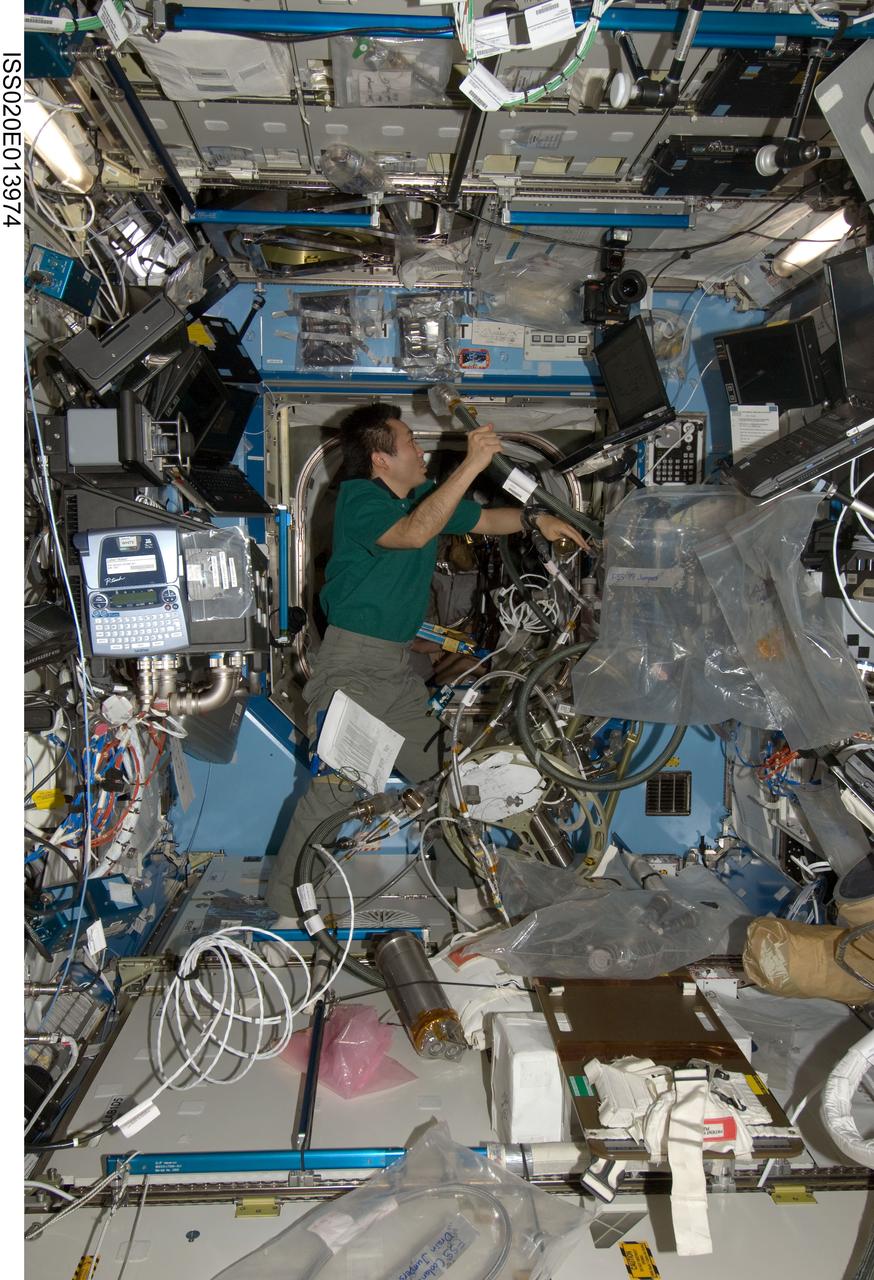

ISS020-E-013974 (23 June 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 20 flight engineer, works with the Fluid Control Pump Assembly (FCPA), which is a part of the Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station.
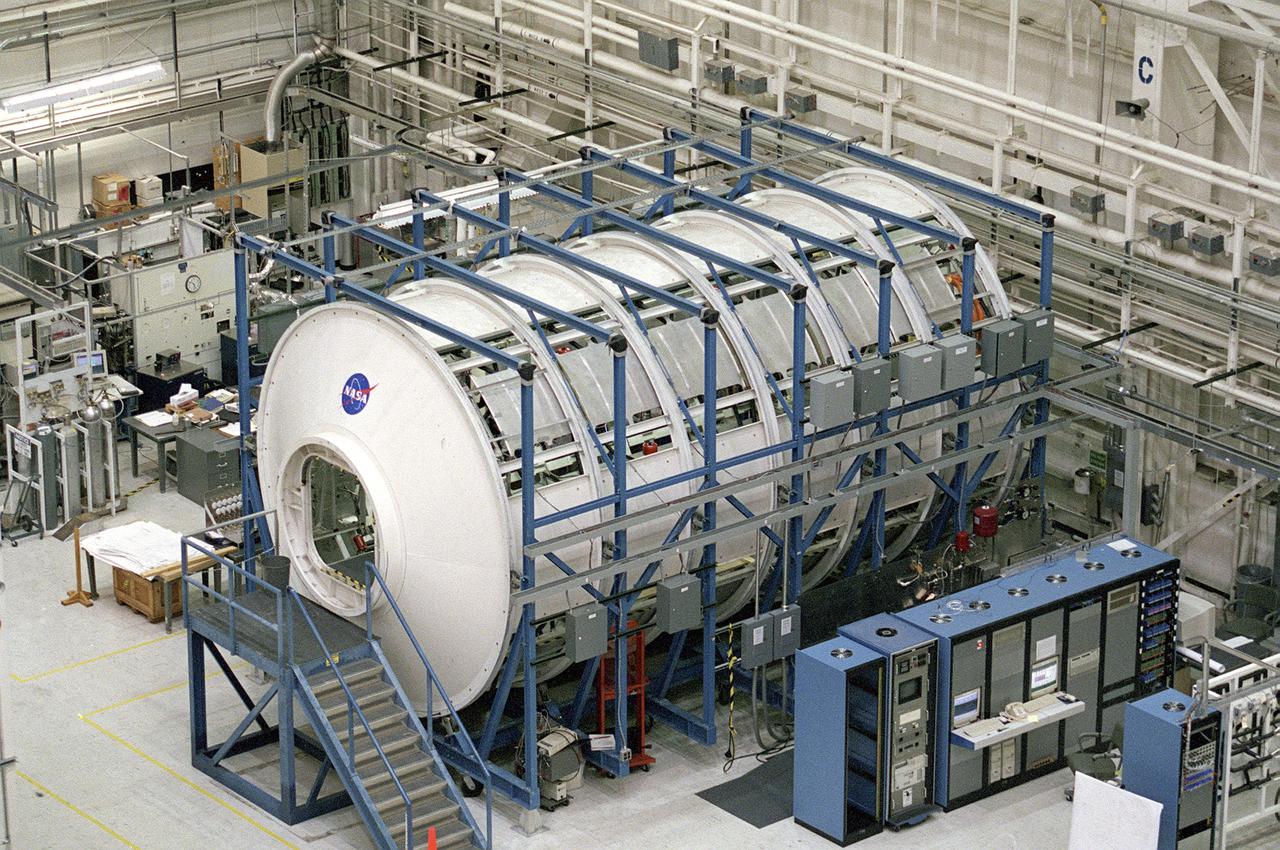

The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) is responsible for designing and building the life support systems that will provide the crew of the International Space Station (ISS) a comfortable environment in which to live and work. Scientists and engineers at the MSFC are working together to provide the ISS with systems that are safe, efficient and cost-effective. These compact and powerful systems are collectively called the Environmental Control and Life Support Systems, or simply, ECLSS. This is an exterior view of the U.S. Laboratory Module Simulator containing the ECLSS Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) testing facility at MSFC. At the bottom right is the data acquisition and control computers (in the blue equipment racks) that monitor the testing in the facility. The ITCS simulator facility duplicates the function, operation, and troubleshooting problems of the ITCS. The main function of the ITCS is to control the temperature of equipment and hardware installed in a typical ISS Payload Rack.
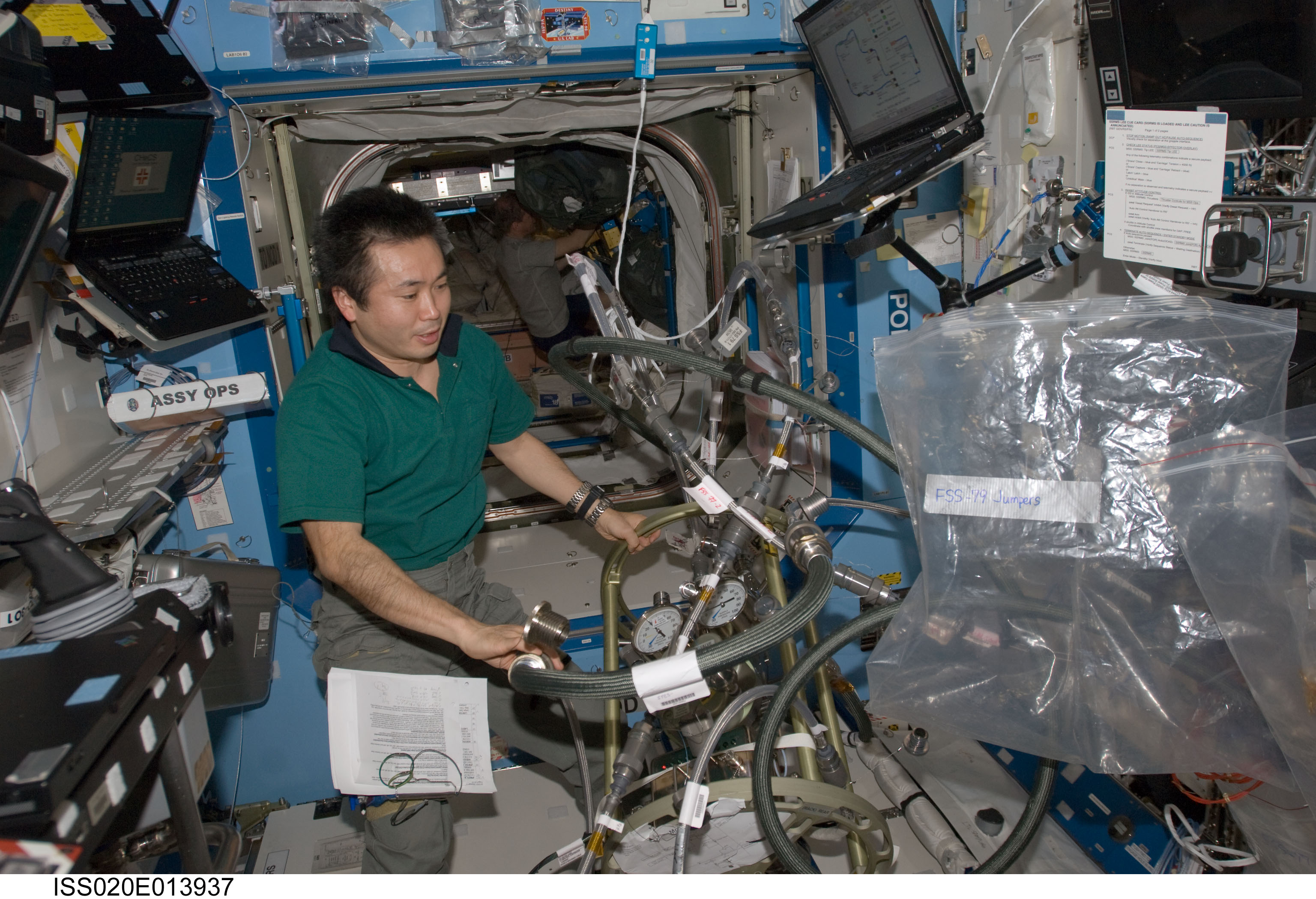

ISS020-E-013937 (23 June 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 20 flight engineer, works with the Fluid Control Pump Assembly (FCPA), which is a part of the Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station.
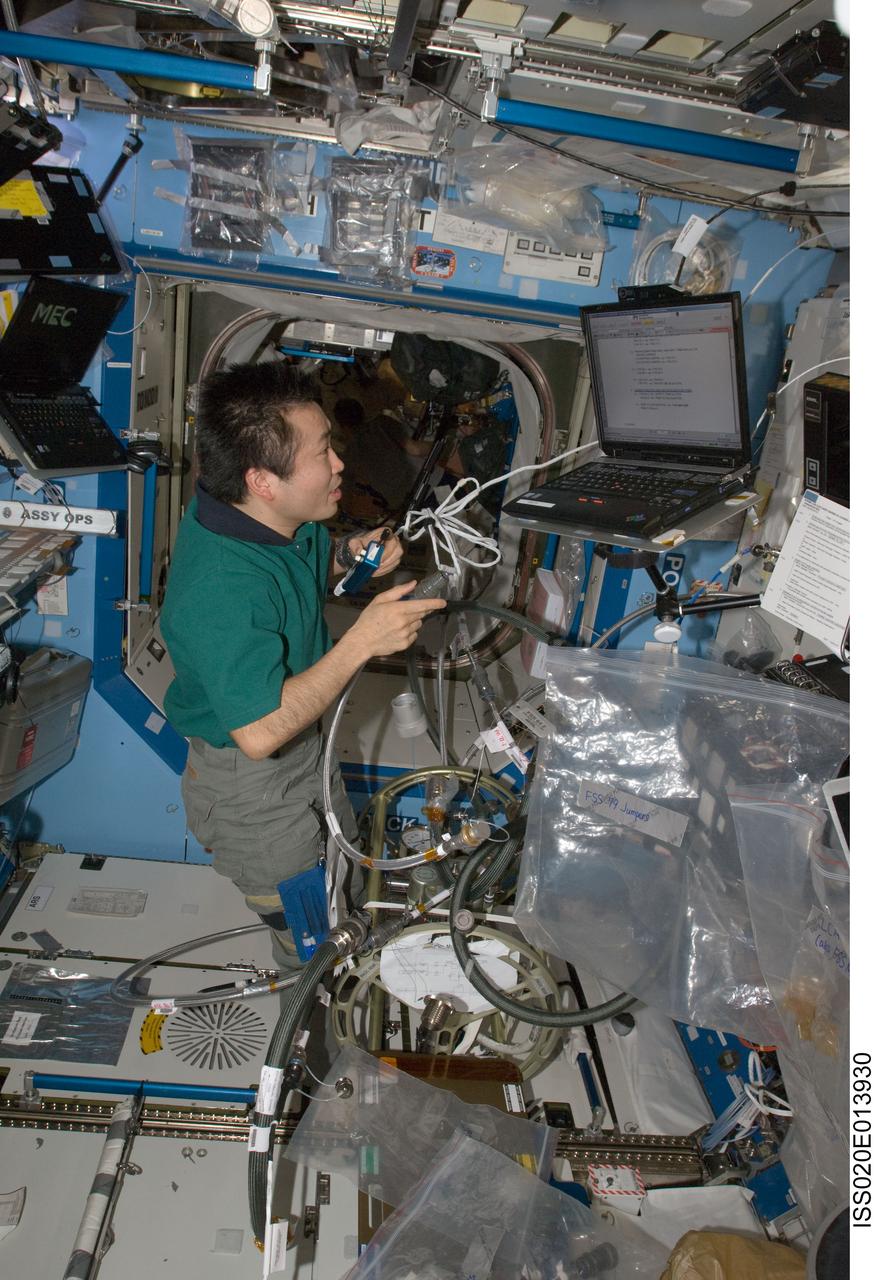

ISS020-E-013930 (23 June 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 20 flight engineer, works with the Fluid Control Pump Assembly (FCPA), which is a part of the Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station.
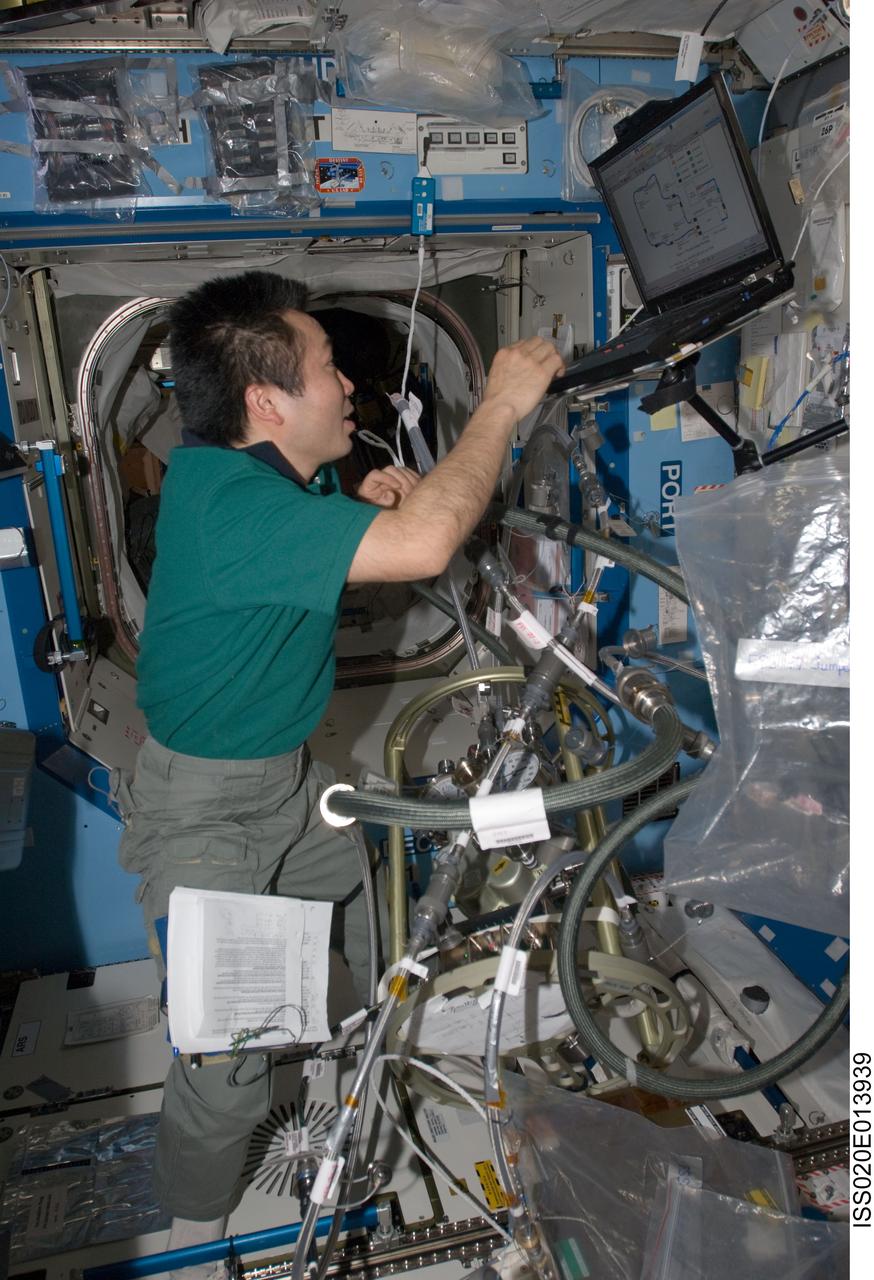

ISS020-E-013939 (23 June 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 20 flight engineer, uses a computer while working with the Fluid Control Pump Assembly (FCPA), which is a part of the Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station.
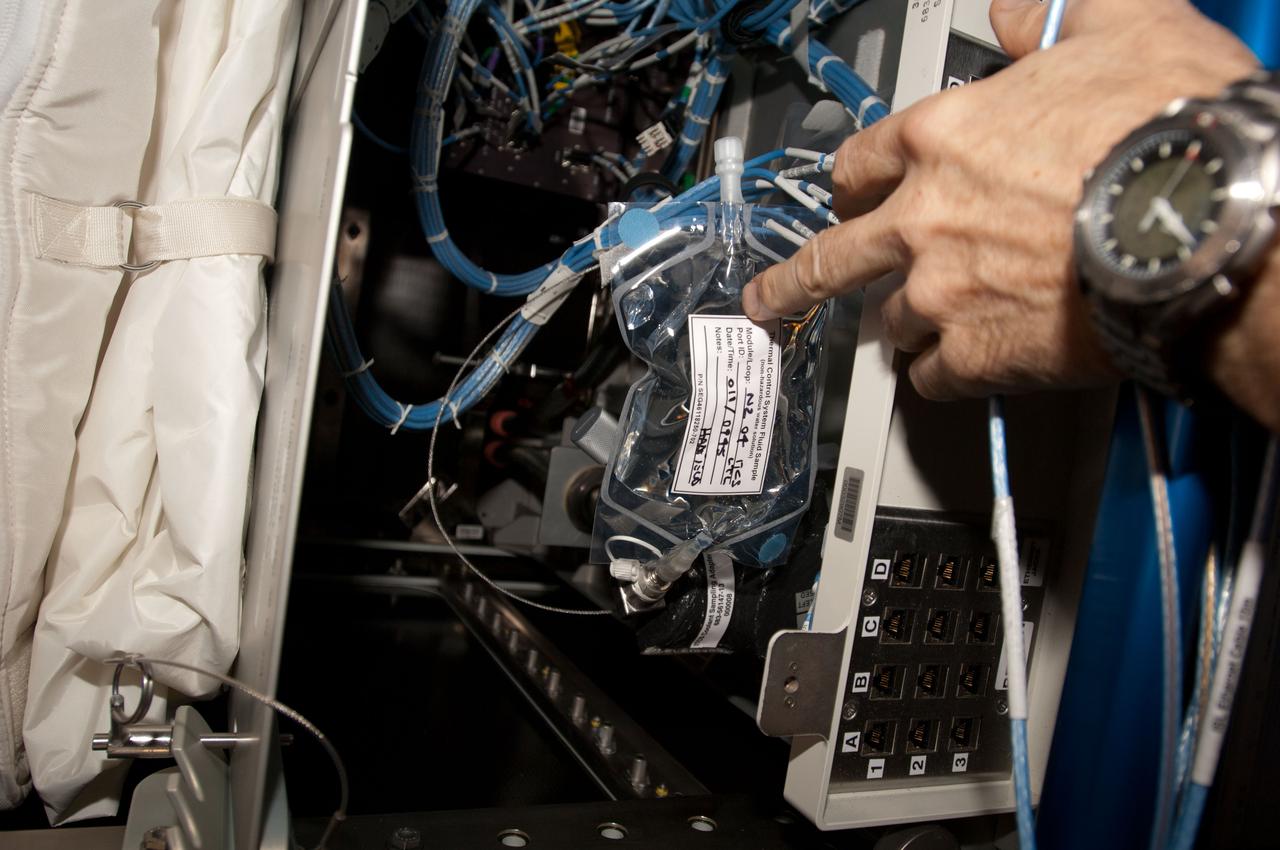
View during Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) - Measuring valve parameters in the Node 3. Photo was taken during Expedition 34.
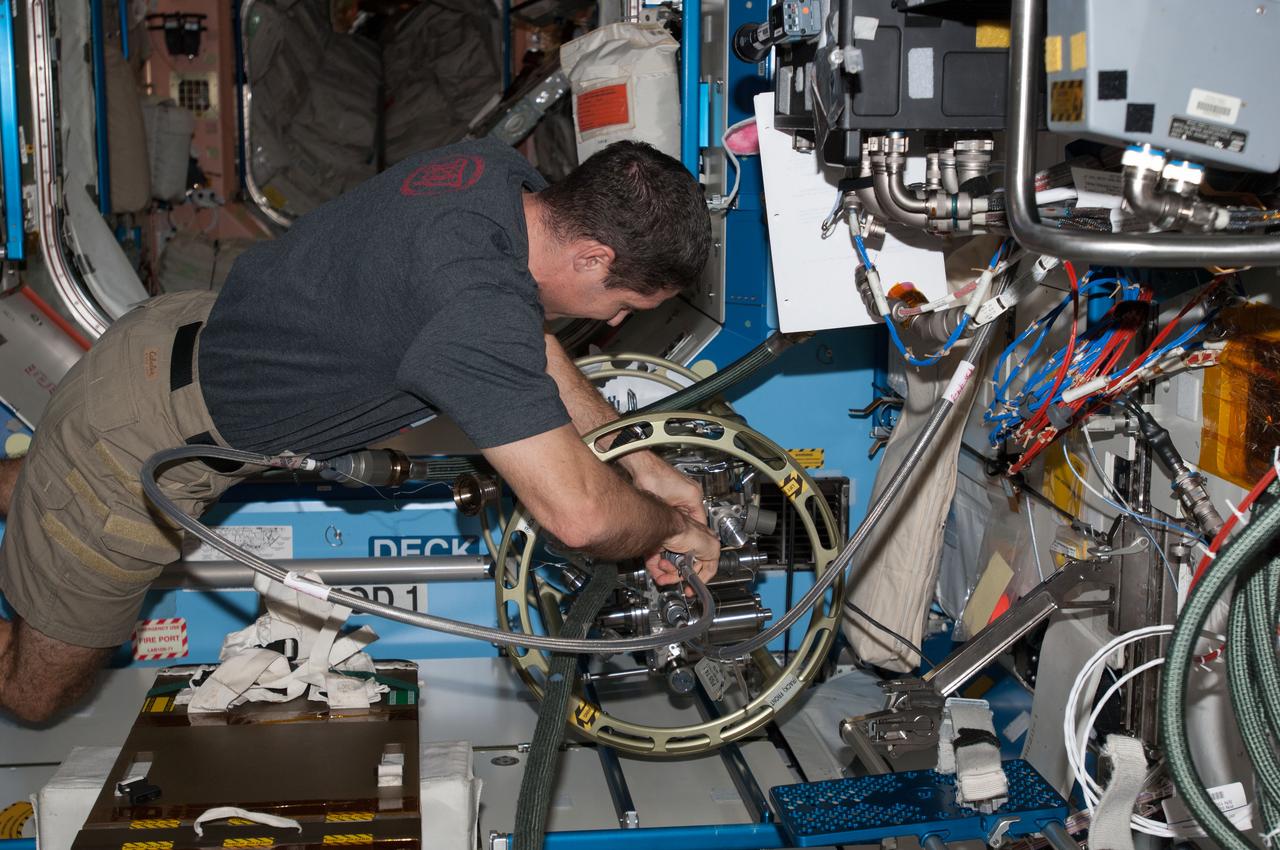

ISS038-E-040139 (31 Jan. 2014) --- NASA astronaut Mike Hopkins, Expedition 38 flight engineer, uses the Fluid Servicing System (FSS) to refill Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) loops with fresh coolant in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
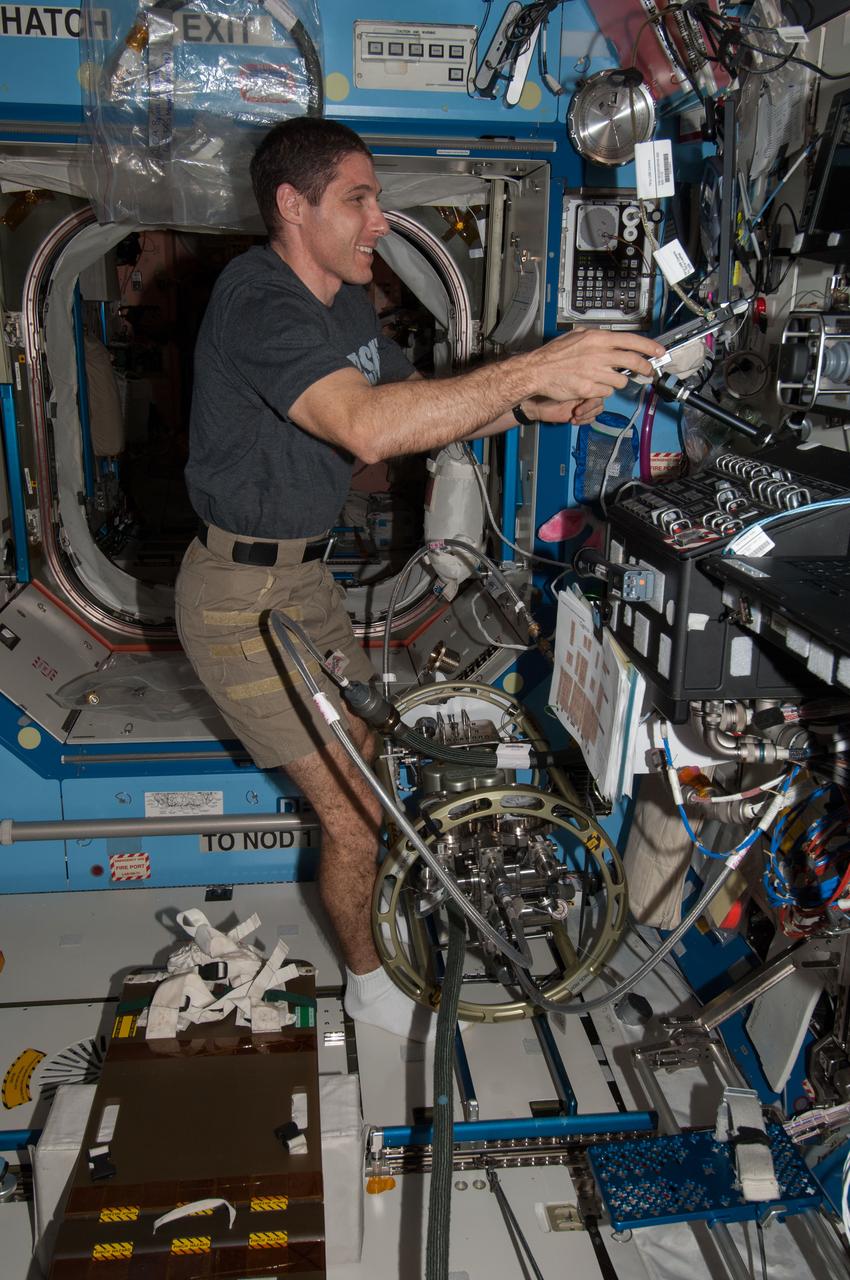

ISS038-E-040111 (31 Jan. 2014) --- NASA astronaut Mike Hopkins, Expedition 38 flight engineer, uses the Fluid Servicing System (FSS) to refill Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) loops with fresh coolant in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
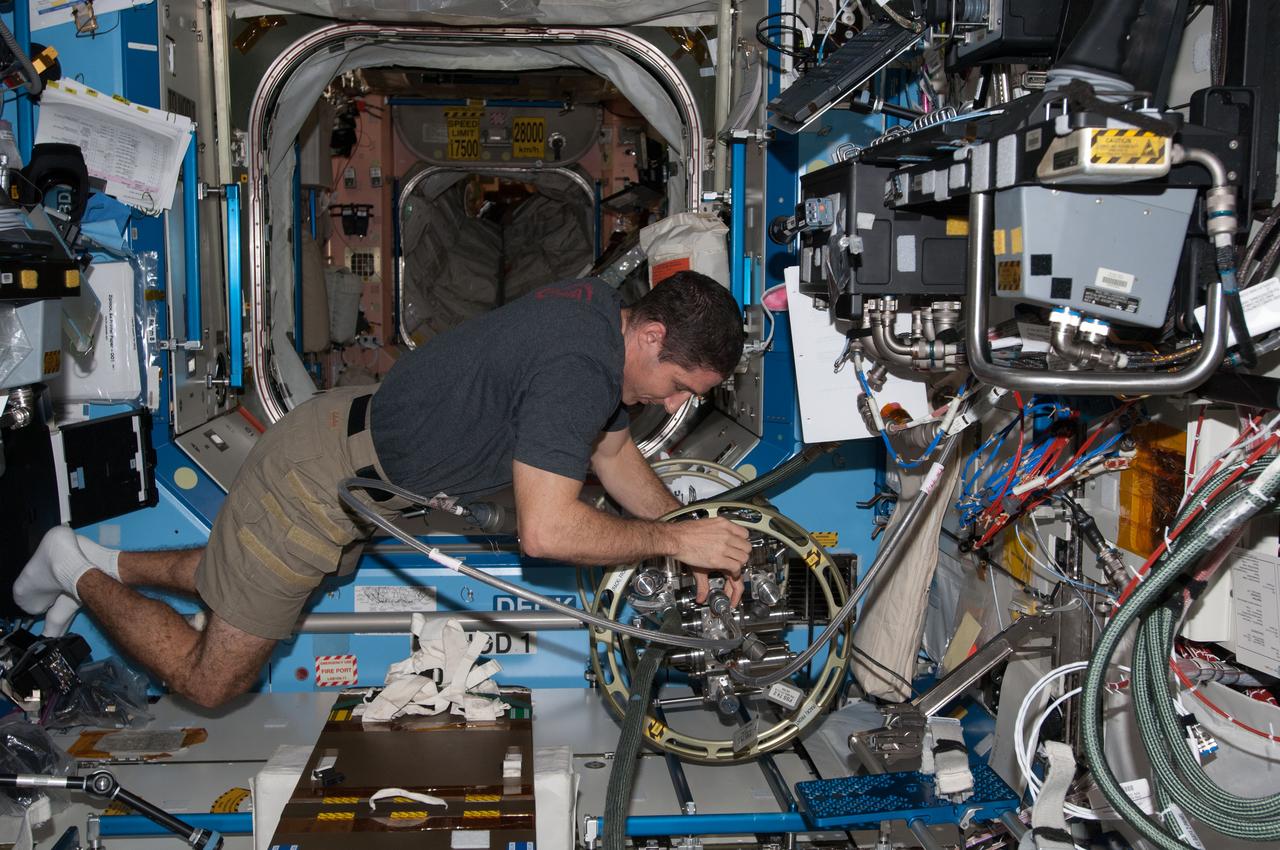

ISS038-E-040140 (31 Jan. 2014) --- NASA astronaut Mike Hopkins, Expedition 38 flight engineer, uses the Fluid Servicing System (FSS) to refill Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) loops with fresh coolant in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
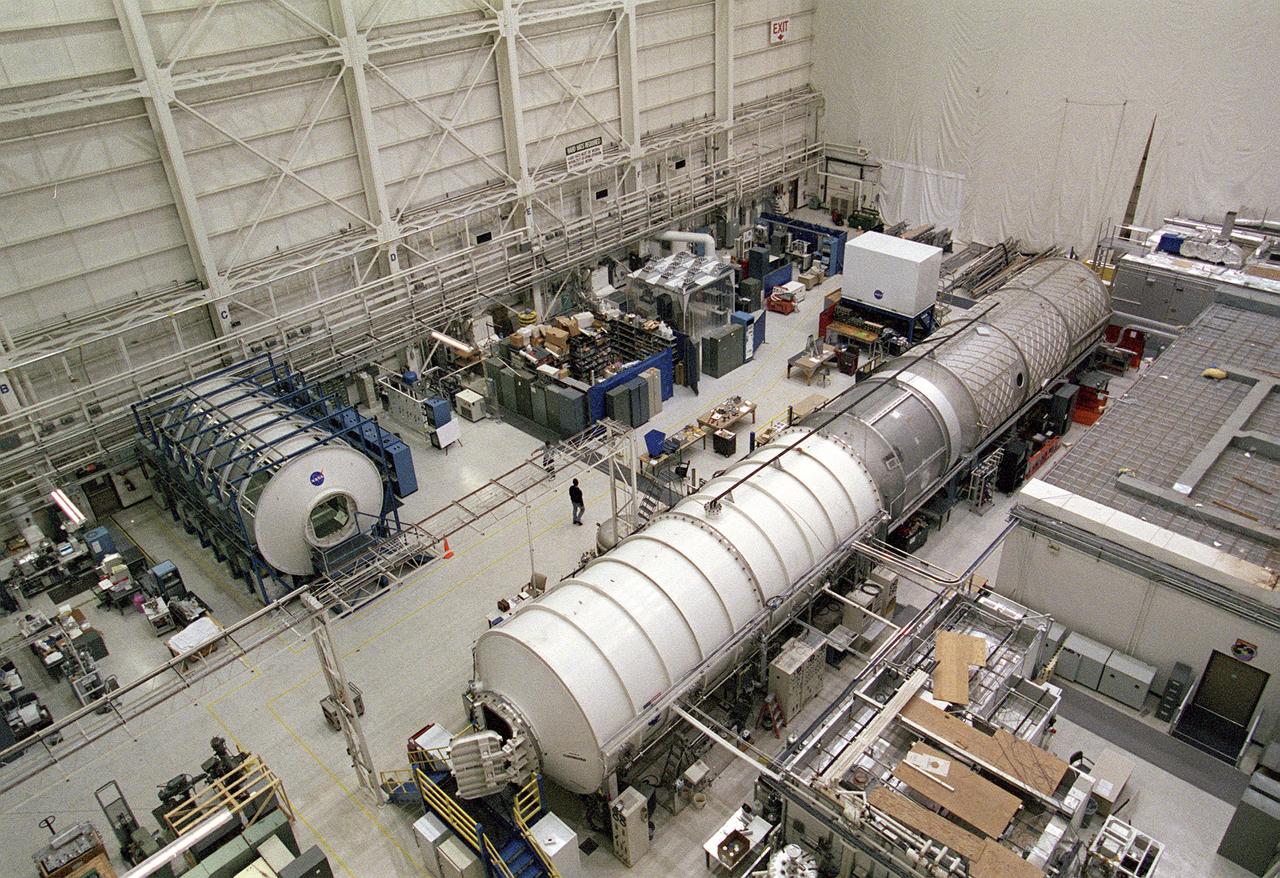
The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) is responsible for designing and building the life support systems that will provide the crew of the International Space Station (ISS) a comfortable environment in which to live and work. Scientists and engineers at the MSFC are working together to provide the ISS with systems that are safe, efficient, and cost-effective. These compact and powerful systems are collectively called the Environmental Control and Life Support Systems, or simply, ECLSS. This is a view of the ECLSS and the Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) Test Facility in building 4755, MSFC. In the foreground is the 3-module ECLSS simulator comprised of the U.S. Laboratory Module Simulator, Node 1 Simulator, and Node 3/Habitation Module Simulator. At center left is the ITCS Simulator. The main function of the ITCS is to control the temperature of equipment and hardware installed in a typical ISS Payload Rack.
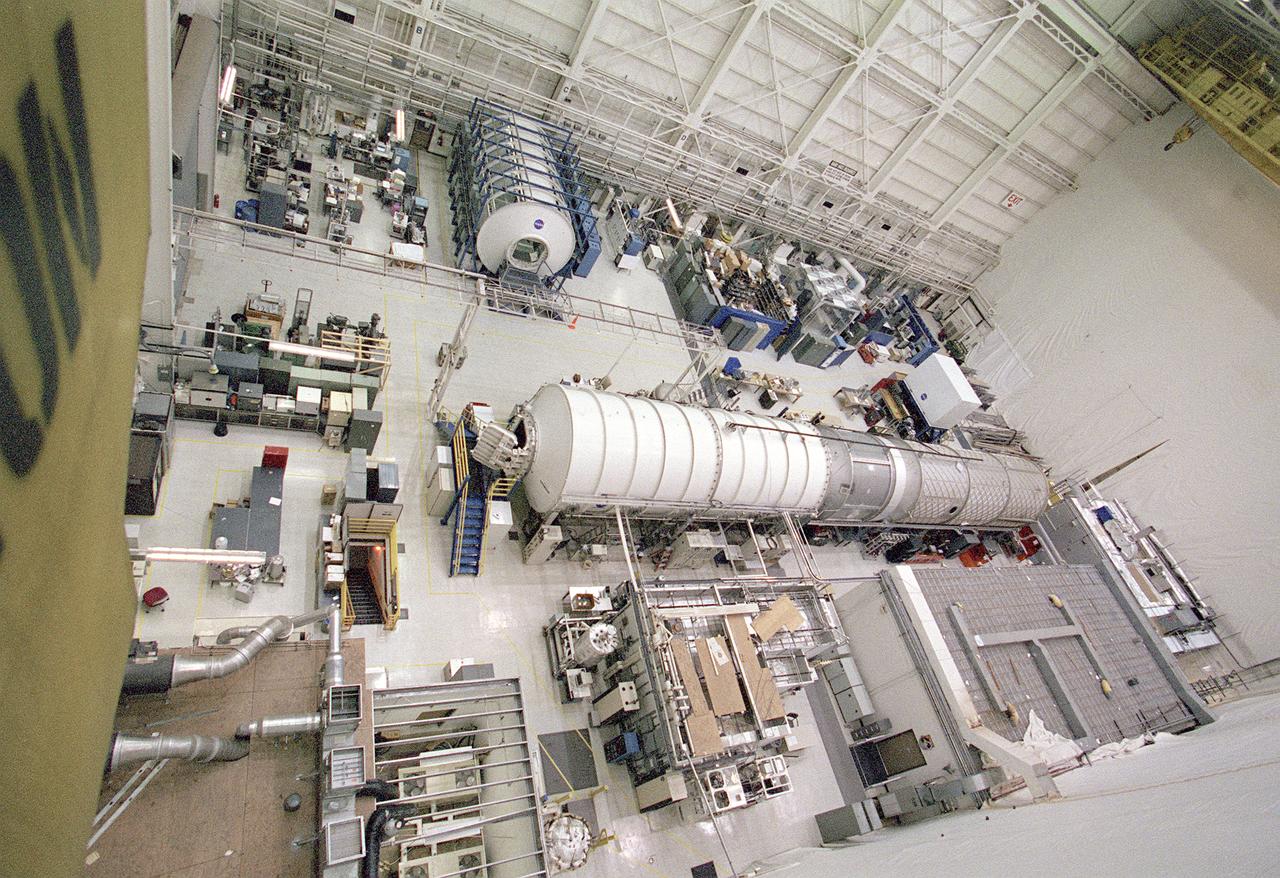
The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) is responsible for designing and building the life support systems that will provide the crew of the International Space Station (ISS) a comfortable environment in which to live and work. Scientists and engineers at the MSFC are working together to provide the ISS with systems that are safe, efficient, and cost-effective. These compact and powerful systems are collectively called the Environmental Control and Life Support Systems, or simply, ECLSS. This is a view of the ECLSS and the Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) Test Facility in building 4755, MSFC. In the foreground is the 3-module ECLSS simulator comprised of the U.S. Laboratory Module Simulator, Node 1 Simulator, and Node 3/Habitation Module Simulator. On the left is the ITCS Simulator. The main function of the ITCS is to control the temperature of equipment and hardware installed in a typical ISS Payload Rack.
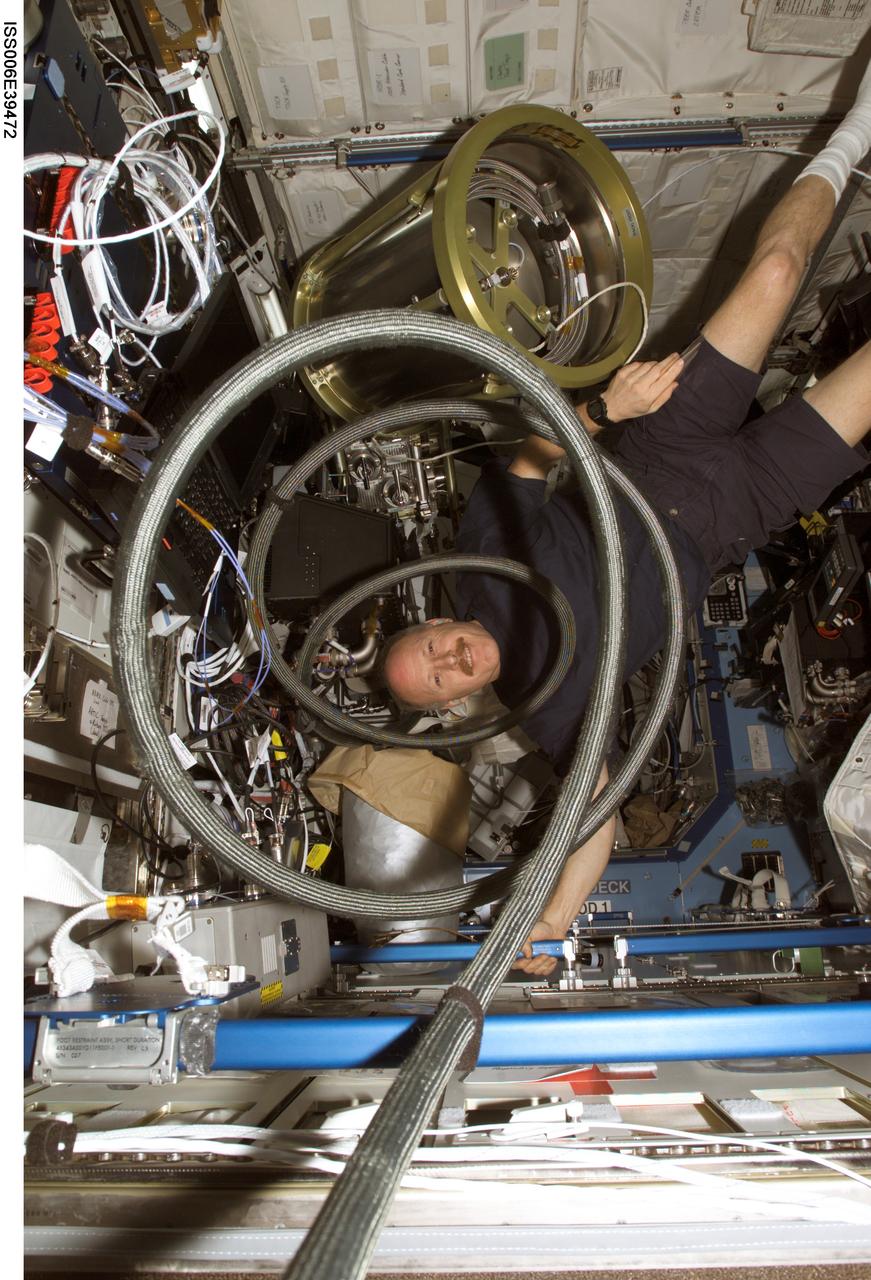

ISS006-E-39472 (18 March 2003) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, Expedition Six mission commander, floats with a supply tank, which is a part of the Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).
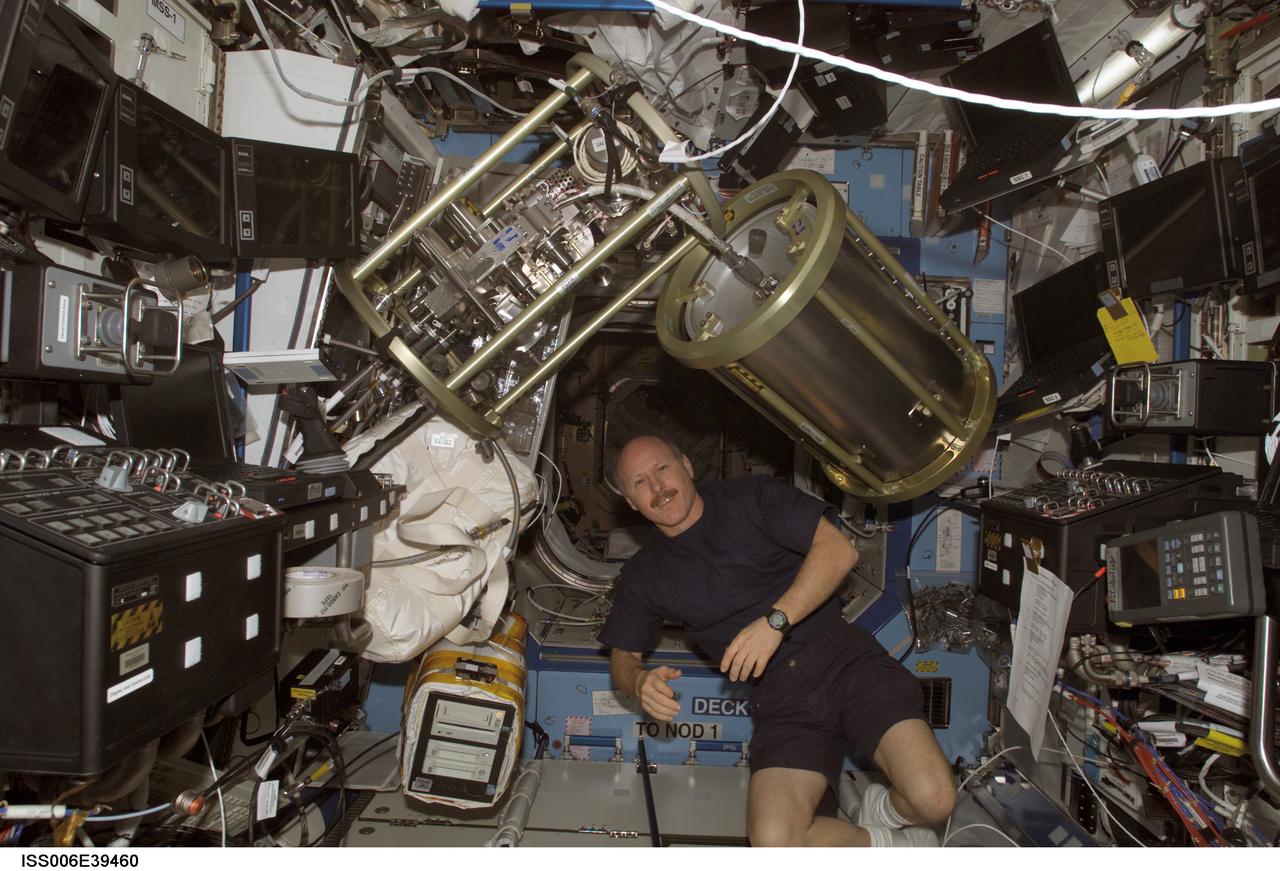

ISS006-E-39460 (18 March 2003) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, Expedition Six mission commander, is pictured in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). The supply tank and Fluid Control Pump Assembly (FCPA), which are a part of the Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS), are visible floating freeing above Bowersox.
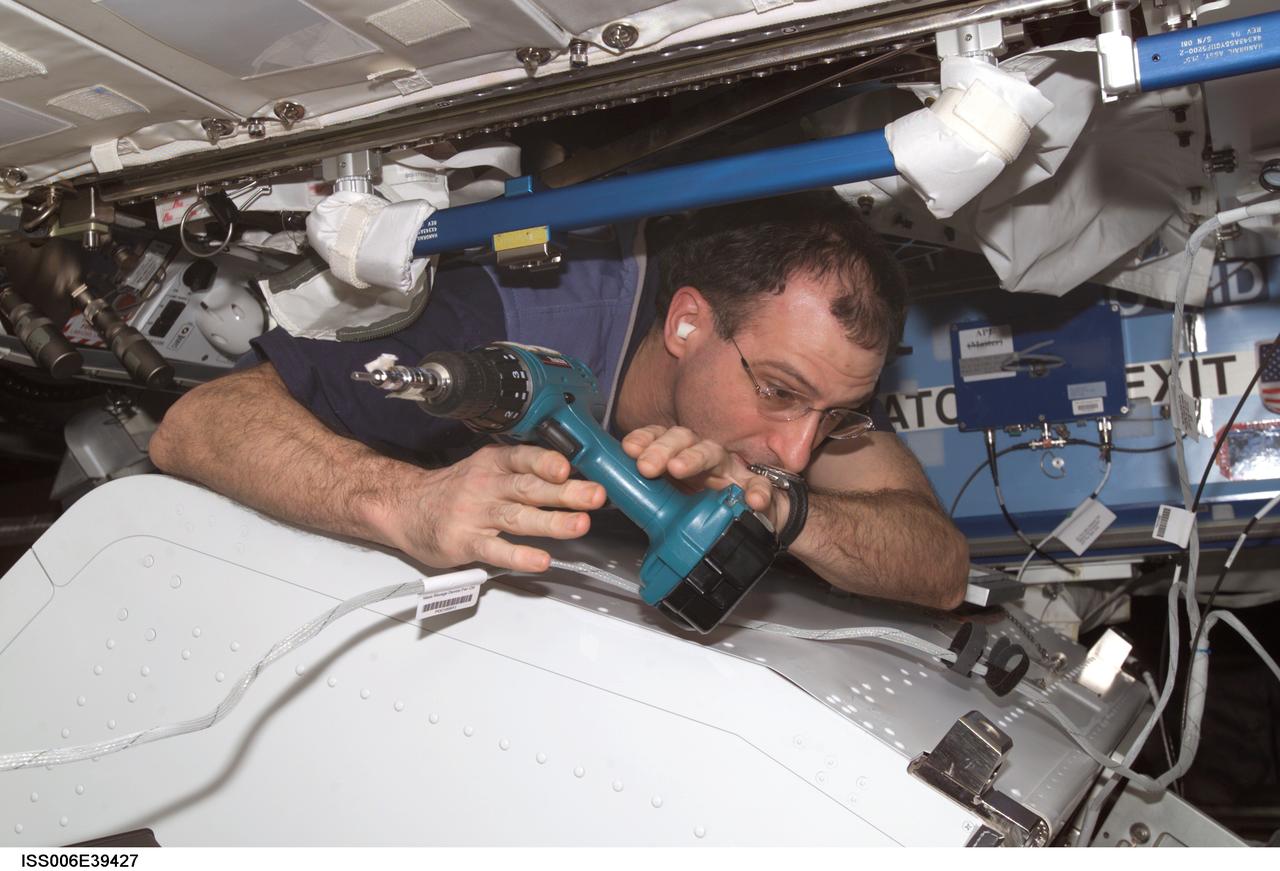

ISS006-E-39427 (17 March 2003) --- Astronaut Donald R. Pettit, Expedition Six NASA ISS science officer, uses a drill to disassemble framework of the Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).

Imaging Technology Center, ITC, Engineering Team
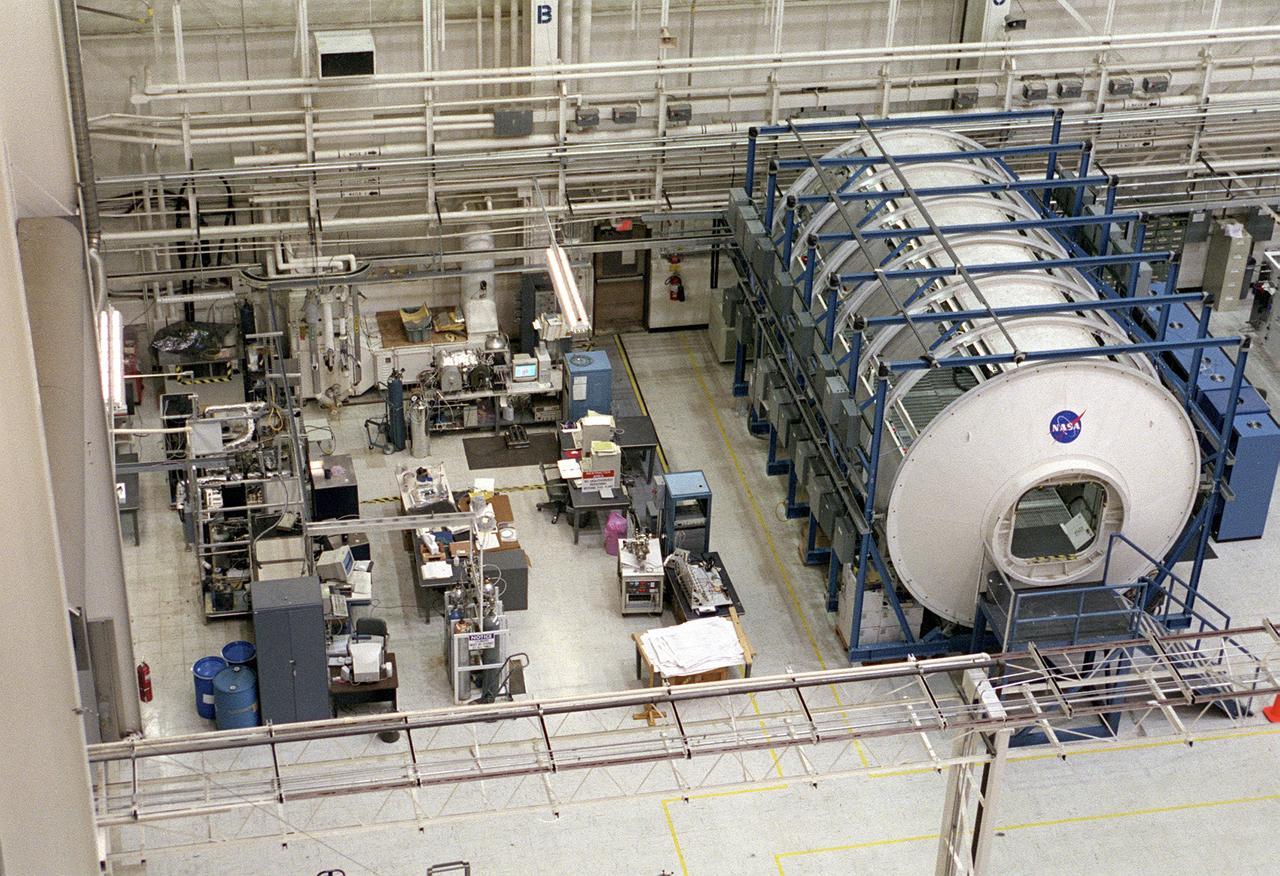

The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) is responsible for designing and building the life support systems that will provide the crew of the International Space Station (ISS) a comfortable environment in which to live and work. Scientists and engineers at the MSFC are working together to provide the ISS with systems that are safe, efficient, and cost-effective. These compact and powerful systems are collectively called the Environmental Control and Life Support Systems, or simply, ECLSS. In this photograph, the life test area on the left of the MSFC ECLSS test facility is where various subsystems and components are tested to determine how long they can operate without failing and to identify components needing improvement. Equipment tested here includes the Carbon Dioxide Removal Assembly (CDRA), the Urine Processing Assembly (UPA), the mass spectrometer filament assemblies and sample pumps for the Major Constituent Analyzer (MCA). The Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) simulator facility (in the module in the right) duplicates the function and operation of the ITCS in the ISS U.S. Laboratory Module, Destiny. This facility provides support for Destiny, including troubleshooting problems related to the ITCS.
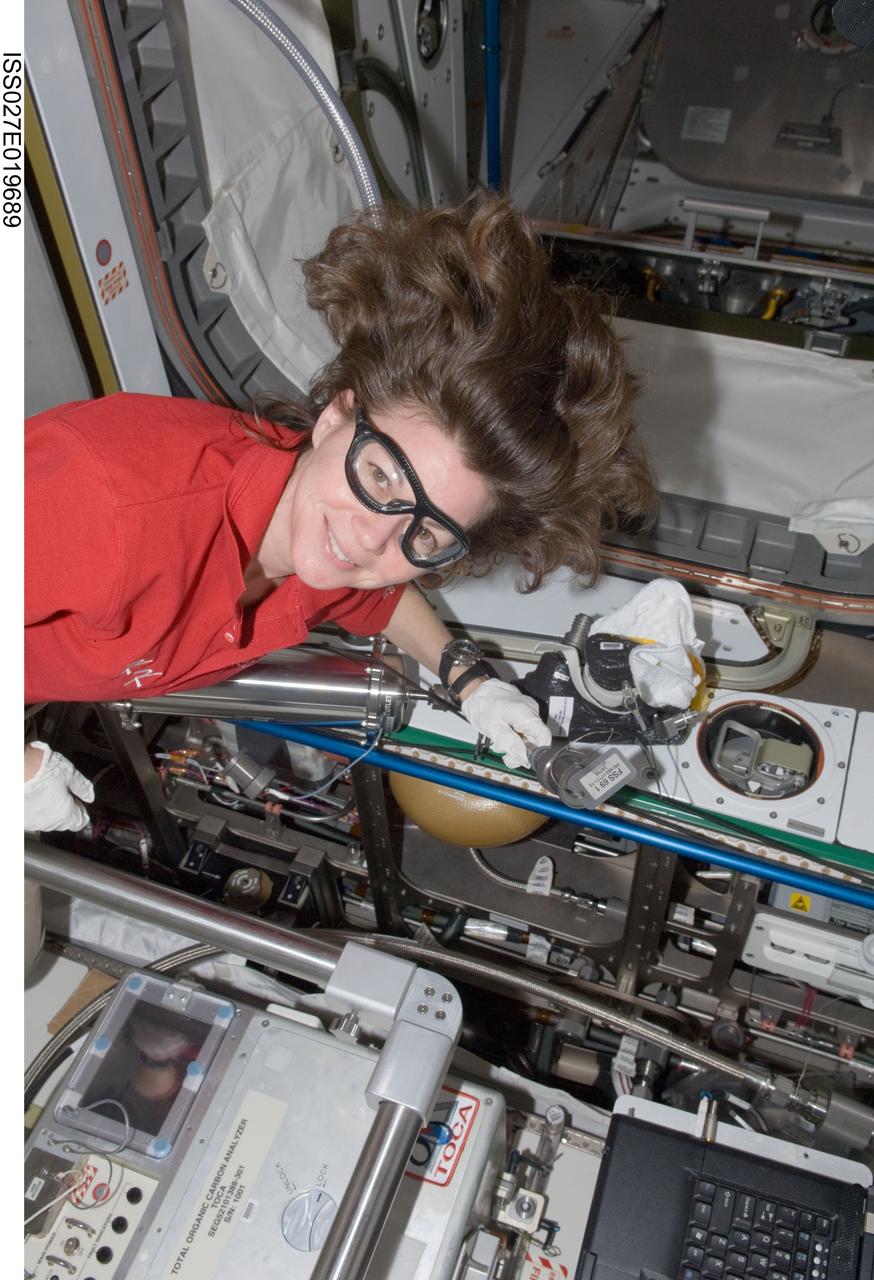

ISS027-E-019689 (22 April 2011) --- NASA astronaut Cady Coleman, Expedition 27 flight engineer, works with the Internal Thermal Control System Moderate Temperature Loop (ITCS MTL) in the Tranquility node of the International Space Station.
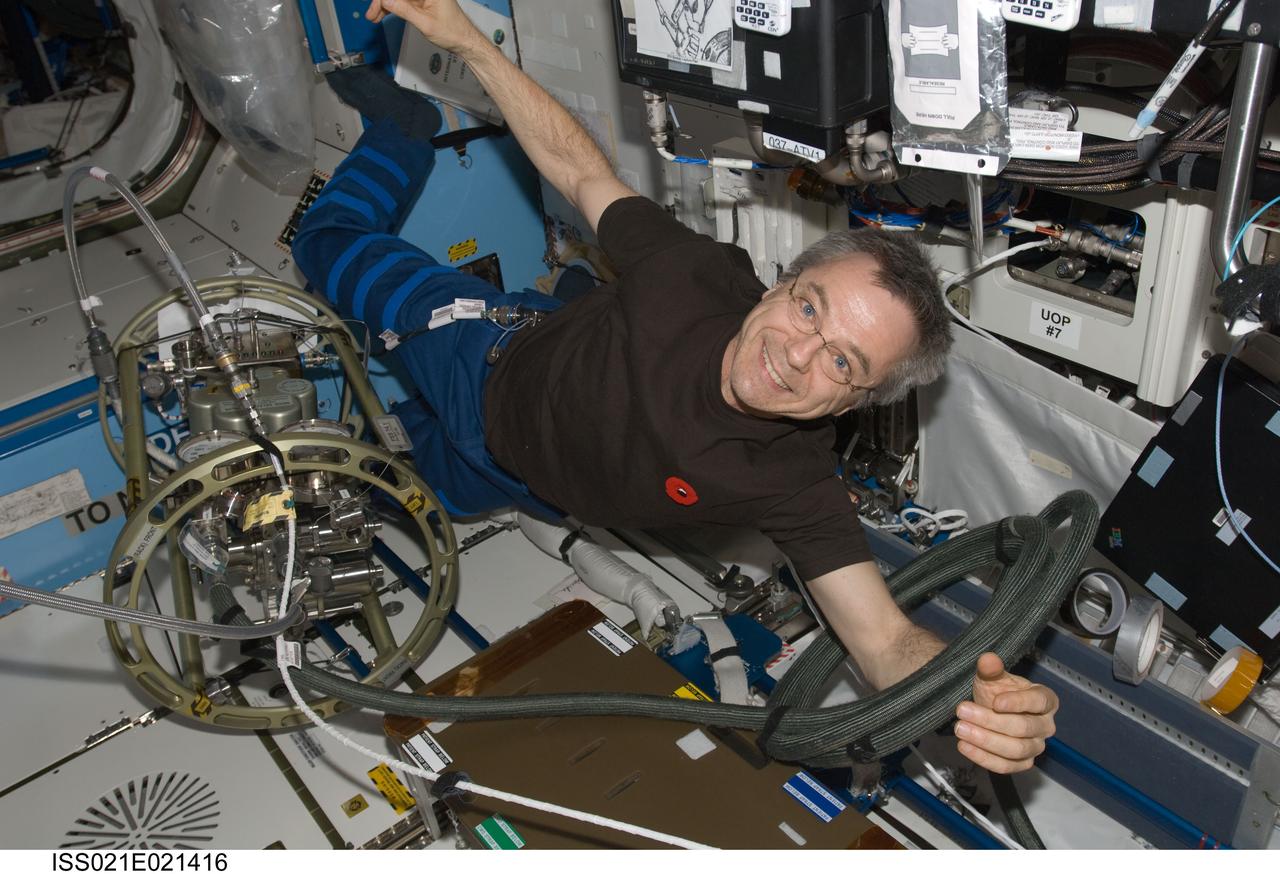

ISS021-E-021416 (5 Nov. 2009) --- Canadian Space Agency astronaut Robert Thirsk, Expedition 21 flight engineer, uses the Fluid Servicing System (FSS) to refill Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) loops with fresh coolant in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
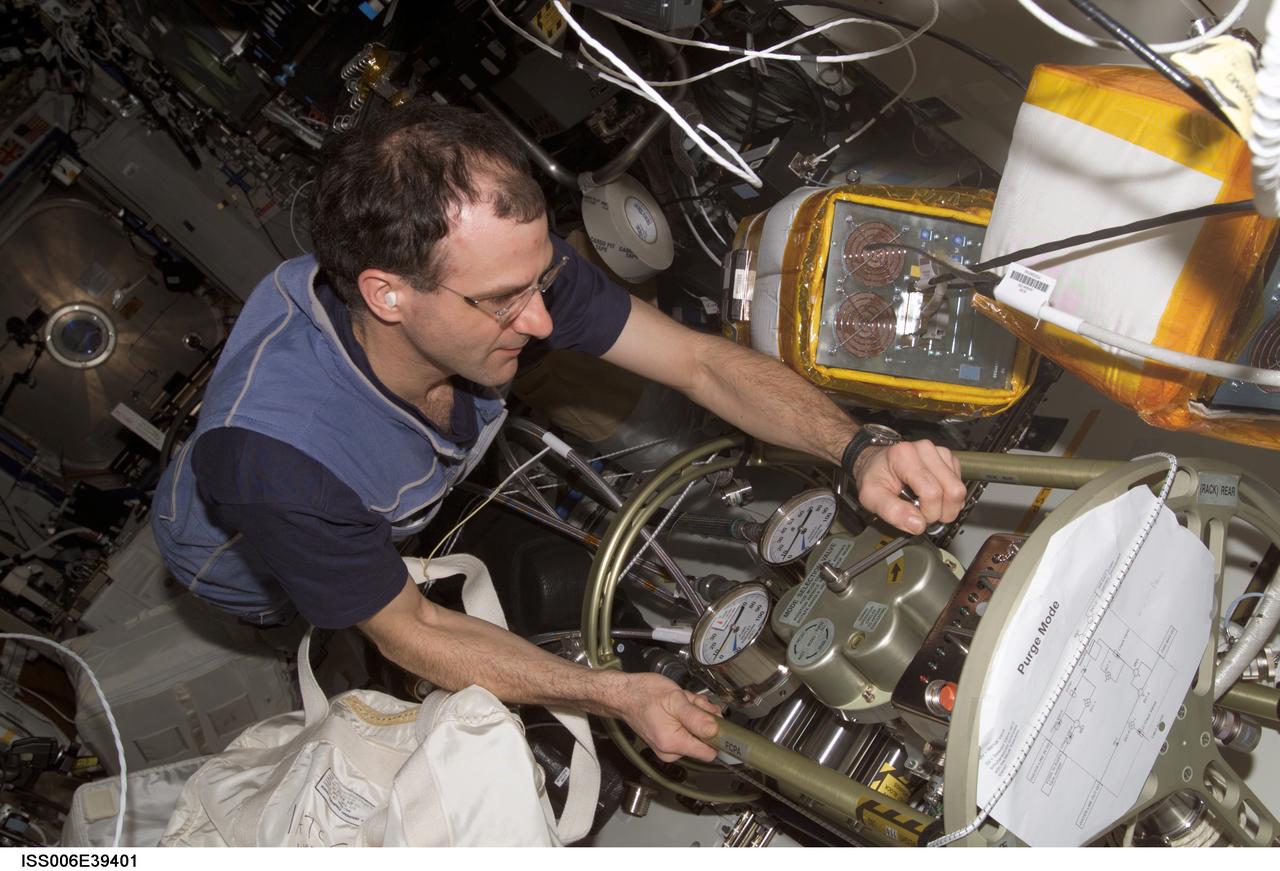

ISS006-E-39401 (17 March 2003) --- Astronaut Donald R. Pettit, Expedition Six NASA ISS science officer, makes a valve adjustment to the Fluid Control Pump Assembly (FCPA), which is a part of the Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).
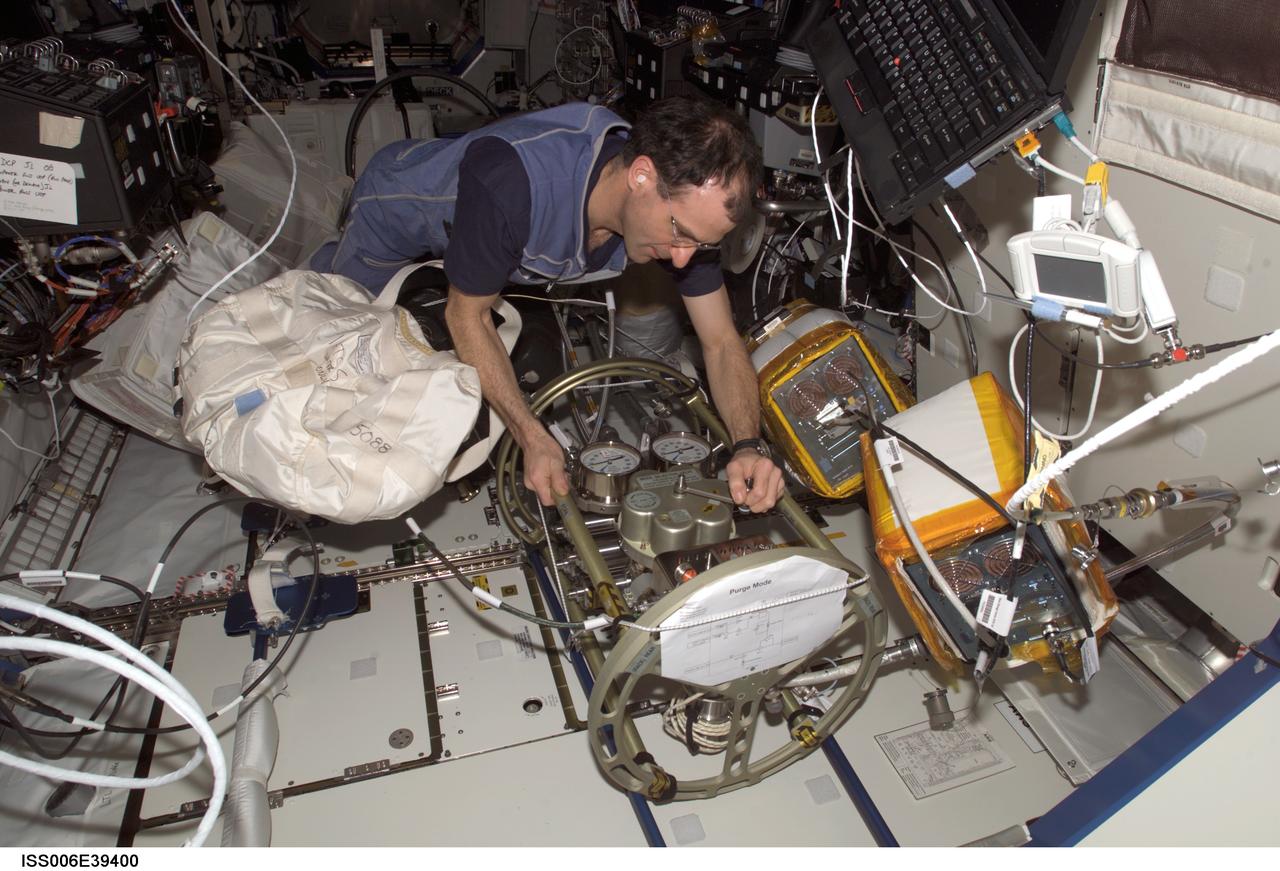

ISS006-E-39400 (17 March 2003) --- Astronaut Donald R. Pettit, Expedition Six NASA ISS science officer, makes a valve adjustment to the Fluid Control Pump Assembly (FCPA), which is a part of the Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS) in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).
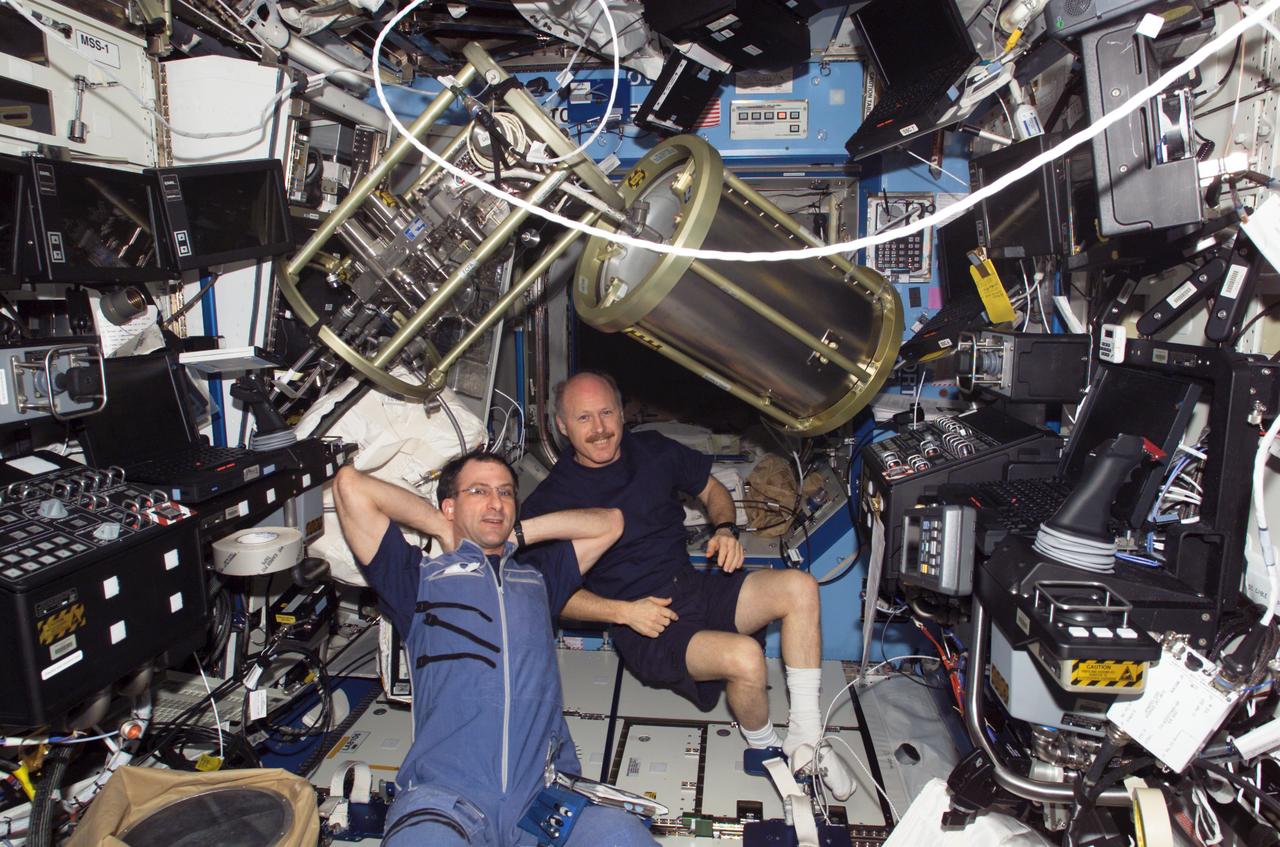

ISS006-E-39461 (18 March 2003) --- Astronauts Donald R. Pettit (left), Expedition 6 NASA ISS Science Officer, and Kenneth D. Bowersox, mission commander, are pictured in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). The supply tank and Fluid Control Pump Assembly (FCPA), which are a part of the Internal Thermal Control System (ITCS), are visible floating freeing above them.
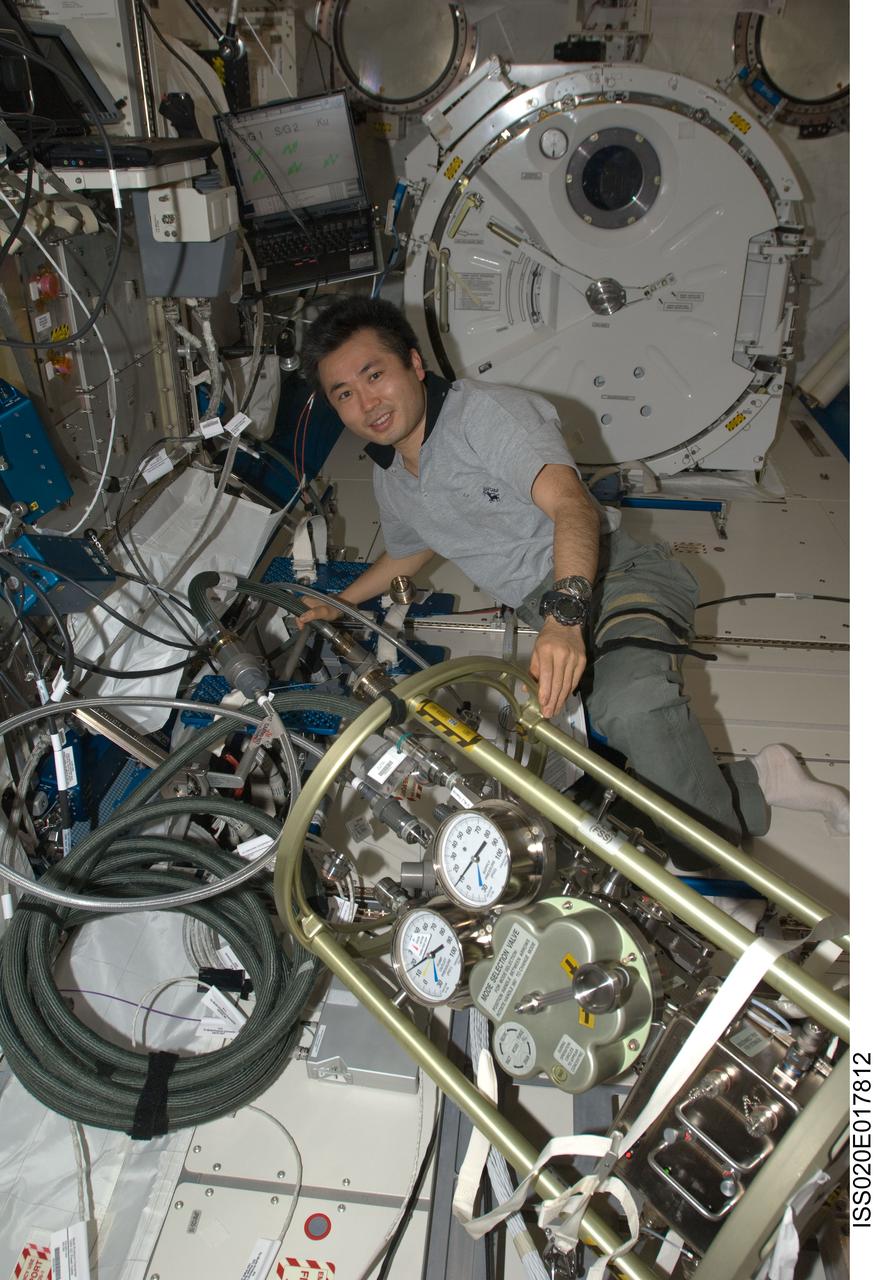

ISS020-E-017812 (7 July 2009) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Koichi Wakata, Expedition 20 flight engineer, works with the Fluid Control Pump Assembly (FCPA) in the Kibo laboratory on the International Space Station.
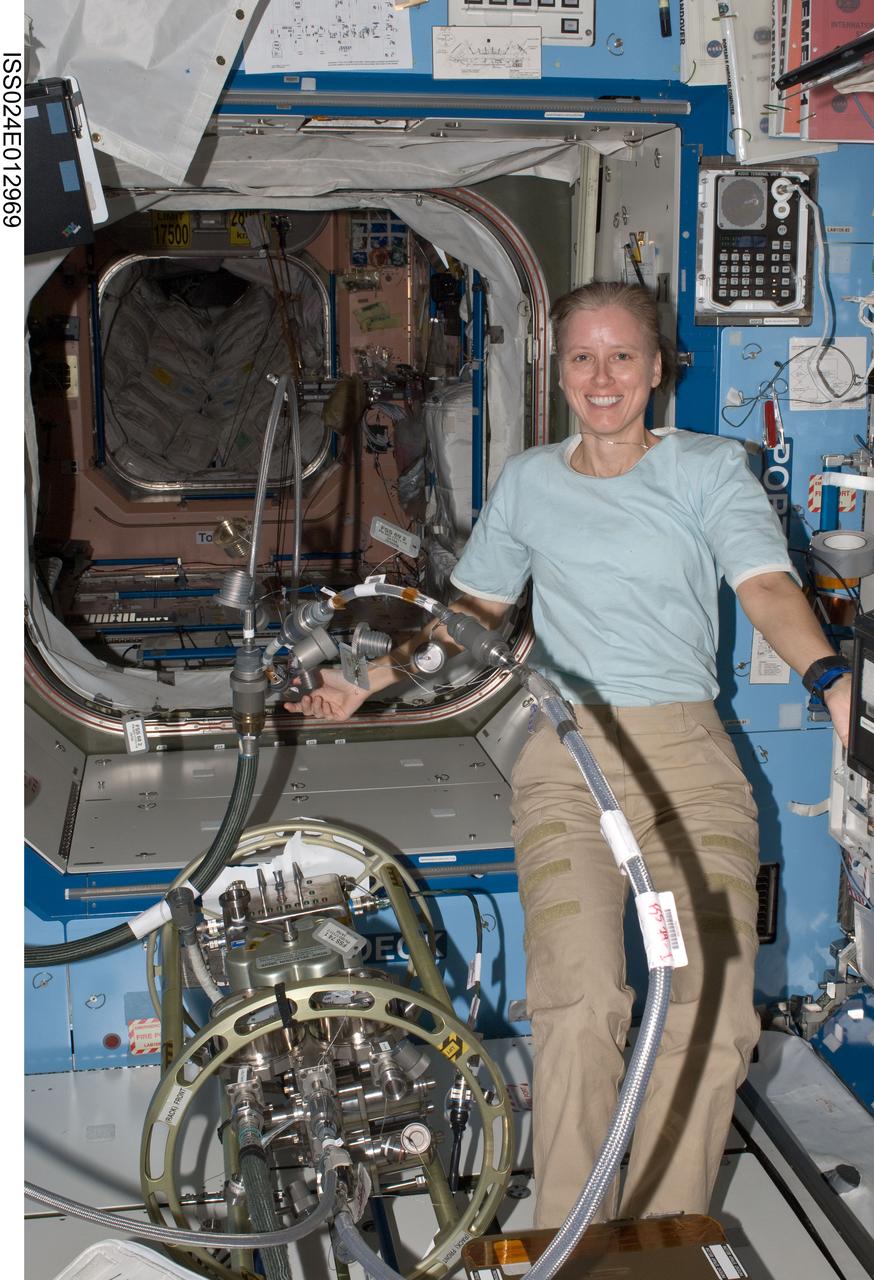

ISS024-E-012969 (31 Aug. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Shannon Walker, Expedition 24 flight engineer, works with the Fluid Servicing System (FSS) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
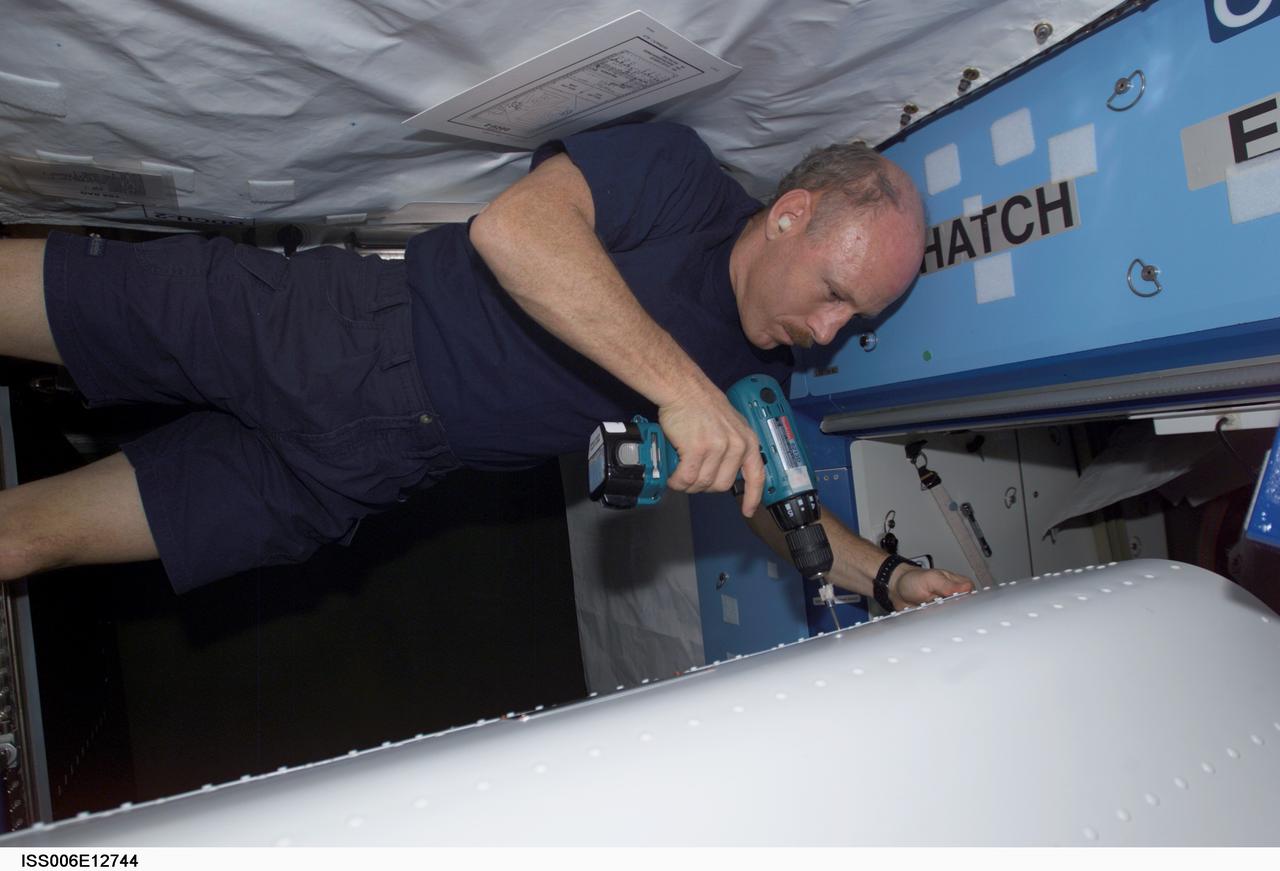

ISS006-E-12744 (30 December 2002) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, Expedition Six mission commander, performs in-flight maintenance (IFM) in the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).
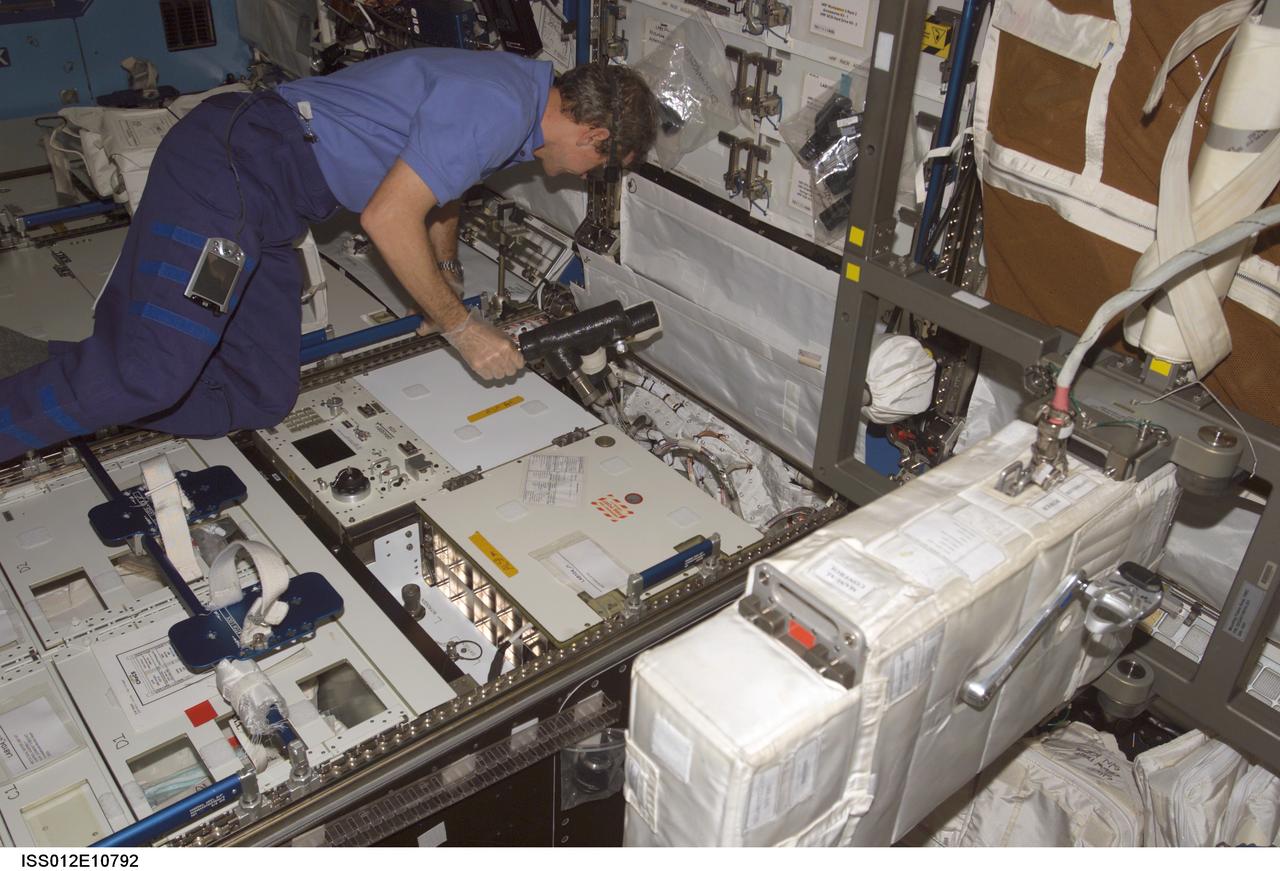

ISS012-E-10792 (9 December 2005) --- Astronaut William S. (Bill) McArthur Jr., Expedition 12 commander and NASA space station science officer, prepares to remove the Avionics Air Assembly (AAA) from the Crew Health Care System (CHeCS) rack during in-flight maintenance (IFM) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.