Cratos II: Modular ISRU Excavation Tools

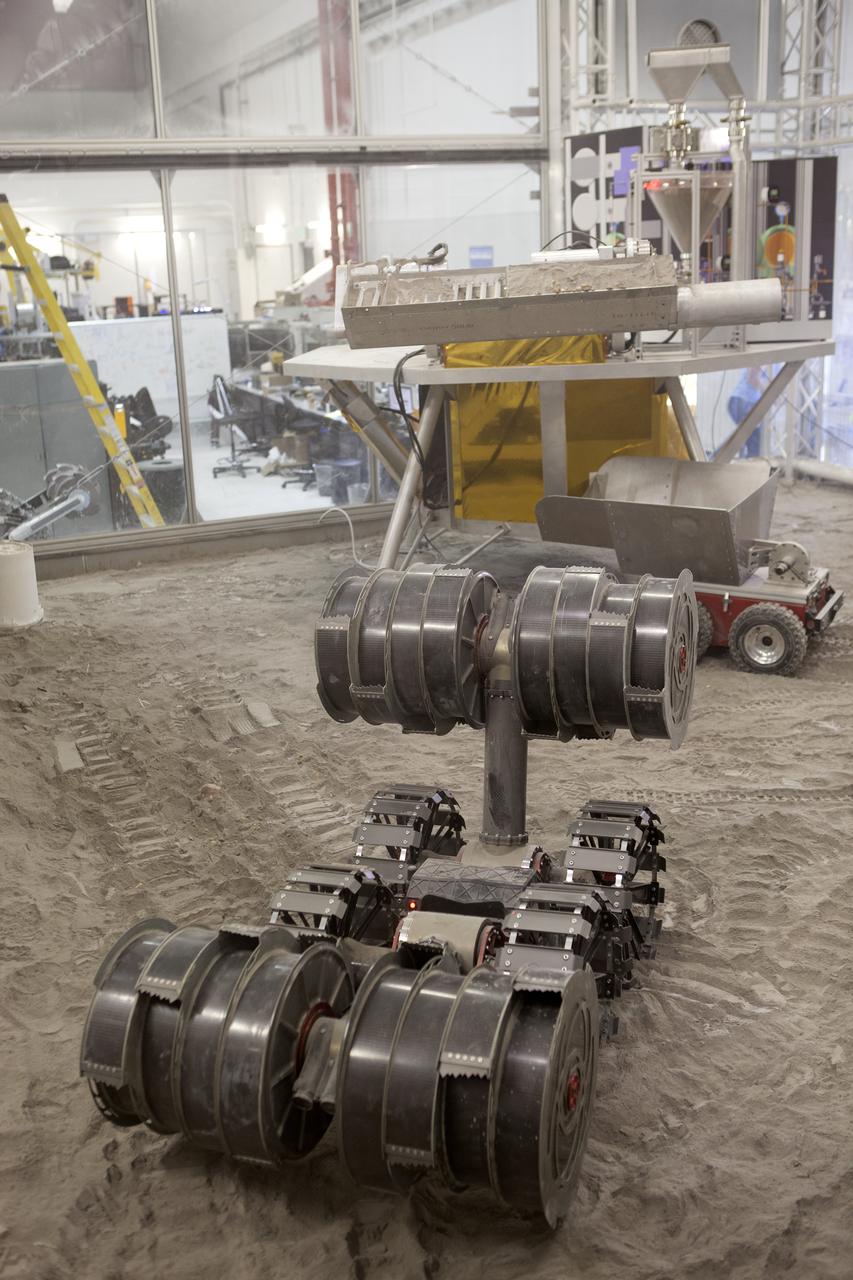
With the lights out, the ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

With the lights out, the ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

The ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in the regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

With the lights out, the ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in the regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

The ISRU Pilot Excavator digs its way through the regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

The ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in the regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.

A team from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab operates a test of the ISRU Pilot Excavator in regolith bin inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
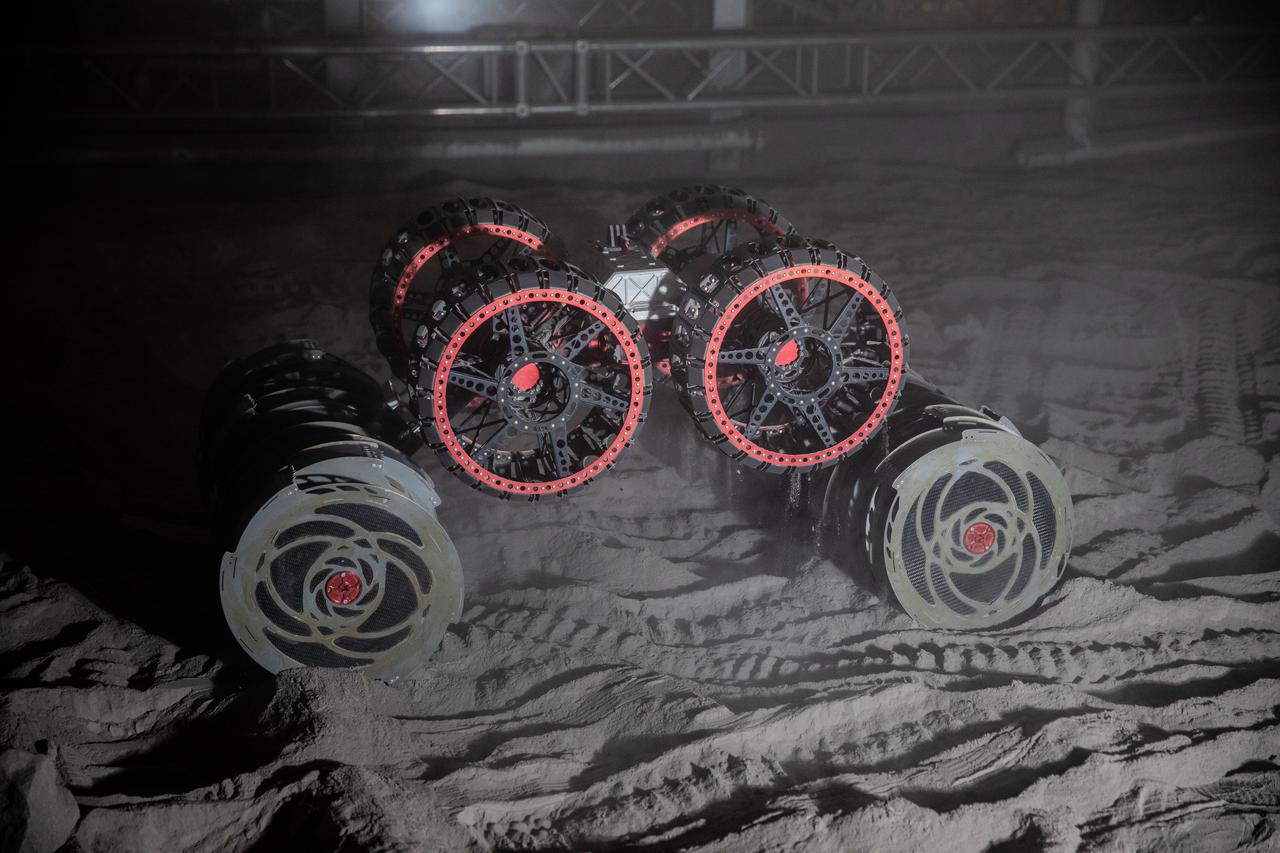

With the lights out, the ISRU Pilot Excavator digs in regolith bin during testing inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
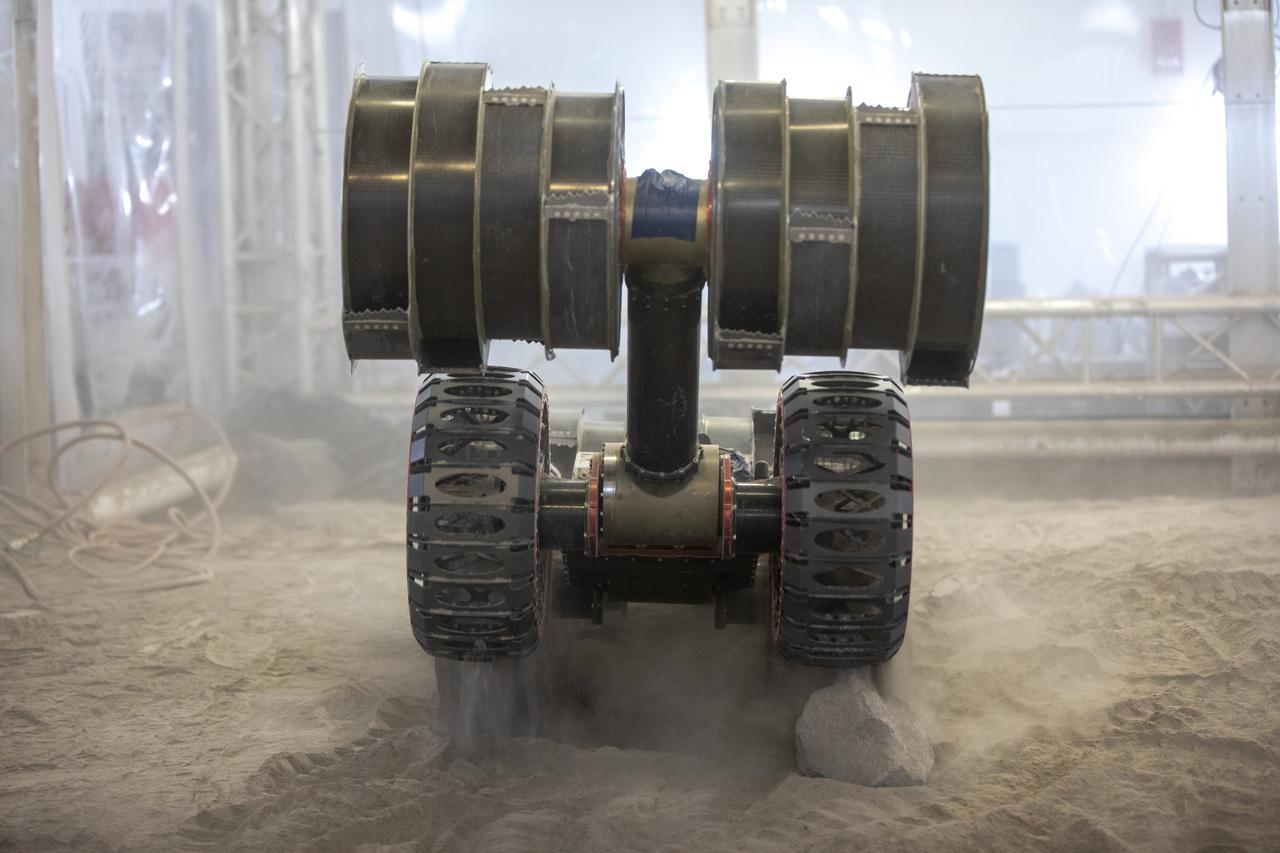

The ISRU Pilot Excavator is tested in the regolith bin inside Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2022. Tests use a gravity assist offload system to simulate reduced gravity conditions found on the Moon. On the surface of the Moon, mining robots like the Pilot Excavator will excavate the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. The Pilot Excavator can scoop up icy regolith which can be used to make operations on the Moon sustainable.
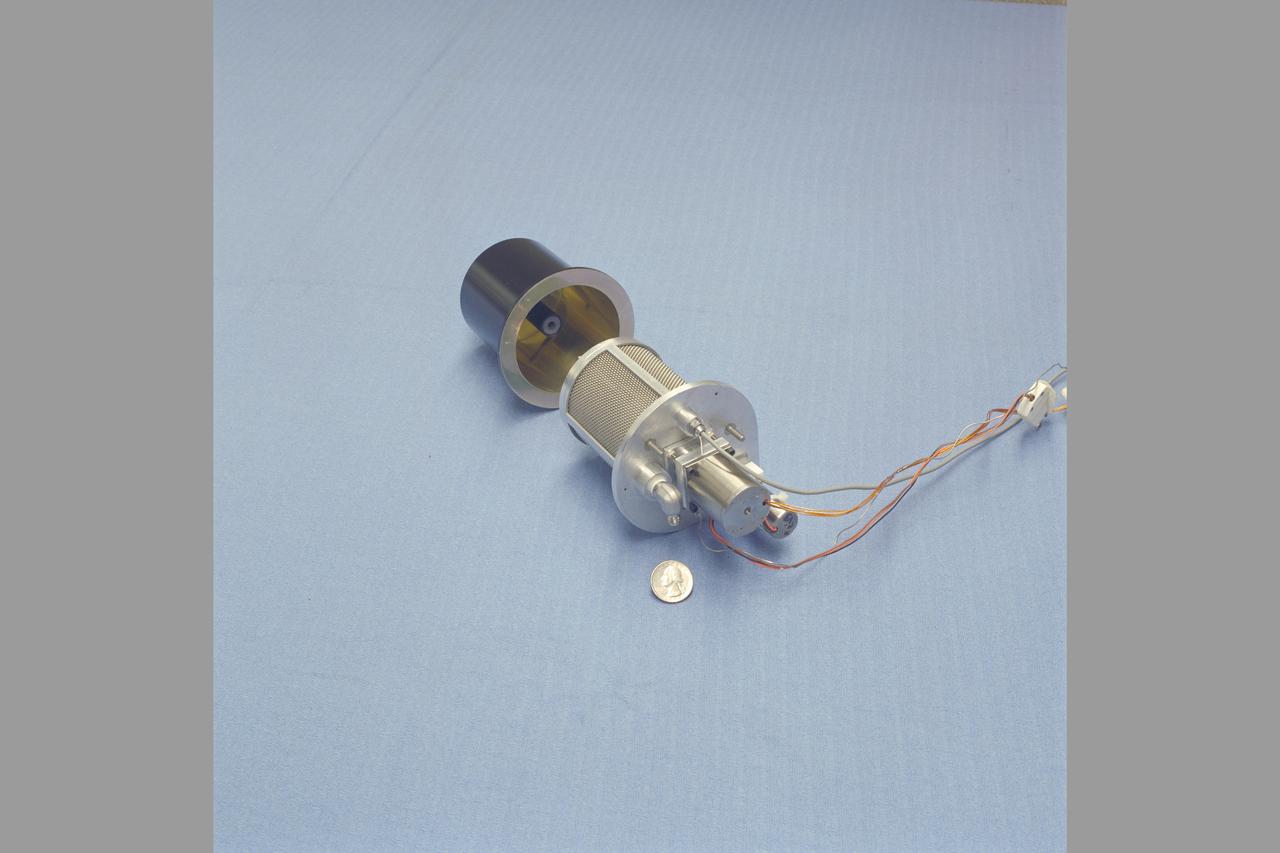
adsorption compression for Mars ISRU ( In-SITU Resource Utilization) N-239 lab
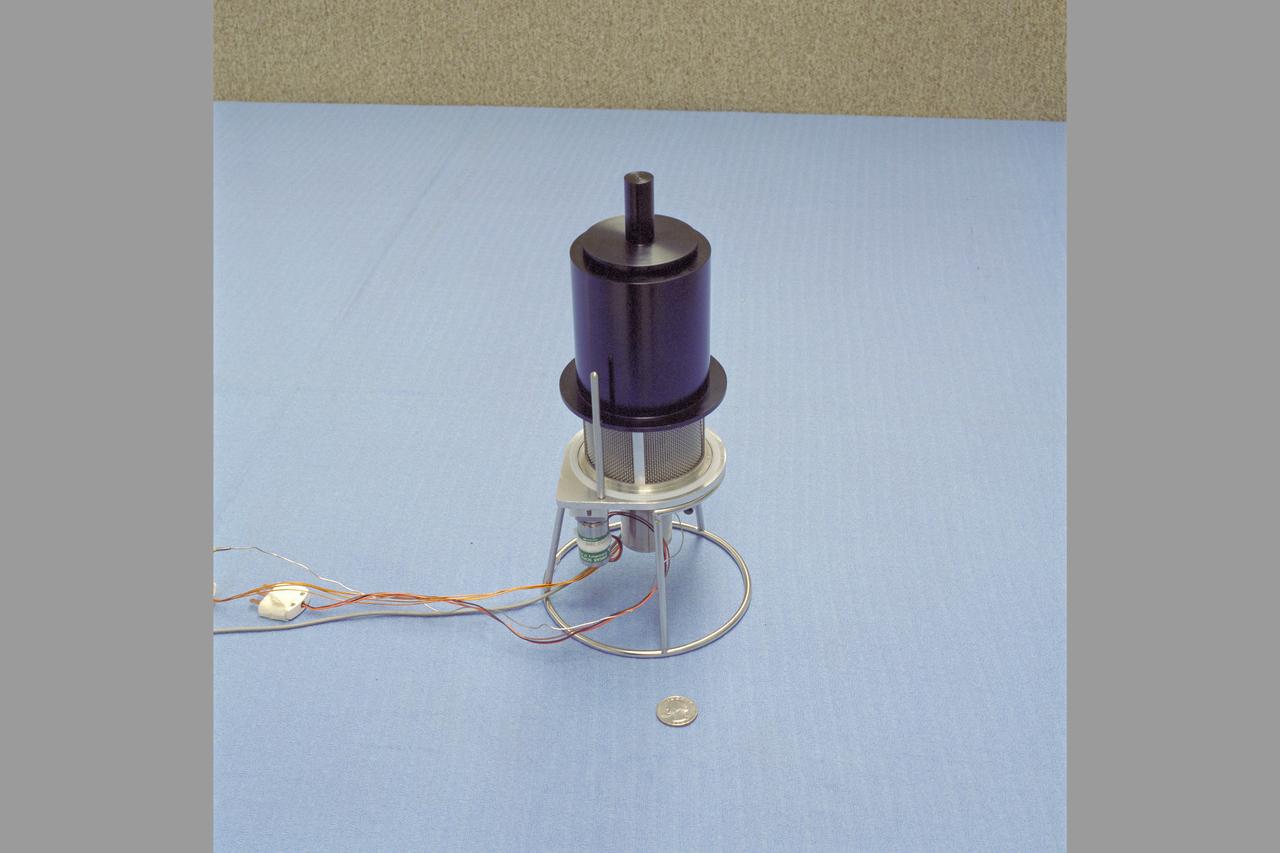
adsorption compression for Mars ISRU ( In-SITU Resource Utilization) N-239 lab
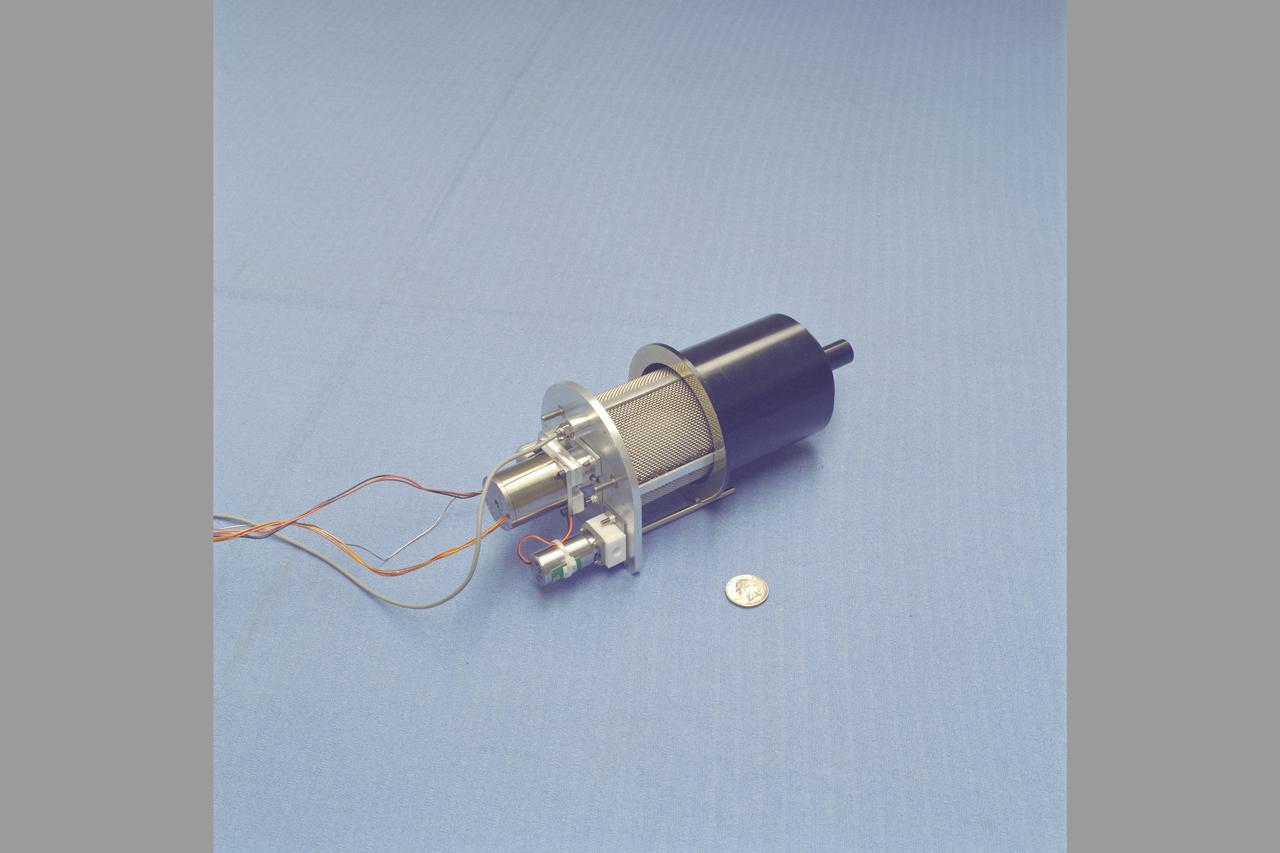
adsorption compression for Mars ISRU ( In-SITU Resource Utilization) N-239 lab

adsorption compression for Mars ISRU ( In-SITU Resource Utilization) N-239 lab

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Courtyard by Marriott hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., William Larson, retired NASA ISRU project manager, talks to participants in the room and those participating online during the Third International Workshop on Lunar Superconductor Applications. The workshop included presentations from several engineers and researchers at Kennedy Space Center. The three-day workshop included presentations from speakers throughout the country and focused on Lunar in-situ resource utilization, NASA’s Lunar Ice Prospector called RESOLVE, CubeSats, cryogenic storage and many other topics related to lunar exploration. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
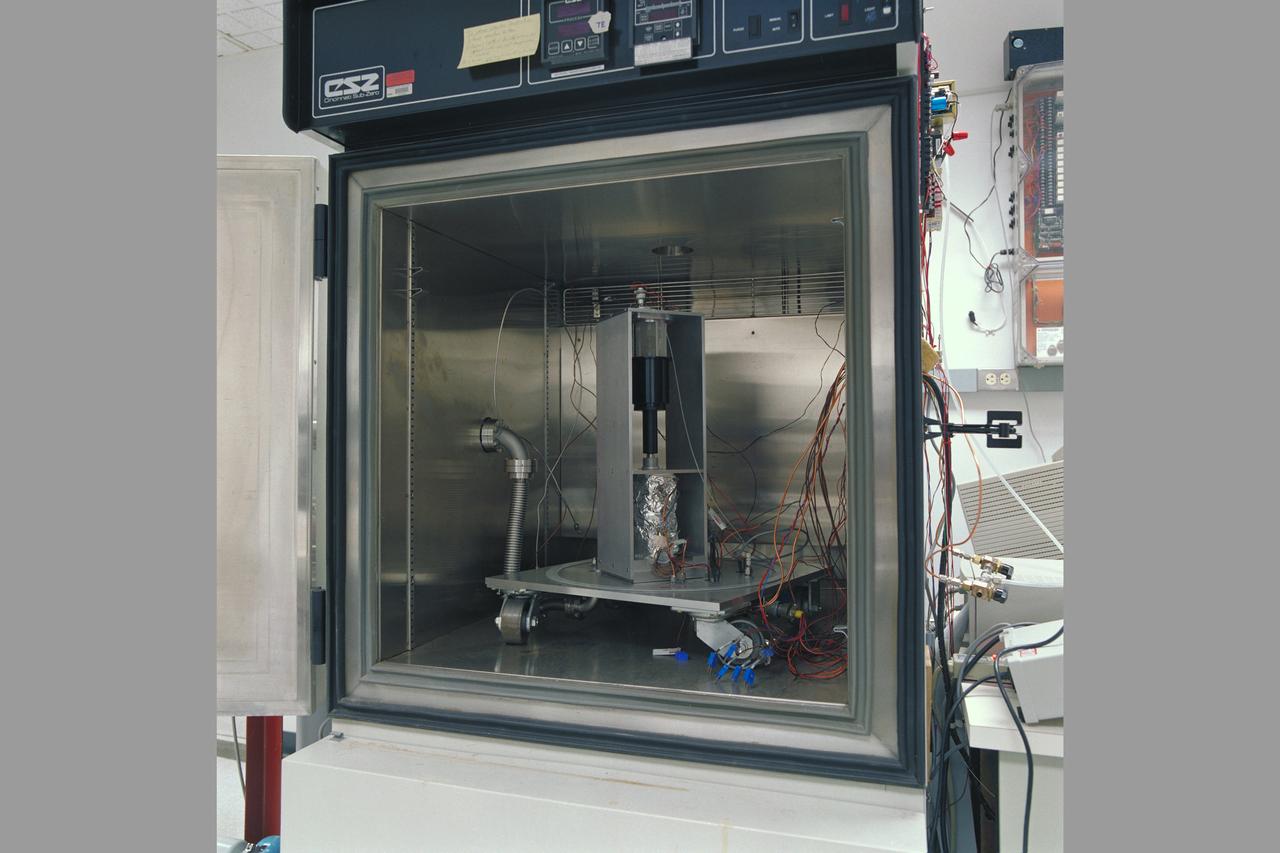

Mars Environmental Chamber. Absorption Compression for Mars ISRU (In-SITU Resource Utilization) N-239.
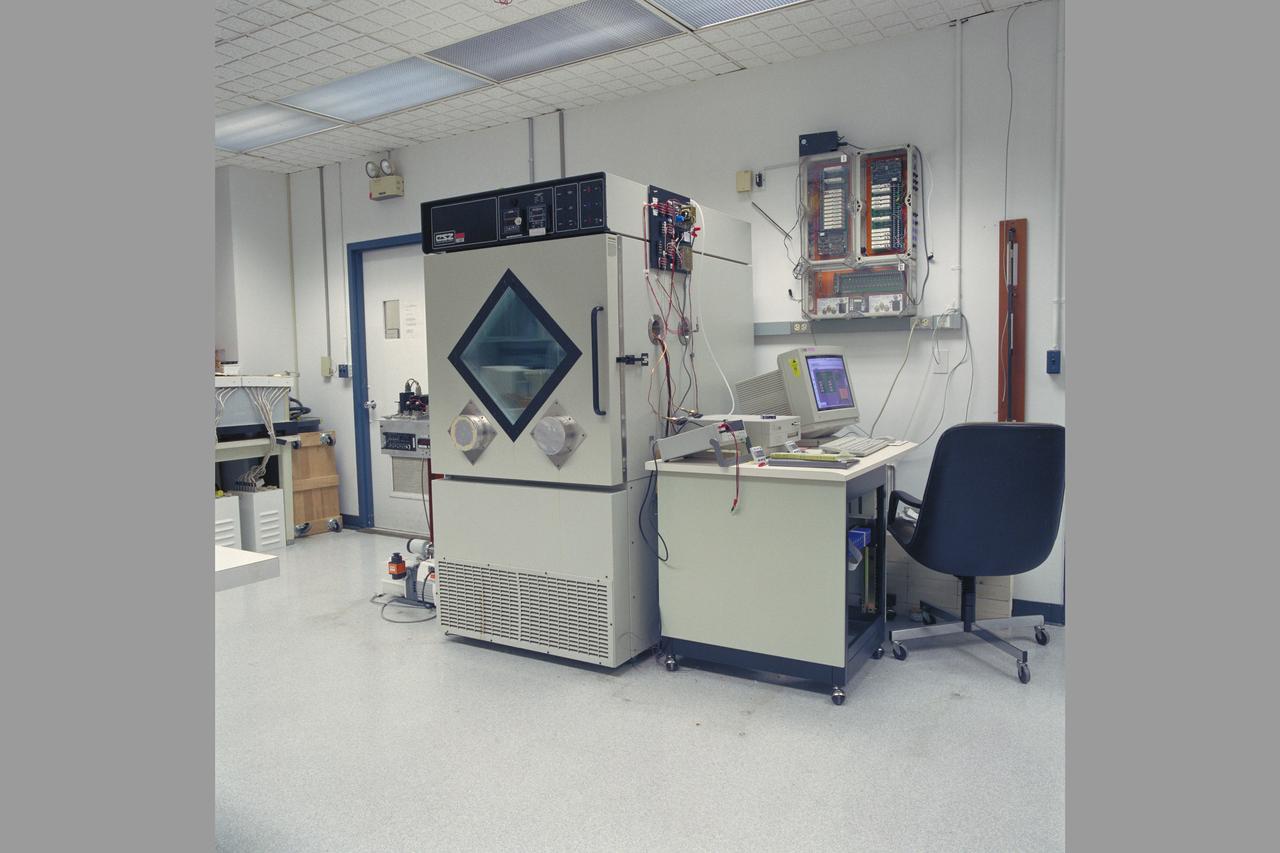

Mars Environmental Chamber. Absorption Compression for Mars ISRU (In-SITU Resource Utilization) N-239.
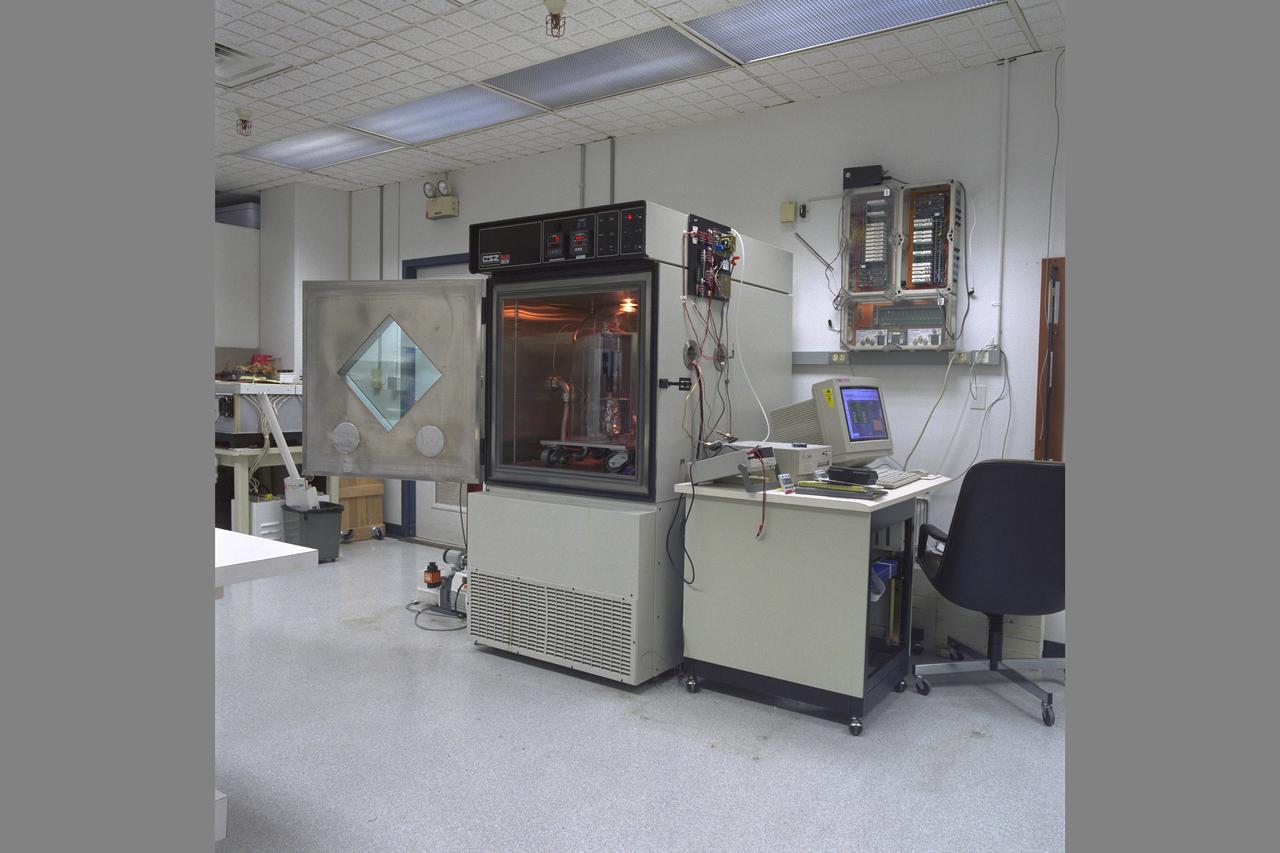

Mars Environmental Chamber. Absorption Compression for Mars ISRU (In-SITU Resource Utilization) N-239.
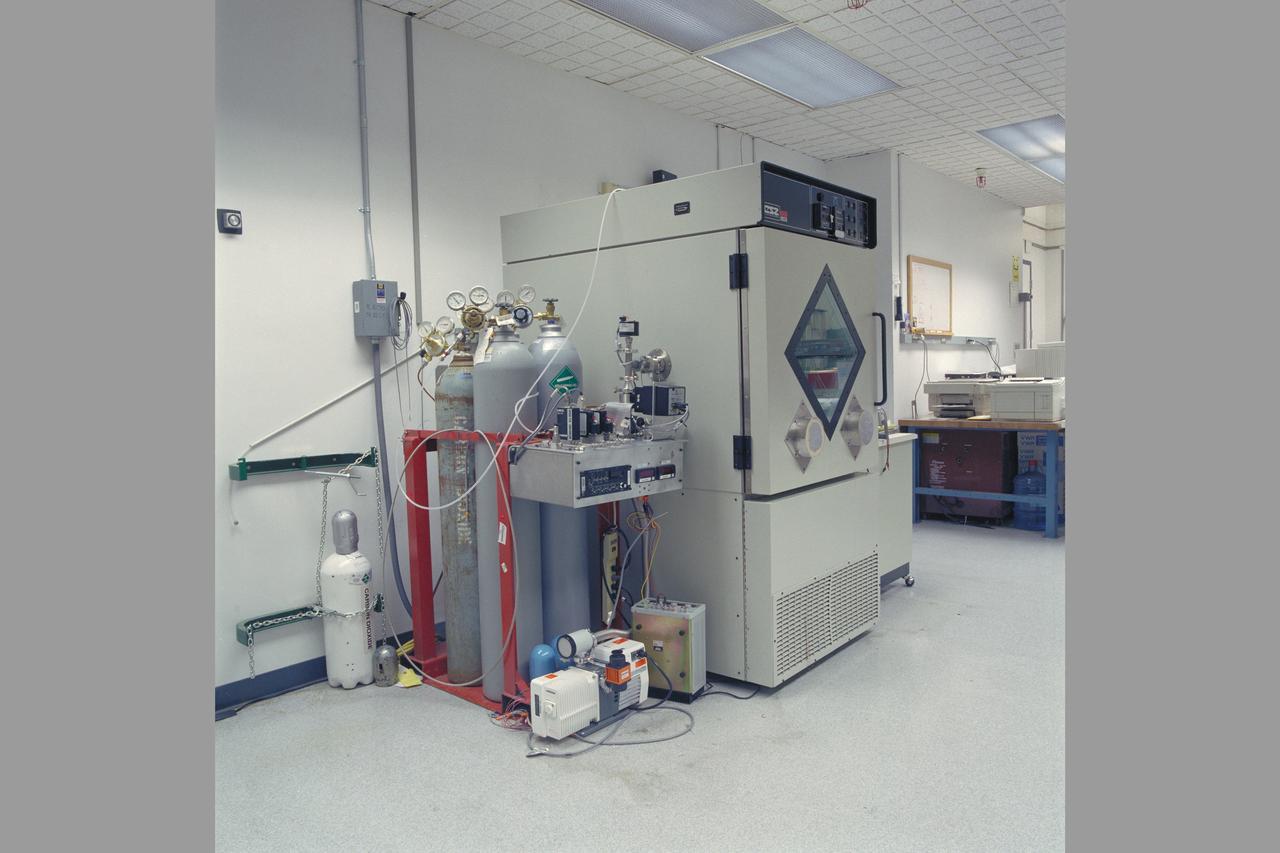

Mars Environmental Chamber. Absorption Compression for Mars ISRU (In-SITU Resource Utilization) N-239.

Mars Environmental Chamber. Absorption Compression for Mars ISRU (In-SITU Resource Utilization) N-239.
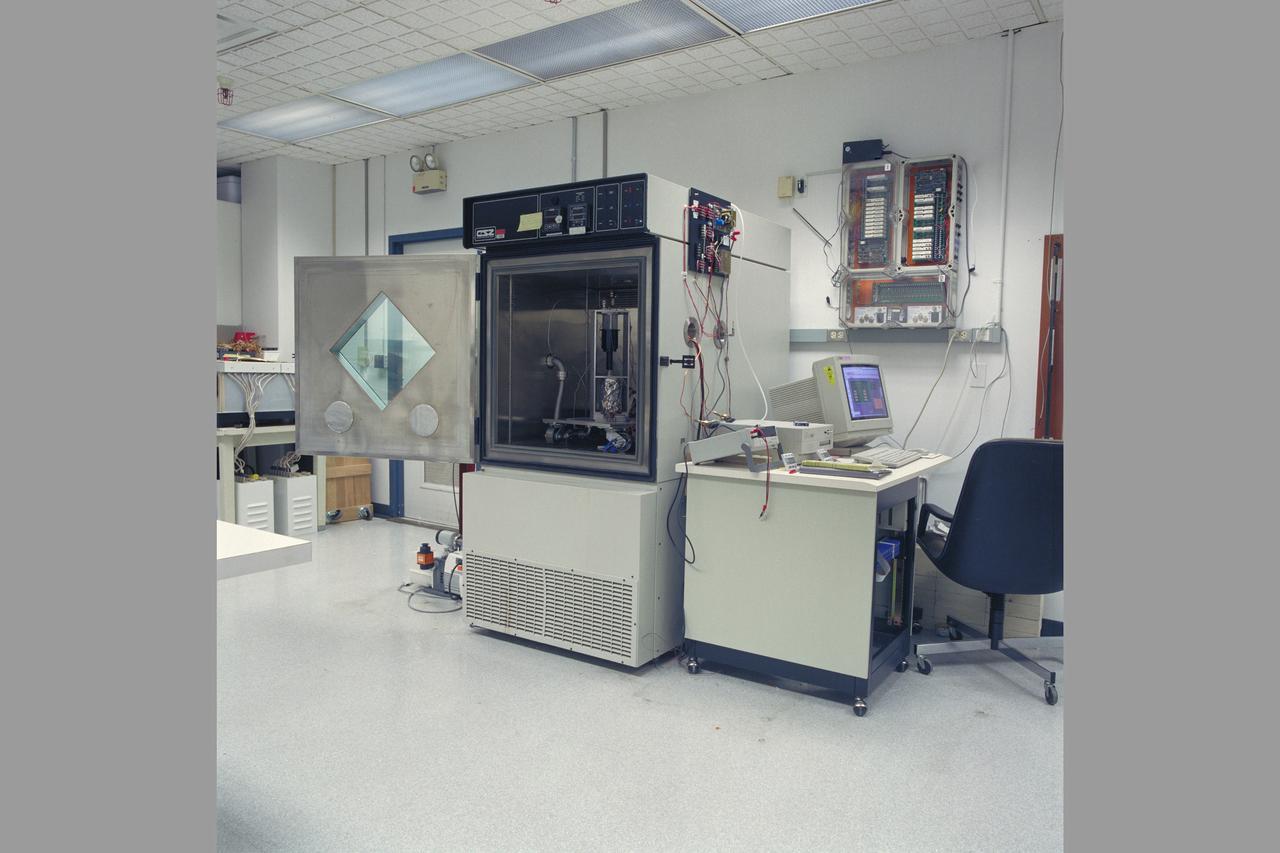

Mars Environmental Chamber. Absorption Compression for Mars ISRU (In-SITU Resource Utilization) N-239.
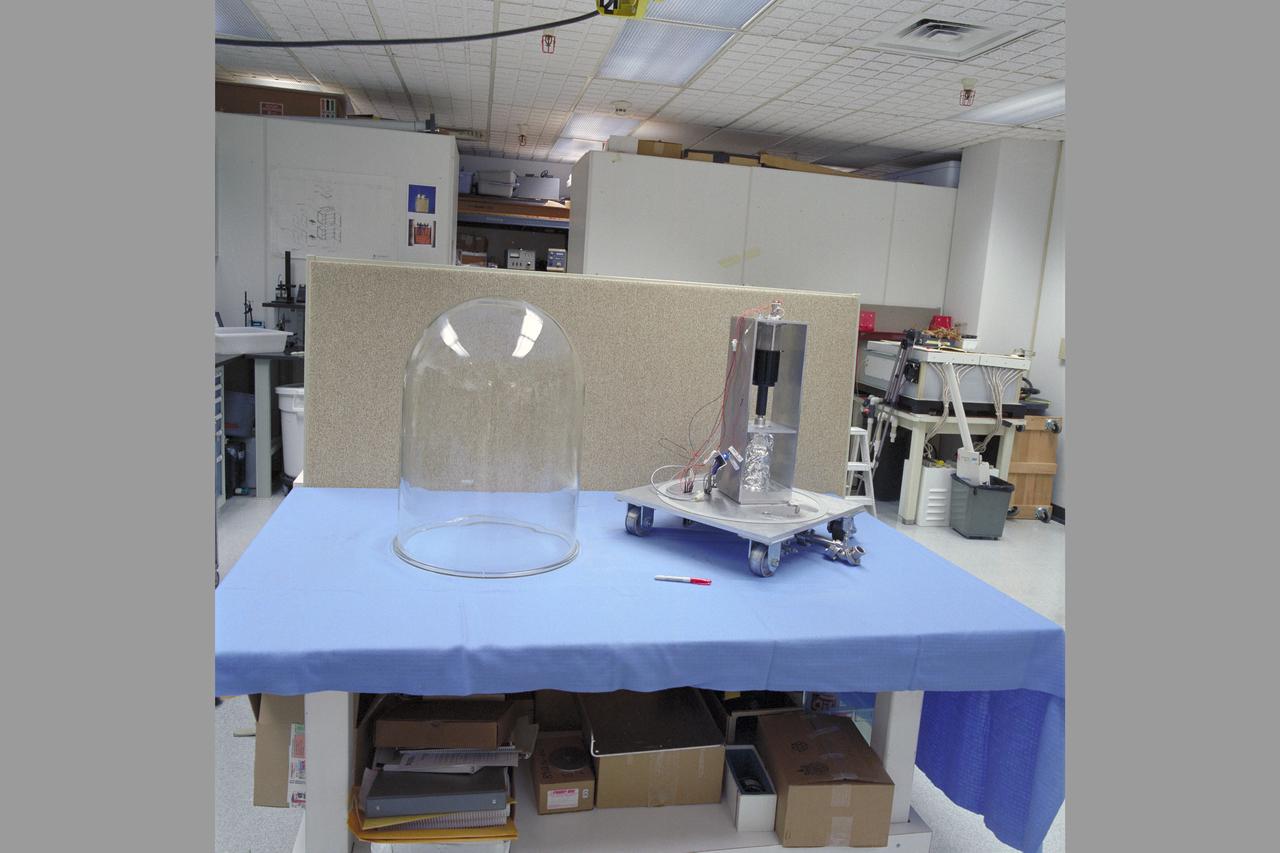

Mars Environmental Chamber. Absorption Compression for Mars ISRU (In-SITU Resource Utilization) N-239.
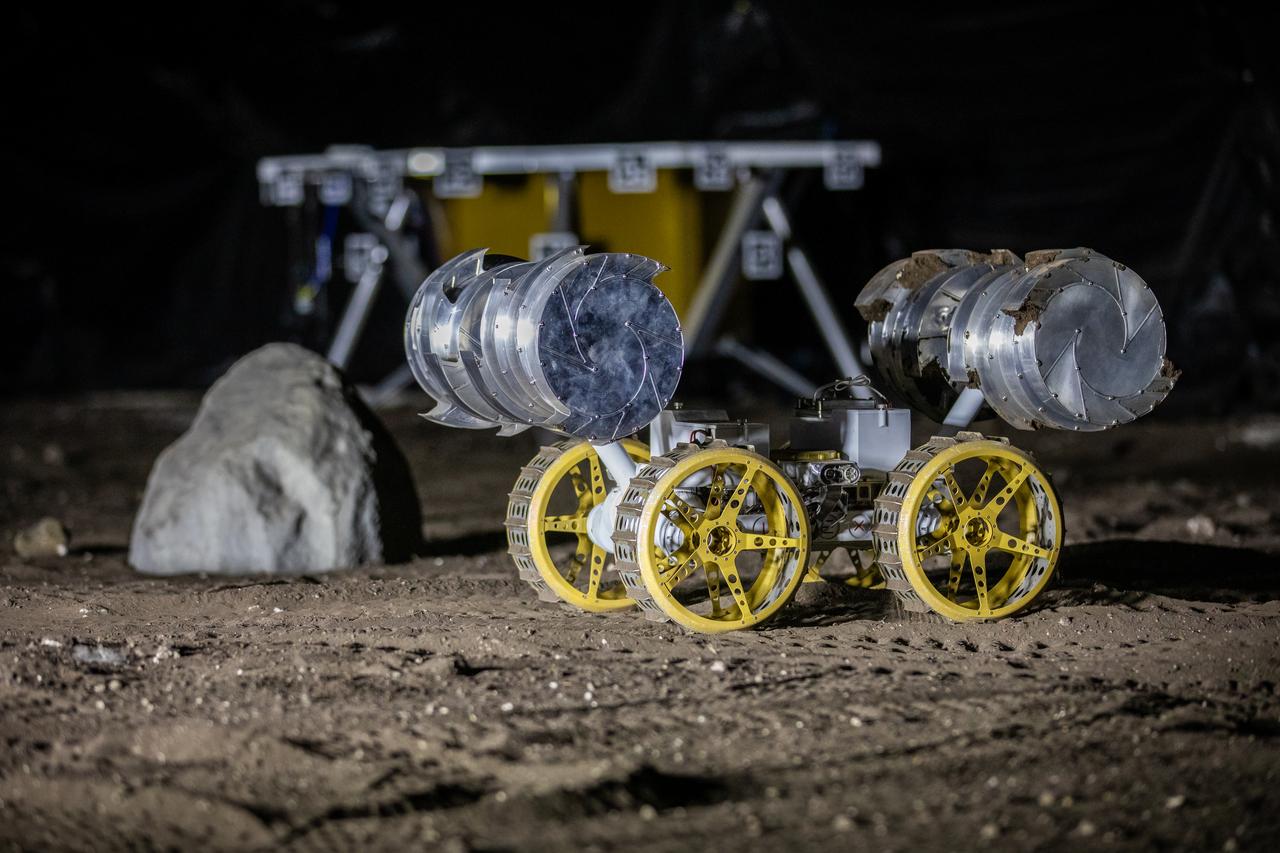

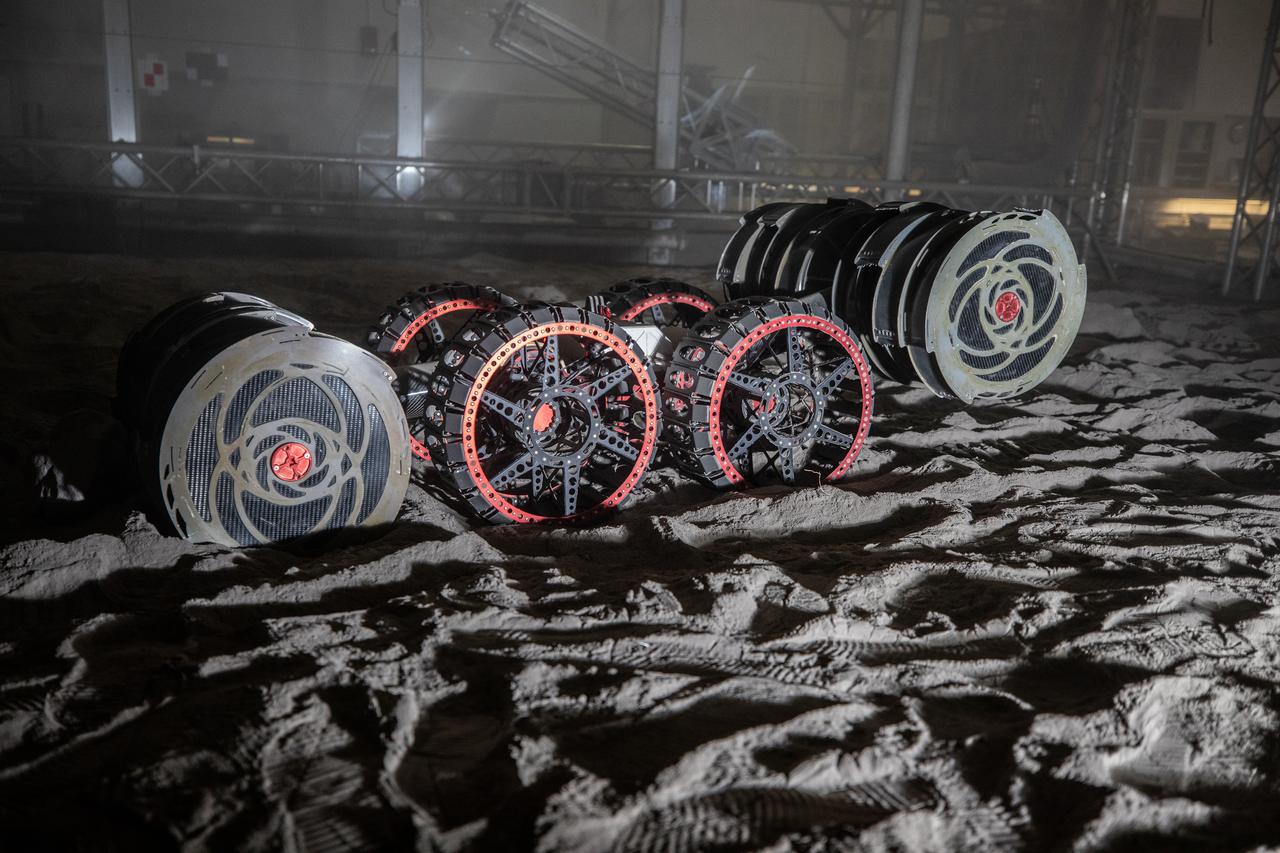
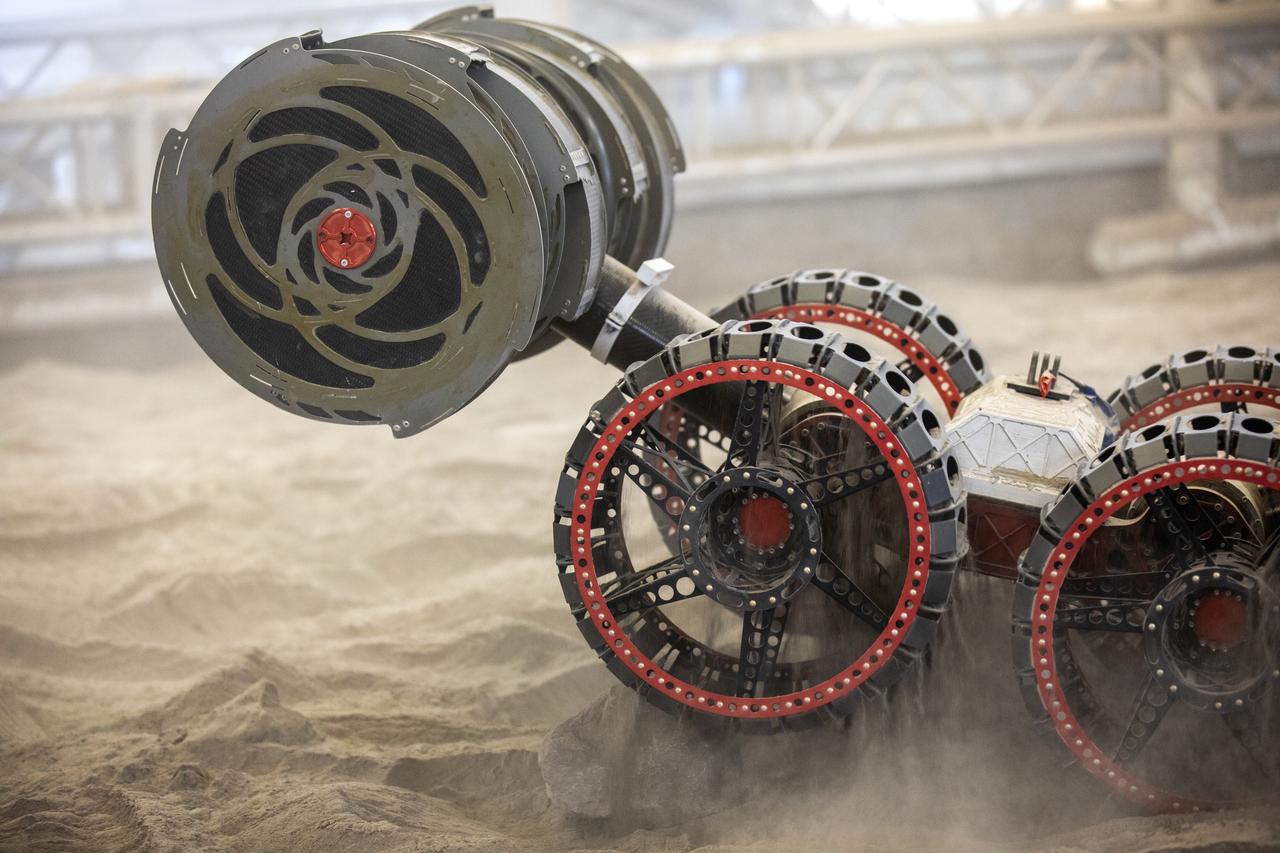
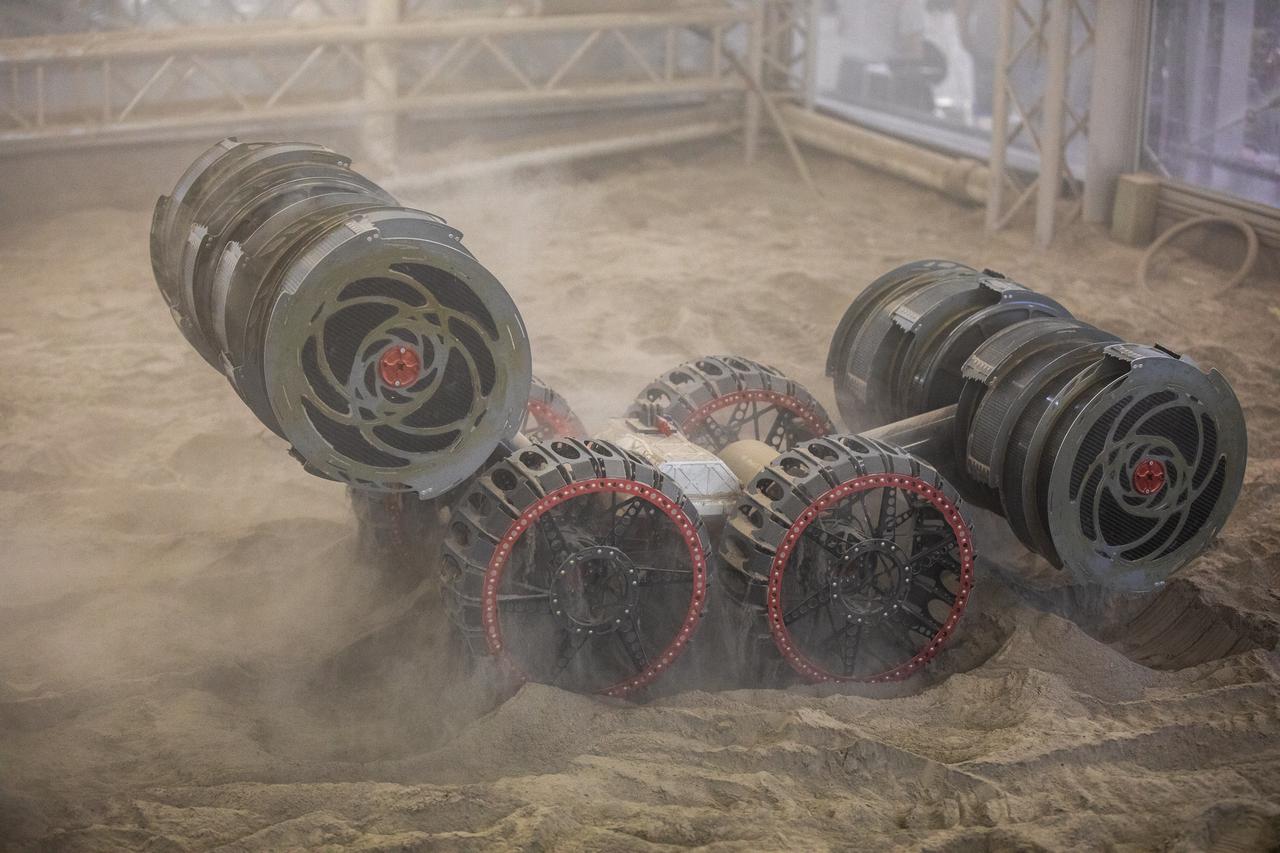
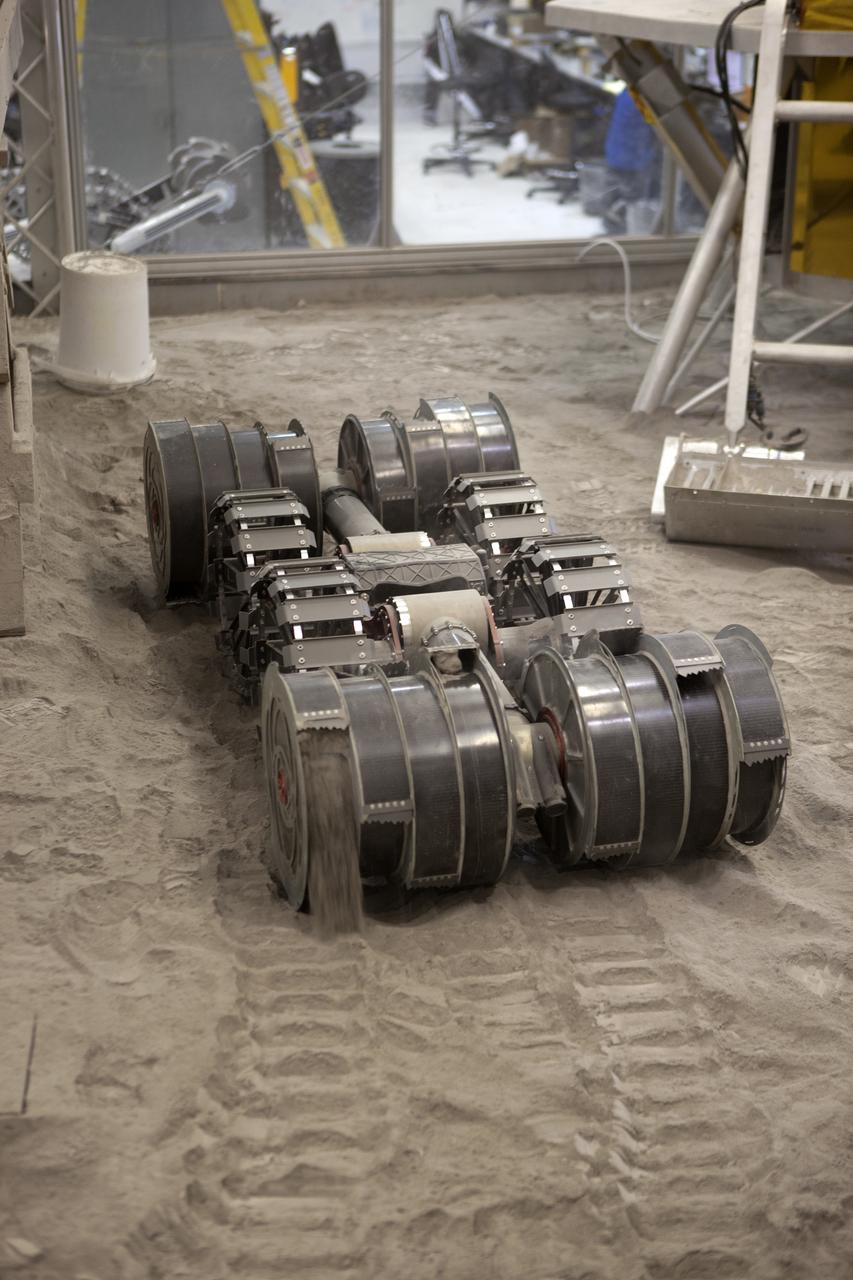
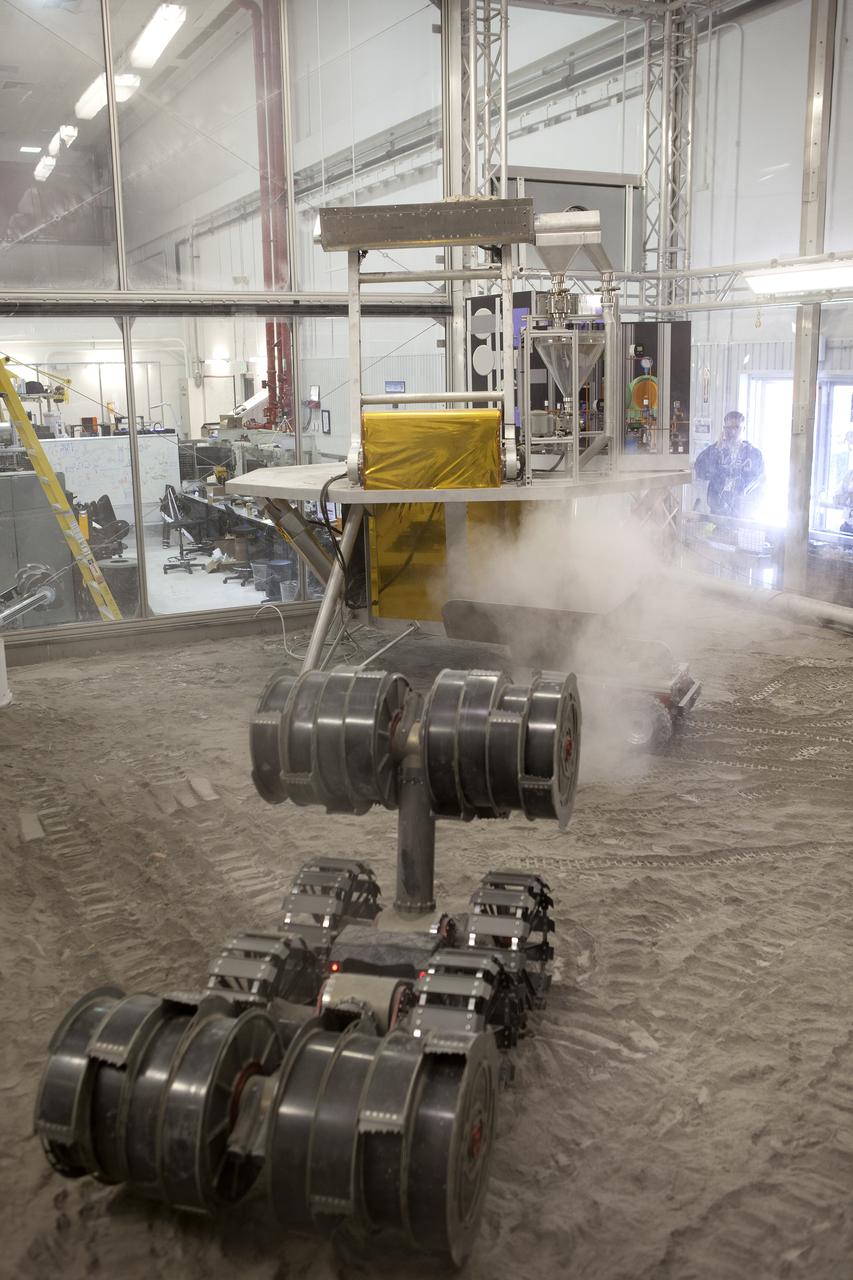
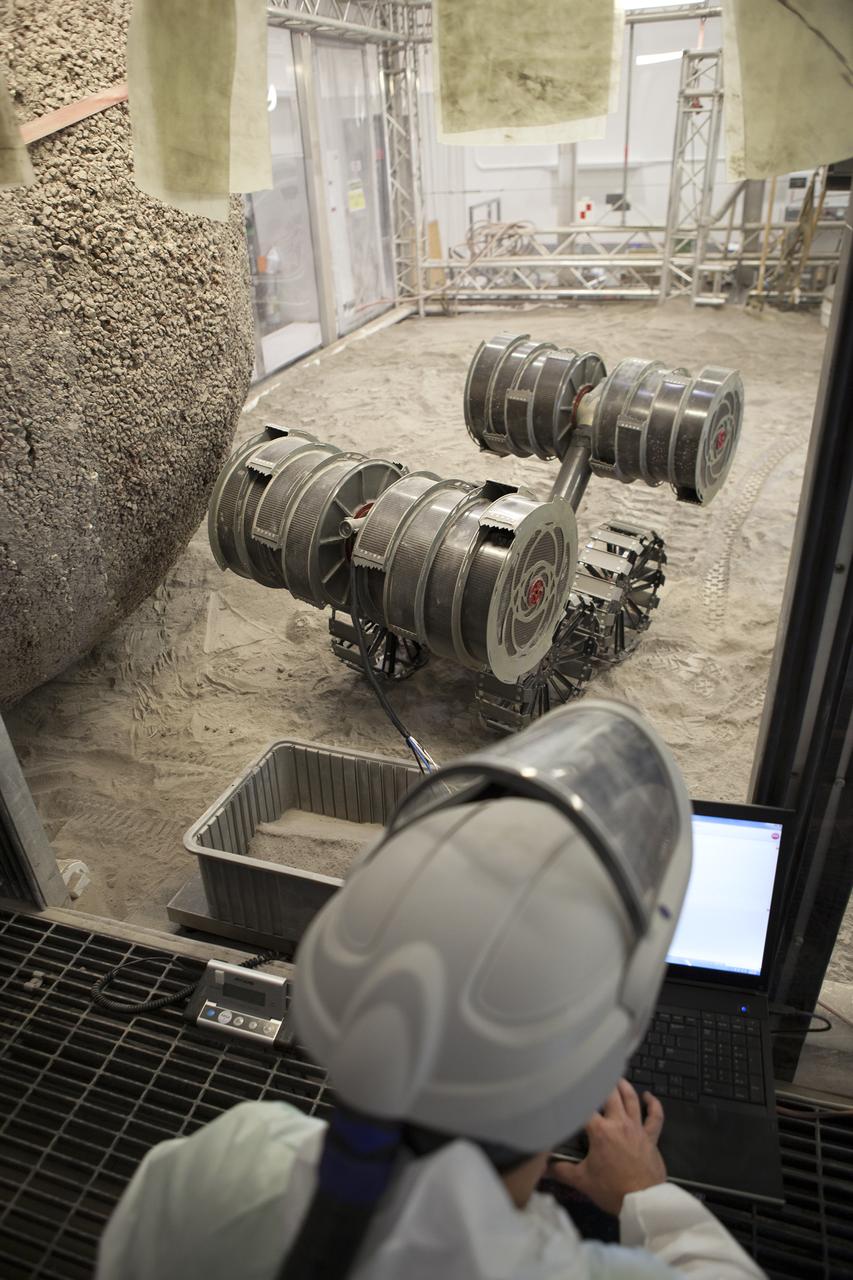
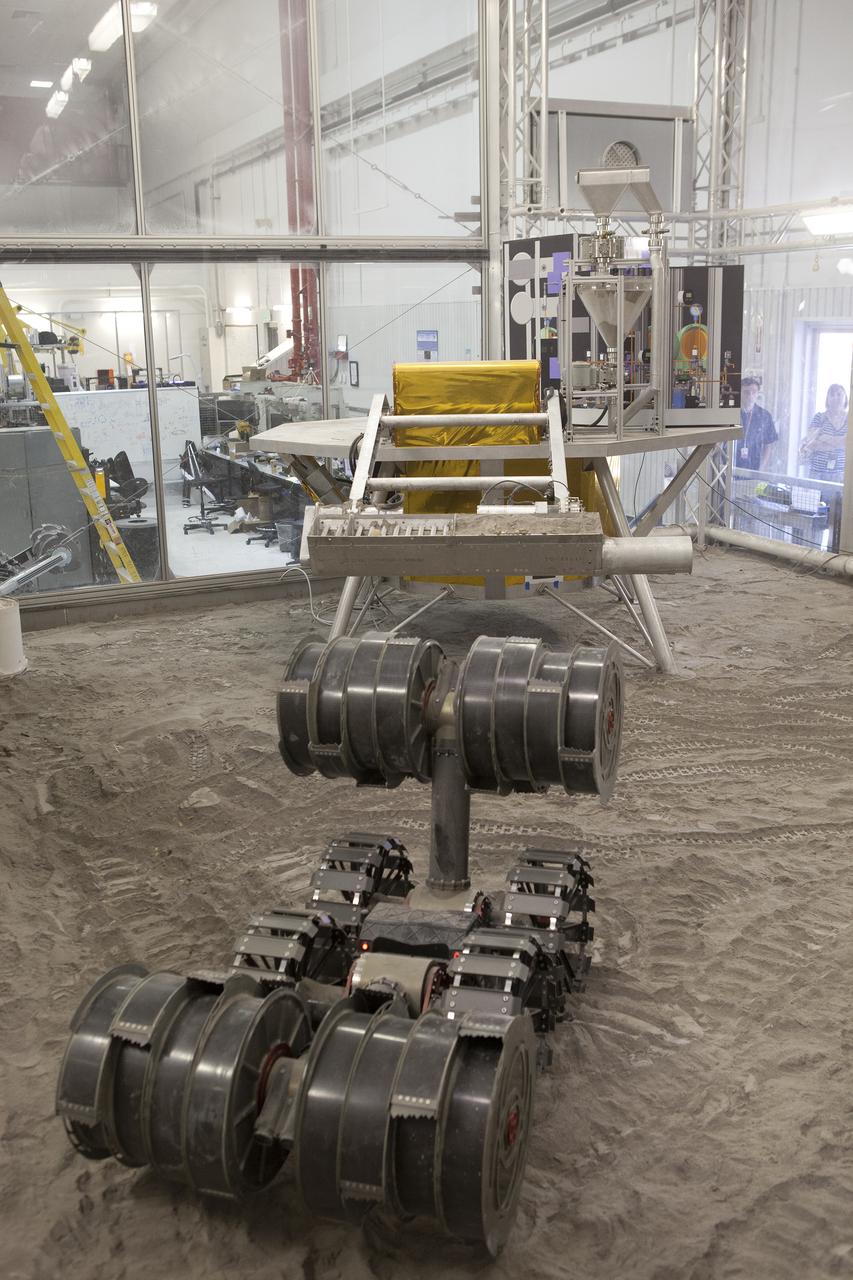
NASA’s ISRU Pilot Excavator (IPEx) performs a simulated lunar mission in a testbed at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center on Friday, Aug. 30, 2024. IPEx functions as both an excavator and a dump truck to mine and transport lunar regolith, the loose rocky material on the Moon’s surface, which is crucial for future lunar missions and In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) processes. This dual capability makes IPEx an indispensable tool for sustainable lunar exploration.
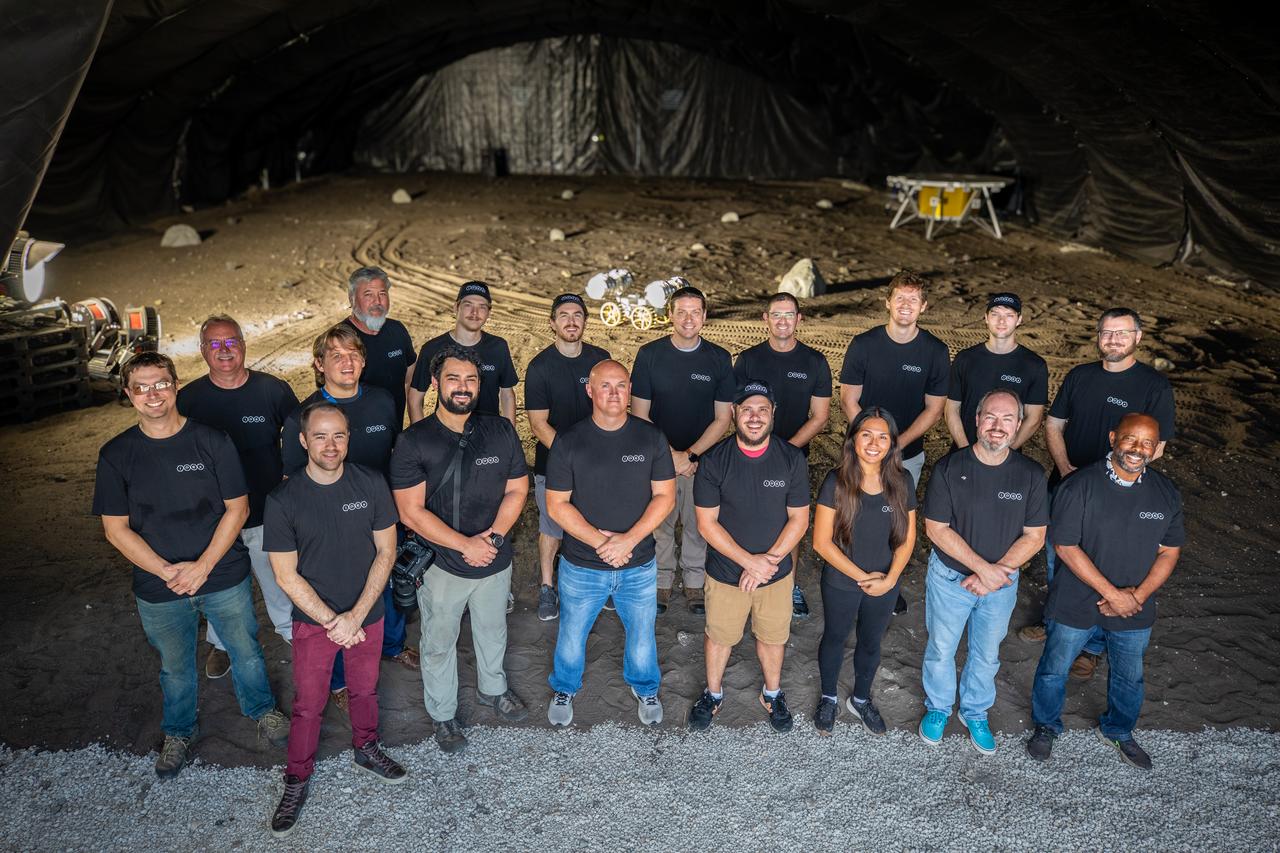

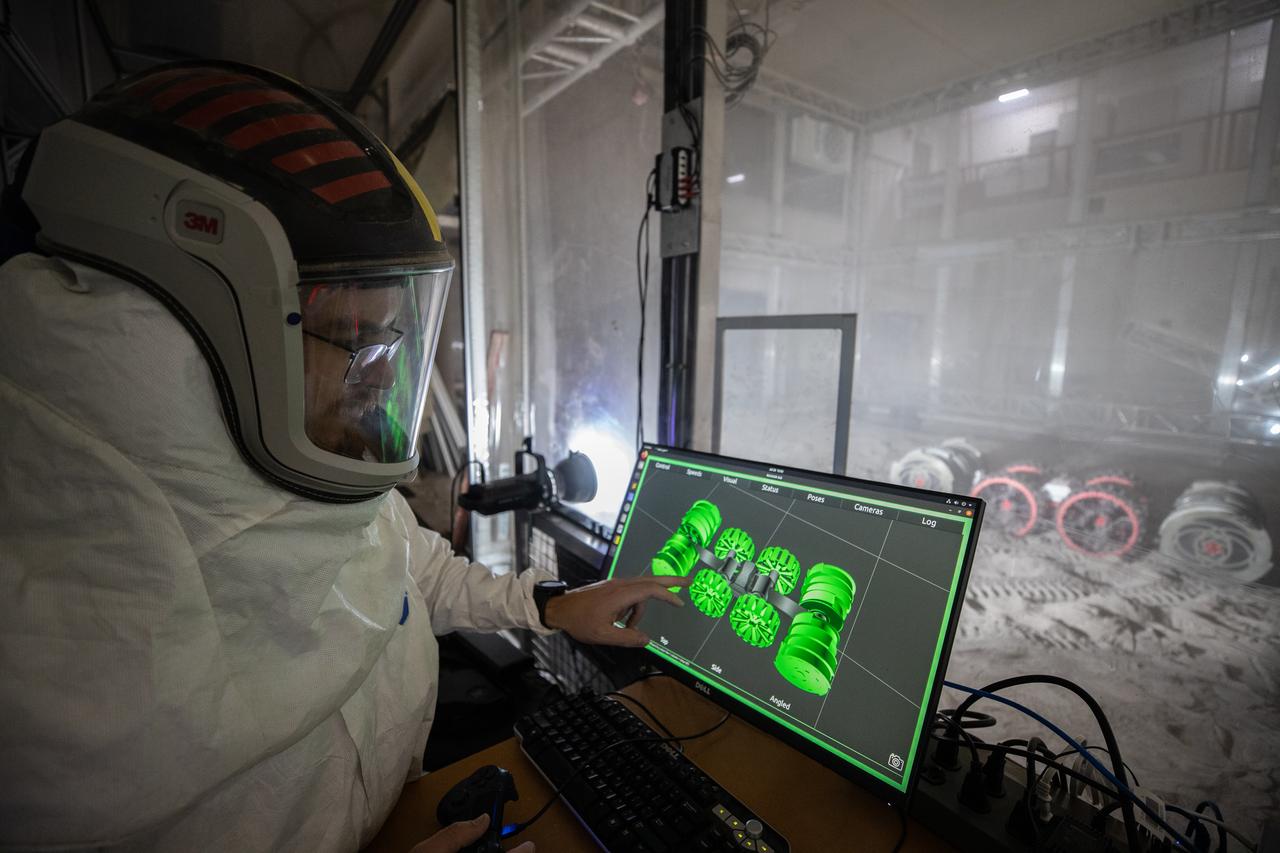
A team from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations lab who developed and tested NASA’s ISRU Pilot Excavator (IPEx) pose for a photo on Friday, Aug. 30, 2024, in a testbed located at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IPEx functions as both an excavator and a dump truck to mine and transport lunar regolith, the loose rocky material on the Moon’s surface, which is crucial for future lunar missions and In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) processes. This dual capability makes IPEx an indispensable tool for sustainable lunar exploration.
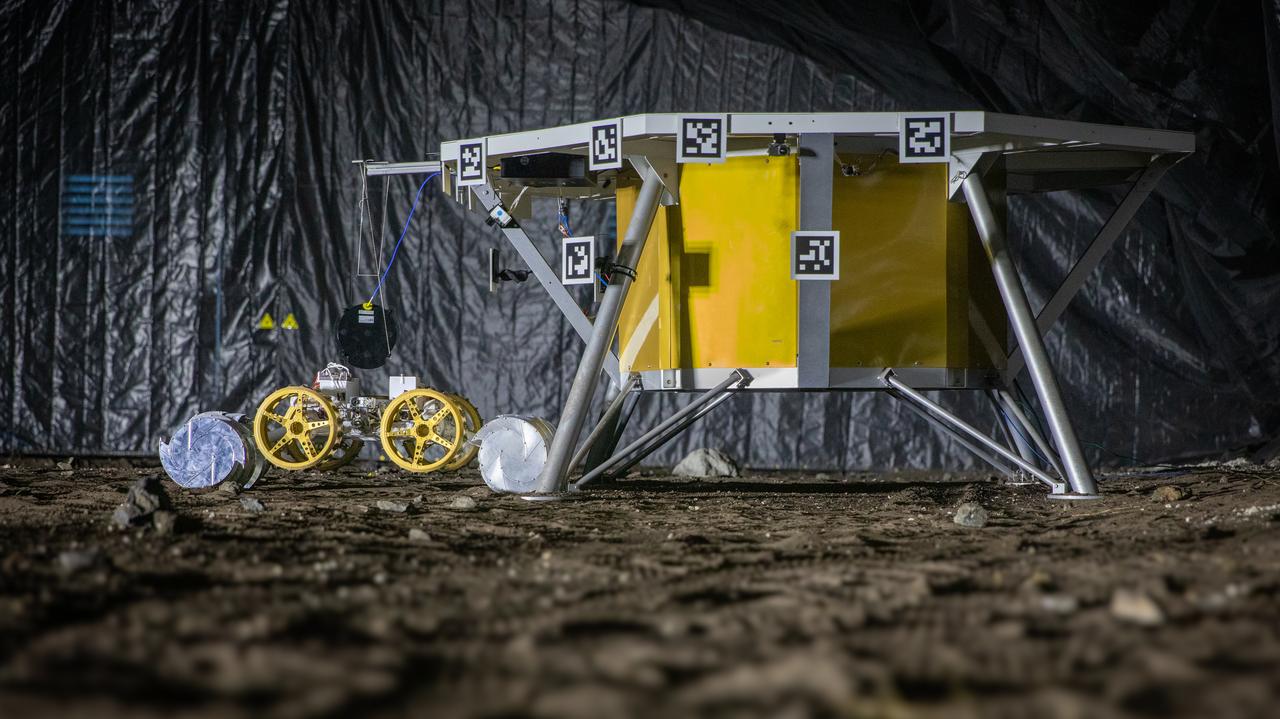

NASA’s ISRU Pilot Excavator (IPEx) performs a simulated lunar mission in a testbed at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center on Friday, Aug. 30, 2024. IPEx functions as both an excavator and a dump truck to mine and transport lunar regolith, the loose rocky material on the Moon’s surface, which is crucial for future lunar missions and In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) processes. This dual capability makes IPEx an indispensable tool for sustainable lunar exploration.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Courtyard by Marriott hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Rob Mueller, senior technologist in the Surface Systems Office of the Engineering and Technology Directorate at Kennedy Space Center, talks to participants in the room and those participating online during the Third International Workshop on Lunar Superconductor Applications. The workshop included presentations from several engineers and researchers at Kennedy Space Center. The three-day workshop included presentations from speakers throughout the country and focused on Lunar in-situ resource utilization, NASA’s Lunar Ice Prospector called RESOLVE, CubeSats, cryogenic storage and many other topics related to lunar exploration. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Courtyard by Marriott hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Russell Cox, director of research with Flexure Engineering, welcomes participants in the room and those participating online to the Third International Workshop on Lunar Superconductor Applications. The workshop included presentations from several engineers and researchers at Kennedy Space Center. The three-day workshop included presentations from speakers throughout the country and focused on Lunar in-situ resource utilization, NASA’s Lunar Ice Prospector called RESOLVE, CubeSats, cryogenic storage and many other topics related to lunar exploration. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Courtyard by Marriott hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Bonnie Dubrow, business development manager with Flexure Engineering, welcomes participants in the room and those participating online to the Third International Workshop on Lunar Superconductor Applications. The workshop included presentations from several engineers and researchers at Kennedy Space Center. The three-day workshop included presentations from speakers throughout the country and focused on Lunar in-situ resource utilization, NASA’s Lunar Ice Prospector called RESOLVE, CubeSats, cryogenic storage and many other topics related to lunar exploration. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Courtyard by Marriott hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Pat Simpkins, director of Engineering and Technology at Kennedy Space Center talks to participants in the room and those participating online during the Third International Workshop on Lunar Superconductor Applications. The workshop included presentations from several engineers and researchers at Kennedy Space Center. The three-day workshop included presentations from speakers throughout the country and focused on Lunar in-situ resource utilization, NASA’s Lunar Ice Prospector called RESOLVE, CubeSats, cryogenic storage and many other topics related to lunar exploration. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
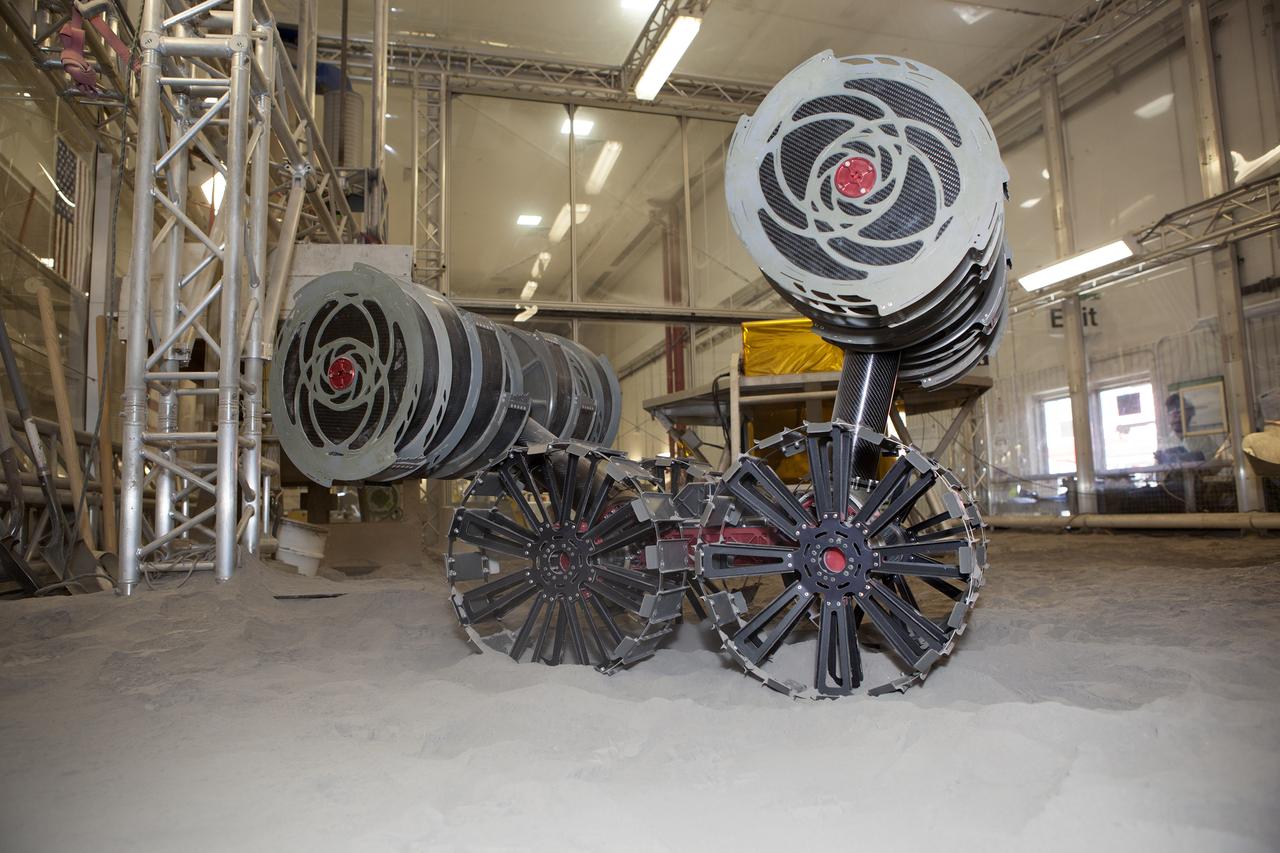

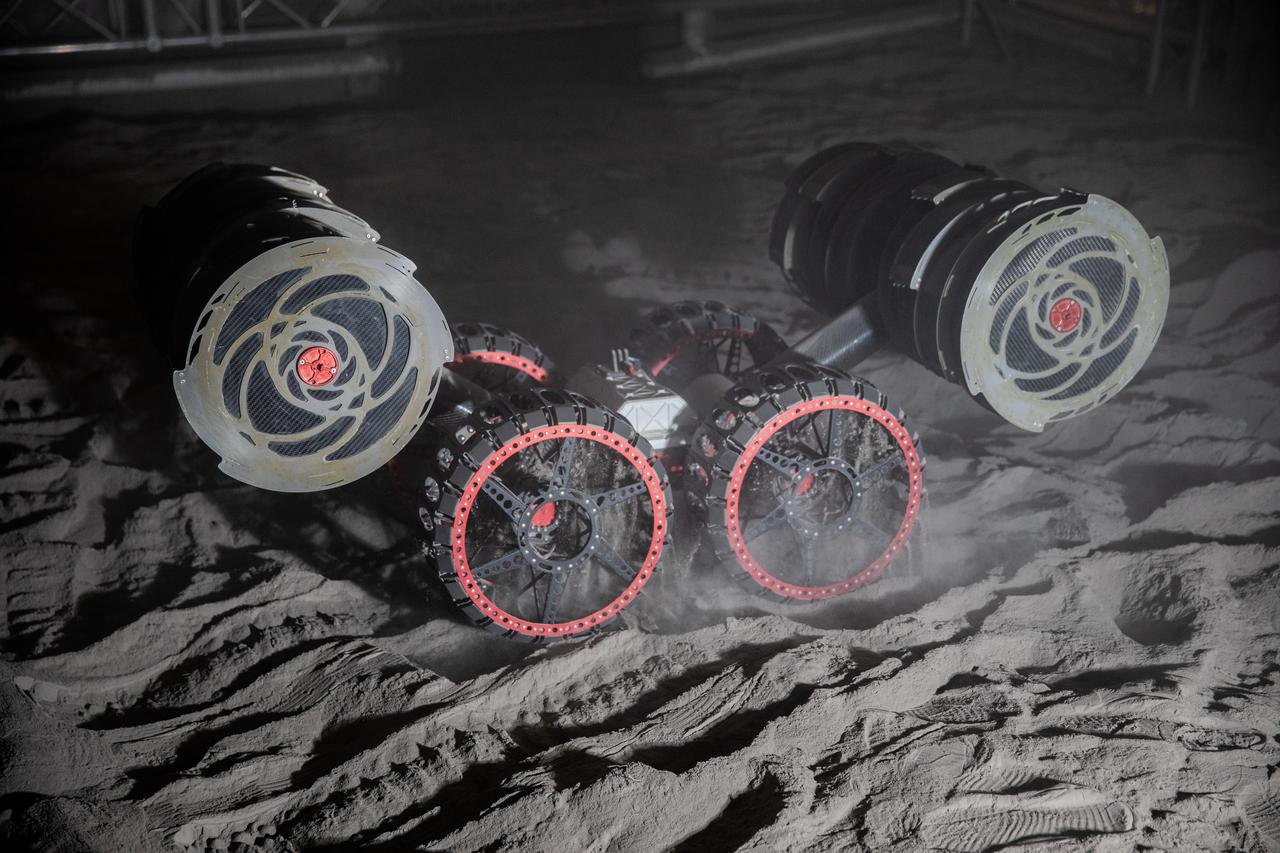
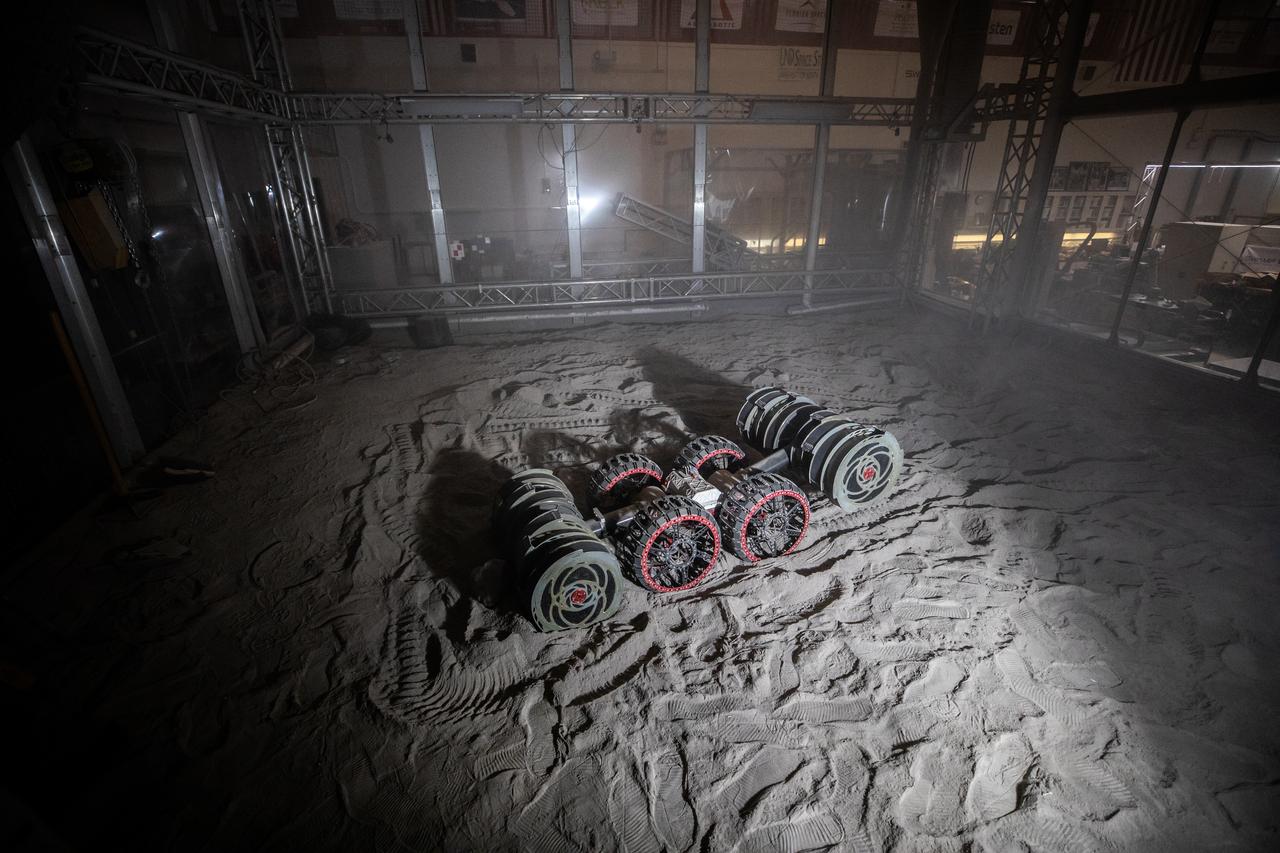
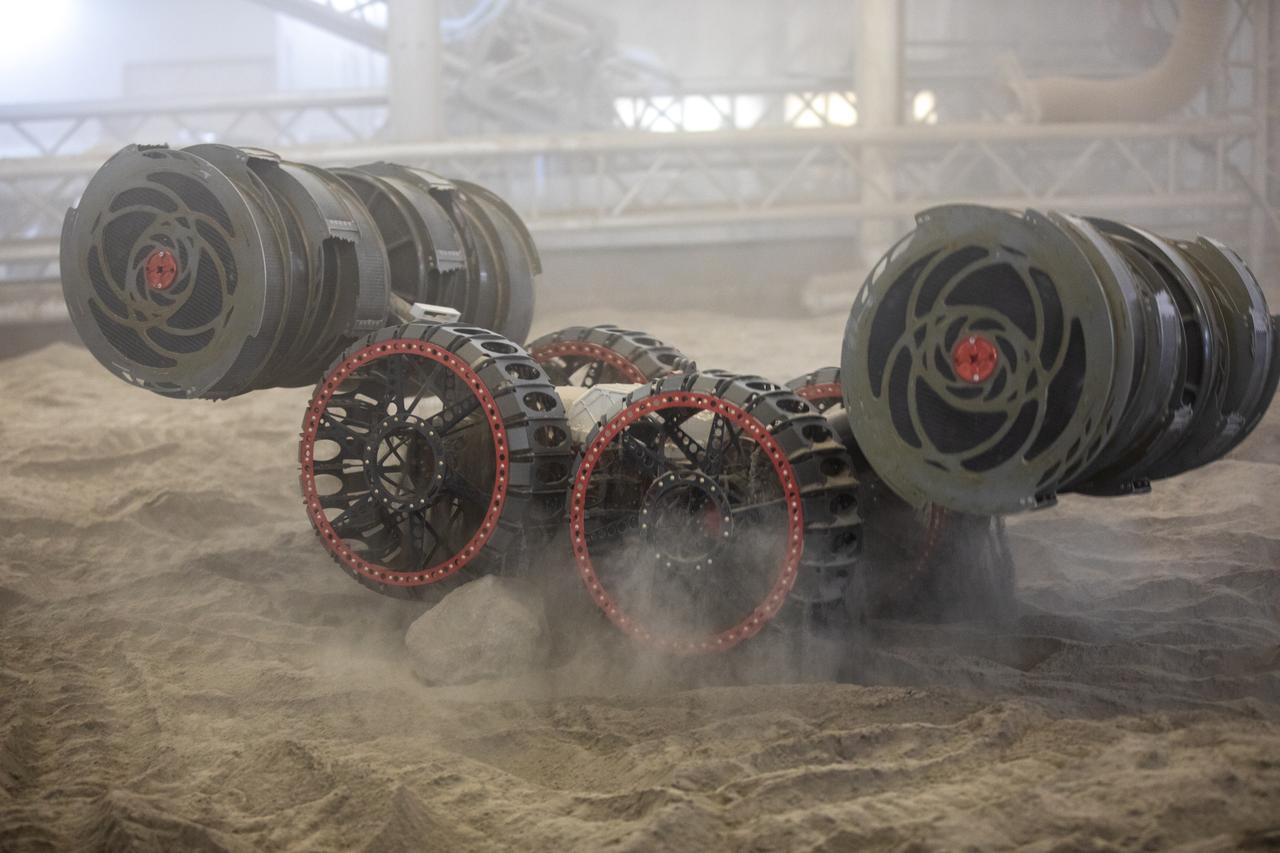
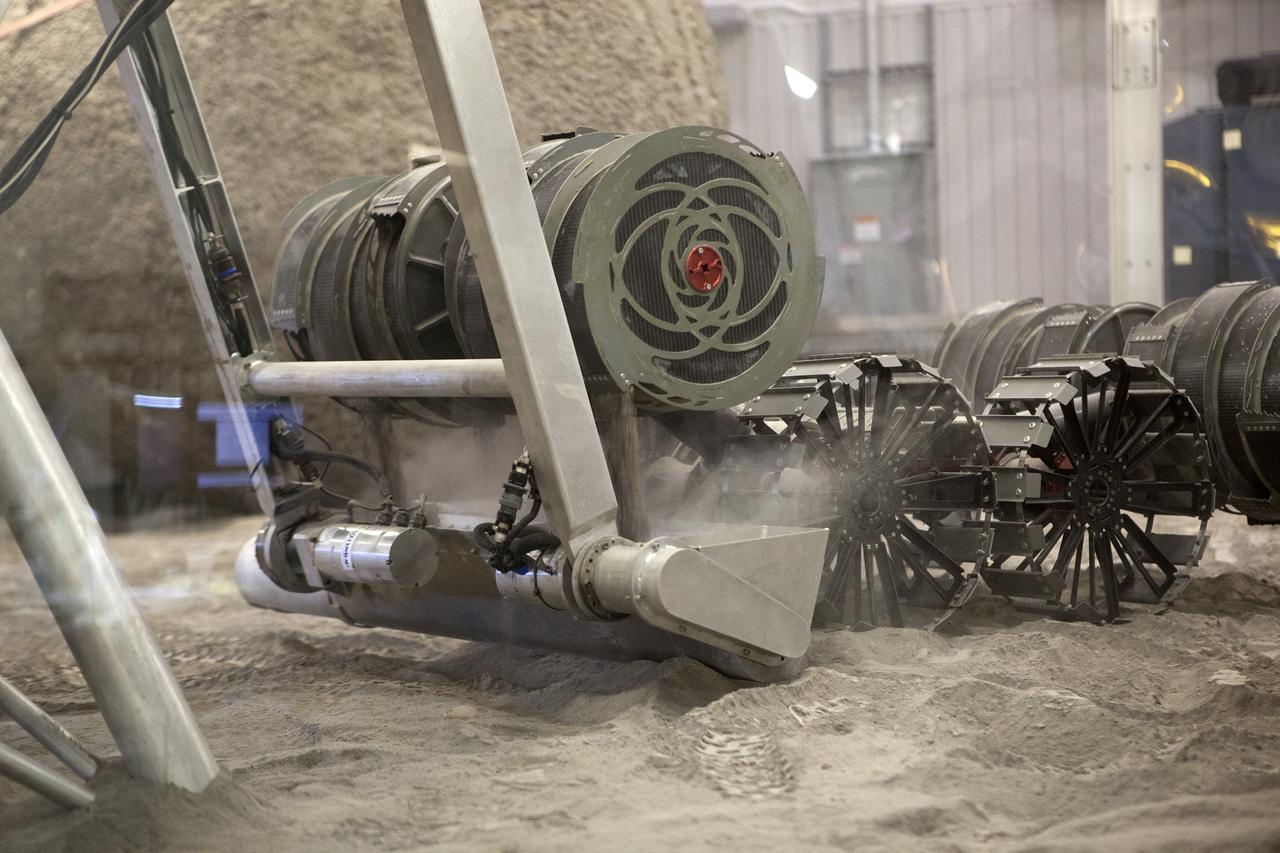
An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.
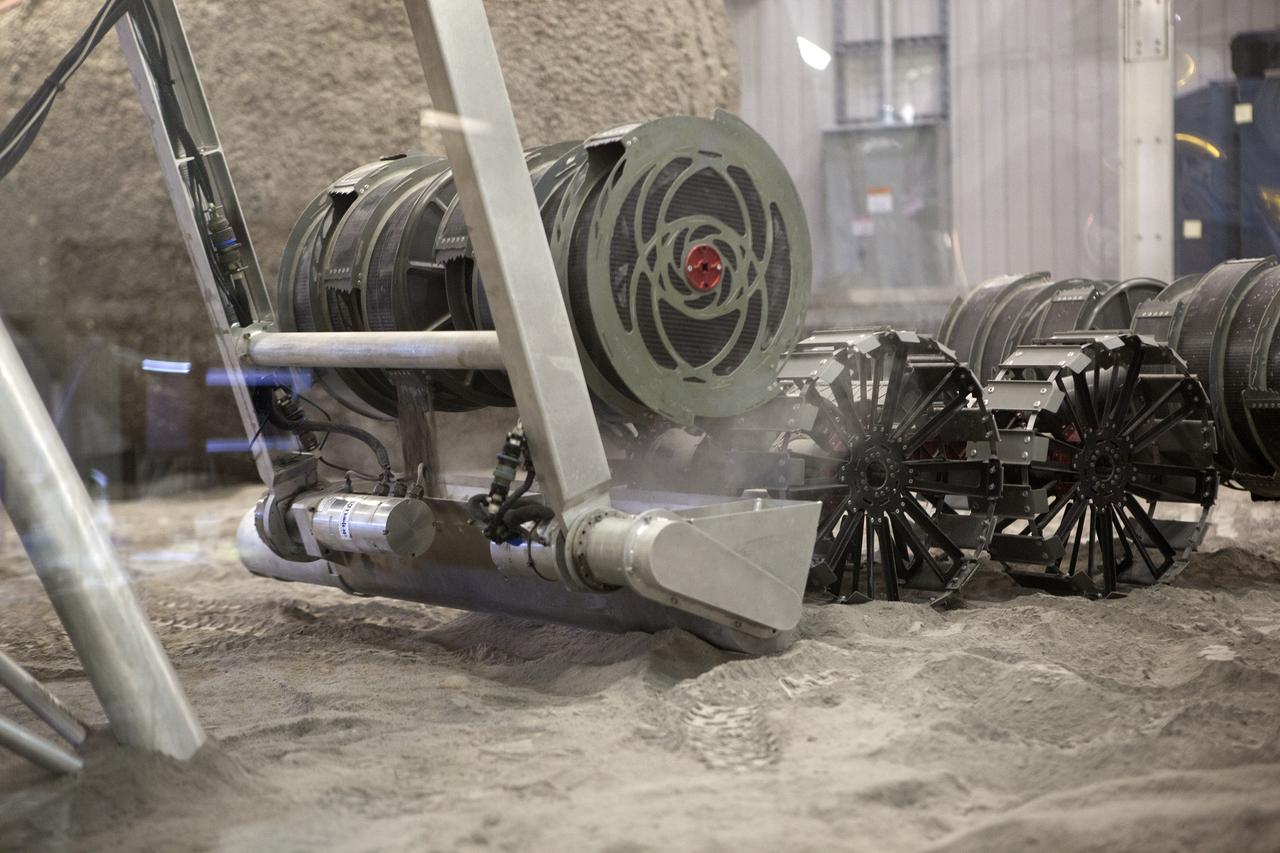

An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.

An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.

An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.

An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.

An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.

An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.
An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.

An integrated test of the MARCO POLO/Mars Pathfinder in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU, system takes place at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A mockup of MARCO POLO, an ISRU propellant production technology demonstration simulated mission, is tested in a regolith bin with RASSOR 2.0, the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot. On the surface of Mars, mining robots like RASSOR will dig down into the regolith and take the material to a processing plant where usable elements such as hydrogen, oxygen and water can be extracted for life support systems. Regolith also shows promise for both construction and creating elements for rocket fuel.
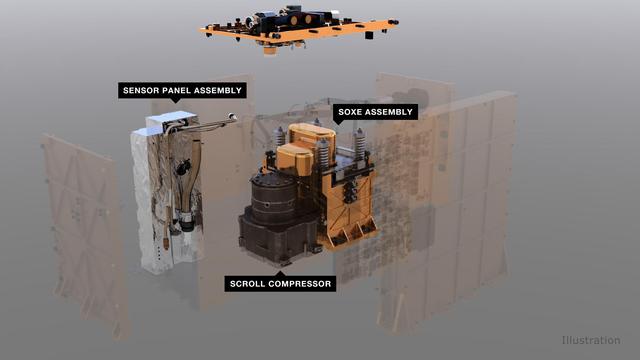
An illustration of MOXIE (Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment) and its components. An air pump pulls in carbon dioxide gas from the Martian atmosphere, which is then regulated and fed to the Solid OXide Electrolyzer (SOXE), where it is electrochemically split to produce pure oxygen. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24177

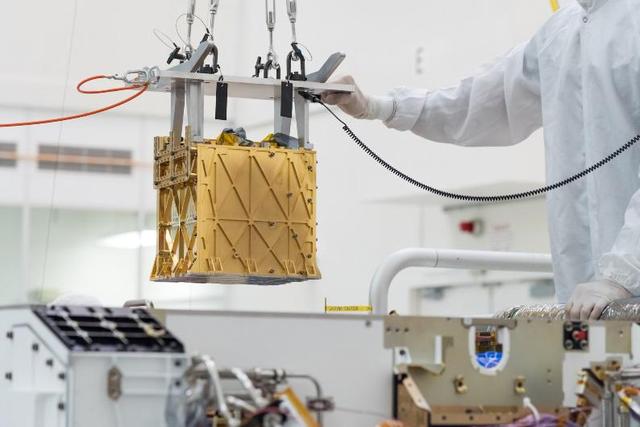
Engineers lower MOXIE (the Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment) into the belly of NASA's Perseverance rover. MOXIE is a technology demonstration designed to convert carbon dioxide in the Martian atmosphere into oxygen. In the distant future, astronauts could use technology like MOXIE for breathing and to generate industrial quantities of rocket propellant in order to launch themselves back to Earth. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24176
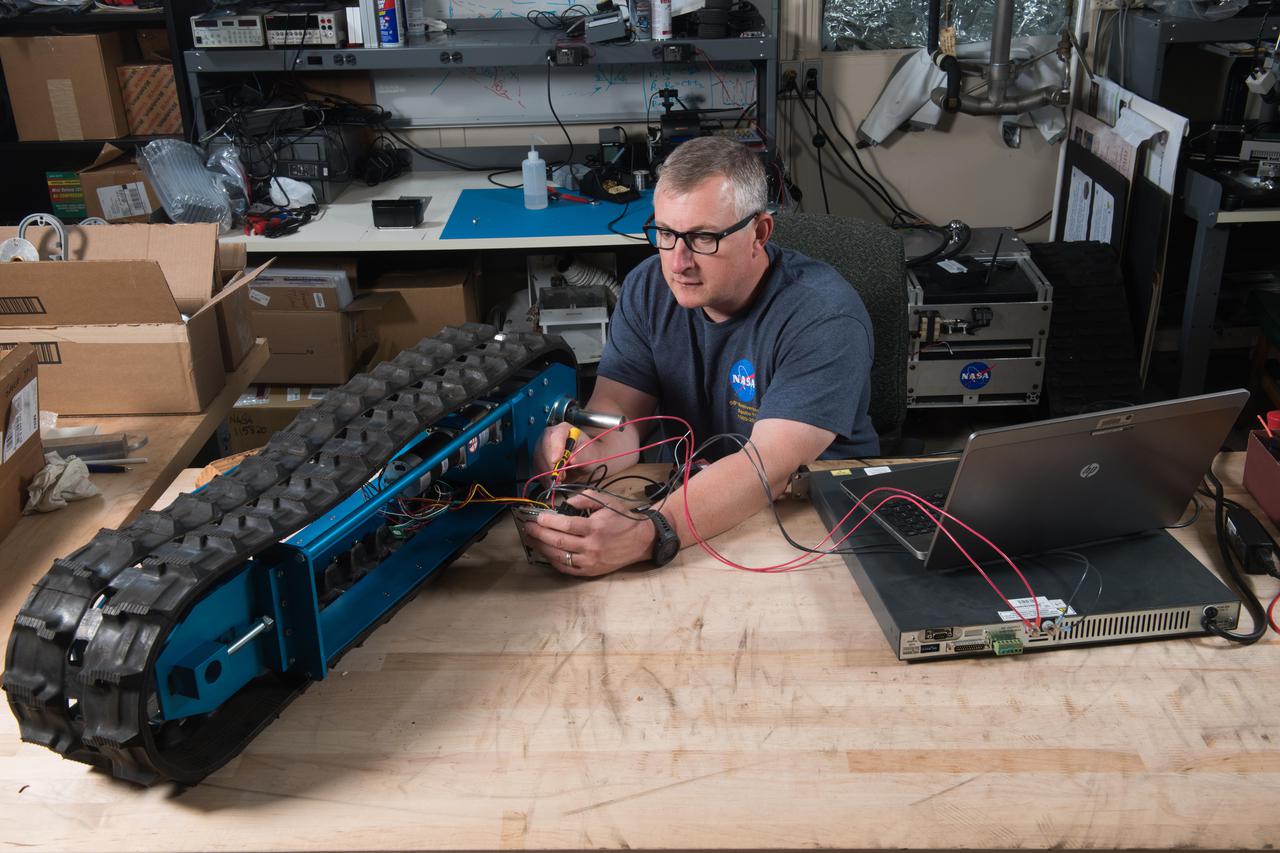
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
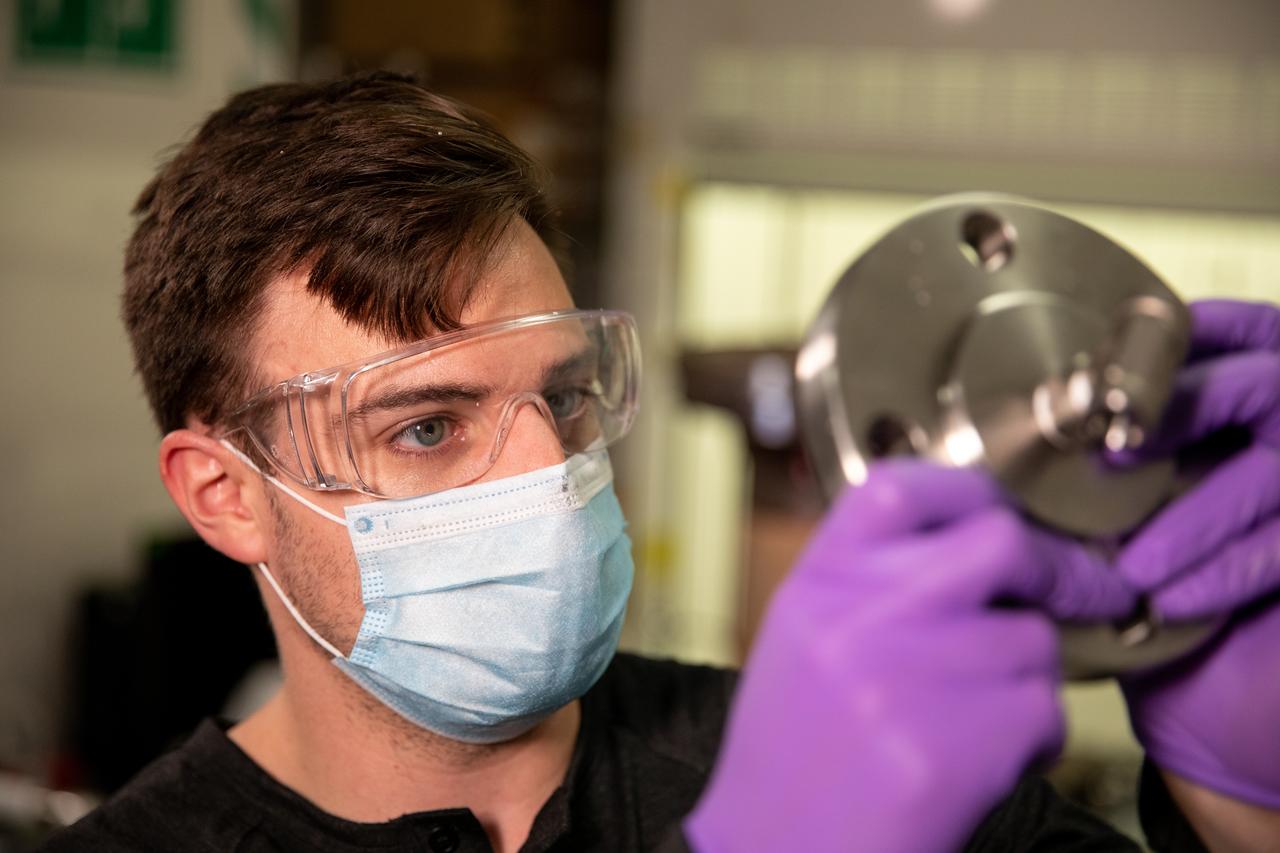

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
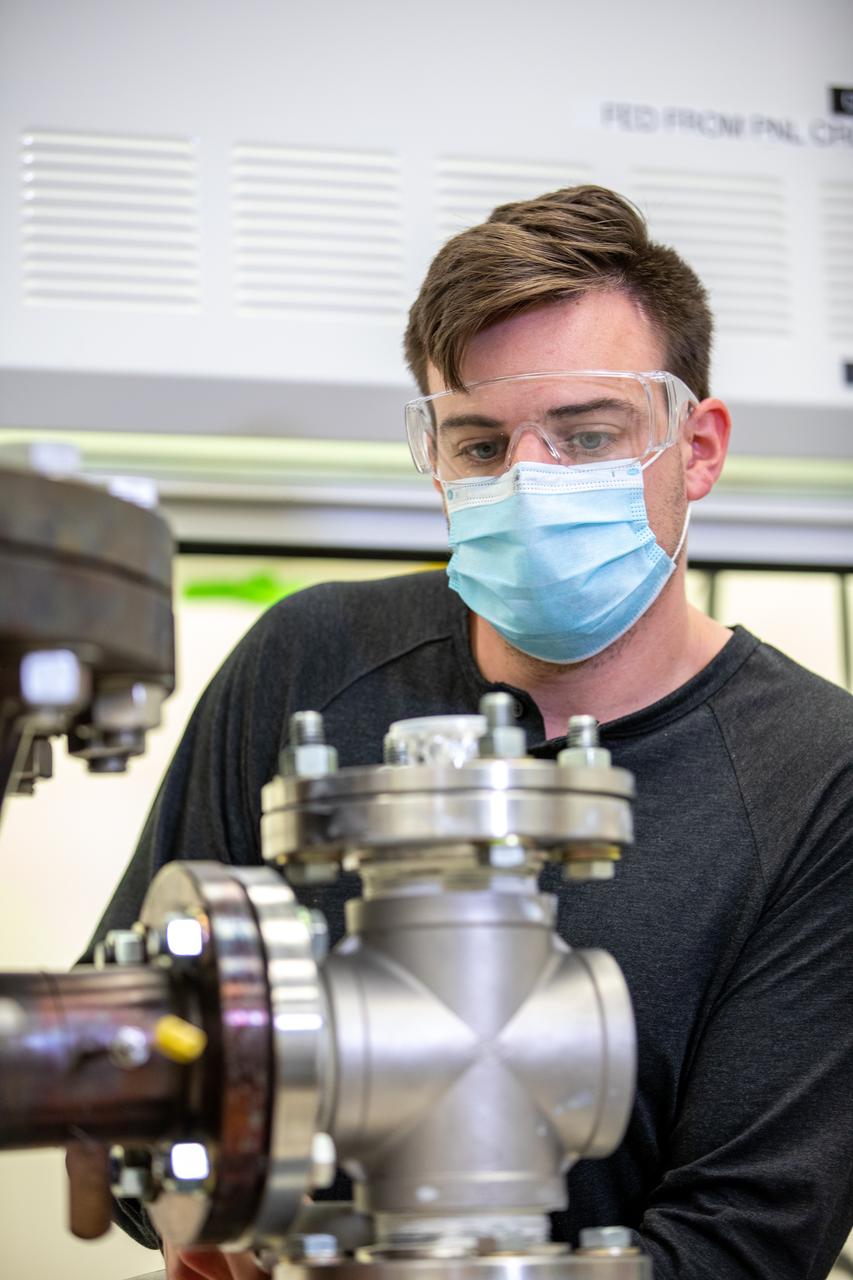

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
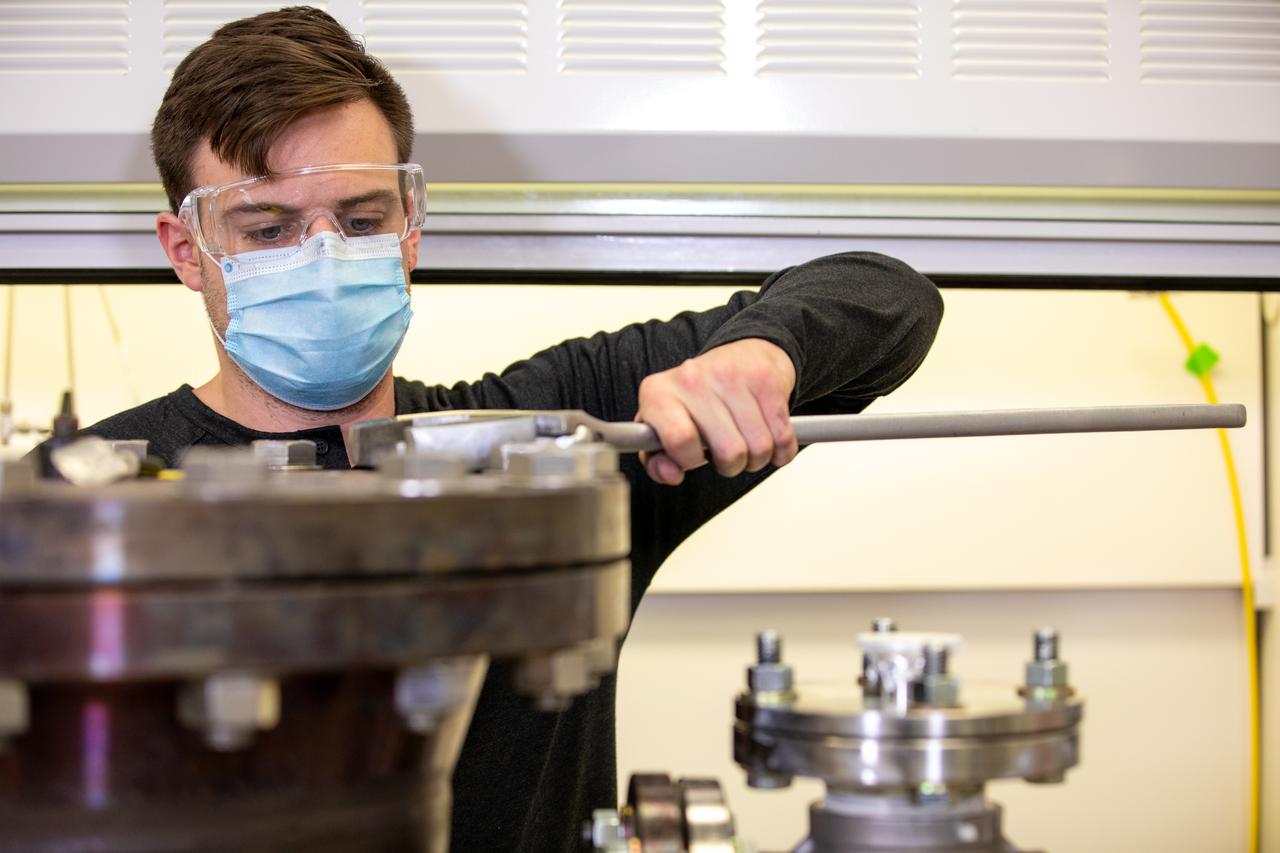

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
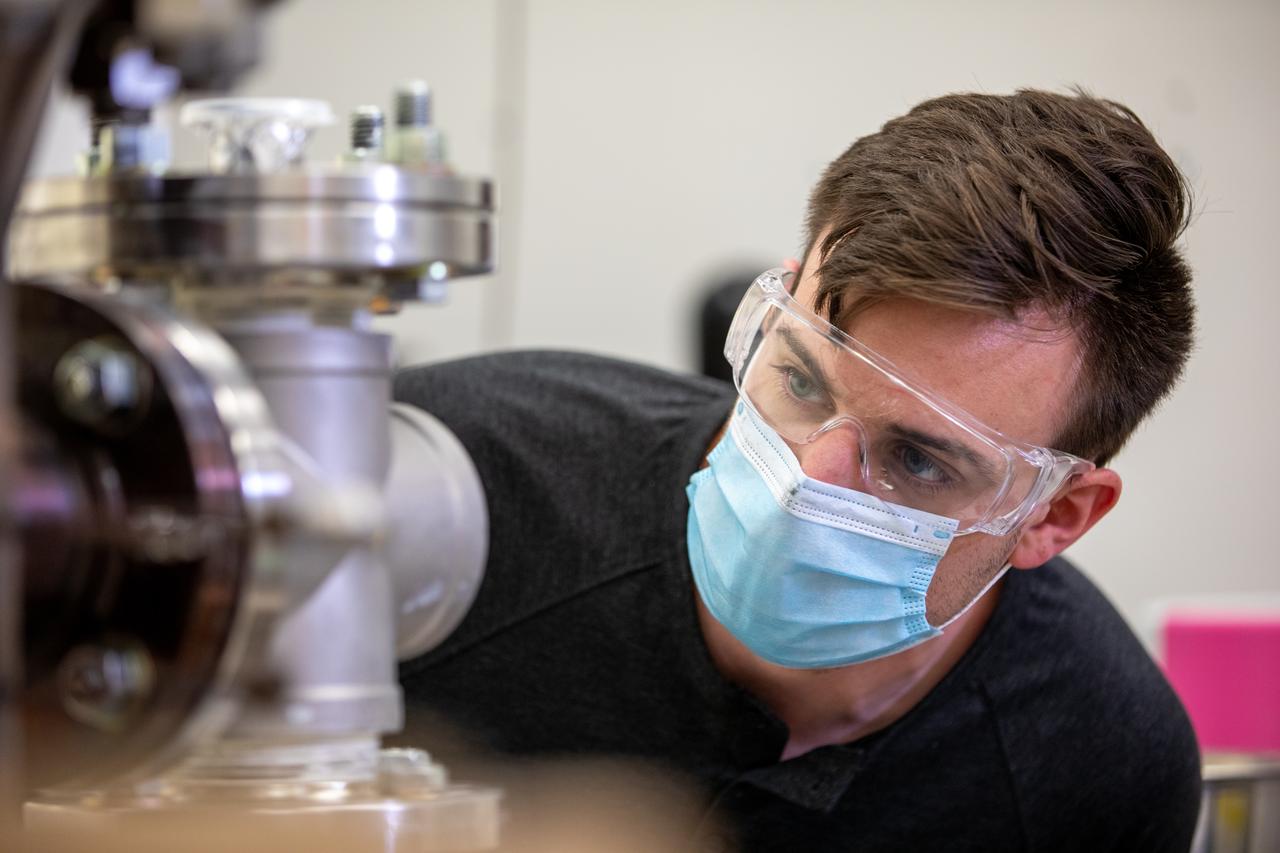

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
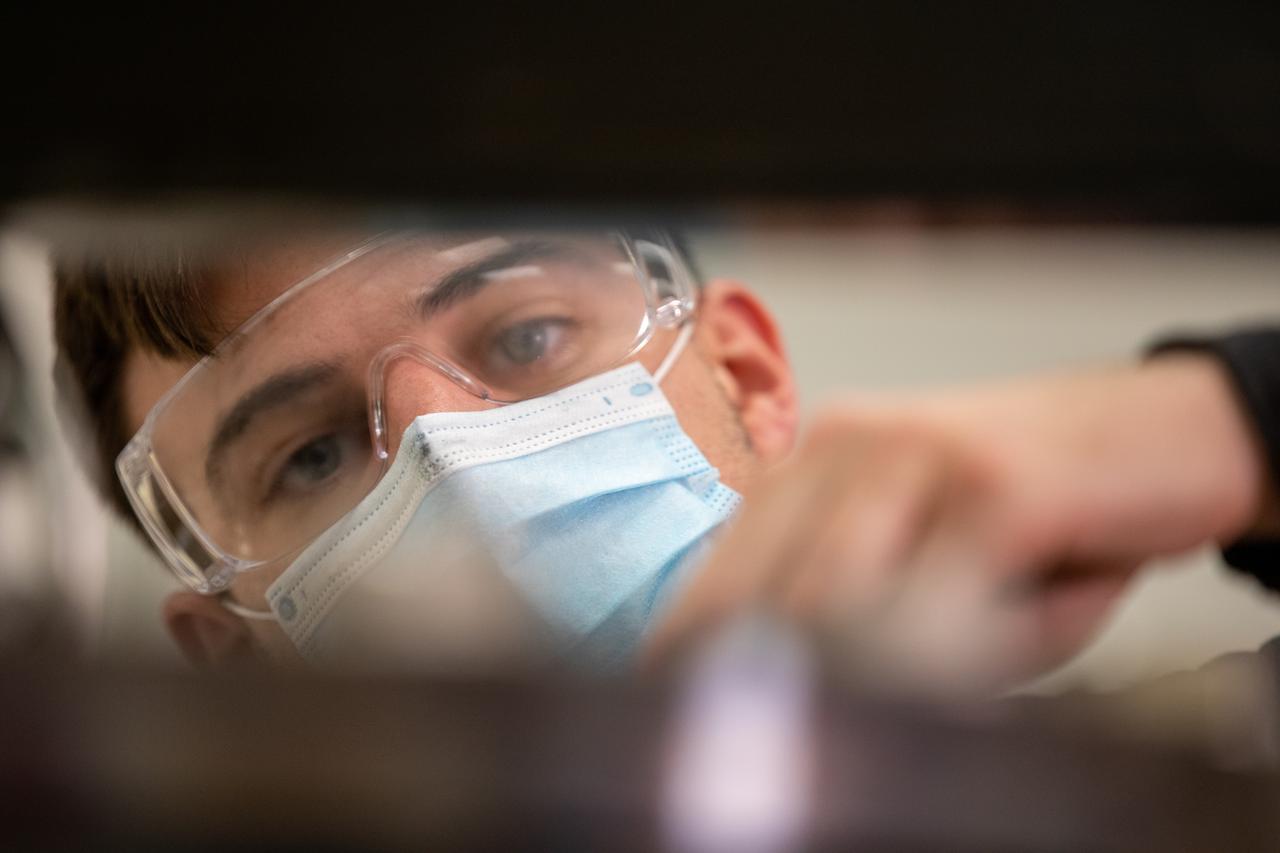

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, works on the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
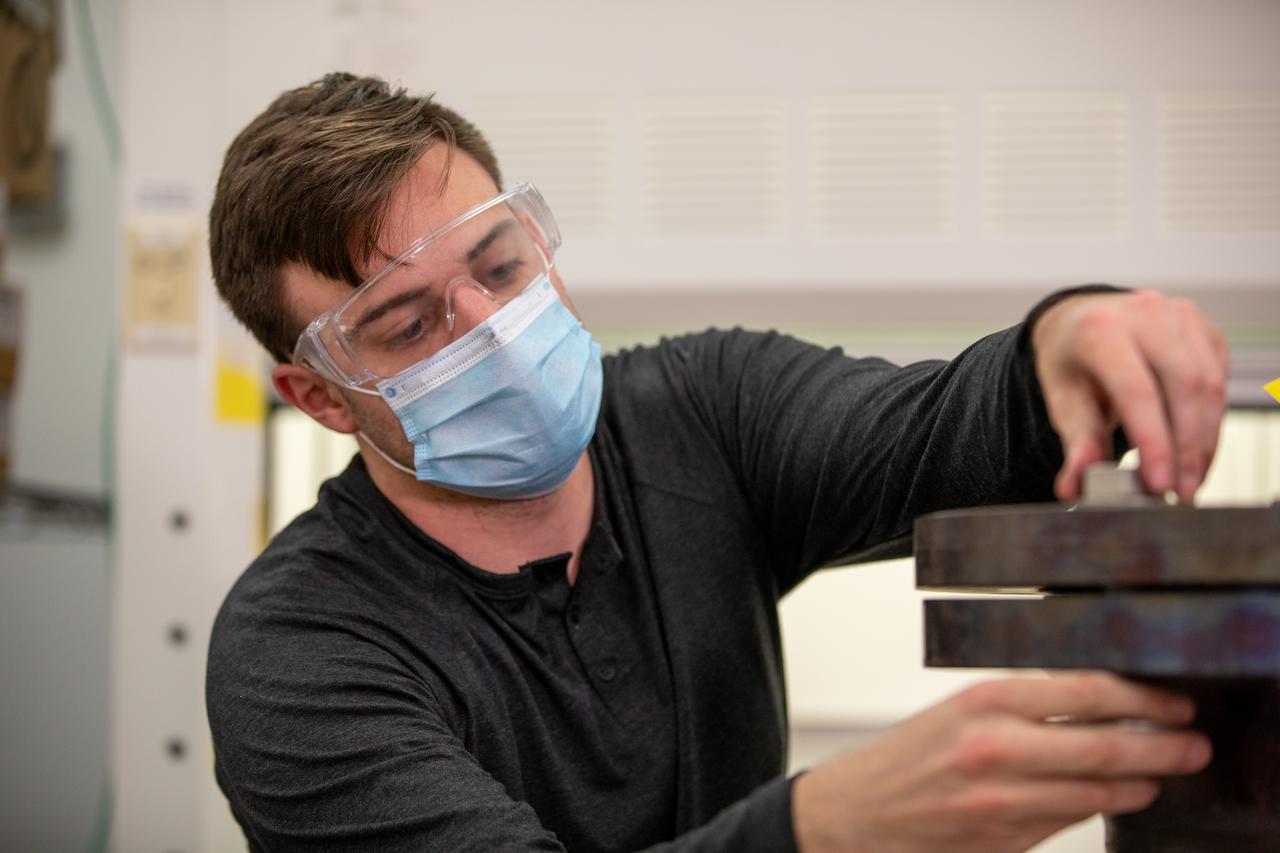

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
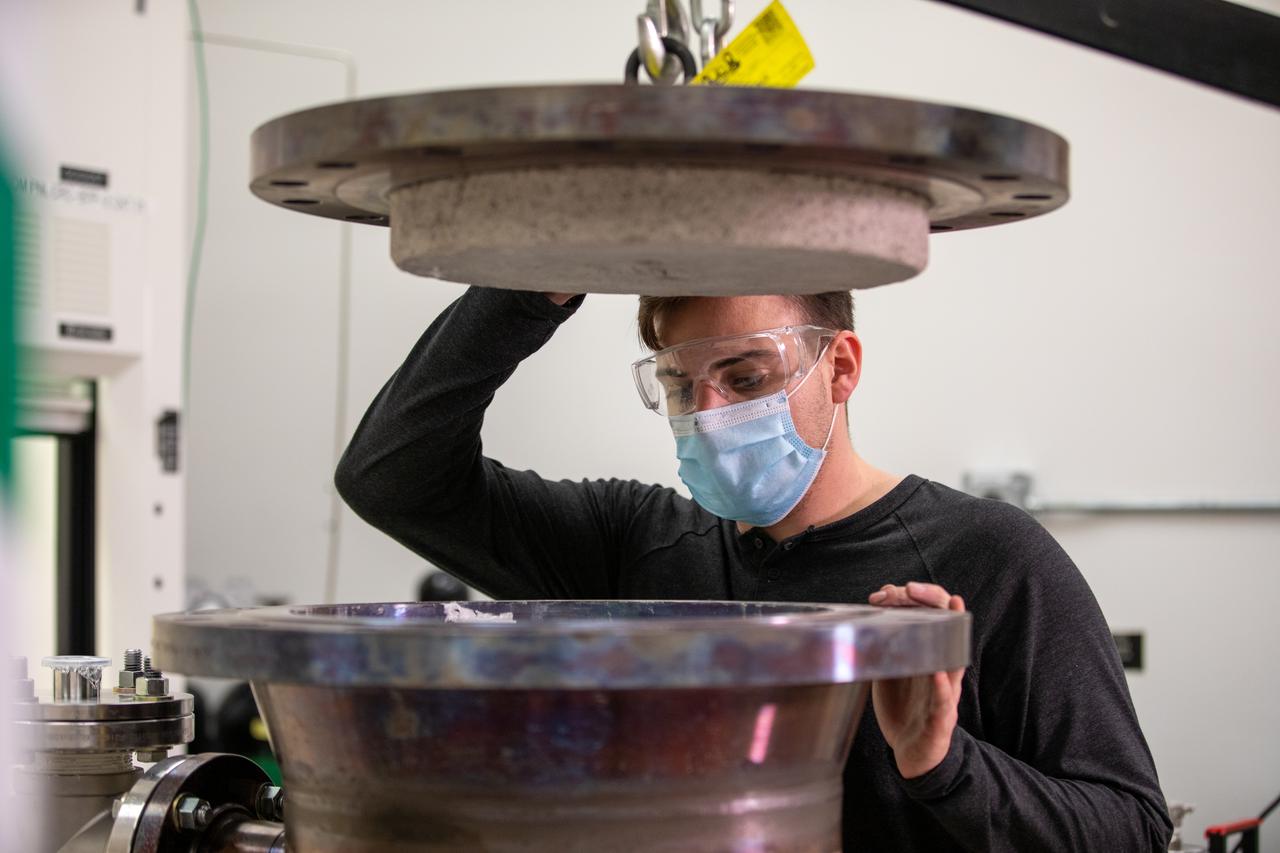

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, checks the hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
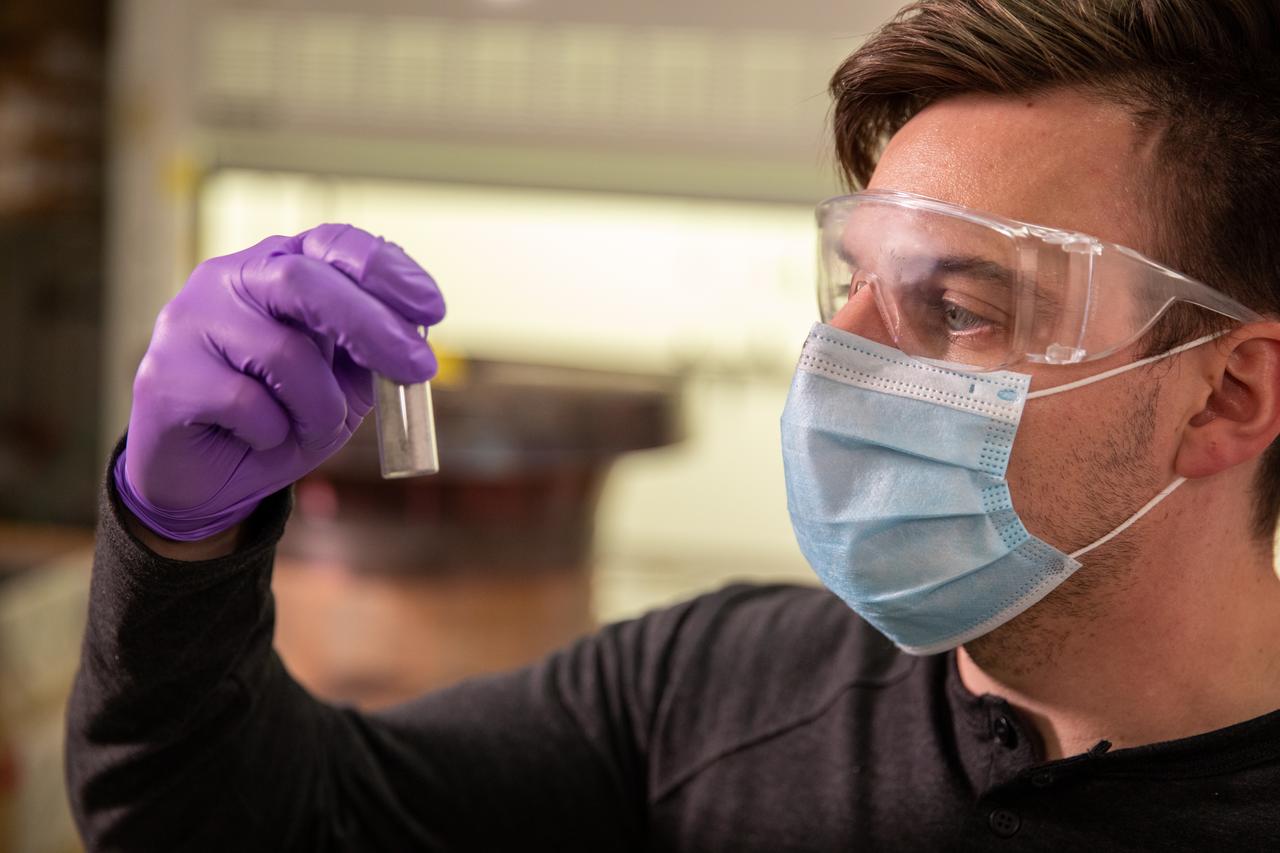

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
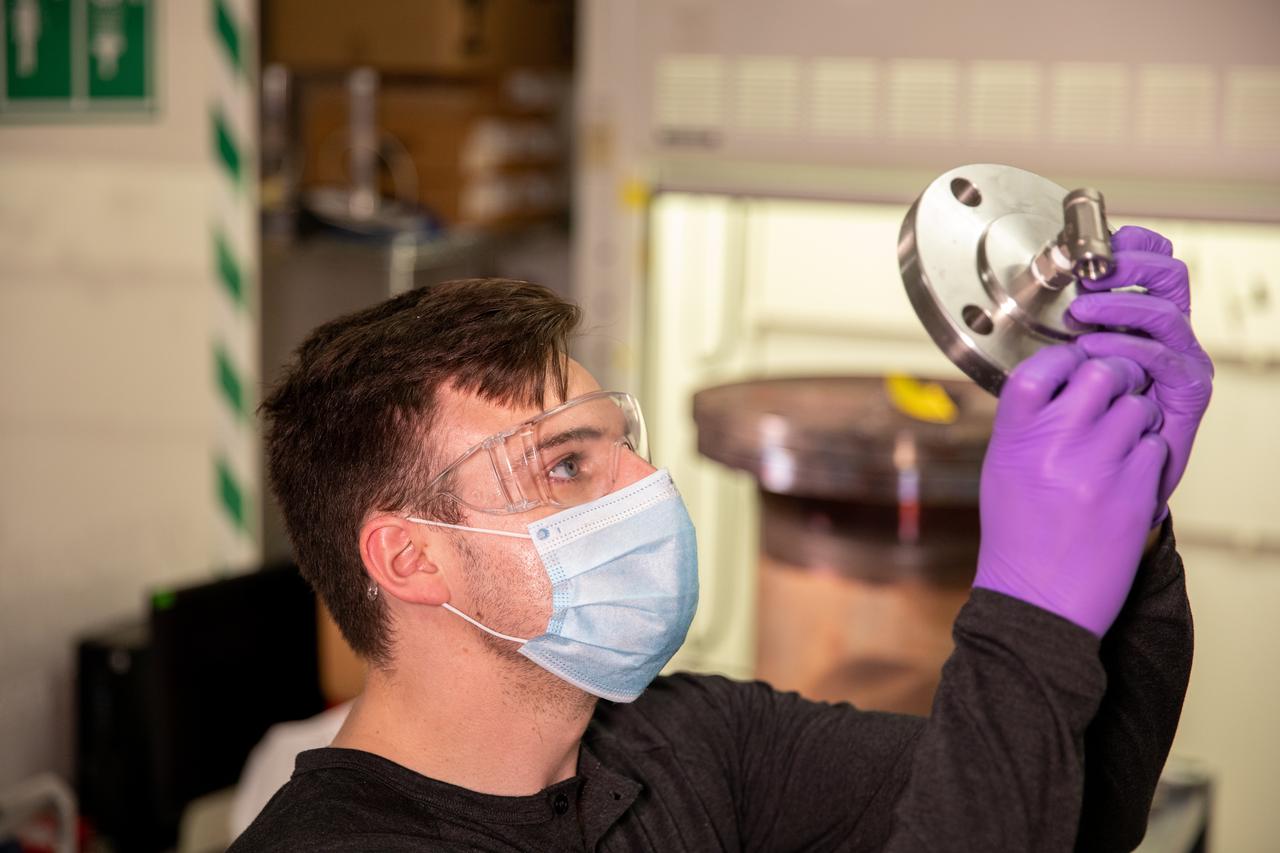

Kevin Grossman, project lead for the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Swamp Works, inspects a piece of hardware for GaLORE on July 21, 2020, inside a laboratory at the center’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. Grossman is leading an Early Career Initiative project that is investing in turning lunar regolith into oxygen that could be used for life support for sustainable human lunar exploration on long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by NASA’s Space Technology Mission directorate.

Office of the Chief Technologist, OCT Innovation Workshop, and Facility Tours

MOXIE (Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment) was launched aboard NASA's Perseverance rover to test a technology for extracting oxygen from the Red Planet's carbon dioxide-rich atmosphere. Audio of MOXIE's air compressor at work on Mars was captured by the microphone on Perseverance's SuperCam instrument on May 27, 2021, the 96th day of the rover's mission. Since Perseverance landed on Mars in 2021, MOXIE generated a total of 122 grams of oxygen – about what a small dog breathes in 10 hours. At its most efficient, MOXIE was able to produce 12 grams of oxygen an hour – twice as much as NASA's original goals for the instrument – at 98% purity or better. On its final, 16th run, on Aug. 7, 2023, the instrument made 9.8 grams of oxygen. MOXIE successfully completed all of its technical requirements and was operated at a variety of conditions throughout a full Mars year, allowing the instrument's developers to learn a great deal about the technology. MOXIE produces molecular oxygen through an electrochemical process that separates one oxygen atom from each molecule of carbon dioxide pumped in from Mars' thin atmosphere. As these gases flow through the system, they're analyzed to check the purity and quantity of oxygen produced. While many of Perseverance's experiments are addressing primary science goals, MOXIE was focused on future human exploration. MOXIE served as the first-ever demonstration of technology that humans could use to survive on, and leave, the Red Planet. An oxygen-producing system could help future missions in various ways, but the most important of them would be as a source of rocket propellant, which would be required in industrial quantities to launch rockets with astronauts for their return trip home. Rather than bringing large quantities of oxygen with them to Mars, future astronauts could live off the land, using materials they find on the planet's surface to survive. This concept – called in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU – has evolved into a growing area of research. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Audio file available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26041
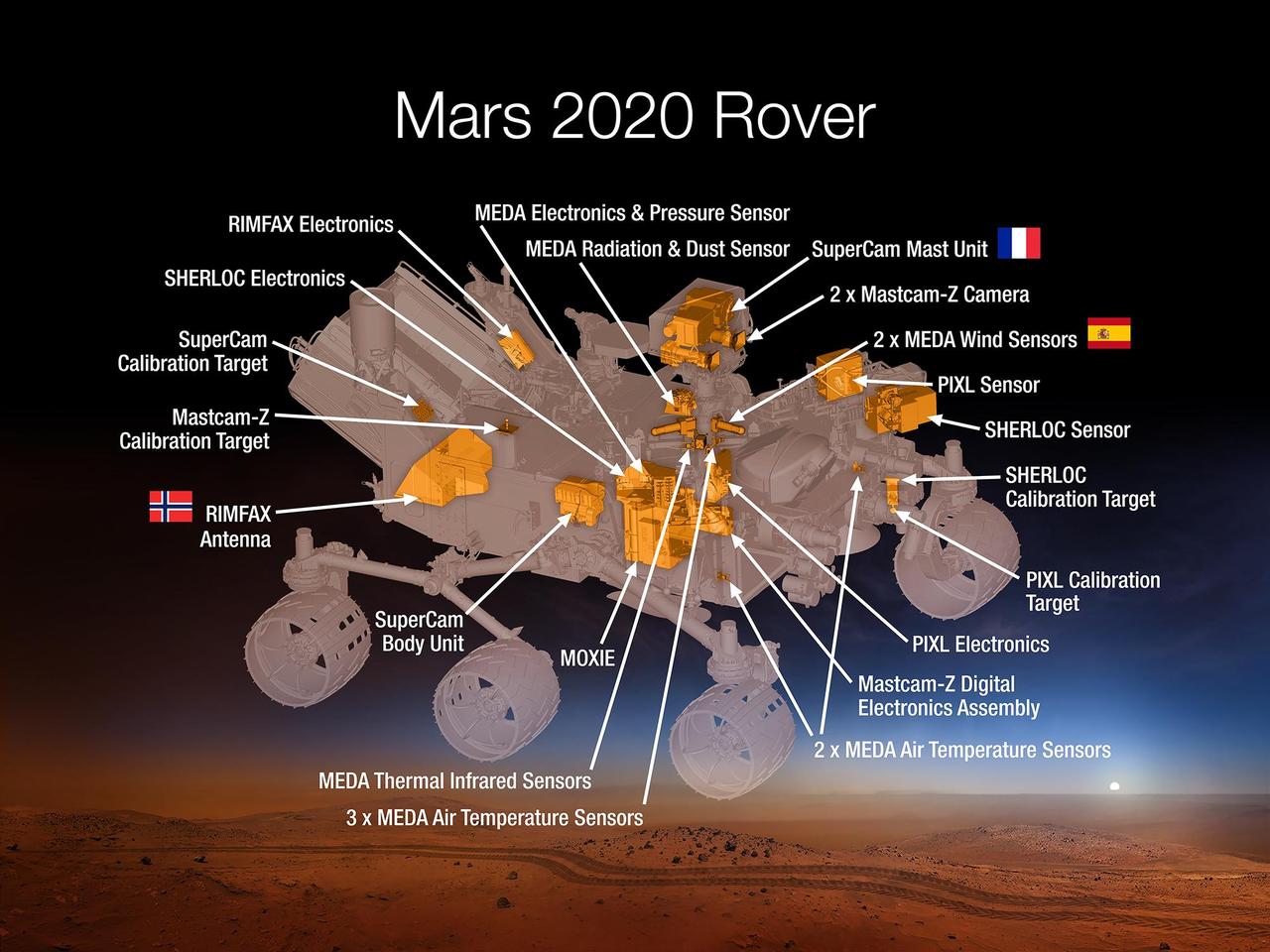
This 2015 diagram shows components of the investigations payload for NASA's Mars 2020 rover mission. Mars 2020 will re-use the basic engineering of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory to send a different rover to Mars, with new objectives and instruments, launching in 2020. The rover will carry seven instruments to conduct its science and exploration technology investigations. They are: Mastcam-Z, an advanced camera system with panoramic and stereoscopic imaging capability and the ability to zoom. The instrument also will determine mineralogy of the Martian surface and assist with rover operations. The principal investigator is James Bell, Arizona State University in Tempe. SuperCam, an instrument that can provide imaging, chemical composition analysis, and mineralogy. The instrument will also be able to detect the presence of organic compounds in rocks and regolith from a distance. The principal investigator is Roger Wiens, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico. This instrument also has a significant contribution from the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales, Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie (CNES/IRAP) France. Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry (PIXL), an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer that will also contain an imager with high resolution to determine the fine-scale elemental composition of Martian surface materials. PIXL will provide capabilities that permit more detailed detection and analysis of chemical elements than ever before. The principal investigator is Abigail Allwood, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California. Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics and Chemicals (SHERLOC), a spectrometer that will provide fine-scale imaging and uses an ultraviolet (UV) laser to determine fine-scale mineralogy and detect organic compounds. SHERLOC will be the first UV Raman spectrometer to fly to the surface of Mars and will provide complementary measurements with other instruments in the payload. SHERLOC includes a high-resolution color camera for microscopic imaging of Mars' surface. The principal investigator is Luther Beegle, JPL. The Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment (MOXIE), an exploration technology investigation that will produce oxygen from Martian atmospheric carbon dioxide. The principal investigator is Michael Hecht, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts. Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer (MEDA), a set of sensors that will provide measurements of temperature, wind speed and direction, pressure, relative humidity and dust size and shape. The principal investigator is Jose Rodriguez-Manfredi, Centro de Astrobiologia, Instituto Nacional de Tecnica Aeroespacial, Spain. The Radar Imager for Mars' Subsurface Experiment (RIMFAX), a ground-penetrating radar that will provide centimeter-scale resolution of the geologic structure of the subsurface. The principal investigator is Svein-Erik Hamran, the Norwegian Defence Research Establishment, Norway. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19672