
Iron Meteorite on Mars

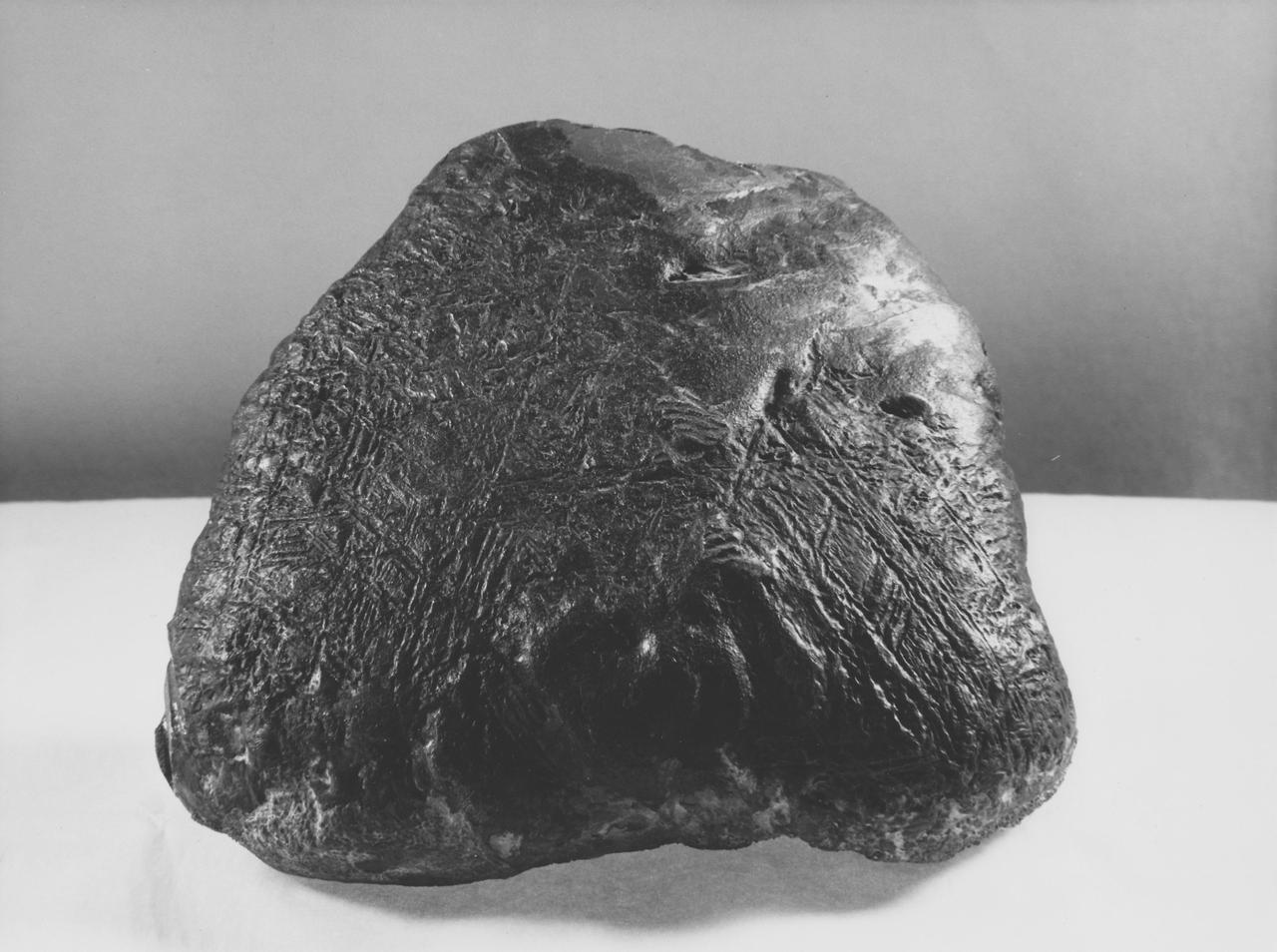
This rock encountered by NASA Curiosity Mars rover is an iron meteorite called Lebanon, similar in shape and luster to iron meteorites found on Mars by the previous generation of rovers, Spirit and Opportunity.
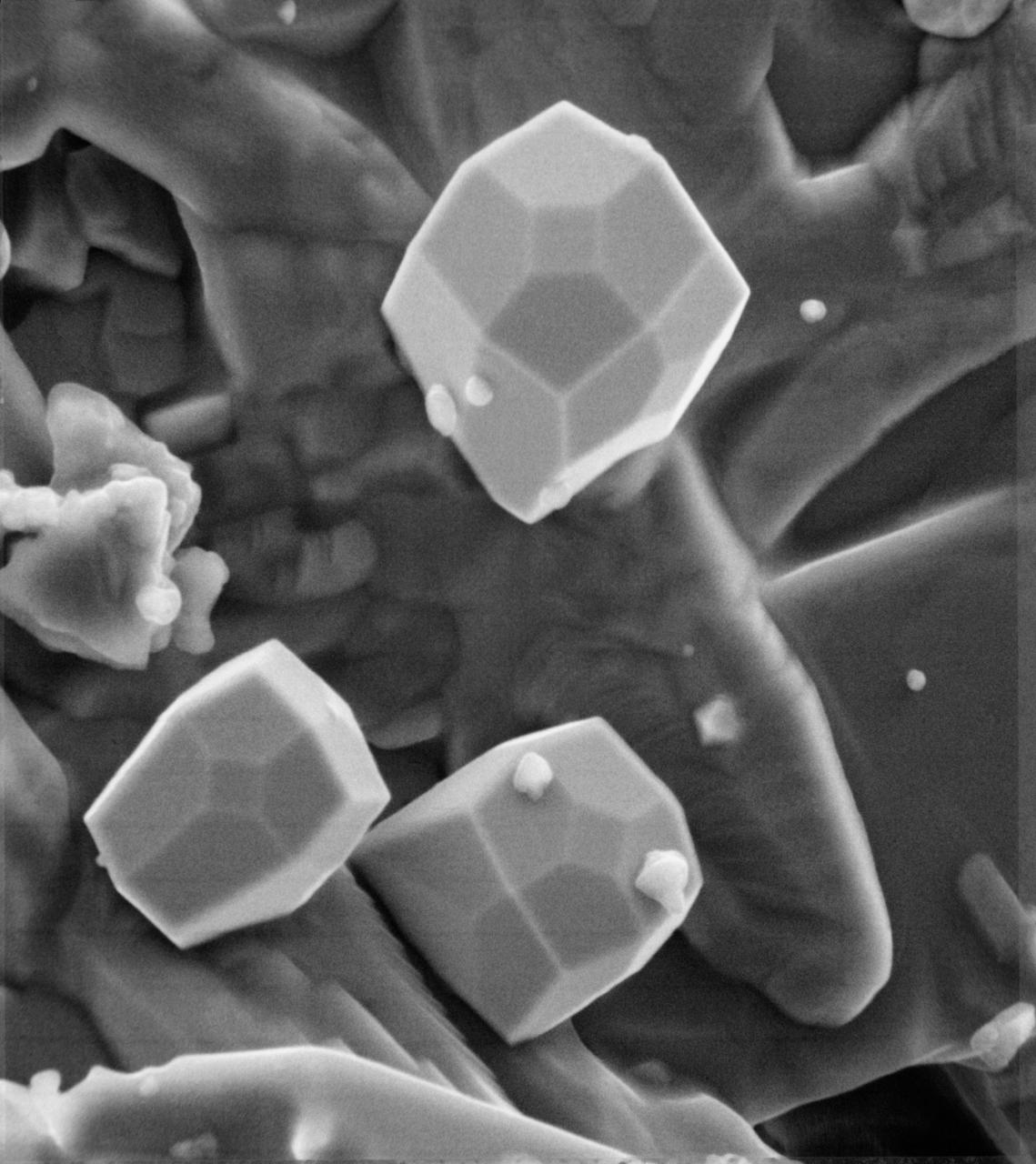

A scanning electron microscope photograph of iron crystals which grow in a small vug or cavity in a recrystallized breccia (fragmented rock) from the Apollo 15 Hadley-Apennino lunar landing site. The largest crystal is three microns across. Perfectly developed crystals such as these indicate slow formation from a hot vapor as the rock was cooling. The crystals are resting on an interlocking lattice of pyroxene (calsium-magnesium-iron silicate).
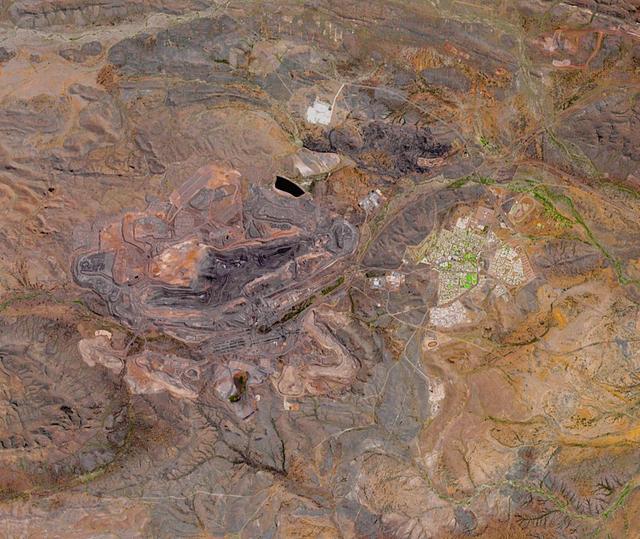

The Mount Whaleback open pit iron ore mine is located 6 km west of the town of Newman in the Pilbara region of Western Australia. It is currently the fifth largest iron mine in the world. The iron occurs in banded iron ore formations, created about 2.5 billion years ago when microorganisms first produced massive amounts of oxygen, oxidizing and precipitating the free iron in the oceans. The image was acquired October 2, 2017, covers an area of 14.4 by 17 km, and is located at 23.3 degrees south, 119.7 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24016

Mercury Surface Has More Iron + Titanium Than Previously Thought

This iron-nickel meteorite found near Fort Stockton, Texas, in 1952 shows a surface texture similar to some portions of the surface of an iron-nickel meteorite that NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity found on Mars in July, 2009.
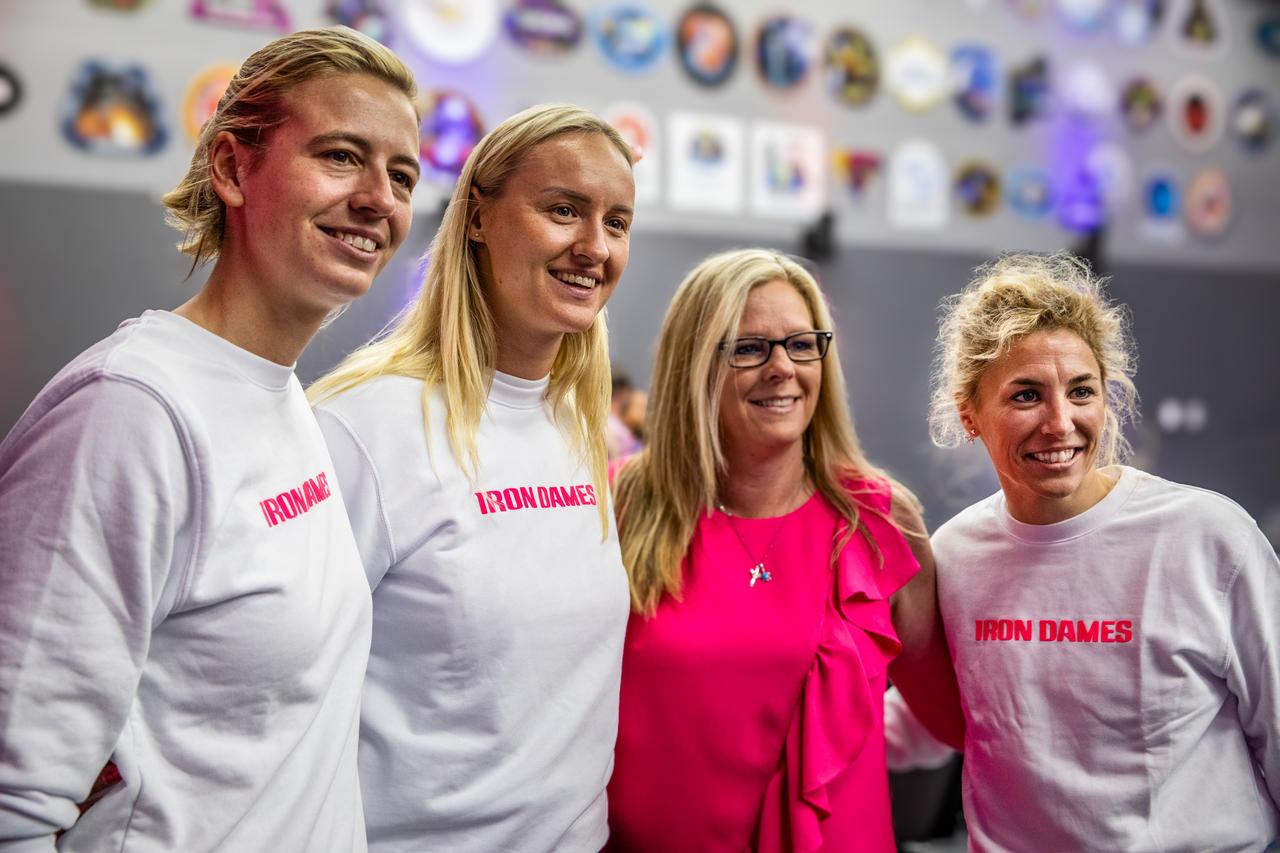

Members of the Iron Dames, from left to right, Sarah Bovy, Michelle Gatting, Christina Williams, business development specialist NASA Kennedy; and Iron Dames Rahel Frey, visit NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, March 13, 2024, to discuss their project to promote and support women in sports, and enable them to compete on equal terms with men in fields of jobs including driving, mechanics, engineers, and team leaders. The all-female team started in motorsports and became the first all-female team to win a race in the 2023 FIA World Endurance Championships at Sebring International Raceway in Sebring, Florida.
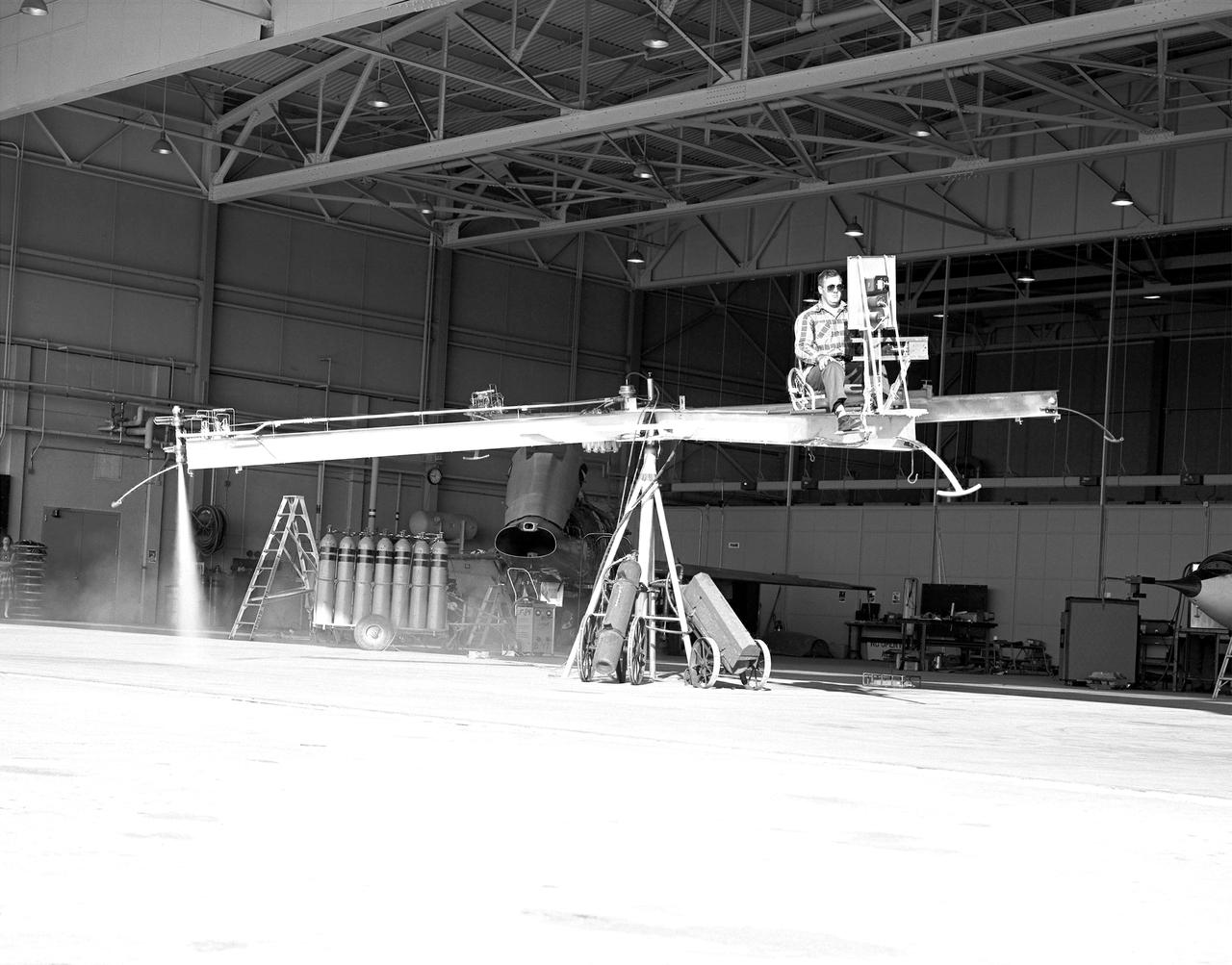

NACA High-Speed Flight Station test pilot Stan Butchart flying the Iron Cross, the mechanical reaction control simulator. High-pressure nitrogen gas expanded selectively, by the pilot, through the small reaction control thrusters maneuvered the Iron Cross through the three axes. The exhaust plume can be seen from the aft thruster. The tanks containing the gas can be seen on the cart at the base of the pivot point of the Iron Cross. NACA technicians built the iron-frame simulator, which matched the inertia ratios of the Bell X-1B airplane, installing six jet nozzles to control the movement about the three axes of pitch, roll, and yaw.
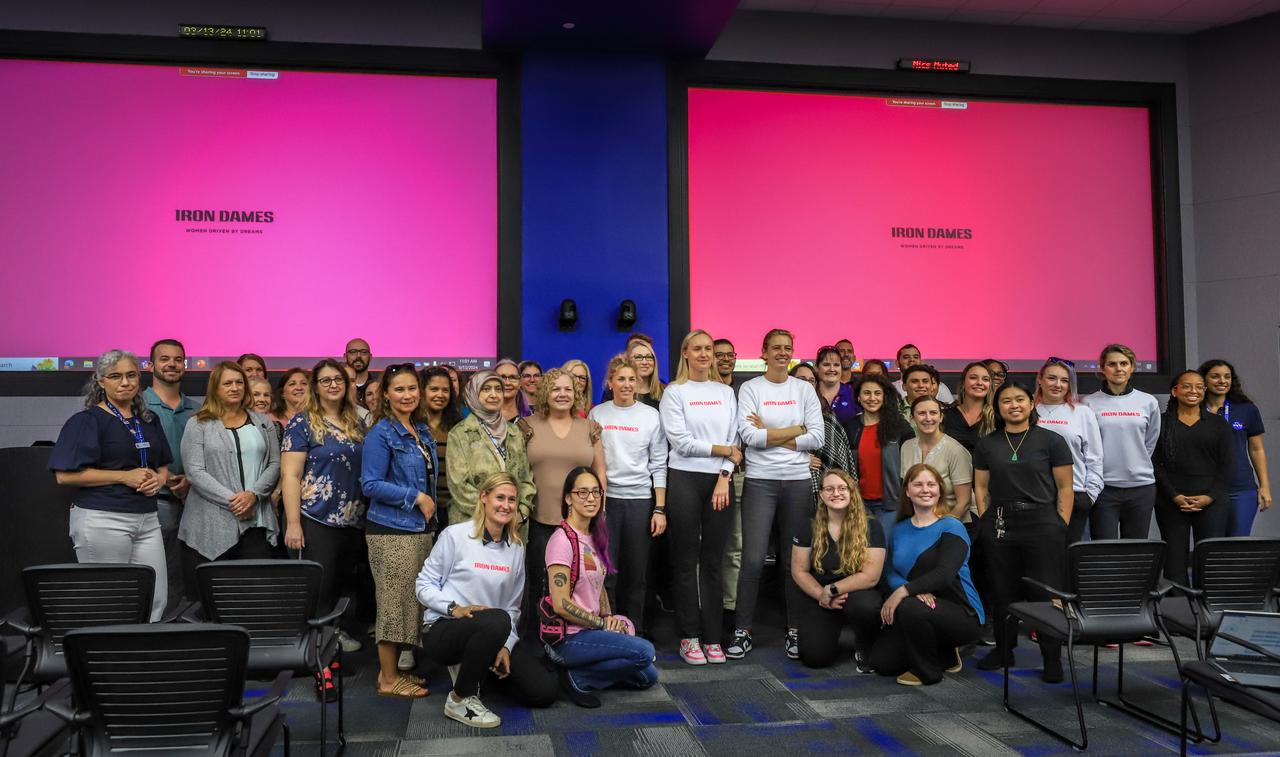

NASA’s Office of Communication, along with Kennedy Space Center's Network of Women and New Americans Employee Resource Groups host a special presentation with guests of the Iron Dames, an all-female motorsports team on Wednesday, March 13, 2024, inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The all-female team started in motorsports and became the first all-female team to win a race in the 2023 FIA World Endurance Championships at Sebring International Raceway in Sebring, Florida.
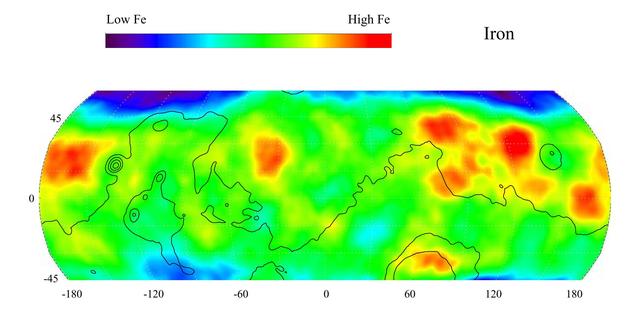
This gamma ray spectrometer map from NASA Mars Odyssey of the mid-latitude region of Mars is based on gamma-rays from the element iron, one of the most abundant elements on Mars and Earth. It is responsible for the red color on the surface of Mars.
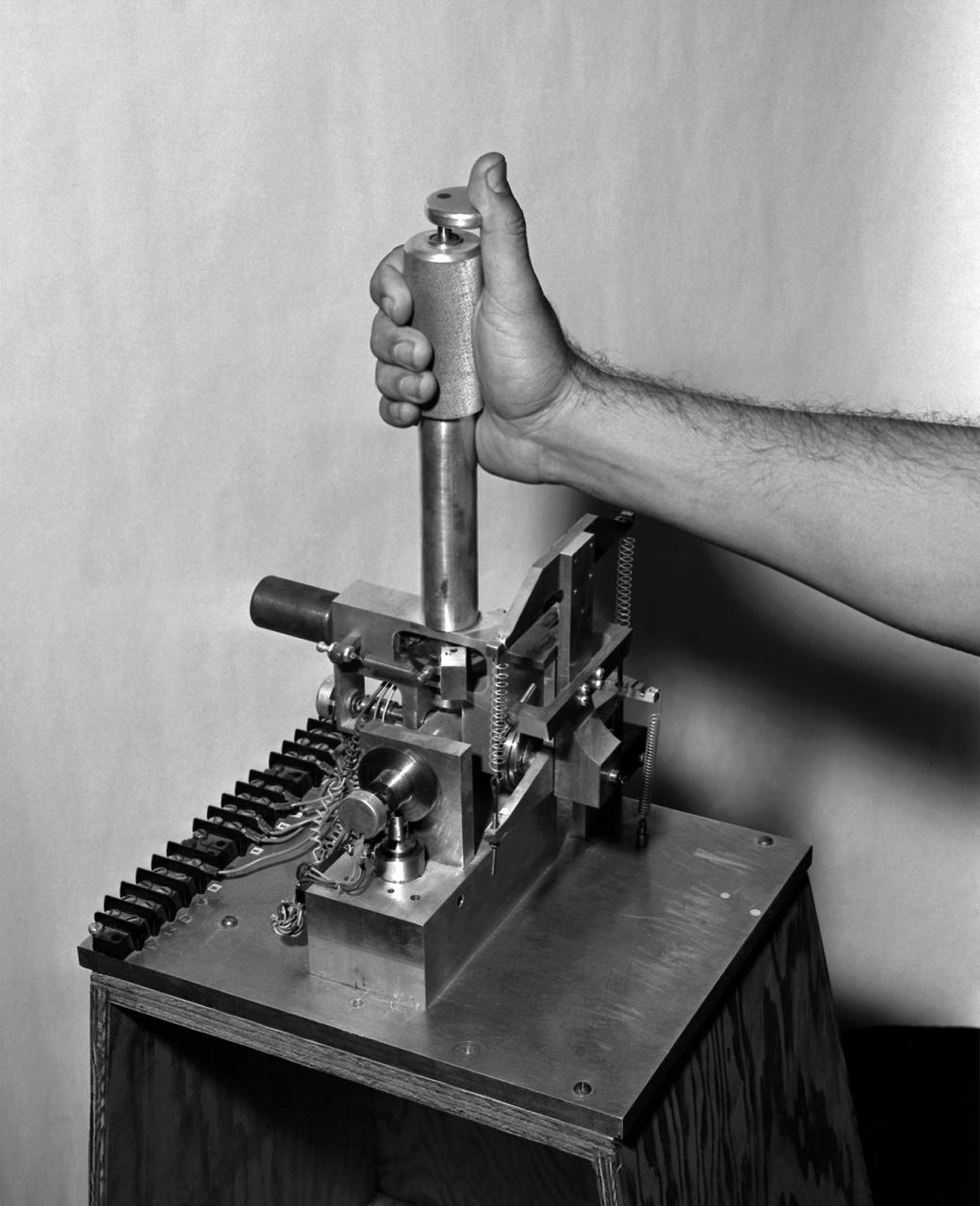

A photo of the control stick used on the Iron Cross Attitude Simulator. Although it resembled today's desktop computer flight sticks, its operation was different. As with a standard control stick, moving it back and forth raised and lowered the nose resulting in changes in pitch. Moving the stick to the right or left raised or lowered the wing, resulted in changes in roll. This control stick had a third axis, not found in standard control sticks. Twisting the stick to the right or left caused the airplane's nose to move horizontally in the same direction, resulting in changes in yaw.
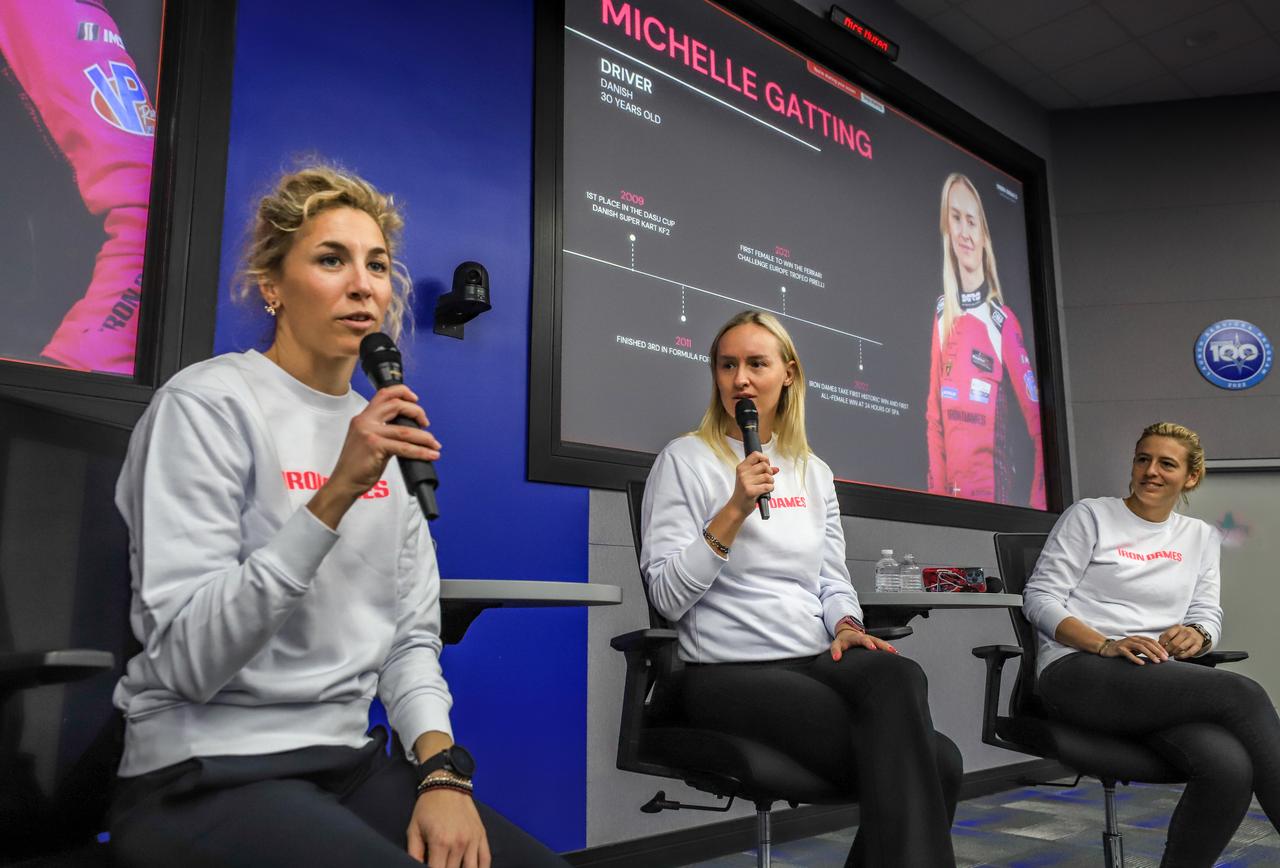

Members of the Iron Dames, from left to right, Rahel Frey, Michelle Gatting, and Sarah Bovy, visit with NASA’s Office of Communication, along with Kennedy Space Center's Network of Women and New Americans Employee Resource Groups inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, March 13, 2024, to discuss their project to promote and support women in sports, and enable them to compete on equal terms with men in fields of jobs including driving, mechanics, engineers, and team leaders. The all-female team started in motorsports and became the first all-female team to win a race in the 2023 FIA World Endurance Championships at Sebring International Raceway in Sebring, Florida.

On Nov. 5, 2015, a dam at an iron-ore mine in southeastern Brazil burst, sending a wall of water, clay-red mud and debris downstream, overwhelming several villages in the path as seen by NASA Terra spacecraft. The Germano mine is near the town of Mariana in Minas Gerais state. The region is seen in this image from the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument aboard NASA's Terra spacecraft was acquired Nov. 12, 2015, covers an area of 6.8 by 14.3 miles (11 by 23 kilometers), and is located at 20.2 degrees south, 43.5 degrees west. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20156
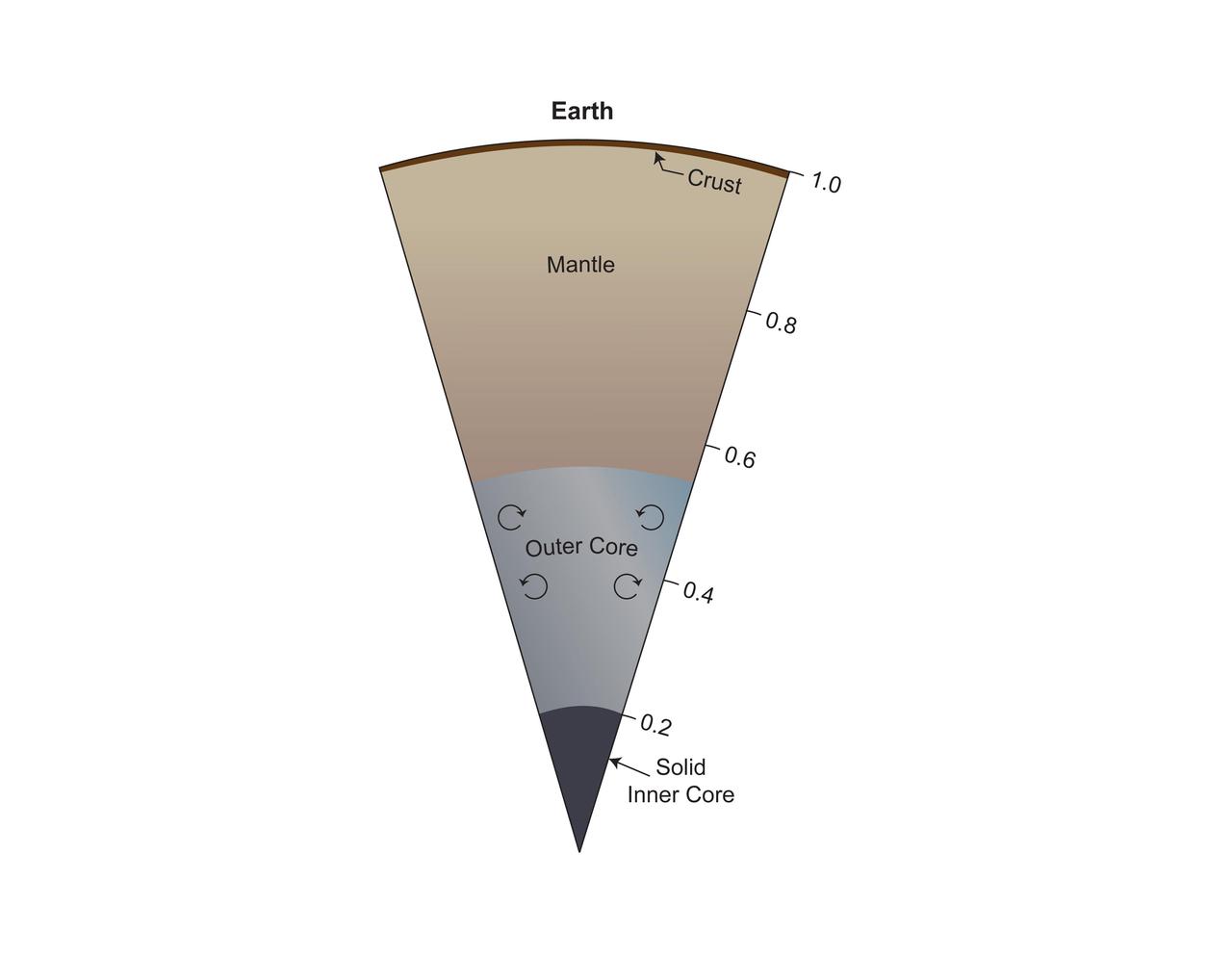
This model of Earth's interior includes a solid, mostly iron inner core beneath a convective liquid iron core that extends to half Earth's radius. Above that is a silicate mantle rich in iron and magnesium and a thin crust of lighter silicates. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25063
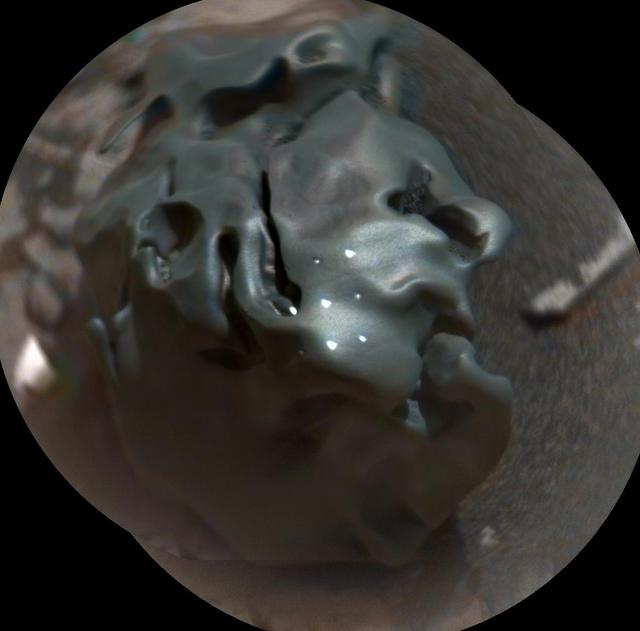
The dark, golf-ball-size object in this composite, colorized view from the Chemistry and Camera (ChemCam) instrument on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover shows a grid of shiny dots where ChemCam had fired laser pulses used for determining the chemical elements in the target's composition. The analysis confirmed that this object, informally named "Egg Rock," is an iron-nickel meteorite. Iron-nickel meteorites are a common class of space rocks found on Earth, and previous examples have been found on Mars, but Egg Rock is the first on Mars to be examined with a laser-firing spectrometer. The laser pulses on Oct. 30, 2016, induced bursts of glowing gas at the target, and ChemCam's spectrometer read the wavelengths of light from those bursts to gain information about the target's composition. The laser pulses also burned through the dark outer surface, exposing bright interior material. This view combines two images taken later the same day by ChemCam's remote micro-imager (RMI) camera, with color added from an image taken by Curiosity's Mast Camera (Mastcam). A Mastcam image of Egg Rock is at PIA21134. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21133
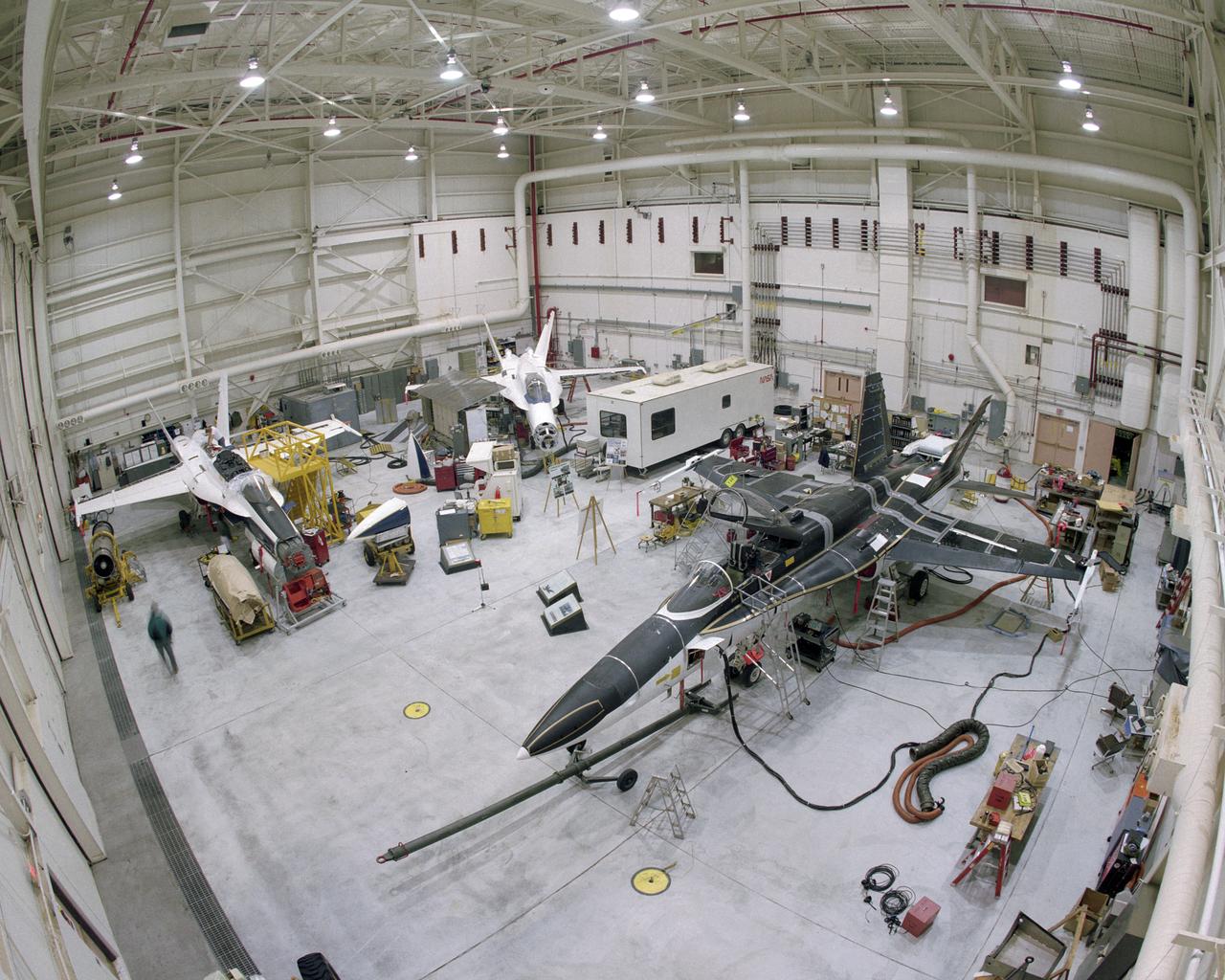

RAIF Hangar Bays 1 and 2. Three of NASA's F-18 aircraft can be seen in this photo. The SRA, or Systems Research Aircraft, is at the far left. In the middle is the F-18 Iron Bird, used for full-scale, hardware-in-the-loop simulations. On the right is the F-18 High Alpha Research Vehicle, or HARV.
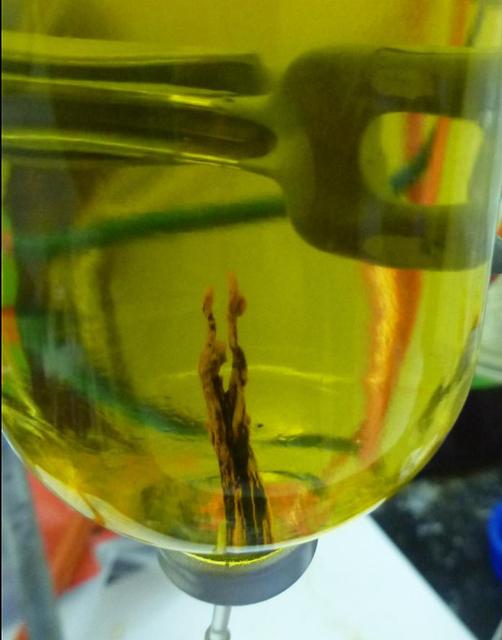

A laboratory-created "chemical garden" made of a combination of black iron sulfide and orange iron hydroxide/oxide is shown in this photo. Chemical gardens are a nickname for chimney-like structures that form at bubbling vents on the seafloor. Some researchers think that life may have originated at structures like these billions of years ago. JPL's research team is part of the Icy Worlds team of the NASA Astrobiology Institute, based at NASA's Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, California. JPL is managed by the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena for NASA. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19835
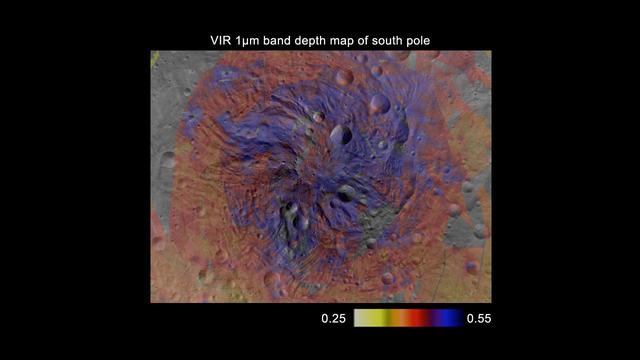
This map, made from data obtained by NASA Dawn spacecraft, shows the distribution of pyroxene, an iron- and magnesium-rich mineral, in the southern hemisphere of the giant asteroid Vesta.
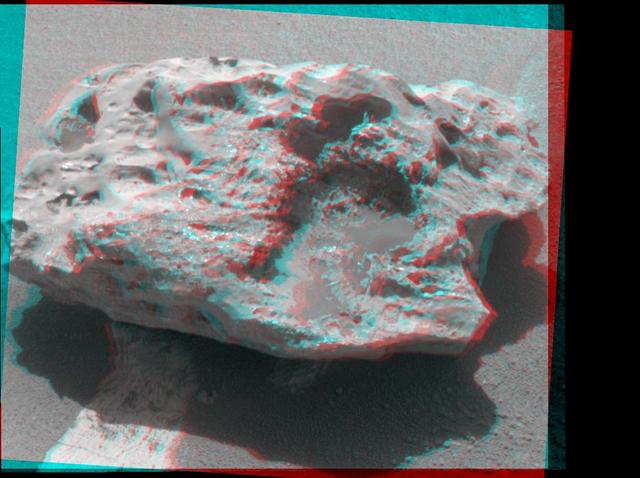
Composition measurements by NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity confirm that this rock on the Martian surface is an iron-nickel meteorite. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
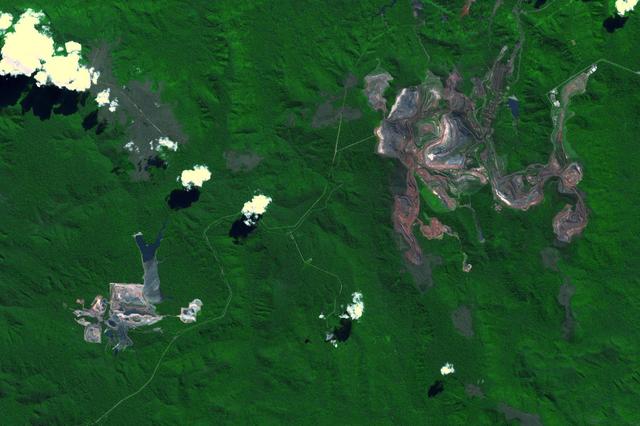

The Carajas Mine is the largest open-pit iron ore mine in the world. It is located in the state of Para, northern Brazil. The mine is estimated to contain over 7 billion tons of iron ore, plus gold, manganese, bauxite, copper and nickel. Ore is loaded into rail cars, and shipped to the Atlantic port city of Sao Luis over 250 kilometers away. The image was acquired June 19, 2017, covers an area of 18 by 27 kilometers, and is located at 6.1 degrees south, 50.2 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22861
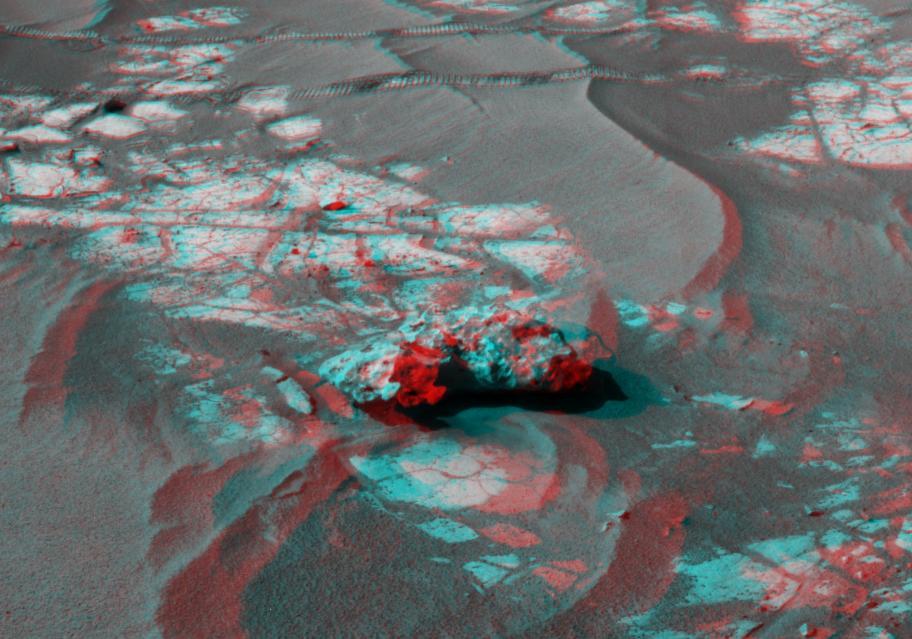
An iron meteorite is the latest quarry for NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity. Shown here is the left-eye view of a stereo pair of images. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.

This plot segregates various minerals examined by NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity according to their different compositions; for example, those with more iron and magnesium oxides are located in the lower right corner.
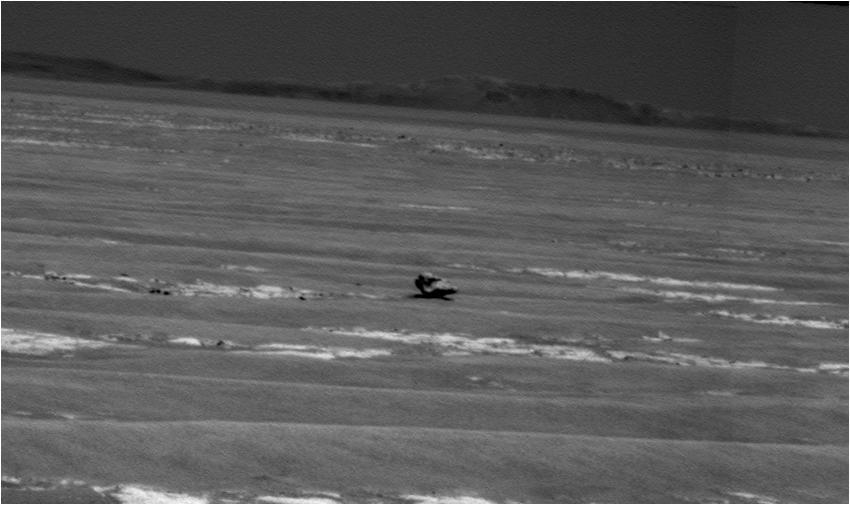

NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity used its panoramic camera to capture this view of a dark rock the size of a toaster that may be an iron meteorite. Part of the rim of Endurance Crater is on the horizon.
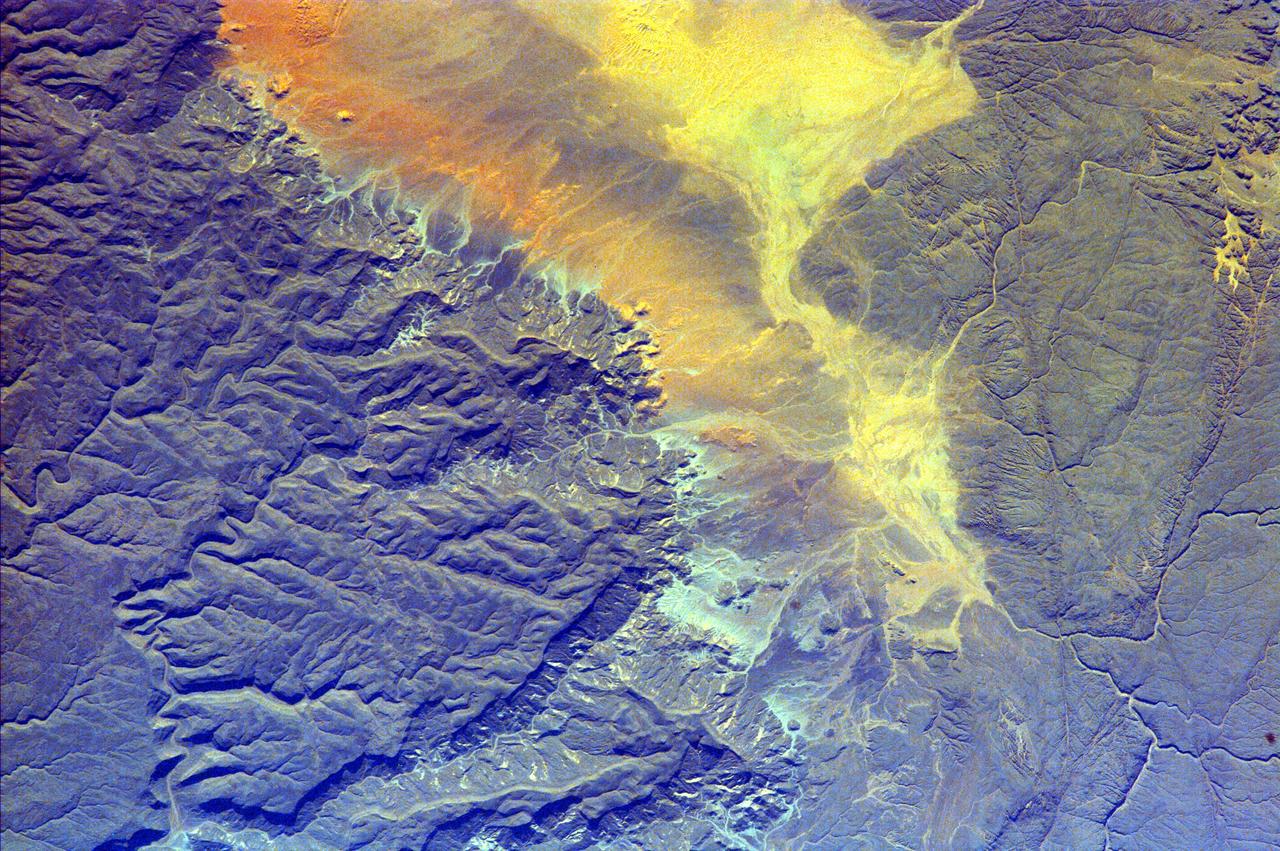

The impermanent waterways shown here from NASA EarthKAM are part of Oued Irharrhar, which appear to be carrying sulfur yellow and iron red deposits. The city of Amguid is located on these waterways, and all lie in the Mouydir Mountains in Algeria.
This image taken at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory shows the Moessbauer spectrometer, an instrument on NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit that detects iron-bearing minerals in martian rocks and soil.

A massive star left, which has created elements as heavy as iron in its interior, blows up in a tremendous explosion middle, scattering its outer layers in a structure called a supernova remnant right.
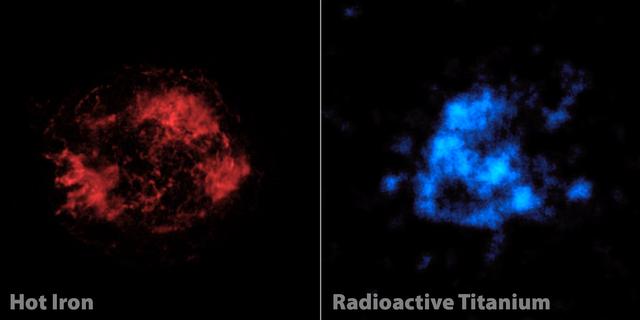
When astronomers first looked at images of a supernova remnant called Cassiopeia A, captured by NASA NuSTAR. The mystery of Cassiopeia A Cas A, a massive star that exploded in a supernova more than 11,000 years ago continues to confound scientists.
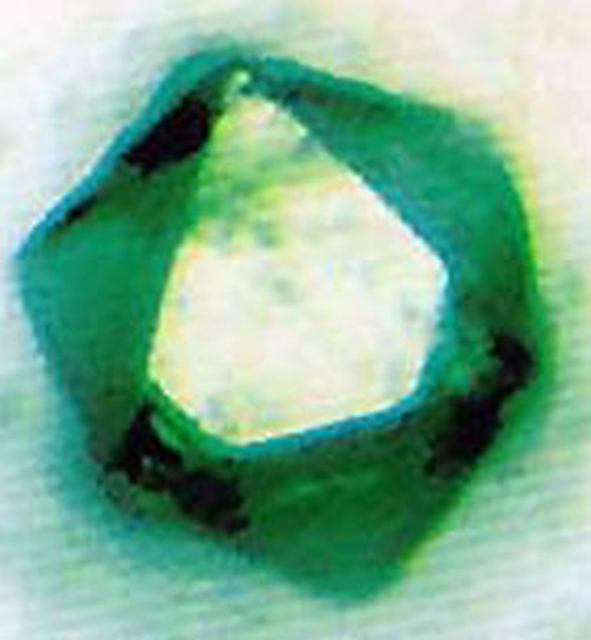

The demetalized form of the major iron storage protein from horse spleen.
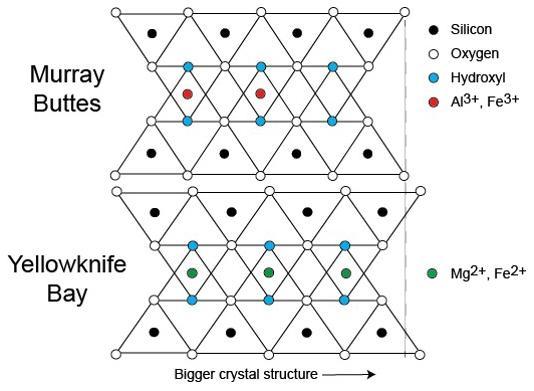
This diagram illustrates how the dimensions of clay minerals' crystal structure are affected by which ions are present in the composition of the mineral. Different clay minerals were identified this way at two sites in Mars' Gale Crater: "Murray Buttes" and "Yellowknife Bay." In otherwise identical clay minerals, a composition that includes aluminum and ferric iron ions (red dots) results in slightly smaller crystalline unit cells than one that instead includes magnesium and ferrous iron ions (green dots). Ferric iron is more highly oxidized than ferrous iron. Crystalline cell units are the basic repeating building blocks that define minerals. X-ray diffraction analysis, a capability of the Chemistry and Mineralogy (CheMin) instrument on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover, identifies minerals from their crystalline structure. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21148
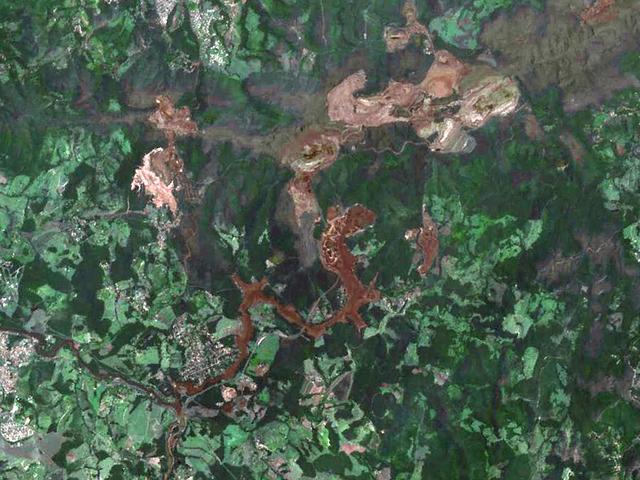

On January 25, 2019, a dam burst at a Brazilian iron ore mine. The dam's breach unleashed a torrent of mud and mine debris, covering the city of Brumadinho. The image was acquired by ASTER on February 1, 2019, covers an area of 10.8 by 14.8 kilometers, and is located at 20.1 degrees south, 44.1 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22824
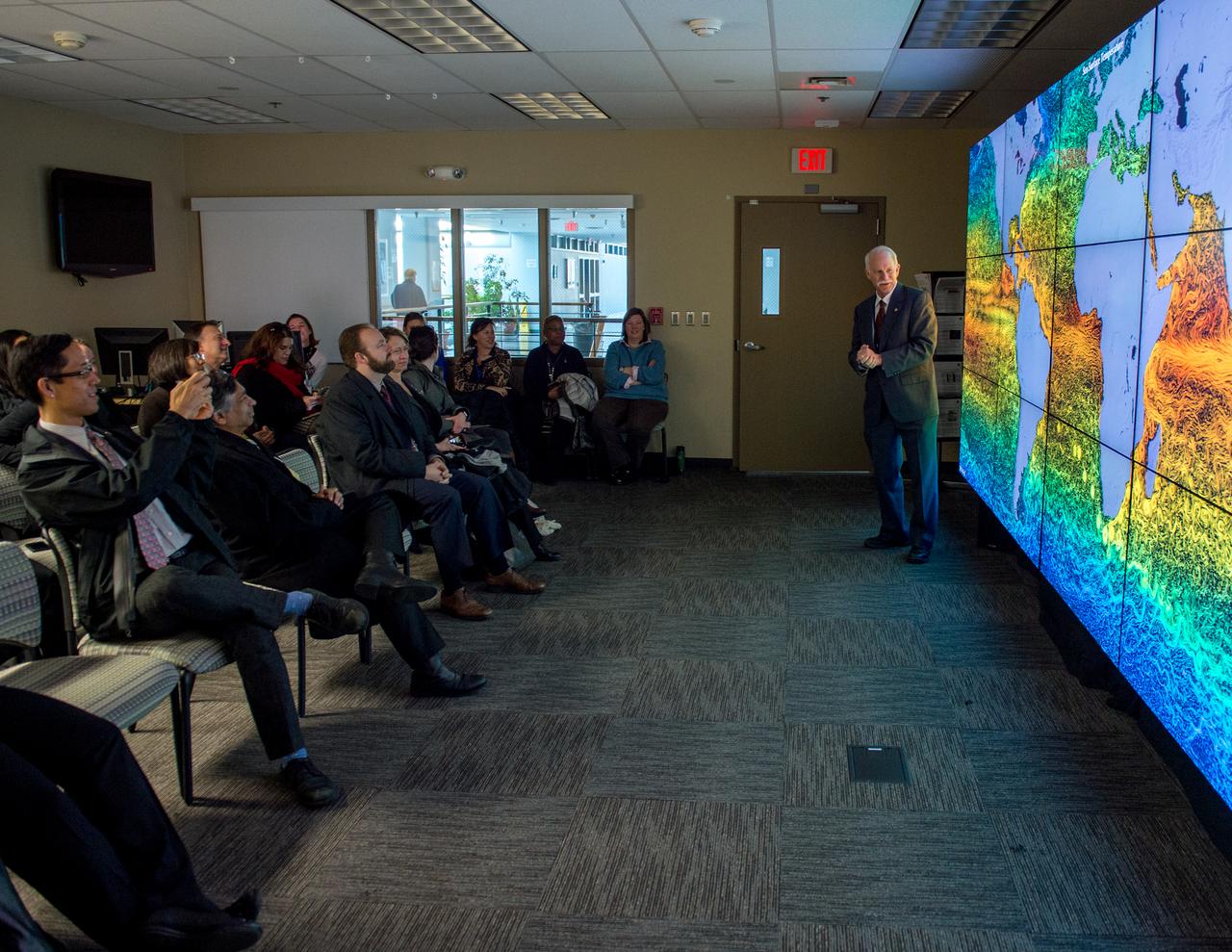

White House Office of Science & Technology Policy tours Goddard Space Flight Center. Dr. Jim Irons at the hyperwall.
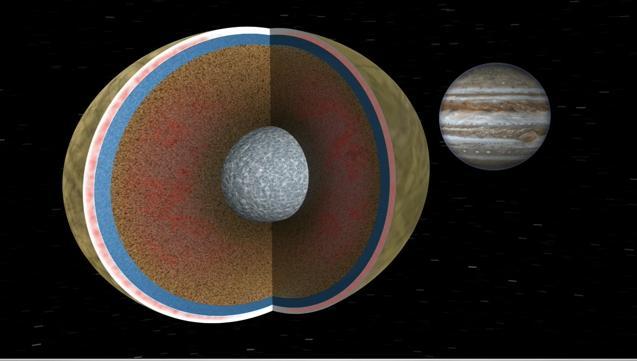
In this image, Europa is seen in a cutaway view through two cycles of its 3.5 day orbit about the giant planet Jupiter. Like Earth, Europa is thought to have an iron core, a rocky mantle and a surface ocean of salty water. Animation available at the Photo
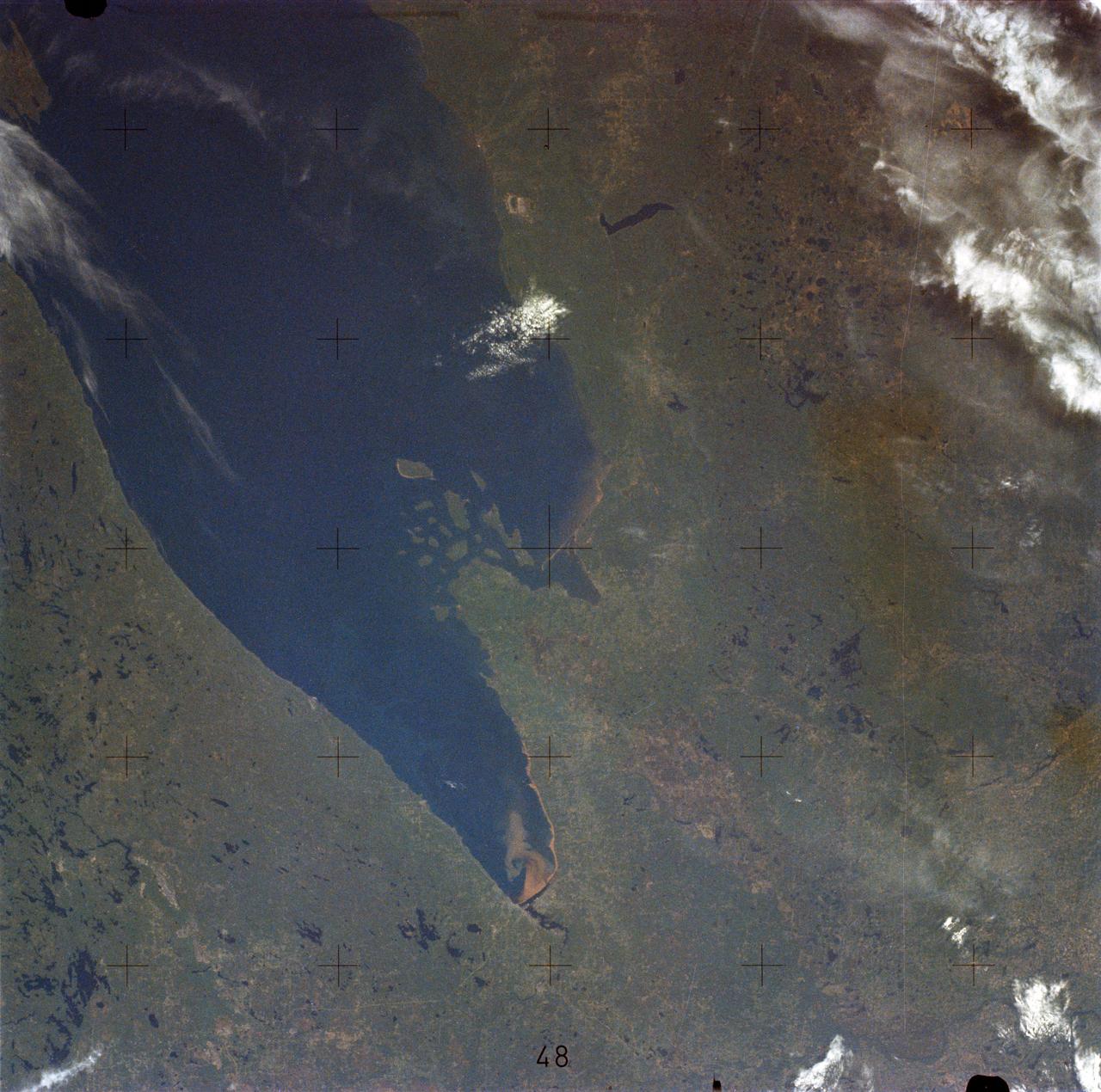
SL2-05-454 (22 June 1973) --- This view shows the west end of Lake Superior and Duluth, MN (47.0N, 91.0W). Portions of Minnesota, Michigan and Ontario, Canada are in the scene. The Duluth metropolitan area is at the west end of the lake. The discoloration plume in the water at Duluth is the result of tailings from the iron ore smelters that process the iron ore from the nearby open pit mines seen near the upper left corner of the photo. Photo credit: NASA

This is a macro photograph of an etched surface of the Mundrabilla meteorite, a small piece of the approximately 3.9 billion-year-old meteorite that was first discovered in Western Australia in 1911. Two more giant chunks, together weighing about 17 tons, were found in 1966. Researchers can learn much from this natural crystal growth experiment since it has spent several hundred million years cooling, and would be impossible to emulate in a lab. This single slice, taken from a 6 ton piece recovered in 1966, measures only 2 square inches. The macro photograph shows a metallic iron-nickel alloy phase of kamcite (38% Ni) and taenite (6% Ni) at bottom right, bottom left, and top left. The darker material is an iron sulfide (FeS or troilite) with a parallel precipitates of duabreelite (iron chromium sulfide (FeCr2S4).
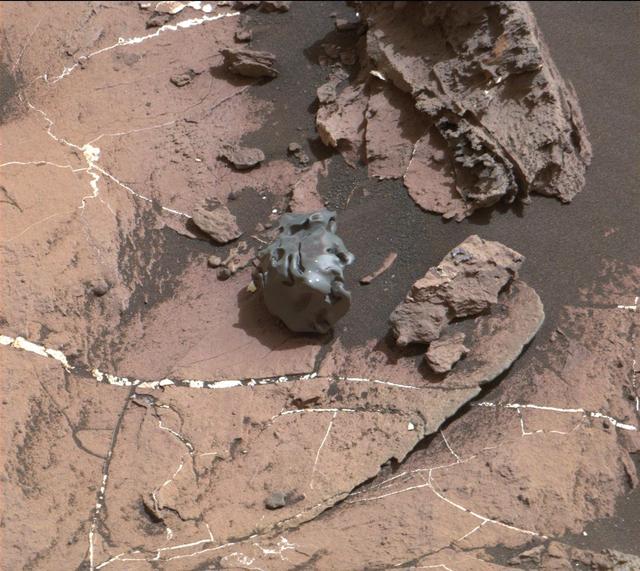

The dark, smooth-surfaced object at the center of this Oct. 30, 2016, image from the Mast Camera (Mastcam) on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover was examined with laser pulses and confirmed to be an iron-nickel meteorite. The grid of shiny points visible on the object resulted from that laser zapping by Curiosity's Chemistry and Camera (ChemCam) instrument. The meteorite is about the size of a golf ball. It is informally named "Egg Rock," for a site in Maine. Locations around Bar Harbor, Maine, are the naming theme for an area on Mars' Mount Sharp that Curiosity reached in October. Iron-nickel meteorites are a common class of space rocks found on Earth, and previous examples have been found on Mars, but Egg Rock is the first on Mars to be examined with a laser-firing spectrometer. The scene is presented with a color adjustment that approximates white balancing, to resemble how the rocks and sand would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. Figure 1 includes a scale bar of 5 centimeters (about 2 inches). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21134
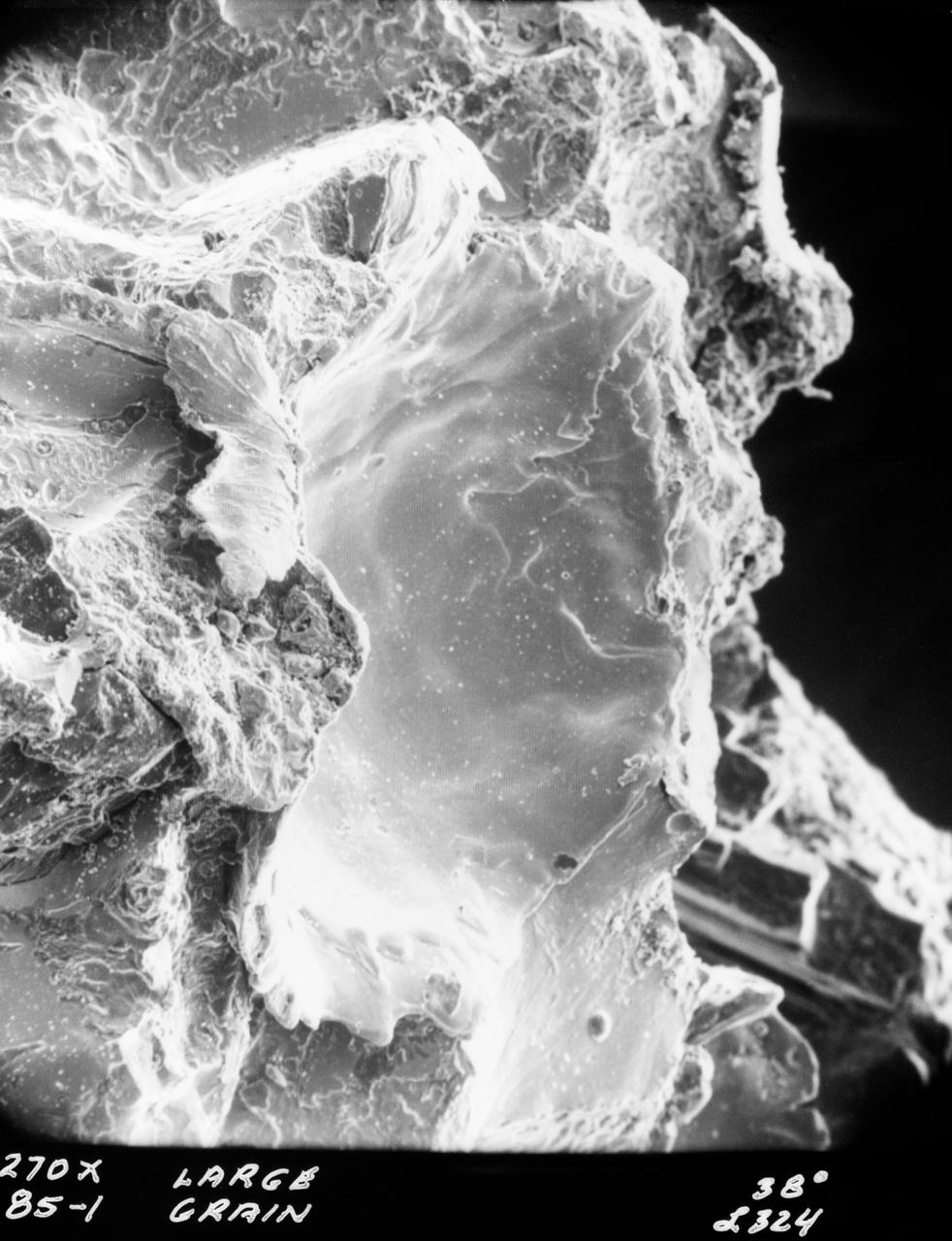
S70-20416 (December 1969) --- Enlarged view show hypervelocity impact on iron particles of lunar surface material returned to Earth by the crew of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. This photograph, enlarged to 270 times the actual size, was taken by Dr. G. J. Wasserberg, J. DeVaney and K. Evans at the California Institute of Technology.
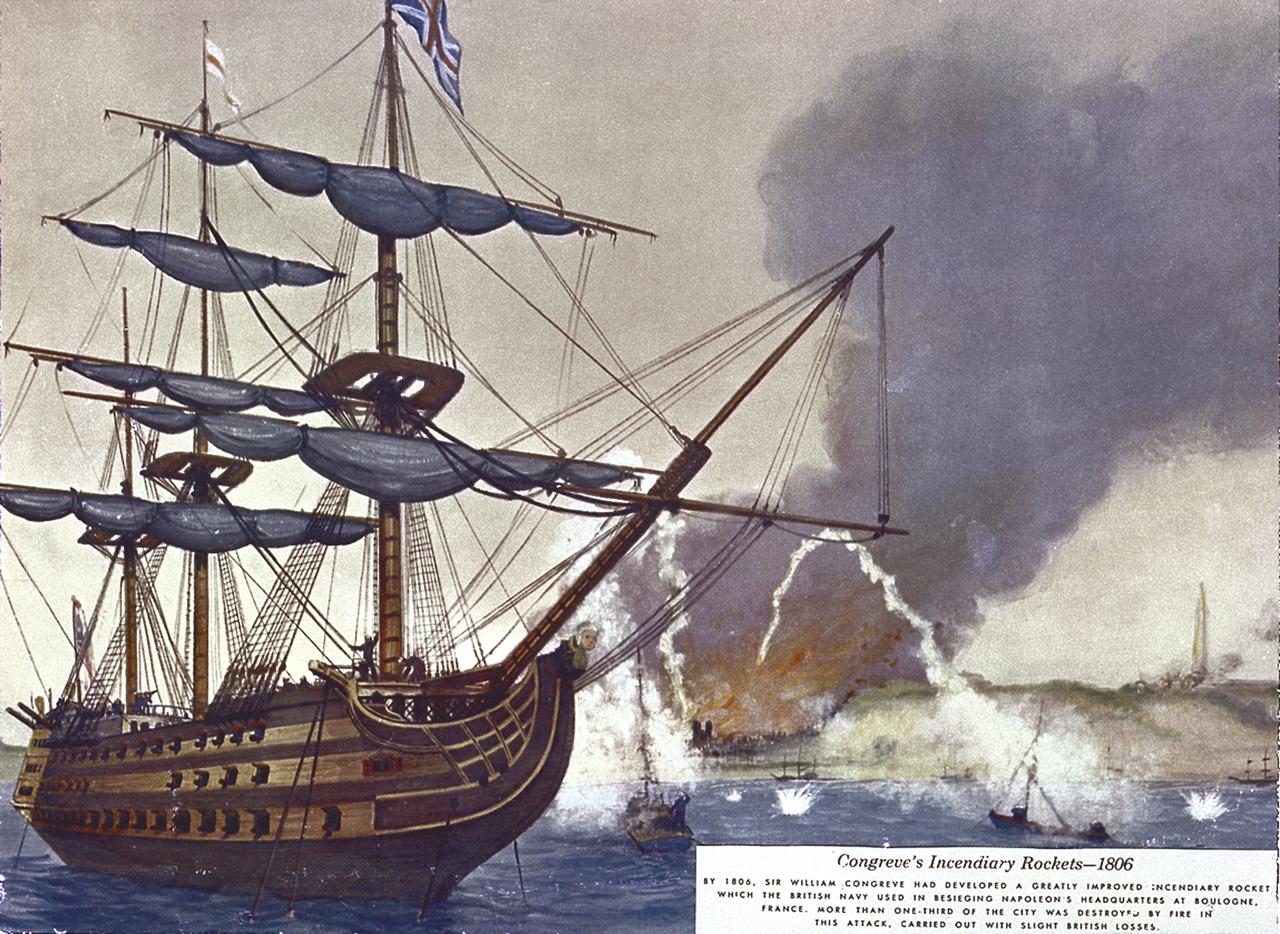
Sir William Congreve developed a rocket with a range of about 9,000 feet. The incendiary rocket used black powder, an iron case, and a 16-foot guide stick. In 1806, British used Congreve rockets to attack Napoleon's headquarters in France. In 1807, Congreve directed a rocket attack against Copenhagen.
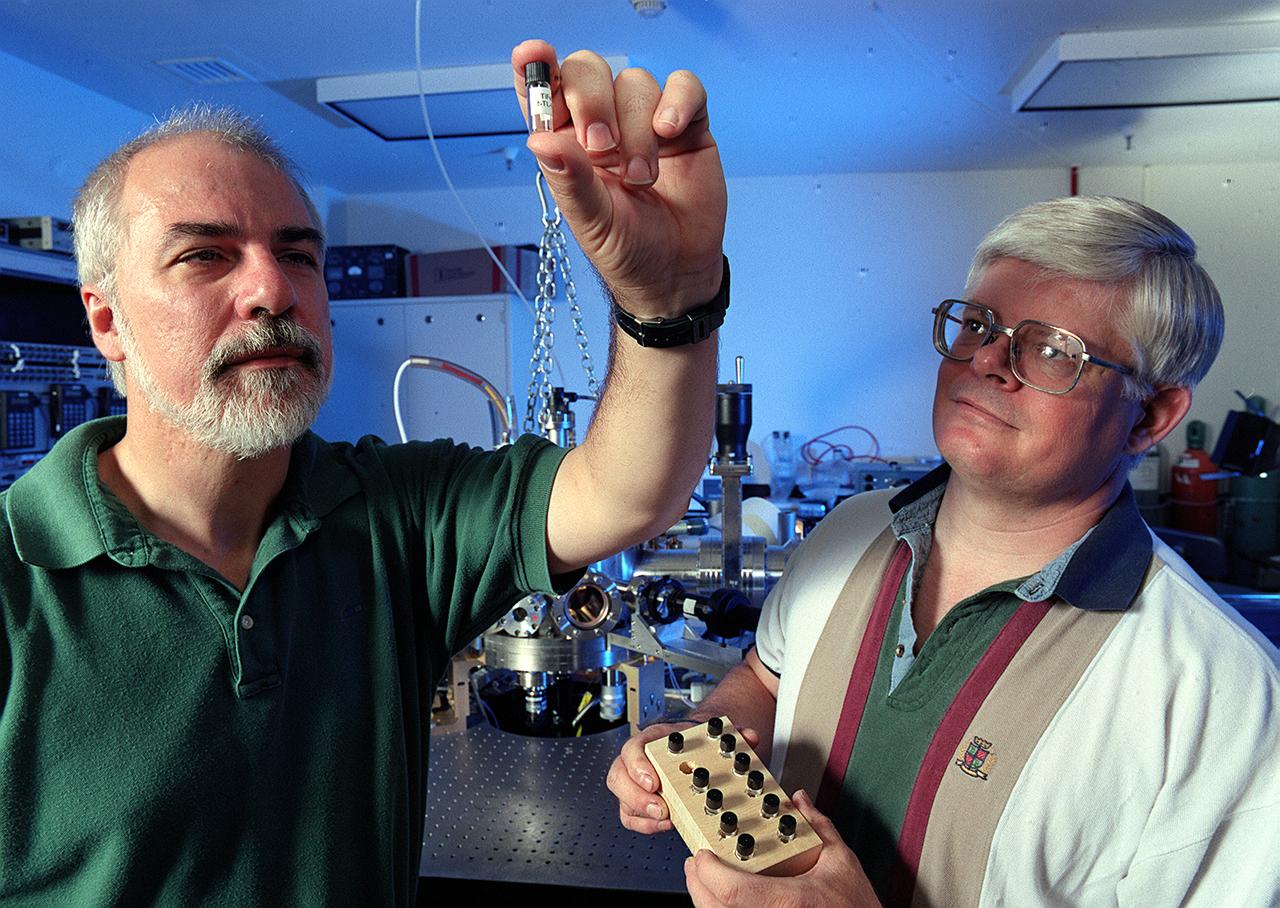

Prof. Kerneth Kelton of Washington University in St. Lous, MO, (L) and Dr. Michael Robinson of NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) examine a titanium-iron silicate (TiFeSiO)sample processed in MSFC's Electrostatic Levitator (ESL) Facility (background). Kelton is investigating undercooling of polytetrahedral phase-forming liquids.
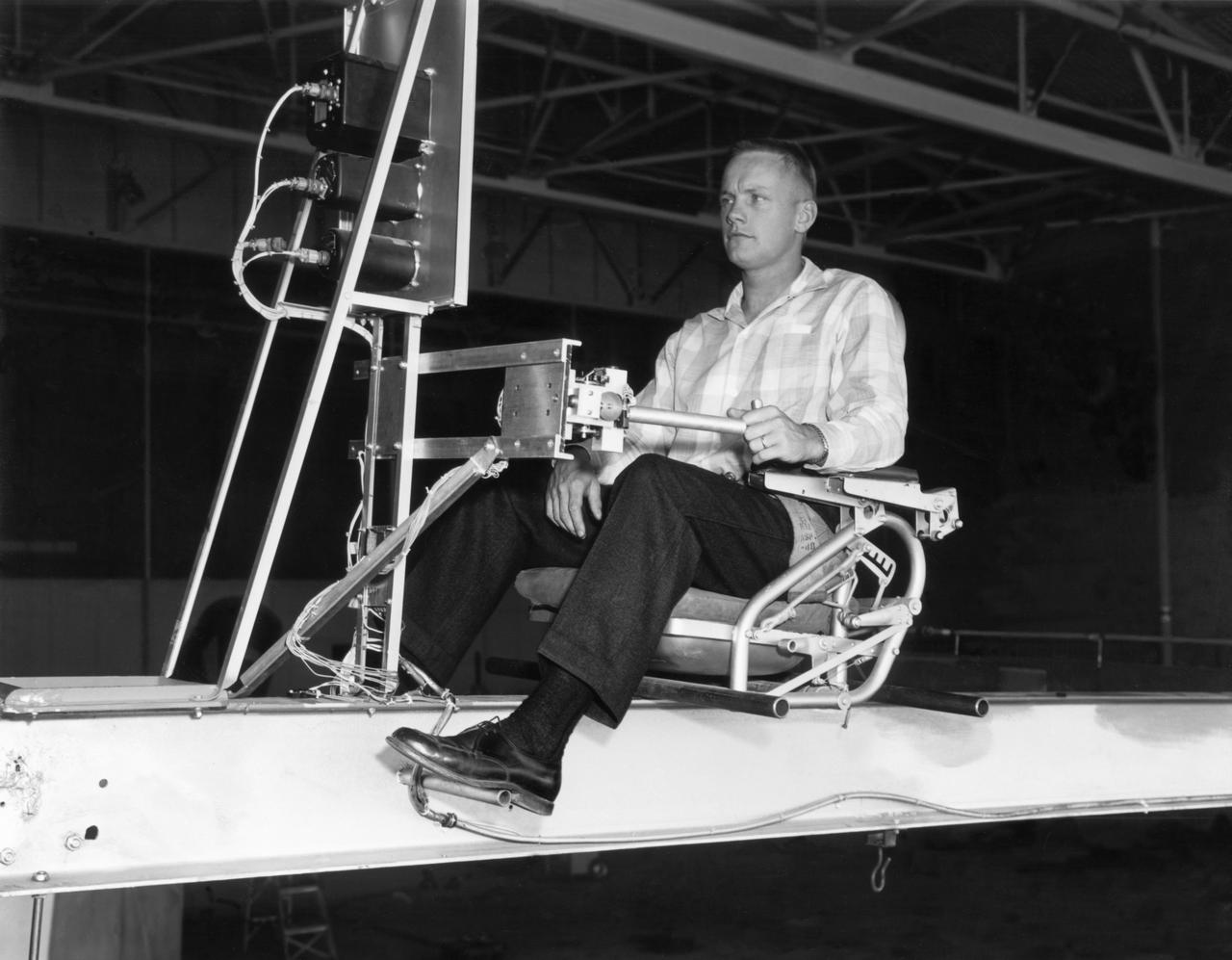

Famed astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, the first man to set foot on the moon during the historic Apollo 11 space mission in July 1969, served for seven years as a research pilot at the NACA-NASA High-Speed Flight Station, now the Dryden Flight Research Center, at Edwards, California, before he entered the space program. Armstrong joined the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) at the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory (later NASA's Lewis Research Center, Cleveland, Ohio, and today the Glenn Research Center) in 1955. Later that year, he transferred to the High-Speed Flight Station at Edwards as an aeronautical research scientist and then as a pilot, a position he held until becoming an astronaut in 1962. He was one of nine NASA astronauts in the second class to be chosen. As a research pilot Armstrong served as project pilot on the F-100A and F-100C aircraft, F-101, and the F-104A. He also flew the X-1B, X-5, F-105, F-106, B-47, KC-135, and Paresev. He left Dryden with a total of over 2450 flying hours. He was a member of the USAF-NASA Dyna-Soar Pilot Consultant Group before the Dyna-Soar project was cancelled, and studied X-20 Dyna-Soar approaches and abort maneuvers through use of the F-102A and F5D jet aircraft. Armstrong was actively engaged in both piloting and engineering aspects of the X-15 program from its inception. He completed the first flight in the aircraft equipped with a new flow-direction sensor (ball nose) and the initial flight in an X-15 equipped with a self-adaptive flight control system. He worked closely with designers and engineers in development of the adaptive system, and made seven flights in the rocket plane from December 1960 until July 1962. During those fights he reached a peak altitude of 207,500 feet in the X-15-3, and a speed of 3,989 mph (Mach 5.74) in the X-15-1. Armstrong has a total of 8 days and 14 hours in space, including 2 hours and 48 minutes walking on the Moon. In March 1966 he was commander of the Gemini 8 or
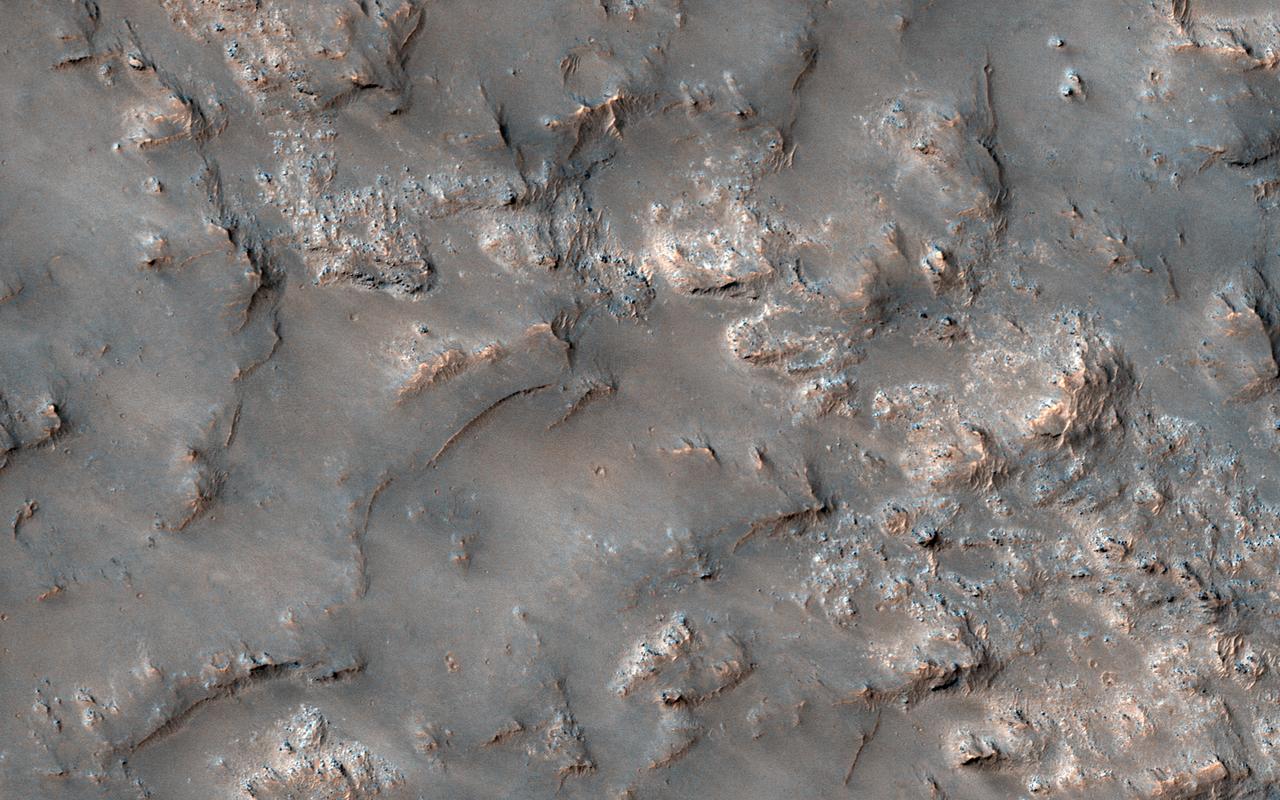

This image shows partially exposed bedrock within the Koval'sky impact basin, which is on the outskirts of the extensive lava field of Daedalia Planum. Daedalia Planum is located southwest of Arsia Mons, which may be the source responsible for filling the crater with lava flows and ash deposits. On one side, bright bedrock with scattered dark blue spots are seen. The dark blue spots are boulders shedding from the outcrops. The color range of the bedrock provides some information on its composition. The blue color is indicative of the presence of iron-rich minerals that are generally not oxidized (i.e., rusted), unlike most of the ruddy Martian surface. Volcanic rocks are common on Mars. Possible candidate minerals for the bluish materials are often consistent with iron-rich minerals, such as pyroxene and olivine. The ridges may represent remnants of the original surface of the lava flows that filled the Koval'sky impact basin. NB: The region is named for M. A. Koval'sky, a Russian astronomer. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21765

This artist's impression depicts the accretion disc surrounding a black hole, in which the inner region of the disc precesses. "Precession" means that the orbit of material surrounding the black hole changes orientation around the central object. In these three views, the precessing inner disc shines high-energy radiation that strikes the matter in the surrounding accretion disc. This causes the iron atoms in that disc to emit X-rays, depicted as the glow on the accretion disc to the right (in view a), to the front (in view b) and to the left (in view c) (see Figure 1). In a study published in July 2016, astronomers used data from ESA's XMM-Newton X-ray Observatory and NASA's NuSTAR telescope to measure this "wobble" in X-ray emission from excited iron atoms. Scientists interpreted this as evidence for the Lense-Thirring effect -- a name for the precession phenomenon -- in the strong gravitational field of a black hole. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20697
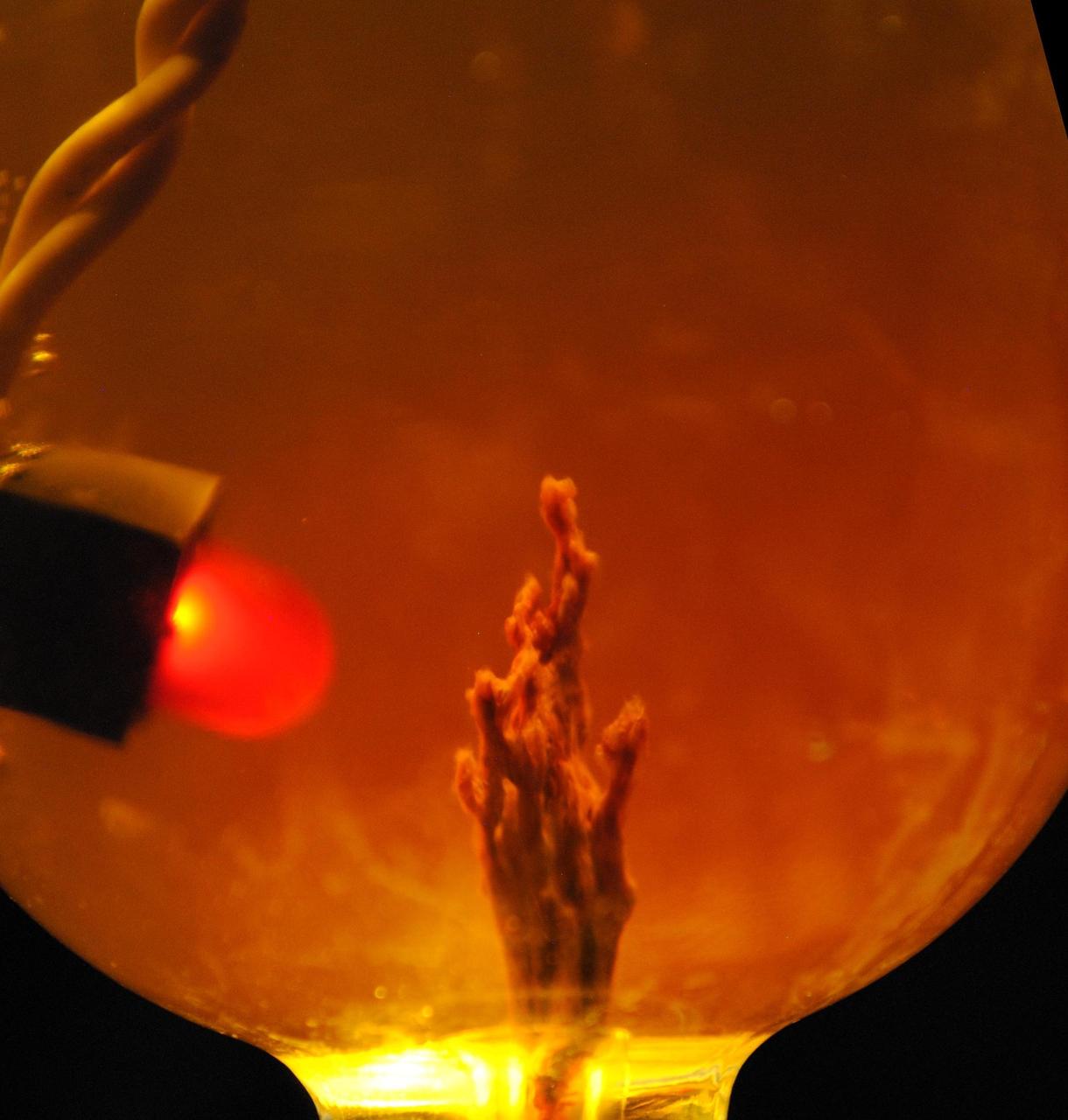

This photo simulation shows a laboratory-created "chemical garden," which is a chimney-like structure found at bubbling vents on the seafloor. Some researchers think life on Earth might have got its start at structures like these billions of years ago, partly due to their ability to transfer electrical currents -- an essential trait of life as we know it. The battery-like property of these chemical gardens was demonstrated by linking several together in series to light an LED (light-emitting diode) bulb. In this photo simulation, the bulb is not really attached to the chimney. The chimney membranes are made of iron sulfides and iron hydroxides, geologic materials that conduct electrons. JPL's research team is part of the Icy Worlds team of the NASA Astrobiology Institute, based at NASA's Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, California. JPL is managed by the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena for NASA. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19834
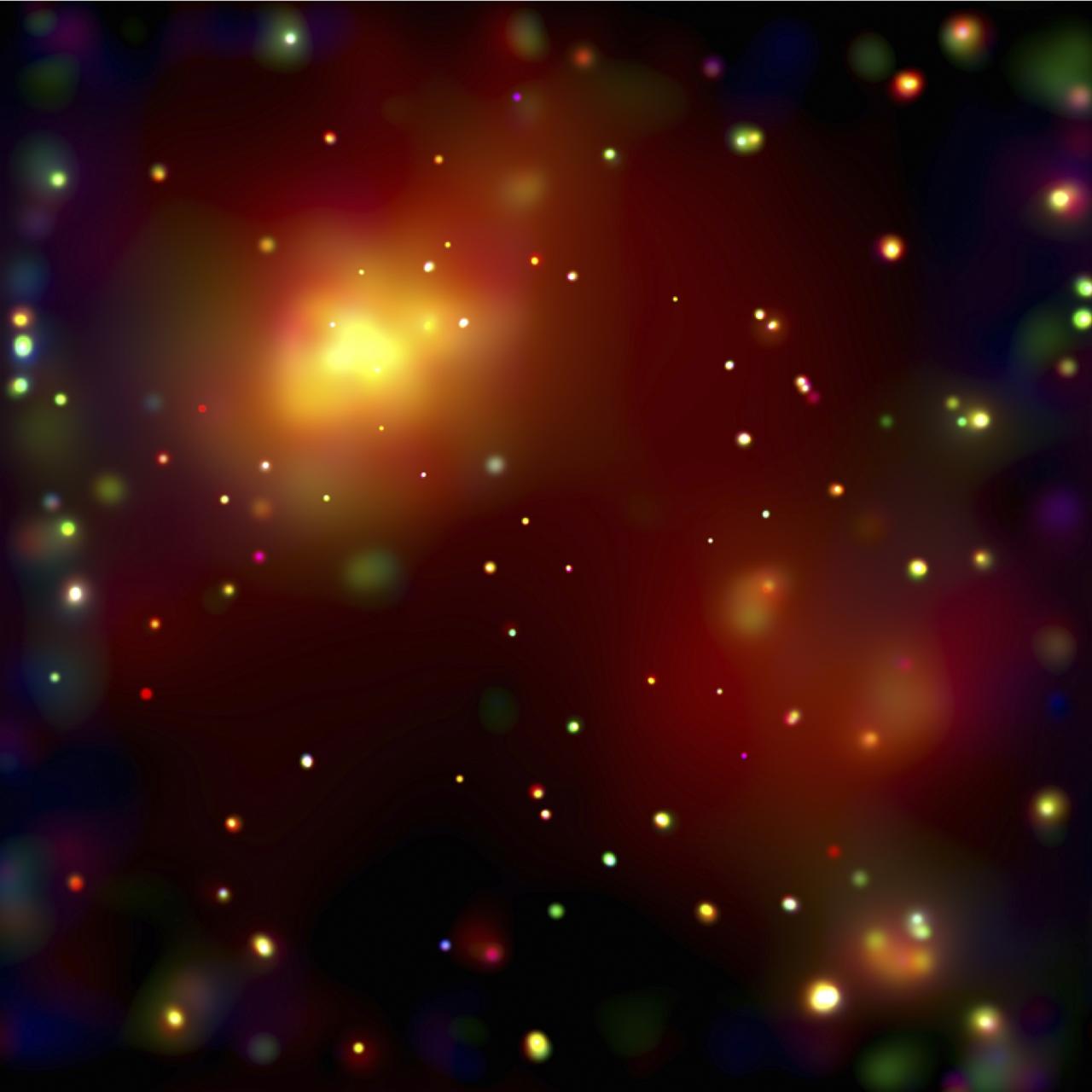

This image of the galaxy cluster Abell 2125, provided by the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), reveals several massive multimillion degree Celsius gas clouds that appear to be in the process of merging. Ten of the point-like sources are associated with galaxies in the cluster and the rest are probably distant background galaxies. The small bright feature in the extreme lower right-hand corner is probably a background galaxy cluster not associated with Abell 2125. The bright gas cloud on the upper left is the core of the cluster and envelopes hundreds of galaxies. It consists of several elongated clouds that are merging. Chandra, Hubble Space Telescope (HST), and Very Large Array radio telescope data show that several galaxies in the Abell 2125 core cluster are being stripped of their gas as they fall through surrounding high-pressure hot gas. This stripping process has enriched the core cluster's gas in heavy elements such as iron. In contrast, the bright large cloud on the lower right envelopes hundreds of galaxies and has an extraordinarily low concentration of iron atoms. It is thought that this cloud, which is several million light years from the core cluster, has not yet been enriched by the stripping of iron-rich gas from its member galaxies. Over time, as this cloud merges into the core and the hot gas pressure increases, iron atoms should be swept from the galaxies. Building a massive galaxy cluster is a step-by-step enterprise that takes billions of years and affects the growth and evolution of the member galaxies. The observations of A 2125 provide a rare glimpse into the early steps in this process. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama manages both the Chandra and Hubble programs. (NASA/UMass/D. Wang et al.))

This illustration shows three possible interiors of the seven rocky exoplanets in the TRAPPIST-1 system, based on precision measurements of the planet densities. Overall the TRAPPIST-1 worlds have remarkably similar densities, which suggests they may share the same ratio of common planet-forming elements. The planet densities are slightly lower than those of Earth or Venus, which could mean they contain fractionally less iron (a highly dense material) or more low-density materials, such as water or oxygen. In the first model (left), the interior of the planet is composed of rock mixed with iron bound to oxygen. There is no solid iron core, which is the case with Earth and the other rocky planets in our own solar system. The second model shows an overall composition similar to Earth's, in which the densest materials have settled to the center of the planet, forming an iron-rich core proportionally smaller than Earth's core. A variation is shown in the third panel, where a larger, denser core could be balanced by an extensive low-density ocean on the planet's surface. However, this scenario can be applied only to the outer four planets in the TRAPPIST-1 system. On the inner three planets, any oceans would vaporize due to the higher temperatures near their star, and a different composition model is required. Since all seven planets have remarkably similar densities, it is more likely that all the planets share a similar bulk composition, making this fourth scenario unlikely but not impossible. The high-precision mass and diameter measurements of the exoplanets in the TRAPPIST-1 system have allowed astronomers to calculate the overall densities of these worlds with an unprecedented degree of accuracy in exoplanet research. Density measurements are a critical first step in determining the composition and structure of exoplanets, but they must be interpreted through the lens of scientific models of planetary structure. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24372
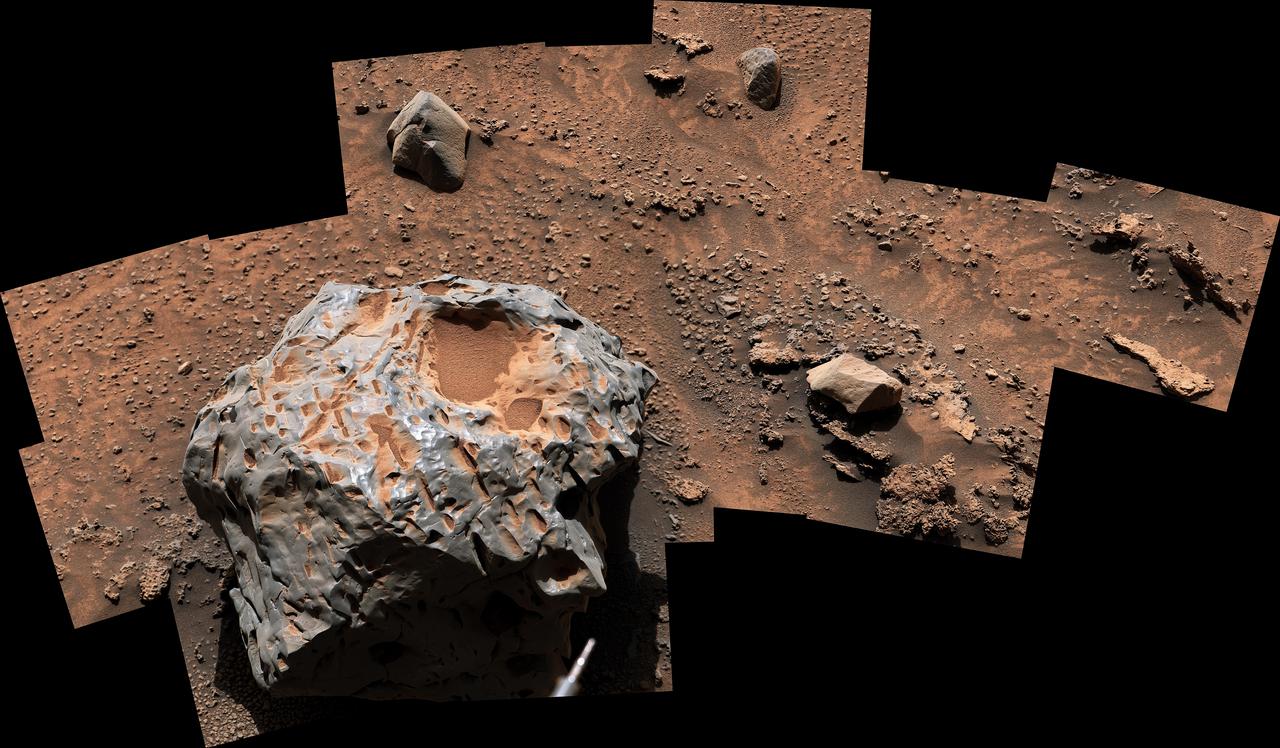

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover captured this image of an iron-nickel meteorite nicknamed "Cacao" on Jan, 28, 2023, the 3,725th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This meteorite, discovered in the "sulfate-bearing unit," a region on Mars' Mount Sharp, is estimated to be about 1 foot (30 centimeters) across. It's one of several meteorites Curiosity has seen while exploring Mars. Curiosity's Mast Camera, or Mastcam, took the panorama with its 100-millimeter focal length lens. The panorama is made up of 19 individual images that were stitched together after being sent to Earth. The color has been adjusted to match lighting conditions as the human eye would perceive them on Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25737
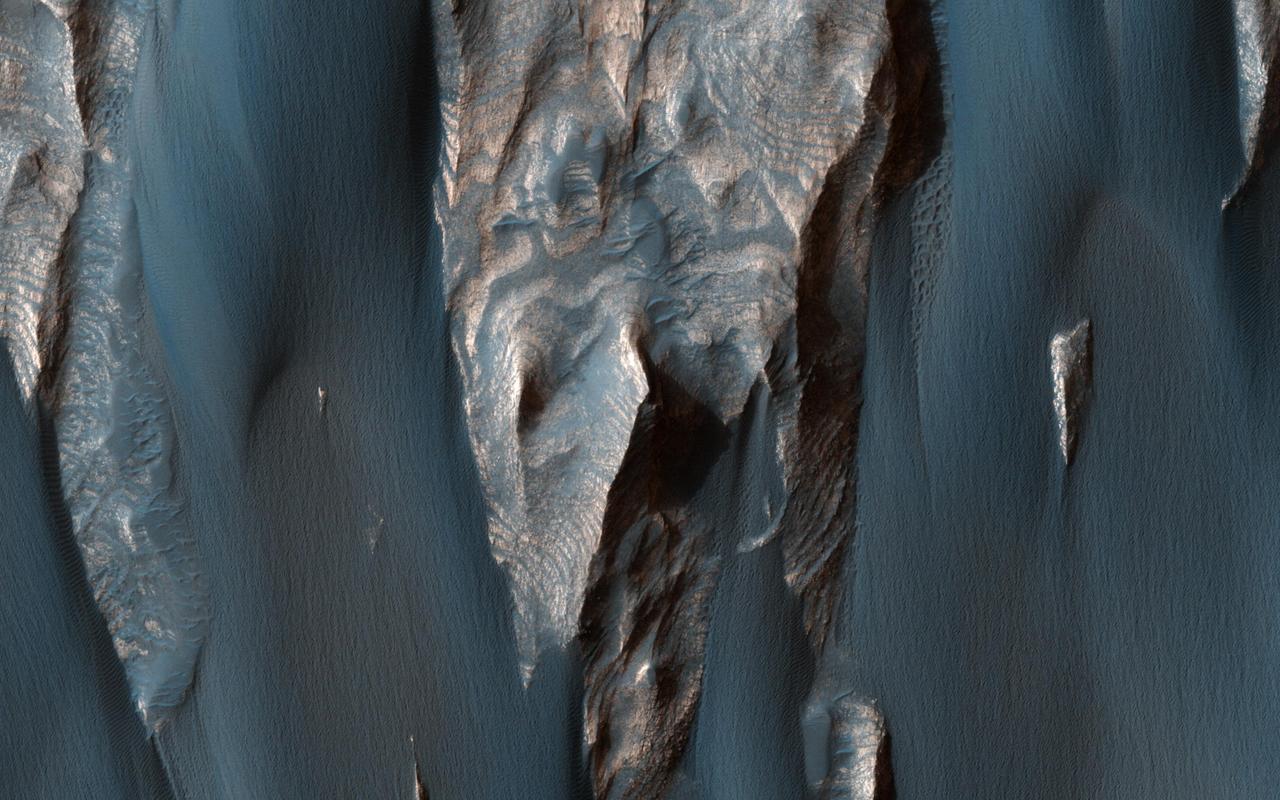

Dark, windblown sand covers intricate sedimentary rock layers in this image captured by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) from Ganges Chasma, a canyon in the Valles Marineris system. These features are at once familiar and unusual to those familiar with Earth's beaches and deserts. Most sand dunes on Earth are made of silica-rich sand, giving them a light color; these Martian dunes owe their dark color to the iron and magnesium-rich sand found in the region. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21600
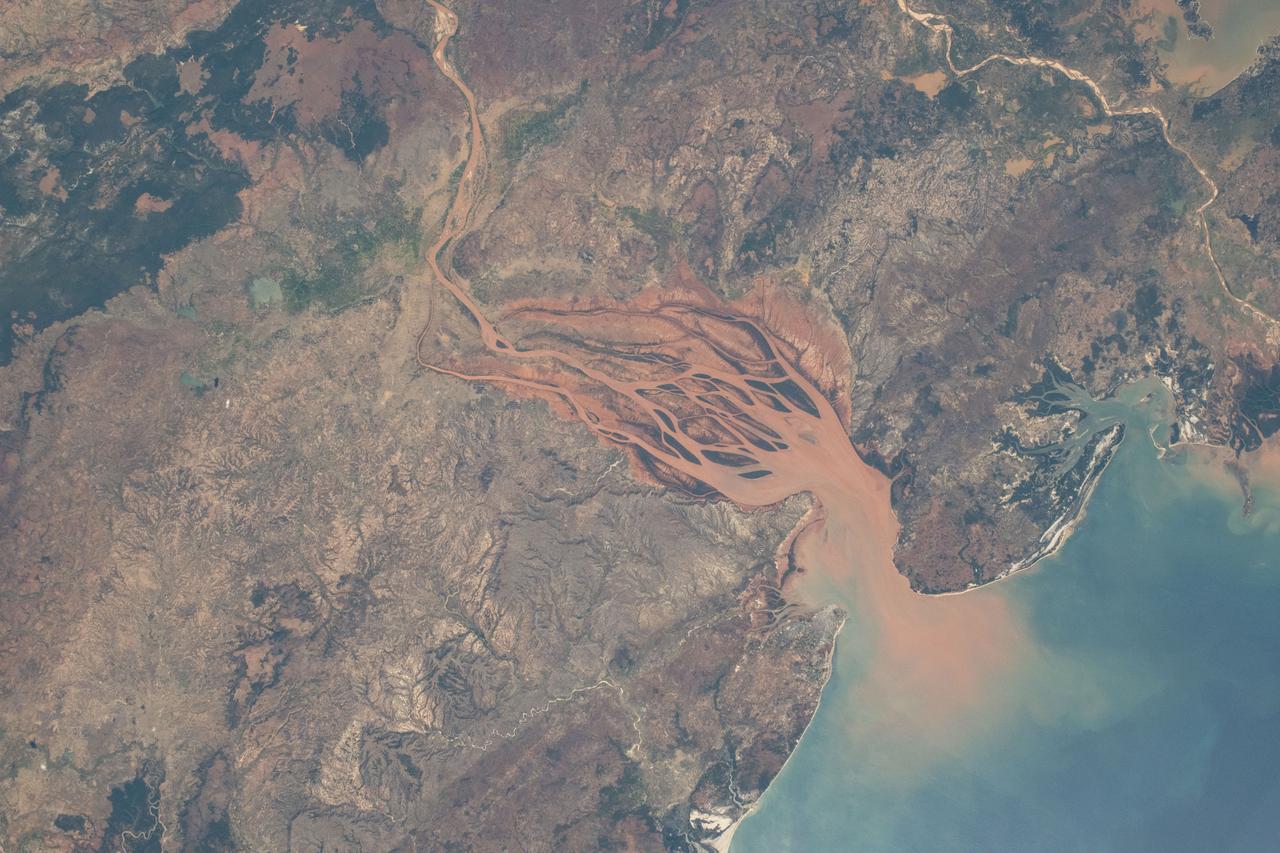

iss071e218069 (June 26, 2024) -- On Madagascar's northwestern coast, the Mozambique Channel flows inland to the Betsiboka River, forming Bombetoka Bay. The reddish-brown color is the result of iron-rich sediment transporting through, creating a striking visual marker for astronauts aboard the International Space Station. This photograph was taken as the orbiting laboratory soared 266 miles above Earth.
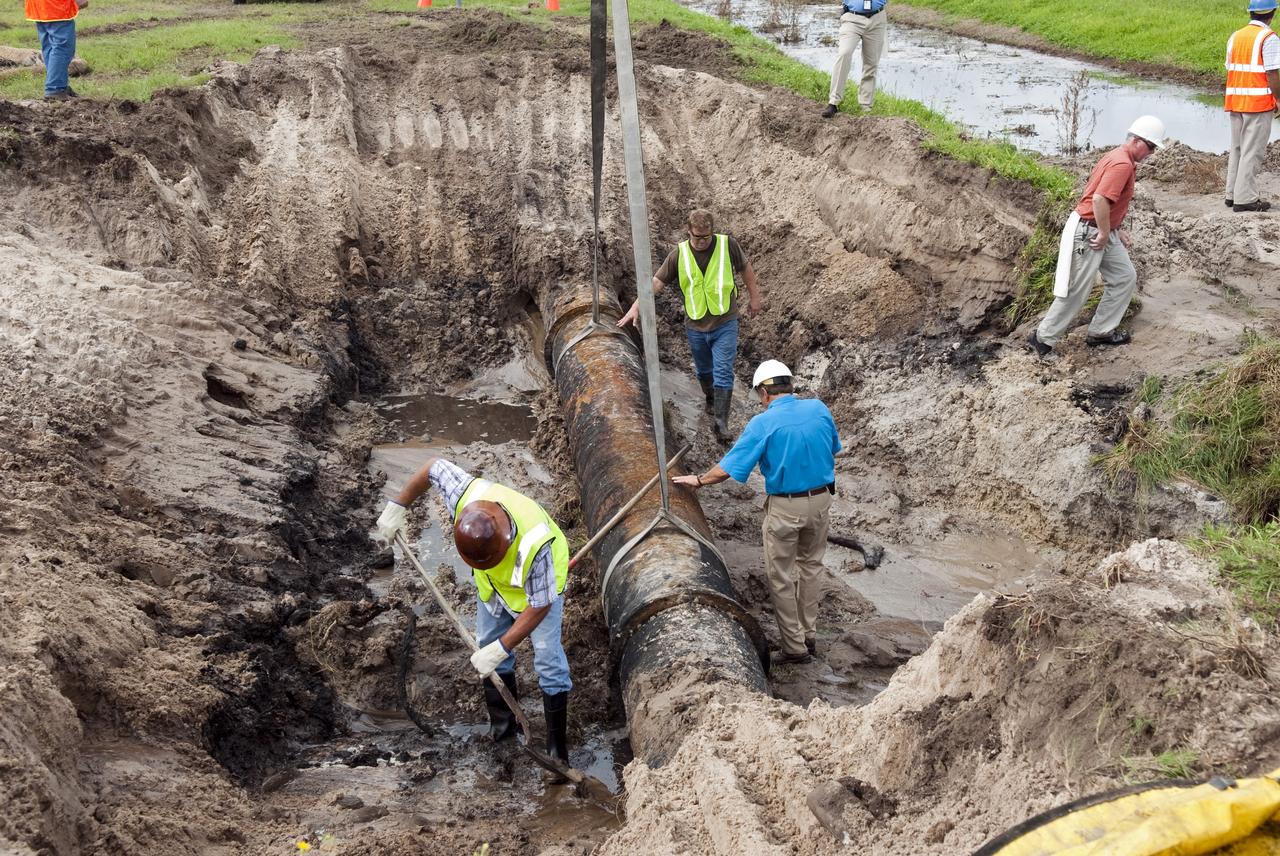

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crew begins to fix a major water main break in a 24-inch cast iron pipe in the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building and the Launch Control Center. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

iss071e040346 (4/23/2024) ---A view aboard the International Space Station (ISS) of the Higher Orbits Multi Experiment Module #5 (HIOR_EDU05) continues a series of student-led experiments aboard the International Space Station. This module includes three experiments: Radiation and Fungus, which tests fungal growth in space; Project Bones, which compares iron levels in fruit flies fed different diets; and Cells in Space, which examines the effect of radiation on cellular respiration in yeast.

jsc2023e065188 (1/27/2023) --- Student researchers work on their experiment, which will be included in the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Orbiter-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 17 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Orbiter-SSEP). Edina High School students Josh Cram, Colin Shaw and Grayson Irons, work together to create a seed holder device meant to minimize vibrations and guide roots of growing bean plants while aboard the ISS.
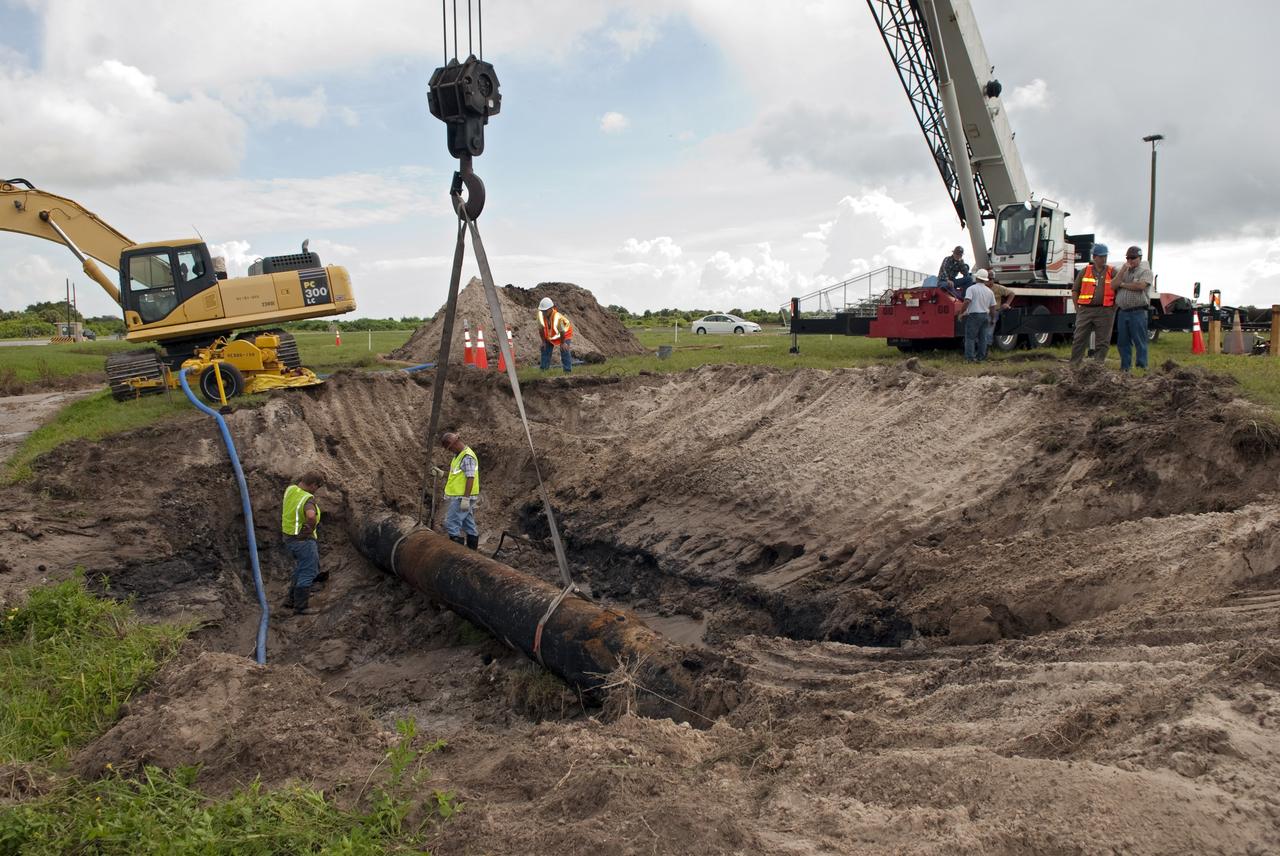

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crew begins to fix a major water main break in a 24-inch cast iron pipe in the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building and the Launch Control Center. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
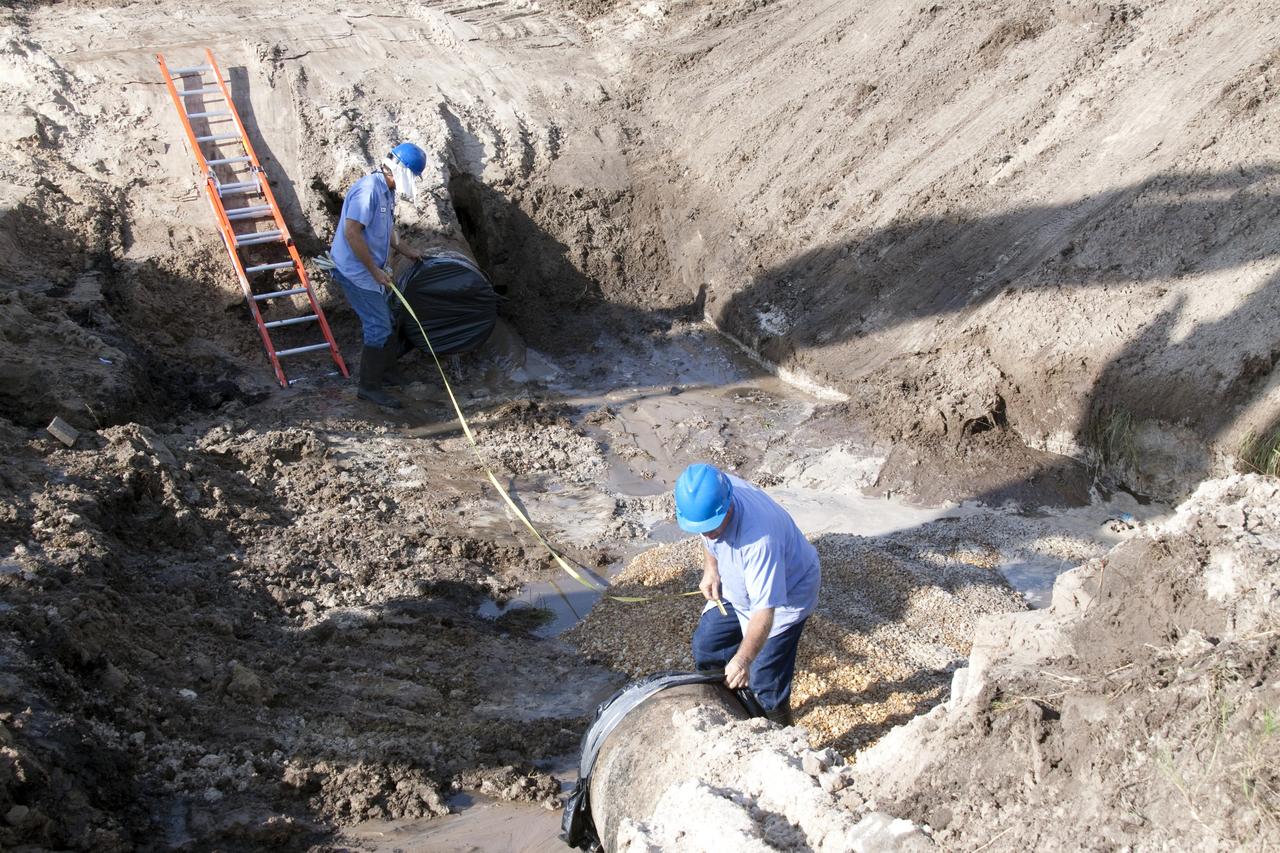

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers take measurements for replacement sections of a 24-inch cast iron water main pipe. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the water main break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
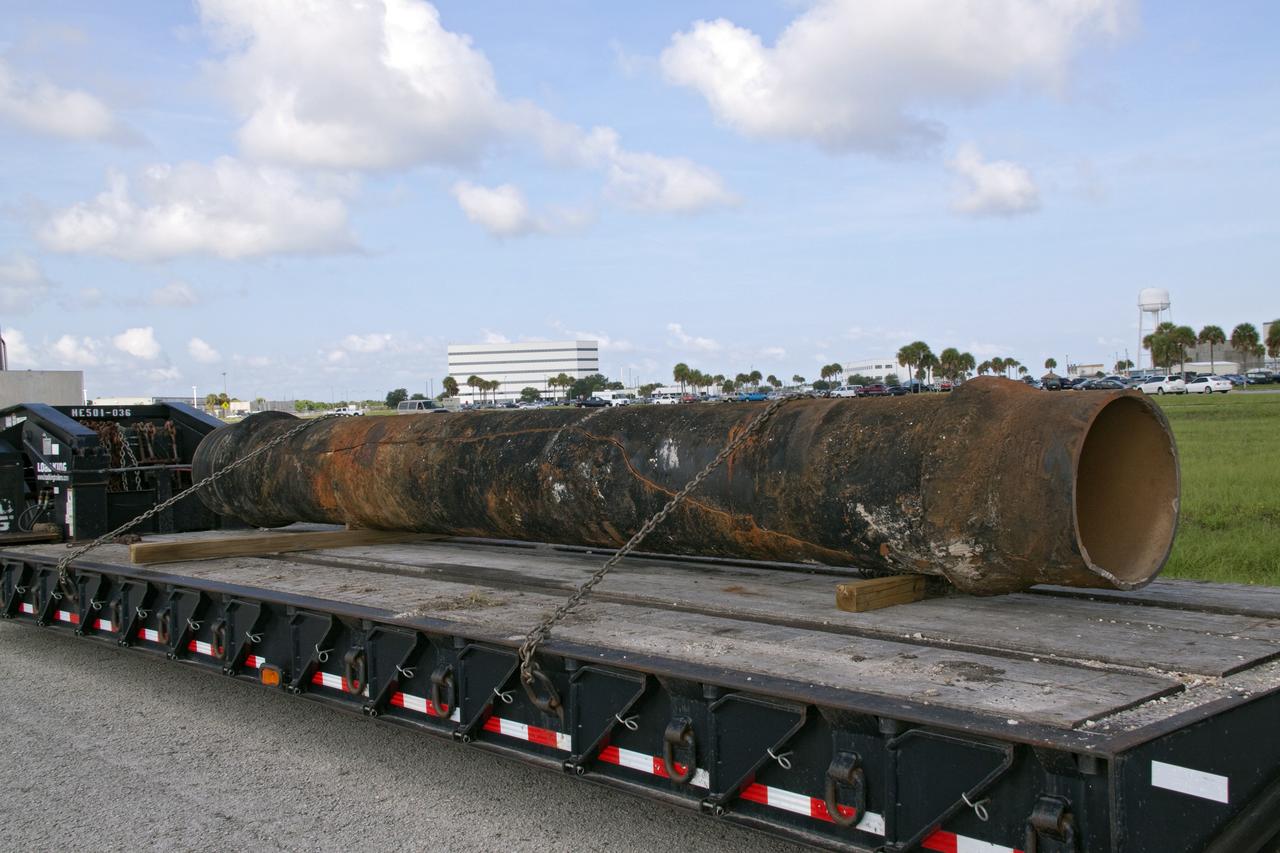

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the section of a 24-inch cast iron water main pipe that failed is hauled away by a transport truck. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the water main break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
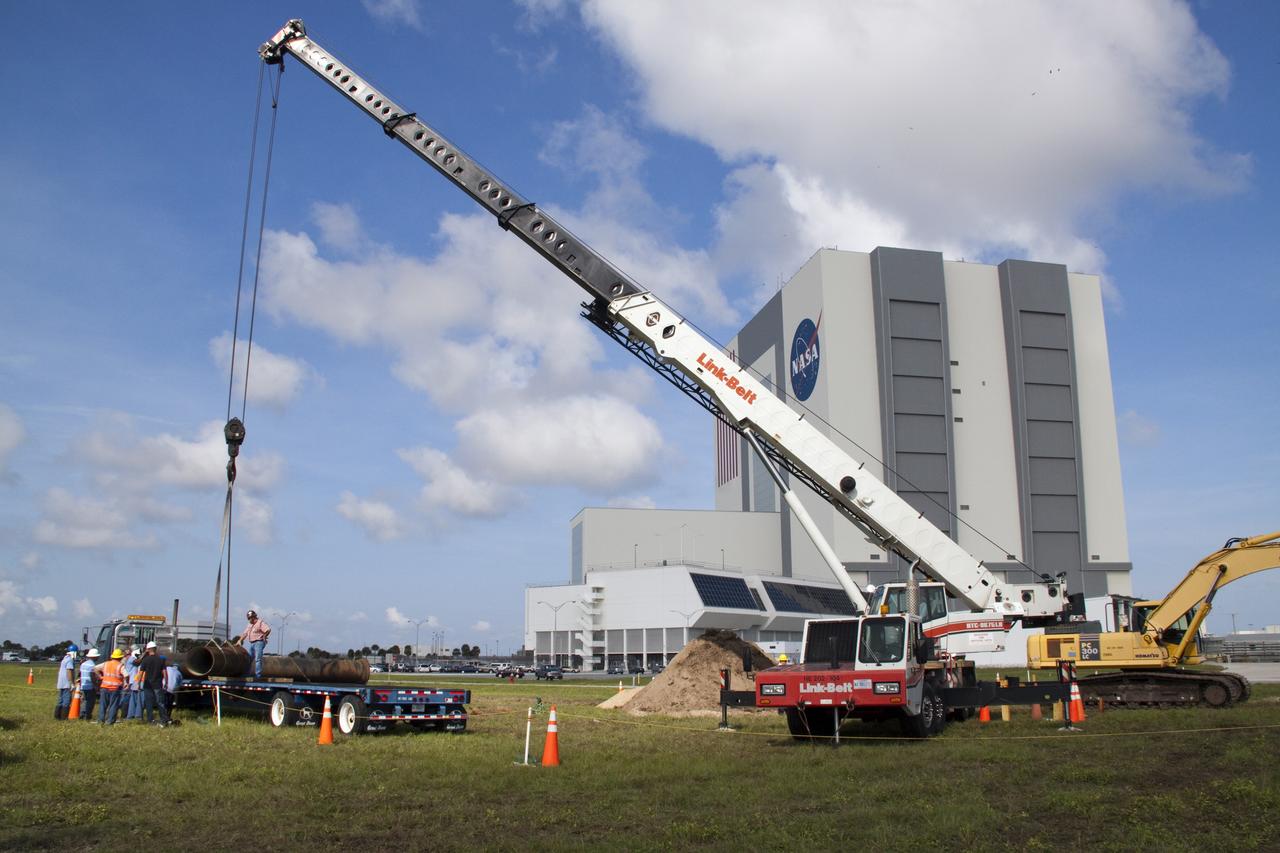

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. --In the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, assisted by an overhead crane maneuver the replacement section of a 24-inch cast iron water main pipe off of a transport truck. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the water main break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
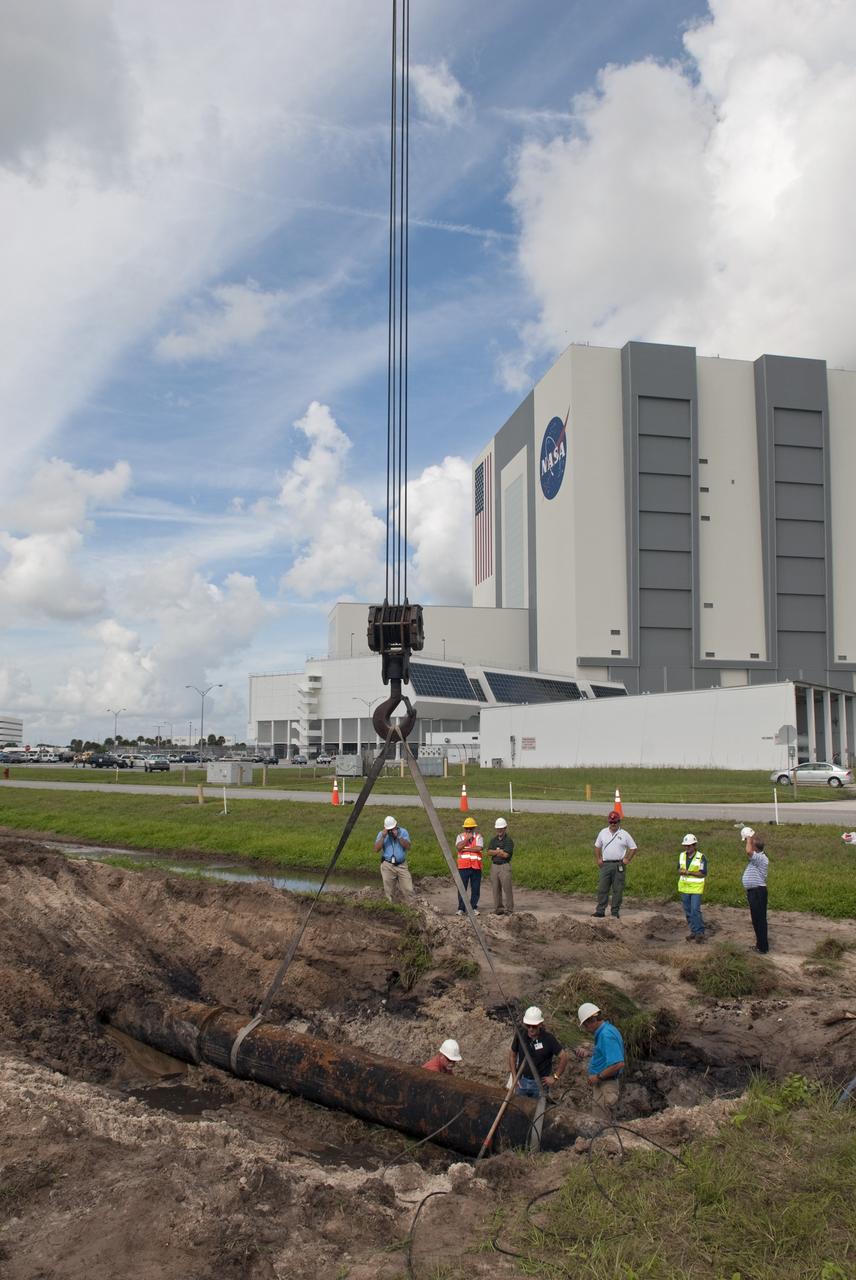

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crew begins to fix a major water main break in a 24-inch cast iron pipe in the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building and the Launch Control Center. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
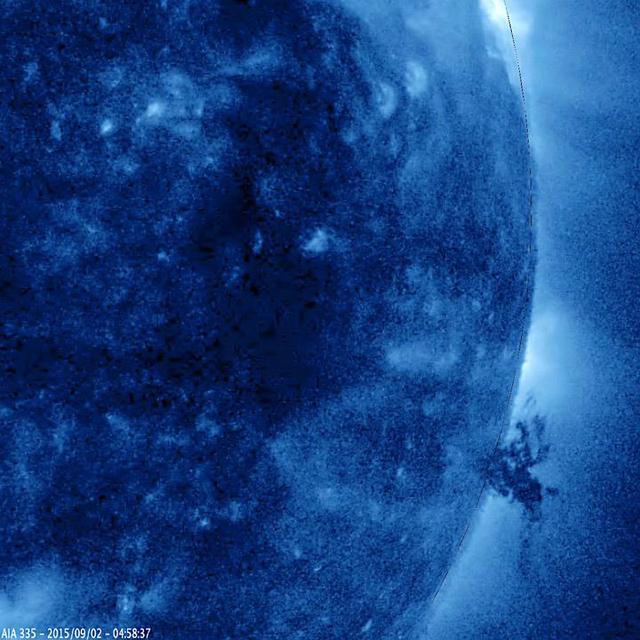

A small, but complex mass of plasma gyrated and spun about over the course of 40 hours above the surface of the Sun (Sept. 1-3, 2015). It was stretched and pulled back and forth by powerful magnetic forces but not ripped apart in this sequence. The temperature of the ionized iron particles observed in this extreme ultraviolet wavelength of light was about 2.8 million degrees C. (or 5 million degrees F.) http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19878
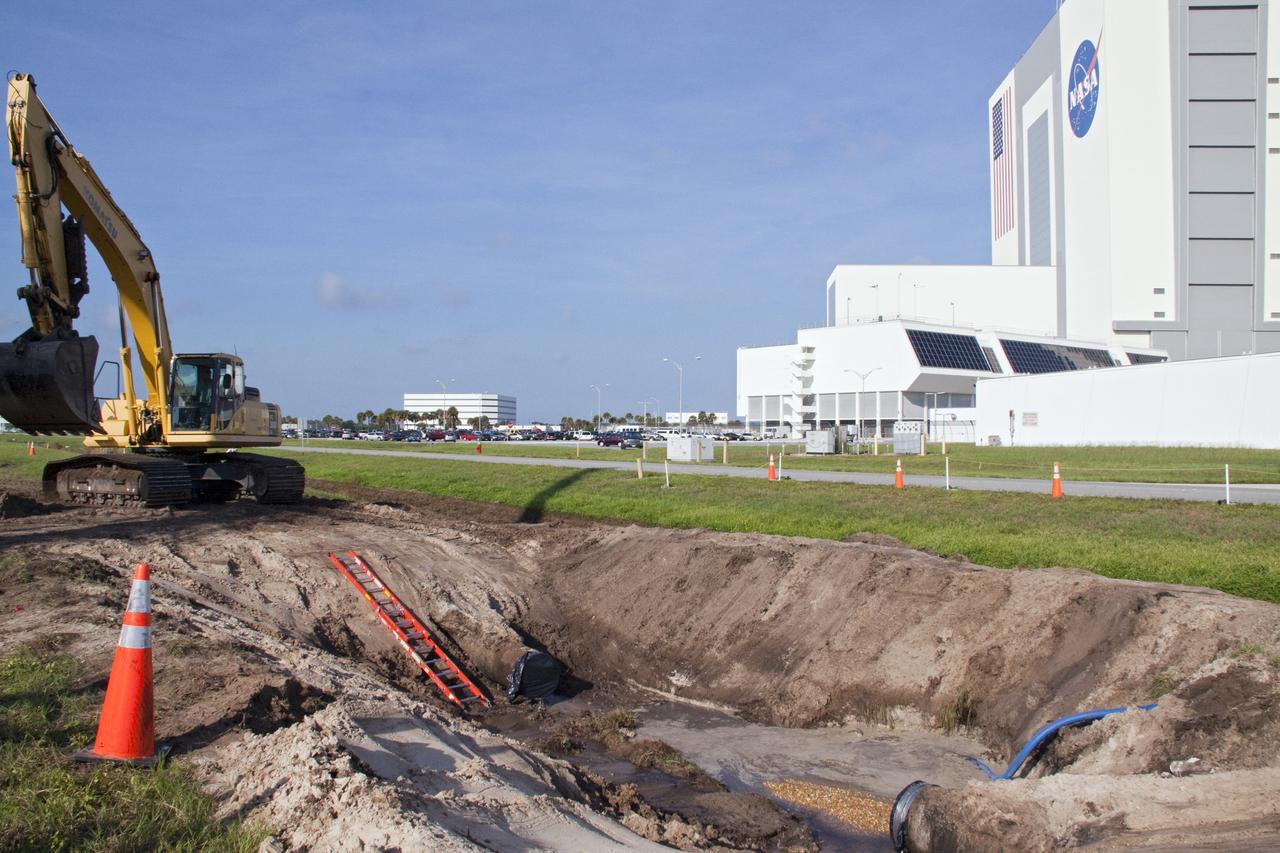

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a work crew has removed a large section of a 24-inch cast iron water main pipe located in the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building and the Launch Control Center. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
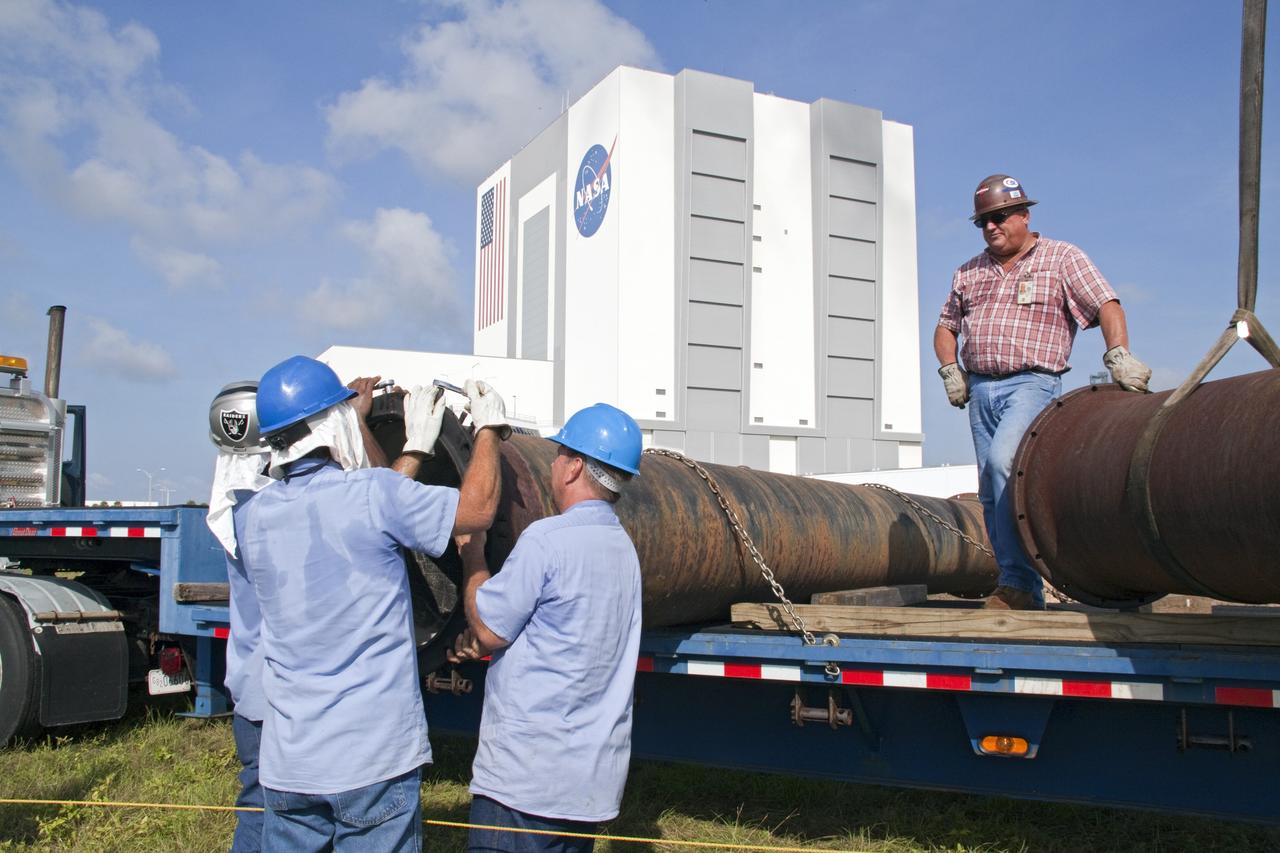

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers maneuver the replacement section of a 24-inch cast iron water main pipe off of a transport truck. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the water main break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
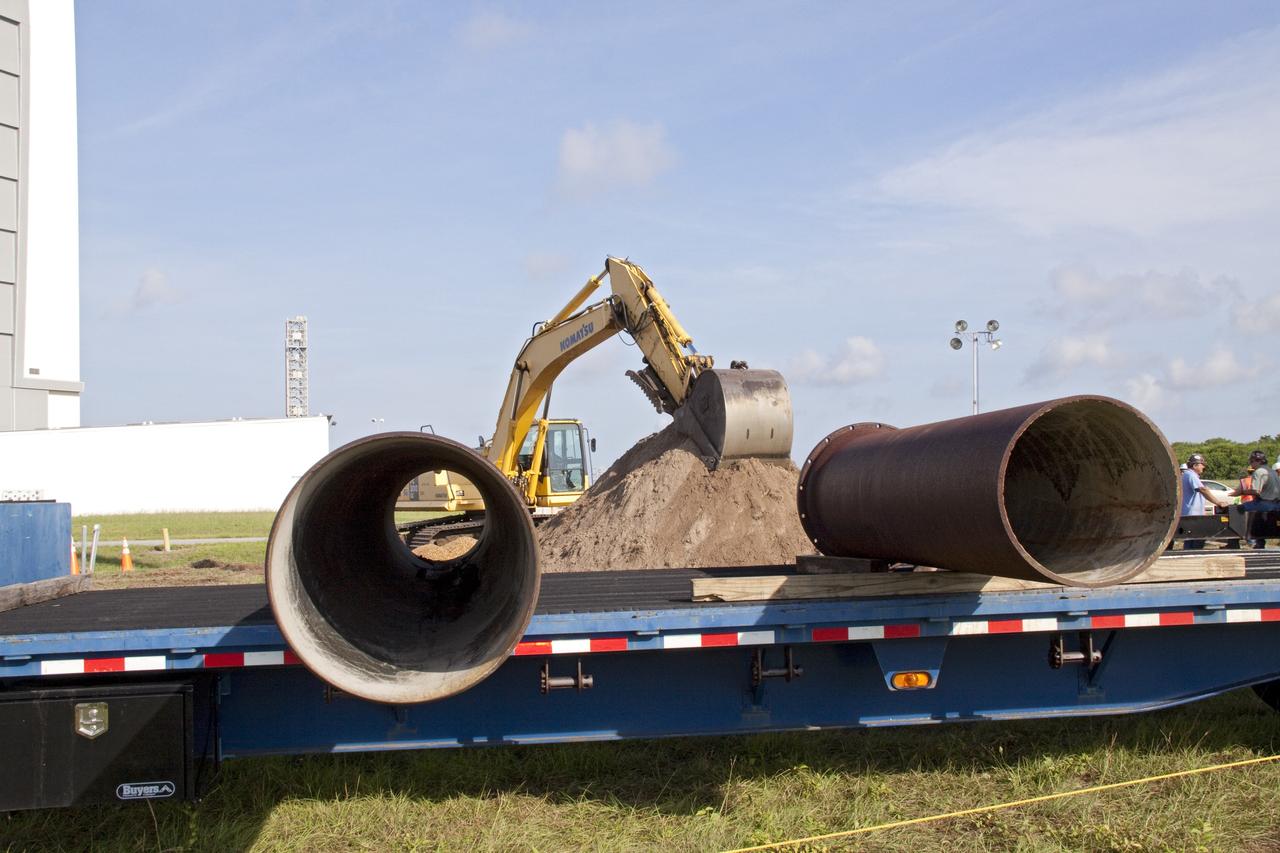

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, replacement sections of a 24-inch cast iron water main pipe awaits installation. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the water main break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
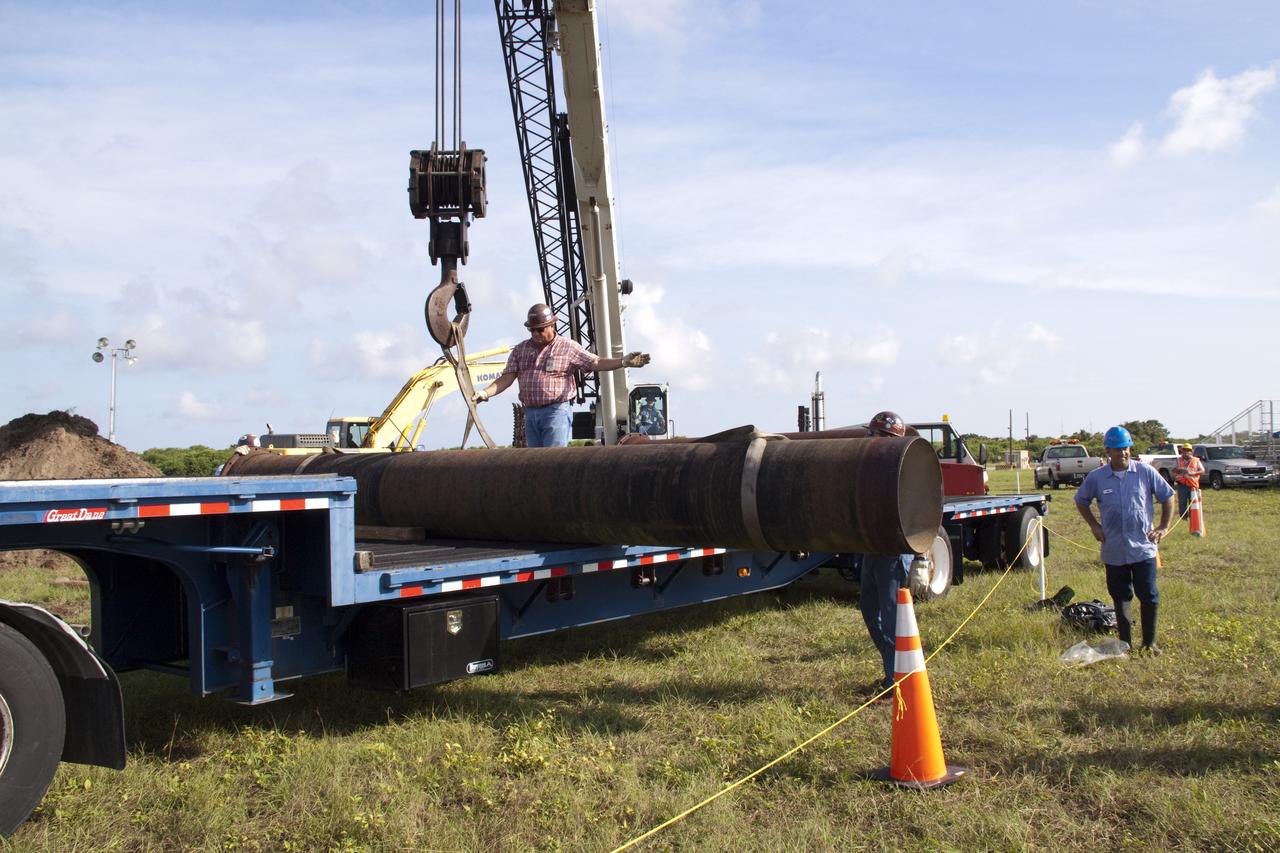

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers maneuver the replacement sections of a 24-inch cast iron water main pipe off of a transport truck. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the water main break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
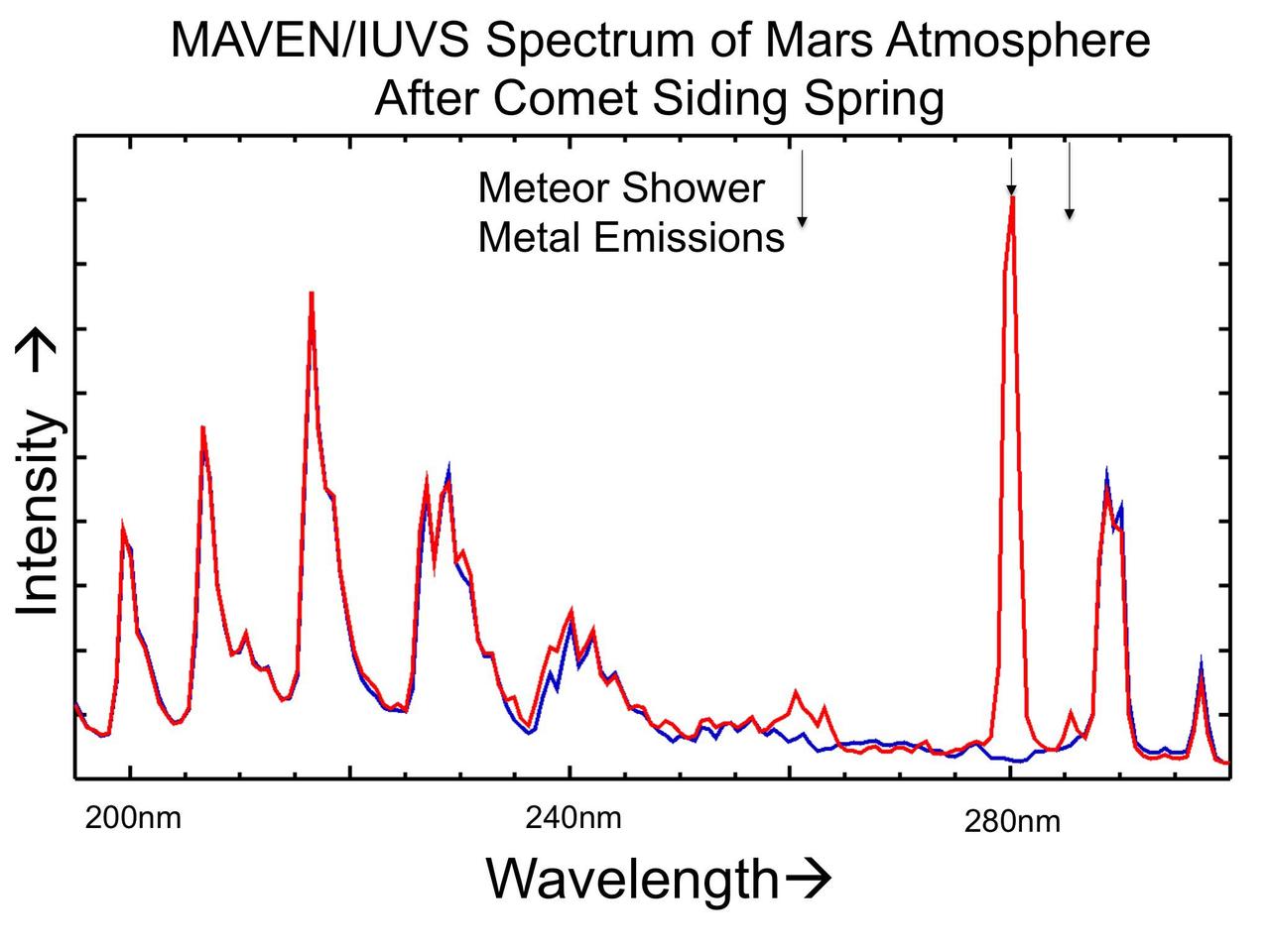
The places where the red line on this graph extends higher than the blue line show detection of metals added to the Martian atmosphere from dust particles released by a passing comet on Oct. 19, 2014. The graphed data are from NASA MAVEN spacecraft.
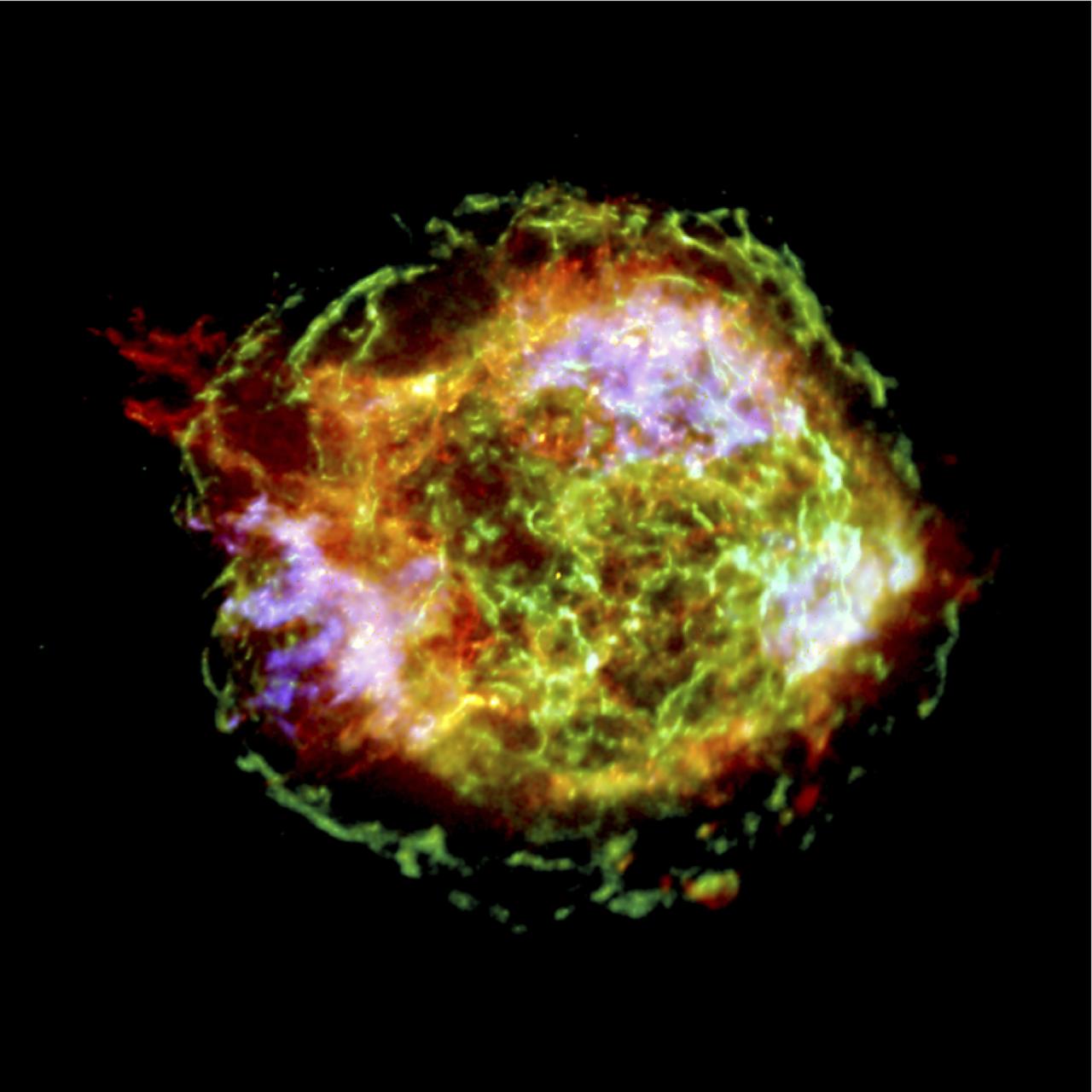
This spectacular Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO) image of the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A is the most detailed image ever made of the remains of an exploded star. The one-million-second image shows a bright outer ring (green) 10 light years in diameter that marks the location of a shock wave generated by the supernova explosion. In the upper left corner is a large jet-like structure that protrudes beyond the shock wave, and a counter-jet can be seen on the lower right. The x-ray spectra show that the jets are rich in silicon atoms, and relatively poor in iron atoms. This indicates that the jets formed soon after the initial explosion of the star, otherwise, the jets should have contained large quantities of iron from the star’s central regions. The bright blue areas are composed almost purely of iron gas, which was produced in the central, hottest regions of the star and somehow ejected in a direction almost perpendicular to the jets. The bright source at the center of the image is presumed to be a neutron star created during the supernova. Unlike most others, this neutron star is quiet, faint, and so far shows no evidence of pulsed radiation. A working hypothesis is that the explosion that created Cassiopeia A produced high speed jets similar to, but less energetic than, the hyper nova jets thought to produce gamma-ray bursts. During the explosion, the star may have developed an extremely strong magnetic filed that helped to accelerate the jets and later stifled any pulsar wind activity. CXO project management is the responsibility of NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.
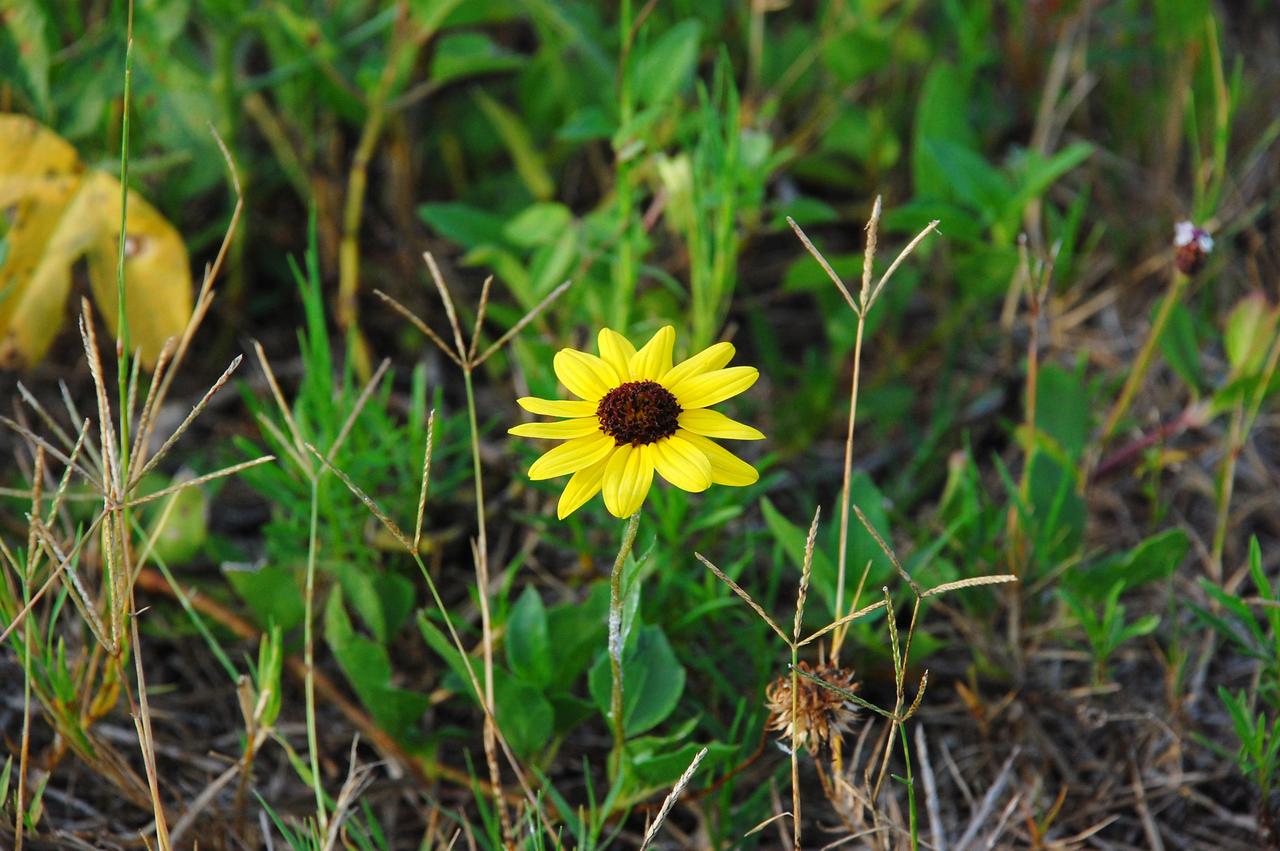

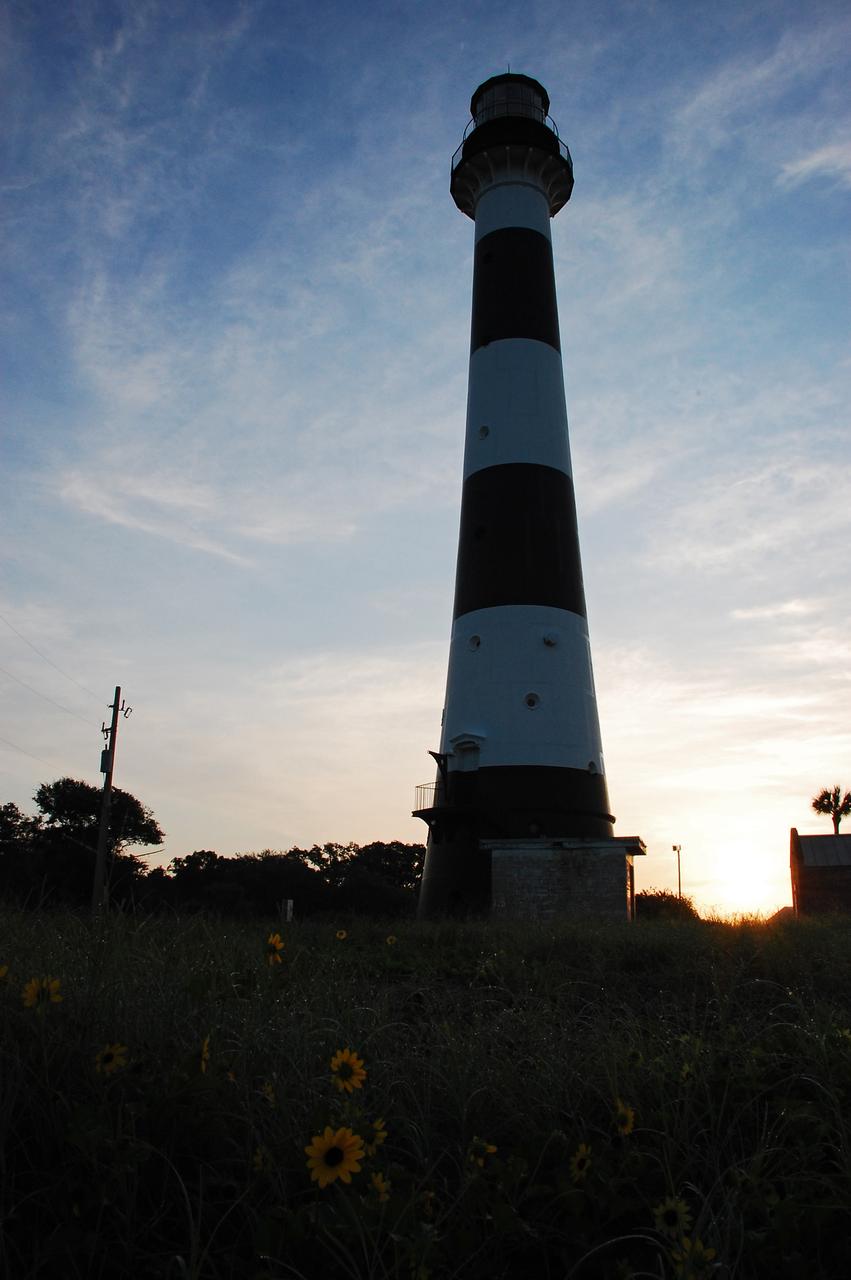
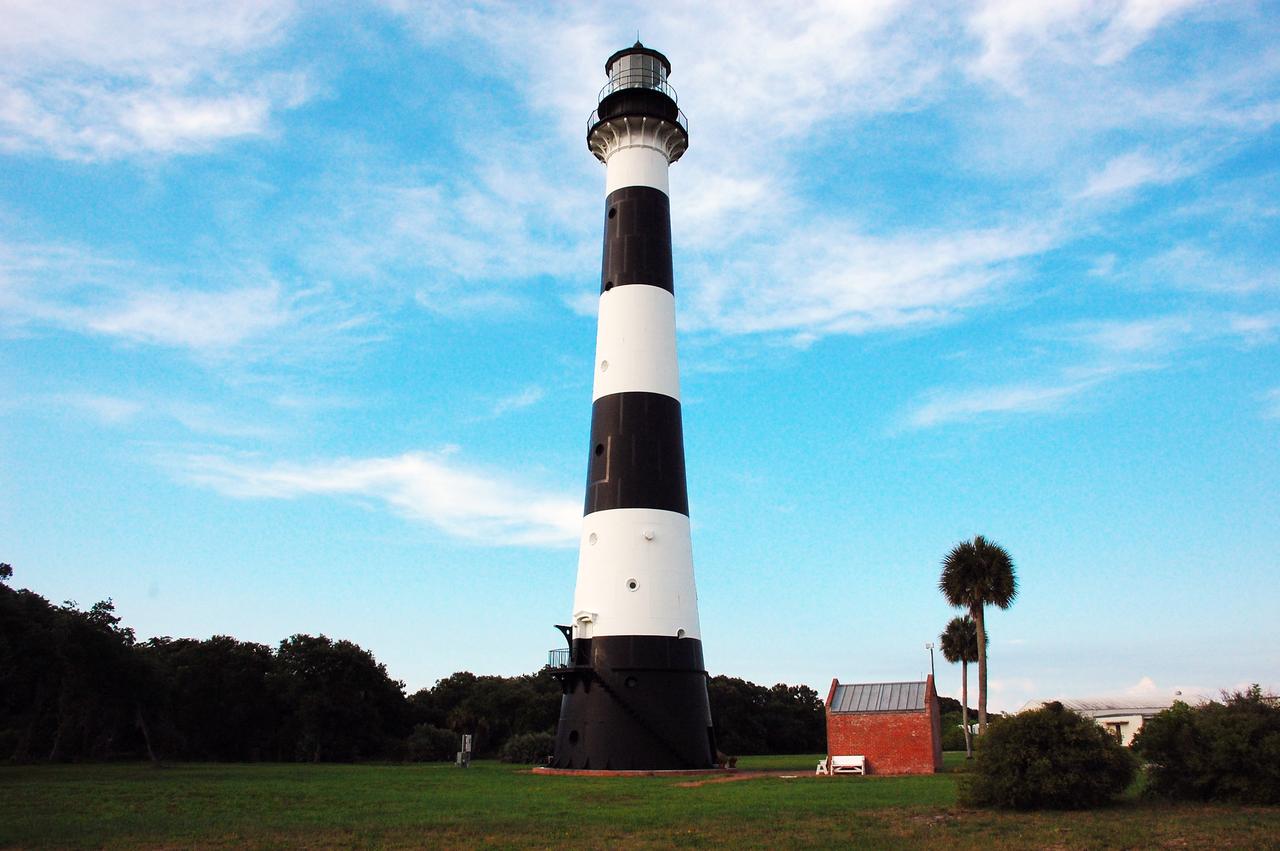
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A daisy thrives amidst the natural vegetation surrounding the historic Cape Canaveral Light on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lighthouse currently is owned by the U.S. Air Force. The first lighthouse on Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse was not finished until 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to a new location about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. For more information on the lighthouse, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy/about/history/lighthouse.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
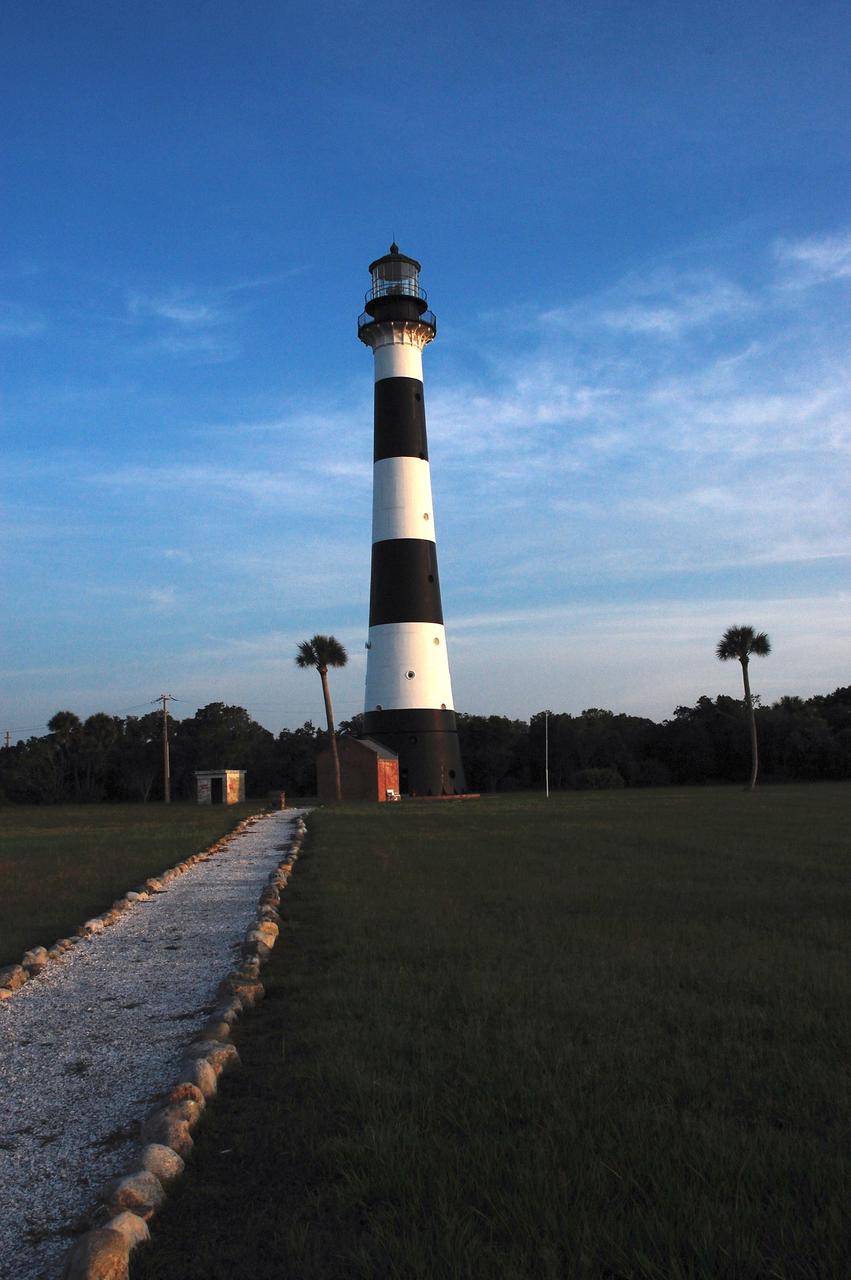

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- A warm glow envelopes the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse as dawn breaks over the Cape.. The Canaveral light is the only operating lighthouse owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the modern first-order beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
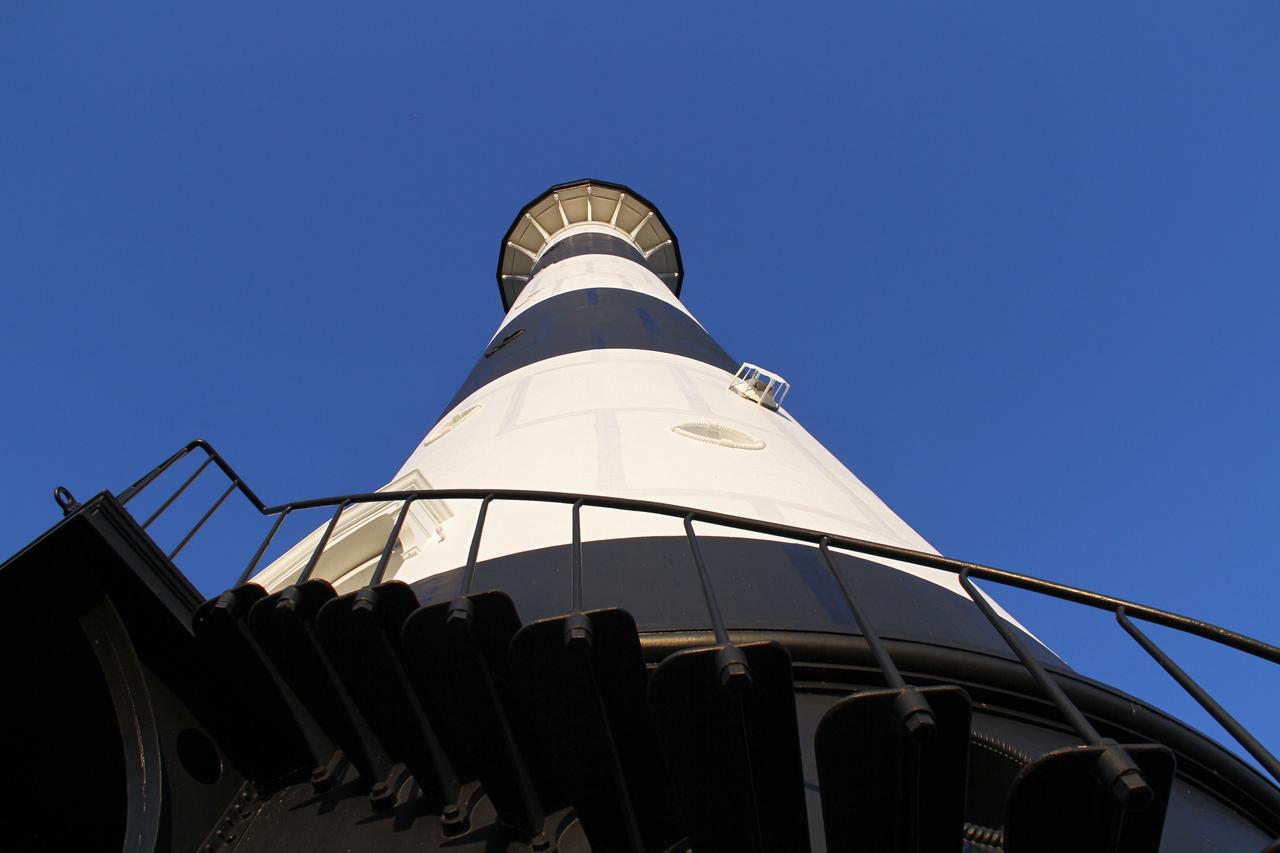

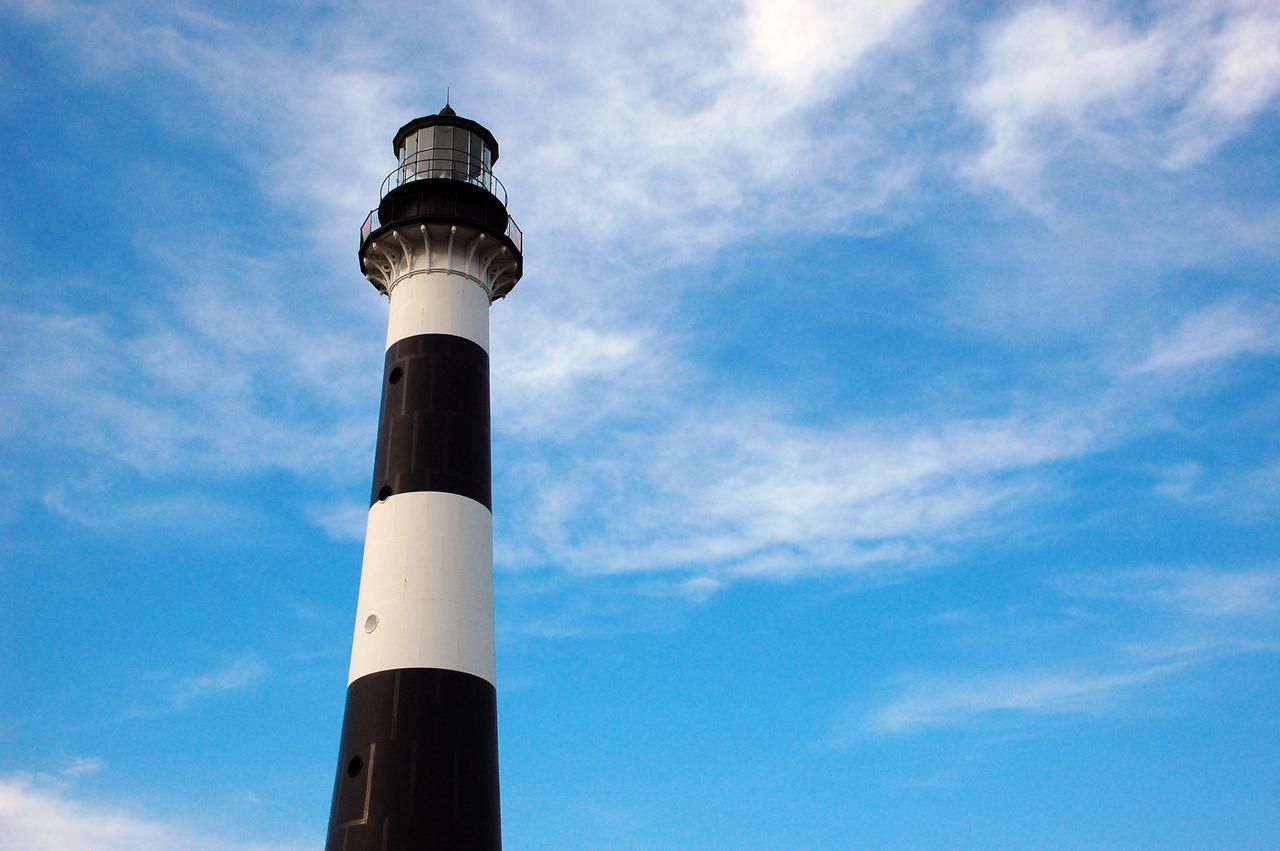
CAPE CANAVERAL AIR FORCE STATION, Fla. – This view looking up contrasts the black and white lighthouse at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station against the Florida sky. The Canaveral light is the only one owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
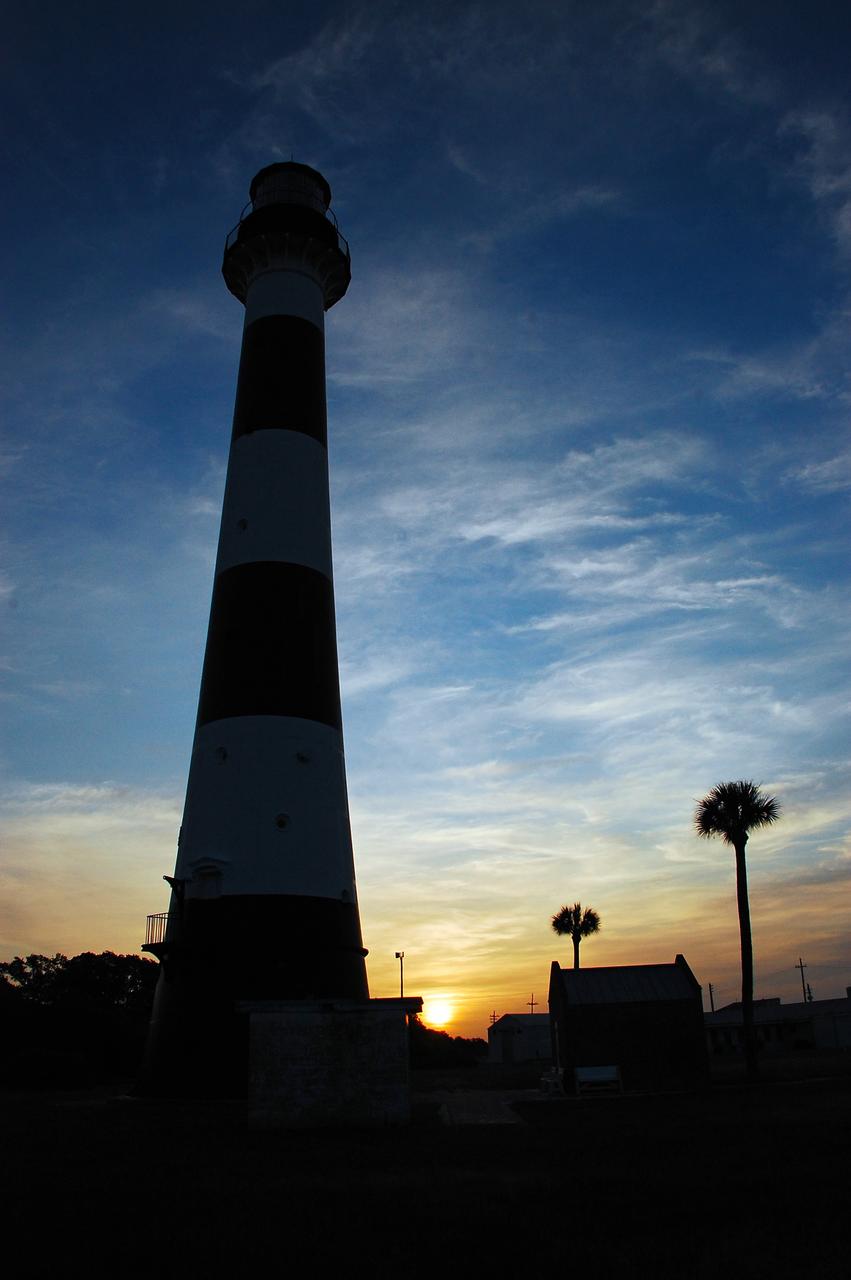

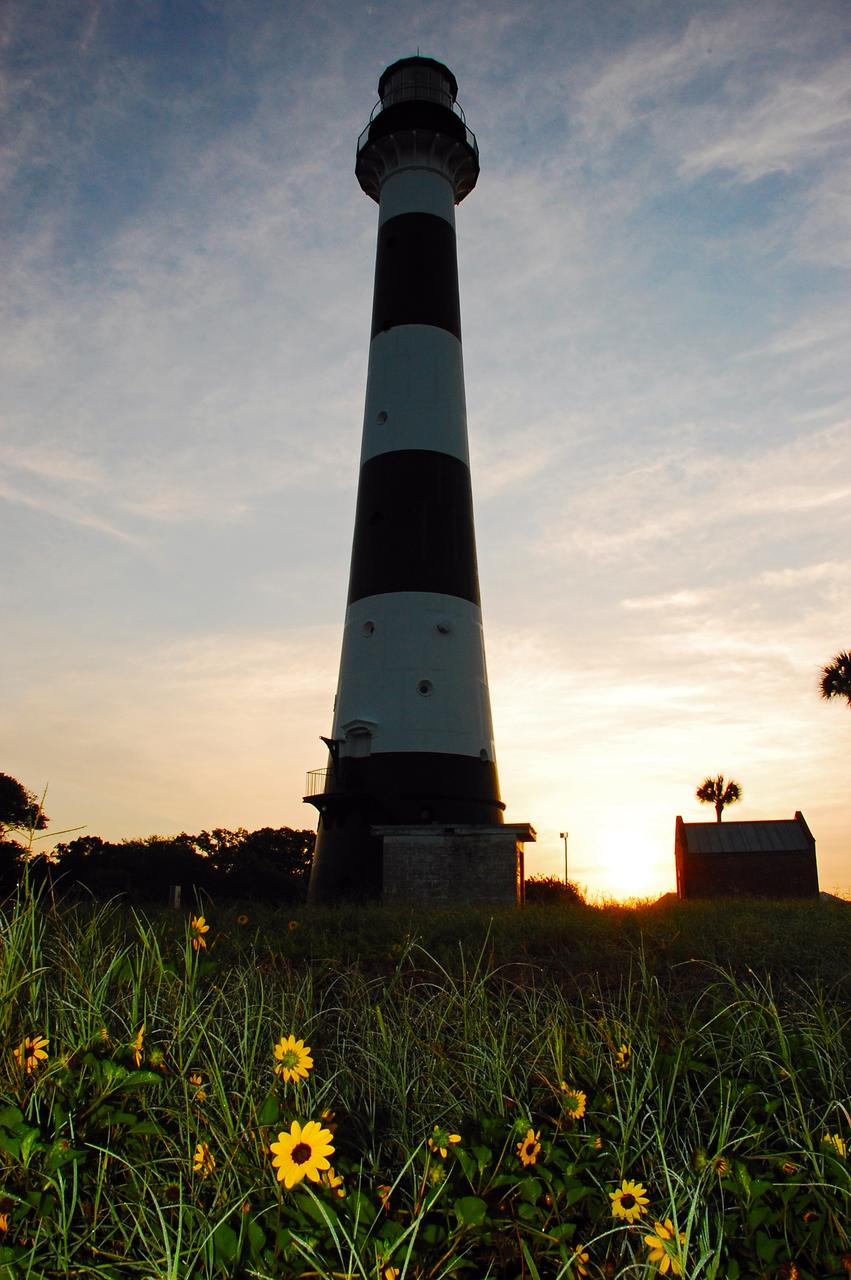
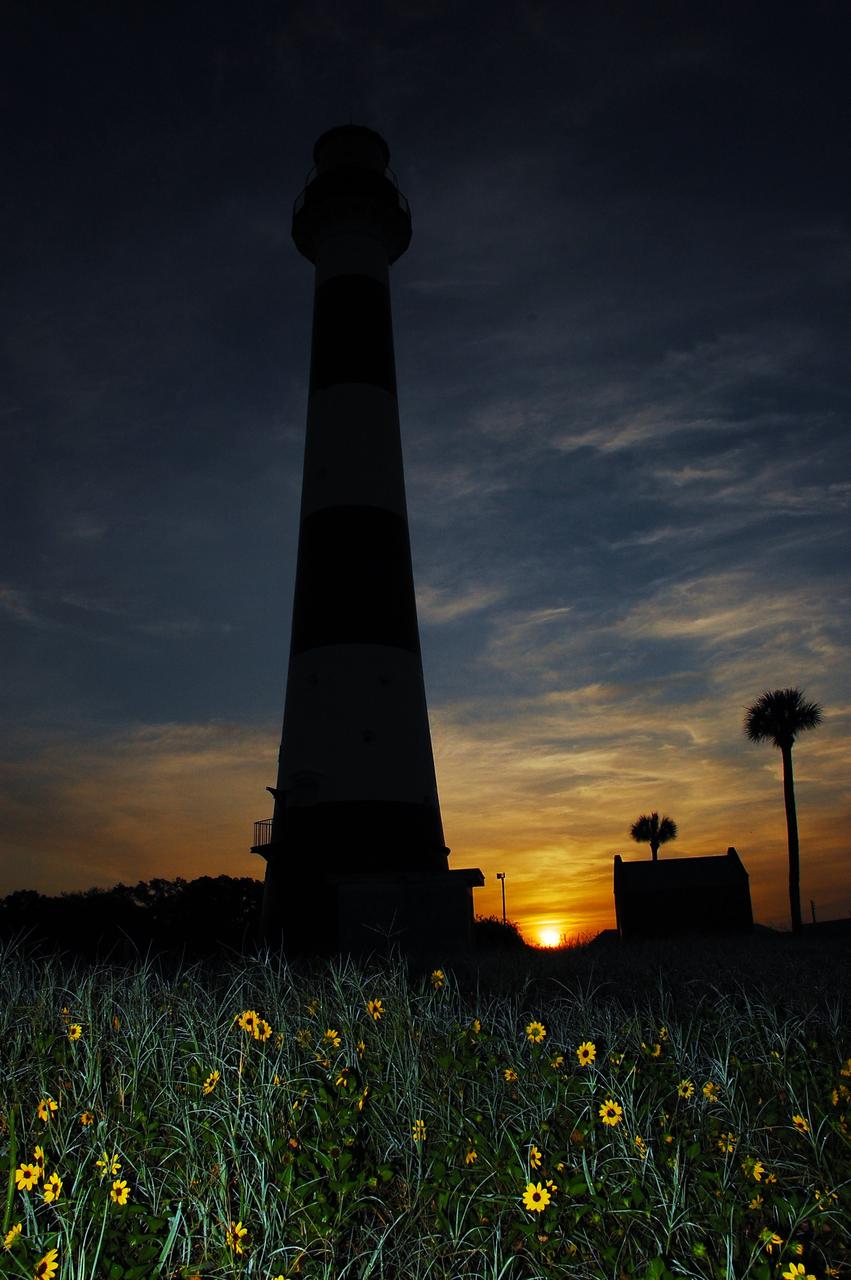
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- As the sun rises, the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse is silhouetted against the early morning sky. The Canaveral light is the only operating lighthouse owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the modern first-order beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
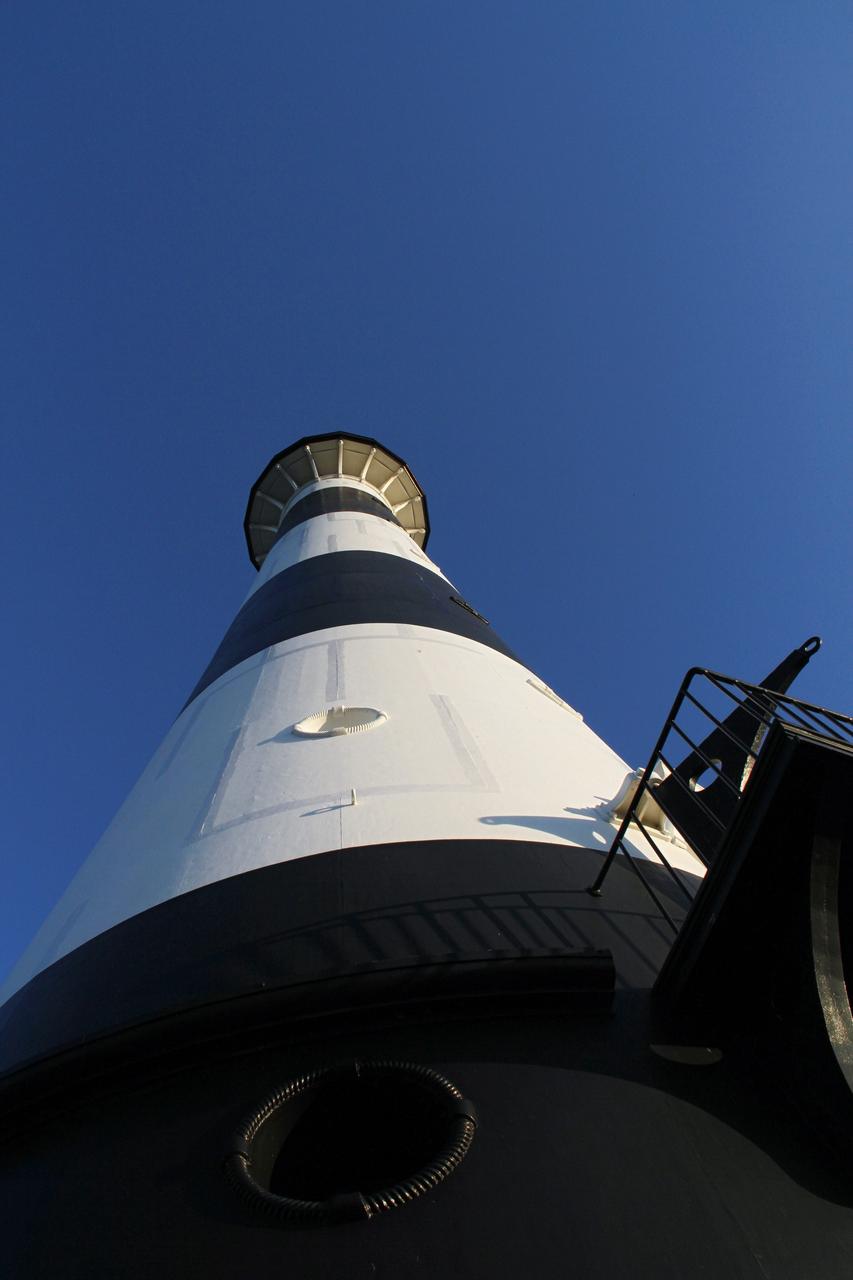

CAPE CANAVERAL AIR FORCE STATION, Fla. – This view looking up contrasts the black and white lighthouse at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station against the Florida sky. The Canaveral light is the only one owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
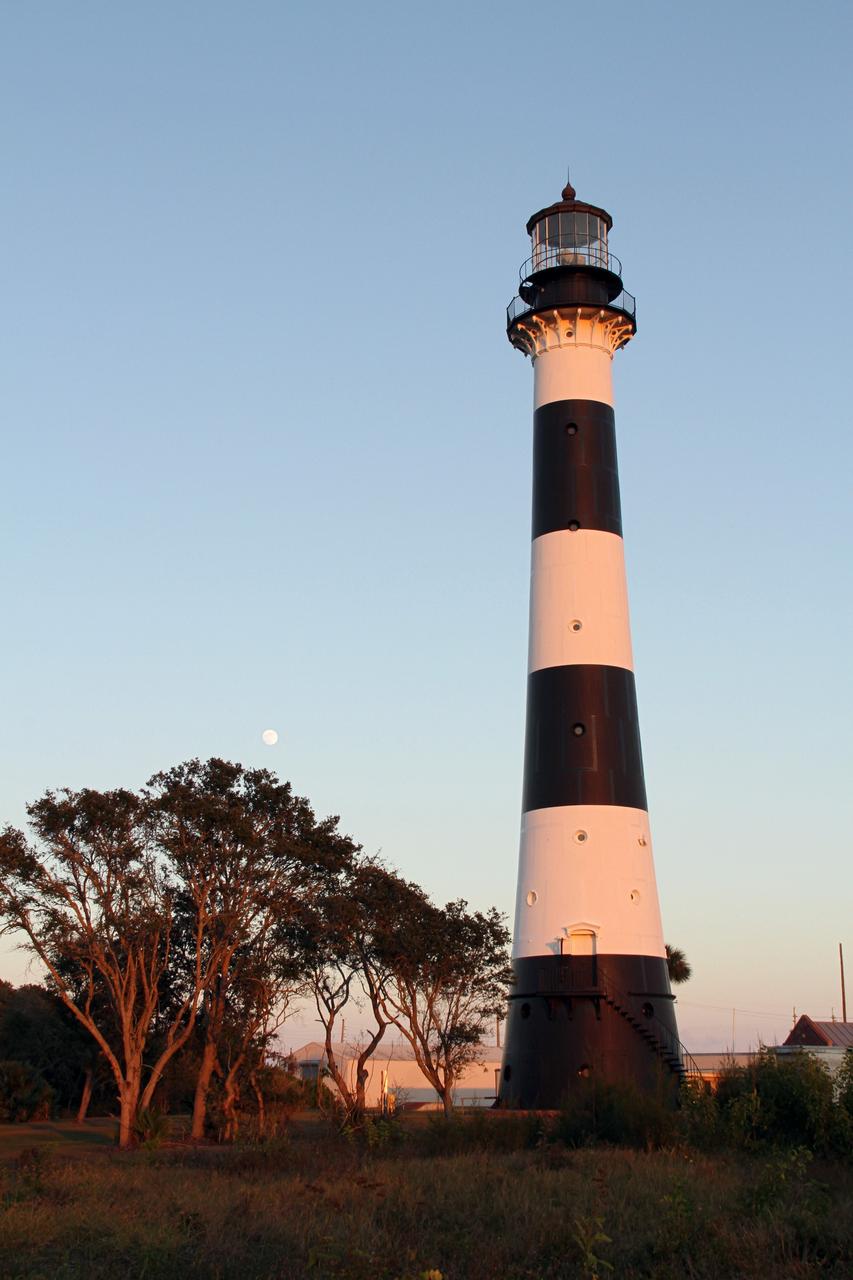

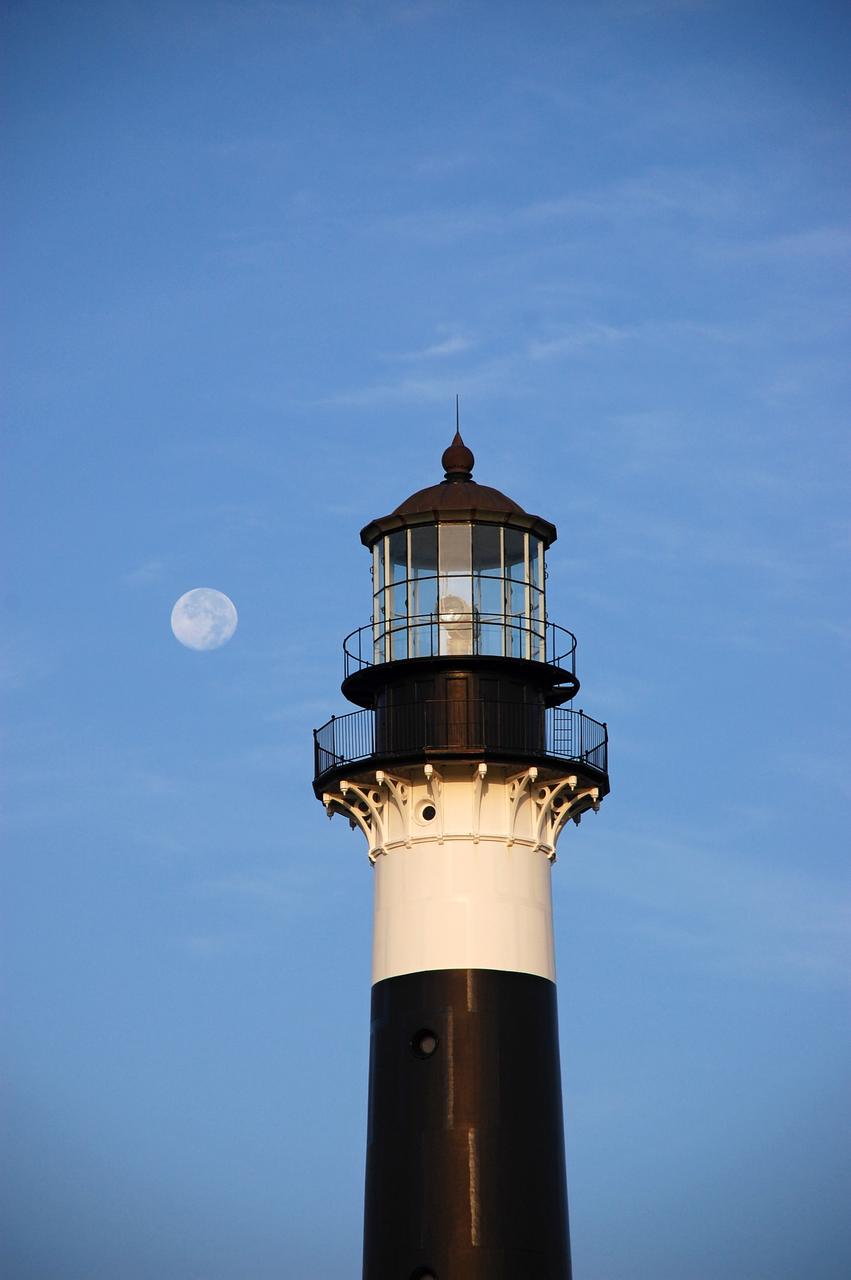
CAPE CANAVERAL AIR FORCE STATION, Fla. – The Cape Canaveral Air Force Station lighthouse takes on a warm glow as dawn breaks and a full moon still shines in the background. The Canaveral light is the only one owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
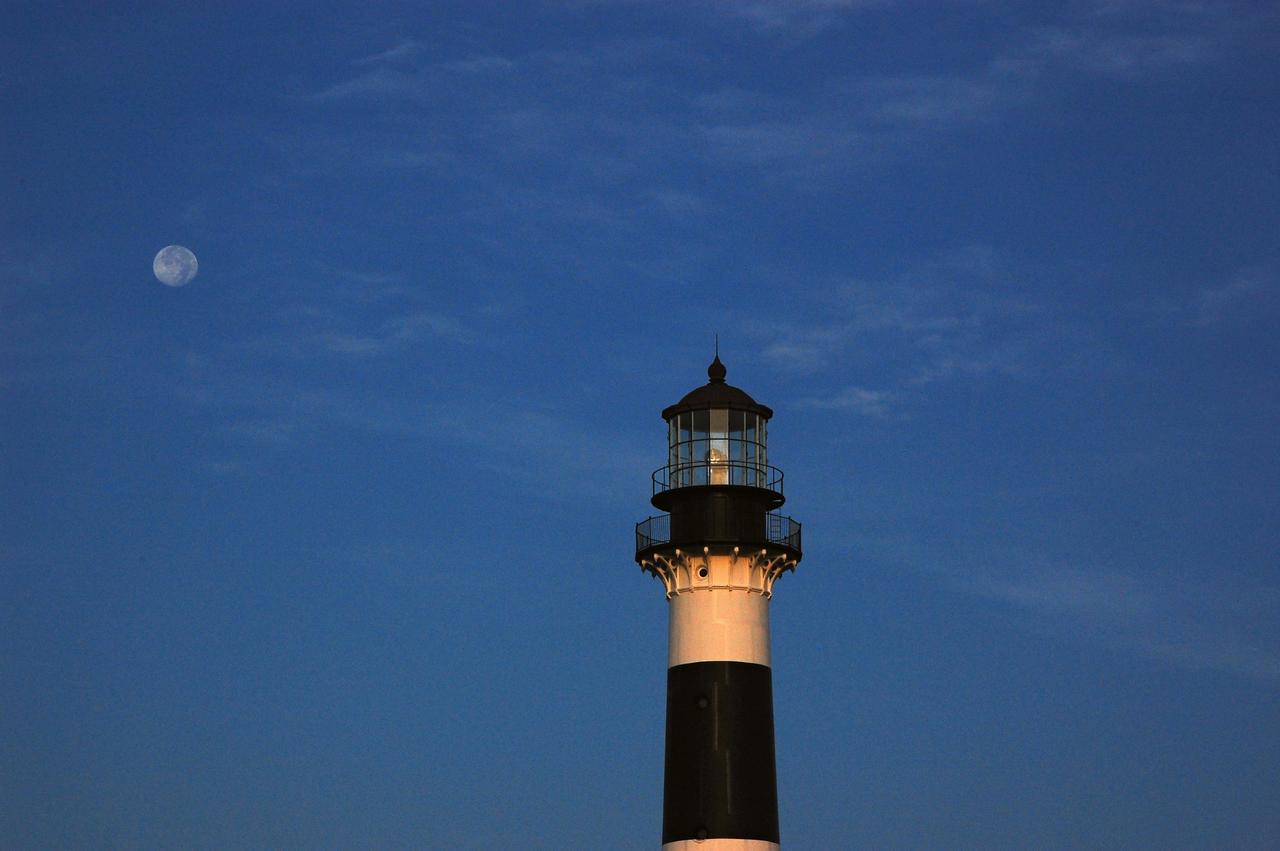

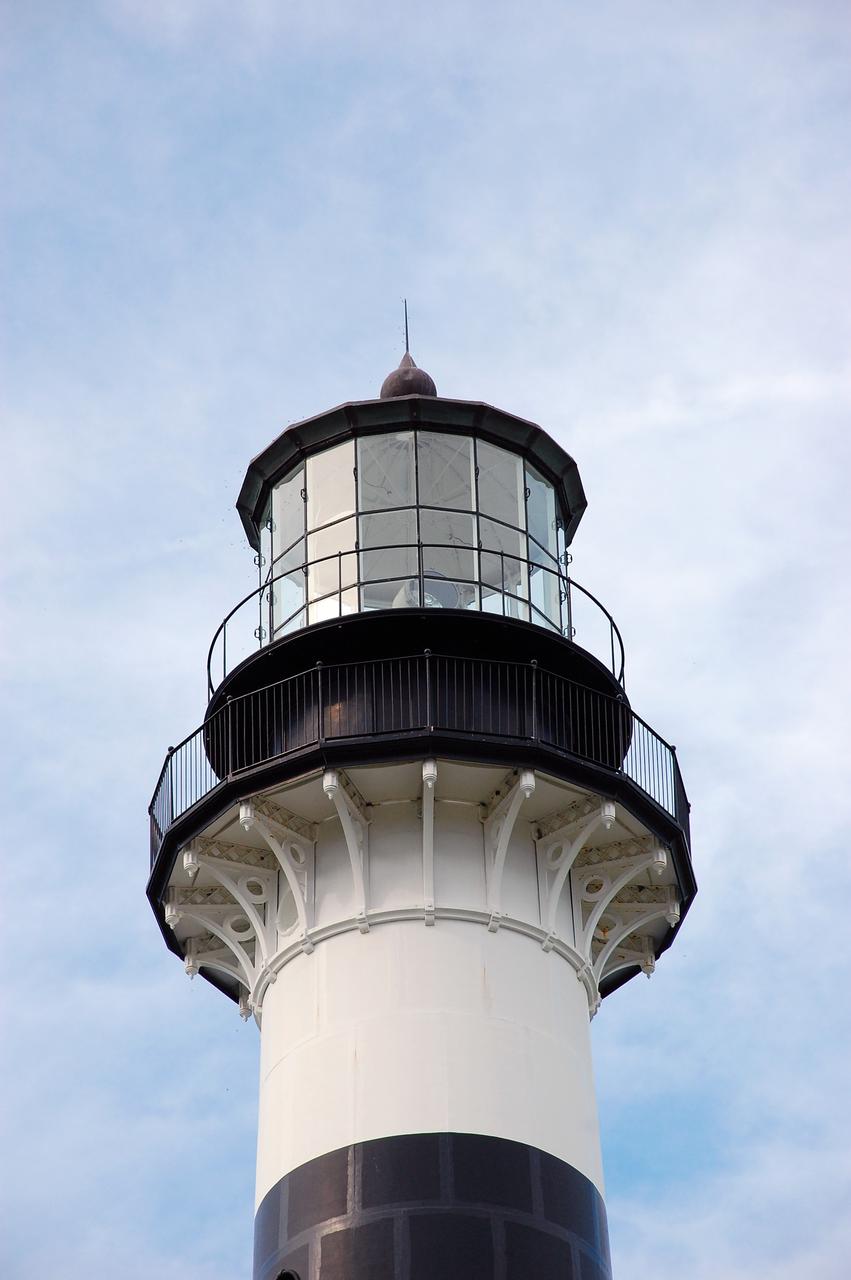
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- The lantern room of the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse, with its modern first-order optic, takes on a warm glow as dawn breaks and a full moon still shines overhead. The Canaveral light is the only operating lighthouse owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
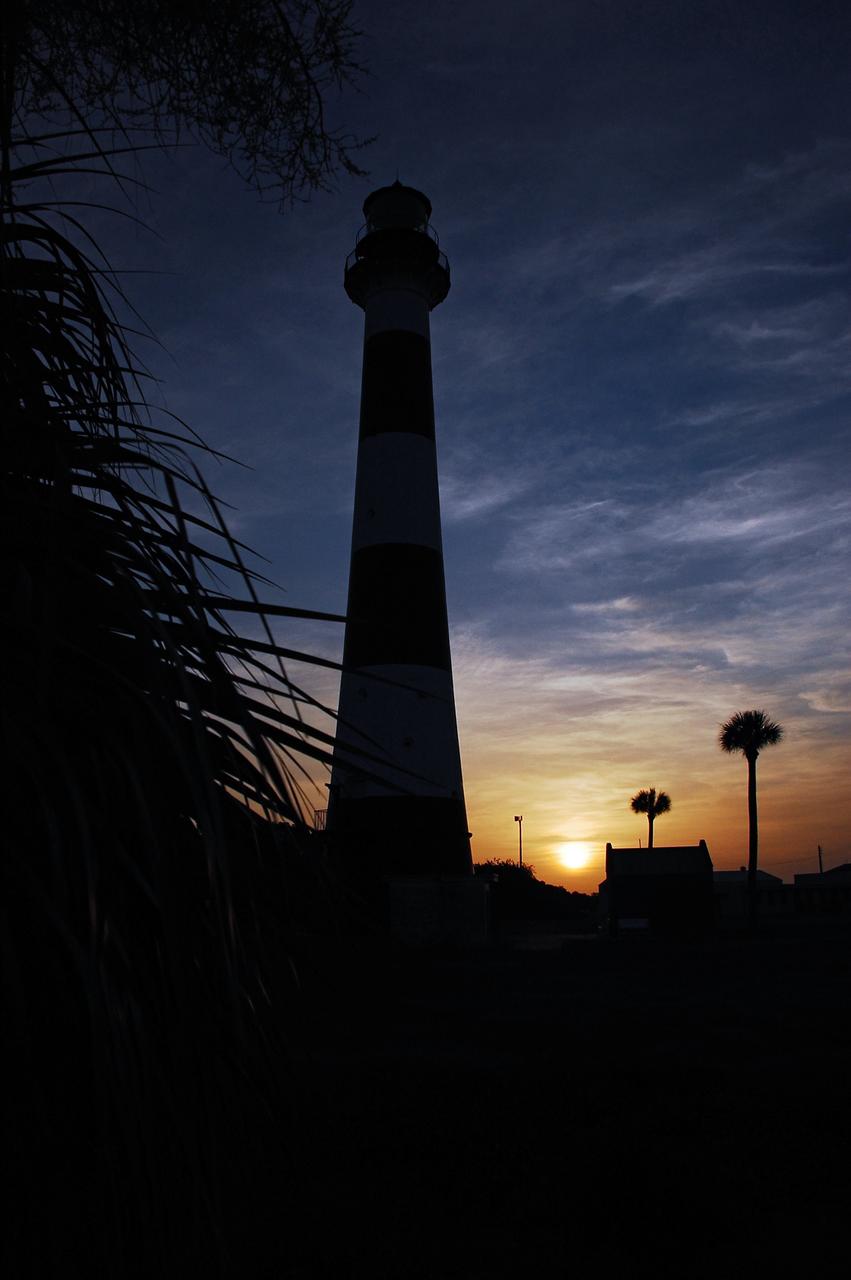

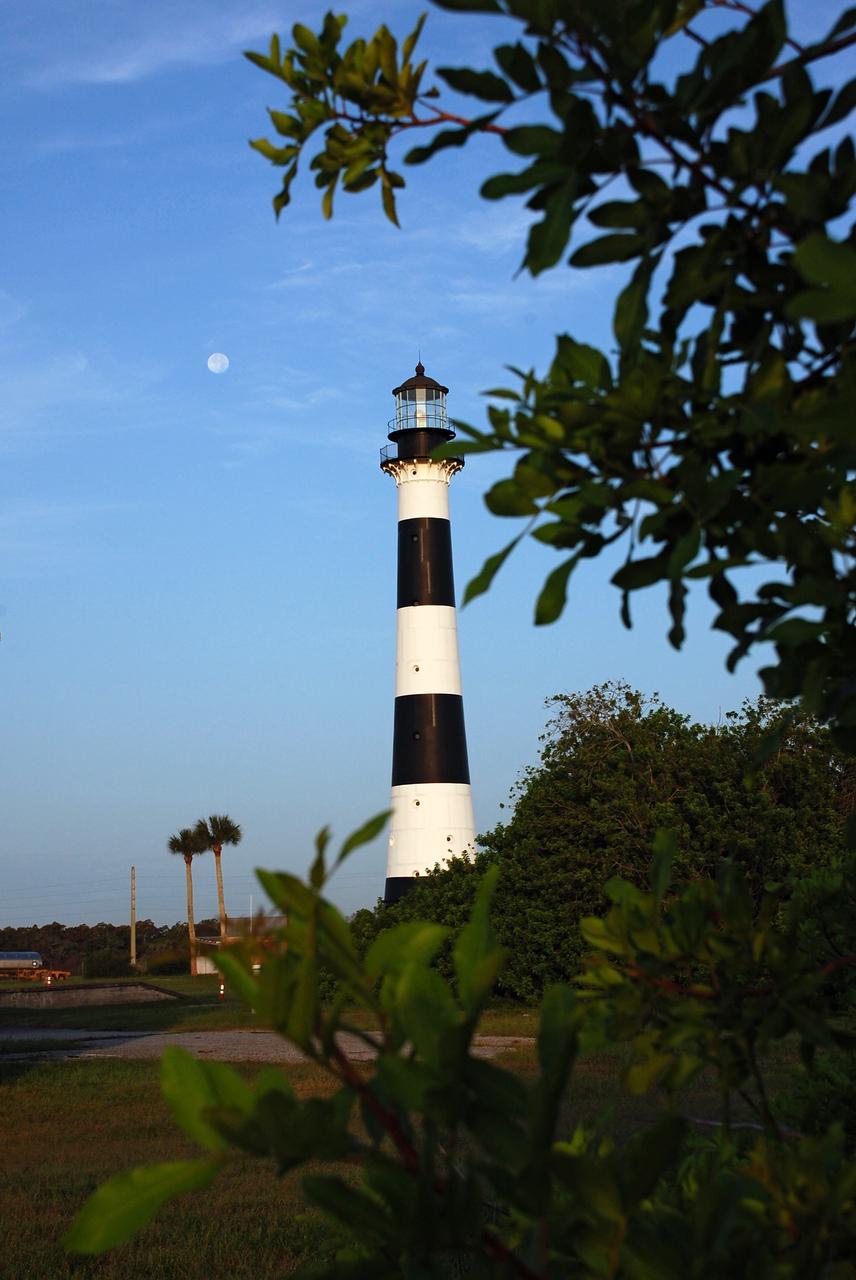
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- As the sun rises, the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse is silhouetted against the early morning sky. The Canaveral light is the only operating lighthouse owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the modern first-order beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
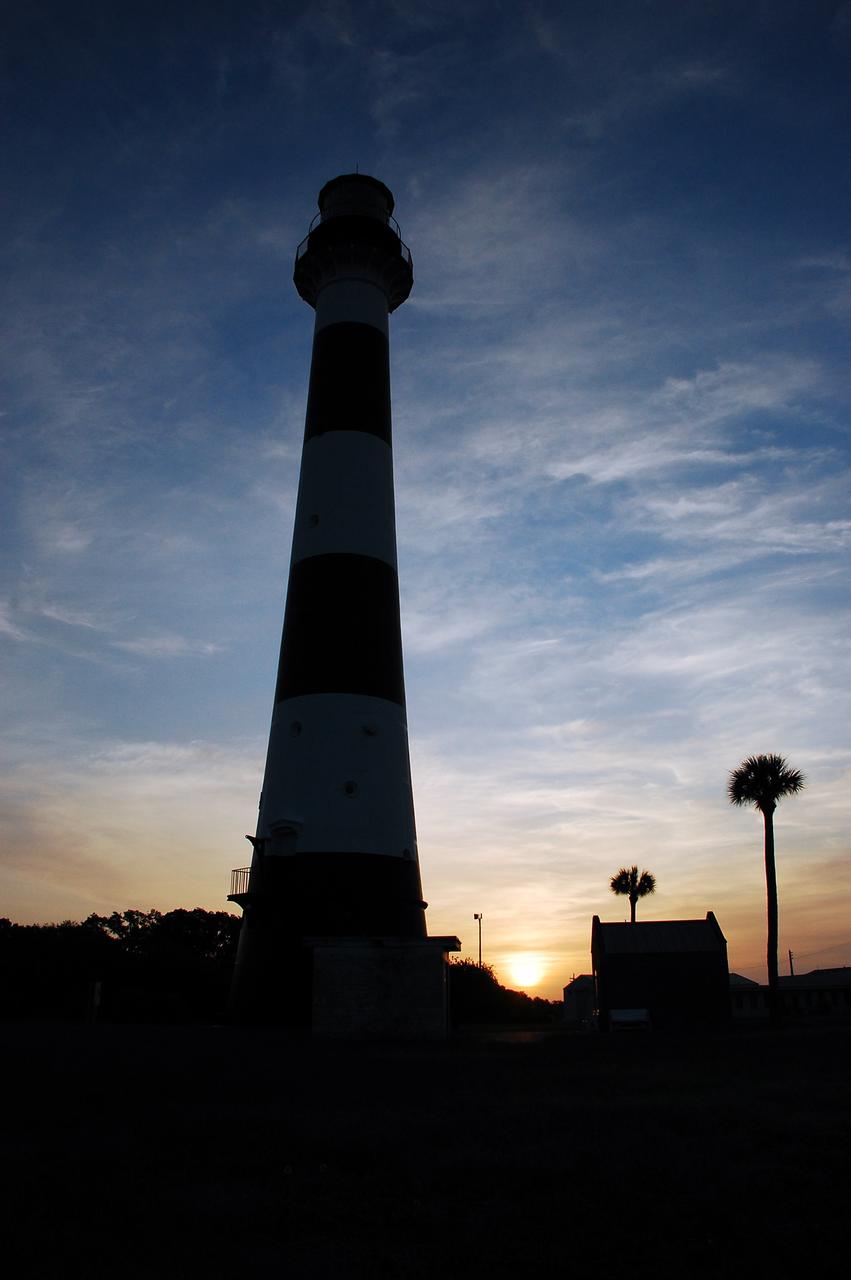

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- As the sun rises, the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse is silhouetted against the early morning sky. The Canaveral light is the only operating lighthouse owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the modern first-order beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
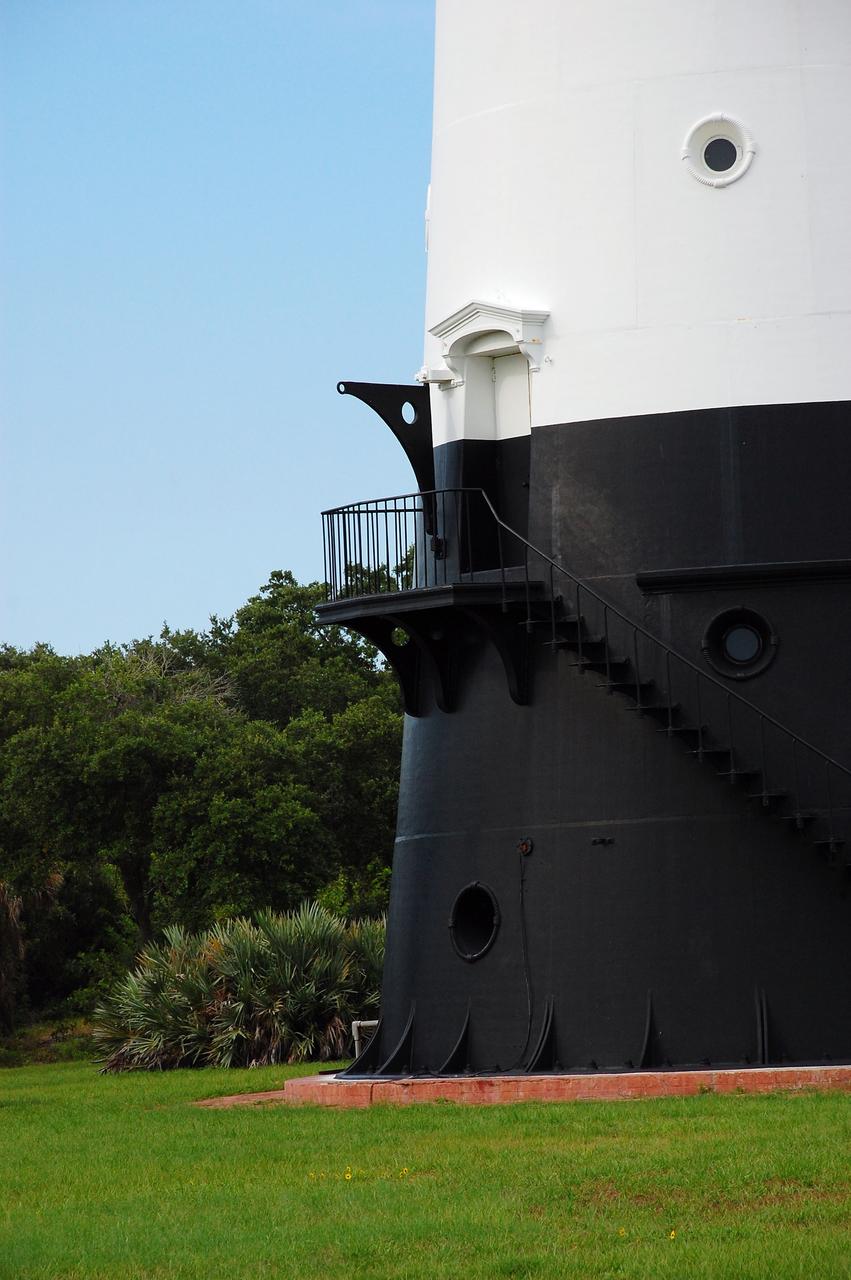

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The historic Cape Canaveral Light, now owned by the U.S. Air Force, has resided in its current spot on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida since 1894. The first lighthouse on Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse was not finished until 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to a new location about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. For more information on the lighthouse, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy/about/history/lighthouse.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- The lantern room of the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse, with its modern first-order optic, takes on a warm glow as dawn breaks and a full moon still shines overhead. The Canaveral light is the only operating lighthouse owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- A warm glow envelopes the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse as dawn breaks and a full moon still shines overhead. The Canaveral light is the only operating lighthouse owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the modern first-order beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- As the sun rises, the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse is silhouetted against the early morning sky. The Canaveral light is the only operating lighthouse owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the modern first-order beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
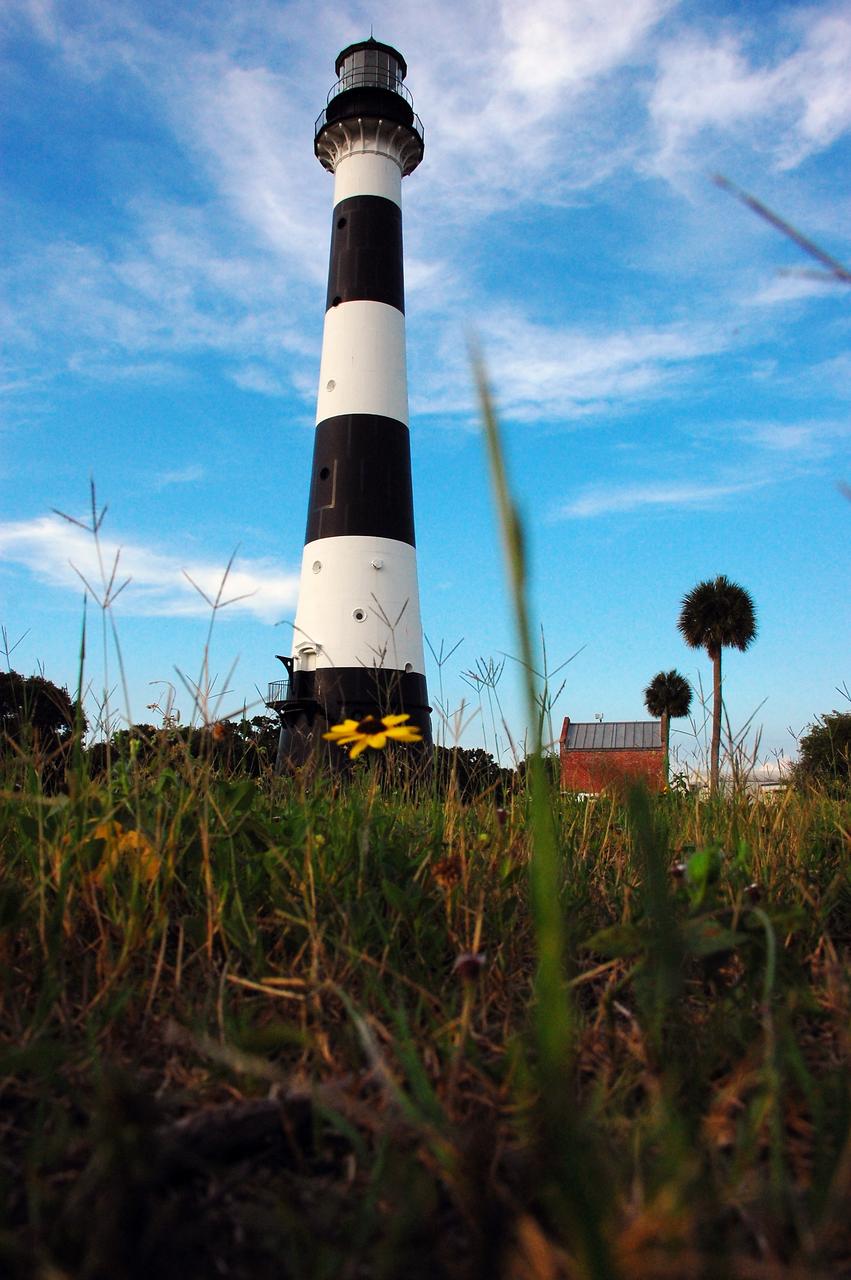

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Natural vegetation surrounds the historic Cape Canaveral Light on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The low structure to the right of the lighthouse is the original oil house. The U.S. Air Force now owns the lighthouse. The first lighthouse on Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse was not finished until 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to a new location about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. For more information on the lighthouse, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy/about/history/lighthouse.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- As the sun rises, the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse is silhouetted against the early morning sky. The Canaveral light is the only operating lighthouse owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the modern first-order beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The U.S. Coast Guard operates the beacon of the historic Cape Canaveral Light as an active navigational aid. The lighthouse resides on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida and is owned by the U.S. Air Force. The first lighthouse on Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse was not finished until 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to a new location about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. For more information on the lighthouse, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy/about/history/lighthouse.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The historic Cape Canaveral Light on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida serves as a navigational aid for boaters and fishing interests along Florida's Atlantic coast. The U.S. Coast Guard operates the lighthouse's beacon the U.S. Air Force owns the lighthouse. The first lighthouse on Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse was not finished until 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to a new location about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. For more information on the lighthouse, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy/about/history/lighthouse.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- As the sun rises, the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse is silhouetted against the early morning sky. The Canaveral light is the only operating lighthouse owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the modern first-order beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
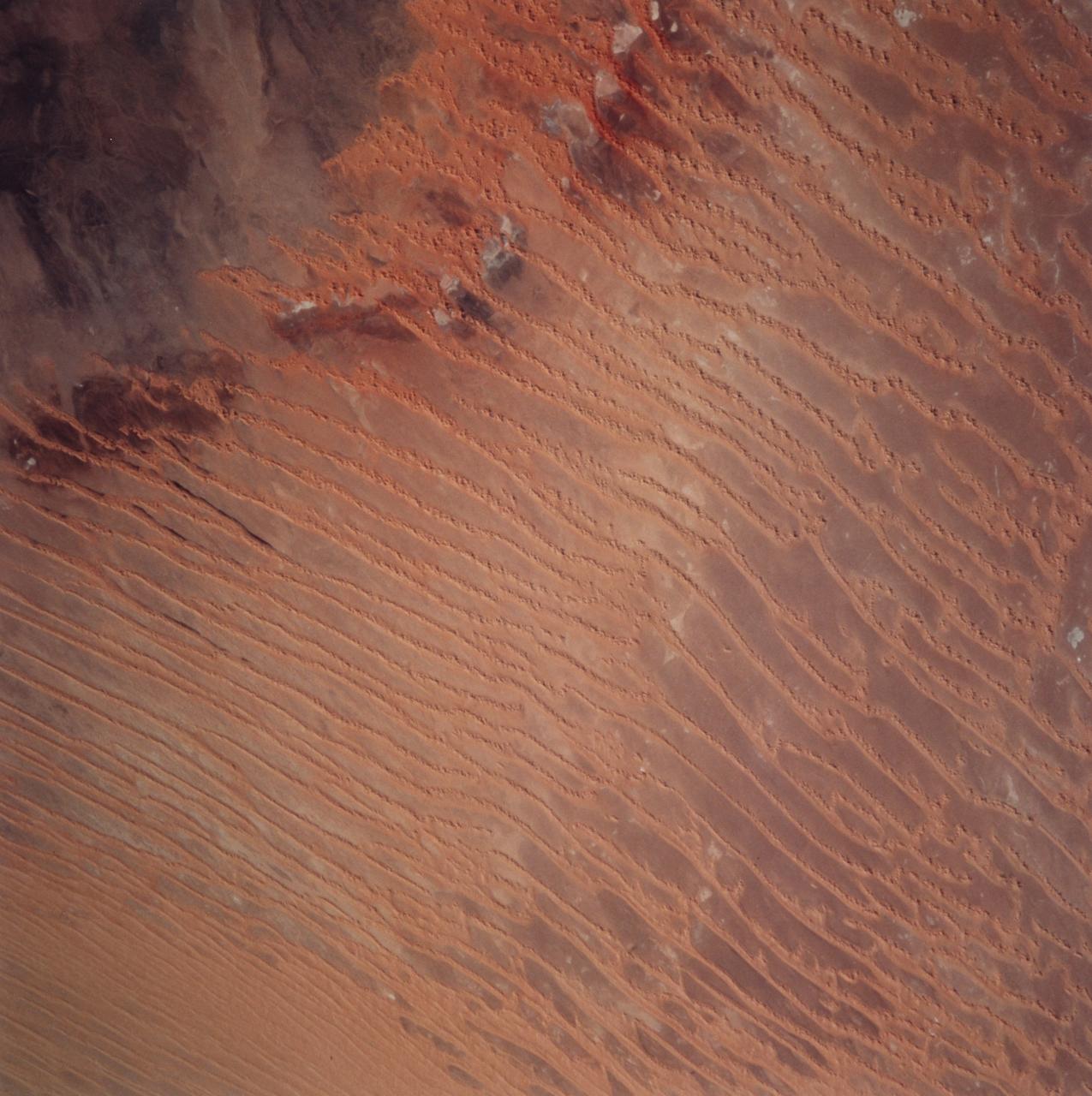

STS099-729-045 (11-22 February 2000) ---This Earth scene from the Space Shuttle Endeavour features linear dunes in the Algerian Saharan sand sea known as the Erg Chech. The dunes, according to NASA scientists, have been built up over thousands of years into masses elongated roughly parallel with the prevailing northeast winds. Dune chains in the northern (upper) half of the view are 5-8 kilometers apart. A slight change in orientation and an increase in the density of dunes appear across the middle of the view. Such changes usually relate to changes in sand supply, and also to topographic scarps over which the dunes pass. Obstacles like scarps and hills locally cause a leftward deflection (in the Northern Hemisphere) in wind direction, an effect that can be seen here in the dune orientation in the middle of the photo. Dunes in the lower part of the view are 2-5 kilometers apart. White patches are small dry lakes at low points in the underlying rock surface. The strong red color in some dunes near the edge of the dune field (left margin) is iron staining derived from sand particles blown into the dunes from the underlying iron-rich soils. A dune-free area appears in the lower left corner.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Reconstruction from the original architectural plans of the keeper's house, next to the historic Cape Canaveral Light on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, is planned by the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse Foundation. The lighthouse currently is owned by the U.S. Air Force. The first lighthouse on Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse was not finished until 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to a new location about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. For more information on the lighthouse, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy/about/history/lighthouse.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
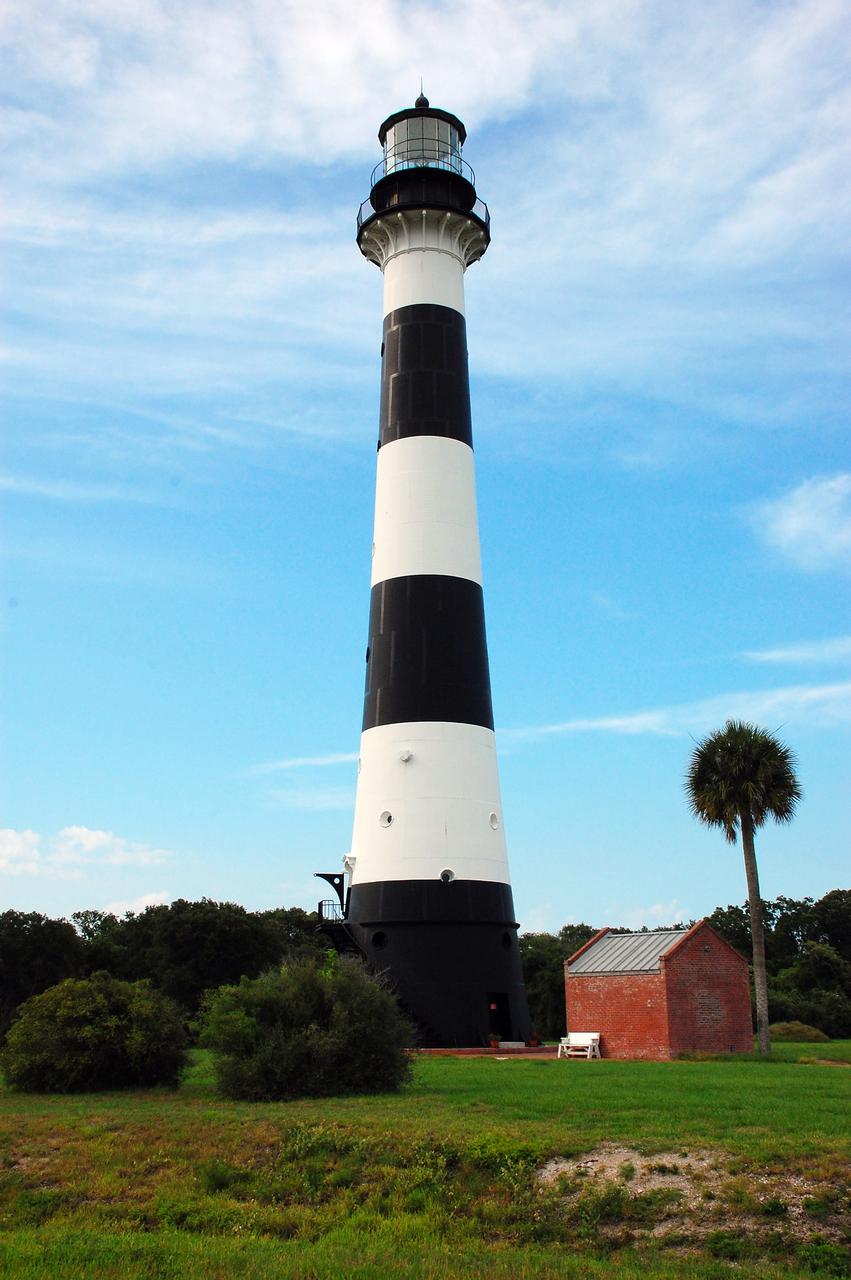

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida is home to the historic Cape Canaveral Light, a lighthouse built circa 1868 and now owned by the U.S. Air Force. The first lighthouse on Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse was not finished until 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to a new location about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. For more information on the lighthouse, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy/about/history/lighthouse.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
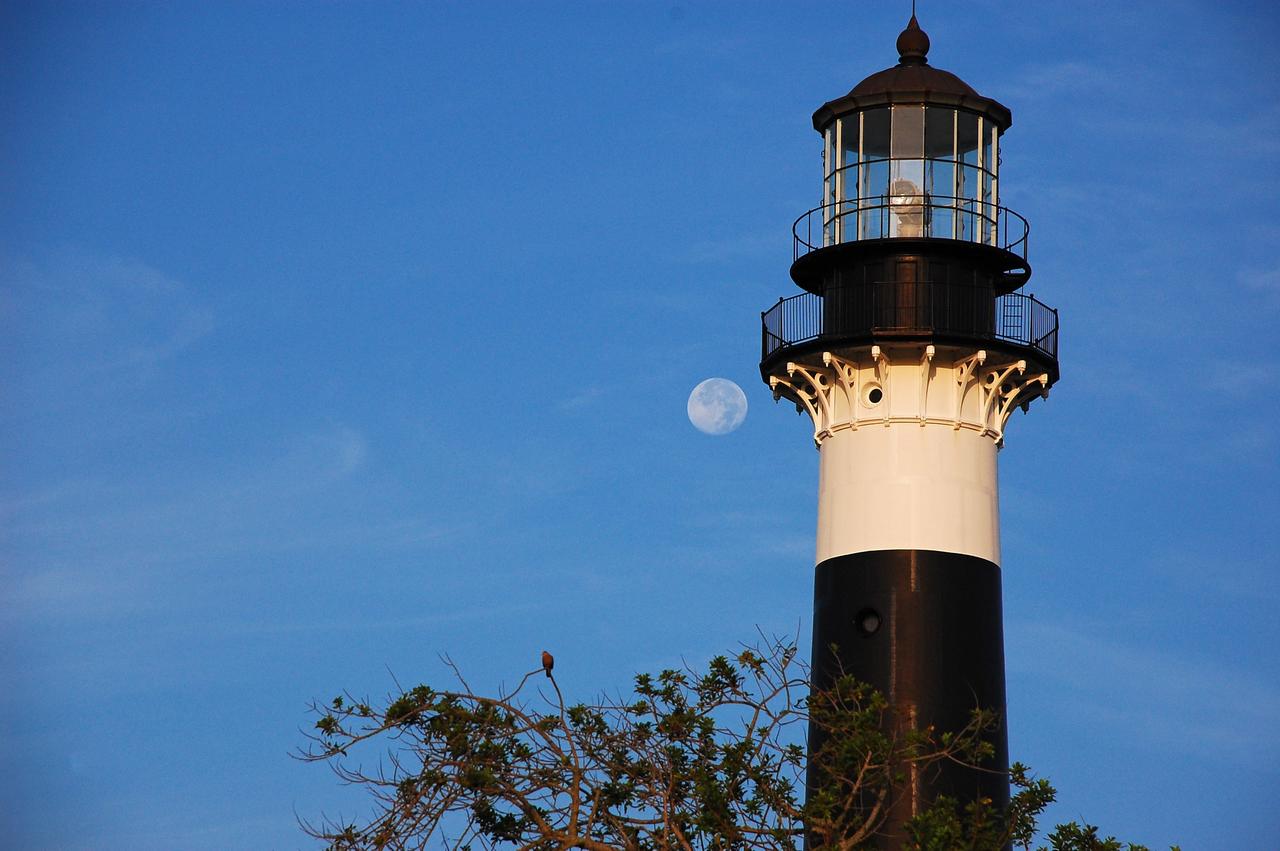

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- The lantern room of the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse, with its modern first-order optic, takes on a warm glow as dawn breaks and a full moon still shines overhead. The Canaveral light is the only operating lighthouse owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
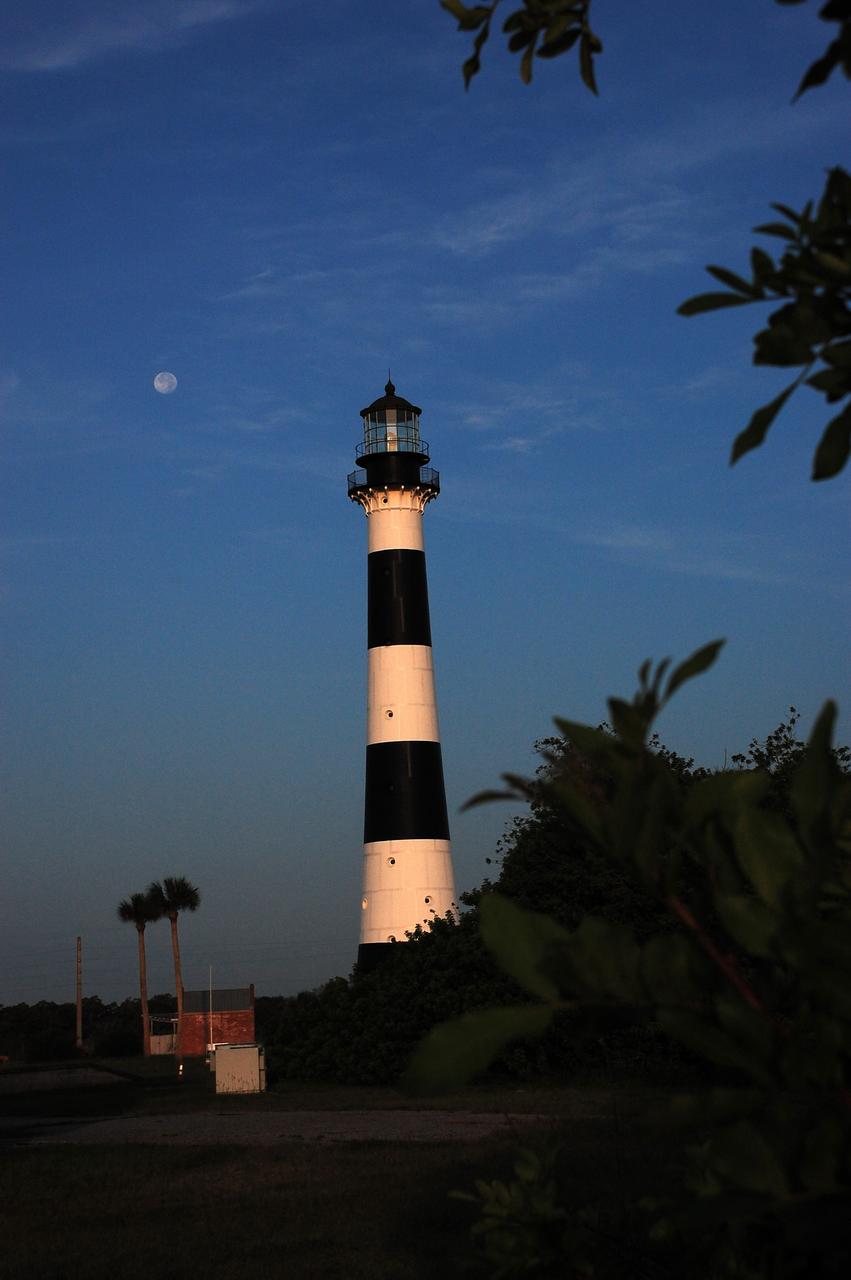

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- A warm glow envelopes the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse as dawn breaks and a full moon still shines overhead. The Canaveral light is the only operating lighthouse owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the modern first-order beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
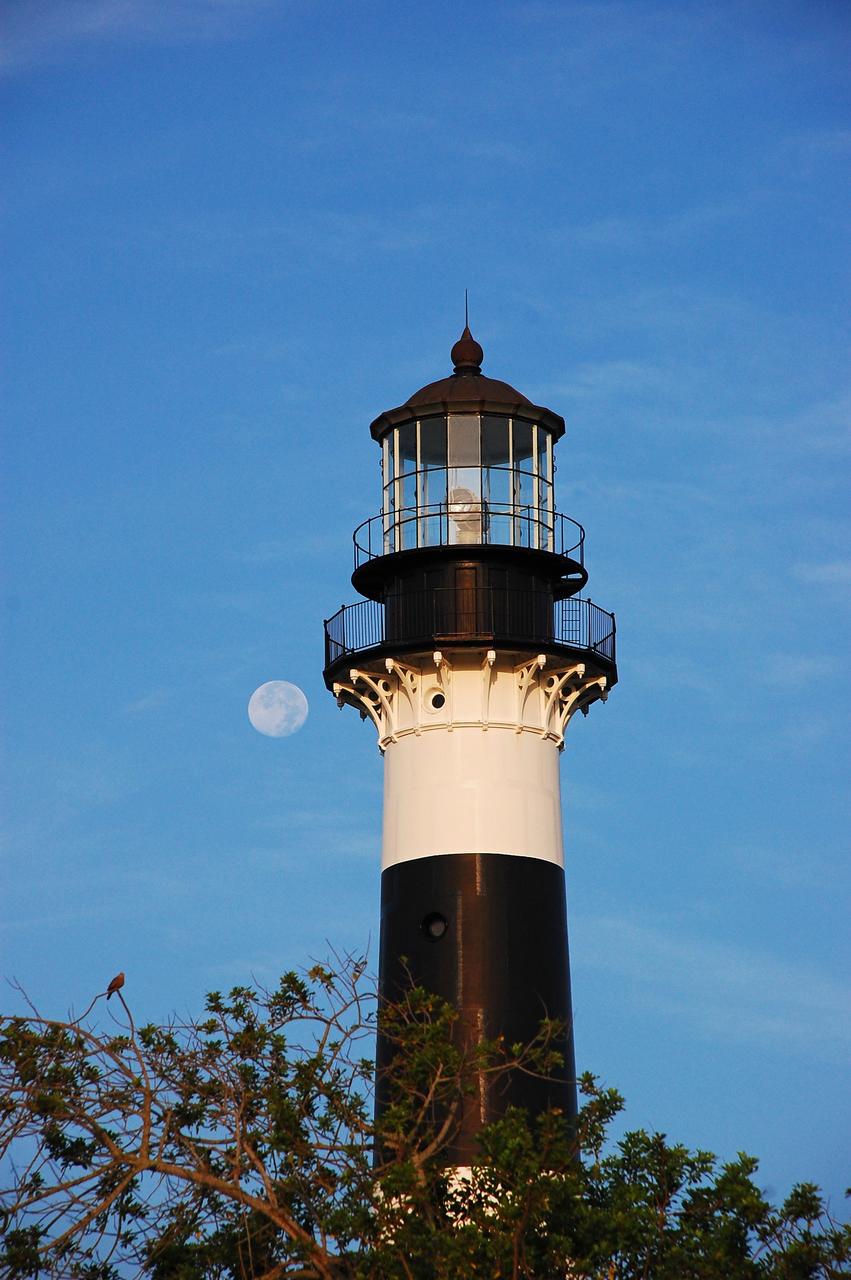

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- The lantern room of the Cape Canaveral Lighthouse, with its modern first-order optic, takes on a warm glow as dawn breaks and a full moon still shines overhead. The Canaveral light is the only operating lighthouse owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
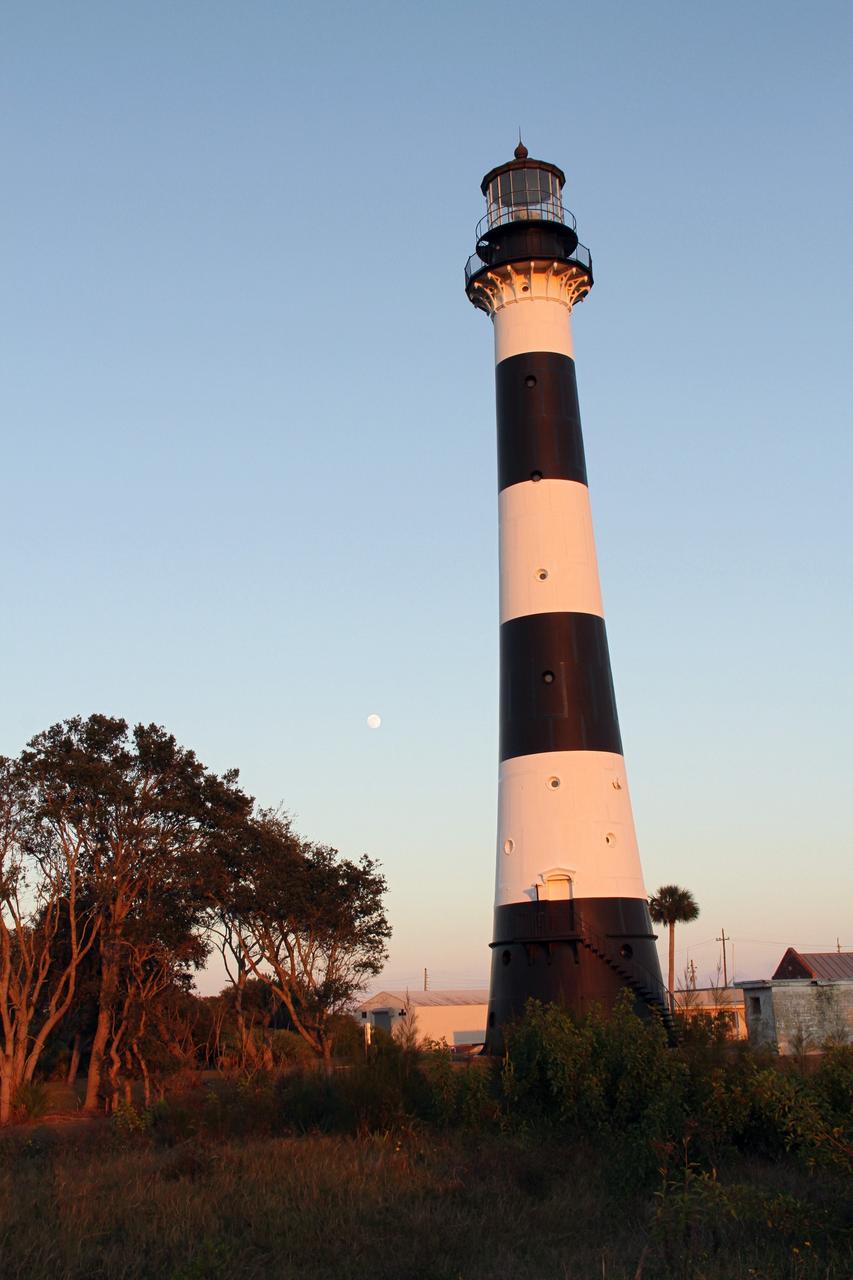

CAPE CANAVERAL AIR FORCE STATION, Fla. – The Cape Canaveral Air Force Station lighthouse takes on a warm glow as dawn breaks and a full moon still shines in the background. The Canaveral light is the only one owned by the U.S. Air Force. In 2000, the Coast Guard transferred ownership of the lighthouse structure and its grounds to the Air Force, which is now responsible for maintaining it. The U.S. Coast Guard continues to operate the beacon as an active navigational aid. The first lighthouse at Cape Canaveral was built near the tip of the Cape in 1848. The structure was only about 60 feet high with a rather dim light powered by whale oil. In 1859, work began nearby on a new, taller iron structure. Construction was halted during the Civil War, and the lighthouse finally was finished in 1868. The structure, with a brick lining inside its iron exterior, was painted with its "daymark" black and white horizontal bands in 1873 to make it easier to identify during the day as a navigation point. Between 1892 and 1894, the lighthouse was dismantled and moved to its new home about a mile from the coast, where it stands today. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
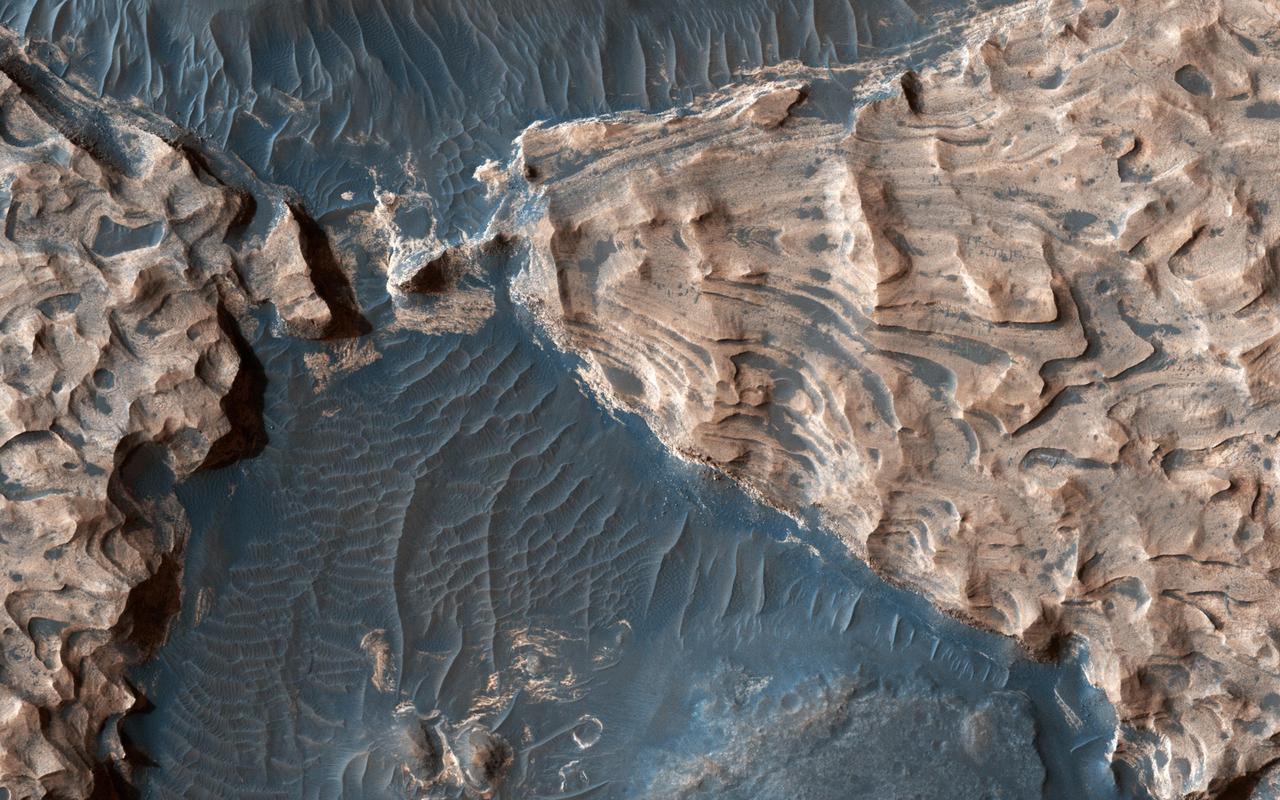

Acquired on April 1, 2018, this image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows Aram Chaos, a 280 kilometer-diameter ancient impact crater that lies within in the Southern Highlands of Mars. Uplifted blocks of light-toned layers, composed largely of the iron-oxide hematite and water-altered silicates, indicate that this crater once held a lake. Scientists suggest that these enormous flood channels were carved quickly within just weeks or months by catastrophic outflows of groundwater over 2.5 billion years ago from beneath Aram Chaos and nearby regions. Today dark (basaltic) dunes fill most of the low regions and the etched areas of the uplifted blocks obscure much of the original crater floor. Aram Chaos is located near the headwaters of Ares Vallis, a large outflow channel system that extends about 1700 kilometers towards the northwest across the ancient cratered highlands before emptying into the Northern Lowlands at Chryse Planitia near the Mars Pathfinder landing site. More information is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22585
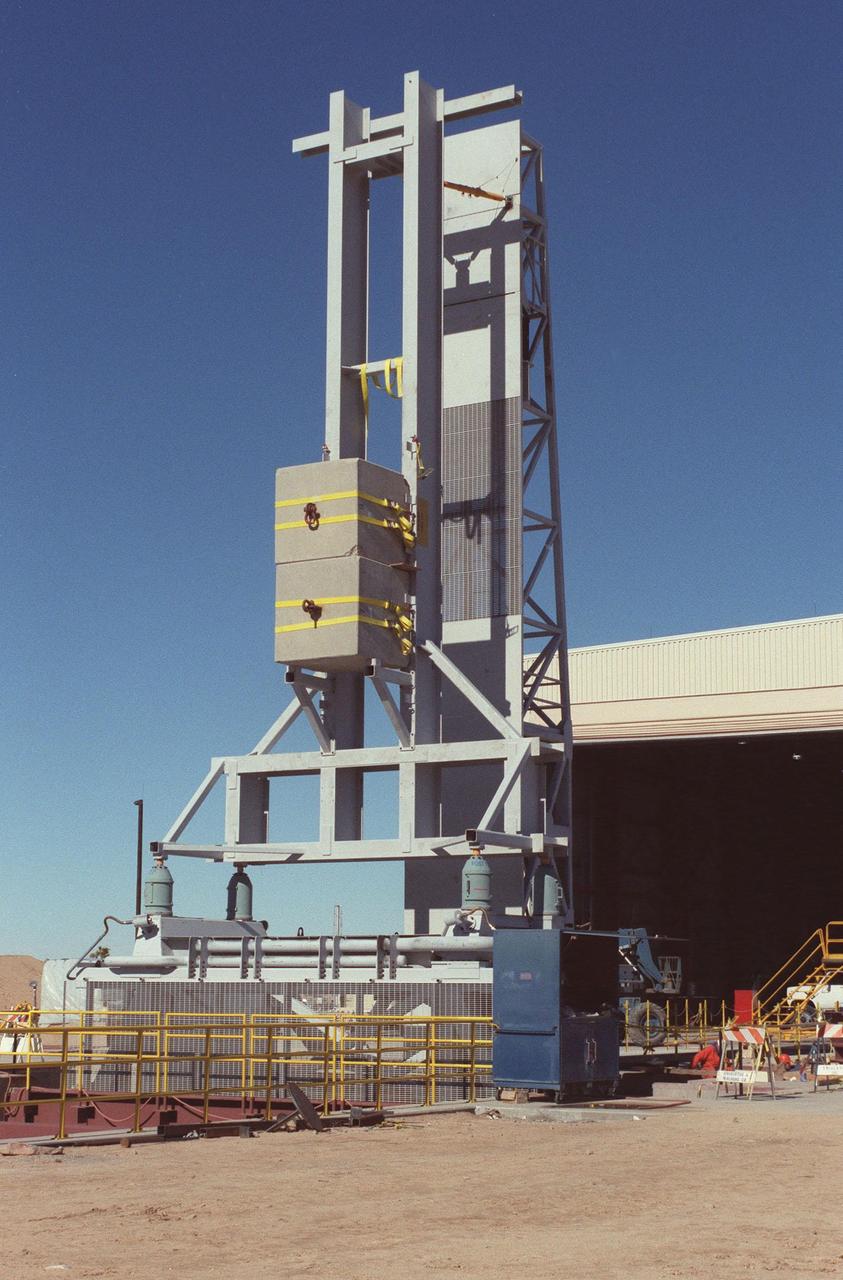

The KSC-developed X-33 weight simulator (left), known as the "iron bird," is fully raised to a vertical position at the X-33 launch site as part of launch equipment testing on Edwards Air Force Base, CA. The simulator matches the 75,000-pound weight and 63-foot height of the X-33 vehicle that will be using the launch equipment. KSC's Vehicle Positioning System (VPS) placed the simulator on the rotating launch platform prior to the rotation. The new VPS will dramatically reduce the amount of manual labor required to position a reusable launch vehicle for liftoff
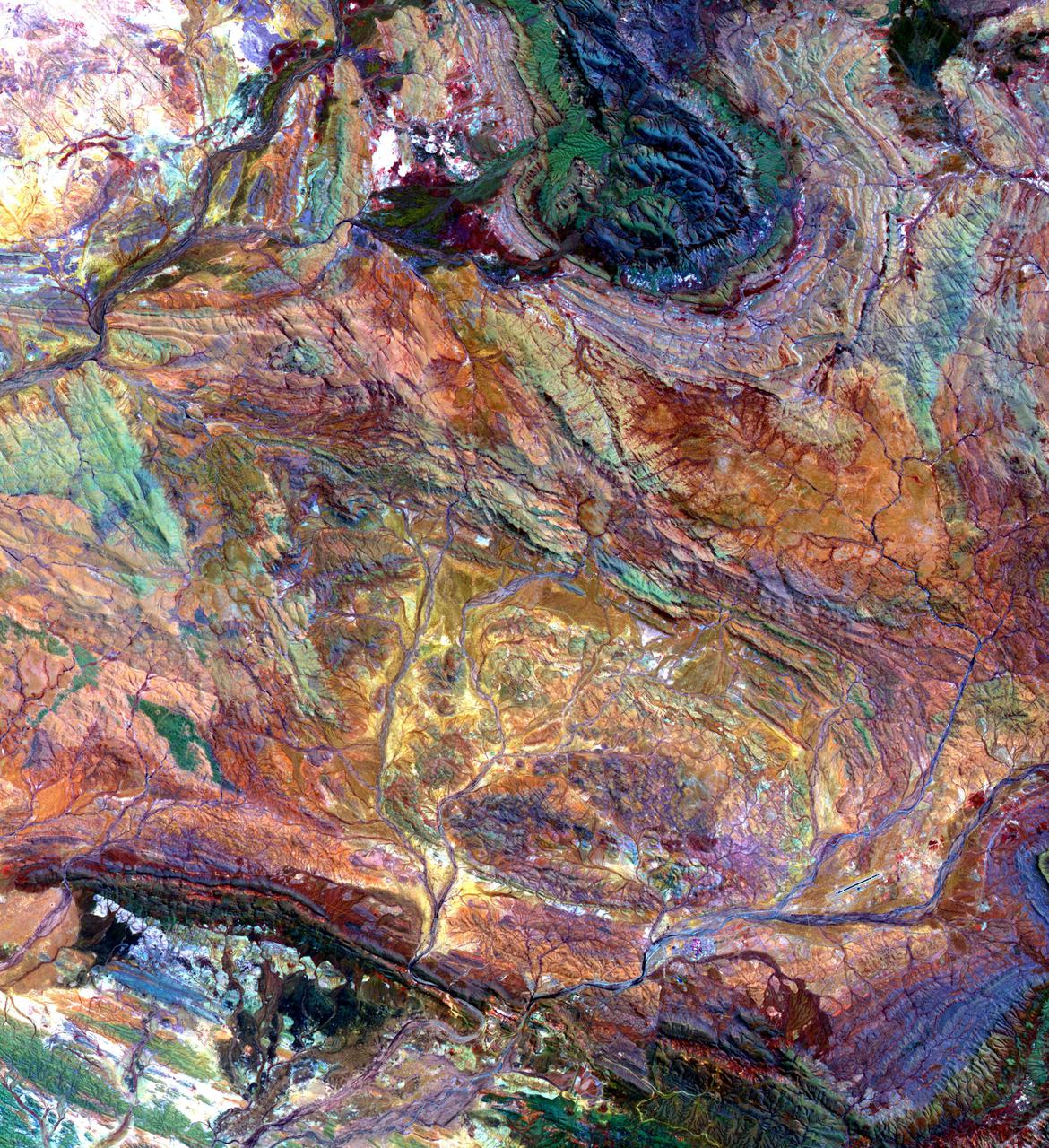

The Pilbara in northwestern Australia exposes some of the oldest rocks on Earth, over 3.6 billion years old. The iron-rich rocks formed before the presence of atmospheric oxygen, and life itself. Found upon these rocks are 3.45 billion-year-old fossil stromatolites, colonies of microbial cyanobacteria. The image is a composite of ASTER bands 4-2-1 displayed in RGB. The image was acquired October 12, 2004, covers an area of 49.1 by 55.2 km, and is located at 22.8 degrees south, 117.6 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25122
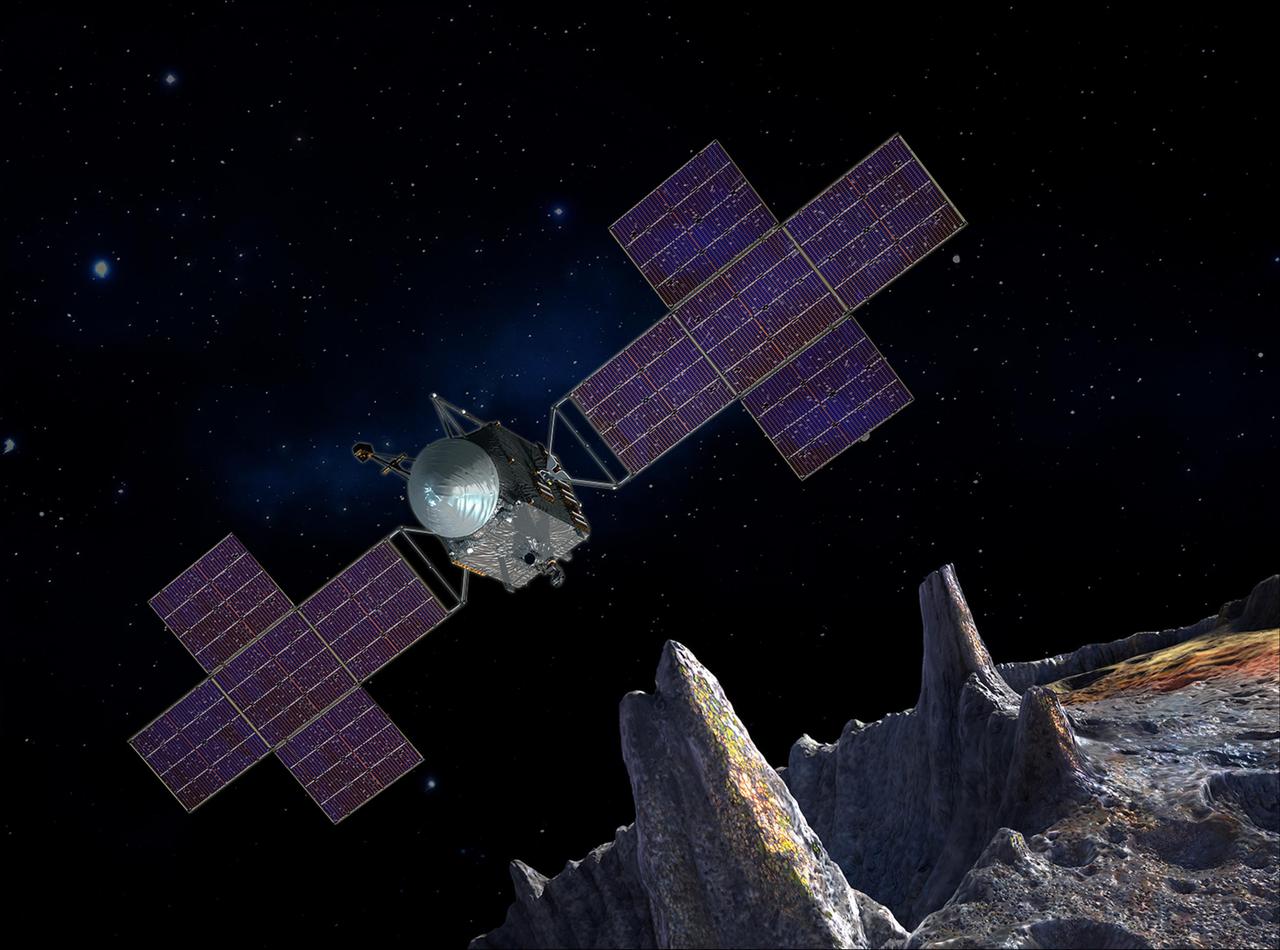

This artist's-concept illustration depicts the spacecraft of NASA's Psyche mission near the mission's target, the metal asteroid Psyche. The artwork was created in May 2017 to show the five-panel solar arrays planned for the spacecraft. The spacecraft's structure will include power and propulsion systems to travel to, and orbit, the asteroid. These systems will combine solar power with electric propulsion to carry the scientific instruments used to study the asteroid through space. The mission plans launch in 2022 and arrival at Psyche, between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, in 2026. This selected asteroid is made almost entirely of nickel-iron metal. It offers evidence about violent collisions that created Earth and other terrestrial planets. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21499
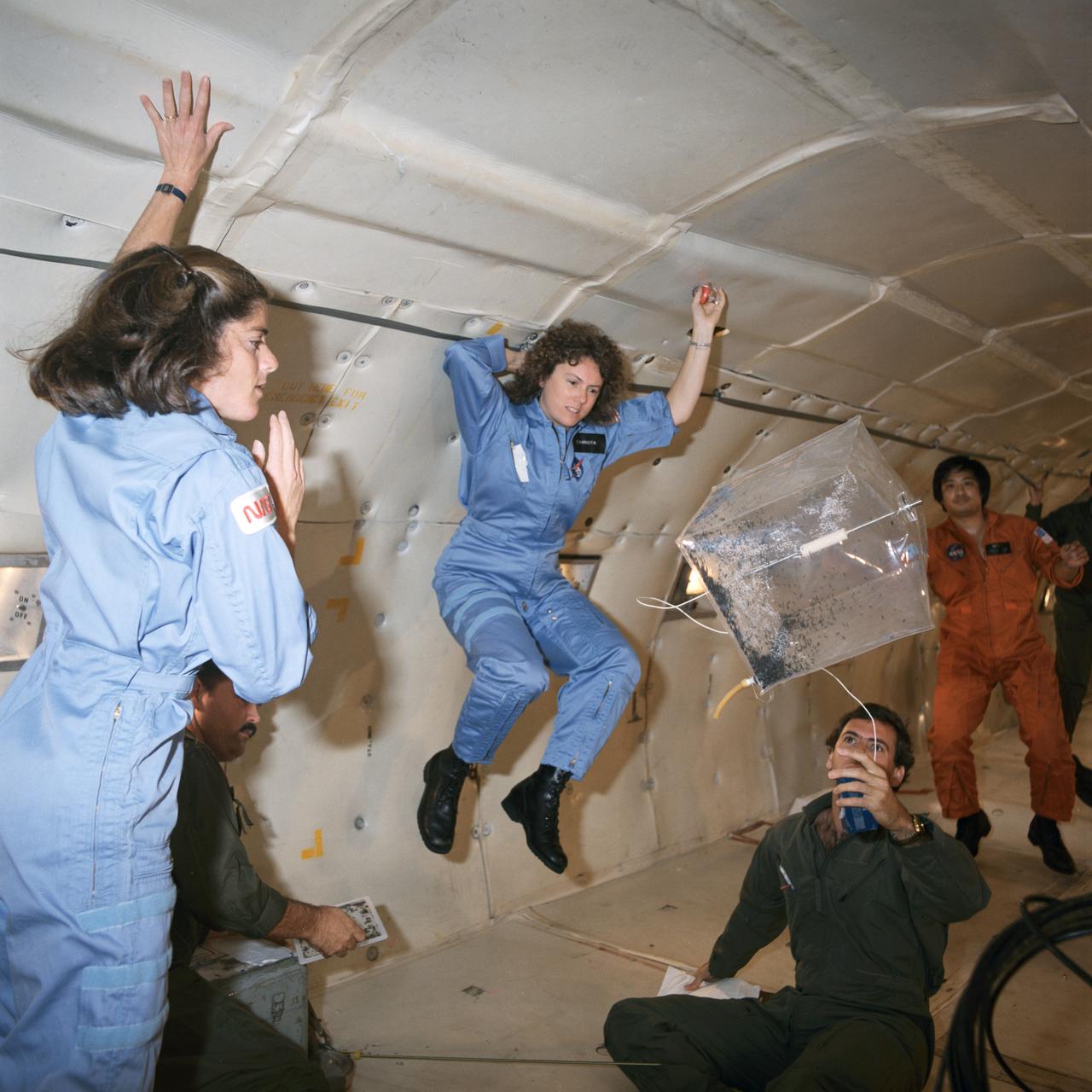

S85-42474 (16 Oct. 1985) --- A KC-135 aircraft provides a brief period of weightlessness as a preview for a teacher, in training to fly onboard a space shuttle for the Teacher-in-Space Project, and her backup. Sharon Christa McAuliffe (center frame), STS-51L prime crew member, and Barbara Morgan, her backup, monitor an experiment involving magnetic effects - one of the tests to be performed on the STS-51L flight. The experiment uses a control box, a square receptacle containing rubber tubing, stainless steel rod, a filter with desiccant, soft iron wire and a magnet. Photo credit: NASA
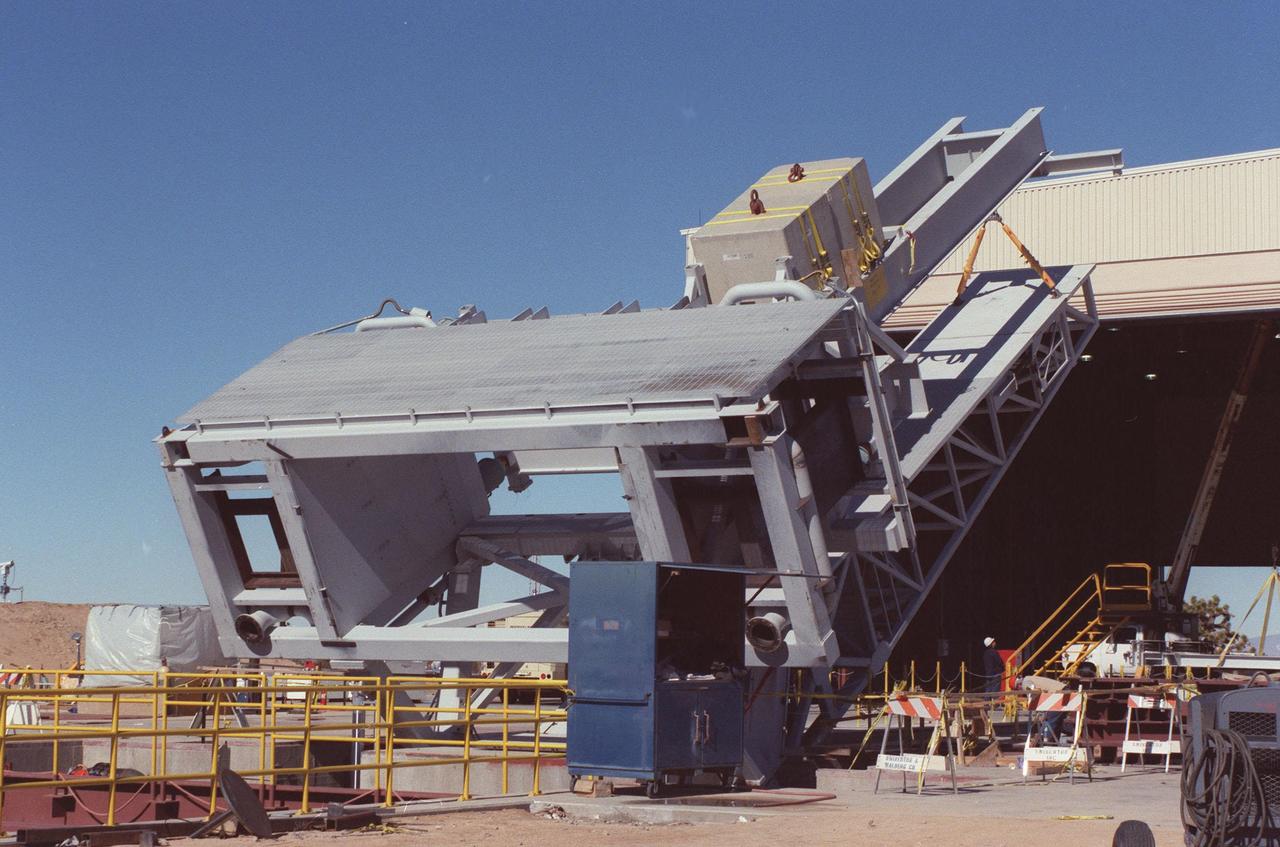

The KSC-developed X-33 weight simulator (top), known as the "iron bird," is lifted to a vertical position at the X-33 launch site as part of launch equipment testing on Edwards Air Force Base, CA. The simulator matches the 75,000-pound weight and 63-foot height of the X-33 vehicle that will be using the launch equipment. KSC's Vehicle Positioning System (VPS) placed the simulator on the rotating launch platform prior to the rotation. The new VPS will dramatically reduce the amount of manual labor required to position a reusable launch vehicle for liftoff
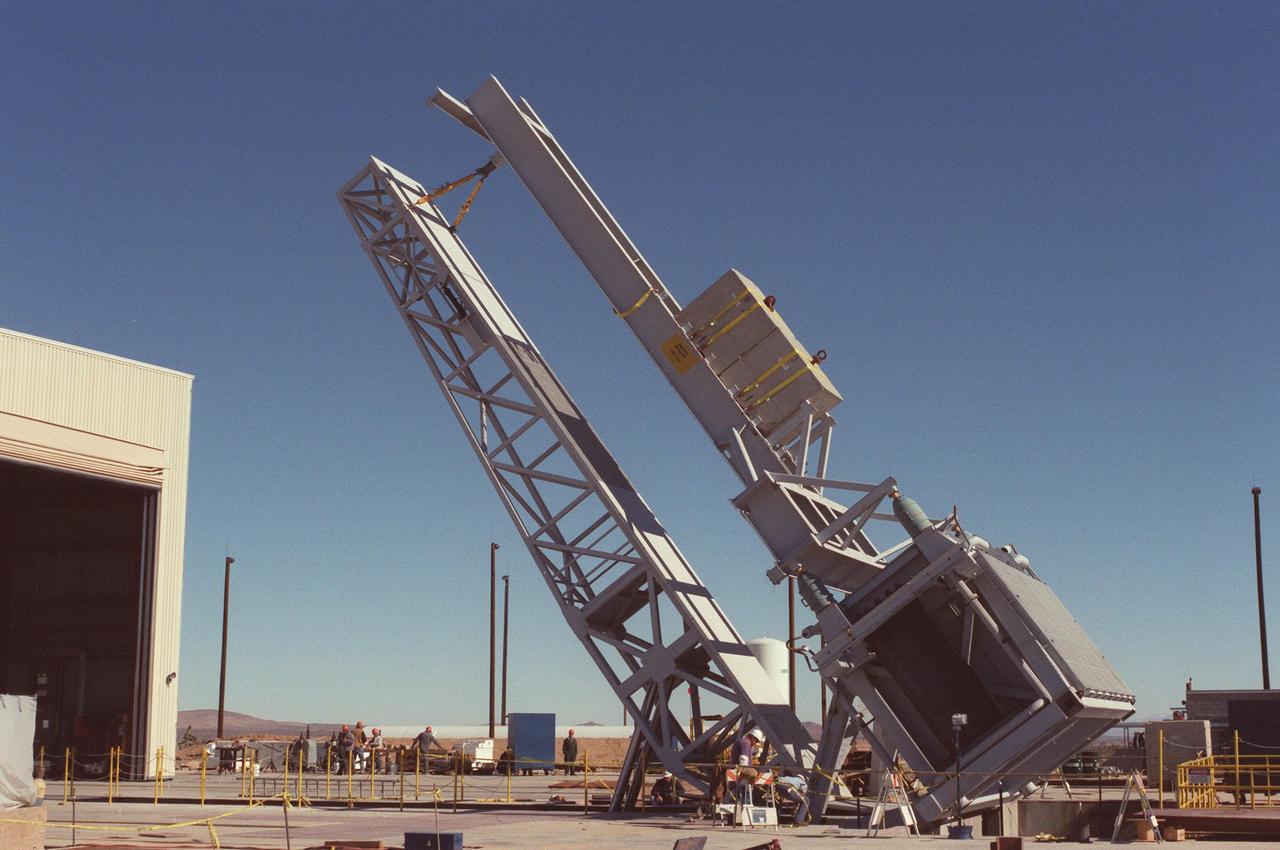

The KSC-developed X-33 weight simulator (top, right), known as the "iron bird," is lifted to a vertical position at the X-33 launch site as part of launch equipment testing on Edwards Air Force Base, CA. The simulator matches the 75,000-pound weight and 63-foot height of the X-33 vehicle that will be using the launch equipment. KSC's Vehicle Positioning System (VPS) placed the simulator on the rotating launch platform prior to the rotation. The new VPS will dramatically reduce the amount of manual labor required to position a reusable launch vehicle for liftoff

S69-45009 (27 July 1969) --- This is the first lunar sample that was photographed in detail in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The photograph shows a granular, fine-grained, mafic (iron magnesium rich) rock. At this early stage of the examination, this rock appears similar to several igneous rock types found on Earth. The scale is printed backwards due to the photographic configuration in the Vacuum Chamber. The sample number is 10003. This rock was among the samples collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) on July 20, 1969.

Giant, bright coronal loops trace out the magnetic field lines above an active region from June 4-6, 2018. The wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light shown here is emitted by ionized iron travelling along the field lines, super-heated to approximately 1 million degrees K. Coronal loops were not seen in this level of detail until the Solar Dynamics Observatory was launched in 2010 and came online, giving solar scientists new data with which to study the Sun and its processes. Videos are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22508
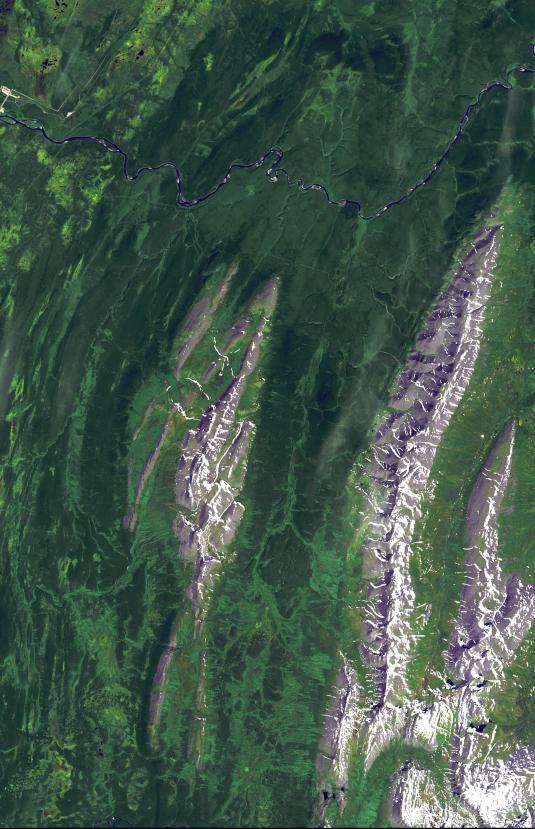

This image from NASA Terra spacecraft shows the Ural Mountains, which run 2500 km north-south through western Russia, and form the boundary between Europe and Asia. Since the 17th century, the mountains were exploited for their deposits of iron, copper, gold, coal, oil, mica and gemstones. The Urals are among the world's oldest existing mountain ranges, having been formed about 275 million years ago due to the collision of the Laurussia supercontinent with the continent of Kazakhstania. The image was acquired July 13, 2011, covers an area of 39 by 62 km, and is located near 65.5 degrees north, 59.9 degrees east. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19795
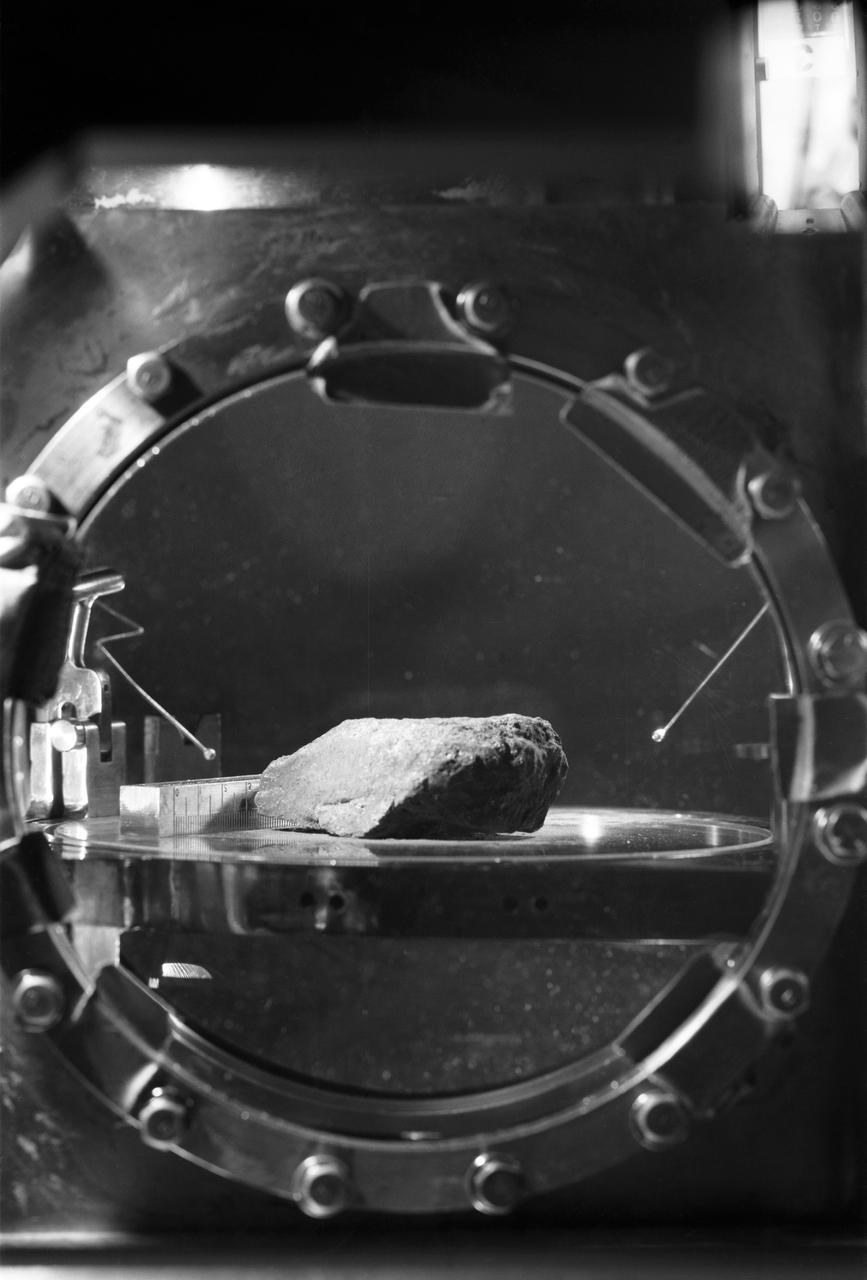

S69-45025 (27 July 1969) --- This is the first lunar sample that was photographed in detail in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center. The photograph shows a granular, fine-grained, mafic (iron magnesium rich) rock. At this early stage of the examination, this rock appears similar to several igneous rock types found on Earth. The scale is printed backwards due to the photographic configuration in the Vacuum Chamber. The sample number is 10003. This rock was among the samples collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity on July 20, 1969.
STS103-728-022 (19-27 December 1999)--- One of the astronauts aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Discovery used a handheld 70mm camera to photograph the Tifernine dunes (note, the dunes are below the "beak" of sandstone rock). According to NASA scientists studying the STS-103 photo collection, the dunes were created when the dark sandstone rocks trapped sand. Winds, they continued, then piled the sand into dunes up to 457.2 m (1,500 ft). The color of the sandstone is due to a desert varnish, the scientists reported. The varnish is composed of manganese, iron oxides, hydroxides, and clay minerals, they said.

This still image from an animation from NASA GSFC Solar Dynamics Observatory shows magnetically charged particles forming a nicely symmetrical arch at the edge of the Sun as they followed the magnetic field lines of an active region Aug.4-5, 2015. Before long the arch begins to fade, but a fainter and taller arch appears for a time in the same place. Note that several other bright active regions display similar kinds of loops above them. These images of ionized iron at about one million degrees were taken in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. The video covers about 30 hours of activity. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19874