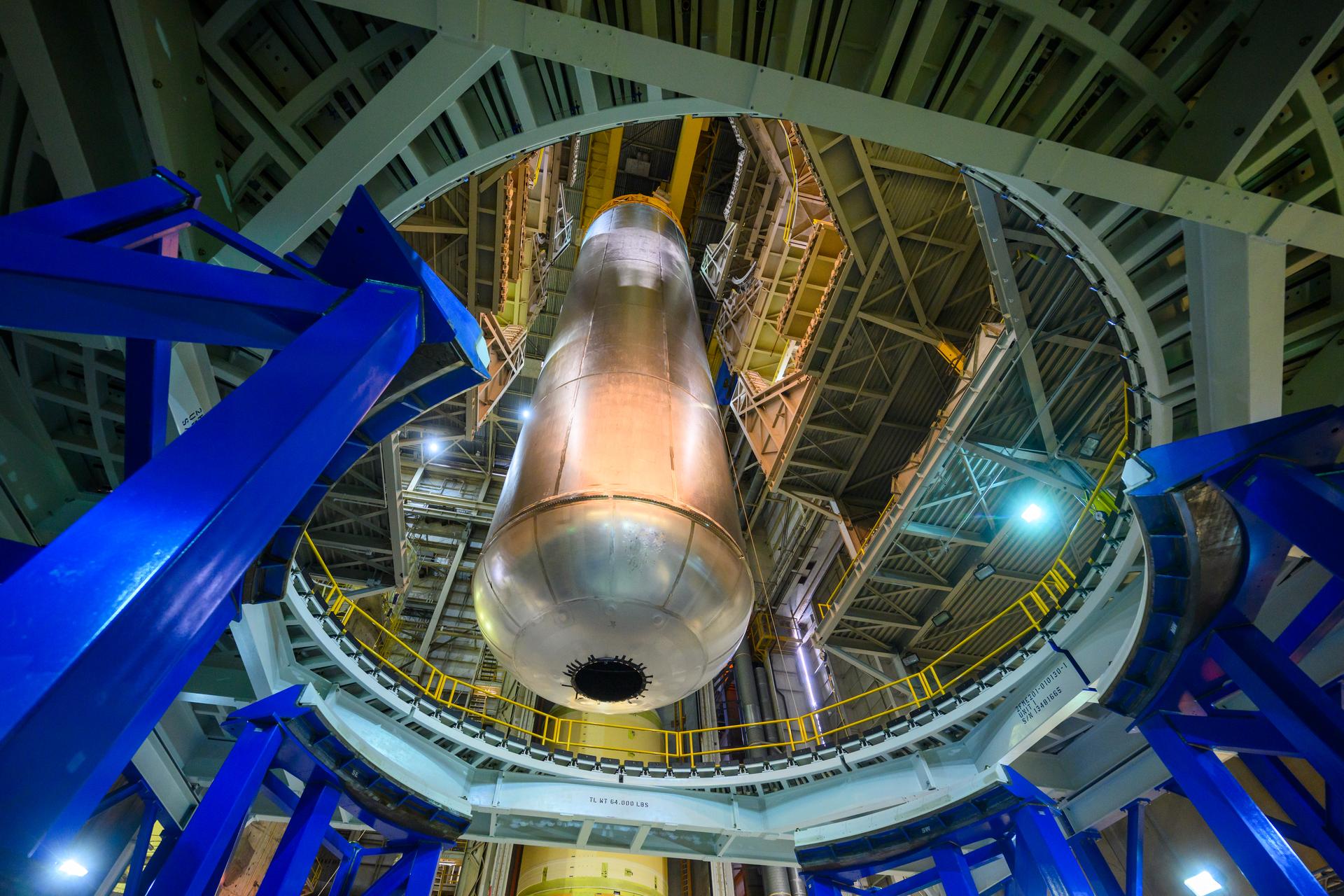

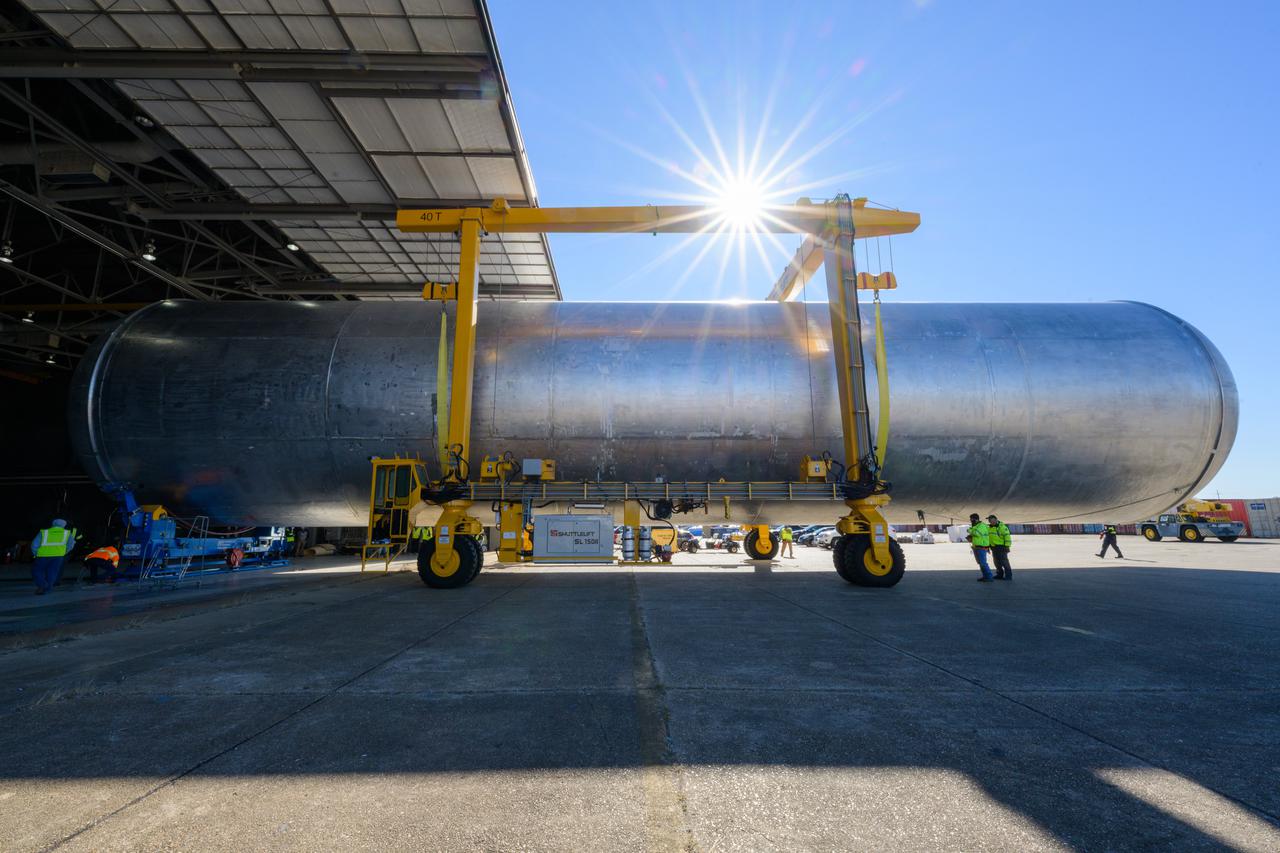
Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the 130-foot-tall liquid hydrogen tank off the vertical assembly center on Nov. 14. This is the fourth liquid hydrogen tank manufactured at the facility for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The completed tank will be loaded into a production cell for technicians to remove the lift tool, perform dimensional scans, and then install brackets, which will allow the move crew to break the tank over from a vertical to a horizontal configuration.

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the 130-foot-tall liquid hydrogen tank off the vertical assembly center on Nov. 14. This is the fourth liquid hydrogen tank manufactured at the facility for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The completed tank will be loaded into a production cell for technicians to remove the lift tool, perform dimensional scans, and then install brackets, which will allow the move crew to break the tank over from a vertical to a horizontal configuration.

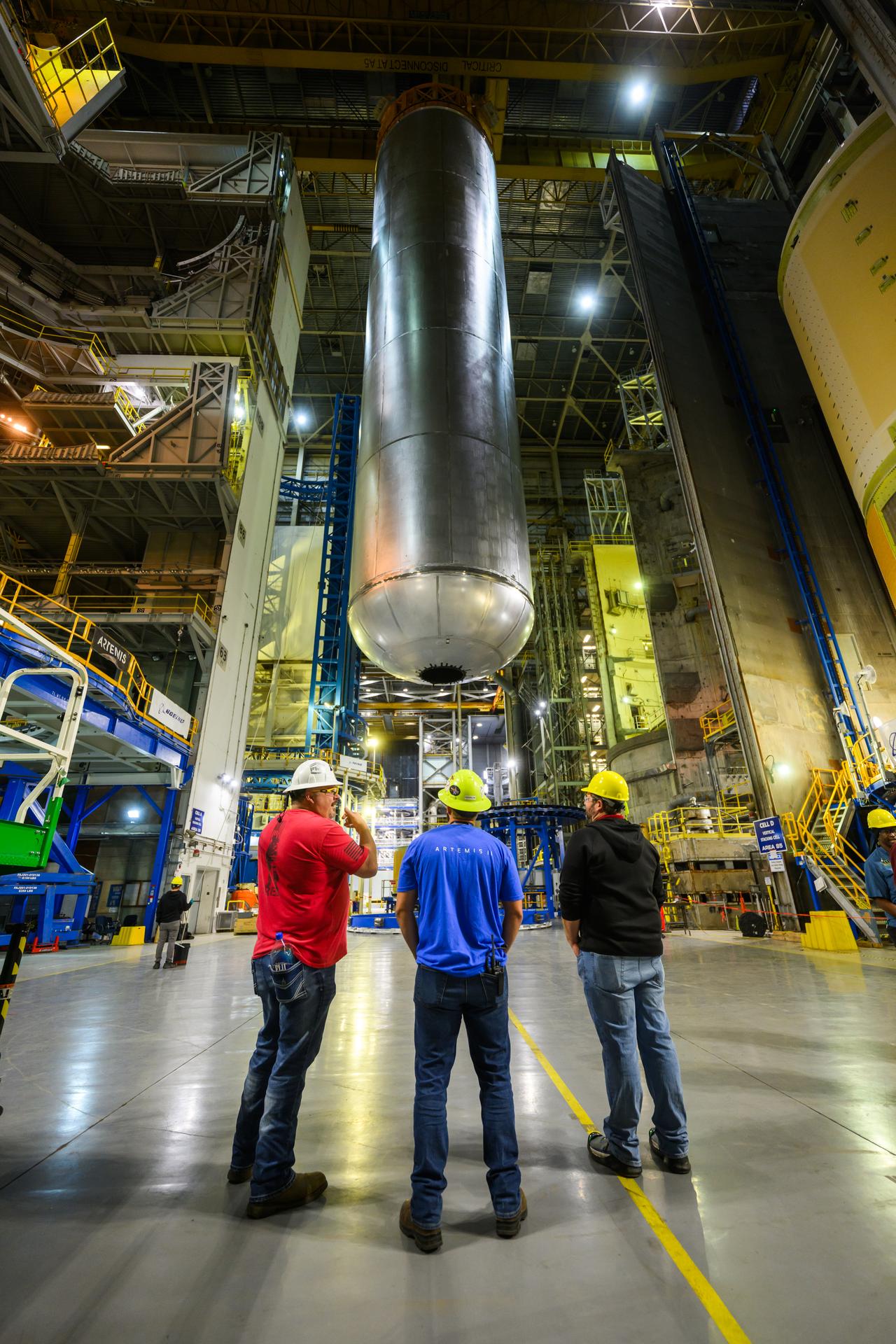
The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the 130-foot-tall liquid hydrogen tank off the vertical assembly center on Nov. 14. This is the fourth liquid hydrogen tank manufactured at the facility for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The completed tank will be loaded into a production cell for technicians to remove the lift tool, perform dimensional scans, and then install brackets, which will allow the move crew to break the tank over from a vertical to a horizontal configuration. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the 130-foot-tall liquid hydrogen tank off the vertical assembly center on Nov. 14. This is the fourth liquid hydrogen tank manufactured at the facility for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The completed tank will be loaded into a production cell for technicians to remove the lift tool, perform dimensional scans, and then install brackets, which will allow the move crew to break the tank over from a vertical to a horizontal configuration. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the 130-foot-tall liquid hydrogen tank off the vertical assembly center on Nov. 14. This is the fourth liquid hydrogen tank manufactured at the facility for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The completed tank will be loaded into a production cell for technicians to remove the lift tool, perform dimensional scans, and then install brackets, which will allow the move crew to break the tank over from a vertical to a horizontal configuration. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the 130-foot-tall liquid hydrogen tank off the vertical assembly center on Nov. 14. This is the fourth liquid hydrogen tank manufactured at the facility for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The completed tank will be loaded into a production cell for technicians to remove the lift tool, perform dimensional scans, and then install brackets, which will allow the move crew to break the tank over from a vertical to a horizontal configuration. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the 130-foot-tall liquid hydrogen tank off the vertical assembly center on Nov. 14. This is the fourth liquid hydrogen tank manufactured at the facility for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The completed tank will be loaded into a production cell for technicians to remove the lift tool, perform dimensional scans, and then install brackets, which will allow the move crew to break the tank over from a vertical to a horizontal configuration. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
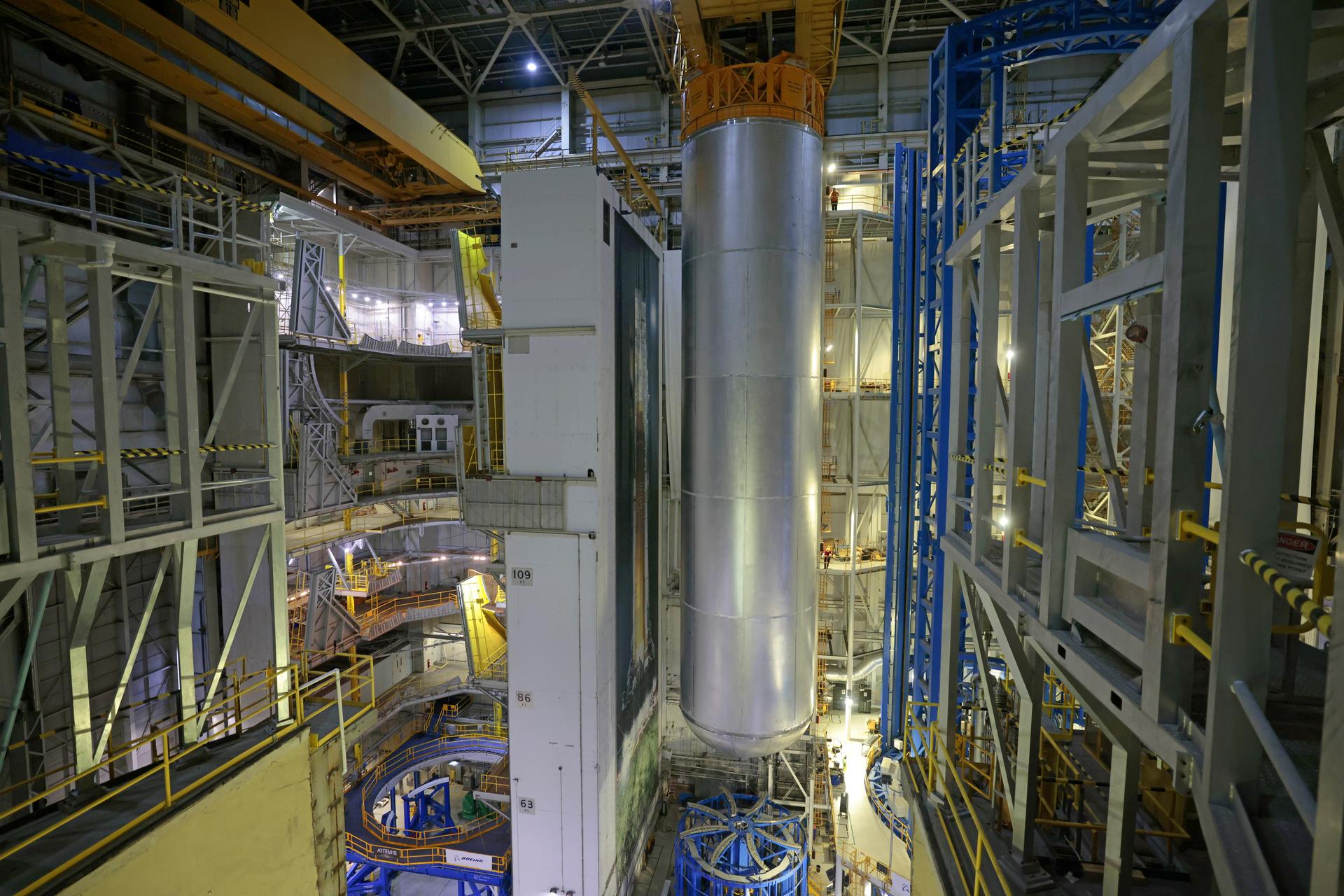

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the 130-foot-tall liquid hydrogen tank off the vertical assembly center on Nov. 14. This is the fourth liquid hydrogen tank manufactured at the facility for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The completed tank will be loaded into a production cell for technicians to remove the lift tool, perform dimensional scans, and then install brackets, which will allow the move crew to break the tank over from a vertical to a horizontal configuration. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
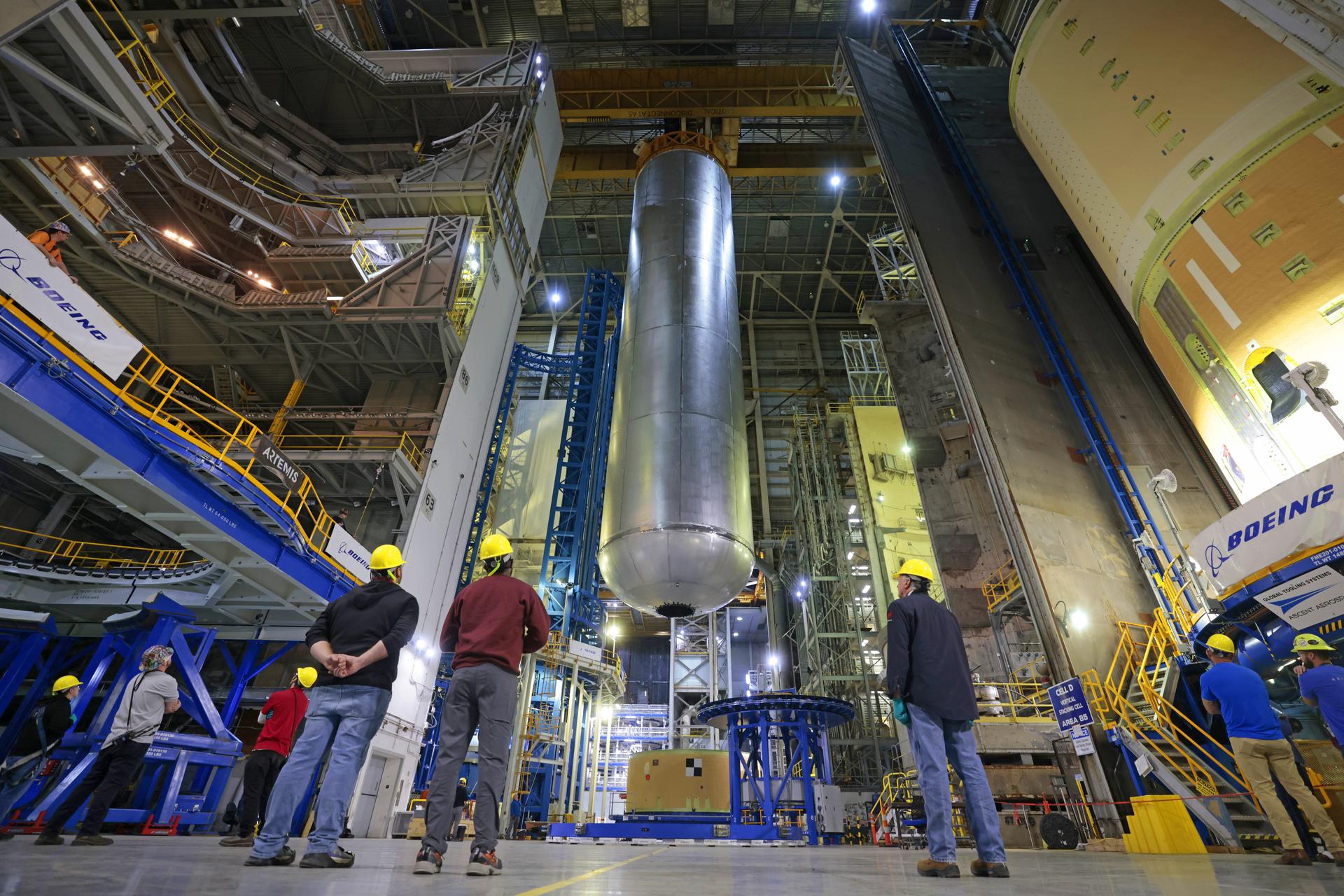

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the 130-foot-tall liquid hydrogen tank off the vertical assembly center on Nov. 14. This is the fourth liquid hydrogen tank manufactured at the facility for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The completed tank will be loaded into a production cell for technicians to remove the lift tool, perform dimensional scans, and then install brackets, which will allow the move crew to break the tank over from a vertical to a horizontal configuration. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams lift a liquid hydrogen tank barrel into the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, on July 25, 2025. Inside the center, teams will perform a circumferential weld to connect the barrel to the previously loaded forward dome. The barrel is one of five barrels, which along with the forward and aft domes, make up the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage manufactured at the site. Artemis will pave the way for a long-term human presence on the lunar surface while ushering in the Golden Age of Innovation and Exploration.

Teams lift a liquid hydrogen tank barrel into the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, on July 25, 2025. Inside the center, teams will perform a circumferential weld to connect the barrel to the previously loaded forward dome. The barrel is one of five barrels, which along with the forward and aft domes, make up the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage manufactured at the site. Artemis will pave the way for a long-term human presence on the lunar surface while ushering in the Golden Age of Innovation and Exploration.

Teams lift a liquid hydrogen tank barrel into the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, on July 25, 2025. Inside the center, teams will perform a circumferential weld to connect the barrel to the previously loaded forward dome. The barrel is one of five barrels, which along with the forward and aft domes, make up the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage manufactured at the site. Artemis will pave the way for a long-term human presence on the lunar surface while ushering in the Golden Age of Innovation and Exploration.

Teams lift a liquid hydrogen tank barrel into the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, on July 25, 2025. Inside the center, teams will perform a circumferential weld to connect the barrel to the previously loaded forward dome. The barrel is one of five barrels, which along with the forward and aft domes, make up the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage manufactured at the site. Artemis will pave the way for a long-term human presence on the lunar surface while ushering in the Golden Age of Innovation and Exploration.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. The engine section is still being outfitted, so for this test crews attached an engine section aft simulator during proof testing on January 27, 2022. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. The engine section is still being outfitted, so for this test crews attached an engine section aft simulator during proof testing on January 27, 2022. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
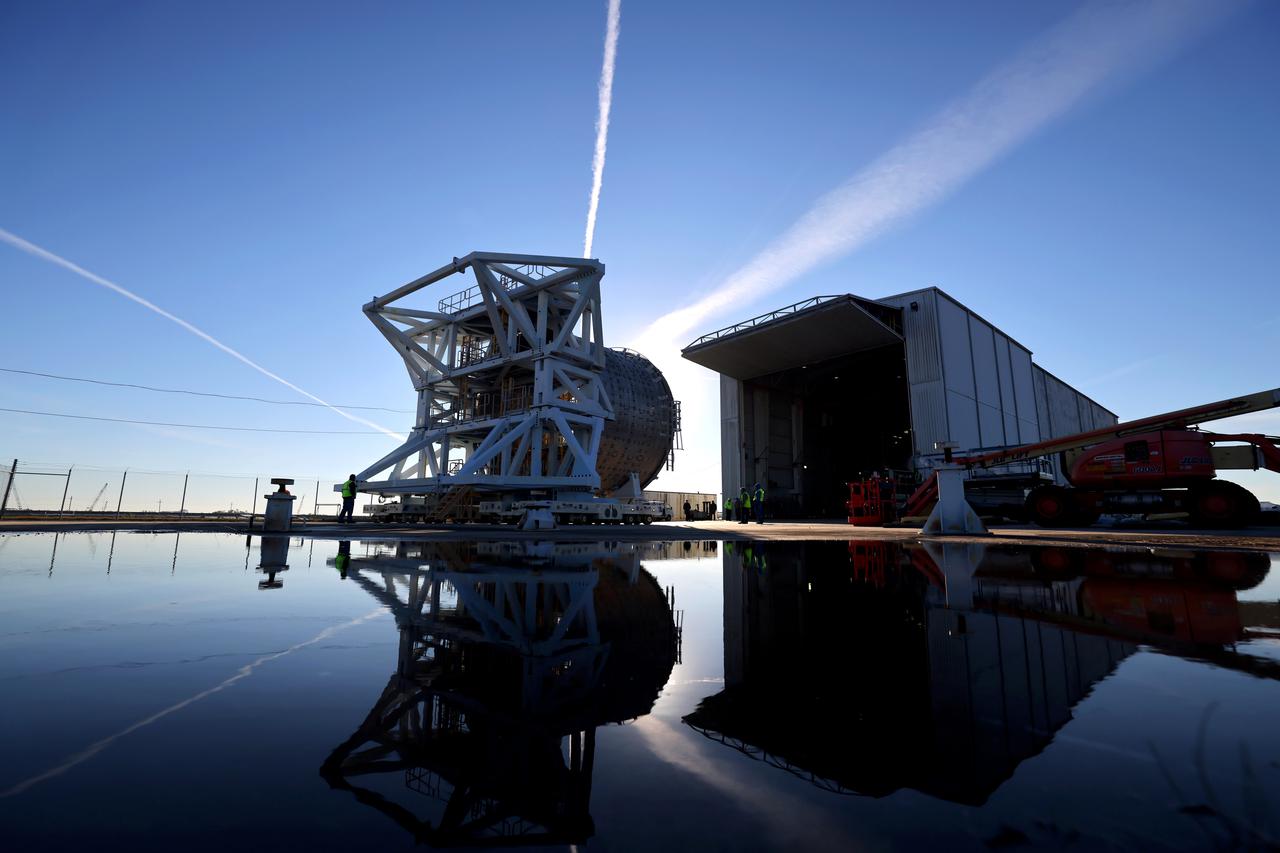

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. The engine section is still being outfitted, so for this test crews attached an engine section aft simulator during proof testing on January 27, 2022. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
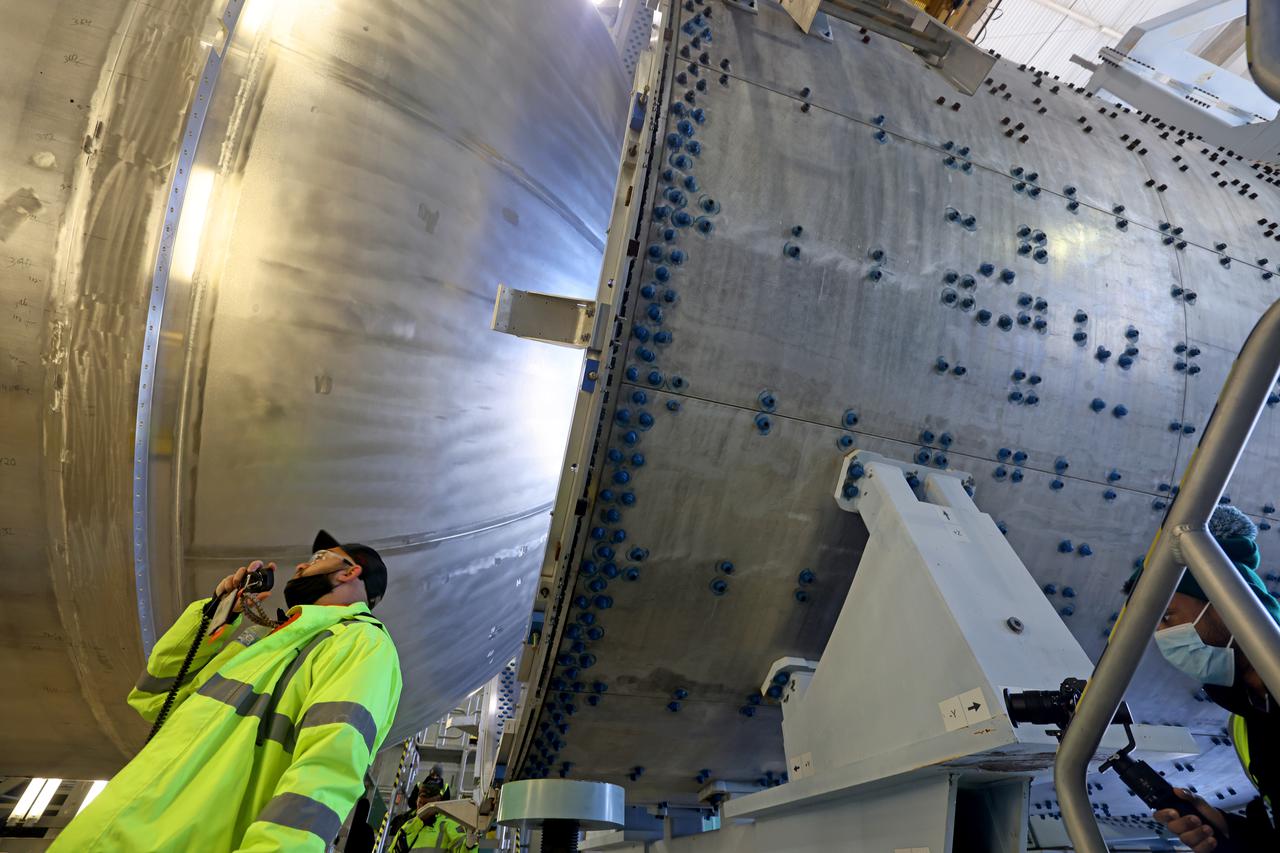

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. The engine section is still being outfitted, so for this test crews attached an engine section aft simulator during proof testing on January 27, 2022. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
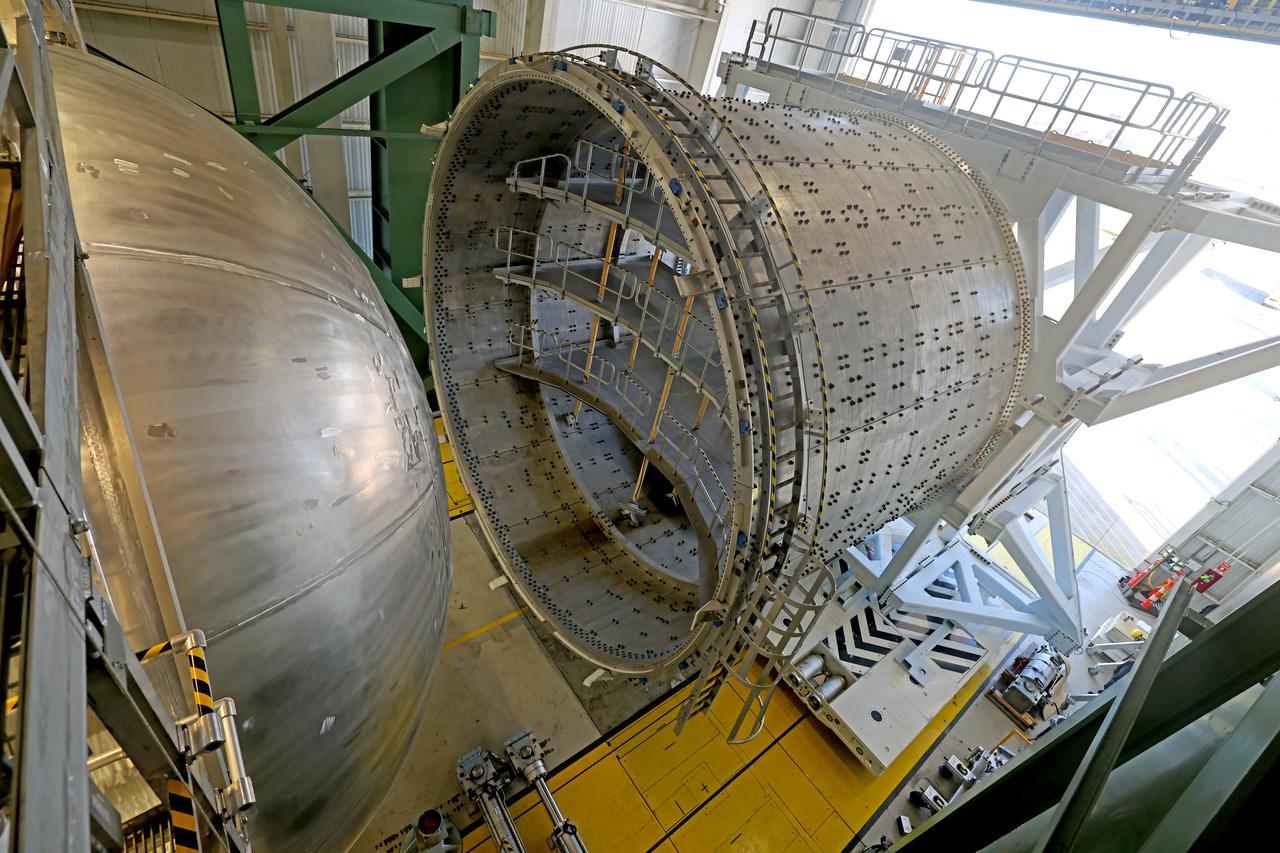

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the RS-25 engines. The engine section is still being outfitted, so for this test crews attached an engine section aft simulator during proof testing on January 27, 2022. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

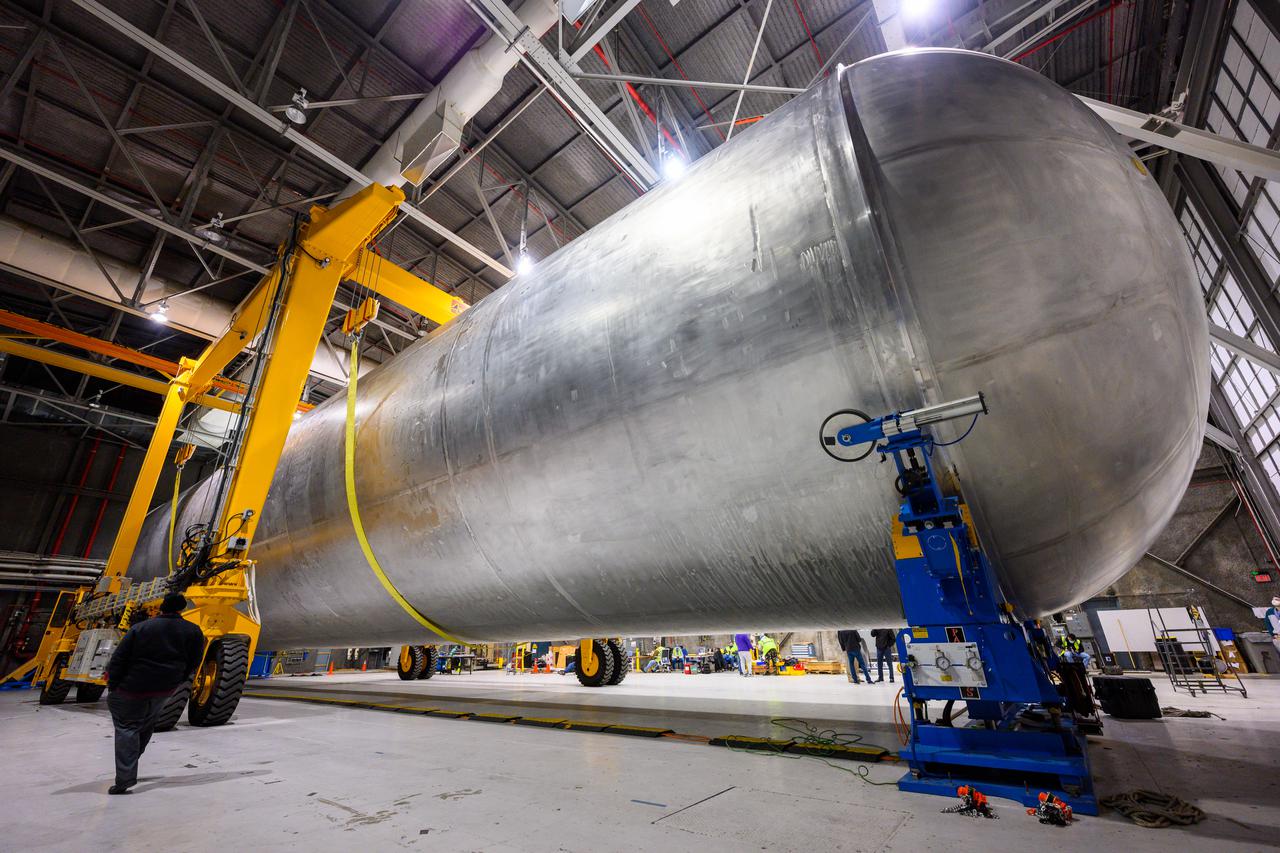
These photos show how teams moved and prepared a liquid hydrogen tank for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for priming in the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 14, 2023. The hardware will form part of the core stage for the SLS rocket that will power Artemis III. To prepare the flight hardware for primer, the tank underwent internal cleaning in nearby Cell E in October. Internal cleaning is part of the manufacturing process for the core stage. After testing, both of the stage’s propellant tanks and its dry structures – the elements that do not hold fuel – are cleaned, primed, and readied for the next phase of production Technichians will next sand down and prepare the surface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. The propellant tank is the largest of the five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall Moon rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
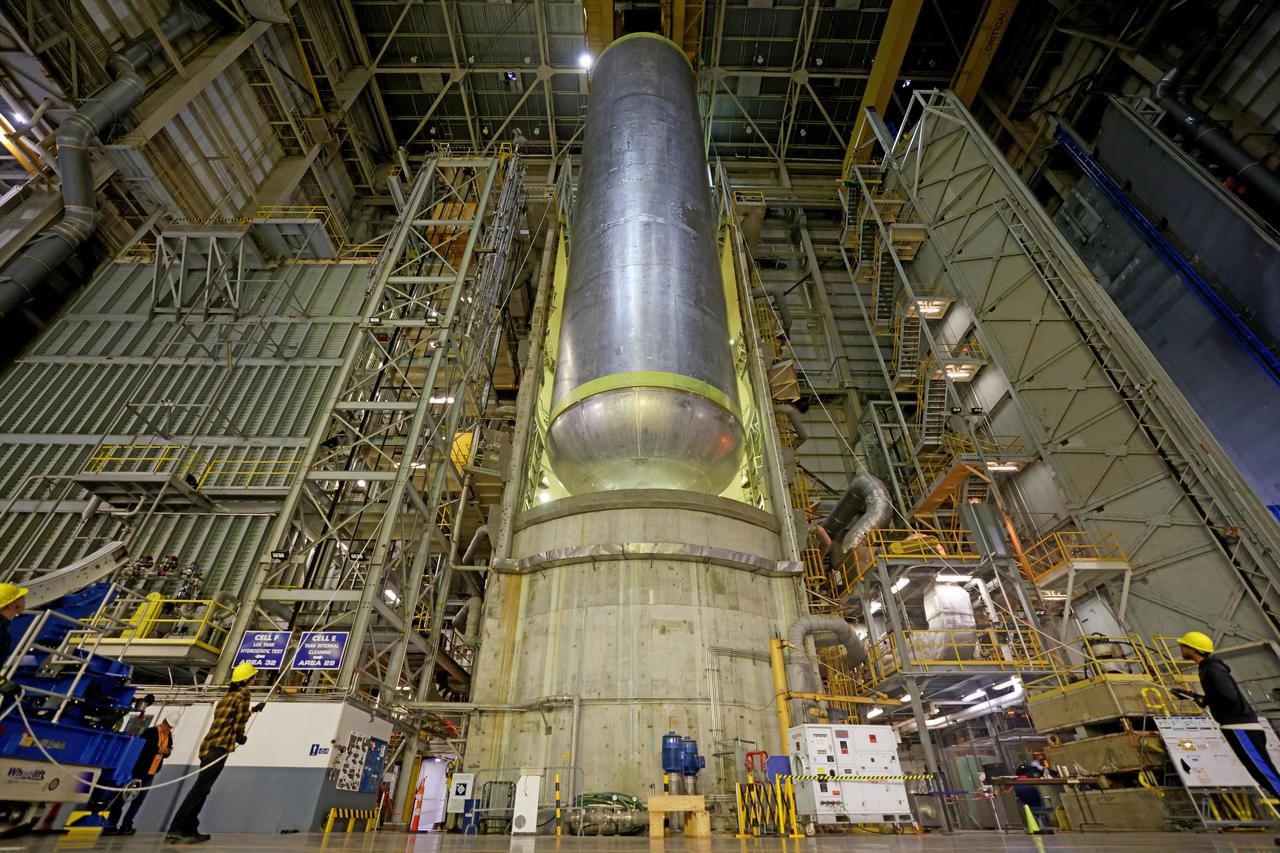

These photos show how teams moved and prepared a liquid hydrogen tank for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for priming in the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 14, 2023. The hardware will form part of the core stage for the SLS rocket that will power Artemis III. To prepare the flight hardware for primer, the tank underwent internal cleaning in nearby Cell E in October. Internal cleaning is part of the manufacturing process for the core stage. After testing, both of the stage’s propellant tanks and its dry structures – the elements that do not hold fuel – are cleaned, primed, and readied for the next phase of production Technichians will next sand down and prepare the surface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. The propellant tank is the largest of the five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall Moon rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
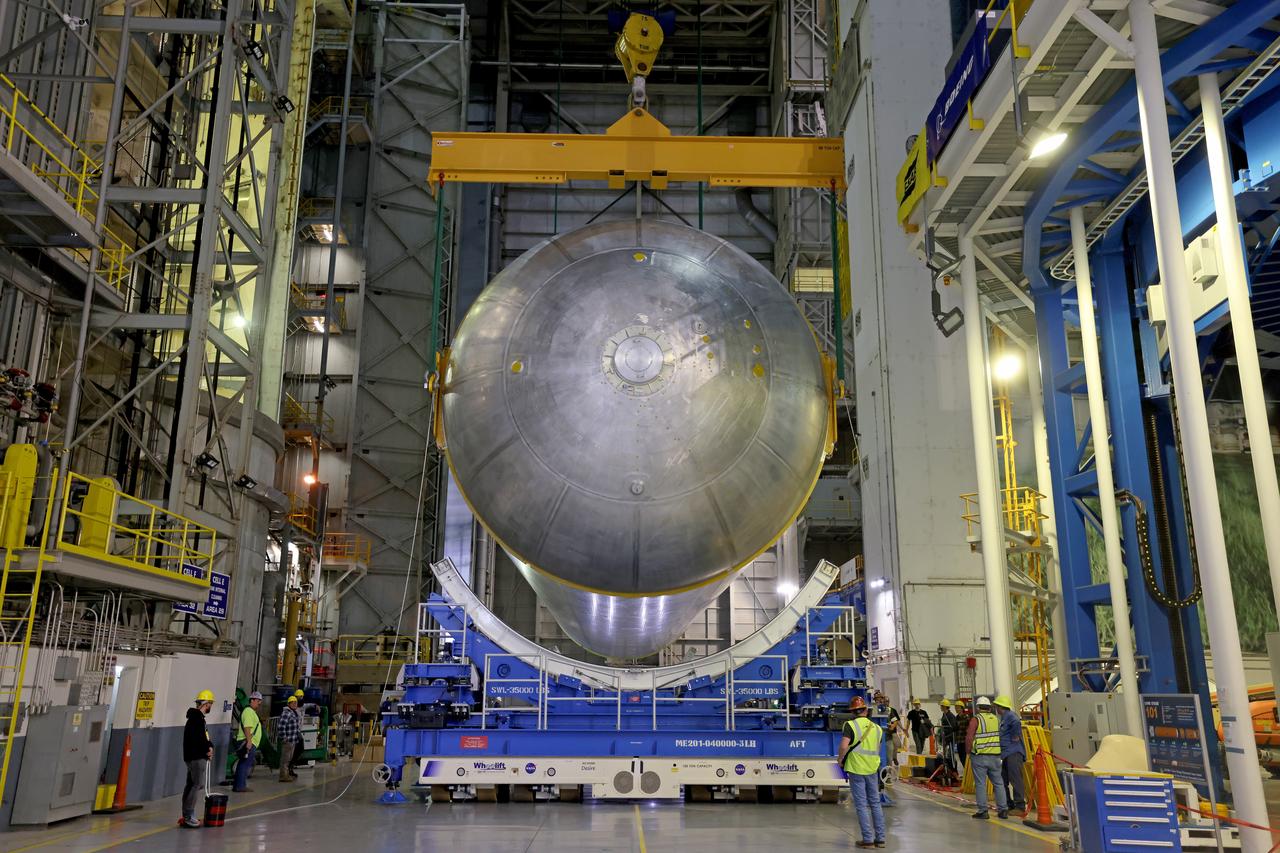

These photos show how teams moved and prepared a liquid hydrogen tank for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for priming in the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 14, 2023. The hardware will form part of the core stage for the SLS rocket that will power Artemis III. To prepare the flight hardware for primer, the tank underwent internal cleaning in nearby Cell E in October. Internal cleaning is part of the manufacturing process for the core stage. After testing, both of the stage’s propellant tanks and its dry structures – the elements that do not hold fuel – are cleaned, primed, and readied for the next phase of production Technichians will next sand down and prepare the surface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. The propellant tank is the largest of the five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall Moon rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
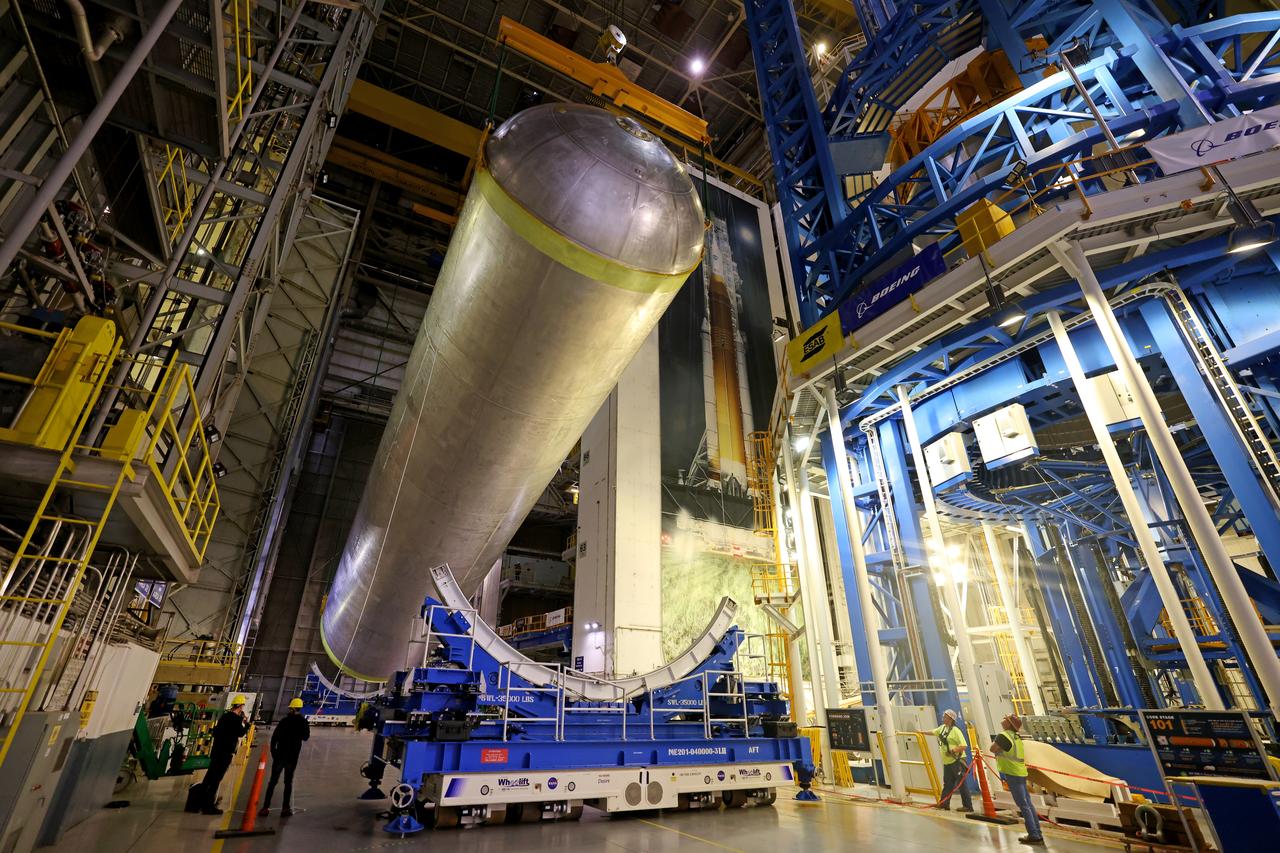

These photos show how teams moved and prepared a liquid hydrogen tank for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for priming in the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 14, 2023. The hardware will form part of the core stage for the SLS rocket that will power Artemis III. To prepare the flight hardware for primer, the tank underwent internal cleaning in nearby Cell E in October. Internal cleaning is part of the manufacturing process for the core stage. After testing, both of the stage’s propellant tanks and its dry structures – the elements that do not hold fuel – are cleaned, primed, and readied for the next phase of production Technichians will next sand down and prepare the surface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. The propellant tank is the largest of the five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall Moon rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

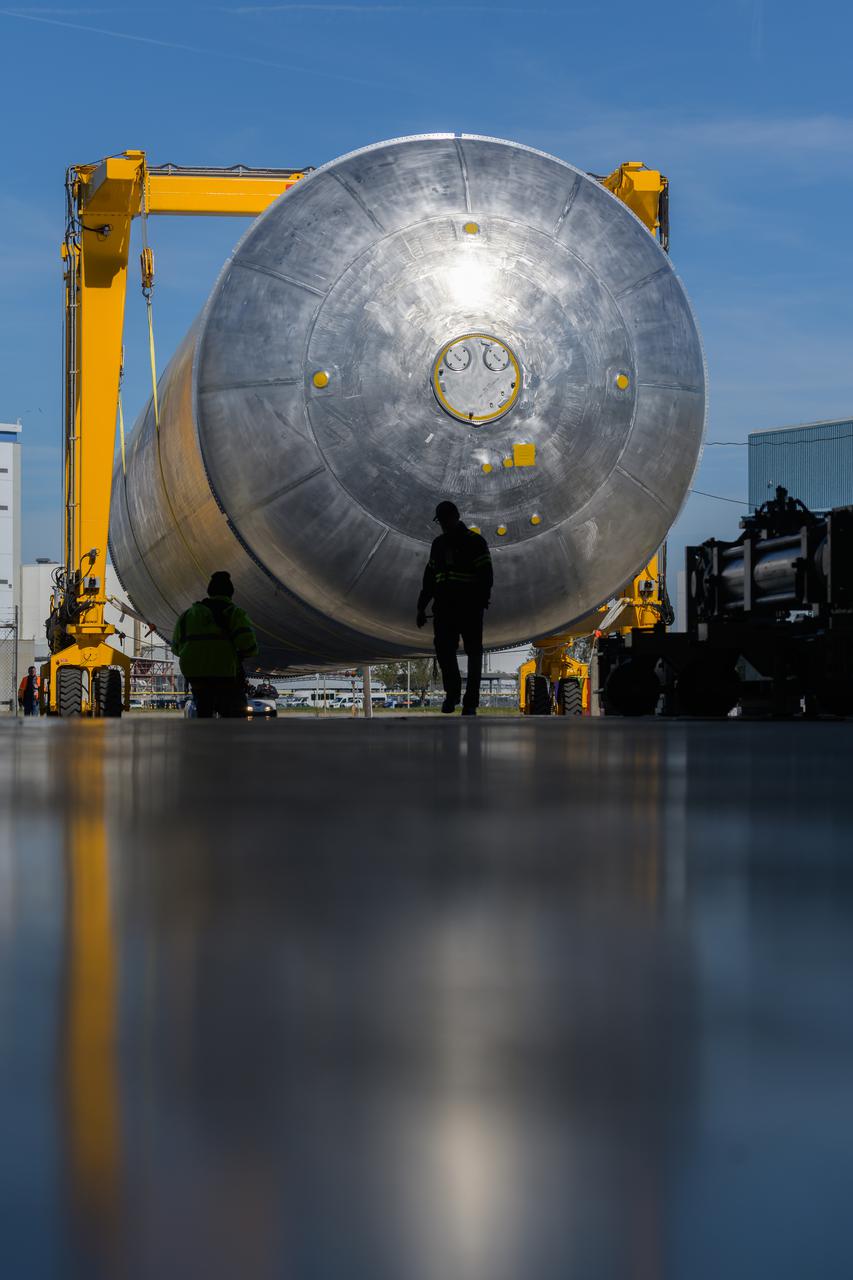
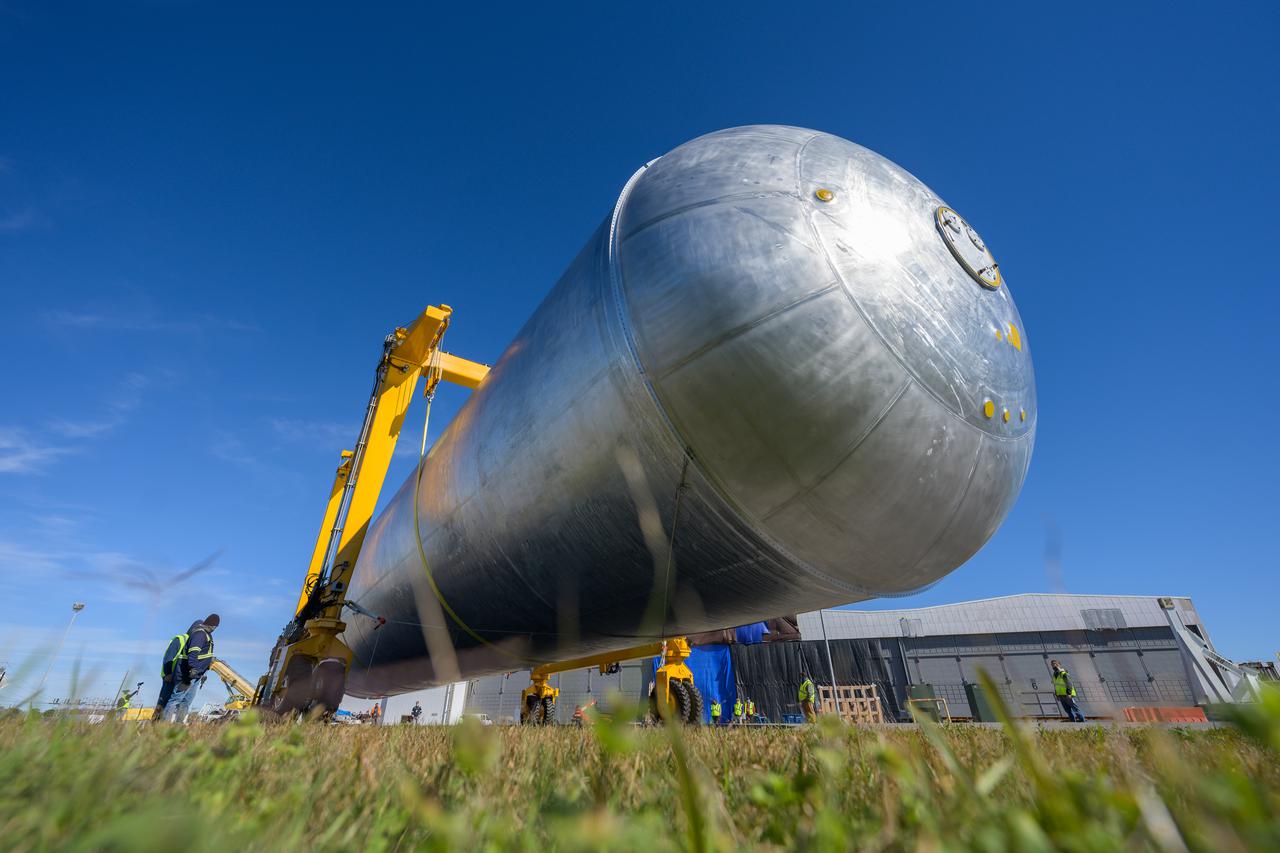
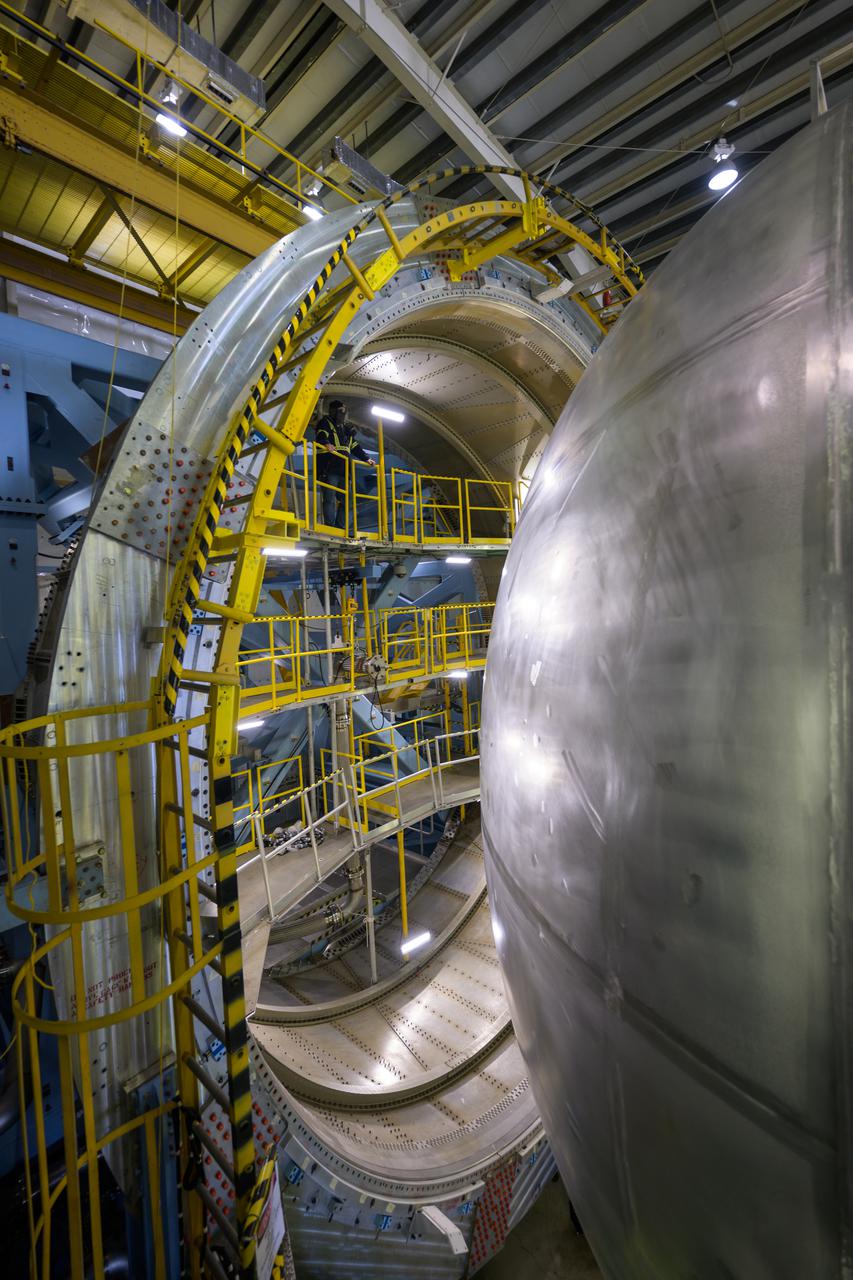
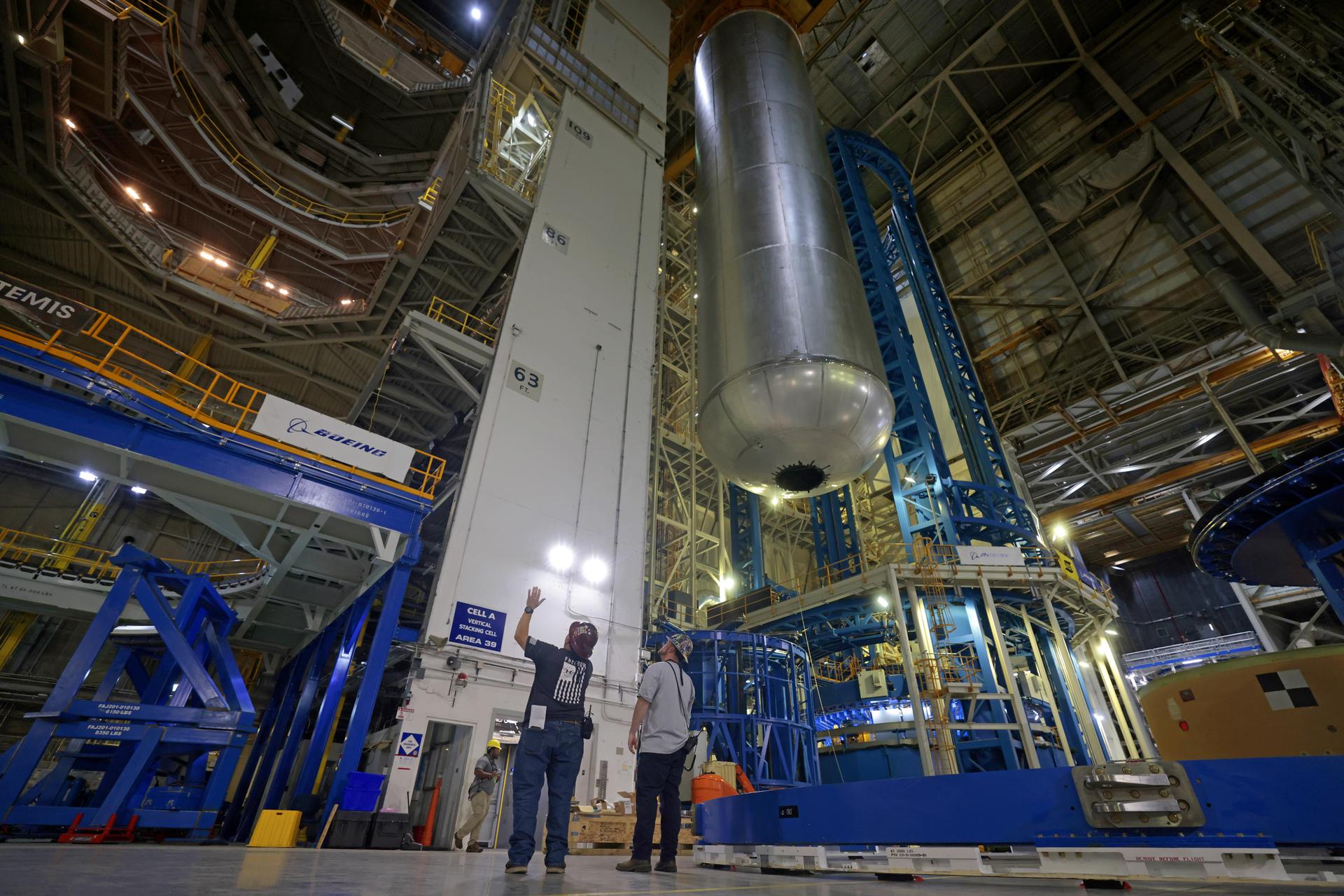
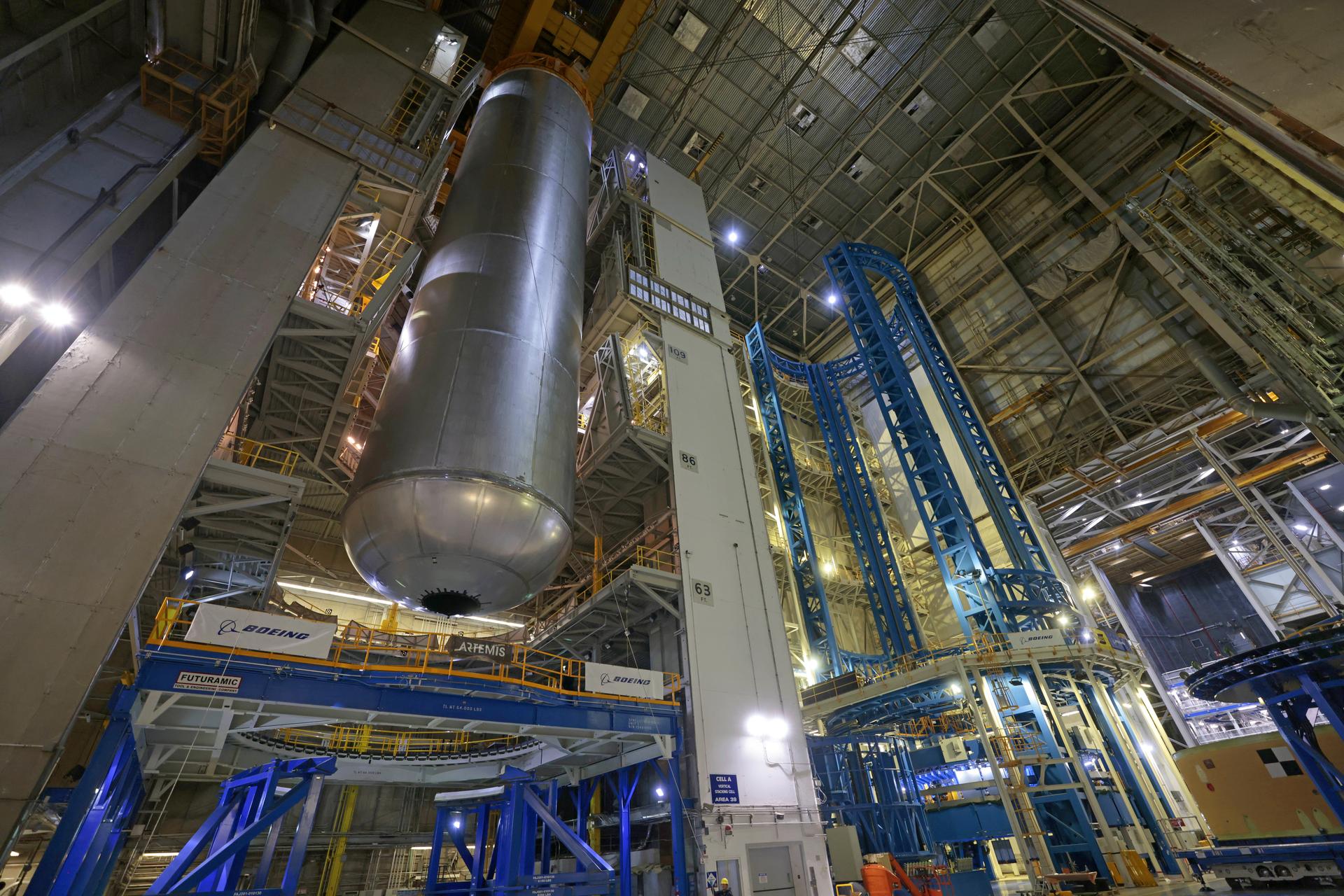
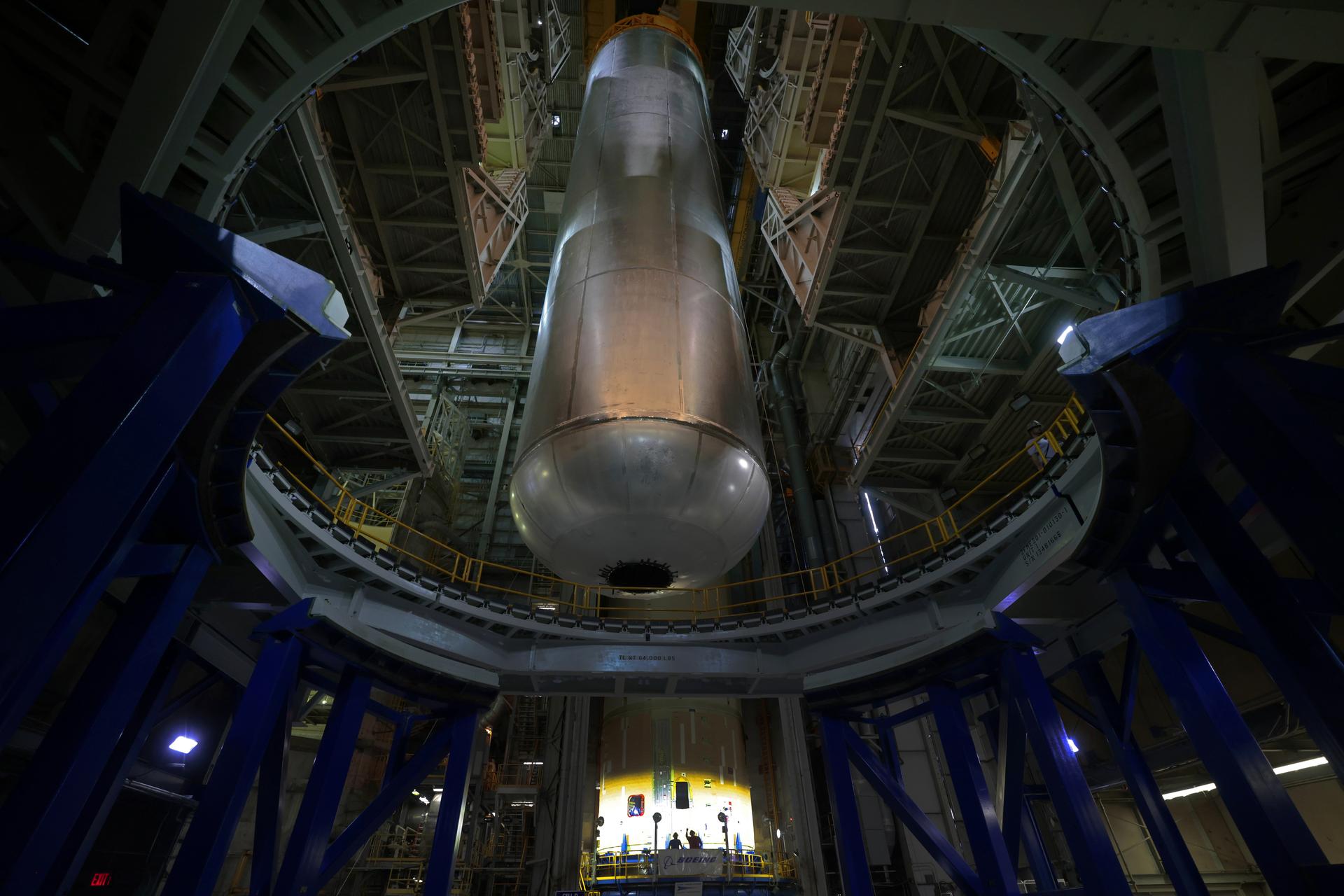
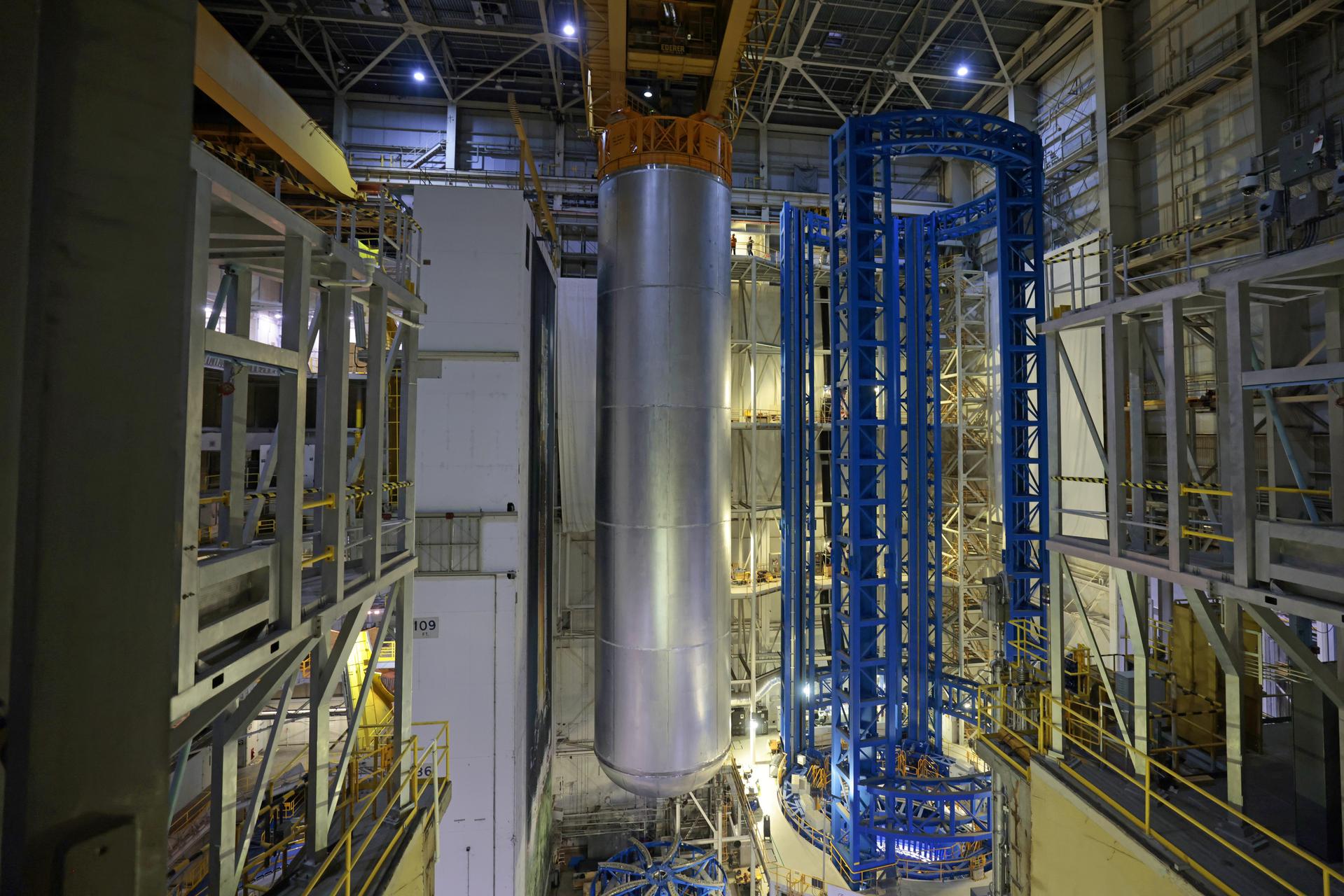
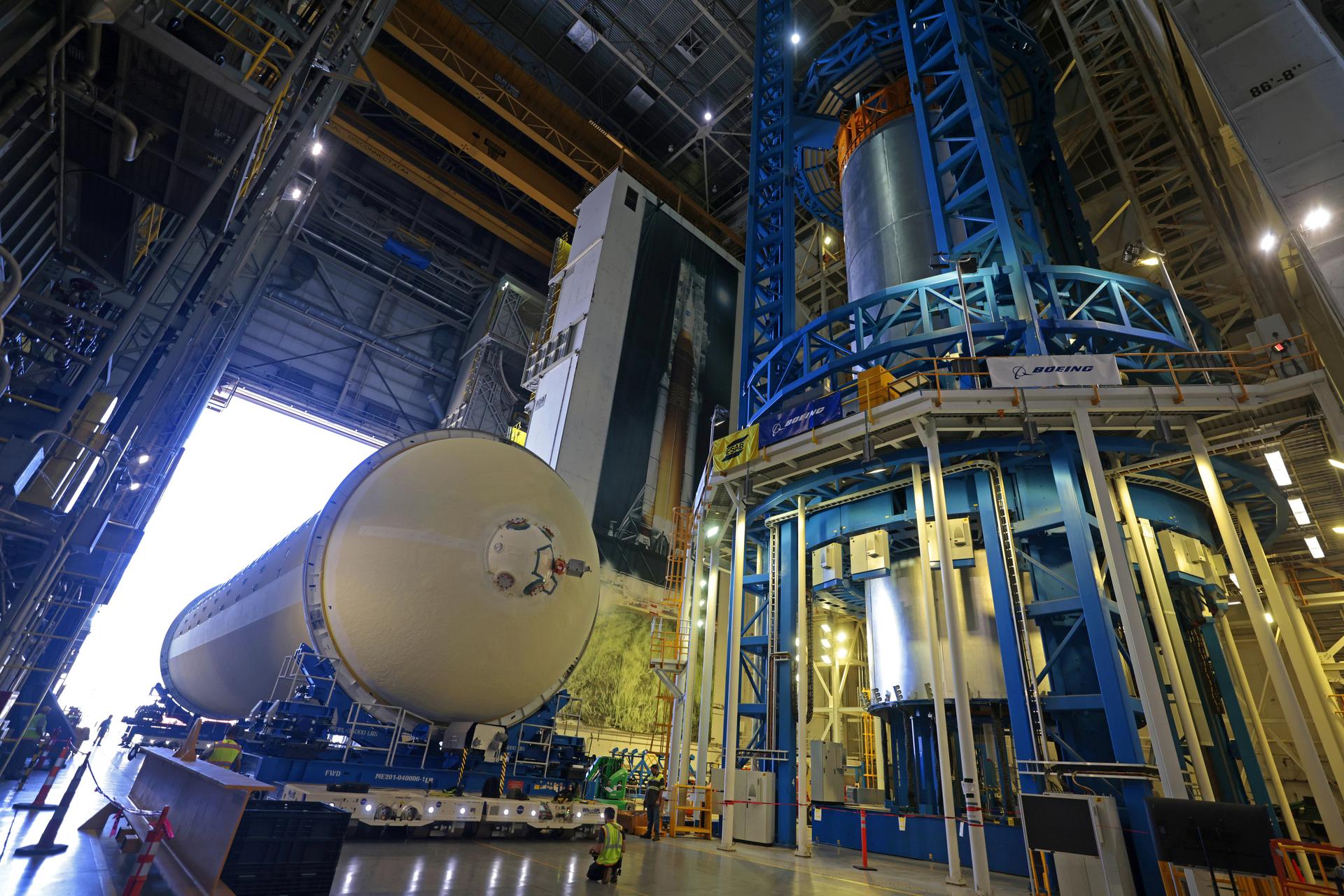
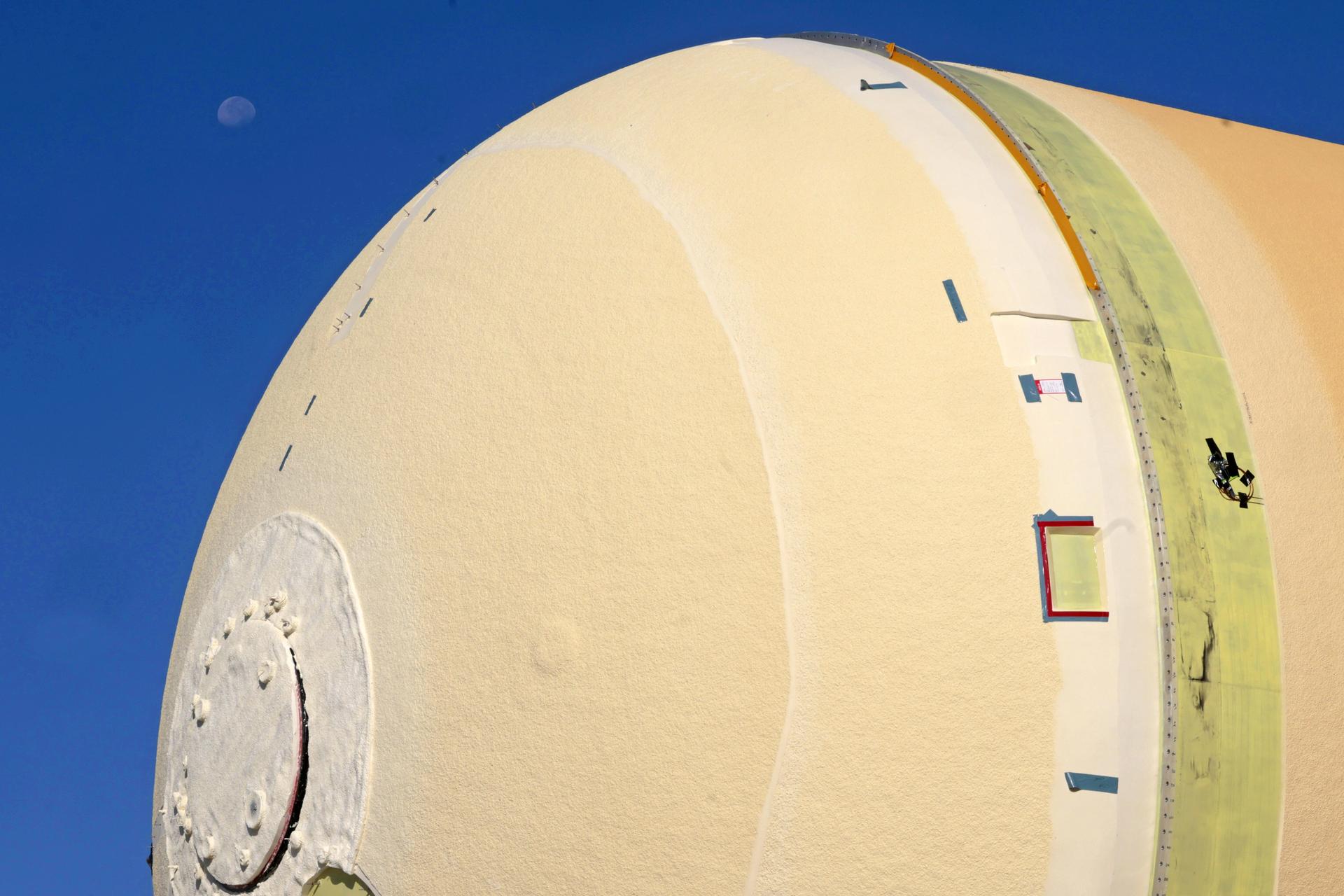
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid hydrogen tank of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Cell A for white light scans of the tank’s dimensions in preparation of multiple join activities throughout the manufacturing process. The flight hardware will be used for Artemis III, one of the first crewed Artemis missions. The liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and is the largest of the five elements that make up the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank is situated between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid hydrogen tank of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Cell A for white light scans of the tank’s dimensions in preparation of multiple join activities throughout the manufacturing process. The flight hardware will be used for Artemis III, one of the first crewed Artemis missions. The liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and is the largest of the five elements that make up the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank is situated between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
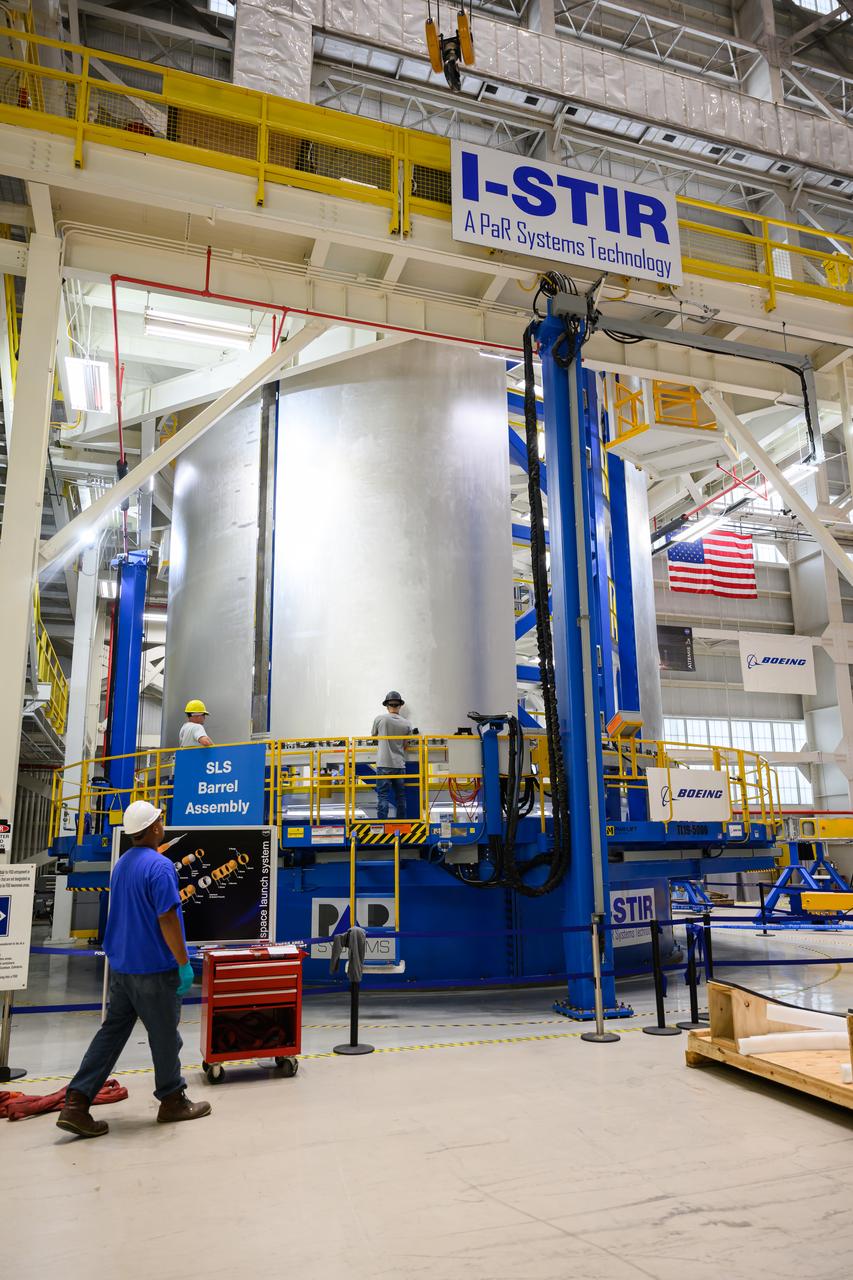

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans load alluminum alloy panels into the Vertical Weld Center June 1. The Vertical Weld Center is a friction-stir weld tool for the large structures of the core stage for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. Teams load the panels into the VWC using an overhead crane system, then multiple panels are welded together to create entire barrels. The panels in these images are some of the five barrels that will form the SLS liquid hydrogen propellant tank for the SLS rocket that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which is also the first flight of SLS in its more powerful Block 1B configuration. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid hydrogen propellant tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, provides propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis IV mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
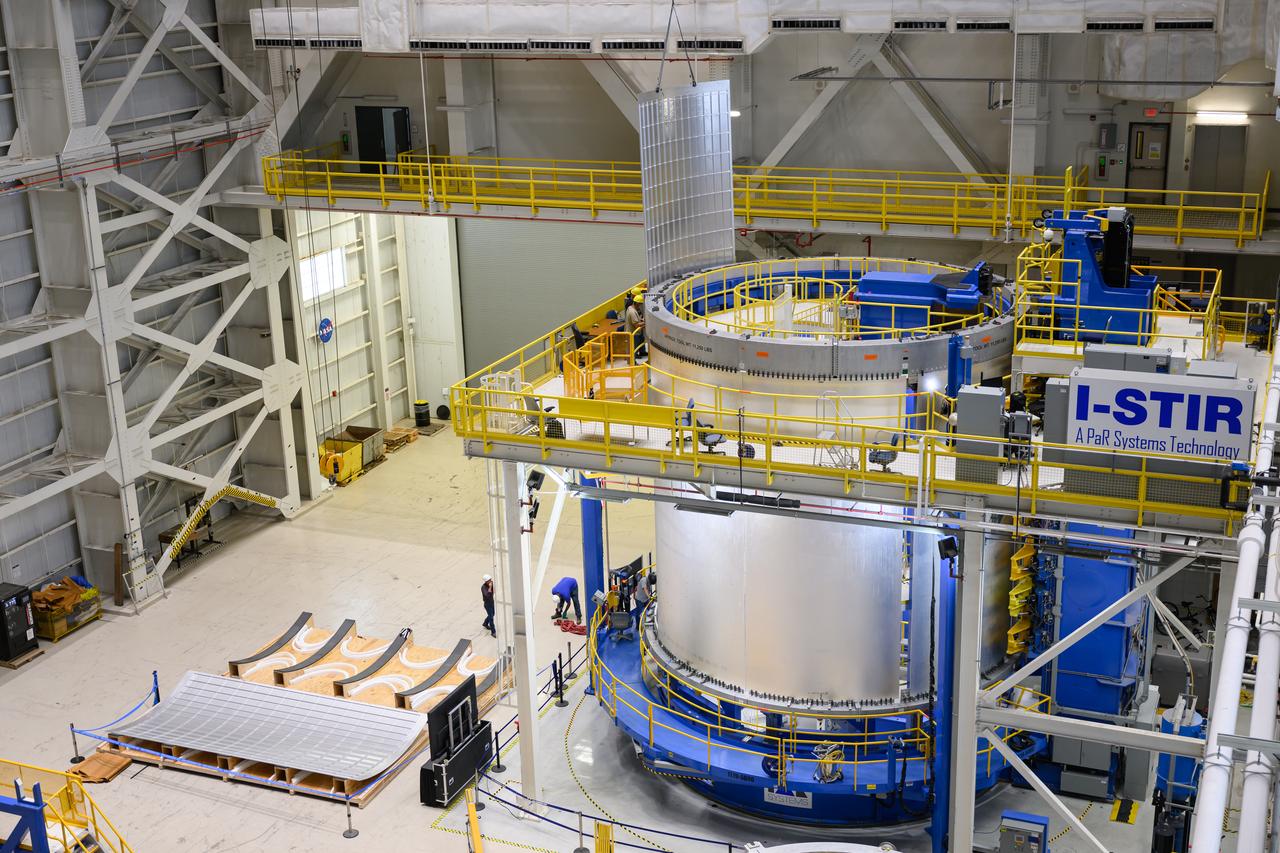

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans load alluminum alloy panels into the Vertical Weld Center June 1. The Vertical Weld Center is a friction-stir weld tool for the large structures of the core stage for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. Teams load the panels into the VWC using an overhead crane system, then multiple panels are welded together to create entire barrels. The panels in these images are some of the five barrels that will form the SLS liquid hydrogen propellant tank for the SLS rocket that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which is also the first flight of SLS in its more powerful Block 1B configuration. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid hydrogen propellant tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, provides propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis IV mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid hydrogen tank of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Cell A for white light scans of the tank’s dimensions in preparation of multiple join activities throughout the manufacturing process. The flight hardware will be used for Artemis III, one of the first crewed Artemis missions. The liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and is the largest of the five elements that make up the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank is situated between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid hydrogen tank of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Cell A for white light scans of the tank’s dimensions in preparation of multiple join activities throughout the manufacturing process. The flight hardware will be used for Artemis III, one of the first crewed Artemis missions. The liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and is the largest of the five elements that make up the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank is situated between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
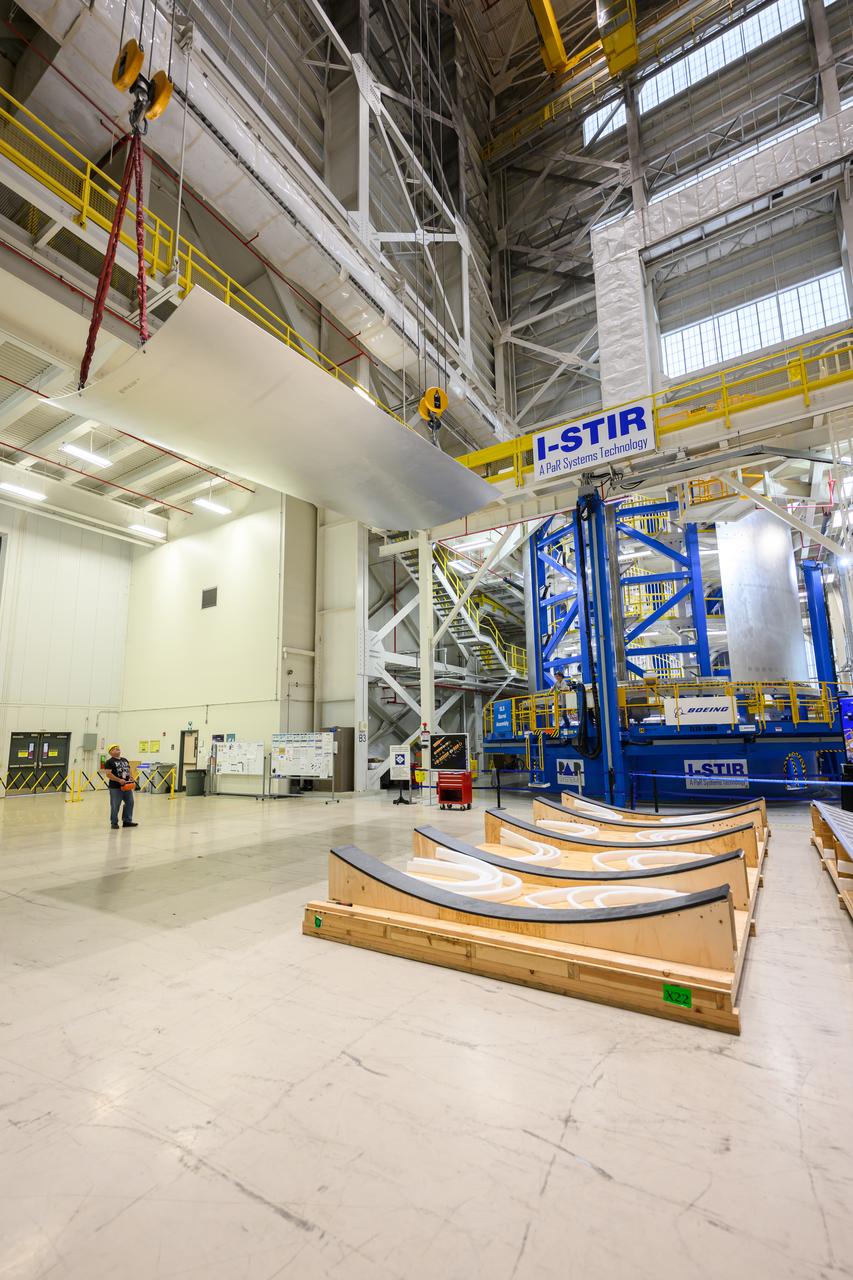

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans load alluminum alloy panels into the Vertical Weld Center June 1. The Vertical Weld Center is a friction-stir weld tool for the large structures of the core stage for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. Teams load the panels into the VWC using an overhead crane system, then multiple panels are welded together to create entire barrels. The panels in these images are some of the five barrels that will form the SLS liquid hydrogen propellant tank for the SLS rocket that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which is also the first flight of SLS in its more powerful Block 1B configuration. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid hydrogen propellant tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, provides propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis IV mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans load alluminum alloy panels into the Vertical Weld Center June 1. The Vertical Weld Center is a friction-stir weld tool for the large structures of the core stage for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. Teams load the panels into the VWC using an overhead crane system, then multiple panels are welded together to create entire barrels. The panels in these images are some of the five barrels that will form the SLS liquid hydrogen propellant tank for the SLS rocket that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which is also the first flight of SLS in its more powerful Block 1B configuration. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid hydrogen propellant tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, provides propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis IV mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
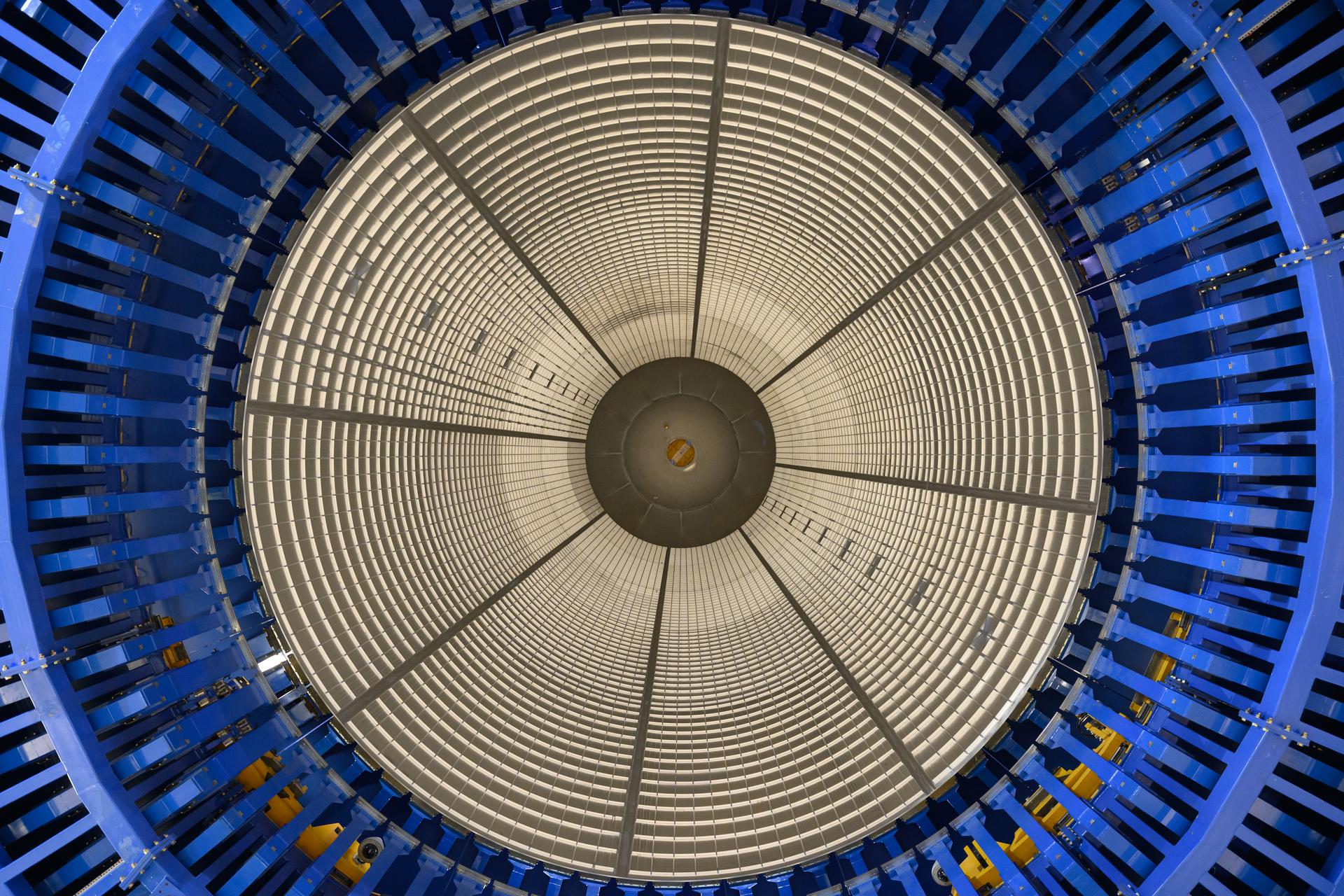

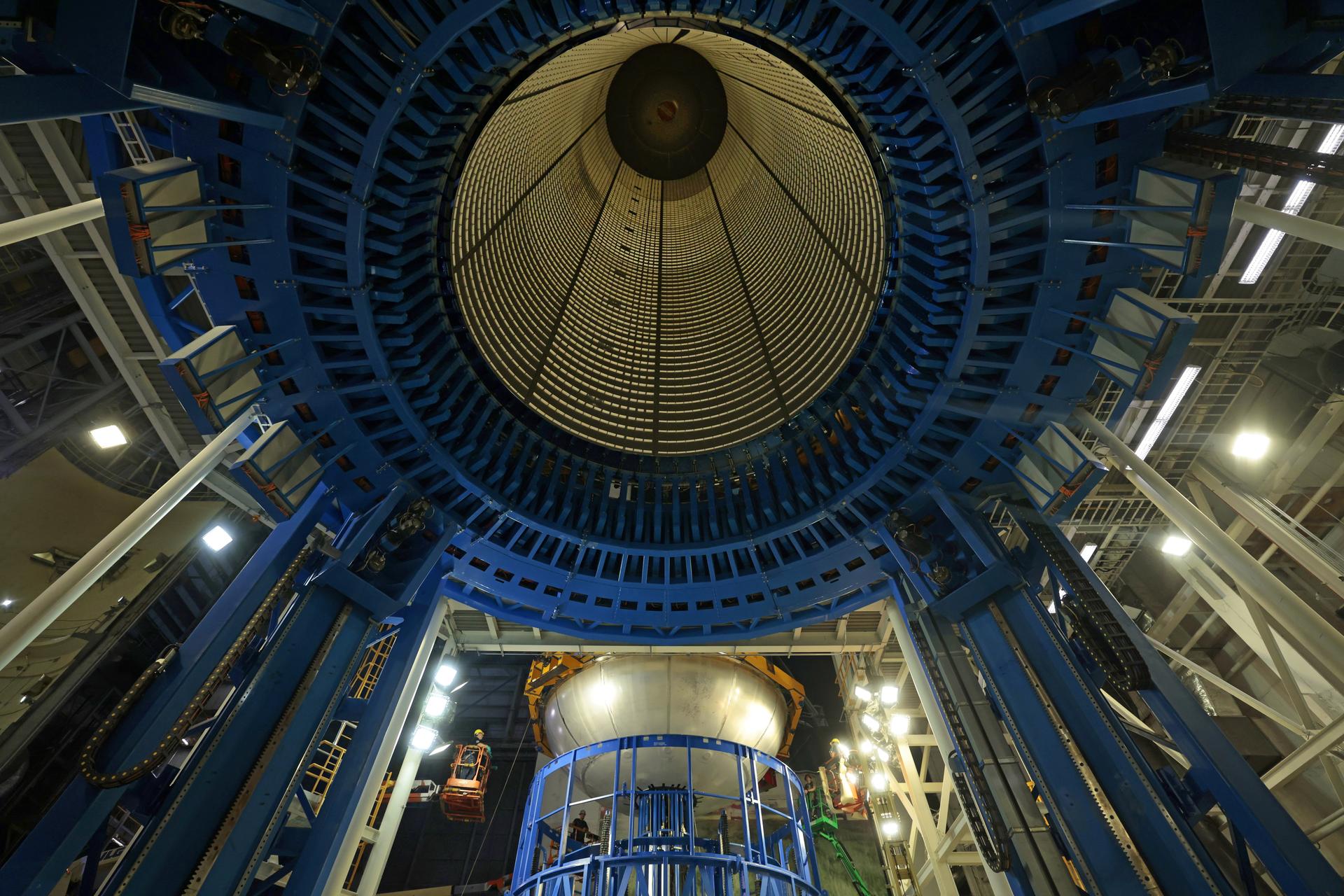
Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the aft dome for the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System), into the in-feeder of the facility’s vertical assembly center. Once loaded into the production tool, teams with SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will circumferentially friction-stir weld the dome to the previously-welded forward dome and five barrels that make up the liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
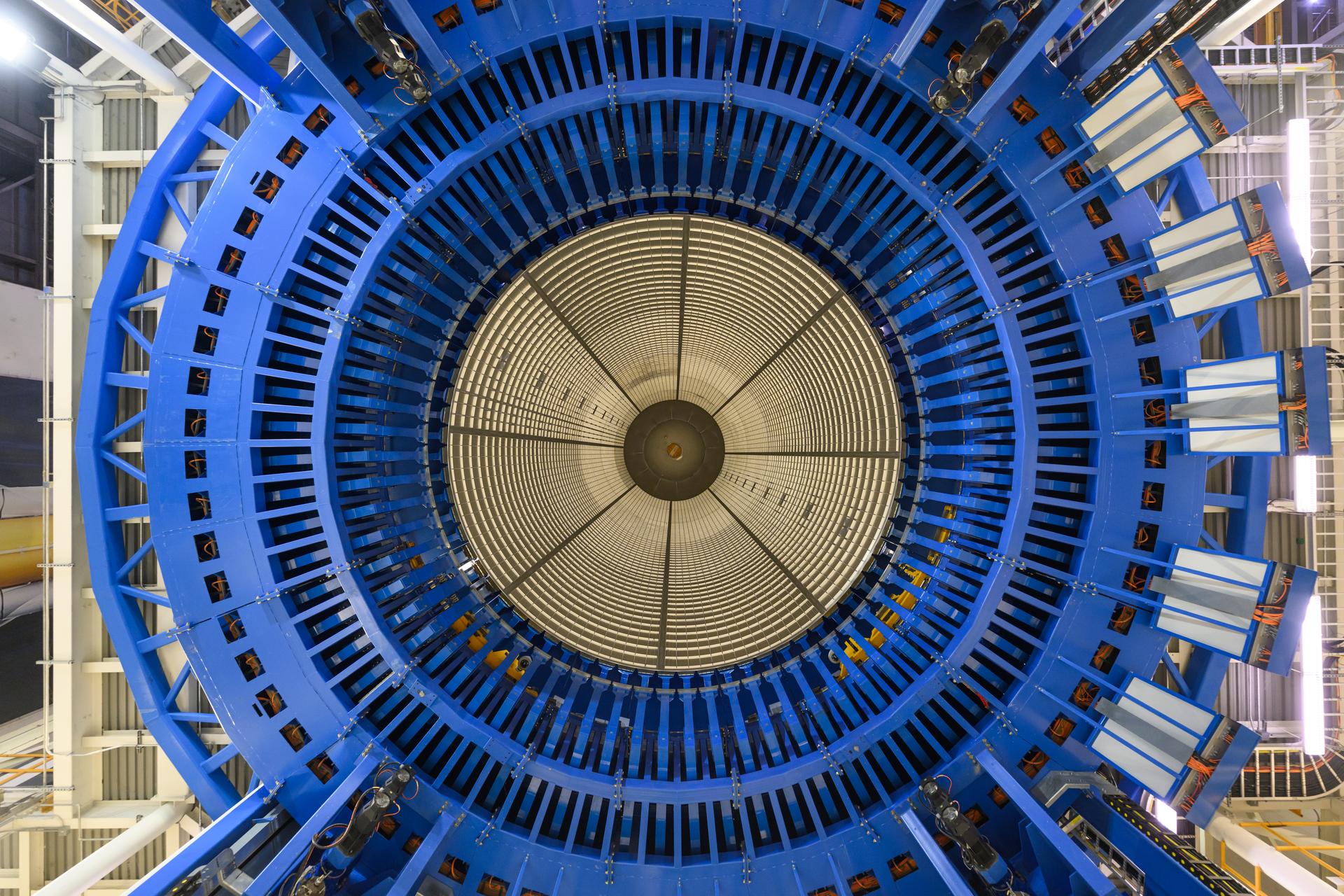
Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the aft dome for the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System), into the in-feeder of the facility’s vertical assembly center. Once loaded into the production tool, teams with SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will circumferentially friction-stir weld the dome to the previously-welded forward dome and five barrels that make up the liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
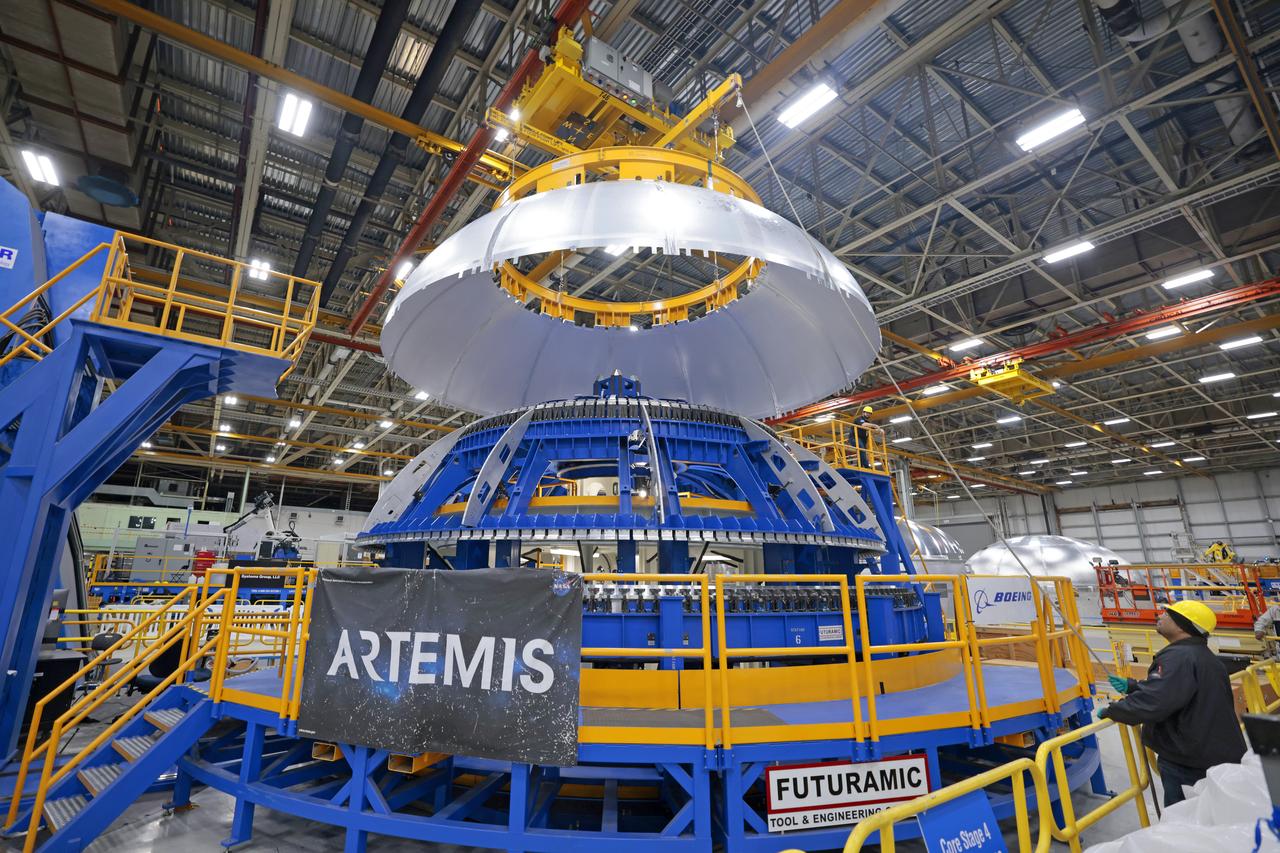

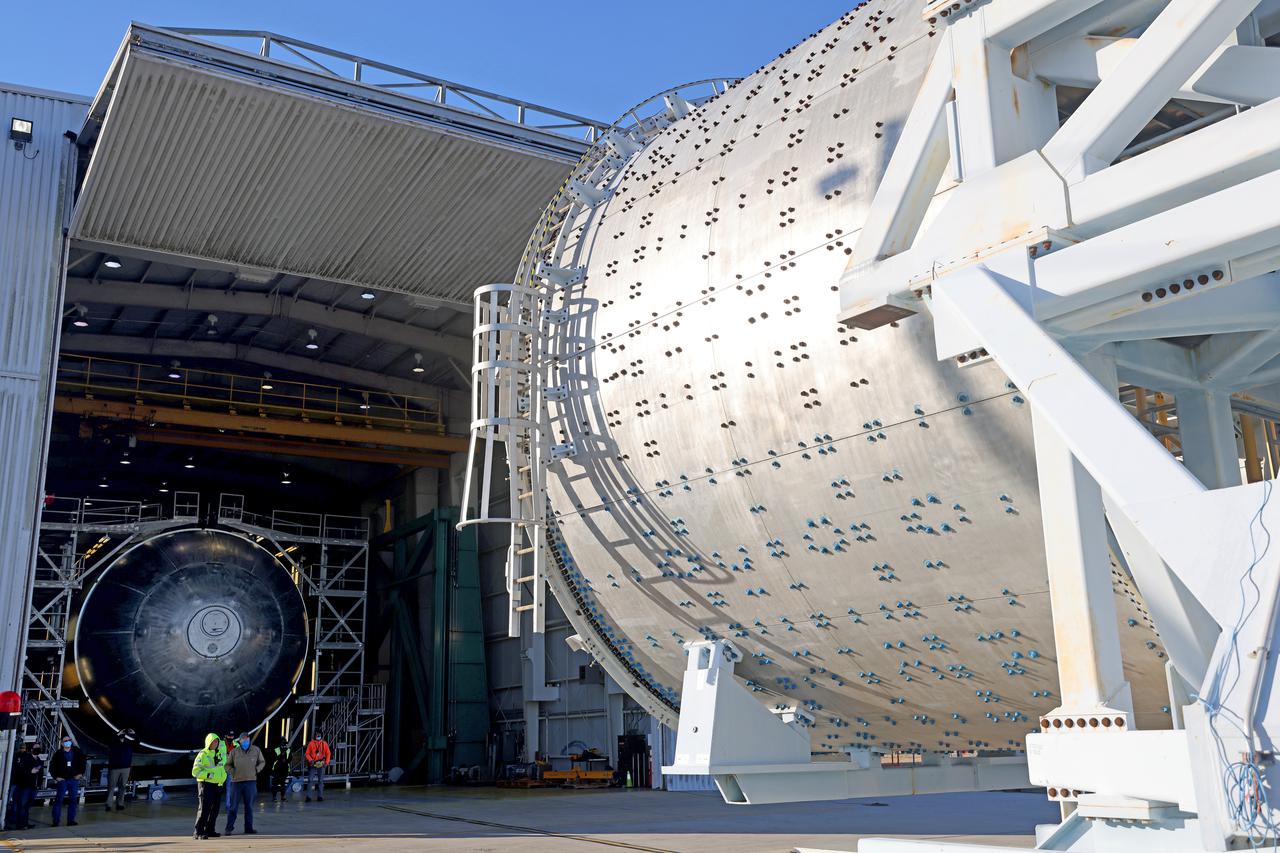
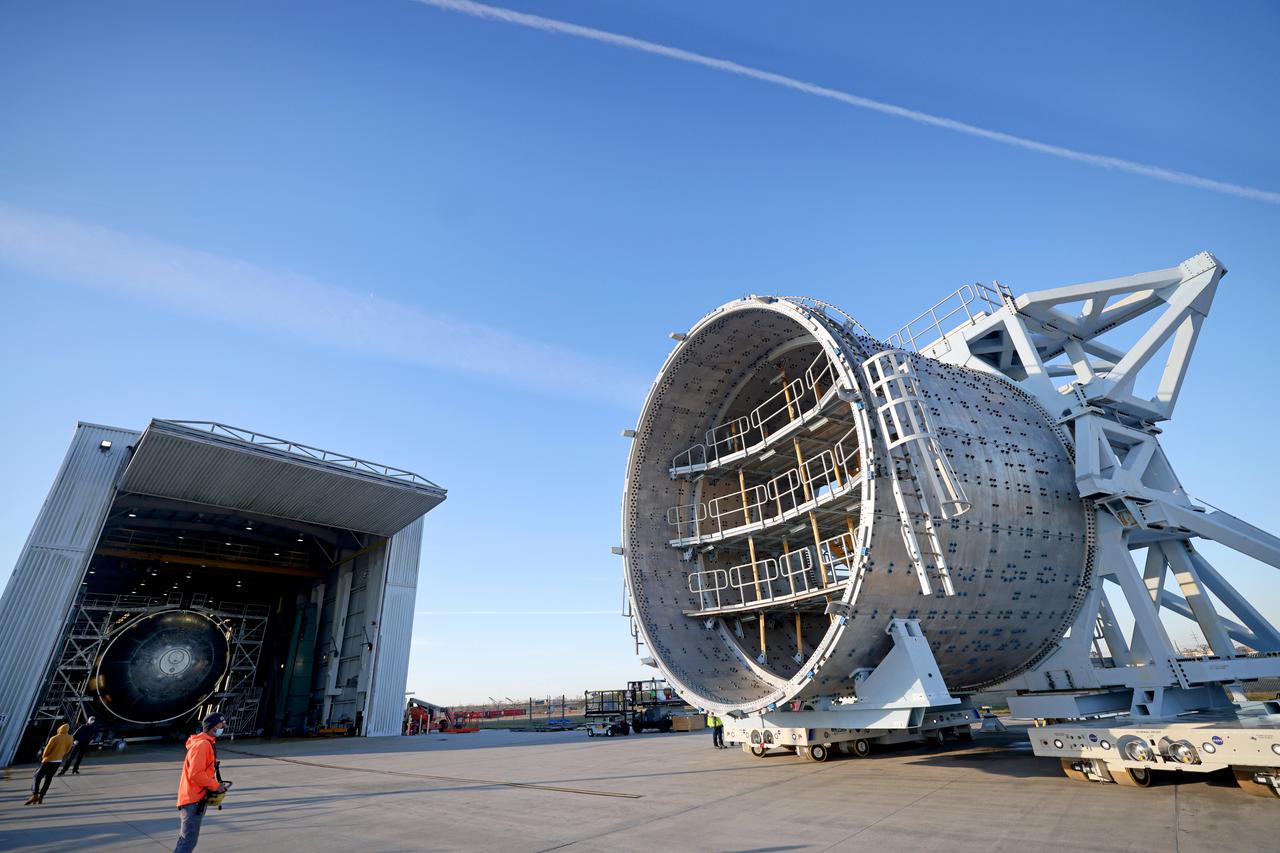
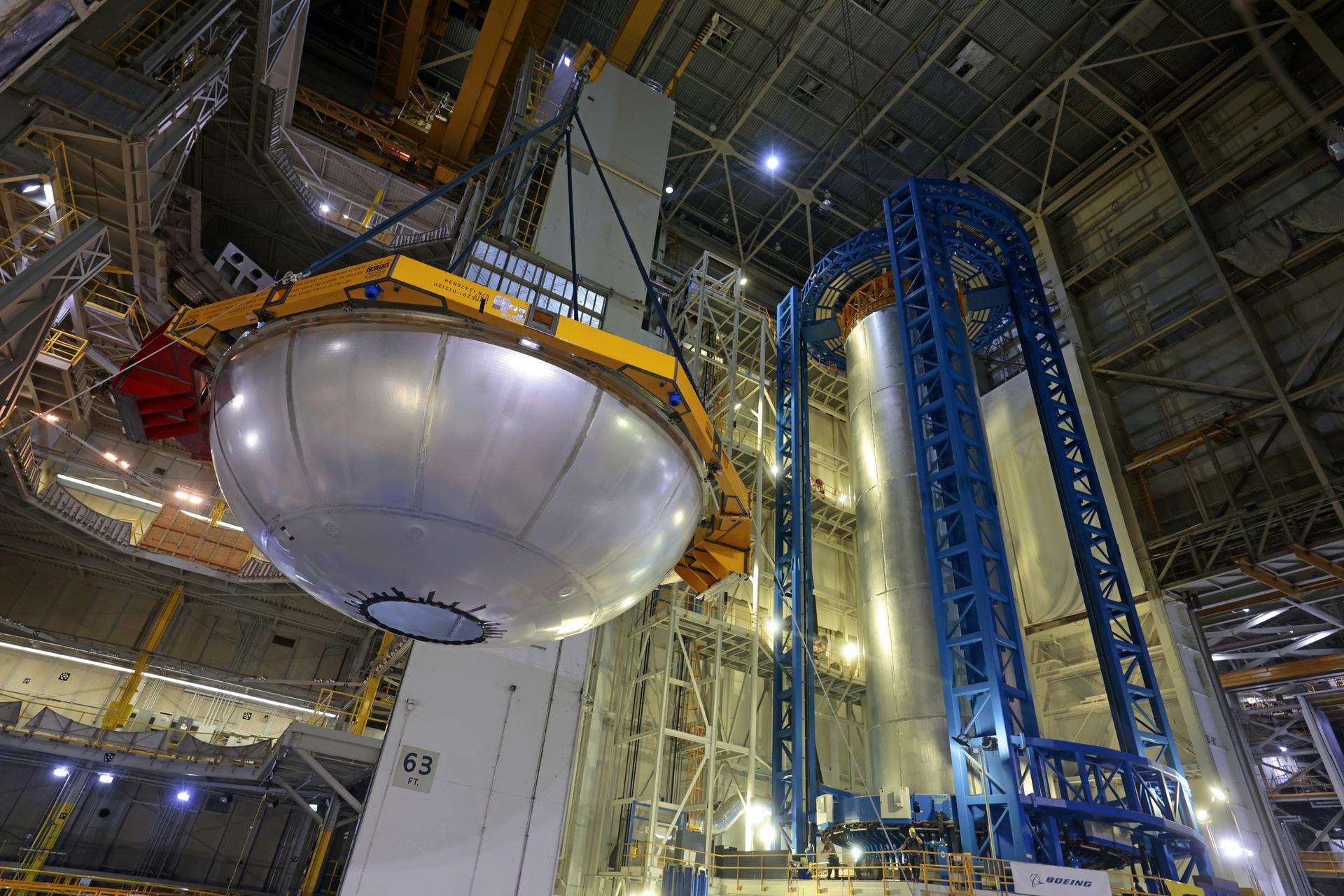
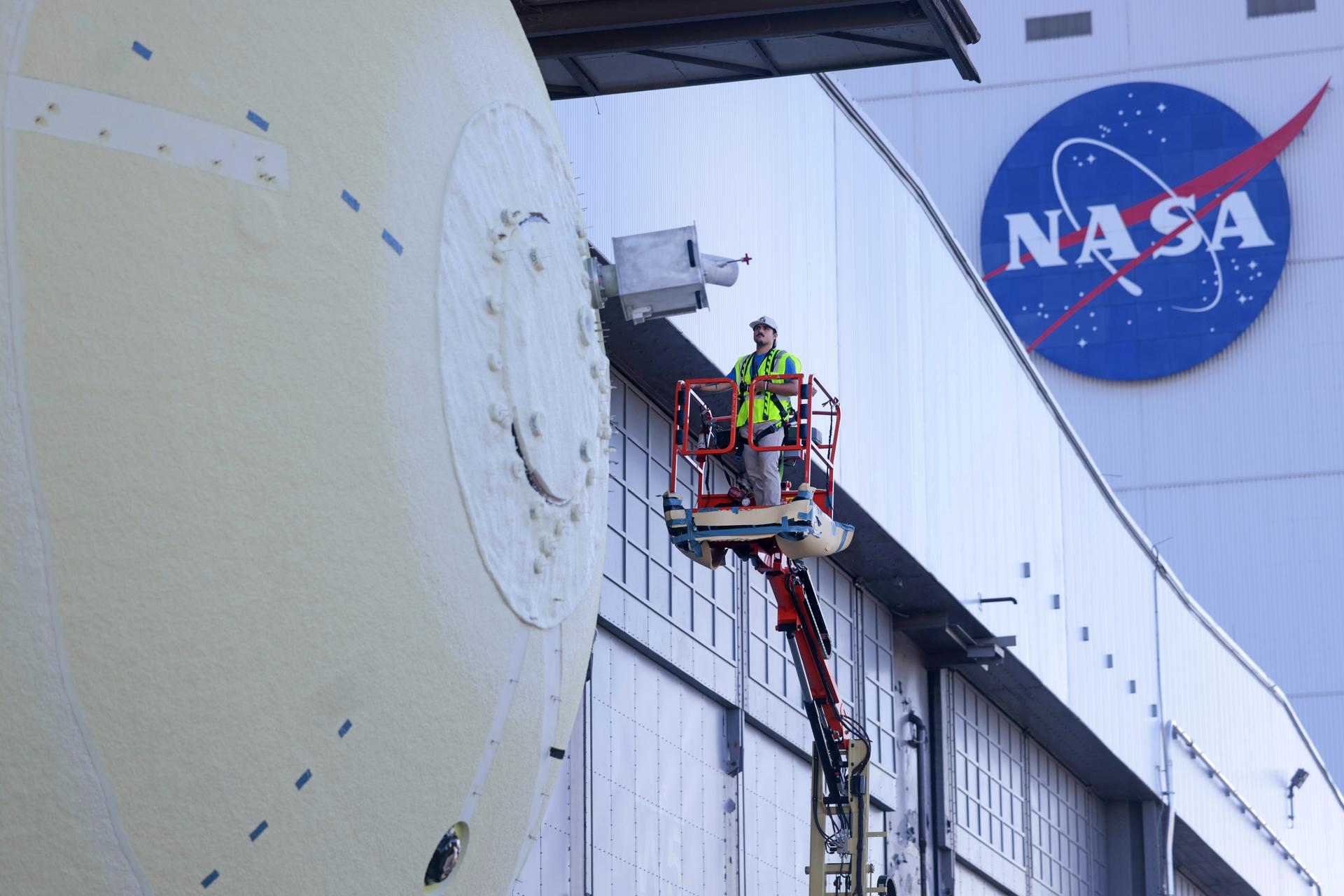
This image shows teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lifting a completed dome off of a robotic weld tool on Nov. 21. The dome, which will cap off the aft end of the liquid hydrogen tank, will be used on the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis IV mission. Later, technicians from Boeing – NASA’s prime contractor for SLS – will join the aft dome with five barrels and a forward dome to complete the liquid hydrogen tank. Artemis IV is the first flight of SLS in its Block 1B configuration. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
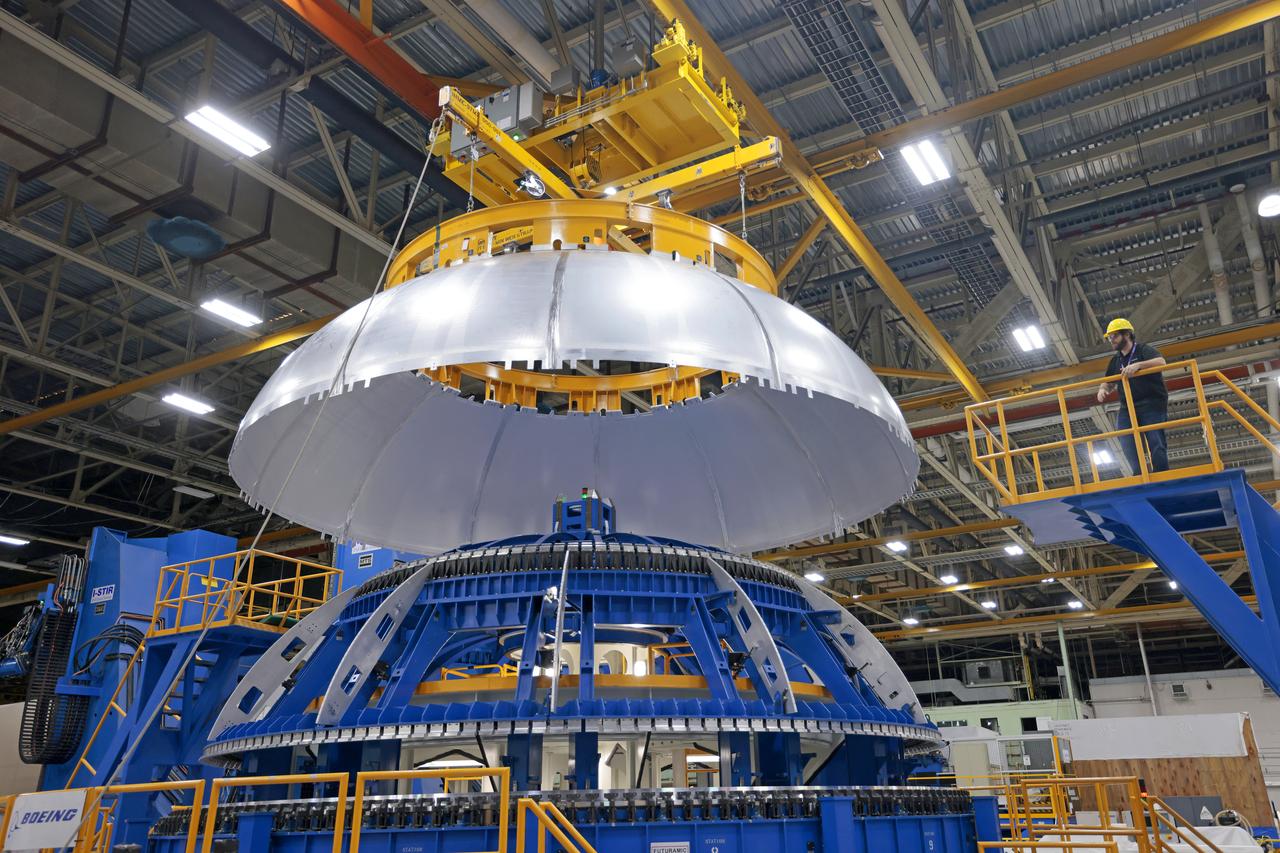

This image shows teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lifting a completed dome off of a robotic weld tool on Nov. 21. The dome, which will cap off the aft end of the liquid hydrogen tank, will be used on the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis IV mission. Later, technicians from Boeing – NASA’s prime contractor for SLS – will join the aft dome with five barrels and a forward dome to complete the liquid hydrogen tank. Artemis IV is the first flight of SLS in its Block 1B configuration. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
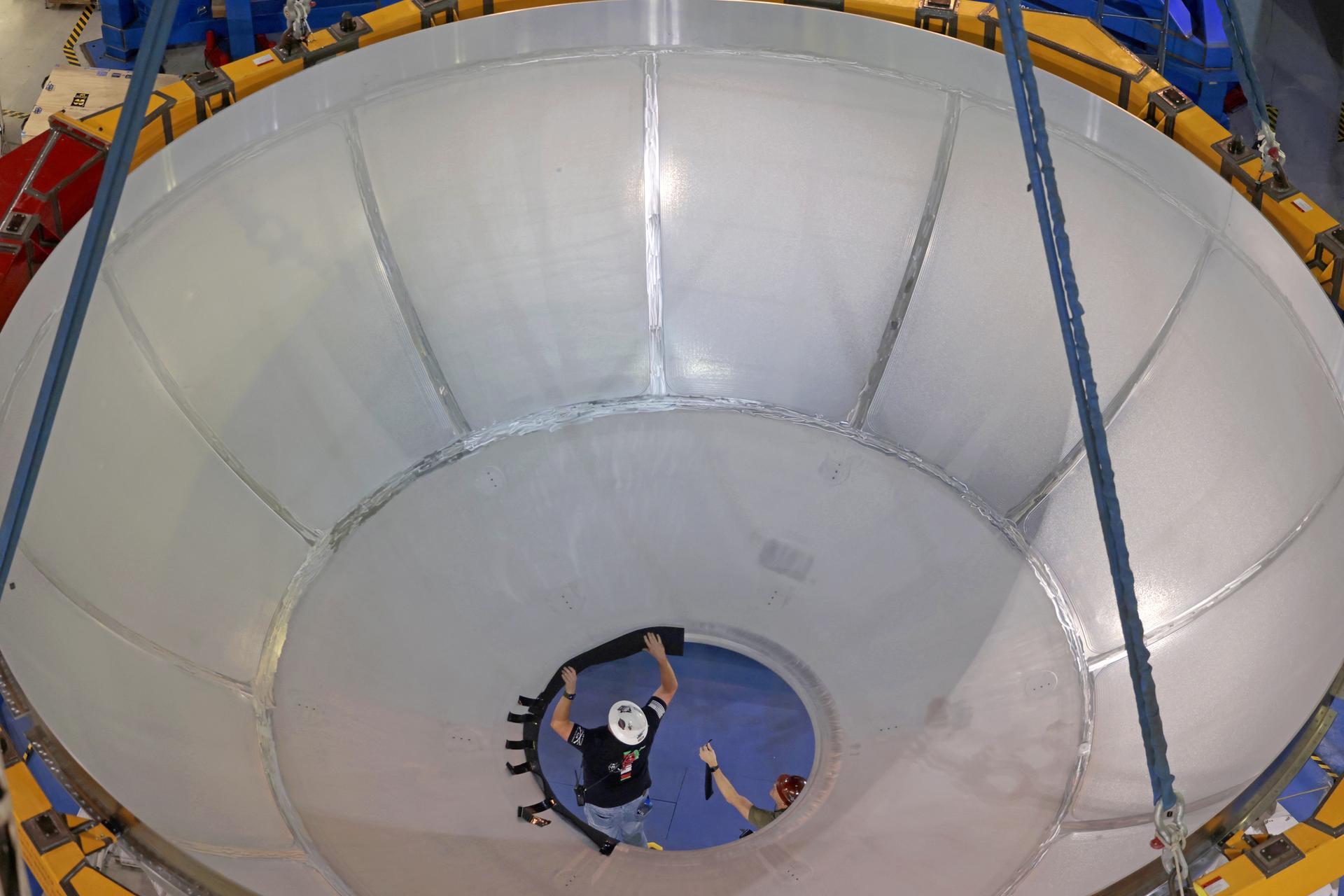

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the aft dome for the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System), into the in-feeder of the facility’s vertical assembly center. Once loaded into the production tool, teams with SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will circumferentially friction-stir weld the dome to the previously-welded forward dome and five barrels that make up the liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
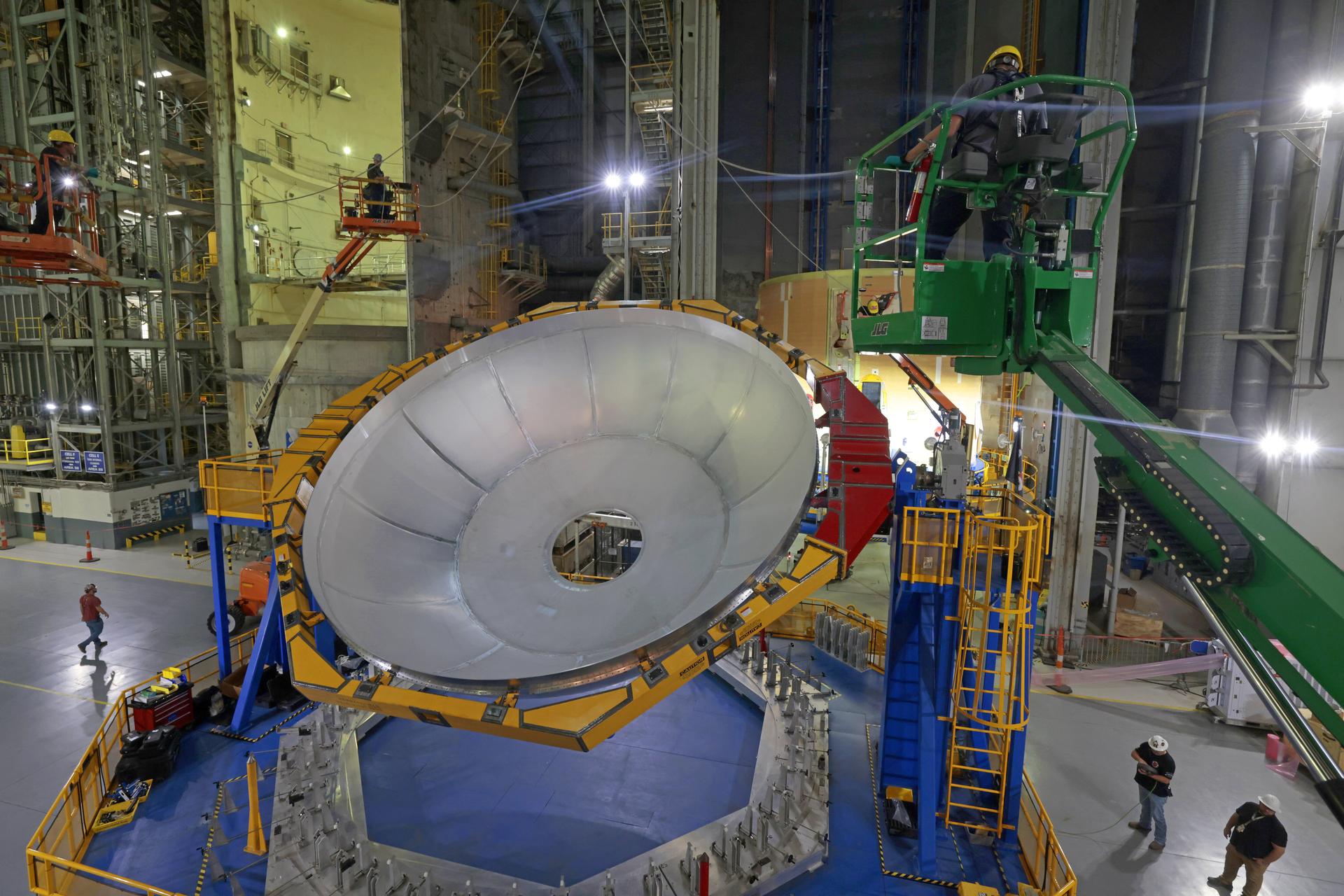

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the aft dome for the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System), into the in-feeder of the facility’s vertical assembly center. Once loaded into the production tool, teams with SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will circumferentially friction-stir weld the dome to the previously-welded forward dome and five barrels that make up the liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
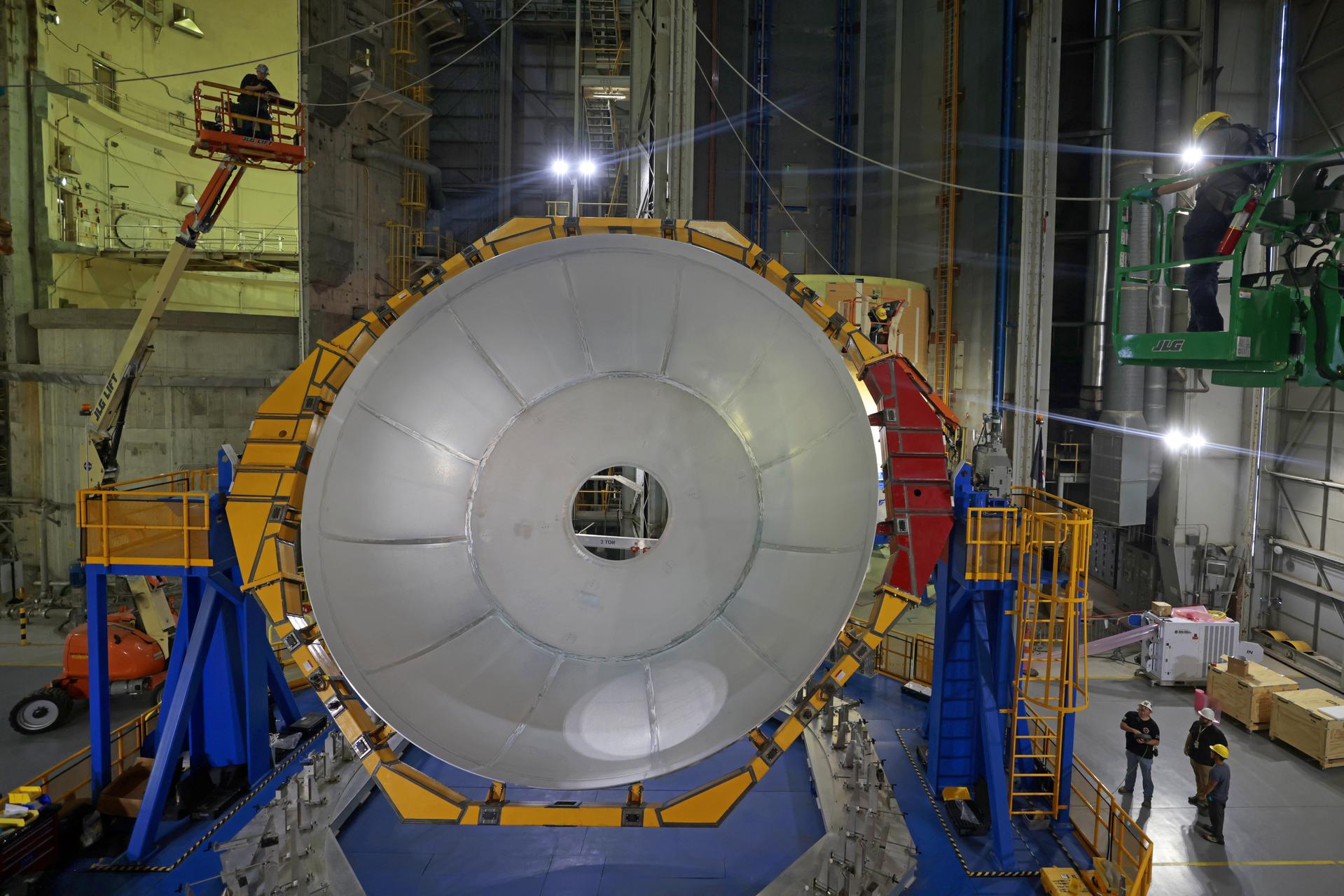

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the aft dome for the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System), into the in-feeder of the facility’s vertical assembly center. Once loaded into the production tool, teams with SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will circumferentially friction-stir weld the dome to the previously-welded forward dome and five barrels that make up the liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the aft dome for the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System), into the in-feeder of the facility’s vertical assembly center. Once loaded into the production tool, teams with SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will circumferentially friction-stir weld the dome to the previously-welded forward dome and five barrels that make up the liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the aft dome for the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System), into the in-feeder of the facility’s vertical assembly center. Once loaded into the production tool, teams with SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will circumferentially friction-stir weld the dome to the previously-welded forward dome and five barrels that make up the liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
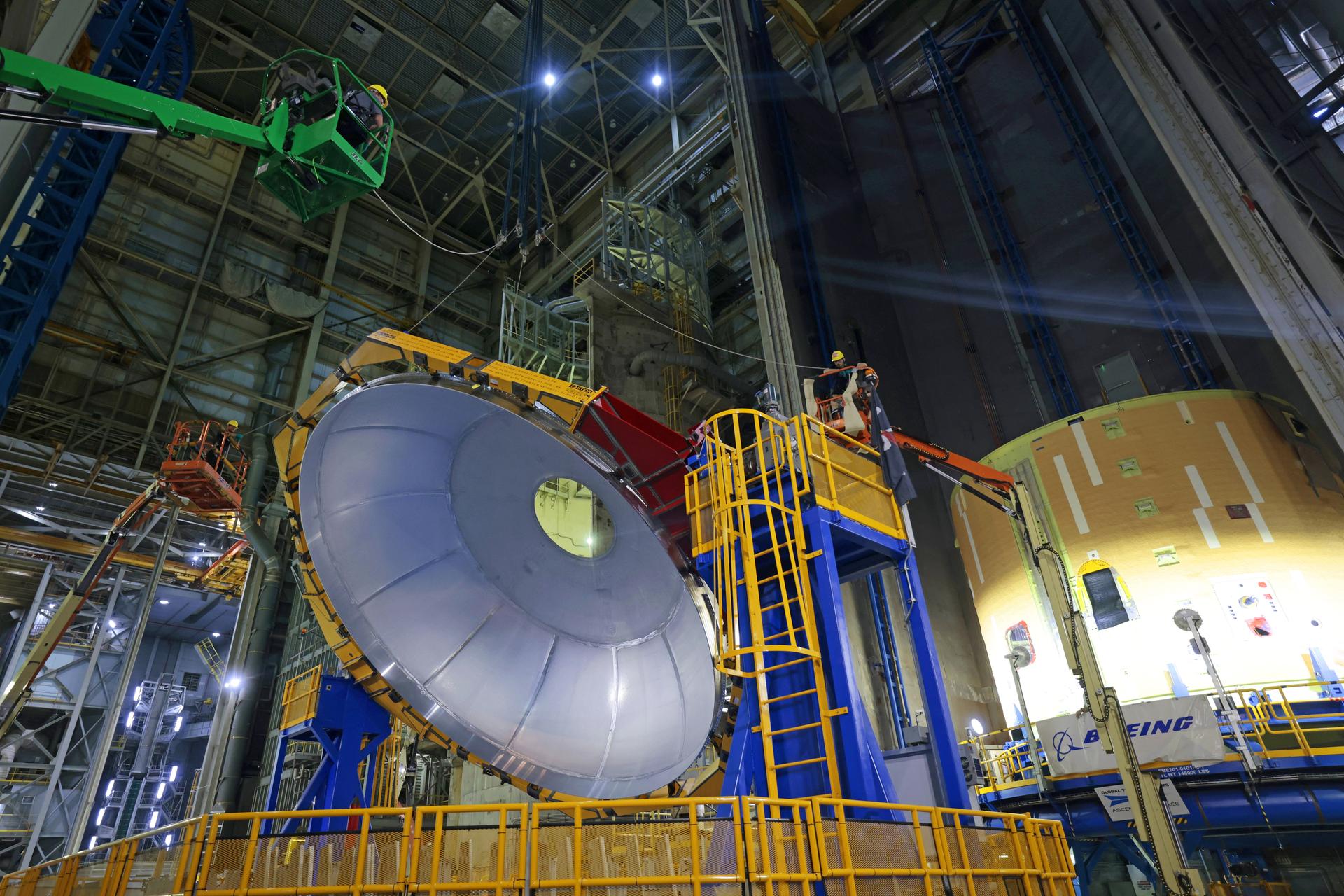

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the aft dome for the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System), into the in-feeder of the facility’s vertical assembly center. Once loaded into the production tool, teams with SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will circumferentially friction-stir weld the dome to the previously-welded forward dome and five barrels that make up the liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the aft dome for the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System), into the in-feeder of the facility’s vertical assembly center. Once loaded into the production tool, teams with SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will circumferentially friction-stir weld the dome to the previously-welded forward dome and five barrels that make up the liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
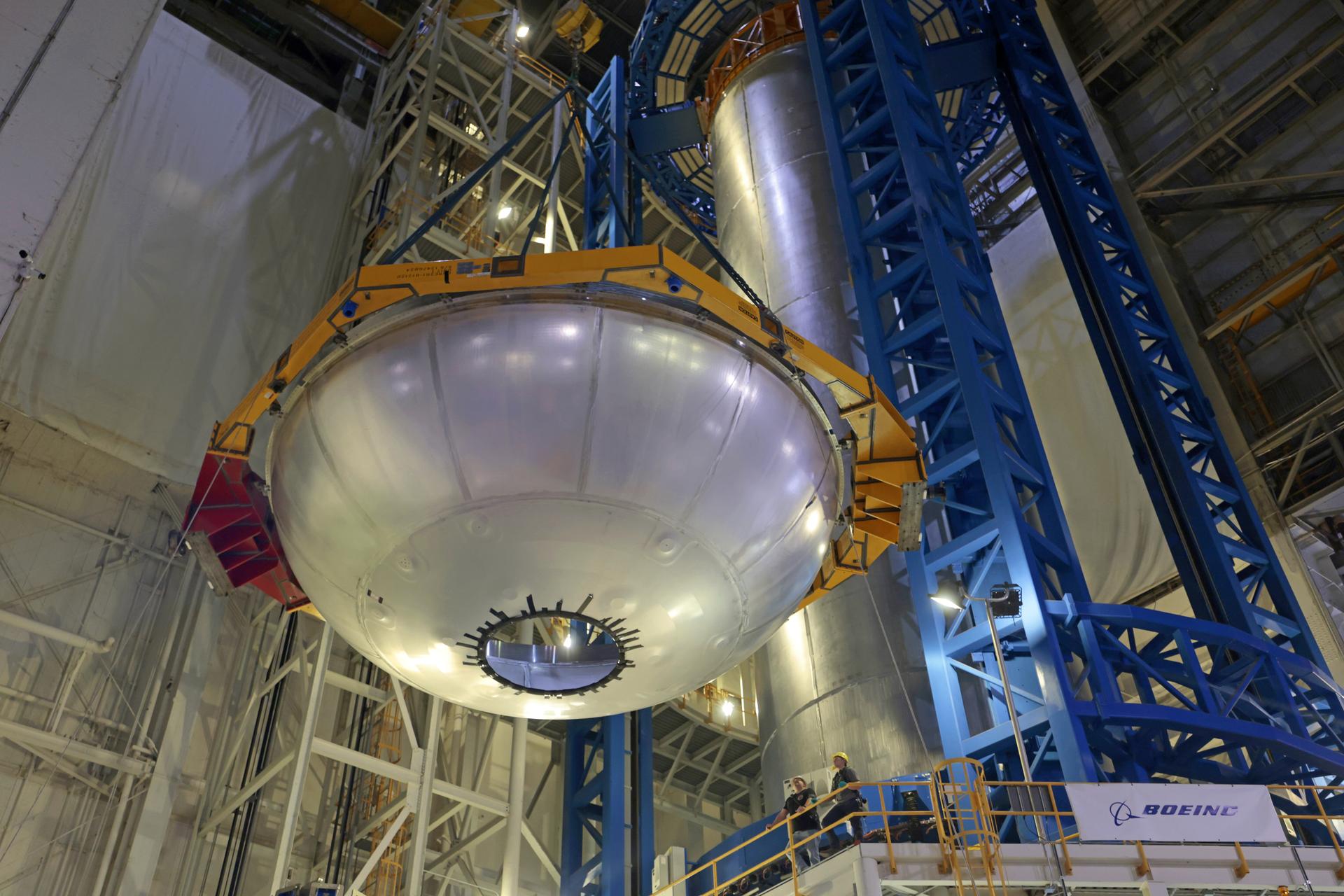

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the aft dome for the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System), into the in-feeder of the facility’s vertical assembly center. Once loaded into the production tool, teams with SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will circumferentially friction-stir weld the dome to the previously-welded forward dome and five barrels that make up the liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
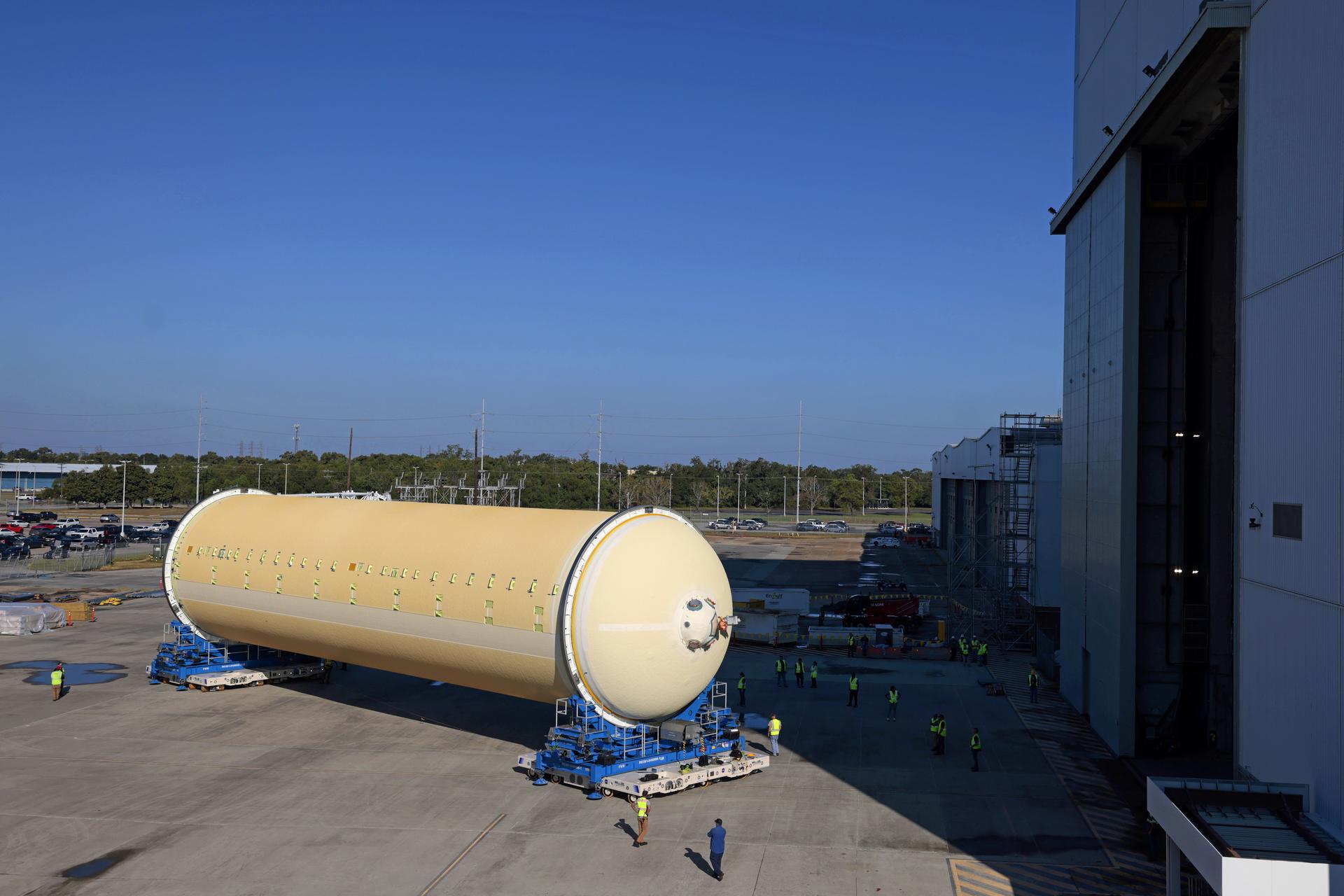

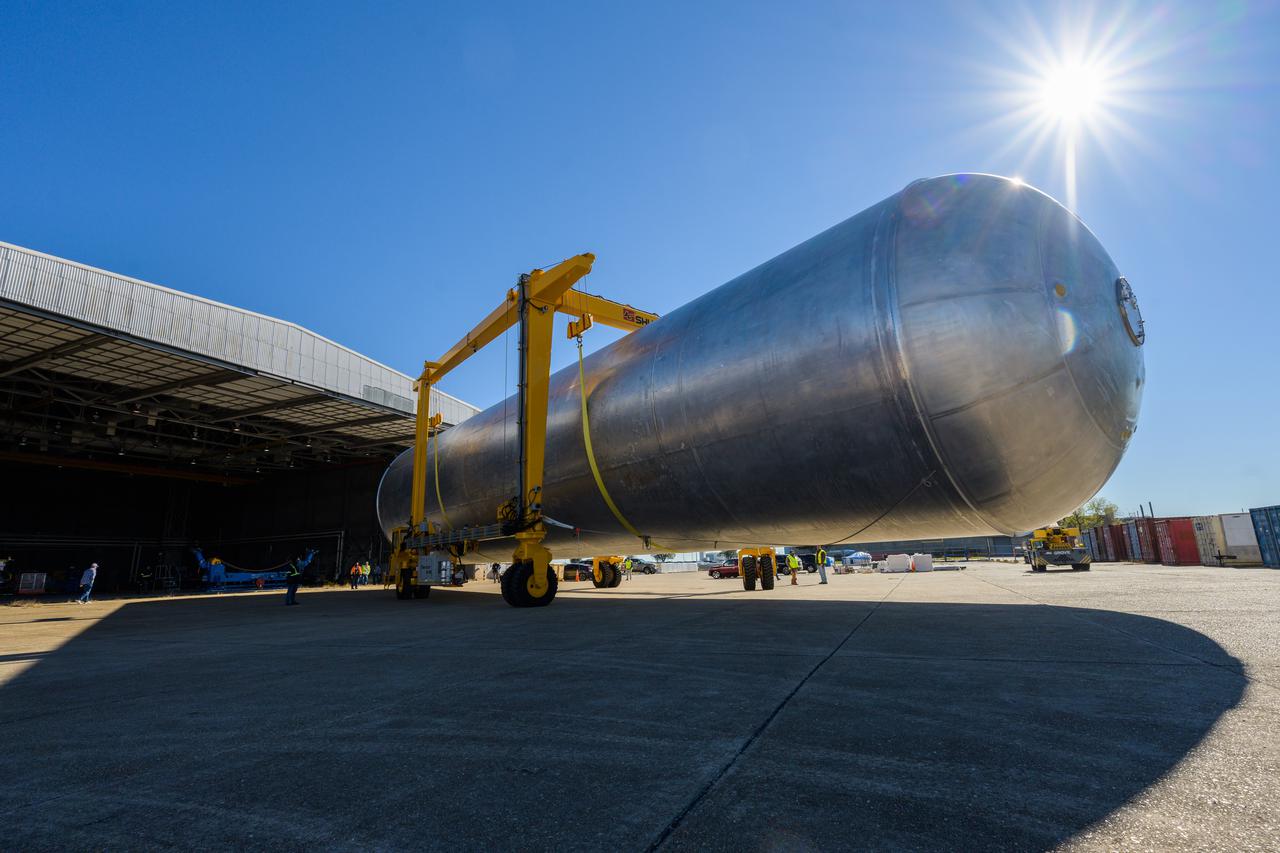
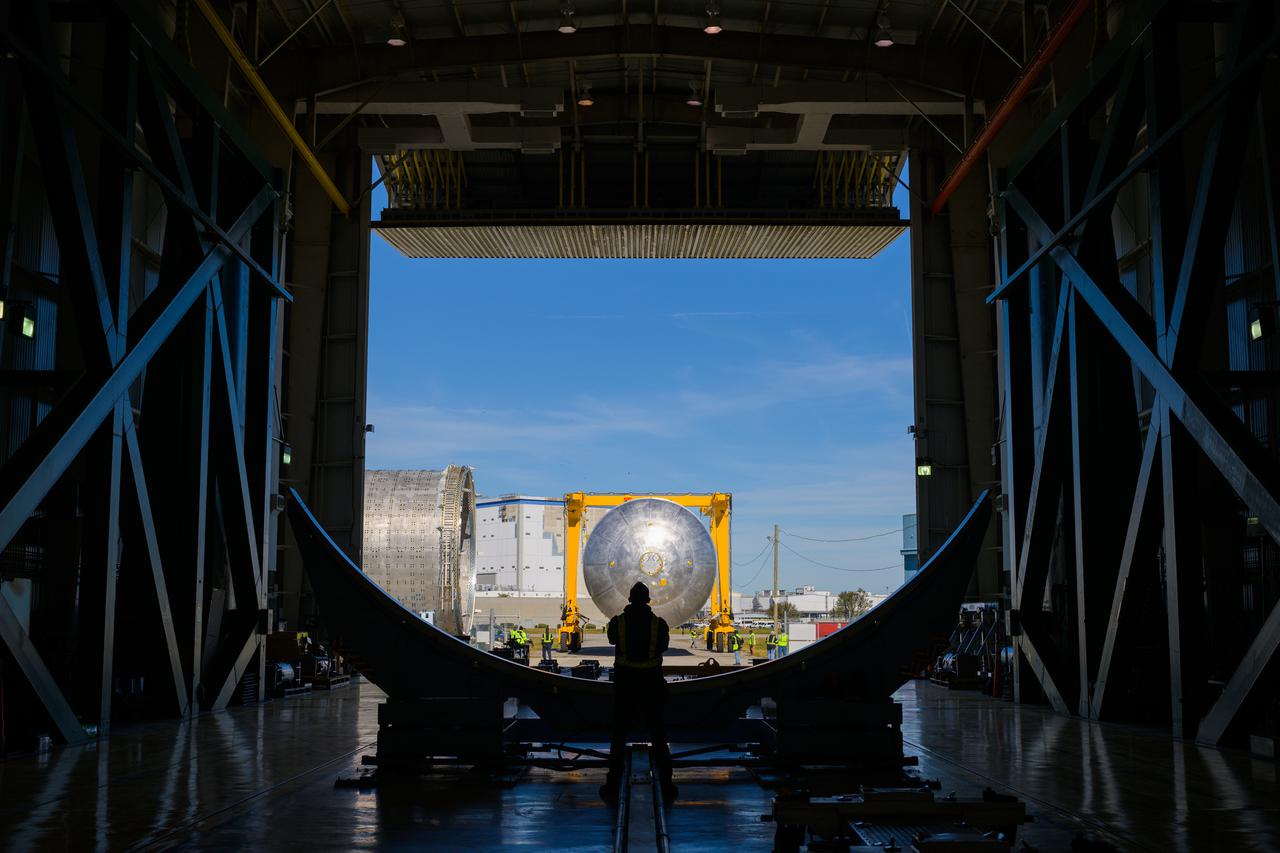
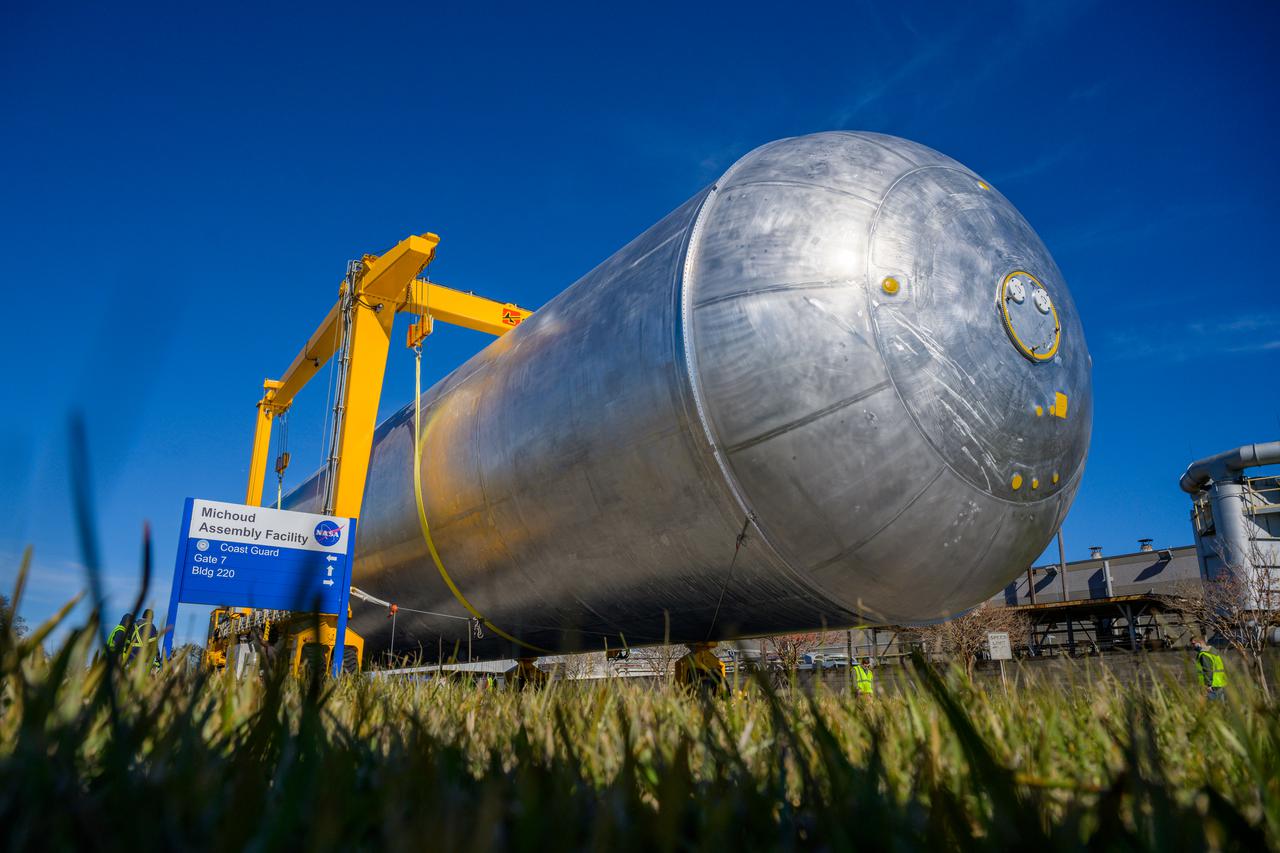
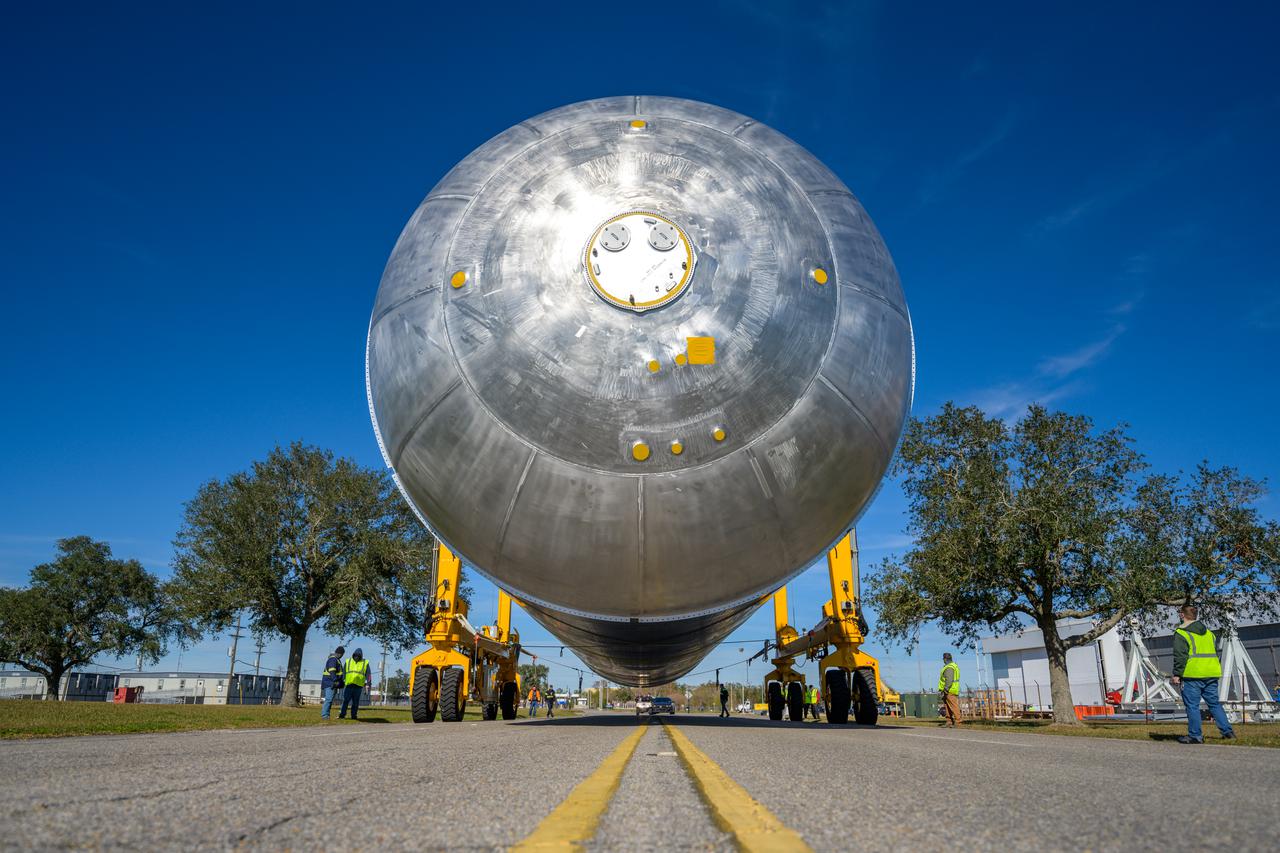
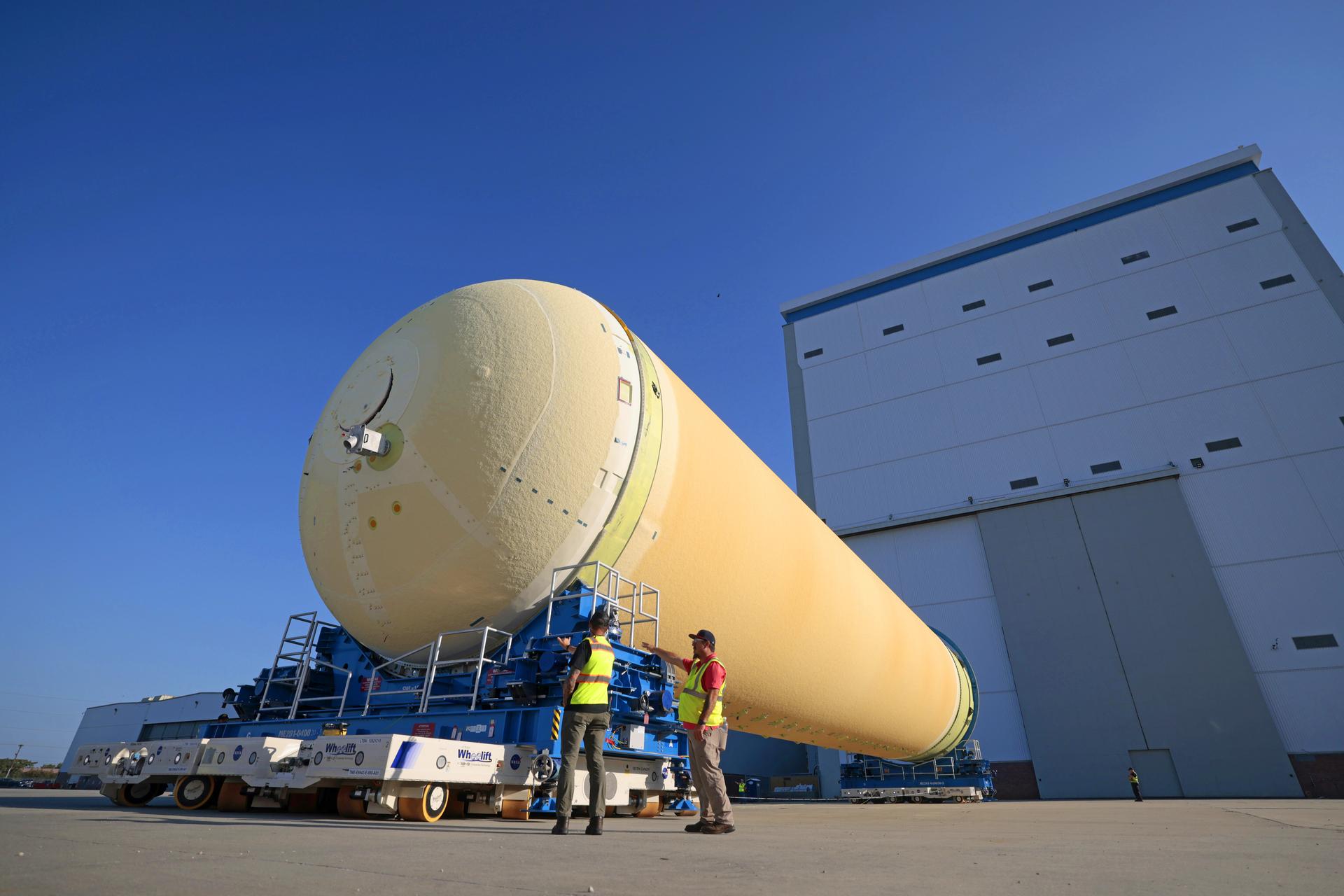
Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
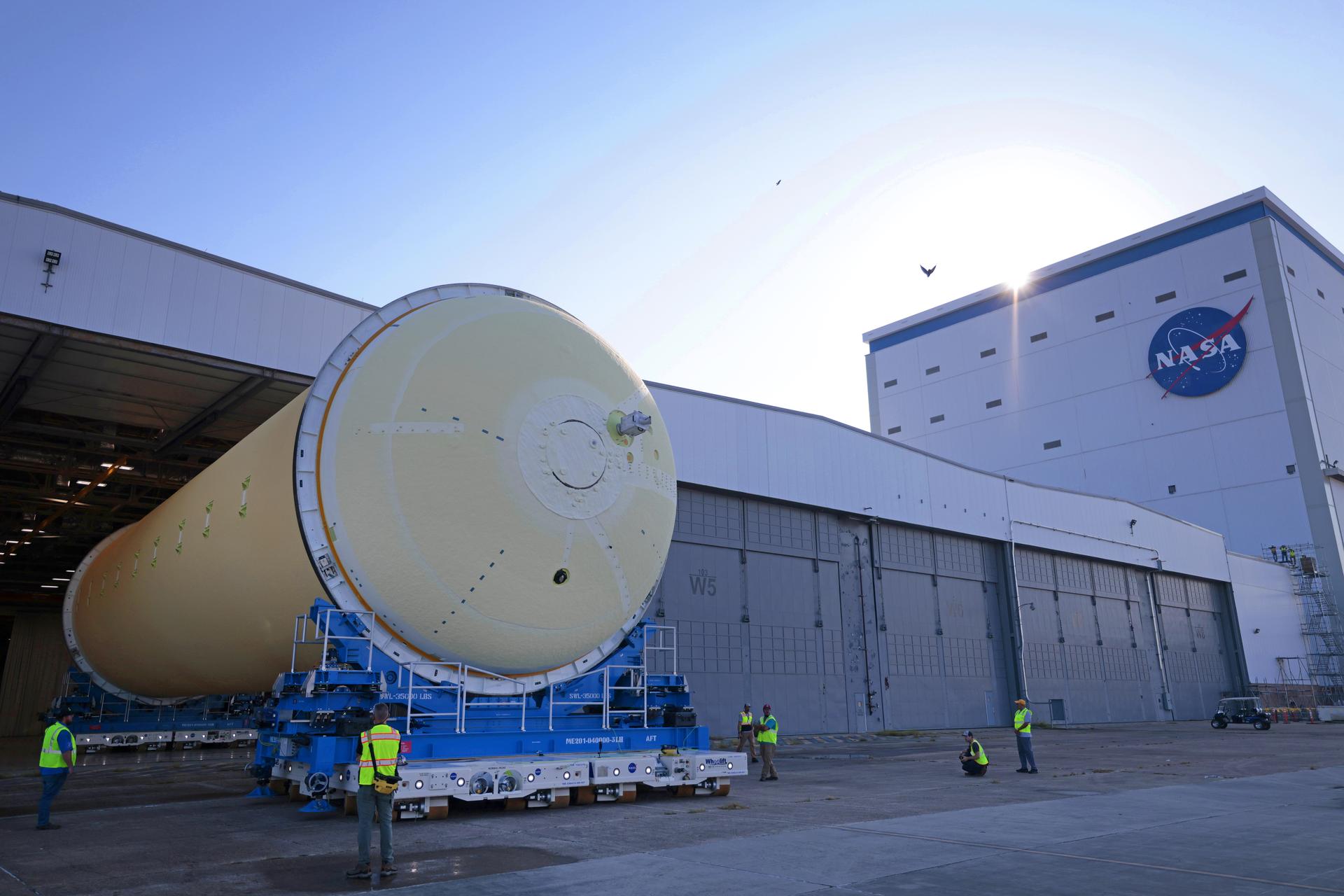

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
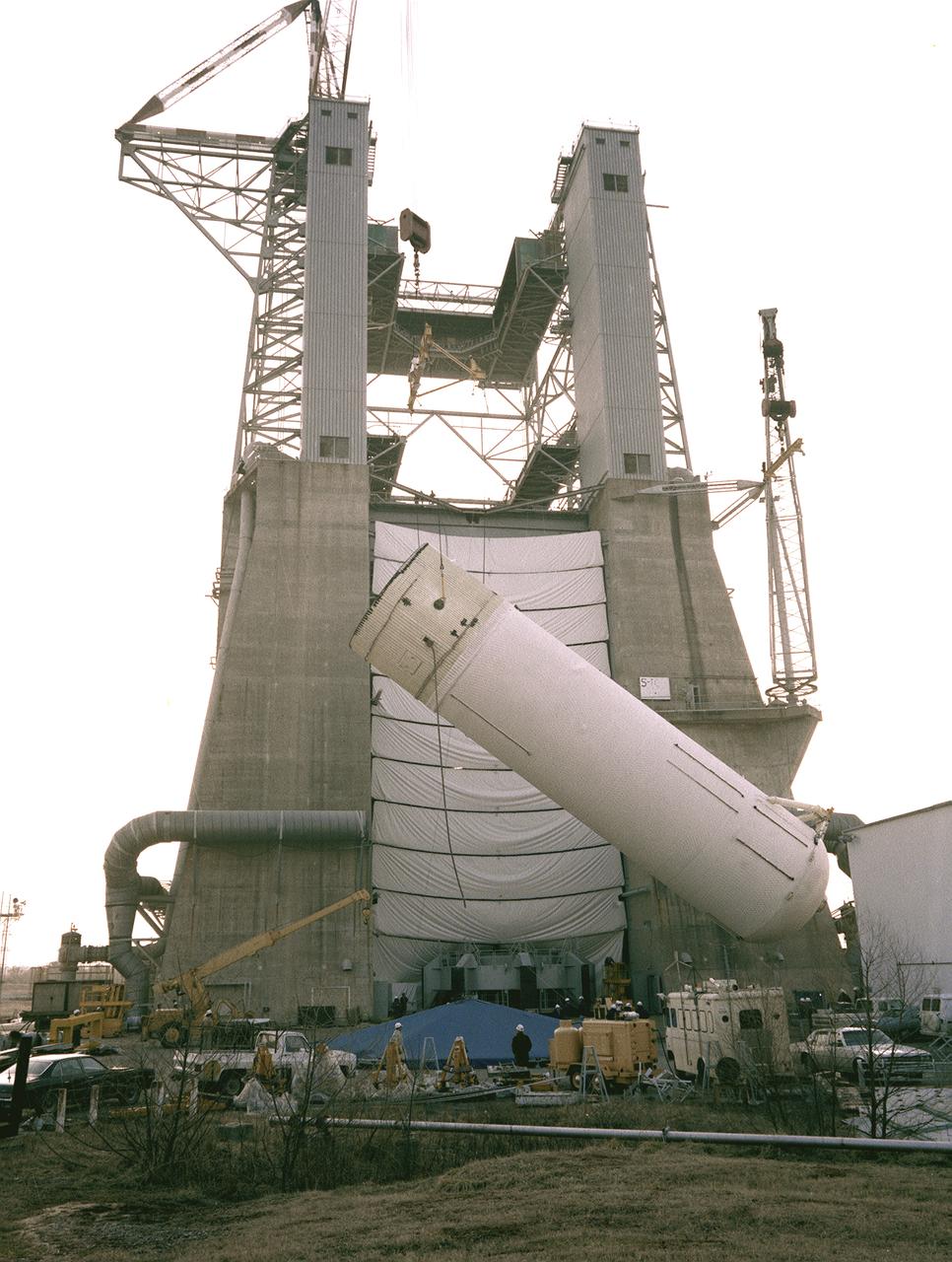

A liquid hydrogen tank of the Shuttle's external tank (ET) is installed into the S-1C Test Stand for a structural test at the Marshall Space Flight Center. At 154-feet long and more than 27-feet in diameter, the ET is the largest component of the Space Shuttle, the structural backbone of the entire Shuttle system, and is the only part of the vehicle that is not reusable. The ET is manufactured at the Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans, Louisiana, by the Martin Marietta Corporation under management of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
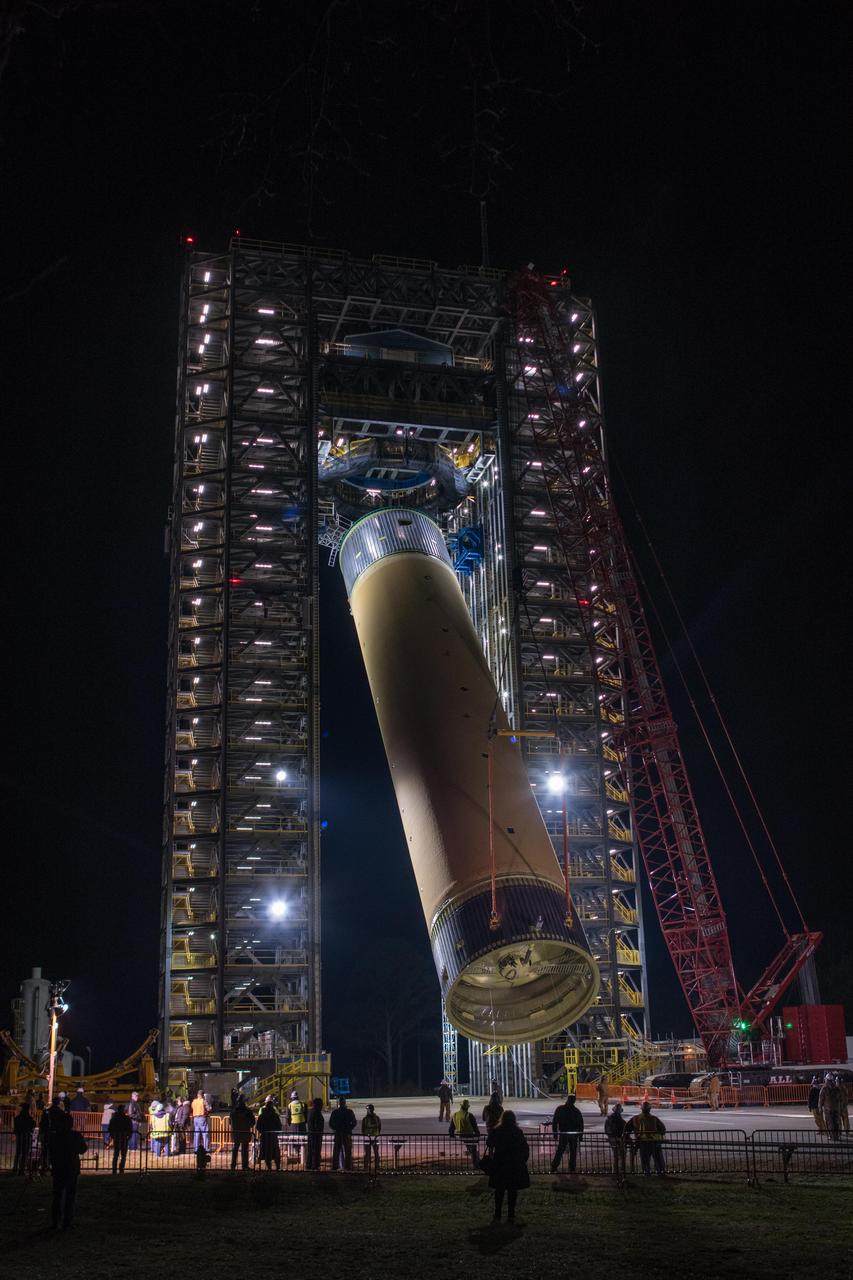

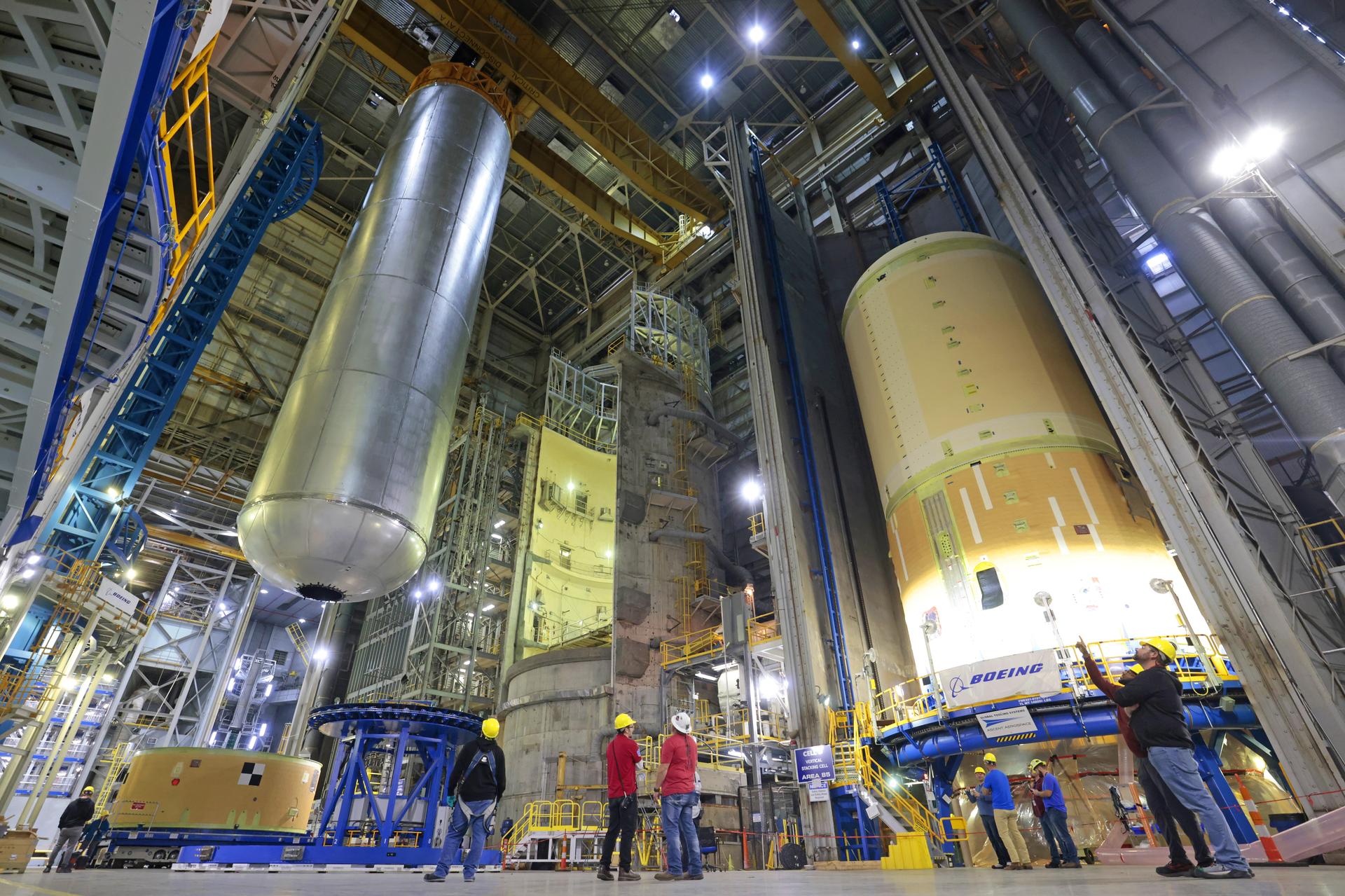
The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
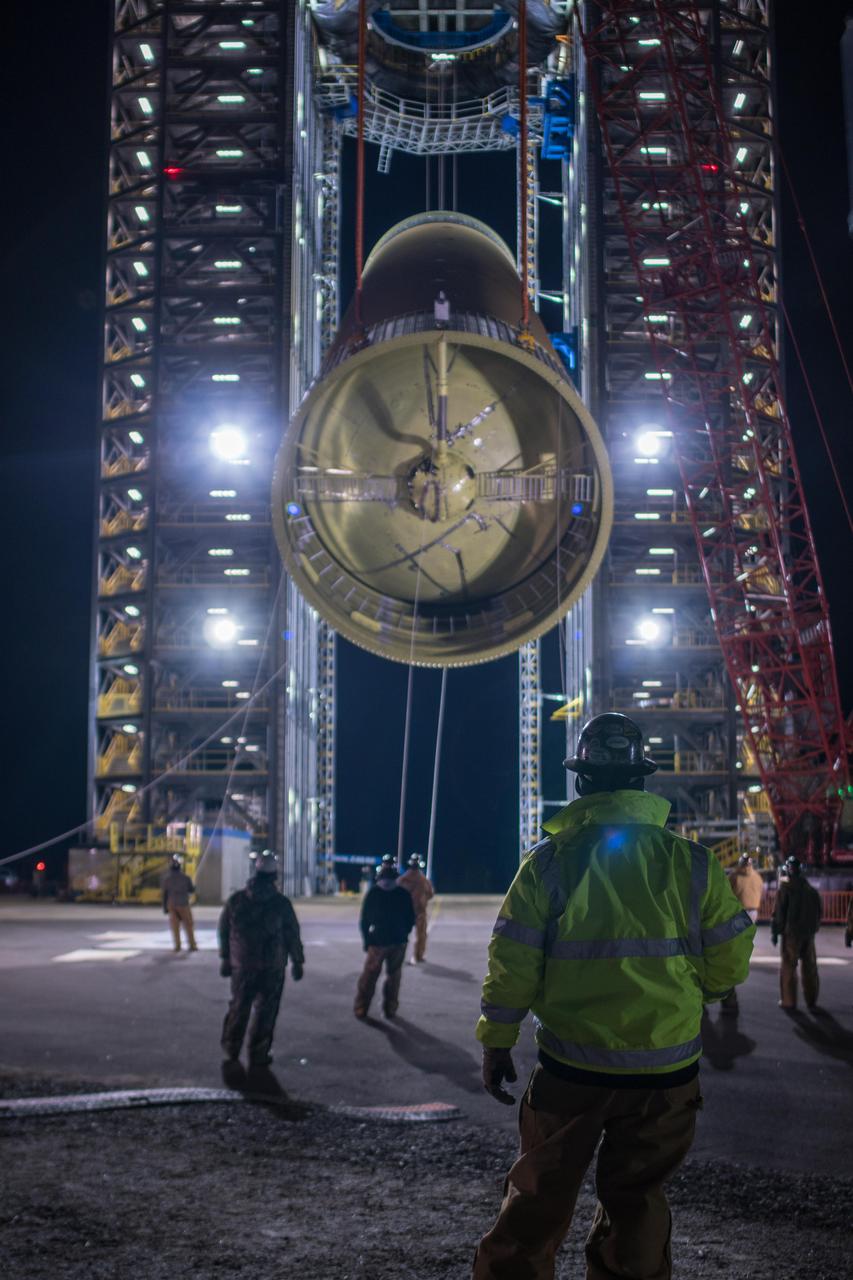

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
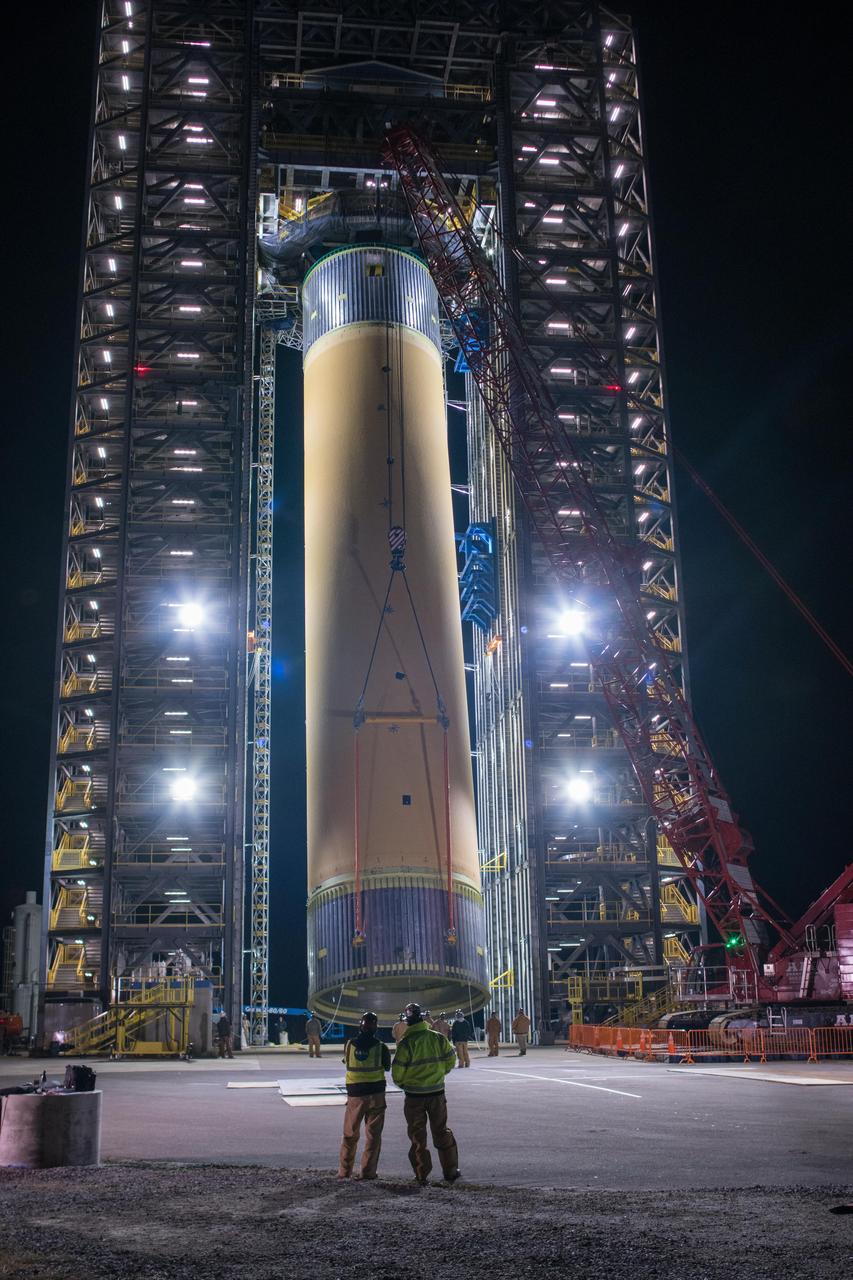

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
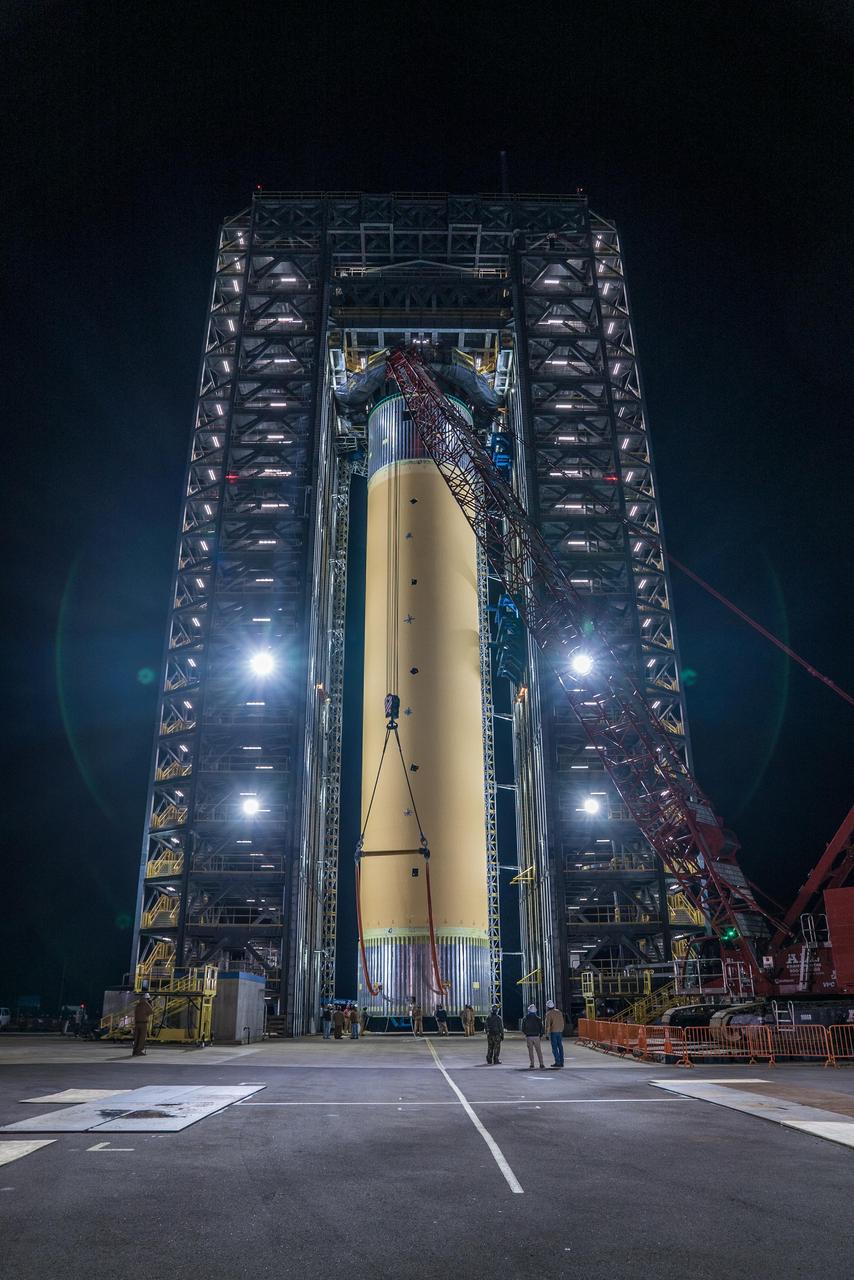

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
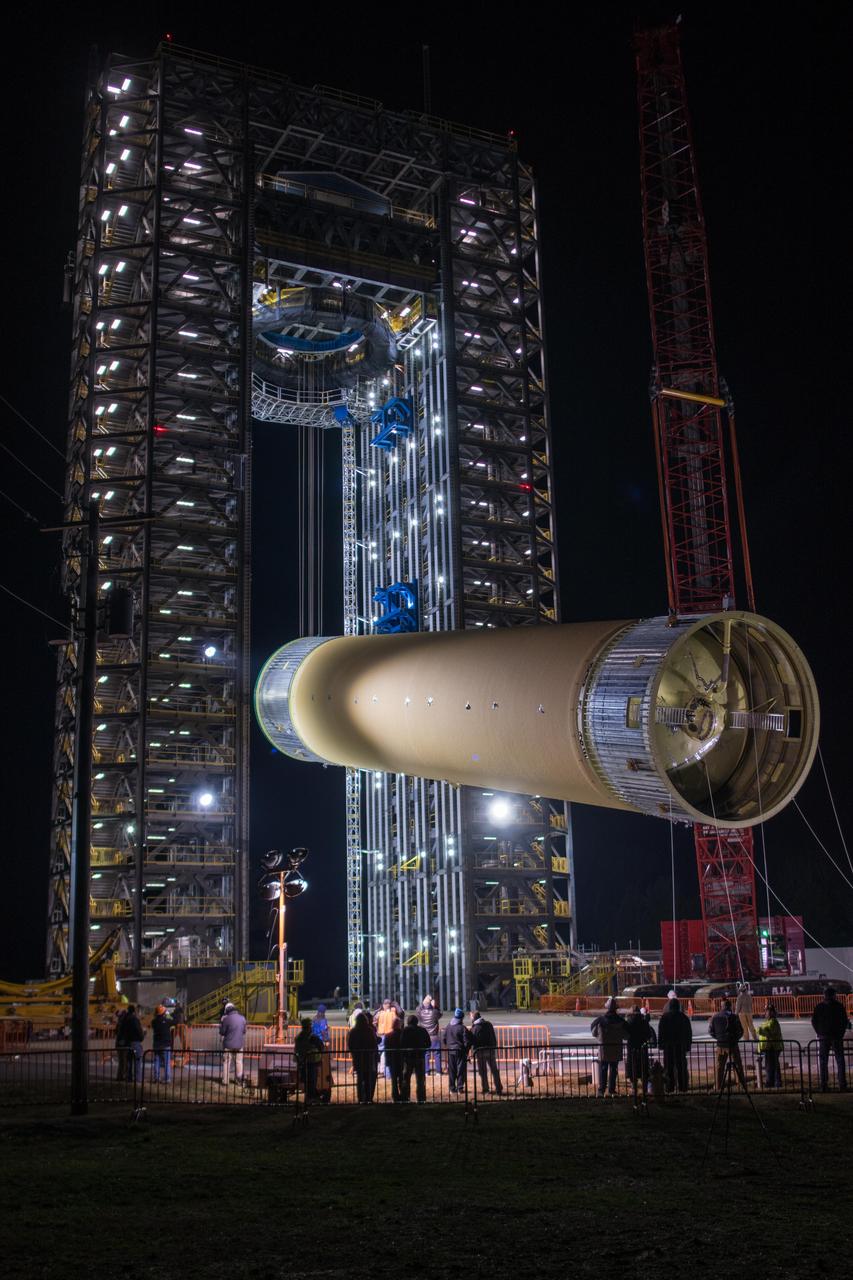

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
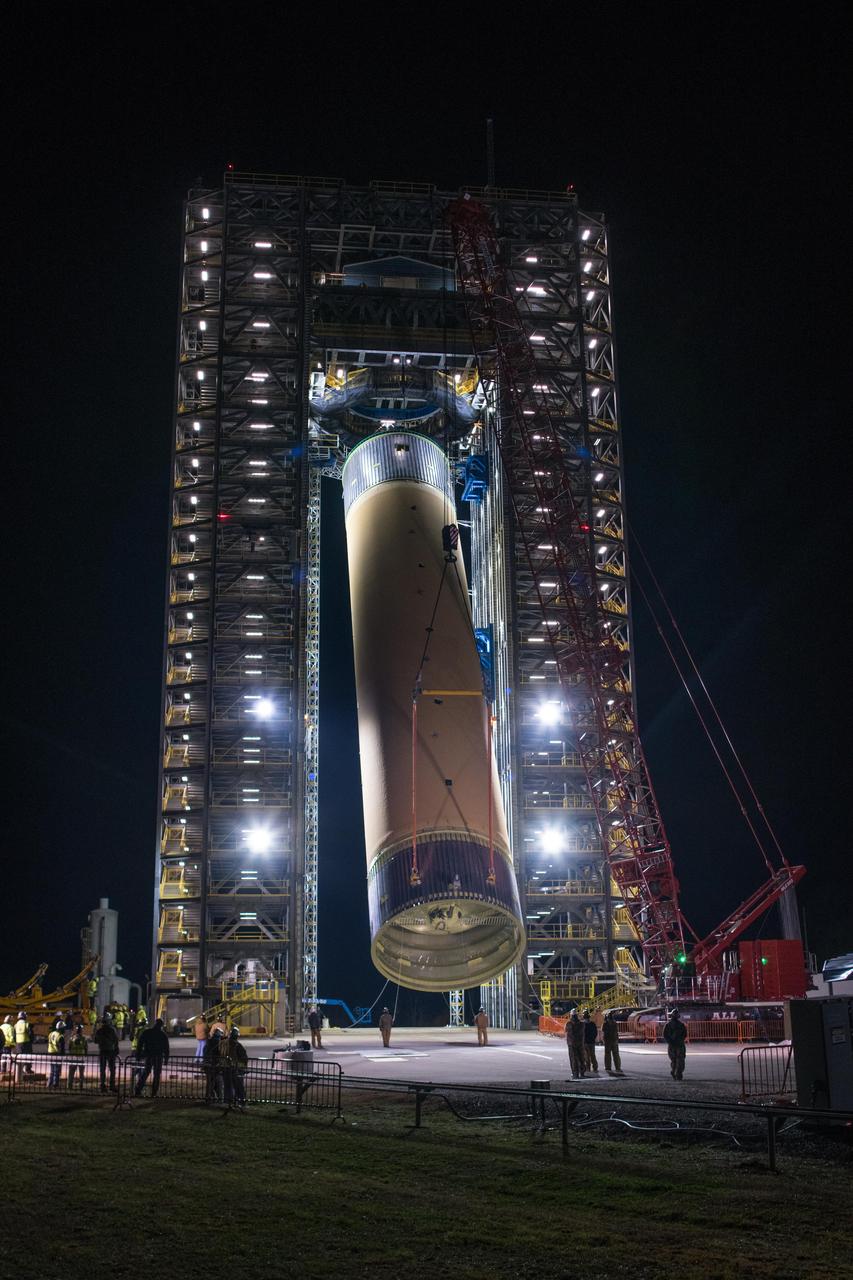

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
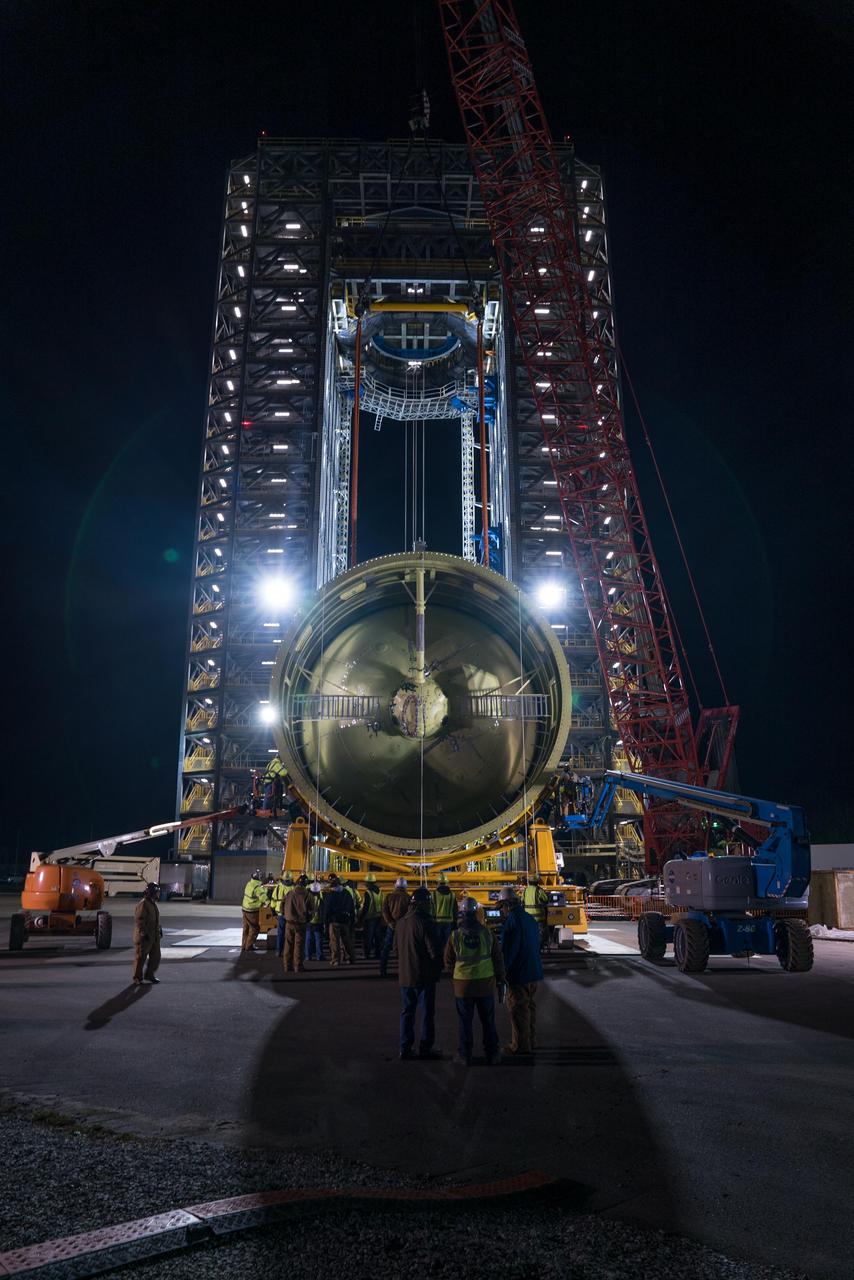

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.

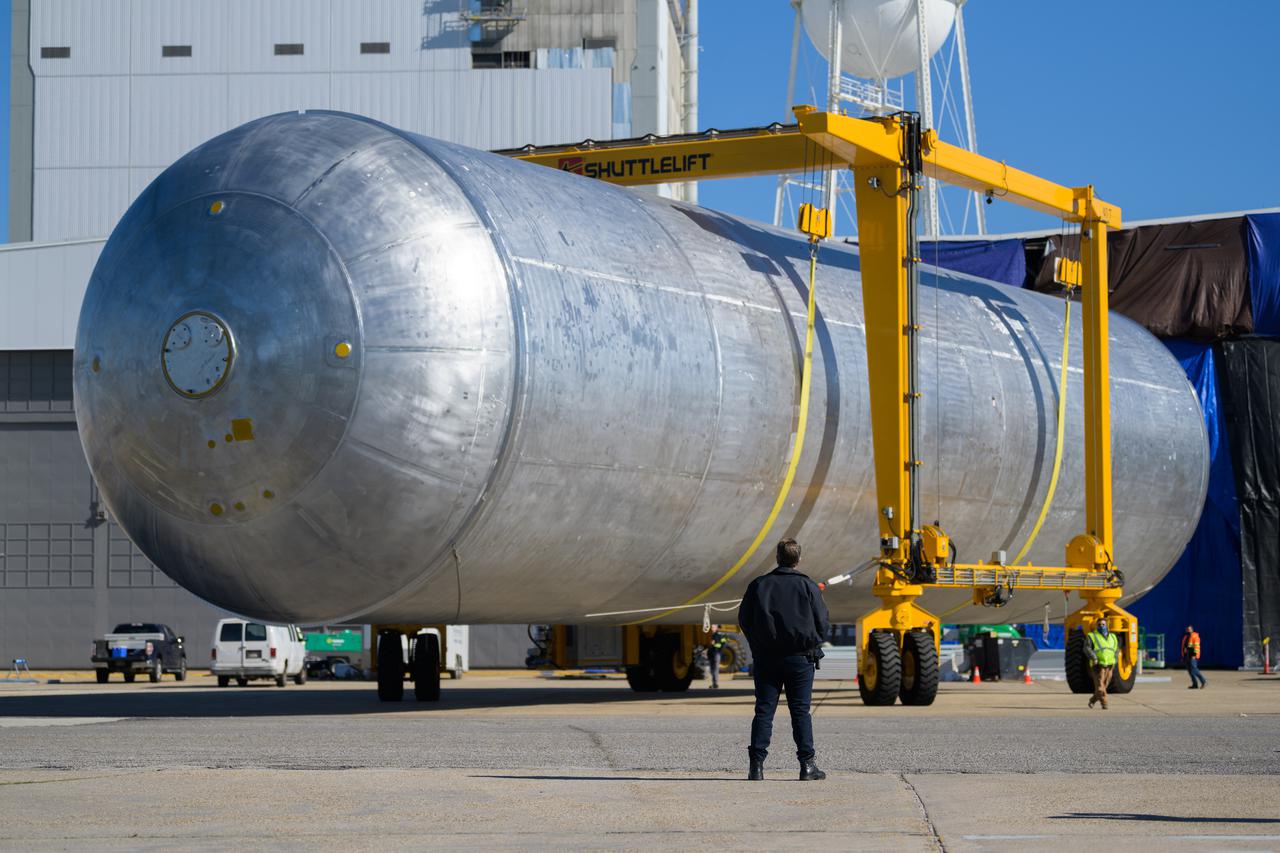
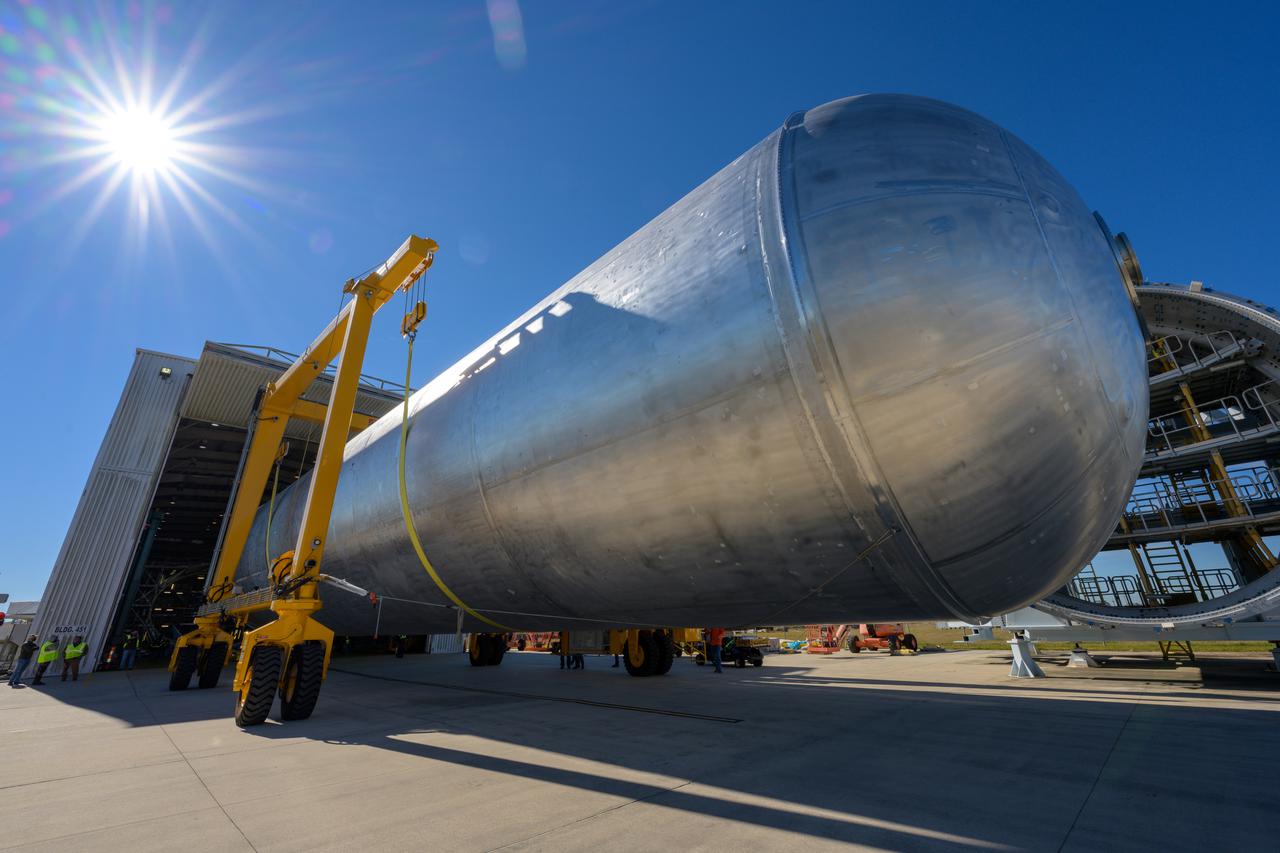
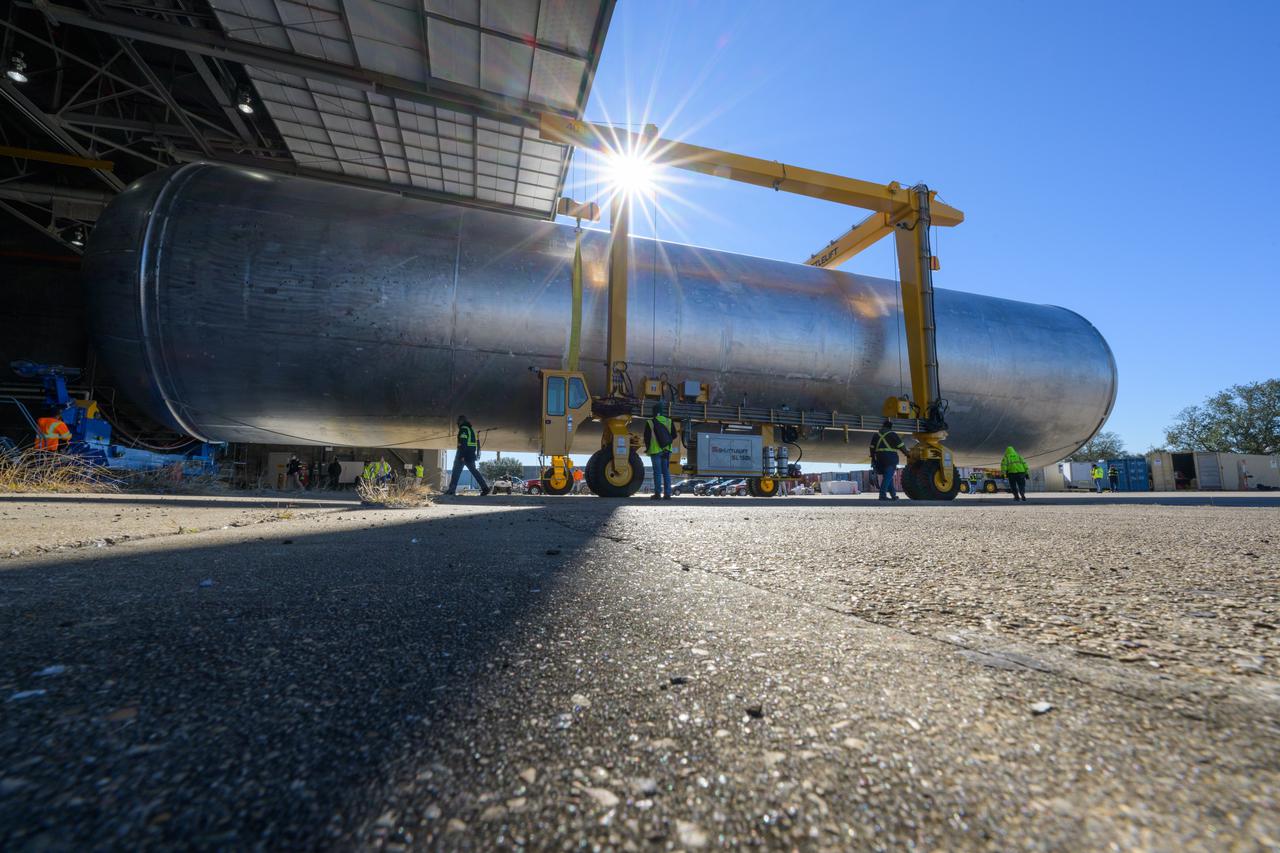
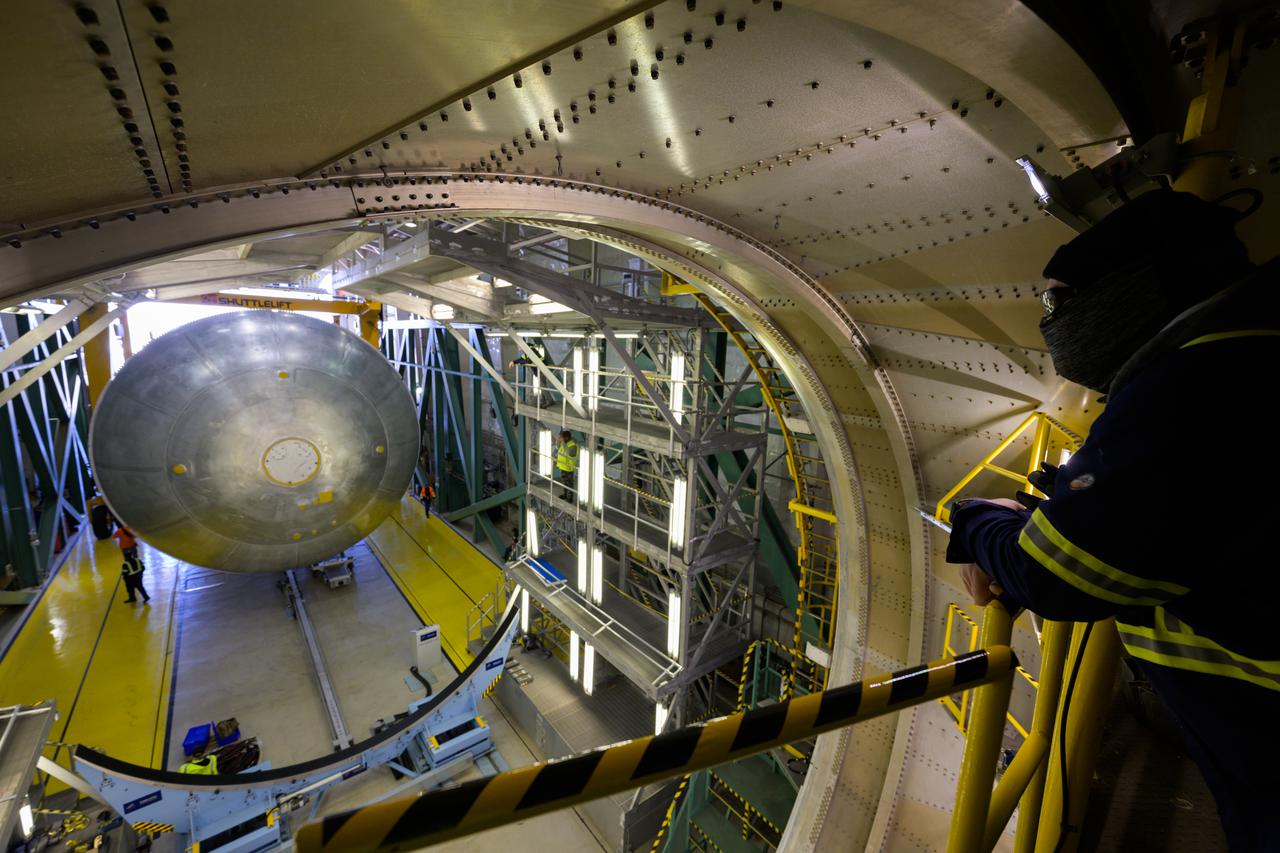
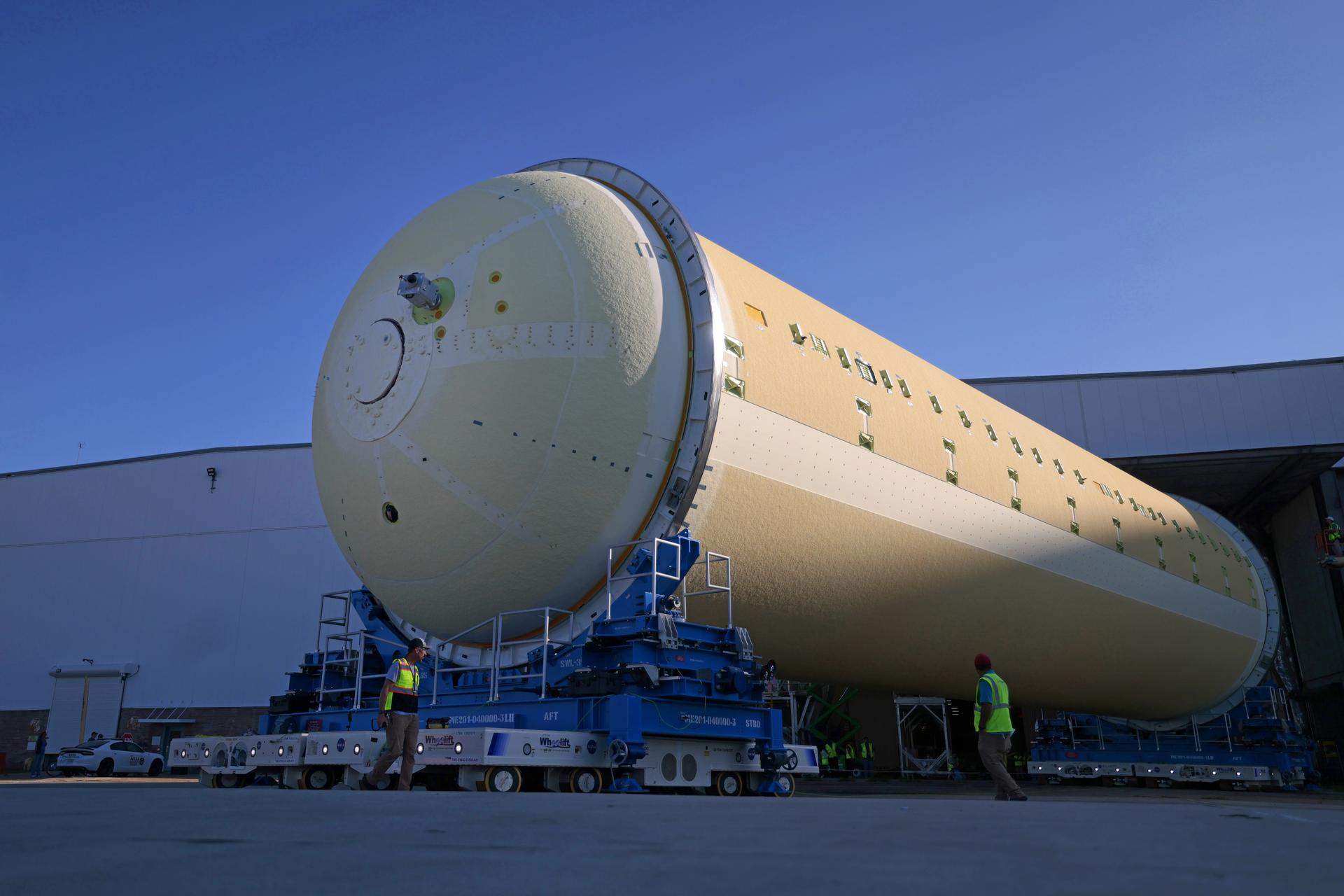
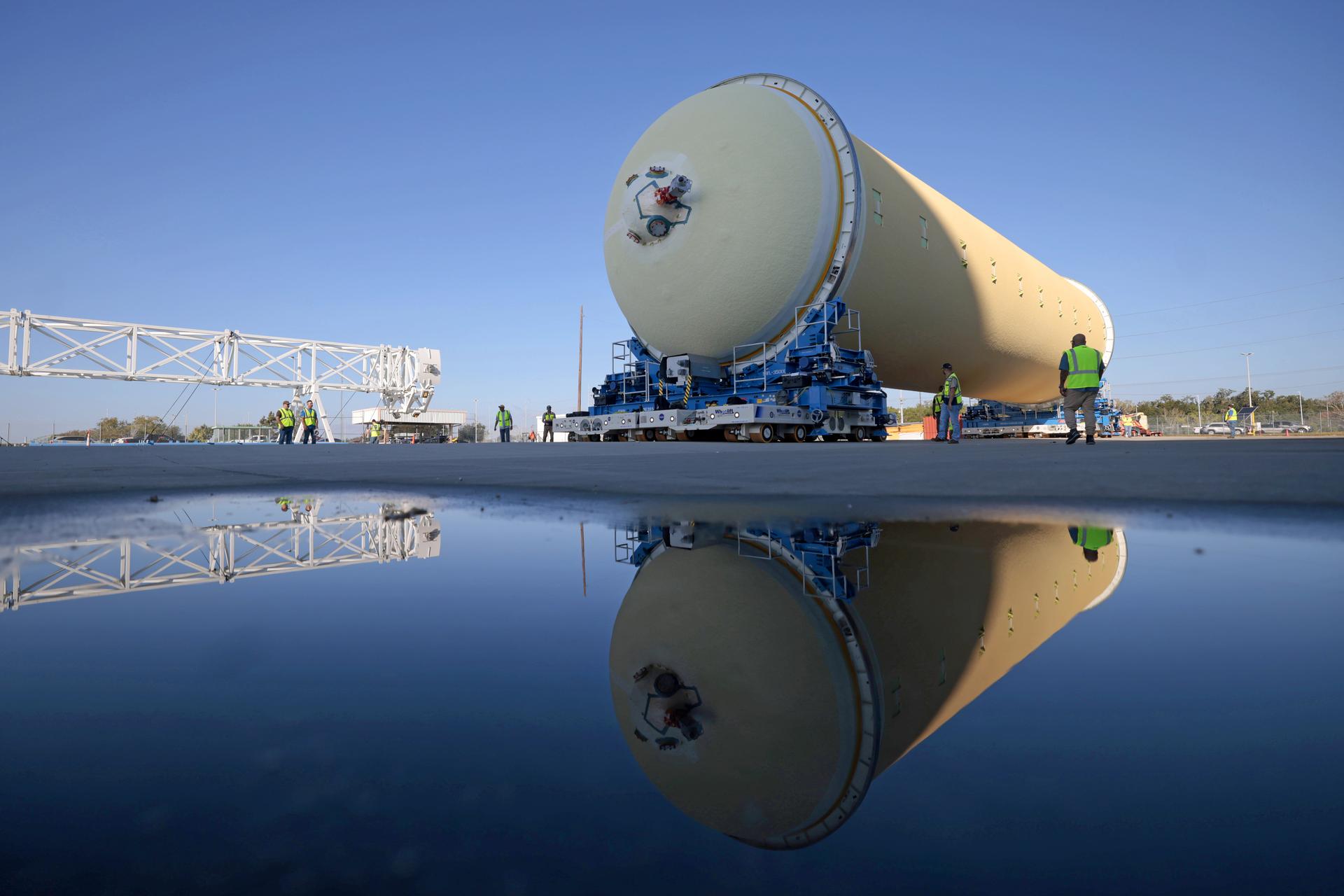
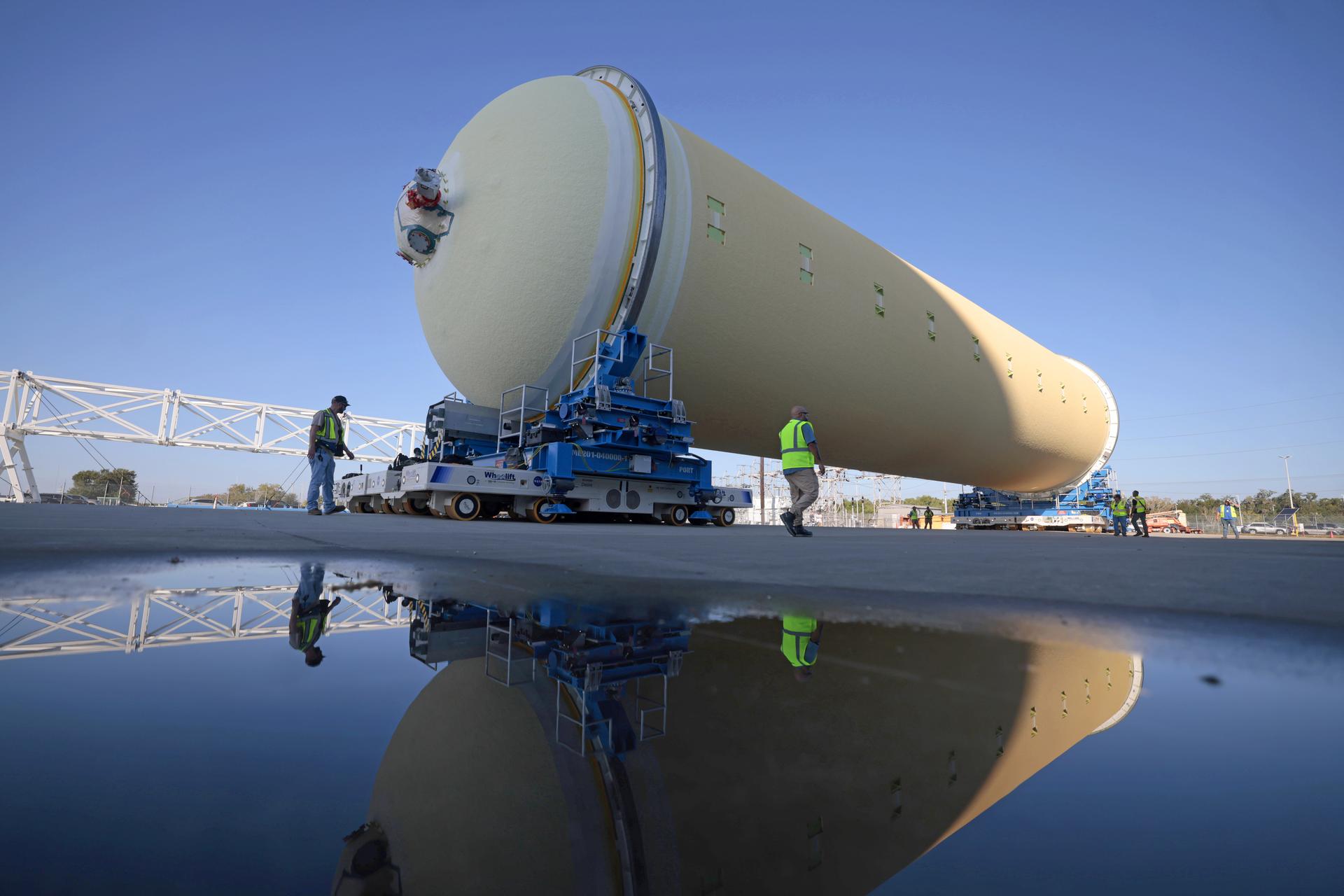
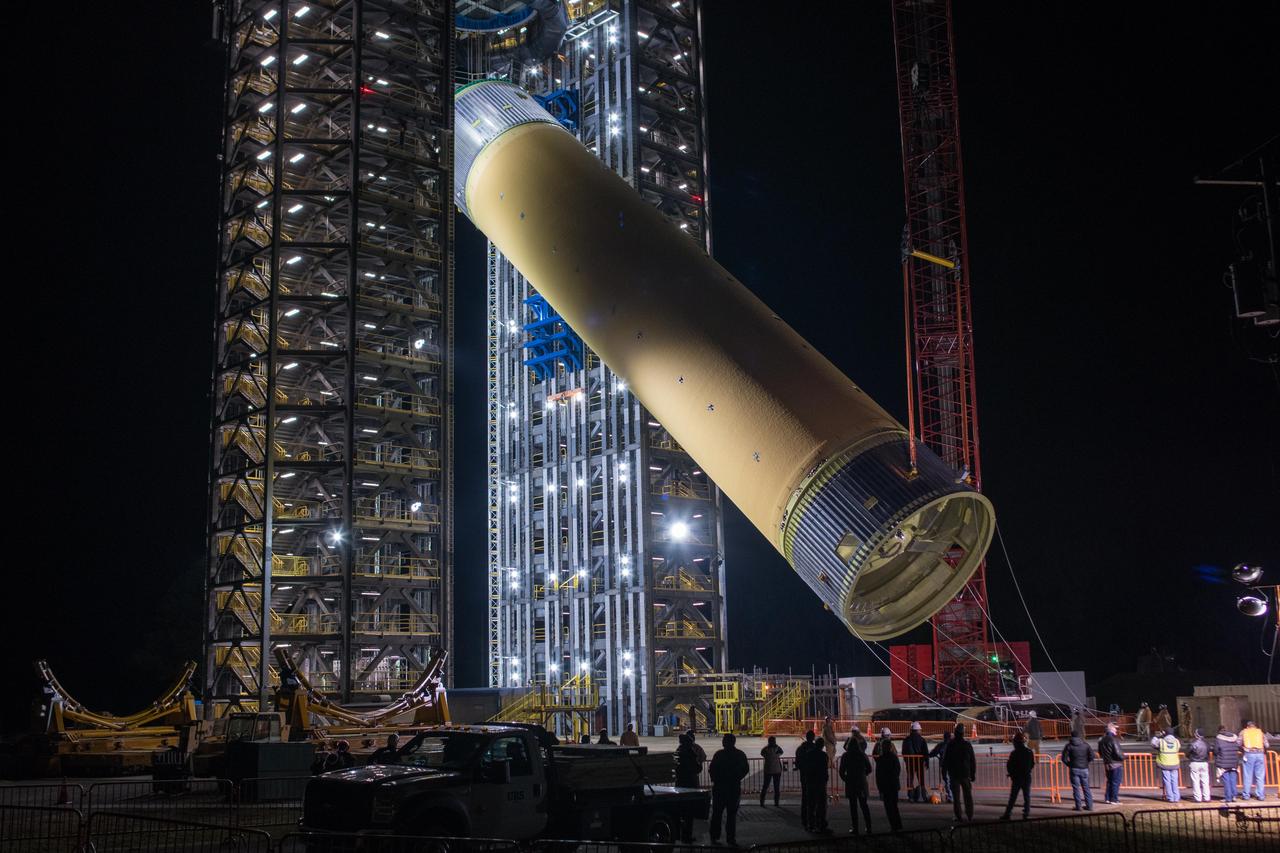
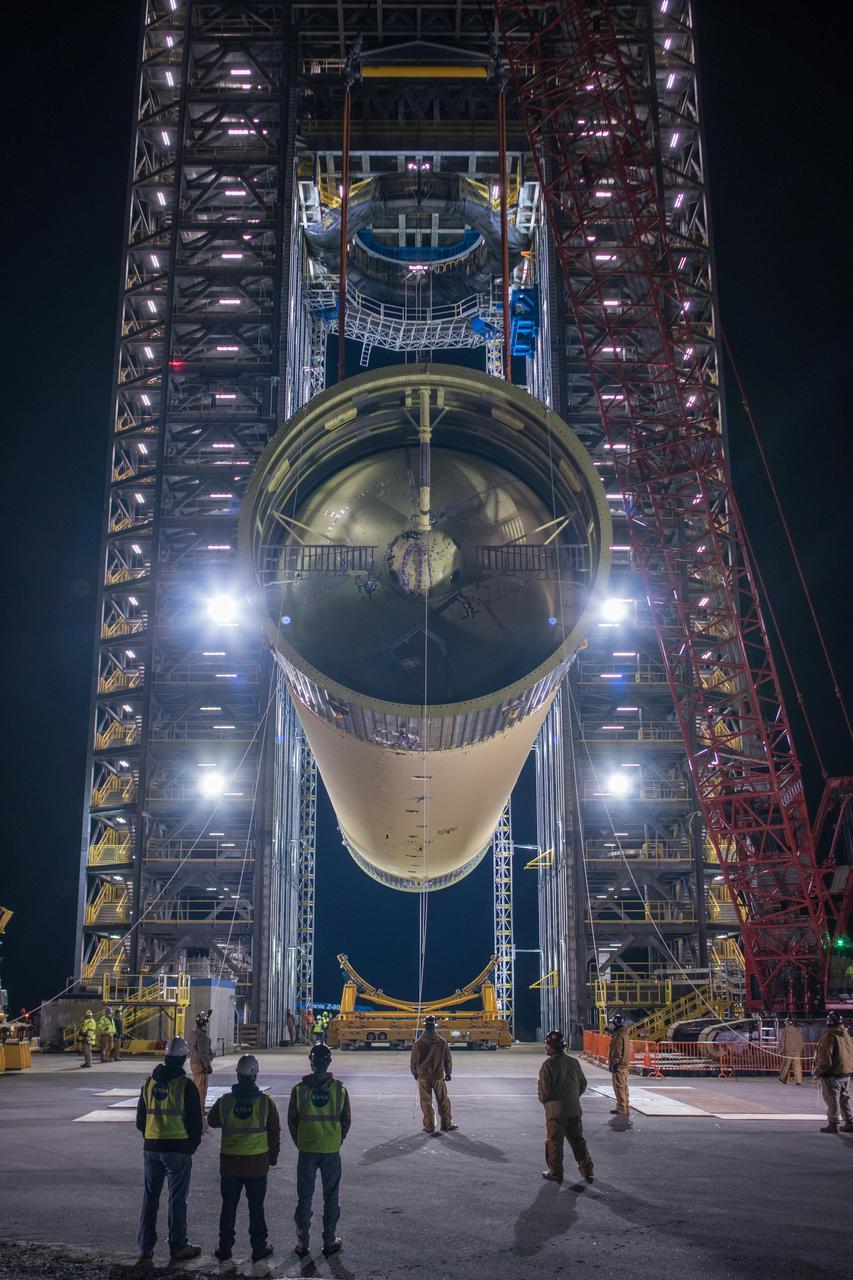
NASA’s Michoud Assembly move crews lift the liquid hydrogen tank for its Artemis III mission out of a production cell and move it into the final assembly manufacturing area on Oct. 10, 2025. Teams with SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing, recently mated the tank to the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly, which will allow the stage to be securely transported by barge to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center once it’s mated to the forward end of the core stage. The LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly serves as a temporary place holder for the engine section, which was previously shipped from Michoud to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center for further integration. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

NASA’s Michoud Assembly move crews lift the liquid hydrogen tank for its Artemis III mission out of a production cell and move it into the final assembly manufacturing area on Oct. 10, 2025. Teams with SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing, recently mated the tank to the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly, which will allow the stage to be securely transported by barge to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center once it’s mated to the forward end of the core stage. The LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly serves as a temporary place holder for the engine section, which was previously shipped from Michoud to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center for further integration. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
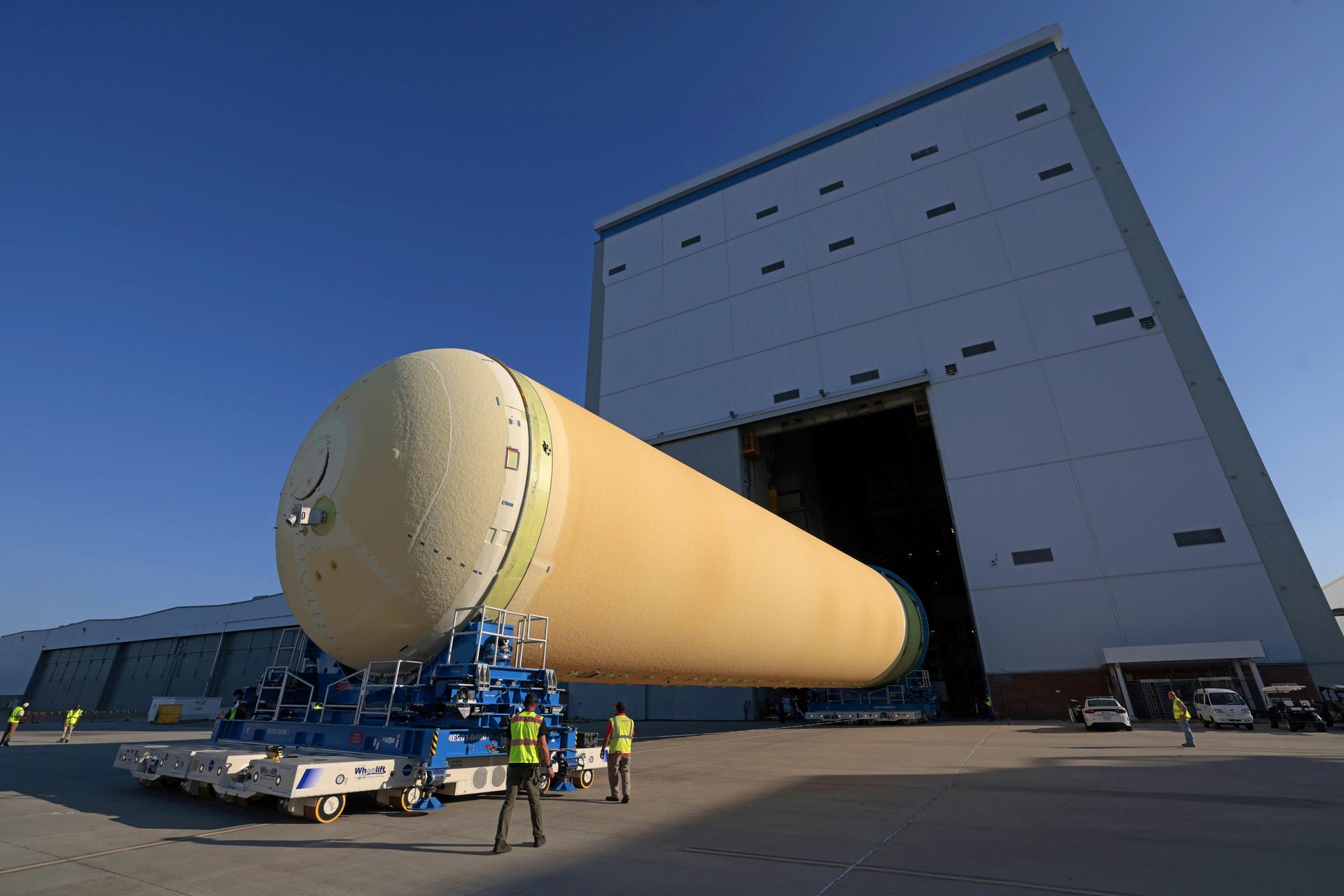

NASA’s Michoud Assembly move crews lift the liquid hydrogen tank for its Artemis III mission out of a production cell and move it into the final assembly manufacturing area on Oct. 10, 2025. Teams with SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing, recently mated the tank to the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly, which will allow the stage to be securely transported by barge to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center once it’s mated to the forward end of the core stage. The LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly serves as a temporary place holder for the engine section, which was previously shipped from Michoud to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center for further integration. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
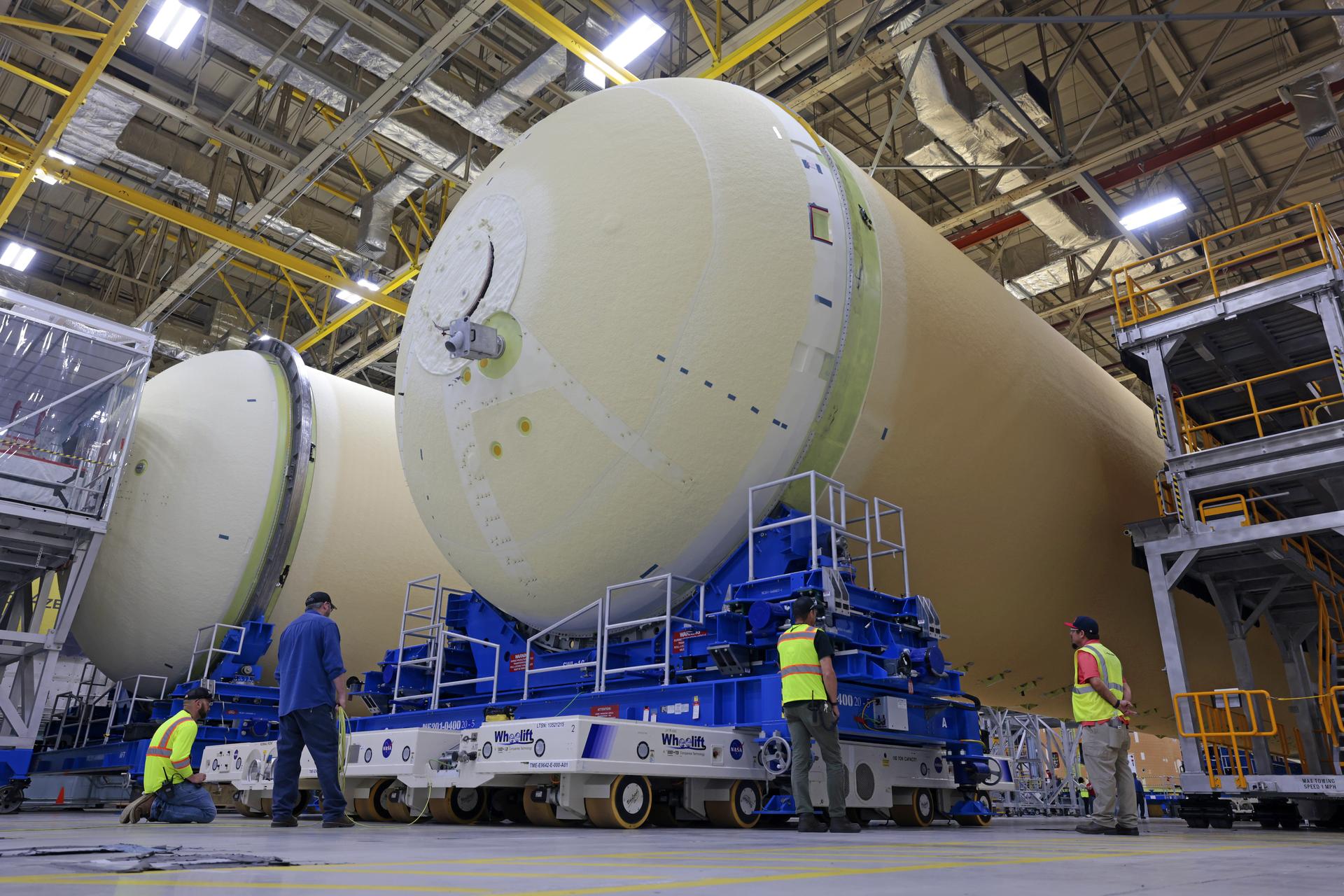

NASA’s Michoud Assembly move crews lift the liquid hydrogen tank for its Artemis III mission out of a production cell and move it into the final assembly manufacturing area on Oct. 10, 2025. Teams with SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing, recently mated the tank to the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly, which will allow the stage to be securely transported by barge to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center once it’s mated to the forward end of the core stage. The LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly serves as a temporary place holder for the engine section, which was previously shipped from Michoud to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center for further integration. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
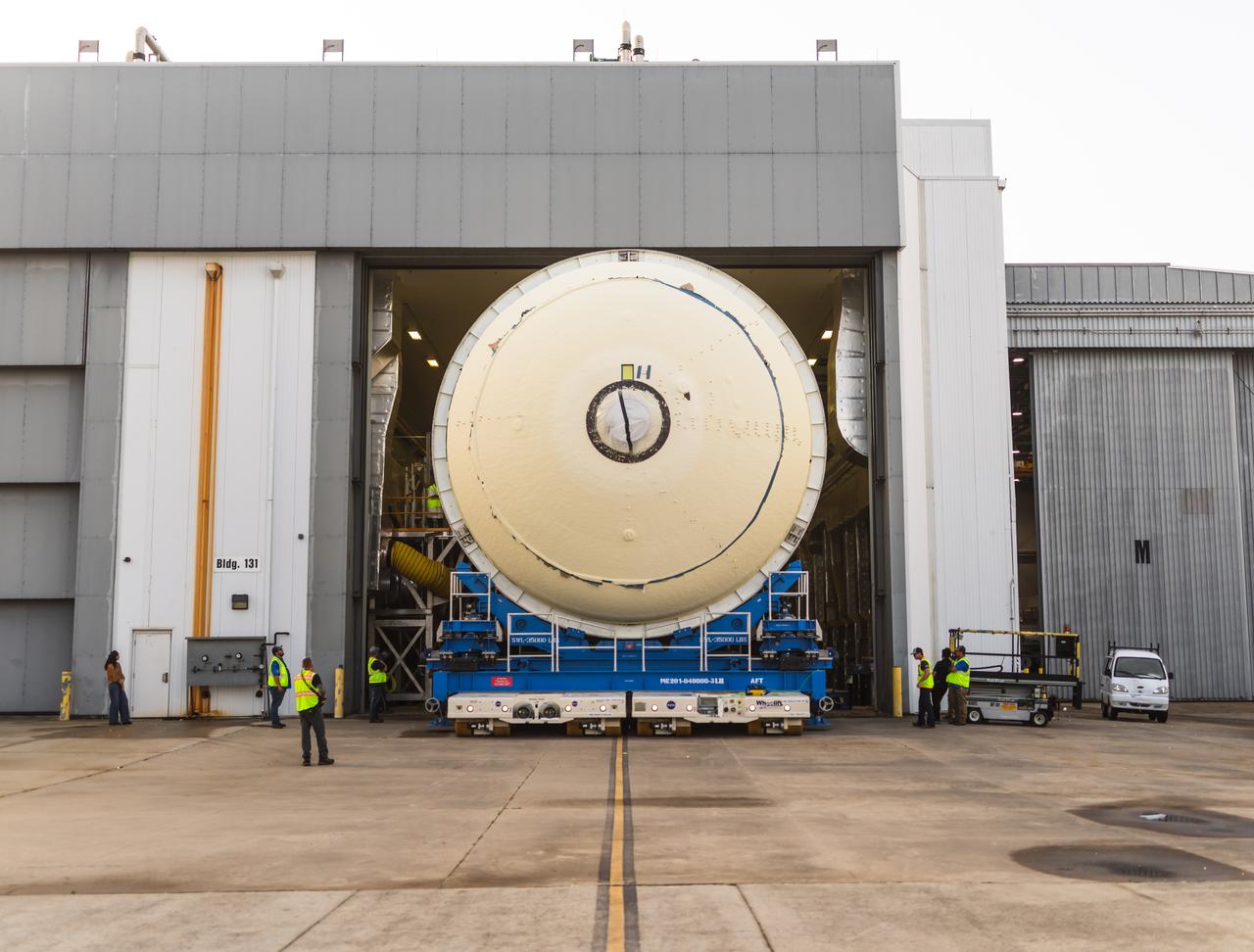

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
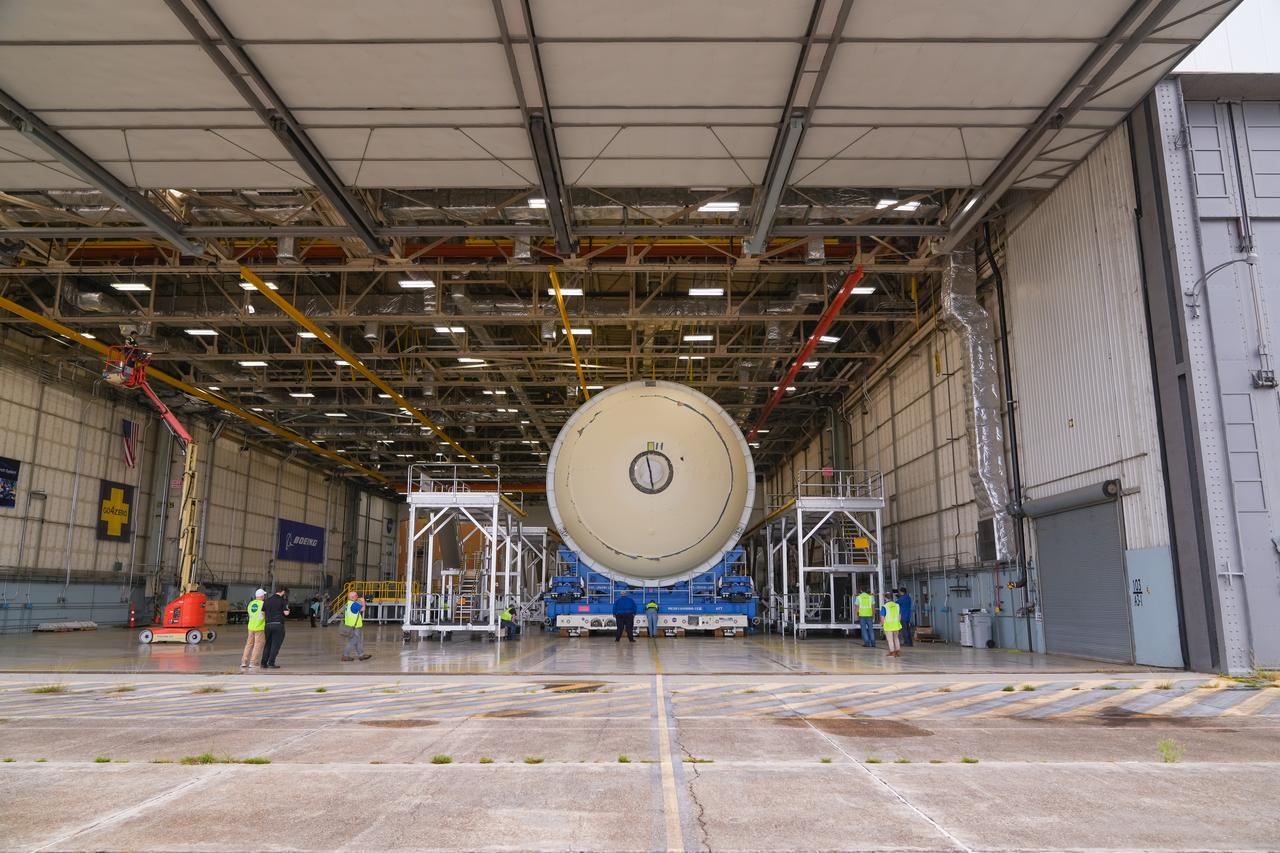

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
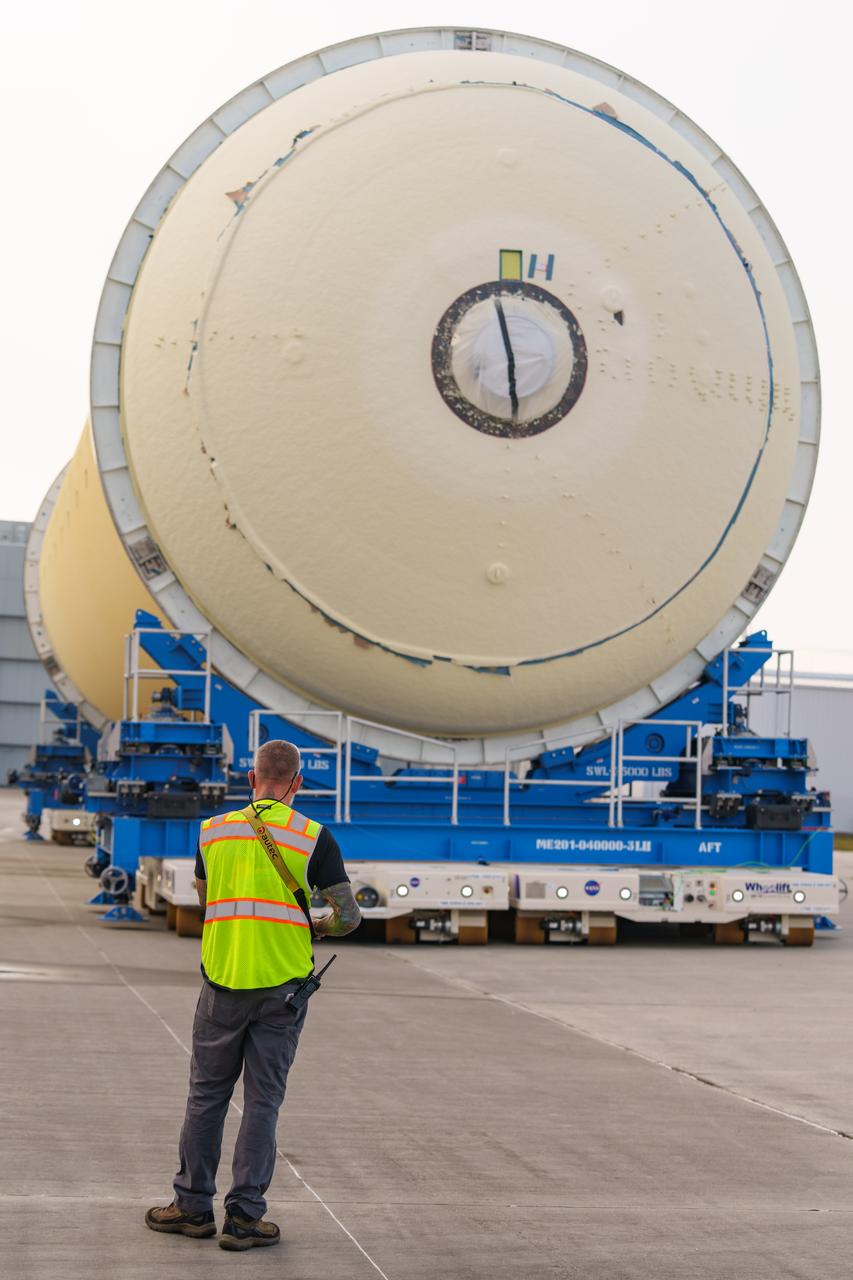

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
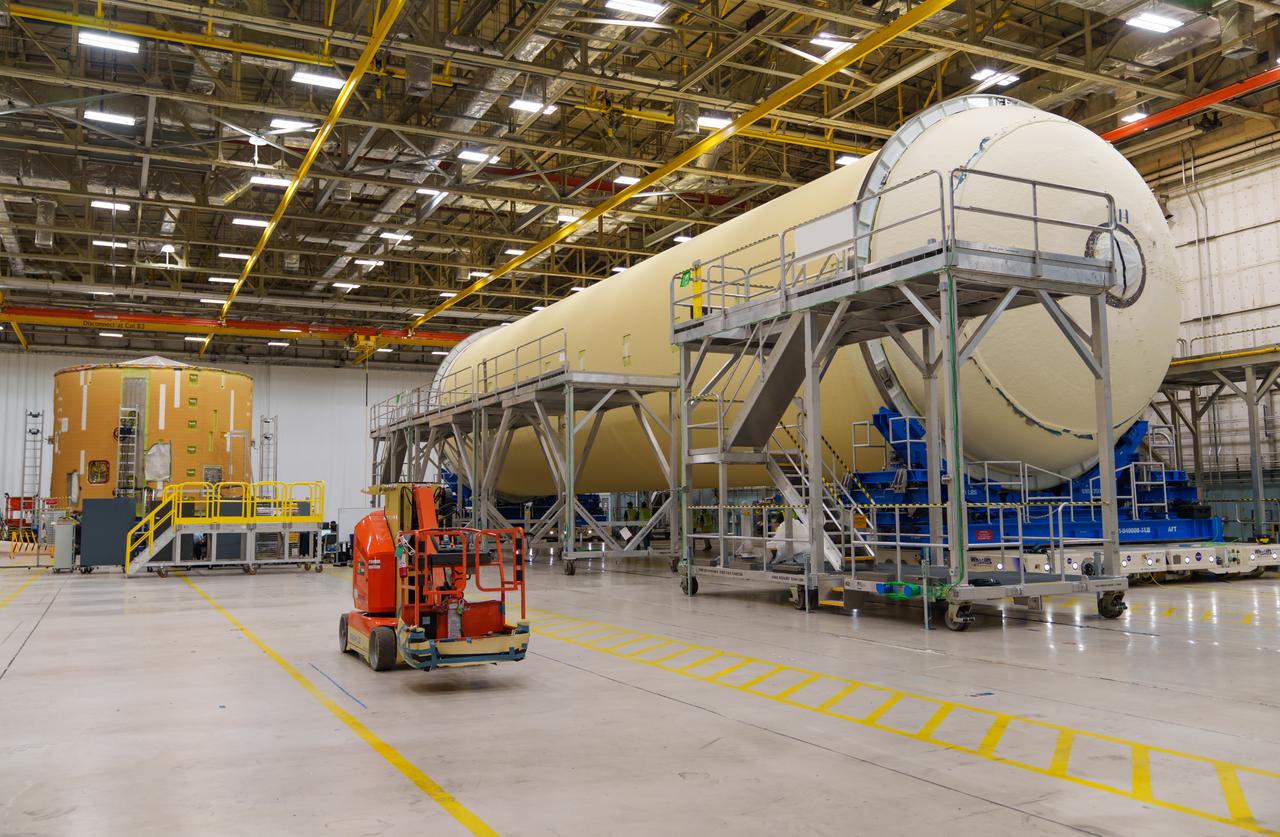

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
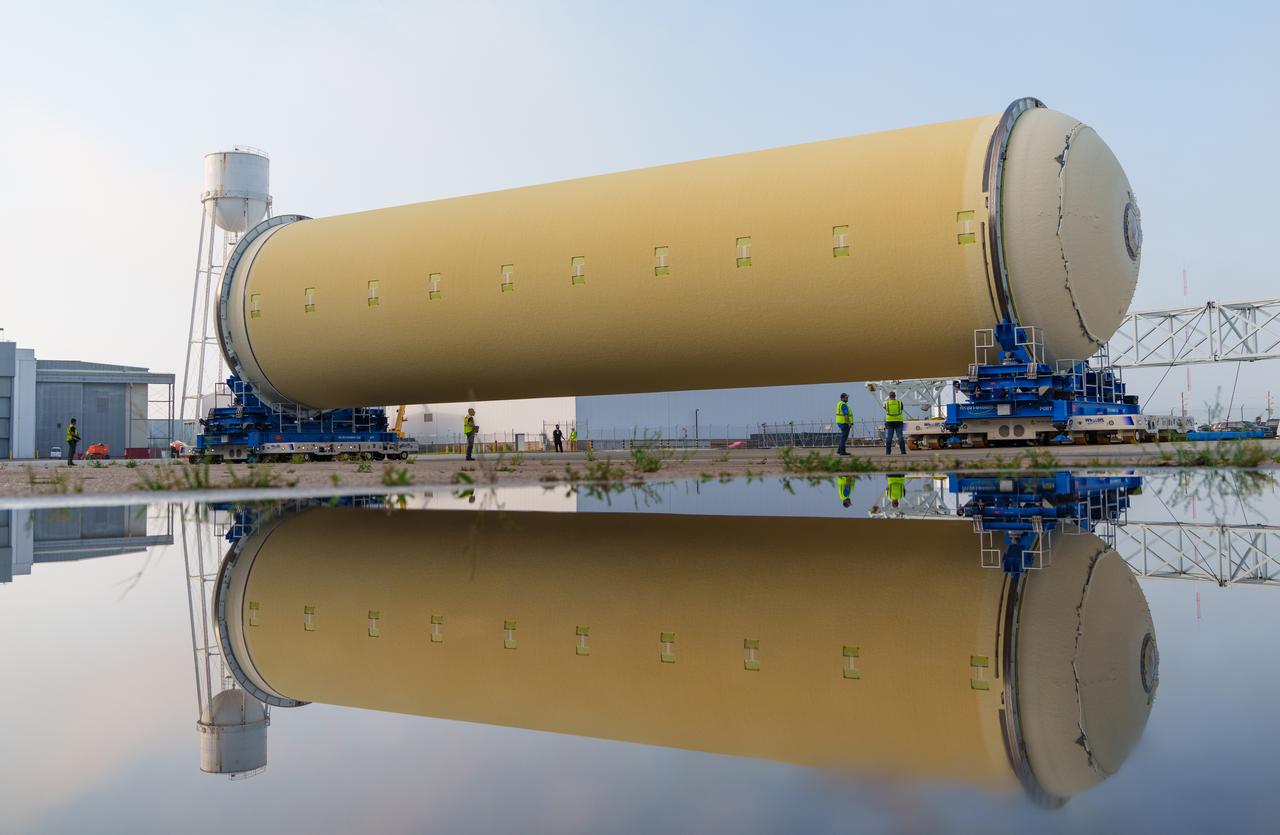

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
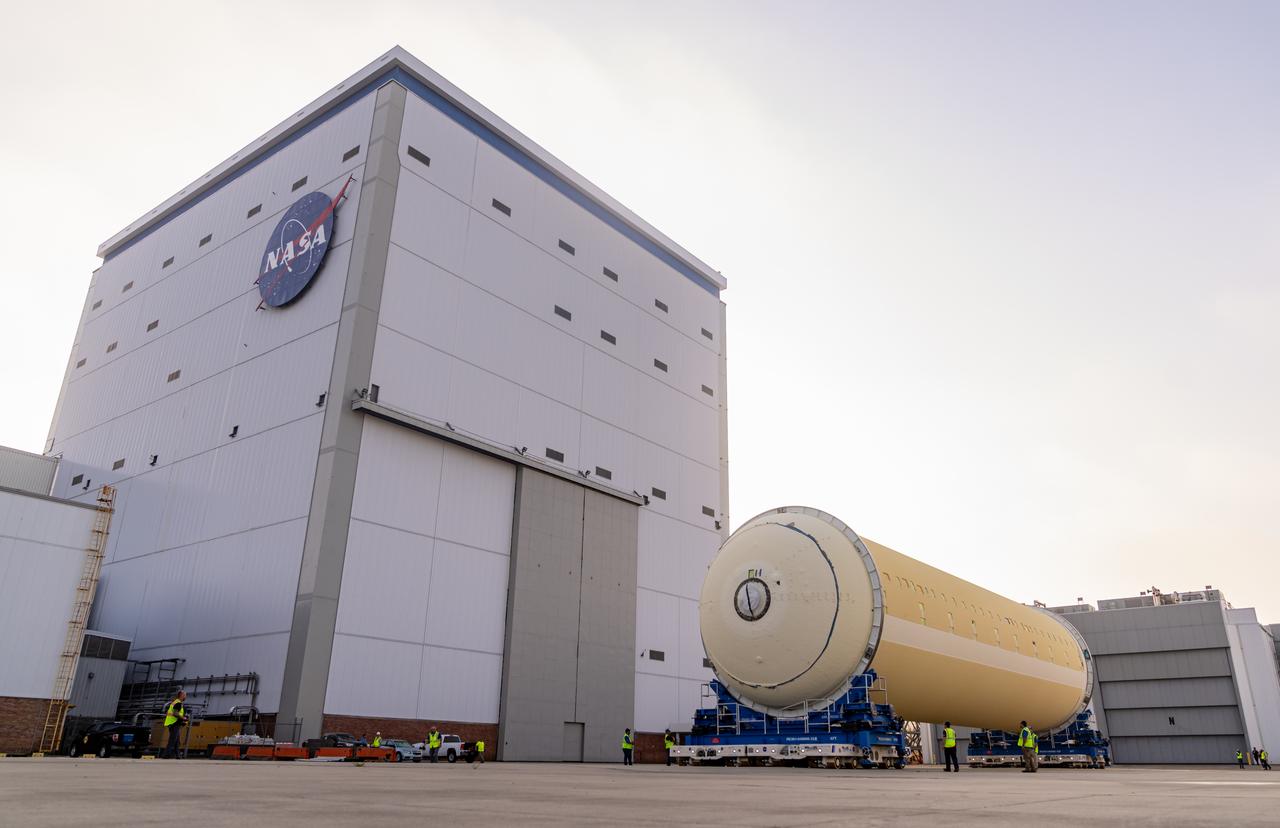

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
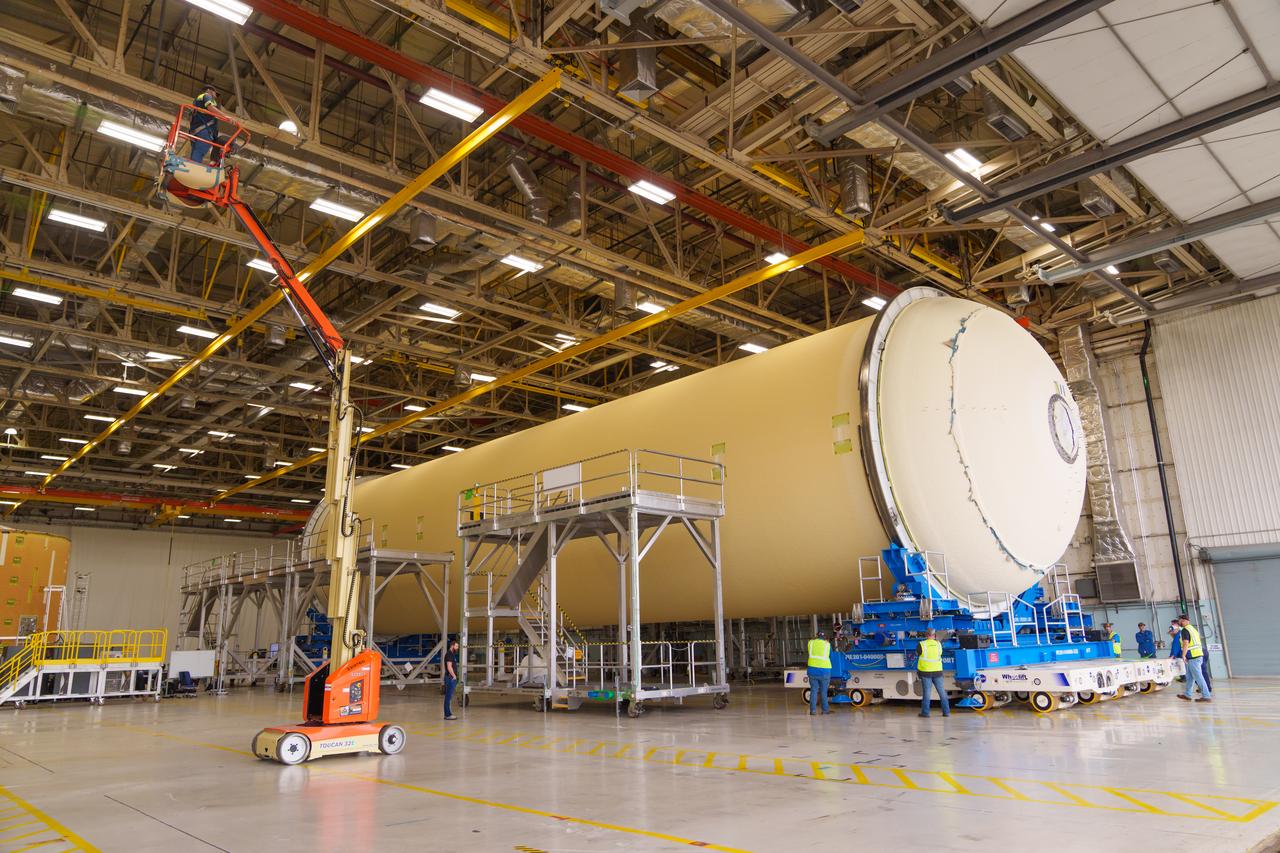

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
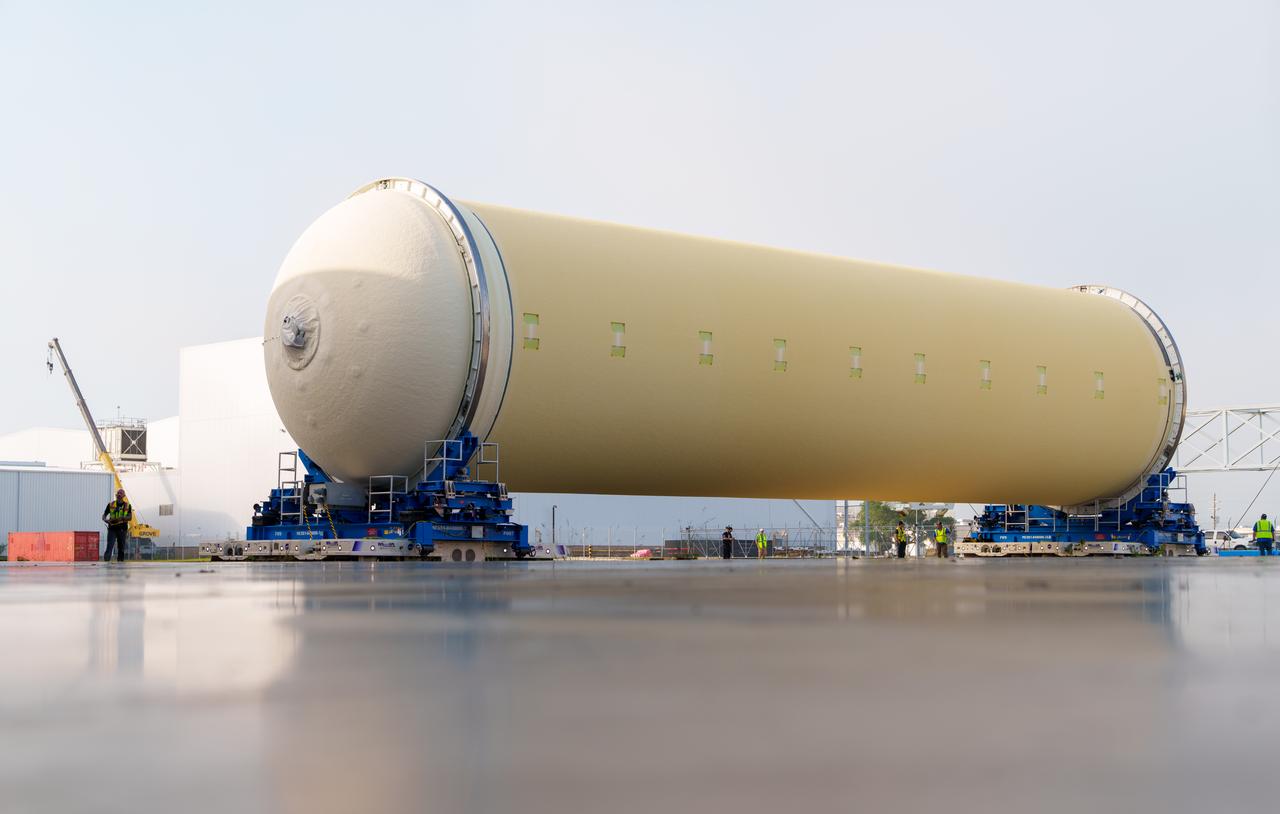

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
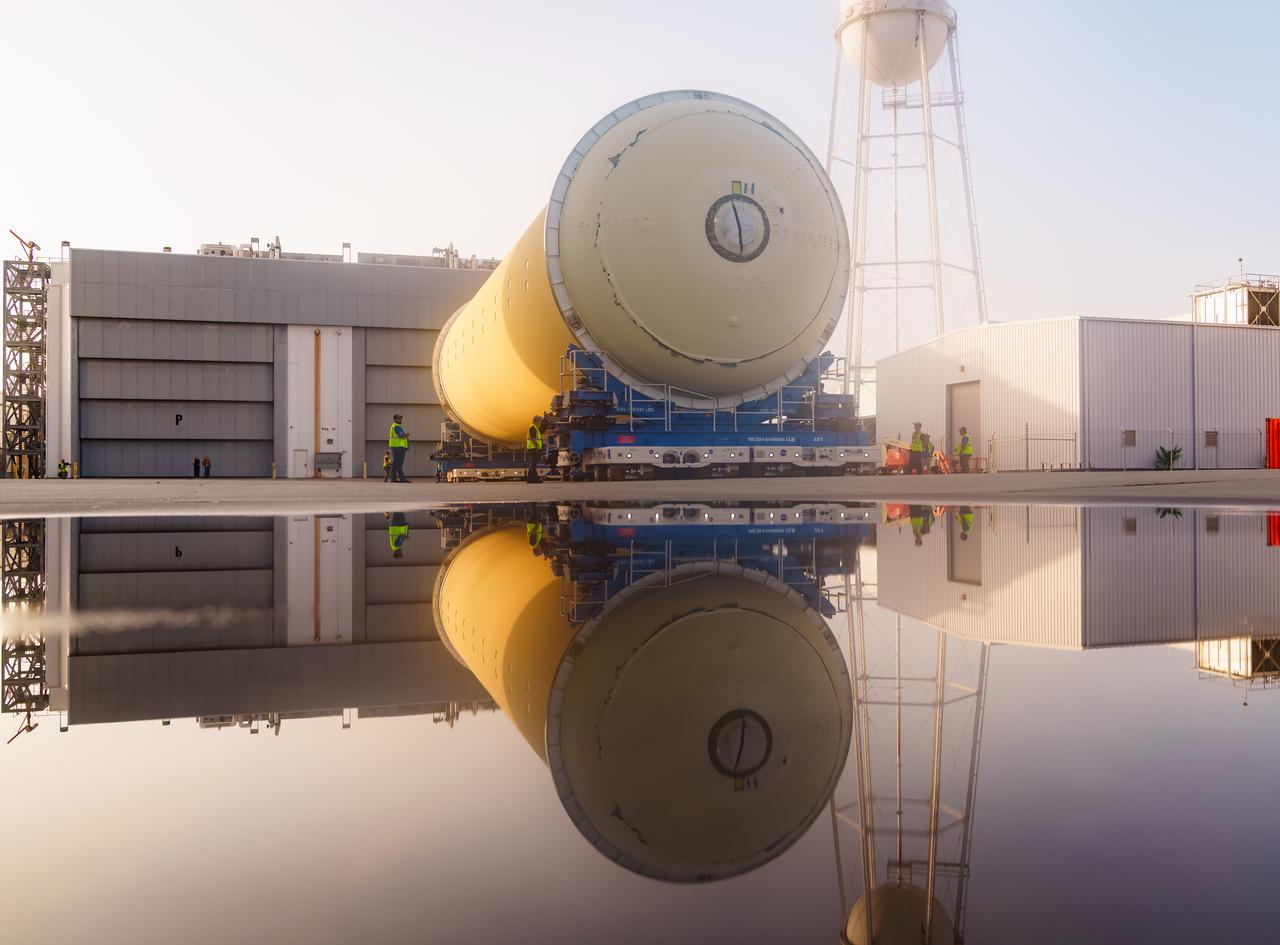

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
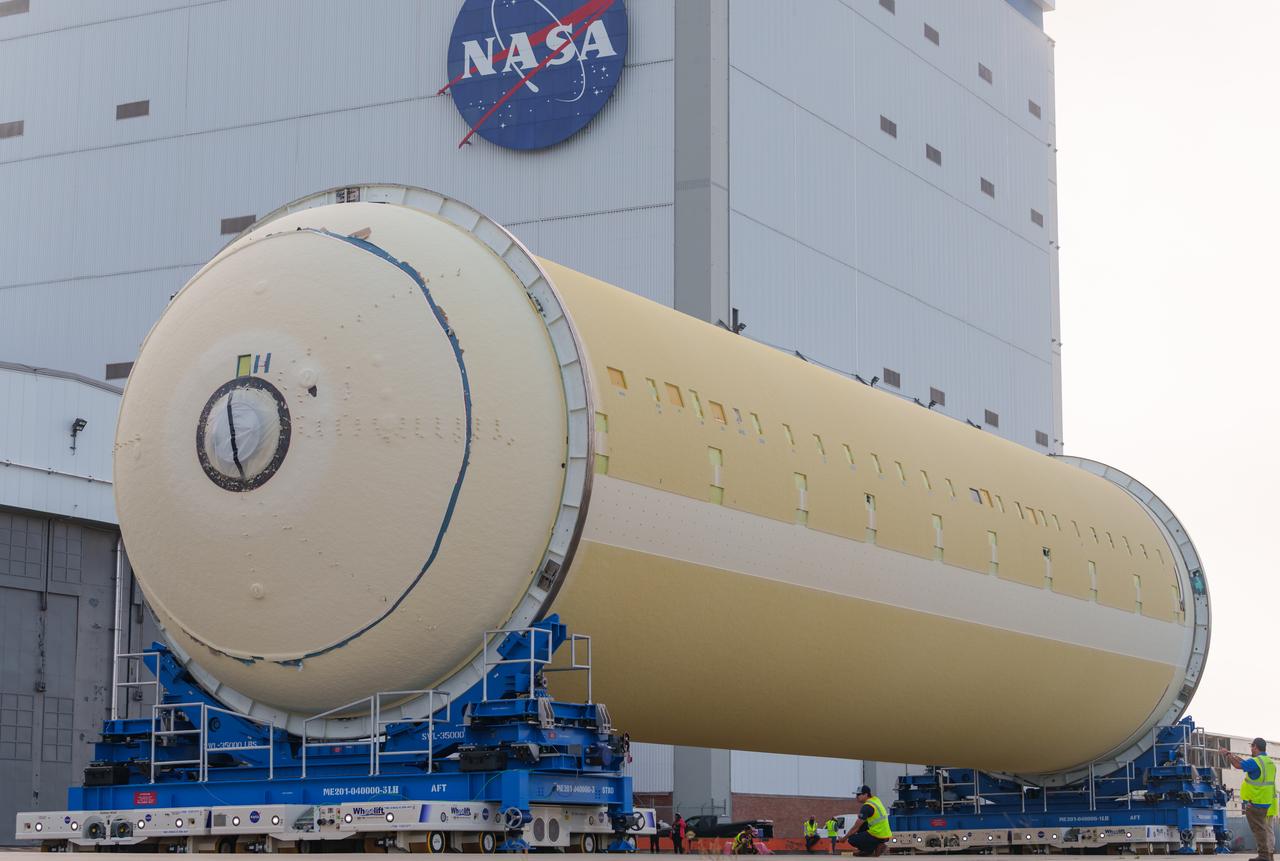

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
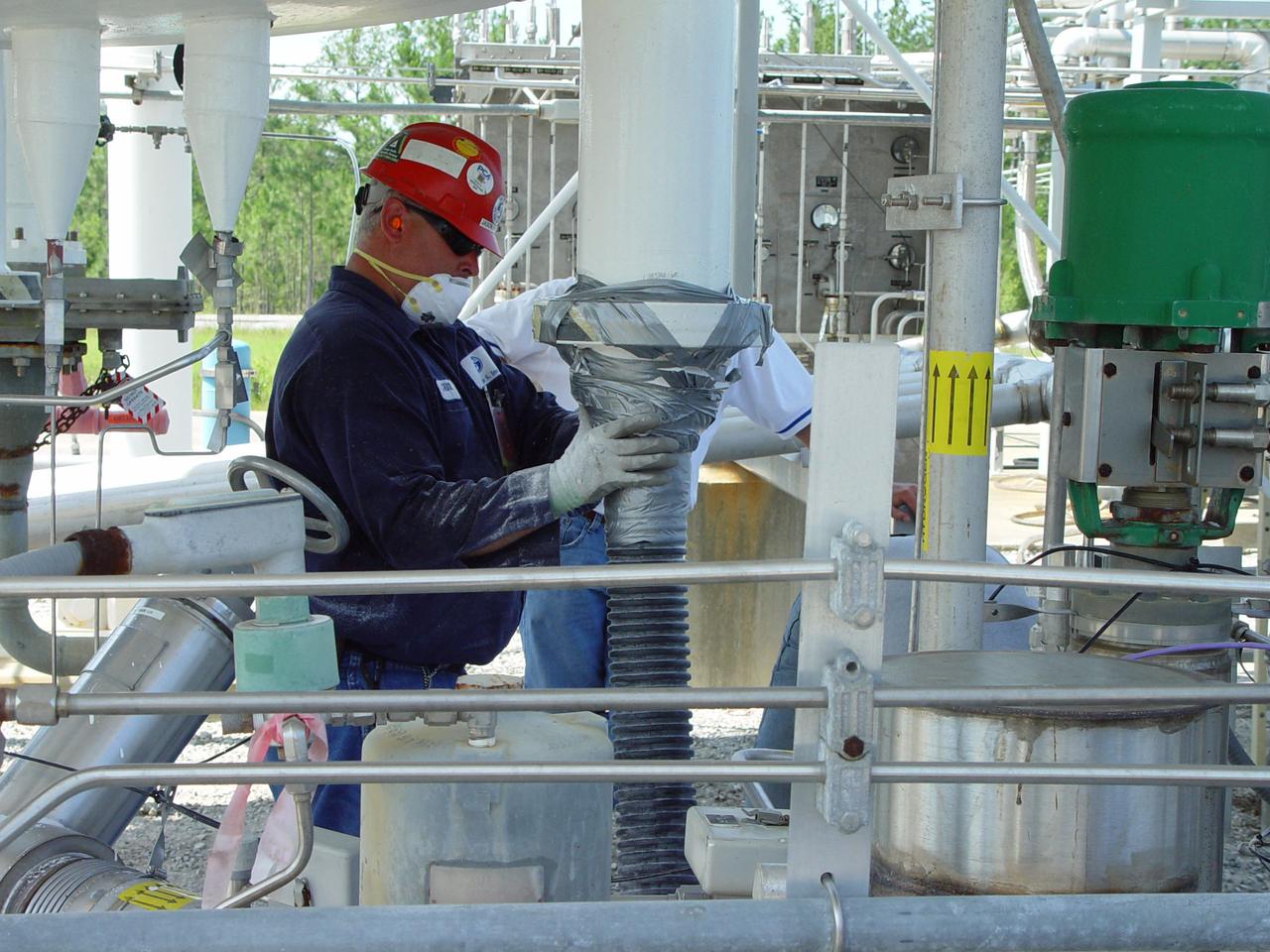

A worker removes Perlite insulation from a liquid hydrogen storage tank to replace it with glass bubble insulation.
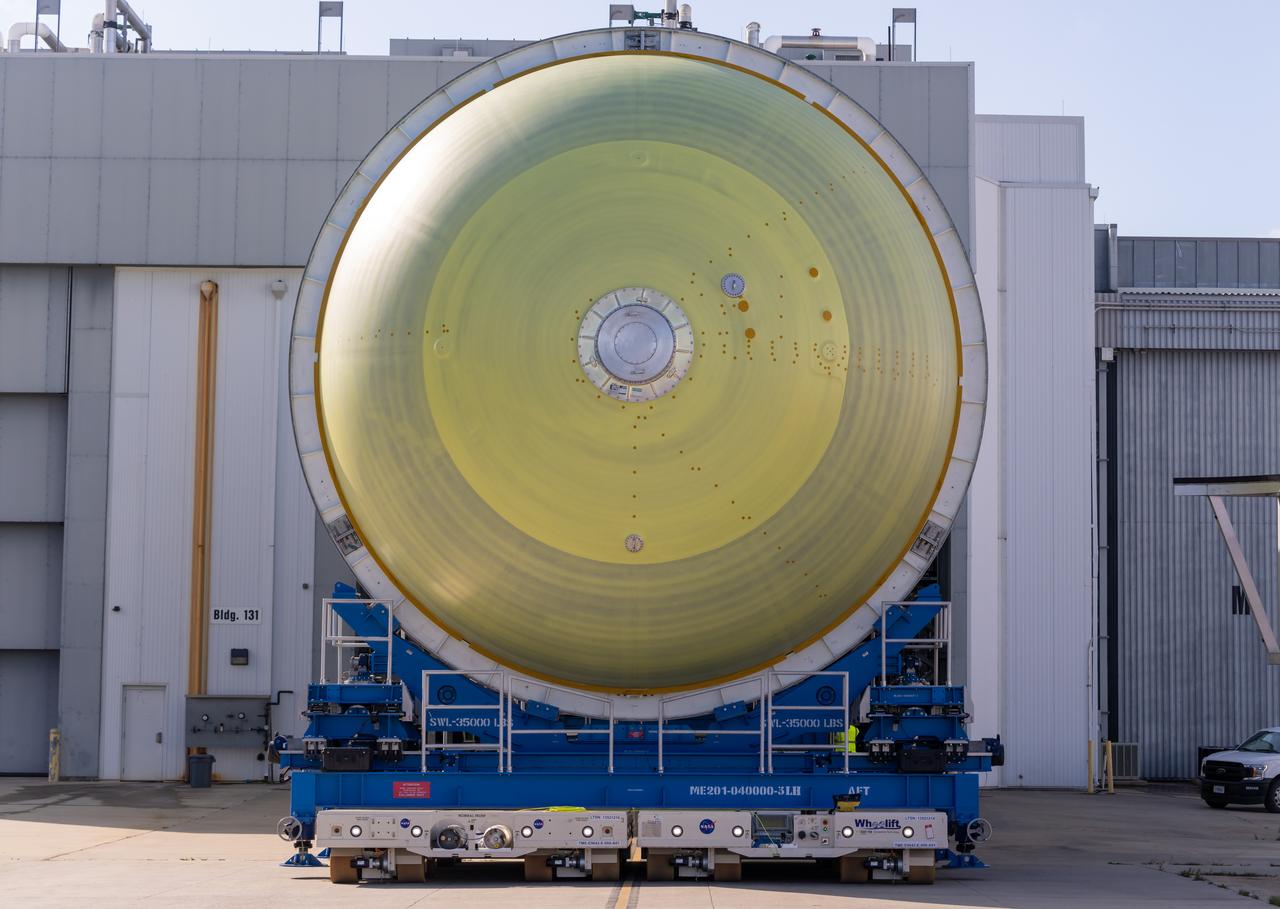

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.
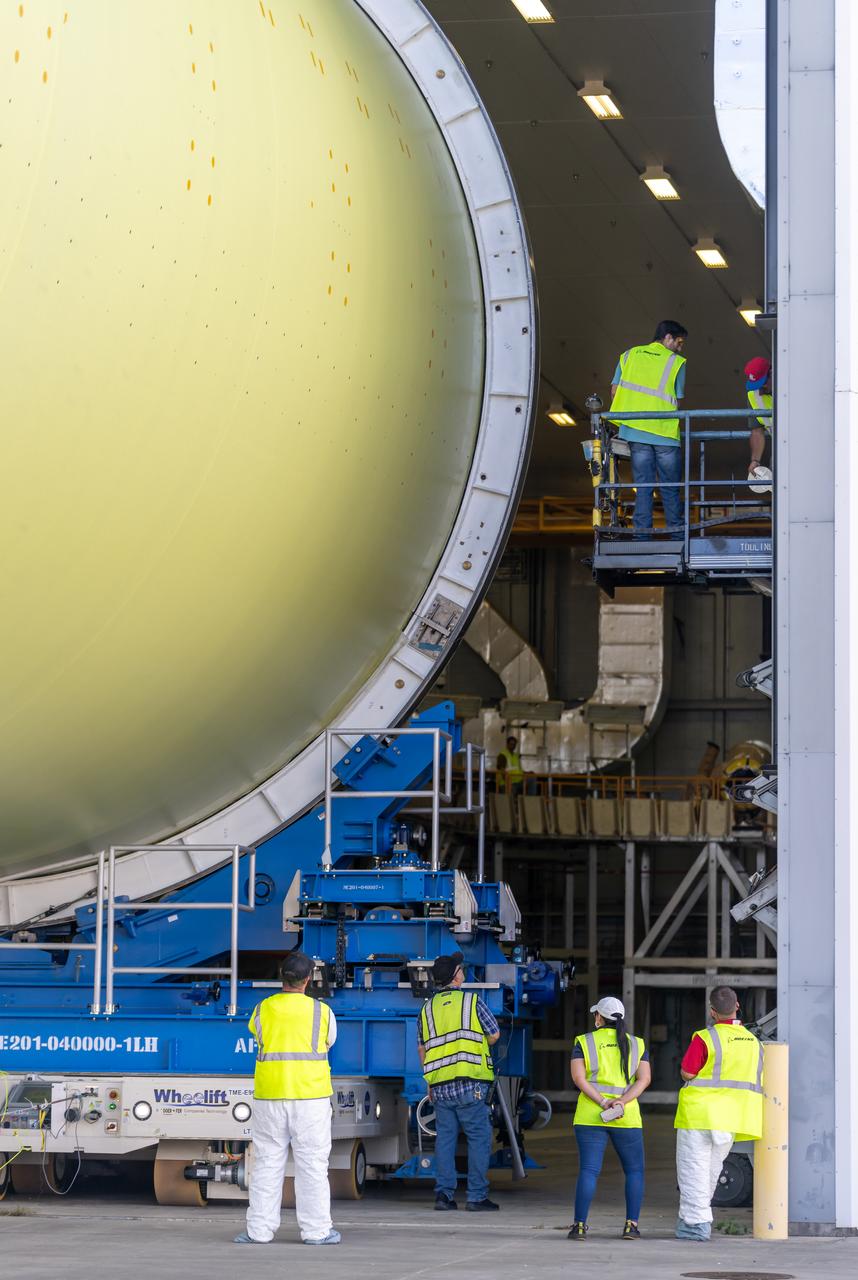

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.
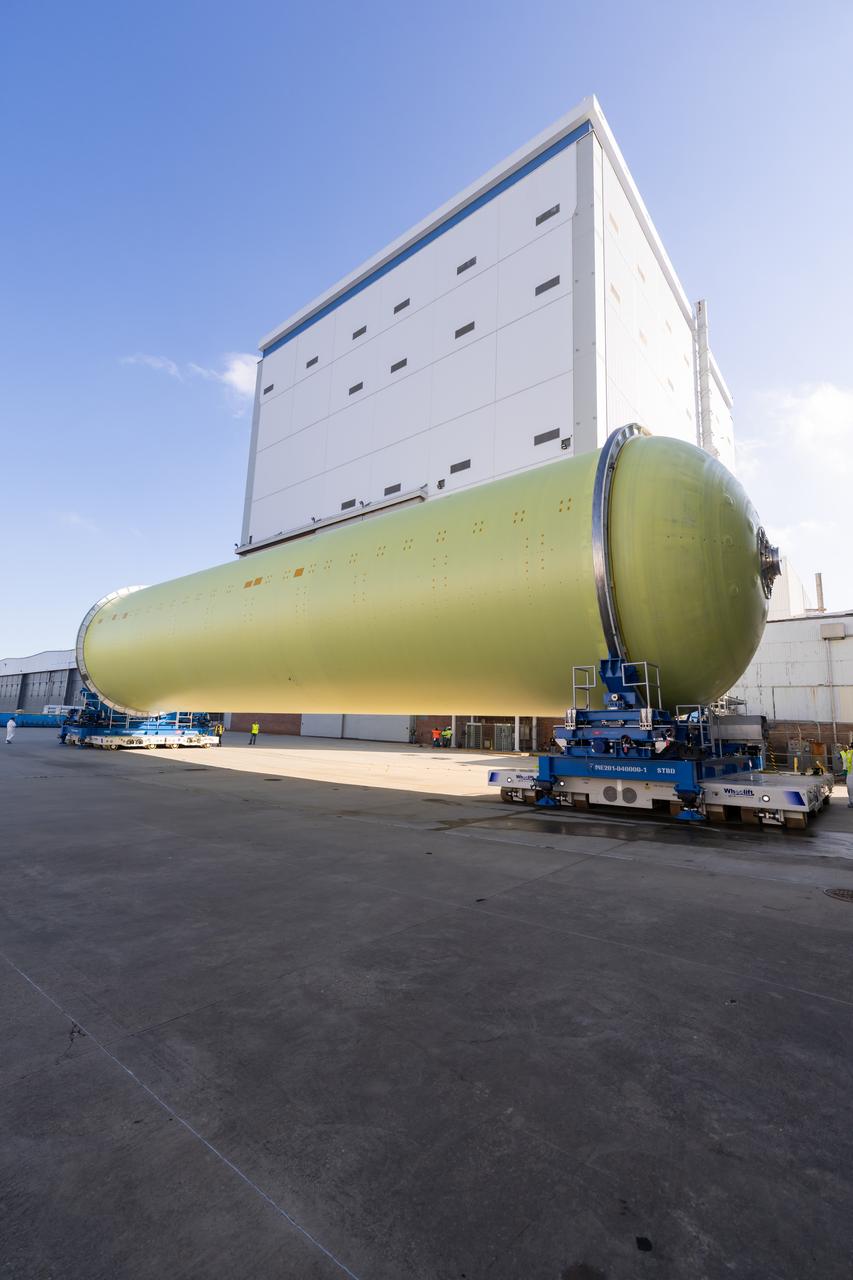

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.
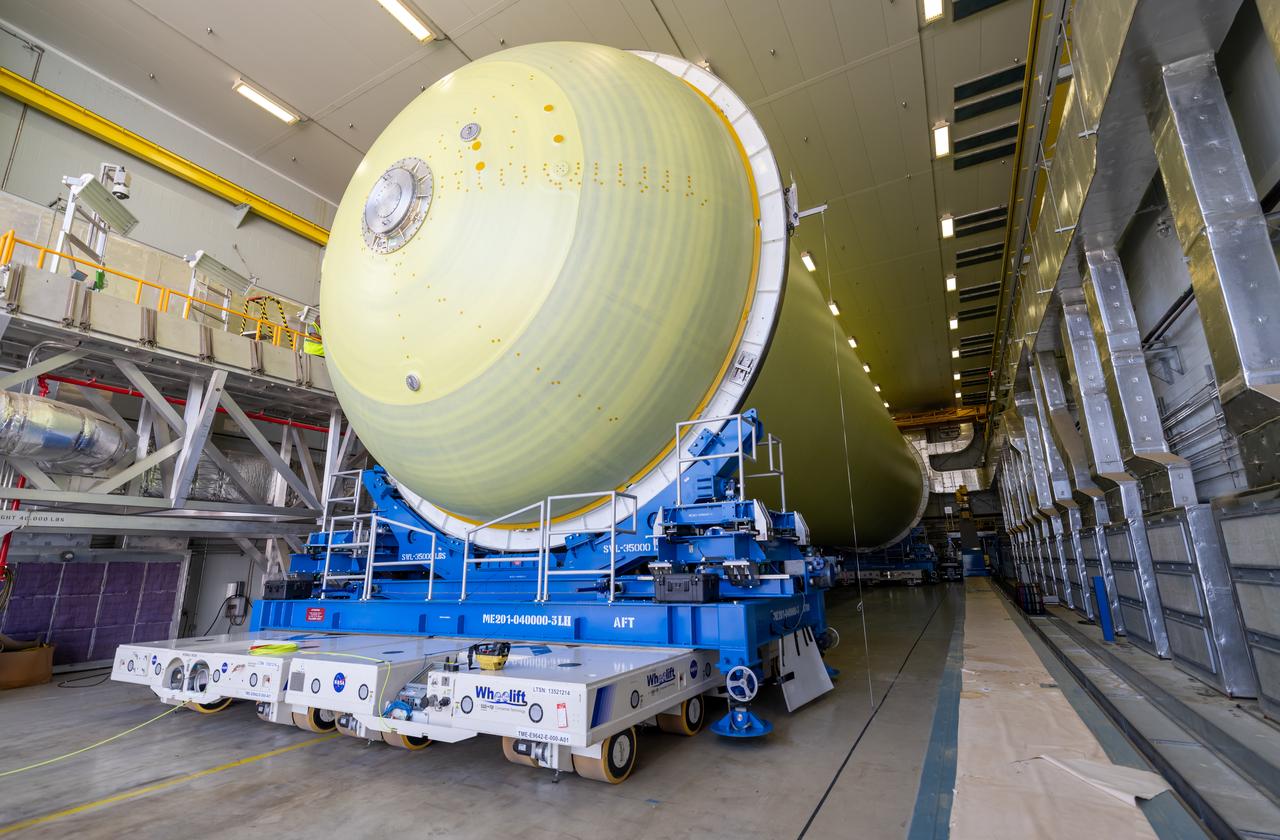

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.
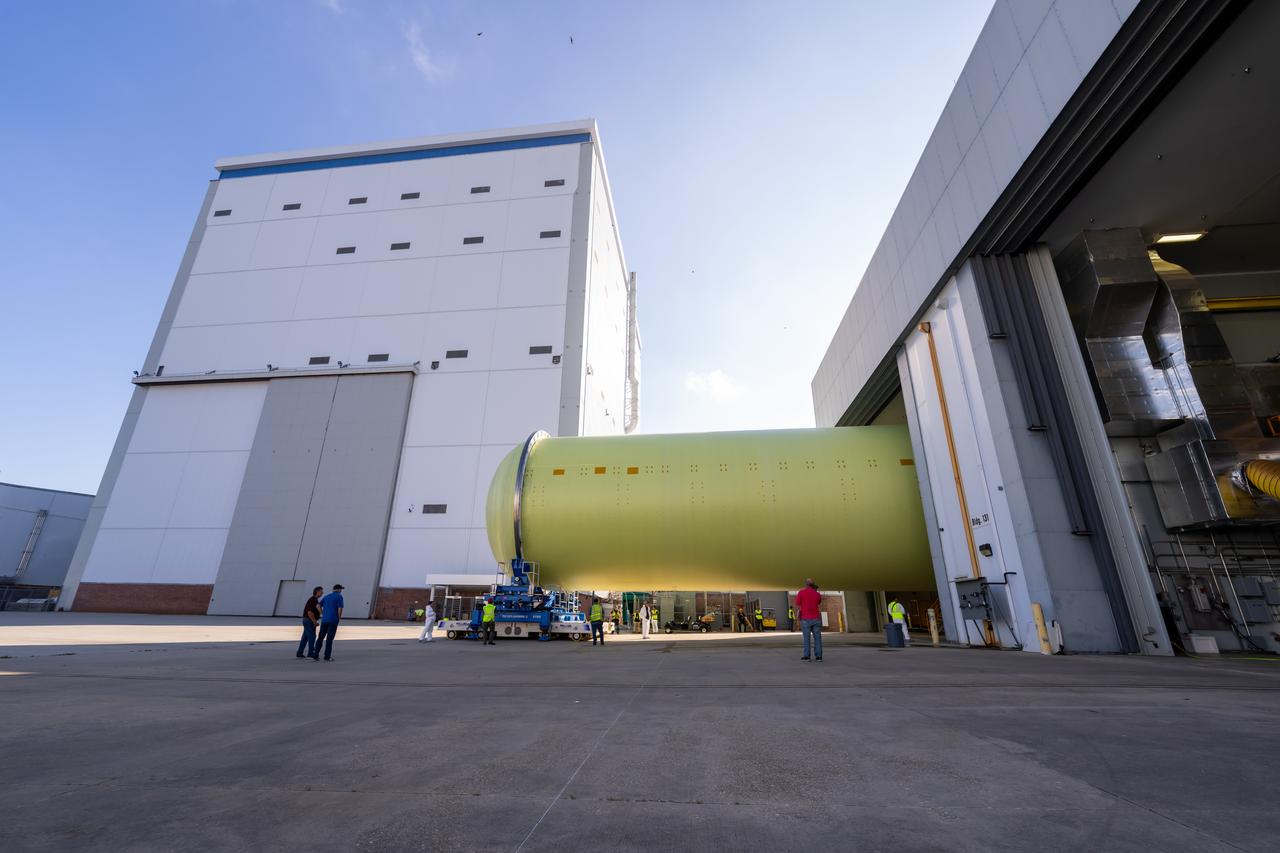

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.
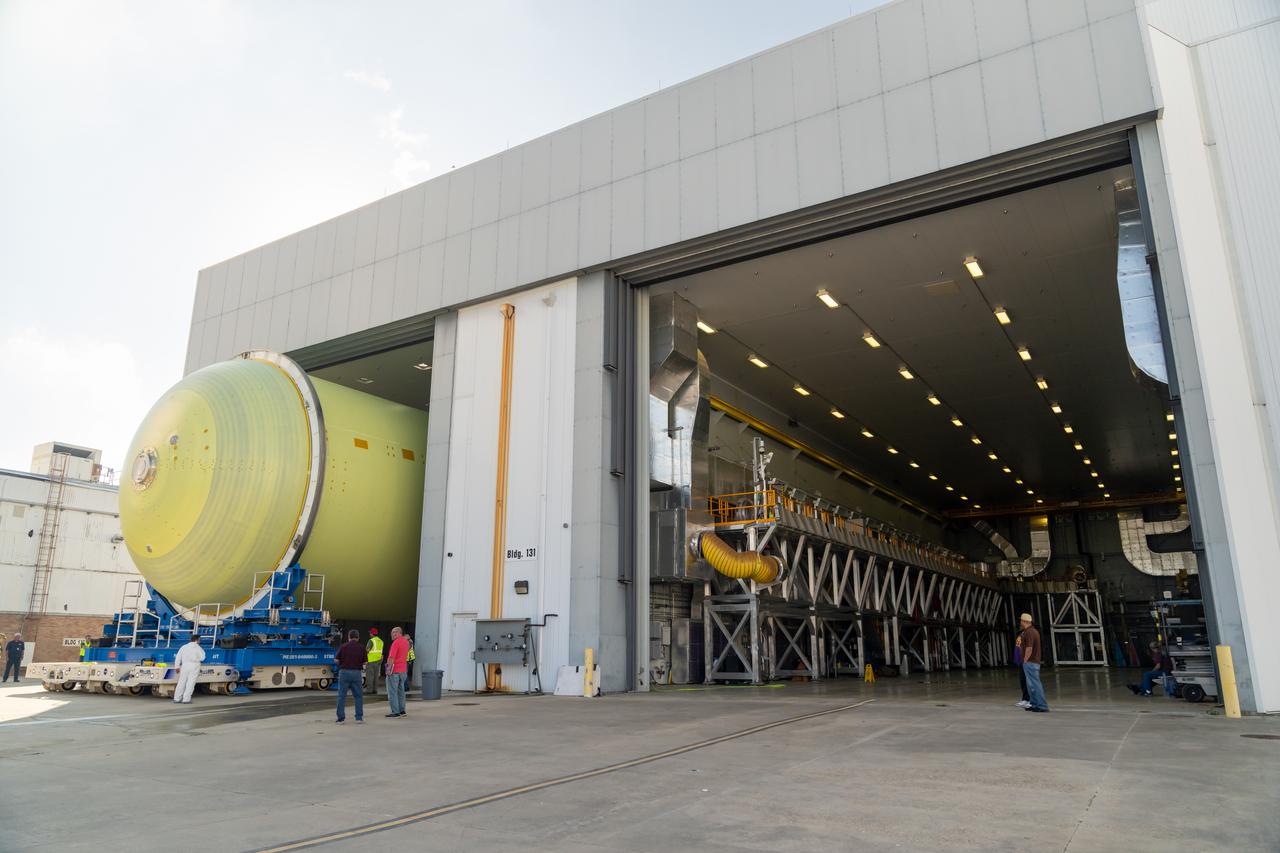

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.
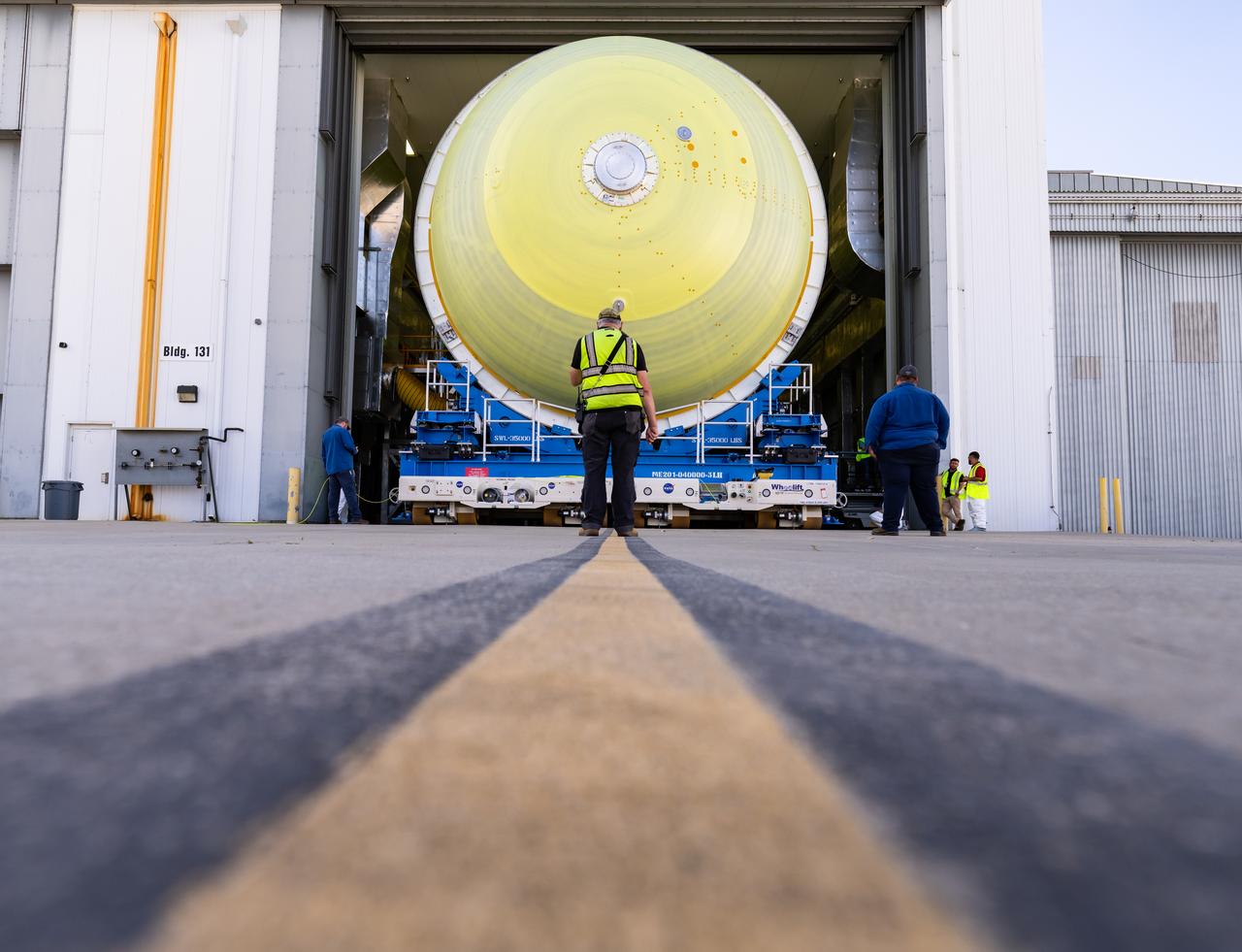

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.
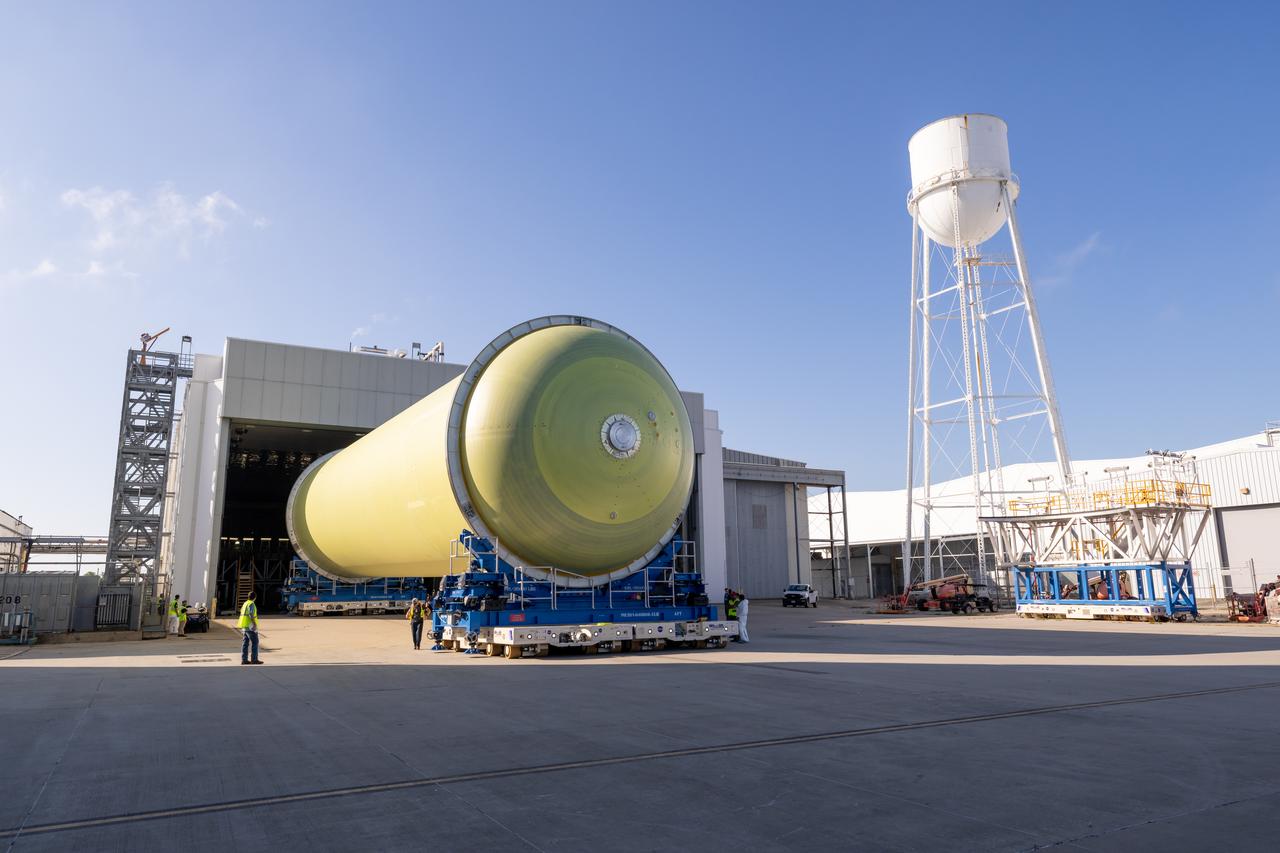

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.
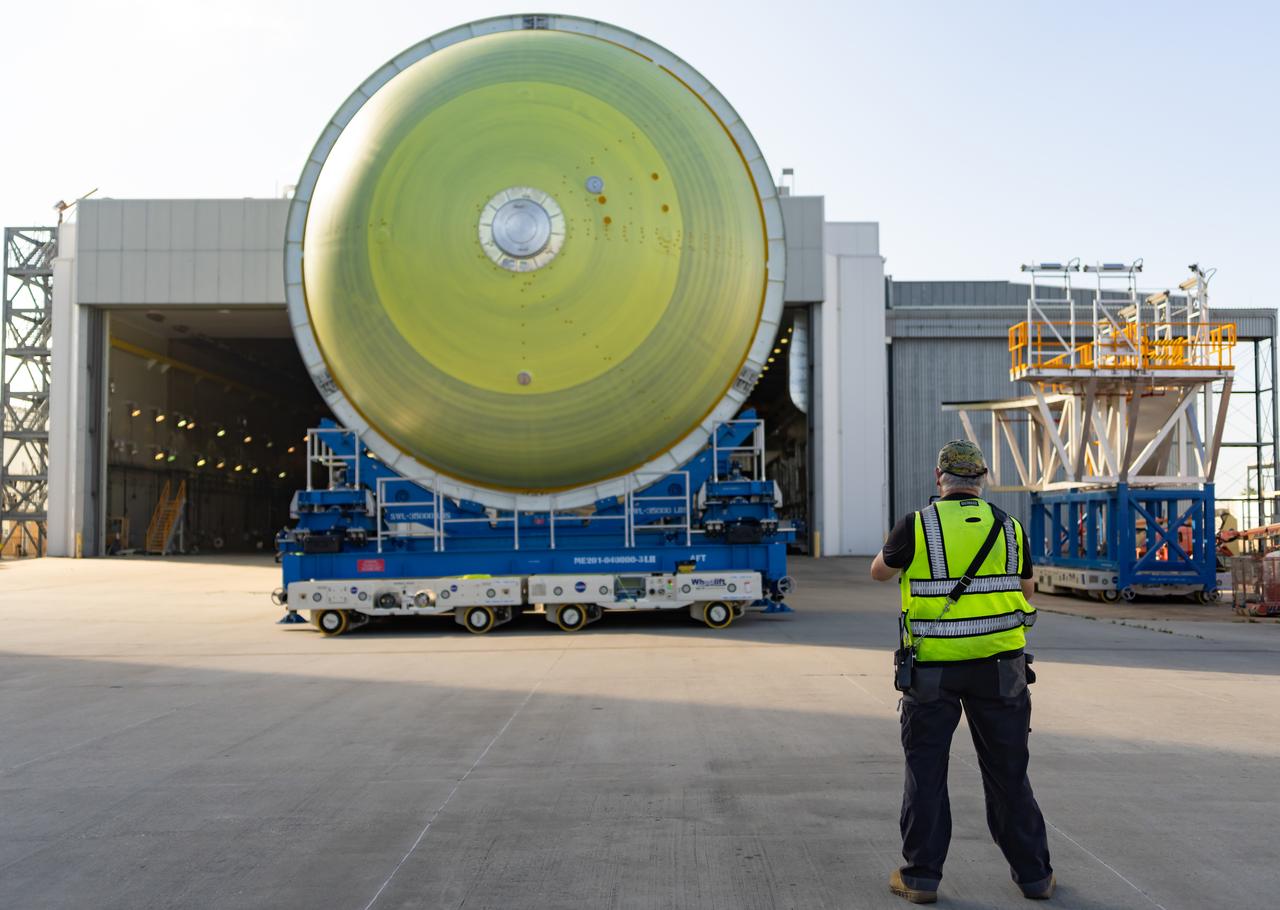

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.
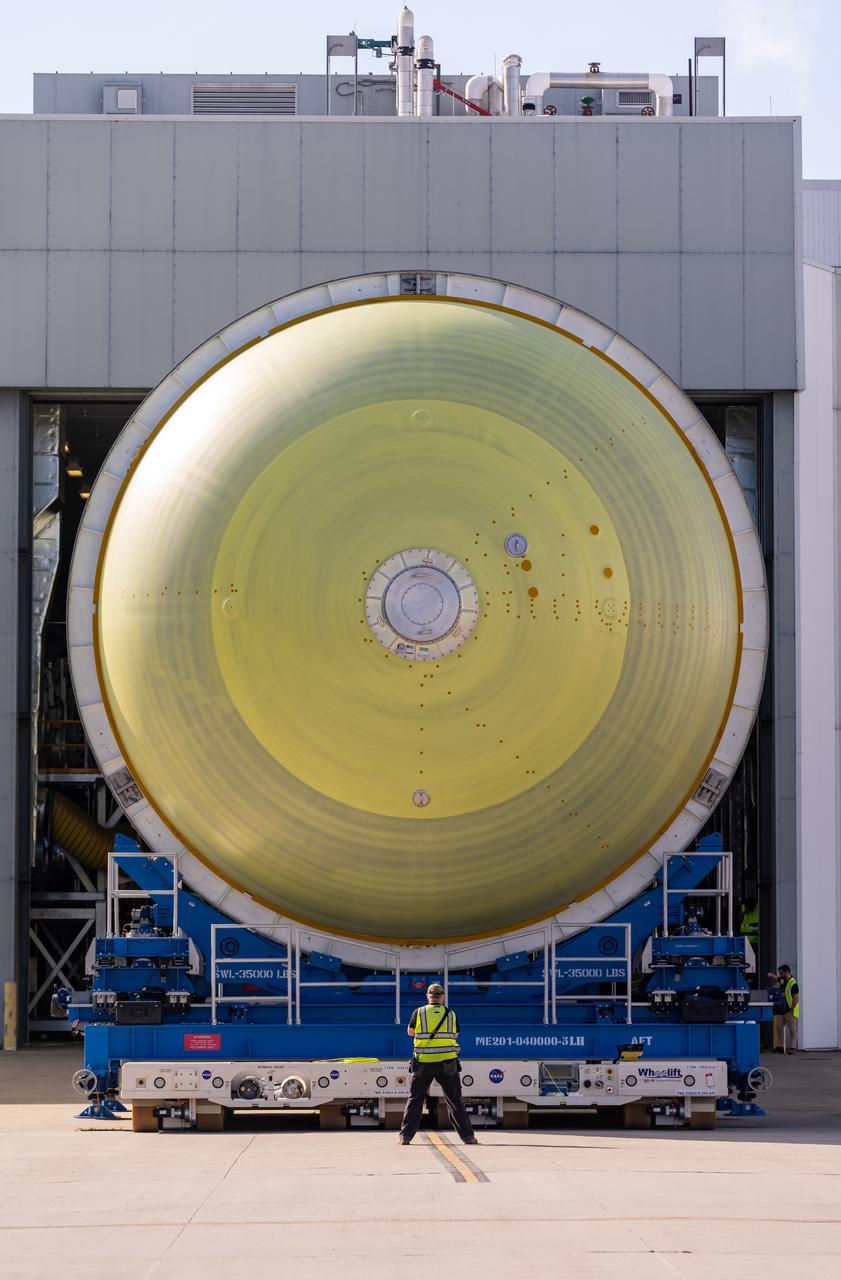

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.
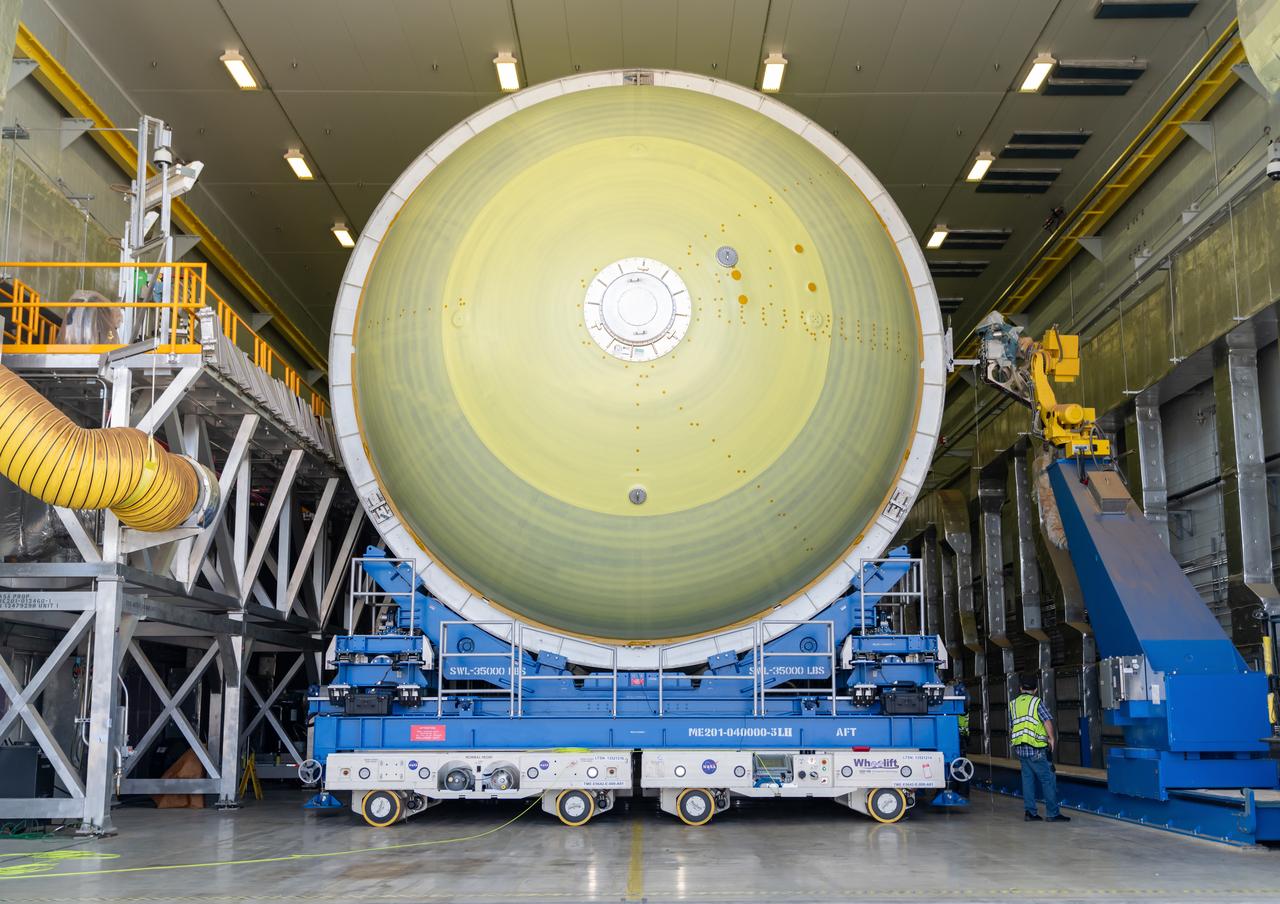

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.