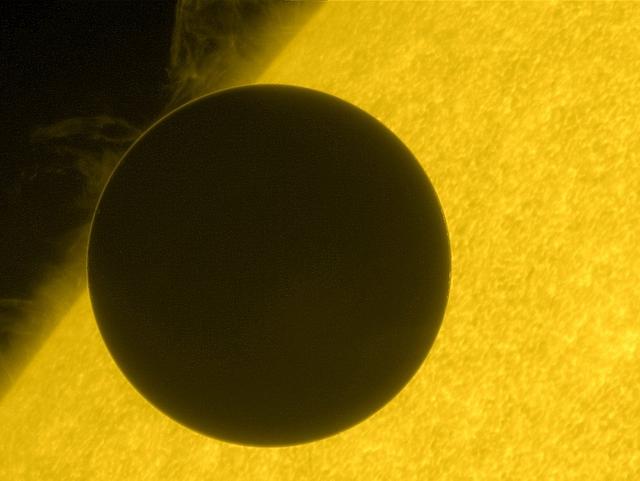

On June 5, 2012, Hinode captured this stunning view of the transit of Venus -- the last instance of this rare phenomenon until 2117. Hinode is a joint JAXA/NASA mission to study the connections of the sun's surface magnetism, primarily in and around sunspots. NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala., manages Hinode science operations and oversaw development of the scientific instrumentation provided for the mission by NASA, and industry. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory in Cambridge, Mass., is the lead U.S. investigator for the X-ray Telescope. Image credit: JAXA/NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Hinode (Sunrise), formerly known as Solar-B before reaching orbit, was launched from the Uchinoura Space Center in Japan on September 23, 2006. Hinode was designed to probe into the Sun’s magnetic field to better understand the origin of solar disturbances which interfere with satellite communications, electrical power transmission grids, and the safety of astronauts traveling beyond the Earth’s magnetic field. Hinode is circling Earth in a polar orbit that places the instruments in continuous sunlight for nine months each year and allows data dumps to a high latitude European Space Agency (ESA) ground station every orbit. NASA and other science teams will support instrument operations and data collection from the spacecraft’s operation center at the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA’s) Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science facility located in Tokyo. The Hinode spacecraft is a collaboration among space agencies of Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Europe. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed development of three instruments comprising the spacecraft; the Solar Optical Telescope (SOT); the X-Ray Telescope (XRT); and the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Imaging Spectrometer (EIS). This image of a sunspot, taken by Hinode, is a prime example of what the spacecraft can offer.
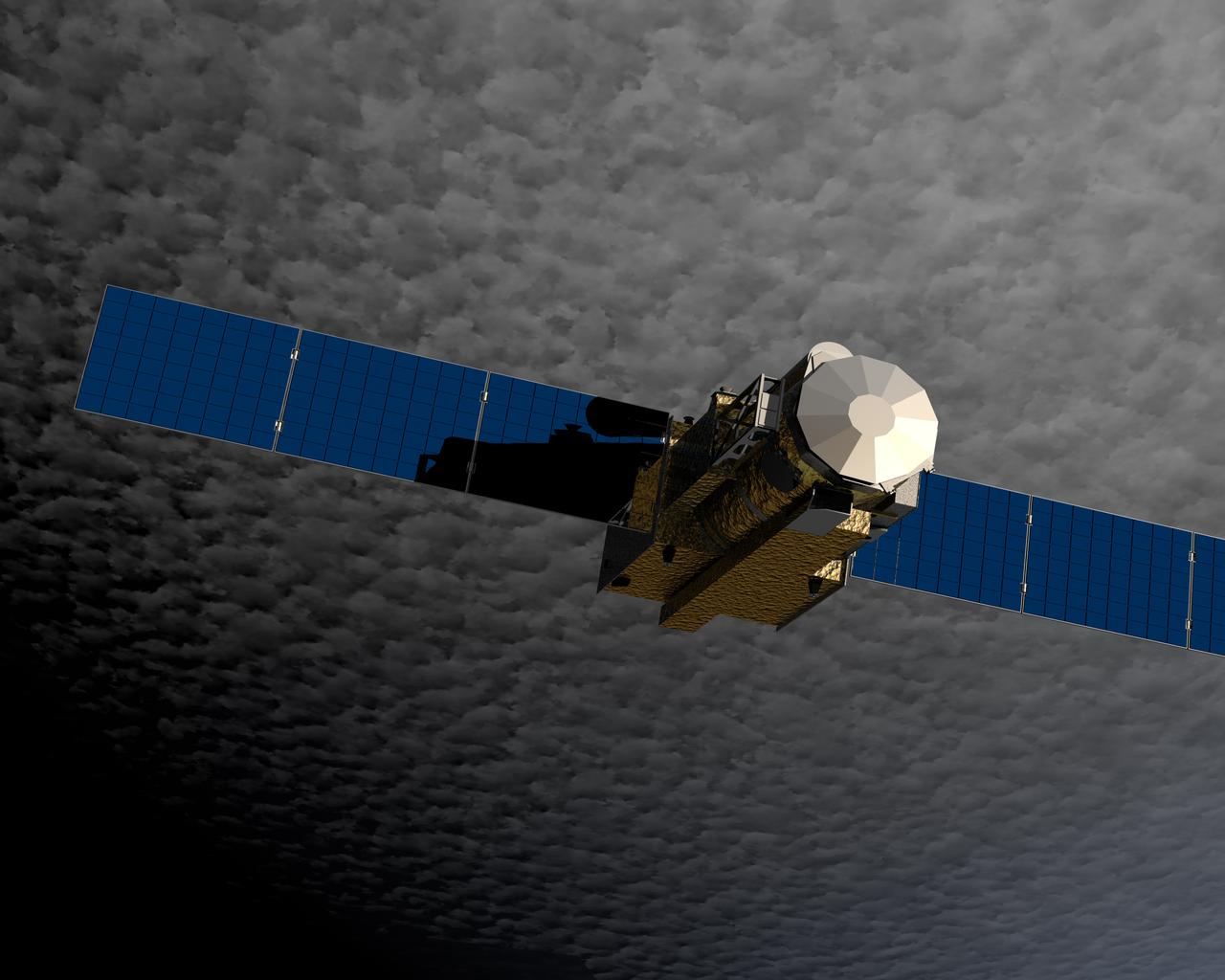

Hinode (Sunrise), formerly known as Solar-B before reaching orbit, was launched from the Uchinoura Space Center in Japan on September 23, 2006. Hinode was designed to probe into the Sun’s magnetic field to better understand the origin of solar disturbances which interfere with satellite communications, electrical power transmission grids, and the safety of astronauts traveling beyond the Earth’s magnetic field. Hinode is circling Earth in a polar orbit that places the instruments in continuous sunlight for nine months each year and allows data dumps to a high latitude European Space Agency (ESA) ground station every orbit. NASA and other science teams will support instrument operations and data collection from the spacecraft’s operation center at the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA’s) Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science facility located in Tokyo. The Hinode spacecraft is a collaboration among space agencies of Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Europe. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed development of three instruments comprising the spacecraft; the Solar Optical Telescope (SOT); the X-Ray Telescope (XRT); and the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Imaging Spectrometer (EIS). Provided by the Multimedia support group at MSFC, this rendering illustrates the Solar-B Spacecraft in earth orbit with its solar panels completely extended.
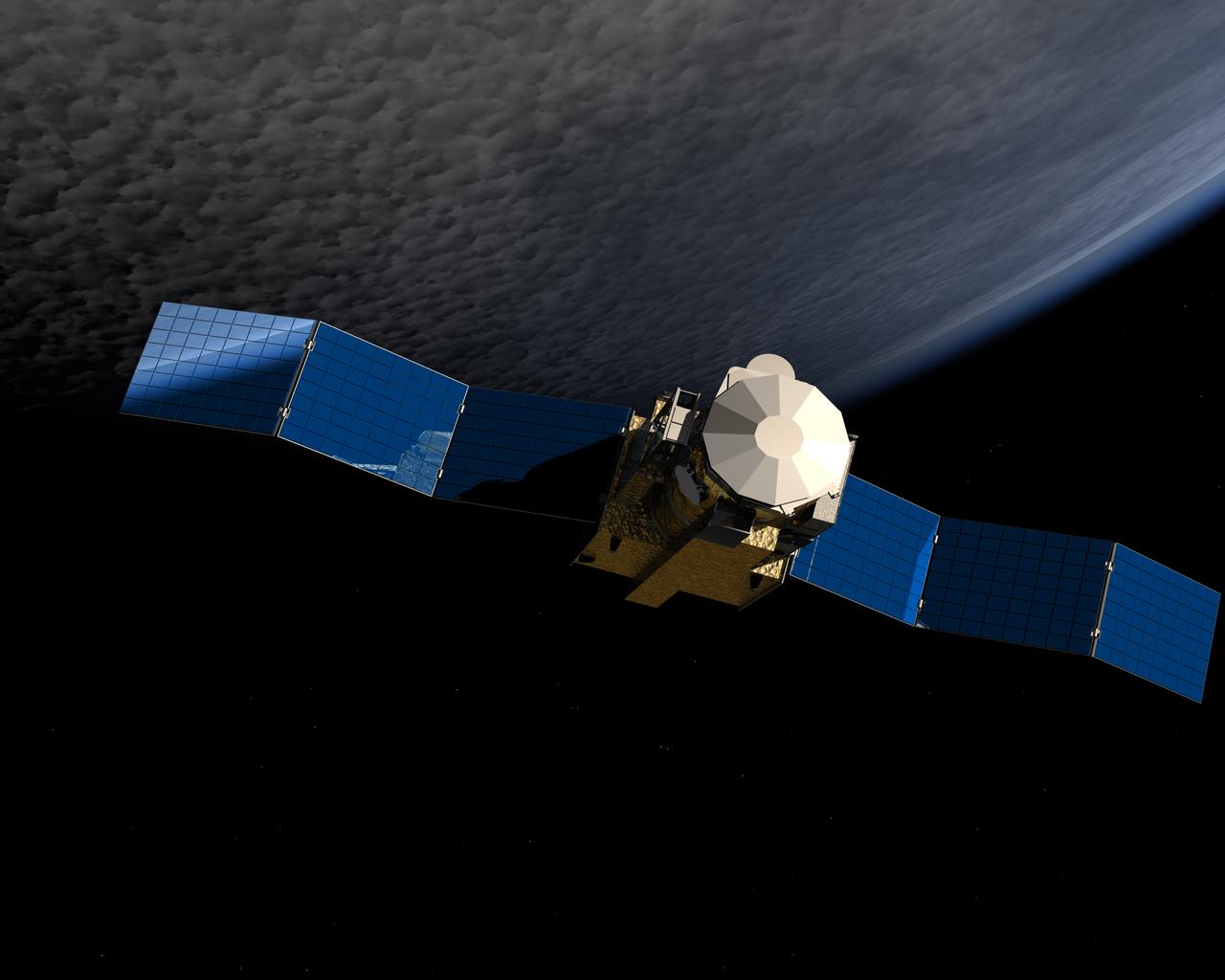

Hinode (Sunrise), formerly known as Solar-B before reaching orbit, was launched from the Uchinoura Space Center in Japan on September 23, 2006. Hinode was designed to probe into the Sun’s magnetic field to better understand the origin of solar disturbances which interfere with satellite communications, electrical power transmission grids, and the safety of astronauts traveling beyond the Earth’s magnetic field. Hinode is circling Earth in a polar orbit that places the instruments in continuous sunlight for nine months each year and allows data dumps to a high latitude European Space Agency (ESA) ground station every orbit. NASA and other science teams will support instrument operations and data collection from the spacecraft’s operation center at the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA’s) Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science facility located in Tokyo. The Hinode spacecraft is a collaboration among space agencies of Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Europe. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed development of three instruments comprising the spacecraft; the Solar Optical Telescope (SOT); the X-Ray Telescope (XRT); and the Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Imaging Spectrometer (EIS). Provided by the Multimedia support group at MSFC, this rendering illustrates the Solar-B Spacecraft in earth orbit with its solar panels partially extended.
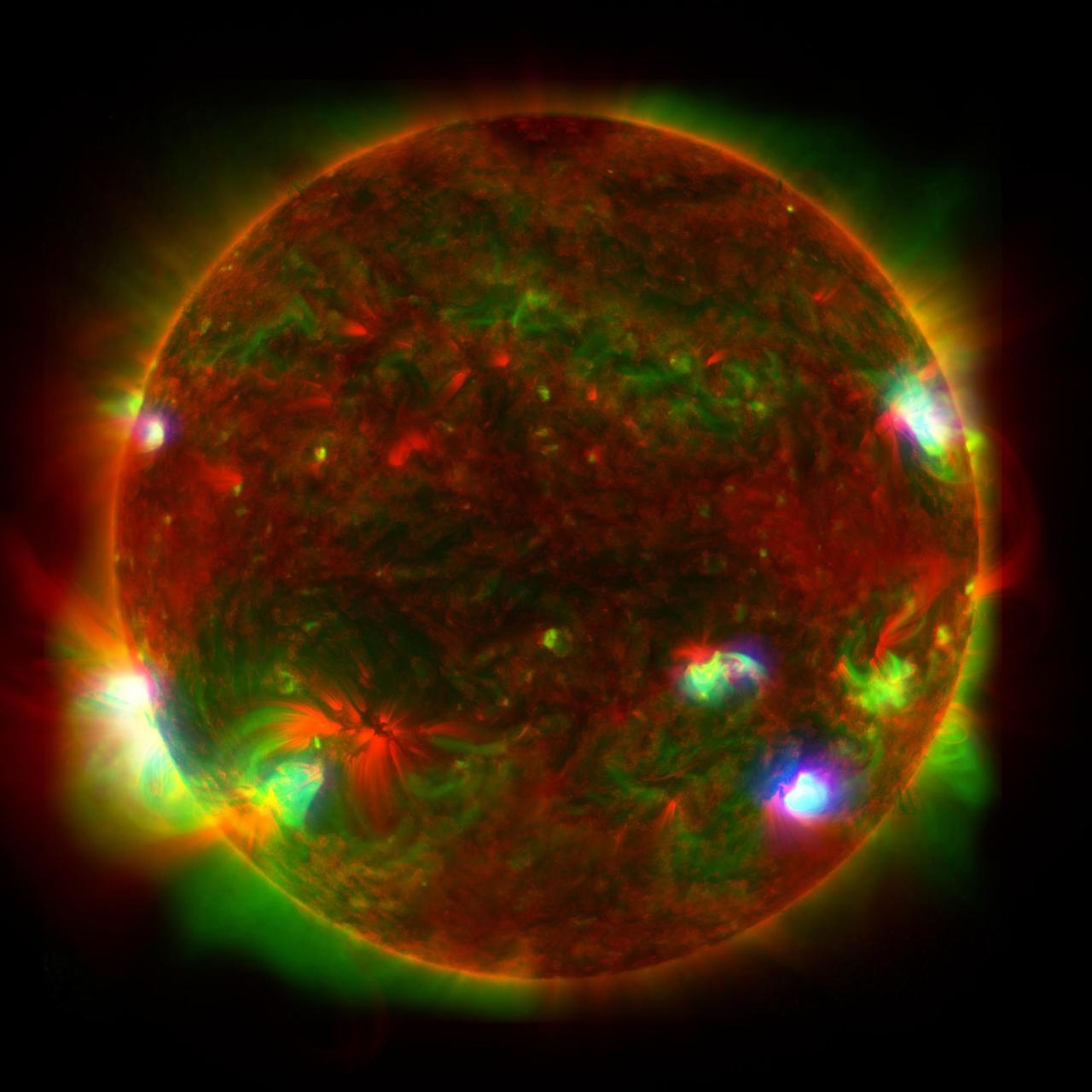
This composite image of the Sun includes high-energy X-ray data from NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) shown in blue; lower energy X-ray data from the X-ray Telescope (XRT) on the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode mission shown in green; and ultraviolet light detected by the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) shown in red. NuSTAR's relatively small field of view means it can't see the entire Sun from its position in Earth orbit, so Figure A is a composite of 25 images, which were taken by the observatory in June 2022. NuSTAR sees high-energy X-rays that appear at only a few locations, where the hottest material is present in the Sun's atmopshere. By contrast, Hinode's XRT and SDO's AIA detect detect wavelengths emitted across the entire face of the Sun. The hotspots observed by NuSTAR might be caused by collections of nanoflares, or small outbursts of heat, light, and particles from the Sun's surface that subsequently heat the atmosphere. Individual nanoflares are too faint to directly observe amid the Sun's blazing light. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25628

Flaring, active regions of our sun are highlighted in this image combining observations from several telescopes. High-energy X-rays from NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) are shown in blue; low-energy X-rays from Japan's Hinode spacecraft are green; and extreme ultraviolet light from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) is yellow and red. All three telescopes captured their solar images around the same time on April 29, 2015. The NuSTAR image is a mosaic made from combining smaller images. The active regions across the sun's surface contain material heated to several millions of degrees. The blue-white areas showing the NuSTAR data pinpoint the most energetic spots. During the observations, microflares went off, which are smaller versions of the larger flares that also erupt from the sun's surface. The microflares rapidly release energy and heat the material in the active regions. NuSTAR typically stares deeper into the cosmos to observe X-rays from supernovas, black holes and other extreme objects. But it can also look safely at the sun and capture images of its high-energy X-rays with more sensitivity than before. Scientists plan to continue to study the sun with NuSTAR to learn more about microflares, as well as hypothesized nanoflares, which are even smaller. In this image, the NuSTAR data shows X-rays with energies between 2 and 6 kiloelectron volts; the Hinode data, which is from the X-ray Telescope instrument, has energies of 0.2 to 2.4 kiloelectron volts; and the Solar Dynamics Observatory data, taken using the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly instrument, shows extreme ultraviolet light with wavelengths of 171 and 193 Angstroms. Note the green Hinode image frame edge does not extend as far as the SDO ultraviolet image, resulting in the green portion of the image being truncated on the right and left sides. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19821
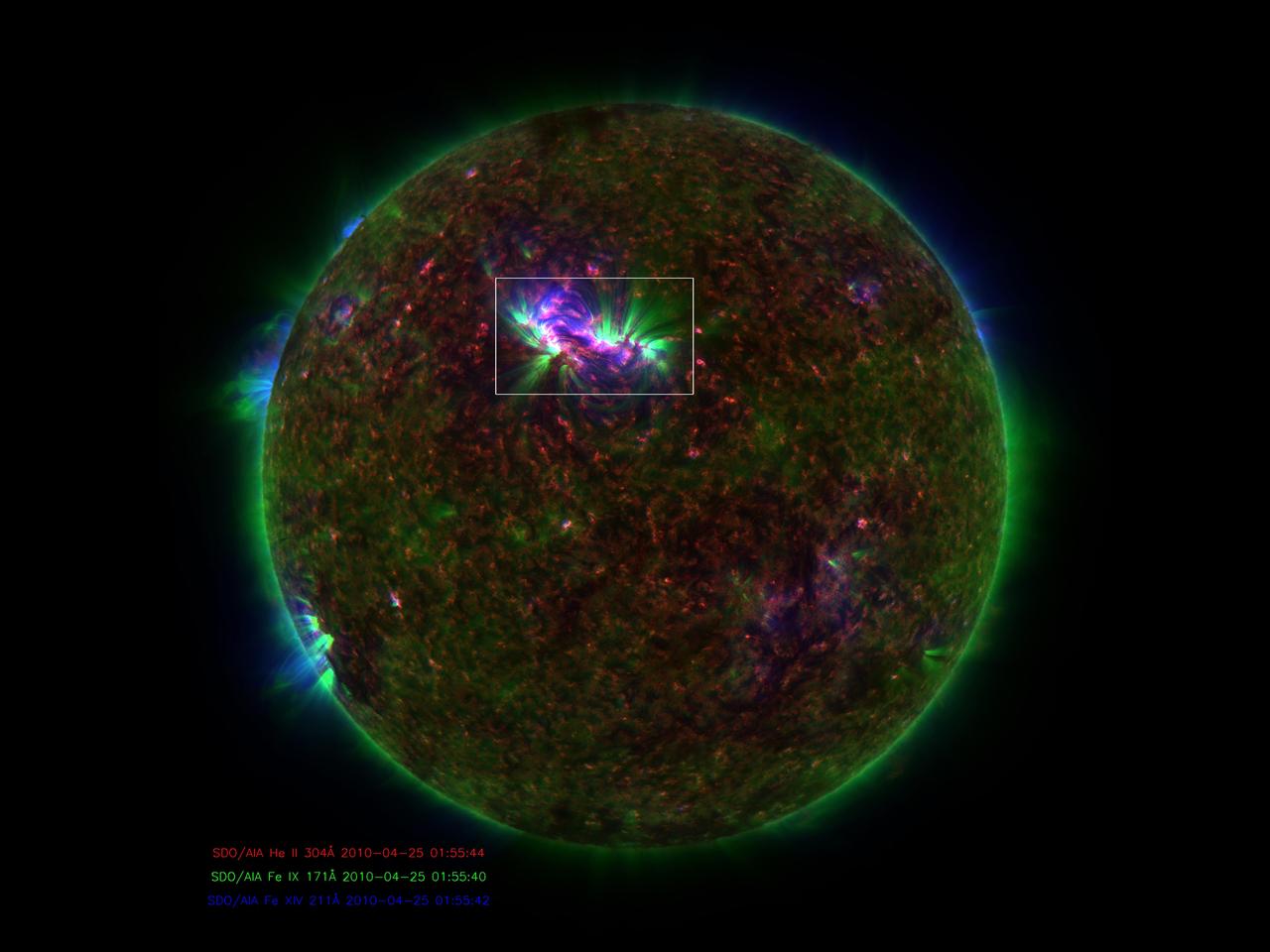
NASA image release January 6, 2010 Caption: Spicules on the sun, as observed by the Solar Dynamics Observatory. These bursts of gas jet off the surface of the sun at 150,000 miles per hour and contain gas that reaches temperatures over a million degrees. GREENBELT, Md. -- Observations from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and the Japanese satellite Hinode show that some gas in the giant, fountain-like jets in the sun's atmosphere known as spicules can reach temperatures of millions of degrees. The finding offers a possible new framework for how the sun's high atmosphere gets so much hotter than the surface of the sun. What makes the high atmosphere, or corona, so hot – over a million degrees, compared to the sun surface's 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit -- remains a poorly understood aspect of the sun's complicated space weather system. That weather system can reach Earth, causing auroral lights and, if strong enough, disrupting Earth's communications and power systems. Understanding such phenomena, therefore, is an important step towards better protecting our satellites and power grids. "The traditional view is that all the heating happens higher up in the corona," says Dean Pesnell, who is SDO's project scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. "The suggestion in this paper is that cool gas is being ejected from the sun's surface in spicules and getting heated on its way to the corona." Spicules were first named in the 1940s, but were hard to study in detail until recently, says Bart De Pontieu of Lockheed Martin's Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory, Palo Alto, Calif. who is the lead author on a paper on this subject in the January 7, 2011 issue of Science magazine. In visible light, spicules can be seen to send large masses of so-called plasma – the electromagnetic gas that surrounds the sun – up through the lower solar atmosphere or photosphere. The amount of material sent up is stunning, some 100 times as much as streams away from the sun in the solar wind towards the edges of the solar system. But nobody knew if they contained hot gas. "Heating of spicules to the necessary hot temperatures has never been observed, so their role in coronal heating had been dismissed as unlikely," says De Pontieu. Now, De Pontieu's team -- which included researchers at Lockheed Martin, the High Altitude Observatory of the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in Colorado and the University of Oslo, Norway -- was able to combine images from SDO and Hinode to produce a more complete picture of the gas inside these gigantic fountains. The scientists found that a large fraction of the gas is heated to a hundred thousand degrees, while a small fraction is heated to millions of degrees. Time-lapsed images show that this material spews up into the corona, with most falling back down towards the surface of the sun. However, the small fraction of the gas that is heated to millions of degrees does not immediately return to the surface. Given the large number of spicules on the Sun, and the amount of material in the spicules, the scientists believe that if even some of that super hot plasma stays aloft it would make a contribution to coronal heating. Astrophysicist Jonathan Cirtain, who is the U.S. project scientist for Hinode at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Ala., says that incorporating such new information helps address an important question that reaches far beyond the sun. "This breakthrough in our understanding of the mechanisms which transfer energy from the solar photosphere to the corona addresses one of the most compelling questions in stellar astrophysics: How is the atmosphere of a star heated?" he says. "This is a fantastic discovery, and demonstrates the muscle of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, comprised of numerous instruments on multiple observatories." Hinode is the second mission in NASA's Solar Terrestrial Probes program, the goal of which is to improve understanding of fundamental solar and space physics processes. The mission is led by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ). The collaborative mission includes the U.S., the United Kingdom, Norway and Europe. NASA Marshall manages Hinode U.S. science operations and oversaw development of the scientific instrumentation provided for the mission by NASA, academia and industry. The Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center is the lead U.S. investigator for the Solar Optical Telescope on Hinode. SDO is the first mission in a NASA science program called Living With a Star, the goal of which is to develop the scientific understanding necessary to address those aspects of the sun-Earth system that directly affect our lives and society. NASA Goddard built, operates, and manages the SDO spacecraft for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/news20110106-spicules.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/news20110106-spicules...</a> Credit: NASA Goddard/SDO/AIA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
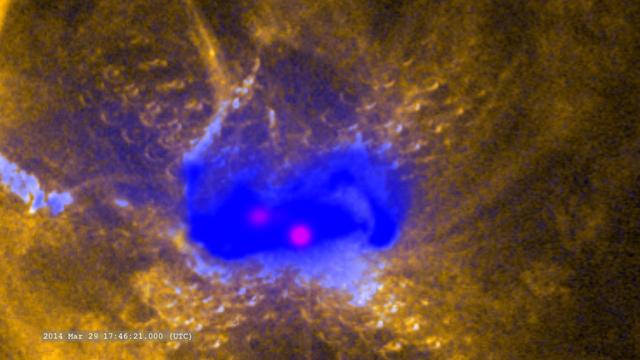
Zoom in on the flare in ultraviolet (SDO/AIA), X-rays (Hinode) and gamma-rays (RHESSI) -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
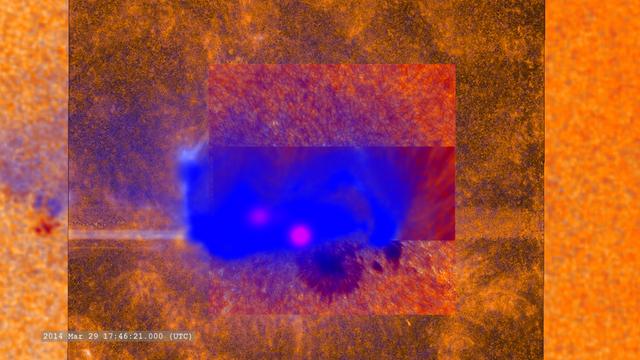
A combination of many (but not all) of the datasets which observed this flare. -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The March 29, 2014, X-class flare appears as a bright light on the upper right in this image from SDO, showing light in the 304 Angstrom wavelength. This wavelength shows material on the sun in what's called the transition region, where the chromosphere transitions into the upper solar atmosphere, the corona. Some light of the flare is clearly visible, but the flare appears brighter in other images that show hotter temperature material. Credit: NASA/SDO/AIA -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
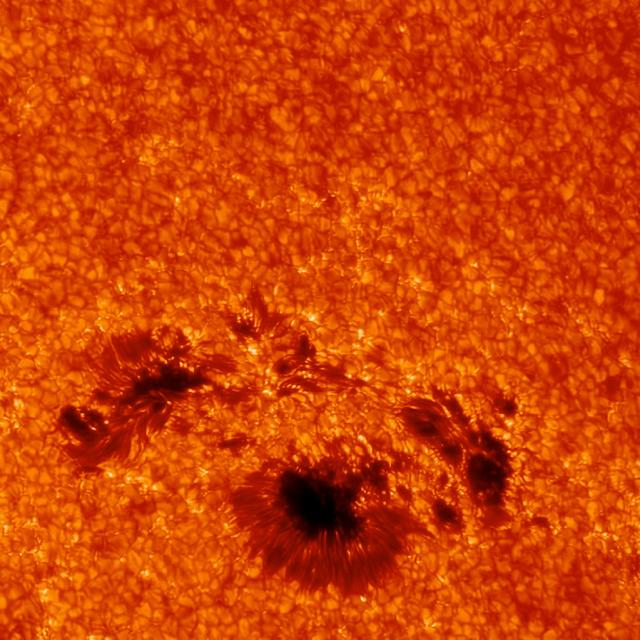

This close-up of the sunspot underneath the March 29, 2014, flare shows incredible detail. The image was captured by the G-band camera at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. This instrument can focus on only a small area at once, but provide very high resolution. Ground-based telescope data can be hindered by Earth's atmosphere, which blocks much of the sun's ultraviolet and X-ray light, and causes twinkling even in the light it does allow through. As it happens, the March 29 flare occurred at a time of day in New Mexico that often results in the best viewing times from the ground. Credit: Kevin Reardon (National Solar Observatory), Lucia Kleint (BAER Institute) -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
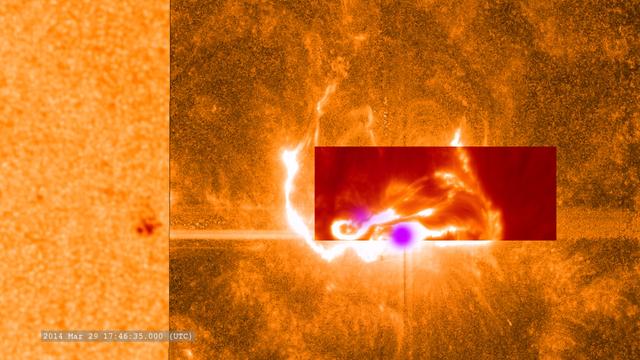
This combined image shows the March 29, 2014, X-class flare as seen through the eyes of different observatories. SDO is on the bottom/left, which helps show the position of the flare on the sun. The darker orange square is IRIS data. The red rectangular inset is from Sacramento Peak. The violet spots show the flare's footpoints from RHESSI. -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
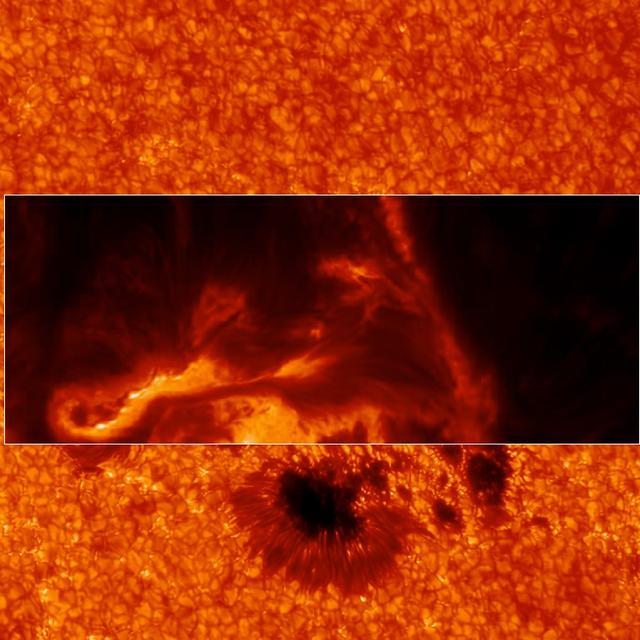

IBIS can focus in on different wavelengths of light, and so reveal different layers at different heights in the sun's lower atmosphere, the chromosphere. This image shows a region slightly higher than the former one. Credit: Lucia Kleint (BAER Institute), Paul Higgins (Trinity College Dublin, Ireland) -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
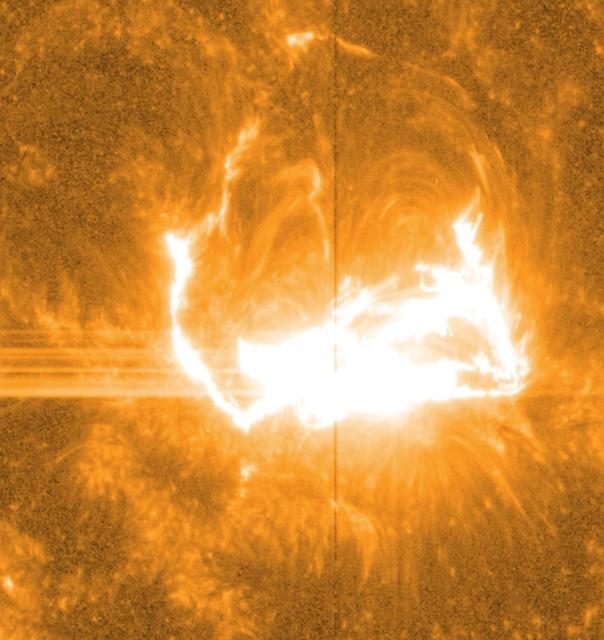
Like almost all solar observatories, NASA's IRIS can provide images of different layers of the sun's atmosphere, which together create a whole picture of what's happening. This image shows light at a wavelength of 1400 Angstrom, which highlights material some 650 miles above the sun's surface. The vertical line in the middle shows the slit for IRIS's spectrograph, which can separate light into its many wavelengths to provide even more information about the temperature and velocity of material during a flare. Credit: NASA/IRIS/Goddard Space Flight Center -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>