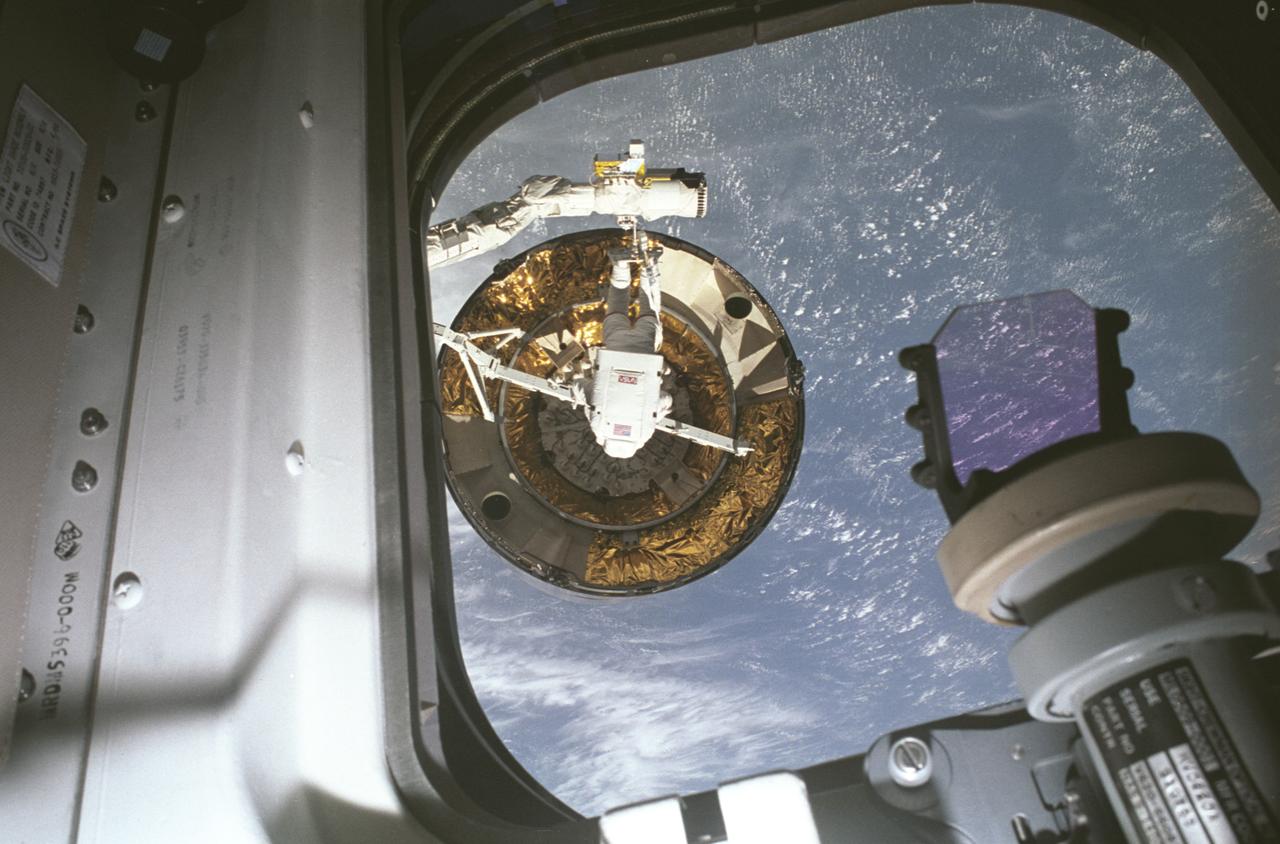

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. Recorded with a 35 mm camera inside Endeavour’s cabin, is astronaut Pierre Thuot after his second unsuccessful attempt to affix a specially designed grapple bar to the 4.5 ton INTELSAT VI.
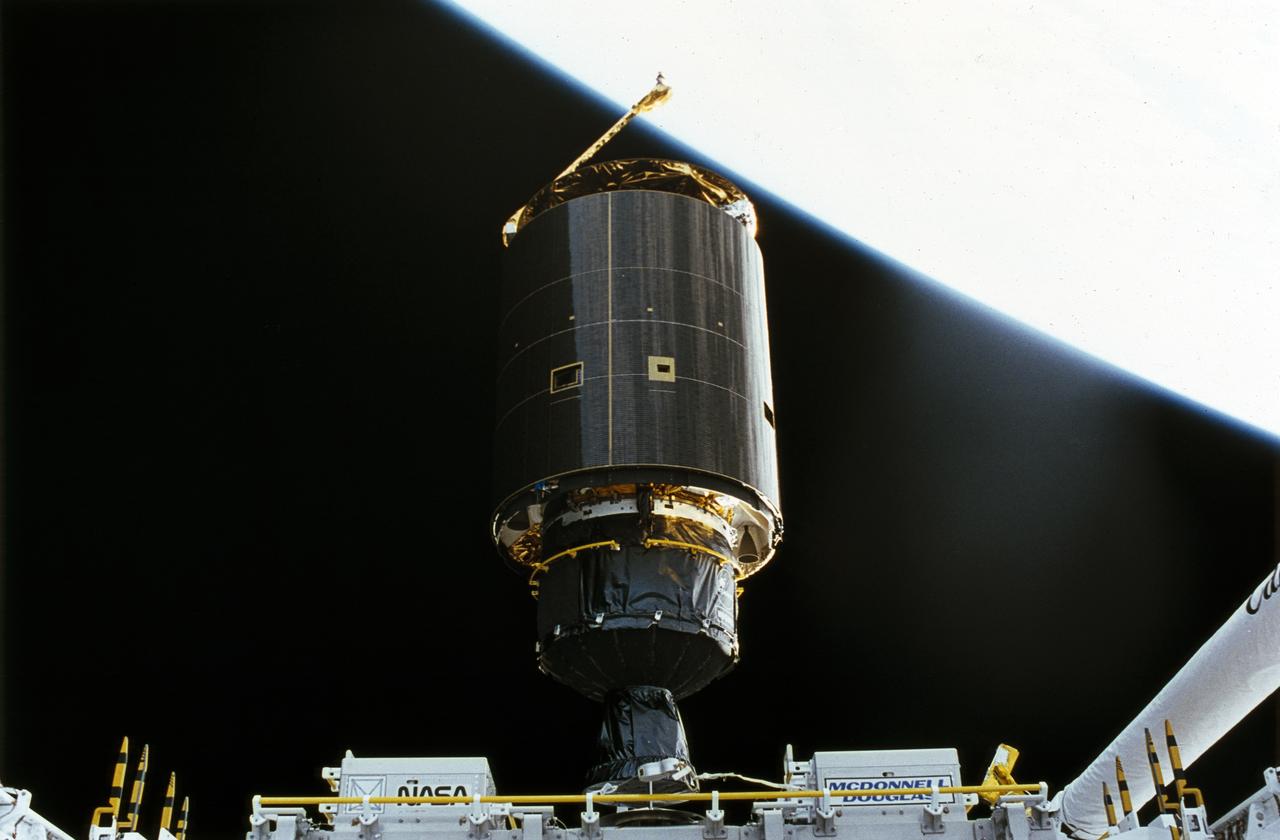

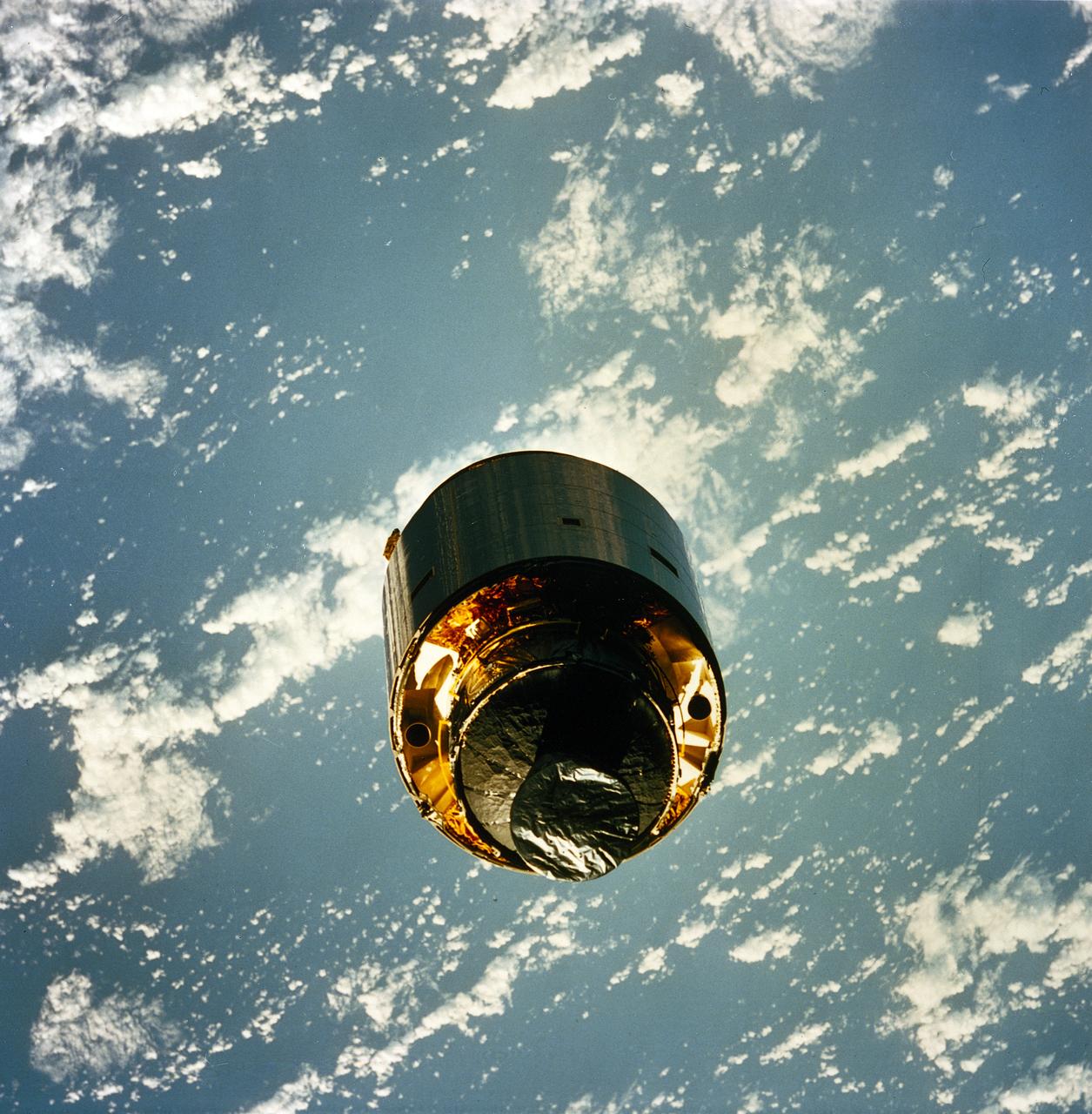
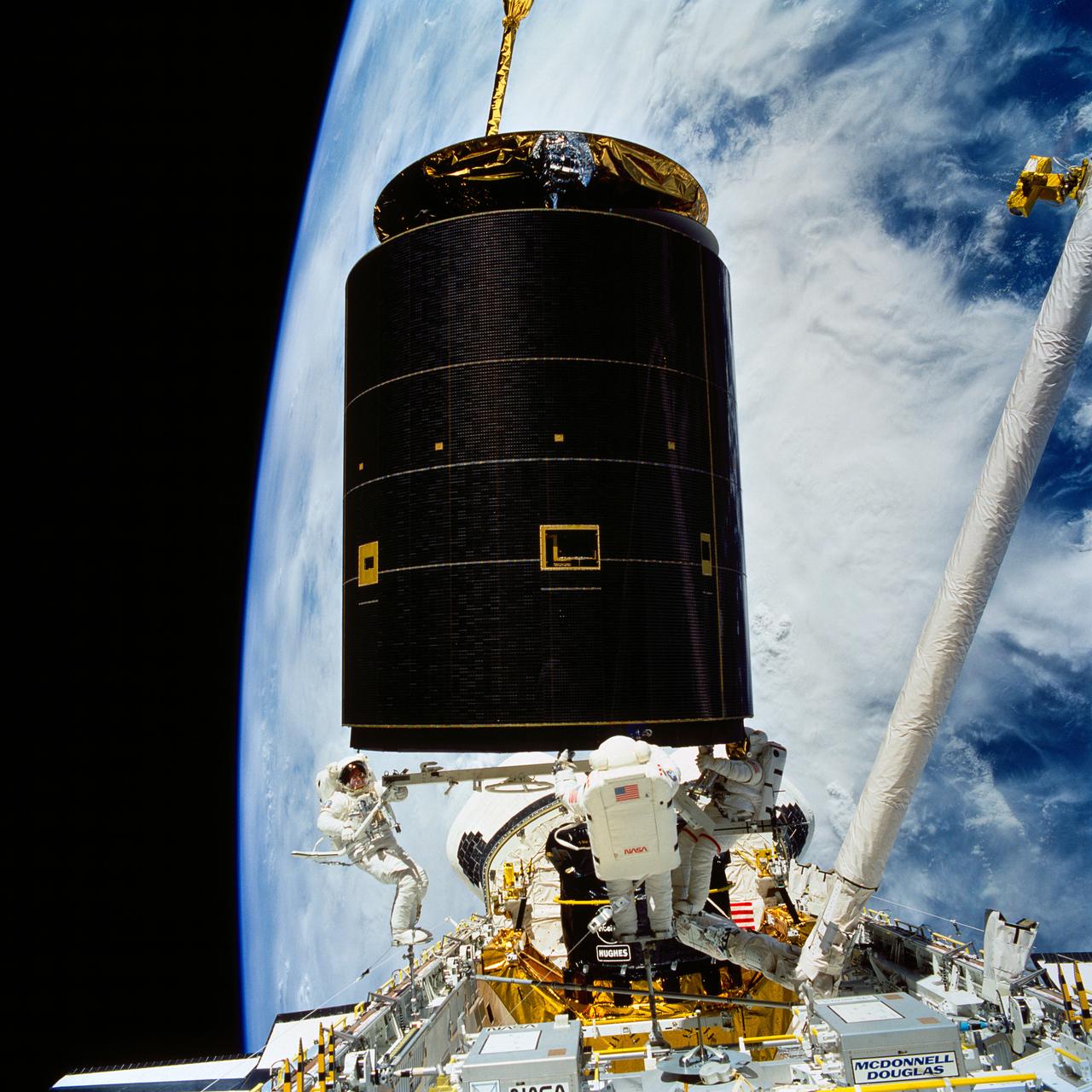
STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. The 4.5 ton INTELSAT VI was successfully snared by three astronauts on a third EVA. In this photo, the satellite, with its newly deployed perigee stage, begins its separation from the Shuttle.

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. After securing the satellite with the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), the crew proceeded with preparing the satellite for its release into space.
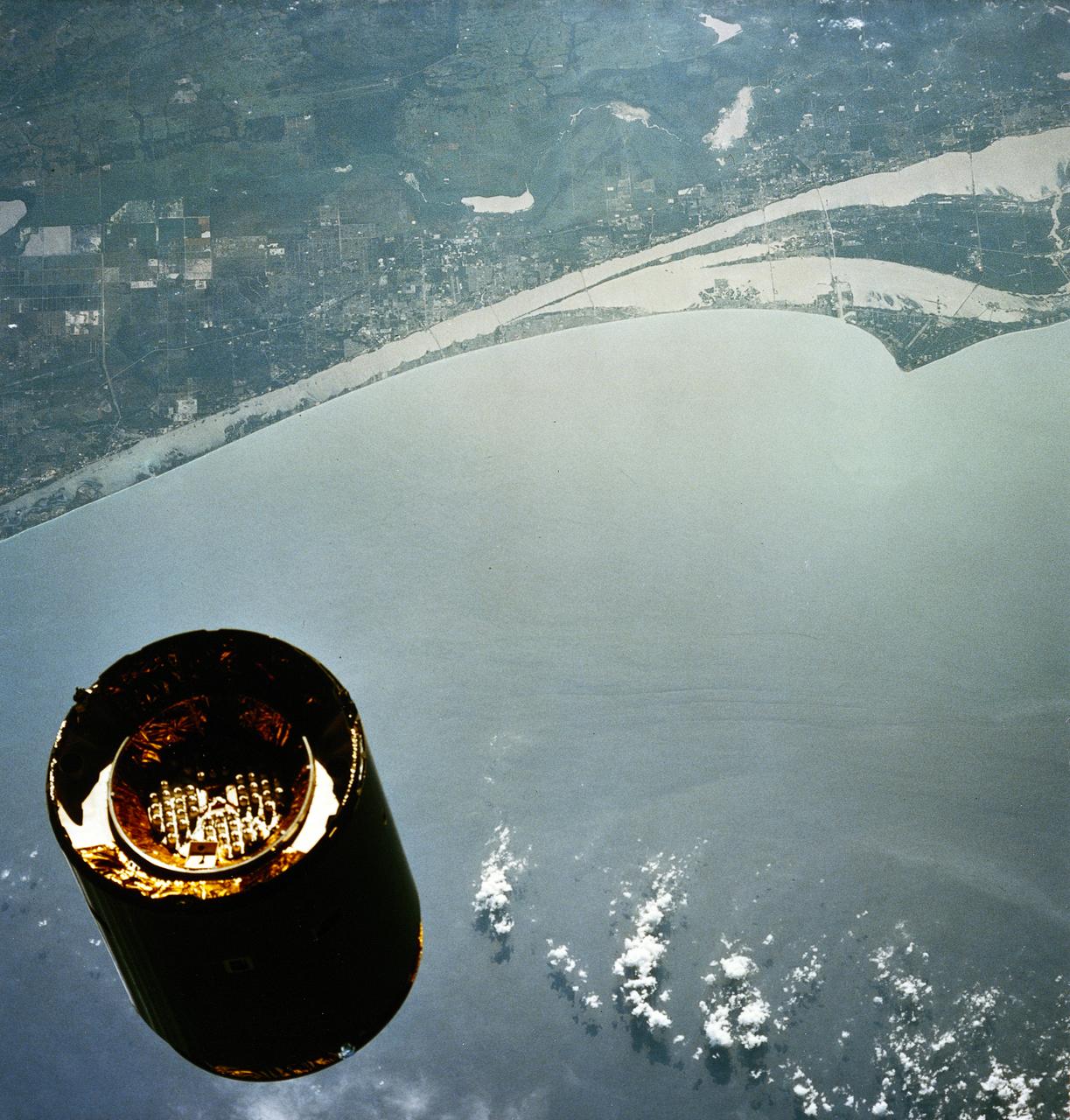

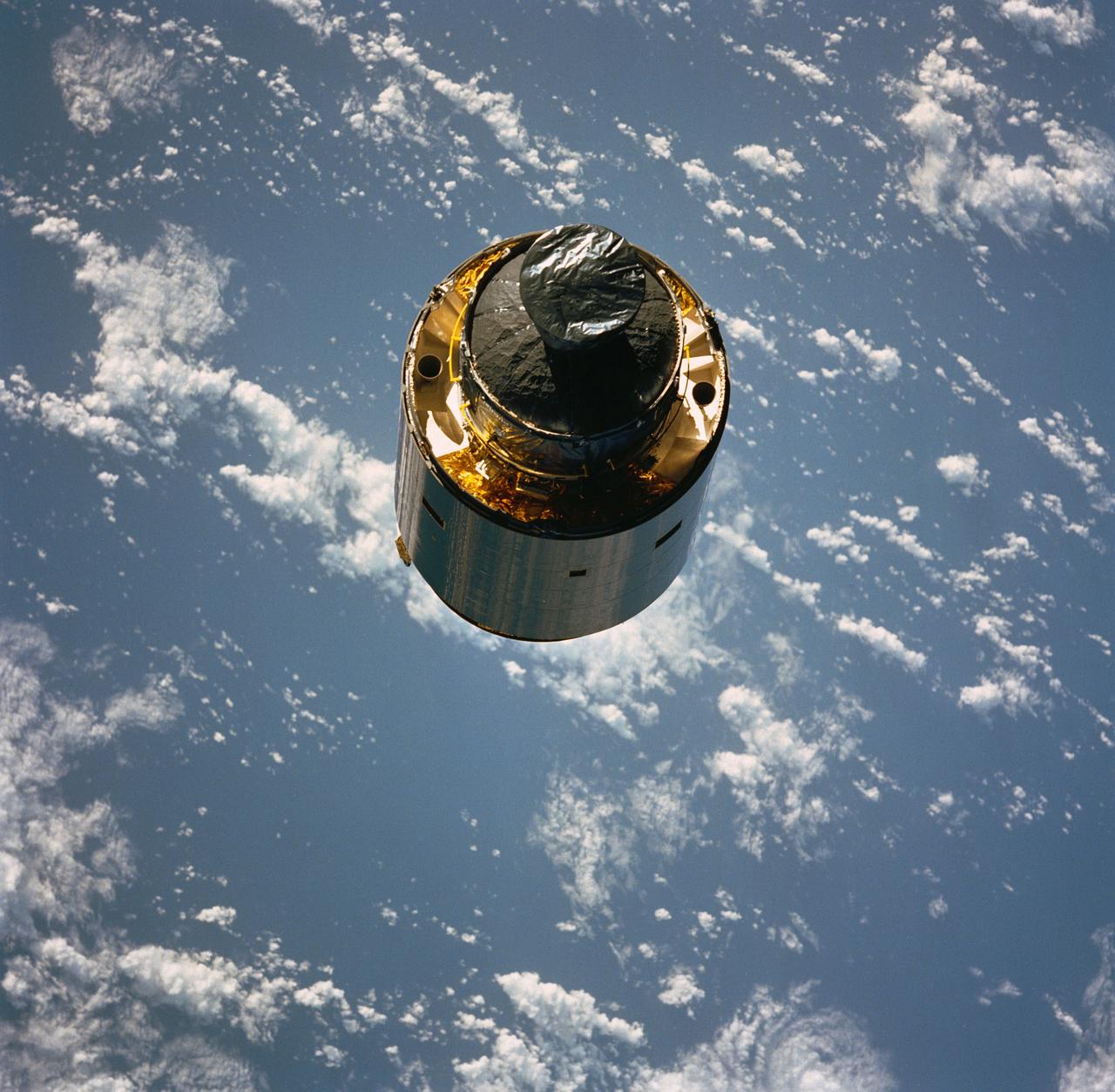
STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. This onboard photo depicts Florida’s Atlantic coast and the Cape Canaveral area as the backdrop for this scene of the INTELSAT VI’s approach to the Shuttle Endeavour.

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. The 4.5 ton INTELSAT VI was successfully snared by three astronauts on a third EVA. The three hand-grabbed the errant satellite, pulled it into the cargo bay, and attached a boost-given perigee stage before its release.

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. The 4.5 ton INTELSAT VI was successfully snared by three astronauts on a third EVA. The three hand-grabbed the errant satellite, pulled it into the cargo bay, and attached a boost-given perigee stage before its release.
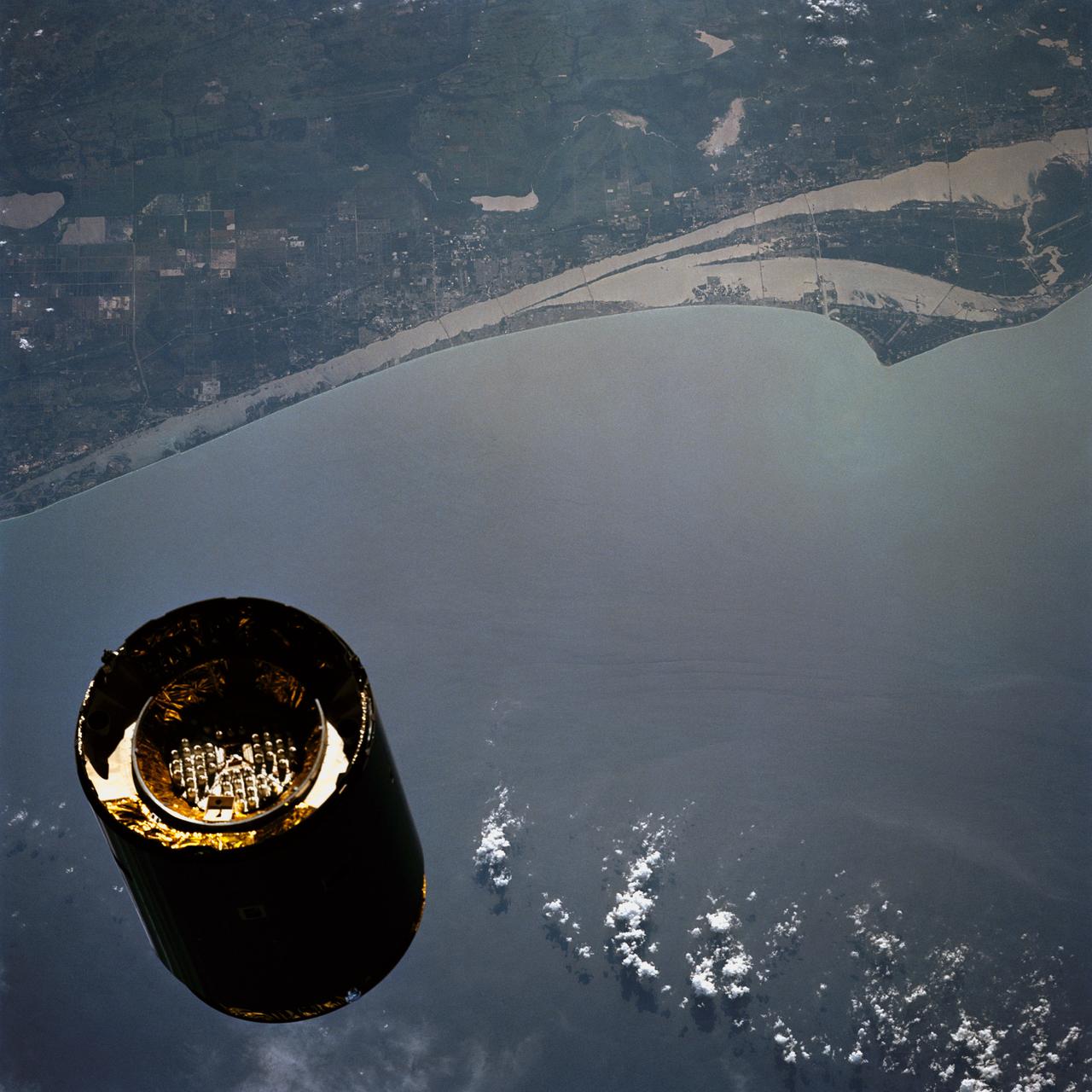

STS049-79-024 (13 May 1992) --- Florida's Atlantic Coast and the Cape Canaveral area form the backdrop for this 70mm scene of Intelsat VI's approach to the Space Shuttle Endeavour. Later, the seven-member crew was successful in capturing the satellite and adding a perigee phase. The new motor allowed the needed boost for Intelsat, once the crew members had released it into space.

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. The 4.5 ton satellite was successfully snared by three astronauts on a third EVA. The three hand-grabbed the errant satellite, pulled it into the cargo bay, and attached a boost-given perigee stage before its release. In this photo, the satellite spins slowly out of cargo bay to begin its “new lift”.
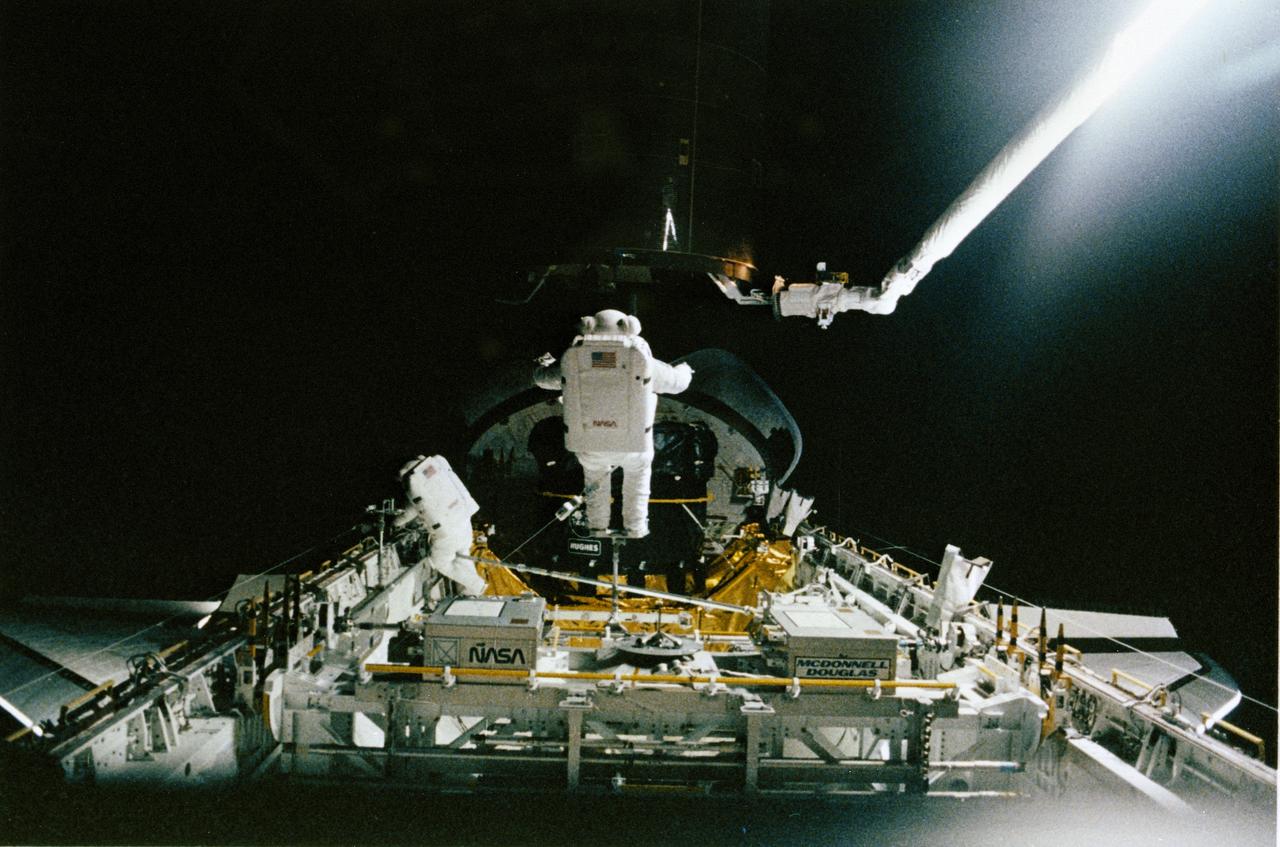
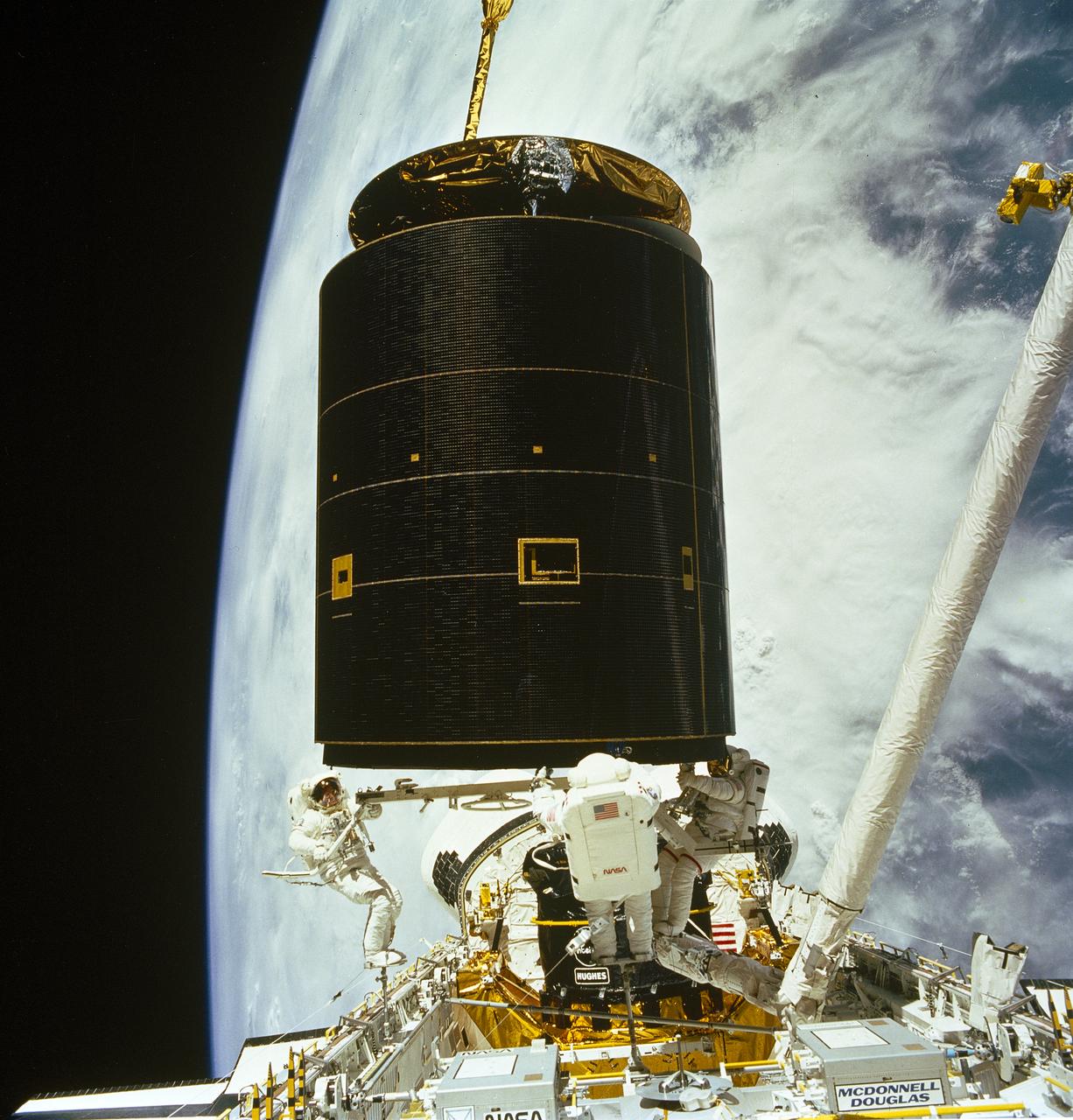
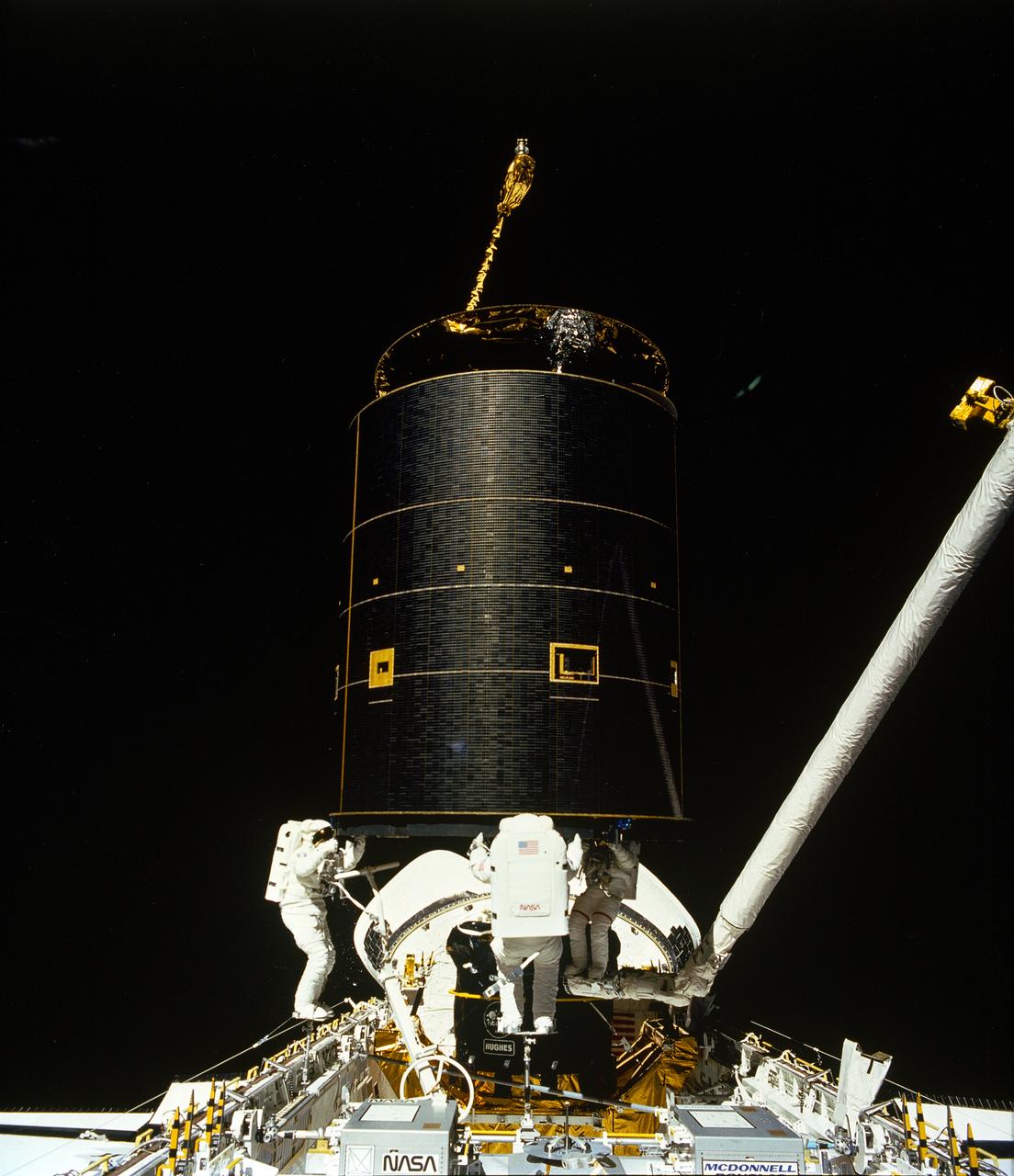
STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. In this onboard photo, astronauts Hieb, Akers, and Thuot have handholds on the satellite.
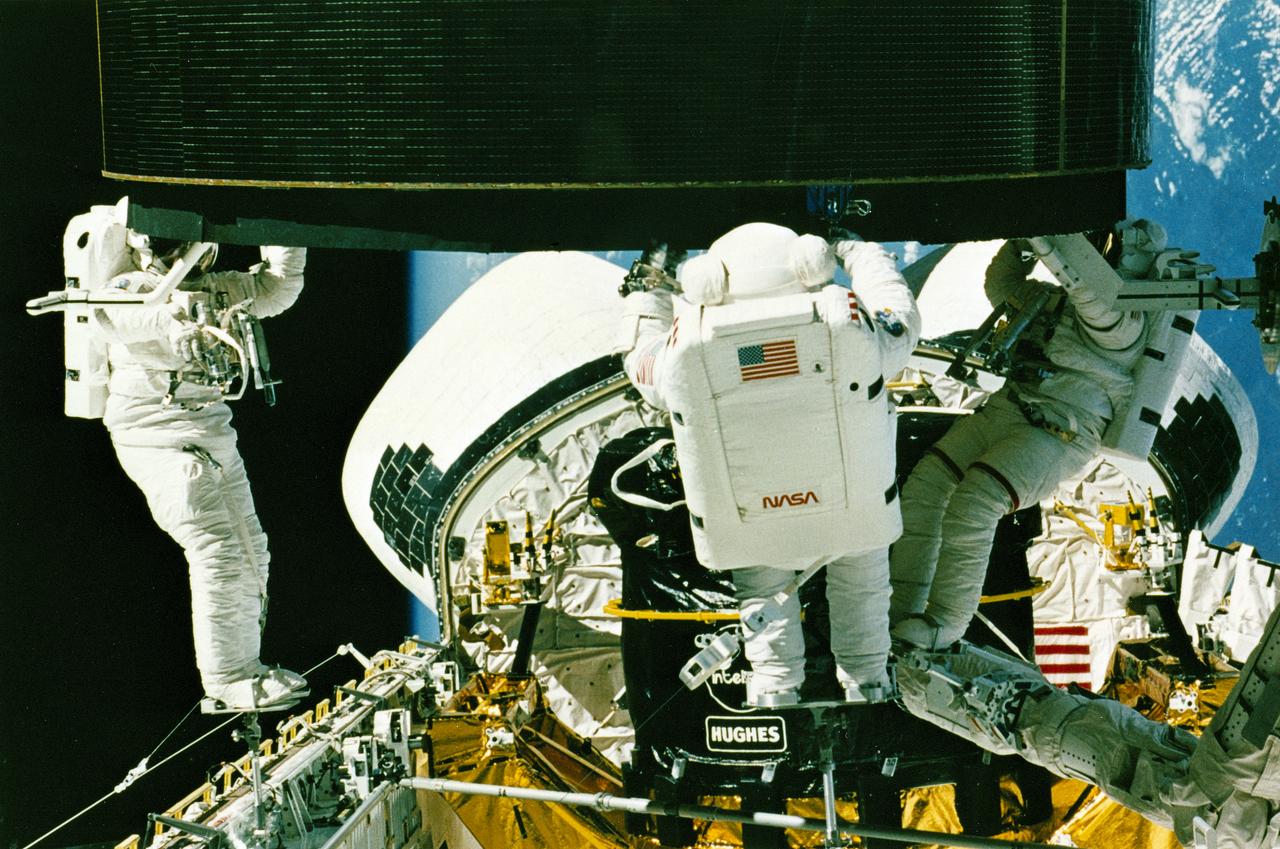
STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. In this onboard photo, astronauts Hieb, Akers, and Thuot have handholds on the satellite.
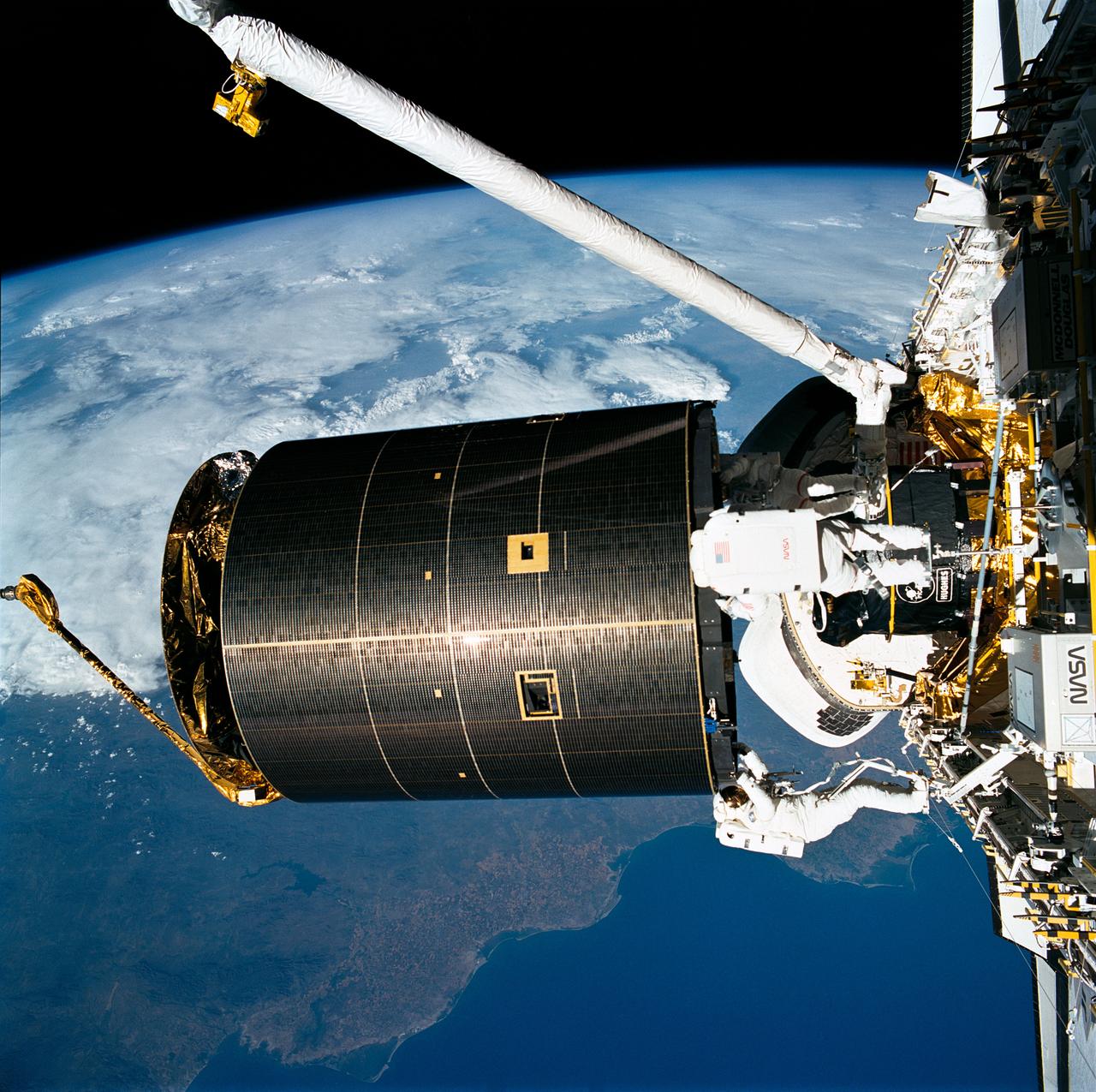

STS049-91-020 (13 May 1992) --- The successful capture of Intelsat VI satellite is recorded over Mexico on this 70mm frame, from inside the Space Shuttle Endeavour's cabin. Left to right, astronauts Richard J. Hieb, Thomas D. Akers and Pierre J. Thuot have handholds on the satellite. Ground coverage in the frame includes an area from Hermosillo, Sonara to Los Mochis in the state of Sinaloa. The nine-day mission accomplished the capture of the Intelsat, subsequent mating of the satellite to a booster and its eventual deployment, as well as a Space Station Freedom preview Extravehicular Activity (EVA). Endeavour's crew members were astronauts Daniel C. Brandenstein, mission commander; Kevin P. Chilton, pilot; and Thomas D. Akers, Richard J. Hieb, Bruce E. Melnick, Kathryn C. Thornton and Pierre J. Thuot, all mission specialists.

STS049-91-056 (13 May 1992) --- The 4.5-ton Intelsat VI communications satellite begins its separation from the Space Shuttle Endeavour. Crew members deployed a new perigee stage on the satellite after three astronauts on a third extravehicular activity (EVA) successfully snared it. Clouds over the open ocean serve as backdrop for the 70mm image.
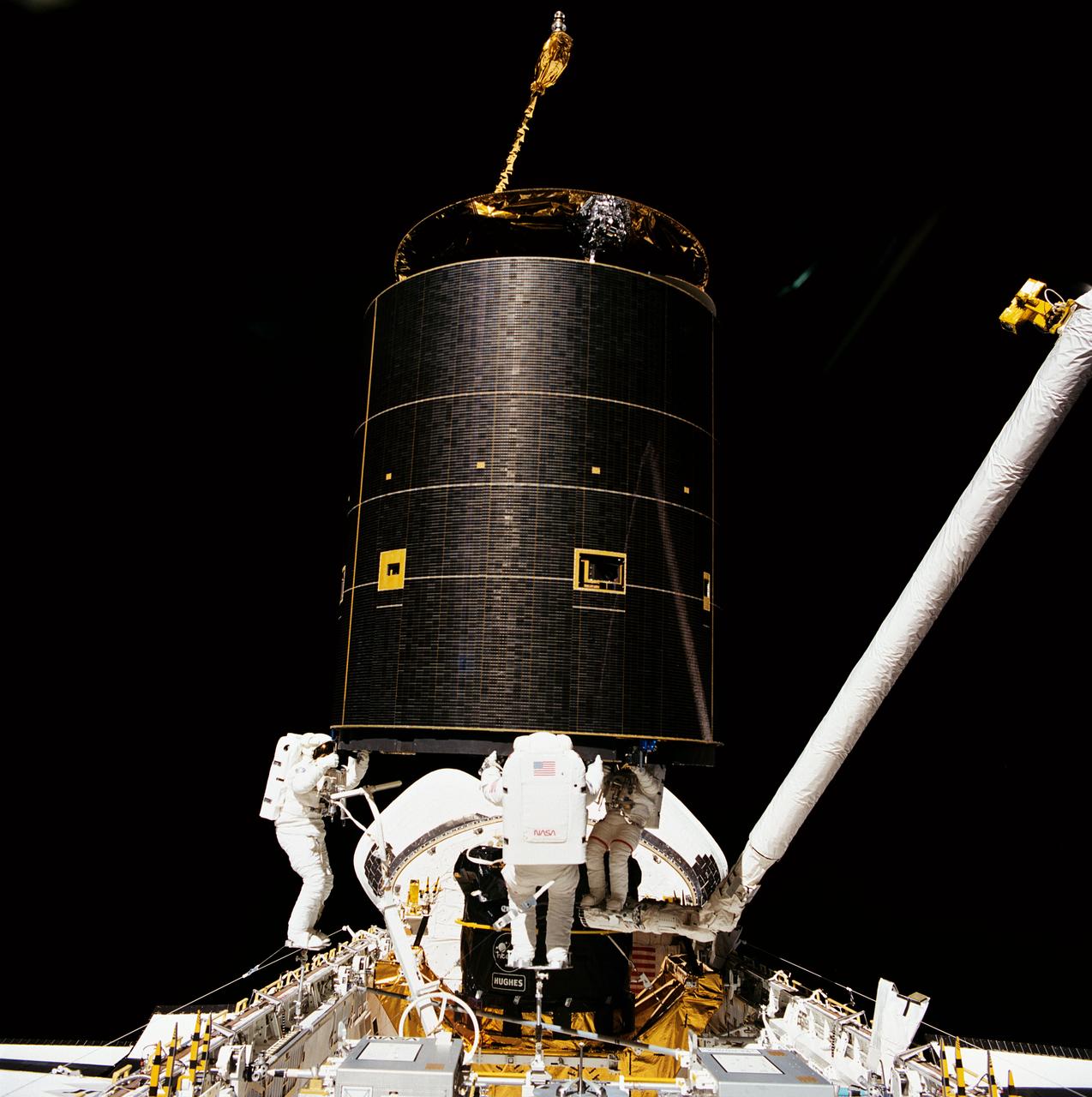

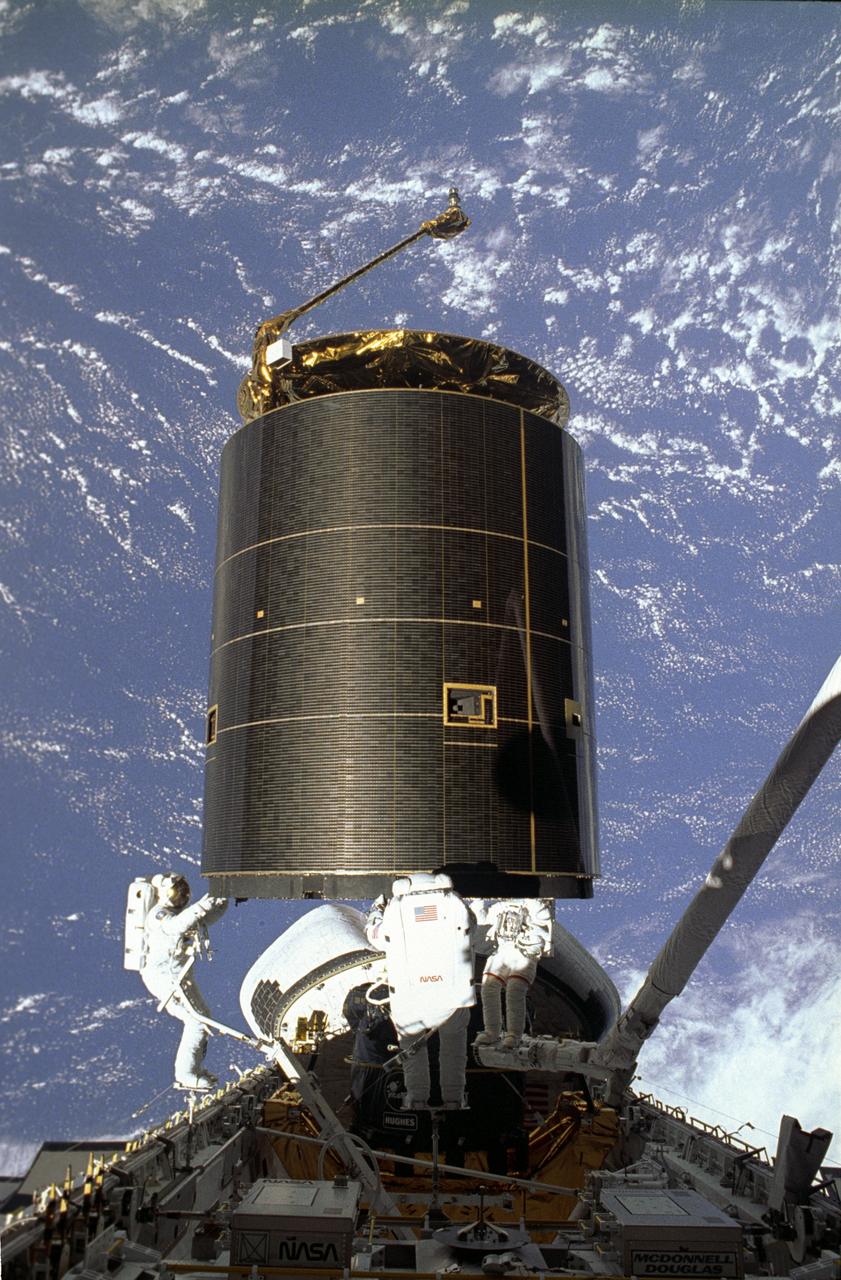
STS049-91-026 (13 May 1992) --- Three astronauts hold onto the 4.5-ton Intelsat VI satellite after a six-handed "capture" was made minutes earlier. Left to right are astronauts Richard J. Hieb, Thomas D. Akers and Pierre J. Thuot. Thuot stands on the end of the remote manipulator system arm, from which he had made two earlier unsuccessful grapple attempts on two-person extravehicular activity sessions. Ground controllers and crew members agreed that a third attempt, using three mission specialists in the cargo bay of the space shuttle Endeavour, was the effort needed to accomplish the capture feat.

STS049-91-029 (13 May 1992) --- Following the successful capture of Intelsat VI satellite, three astronauts continue their chores toward moving the 4.5 ton communications satellite into the space shuttle Endeavour's cargo bay. A fellow crew member recorded this 70mm still frame from inside Endeavour's cabin. Left to right, astronauts Richard J. Hieb, Thomas D. Akers and Pierre J. Thuot, cooperate on the effort to attach a specially designed grapple bar underneath the satellite. Thuot stands on the end of the Remote Manipulator System's (RMS) arm while Hieb and Akers are on Portable Foot Restraints (PFR) affixed to Endeavour's portside and the Multipurpose Support Structure (MPESS), respectively. The sections of Earth which form the backdrop for the scene are blanketed with thousands of square miles of clouds. Photo credit: NASA
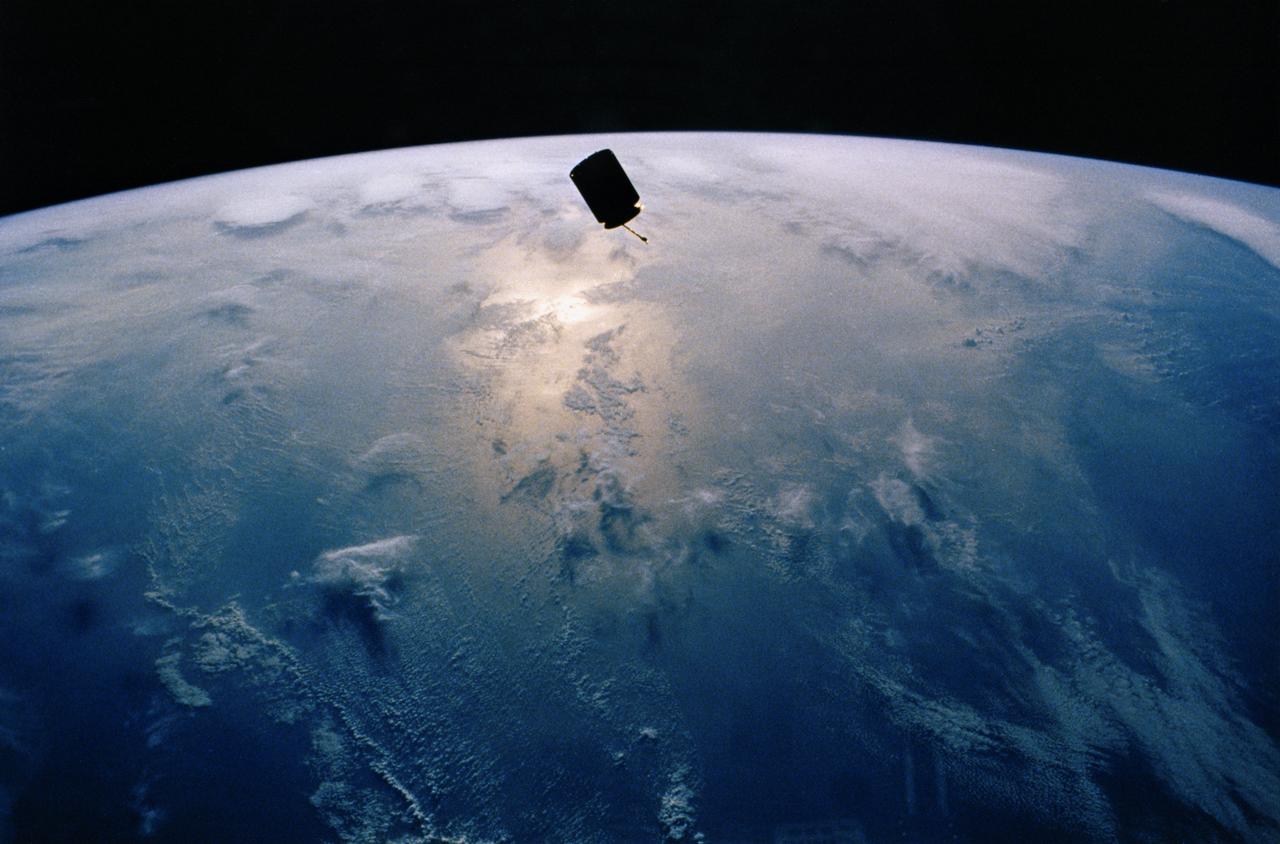

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. This onboard photo captures the free flying INTELSAT IV.
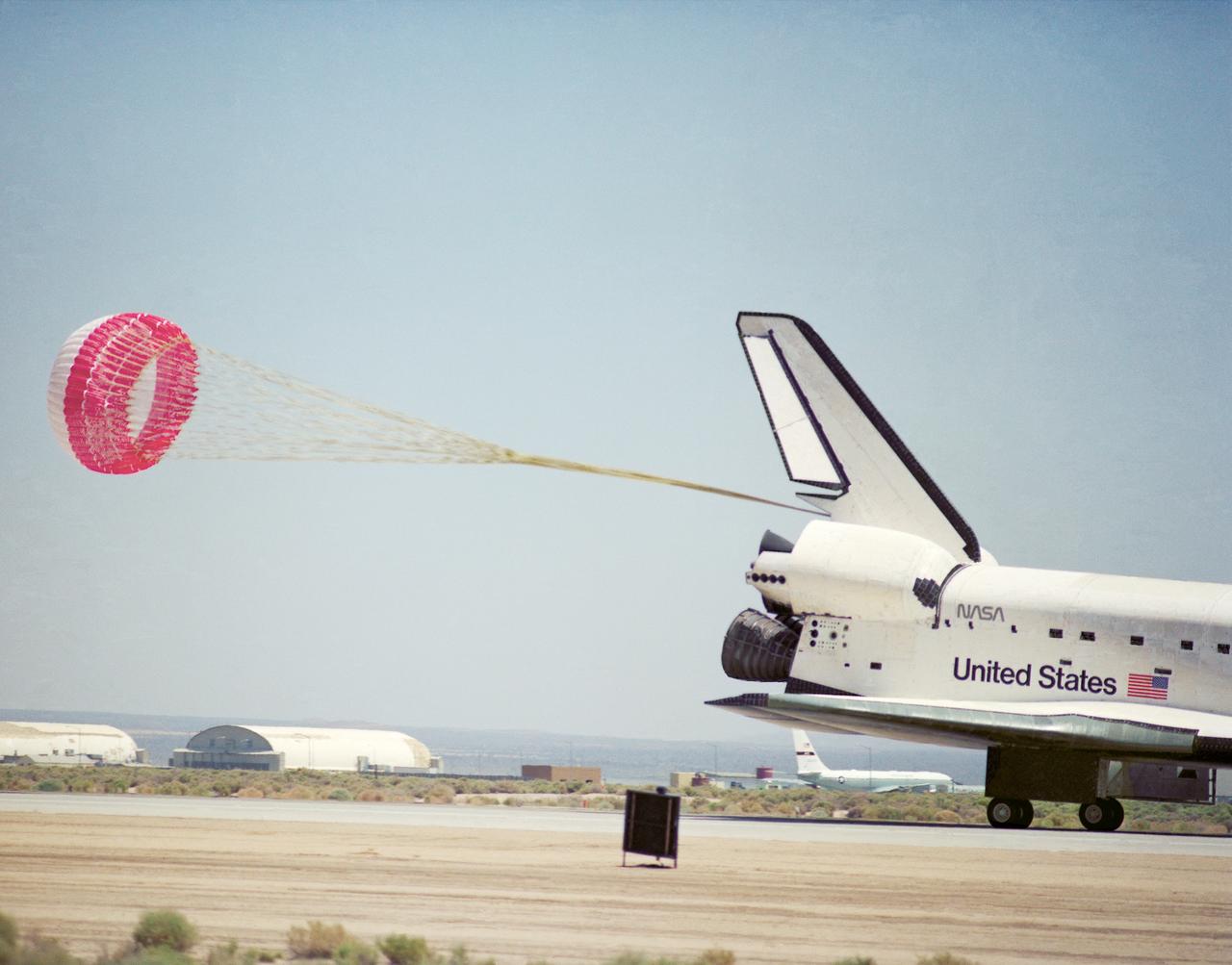

The Space Shuttle Endeavour concludes mission STS-49 at NASA's Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility (later redesignated Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California, with a 1:57 p.m. (PDT) landing 16 May on Edward's concrete runway 22. The planned 7-day mission, which began with a launch from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 4:41 p.m. (PFT), 7 May, was extended two days to allow extra time to rescue the Intelsat VI satellite and complete Space Station assembly techniques originally planned. After a perfect rendezvous in orbit and numerous attempts to grab the satellite, space walking astronauts Pierre Thuot, Rick Hieb and Tom Akers successfully rescued it by hand on the third space walk with the support of mission specialists Kathy Thornton and Bruce Melnick. The three astronauts, on a record space walk, took hold of the satellite and directed it to the shuttle where a booster motor was attached to launch it to its proper orbit. Commander Dan Brandenstein and Pilot Kevin Chilton brought Endeavours's record setting maiden voyage to a perfect landing at Edwards AFB with the first deployment of a drag chute on a shuttle mission.
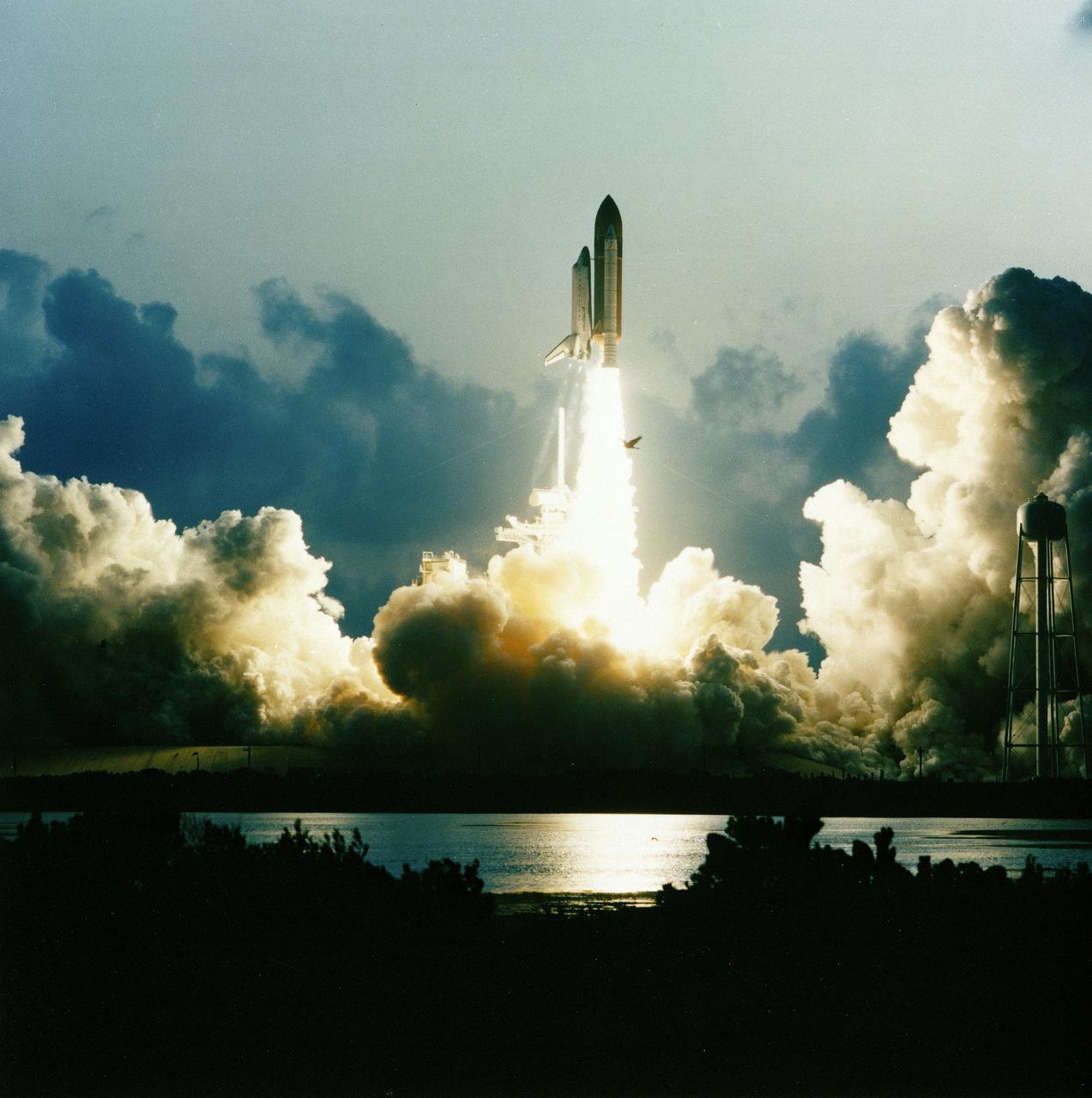

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3) which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990.
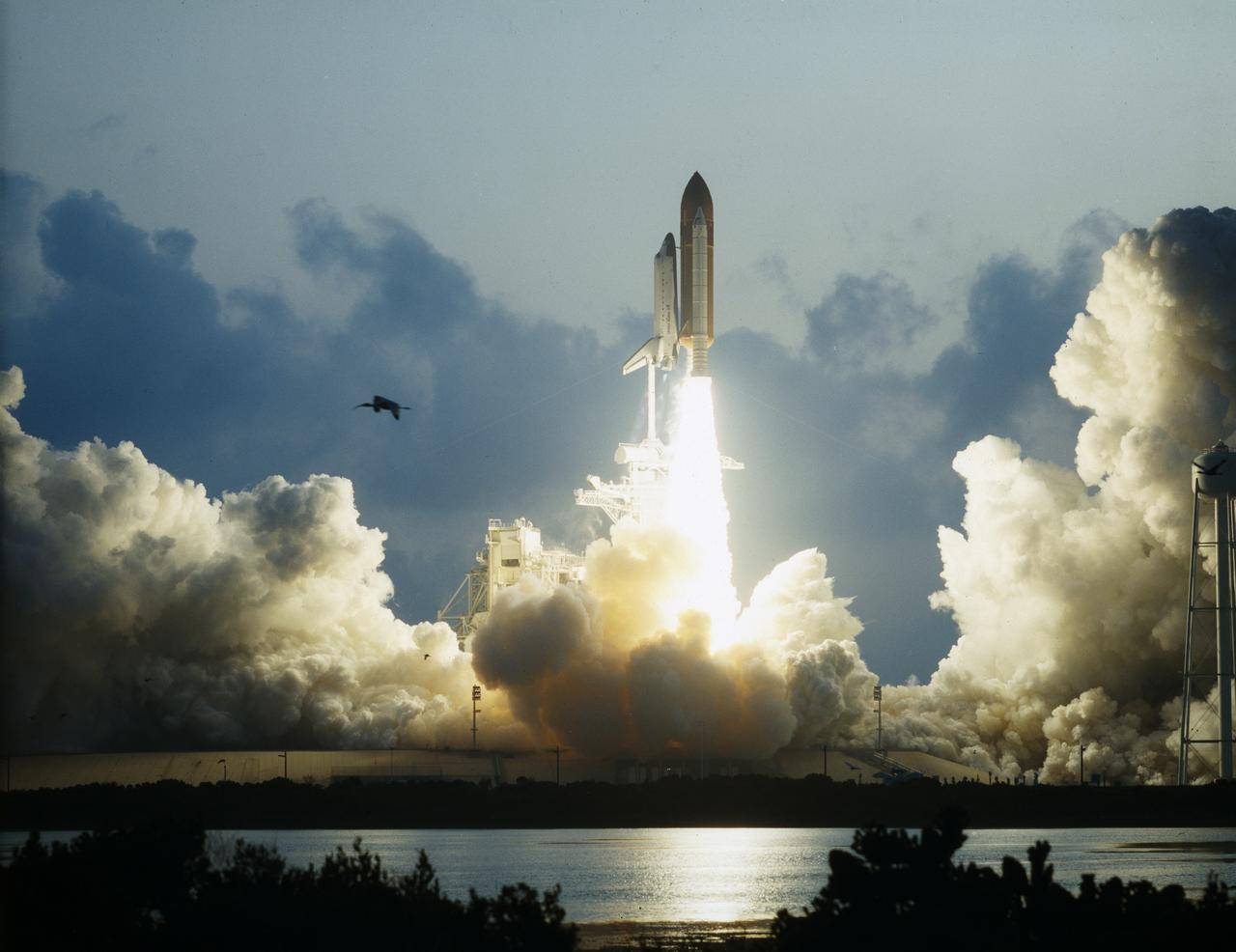

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3) which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990.
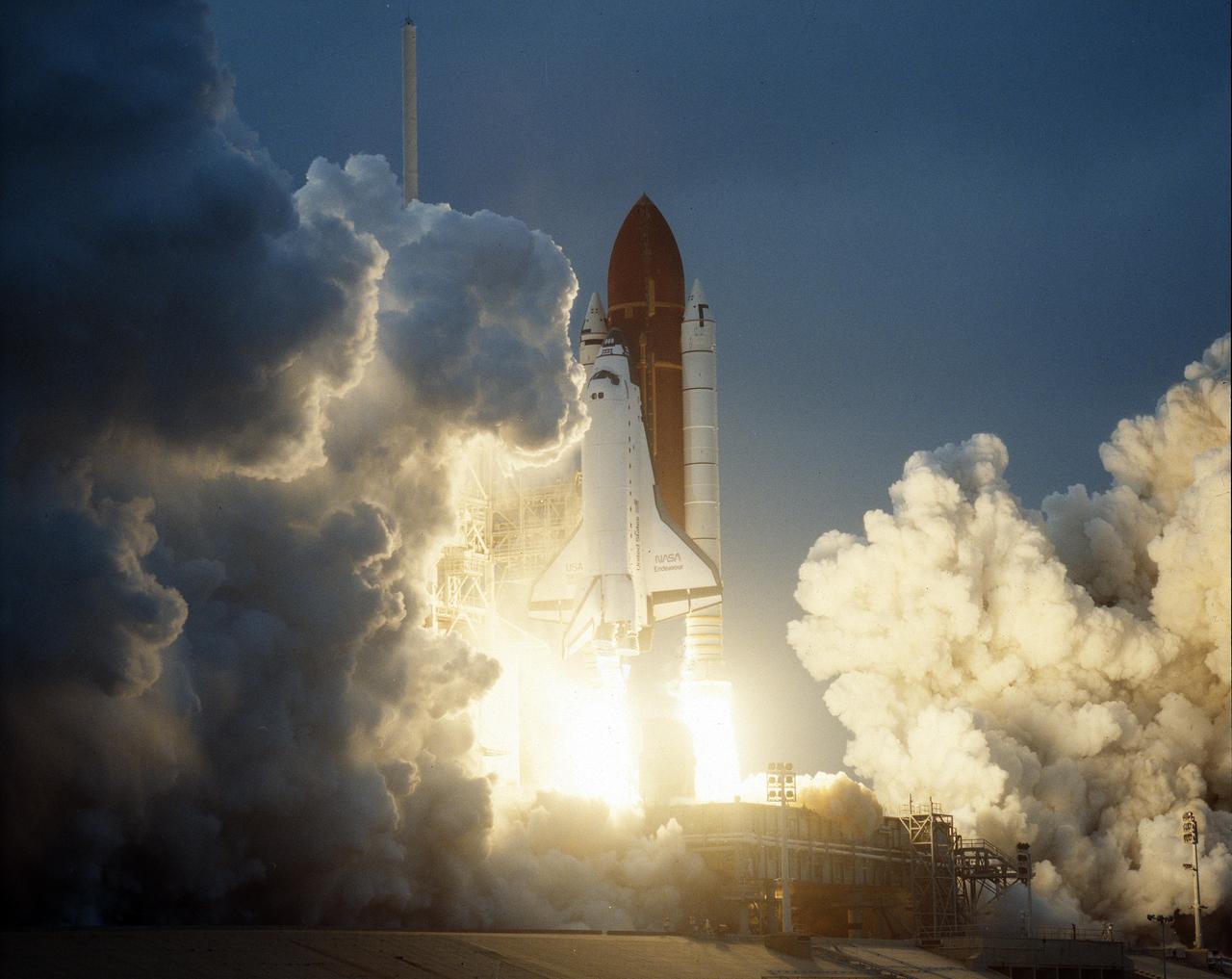

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3) which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990.
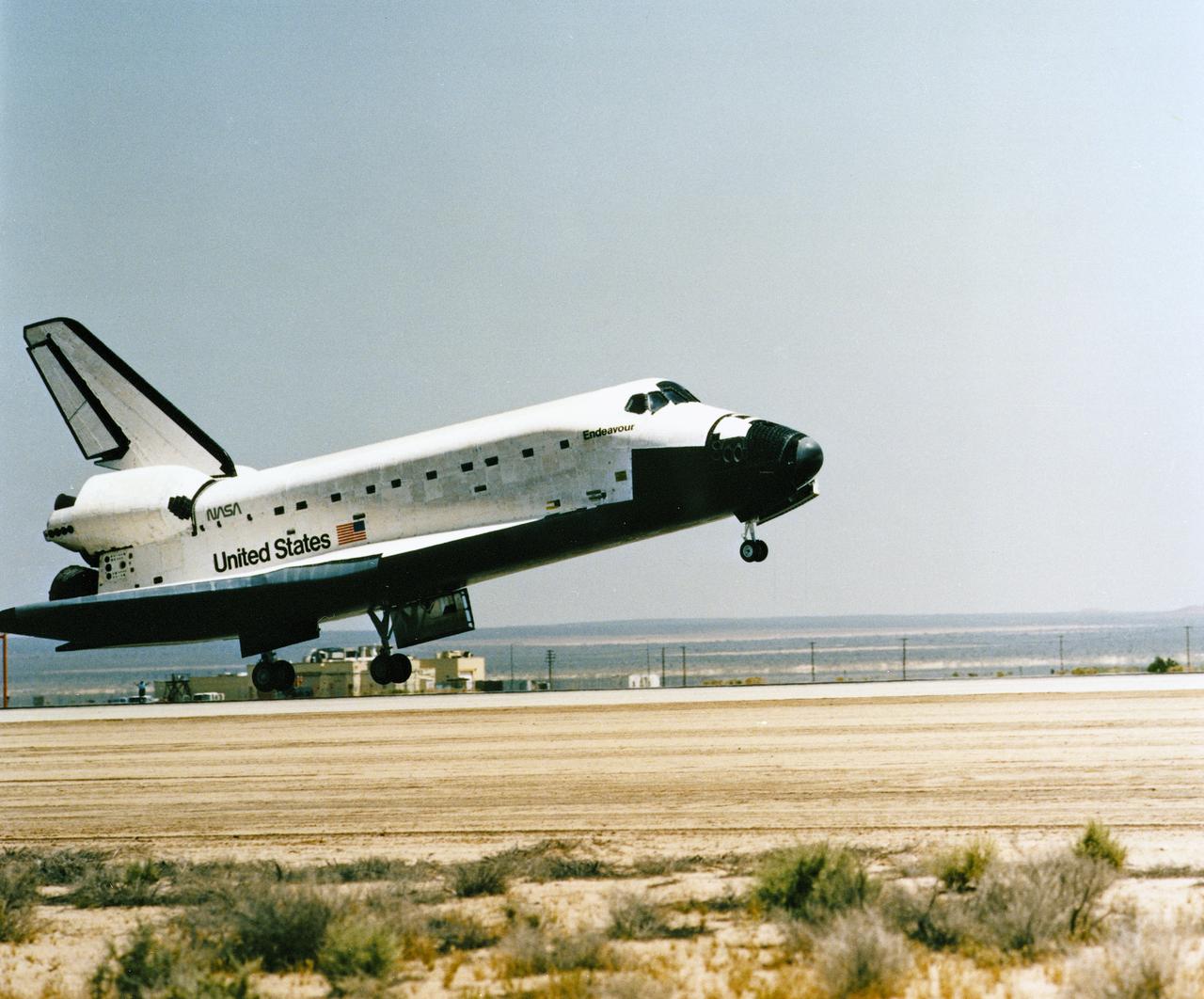

STS-49 Orbiter Endeavour landed at Edwards Air Force Base on May 16, 1992 after a successful nine day mission dedicated to the retrieval, repair, and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3) satellite. The communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization had been stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. The mission marked the first time 3 astronauts worked simultaneously outside the space craft.

One step closer to its maiden voyage, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour rolls out of the Vehicle Assembly Building, headed to Launch Pad 39B. Launched on May 7th 1992, the STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3) which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990.
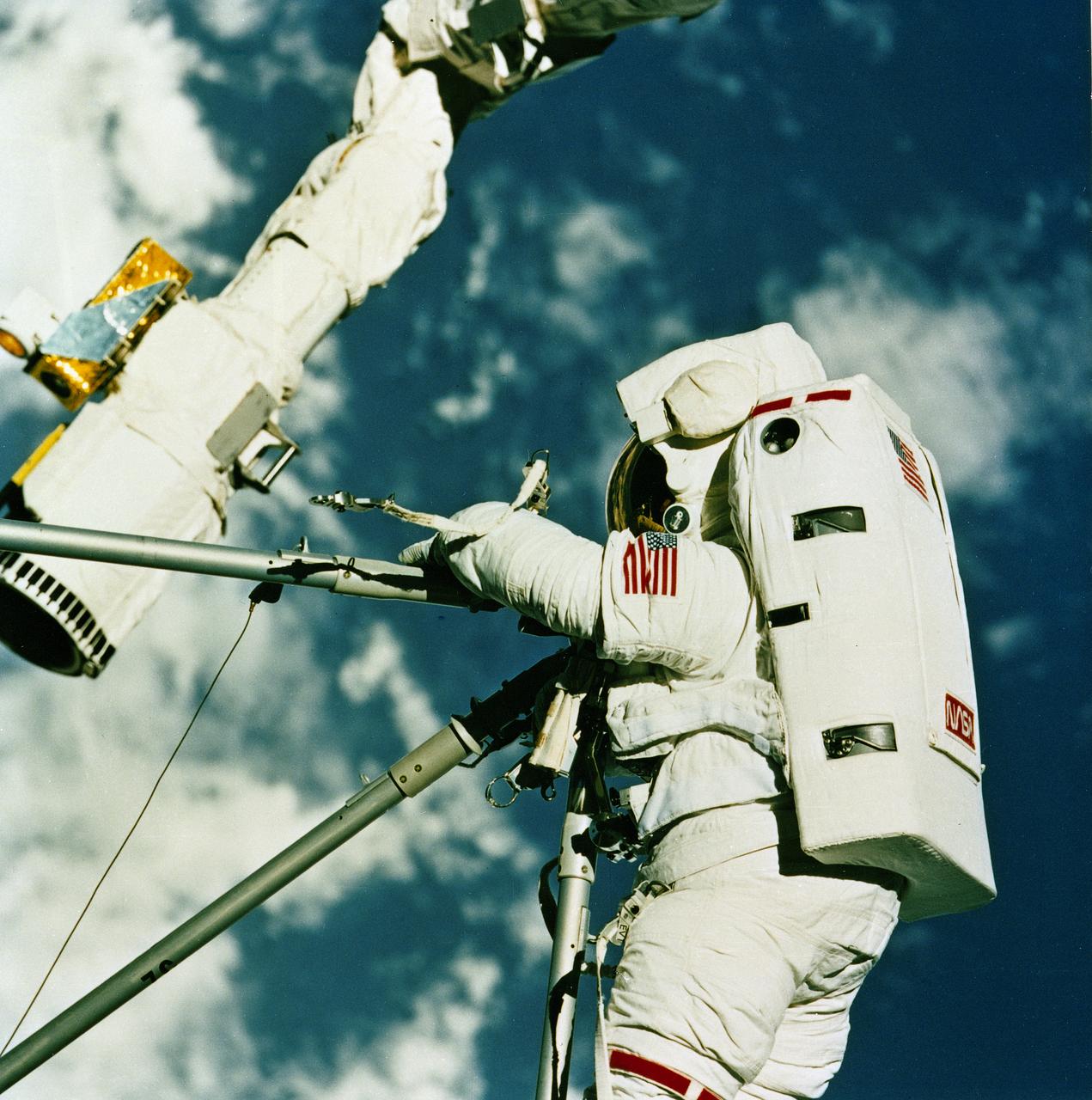

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3) which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. In this STS-49 onboard photo, Astronaut Kathryn Thornton joins three struts together during her Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA).
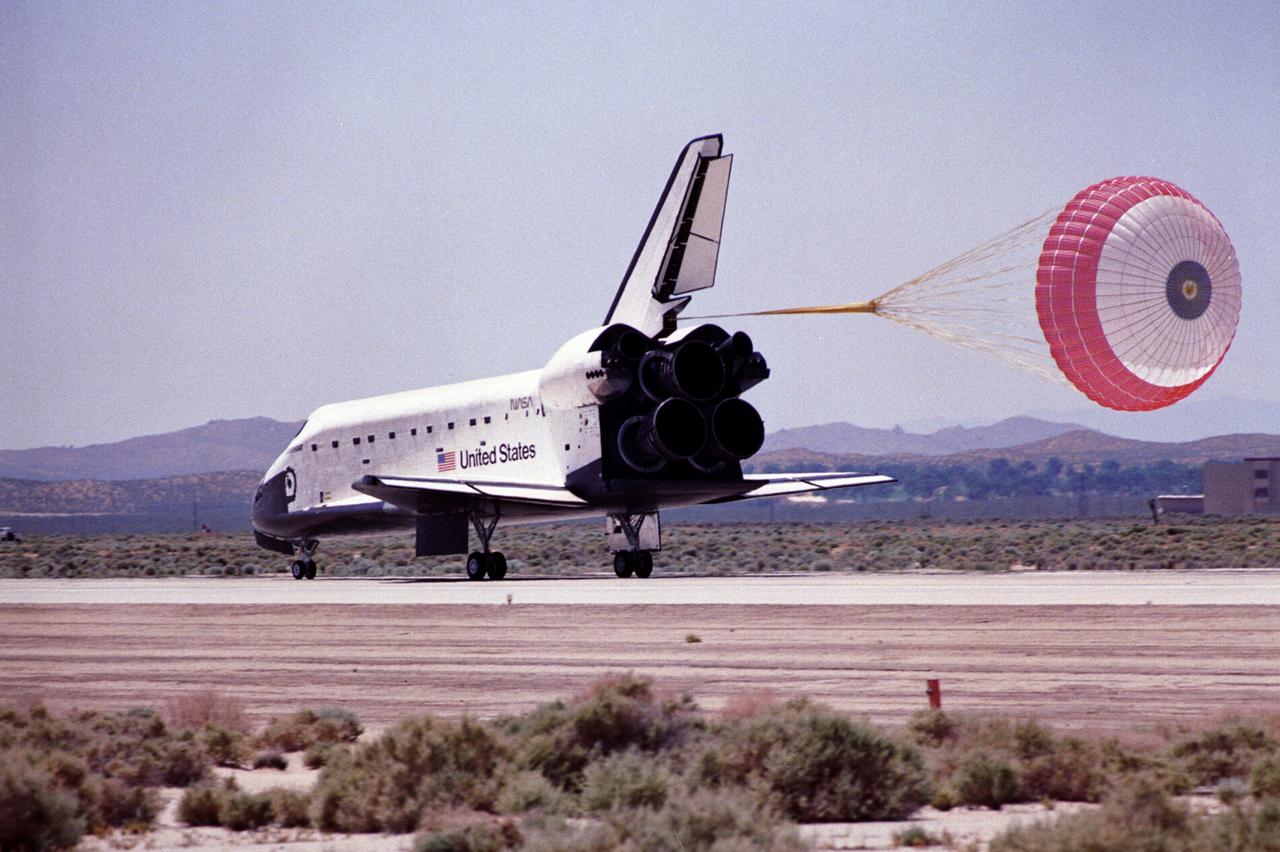

STS-49 Orbiter Endeavour landed at Edwards Air Force Base on May 16, 1992 The drogue chute precedes the main chute in NASA’s first exercise of its detailed test objective on the drag chute system. STS-49 ended its successful nine day mission dedicated to the retrieval, repair, and redeployment of the the INTELSAT VI (F-3) satellite. The communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization had been stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. The mission marked the first time 3 astronauts worked simultaneously outside the space craft.
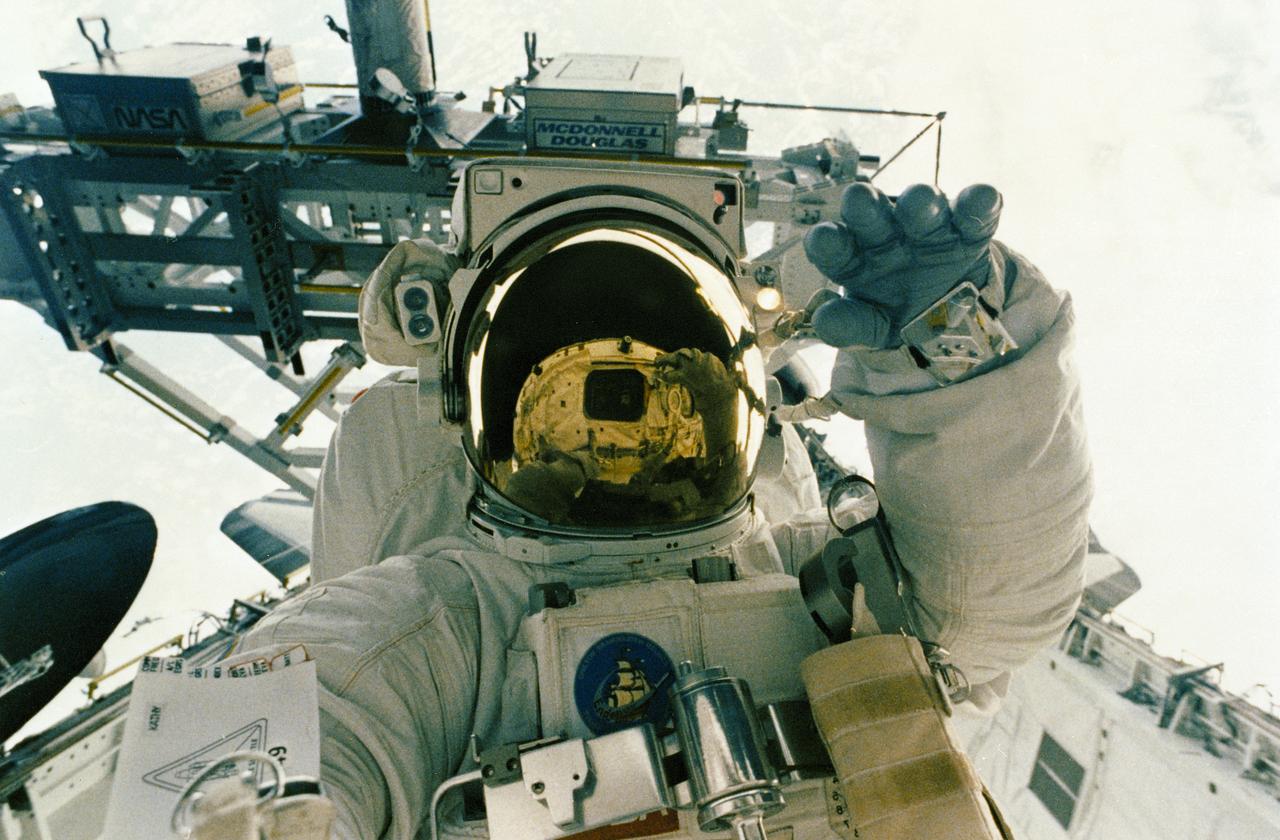

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. In this onboard photo, astronaut Kathryn Thornton is working on the Assembly of Station by EVA Methods (ASEM) in the cargo bay.
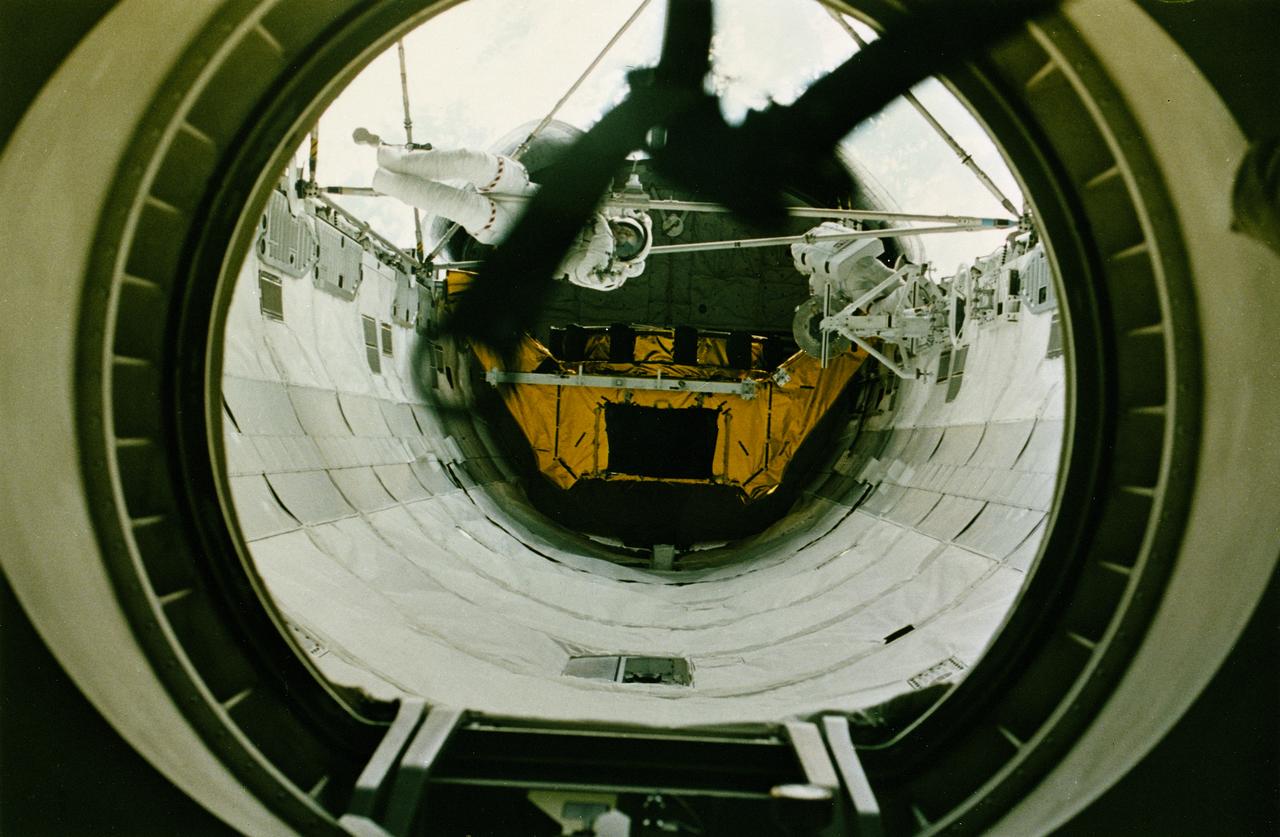

STS-49, the first flight of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, lifted off from launch pad 39B on May 7, 1992 at 6:40 pm CDT. The STS-49 mission was the first U.S. orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members working simultaneously outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3), a communication satellite for the International Telecommunication Satellite organization, which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990. A view through Endeavour’s busy airlock reveals astronauts Thomas Akers and Kathryn Thornton.
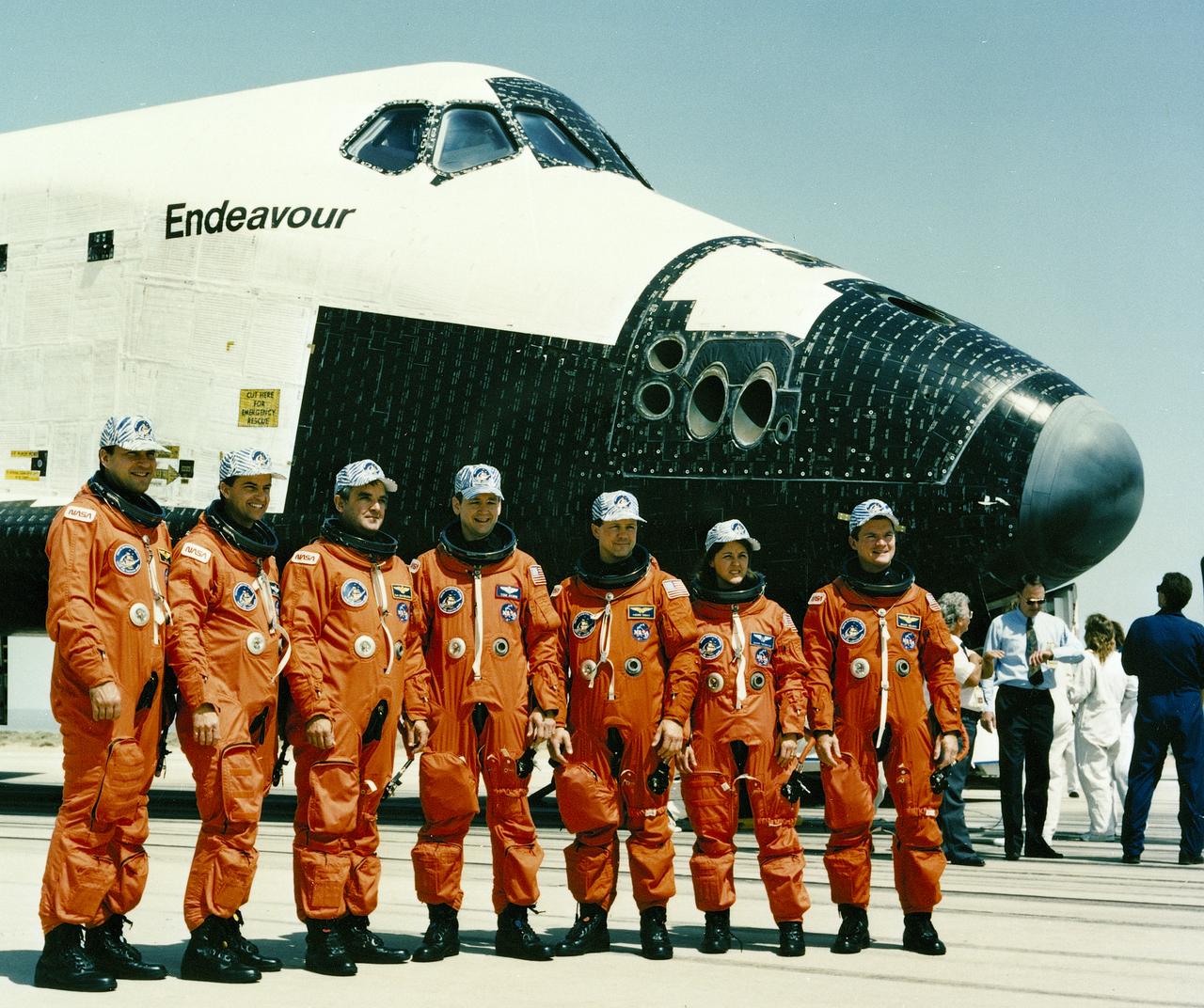

The STS-49 crew members pose near Endeavour after landing. Pictured left to right are: Richard J. Hieb, mission specialist; Kevin P. Chiltin, pilot; Daniel C. Brandenstein, commander; and mission specialists Thomas D. Akers, Pierre J. Thuot, Kathryn C. Thornton, and Bruce E. Melnick. Launched on May 7, 1992 at 7:40:00 pm (EDT), the crew of seven was the first to fly aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavor. The mission was the first US orbital flight to feature 4 extravehicular activities (EVAs), and the first flight to involve 3 crew members simultaneously working outside of the spacecraft. The primary objective was the capture and redeployment of the INTELSAT VI (F-3) which was stranded in an unusable orbit since its launch aboard the Titan rocket in March 1990.
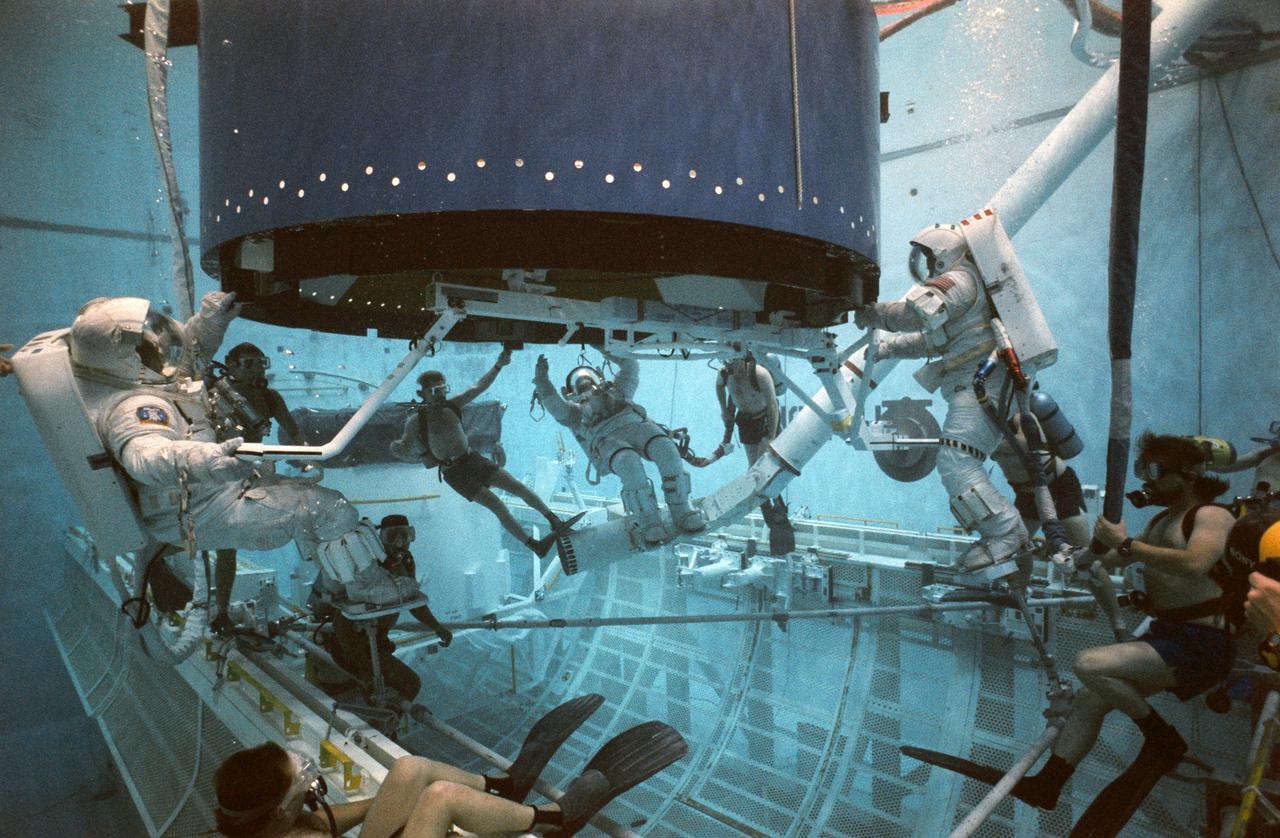
S92-35764 (12 May 1992) --- Wearing extravehicular mobility units (EMU's) and fitted with weights for neutral buoyancy are three trouble-shooting astronauts. The astronauts practiced techniques for capturing Intelsat, and climbing into the airlock mockup in the Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF). No apparent problems were identified in placing three astronauts in the airlock at one time. Left to right are, Michael R. (Rich) Clifford, Story Musgrave, and James S. Voss. Three Endeavour astronauts, Pierre J. Thuot, Richard J. Hieb and Thomas D. Akers, will attempt to capture Intelsat again on May 13. Clifford played the role of Hieb, Musgrave for Thuot, and Voss, Akers.
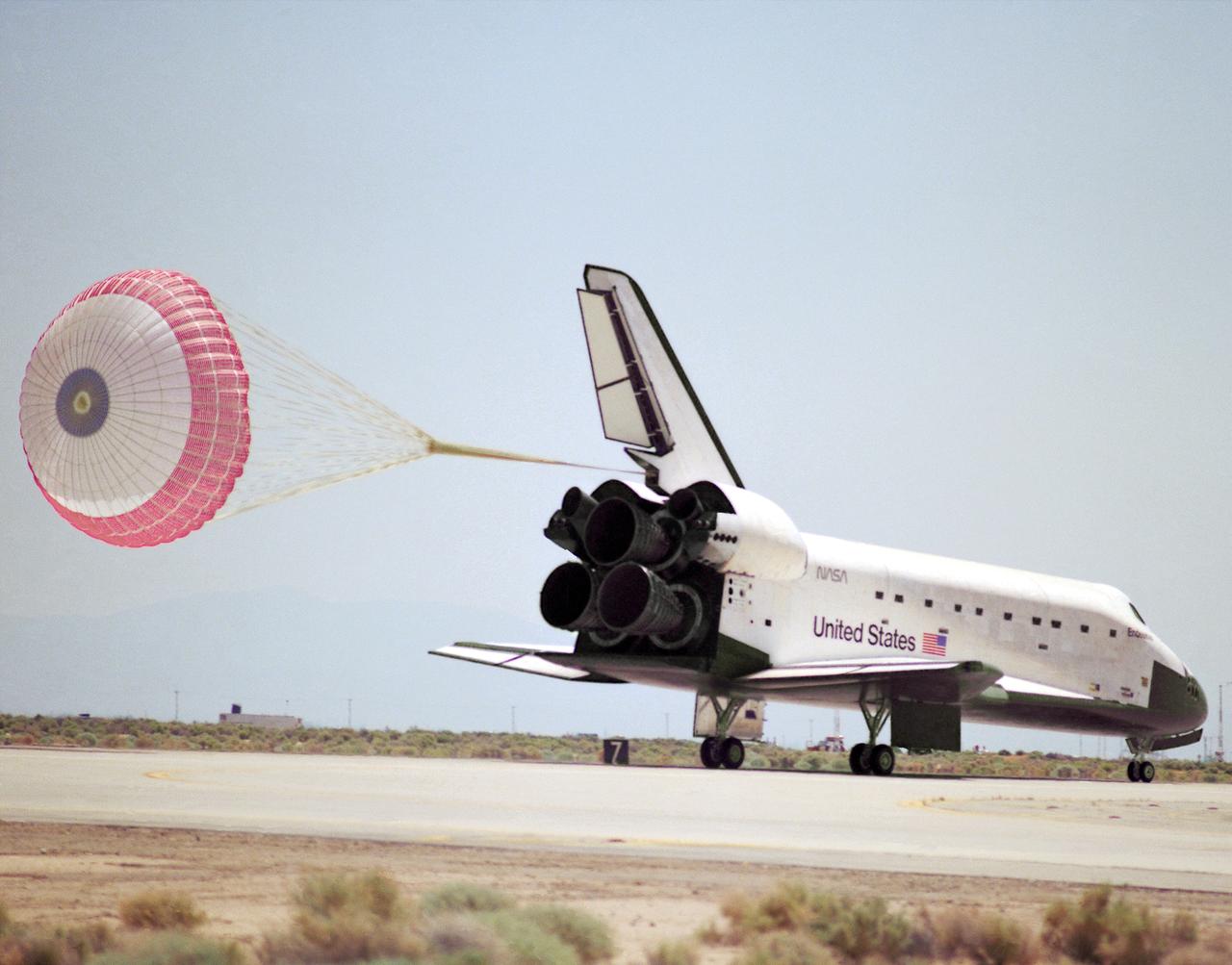

The Space Shuttle Endeavour concludes mission STS-49 at NASA's Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility (later redesignated Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California, with a 1:57 p.m. (PDT) landing May 16 on Edward's concrete runway 22. The planned 7-day mission, which began with a launch from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 4:41 p.m. (PFT), 7 May, was extended two days to allow extra time to rescue the Intelsat VI satellite and complete Space Station assembly techniques originally planned. After a perfect rendezvous in orbit and numerous attempts to grab the satellite, space walking astronauts Pierre Thuot, Rick Hieb and Tom Akers successfully rescued it by hand on the third space walk with the support of mission specialists Kathy Thornton and Bruce Melnick. The three astronauts, on a record space walk, took hold of the satellite and directed it to the shuttle where a booster motor was attached to launch it to its proper orbit. Commander Dan Brandenstein and Pilot Kevin Chilton brought Endeavours's record setting maiden voyage to a perfect landing at Edwards with the first deployment of a drag chute on a shuttle mission.