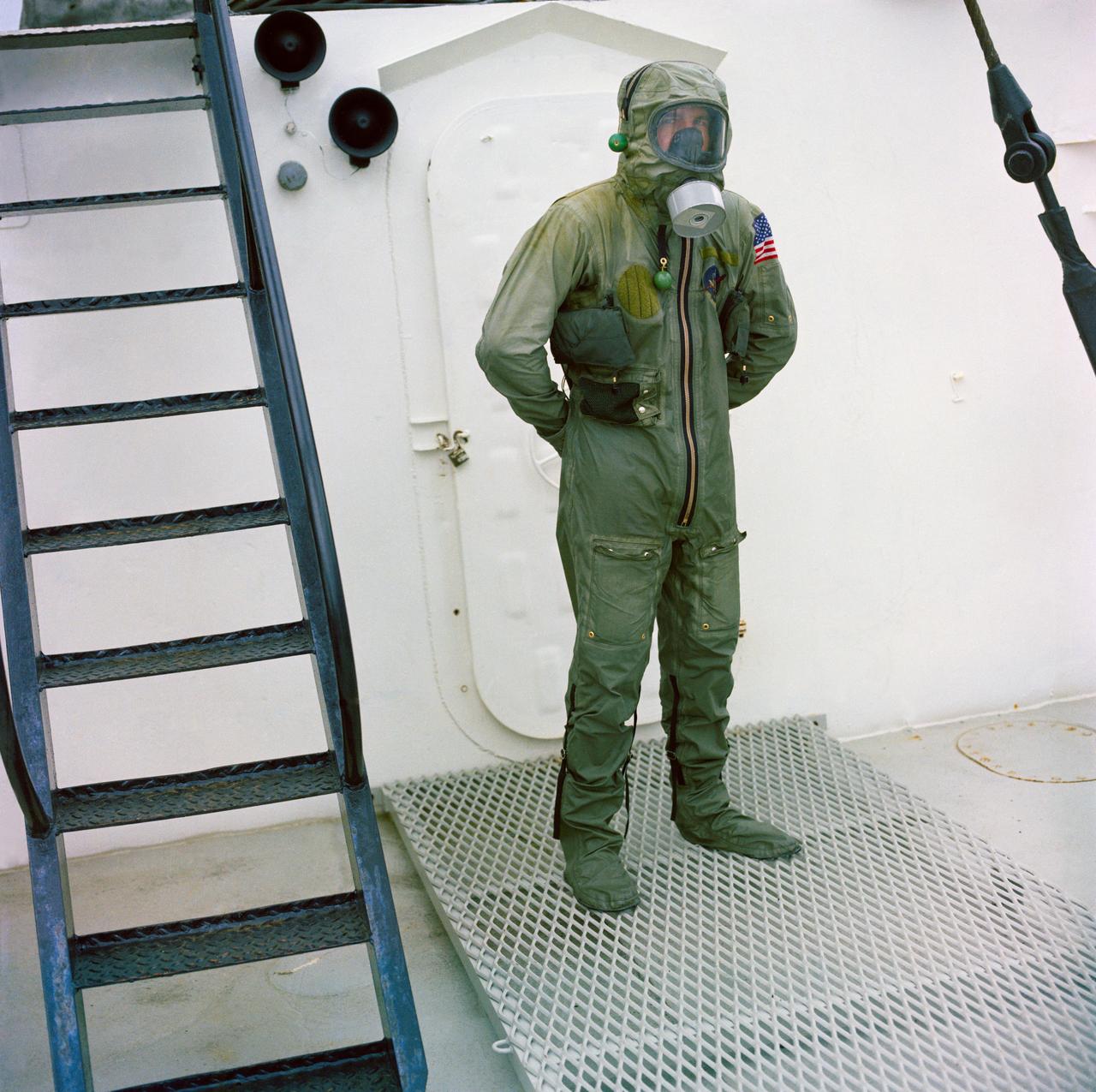

View of subject wearing Biological Isolation Garment (BIG) during a qualification test.

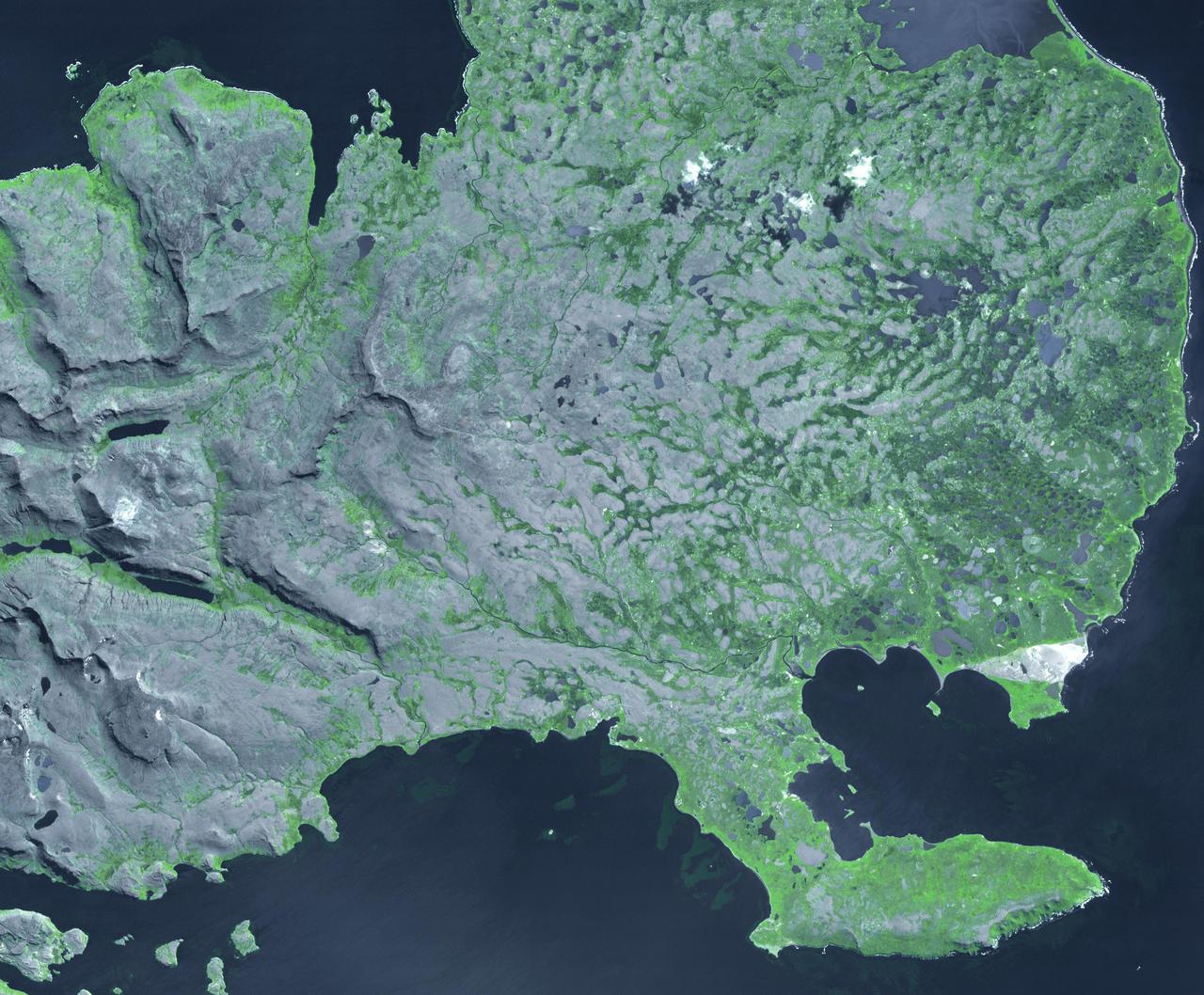
Isolated Northern Dunes
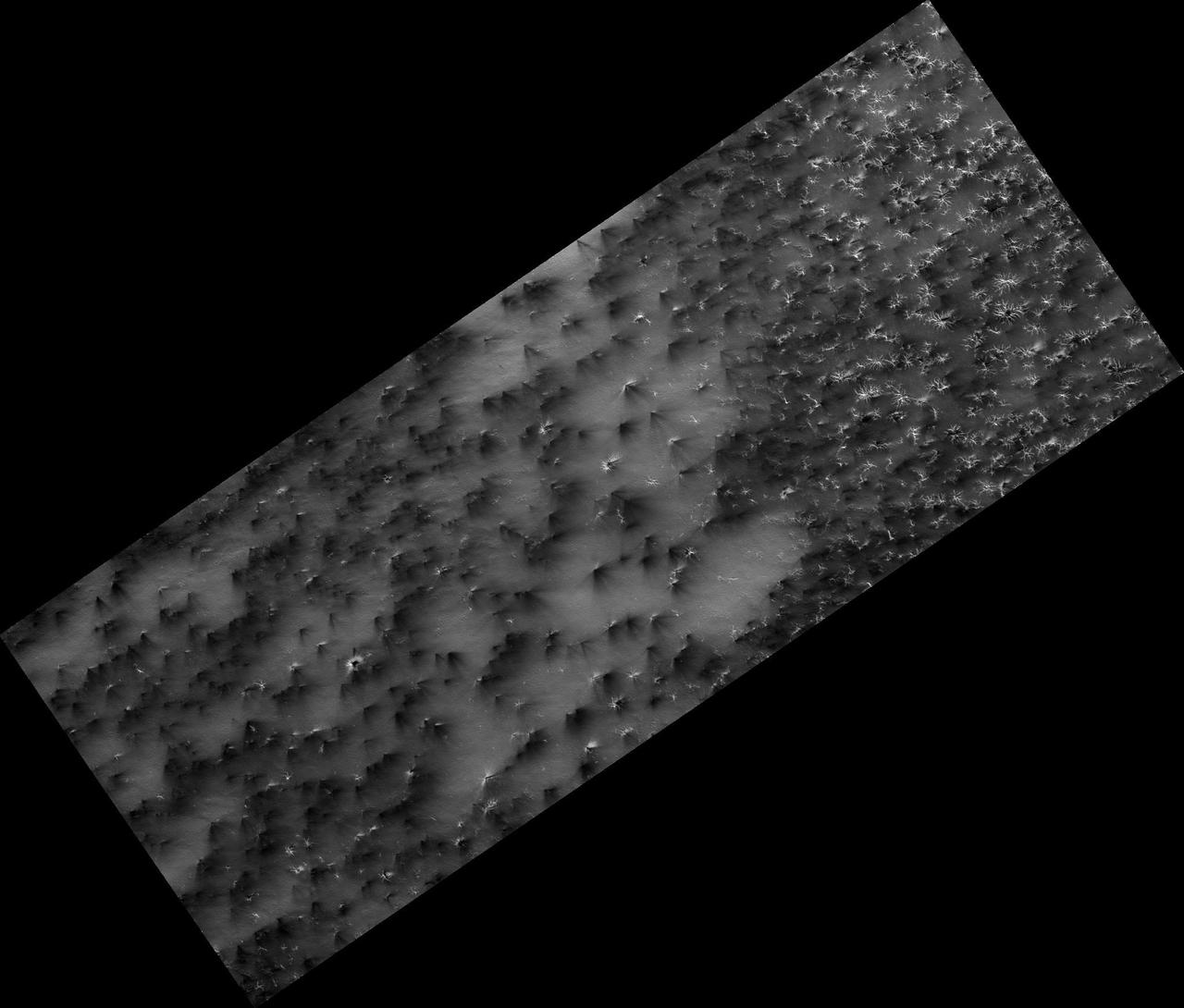
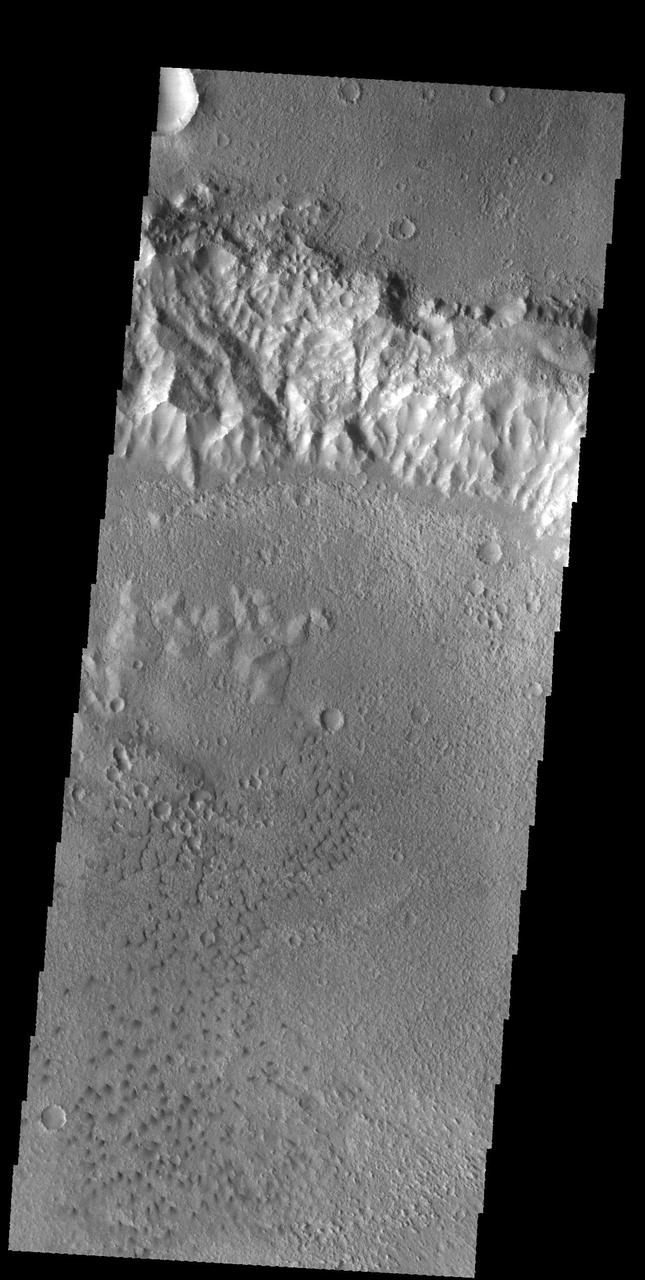
Science in Motion: Isolated Araneiform Topography
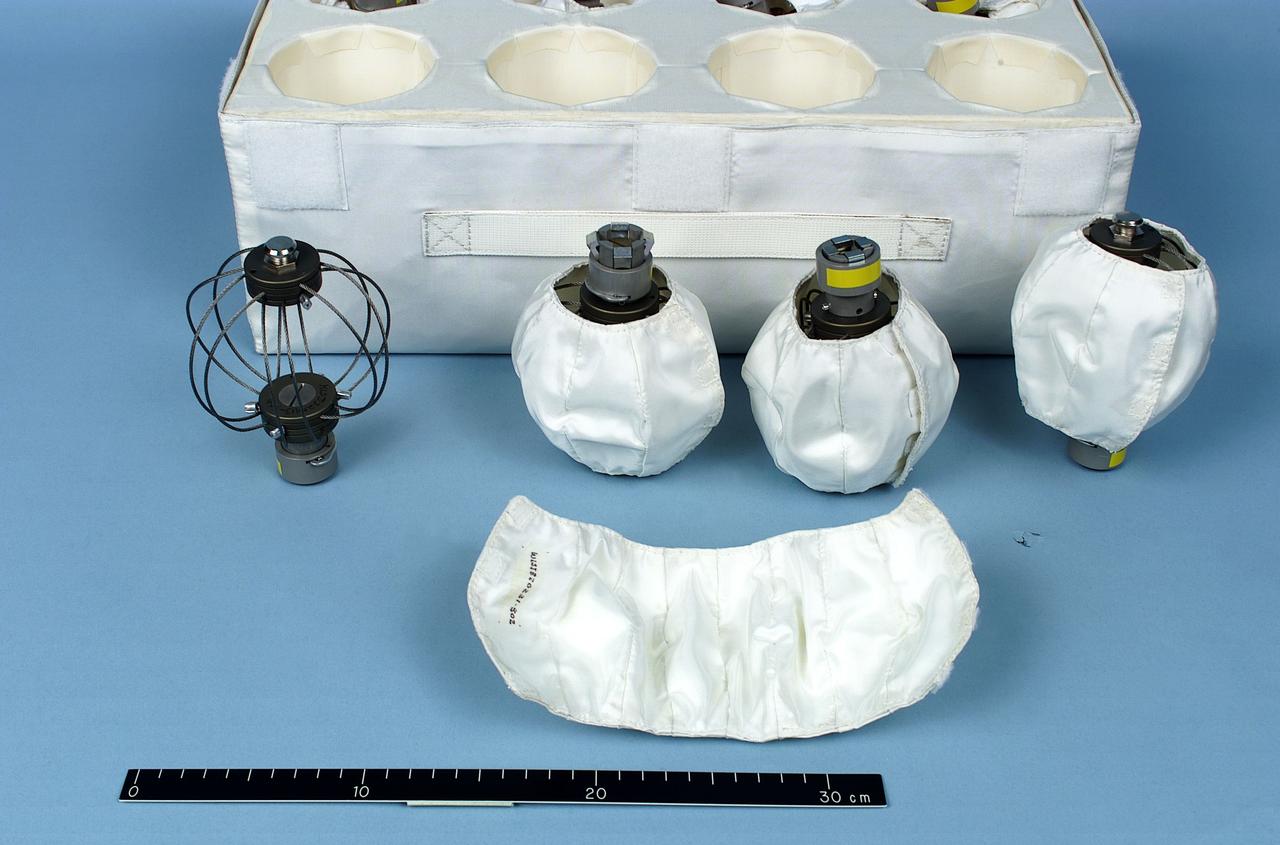

jsc2000e18537 (7/06/2000) --- The small isolators unpacked in front of the Cycle Ergometer / Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) isolator kit.

Gusev Dust Devil Movie, Sol 456 Plain and Isolated
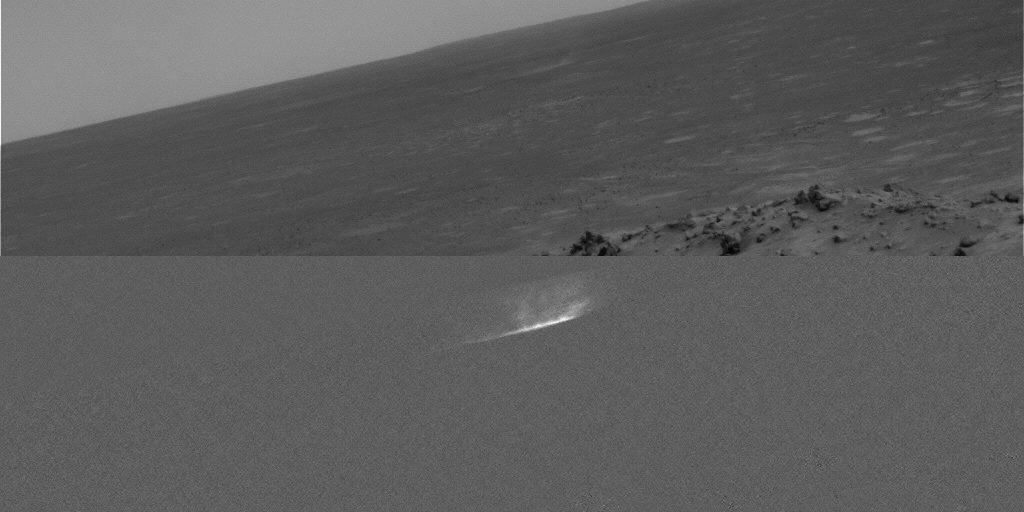

Gusev Dust Devil Movie, Sol 459 Plain and Isolated
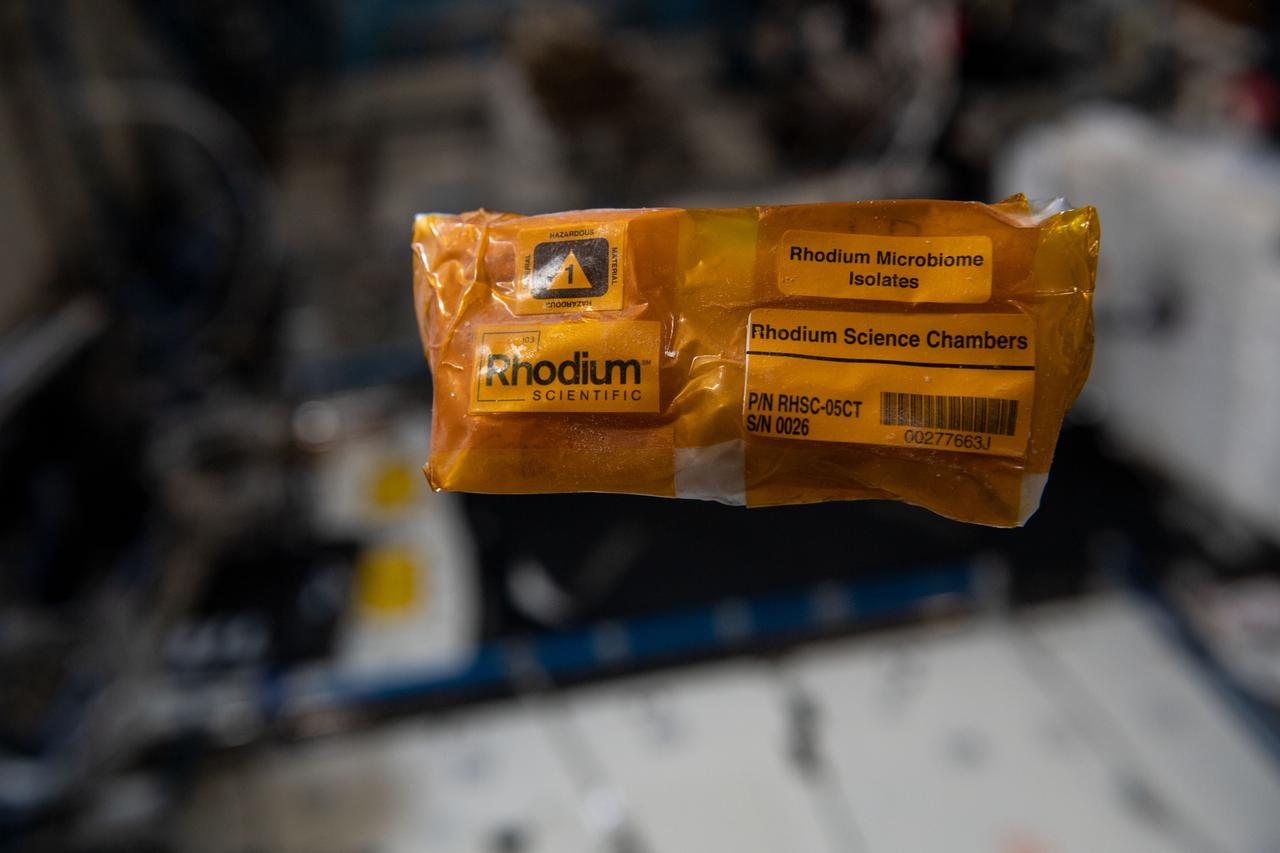

iss068e012558 (10/7/2022) --- A view of the Rhodium Space Microbiome Isolates sample aboard the International space Station (ISS). Characterization of Targeted Space Gut Microbiome Isolates to Advance Astronaut Gut-On-A-Chip Platform Development (Rhodium Space Microbiome Isolates) characterizes individual bacterial species from the human gut microbiome that change during spaceflight. Research shows a connection between alterations in the gut microbiome and multiple chronic and acute diseases.
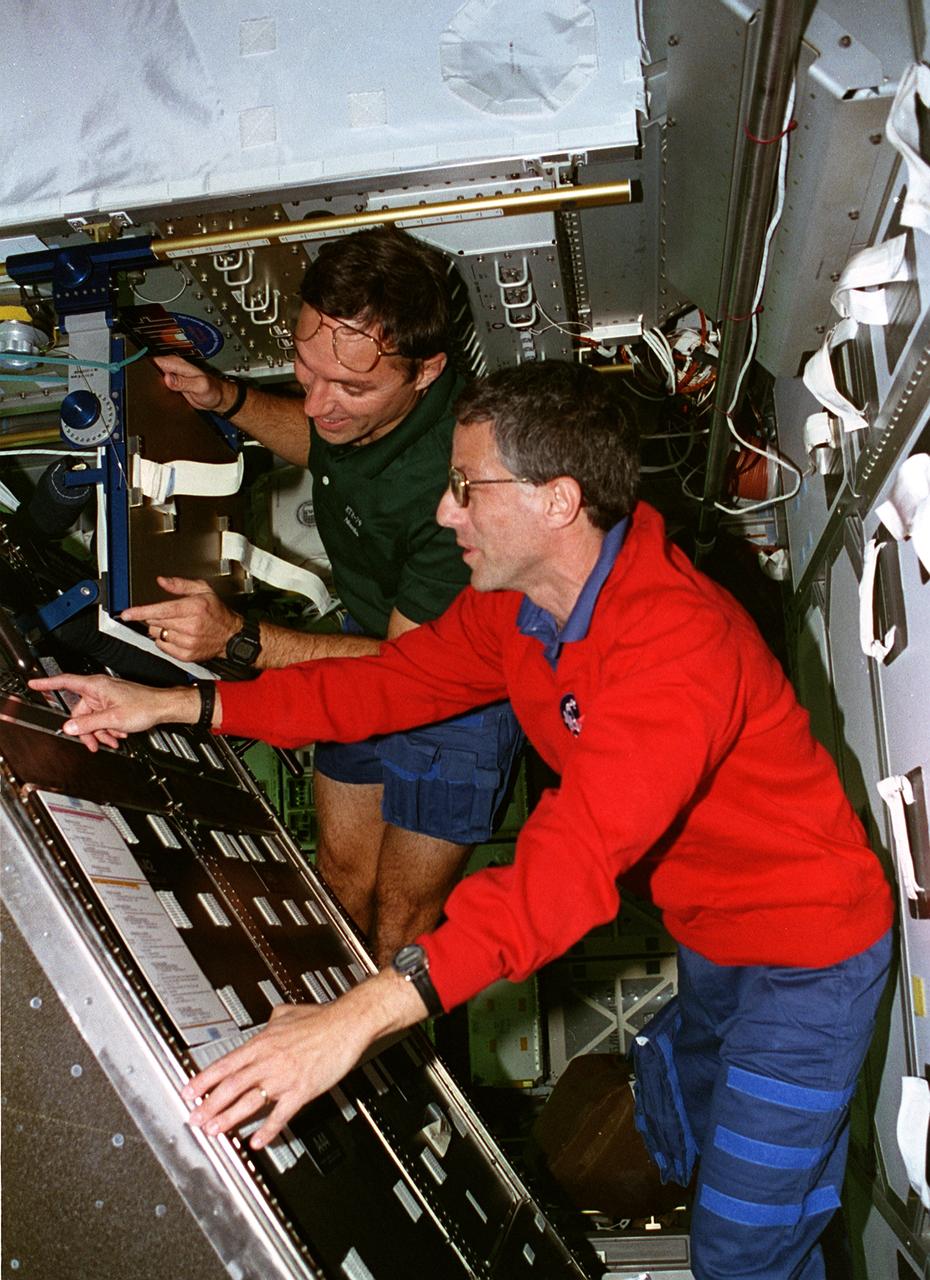

STS079-302-006 (16-26 Sept. 1996) --- Astronauts Jerome (Jay) Apt (right) and Carl E. Walz, both mission specialists, tilt the Active Rack Isolation System (ARIS) hardware which was included on this flight to evaluate conditions and hardware requirements for the International Space Station (ISS). The ARIS is designed to isolate certain experiments from major disturbances that are expected to be found on the ISS, such as vibrations caused by the movement of mechanisms and crew members and the operation of equipment. STS-79 was chosen for the inclusion of the experiment because the Shuttle-Mir complex more closely approximates the acceleration environment of the ISS.
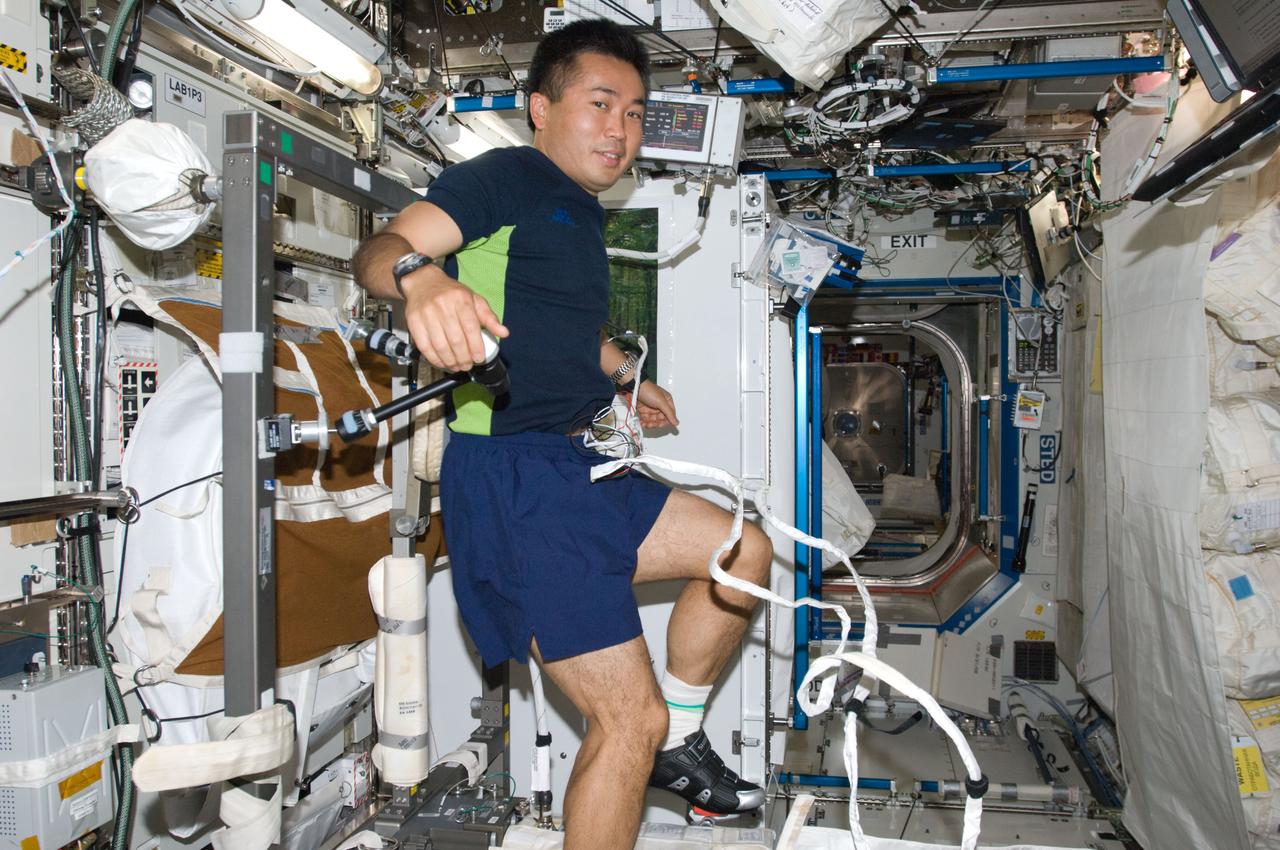

ISS018-E-043723 (30 March 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 18/19 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.

ISS018-E-043414 (26 March 2009) --- Astronaut Michael Fincke, Expedition 18 commander, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
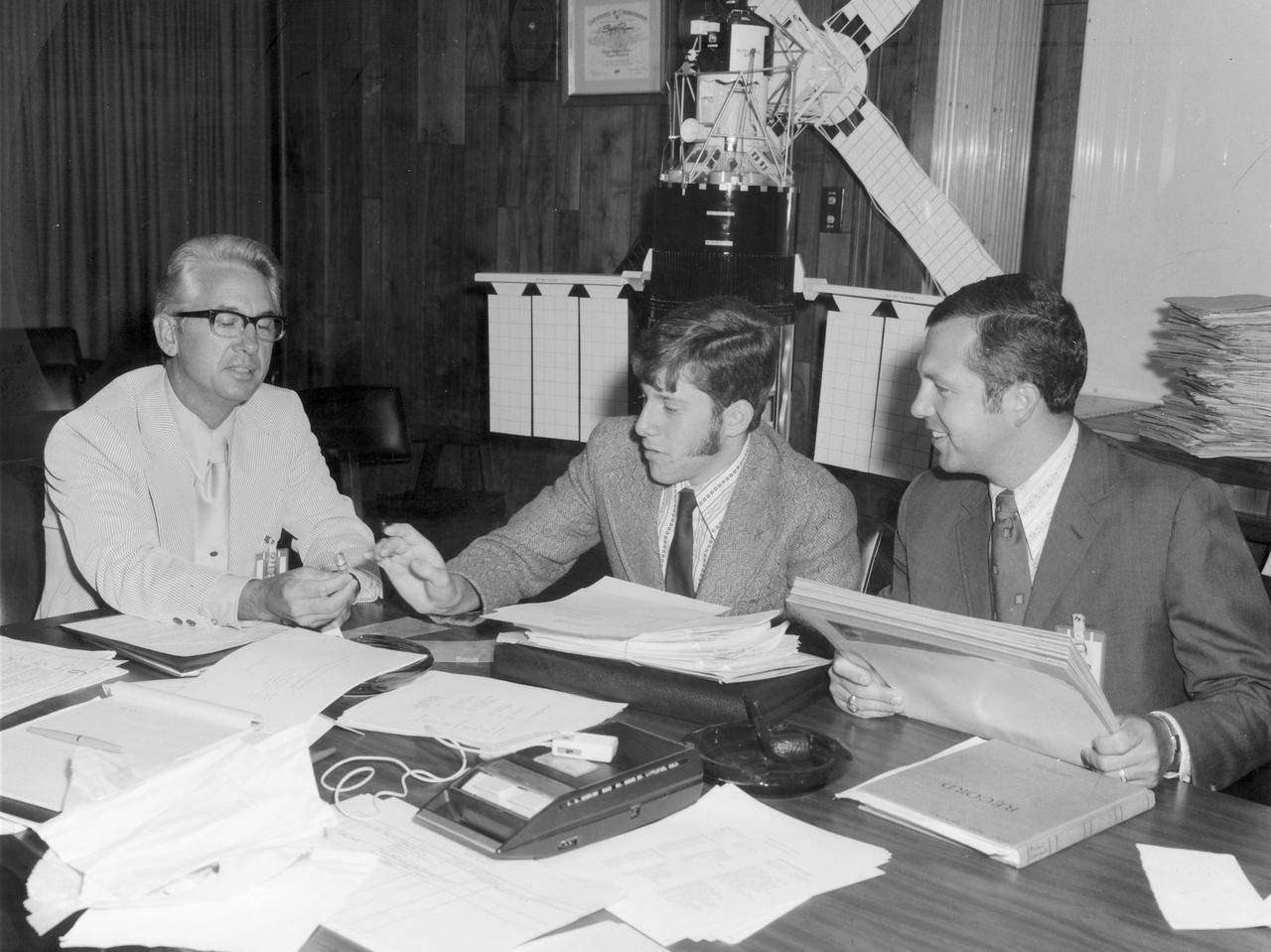

Todd Meister(center), high school student of the Bronx High School of Science, discusses his experiment “An Invitro Study of Selected Isolated Immune Phenomena” with his advisor, Dr. Robert Allen (right) and Henry Floyd, both of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). His experiment was aimed at discovering whether or not the absence of gravity affects the representative life processes. Meister was one of the 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of equipment.
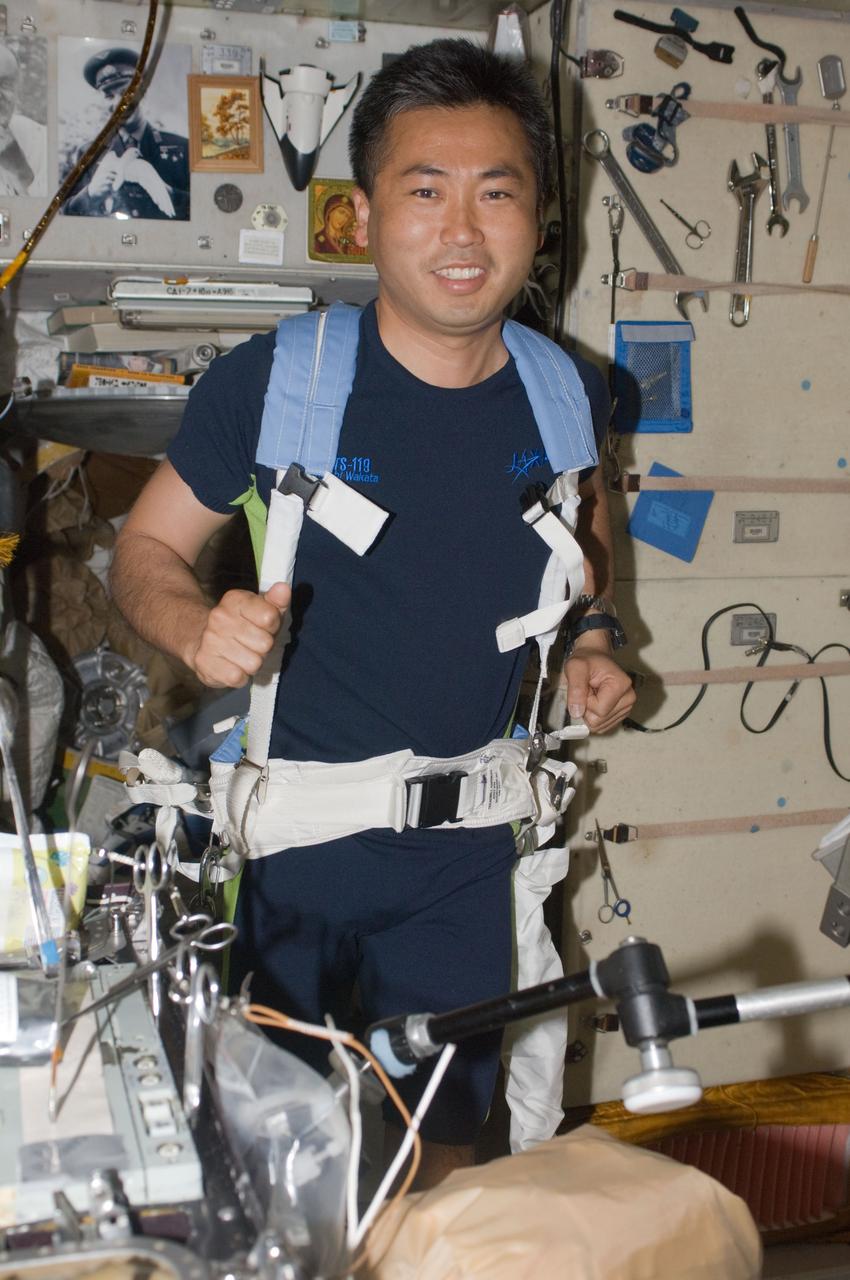

ISS018-E-042662 (22 March 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 18 flight engineer, equipped with a bungee harness, exercises on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station while Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-119) remains docked with the station.
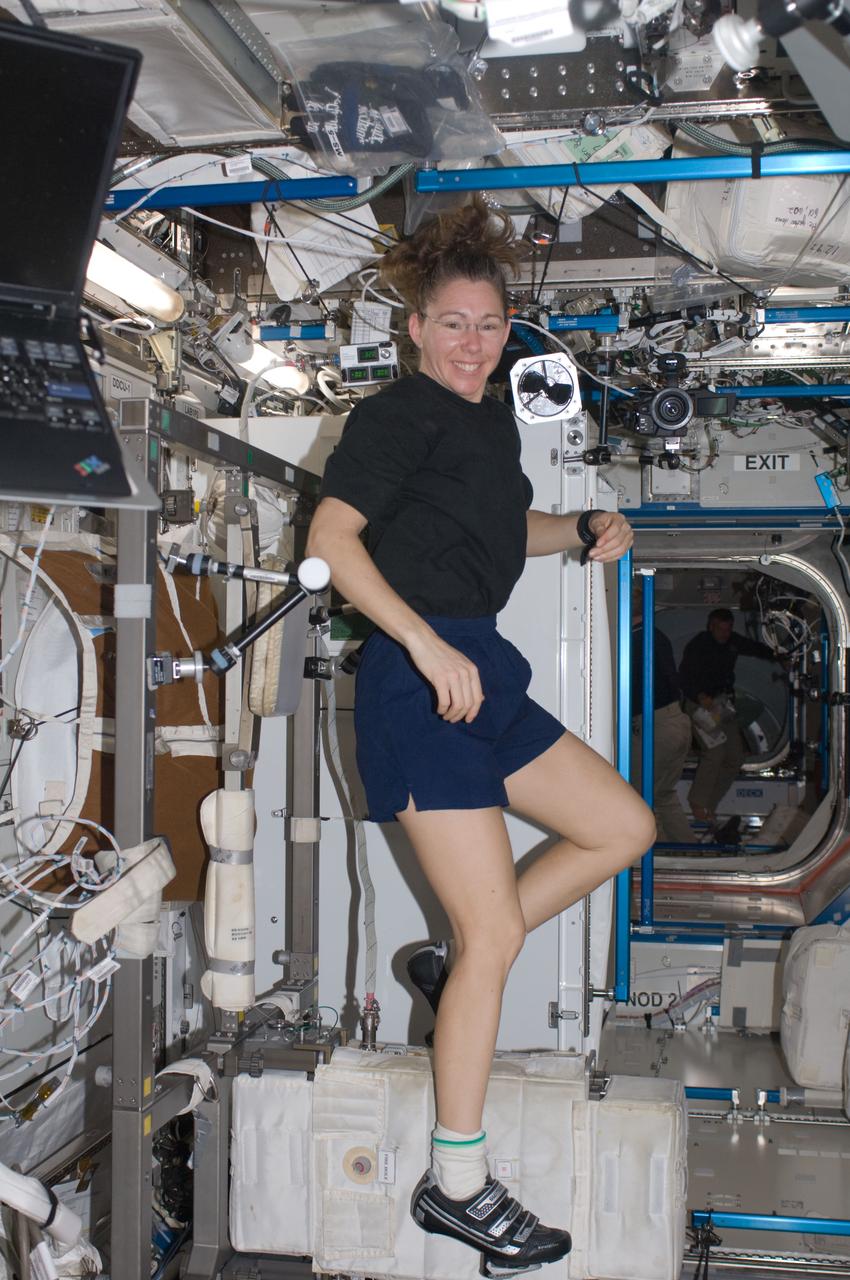

ISS018-E-042649 (22 March 2009) --- Astronaut Sandra Magnus, STS-119 mission specialist, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station while Space Shuttle Discovery remains docked with the station.
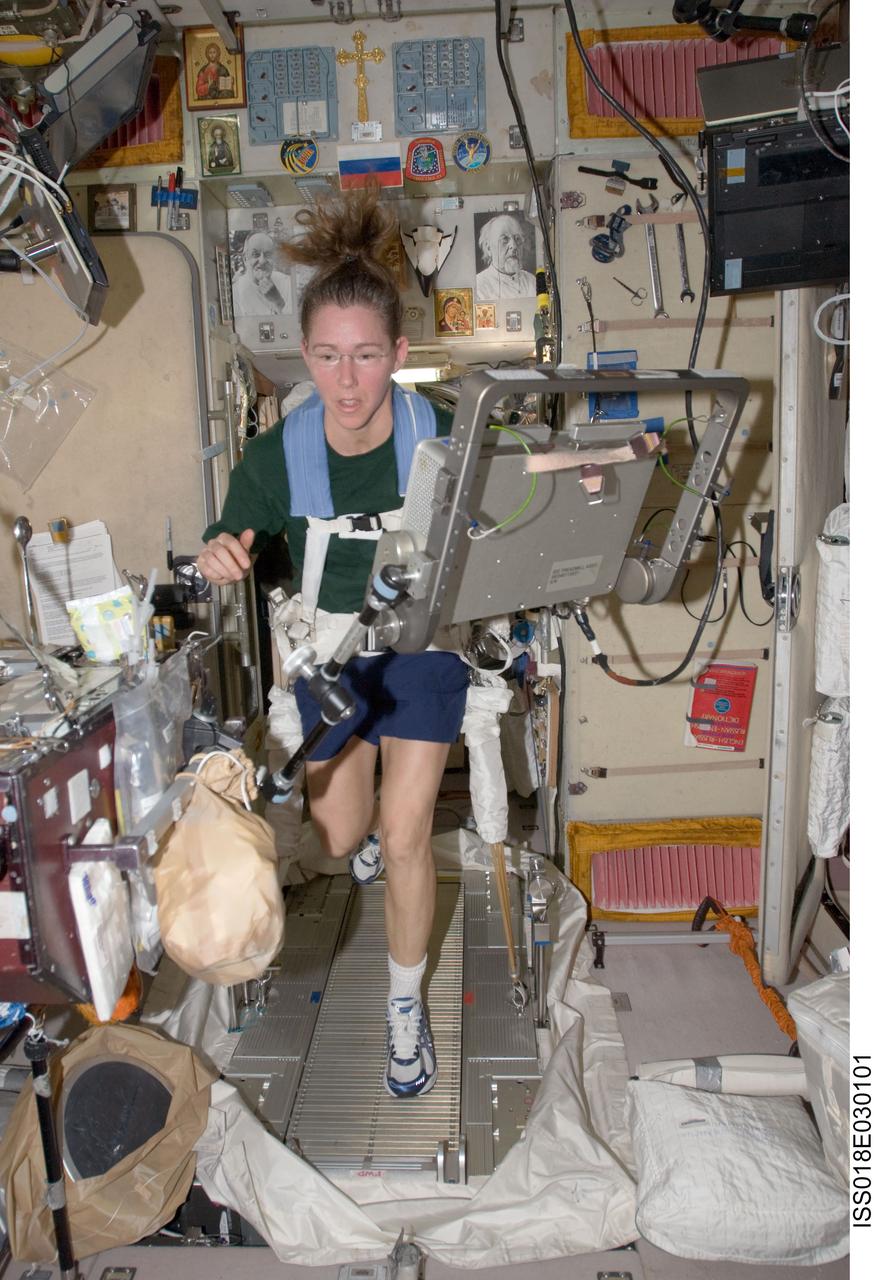

ISS018-E-030101 (12 Feb. 2009) --- Astronaut Sandra Magnus, Expedition 18 flight engineer, equipped with a bungee harness, exercises on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
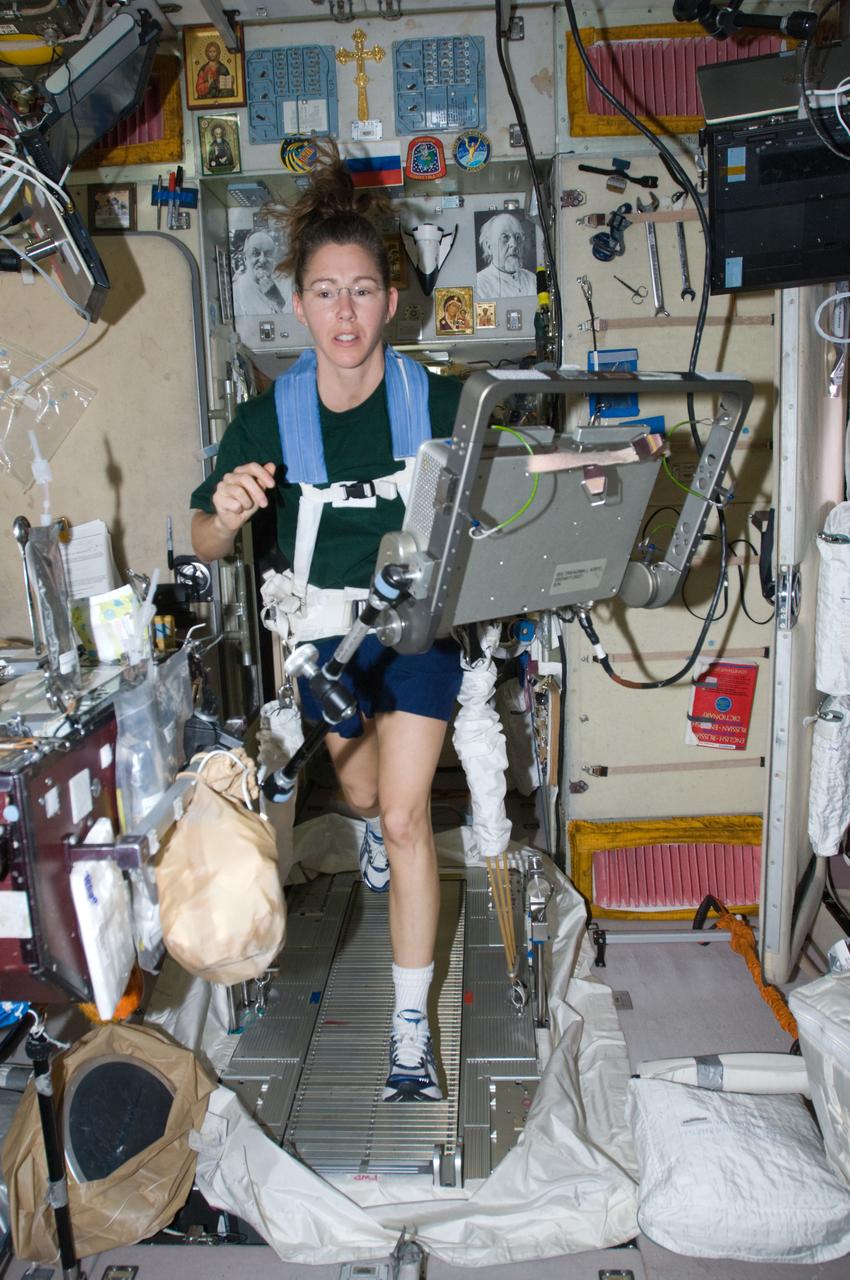
ISS018-E-030096 (12 Feb. 2009) --- Astronaut Sandra Magnus, Expedition 18 flight engineer, equipped with a bungee harness, exercises on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
![This isolated mesa [lower left center of the image] has an almost heart-shaped margin. Happy Valentine Day from Mars](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA02174/PIA02174~medium.jpg)
This isolated mesa [lower left center of the image] has an almost heart-shaped margin. Happy Valentine Day from Mars
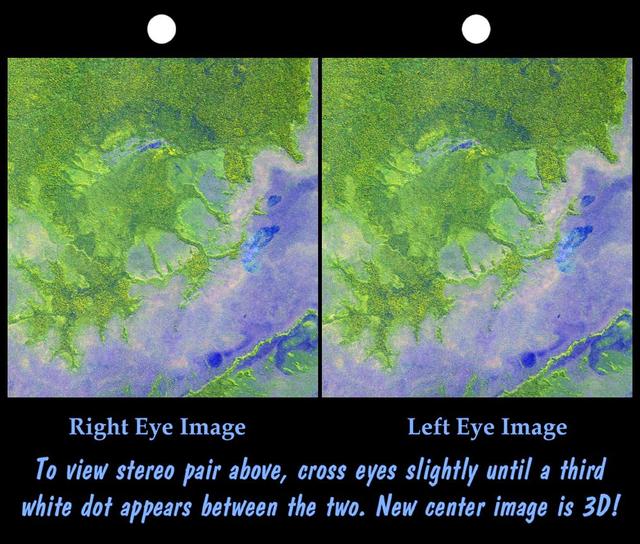
An 8-kilometer 5-mile wide crater of possible impact origin is shown in this stereoscopic view of an isolated part of the Bolivian Amazon.
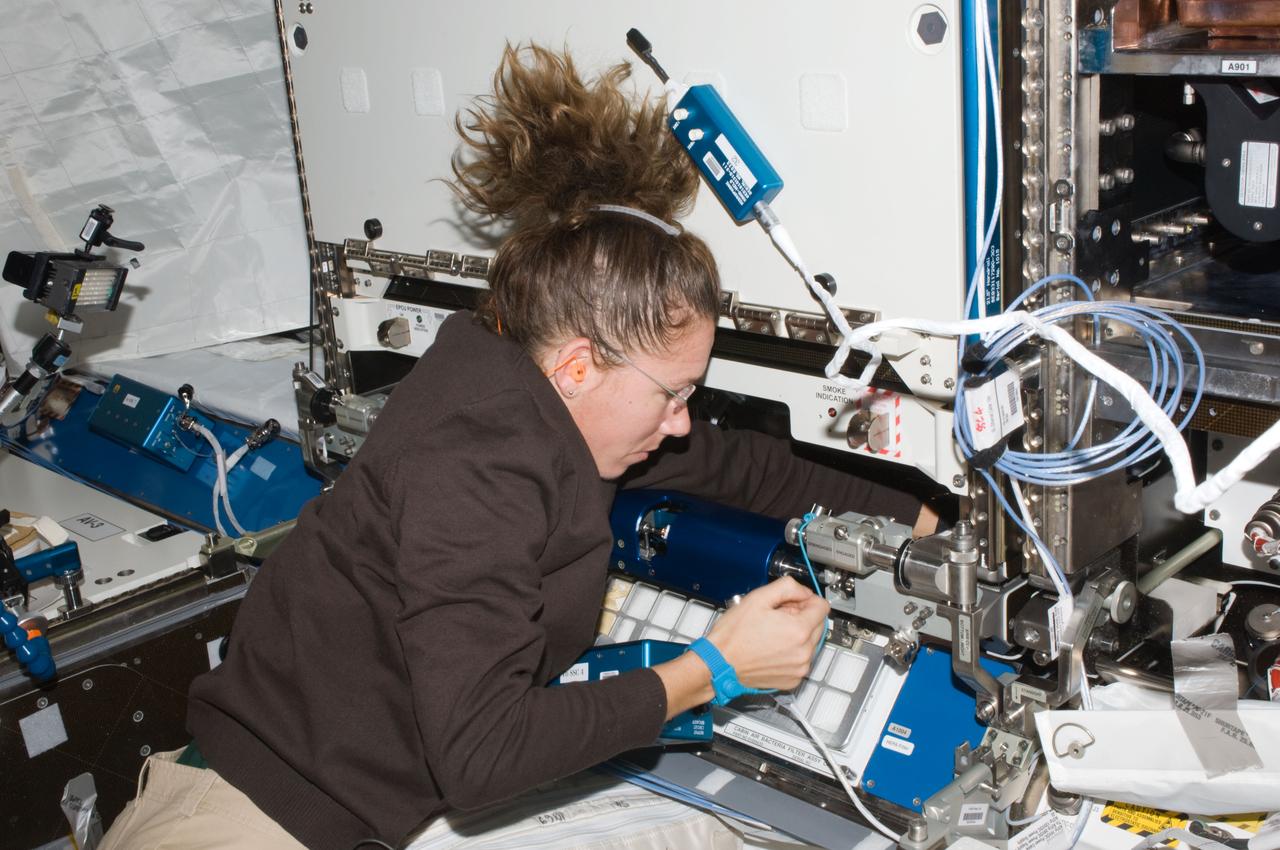

ISS018-E-017796 (5 Jan. 2009) --- Astronaut Sandra Magnus, Expedition 18 flight engineer, works on the Fluids and Combustion Facility (FCF) Combustion Integration Rack (CIR) Passive Rack Isolation System (PaRIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
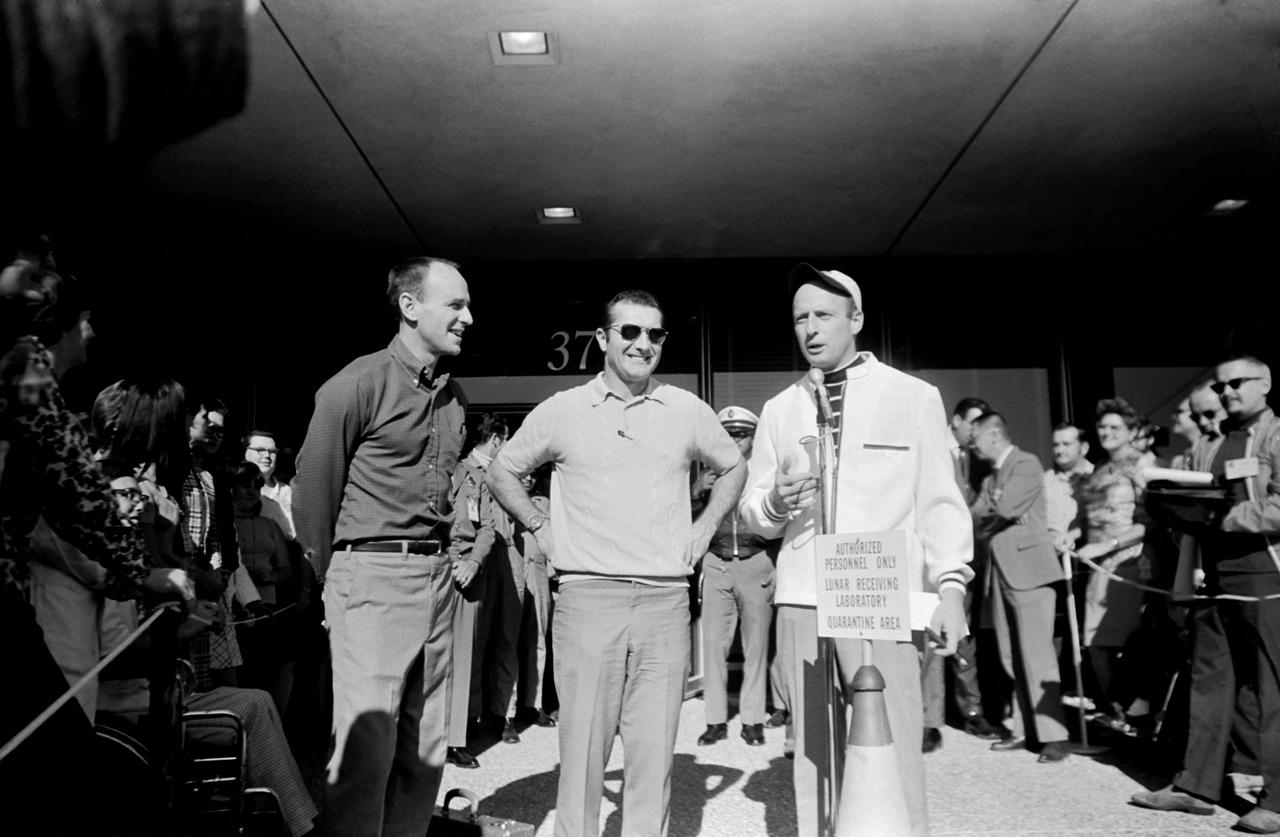

S69-62884 (10 Dec. 1969) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, makes several remarks publicly in response to the welcome given him and other members of the Apollo 12 crew upon their release from post-mission isolation in the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). Pictured with Conrad outside Building 37, which houses the LRL, are his fellow crewmembers for the Apollo 12 mission, astronauts Alan L. Bean (left), lunar module pilot; and Richard F. Gordon Jr. (center), command module pilot.
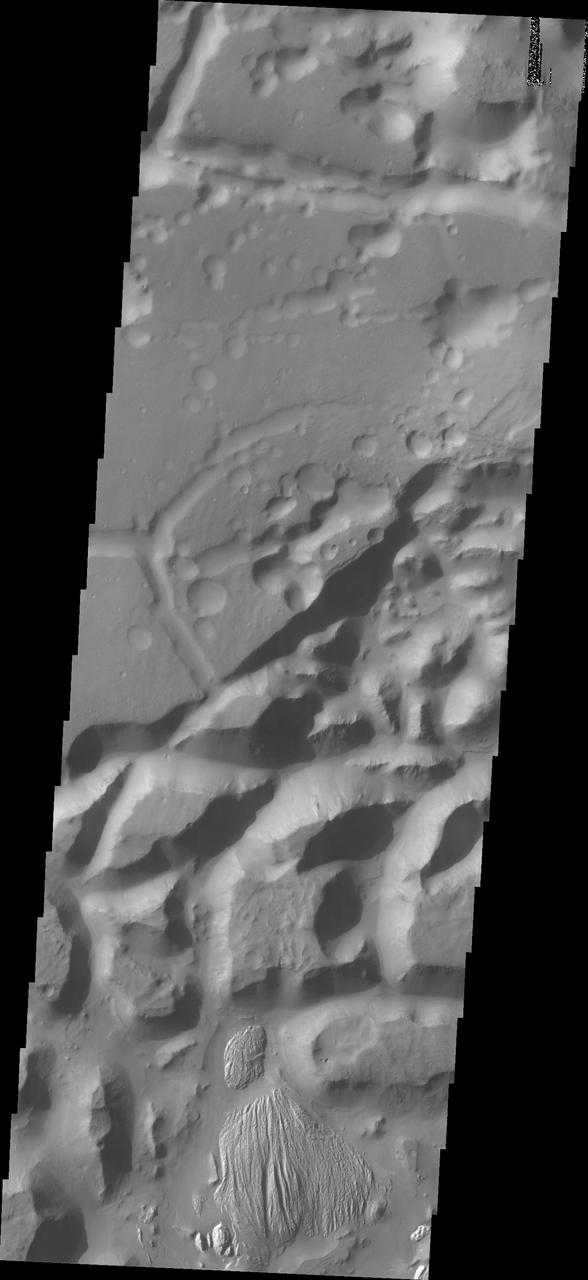

The isolated mesas in this image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft are part of Arsinoes Chaos. There is a material that differs from the rest of the chaos visible at the bottom of the image.
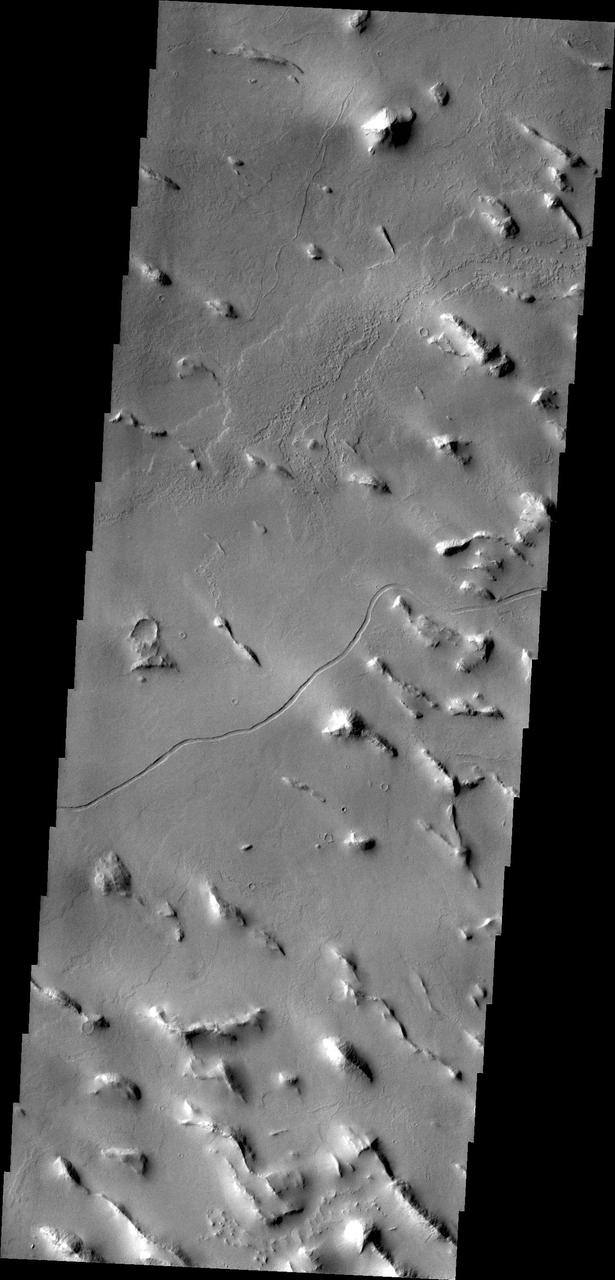

Isolated hills and a small channel are visible in this image of Gigas Sulci captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft . Gigas Sulci is located southeast of Olympus Mons.

The large isolated dune in this VIS image is located on the floor of an unnamed crater in Terra Sabaea. Orbit Number: 64218 Latitude: 26.2102 Longitude: 57.11 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2016-06-05 12:48 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20802
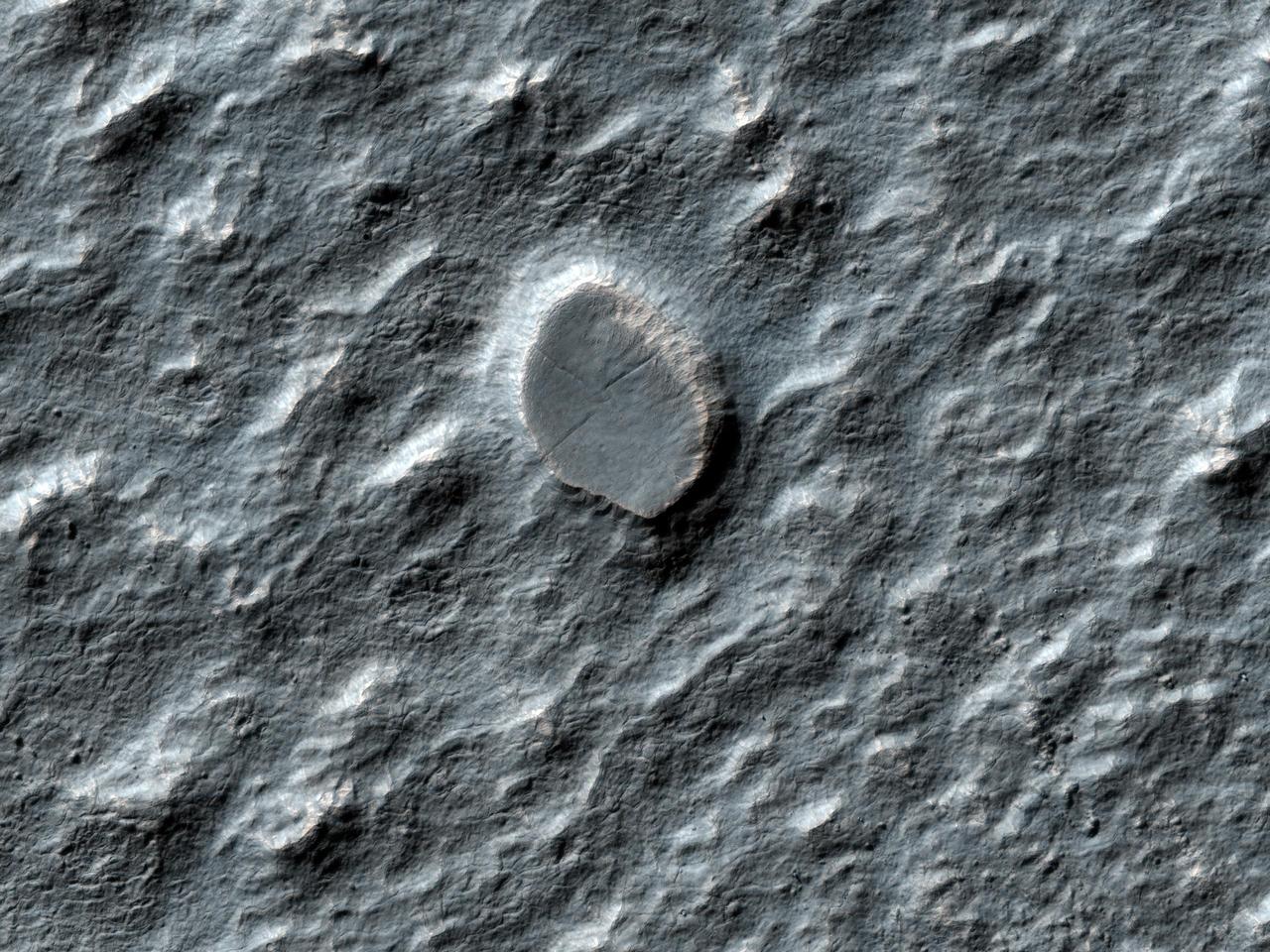

This image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows a swath of a debris apron east of Hellas Basin. Features like this are often found surrounding isolated mountains in this area. Original release date March 3, 2010.
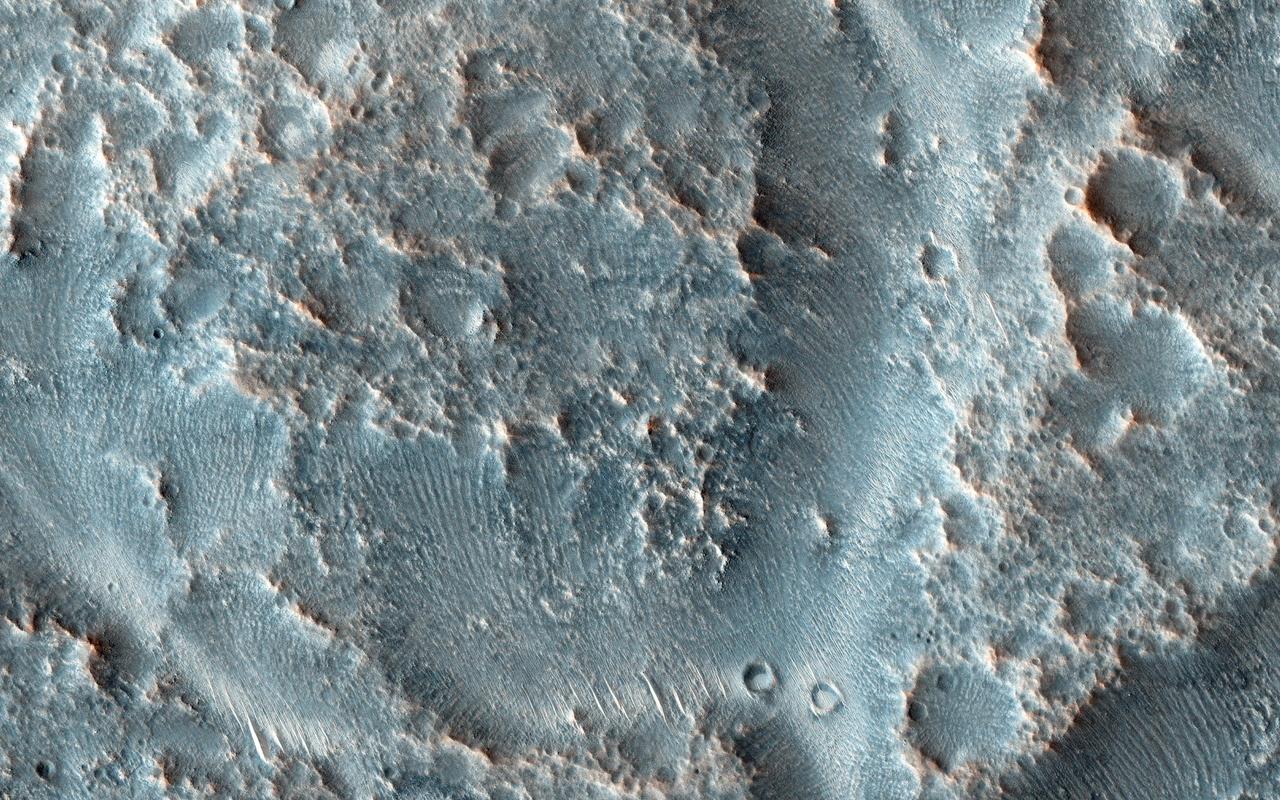

As rivers age they can meander and occasionally these meanders get so pronounced that the river cuts off these curving loops at their narrow end leaving them as isolated as oxbow lakes. Image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.

Just north of the hematite deposit in Meridiani Planum, the remnants of a formerly extensive layer of material remain as isolated knobs and buttes in this image from NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft.
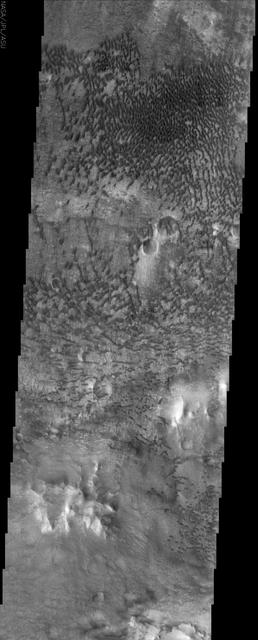
This NASA Mars Odyssey image shows a remarkable array of dunes on the floor of a large impact crater named Baldet. Many of the dunes in this region are isolated features with large, sand-free interdune surfaces between the individual dunes.
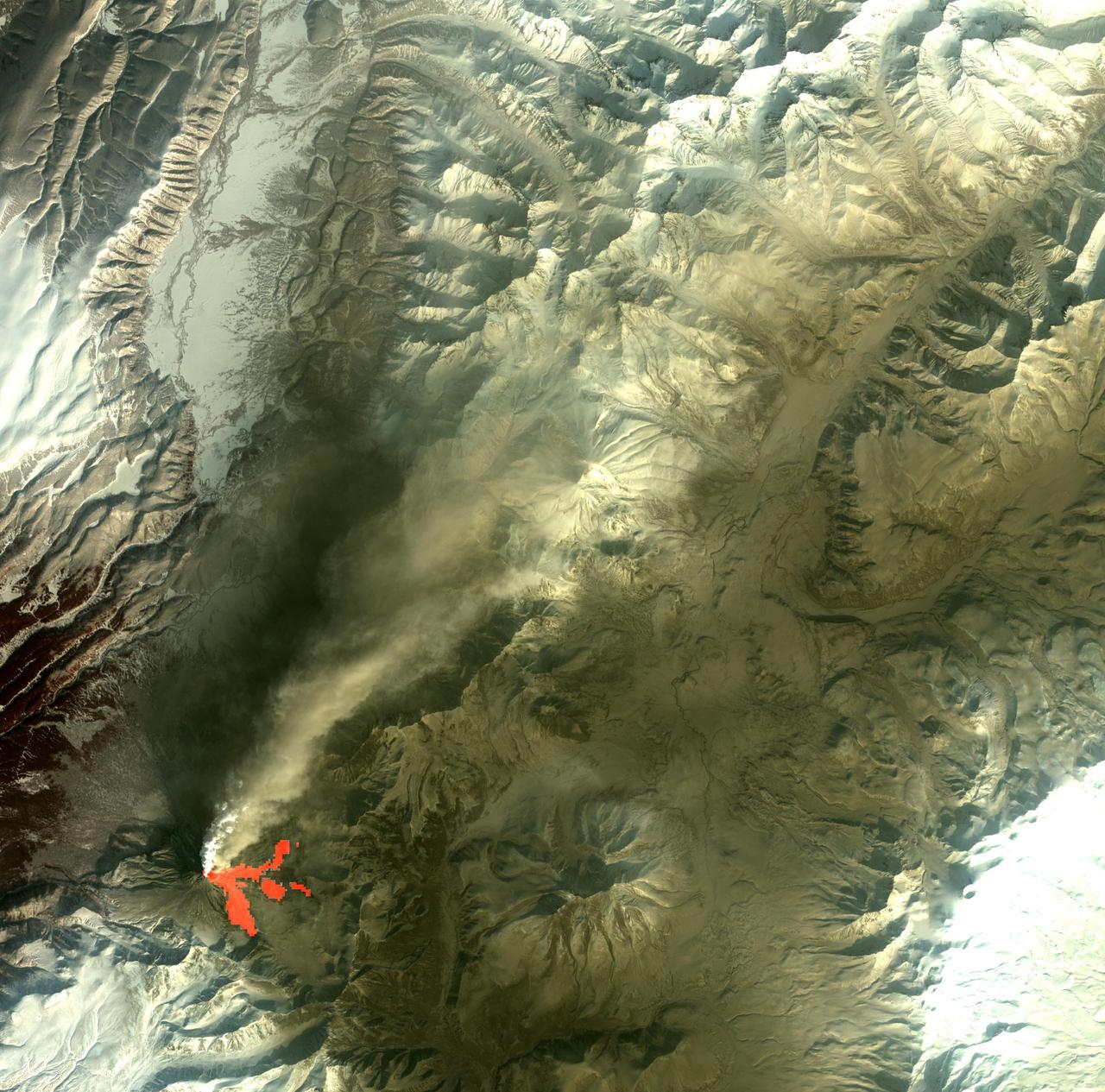
On Feb. 25, 2011, NASA Terra spacecraft captured this image of a large ash-laden eruption plume drifting towards the northeast from Kizimen volcano, an isolated stratovolcano, in Kamchatka, Russia.
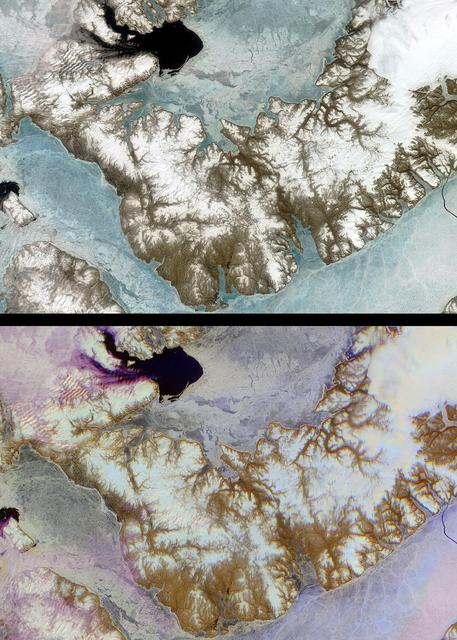

Devon Island is situated in an isolated part of Canada Nunavut Territory, and is usually considered to be the largest uninhabited island in the world. These images were acquired by NASA Terra satellite on June 28, 2001.

This image from NASA Terra spacecraft shows the Kerguelen Islands also known as the Desolation Islands, which are part of the French Southern and Antarctic lands. The islands are among the most isolated places on Earth.

An isolated mesa east of the Phlegra Montes in northeastern Elysium Planitia has a cracked surface that, combined with its overall shape, gives the appearance of a giant loaf of bread in this image from NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft.

This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of Aspledon Undae, a region of dunes near the north pole. The right side of the image shows hundreds of small, isolated dunes.

Tectonics played the major role in shaping the surface of this image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft. This image contains arcuate fractures and isolated depressions containing chaos.
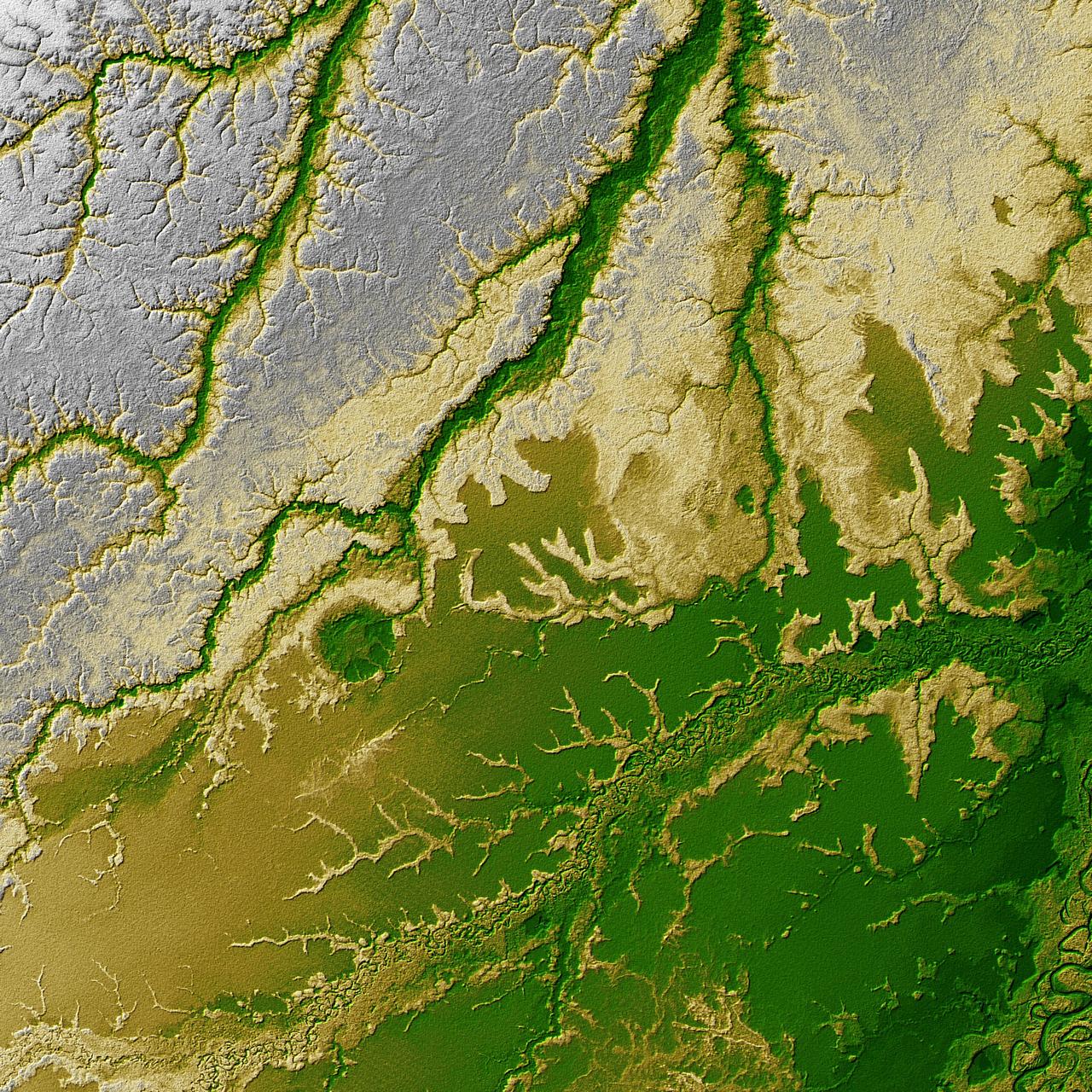

An 8-kilometer 5-mile wide crater of possible impact origin is shown in this view of an isolated part of the Bolivian Amazon from NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission.
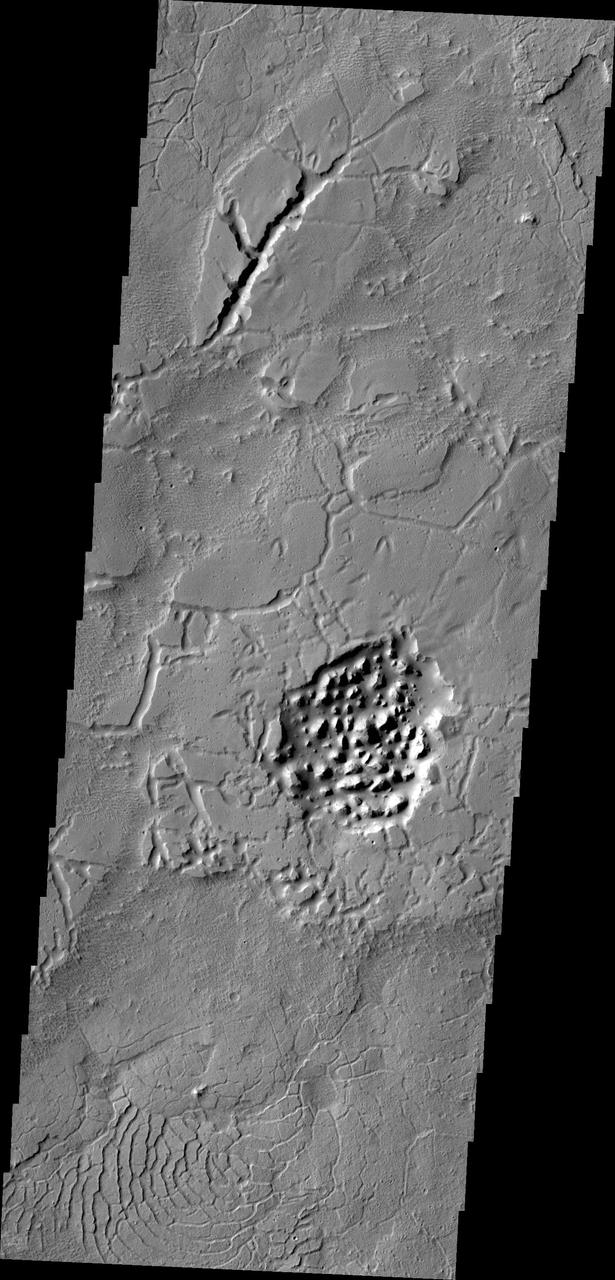

The Avernus region contains several different surface features. These include tectonic fractures, ridges, hills, and regions of chaos within isolated depressions termed cavi. This image was captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft.

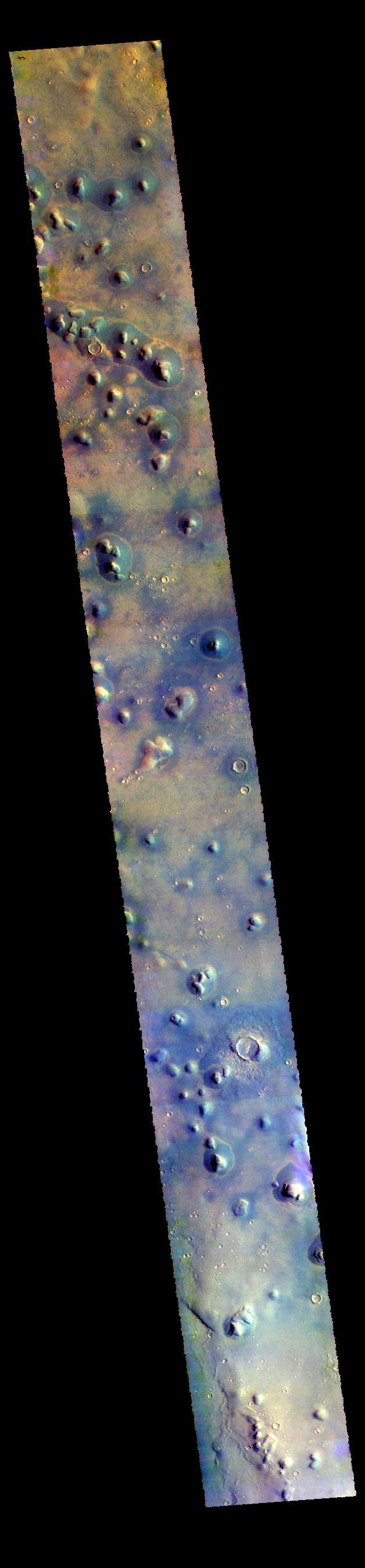
This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows a region of small isolated dunes on the floor of an unnamed crater in Terra Cimmeria. Orbit Number: 59106 Latitude: -30.4214 Longitude: 145.4 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2015-04-11 11:57 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19477

iss068e013749 (10/8/2022) --- A view of the Rhodium Space Microbiome Isolates sample aboard the International space Station (ISS). Characterization of Targeted Space Gut Microbiome Isolates to Advance Astronaut Gut-On-A-Chip Platform Development (Rhodium Space Microbiome Isolates) characterizes individual bacterial species from the human gut microbiome that change during spaceflight. Research shows a connection between alterations in the gut microbiome and multiple chronic and acute diseases.

A severe drought in the Amazon is disrupting transportation, isolating communities and putting wildlife at risk. The Amazon and its tributaries, including the Rio Negro that joins the Amazon at Manaus (2023 image), fell to their lowest level in over a century. The images were acquired October 9, 2023 and August 15, 2020. They cover an area of 30 by 45 km, and are located at 2.8 degrees south, 60.7 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26196
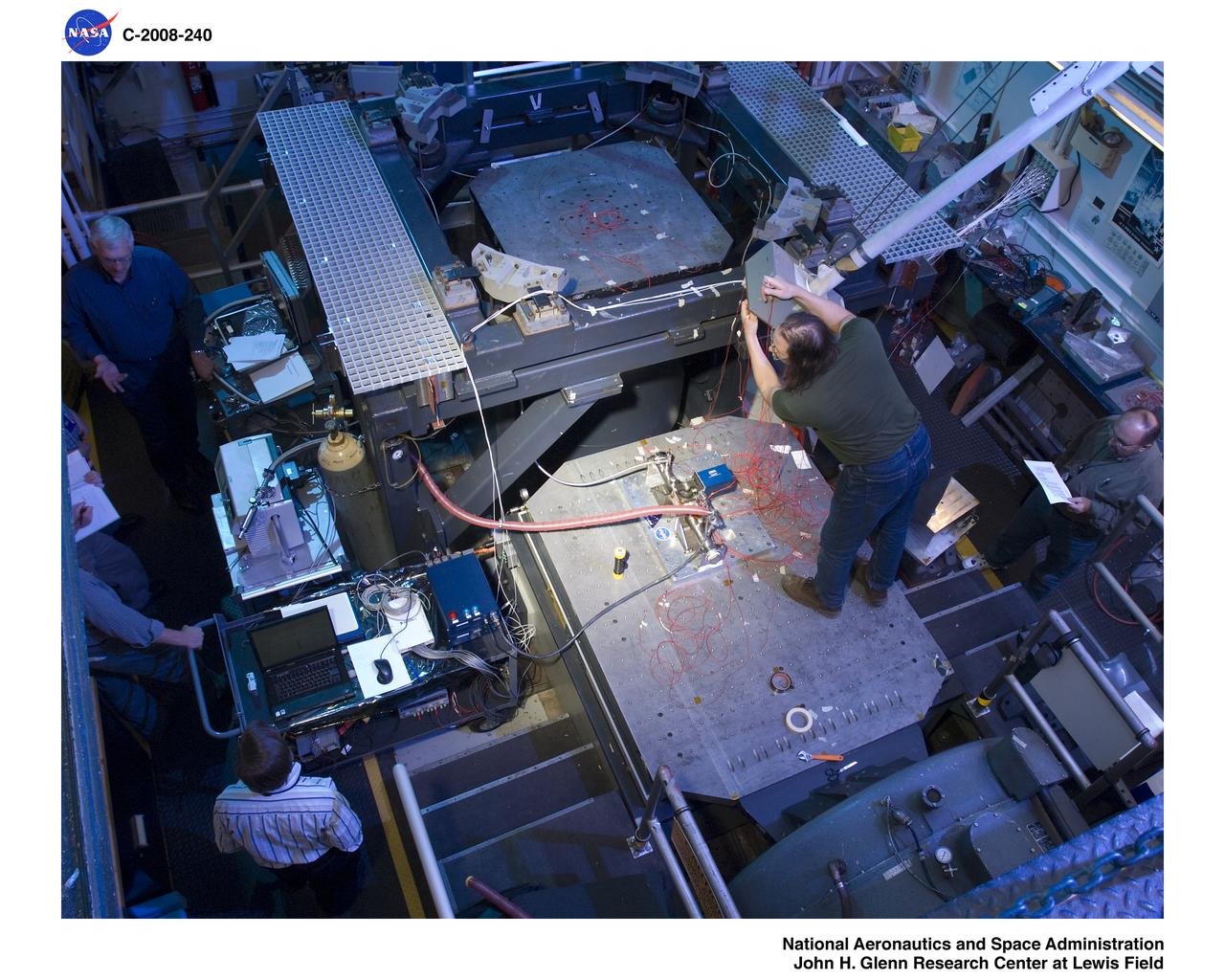
Vibration test of the Orion Service Module advanced development propellant isolation valve. "X: Angle of Rotation".

Vibration test of the Orion Service Module advanced development propellant isolation valve. "X: Angle of Rotation".
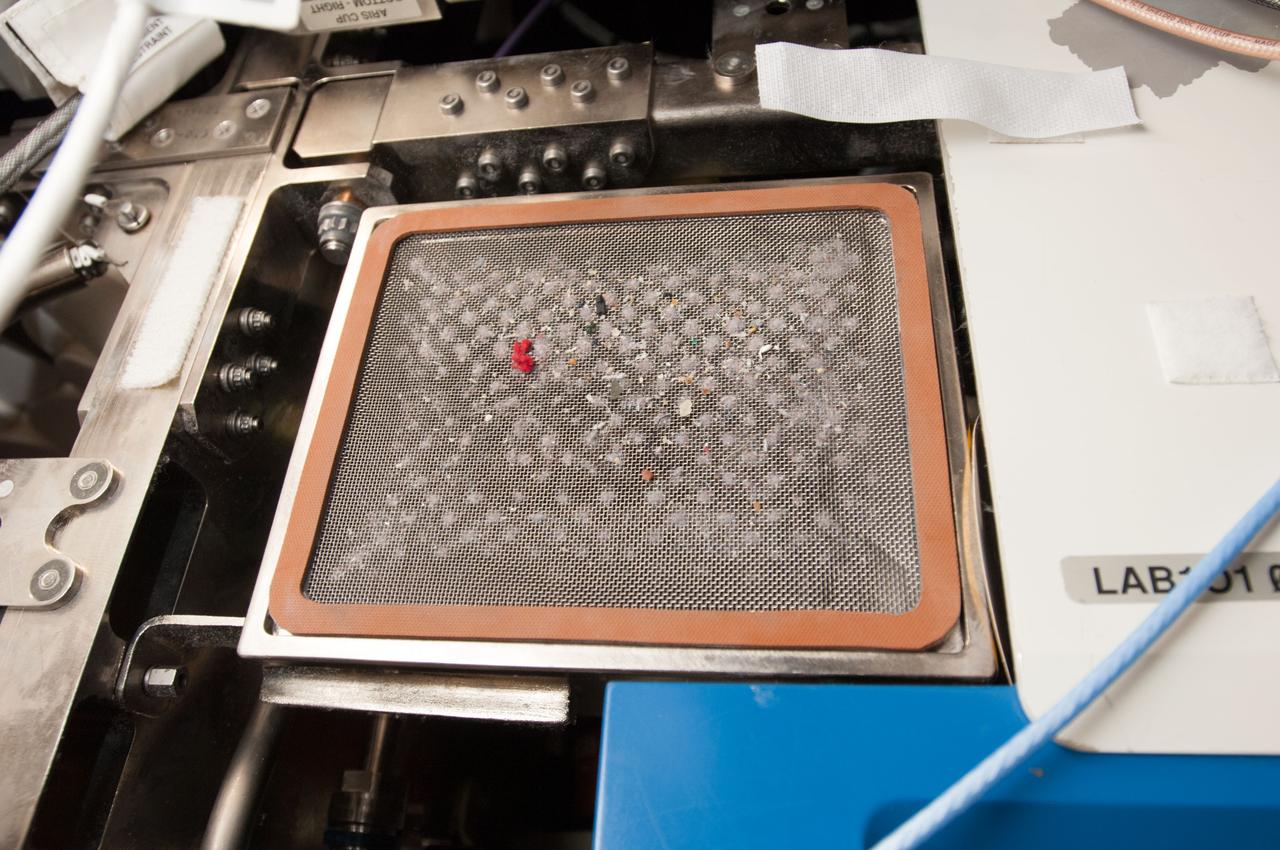
View of filter during cleaning on the Active Rack Isolation System (ARIS). Photo was taken during Expedition 34.

In this NASA Mars Odyssey image of eastern Arabia Terra, remnants of a once vast layered terrain are evident as isolated buttes, mesas, and deeply-filled craters. The origin of the presumed sediments that created the layers is unknown, but those same sediments, now eroded, may be the source of the thick mantle of dust that covers much of Arabia Terra today. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04400

This VIS image shows an isolated mountain east of Hellas Planitia. Erosion is moving material down hill towards the lower elevations. The linear features on the hill debris indicate that volatiles such as ice may play a part in the erosion. Orbit Number: 74924 Latitude: -42.7071 Longitude: 108.078 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2018-11-04 11:37 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22999

This VIS image shows some of the plains of Arcadia Planitia. Isolated small hills are a common feature in this part of the planitia. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Orbit Number: 61382 Latitude: 37.5959 Longitude: 171.296 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2015-10-15 23:03 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22791
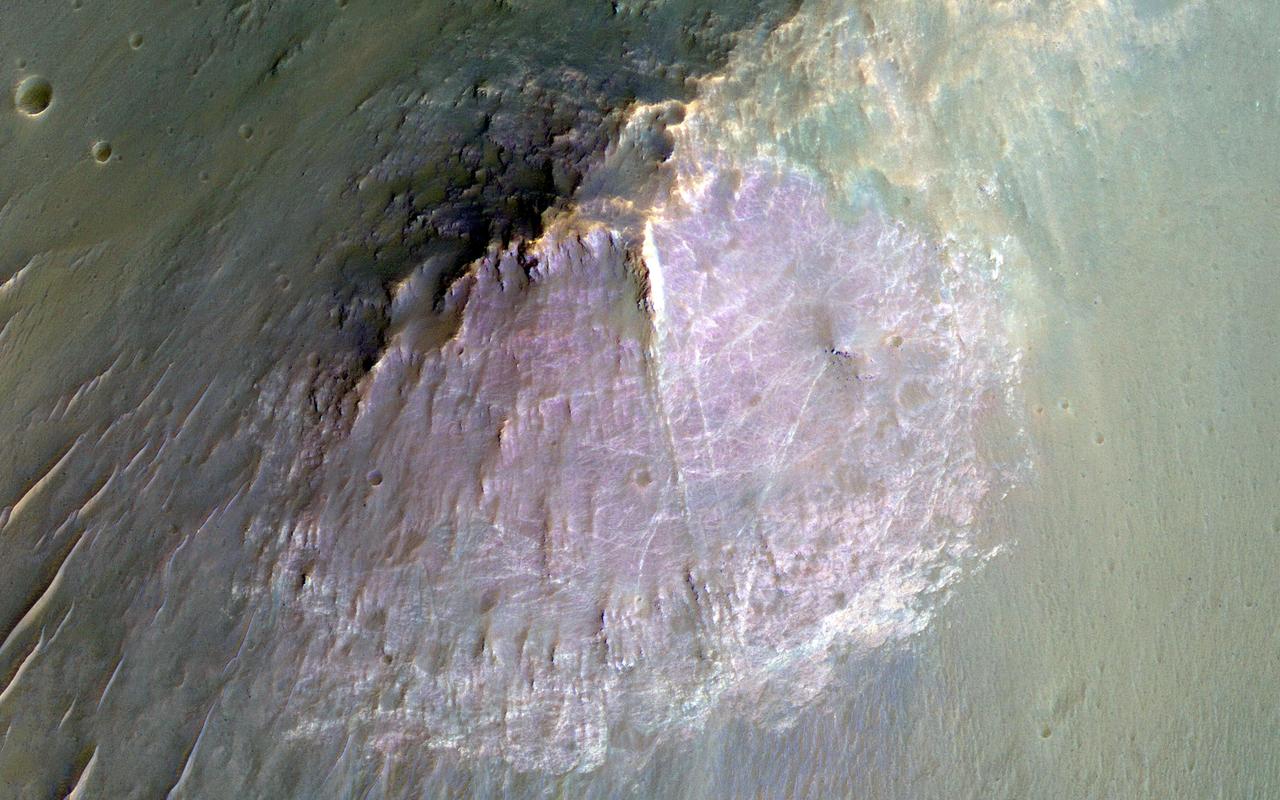

NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbite observed this image of an isolated mountain in the Southern highlands reveals a large exposure of purplish bedrock. Since HiRISE color is shifted to longer wavelengths than visible color and given relative stretches, this really means that the bedrock is roughly dark in the broad red bandpass image compared to the blue-green and near-infrared bandpass images. In the RGB (red-green-blue) color image, which excludes the near-infrared bandpass image, the bedrock appears bluish in color. This small mountain is located near the northeastern rim of the giant Hellas impact basin, and could be impact ejecta. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19854
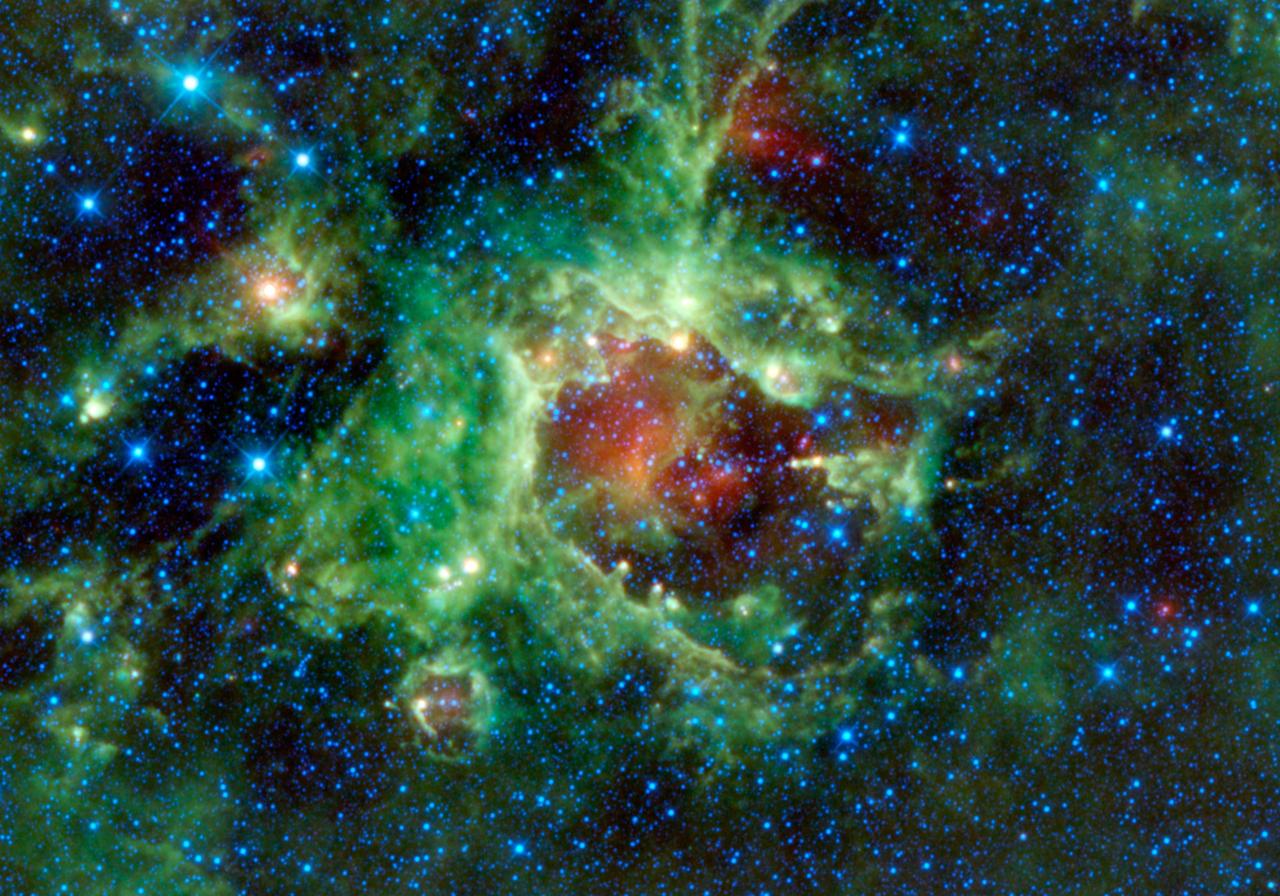

NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, captured this image of a star-forming cloud of dust and gas located in the constellation of Monoceros. Sh2-284 is relatively isolated at the very end of an outer spiral arm of our Milky Way galaxy.
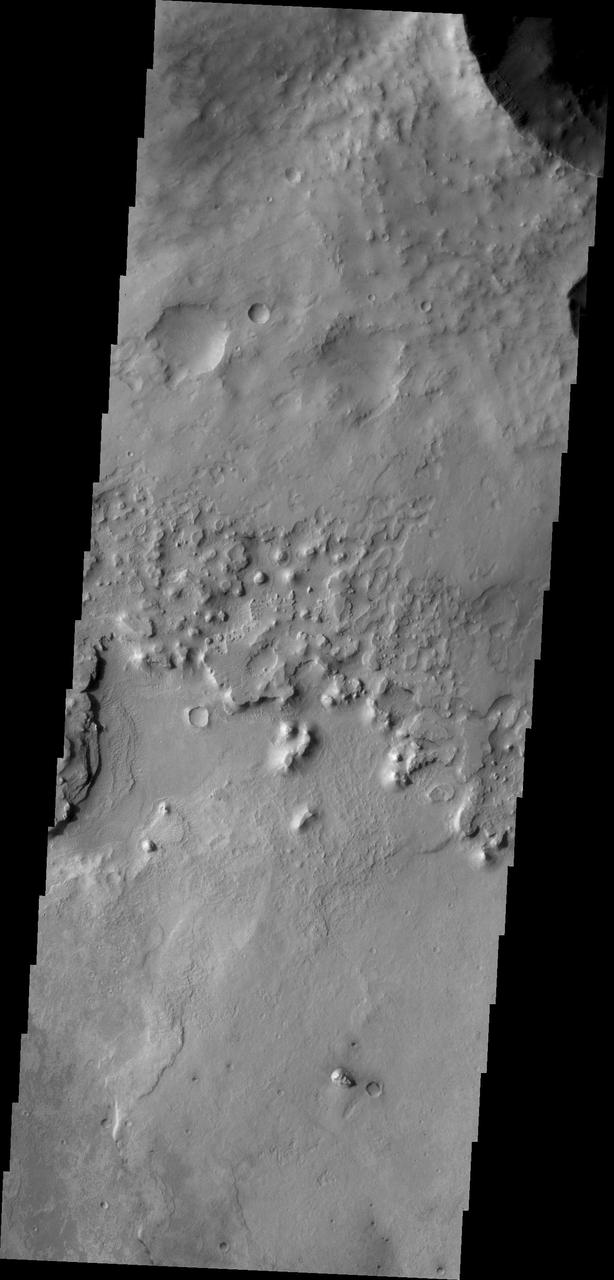

The ejecta blanket created around impact craters is often much more resistant to erosion than surrounding surface materials. As seen by NASA Mars Odyssey, the ejecta material creates isolated highs as surrounding surface is eroded near Meridiani Planum.
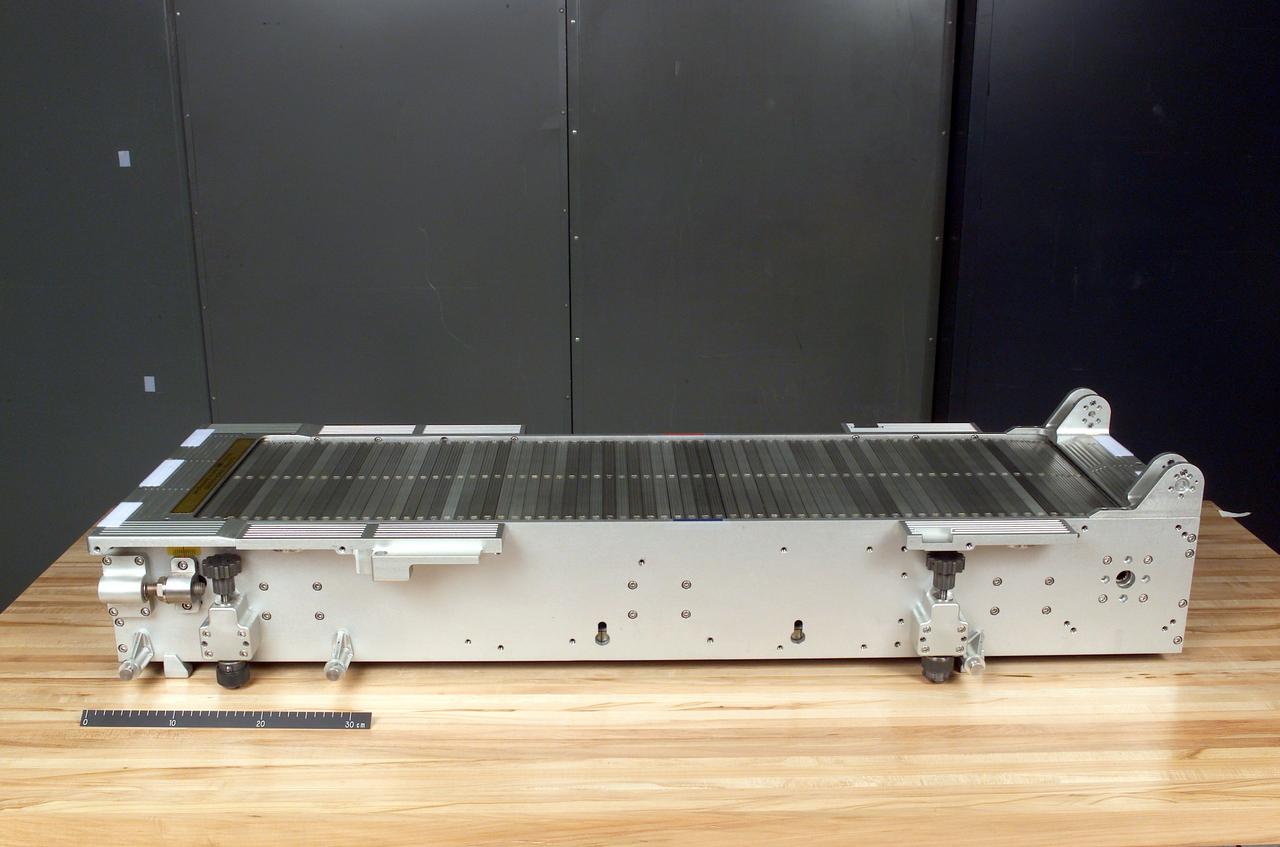

jsc2002e38731 (2002) --- Overall oblique view of the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) Chassis Assembly for use in the International Space Station (ISS) Service Module (SM).
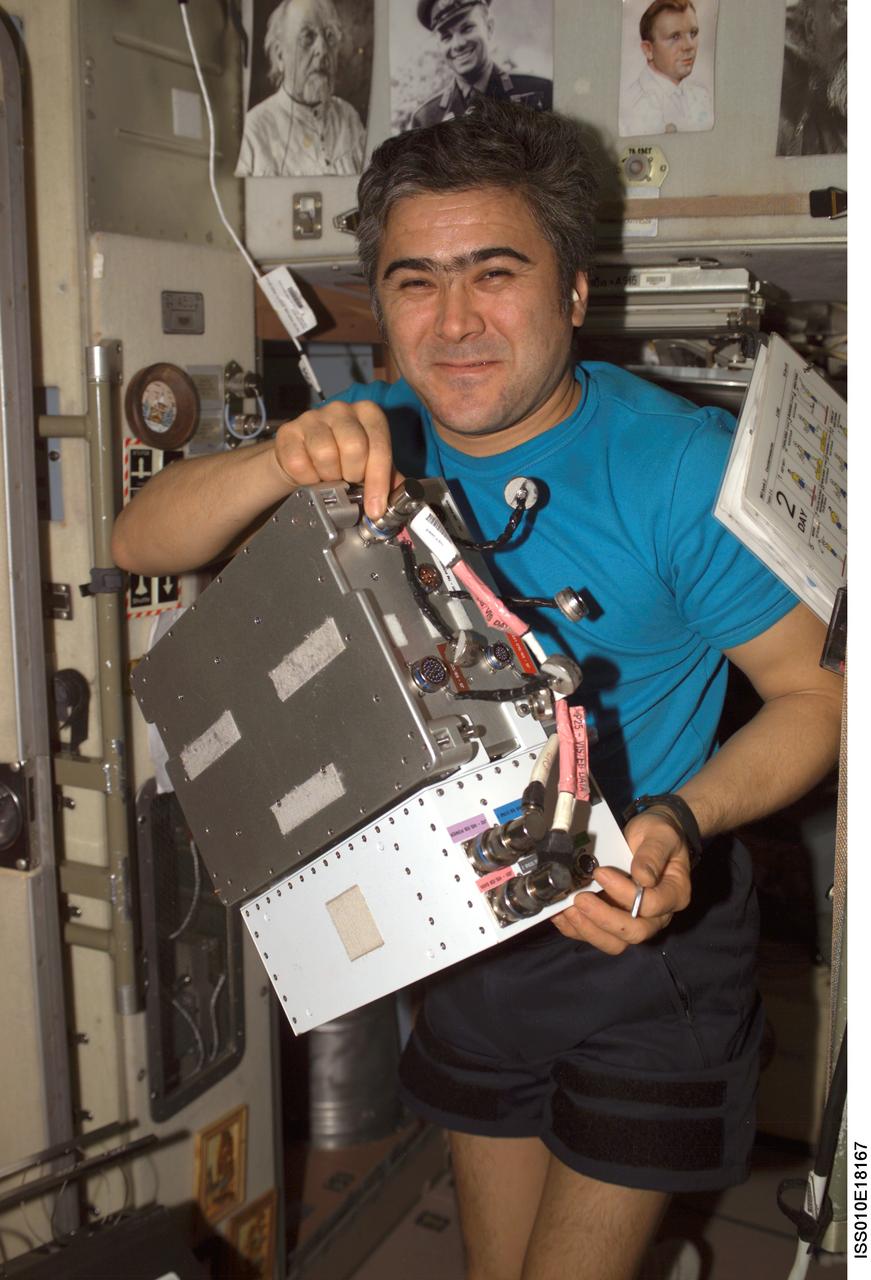

ISS010-E-18167 (17 February 2005) --- Cosmonaut Salizhan S. Sharipov, Expedition 10 flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, holds an Electronic Box Assembly, and Violation Isolation and Stabilization (VIS) Controller Assembly, which is part of the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station (ISS). Also in view is a VIS/TM data cable and VIS/TM power cable. This box receives power and distributes it between the treadmill and the VIS subassemblies.
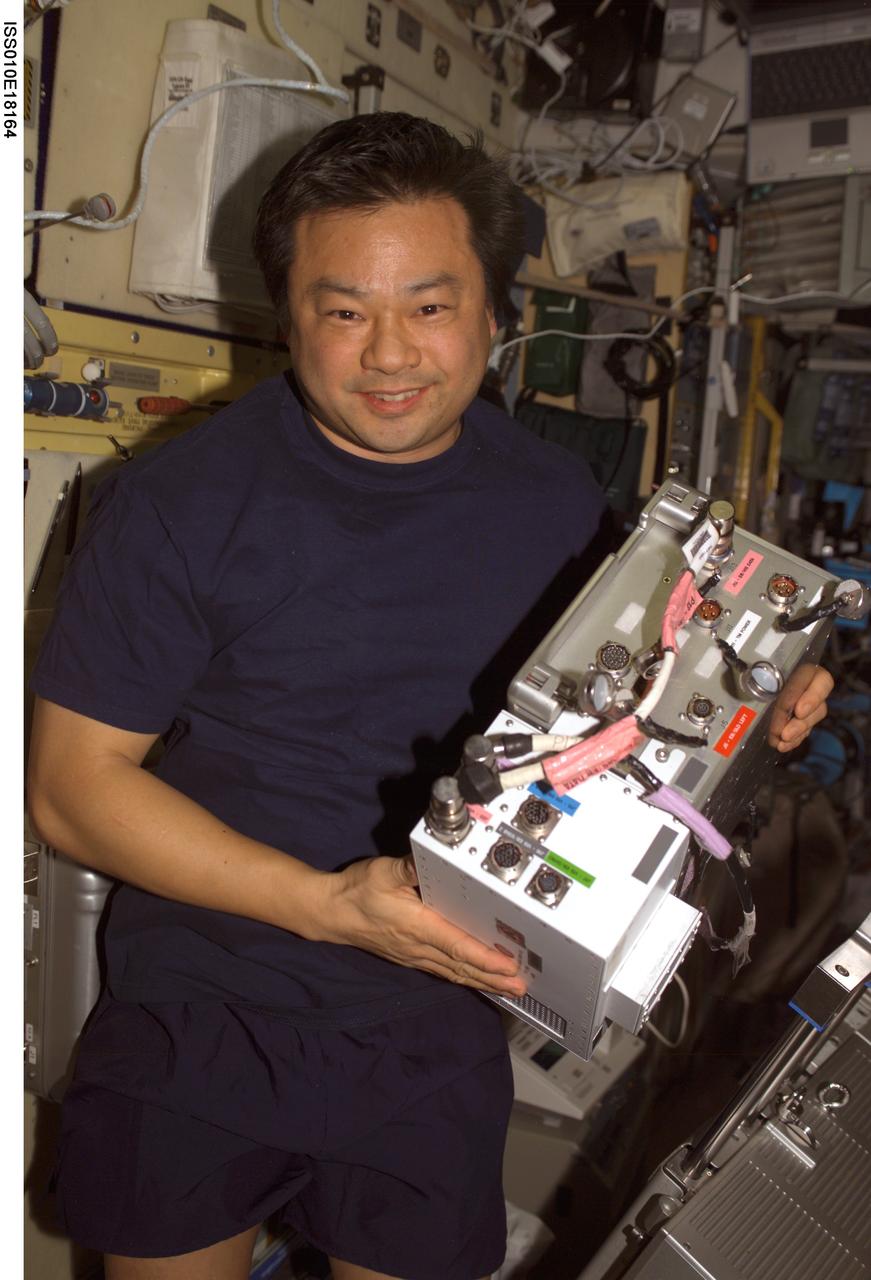
ISS010-E-18164 (17 February 2005) --- Astronaut Leroy Chiao, Expedition 10 commander and NASA ISS science officer, holds an Electronic Box Assembly, and Violation Isolation and Stabilization (VIS) Controller Assembly, which is part of the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station (ISS). Also in view is a VIS/TM data cable and VIS/TM power cable. This box receives power and distributes it between the treadmill and the VIS subassemblies.
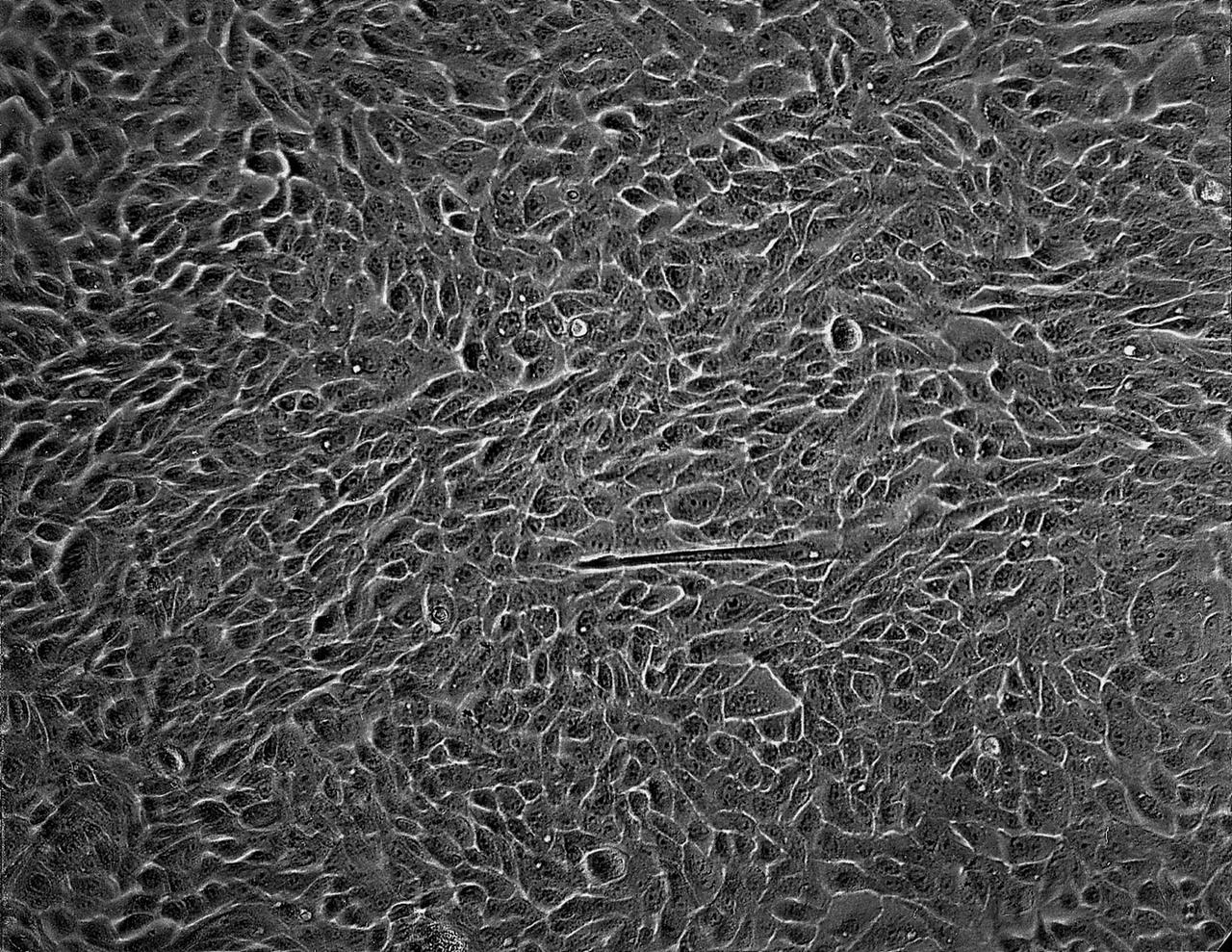
Isolation of human mammary epithelial cells (HMEC) from breast cancer susceptible tissue. Isolate of long-term growth human mammary epithelial cells (HMEC) from outgrowth of duct element; cells shown soon after isolation and early in culture in a dish. NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) is sponsoring research with Bioreactors, rotating wall vessels designed to grow tissue samples in space, to understand how breast cancer works. This ground-based work studies the growth and assembly of human mammary epithelial cell (HMEC) from breast cancer susceptible tissue. Radiation can make the cells cancerous, thus allowing better comparisons of healthy vs. tunorous tissue. Credit: Dr. Robert Tichmond, NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).

In planetary nomenclature, the descriptor term chaos means "distinctive area of broken terrain". The general morphology of chaos is steep-sided mesas in close proximity. This VIS image shows a region of chaos where the isolated mesas are still very large, as well as other locations that are already reduced by erosion into small mesas. This image is located south of Eos Chasma. Orbit Number: 82896 Latitude: -16.1936 Longitude: 319.319 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-08-21 23:16 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24181
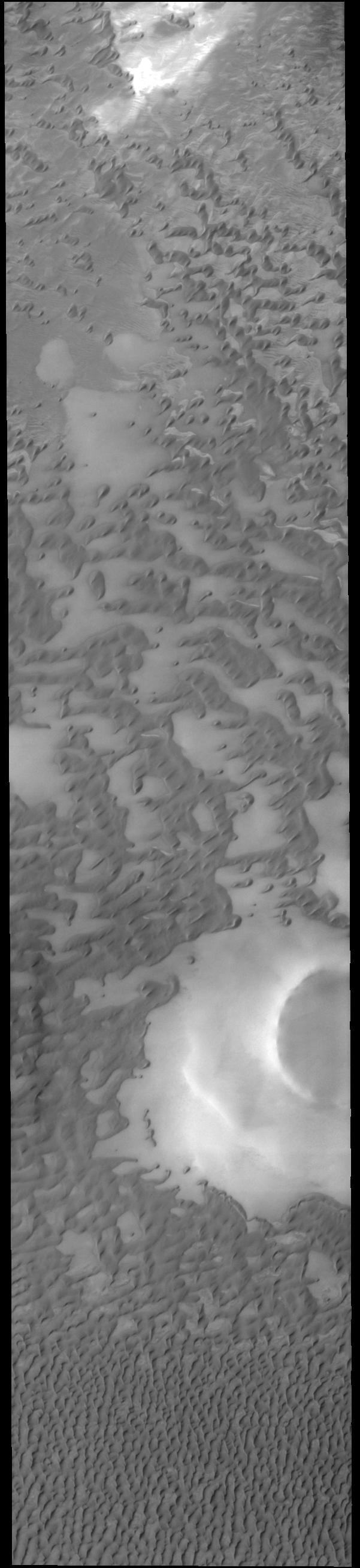

This VIS image shows part of Olympia Undae, a large dune field that surrounds part of the north polar cap. At the top of the image the dunes are small and isolated. As the amount of available sand increases the density of dunes increases. This is seen at the bottom of the image. Collected during northern summer, the dunes are completely free of ice and frost. Orbit Number: 71822 Latitude: 79.9343 Longitude: 143.91 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2018-02-22 00:15 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22400
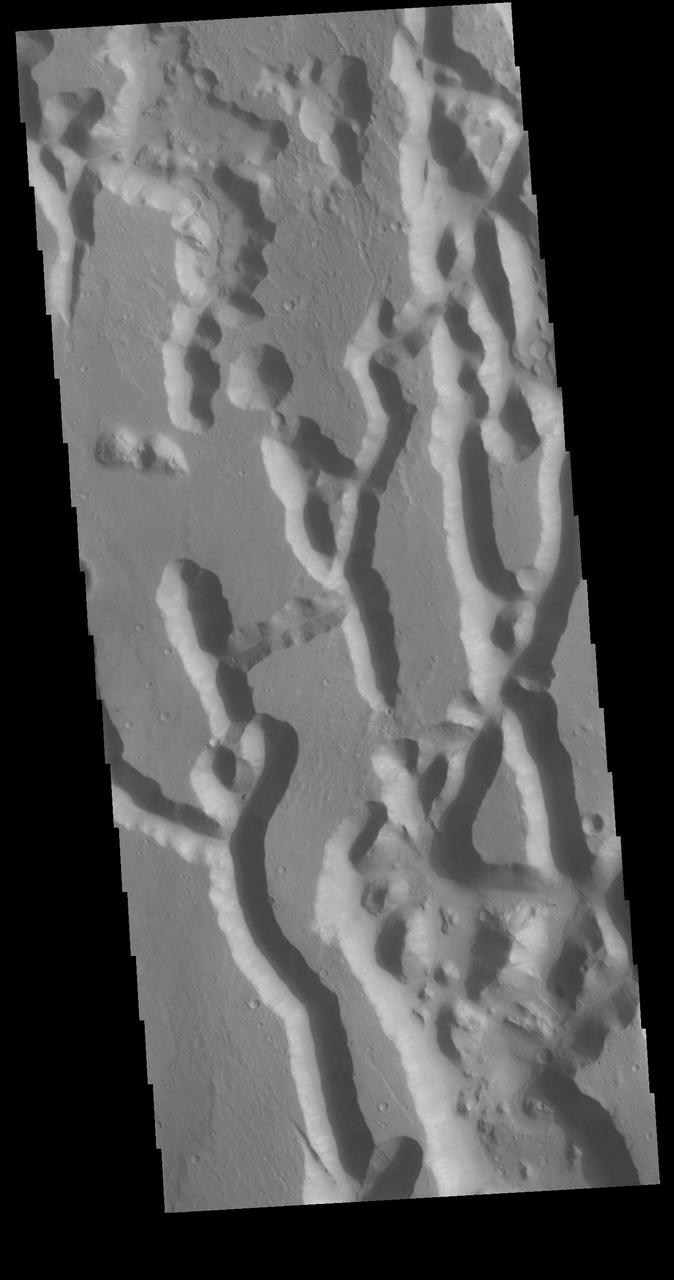

In planetary nomenclature, the descriptor term chaos means "distinctive area of broken terrain". The general morphology of chaos is steep-sided mesas in close proximity. This VIS image shows a region of Chryse Chaos where the isolated mesas are beginning to be formed. The interconnected channel forms erode, and mesas are created by erosion of the bounding channels. The bottom of the image shows some of the resultant mesas. Orbit Number: 71455 Latitude: 13.1491 Longitude: 318.592 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2018-01-22 18:16 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22395
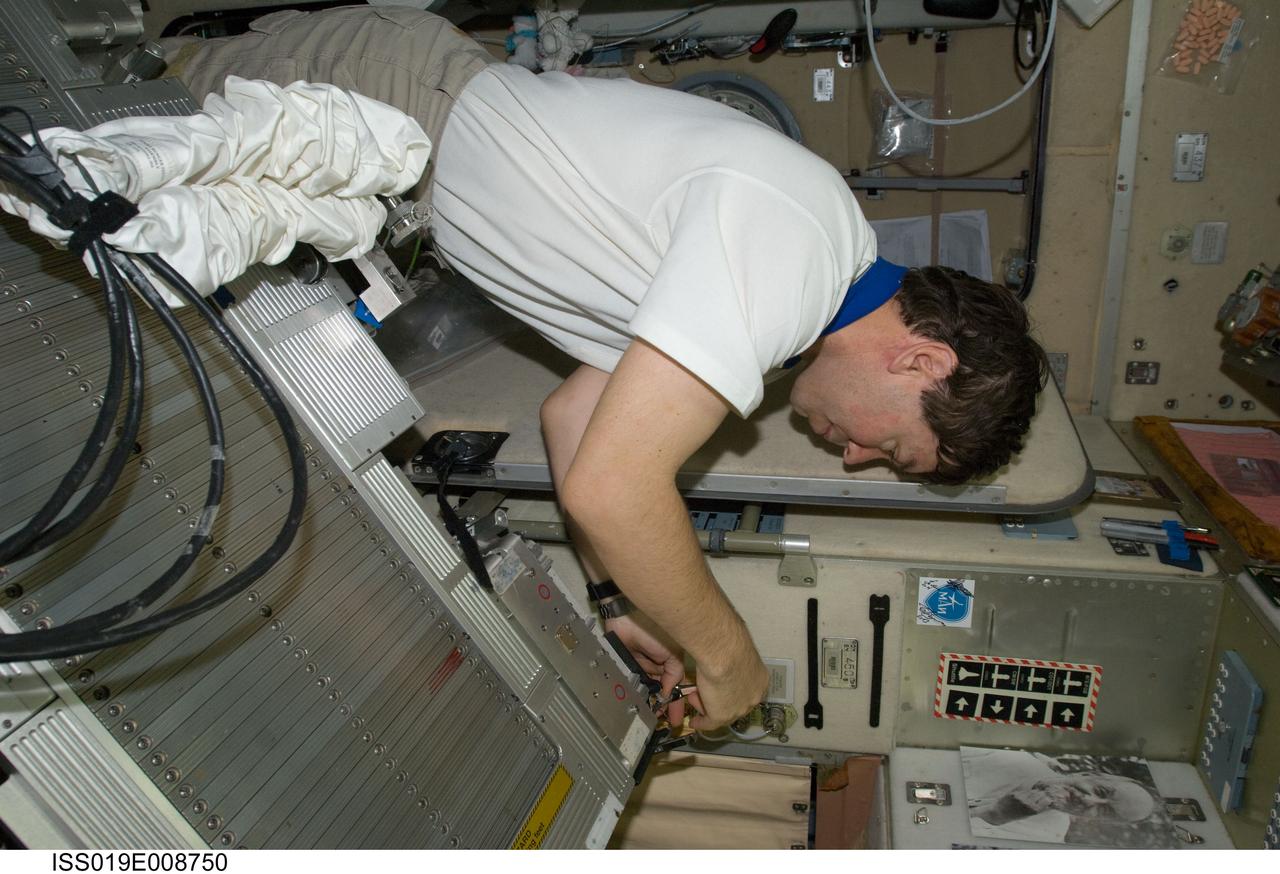

ISS019-E-008750 (21 April 2009) --- Astronaut Michael Barratt, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
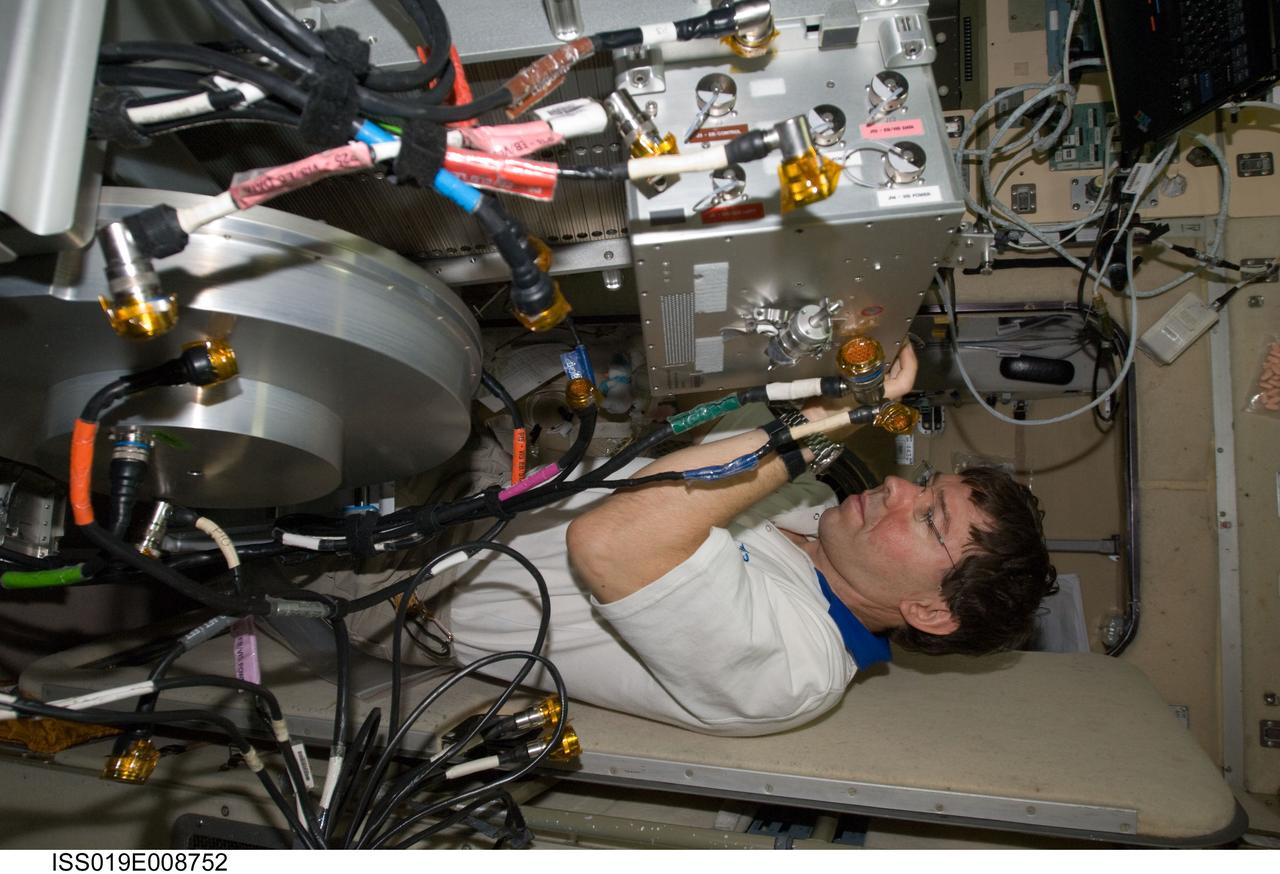

ISS019-E-008752 (21 April 2009) --- Astronaut Michael Barratt, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
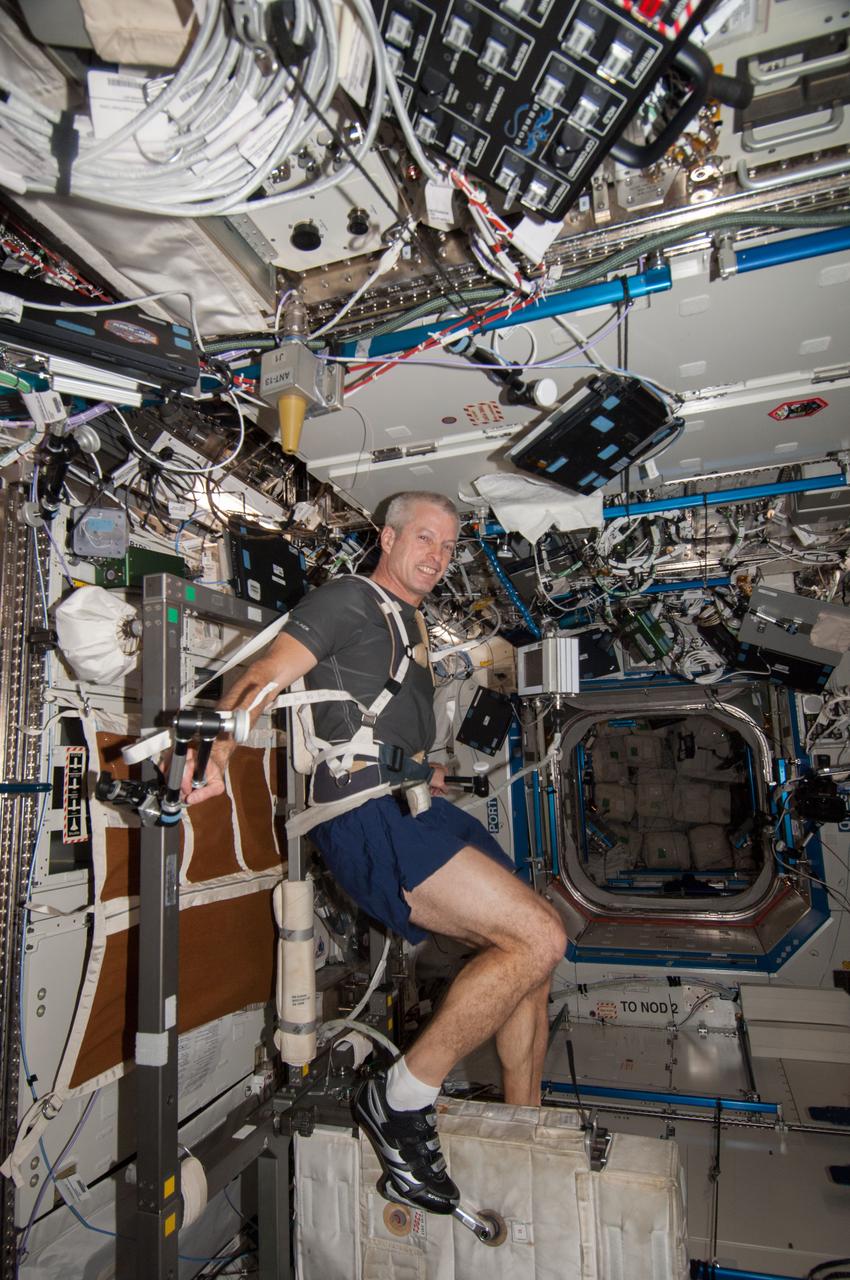

ISS039-E-014696 (22 April 2014) --- Expedition 39 Flight Engineer Steve Swanson of NASA, works out on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the U.S. lab Destiny of the International Space Station.
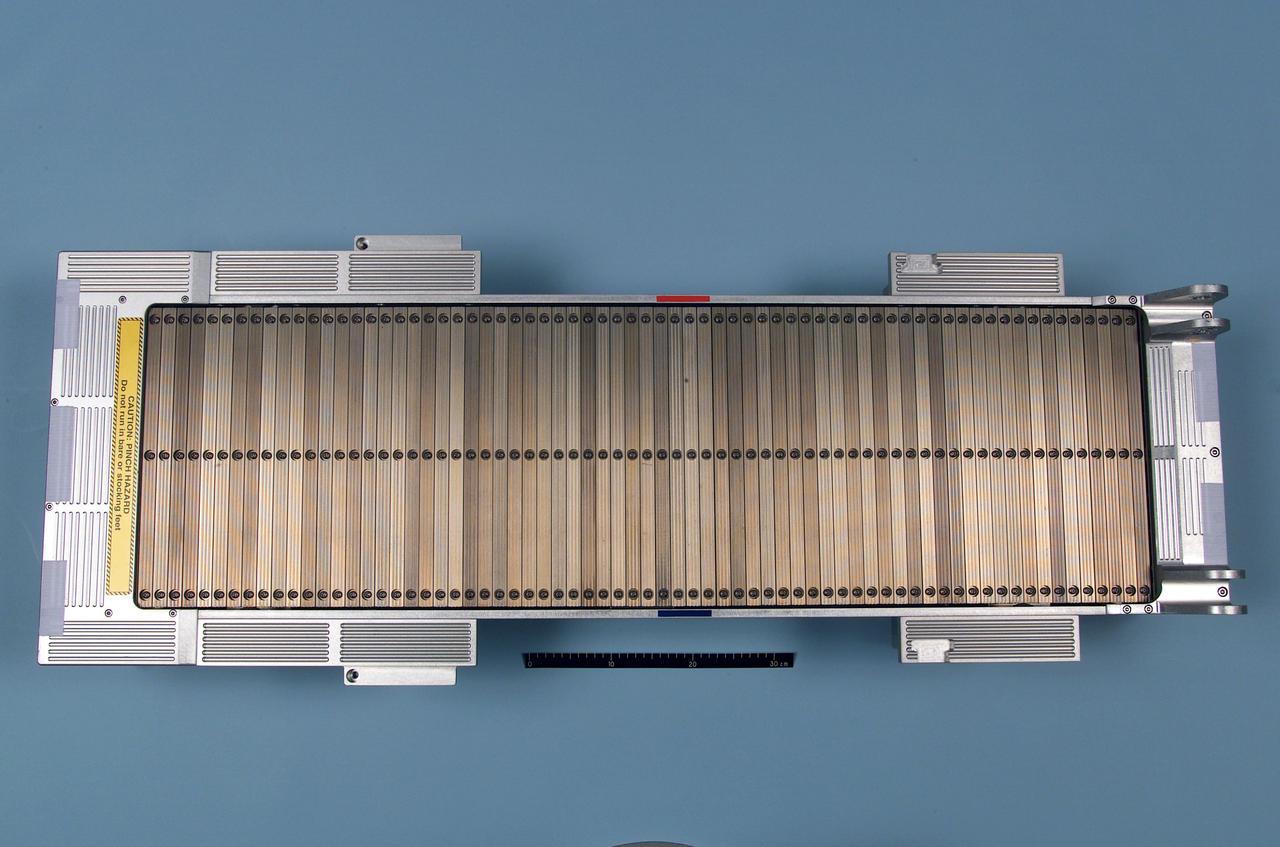

jsc2002e38738 (2002) --- Top view of the Treadmill Belt Assembly on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) Chassis Assembly for use in the International Space Station (ISS) Service Module (SM).
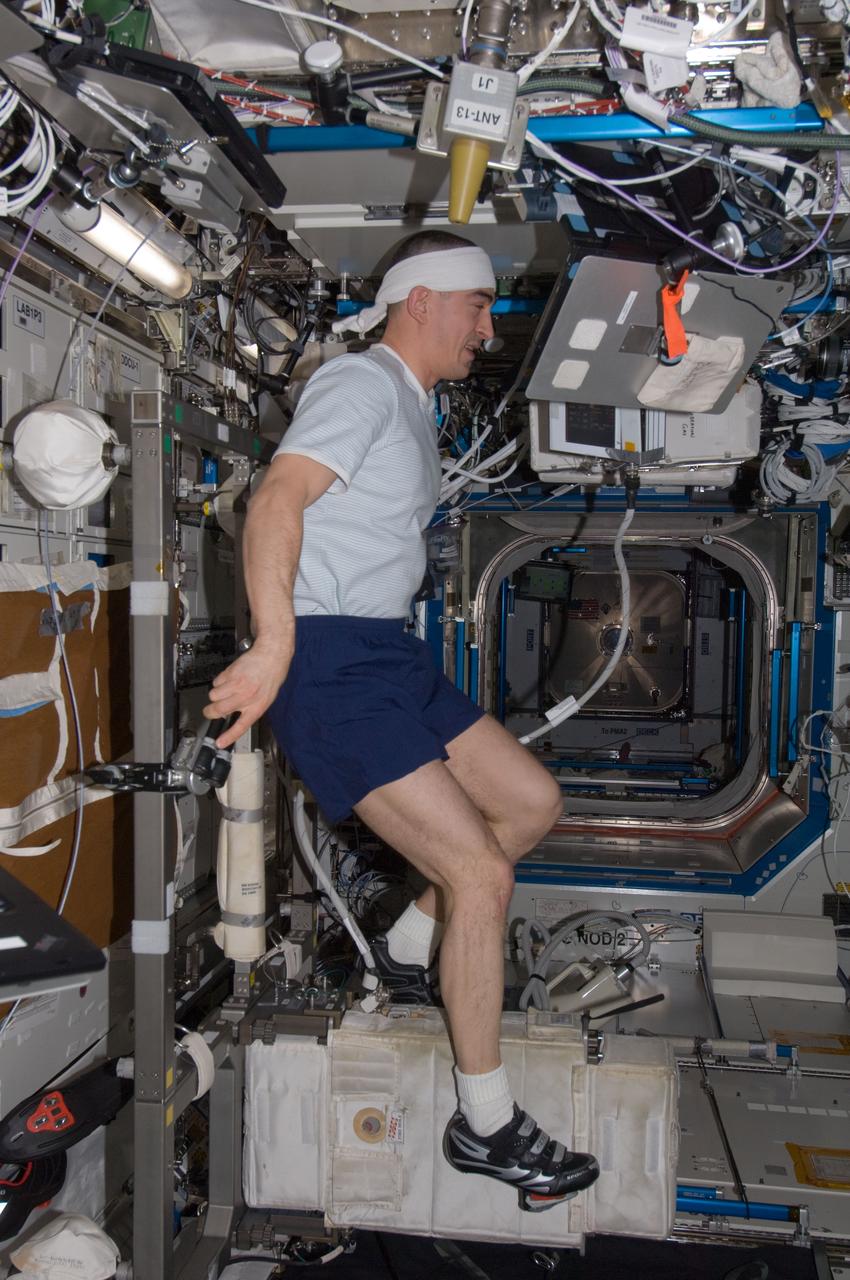

ISS030-E-012738 (10 Dec. 2011) --- Russian cosmonaut Anatoly Ivanishin, Expedition 30 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
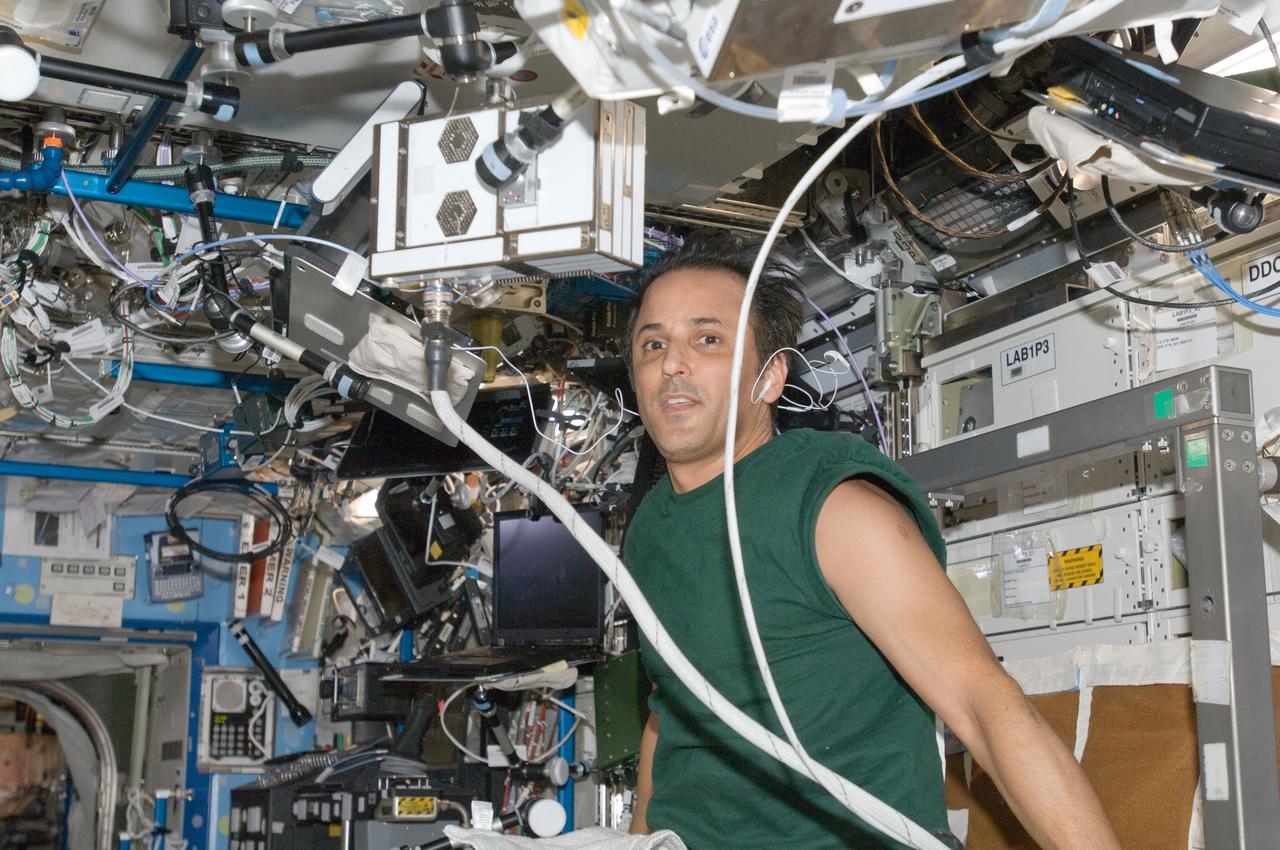

ISS032-E-009028 (21 July 2012) --- NASA astronaut Joe Acaba, Expedition 32 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
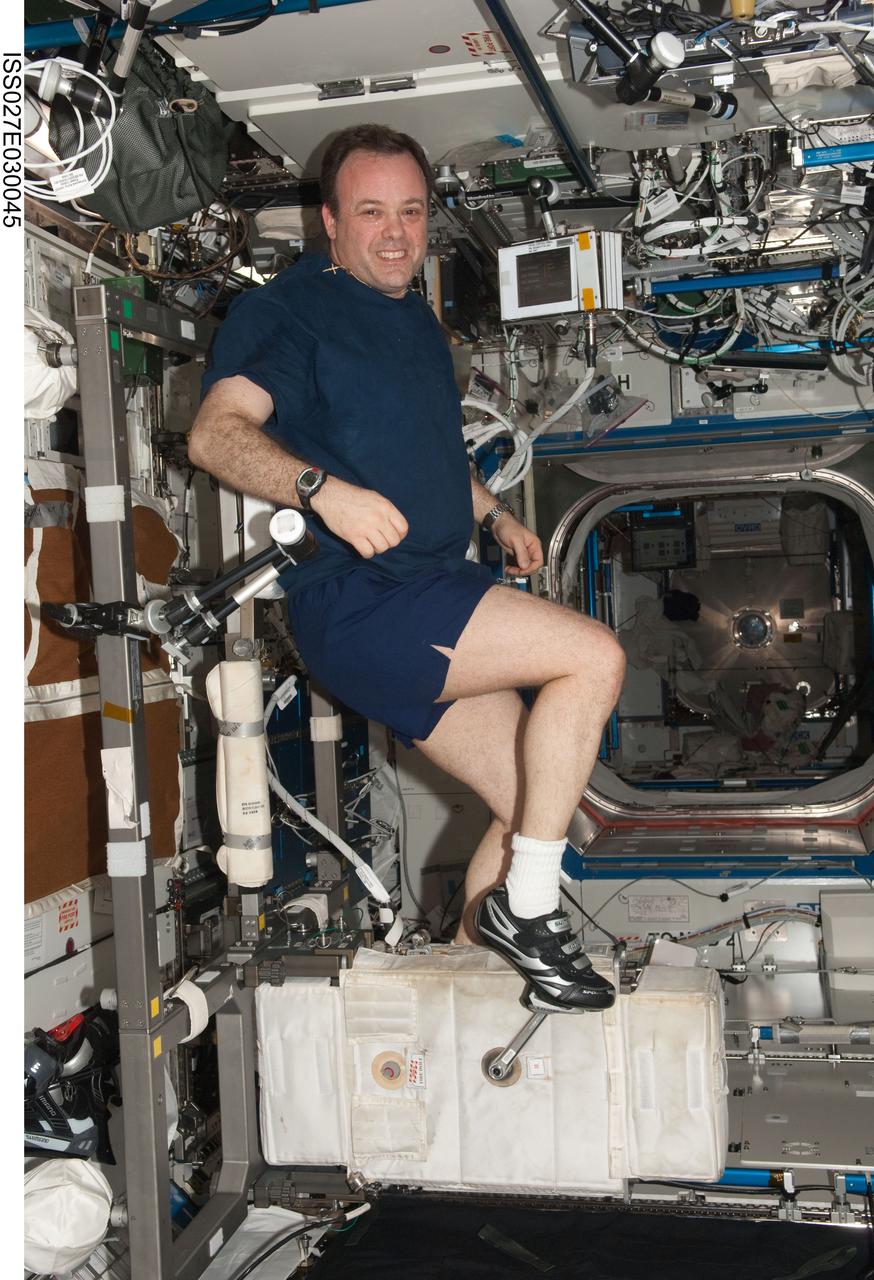

ISS027-E-030045 (11 May 2011) --- NASA astronaut Ron Garan, Expedition 27 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
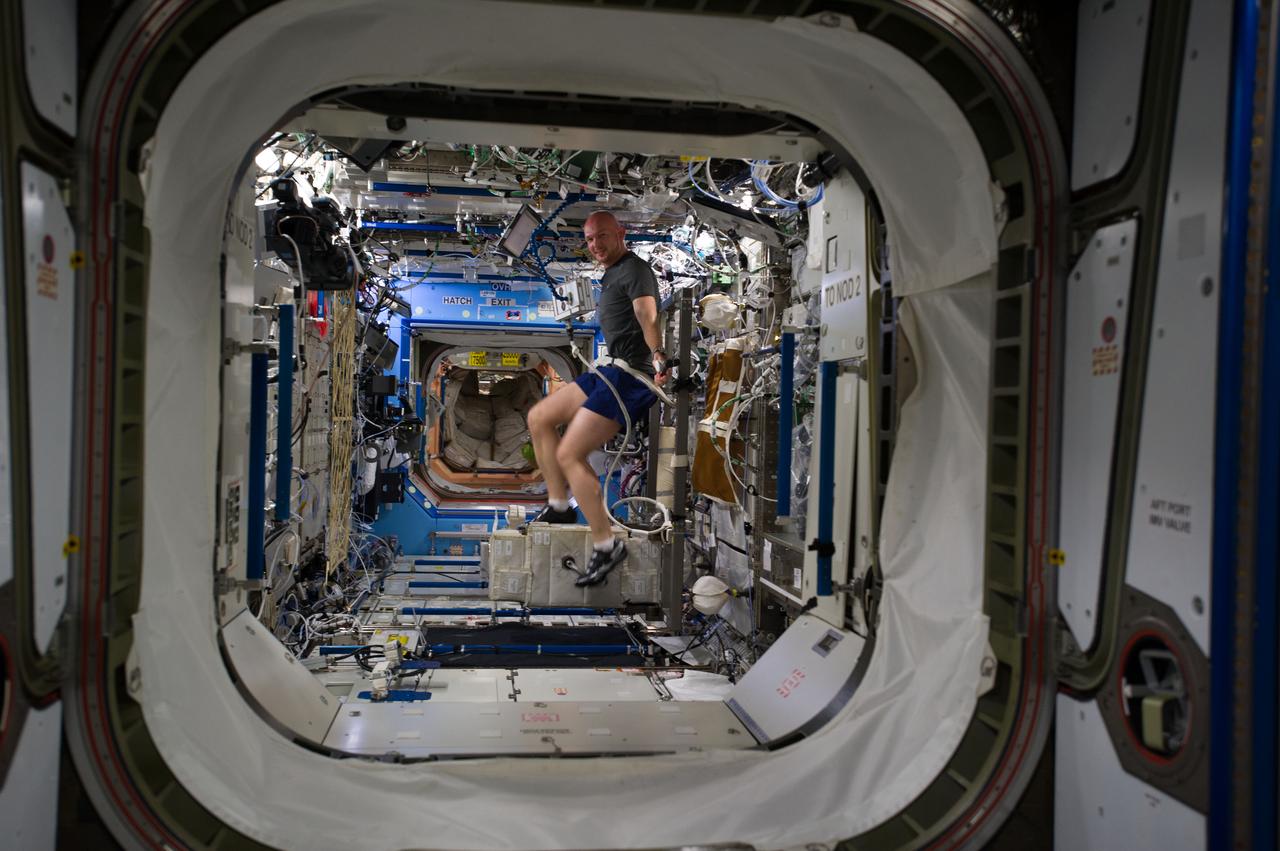

ISS040-E-006699 (2 June 2014) --- European Space Agency astronaut Alexander Gerst, Expedition 40 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
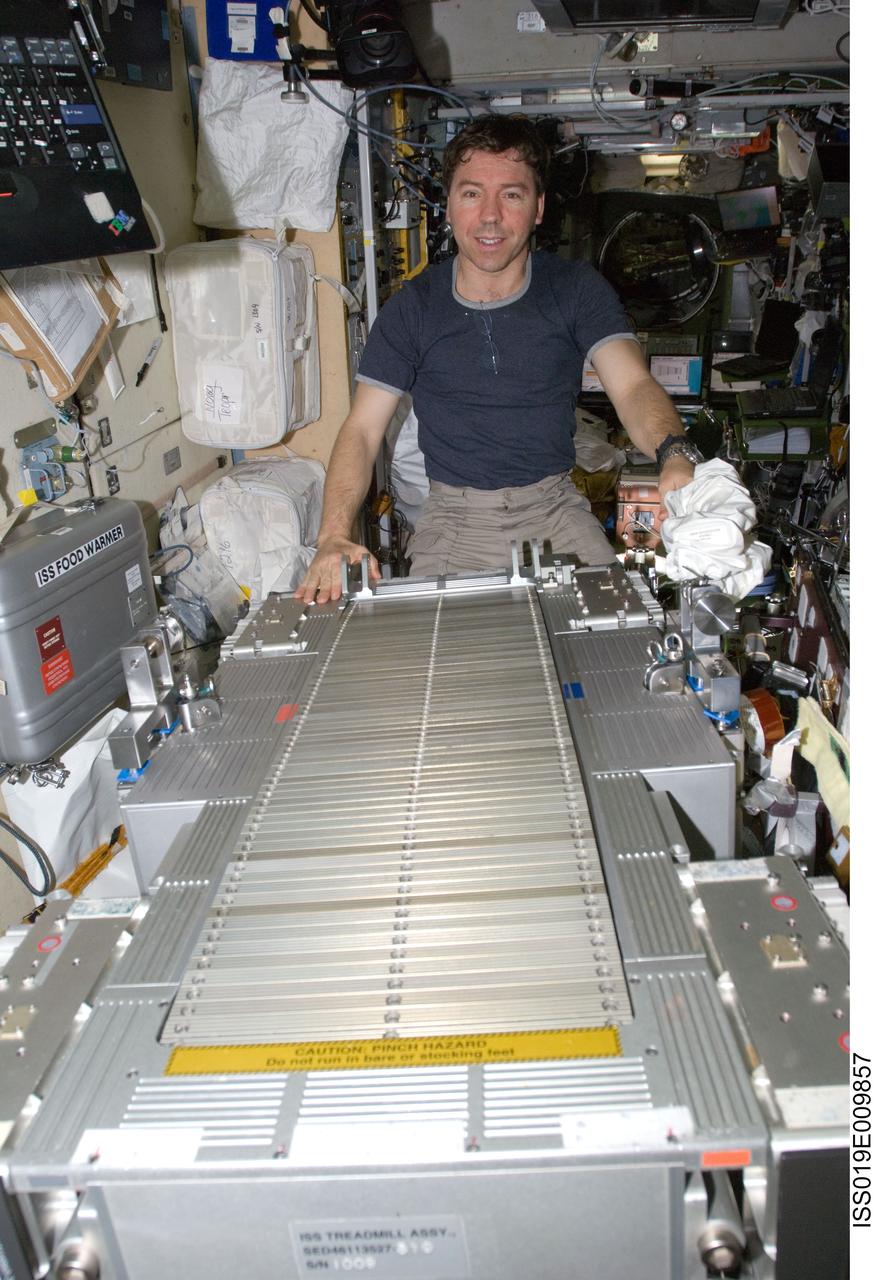

ISS019-E-009857 (23 April 2009) --- Astronaut Michael Barratt, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
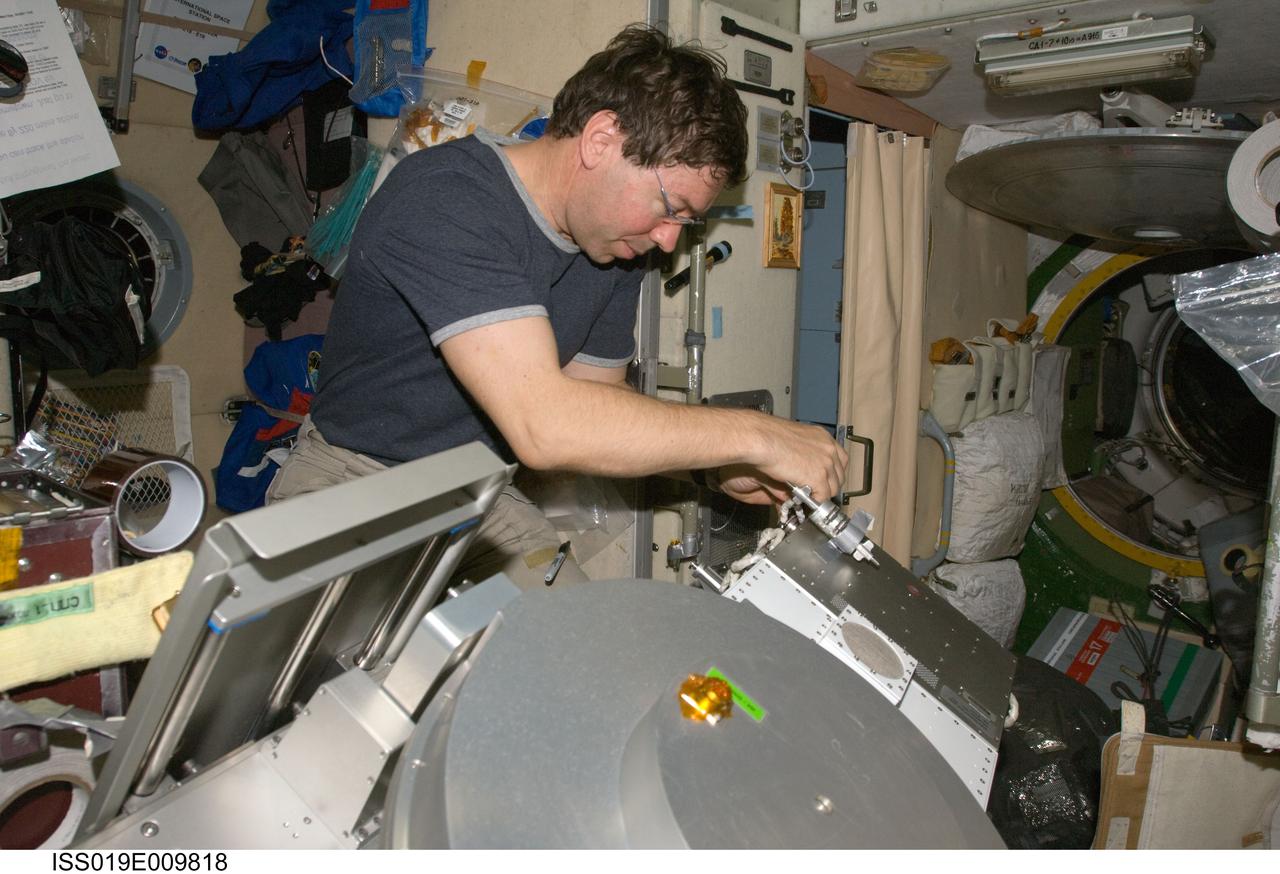

ISS019-E-009818 (23 April 2009) --- Astronaut Michael Barratt, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
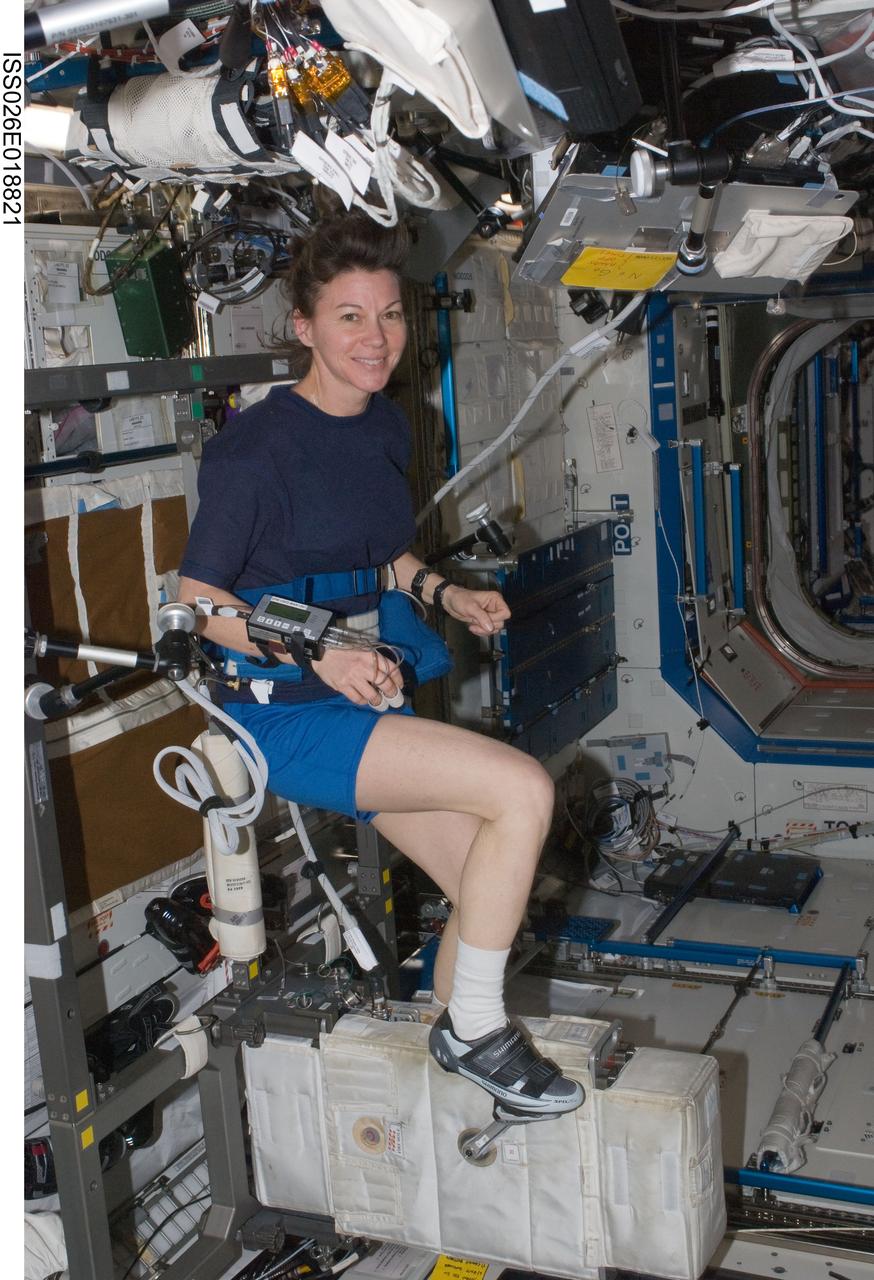

ISS026-E-018821 (20 Jan. 2011) --- NASA astronaut Catherine (Cady) Coleman, Expedition 26 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
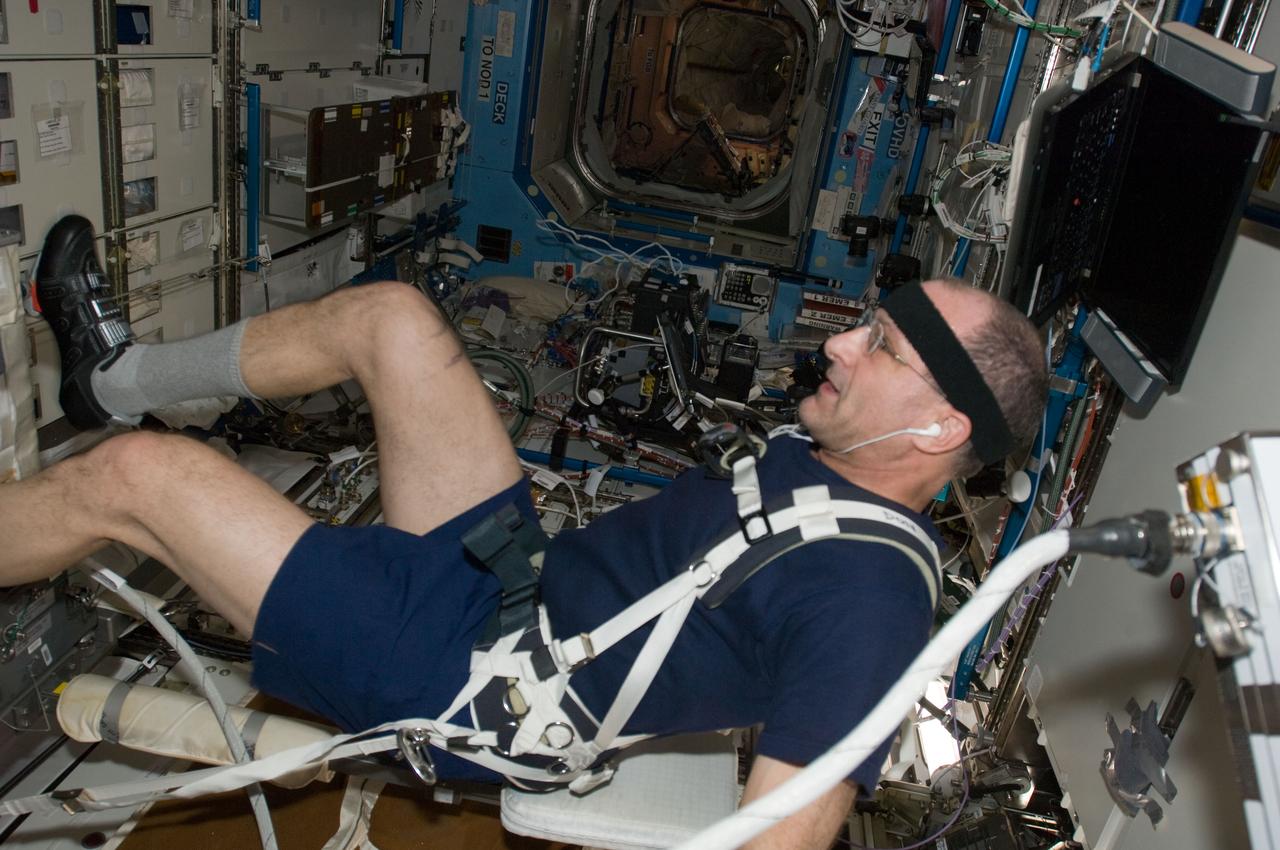

ISS030-E-032768 (15 Jan. 2012) --- NASA astronaut Don Pettit, Expedition 30 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
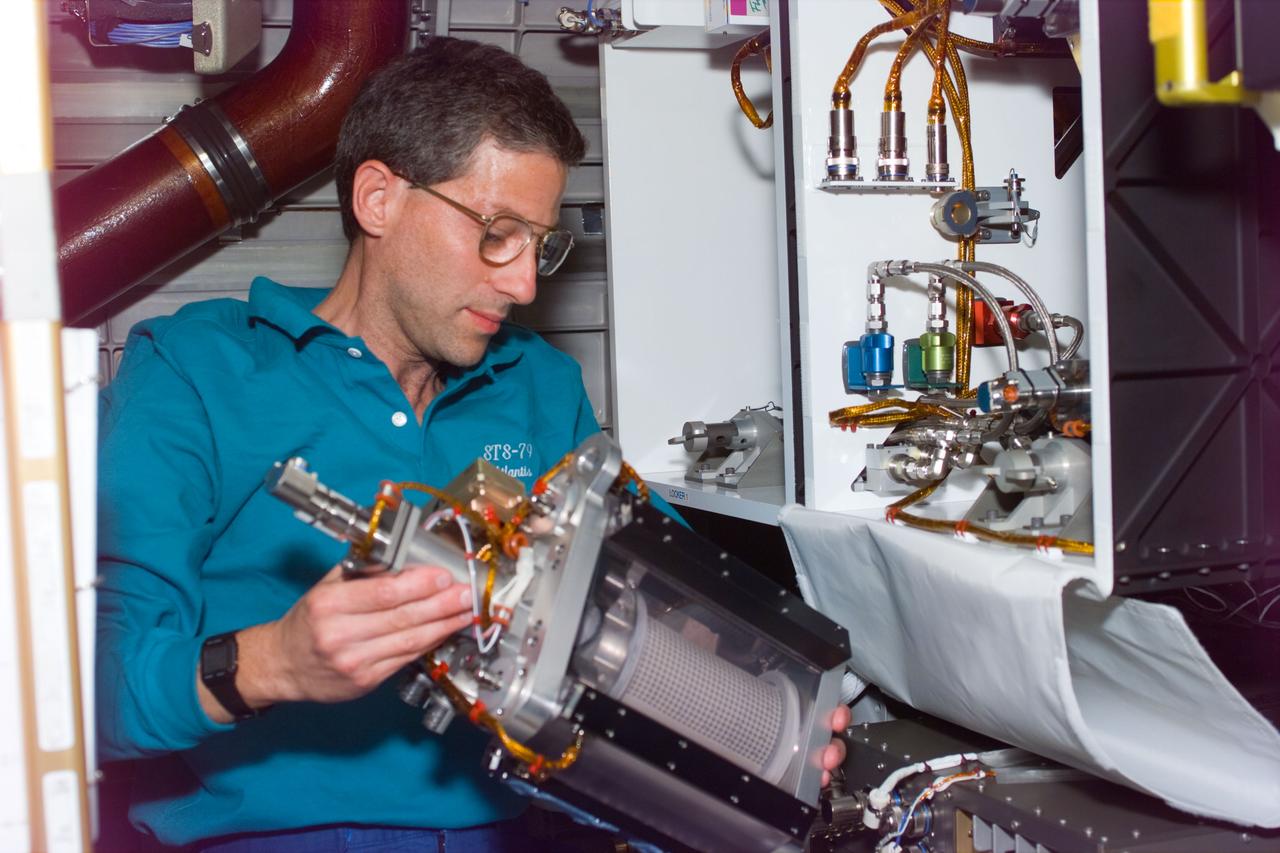

STS79-E-5042 (18 September 1996) --- Astronaut Jerome (Jay) Apt performs In-Flight Maintenance (IFM) on Active Rack Isolation System (ARIS) experiment, on Flight Day 3.
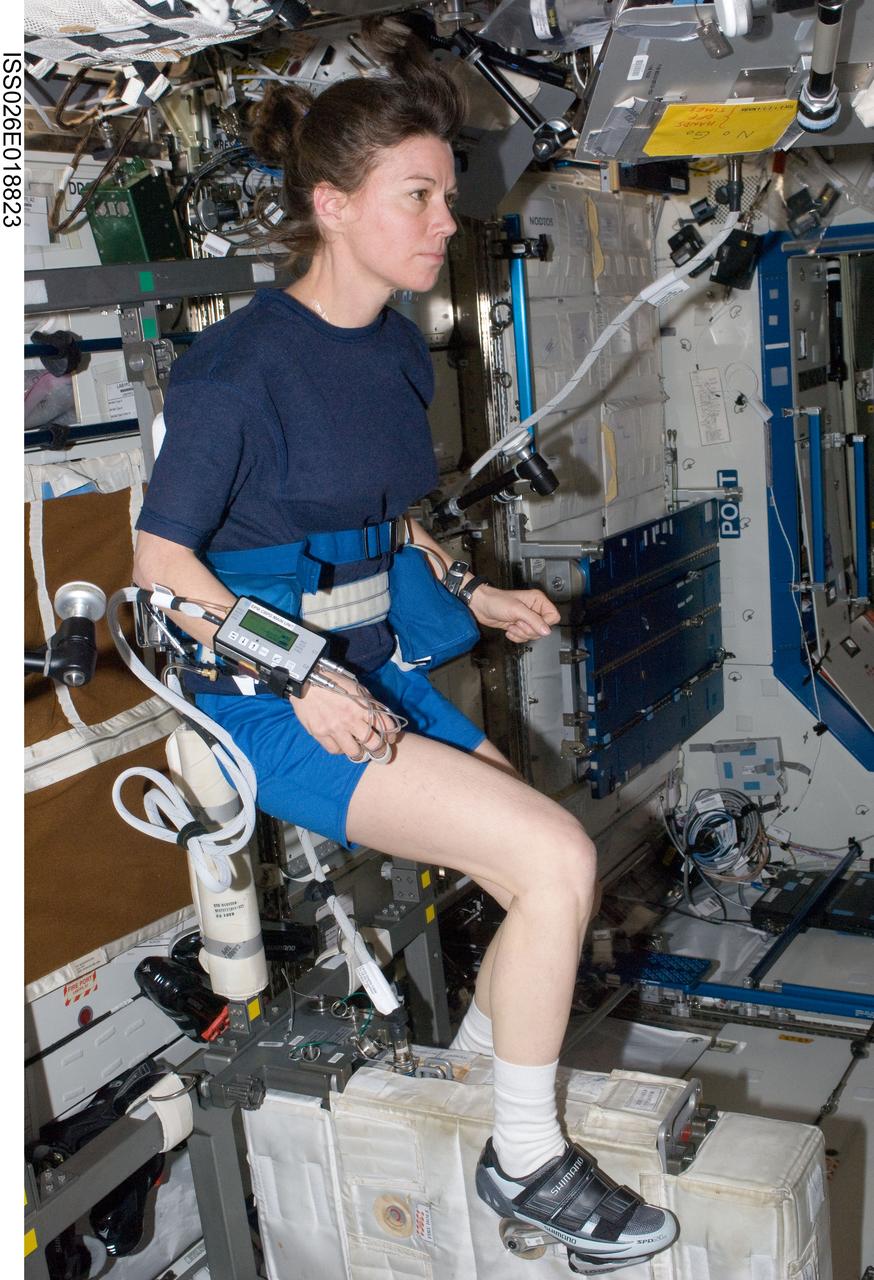

ISS026-E-018823 (20 Jan. 2011) --- NASA astronaut Catherine (Cady) Coleman, Expedition 26 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
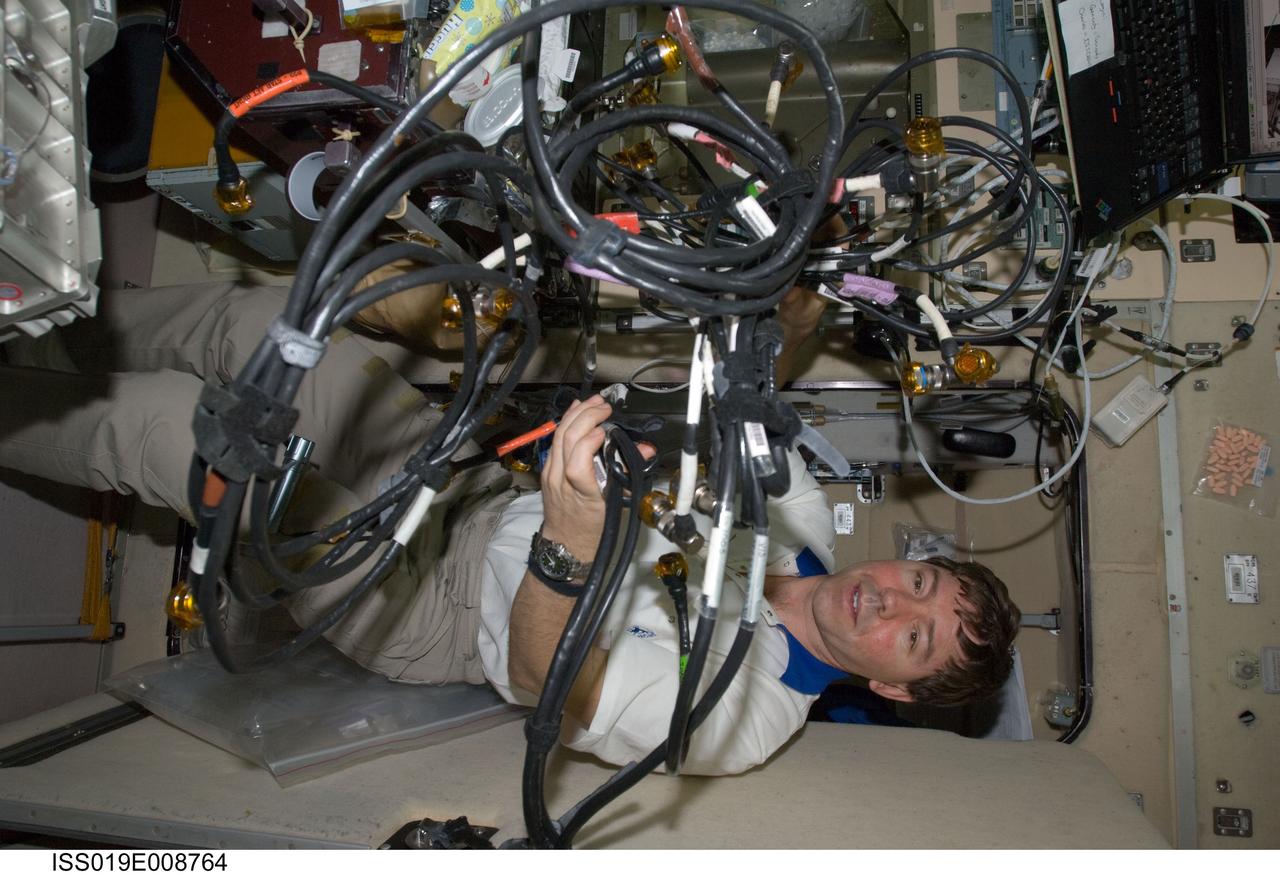

ISS019-E-008764 (21 April 2009) --- Astronaut Michael Barratt, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
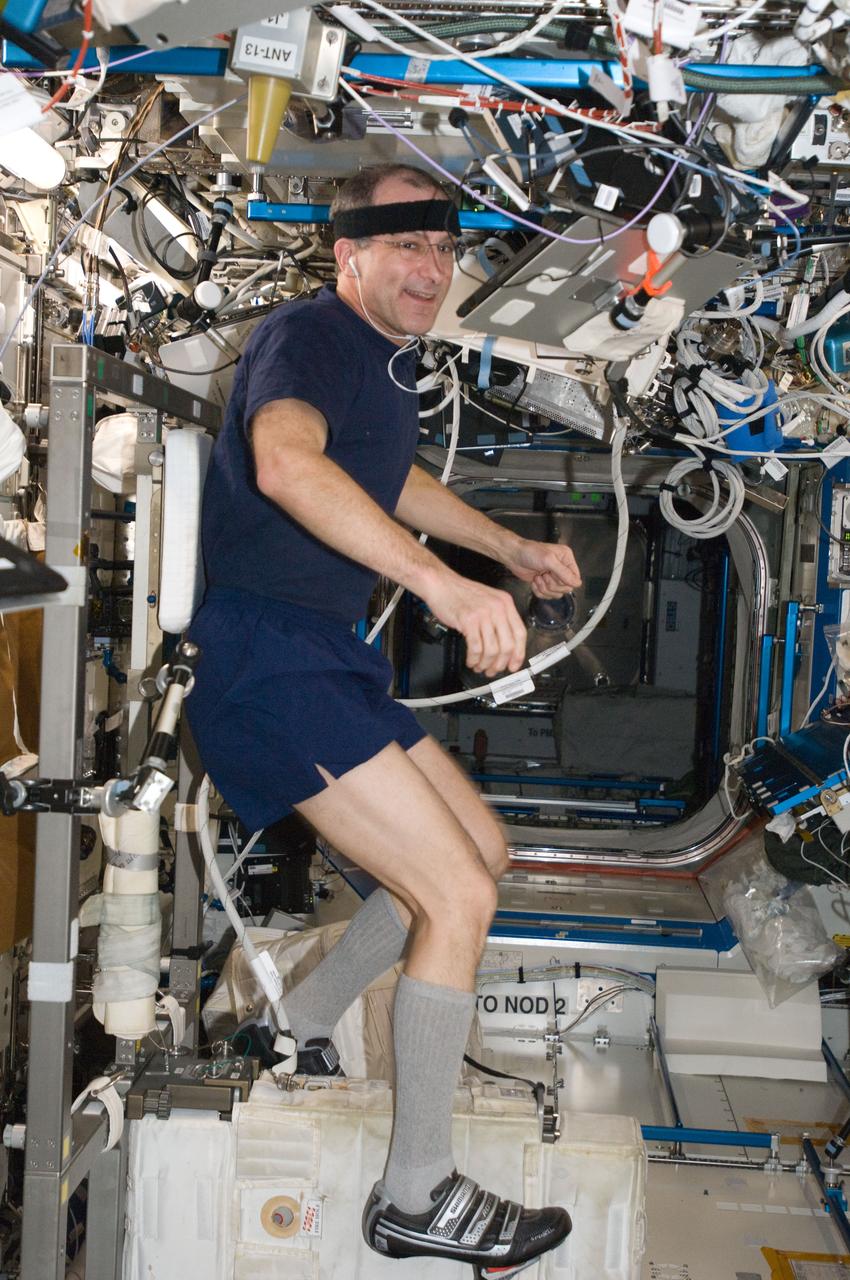

ISS030-E-063871 (5 Feb. 2012) --- NASA astronaut Don Pettit, Expedition 30 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
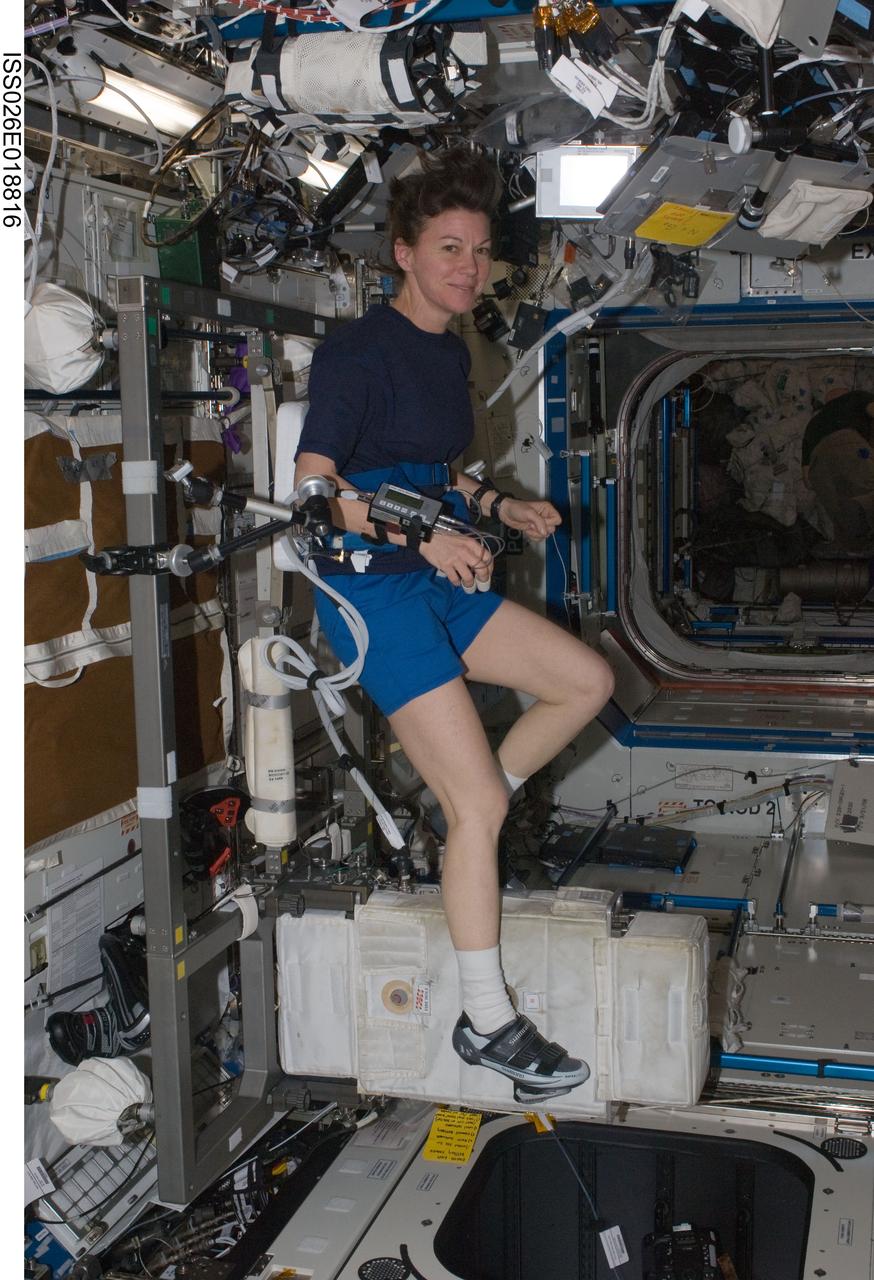

ISS026-E-018816 (20 Jan. 2011) --- NASA astronaut Catherine (Cady) Coleman, Expedition 26 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
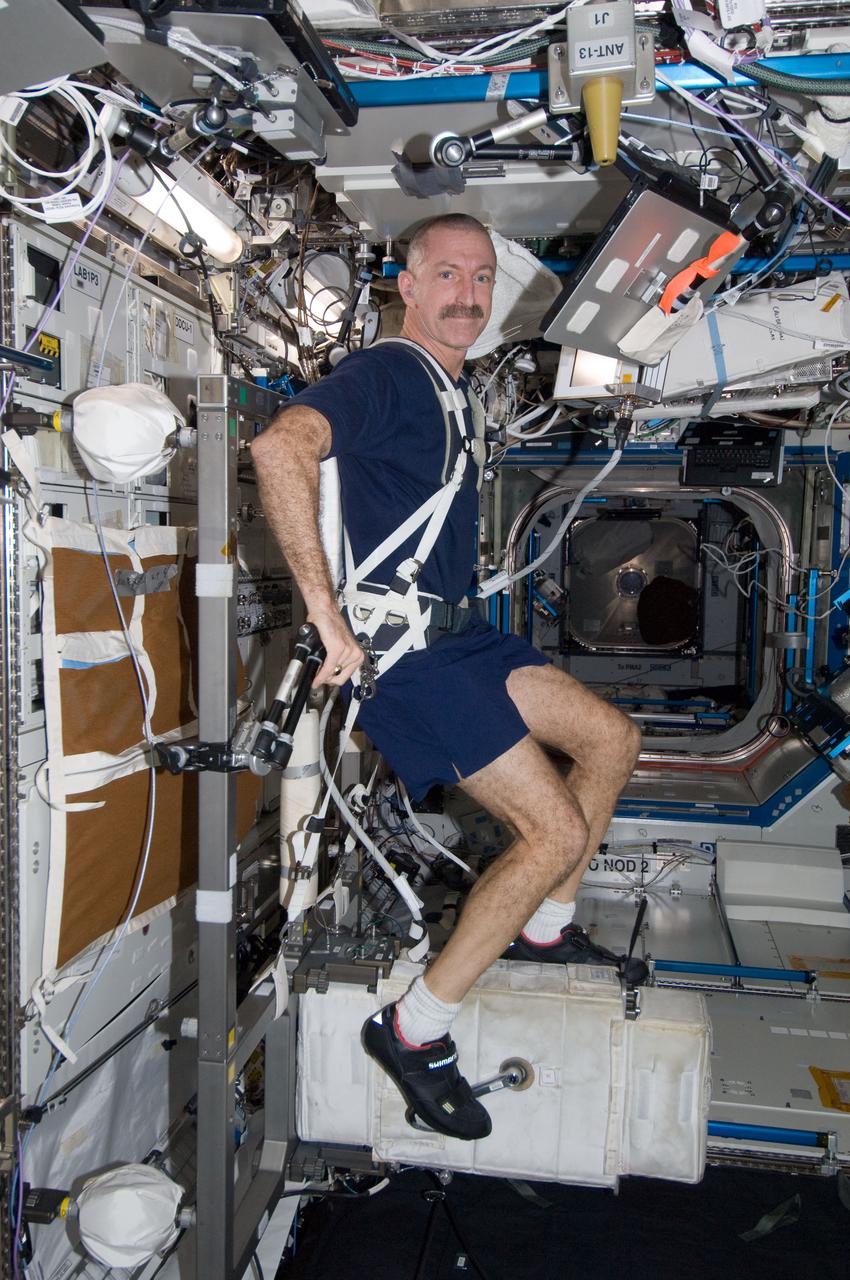

ISS030-E-032829 (2 Jan. 2012) --- NASA astronaut Dan Burbank, Expedition 30 flight commander, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
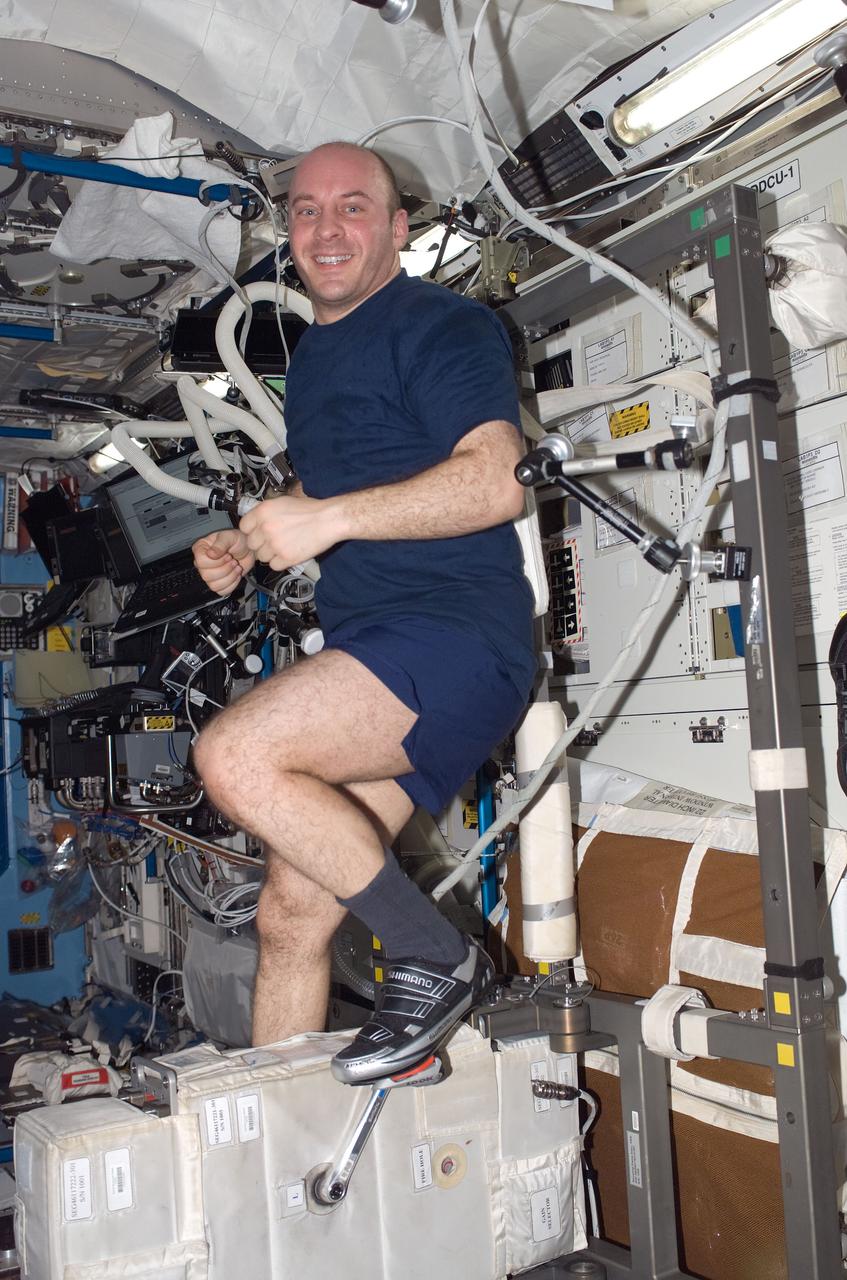

ISS017-E-006668 (11 May 2008) --- NASA astronaut Garrett Reisman, Expedition 17 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
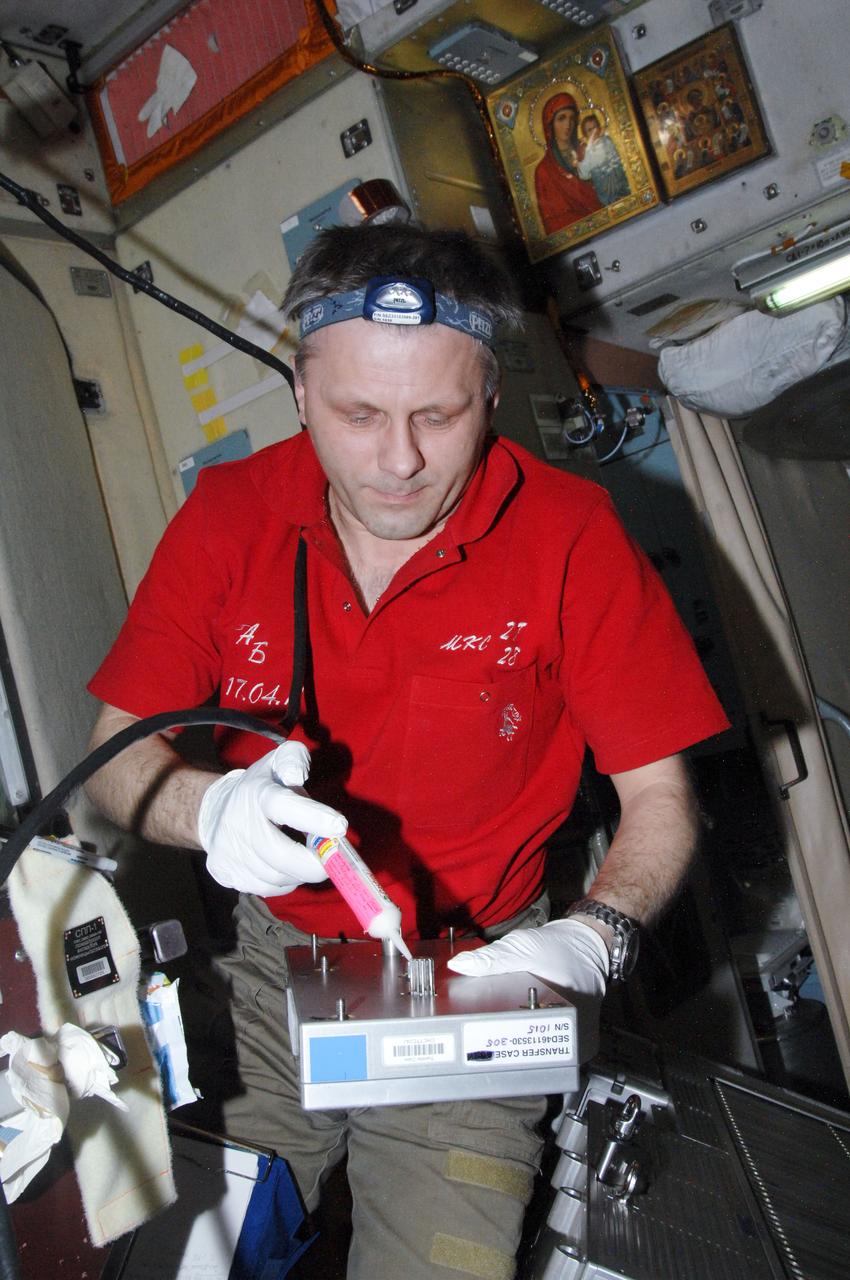

ISS028-E-013757 (1 July 2011) --- Russian cosmonaut Andrey Borisenko, Expedition 28 commander, performs in-flight maintenance on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
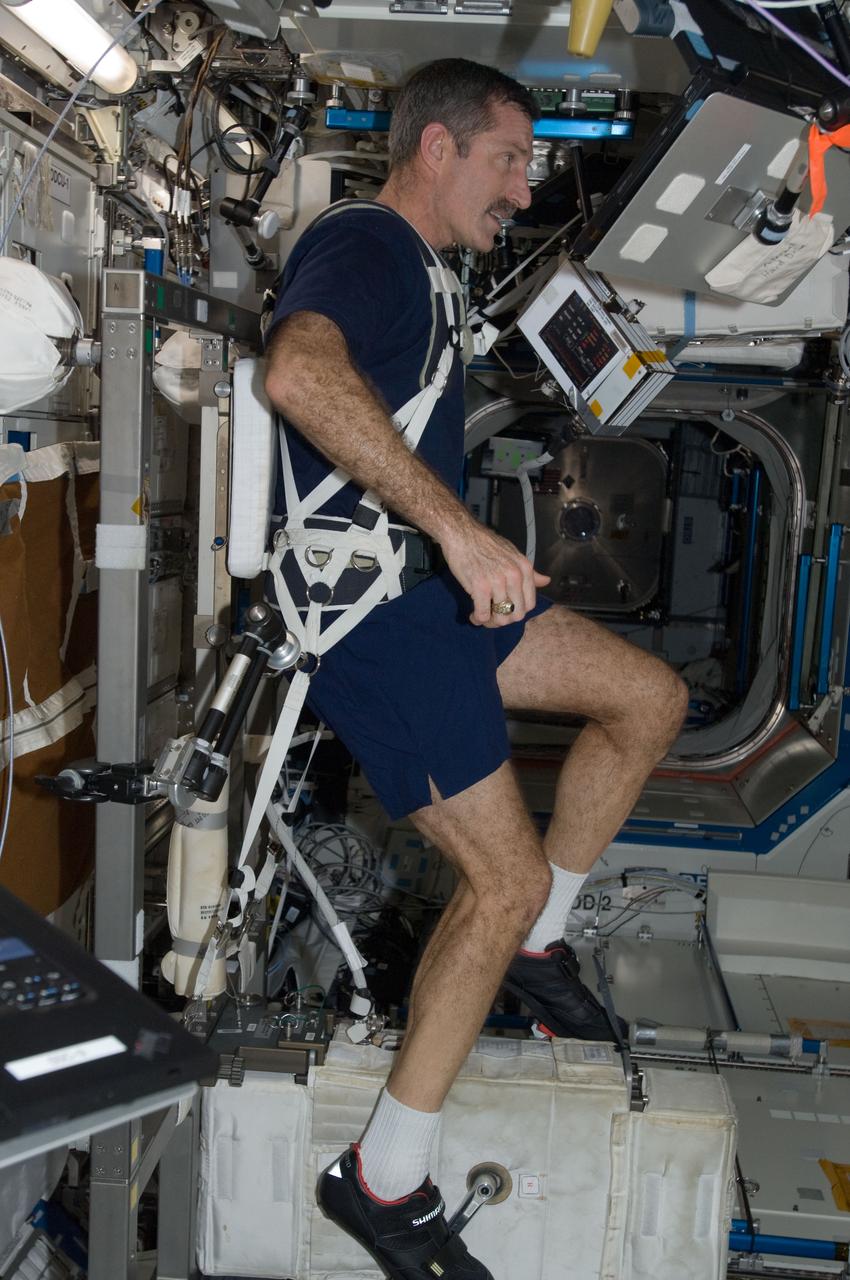

ISS030-E-010646 (9 Dec. 2011) --- NASA astronaut Dan Burbank, Expedition 30 commander, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
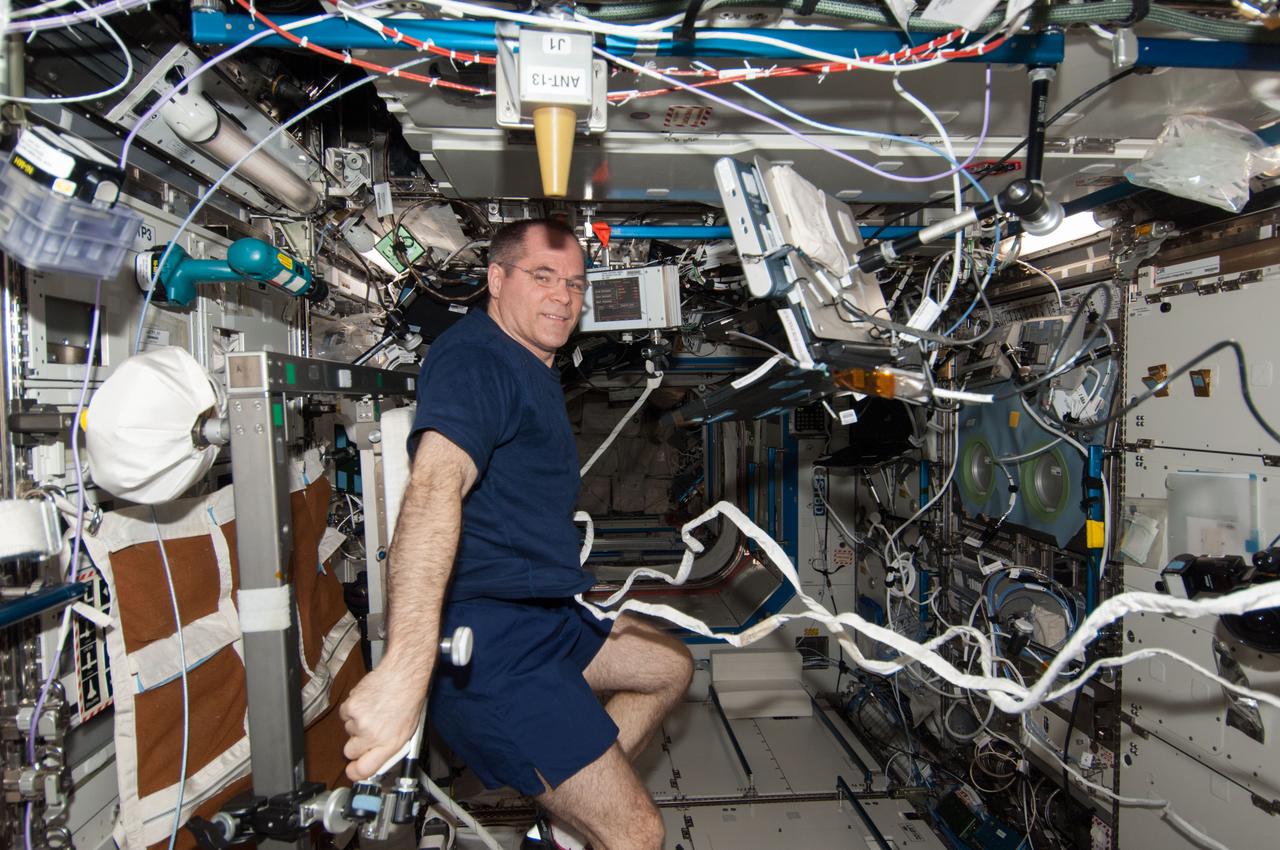

ISS034-E-061648 (4 March 2013) --- Inside the U.S. lab Destiny on the Earth-orbiting International Space Station, Expedition 34 Commander Kevin Ford exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS).
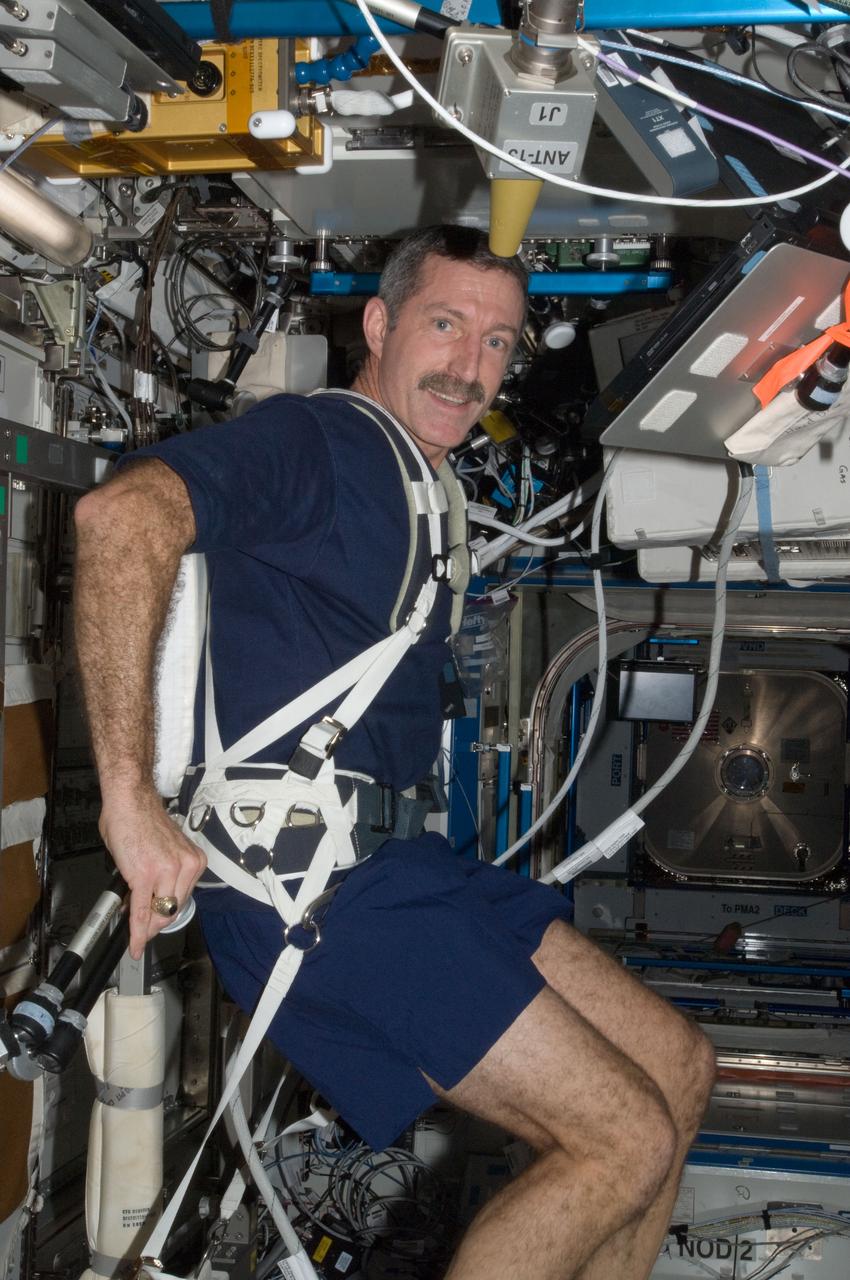
ISS030-E-007559 (4 Dec. 2011) --- NASA astronaut Dan Burbank, Expedition 30 commander, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
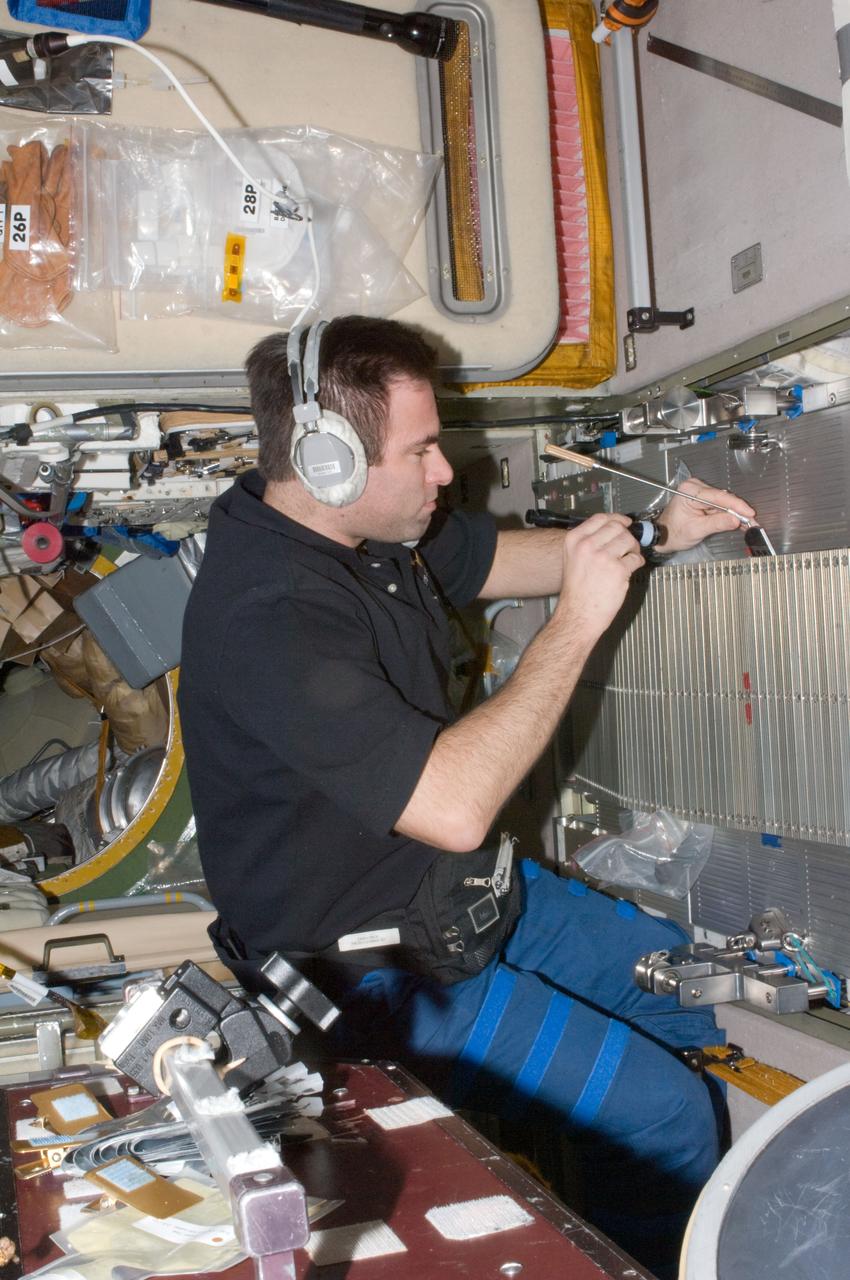

ISS017-E-012105 (1 Aug. 2008) --- NASA astronaut Greg Chamitoff, Expedition 17 flight engineer, works with the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
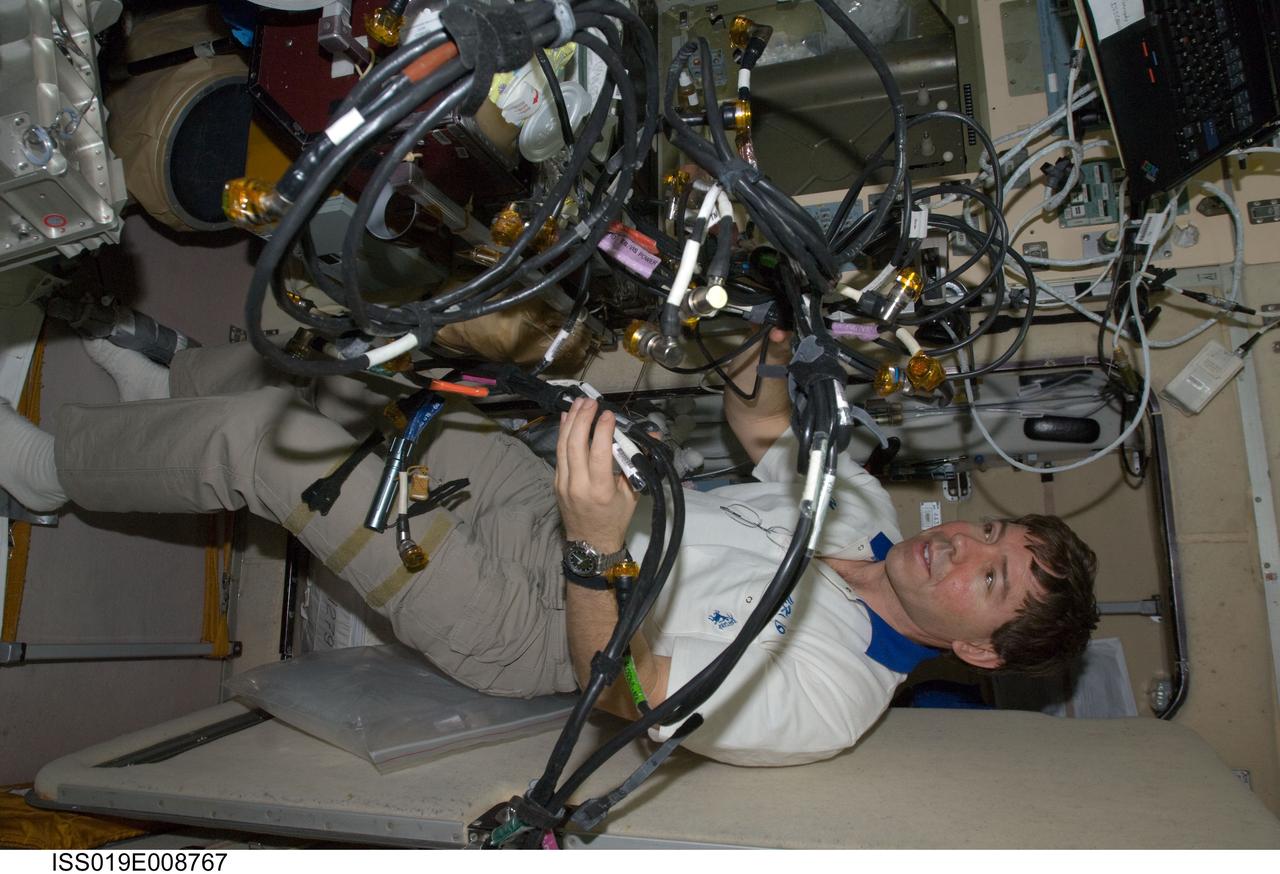

ISS019-E-008767 (21 April 2009) --- Astronaut Michael Barratt, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
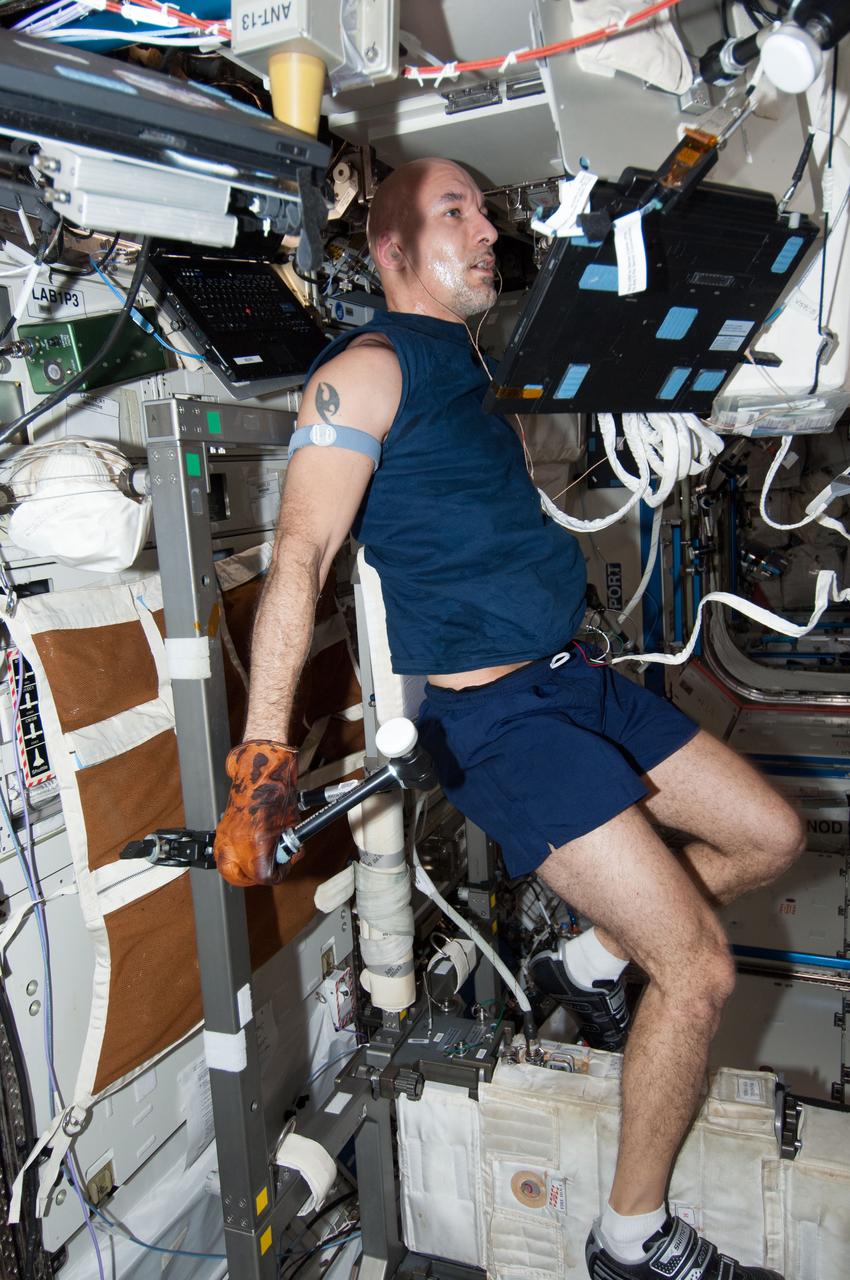

ISS037-E-006471 (3 Oct. 2013) --- European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano, Expedition 37 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
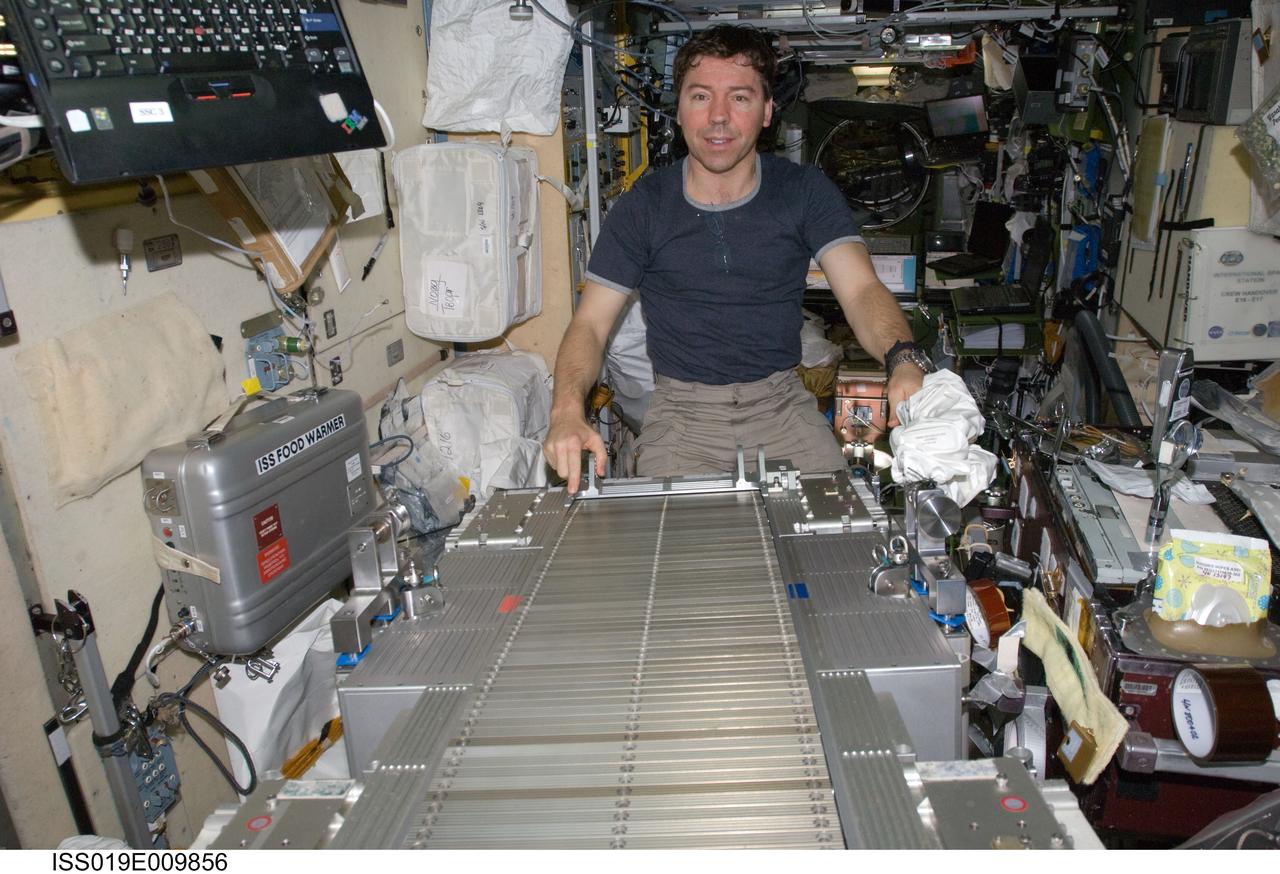

ISS019-E-009856 (23 April 2009) --- Astronaut Michael Barratt, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
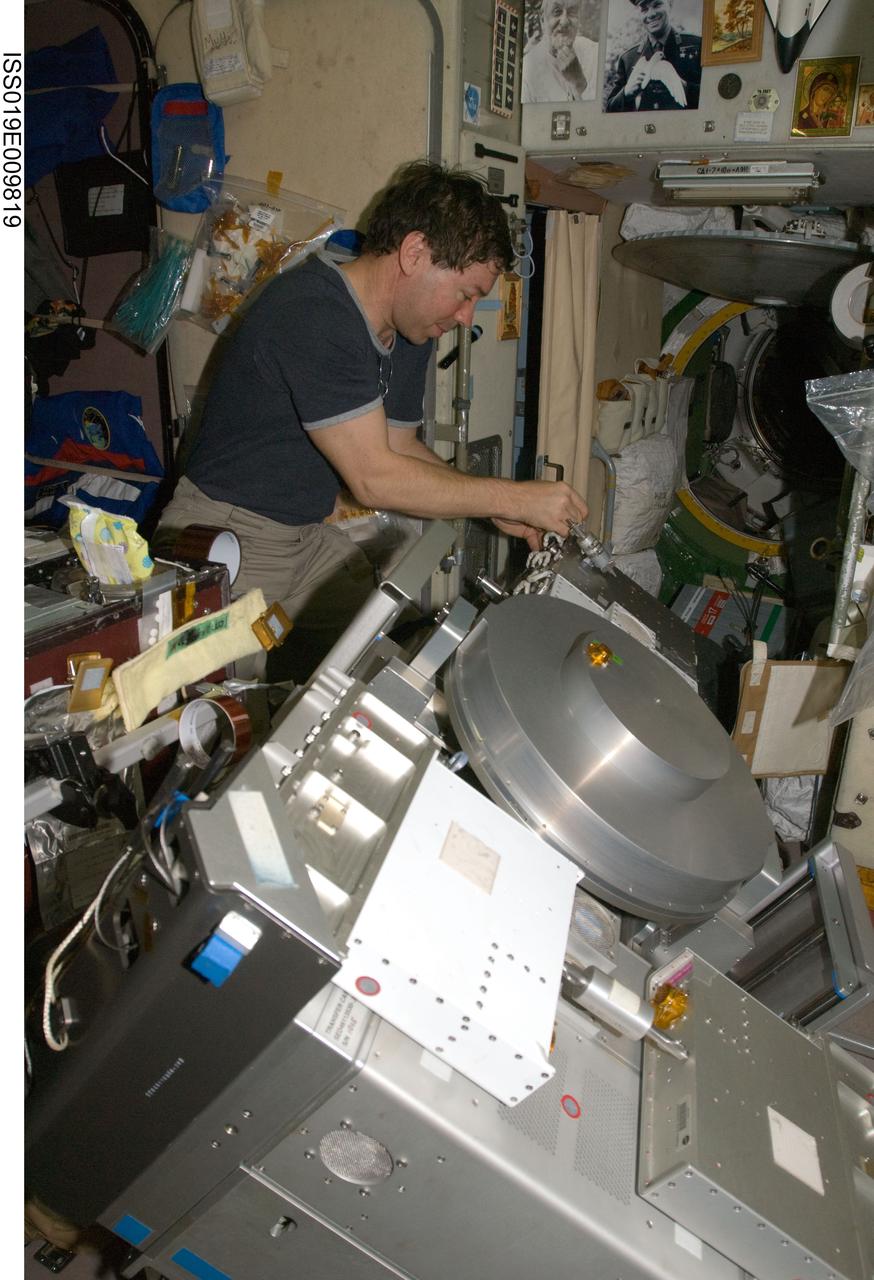

ISS019-E-009819 (23 April 2009) --- Astronaut Michael Barratt, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
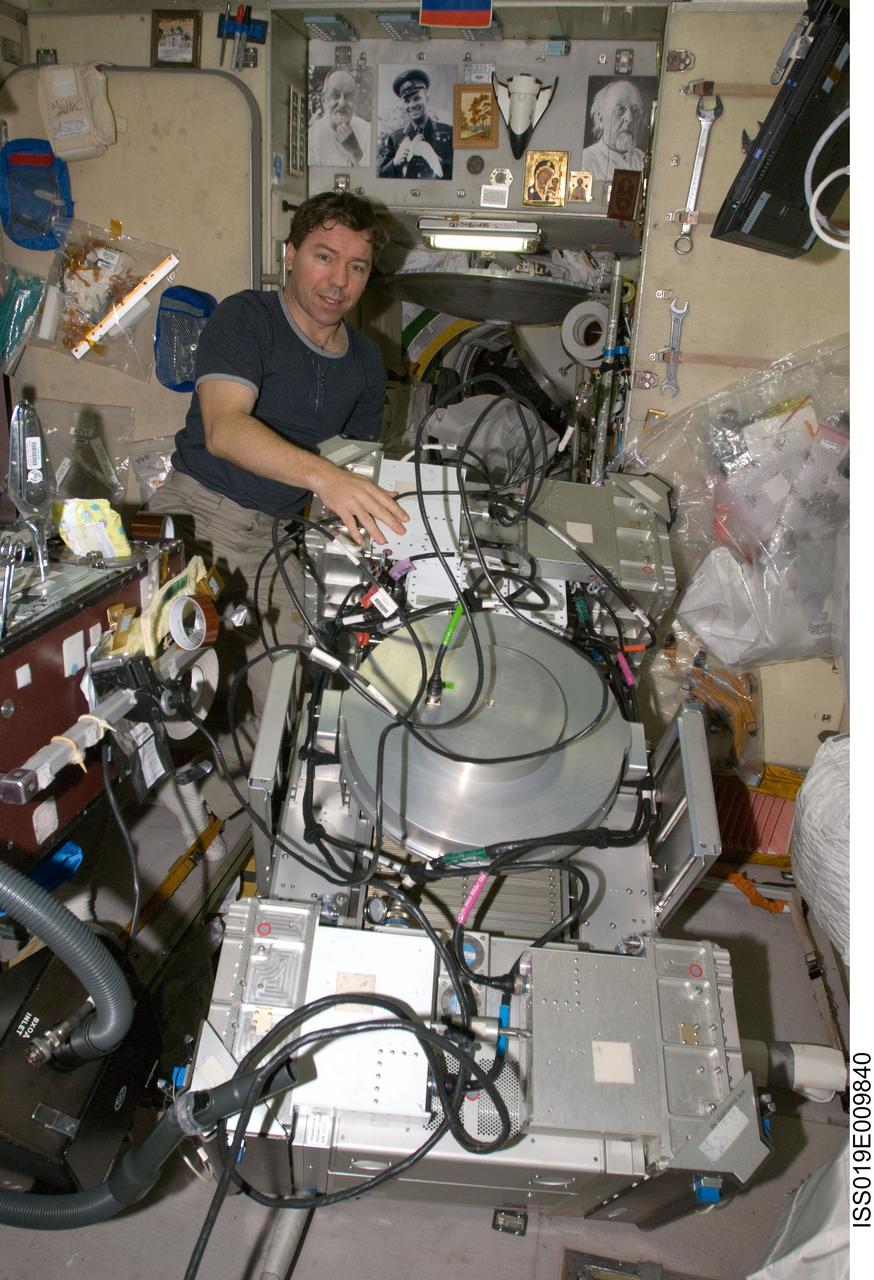

ISS019-E-009840 (23 April 2009) --- Astronaut Michael Barratt, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
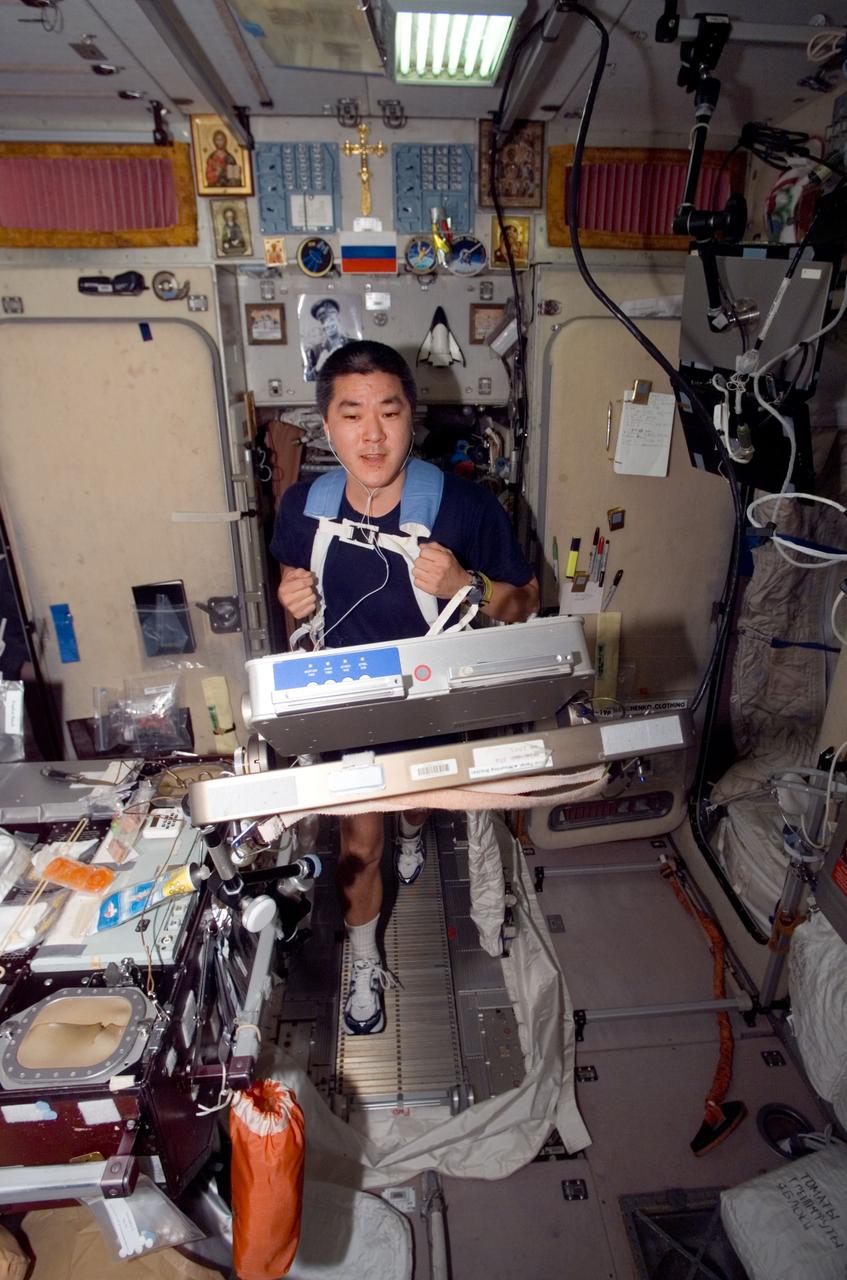

ISS016-E-024679 (22 Jan. 2008) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, works out on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) onboard the International Space Station.

iss047e154247 (6/16/2016) --- View of Commander Tim Kopra exercising on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation and Stabilization (CEVIS) in the U.S. Laboratory. Photo was taken during Expedition 47.
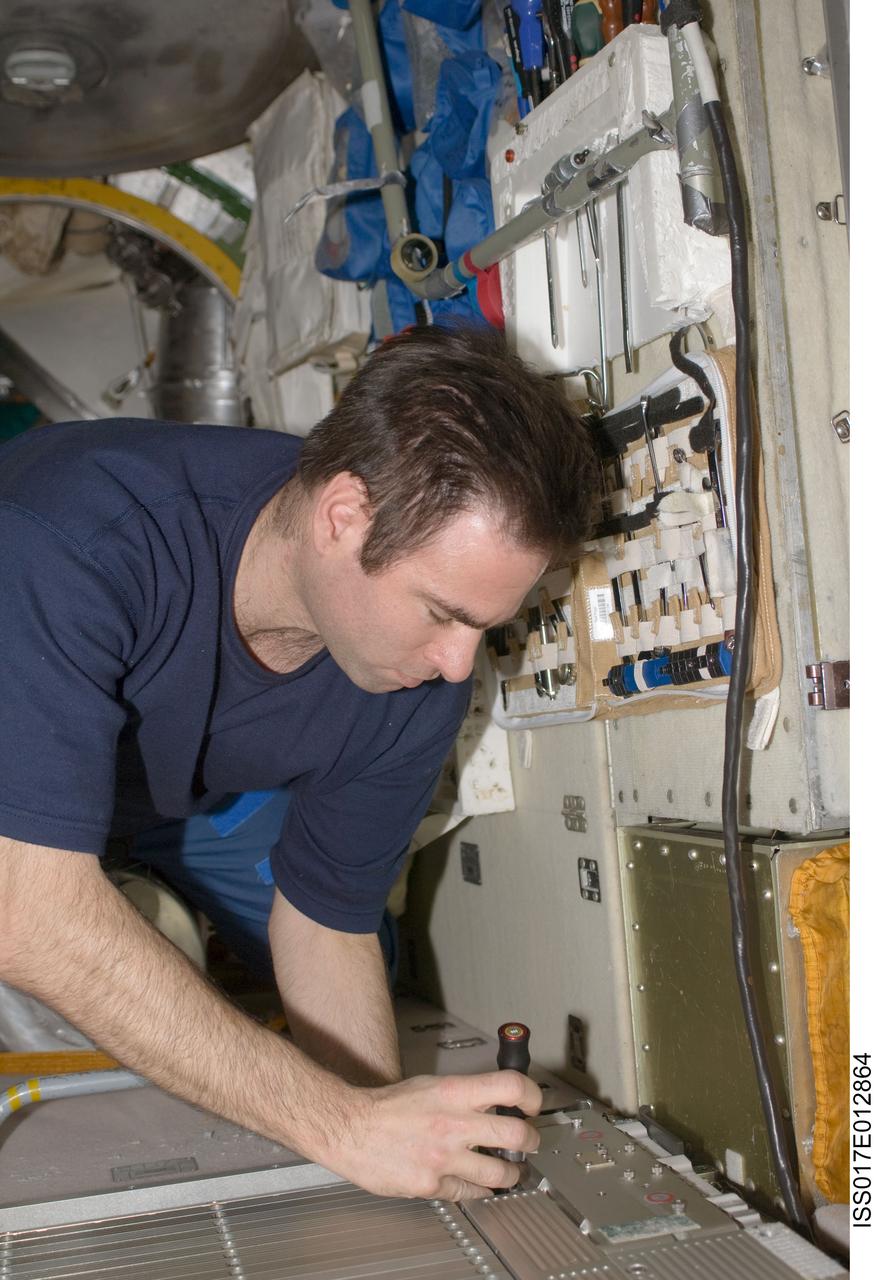

ISS017-E-012864 (12 Aug. 2008) --- NASA astronaut Greg Chamitoff, Expedition 17 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
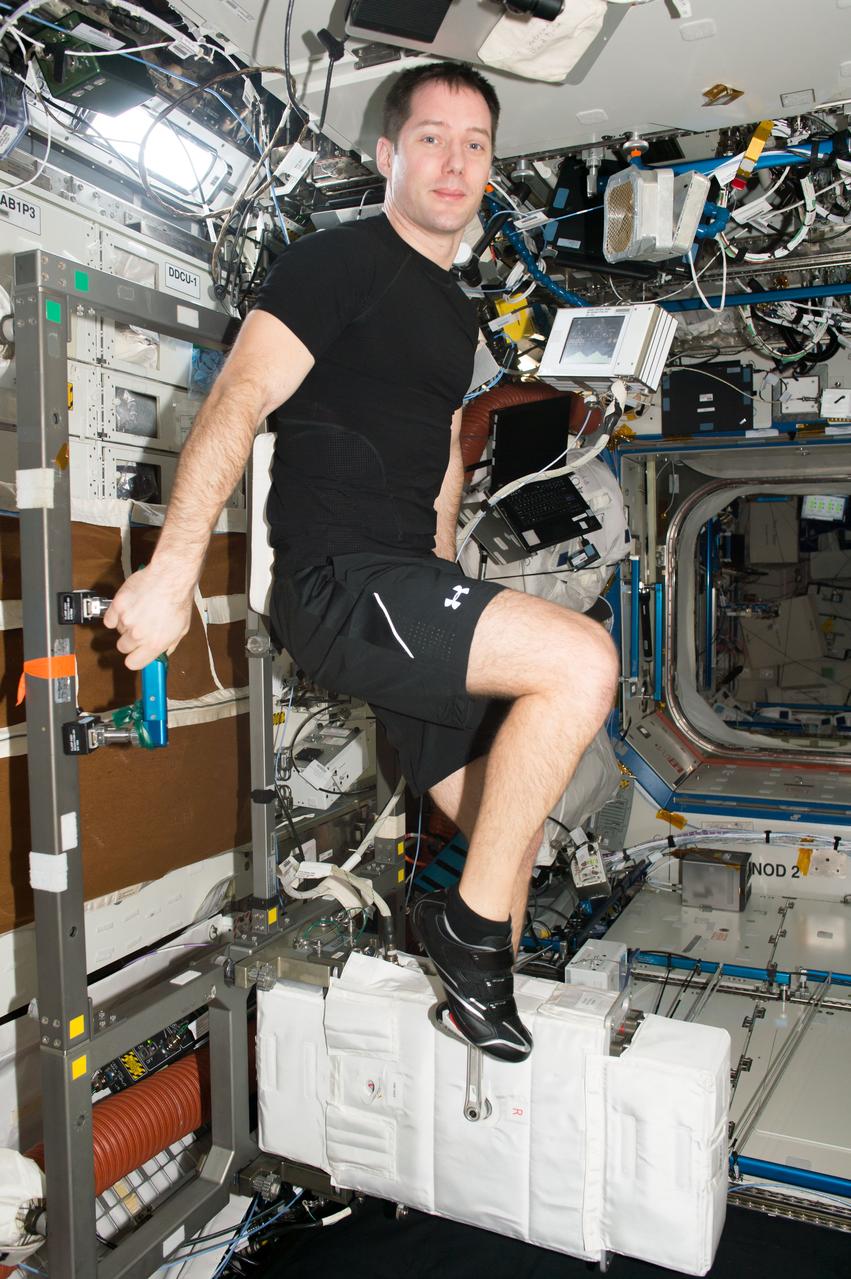

iss051e029335 (April 30, 2017) --- European Space Agency astronaut Thomas Pesquet exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation and Stabilization System (CEVIS), the station’s exercise bike, inside the Destiny laboratory module.
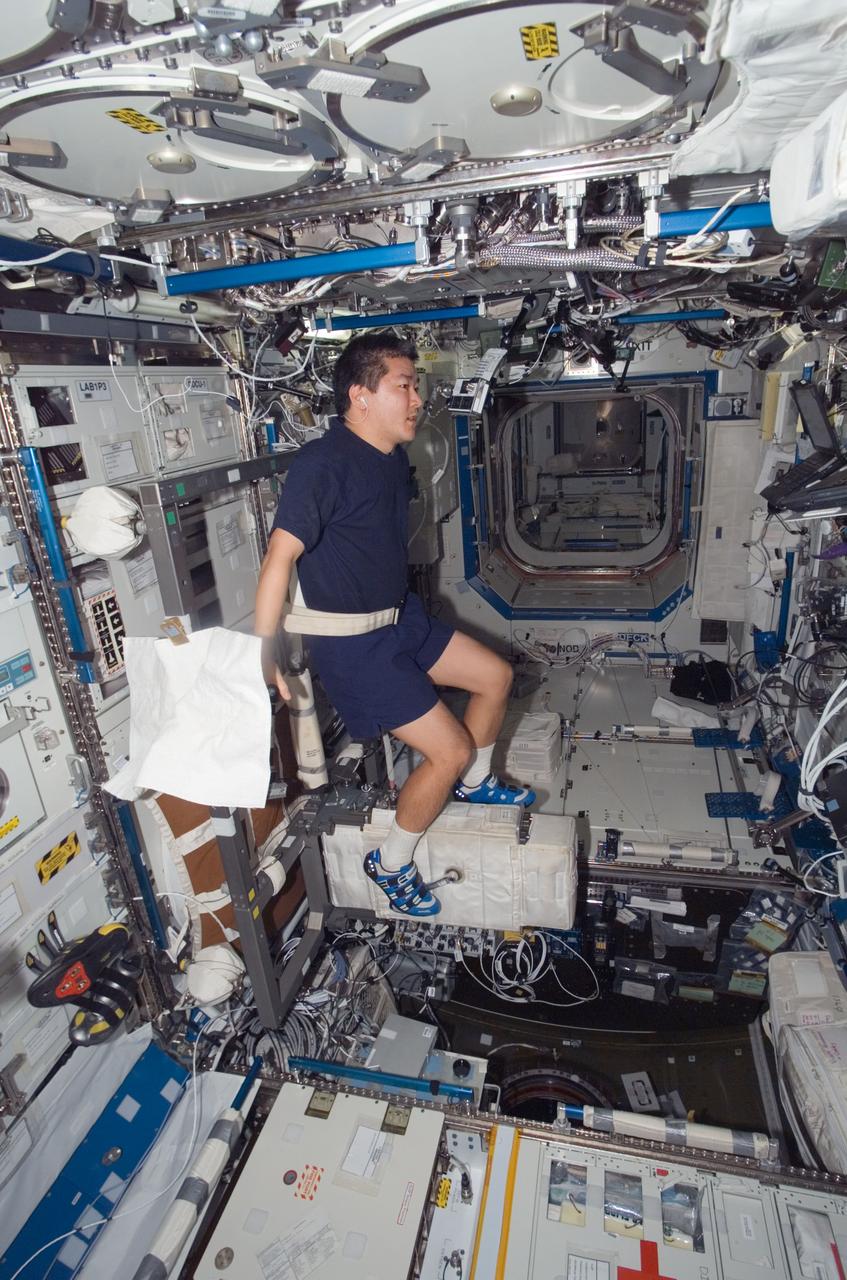

ISS016-E-027899 (6 Feb. 2008) --- Astronauts Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
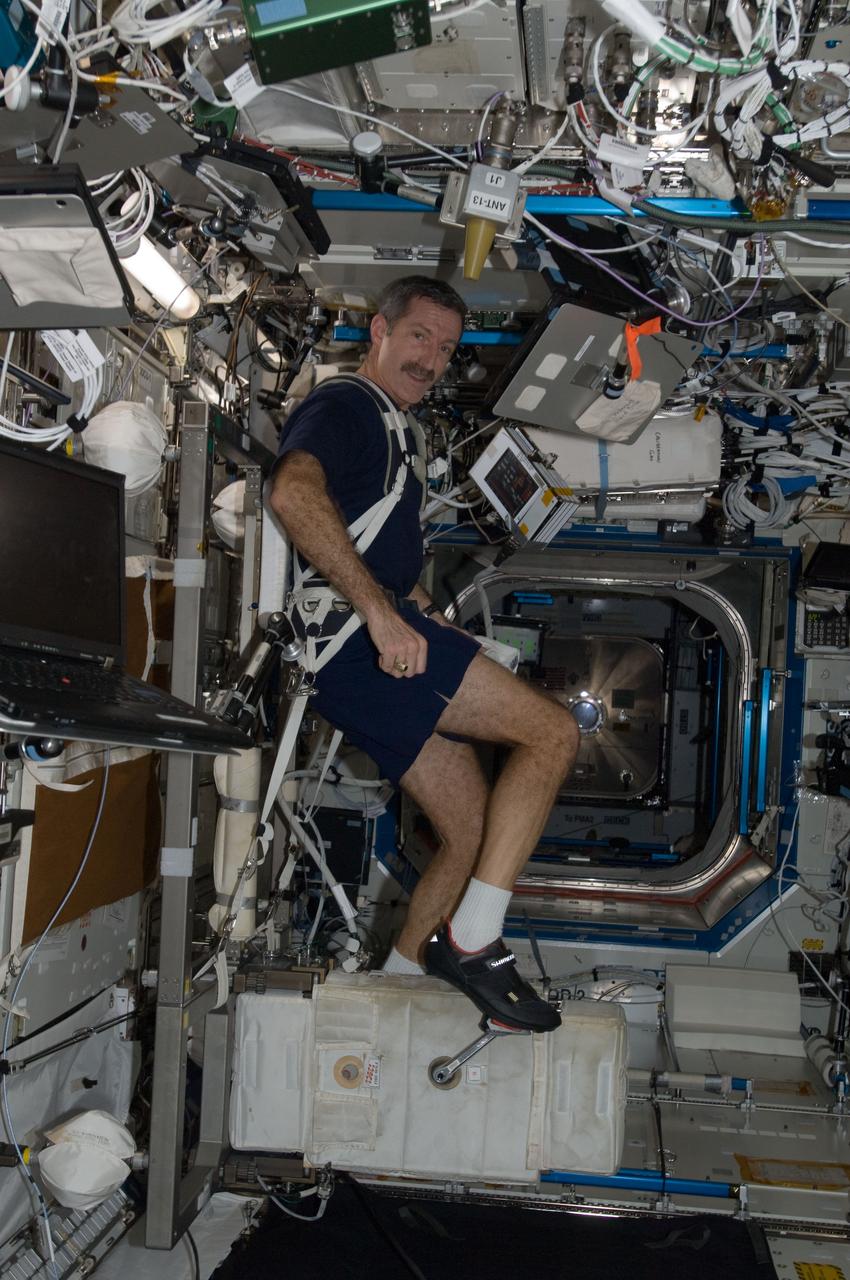

ISS030-E-010644 (9 Dec. 2011) --- NASA astronaut Dan Burbank, Expedition 30 commander, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
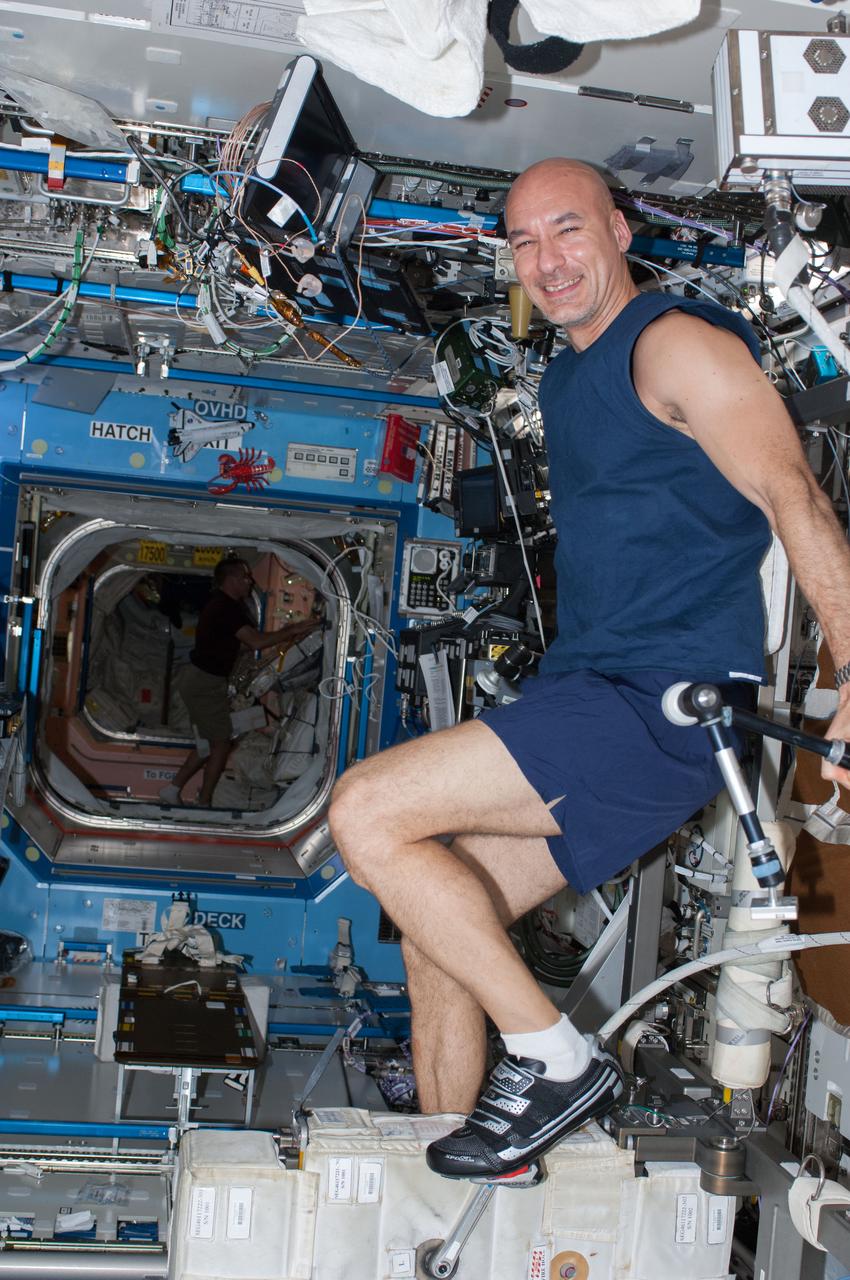

ISS036-E-015570 (6 July 2013) --- European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano, Expedition 36 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
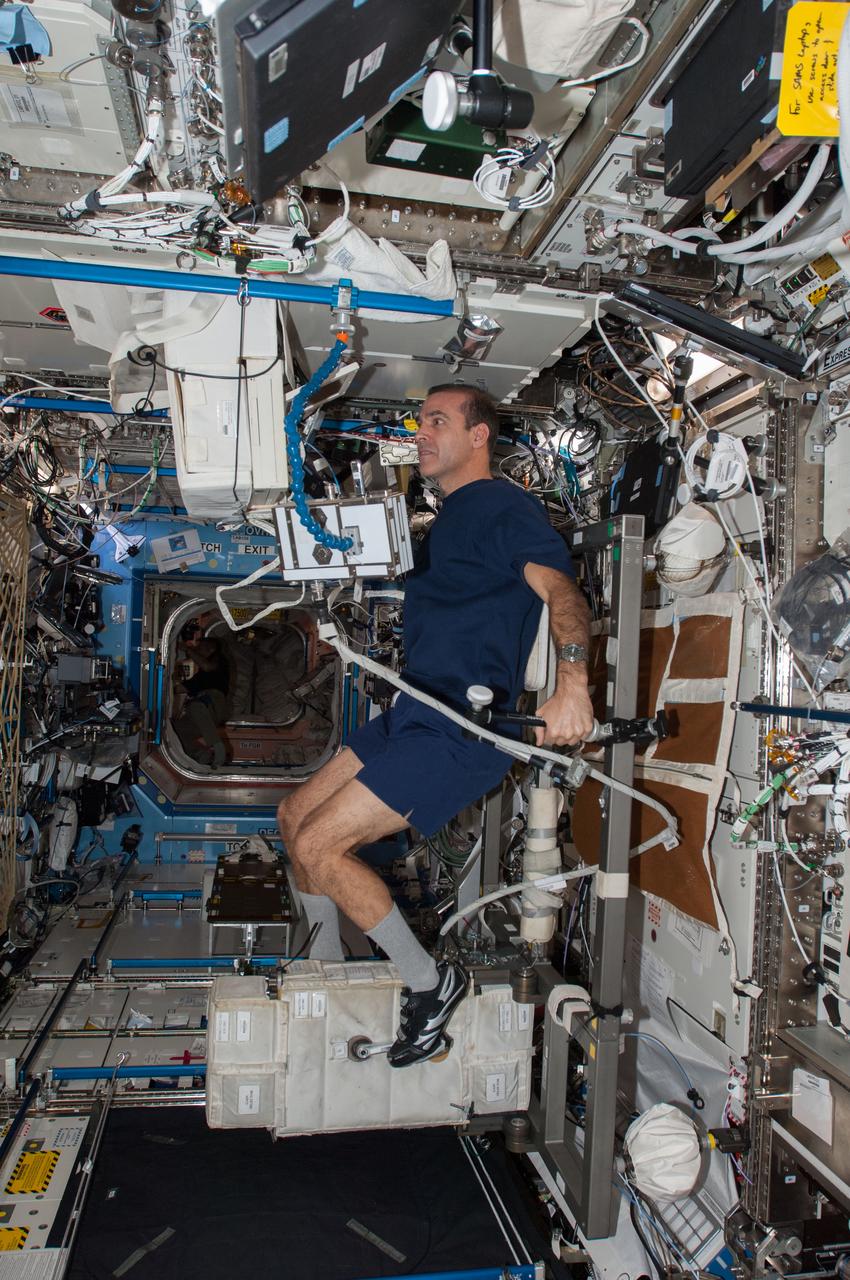

ISS038-E-007156 (22 Nov. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Rick Mastracchio, Expedition 38 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
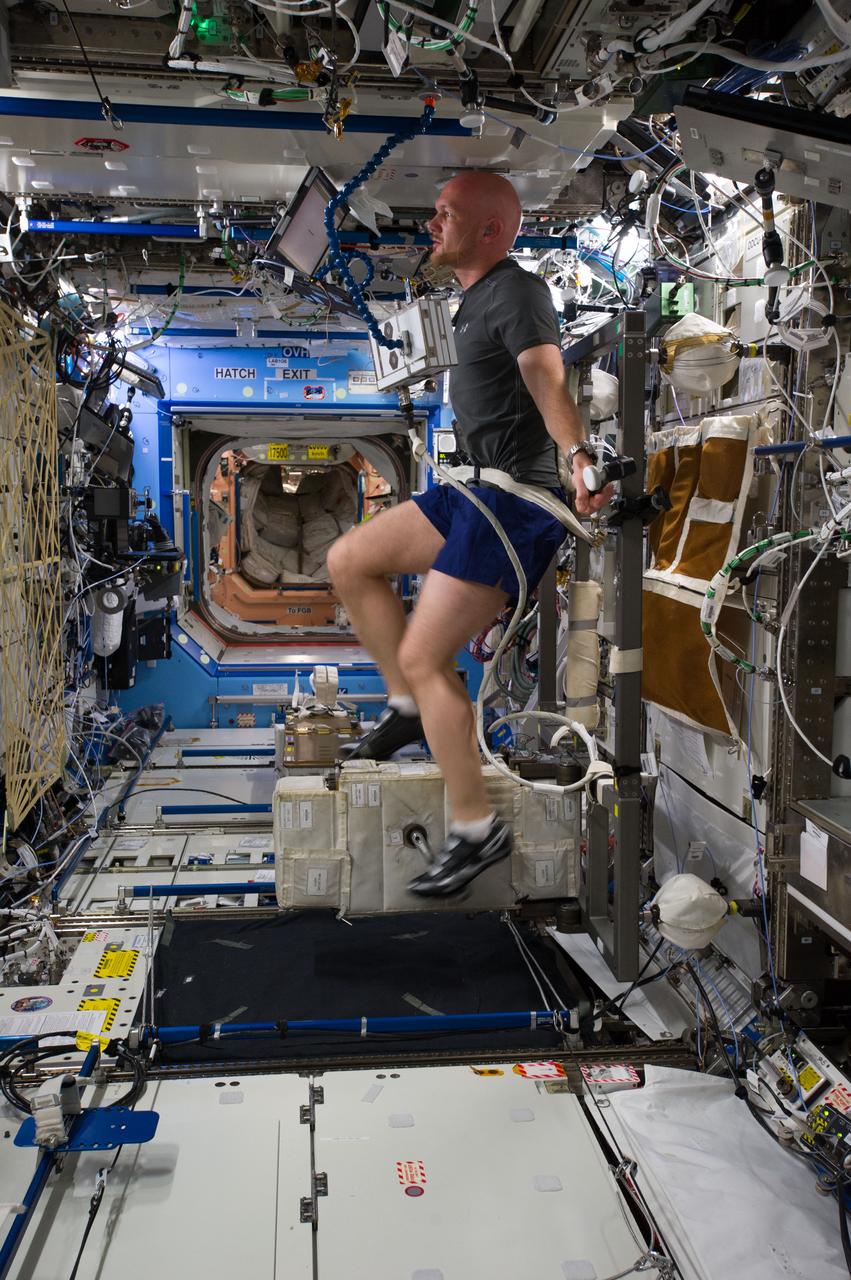

ISS040-E-006700 (2 June 2014) --- European Space Agency astronaut Alexander Gerst, Expedition 40 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
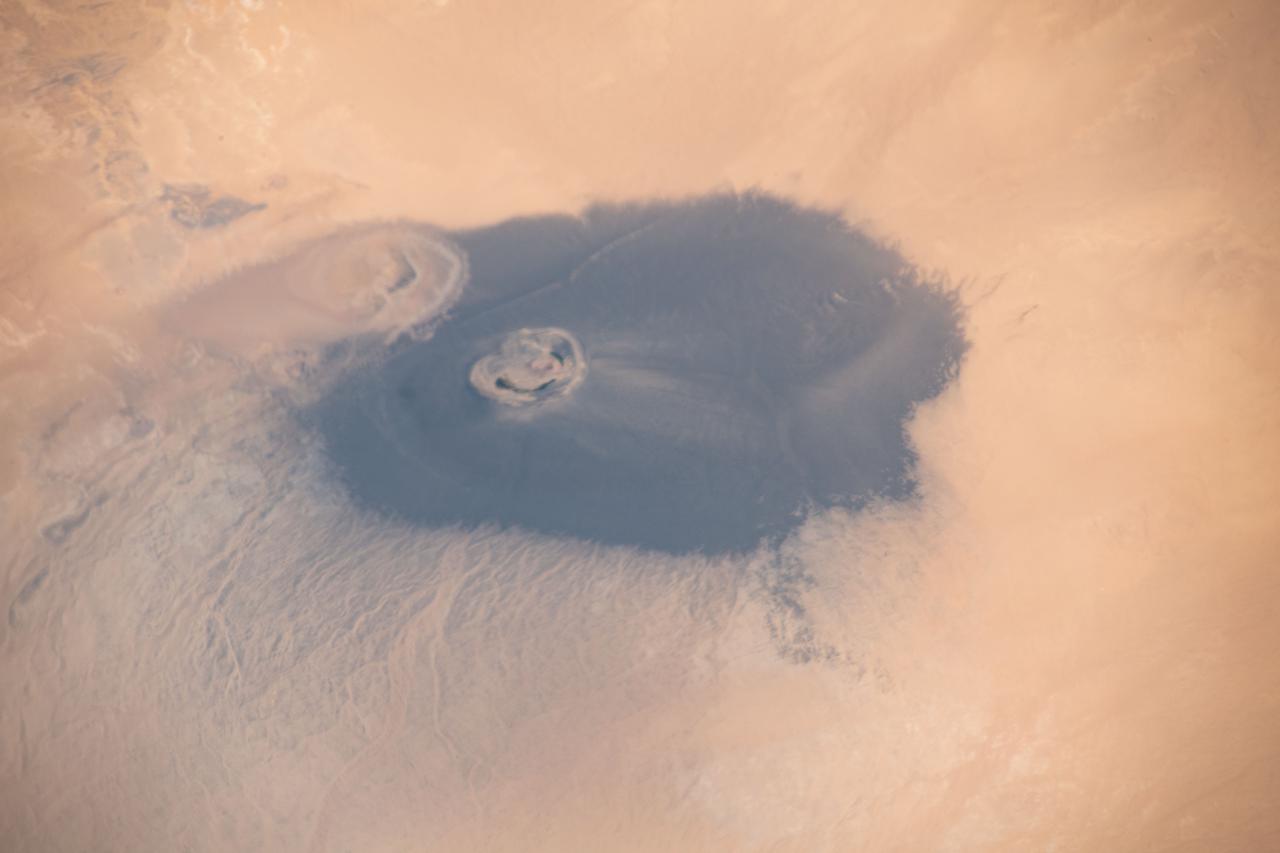

iss065e009516 (April 29, 2021) --- The isolated volcanic crater Waw an Namus in Libya with three small saltwater lakes is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 263 miles above the Sahara Desert.
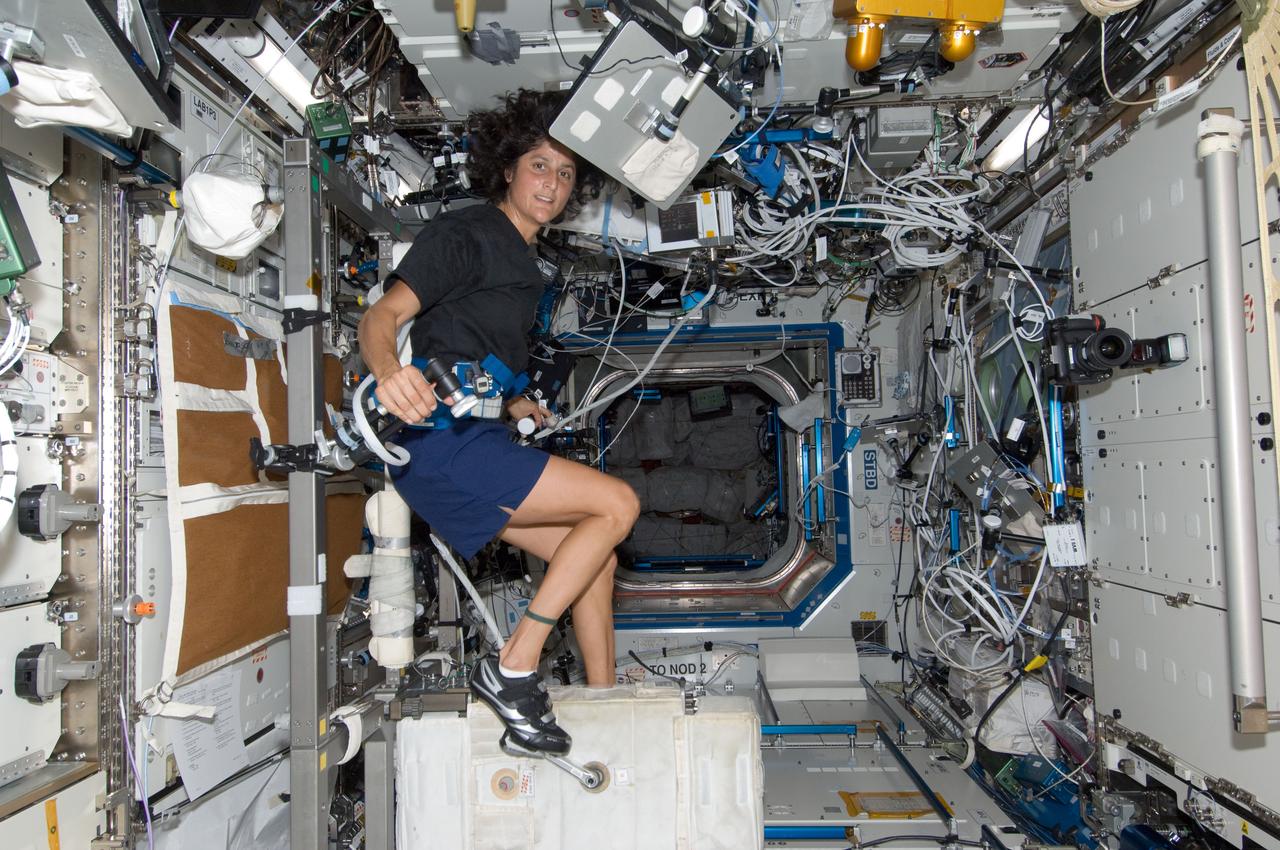

ISS032-E-008595 (20 July 2012) --- NASA astronaut Sunita Williams, Expedition 32 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
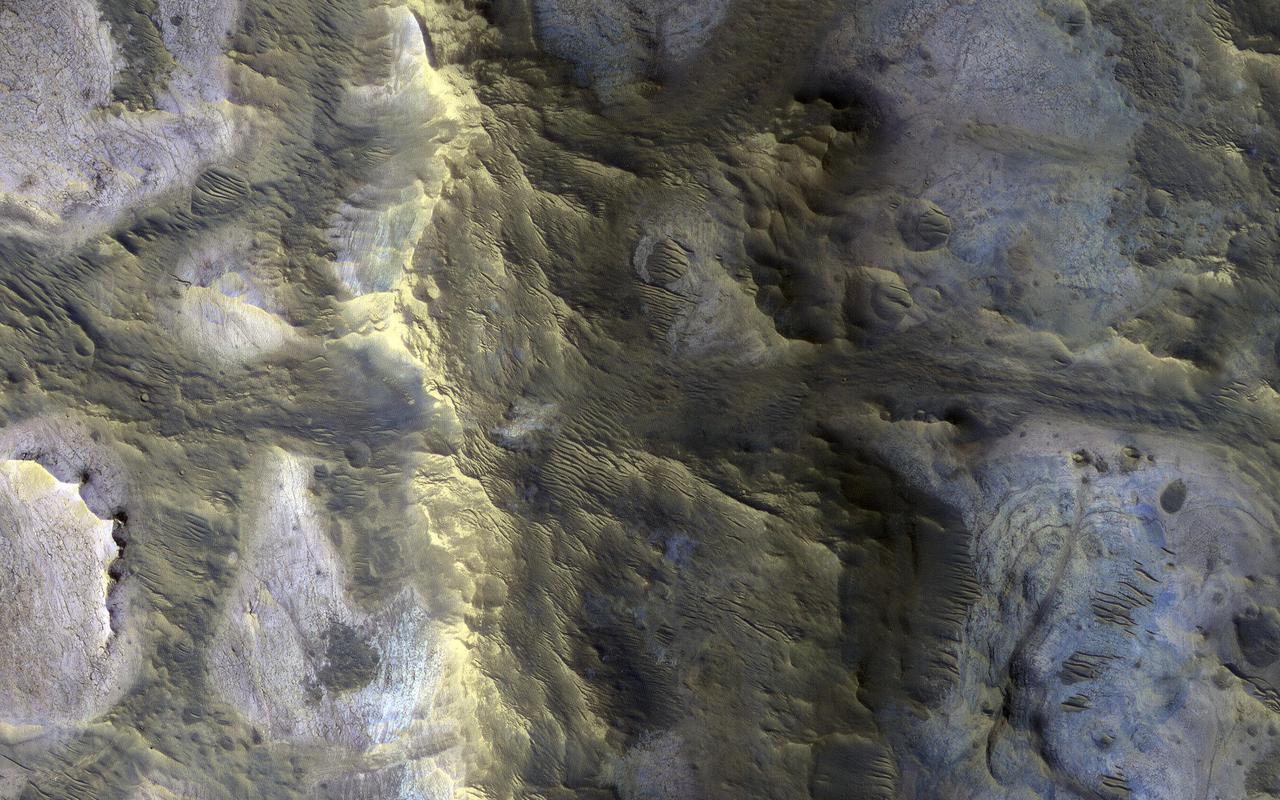

An isolated, elongated mound (about 1 mile wide and 3.75 miles long) rises above the smooth, surrounding plains. Horizontal layers are exposed at the northern end of the mound, and its surface is characterized by a very unusual quasi-circular pattern with varying colors that likely reflect diverse mineral compositions. A closer view shows that the rock has a range of textures, from massive and fractured on the left, to subtle banding or layering on the right. The origin of this mound is unknown, but its formation may be related to the clay-bearing rocks in the nearby Oxia Planum region. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24387

Isolation of human mammary epithelial cells (HMEC) from breast cancer susceptible tissue; A: Duct element recovered from breast tissue digest. B: Outgrowth of cells from duct element in upper right corner cultured in a standard dish; most cells spontaneousely die during early cell divisions, but a few will establish long-term growth. C: Isolate of long-term frowth HMEC from outgrowth of duct element; cells shown soon after isolation and in early full-cell contact growth in culture in a dish. D: same long-term growth HMEC, but after 3 weeks in late full-cell contact growth in a continuous culture in a dish. Note attempts to reform duct elements but this in two demensions in a dish rather than in three dimensions in tissue. NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) is sponsoring research with Bioreactors, rotating wall vessels designed to grow tissue samples in space, to understand how breast cancer works. This ground-based work studies the growth and assembly of human mammary epithelial cell (HMEC) from breast cancer susceptible tissue. Radiation can make the cells cancerous, thus allowing better comparisons of healthy vs. tunorous tissue. Credit: Dr. Robert Richmond, NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).

ISS037-E-006454 (3 Oct. 2013) --- European Space Agency astronaut Luca Parmitano, Expedition 37 flight engineer, prepares to use the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
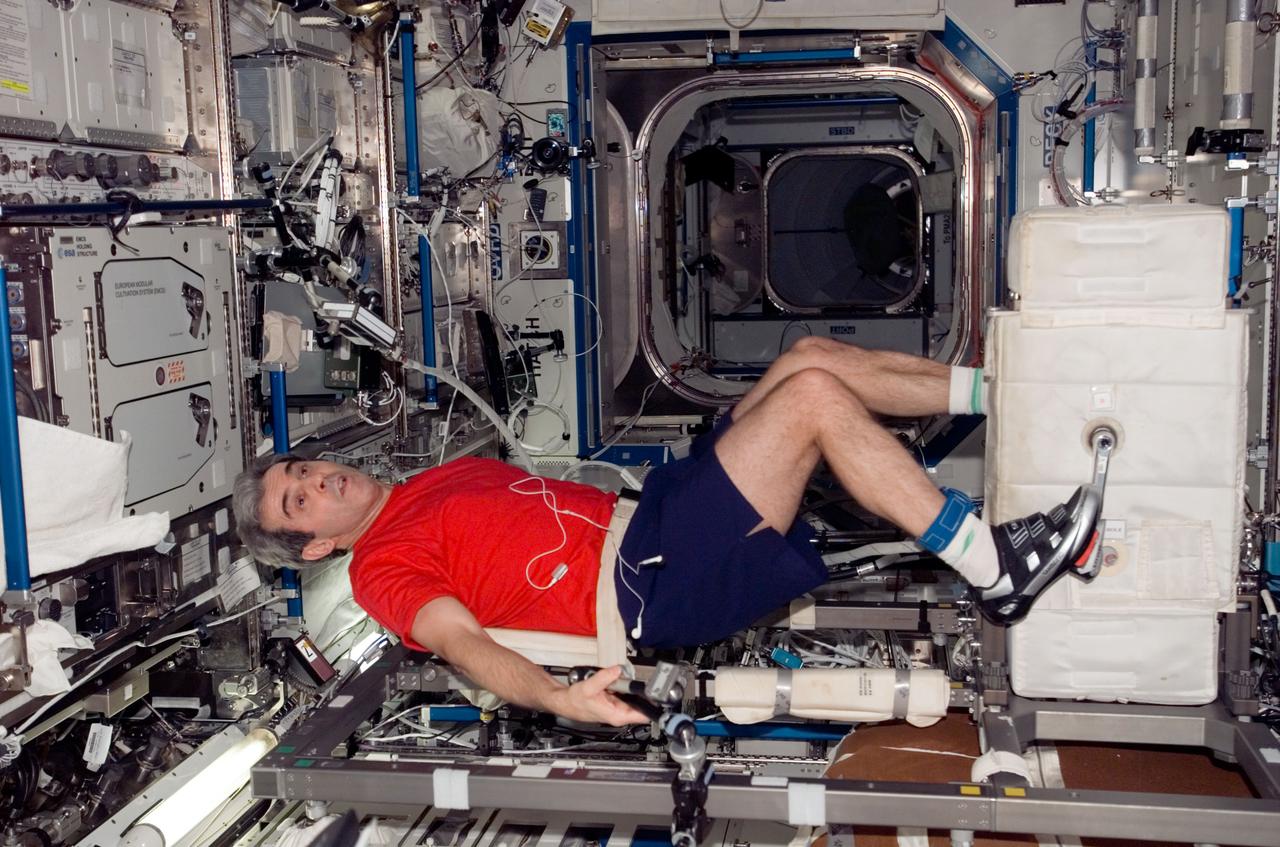

ISS016-E-032805 (16 March 2008) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Leopold Eyharts, Expedition 16 flight engineer, exercises on the Cycle Ergometer with Vibration Isolation System (CEVIS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station while Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-123) remains docked with the station.
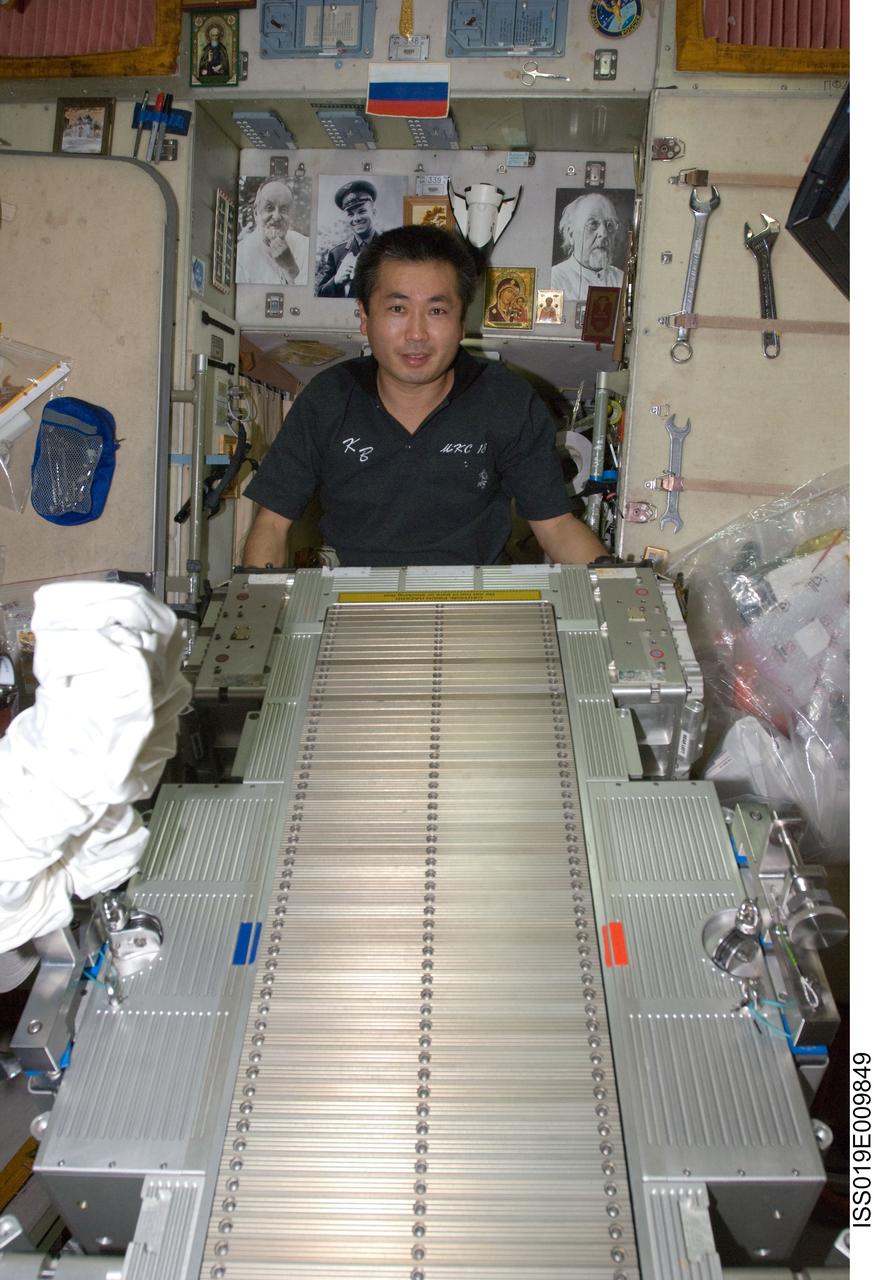

ISS019-E-009849 (23 April 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 19/20 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
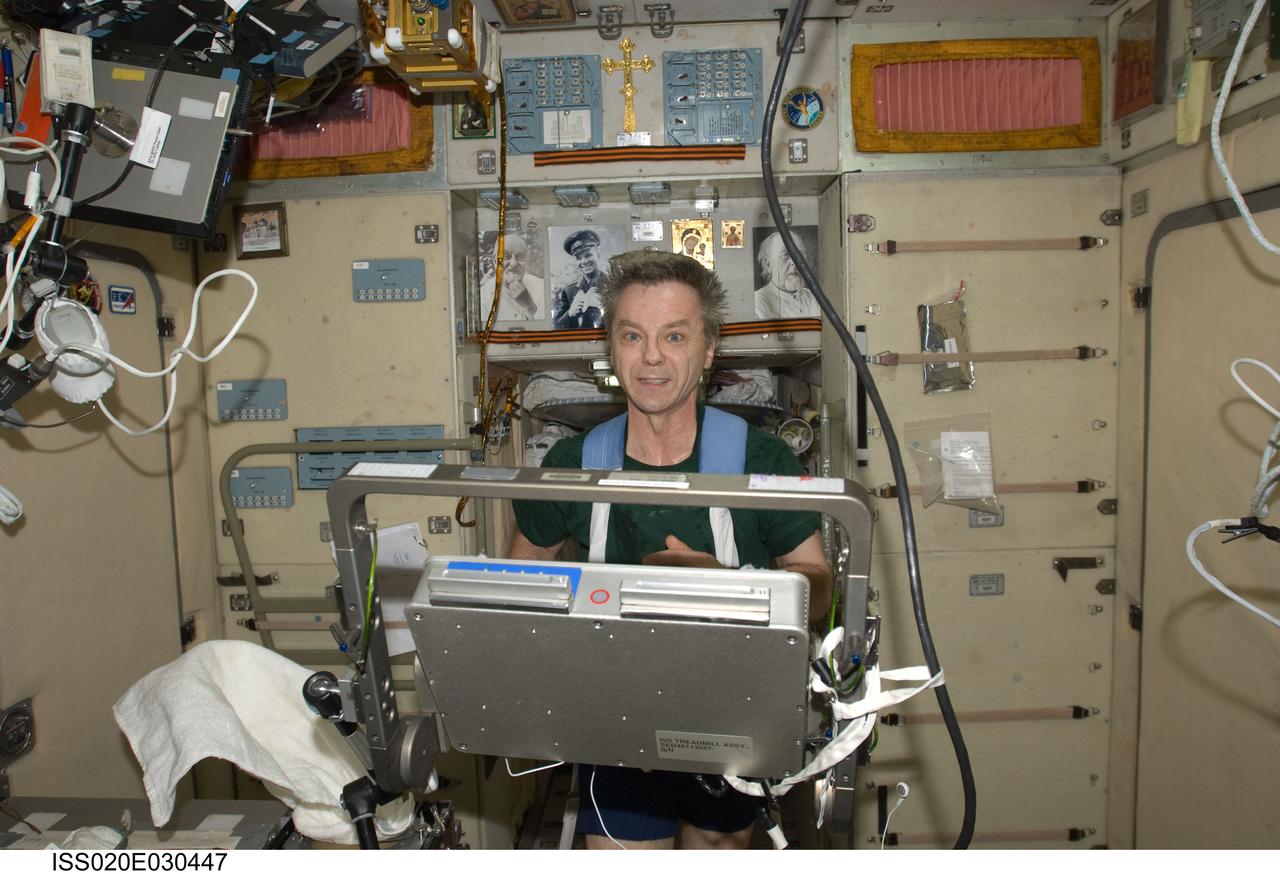

ISS020-E-030447 (13 Aug. 2009) --- Canadian Space Agency astronaut Robert Thirsk, Expedition 20 flight engineer, equipped with a bungee harness, exercises on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station.
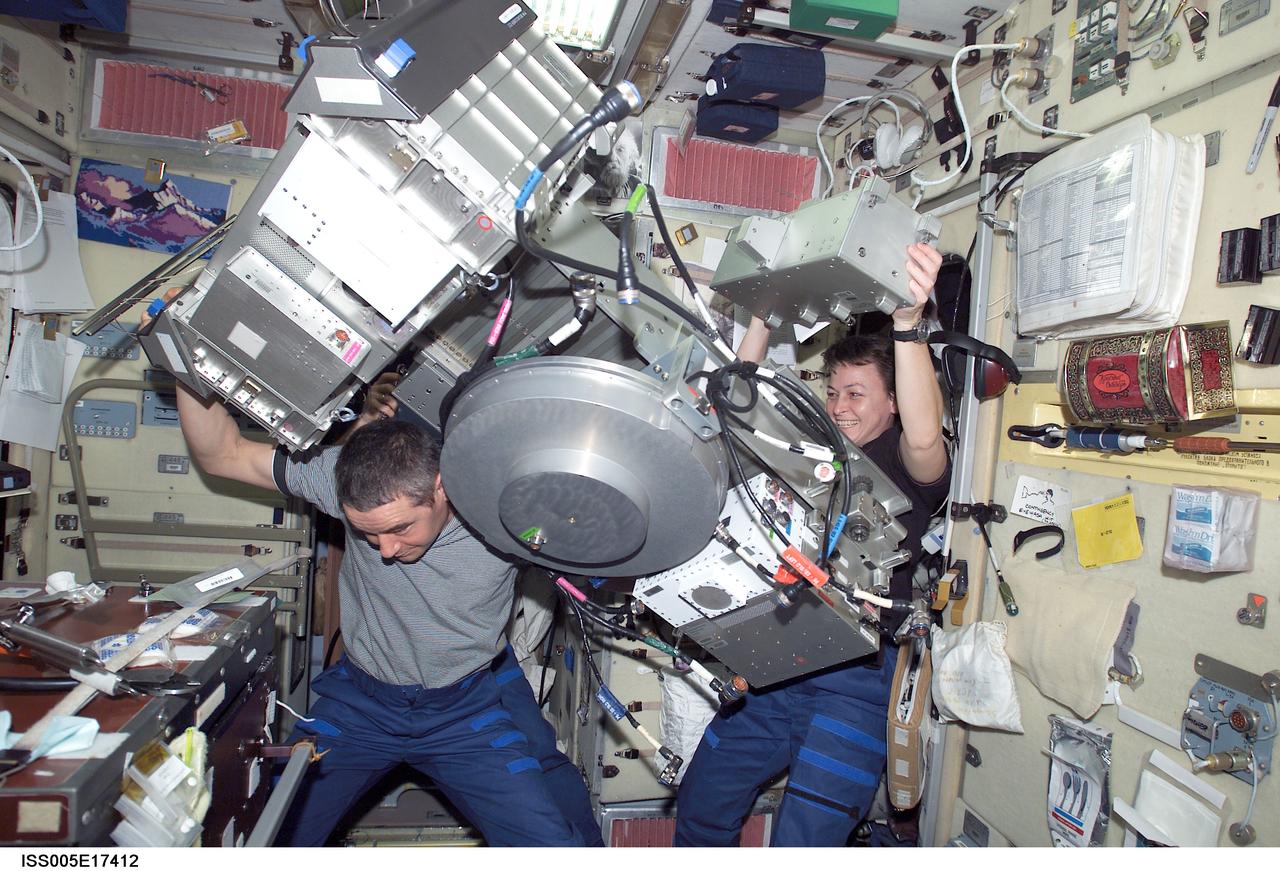

ISS005-E-17412 (13 October 2002) --- Cosmonaut Valery G. Korzun (left), Expedition Five mission commander, and astronaut Peggy A. Whitson, Expedition Five flight engineer, perform maintenance on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). Korzun represents Rosaviakosmos.