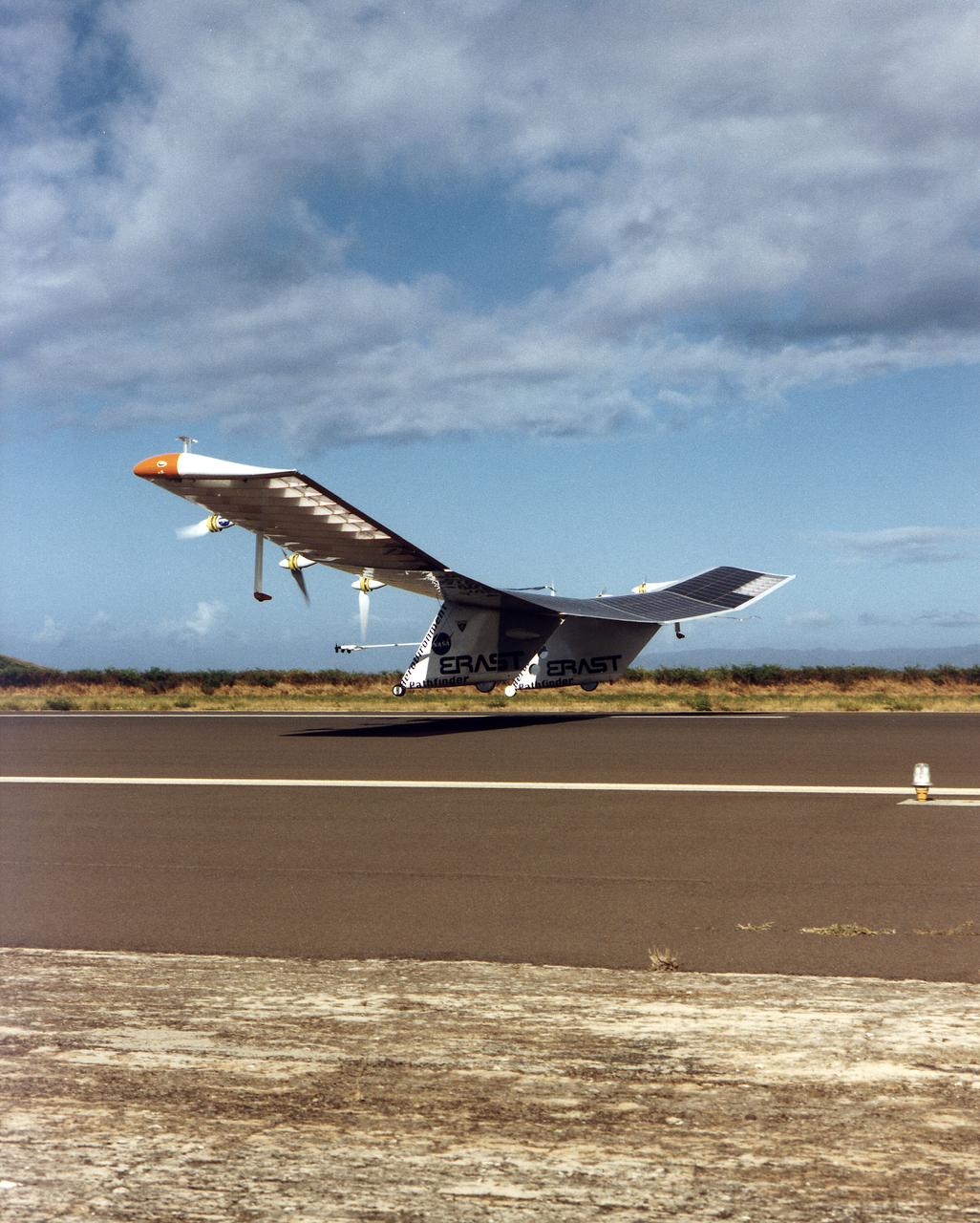

The Pathfinder aircraft has set a new unofficial world record for high-altitude flight of over 71,500 feet for solar-powered aircraft at the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility, Kauai, Hawaii. Pathfinder was designed and manufactured by AeroVironment, Inc, of Simi Valley, California, and was operated by the firm under a jointly sponsored research agreement with NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. Pathfinder's record-breaking flight occurred July 7, 1997. The aircraft took off at 11:34 a.m. PDT, passed its previous record altitude of 67,350 feet at about 5:45 p.m. and then reached its new record altitude at 7 p.m. The mission ended with a perfect nighttime landing at 2:05 a.m. PDT July 8. The new record is the highest altitude ever attained by a propellor-driven aircraft. Before Pathfinder, the altitude record for propellor-driven aircraft was 67,028 feet, set by the experimental Boeing Condor remotely piloted aircraft.
The Gamma-Ray Imager/Polarimeter for Solar flares (GRIPS) instrument is installed in the B-2 vacuum chamber for a full-instrument thermal-vacuum test in 2015. The GRIPS telescope was launched via balloon in January 2016 on a high-altitude flight over Antarctica to study the acceleration and transport of solar flare particles.
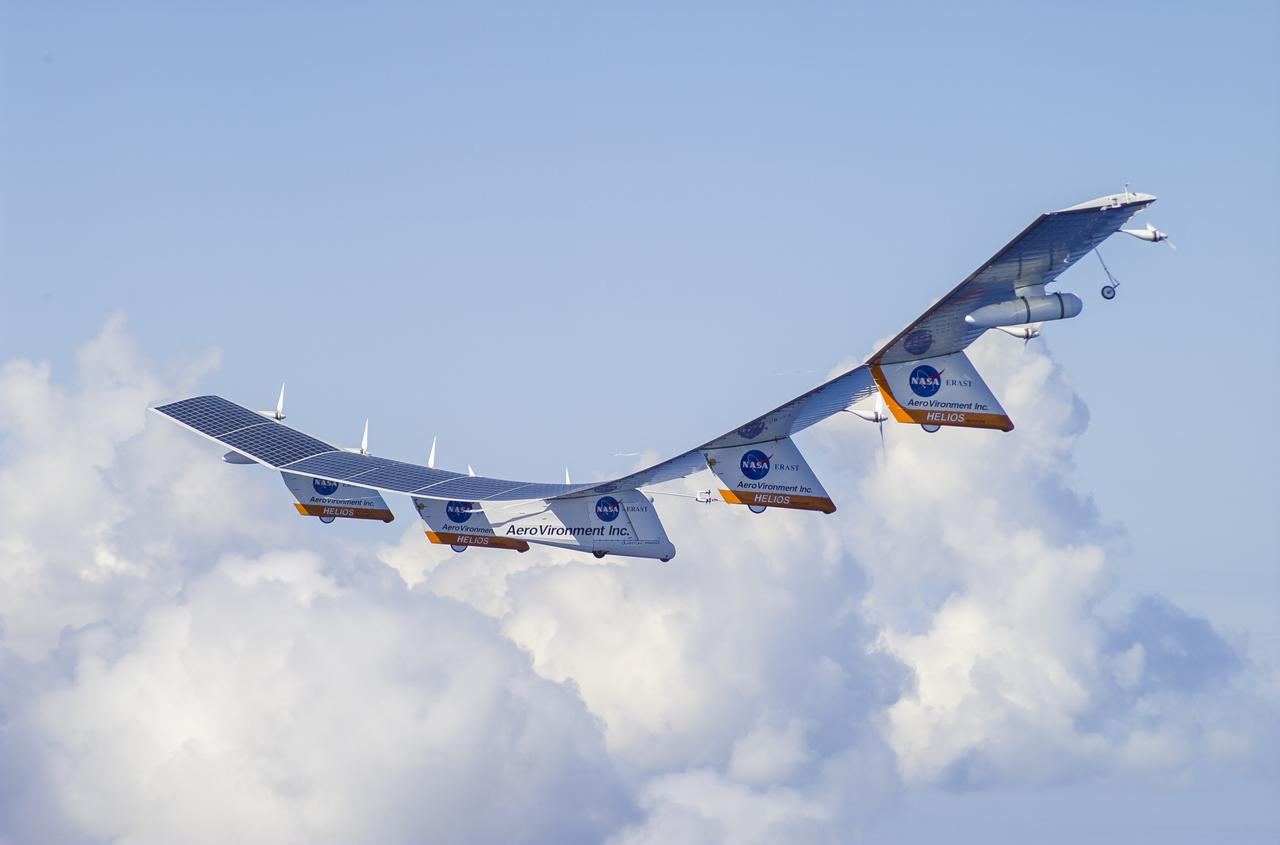

The AeroVironment Helios high-altitude, solar-powered aircraft flies in Kauai, Hawaii. Helios reached 96,300 feet altitude, the record for sustained, level flight for a winged aircraft.
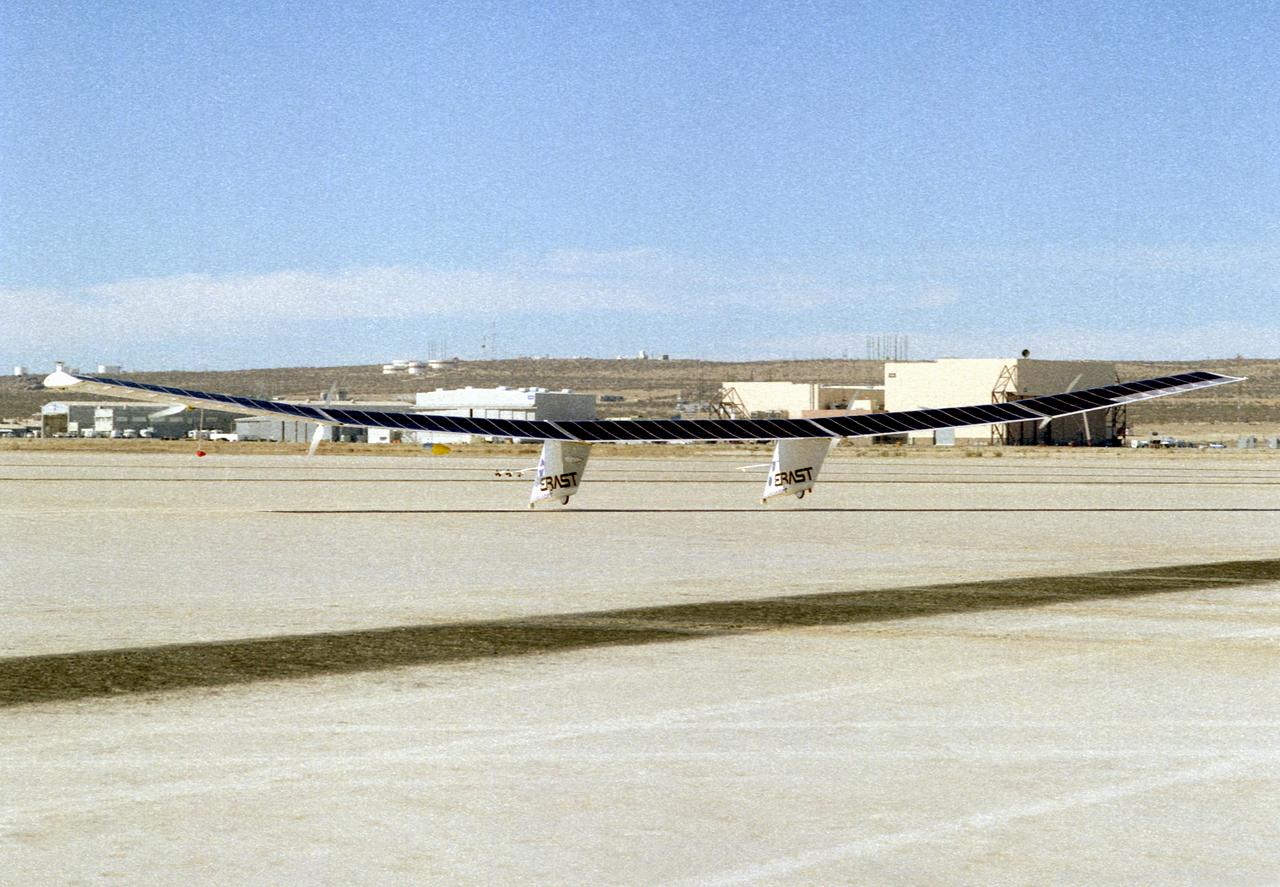

The Pathfinder research aircraft's solar cell arrays are prominently displayed as it touches down on the bed of Rogers Dry Lake at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, following a test flight. The solar arrays covered more than 75 percent of Pathfinder's upper wing surface, and provided electricity to power its six electric motors, flight controls, communications links and a host of scientific sensors.
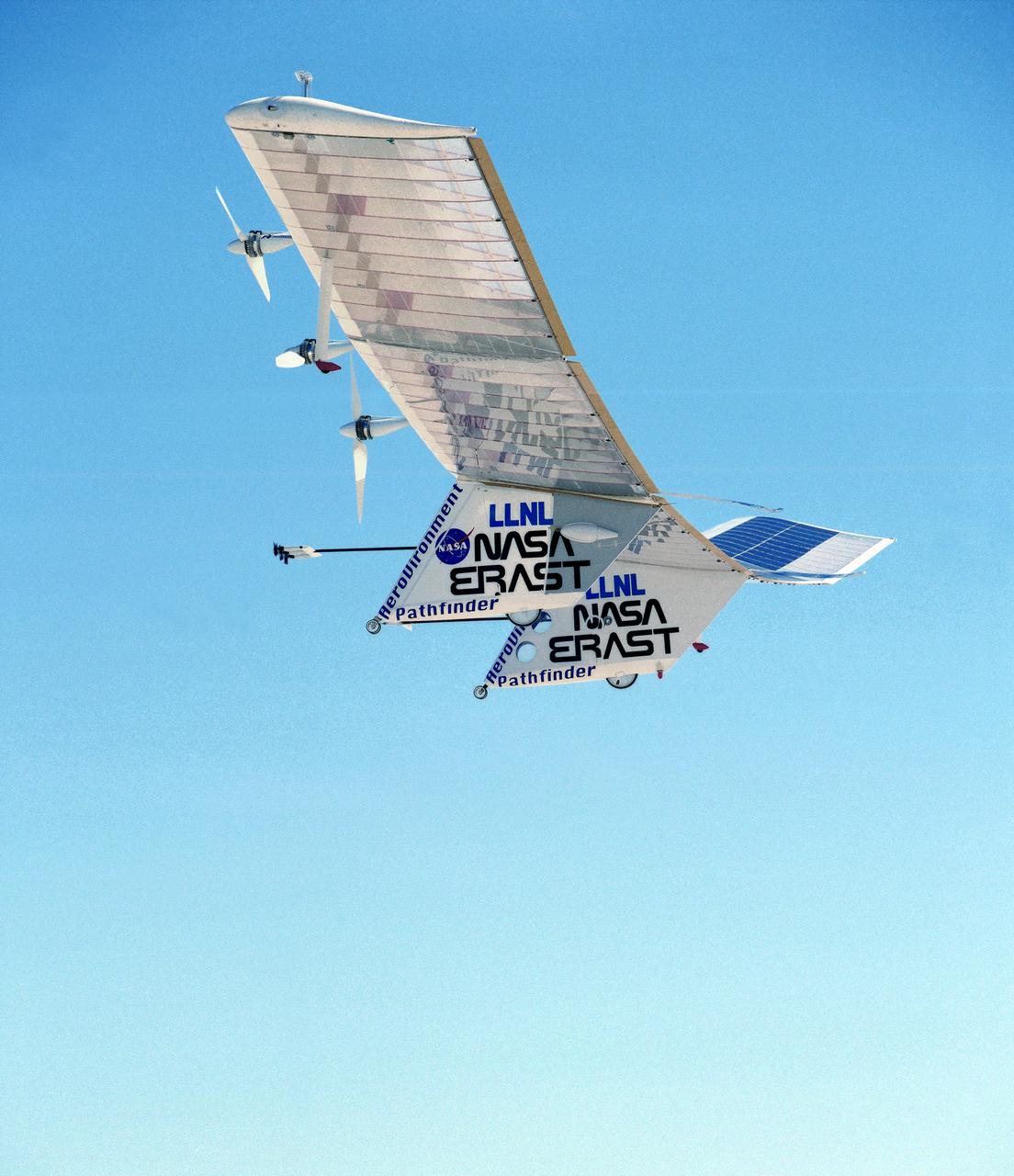

The Pathfinder solar-powered remotely piloted aircraft climbs to a record-setting altitude of 50,567 feet during a flight Sept. 11, 1995, at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.
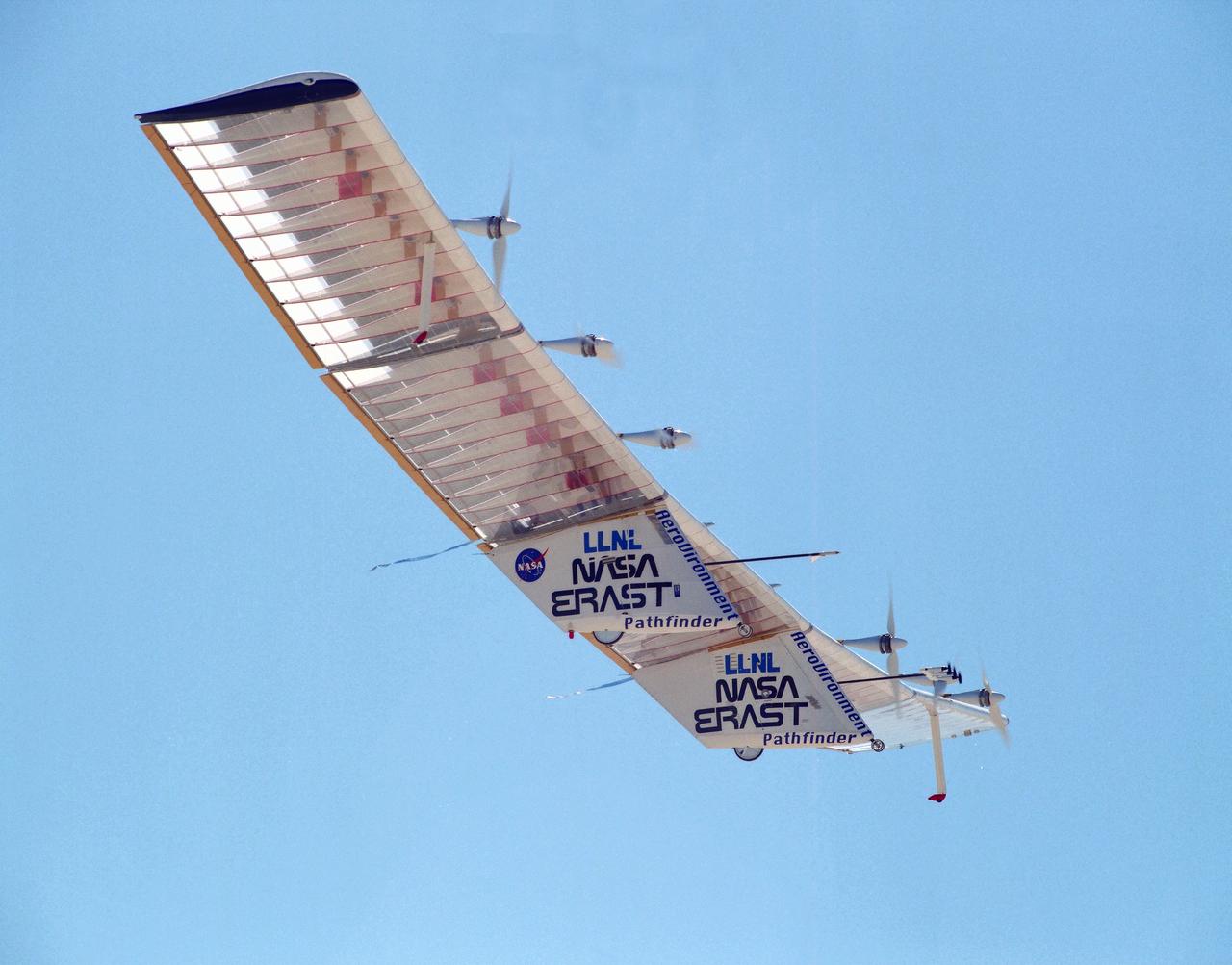

The Pathfinder research aircraft's wing structure was clearly defined as it soared under a clear blue sky during a test flight July 27, 1995, from Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The center section and outer wing panels of the aircraft had ribs constructed of thin plastic foam, while the ribs in the inner wing panels are fabricated from lightweight composite material. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., the Pathfinder was one of several unmanned aircraft being evaluated under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program.
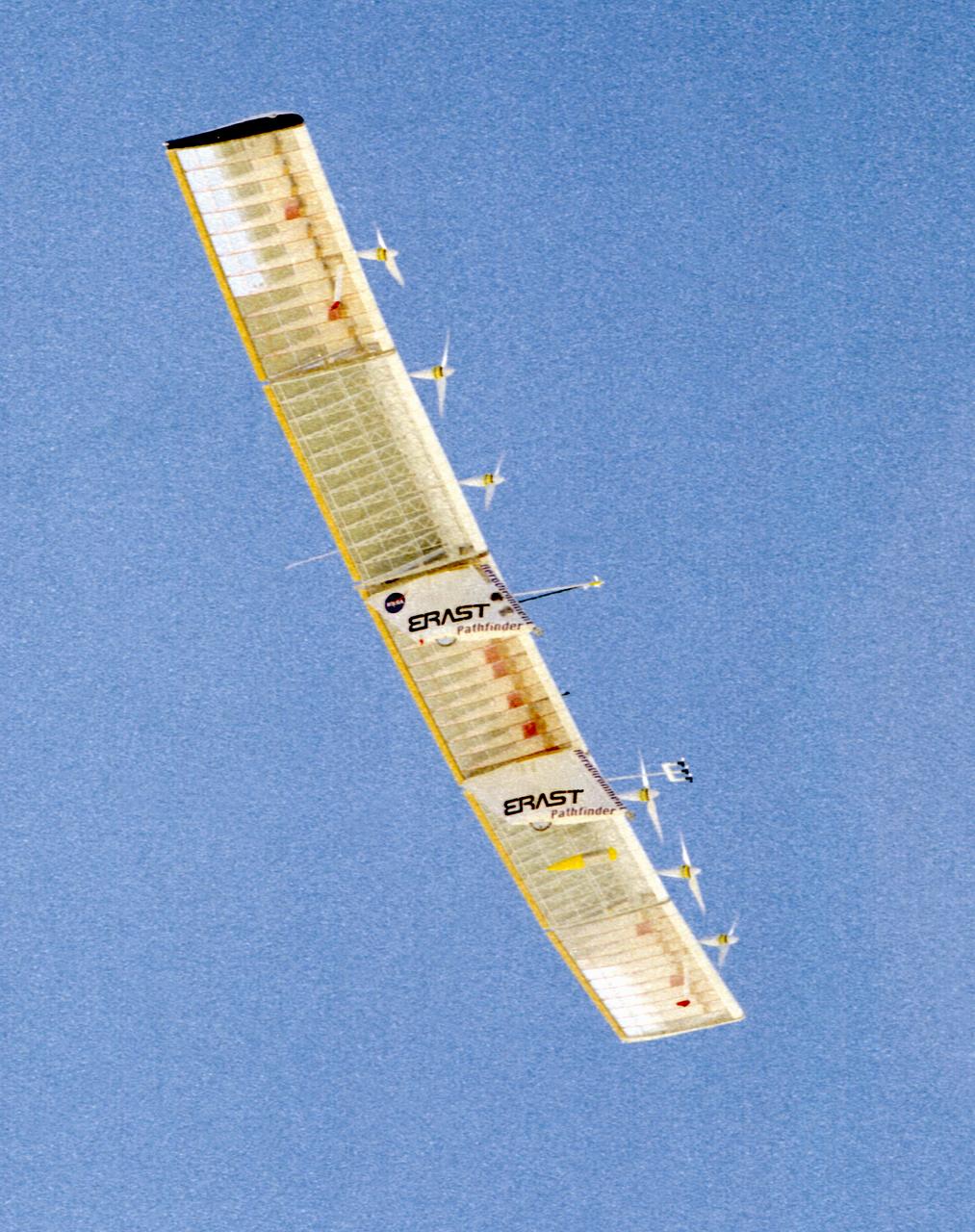

The Pathfinder research aircraft's wing structure is clearly defined as it soars under a clear blue sky during a test flight from Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, in November of 1996.
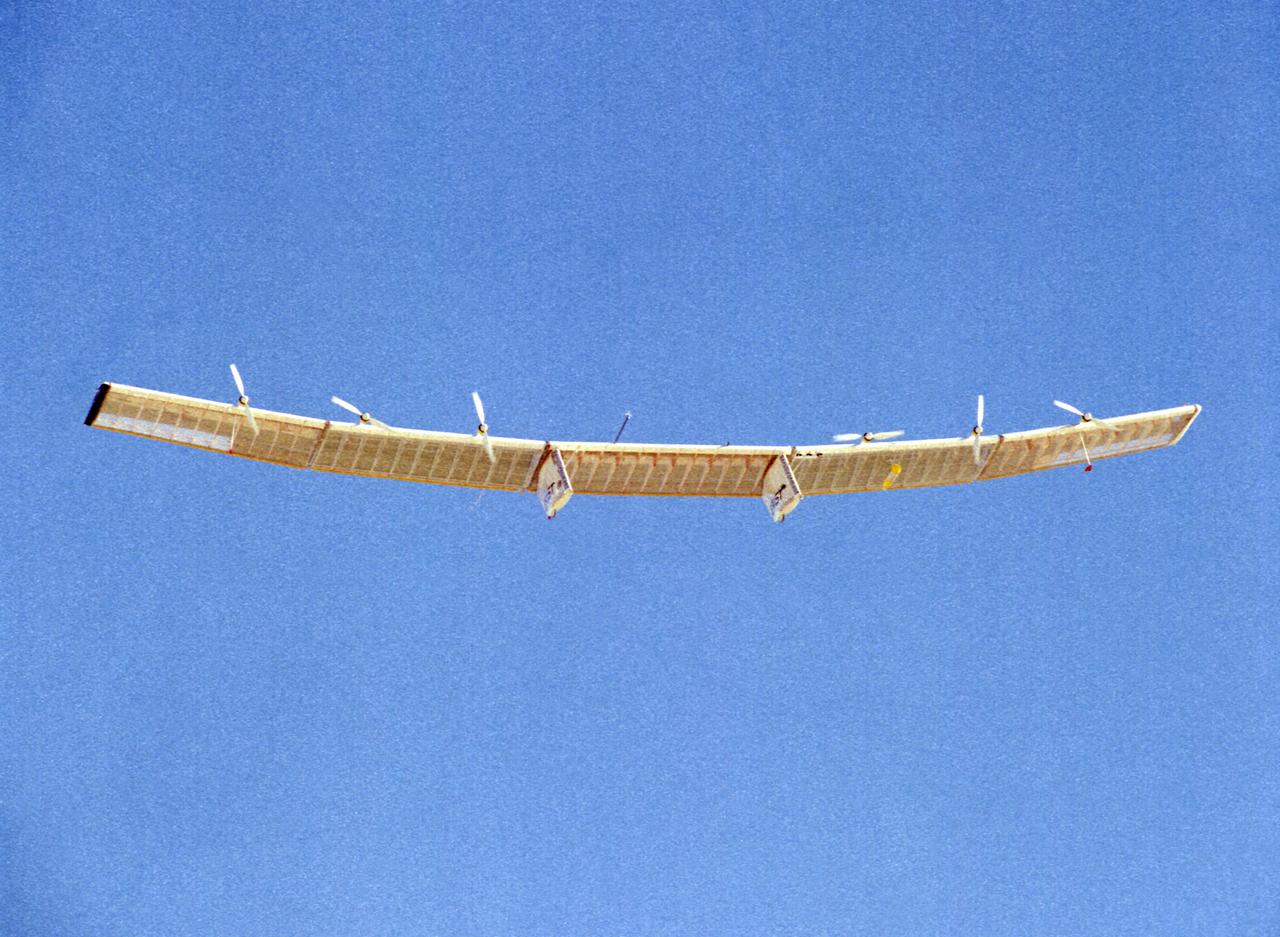
The Pathfinder solar-powered research aircraft is silhouetted against a clear blue sky as it soars aloft during a checkout flight from the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, November, 1996.
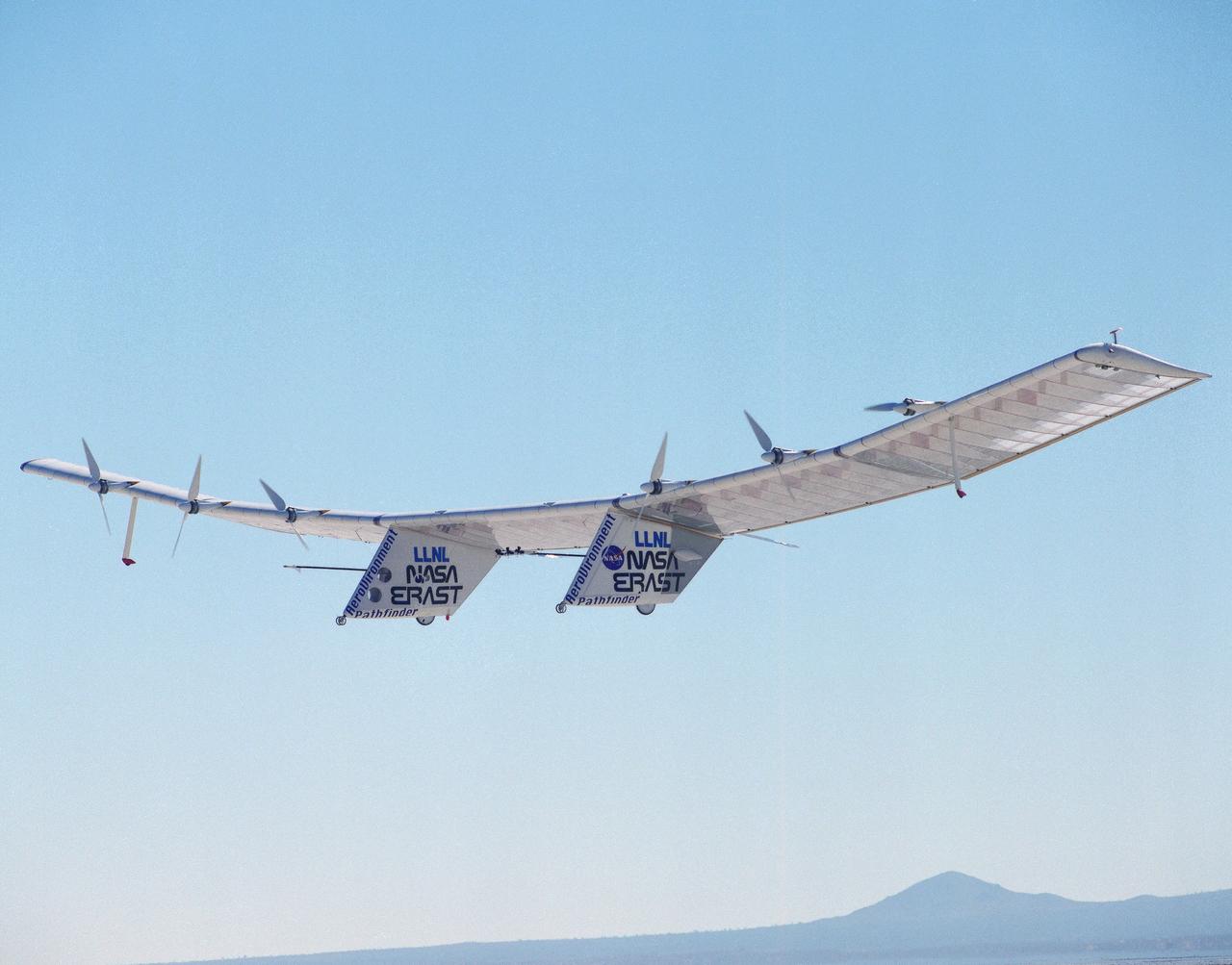

The Pathfinder solar-powered remotely piloted aircraft climbs to a record-setting altitude of 50,567 feet during a flight Sept. 11, 1995, at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The flight was part of the NASA ERAST (Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology) program. The Pathfinder was designed and built by AeroVironment Inc., Monrovia, California. Solar arrays cover nearly all of the upper wing surface and produce electricity to power the aircraft's six motors.

Pathfinder, NASA's solar-powered, remotely-piloted aircraft is shown while it was conducting a series of science flights to highlight the aircraft's science capabilities while collecting imagery of forest and coastal zone ecosystems on Kauai, Hawaii. The flights also tested two new scientific instruments, a high-spectral-resolution Digital Array Scanned Interferometer (DASI) and a high-spatial-resolution Airborne Real-Time Imaging System (ARTIS). The remote sensor payloads were designed by NASA's Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California, to support NASA's Mission to Planet Earth science programs.

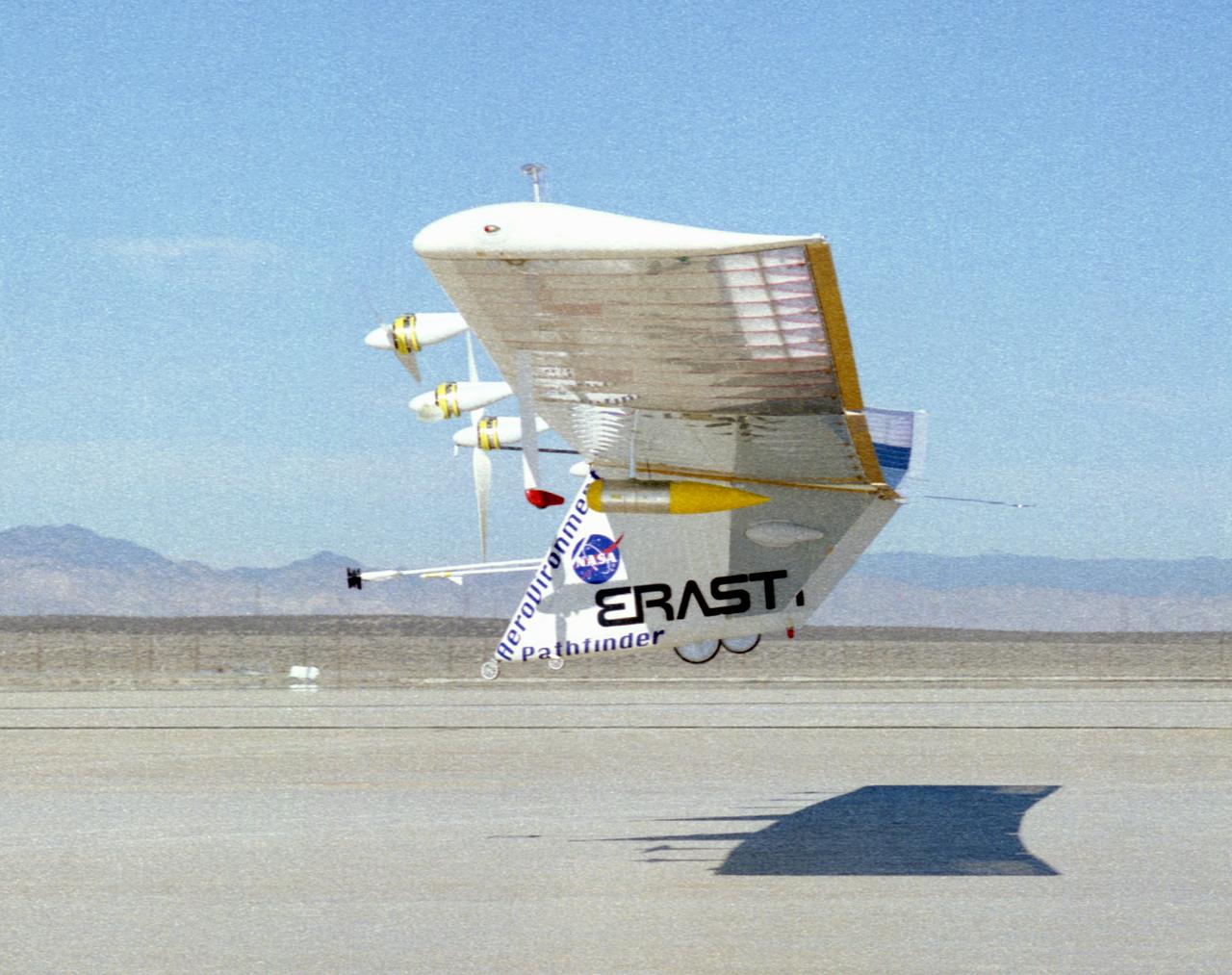
The Pathfinder solar-powered aircraft sits on Rogers Dry Lake at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, before a research flight.

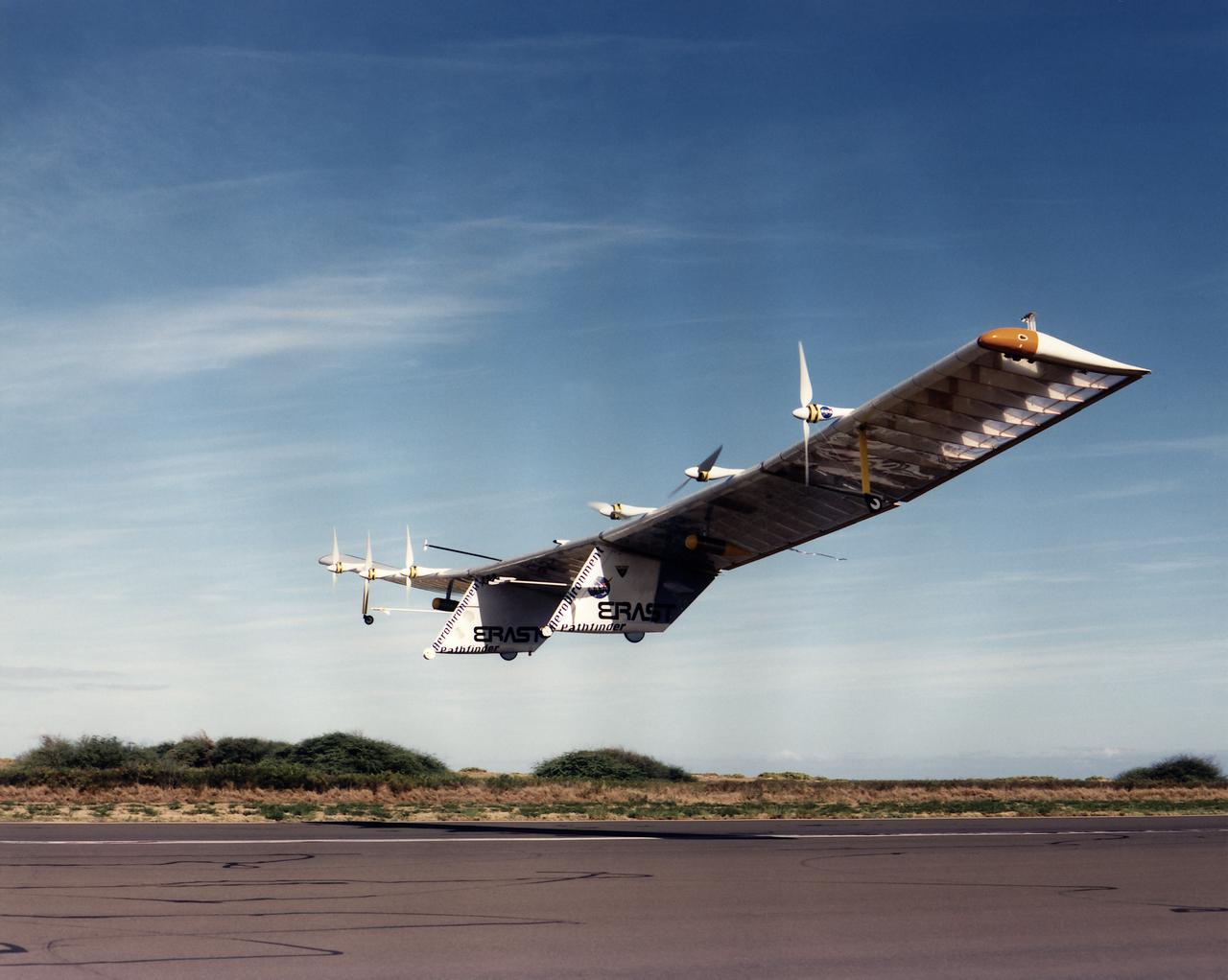
The Pathfinder solar-powered research aircraft heads for landing on the bed of Rogers Dry Lake at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, after a successful test flight Nov. 19, 1996.
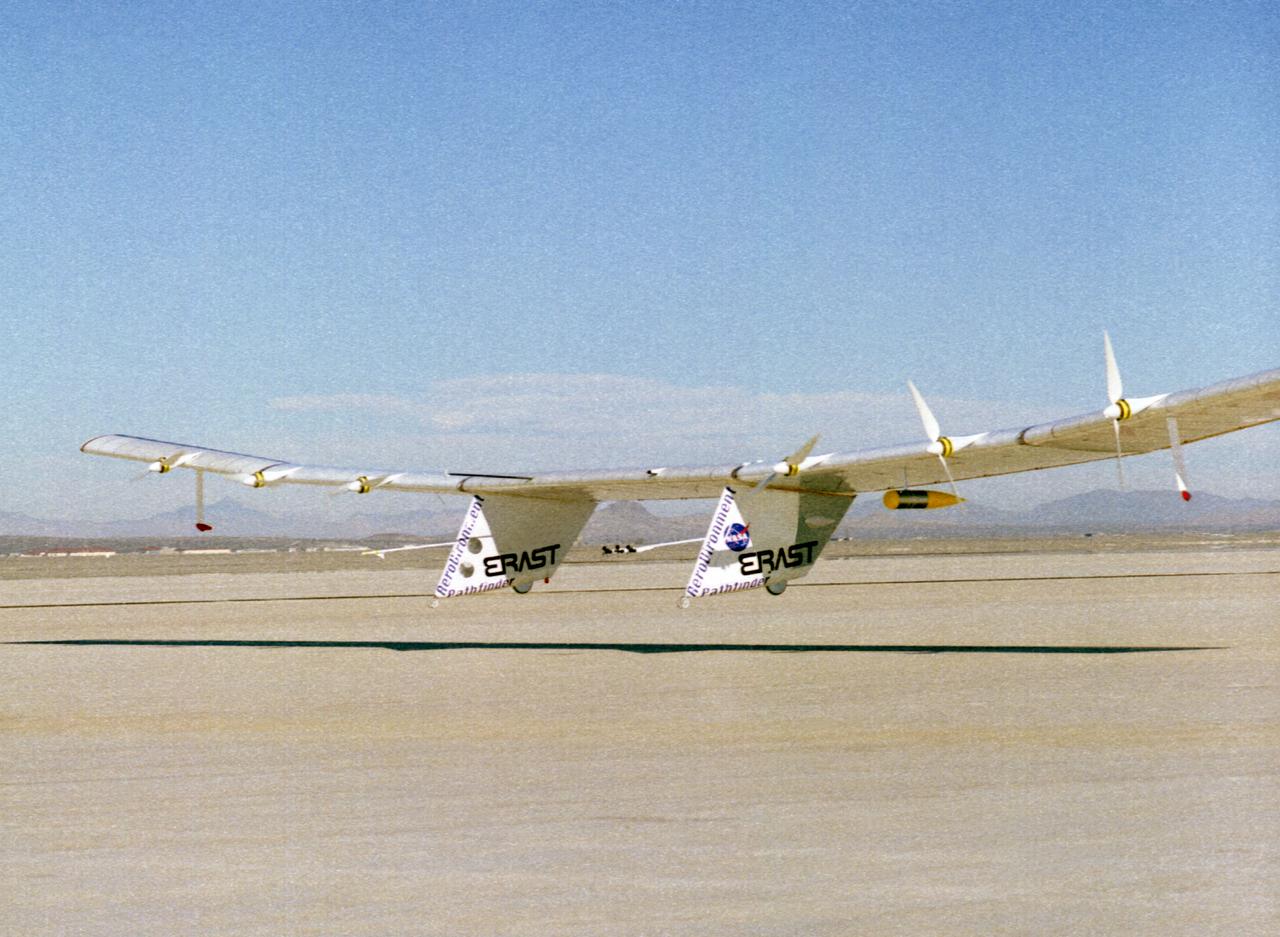

The Pathfinder solar-powered research aircraft settles in for landing on the bed of Rogers Dry Lake at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, after a successful test flight Nov. 19, 1996. The ultra-light craft flew a racetrack pattern at low altitudes over the flight test area for two hours while project engineers checked out various systems and sensors on the uninhabited aircraft. The Pathfinder was controlled by two pilots, one in a mobile control unit which followed the craft, the other in a stationary control station. Pathfinder, developed by AeroVironment, Inc., is one of several designs being evaluated under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program.
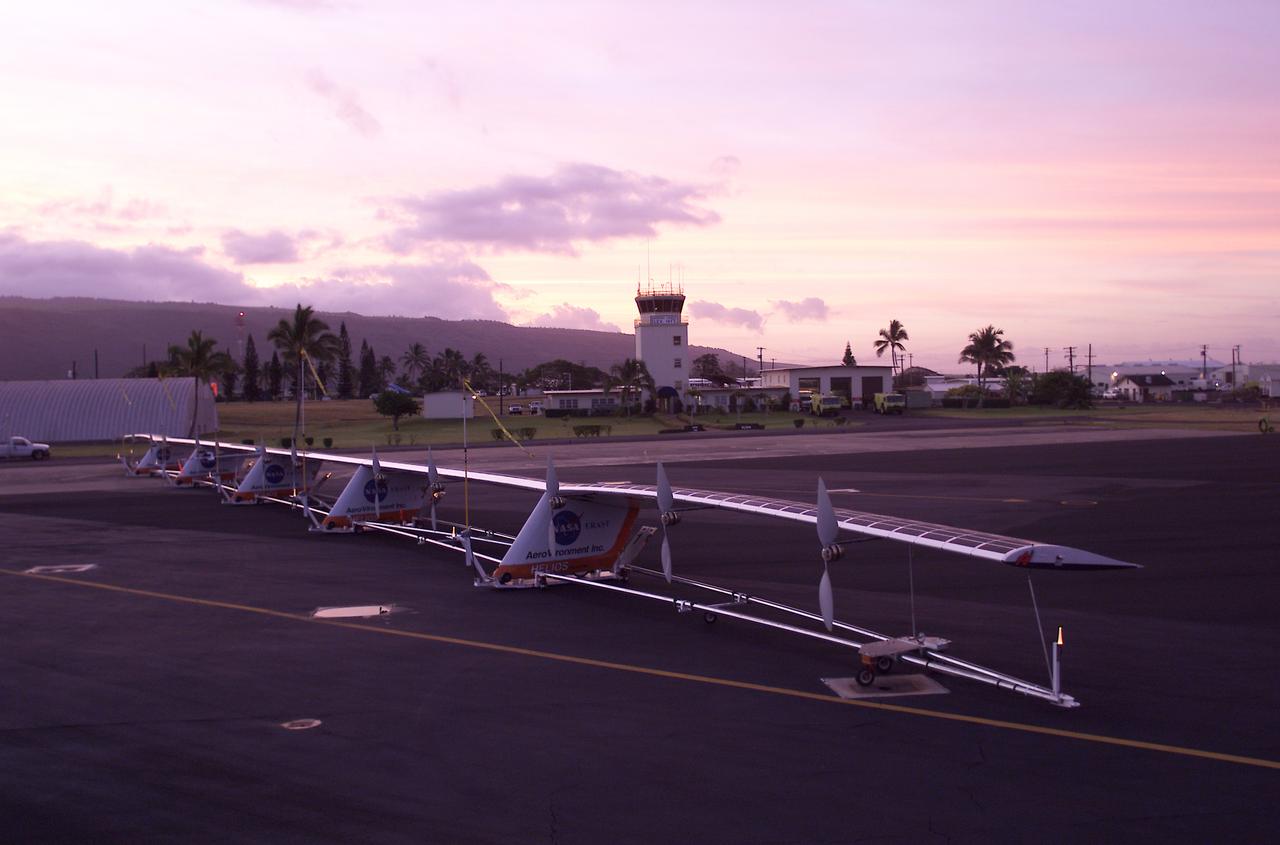

The 247-foot length of the Helios prototype wing is in evidence as the high-altitude, solar-powered flying wing rests on its ground dolly during pre-flight tests at the U.S. Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility on Kaua'i, Hawaii.
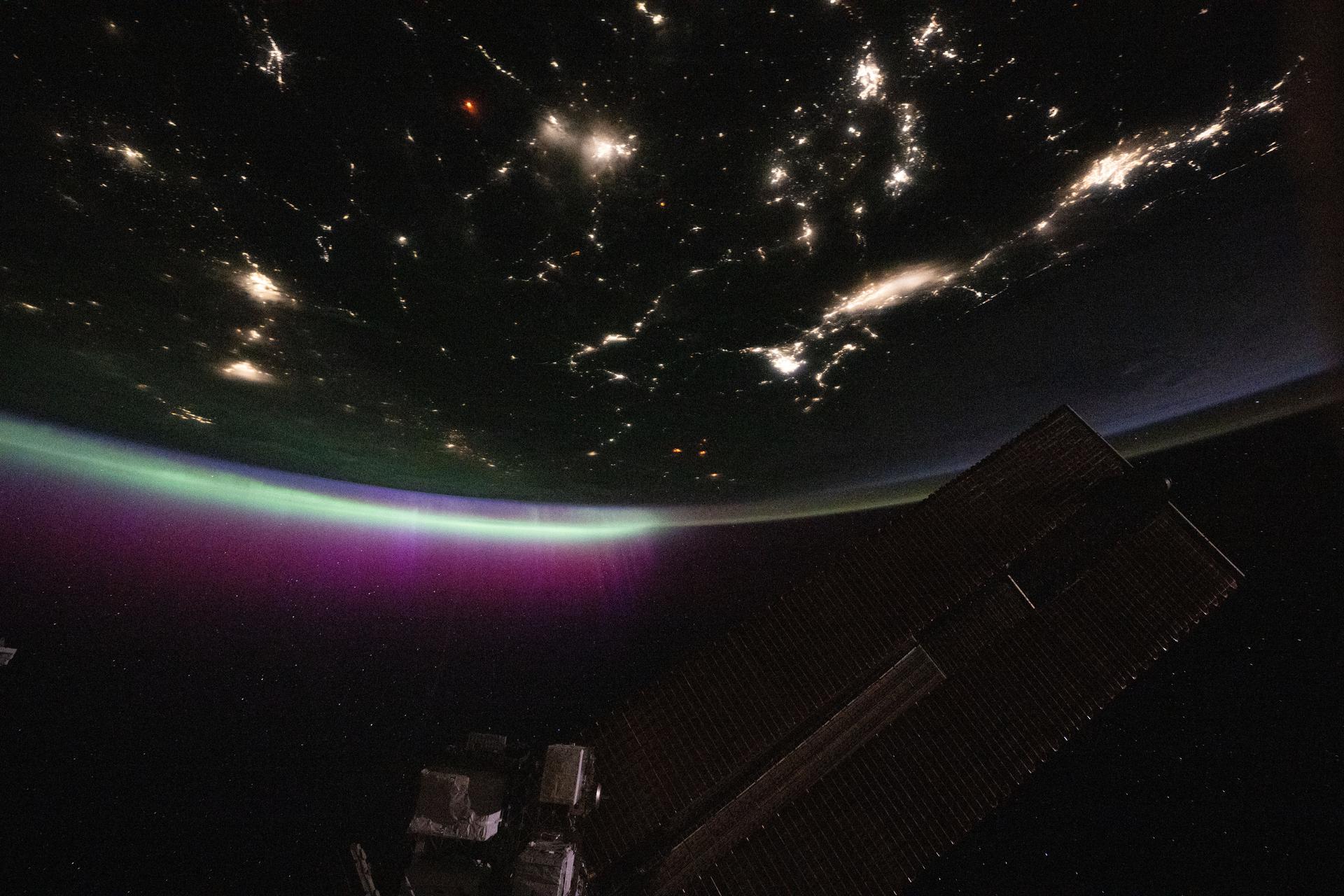

iss073e0780439 (Sept. 2, 2025) --- A diffuse aurora glows above Earth's horizon over Canada as its red and green hues shimmer like neon lights—an effect created by excited oxygen atoms high in the atmosphere. The city lights of the U.S.-Canadian Pacific Northwest (toward upper right) trace the continent eastward. The red aurora is produced by high-altitude oxygen atoms (~300 km), while the green glow comes from lower-altitude oxygen (~100 km), both excited by energetic electrons guided into the atmosphere by Earth's magnetic field during solar activity.
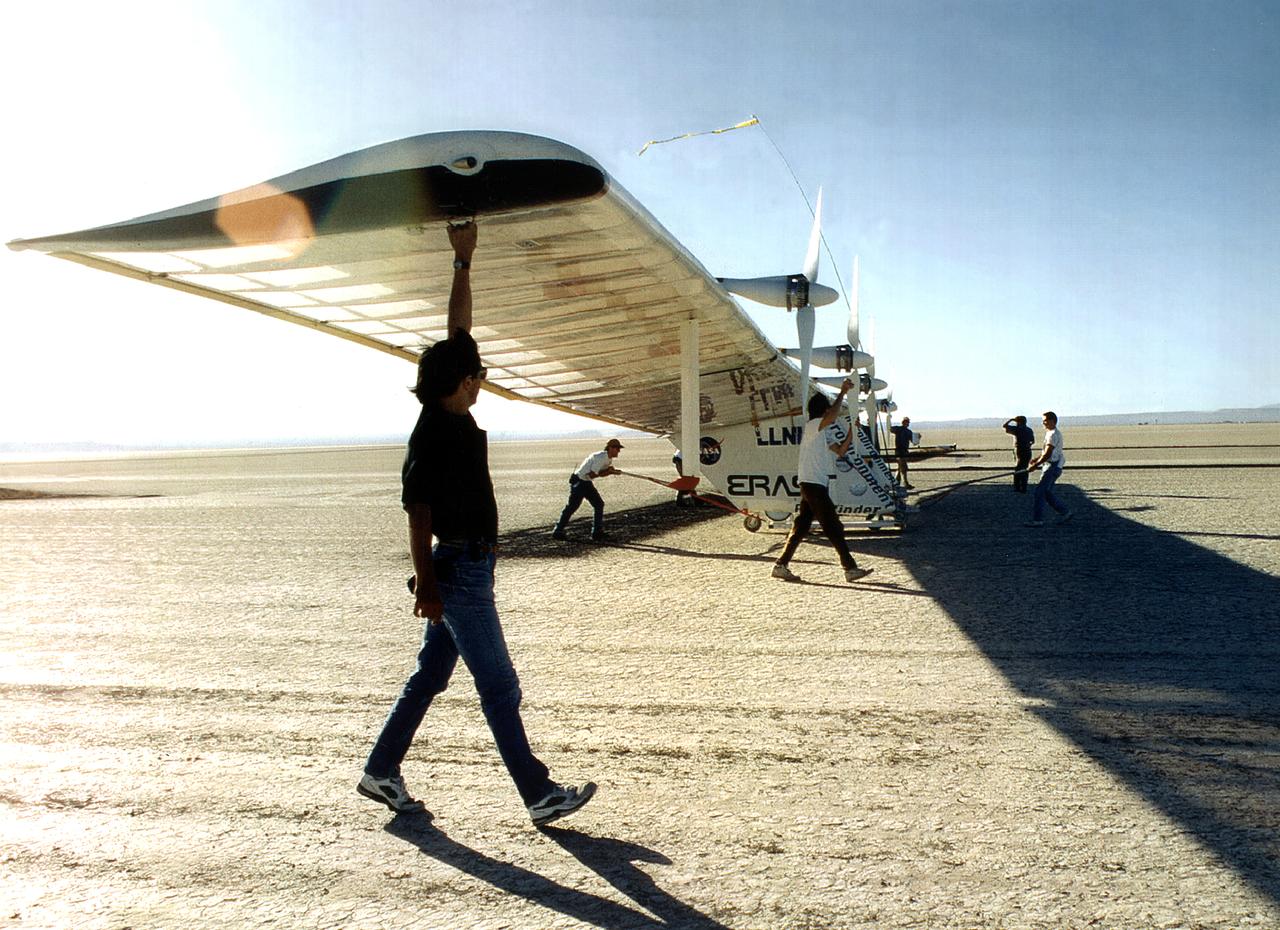

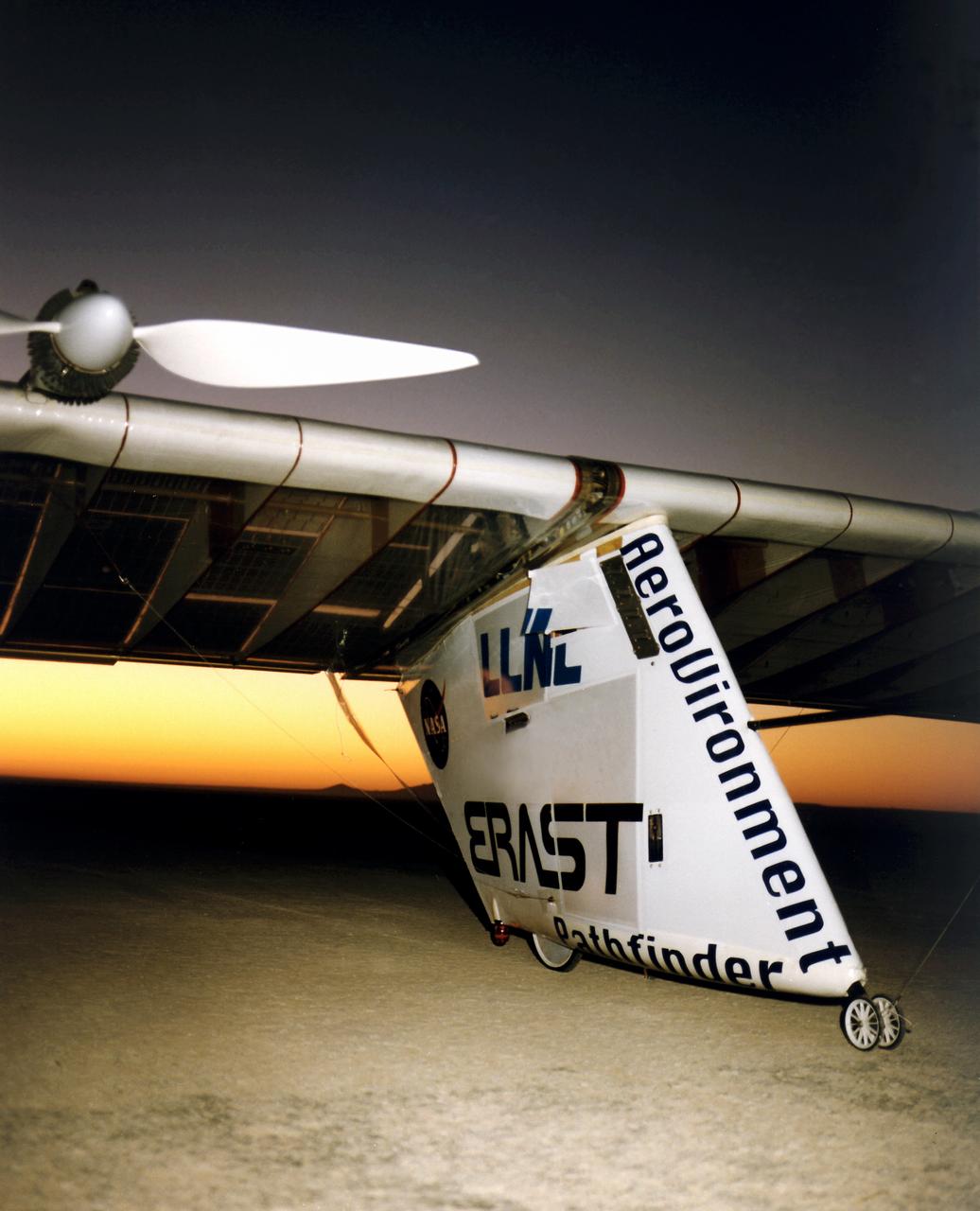
The Pathfinder research aircraft's wing structure is clearly defined in this photo as personnel from AeroVironment rolled it out onto the lakebed at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, for another test flight.
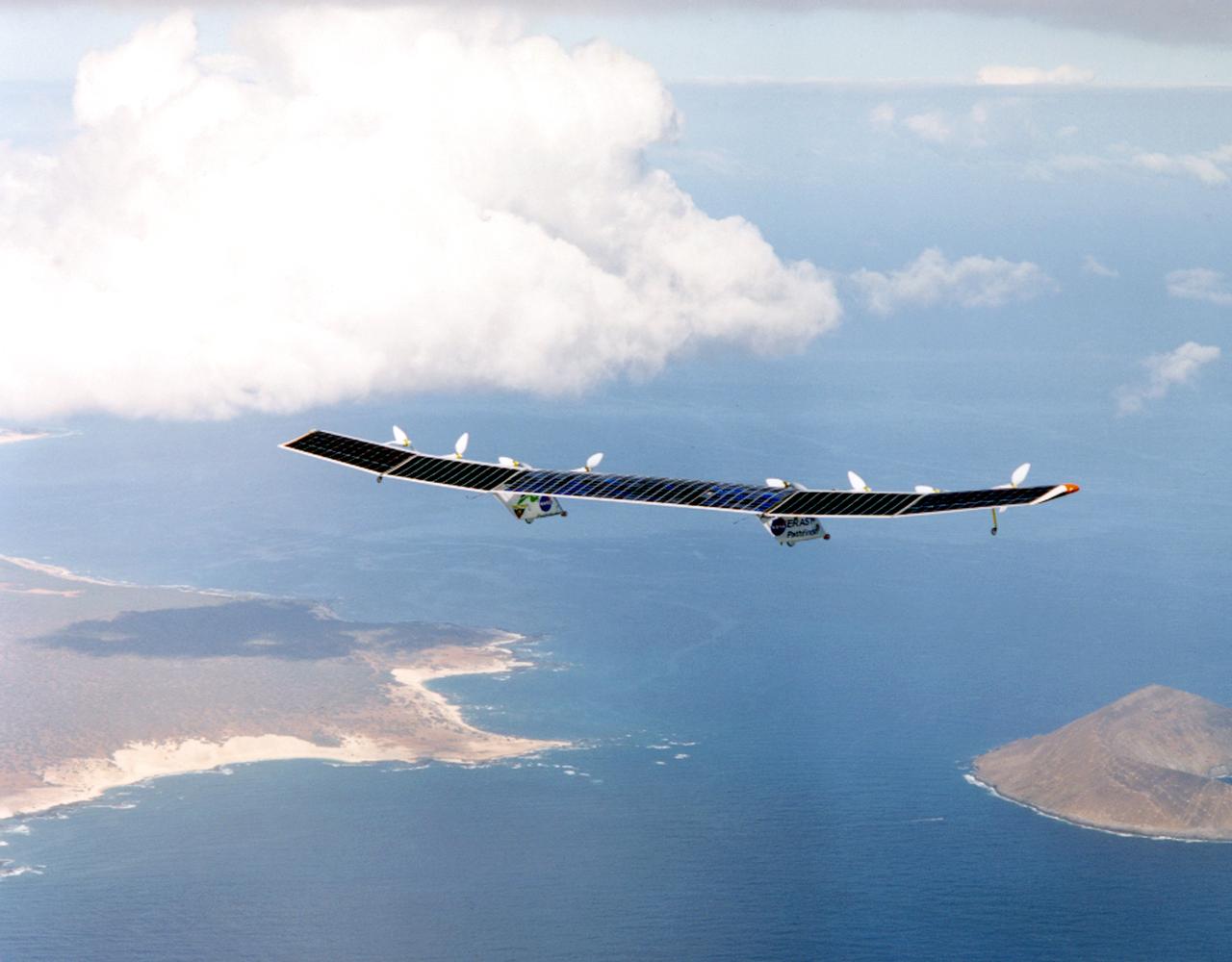

Pathfinder-Plus on flight over Hawaiian Islands, with N'ihau and Lehua in the background.
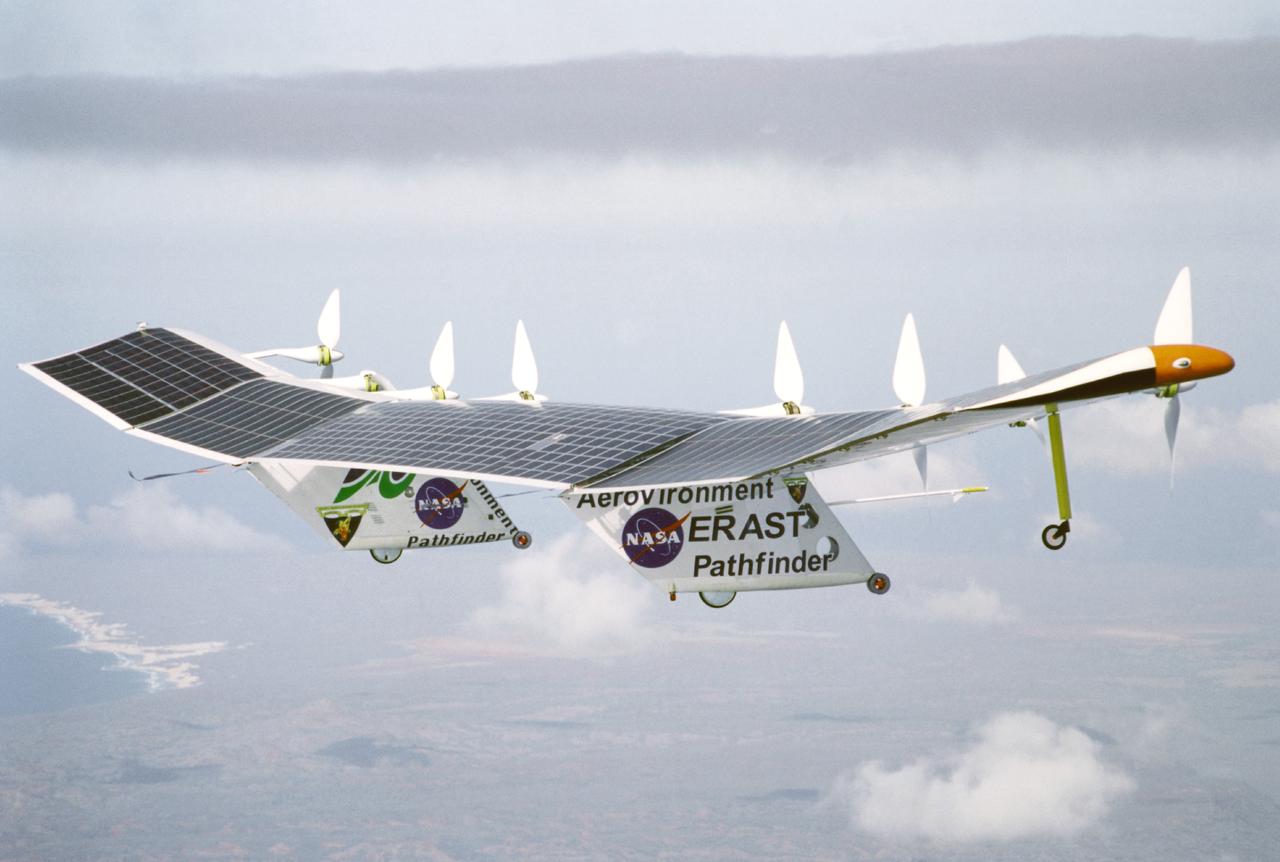

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight over the Hawaiian island of N'ihau in 1998.

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight in 1998 over Hawaiian waters.
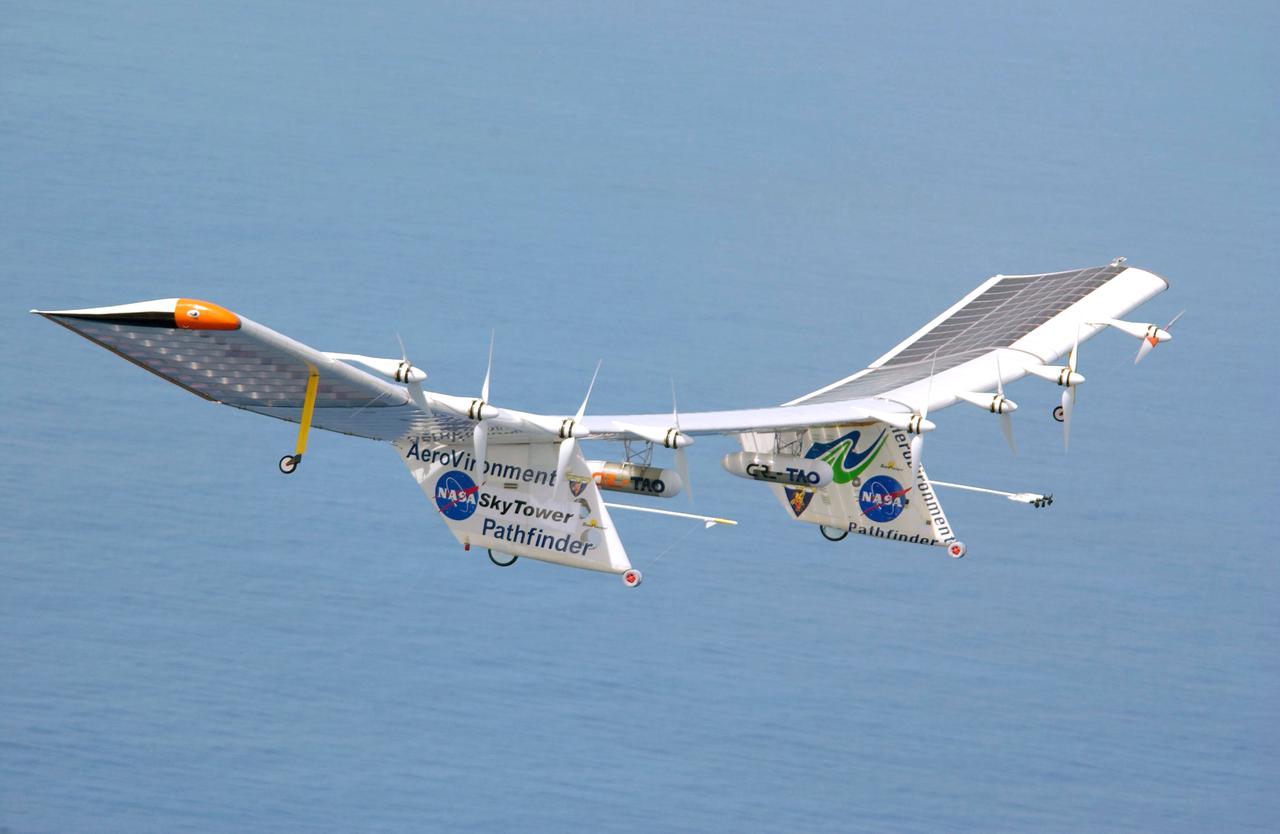

Pathfinder-Plus flight in Hawaii June 2002
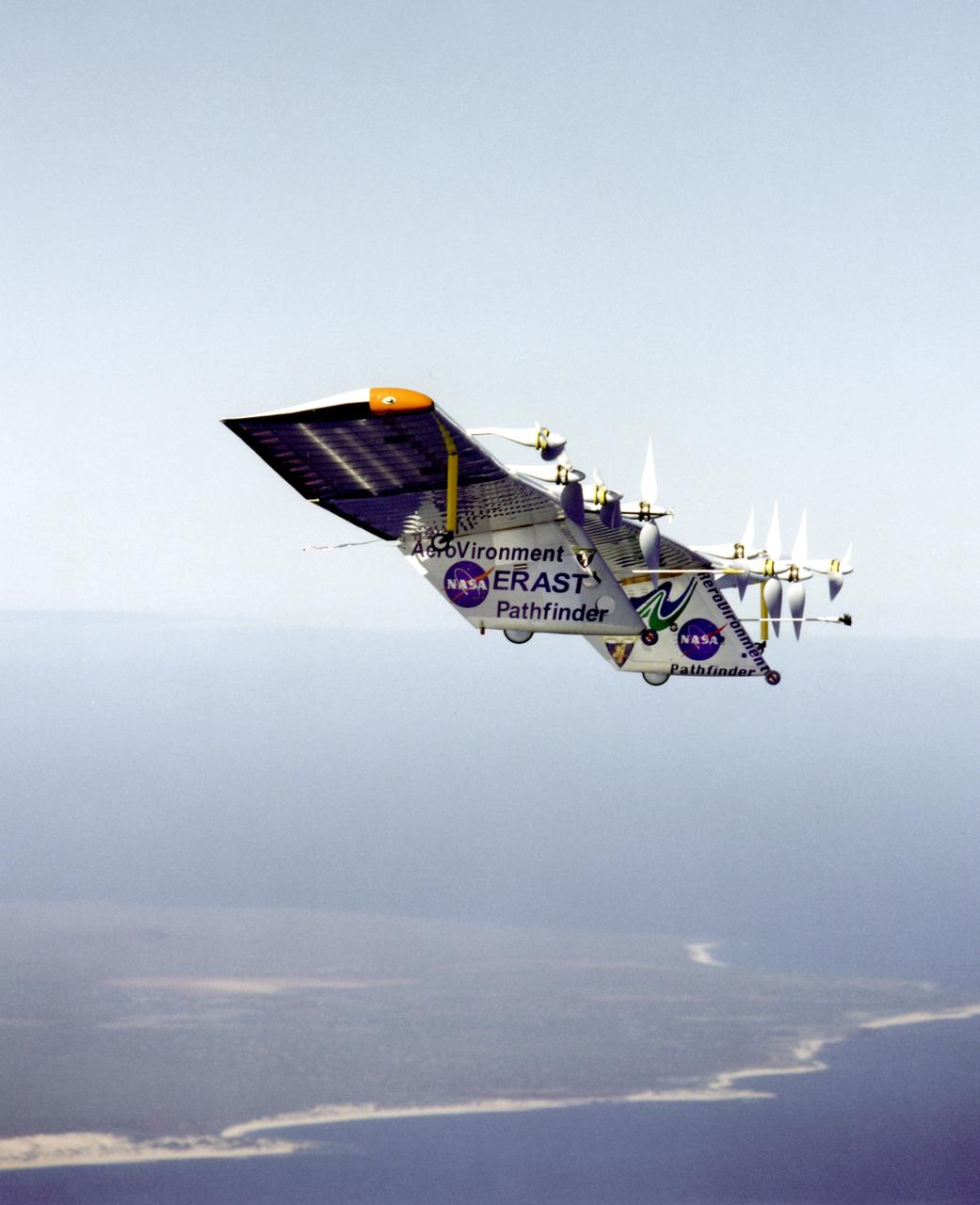

Pathfinder-Plus flying over the Hawaiian Islands in 1998 with Ni'ihau Island in the background.
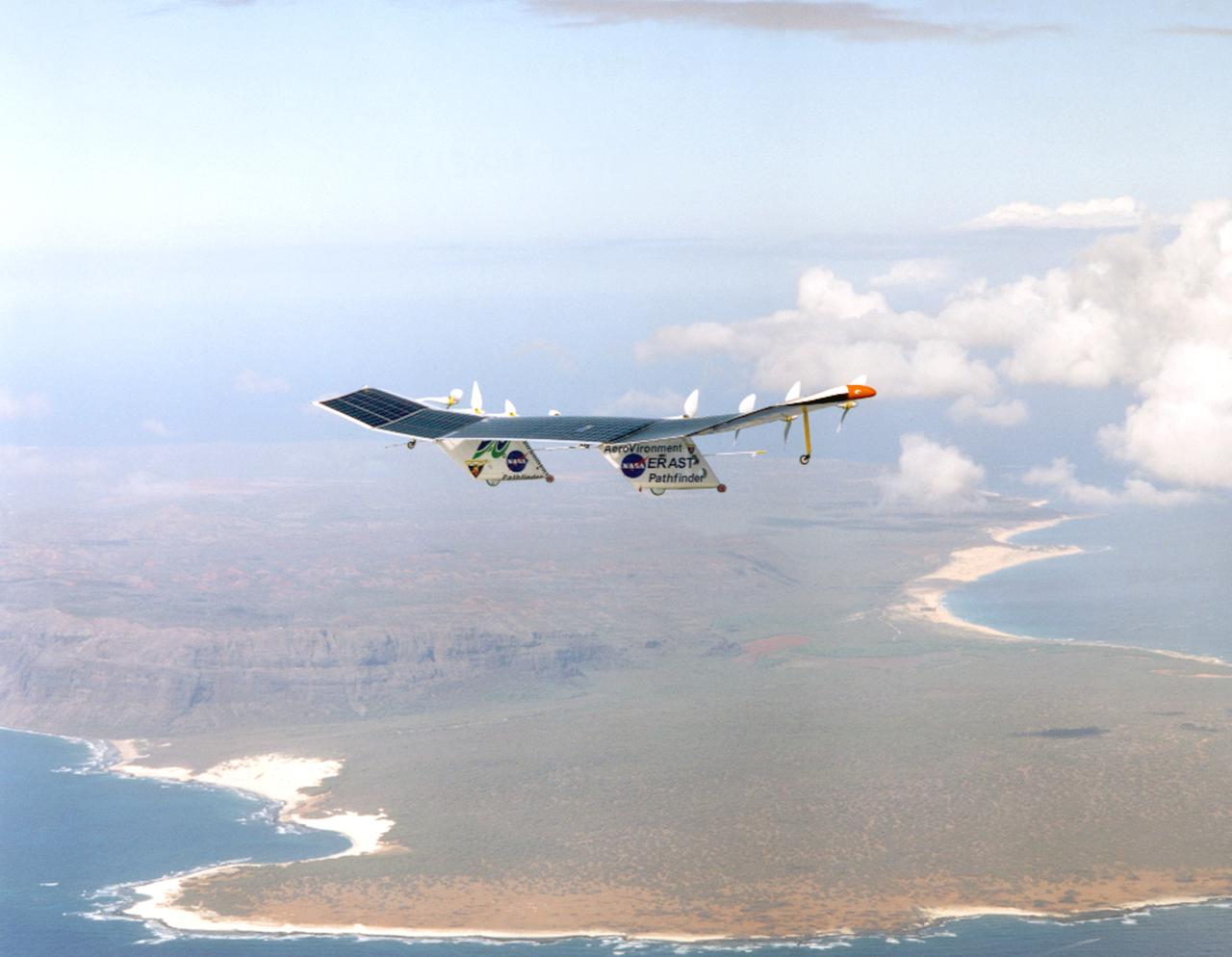

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight with the Hawaiian island of N'ihau in the background.
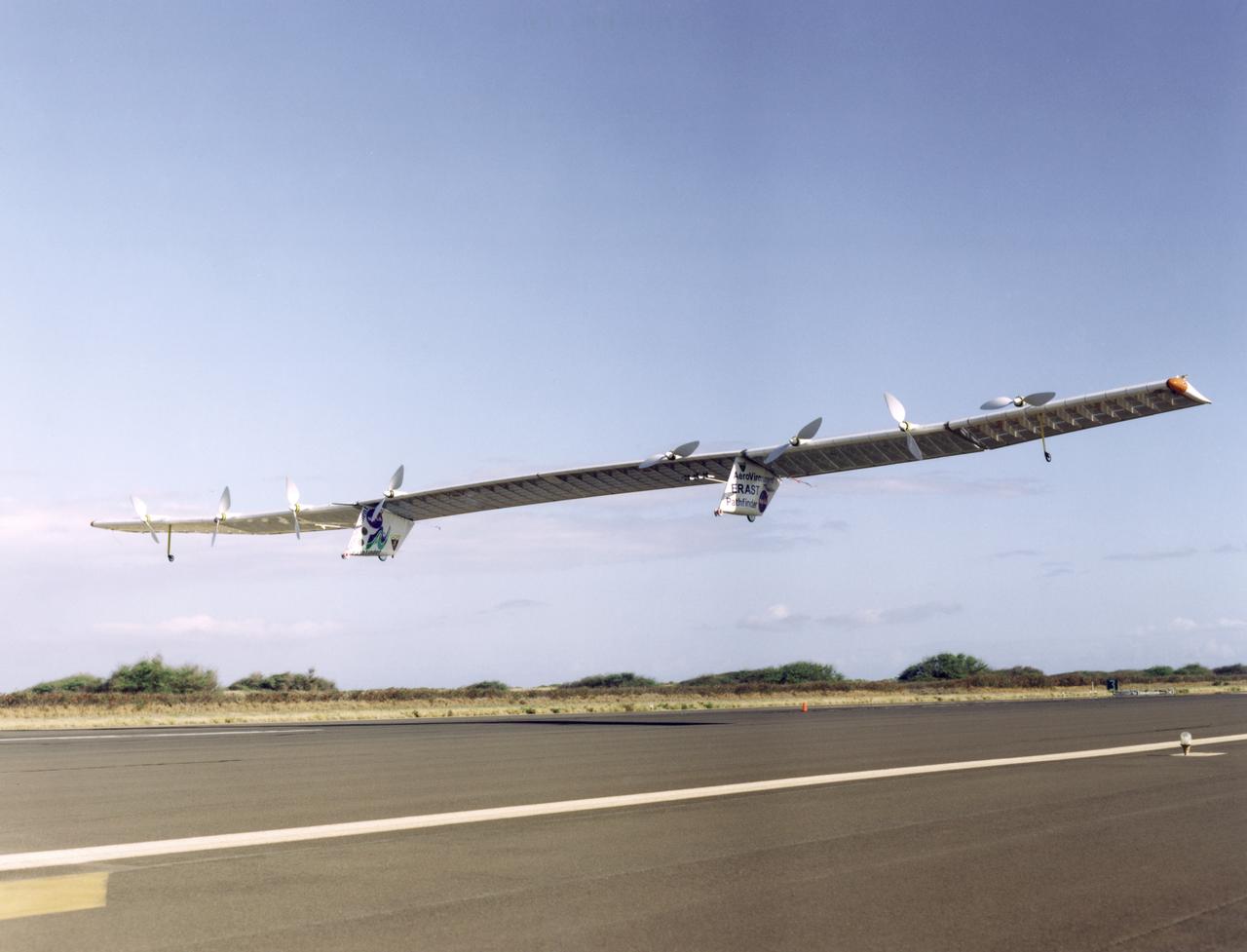

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight over Hawaii in 1998.
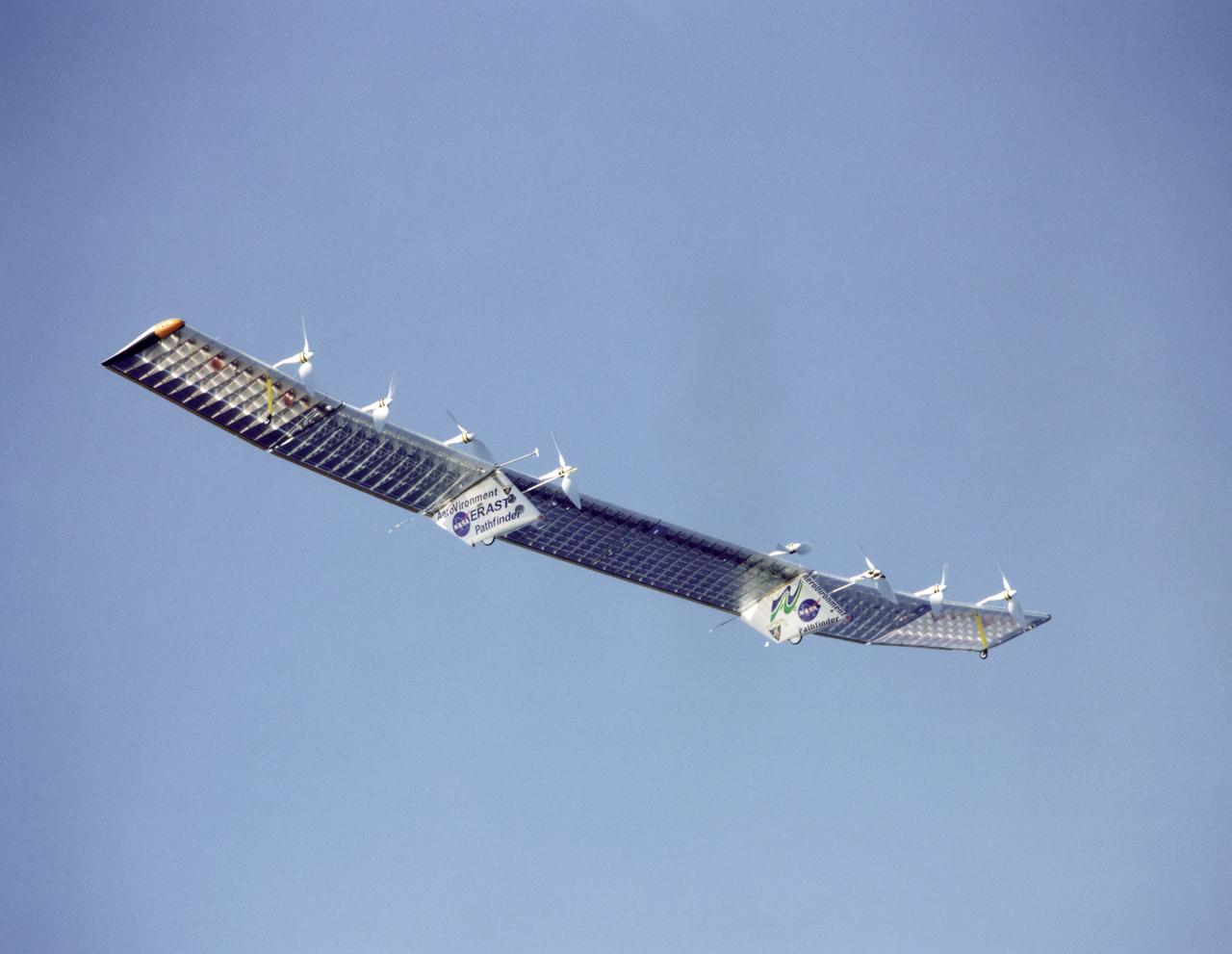

Pathfinder-Plus on flight over Hawaii.
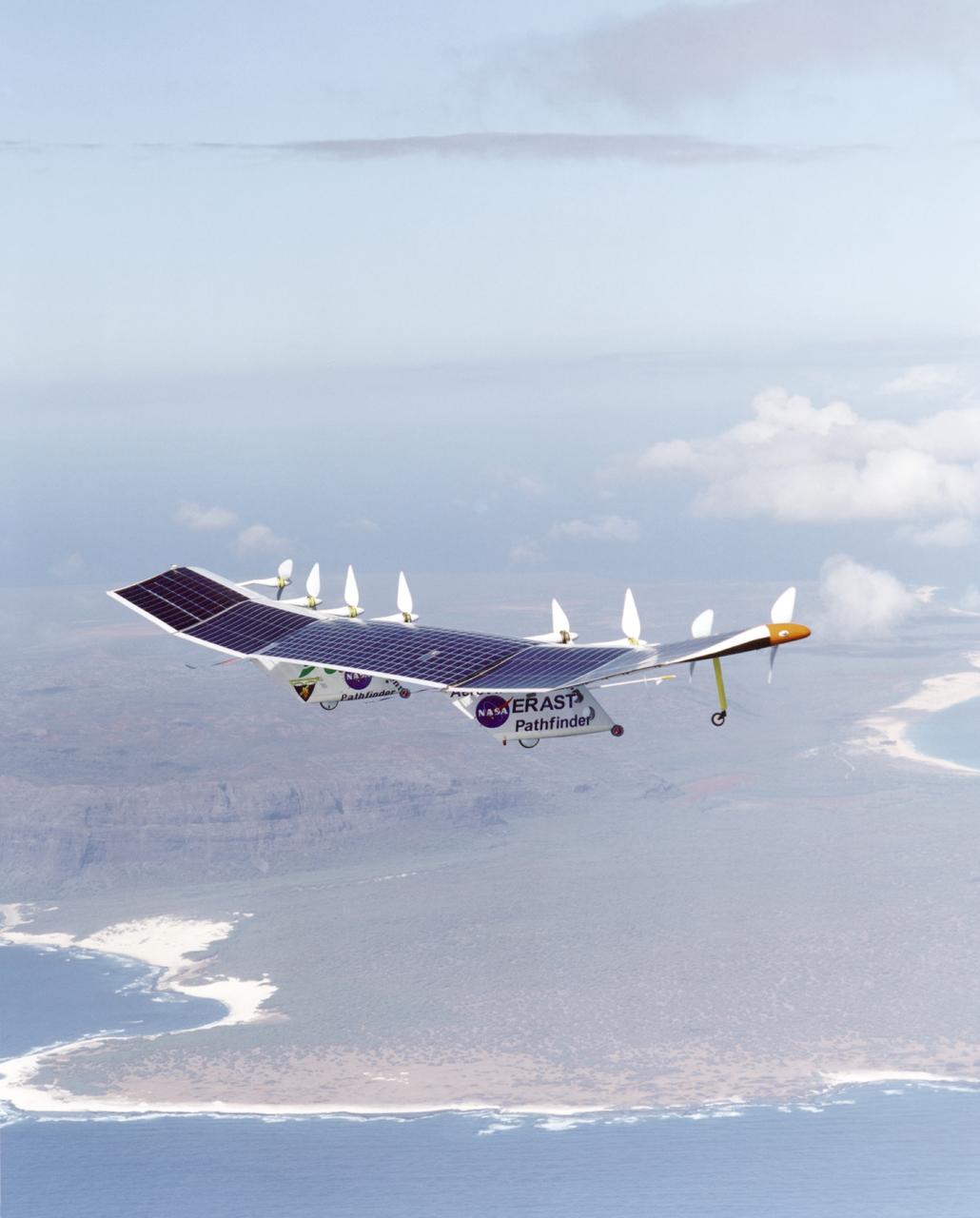

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight over the Hawaiian island of N'ihau in 1998.
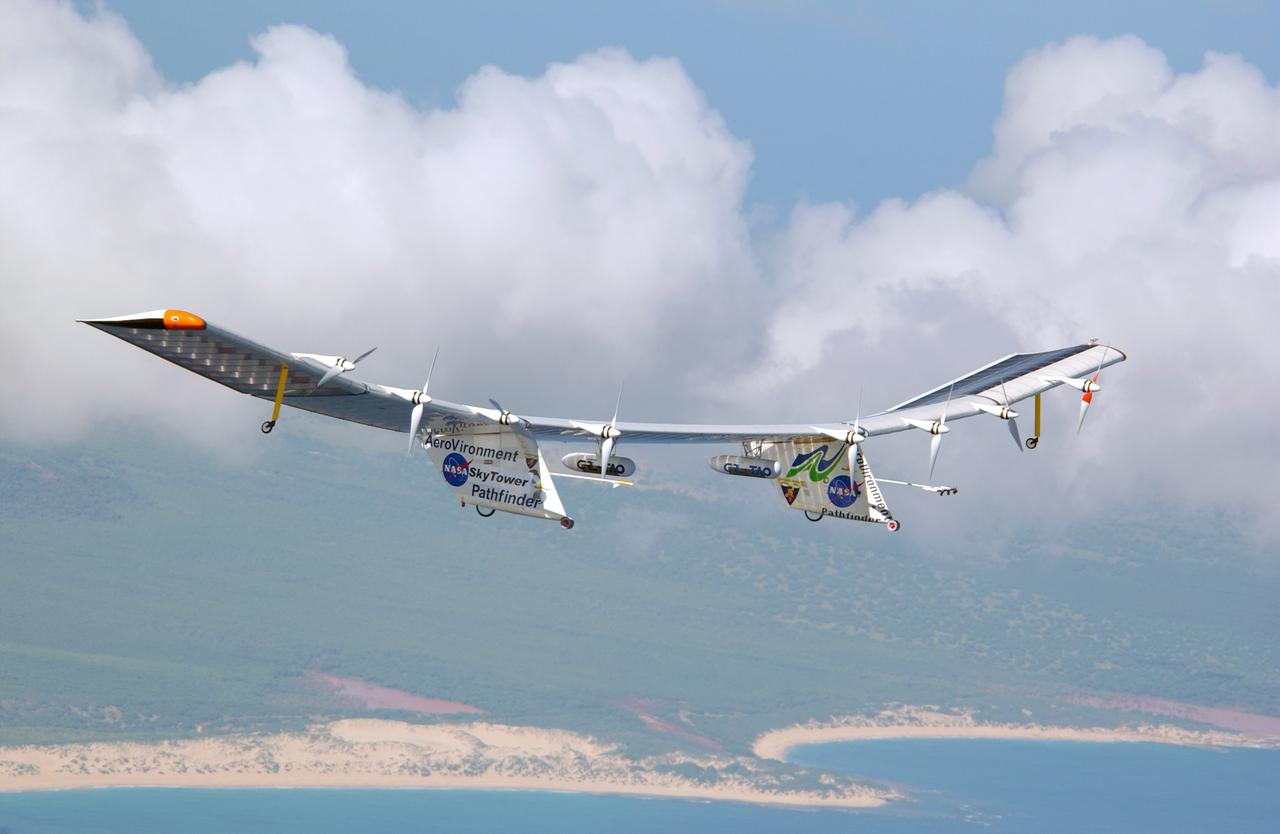

Pathfinder-Plus flight in Hawaii June 2002
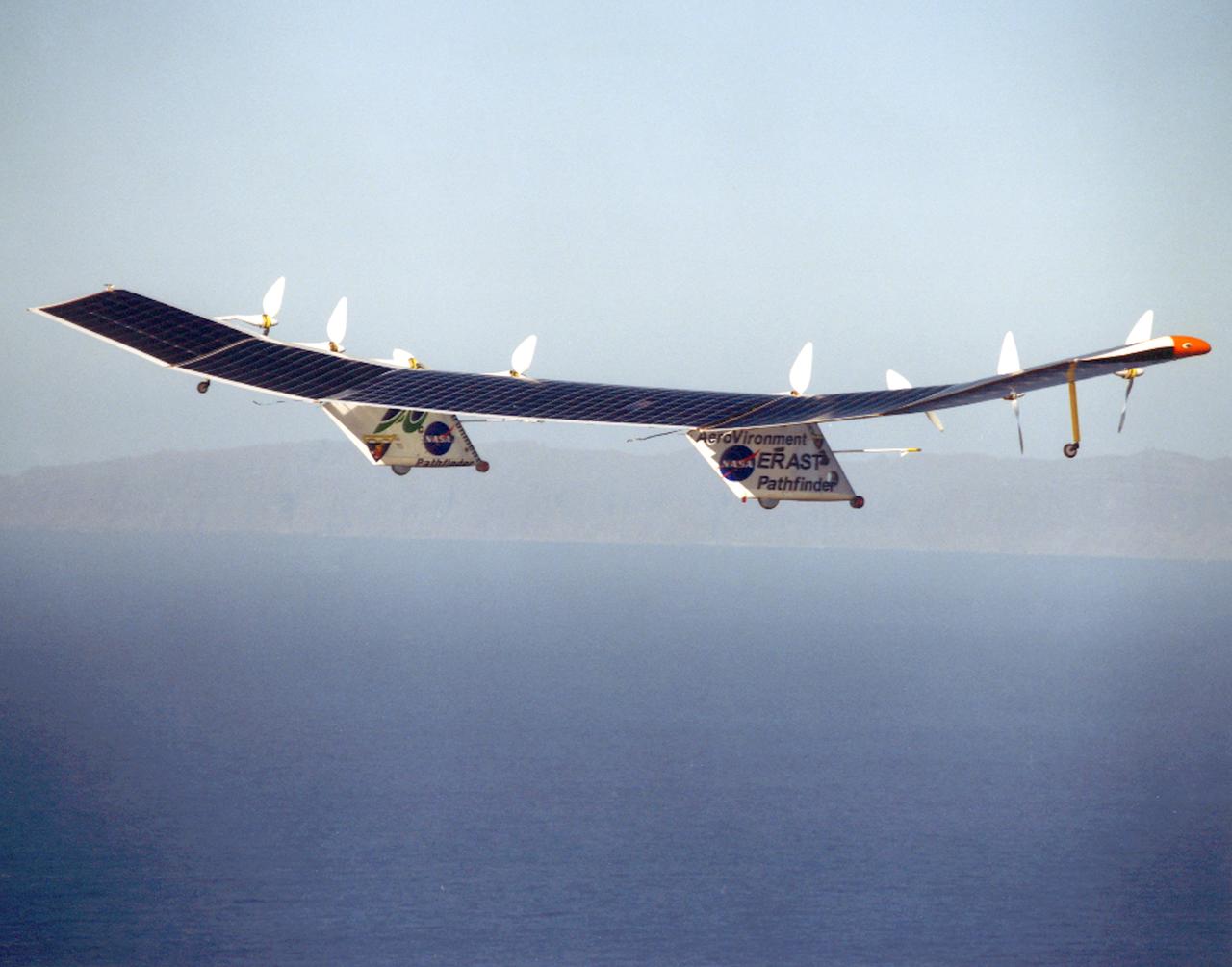

Pathfinder-Plus on flight over Hawaiian Islands in 1998.

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight over the Hawaiian island of N'ihau in 1998.
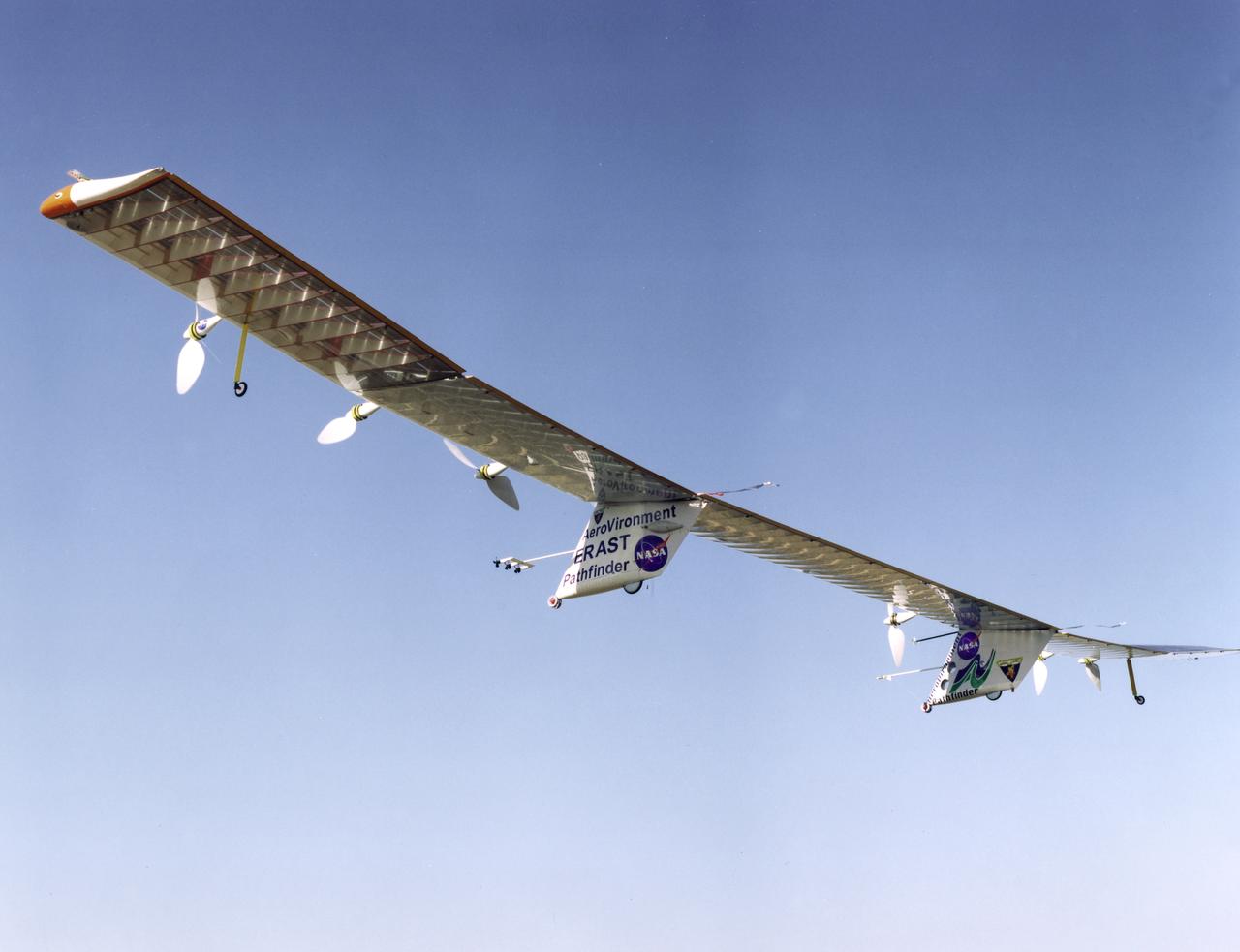

Pathfinder-Plus on a flight over Hawaii in 1998.
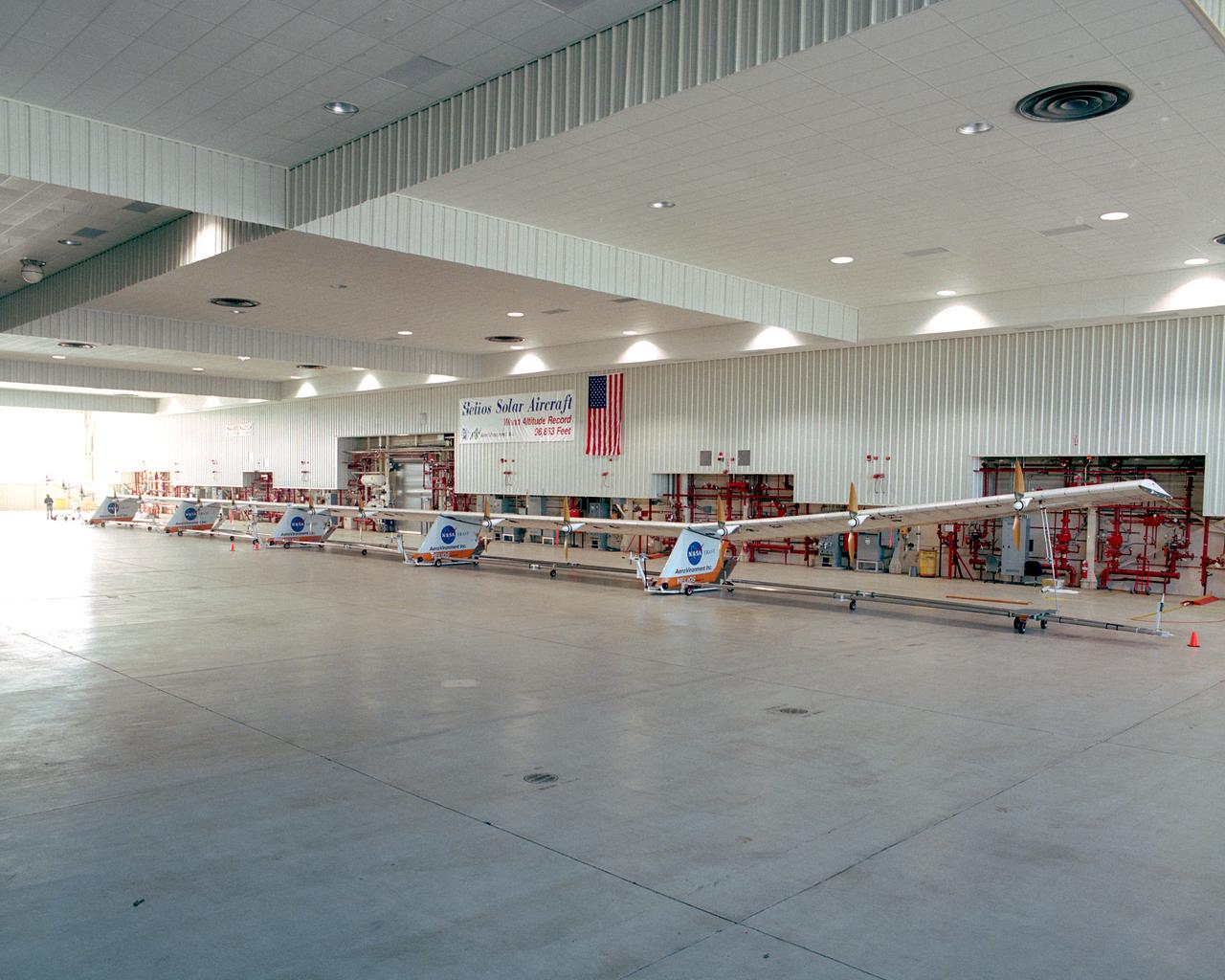

The Helios Prototype flying wing stretches almost the full length of the 300-foot-long hangar at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The 247-foot span solar-powered aircraft, resting on its ground maneuvering dolly, was on display for a visit of NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe and other NASA officials on January 31, 2002. The unique solar-electric flying wing reached an altitude of 96,863 feet during an almost 17-hour flight near Hawaii on August 13, 2001, a world record for sustained horizontal flight by a non-rocket powered aircraft. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) project, the Helios Prototype is the forerunner of a planned fleet of slow-flying, long duration, high-altitude uninhabited aerial vehicles (UAV) which can serve as "atmospheric satellites," performing Earth science missions or functioning as telecommunications relay platforms in the stratosphere.

Red and Green colors predominate in this view of the Aurora Australis photographed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-39) in May 1991 at the peak of the last geomagnetic maximum. The payload bay and tail of the shuttle can be seen on the left hand side of the picture. Auroras are caused when high-energy electrons pour down from the Earth's magnetosphere and collide with atoms. Red aurora occurs from 200 km to as high as 500 km altitude and is caused by the emission of 6300 Angstrom wavelength light from oxygen atoms. Green aurora occurs from about 100 km to 250 km altitude and is caused by the emission of 5577 Angstrom wavelength light from oxygen atoms. The light is emitted when the atoms return to their original unexcited state. At times of peaks in solar activity, there are more geomagnetic storms and this increases the auroral activity viewed on Earth and by astronauts from orbit.
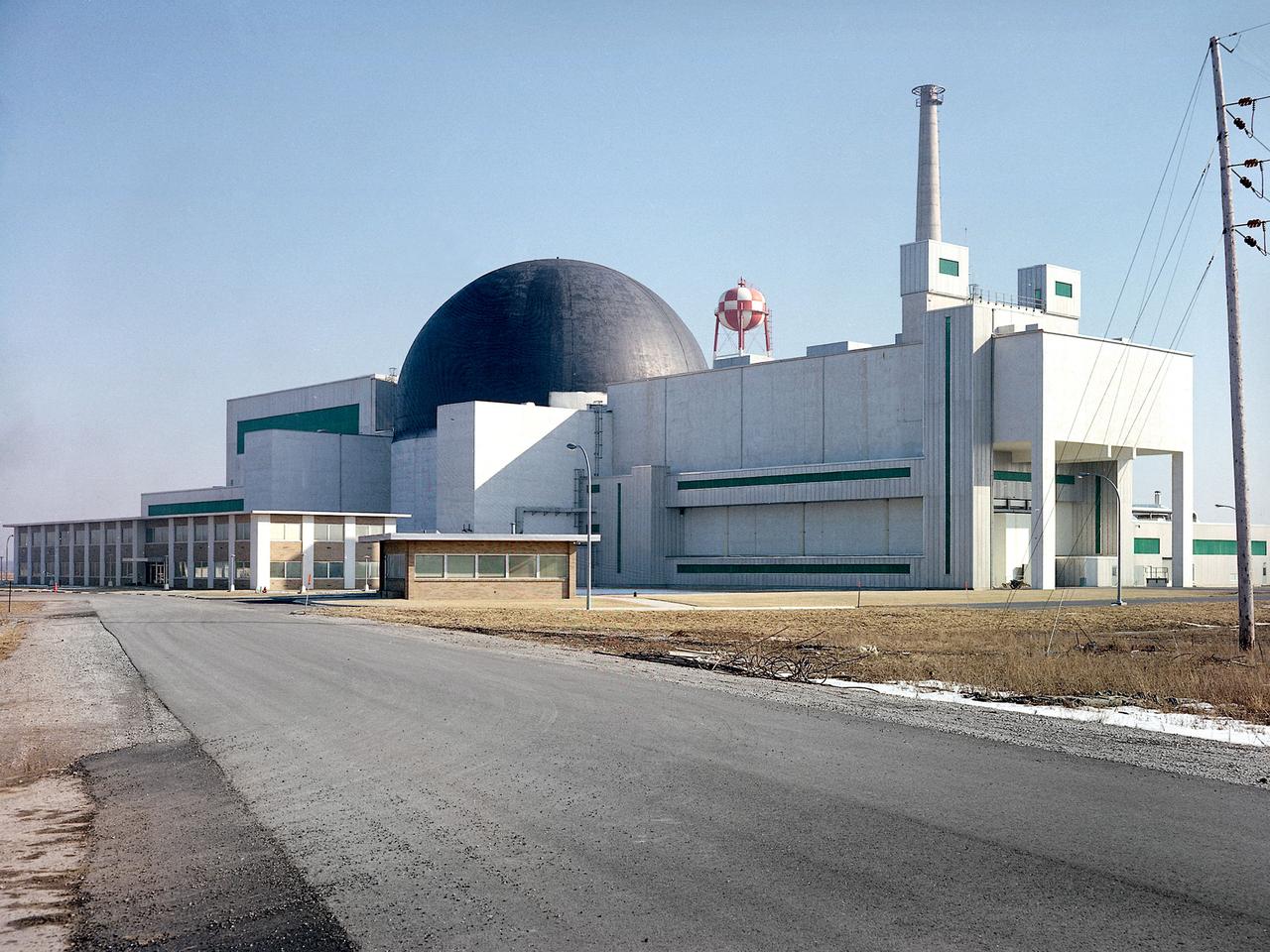

Exterior view of the Space Power Facility at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio. The $28.4-million facility, which began operations in 1969, is the largest high vacuum chamber ever built. The chamber is 100 feet in diameter and 120 feet high. It produces a vacuum deep enough to simulate the conditions at 300 miles altitude. The facility can sustain a high vacuum; simulate solar radiation via a 4-megawatt quartz heat lamp array, solar spectrum by a 400-kilowatt arc lamp, and cold environments. The Space Power Facility was originally designed to test nuclear power sources for spacecraft during long durations in a space atmosphere, but it was never used for that purpose. The facility’s first test in 1970 involved a 15 to 20-kilowatt Brayton Cycle Power System for space applications. Three different methods of simulating solar heat were employed during the Brayton tests. The facility was also used for jettison tests of the Centaur Standard Shroud. The shroud was designed for the new Titan-Centaur rocket that was scheduled to launch the Viking spacecraft to Mars. The new shroud was tested under conditions that simulated the time from launch to the separation of the stages. Test programs at the facility include high-energy experiments, shroud separation tests, Mars Lander system tests, deployable Solar Sail tests and International Space Station hardware tests.
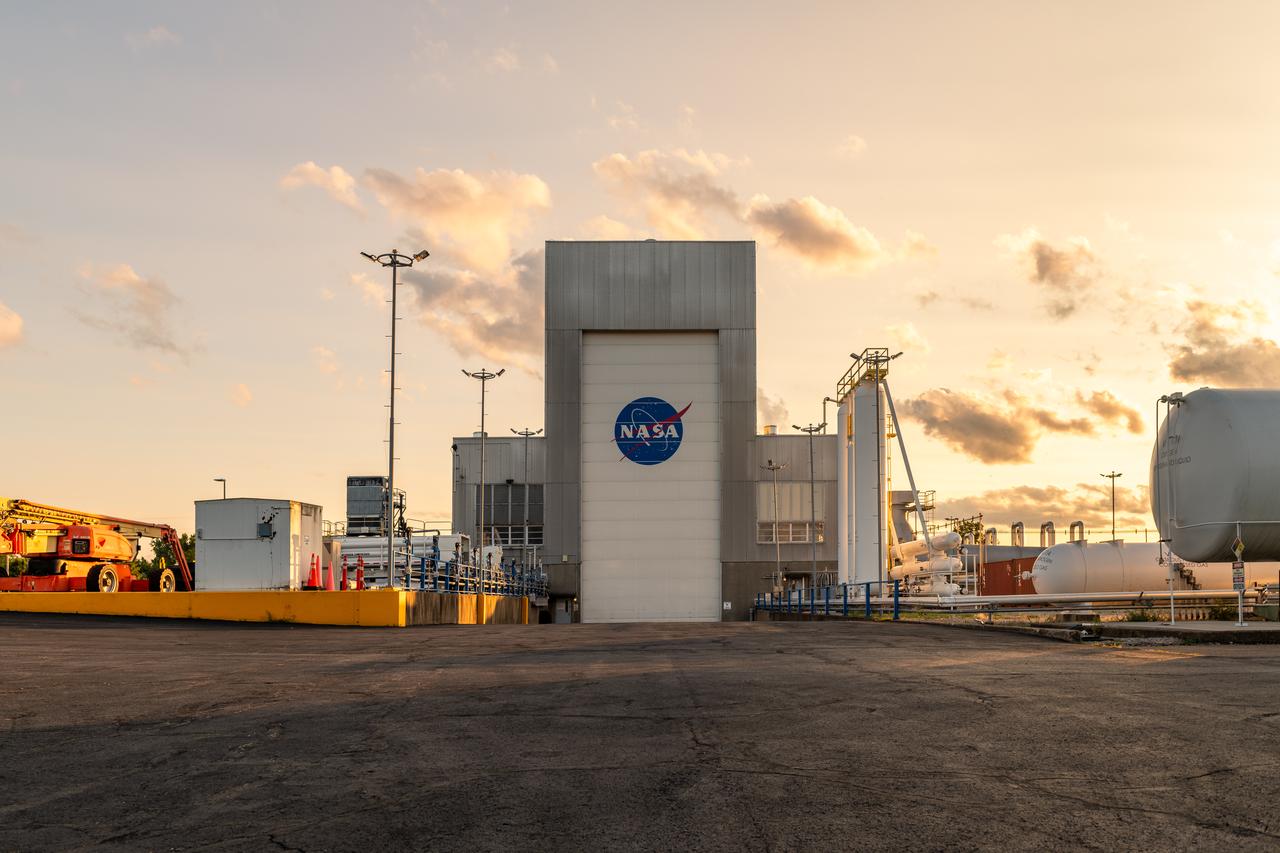

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
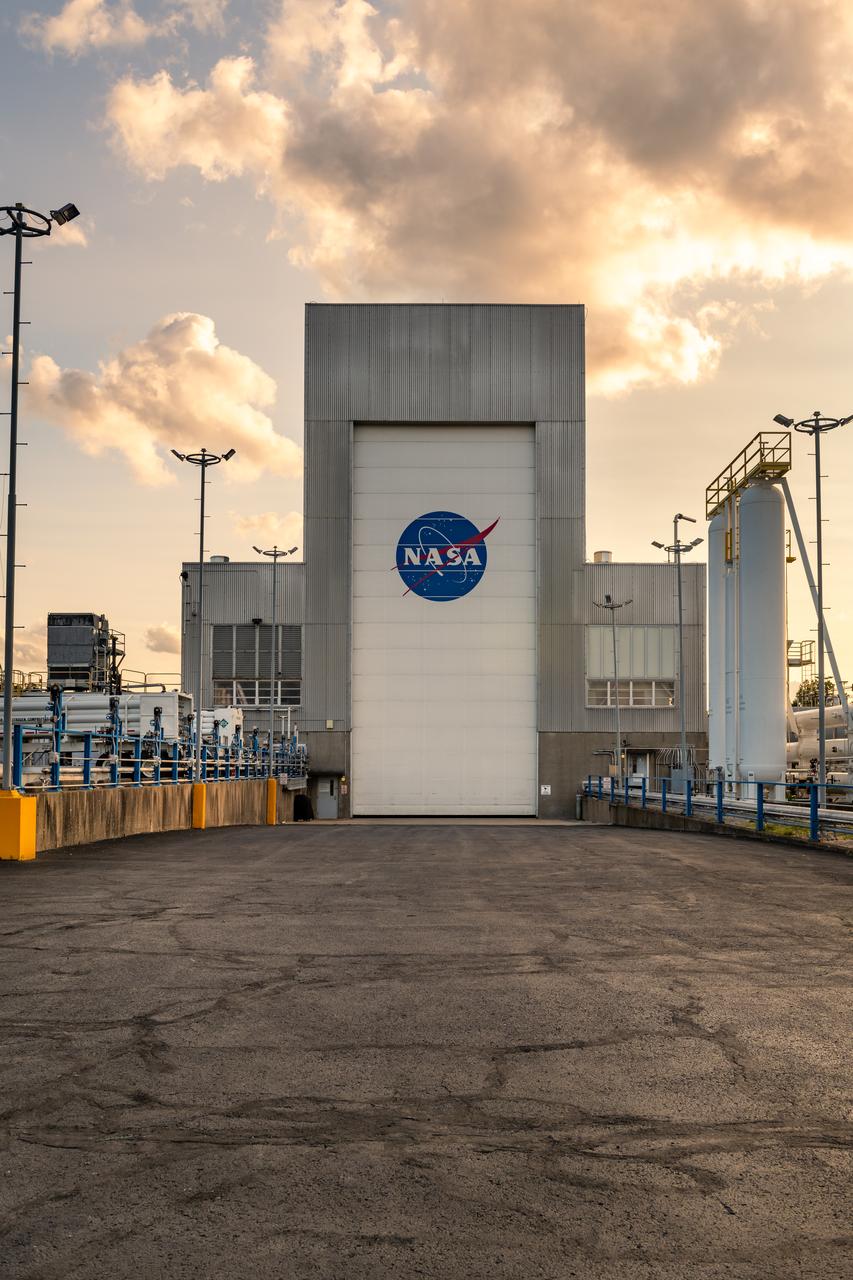

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
This image is the first observation of "shallow lightning" flashes — signatures of high-altitude Jovian thunderstorms that may fundamentally influence the composition of Jupiter's atmosphere. The image of was acquired by NASA's Juno mission using the spacecraft's sensitive Stellar Reference Unit navigation camera during Juno's 10th science flyby on Feb. 7, 2018. The solar-powered Jupiter explorer launched on Aug. 5, 2011 and went into orbit around the gas giant on July 4, 2016. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24301

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
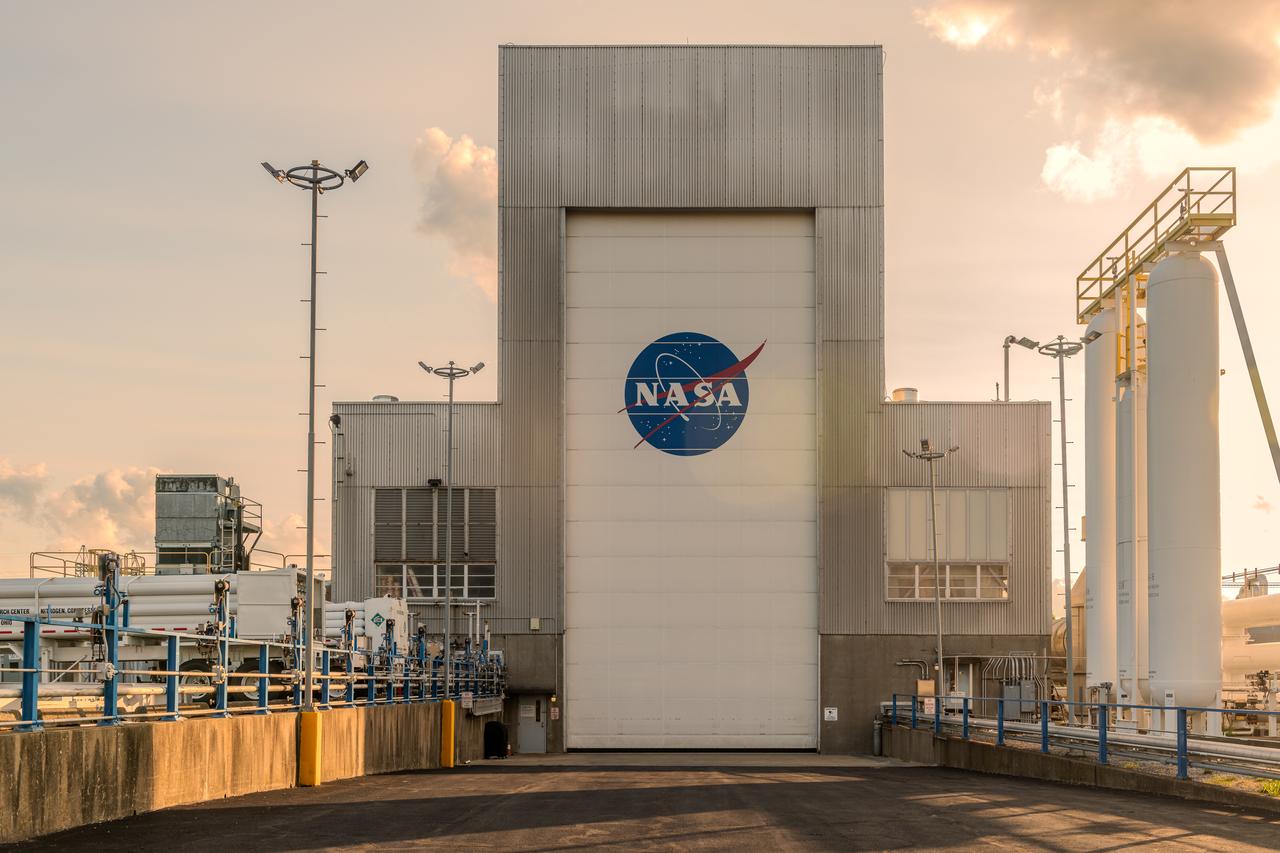

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
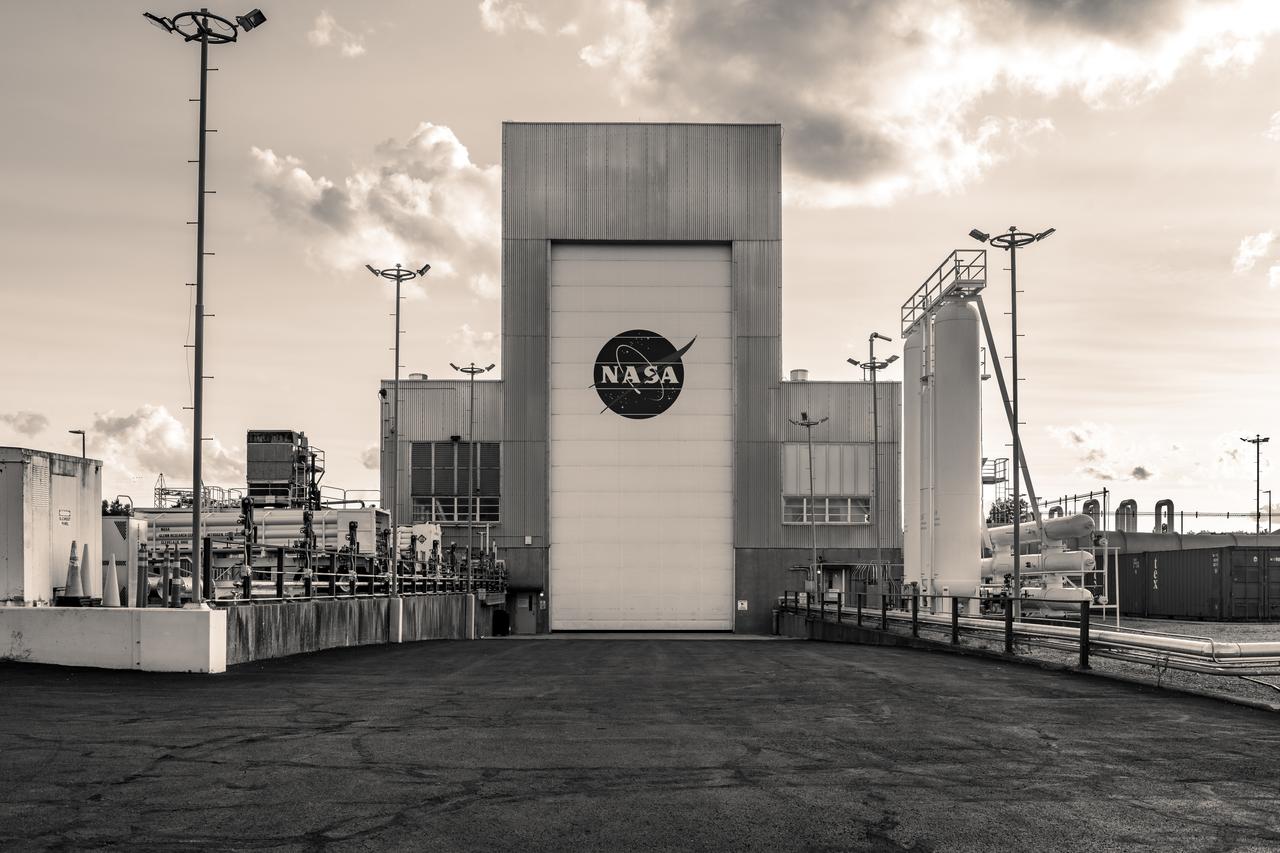

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
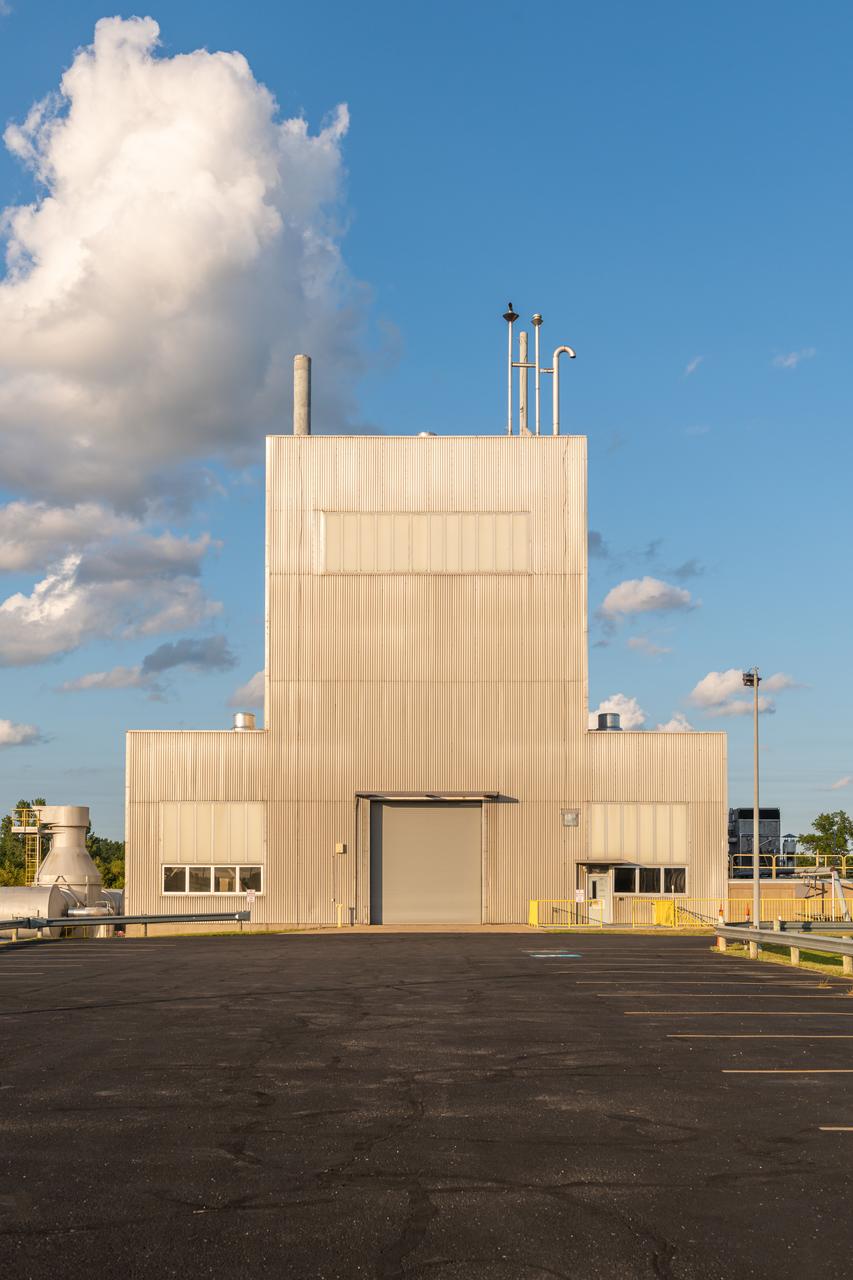

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
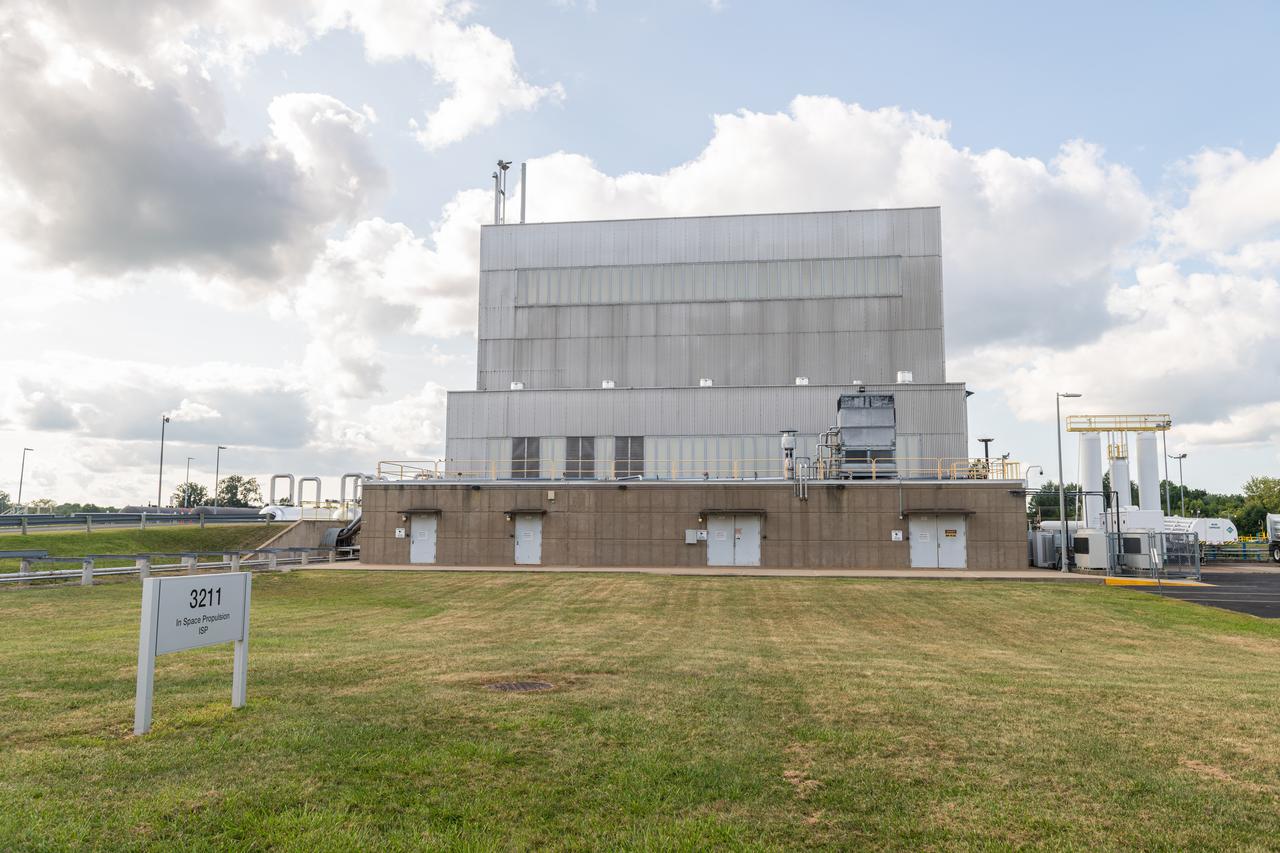

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
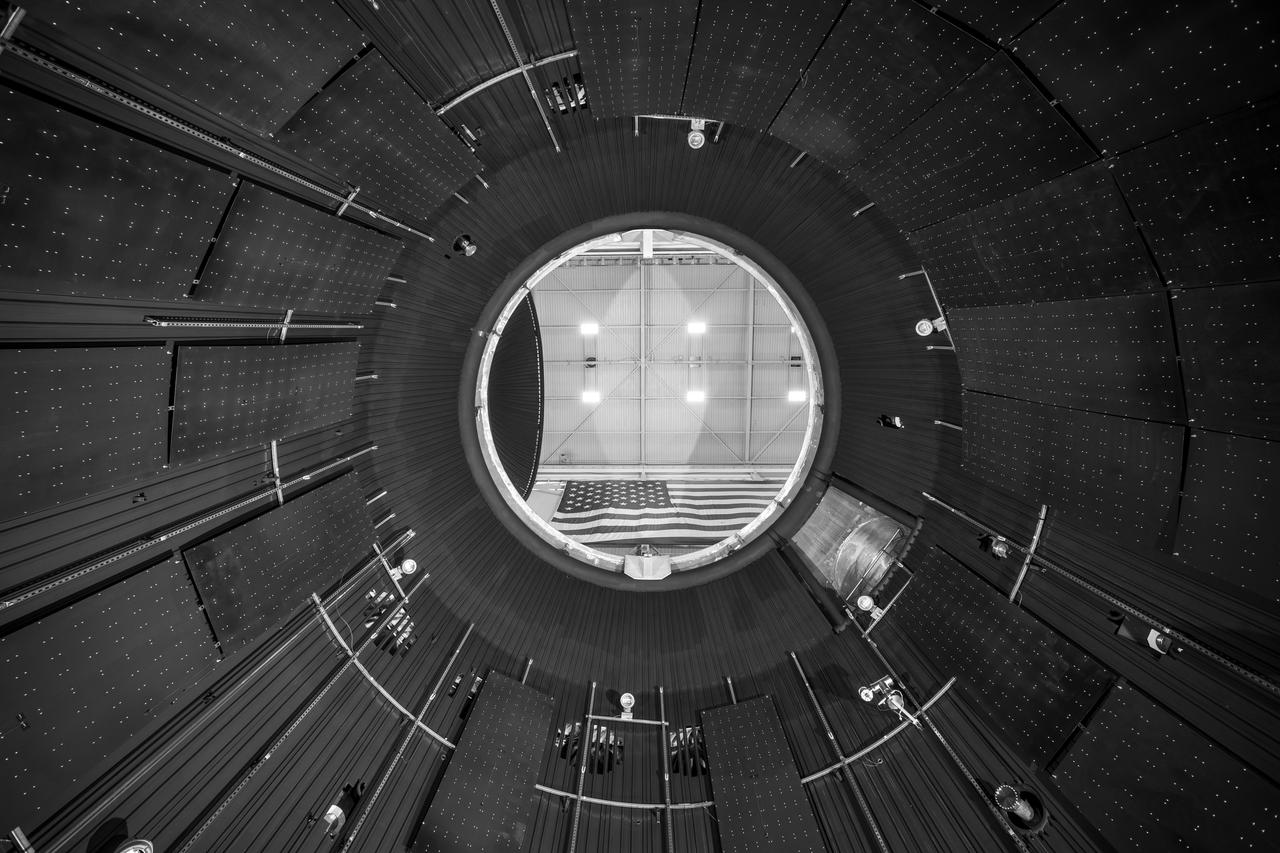

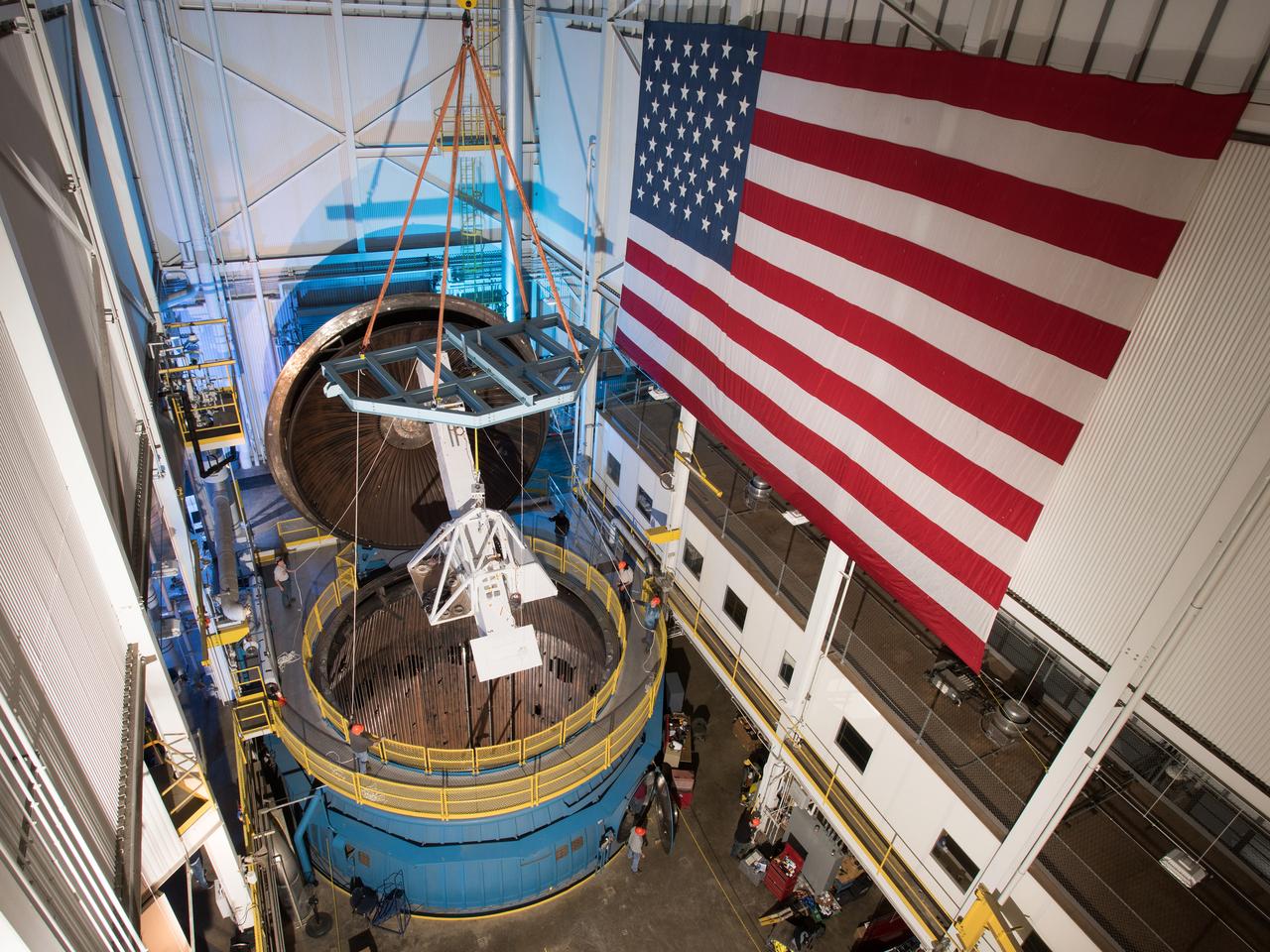
NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. This is a view from inside the chamber looking up toward the American flag. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
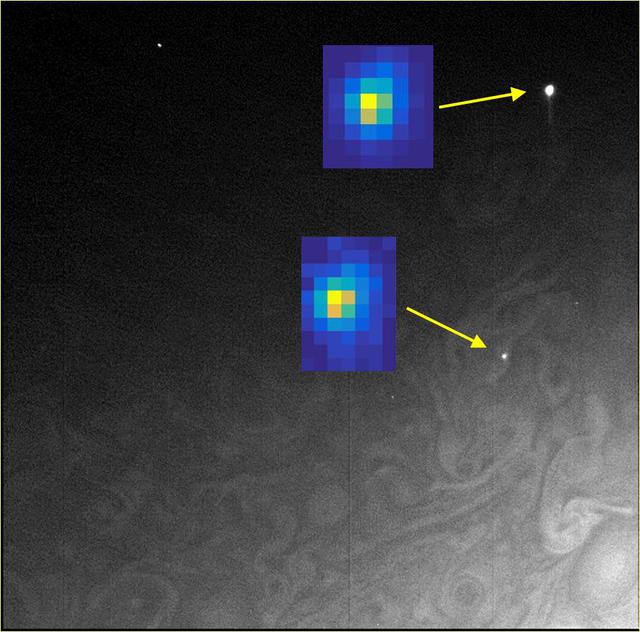

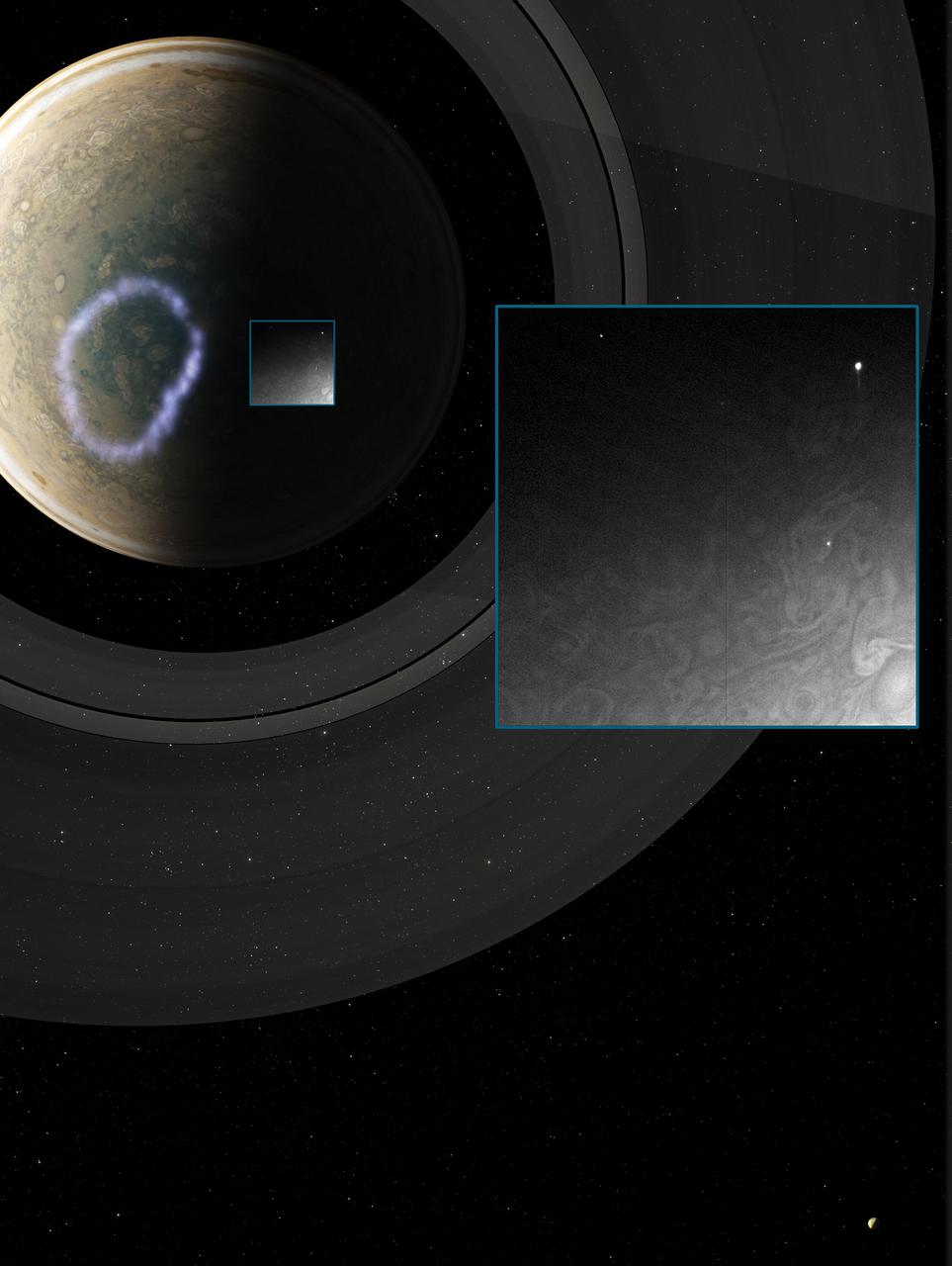
In this composite image taken by Juno's Stellar Reference Unit, the arrows point to small lightning flashes observed on Jupiter's cloud tops; the magnified insets show how they appeared in the science imager. The small size is evidence that the lighting is shallow, originating at unexpectedly high altitudes where it is too cold for liquid water to exist. Designed to detect dim stars, the Stellar Reference Unit's optics enable identification of tiny points of light. The data for this composite was taken by the Stellar Reference Unit on Feb. 7, 2018. The solar-powered Jupiter explorer launched on Aug. 5, 2011 and went into orbit around the gas giant on July 4, 2016. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24302
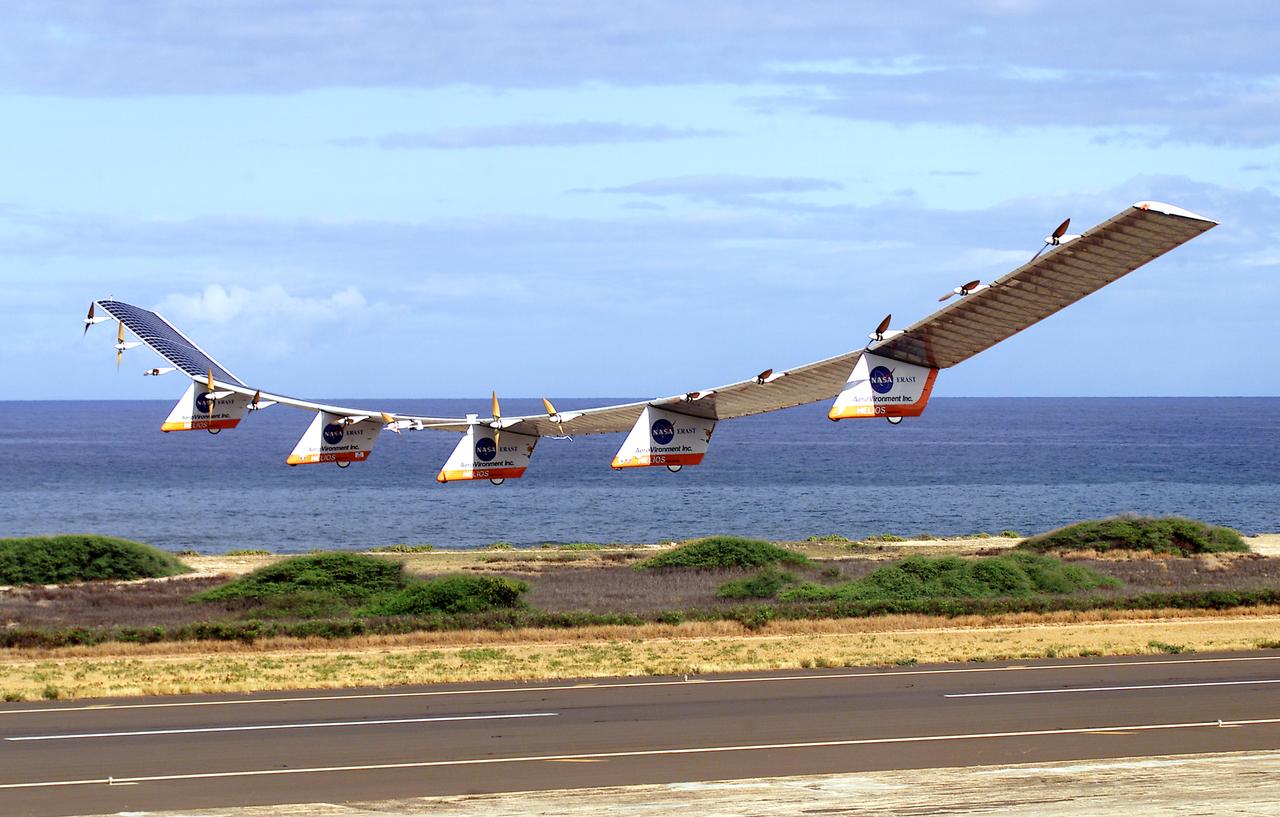

NASA's Helios Prototype aircraft taking off from the Pacific Missile Range Facility, Kauai, Hawaii, for the record flight. As a follow-on to the Centurion (and earlier Pathfinder and Pathfinder-Plus) aircraft, the solar-powered Helios Prototype is the latest and largest example of a slow-flying ultralight flying wing designed for long-duration, high-altitude Earth science or telecommunications relay missions in the stratosphere. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, California, under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) project, the unique craft is intended to demonstrate two key missions: the ability to reach and sustain horizontal flight at 100,000 feet altitude on a single-day flight in 2001, and to maintain flight above 50,000 feet altitude for at least four days in 2003, with the aid of a regenerative fuel cell-based energy storage system now in development. Both of these missions will be powered by electricity derived from non-polluting solar energy. The Helios Prototype is an enlarged version of the Centurion flying wing, which flew a series of test flights at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in late 1998. The craft has a wingspan of 247 feet, 41 feet greater than the Centurion, 2 1/2 times that of its solar-powered Pathfinder flying wing, and longer than the wingspans of either the Boeing 747 jetliner or Lockheed C-5 transport aircraft. The remotely piloted, electrically powered Helios Prototype went aloft on its maiden low-altitude checkout flight Sept. 8, 1999, over Rogers Dry Lake adjacent to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in the Southern California desert. The initial flight series was flown on battery power as a risk-reduction measure. In all, six flights were flown in the Helios Protoype's initial development series. In upgrading the Centurion to the Helios Prototype configuration, AeroVironment added a sixth wing section and a fifth landing gear pod, among other improvements. The additional wingsp
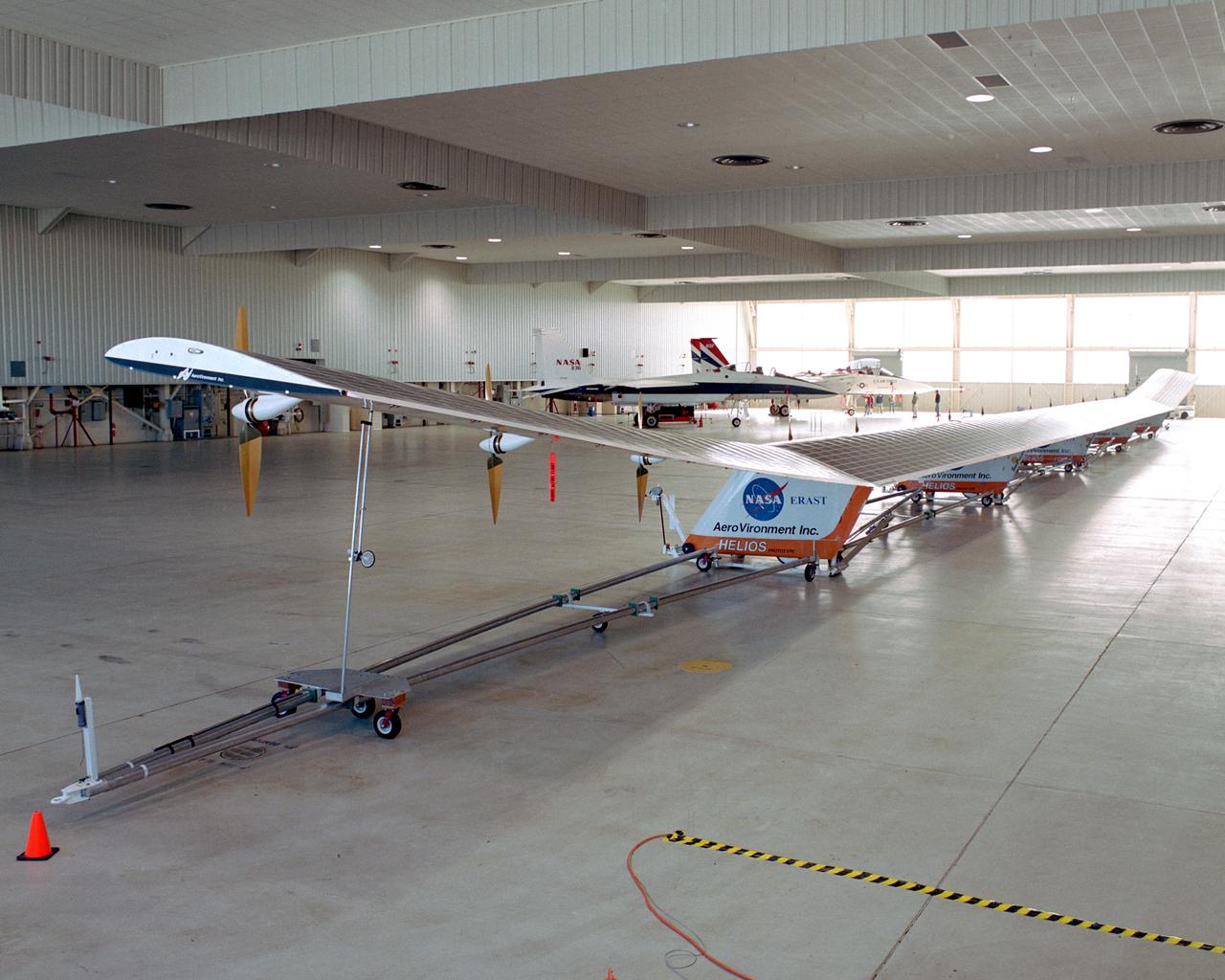

The solar-powered Helios Prototype flying wing frames two modified F-15 research aircraft in a hangar at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The elongated 247-foot span lightweight aircraft, resting on its ground maneuvering dolly, stretched almost the full length of the 300-foot long hangar while on display during a visit of NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe and other NASA officials on Jan. 31, 2002. The unique solar-electric flying wing reached an altitude of 96,863 feet during an almost 17-hour flight near Hawaii on Aug. 13, 2001, a world record for sustained horizontal flight by a non-rocket powered aircraft. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) project, the Helios Prototype is the forerunner of a planned fleet of slow-flying, long duration, high-altitude uninhabited aerial vehicles (UAV) which can serve as "atmospheric satellites," performing Earth science missions or functioning as telecommunications relay platforms in the stratosphere.
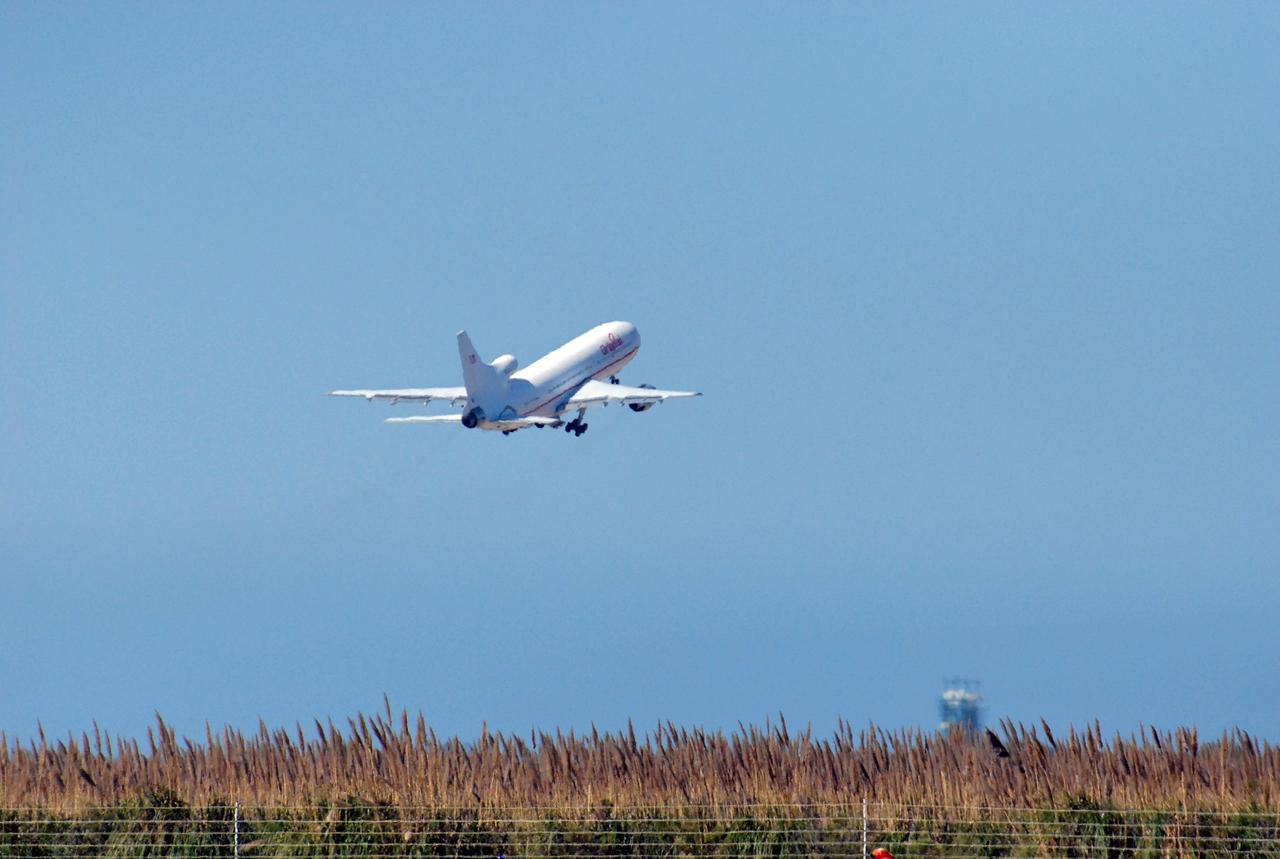

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft takes off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California for the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Under its wing is NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft begins rolling for takeoff from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Under its wing is NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
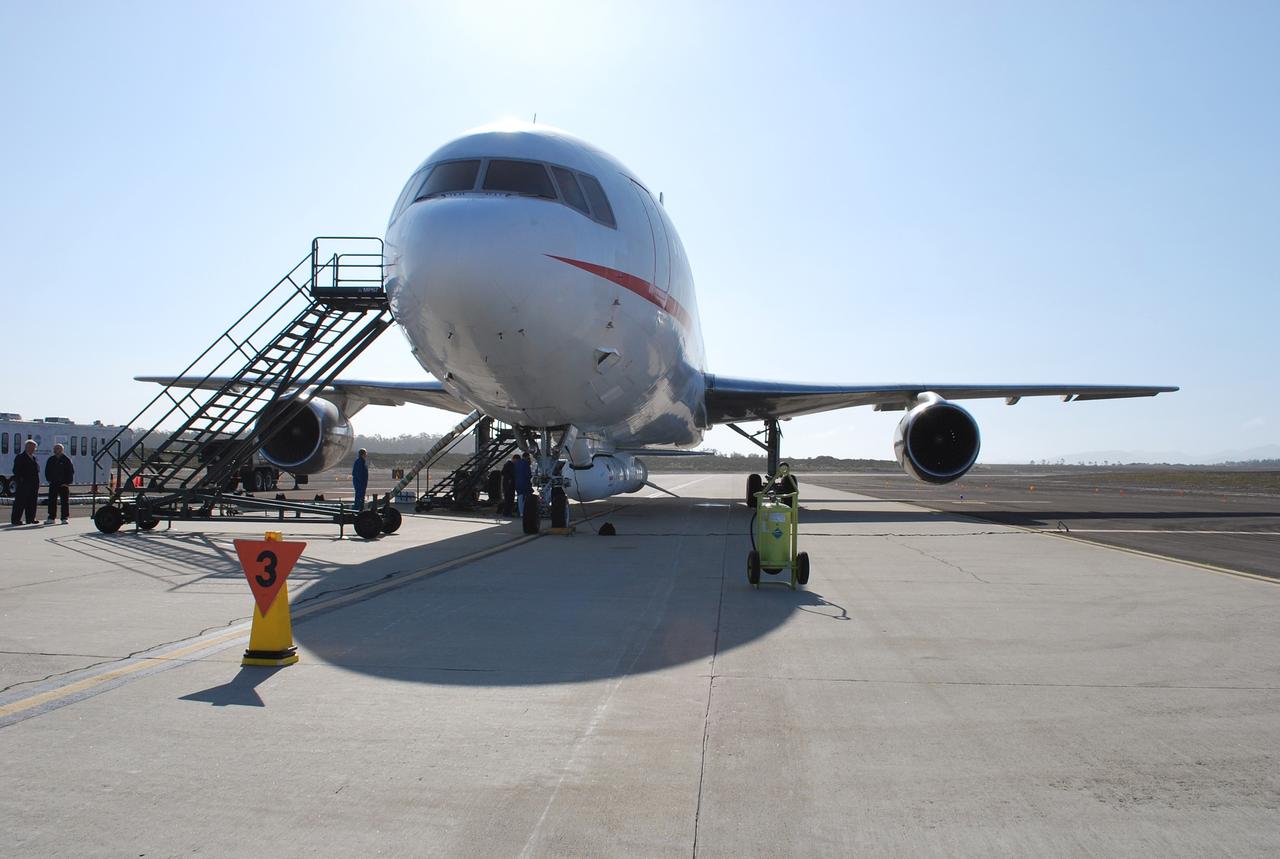

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – On the ramp of Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft awaits departure for the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean, with NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket. The Pegasus is attached under the wing of the aircraft for launch. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
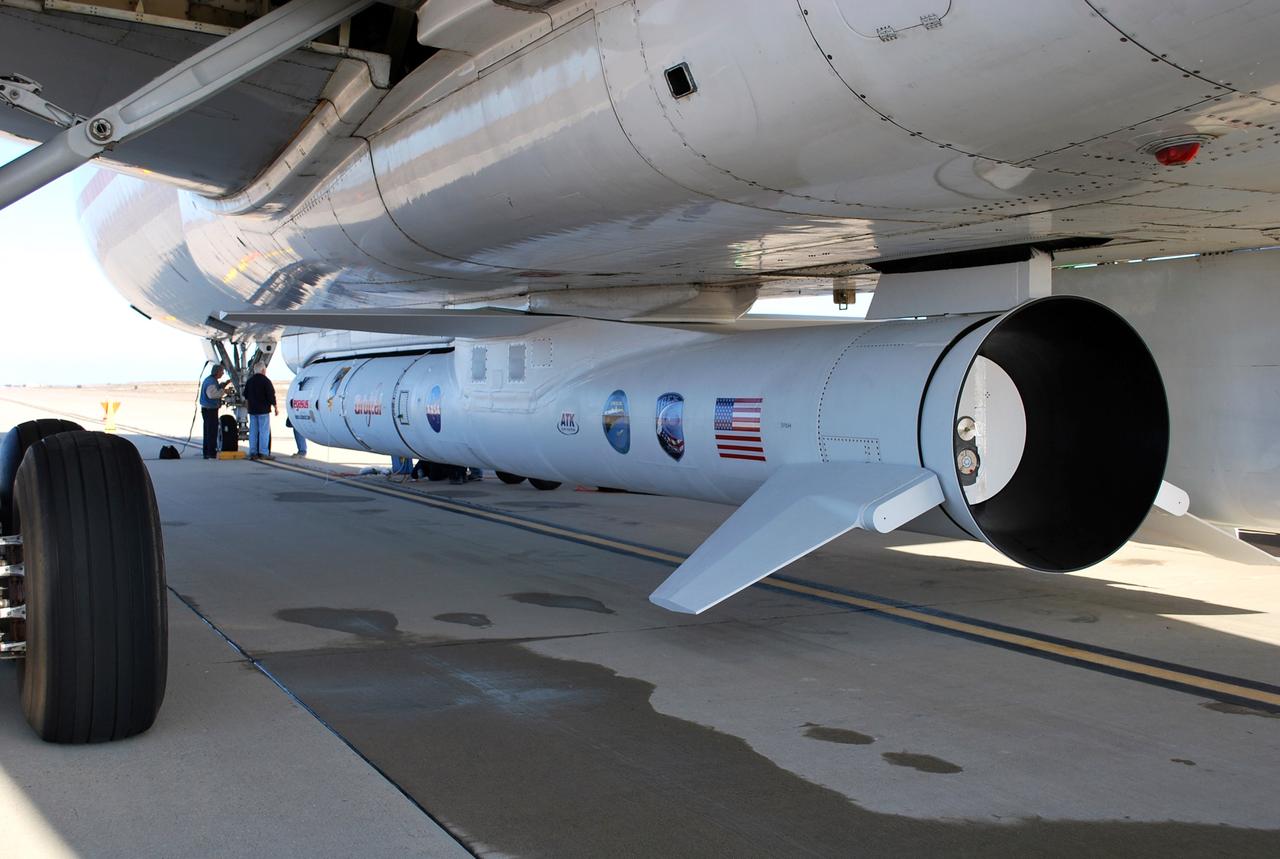

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – On the ramp of Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers make final checks of the Pegasus XL rocket before departure for the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Mated to NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft, the Pegasus is attached under the wing of the aircraft for launch. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
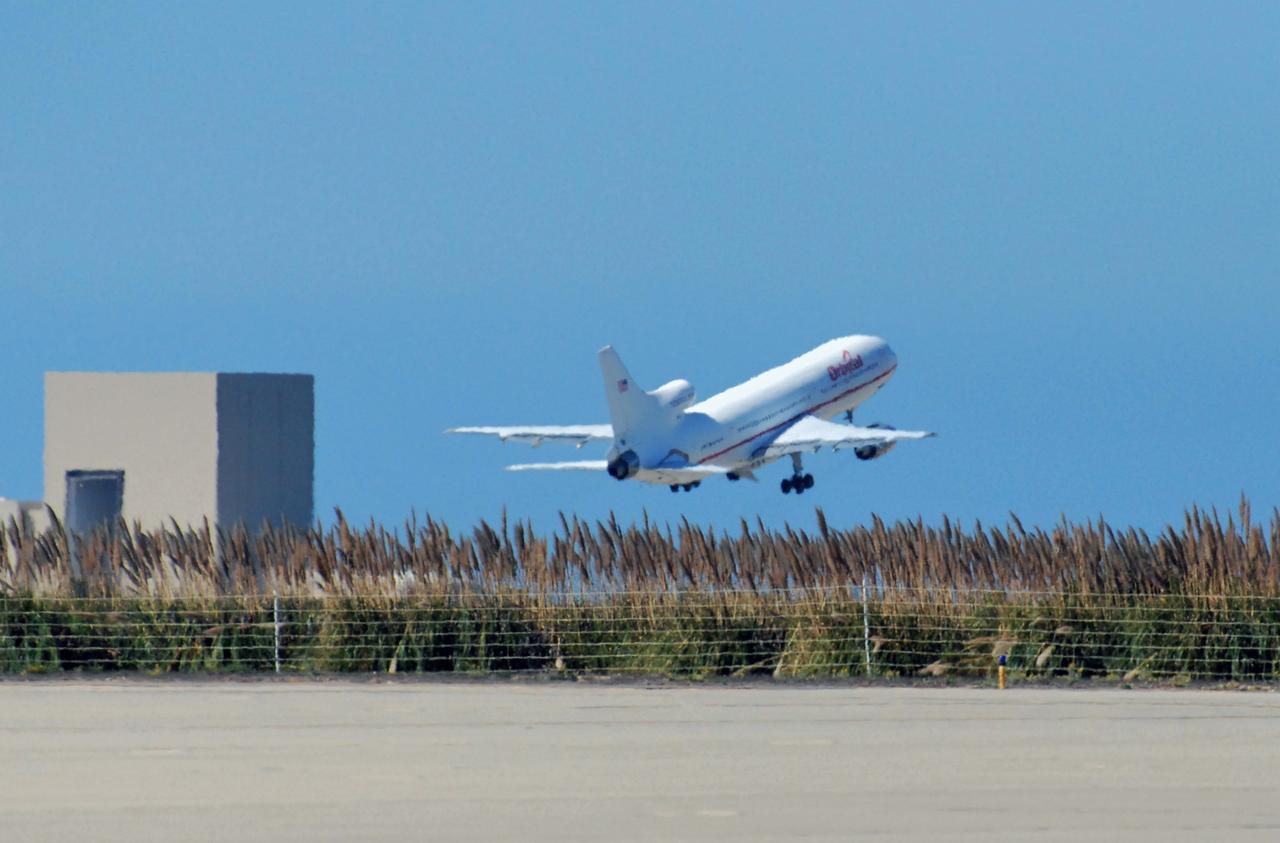

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft takes off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California for the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Under its wing is NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
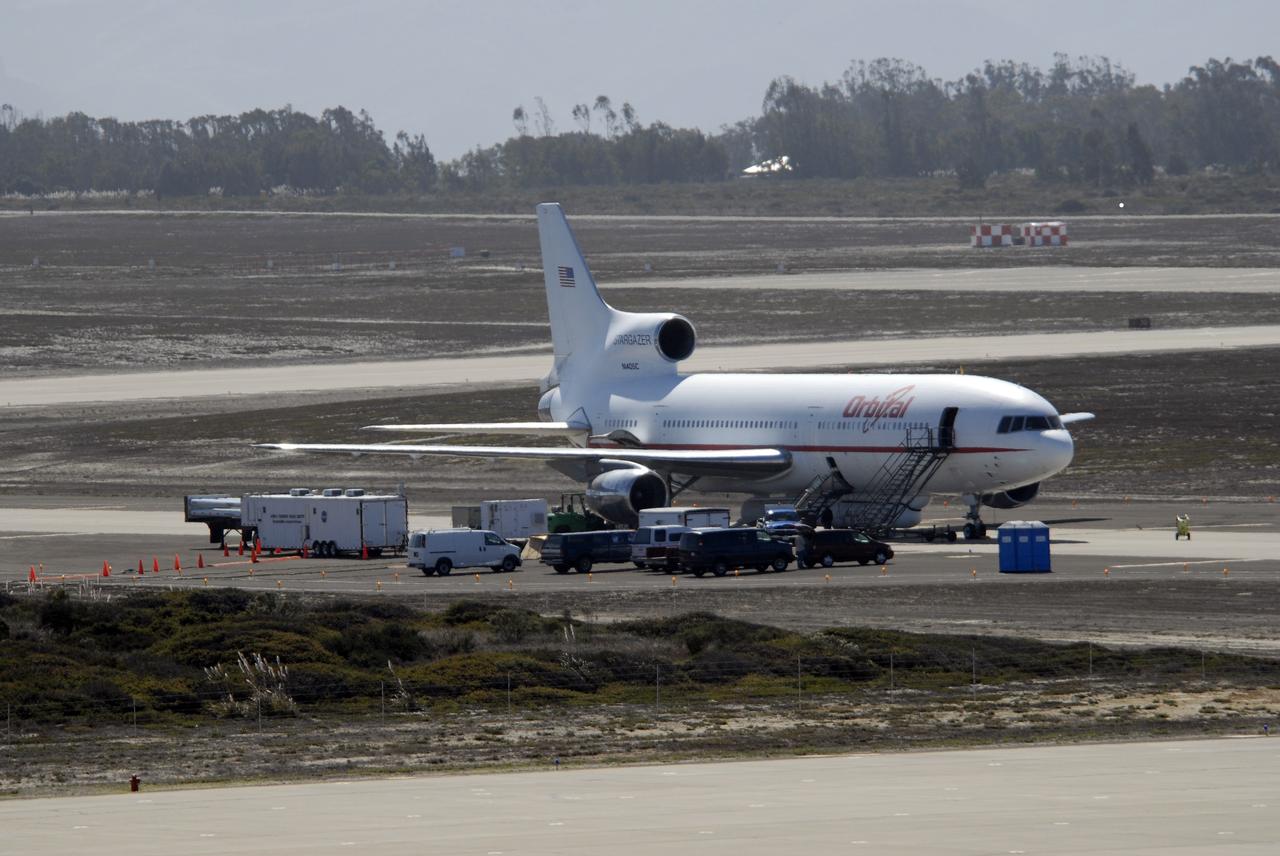

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – On the ramp of Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft awaits departure for the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean, with NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket. The Pegasus is attached under the wing of the aircraft for launch. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/CIV USAF/Daniel Liberotti
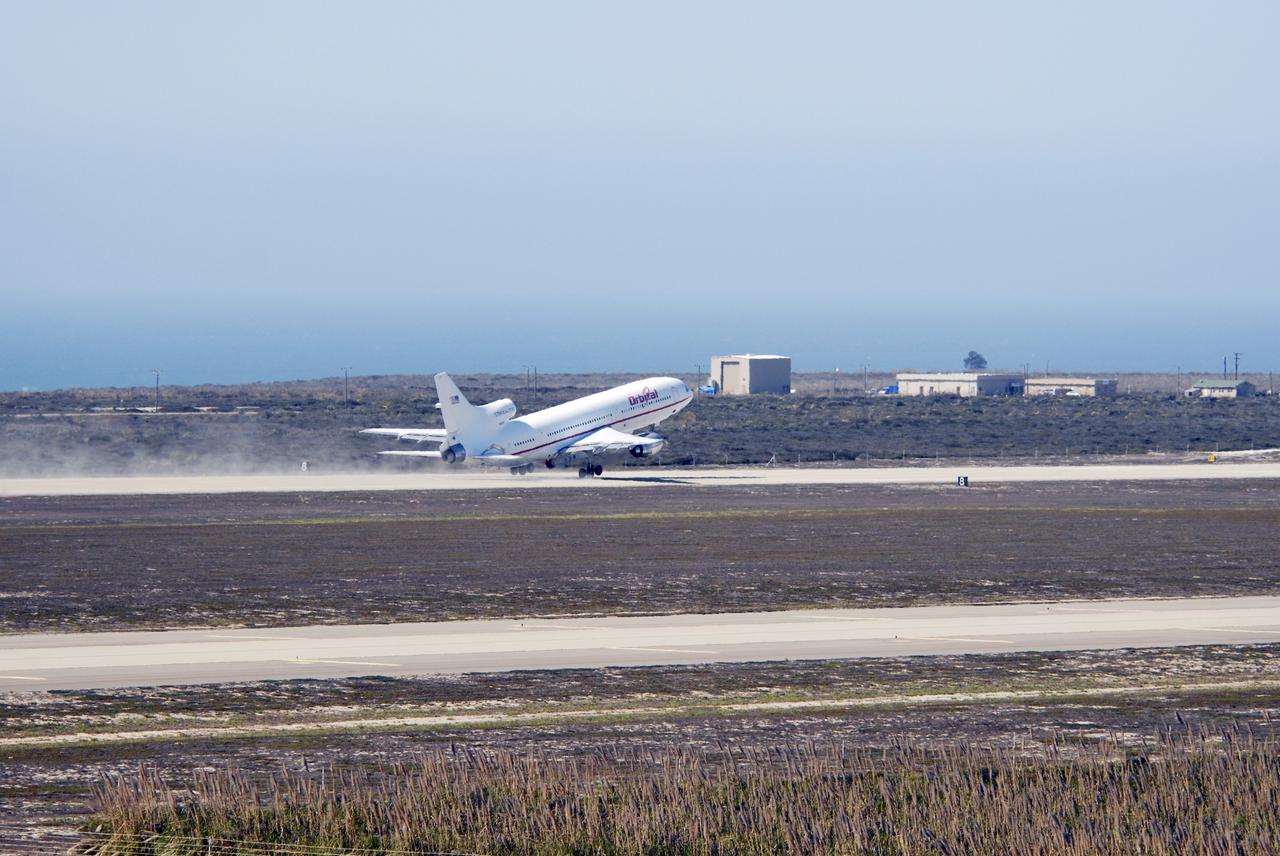

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft takes off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California for the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Under its wing is NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
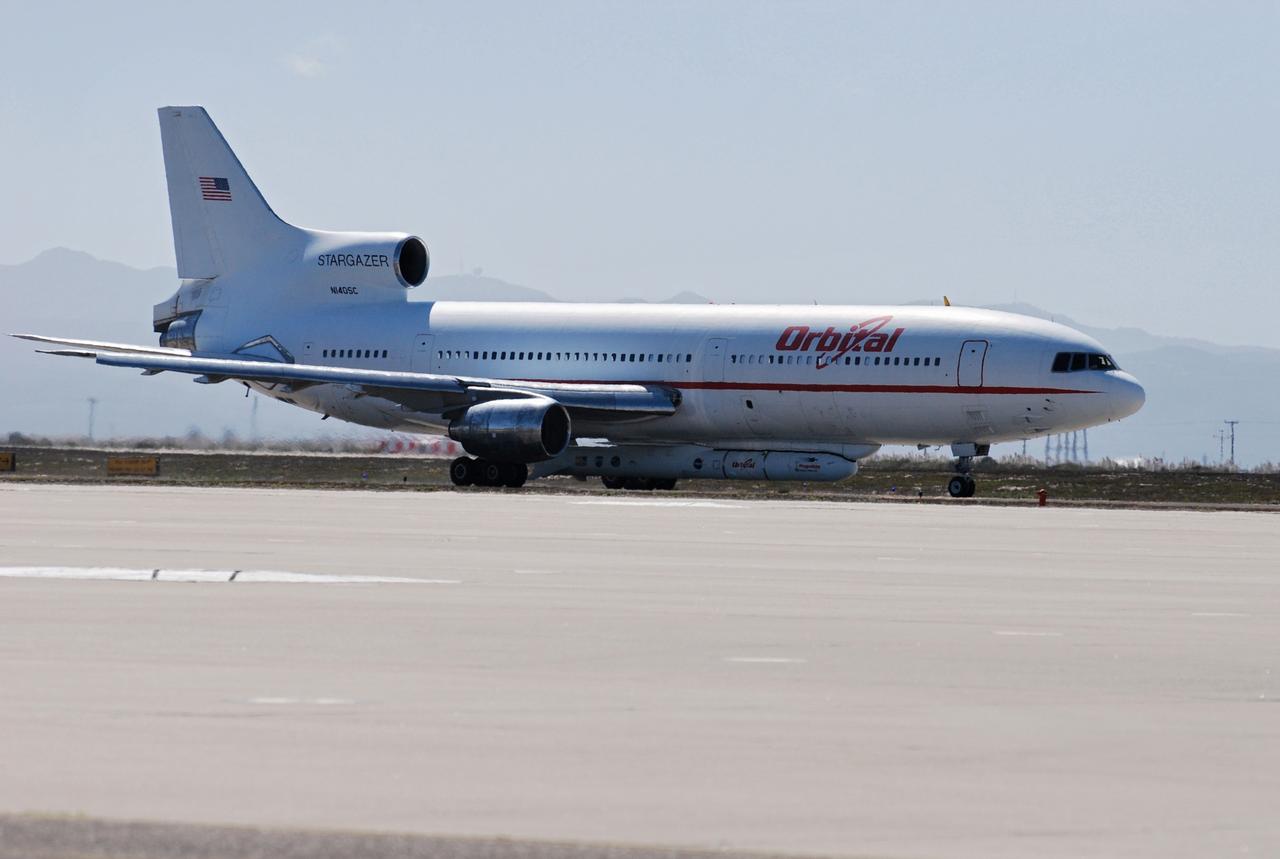

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft begins rolling for takeoff from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Under its wing is NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
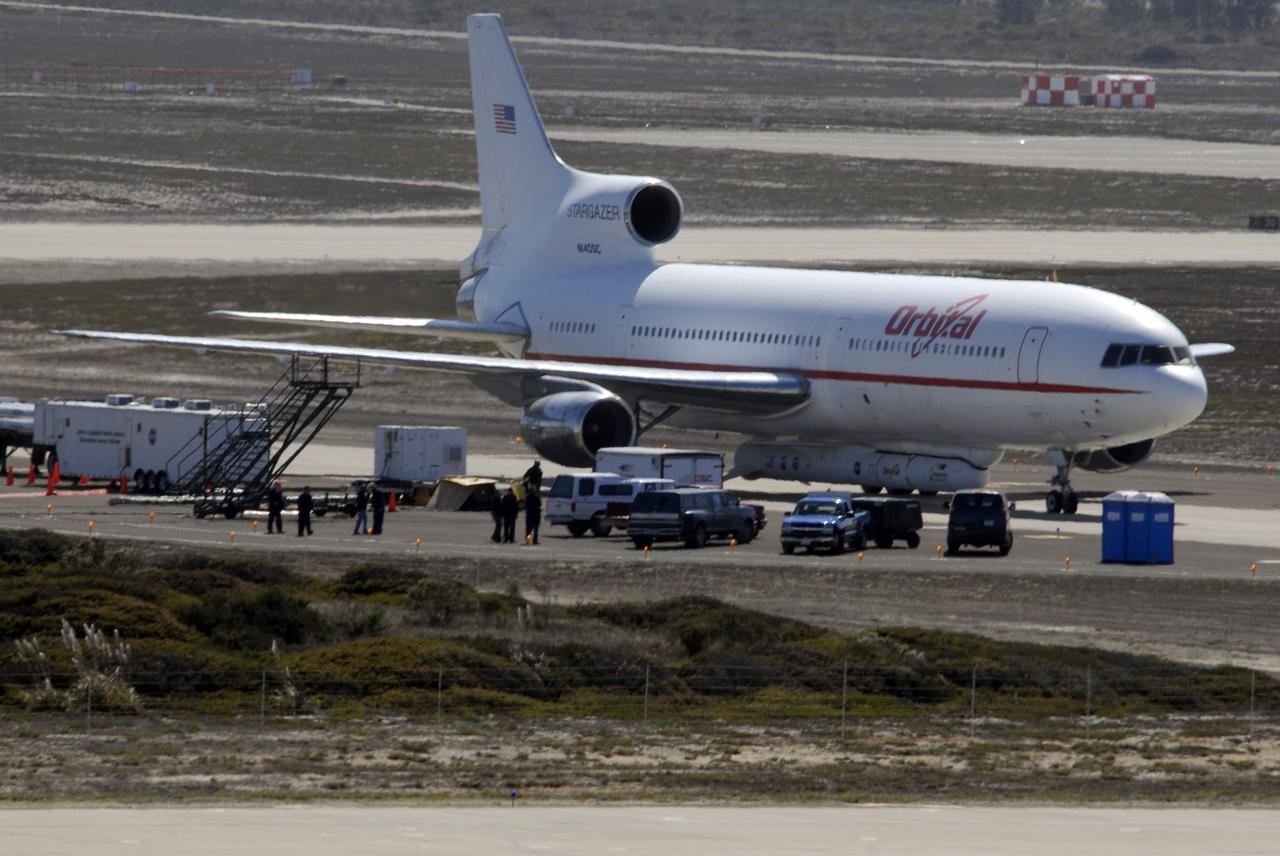

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – On the ramp of Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft awaits departure for the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean, with NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket. The Pegasus is attached under the wing of the aircraft for launch. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/CIV USAF/Daniel Liberotti
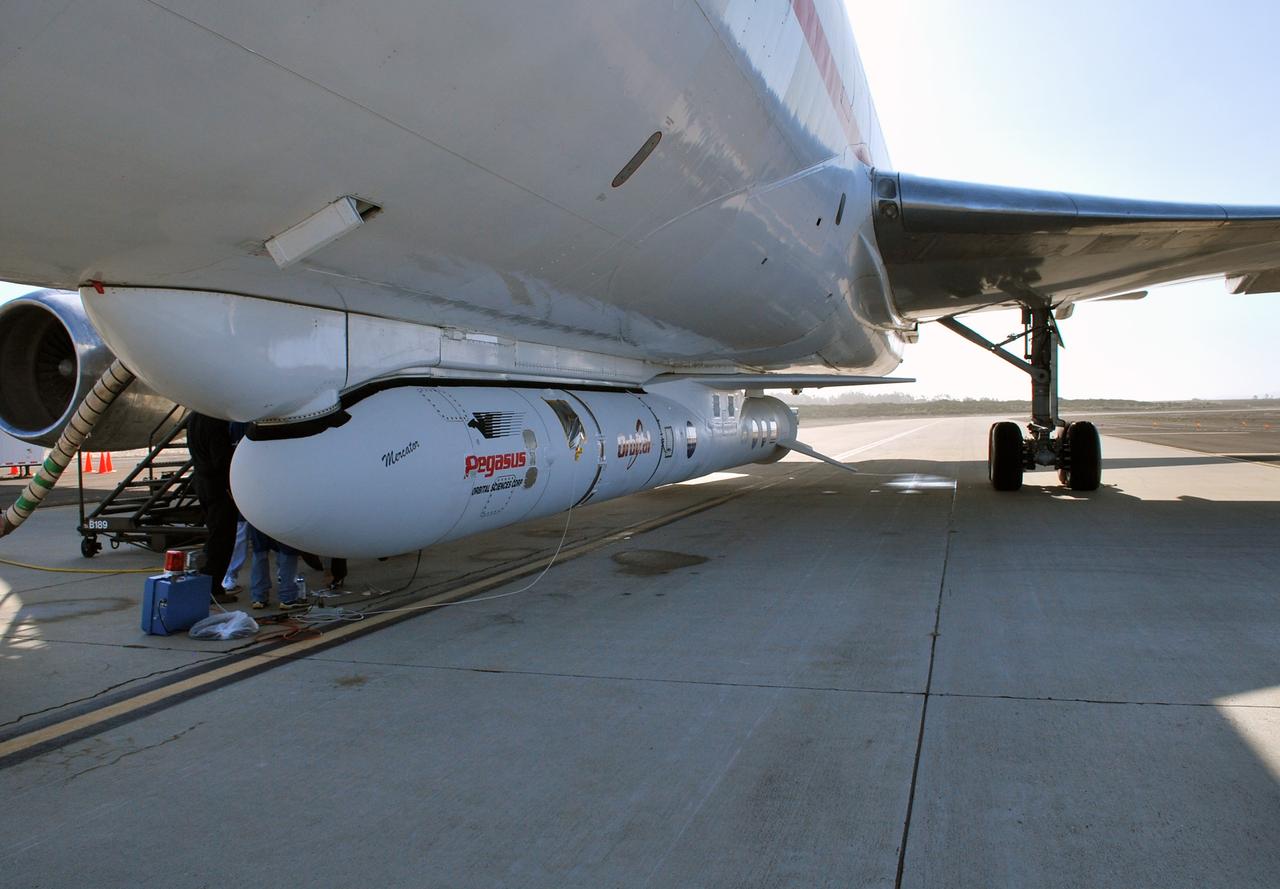

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – On the ramp of Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft awaits departure for the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean, with NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket. The Pegasus is attached under the wing of the aircraft for launch. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft begins to taxi for takeoff from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Under its wing is NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/CIV USAF/Daniel Liberotti
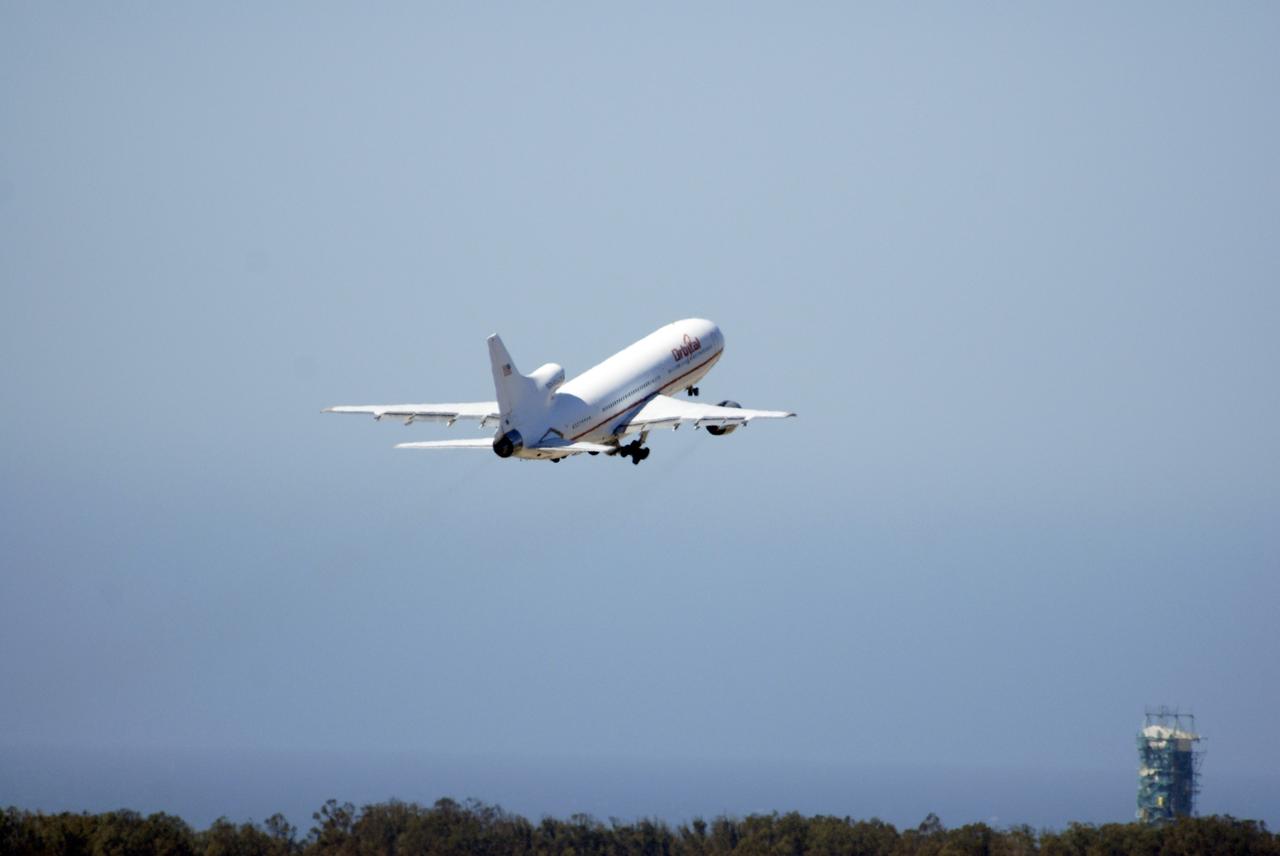

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft takes off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California for the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Under its wing is NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
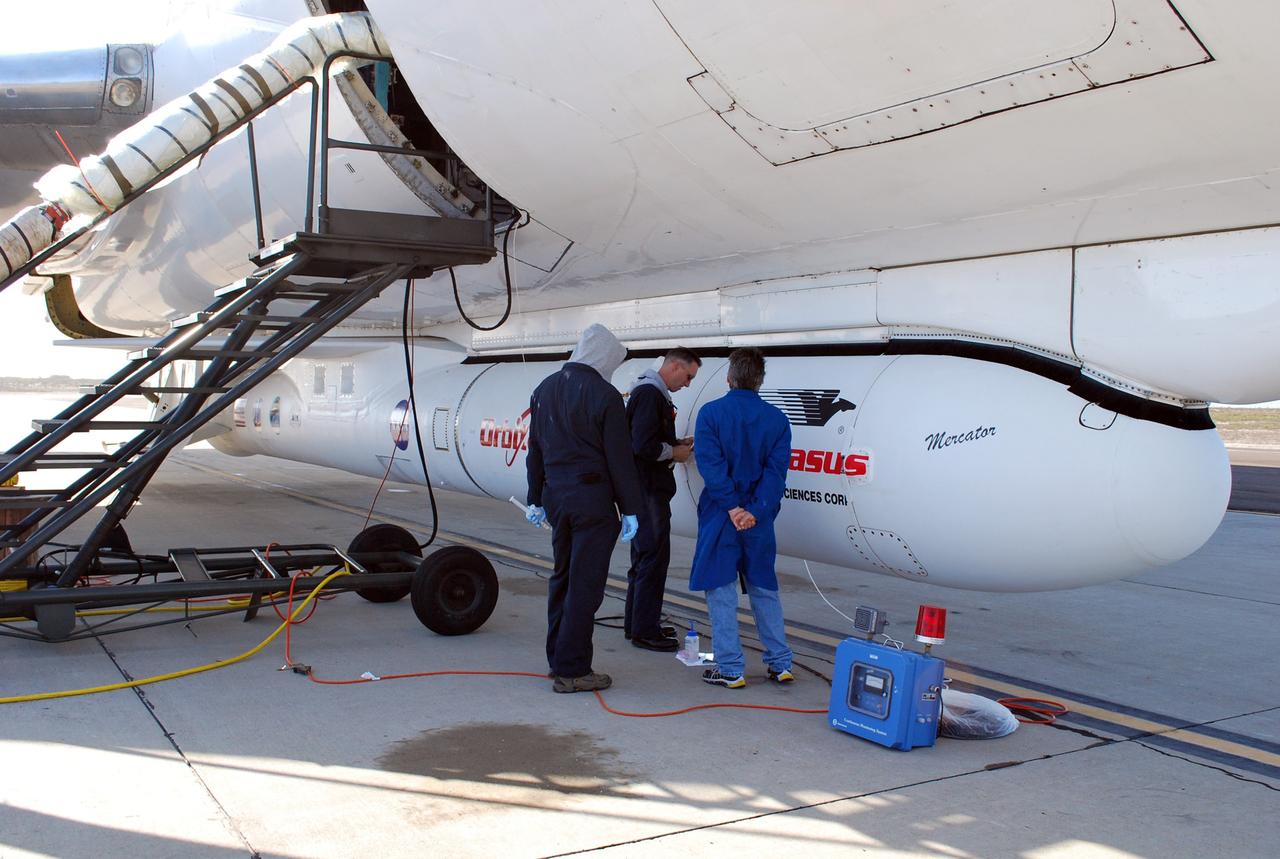

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – On the ramp of Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers make final checks of the Pegasus XL rocket before departure for the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Mated to NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft, the Pegasus is attached under the wing of the aircraft for launch. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
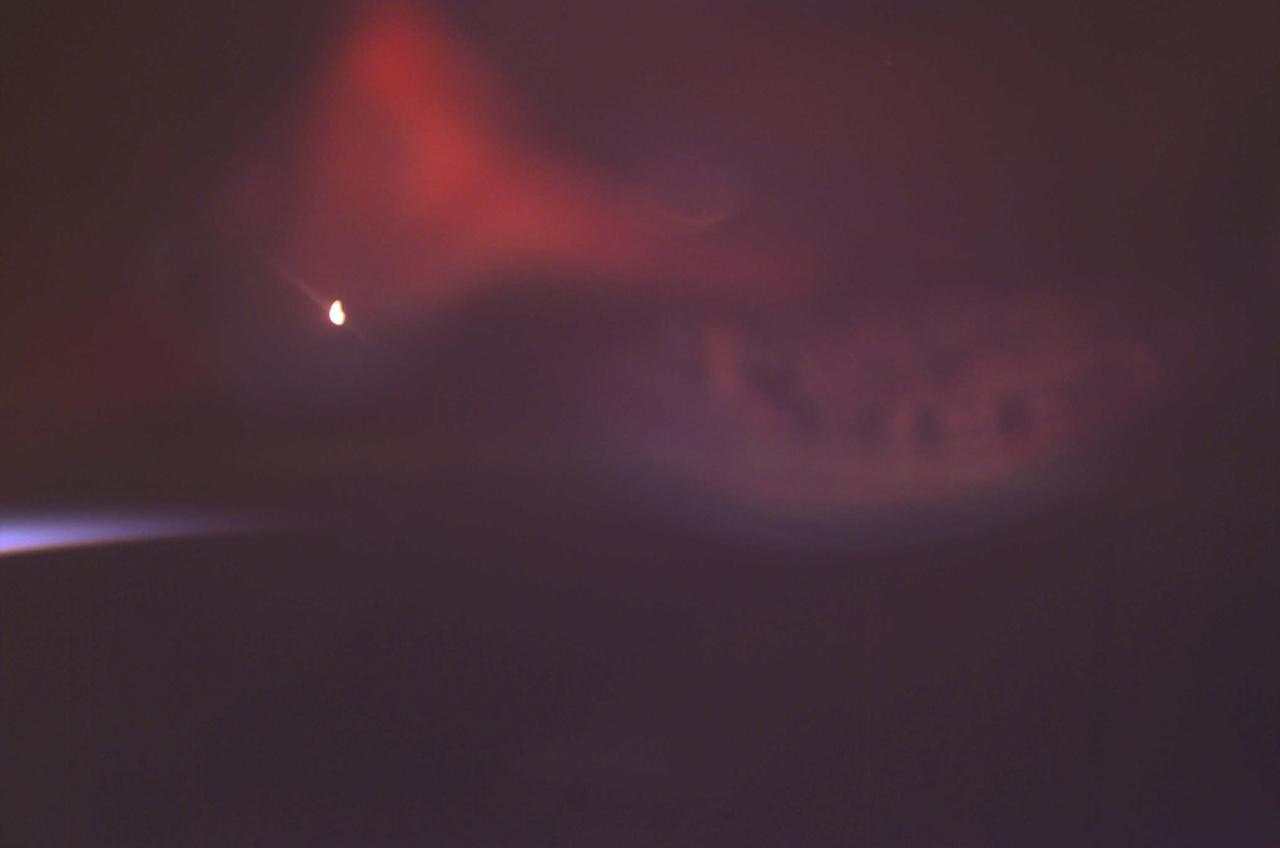
Auroras are caused when high-energy electrons pour down from the Earth's magnetosphere and collide with atoms. Red aurora, as captured here by a still digital camera aboard the International Space Station (ISS), occurs from 200 km to as high as 500 km altitude and is caused by the emission of 6300 Angstrom wavelength light from oxygen atoms. The light is emitted when the atoms return to their original unexcited state. The white spot in the image is from a light on inside of the ISS that is reflected off the inside of the window. The pale blue arch on the left side of the frame is sunlight reflecting off the atmospheric limb of the Earth. At times of peaks in solar activity, there are more geomagnetic storms and this increases the auroral activity viewed on Earth and by astronauts from orbit.
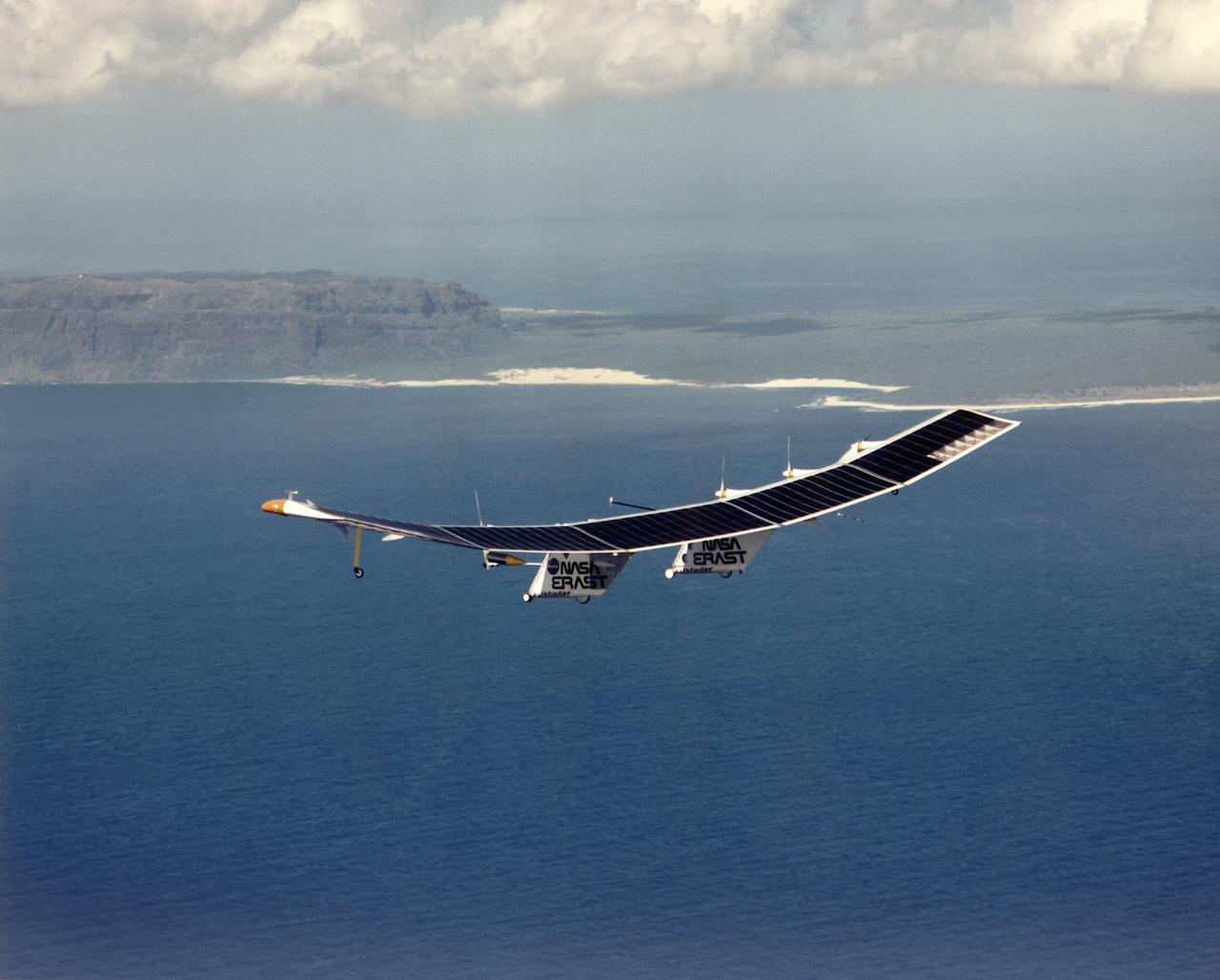

Pathfinder, NASA's solar-powered, remotely-piloted aircraft is shown while it was conducting a series of science flights to highlight the aircraft's science capabilities while collecting imagery of forest and coastal zone ecosystems on Kauai, Hawaii. The flights also tested two new scientific instruments, a high spectral resolution Digital Array Scanned Interferometer (DASI) and a high spatial resolution Airborne Real-Time Imaging System (ARTIS). The remote sensor payloads were designed by NASA's Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California, to support NASA's Mission to Planet Earth science programs.
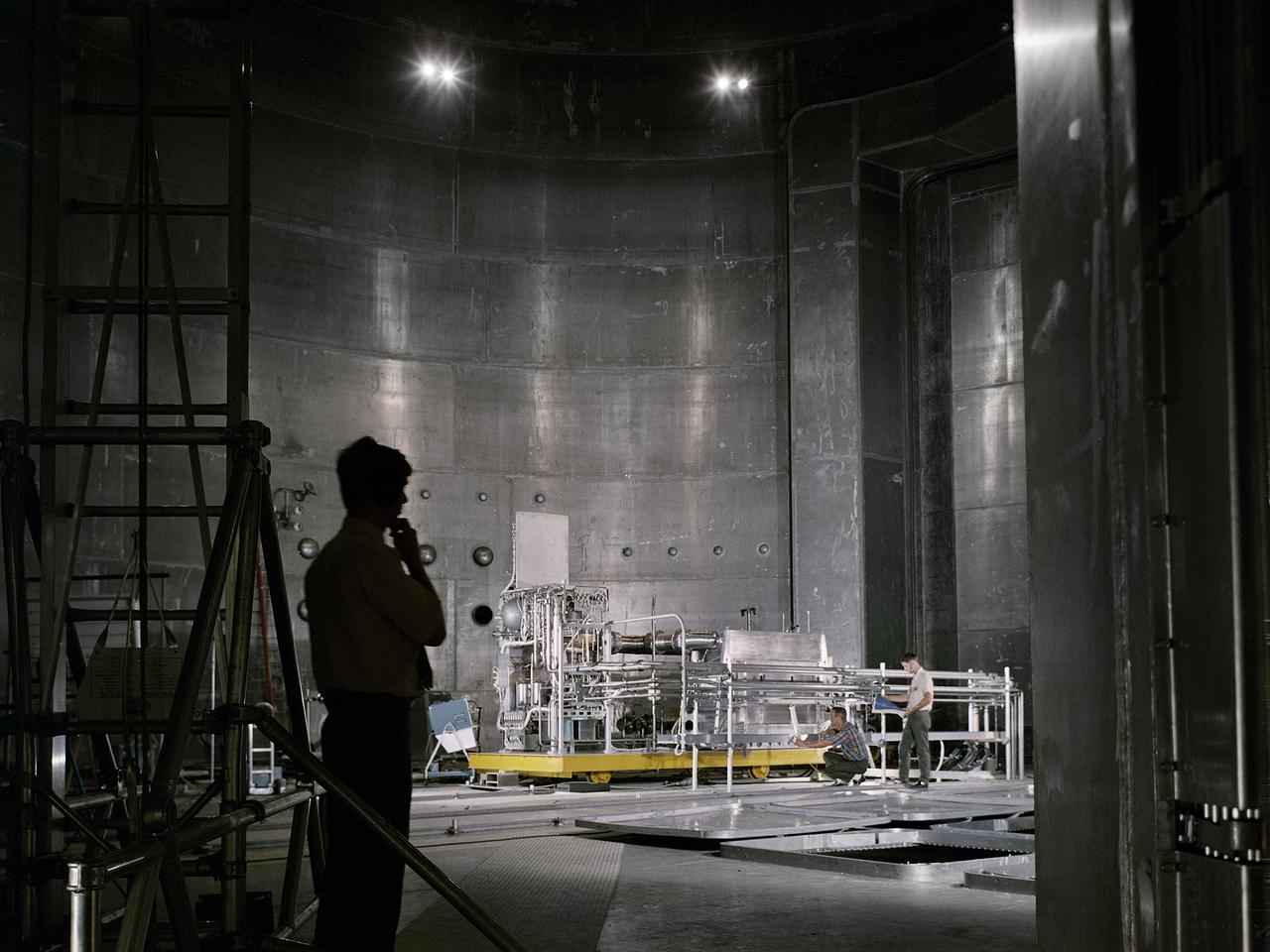

Set up of a Brayton Cycle Power System test in the Space Power Facility’s massive vacuum chamber at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio. The $28.4-million facility, which began operations in 1969, is the largest high vacuum chamber ever built. The chamber is 100 feet in diameter and 120 feet high. It can produce a vacuum deep enough to simulate the conditions at 300 miles altitude. The Space Power Facility was originally designed to test nuclear-power sources for spacecraft, but it was never used for that purpose. The Space Power Facility was first used to test a 15 to 20-kilowatt Brayton Cycle Power System for space applications. Three different methods of simulating solar heat were employed during the tests. Lewis researchers studied the Brayton power system extensively in the 1960s and 1970s. The Brayton engine converted solar thermal energy into electrical power. The system operated on a closed-loop Brayton thermodynamic cycle with a helium-xenon gas mixture as its working fluid. A space radiator was designed to serve as the system’s waste heat rejecter. The radiator was later installed in the vacuum chamber and tested in a simulated space environment to determine its effect on the power conversion system. The Brayton system was subjected to simulated orbits with 62 minutes of sun and 34 minutes of shade.
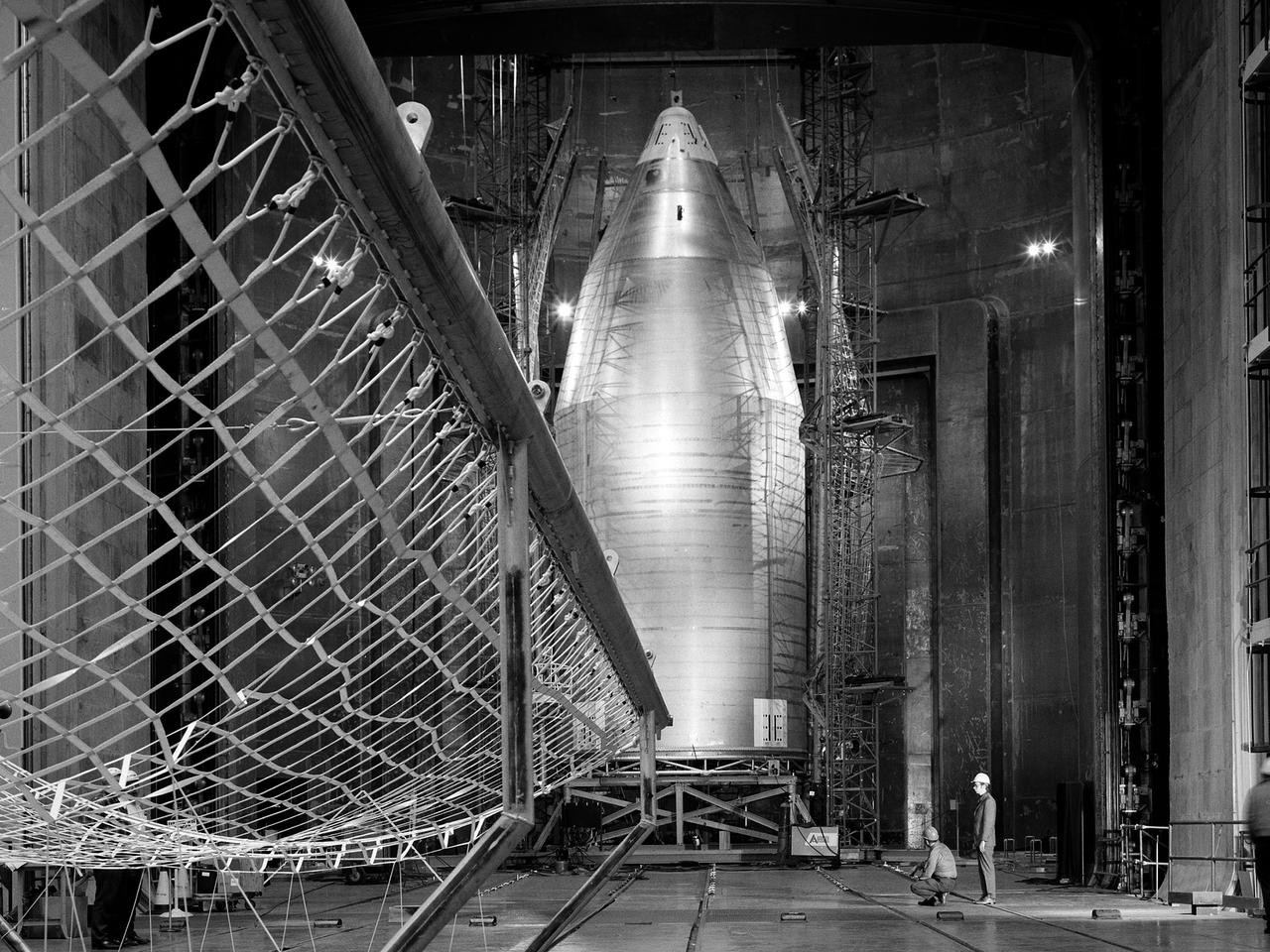

The 56-foot tall, 24,400-pound Skylab shroud installed in the Space Power Facility’s vacuum chamber at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station. The Space Power Facility, which began operations in 1969, is the largest high vacuum chamber ever built. The chamber is 100 feet in diameter and 120 feet high. It can produce a vacuum deep enough to simulate the conditions at 300 miles altitude. The Space Power Facility was originally designed to test nuclear-power sources for spacecraft during long durations in a space atmosphere, but it was never used for that purpose. Payload shrouds are aerodynamic fairings to protect the payload during launch and ascent to orbit. The Skylab mission utilized the largest shroud ever attempted. Unlike previous launches, the shroud would not be jettisoned until the spacecraft reached orbit. NASA engineers designed these tests to verify the dynamics of the jettison motion in a simulated space environment. Fifty-four runs and three full-scale jettison tests were conducted from mid-September 1970 to June 1971. The shroud behaved as its designers intended, the detonators all fired, and early design issues were remedied by the final test. The Space Power Facility continues to operate today. The facility can sustain a high vacuum; simulate solar radiation via a 4-megawatt quartz heat lamp array, solar spectrum by a 400-kilowatt arc lamp, and cold environments. Test programs at the facility include high-energy experiments, shroud separation tests, Mars Lander system tests, deployable Solar Sail tests and International Space Station hardware tests.
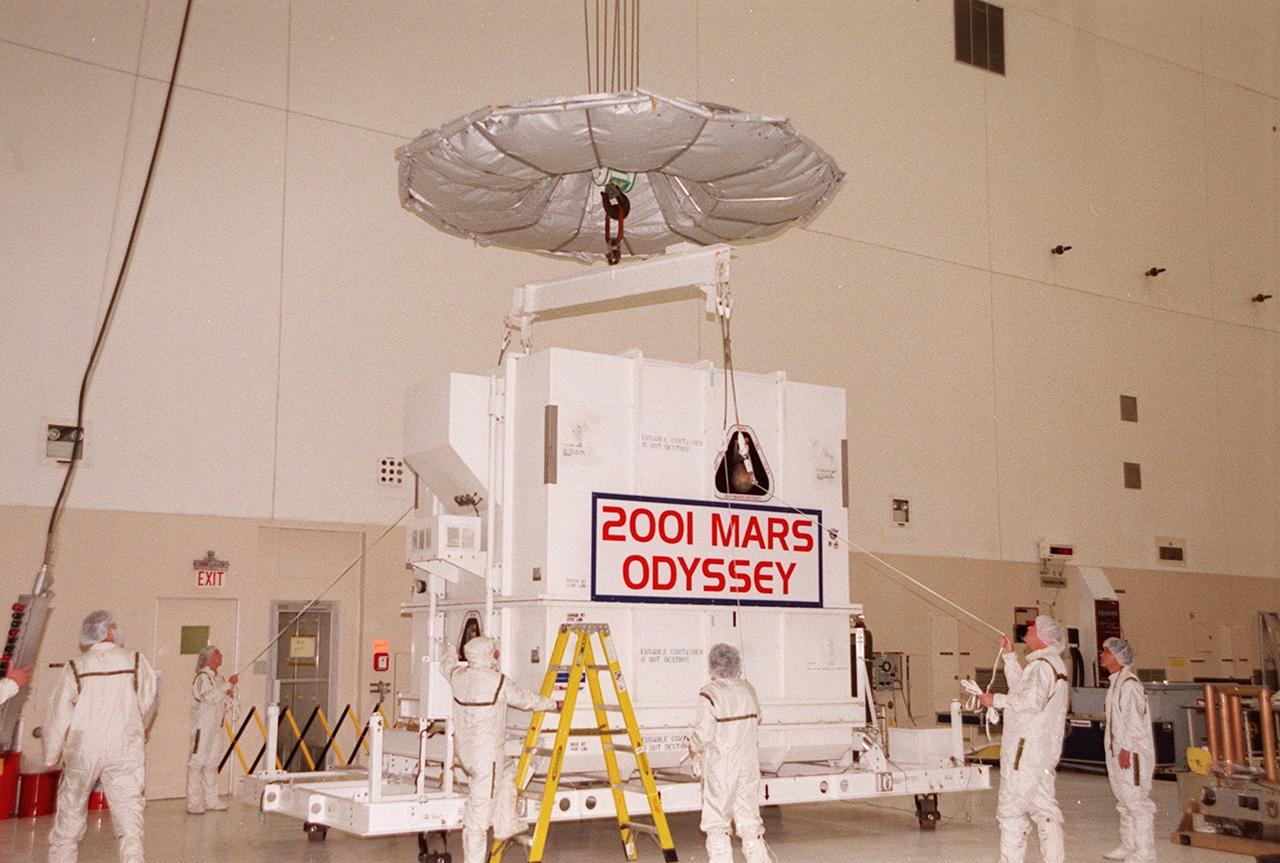

Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2)secure an overhead crane to the crate containing the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. The spacecraft will undergo final assembly and checkout, which includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. Launch aboard a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A, Complex 17, CCAFS, is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet’s surface and measuring its environment
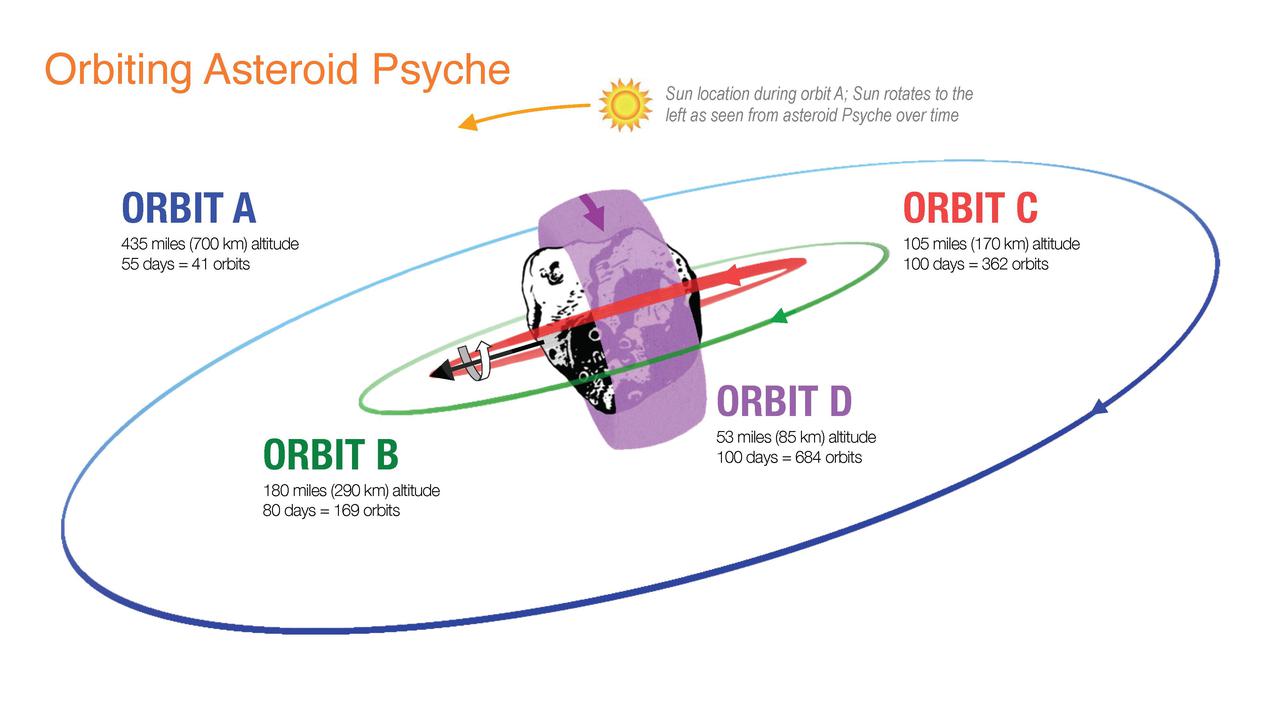
This illustration shows how NASA's Psyche spacecraft will explore the asteroid Psyche, beginning with Orbit A when it arrives at the asteroid in early 2026. The initial orbit is designed to be at a high altitude – about 435 miles (700 kilometers) above the asteroid's surface. Over the following 20 months, the spacecraft will use its electric propulsion system to dip into lower and lower orbits as it conducts its science investigation. Eventually, the spacecraft will establish a final orbit (Orbit D) about 53 miles (85 kilometers) above the surface. Set to launch in August 2022, Psyche will investigate a metal-rich asteroid of the same name, which lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Scientists believe the asteroid could be part or all of the iron-rich interior of an early planetary building block that was stripped of its outer rocky shell as it repeatedly collided with other large bodies during the early formation of the solar system. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24896

In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 , an overhead crane lifts the crate covering the Mars Odyssey spacecraft. The spacecraft, which arrived from Denver, Colo., Jan. 4, will undergo final assembly and checkout. That includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. Launch aboard a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A, Complex 17, CCAFS, is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet’s surface and measuring its environment

Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 move the shipping crate away from the 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft, at left on the stand. Odyssey is still covered by a protective sheet. The spacecraft, which arrived from Denver, Colo., Jan. 4, will undergo final assembly and checkout in the SAEF-2. That includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. Launch aboard a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A, Complex 17, CCAFS, is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet’s surface and measuring its environment
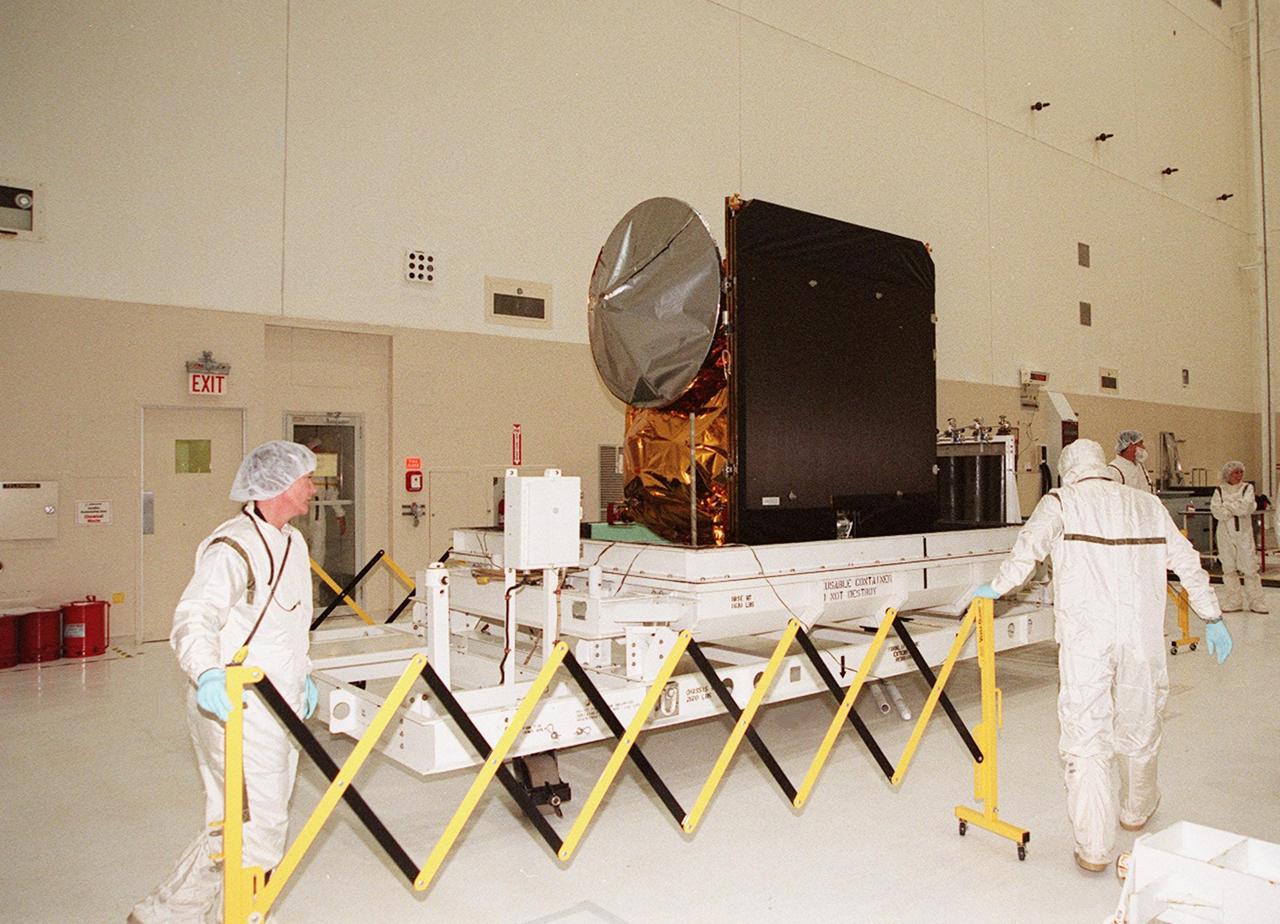

In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2, workers place a protective barrier around the 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft. Odyssey will undergo final assembly and checkout in the SAEf-2, which includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. Odyssey, which arrived from Denver, Colo., Jan. 4, will be launched aboard a Boeing Delta II vehicle from Pad A, Complex 17, CCAFS. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet’s surface and measuring its environment
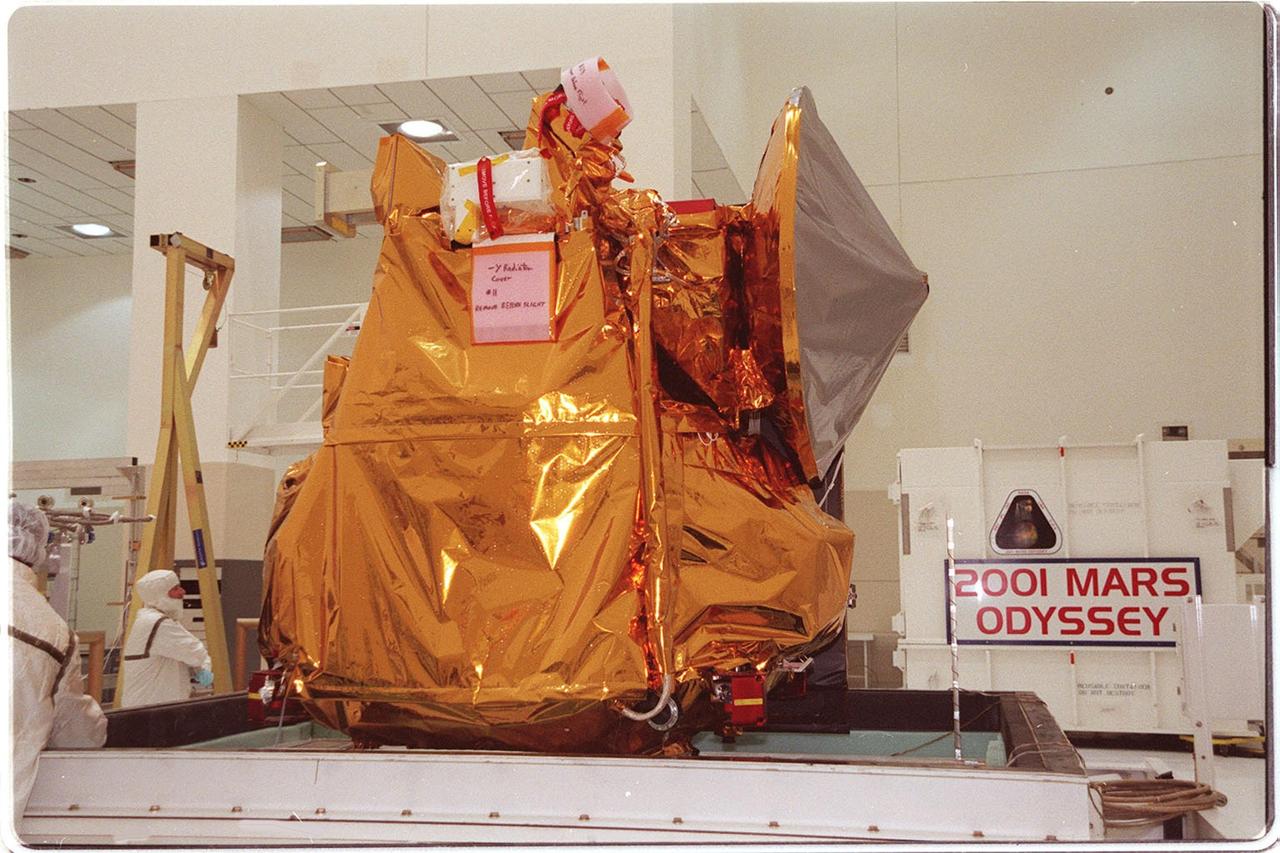
In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2, the 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft sits on a workstand, ready for final assembly and checkout. That includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. Odyssey, which arrived from Denver, Colo., Jan. 4, will be launched aboard a Boeing Delta II vehicle from Pad A, Complex 17, CCAFS. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet’s surface and measuring its environment
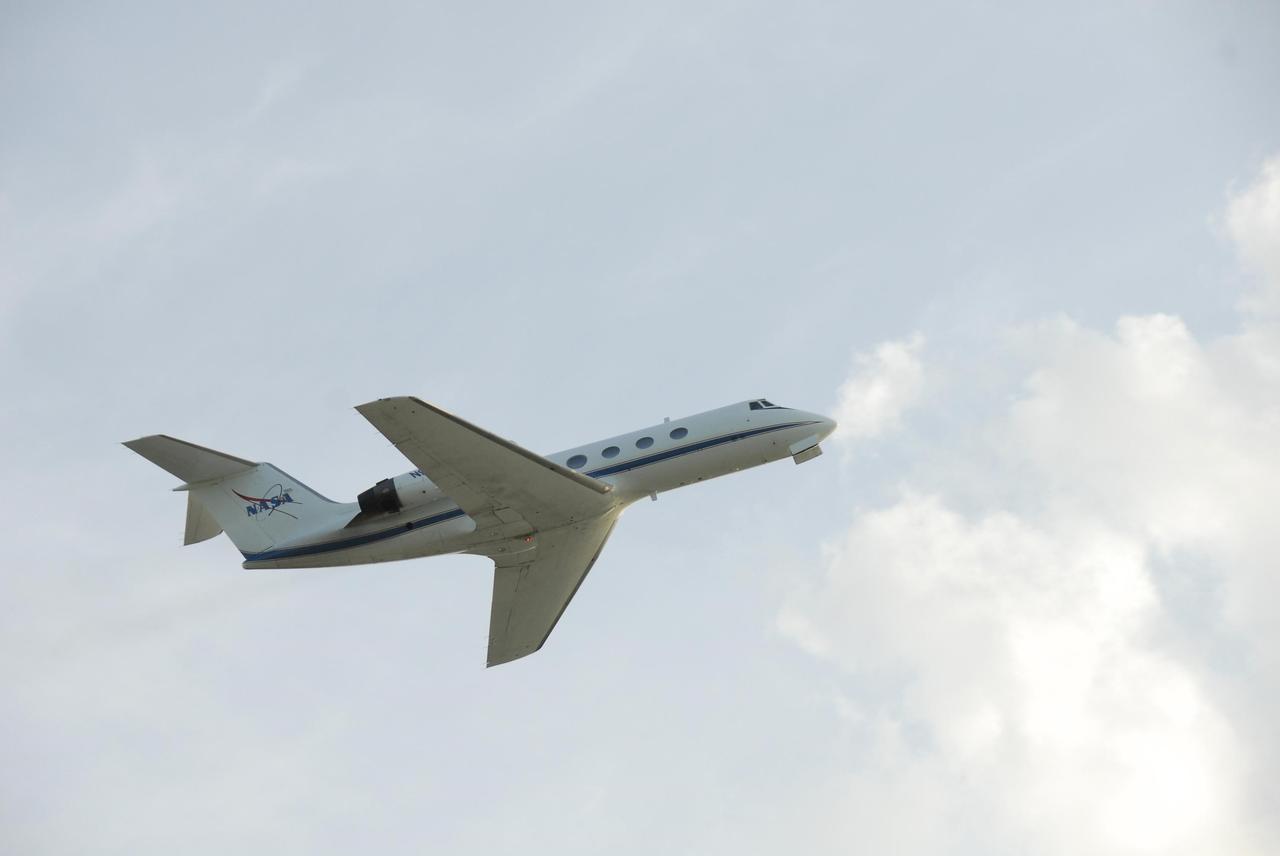

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-117 Commander Frederick Sturckow and Pilot Lee Archambault aim high to begin landing practice in the shuttle training aircraft (STA). The STA is a Grumman American Aviation-built Gulf Stream II jet that was modified to simulate an orbiter's cockpit, motion and visual cues, and handling qualities. In flight, the STA duplicates the orbiter's atmospheric descent trajectory from approximately 35,000 feet altitude to landing on a runway. STS-117 is scheduled to launch at 7:38 p.m. June 8. During the 11-day mission and three spacewalks, the crew will work with flight controllers at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston to install the 17-ton segment on the station's girder-like truss and deploy the set of solar arrays, S3/S4. The mission will increase the space station's power capability in preparation for the arrival of new science modules from the European and Japanese space agencies. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

In the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2, workers remove the protective sheet from around the 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft. Odyssey, which arrived from Denver, Colo., Jan. 4, will undergo final assembly and checkout in the SAEF-2. That includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. Launch aboard a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A, Complex 17, CCAFS, is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet’s surface and measuring its environment

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – On the ramp of Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Pathfinder aircraft waits for its passengers to arrive before takeoff. The Pathfinder will accompany Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft carrying NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket on its flight to the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. The Pathfinder will carry the contingency crew and launch team members. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/CIV USAF/Daniel Liberotti

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – On the runway of Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Pathfinder aircraft taxis down the runway for takeoff. The Pathfinder will accompany Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft carrying NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket on its flight to the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. The Pathfinder will carry the contingency crew and launch team members. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/CIV USAF/Daniel Liberotti
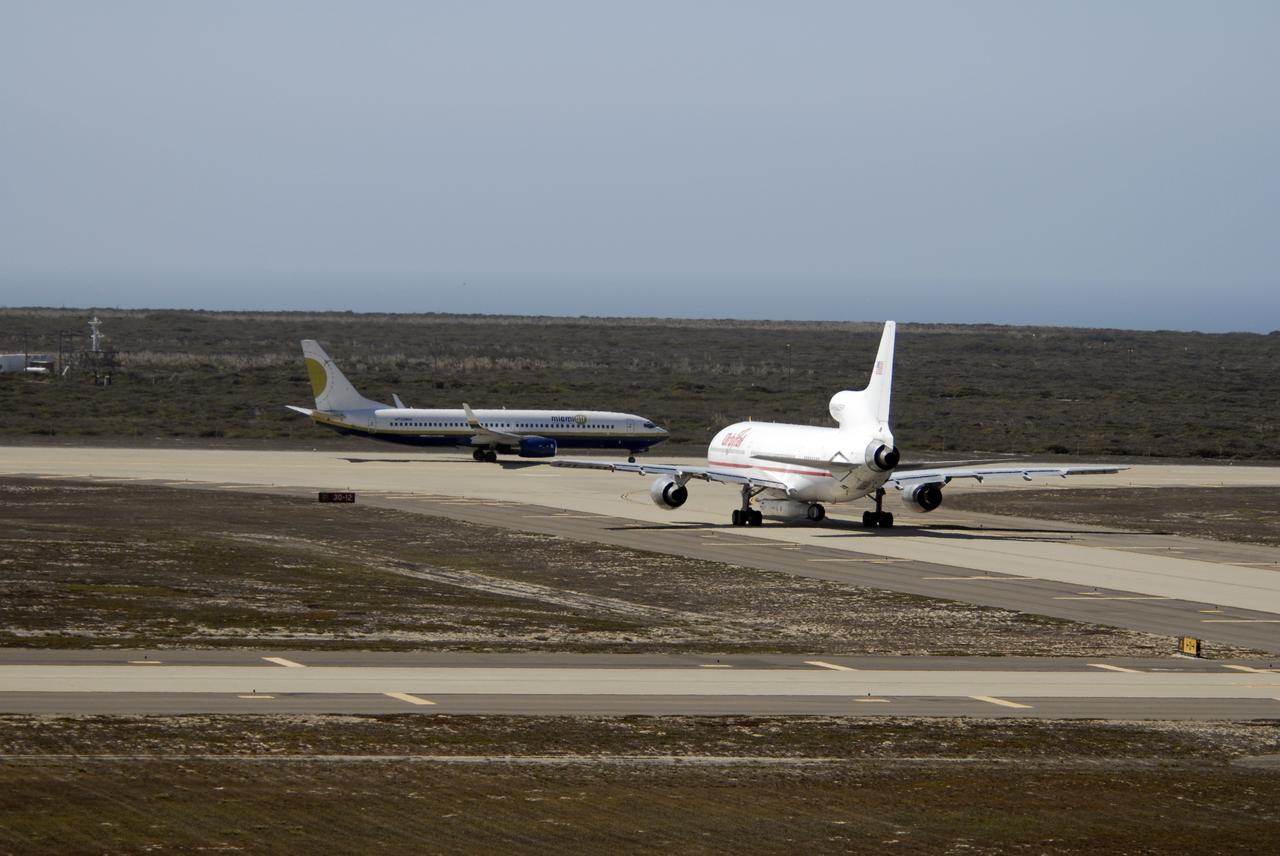

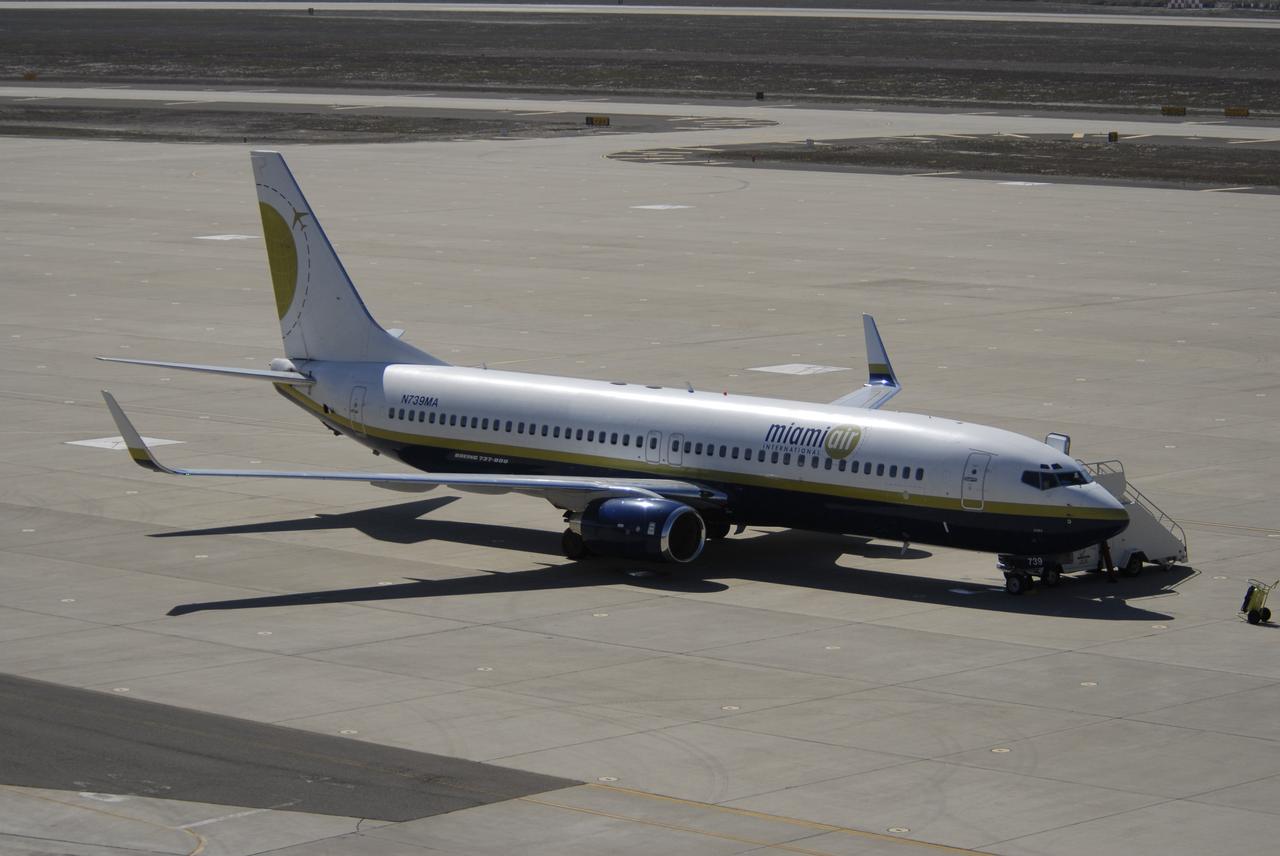
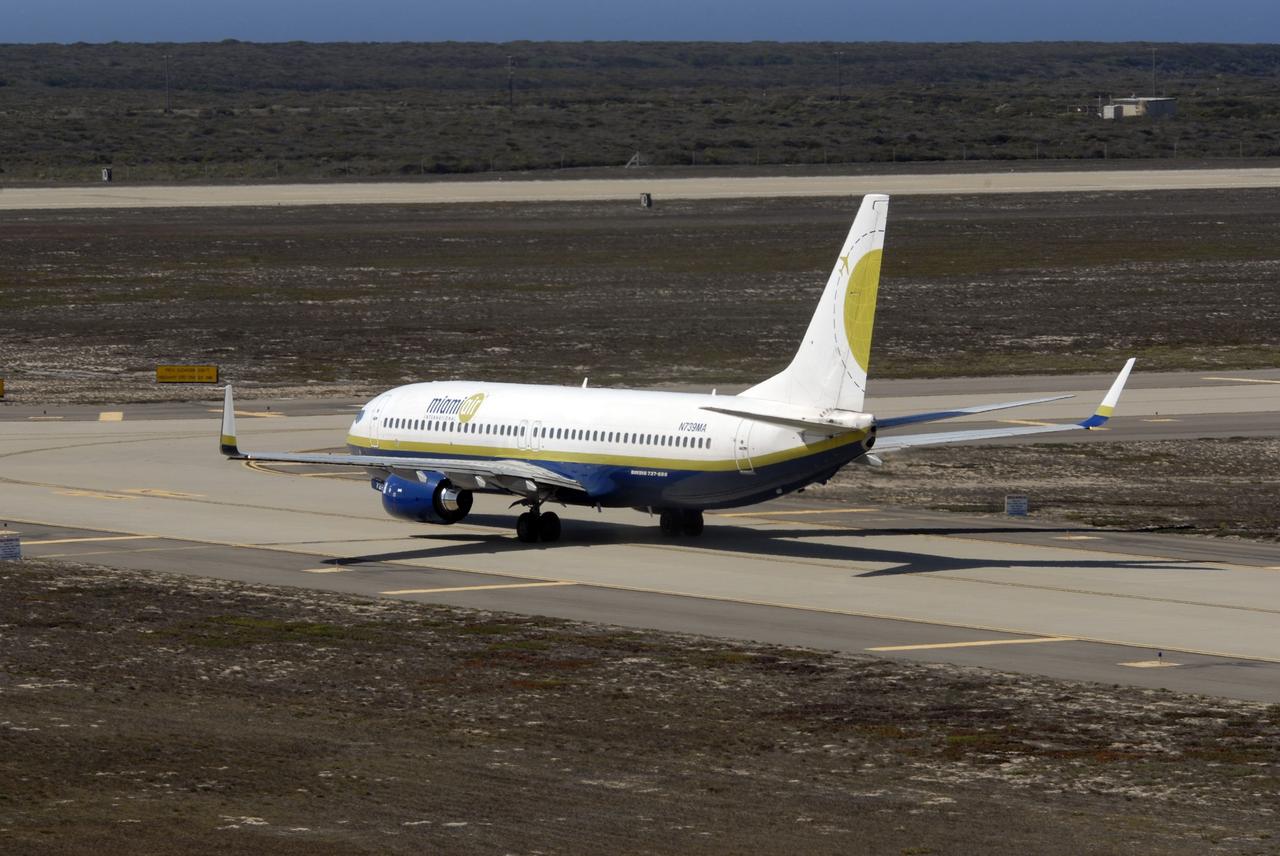
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft (right) taxis on the runway for takeoff from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Under its wing is NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket. At left is the Pathfinder aircraft that will accompany the L-1011, carrying the contingency crew and launch team members. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
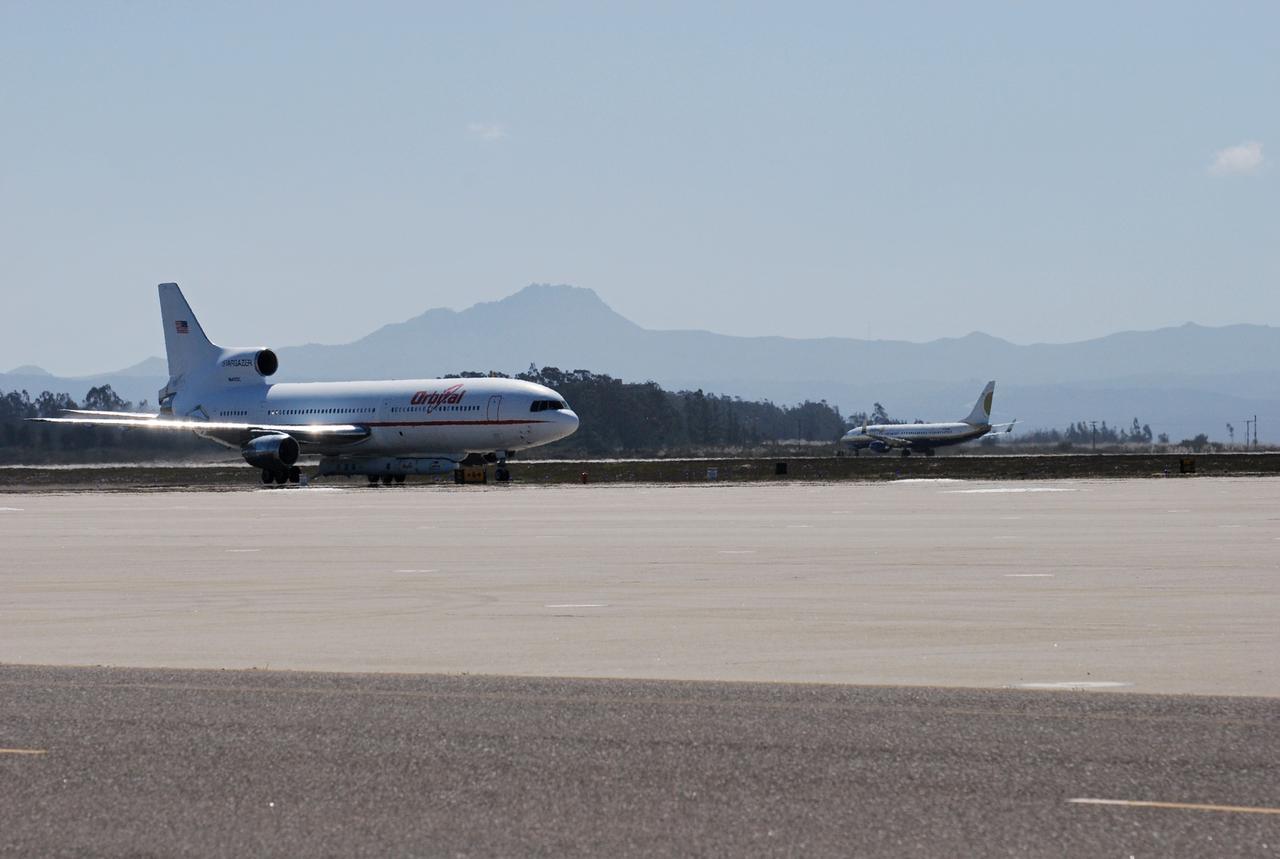

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – On the ramp of Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft awaits departure for the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean, with NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket. The Pegasus is attached under the wing of the aircraft for launch. In the background at right is the Pathfinder aircraft that will accompany the L-1011 with a contingency crew and launch team members. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
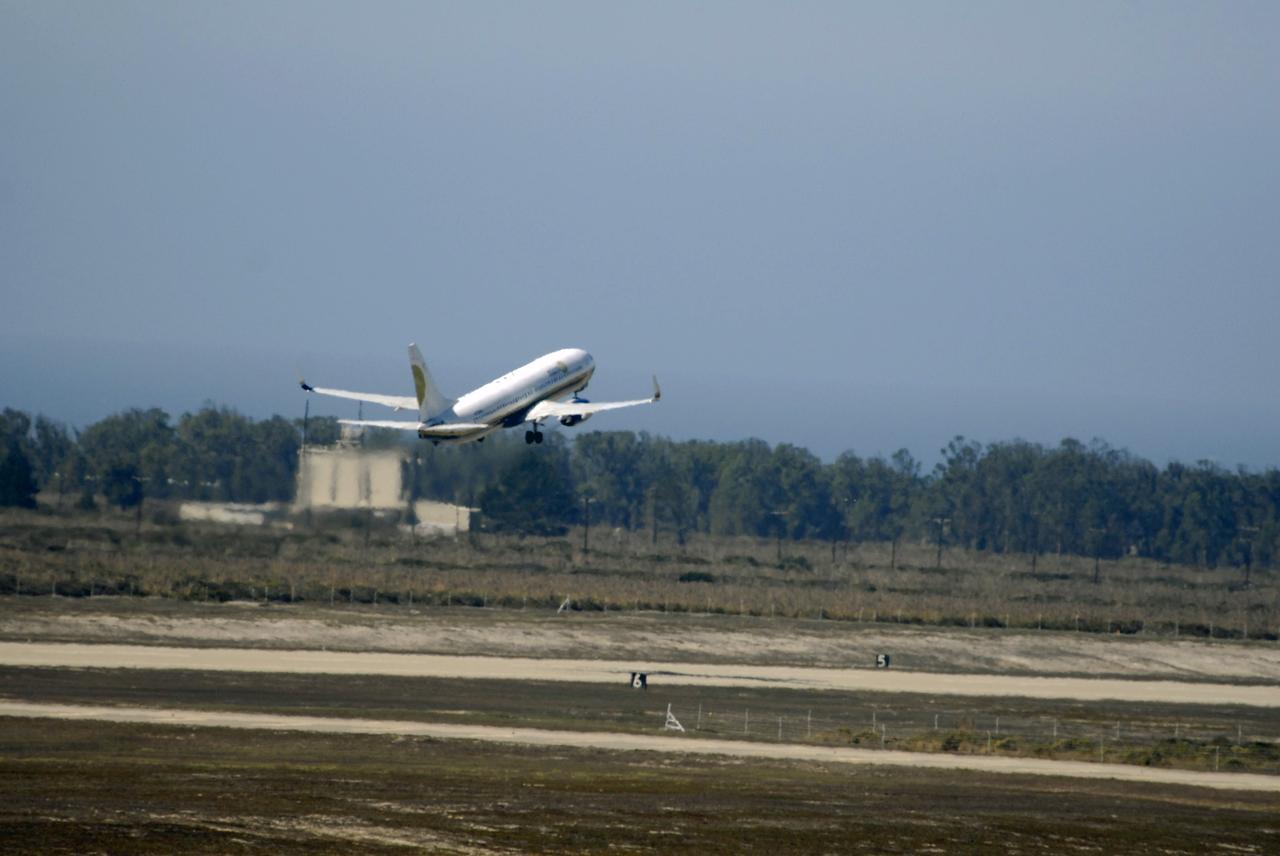

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – From the runway of Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Pathfinder aircraft takes off. The Pathfinder will accompany Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft carrying NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft and Pegasus XL rocket on its flight to the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. The Pathfinder will carry the contingency crew and launch team members. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/CIV USAF/Daniel Liberotti
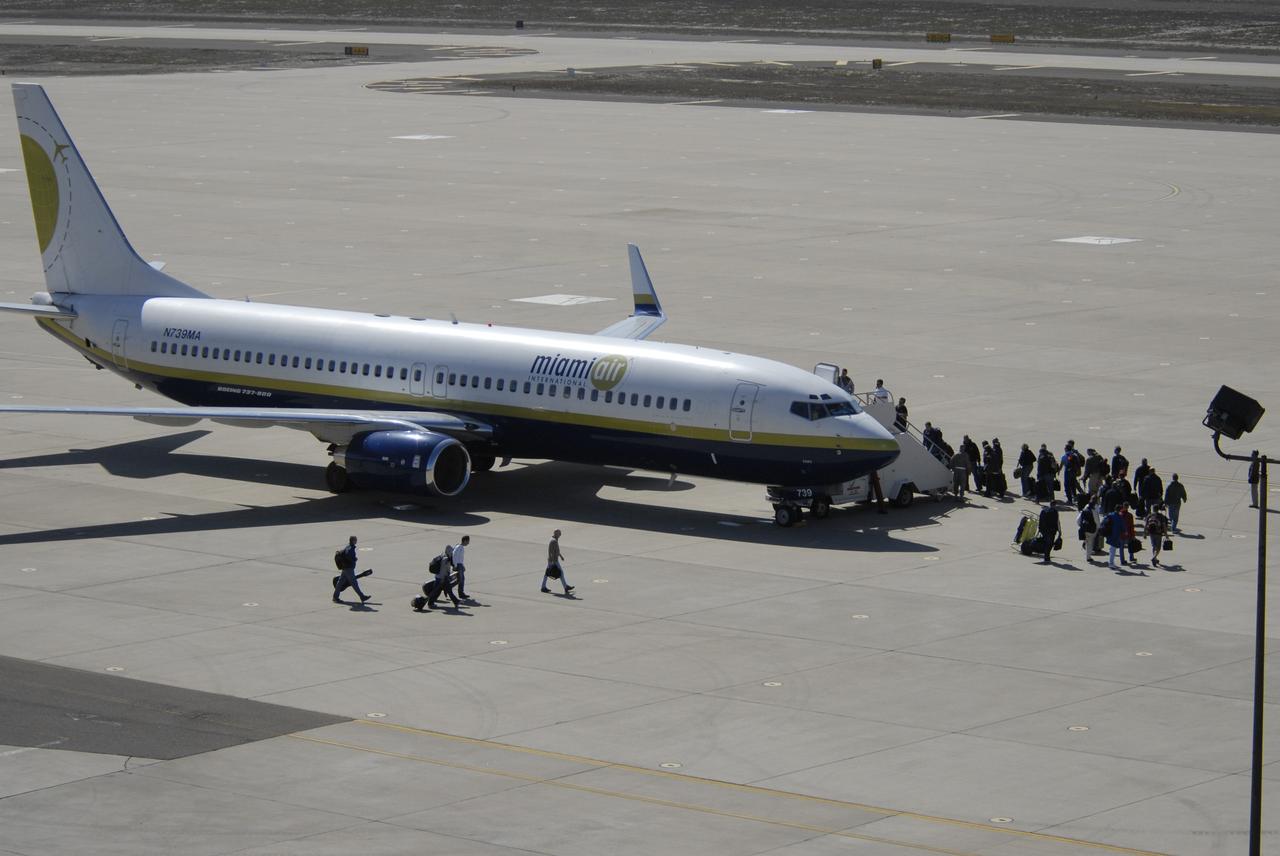

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – On the ramp of Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the contingency crew and launch team members for NASA’s Interstellar Boundary Explorer, or IBEX, spacecraft embark on the Pathfinder aircraft that will accompany Orbital Sciences’ L-1011 aircraft. The L-1011 will carry IBEX and Pegasus XL rocket on its flight to the Kwajalein Atoll, a part of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Departing from Kwajalein, the Pegasus rocket will be dropped from under the wing of the L-1011 over the Pacific Ocean to carry the spacecraft approximately 130 miles above Earth and place it in orbit. Then, the spacecraft’s own engine will boost it to its final high-altitude orbit (about 200,000 miles high) — most of the way to the Moon. The IBEX satellite will make the first map of the boundary between the Solar System and interstellar space. IBEX science will be led by the Southwest Research Institute of San Antonio, Texas. IBEX is targeted for launch over the Pacific Oct. 19. Photo credit: NASA/CIV USAF/Daniel Liberotti
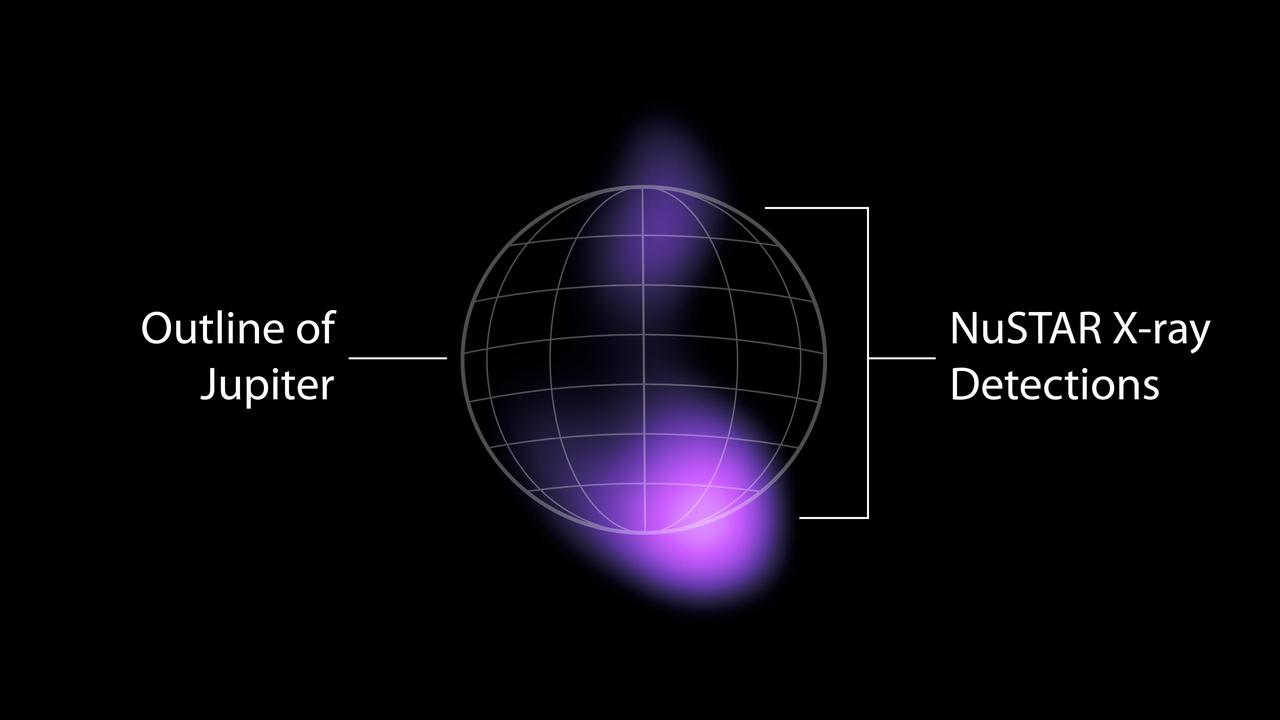
The areas where high-energy X-rays were detected by NASA's NuSTAR (Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array) from the auroras near Jupiter's north and south poles are shown in purple in this graphic. The emissions are the highest-energy light ever seen at Jupiter and the highest-energy light ever detected from a planet in our solar system other than Earth. The light comes from accelerated electrons colliding with the atmosphere. NuSTAR cannot pinpoint the source of the light with high precision, but can only find that it is coming from somewhere in the purple-colored regions. X-rays are a form of light, but with much higher energies and shorter wavelengths than the visible light human eyes can see. NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and the ESA (European Space Agency) XMM-Newton observatory have both studied X-rays from Jupiter's auroras – produced when volcanos on Jupiter's moon Io shower the planet with ions (atoms stripped of their electrons). Jupiter's powerful magnetic field accelerates the particles and funnels them toward the planet's poles, where they collide with its atmosphere and release energy in the form of light, including X-rays. Electrons from Io are also accelerated by the planet's magnetic field, according to observations by the Jovian Auroral Distributions Experiment (JADE) and Jupiter Energetic-particle Detector Instrument (JEDI) on NASA's Juno spacecraft, which arrived at Jupiter in 2016. Researchers suspected that those electrons should produce even higher-energy X-rays than those observed by Chandra and XMM-Newton, and the NuSTAR detections confirm that hypothesis. The high-energy X-rays are relatively faint, and required a week of NuSTAR observations to detect. Scientists have detected X-rays in Earth's auroras with even higher energies than what NuSTAR saw at Jupiter, but those emissions can only be spotted by small satellites or high-altitude balloons that get extremely close to the locations in the atmosphere that generate those X-rays. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25131

A forklift carries the crated Mars Odyssey spacecraft from the Air Force C-17 cargo airplane that brought it from Denver, Colo.., location of the Lockheed Martin plant where the spacecraft was built. The crate will placed on a transport trailer to take it from KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2) located in the KSC Industrial Area. In the SAEF it will undergo final assembly and checkout. This includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. It will be fueled and then mated to an upper stage booster, the final activities before going to the launch pad. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. Mars Odyssey will be inserted into an interplanetary trajectory by a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A at Complex 17 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet's surface and measuring its environment
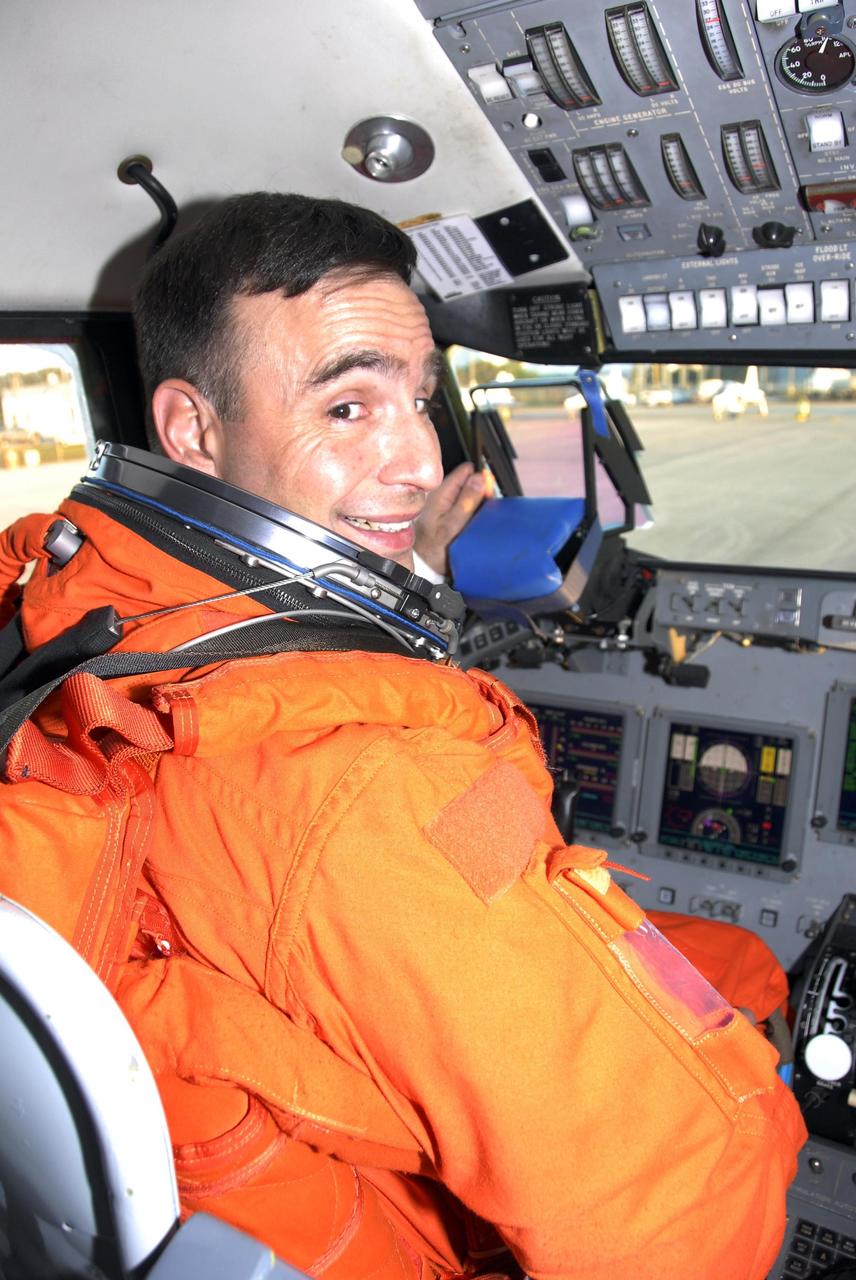

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility, Mission STS-117 Pilot Lee Archambault sits in the cockpit of the shuttle training aircraft (STA) ready to begin practice flights as part of the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The STA is a Grumman American Aviation-built Gulf Stream II jet that was modified to simulate an orbiter's cockpit, motion and visual cues, and handling qualities. In flight, the STA duplicates the orbiter's atmospheric descent trajectory from approximately 35,000 feet altitude to landing on a runway. Because the orbiter is unpowered during re-entry and landing, its high-speed glide must be perfectly executed the first time. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. STS-117 is the 118th space shuttle flight and the 21st flight to the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
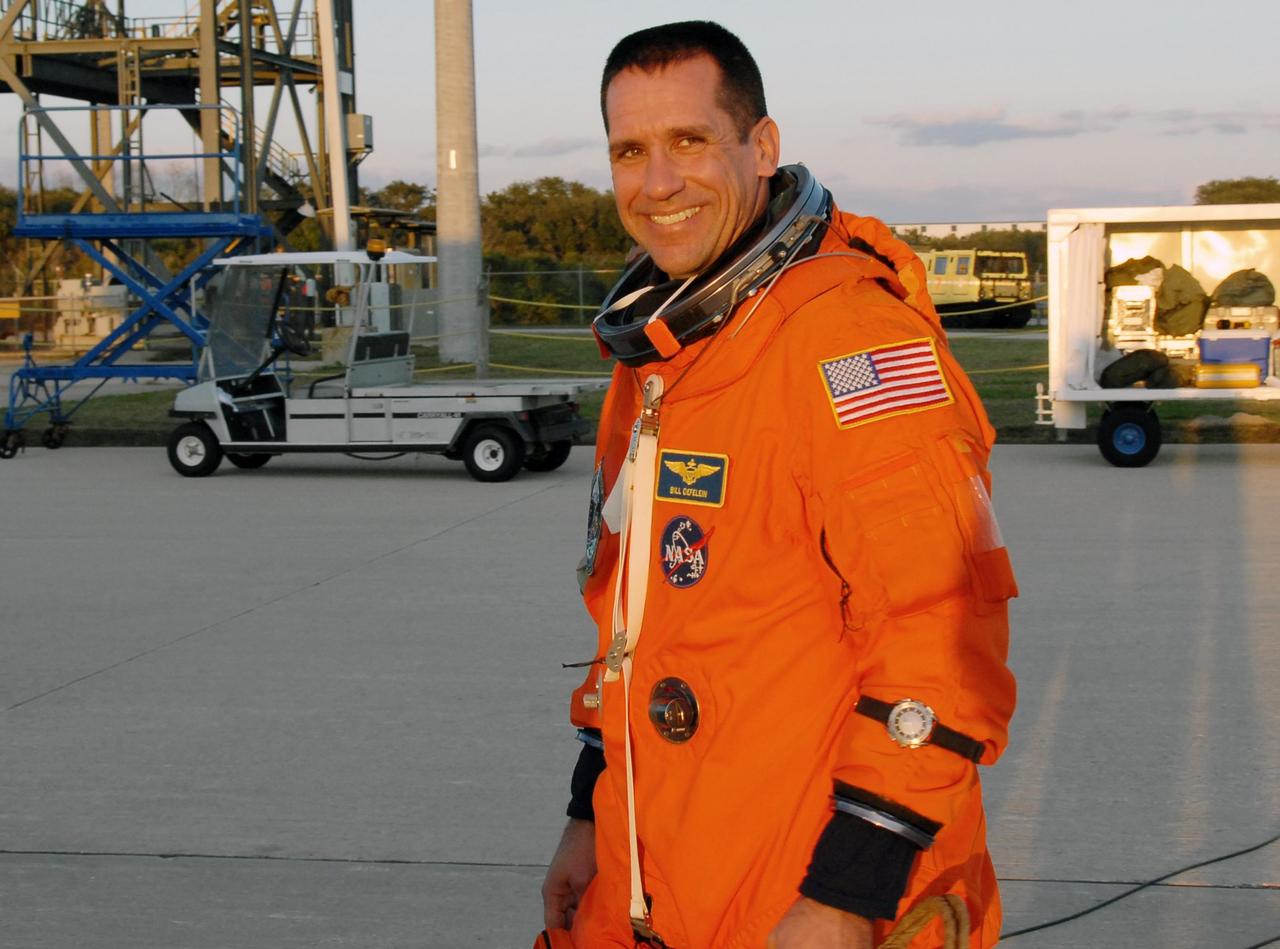

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-116 Pilot William Oefelein is suited and ready to begin practice flights on the shuttle training aircraft (STA) two days before launch. The STA is a Grumman American Aviation-built Gulf Stream II jet that was modified to simulate an orbiter's cockpit, motion and visual cues, and handling qualities. In flight, the STA duplicates the orbiter's atmospheric descent trajectory from approximately 35,000 feet altitude to landing on a runway. Because the orbiter is unpowered during re-entry and landing, its high-speed glide must be perfectly executed the first time. Launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-116 is scheduled for 9:35 p.m. Dec. 7. On the mission, the STS-116 crew will deliver truss segment, P5, to the International Space Station and begin the intricate process of reconfiguring and redistributing the power generated by two pairs of U.S. solar arrays. The P5 will be mated to the P4 truss that was delivered and attached during the STS-115 mission in September. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
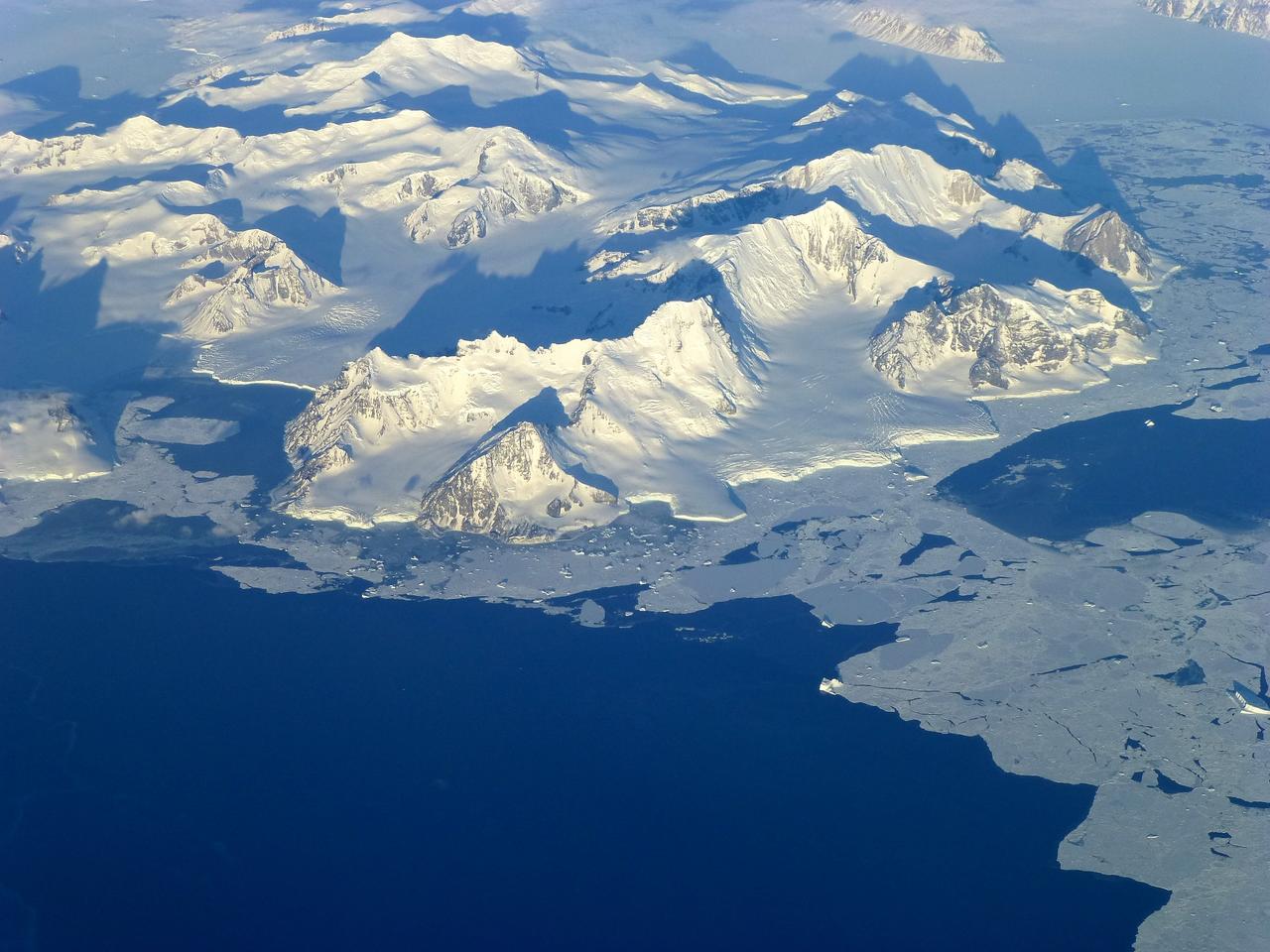

View of the northern Antarctic Peninsula from high altitude during IceBridge's flight back from the Foundation Ice Stream, on Oct. 28. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Maria-Jose Vinas NASA's Operation IceBridge is an airborne science mission to study Earth's polar ice. For more information about IceBridge, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/icebridge" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/icebridge</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
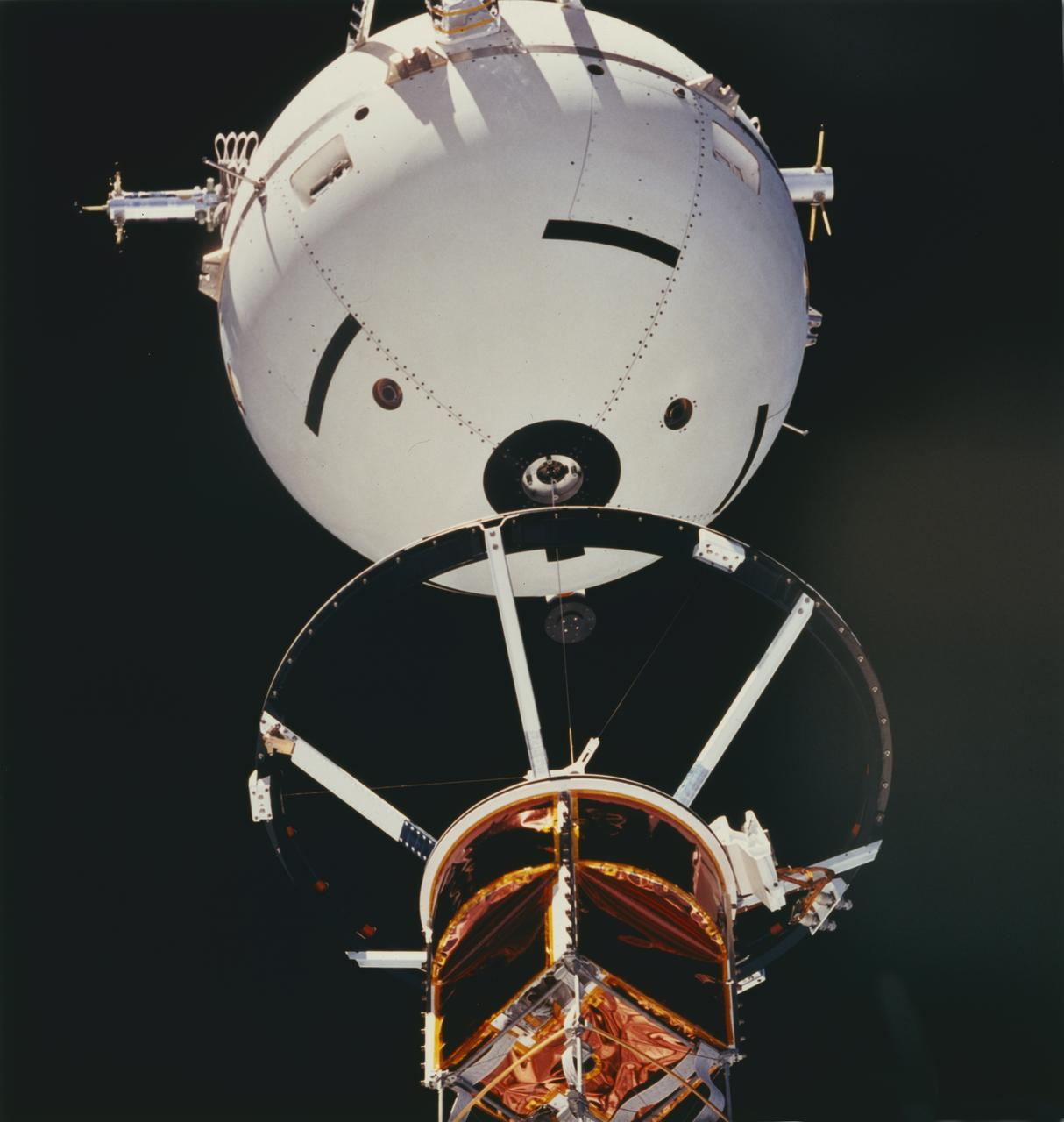

A crewmember aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis (STS-46) used a 70mm handheld camera to capture this medium closeup view of early operations with the Tethered Satellite System (TSS). TSS-1 is being deployed from its boom as it is perched above the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting Shuttle circling the Earth at an altitude of 296 kilometers (184 miles), the TSS-1 will be well within the tenuous, electrically charged layer of the atmosphere known as the ionosphere. There, a satellite attached to the orbiter by a thin conducting cord, or tether, will be reeled from the Shuttle payload bay. On this mission the satellite was plarned to be deployed 20 kilometers (12.5 miles) above the Shuttle. The conducting tether will generate high voltage and electrical currents as it moves through the atmosphere allowing scientists to examine the electrodynamics of a conducting tether system. These studies will not only increase our understanding of physical processes in the near-Earth space environment, but will also help provide an explanation for events witnessed elsewhere in the solar system. The crew of the STS-46 mission were unable to reel the satellite as planned. After several unsuccessful attempts, they were only able to extend the satellite 9.8 kilometers (6.1 miles). The TSS was a cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI), and NASA.

The Mars Odyssey spacecraft is removed from the Air Force C-17 cargo airplane that brought it from Denver, Colo.., location of the Lockheed Martin plant where the spacecraft was built. Mars Odyssey will be moved on a transport trailer from KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2) located in the KSC Industrial Area. In the SAEF it will undergo final assembly and checkout. This includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. It will be fueled and then mated to an upper stage booster, the final activities before going to the launch pad. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. Mars Odyssey will be inserted into an interplanetary trajectory by a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A at Complex 17 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet's surface and measuring its environment
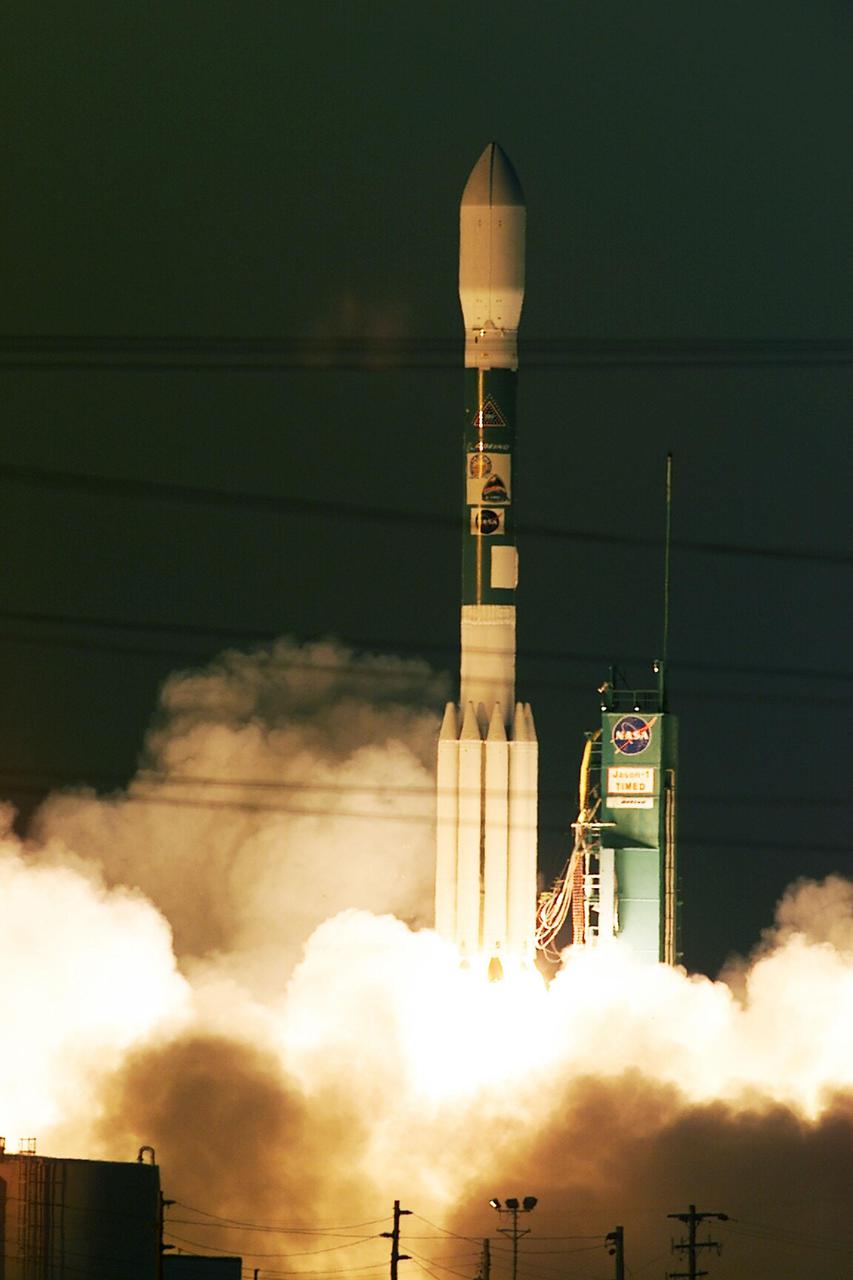

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A Delta II rocket launches successfully with the joint NASA_French Space Agency oceanography satellite Jason 1 and Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics satellite aboard. Liftoff from Launch Complex 2W occurred at 7:07 a.m. PST (10:07 a.m. EST or 15:07 GMT). Jason 1 joins the orbiting Topex_Poseidon satellite to continue observations of the global climate interaction occurring between the sea and the atmosphere as a result of stored solar energy. Instruments on Jason 1 will map variations in ocean surface topography to monitor world ocean circulation, study interactions of the oceans and atmosphere, improve climate predictions and observe events like El Nino. The mission is expected to last three years. The TIMED satellite will study a little-known region above the atmosphere, some 40 to 110 miles from the Earth's surface. Studying this region has been nearly impossible until now because conventional airplanes and balloons cannot reach this high altitude, and it is too low for direct satellite measurements
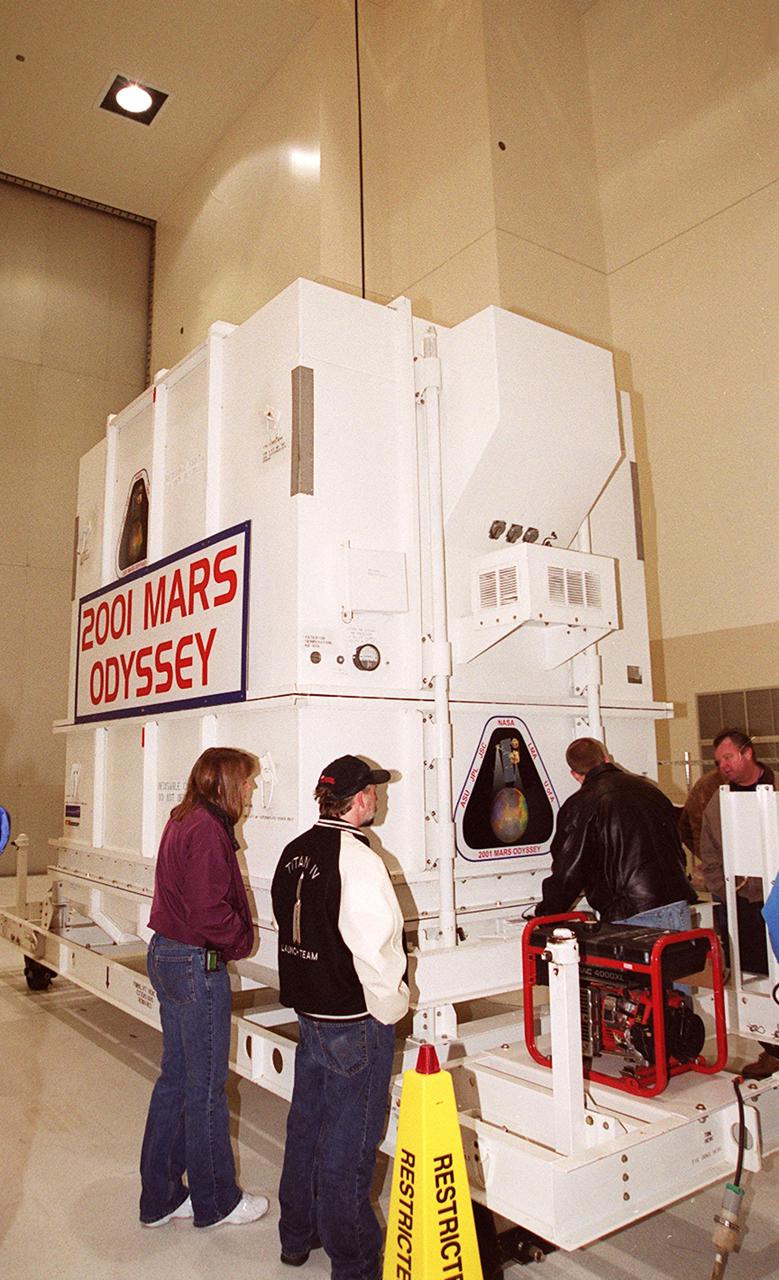

The crated 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft rests safely inside the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2) located in the KSC Industrial Area. The spacecraft arrived at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility aboard an Air Force C-17 cargo airplane that brought it from Denver, Colo.., location of the Lockheed Martin plant where the spacecraft was built. In the SAEF, Odyssey will undergo final assembly and checkout. This includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. It will be fueled and then mated to an upper stage booster, the final activities before going to the launch pad. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. Mars Odyssey will be inserted into an interplanetary trajectory by a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A at Complex 17 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet's surface and measuring its environment

The 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft arrives at the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2) located in the KSC Industrial Area. The spacecraft arrived at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility aboard an Air Force C-17 cargo airplane that brought it from Denver, Colo.., location of the Lockheed Martin plant where the spacecraft was built. In the SAEF, Odyssey will undergo final assembly and checkout. This includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. It will be fueled and then mated to an upper stage booster, the final activities before going to the launch pad. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. Mars Odyssey will be inserted into an interplanetary trajectory by a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A at Complex 17 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet's surface and measuring its environment
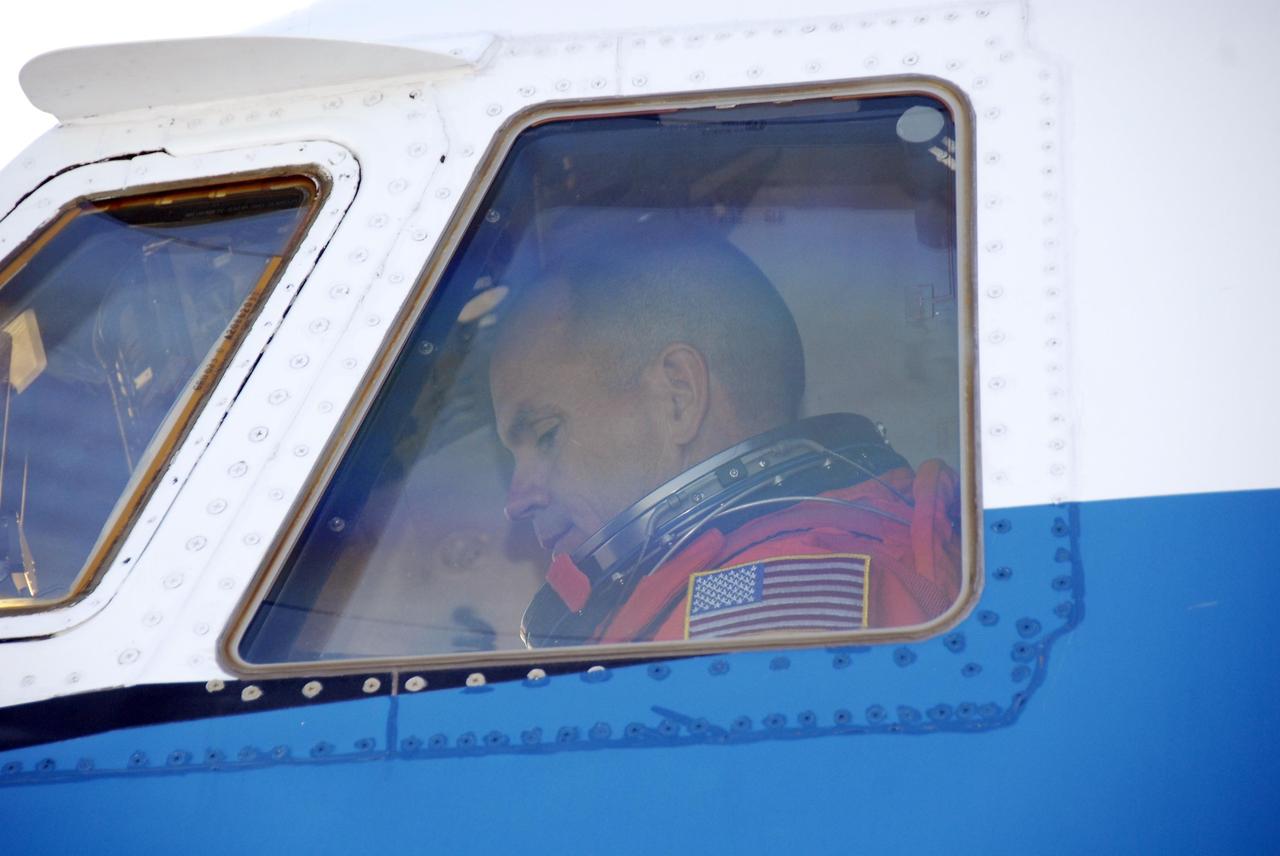

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility, Mission STS-117 Commander Rick Sturckow sits in the cockpit of the shuttle training aircraft (STA) ready to begin practice flights as part of the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The STA is a Grumman American Aviation-built Gulf Stream II jet that was modified to simulate an orbiter's cockpit, motion and visual cues, and handling qualities. In flight, the STA duplicates the orbiter's atmospheric descent trajectory from approximately 35,000 feet altitude to landing on a runway. Because the orbiter is unpowered during re-entry and landing, its high-speed glide must be perfectly executed the first time. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. STS-117 is the 118th space shuttle flight and the 21st flight to the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
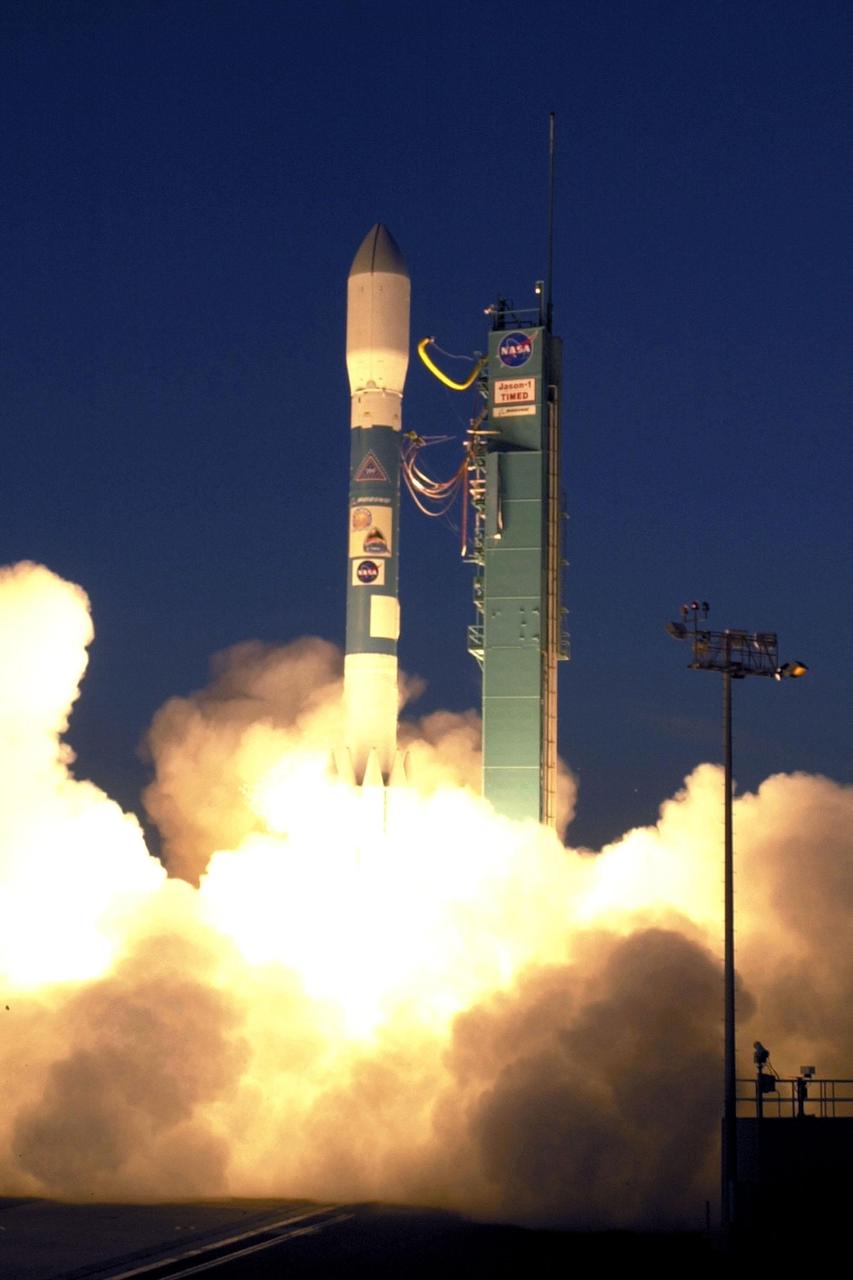

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif.. -- A Delta rocket leaps off Launch Complex 2W carrying the joint NASA/French Space Agency oceanography satellite Jason 1 and Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics satellite aboard. Liftoff occurred at 7:07 a.m. PST (10:07 a.m. EST or 15:07 GMT). Jason 1 joins the orbiting Topex/Poseidon satellite to continue observations of the global climate interaction occurring between the sea and the atmosphere as a result of stored solar energy. Instruments on Jason 1 will map variations in ocean surface topography to monitor world ocean circulation, study interactions of the oceans and atmosphere, improve climate predictions and observe events like El Nino. The mission is expected to last three years. The TIMED satellite will study a little-known region above the atmosphere, some 40 to 110 miles from the Earth's surface. Studying this region has been nearly impossible until now because conventional airplanes and balloons cannot reach this high altitude, and it is too low for direct satellite measurements

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif.. -- A Delta rocket leaps off Launch Complex 2W carrying the joint NASA_French Space Agency oceanography satellite Jason 1 and Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics satellite aboard. Liftoff occurred at 7:07 a.m. PST (10:07 a.m. EST or 15:07 GMT). Jason 1 joins the orbiting Topex_Poseidon satellite to continue observations of the global climate interaction occurring between the sea and the atmosphere as a result of stored solar energy. Instruments on Jason 1 will map variations in ocean surface topography to monitor world ocean circulation, study interactions of the oceans and atmosphere, improve climate predictions and observe events like El Nino. The mission is expected to last three years. The TIMED satellite will study a little-known region above the atmosphere, some 40 to 110 miles from the Earth's surface. Studying this region has been nearly impossible until now because conventional airplanes and balloons cannot reach this high altitude, and it is too low for direct satellite measurements

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With the sun just peaking above the horizon, the shuttle training aircraft (STA) sits on the tarmac at the Shuttle Landing Facility, ready for practice flights by Mission STS-117 Commander Rick Sturckow and Pilot Lee Archambault. The STA is a Grumman American Aviation-built Gulf Stream II jet that was modified to simulate an orbiter's cockpit, motion and visual cues, and handling qualities. In flight, the STA duplicates the orbiter's atmospheric descent trajectory from approximately 35,000 feet altitude to landing on a runway. Because the orbiter is unpowered during re-entry and landing, its high-speed glide must be perfectly executed the first time. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. STS-117 is the 118th space shuttle flight and the 21st flight to the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
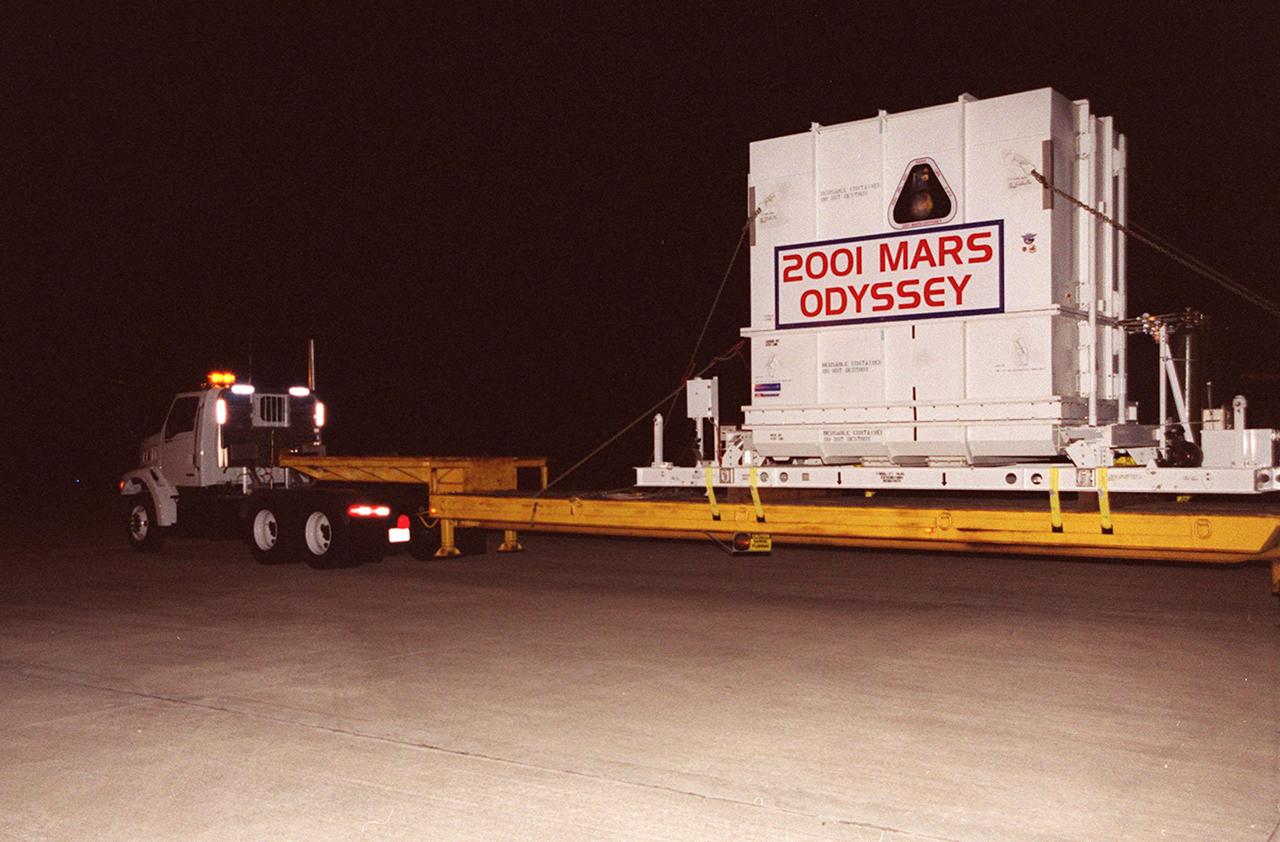

The 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft leaves the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility on the bed of a transport trailer. The spacecraft is being moved to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2) located in the KSC Industrial Area. The spacecraft arrived at the SLF aboard an Air Force C-17 cargo airplane that brought it from Denver, Colo.., location of the Lockheed Martin plant where the spacecraft was built. In the SAEF, Odyssey will undergo final assembly and checkout. This includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. It will be fueled and then mated to an upper stage booster, the final activities before going to the launch pad. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. Mars Odyssey will be inserted into an interplanetary trajectory by a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A at Complex 17 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet's surface and measuring its environment
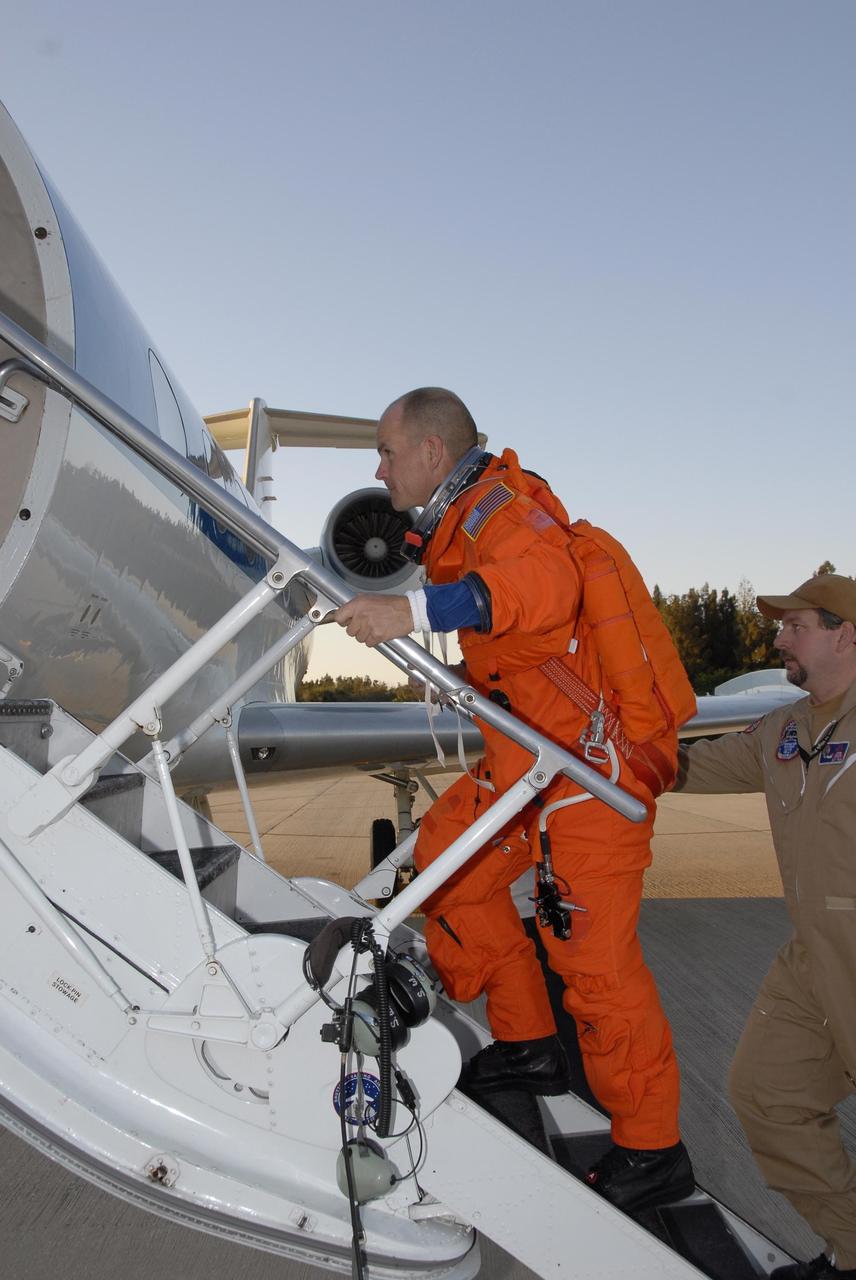

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Shuttle Landing Facility, Mission STS-117 Commander Rick Sturckow is ready to begin practice flights on the shuttle training aircraft (STA) during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) Activities. The STA is a Grumman American Aviation-built Gulf Stream II jet that was modified to simulate an orbiter's cockpit, motion and visual cues, and handling qualities. In flight, the STA duplicates the orbiter's atmospheric descent trajectory from approximately 35,000 feet altitude to landing on a runway. Because the orbiter is unpowered during re-entry and landing, its high-speed glide must be perfectly executed the first time. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. STS-117 is the 118th space shuttle flight and the 21st flight to the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
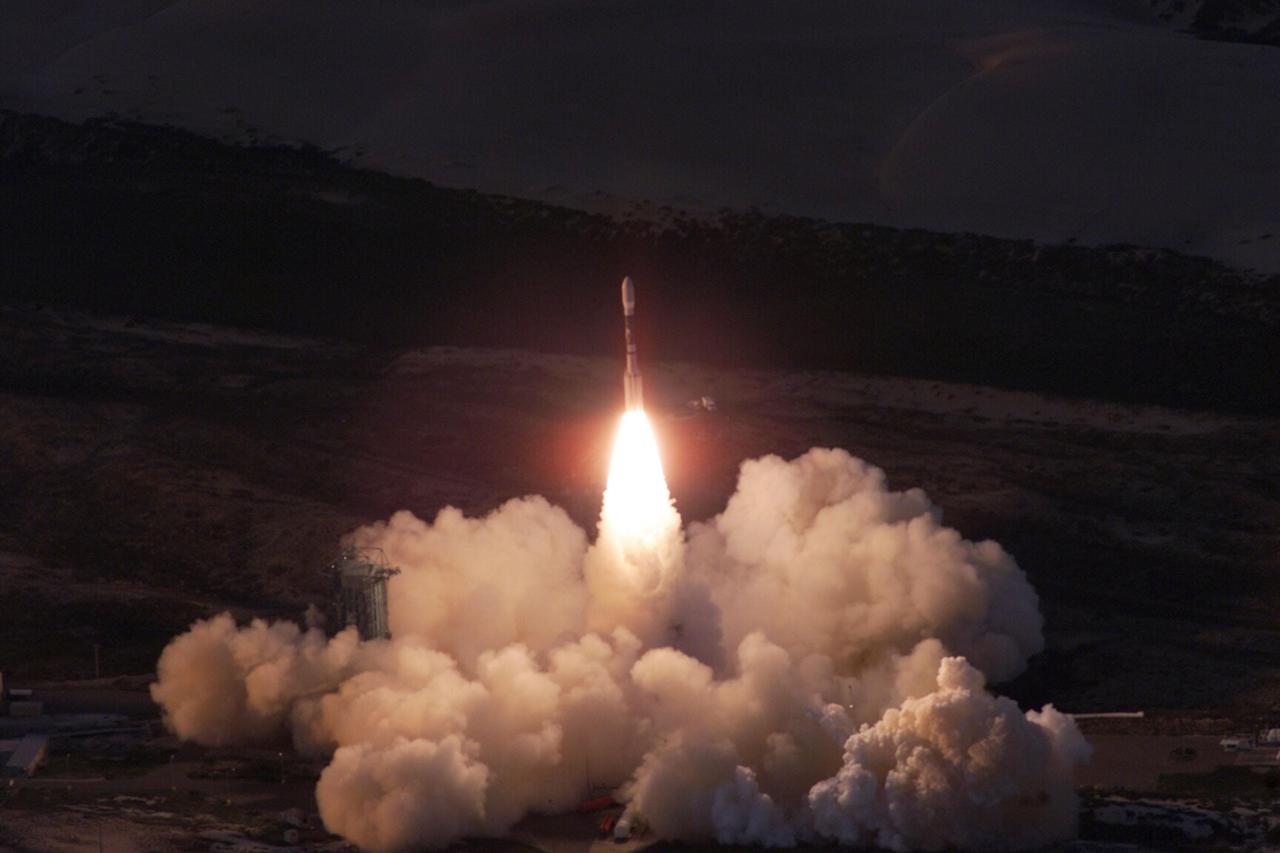

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A Delta II rocket appears to erupt from the undulating clouds of smoke below as it launches with the joint NASA/French Space Agency oceanography satellite Jason 1 and Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics satellite aboard. Liftoff from Launch Complex 2W occurred at 7:07 a.m. PST (10:07 a.m. EST or 15:07 GMT). Jason 1 joins the orbiting Topex/Poseidon satellite to continue observations of the global climate interaction occurring between the sea and the atmosphere as a result of stored solar energy. Instruments on Jason 1 will map variations in ocean surface topography to monitor world ocean circulation, study interactions of the oceans and atmosphere, improve climate predictions and observe events like El Nino. The mission is expected to last three years. The TIMED satellite will study a little-known region above the atmosphere, some 40 to 110 miles from the Earth's surface. Studying this region has been nearly impossible until now because conventional airplanes and balloons cannot reach this high altitude, and it is too low for direct satellite measurements
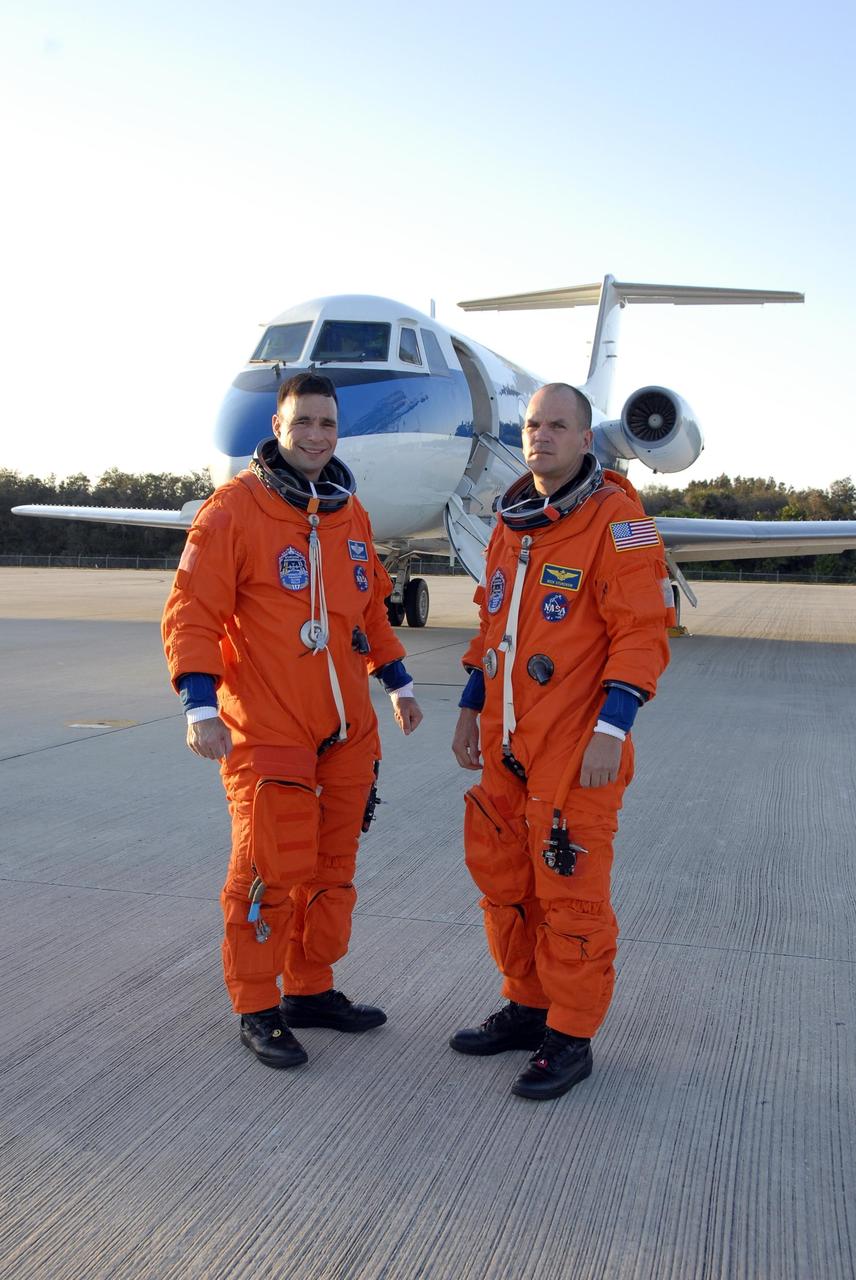

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Mission STS-117 Commander Rick Sturckow (left) and Pilot Lee Archambault, dressed in their launch suits, arrive at the Shuttle Landing Facility to begin practice flights on the shuttle training aircraft (STA) during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The STA is a Grumman American Aviation-built Gulf Stream II jet that was modified to simulate an orbiter's cockpit, motion and visual cues, and handling qualities. In flight, the STA duplicates the orbiter's atmospheric descent trajectory from approximately 35,000 feet altitude to landing on a runway. Because the orbiter is unpowered during re-entry and landing, its high-speed glide must be perfectly executed the first time. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. STS-117 is the 118th space shuttle flight and the 21st flight to the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
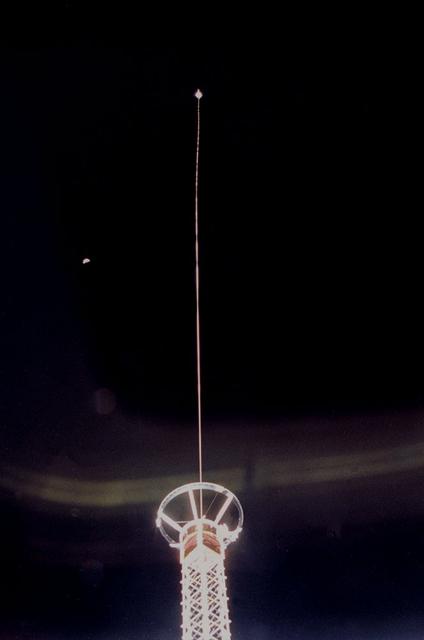

This STS-46 onboard photo is of the Tethered Satellite System-1 (TSS-1) being deployed from its boom as it is perched above the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Atlantis. Circling the Earth at an altitude of 296 kilometers (184 miles), the TSS-1 will be well within the tenuous, electrically charged layer of the atmosphere known as the ionosphere. There, a satellite attached to the orbiter by a thin conducting cord, or tether, will be reeled from the Shuttle payload bay. On this mission the satellite was plarned to be deployed 20 kilometers (12.5 miles) above the Shuttle. The conducting tether will generate high voltage and electrical currents as it moves through the atmosphere allowing scientists to examine the electrodynamics of a conducting tether system. These studies will not only increase our understanding of physical processes in the near-Earth space environment, but will also help provide an explanation for events witnessed elsewhere in the solar system. The crew of the STS-46 mission were unable to reel the satellite as planned. After several unsuccessful attempts, they were only able to extend the satellite 9.8 kilometers (6.1 miles). The TSS was a cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI), and NASA.
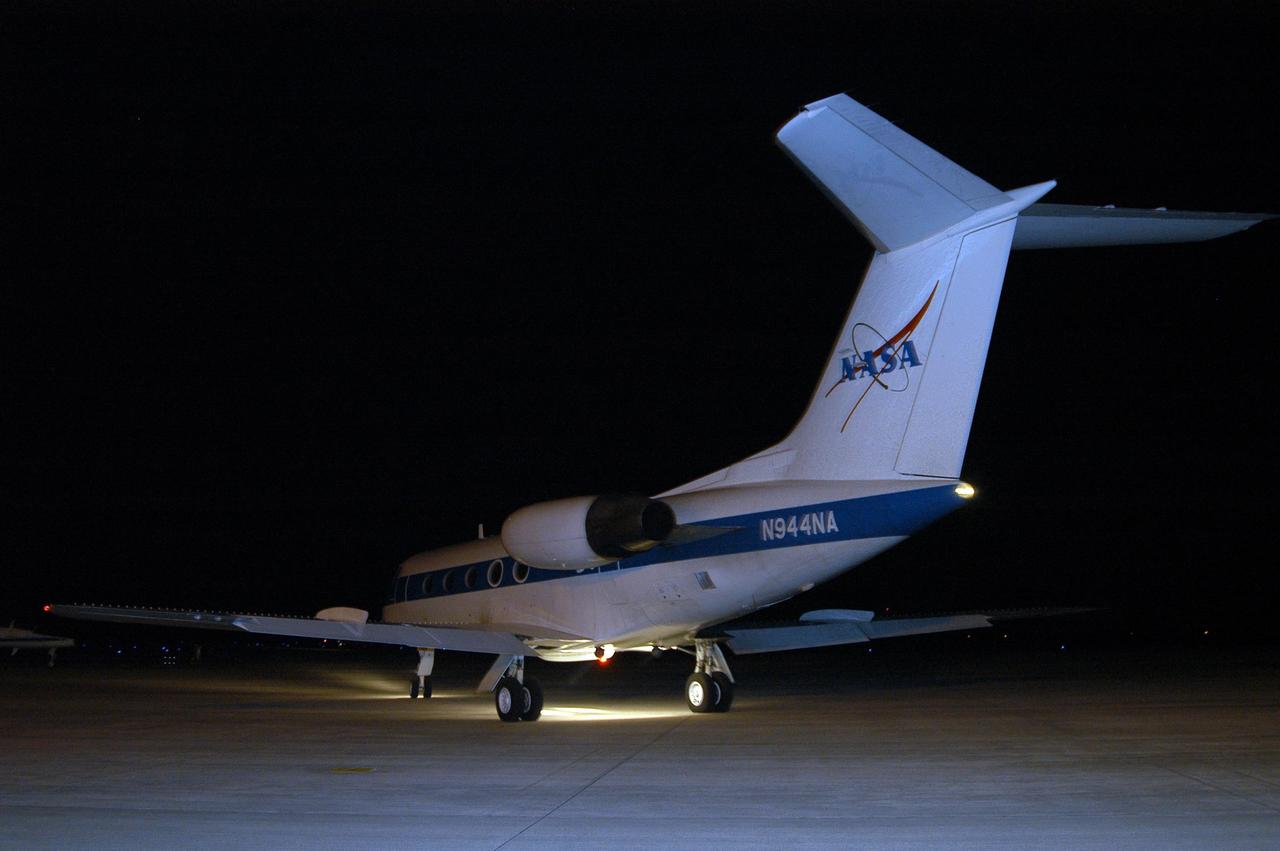

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The shuttle training aircraft (STA), with STS-116 Commander Mark Polansky in the pilot's seat, taxis to the runway of the Shuttle Landing Facility. Polansky will be practicing landing the orbiter. The STA is a Grumman American Aviation-built Gulf Stream II jet that was modified to simulate an orbiter's cockpit, motion and visual cues, and handling qualities. In flight, the STA duplicates the orbiter's atmospheric descent trajectory from approximately 35,000 feet altitude to landing on a runway. Because the orbiter is unpowered during re-entry and landing, its high-speed glide must be perfectly executed the first time. Launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-116 is scheduled for 9:35 p.m. Dec. 7. On the mission, the STS-116 crew will deliver truss segment, P5, to the International Space Station and begin the intricate process of reconfiguring and redistributing the power generated by two pairs of U.S. solar arrays. The P5 will be mated to the P4 truss that was delivered and attached during the STS-115 mission in September. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
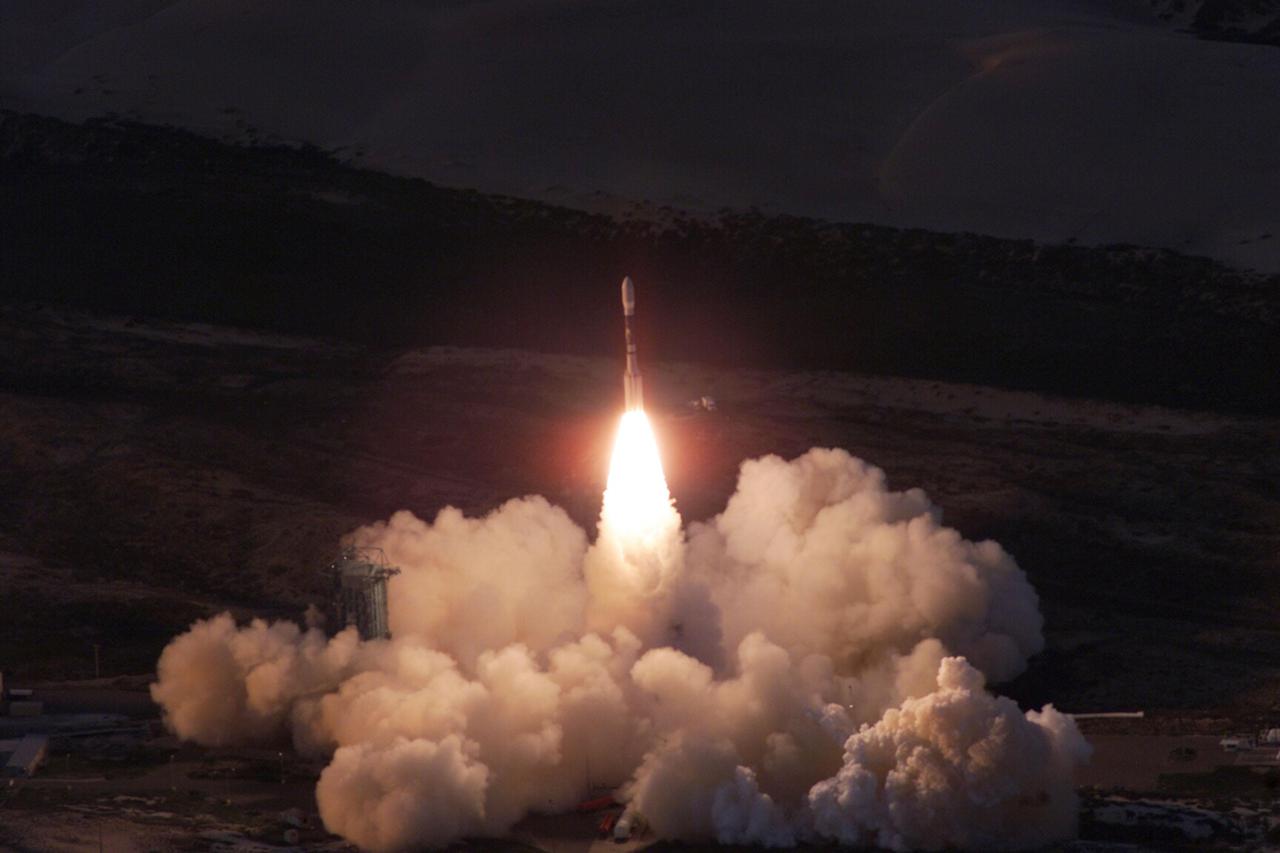

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A Delta II rocket appears to erupt from the undulating clouds of smoke below as it launches with the joint NASA_French Space Agency oceanography satellite Jason 1 and Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics satellite aboard. Liftoff from Launch Complex 2W occurred at 7:07 a.m. PST (10:07 a.m. EST or 15:07 GMT). Jason 1 joins the orbiting Topex_Poseidon satellite to continue observations of the global climate interaction occurring between the sea and the atmosphere as a result of stored solar energy. Instruments on Jason 1 will map variations in ocean surface topography to monitor world ocean circulation, study interactions of the oceans and atmosphere, improve climate predictions and observe events like El Nino. The mission is expected to last three years. The TIMED satellite will study a little-known region above the atmosphere, some 40 to 110 miles from the Earth's surface. Studying this region has been nearly impossible until now because conventional airplanes and balloons cannot reach this high altitude, and it is too low for direct satellite measurements
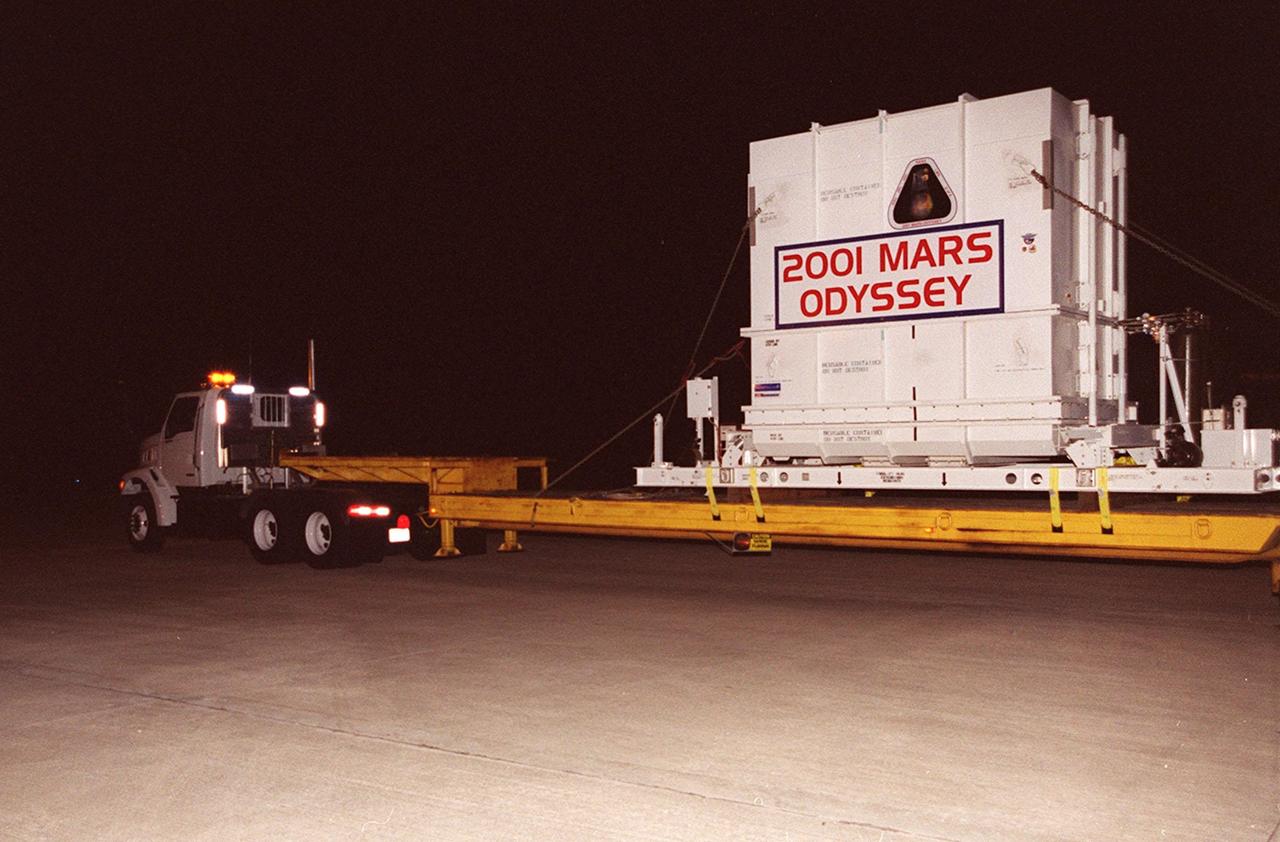

The 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft leaves the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility on the bed of a transport trailer. The spacecraft is being moved to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2) located in the KSC Industrial Area. The spacecraft arrived at the SLF aboard an Air Force C-17 cargo airplane that brought it from Denver, Colo.., location of the Lockheed Martin plant where the spacecraft was built. In the SAEF, Odyssey will undergo final assembly and checkout. This includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. It will be fueled and then mated to an upper stage booster, the final activities before going to the launch pad. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. Mars Odyssey will be inserted into an interplanetary trajectory by a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A at Complex 17 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet's surface and measuring its environment