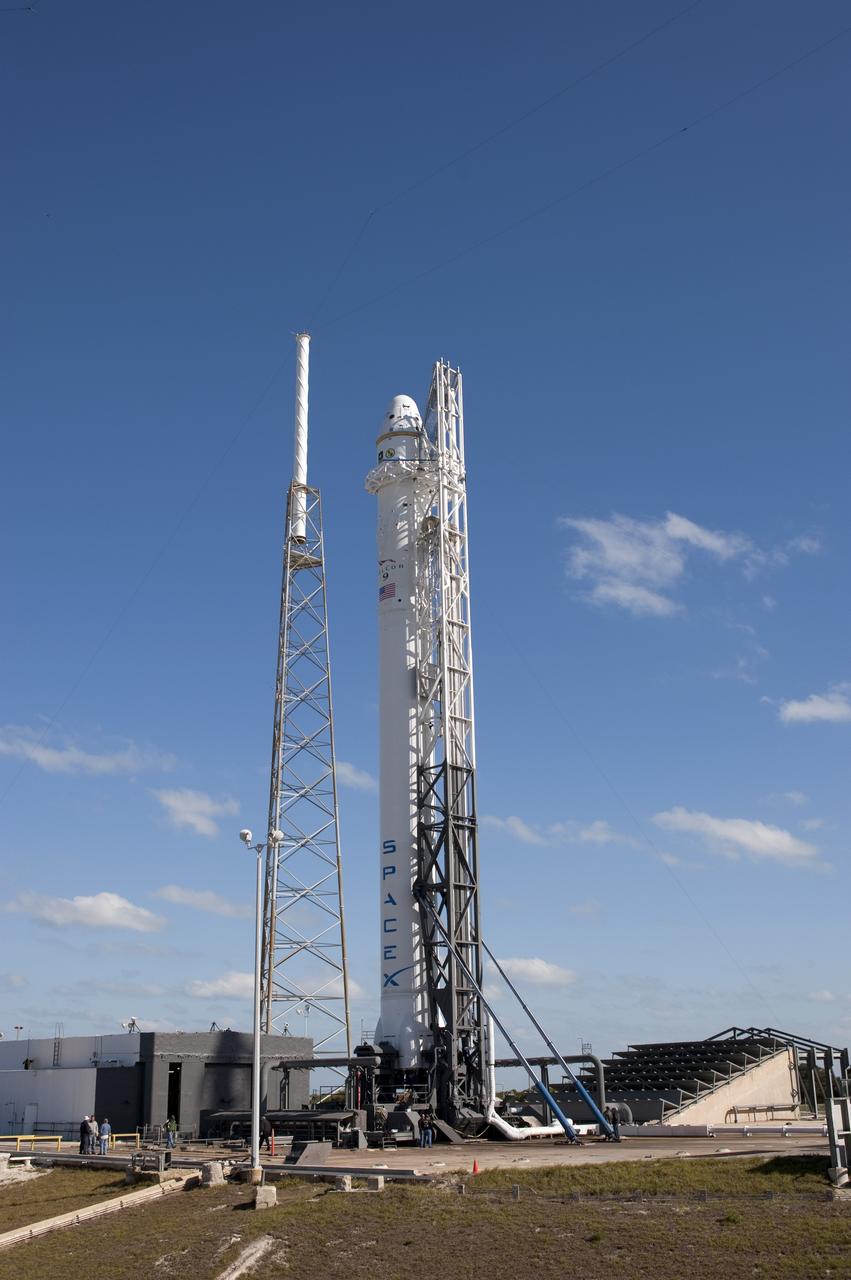

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket awaits a static fire test on Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, in which all nine Merlin engines will fire at once. The engines use rocket-grade kerosene and liquid oxygen to produce 1 million pounds of thrust. After the test, SpaceX will conduct a thorough review of all data as engineers make final preparations for the first launch of the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) Dragon spacecraft to low Earth orbit atop the Falcon 9. This first stage firing is part of a full launch dress rehearsal, which will end after the engines fire at full power for two seconds, with only the hold-down system restraining the rocket from flight. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Kevin O'Connell
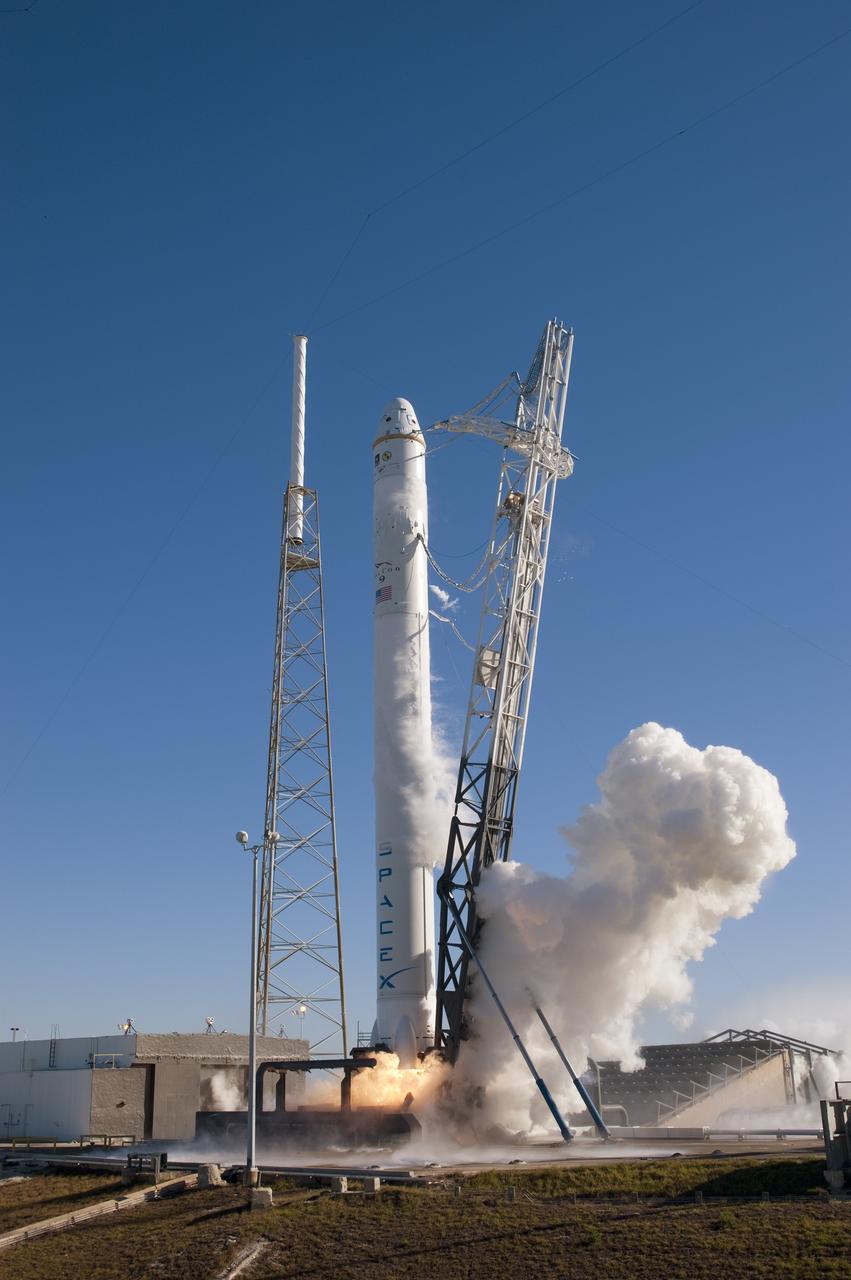

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a static fire test on Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, all nine Merlin engines of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket fire at once. The engines use rocket-grade kerosene and liquid oxygen to produce 1 million pounds of thrust. After the test, SpaceX began to conduct a thorough review of all data as engineers make final preparations for the first launch of the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) Dragon spacecraft to low Earth orbit atop the Falcon 9. This first stage firing is part of a full launch dress rehearsal, which ended after the engines fired at full power for two seconds, with only the hold-down system restraining the rocket from flight. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Kevin O'Connell
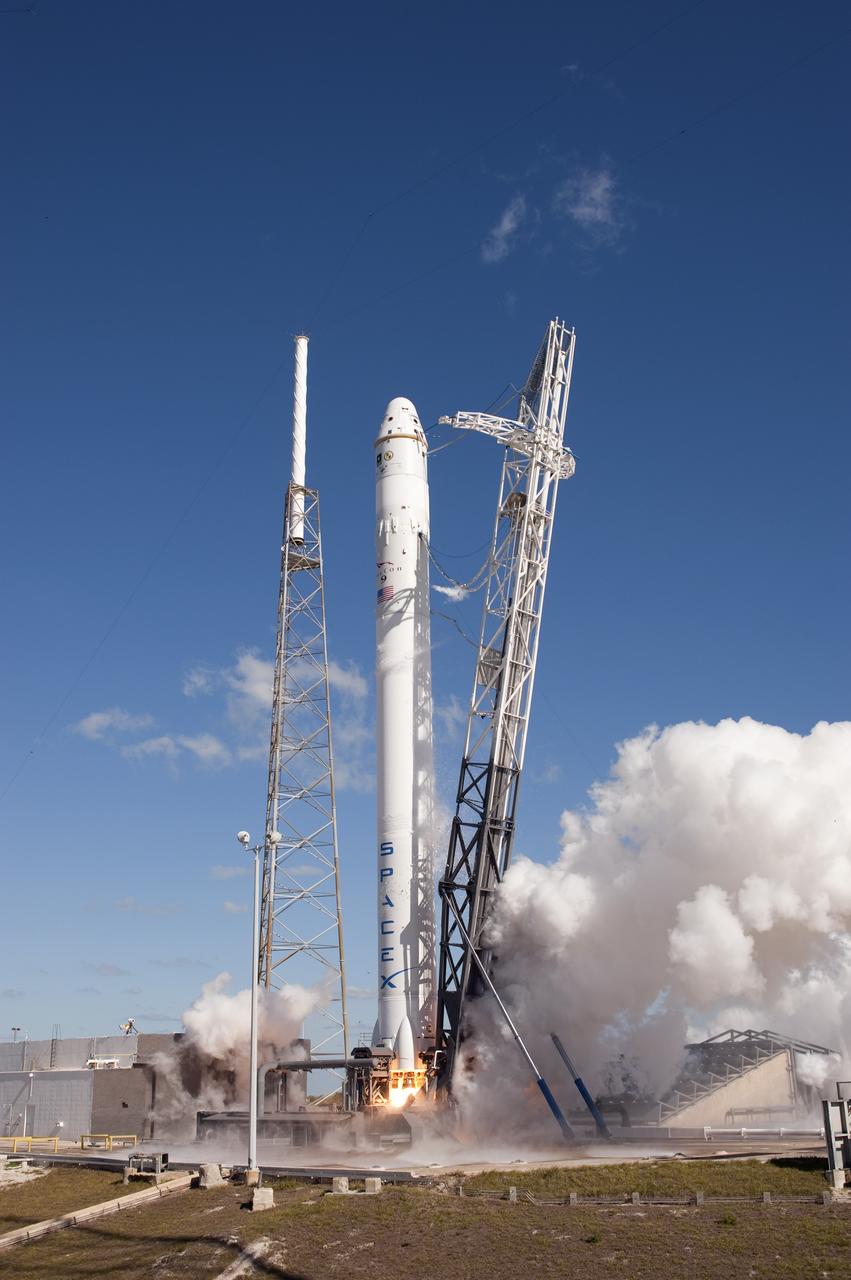

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket static fire test on Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was aborted at T minus 1.1 seconds due to high engine chamber pressure. During the test, all nine Merlin engines, which use rocket-grade kerosene and liquid oxygen to produce 1 million pounds of thrust, are expected to fire at once. After the test, SpaceX will conduct a thorough review of all data as engineers make final preparations for the first launch of the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) Dragon spacecraft to low Earth orbit atop the Falcon 9. This first stage firing is part of a full launch dress rehearsal, which will end after the engines fire at full power for two seconds, with only the hold-down system restraining the rocket from flight. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Kevin O'Connell
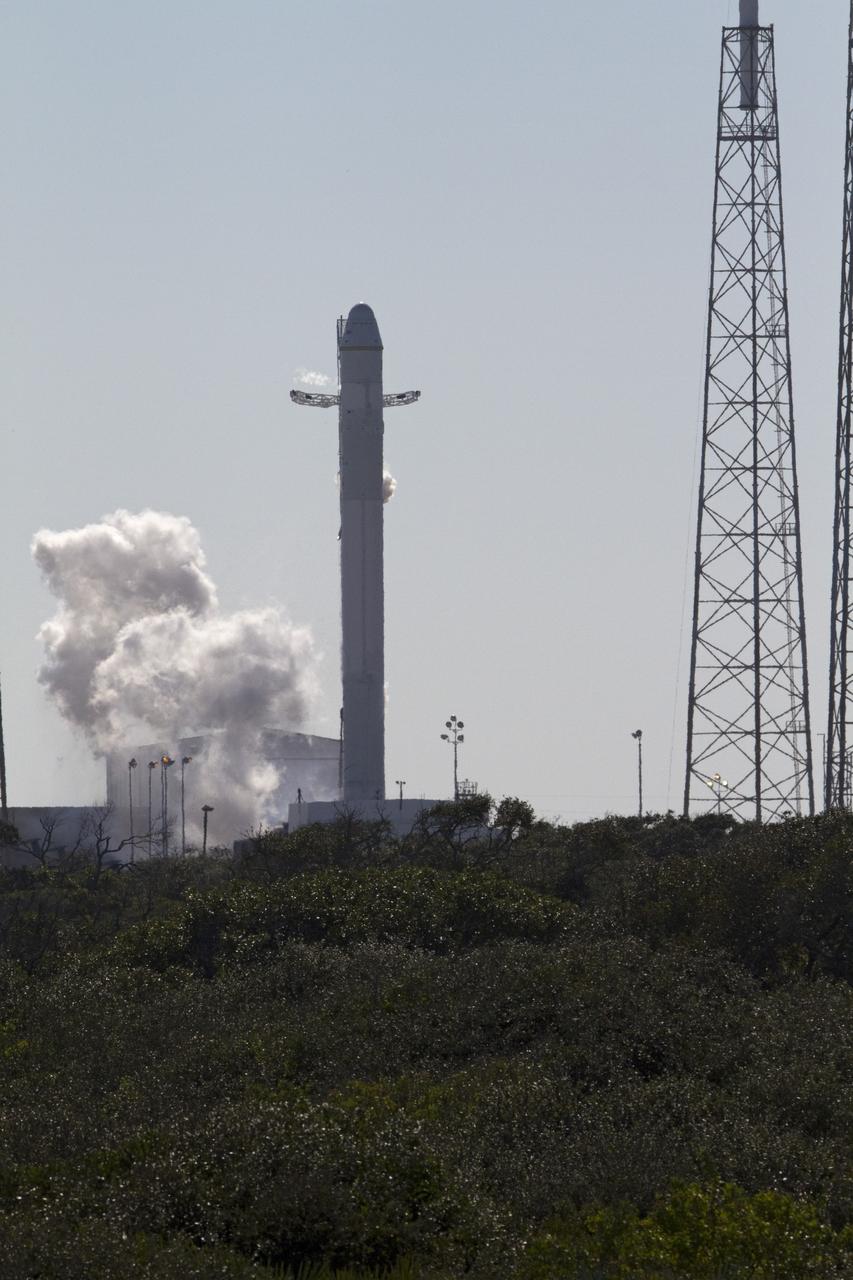

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket static fire test on Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was aborted at T minus 1.1 seconds due to high engine chamber pressure. During the test, all nine Merlin engines, which use rocket-grade kerosene and liquid oxygen to produce 1 million pounds of thrust, are expected to fire at once. After the test, SpaceX will conduct a thorough review of all data as engineers make final preparations for the first launch of the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) Dragon spacecraft to low Earth orbit atop the Falcon 9. This first stage firing is part of a full launch dress rehearsal, which will end after the engines fire at full power for two seconds, with only the hold-down system restraining the rocket from flight. Photo credit: NASA/Rusty Backer
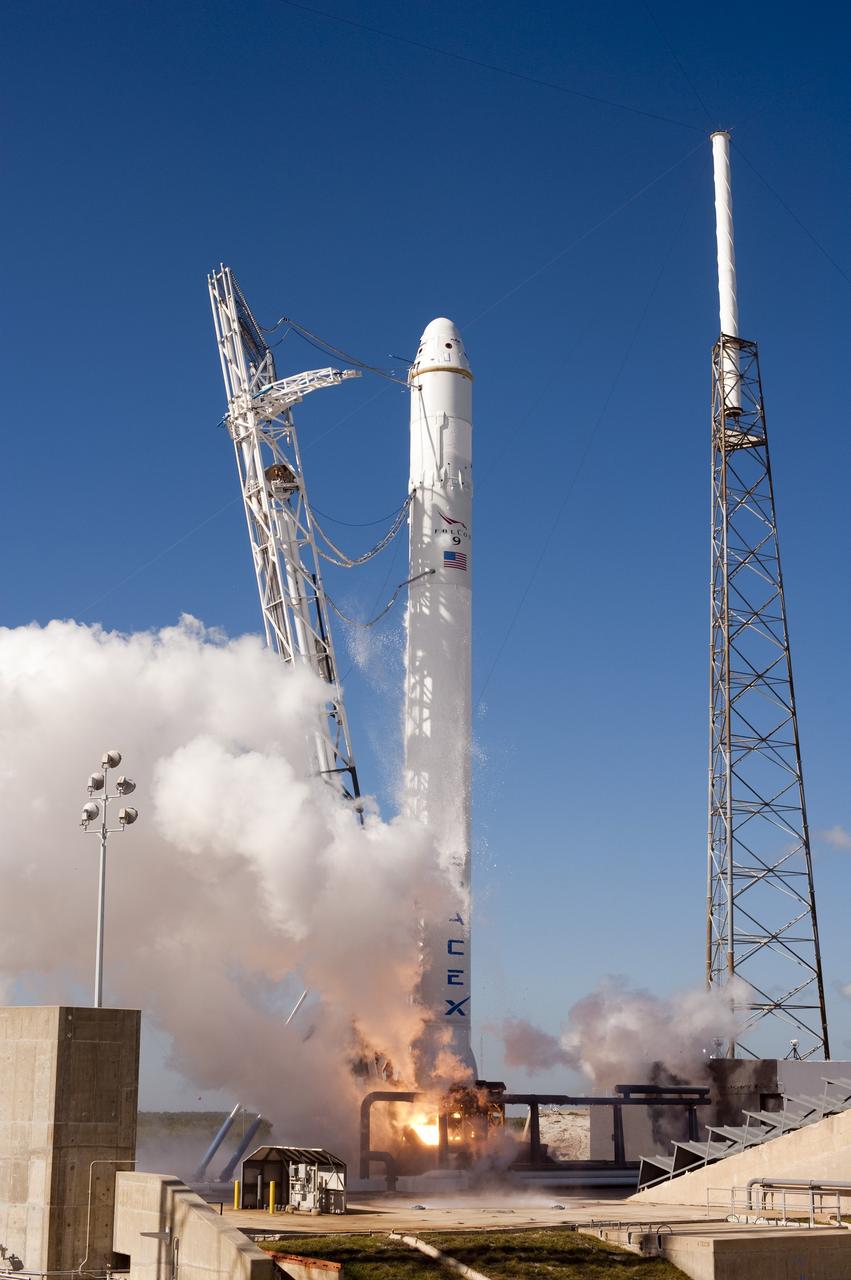

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket static fire test on Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was aborted at T minus 1.1 seconds due to high engine chamber pressure. During the test, all nine Merlin engines, which use rocket-grade kerosene and liquid oxygen to produce 1 million pounds of thrust, are expected to fire at once. After the test, SpaceX will conduct a thorough review of all data as engineers make final preparations for the first launch of the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) Dragon spacecraft to low Earth orbit atop the Falcon 9. This first stage firing is part of a full launch dress rehearsal, which will end after the engines fire at full power for two seconds, with only the hold-down system restraining the rocket from flight. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Kevin O'Connell
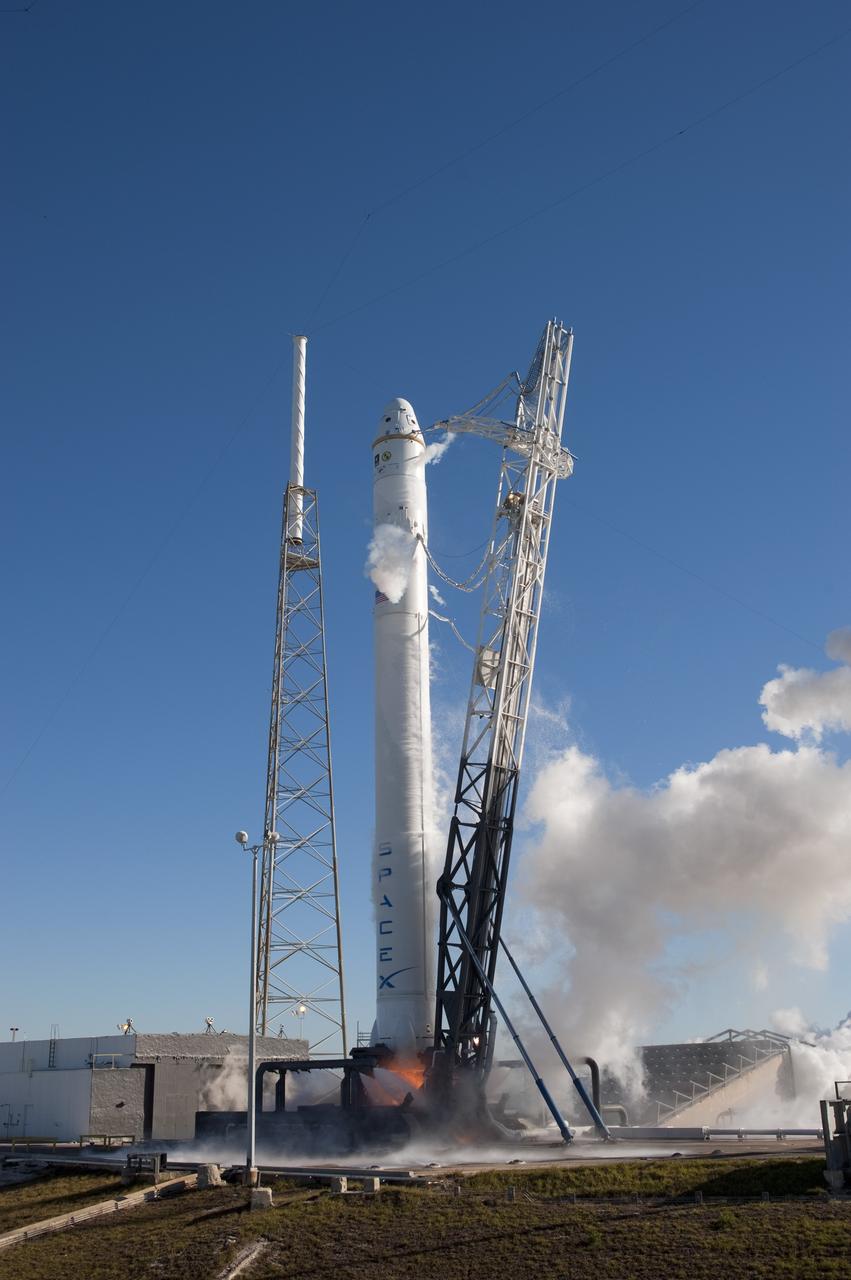

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a static fire test on Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, all nine Merlin engines of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket fire at once. The engines use rocket-grade kerosene and liquid oxygen to produce 1 million pounds of thrust. After the test, SpaceX began to conduct a thorough review of all data as engineers make final preparations for the first launch of the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) Dragon spacecraft to low Earth orbit atop the Falcon 9. This first stage firing is part of a full launch dress rehearsal, which ended after the engines fired at full power for two seconds, with only the hold-down system restraining the rocket from flight. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Kevin O'Connell
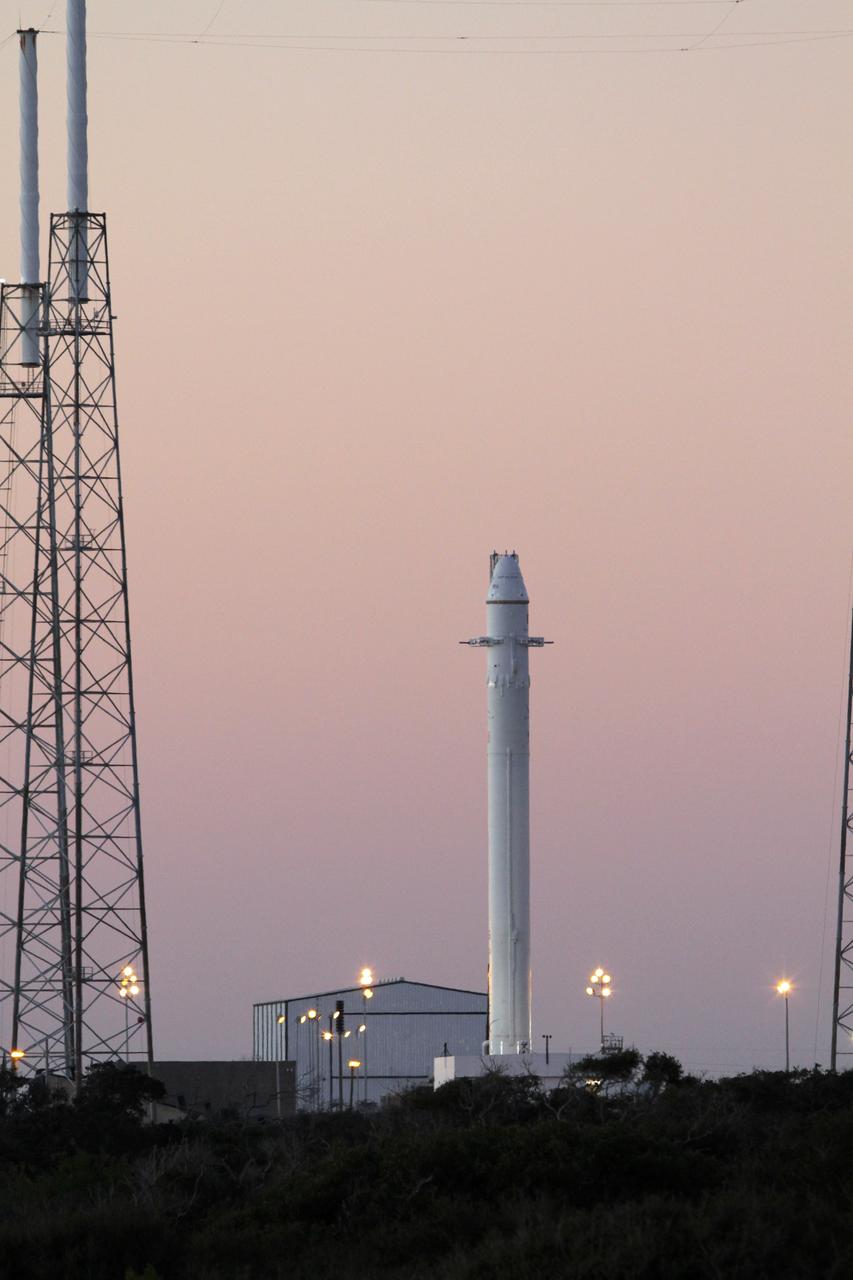

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket awaits a static fire test on Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, in which all nine Merlin engines will fire at once. The engines use rocket-grade kerosene and liquid oxygen to produce 1 million pounds of thrust. After the test, SpaceX will conduct a thorough review of all data as engineers make final preparations for the first launch of the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) Dragon spacecraft to low Earth orbit atop the Falcon 9. This first stage firing is part of a full launch dress rehearsal, which will end after the engines fire at full power for two seconds, with only the hold-down system restraining the rocket from flight. Photo credit: NASA/Rusty Backer
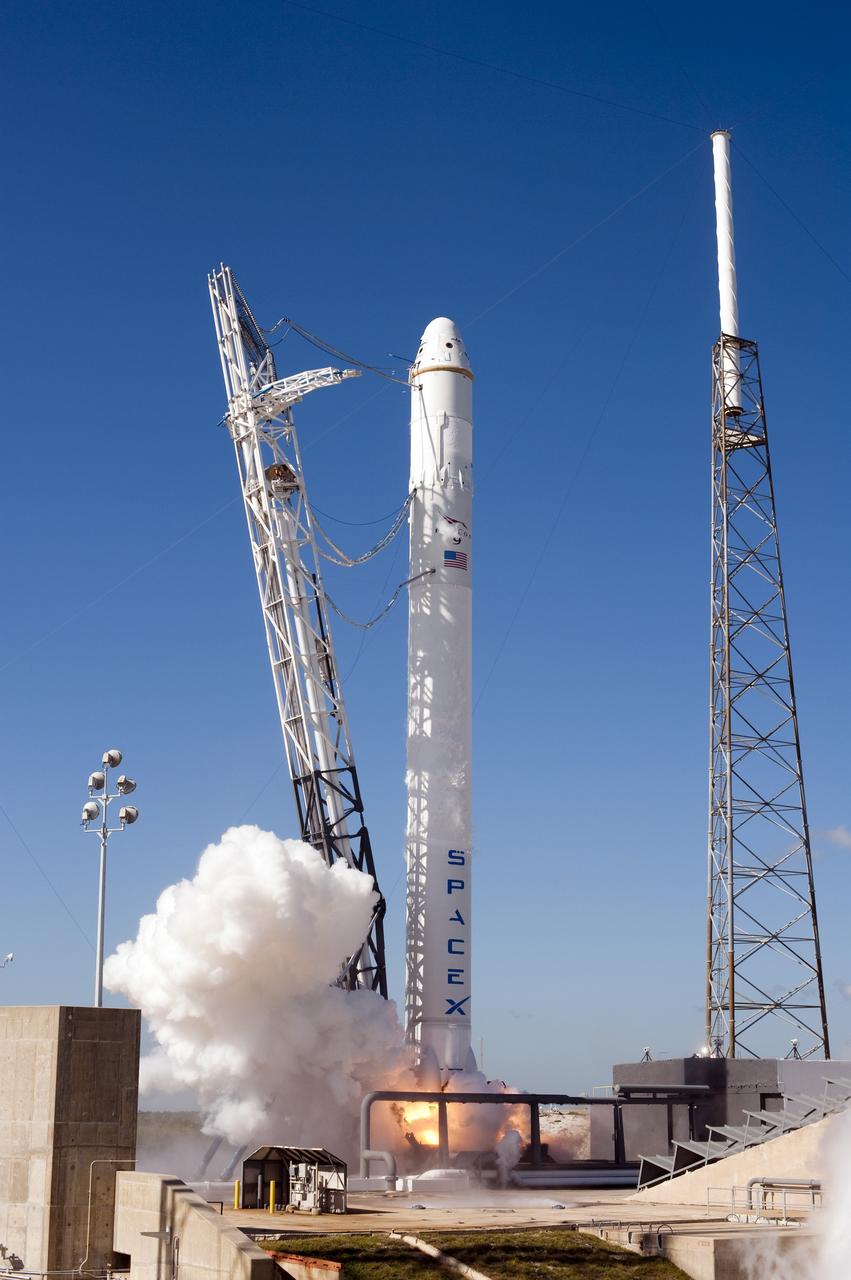

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket static fire test on Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station was aborted at T minus 1.1 seconds due to high engine chamber pressure. During the test, all nine Merlin engines, which use rocket-grade kerosene and liquid oxygen to produce 1 million pounds of thrust, are expected to fire at once. After the test, SpaceX will conduct a thorough review of all data as engineers make final preparations for the first launch of the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) Dragon spacecraft to low Earth orbit atop the Falcon 9. This first stage firing is part of a full launch dress rehearsal, which will end after the engines fire at full power for two seconds, with only the hold-down system restraining the rocket from flight. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Kevin O'Connell
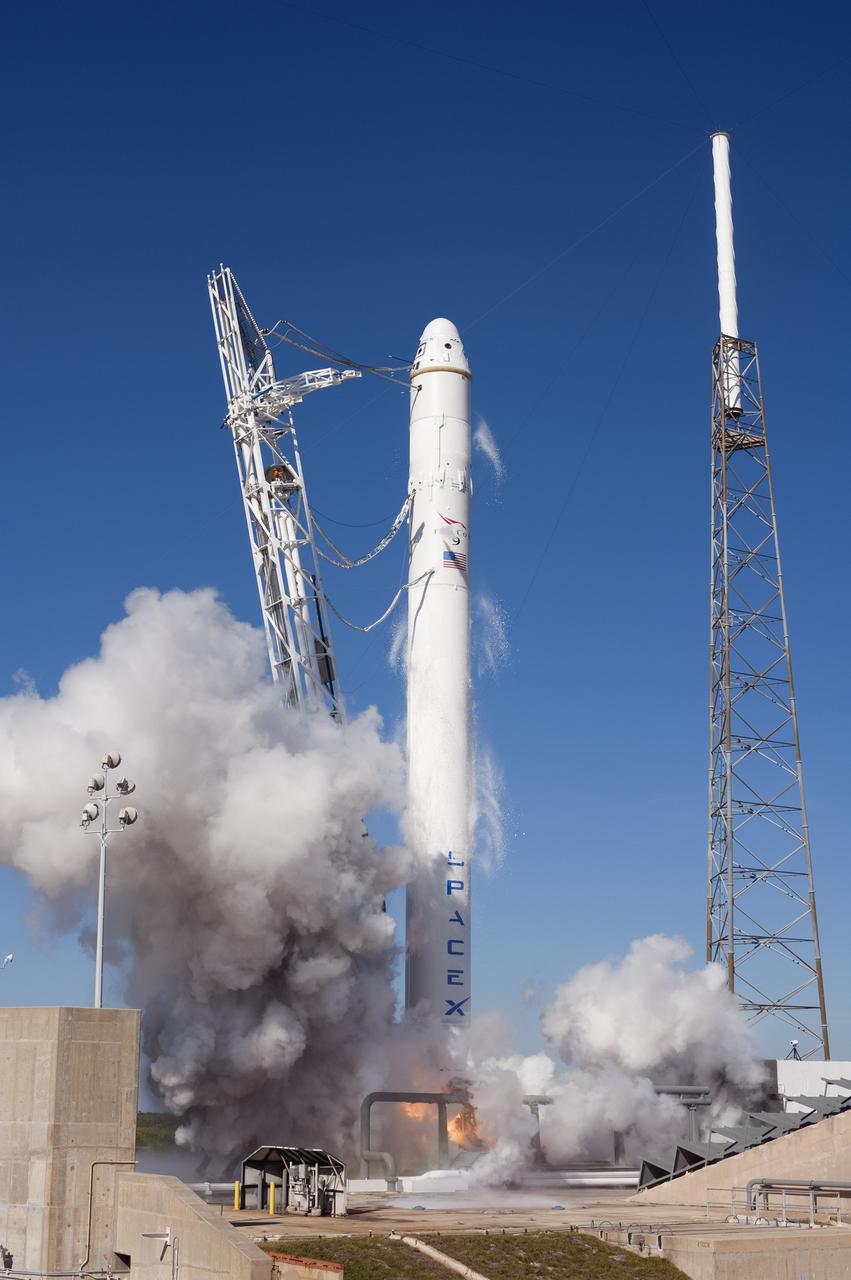

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a static fire test on Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, all nine Merlin engines of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket fire at once. The engines use rocket-grade kerosene and liquid oxygen to produce 1 million pounds of thrust. After the test, SpaceX began to conduct a thorough review of all data as engineers make final preparations for the first launch of the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) Dragon spacecraft to low Earth orbit atop the Falcon 9. This first stage firing is part of a full launch dress rehearsal, which ended after the engines fired at full power for two seconds, with only the hold-down system restraining the rocket from flight. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Kevin O'Connell
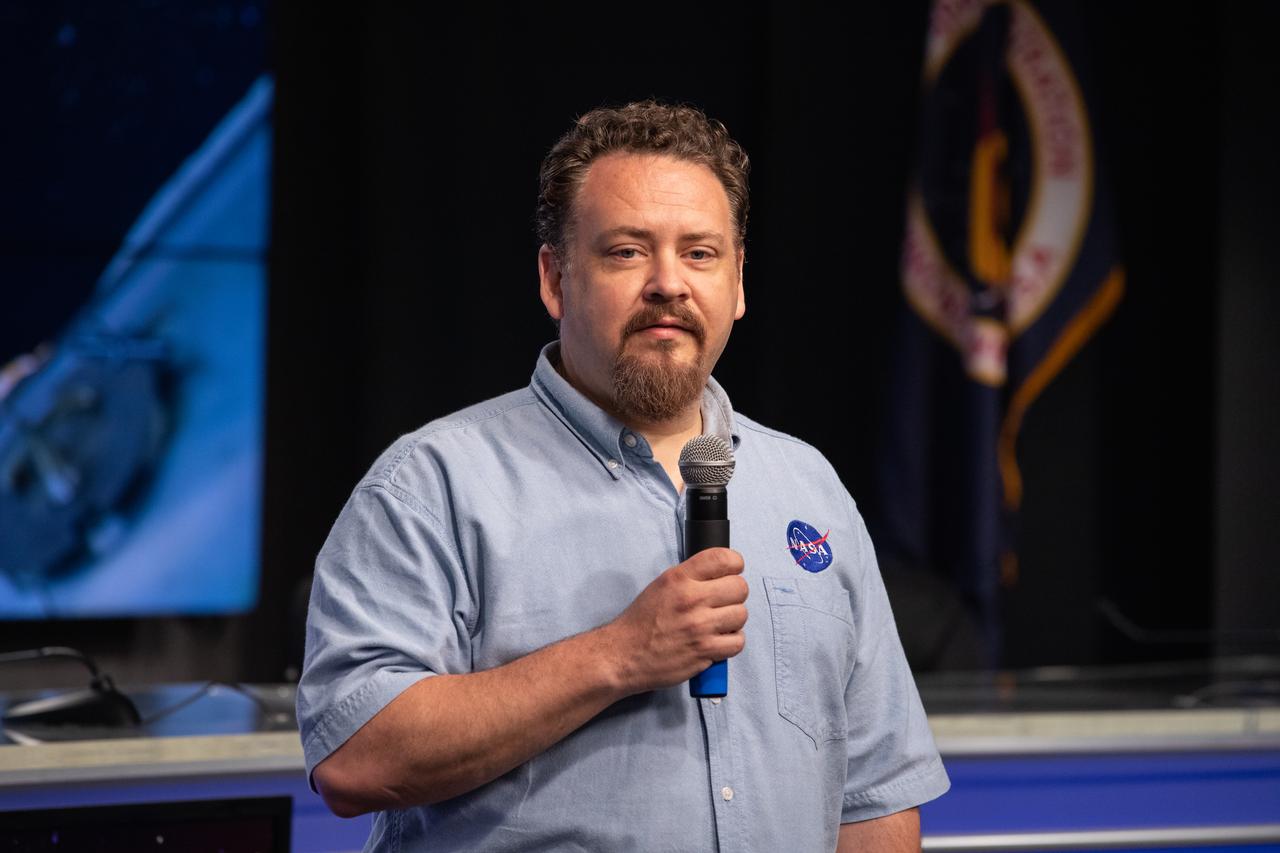

Dr. Kirt Costello, chief scientist for the ISS Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
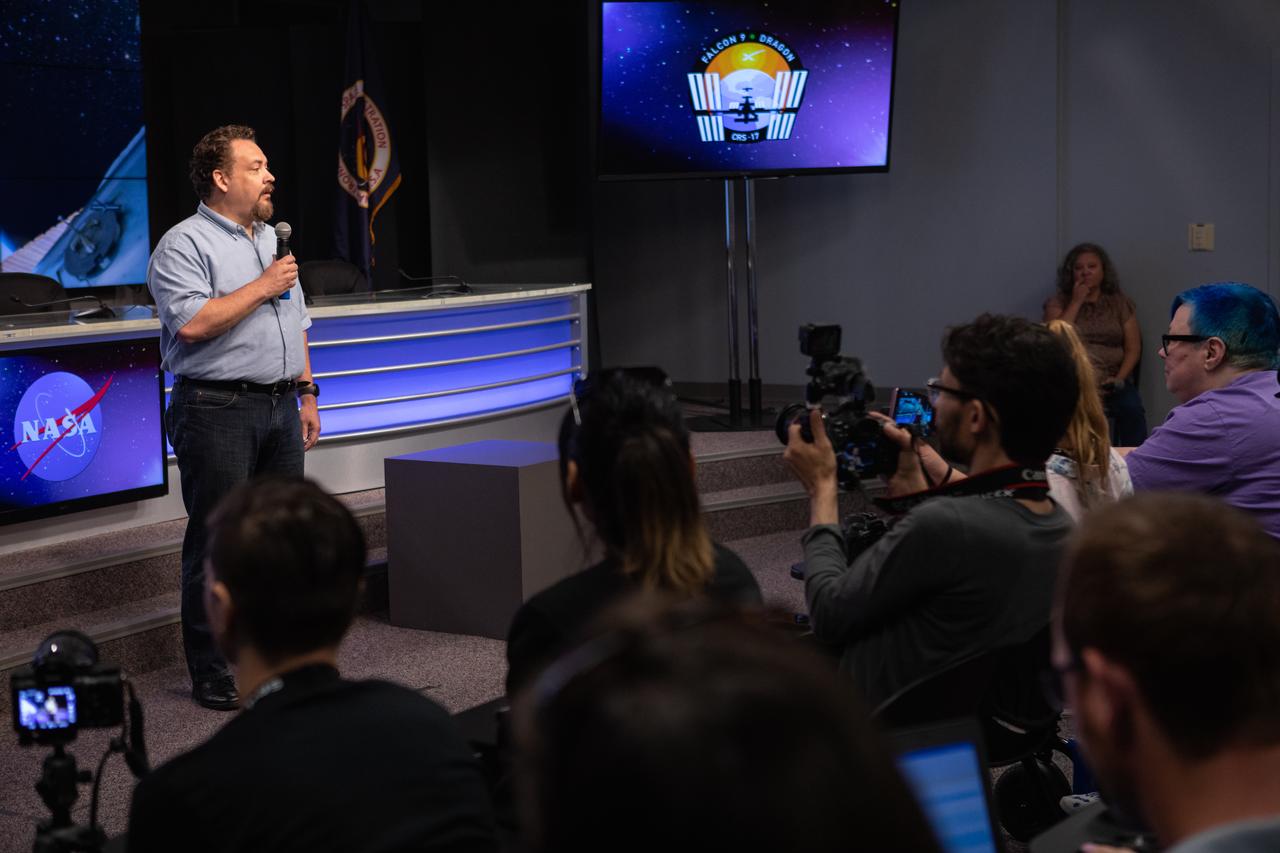

Dr. Kirt Costello, chief scientist for the ISS Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
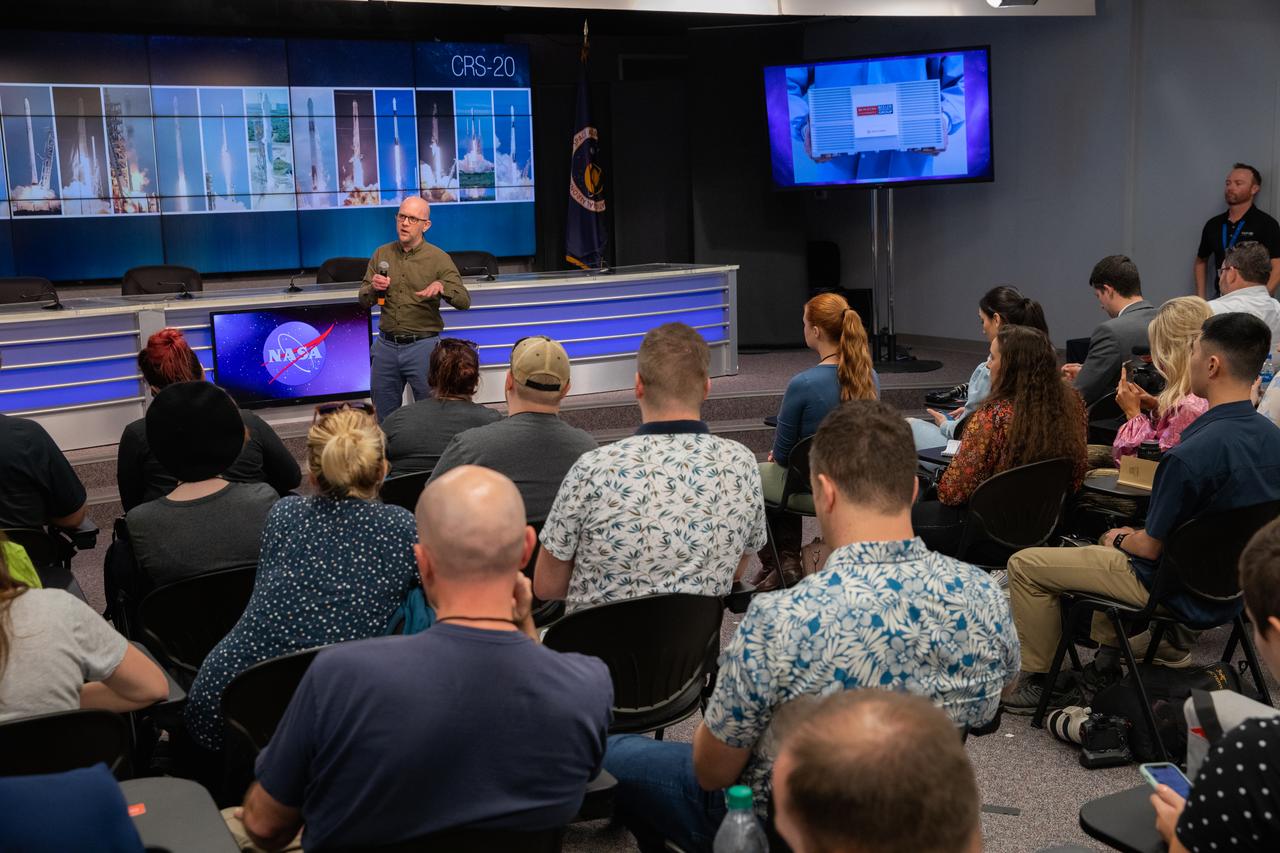

Aaron Beeler, professor of chemistry at Boston University and principal investigator of the Flow Chemistry Platform for Synthetic Reactions on ISS study, addresses NASA Social participants during a What’s on Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 5, 2020. The briefing provided a closer look at some of the payloads launching on SpaceX’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission to the International Space Station. The company’s Falcon 9 rocket is scheduled to lift off from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40 at 11:50 p.m. EST on March 6, 2020.
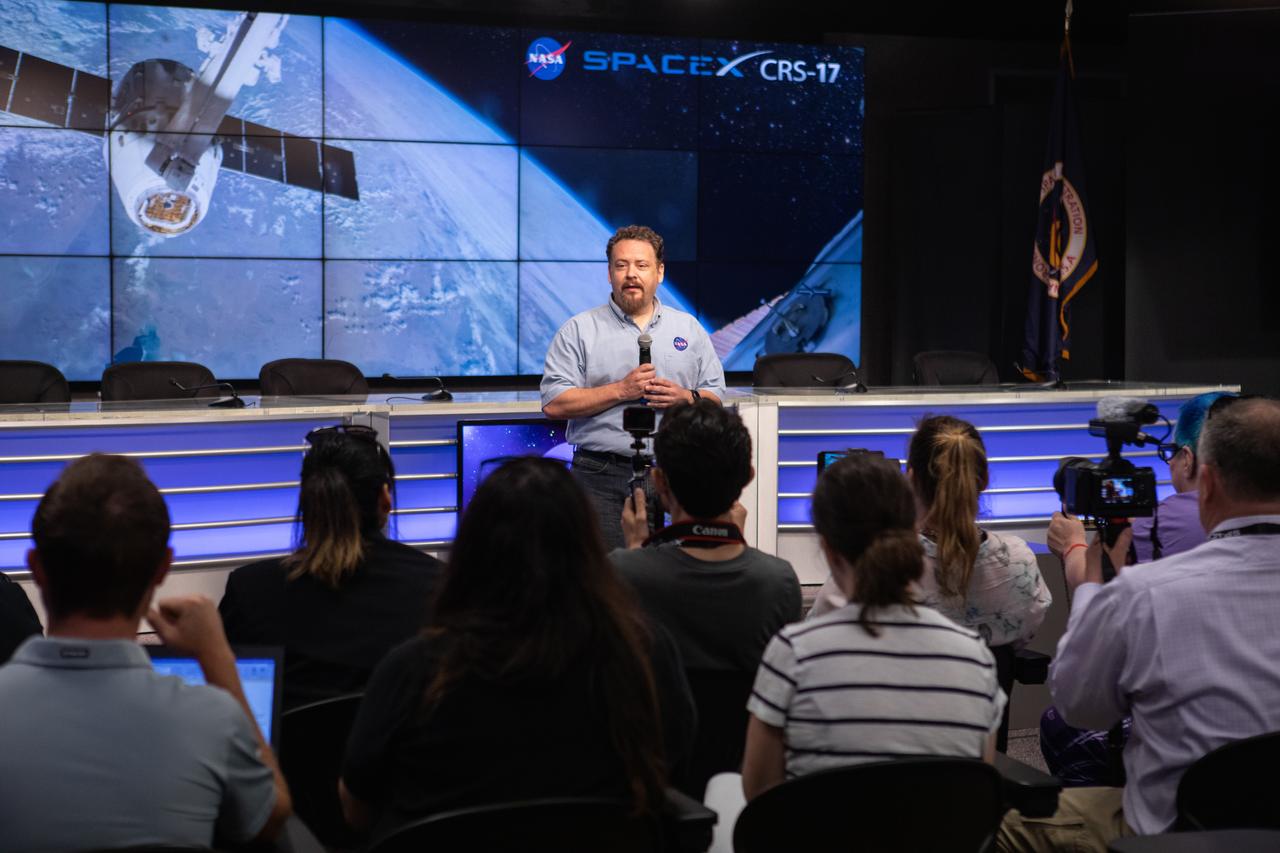

Dr. Kirt Costello, chief scientist for the ISS Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

Aaron Beeler, professor of chemistry at Boston University and principal investigator of the Flow Chemistry Platform for Synthetic Reactions on ISS study, addresses NASA Social participants during a What’s on Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 5, 2020. The briefing provided a closer look at some of the payloads launching on SpaceX’s 20th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-20) mission to the International Space Station. The company’s Falcon 9 rocket is scheduled to lift off from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40 at 11:50 p.m. EST on March 6, 2020.
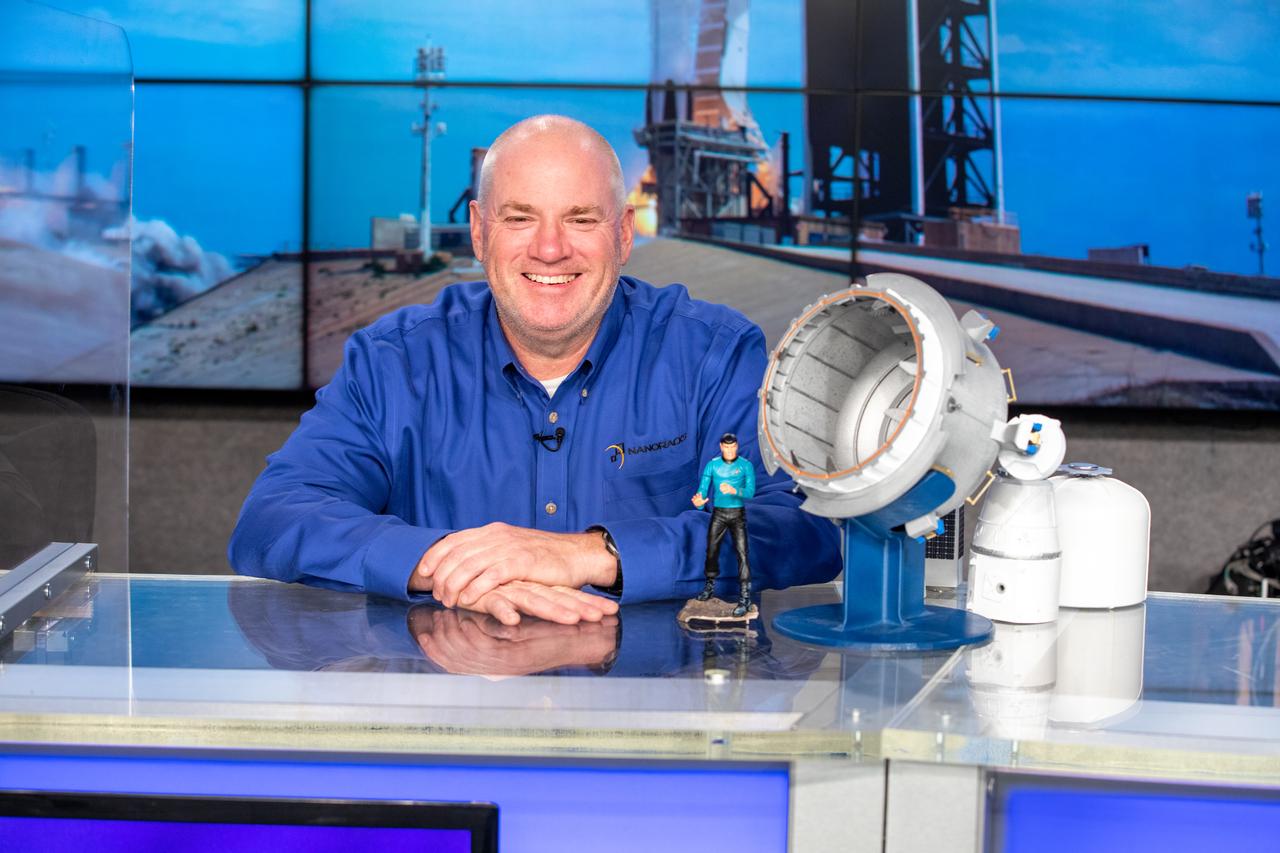

Brock Howe, airlock program manager, Nanoracks, participates in a #NASASocial Science and Station Q&A show at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 4, 2020. Jennifer Scott-Williams, ISS Program Research Office; and Pinar Mesci, project scientist, Sanford Consortium for Regenerative Medicine, UC San Diego, also participated in the event, which was moderated by NASA Communications’ Kenna Pell. SpaceX’s 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) mission is scheduled to launch from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A on Dec. 5, 2020. Liftoff of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and cargo Dragon spacecraft is targeted for 11:39 a.m. EST.
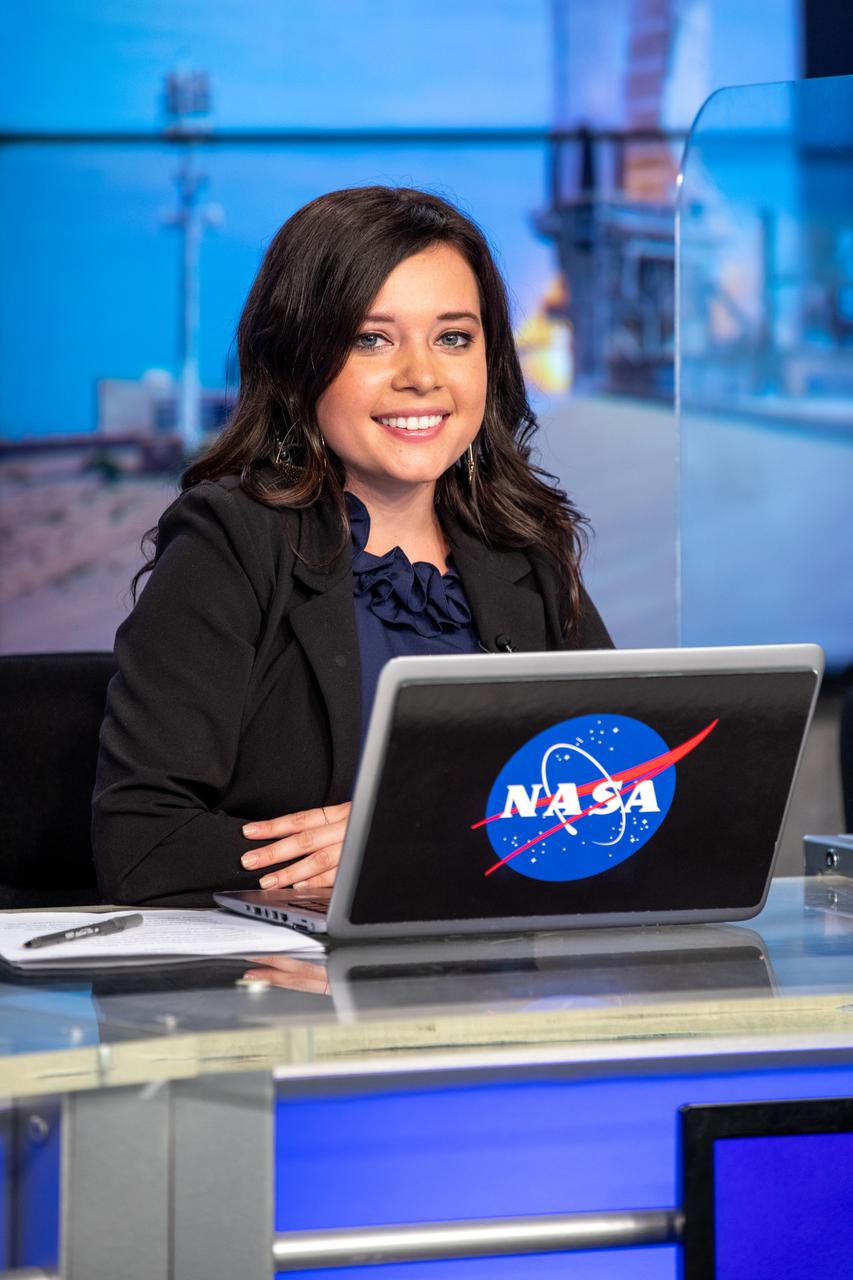

NASA Communications’ Kenna Pell moderates a #NASASocial Science and Station Q&A show at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 4, 2020. Participants included Brock Howe, airlock program manager, Nanoracks; Jennifer Scott-Williams, ISS Program Research Office; and Pinar Mesci, project scientist, Sanford Consortium for Regenerative Medicine, UC San Diego. SpaceX’s 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) mission is scheduled to launch from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A on Dec. 5, 2020. Liftoff of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and cargo Dragon spacecraft is targeted for 11:39 a.m. EST.
Props are used by Brock Howe, airlock program manager, Nanoracks, during a #NASASocial Science and Station Q&A show at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 4, 2020. NASA Communications’ Kenna Pell moderated the program, which also included Jennifer Scott-Williams, ISS Program Research Office; and Pinar Mesci, project scientist, Sanford Consortium for Regenerative Medicine, UC San Diego. SpaceX’s 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) mission is scheduled to launch from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A on Dec. 5, 2020. Liftoff of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and cargo Dragon spacecraft is targeted for 11:39 a.m. EST.
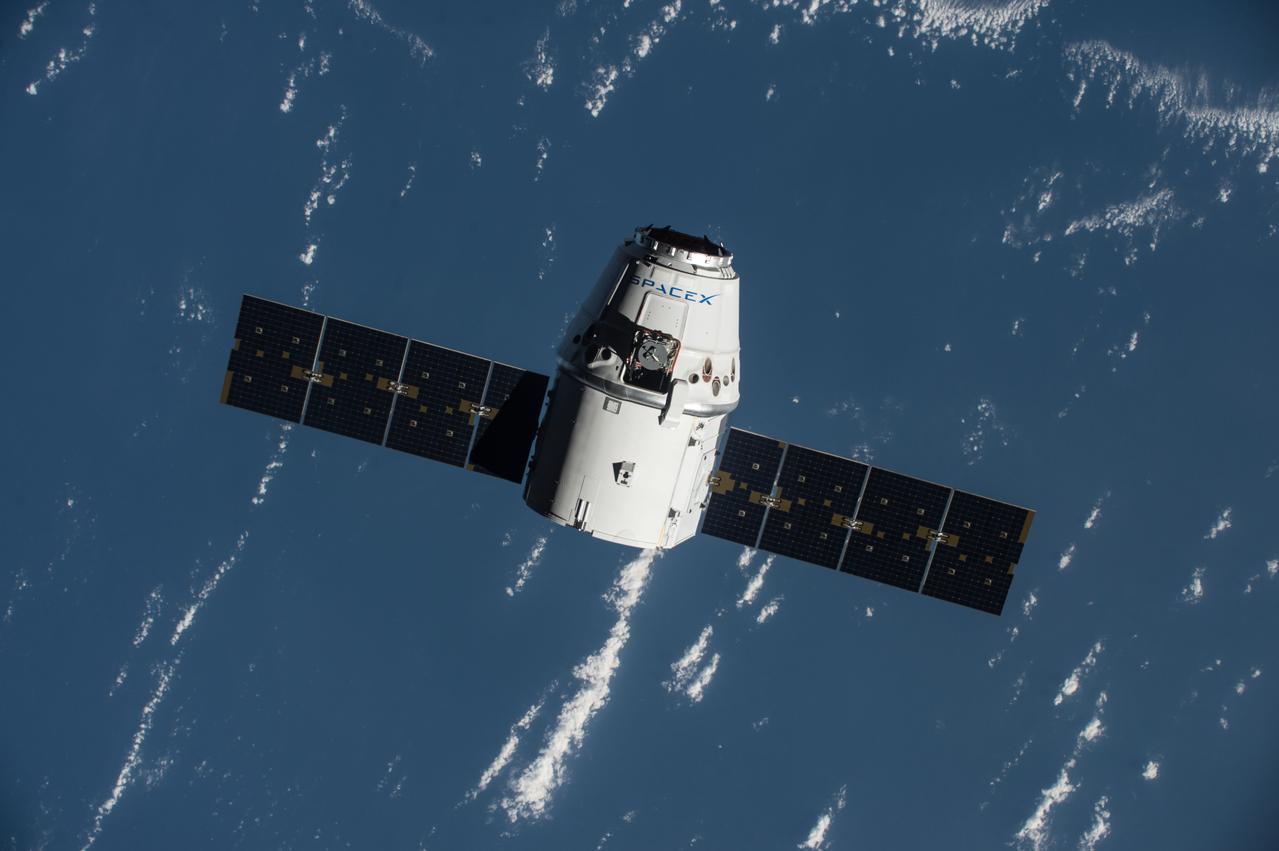

The SpaceX Dragon Commercial Resupply Services-9 (CRS-9) spacecraft approaches the ISS for rendezvous and grapple operations. Earth provides the backdrop for this image.
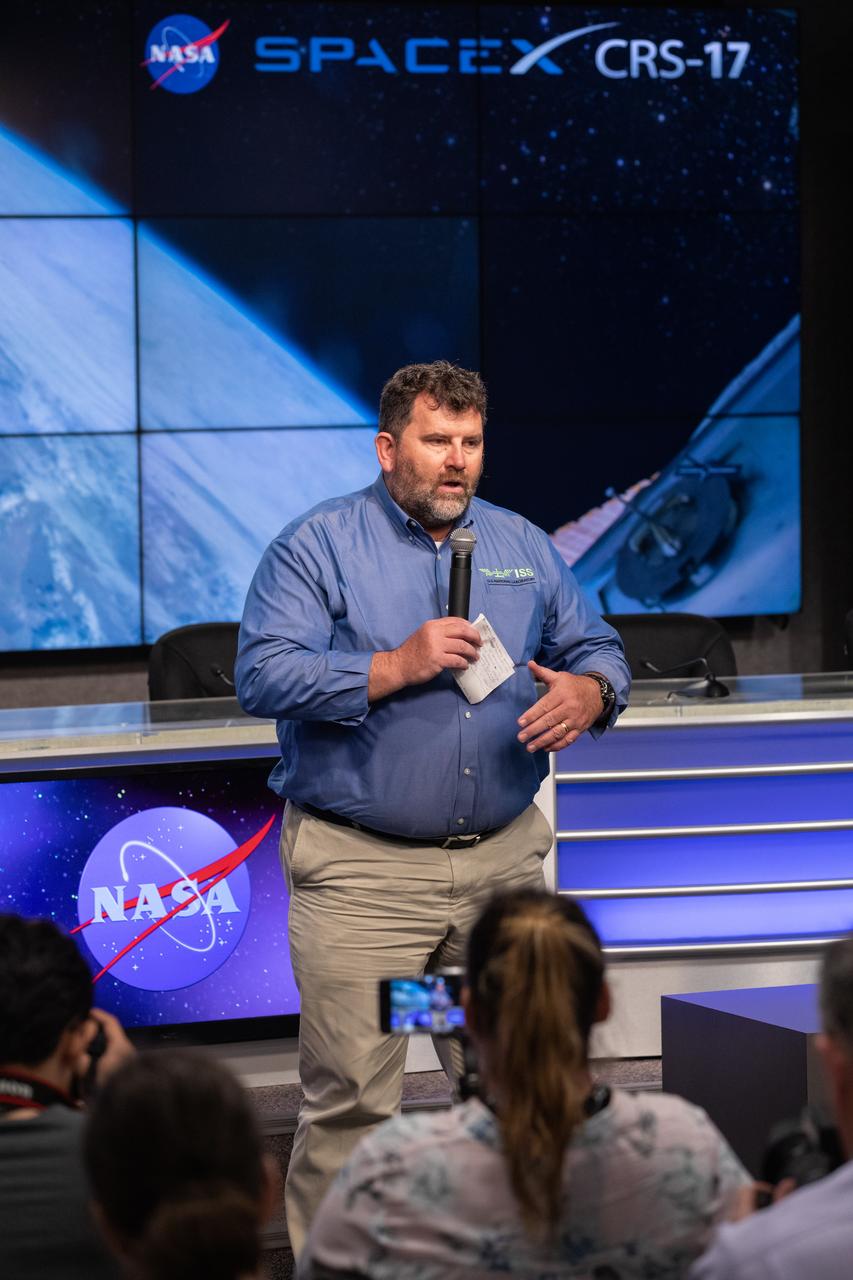

Mike Roberts, deputy chief scientist for the ISS Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
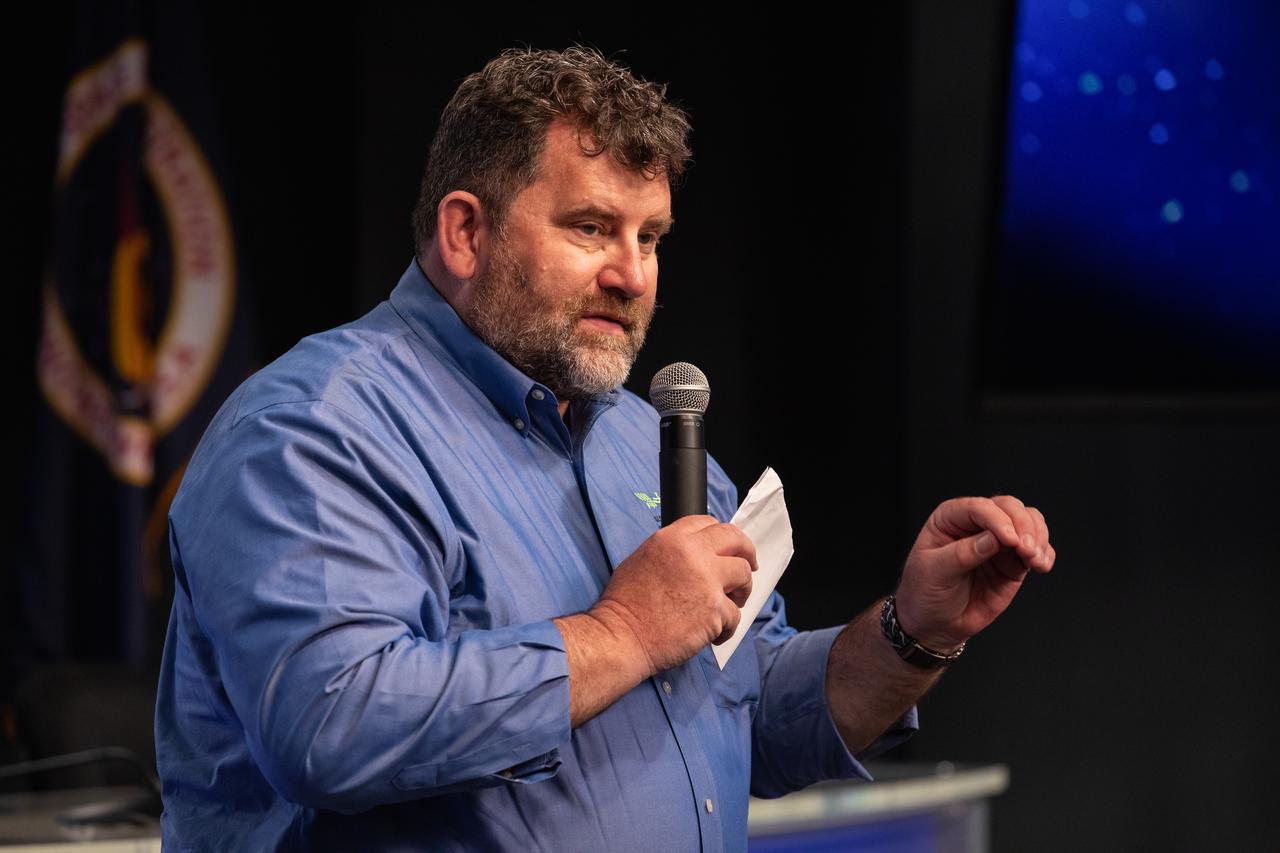

Mike Roberts, deputy chief scientist for the ISS Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
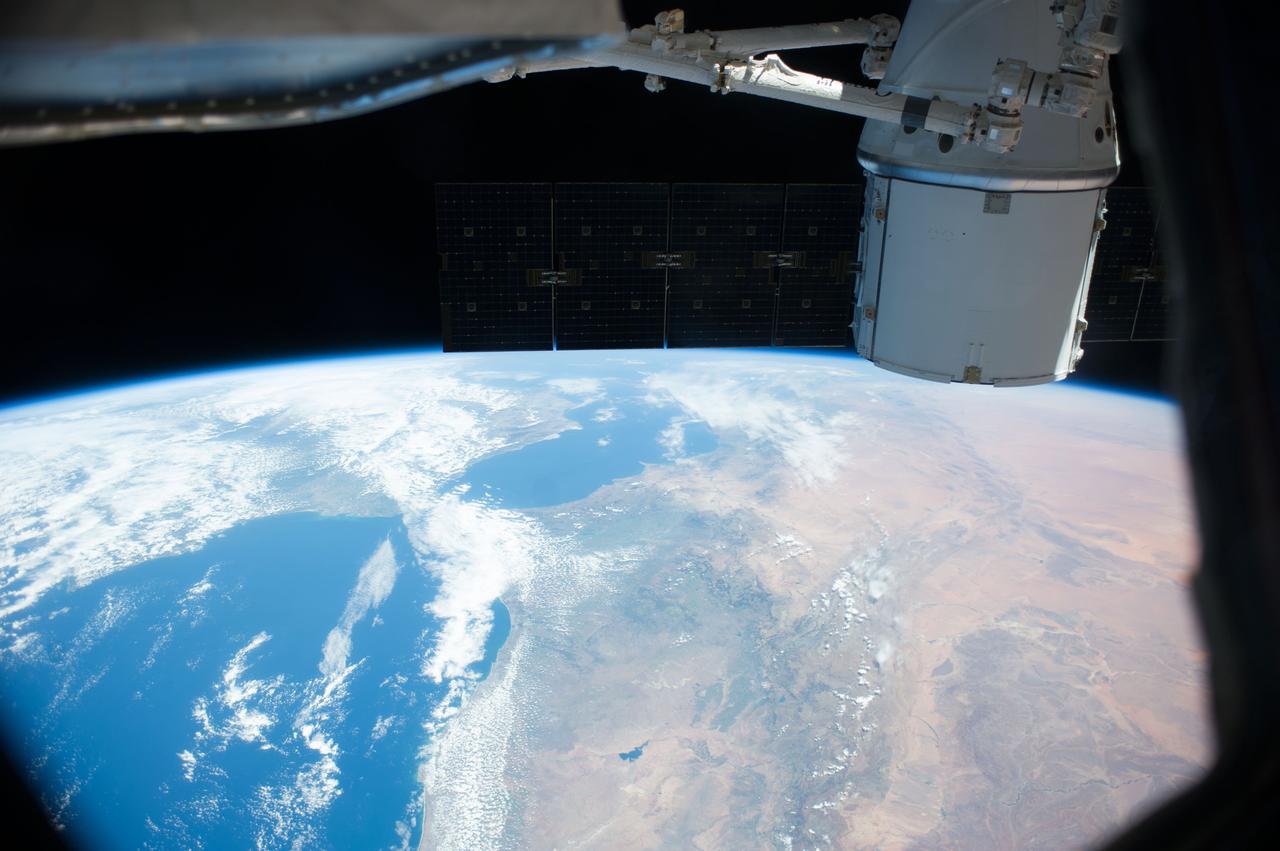

Earth observation taken by the Expedition 39 crew aboard the ISS. A portion of the SpaceX Dragon Commercial Resupply Services-3 (CRS-3) spacecraft is in view. Image was released by astronaut on Twitter and downlinked in folder: Europe.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida comes alive as the Merlin engines ignite under the Falcon 9 rocket carrying a Dragon capsule to orbit. Liftoff was at 8:35 p.m. EDT. Space Exploration Technologies Corp., or SpaceX, built both the rocket and capsule for NASA's first Commercial Resupply Services, or CRS-1, mission to the International Space Station. SpaceX CRS-1 is an important step toward making America’s microgravity research program self-sufficient by providing a way to deliver and return significant amounts of cargo, including science experiments, to and from the orbiting laboratory. NASA has contracted for 12 commercial resupply flights from SpaceX and eight from the Orbital Sciences Corp. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/living/launch/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Rick Wetherington and Tim Powers
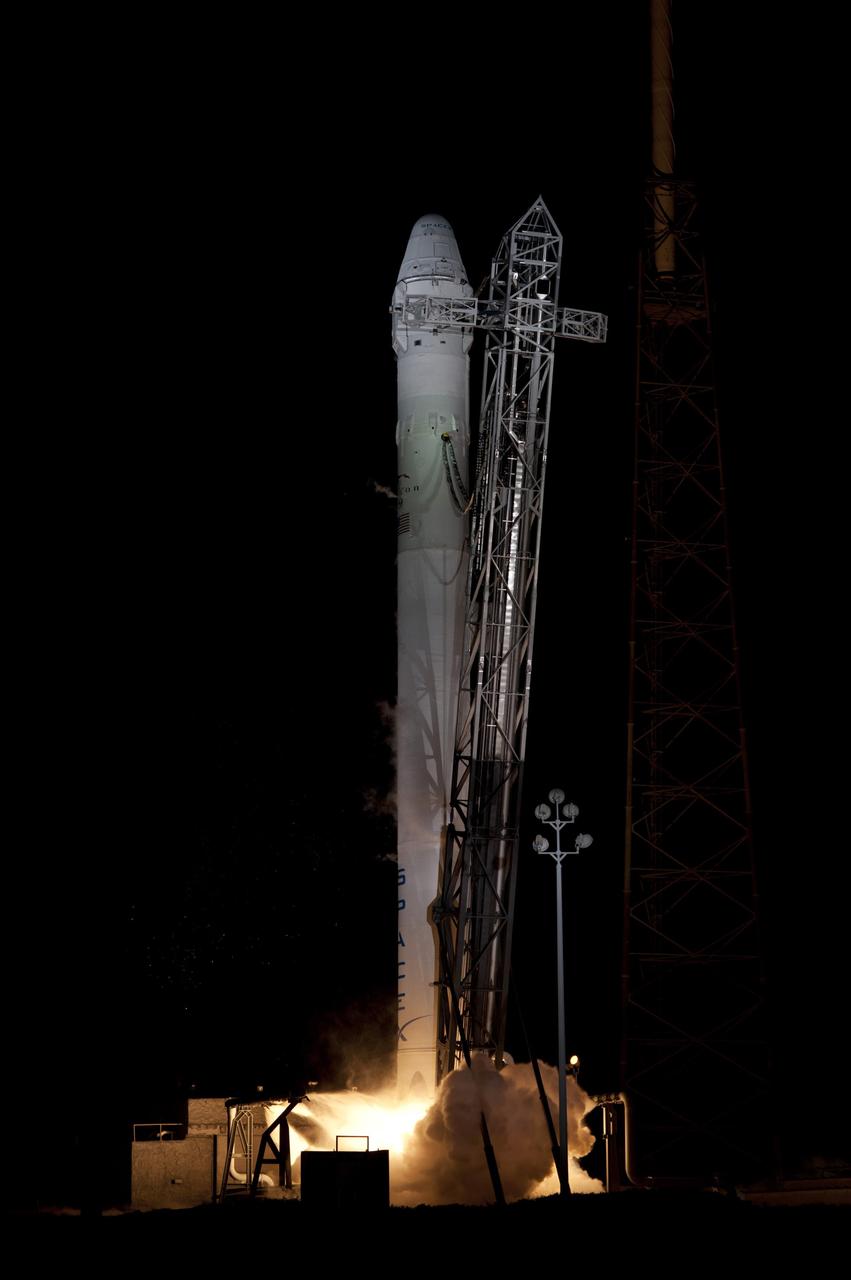

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida comes alive as the Merlin engines ignite under the Falcon 9 rocket carrying a Dragon capsule to orbit. Liftoff was at 8:35 p.m. EDT. Space Exploration Technologies Corp., or SpaceX, built both the rocket and capsule for NASA's first Commercial Resupply Services, or CRS-1, mission to the International Space Station. SpaceX CRS-1 is an important step toward making America’s microgravity research program self-sufficient by providing a way to deliver and return significant amounts of cargo, including science experiments, to and from the orbiting laboratory. NASA has contracted for 12 commercial resupply flights from SpaceX and eight from the Orbital Sciences Corp. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/living/launch/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Rick Wetherington and Tim Powers
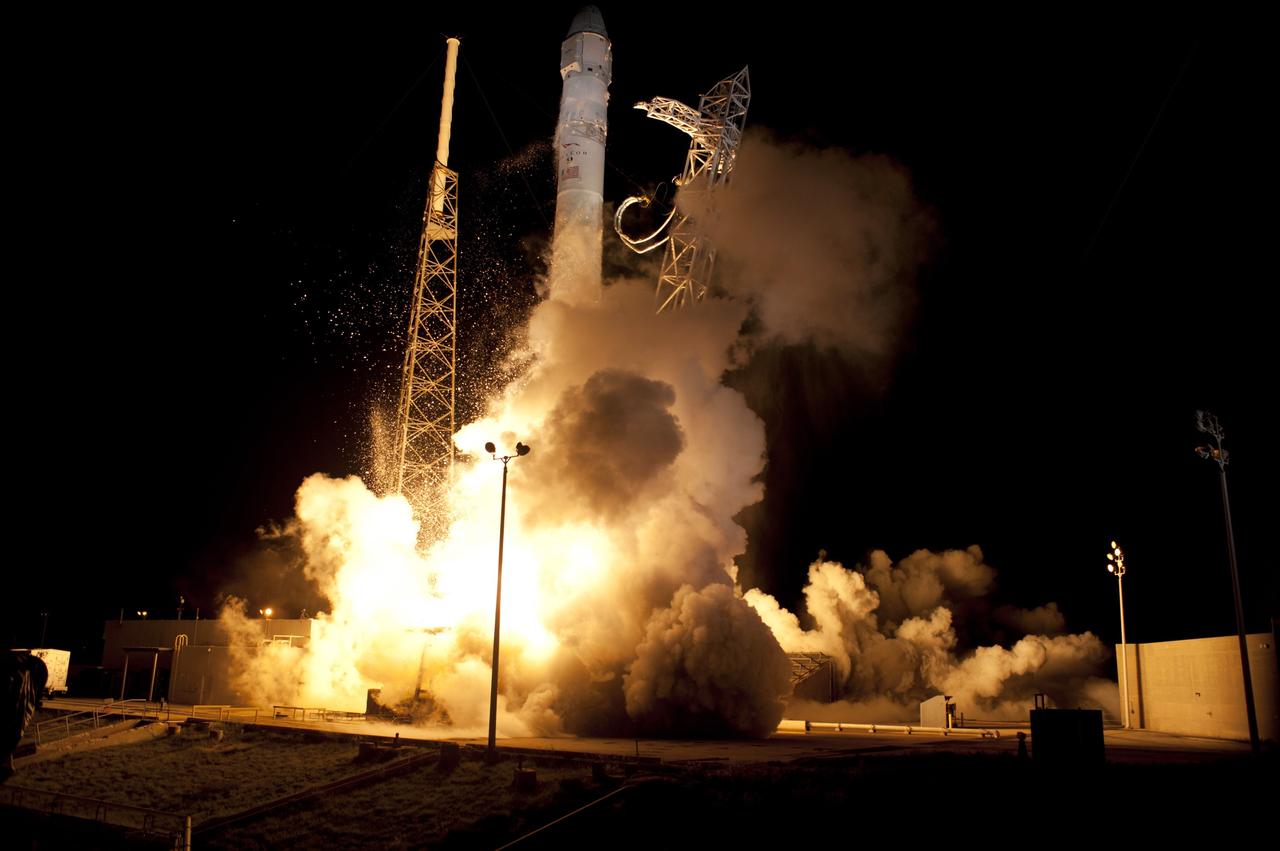

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida comes alive as the Merlin engines ignite under the Falcon 9 rocket carrying a Dragon capsule to orbit. Liftoff was at 8:35 p.m. EDT. Space Exploration Technologies Corp., or SpaceX, built both the rocket and capsule for NASA's first Commercial Resupply Services, or CRS-1, mission to the International Space Station. SpaceX CRS-1 is an important step toward making America’s microgravity research program self-sufficient by providing a way to deliver and return significant amounts of cargo, including science experiments, to and from the orbiting laboratory. NASA has contracted for 12 commercial resupply flights from SpaceX and eight from the Orbital Sciences Corp. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/living/launch/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Rick Wetherington and Tim Powers
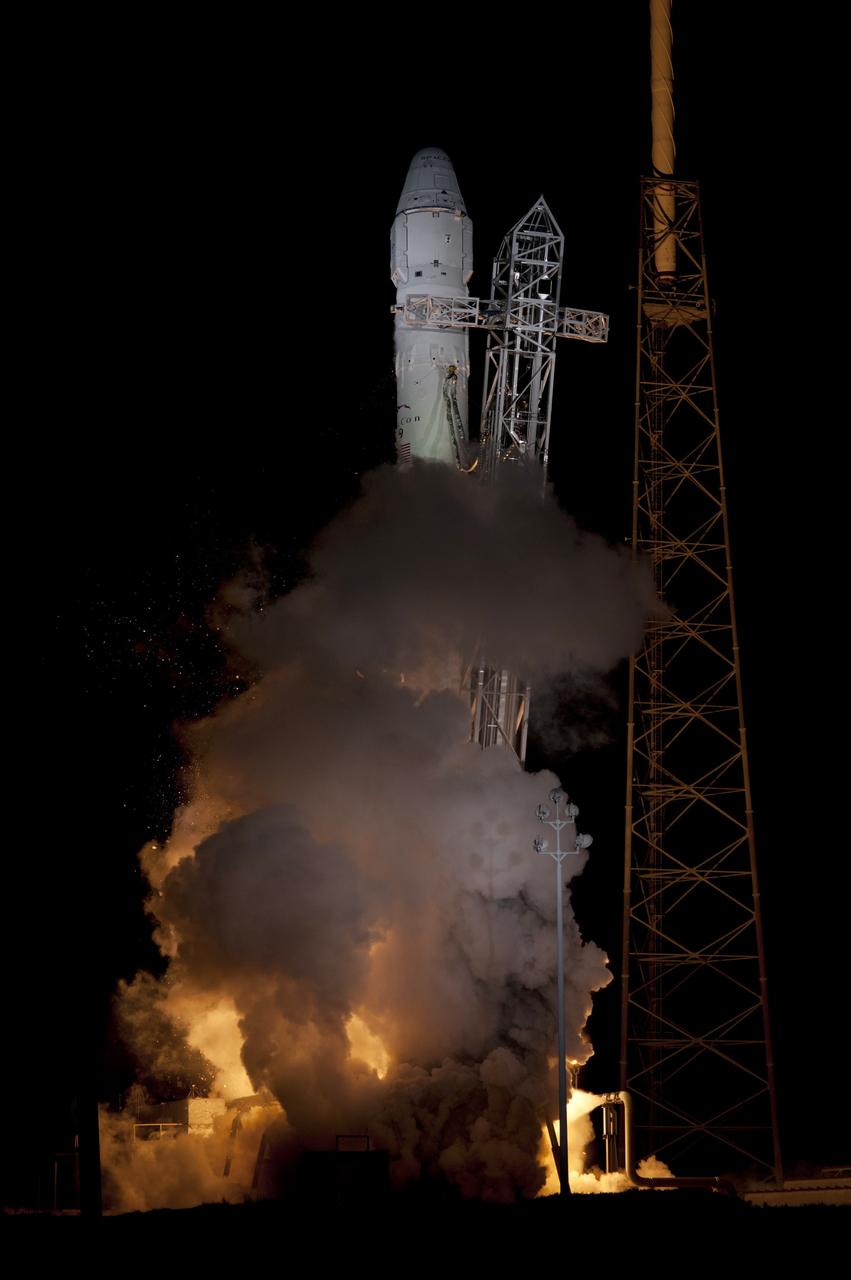

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida comes alive as the Merlin engines ignite under the Falcon 9 rocket carrying a Dragon capsule to orbit. Liftoff was at 8:35 p.m. EDT. Space Exploration Technologies Corp., or SpaceX, built both the rocket and capsule for NASA's first Commercial Resupply Services, or CRS-1, mission to the International Space Station. SpaceX CRS-1 is an important step toward making America’s microgravity research program self-sufficient by providing a way to deliver and return significant amounts of cargo, including science experiments, to and from the orbiting laboratory. NASA has contracted for 12 commercial resupply flights from SpaceX and eight from the Orbital Sciences Corp. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/living/launch/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Rick Wetherington and Tim Powers
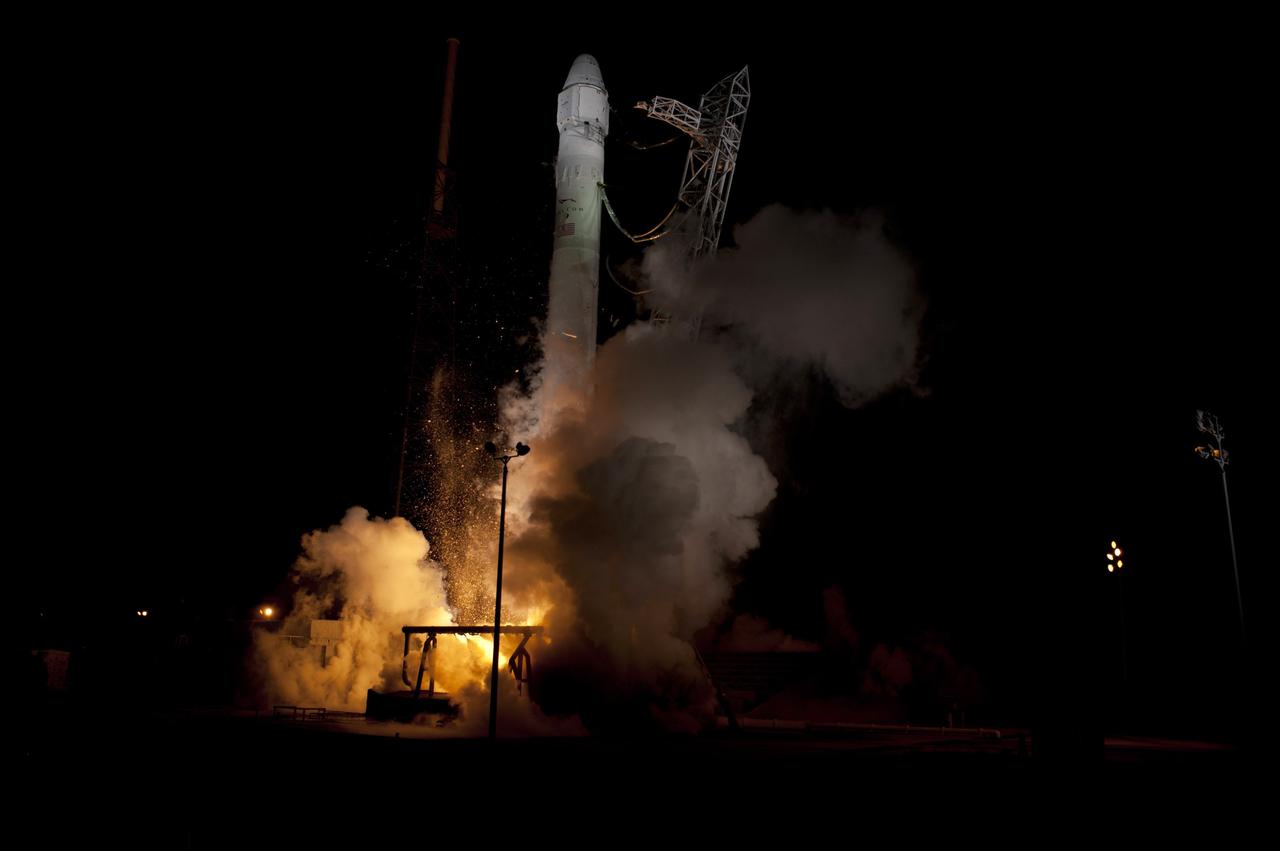

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida comes alive as the Merlin engines ignite under the Falcon 9 rocket carrying a Dragon capsule to orbit. Liftoff was at 8:35 p.m. EDT. Space Exploration Technologies Corp., or SpaceX, built both the rocket and capsule for NASA's first Commercial Resupply Services, or CRS-1, mission to the International Space Station. SpaceX CRS-1 is an important step toward making America’s microgravity research program self-sufficient by providing a way to deliver and return significant amounts of cargo, including science experiments, to and from the orbiting laboratory. NASA has contracted for 12 commercial resupply flights from SpaceX and eight from the Orbital Sciences Corp. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/living/launch/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Rick Wetherington and Tim Powers
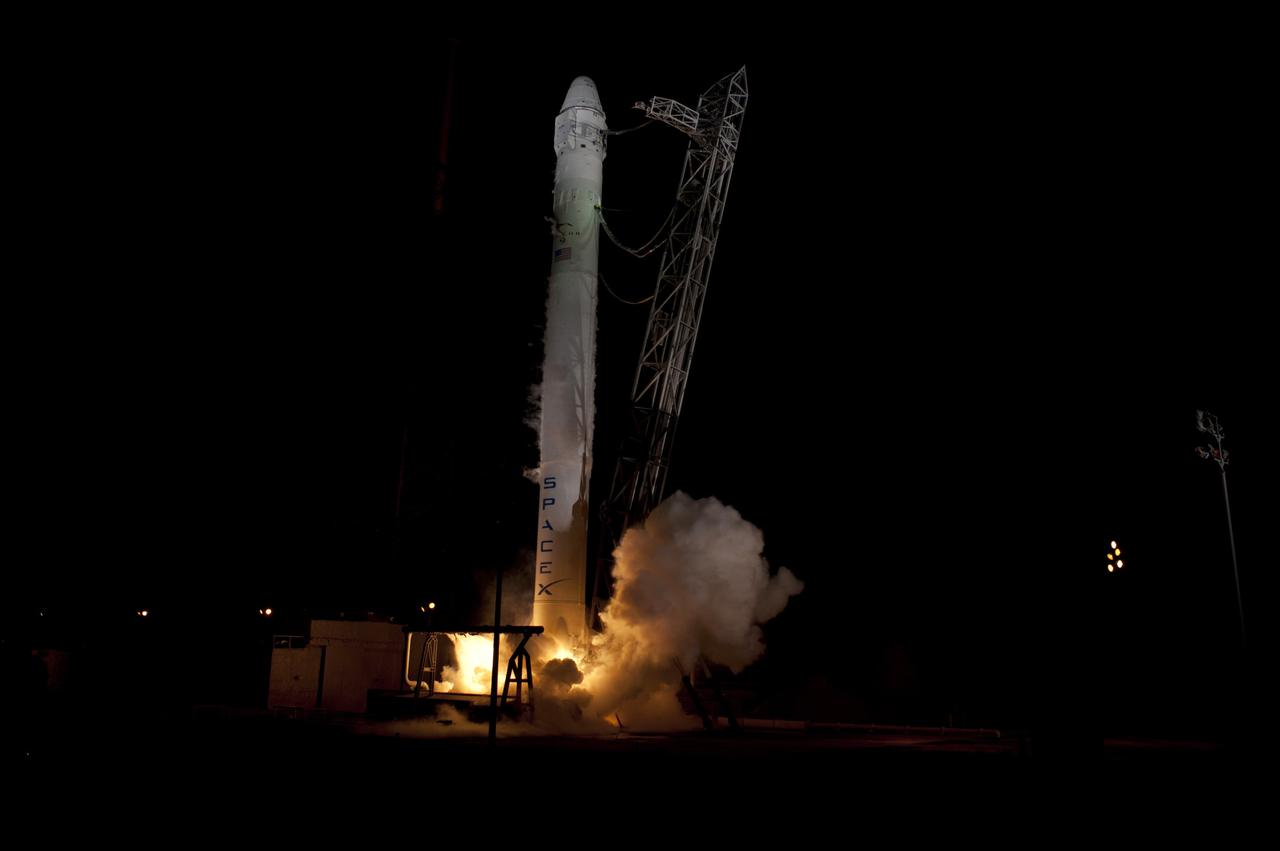

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida comes alive as the Merlin engines ignite under the Falcon 9 rocket carrying a Dragon capsule to orbit. Liftoff was at 8:35 p.m. EDT. Space Exploration Technologies Corp., or SpaceX, built both the rocket and capsule for NASA's first Commercial Resupply Services, or CRS-1, mission to the International Space Station. SpaceX CRS-1 is an important step toward making America’s microgravity research program self-sufficient by providing a way to deliver and return significant amounts of cargo, including science experiments, to and from the orbiting laboratory. NASA has contracted for 12 commercial resupply flights from SpaceX and eight from the Orbital Sciences Corp. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/living/launch/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Rick Wetherington and Tim Powers
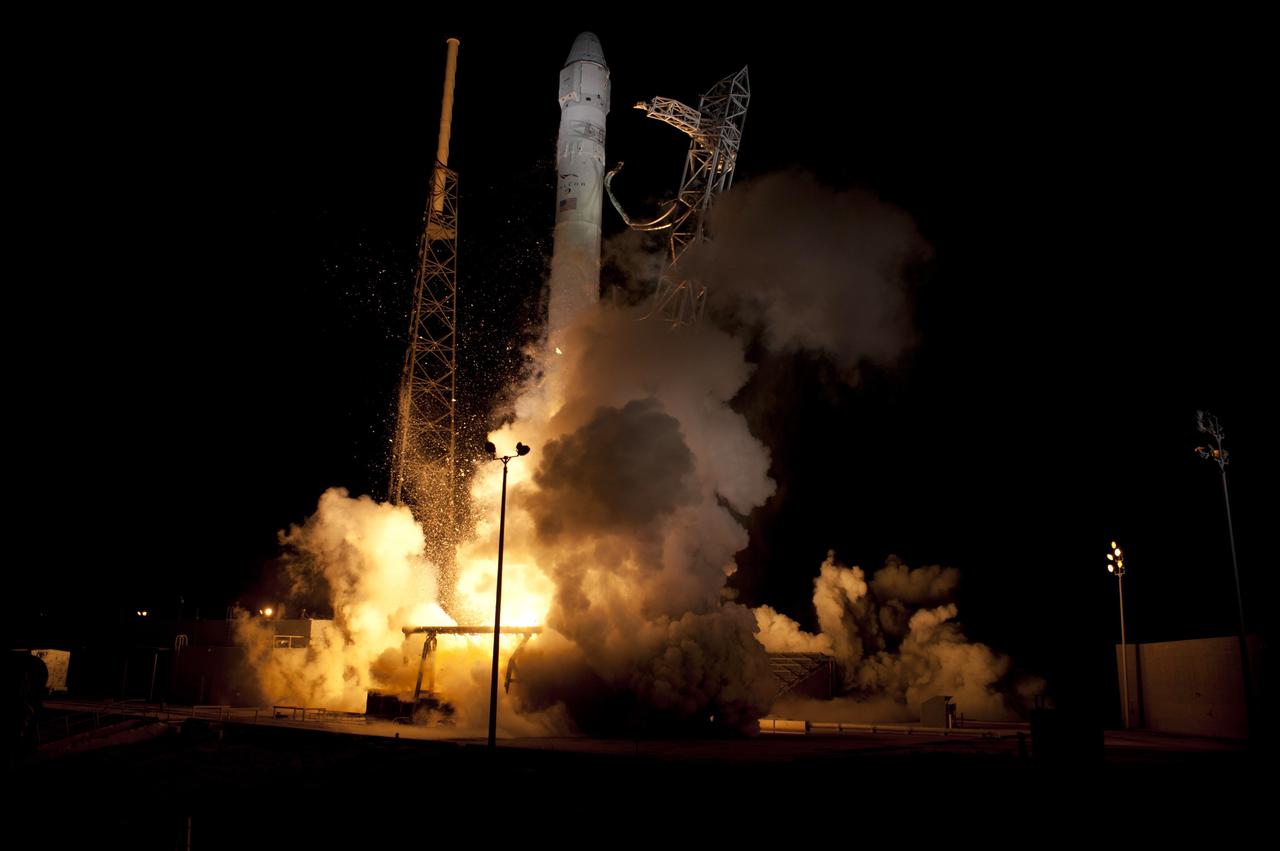

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida comes alive as the Merlin engines ignite under the Falcon 9 rocket carrying a Dragon capsule to orbit. Liftoff was at 8:35 p.m. EDT. Space Exploration Technologies Corp., or SpaceX, built both the rocket and capsule for NASA's first Commercial Resupply Services, or CRS-1, mission to the International Space Station. SpaceX CRS-1 is an important step toward making America’s microgravity research program self-sufficient by providing a way to deliver and return significant amounts of cargo, including science experiments, to and from the orbiting laboratory. NASA has contracted for 12 commercial resupply flights from SpaceX and eight from the Orbital Sciences Corp. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/living/launch/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Rick Wetherington and Tim Powers

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida comes alive as the Merlin engines ignite under the Falcon 9 rocket carrying a Dragon capsule to orbit. Liftoff was at 8:35 p.m. EDT. Space Exploration Technologies Corp., or SpaceX, built both the rocket and capsule for NASA's first Commercial Resupply Services, or CRS-1, mission to the International Space Station. SpaceX CRS-1 is an important step toward making America’s microgravity research program self-sufficient by providing a way to deliver and return significant amounts of cargo, including science experiments, to and from the orbiting laboratory. NASA has contracted for 12 commercial resupply flights from SpaceX and eight from the Orbital Sciences Corp. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/living/launch/index.html Photo credit: NASA/ Rick Wetherington and Tim Powers
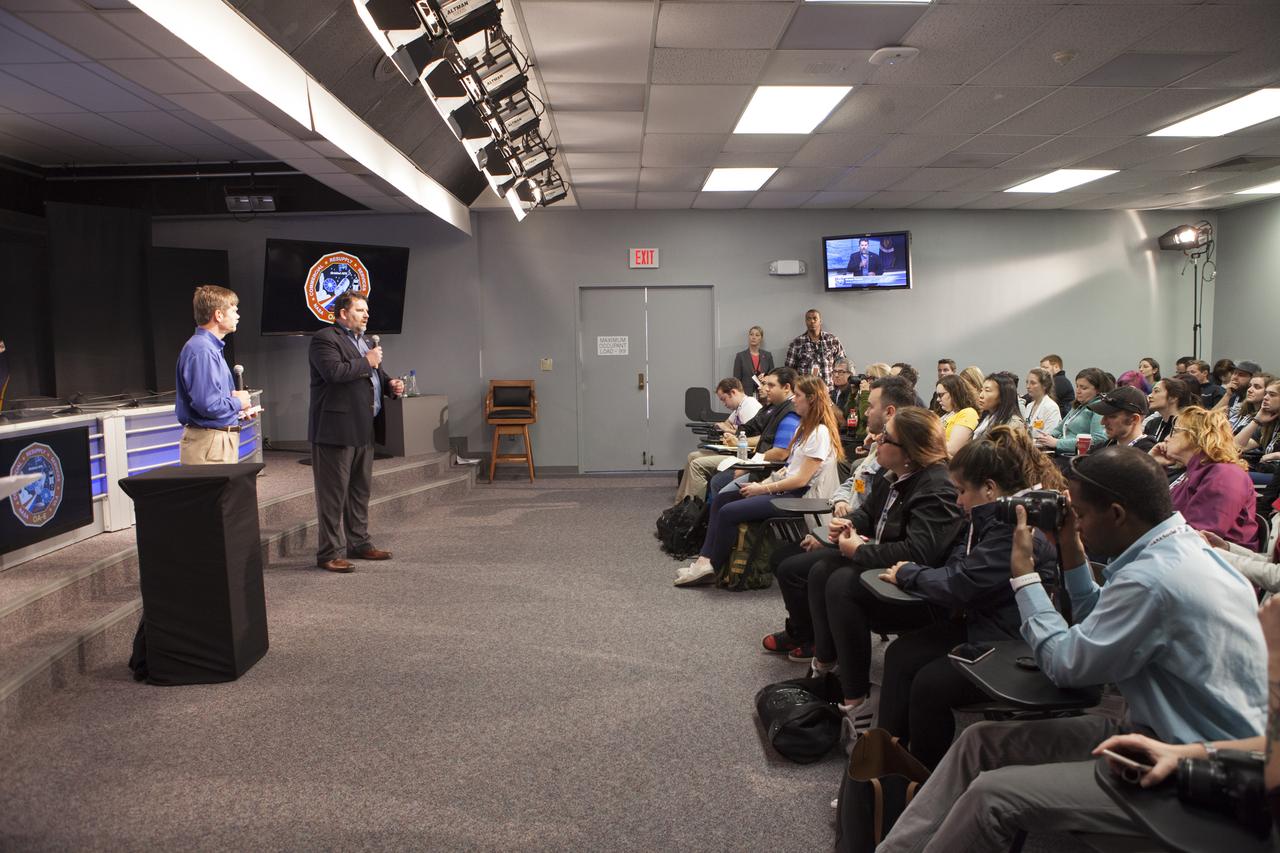

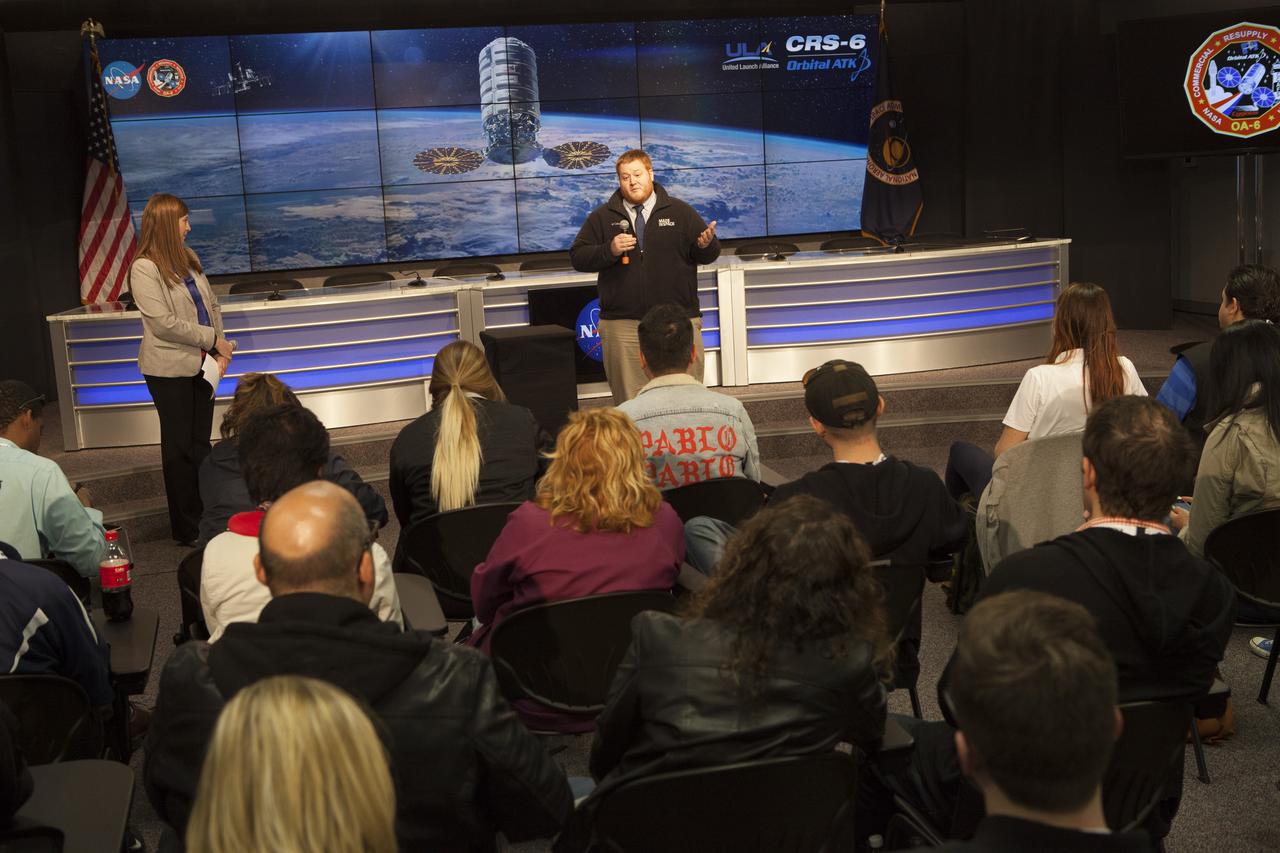
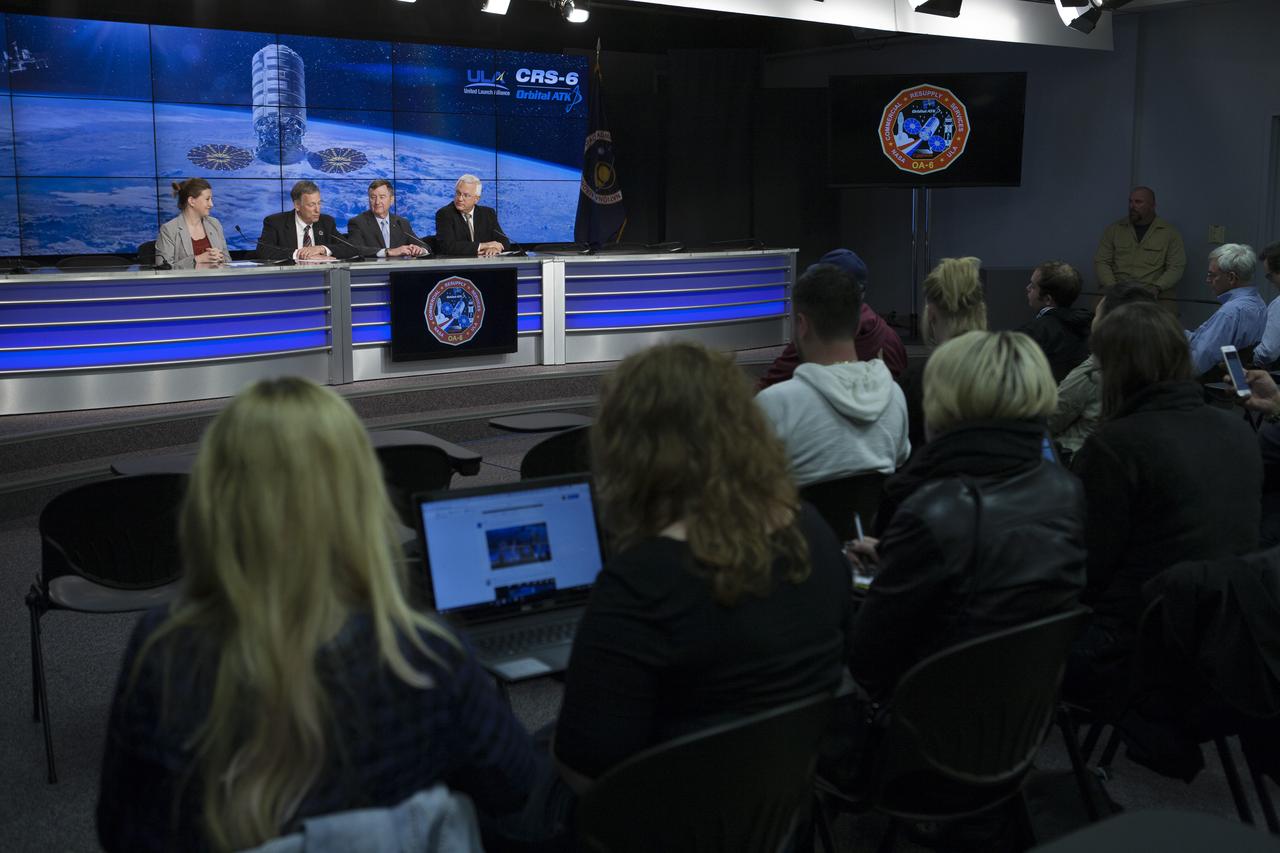
In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, members of the media participate in a briefing on science research and technology work planned for the International Space Station, or ISS. NASA is preparing for the launch of a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission to the ISS. From left are: Pete Hasbrook, NASA associate program scientist for the ISS Program at the Johnson Space Center in Houston, and Dr. Michael Roberts, deputy chief scientist for the Center for the Advancement for Science in Space, or CASIS.
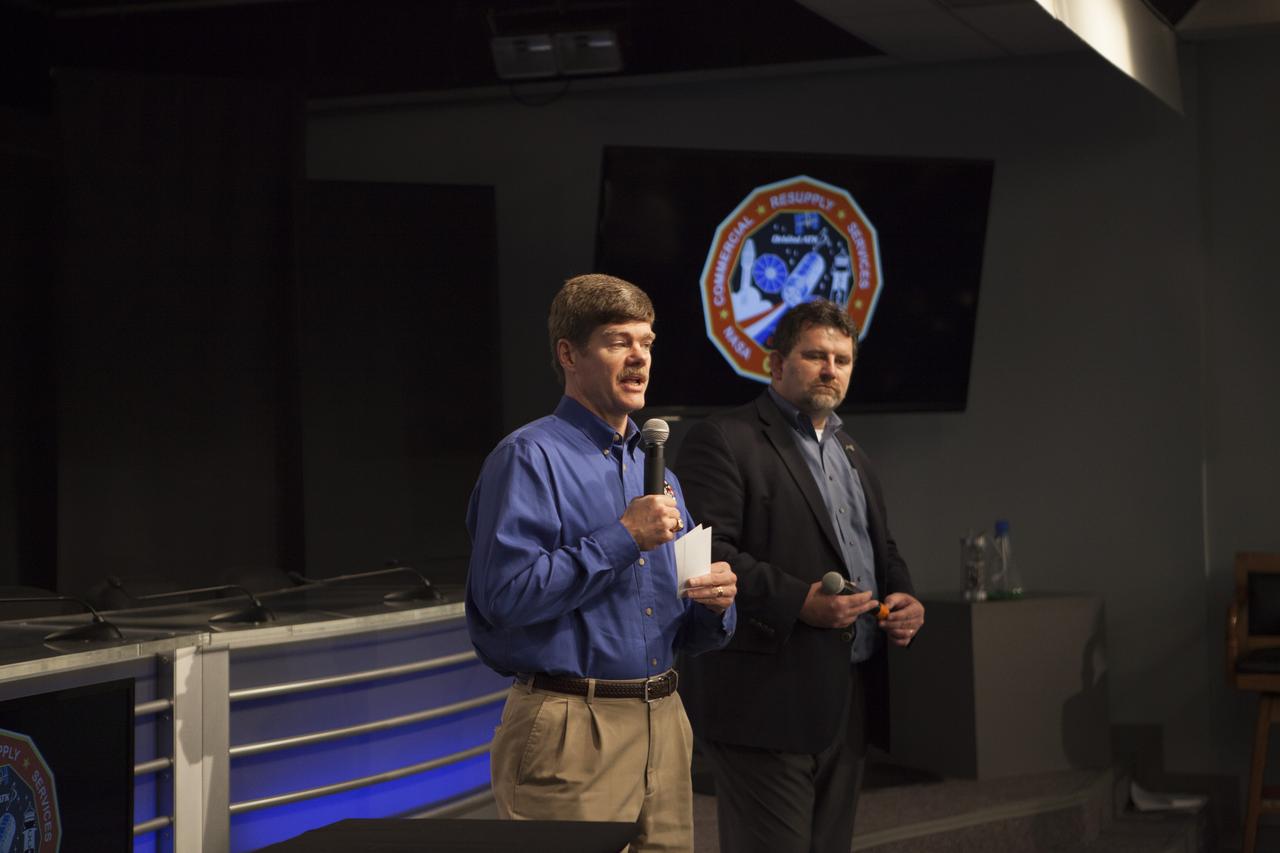

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, members of the media participate in a briefing on science research and technology work planned for the International Space Station, or ISS. NASA is preparing for the launch of a Cygnus spacecraft on the Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission to the ISS. From left are: Pete Hasbrook, NASA associate program scientist for the ISS Program at the Johnson Space Center in Houston, and Dr. Michael Roberts, deputy chief scientist for the Center for the Advancement for Science in Space, or CASIS.
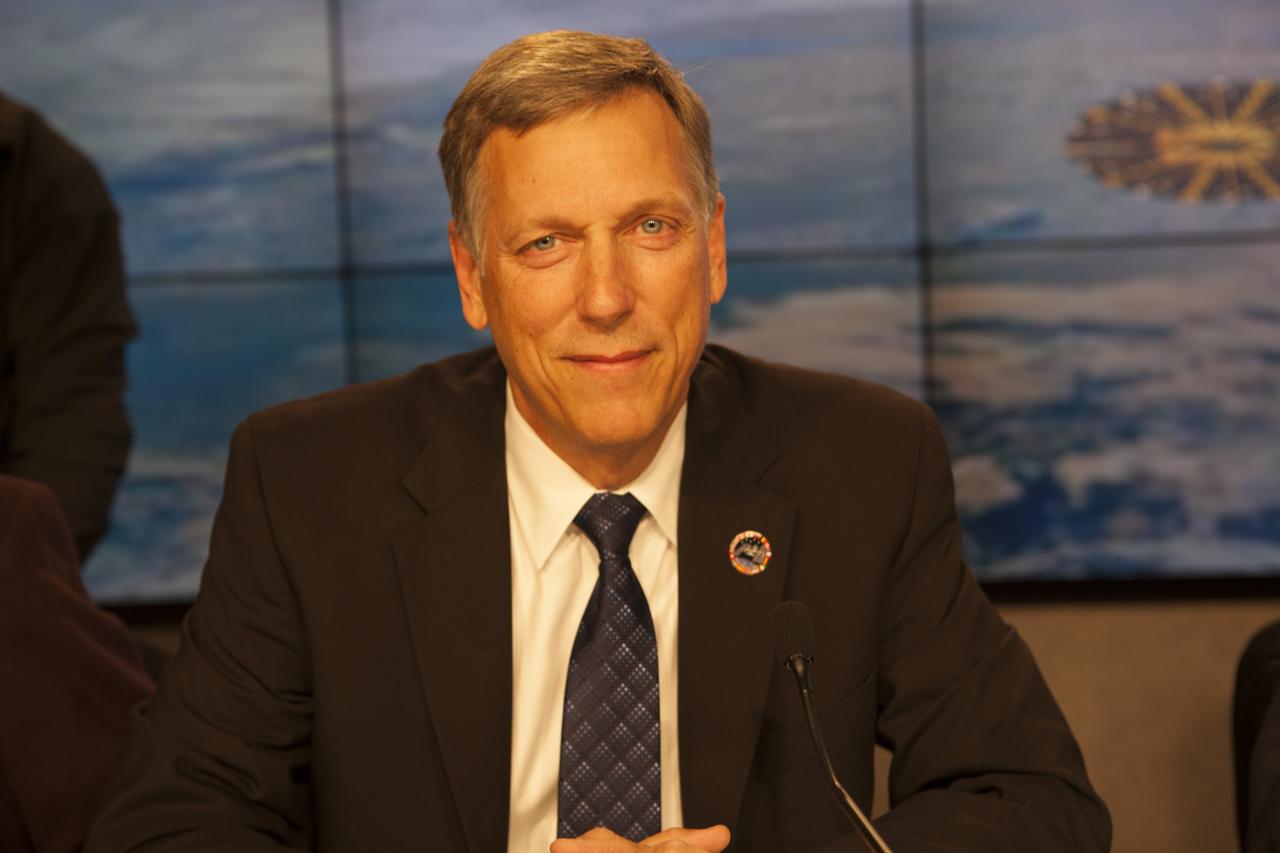

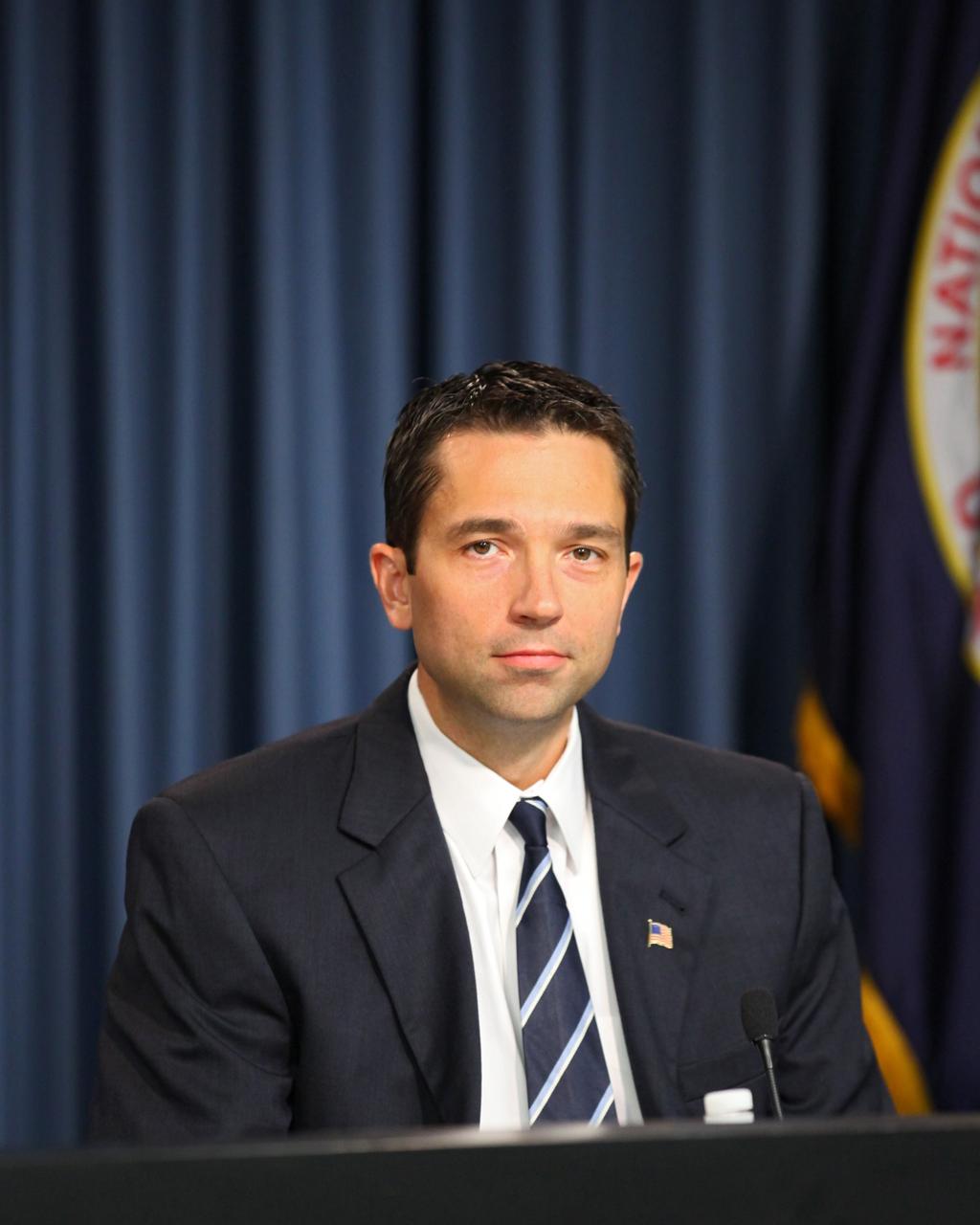
In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, Kenneth Todd, NASA ISS Operations Integration manager; speaks to members of the media at a prelaunch news conference for Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station.
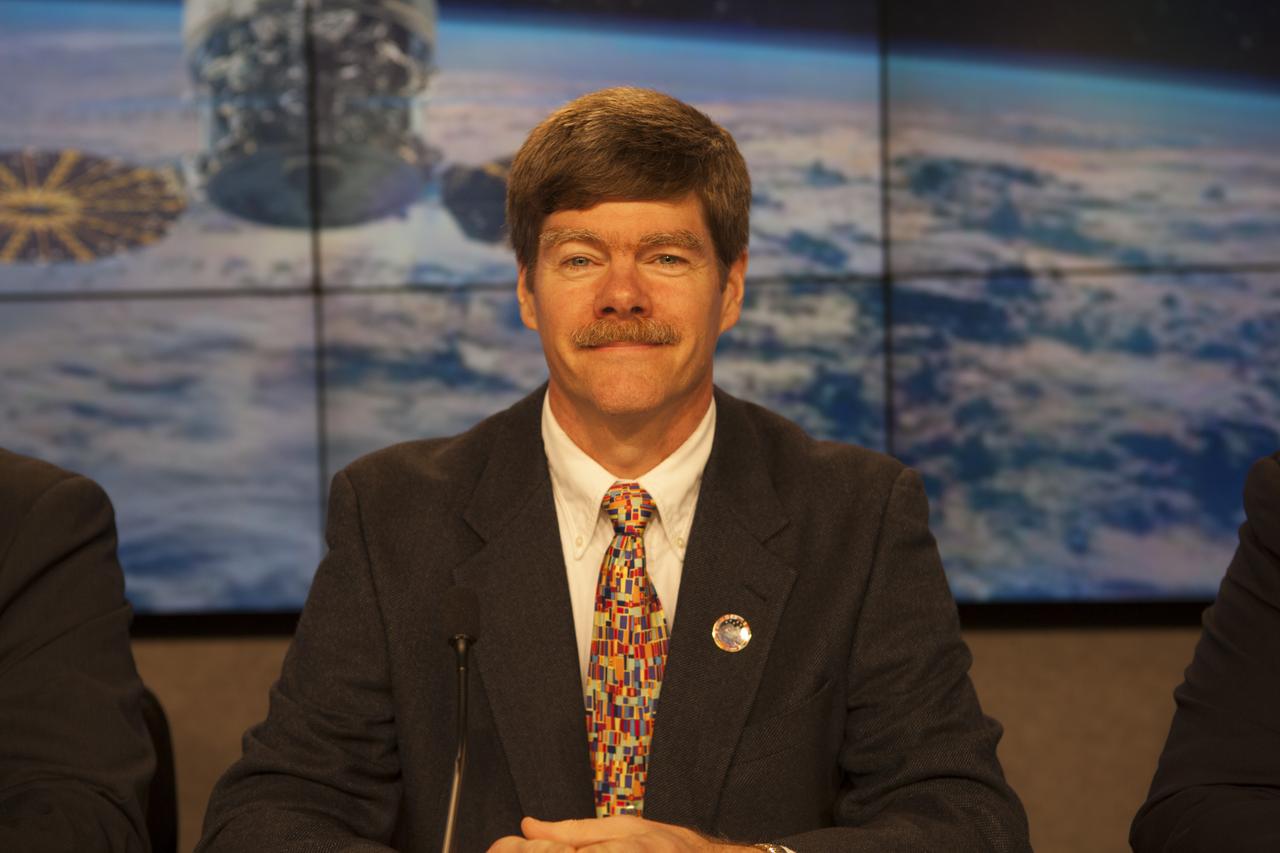

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, Pete Hasbrook, NASA associate program scientist for the ISS Program at the Johnson Space Center in Houston, speaks to members of the media at a prelaunch news conference for Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station.

Commercial Crew Program: The Commercial Crew Program at Kennedy Space Center is leading NASA’s efforts to develop the next United States capability for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the International Space Station ISS and other low Earth orbit destinations by the middle of the decade. The outcome of this capability is expected to stimulate and expand the U.S. space transportation industry. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the media during a prelaunch news conference for the SpaceX CRS-14 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. From left, are Stephanie Schierholz, of NASA Communications; Jessica Jensen, director, Dragon Mission Management, SpaceX; Pete Hasbrook, associate program scientist, ISS Program Science Office at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston; and Mike McAleenan, weather officer, 45th Weather Squadron. Joining on the phone is Joel Montalbano, deputy manager, ISS Program at Johnson. A Dragon spacecraft is scheduled to be launched from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 4:30 p.m. EST, on April 2, 2018. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will lift off on the company's 14th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
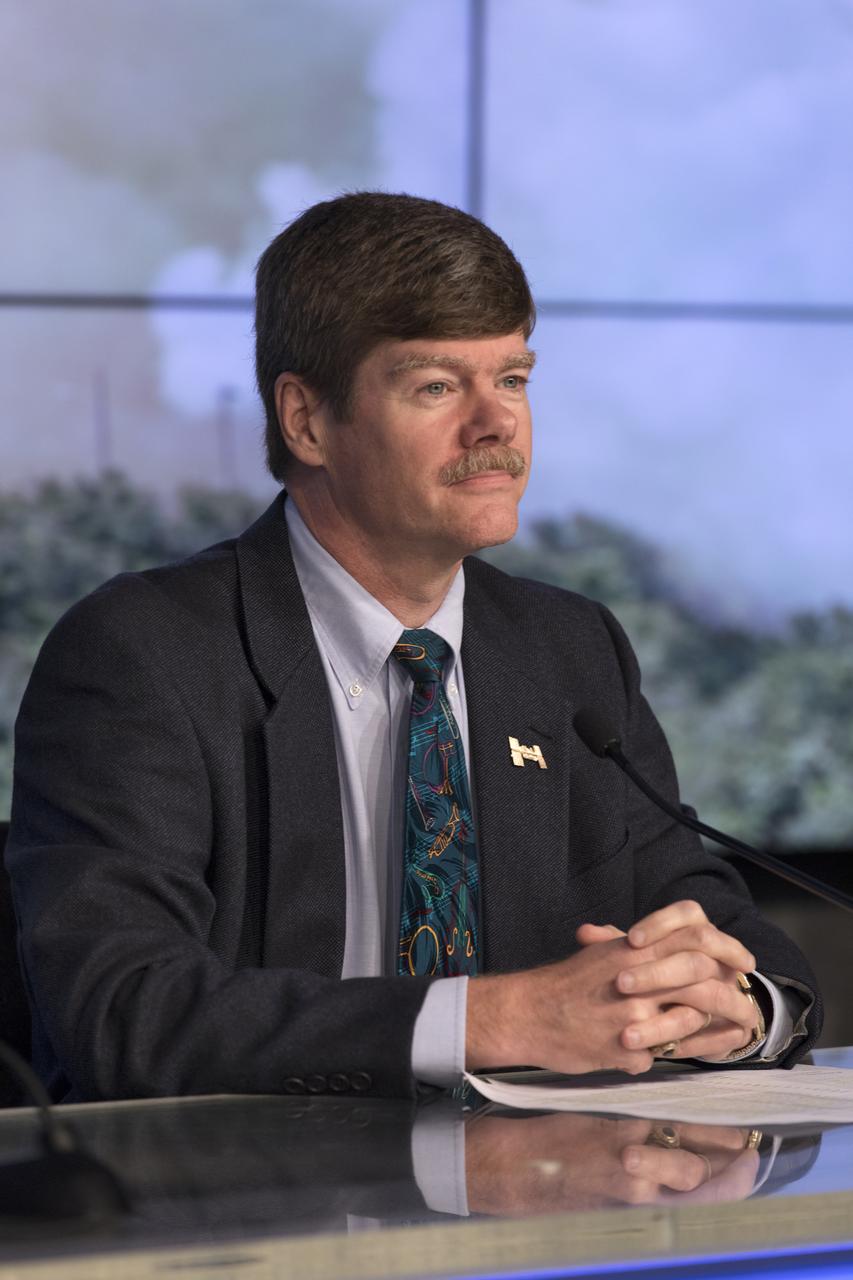

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the media during a prelaunch news conference for the SpaceX CRS-14 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Pete Hasbrook, associate program scientist, ISS Program Science Office at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston; participates in the news conference. A Dragon spacecraft is scheduled to be launched from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 4:30 p.m. EST, on April 2, 2018. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will lift off on the company's 14th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
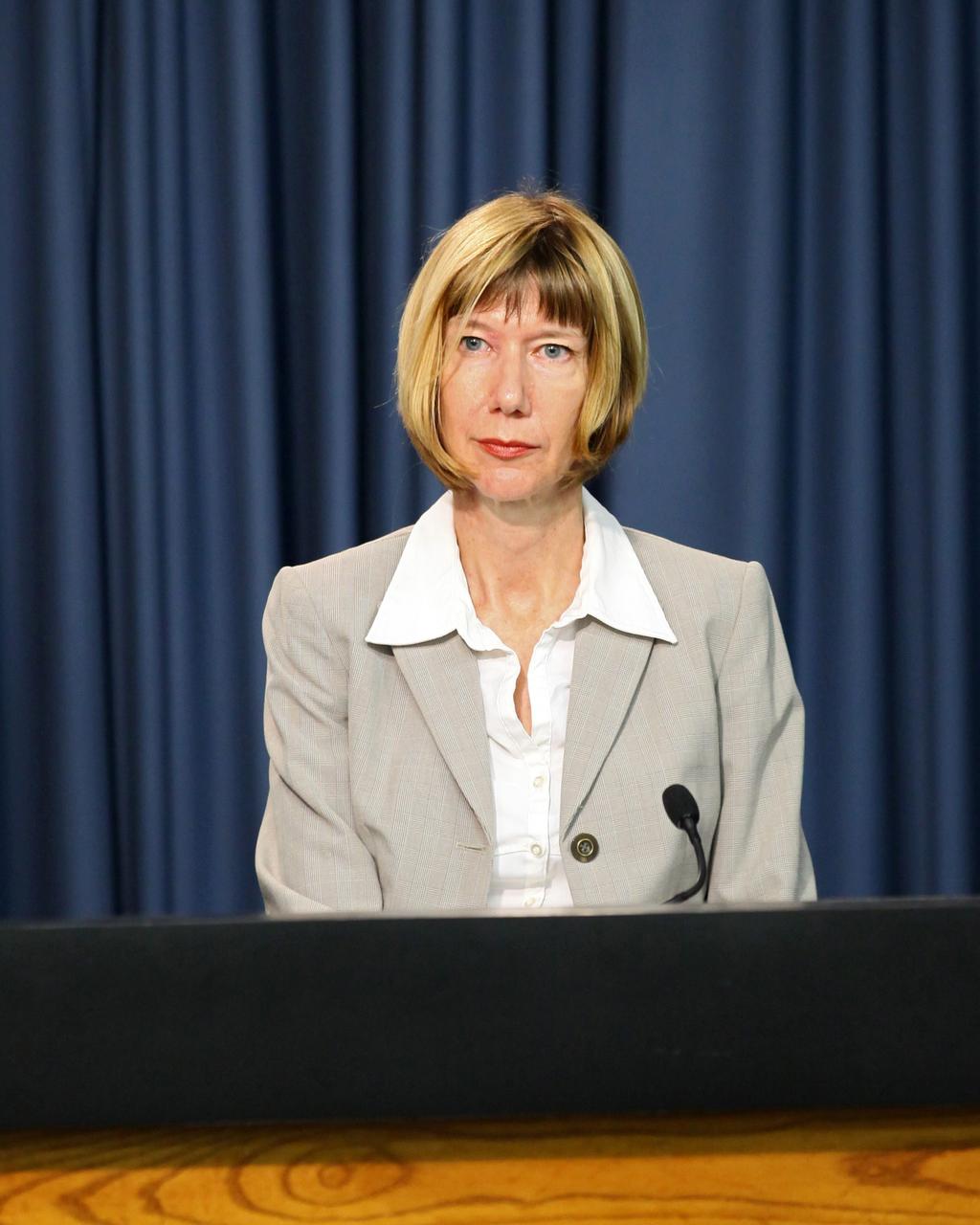

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Kathy Lueders, manager of the International Space Station, or ISS, Transportation Integration Office, participates in a NASA Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, pre-proposal conference. The conference informed prospective companies about the recently released request for contract proposals and updates to the certification requirements for crewed missions to ISS. The two-phase certification process, called Certification Products Contract, or CPC, will enable NASA to eventually purchase service missions to fly astronauts to and from the ISS. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
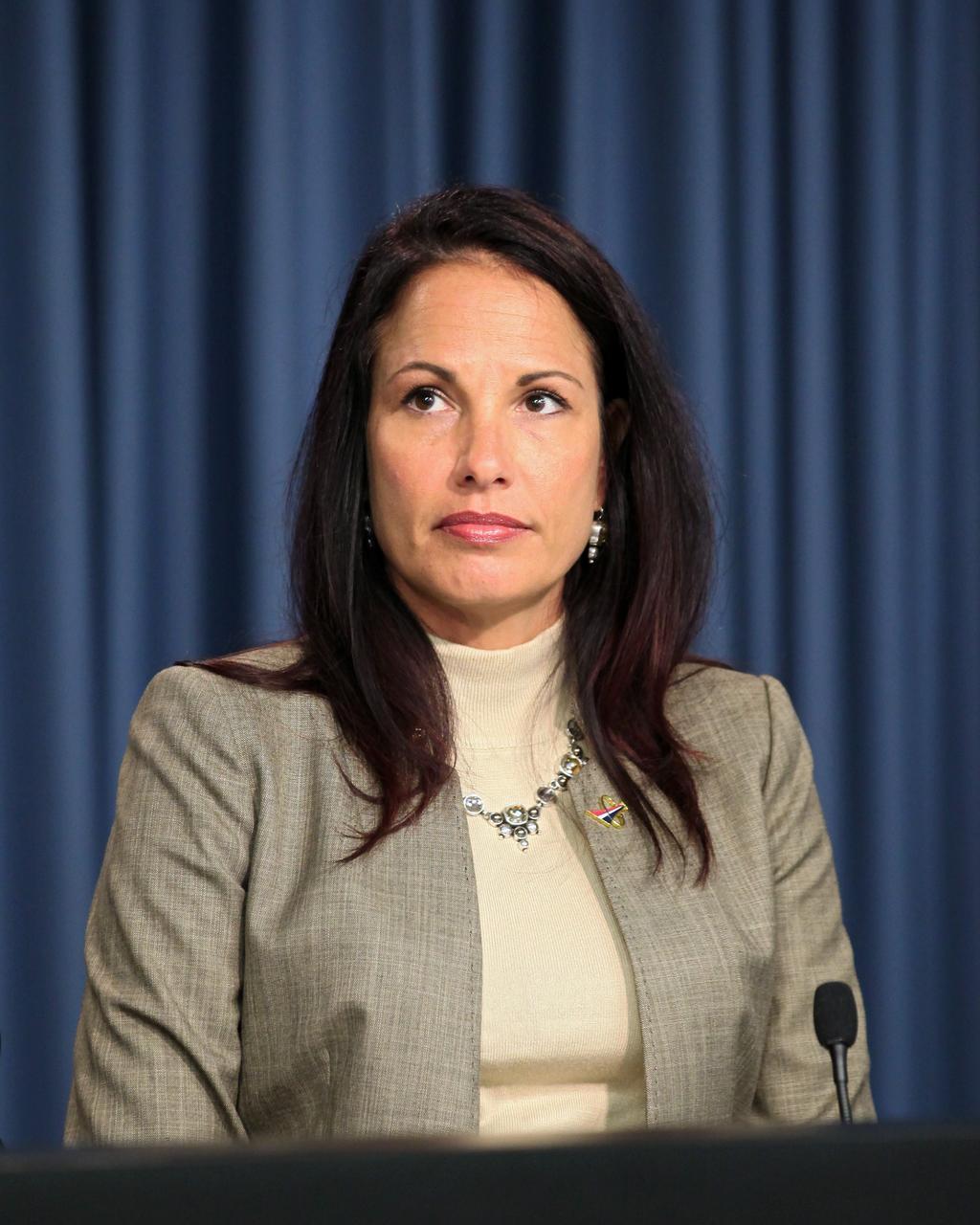

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Maria Collura of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, talks to aerospace industry representatives during a pre-proposal conference to inform prospective companies about the recently released request for contract proposals and updates to the certification requirements for crewed missions to the International Space Station, or ISS. The two-phase certification process, called Certification Products Contract, or CPC, will enable NASA to eventually purchase service missions to fly astronauts to and from the ISS. Collura serves as a CCP certification manager. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
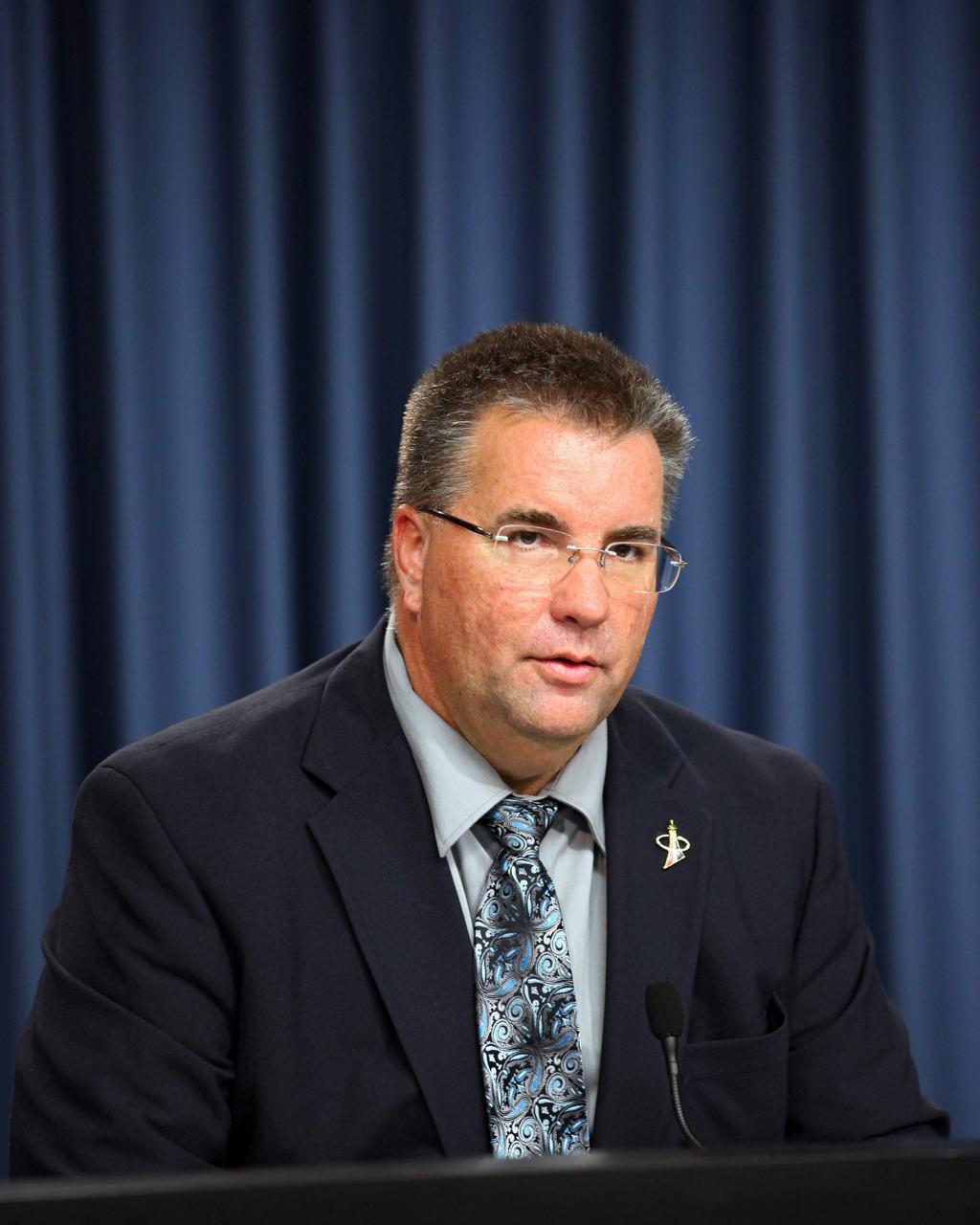

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Ed Mango, manager of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, talks to aerospace industry representatives during a pre-proposal conference to inform prospective companies about the recently released request for contract proposals and updates to the certification requirements for crewed missions to the International Space Station, or ISS. The two-phase certification process, called Certification Products Contract, or CPC, will enable NASA to eventually purchase service missions to fly astronauts to and from the ISS. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
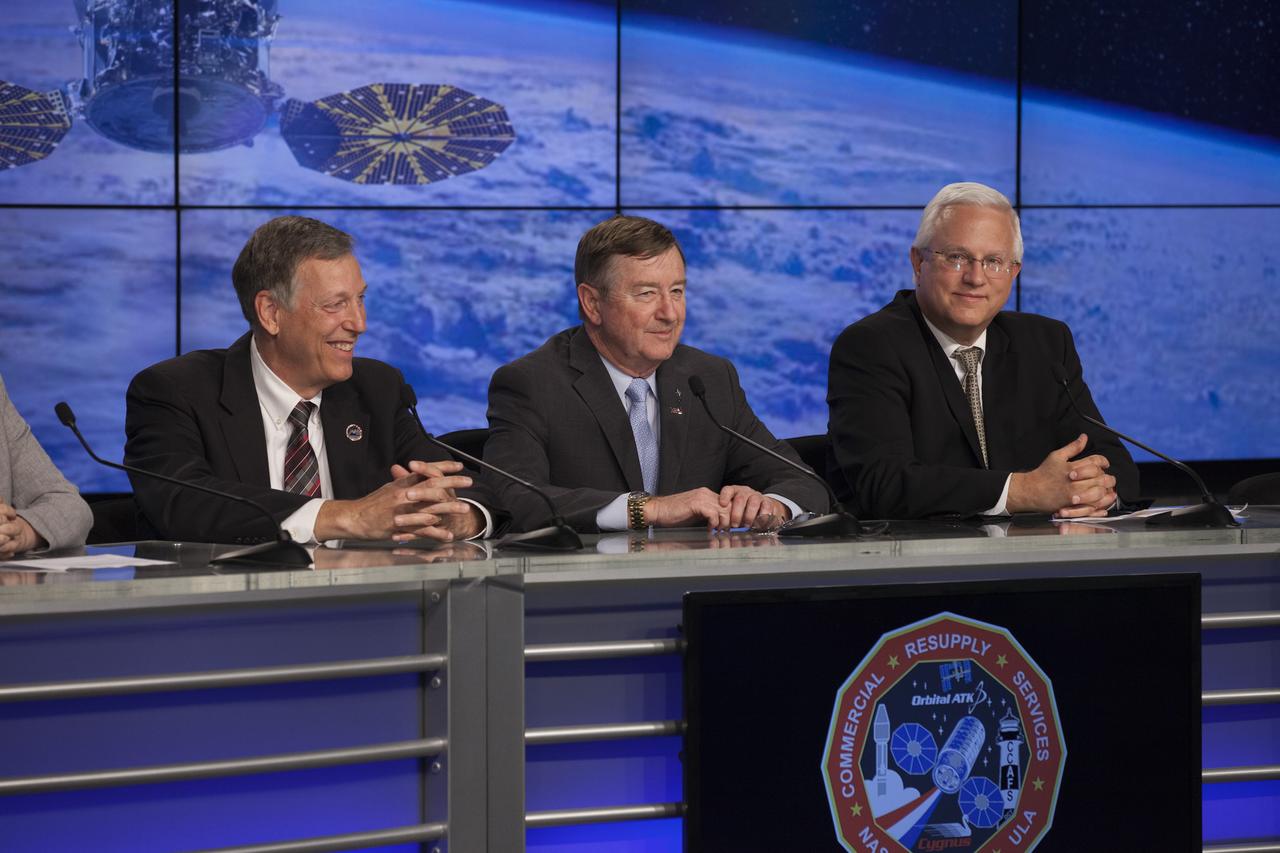

In the Press Site auditorium of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the news media at a post-launch news conference following the liftoff of Orbital ATK CRS-6, a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station, or ISS. From left are: Kenneth Todd, NASA ISS Operations Integration manager; Frank Culbertson, president of Orbital ATK's Space System Group; Vern Thorp, United Space Alliance's program manager for NASA missions. The Cygnus spacecraft lifted off atop an Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 11:05 p.m. EDT.
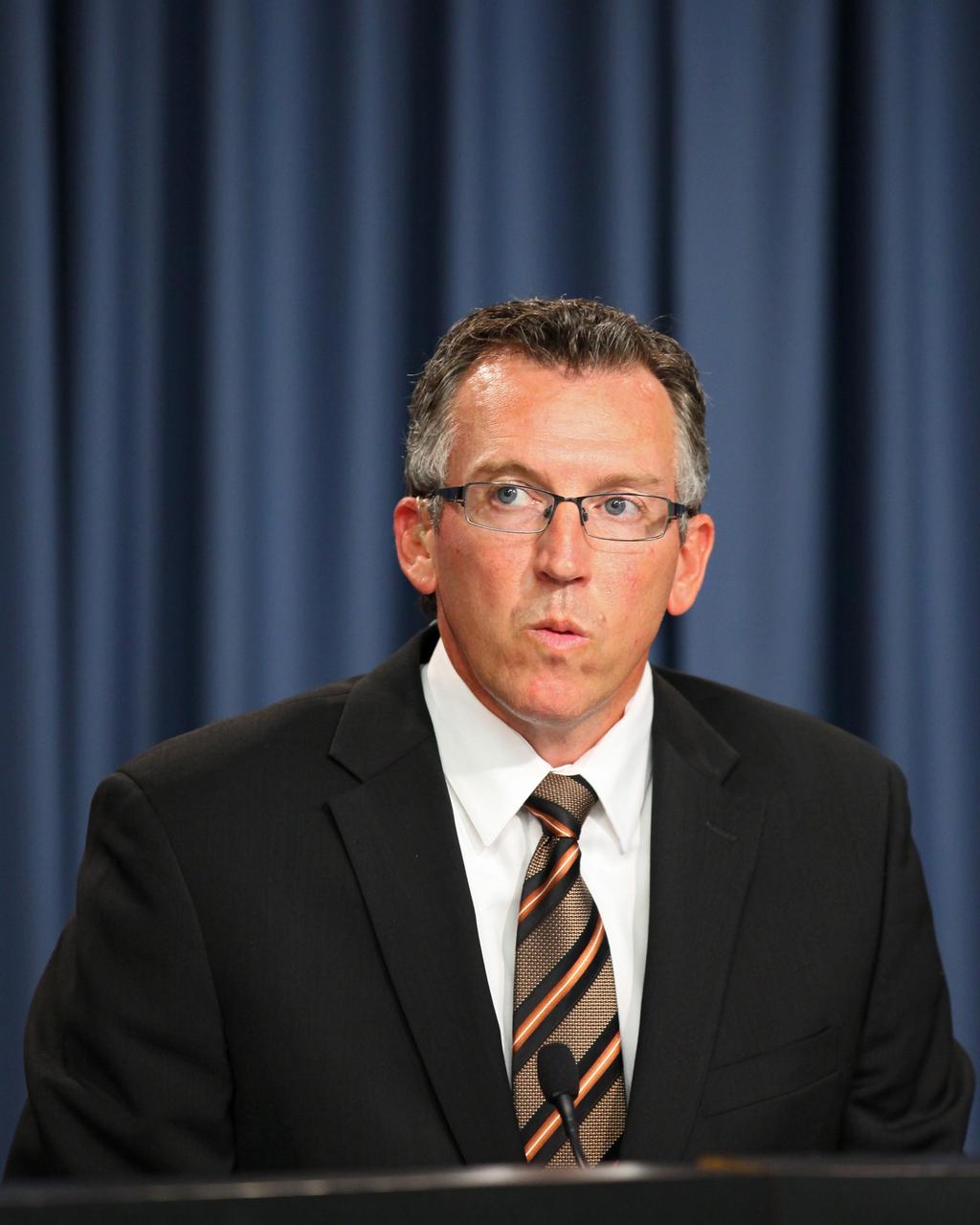

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Steve Janney of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, talks to aerospace industry representatives during a pre-proposal conference to inform prospective companies about the recently released request for contract proposals and updates to the certification requirements for crewed missions to the International Space Station, or ISS. The two-phase certification process, called Certification Products Contract, or CPC, will enable NASA to eventually purchase service missions to fly astronauts to and from the ISS. Janney serves as the contracting officer during CPC procurement. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
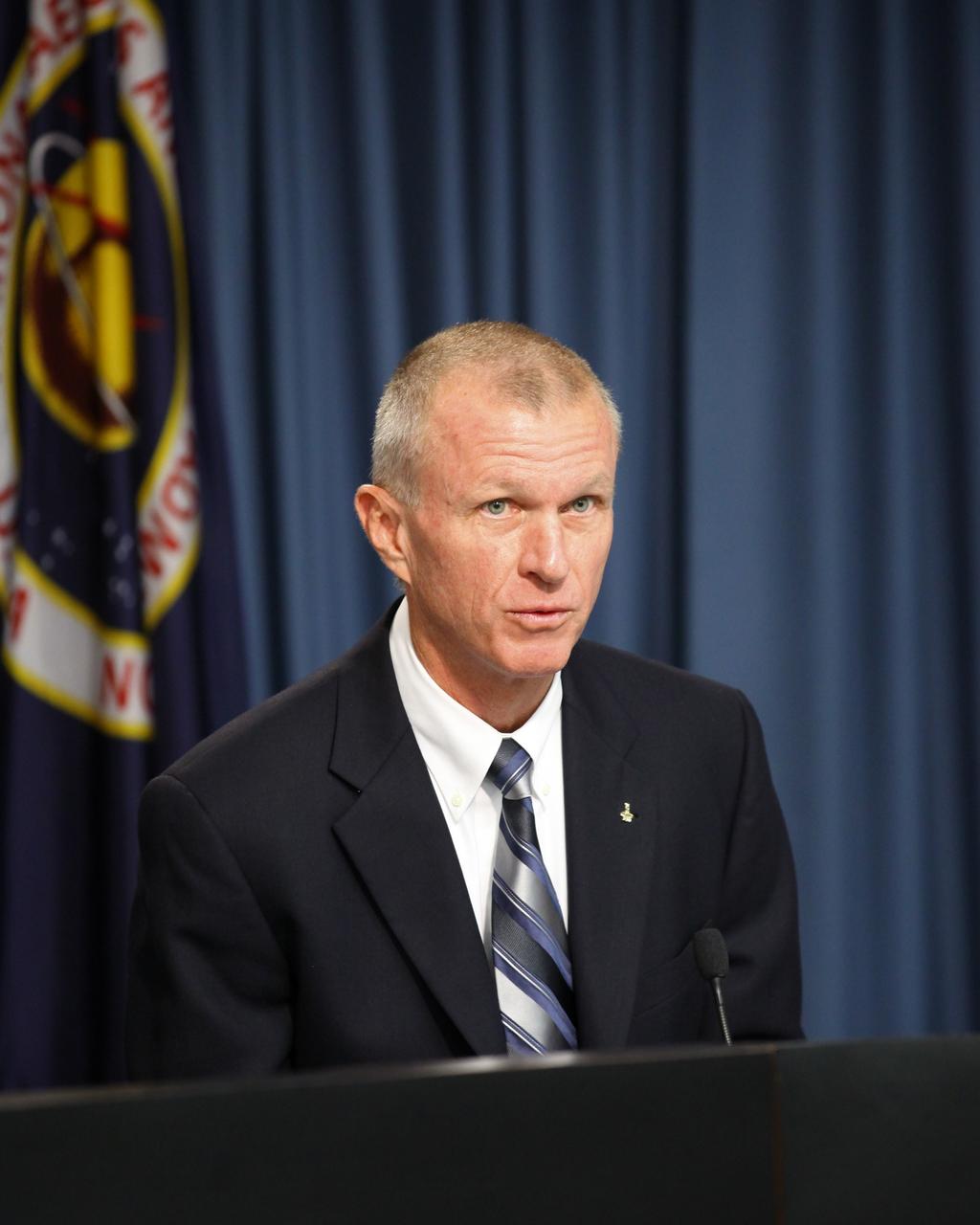

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Brent Jett, deputy manager of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, talks to aerospace industry representatives during a pre-proposal conference to inform prospective companies about the recently released request for contract proposals and updates to the certification requirements for crewed missions to the International Space Station, or ISS. The two-phase certification process, called Certification Products Contract, or CPC, will enable NASA to eventually purchase service missions to fly astronauts to and from the ISS. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
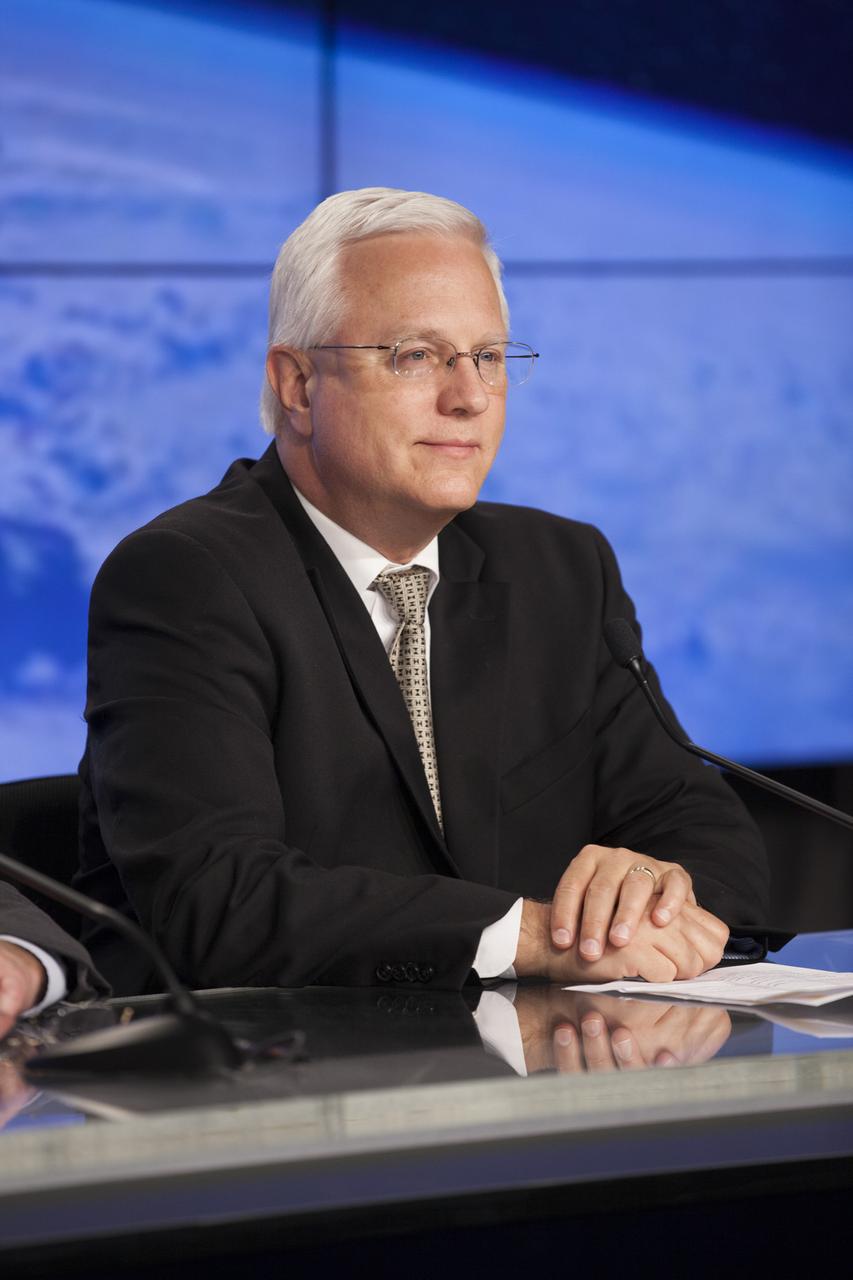

In the Press Site auditorium of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Vern Thorp, United Space Alliance's program manager for NASA missions, speaks to members of the news media at a post-launch news conference following the liftoff of Orbital ATK CRS-6, a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station, or ISS. The Cygnus spacecraft lifted off atop an Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 11:05 p.m. EDT.
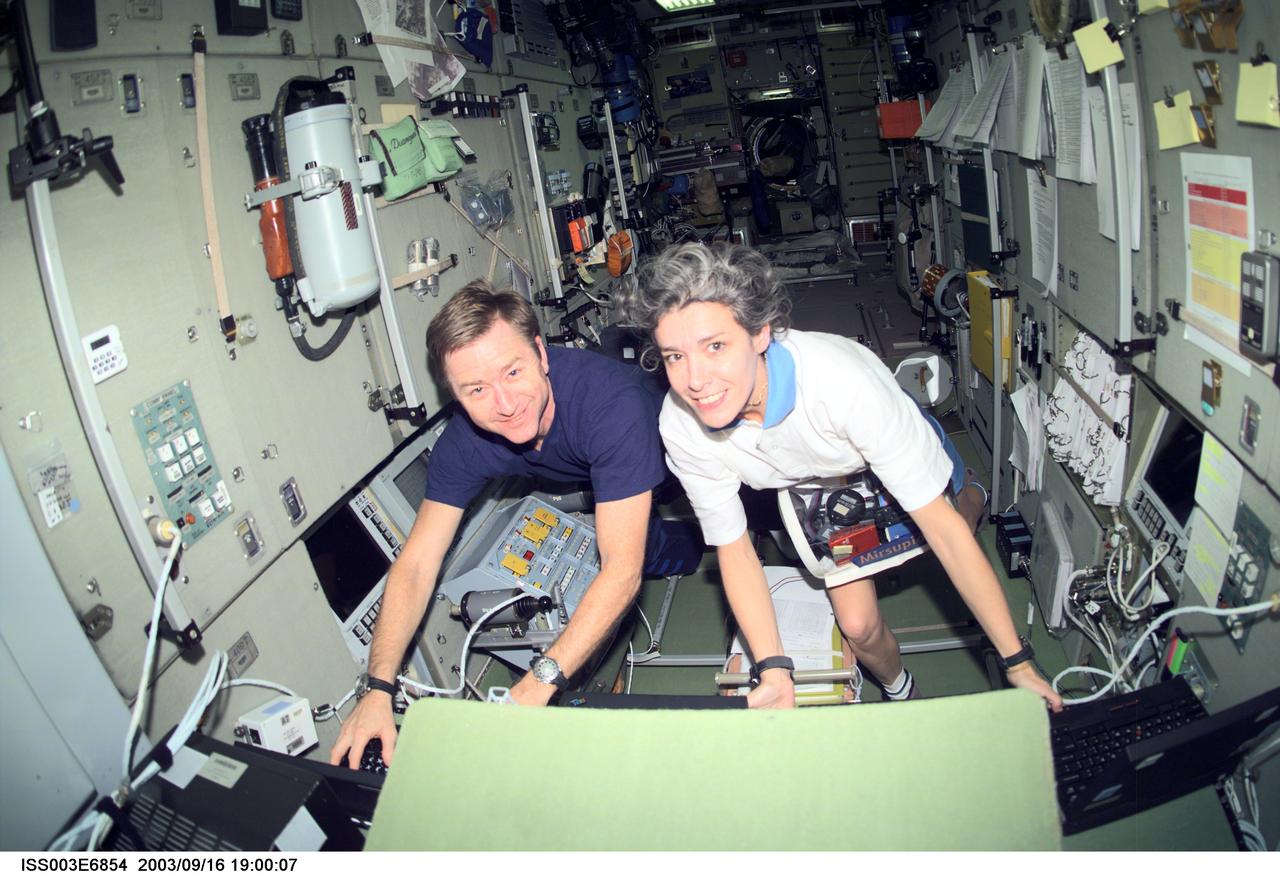

ISS003-E-6854 (23-31 October 2001) --- Astronaut Frank L. Culbertson, Jr. (left), Expedition Three mission commander, and French Flight Engineer Claudie Haignere, work in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). Haignere represents ESA, carrying out a flight program for CNES, the French Space Agency, under a commercial contract with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. This image was taken with a digital still camera.
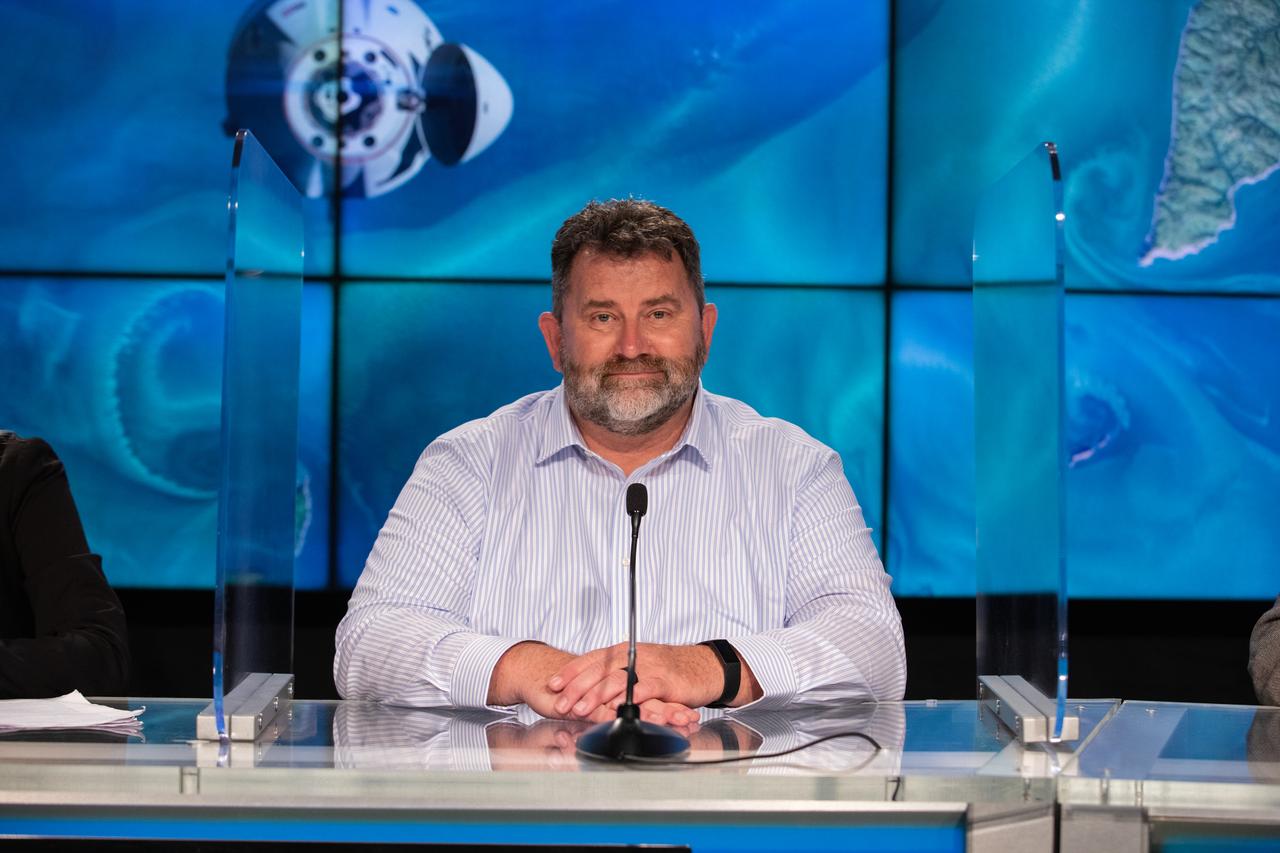

Mike Roberts, chief scientist, ISS National Lab, participates in a climate conversation at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 13, 2022, leading up to SpaceX’s 25th Commercial Resupply Services mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon capsule atop SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket is scheduled to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A on July 14 at 8:44 p.m. EDT. Dragon will deliver more than 5,800 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, to the space station.

ISS003-E-6855 (23-31 October 2001) --- French Flight Engineer Claudie Haignere, works in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). Haignere represents ESA, carrying out a flight program for CNES, the French Space Agency, under a commercial contract with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. This image was taken with a digital still camera.
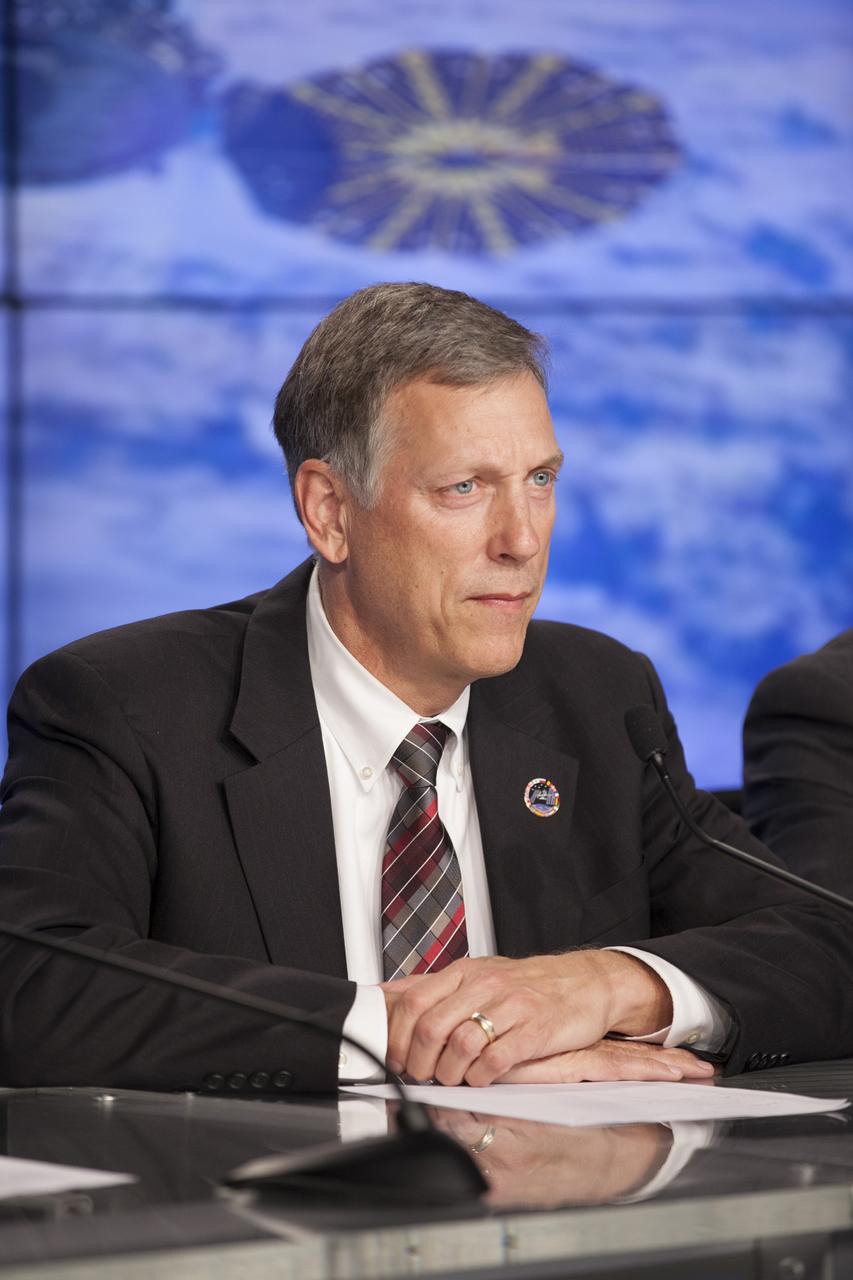

In the Press Site auditorium of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Kenneth Todd, NASA's International Space Staton Operations Integration manager, speaks to members of the news media at a post-launch news conference following the liftoff of Orbital ATK CRS-6, a commercial resupply services mission to the ISS. The Cygnus spacecraft lifted off atop an Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 11:05 p.m. EDT.
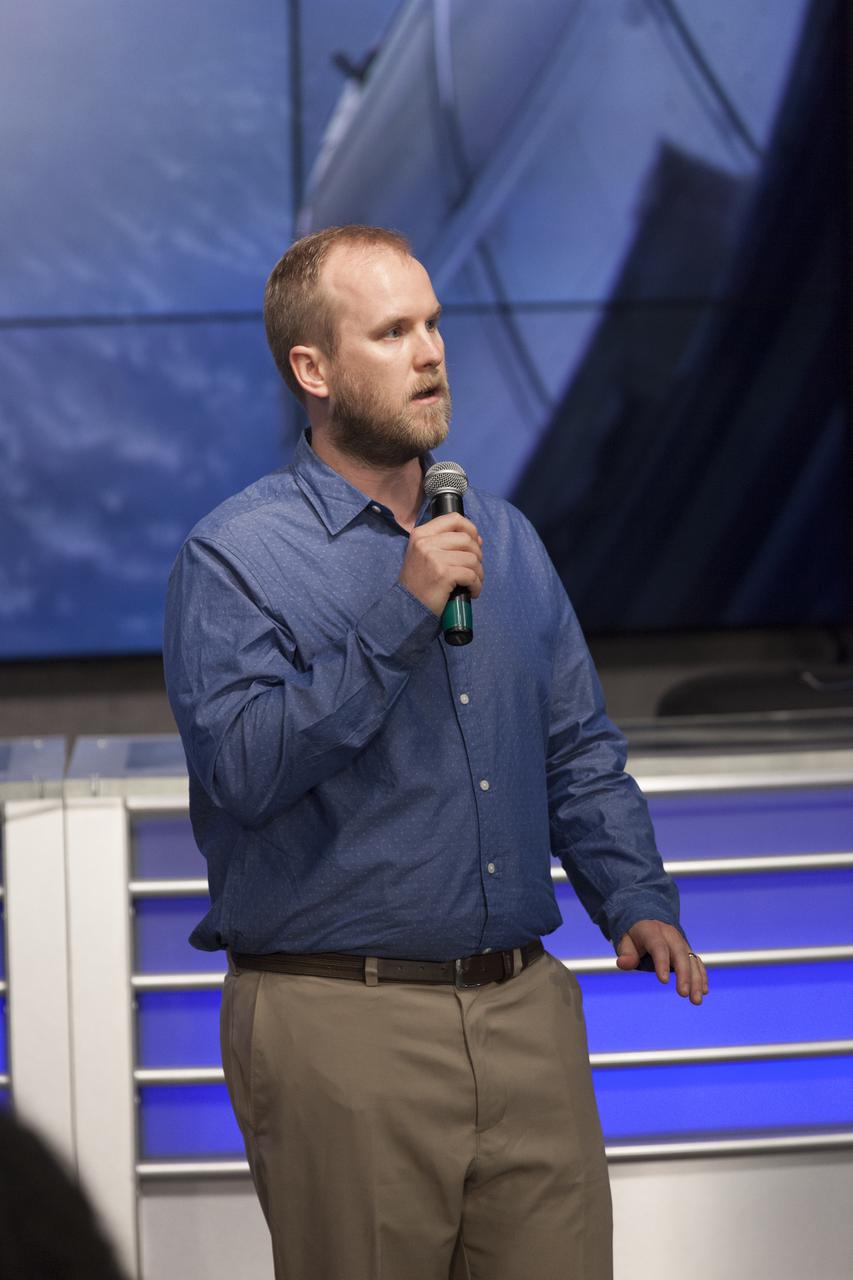

Jacob Smith of the University of Maryland speaks to members of social media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. He is operations lead for the International Space Station Cosmic Ray Energetics and Mass, or ISS-CREAM, investigation. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for launch from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A on Aug. 14 atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on the company's 12th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
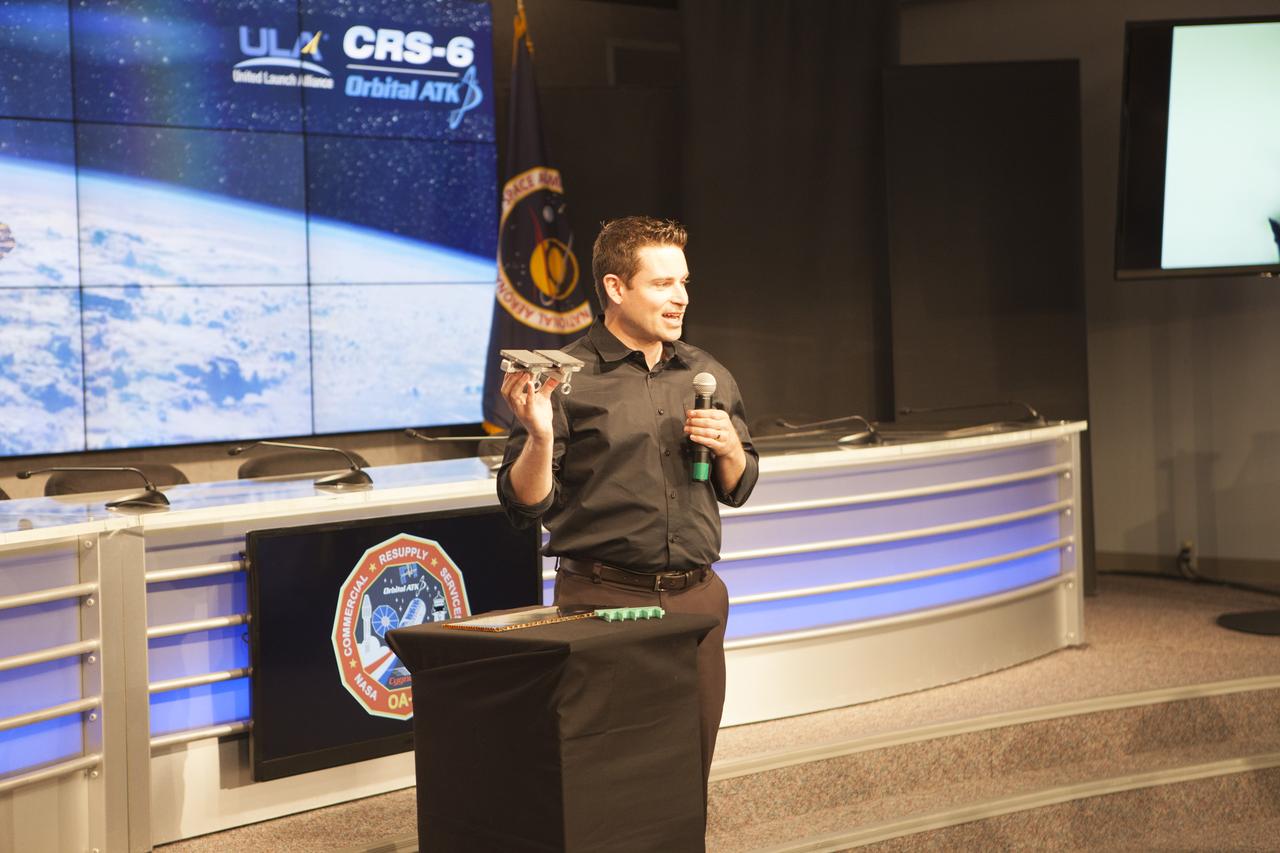

Dr. Aaron Parness, group leader at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, who is working the Extreme Environment Robots Group on the Gecko Grippers experiment, speaks to members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on science research and technology work planned for the International Space Station, or ISS, following the arrival of a Cygnus spacecraft. The Cygnus is scheduled to be launched March 22 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on the Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission.
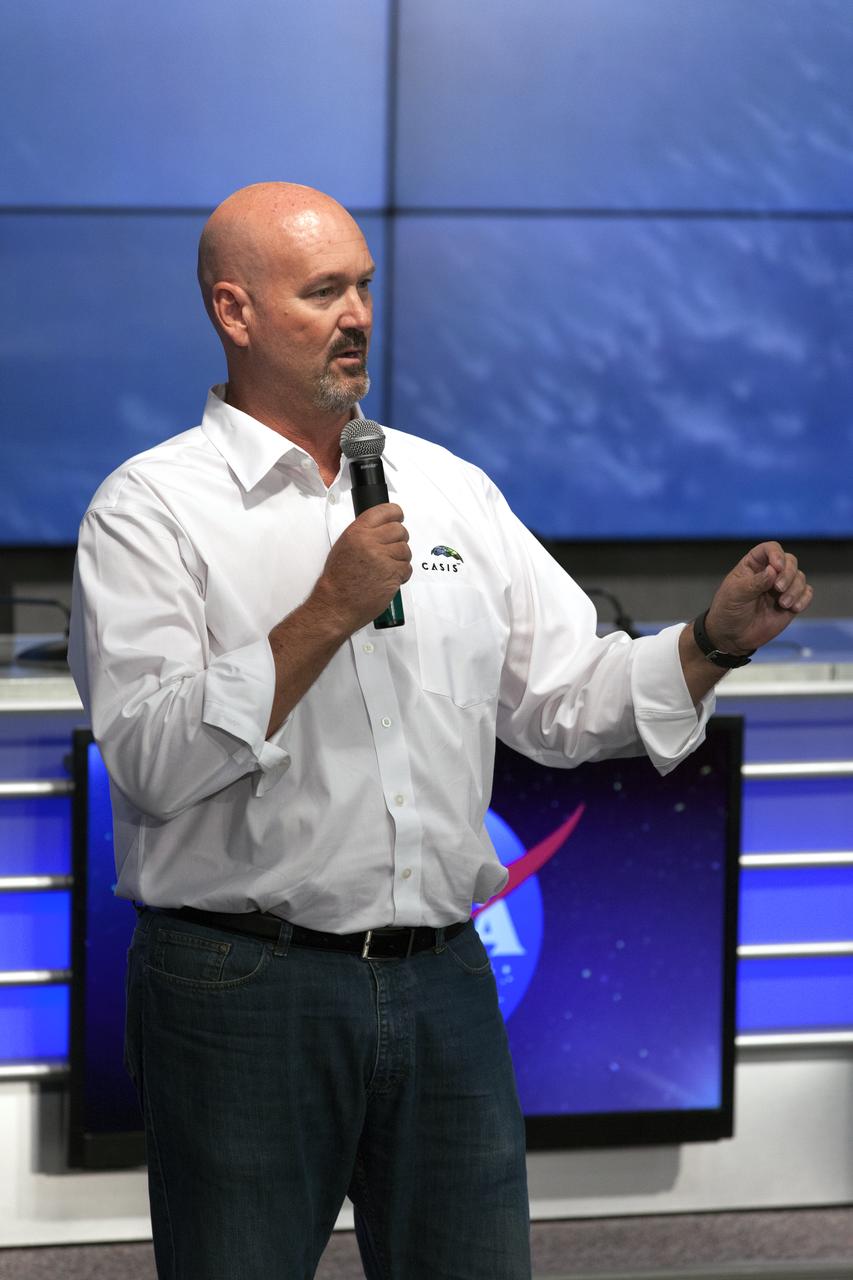

Ken Shields, director of Operations for Center for the Advancement of Science in Space/ISS National Lab, speaks to members of social media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for launch from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A on Aug. 14 atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on the company's 12th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
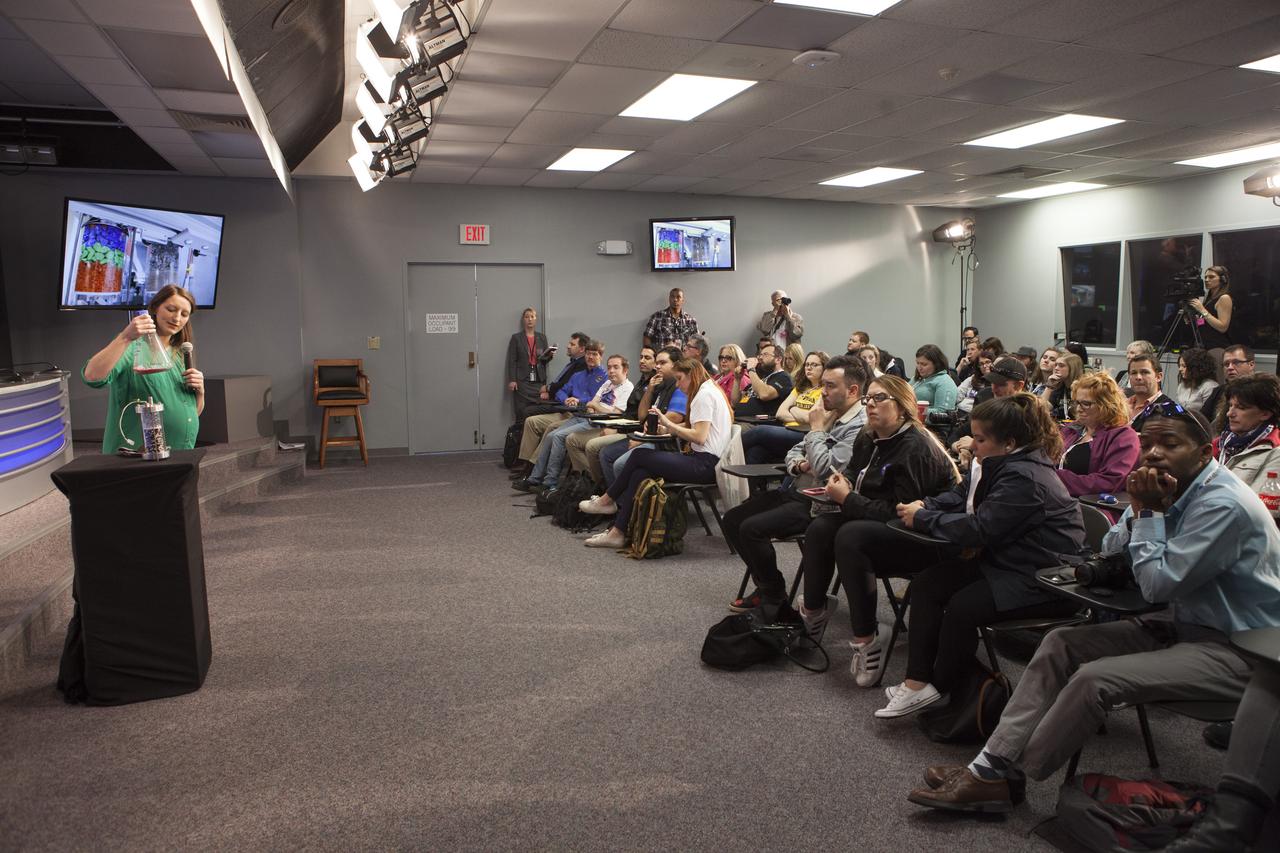

Dr. Kristen John, deputy project manager and co-investigator for the Strata-1 experiment at the Johnson Space Center in Houston , speaks to members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on science research and technology work planned for the International Space Station, or ISS, following the arrival of a Cygnus spacecraft. The Cygnus is scheduled to be launched March 22 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on the Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission.
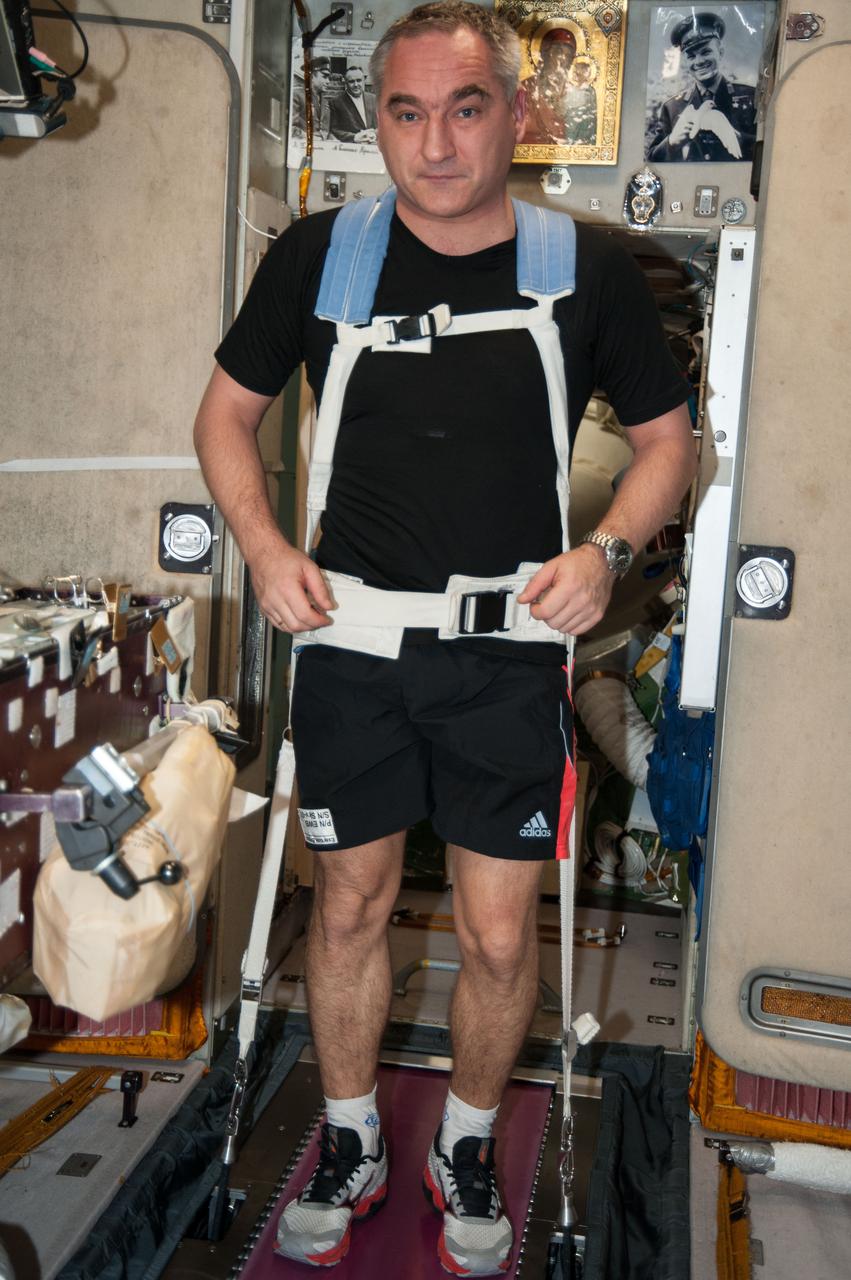

iss040e071323 (7/23/2014) --- Russian cosmonaut Alexander Skvortsov, exercises on the Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS) in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station (ISS). Photo is part of IVA clothing study. The Intravehicular Activity Clothing Study (IVA Clothing Study) dresses crewmembers in commercially available lightweight clothes that have been designed to resist odors.
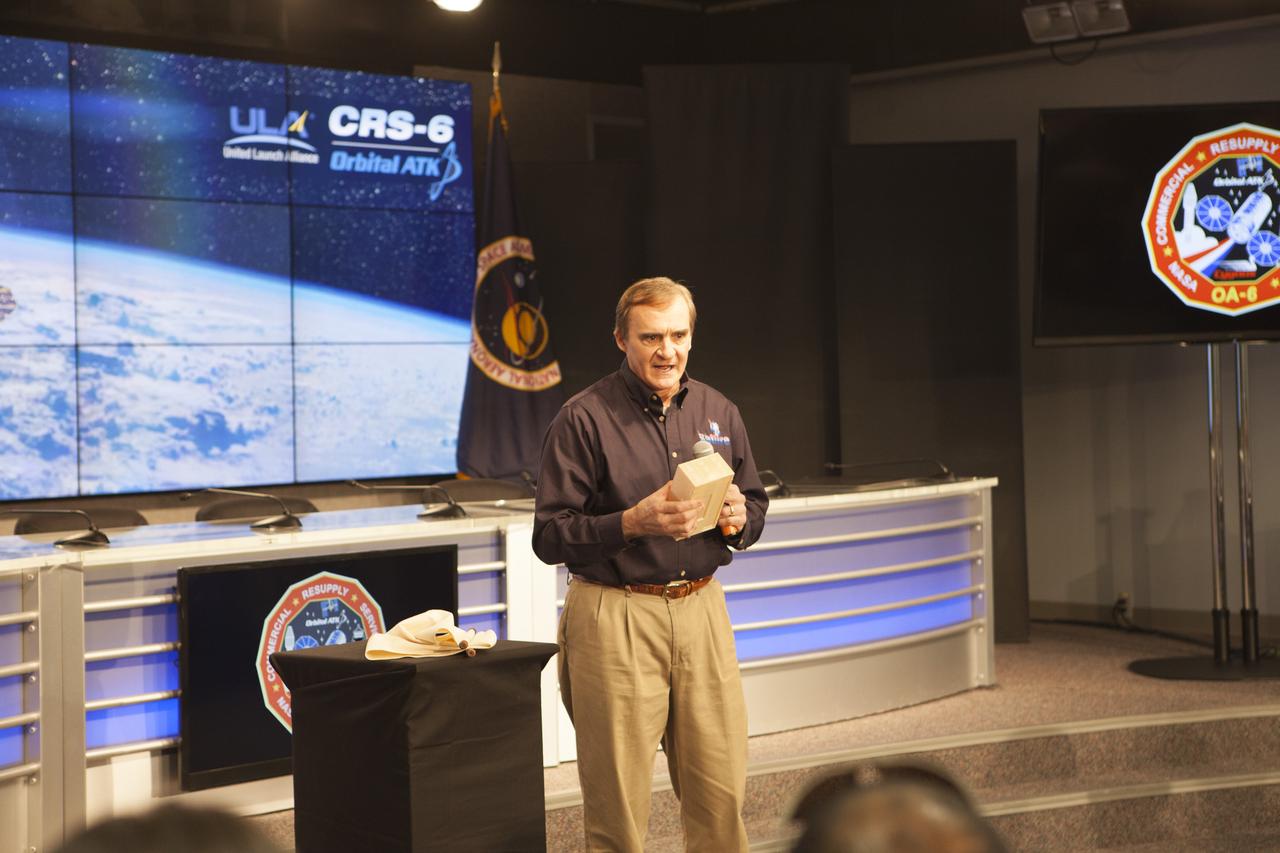

Gary Ruff, NASA project manager and co-investigator for the Spacecraft Fire Safety Demonstration Project, or Saffire, at the Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, speaks to members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on science research and technology work planned for the International Space Station, or ISS, following the arrival of a Cygnus spacecraft. The Cygnus is scheduled to be launched March 22 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on the Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission.
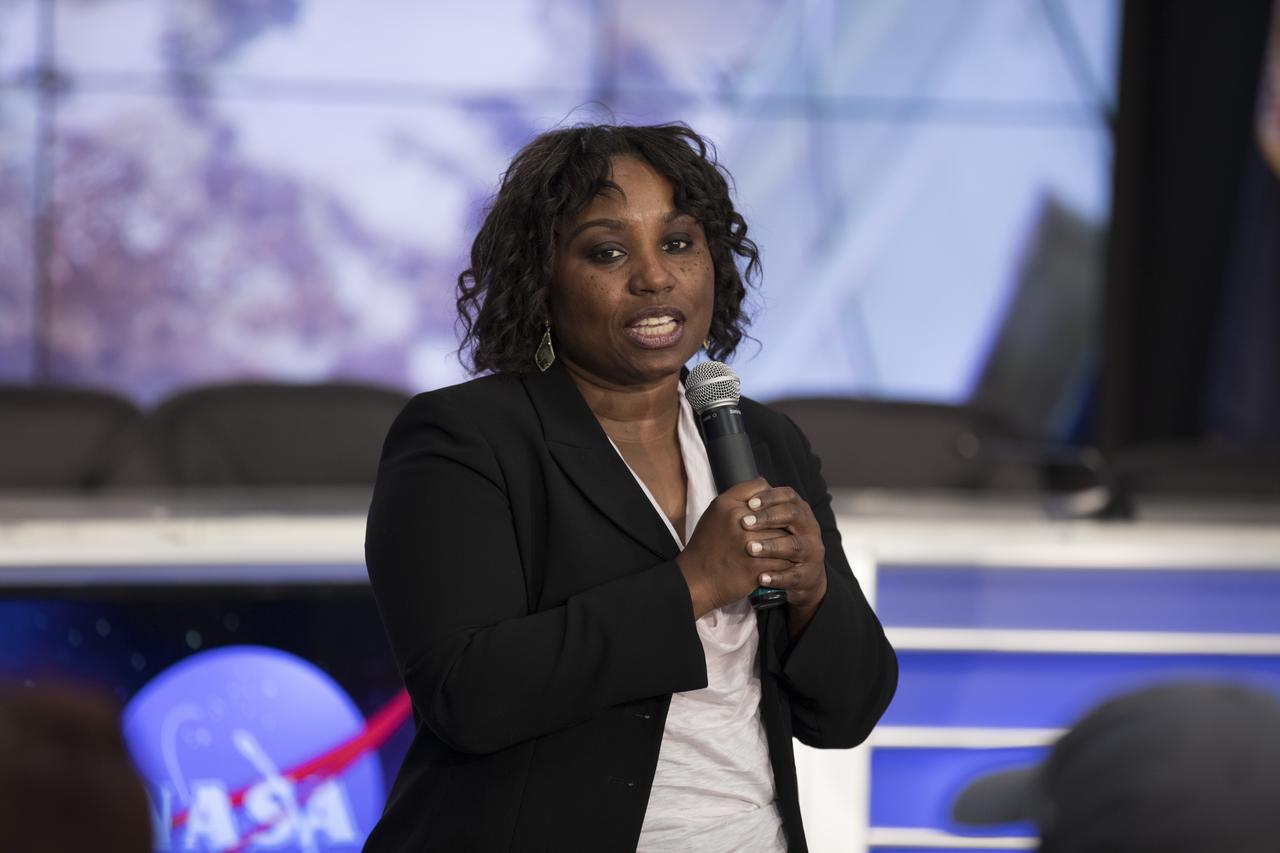

Dr. Camille Alleyne, associate program scientist for the International Space Station (ISS) at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, speaks to members of social media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for launch from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A on June 1 atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on the company's 11th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
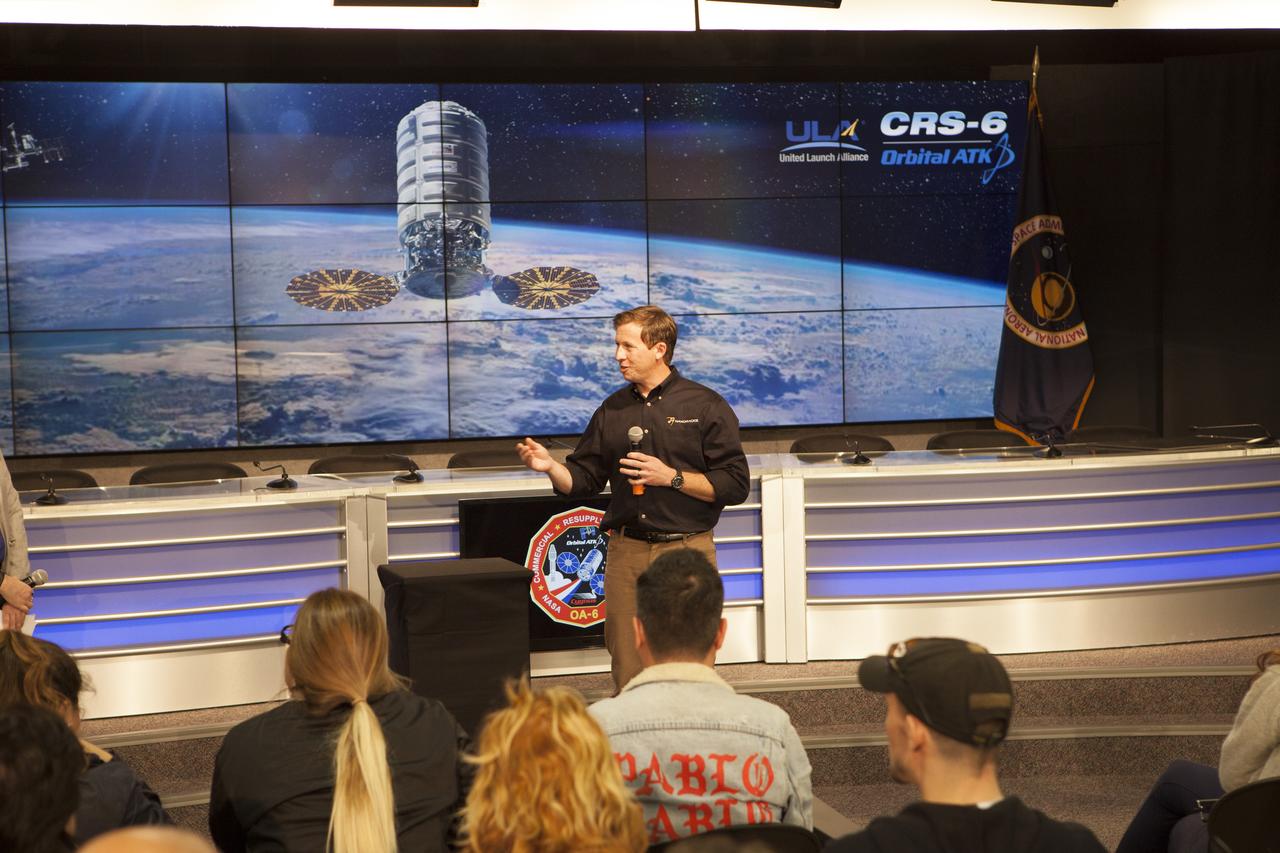

Michael Lewis, chief technology officer for NanoRacks, speaks to members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on science research and technology work planned for the International Space Station, or ISS, following the arrival of a Cygnus spacecraft. The Cygnus is scheduled to be launched March 22 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on the Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission.
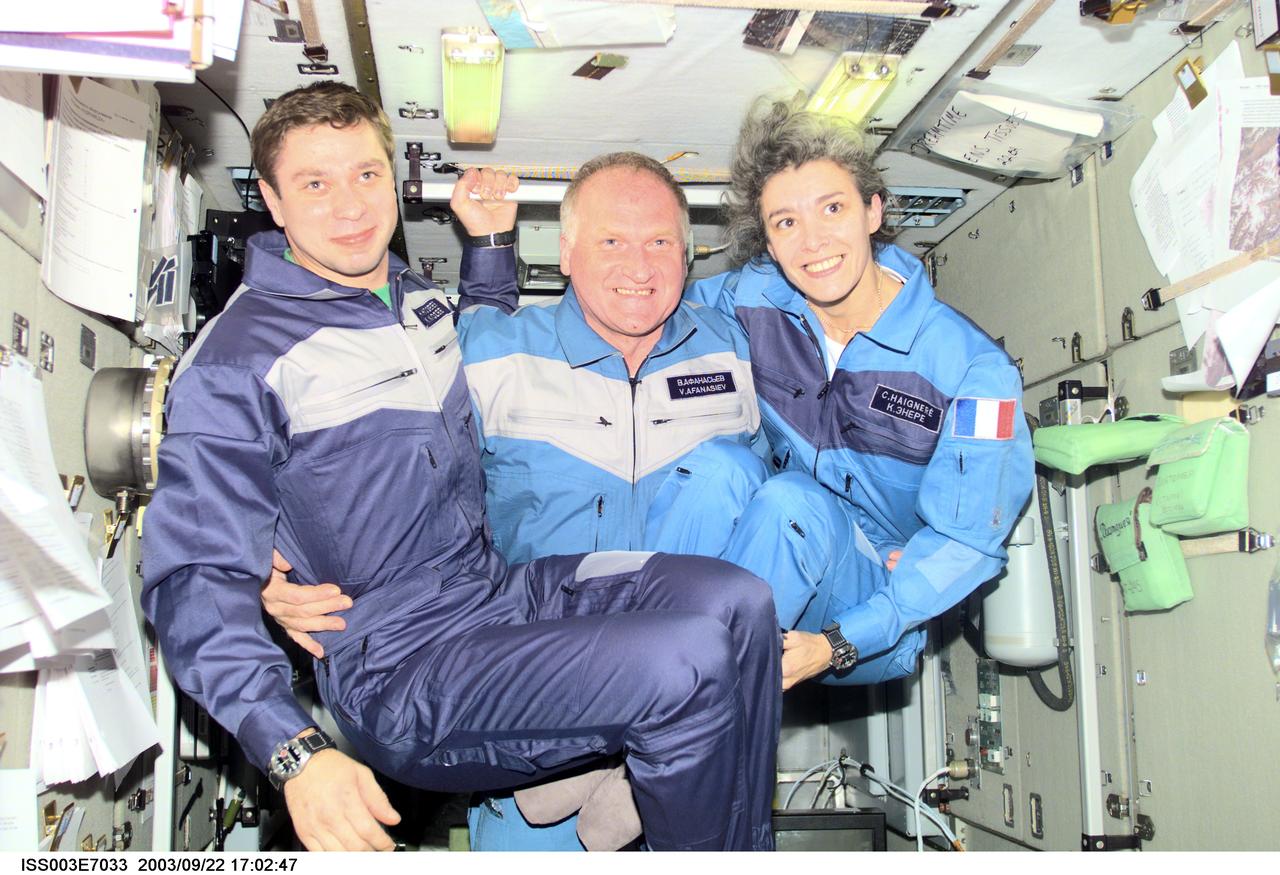

ISS003-E-7033 (23-31 October 2001) --- The Soyuz Taxi crewmembers assemble for a group photo in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). From the left are Flight Engineer Konstantin Kozeev, Commander Victor Afanasyev, and French Flight Engineer Claudie Haignere. Afanasyev and Kozeev represent Rosaviakosmos, and Haignere represents ESA, carrying out a flight program for CNES, the French Space Agency, under a commercial contract with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. This image was taken with a digital still camera.
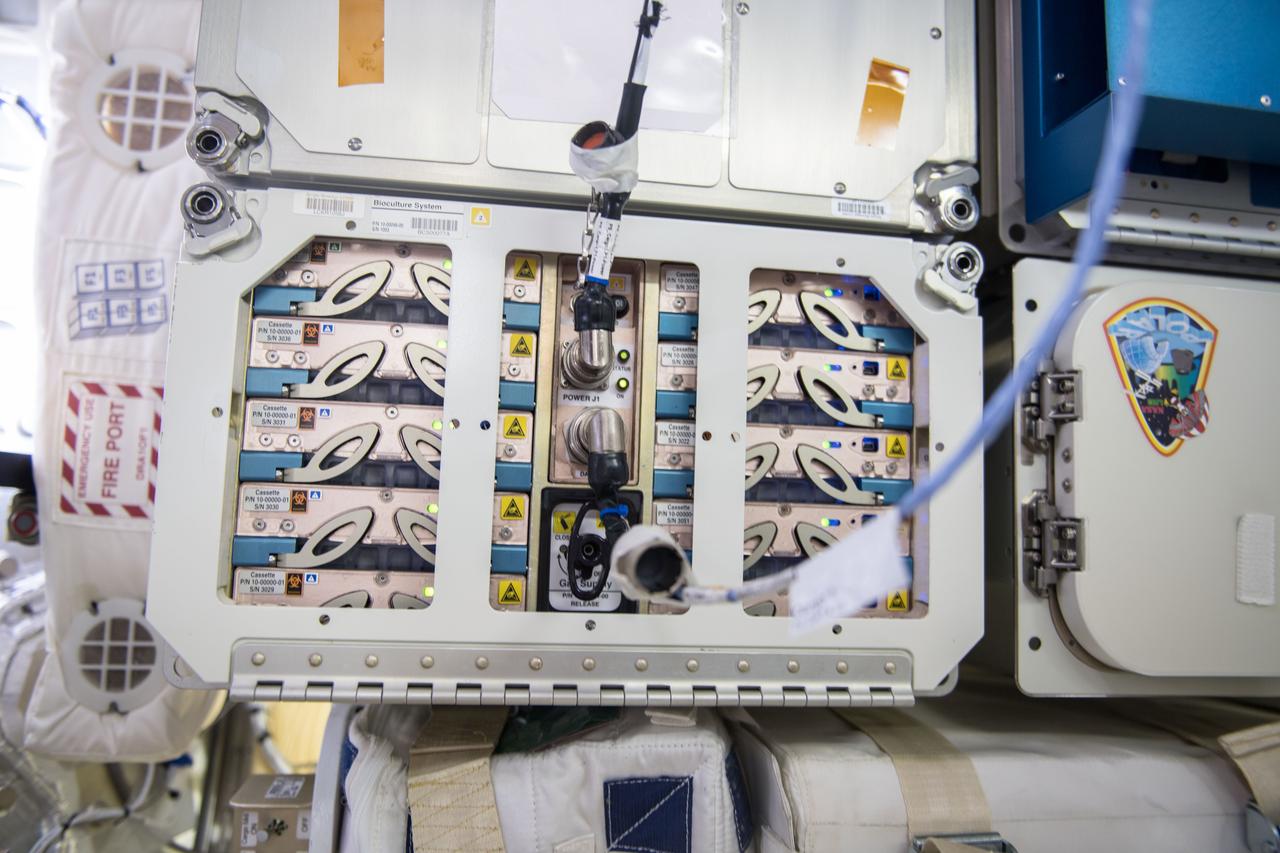
iss054e020928 (1/12/2018) --- Photo documentation of the Bioculture System Facility installed in the SpaceX Dragon Commercial Resupply Services-13 (CRS-13) spacecraft for return to Earth. The Bioculture System Hardware Validation (Cell Science-Validation) tests the performance and life-support capability of a new cell culture hardware system for use aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
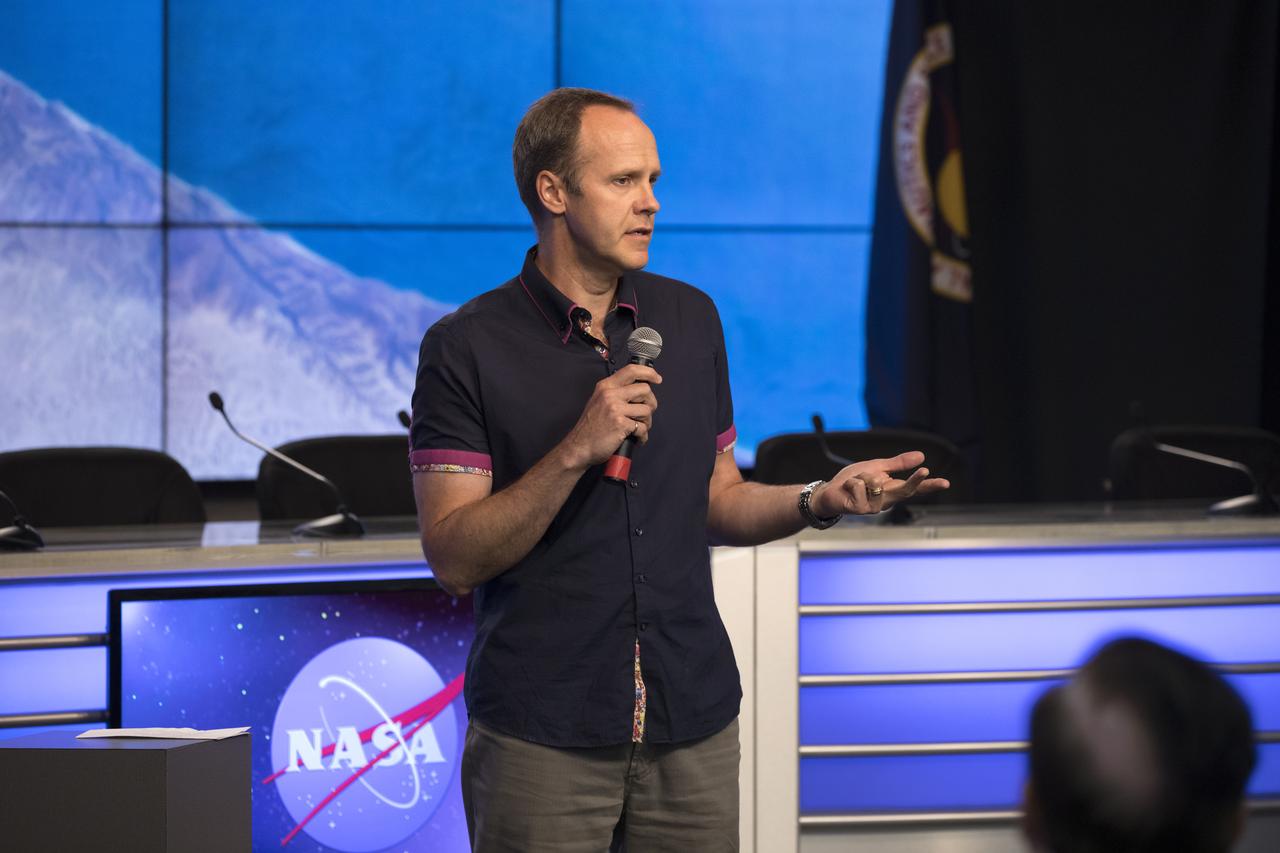

Ken Podwalski, Canadian ISS program manager, talks to members of the media during a briefing in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 15th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
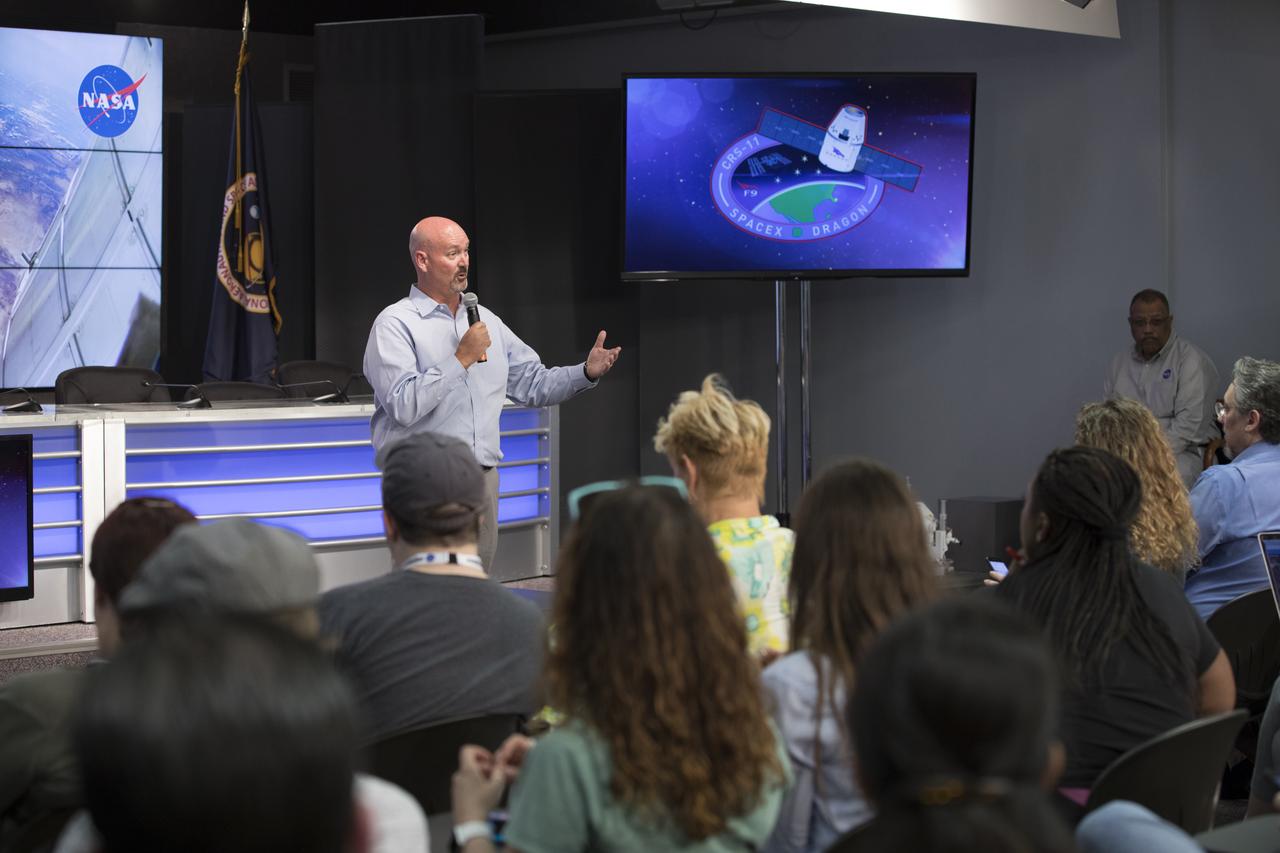

Ken Shields, director of Operations for the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS)/ISS National Lab, speaks to members of social media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for launch from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A on June 1 atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on the company's 11th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
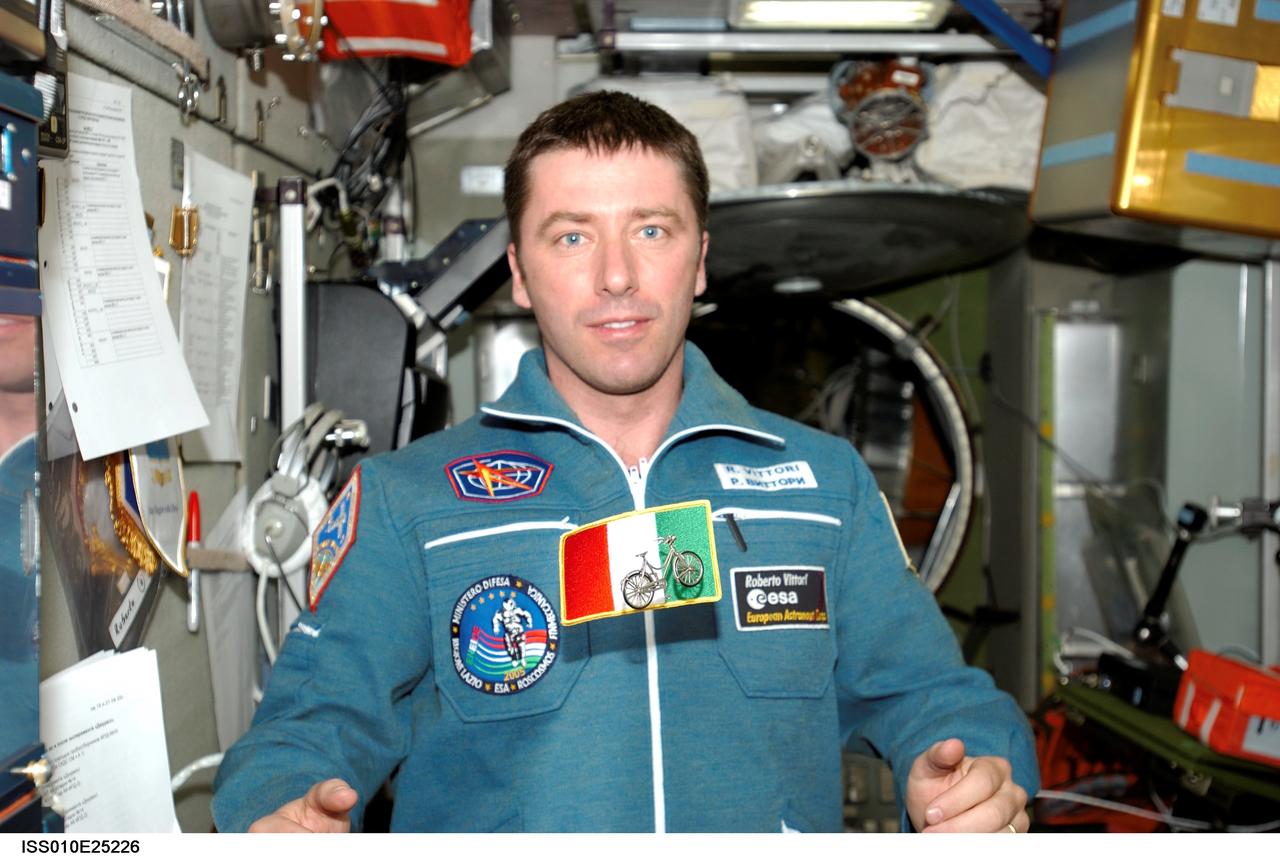

ISS010-E-25226 (20 April 2005) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Roberto Vittori of Italy is pictured in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station (ISS). A patch representing the Italian flag and a toy bicycle float freely near Vittori. After spending eight days on the Station under a commercial contract between ESA and the Russian Federal Space Agency, Vittori will return to Earth with the Expedition 10 crew on April 24 (CDT).
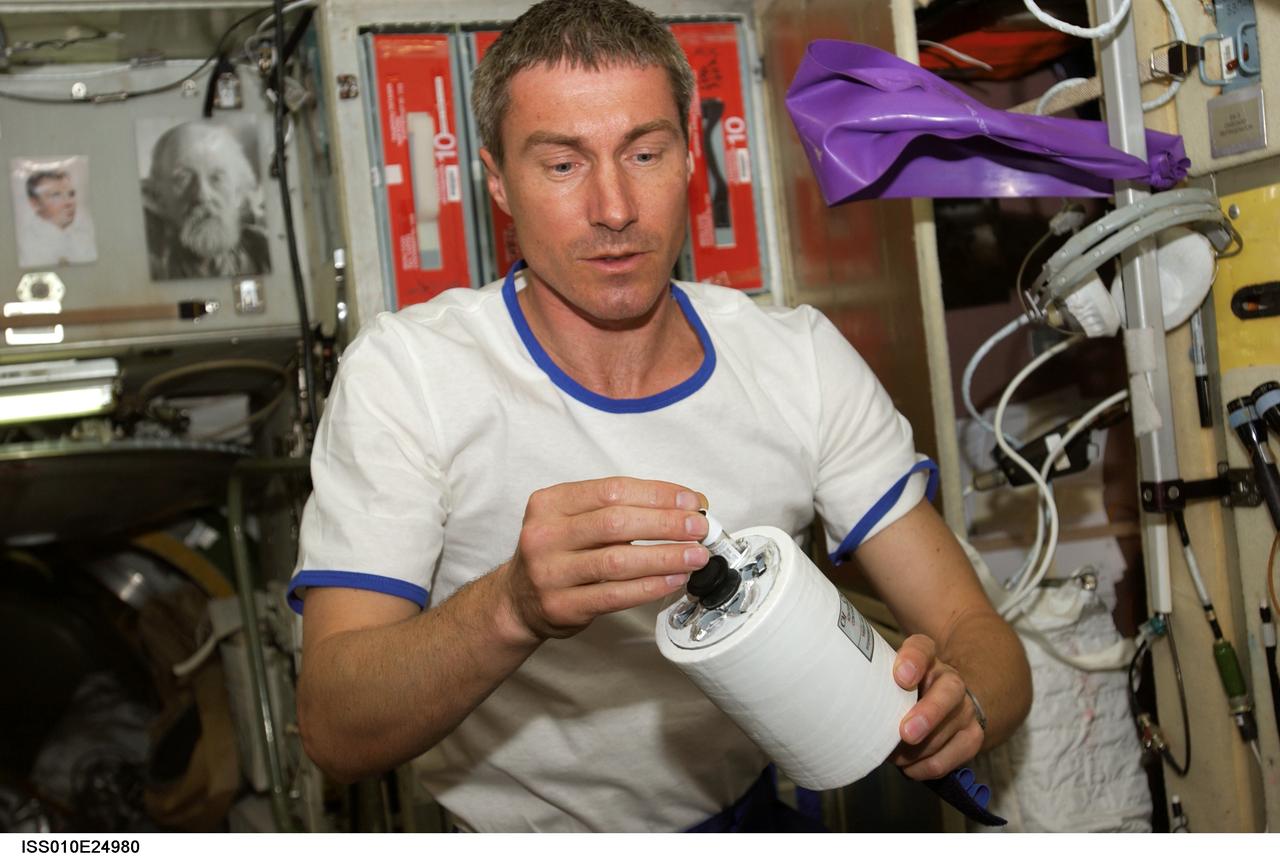

ISS010-E-24980 (18 April 2005) --- Cosmonaut Sergei K. Krikalev, Expedition 11 commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, holds a sample tube within the Commercial Protein Crystallization Facility-2 (CPCF-2) Activation Mechanism which is part of the Kriogem-03 refrigerator in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station (ISS).

In the Press Site auditorium of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Frank Culbertson, president of Orbital ATK's Space System Group, speaks to members of the news media at a post-launch news conference following the liftoff of Orbital ATK CRS-6, a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station, or ISS. The Cygnus spacecraft lifted off atop an Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 11:05 p.m. EDT.
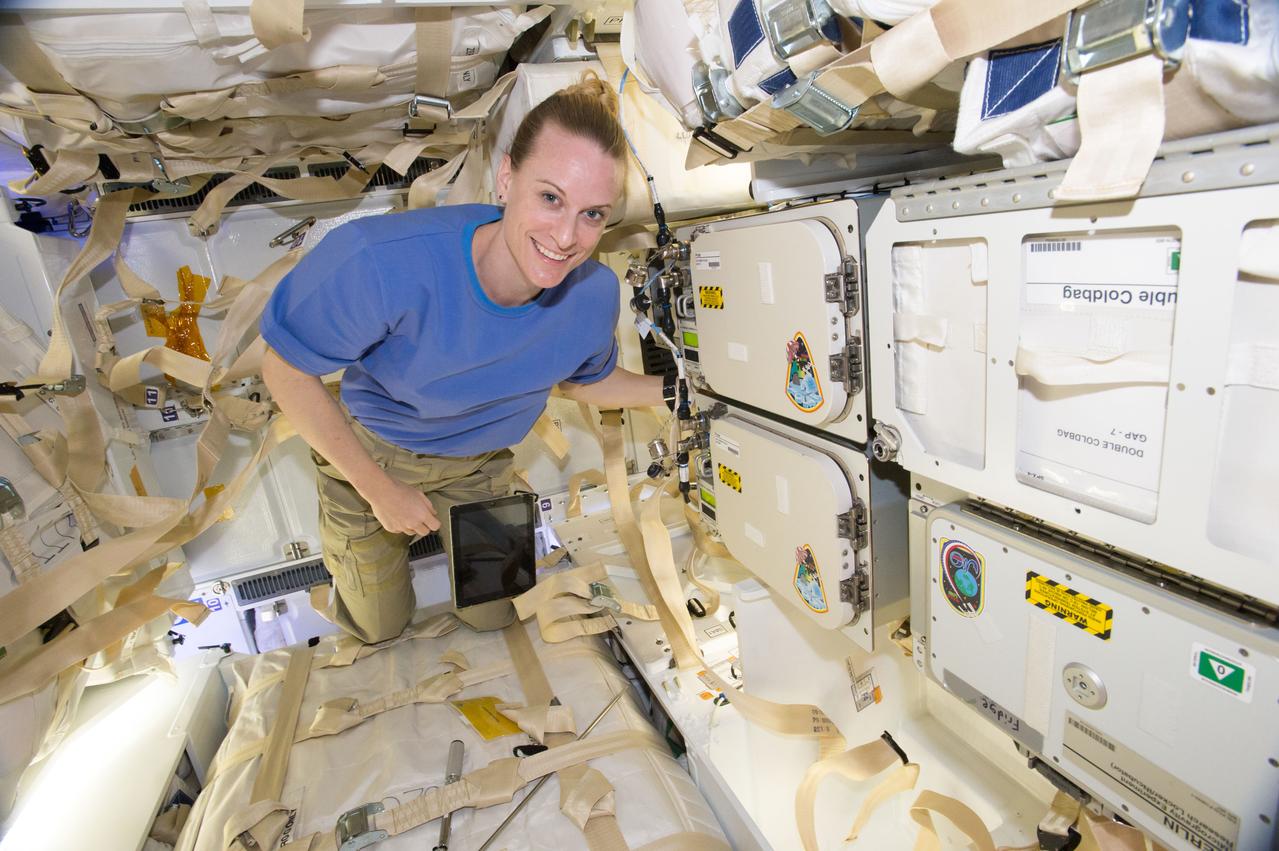

iss048e065818 (8/24/2016) --- NASA astonaut Kate Rubins poses for a photo next to Polar Facilities 2 and 4 installed in the SpaceX Dragon Commercial Resupply Services-9 (CRS-9) spacecraft for return to Earth. Polar is a Cold Stowage managed facility that provides transport and storage of science samples at cryogenic temperatures (-80ºC) to and from the International Space Station (ISS).

Michael Snyder, chief engineer for Made in Space, speaks to members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on science research and technology work planned for the International Space Station, or ISS, following the arrival of a Cygnus spacecraft. The Cygnus is scheduled to be launched March 22 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on the Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission.
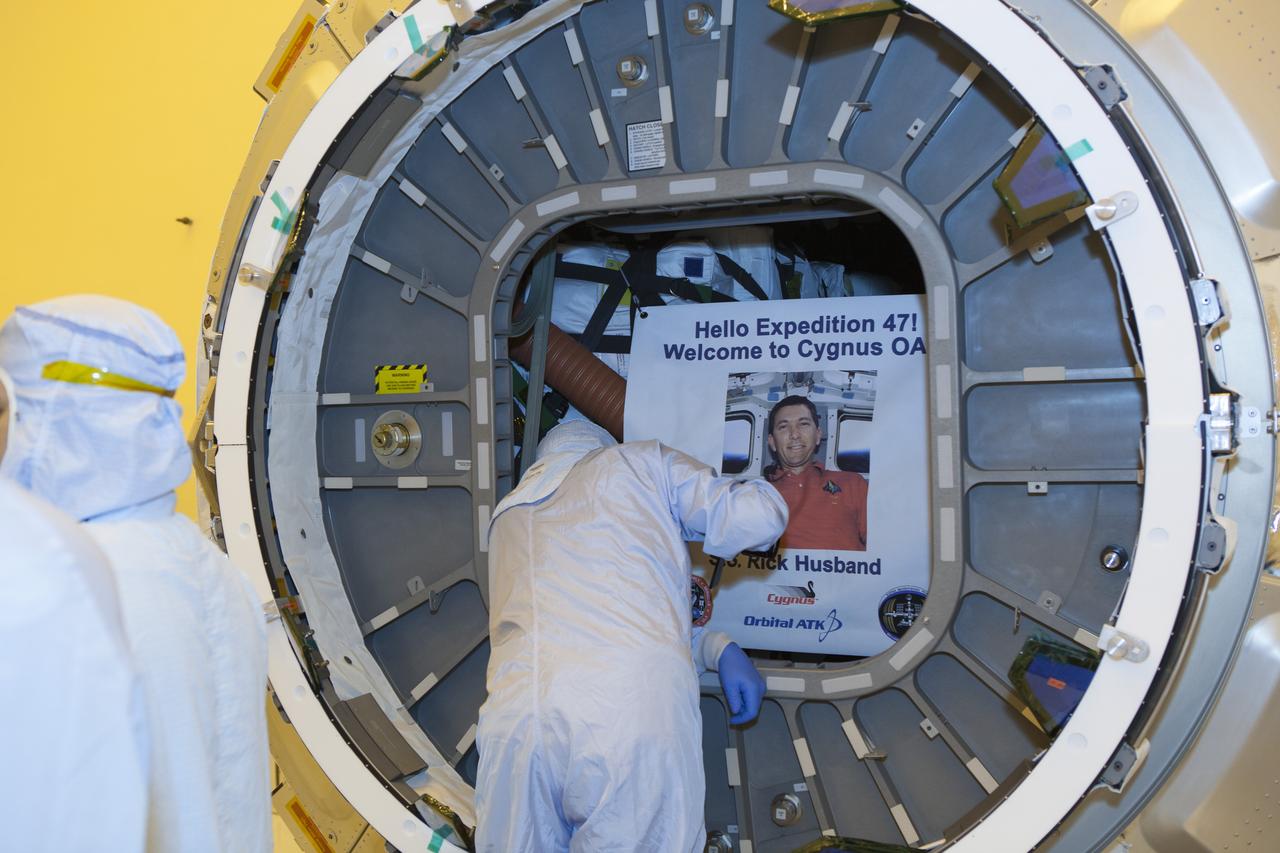

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the hatch is closed for the upcoming flight of a Cygnus cargo vessel. The spacecraft is scheduled for the upcoming Orbital ATK Commercial Resupply Services-6 mission to deliver hardware and supplies to the International Space Station. When members of the ISS Expedition 47 crew open the hatch, they will be greeted with a sign noting the spacecraft was named SS Rick Husband in honor of the commander of the STS-107 mission. On that flight, the crew of the space shuttle Columbia was lost during re-entry on Feb. 1, 2003. The Cygnus is scheduled to lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on March 22.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the upgraded version of the Cargo Dragon spacecraft, is seen inside the company’s hangar at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 2, 2020, prior to being rolled out to the launch pad in preparation for the 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) launch. The first launch for SpaceX under NASA’s second Commercial Resupply Services contract, CRS-21 will deliver critical supplies, equipment, and material to support a variety of science and research investigations that will take place aboard the International Space Station. Liftoff is scheduled for 11:39 a.m. EST on Saturday, Dec. 5, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
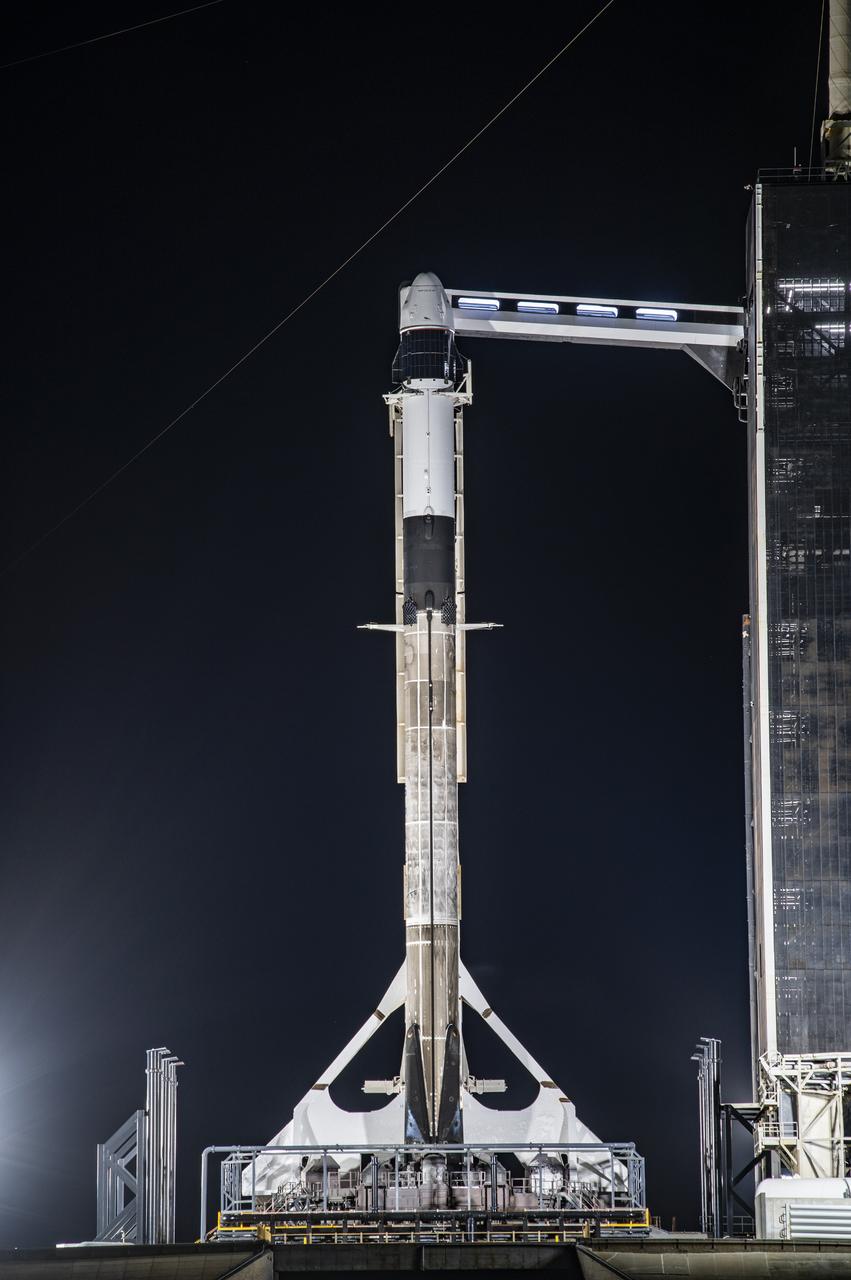

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the company’s upgraded version of the Dragon spacecraft, stands vertical at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida on Wednesday, Dec. 2, 2020. The first mission for SpaceX under NASA’s second Commercial Resupply Services contract, CRS-21 is scheduled to lift off from Launch Complex 39A on Saturday, Dec. 5, at 11:39 a.m. EST. The mission will deliver critical supplies and equipment to the International Space Station.
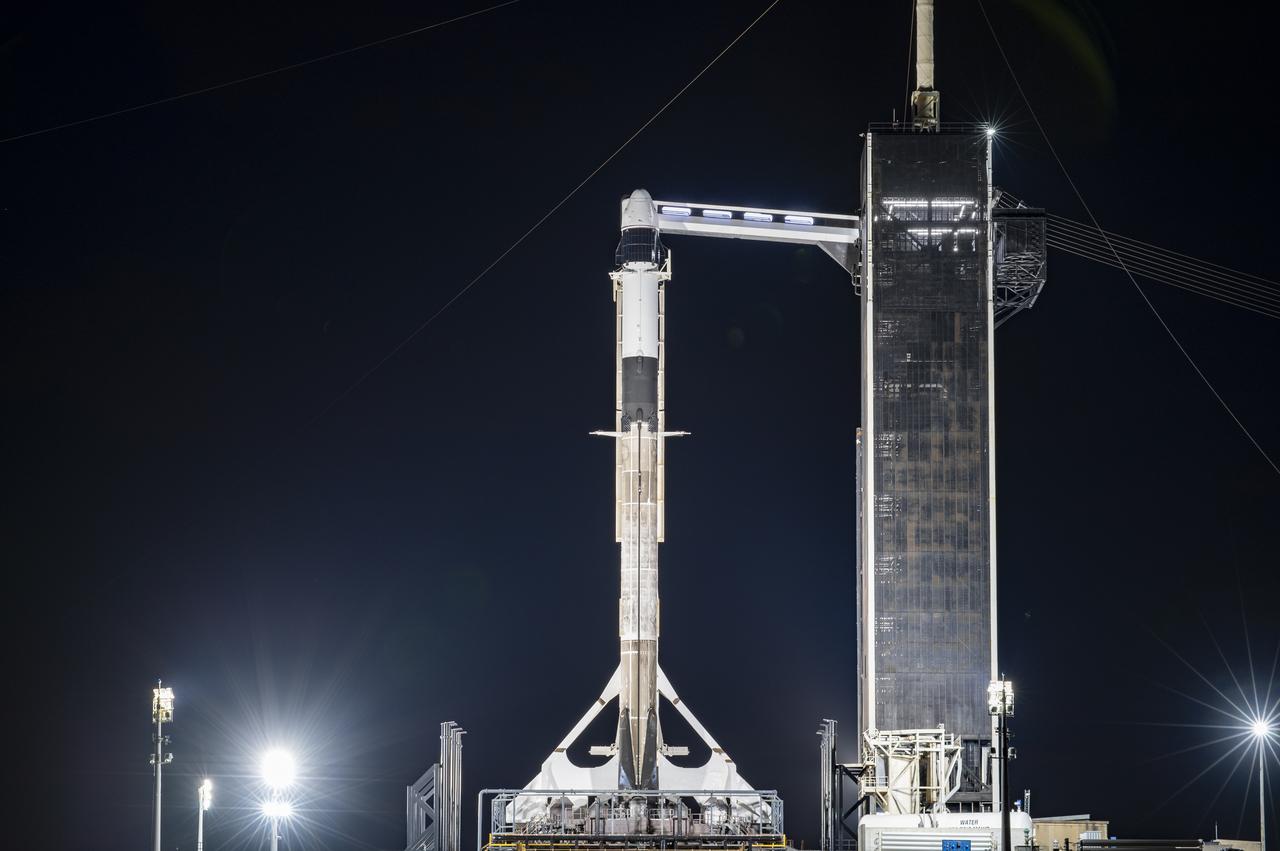

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the company’s upgraded version of the Dragon spacecraft, stands vertical at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida on Wednesday, Dec. 2, 2020. The first mission for SpaceX under NASA’s second Commercial Resupply Services contract, CRS-21 is scheduled to lift off from Launch Complex 39A on Saturday, Dec. 5, at 11:39 a.m. EST. The mission will deliver critical supplies and equipment to the International Space Station.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the upgraded version of the Cargo Dragon spacecraft, is seen inside the company’s hangar at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 2, 2020, prior to being rolled out to the launch pad in preparation for the 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) launch. The first launch for SpaceX under NASA’s second Commercial Resupply Services contract, CRS-21 will deliver critical supplies, equipment, and material to support a variety of science and research investigations that will take place aboard the International Space Station. Liftoff is scheduled for 11:39 a.m. EST on Saturday, Dec. 5, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
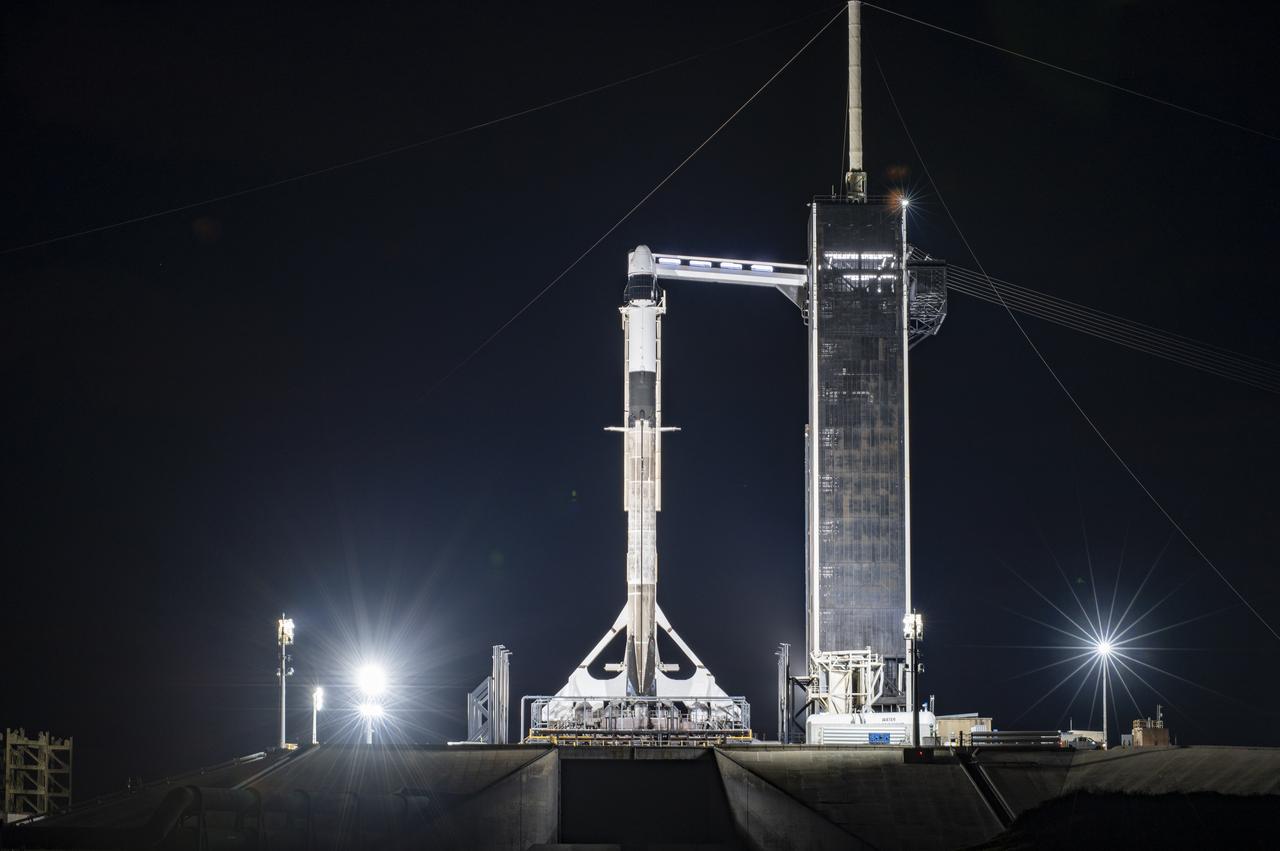

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the company’s upgraded version of the Dragon spacecraft, stands vertical at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida on Wednesday, Dec. 2, 2020. The first mission for SpaceX under NASA’s second Commercial Resupply Services contract, CRS-21 is scheduled to lift off from Launch Complex 39A on Saturday, Dec. 5, at 11:39 a.m. EST. The mission will deliver critical supplies and equipment to the International Space Station.

The upgraded version of SpaceX’s Cargo Dragon spacecraft, Dragon 2, is seen atop a Falcon 9 rocket on Dec. 2, 2020, as they prepare to be rolled out to Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the company’s 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) launch. The first launch for SpaceX under NASA’s second Commercial Resupply Services contract, CRS-21 will deliver critical supplies, equipment, and material to support a variety of science and research investigations that will take place aboard the International Space Station. Liftoff is scheduled for 11:39 a.m. EST on Saturday, Dec. 5.
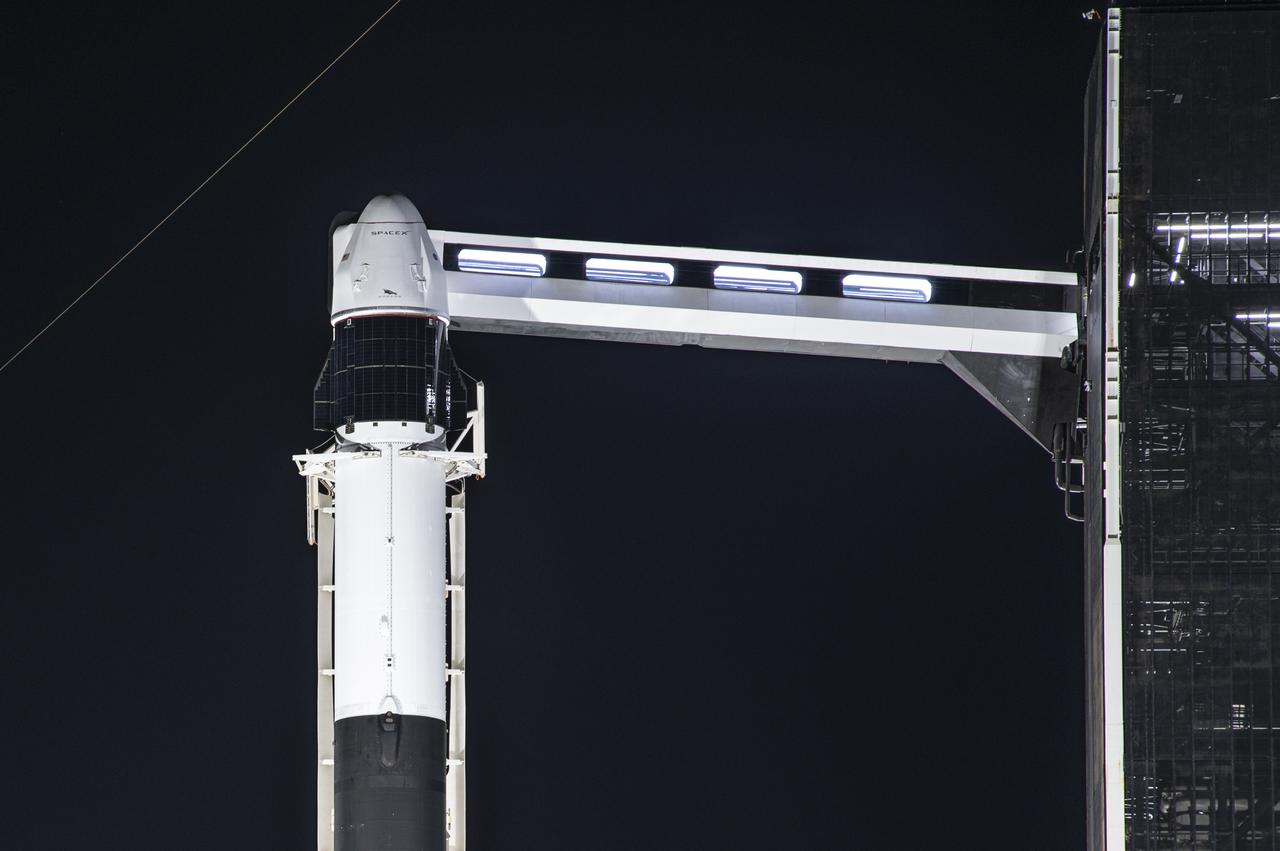

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the company’s upgraded version of the Dragon spacecraft, stands vertical at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida on Wednesday, Dec. 2, 2020. The first mission for SpaceX under NASA’s second Commercial Resupply Services contract, CRS-21 is scheduled to lift off from Launch Complex 39A on Saturday, Dec. 5, at 11:39 a.m. EST. The mission will deliver critical supplies and equipment to the International Space Station.
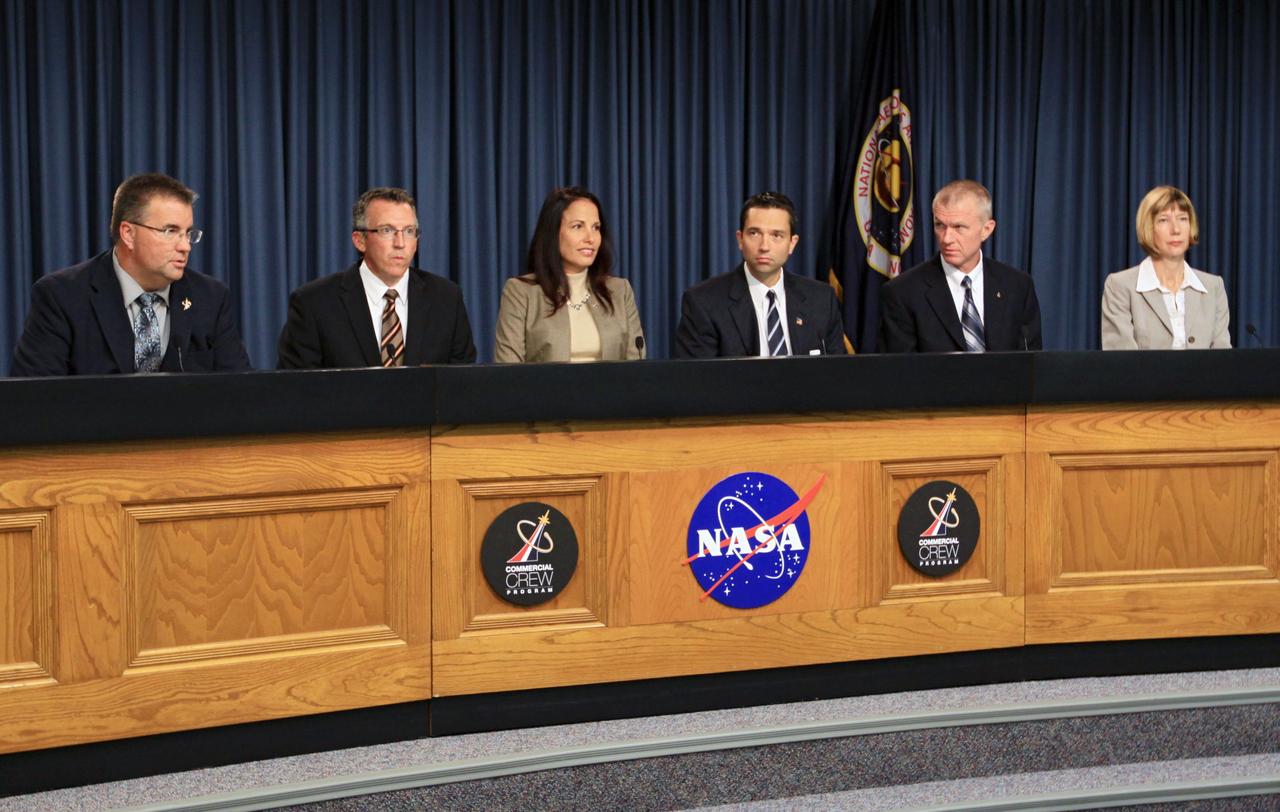

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, hosts a pre-proposal conference to inform prospective companies about the recently released request for contract proposals and updates to the certification requirements for crewed missions to the International Space Station, or ISS. The two-phase certification process, called Certification Products Contract, or CPC, will enable NASA to eventually purchase service missions to fly astronauts to and from the ISS. From left, Ed Mango, CCP's program manager Steve Janney, CPC contracting officer Maria Collura, CCP certification manager Tom Simon, CPC Evaluation Team chair Brent Jett, CCP deputy program manager and Kathy Lueders, manager of the ISS Transportation Integration Office. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
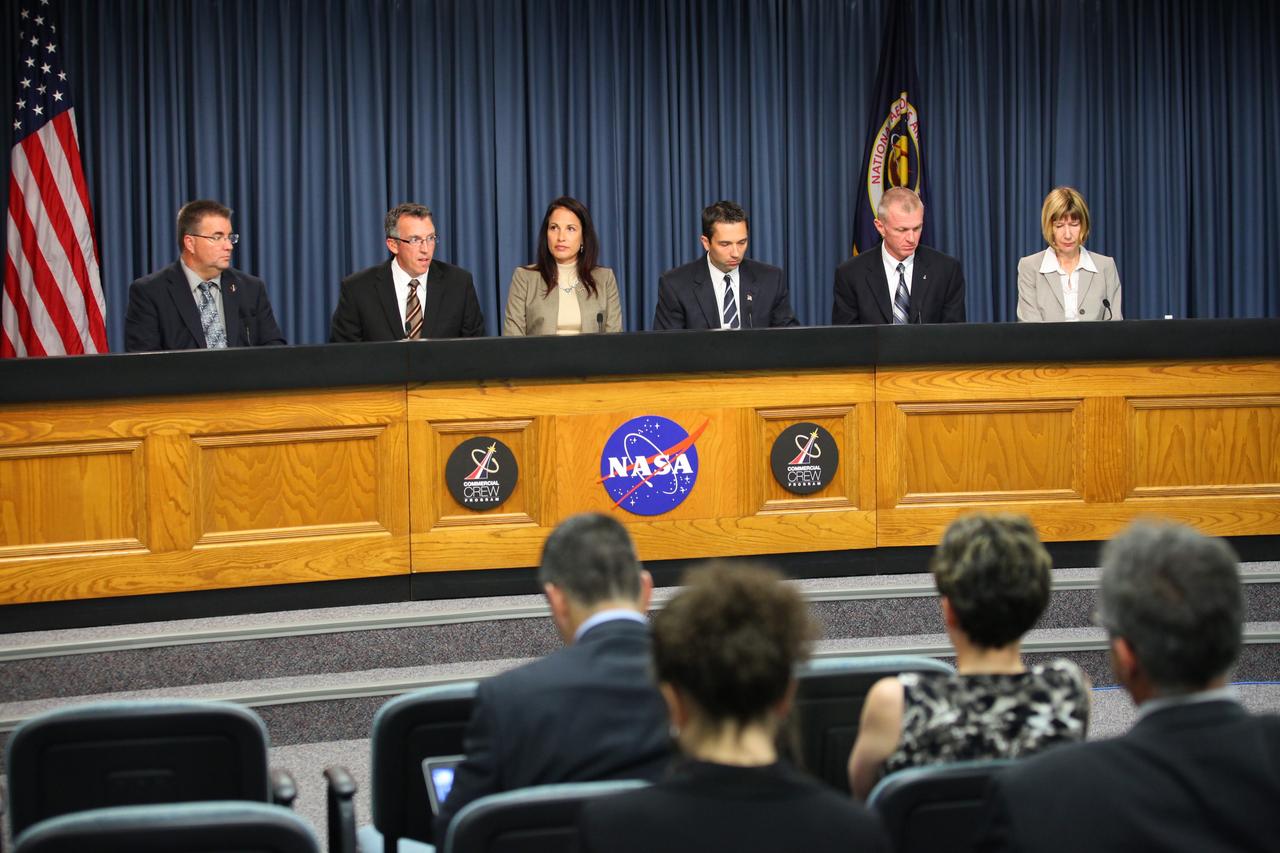

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, hosts a pre-proposal conference to inform prospective companies about the recently released request for contract proposals and updates to the certification requirements for crewed missions to the International Space Station, or ISS. The two-phase certification process, called Certification Products Contract, or CPC, will enable NASA to eventually purchase service missions to fly astronauts to and from the ISS. From left, Ed Mango, CCP's program manager Steve Janney, CPC contracting officer Maria Collura, CCP certification manager Tom Simon, CPC Evaluation Team chair Brent Jett, CCP deputy program manager and Kathy Lueders, manager of the ISS Transportation Integration Office. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

A Nasdaq moderator, center, talks with NASA Director of Commercial Spaceflight Development Phil McAlister, left, ISS National Lab Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Ken Shields, NASA Advisory Council Regulatory and Policy Committee Chair Mike Gold, and NASA Deputy Chief Financial Officer for Integration Doug Comstock, right, during a live social media event shortly after NASA announced a five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Nasdaq moderator, center, talks with NASA Director of Commercial Spaceflight Development Phil McAlister, left, ISS National Lab Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Ken Shields, NASA Advisory Council Regulatory and Policy Committee Chair Mike Gold, and NASA Deputy Chief Financial Officer for Integration Doug Comstock, right, during a live social media event shortly after NASA announced a five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

In the Press Site auditorium of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the news media at a post-launch news conference following the liftoff of Orbital ATK CRS-6, a commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station, or ISS. From left are: Kathryn Hambleton of NASA Communications; Kenneth Todd, NASA ISS Operations Integration manager; Frank Culbertson, president of Orbital ATK's Space System Group; Vern Thorp, United Space Alliance's program manager for NASA missions. The Cygnus spacecraft lifted off atop an Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 11:05 p.m. EDT.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Tom Simon of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, talks to aerospace industry representatives during a pre-proposal conference to inform prospective companies about the recently released request for contract proposals and updates to the certification requirements for crewed missions to the International Space Station, or ISS. The two-phase certification process, called Certification Products Contract, or CPC, will enable NASA to eventually purchase service missions to fly astronauts to and from the ISS. Simon will serve as chair of the CPC Evaluation Team that will come together to identify, research and ensure that the selected companies can comply with NASA's contract requirements. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
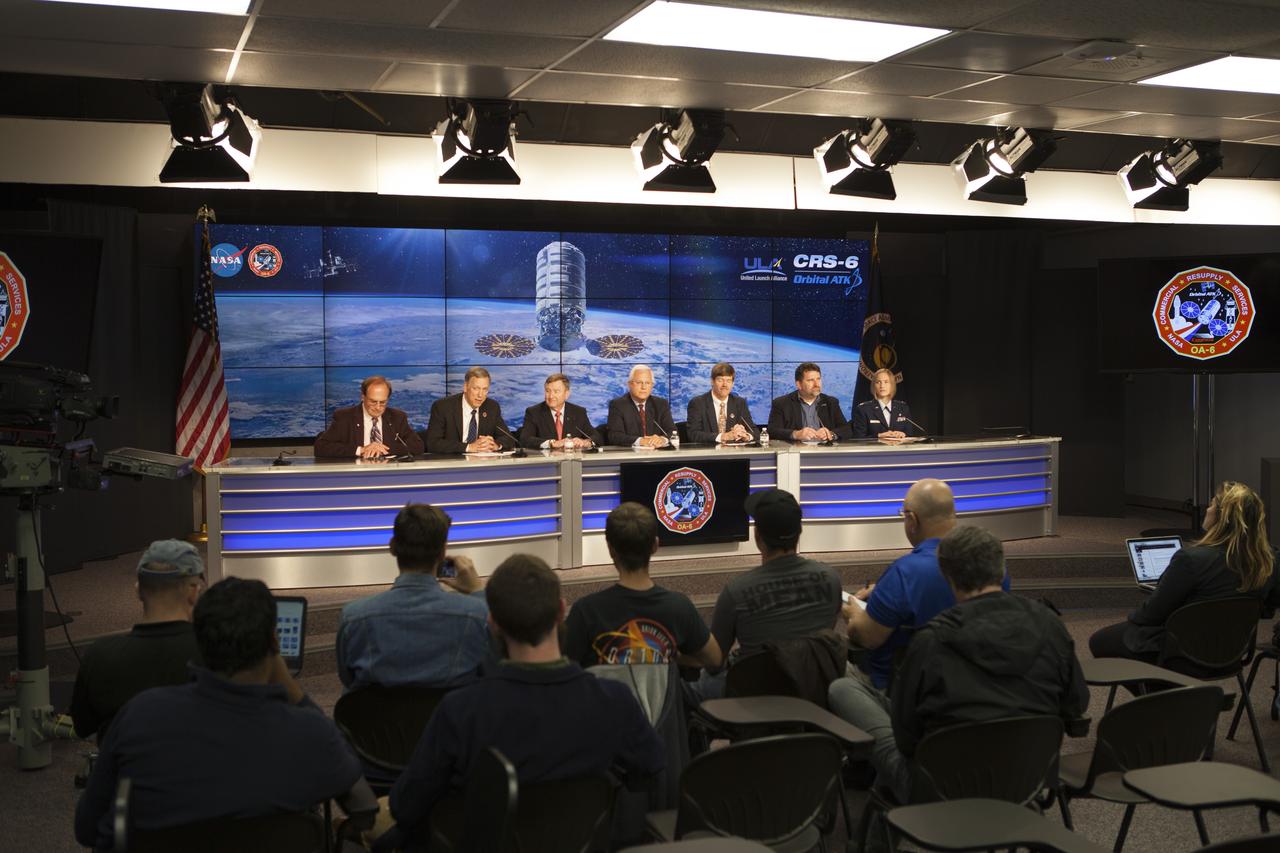

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, agency and industry leaders speak to members of the media at a prelaunch news conference for Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. From left are: George Diller of NASA Communications; Kenneth Todd, NASA ISS Operations Integration manager; Frank Culbertson, president of Orbital ATK's Space System Group; Vern Thorp, United Space Alliance's program manager for NASA missions; Pete Hasbrook, NASA associate program scientist for the ISS Program at the Johnson Space Center in Houston; Dr. Michael Roberts deputy chief scientist for the Center for the Advancement for Science in Space, or CASIS; and Capt. Laura Godoy, launch weather officer of the U.S. Air Force 45th Weather Squadron.
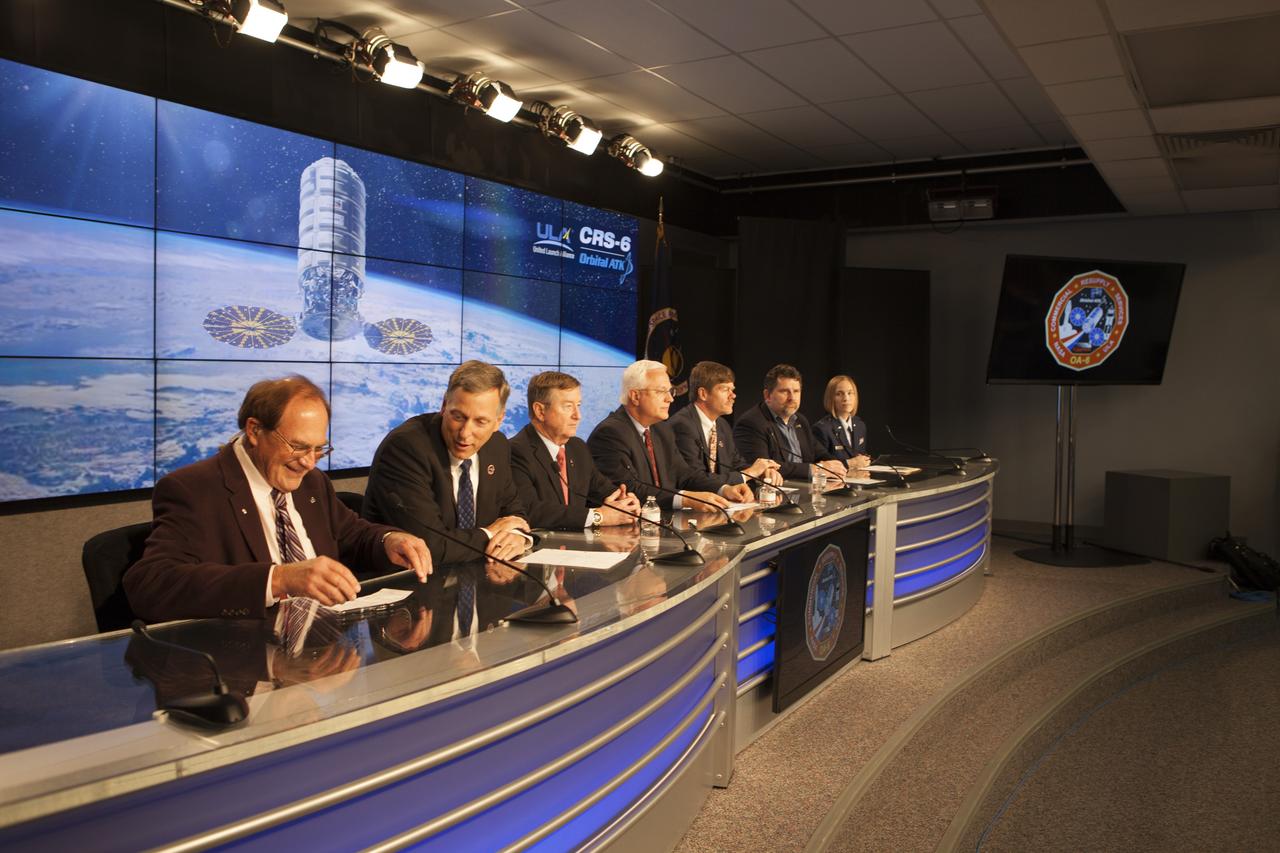

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, agency and industry leaders speak to members of the media at a prelaunch news conference for Orbital ATK CRS-6 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. From left are: George Diller of NASA Communications; Kenneth Todd, NASA ISS Operations Integration manager; Frank Culbertson, president of Orbital ATK's Space System Group; Vern Thorp, United Space Alliance's program manager for NASA missions; Pete Hasbrook, NASA associate program scientist for the ISS Program at the Johnson Space Center in Houston; Dr. Michael Roberts deputy chief scientist for the Center for the Advancement for Science in Space, or CASIS; and Capt. Laura Godoy, launch weather officer of the U.S. Air Force 45th Weather Squadron.
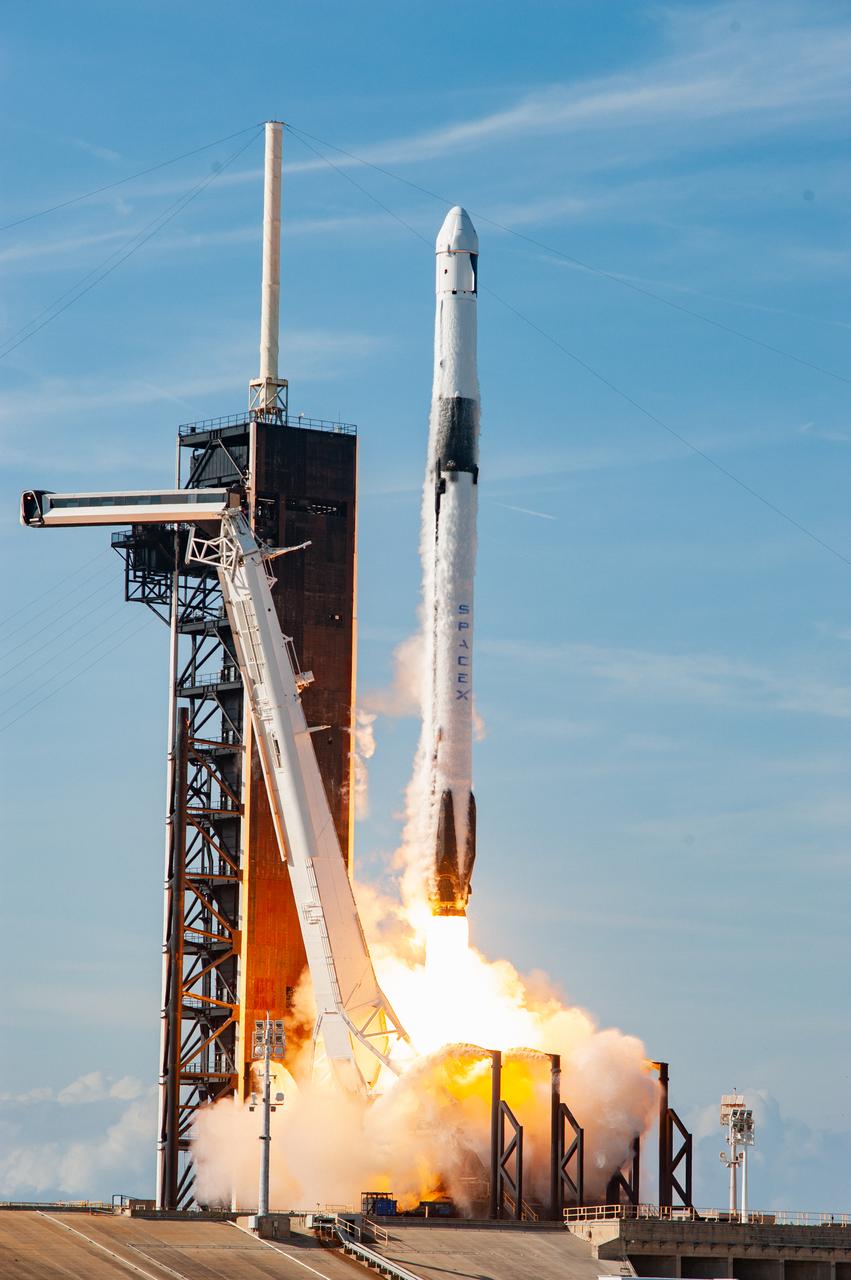

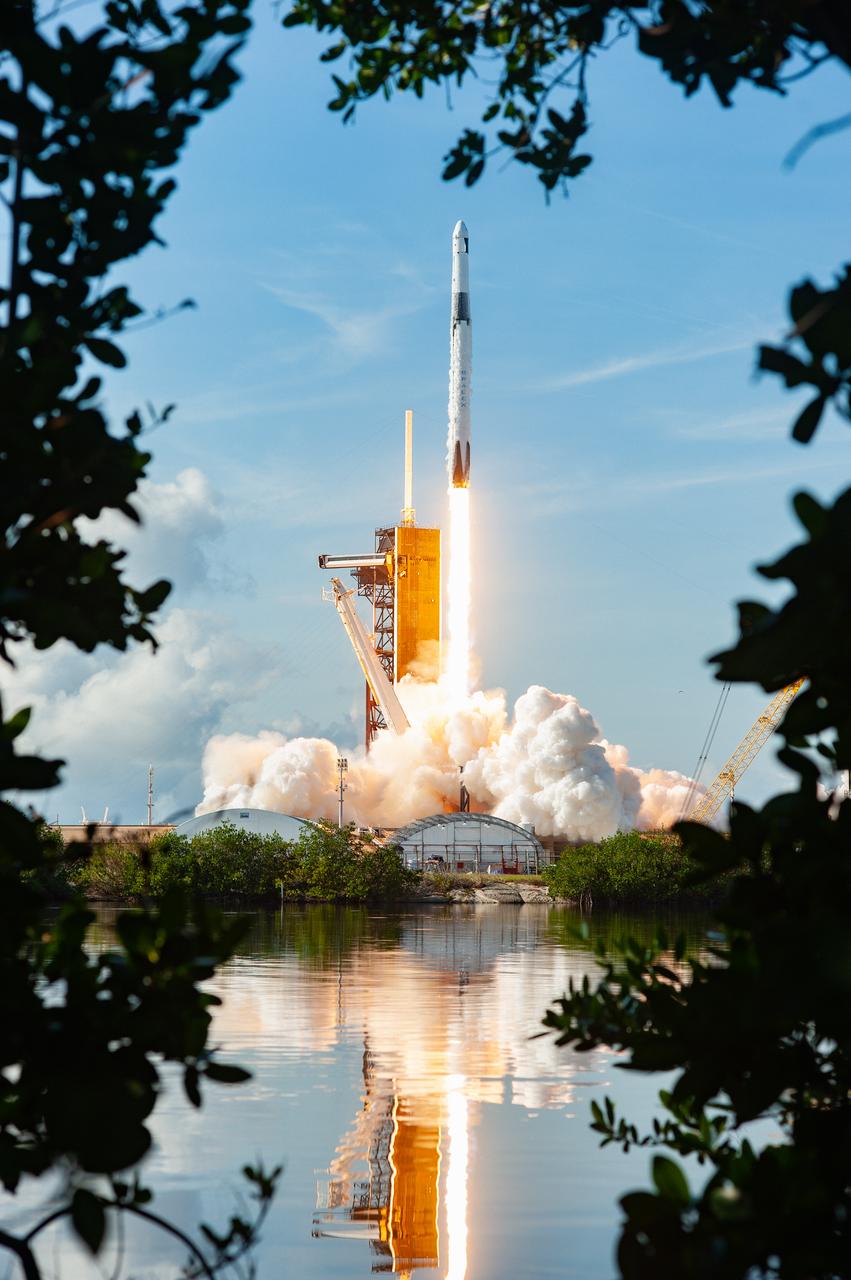
The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
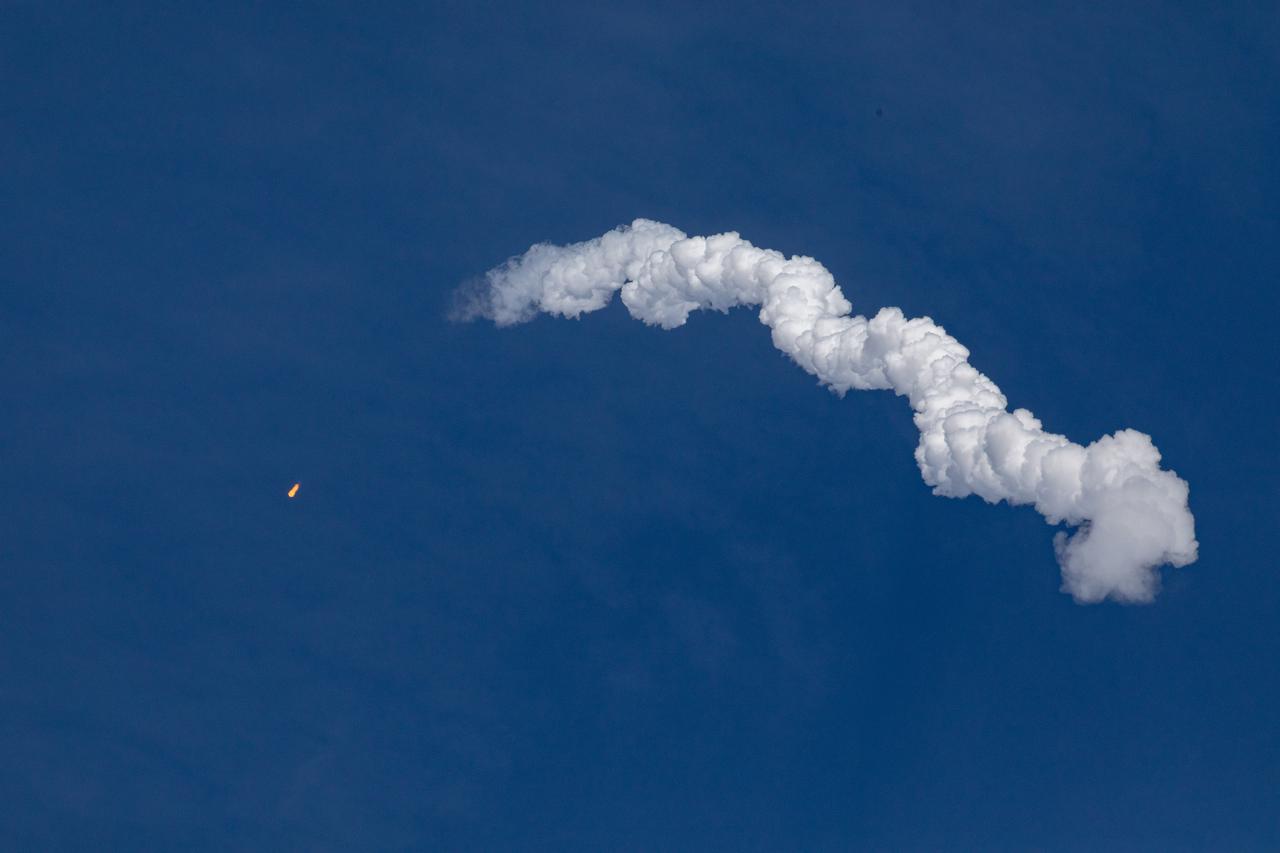

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after its liftoff from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th Commercial Resupply Services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo spacecraft will deliver about 7,700 pounds of science and research, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
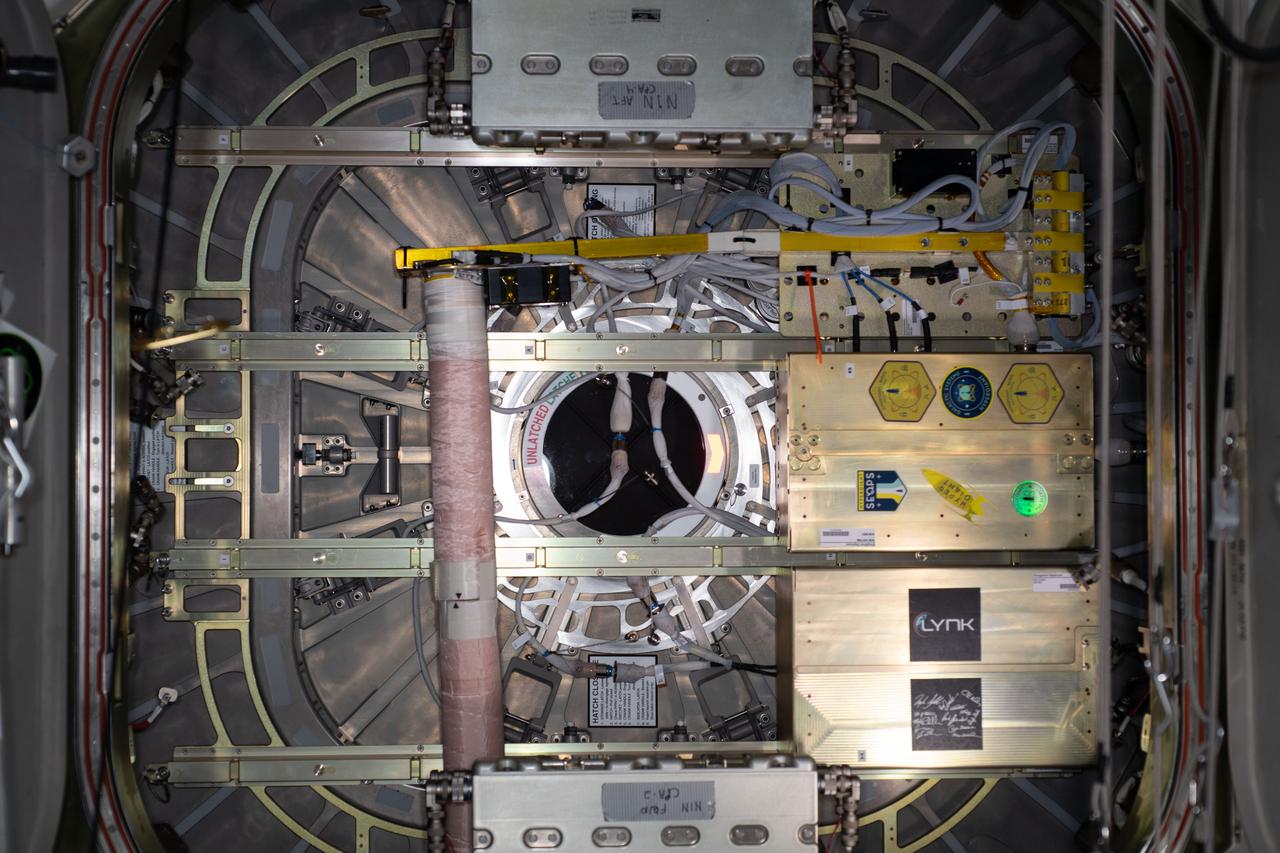
iss063e010534 (5/10/2020) --- A view from the Unity module aboard the International Space Station (ISS) of the Northrop Grumman NG-13 hatch. Attached to the hatch is the SlingShot small satellite deployer loaded with two CubeSats that will be deployed into Earth orbit after Cygnus departs the orbiting lab on May 11, 2020. The SEOPS-UbiquitiLink investigation furthers demonstrates the premise that small satellites/nano satellites can perform vital communications missions and provide valuable communications services. The SEOPS-WIDAR investigation demonstrates technologies that increase the utility of low-cost microsatellites, contributing to the increased commercialization of the International Space Station and low-Earth orbit.
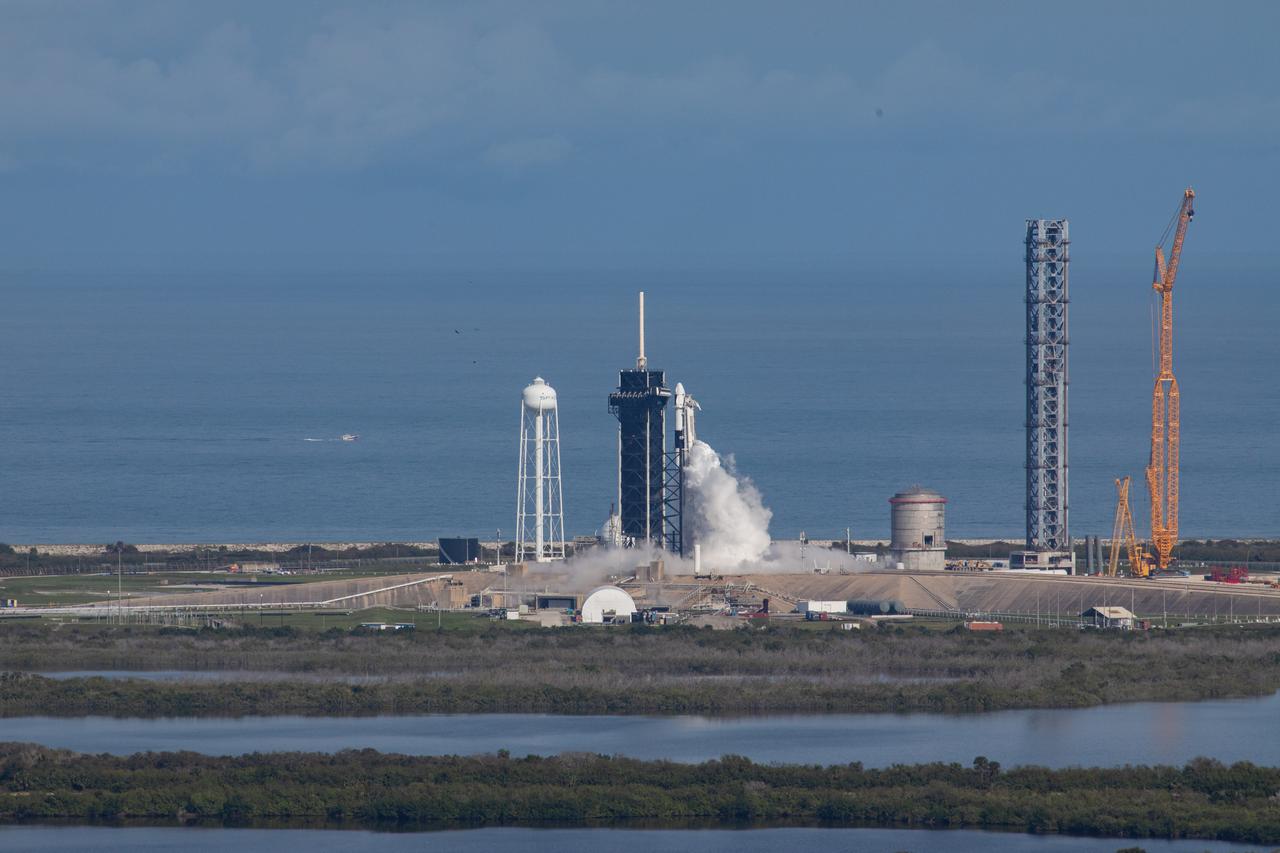

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
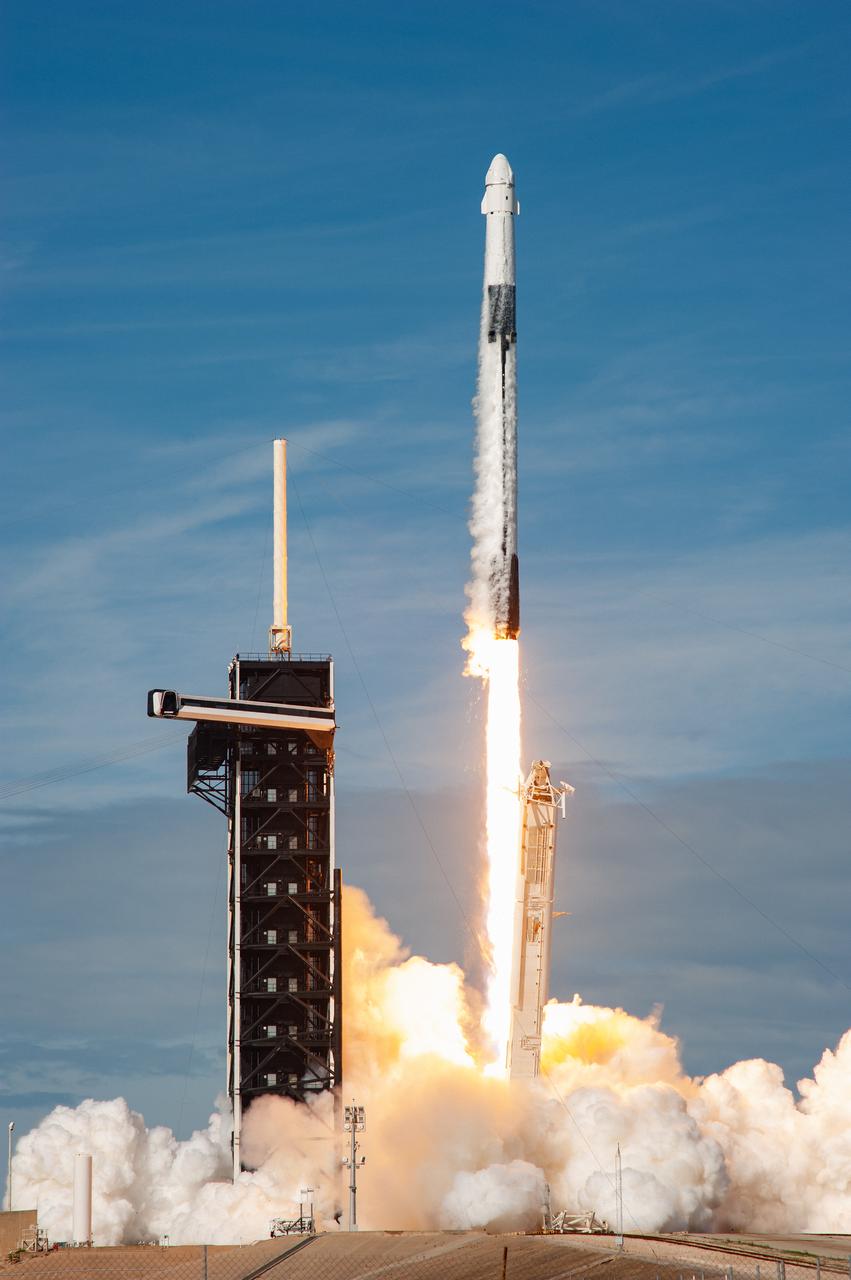

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
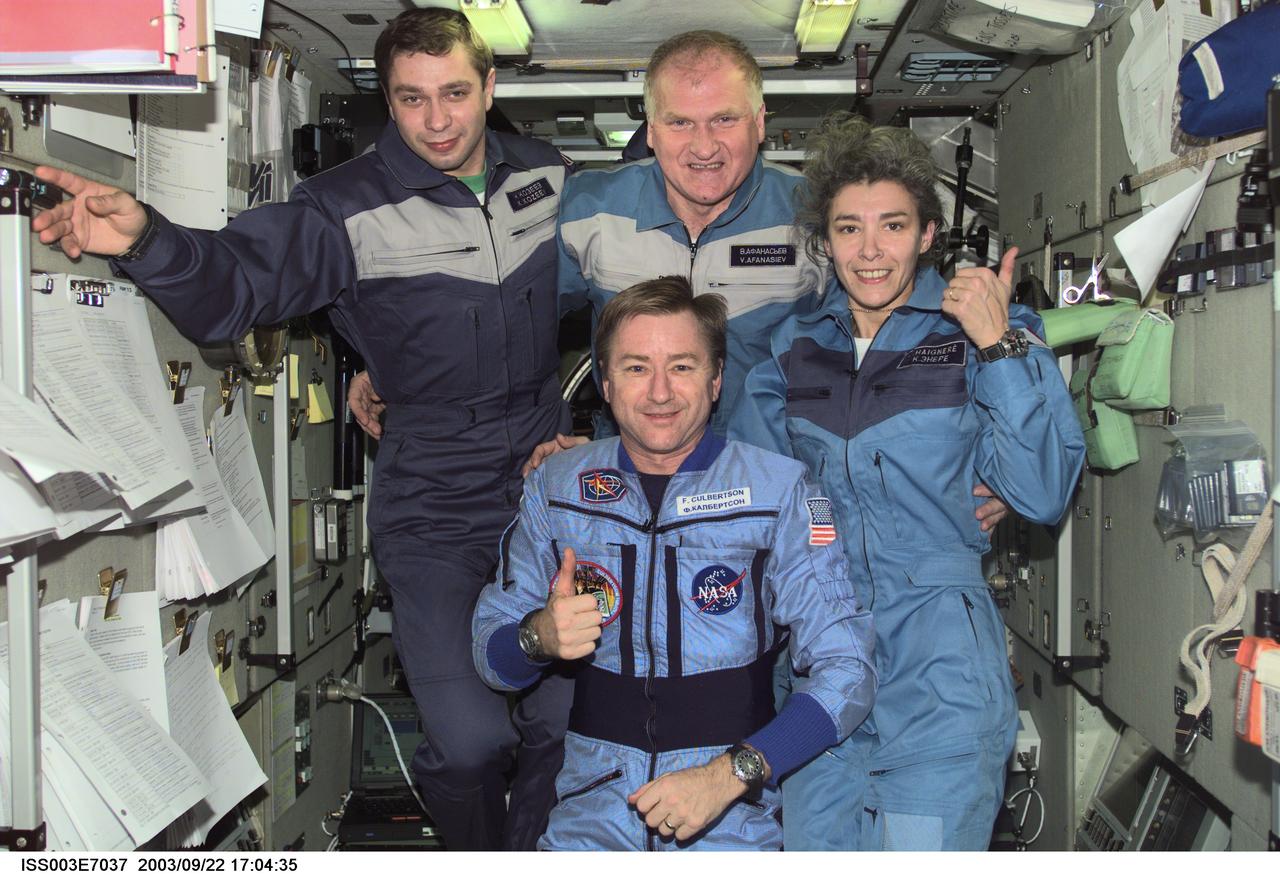

ISS003-E-7037 (23-31 October 2001) --- Astronaut Frank L. Culbertson, Jr. (foreground), Expedition Three mission commander, and the Soyuz Taxi crewmembers assemble for a group photo in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). From the left are Flight Engineer Konstantin Kozeev, Commander Victor Afanasyev, and French Flight Engineer Claudie Haignere. Afanasyev and Kozeev represent Rosaviakosmos, and Haignere represents ESA, carrying out a flight program for CNES, the French Space Agency, under a commercial contract with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. This image was taken with a digital still camera.
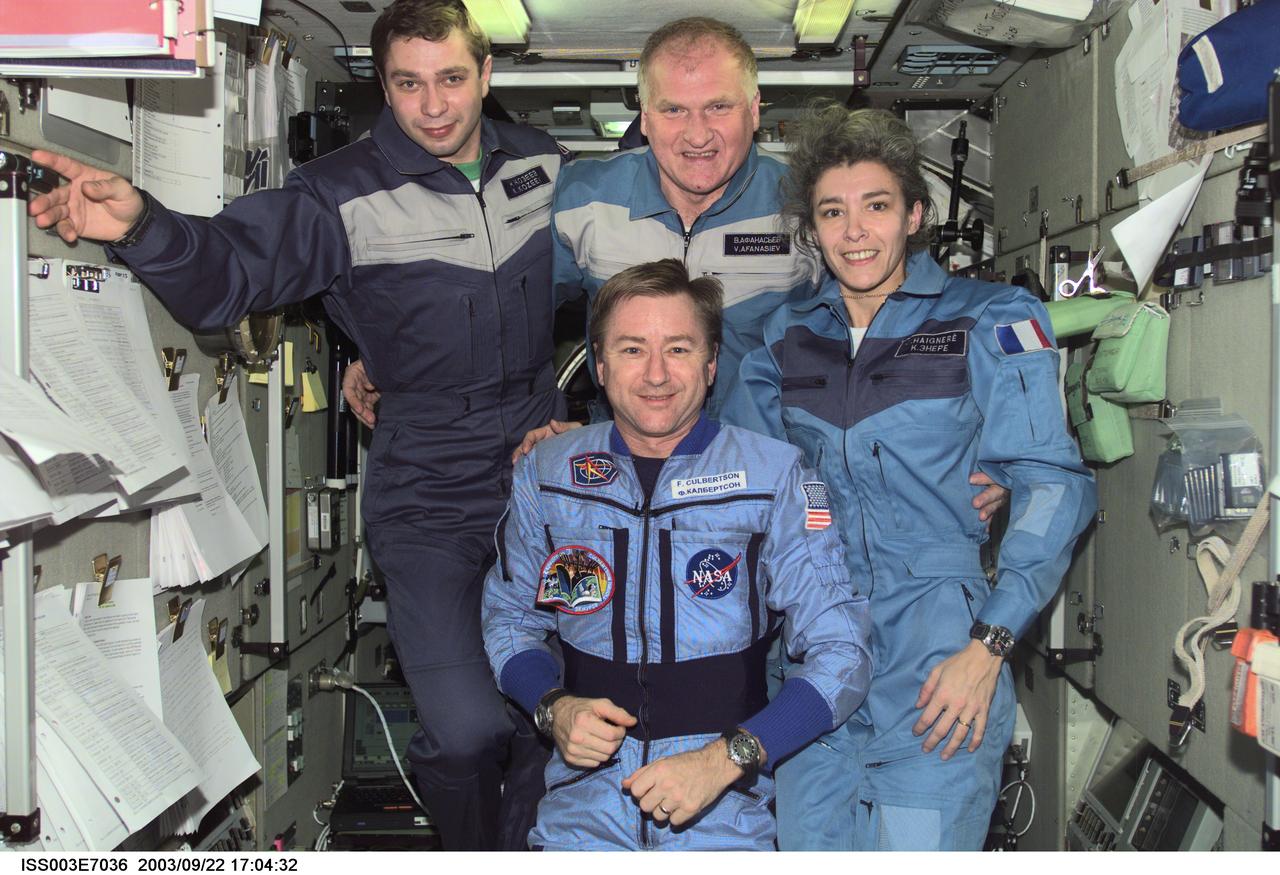

ISS003-E-7036 (23-31 October 2001) --- Astronaut Frank L. Culbertson, Jr. (foreground), Expedition Three mission commander, and the Soyuz Taxi crewmembers assemble for a group photo in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). From the left are Flight Engineer Konstantin Kozeev, Commander Victor Afanasyev, and French Flight Engineer Claudie Haignere. Afanasyev and Kozeev represent Rosaviakosmos, and Haignere represents ESA, carrying out a flight program for CNES, the French Space Agency, under a commercial contract with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. This image was taken with a digital still camera.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
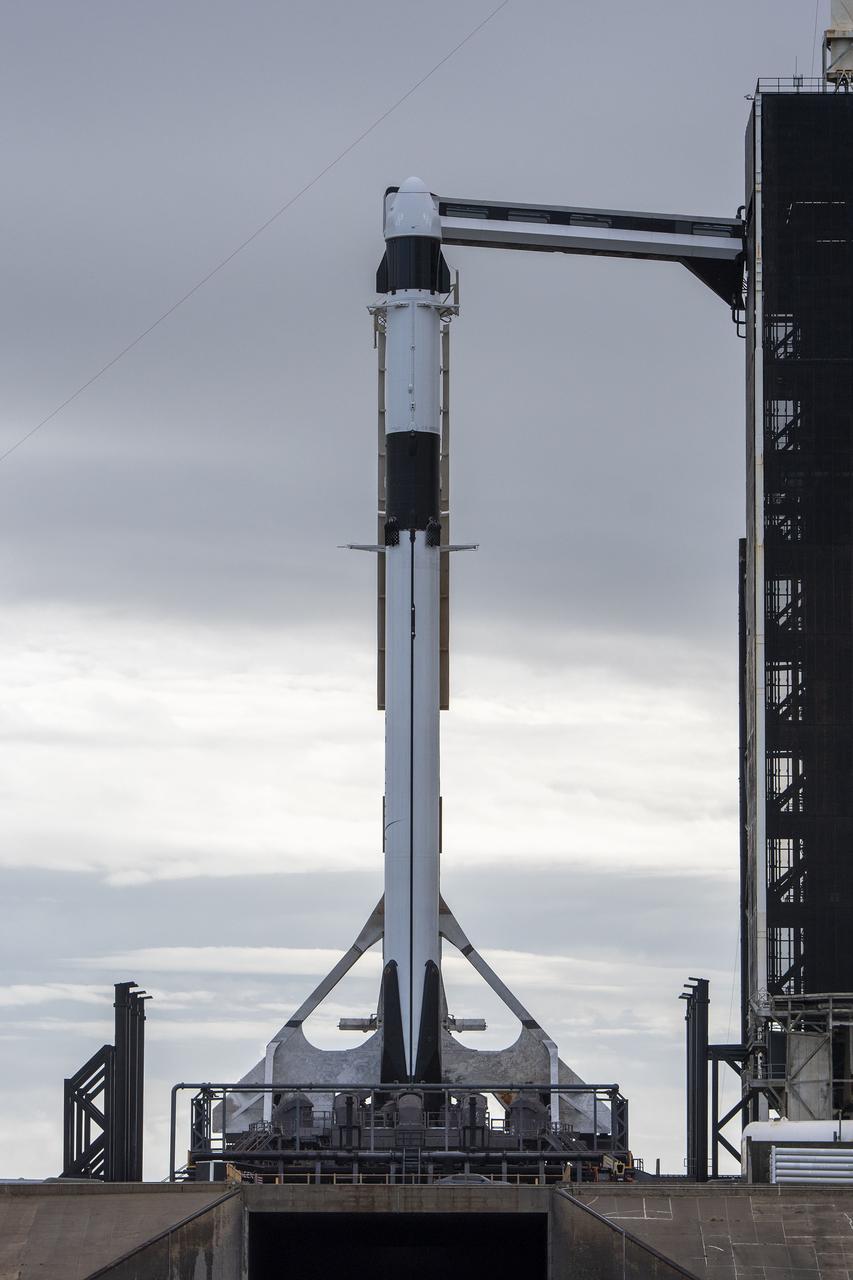

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, with the company’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop, is raised to a vertical position at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A on Nov. 21, 2022, in preparation for the 26th commercial resupply services launch to the International Space Station. The mission will deliver new science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). Liftoff is scheduled for 3:54 p.m. EST on Monday, Nov. 22, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.

Ken Shields, director of Operations for Center for the Advancement of Science in Space/ISS National Lab, left, and Pete Hasbrook, associate program scientist for the International Space Station Program, speak to members of social media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for launch from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A on Aug. 14 atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on the company's 12th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
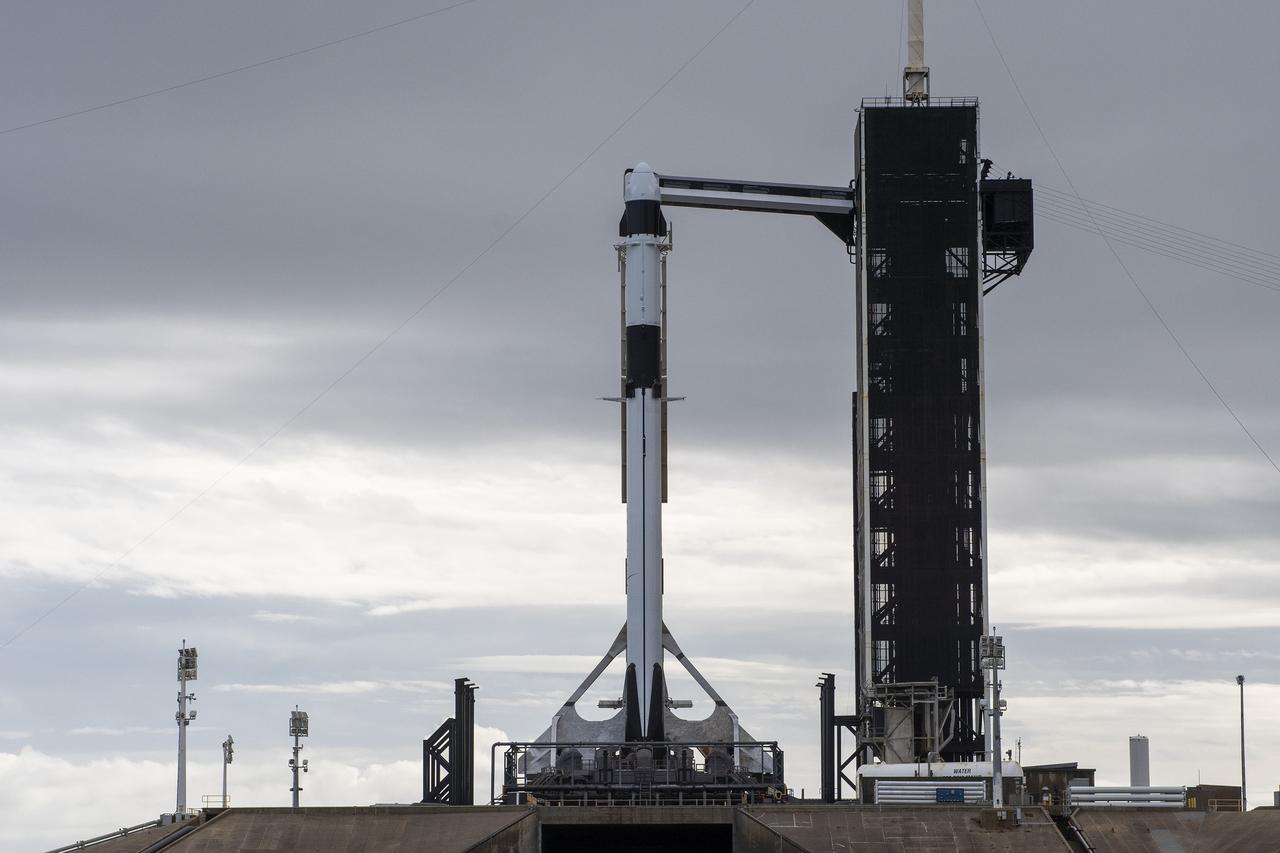

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, with the company’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop, is raised to a vertical position at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A on Nov. 21, 2022, in preparation for the 26th commercial resupply services launch to the International Space Station. The mission will deliver new science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). Liftoff is scheduled for 3:54 p.m. EST on Monday, Nov. 22, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
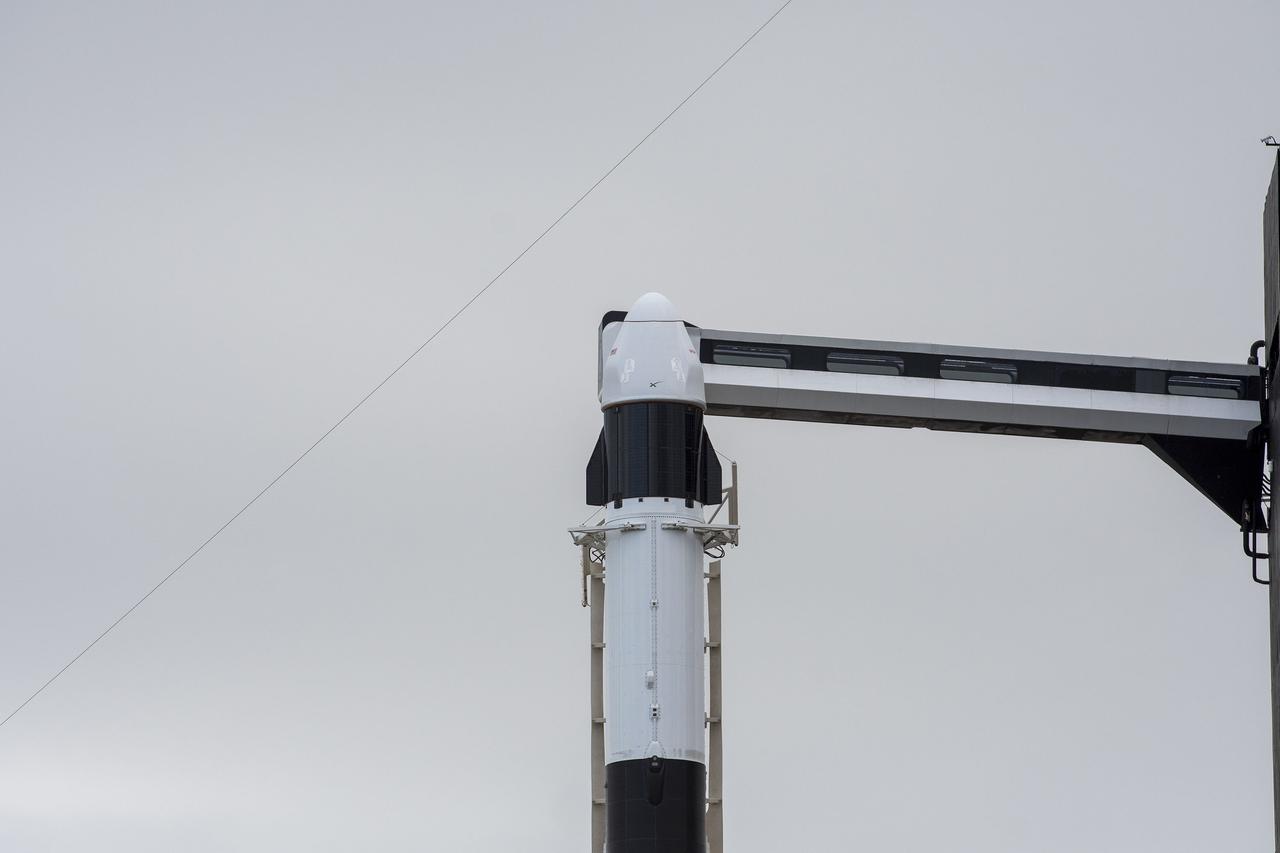

Seen here is the SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket after being raised to a vertical position at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2022, in preparation for the 26th commercial resupply services launch to the International Space Station. The mission will deliver new science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). Liftoff is scheduled for 3:54 p.m. EST on Monday, Nov. 22, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
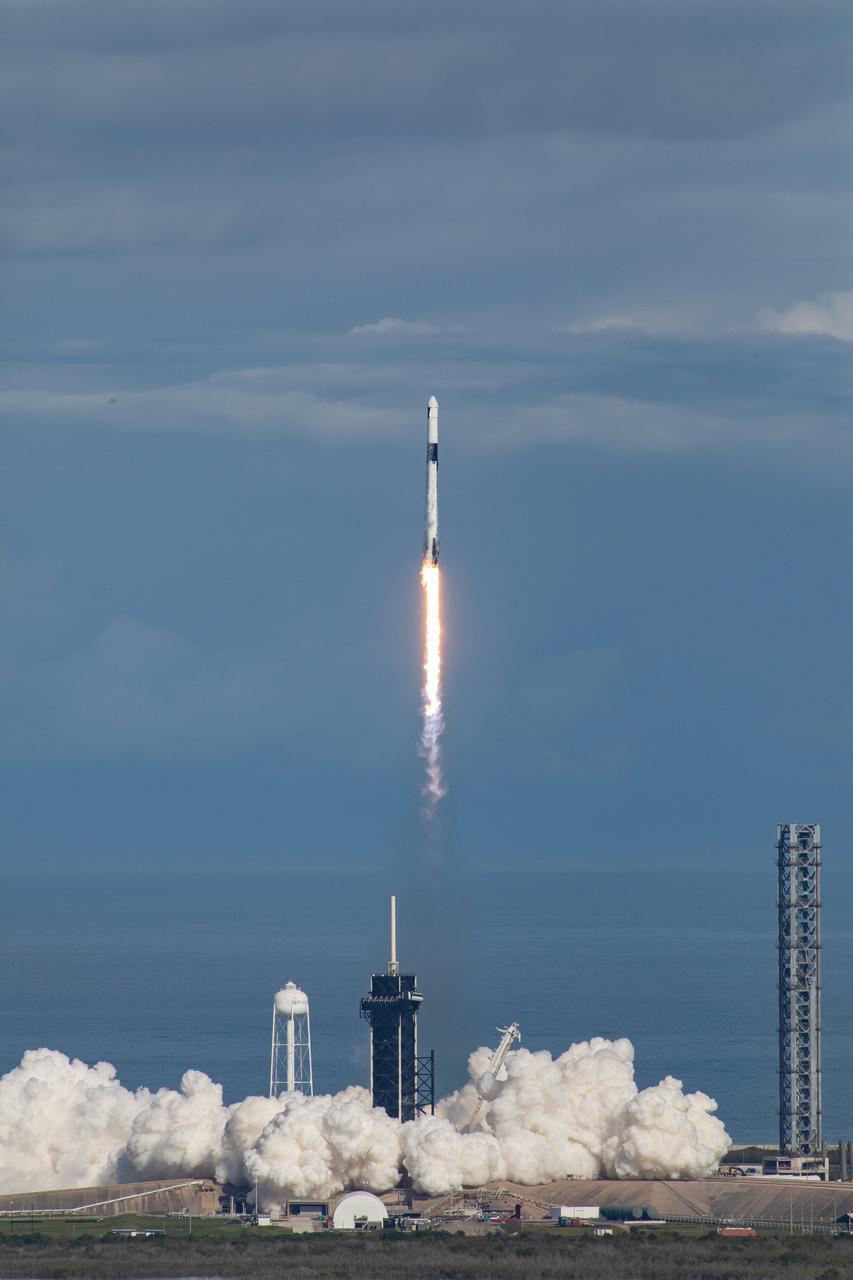

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
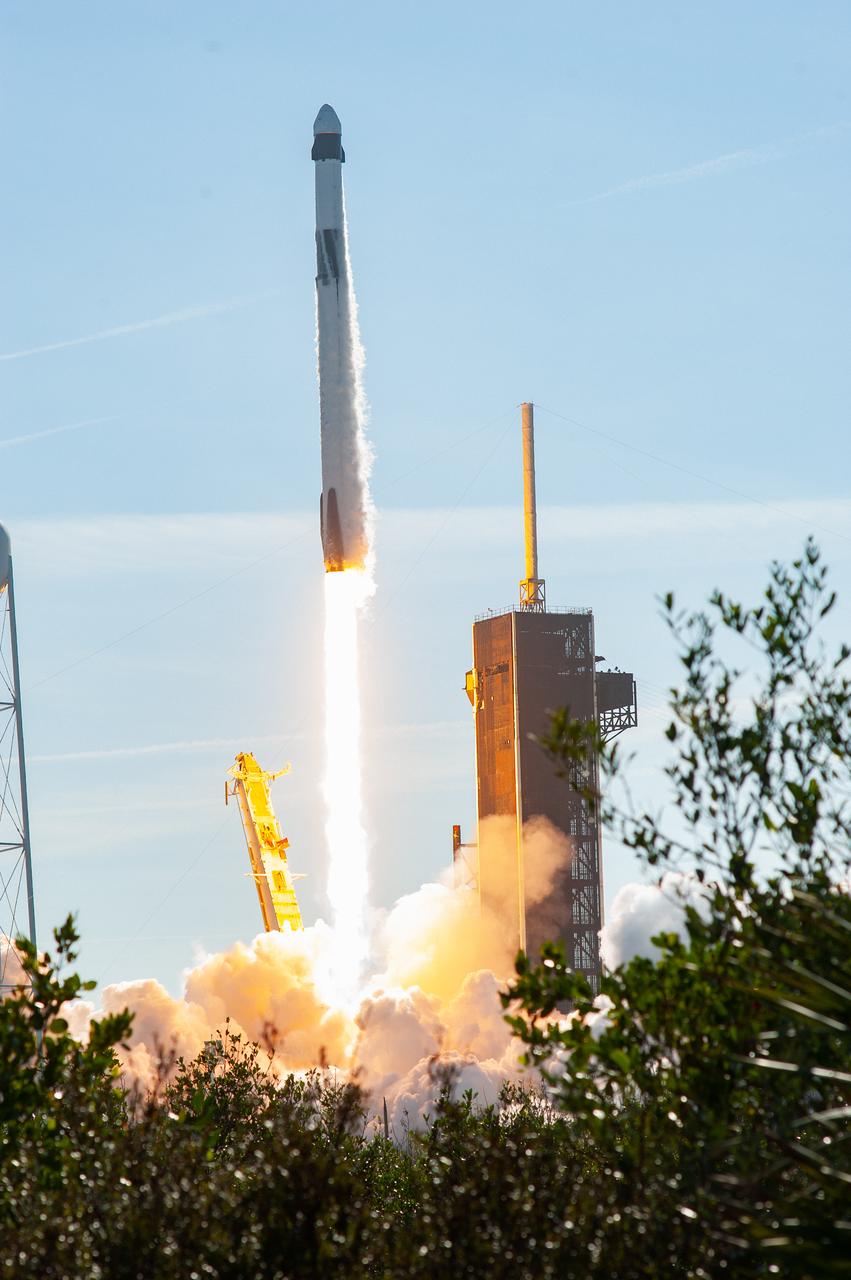

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
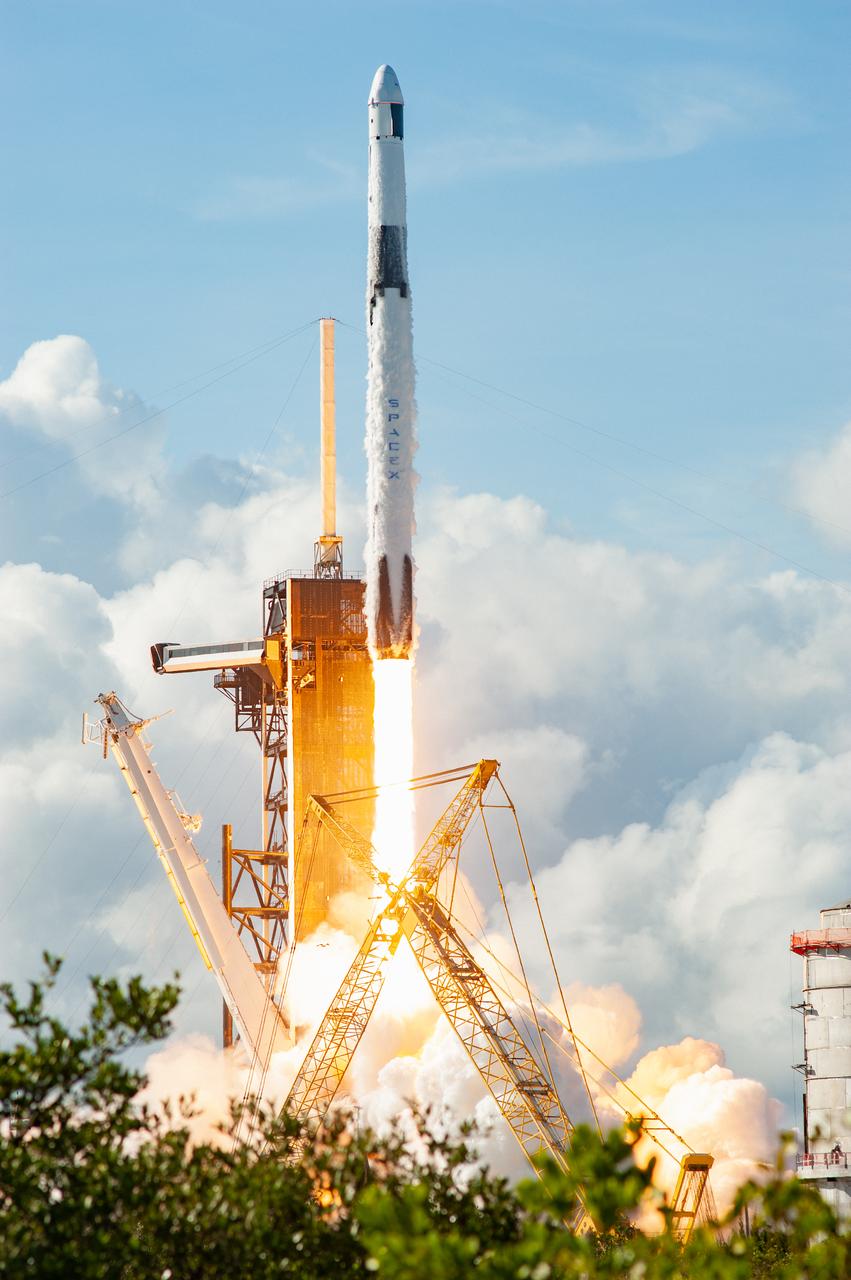

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
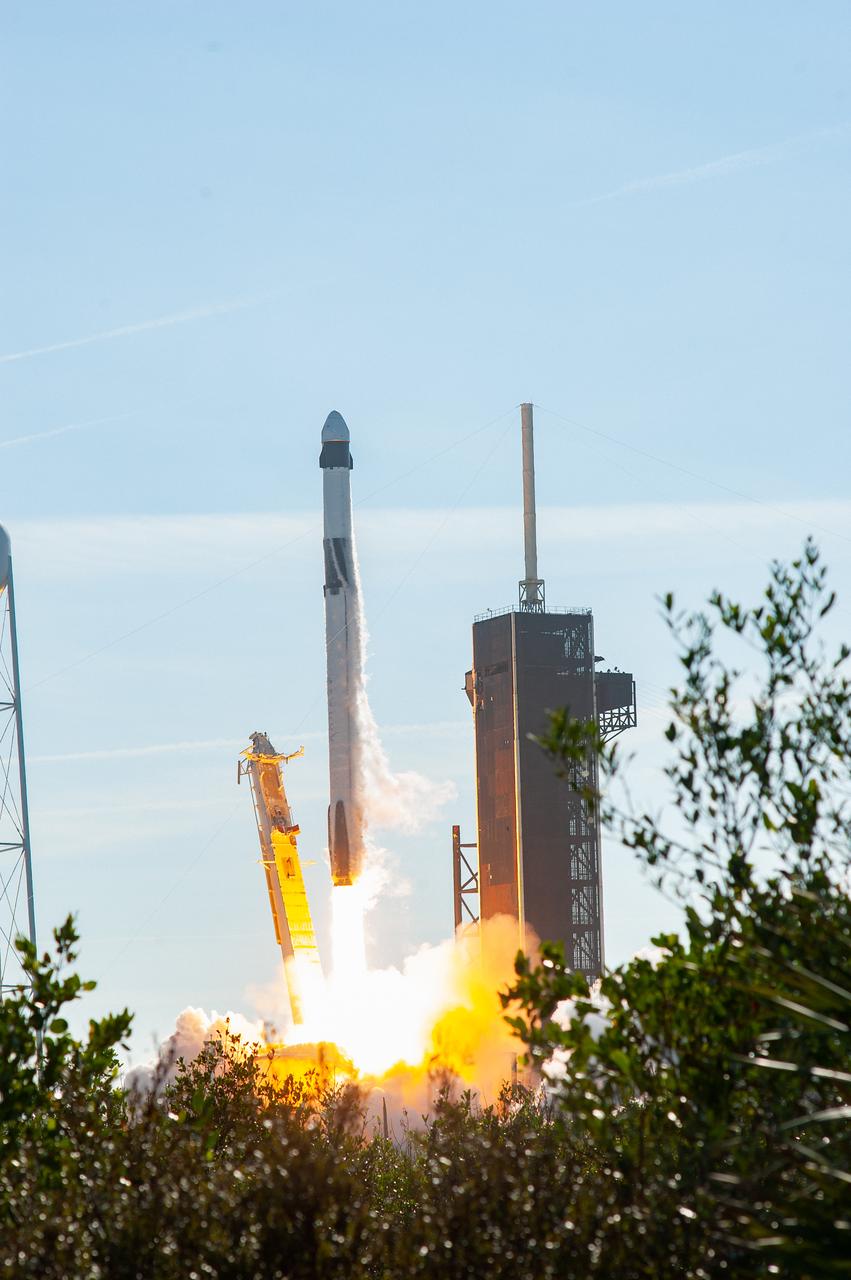

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
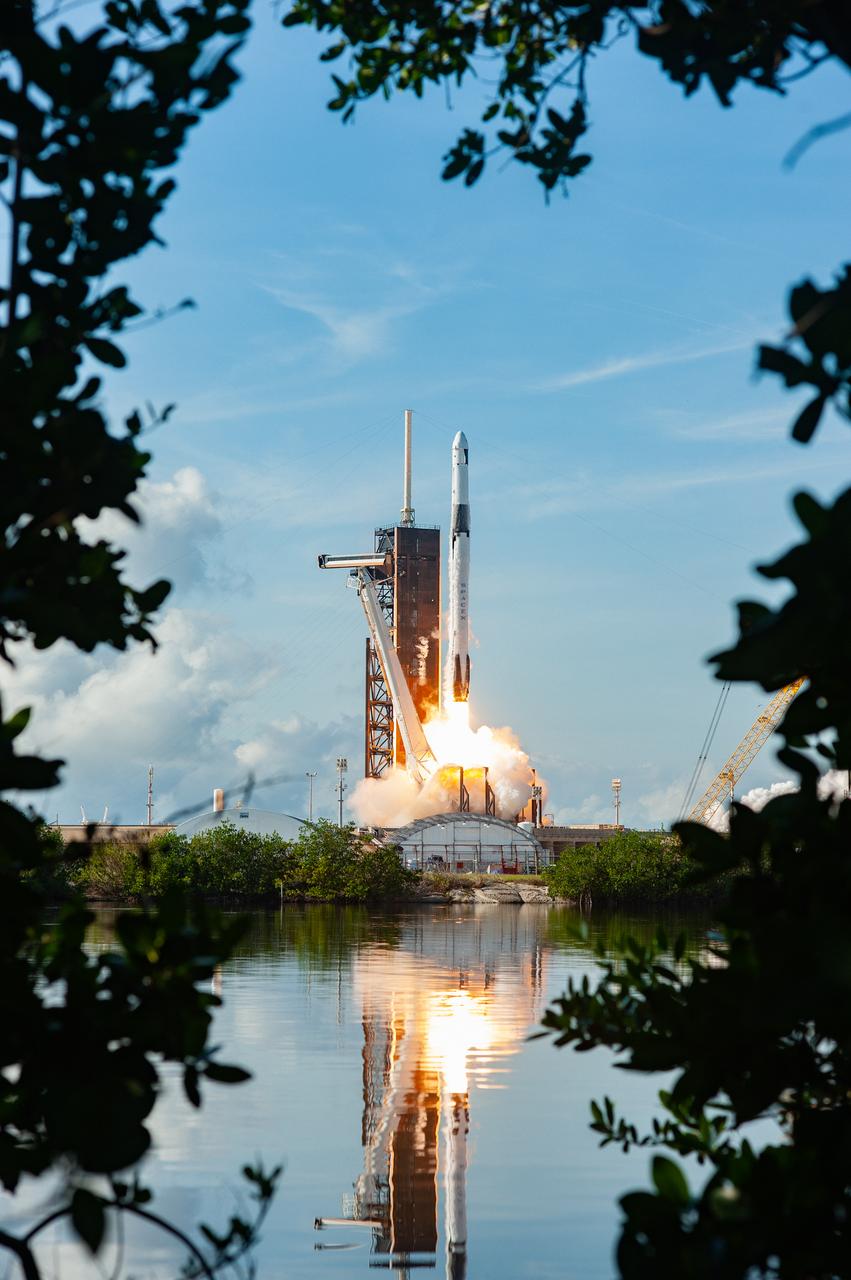

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
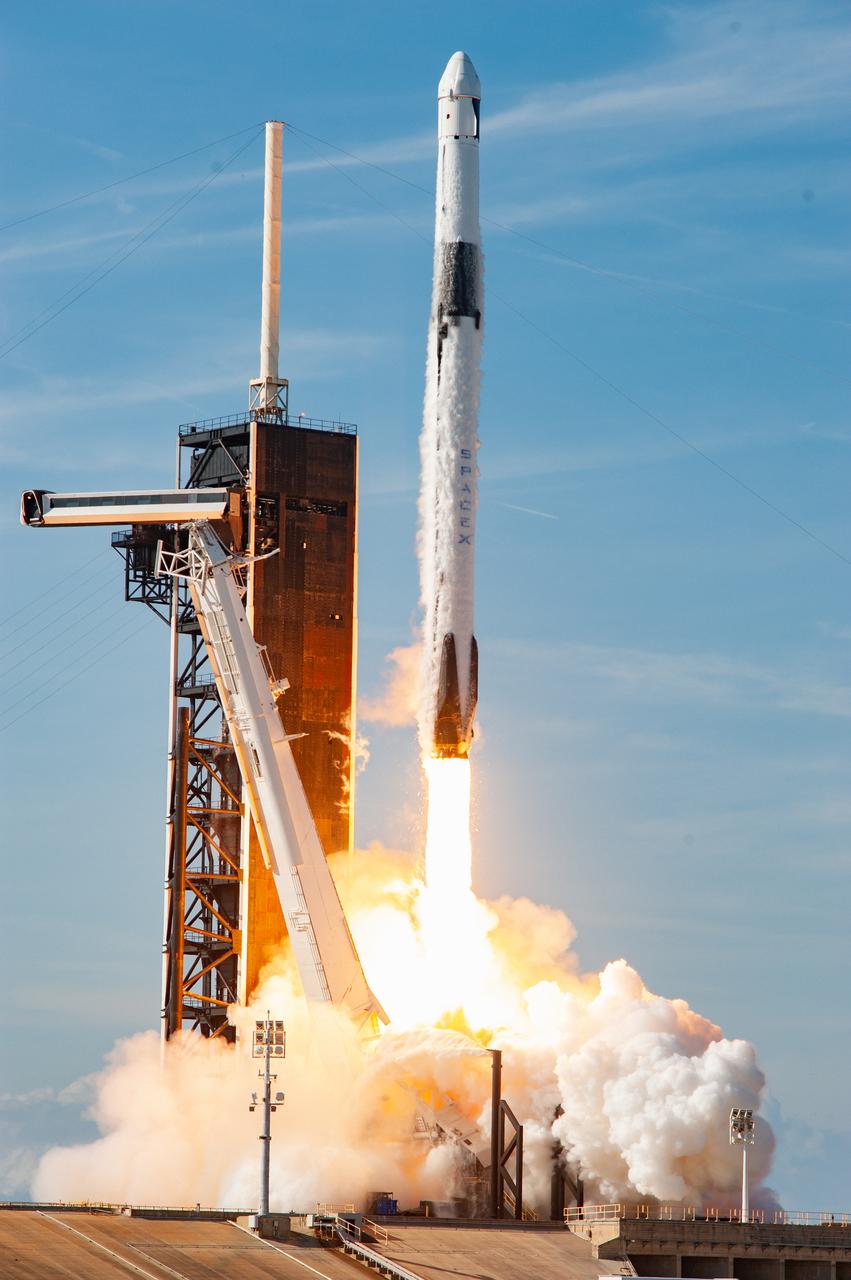

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
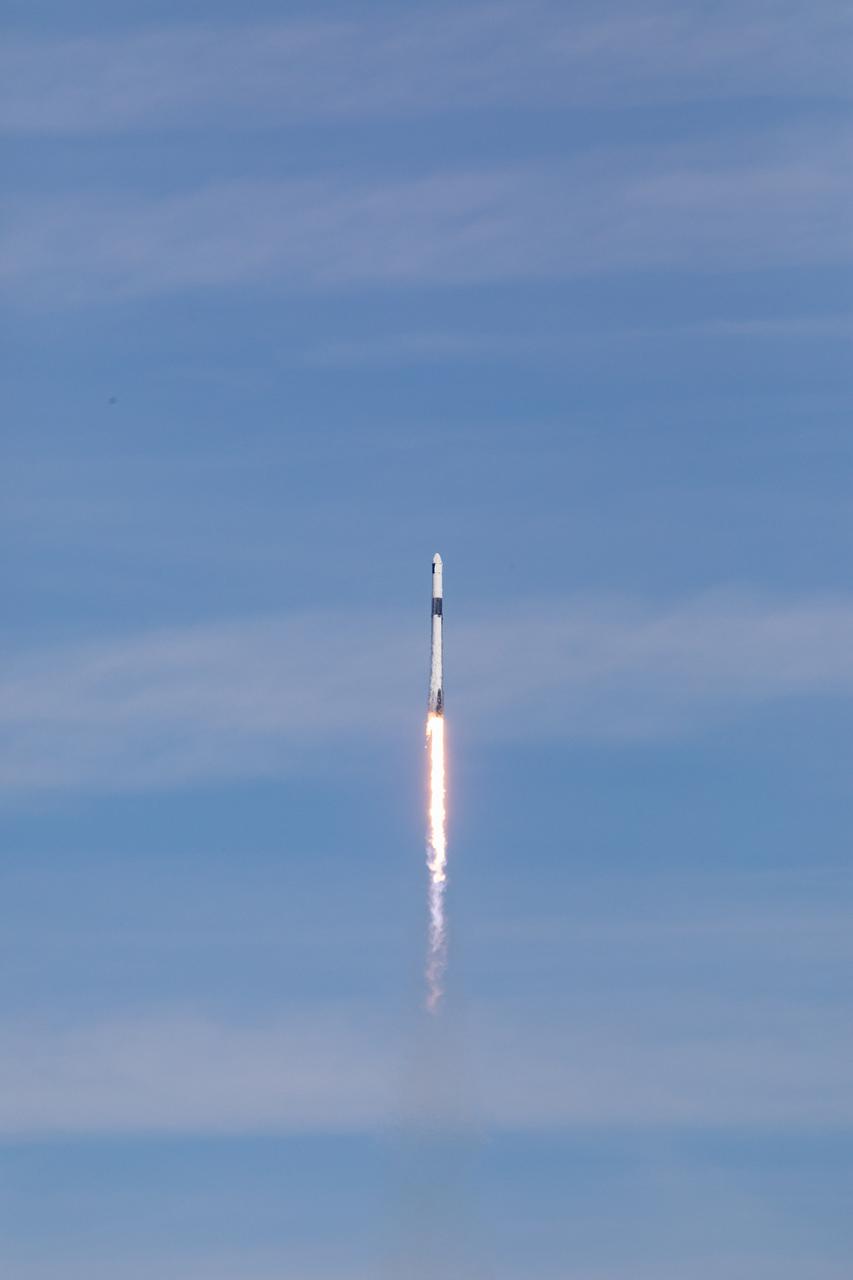

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after its liftoff from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th Commercial Resupply Services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo spacecraft will deliver about 7,700 pounds of science and research, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.