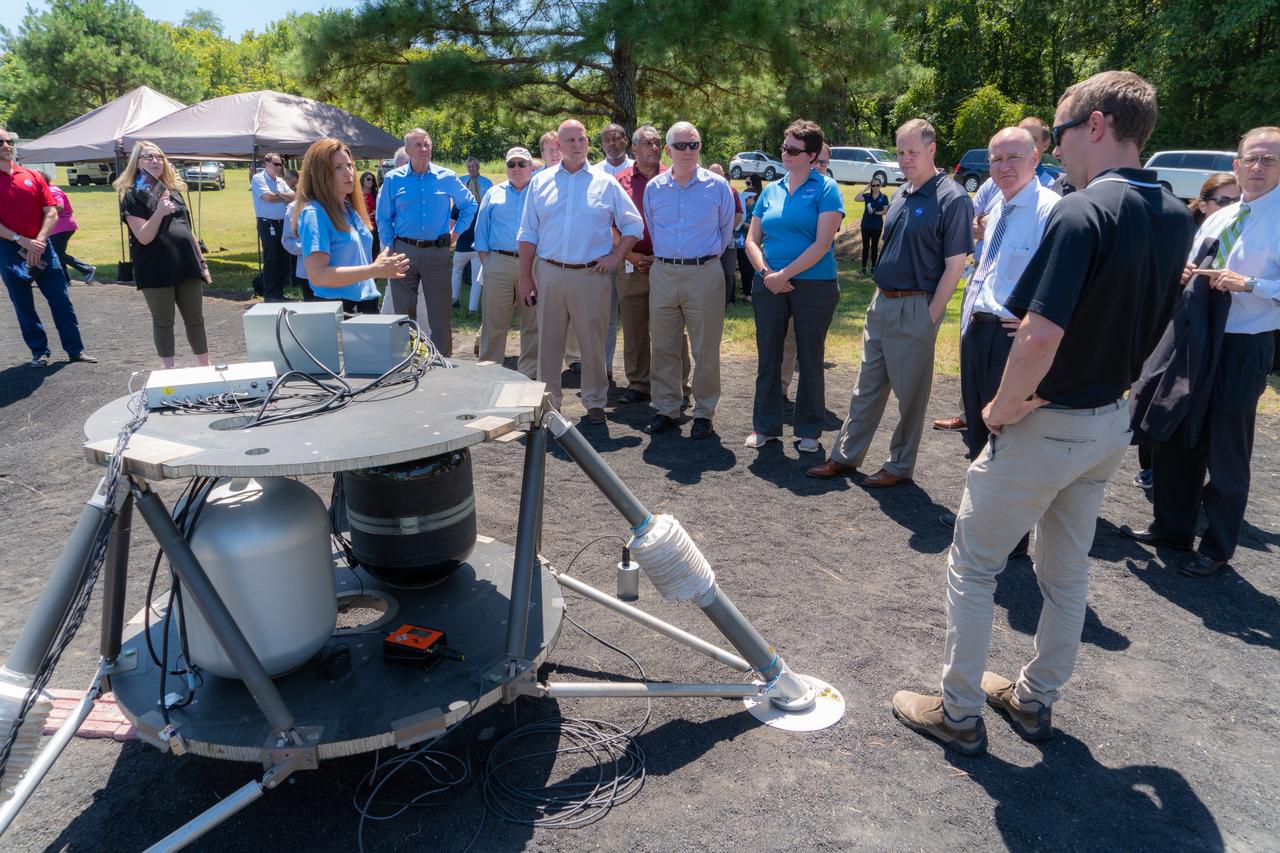

Lisa Watson-Morgan, center left, program manager of NASA’s Human Landing System Program at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, shows NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine equipment used to test seismic sensors on a lunar lander platform on a simulated lunar surface at the center Aug. 16, 2019. Bridenstine was joined by Representatives Mo Brooks and Robert Aderholt of Alabama and Representative Scott DesJarlais of Tennessee. Planetary scientists performed the experiment to learn how these waves travel through simulated regolith, which is material similar to the Moon’s surface. The experiment will help guide instrument deployment scenarios for NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Service (CLPS) Program, delivering small science and technology payloads for Artemis. That same day, Bridenstine announced Marshall will lead the agency’s Human Landing System Program. (NASA/Fred Deaton) For more information: https://www.nasa.gov/artemis-1
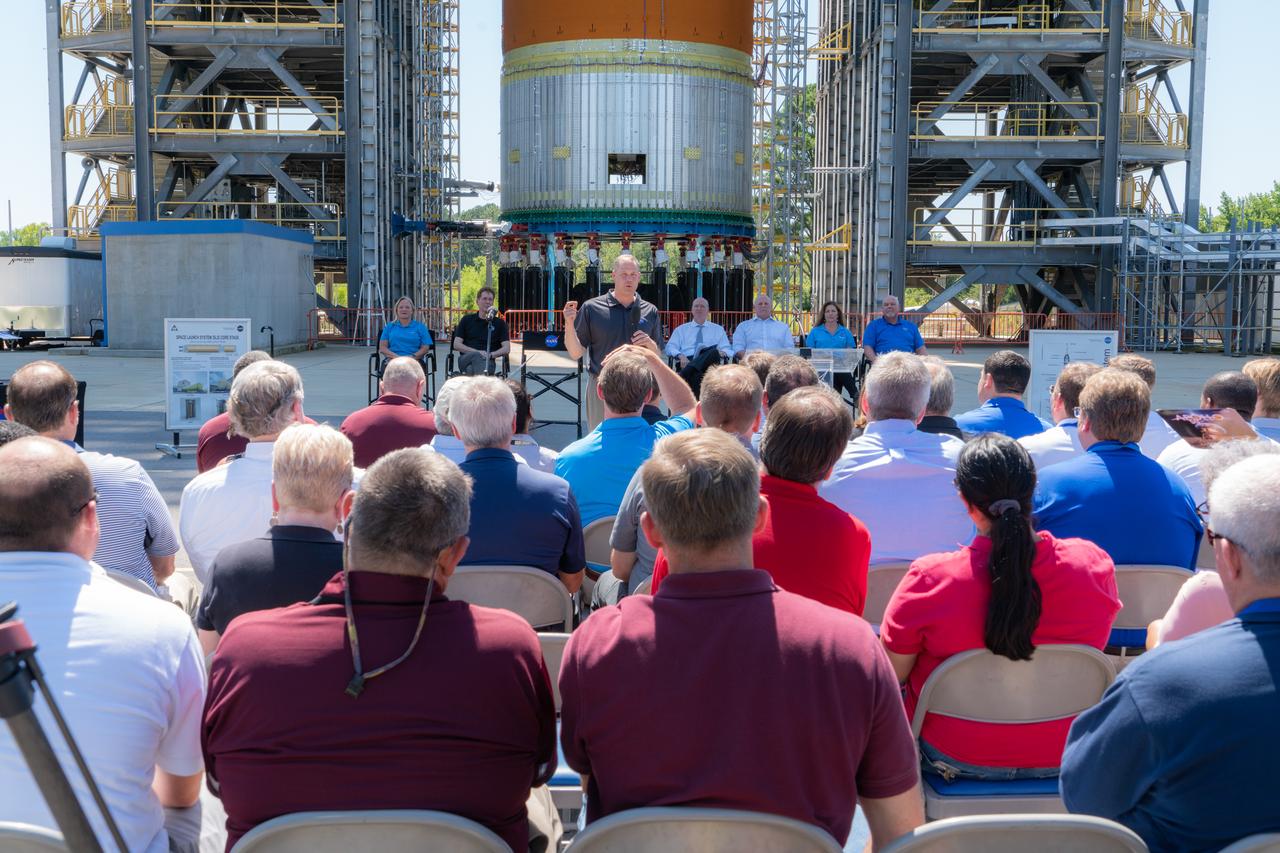

On Aug. 16, 2019, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine announced the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, will lead the Human Landing System Program. Bridenstine was joined by Representatives Mo Brooks and Robert Aderholt of Alabama and Representative Scott DesJarlais of Tennessee. NASA will rapidly develop the lander for safely carrying the first woman and the next man to the Moon’s surface in 2024. The Artemis missions will start with launch by the world’s most powerful rocket, NASA’s Space Launch System, also managed by Marshall. Bridenstine made the announcement in front of the 149-foot-tall SLS liquid hydrogen structural test article, currently being tested to help ensure the structure can safely launch astronauts on the Artemis lunar missions. (NASA/Fred Deaton) For more information: https://www.nasa.gov/artemis-1

Human Landing System Program Manager Lisa Watson-Morgan gives remarks during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
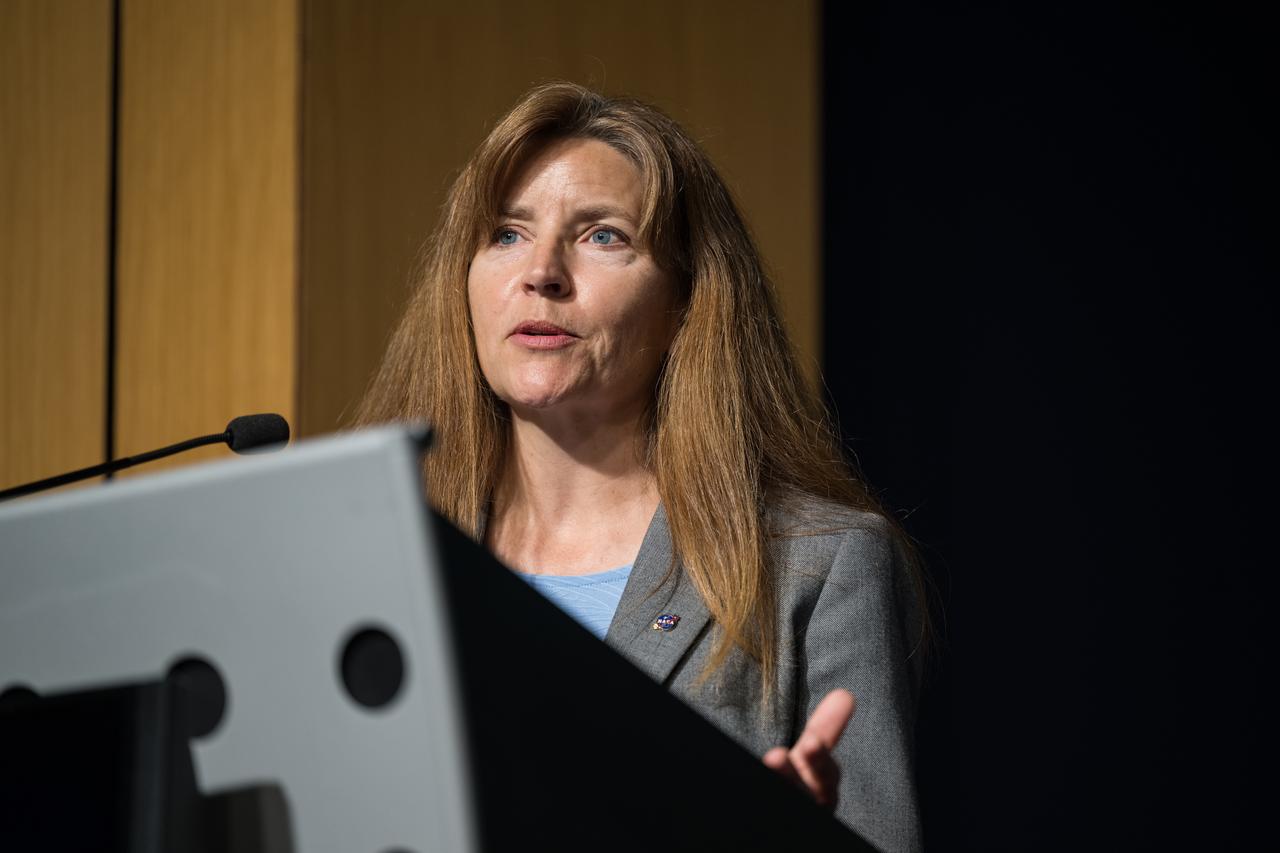

Human Landing System Program Manager Lisa Watson-Morgan gives remarks during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
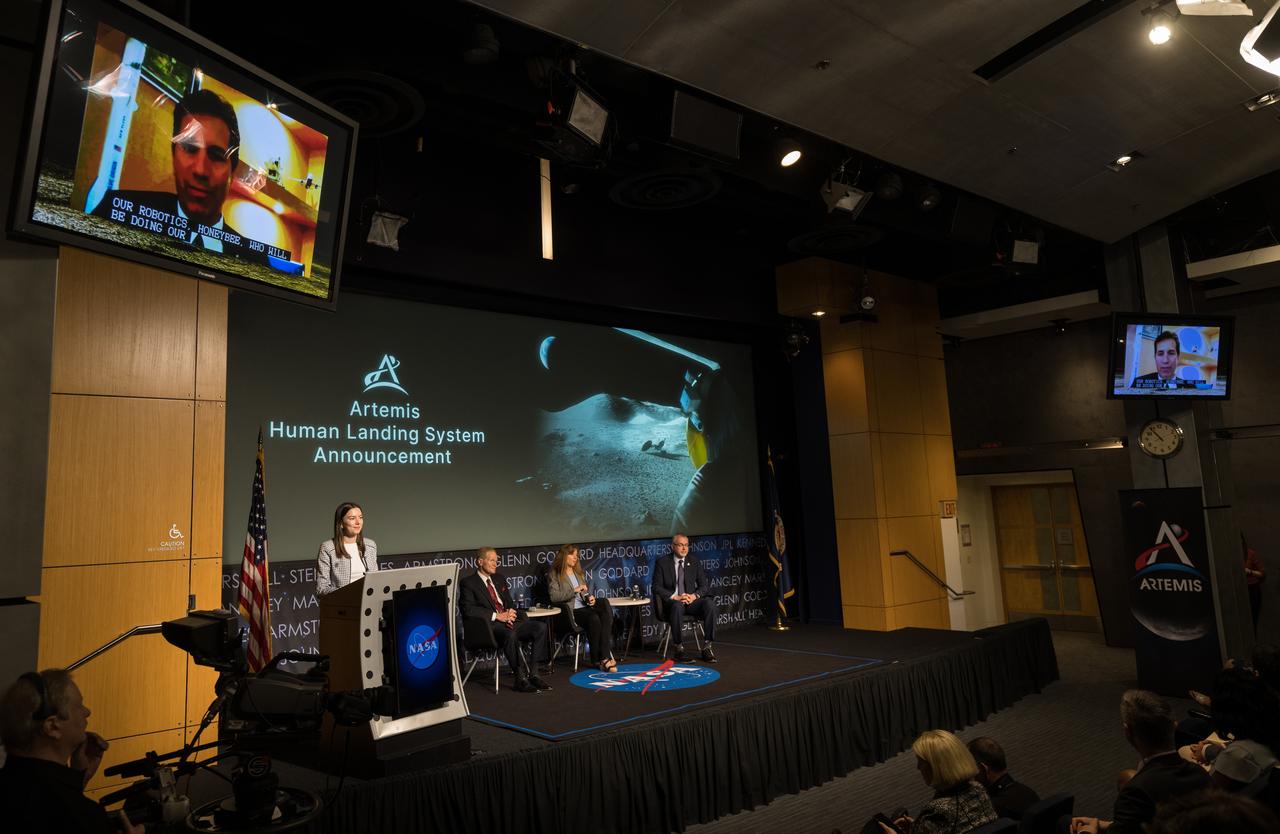

Blue Origin Human Landing System Program Manager, John Couluris, gives remarks during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
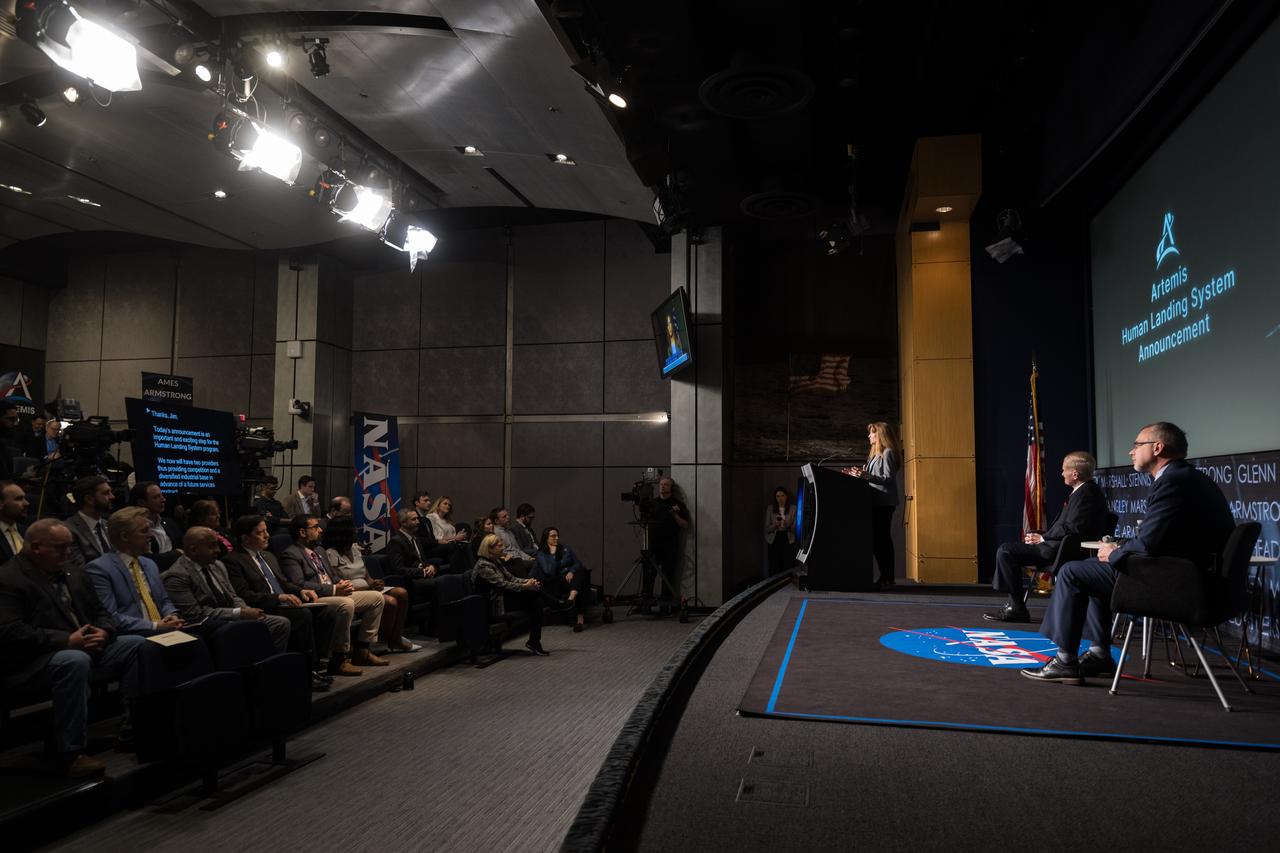

Human Landing System Program Manager Lisa Watson-Morgan gives remarks during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Human Landing System Program Manager Lisa Watson-Morgan gives remarks as NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, left, and NASA Associate Administrator for the Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate Jim Free, right, look on during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
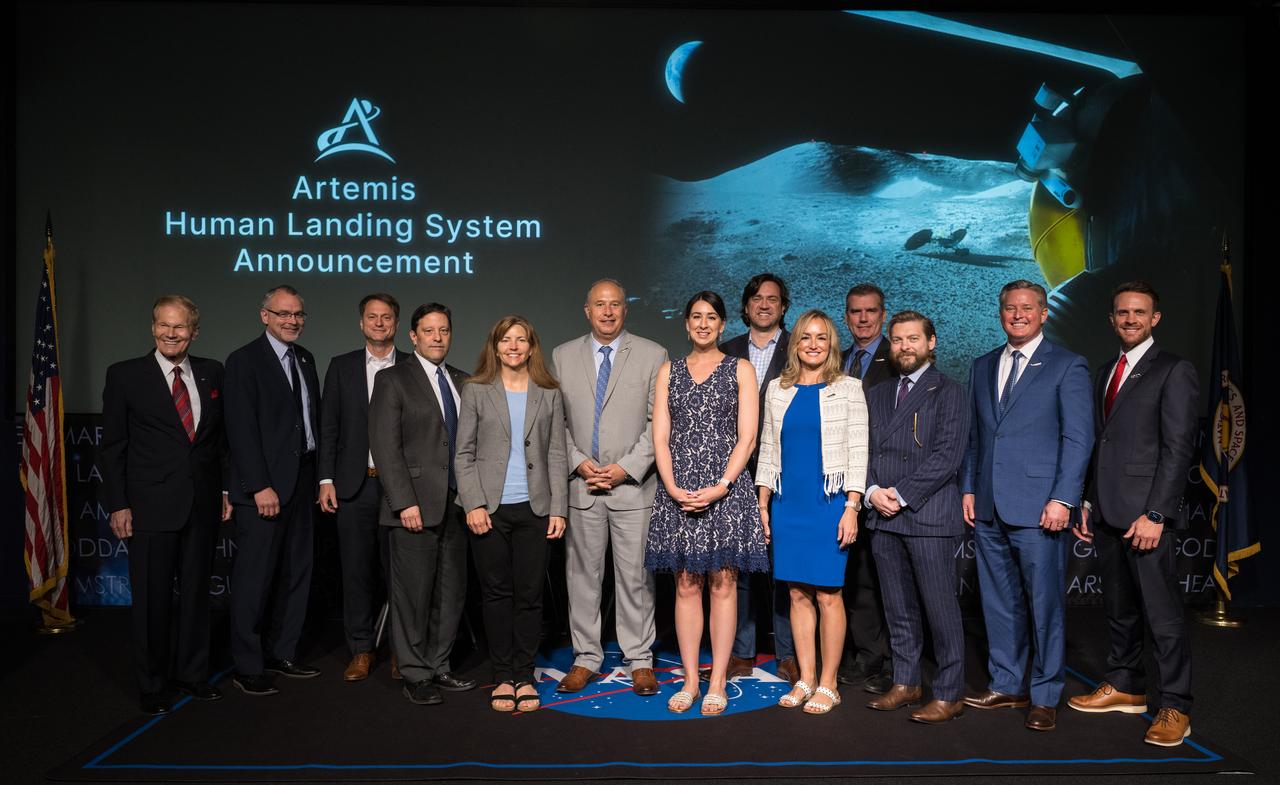

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, NASA Associate Administrator for the Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate Jim Free, Human Landing System Program Manager Lisa Watson-Morgan, members of Blue Origin’s team, and others pose for a photo at the conclusion of an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
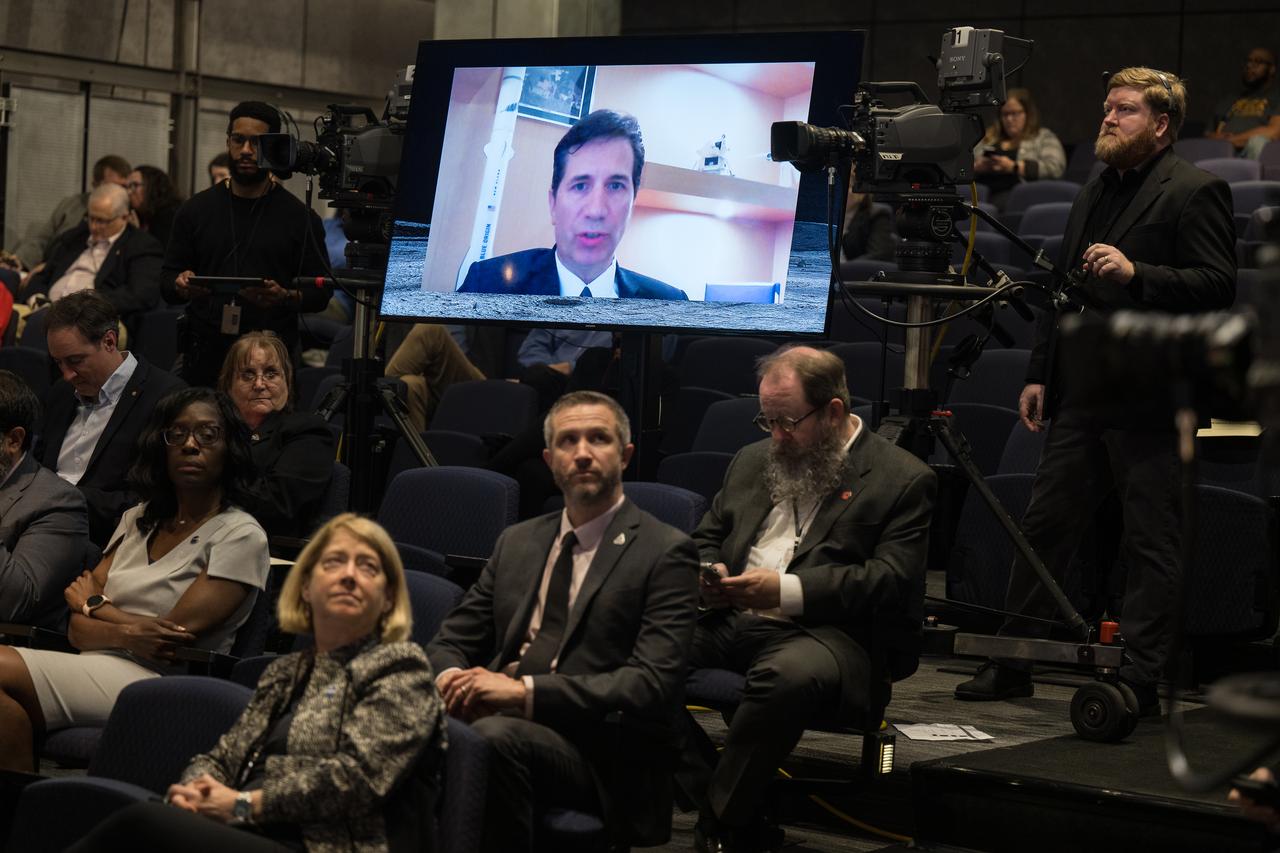

Blue Origin Human Landing System Program Manager, John Couluris, is seen on the monitor answering a question during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
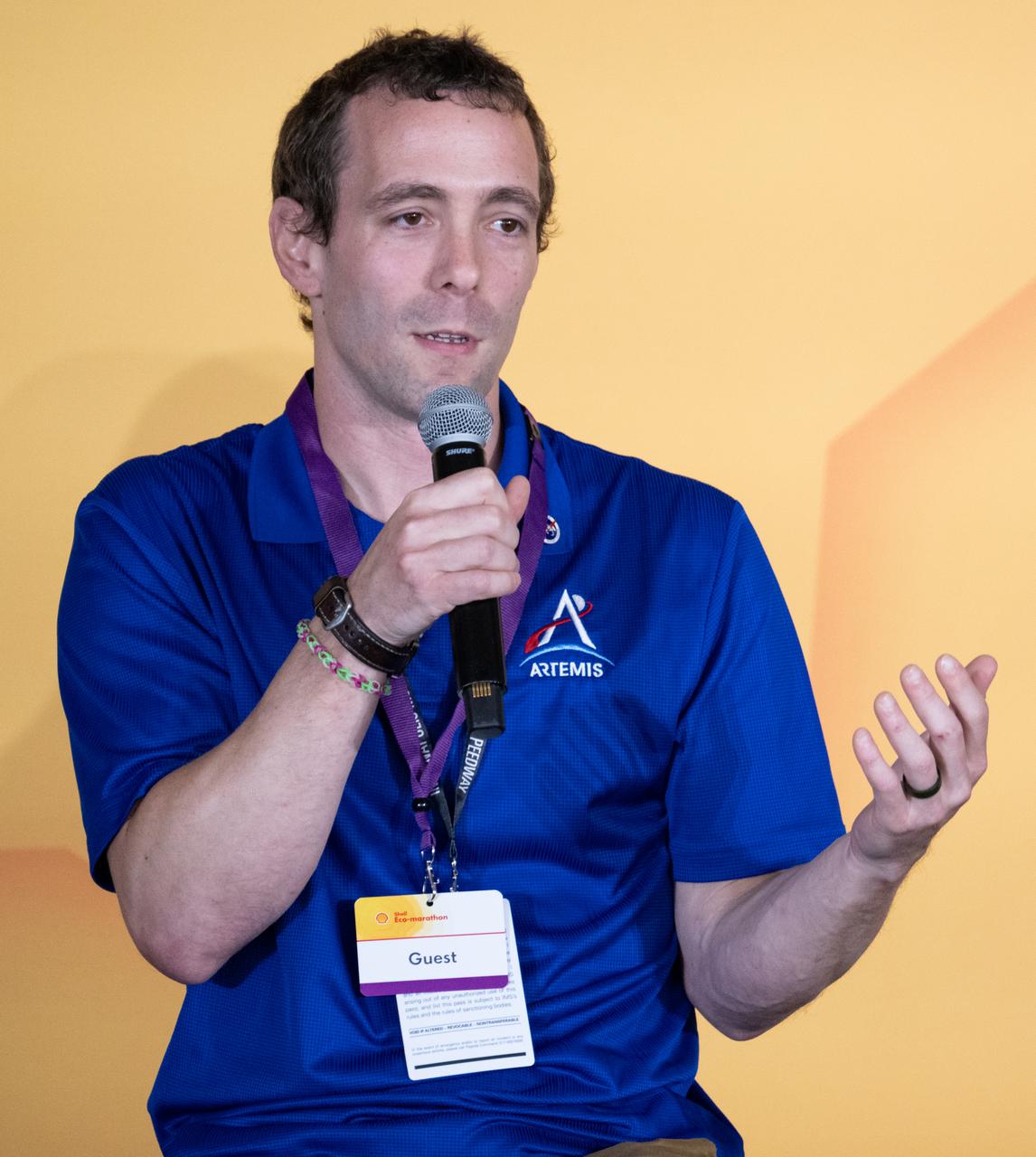

Logan Kennedy, surface lead for Human Landing System Programs in NASA's Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, speaks to students about power production and energy for the Artemis Program at the Shell Eco-marathon Americas, Saturday, April 6, 2024, at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Indianapolis, Ind. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
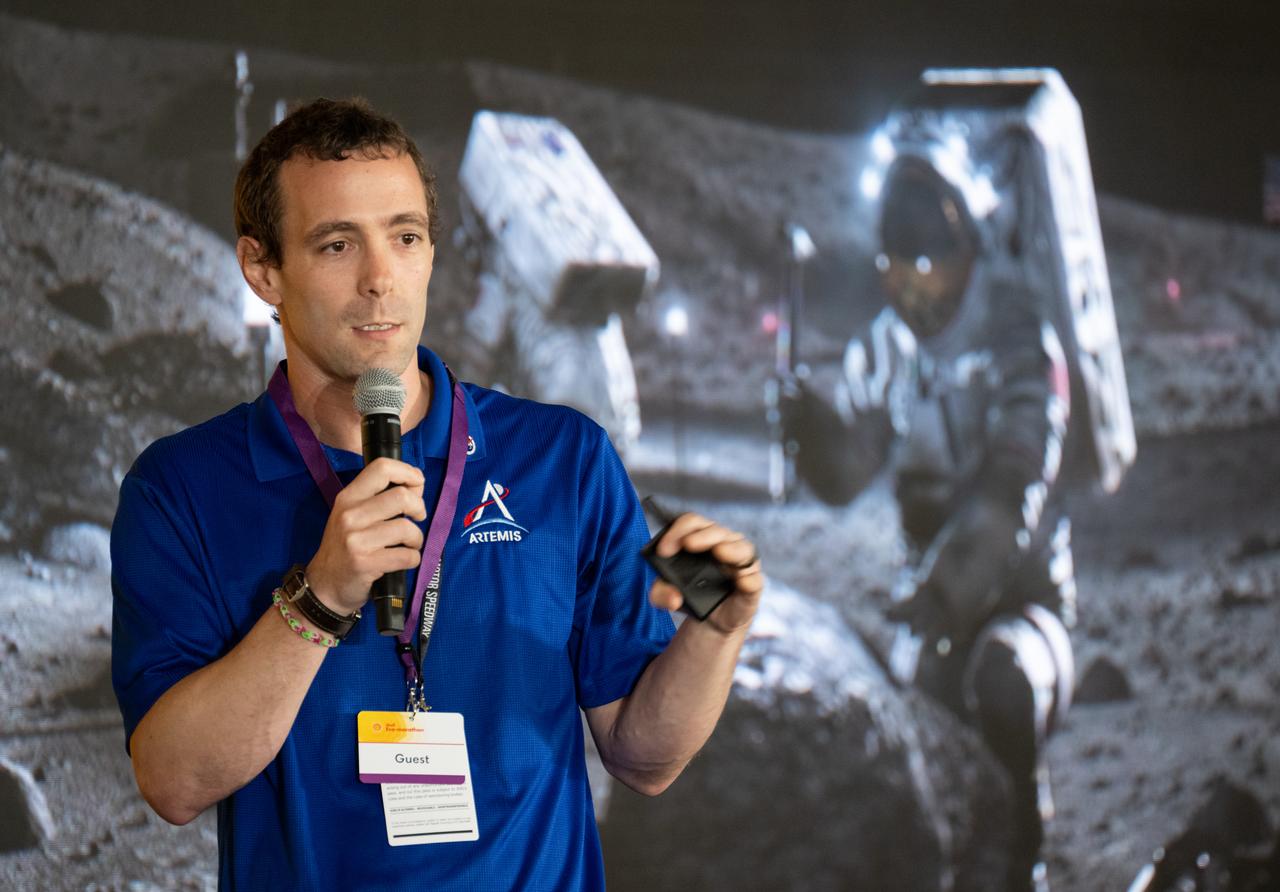

Logan Kennedy, surface lead for Human Landing System Programs in NASA's Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, speaks to students about power production and energy for the Artemis Program at the Shell Eco-marathon Americas, Saturday, April 6, 2024, at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Indianapolis, Ind. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
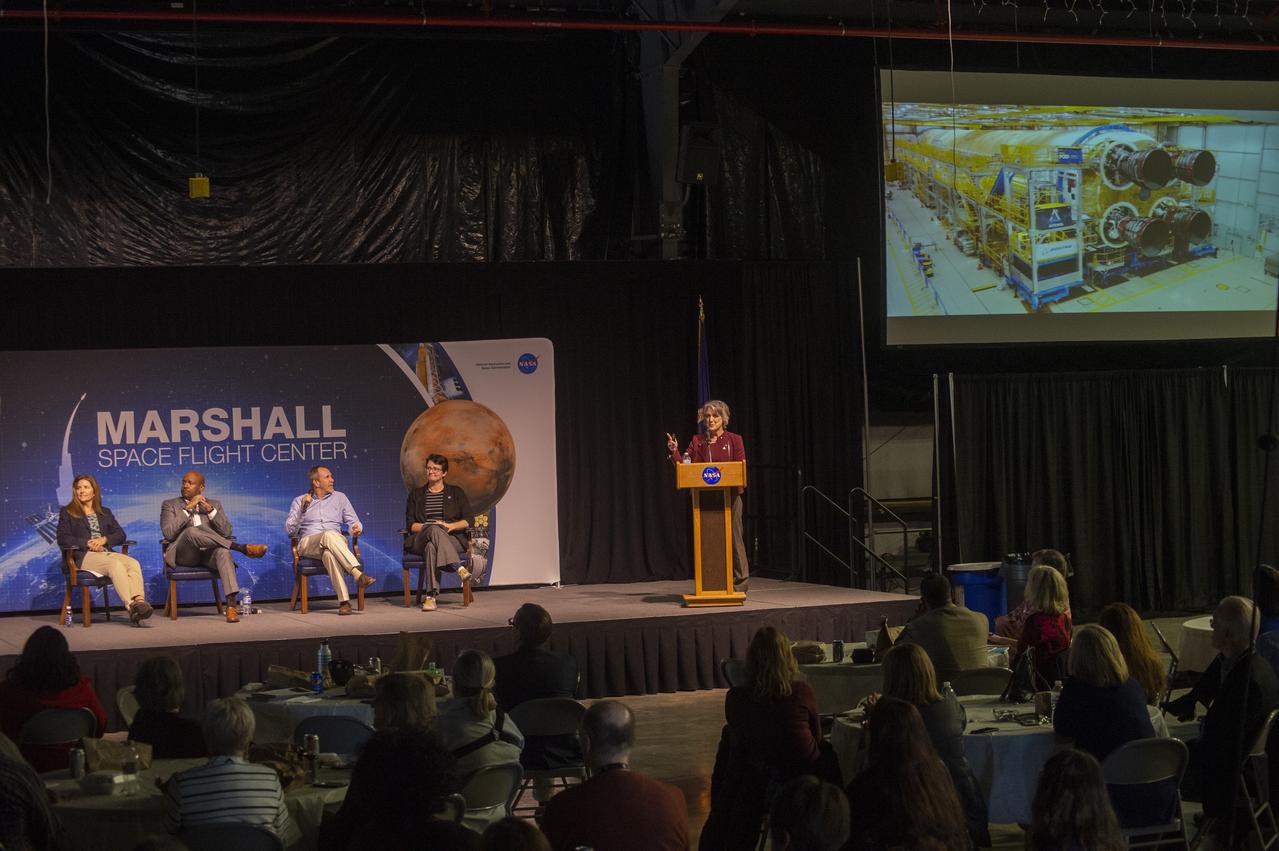

MARCIA LINDSTROM, AT PODIUM, FACILITATES ARTEMIS PROGRAM PANEL DISCUSSION AT NOVEMBER MARSHALL ASSOCIATION LUNCHEON. (L TO R), LISA WATSON-MORGAN, PROGRAM MANAGER, HUMAN LANDING SYSTEM; BOBBY WATKINS, DIRECTOR HUMAN EXPLORATION DEVELOPMENT & OPERATIONS OFFICE; DAVID BEAMAN, MANAGER, SYSTEMS ENGINEERING & INTEGRATION OFFICE, RENEE WEBER, ACTING CENTER CHIEF SCIENTIST
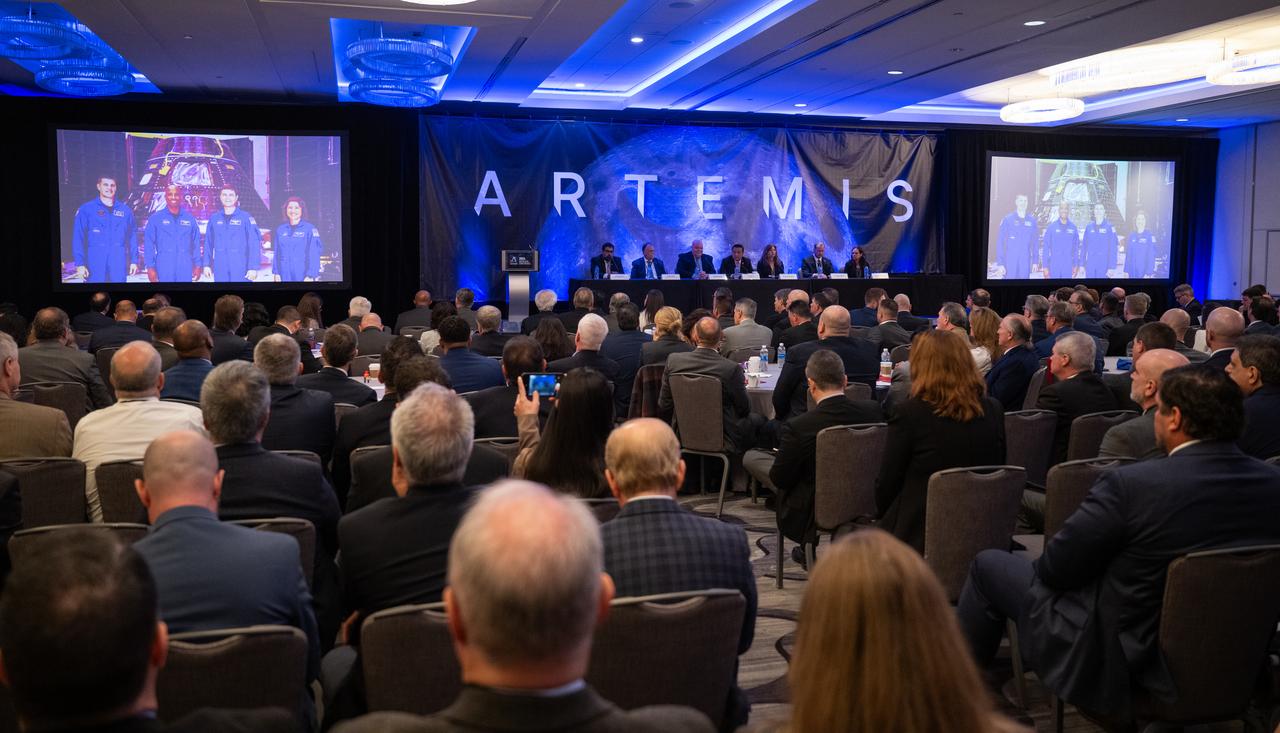

Howard Hu, manager of the Orion Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, center, speaks during an Artemis Program progress update panel at the 2024 Artemis Suppliers Conference, Tuesday, Feb. 27, 2024, at the Grand Hyatt Hotel in Washington. Also participating in the panel was, from left, Amit Kshatriya, deputy associate administrator for the Moon to Mars Program in NASA’s Explorations Systems Development Mission Directorate; Shawn Quinn, manager of Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center; John Honeycutt, manager of the Space Launch System Program at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; Lisa Watson-Morgan, manager of the Human Landing System Program at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; Jon B. Olansen, manager of the Gateway Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center; and Lara Kearney, manager of Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
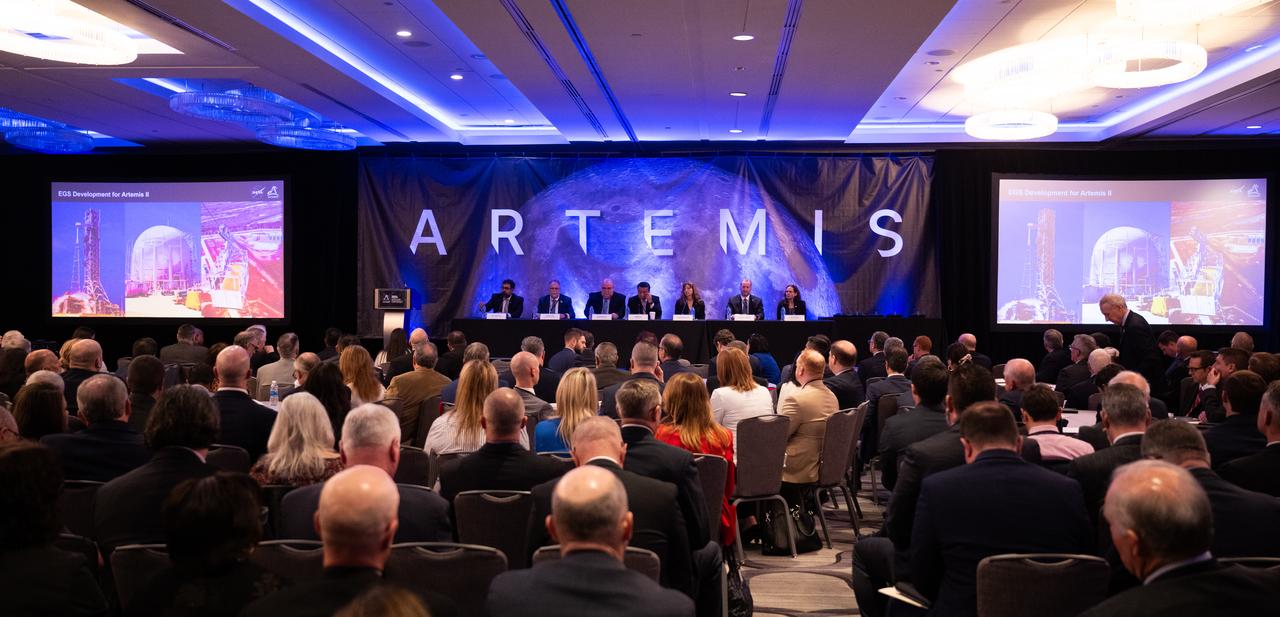

Shawn Quinn, manager of Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, second from left, speaks during an Artemis Program progress update panel at the 2024 Artemis Suppliers Conference, Tuesday, Feb. 27, 2024, at the Grand Hyatt Hotel in Washington. Also participating in the panel was, from left, Amit Kshatriya, deputy associate administrator for the Moon to Mars Program in NASA’s Explorations Systems Development Mission Directorate; John Honeycutt, manager of the Space Launch System Program at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; Howard Hu, manager of the Orion Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center; Lisa Watson-Morgan, manager of the Human Landing System Program at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; Jon B. Olansen, manager of the Gateway Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center; and Lara Kearney, manager of Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Howard Hu, manager of the Orion Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, center, speaks during an Artemis Program progress update panel at the 2024 Artemis Suppliers Conference, Tuesday, Feb. 27, 2024, at the Grand Hyatt Hotel in Washington. Also participating in the panel was, from left, Amit Kshatriya, deputy associate administrator for the Moon to Mars Program in NASA’s Explorations Systems Development Mission Directorate; Shawn Quinn, manager of Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center; John Honeycutt, manager of the Space Launch System Program at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; Lisa Watson-Morgan, manager of the Human Landing System Program at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; Jon B. Olansen, manager of the Gateway Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center; and Lara Kearney, manager of Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
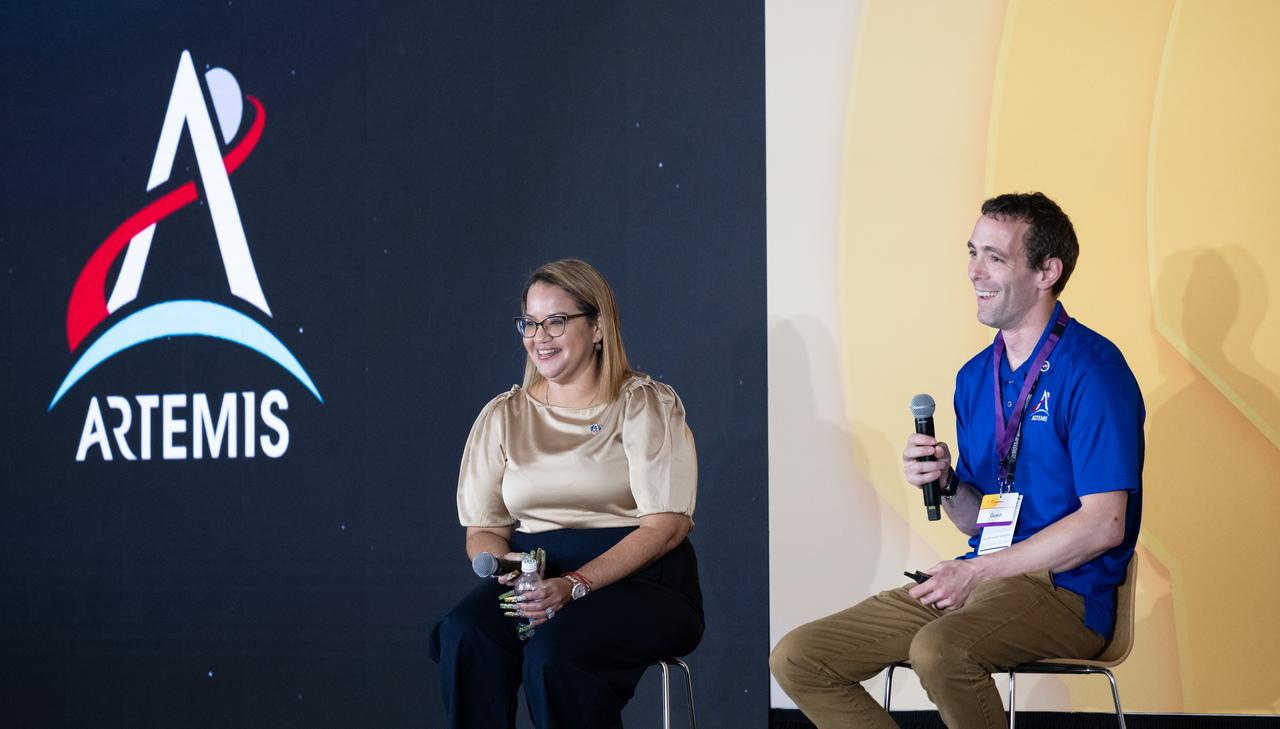

Dr. Dionne Hernandez-Lugo, Power and Propulsion Element Contracting Officer Representative in the Gateway & Power and Propulsion Element Office of NASA's Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, left, and Logan Kennedy, surface lead for Human Landing System Programs in NASA's Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, right, speaks to students about power production and energy for the Artemis Program at the Shell Eco-marathon Americas, Saturday, April 6, 2024, at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Indianapolis, Ind. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
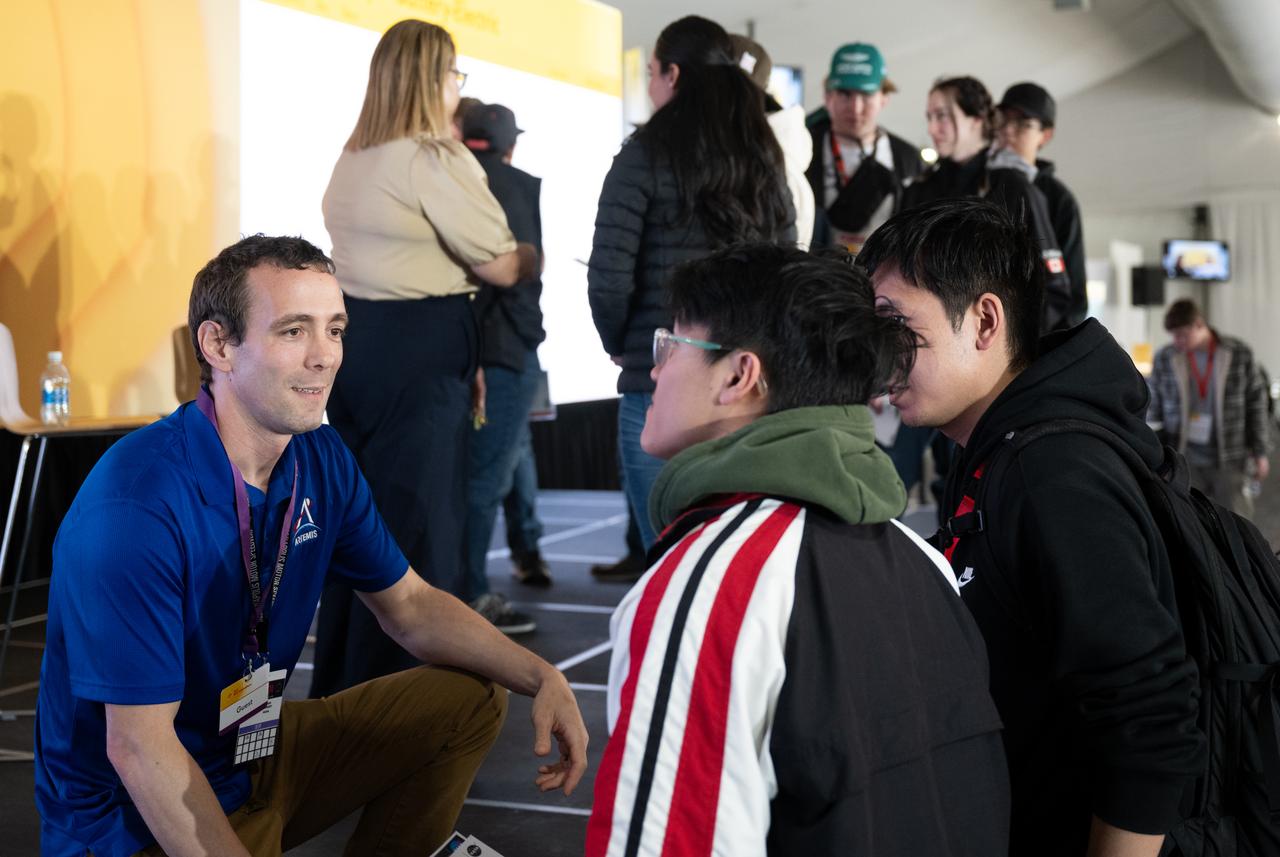

Logan Kennedy, surface lead for Human Landing System Programs in NASA's Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, speaks to students after discussing about power production and energy for the Artemis Program at the Shell Eco-marathon Americas, Saturday, April 6, 2024, at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Indianapolis, Ind. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
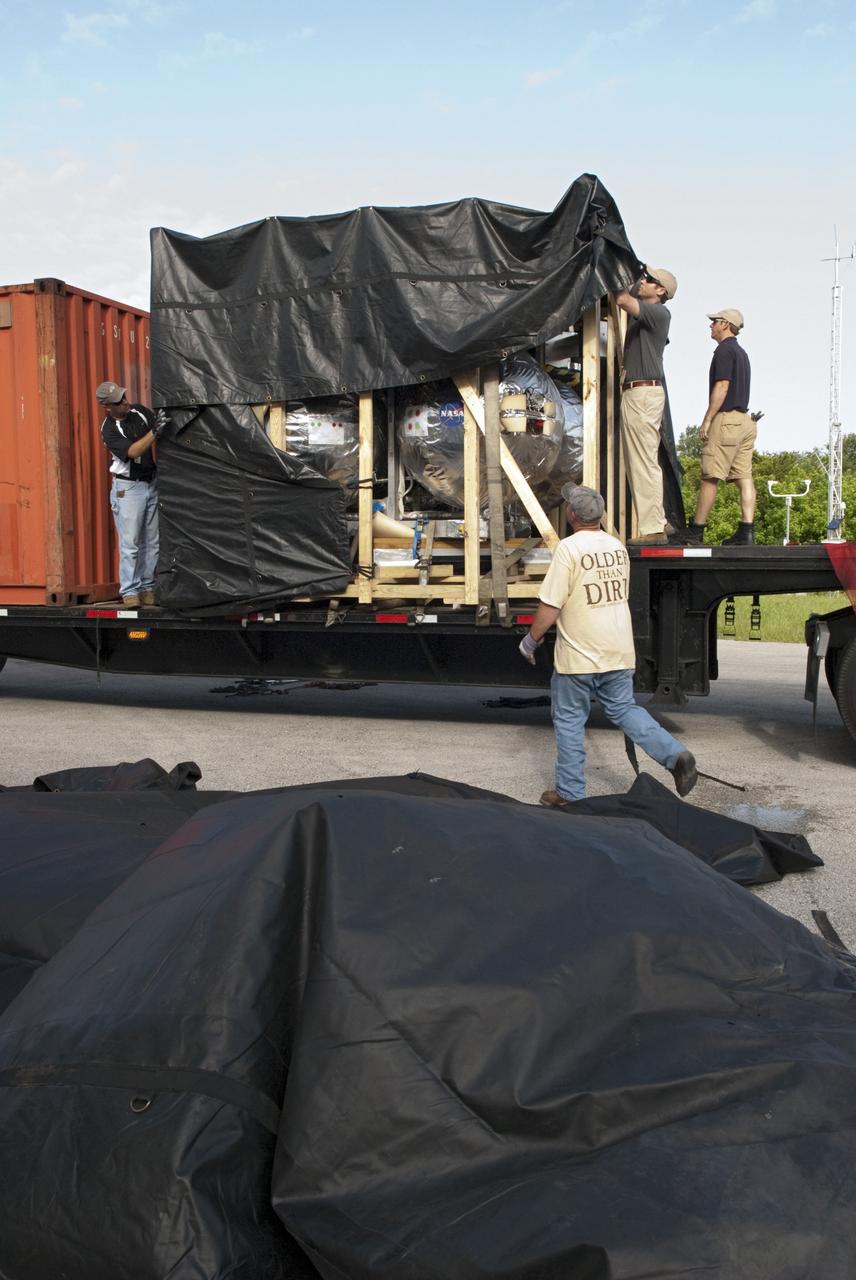

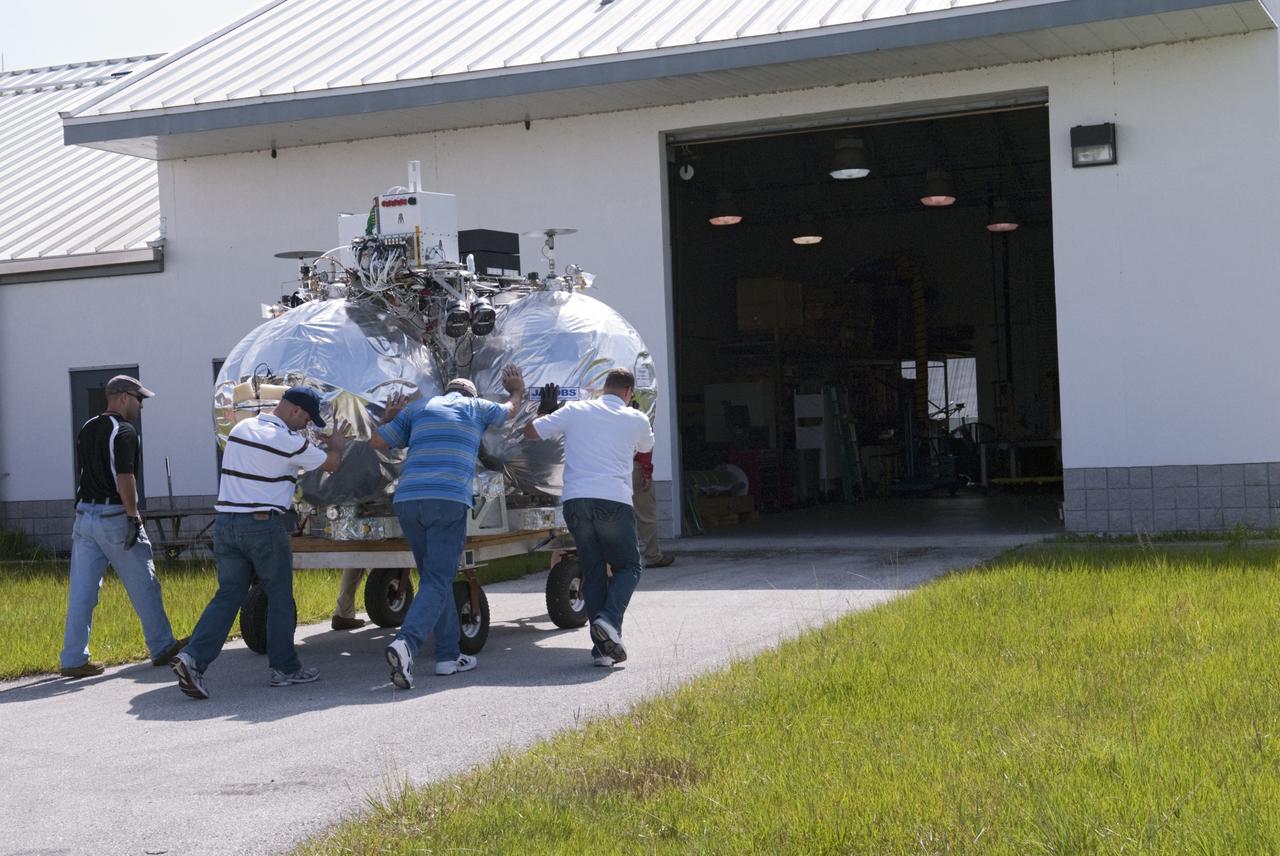
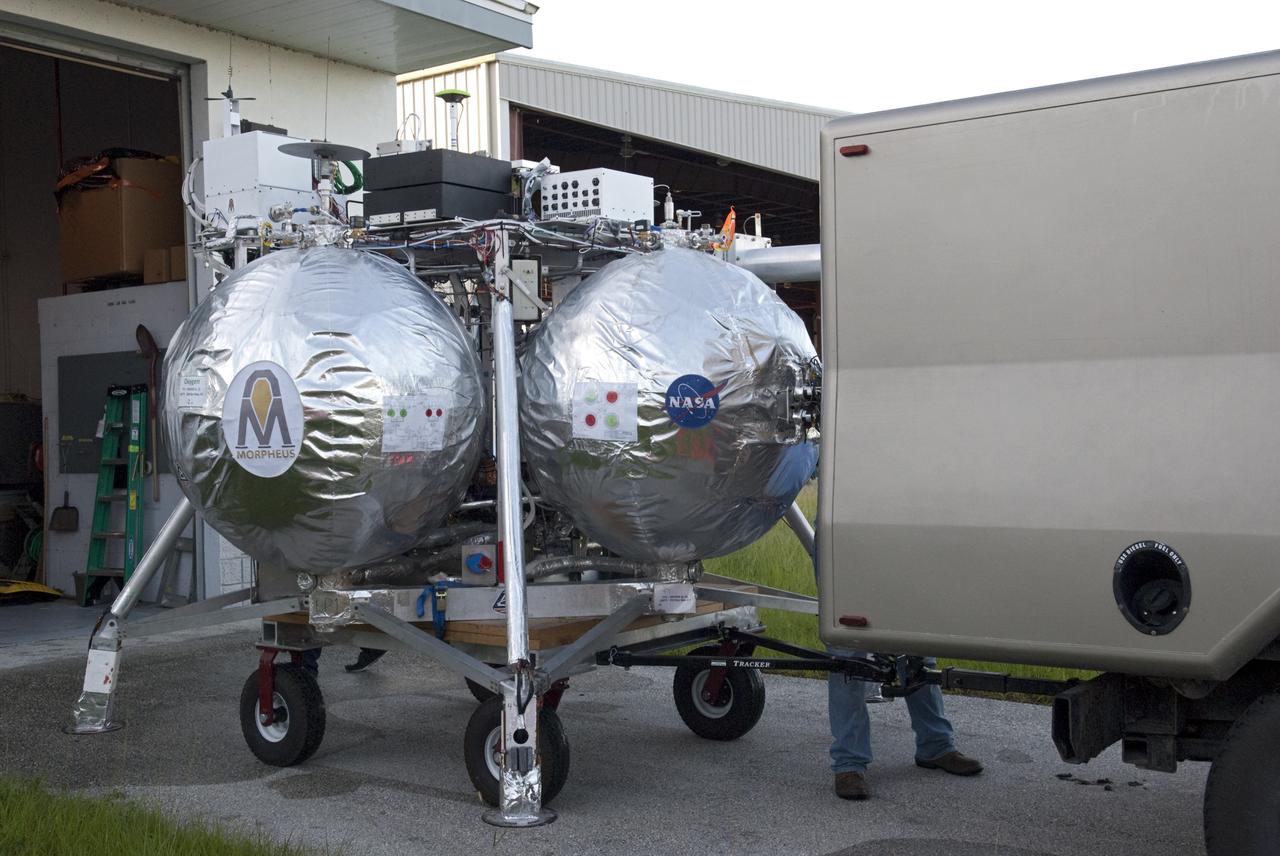
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
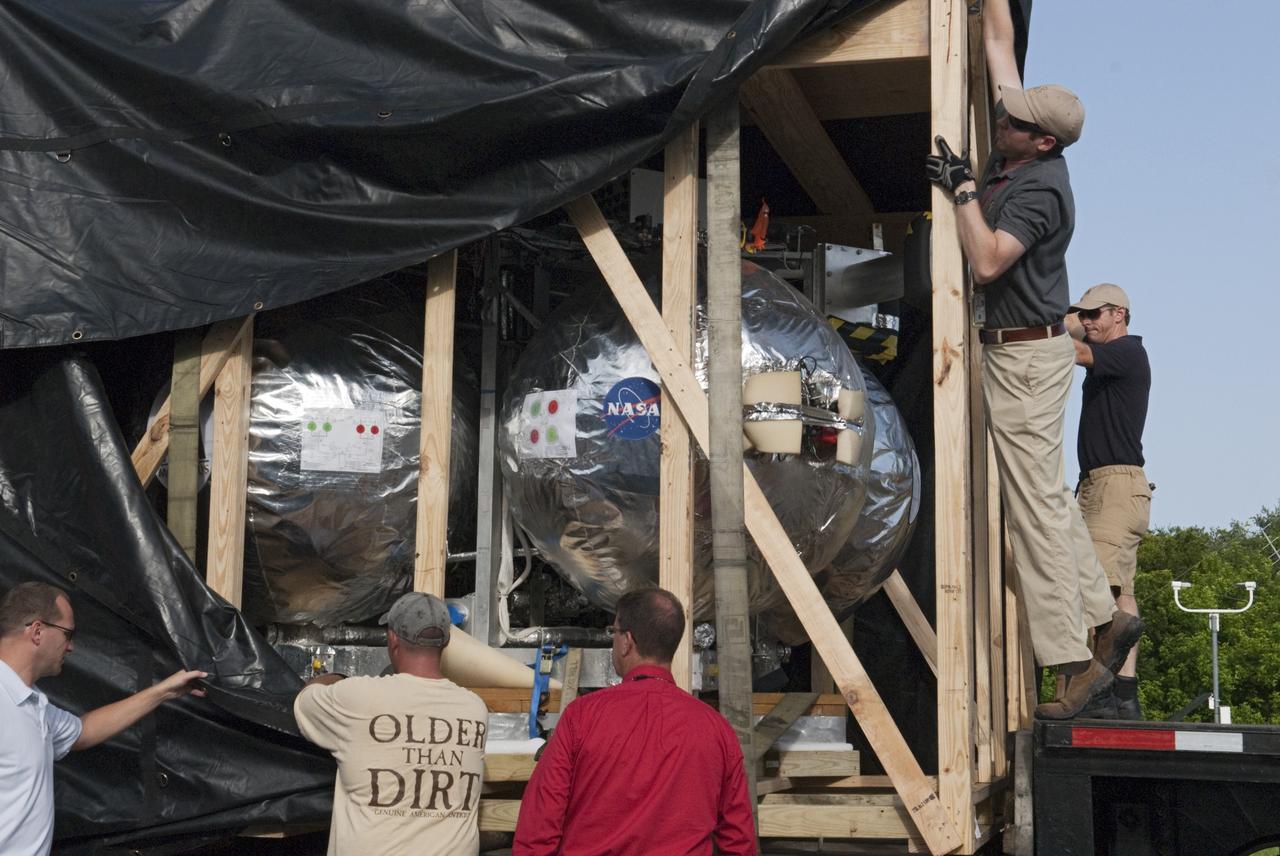

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
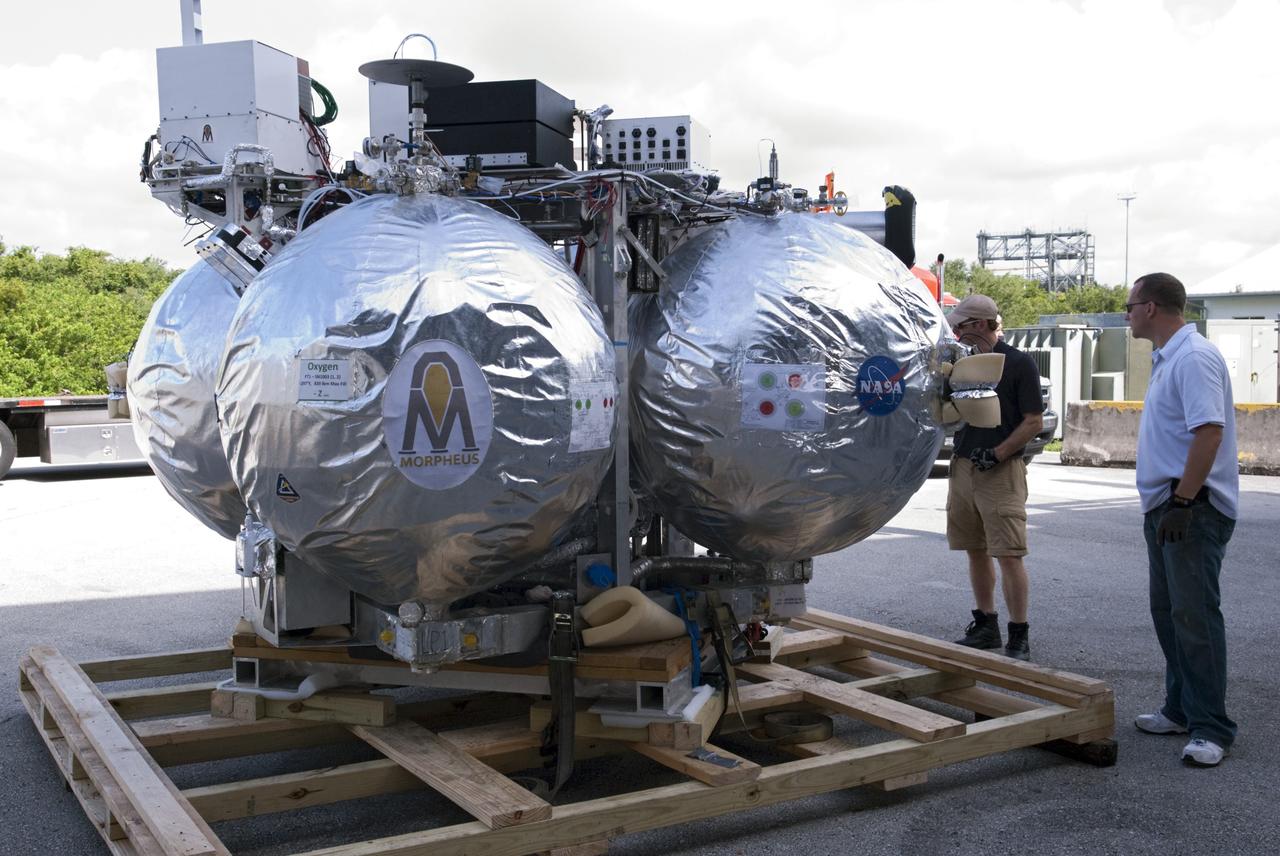

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
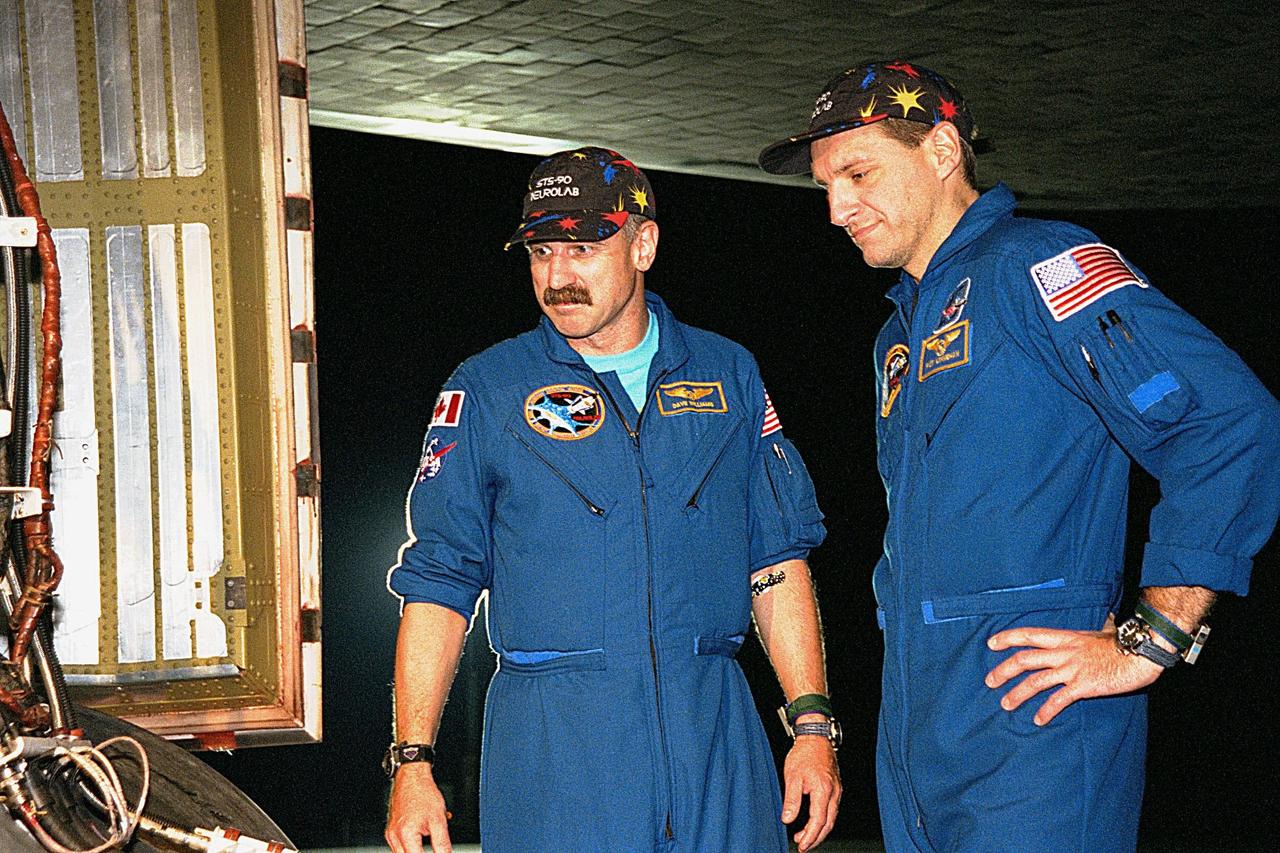

STS-90 Mission Specialists Dafydd (Dave) Williams, M.D., with the Canadian Space Agency (left) and Richard Linnehan, D.V.M., inspect the orbiter Columbia's tires in the evening after their midday arrival on May 3, ending their nearly 16-day Neurolab mission. The 90th Shuttle mission was Columbia's 13th landing at the space center and the 43rd KSC landing in the history of the Space Shuttle program. During the mission, the crew conducted research to contribute to a better understanding of the human nervous system

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s parachute systems successfully completed a “lawn dart” test at the Yuma Proving Ground in Arizona in February. The test involved dropping the dart from a C-17 aircraft. This reliability test was part of a special studies program NASA initiated to validate the robust design of Starliner’s parachute systems, and is an important milestone in proving the systems are ready to safely land Starliner. NASA and Boeing are preparing for the company’s uncrewed and crewed flight tests of Starliner as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which will return human spaceflight launches into low-Earth orbit from U.S. soil
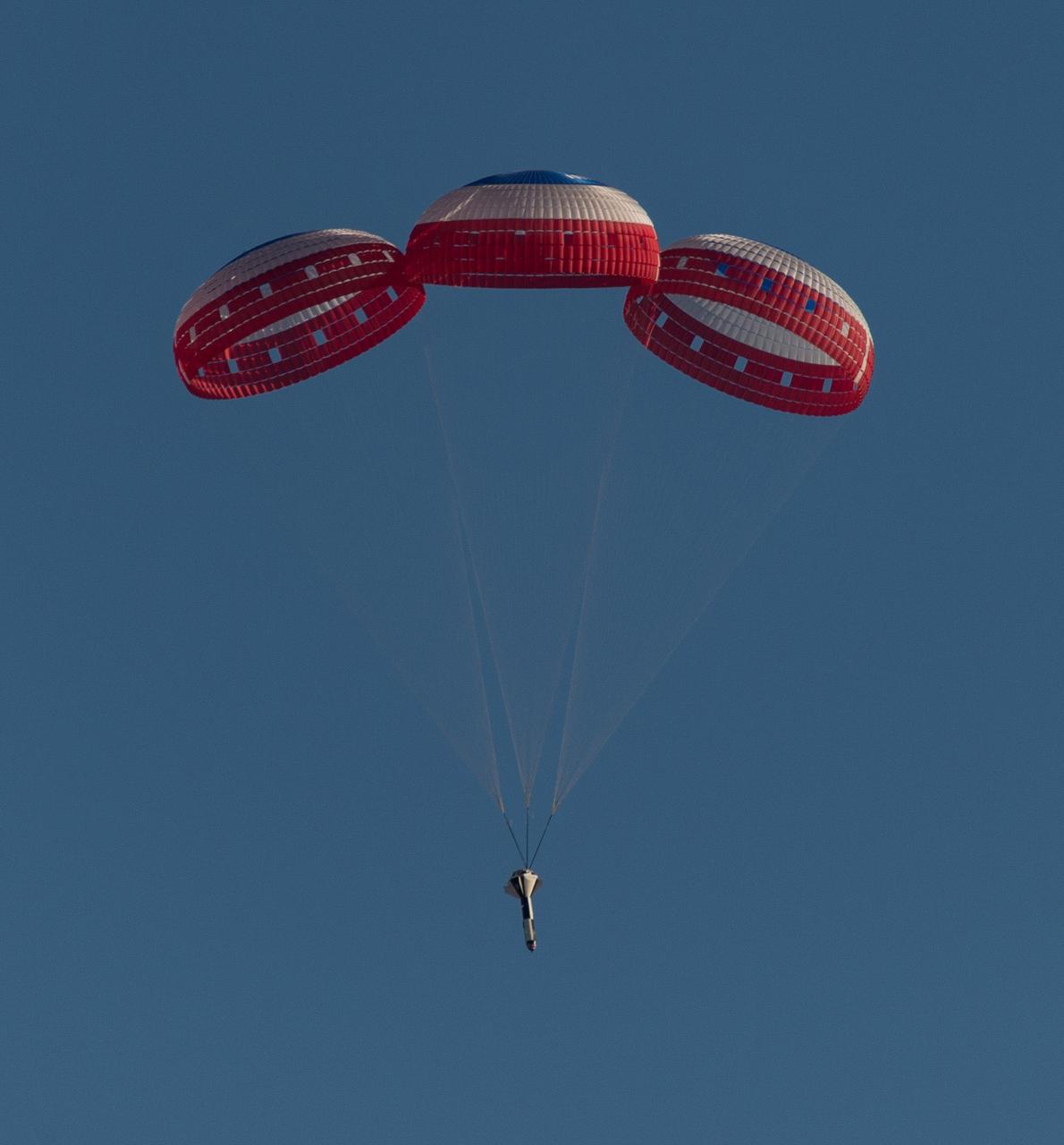

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s parachute systems successfully completed a “lawn dart” test at the Yuma Proving Ground in Arizona in February. The test involved dropping the dart from a C-17 aircraft. This reliability test was part of a special studies program NASA initiated to validate the robust design of Starliner’s parachute systems, and is an important milestone in proving the systems are ready to safely land Starliner. NASA and Boeing are preparing for the company’s uncrewed and crewed flight tests of Starliner as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which will return human spaceflight launches into low-Earth orbit from U.S. soil
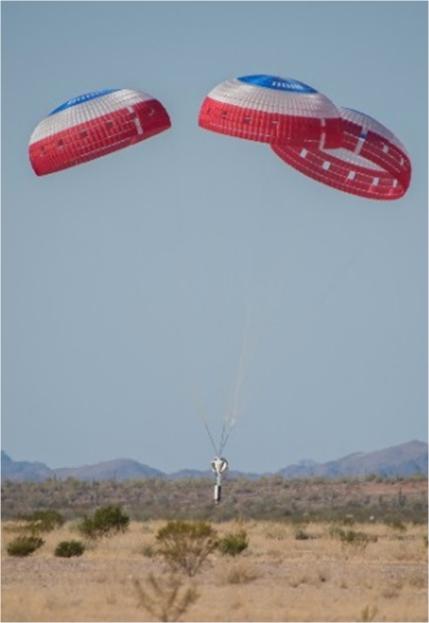

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s parachute systems successfully completed a “lawn dart” test at the Yuma Proving Ground in Arizona in February. The test involved dropping the dart from a C-17 aircraft. This reliability test was part of a special studies program NASA initiated to validate the robust design of Starliner’s parachute systems, and is an important milestone in proving the systems are ready to safely land Starliner. NASA and Boeing are preparing for the company’s uncrewed and crewed flight tests of Starliner as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which will return human spaceflight launches into low-Earth orbit from U.S. soil.
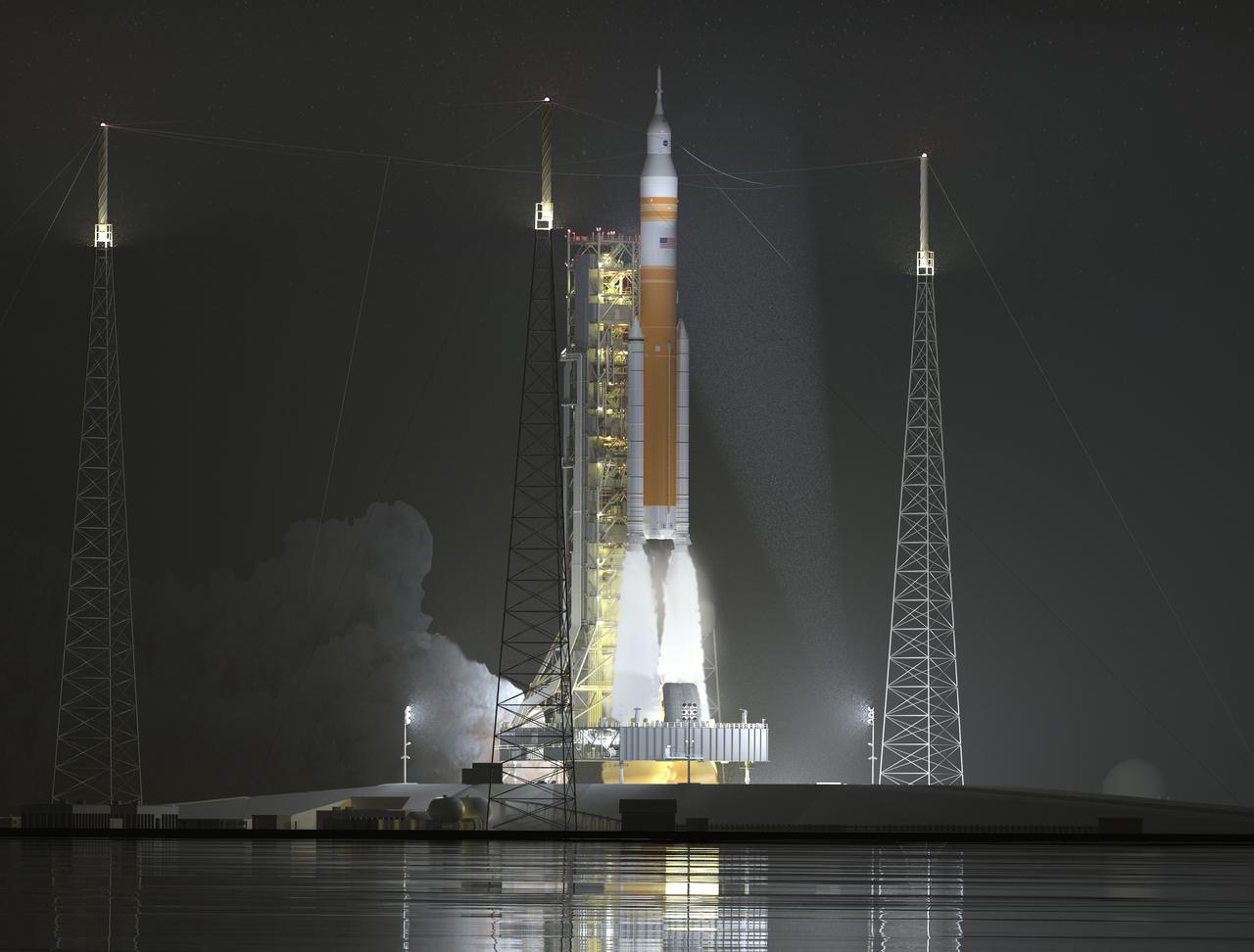

Illustration of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant night launch. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA) In album: B1B_Crew_SLS
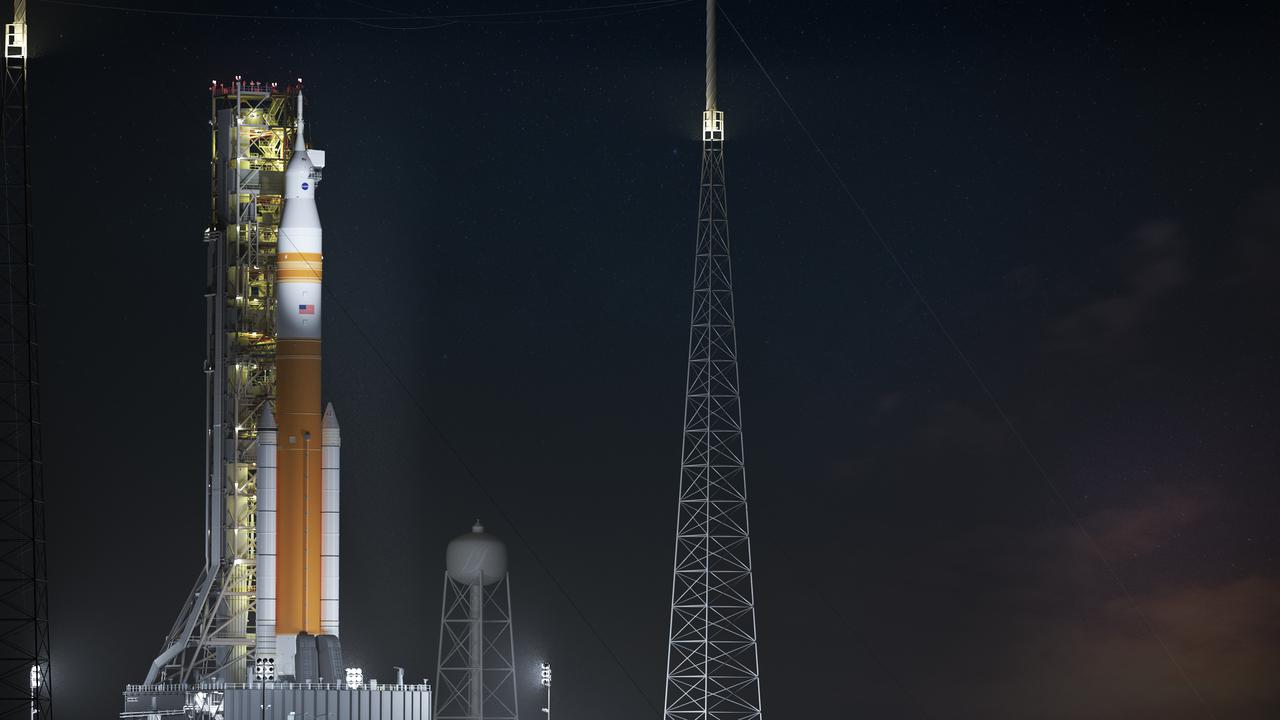

Illustration of nighttime scene of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant on Pad 39B.. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)

Illustration of the SLS Exploration Upper Stage, or EUS. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)

Seen here, is a nighttime rendering of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant positioned on the mobile launcher. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
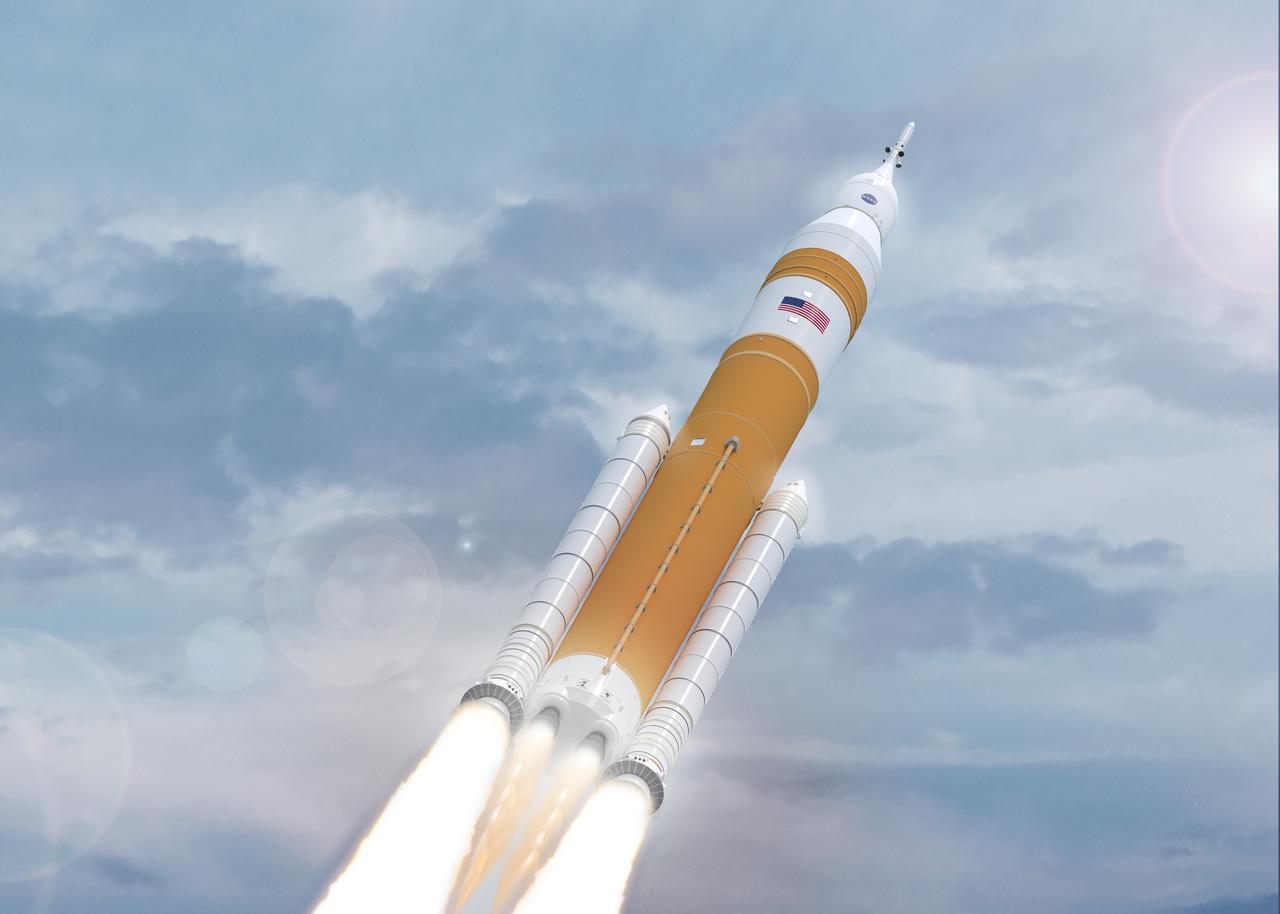

Illustration of evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant in flight. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)

Illustration of the SLS Exploration Upper Stage, or EUS. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
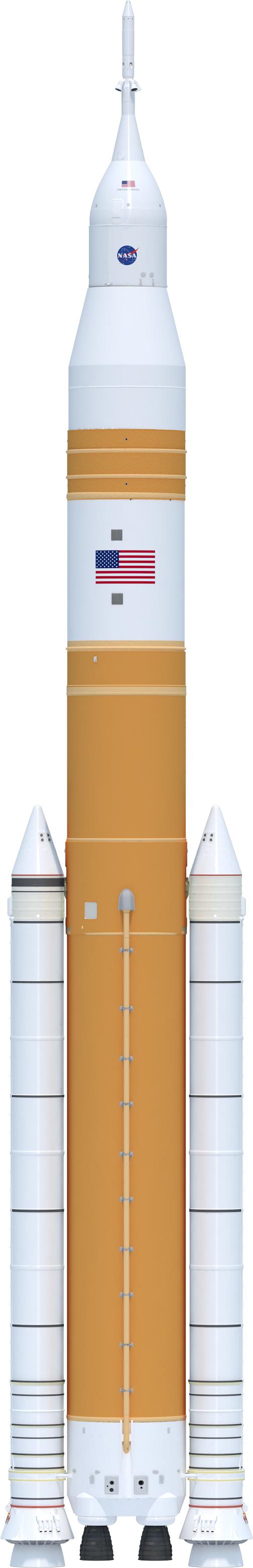

Illustration of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant outer mold line. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
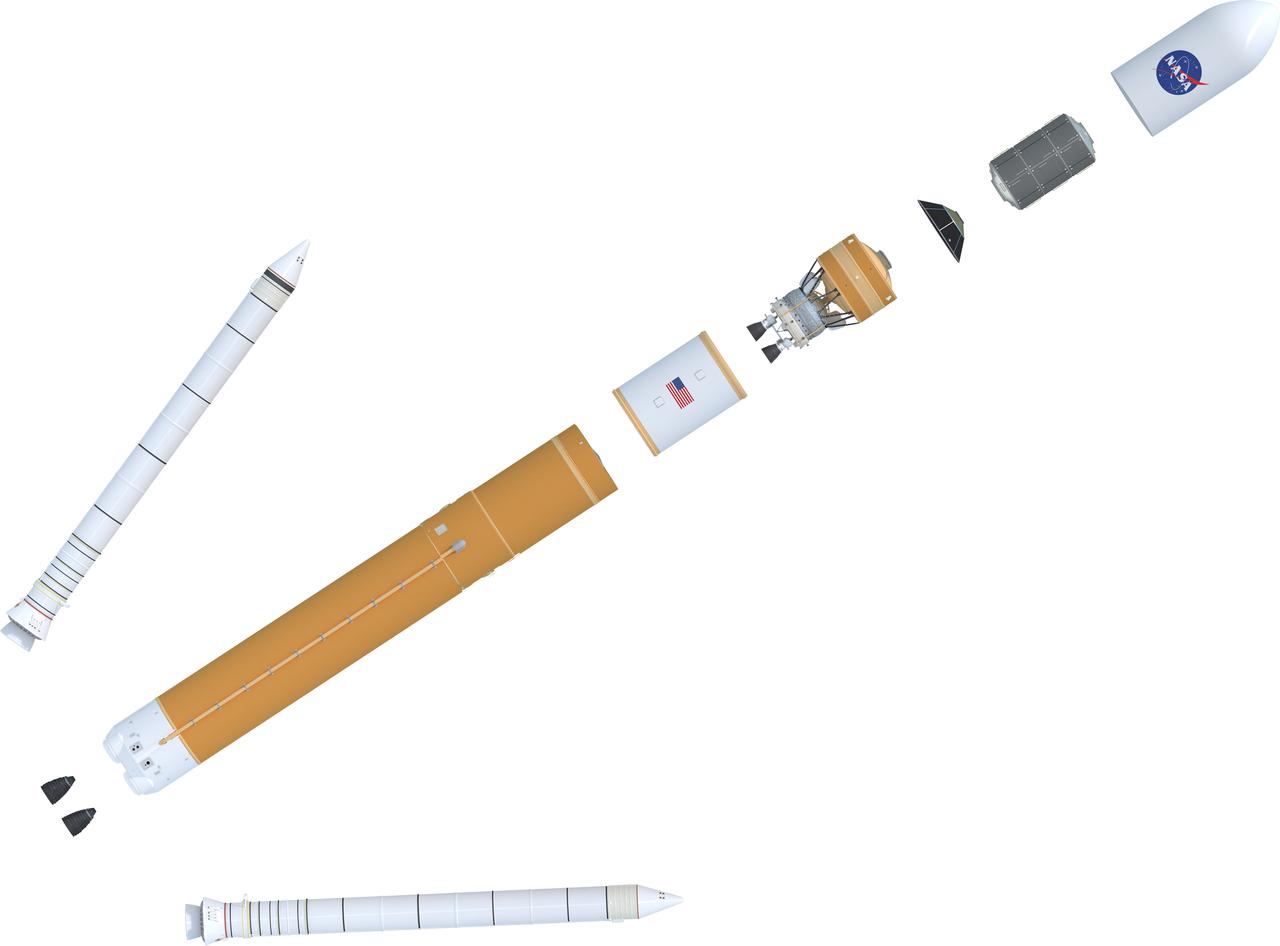
Expanded view illustration of elements of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
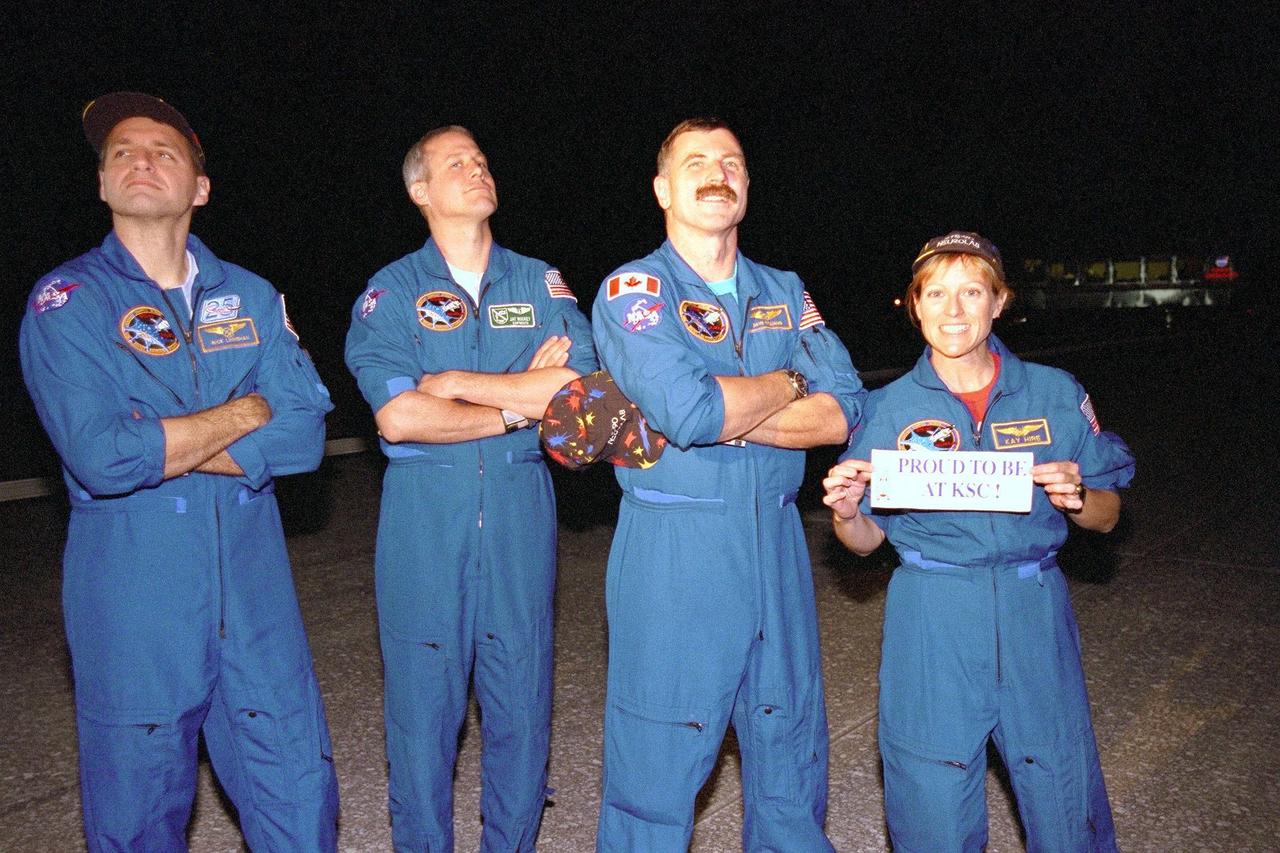

Some of the STS-90 crew members pose at the Shuttle Landing Facility hours after arrival on May 3, ending their nearly 16-day Neurolab mission. Shown left to right are Mission Specialist Richard Linnehan, D.V.M.; Payload Specialist Jay Buckey, M.D.; and Mission Specialists Dafydd (Dave) Williams, M.D., with the Canadian Space Agency and Kathryn (Kay) Hire holding a sign that states "Proud to be at KSC." The 90th Shuttle mission was Columbia's 13th landing at the space center and the 43rd KSC landing in the history of the Space Shuttle program. During the mission, the crew conducted research to contribute to a better understanding of the human nervous system
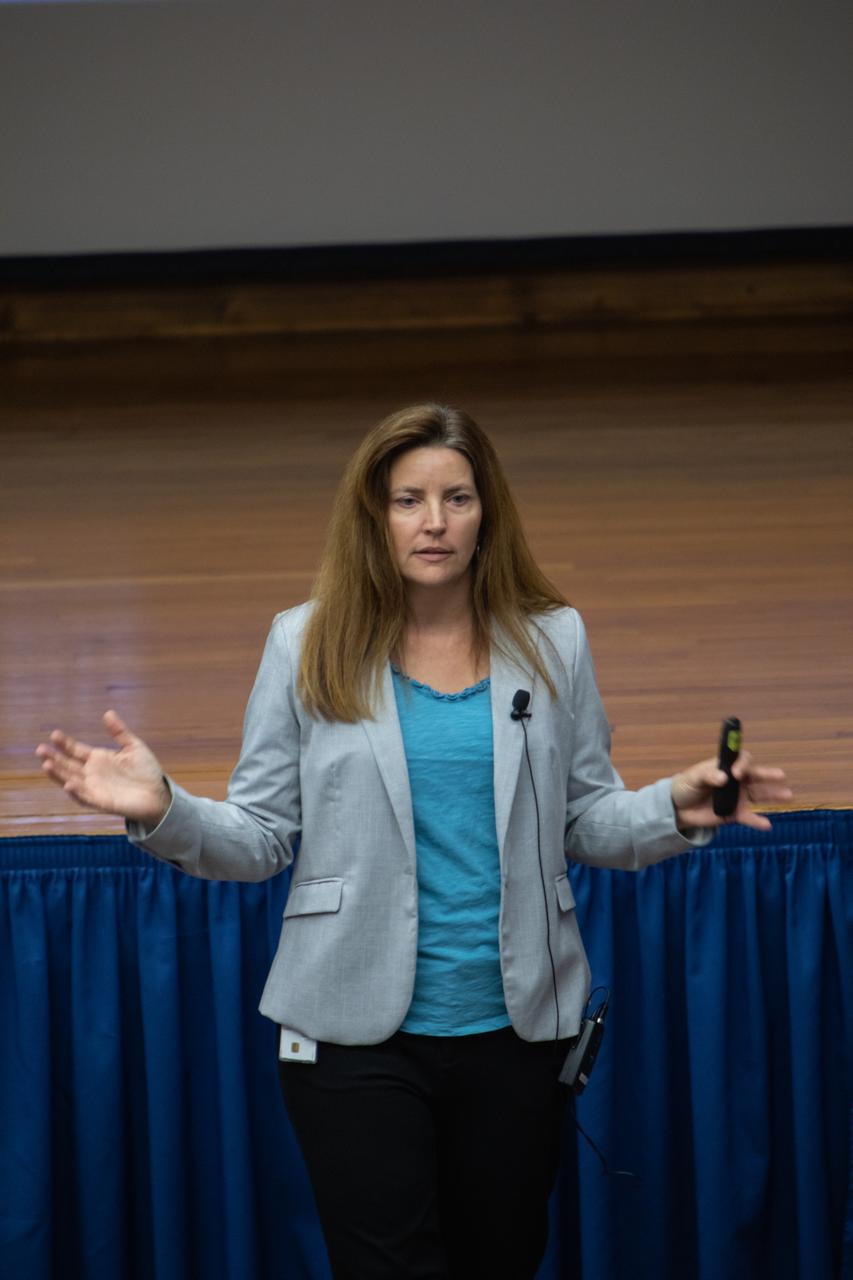

Lisa-Watson Morgan, NASA’s Human Landing System program manager, provides an overview of the program to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on Nov. 19, 2019. Watson-Morgan’s presentation was part of the center’s Innovation Days, one of several events throughout the year aimed at fostering and encouraging an innovative culture at Kennedy. In addition to the presentation, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend an innovation showcase, where nearly 50 exhibitors demonstrated new technologies and innovations. Showcase participants included individuals from multiple directorates, programs and organizations throughout Kennedy.
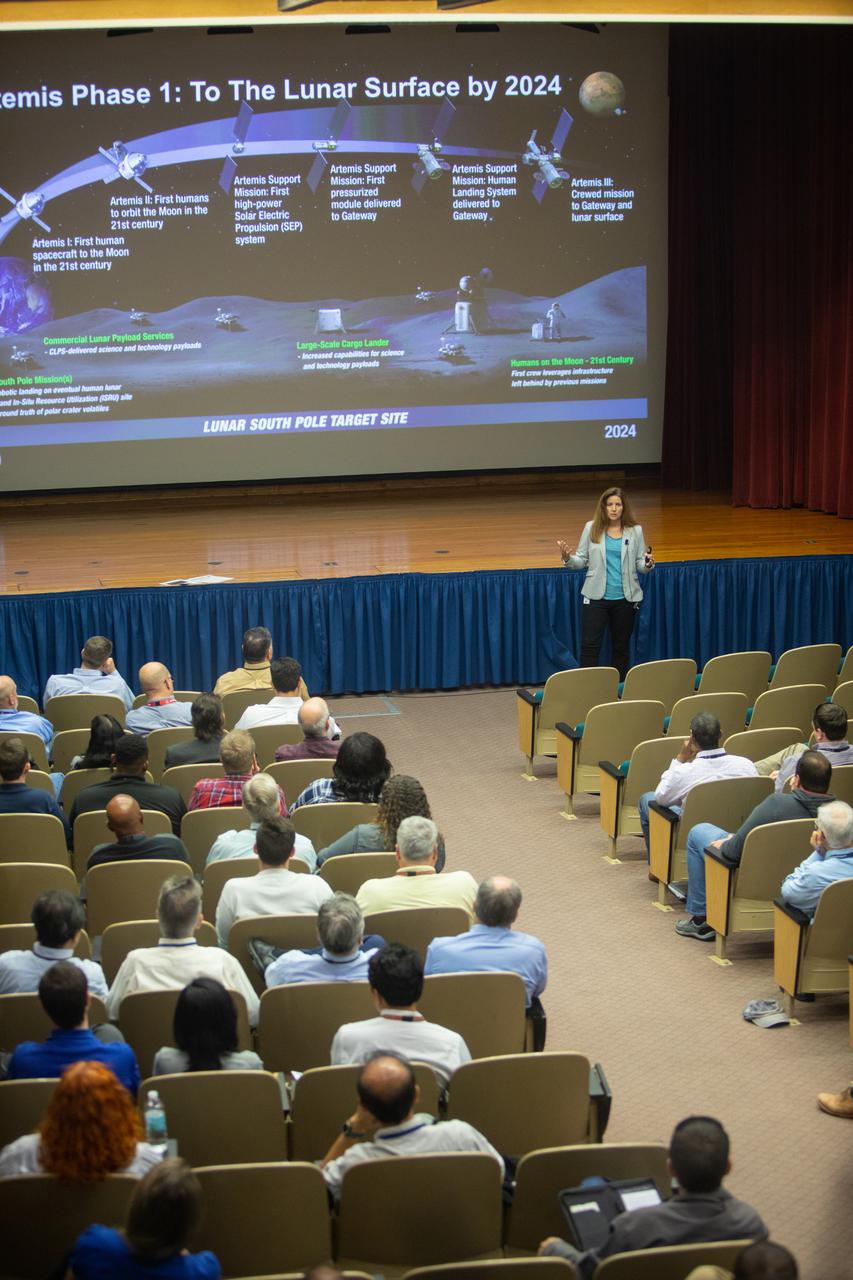

Lisa-Watson Morgan, NASA’s Human Landing System program manager, provides an overview of the program to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on Nov. 19, 2019. Watson-Morgan’s presentation was part of the center’s Innovation Days, one of several events throughout the year aimed at fostering and encouraging an innovative culture at Kennedy. In addition to the presentation, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend an innovation showcase, where nearly 50 exhibitors demonstrated new technologies and innovations. Showcase participants included individuals from multiple directorates, programs and organizations throughout Kennedy.
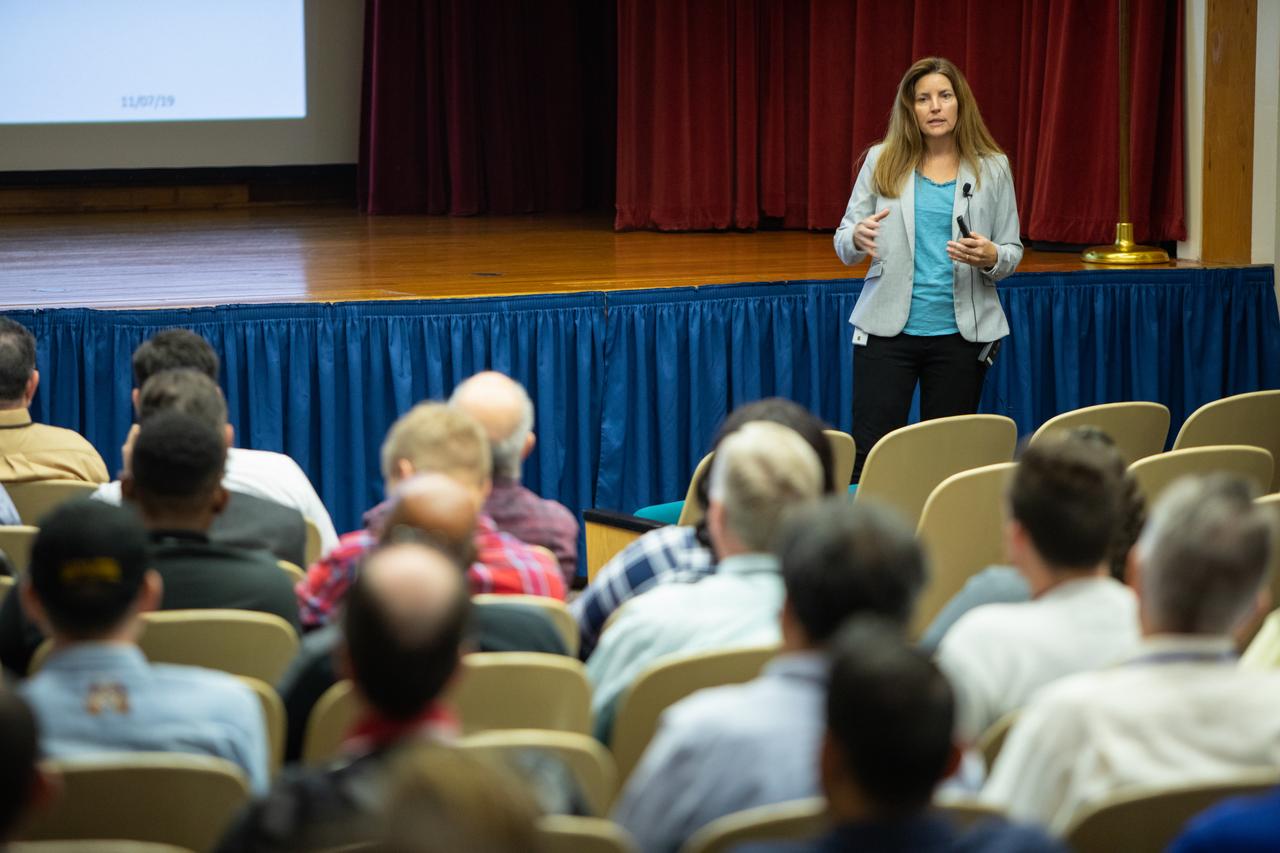

Lisa-Watson Morgan, NASA’s Human Landing System program manager, provides an overview of the program to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on Nov. 19, 2019. Watson-Morgan’s presentation was part of the center’s Innovation Days, one of several events throughout the year aimed at fostering and encouraging an innovative culture at Kennedy. In addition to the presentation, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend an innovation showcase, where nearly 50 exhibitors demonstrated new technologies and innovations. Showcase participants included individuals from multiple directorates, programs and organizations throughout Kennedy.
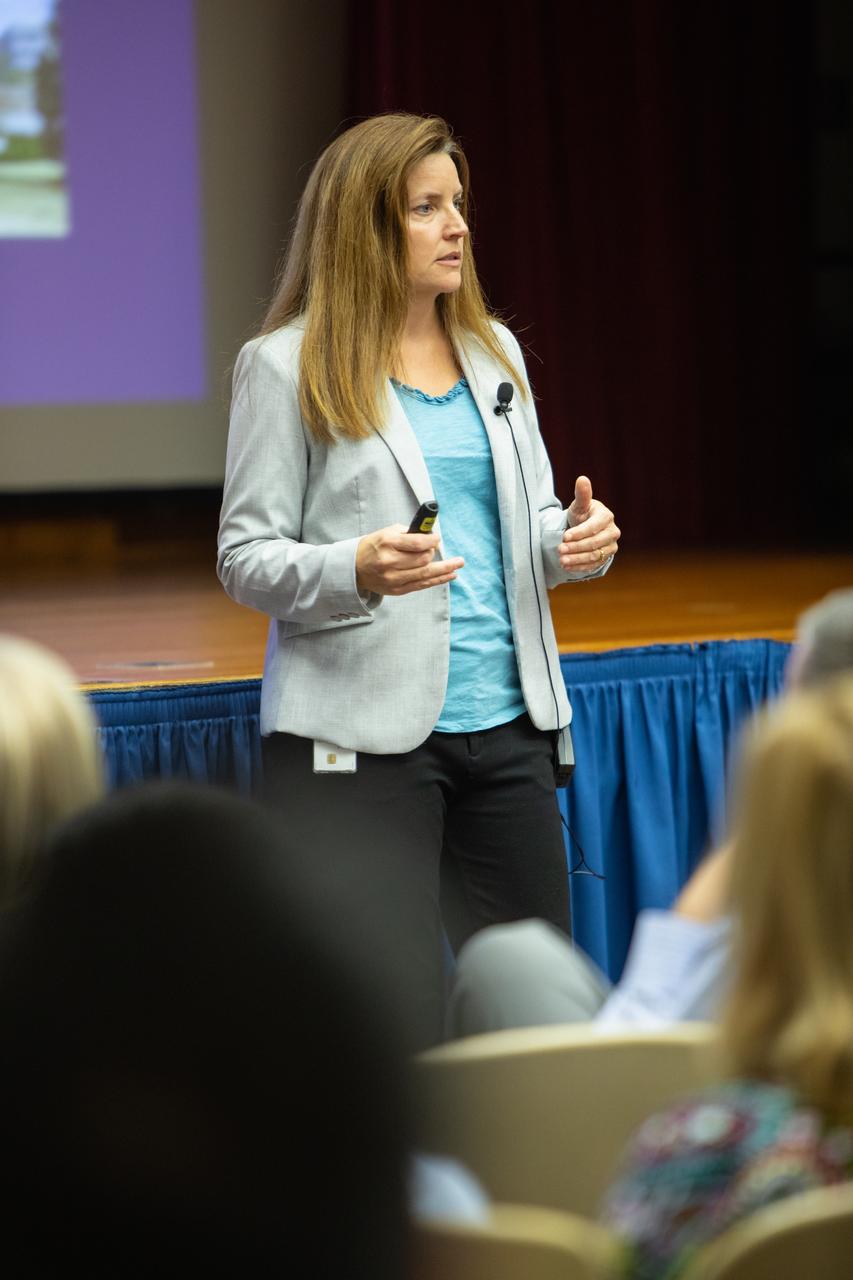

Lisa-Watson Morgan, NASA’s Human Landing System program manager, provides an overview of the program to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Florida spaceport’s Training Auditorium on Nov. 19, 2019. Watson-Morgan’s presentation was part of the center’s Innovation Days, one of several events throughout the year aimed at fostering and encouraging an innovative culture at Kennedy. In addition to the presentation, Kennedy employees had the opportunity to attend an innovation showcase, where nearly 50 exhibitors demonstrated new technologies and innovations. Showcase participants included individuals from multiple directorates, programs and organizations throughout Kennedy.
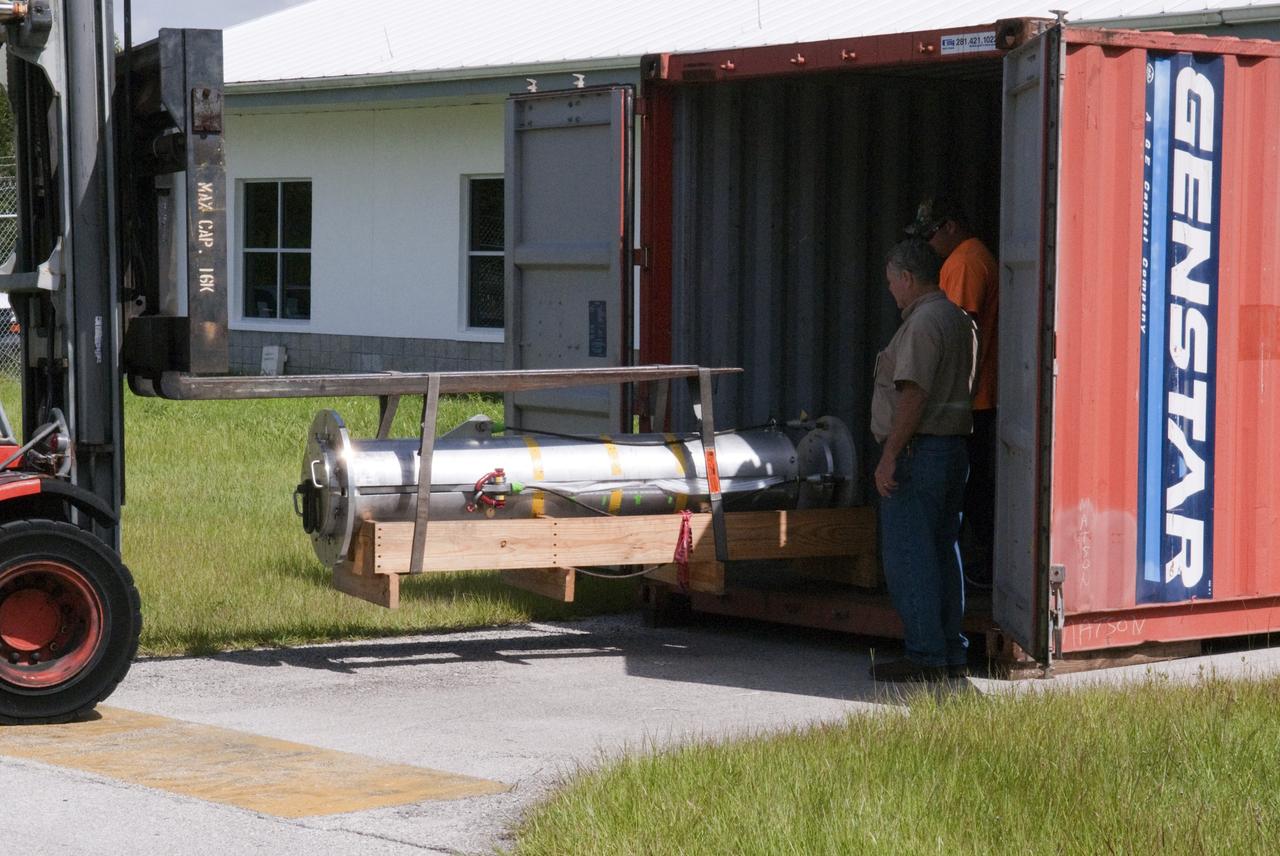

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Support equipment for NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
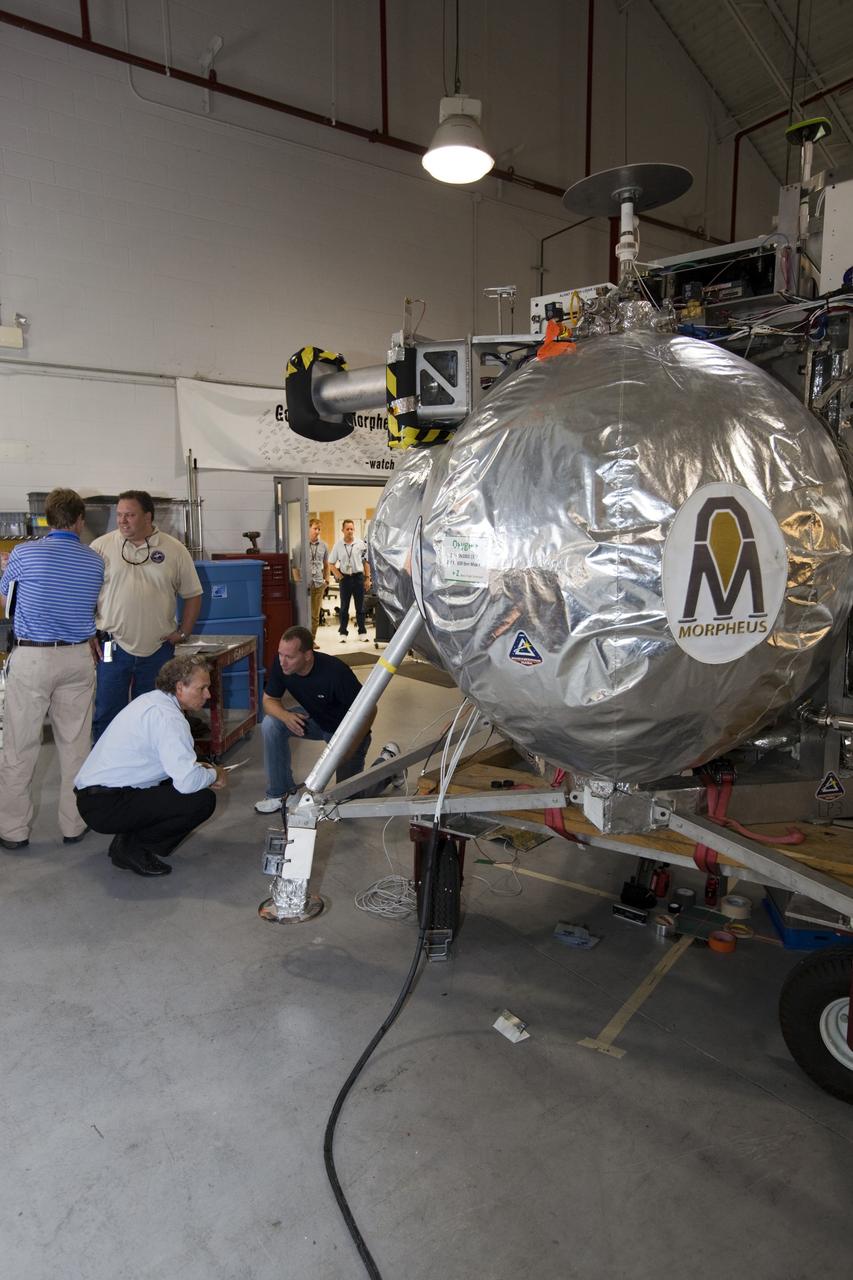

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Russell Romanella, director of Safety and Mission Assurance at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, kneeling on the left, is briefed on NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle. Morpheus is being checked out by technicians and engineers in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at Kennedy. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
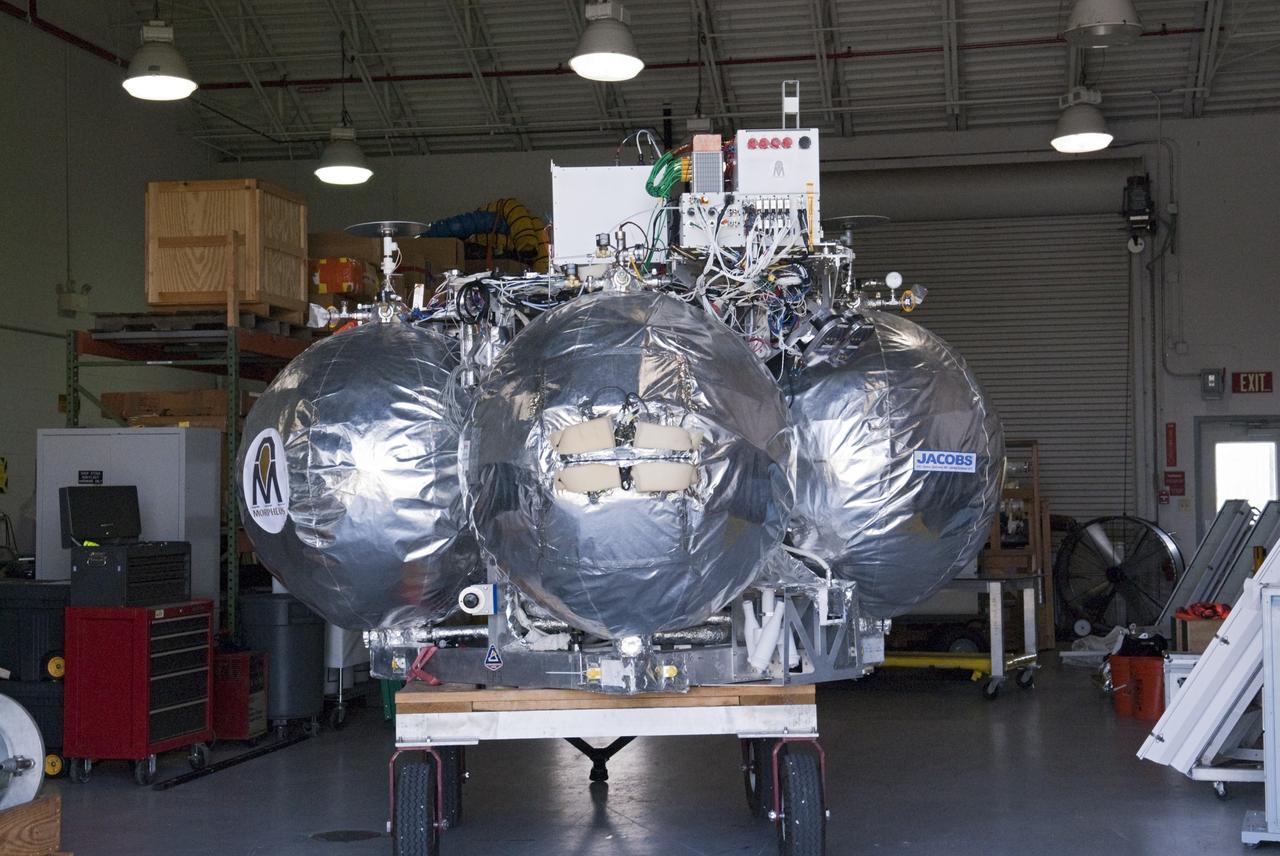

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, has been moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
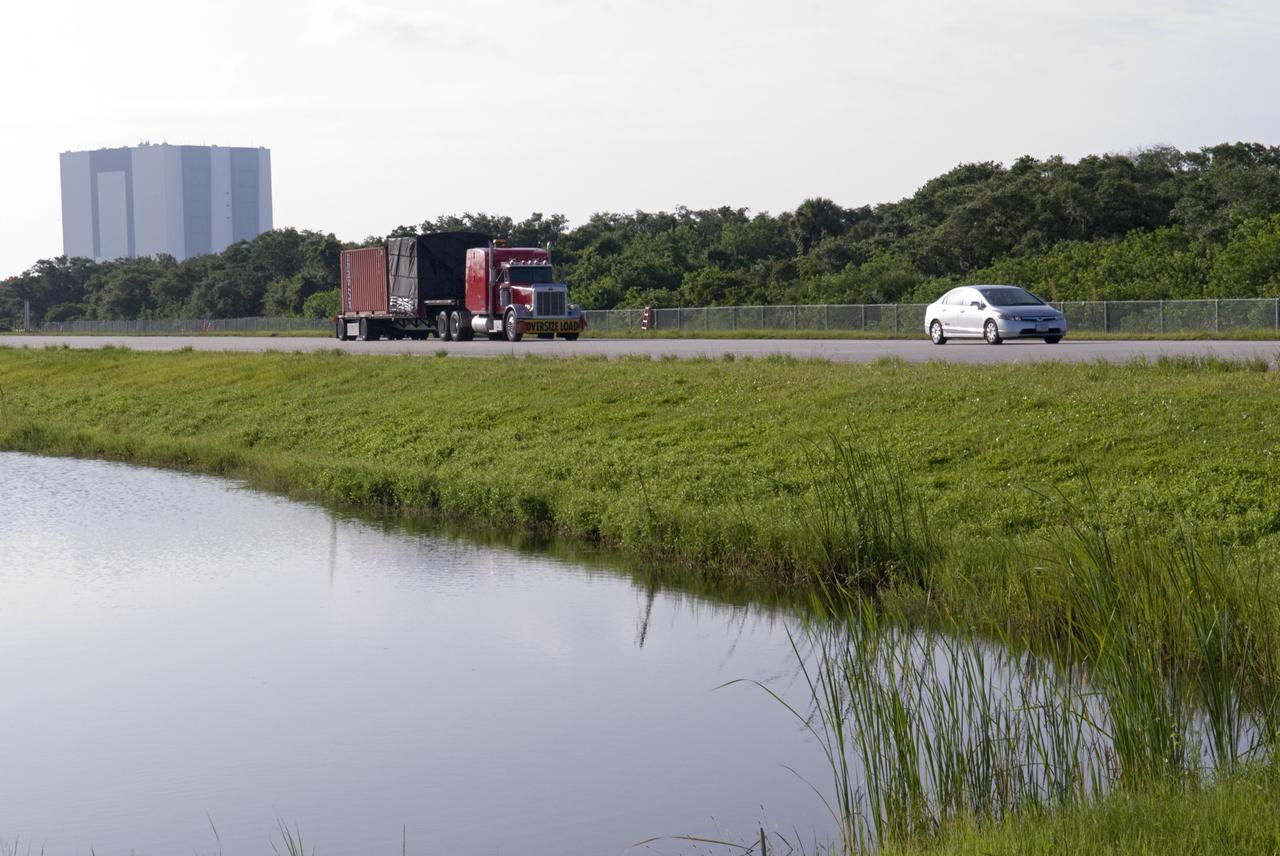

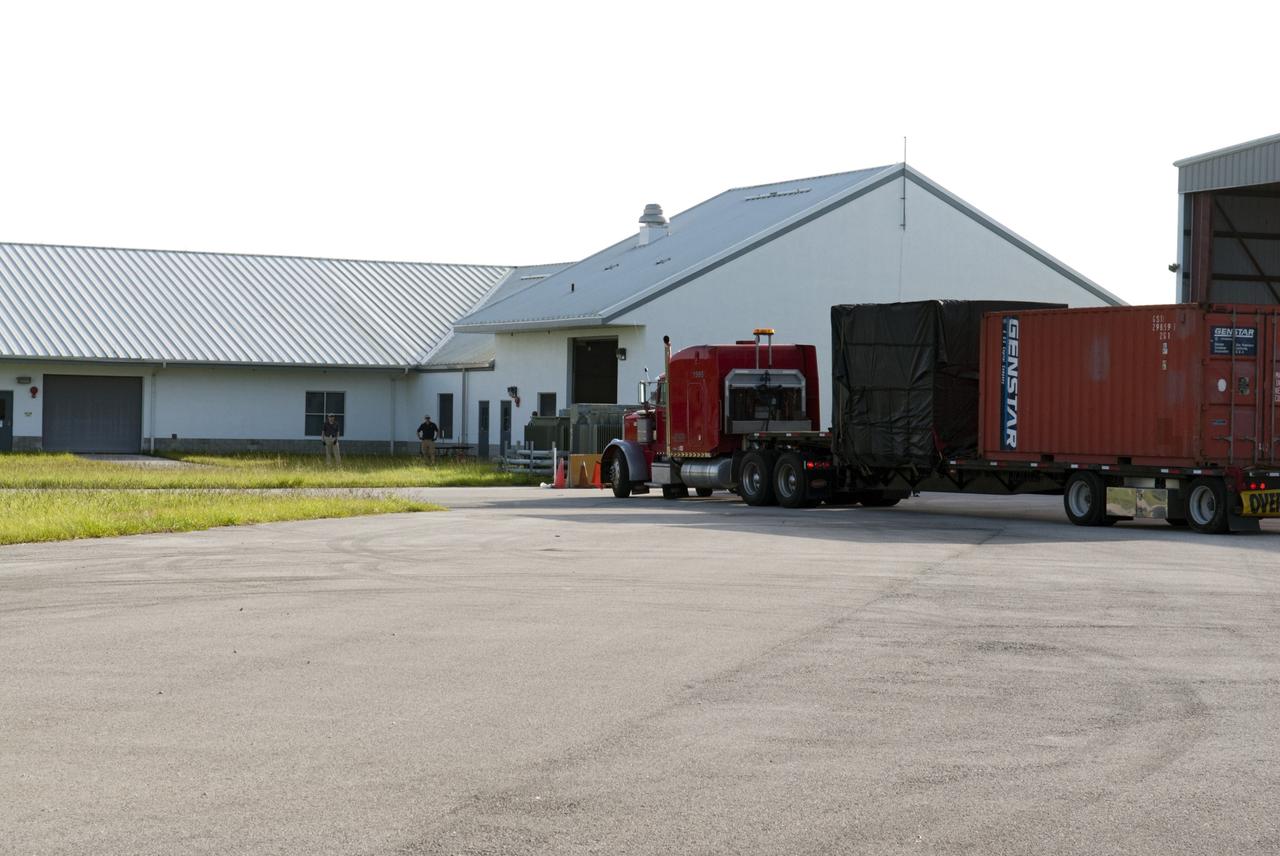
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A truck transporting NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, heads towards the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida for unloading. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
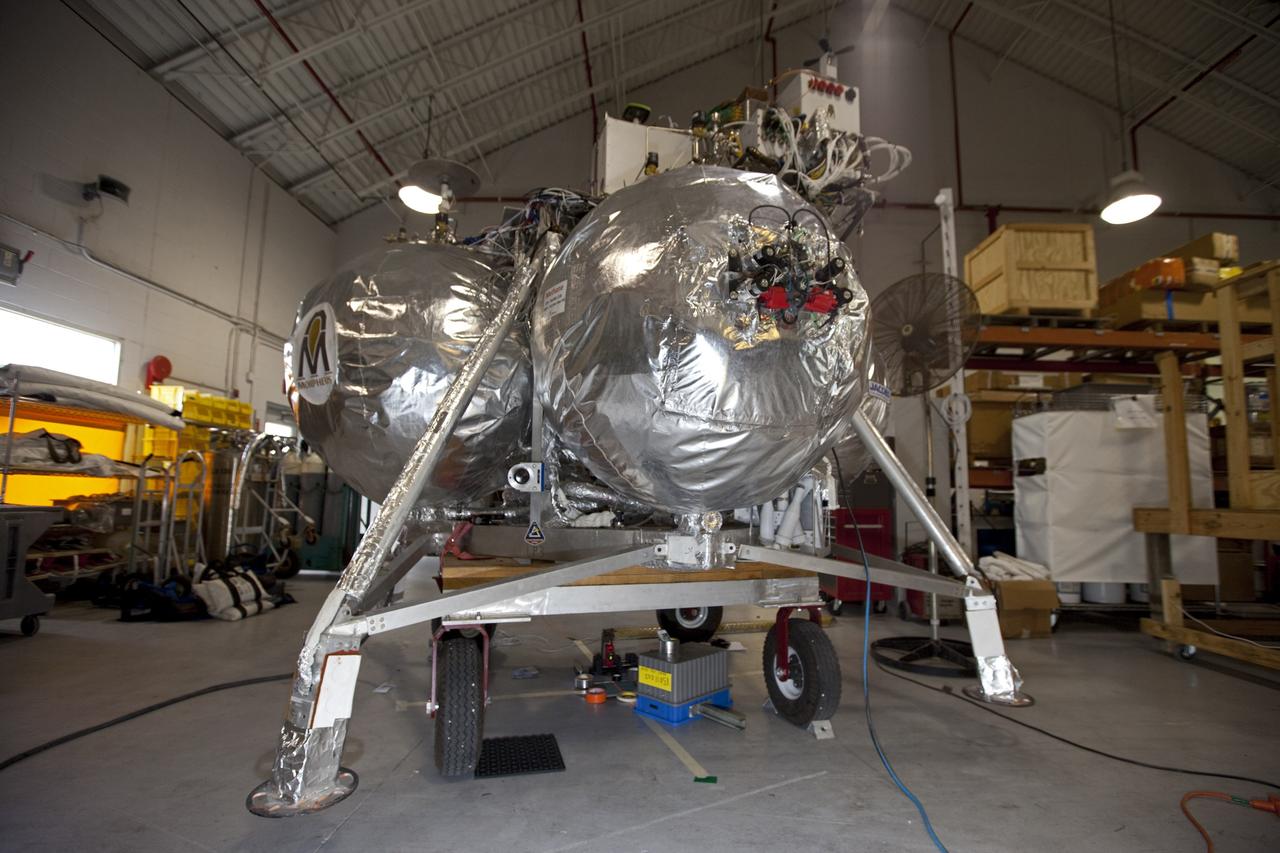

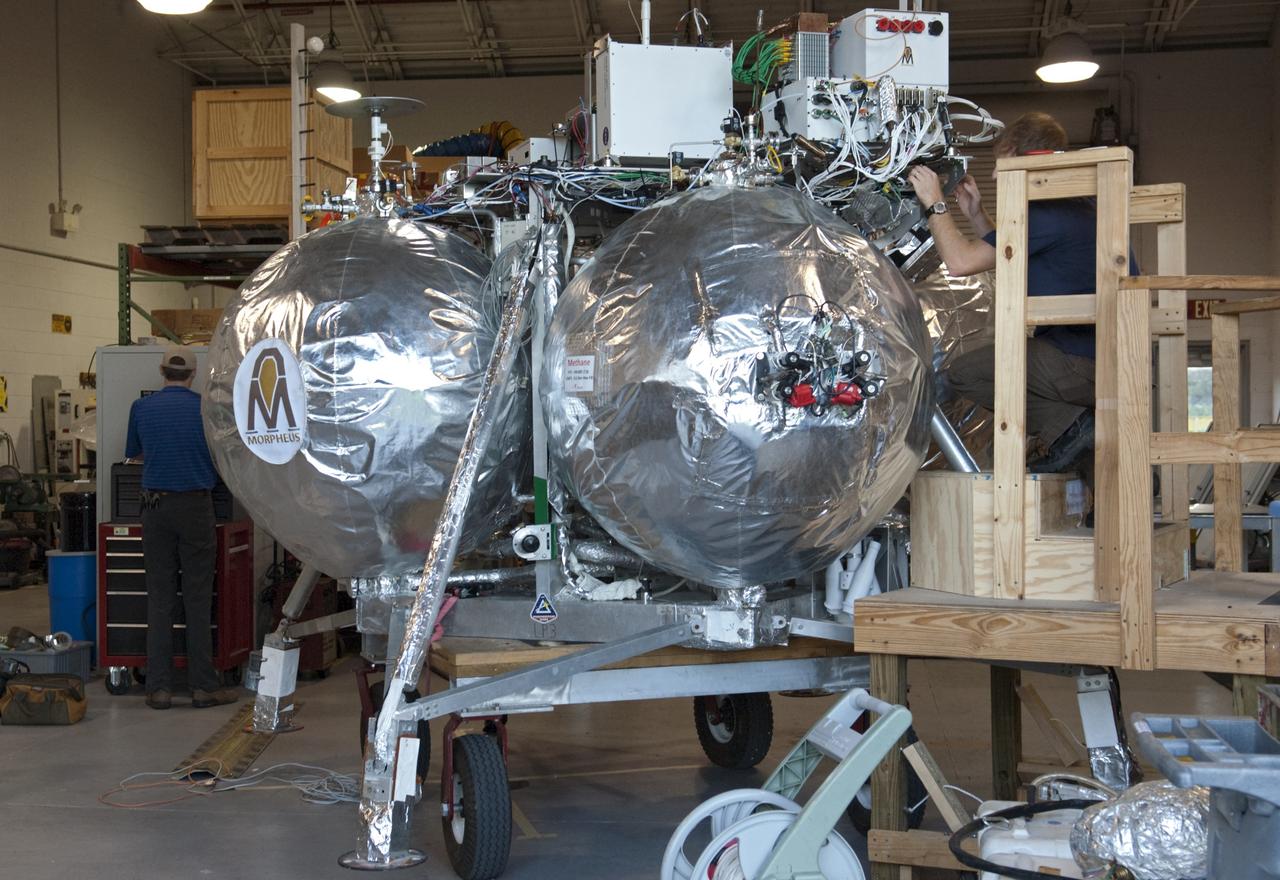
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being checked out in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
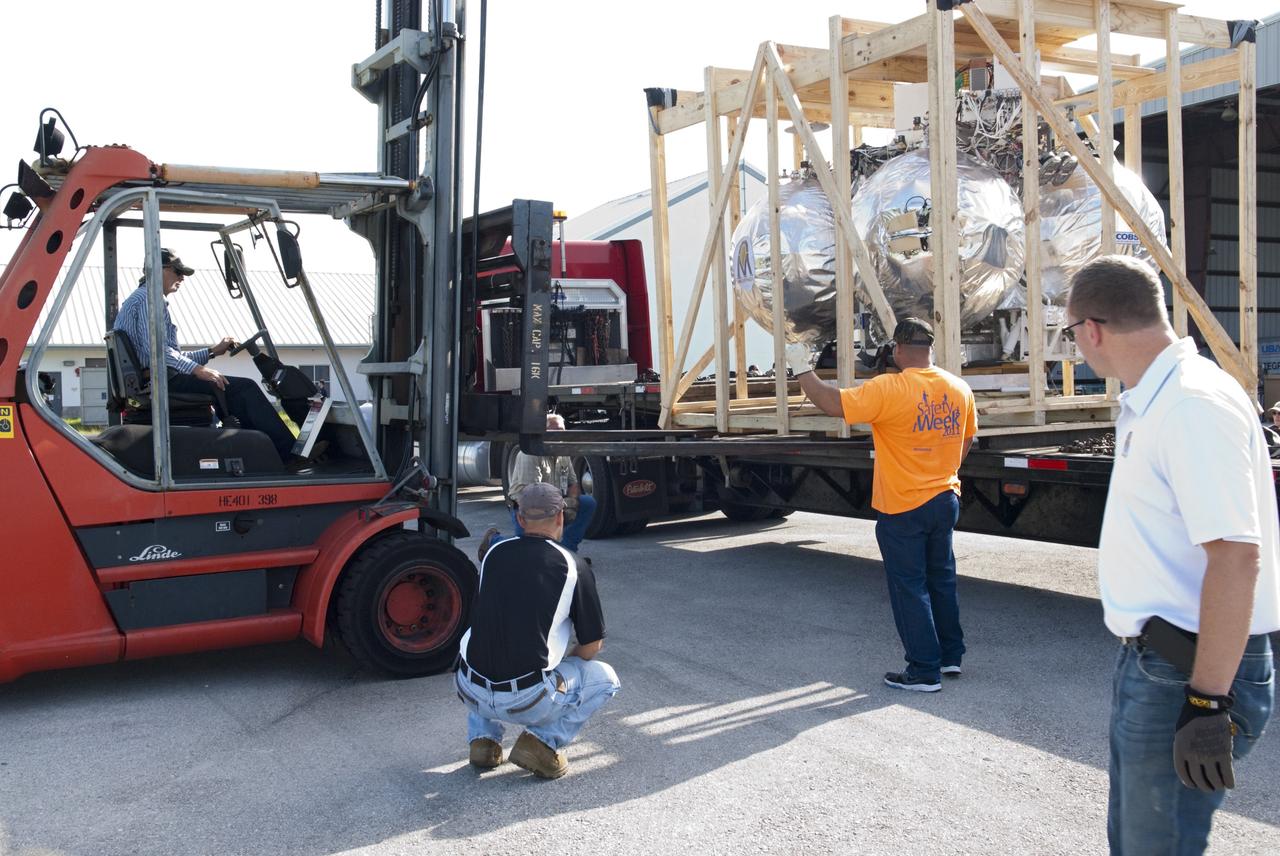

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
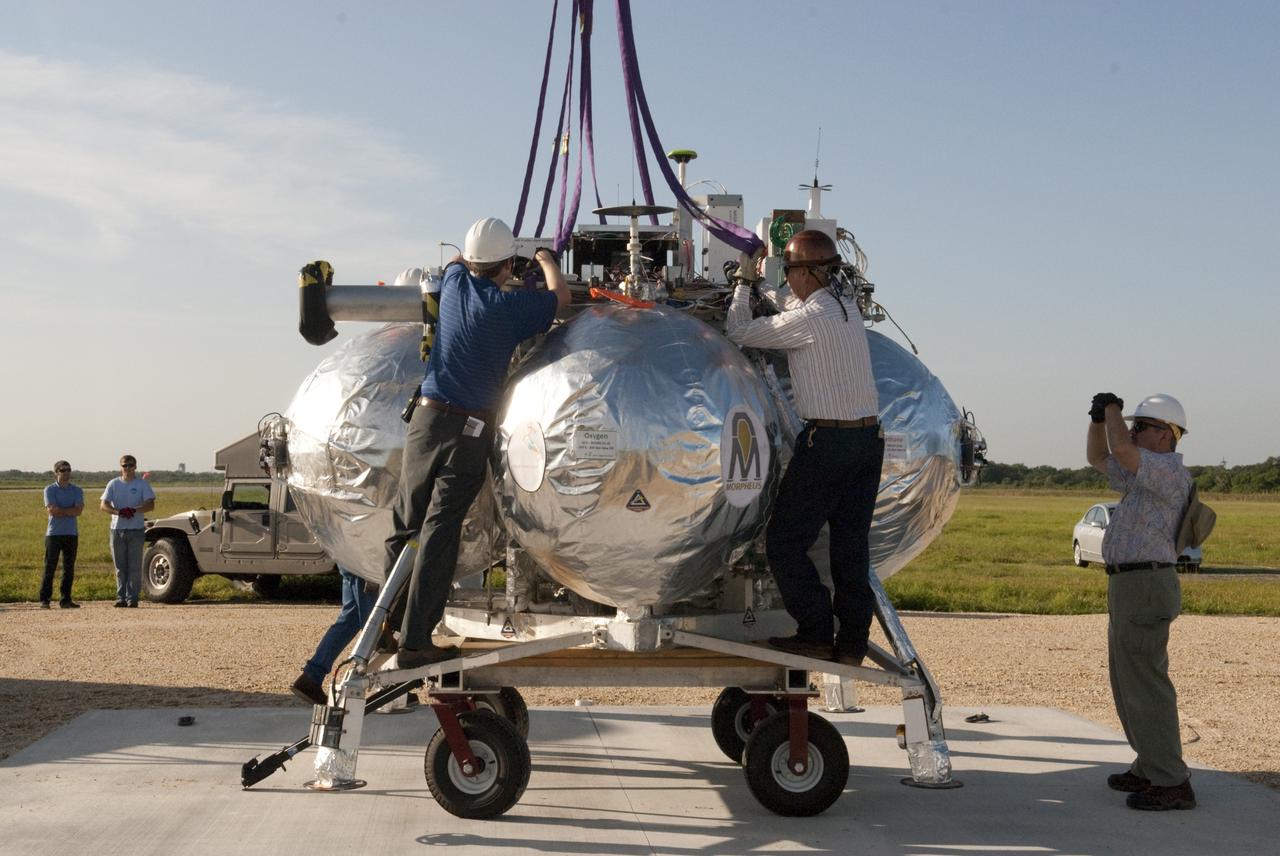

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Technicians secure connections for a crane which will be used to set up NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, at its launch position along the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
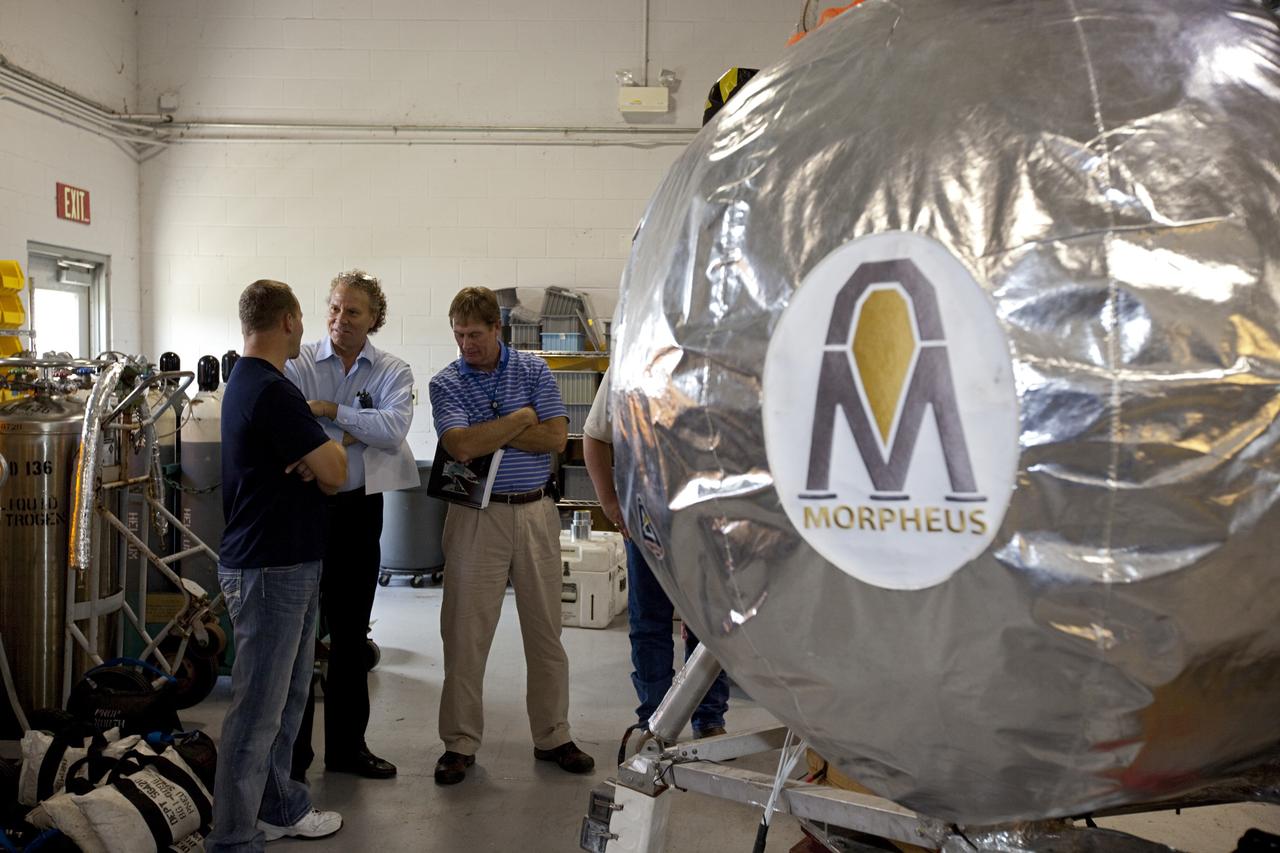

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Russell Romanella, director of Safety and Mission Assurance at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, center, is briefed on NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle. Morpheus is being checked out by technicians and engineers in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at Kennedy. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
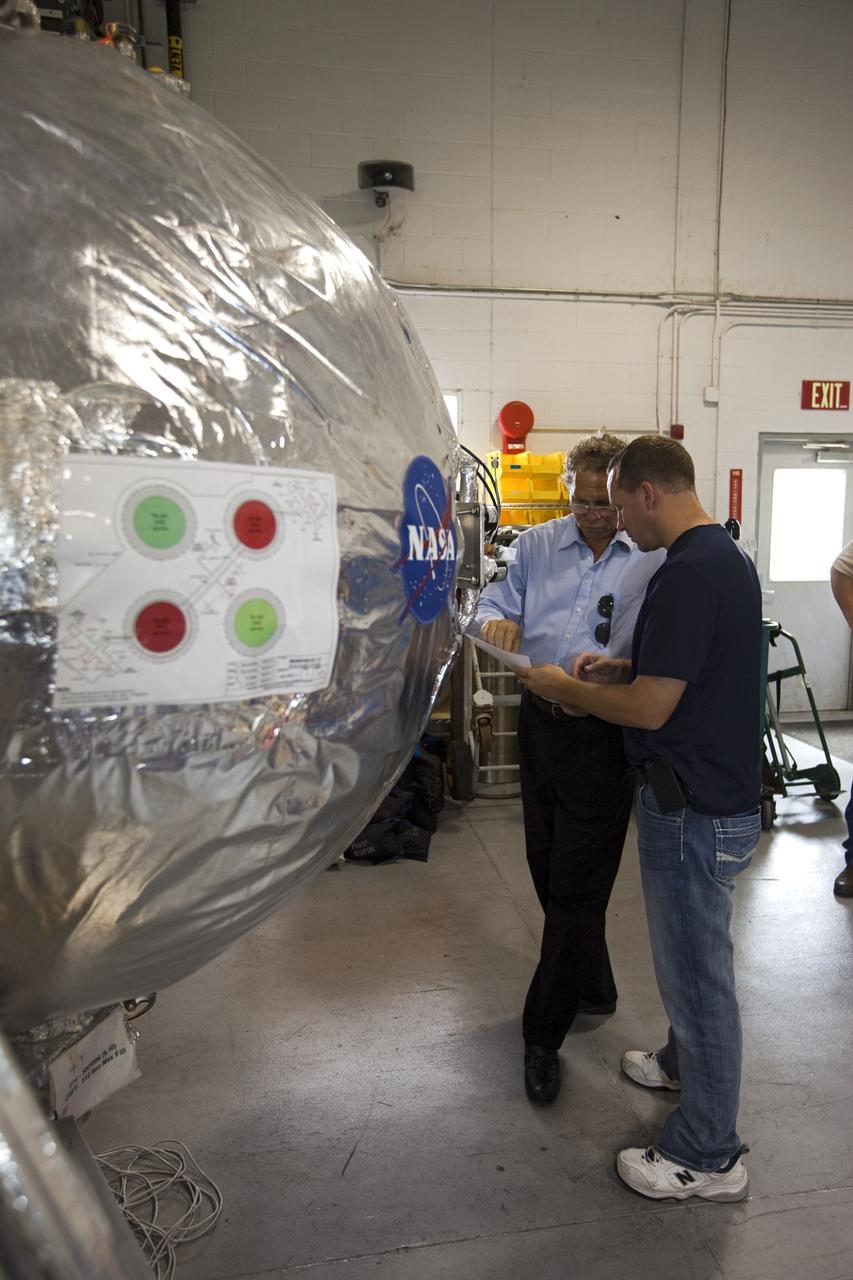

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Russell Romanella, director of Safety and Mission Assurance at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, left, is briefed on NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle. Morpheus is being checked out by technicians and engineers in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at Kennedy. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Russell Romanella, director of Safety and Mission Assurance at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, right-center, is briefed on NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle. Morpheus is being checked out by technicians and engineers in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at Kennedy. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
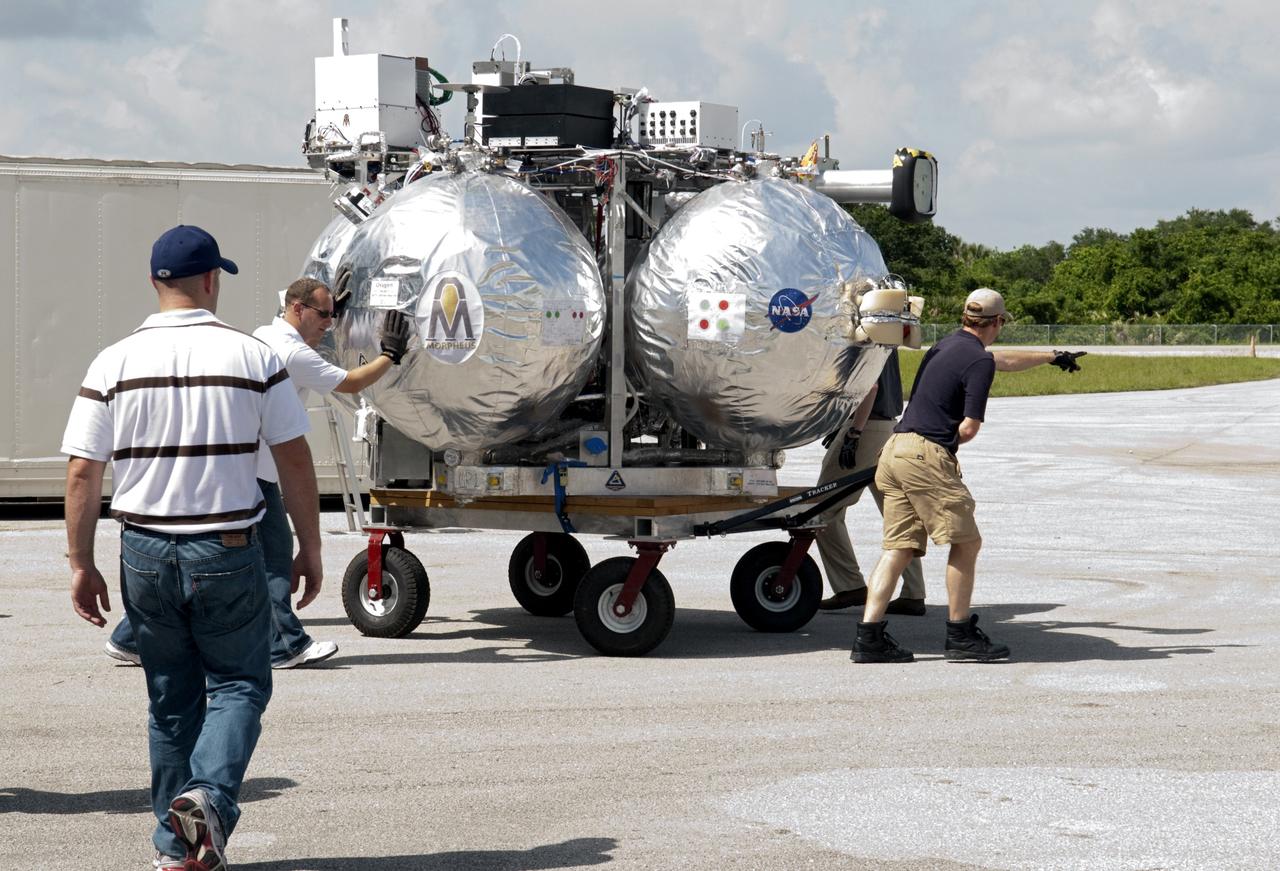

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
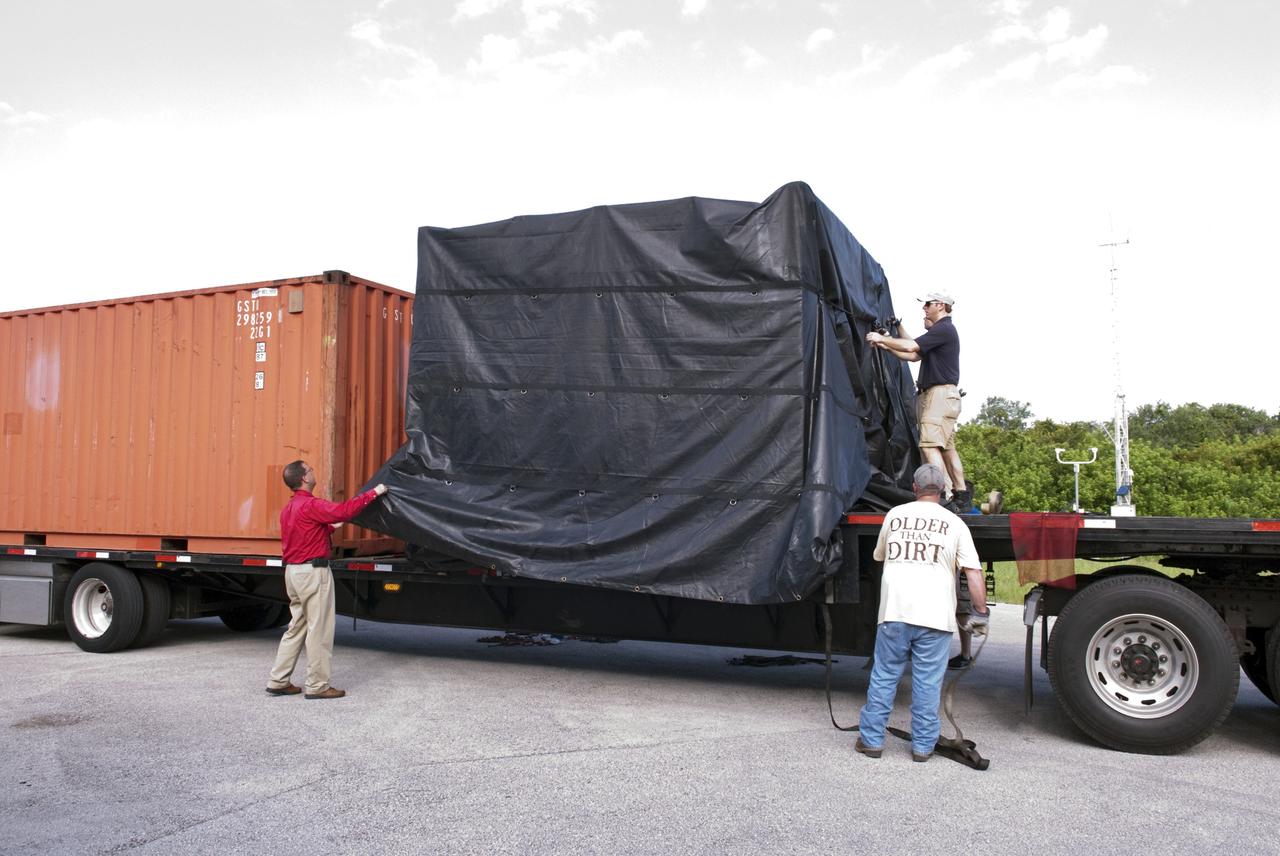

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is unloaded at a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
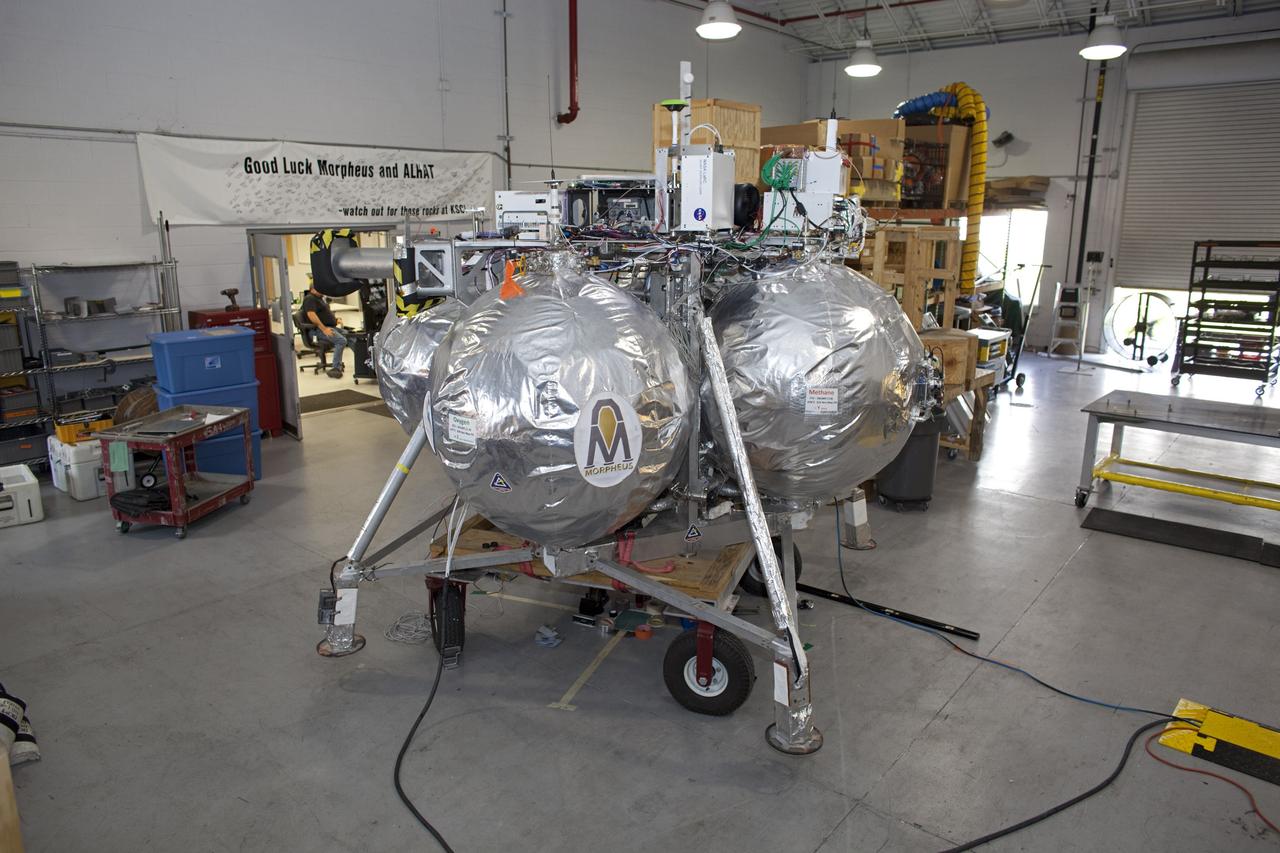

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being checked out in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, arrives at its launch position along the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
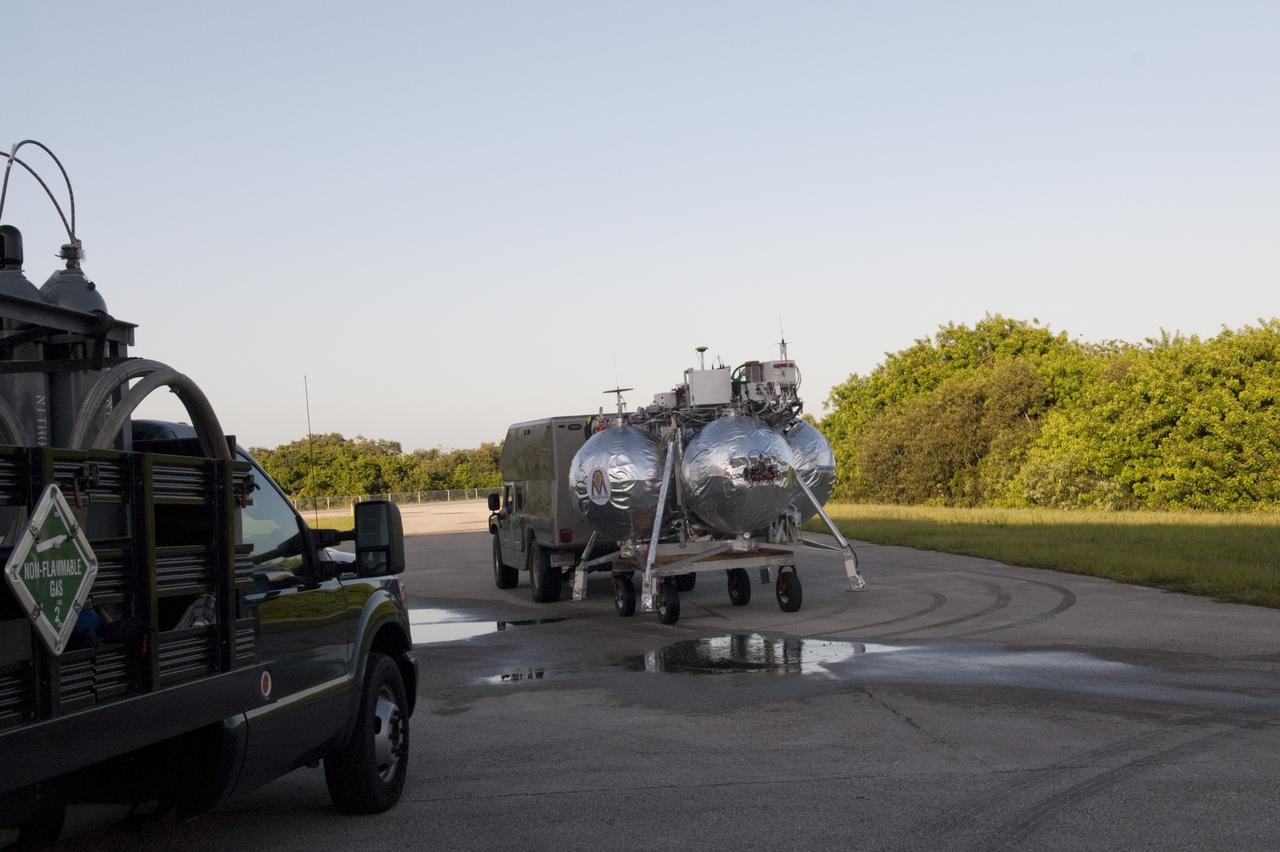

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being transported out from its checkout building for a short trip to a launch position at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

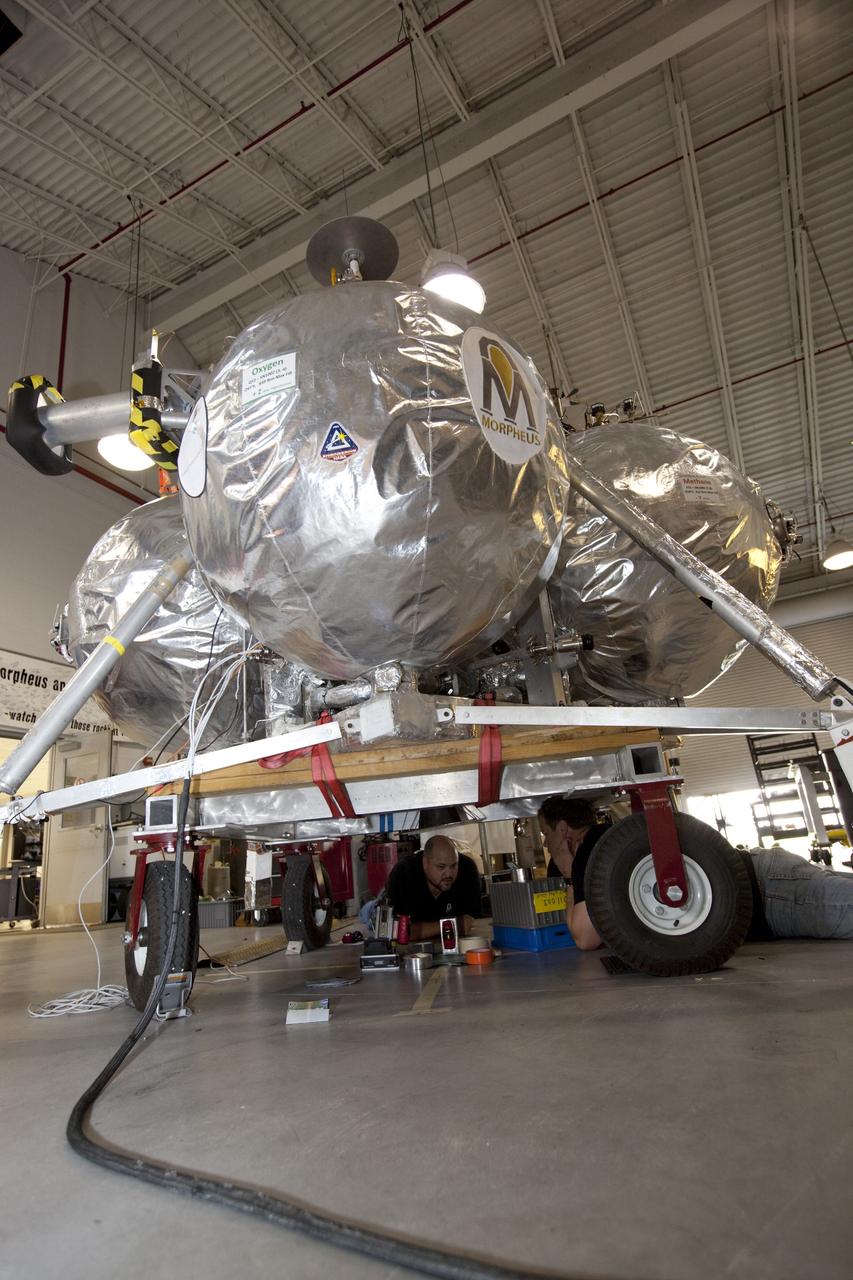
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Russell Romanella, director of Safety and Mission Assurance at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, right, is briefed on NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle. Morpheus is being checked out by technicians and engineers in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at Kennedy. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
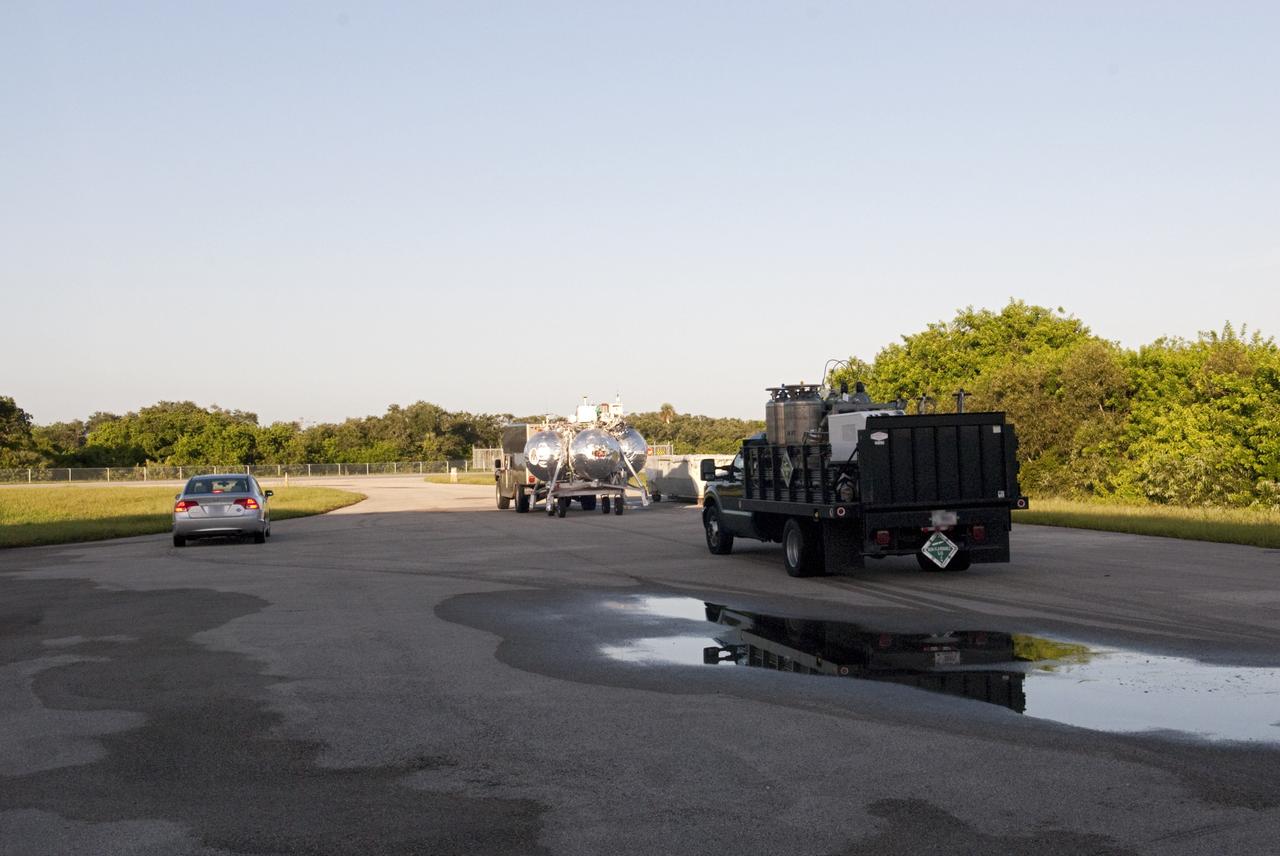

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being transported out from its checkout building for a short trip to a launch position at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
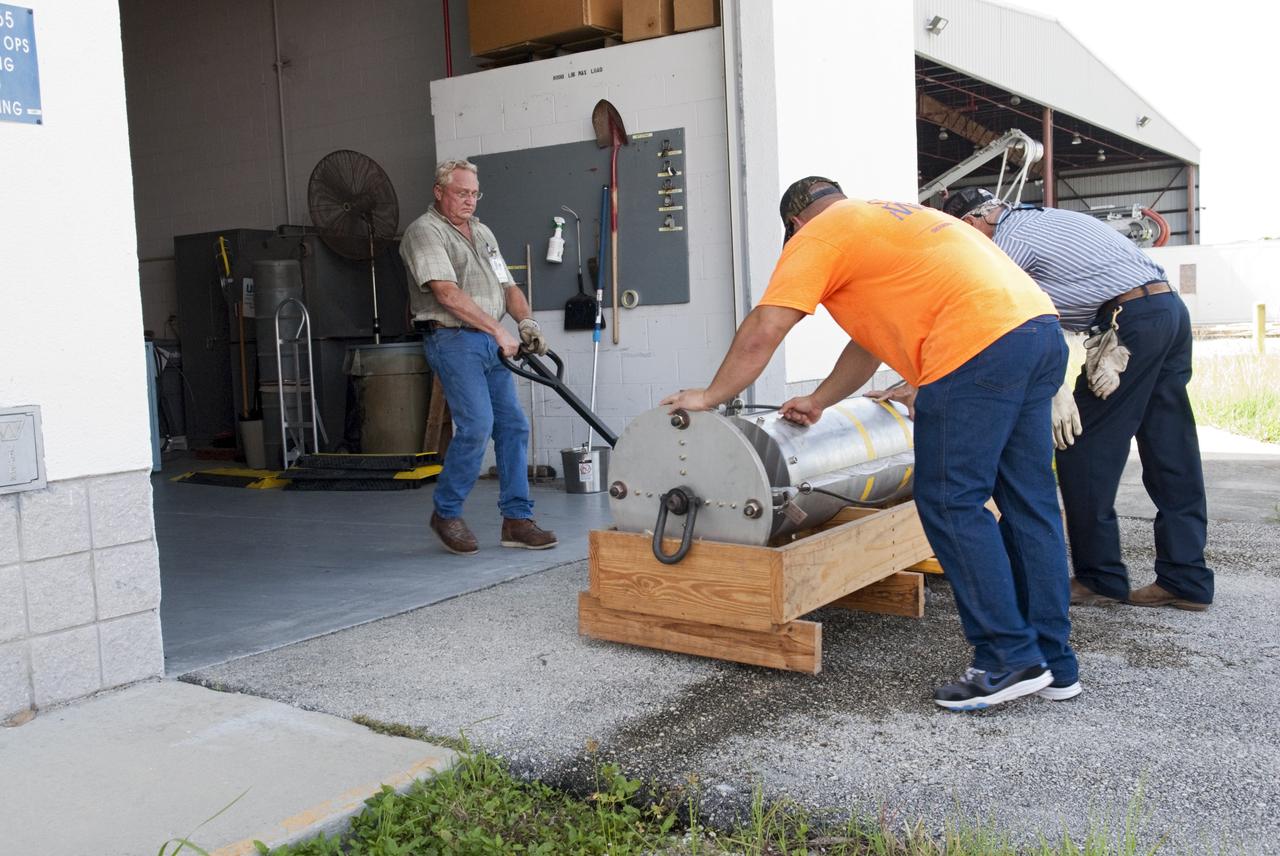

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Support equipment for NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A crane is being used to set up NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, at its launch position along the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

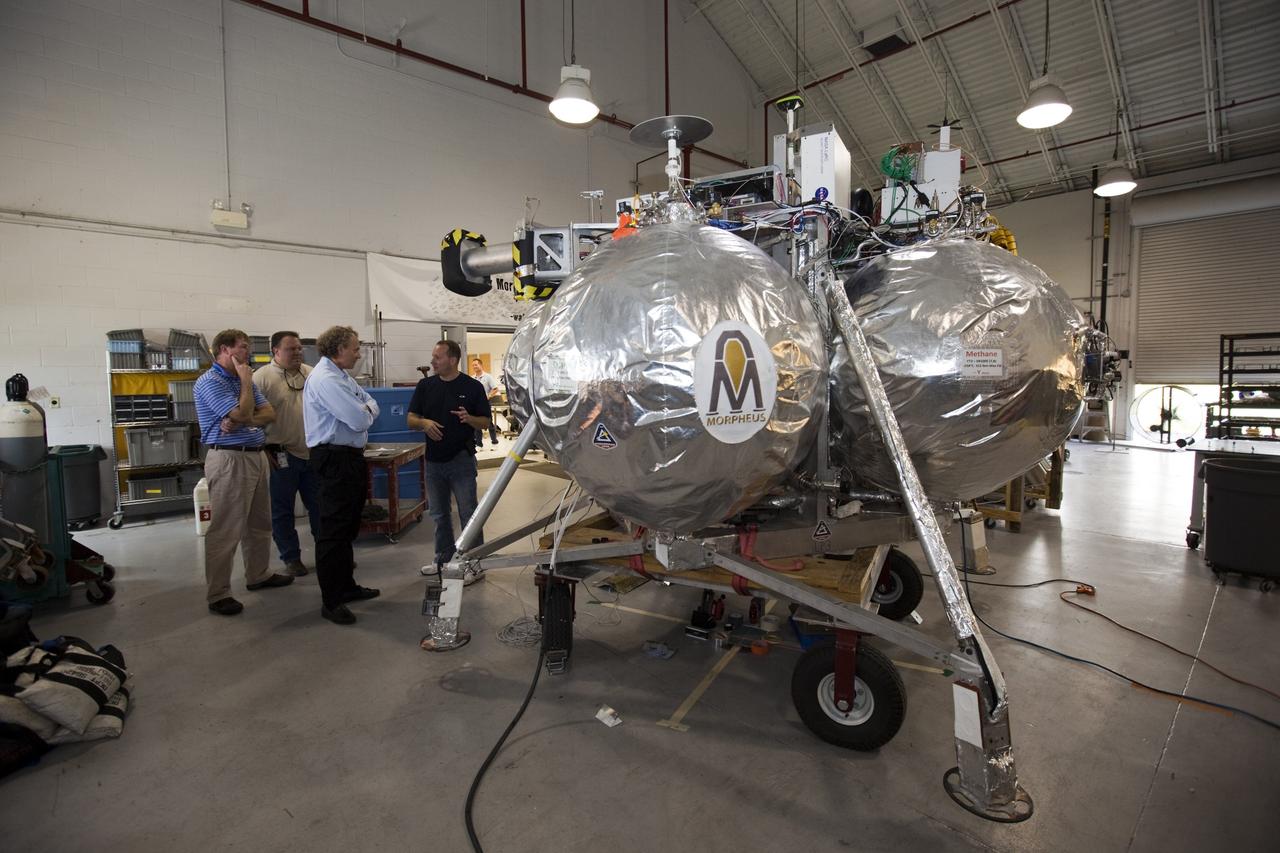
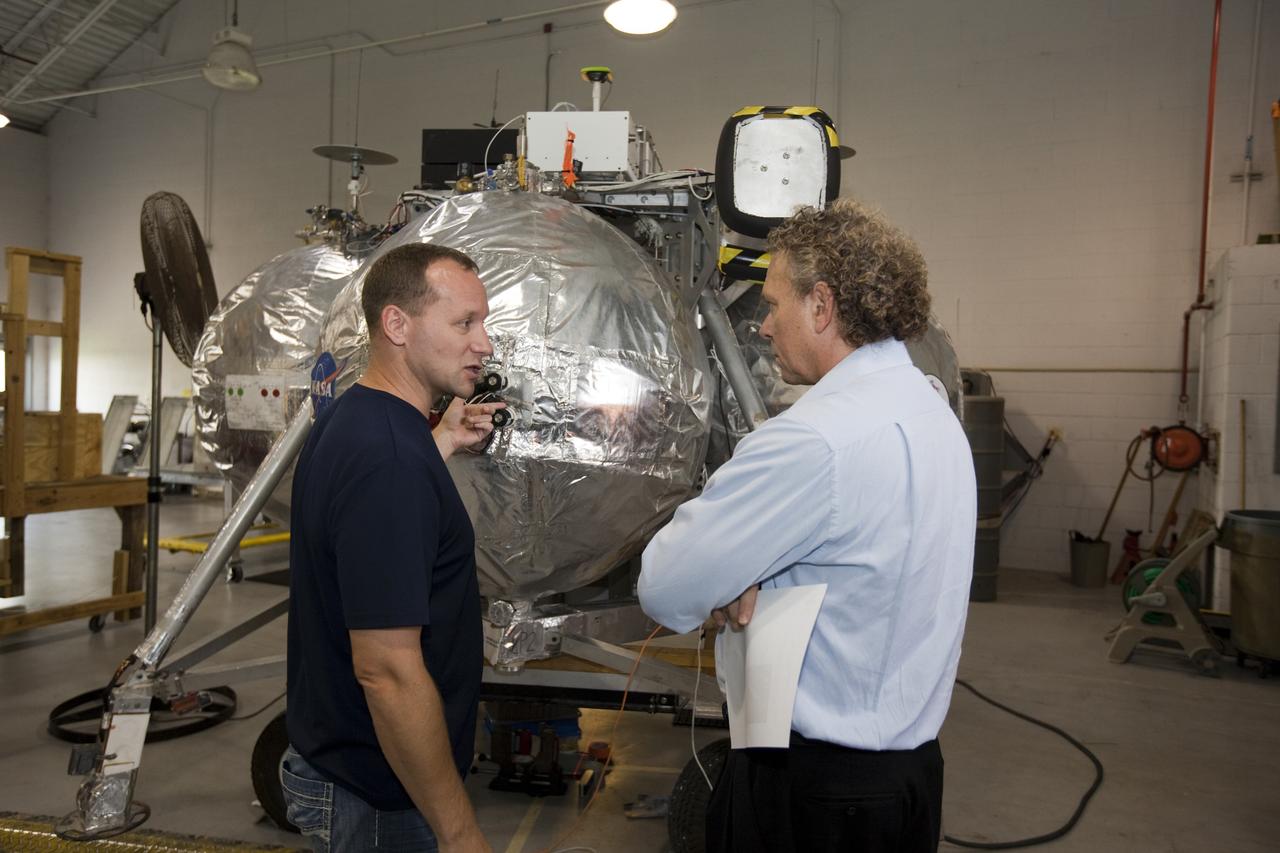
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is checked out by technicians in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A truck transporting NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, arrives at a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida for unloading. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being transported out of its checkout building for a short trip to a launch position at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being checked out in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
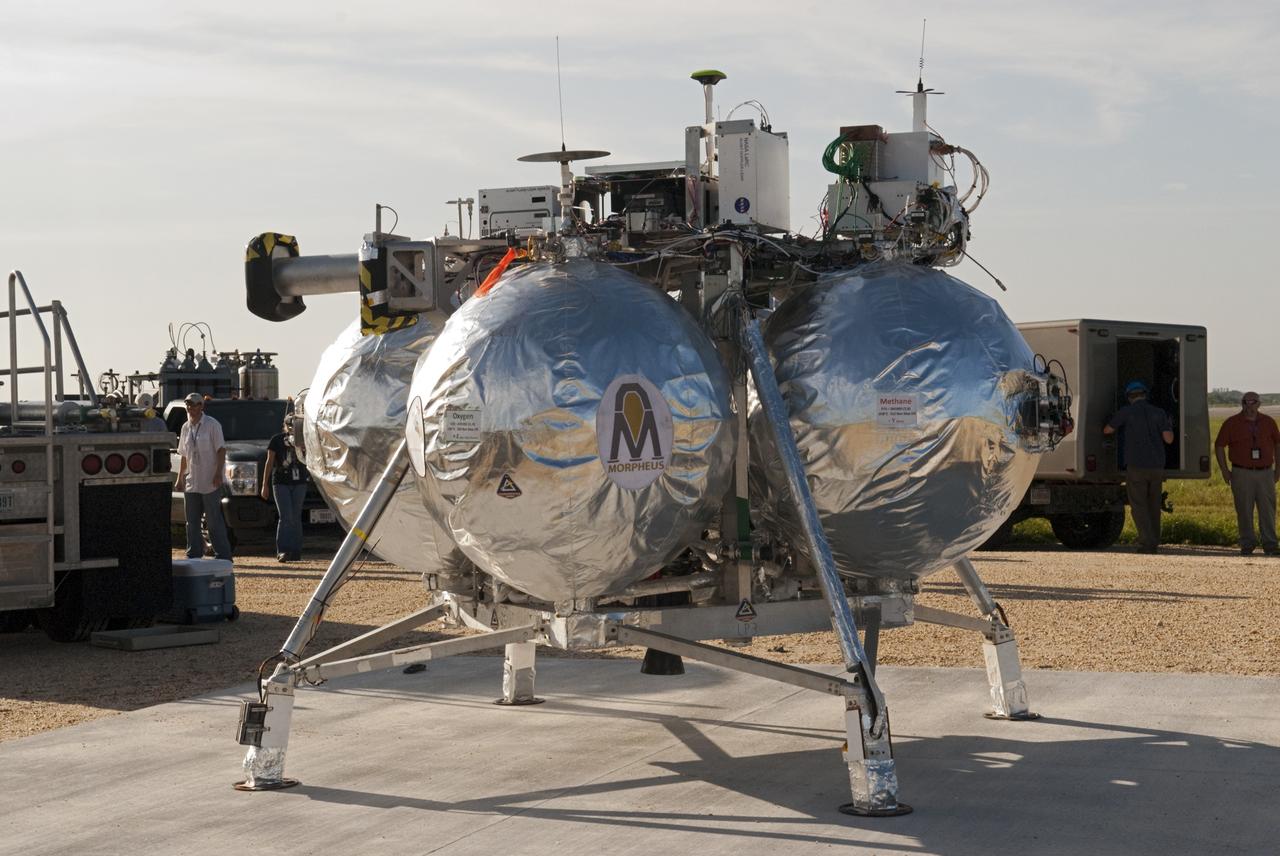

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, has been set up at its launch position along the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
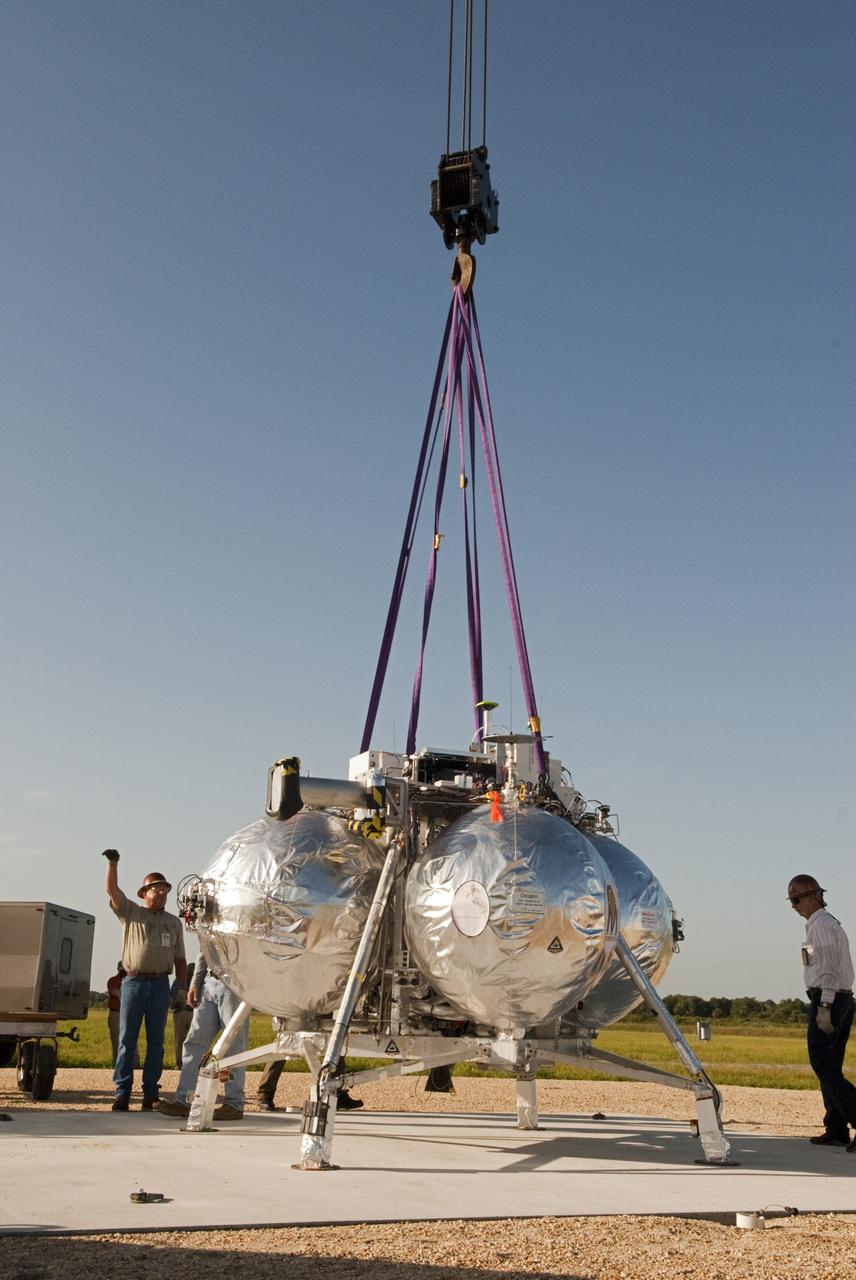

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A crane is being used to set up NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, at its launch position along the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
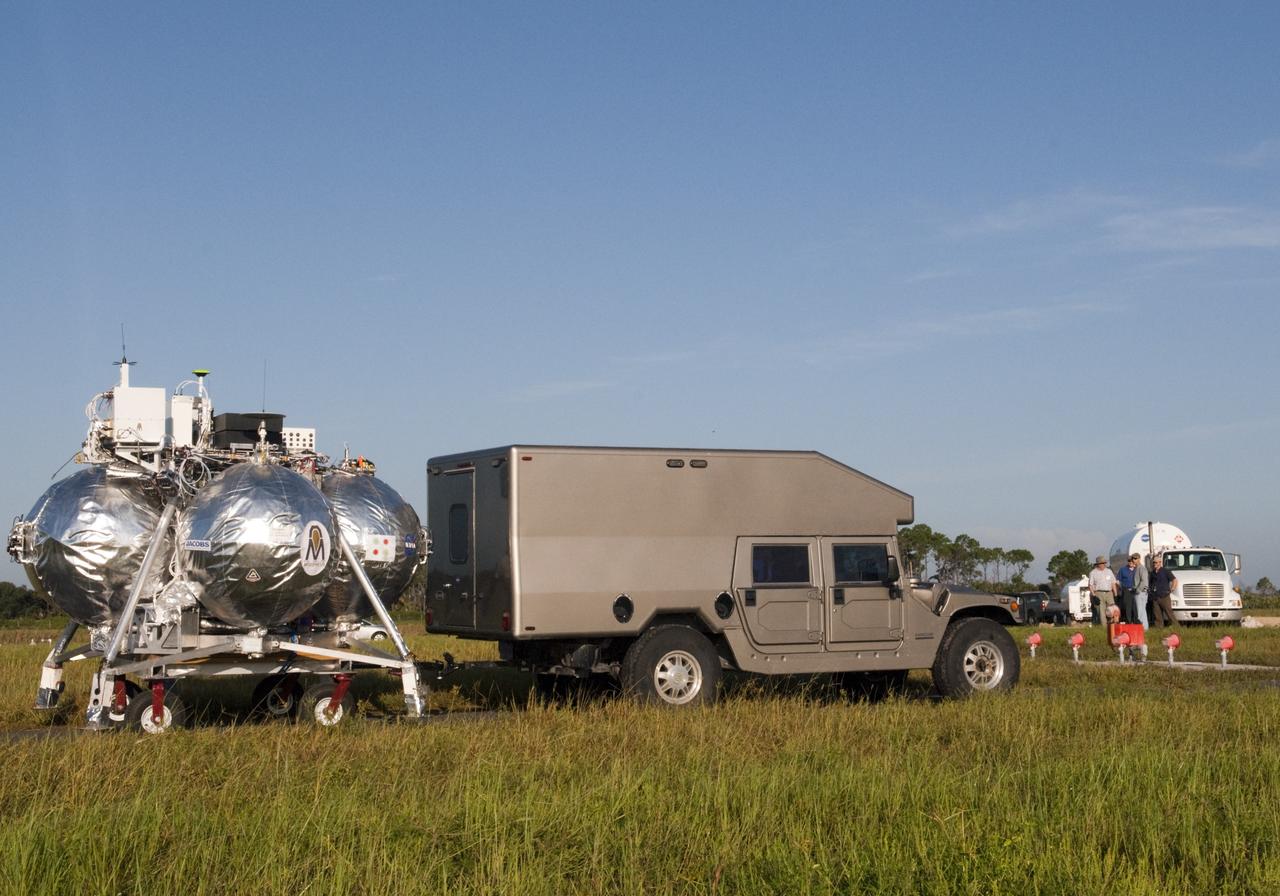

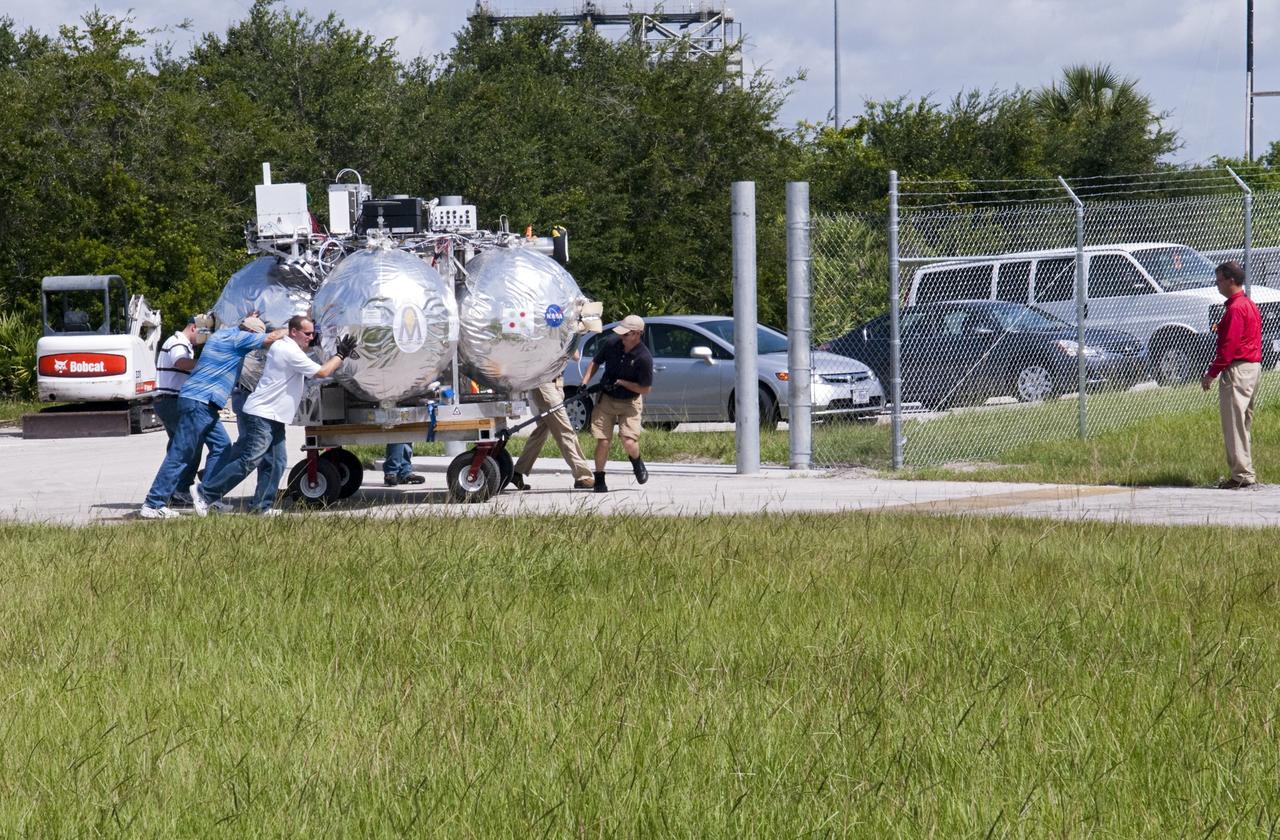
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being transported along the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida for a short trip to a launch position along the runway. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being transported along the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida for a short trip to a launch position along the runway. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
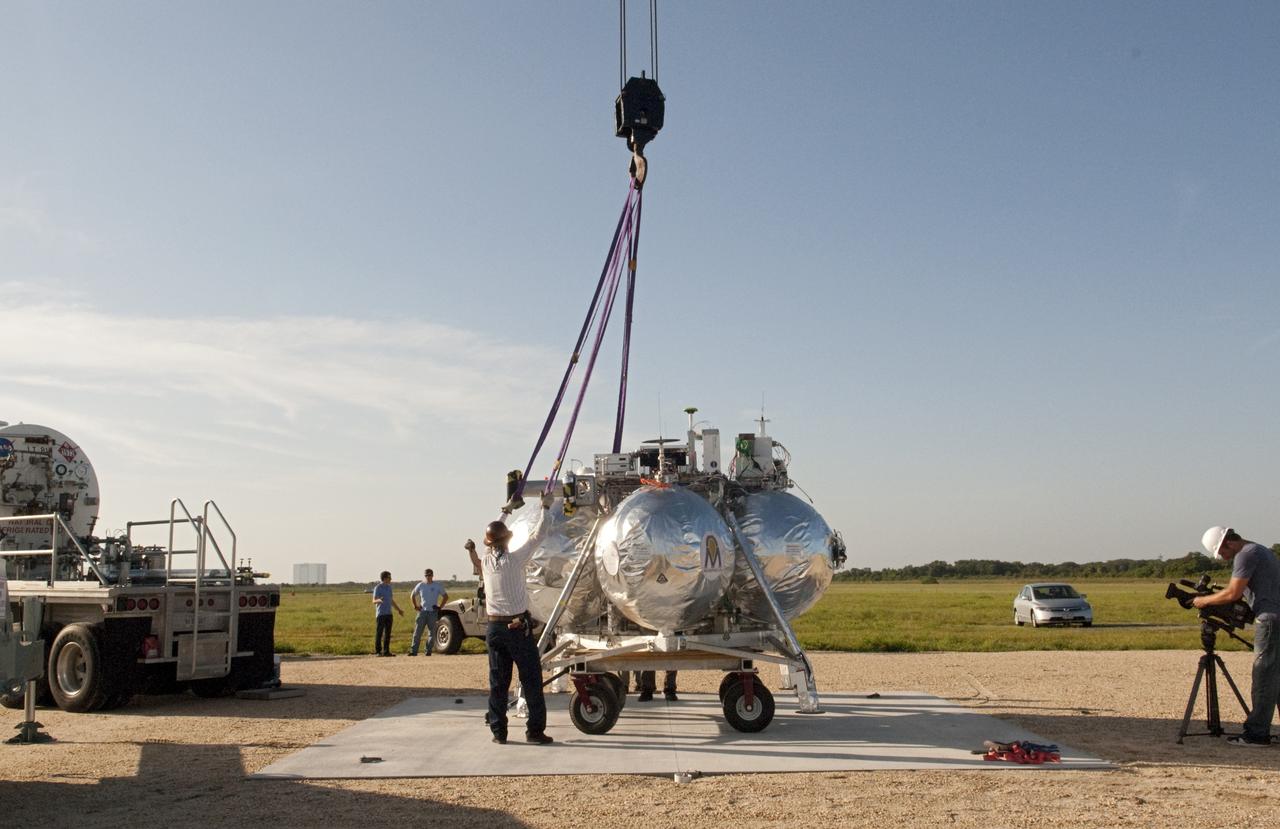

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A crane is being used to set up NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, at its launch position along the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
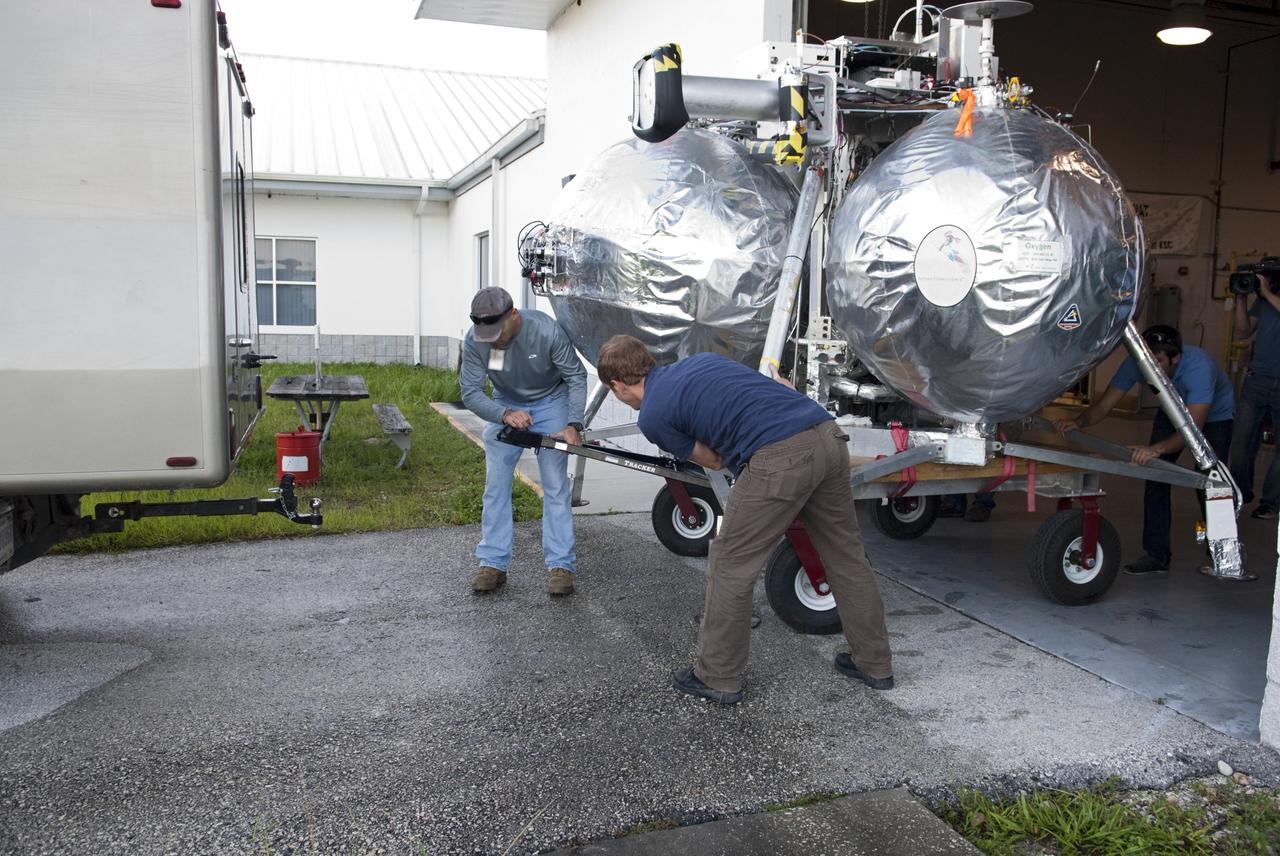

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being moved out of its checkout building for a short trip to a launch position at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
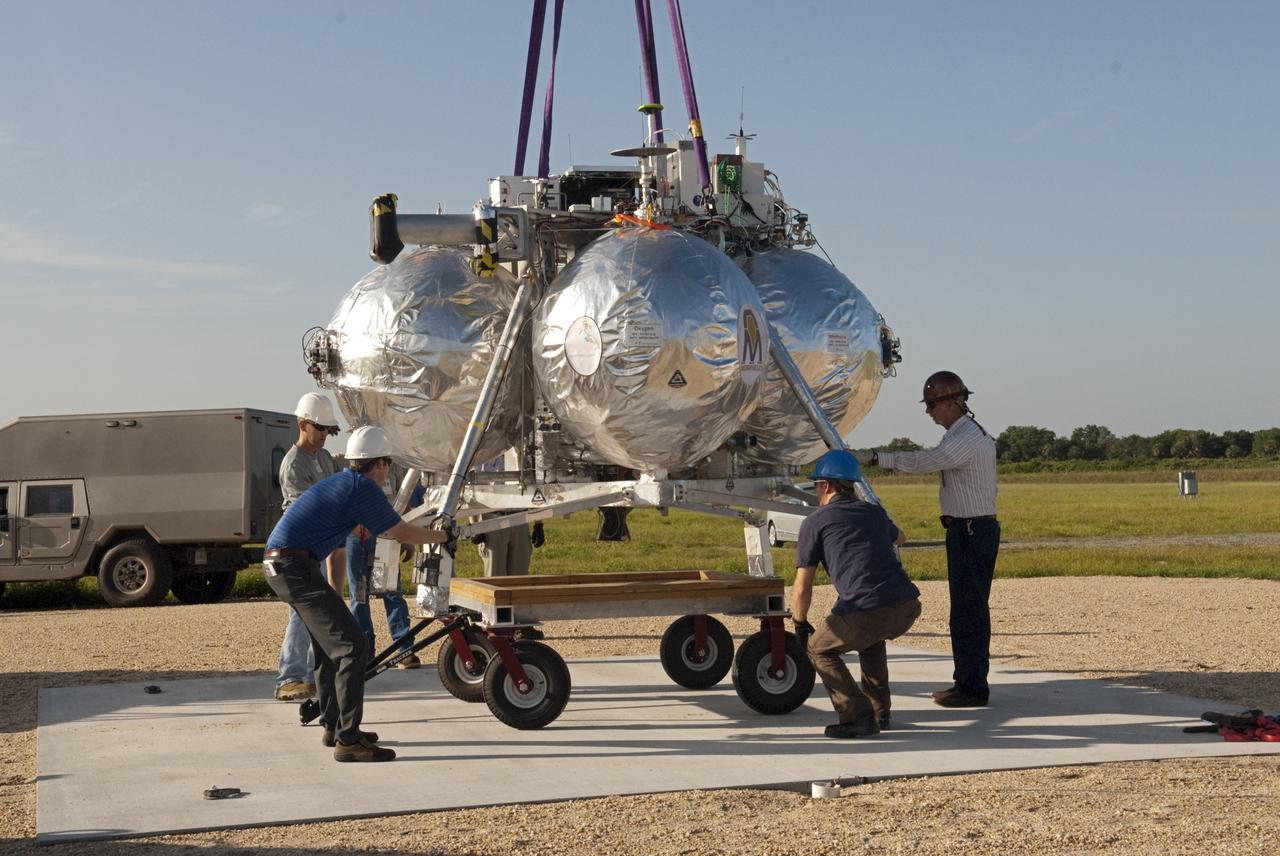

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Technicians set up NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, at its launch position along the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
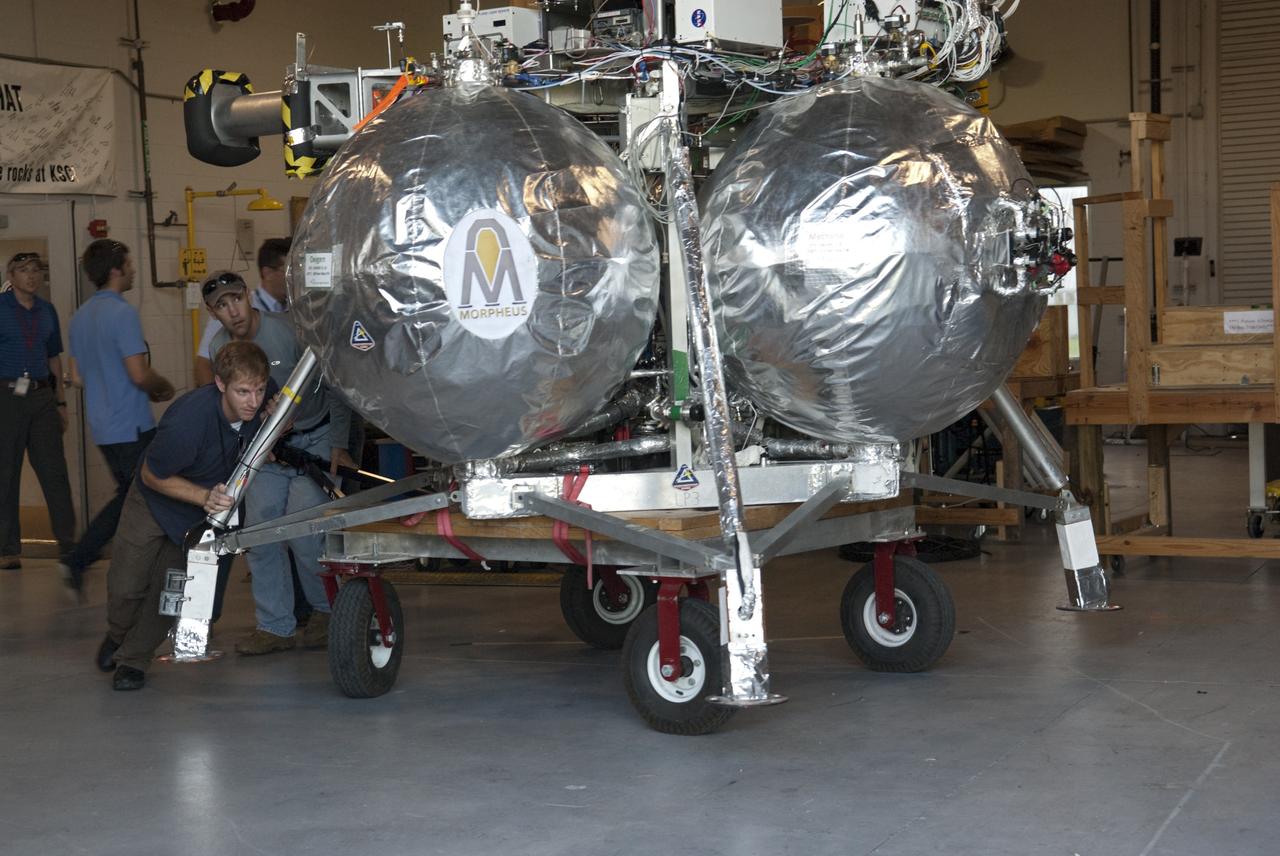

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being moved out of its checkout building for a short trip to a launch position at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
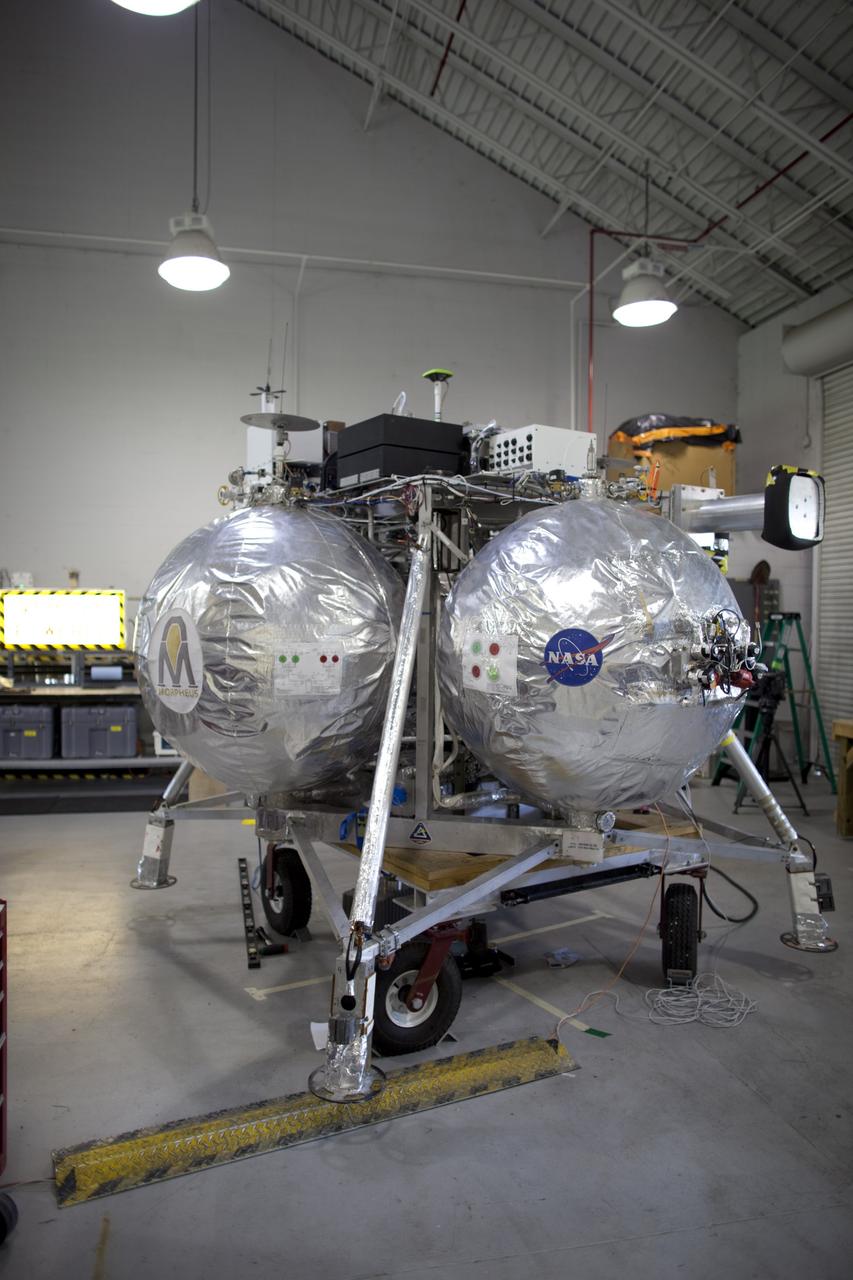

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being checked out in a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
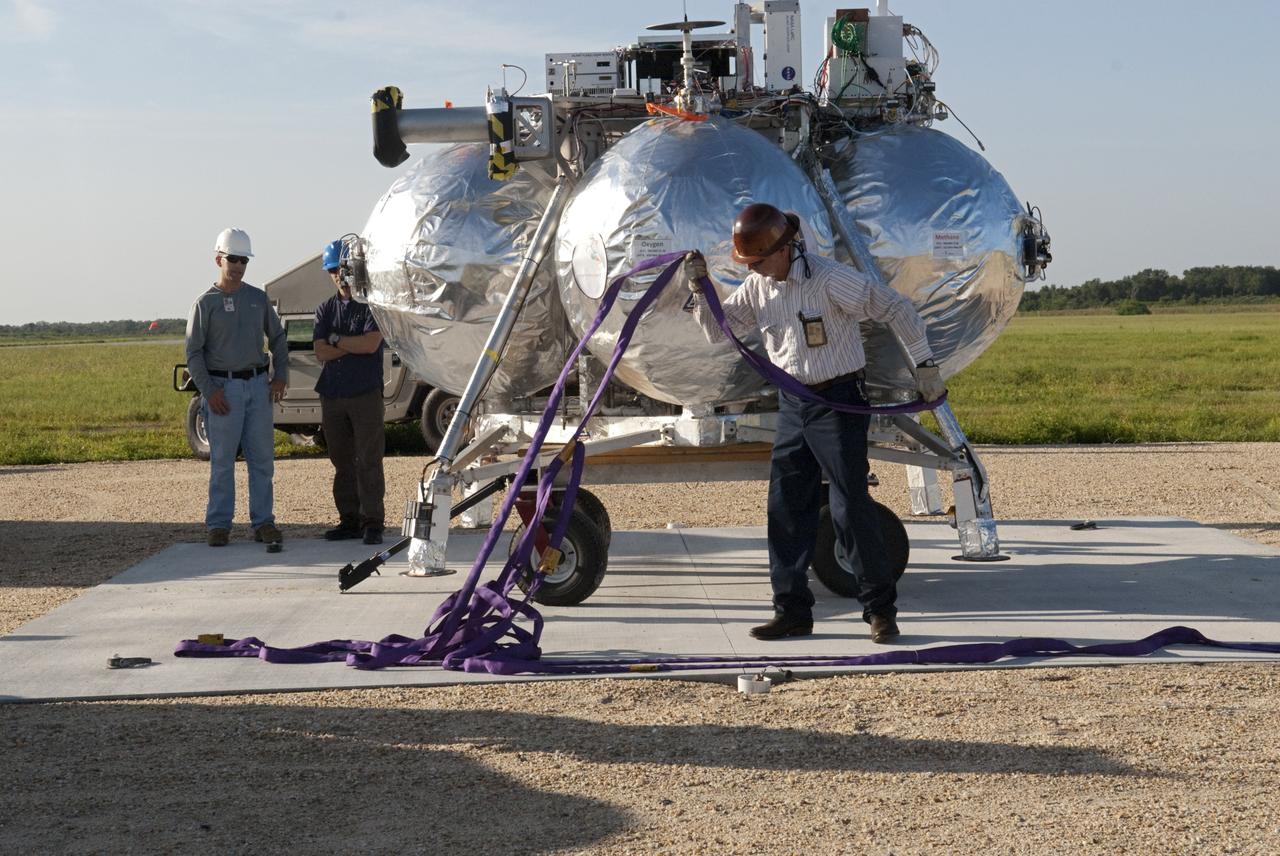

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being set up at its launch position along the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
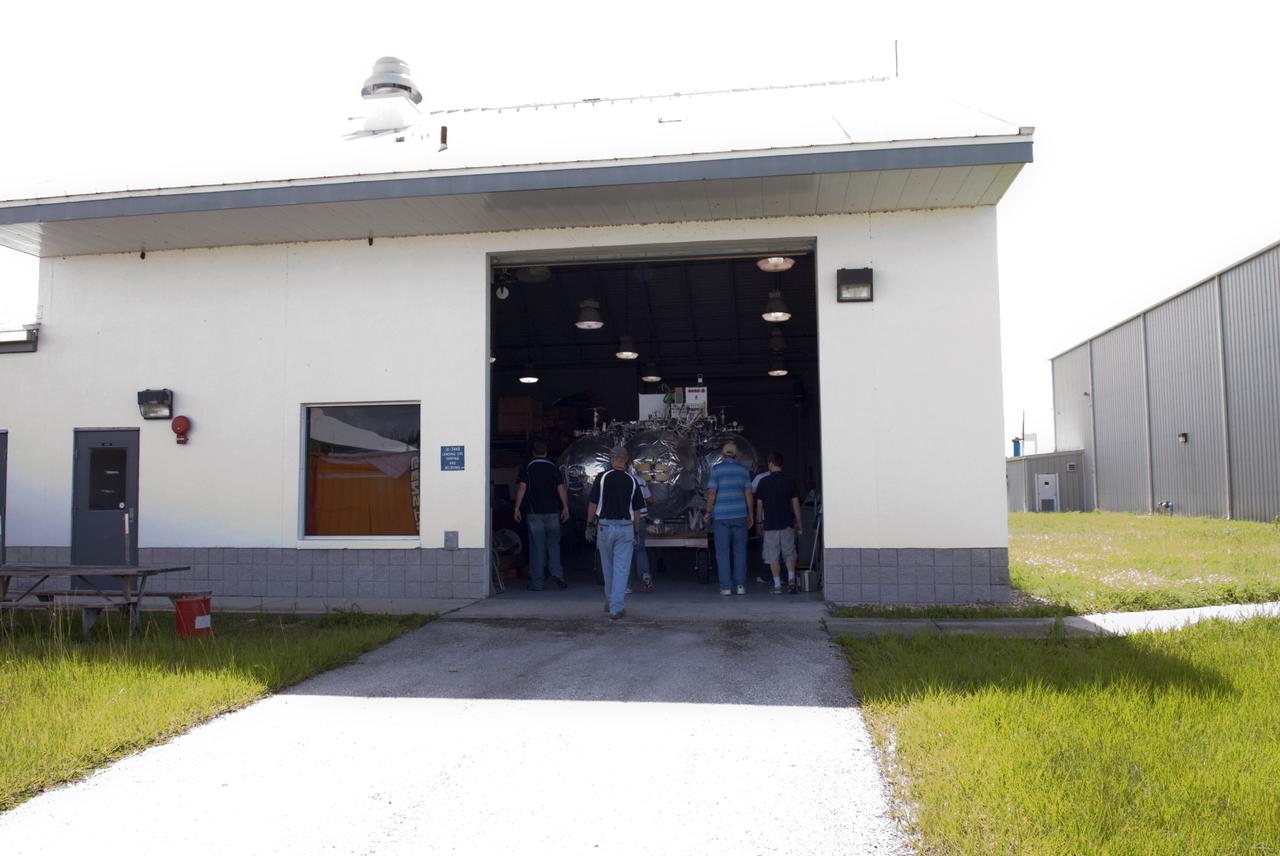

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, has been moved into a building at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
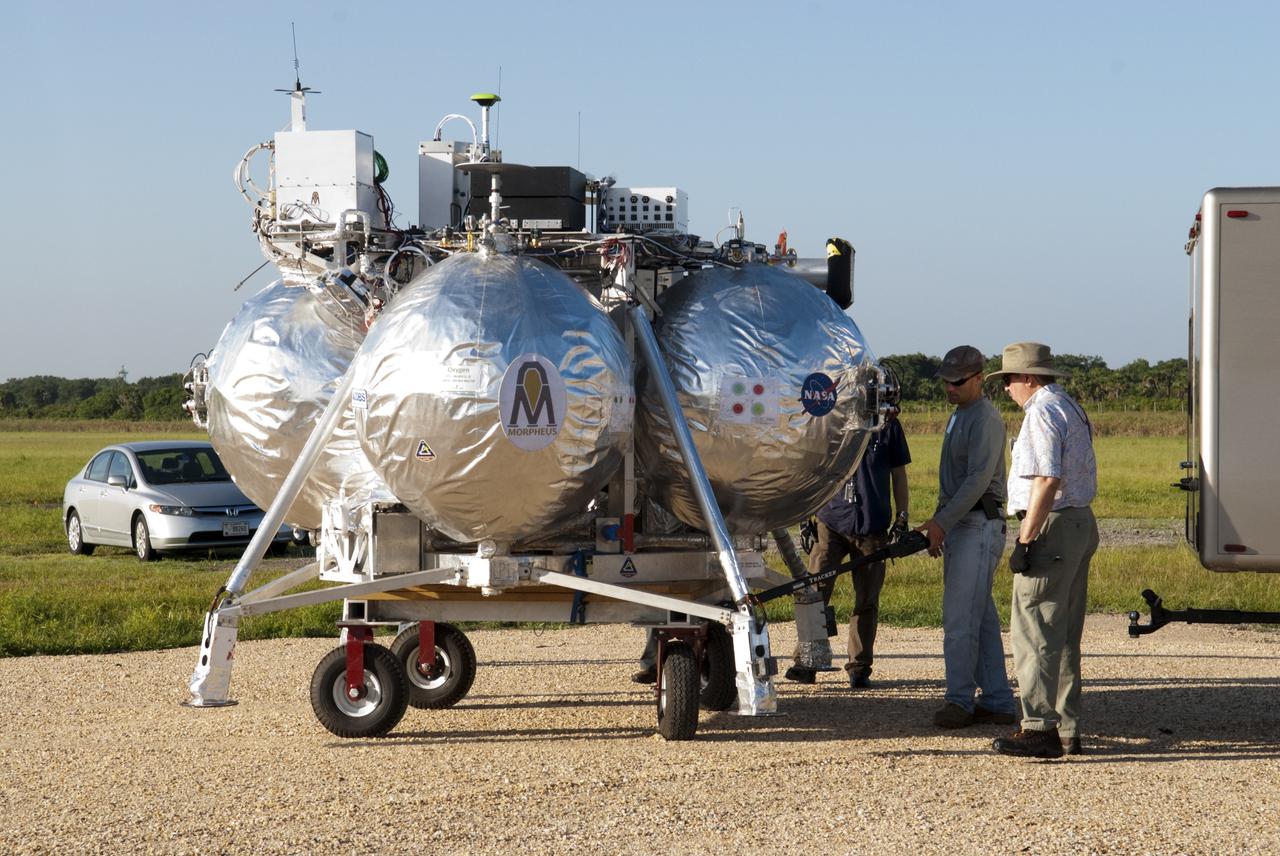

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being set up at its launch position along the runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
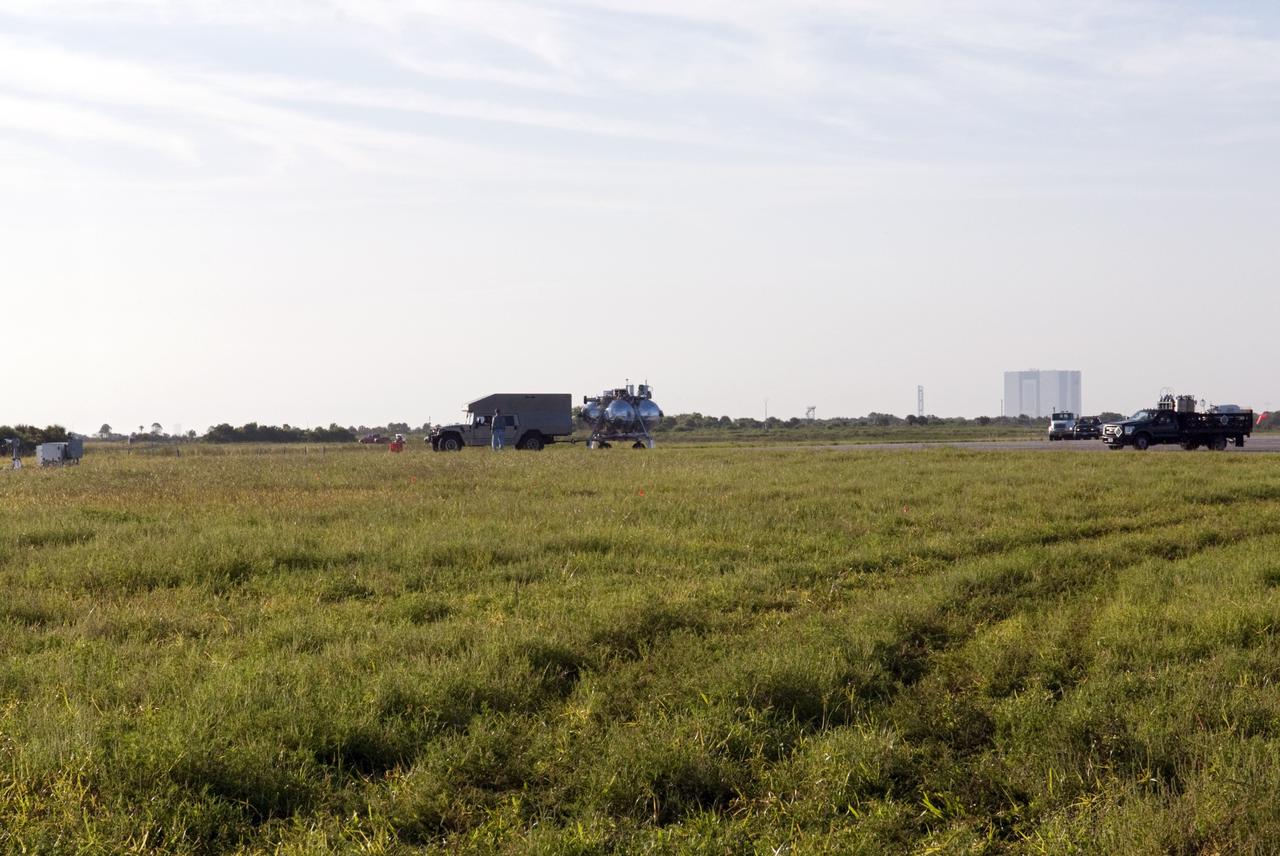

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - NASA's Morpheus lander, a vertical test bed vehicle, is being transported along the Shuttle Landing Facility, or SLF, at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida for a short trip to a launch position along the runway. Morpheus is designed to demonstrate new green propellant propulsion systems and autonomous landing and an Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, system. Checkout of the prototype lander has been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free flight. The SLF site will provide the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing. Project Morpheus is one of 20 small projects comprising the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/johnson/exploration/morpheus/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
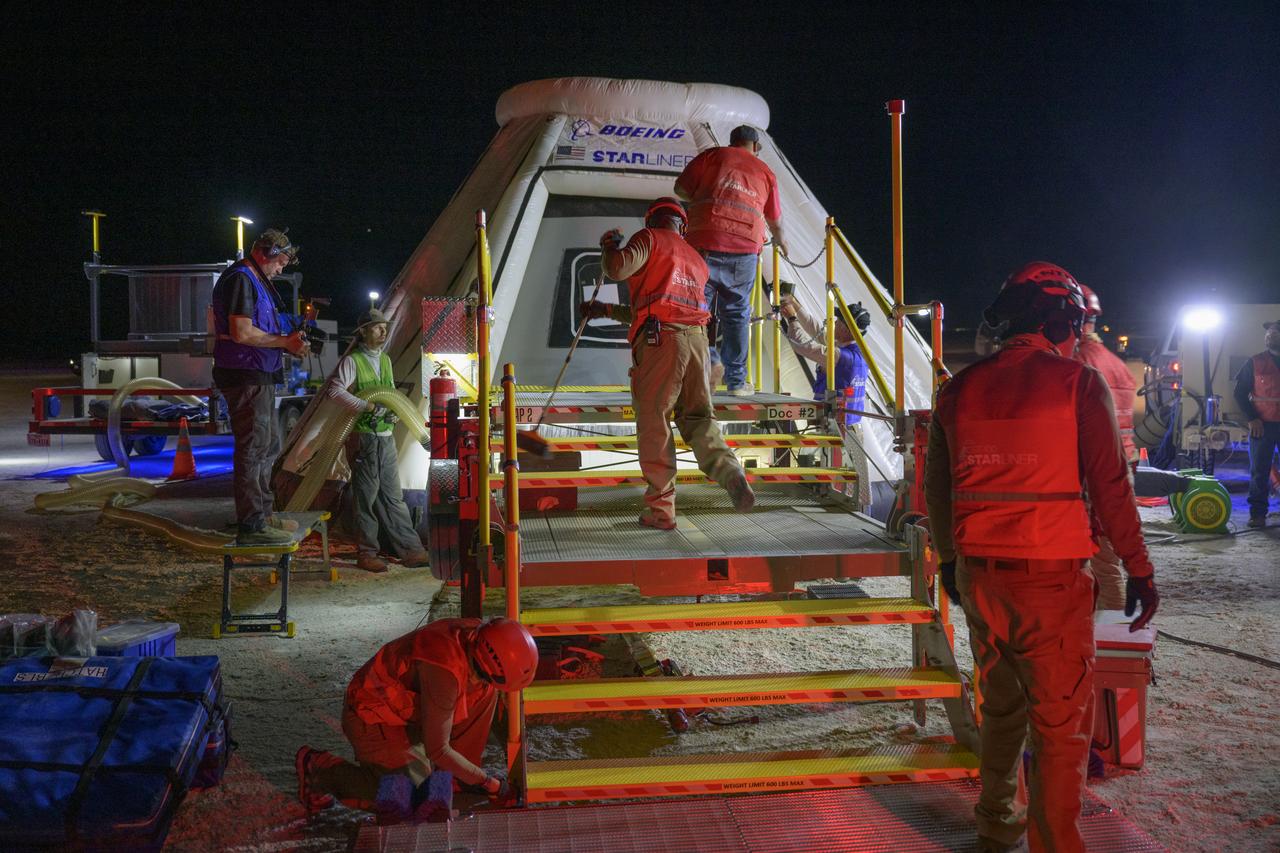

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
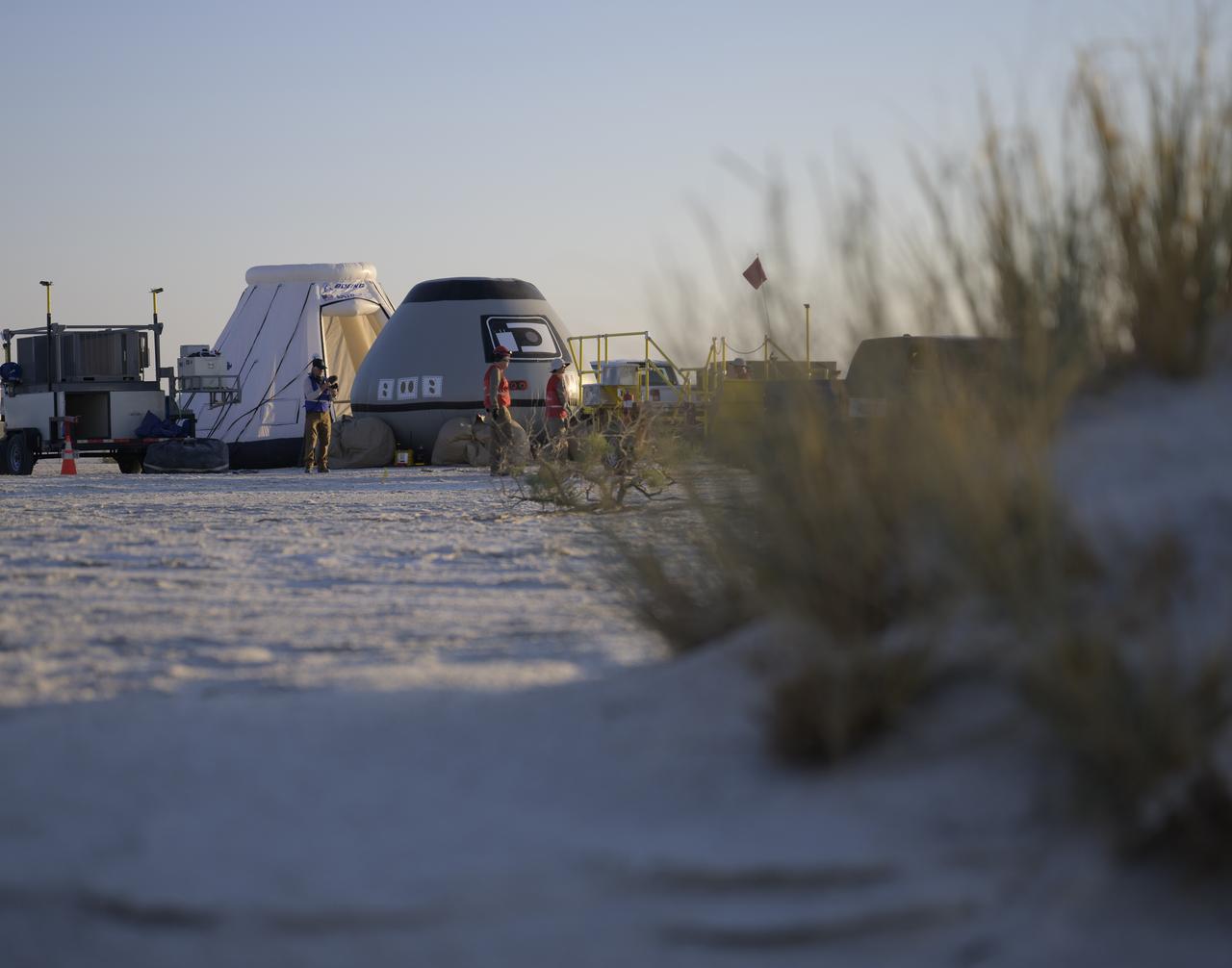

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
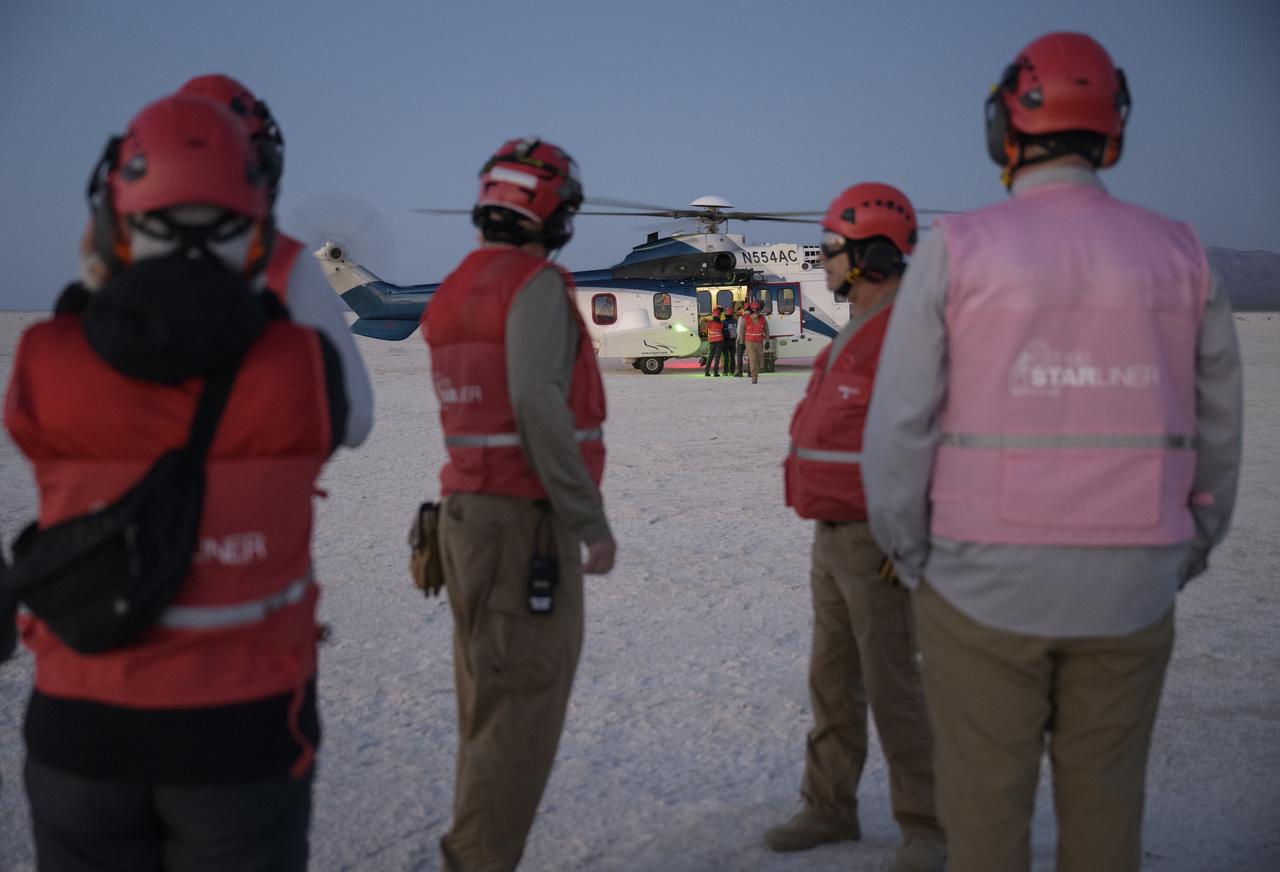

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
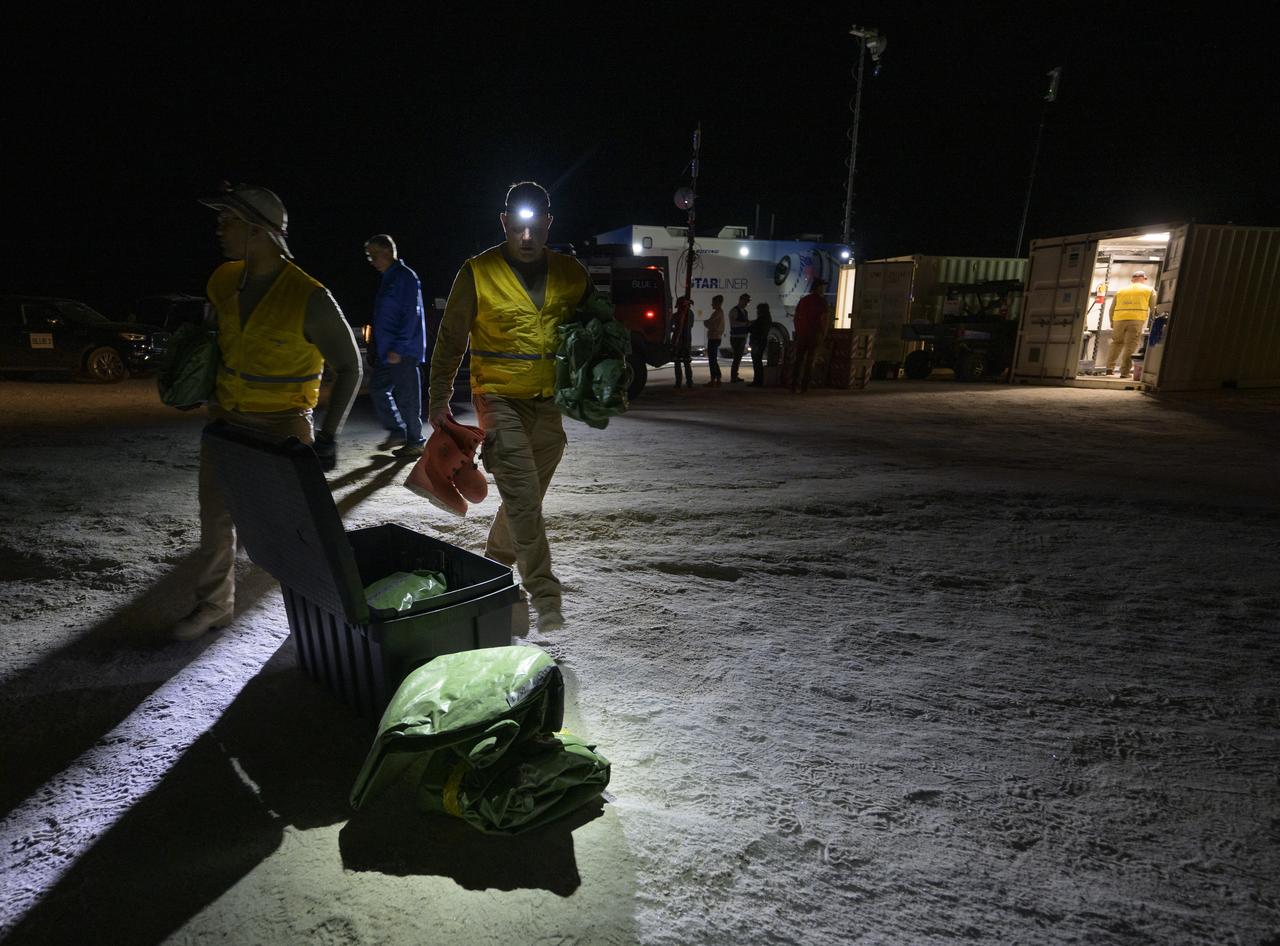

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
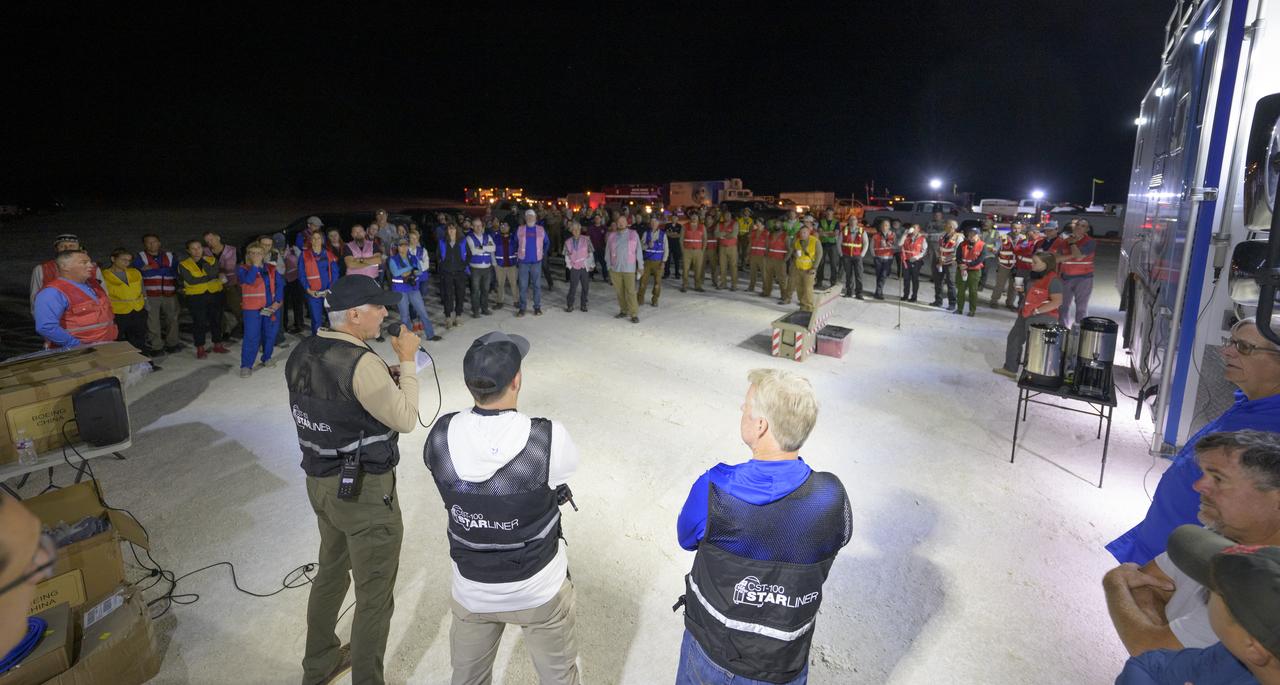

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
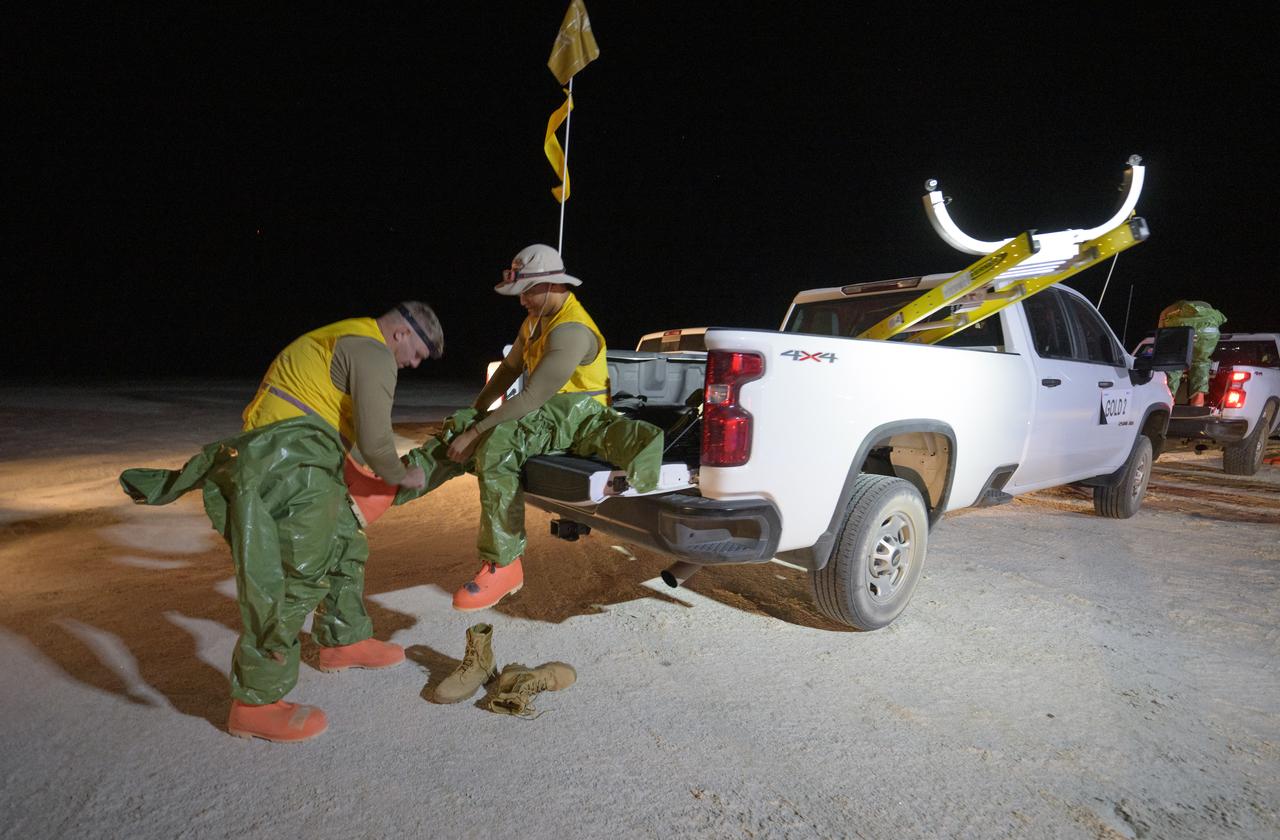

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
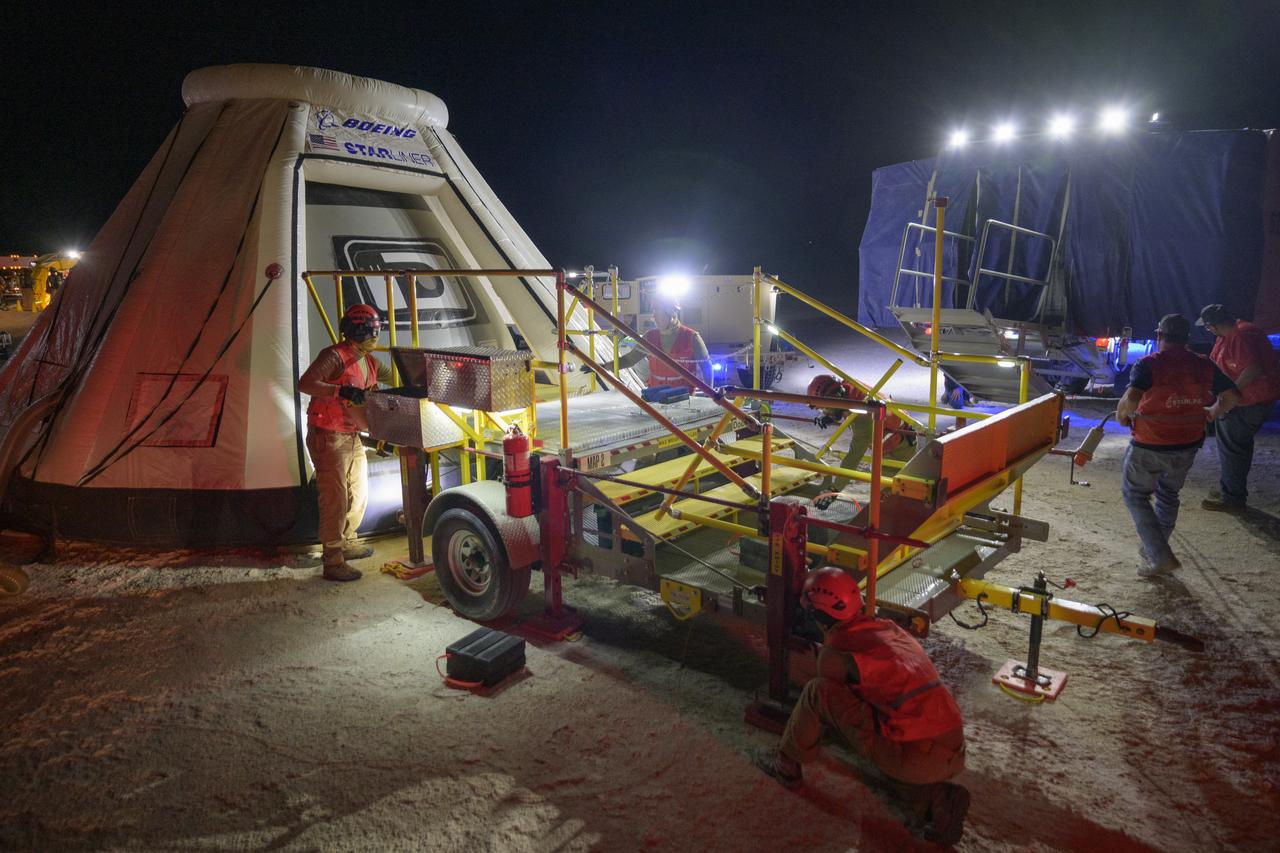

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
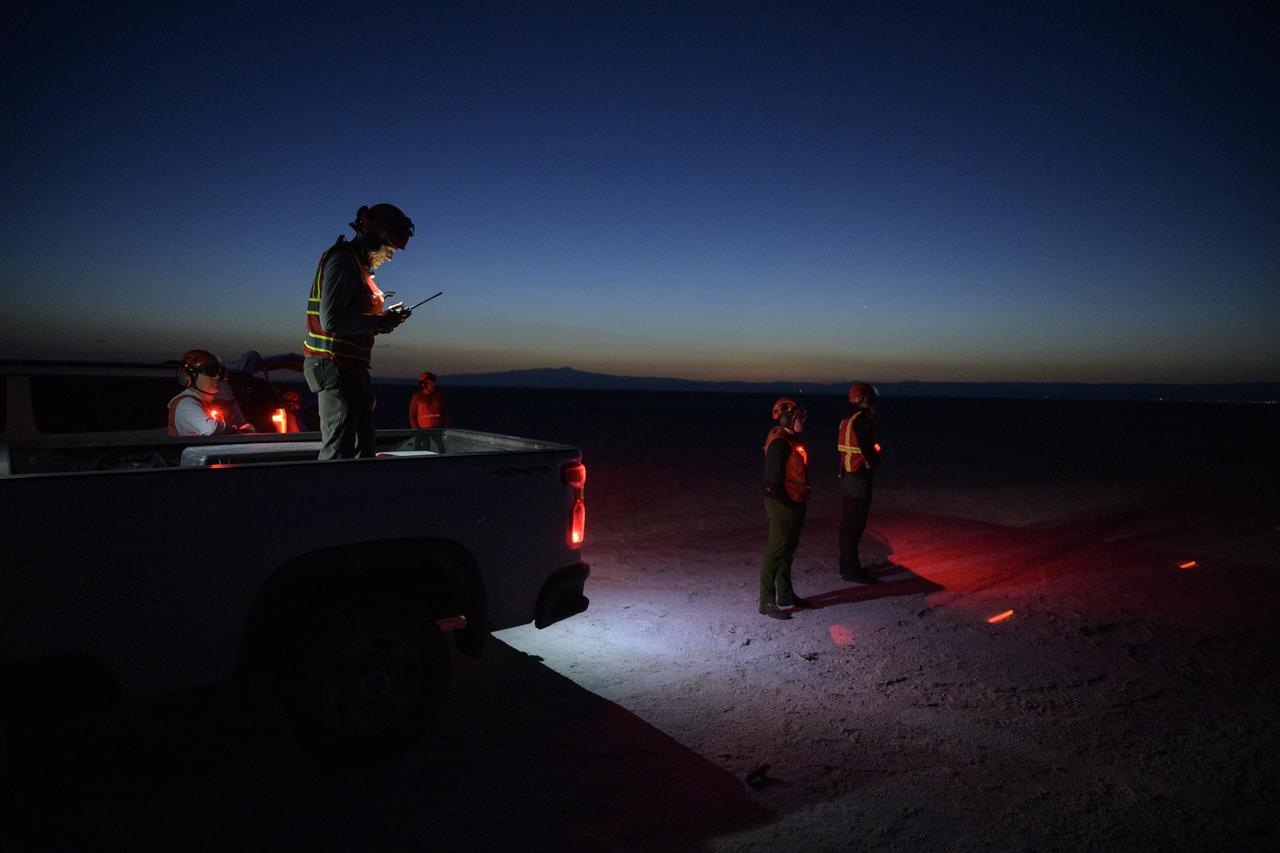

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
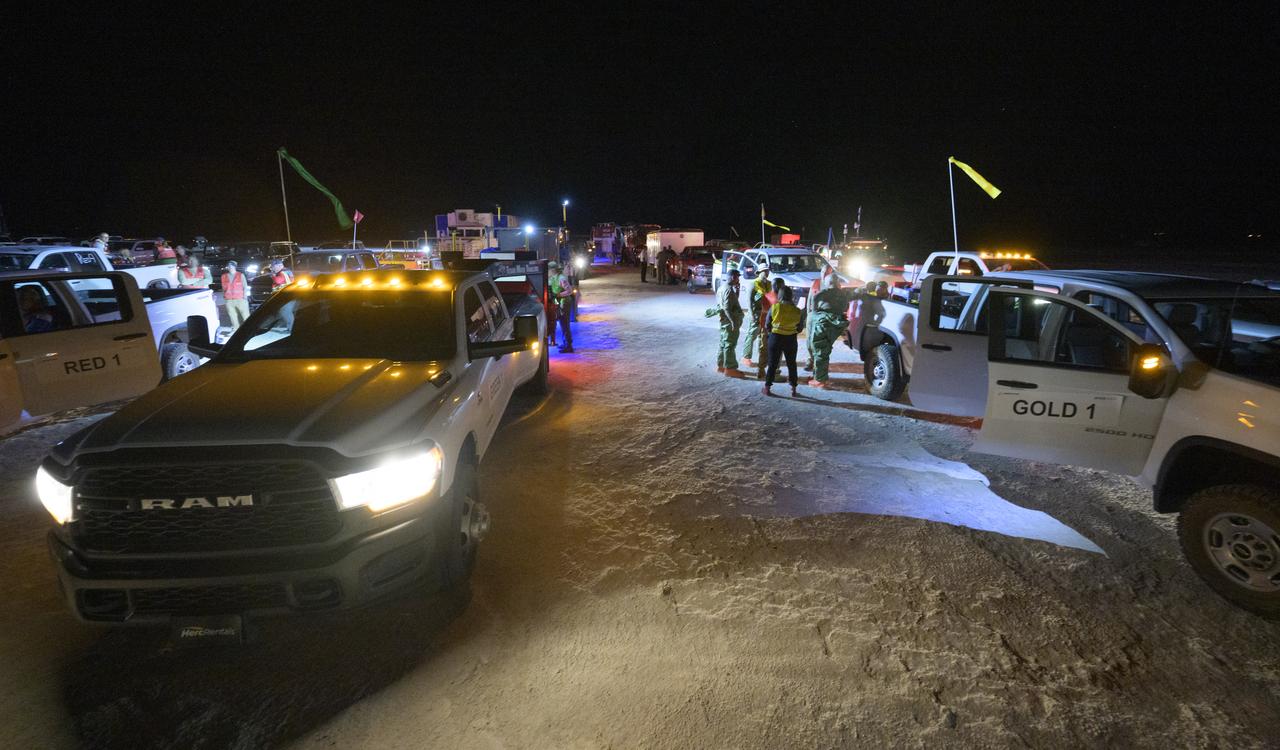

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
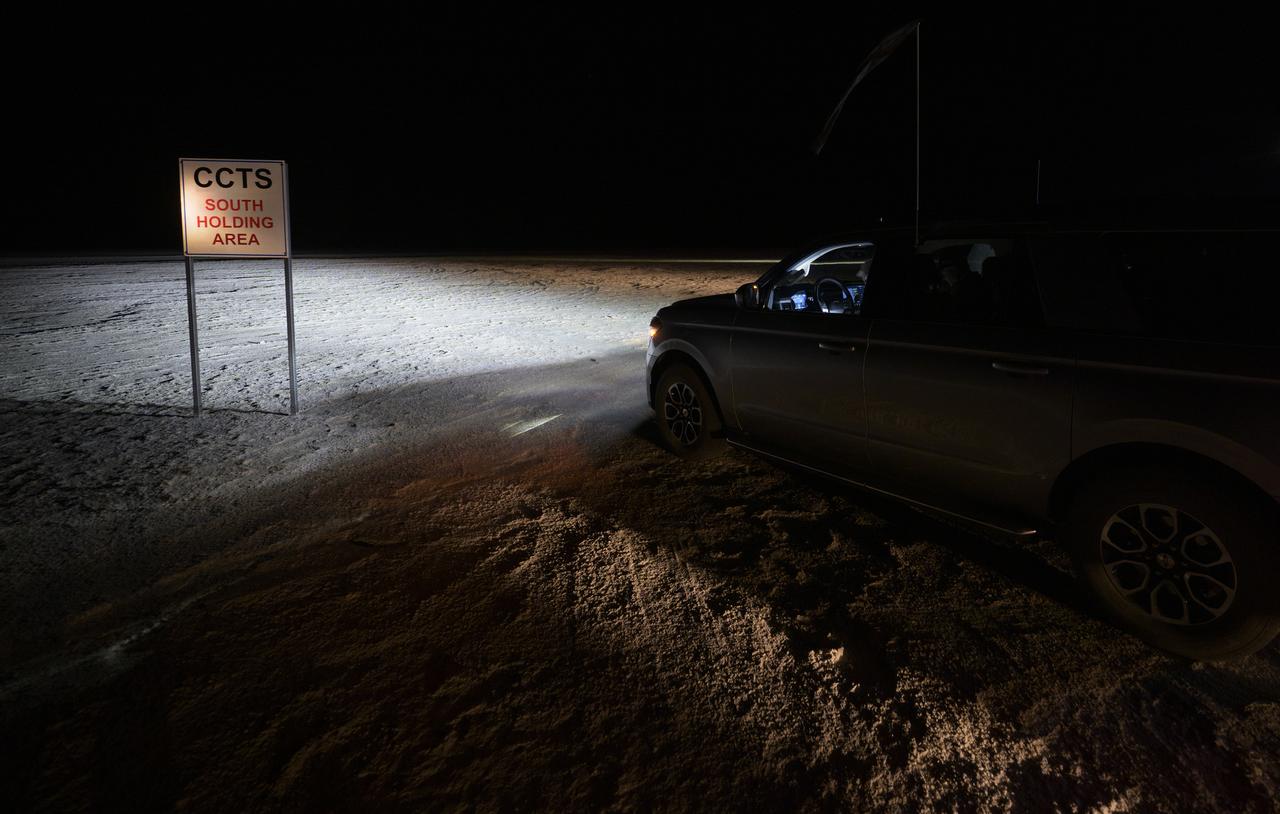

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
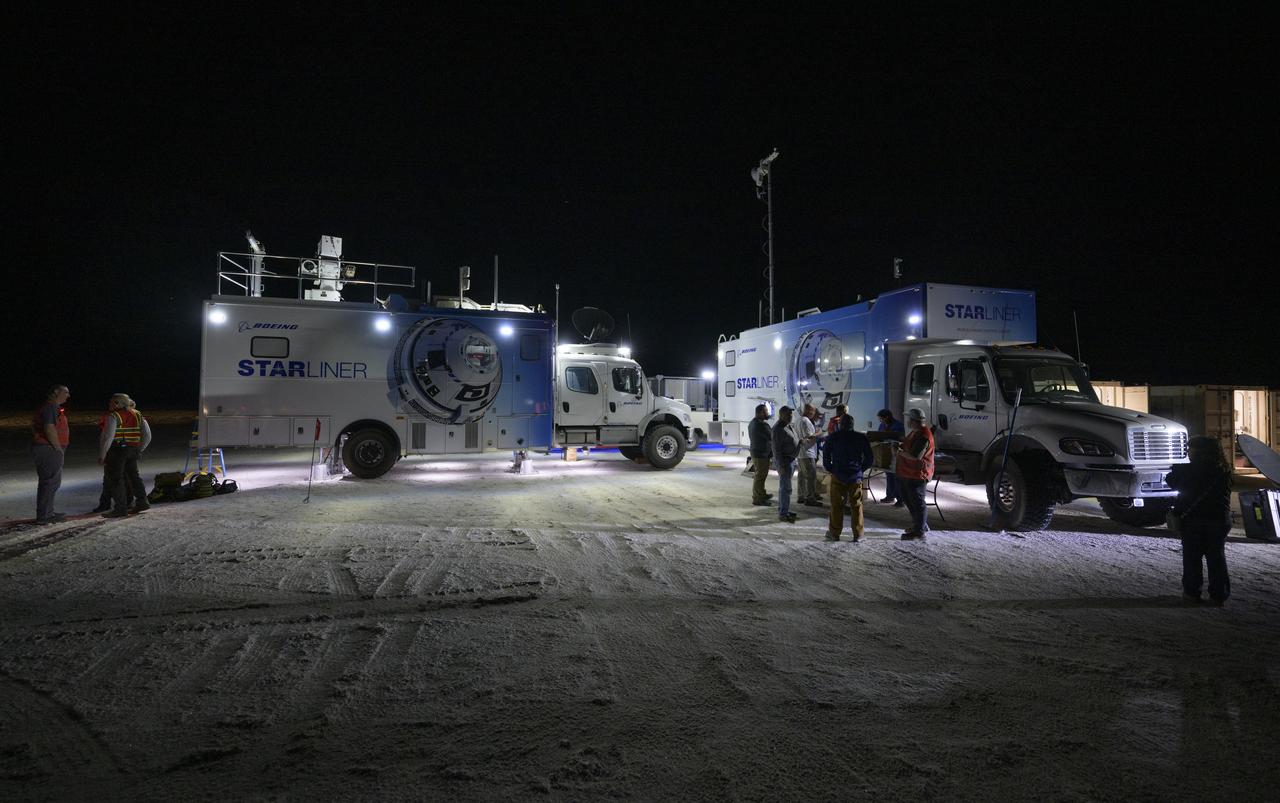

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
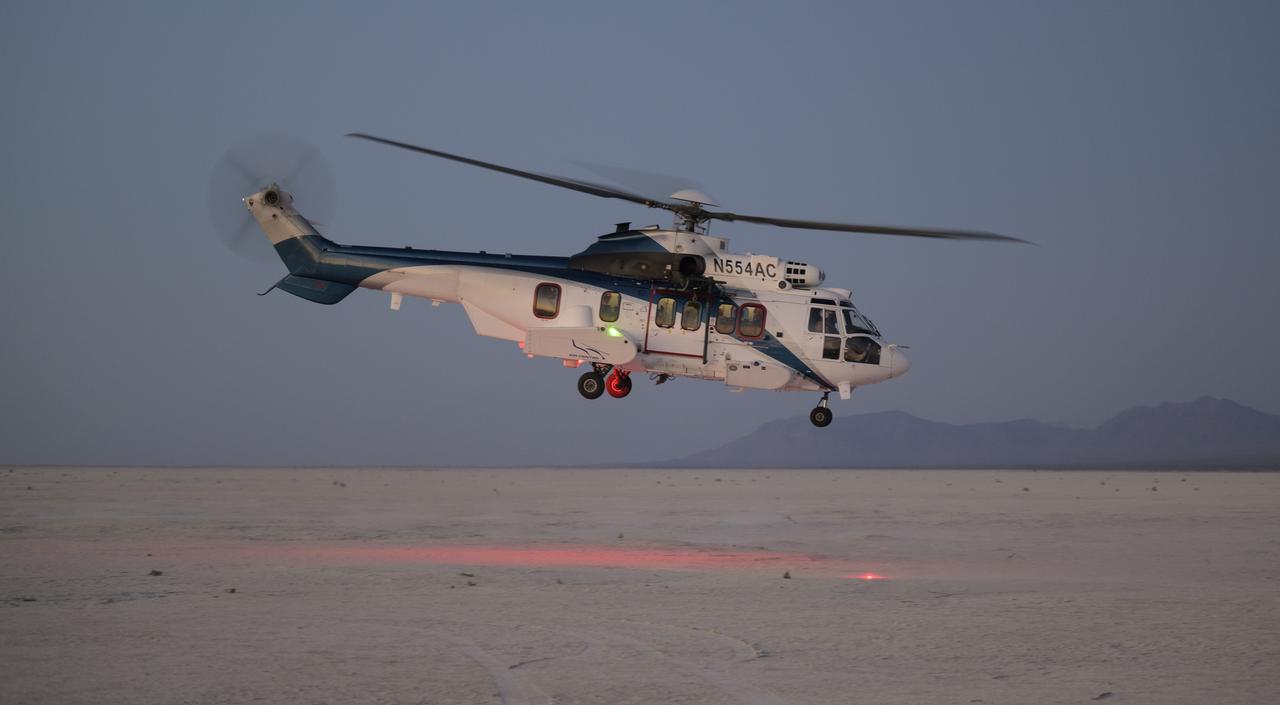

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
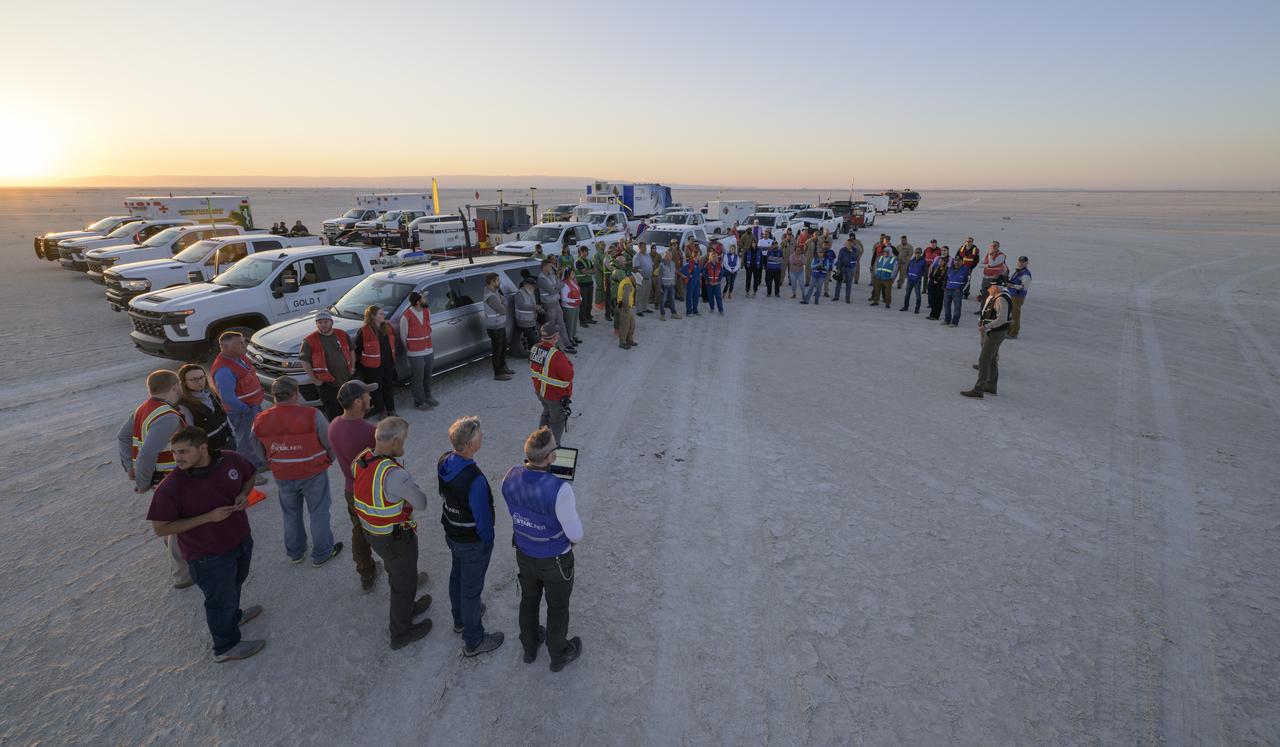

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
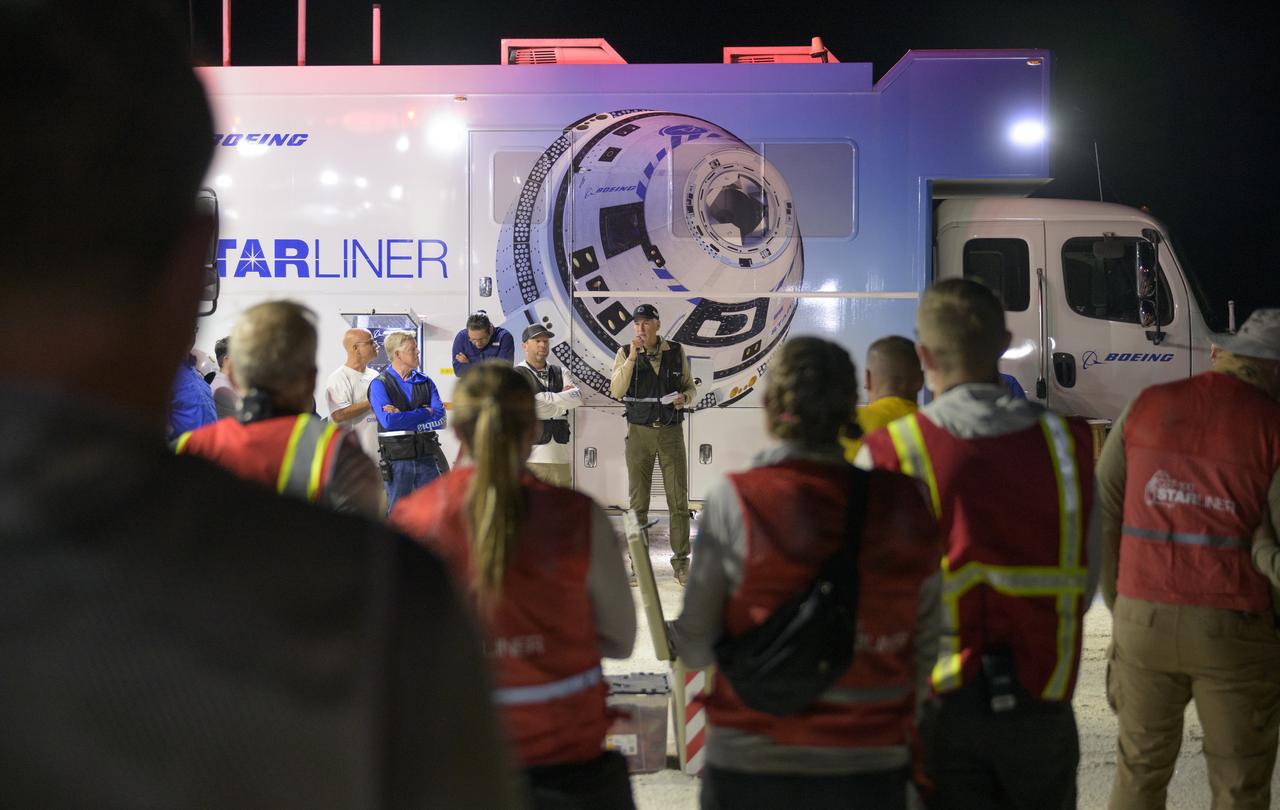

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
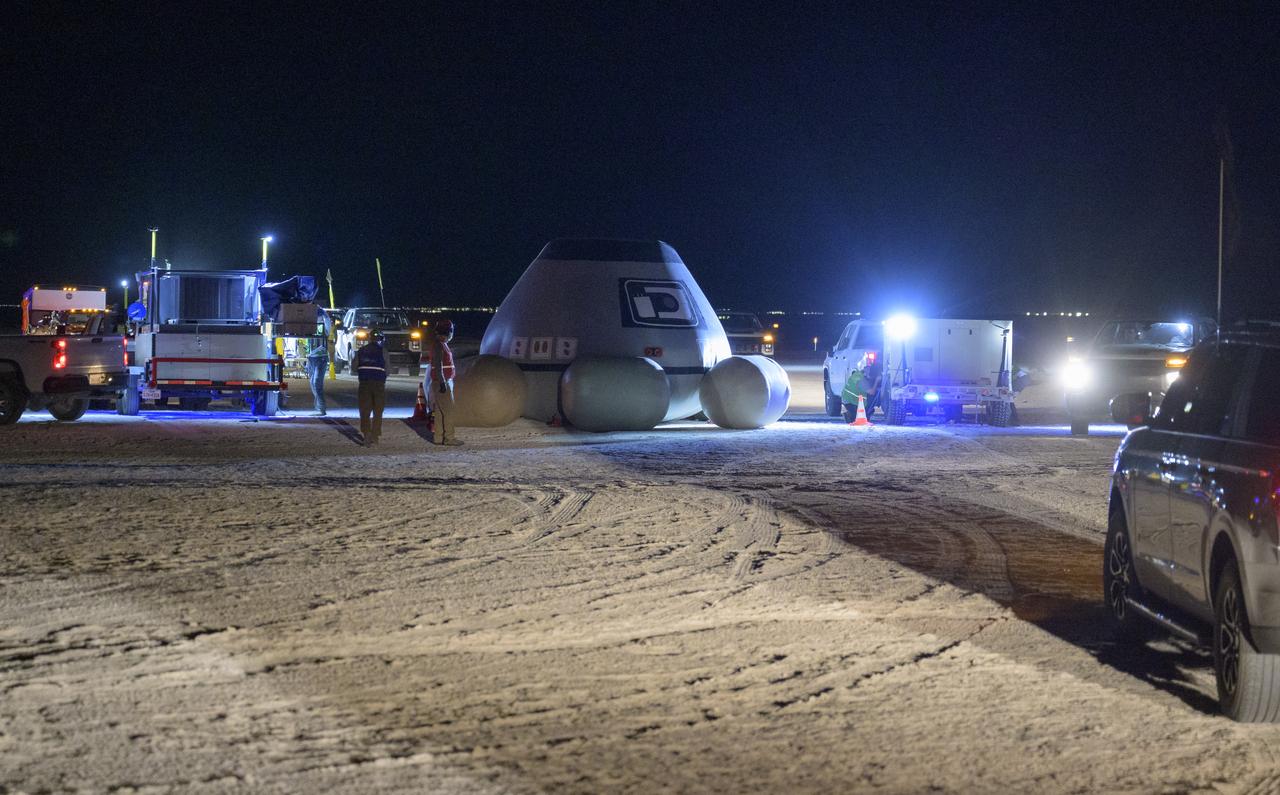

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
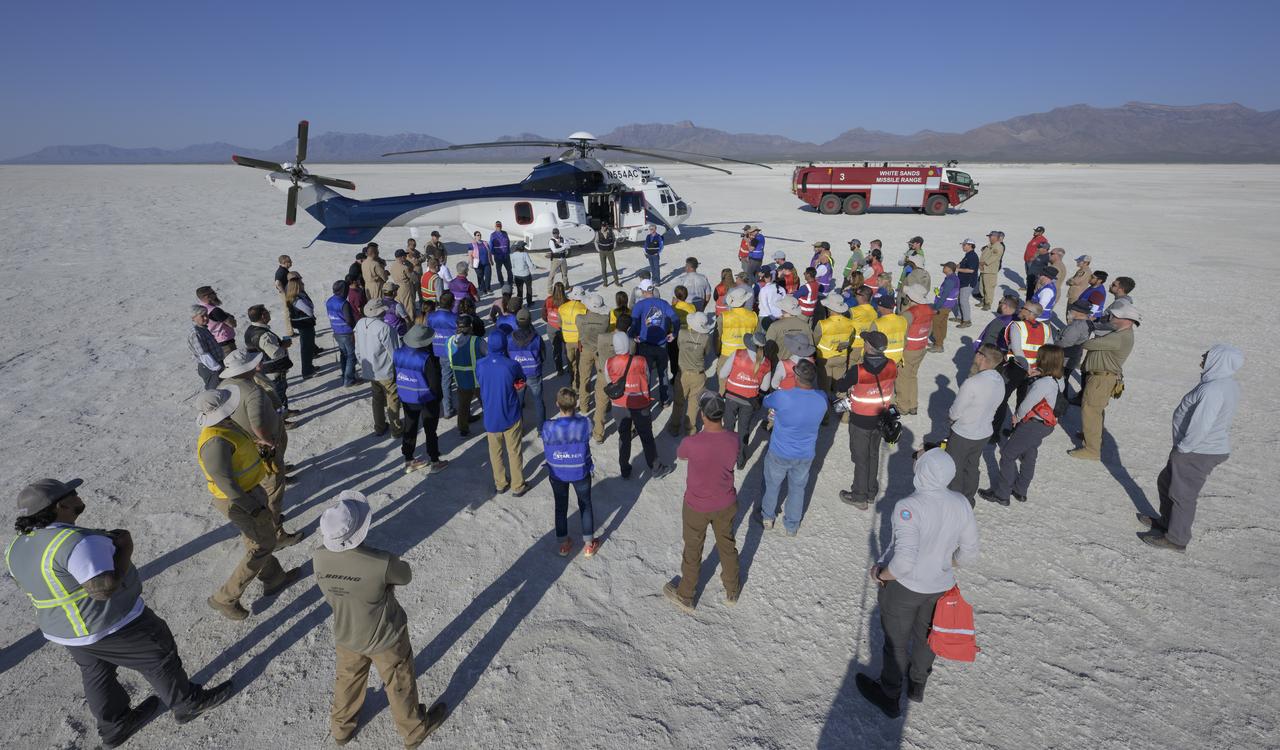

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
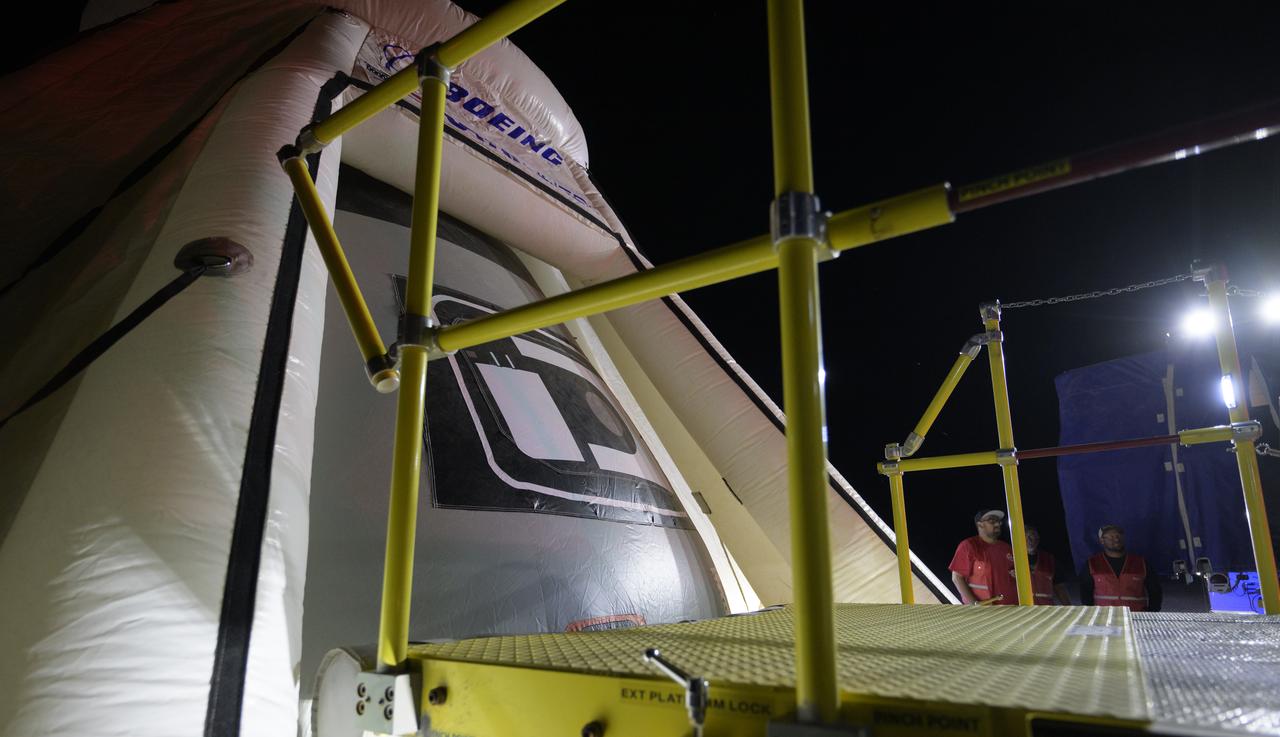

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
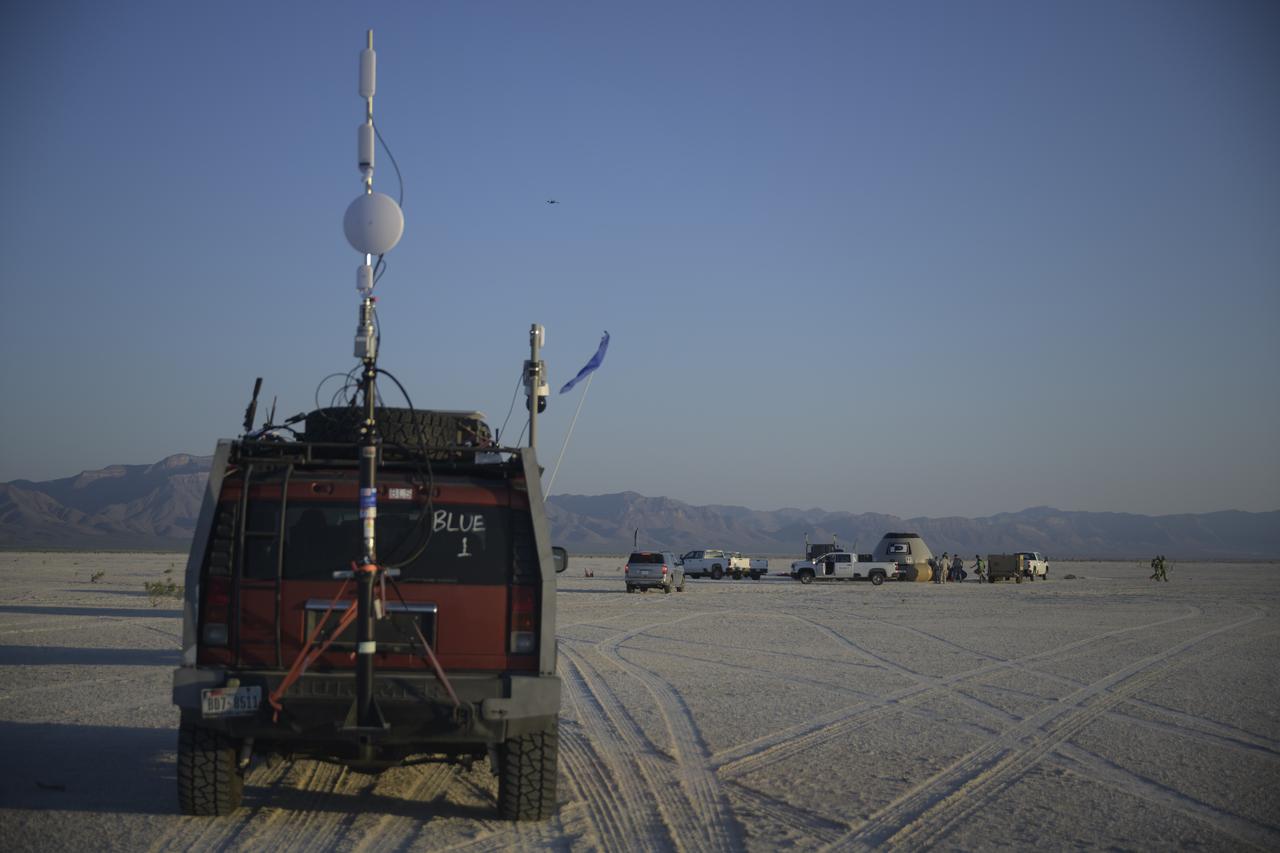

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
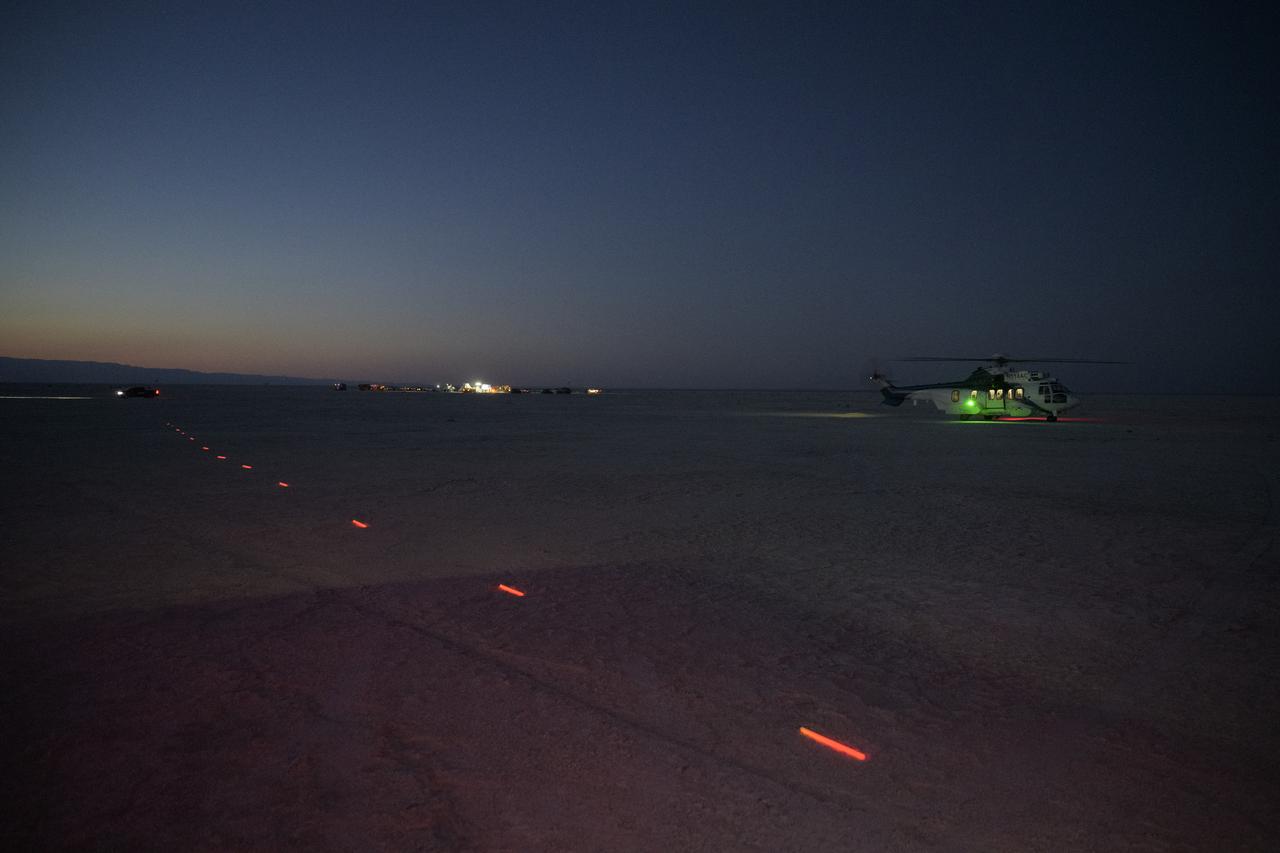

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
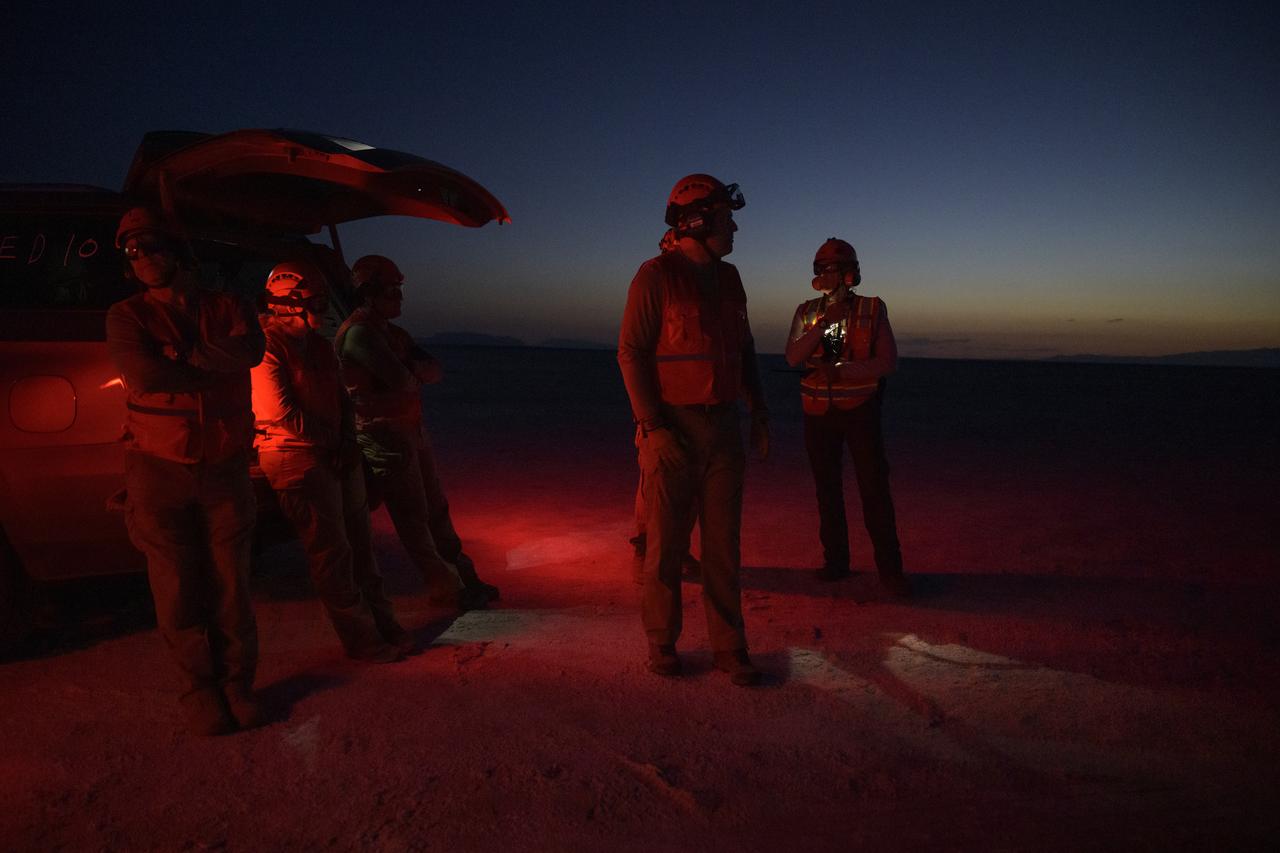

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
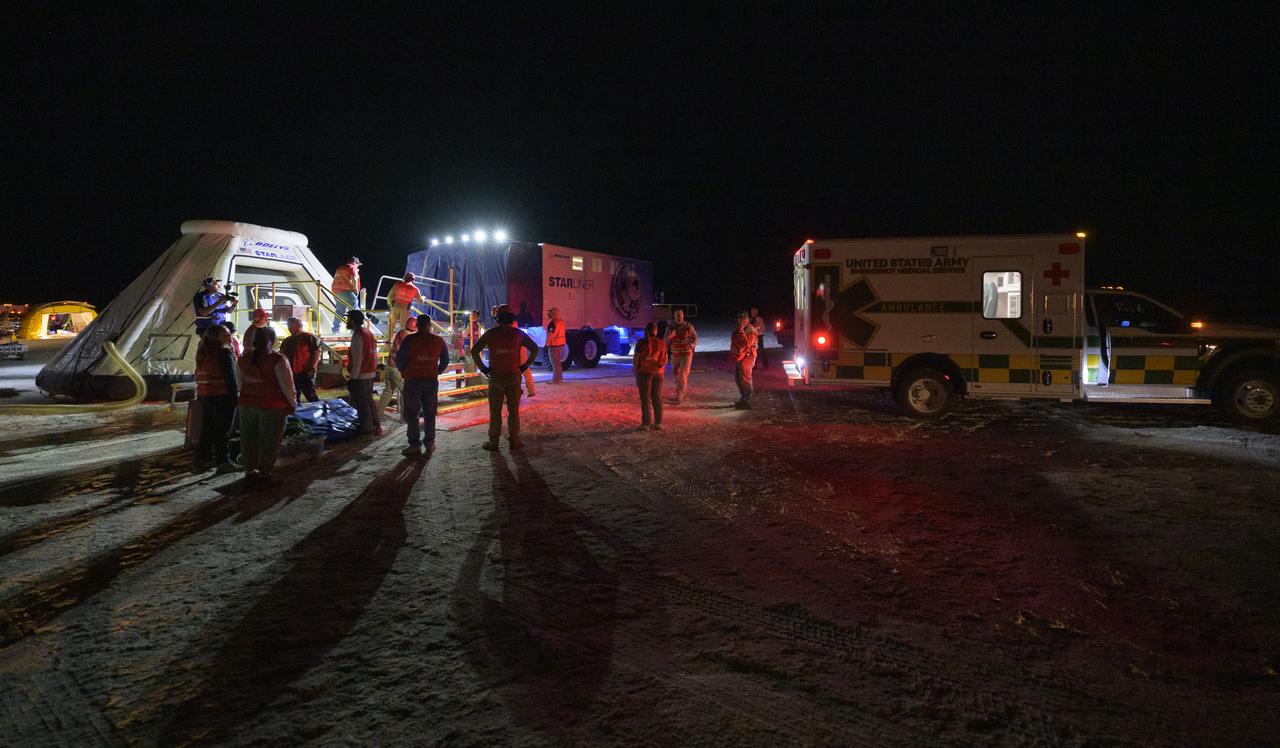

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
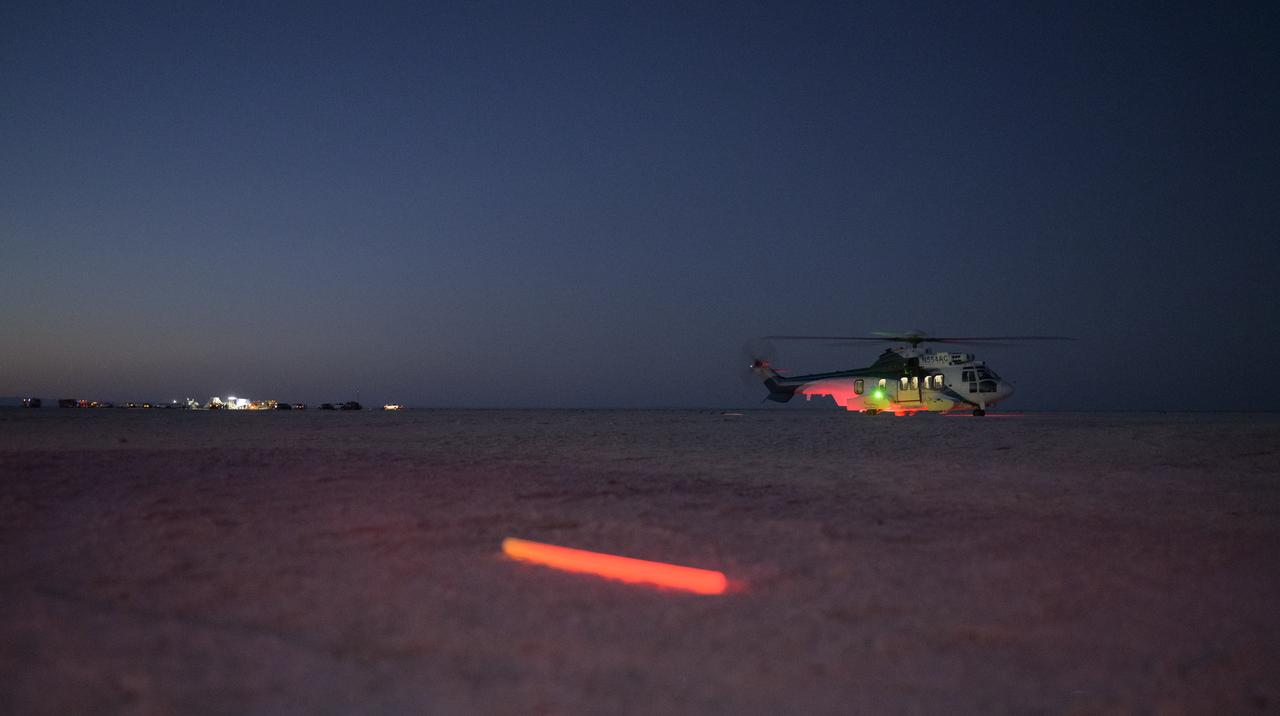

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
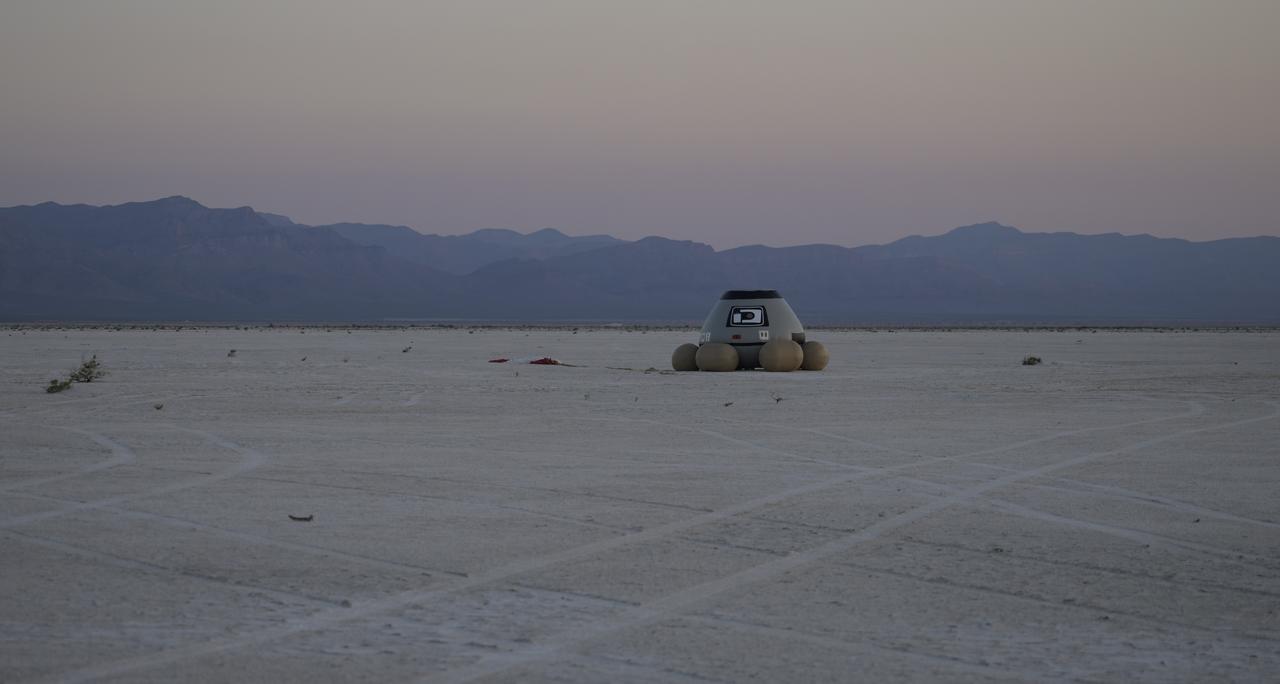

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
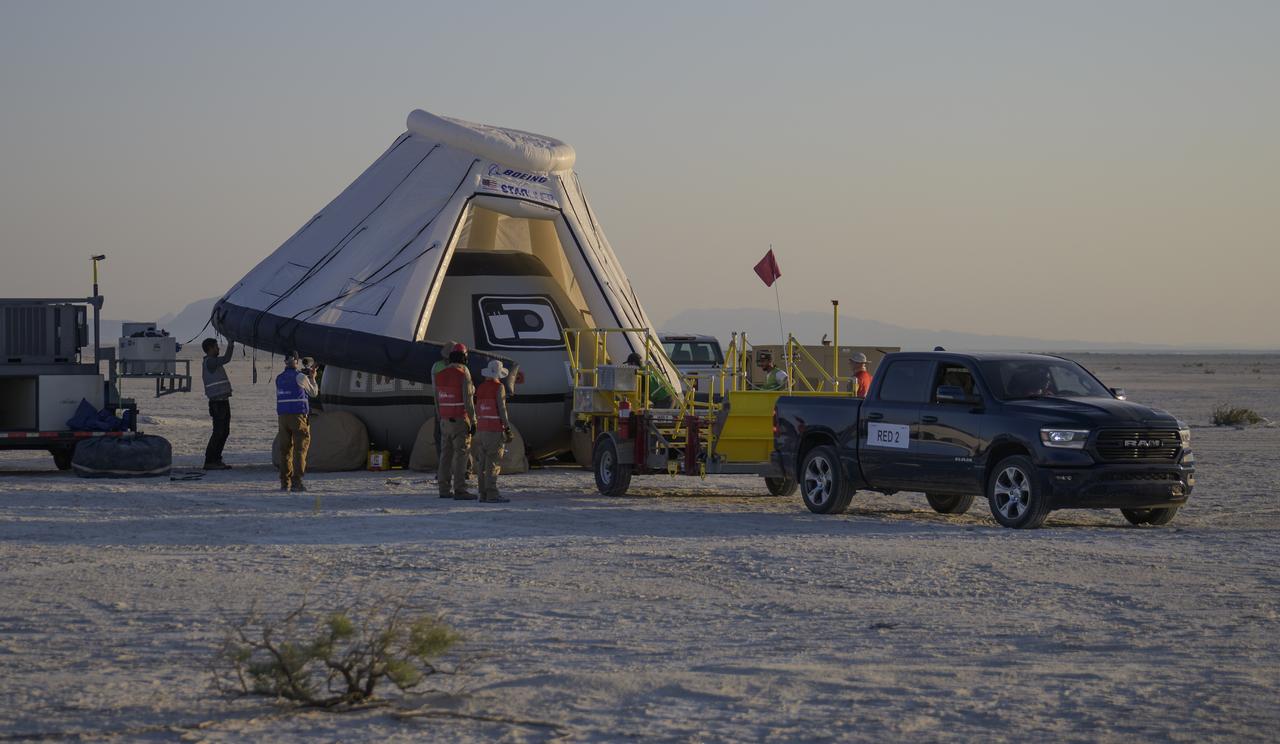

Boeing and NASA teams participate in a mission dress rehearsal to prepare for the landing of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, June 16, 2024. NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams are Starliner’s first human crew and travelled to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test. The mission serves as an end-to-end demonstration of Boeing’s crew transportation system as a provider for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)