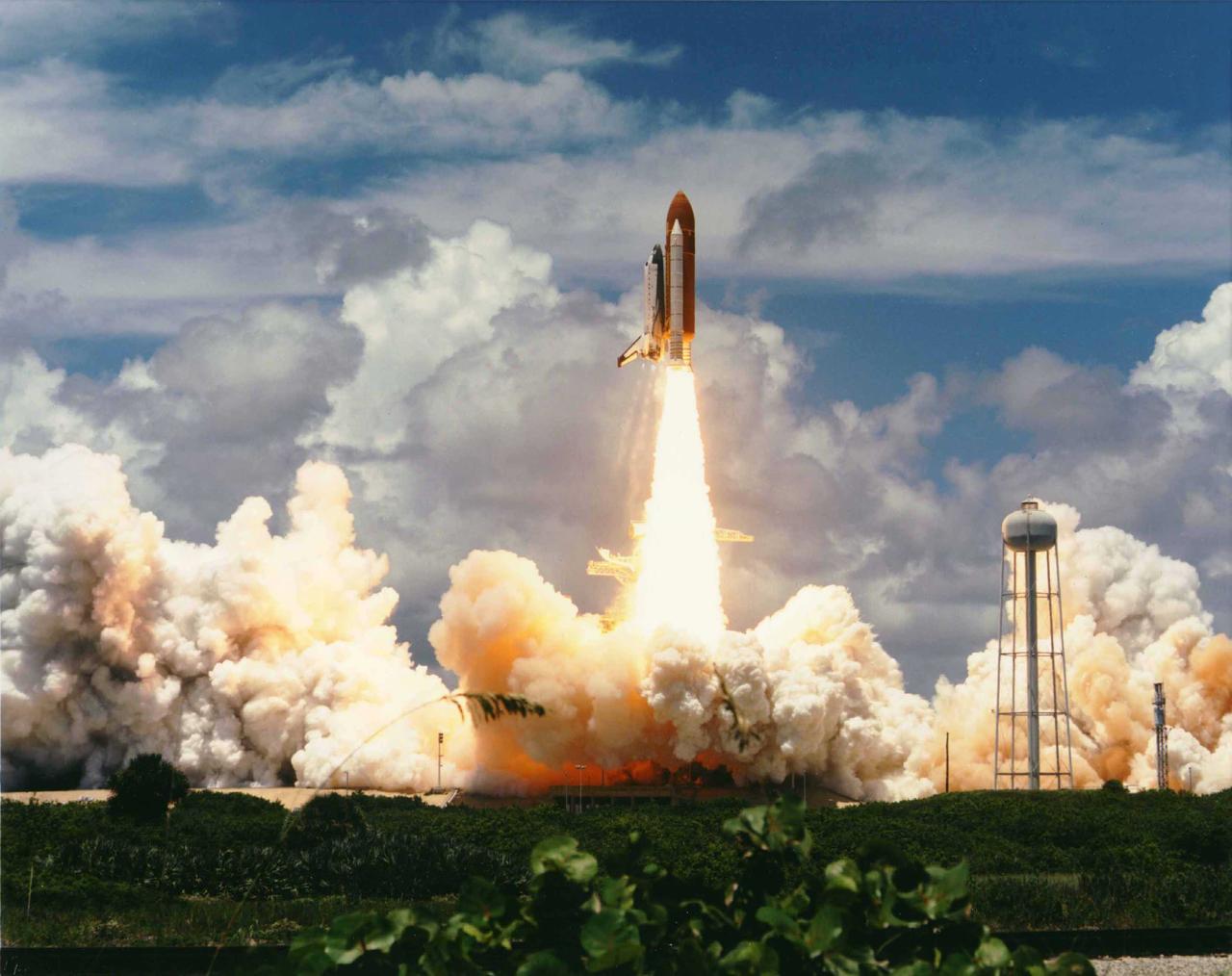

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The second International Microgravity Laboratory-2 (IML-2) is off to an ontime start as the Space Shuttle Columbia lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at 12:43:00 p.m. EDT. On board are a crew of seven and more than 80 investigations developed by more than 200 scientists from 13 countries. The IML-2 complement includes materials science, bioprocessing, space and radiation biology, and human physiology experiments that will be carried out over the course of the 14-day flight. The commander of Space Shuttle Mission STS-65 is Robert D. Cabana. James D. Halsell Jr. is the pilot; the payload commander is Richard J. Hieb; the three mission specialists are Carl E. Walz, Leroy Chiao and Donald A. Thomas. Dr. Chiaki Mukai, representing NASDA, the National Space Development Agency of Japan, is the payload specialist. Mukai becomes the first Japanese woman to fly into space.

The primary payload for Space Shuttle Mission STS-42, launched January 22, 1992, was the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), a pressurized manned Spacelab module. The goal of IML-1 was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. Around-the-clock research was performed on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and effects of microgravity on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Materials processing experiments were also conducted, including crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury iodide and a virus. More than 200 scientists from 16 countries participated in the investigations. This is the logo or emblem that was designed to represent the IML-1 payload.
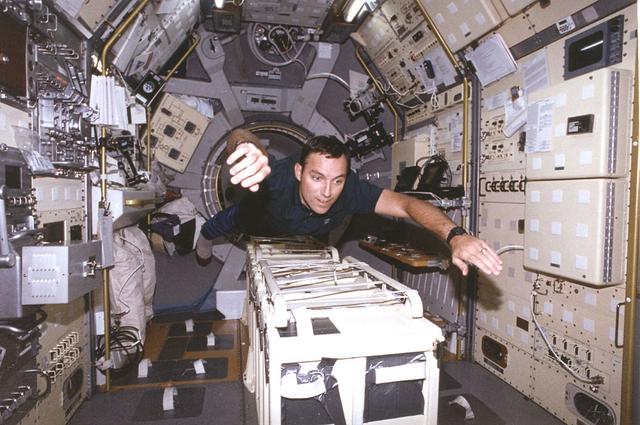

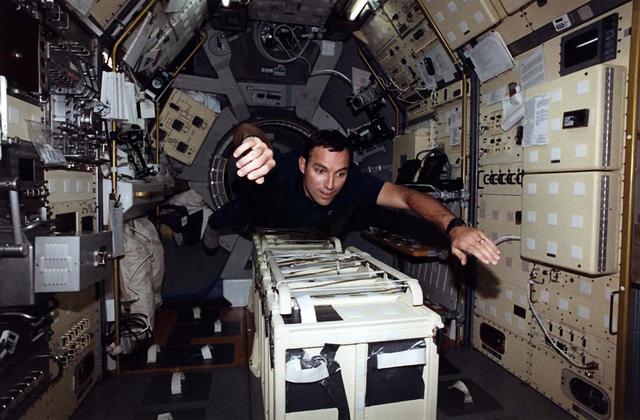
Astronaut Carl E. Walz, mission specialist, flies through the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) science module, STS-65 mission. IML was dedicated to study fundamental materials and life sciences in a microgravity environment inside Spacelab, a laboratory carried aloft by the Shuttle. The mission explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. The IML program gave a team of scientists from around the world access to a unique environment, one that is free from most of Earth's gravity. Managed by the NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (SCA), the French National Center for Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DARA/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) participated in developing hardware and experiments for the IML missions. The missions were managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. The Orbiter Columbia was launched on July 8, 1994 for the IML-2 mission.
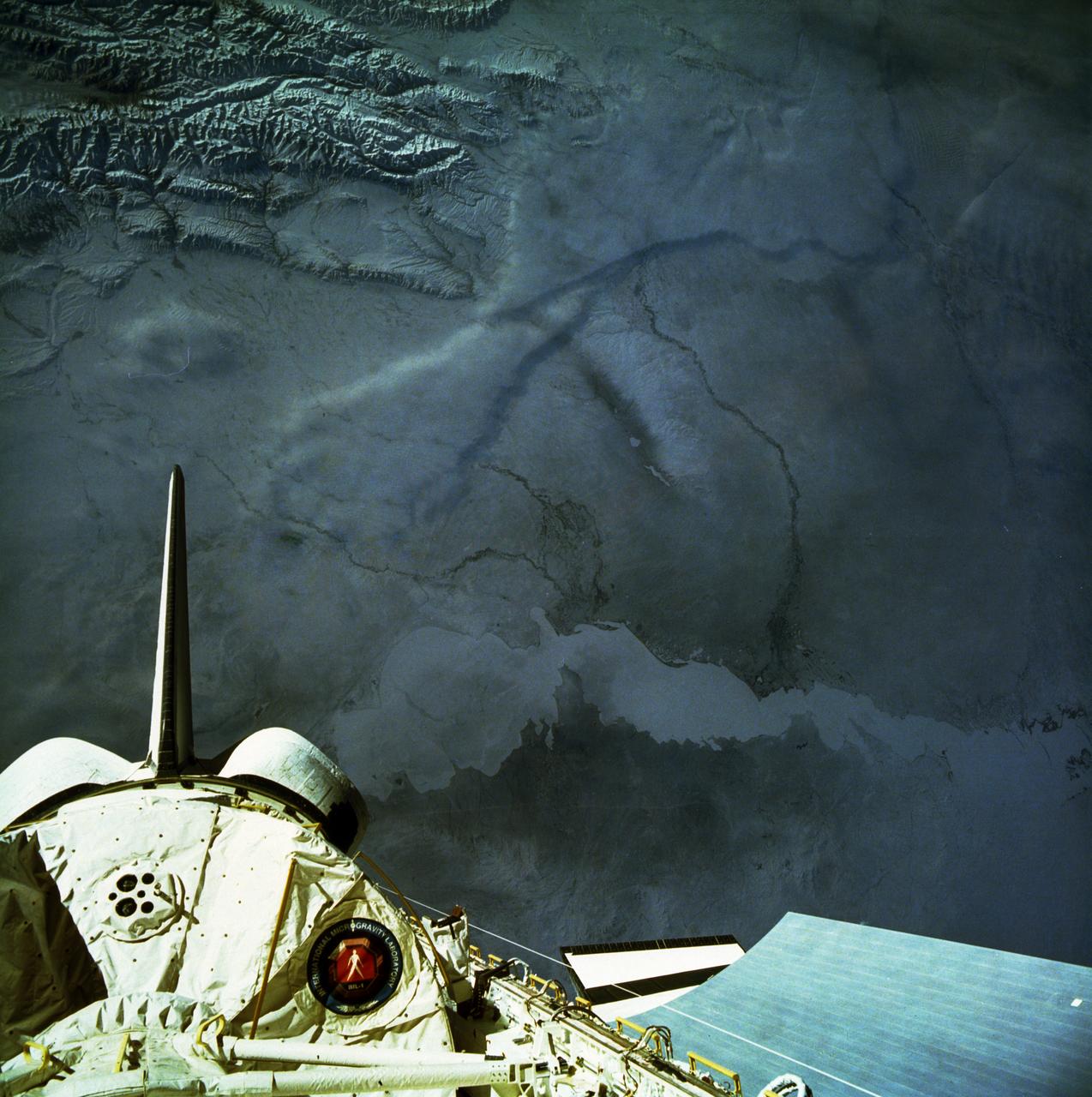

STS-42, Viewing earth with lots of snow, partial view of IML-1 (International Microgravity Laboratory) in cargo bay.
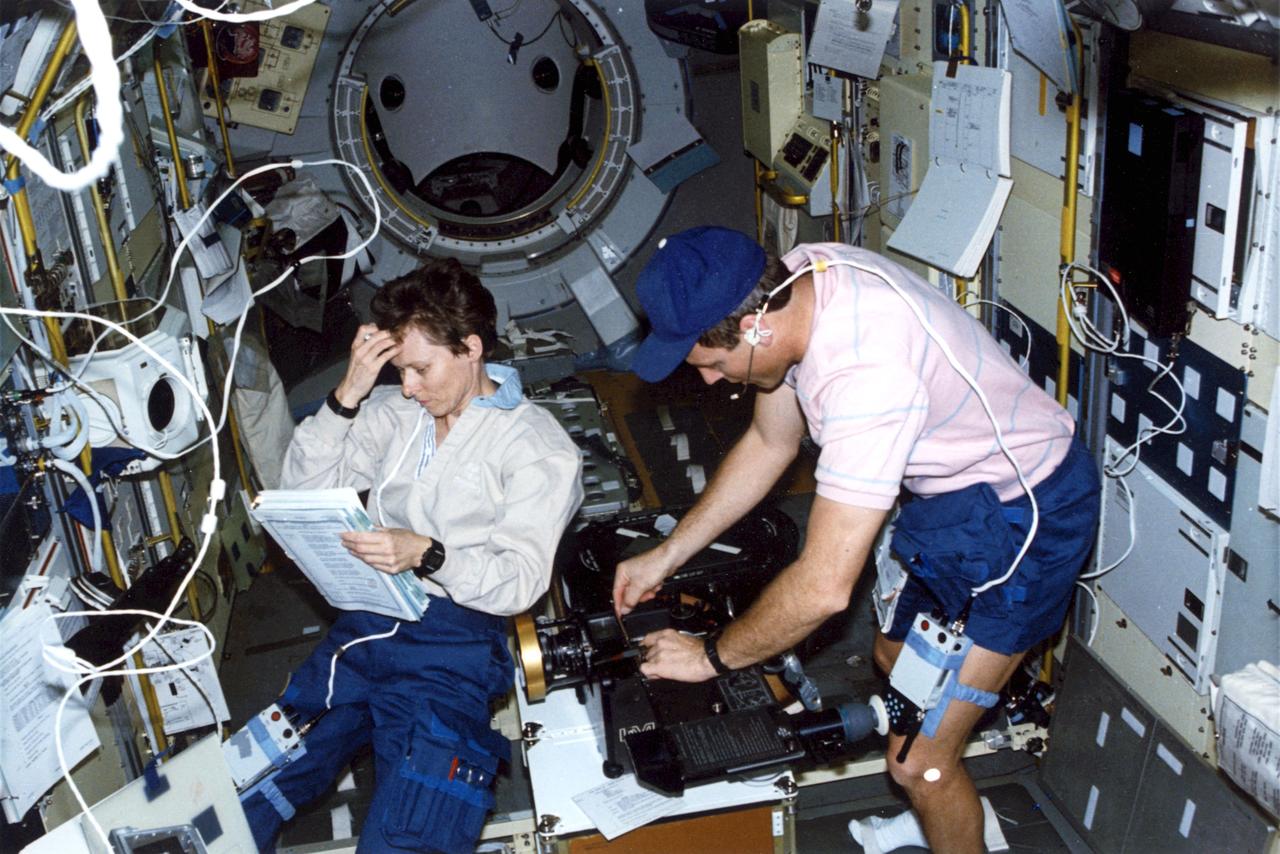

STS-42, Astronauts Steve Oswald and Canadian Roberta Bondar working in IML-1 (International Microgravity Laboratory).
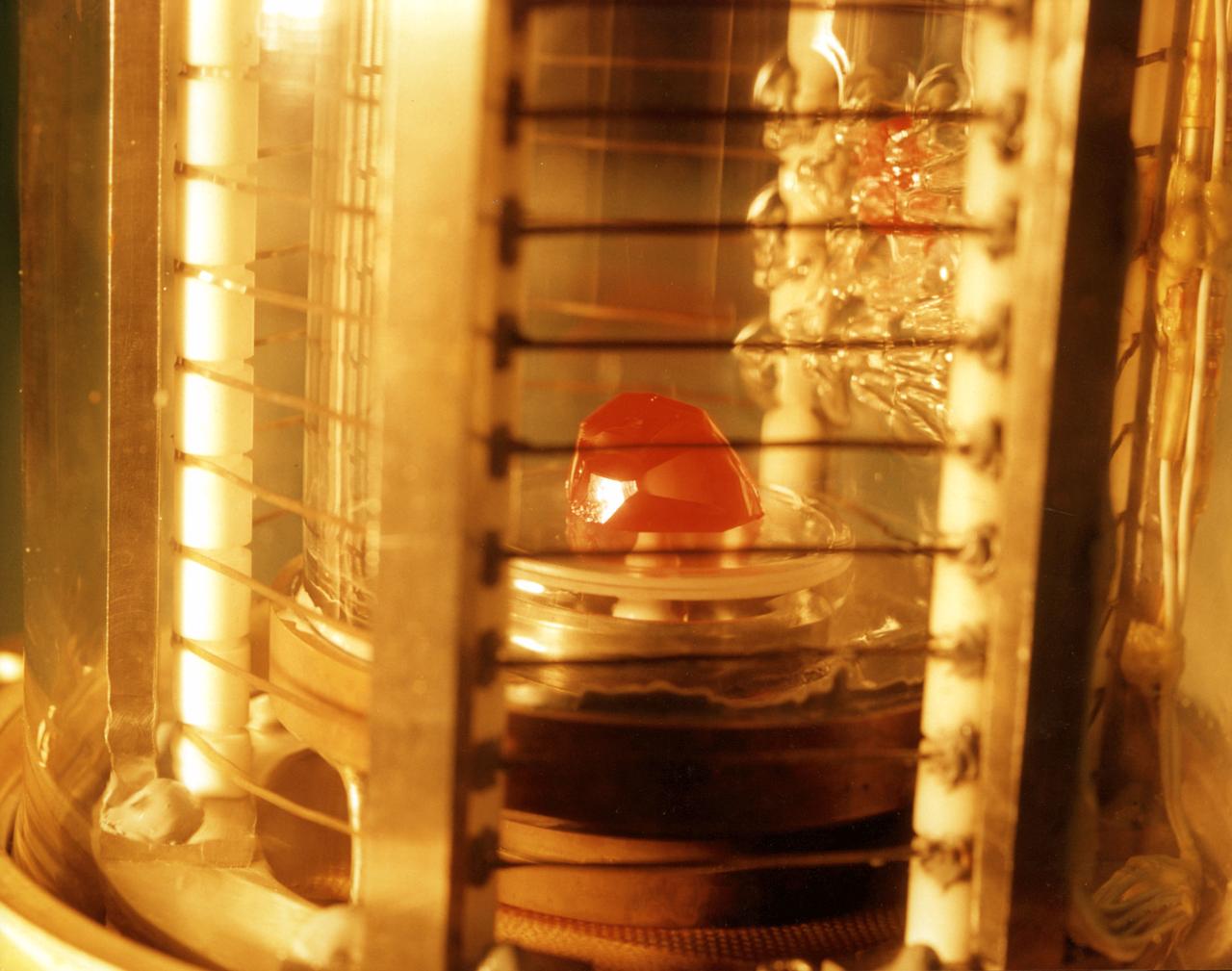

The image shows a test cell of Crystal Growth experiment inside the Vapor Crystal Growth System (VCGS) furnace aboard the STS-42, International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), mission. The goal of IML-1, a pressurized marned Spacelab module, was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. More than 200 scientists from 16 countires participated in the investigations.
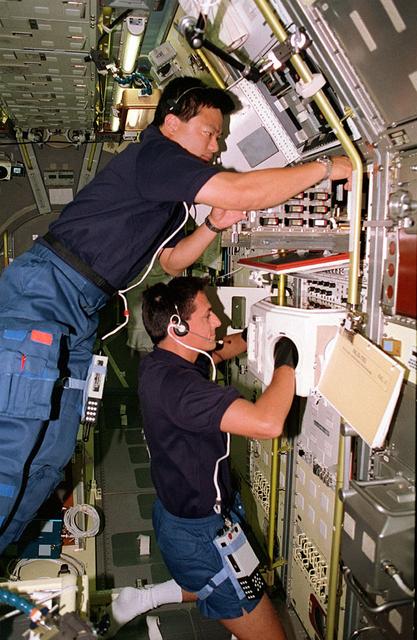

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-65) Mission Specialist Leroy Chiao (top) and Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas are seen at work in the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) spacelab science module. The two crewmembers are conducting experiments at the IML-2 Rack 5 Biorack (BR). Chiao places a sample in the BR incubator as Thomas handles another sample inside the BR glovebox. The glovebox is used to prepare samples for BR and slow rotating centrifuge microscope (NIZEMI) experiments.
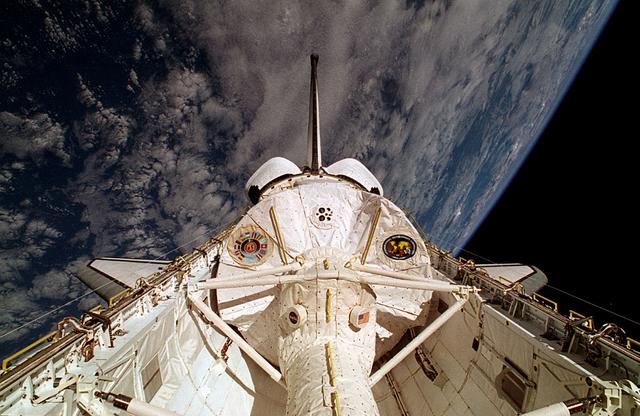

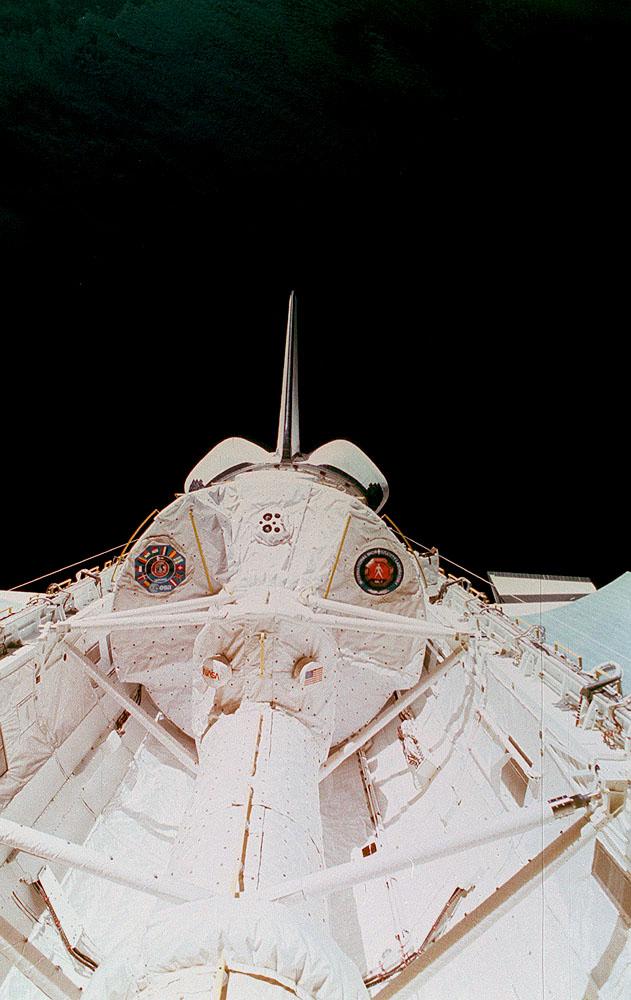
This is a Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-65) onboard photo of the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) in the cargo bay with Earth in the background. Mission objectives of IML-2 were to conduct science and technology investigations that required the low-gravity environment of space, with emphasis on experiments that studied the effects of microgravity on materials processes and living organisms. Materials science and life sciences are two of the most exciting areas of microgravity research because discoveries in these fields could greatly enhance the quality of life on Earth. If the structure of certain proteins can be determined by examining high-quality protein crystals grown in microgravity, advances can be made to improve the treatment of many human diseases. Electronic materials research in space may help us refine processes and make better products, such as computers, lasers, and other high-tech devices. The 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (SCA), the French National Center for Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DARA/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) participated in developing hardware and experiments for the IML missions. The missions were managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. The Orbiter Columbia was launched from the Kennedy Space Center on July 8, 1994 for the IML-2 mission.

Documentation of the AFE (Aero Flight Experiment) - IML (International Microgravity Laboratory) construction progress through the year 1988.

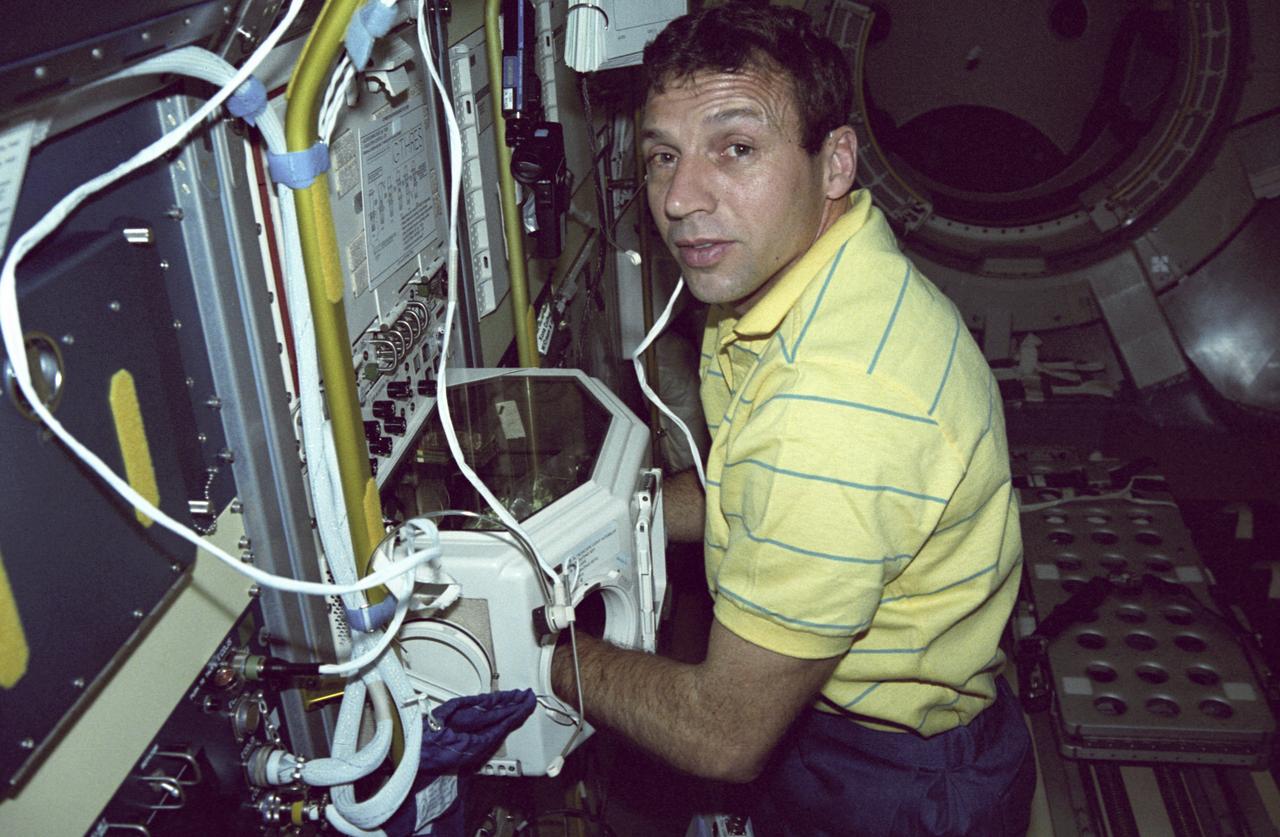
This is an onboard photo of space shuttle Atlantis (STS-66) astronaut Scott E. Parazynski, in the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML), performing a series of experiments devoted to material and life sciences studies using the Spacelab Long Module (SLM). STS-066 was launched on November 3, 1994.
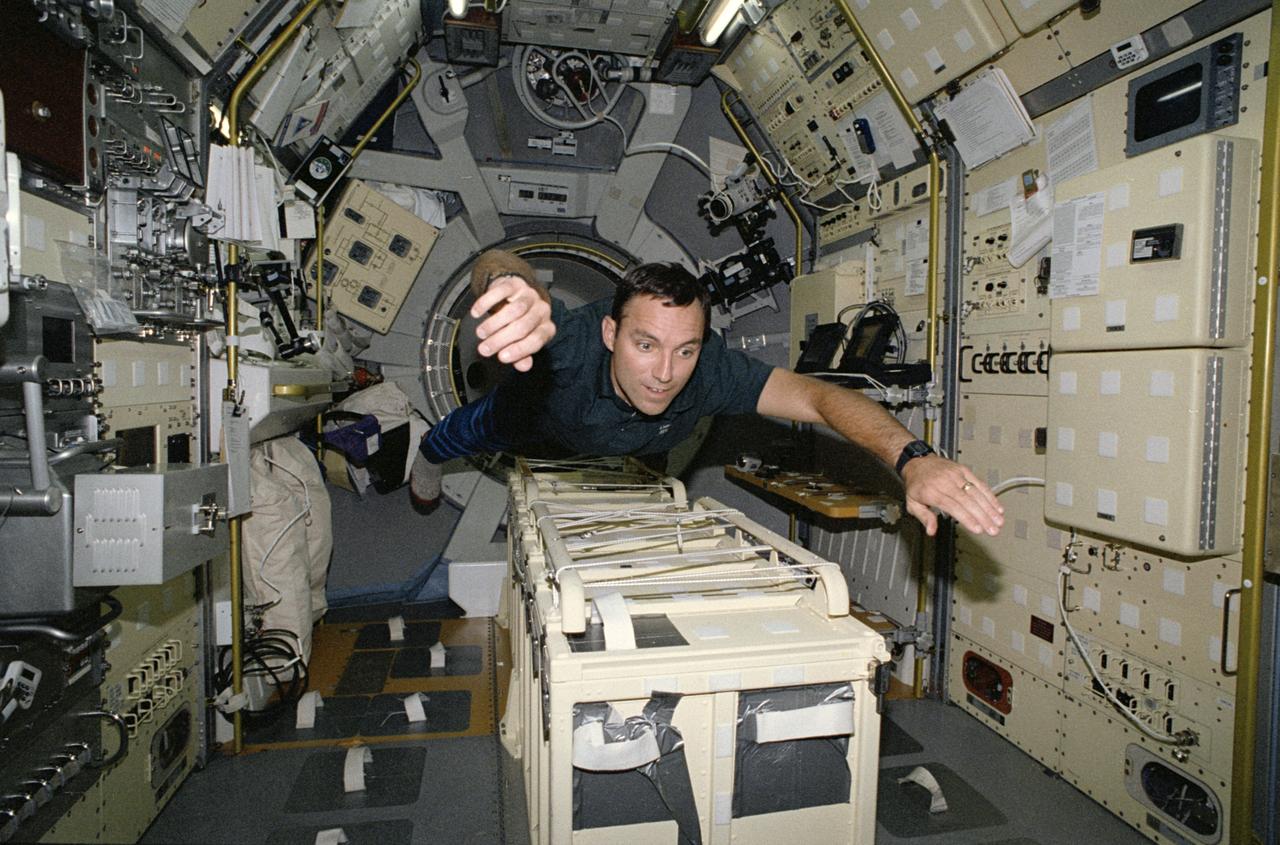

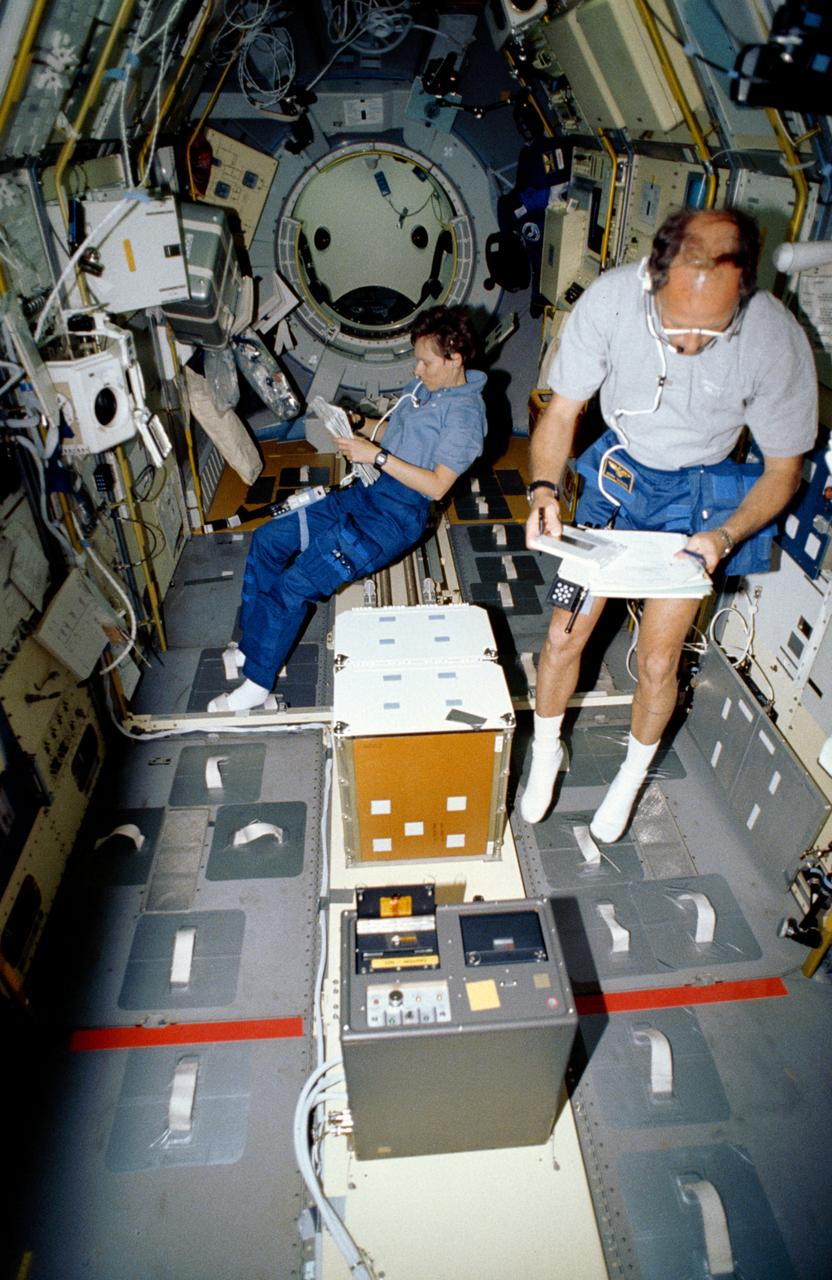
STS-65 Mission Specialist Carl E. Walz floats above center aisle equipment in the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) spacelab science module. Walz has just entered the IML-2 module via the spacelab tunnel (note hatch opening behind him). The tunnel connects the IML-2 module with Columbia's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102's, crew compartment. Walz along with five other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist spent more than two weeks in Earth orbit conducting IML-2 experiments. This photo was among the first released by NASA following IML-2.
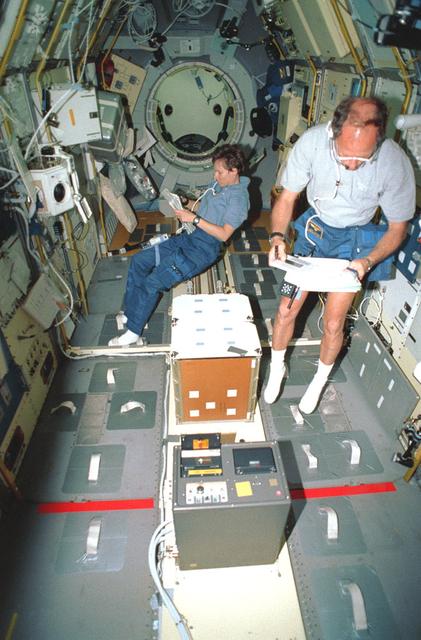

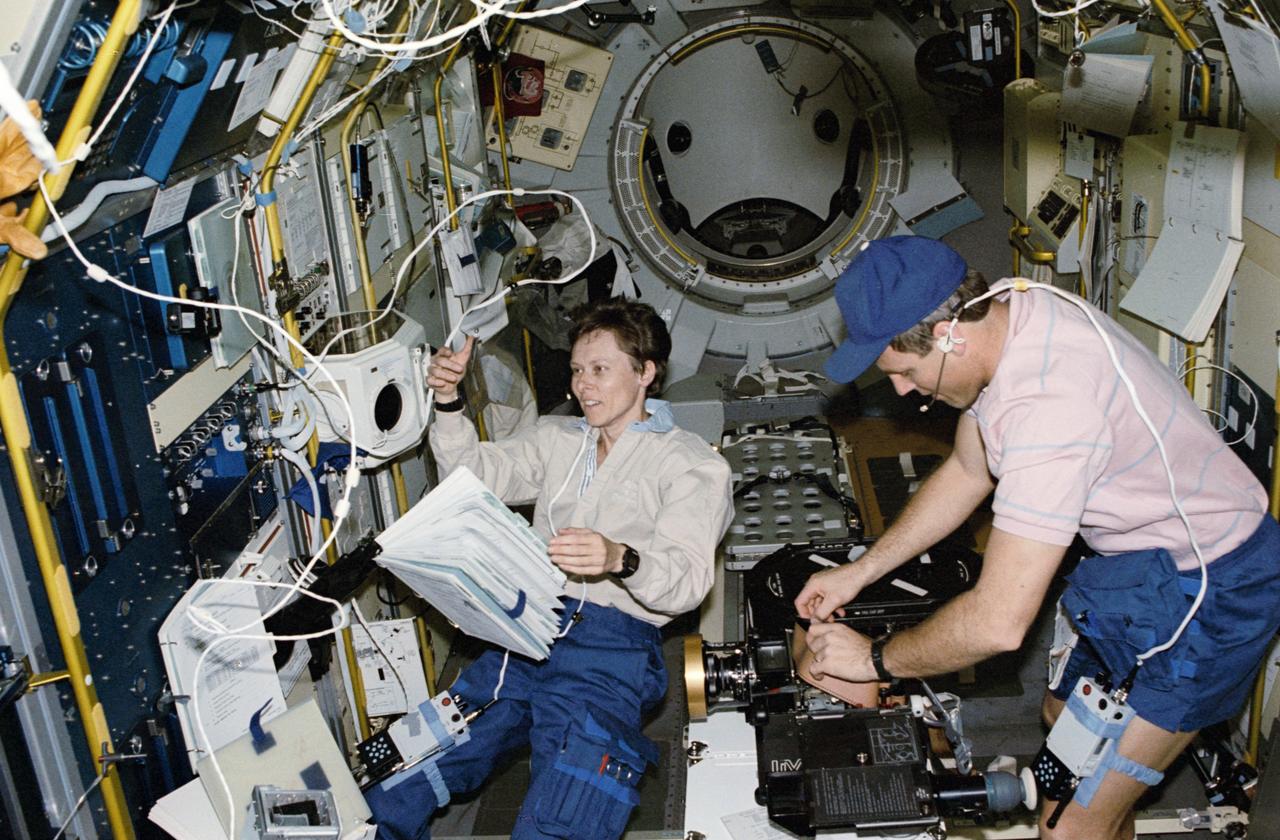
Onboard Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-42) Astronaut Norman E. Thagard, payload commander, and Canadian payload specialist Roberta L. Bondar are busily engaged with experiments in the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) science module. Bondar reads a checklist near the Biorack while Thagard performs a VCR tape change-out. The two, along with four other NASA astronauts and a second IML-1 payload specialist spent more than eight days conducting experiments in Earth orbit. Part of the Space Acceleration Measurement System is in center foreground.

In this photograph, astronaut David Hilmers conducts a life science experiment by using the Biorack Glovebox (GBX) during the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) mission. The Biorack was a large multipurpose facility designed for studying the effects of microgravity and cosmic radiation on numerous small life forms such as cells, tissues, small organisms, and plants. Located at the Biorack, the GBX was an enclosed environment that protected samples from contamination and prevented liquid from escaping. Crewmembers handled the specimens with their hands inside gloves that extended into the sealed work area. A microscope and video camera mounted on the GBX door were used to observe and document experiments. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research and was launched aboard the Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42) on January 22, 1992.
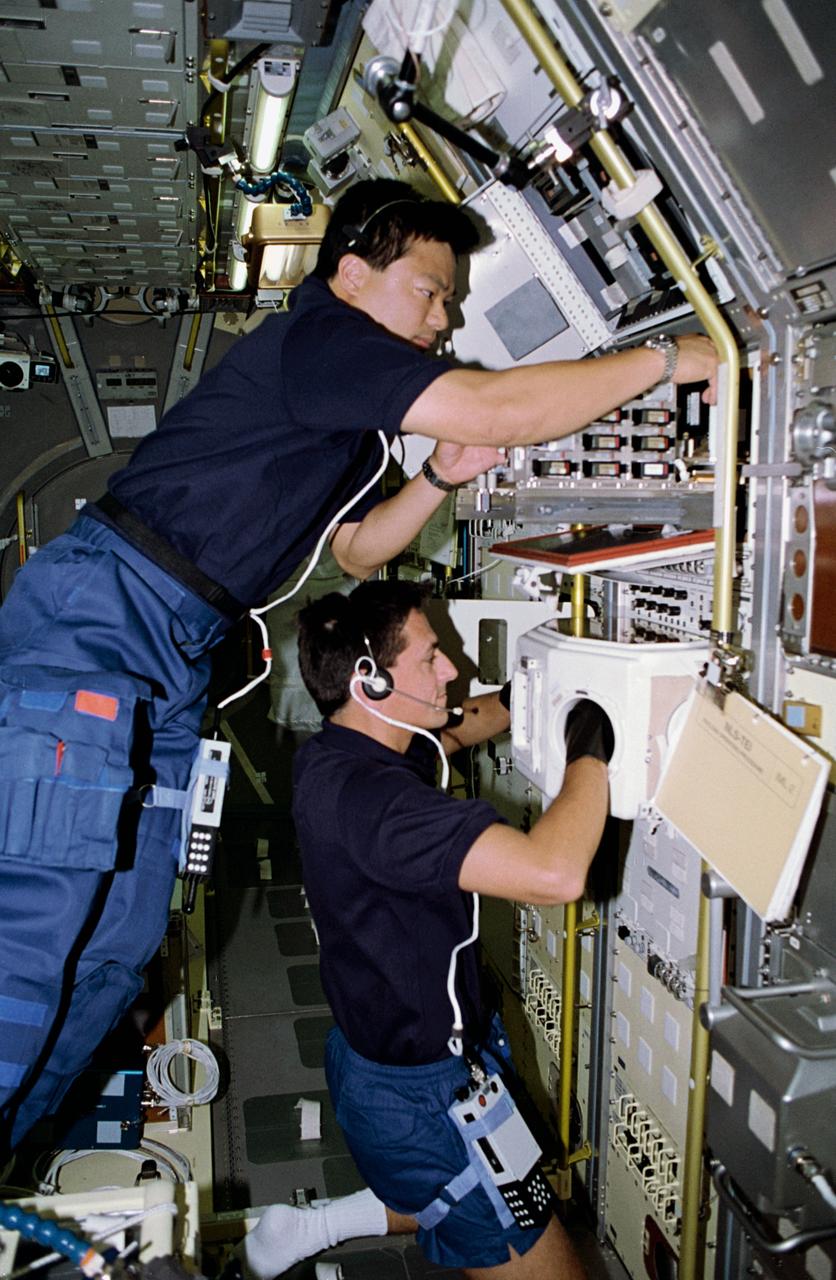

STS-65 Mission Specialist (MS) Leroy Chiao (top) and MS Donald A. Thomas are seen at work in the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) spacelab science module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102. The two crewmembers are conducting experiments at the IML-2 Rack 5 Biorack (BR). Chiao places a sample in the BR incubator as Thomas handles another sample inside the BR glovebox. The glovebox is used to prepare samples for BR and slow rotating centrifuge microscope (NIZEMI) experiments.

STS042-11-016 (30 Jan 1992) --- Astronaut Norman E. Thagard, STS-42 missions specialist and payload commander, and payload specialist Roberta L. Bondar are busily engaged with experiments in the International Microgravity Laboratory 1 (IML-1) Spacelab module. Bondar reads a checklist near the Rack 5 Biorack and glovebox while Thagard performs a VCR tape change-out. The Space Acceleration Measurement System (SAMS) (foreground) and shuttle middeck lockers are secured in IML-1's center aisle. In the background the open hatch and Spacelab tunnel interior are visible. Crewmembers enter and exit the IML-1 module via the Spacelab tunnel which connects to Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, airlock.

S91-52649 (Nov 1991) ---- Astronaut Ulf Merbold, PhD, European Space Agency (ESA) Payload Specialist for STS-42, International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1).
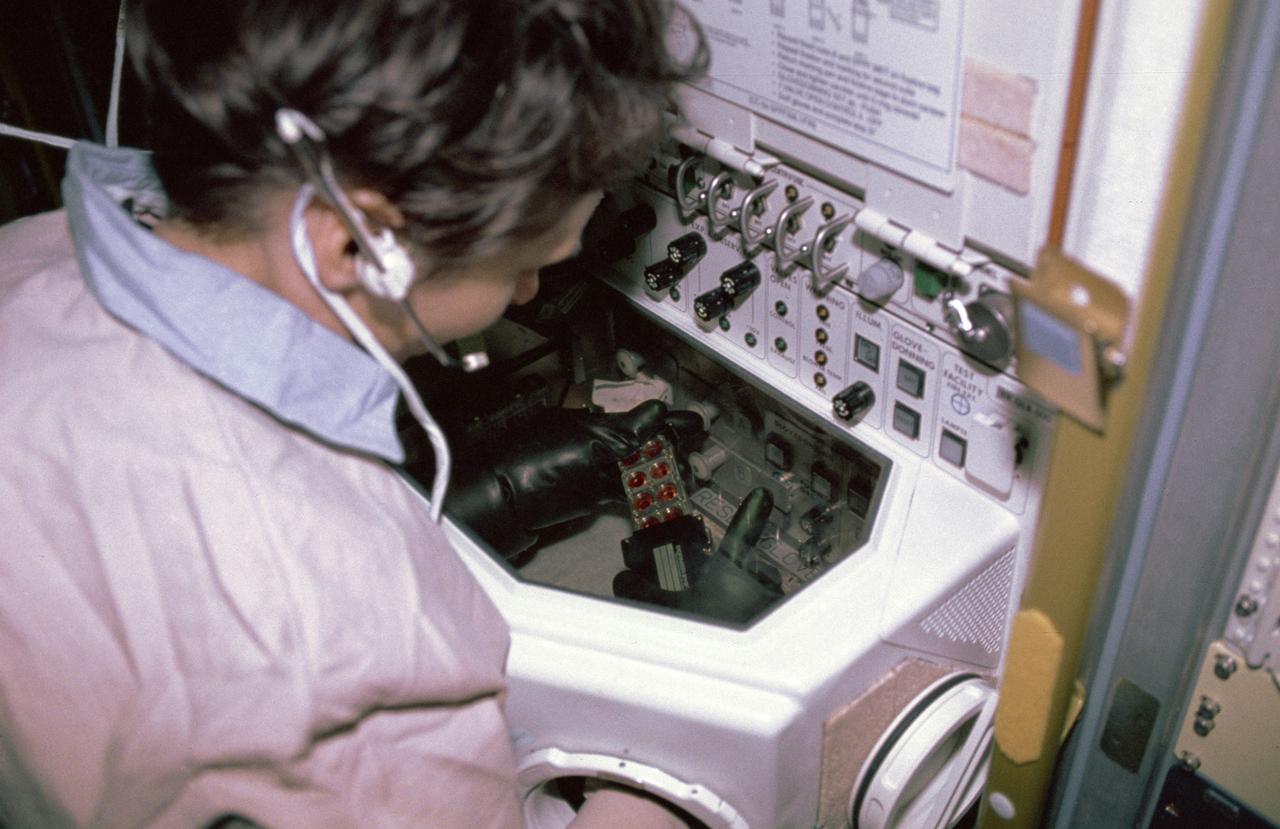

In this photograph, astronaut Roberta Bondar conducts a life science experiment by using the Biorack Glovebox (GBX) during the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) mission. The Biorack was a large multipurpose facility designed for studying the effects of microgravity and cosmic radiation on numerous small life forms such as cells, tissues, small organisms, and plants. Located at the Biorack, the GBX was an enclosed environment that protected samples from contamination and prevented liquid from escaping. Crewmembers handled the specimens with their hands inside gloves that extended into the sealed work area. A microscope and video camera mounted on the GBX door were used to observe and document experiments. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research and was launched aboard the Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42) on January 22, 1992.
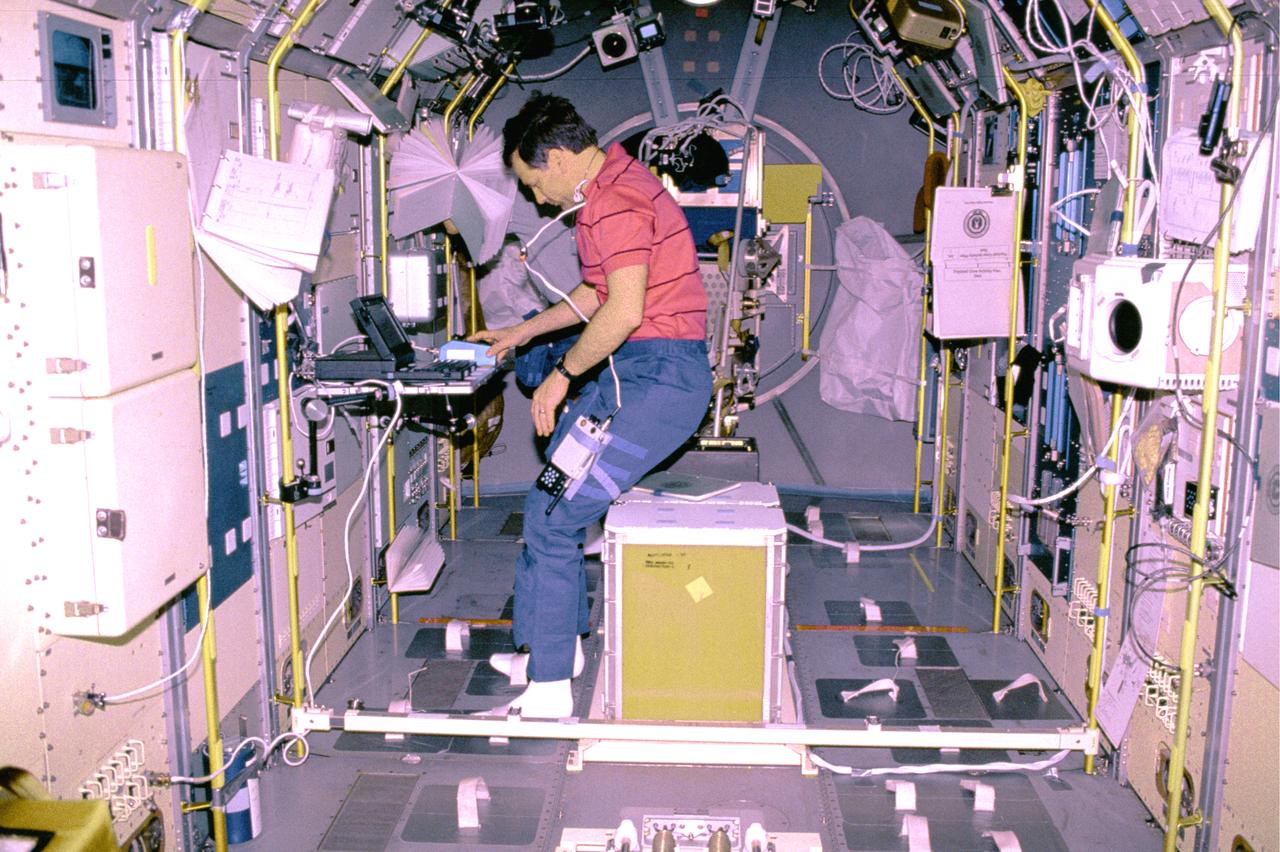

The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research with the international partners. The participating space agencies included: NASA, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), the French National Center of Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DAR/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Dedicated to the study of life and materials sciences in microgravity, the IML missions explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. Both life and materials sciences benefited from the extended periods of microgravity available inside the Spacelab science module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter. In this photograph, Commander Ronald J. Grabe works with the Mental Workload and Performance Evaluation Experiment (MWPE) in the IML-1 module. This experiment was designed as a result of difficulty experienced by crewmembers working at a computer station on a previous Space Shuttle mission. The problem was due to the workstation's design being based on Earthbound conditions with the operator in a typical one-G standing position. Information gained from this experiment was used to design workstations for future Spacelab missions and the International Space Station. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, IML-1 was launched on January 22, 1992 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42 mission).

STS042-201-009 (22-30 Jan 1992) --- Canadian Roberta L. Bondar, payload specialist representing the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), works at the International Microgravity Laboratory's (IML-1) biorack while astronaut Stephen S. Oswald, pilot, changes a film magazine on the IMAX camera. The two were joined by five fellow crew members for eight-days of scientific research aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery in Earth-orbit. Most of their on-duty time was spent in this IML-1 Science Module, positioned in the cargo bay and attached via a tunnel to Discovery's airlock.
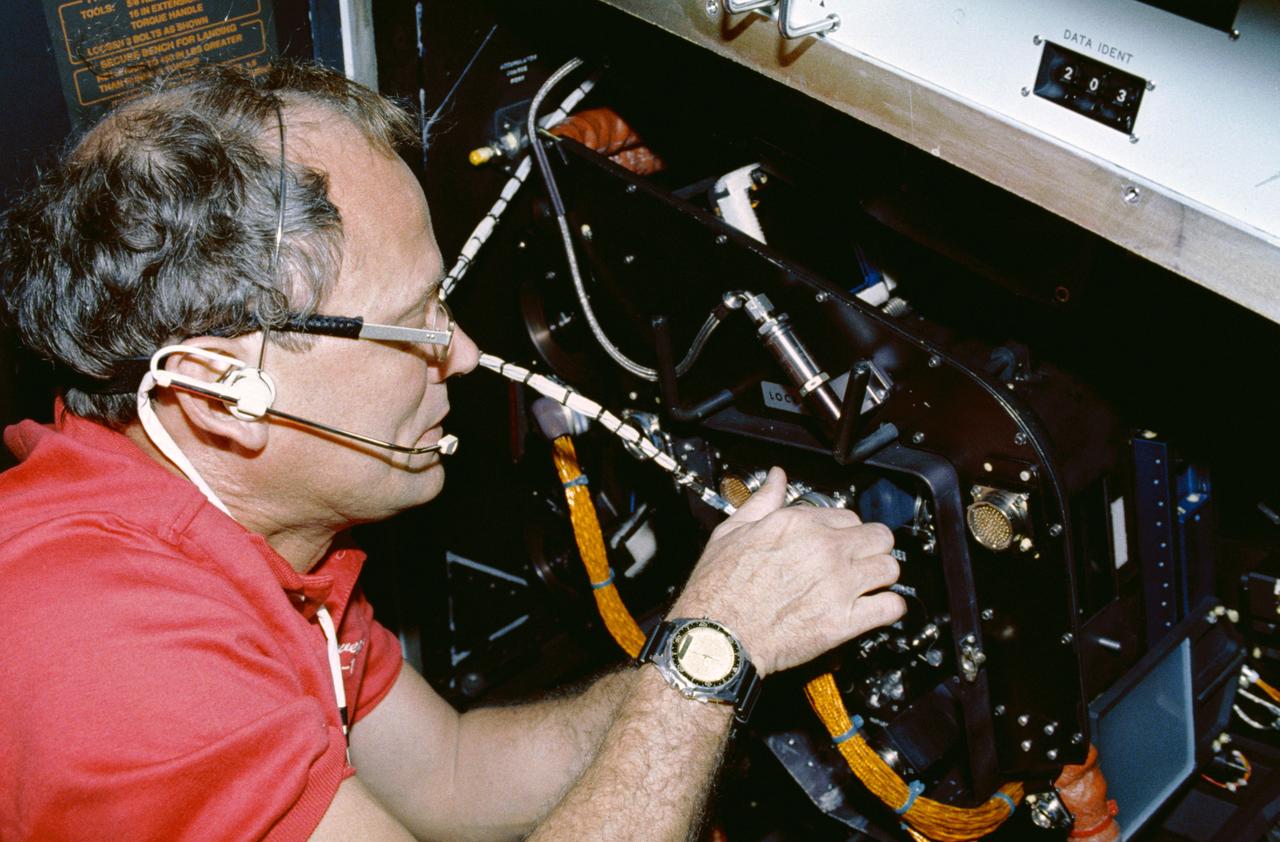

STS042-05-006 (22-30 Jan 1992) --- Astronaut Norman E. Thagard, payload commander, performs the Fluids Experiment System (FES) in the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) science module. The FES is a NASA-developed facility that produces optical images of fluid flows during the processing of materials in space. The system's sophisticated optics consist of a laser to make holograms of samples and a video camera to record images of flows in and around samples. Thagard was joined by six fellow crewmembers for eight days of scientific research aboard Discovery in Earth-orbit. Most of their on-duty time was spent in this IML-1 science module, positioned in the cargo bay and attached via a tunnel to Discovery's airlock.
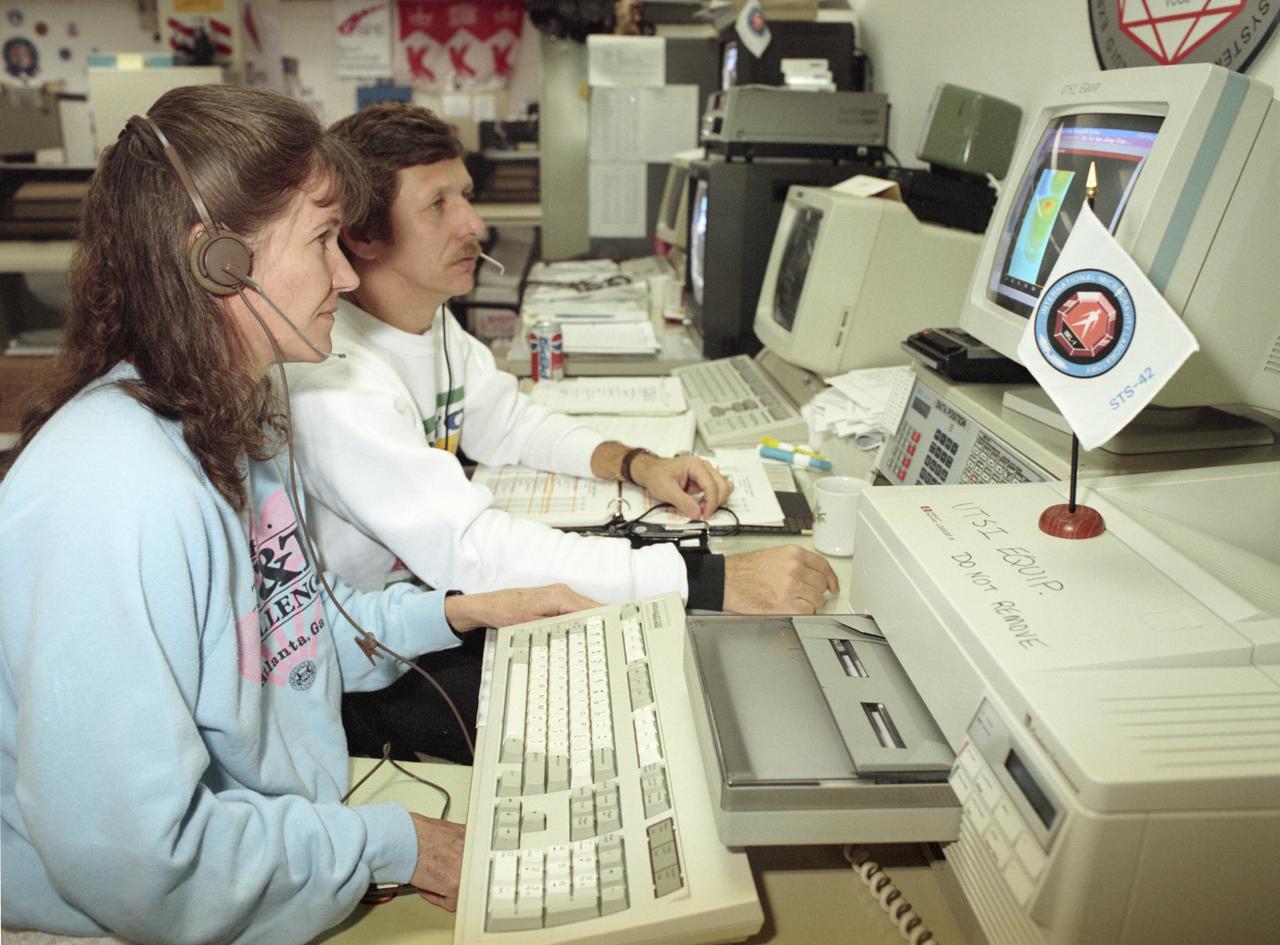

The primary payload for Space Shuttle Mission STS-42, launched January 22, 1992, was the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), a pressurized manned Spacelab module. The goal of IML-1 was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. Around-the-clock research was performed on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and effects of microgravity on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Materials processing experiments were also conducted, including crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury iodide, and a virus. The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Featured are activities in the SL POCC during STS-42, IML-1 mission.
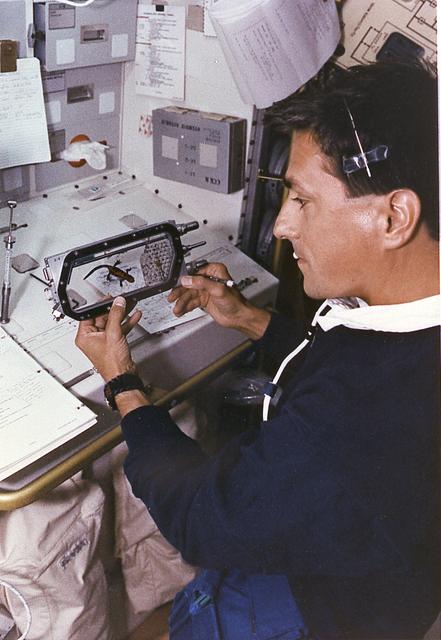

Astronaut Donald Thomas conducts the Fertilization and Embryonic Development of Japanese Newt in Space (AstroNewt) experiment at the Aquatic Animal Experiment Unit (AAEU) inside the International Microgravity Laboratory-2 (IML-2) science module. The AstroNewt experiment aims to know the effects of gravity on the early developmental process of fertilized eggs using a unique aquatic animal, the Japanese red-bellied newt. The newt egg is a large single cell at the begirning of development. The Japanese newt mates in spring and autumn. In late autumn, female newts enter hibernation with sperm in their body cavity and in spring lay eggs and fertilized them with the stored sperm. The experiment takes advantage of this feature of the newt. Groups of newts were sent to the Kennedy Space Center and kept in hibernation until the mission. The AAEU cassettes carried four newts aboard the Space Shuttle. Two newts in one cassette are treated by hormone injection on the ground to simulate egg laying. The other two newts are treated on orbit by the crew. The former group started maturization of eggs before launch. The effects of gravity on that early process were differentiated by comparison of the two groups. The IML-2 was the second in a series of Spacelab flights designed to conduct research by the international science community in a microgravity environment. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the IML-2 was launch on July 8, 1994 aboard the STS-65 Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia mission.
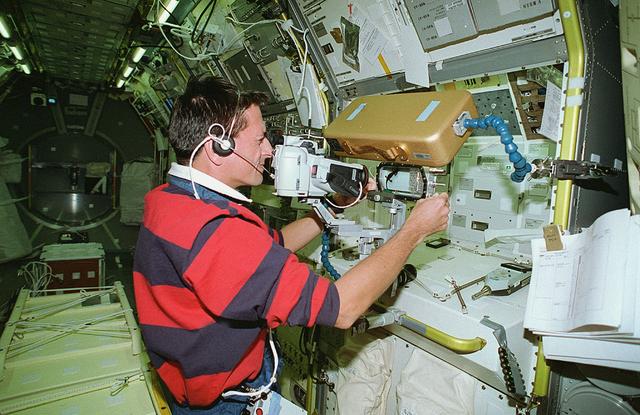

Astronaut Donald Thomas conducts the Fertilization and Embryonic Development of Japanese Newt in Space (AstroNewt) experiment at the Aquatic Animal Experiment Unit (AAEU) inside the International Microgravity Laboratory-2 (IML-2) science module. The AstroNewt experiment aims to know the effects of gravity on the early developmental process of fertilized eggs using a unique aquatic animal, the Japanese red-bellied newt. The newt egg is a large single cell at the begirning of development. The Japanese newt mates in spring and autumn. In late autumn, female newts enter hibernation with sperm in their body cavity and in spring lay eggs and fertilize them with the stored sperm. The experiment takes advantage of this feature of the newt. Groups of newts were sent to the Kennedy Space Center and kept in hibernation until the mission. The AAEU cassettes carried four newts aboard the Space Shuttle. Two newts in one cassette are treated by hormone injection on the ground to simulate egg laying. The other two newts are treated on orbit by the crew. The former group started maturization of eggs before launch. The effects of gravity on that early process were differentiated by comparison of the two groups. The IML-2 was the second in a series of Spacelab flights designed to conduct research by the international science community in a microgravity environment. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the IML-2 was launched on July 8, 1994 aboard the STS-65 Space Shuttle mission, Orbiter Columbia.
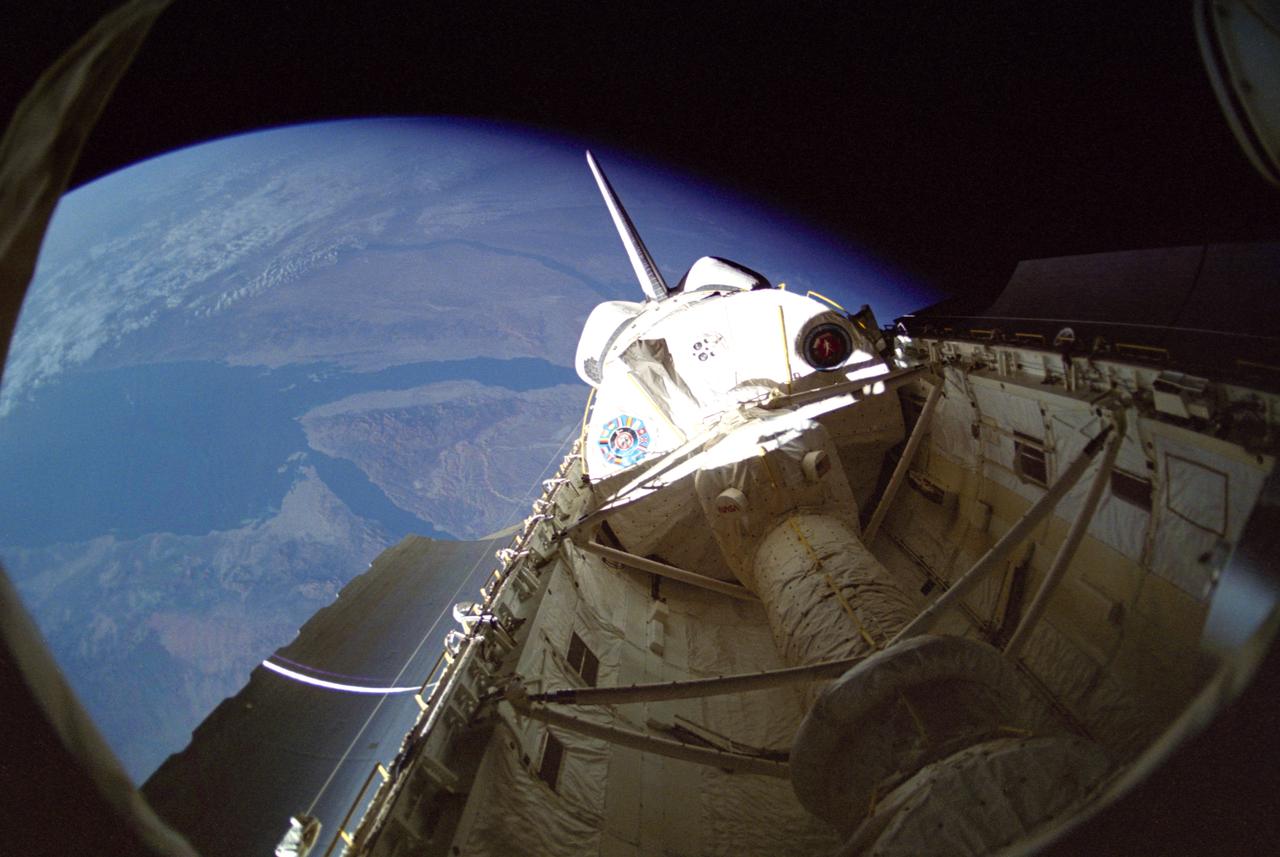

STS042-25-027 (30 Jan 1992) --- STS-42 International Microgravity Laboratory 1 (IML-1) Spacelab module and Spacelab tunnel (foreground) exteriors are documented in the payload bay (PLB) of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, and backdropped against the Red Sea and part of the Sinai Peninsula.
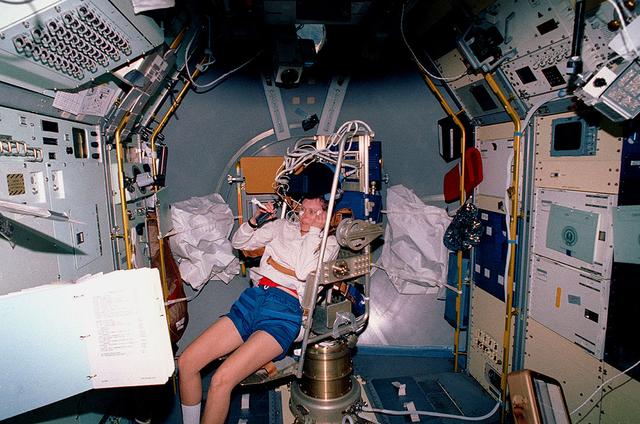

This Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42) onboard photo shows Canadian Payload Specialist Roberta Bondar getting into the Microgravity Vestibular Investigation (MVI) chair to begin an experiment in the International Microgravity Lab-1 (IML-1) Science Module. The (MVI) chair was designed to test the crew member's visual and vestibular responses to head and body movements.

STS065-214-037 (8-23 July 1994) --- Ready to begin one of her busy twelve hour shifts, payload specialist Dr. Chiaki Naito-Mukai enters the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) science module in the cargo bay via the tunnel connecting it to the Space Shuttle Columbia's cabin. Dr. Mukai joined six NASA astronauts for more than two weeks of experimenting in Earth orbit. This photo was among the first released by NASA following IML-2. Also onboard were NASA astronauts Robert D. Cabana, James D. Halsell, Jr., Richard J. Hieb, Carl E. Walz, Donald A. Thomas and Leroy Chiao. Dr. Mukai represented the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan.
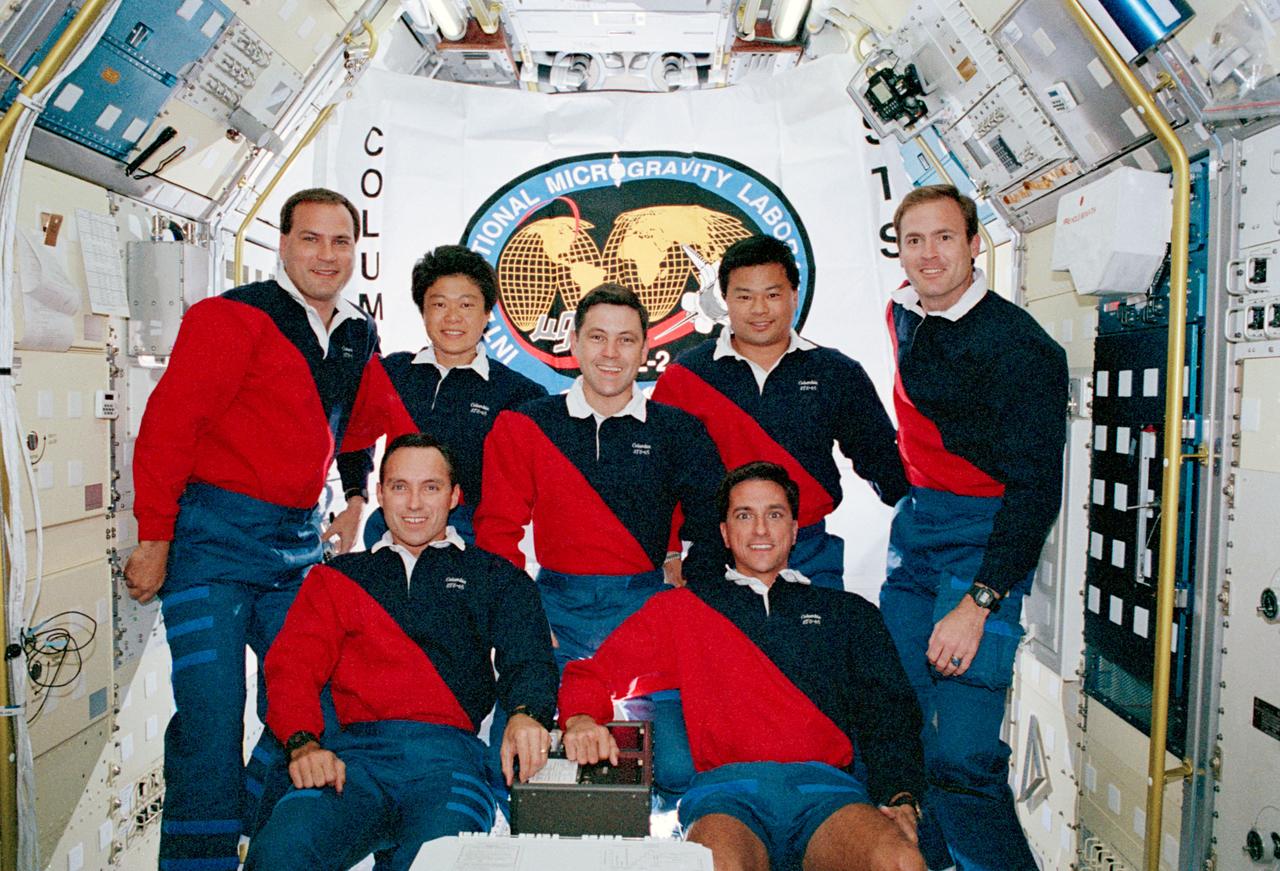

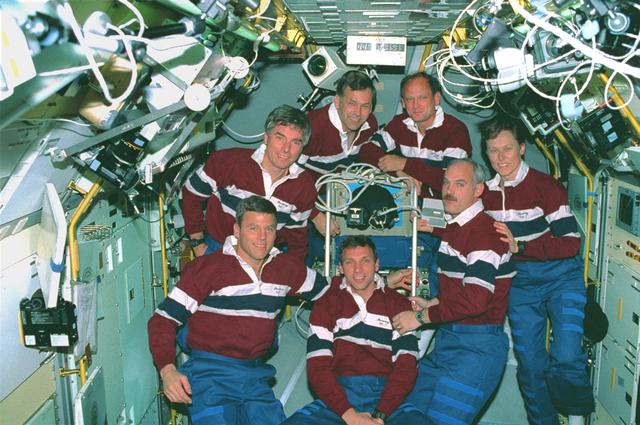
In the spacelab science module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, the seven crewmembers pose for the traditional onboard (inflight) crew portrait. Displayed in the background is a flag with the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) insignia and Columbia inscribed along the edge. In the front row (left to right) are Mission Specialist (MS) Carl E. Walz and MS Donald A. Thomas. Behind them (left to right) are Payload Commander (PLC) Richard J. Hieb, Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, Commander Robert D. Cabana, MS Leroy Chiao, and Pilot James D. Halsell, Jr. Mukai represents the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan. Crewmembers are wearing their mission polo shirts for the portrait. Inside this module, the crew conducted experiments in support of the IML-2 mission.
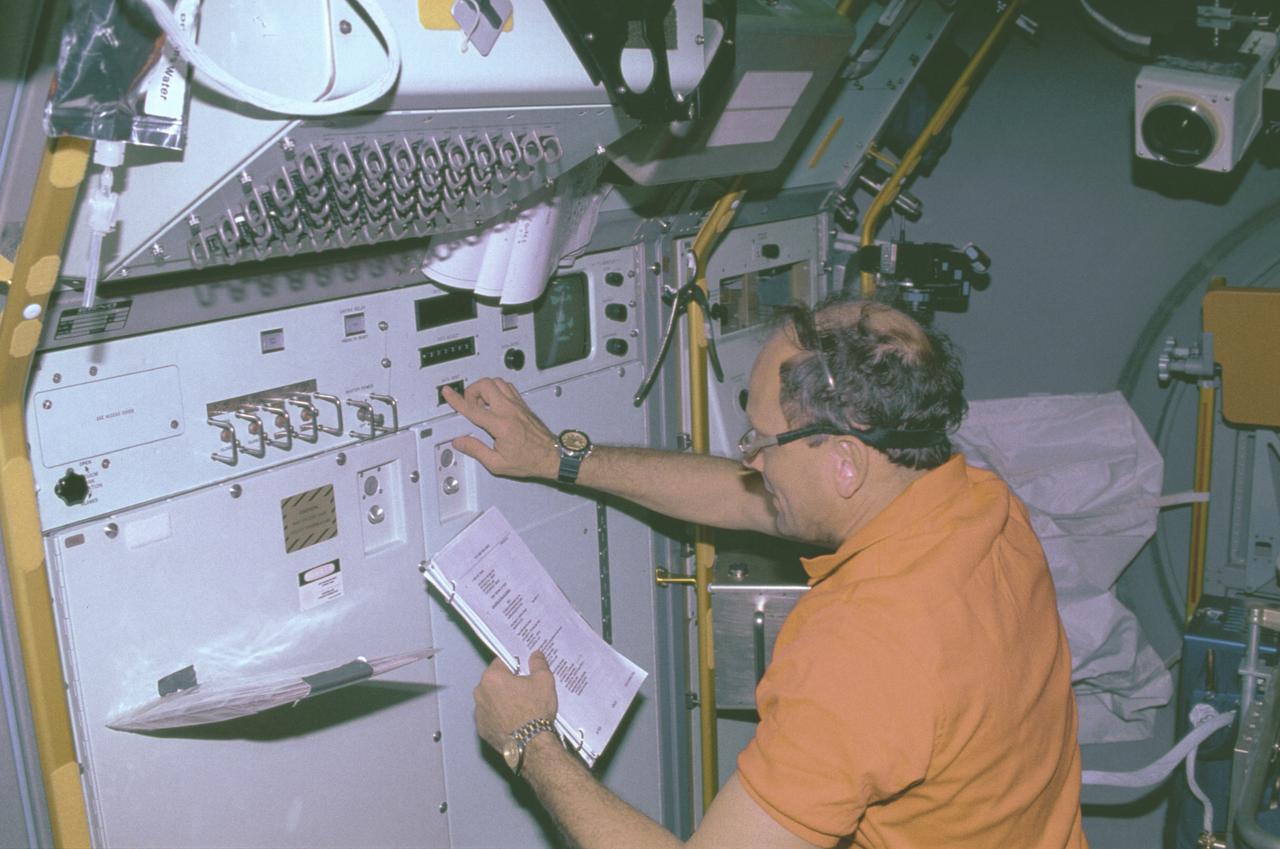

The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research with the international partners. The participating space agencies included: NASA, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), The French National Center of Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DAR/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Dedicated to the study of life and materials sciences in microgravity, the IML missions explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. Both life and materials sciences benefited from the extended periods of microgravity available inside the Spacelab science module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter. This photograph shows Astronaut Norman Thagard performing the fluid experiment at the Fluid Experiment System (FES) facility inside the laboratory module. The FES facility had sophisticated optical systems for imaging fluid flows during materials processing, such as experiments to grow crystals from solution and solidify metal-modeling salts. A special laser diagnostic technique recorded the experiments, holograms were made for post-flight analysis, and video was used to view the samples in space and on the ground. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the IML-1 mission was launched on January 22, 1992 aboard the Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42).
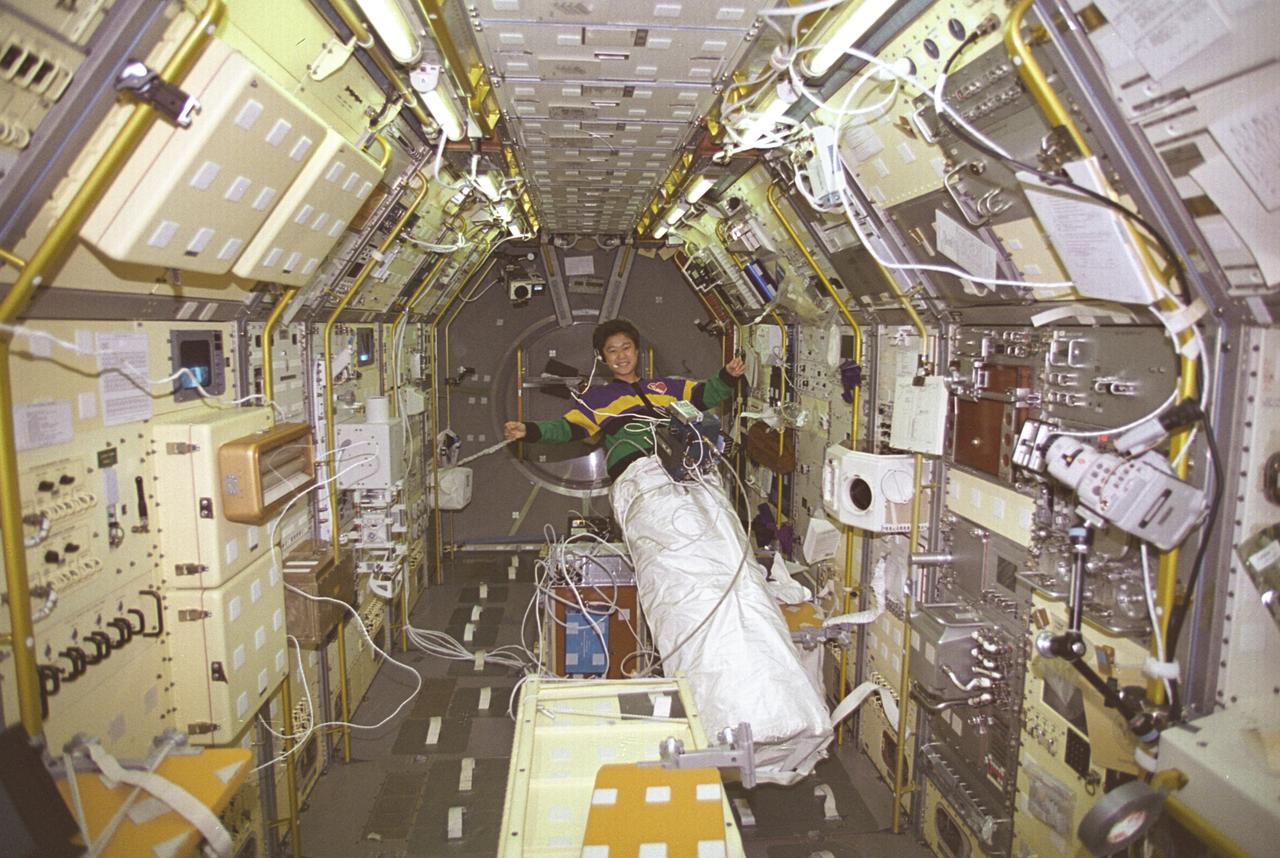

Astronaut Chiaki Mukai conducts the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) experiment inside the International Microgravity Laboratory-2 (IML-2) mission science module. Dr. Chiaki Mukai is one of the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) astronauts chosen by NASA as a payload specialist (PS). She was the second NASDA PS who flew aboard the Space Shuttle, and was the first female astronaut in Asia. When humans go into space, the lack of gravity causes many changes in the body. One change is that fluids normally kept in the lower body by gravity shift upward to the head and chest. This is why astronauts' faces appear chubby or puffy. The change in fluid volume also affects the heart. The reduced fluid volume means that there is less blood to circulate through the body. Crewmembers may experience reduced blood flow to the brain when returning to Earth. This leads to fainting or near-fainting episodes. With the use of the LBNP to simulate the pull of gravity in conjunction with fluids, salt tablets can recondition the cardiovascular system. This treatment, called "soak," is effective up to 24 hours. The LBNP uses a three-layer collapsible cylinder that seals around the crewmember's waist which simulates the effects of gravity and helps pull fluids into the lower body. The data collected will be analyzed to determine physiological changes in the crewmembers and effectiveness of the treatment. The IML-2 was the second in a series of Spacelab flights designed by the international science community to conduct research in a microgravity environment Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the IML-2 was launched on July 8, 1994 aboard the STS-65 Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia mission.
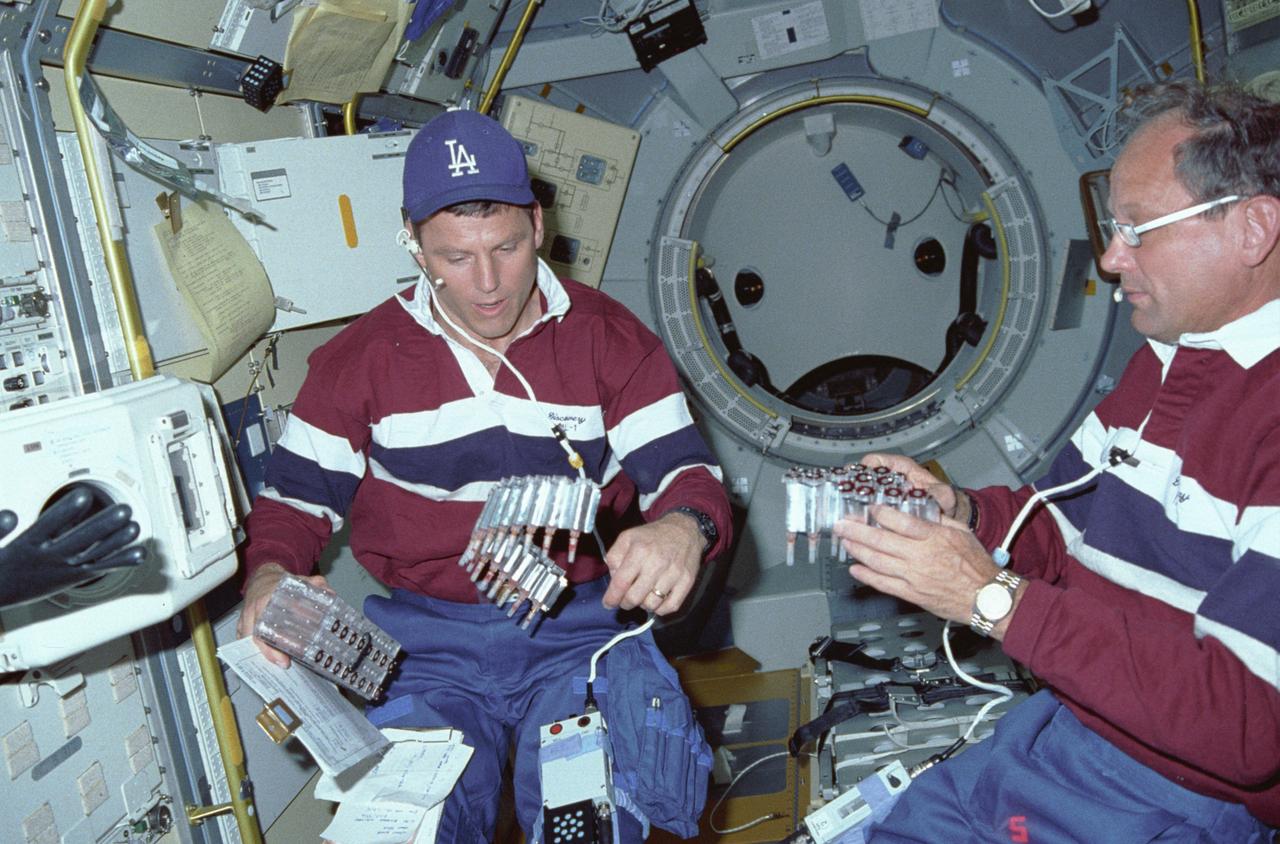

International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research with the international partners. The participating space agencies included: NASA, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), the French National Center of Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DAR/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Dedicated to the study of life and materials sciences in microgravity, the IML missions explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. Both life and materials sciences benefited from the extended periods of microgravity available inside the Spacelab science module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter. In this photograph, Astronauts Stephen S. Oswald and Norman E. Thagard handle ampoules used in the Mercuric Iodide Crystal Growth (MICG) experiment. Mercury Iodide crystals have practical uses as sensitive x-ray and gamma-ray detectors. In addition to their exceptional electronic properties, these crystals can operate at room temperature rather than at the extremely low temperatures usually required by other materials. Because a bulky cooling system is urnecessary, these crystals could be useful in portable detector devices for nuclear power plant monitoring, natural resource prospecting, biomedical applications in diagnosis and therapy, and astronomical observation. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, IML-1 was launched on January 22, 1992 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42 mission).
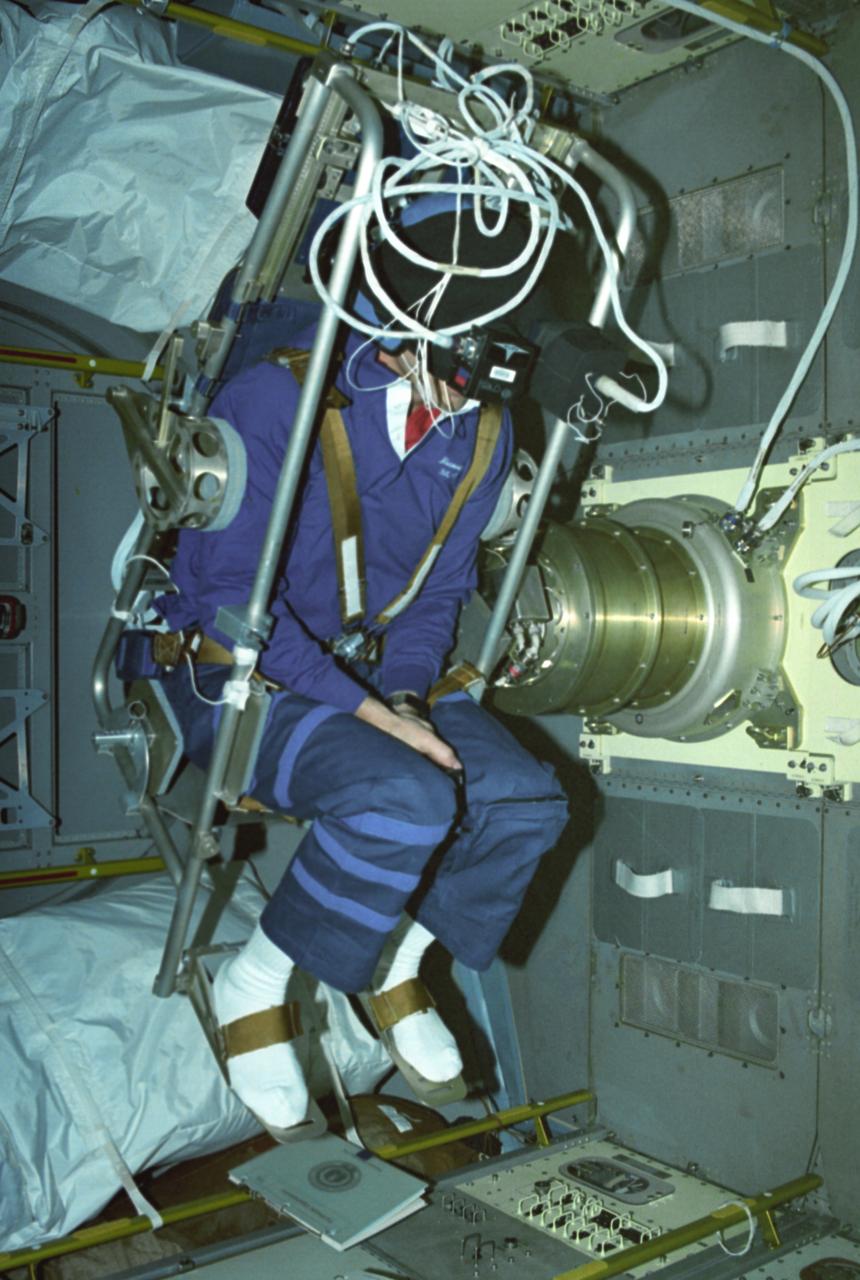

Astronaut David C. Hilmers conducts the Microgravity Vestibular Investigations (MVI) sitting in its rotator chair inside the IML-1 science module. When environmental conditions change so that the body receives new stimuli, the nervous system responds by interpreting the incoming sensory information differently. In space, the free-fall environment of an orbiting spacecraft requires that the body adapts to the virtual absence of gravity. Early in flights, crewmembers may feel disoriented or experience space motion sickness. MVI examined the effects of orbital flight on the human orientation system to obtain a better understanding of the mechanisms of adaptation to weightlessness. By provoking interactions among the vestibular, visual, and proprioceptive systems and then measuring the perceptual and sensorimotor reactions, scientists can study changes that are integral to the adaptive process. The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research with the international partners. The participating space agencies included: NASA, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), the French National Center of Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DAR/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Both life and materials sciences benefited from the extended periods of microgravity available inside the Spacelab science module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, IML-1 was launched on January 22, 1992 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42 mission).
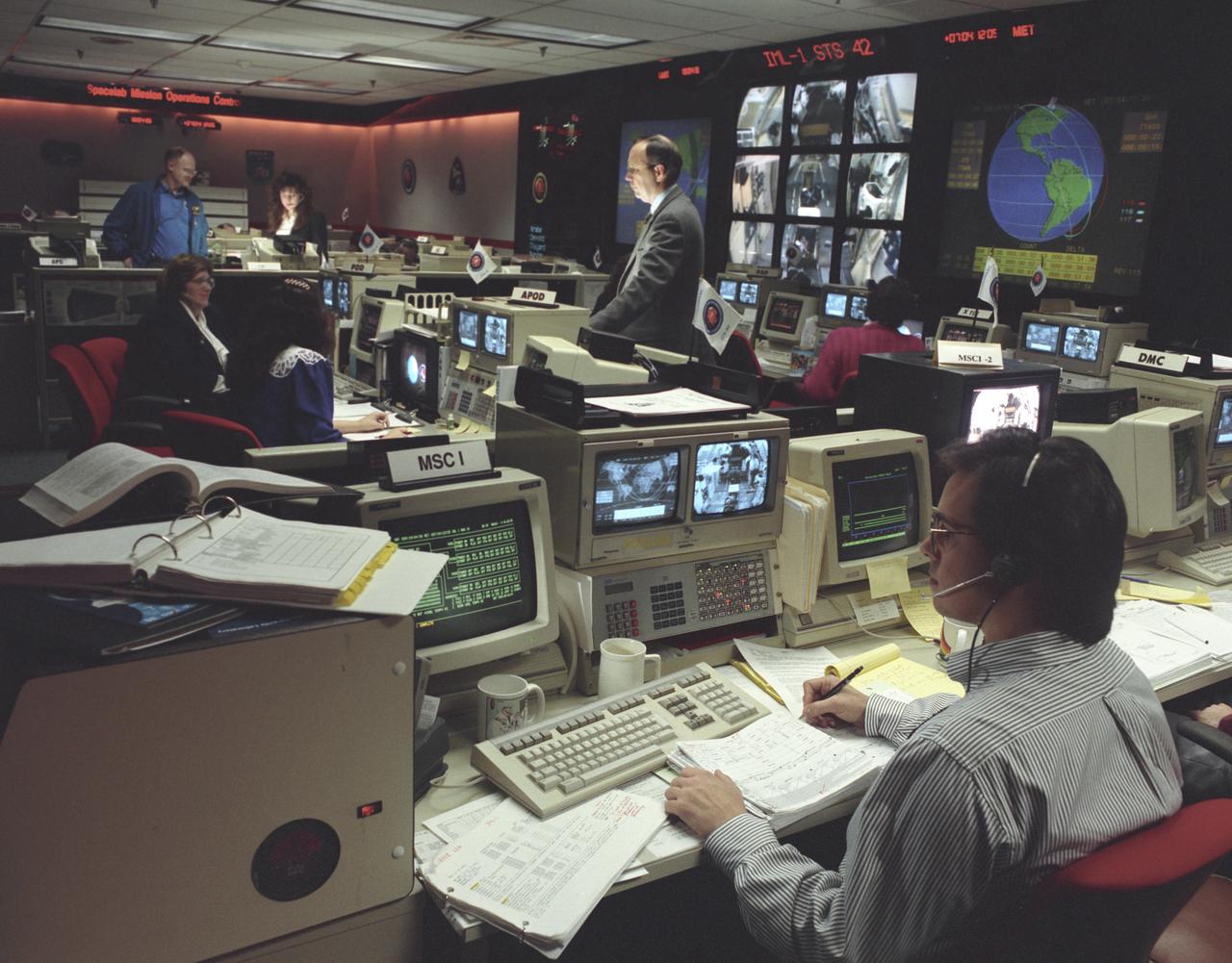

This photograph shows activities during the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) mission (STS-42) in the Payload Operations Control Center (POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research. The mission was to explore, in depth, the complex effects of weightlessness on living organisms and materials processing. The crew conducted experiments on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and the effects on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Low gravity materials processing experiments included crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury, iodine, and virus. The International space science research organizations that participated in this mission were: The U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration, the European Space Agency, the Canadian Space Agency, the French National Center for Space Studies, the German Space Agency, and the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The POCC was the air/ground communication charnel used between the astronauts aboard the Spacelab and scientists, researchers, and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. The facility made instantaneous video and audio communications possible for scientists on the ground to follow the progress and to send direct commands of their research almost as if they were in space with the crew.
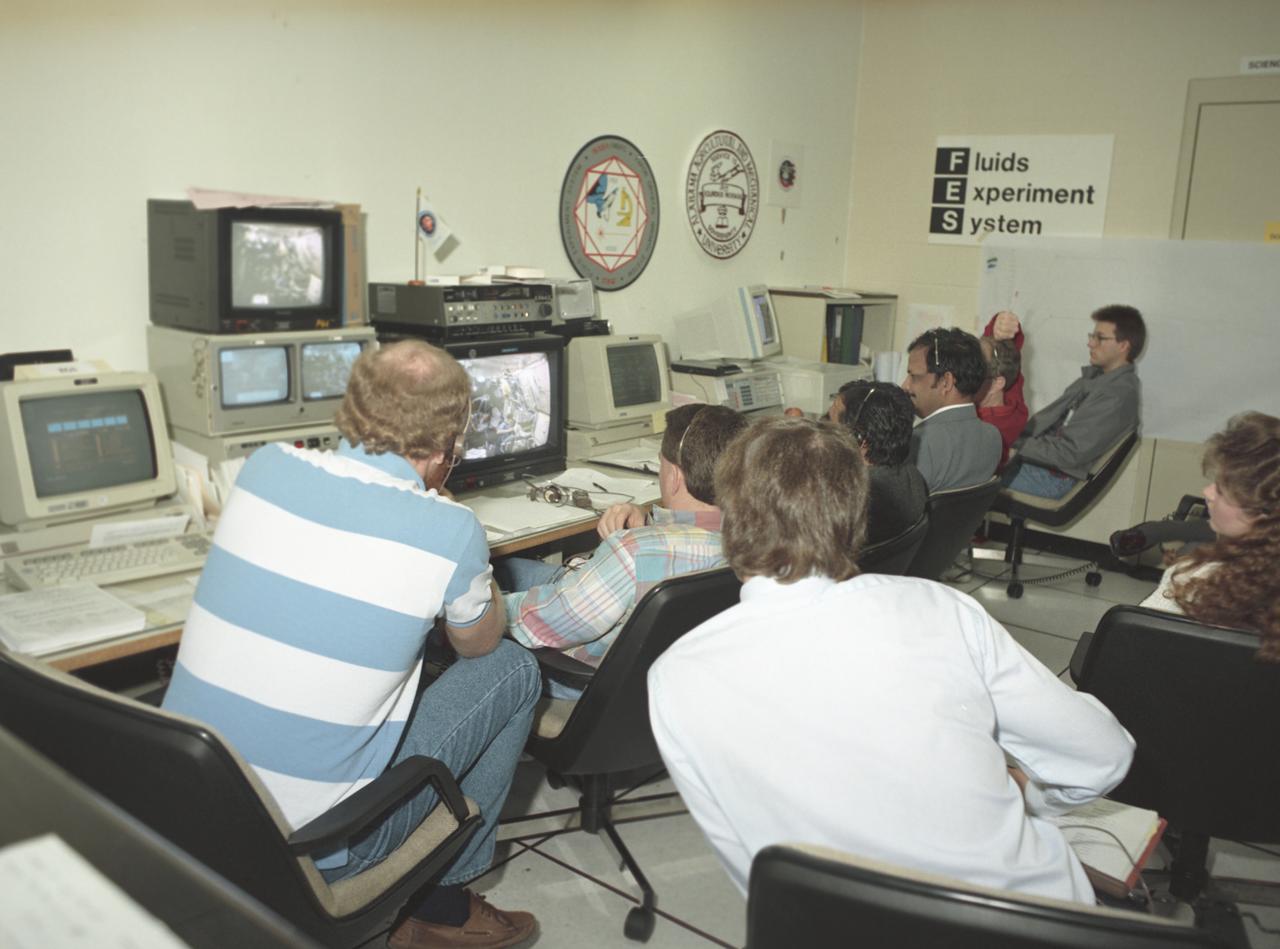

This photograph shows activities during the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1) mission (STS-42) in the Payload Operations Control Center (POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center. Members of the Fluid Experiment System (FES) group monitor the progress of their experiment through video at the POCC. The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research. The mission was to explore, in depth, the complex effects of weightlessness on living organisms and materials processing. The crew conducted experiments on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and the effects on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Low gravity materials processing experiments included crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury, iodine, and virus. The International space science research organizations that participated in this mission were: The U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administion, the European Space Agency, the Canadian Space Agency, the French National Center for Space Studies, the German Space Agency, and the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The POCC was the air/ground communication charnel used between astronauts aboard the Spacelab and scientists, researchers, and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. The facility made instantaneous video and audio communications possible for scientists on the ground to follow the progress and to send direct commands of their research almost as if they were in space with the crew.

The primary payload for Space Shuttle Mission STS-42, launched January 22, 1992, was the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), a pressurized manned Spacelab module. The goal of IML-1 was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. Around-the-clock research was performed on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and effects of microgravity on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Materials processing experiments were also conducted, including crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury iodide, and a virus. The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Featured activities are of the Mental Workload and Performance Experiment (MWPE) team in the SL POCC during the IML-1 mission.
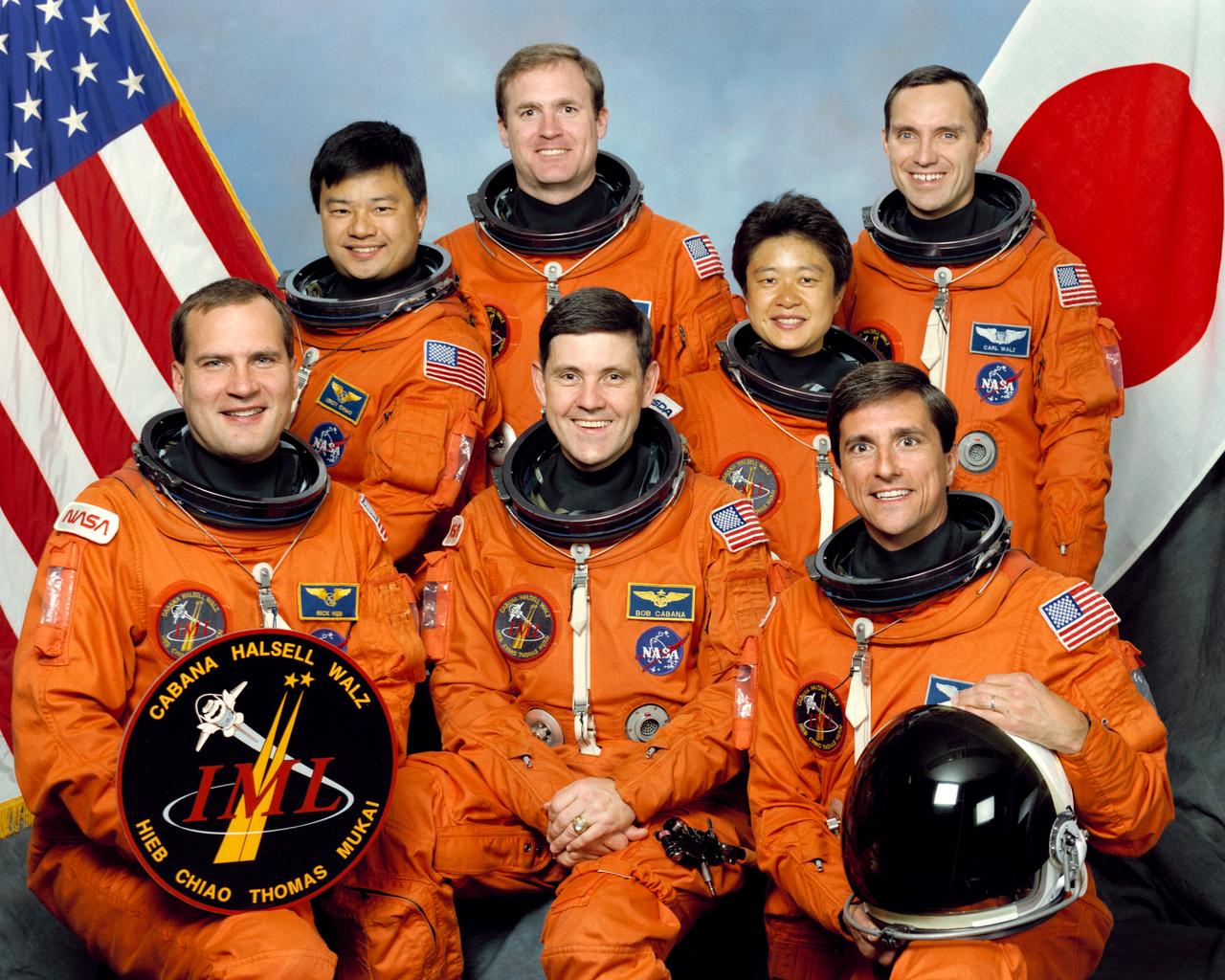

STS065-S-002 (April 1994) --- Six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist take a break from training to pose for their crew portrait. Left to right are Richard J. Hieb, Leroy Chiao, James D. Halsell Jr., Robert D. Cabana, Dr. Chiaki Mukai, Donald A. Thomas and Carl E. Walz. Cabana is mission commander, and Halsell has been assigned as pilot. Hieb is payload commander, with Walz, Thomas and Chiao serving as mission specialist. Dr. Mukai represents the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan as payload specialist on the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML) mission.
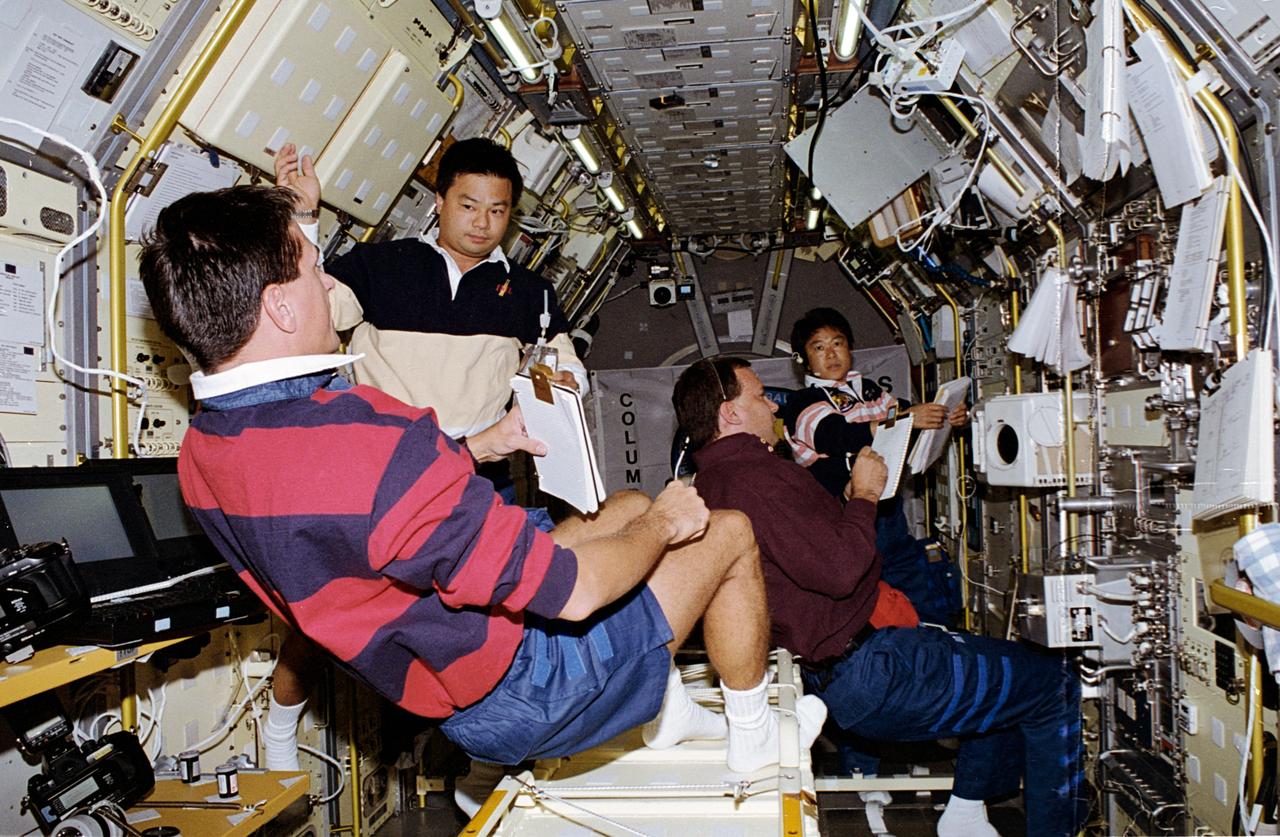

STS065-05-037 (8-23 July 1994) --- In the science module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, four members of the crew busy themselves with experiments in support of the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) mission. Left to right are Donald A. Thomas and Leroy Chiao, both mission specialists; Richard J. Hieb, payload commander, and Dr. Chiaki Mukai of NASDA, payload specialist.
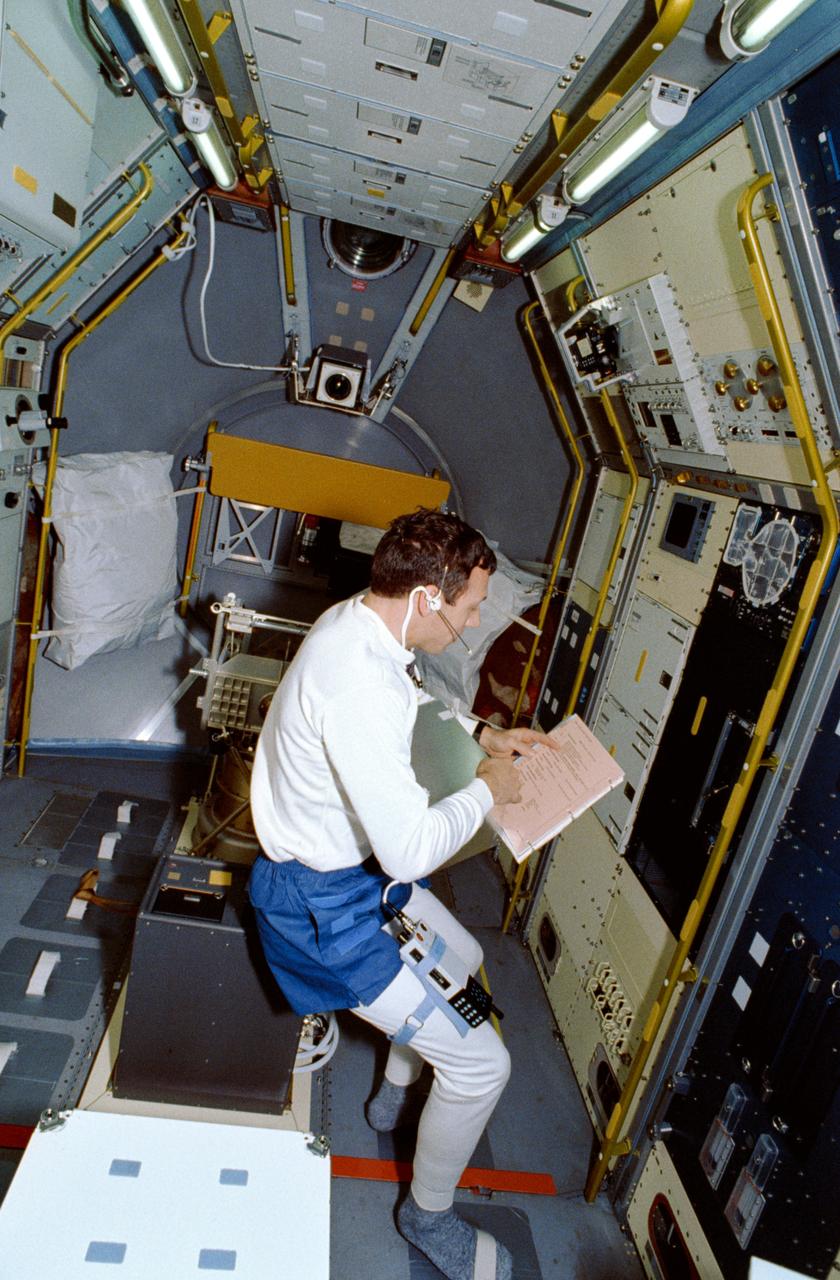

STS042-17-001 (22 Jan 1992) --- Astronaut David C. Hilmers, mission specialist, looks over a checklist at the Johnson Space Center refrigerator/freezer, in which perishable samples are stowed. The view gives an overall perspective of the science module -- heavily utilized for eight-days of scientific research supporting the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) -- in Discovery's cargo bay.
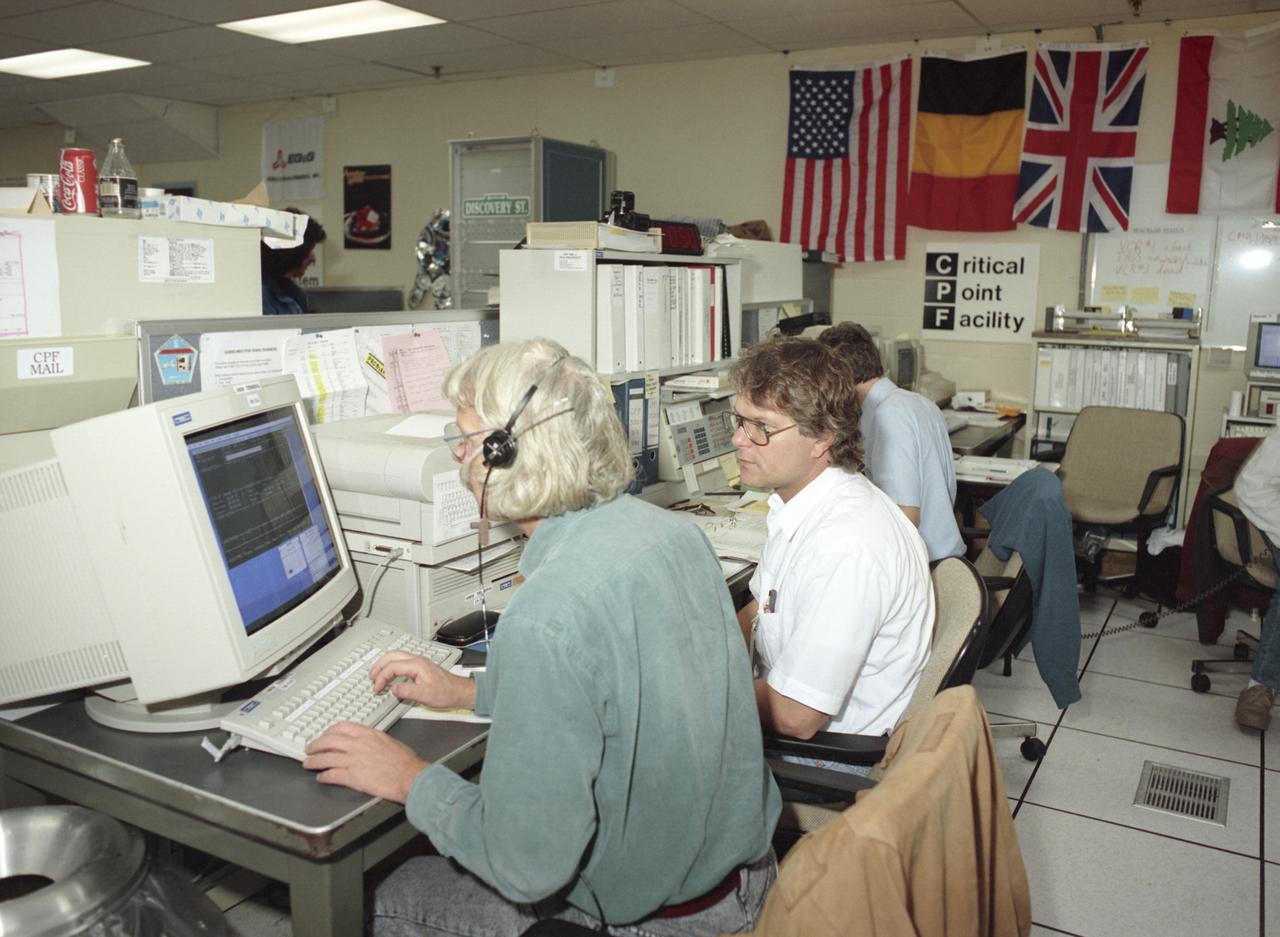

The primary payload for Space Shuttle Mission STS-42, launched January 22, 1992, was the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), a pressurized manned Spacelab module. The goal of IML-1 was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. Around-the-clock research was performed on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and effects of microgravity on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Materials processing experiments were also conducted, including crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury iodide, and a virus. The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Featured is the Critical Point Facility (CPF) team in the SL POCC during the IML-1 mission.
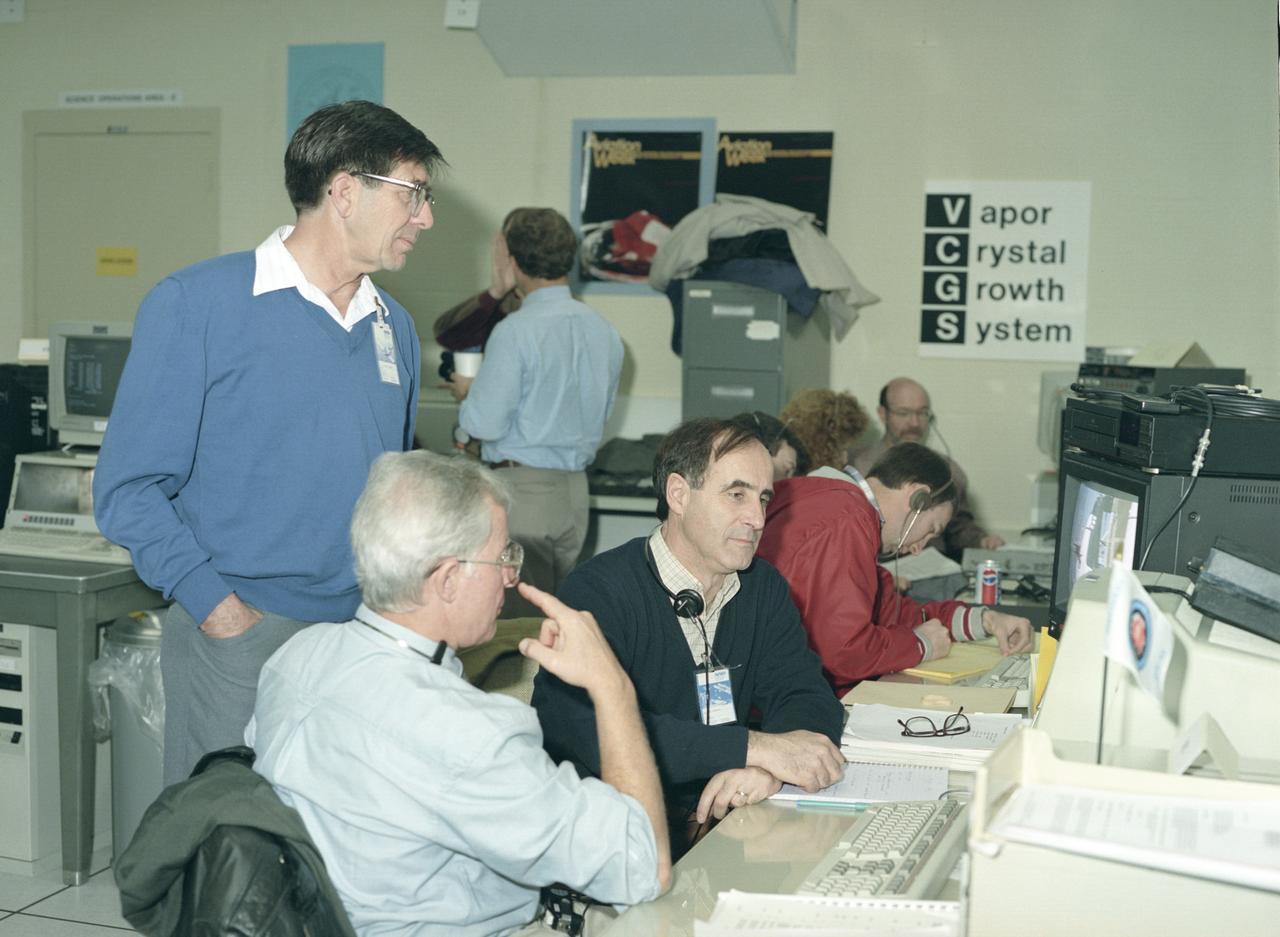

The primary payload for Space Shuttle Mission STS-42, launched January 22, 1992, was the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), a pressurized manned Spacelab module. The goal of IML-1 was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. Around-the-clock research was performed on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and effects of microgravity on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Materials processing experiments were also conducted, including crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury iodide, and a virus. The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Featured is the Vapor Crystal Growth System (VCGS) team in SL POCC), during STS-42, IML-1 mission.
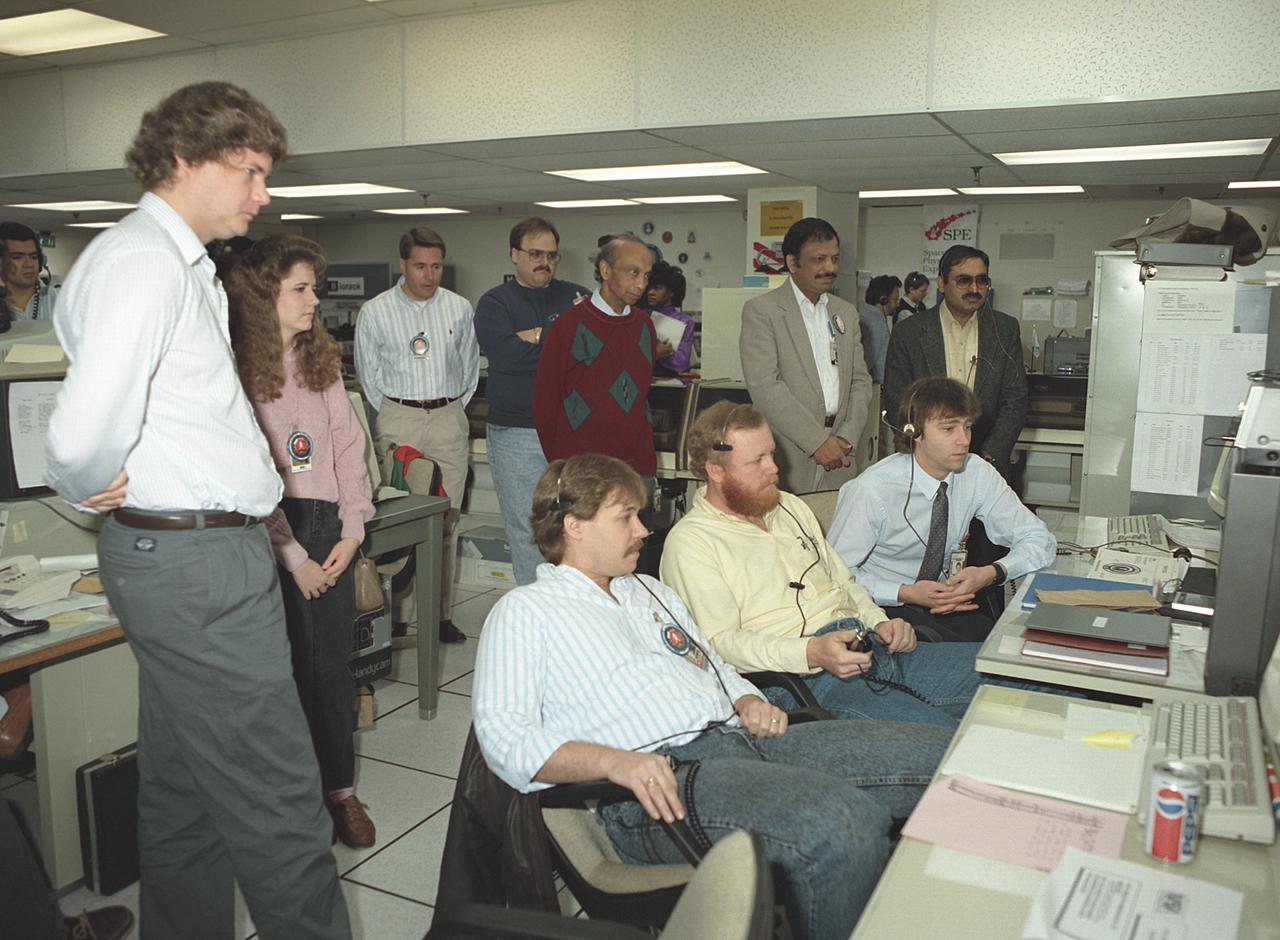

The primary payload for Space Shuttle Mission STS-42, launched January 22, 1992, was the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), a pressurized manned Spacelab module. The goal of IML-1 was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. Around-the-clock research was performed on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and effects of microgravity on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Materials processing experiments were also conducted, including crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury iodide, and a virus. The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Featured is the Crystal Growth team in the SL POCC during STS-42, IML-1 mission.
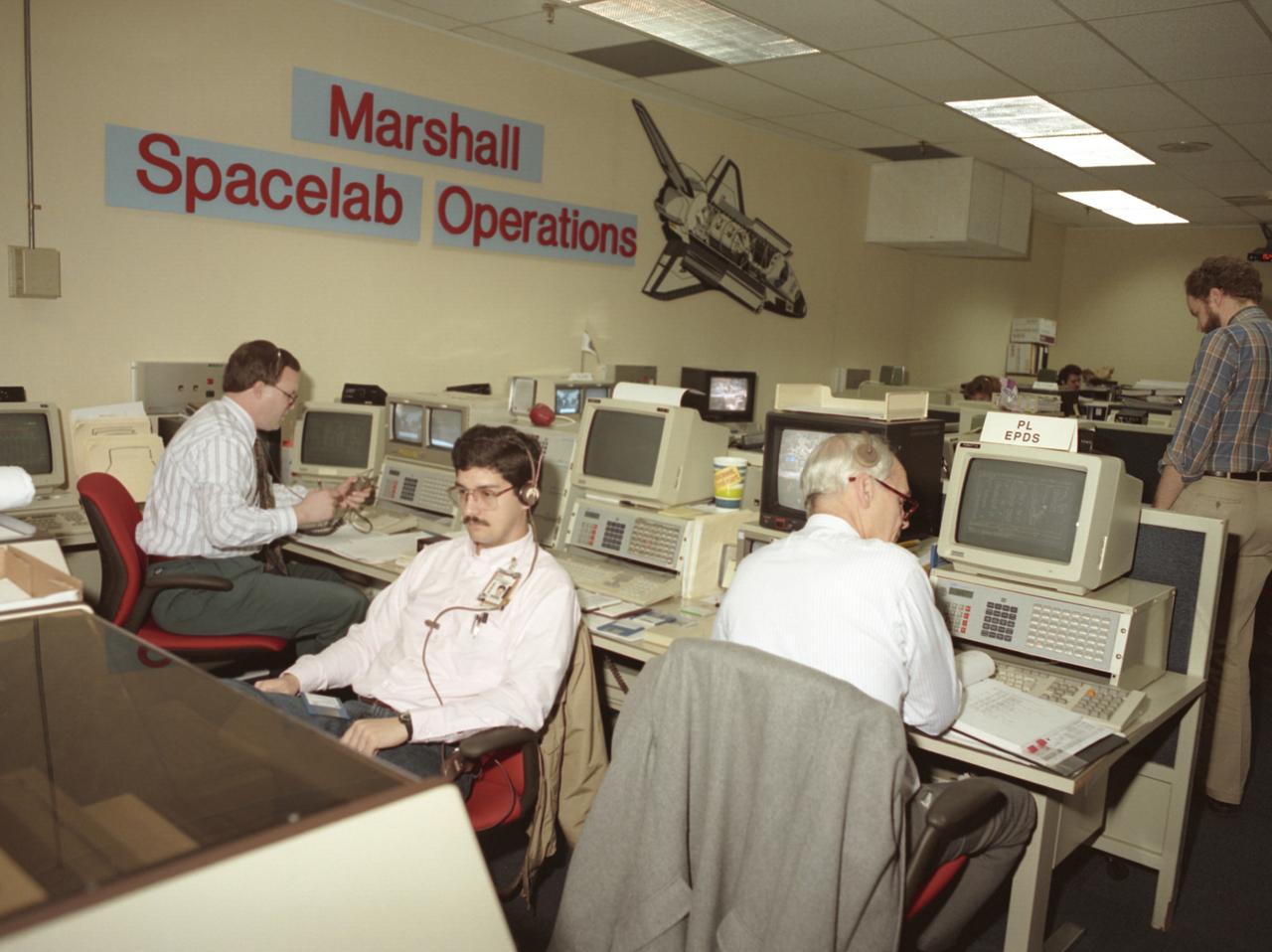

The primary payload for Space Shuttle Mission STS-42, launched January 22, 1992, was the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), a pressurized manned Spacelab module. The goal of IML-1 was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. Around-the-clock research was performed on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and effects of microgravity on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Materials processing experiments were also conducted, including crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury iodide, and a virus. The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Featured is the Spacelab Operations Support Room Space Engineering Support team in the SL POCC during STS-42, IML-1 mission.
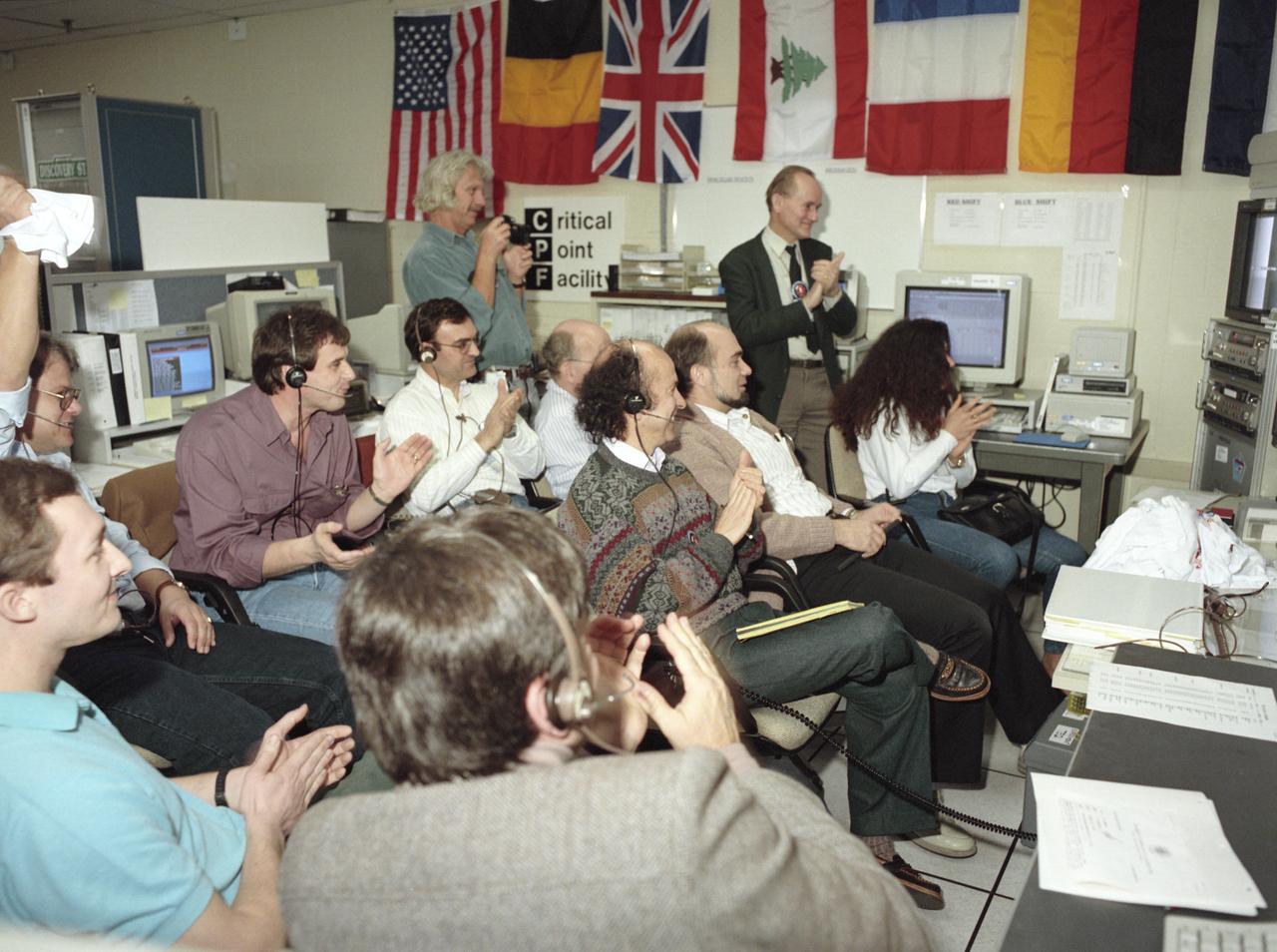

The primary payload for Space Shuttle Mission STS-42, launched January 22, 1992, was the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), a pressurized manned Spacelab module. The goal of IML-1 was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. Around-the-clock research was performed on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and effects of microgravity on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Materials processing experiments were also conducted, including crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury iodide, and a virus. The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Featured is the Critical Point Facility (CPE) group in the SL POCC during STS-42, IML-1 mission.
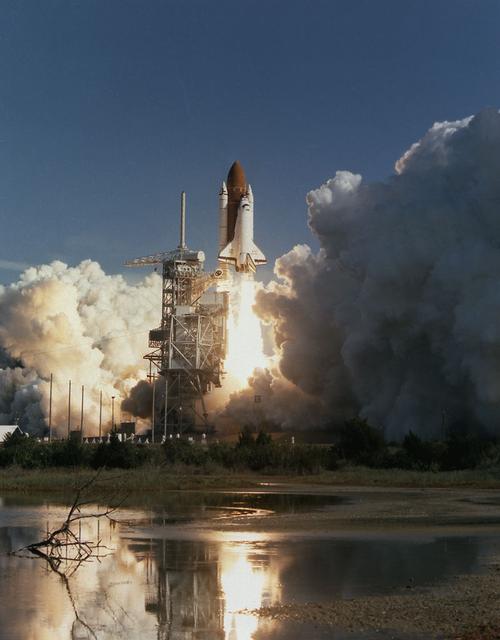

Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-42) lifted off from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) with International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) aboard the orbiter's cargo bay. IML missions were devoted to material and life sciences studies using the Spacelab Long Module.
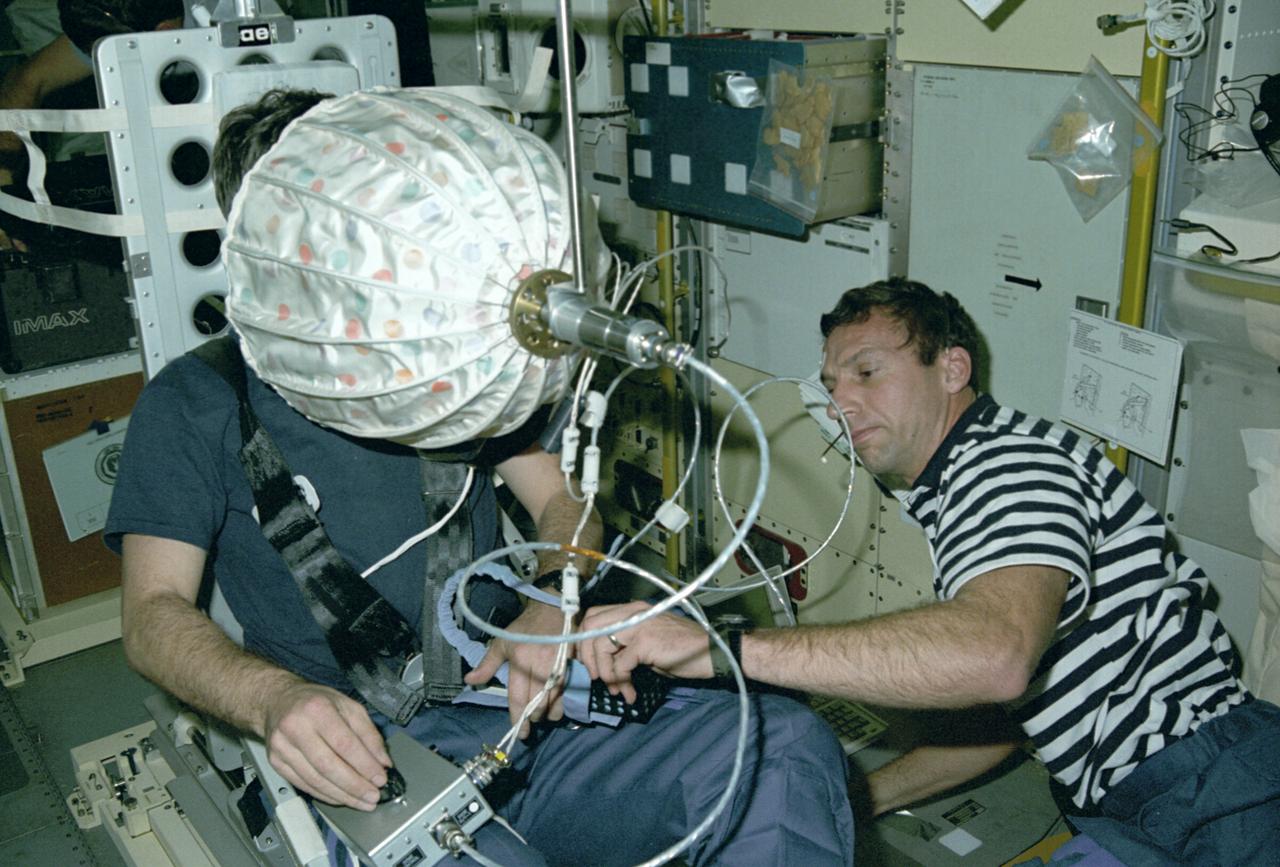

Astronaut Ulf Merbold on the stationary seat of the mini-sled, stares into an umbrella-shaped rotating dome with colored dots. Astronaut Merbold, assisted by astronaut David Hilmer, are conducting the Visual Simulator Experiment, a space physiology experiment. The Visual Stimulator Experiment measures the relative importance of visual and vestibular information in determining body orientation. When a person looks at a rotating visual field, a false sensation of self-rotation, called circularvection, results. In weightlessness, circularvection should increase immediately and may continue to increase as the nervous system comes to rely more on visual than vestibular cues. As Astronaut Merbold stares into the rotating dome with a pattern of colored dots and its interior, he turns a knob to indicate his perception of body rotation. The strength of circularvection is calculated by comparing signals from the dome and the knob. The greater the false sense of circularvection, the more the subject is relying on visual information instead of otolith information. The IML-1 mission was the first in a series of Shuttle flights dedicated to fundamental materials and life sciences research with the international partners. The participating space agencies included: NASA, the 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), the French National Center of Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DAR/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, IML-1 was launched on January 22, 1992 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery (STS-42 mission).
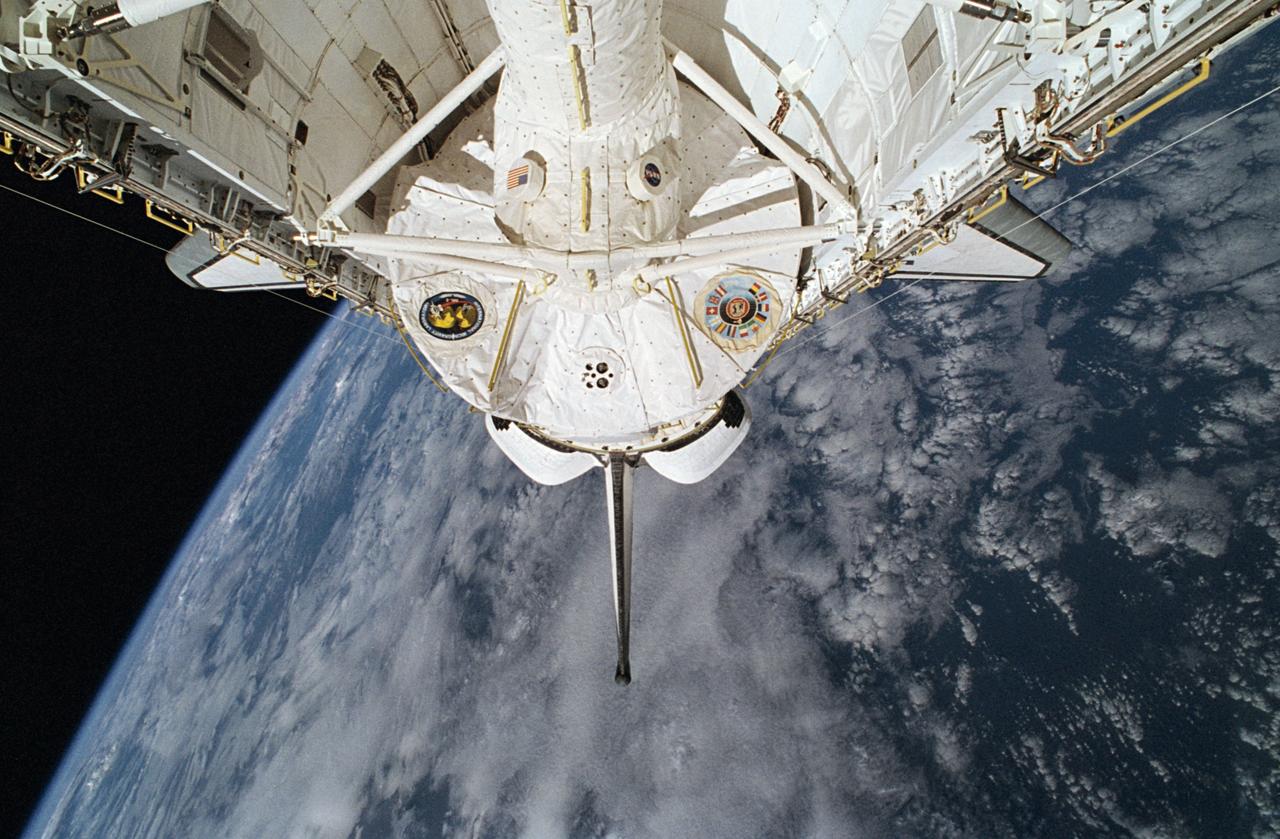

STS065-34-016 (8-23 July 1994) --- Clouds over the ocean form the backdrop for this scene of the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) science module in the Space Shuttle Columbia's cargo bay during the two-week mission. Part of the tunnel that served as passageway for the seven crew members to and from the lab is seen in center foreground. Onboard Columbia were astronauts Robert D. Cabana, James D. Halsell, Jr., Richard J. Hieb, Carl E. Walz, Donald A. Thomas and Leroy Chiao, along with (NASDA) Japanese payload specialist Dr. Chiaki Naito-Mukai.
This is the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery, STS-42 mission, with the First International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) module shown in the cargo bay. IML-1, the first in a series of Shuttle flights, was dedicated to study the fundamental materials and life sciences in the microgravity environment inside Spacelab, a laboratory carried aloft by the Shuttle. The mission explored how life forms adapt to weightlessness and investigated how materials behave when processed in space. The IML program gave a team of scientists from around the world access to a unique environment, one that is free from most of Earth's gravity. The 14-nation European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (SCA), the French National Center for Space Studies (CNES), the German Space Agency and the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DARA/DLR), and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) participated in developing hardware and experiments for the IML missions. The missions were managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. The Orbiter Discovery was launched on January 22, 1992 for the IML-1 mission.
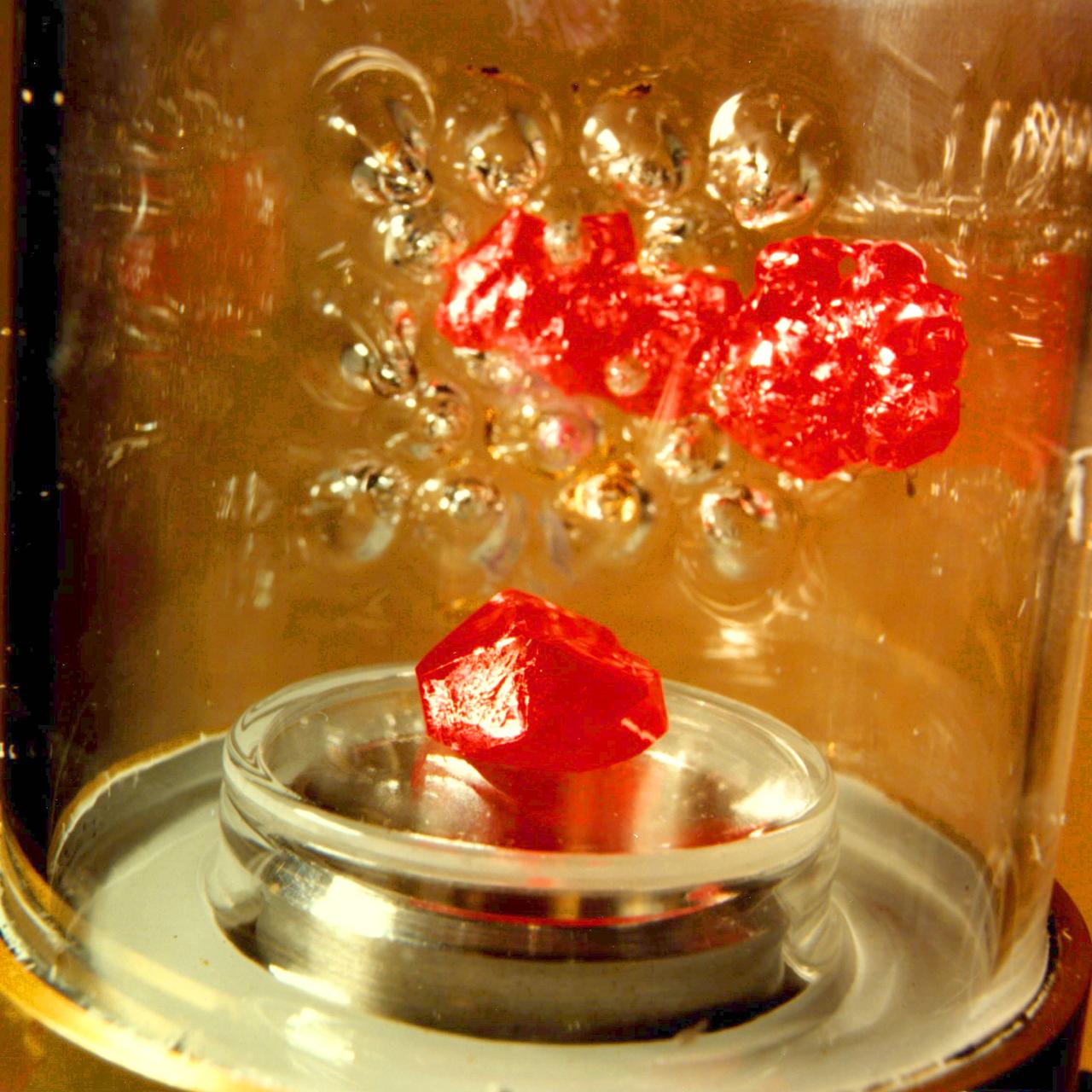

Vapor Crystal Growth System (VCGS), Flown on IML-1, Spacelab 3, Principal Investigator: Lodewijk van den Berg
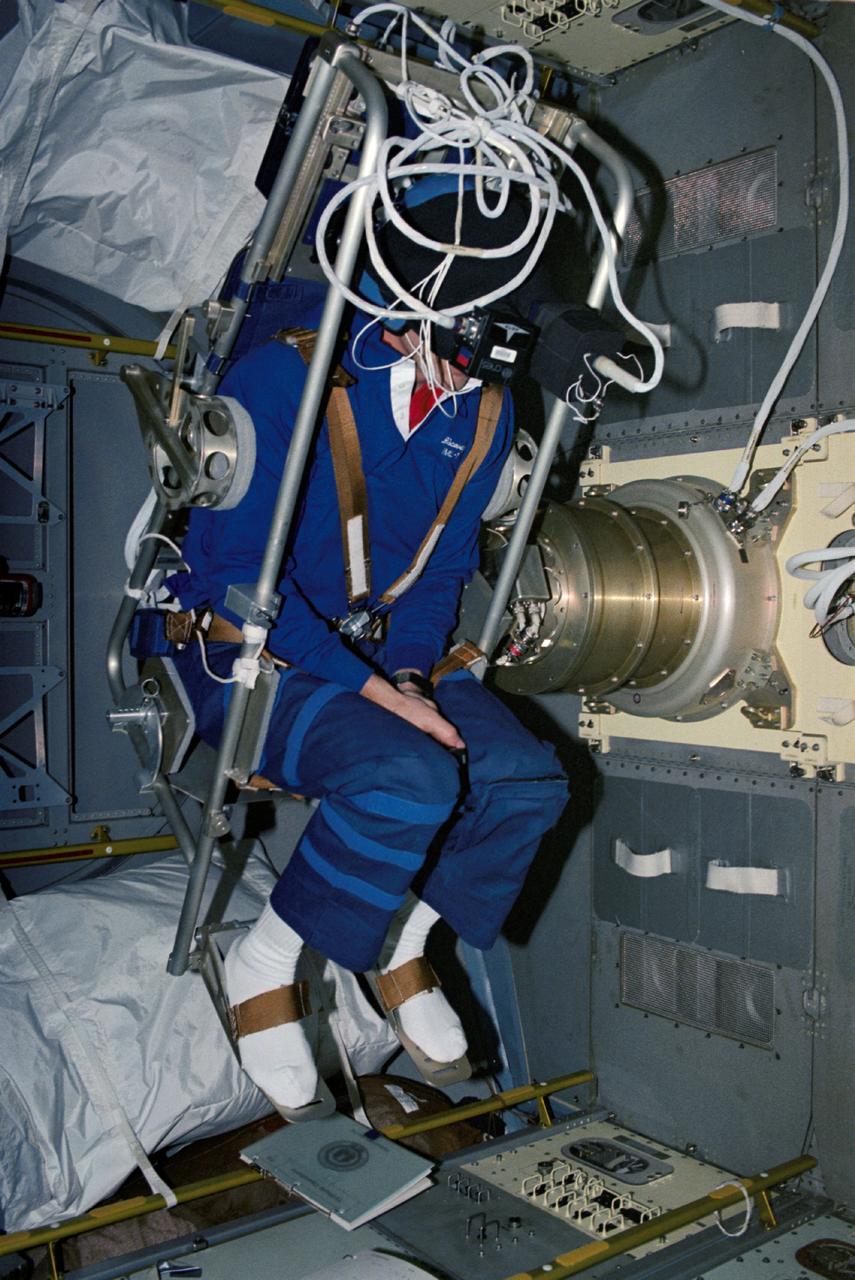

STS042-27-037 (22-30 Jan. 1992) --- Astronaut David C. Hilmers, STS-42 mission specialist, wearing a helmet assembly, sits in the Microgravity Vestibular Investigation (MVI) rotating chair. The scene is in the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) science module aboard Discovery. Hilmers, a mission specialist, and six other crewmembers spent more than eight days in Earth-orbit conducting experiments. Hilmer's helmet assembly is outfitted with accelerometers to measure head movements and visors that fit over each eye independently to provide visual stimuli. The chair system has three movement patterns: "sinusoidal" or traveling predictably back and forth over the same distance at a constant speed; "pseudorandom" or moving back and forth over the varying distances; and "stepped" or varying speeds beginning and stopping suddenly.
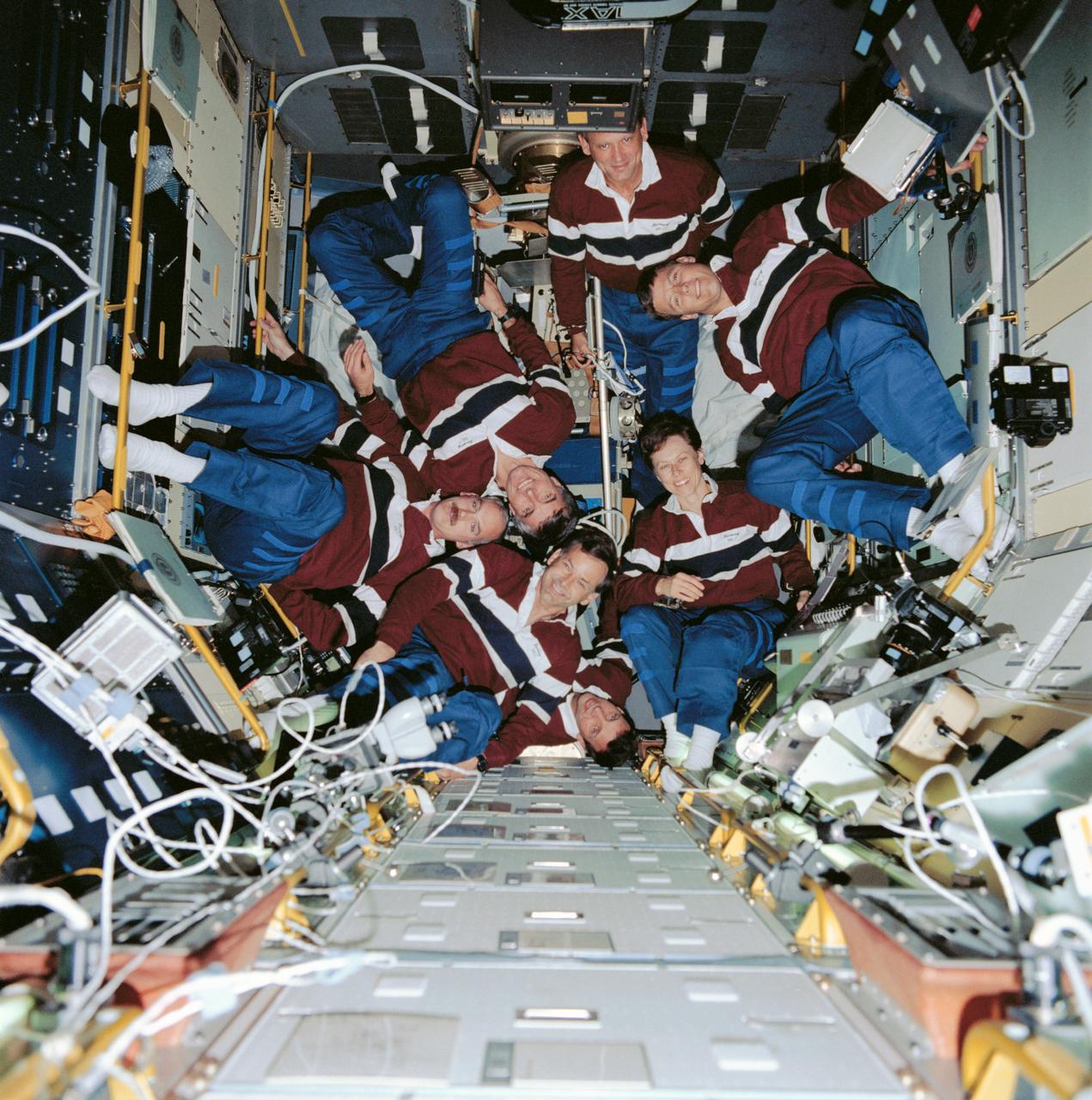

STS042-78-061 (22-30 Jan. 1992) --- The seven STS-42 crewmembers pose for a traditional in-space portrait in the shirt-sleeve environment of the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) science module in the shuttle's cargo bay. (Hold picture with index numbers at top.) David C. Hilmers, mission specialist, is at top center of the 70mm image. Others pictured are (clockwise) Ronald J. Grabe, mission commander; William F. Readdy; mission specialist; Ulf Merbold, European Space Agency (ESA) payload specialist; Norman E. Thagard, payload commander; Stephen S. Oswald, pilot; and Roberta L. Bondar, Canadian payload specialist. The rotating chair, used often in biomedical tests on the eight-day flight, is (partially obscured) in center frame.
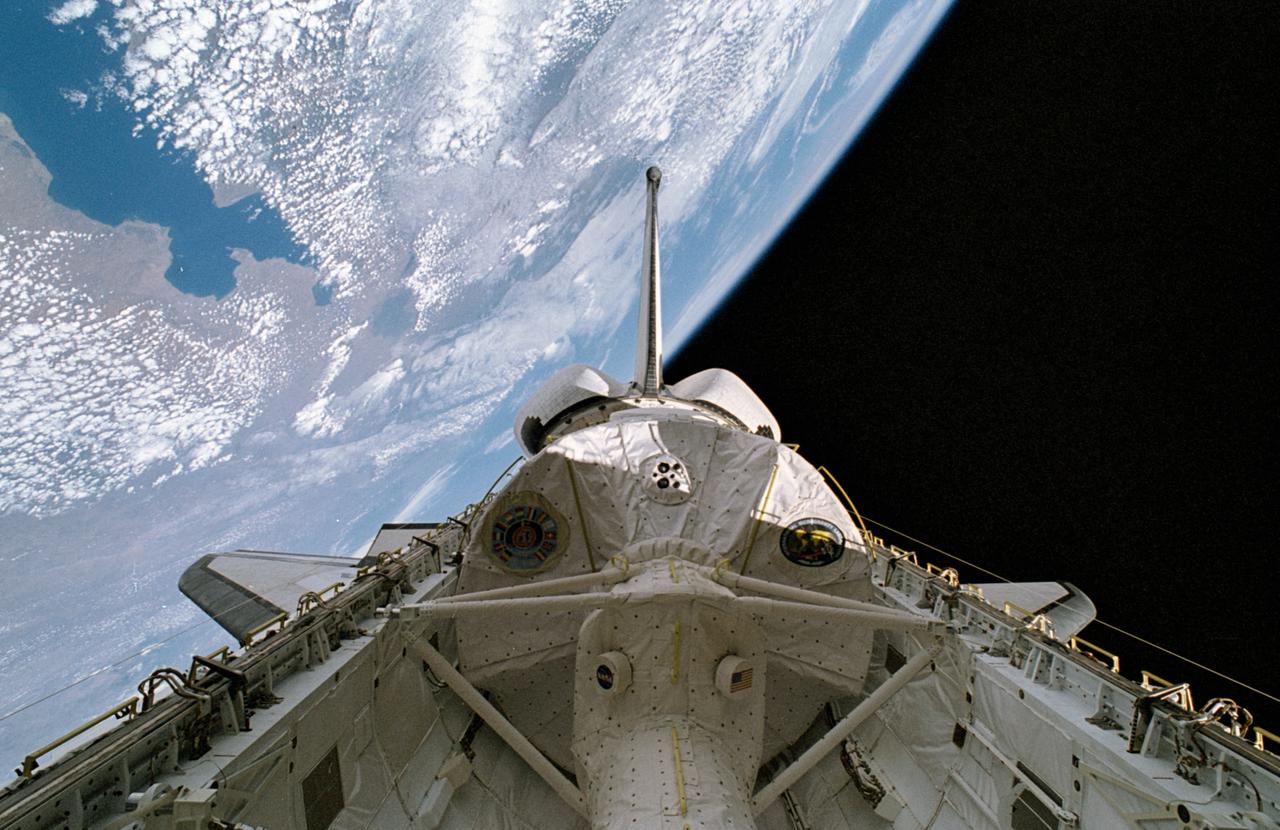

STS065-42-017 (8-23 July 1994) --- This 35mm panorama shows the science module, for the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) and the Space Shuttle Columbia's cargo bay, backdropped against the darkness of space over part of Africa, on Earth's horizon. Lake Nyasa in Malawi can easily be delineated. Also visible are part of the country of Mozambique and the Indian Ocean. Six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist spent more than two weeks of experimenting in Earth-orbit. Onboard were NASA astronauts Robert D. Cabana, James D. Halsell, Jr., Richard J. Hieb, Carl E. Walz, Donald A. Thomas and Leroy Chiao along with payload specialist Dr. Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan.
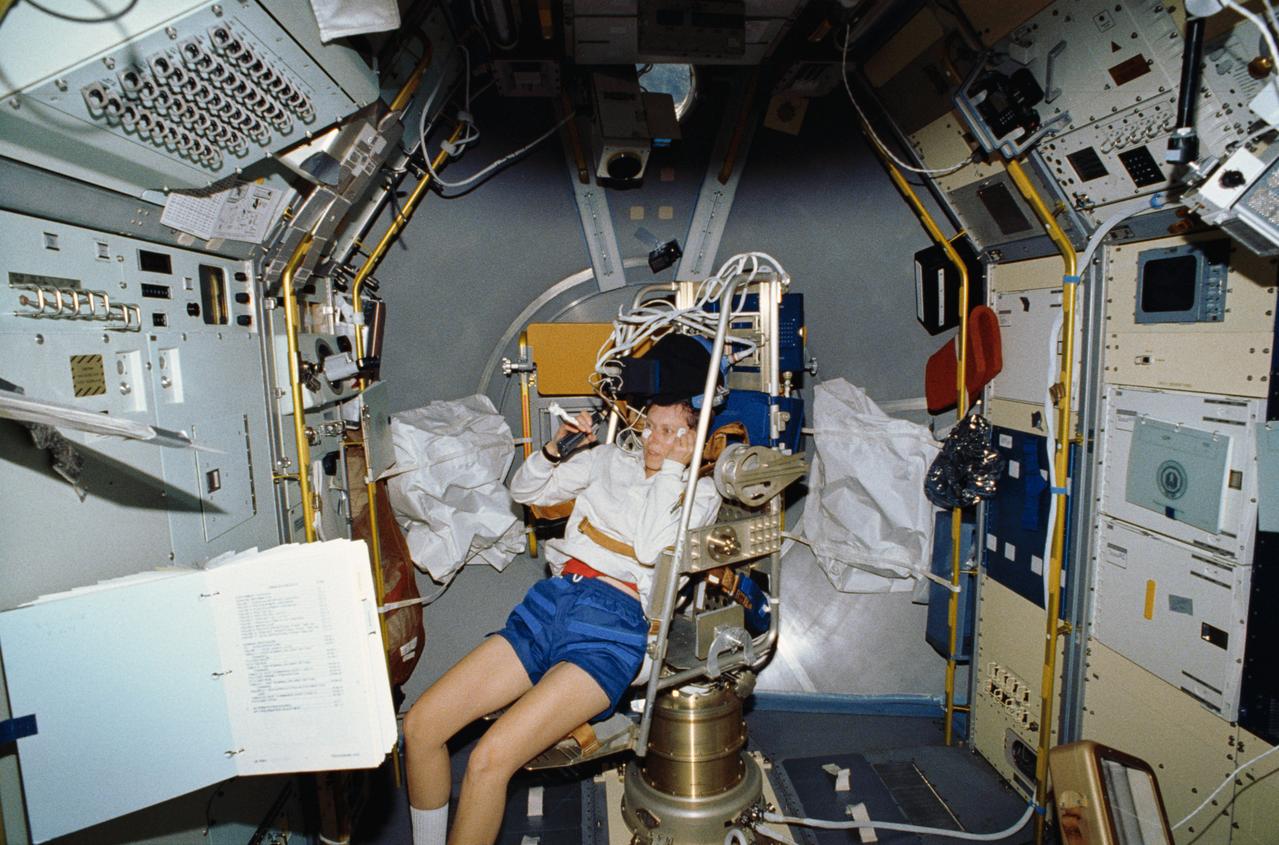

STS042-06-031 (30 Jan 1992) - - - STS-42 Payload Specialist Roberta L. Bondar gets into the Microgravity Vestibular Investigations (MVI) rotator chair to begin an experiment. The chair is mounted in the center aisle of the International Microgravity Laboratory 1 (IML-1) Spacelab (SL) module. Just above Bondar's head is the helmet assembly which is outfitted with accelerometers to measure head movements and visors that fit over each eye independently to provide visual stimuli. The chair system has three movement patterns: "sinusoidal" or traveling predictably back and forth over the same distance at a constant speed; "pseudorandom" or moving back and forth over varying distances; and "stepped" or varying speeds beginning and stopping suddenly.
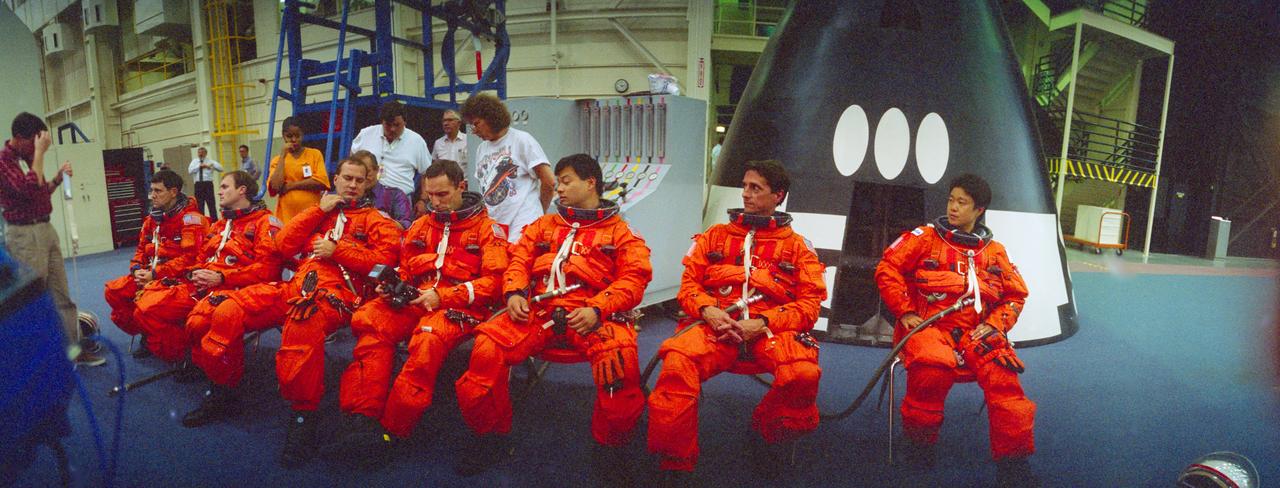

S94-31388 (25 Mar 1994) --- Six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist listen to a briefing by a crew training staffer. From the left are astronauts Robert D. Cabana, mission commander; James D. Halsell Jr., pilot; Richard J. Hieb, payload commander; and Carl E. Walz, Leroy Chiao and Donald A. Thomas, all mission specialists; along with Dr. Chiaki Mukai, payload specialist. Dr. Mukai represents the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan. The STS-65 crew was in the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Shuttle mockup and integration laboratory for crew egress training. The full fuselage trainer, used for the rehearsals, is just out of frame. The seven-member crew will support the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) mission aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia later this year.

STS065-S-001 (March 1994) --- Designed by the crew members, the STS-65 insignia features the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) mission and its Spacehab module which will fly aboard the space shuttle Columbia. IML-2 is reflected in the emblem by two gold stars shooting toward the heavens behind the IML lettering. The space shuttle Columbia is depicted orbiting the logo and reaching into space, with Spacehab on an international quest for a better understanding of the effects of spaceflight on materials processing and life sciences. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
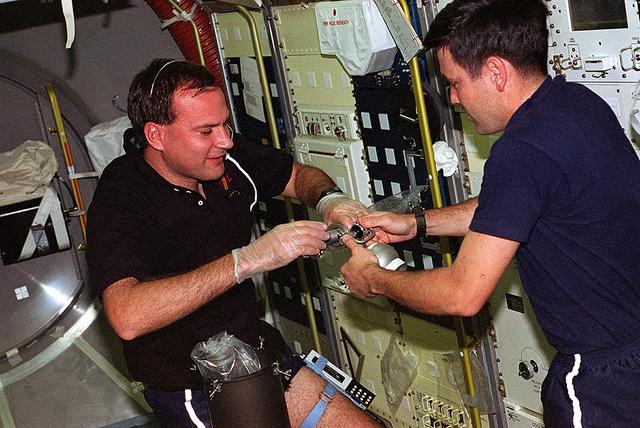

Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-65) onboard photo of Payload specialist Richard J. Hieb (right) and Shuttle Pilot James D. Halsell Jr. working on experiments in the Spacelab in the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2).
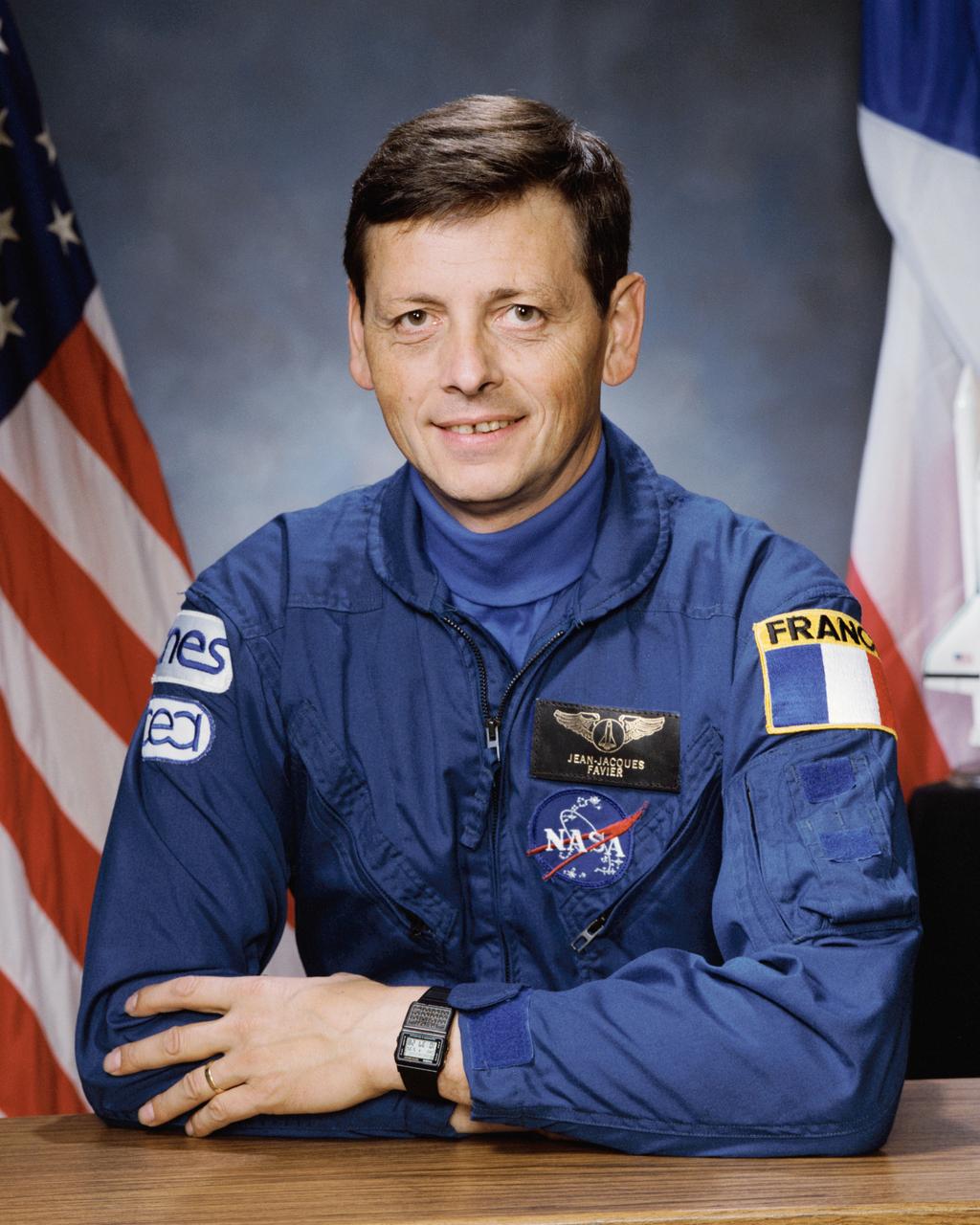

Official portrait of STS-65 International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) backup Payload Specialist Jean-Jacques Favier. Favier is a member of the Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), the French space agency.
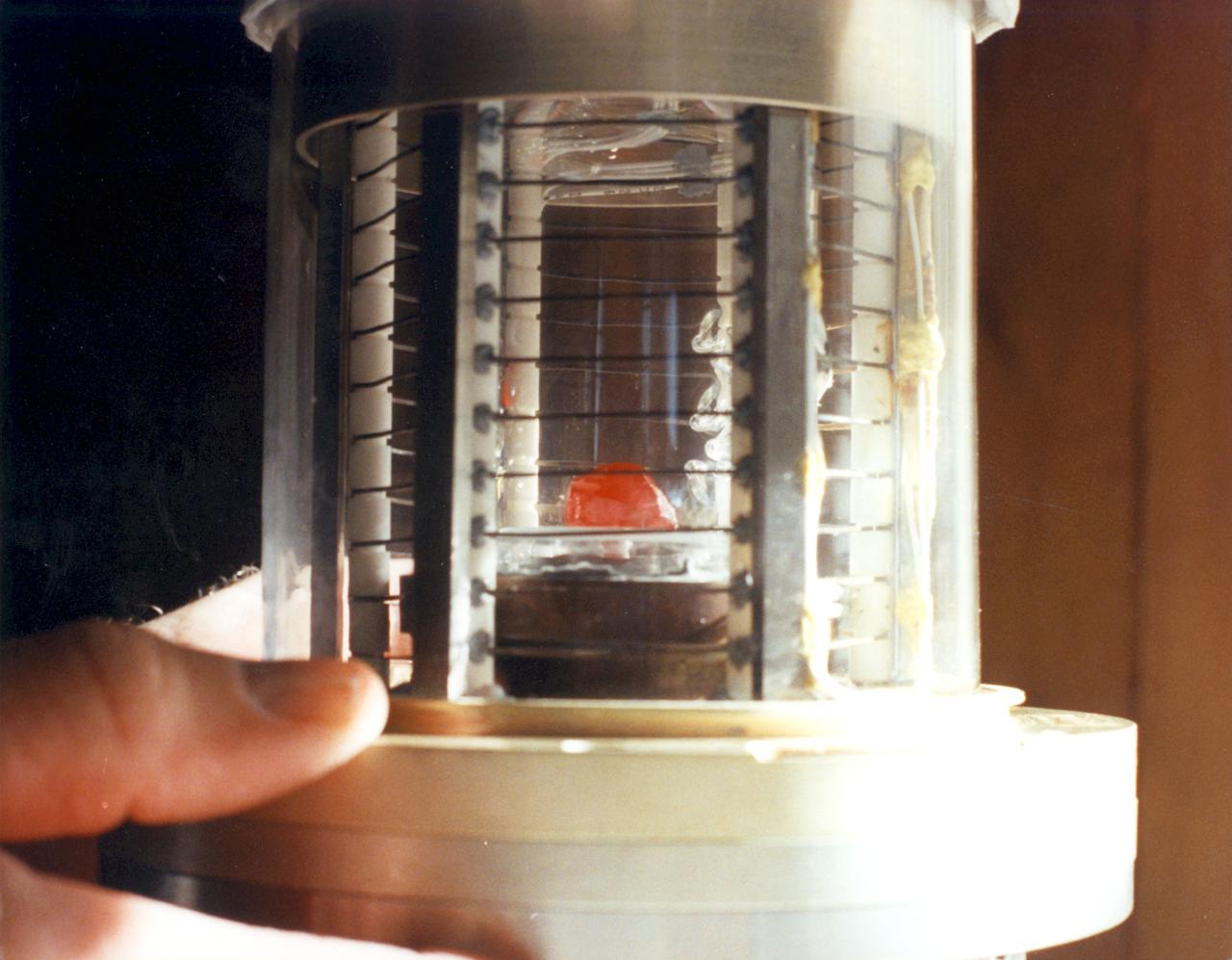
Ampoule view of the Vapor Crystal Growth System (VCGS) Furnace. Used on IML-1 International Microgravity Laboratory Spacelab 3. Prinicipal Investigator and Payload Specialist was Lodewijk van den Berg.
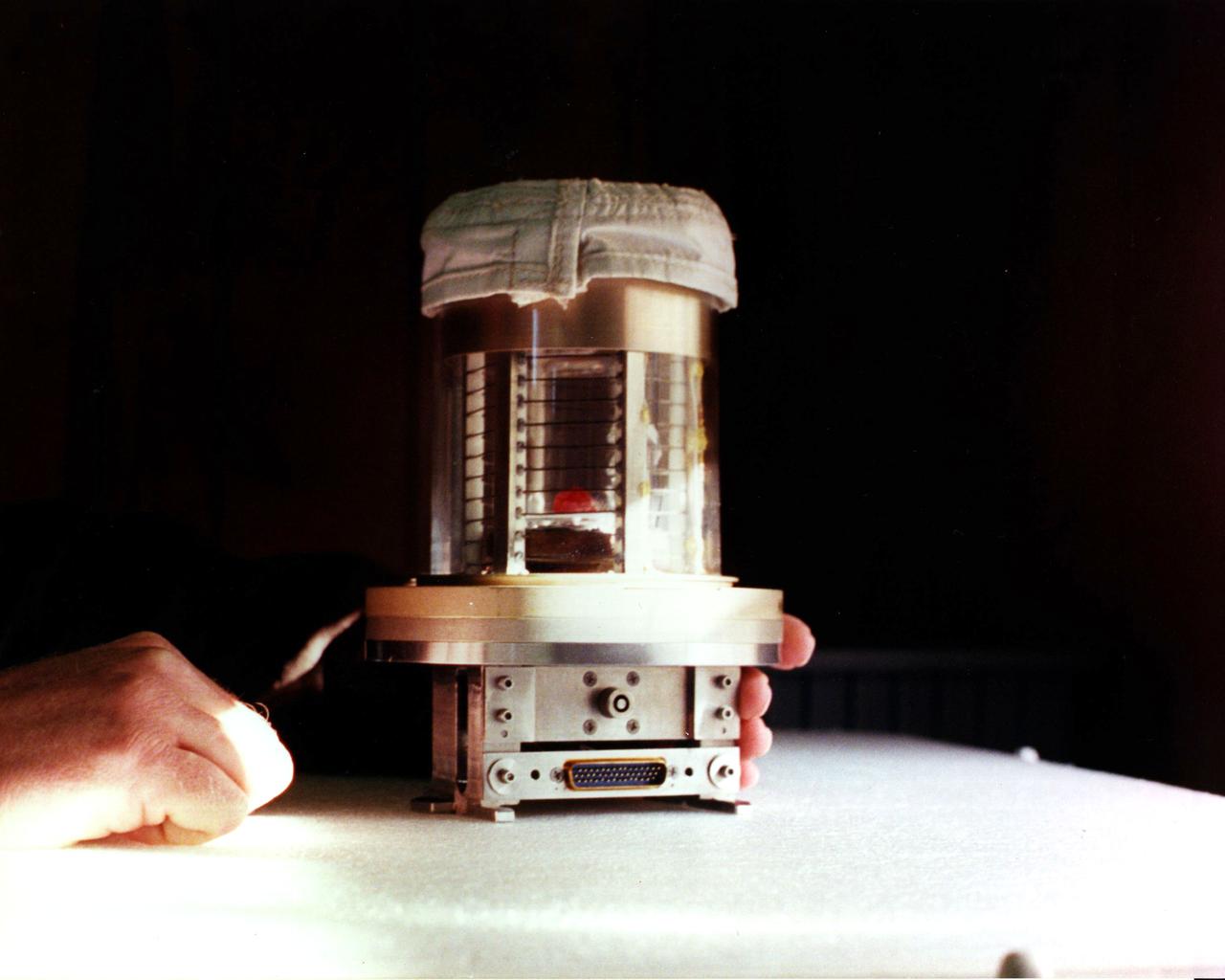
Overall view of the Vapor Crystal Growth System (VCGS) Furnace. Used on IML-1 International Microgravity Laboratory Spacelab 3. Principal Investigator and Payload Specialist was Lodewijk van den Berg.
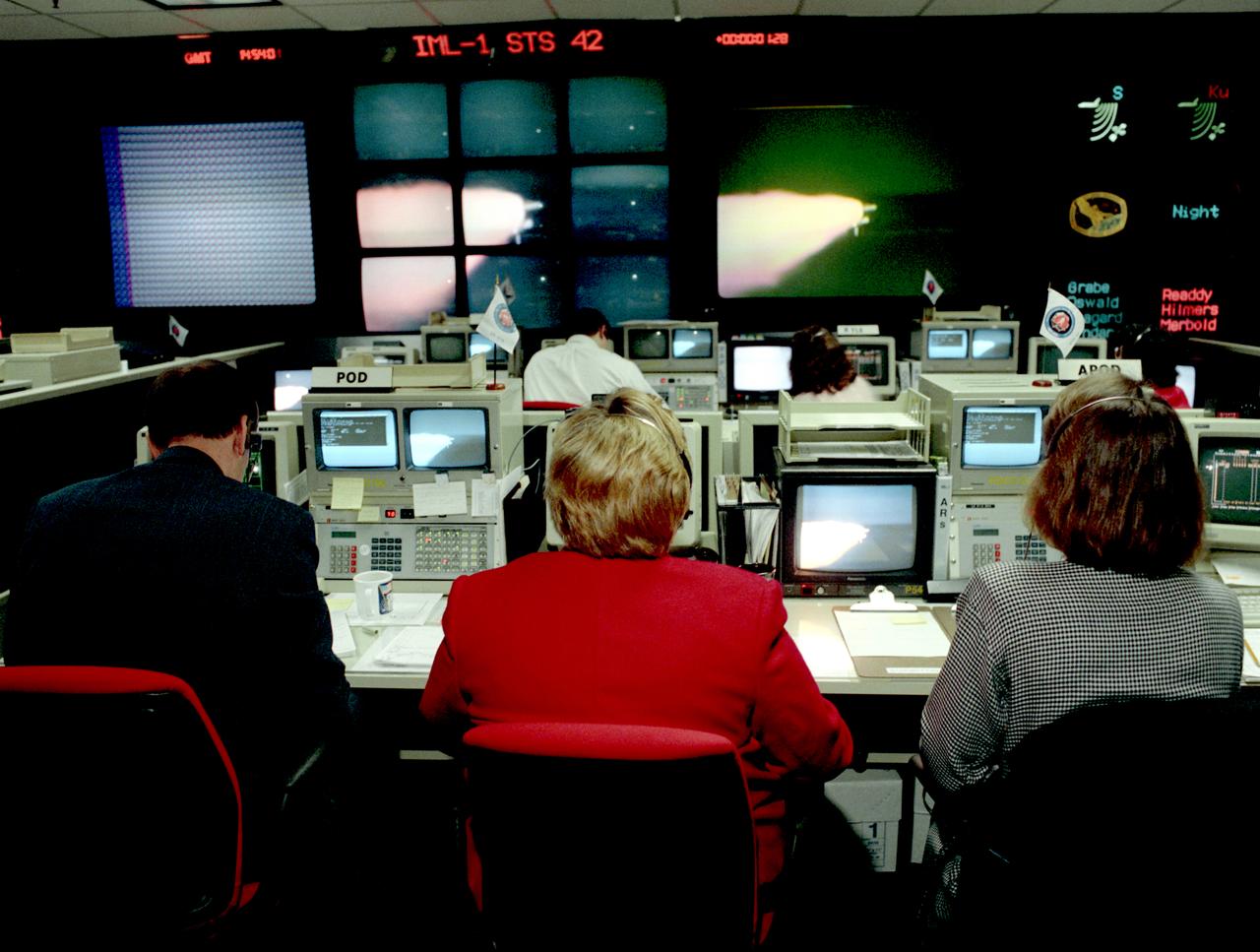

The primary payload for Space Shuttle Mission STS-42, launched January 22, 1992, was the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), a pressurized manned Spacelab module. The goal of IML-1 was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. Around-the-clock research was performed on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and effects of microgravity on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Materials processing experiments were also conducted, including crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury iodide and a virus. The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts aboard the Spacelab and scientists, researchers, and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. The facility made instantaneous video and audio communications possible for scientists on the ground to follow the progress and to send direct commands of their research almost as if they were in space with the crew. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. In this photograph the Payload Operations Director (POD) views the launch.
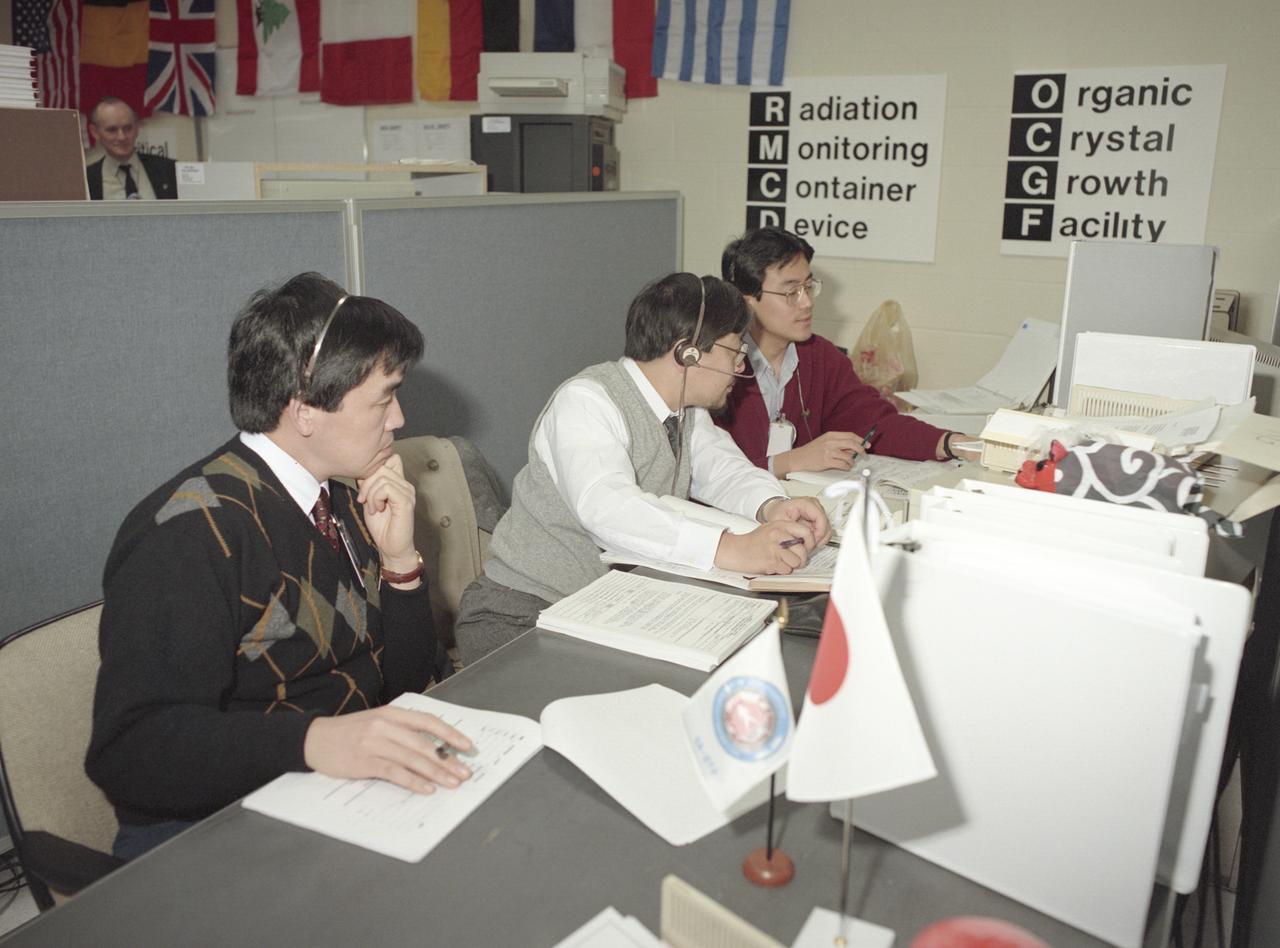

The primary payload for Space Shuttle Mission STS-42, launched January 22, 1992, was the International Microgravity Laboratory-1 (IML-1), a pressurized manned Spacelab module. The goal of IML-1 was to explore in depth the complex effects of weightlessness of living organisms and materials processing. Around-the-clock research was performed on the human nervous system's adaptation to low gravity and effects of microgravity on other life forms such as shrimp eggs, lentil seedlings, fruit fly eggs, and bacteria. Materials processing experiments were also conducted, including crystal growth from a variety of substances such as enzymes, mercury iodide, and a virus. The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Featured are activities of the Organic Crystal Growth Facility (OCGF) and Radiation Monitoring Container Device (RMCD) groups in the SL POCC during the IML-1 mission.
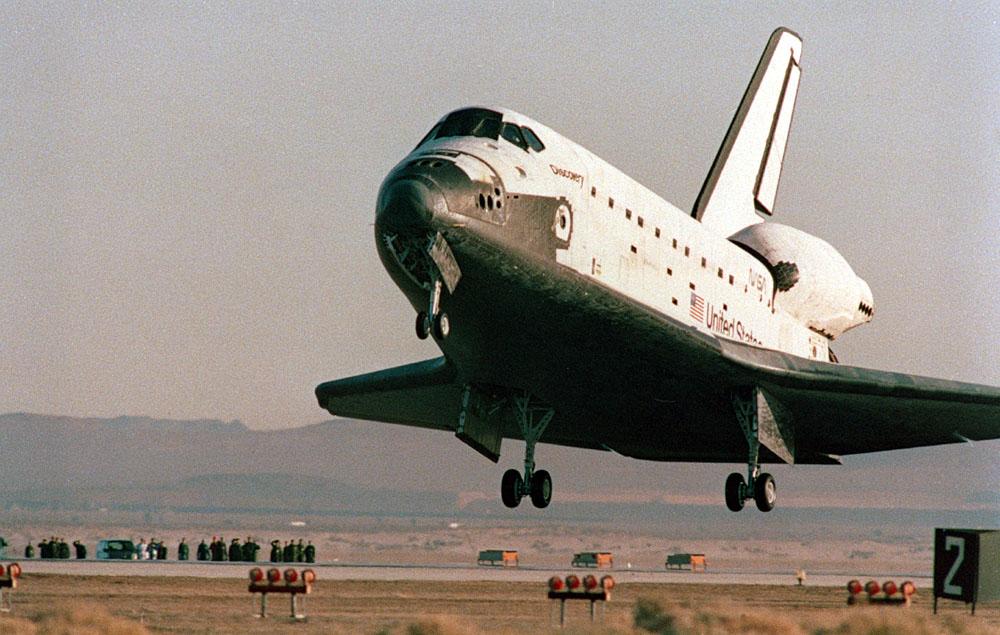

Space Shuttle Discovery STS-42) is just about to ease down its main gear on Runway 22 at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California. The successful landing completed an eight-day mission for five NASA astronauts and two payload specialists supporting the first International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) mission.

Astronaut Carl E. Walz, mission specialist, enters the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) science module in the cargo bay via the turnel connecting it to Columbia's cabin. Walz joined five other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist for more than two weeks of experimenting in Earth orbit.

Payload Specialist Larry DeLucas and Payload Commander Bornie Dunbar working in USML-1.
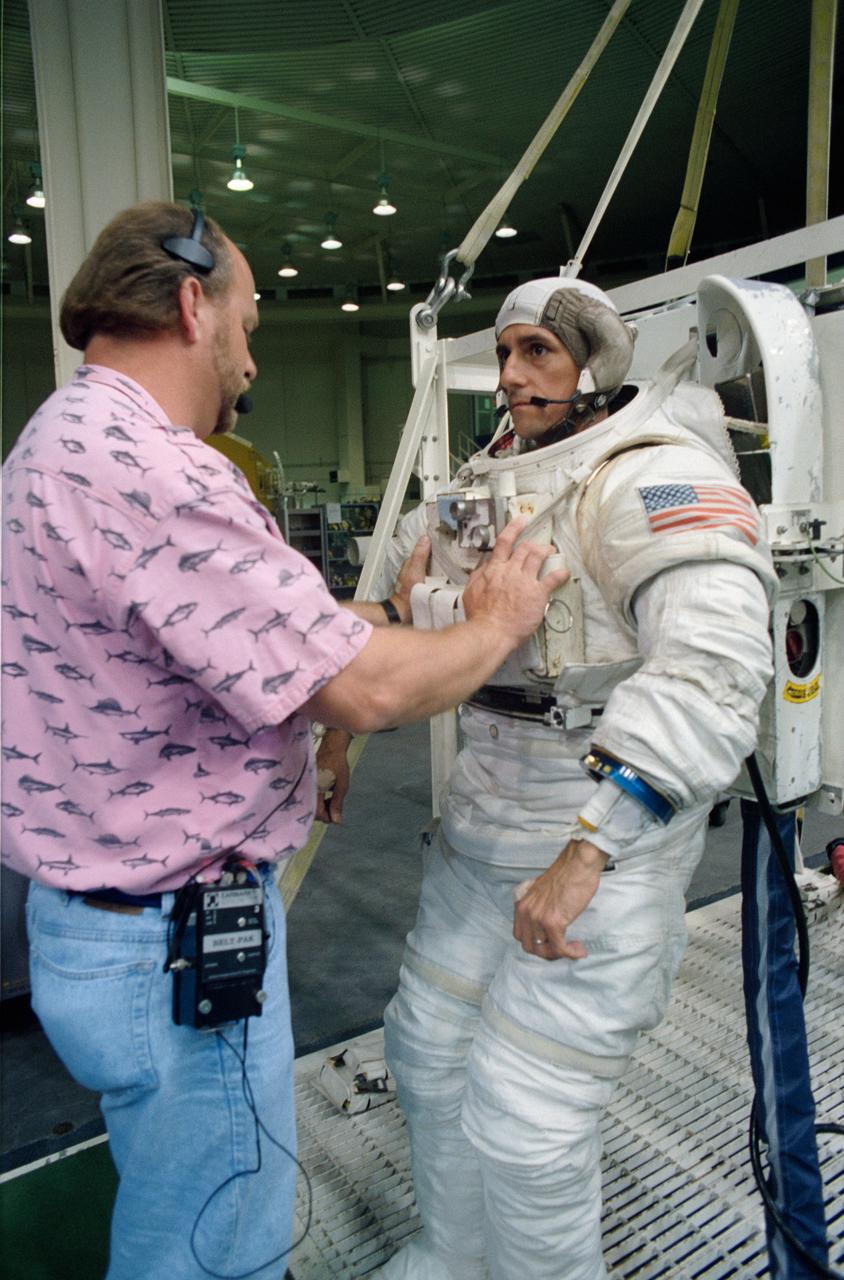

S94-29981 (8 March 1994) --- Astronaut Donald A. Thomas, mission specialist, awaits his helmet as he prepares to be lowered into a 25-feet deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Astronauts Thomas and Leroy Chiao were about to be submerged and made to be neutrally buoyant in order to rehearse several contingency tasks that would require a spacewalk. No spacewalks are scheduled for the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2).

S94-29978 (8 March 1994) --- Astronaut Donald A. Thomas, mission specialist, prepares to be lowered into a 25-feet deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Astronauts Thomas and Leroy Chiao were about to be submerged and made to be neutrally buoyant in order to rehearse several contingency tasks that would require a spacewalk. No spacewalks are scheduled for the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2).
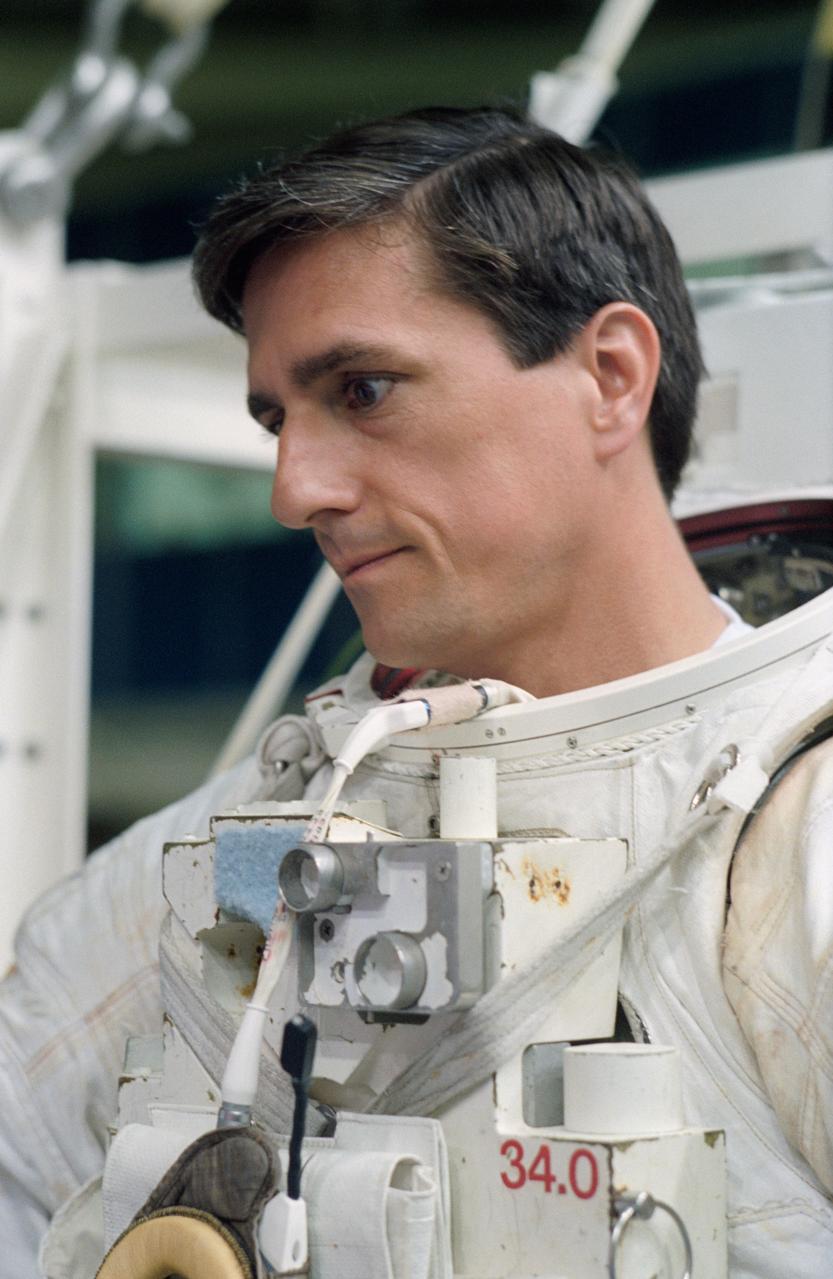

S94-29976 (8 March 1994) --- Astronaut Donald A. Thomas, mission specialist, awaits his helmet as he prepares to be lowered into a 25-feet deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Astronauts Thomas and Leroy Chiao were about to be submerged and made to be neutrally buoyant in order to rehearse several contingency tasks that would require a spacewalk. No spacewalks are scheduled for the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2).
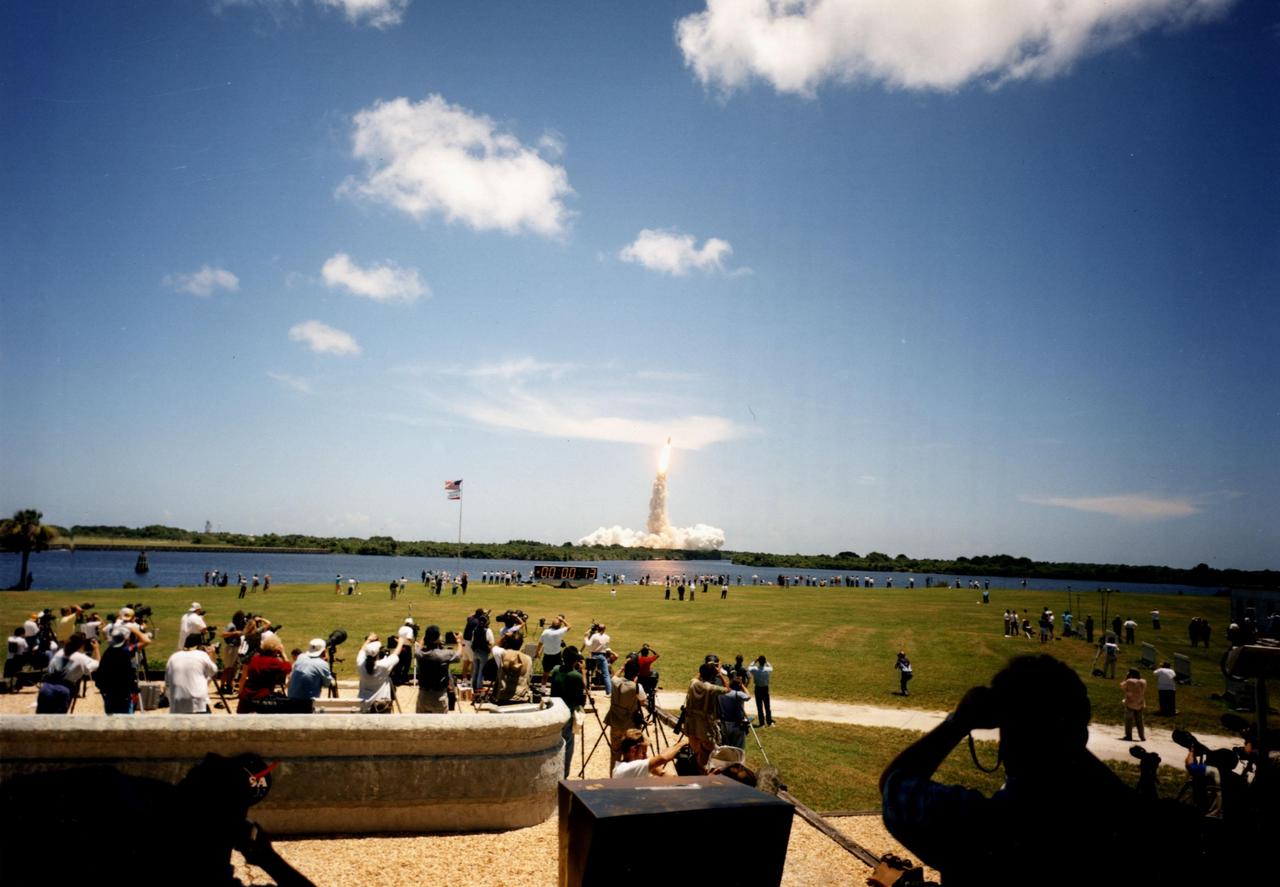

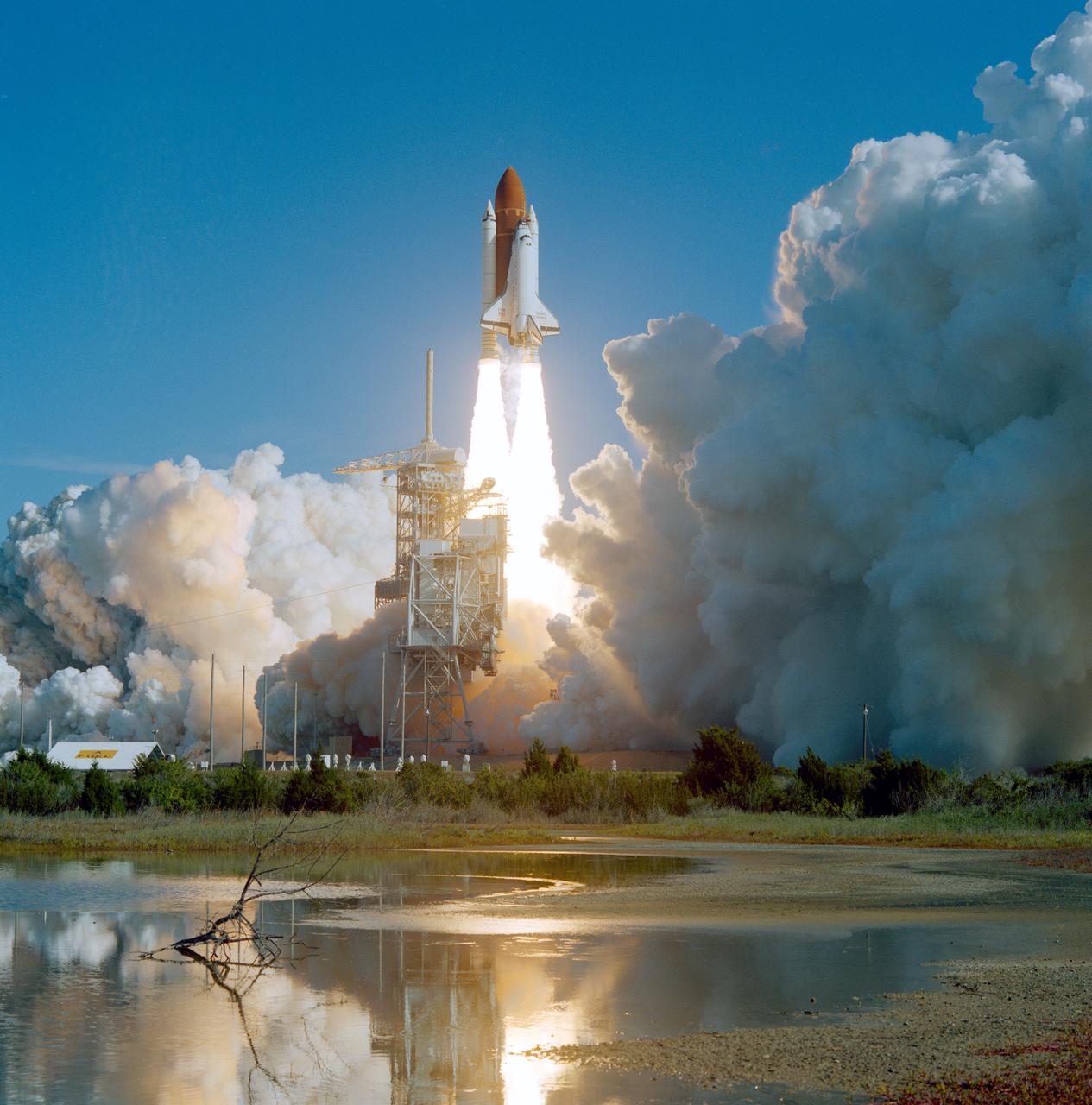
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle Columbia lifts off from Launch Pad 39A on July 8, 1994 at 12:43 p.m. EDT to begin the 14-day STS-65/Internatinal Microgravity Laboratory-2 (IML-2) mission. The mission countdown clock also can be seen, giving the time into the mission after liftoff. The STS-65 mission is scheduled to end with a landing at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility
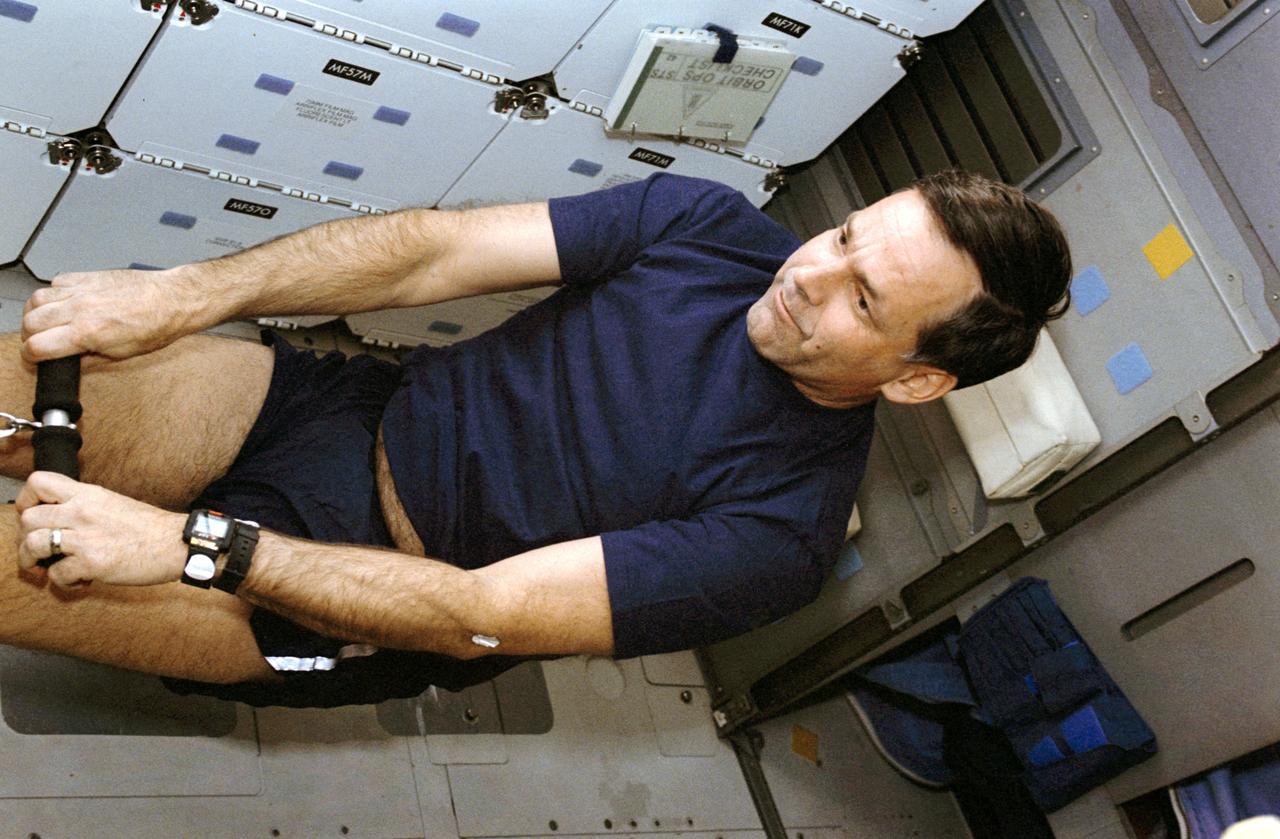

STS042-209-002 (22-30 Jan 1992) --- Astronaut Ronald J. Grabe, STS-42 mission commander, exercises on Discovery's middeck. Grabe, along with four other NASA astronauts and two International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) payload specialists spent more than eight days conducting experiments in Earth orbit.
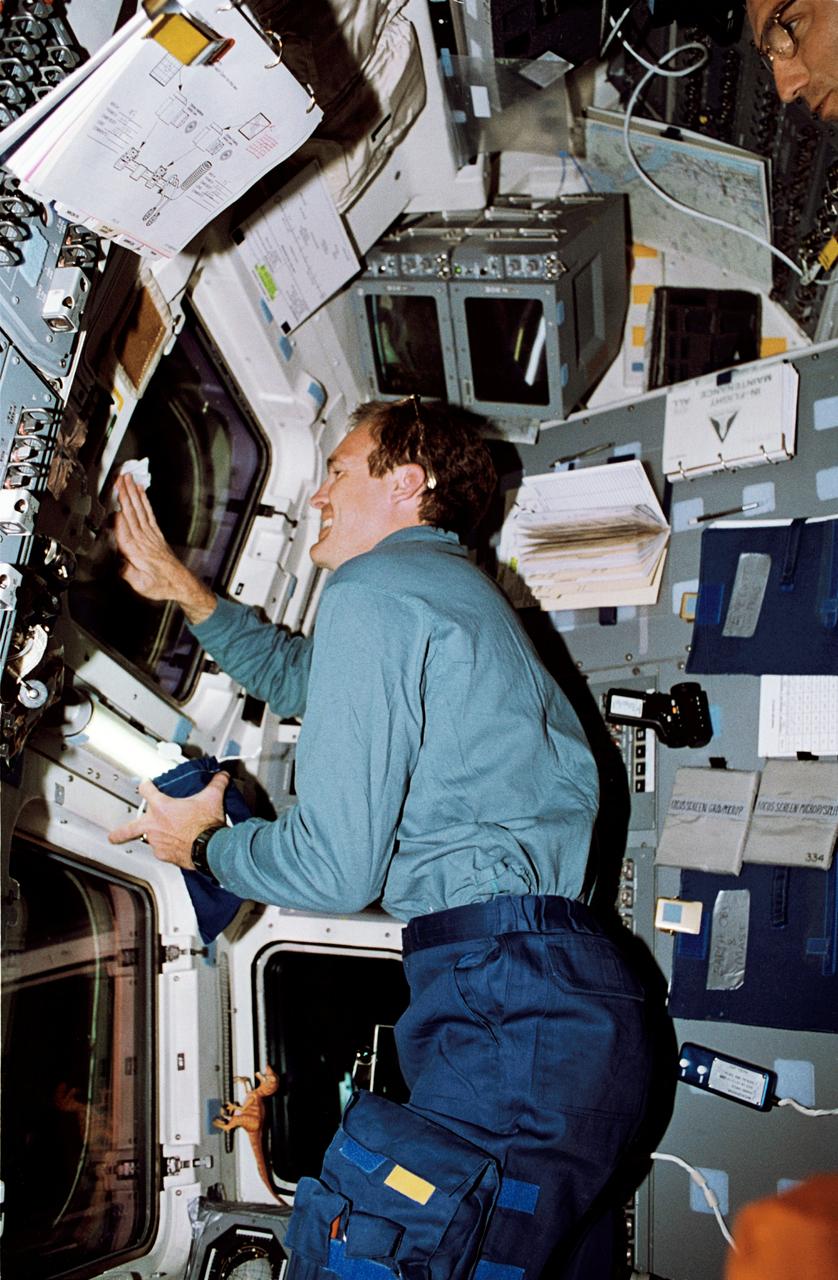

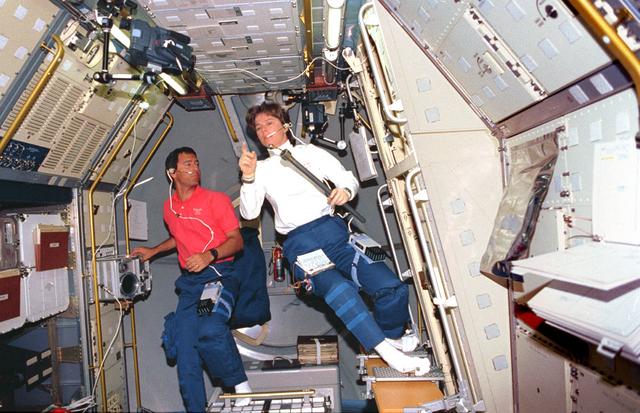
STS065-52-034 (8-23 July 1994) --- On the Space Shuttle Columbia's aft flight deck, astronaut James D. Halsel,l Jr., pilot, cleans off one of the overhead windows. Astronaut Carl E. Walz, mission specialist, looks on (photo's edge). The two shared over fourteen days in Earth-orbit with four other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist in support of the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) mission.
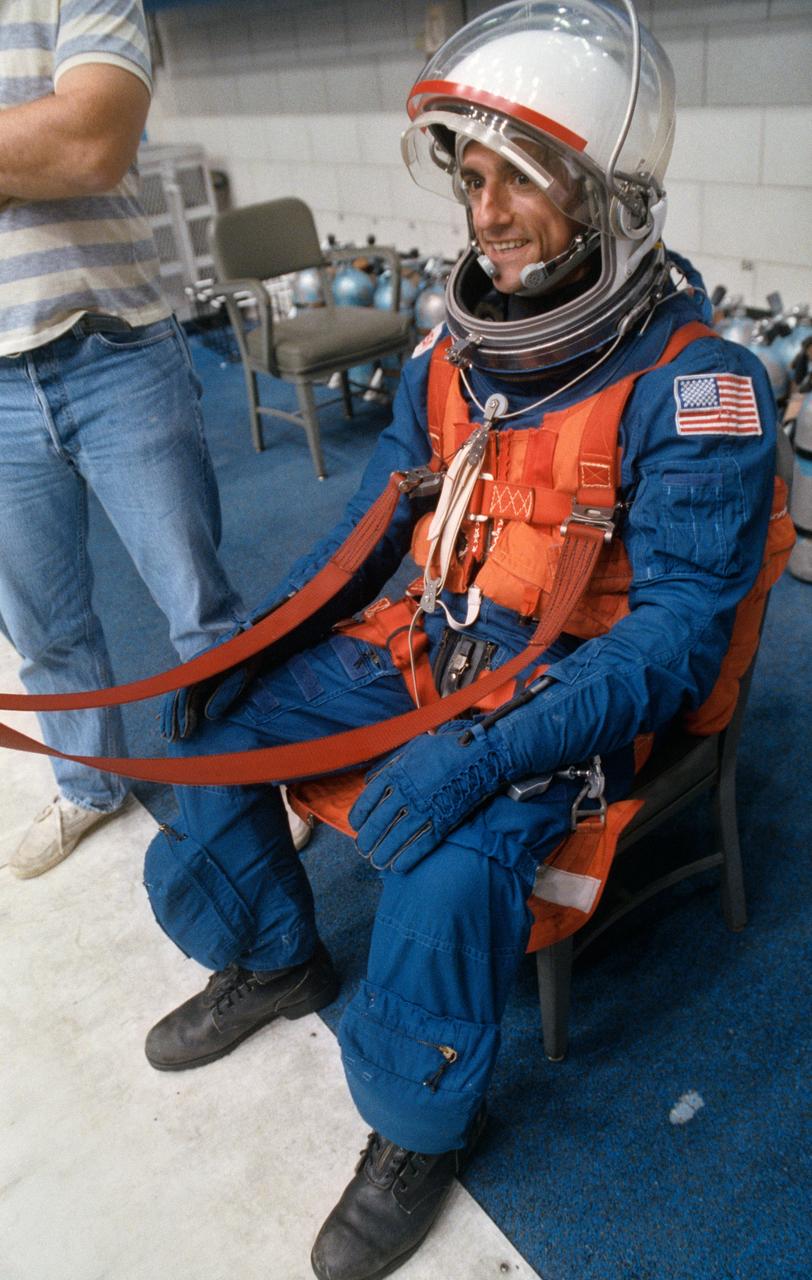

S93-43113 (Nov 1993) --- Astronaut Donald A. Thomas, mission specialist, is pictured during a bailout training session at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Test Facility (WET-F). Thomas was joined by five other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist for the training session. The crew will spend approximately two weeks aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia next year in support of the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) mission.
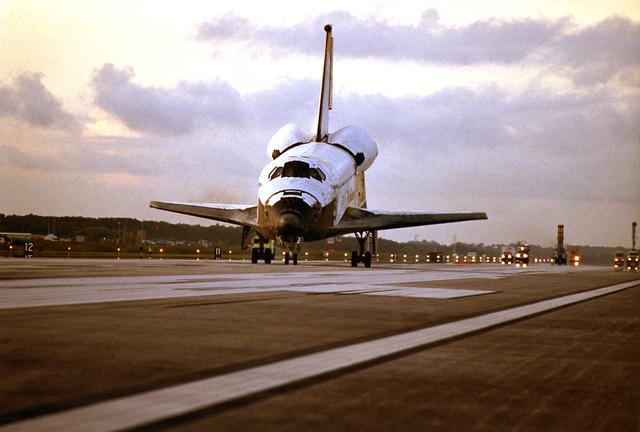

The Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-65) came to a stop at Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility to complete the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) mission. During the record-setting spaceflight of 14 days, 17 hours, and 56 minutes, the seven-person crew conducted more than 80 materials and life sciences experiments,
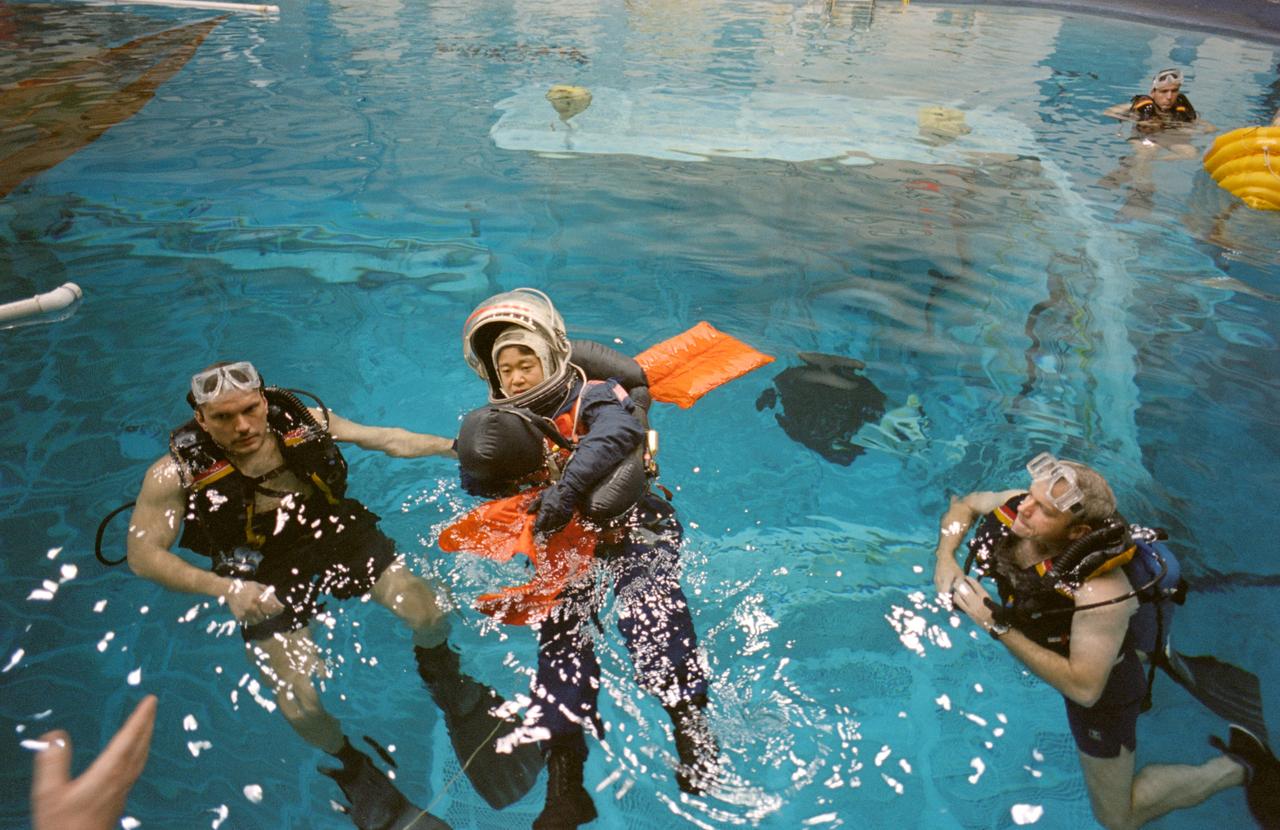
S94-29355 (28 Feb 1994) --- Dr. Chiaki Mukai, payload specialist, is assisted by a team of SCUBA-equipped divers during emergency egress training. The STS-65 crew was in the Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F) for the bailout training exercise. Dr. Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency (NASDA), will join six NASA astronauts for the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) mission aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia later this year.

Dr. Chiaki Mukai of Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA) speaks to students at the California Science Center during the outreach session of the Pan Pacific Microgravity Conference on May 2, 2001. She flew as a payload specialist on two NASA Space Shuttle missions, STS-65 carrying the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2, 1994) and STS-95 (1998).
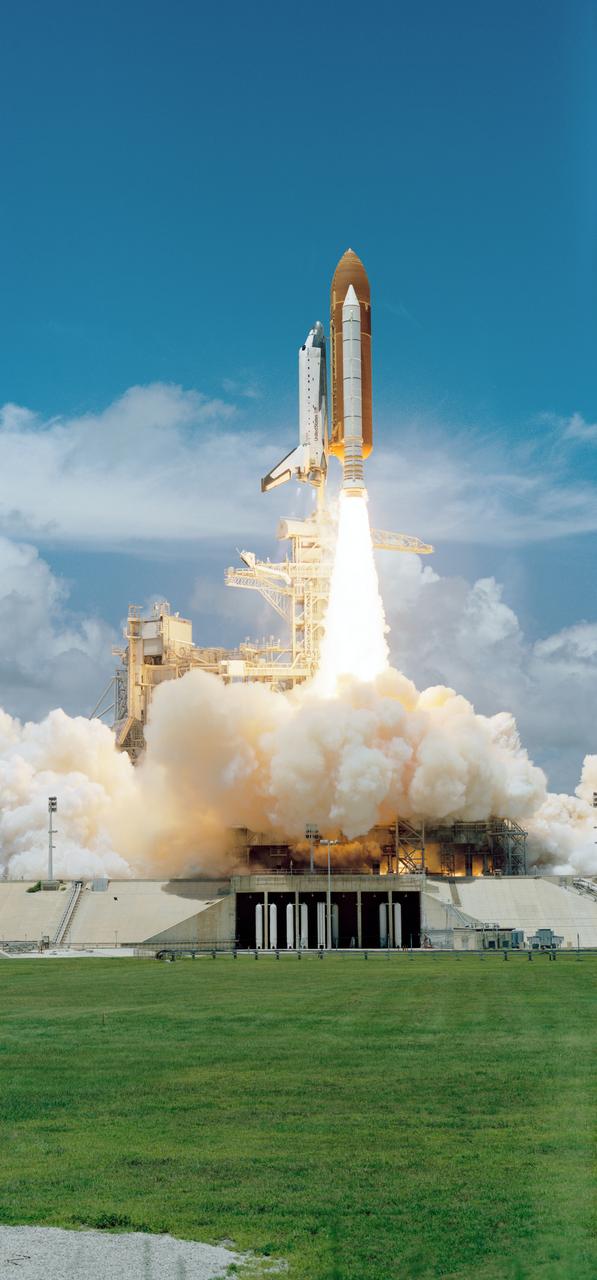

STS065-S-048 (8 July 1994) --- The Space Shuttle Columbia, with six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist aboard, heads toward Earth-orbit. A short time later, the crew began setting up the science module for two weeks of experimentation in support of the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2). Launch occurred at 12:43 p.m. (EDT), July 8, 1994. Onboard were astronauts Robert D. Cabana, James D. Halsell, Jr., Richard J. Hieb, Carl E. Walz, Leroy Chiao, and Donald A. Thomas along with NASDA payload specialist Dr. Chiaki Mukai.
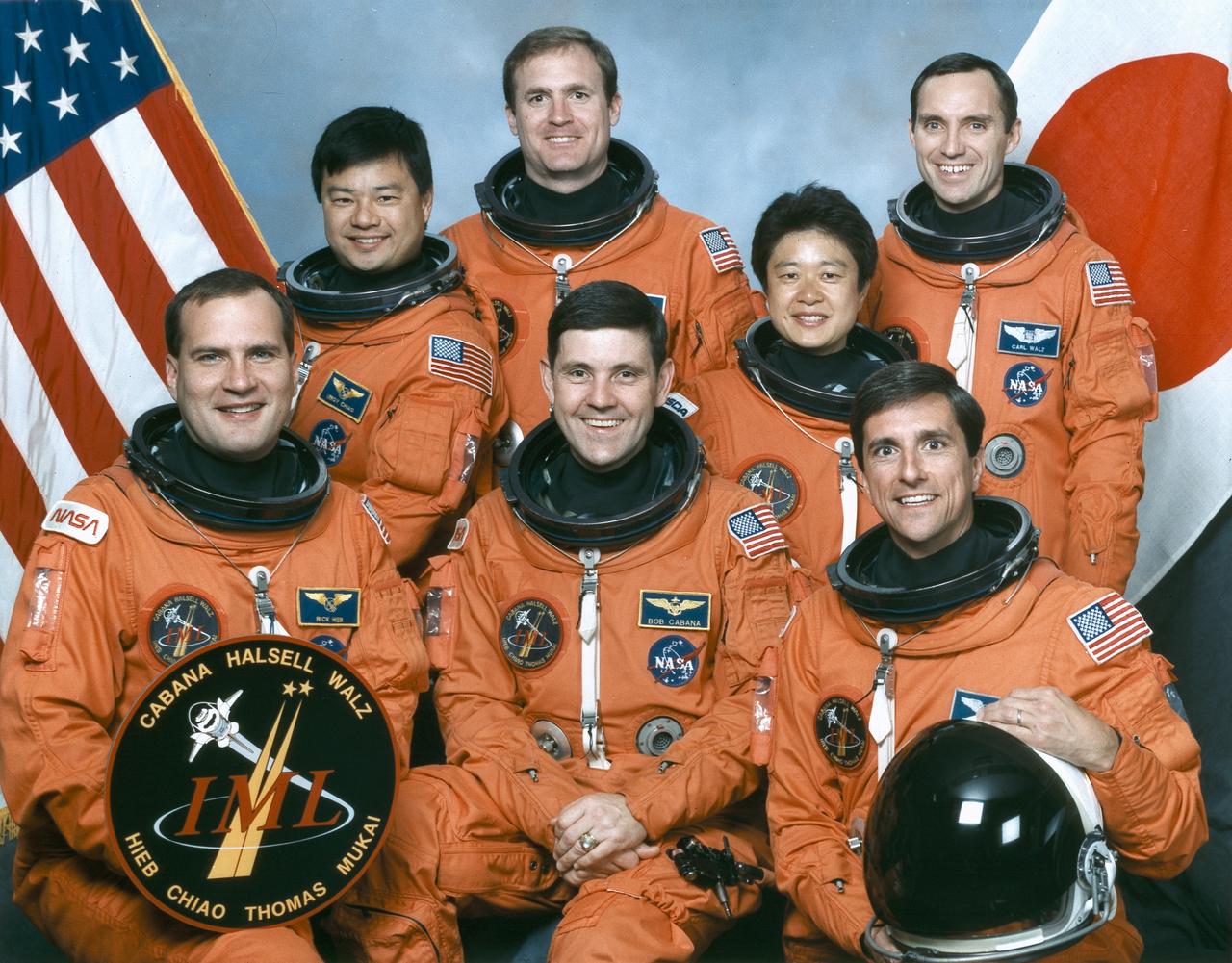

The crew assigned to the STS-65 mission included (seated left to right) Richard J. (Rick) Hieb, payload commander; Robert D. (Bob) Cabana, commander; and Donald A. Thomas, mission specialist. Standing, from left to right, are Leroy Chiao, mission specialist; James D. Halsell, pilot; Chiaki Naito-Mukai, payload specialist; and Carl E. Walz, mission specialist. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on July 8, 1994 at 12:43:00 pm (EDT), the STS-64 mission marked the second flight of the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) and the first flight of a female Japanese crew member.
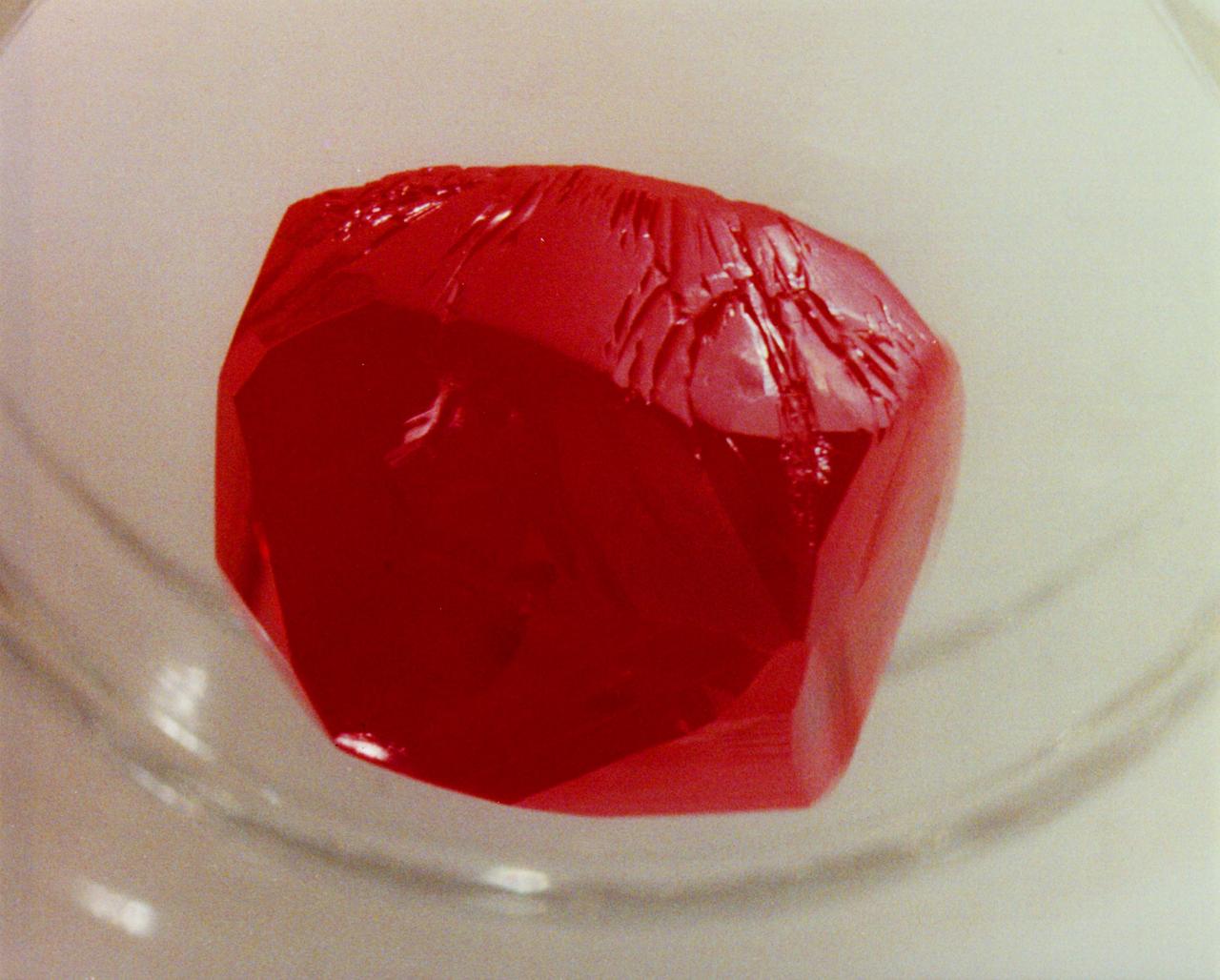

Vapor Crystal Growth System developed in IML-1, Mercuric Iodide Crystal grown in microgravity FES/VCGS (Fluids Experiment System/Vapor Crystal Growth Facility). During the mission, mercury iodide source material was heated, vaporized, and transported to a seed crystal where the vapor condensed. Mercury iodide crystals have practical uses as sensitive X-ray and gamma-ray detectors. In addition to their excellent optical properties, these crystals can operate at room temperature, which makes them useful for portable detector devices for nuclear power plant monitoring, natural resource prospecting, biomedical applications, and astronomical observing.
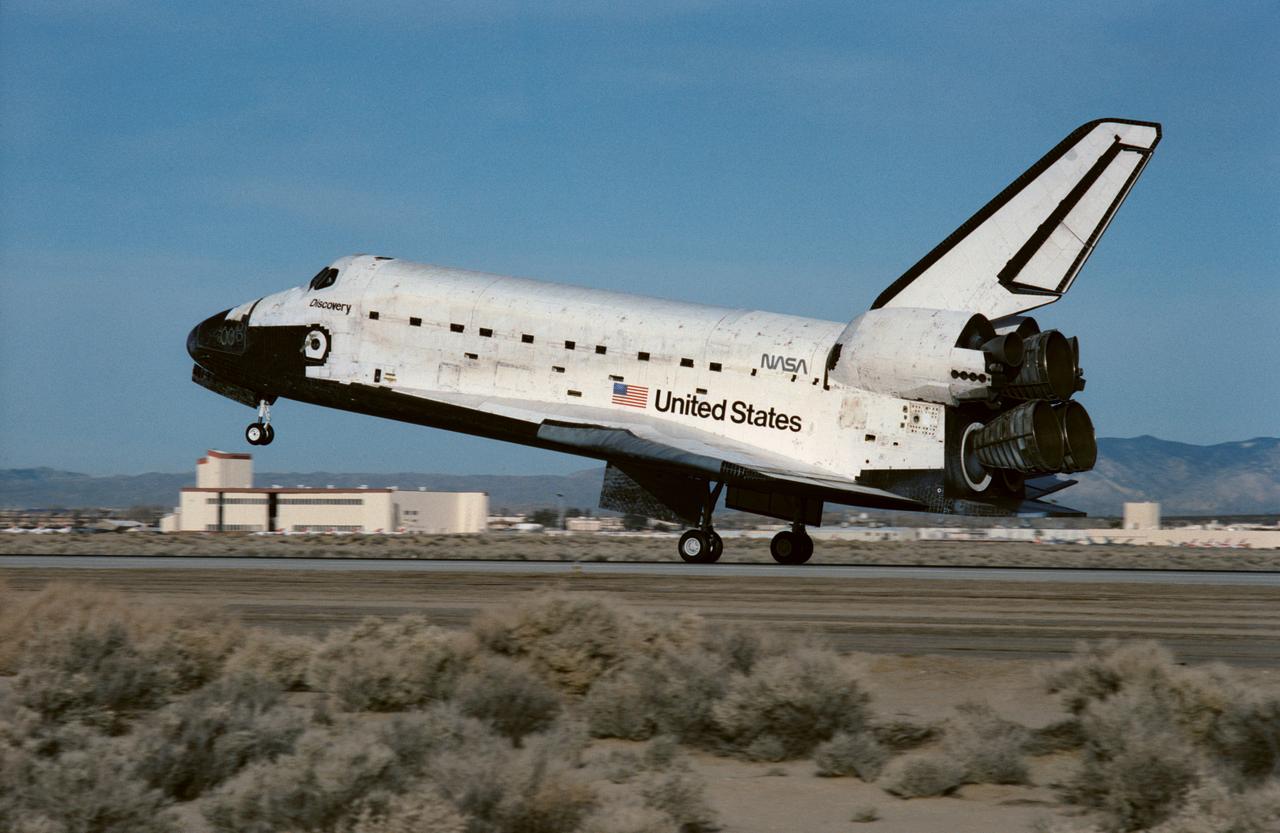

STS042-S-094 (30 Jan 1992) --- Space Shuttle Discovery lands on Runway 22 at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California to complete an eight-day mission. Main gear touchdown occurred at 8:07:18 a.m. (PST), Jan. 30, 1992. The crewmembers aboard Discovery for the first International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) mission were astronauts Ronald J. Grabe, mission commander; Stephen S. Oswald, pilot; Norman E. Thagard, payload commander; and David C. Hilmers and William F. Readdy, both mission specialists; and payload specialists Roberta L. Bondar of Canada and Ulf Merbold, representing the European Space Agency (ESA).
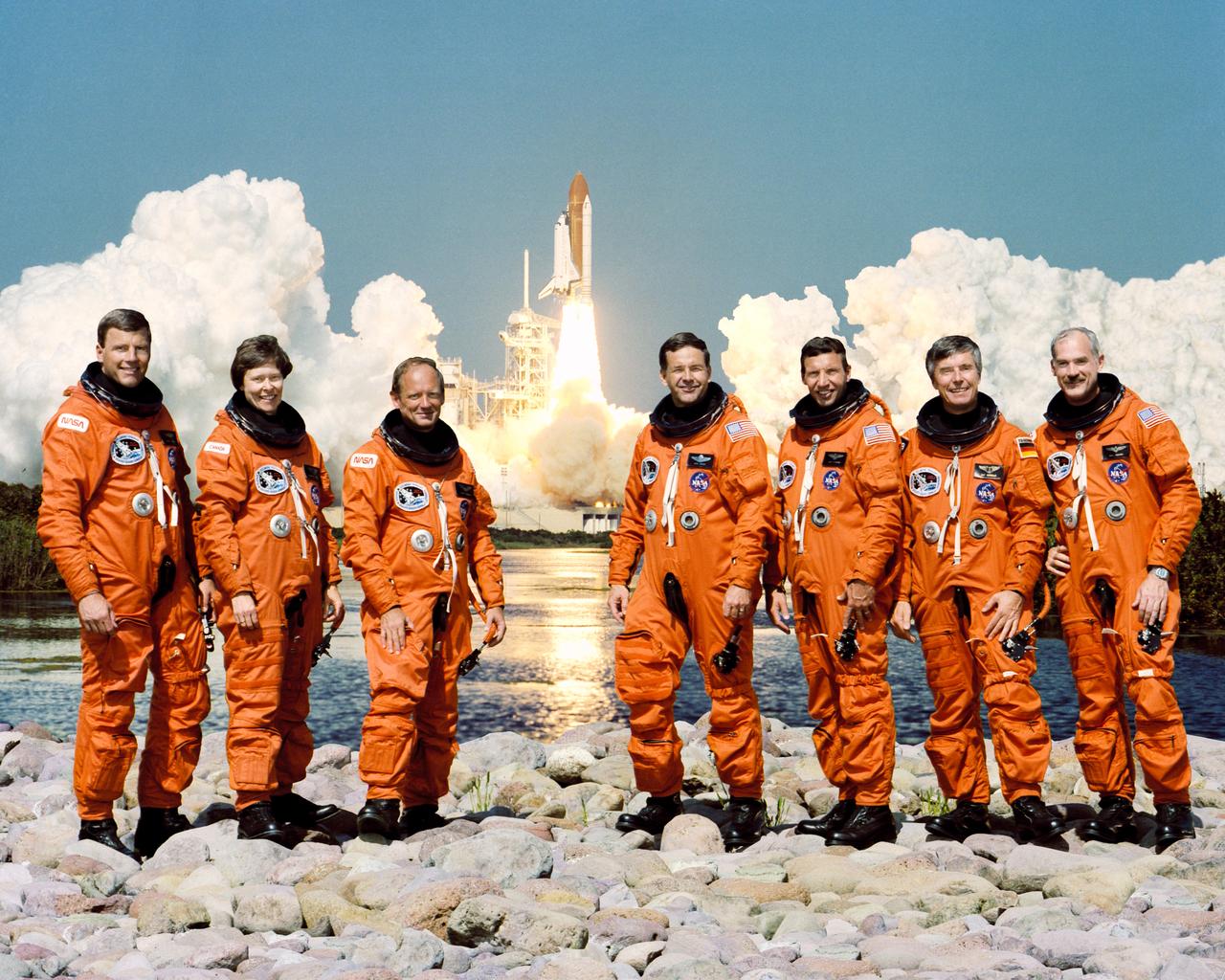

STS042-S-002 (November 1991) --- Payload specialists representing Canada and the European Space Agency (CSA - ESA) join five NASA astronauts for the January 1992 scheduled STS-42 mission. Left to right are astronauts Stephen S. Oswald, pilot; Roberta L. Bondar, payload specialist; Norman E. Thagard, payload commander; Ronald J. Grabe, mission commander; David C. Hilmers, mission specialist; Ulf Merbold, payload specialist; and William F. Readdy, mission specialist. The STS-42 mission will utilize the Space Shuttle Discovery to carry out experiments for the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1).
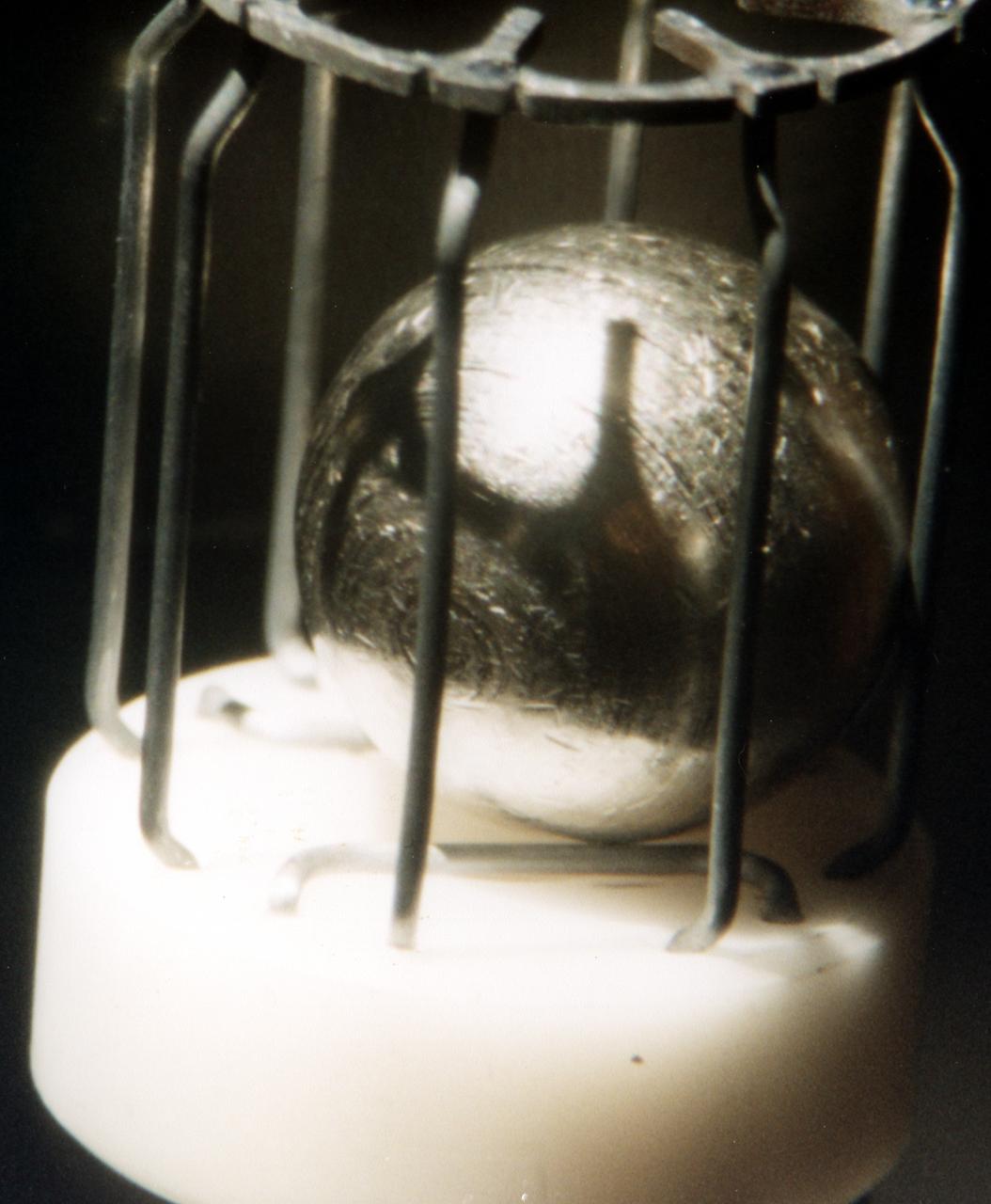

Typical metal sample that was processed by TEMPUS (Tiegelfreies Elektromagnetisches Prozessieren Unter Schwerelosigkeit), an electromagnetic levitation facility developed by German researchers and flown on the IML-2 and MSL-1 and 1R Spacelab missions. Electromagnetic levitation is used commonly in ground-based experiments to melt and then cool metallic melts below their freezing points without solidification occurring. Sample size is limited in ground-based experiments. Research with TEMPUS aboard Spacelab allowed scientists to study the viscosity, surface tension, and other properties of several metals and alloys while undercooled (i.e., cooled below their normal solidification points). The sample is about 1 cm (2/5 inch) in diameter.

STS042-S-064 (22 Jan 1992) --- A horizontal image of liftoff of STS-42, with a crew of seven and the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) onboard. Crewmembers are astronauts Ronald J. Grabe, mission commander; Stephen S. Oswald, pilot; Norman E. Thagard, payload commander; David C. Hilmers and William F. Readdy, both mission specialists; and payload specialists Roberta L. Bondar of Canada and Ulf Merbold, representing the European Space Agency (ESA). Liftoff occurred at 9:52:33 a.m. (EST), Jan. 22, 1992.
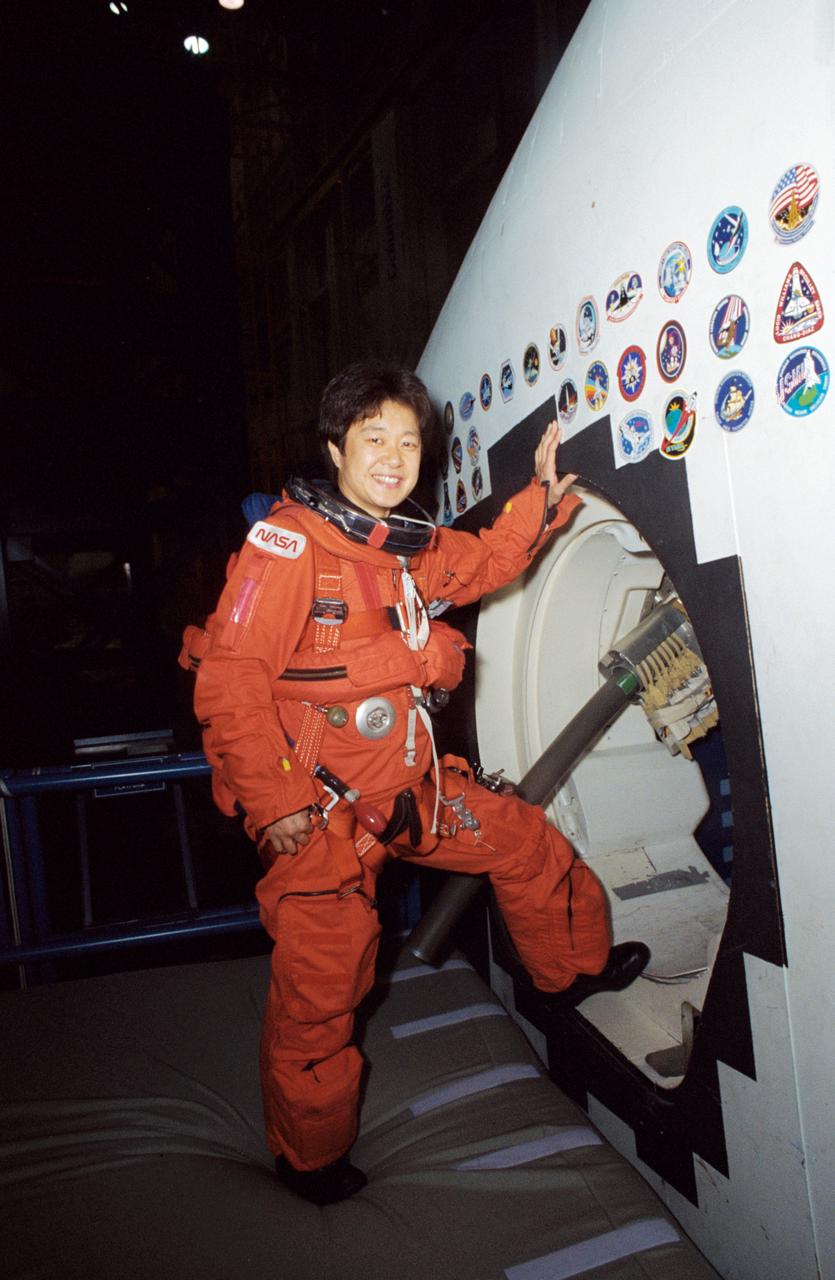

STS-65 Japanese Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai takes a break from training at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Wearing a training version of the orange launch and entry suit (LES), Mukai stands at the crew compartment trainer (CCT) side hatch in the Mockup and Integration Laboratory (MAIL) Bldg 9NE. Note the crew escape system (CES) pole device extending out the side hatch which would accommodate crewmembers in bailout from a troubled spacecraft. Mukai represents the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan and will serve as a payload specialist aboard Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, during the STS-65 International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) mission.

Onboard Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-42) the seven crewmembers pose for a traditional in-space portrait in the shirt-sleeve environment of the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) science module in the Shuttle's cargo bay. Pictured are (clockwise from top),Commander Ronald J. Grabe, payload commander Norman E. Thagard, payload specialist Roberta L. Bondar; mission specialists William F. Readdy and David C. Hilmers; pilot Stephen S. Oswald and payload specialist Ulf Merbold. The rotating chair, used often in biomedical tests on the eight-day flight, is in center frame.
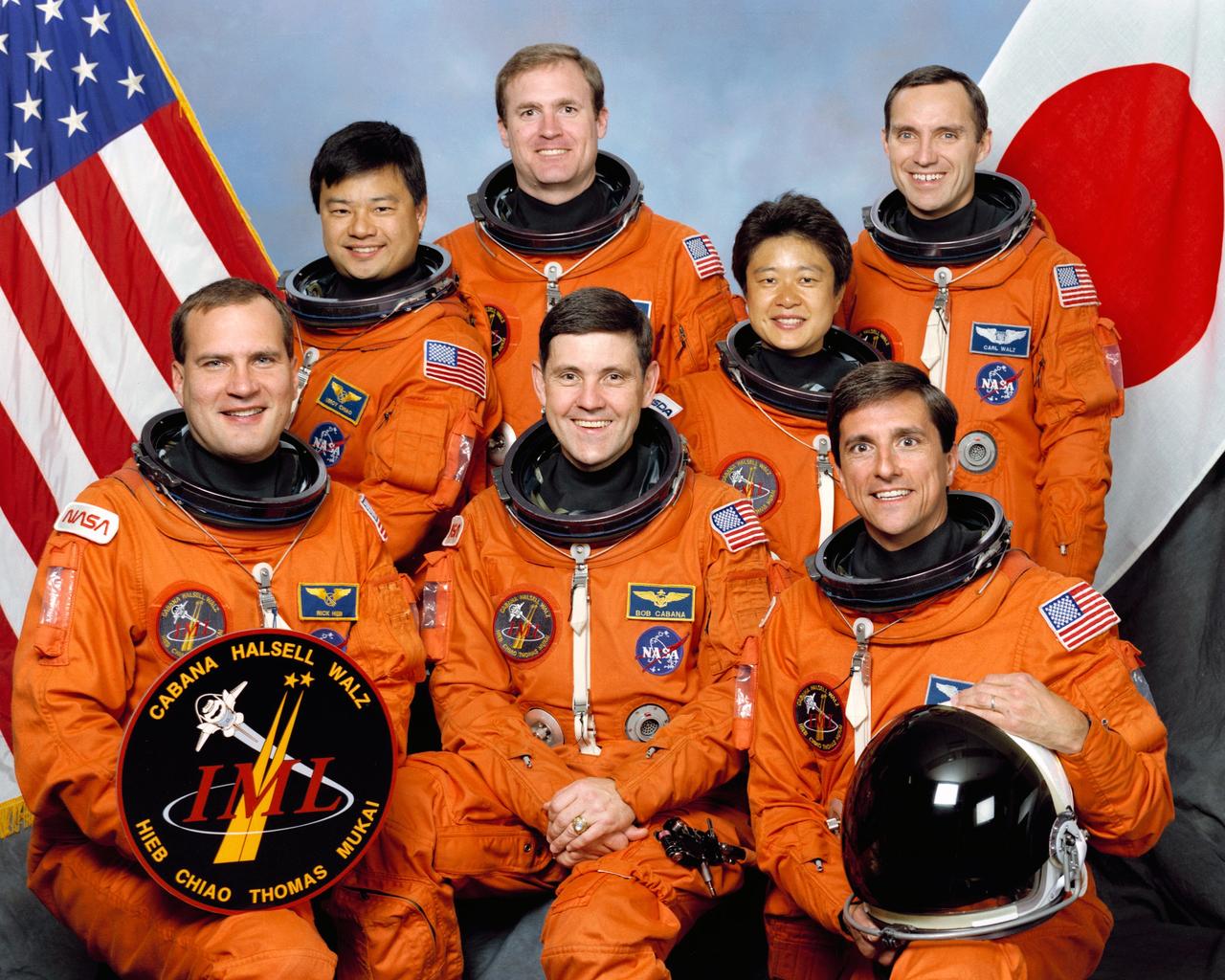

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, Houston, Texas -- -- STS065(S)002 -- STS-65 Official Crew Portrait --- Six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist take a break from STS-65 training to pose for their crew portrait. Left to right are Richard J. Hieb, Leroy Chiao, James D. Halsell Jr., Robert D. Cabana, Dr. Chiaki Mukai, Donald A. Thomas and Carl E. Walz. Cabana is mission commander, and Halsell has been assigned as pilot. Hieb is payload commander, with Walz, Thomas and Chiao serving as mission specialists. Dr. Mukai represents the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan as payload specialist on the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML) mission.
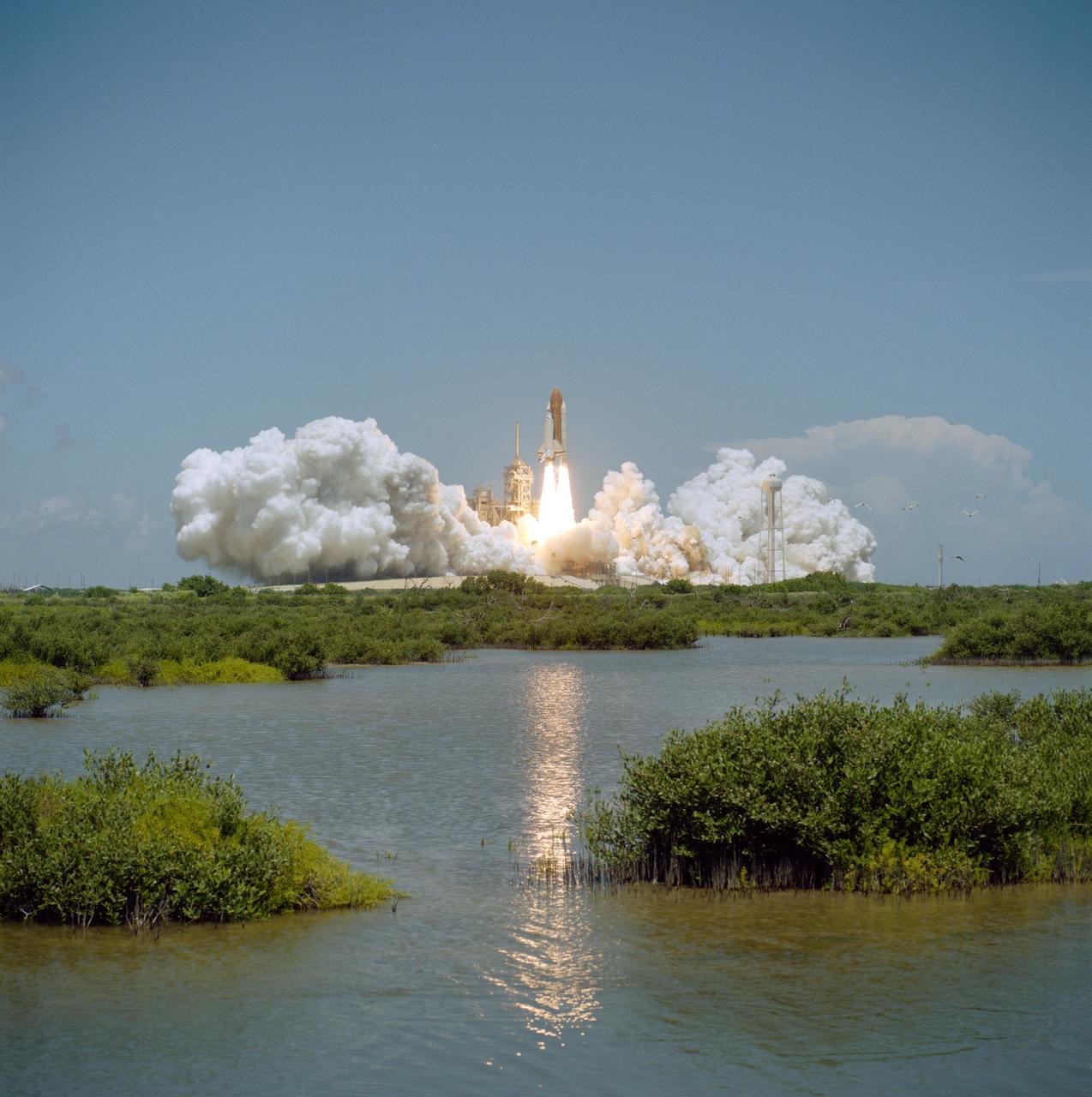

Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, rises above Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39A after liftoff at 12:43 pm Eastern Daylight Time (EDT). An exhaust cloud covers the launch pad area and the glow of the space shuttle main engine (SSME) and solid rocket booster (SRB) firings is reflected in a nearby marsh as OV-102 atop its external tank (ET) heads toward Earth orbit. A small flock of birds is visible at the right. Once in Earth's orbit, STS-65's six NASA astronauts and a Japanese Payload Specialist aboard OV-102 will begin two weeks of experimentation in support of the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) mission.
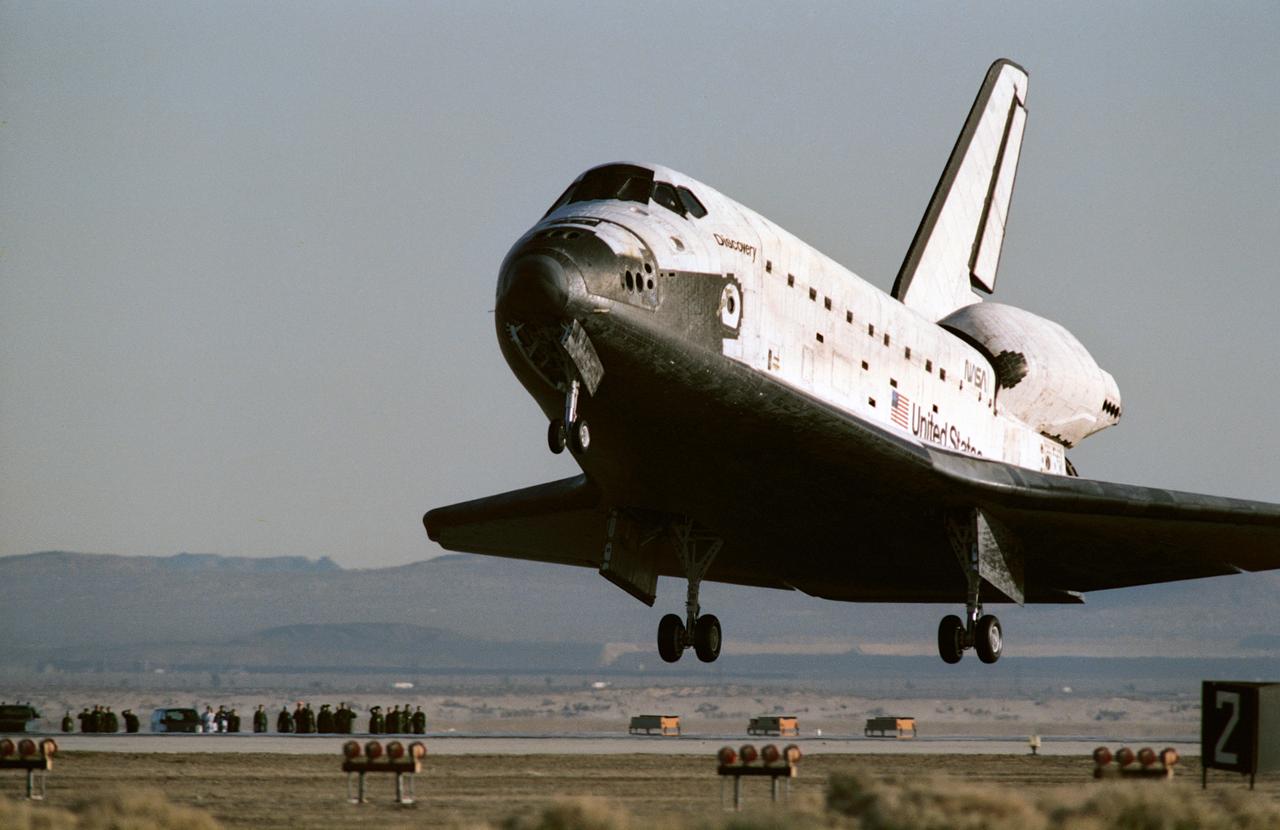

STS042-S-093 (30 Jan 1992) --- Space Shuttle Discovery is just about to ease down its main gear on Runway 22 at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California. Main gear touchdown occurred at 8:07:18 a.m. (PST), Jan. 30, 1992. The successful landing completed an eight-day mission for five NASA astronauts and two payload specialists supporting the first International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) mission. Onboard were astronauts Ronald J. Grabe, mission commander; Stephen S. Oswald, pilot; Norman E. Thagard, payload commander; David C. Hilmers and William F. Readdy, both mission specialists; and payload specialists Roberta L. Bondar of Canada and Ulf Merbold, representing the European Space Agency (ESA).
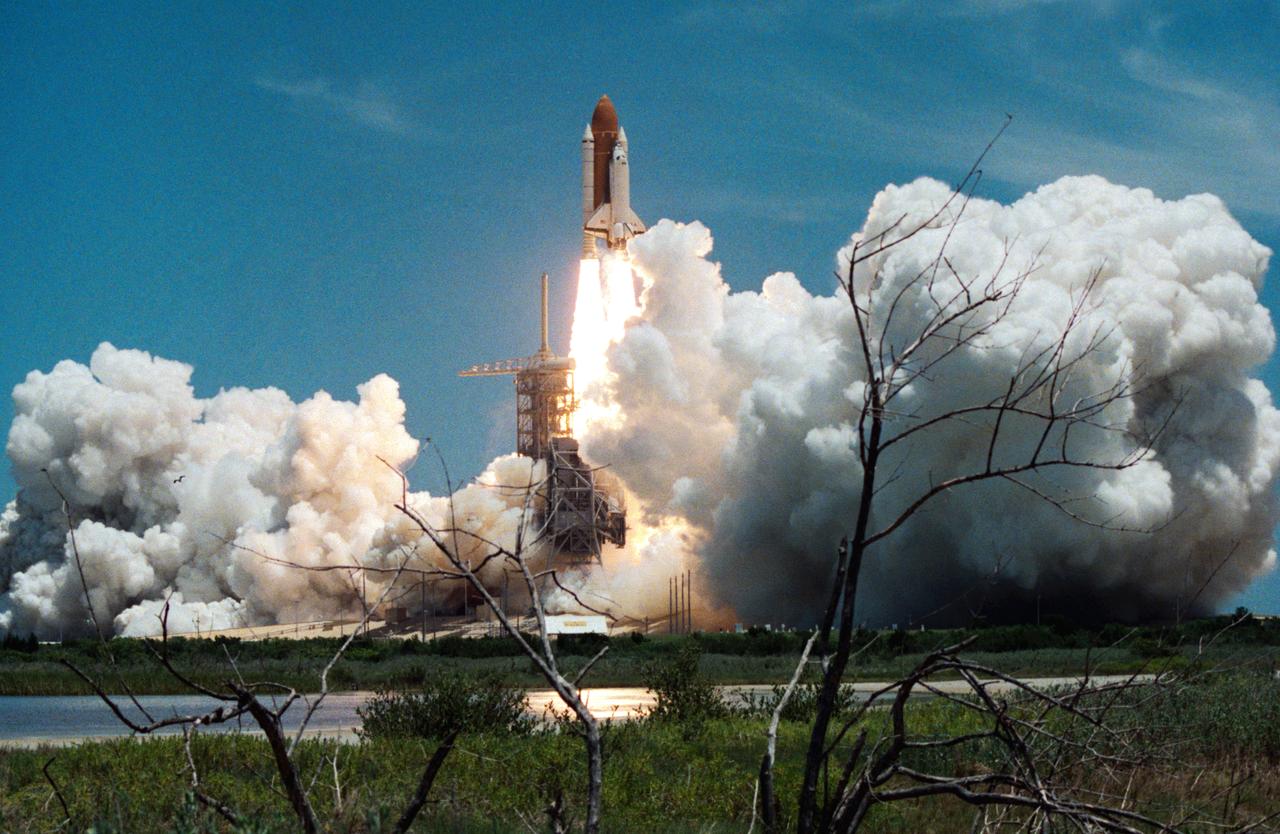

Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, begins its roll maneuver after clearing the fixed service structure (FSS) tower as it rises above Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39A. In the foreground of this horizontal scene is Florida brush and a waterway. Beyond the brush, the shuttle's exhaust cloud envelops the immediate launch pad area. Launch occurred at 12:43 pm Eastern Daylight Time (EDT). The glow of the space shuttle main engine (SSME) and solid rocket booster (SRB) firings is reflected in the nearby waterway. Once in Earth orbit, STS-65's six NASA astronauts and a Japanese Payload Specialist aboard OV-102 will begin two weeks of experimentation in support of the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2).
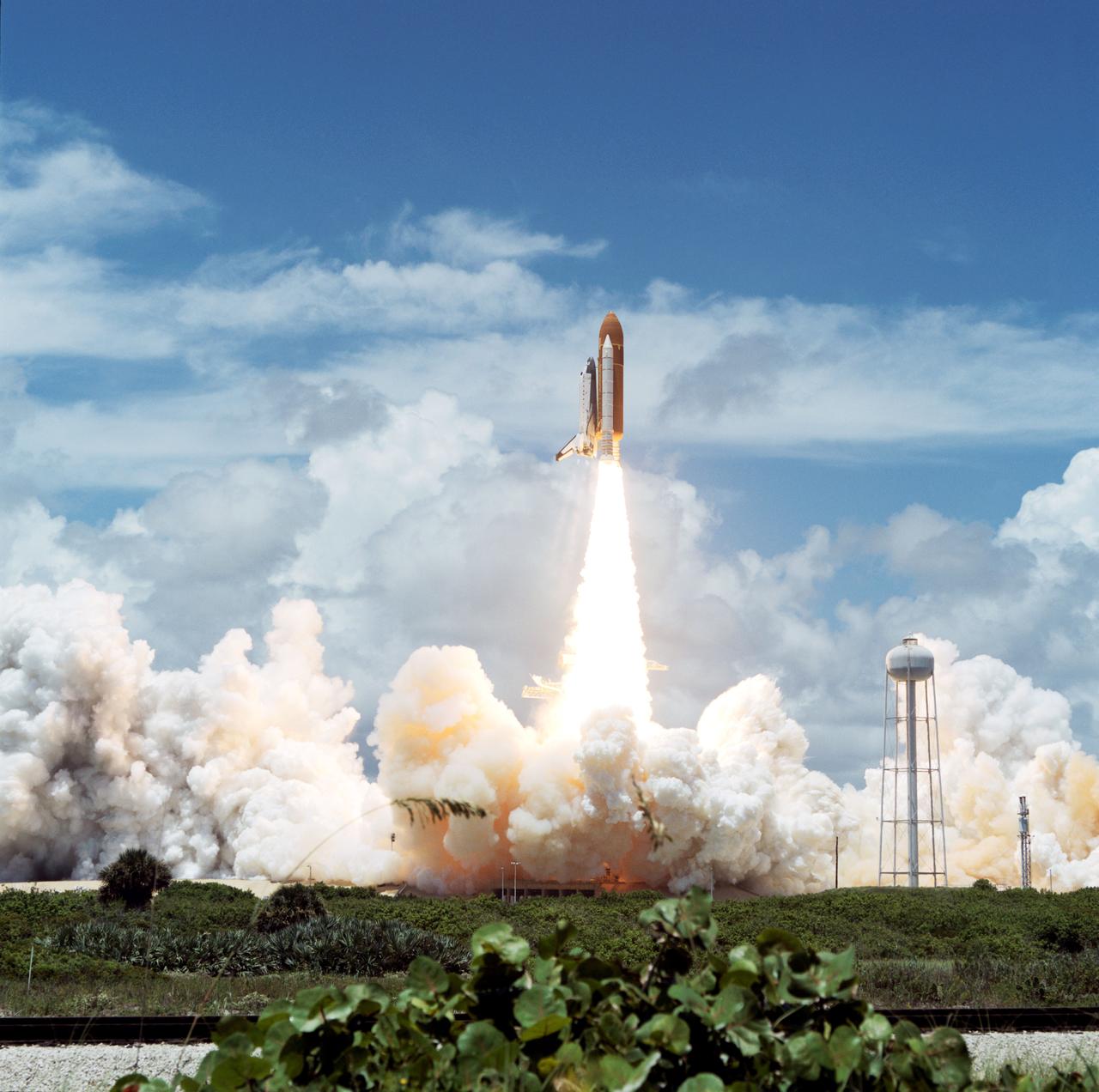

Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, heads skyward after clearing the fixed service structure (FSS) tower at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39A. Florida plant life appears in the foreground. The exhaust cloud produced by OV-102's solid rocket boosters (SRBs) covers the launch pad area with the exception of the sound suppression water system tower. OV-102's starboard side and the right SRB are visible from this angle. Launch occurred at 12:43 pm Eastern Daylight Time (EDT). Once in Earth orbit, STS-65's six NASA astronauts and a Japanese Payload Specialist aboard OV-102 will begin two weeks of experimentation in support of the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2).
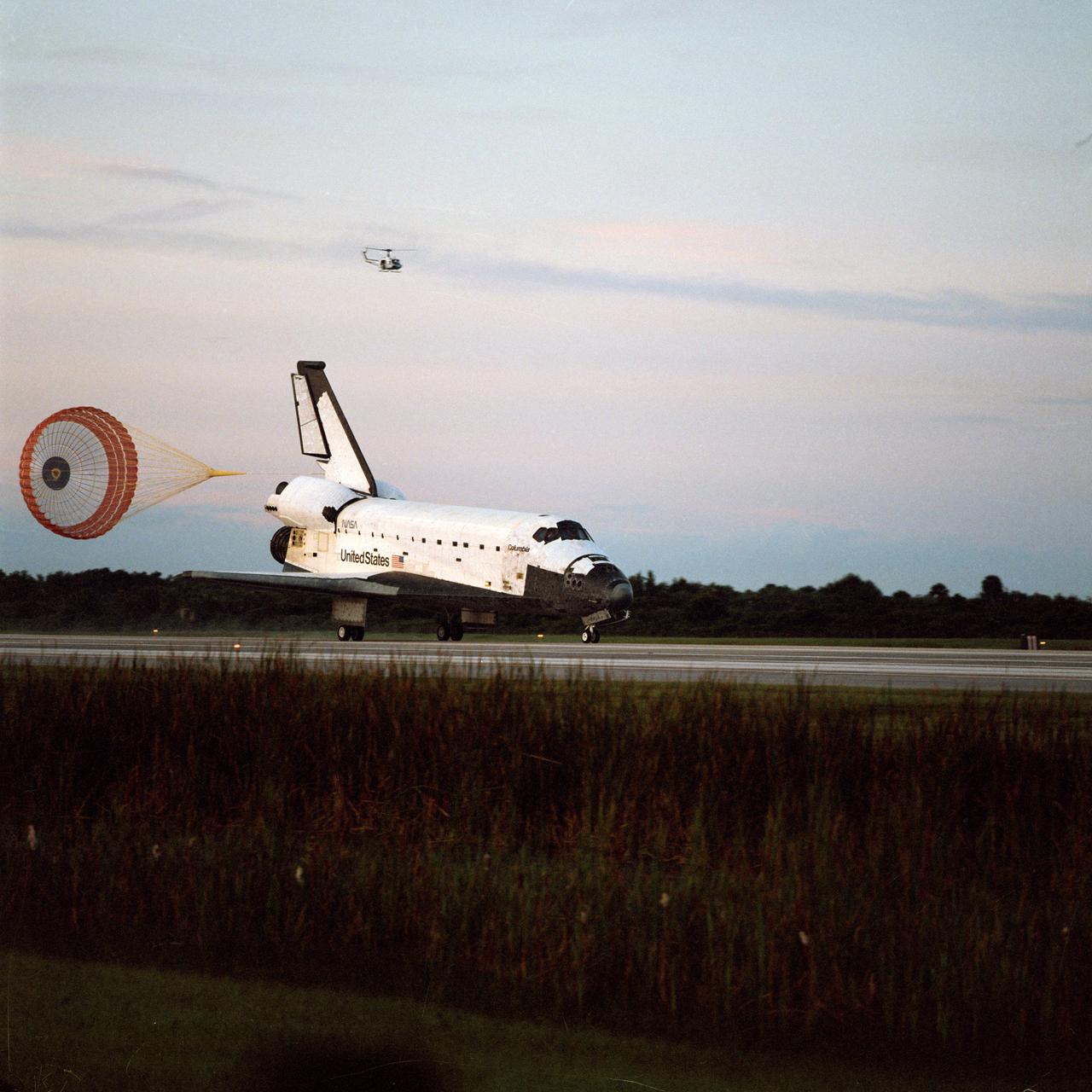

The Space Shuttle Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, its drag chute fully deployed, completes a record duration mission as it lands on Runway 33 at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF). A helicopter flying overhead observes as OV-102's nose landing gear (NLG) and main landing gear (MLG) roll along the runway. Landing occurred at 6:38 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). STS-65 mission duration was 14 days 17 hours and 56 minutes. Onboard were six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist who conducted experiments in support of the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) during the mission.
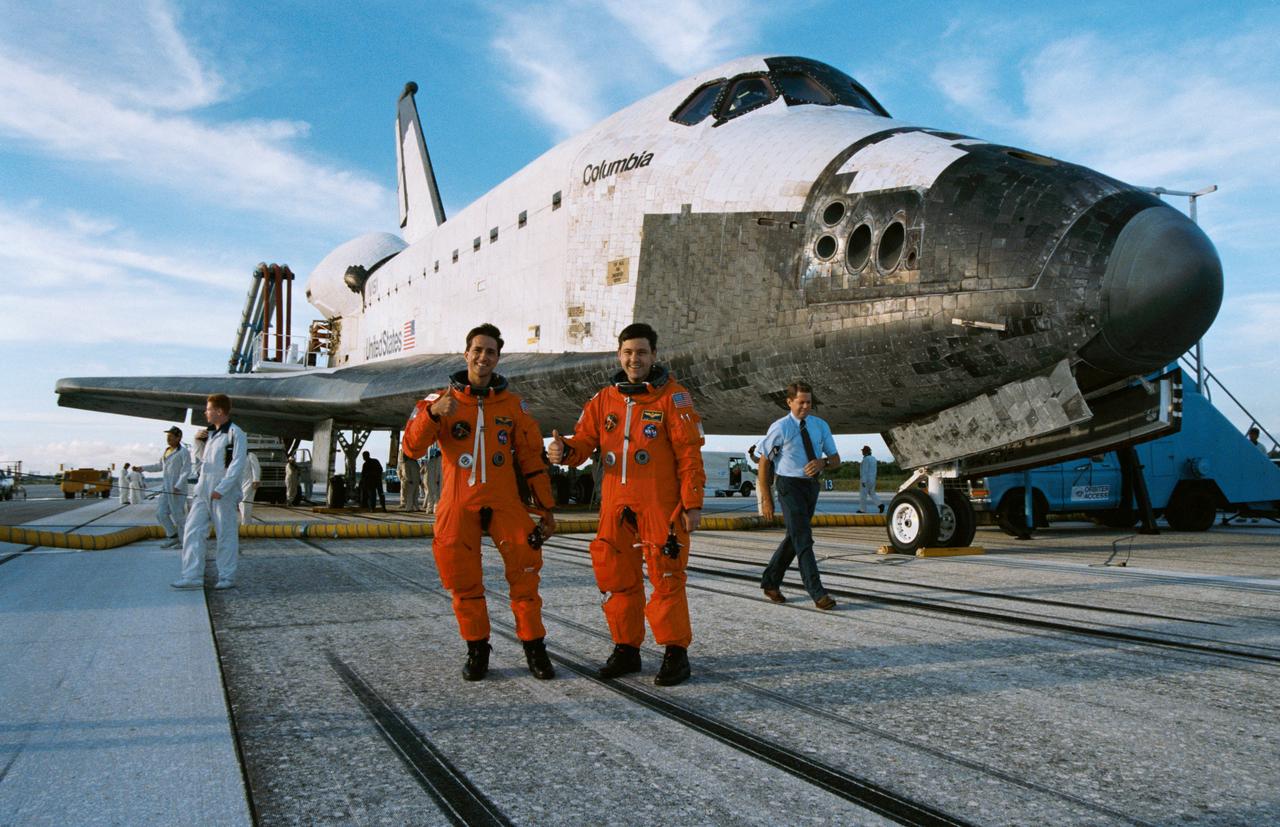

STS-65 Commander Robert D. Cabana (right) and Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas, wearing launch and entry suits (LESs), signal mission success with a "thumbs up" gesture as they stand in front of Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102. The two crewmembers are all smiles after OV-102's landing at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF). The two, along with four other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist, had just broken a Shuttle duration record as they ran almost 18 hours over two weeks in space in support of the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) mission. Landing occurred at 6:38 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). Mission duration was 14 days, 17 hours and 56 minutes. In the background, KSC personnel conduct postflight servicing of the vehicle.
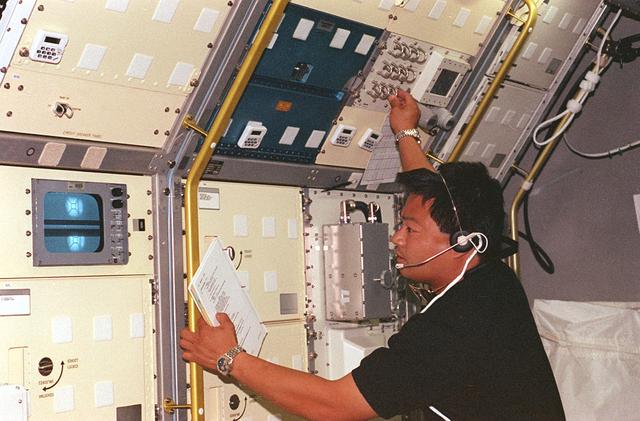

TEMPUS, an electromagnetic levitation facility that allows containerless processing of metallic samples in microgravity, first flew on the IML-2 Spacelab mission. The principle of electromagnetic levitation is used commonly in ground-based experiments to melt and then cool metallic melts below their freezing points without solidification occurring. The TEMPUS operation is controlled by its own microprocessor system; although commands may be sent remotely from the ground and real time adjustments may be made by the crew. Two video cameras, a two-color pyrometer for measuring sample temperatures, and a fast infrared detector for monitoring solidification spikes, will be mounted to the process chamber to facilitate observation and analysis. In addition, a dedicated high-resolution video camera can be attached to the TEMPUS to measure the sample volume precisely.

S91-51633 (November 1991) --- Astronaut Roberta L. Bondar, Canadian payload specialist.
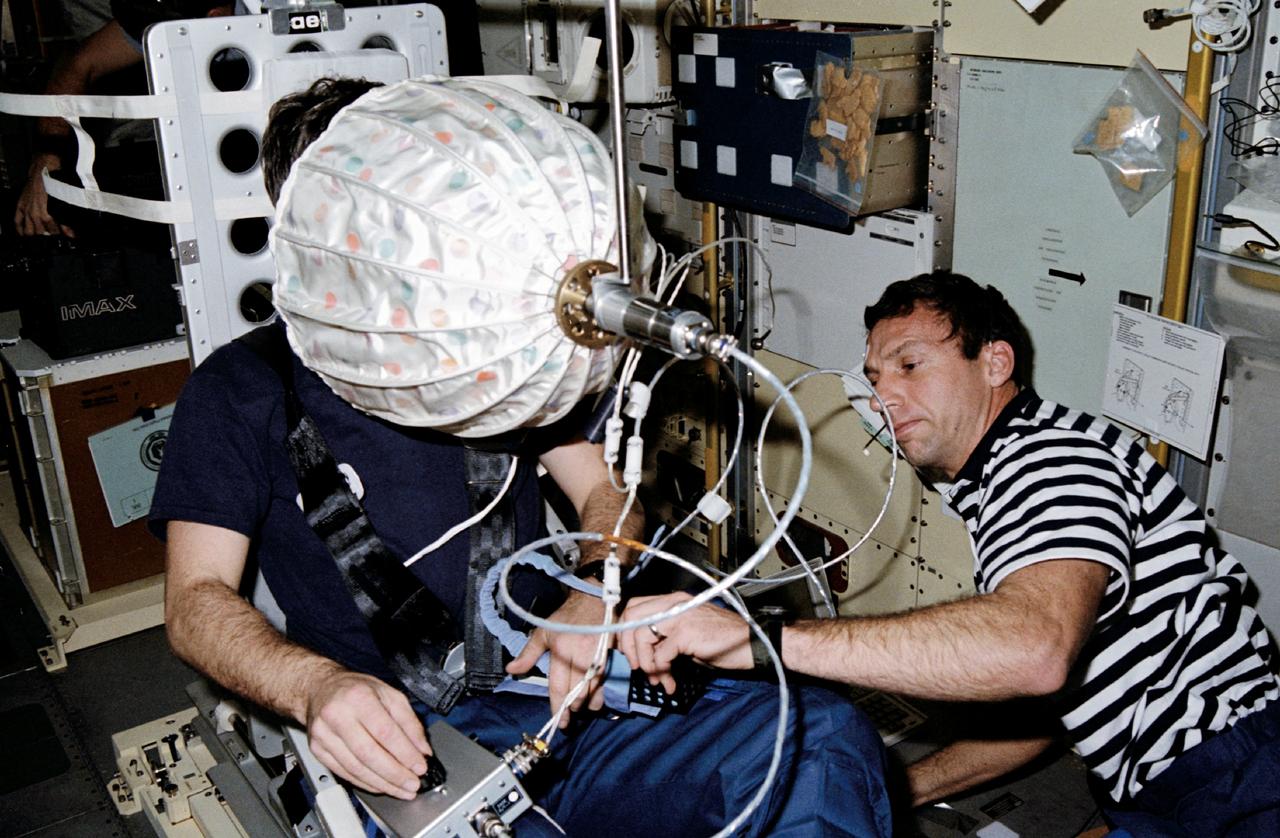

STS042-203-024 (22-30 Jan. 1992) --- Astronaut David C. Hilmers (right), STS-42 mission specialist, assists European Space Agency (ESA) payload specialist Ulf Merbold with the visual stimulator experiment on the Space Shuttle Discovery's middeck. This particular test is part of an ongoing study of the Space Adaptation Syndrome (SAS). Seated in a stationary mini-sled, Merbold (or any other subject for this test) stares at an umbrella-shaped rotating dome with a pattern of colored dots on its interior. While observing the rotating dome, the subject turns a knob to indicate his perception of body rotation. The strength of circular vection is calculated by comparing the signals from the dome and the knob. The greater the false sense of circular vection, the more the subject is relying on visual information instead of otolith information.

STS042-S-001 (October 1991) --- Designed by the crew members, the International Microgravity Lab-1 (IML-1) insignia depicts the orbiter with the Spacelab Module aboard. The spacecraft is oriented in a quiescent, tail-to-Earth, gravity-gradient attitude to best support the various microgravity payloads and experiments. The international composition of the crew is depicted by symbols representing both the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and the European Space Agency (ESA). The number 42 is represented by six white stars -- four on one side of the orbiter and two on the other. The single gold star above Earth's horizon honors the memory of astronaut Manley L. (Sonny) Carter, who was killed earlier this year in a commuter plane crash. A crew spokesperson stated that Carter "...was our crew mate, colleague and friend." Blue letters set against white give the surnames of the five astronauts and two payload specialists for the flight. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, it will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA