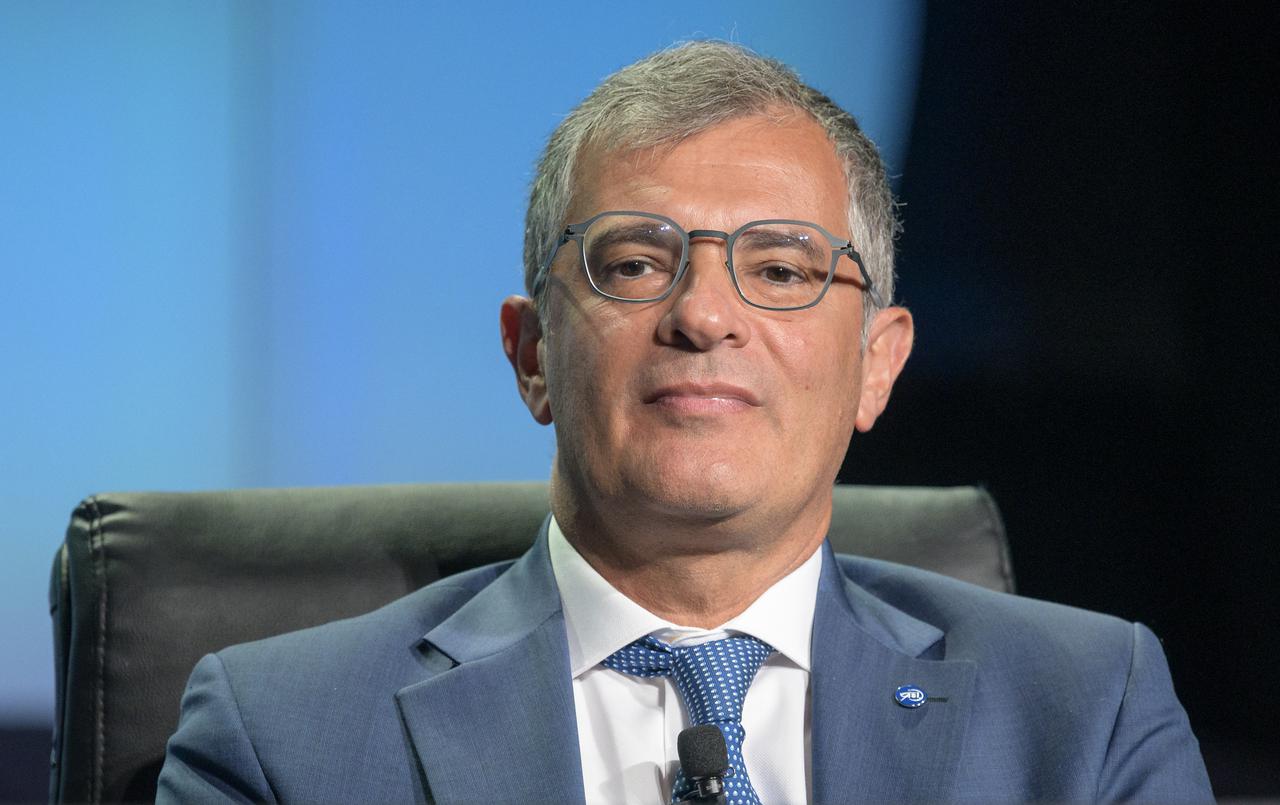

Giorgio Saccoccia, President, Italian Space Agency (ASI), gives remarks in a Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
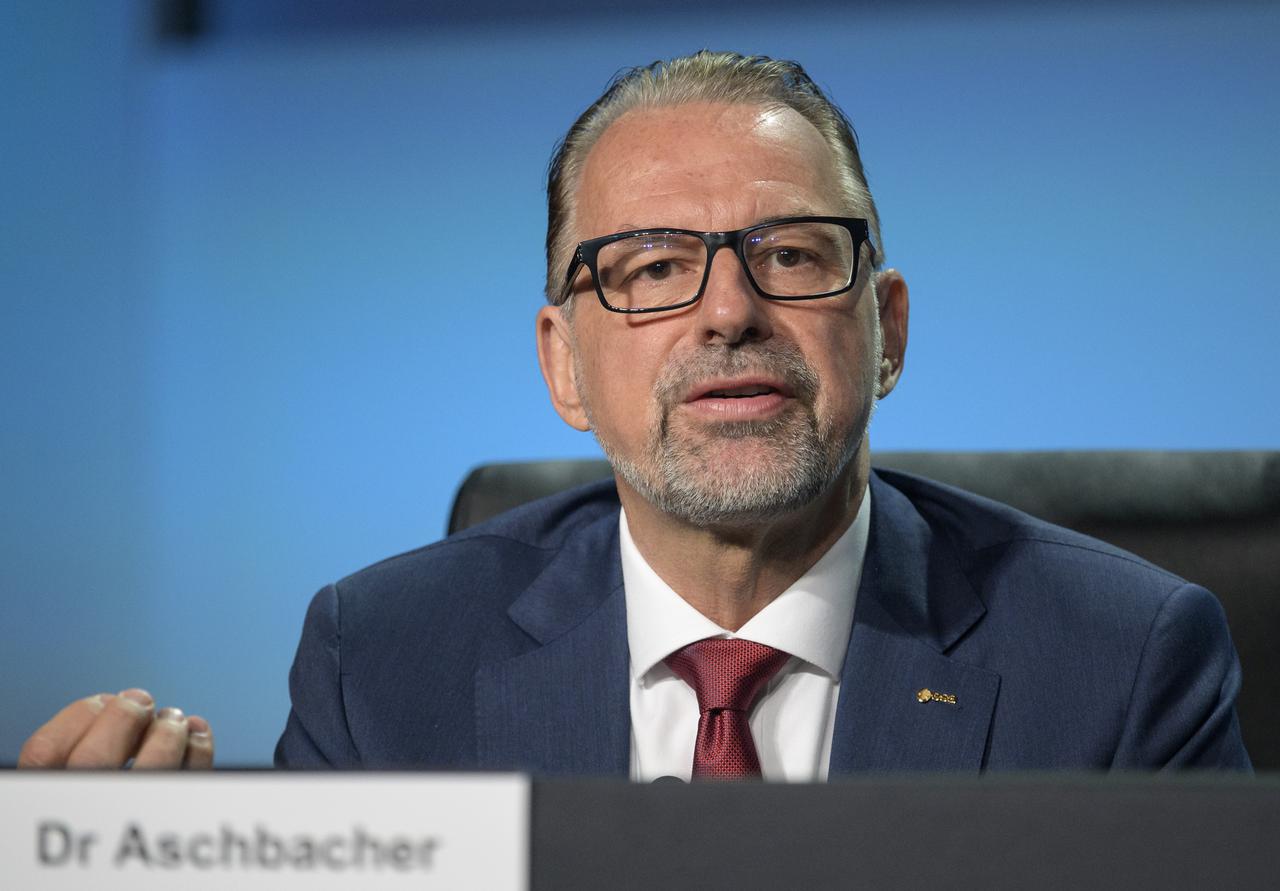

Dr. Josef Aschbacher, Director General, European Space Agency (ESA) gives remarks in a Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
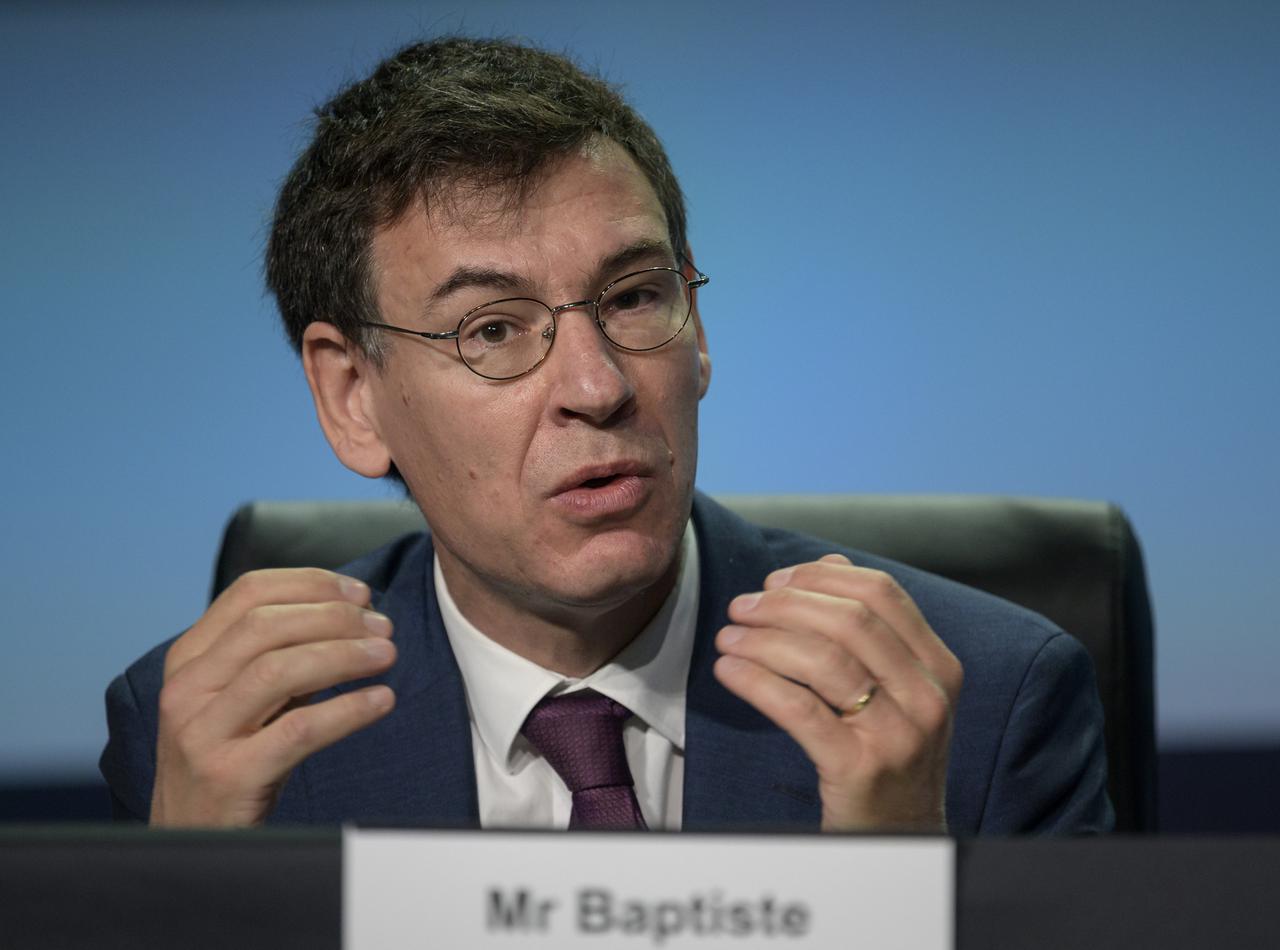

Philippe Baptiste, Chairman and CEO, Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES) gives remarks in a Heads of Agency panel discussion, during the 36th Space Symposium, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
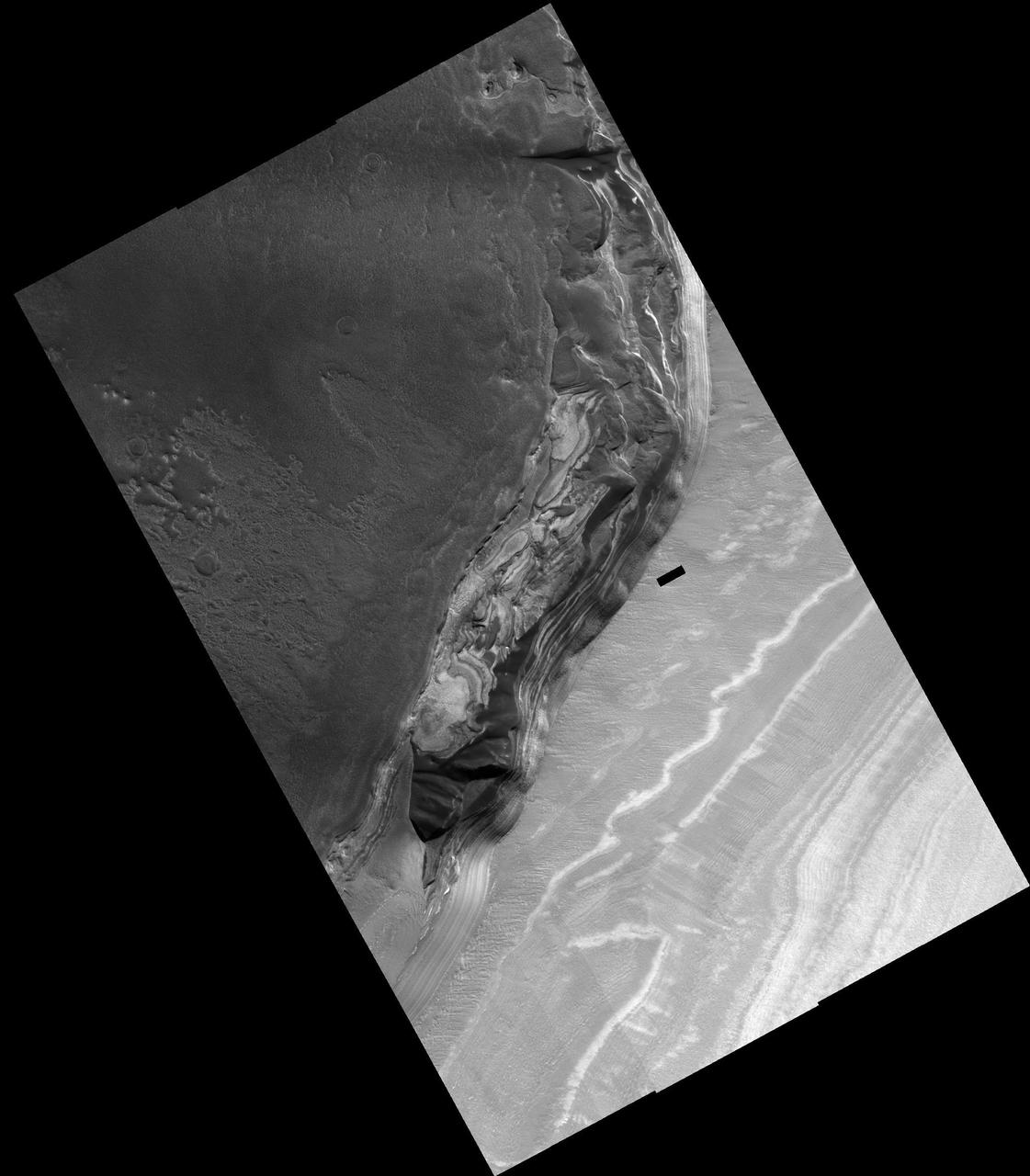

False Color Image of North Polar Layered Deposits in Head Scarp of Chasma Boreale
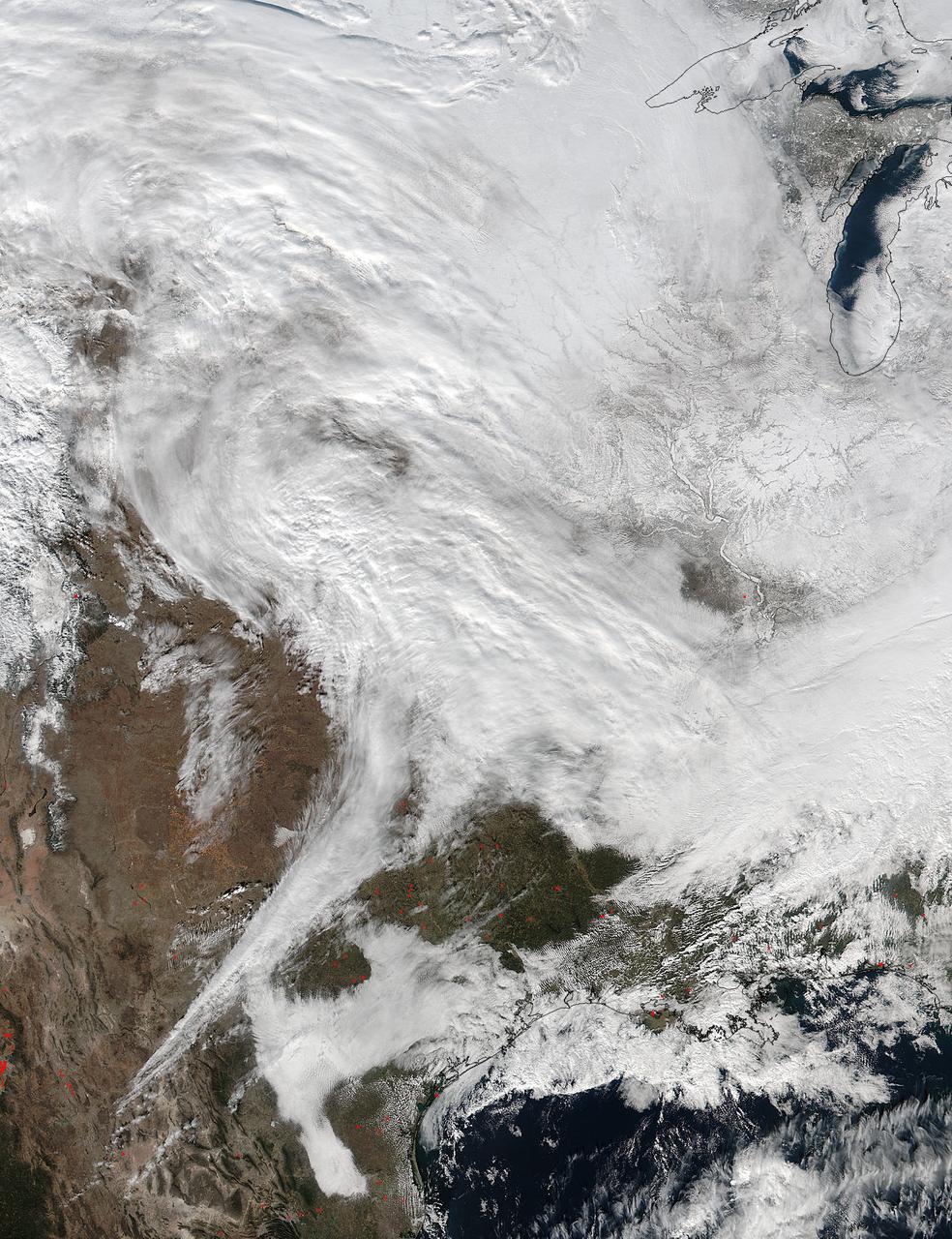
On Jan. 20 at 2:30 p.m. EST the VIIRS instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP captured this image of the winter storm moving through the central U.S. Credits: NASA Goddard Rapid Response The low pressure area from the Eastern Pacific Ocean moved into the western U.S. and tracked across the four corners region into Texas where NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite observed the clouds associated with the storm. The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard Suomi NPP satellite captured the visible image on January 20, 2016 at 19:30 UTC (2:30 p.m. EST) when the storm was over the central U.S. In the image, snow cover is visible in the Rockies and southern Great Lakes states. VIIRS collects visible and infrared imagery and global observations of land, atmosphere, cryosphere and oceans. That low pressure system located over the south central United States on Jan. 21 is expected to track east across the Tennessee Valley and will give way to a deepening coastal low pressure area. The National Weather Service said "This latter feature takes over and becomes a dominant force in setting up heavy snow bands over the Mid-Atlantic and very gusty winds." The storm system is expected to bring an increased risk of severe weather from far southeastern Texas across southern Louisiana/Mississippi, and into the far western Florida Panhandle on Thursday, Jan. 21. That threat for severe weather will move east as the low pressure area continues heading in that direction. The National Weather Service Weather Prediction Center in College Park, Maryland said "A potentially crippling winter storm is anticipated for portions of the mid-Atlantic Friday into early Saturday. Snowfall may approach two feet for some locations, including the Baltimore and Washington, D.C. metro areas. Farther north, there is uncertainty in snowfall for the New York City-to-Boston corridor. Farther south, significant icing is likely for portions of Kentucky and North Carolina." <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Philippe Baptiste, President, French Space Agency (CNES) speaks in a Heads of Agency panel during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy listens in a Heads of Agency panel during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Lisa Campbell, President, Canadian Space Agency (CSA) speaks in a Heads of Agency panel during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks in a Heads of Agency panel during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
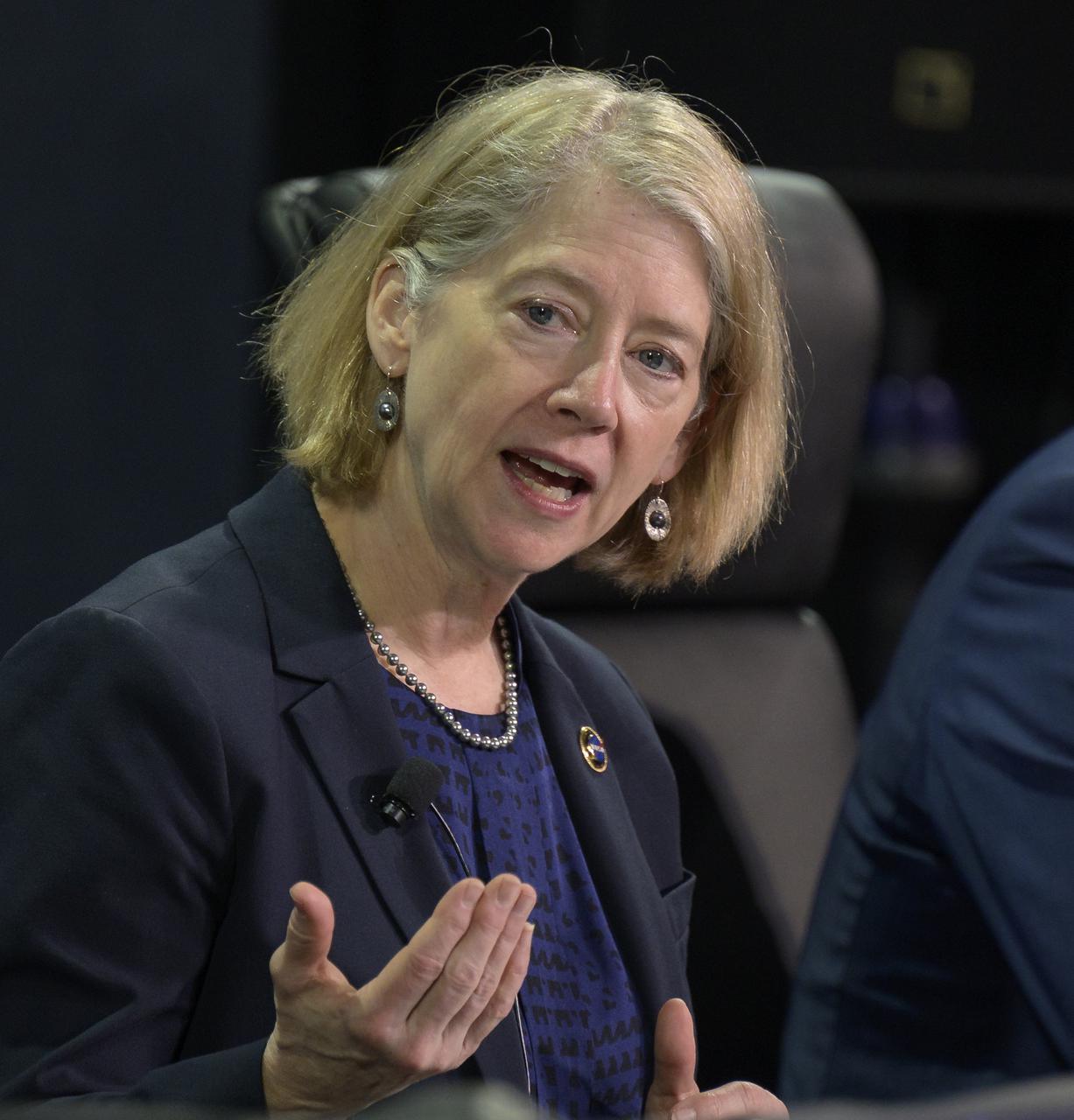

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks in a Heads of Agency panel during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
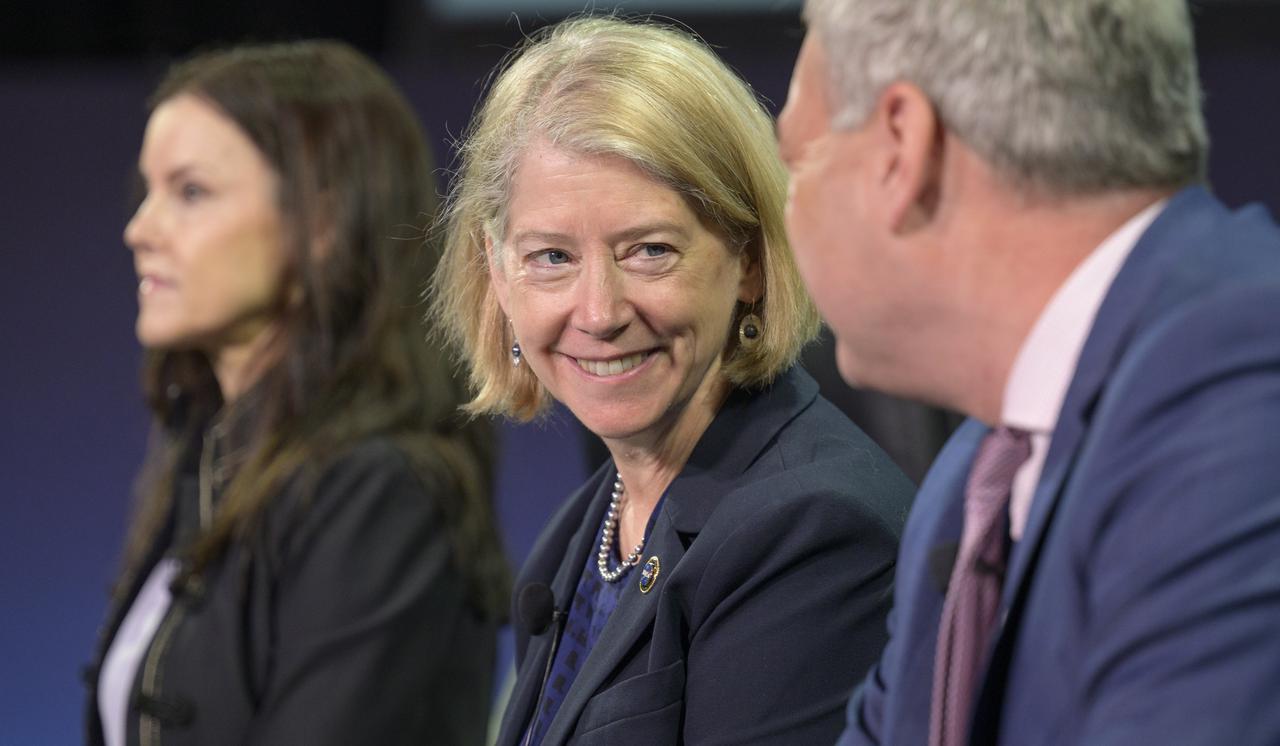

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy listens in a Heads of Agency panel during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Dr. Kathryn C. Thornton, Chairwoman, Space Foundation, moderates a Heads of Agency panel during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
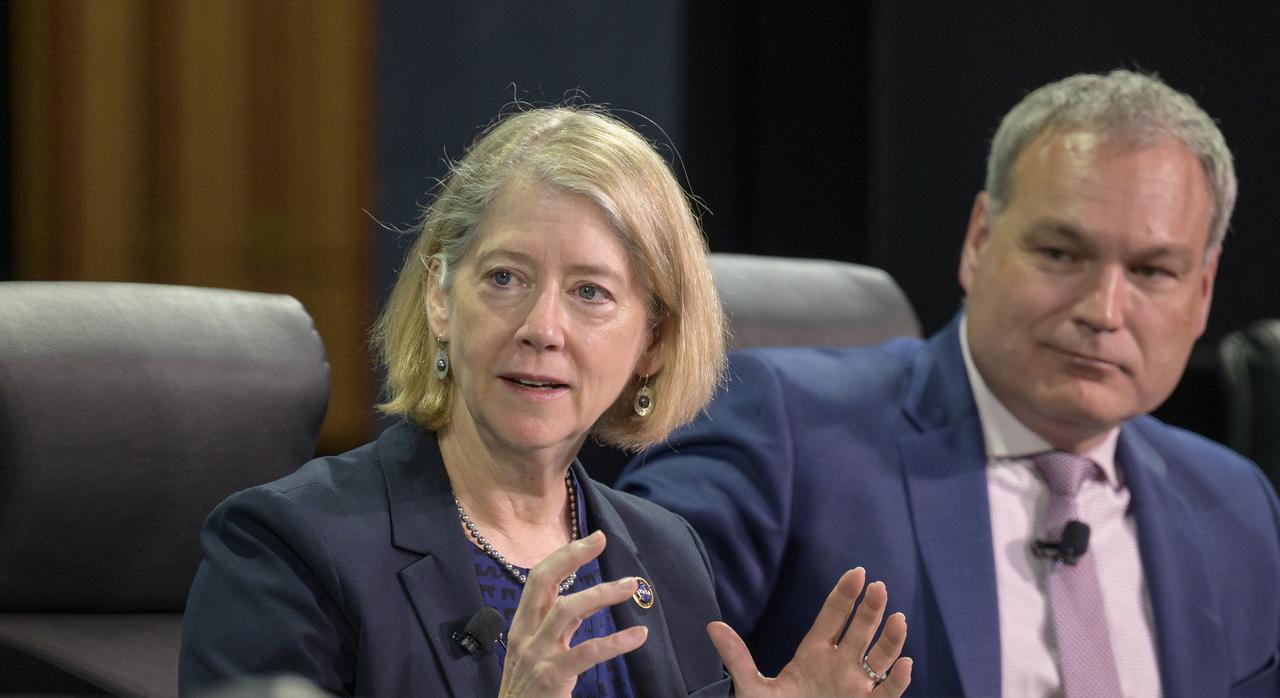

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks in a Heads of Agency panel during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
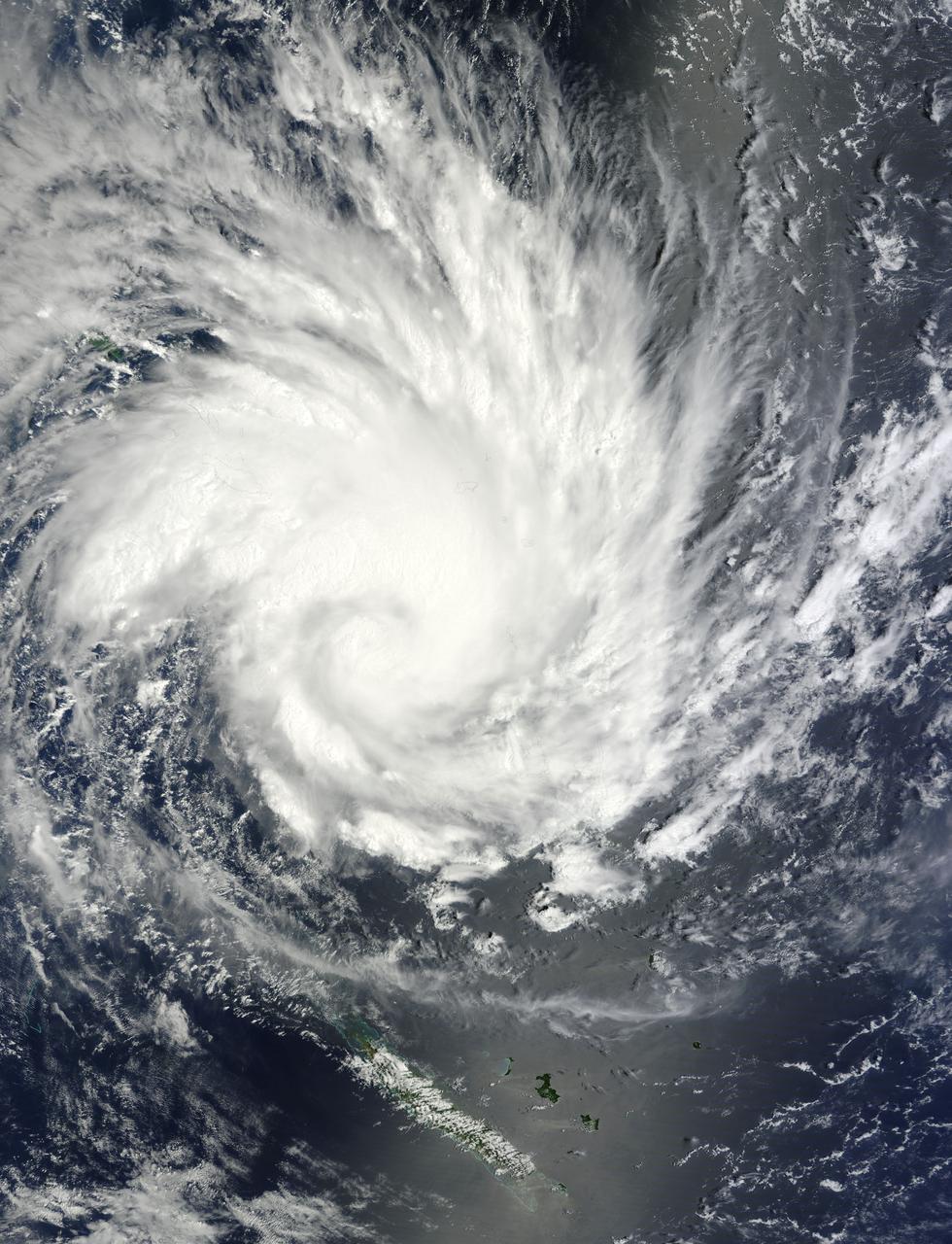

NASA image acquired January 30, 2011 at 23:20 UTC. Satellite: Terra <b> Click here to see the most recent image captured Feb. 1: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5407540724/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5407540724/</a></b> Tropical Storm Anthony made landfall in Queensland, Australia this past weekend, and now the residents are watching a larger, more powerful cyclone headed their way. NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of the large Tropical Cyclone Yasi late yesterday as it makes its way west through the Coral Sea toward Queensland. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured an image of Cyclone Yasi on Jan. 30 at 23:20 UTC (6:20 p.m. EST/09:20 a.m., Monday, January 31 in Australia/Brisbane local time). Although the image did not reveal a visible eye, the storm appears to be well-formed and also appears to be strengthening. Warnings and watches are already in effect throughout the Coral Sea. The Solomon Islands currently have a Tropical Cyclone warning for the provinces of Temotu, Rennell & Bellona, Makira and Guadalcanal. The Australian Bureau of Meteorology has already posted a Tropical Cyclone Watch from Cooktown to Yeppoon and inland to between Georgetown and Moranbah in Queensland, Australia. The Australian Bureau of Meteorology expects damaging winds to develop in coastal and island communities between Cooktown and Yeppoon Wednesday morning, and inland areas on Wednesday afternoon. Updates from the Australian Bureau of Meteorology can be monitored at the Bureau's website at <a href="http://www.bom.gov.au" rel="nofollow">www.bom.gov.au</a>. On January 31 at 1500 UTC (10 a.m. EST/ 1:00 a.m. Tuesday February 1, 2011 in Australia/Brisbane local time), Tropical Cyclone Yasi had maximum sustained winds near 90 knots (103 mph/166 kmh). Yasi is a Category Two Cyclone on the Saffir-Simpson Scale. It was centered about 875 miles E of Cairns, Australia, near 13.4 South latitude and 160.4 East longitude. It was moving west near 19 knots (22 mph/35 kmh). Cyclone-force winds extend out to 30 miles (48 km) from the center. Animated infrared satellite imagery, such as that from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite, showed deep convective (thunderstorm) bands wrapping tighter into the low level circulation center. Wrapping bands of thunderstorms indicate strengthening. Yasi is forecast to move west then southwestward into an area of low vertical wind shear (strong wind shear can weaken a storm). Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) expect Yasi to continue strengthening over the next 36 hours. JTWC forecasts a landfall just south of Cairns as a large 100-plus knot (115 mph/185 kmh)n system by Wednesday. Residents along the Queensland coast should now be making preparations now for the storm's arrival. Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team Click here to see more images from <b><a href="http://rapidfire.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/?latest" rel="nofollow">MODIS</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
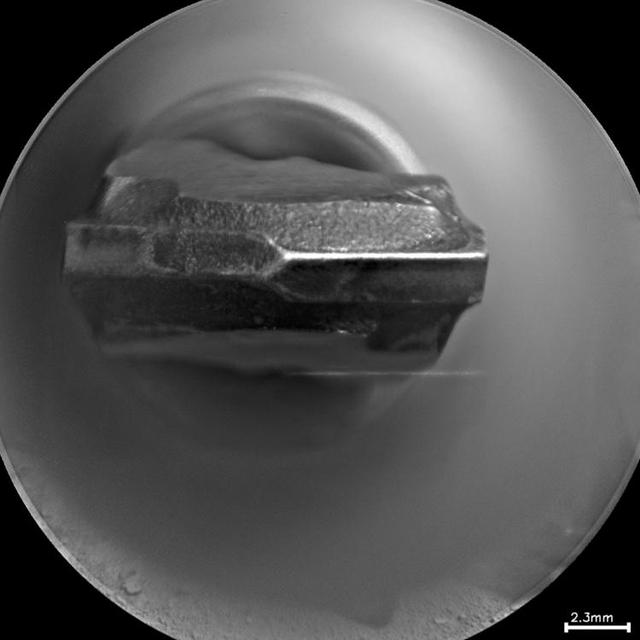
This head-on view shows the tip of the drill bit on NASA Mars rover Curiosity. The view merges two exposures taken by the remote micro-imager in the rover ChemCam instrument at different focus settings.

Dr. Paul Bate, Chief Executive Officer UK Space Agency (UKSA) speaks in a Heads of Agency panel during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Dr. Hiroshi Yamakawa, President, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) speaks in a Heads of Agency panel during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Dr. Josef Aschbacher, Director General, European Space Agency (ESA) speaks during a Heads of Agency panel at the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

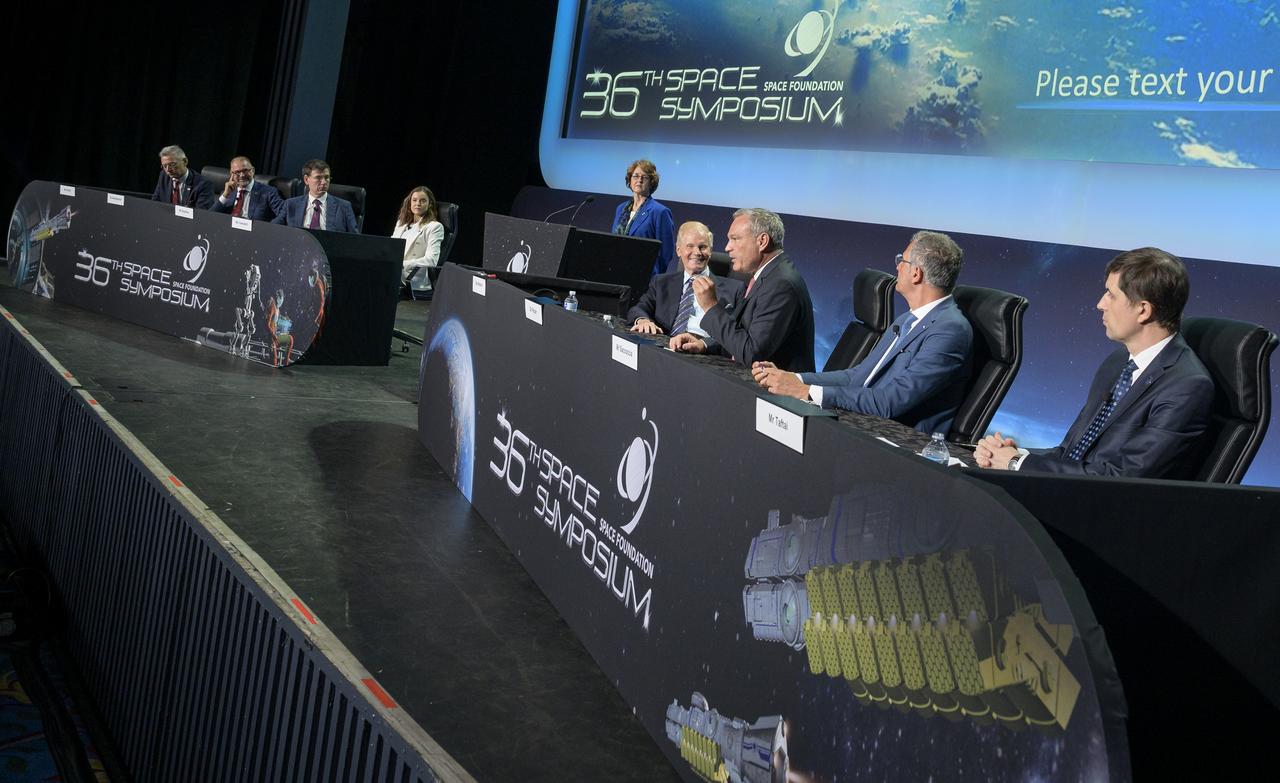
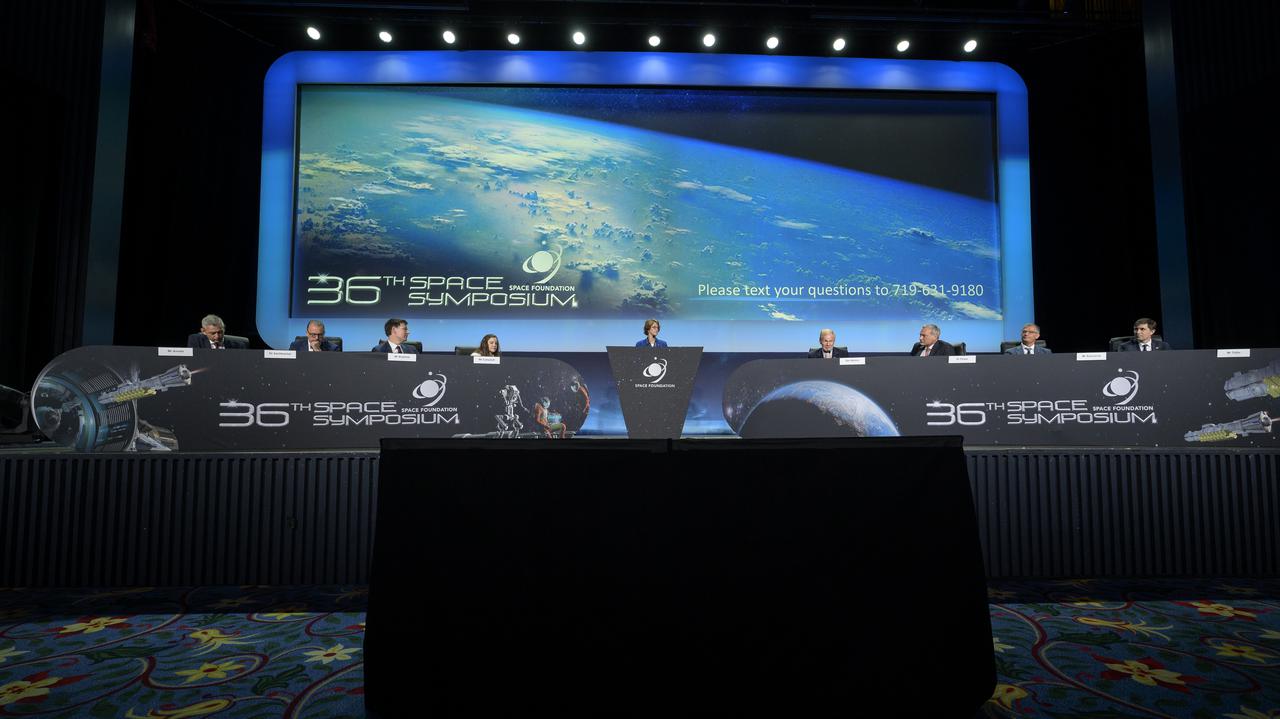
Heads of Agency participate in a panel discussion, from left, Dr. Josef Aschbacher, Director General, European Space Agency (ESA); Dr. Philippe Baptiste, President, French Space Agency (CNES); Dr. Paul Bate, Chief Executive Officer UK Space Agency (UKSA); moderator Dr. Kathryn C. Thornton, Chairwoman, Space Foundation; Lisa Campbell, President, Canadian Space Agency (CSA); NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy; Dr. Walther Pelzer, Executive Board Member and Head of the German Space Agency at the German Aerospace Center (DLR); and Dr. Hiroshi Yamakawa, President, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), right, during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
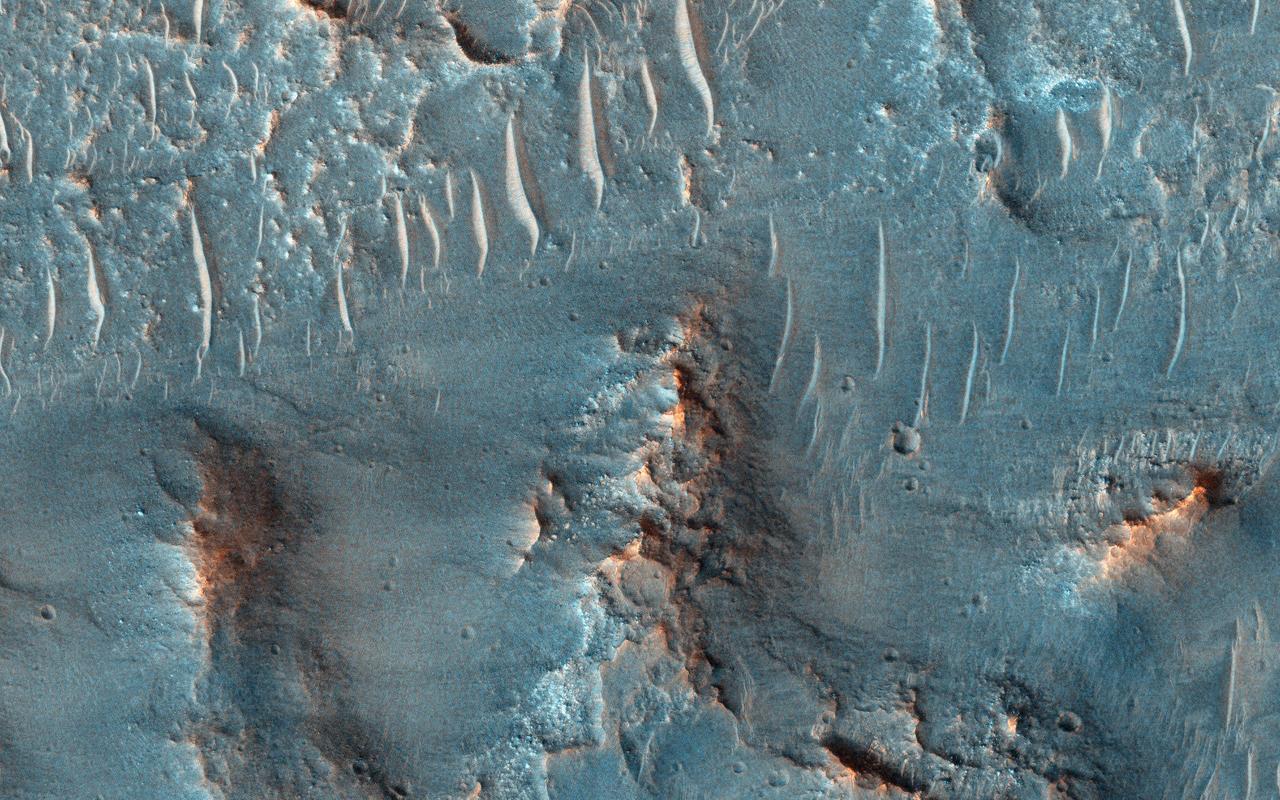

On Earth, cataracts represent regions where a river's gradient increases enough to create so much turbulence, that air gets incorporated into the water body forming a bubbly current sometimes called "whitewater". This image covers a location that may have acted as a cataract in the Kasei valley region. This observation from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows samples of bedrock lithologies which give us a measure of the post-flood erosion and modification history for the floor of Kasei Valles While there is a HiRISE stereo pair adjacent to this location that captures much of this cataract, it also misses some of the head scarp that might be the most useful, scientifically. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19351
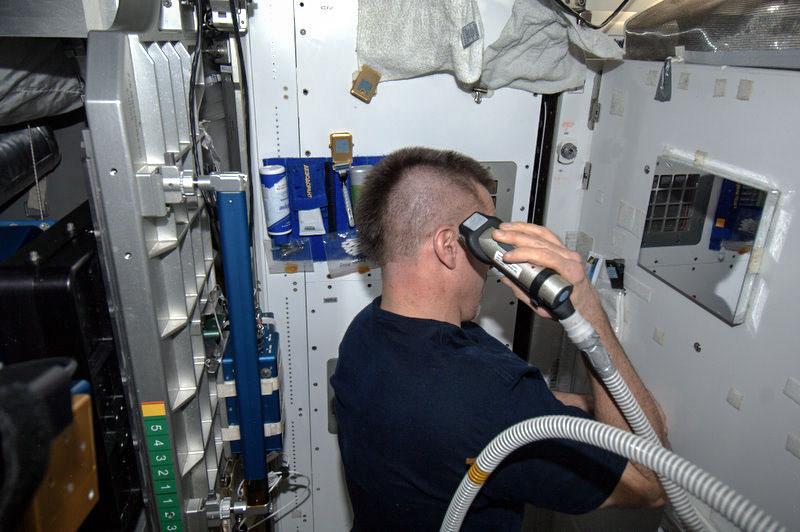

ISS036-E-004795 (29 May 2013) --- NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy, Expedition 36 flight engineer, gives himself a "serious" haircut in the Harmony node onboard the Earth-orbiting International Space Station. Cassidy, who has displayed his sense of humor more than once since coming aboard the orbital outpost in late March, ended up with a completely bald pate when this task was done. The three crew members due to come aboard the station later on this day include one -- Luca Parmitano of the European Space Agency -- who sports a similarly hairless head.
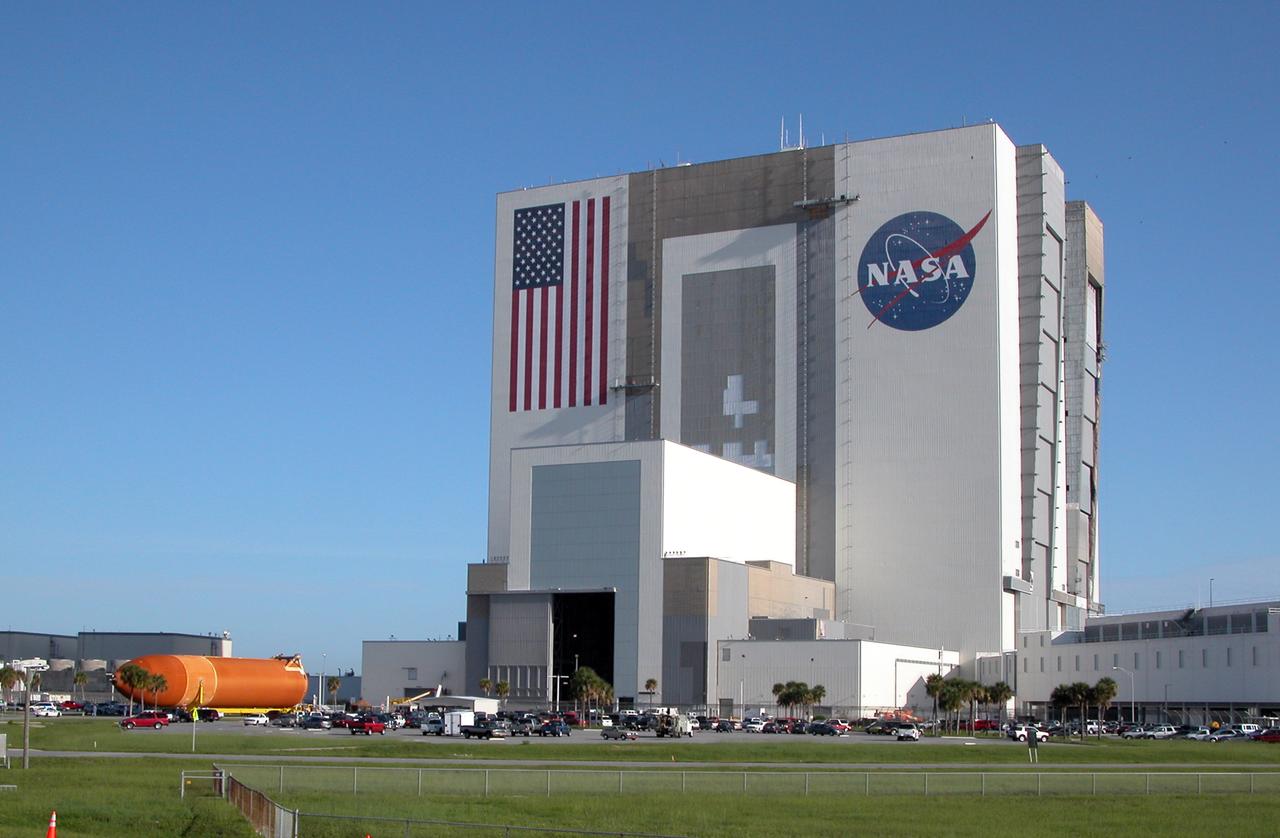
Aboard a transporter, external tank No. 120 heads for the open door of the Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be lifted into a checkout cell. ET-120 will be used for launching Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-120 in October.
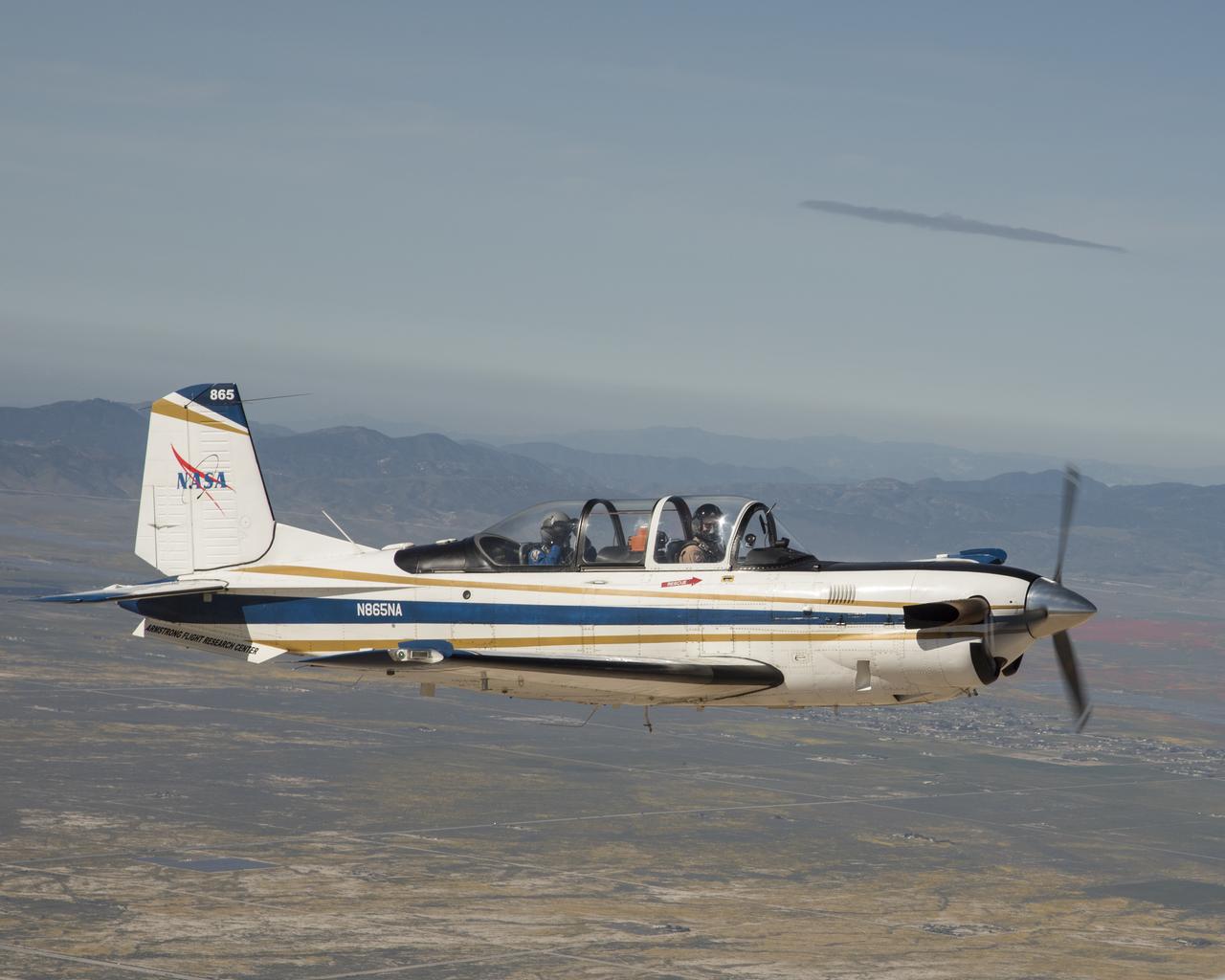

NASA’s T-34 aircraft flown from the agency’s Armstrong Flight Research Center heading toward Southern California’s Antelope Valley Poppy Reserve. The aircraft was flown from the agency’s Armstrong Flight Research Center.

Caption: A NASA Super Pressure Balloon with the COSI payload is ready for launch from McMurdo, Antarctica. Credit: NASA More info: NASA’s globetrotting Balloon Program Office is wrapping up its 2014-2015 Antarctic campaign while prepping for an around-the-world flight launching out of Wanaka, New Zealand, in March. After 16 days, 12 hours, and 56 minutes of flight, operators successfully conducted a planned flight termination of the Suborbital Polarimeter for Inflation Dust and the Epoch of Reionization (SPIDER) mission Saturday, Jan. 18, the final mission of the campaign. Other flights in the 2014-2015 Antarctic campaign included the Antarctic Impulsive Transient Antenna (ANITA-III) mission as well as the Compton Spectrometer and Imager (COSI) payload flown on the developmental Super Pressure Balloon (SPB). ANITA-III successfully wrapped up Jan. 9 after 22 days, 9 hours, and 14 minutes of flight. Flight controllers terminated the COSI flight 43 hours into the mission after detecting a small gas leak in the balloon. Crews are now working to recover all three instruments from different locations across the continent. The 6,480-pound SPIDER payload is stationary at a position about 290 miles from the United Kingdom’s Sky Blu Logistics Facility in Antarctica. The 4,601 pound ANITA-III payload, located about 100 miles from Australia’s Davis Station, and the 2,866 pound COSI payload, located about 340 miles from the United States McMurdo Station both had numerous key components recovered in the past few days. Beginning in late January, the Balloon Program Office will deploy a team to Wanaka, New Zealand, to begin preparations for an SPB flight, scheduled to launch in March. The Program Office seeks to fly the SPB more than 100 days, which would shatter the current flight duration record of 55 days, 1 hour, and 34 minutes for a large scientific balloon. “We’re looking forward to the New Zealand campaign and hopefully a history-making flight with the Super Pressure Balloon,” said Debbie Fairbrother, NASA’s Balloon Program Office Chief. Most scientific balloons see altitude variances based on temperature changes in the atmosphere at night and during the day. The SPB is capable of missions on the order of 100 days or more at constant float altitudes due to the pressurization of the balloon. “Stable, long-duration flights at near-space altitudes above more than 99 percent of the atmosphere are highly desirable in the science community, and we’re ready to deliver,” said Fairbrother. In addition to the SPB flight in March, the Balloon Program Office has 10 more balloon missions planned through September 2015 to include scheduled test flights of the Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator, which is testing new technologies for landing larger, heavier payloads on Mars. NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility manages the agency’s Scientific Balloon Program with 10 to 15 flights each year from launch sites worldwide. The balloons are massive in volume; the average-sized balloon could hold the volume of nearly 200 blimps. Previous work on balloons have contributed to confirming the Big Bang Theory. For more information on NASA’s Scientific Balloon Program, see: <a href="http://sites.wff.nasa.gov/code820/index.html" rel="nofollow">sites.wff.nasa.gov/code820/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA image release Thursday, May 31, 2012 <b>To view a video from this Hubble release go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/7309212940">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/7309212940</a> </b> Caption: This illustration shows a stage in the predicted merger between our Milky Way galaxy and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy, as it will unfold over the next several billion years. In this image, representing Earth's night sky in 3.75 billion years, Andromeda (left) fills the field of view and begins to distort the Milky Way with tidal pull. Credit: NASA; ESA; Z. Levay and R. van der Marel, STScI; T. Hallas; and A. Mellinger To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/milky-way-collide.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/milky-way-colli...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
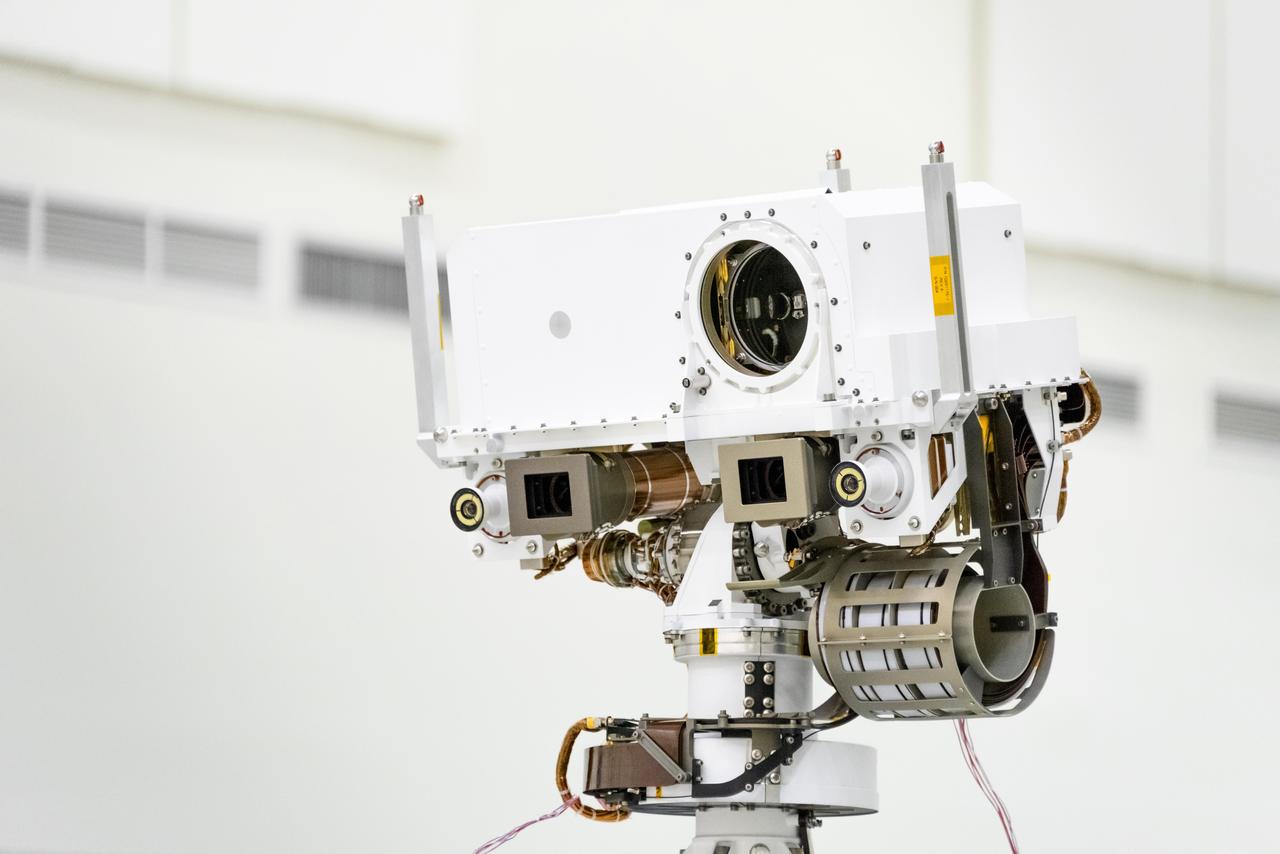
This image, taken in the Spacecraft Assembly Facility's High Bay 1 at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, on July 23, 2019, shows a close-up of the head of Mars 2020's remote sensing mast. The mast head contains the SuperCam instrument (its lens is in the large circular opening). In the gray boxes beneath mast head are the two Mastcam-Z imagers. On the exterior sides of those imagers are the rover's two navigation cameras. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23316
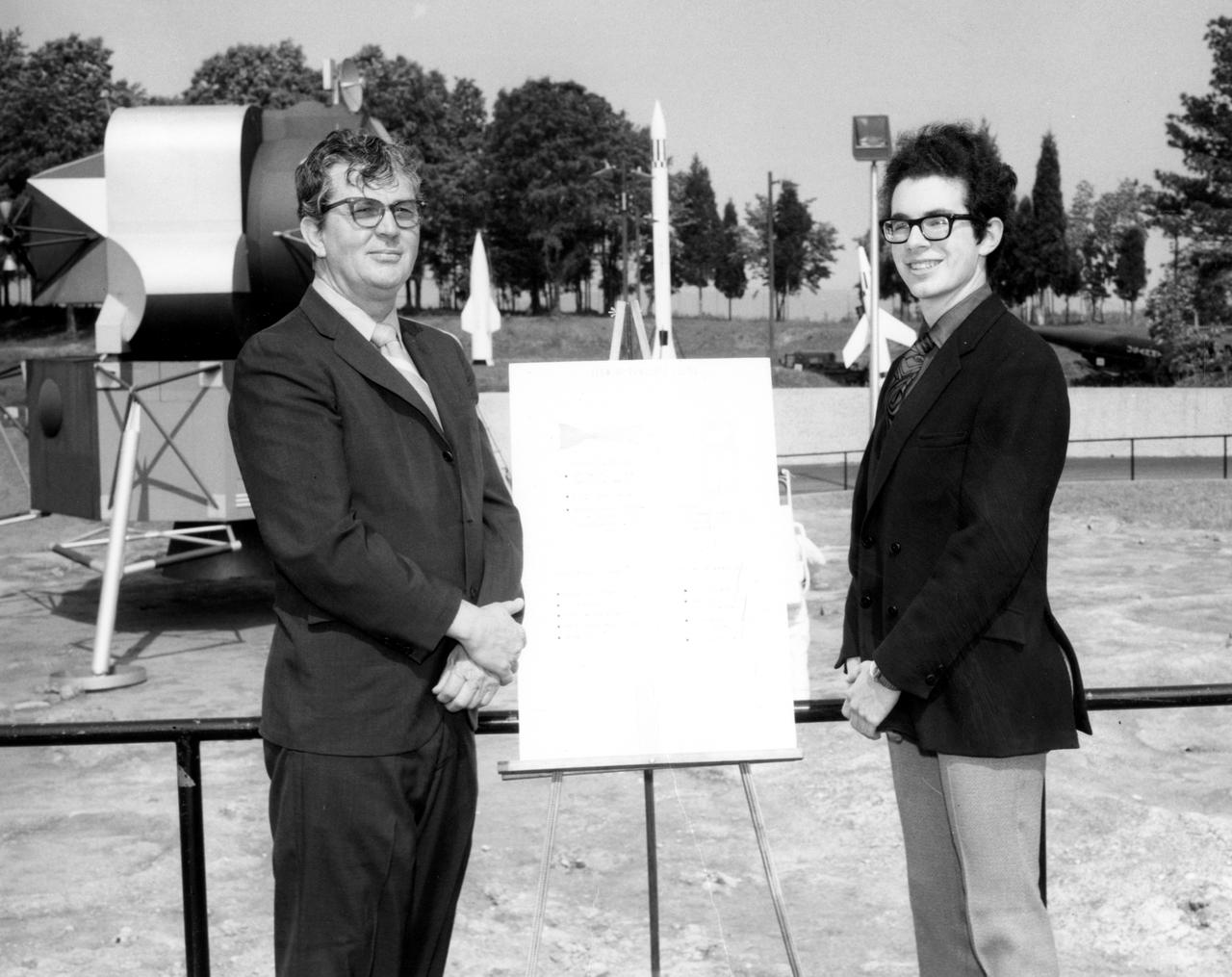

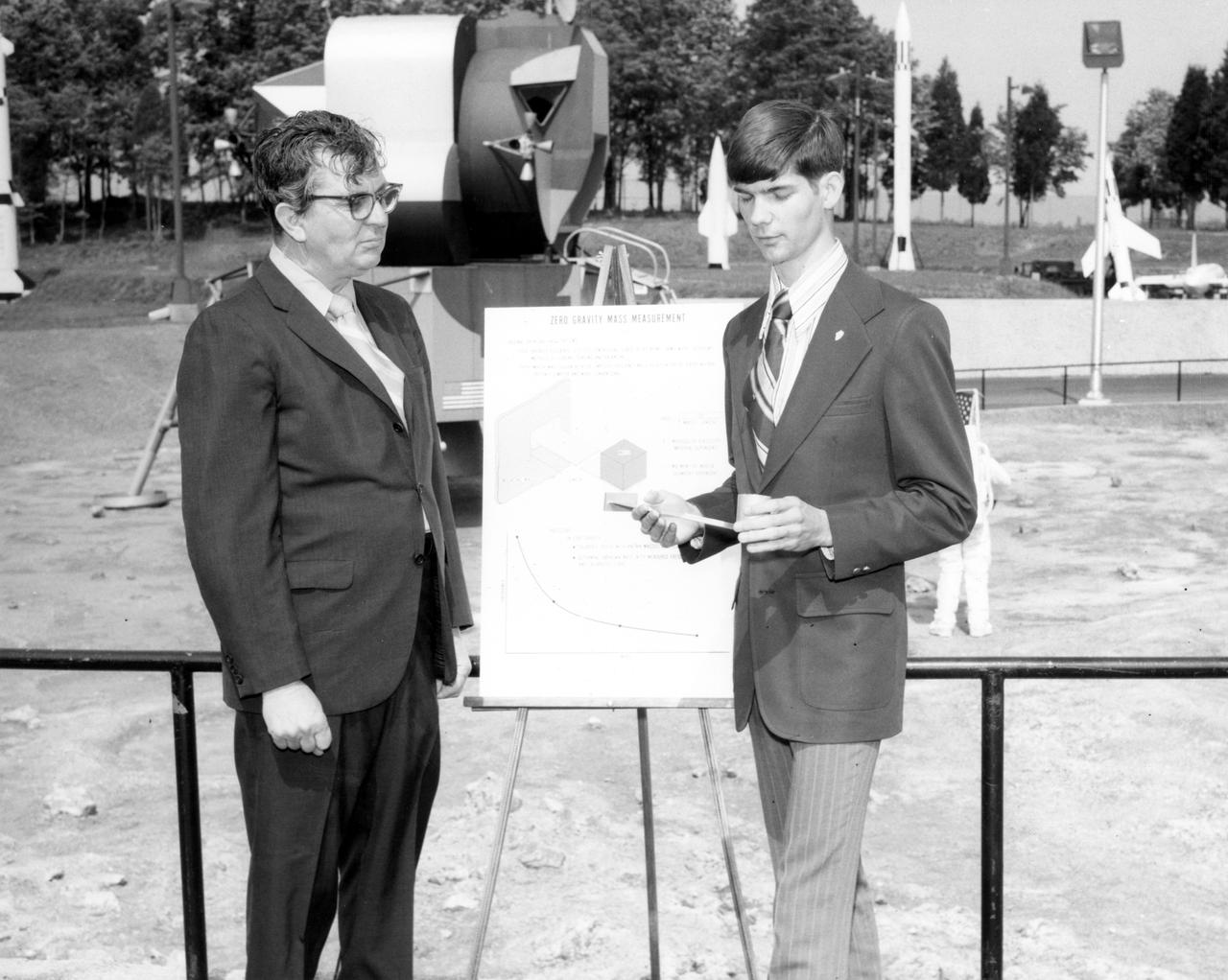
Kirk M. Sherhart, high school student from Berkley, Michigan, discussed a his proposed Skylab experiment with Dr. Robert Head of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) during his visit to the center. The lunar surface scene in the background is one of many space exhibits at the Alabama Space and Rocket Center in nearby Huntsville, Alabama. Sherhart was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
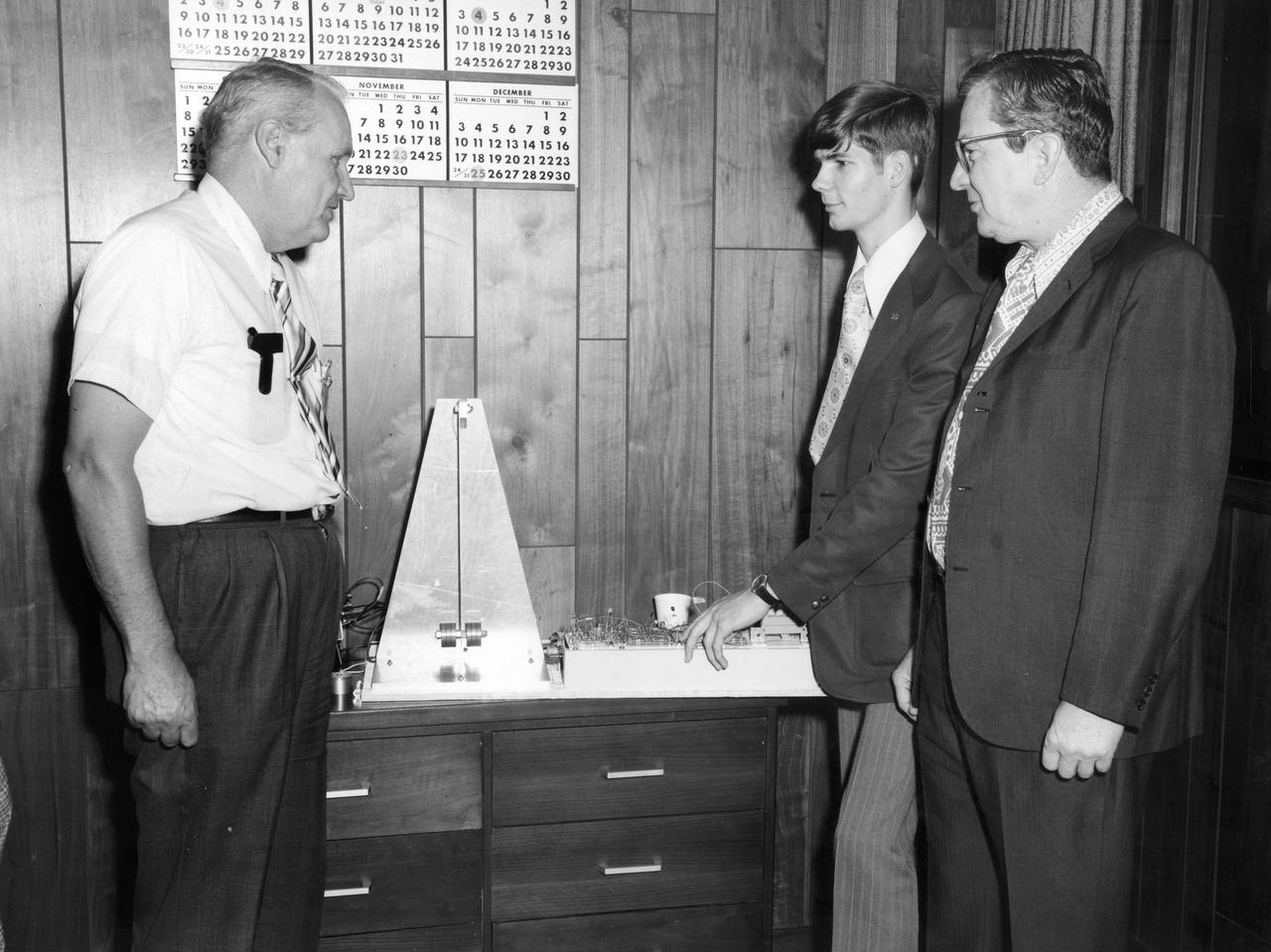

Rockford, Illinois high school student, Vincent Converse, discussed his proposed Skylab experiment with Dr. Robert Head (right) and Gene Greshman of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). His experiment, “Zero Gravity Mass Measurement” used a simple leaf spring with the mass to be weighed attached to the end. The electronic package oscillated the spring at a specific rate and the results were recorded electronically. Converse was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of equipment, such as that of Converse’s experiment.

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover captured this view using its Mast Camera, or Mastcam, while heading west away from Gediz Vallis channel on Nov. 2, 2024, the 4,352nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This panorama is made up of two mosaics: one consisting of 171 individual images taken at 12:16 p.m. local Mars time; and another consisting of 169 at 12:46 p.m. local Mars time. The color has been adjusted to match lighting conditions as the human eye would see them on Earth. Rover tracks can be seen trailing behind Curiosity at right. The difficult, rocky terrain made for slow going. The butte on the left side of the scene is nicknamed "Texoli"; the butte dominating the right side of the scene is nicknamed "Kukenán." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26471
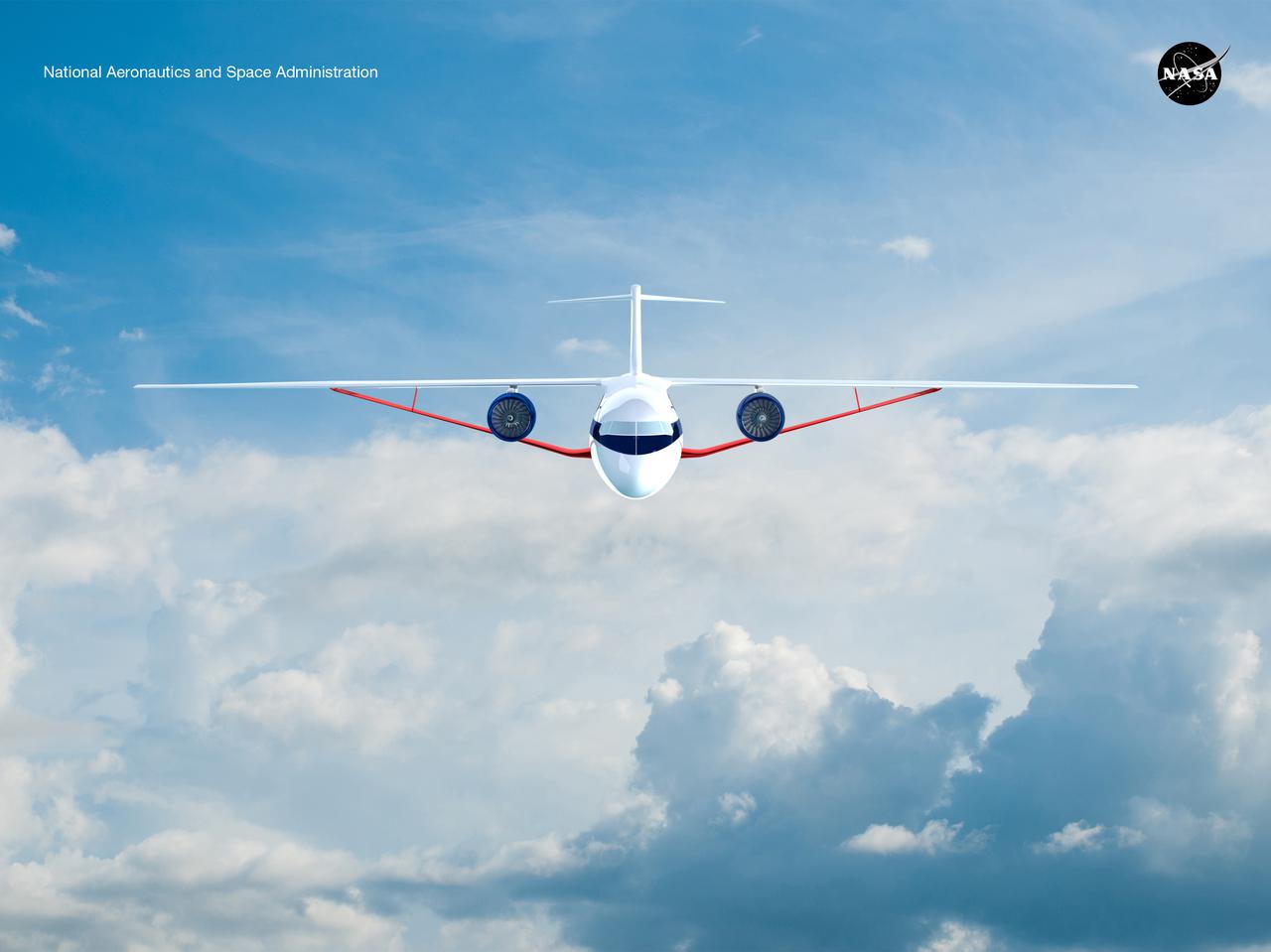

Notice anything different about the wings on this airliner? This conceptual truss-braced wing narrowbody is an aircraft with a 170ft span folding wing. By utilizing trusses, the aircraft can have longer, thinner wings with greater aspect ratios. This, in turn, translates into less drag and 5-10% less fuel burned. The Transonic Truss-Braced Wing aircraft originated from a joint effort by NASA and Boeing to develop subsonic commercial transport concepts – meeting NASA-defined metrics in terms of reduced noise, emissions, and fuel consumption. The design is currently undergoing wind tunnel testing and other studies by NASA researchers.
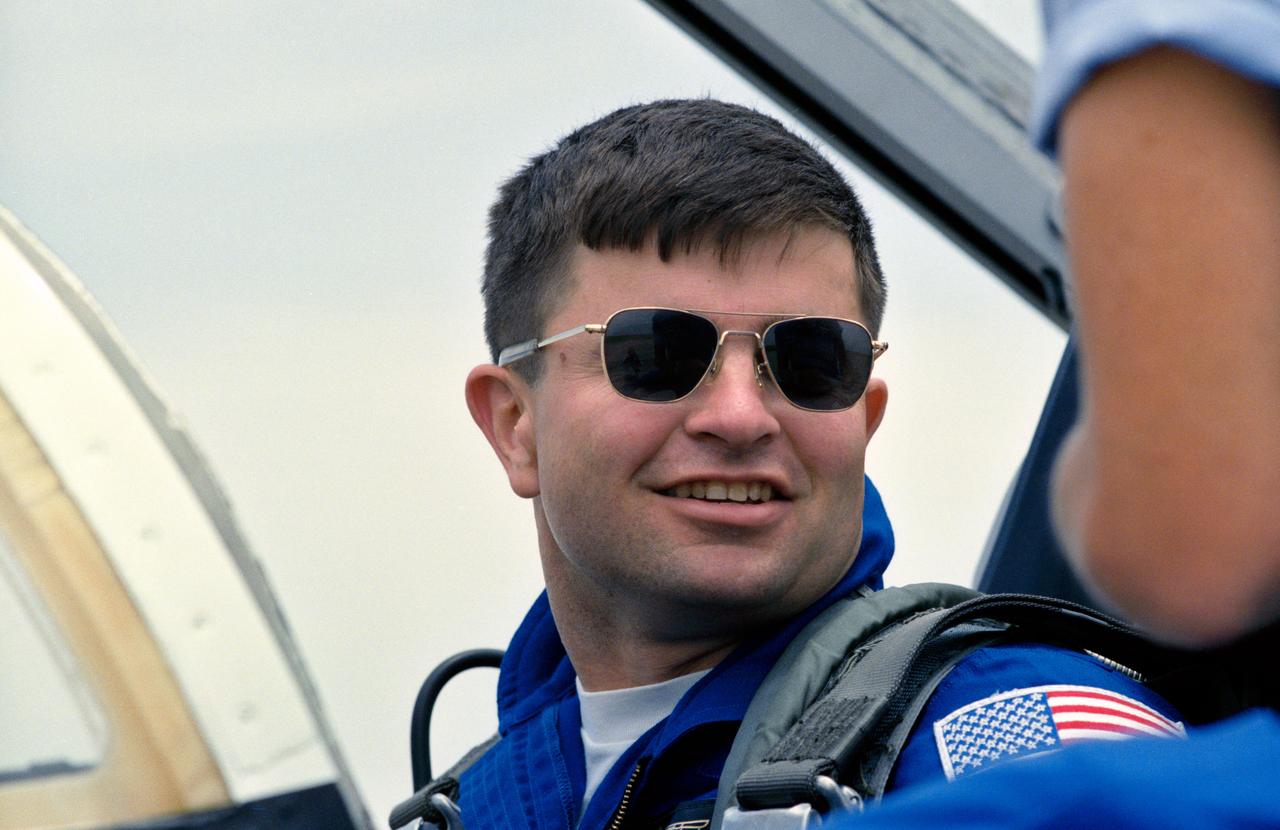

Head and shoulders view of astronaut Ken Cameron sitting in the cockpit of a T 38 at Ellington Field prior to his departure to Fairchild AFB, Washington.

Vincent W. Converse, high school student from Rockford, Illinois, discussed a mass measurement device he proposed for the Skylab mission with Dr. Robert Head of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) during his visit to the center. The lunar surface scene in the background is one of many space exhibits at the Alabama Space and Rocket Center in nearby Huntsville, Alabama. Converse was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
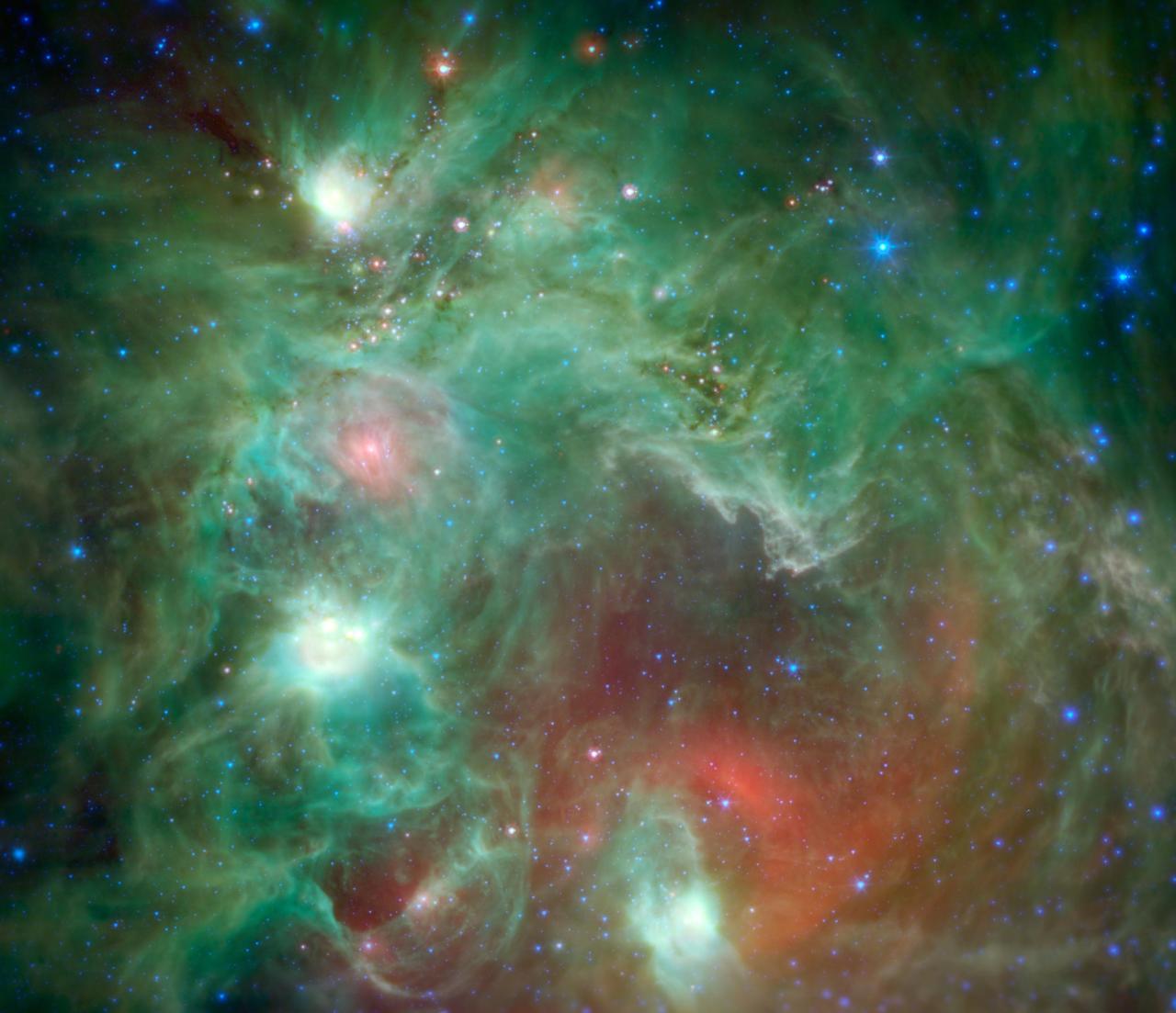

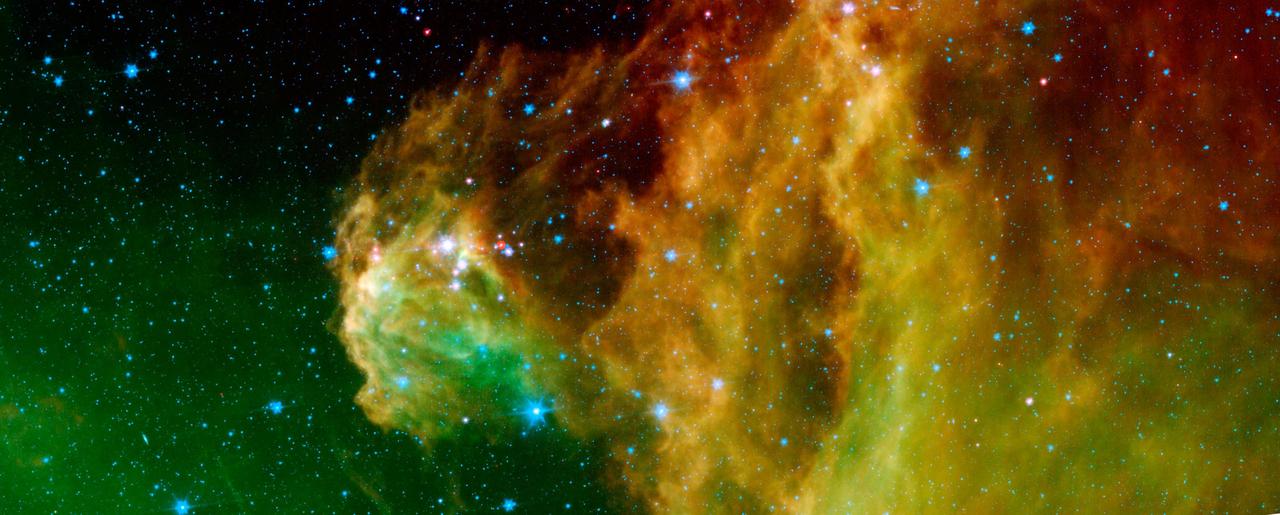
Scores of baby stars shrouded by dust are revealed in this infrared image of the star-forming region NGC 2174, as seen by NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. Found in the constellation Orion, NGC 2174 is located around 6,400 light-years away. Some of the clouds in the region resemble the face of a monkey in visible-light images, hence the nebula's nickname: the "Monkey Head." However, in infrared images such as this, the monkey disappears. That's because different clouds are highlighted in infrared and visible-light images. Found in the northern reaches of the constellation Orion, NGC 2174 is located around 6,400 light-years away. Columns of dust, slightly to the right of center in the image, are being carved out of the dust by radiation and stellar winds from the hottest young stars recently born in the area. Spitzer's infrared view provides us with a preview of the next clusters of stars that will be born in the coming millennia. The reddish spots of light scattered through the darker filaments are infant stars swaddled by blankets of warm dust. The warm dust glows brightly at infrared wavelengths. Eventually, these stars will pop out of their dusty envelopes and their light will carve away at the dust clouds surrounding them. In this image, infrared wavelengths have been assigned visible colors we see with our eyes. Light with a wavelength of 3.5 microns is shown in blue, 8.0 microns is green, and 24 microns in red. The greens show the organic molecules in the dust clouds, illuminated by starlight. Reds are caused by the thermal radiation emitted from the very hottest areas of dust. Areas around the edges that were not observed by Spitzer have been filled in using infrared observations from NASA's Wide Field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19836
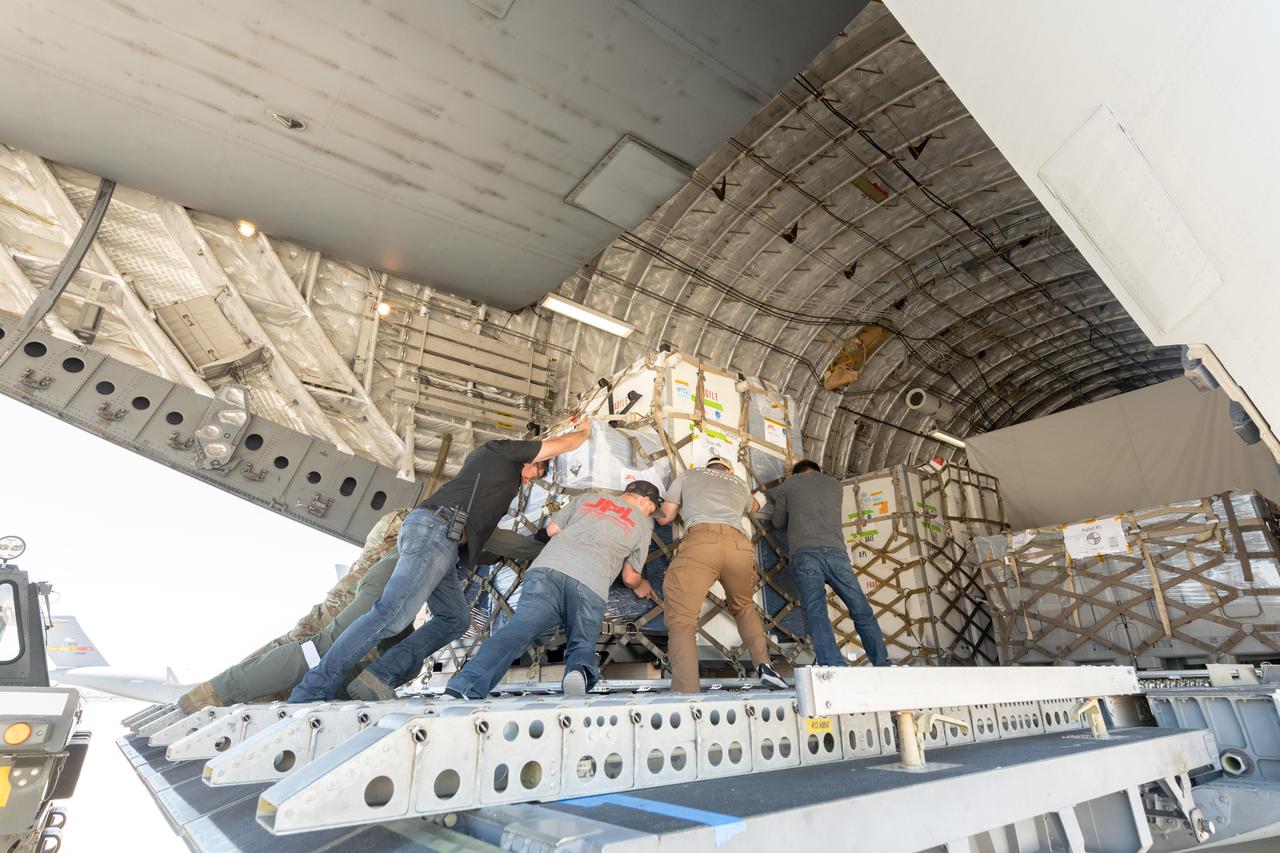

On June 27, 2021, teams from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California and the March Air Reserve Base in Riverside County, California, loaded the scientific heart of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission into a C-17 airplane. The hardware – which includes research instruments – was headed to a clean room facility near Cannes, France, where engineers and technicians completed assembly of the satellite over the next year. The satellite was subsequently shipped back to California for its December 2022 launch from Vandenberg Space Force Base. SWOT will make global surveys of the water on Earth's surface. By measuring its height, researchers can track the volume and location of the finite resource around the world. The data will help with monitoring changes in floodplains and wetlands, measure how much fresh water flows into and out of lakes and rivers and back to the ocean, and track regional shifts in sea level. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25625
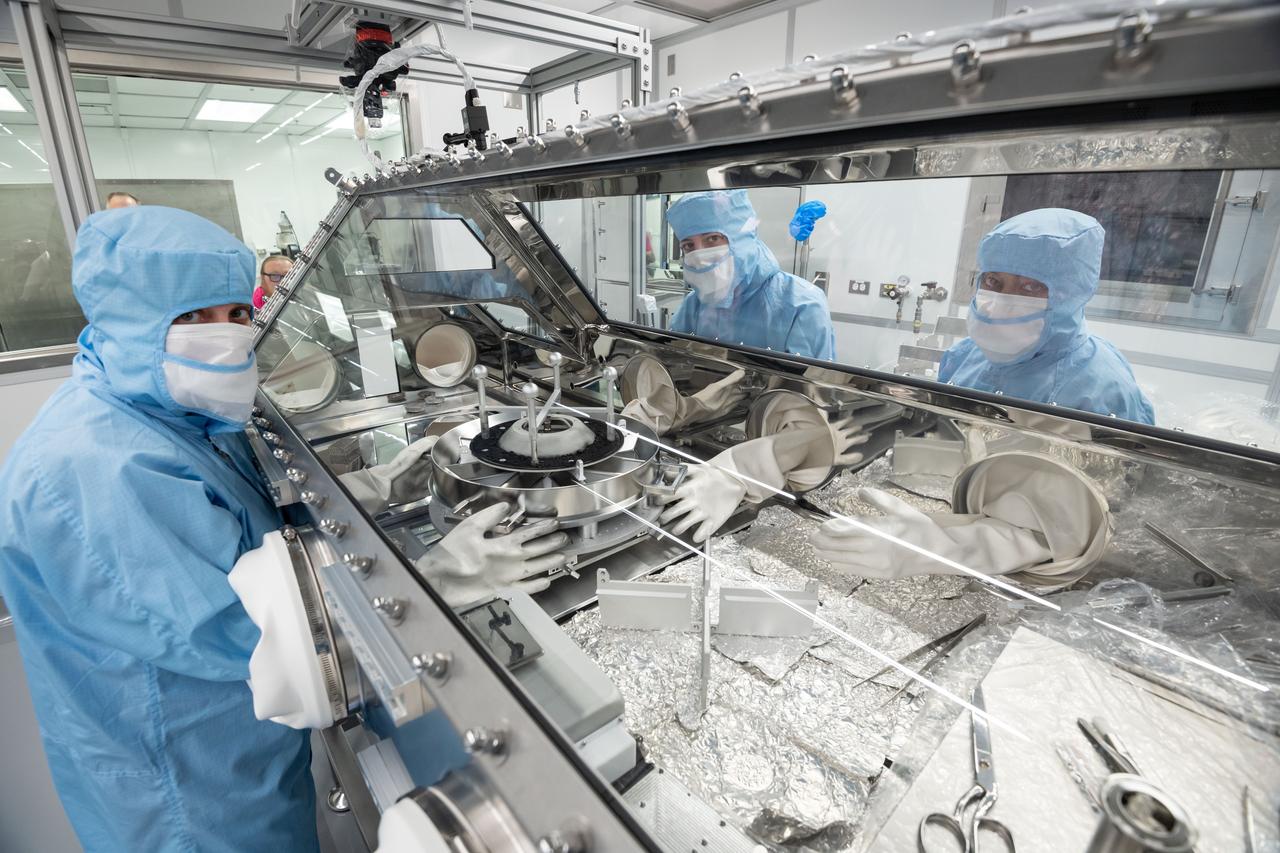

jsc2024e008542 - Curation team members from the Astromaterials Research and Exploration Science (ARES) division at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston perform a pour maneuver to distribute the remaining asteroid sample material from the OSIRIS-REx Touch-and-Go Sample Acquisition Mechanism (TAGSAM) head into sample containers. From left, astromaterials processors Rachel Funk, top right, Julia Plummer, bottom right, Jannatul Ferdous.
NASA's 2001 Mars Odyssey spies what looks likNASA's 2001 Mars Odyssey spies what looks like a barrage of bullets headed its way.e a barrage of bullets headed its way. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21688
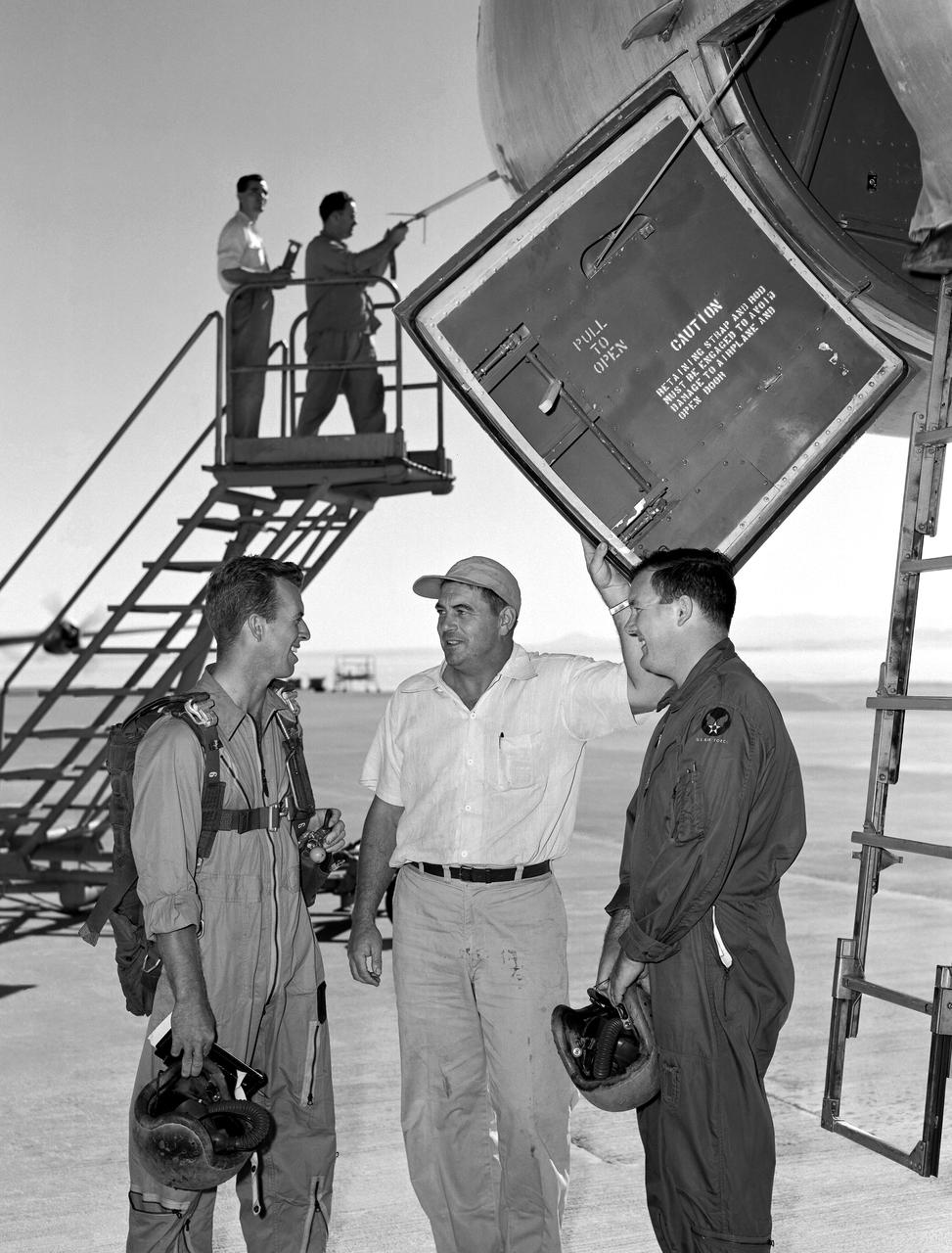

B-47A Stratojet on ramp with pilots and crew. In 1954 after a research flight in the Boeing B-47A Stratojet Crew Chief Wilbur McClenaghan (center) asks of the pilots if there are any "squawks" that should be taken care of before the next flight. Pilots are Joe Walker on the viewer's left and Stanley Butchart on the right. Data system technician Merle Curtis, in coveralls, is busy checking the airdata head mounted on the nose boom with the help of Instrumentation Crew Chief Raymond Langley. The door to the cockpit area is open showing a view of the ladder that folds down to be used by the pilots to enter and leave the area.
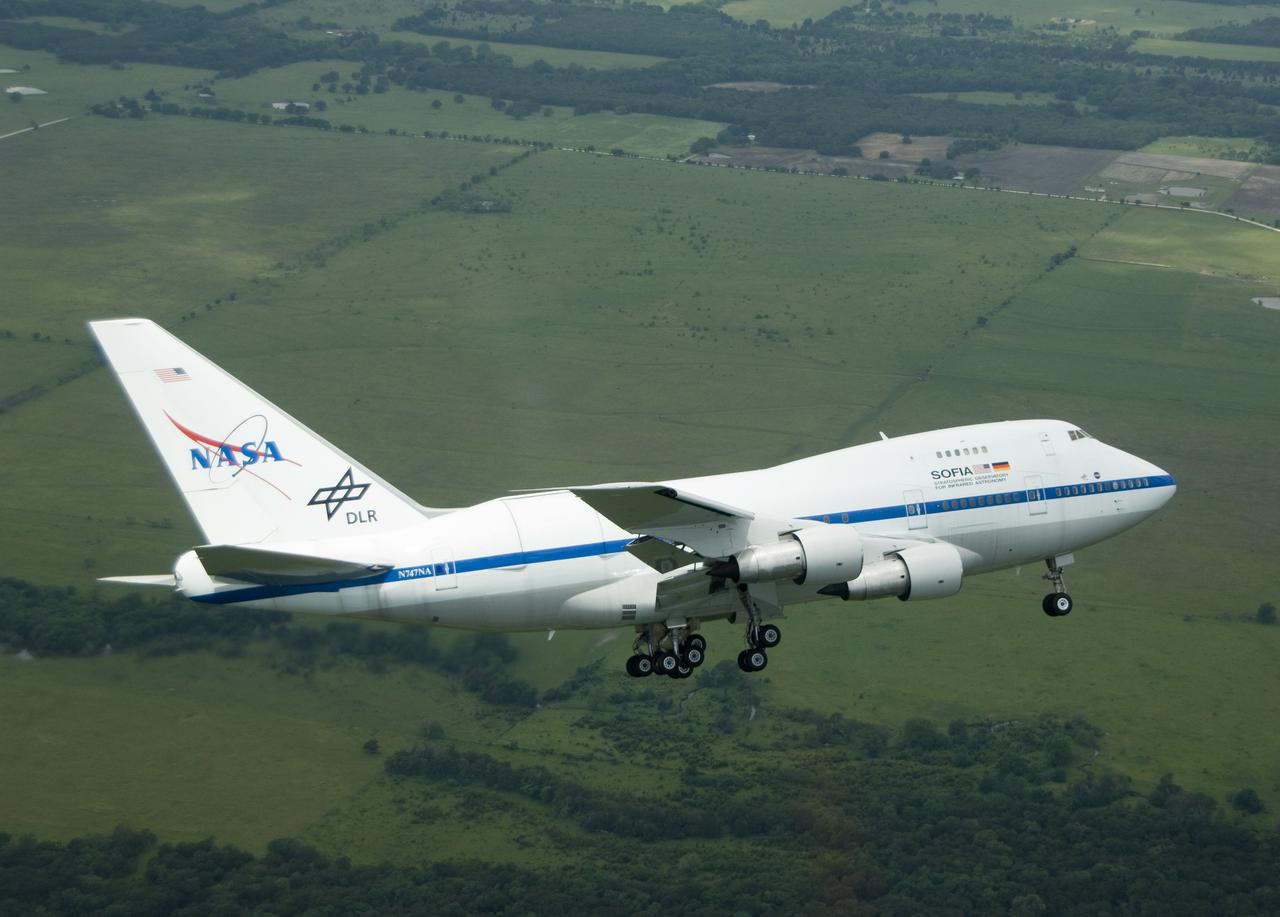

NASA's highly modified Boeing 747SP SOFIA observatory banks low over the Texas countryside as it heads for landing at Waco to conclude its second check flight.
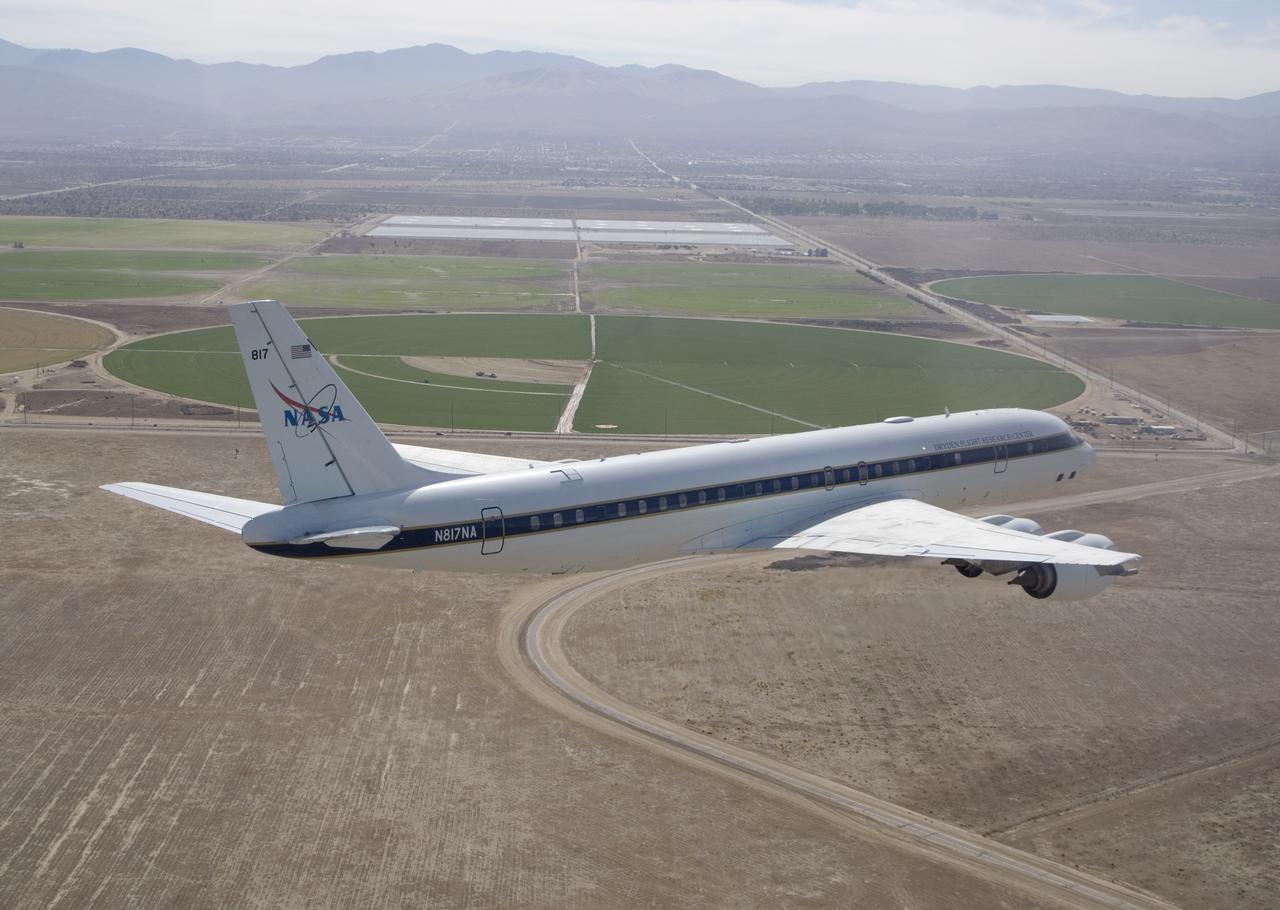

Agricultural fields spread out beyond NASA's DC-8 airborne science laboratory as it heads for landing at Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, Calif.
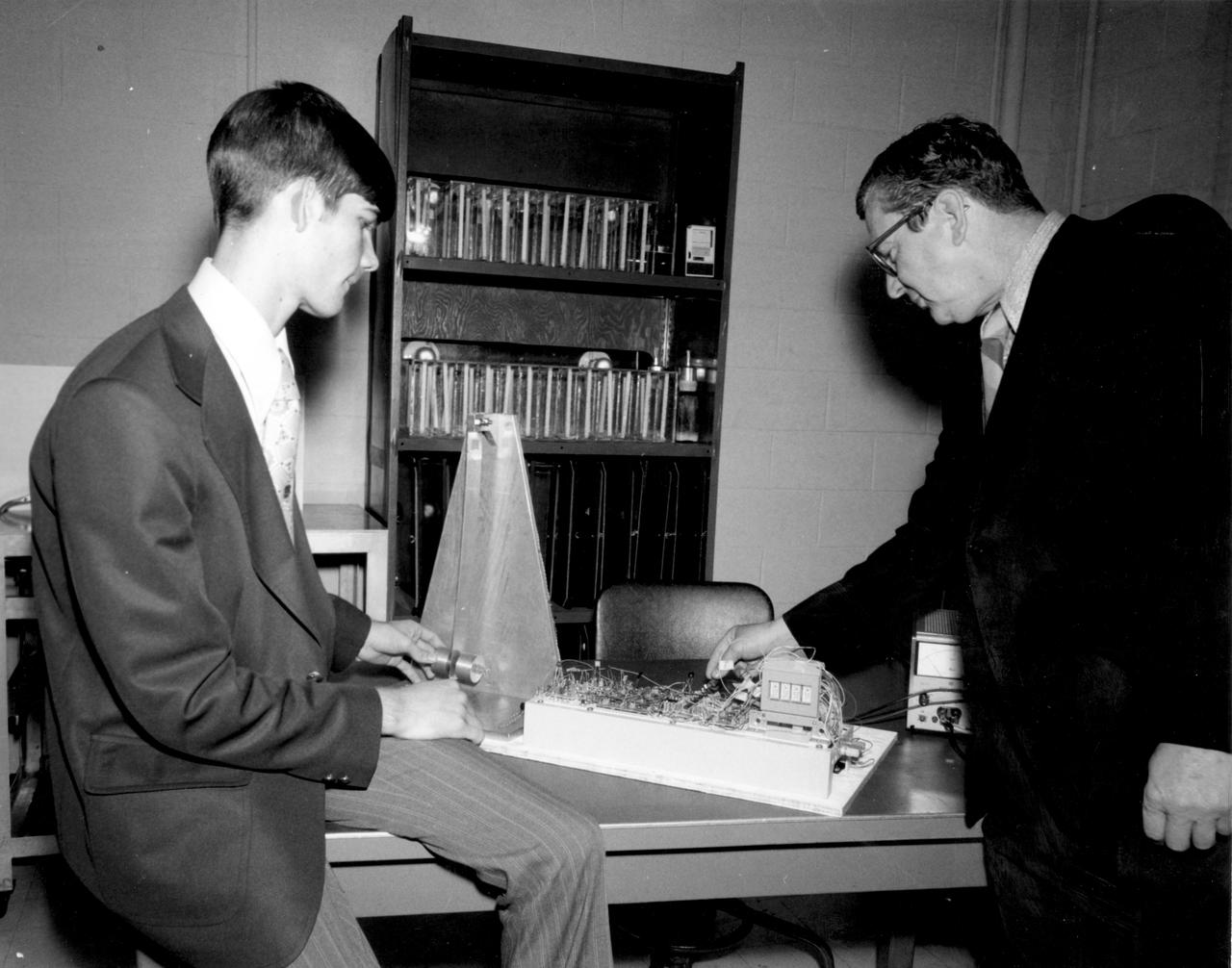

Rockford, Illinois high school student, Vincent Converse (left), and Robert Head of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), check out the equipment to be used in conducting the student’s experiment aboard the Skylab the following year. His experiment, “Zero Gravity Mass Measurement” used a simple leaf spring with the mass to be weighed attached to the end. An electronic package oscillated the spring at a specific rate and the results were recorded electronically. Converse was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC two months earlier where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
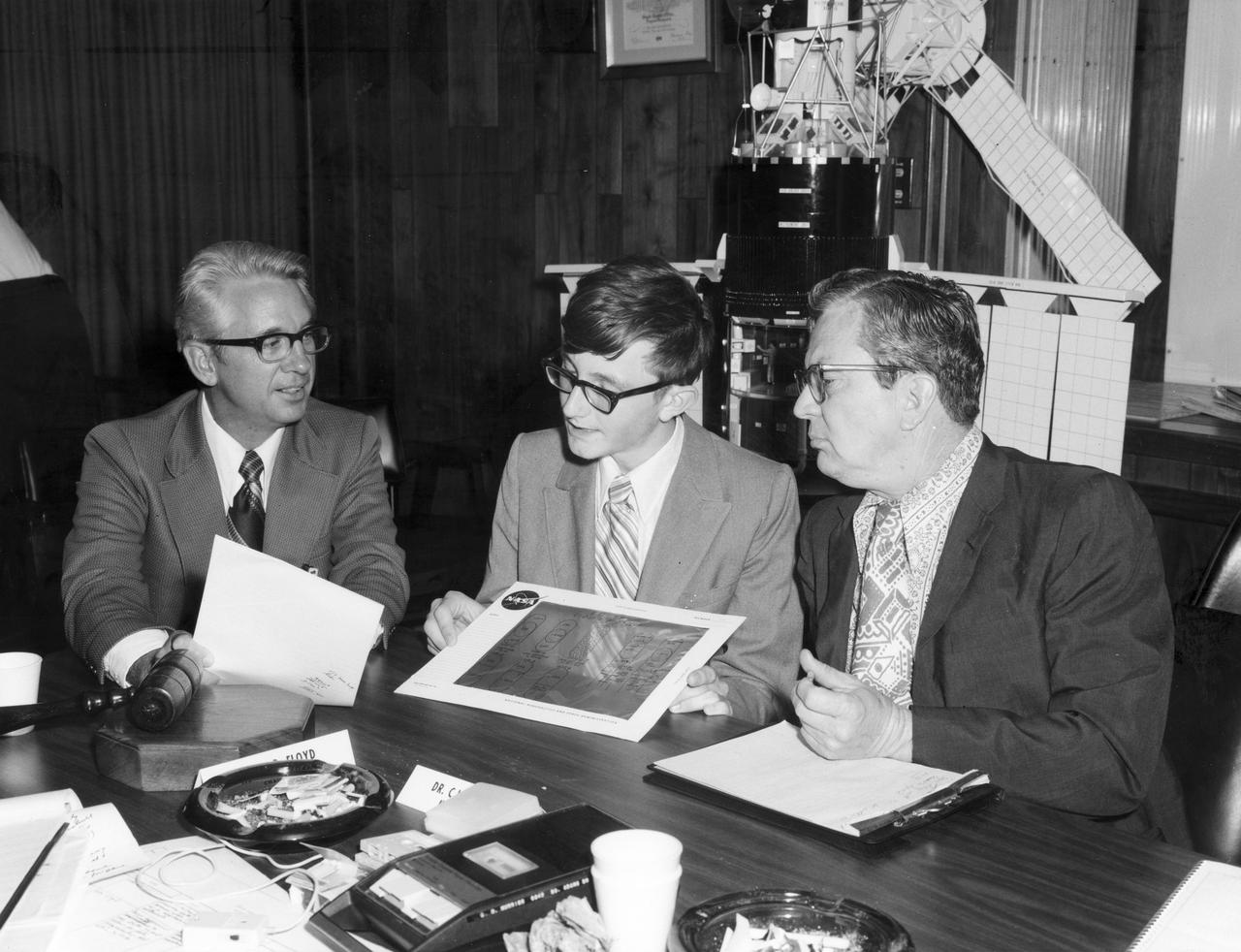

Youngstown, Ohio high school student, W. Brian Dunlap (center), discusses with Dr. Robert Head (right), and Henry Floyd, both of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), his experiment to be performed aboard the Skylab the following year. His experiment, “Wave Motion Trough A Liquid in Zero Gravity” used a container attached to the end of a leaf spring which was oscillated at specific rates using two thickness differentiated types of liquids. Dunlap was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment. The equipment for the experiments was manufactured at MSFC.
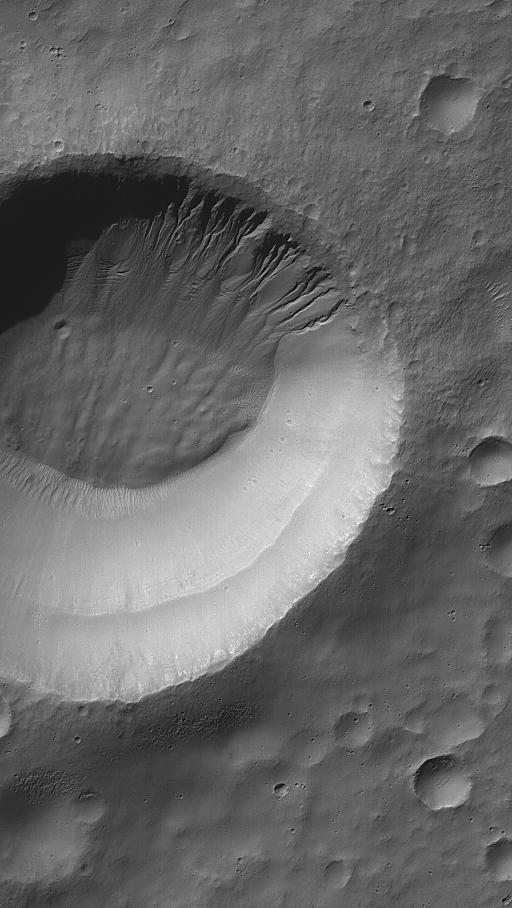

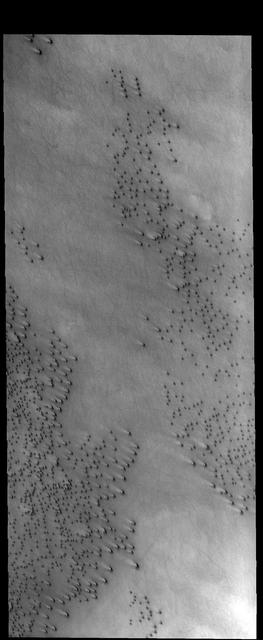
This MOC image shows gullies all of which head at the same level on a south mid-latitude crater wall
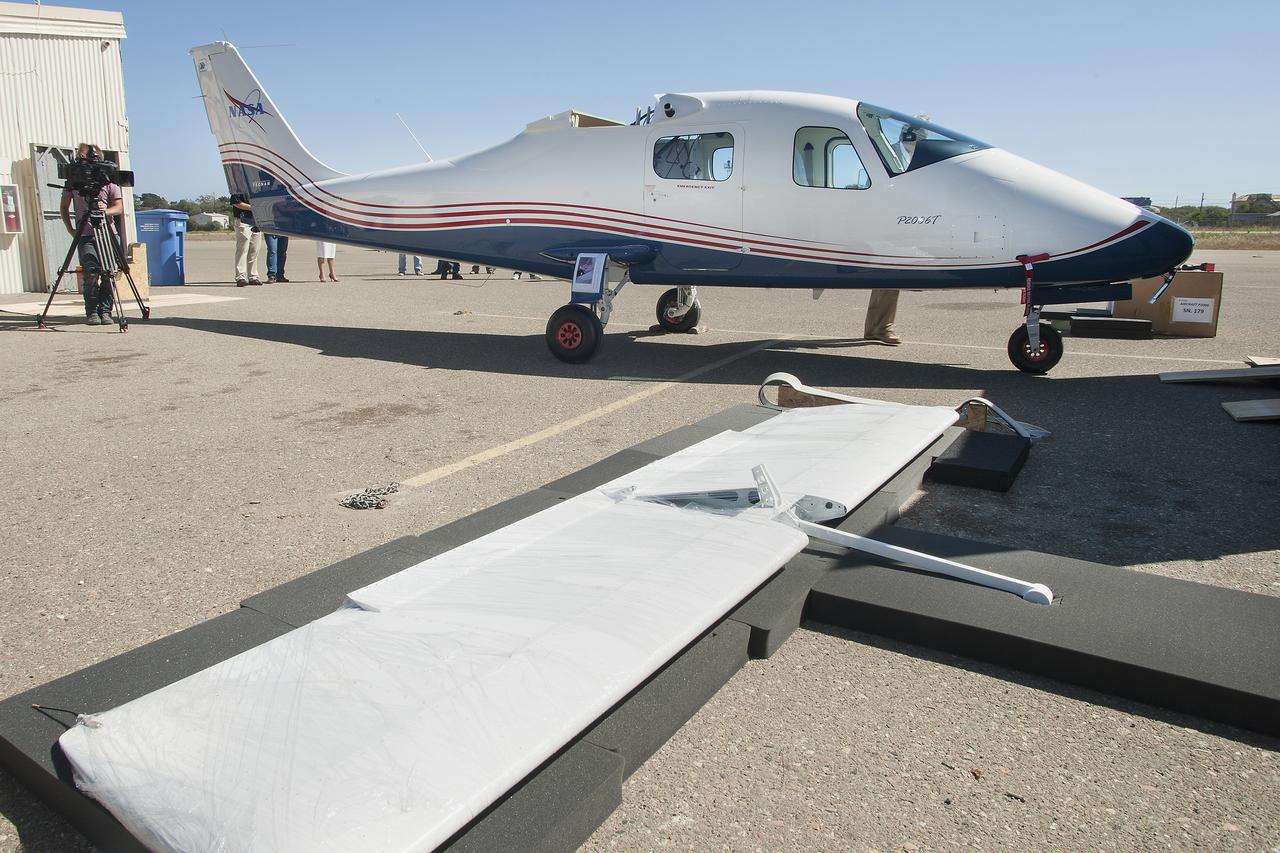

Preparations are underway to inspect, weigh and balance the Tecnam fuselage before it heads to Mojave, California, for wing integration.
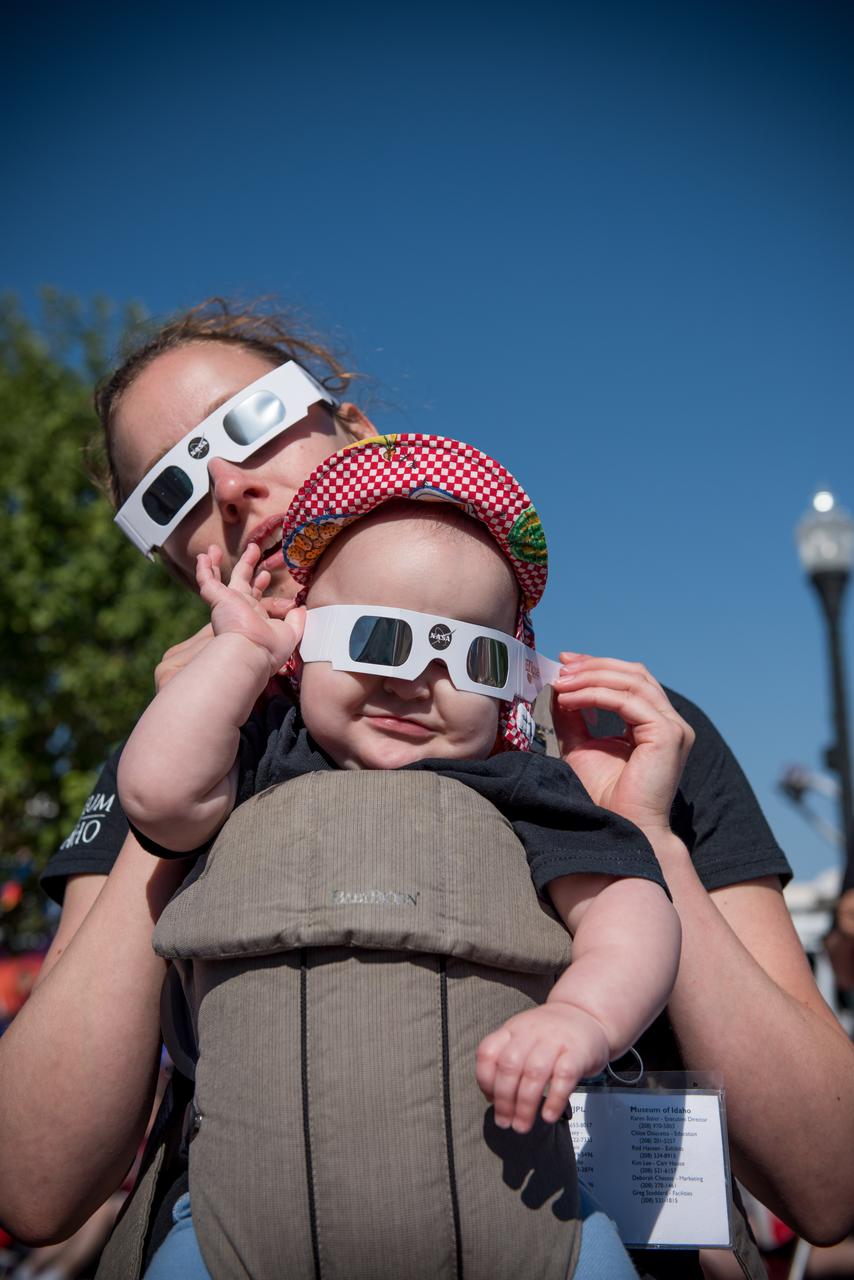

Juniper Doucette and her mother Chloe Doucette, head of education at the museum of Idaho Falls, enjoying the 2017 total solar eclipse.
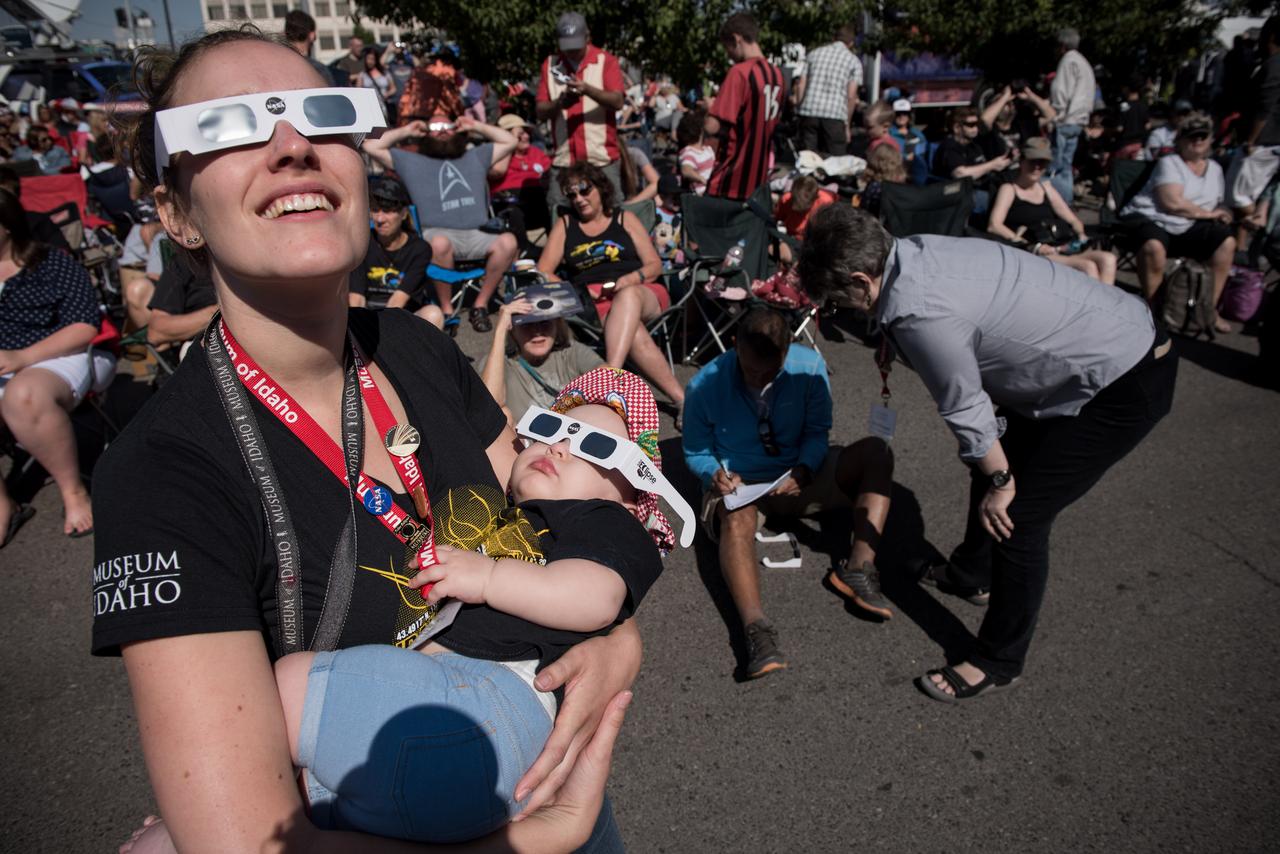

Juniper Doucette with her mother Chloe Doucette, head of education at the museum of Idaho Falls, celebrate the 2017 total solar eclipse.
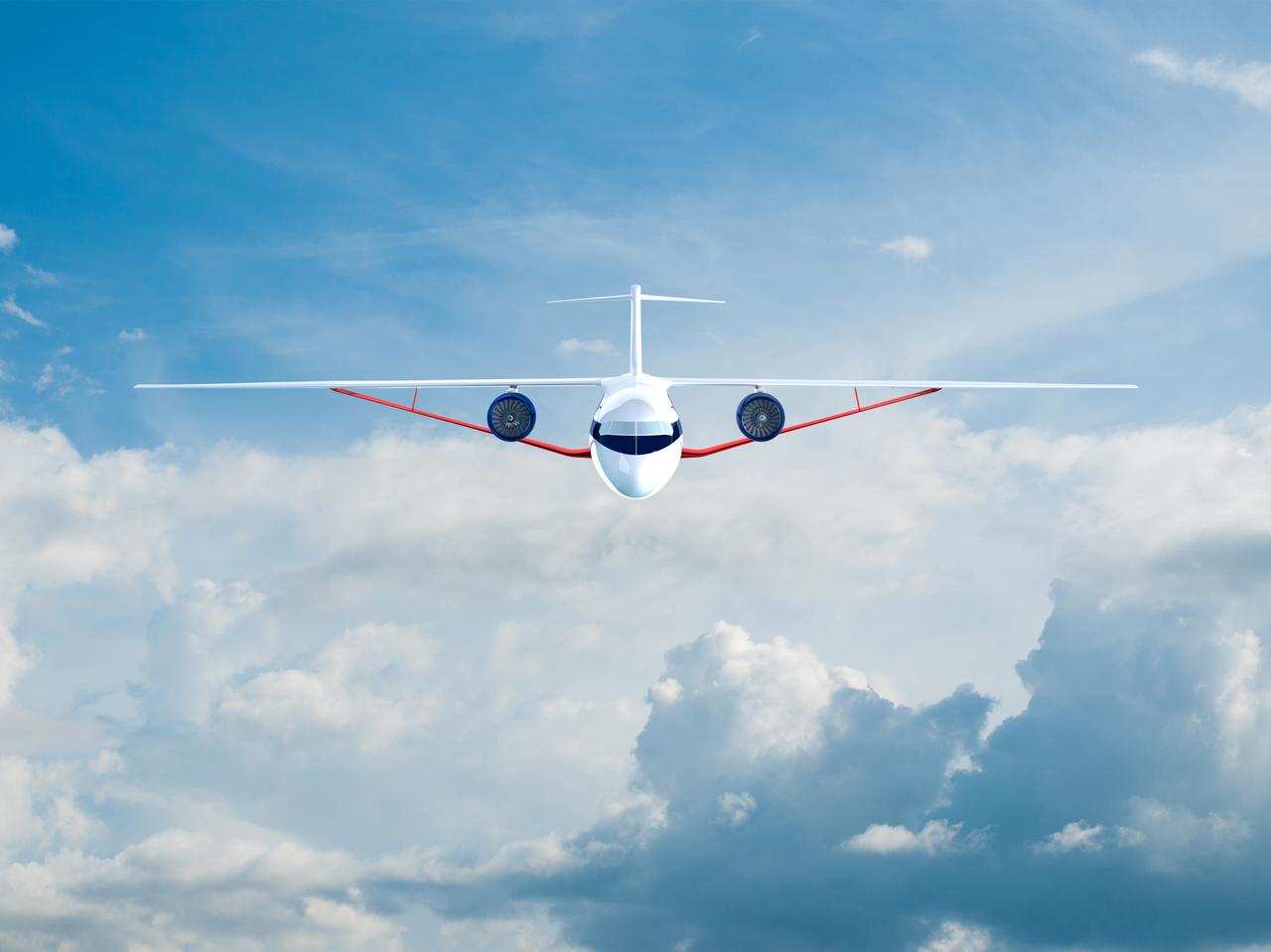

Notice anything different about the wings on this airliner? This conceptual truss-braced wing narrowbody is an aircraft with a 170ft span folding wing. By utilizing trusses, the aircraft can have longer, thinner wings with greater aspect ratios. This, in turn, translates into less drag and 5-10% less fuel burned. The Transonic Truss-Braced Wing aircraft originated from a joint effort by NASA and Boeing to develop subsonic commercial transport concepts – meeting NASA-defined metrics in terms of reduced noise, emissions, and fuel consumption. The design is currently undergoing wind tunnel testing and other studies by NASA researchers.

"Perseverance Valley" lies just on the other side of the dip in the crater rim visible in the left half of this 360-degree panorama from the Navigation Camera (Navcam) on NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity. As the rover arrived at this area in early May 2017, researchers began looking for clues about what process carved the valley. The rover team plans to drive Opportunity all the way down the valley into the interior of Endeavour Crater. The foreground and the area to the right are on the plain just outside of Endeavour Crater. The high point near the center of the image is called "Winnemucca," part of an Endeavour rim segment called "Cape Byron." Endeavour's interior and distant eastern rim are visible at upper left, above the notched portion of the western rim that sits directly above Perseverance Valley. The rover's Navcam took the component images of this scene on May 2 and May 3, 2017, during the 4,718th and 4,719th Martian days, or sols, of Opportunity's work on Mars, two days before a drive that brought Opportunity to the head of the valley. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21495
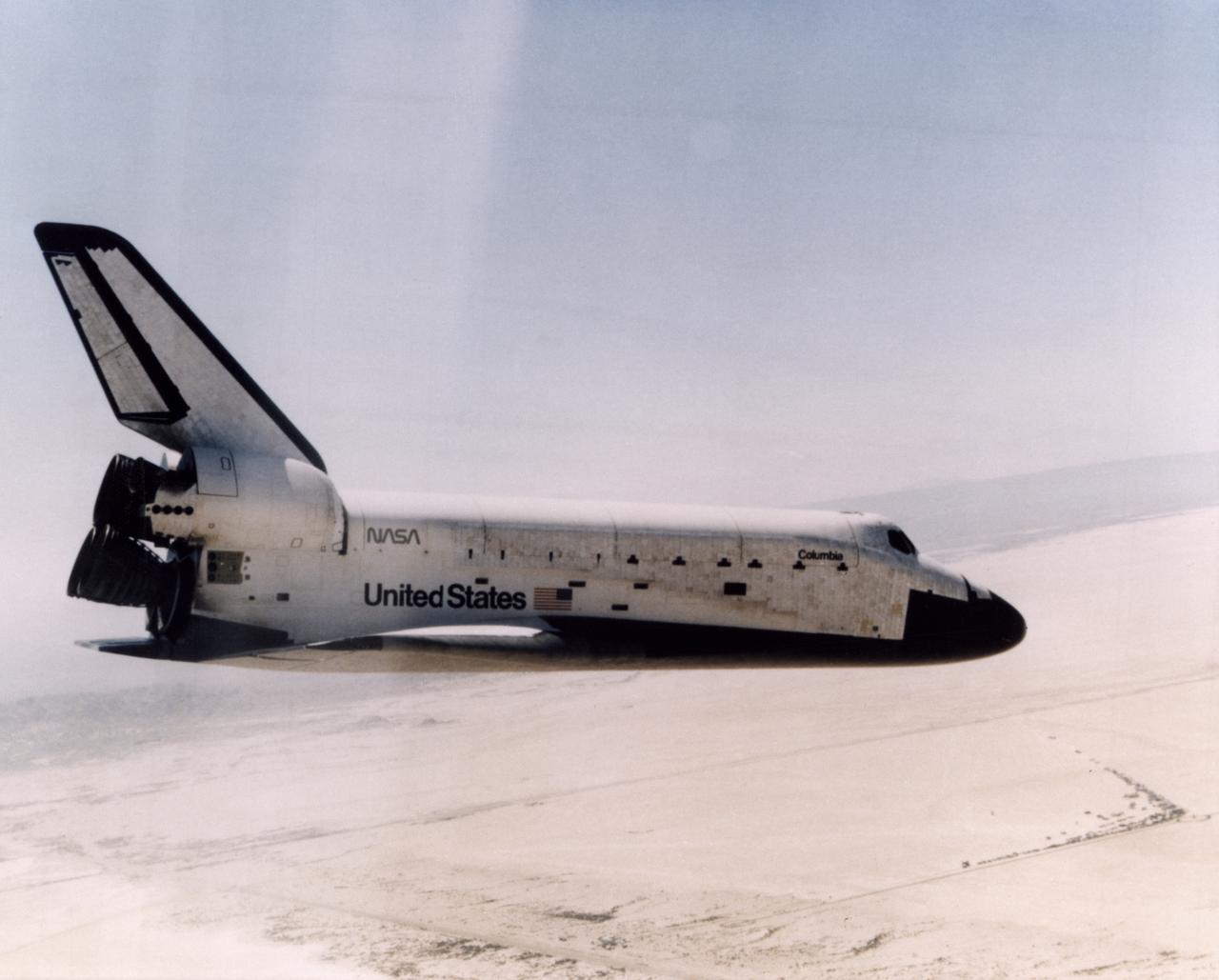

FIRST SHUTTLE LANDING -- The Space Shuttle Columbia glides down over Rogers Dry Lake as it heads for a landing at Edwards Air Force Base at the conclusion of its first orbital mission on April 14, 1981.
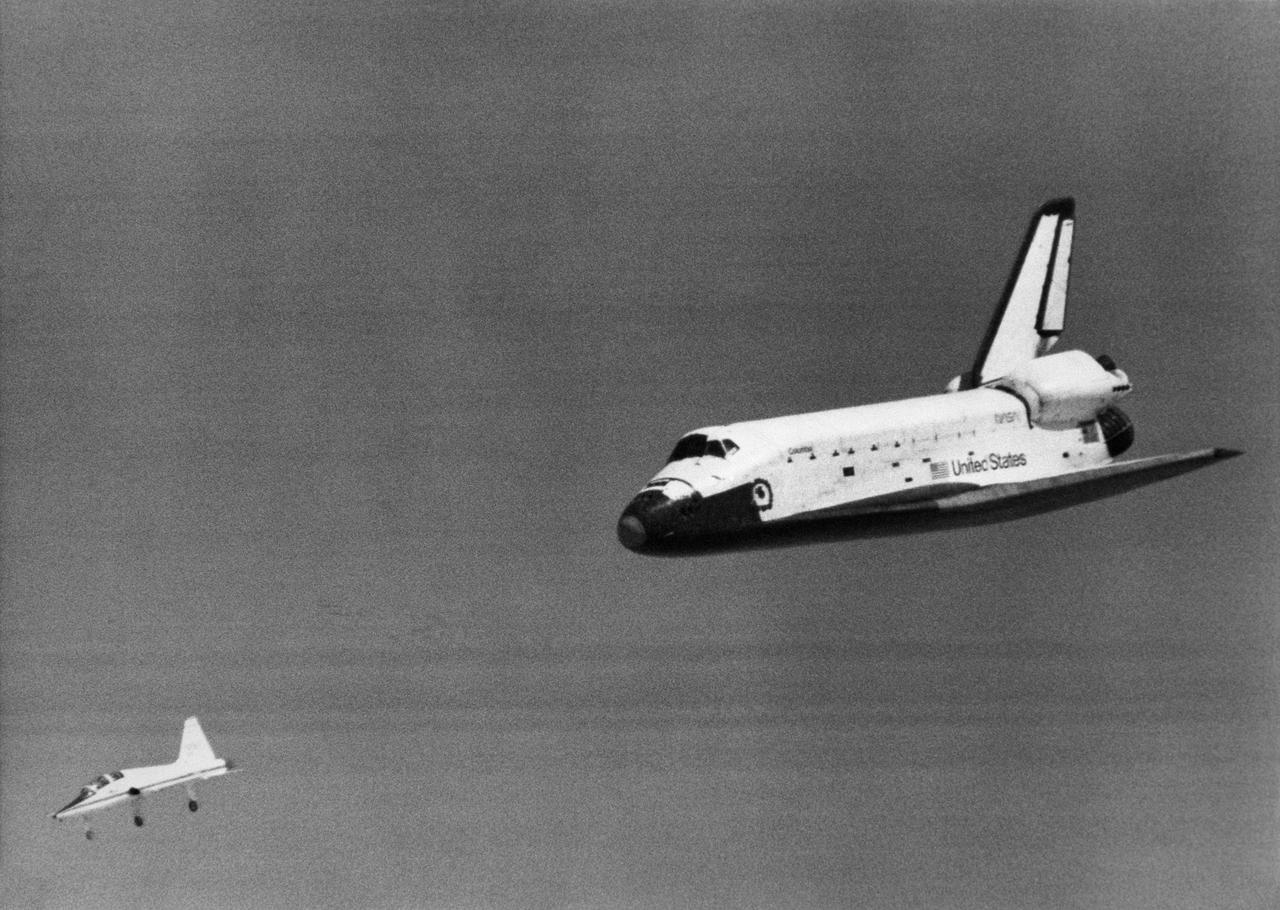

The Space Shuttle Columbia glides down over Rogers Dry Lake as it heads for a landing at Edwards Air Force Base at the conclusion of its first orbital mission on April 14, 1981.
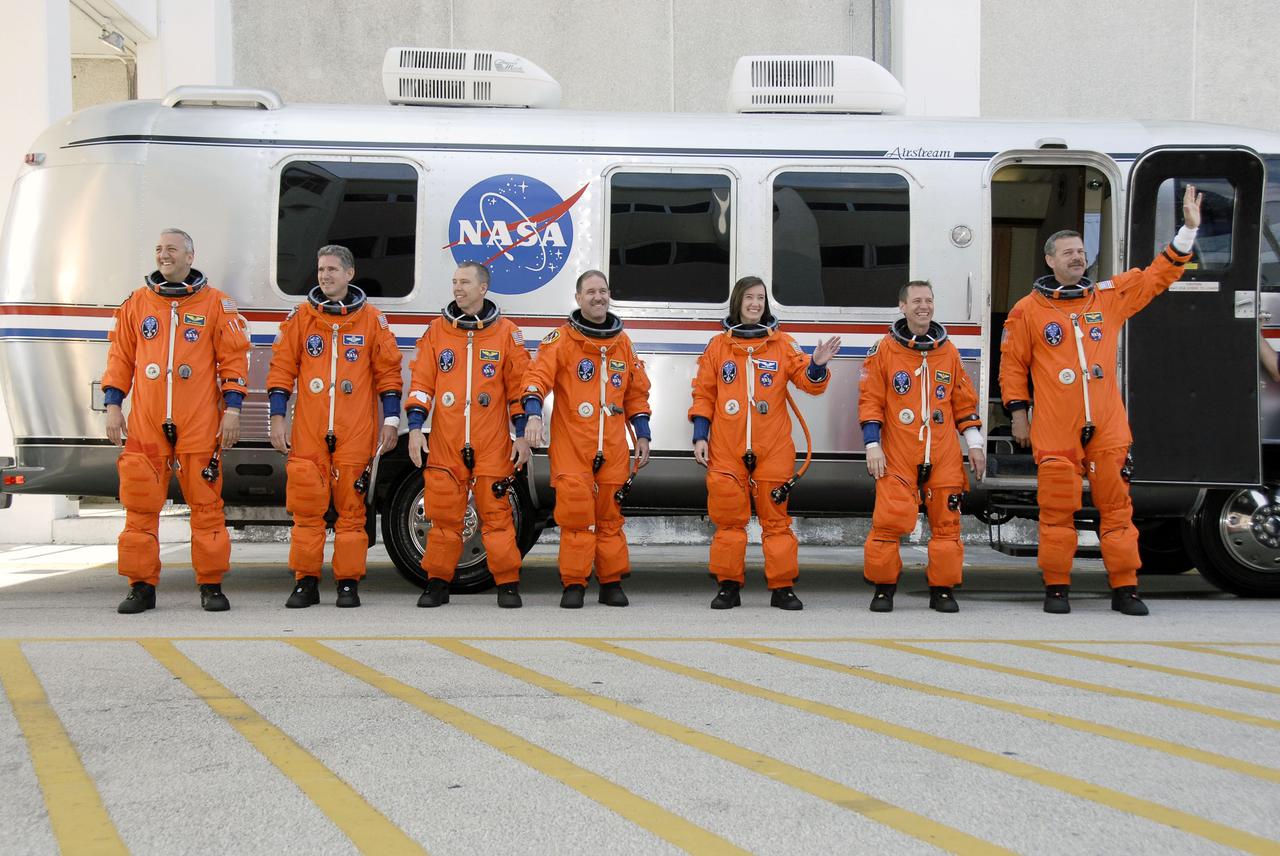

STS125-S-011 (11 May 2009) --- After suiting up, the STS-125 crewmembers pause alongside the Astrovan to wave farewell to onlookers before heading for launch pad 39A for the launch of Space Shuttle Atlantis on the STS-125 mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope. From the right are Scott Altman, commander; Gregory C. Johnson, pilot; Megan McArthur, John Grunsfeld, Andrew Feustel, Michael Good and Mike Massimino, all mission specialists. Atlantis' 11-day flight will include five spacewalks to refurbish and upgrade the telescope with state-of-the-art science instruments that will expand Hubble's capabilities and extend its operational lifespan through at least 2014. The payload includes Wide Field Camera 3, fine guidance sensor and the Cosmic Origins Spectrograph. Launch of Atlantis is scheduled for 2:01 p.m. May 11 EDT.
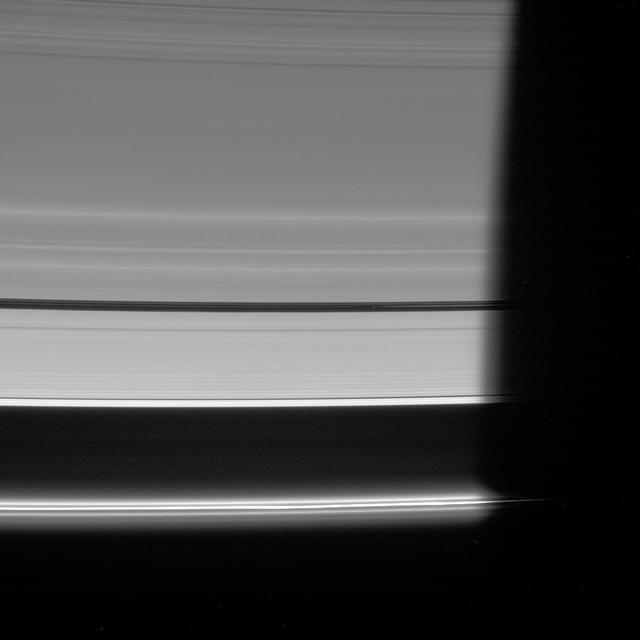

NASA Cassini spacecraft looks down at the unlit side of the rings as Pan heads into Saturn shadow. The moon is accompanied by faint ringlets in the Encke Gap.
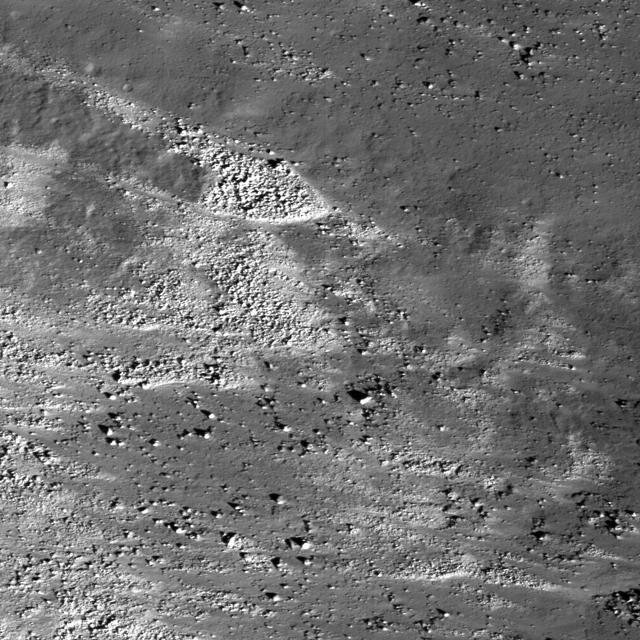

This image taken by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter shows the slopes of the Vallis Schröteri, Cobra Head are boulder-rich and display albedo variations -- bright to dark.
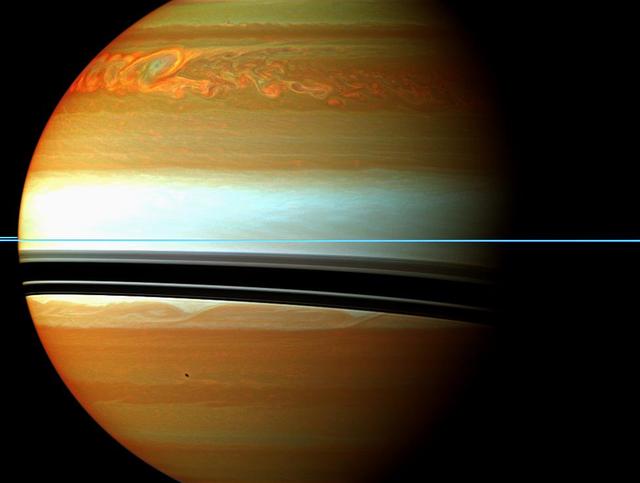

This false-color mosaic from NASA Cassini spacecraft shows the tail of Saturn huge northern storm. The head of the storm is beyond the horizon in this view.
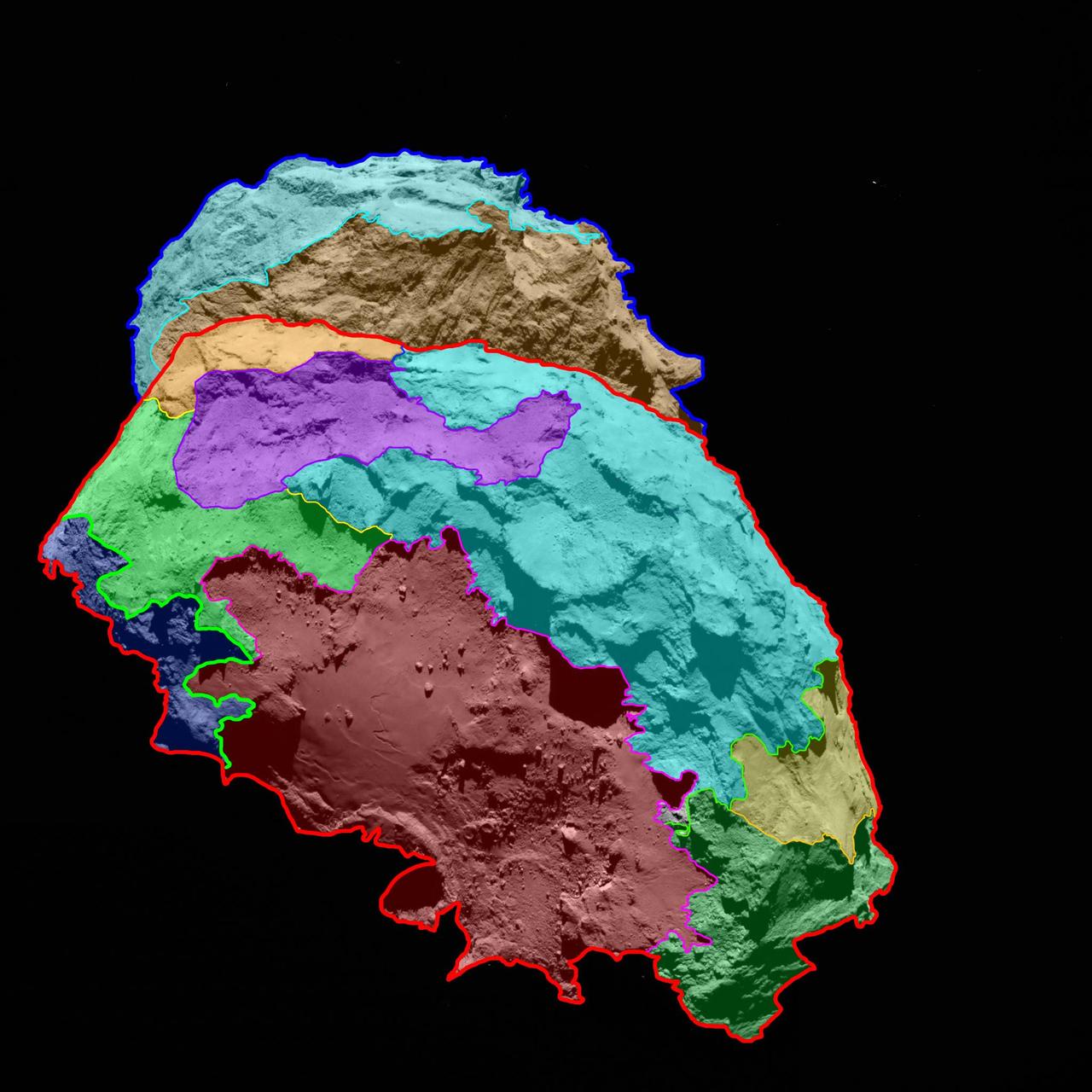

This view of the belly and part of the head of comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko indicates several morphologically different regions as seen by ESA Rosetta spacecraft.