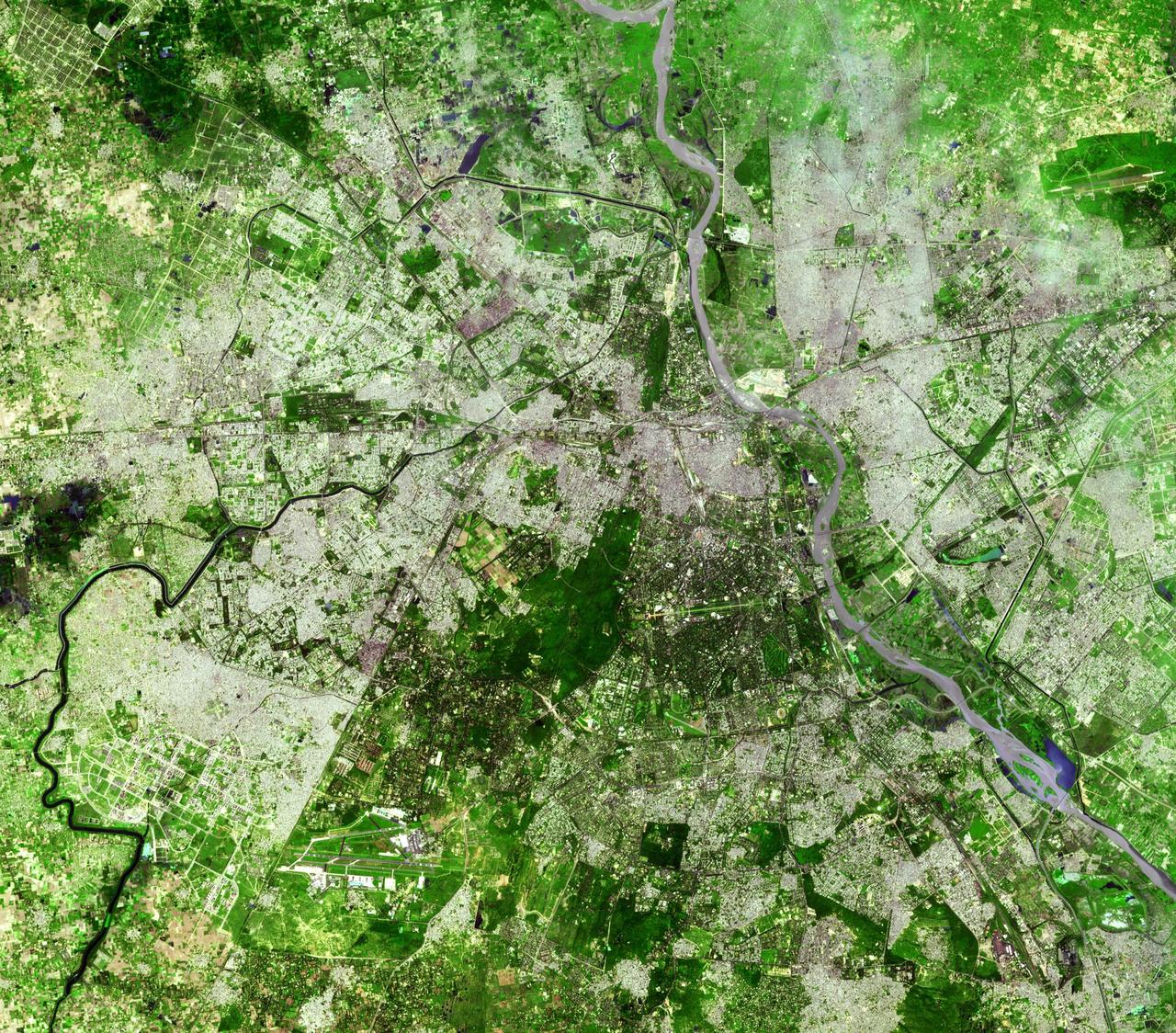

Delhi is the second largest metropolis in India, with a population of 16 million and is located in northern India along the banks of the Yamuna River. This image was acquired by NASA Terra satellite on September 22, 2003.

On January 26, 2001 the Kachchh region in western India suffered the most deadly earthquake in India history.
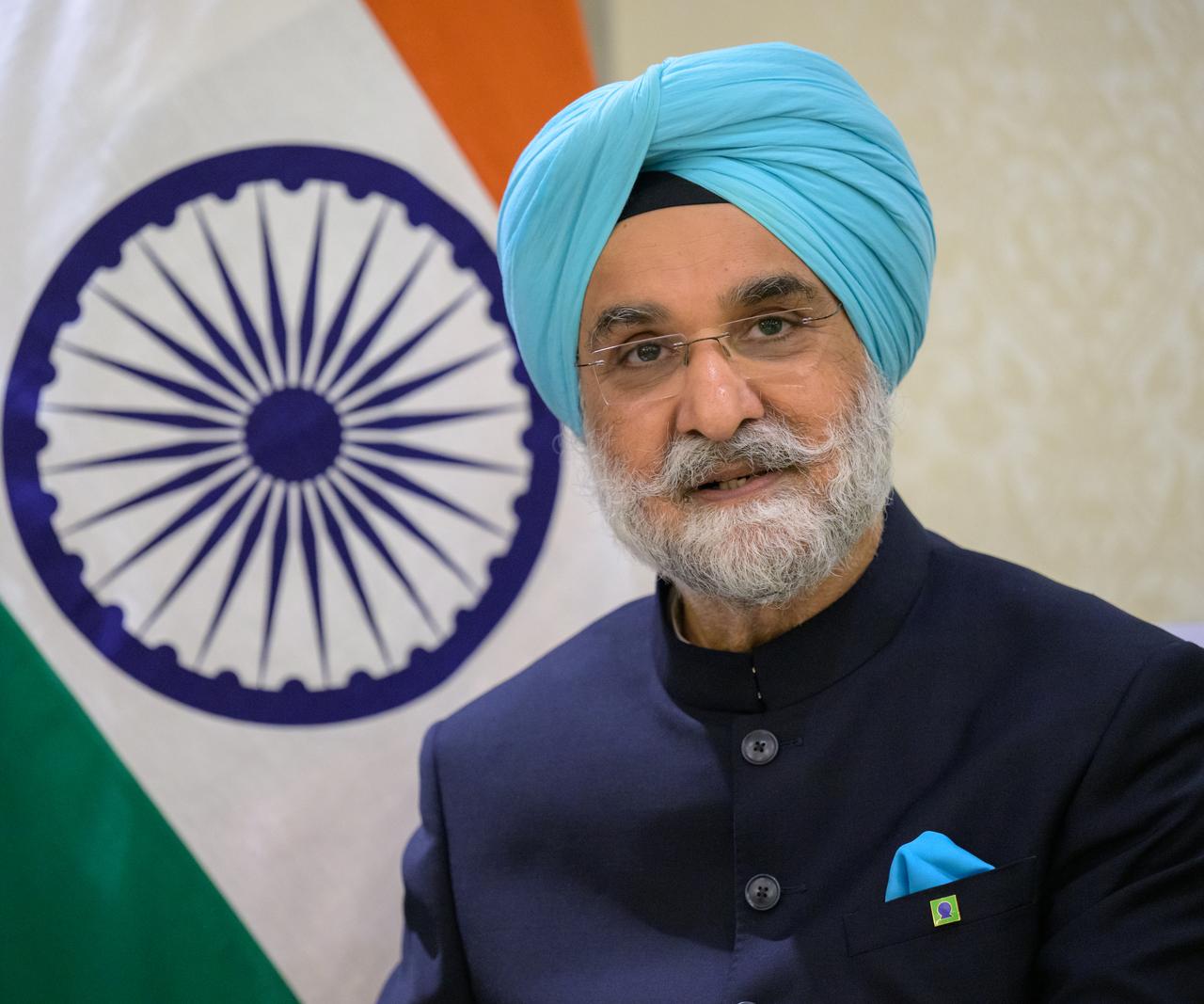

Indian Ambassador Taranjit Sandhu gives remarks after having signed the Artemis Accords, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Willard InterContinental Hotel in Washington. India is the twenty seventh country to sign the Artemis Accords, which establish a practical set of principles to guide space exploration cooperation among nations participating in NASA’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
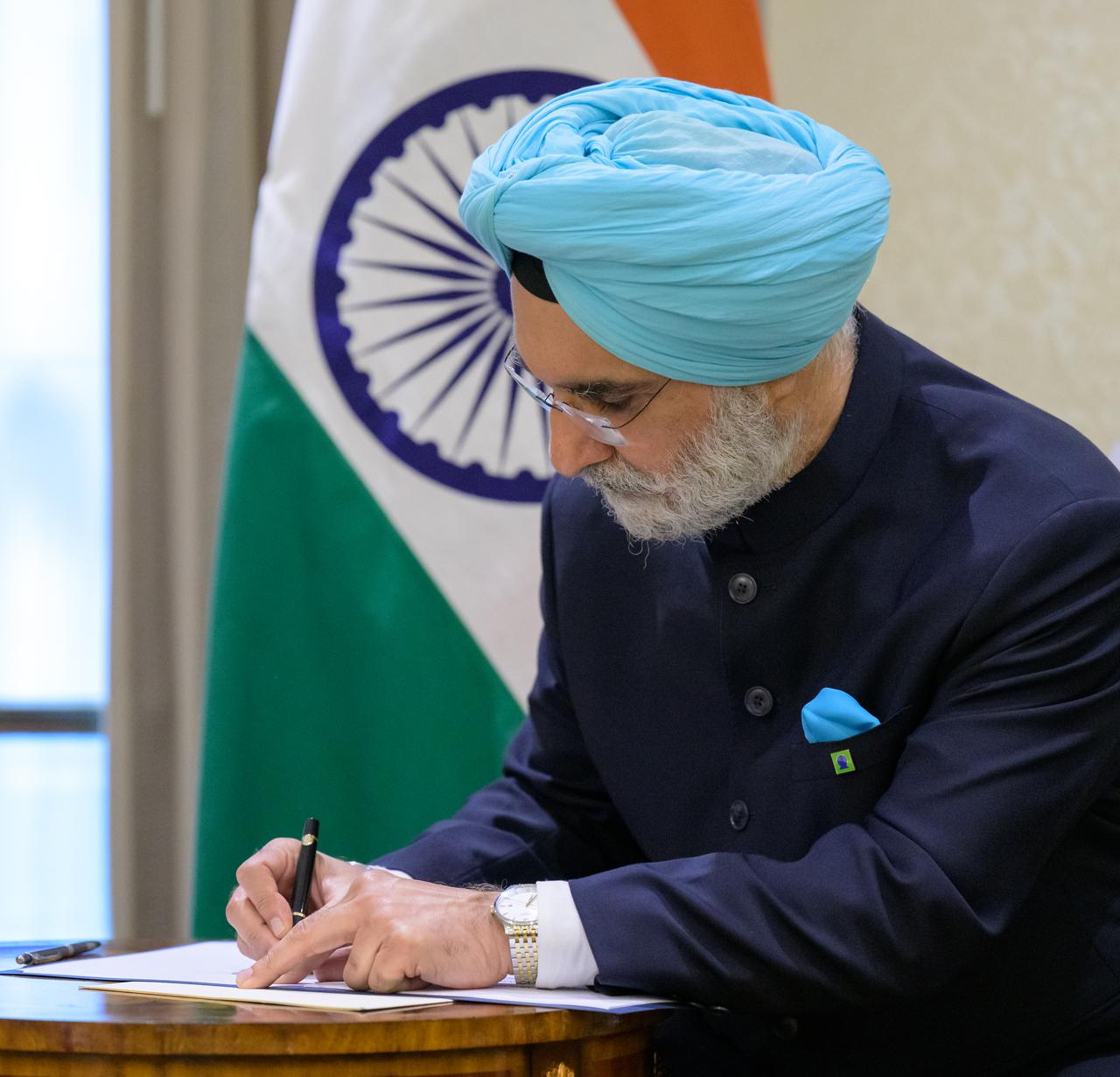

Indian Ambassador Taranjit Sandhu, signs the Artemis Accords, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Willard InterContinental Hotel in Washington. India is the 27th country to sign the Artemis Accords, which establish a practical set of principles to guide space exploration cooperation among nations participating in NASA’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

This image from NASA Terra spacecraft shows a cluster of villages known as Mawsynram in India, which is the current world record holder for the wettest place on earth.

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, 2nd from left, and Indian Ambassador Taranjit Sandhu, 3rd from left, shake hands after the signing of the Artemis Accords, as U.S. Department of State, Deputy Assistant Secretary for India, Nancy Jackson, left, and Indian Space Research Organization, Space Counsellor, Krunal Joshi, right, look on, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Willard InterContinental Hotel in Washington. India is the 27th country to sign the Artemis Accords, which establish a practical set of principles to guide space exploration cooperation among nations participating in NASA’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
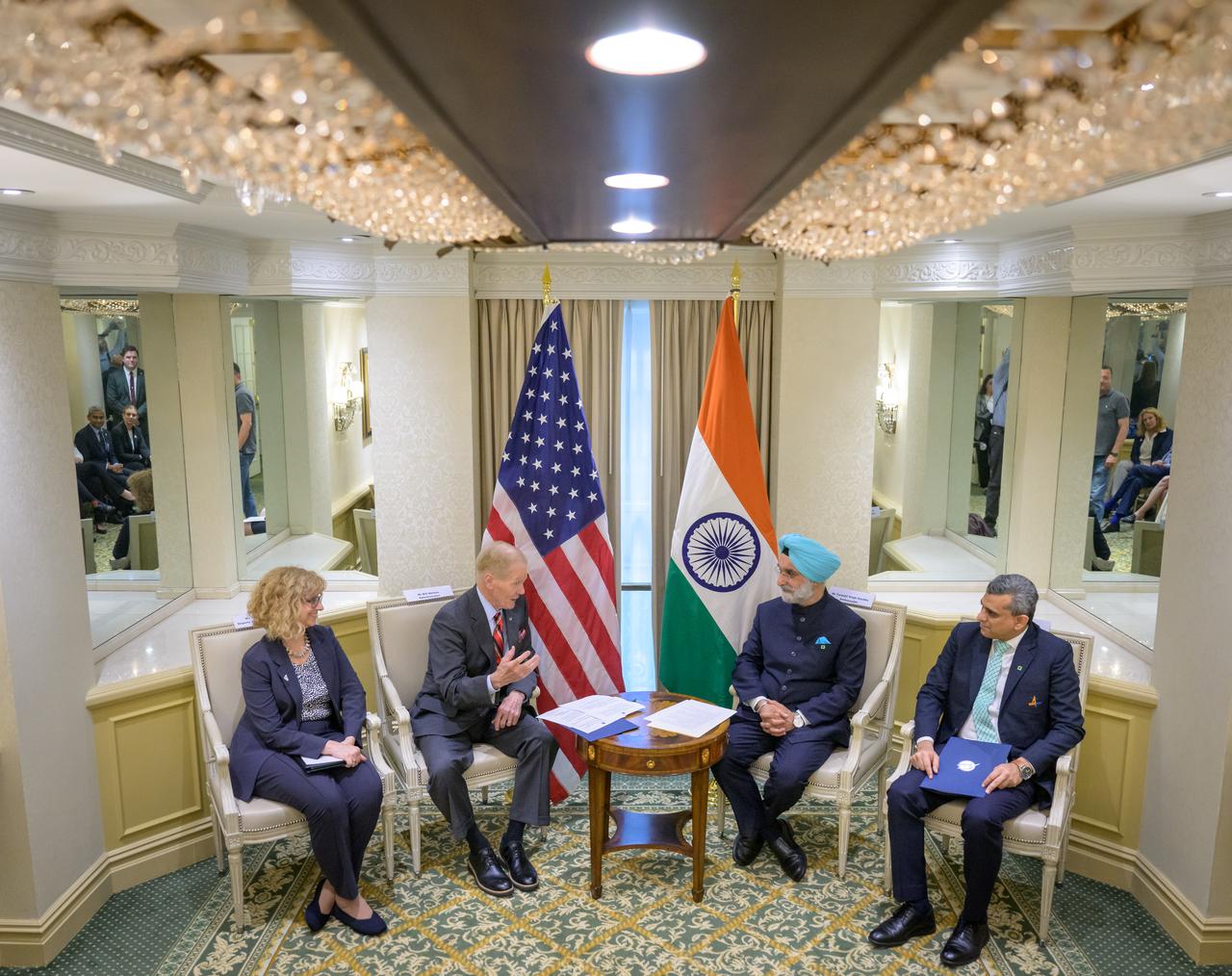

From left; U.S. Department of State, Deputy Assistant Secretary for India, Nancy Jackson, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, Indian Ambassador Taranjit Sandhu, and Indian Space Research Organization, Space Counsellor, Krunal Joshi, talk after the signing of the Artemis Accords, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Willard InterContinental Hotel in Washington. India is the 27th country to sign the Artemis Accords, which establish a practical set of principles to guide space exploration cooperation among nations participating in NASA’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
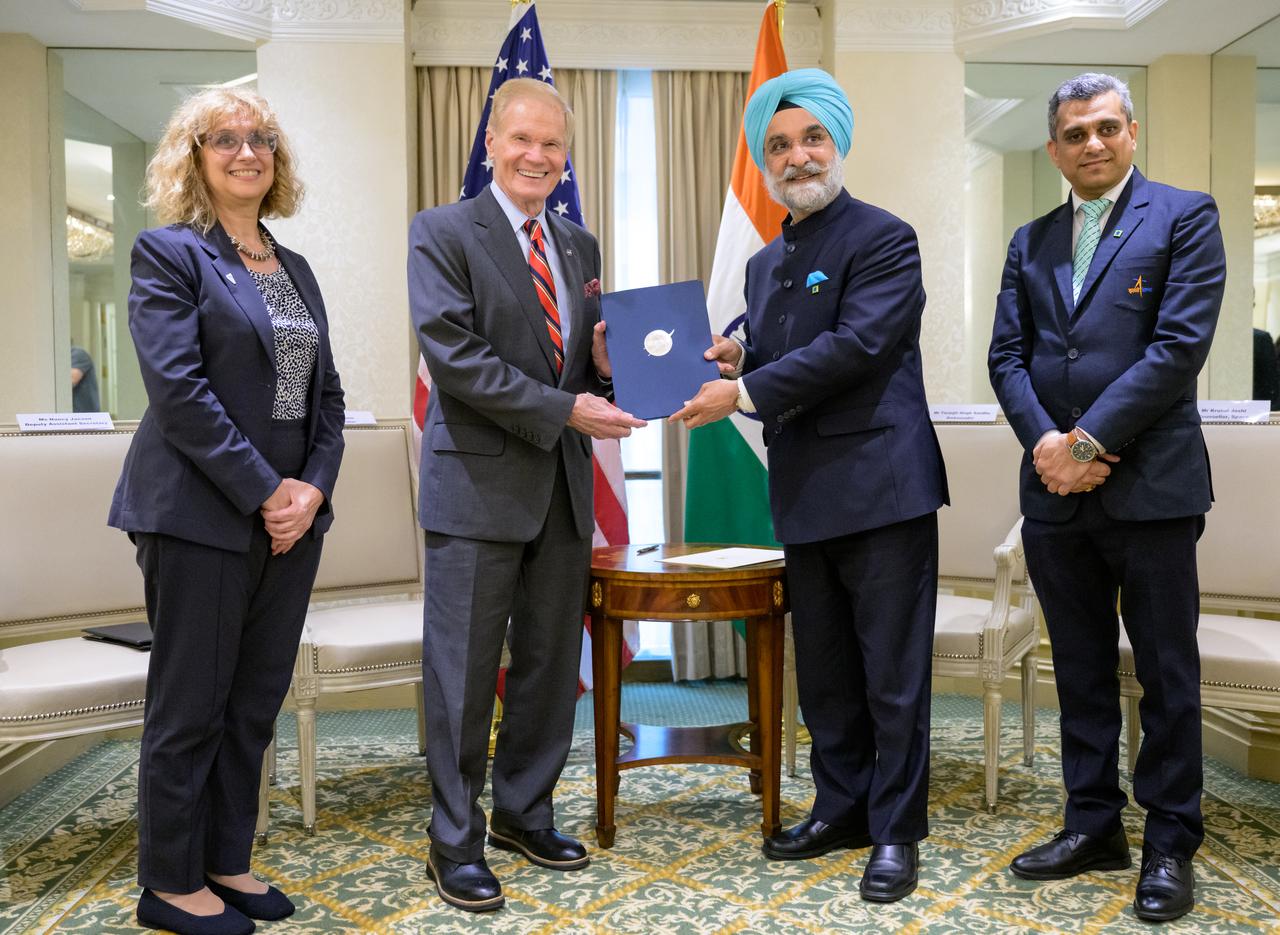

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, 2nd from left, and Indian Ambassador Taranjit Sandhu, 3rd from left, hold the signed Artemis Accords, as U.S. Department of State, Deputy Assistant Secretary for India, Nancy Jackson, left, and Indian Space Research Organization, Space Counsellor, Krunal Joshi, right, join for the group photograph, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Willard InterContinental Hotel in Washington. India is the 27th country to sign the Artemis Accords, which establish a practical set of principles to guide space exploration cooperation among nations participating in NASA’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
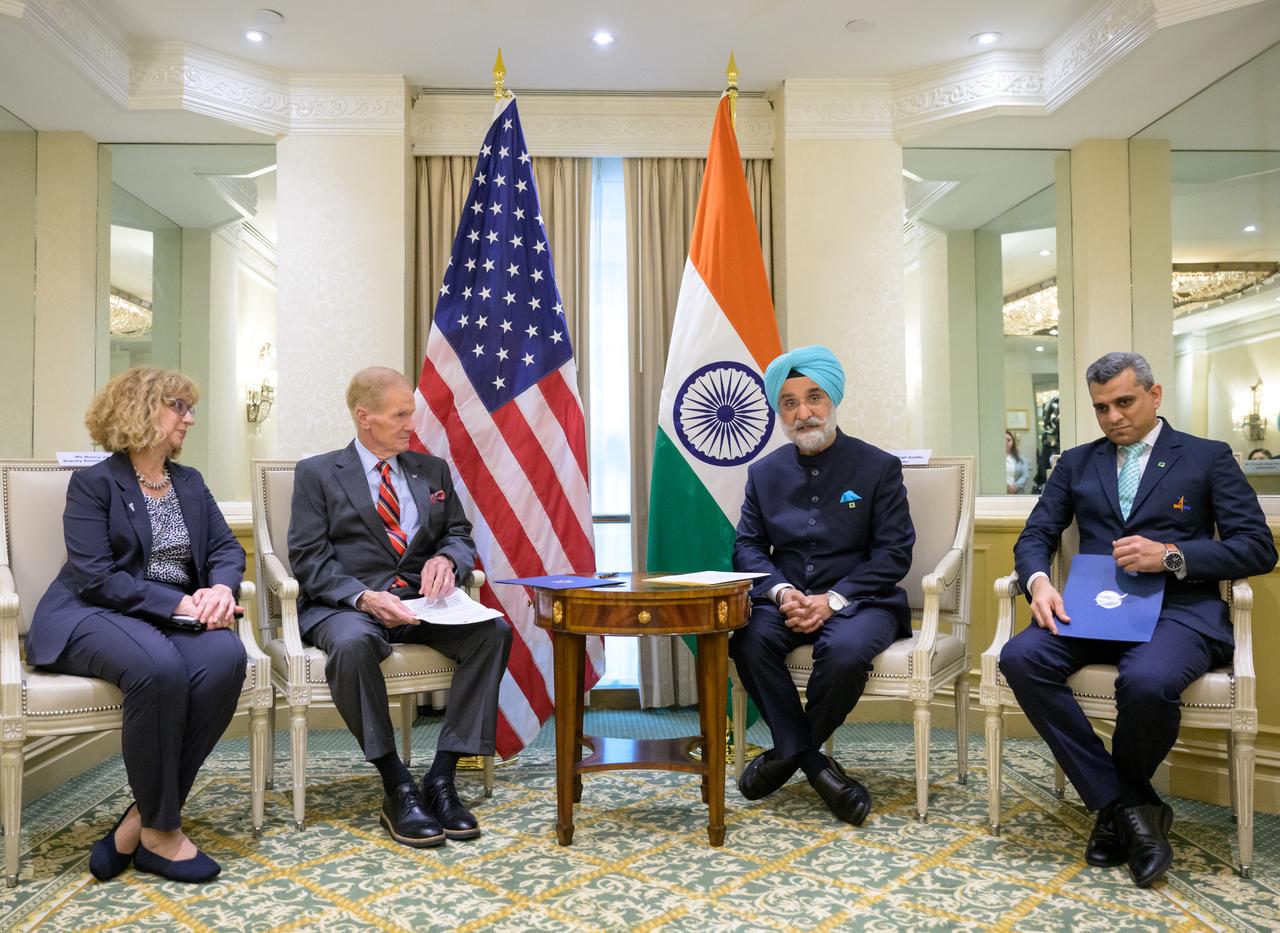

From left; U.S. Department of State, Deputy Assistant Secretary for India, Nancy Jackson, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, Indian Ambassador Taranjit Sandhu, and Indian Space Research Organization, Space Counsellor, Krunal Joshi, talk after the signing of the Artemis Accords, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Willard InterContinental Hotel in Washington. India is the 27th country to sign the Artemis Accords, which establish a practical set of principles to guide space exploration cooperation among nations participating in NASA’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
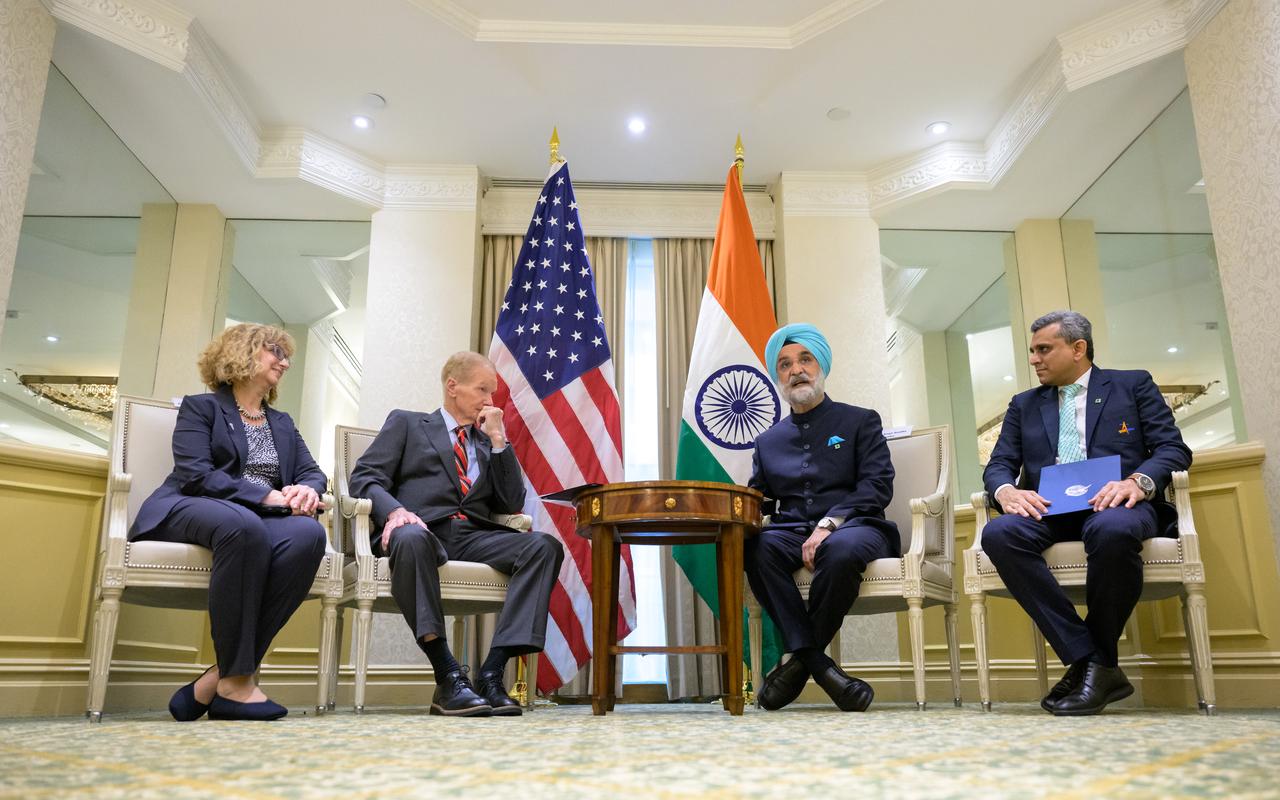

From left; U.S. Department of State, Deputy Assistant Secretary for India, Nancy Jackson, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, Indian Ambassador Taranjit Sandhu, and Indian Space Research Organization, Space Counsellor, Krunal Joshi, talk after the signing of the Artemis Accords, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Willard InterContinental Hotel in Washington. India is the 27th country to sign the Artemis Accords, which establish a practical set of principles to guide space exploration cooperation among nations participating in NASA’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Indian Ambassador Taranjit Sandhu, signs the Artemis Accords, as U.S. Department of State, Deputy Assistant Secretary for India, Nancy Jackson, left, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, and Indian Space Research Organization, Space Counsellor, Krunal Joshi, right, look on, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Willard InterContinental Hotel in Washington. India is the 27th country to sign the Artemis Accords, which establish a practical set of principles to guide space exploration cooperation among nations participating in NASA’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
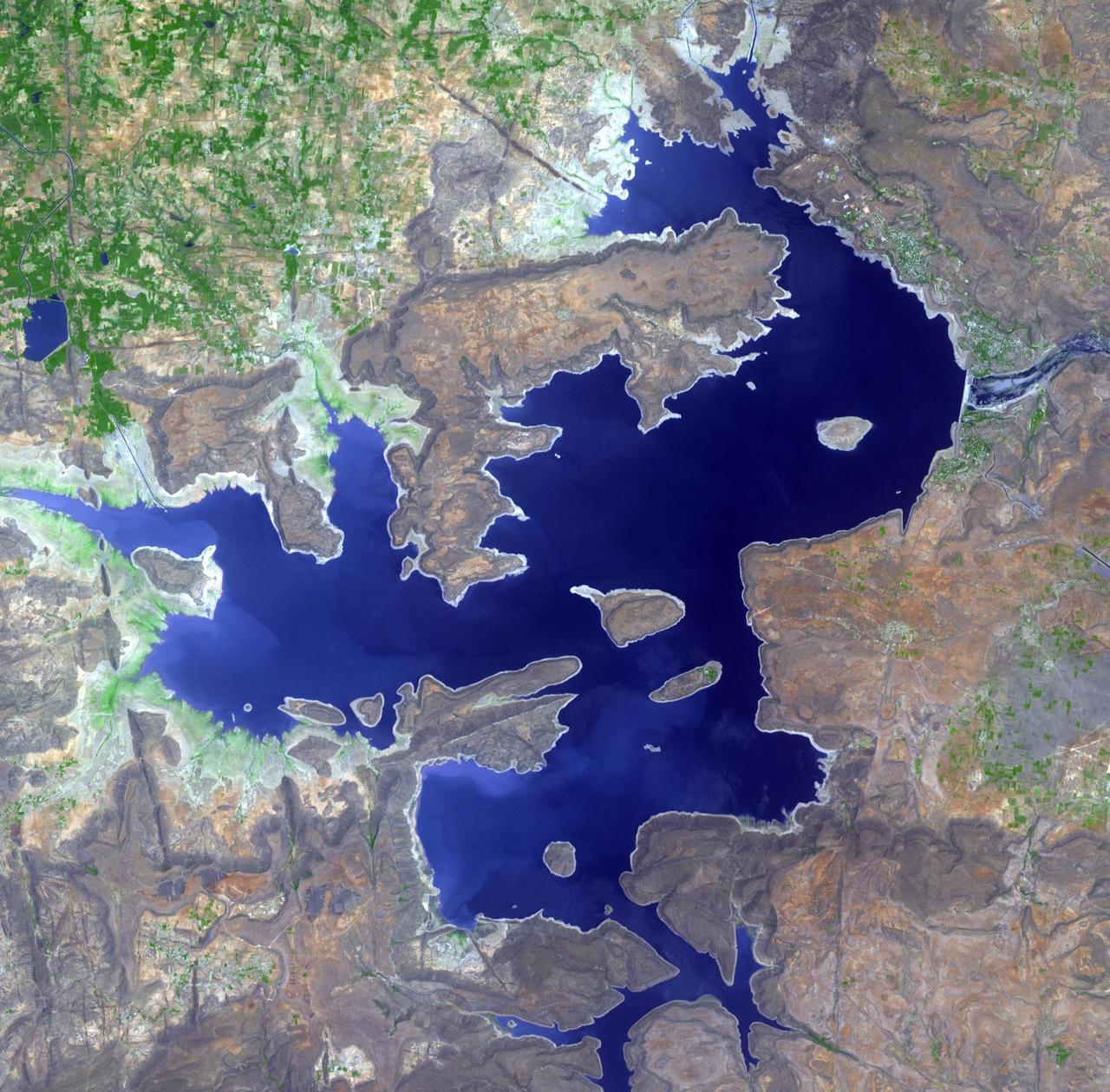
The Nagarunja Sagar Dam on India Krishna River is the largest masonry dam in operation in the world. This image is from NASA Terra spacecraft.
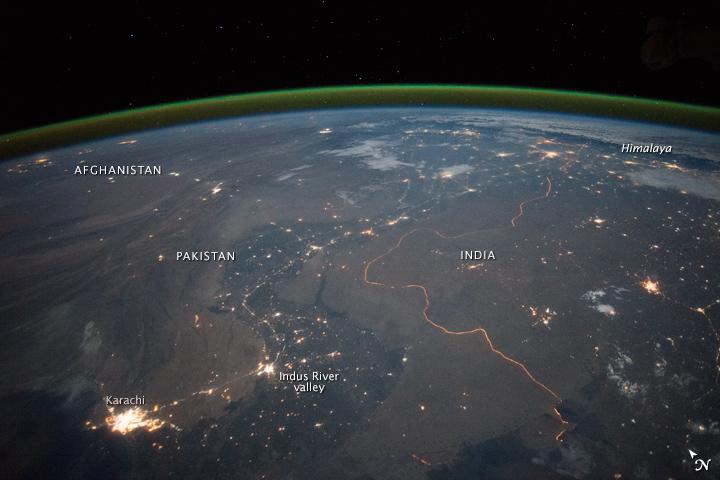

An astronaut aboard the International Space Station took this nighttime panorama while looking north across Pakistan’s Indus River valley. The port city of Karachi is the bright cluster of lights facing the Arabian Sea, which appears completely black. City lights and the dark color of dense agriculture closely track with the great curves of the Indus valley. For scale, the distance from Karachi to the foothills of the Himalaya Mountains is 1,160 kilometers (720 miles). This photograph shows one of the few places on Earth where an international boundary can be seen at night. The winding border between Pakistan and India is lit by security lights that have a distinct orange tone. Astronaut photograph ISS045-E-27869 was acquired on September 23, 2015, with a Nikon D4 digital camera using a 28 millimeter lens, and is provided by the ISS Crew Earth Observations Facility and the Earth Science and Remote Sensing Unit, Johnson Space Center. via NASA Earth Observatory Read more: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=86725&eocn=home&eoci=iotd_title" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=86725&eocn...</a>
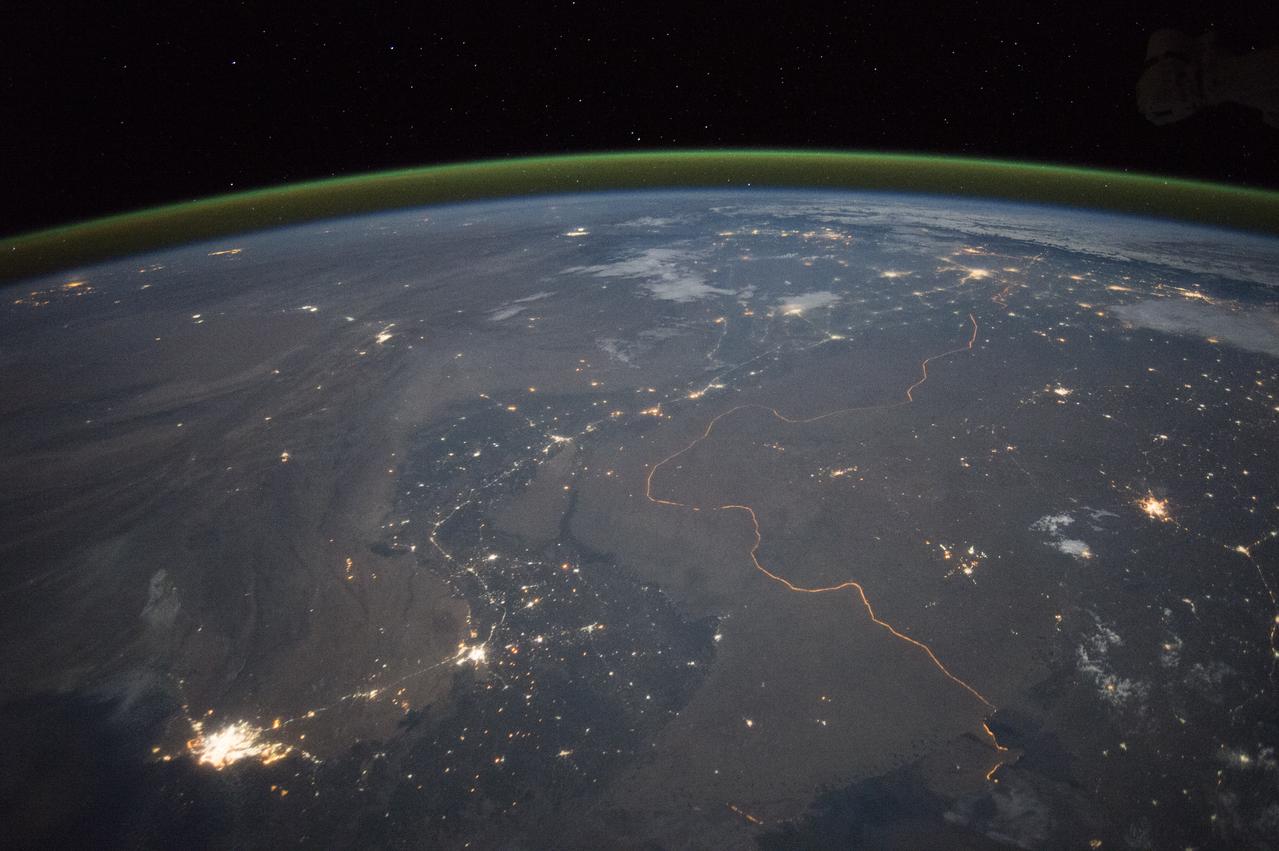

An astronaut aboard the International Space Station took this nighttime panorama while looking north across Pakistan’s Indus River valley. The port city of Karachi is the bright cluster of lights facing the Arabian Sea, which appears completely black. City lights and the dark color of dense agriculture closely track with the great curves of the Indus valley. For scale, the distance from Karachi to the foothills of the Himalaya Mountains is 1,160 kilometers (720 miles). This photograph shows one of the few places on Earth where an international boundary can be seen at night. The winding border between Pakistan and India is lit by security lights that have a distinct orange tone. Astronaut photograph ISS045-E-27869 was acquired on September 23, 2015, with a Nikon D4 digital camera using a 28 millimeter lens, and is provided by the ISS Crew Earth Observations Facility and the Earth Science and Remote Sensing Unit, Johnson Space Center. via NASA Earth Observatory Read more: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=86725&eocn=home&eoci=iotd_title" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=86725&eocn...</a>

On January 26, 2001, the Kachchh region in western India suffered the most deadly earthquake in India history. Geologists traversed the region looking for ground surface disruptions, that could provide clues to the tectonic processes here.

Indian Ambassador Taranjit Sandhu, right, talks with NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, after having signed the Artemis Accords, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Willard InterContinental Hotel in Washington. India is the twenty seventh country to sign the Artemis Accords, which establish a practical set of principles to guide space exploration cooperation among nations participating in NASA’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
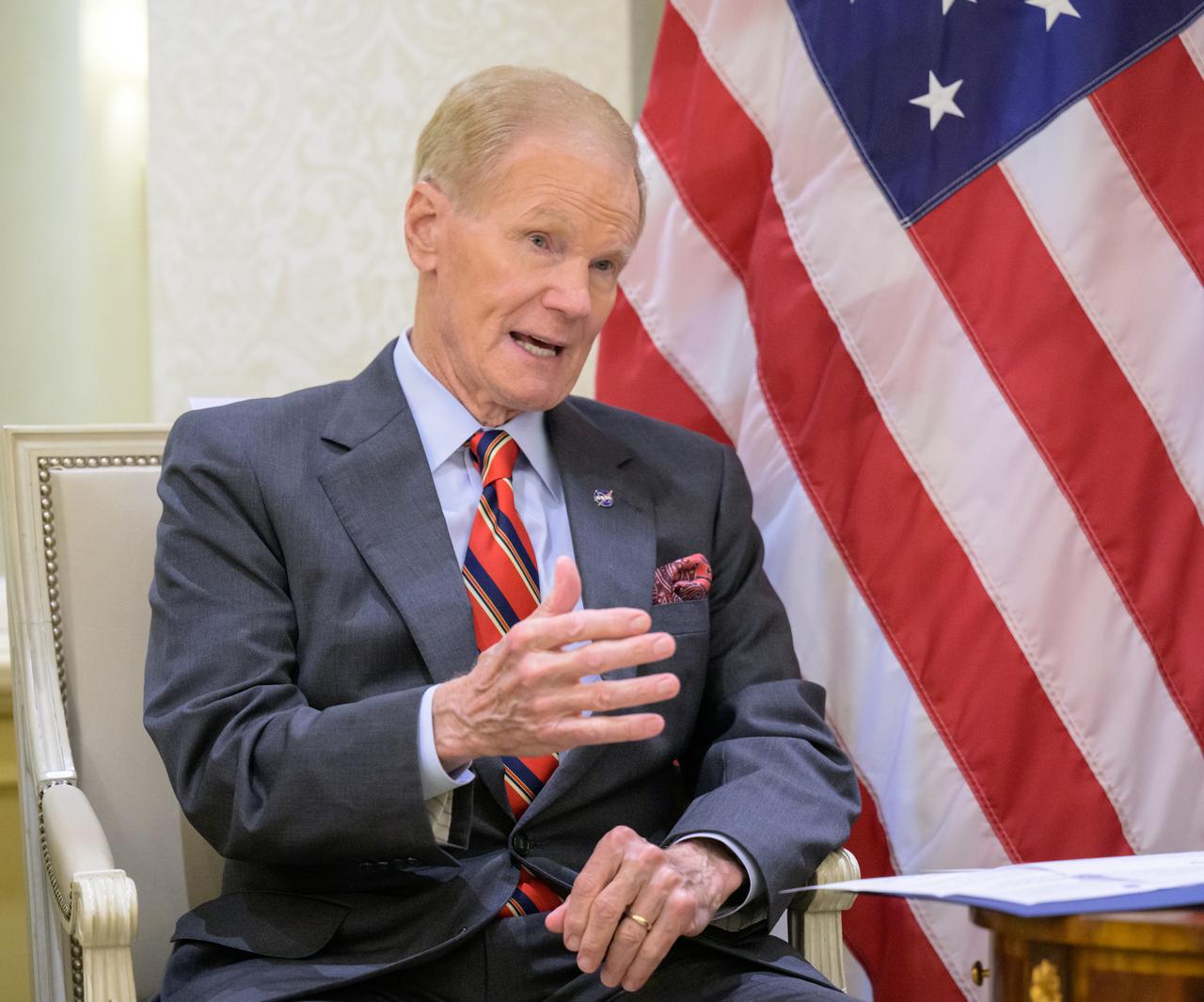

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson gives remarks after Indian Ambassador to the United States Taranjit Sandhu signed the Artemis Accords, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Willard InterContinental Hotel in Washington. India is the twenty seventh country to sign the Artemis Accords, which establish a practical set of principles to guide space exploration cooperation among nations participating in NASA’s Artemis program. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
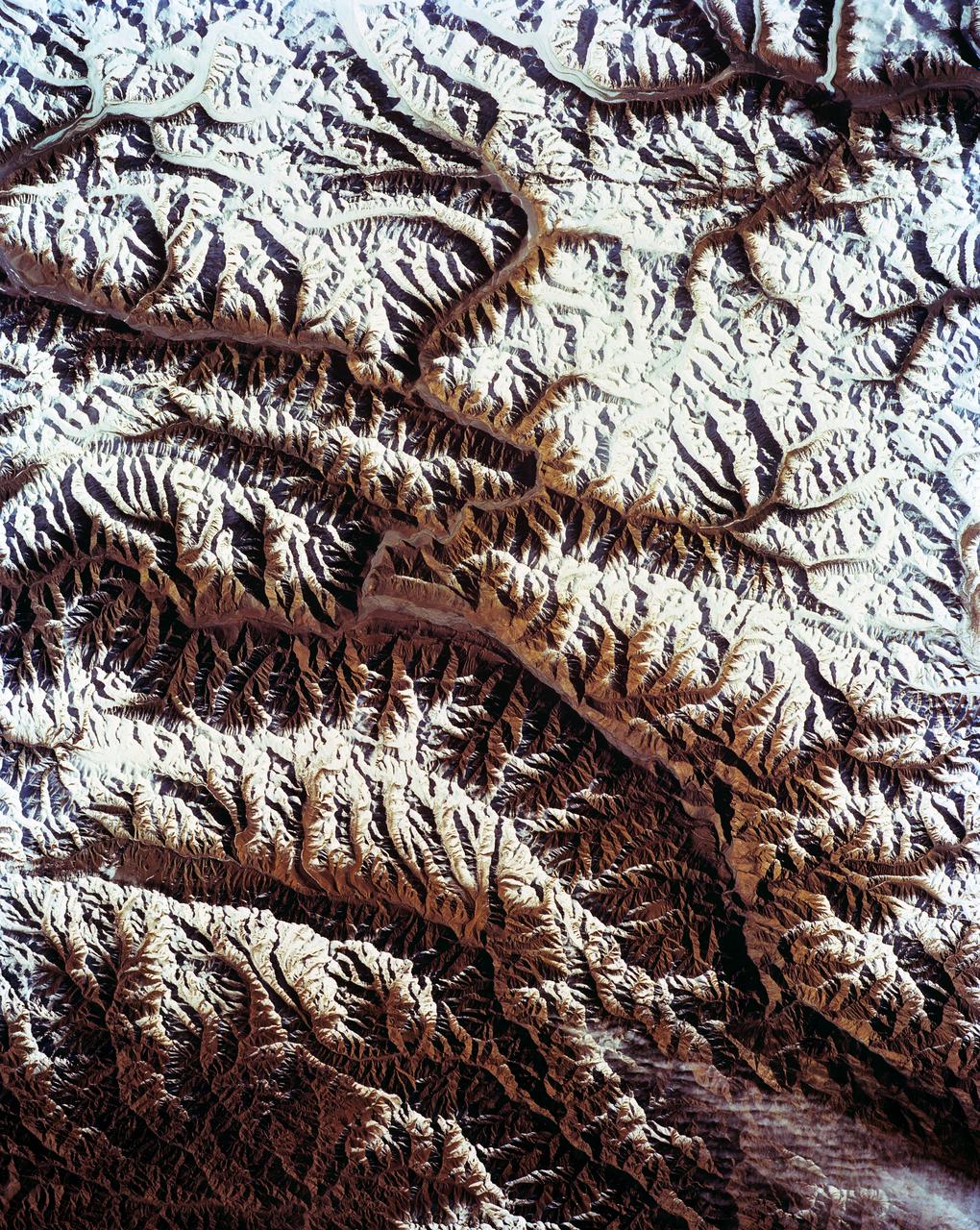

STS-56 Earth observation shows of some of the highest mountain peaks in the world taken from Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, as it passed over India and China. The top of the view shows one of the snow and ice-covered massifs in the great Karakorum Range of north India. A star-shaped peak at top left reaches 23,850 feet. Glaciers can be seen in valleys at these high elevations. The international border between India to the south (top) and China (bottom) snakes left to right along a river near the top of the scene, then veers into the muntains at top left. Larger valleys, despite their elevation (all in excess of 14,000 feet), are occupied by transport routes joining points in India, China and the southern republics of the CIS. The ancient Silk Route between China and the Middle East lies not far to the north (outside the bottom of the frame).
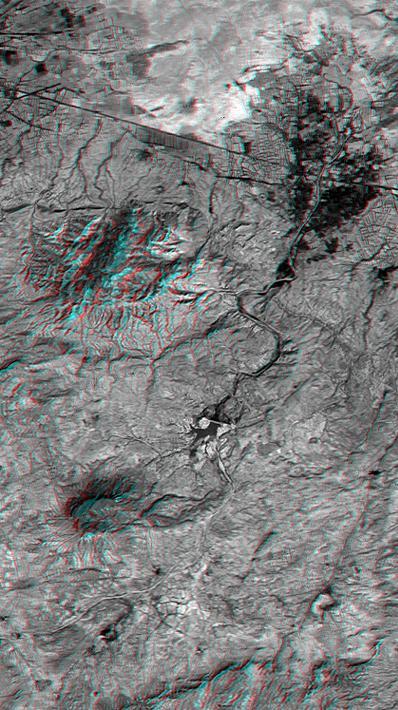
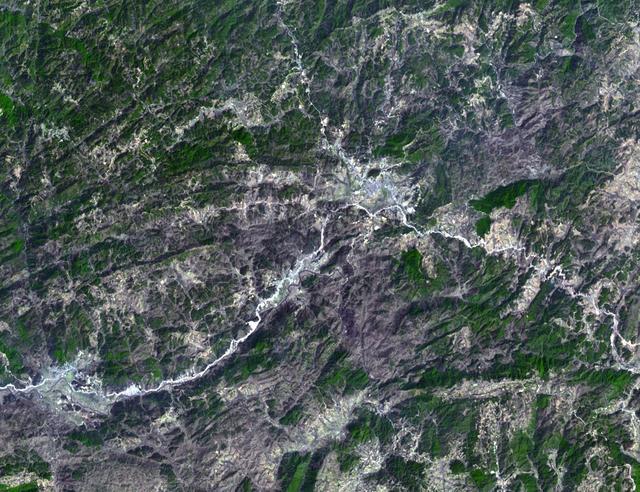
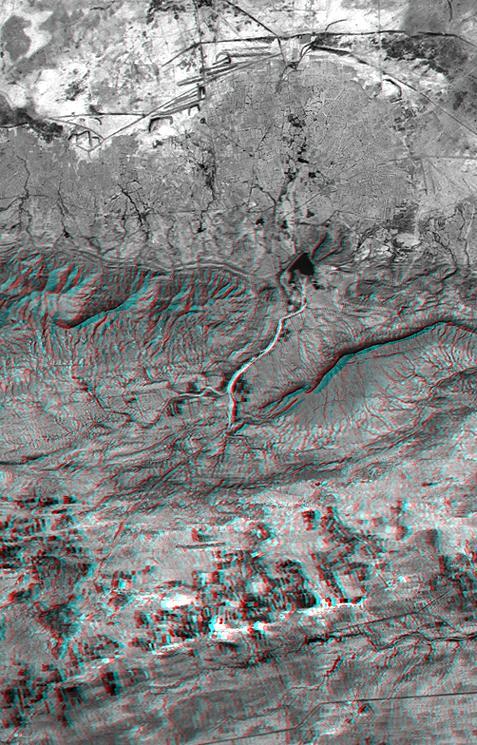
This anaglyph NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, shows the city of Bhuj, India. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
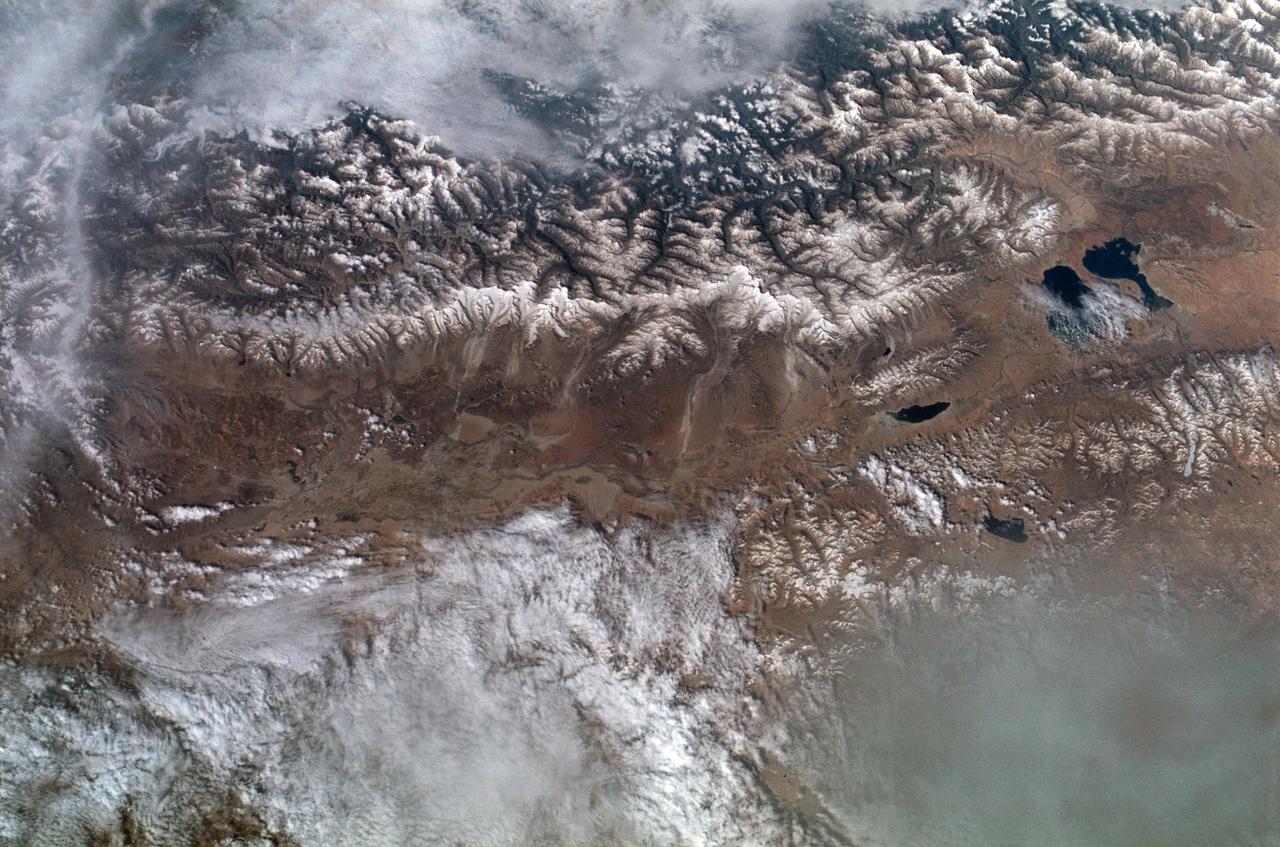

SL2-102-900 (22 June 1973) --- The Great Himalayan Mountain Range, India/Tibet (30.5N, 81.5E) is literally the top of the world where mountains soar to over 20,000 ft. effectively isolating Tibet from the rest of the world. The two lakes seen in the center of the image are the Laga Co and the Kunggyu Co located just inside the Tibet border. Although clouds and rainfall are rare in this region, snow is always present on the mountain peaks. Photo credit: NASA
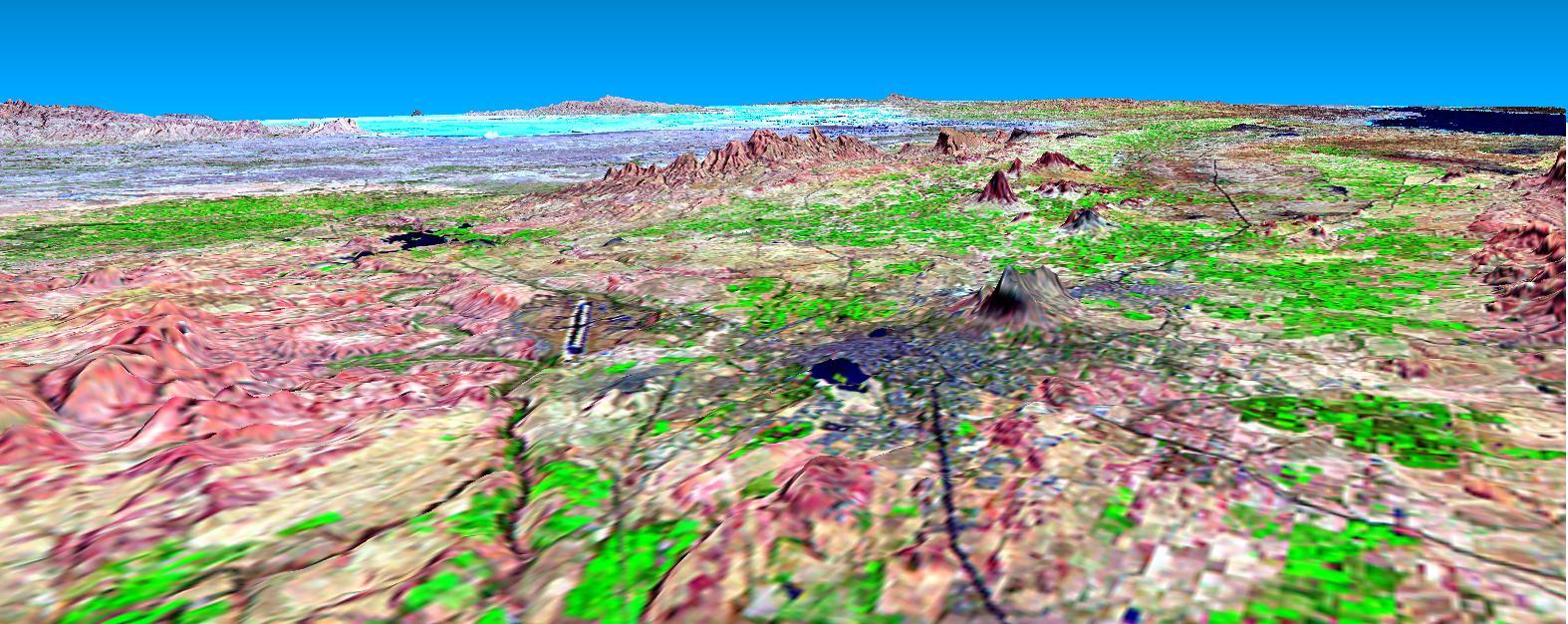
This perspective view shows the city of Bhuj, India, in the foreground gray area after an earthquake in western India on January 26, 2001. This image was generated from NASA Landsat satellite and data from Shuttle Radar Topography Mission SRTM.

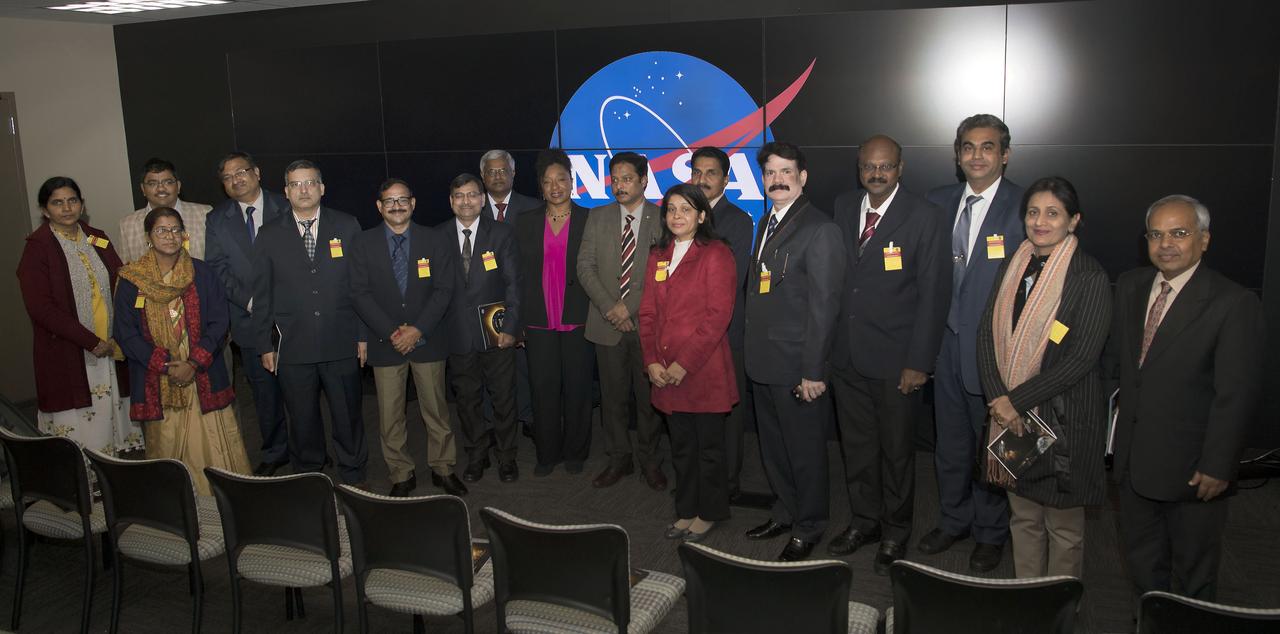
Defence Research & Development Organisation DRDO, Government of India Delegation visited Goddard October 12, 2018. Group visited Goddard Facilities such as Hypewall & Earth Sciences

Delegation Research & Development Organisation DRDO, Delegation of India visited Goddard October 25, 2018. Christyl Johnson welcomed group and receives gift at Hyperwall.

Defence Research & Development Organisation DRDO, Government of India Delegation visited Goddard October 25, 2018. They toured facilities such as Hyperwall, Earth Sciences etc.
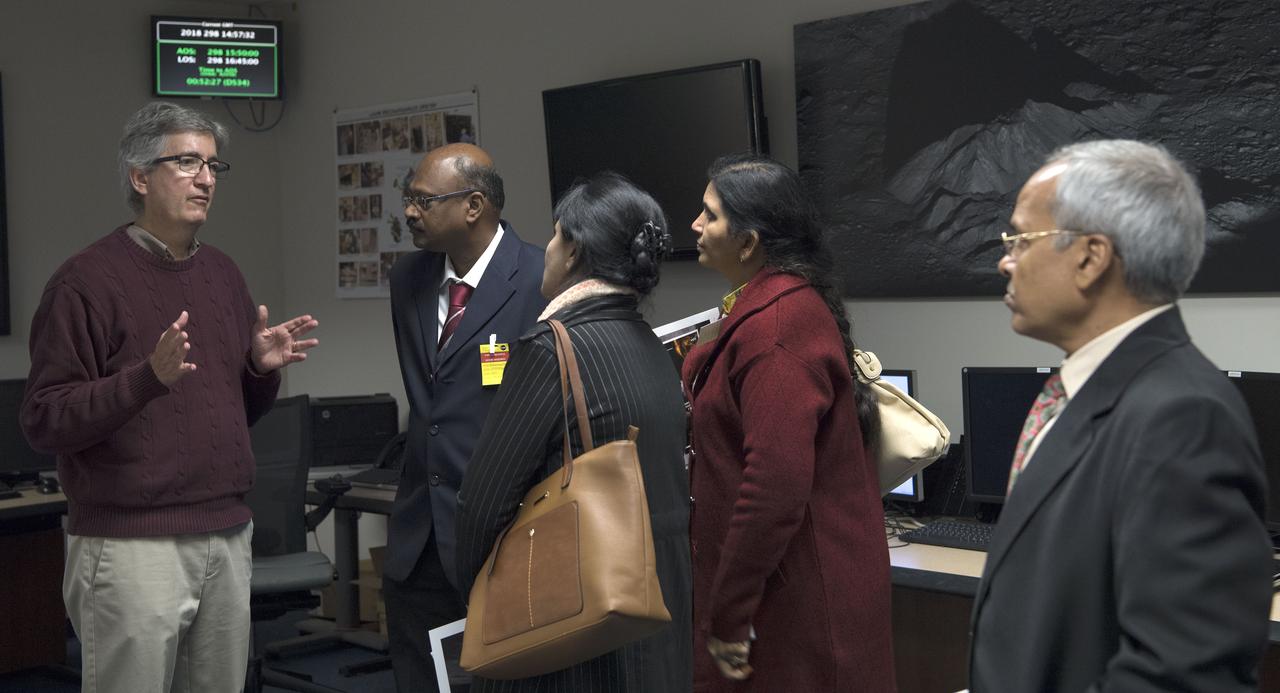

Defence Research & Development Organisation DRDO, Government of India Delegation visited Goddard October 25, 2018. Group toured facilities such as Hyperwall, Earth Sciences and Heliophysics
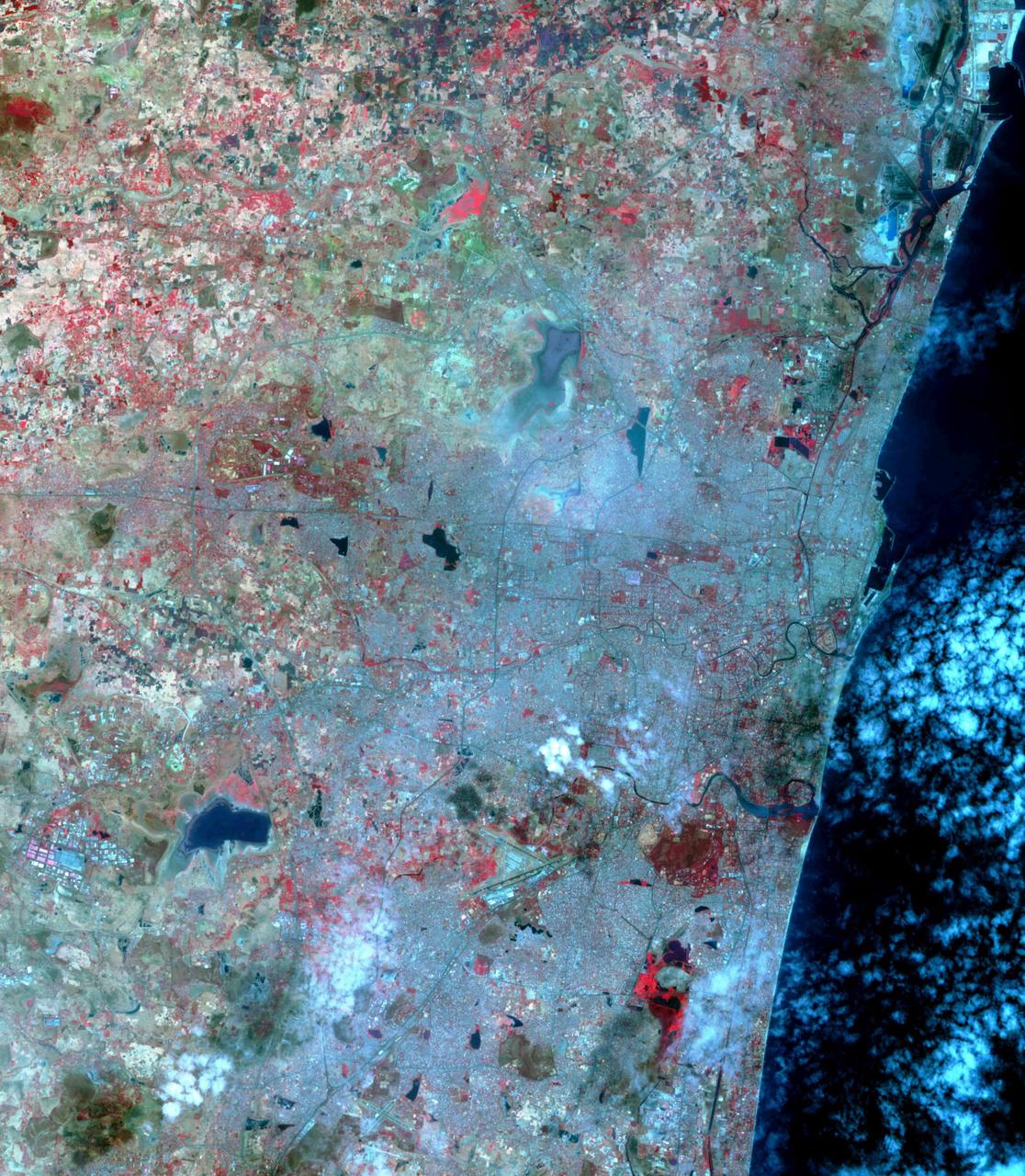

Chennai, India's sixth largest city, has seen no rain for over six months. Its four major reservoirs have virtually run dry, and the city's population of four million is mostly relying on government tankers to provide water, or paying private companies to supply water. The two images were acquired by ASTER on October 6, 2015, and Landsat OLI on June 3, 2019. They cover an area of 29.9 by 45.7 kilometers, and are centered at 13.1 degrees north, 80.3 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23300
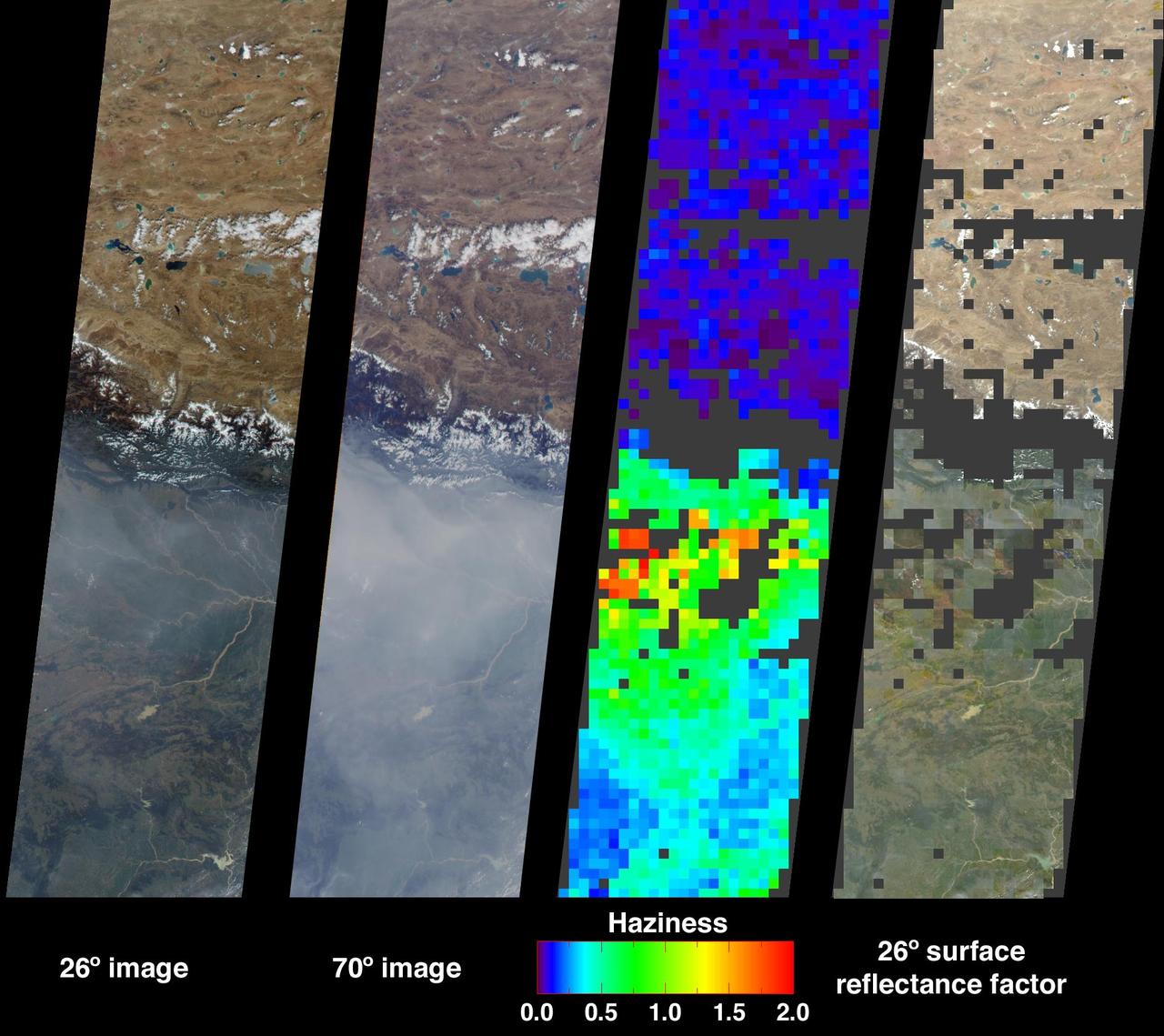
Large abundances of aerosols, or airborne particulates, over the low-lying plains of northeastern India appear in dramatic contrast with the relatively pristine air of the high-altitude Tibetan Plateau in this image from NASA Terra satellite acquired on

S66-54839 (14 Sept. 1966) --- China, India, and Nepal, looking east, as seen from the Gemini-11 spacecraft during its 37th revolution of Earth. The Great Himalaya Mountain Range is clearly visible. Photo credit: NASA

Defence Research & Development Organisation DRDO, Delegation of India visited Goddard October 25, 2018. Christyl Johnson welcomed group at Hyperwall and they toured facilities including Hyperwall, Earth Sciences, and Heliophysics.
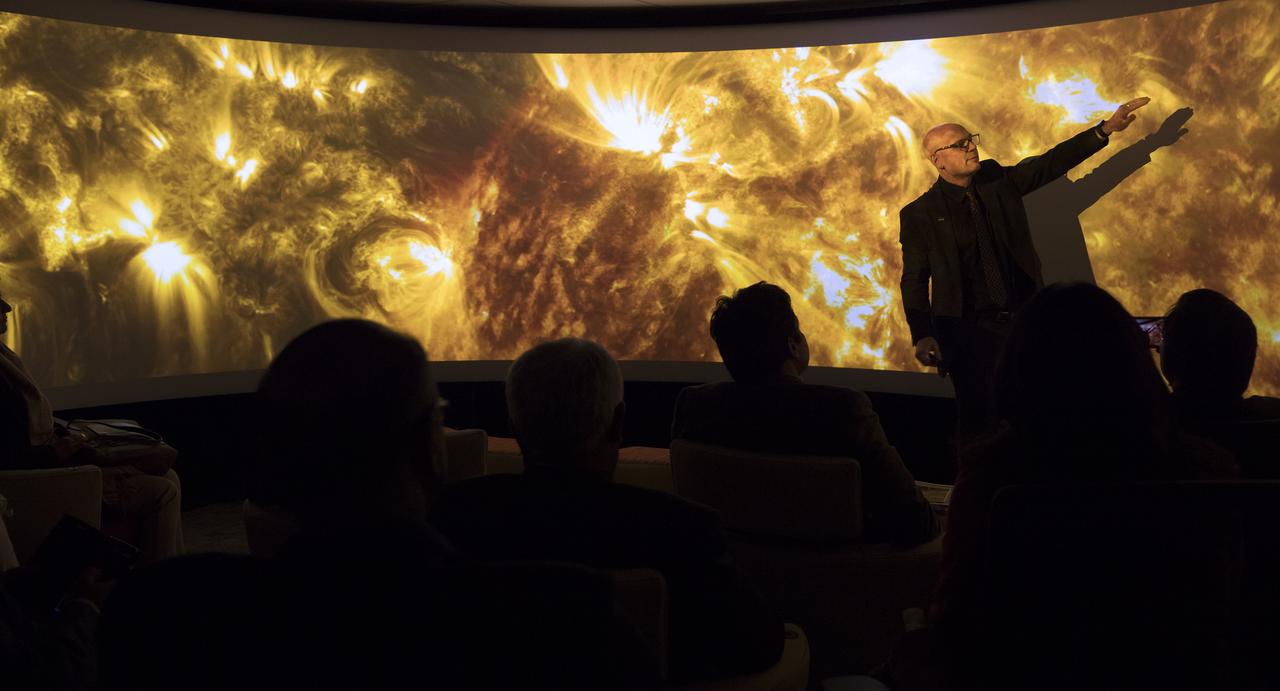

Defence Research & Development Organisation DRDO, Government of India Delegation visited Goddard October 25, 2018. Group toured Goddard facilities such as Hyperwall, Earth Sciences and Heliophysics. Alex Young briefs the group on solar image.
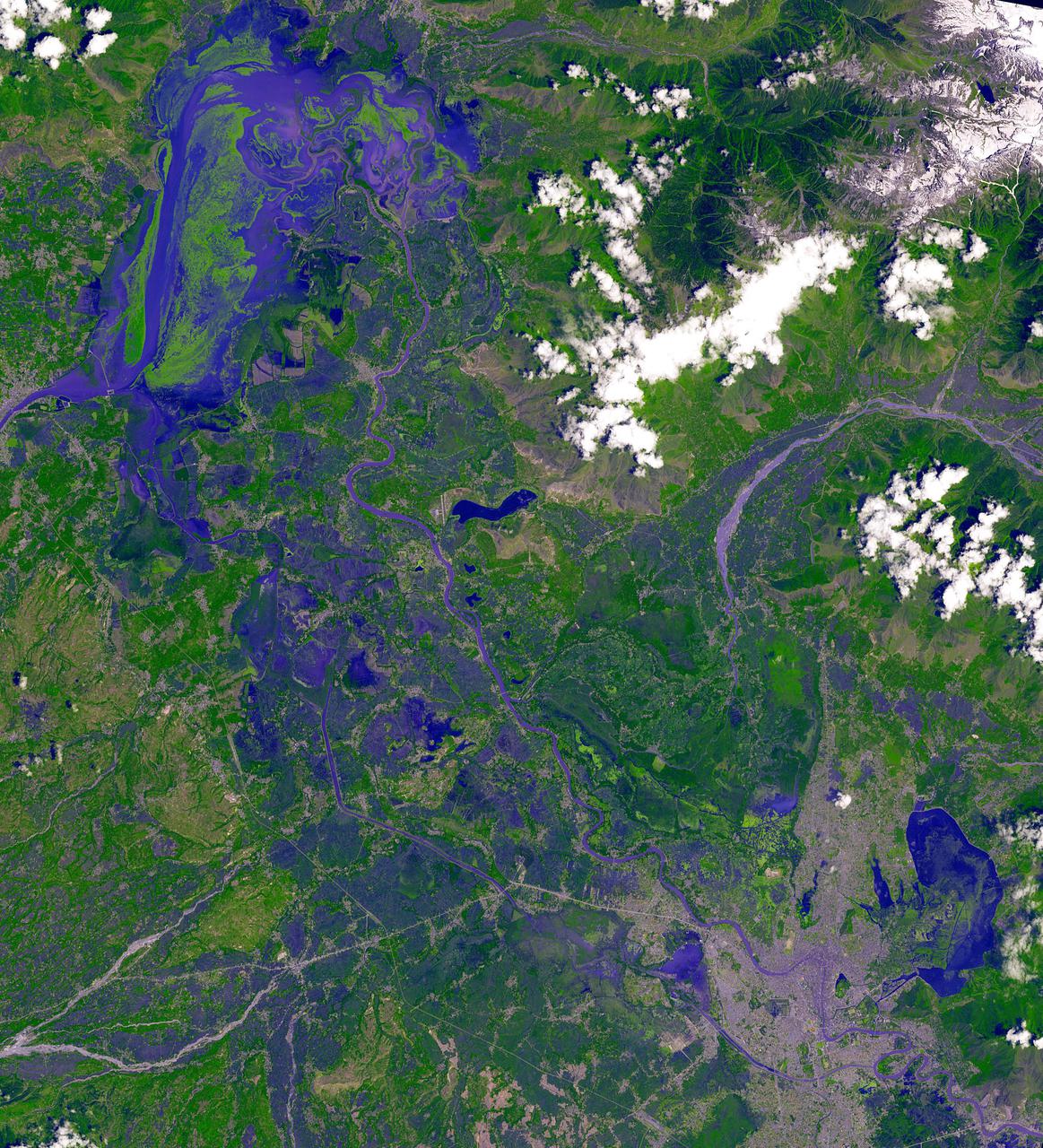

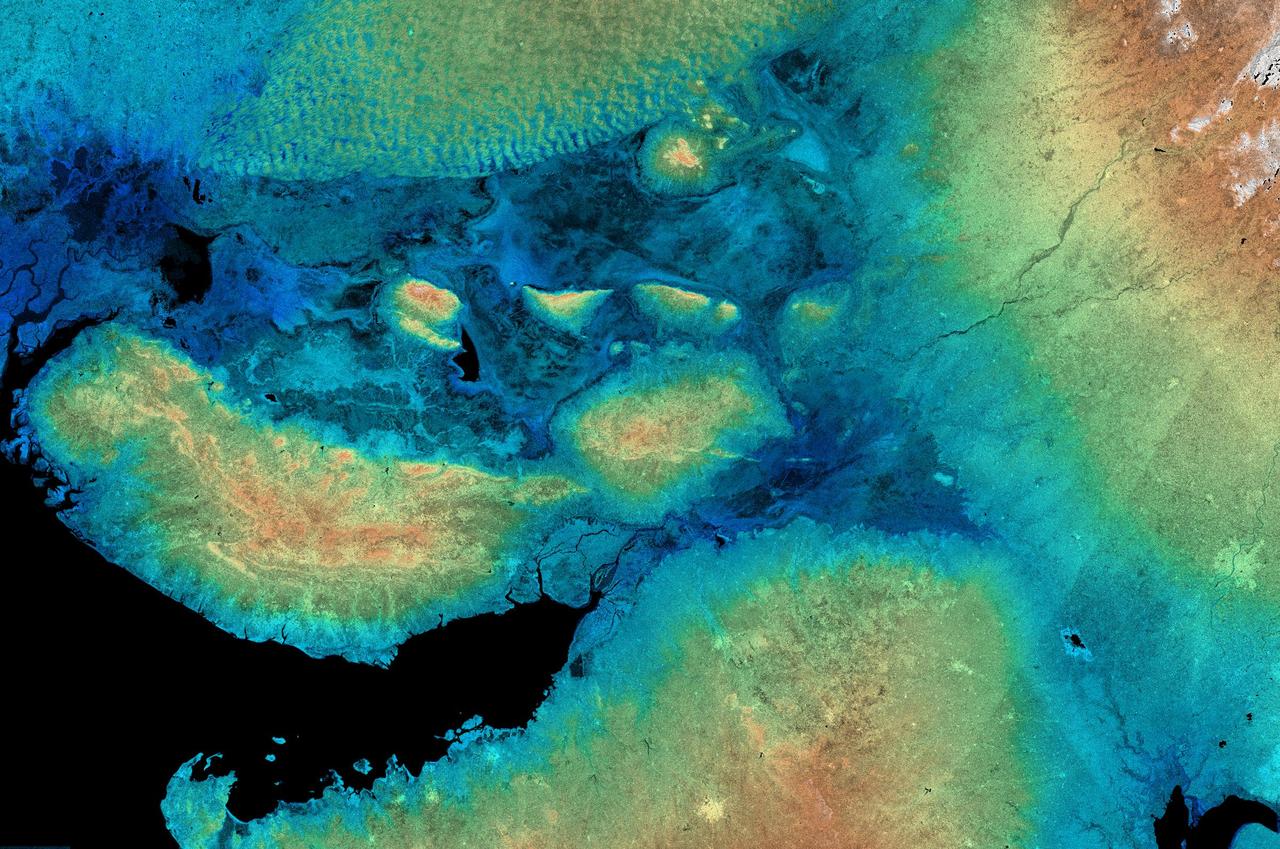
n Jammu and Kashmir, India, along the Jhelum River, Dal and Wular Lakes are remnants of a much larger pre-glacial lake. Wular (in the northwest) is one of the largest freshwater lakes in Asia. Dal Lake (southeast) is an urban lake in Srinagar. It is famous for its Mughal gardens and luxury houseboats. Impressive restoration projects are ongoing to reverse eutrophication. The image was acquired July 3, 2015, covers an area of 39.7 by 43.6 km, and is located at 34.2 degrees north, 74.7 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25123
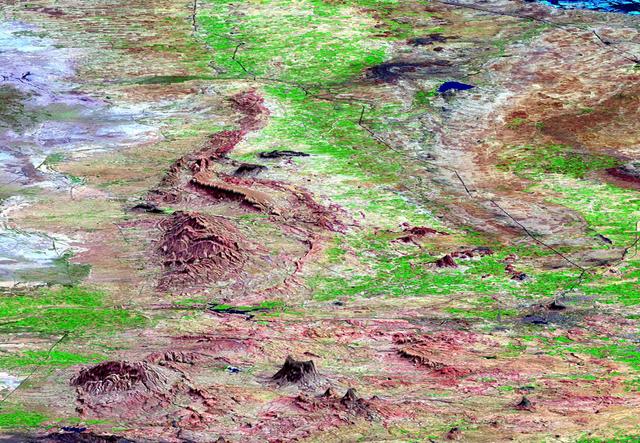

This perspective view shows the city of Bhuj, India, in the foreground near the right side dark gray area. Bhuj and many other towns and cities nearby were almost completely destroyed by the January 26, 2001, earthquake in western India.
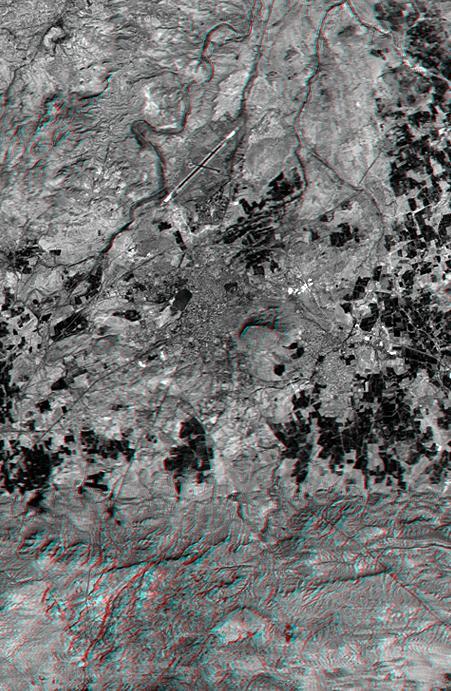
This anaglyph, from NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, shows the city of Bhuj, India. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
This anaglyph NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, shows the city of Bhuj, India. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
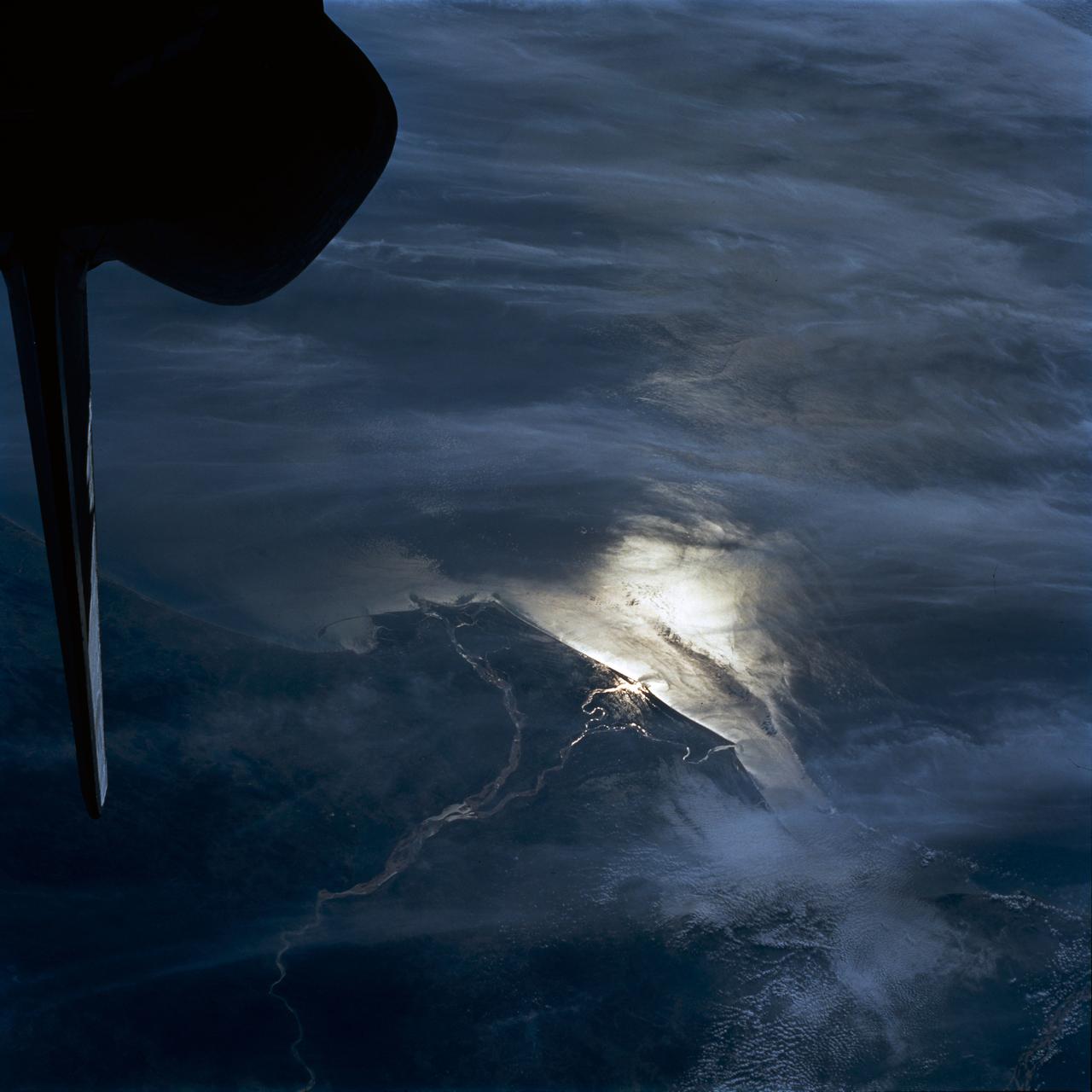

STS054-80-024 (13-19 Jan 1993) --- As the Shuttle was passing southeast over the coast of India, approaching the Bay of Bengal, Endeavour's crew took this picture of the Godavari River Delta. The sun glint pattern was centered directly over the delta and highlighted well the intricate drainage pattern. Offshore, water features associated with current boundaries and river plumes are readily visible. The line of clouds along the coast south of the delta suggest that surface winds are blowing onshore from the Bay of Bengal. As the air passes over the warmer coastal water and land, it is warmed and begins to rise. The moisture in the air condenses, forming a line of low-level clouds.
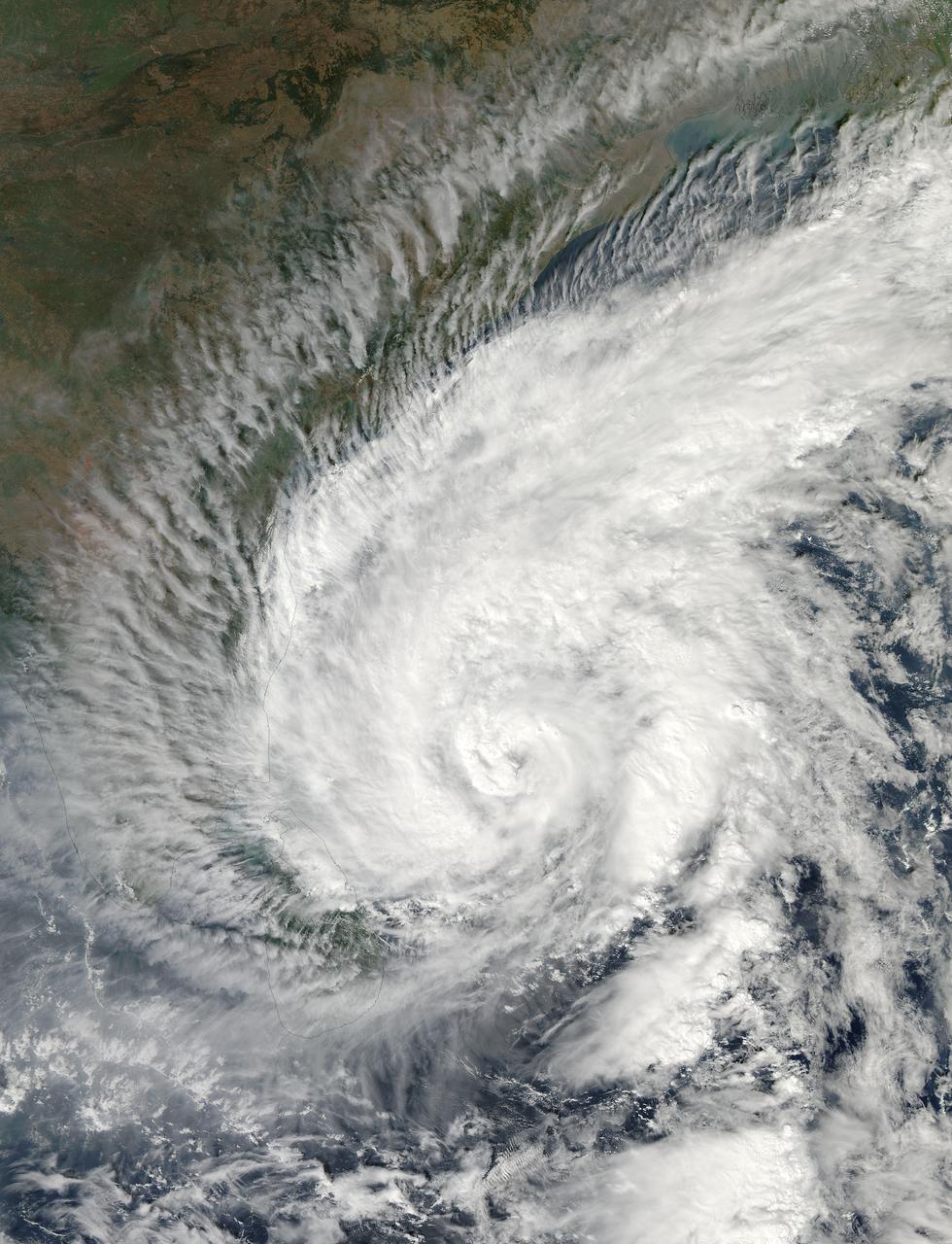
Tropical Cyclone Madi approaching India. Acquired by Aqua/MODIS on 12/07/2013 at 07:55 UTC. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
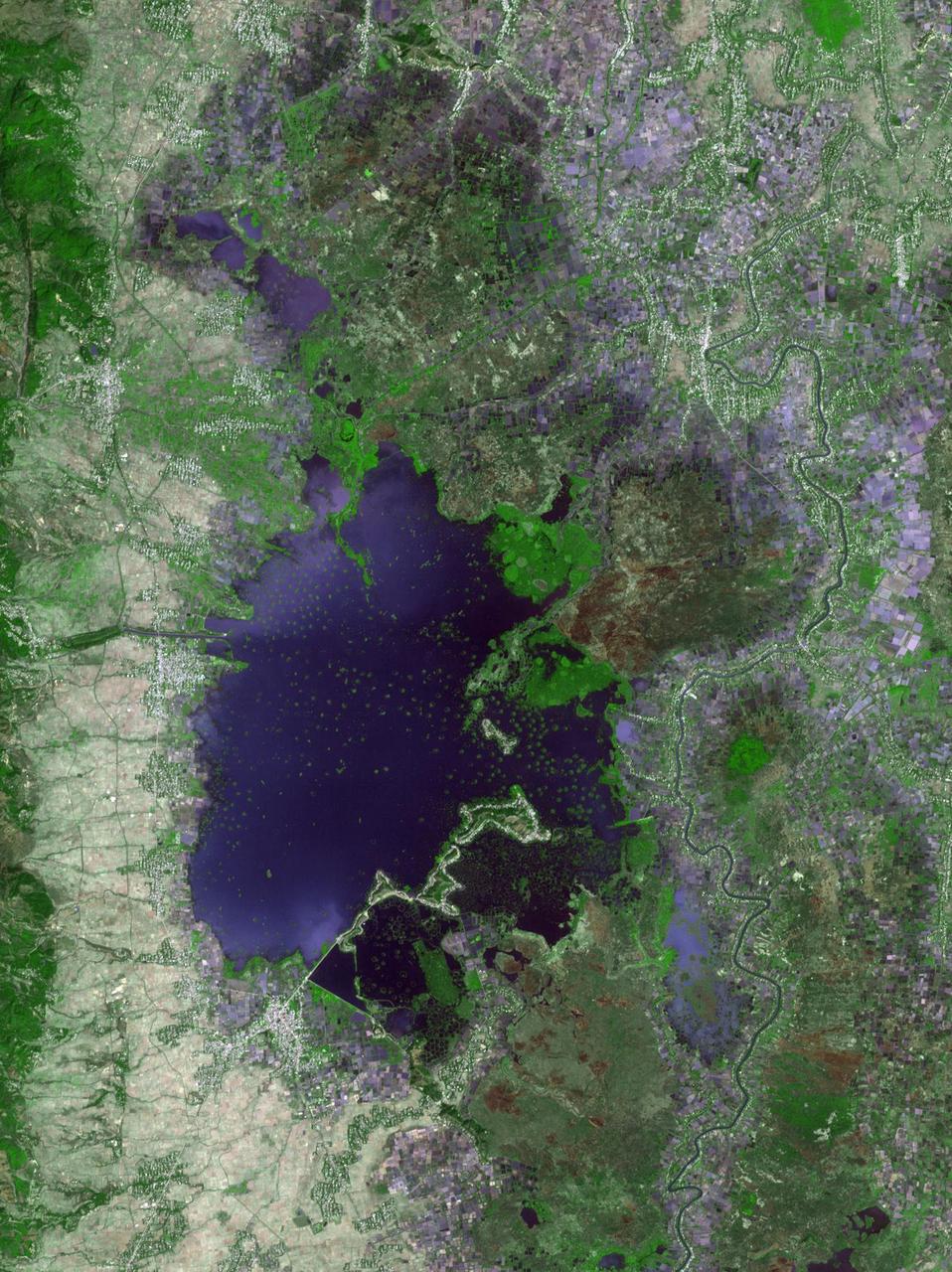

Loktak Lake is the largest freshwater lake in northeast India, and is famous for the floating "phudmis," masses of vegetation, soil and organic material. The lake is a source of water for hydropower, irrigation, drinking water, and livelihood for fish farmers. The image was acquired March 19, 2018, covers an area of 20.5 by 27.3 kilometers, and is located at 24.5 degrees north, 93.8 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22369
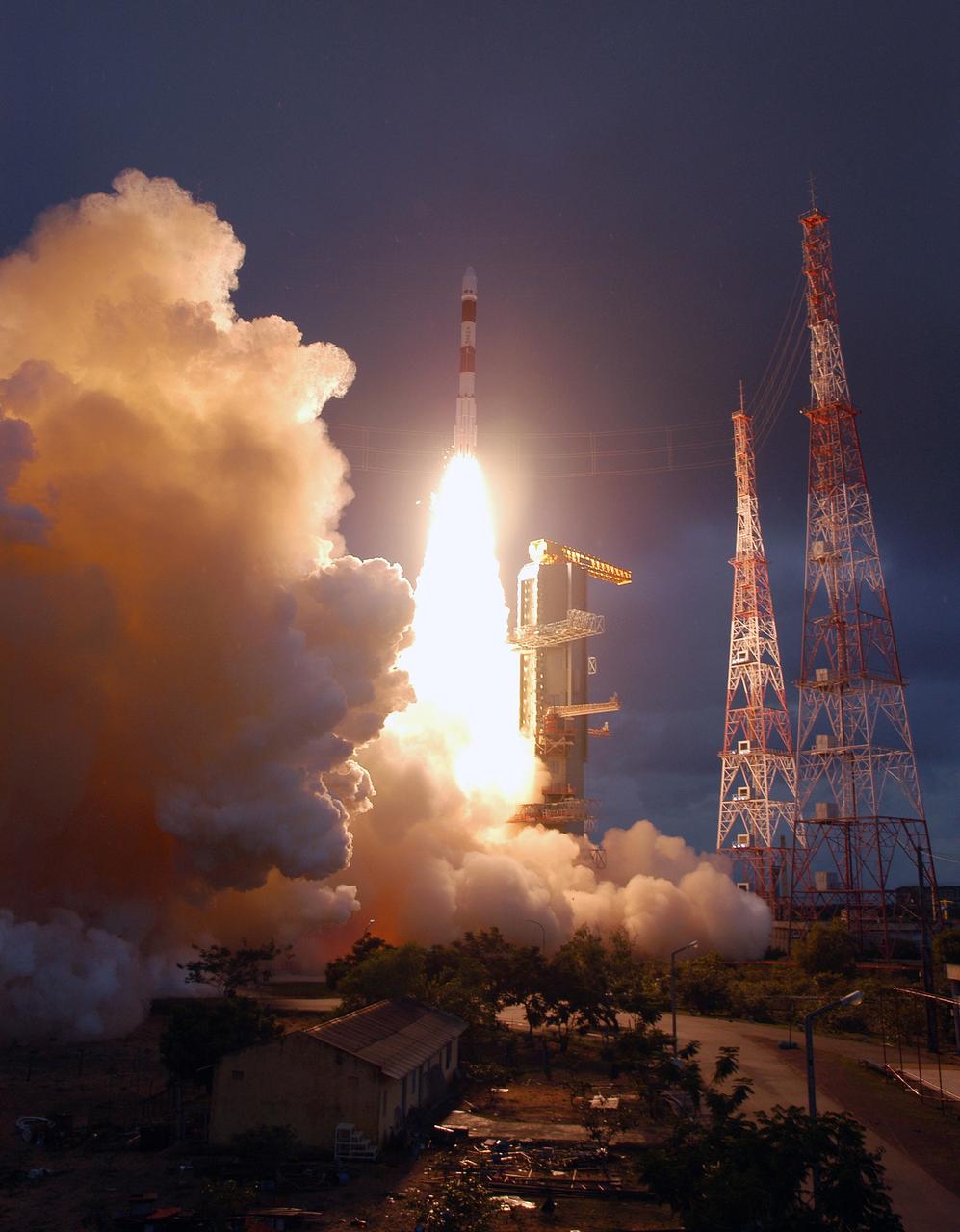

SRIHARIKOTA, India – The Indian Space Research Organization, or ISRO, launches its robotic Chandrayaan-1 rocket with two NASA instruments aboard on India's maiden moon voyage to map the lunar surface. The Moon Mineralogy Mapper will assess mineral resources, and the Miniature Synthetic Aperture Radar, or Mini-SAR, will map the polar regions and look for ice deposits. Data from the two instruments will contribute to NASA's increased understanding of the lunar environment as it implements the nation's space exploration policy, which calls for robotic and human missions to the moon. In addition to the two science instruments, NASA will provide space communications support to Chandrayaan-1. The primary location for the NASA ground tracking station will be at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Md. Photo credit: NASA

Adam's Bridge is a 48 km long chain of limestone shoals, that were formerly a land bridge between India and Sri Lanka. It was reportedly passable until the 15th century, when storms destroyed the integrity of the bridge. The geologic origin of the bridge is still controversial. The image was acquired March 25, 2020, covers an area of 39.6 by 61.7 km, and is located at 9.3 degrees north, 79.3 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24949

iss072e757408 (March 6, 2025) --- Ahmadebad, India—with a metropolitan population of about 9.3 million residents and split by the Sabarmati River—is pictured from the International Space Station at approximately 9:40 p.m. local time as it orbited 258 miles above the South Asian nation. Founded over 600 years ago, India’s first UNESCO World Heritage City is renowned for its thriving textile industry and vibrant street food culture.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Sashikant Dhawan (left), costume director with a film crew from India, and Shirish R. Patel (right), with KSC’s International Space Station Payload Processing, pose for a photo near the viewing stands at the NASA News Center. The crew spent several days at KSC filming at various sites for the movie “Swades,” a story about India’s brain-drain. The writer and director is Ashutosh Gowariker. The lead actors are Shahrukh Khan and Gayatri Joshi. Sunita Gowariker is executive producer.
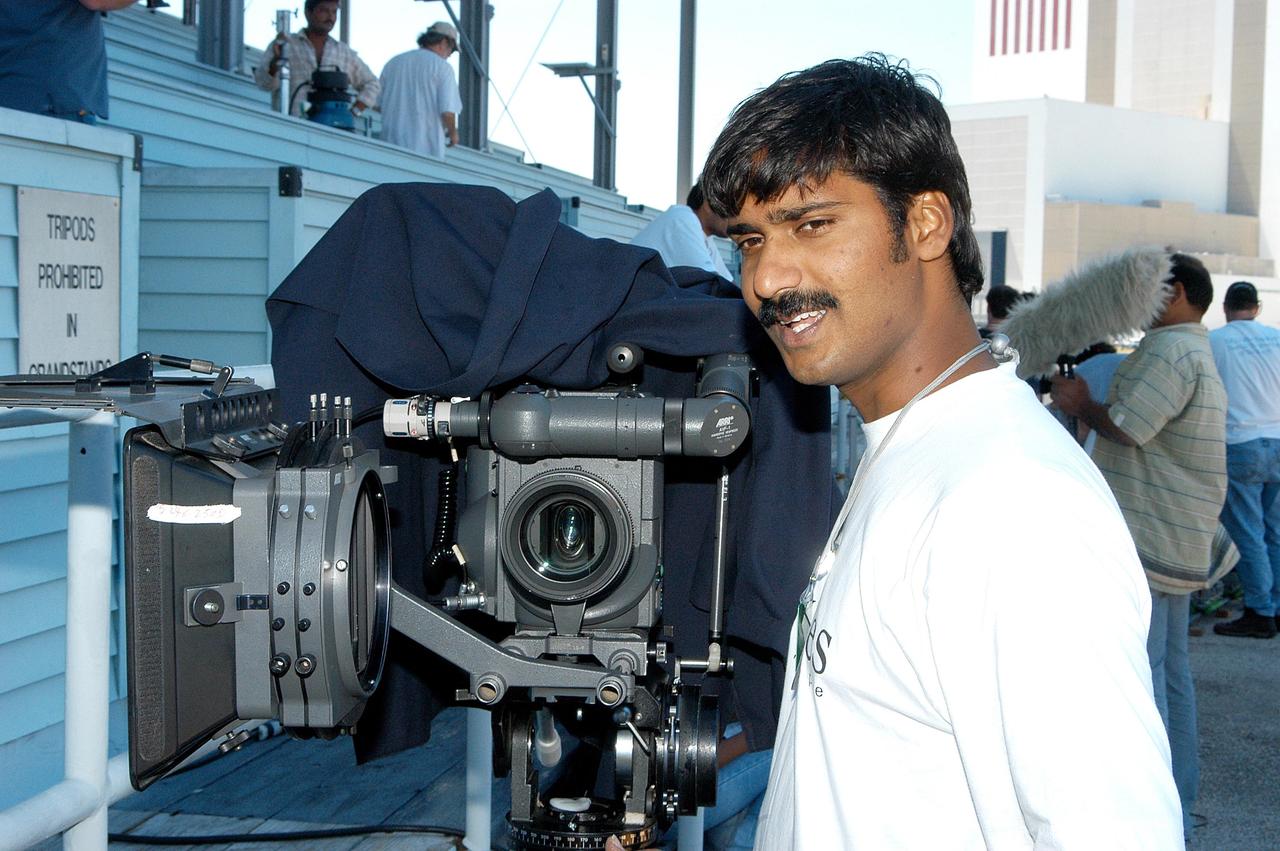

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Sashikant Dhawan is costume director with the film crew from India who spent several days at KSC filming at various sites for the movie “Swades,” a story about India’s brain-drain. Ashutosh Gowariker is the writer-director. The lead actors are Shahrukh Khan and Gayatri Joshi. Sunita Gowariker is executive producer.
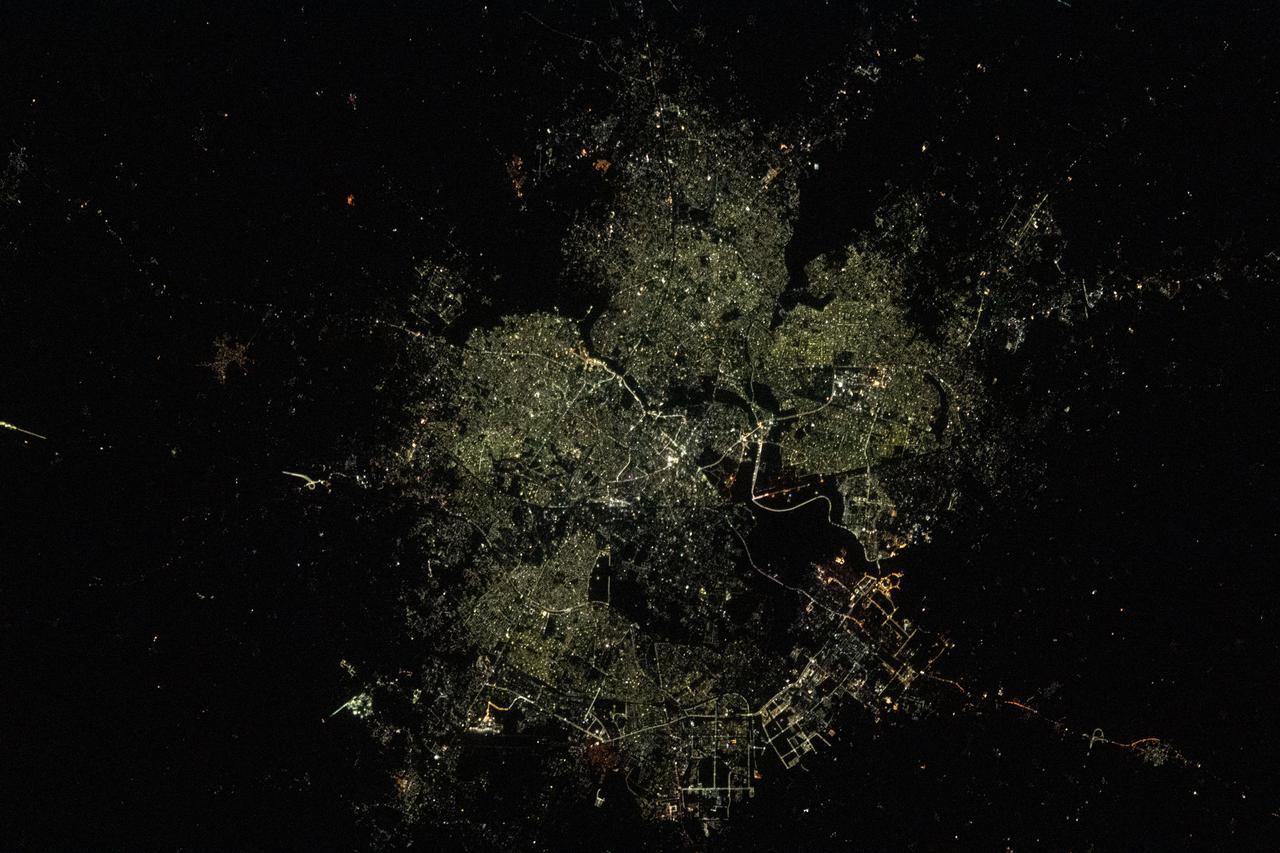

iss069e010770 (May 15, 2023) --- The city lights of Lucknow, in northern India, were pictured by UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Sultan Alneyadi from the International Space Station as it orbited 262 miles above.
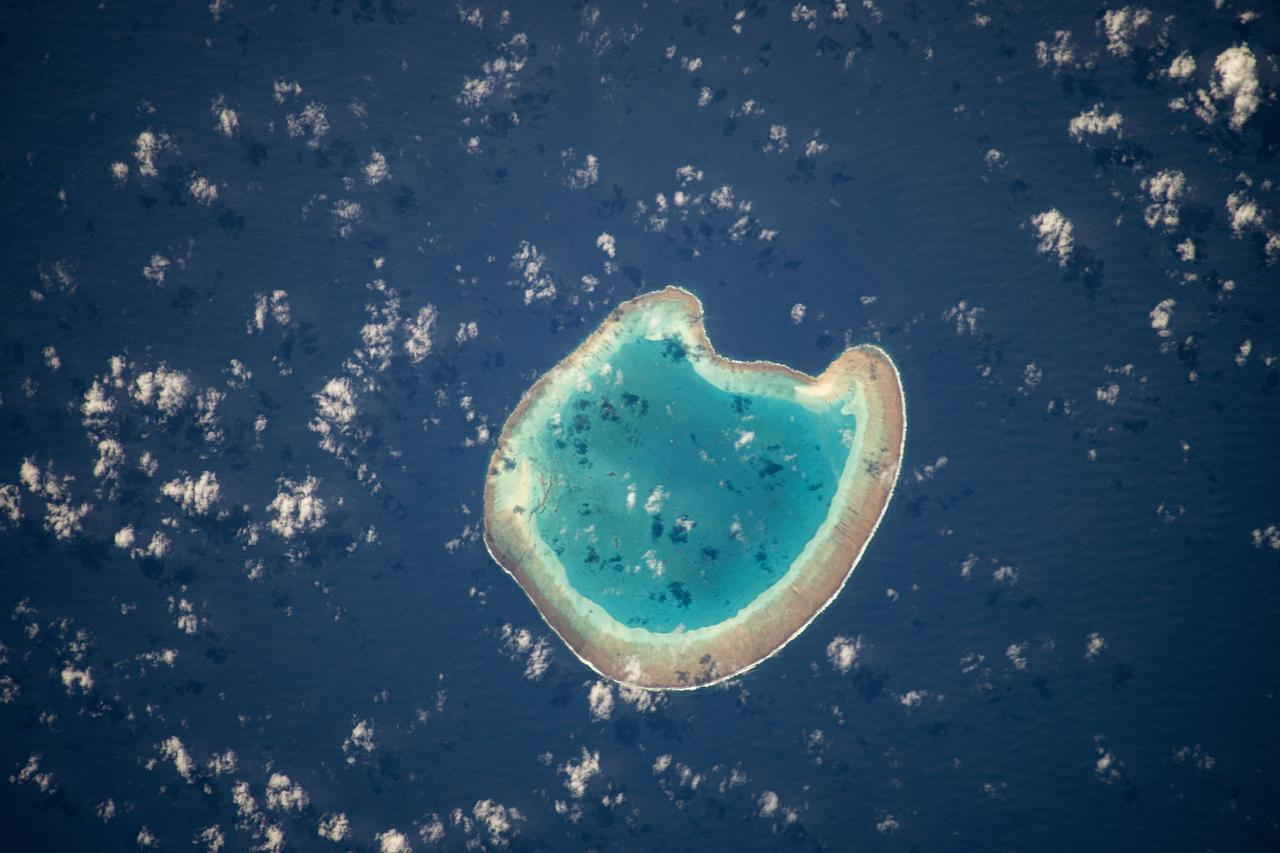

iss071e111610 (May 23, 2024) -- Nearly halfway between Madagascar and Mozambique lies the Bassas da India atoll in the Mozambique Channel. The uninhabited ring-shaped island spans roughly 330 feet (~100 meters) around a shallow lagoon. The International Space Station was soaring 260 miles above as this photo was taken.
This image shows the area around the January 26, 2001, earthquake in western India, the deadliest in the country history with some 20,000 fatalities. The epicenter of the magnitude 7.6 earthquake was just to the left of the center of the image.

On January 26, 2001, the city of Bhuj suffered the most deadly earthquake in India history. This stereoscopic image was generated from NASA Landsat satellite and data from Shuttle Radar Topography Mission SRTM.
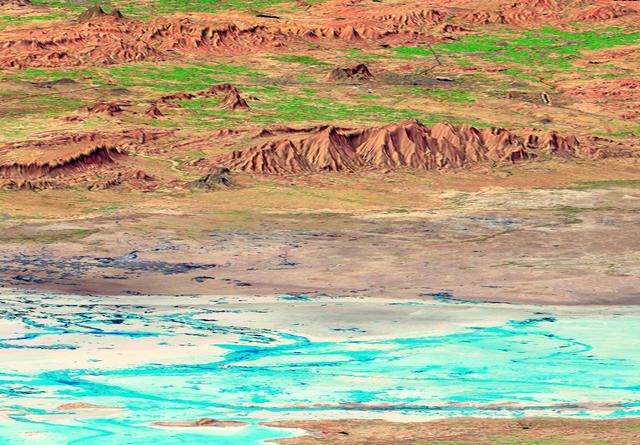

The earthquake that struck western India on January 26, 2001, was the country strongest in the past 50 years. This perspective view shows the area of the earthquake epicenter in the lower left corner.
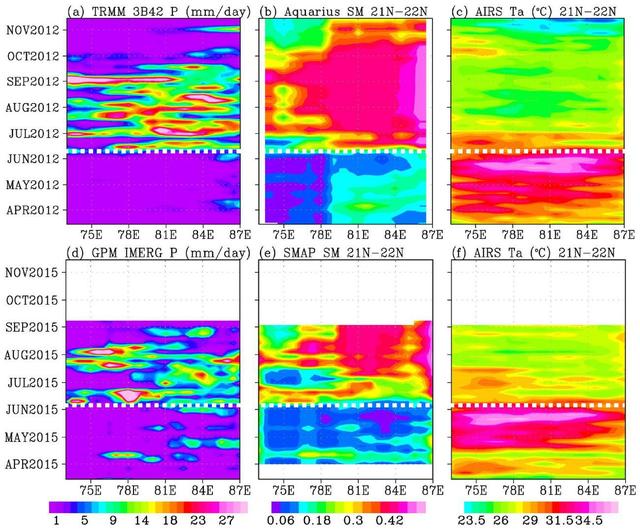
In June 2015, news organizations around the world reported on a deadly heat wave in India that killed more than 2,300 people. Prior to the arrival of the summer monsoon in India, weather conditions had been extremely hot and dry. Such conditions can lead to economic and agricultural disaster, human suffering and loss of life. NASA satellite sensors are allowing scientists to characterize pre-monsoon droughts and heat waves and postulate their scientific cause. This figure shows the longitude-time variations, averaged between 21 and 22 degrees North, across the middle of the India subcontinent from mid-April to mid-June. Longitude from the Arabian Sea to the Bay of Bengal is represented on the horizontal axis; while the vertical axis shows the timeframe. Rainfall is shown on the left, soil moisture is in the center, and surface air temperature is on the right. For both years (2012 and 2015), the summer monsoon begins in June, with sharp rises in rainfall and soil moisture, and a sharp drop in air temperature. The hottest and driest weeks occurred just before the summer monsoon onsets. Similar dry and hot periods, varying from one to a few weeks, were observed in 2013 and 2014. Soil moisture as an indication of drought as measured by NASA's Aquarius mission was first available in 2012. Rainfall data are from NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM), and surface air temperature is from NASA's Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite. The TRMM and Aquarius missions ended in April 2015, before the drought and heat waves. Their data were replaced by those presently available from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive Mission (SMAP) and Global Precipitation Mission (GPM) to show the drought and heatwave in 2015. Scientists from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, have shown that during the summer monsoon season, moisture is transported into the India Subcontinent from the Arabian Sea and out to the Bay of Bengal. The difference between moisture input from the west and output to the east is deposited as rain over land. The pre-monsoon drought and heat waves coincide with the short period when moisture is advected out to the Bay of Bengal ahead of input from the Arabian Sea. The onset of southwest monsoon winds begins in the Bay of Bengal and sucks moisture out from the subcontinent earlier than the onset in the Arabian Sea. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19939
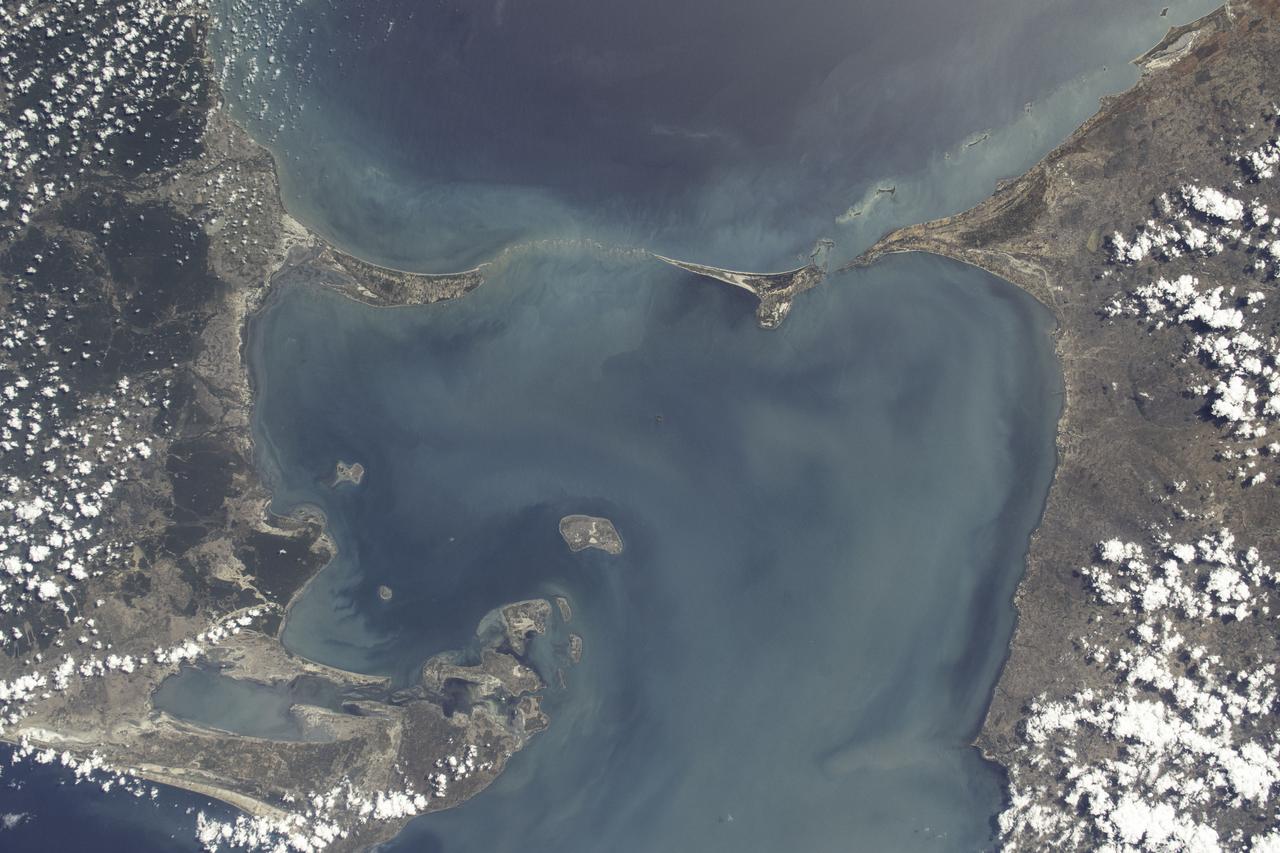

iss071e700080 (Sept. 21, 2024) -- A 48 kilometer ( 30 miles) chain of limestone shoals, formerly a bridge between India and Sri Lanka, are pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 256 miles above. Most often called "Adam's Bridge," it separates the Palk Strait (bottom of image) from the Gulf of Mannar (top). To the right of this image is mainland India, to the left is Sri Lanka.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During filming at KSC by a crew from India, KSC videographer Glen “Mic” Miracle (left) and Bobbie Faye Ferguson talk to actor Rahul Vohra (right). The film crew spent several days at KSC filming at various sites for the movie “Swades,” a story about India’s brain-drain. Vohra is one of the actors in the film that stars Shahrukh Khan and Gayatri Joshi. The writer-director is Ashutosh Gowariker. Sunita Gowariker is executive producer. Ferguson is manager of Multimedia, for NASA Public Affairs.
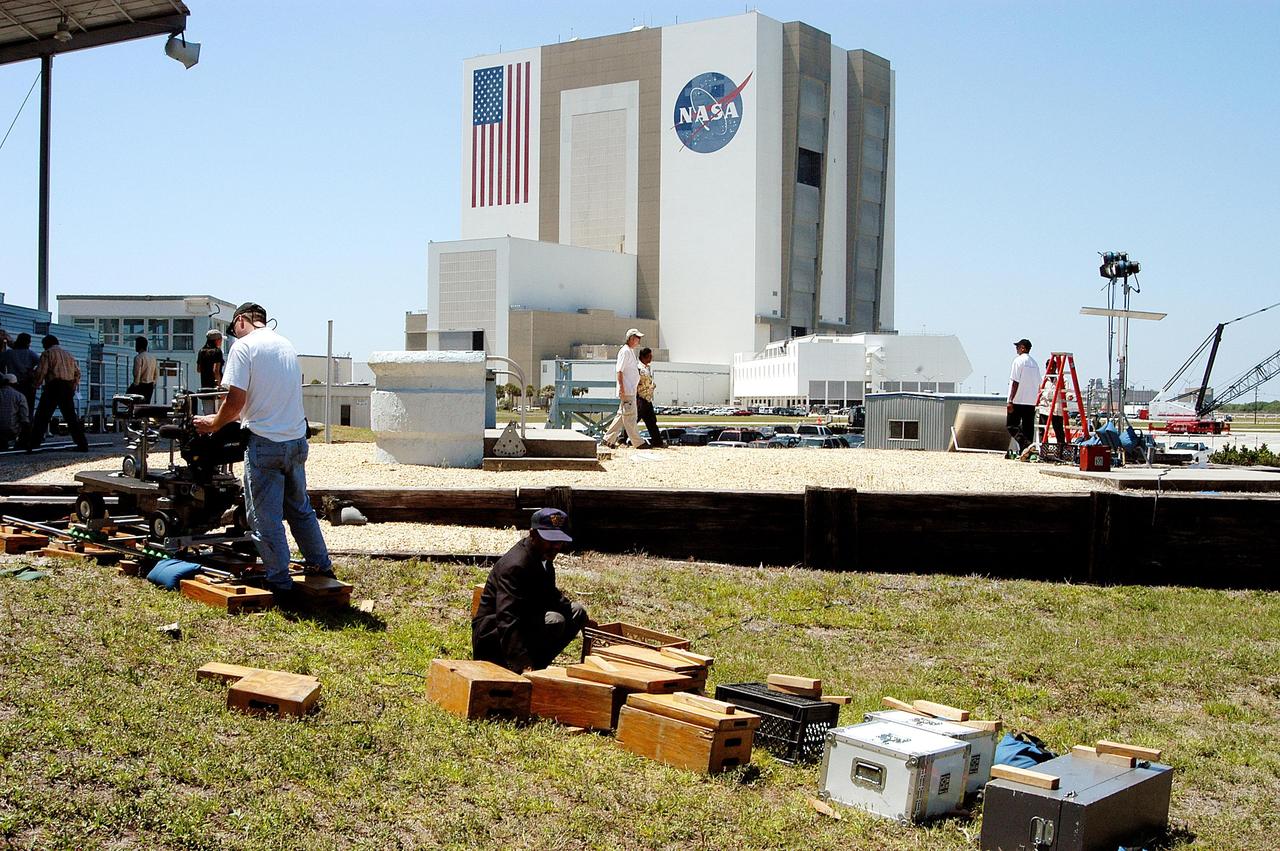

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A film crew from India sets up equipment at the viewing stands near the NASA News Center. The crew spent several days at KSC filming at various sites for the movie “Swades,” a story about India’s brain-drain. The writer and director is Ashutosh Gowariker and lead actors are Shahrukh Khan and Gayatri Joshi. Sunita Gowariker is executive producer.
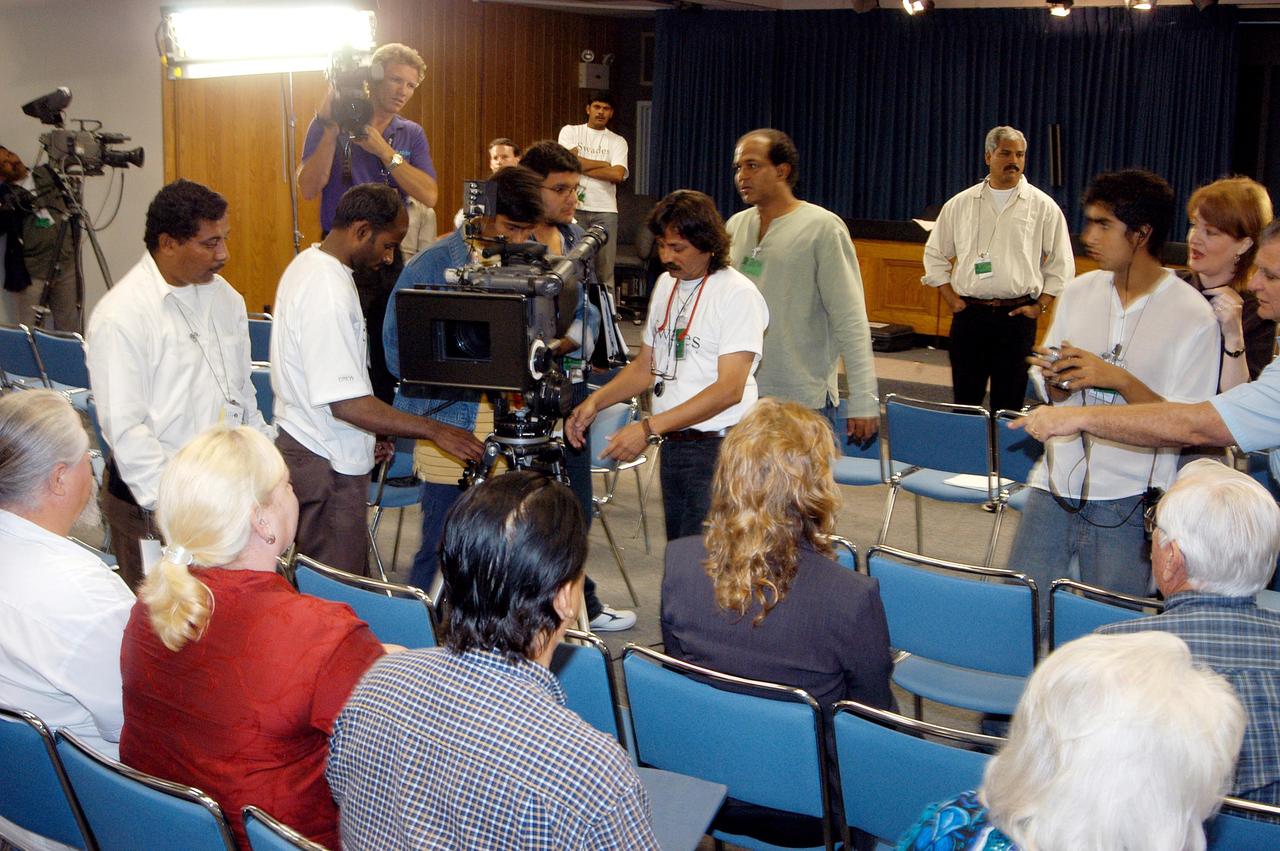

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A film crew from India sets up equipment inside the television studio at the NASA News Center. The crew spent several days at KSC filming at various sites for the movie “Swades,” a story about India’s brain-drain. At center is Mahesh Aney, director of photography. The writer and director is Ashutosh Gowariker (seen to the right of Aney). The lead actors are Shahrukh Khan and Gayatri Joshi. Sunita Gowariker is executive producer.
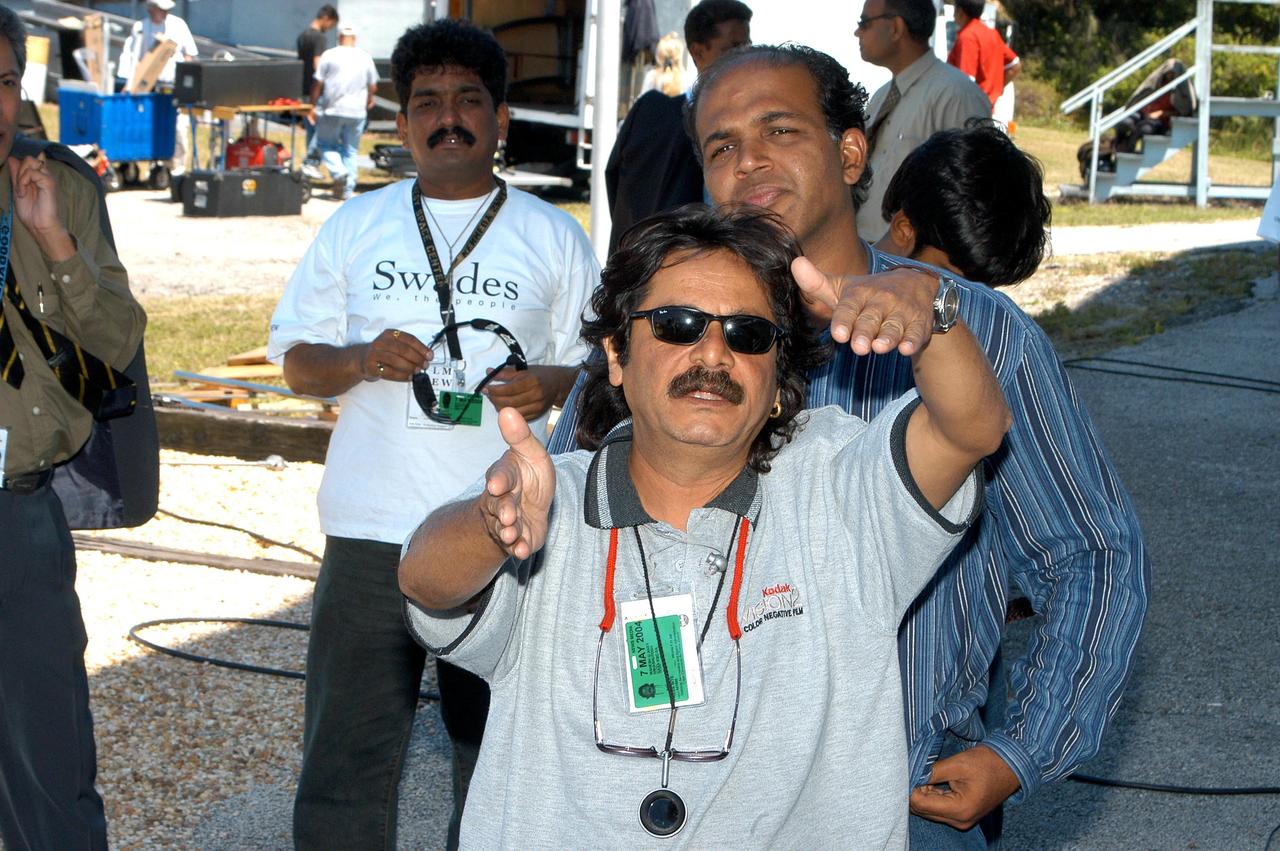

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Part of the crew from India filming at KSC, Director of Photography Mahesh Aney directs a camera setup. Writer and director of the film Ashutosh Gowariker is behind him. The crew spent several days at KSC filming at various sites for the movie “Swades,” a story about India’s brain-drain. The lead actors are Shahrukh Khan and Gayatri Joshi. Sunita Gowariker is executive producer.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During filming at KSC, Shirish R. Patel (left, with KSC’s International Space Station Payload Processing) joins the writer-director Ashutosh Gowariker and actor Rahul Vohra for a photo. The film crew from India spent several days at KSC filming at various sites for the movie “Swades,” a story about India’s brain-drain. The lead actors are Shahrukh Khan and Gayatri Joshi. Sunita Gowariker is executive producer.

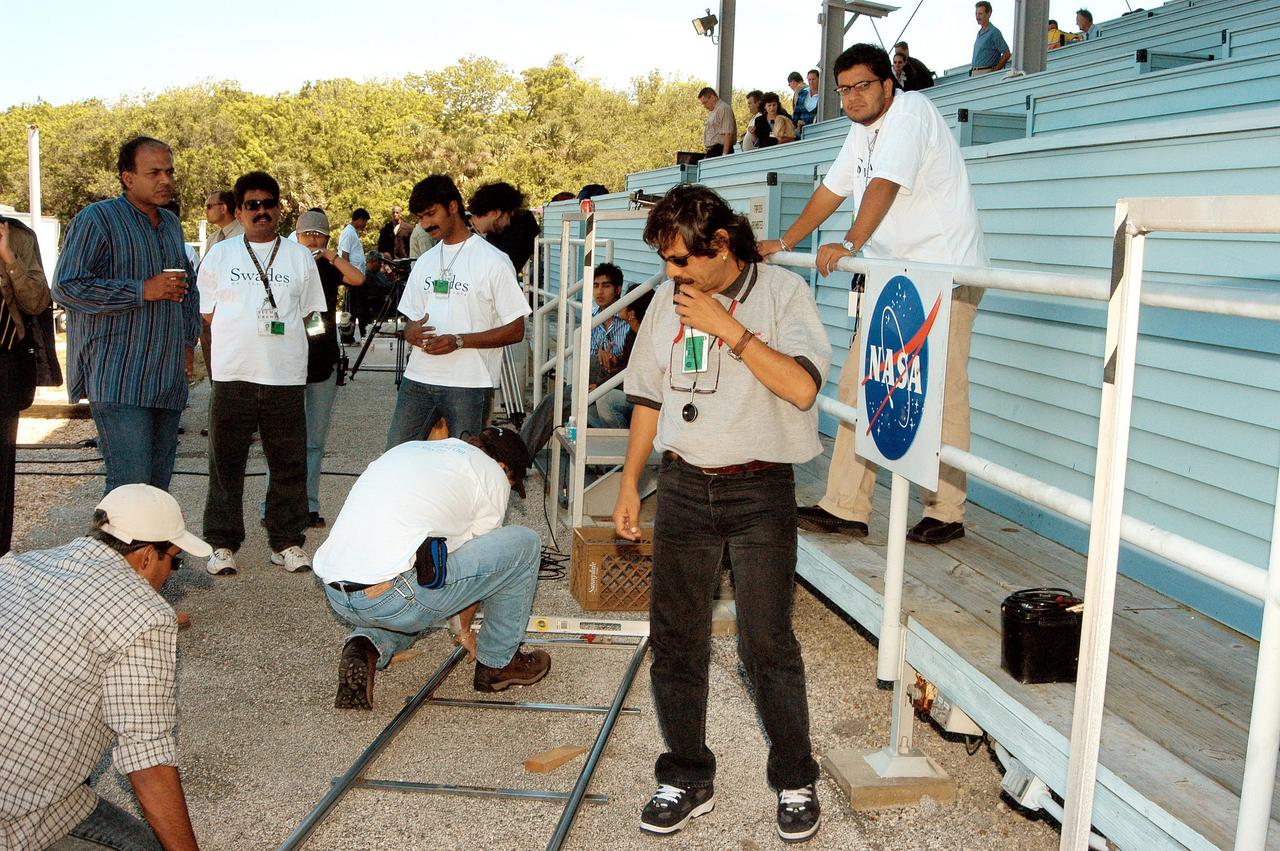
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A film crew from India sets up equipment at the viewing stands near the NASA News Center. The crew spent several days at KSC filming at various sites for the movie “Swades,” a story about India’s brain-drain. The writer and director is Ashutosh Gowariker and lead actors are Shahrukh Khan and Gayatri Joshi. Sunita Gowariker is executive producer.
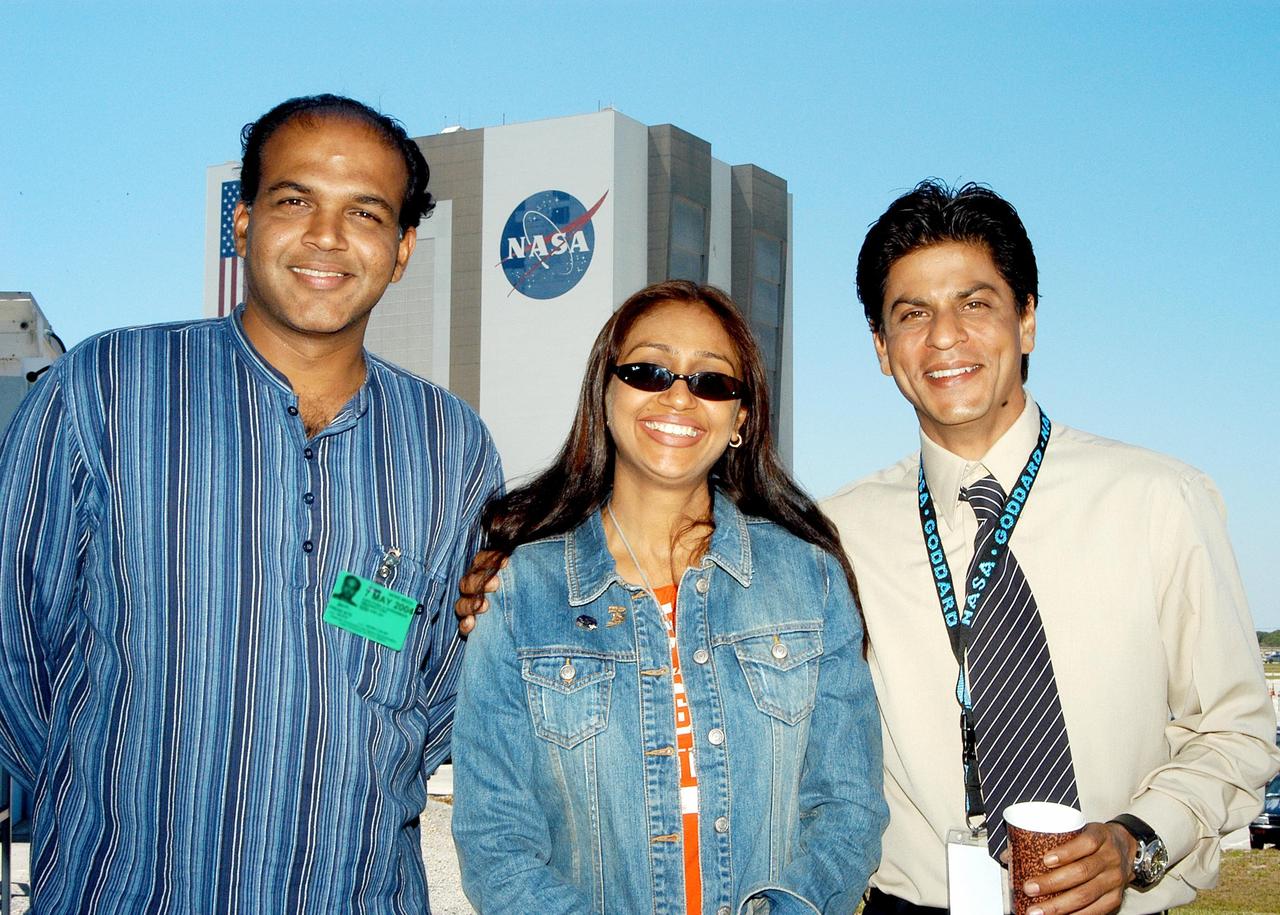

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During filming at KSC, writer-director from India Ashutosh Gowariker, his wife Sunita, and actor Shahrukh Khan pose for a photo with the Vehicle Assembly Building in the background. The film crew spent several days at KSC filming at various sites for the movie “Swades,” a story about India’s brain-drain. Khan is one of the lead actors in the film; the other is Gayatri Joshi. Sunita Gowariker is executive producer.
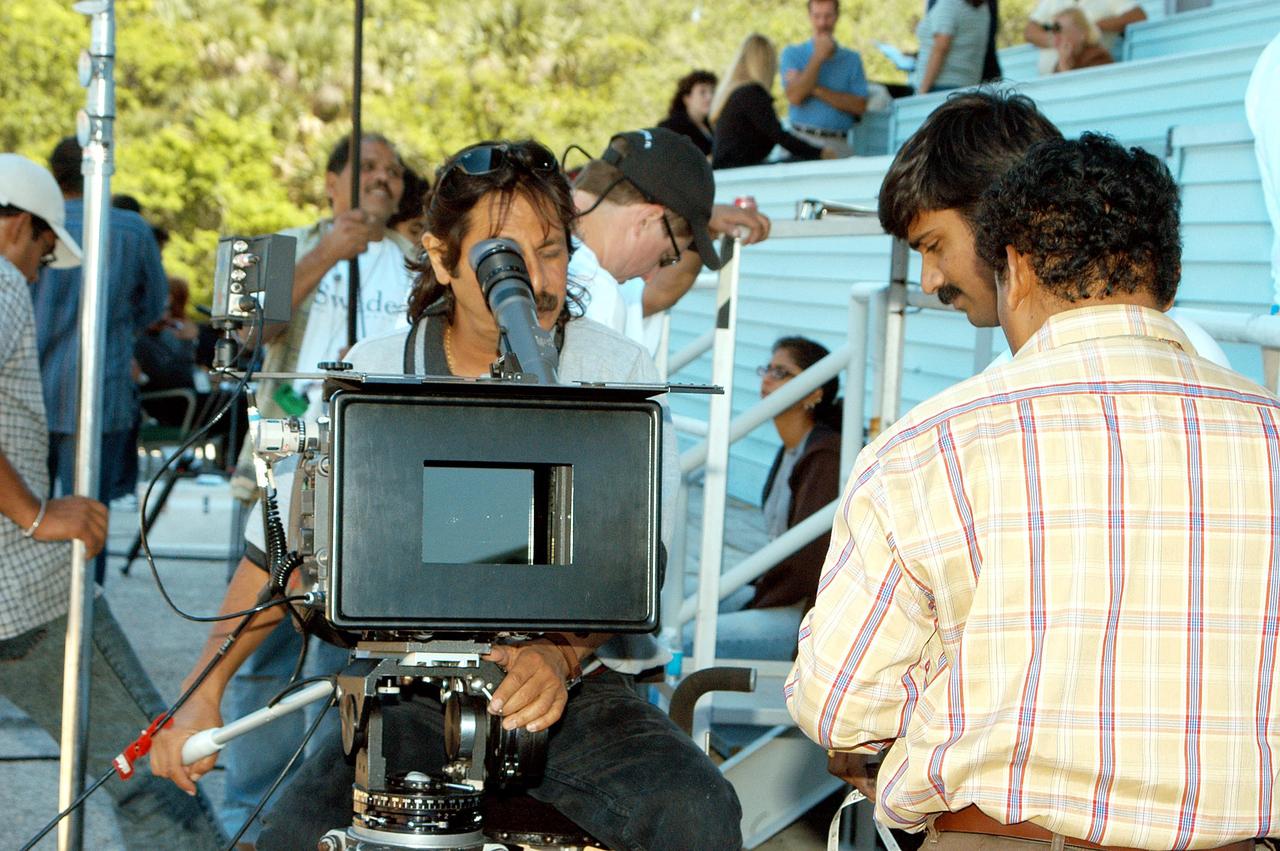

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Mahesh Aney, who is director of photography on a film crew from India, sets up a camera at the stands near the NASA News Center. The crew spent several days at KSC filming at various sites for the movie “Swades,” a story about India’s brain-drain. The writer and director is Ashutosh Gowariker. The lead actors are Shahrukh Khan and Gayatri Joshi. Sunita Gowariker is executive producer.

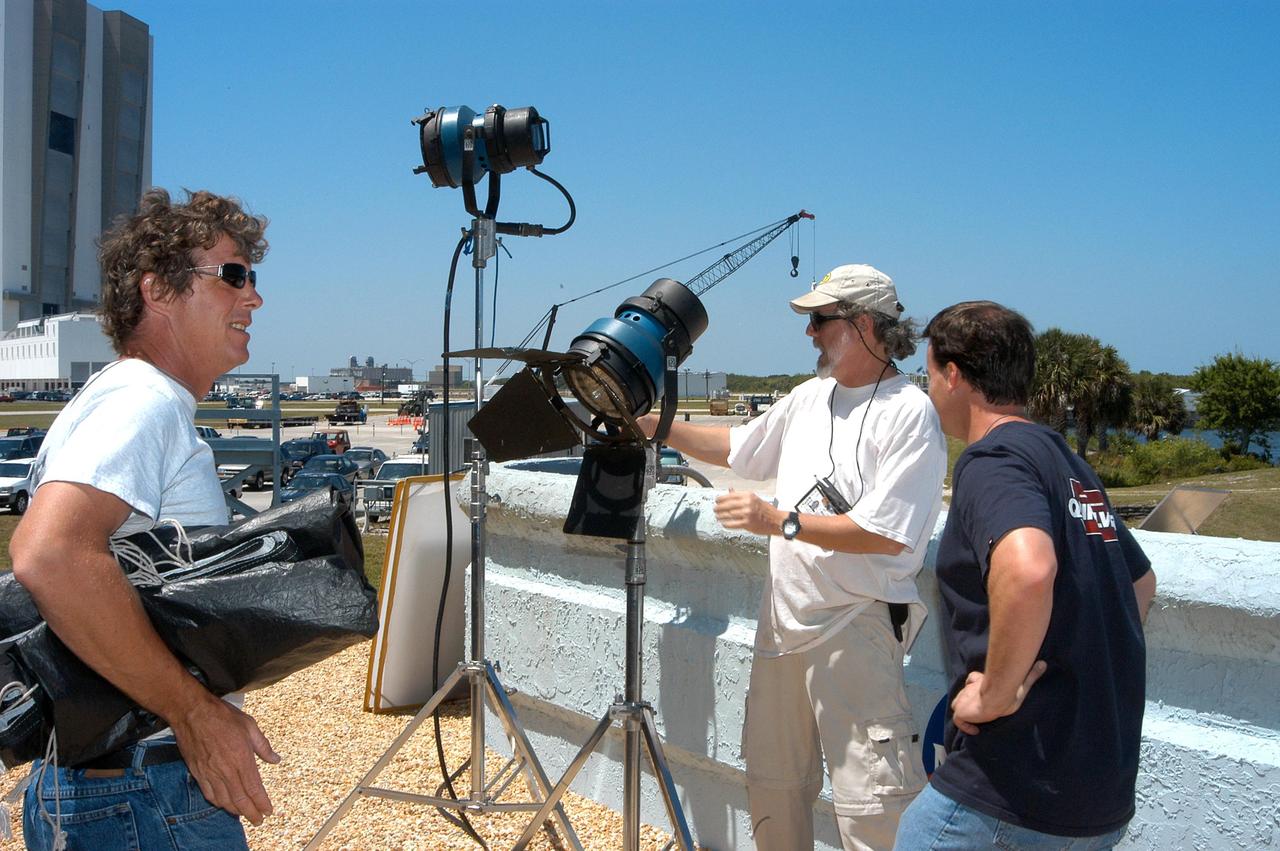
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A film crew from India sets up equipment at the viewing stands near the NASA News Center. The crew spent several days at KSC filming at various sites for the movie “Swades,” a story about India’s brain-drain. The writer and director is Ashutosh Gowariker, standing at left. The lead actors are Shahrukh Khan and Gayatri Joshi. Sunita Gowariker is executive producer.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A film crew from India sets up equipment at the viewing stands near the NASA News Center. Behind the camera at right is Director of Photography Mahesh Aney. The crew spent several days at KSC filming at various sites for the movie “Swades,” a story about India’s brain-drain. The writer and director is Ashutosh Gowariker. The lead actors are Shahrukh Khan and Gayatri Joshi. Sunita Gowariker is executive producer.
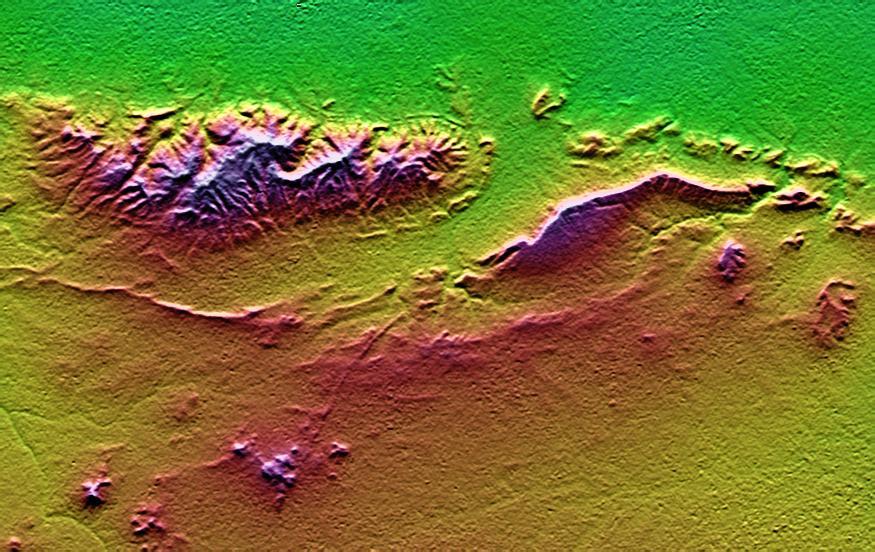

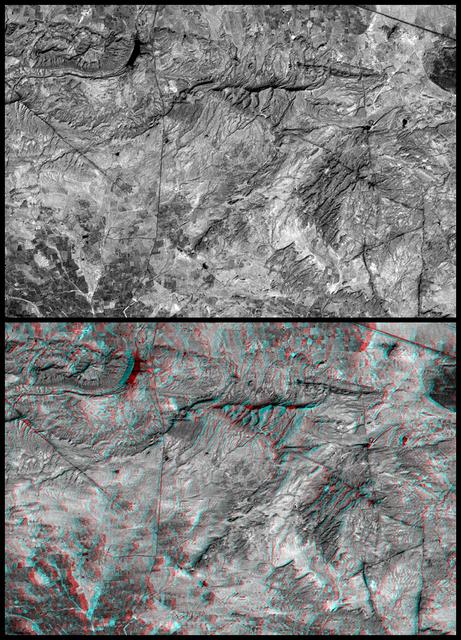
On January 26, 2001, the Kachchh region in western India suffered the most deadly earthquake in India's history. This shaded topography view of landforms northeast of the city of Bhuj depicts geologic structures that are of interest in the study the tectonic processes that may have led to that earthquake. However, preliminary field studies indicate that these structures are composed of Mesozoic rocks that are overlain by younger rocks showing little deformation. Thus these structures may be old, not actively growing, and not directly related to the recent earthquake. The Haro Hills are on the left and the Kas Hills are on the right. The Haro Hills are an "anticline," which is an upwardly convex elongated fold of layered rocks. In this view, the anticline is distinctly ringed by an erosion resistant layer of sandstone. The east-west orientation of the anticline may relate to the crustal compression that has occurred during India's northward movement toward, and collision with, Asia. In contrast, the largest of the Kas Hills appears to be a tilted (to the south) and faulted (on the north) block of layered rocks. Also seen here, the linear feature trending toward the southwest from the image center is an erosion-resistant "dike," which is an igneous intrusion into older "host" rocks along a fault plane or other crack. These features are simple examples of how shaded topography can provide a direct input to geologic studies. In this image, colors show the elevation as measured by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). Colors range from green at the lowest elevations, through yellow and red, to purple at the highest elevations. Elevations here range from near sea level to about 300 meters (about 1000 feet). Shading has been added, with illumination from the north (image top). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03300
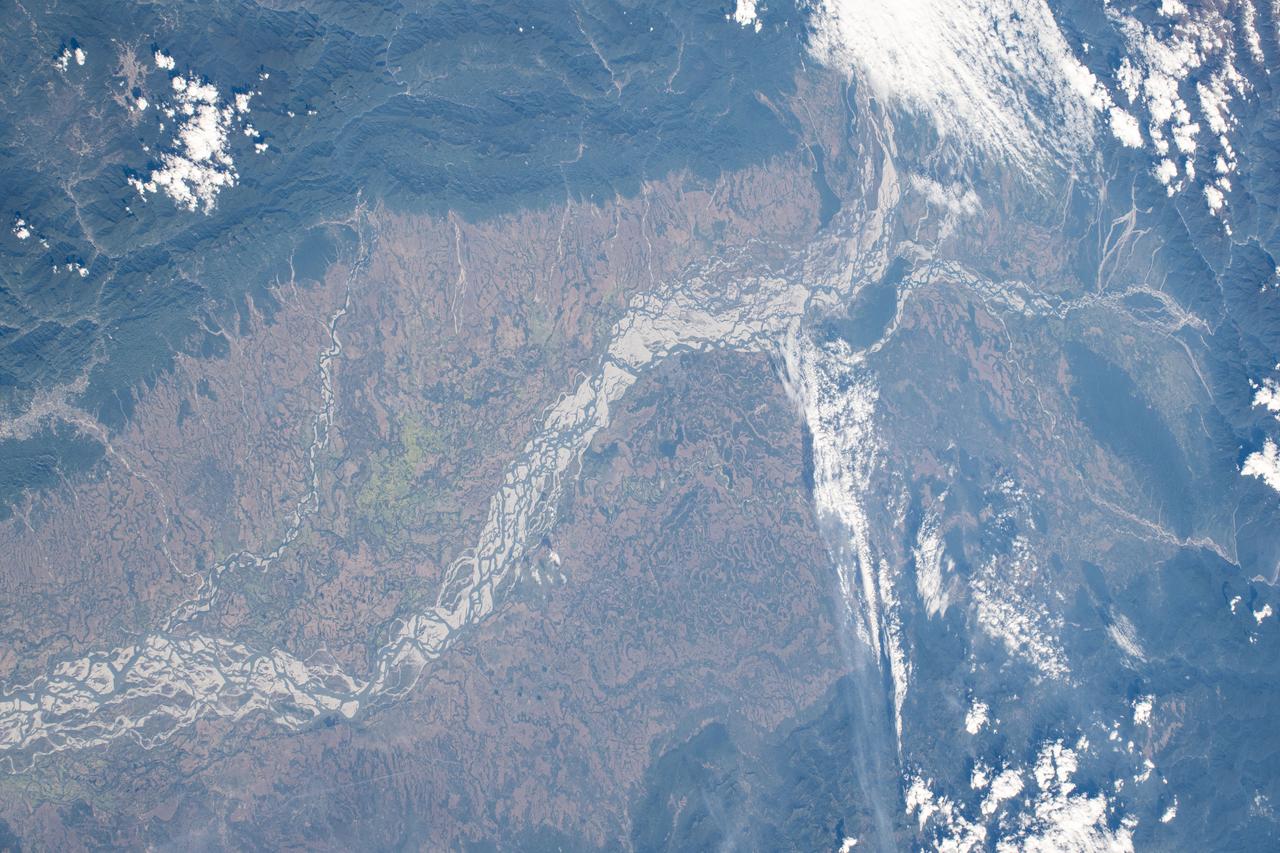

iss072e397228 (Dec. 19, 2024) --- The Brahmaputra River, in eastern India at the foot of the Himalayas near China, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 261 miles above.
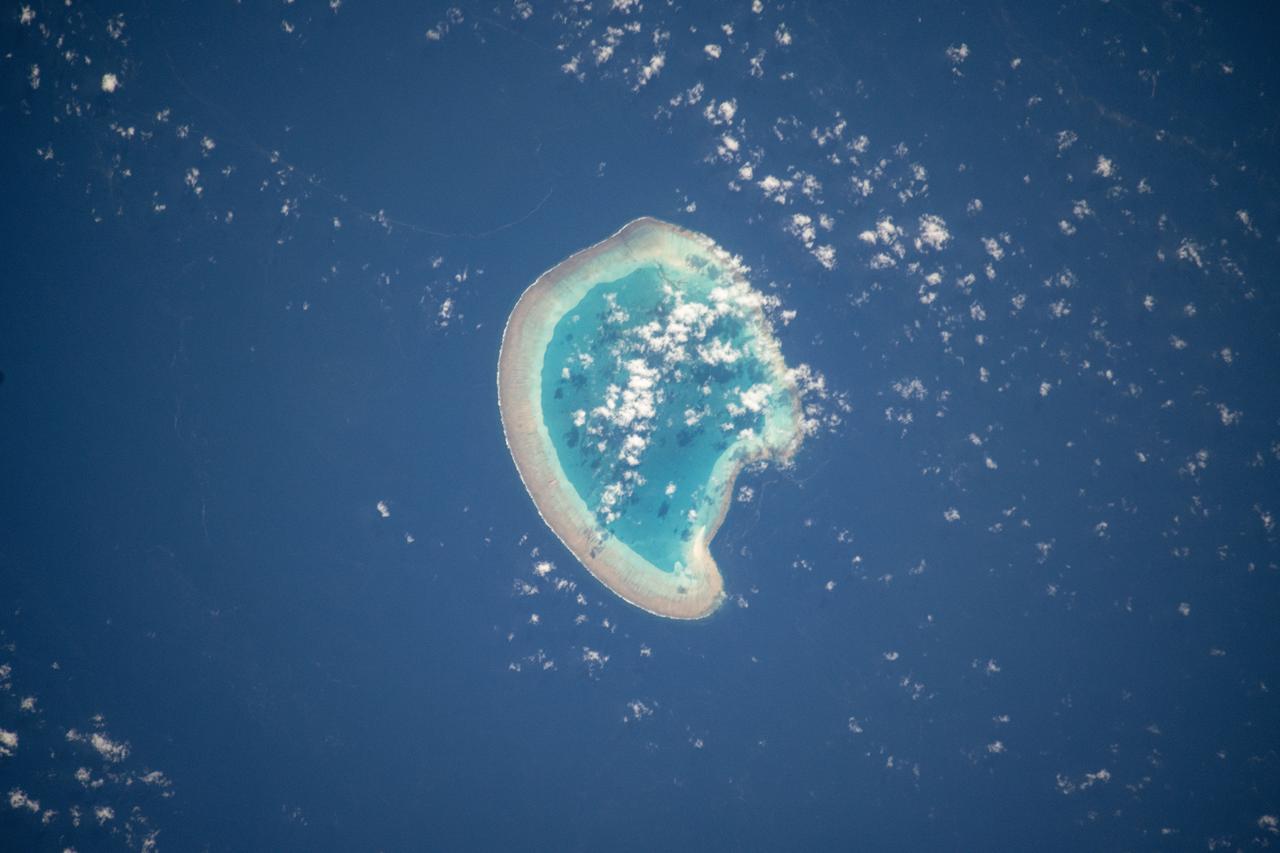

iss072e094988 (Oct. 21, 2024) --- The French atoll of Bassas da India in the Mozambique Channel, halfway beween the African nations of Mozambiue and Madagascar, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 264 miles above.
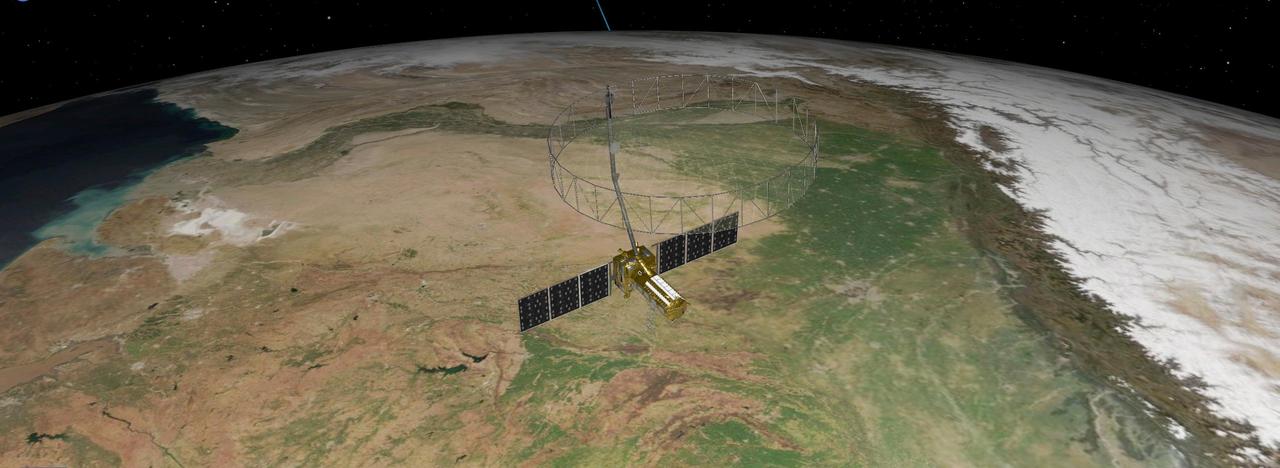

This artist's concept depicts the NISAR satellite orbiting Earth over northeastern India. Short for NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar, the mission is an equal collaboration between the NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation and marks the first time the two agencies have cooperated on hardware development for an Earth-observing mission. Observations from NISAR will benefit humanity by helping researchers around the world better understand changes in our planet's surface, including its ice sheets, glaciers, and sea ice. It also will capture changes in forest and wetland ecosystems and track movement and deformation of our planet's crust by phenomena such as earthquakes, landslides, and volcanic activity. The global and rapid coverage from NISAR will provide unprecedented opportunities for disaster response, producing data to assist in mitigating and assessing damage, with observations before and after catastrophic events available in short time frames. NISAR will launch from ISRO's Satish Dhawan Space Centre on India's southeastern coast in 2025. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26496
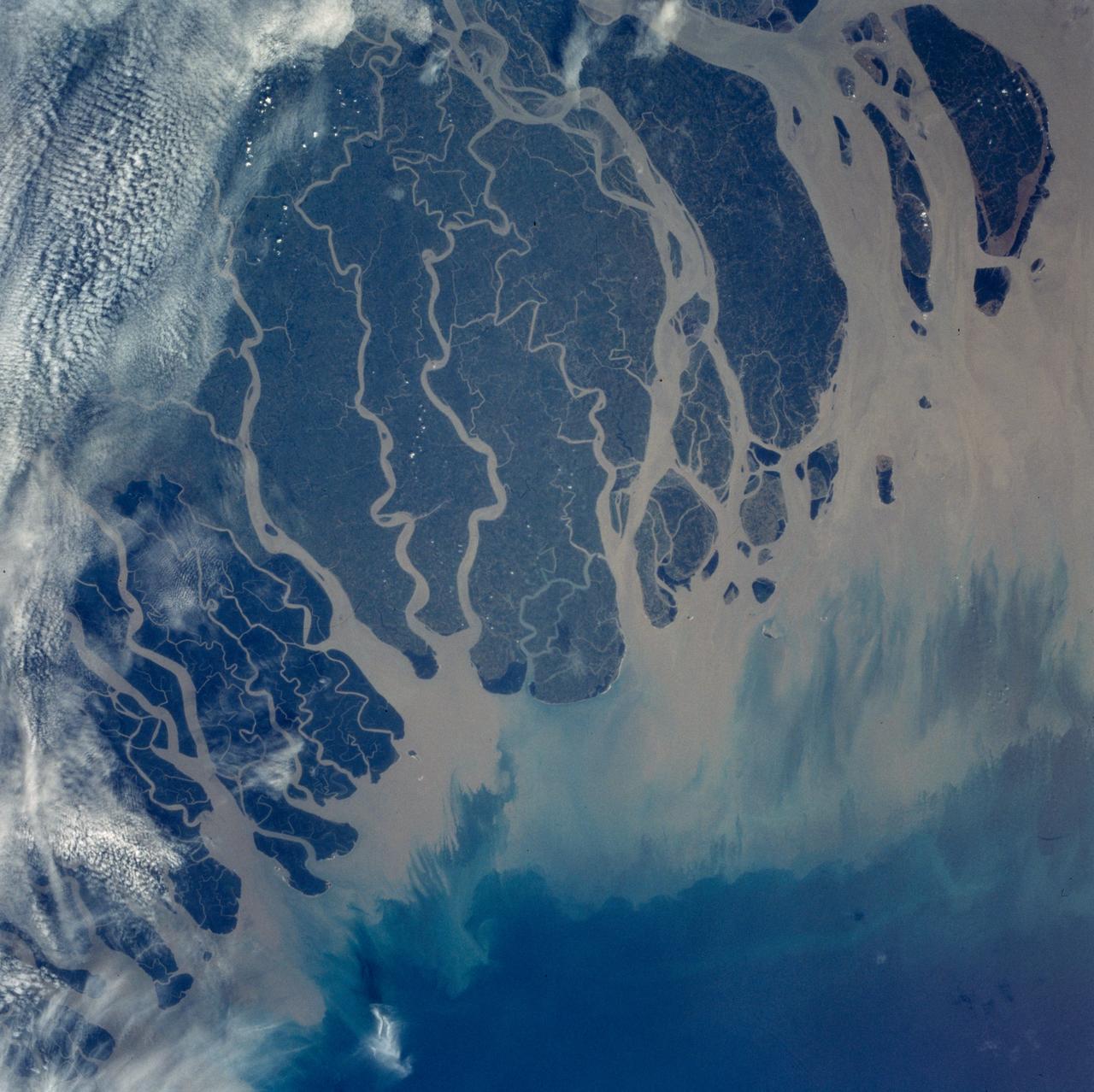

The Ganges River Delta is the largest inter-tidal delta in the world. With its extensive mangrove mud flats, swamp vegetation and sand dunes, it is characteristic of many tropical and subtropical coasts. As seen in this photograph, the tributaries and distributaries of the Ganges and Brahmaputra Rivers deposit huge amounts of silt and clay that create a shifting maze of waterways and islands in the Bay of Bengal.

iss072e757452 (March 6, 2025) --- Delhi, India—the second-largest metropolitan area in the world with a population of approximately 34.7 million—is pictured from the International Space Station at around 11:42 p.m. local time as it orbited 259 miles above. Home to the South Asian nation's capital and Asia’s largest spice market, Delhi is actively combating the effects of its urban heat island status through artificial intelligence, cool roof initiatives, increased tree coverage, modernized urban planning, and updated building codes.
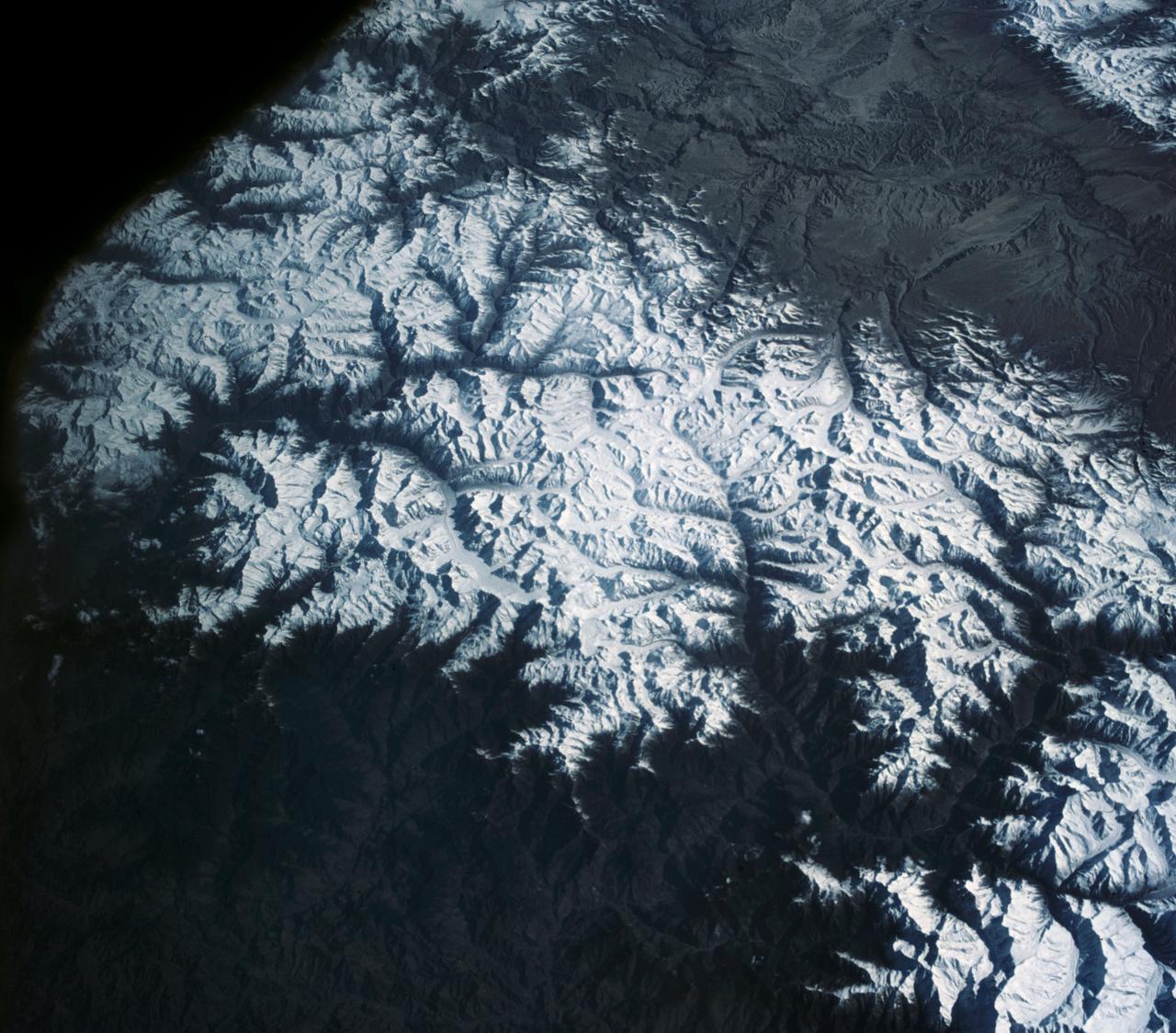

S63-06445 (15-16 May 1963) --- View of the Himalaya Mountain Range in the India-Nepal-Tibet border area, as photographed from the Mercury-Atlas 9 capsule by astronaut L. Gordon Cooper Jr., during his 22-orbit MA-9 spaceflight. Photo credit: NASA
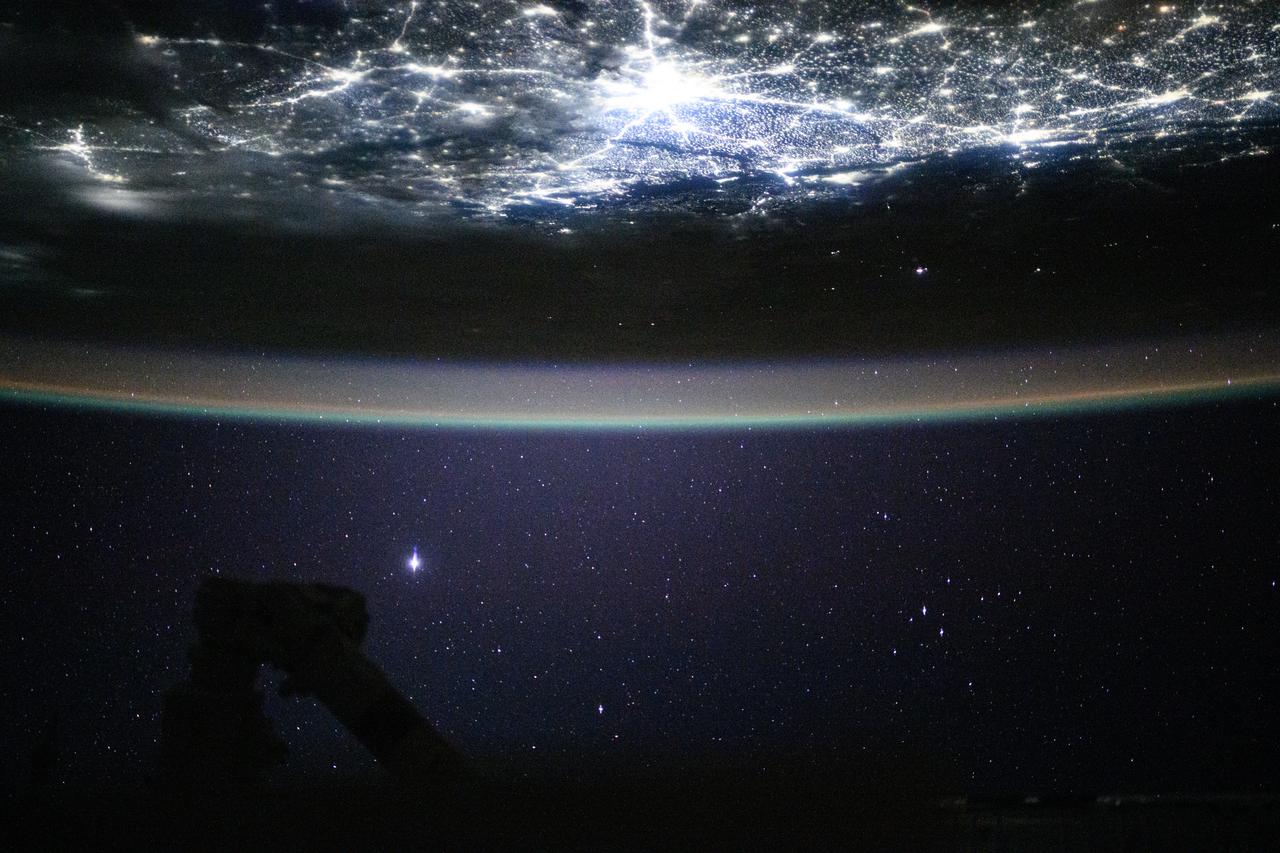

iss073e0685684 (Aug. 21, 2025) --- Underneath a starry night sky, the city lights of New Delhi, India, and its surrounding suburbs glitter below Earth's atmospheric glow and at the edge of the Himalayas. This photograph was taken at approximately 2:55 a.m. local time as the International Space Station orbited 260 miles above.
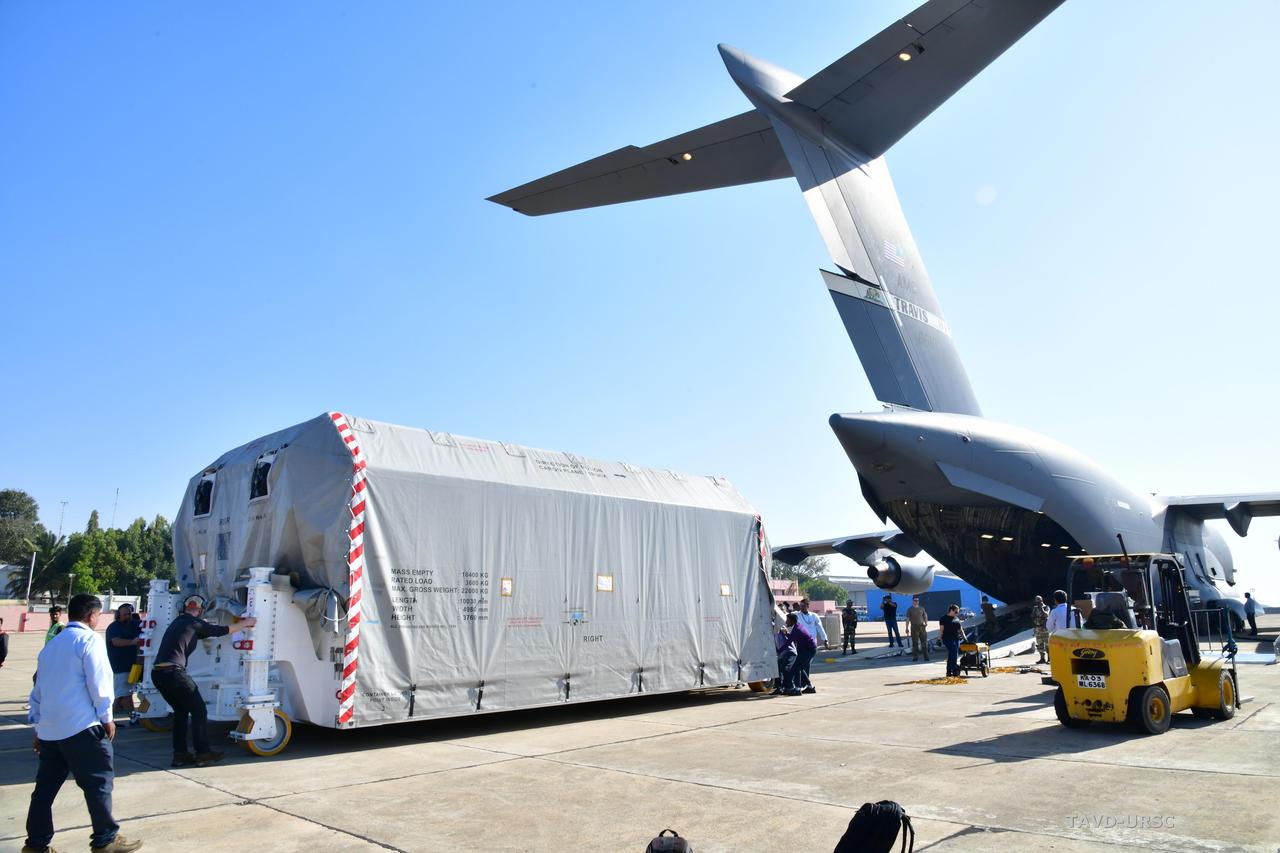

The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) science instrument payload, housed in a specially designed shipping container, sits at Hindustan Aeronautics Limited Airport in Bengaluru, India. The payload left NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Feb. 28, and departed the United States on March 3 aboard a U.S. Air Force cargo plane, arriving in Bengaluru on March 6. From there it was transported to the Indian Space Research Organisation's U R Rao Satellite Centre, where it will be integrated with the satellite body, or bus, and undergo further testing leading up to launch in 2024. The NISAR mission – a joint effort between NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation – will observe nearly all the planet's land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days, measuring movements in extremely fine detail. It will also survey forests and agricultural regions to understand carbon exchange between plants and the atmosphere. NISAR's science payload will be the most advanced radar system ever launched as part of a NASA mission, and it will feature the largest-ever radar antenna of its kind: a drum-shaped, wire mesh reflector nearly 40 feet (12 meters) in diameter that will extend from a 30-foot (9-meter) boom. The mission's science instruments consist of L- and S-band radar, so named to indicate the wavelengths of their signals. ISRO built the S-band radar, which it shipped to JPL in March 2021. Engineers spent much of the last two years integrating the instrument with the JPL-built L-band system, then conducting tests to verify they work well together. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, leads the U.S. component of NISAR. In addition to the L-band radar, NASA is also providing the radar reflector antenna, the deployable boom, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem. In addition to the S-band radar, ISRO is providing the spacecraft bus, the launch vehicle, and associated launch services and satellite mission operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25570
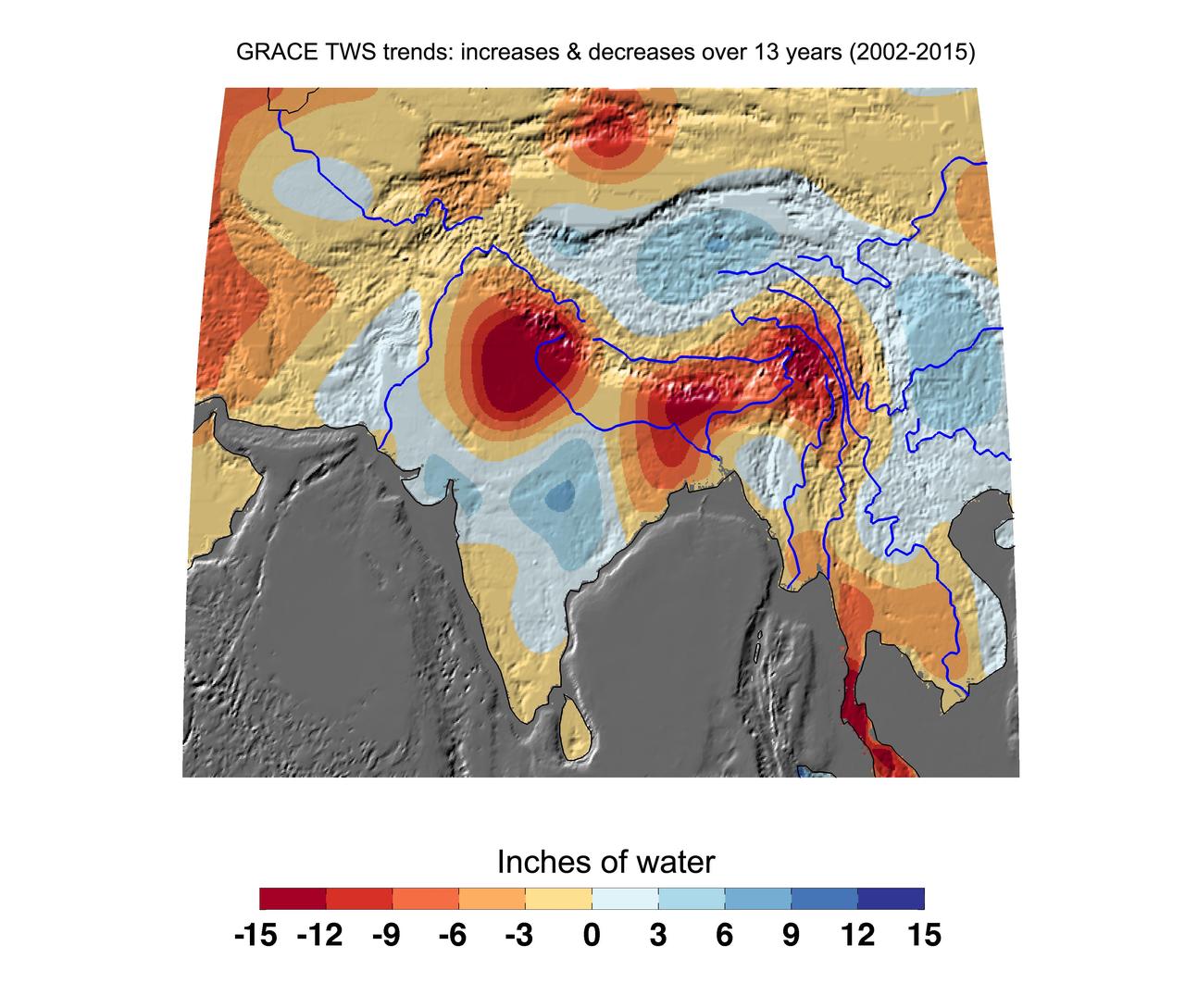
Cumulative total freshwater losses in South Asia from 2002 to 2015 (in inches) observed by NASA's Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) mission. Total water refers to all of the snow, surface water, soil water and groundwater combined. Groundwater depletion in India and Bangladesh continue to dominate total water losses in the region. The persistent drought along the Malaysian Peninsula is also apparent. Regions of increasing total water experience strong interannual variations in the Asian monsoon. Image updated from Rodell et al., 2009. Citation of Record: Rodell, M., I. Velicogna and J. Famiglietti, Satellite-based estimates of groundwater depletion in India, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature08238. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20206
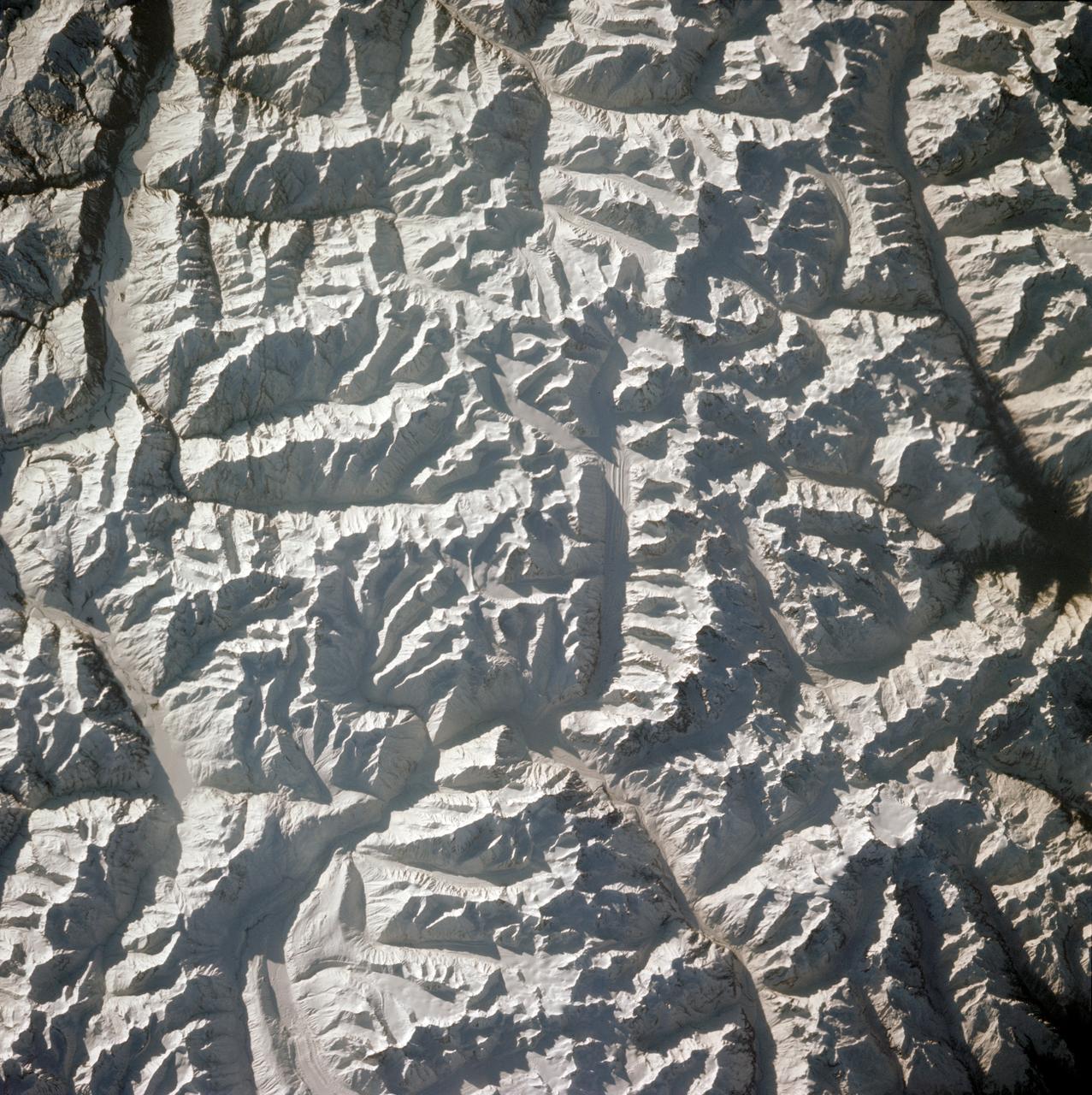

STS001-12-350 (12-14 April 1981) --- India and China, the Ladokh and Zaskar Ranges of the Great Himalaya are clearly etched by snow and shadow. A detailed view shows the glaciation process over a wide area. Photo credit: NASA
This anaglyph, from NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, shows the city of Bhuj, India. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.

The Moon Mineralogy Mapper imaging spectrometer, an instrument on India’s Chandrayaan-1, during development at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
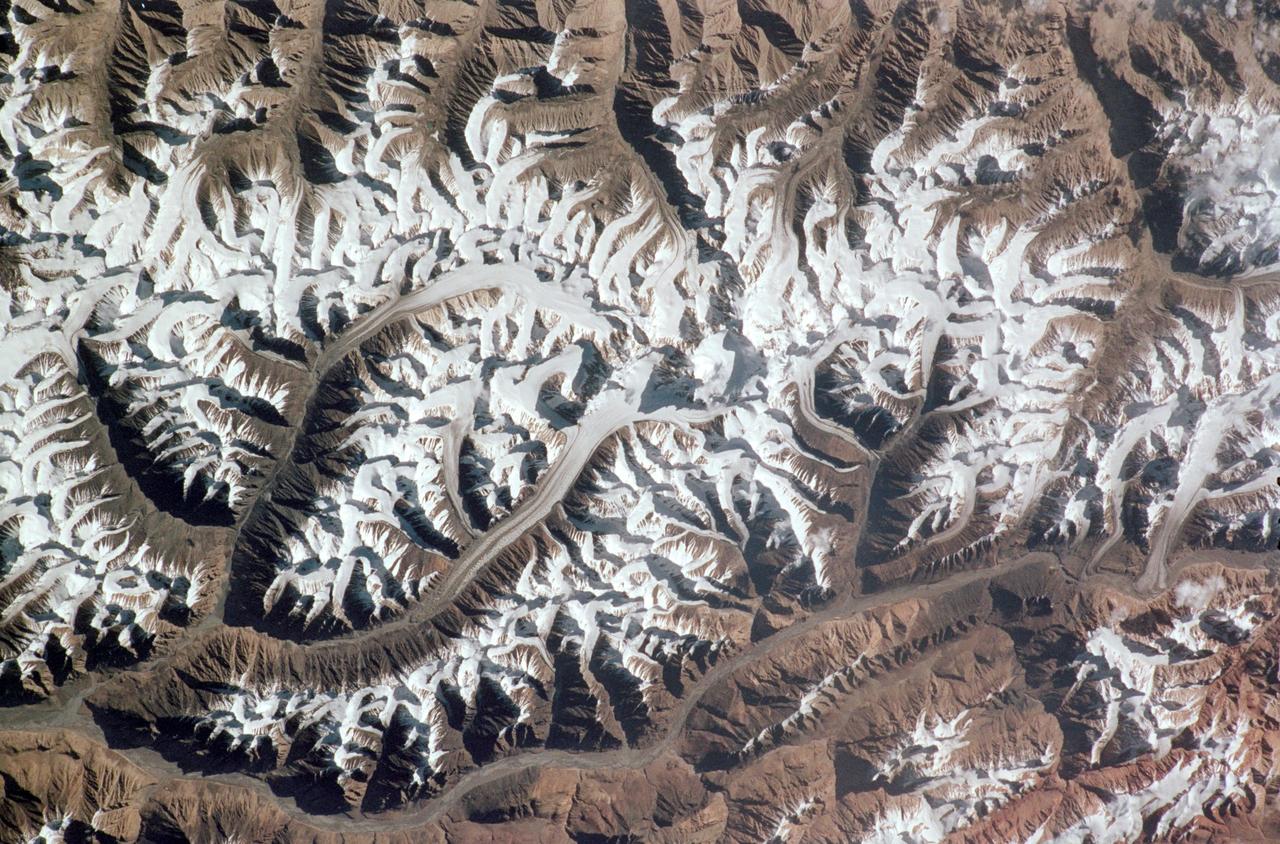

STS121-331-019 (4-17 July 2006) --- (North is toward the lower right corner of the image). This vertical view over glaciers in the Karakoram Mountain range of Northern India was photographed from the Space Shuttle Discovery during the STS-121 mission. The glaciers are centered at 34.8 degrees north latitude and 77.8 degrees east longitude. The small peak in the center of the photo stands 25,170 feet high.
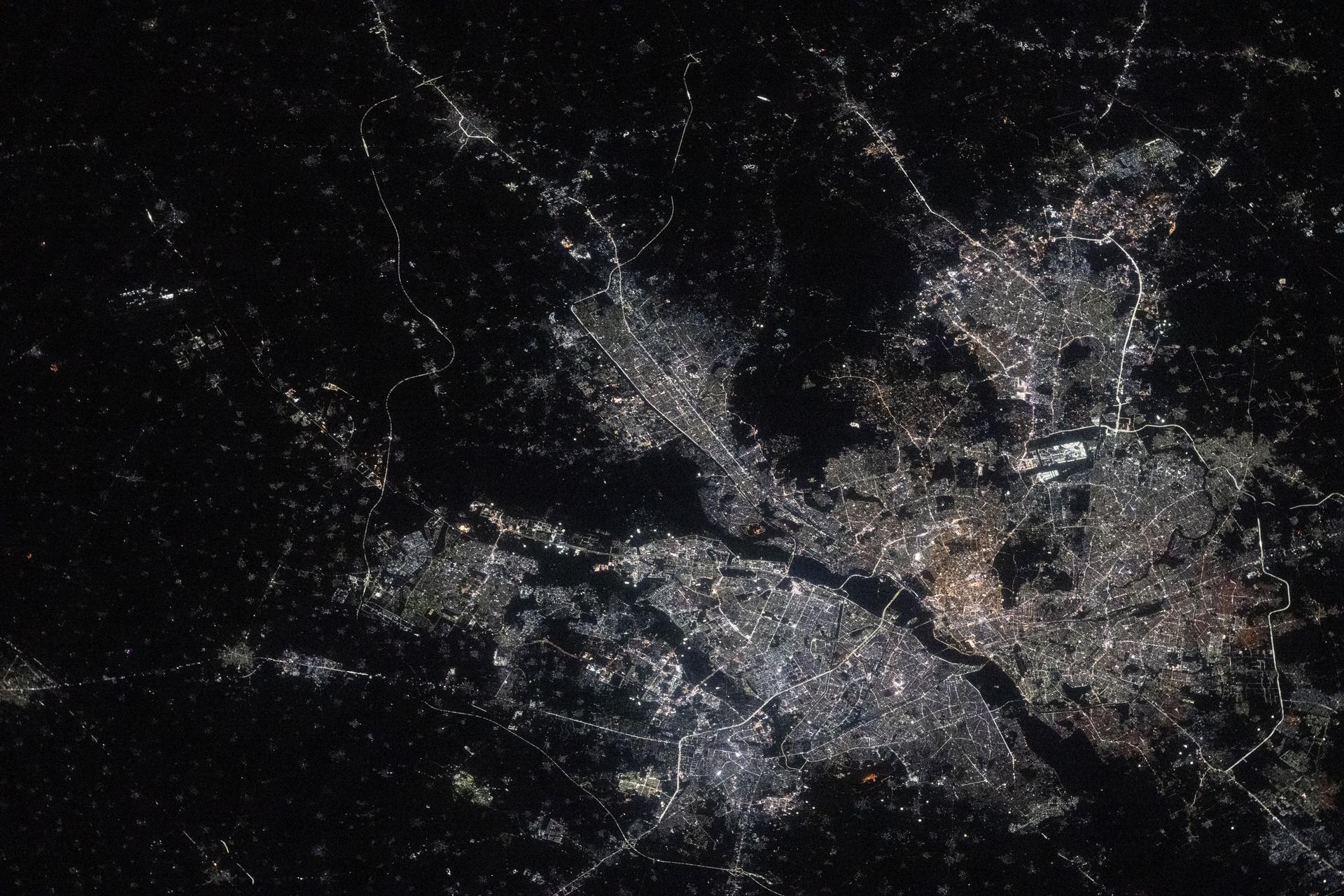

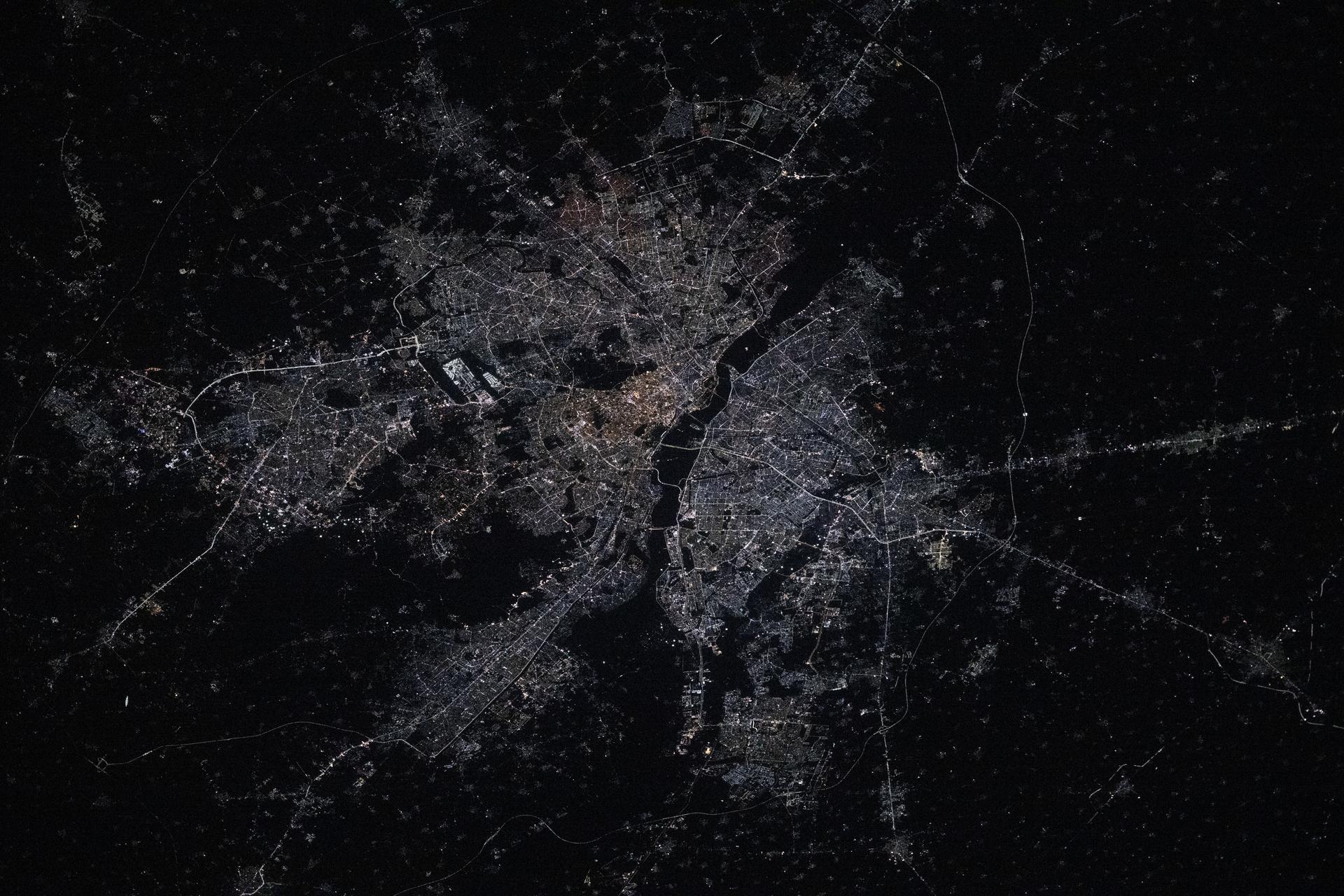
iss073e0763646 (Sept. 21, 2025) --- India’s National Capital Territory of Delhi, home to approximately 34.67 million people, is the second-largest metropolitan area in the world after Tokyo. This nighttime view from the International Space Station, taken at approximately 10:54 p.m. local time, shows the city split by the Yamuna River. The bright rectangular area near the right center marks Indira Gandhi International Airport, one of the busiest aviation hubs in South Asia.
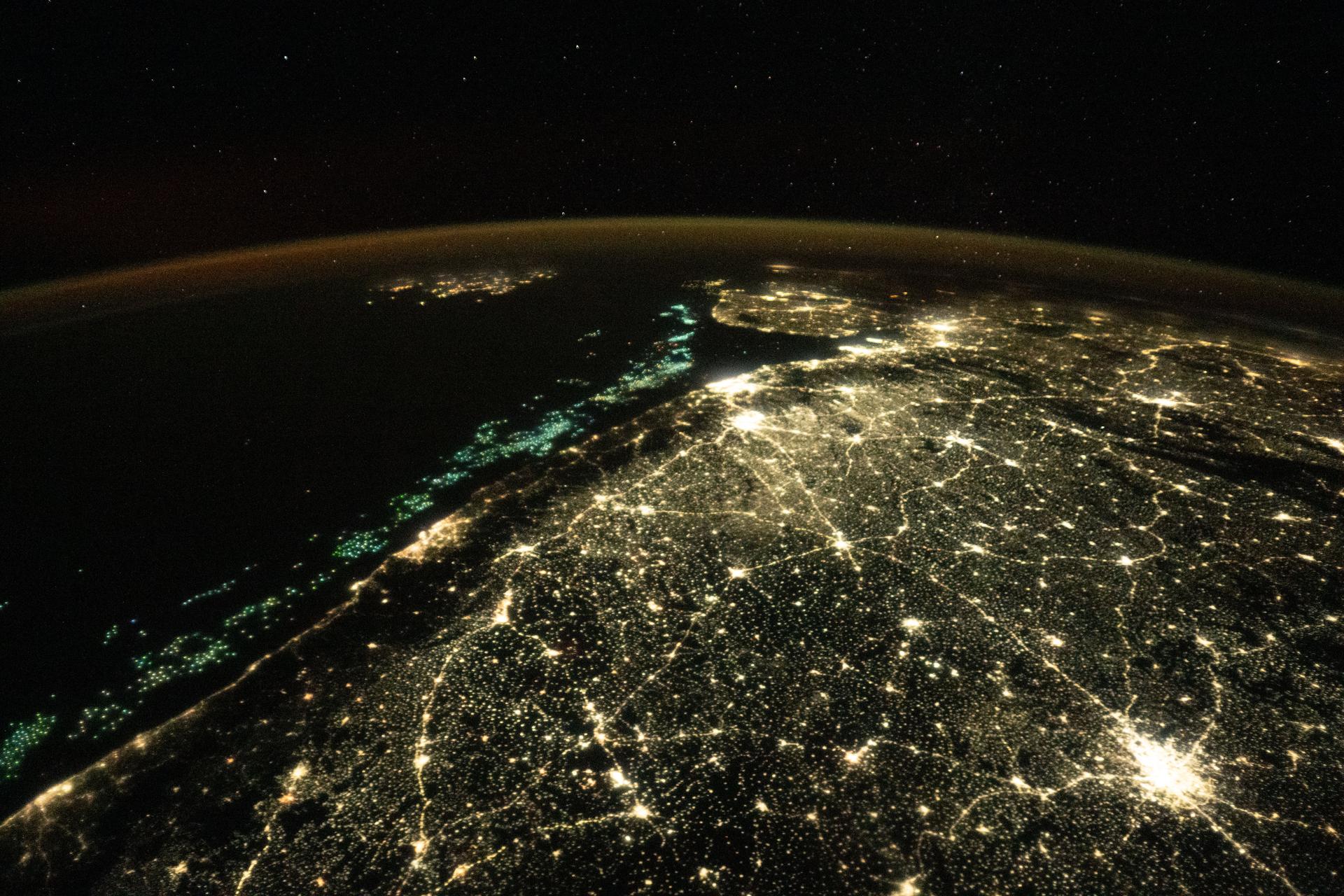

iss074e0044675 (Dec. 25, 2025) --- Fishing boats illuminate the Arabian Sea along India’s west coast with green lights designed to attract squid, shrimp, sardines, and mackerel in this nighttime photograph from the International Space Station, orbiting 259 miles above Earth. At lower right, the city lights of Hyderabad—renowned for its historic diamond and pearl trade—stretch westward toward the Mumbai Metropolitan Region, home to over 26 million people and the heart of Bollywood.
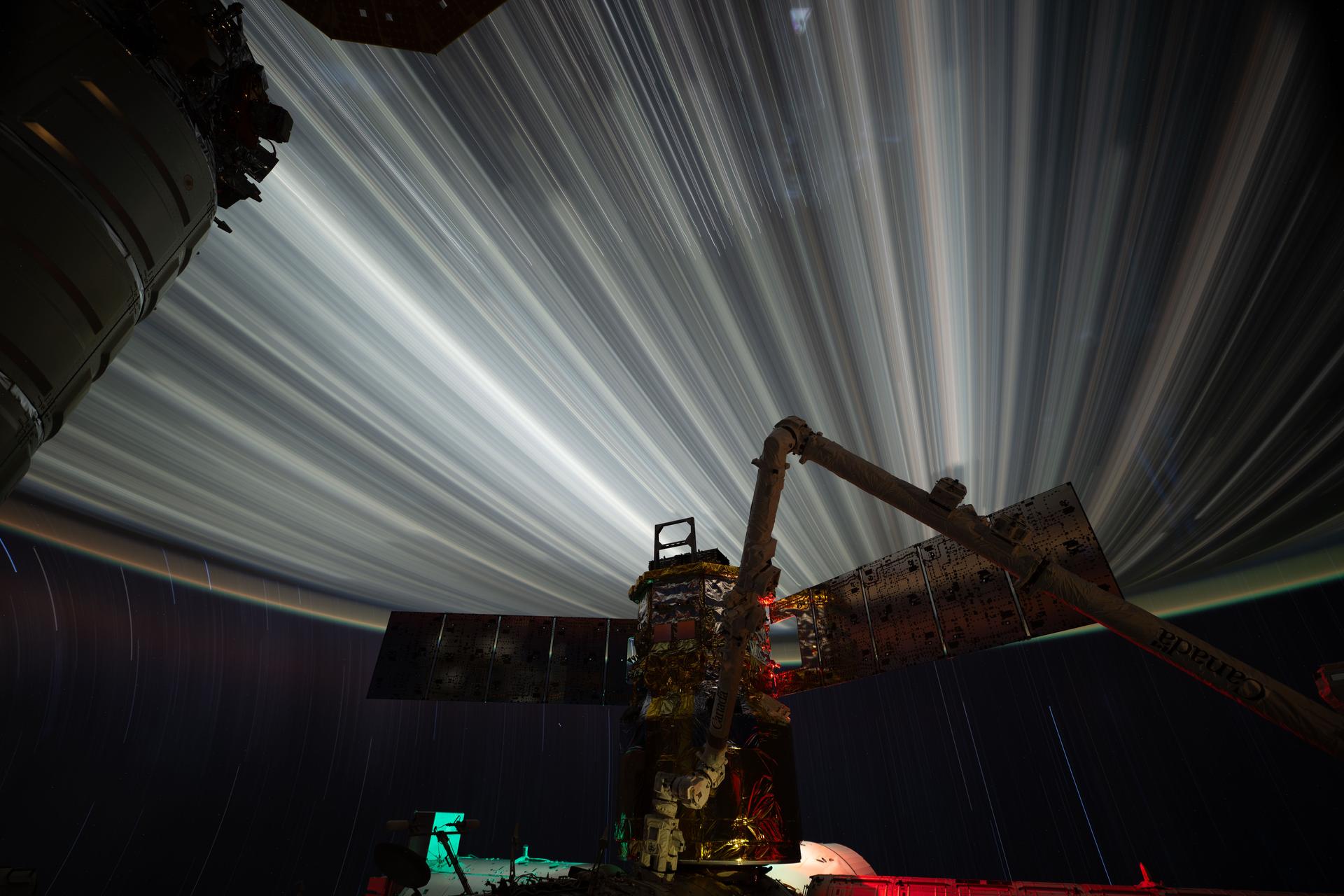

iss074e0319679 (Feb. 19, 2026) --- Star trails and city lights streak by in this long-duration photograph taken from the International Space Station as it orbited 261 miles above the India-Pakistan border at approximately 2:35 a.m. local time. In the foreground is JAXA’s (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) HTV-X1 cargo craft, berthed to the Harmony module’s Earth-facing port, with the Canadarm2 robotic arm perched on a portable data grapple fixture in front. Credit: NASA/Chris Williams
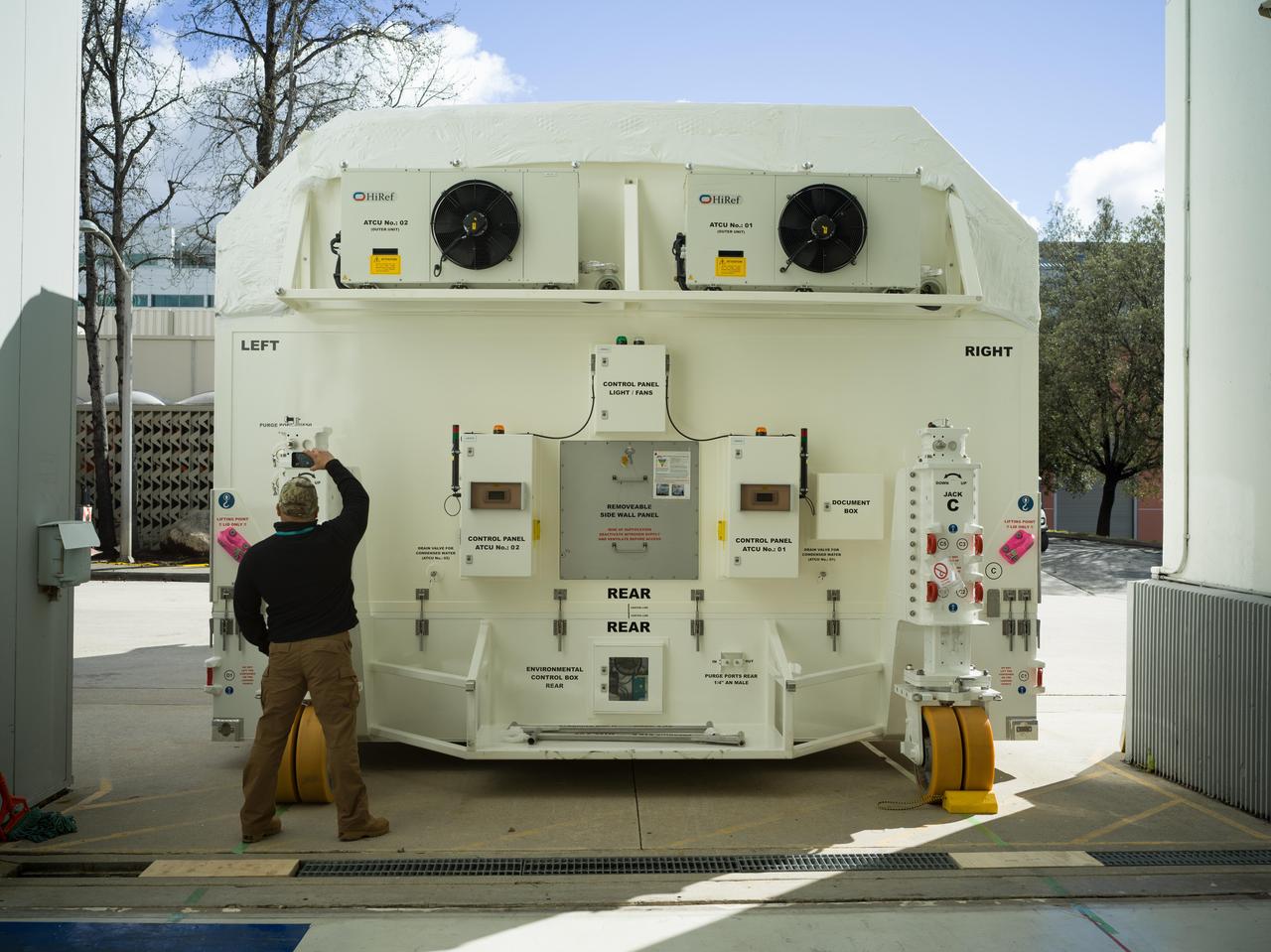

A specially designed, climate-controlled shipping container holding the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) science instrument payload sits outside an airlock at the Spacecraft Assembly Facility at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Feb. 26, 2023. The payload was shipped to Bengaluru, India, on March 3, arriving on March 6. There it will be integrated with the satellite body, or bus, and undergo further testing leading up to launch in 2024. The NISAR mission – a joint effort between NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation – will observe nearly all the planet's land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days, measuring movements in extremely fine detail. It will also survey forests and agricultural regions to understand carbon exchange between plants and the atmosphere. NISAR's science payload will be the most advanced radar system ever launched as part of a NASA mission, and it will feature the largest-ever radar antenna of its kind: a drum-shaped, wire mesh reflector nearly 40 feet (12 meters) in diameter that will extend from a 30-foot (9-meter) boom. The mission's science instruments consist of L- and S-band radar, so named to indicate the wavelengths of their signals. ISRO built the S-band radar, which it shipped to JPL in March 2021. Engineers spent much of the last two years integrating the instrument with the JPL-built L-band system, then conducting tests to verify they work well together. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, leads the U.S. component of NISAR. In addition to the L-band radar, NASA is also providing the radar reflector antenna, the deployable boom, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem. In addition to the S-band radar, ISRO is providing the spacecraft bus, the launch vehicle, and associated launch services and satellite mission operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25568
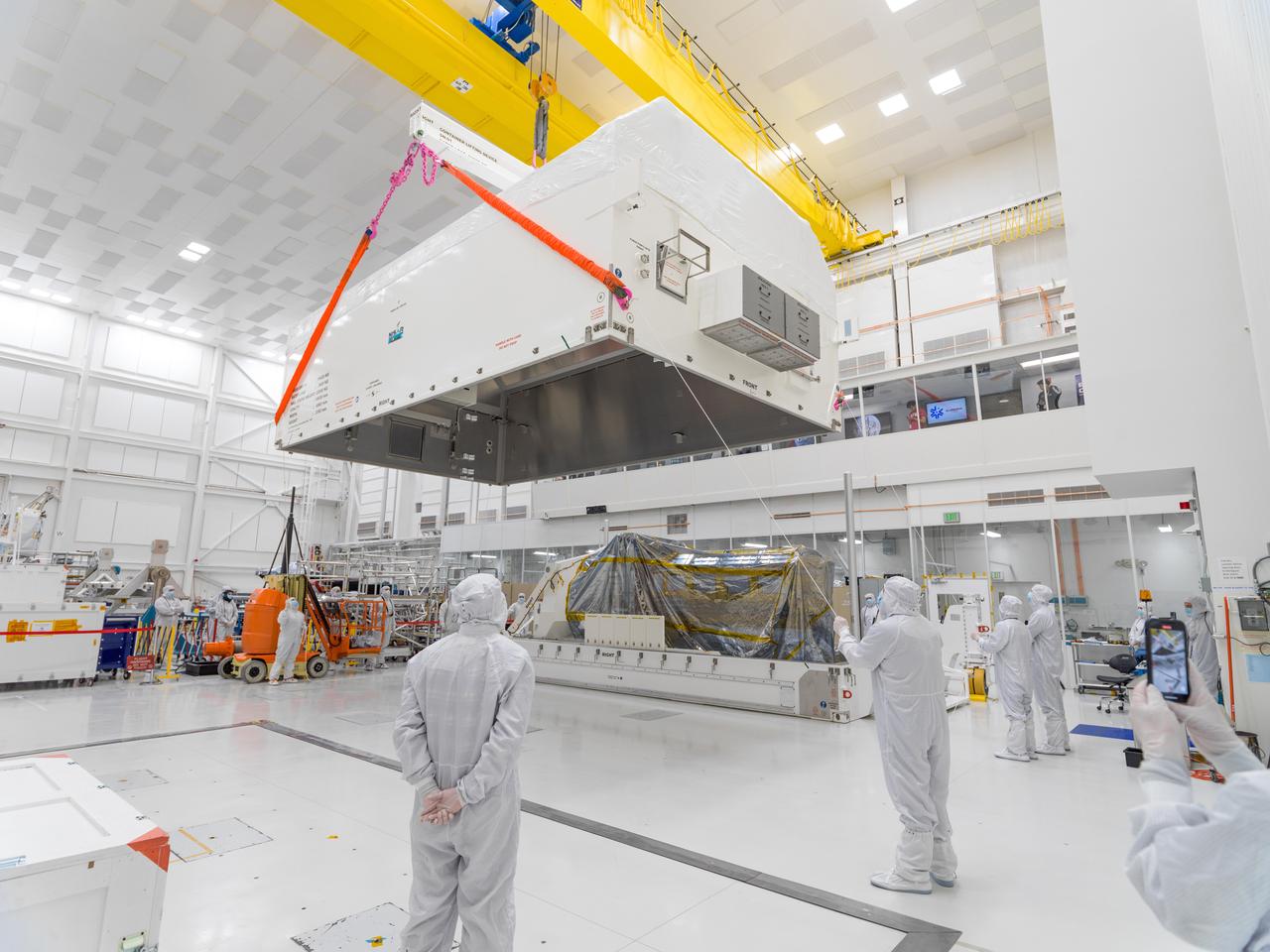

In a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Feb. 23, 2023, engineers and technicians use a crane to prepare to seal a specially designed, climate-controlled shipping container holding the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) science instrument payload. The payload was then shipped to Bengaluru, India, on March 3, arriving on March 6. There it will be integrated with the satellite body, or bus, and undergo further testing leading up to launch in 2024. The NISAR mission – a joint effort between NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation – will observe nearly all the planet's land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days, measuring movements in extremely fine detail. It will also survey forests and agricultural regions to understand carbon exchange between plants and the atmosphere. NISAR's science payload will be the most advanced radar system ever launched as part of a NASA mission, and it will feature the largest-ever radar antenna of its kind: a drum-shaped, wire mesh reflector nearly 40 feet (12 meters) in diameter that will extend from a 30-foot (9-meter) boom. The mission's science instruments consist of L- and S-band radar, so named to indicate the wavelengths of their signals. ISRO built the S-band radar, which it shipped to JPL in March 2021. Engineers spent much of the last two years integrating the instrument with the JPL-built L-band system, then conducting tests to verify they work well together. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, leads the U.S. component of NISAR. In addition to the L-band radar, NASA is also providing the radar reflector antenna, the deployable boom, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem. In addition to the S-band radar, ISRO is providing the spacecraft bus, the launch vehicle, and associated launch services and satellite mission operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25567
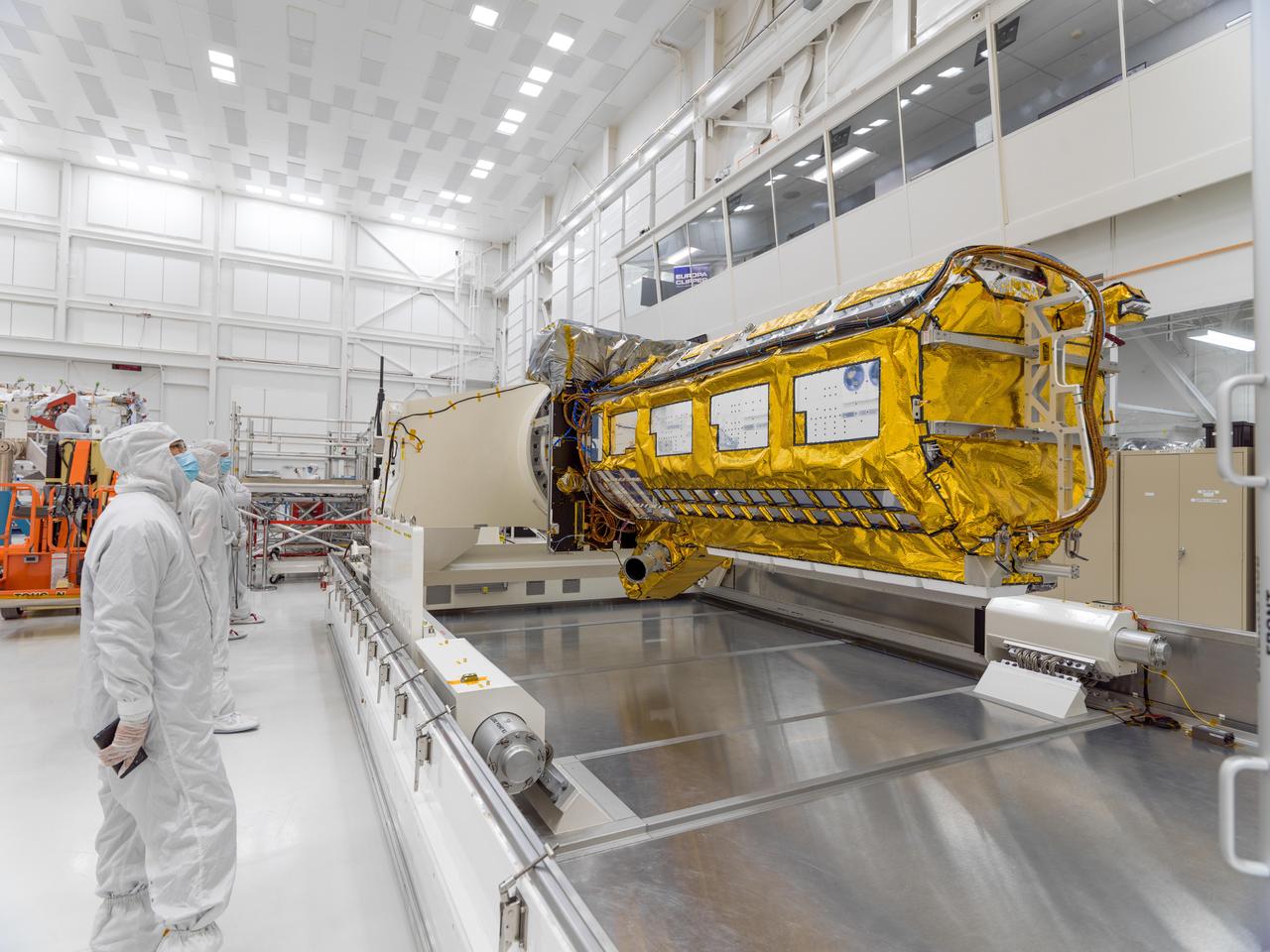

The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) science instrument payload sits in its specially designed, climate-controlled shipping container in a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Feb. 23, 2023. Engineers and technicians used a crane to lift the payload and mount it vertically onto a stage at the far end of the container before tilting it horizontally. The payload was then shipped to Bengaluru, India, on March 3, arriving on March 6. There it will be integrated with the satellite body, or bus, and undergo further testing leading up to launch in 2024. The NISAR mission – a joint effort between NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation – will observe nearly all the planet's land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days, measuring movements in extremely fine detail. It will also survey forests and agricultural regions to understand carbon exchange between plants and the atmosphere. NISAR's science payload will be the most advanced radar system ever launched as part of a NASA mission, and it will feature the largest-ever radar antenna of its kind: a drum-shaped, wire mesh reflector nearly 40 feet (12 meters) in diameter that will extend from a 30-foot (9-meter) boom. The mission's science instruments consist of L- and S-band radar, so named to indicate the wavelengths of their signals. ISRO built the S-band radar, which it shipped to JPL in March 2021. Engineers spent much of the last two years integrating the instrument with the JPL-built L-band system, then conducting tests to verify they work well together. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, leads the U.S. component of NISAR. In addition to the L-band radar, NASA is also providing the radar reflector antenna, the deployable boom, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem. In addition to the S-band radar, ISRO is providing the spacecraft bus, the launch vehicle, and associated launch services and satellite mission operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25566
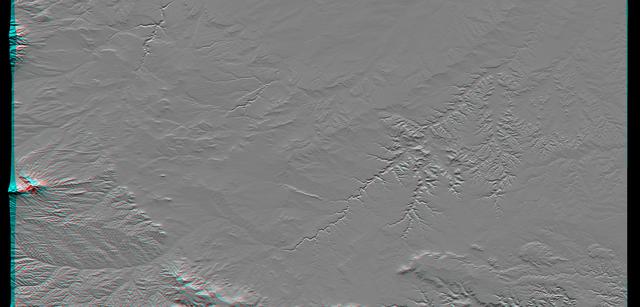
This anaglyph NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, shows the Haro and Kas Hills of the Kachchh region in western India. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
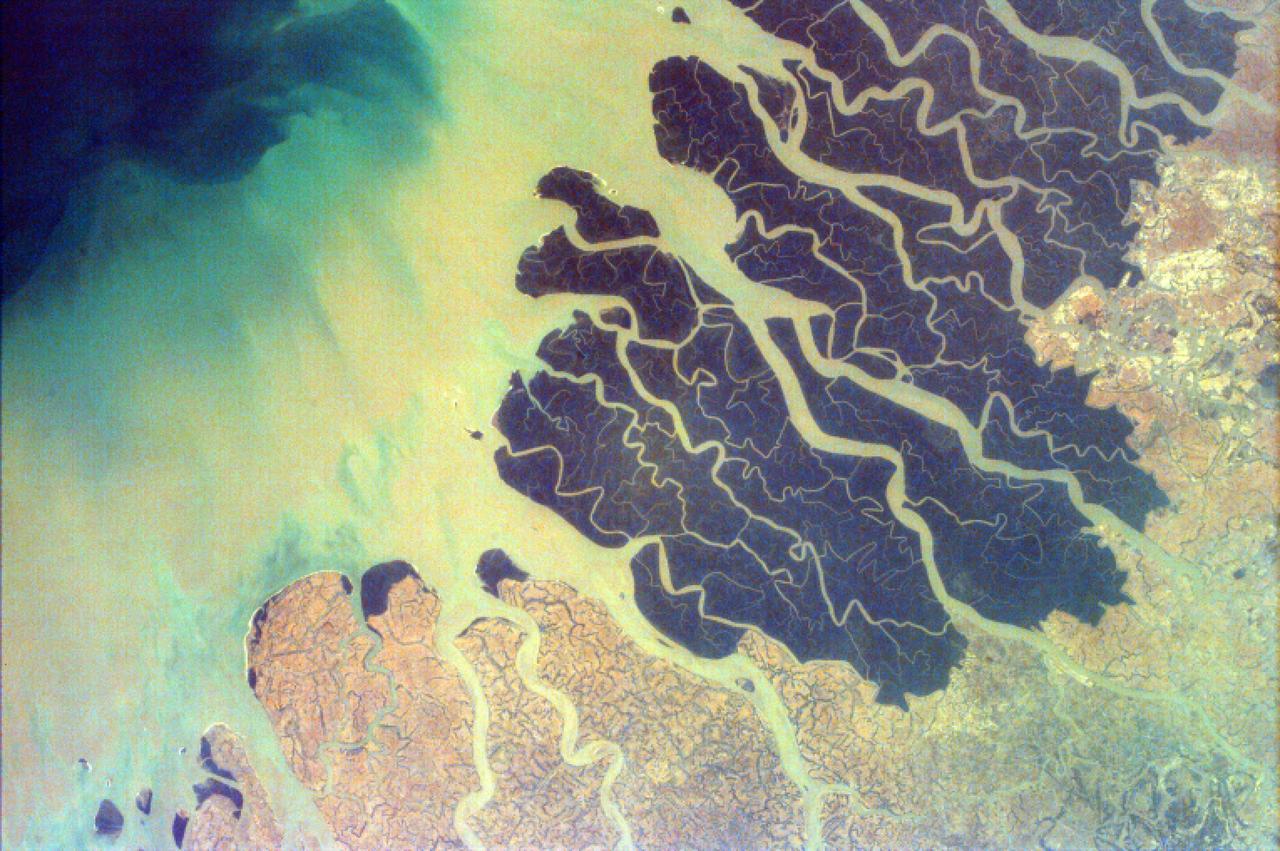

Parts of the vast Ganges delta, in fact the world largest, lie in both Bangladesh and the State of West Bengal, India as seen by NASA EarthKAM.
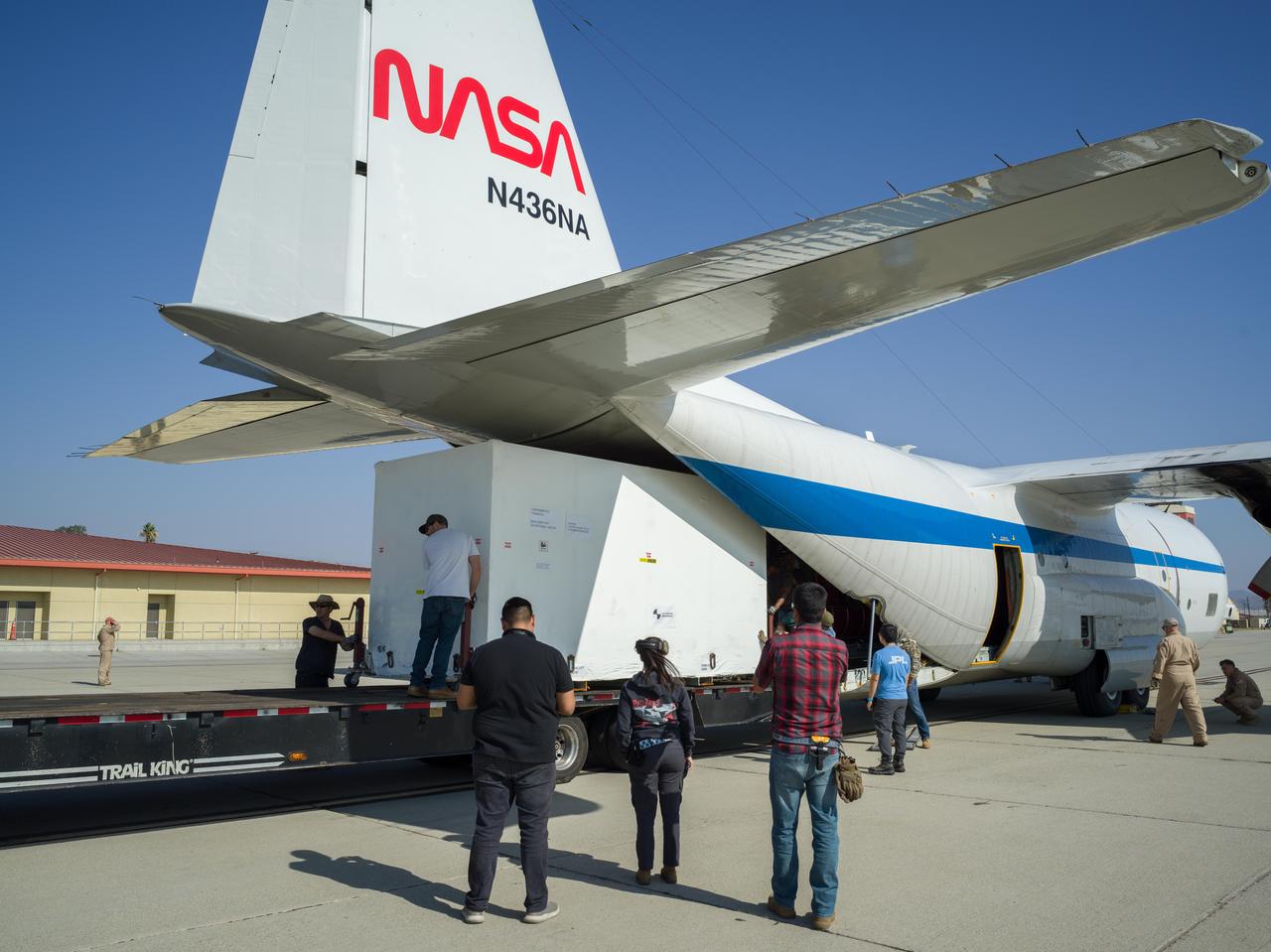

Crews at March Air Reserve Base in Riverside County, California, on Oct. 15, 2024, load a specialized shipping container carrying the NISAR (NASA ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) mission's radar antenna reflector into the hold of NASA's C-130 Hercules plane. The aircraft later departed on a multistage journey to Bengaluru, India, arriving on Oct. 22. A key piece of science hardware for the mission, which is a joint effort of NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation, the reflector had been undergoing work at a specialized facility in California. Engineers there applied reflective tape and took other precautionary measures to mitigate temperature increases that could potentially have affected the deployment of the reflector from its stowed configuration. Drum-shaped and about 39 feet (12 meters) across, the reflector is among NASA's contributions to the mission. The reflector is designed to transmit and receive microwave signals to and from Earth's surface, enabling NISAR to scan nearly all the planet's land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days to collect science data. Once NISAR is in operation, its observations will benefit humanity by helping researchers around the world better understand changes in the planet's surface, including its ice sheets, glaciers, and sea ice. The spacecraft will also capture changes in forest and wetland ecosystems as well as movement and deformation of our planet's crust. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26419
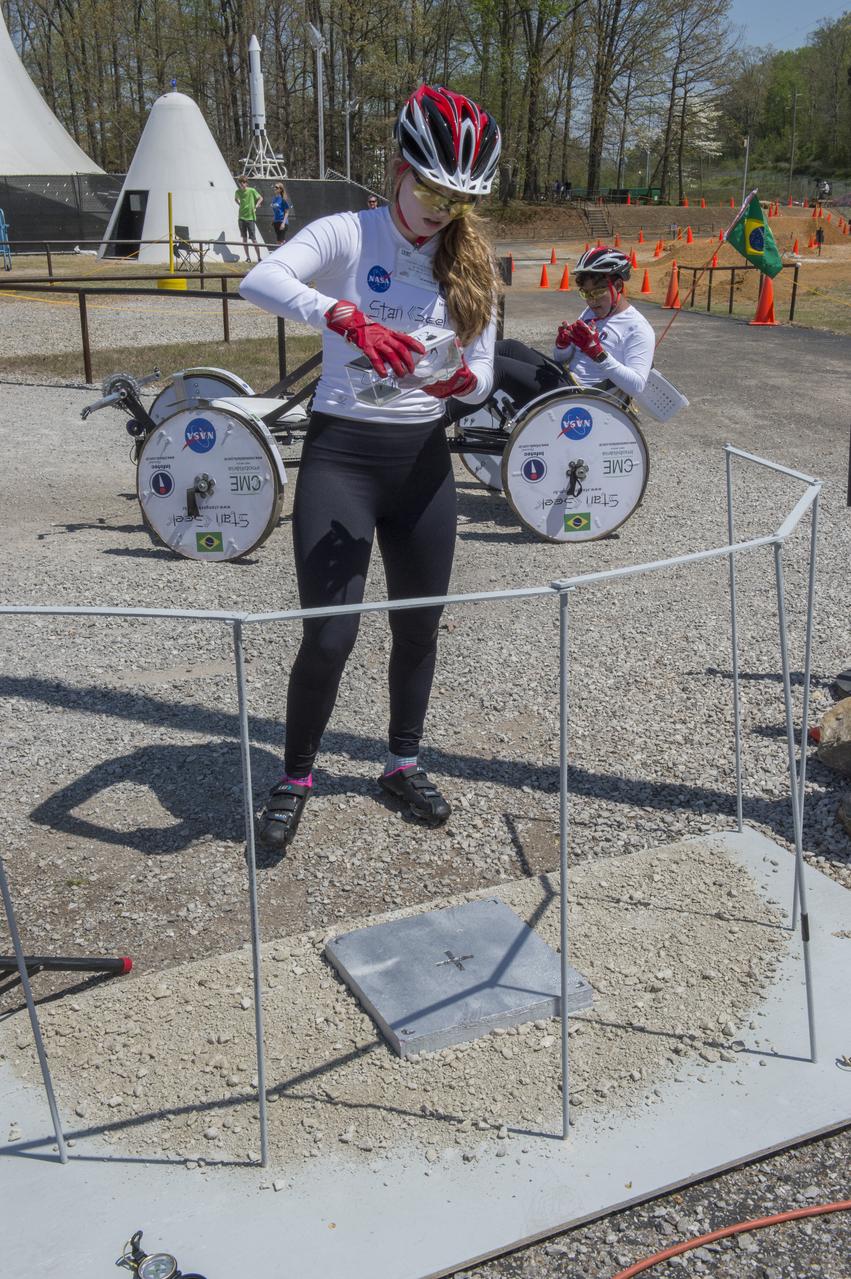

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
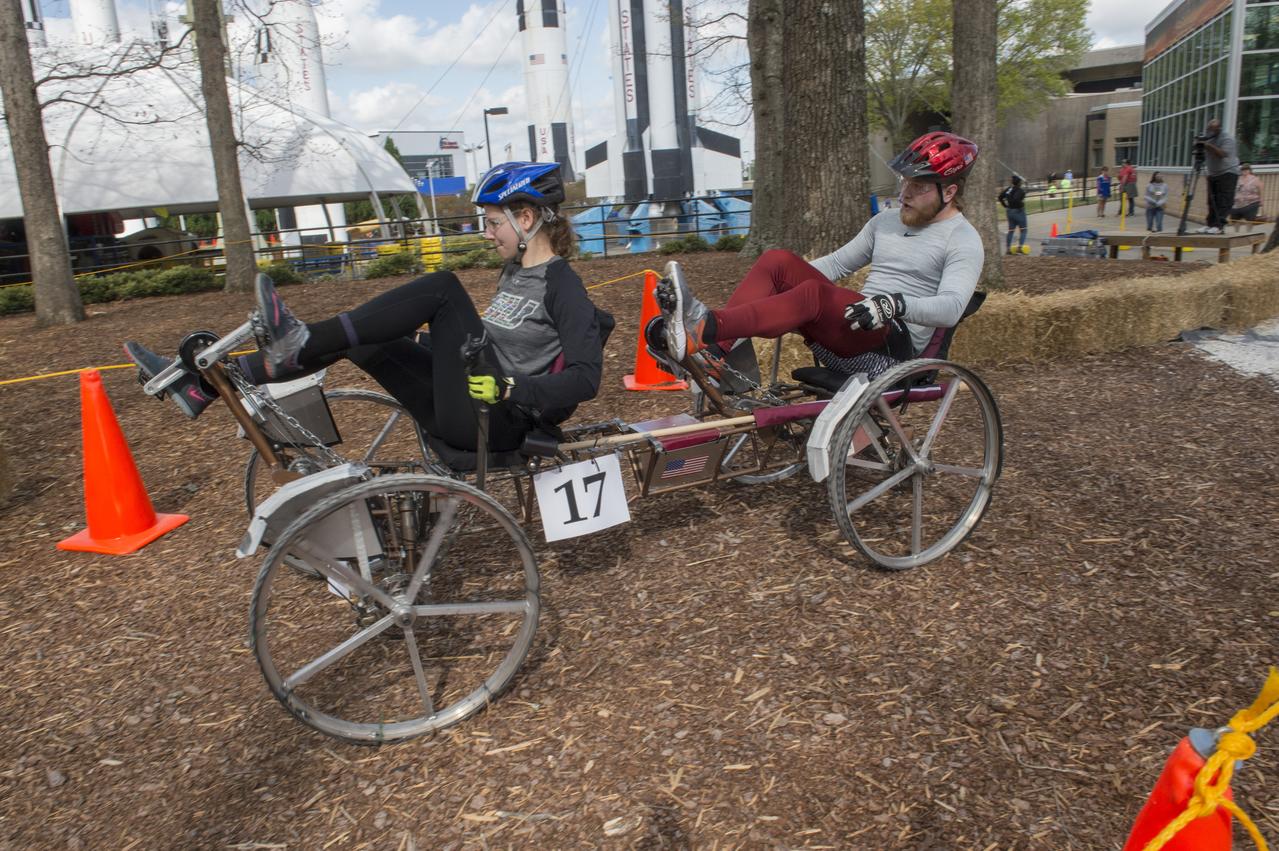

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
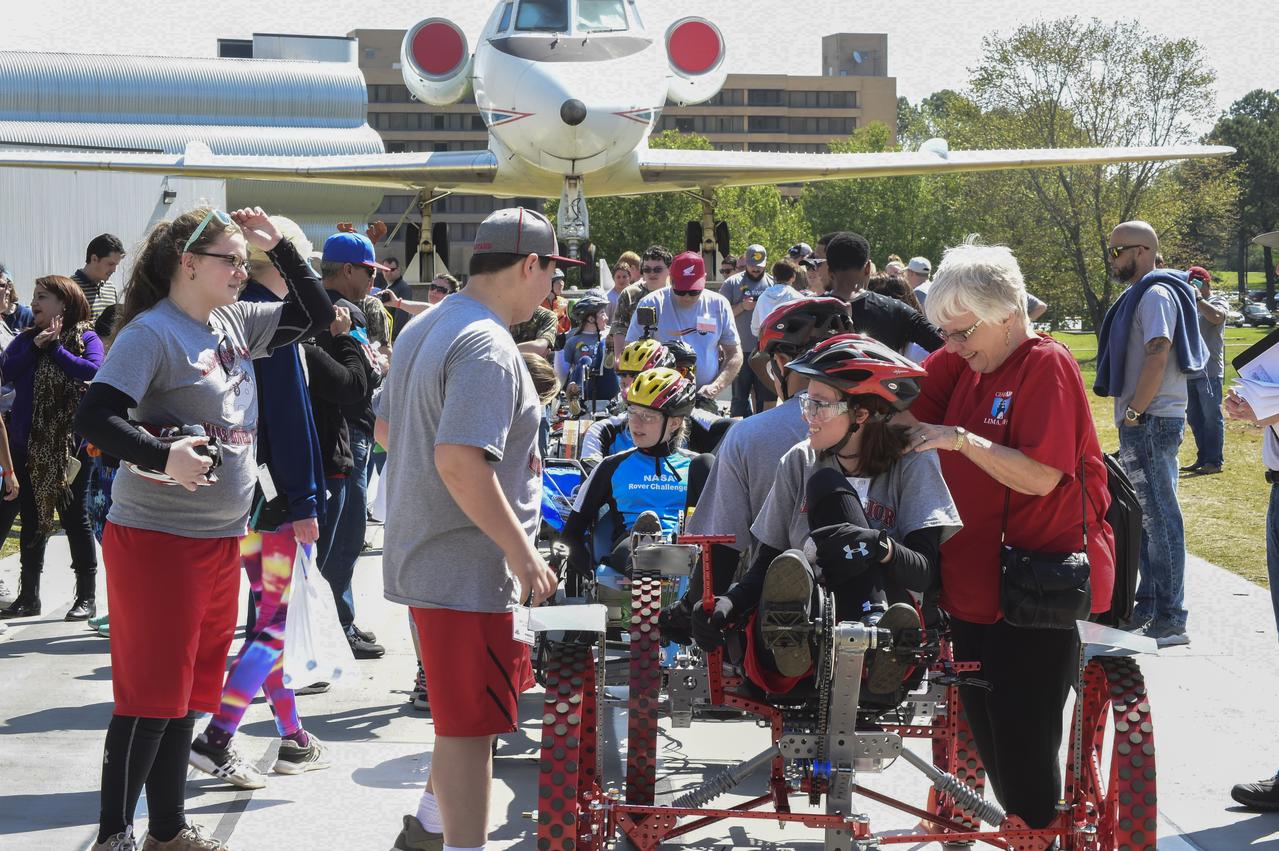

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
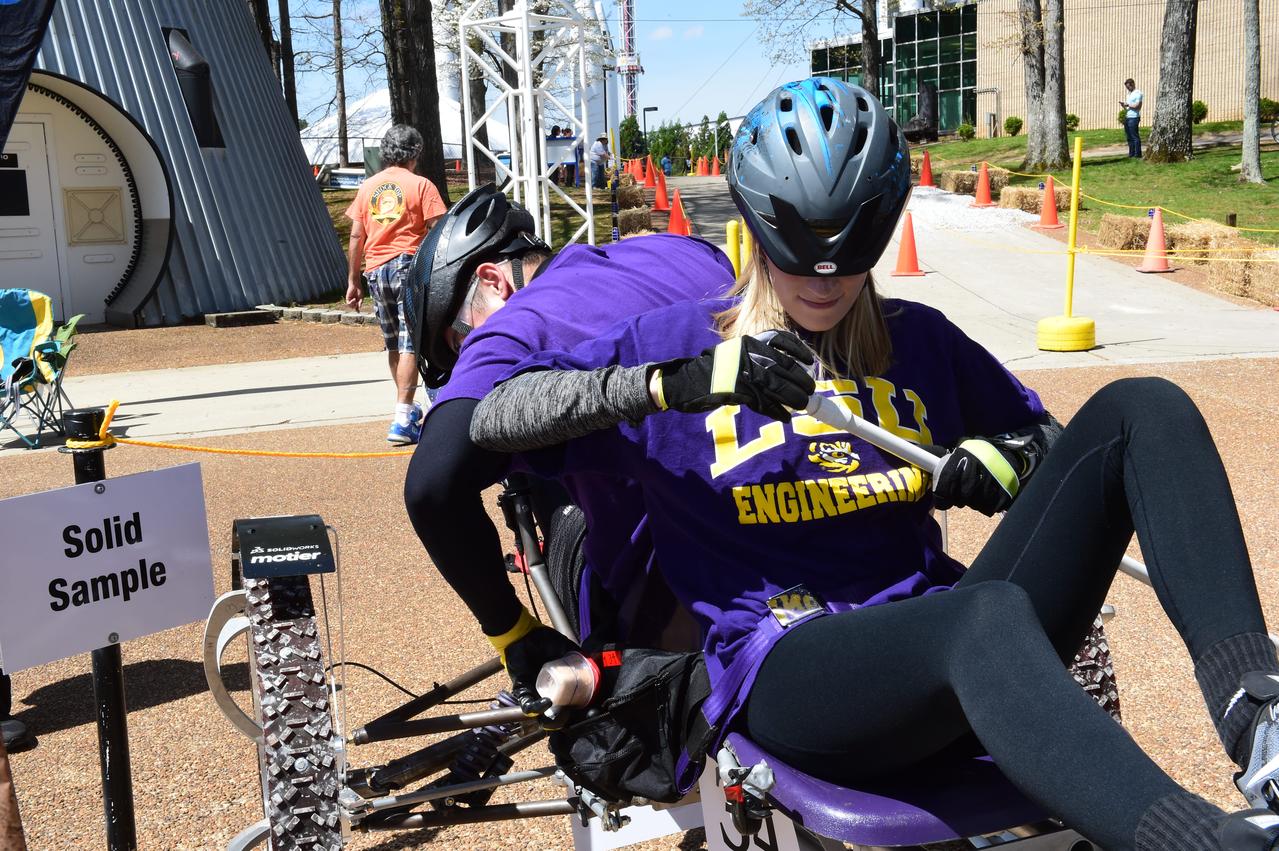

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
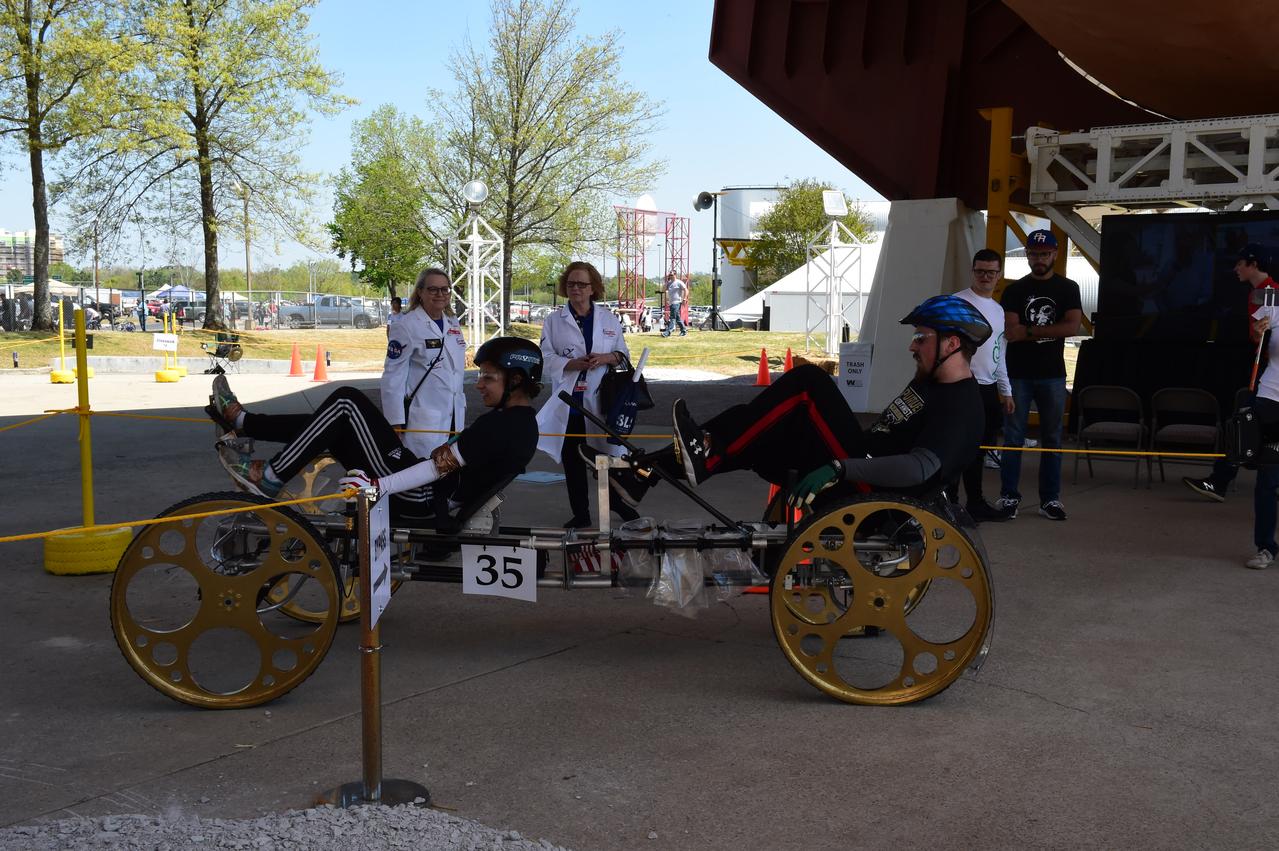

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
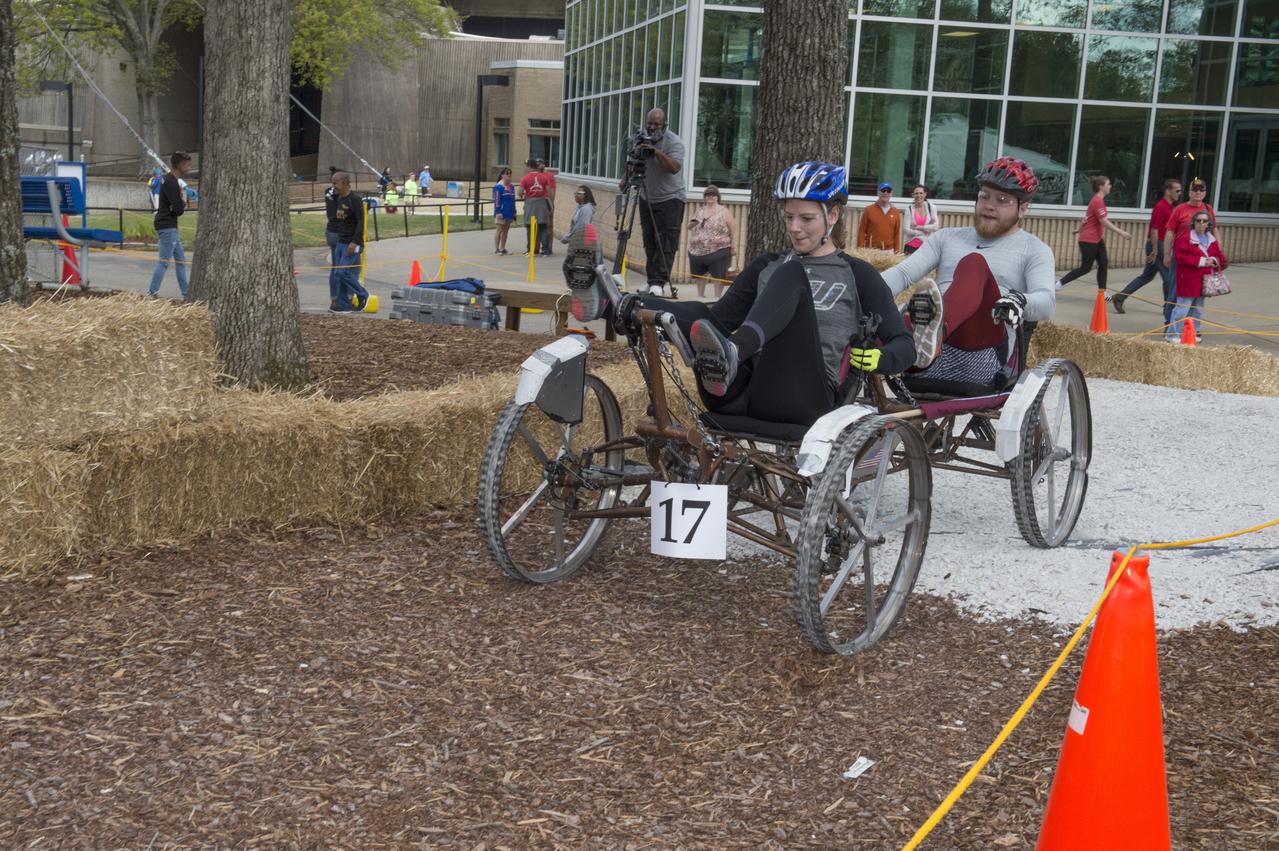

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
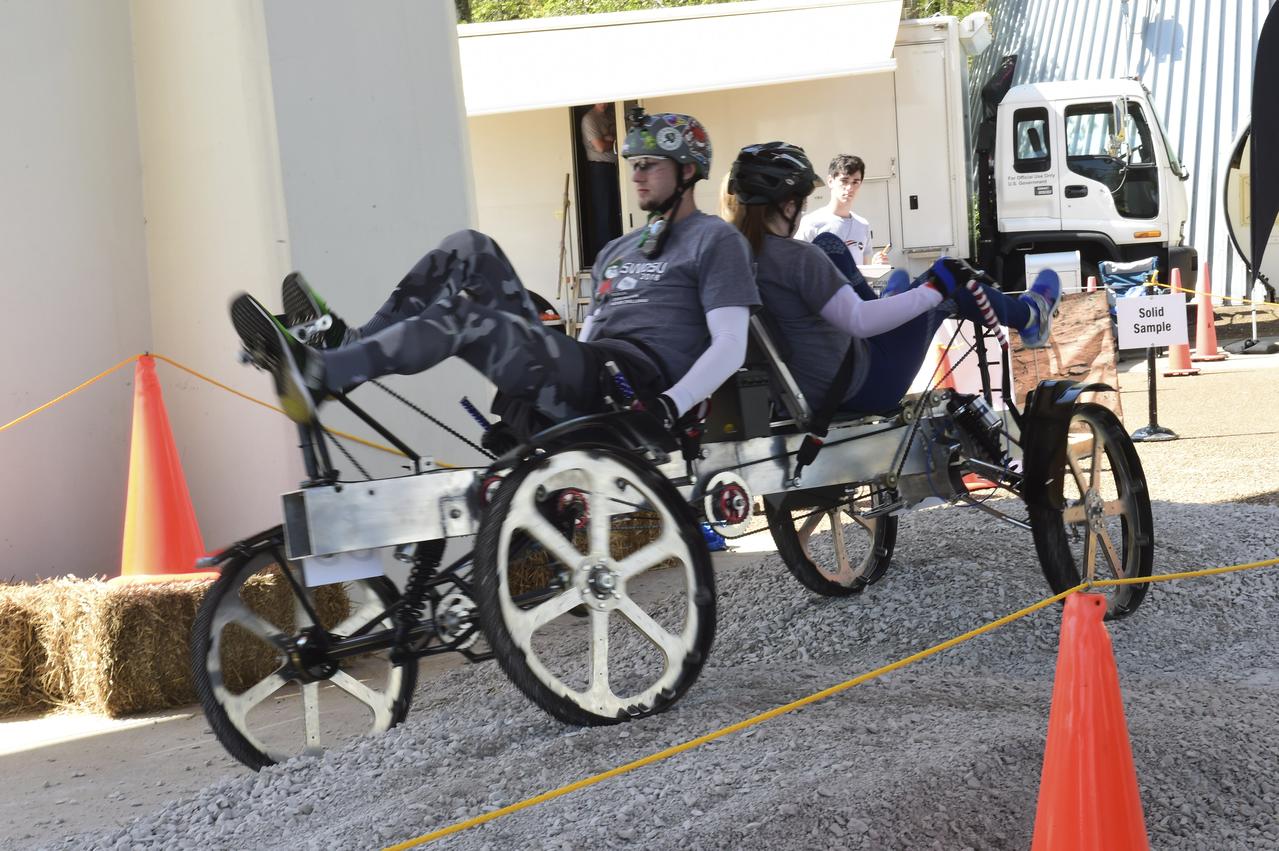

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
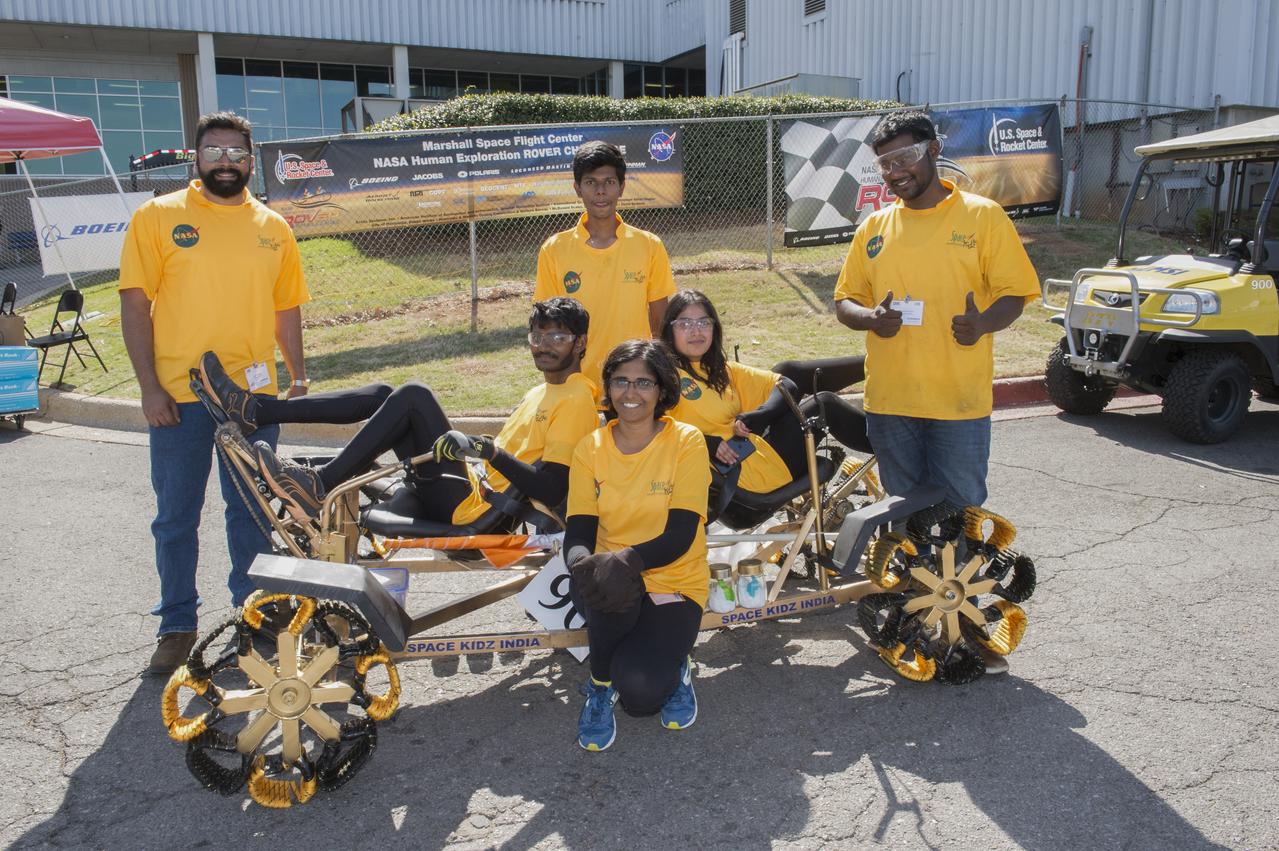

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
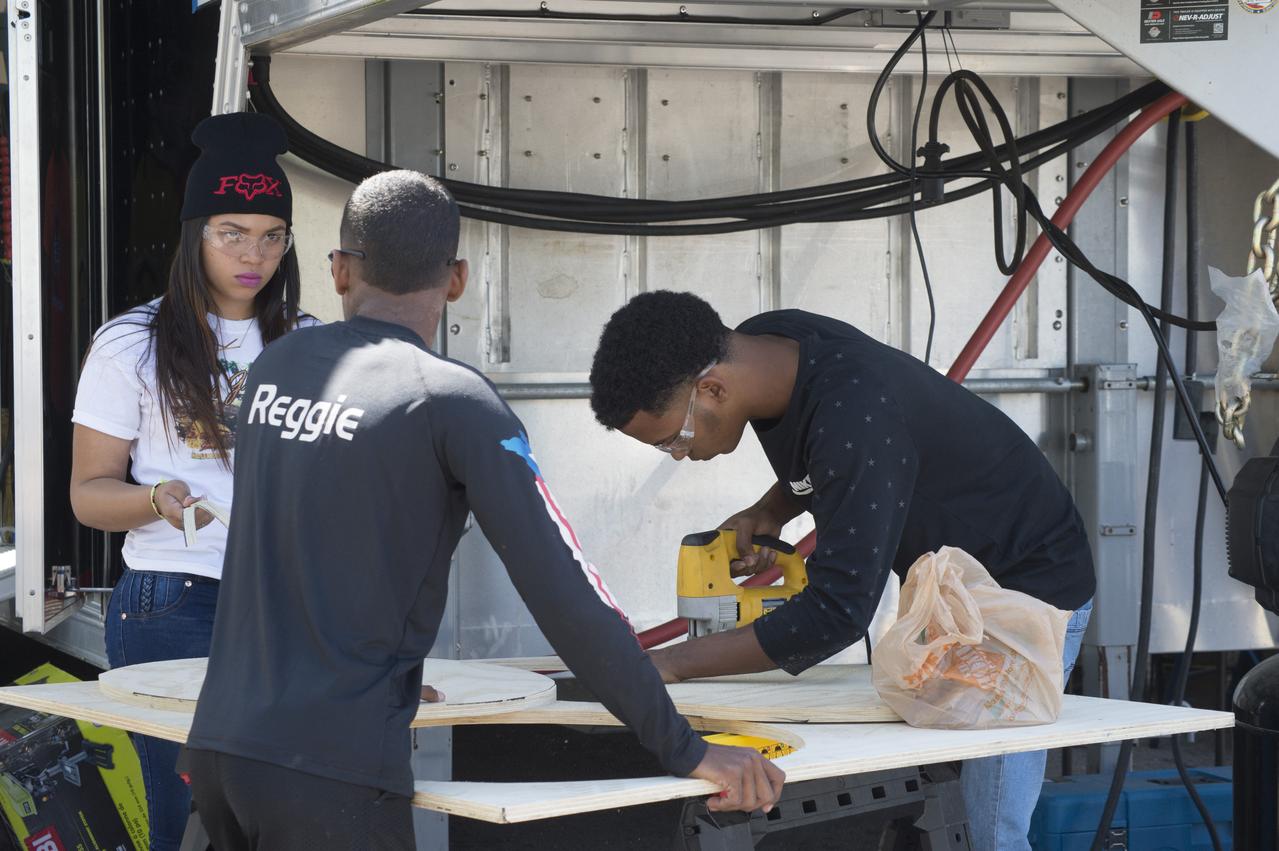

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
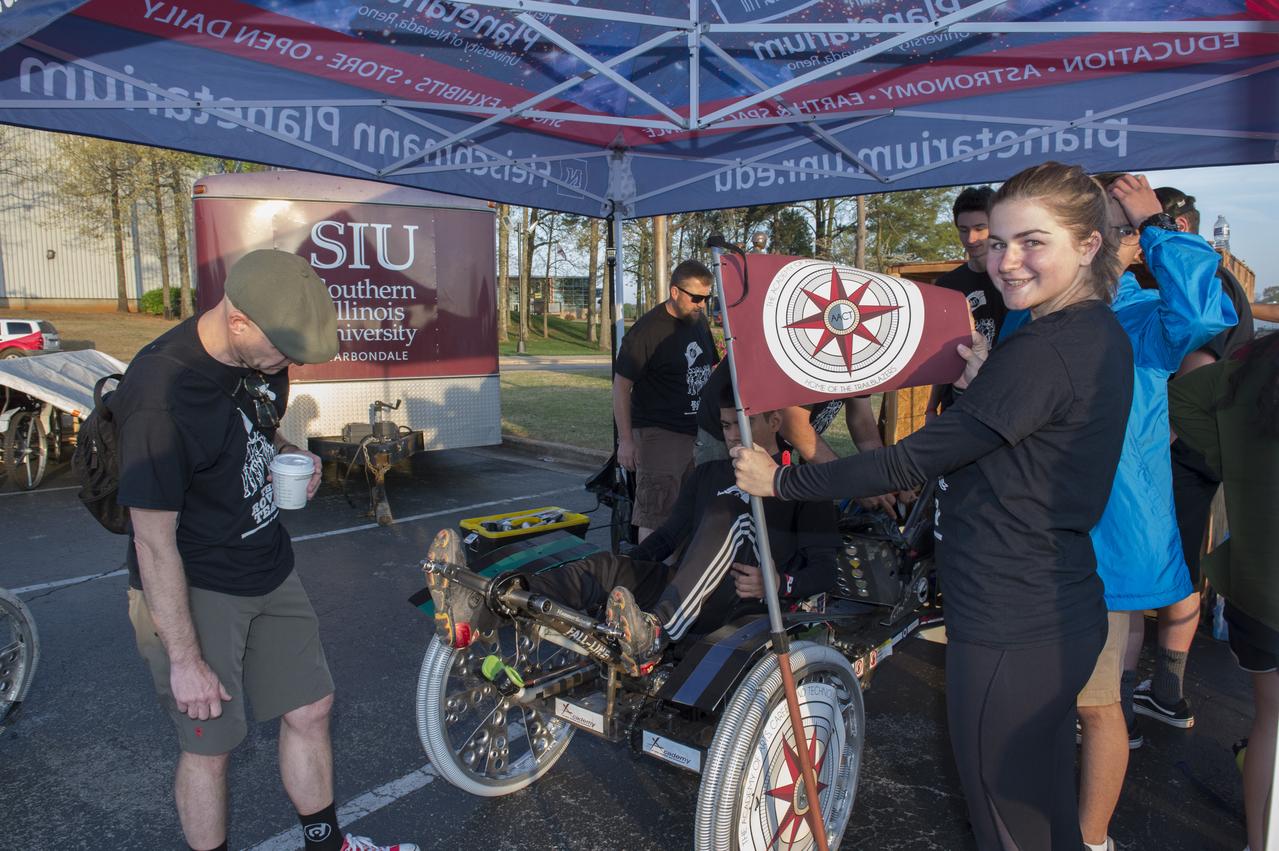

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
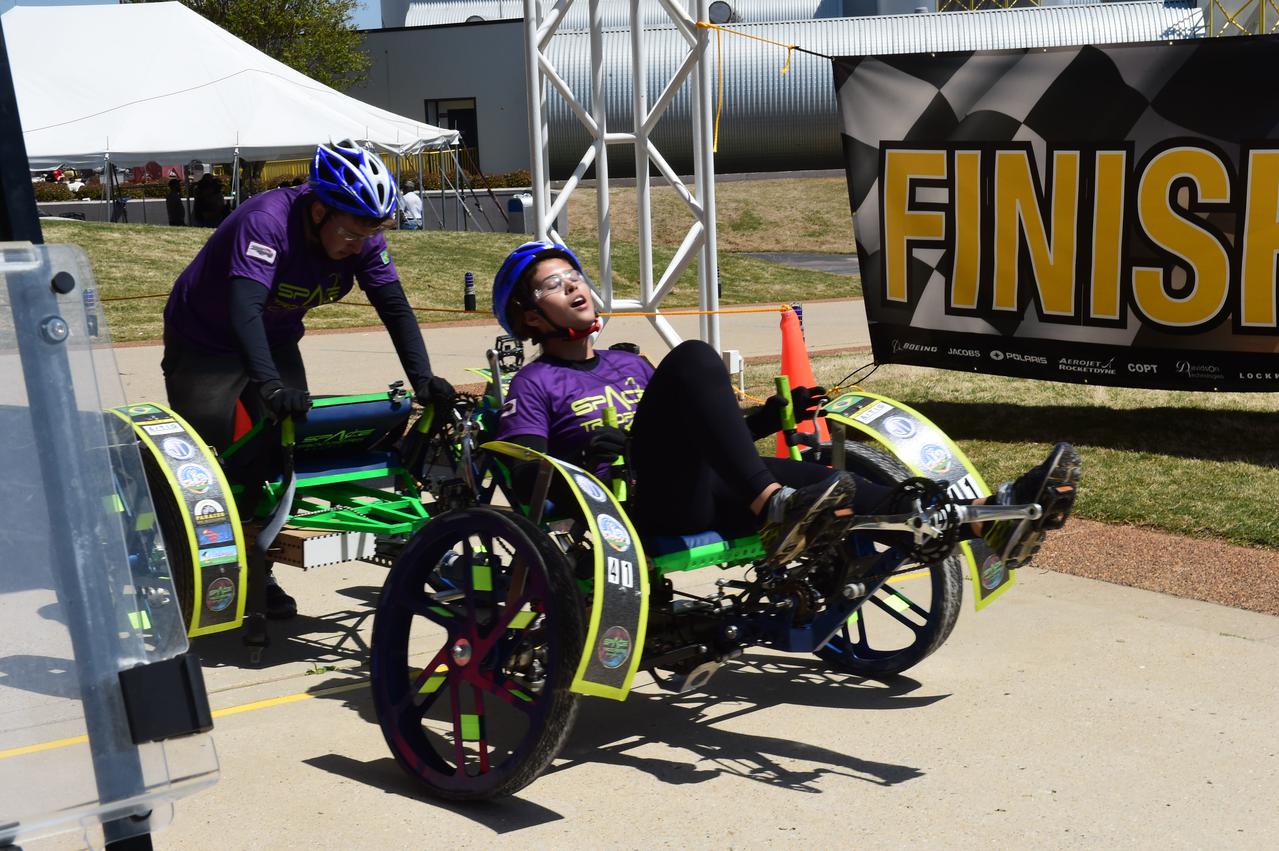

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
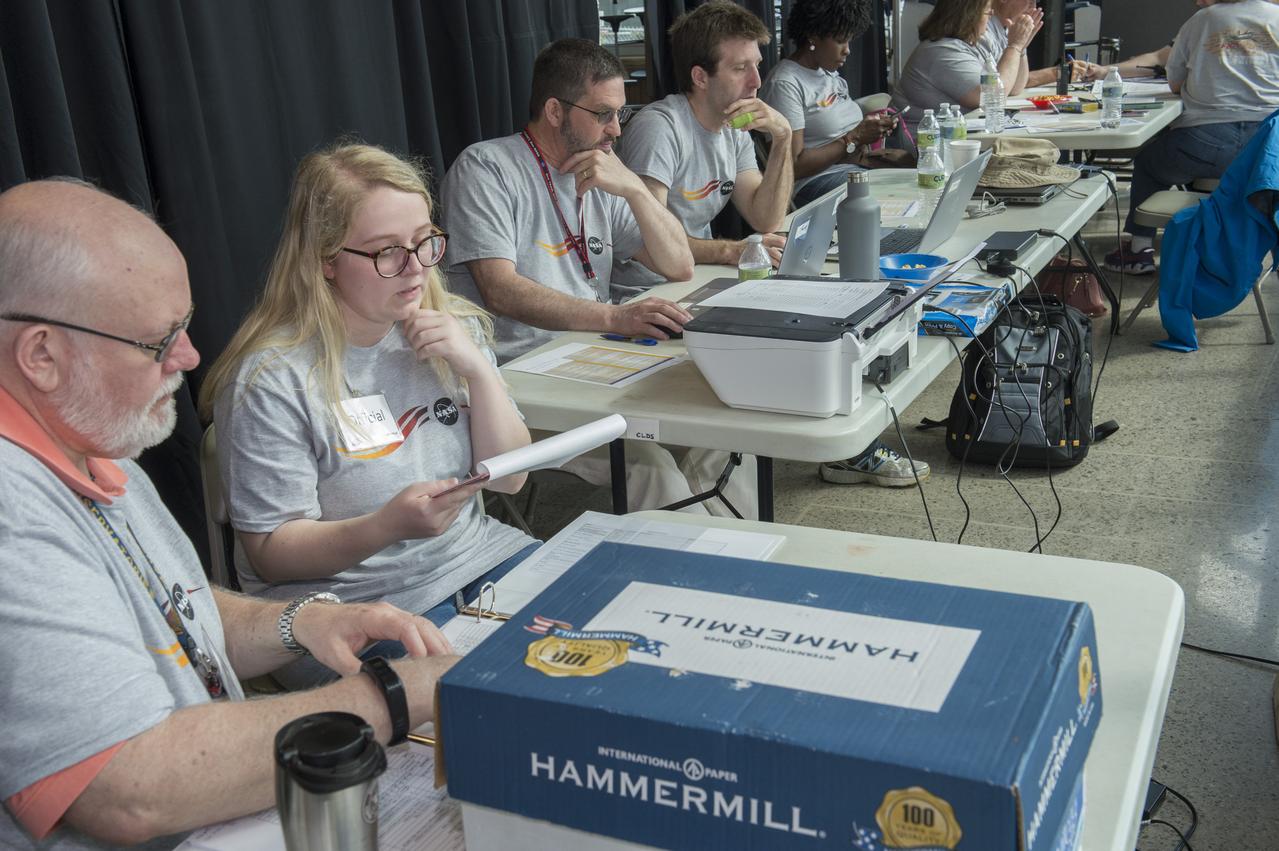

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
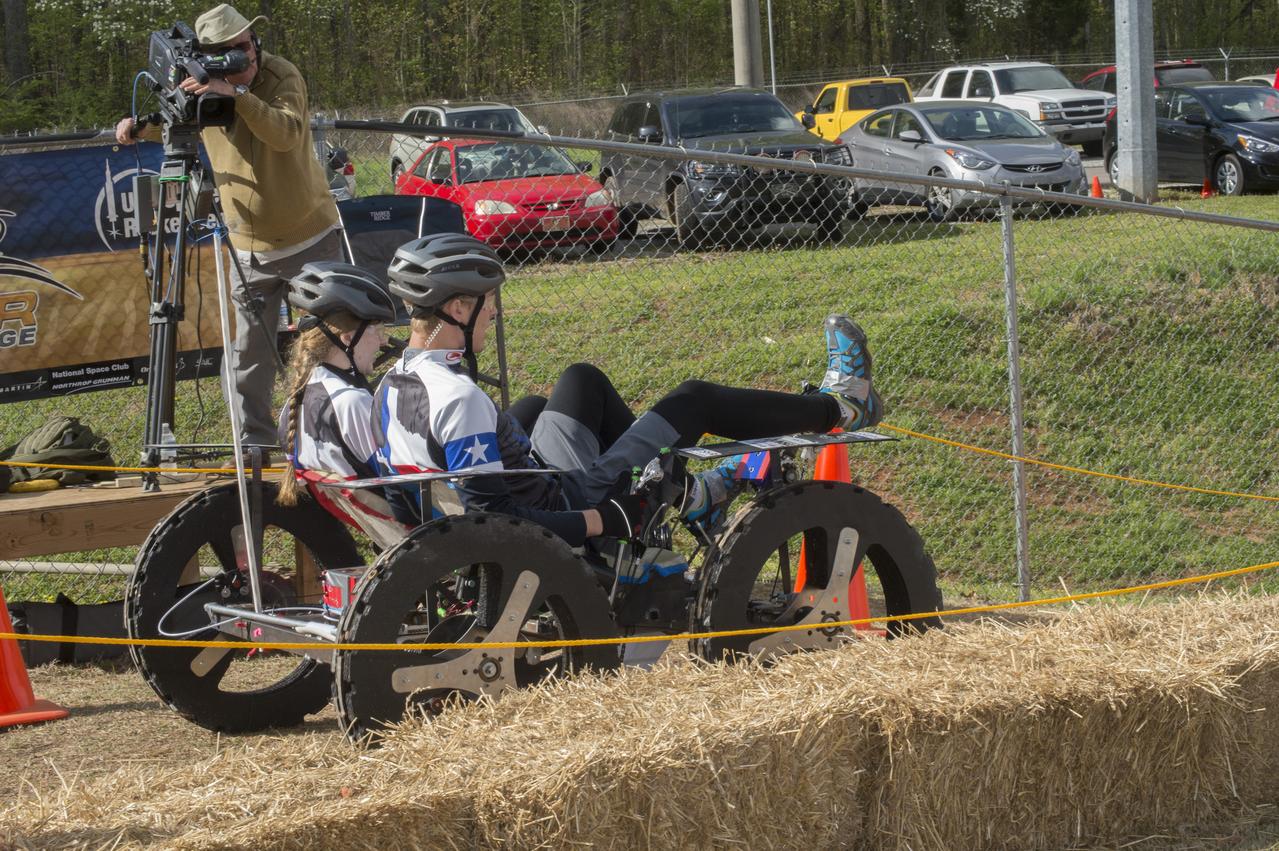

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
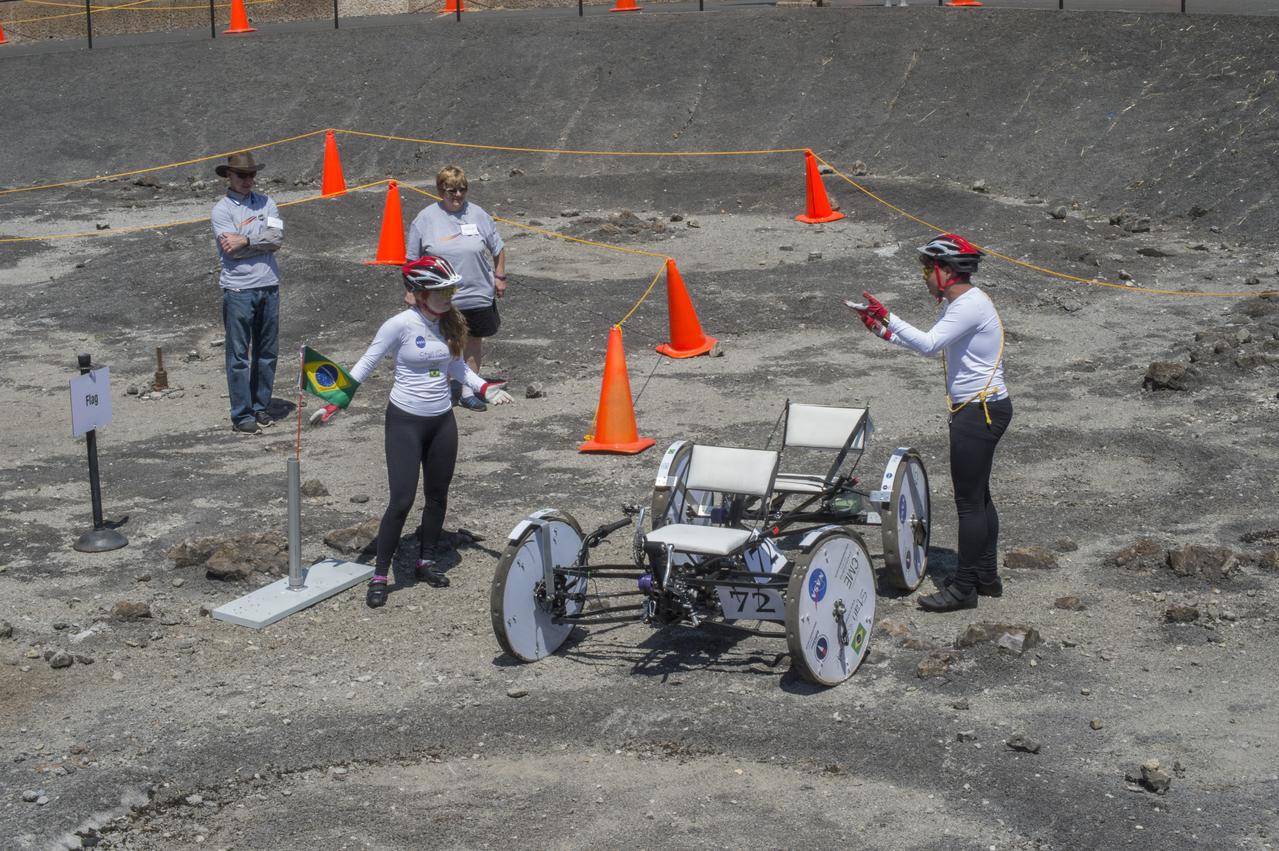

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
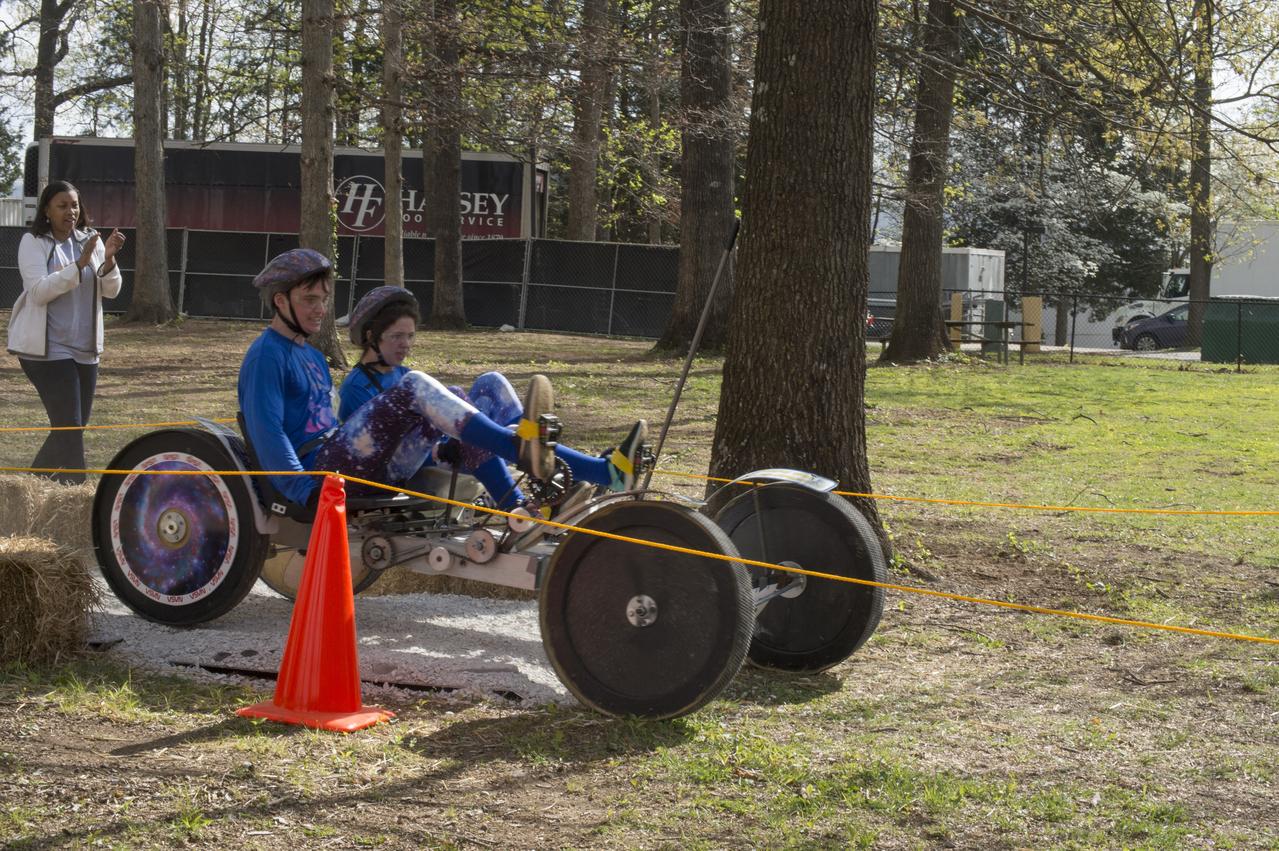

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.
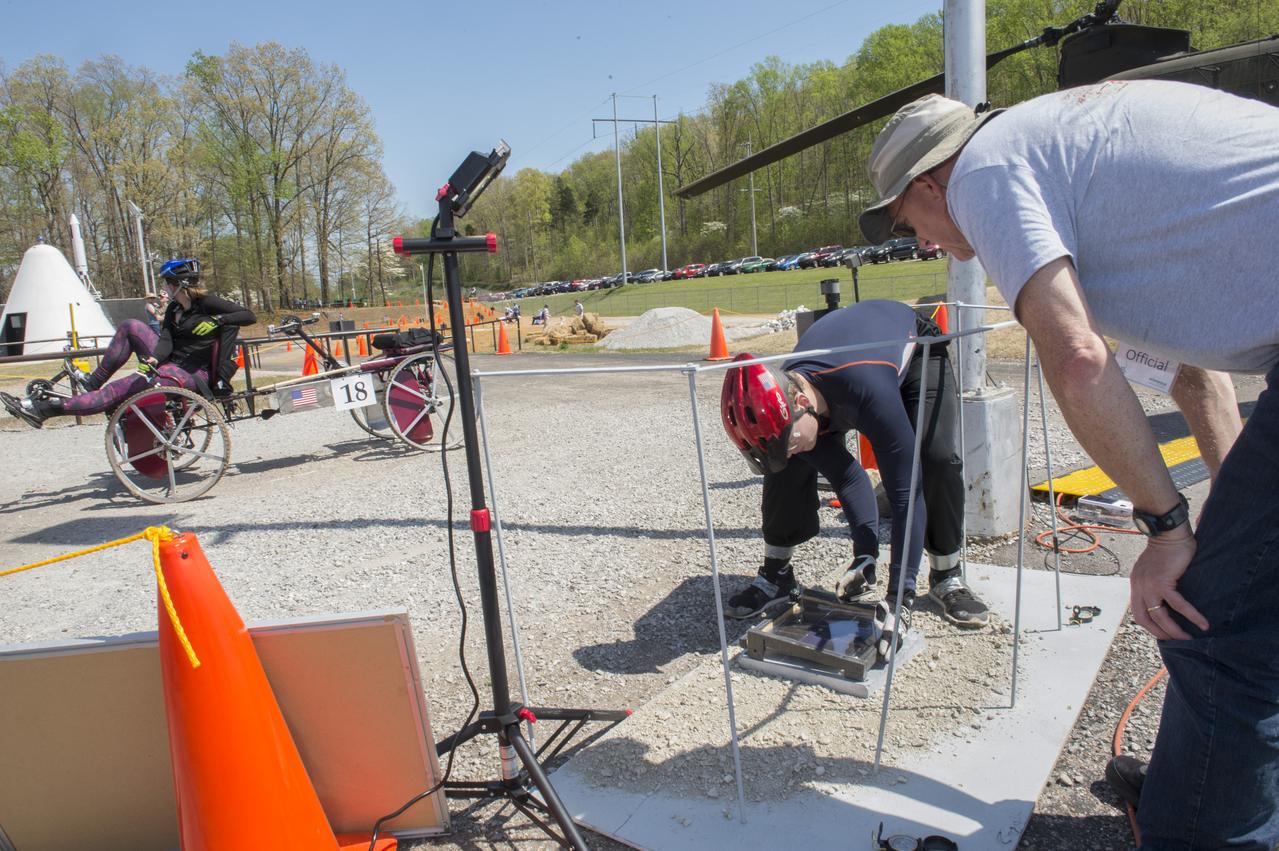

High school and university students competed in the 2018 Human Exploration Rover Challenge event at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Students came from across the U.S. as well as several foreign countries such as Brazil, Germany, India, and Mexico. This event, which is normally a 2 day event, was shortened to 1 day in 2018 due to adverse weather conditions.