
Ius Chasma
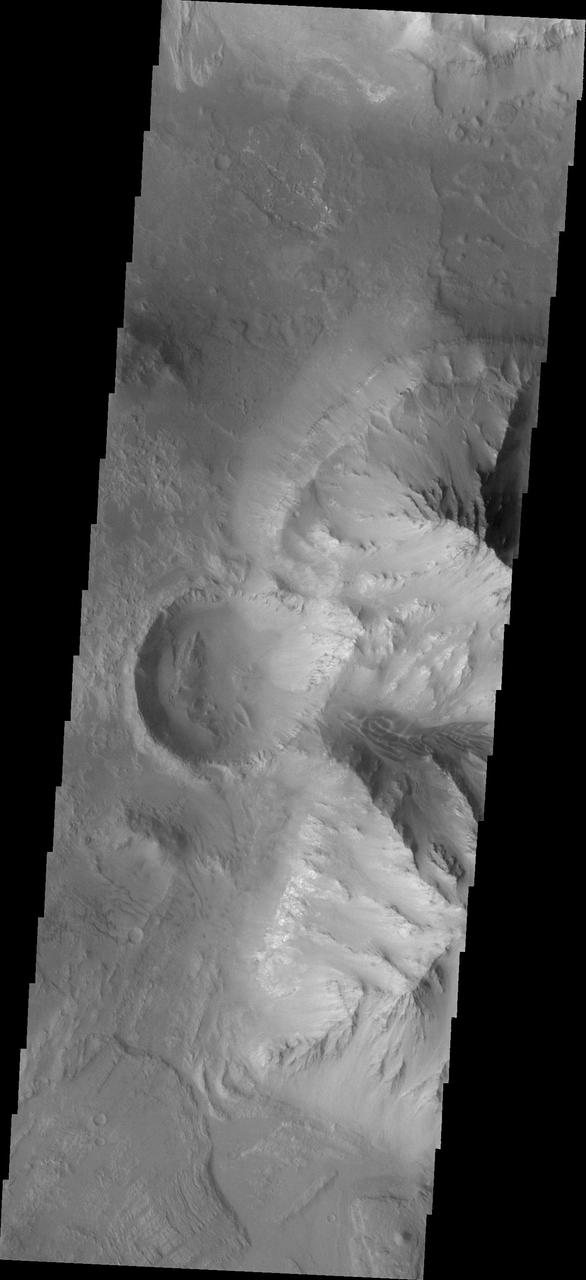

Ius Chasma

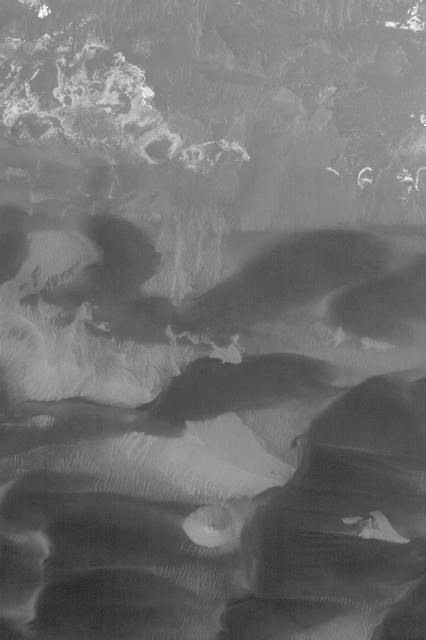
Ius Chasma In False Color
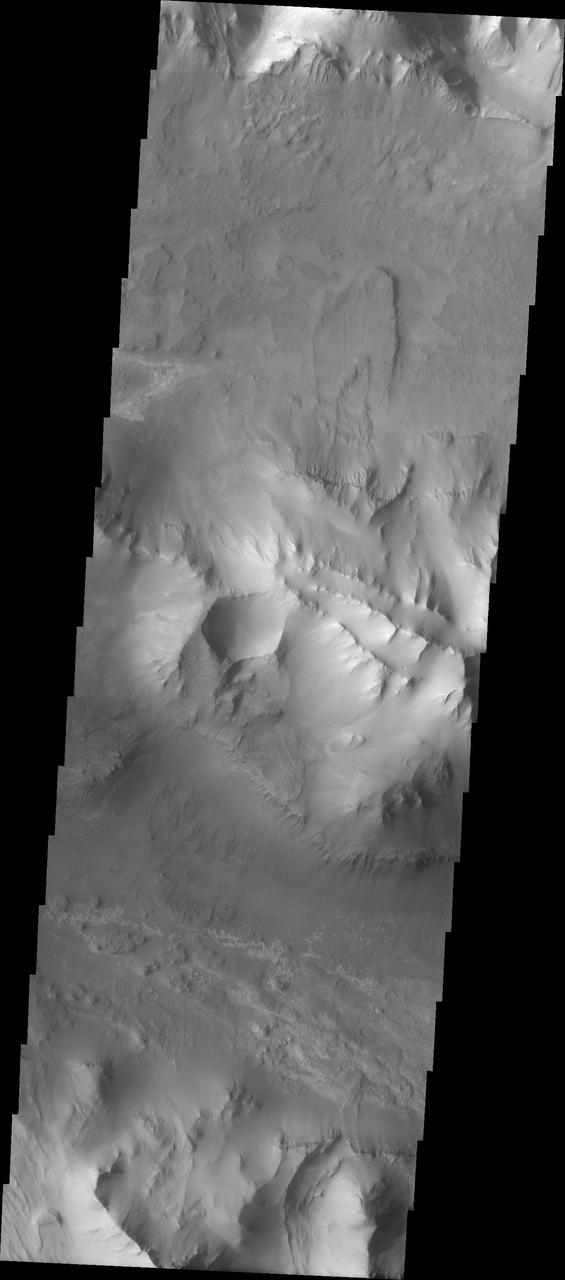

Ius Chasma Ridge

Scene from Ius

Ius Chasma by Day and Night
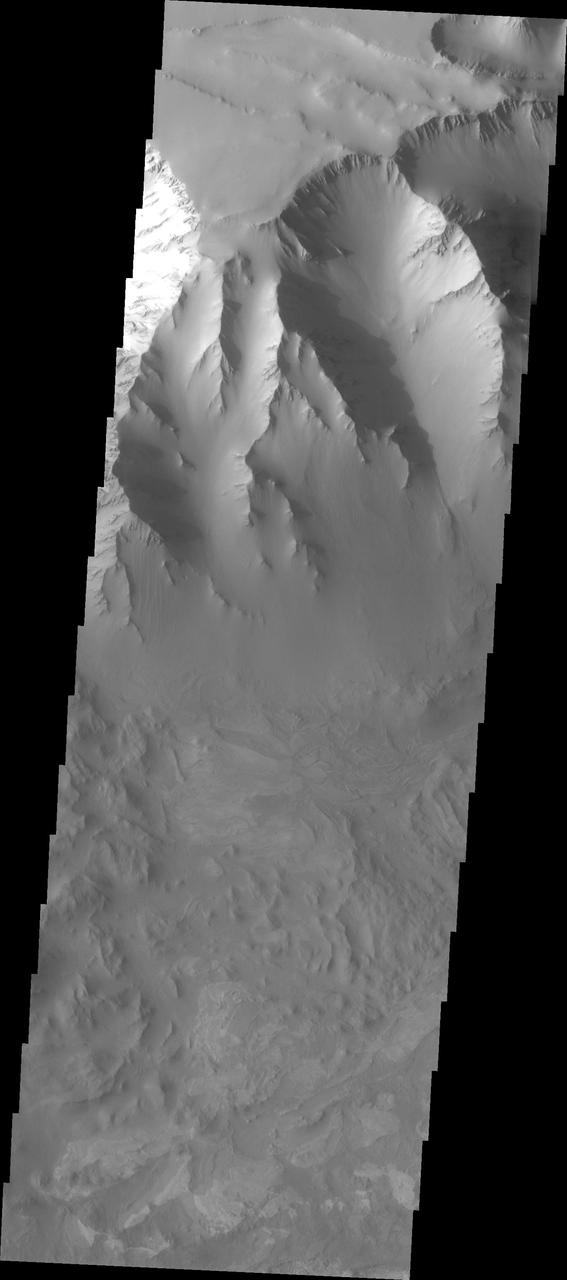

Old Landslide In Ius Chasma

Ius Chasma at Night

Ius Chasma Debris

Tithonium Chasma/Ius Chasma

Ius Chasma Landslide
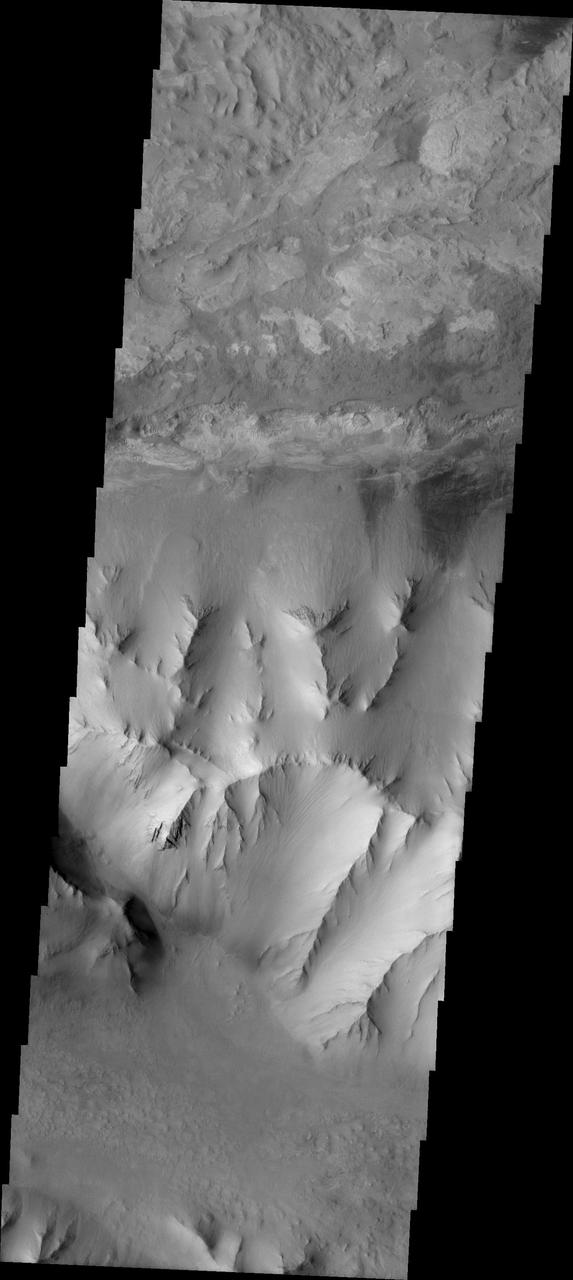

Ius Chasma Ridge
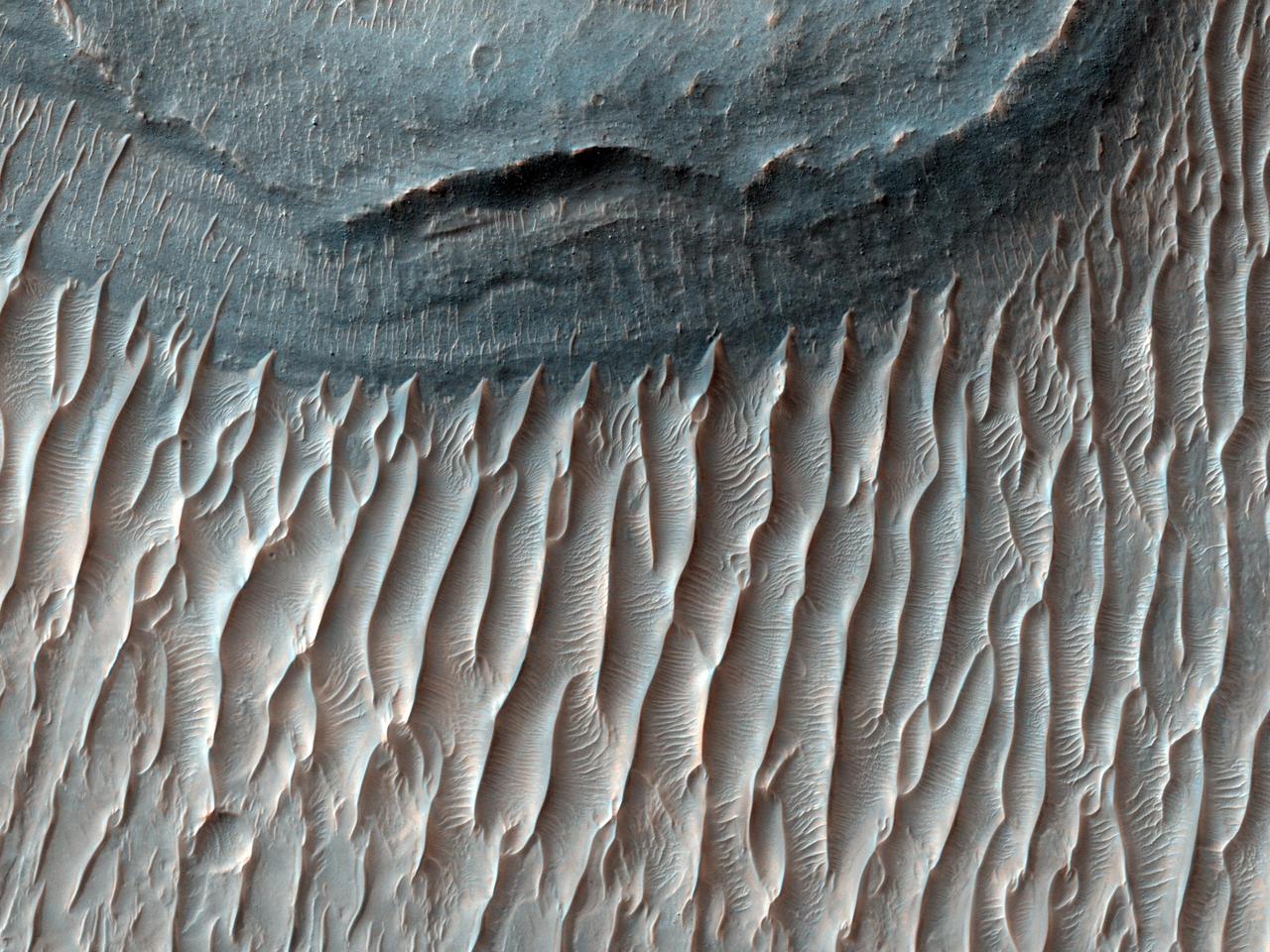

Ius Chasma Floor
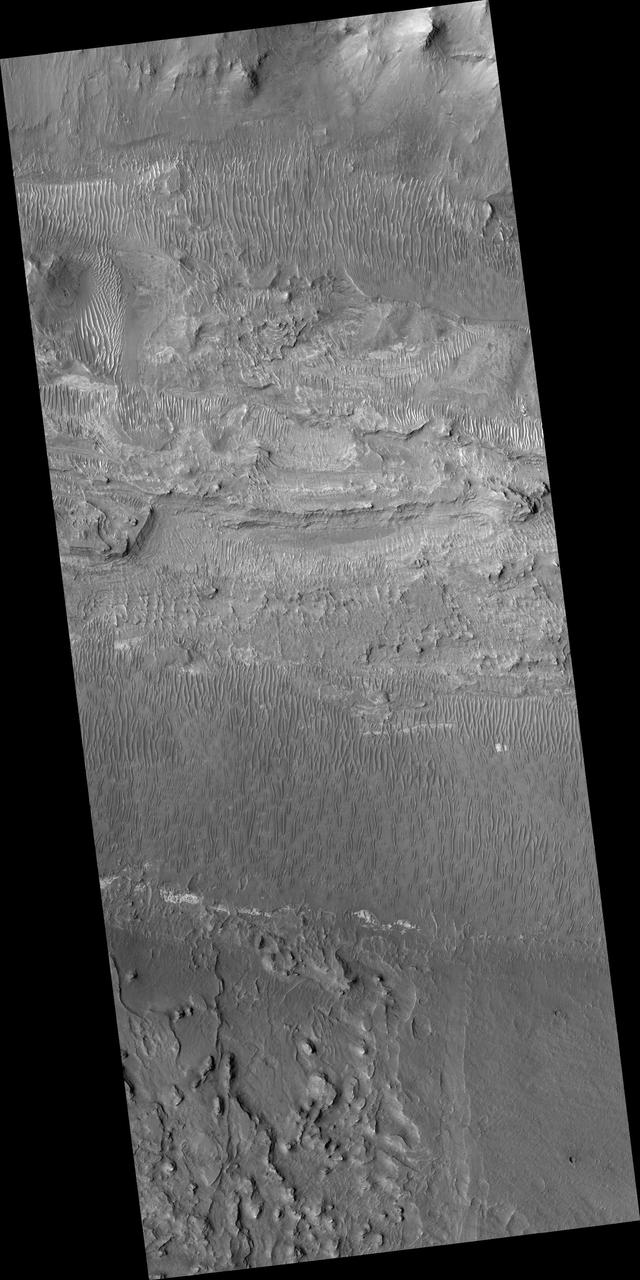

Floor of Ius Chasma
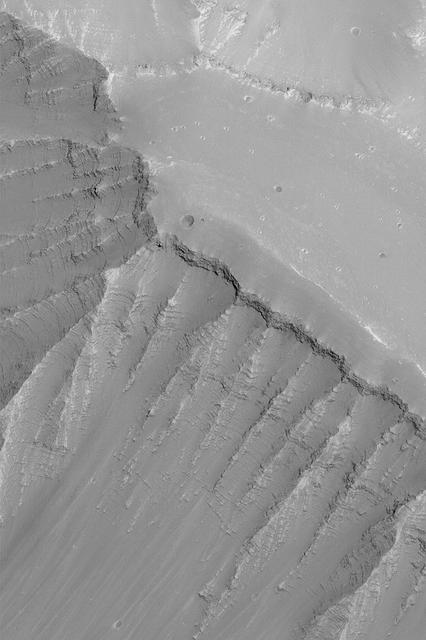

Ius Chasma Layers

Ius Chasma Fault
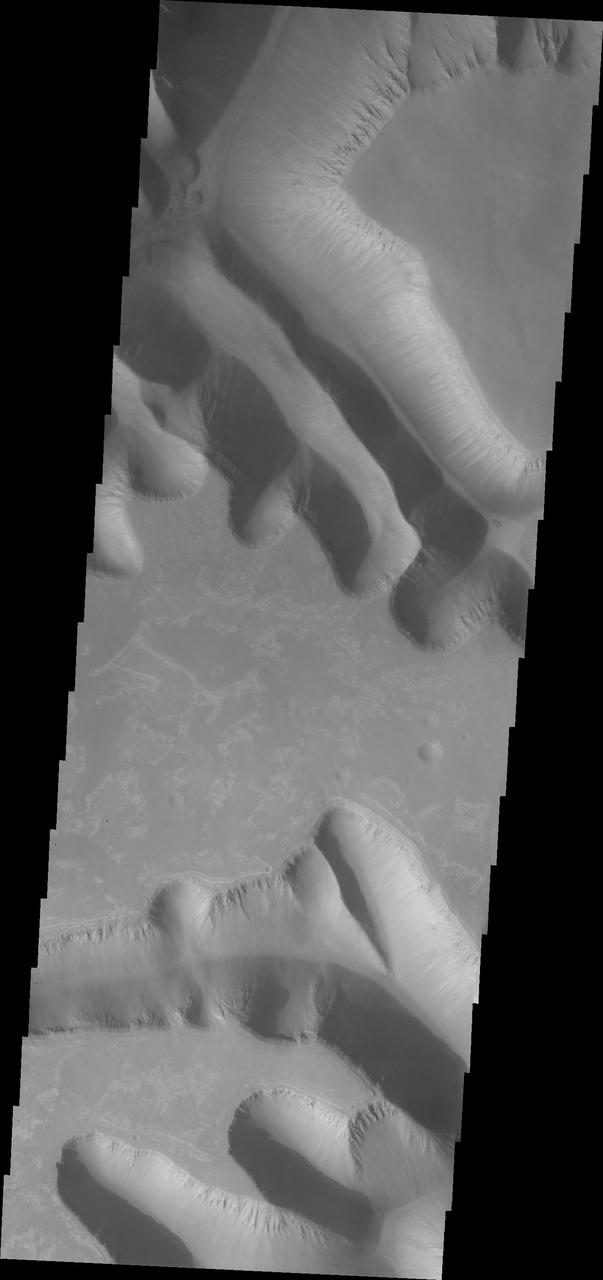
This image captured by NASA Mars Odyssey shows parts of two giant gully that are located on the southern side of Ius Chasma. Ius Chasma has the largest number of mega gullies of any of the chasmata that make up Valles Marineris.

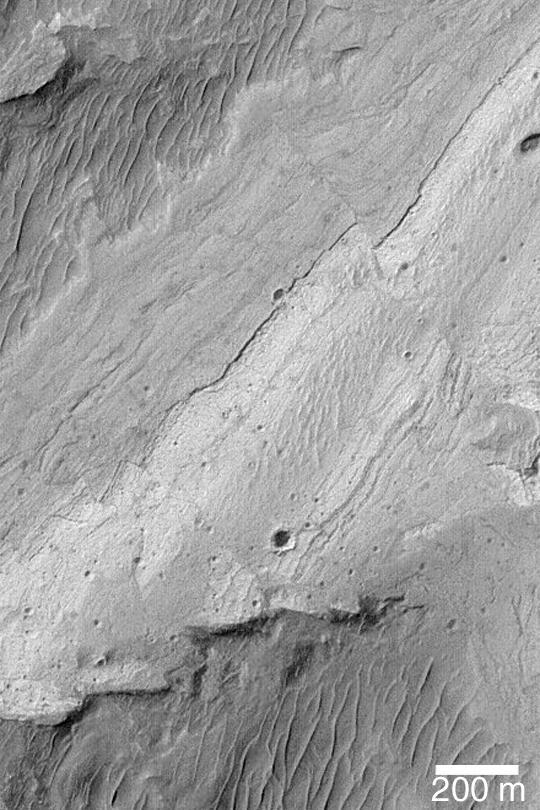
Today's VIS image shows a complete cross section of Ius Chasma. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The rugged floor of Ius Chasma in this image is the result of many large landslides. Orbit Number: 92413 Latitude: -6.89657 Longitude: 272.994 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-10-14 13:17 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25760

Ius Chasma Tributary Valleys and Adjacent Plains

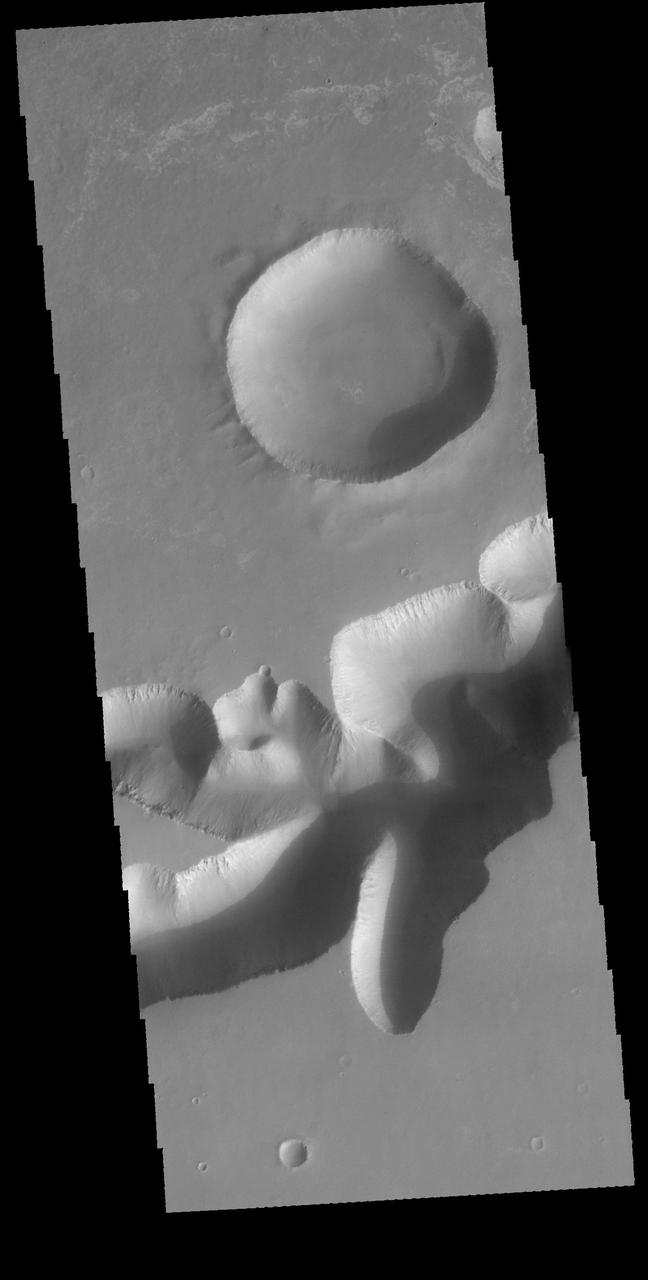
Western Tithonium Chasma/Ius Chasma, Valles Marineris
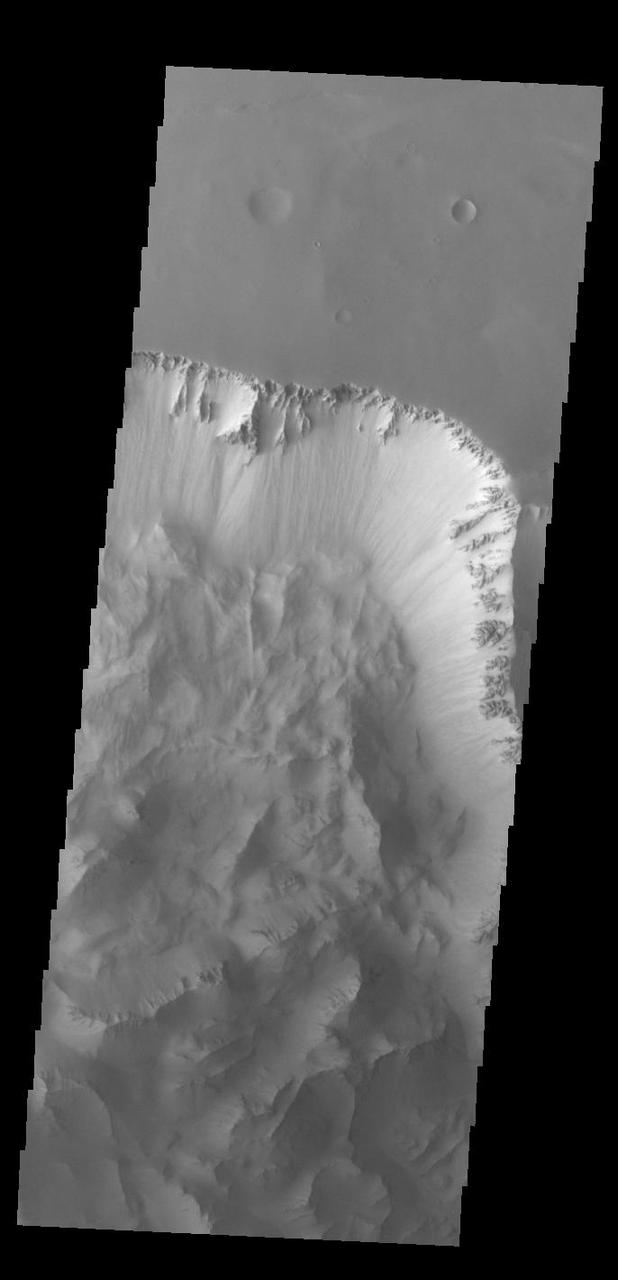

Today's VIS image shows part of Ius Chasma. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The rugged floor of Ius Chasma in this image is the result of many large landslides. Orbit Number: 92987 Latitude: -6.37421 Longitude: 273.45 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-11-30 19:36 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25808

Large landslide deposits dominate this image of Ius Chasma captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey. Dunes are visible at the bottom of the frame.
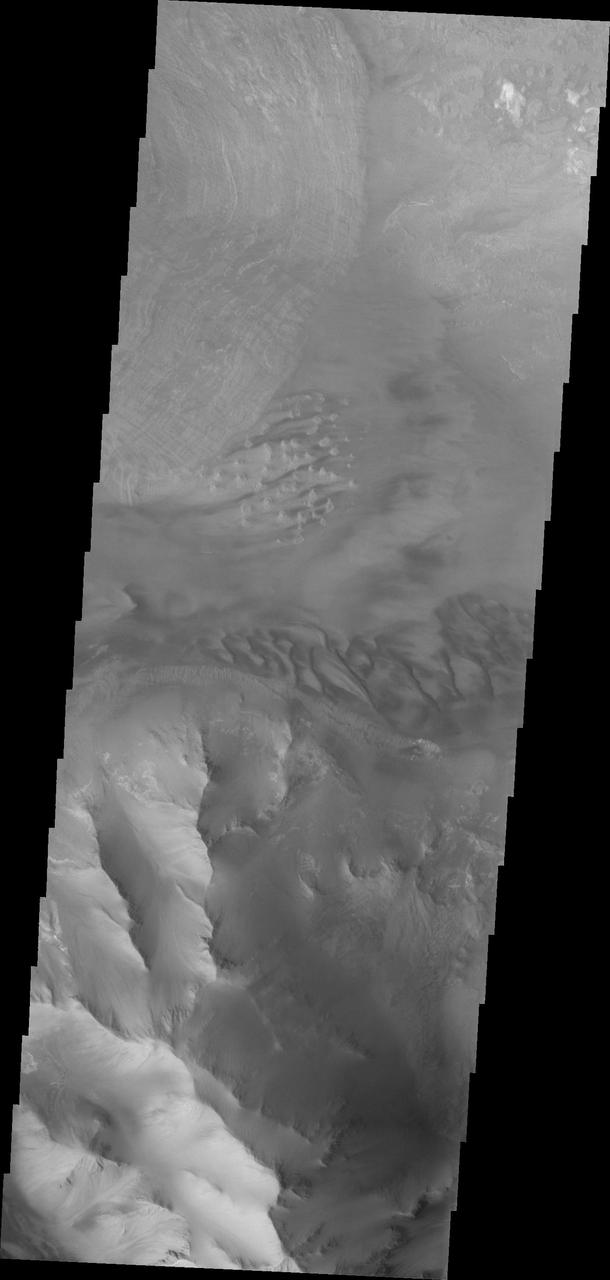

Dunes and the distal end of a landslide deposit are evident in this image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey of eastern Ius Chasma.

Today's VIS image shows part of Ius Chasma and one of its mega gullies (bottom of image). Ius Chasma is unique from the other chasmata of Valles Marineris in possessing mega gullies on both sides of the chasma. The largest mega gullies are located in Sinai Planum, dissecting those plains and emptying into the canyon. Mega gullies are thought to be sapping channels caused by groundwater flow and erosion. The Earth analog is springs – water that flows underground and then breaches the surface creating channels. The morphology of the Mars gullies mirrors terrestrial springs. The channel is fairly uniform in width and the "head" of the channel is rounded like an amphitheater. The channel lengthens by erosion at the "head" backwards as the surface where the spring emerges is undercut. For Mars it is theorized that subsurface water would stay liquid due to underground heating. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris, south of Tithonium Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, almost as wide as the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. Orbit Number: 91408 Latitude: -6.95449 Longitude: 274.37 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-07-23 20:09 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25577

Today's VIS image shows the southern cliffside of Tithonium Chasma (top of image) and the complete cross section of Ius Chasma (center of image). Ius Chasma and Thithonium Chasma are at the western end of Valles Marineris. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Tithonium Chasma is 803 kilometers long (499 miles) while Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The rugged floor of Ius Chasma in this image is the result of many large landslides. Orbit Number: 89711 Latitude: -6.50729 Longitude: 272.316 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-03-06 02:35 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25391
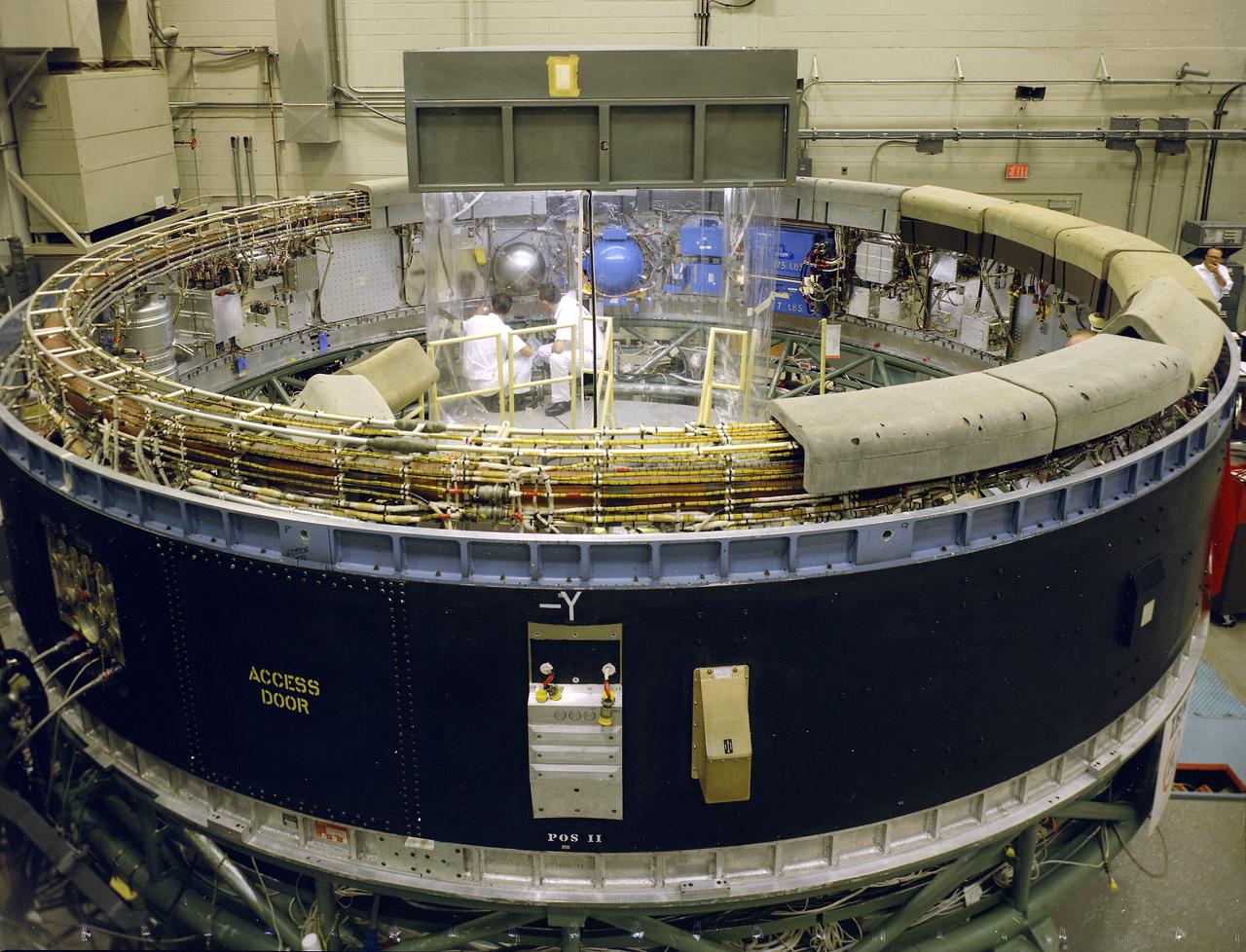
This view depicts engineers conducting a system test on the Saturn V instrument unit (IU) at International Business Machines (IBM) in Huntsville, Alabama. IBM is a prime contractor for development and fabrication of the IU. The IU is vital to the proper flight of the vehicle. It contains navigation, guidance, control, and sequencing equipment for the launch vehicle. Three-feet tall, twenty-one feet in diameter, and weighing about 4,000 pounds, the IU is mounted atop the S-IVB (third) stage, between the S-IVB stage and the Apollo spacecraft.
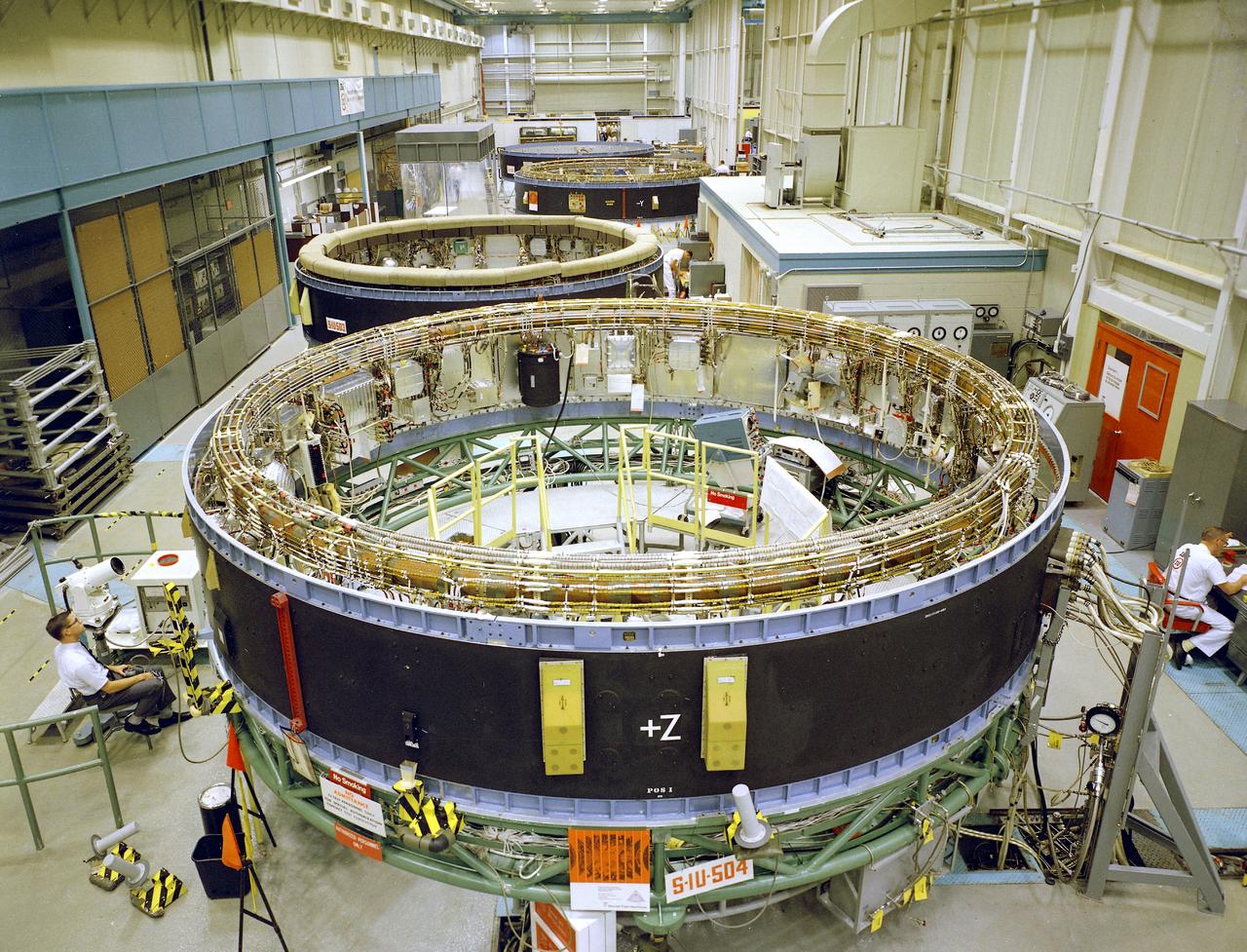
This is a view of the Saturn V instrument unit (IU) being manufactured in the east high bay at International Business Machines (IBM) in Huntsville, Alabama. IBM is a prime contractor for development and fabrication of the IU. The IU is vital to the proper flight of the vehicle. It contains navigation, guidance, control, and sequencing equipment for the launch vehicle. Three feet tall, twenty-one feet in diameter, and weighing about 4,000 pounds, the IU is mounted atop the S-IVB (third) stage, between the S-IVB stage and the Apollo spacecraft.
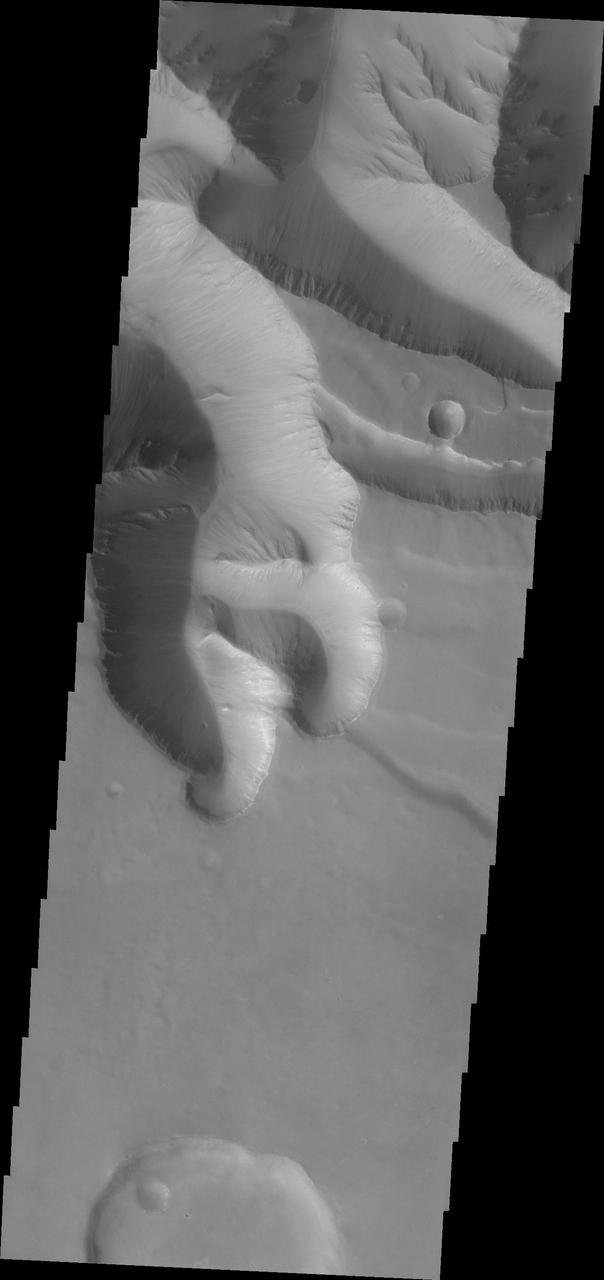

Huge gullies, like these captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey, line both rims of Ius Chasma.

This image from NASA Mars Odyssey shows a portion of a large landslide deposit in Ius Chasma.
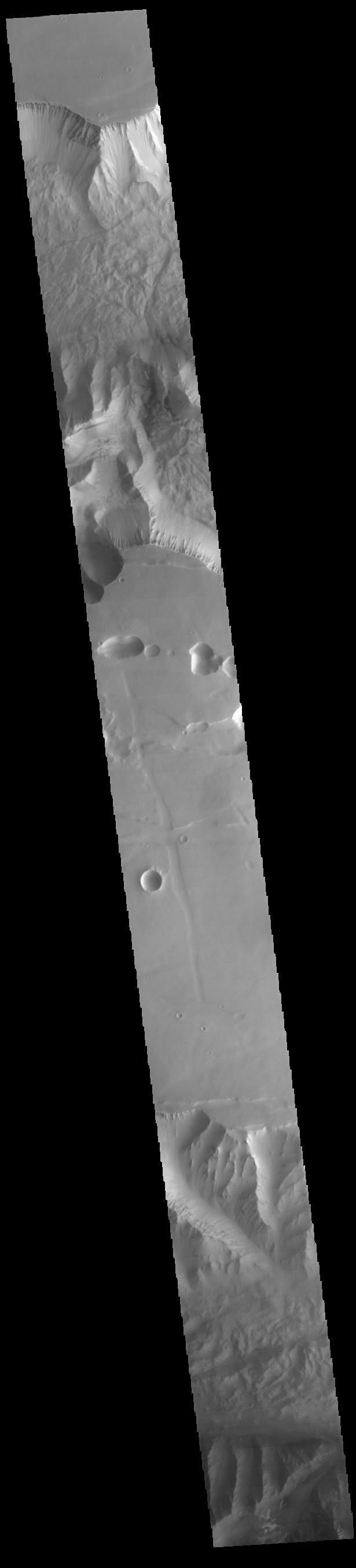

This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft crosses both Tithonium and Ius Chasma.
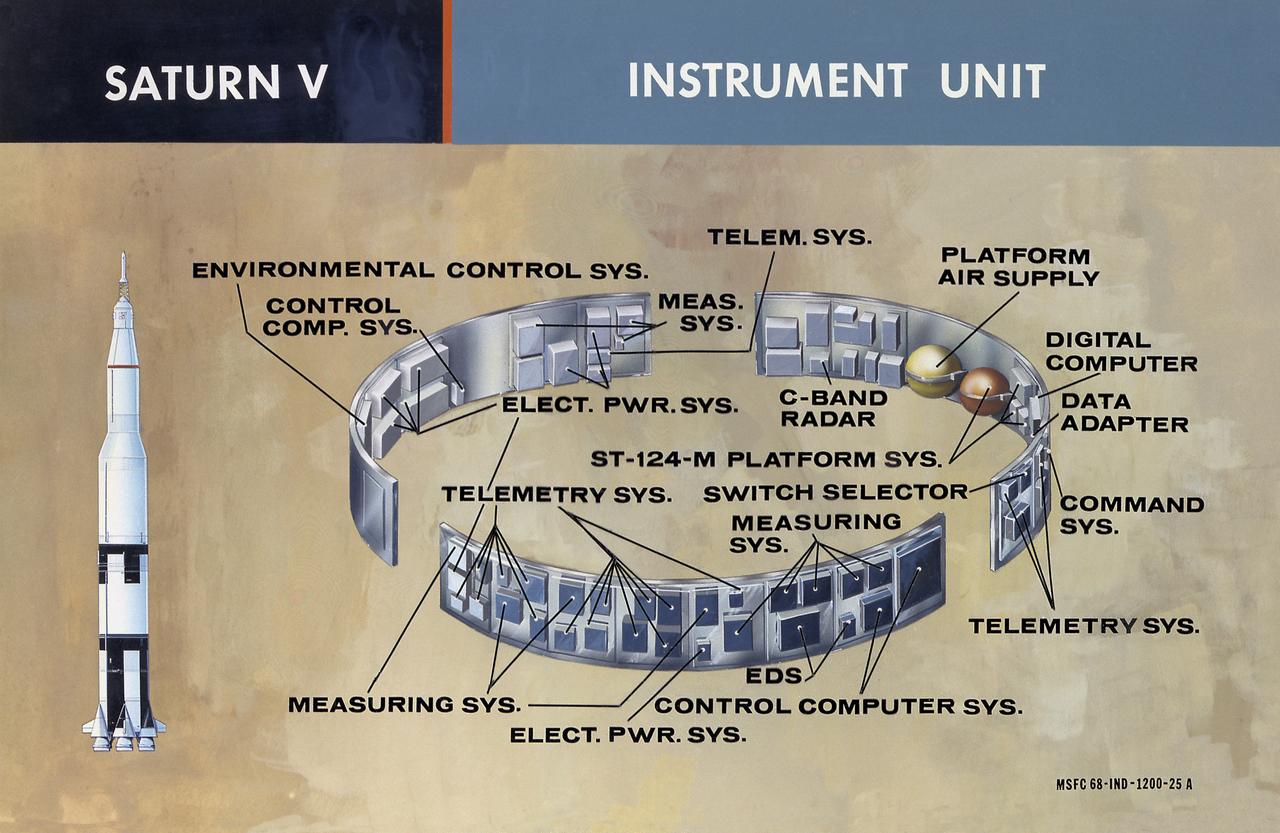
This illustration shows the major components of the instrument unit (IU). Developed and manufactured by International Business Machines, the IU is 3 feet high and 21 feet in diameter and mounted atop an S-IVB, between the third stage and the Apollo spacecraft. It contained the computers, all guidance, control, and sequencing equipment to keep the the launch vehicle properly functioning and on its course. The IU was essentially the same in both the Saturn IB and the Saturn V.

Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris, south of Tithonium Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, almost as wide as the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The rugged floor of Ius Chasma in this image is the result of many large landslides. Orbit Number: 91839 Latitude: -7.09251 Longitude: 272.604 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-08-28 06:58 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25712

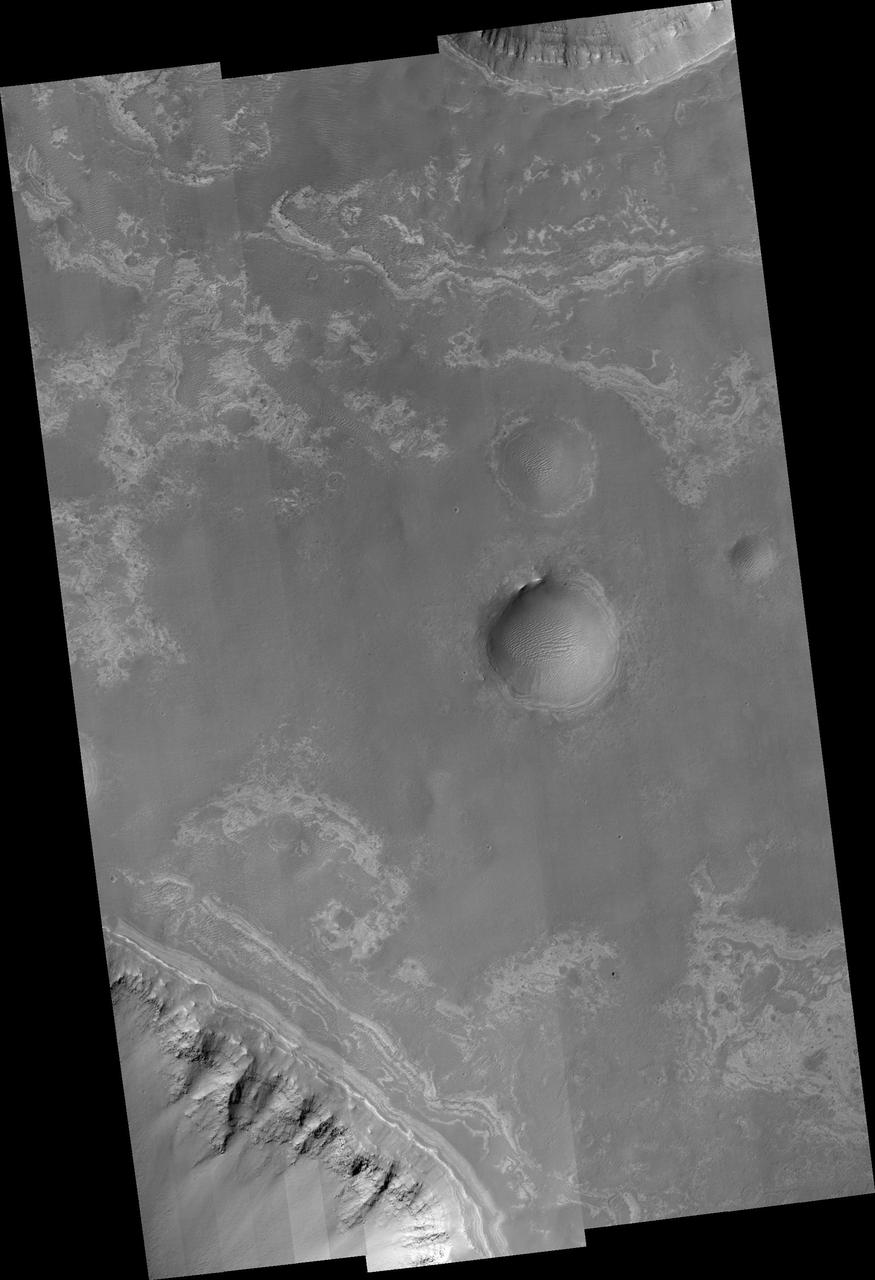
Ius and Tithonium Chasmata are located at the western end of Valles Marineris. Tithonium Chasma is north of Ius Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long (2495 miles), almost as wide as the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 840 kilometers long (522 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. Tithonium Chasma is 803 km (499 miles) long. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long (109 miles), 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The rugged floor of Ius Chasma (bottom of image) is comprised of large landslide deposits. Orbit Number: 92700 Latitude: -5.02133 Longitude: 273.439 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-11-07 04:26 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25769

Ius and Tithonium Chasmata are located at the western end of Valles Marineris. Tithonium Chasma is north of Ius Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long (2495 miles), almost as wide as the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 840 kilometers long (522 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. Tithonium Chasma is 803 km (499 miles) long. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long (109 miles), 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The rugged floor of Ius Chasma (lower half of image) is comprised of large landslide deposits. Orbit Number: 89711 Latitude: -6.50729 Longitude: 272.316 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-03-06 02:35 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25459
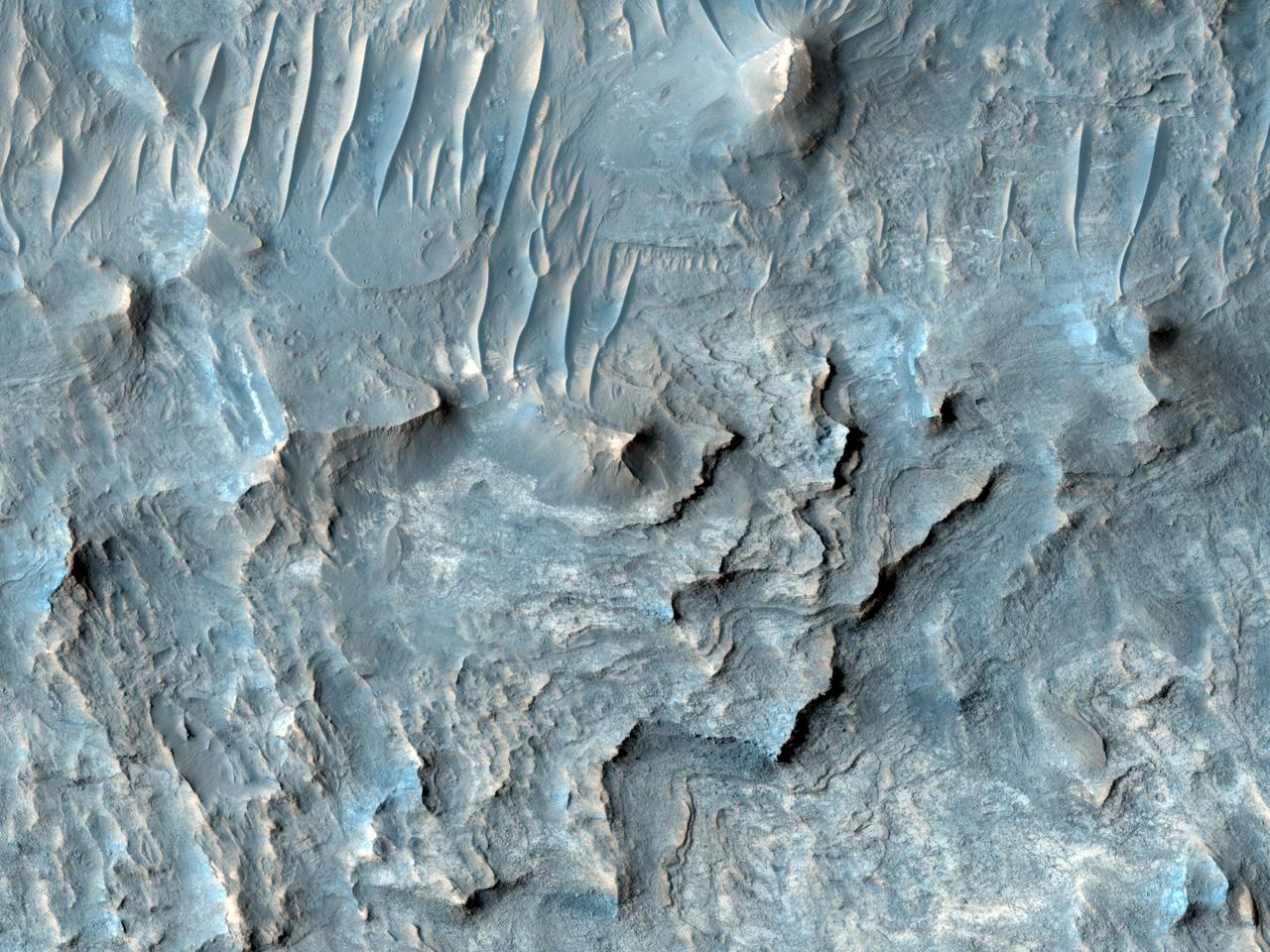

Ius Chasma is one of several canyons that make up Valles Marineris, the largest canyon system in the Solar System as seen by NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
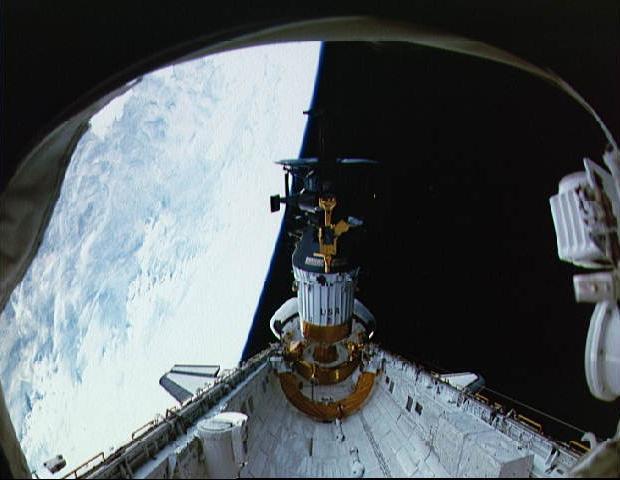

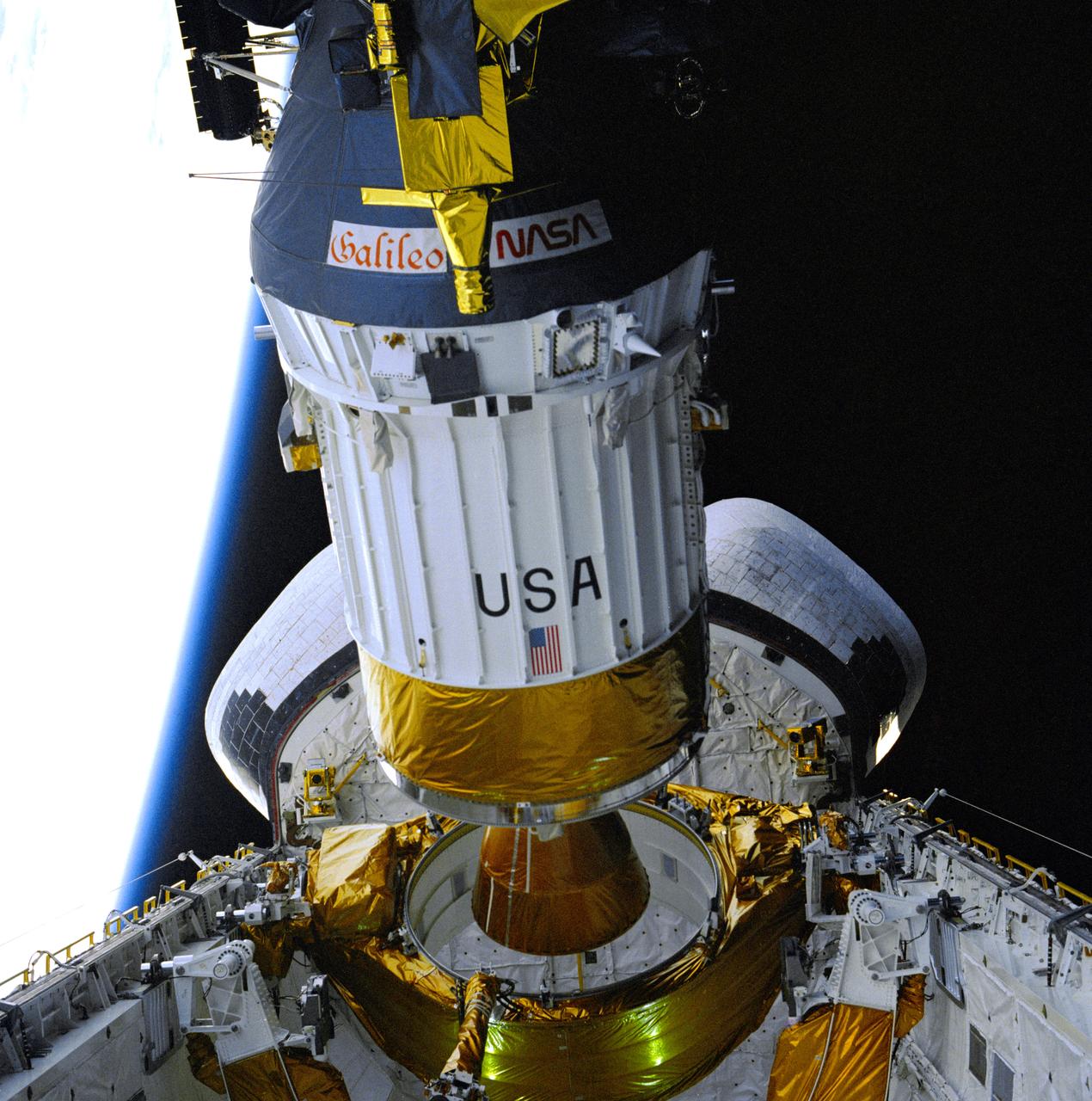
Deployment of NASA Galileo and the IUS from the cargo bay of STS-34 Atlantis at 7:15 p.m. EDT on October 18, 1989. P-35213

Western Tithonium Chasma/Ius Chasma, Valles Marineris - High Resolution Image
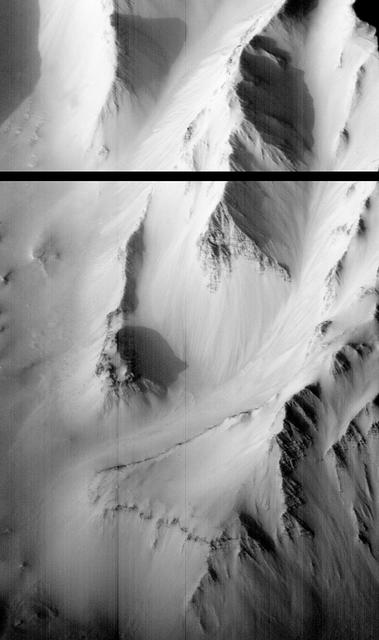
Western Tithonium Chasma/Ius Chasma, Valles Marineris - High Resolution Image
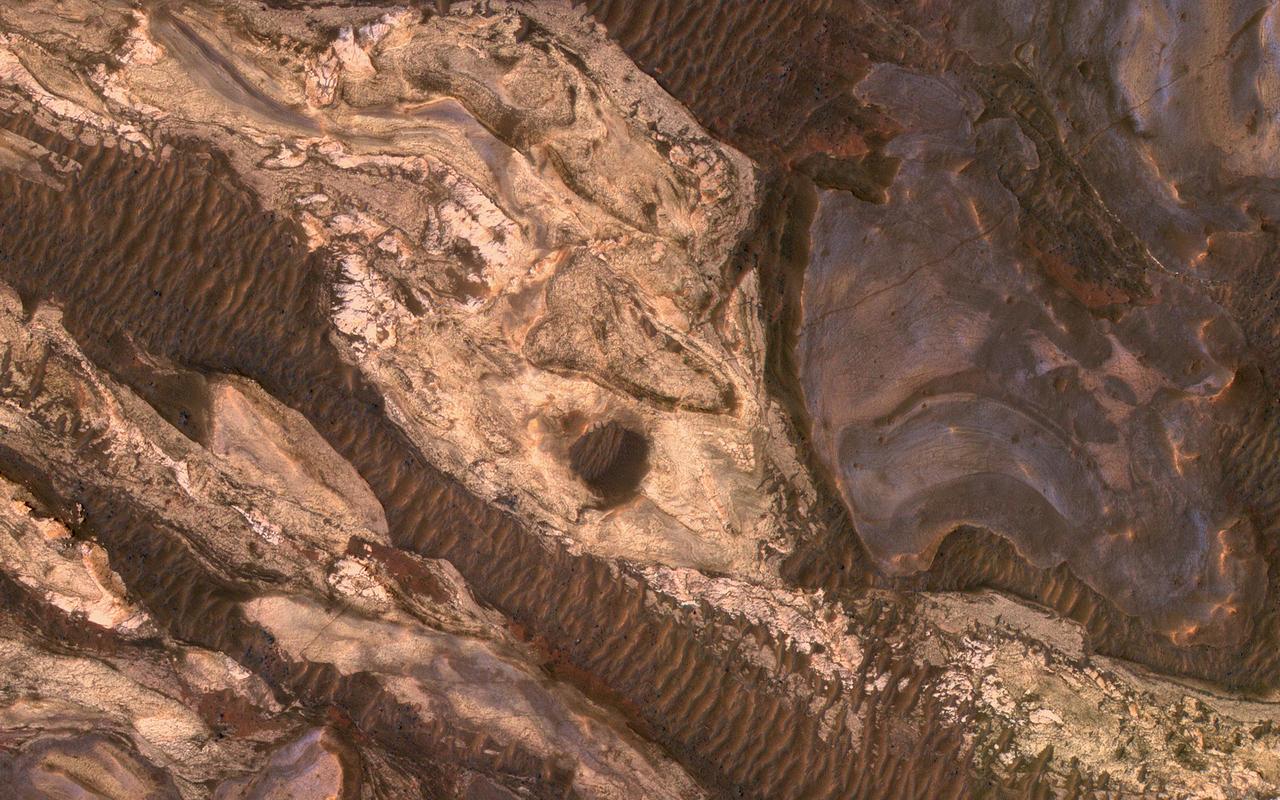

Sometimes Mars' surface is just beautiful as seen through the eyes of HiRISE. This is one example on the floor of Ius Chasma, part of Valles Marineris. The region has had a complex history of sediment deposition, deformation, erosion, and alteration. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23183

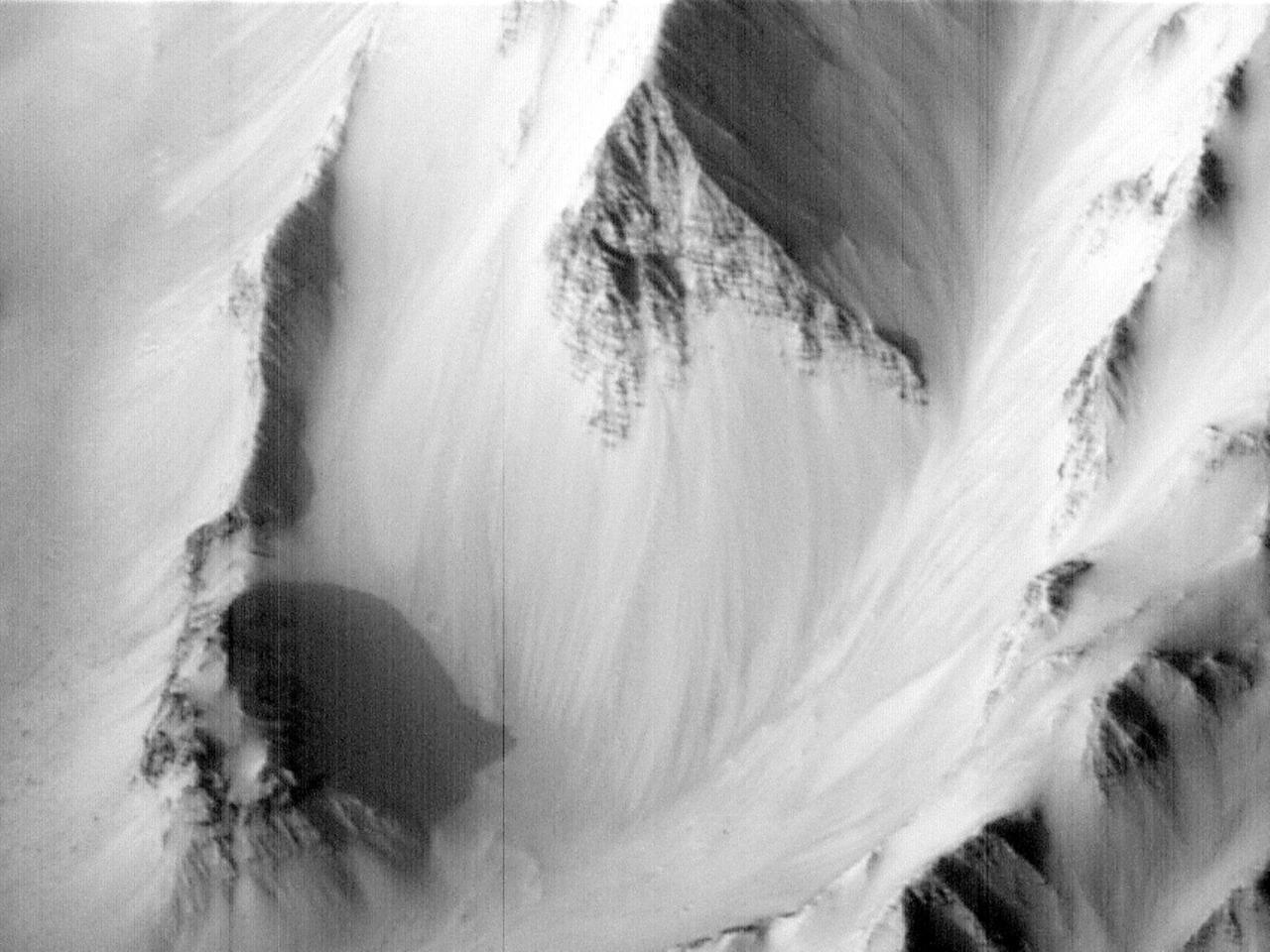
This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows one of the mega sized gullies located on the plains just south of Ius Chasma. Orbit Number: 65907 Latitude: -8.73127 Longitude: 275.005 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2016-10-22 15:44 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21188
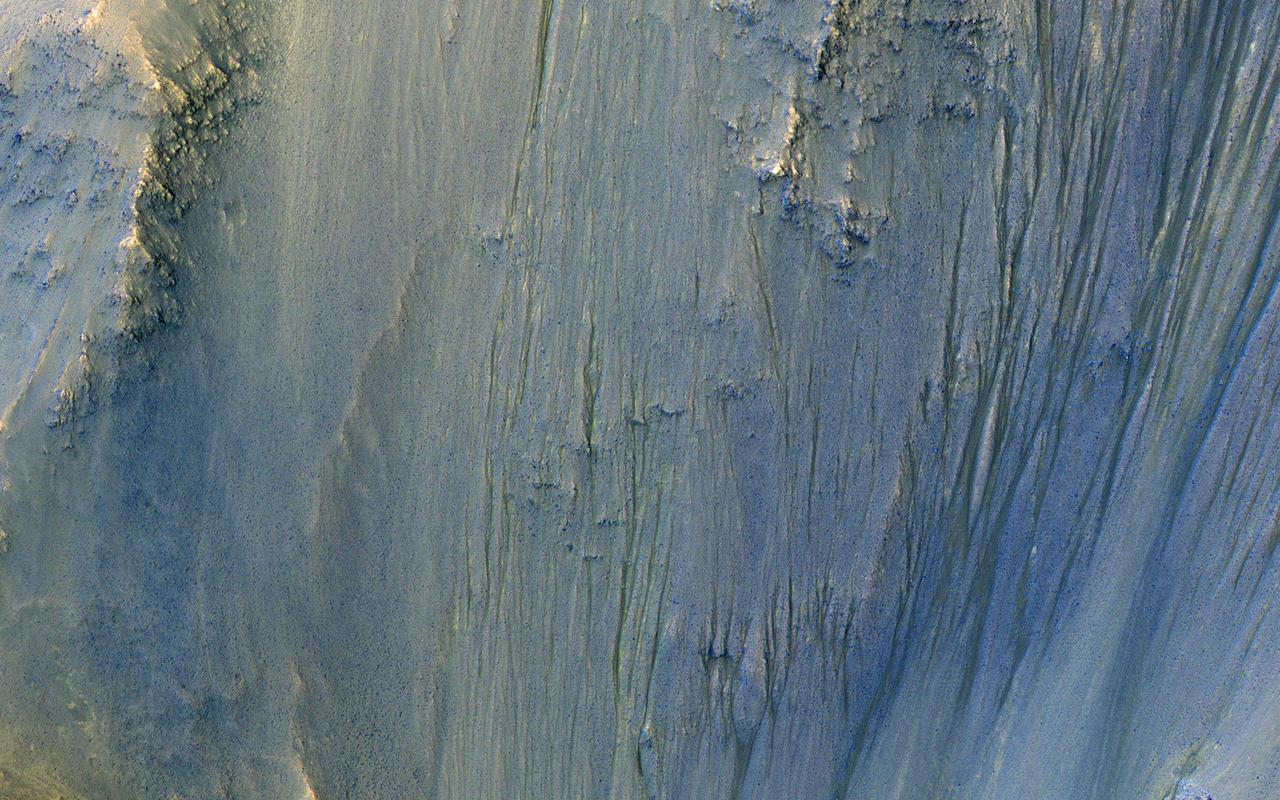

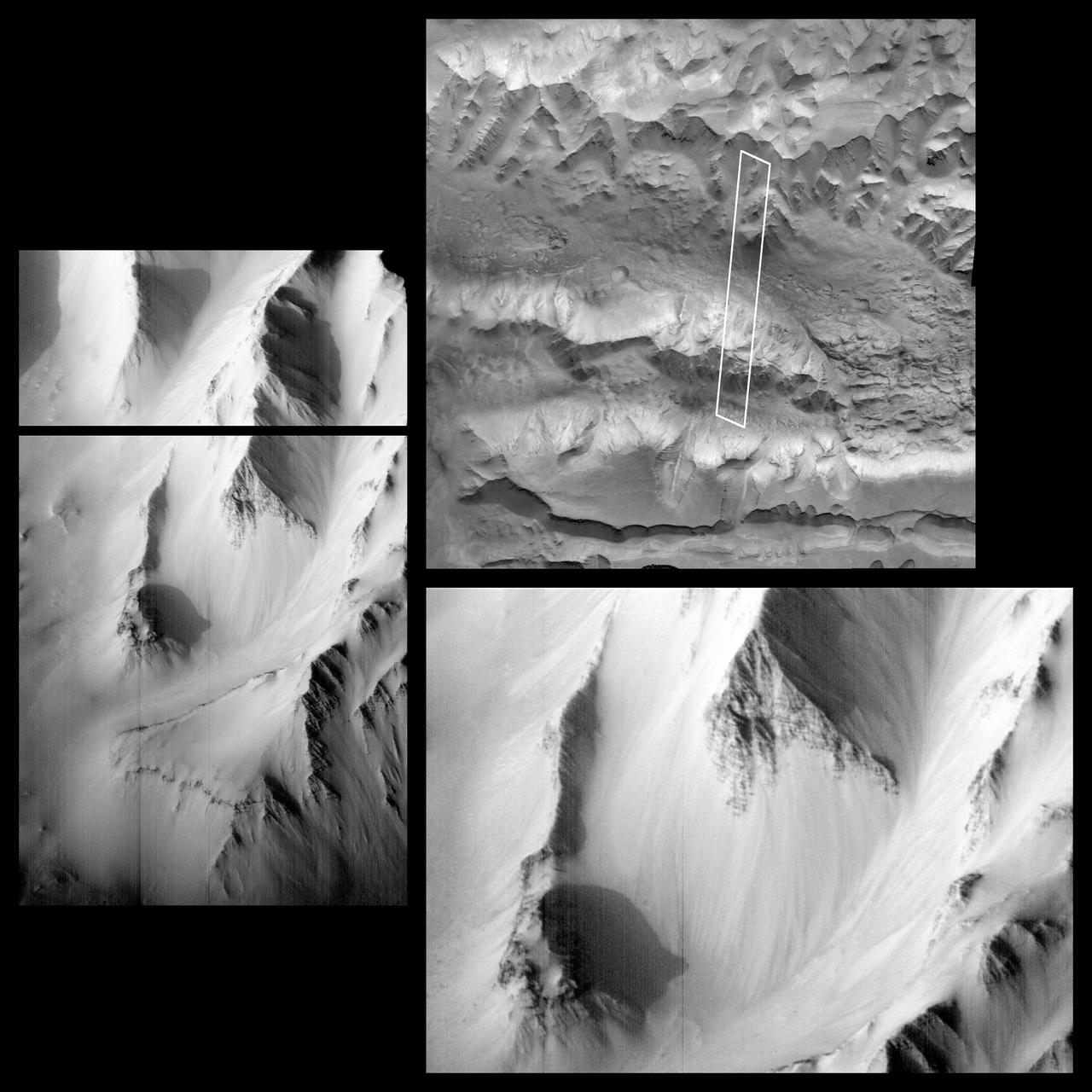
This image was acquired in Ius Chasma, a major section of the western portion of the giant Valles Marineris trough. We see a portion of a steep slope with gullies extending downhill (towards bottom of image). Many of the gully floors are dark, and in some places that dark material extends onto the fan-shaped deposits of the gullies. These dark features are candidates for recurring slope lineae (RSL), which are seasonal features that grow incrementally. The relation between RSL and gullies is not clear: does the RSL activity carve the gullies, or do they simply follow the gully topography created by other processes? Another closeup from this observation shows part of the floor of Ius Chasma, with layered bedrock draped by dunes. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23099
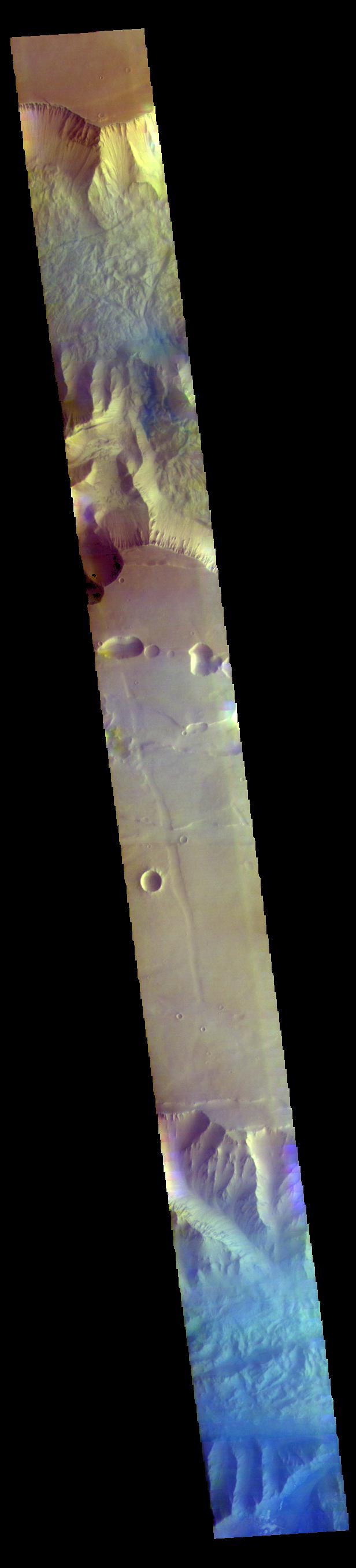

This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows a false color image of the region including both Tithonium and Ius Chasmata, which includes a bluish region in both canyons. This may indicate an atmospheric haze.

This VIS image shows part of the southern cliff face of Ius Chasma. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Orbit Number: 61753 Latitude: -7.27471 Longitude: 274.245 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2015-11-15 12:03 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23070
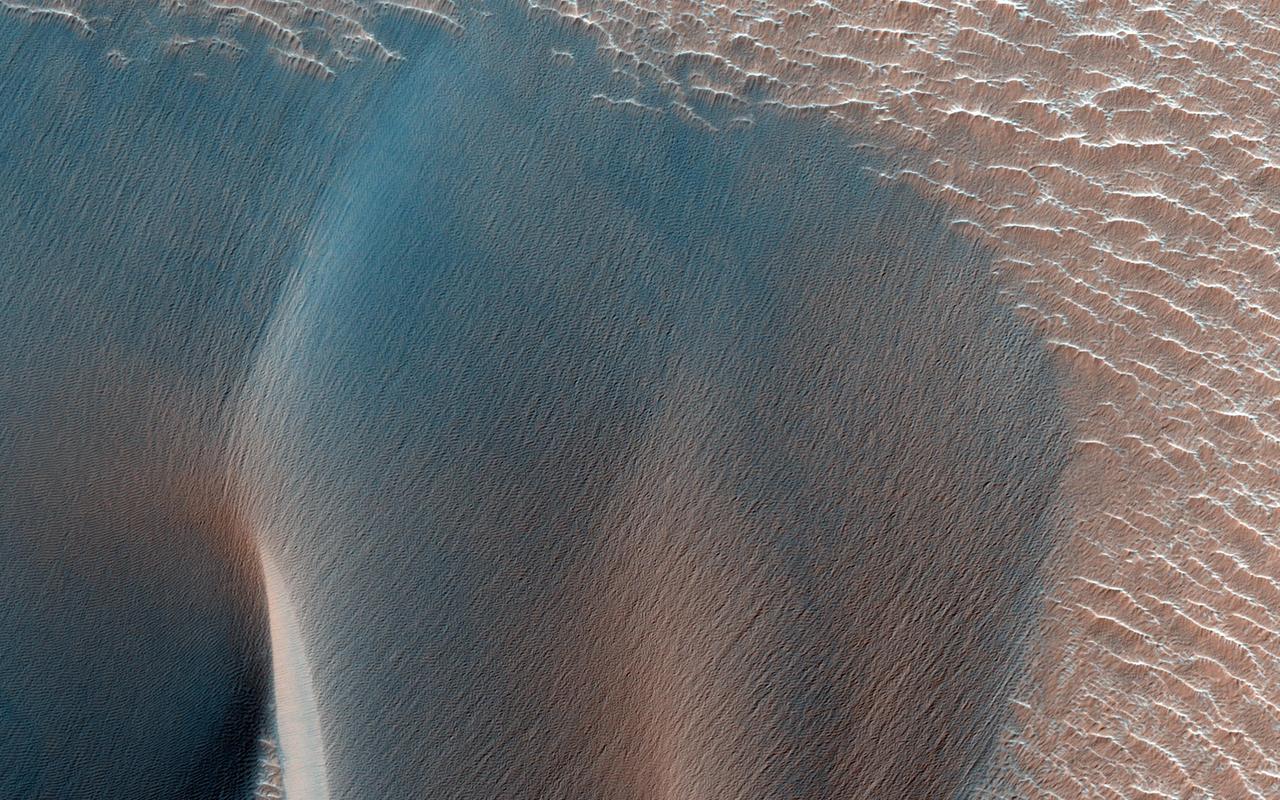

Landslides in Valles Marineris are truly enormous, sometimes stretching from one wall to the base of another. This landslide, known as Ius Labes, would occupy the surface area of the state of Delaware, U.S., seen by NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
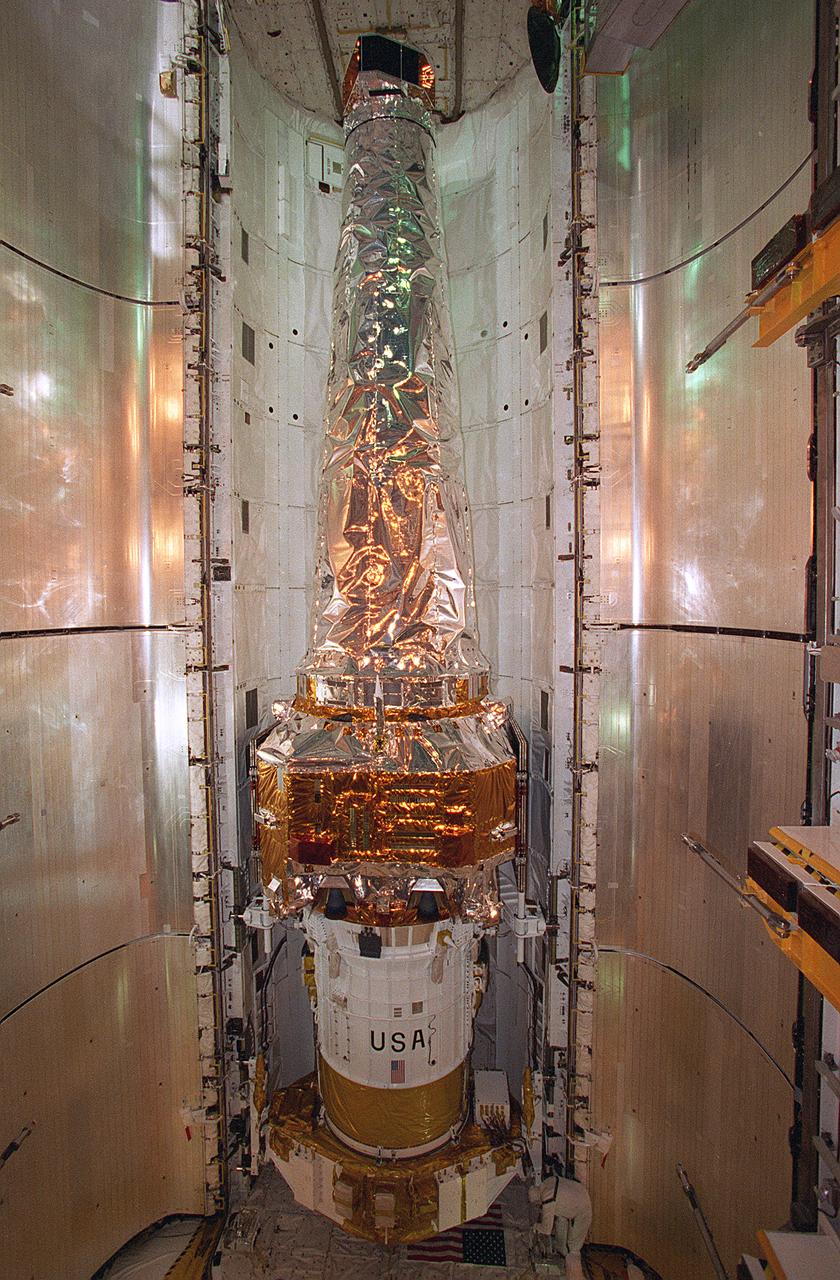

In this photograph, the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO) was installed and mated to the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) inside the Shuttle Columbia's cargo bay at the Kennedy Space Center. The CXO will help astronomers world-wide better understand the structure and evolution of the universe by studying powerful sources of x-rays such as exploding stars, matter falling into black holes, and other exotic celestial objects. X-ray astronomy can only be done from space because Earth's atmosphere blocks x-rays from reaching the surface. The Observatory provides images that are 50 times more detailed than previous x-ray missions. At more than 45 feet in length and weighing more than 5 tons, the CXO was carried into low-Earth orbit by the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93 mission) on July 22, 1999. The Observatory was deployed from the Shuttle's cargo bay at 155 miles above the Earth. Two firings of an attached IUS rocket, and several firings of its own onboard rocket motors, after separating from the IUS, placed the Observatory into its working orbit. The IUS is a solid rocket used to place spacecraft into orbit or boost them away from the Earth on interplanetary missions. Since its first use by NASA in 1983, the IUS has supported a variety of important missions, such as the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, Galileo spacecraft, Magellan spacecraft, and Ulysses spacecraft. The IUS was built by the Boeing Aerospace Co., at Seattle, Washington and managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
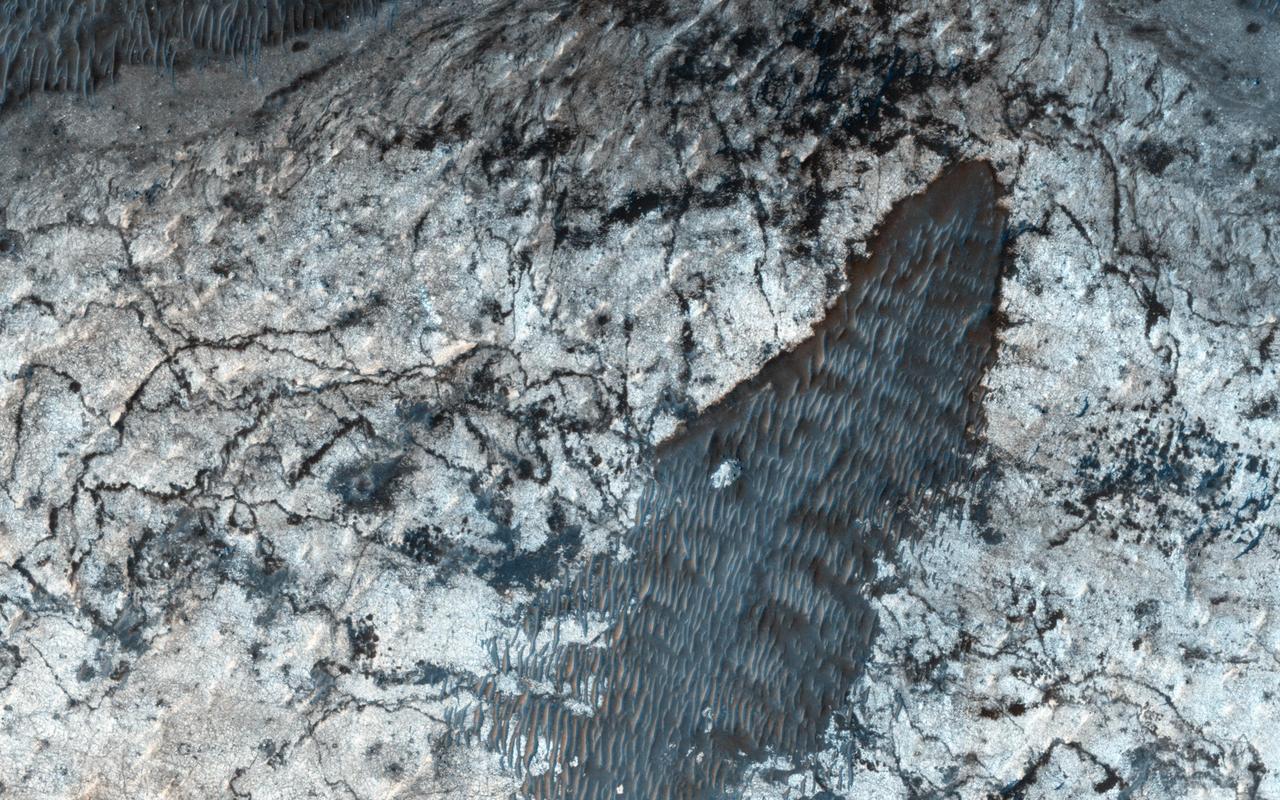

Sedimentary deposits are common within Valles Marineris. Most larger chasmata contain kilometer-thick light-toned layered deposits composed of sulfates. However, some of the chasmata, like Ius Chasma shown in this image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, lack these deposits or have much thinner deposits. The light-toned deposits in Ius Chasma are observed both along the floor and inner wallrock materials. Some of the light-toned deposits appear to post-date formation of the chasma floor, whereas other deposits appear to lie beneath wallrock materials, indicating they are older. By examining the stratigraphy using digital terrain models and 3D images, it should be possible to decipher the relative ages of the different geologic units. CRISM data may also provide insight into the mineralogy, which will tell scientists about the aqueous conditions that emplaced the light-toned deposits. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19855

Continuing eastward along Ius Chasma, this image shows the eastern section of the large landslide deposit seen in yesterday's post. A landslide is a failure of slope due to gravity. They initiate due to several reasons. A lower layer of poorly cemented/resistant material may have been eroded, undermining the wall above which then collapses; earth quake seismic waves can cause the slope to collapse; and even an impact event near the canyon wall can cause collapse. As millions of tons of material fall and slide down slope a scalloped cavity forms at the upper part where the slope failure occurred. At the material speeds downhill it will pick up more of the underlying slope, increasing the volume of material entrained into the landslide. Whereas some landslides spread across the canyon floor forming lobate deposits, very large volume slope failures will completely fill the canyon floor in a large complex region of chaotic blocks. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris, south of Tithonium Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 17902 Latitude: -6.65656 Longitude: 274.872 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2005-12-27 08:01 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22279
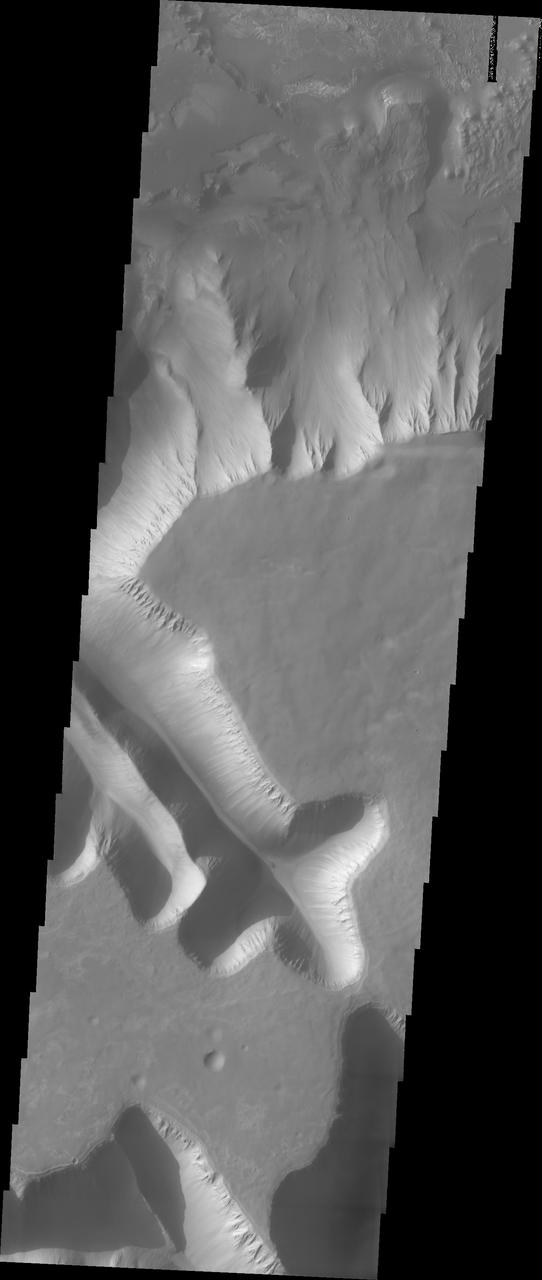

Ius Chasma is unique from the other chasmata of Valles Marineris in possessing mega gullies on both sides of the chasma. The largest mega gullies are located in Sinai Planum, dissecting those plains and emptying into the canyon. These mega gullies are called Louros Valles. Mega gullies are thought to be sapping channels caused by groundwater flow and erosion. The Earth analog is springs - water that flows underground and then breaches the surface creating channels. The morphology of the Mars gullies mirrors terrestrial springs. The channel is fairly uniform in width and the "head" of the channel is rounded like an amphiteater. The channel lengthens by erosion at the "head" backwards as the surface where the spring emerges is undercut. For Mars it is theorized that subsurface water would stay liquid due to underground heating. The "X" in the lower half of the image and the channel at the very bottom are parts of the two largest mega gullies. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris, south of Tithonium Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 11138 Latitude: -7.92828 Longitude: 275.477 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2004-06-18 10:19 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22286
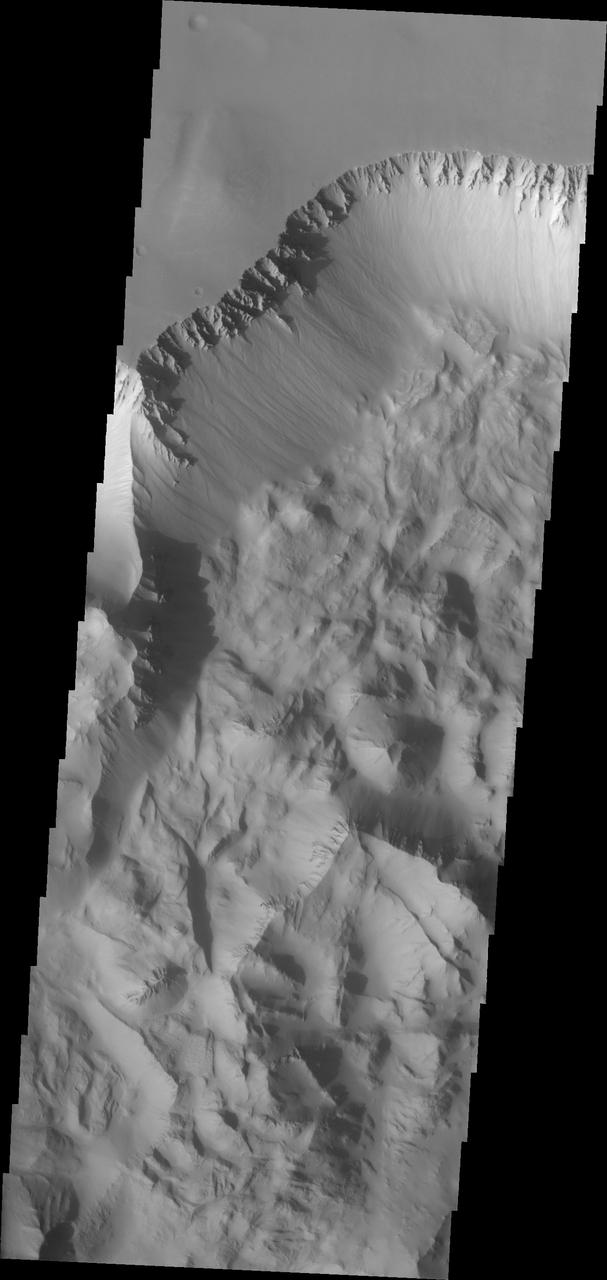

Continuing eastward along Ius Chasma, this section of the canyon floor has been completely filled by blocky deposits from large volume landslides. A landslide is a failure of slope due to gravity. They initiate due to several reasons. A lower layer of poorly cemented/resistant material may have been eroded, undermining the wall above which then collapses; earth quake seismic waves can cause the slope to collapse; and even an impact event near the canyon wall can cause collapse. As millions of tons of material fall and slide down slope a scalloped cavity forms at the upper part where the slope failure occurred. At the material speeds downhill it will pick up more of the underlying slope, increasing the volume of material entrained into the landslide. Whereas some landslides spread across the canyon floor forming lobate deposits, very large volume slope failures will completely fill the canyon floor in a large complex region of chaotic blocks. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris, south of Tithonium Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 17041 Latitude: -6.50422 Longitude: 272.124 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2005-10-17 10:40 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22278
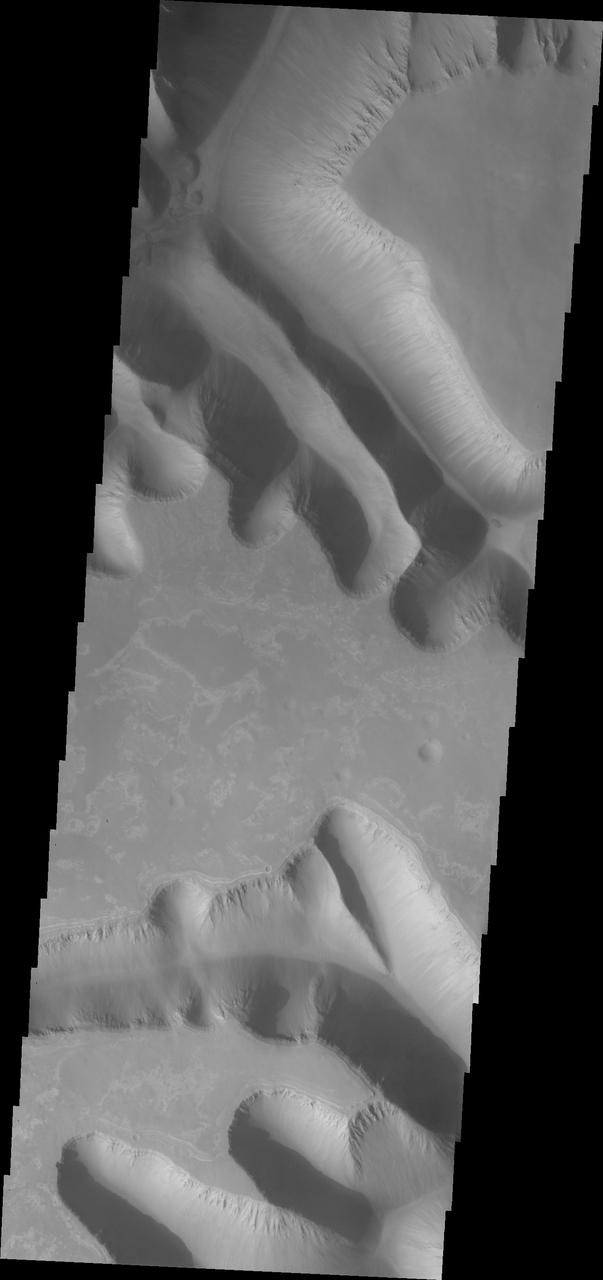
Ius Chasma is unique from the other chasmata of Valles Marineris in possessing mega gullies on both sides of the chasma. The largest mega gullies are located in Sinai Planum, dissecting those plains and emptying into the canyon. These mega gullies are called Louros Valles. Mega gullies are thought to be sapping channels caused by groundwater flow and erosion. The Earth analog is springs - water that flows underground and then breaches the surface creating channels. The morphology of the Mars gullies mirrors terrestrial springs. The channel is fairly uniform in width and the "head" of the channel is rounded like an amphitheater. The channel lengthens by erosion at the "head" backwards as the surface where the spring emerges is undercut. For Mars it is theorized that subsurface water would stay liquid due to underground heating. The channels in this image are parts of the two largest mega gullies. Note how every channel head is the amphitheater bowl shape. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris, south of Tithonium Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 40700 Latitude: -8.16691 Longitude: 275.35 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2011-02-16 12:12 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22287
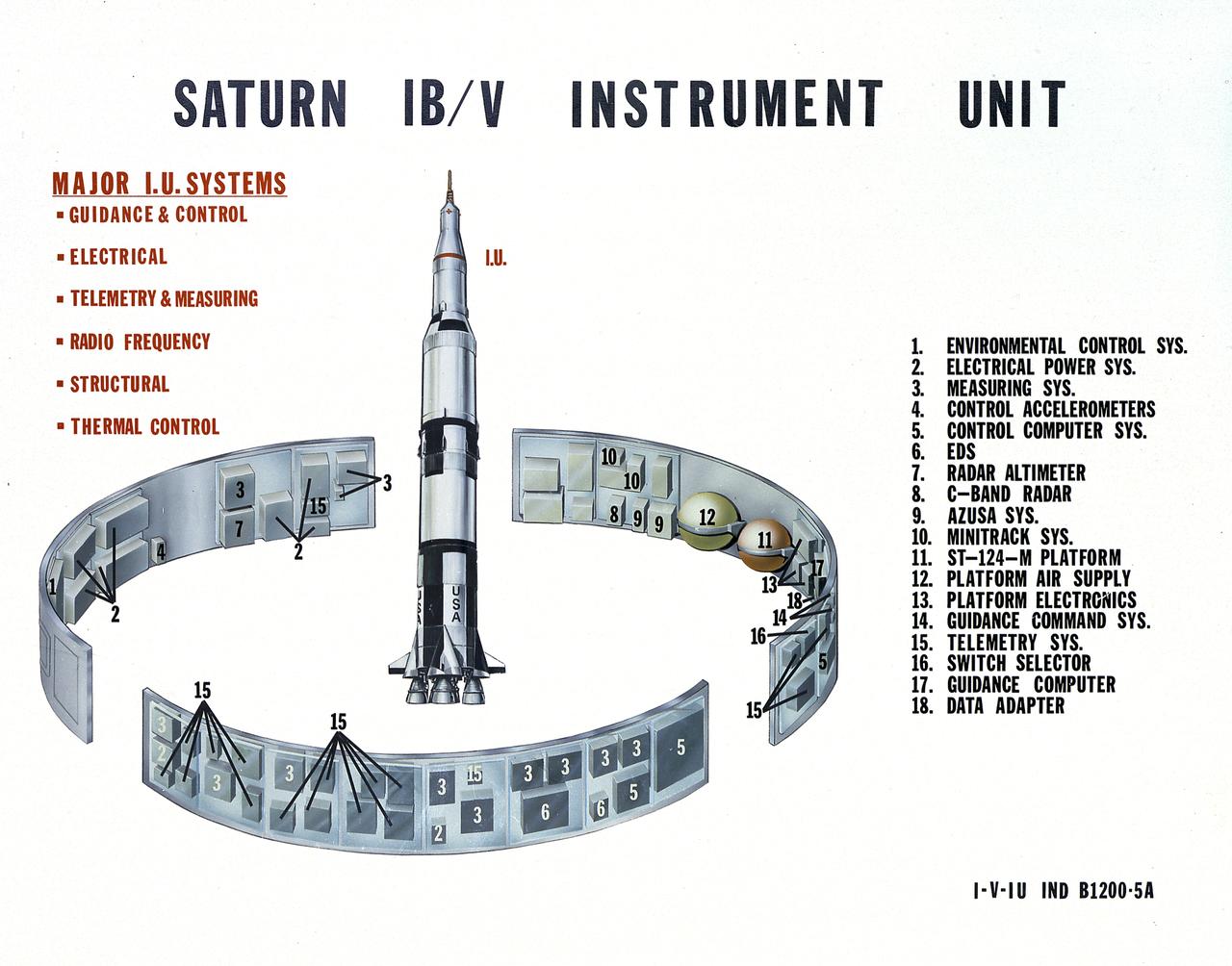
This undated chart provides a description of the Saturn IB and Saturn V's Instrument Unit (IU) and its major components. Designed by NASA at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the Instrument Unit, sandwiched between the S-IVB stage and the Apollo spacecraft, served as the Saturn's "nerve center" providing guidance and control, command and sequence of vehicle functions, telemetry, and environmental control.
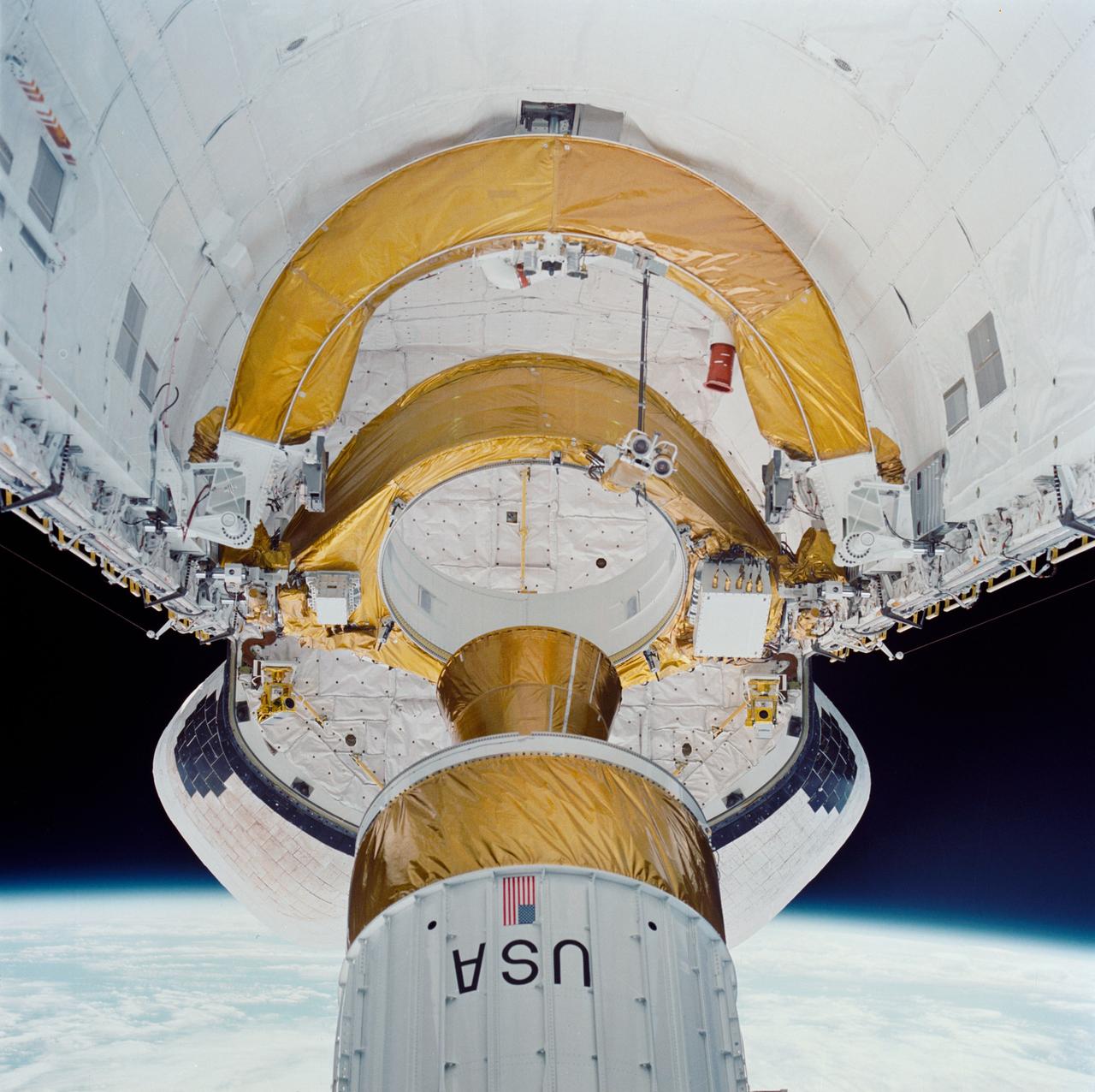

During STS-26, inertial upper stage (IUS) with the tracking and data relay satellite C (TDRS-C) drifts above Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, payload bay (PLB) after being positioned in deployment attitude (an angle of 50 degrees) by the airborne support equipment (ASE). IUS vacates the ASE aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) table in the PLB while the disconnected ASE umbilical boom floats above ASE forward cradle. IUS first stage rocket motor and nozzle and the interstage are visible as the IUS is deployed. In the background are the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and the Earth's limb.
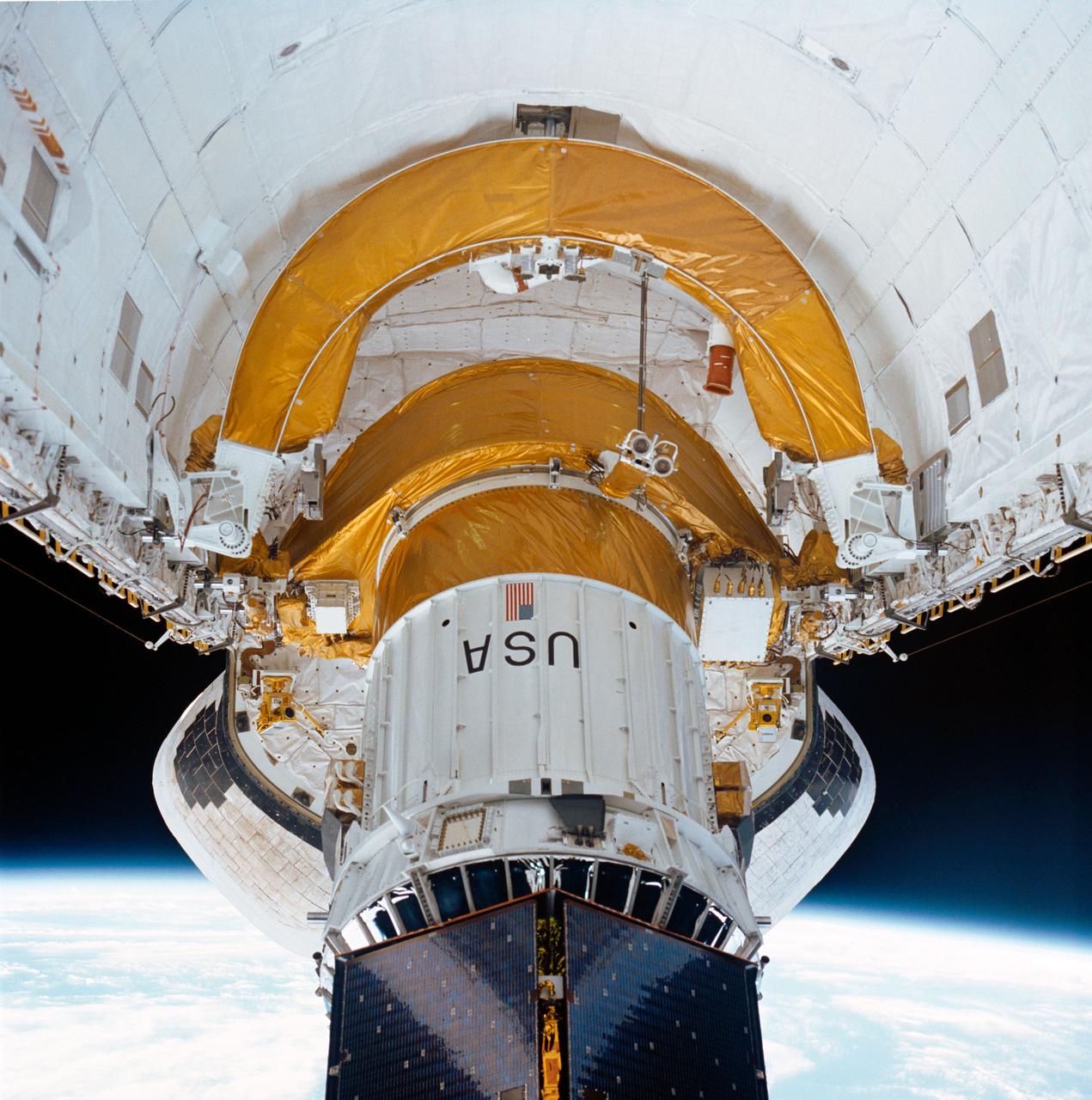

During STS-26, inertial upper stage (IUS) with the tracking and data relay satellite C (TDRS-C) located in the payload bay (PLB) of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is raised into deployment attitude (an angle of 50 degrees) by the airborne support equipment (ASE). ASE aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) table supports the IUS as it is positioned in the PLB and the ASE umbilical boom drifts away from IUS toward ASE forward cradle. TDRS-C solar array panels (in stowed configuration) are visible on top of the IUS. In the background are the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and the Earth's limb.

This VIS image shows part of eastern Ius Chasma. The lower elevations of Geryon Montes are located at the top of the image. Between the montes and the southern wall face is a region of sand and sand dunes. The presence of mobile sand indicates that winds are eroding, depositing and changing the canyon floor. The texture of the canyon floor beneath the dunes and elsewhere in the image is an indication of water, in some form, was part of the process creating the surface. There is a tongue of material emerging from the canyon wall that has steep sides, this may be a delta formed by material washing down the valley and into a body of standing water, like a lake. It may also just be a landslide deposit that has undergone extensive weathering. A landslide is a failure of slope due to gravity. They initiate due to several reasons. A lower layer of poorly cemented/resistant material may have been eroded, undermining the wall above which then collapses; earthquake seismic waves can cause the slope to collapse; and even an impact event near the canyon wall can cause collapse. As millions of tons of material fall and slide down slope a scalloped cavity forms at the upper part where the slope failure occurred. At the material speeds downhill it will pick up more of the underlying slope, increasing the volume of material entrained into the landslide. Whereas some landslides spread across the canyon floor forming lobate deposits, very large volume slope failures will completely fill the canyon floor in a large complex region of chaotic blocks. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris, south of Tithonium Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 10701 Latitude: -8.75442 Longitude: 281.333 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2004-05-13 10:49 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22282

The free-flying Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-E (TDRS-E), still attached to an Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), was photographed by one of the crewmembers during the STS-43 mission. The TDRS-E was boosted by the IUS into geosynchronous orbit and positioned to remain stationary 22,400 miles above the Pacific Ocean southwest of Hawaii. The TDRS system provides almost uninterrupted communications with Earth-orbiting Shuttles and satellites, and had replaced the intermittent coverage provided by globe-encircling ground tracking stations used during the early space program. The TDRS can transmit and receive data, and track a user spacecraft in a low Earth orbit. The IUS is an unmarned transportation system designed to ferry payloads from low Earth orbit to higher orbits that are unattainable by the Shuttle. The Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis for the STS-43 mission was launched on August 2, 1991.
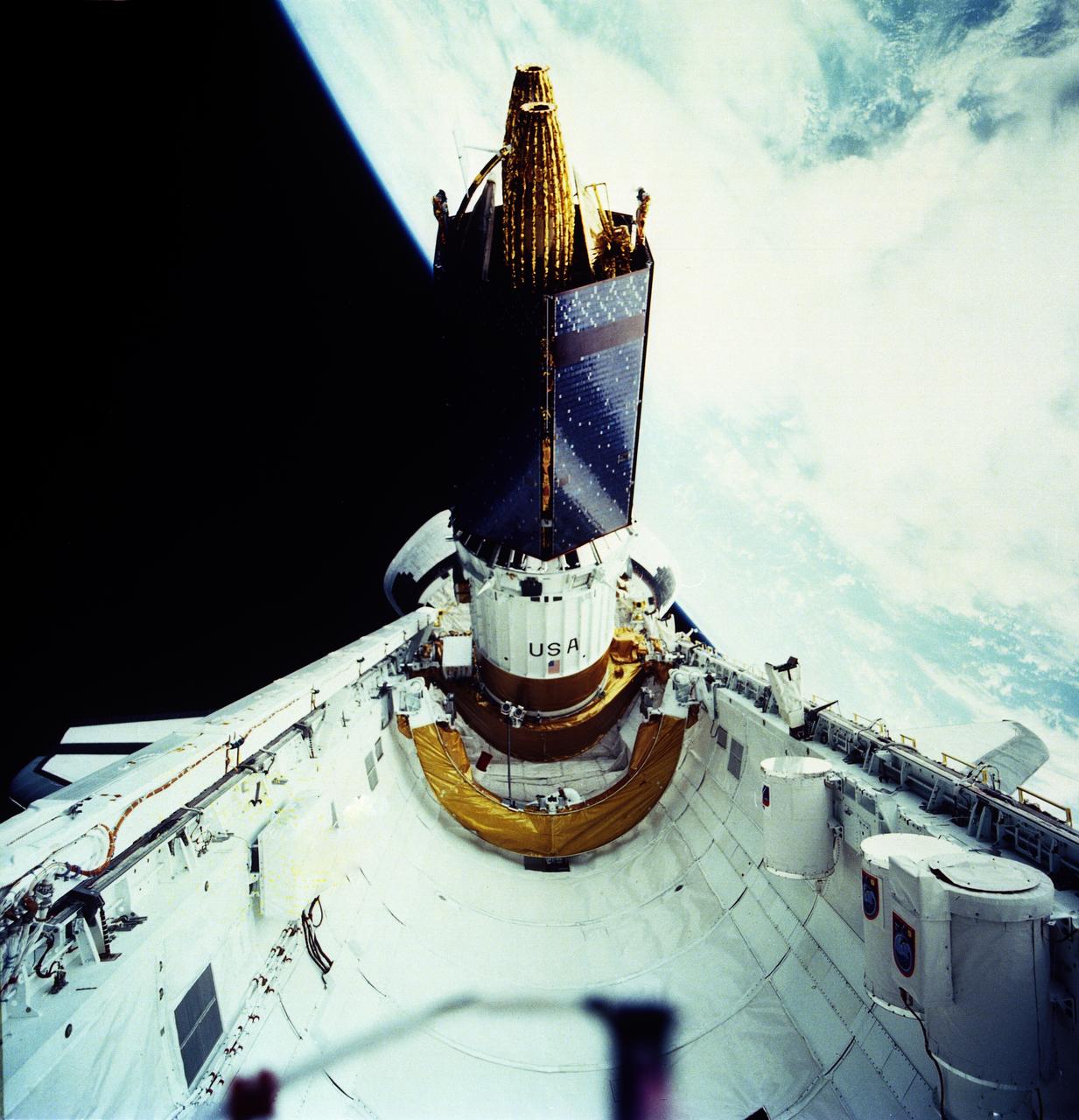

The primary payload of the STS-43 mission, Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-E (TDRS-E) attached to an Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) was photographed at the moment of its release from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis. The TDRS-E was boosted by the IUS into geosynchronous orbit and positioned to remain stationary 22,400 miles above the Pacific Ocean southwest of Hawaii. The TDRS system provides almost uninterrupted communications with Earth-orbiting Shuttles and satellites, and had replaced the intermittent coverage provided by globe-encircling ground tracking stations used during the early space program. The TDRS can transmit and receive data, and track a user spacecraft in a low Earth orbit. The IUS is an unmarned transportation system designed to ferry payloads from low Earth orbit to higher orbits that are unattainable by the Shuttle. The launch of STS-43 occurred on August 2, 1991.
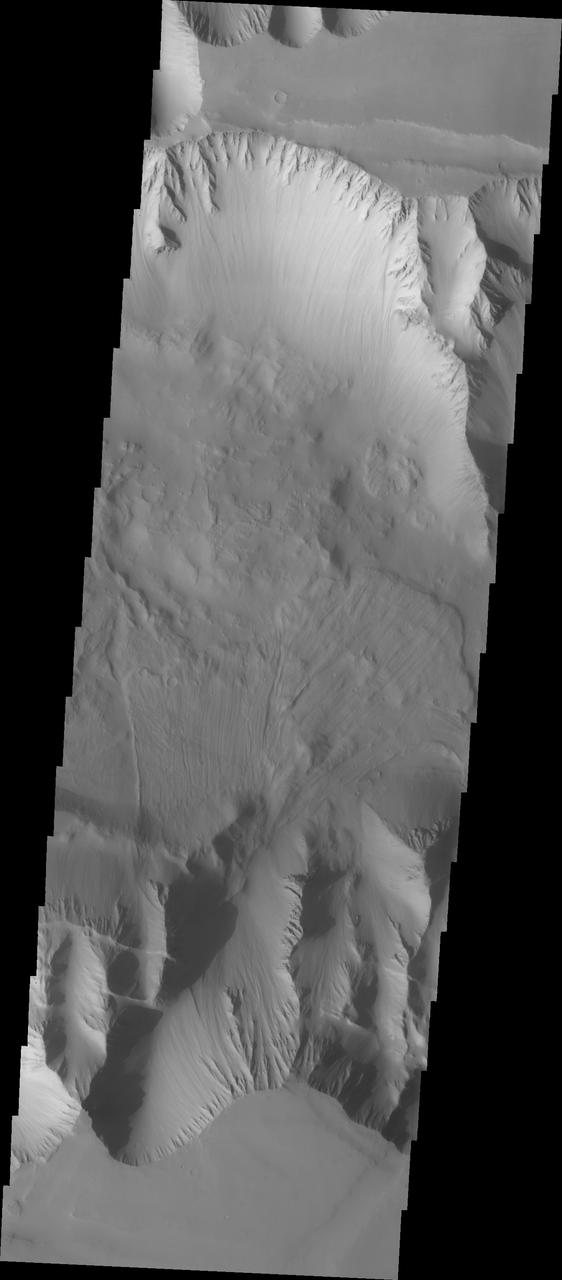

The VIS image shows part of the western end of Ius Chasma. Both the north and south canyon walls are visible in this image. At the top of the frame paired faults have created a graben. On the southern face of the canyon, several linear faults parallel the graben. These faults are part of the tectonic formation of Valles Marineris. Landslides on both walls created deposits on the crater floor. The easiest to identify is the lobate margin at the right side of the images. Lobate margins and radial surface grooves are common features in low volume landslides. A landslide is a failure of slope due to gravity. They initiate due to several reasons. A lower layer of poorly cemented/resistant material may have been eroded, undermining the wall above which then collapses; earth quake seismic waves can cause the slope to collapse; and even an impact event near the canyon wall can cause collapse. As millions of tons of material fall and slide down slope a scalloped cavity forms at the upper part where the slope failure occurred. At the material speeds downhill it will pick up more of the underlying slope, increasing the volume of material entrained into the landslide. Whereas some landslides spread across the canyon floor forming lobate deposits, very large volume slope failures will completely fill the canyon floor in a large complex region of chaotic blocks. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris, south of Tithonium Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 8792 Latitude: -6.69222 Longitude: 270.88 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2003-12-08 06:35 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22277
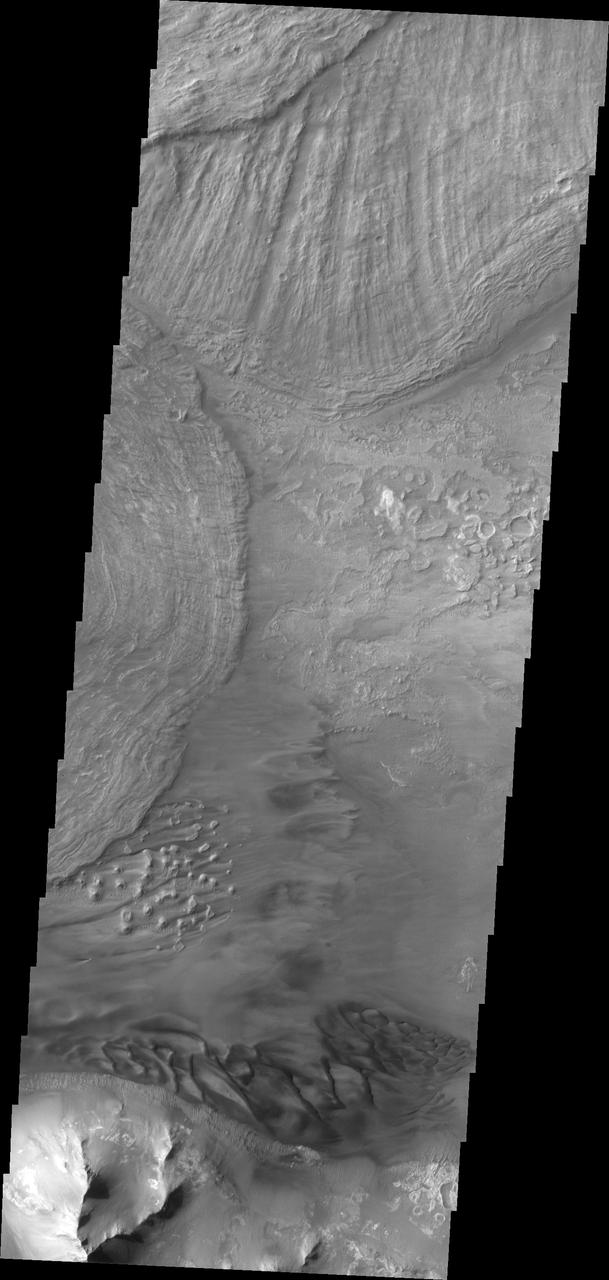

This VIS image shows the eastern end of Ius Chasma. The southern canyon wall is at the bottom of the image, with dark sand and sand dunes. The presence of mobile sand indicates that winds are eroding, depositing and changing the canyon floor. The rest of the image is dominated by large landslide deposits. At the top of the image are two overlapping deposits from landslides originating on the northern chasma wall. The landslide deposit on the left side of the image originate from the southern chasma wall. A landslide is a failure of slope due to gravity. They initiate due to several reasons. A lower layer of poorly cemented/resistant material may have been eroded, undermining the wall above which then collapses; earthquake seismic waves can cause the slope to collapse; and even an impact event near the canyon wall can cause collapse. As millions of tons of material fall and slide down slope a scalloped cavity forms at the upper part where the slope failure occurred. At the material speeds downhill it will pick up more of the underlying slope, increasing the volume of material entrained into the landslide. Whereas some landslides spread across the canyon floor forming lobate deposits, very large volume slope failures will completely fill the canyon floor in a large complex region of chaotic blocks. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris, south of Tithonium Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 36744 Latitude: -8.64709 Longitude: 282.235 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2010-03-27 18:32 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22285
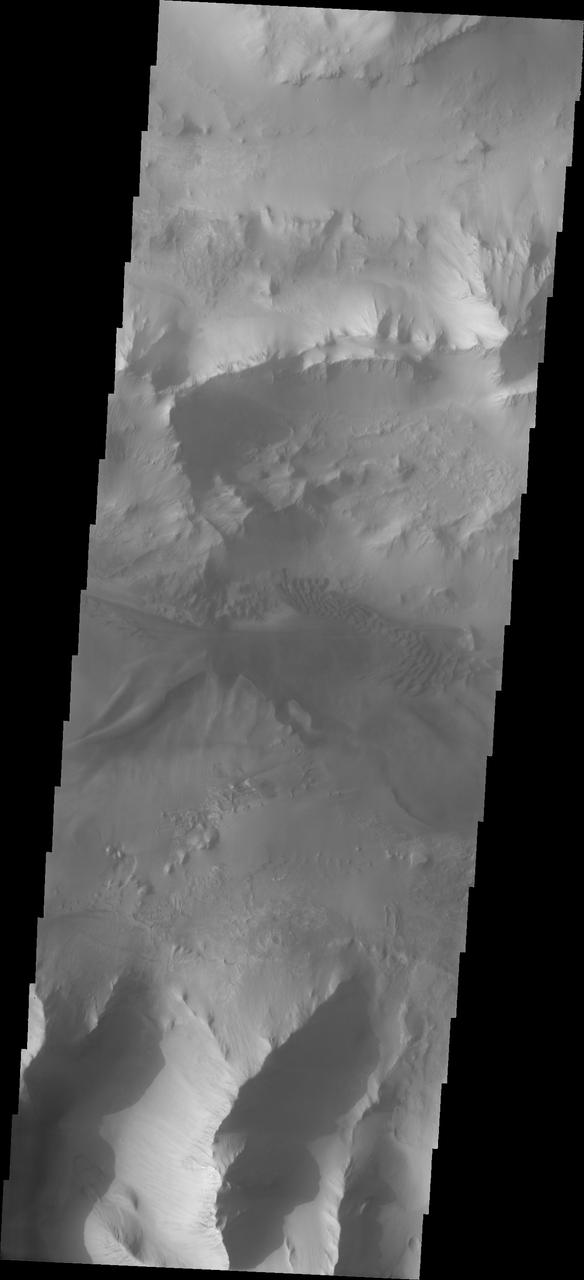

Continuing eastward thru central Ius Chasma, this image shows a section of chasma that is not dominated by landslide deposits. Geryon Montes, in the upper half of the image, has several visible faults, including a pair of faults that divide the uppermost ridge into two sections. Between the montes and the southern wall face is a region of sand and sand dunes. The presence of mobile sand indicates that winds are eroding, depositing and changing the canyon floor. A landslide is a failure of slope due to gravity. They initiate due to several reasons. A lower layer of poorly cemented/resistant material may have been eroded, undermining the wall above which then collapses; earthquake seismic waves can cause the slope to collapse; and even an impact event near the canyon wall can cause collapse. As millions of tons of material fall and slide down slope a scalloped cavity forms at the upper part where the slope failure occurred. At the material speeds downhill it will pick up more of the underlying slope, increasing the volume of material entrained into the landslide. Whereas some landslides spread across the canyon floor forming lobate deposits, very large volume slope failures will completely fill the canyon floor in a large complex region of chaotic blocks. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris, south of Tithonium Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 27012 Latitude: -7.59048 Longitude: 276.328 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2008-01-16 09:47 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22281

This VIS image shows part of the eastern end of Ius Chasma. Geryon Montes are located in the bottom half of the image. Between the montes and the southern wall face is a region of sand and sand dunes. The presence of mobile sand indicates that winds are eroding, depositing and changing the canyon floor. The top of the image is dominated by a large landslide deposit. The radial surface grooves are still visible, but the region as a whole as undergone significant erosion. A landslide is a failure of slope due to gravity. They initiate due to several reasons. A lower layer of poorly cemented/resistant material may have been eroded, undermining the wall above which then collapses; earthquake seismic waves can cause the slope to collapse; and even an impact event near the canyon wall can cause collapse. As millions of tons of material fall and slide down slope a scalloped cavity forms at the upper part where the slope failure occurred. At the material speeds downhill it will pick up more of the underlying slope, increasing the volume of material entrained into the landslide. Whereas some landslides spread across the canyon floor forming lobate deposits, very large volume slope failures will completely fill the canyon floor in a large complex region of chaotic blocks. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris, south of Tithonium Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 17153 Latitude: -8.20738 Longitude: 281.009 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2005-10-26 16:00 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22284
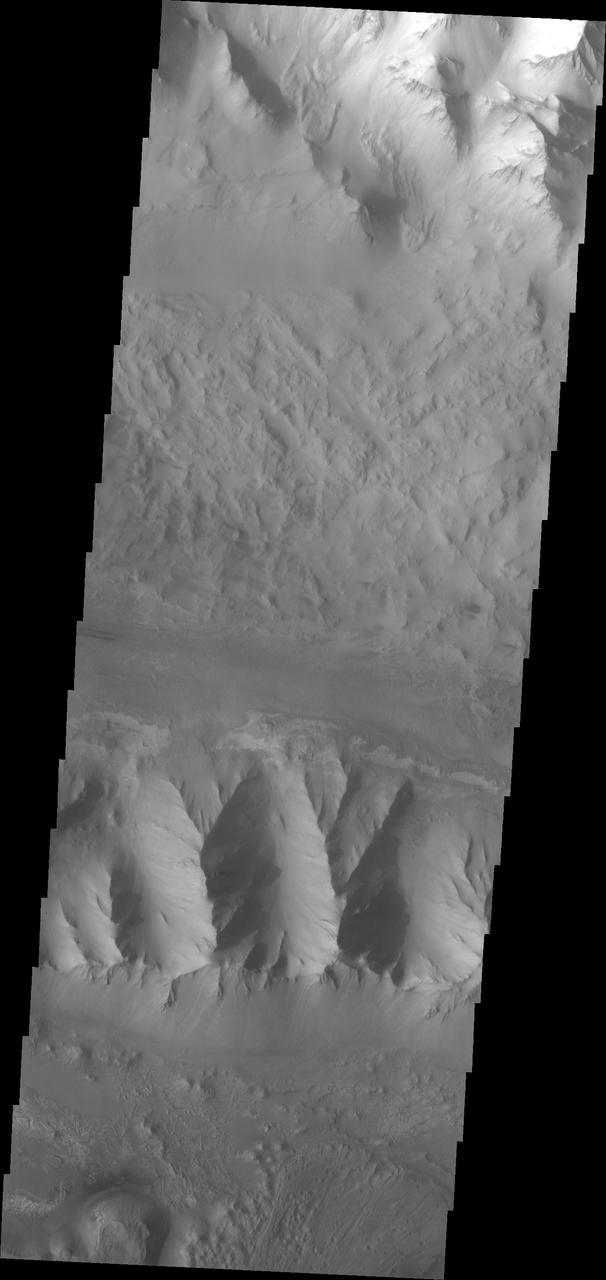

Moving into the central part of Ius Chasma, the canyon profile changes. What started as a large graben south of the main chasma wall, has widened to create a central high ridge separating the chasm into two parallel sections. This interior ridge is called Geryon Montes. The northern canyon wall is at the top of the image, including several tongue shaped landslide deposits. The floor has been covered in deposits that may include landslide material and later materials such as air fall particles like dust and water lain layered deposits. The Geryon Montes are in the lower 1/3 of the image. Just to the top of the Montes are materials with different "colors". These are part of the layered materials inside the canyon. At the very bottom of the image a highly eroded landslide deposit exists. The materials on this side of Geryon Montes are at a higher elevation than the floor on the opposite side. The unusual texture of the canyon floor also points to layered materials that may have been laid down in standing water. A landslide is a failure of slope due to gravity. They initiate due to several reasons. A lower layer of poorly cemented/resistant material may have been eroded, undermining the wall above which then collapses; earth quake seismic waves can cause the slope to collapse; and even an impact event near the canyon wall can cause collapse. As millions of tons of material fall and slide down slope a scalloped cavity forms at the upper part where the slope failure occurred. At the material speeds downhill it will pick up more of the underlying slope, increasing the volume of material entrained into the landslide. Whereas some landslides spread across the canyon floor forming lobate deposits, very large volume slope failures will completely fill the canyon floor in a large complex region of chaotic blocks. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris, south of Tithonium Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. The canyons of Valles Marineris were formed by extensive fracturing and pulling apart of the crust during the uplift of the vast Tharsis plateau. Landslides have enlarged the canyon walls and created deposits on the canyon floor. Weathering of the surface and influx of dust and sand have modified the canyon floor, both creating and modifying layered materials. There are many features that indicate flowing and standing water played a part in the chasma formation. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 71,000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 26151 Latitude: -7.12079 Longitude: 275.703 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2007-11-06 12:17 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22280
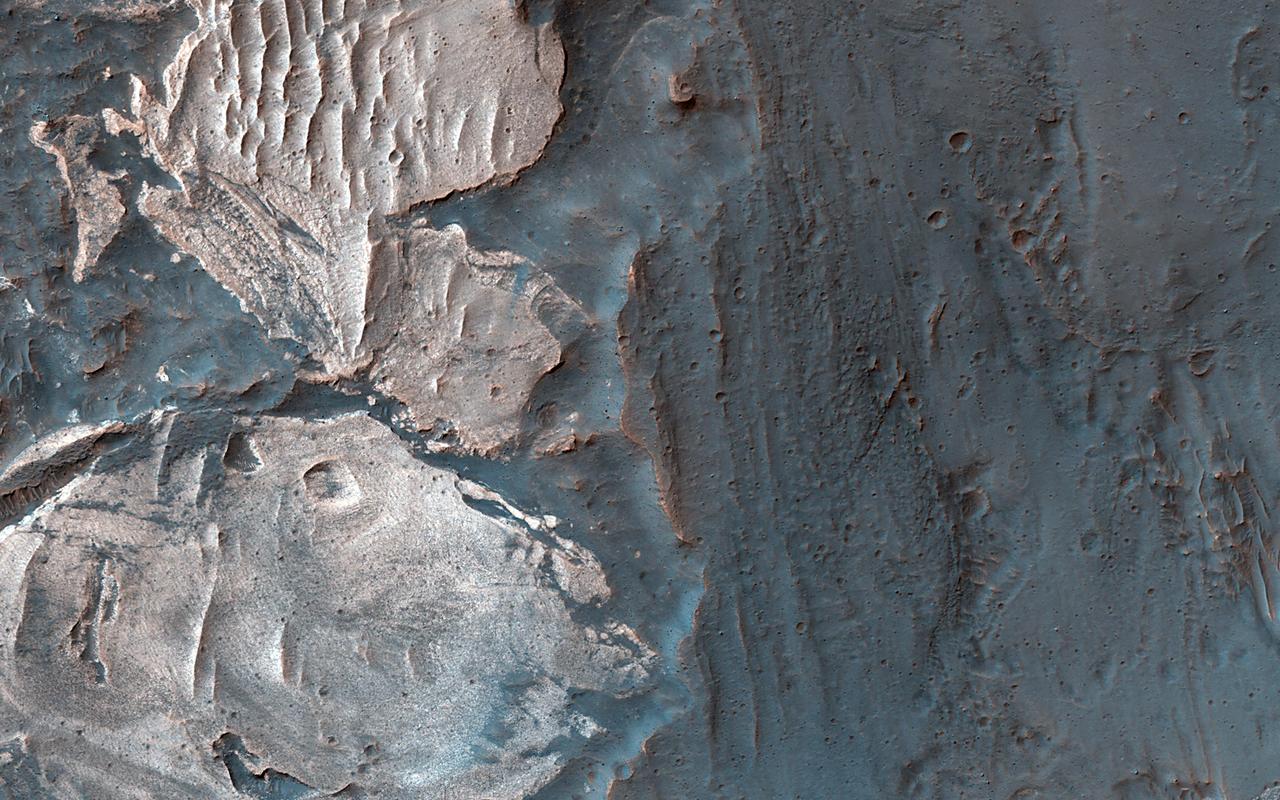

Many of the Valles Marineris canyons, called chasmata, have kilometer-high, light-toned layered mounds made up of sulfate materials. Ius Chasma, near the western end of Valles Marineris, is an exception. The light-toned deposits here are thinner and occur along both the floor and walls, as we see in this HiRISE image. Additionally, the sulfates are mixed with other minerals like clays and hydrated silica. Scientists are trying to use the combination of mineralogy, morphology, and stratigraphy to understand how the deposits formed in Ius Chasma and why they differ from those found elsewhere in Valles Marineris. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25982
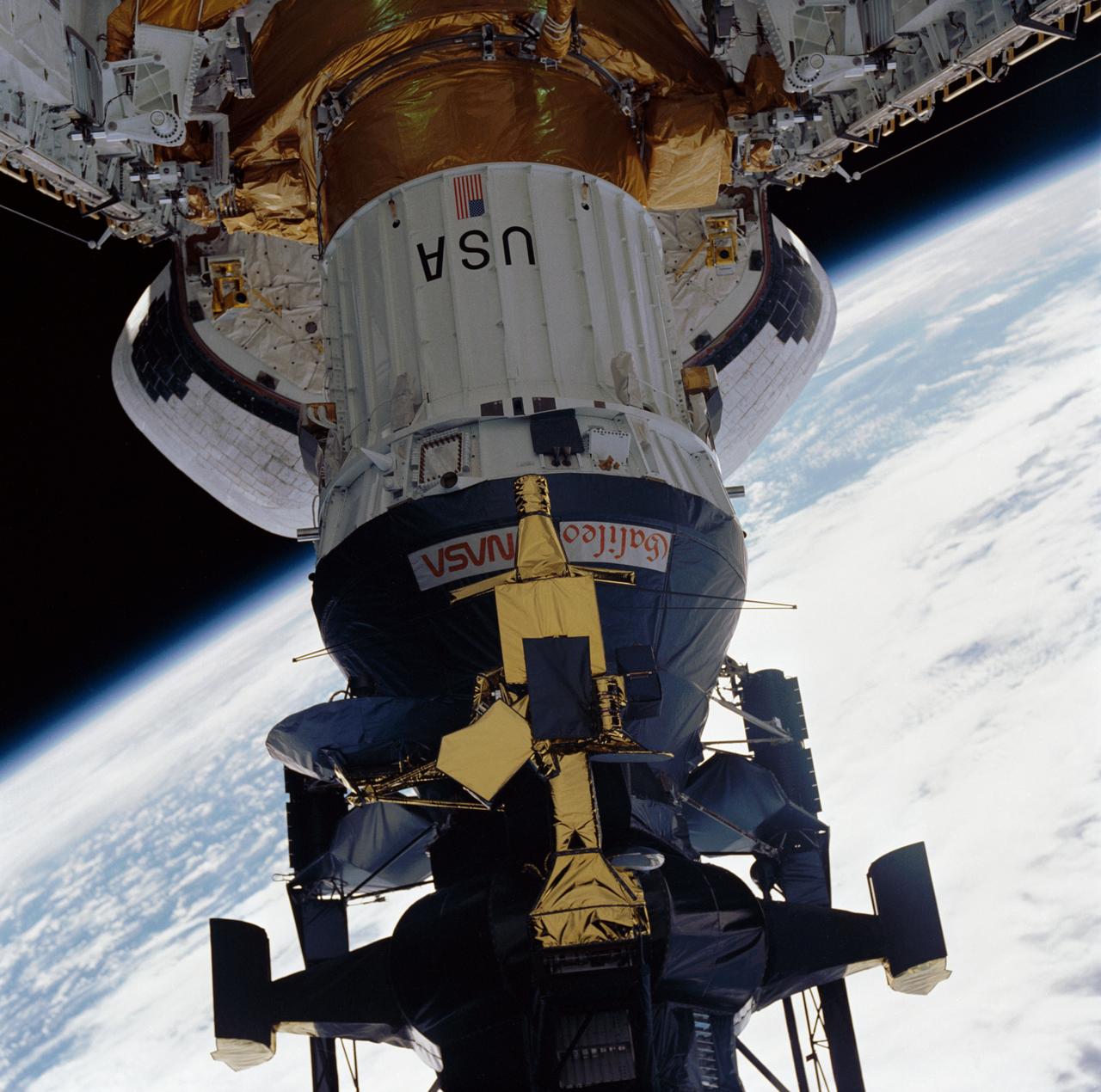

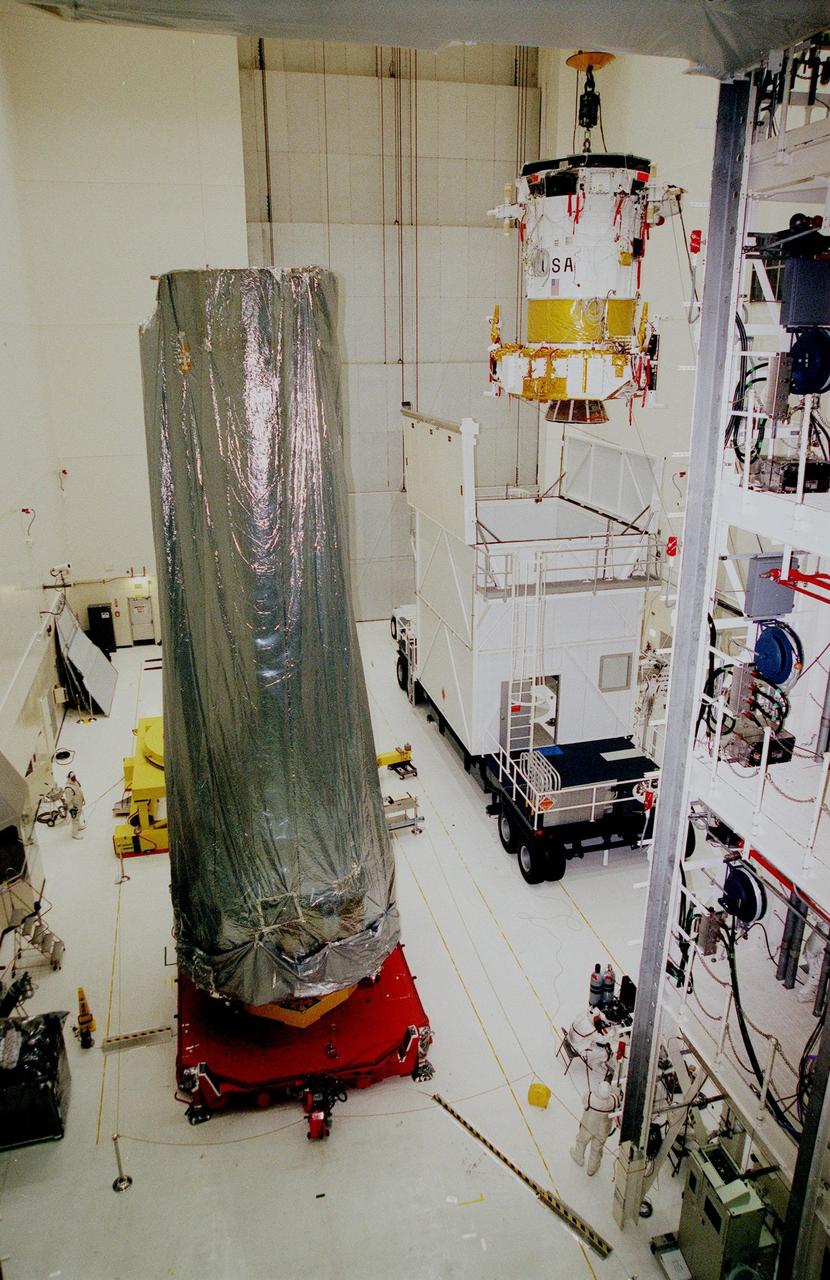
During STS-34 mission, the Galileo spacecraft mounted atop the inertial upper stage (IUS) is tilted to a 58-degree deployment position by the airborne support equipment (ASE) aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) table in Atlantis', Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104's, payload bay (PLB). Visible in the foreground is the ASE forward cradle and the umbilical boom which has fallen away from the IUS. OV-104's orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and the Earth's limb appear in the background.
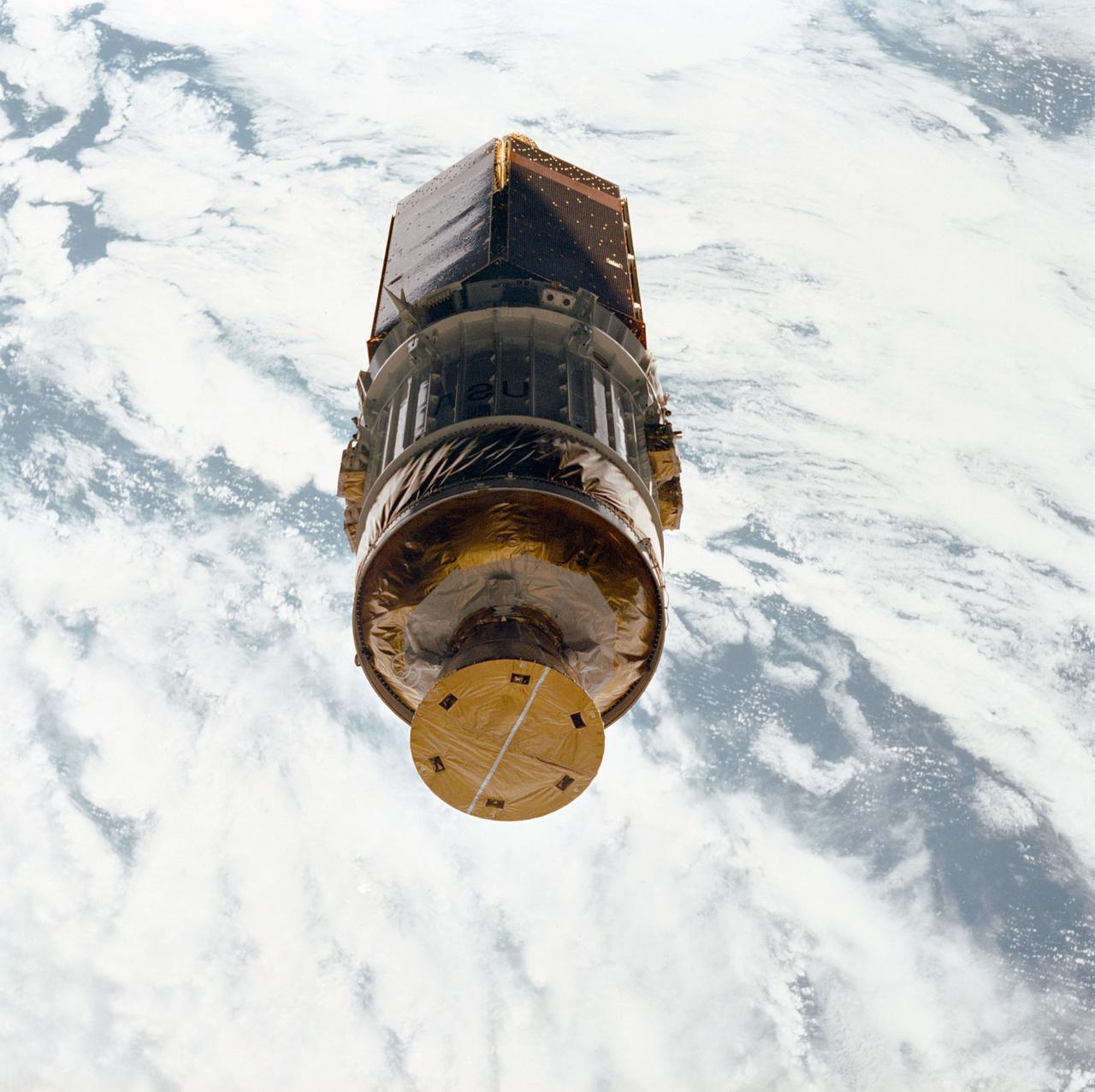

STS026-31-071 (3 Oct 1988) --- After deployment from Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, the inertial upper stage (IUS) with the tracking and data relay satellite C (TDRS-C) drifts above the cloud-covered Earth surface. TDRS-C, in stowed configuration (solar array panels visible), is mounted atop the IUS with the interstage and solid rocket motor and nozzle seen in the foreground.
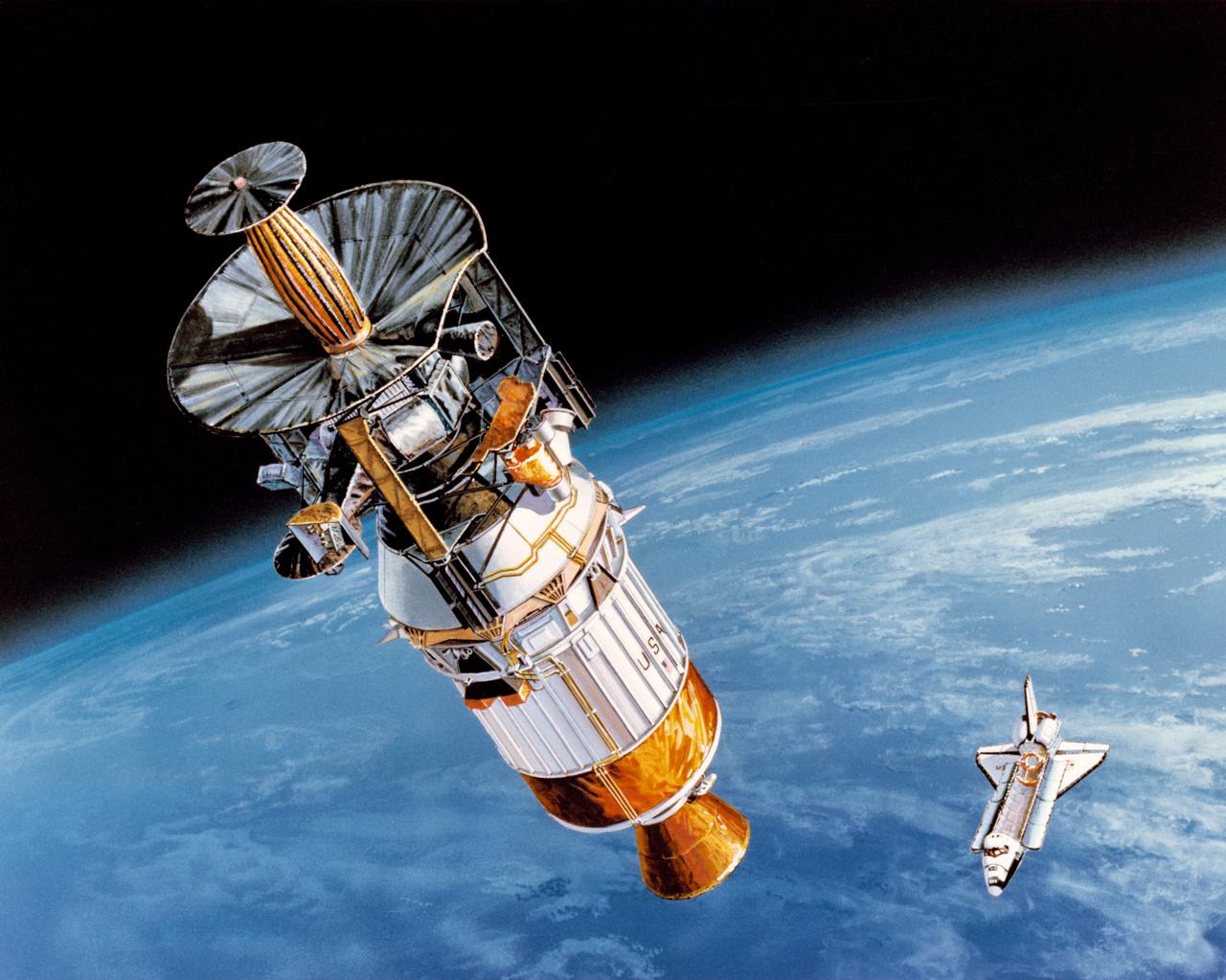

S89-42940 (April 1989) --- In this artist's rendition, the Galileo spacecraft is being boosted into its inter-planetary trajectory by the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) rocket. The Space Shuttle Atlantis, which is scheduled to take Galileo and the IUS from Earth's surface into space, is depicted against the curve of Earth. Galileo will be placed on a trajectory to Venus, from which it will return to Earth at higher velocity and then gain still more energy in two gravity-assist passes, until it has enough velocity to reach Jupiter. Passing Venus, it will take scientific data using instruments designed for observing Jupiter; later, it will make measurements at Earth and the moon, crossing above the moon's north pole in the second pass. Between the two Earth passes, it will edge into the asteroid belt, beyond Mars' orbit; there, the first close-up observation of an asteroid is planned. Crossing the belt later, another asteroid flyby is possible.

During STS-26, inertial upper stage (IUS) with tracking and data relay satellite C (TDRS-C) located in the payload bay (PLB) of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is positioned into its proper deployment attitude (an angle of 50 degrees) by the airborne support equipment (ASE). In the foreground, the ASE forward cradle is visible. The IUS is mounted in the ASE aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) table. TDRS-C components in stowed configuration include solar array panels, TDRS single access #1 and #2, TDRS SGL, and S-Band omni antenna. In the background are the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods, the Earth's cloud-covered surface, and the Earth's limb.
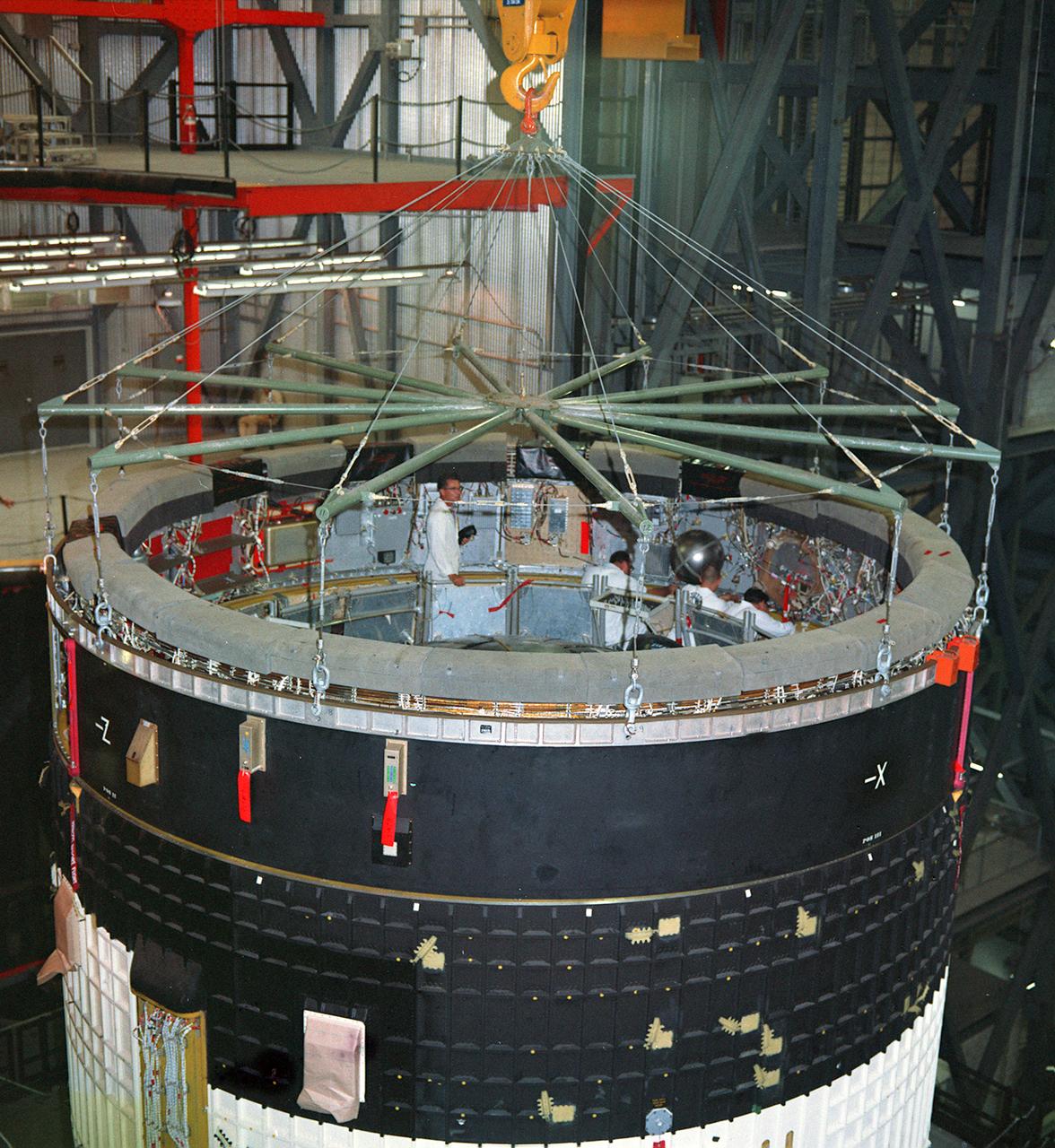

This photograph was taken during the final assembly operation of the Saturn V launch vehicle for the Apollo 4 (SA 501) mission. The instrument unit (IU) was mated atop the S-IC/S-II assembly in the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay at the Kennedy Space Center. The Apollo 4 mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield. The Apollo 4 was launched on November 9, 1967 from KSC.

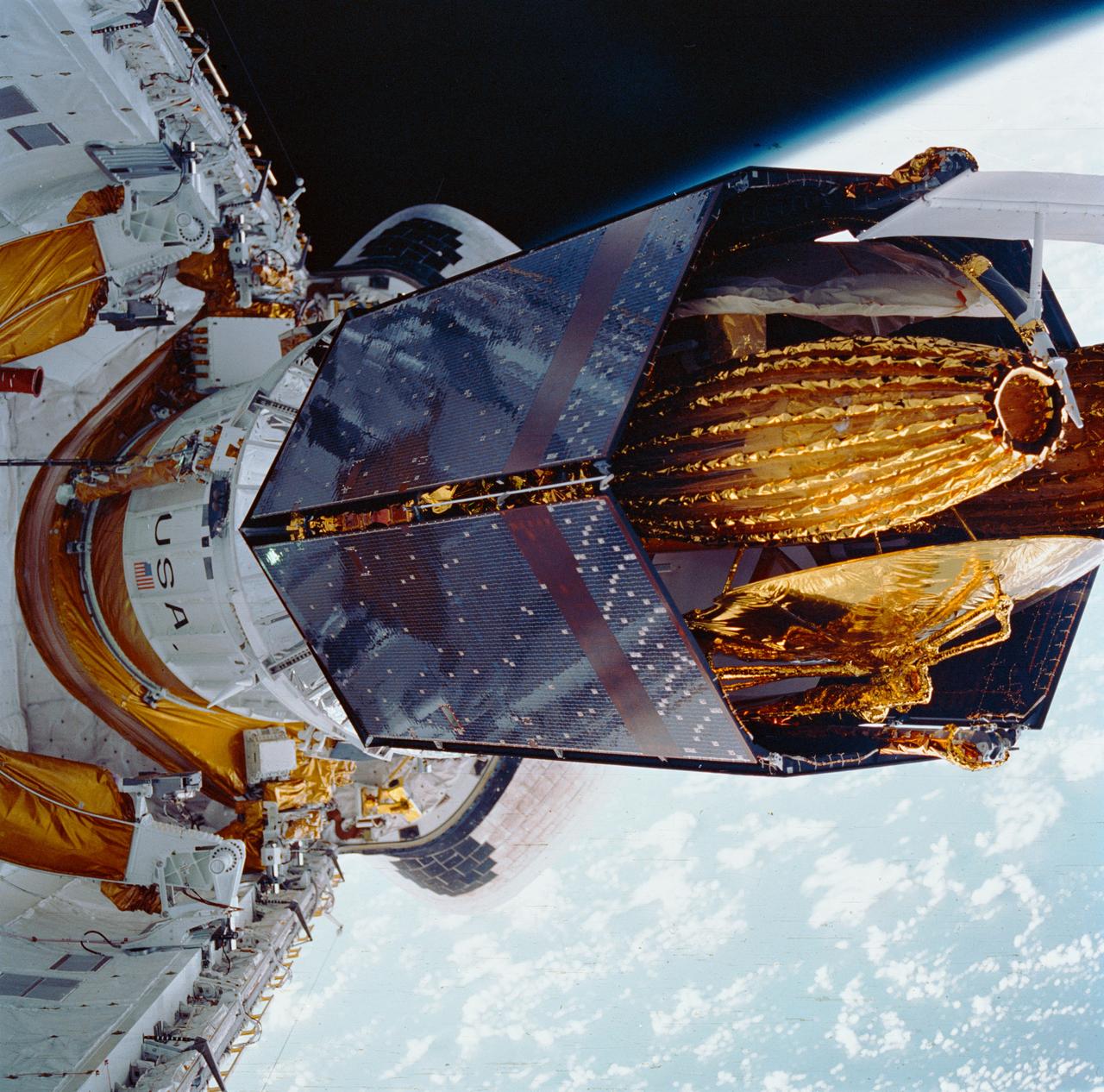
STS034-72-070 (18 Oct 1989) --- Backdropped against the blackness of space, the Galileo spacecraft and its inertial upper stage (IUS) begin relative separation from the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Atlantis. The five-member STS-34 crew deployed the Jupiter-bound satellite within six hours of achieving Earth orbit on Oct. 18, 1989. The scene was exposed with a 70mm handheld Hasselblad camera.

This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft spans from Tithonium Chasma top of image to Ius Chasma bottom of image.
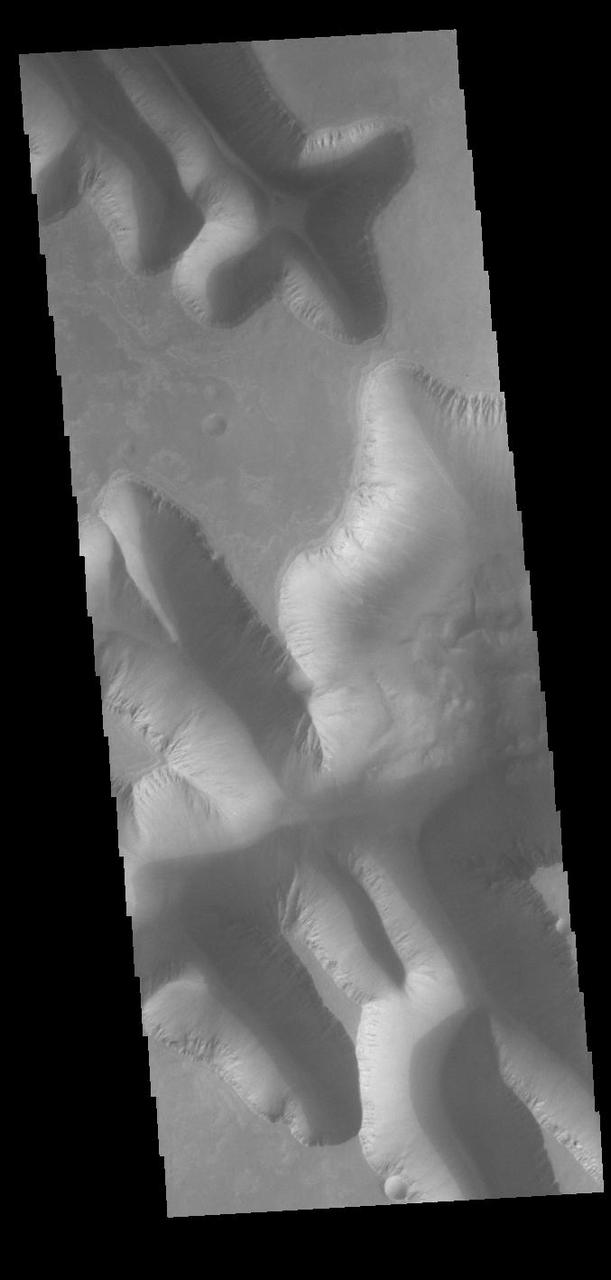

Today's VIS image shows part of Louros Valles on the southern part of Ius Chasma. Louros Valles is a region of mega gullies the empty into Ius Chasma. Ius Chasma is unique from the other chasmata of Valles Marineris in possessing mega gullies on both sides of the chasma. The largest mega gullies are located in Sinai Planum, dissecting those plains and emptying into the canyon. Mega gullies are thought to be sapping channels caused by groundwater flow and erosion. The Earth analog is springs – water that flows underground and then breaches the surface creating channels. The morphology of the Mars gullies mirrors terrestrial springs. The channel is fairly uniform in width and the "head" of the channel is rounded like an amphiteater. The channel lengthens by erosion at the "head" backwards as the surface where the spring emerges is undercut. For Mars it is theorized that subsurface water would stay liquid due to underground heating. Ius Chasma is at the western end of Valles Marineris, south of Tithonium Chasma. Valles Marineris is over 4000 kilometers long, wider than the United States. Ius Chasma is almost 850 kilometers long (528 miles), 120 kilometers wide and over 8 kilometers deep. In comparison, the Grand Canyon in Arizona is about 175 kilometers long, 30 kilometers wide, and only 2 kilometers deep. Orbit Number: 90809 Latitude: -8.38091 Longitude: 275.49 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-06-04 12:25 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25512

Today's VIS image shows part a section of a mega gully. Located on the plains of Sinai Planum, it is just one of a number of huge channels that line the cliff face of Ius Chasma. The linear sides of the channel indicate that the formation of these features included tectonic activity. Ius Chasma is on the western end of Valles Marineris. Orbit Number: 77719 Latitude: -8.12758 Longitude: 274.408 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2019-06-22 16:33 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23368
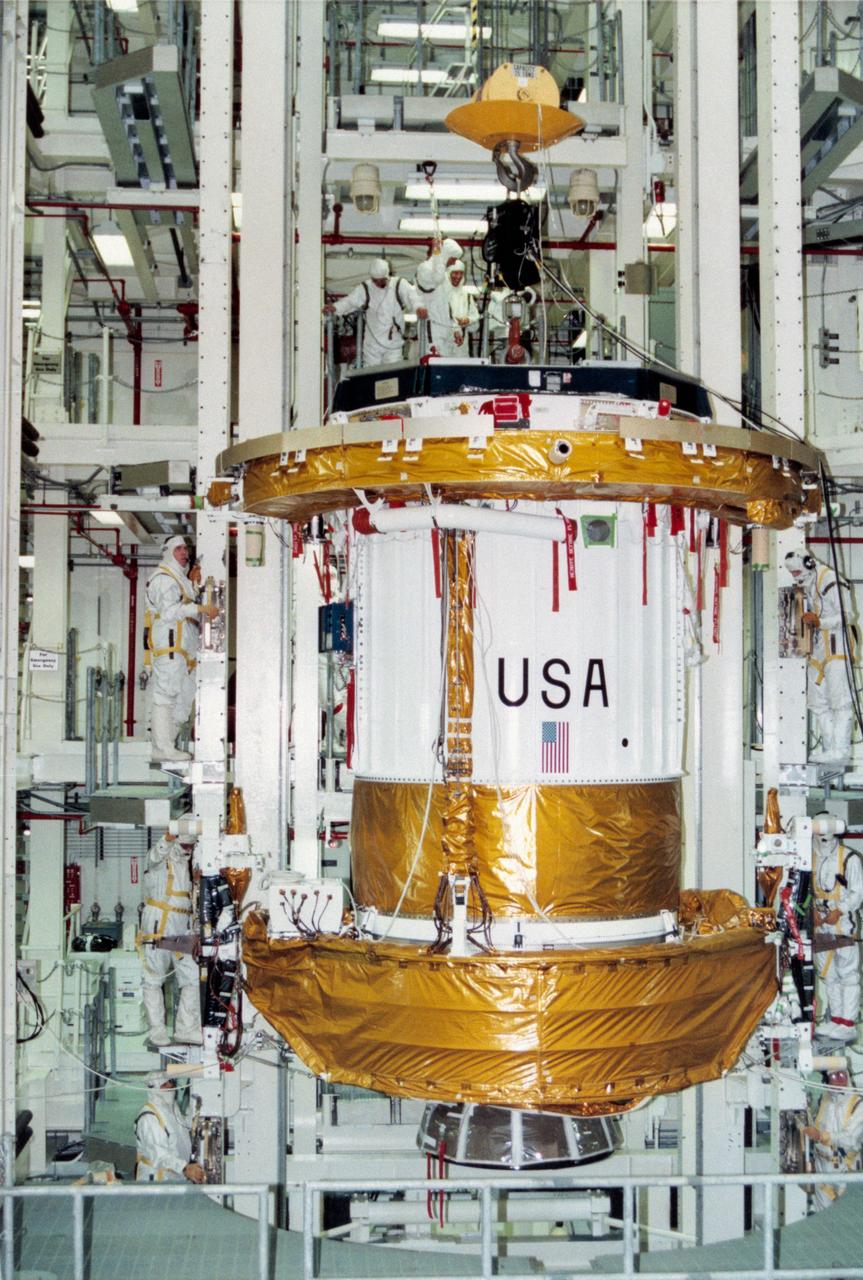
S95-08961 (4 APRIL 1995) --- Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF) oversee and control the lowering of the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) booster into a work stand for preflight processing. The IUS will be attached to the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-G), which will be deployed by the Space Shuttle Discovery on the STS-70 mission. The IUS is scheduled to be mated to the TDRS satellite later in April. Liftoff of STS-70 is slated for no earlier than June 8, 1995.
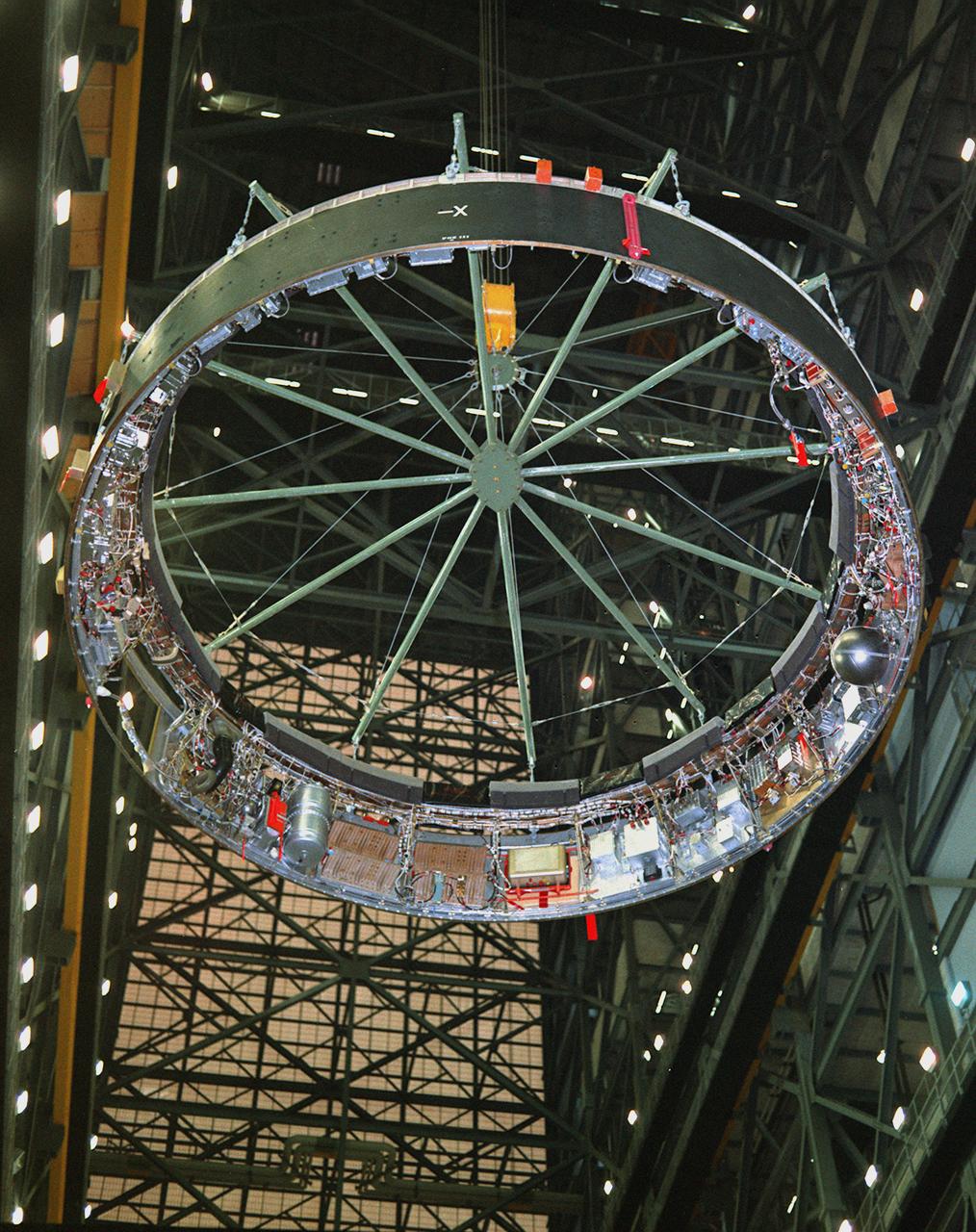

This photograph was taken during the final assembly operation of the Saturn V launch vehicle for the Apollo 4 (SA 501) mission. The instrument unit (IU) was hoisted to be mated to the S-IC/S-II assembly in the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay at the Kennedy Space Center. The Apollo 4 mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield. The Apollo 4 was launched on November 9, 1967 from KSC.
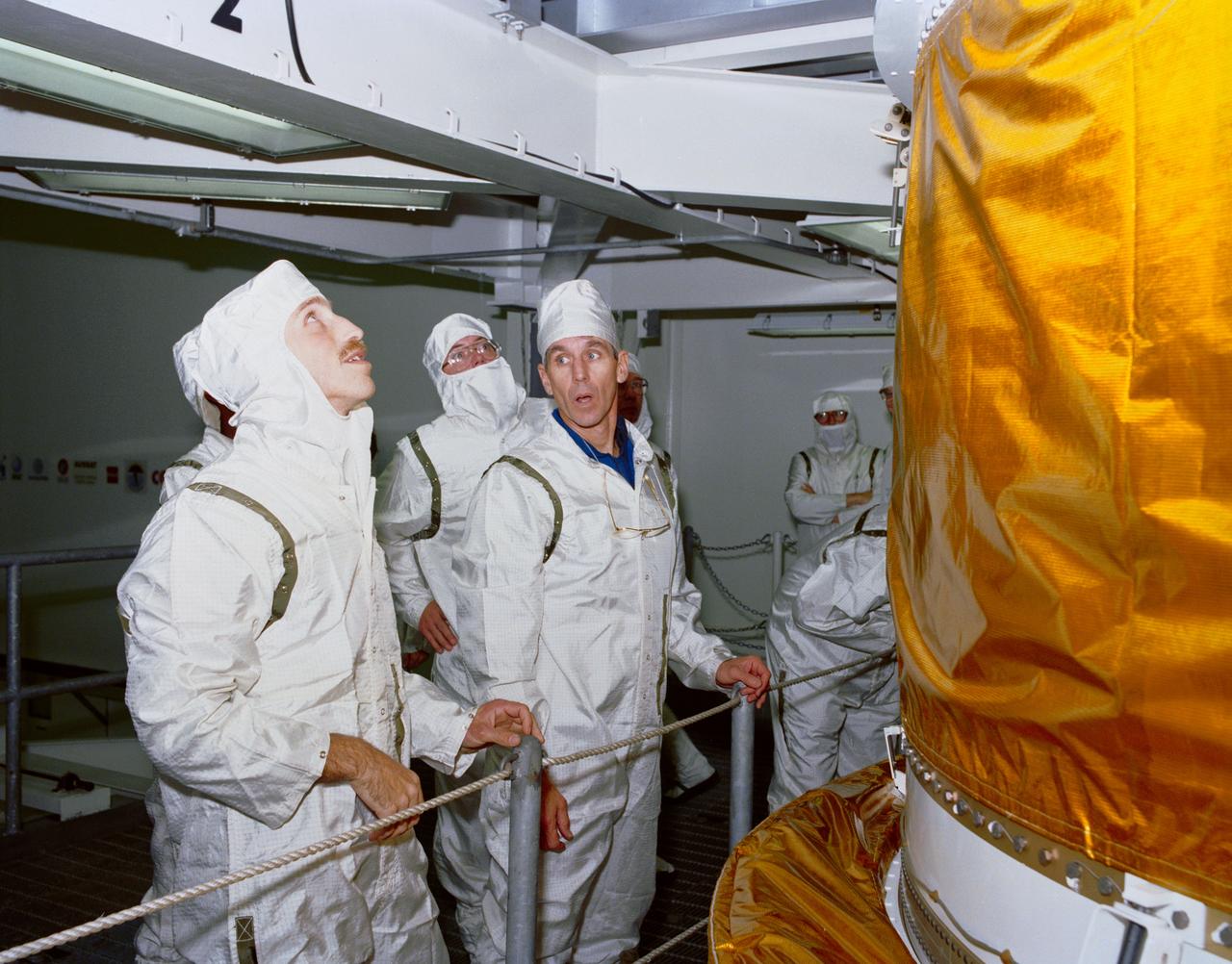

S89-27384 (5 Jan 1989) --- Astronauts James P. Bagian, left, and Robert C. Springer inspect a portion of the first stage of the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS-9) in a test cell of the KSC vertical processing facility. The two, along with three other NASA astronauts, will fly aboard Discovery and are responsible for the deployment of the tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS).
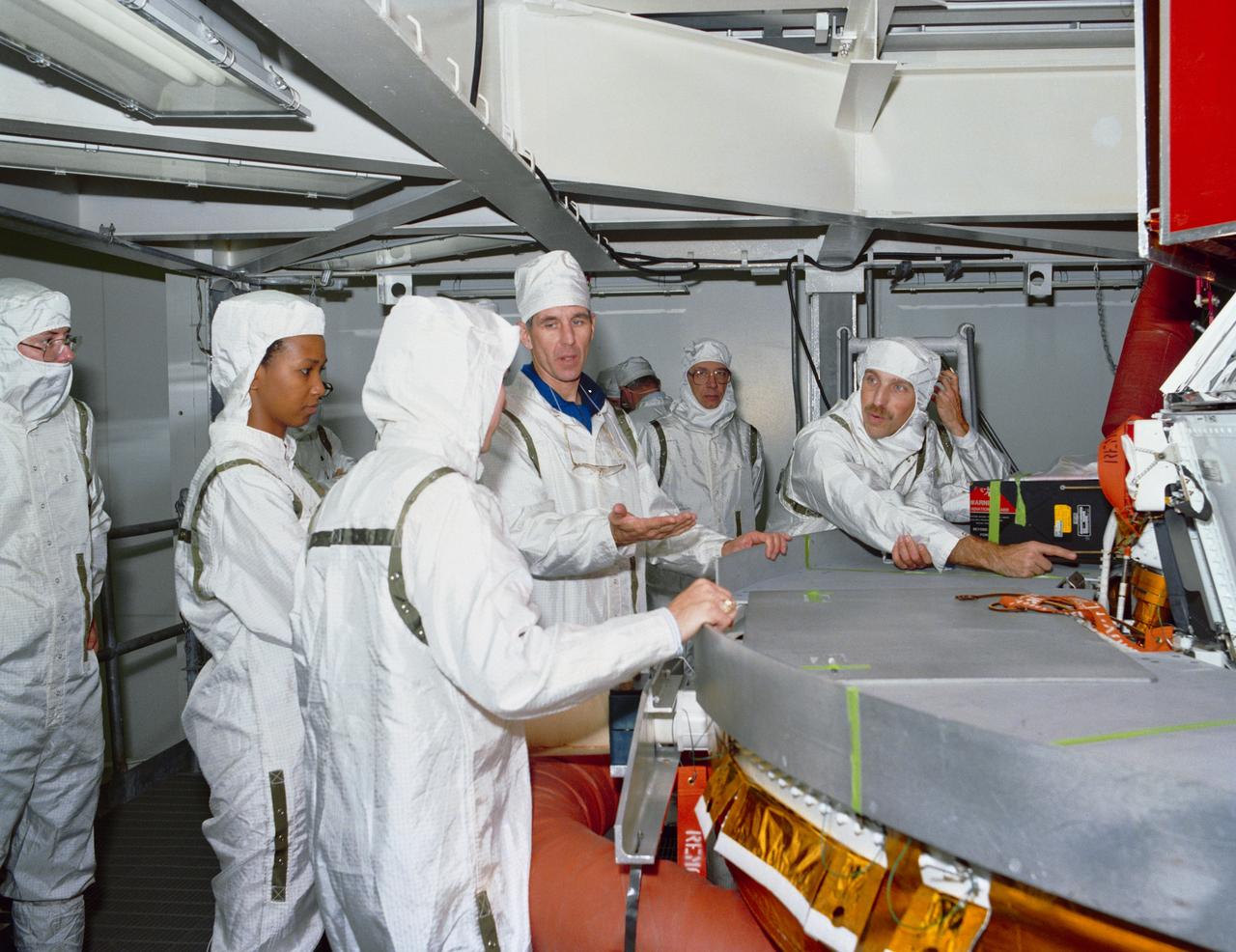

S89-28108 --- Astronaut Mae C. Jemison and STS-29 Mission Specialist James P. Bagian and Robert C. Springer inspect the interface between the tracking and data relay satellite D (TDRS-D) and inertial upper stage (IUS-9) in a test cell located in the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Vertical Processing Facility (VPF). The clean-suited astronauts, engineers, and technicians discuss the payload. Photo credit: NASA
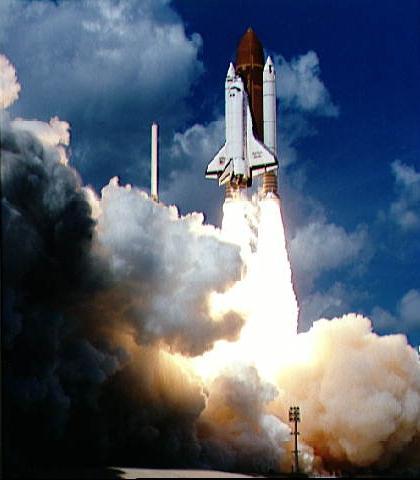

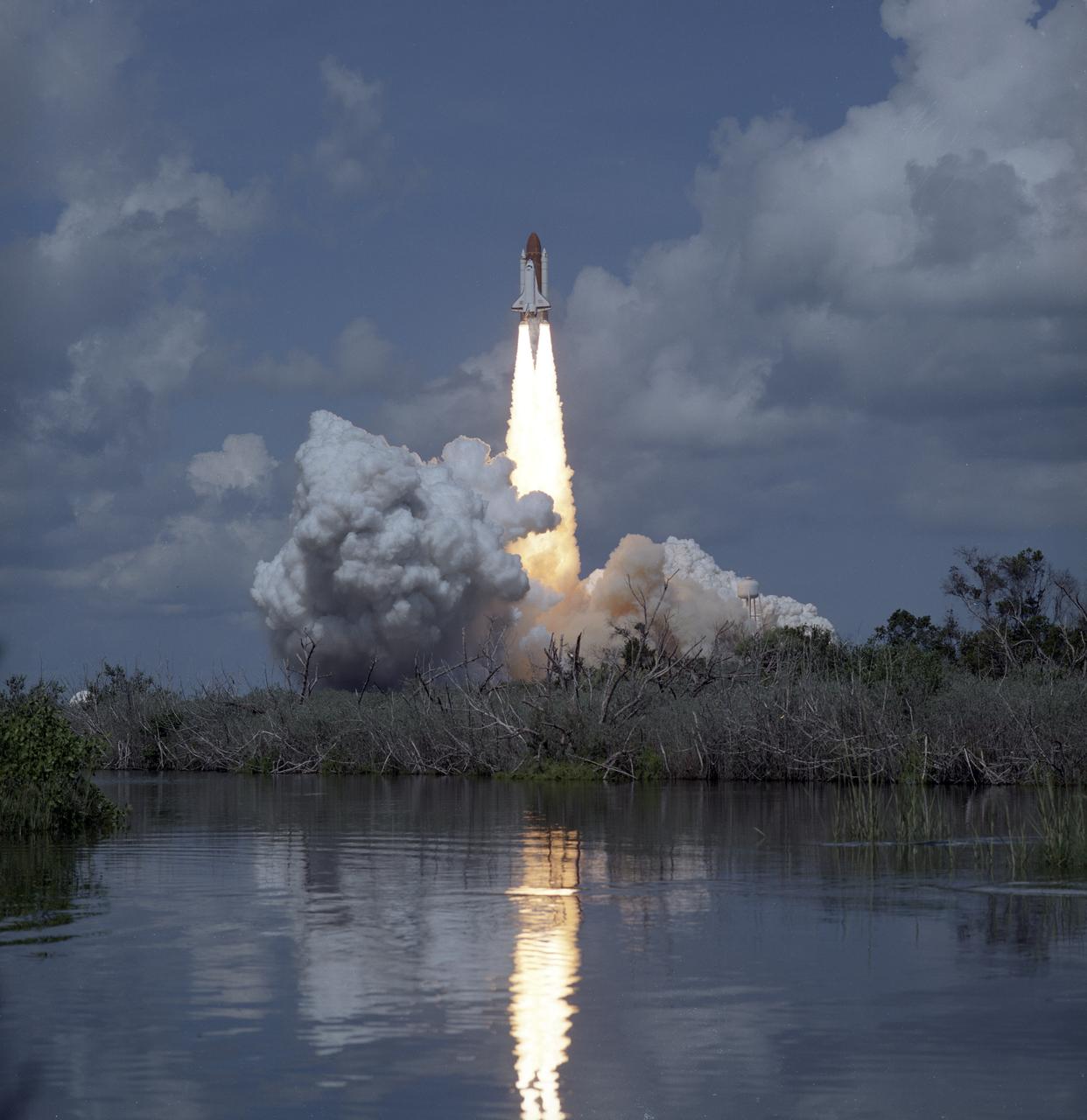
Liftoff of STS-34 Atlantis, carrying NASA Galileo spacecraft and its Inertial Upper Stage IUS booster on October 18, 1989 at 12:35 p.m. EDT. P-35036BC
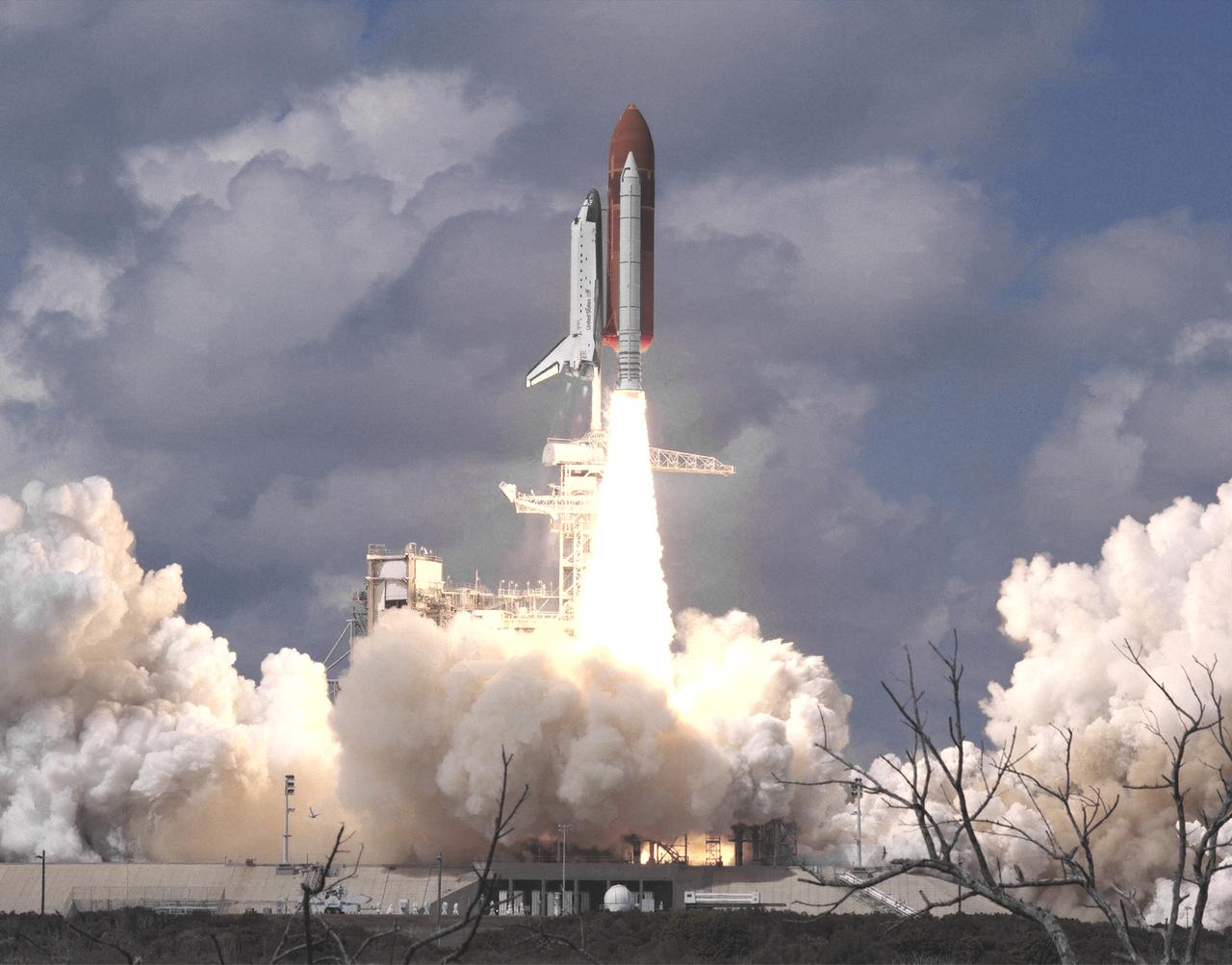

The Space Shuttle Discovery takes off from Launch Pad 39B at the Kennedy Space Center, Florida, to being Mission STS-26 on 29 September 1988,11:37:00 a.m. EDT. The 26th shuttle mission lasted four days, one hour, zero minutes, and 11 seconds. Discovery landed 3 October 1988, 9:37:11 a.m. PDT, on Runway 17 at Edwards Air Force Base, California. Its primary payload, NASA Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-3 (TDRS-3) attached to an Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), became the second TDRS deployed. After deployment, IUS propelled the satellite to a geosynchronous orbit. The crew consisted of Frederick H. Hauck, Commander; Richard O. Covey, Pilot; John M. Lounge, Mission Specialist 1; George D. Nelson, Mission Specialist 2; and David C. Hilmers, Mission Specialist 3.
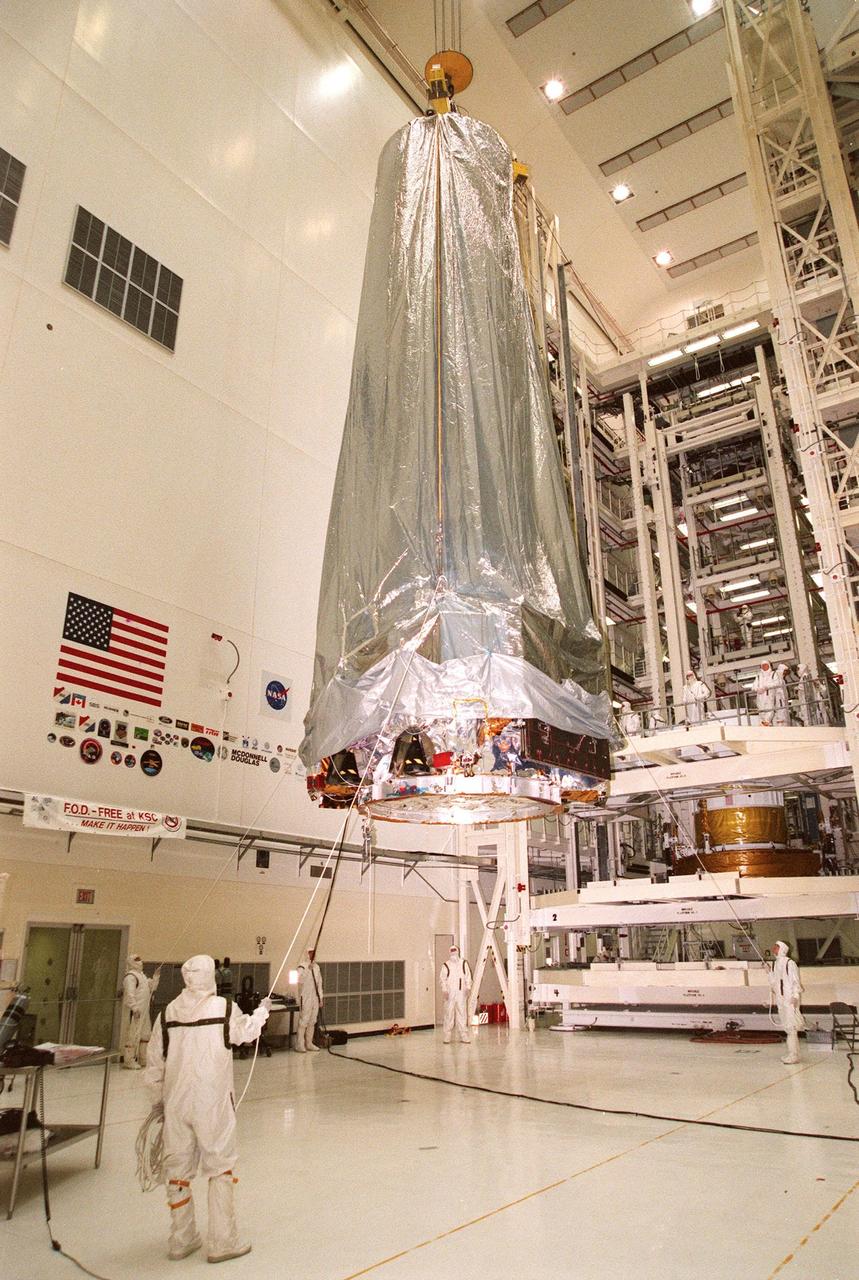

In the Vertical Processing Facility, the Chandra X-ray Observatory is moved toward the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) in a workstand at right. There it will be mated with the IUS and then undergo testing to validate the IUS/Chandra connections and check the orbiter avionics interfaces. Following that, an end-to-end test (ETE) will be conducted to verify the communications path to Chandra, commanding it as if it were in space. With the world's most powerful X-ray telescope, Chandra will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Chandra is scheduled for launch July 22 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia, on mission STS-93
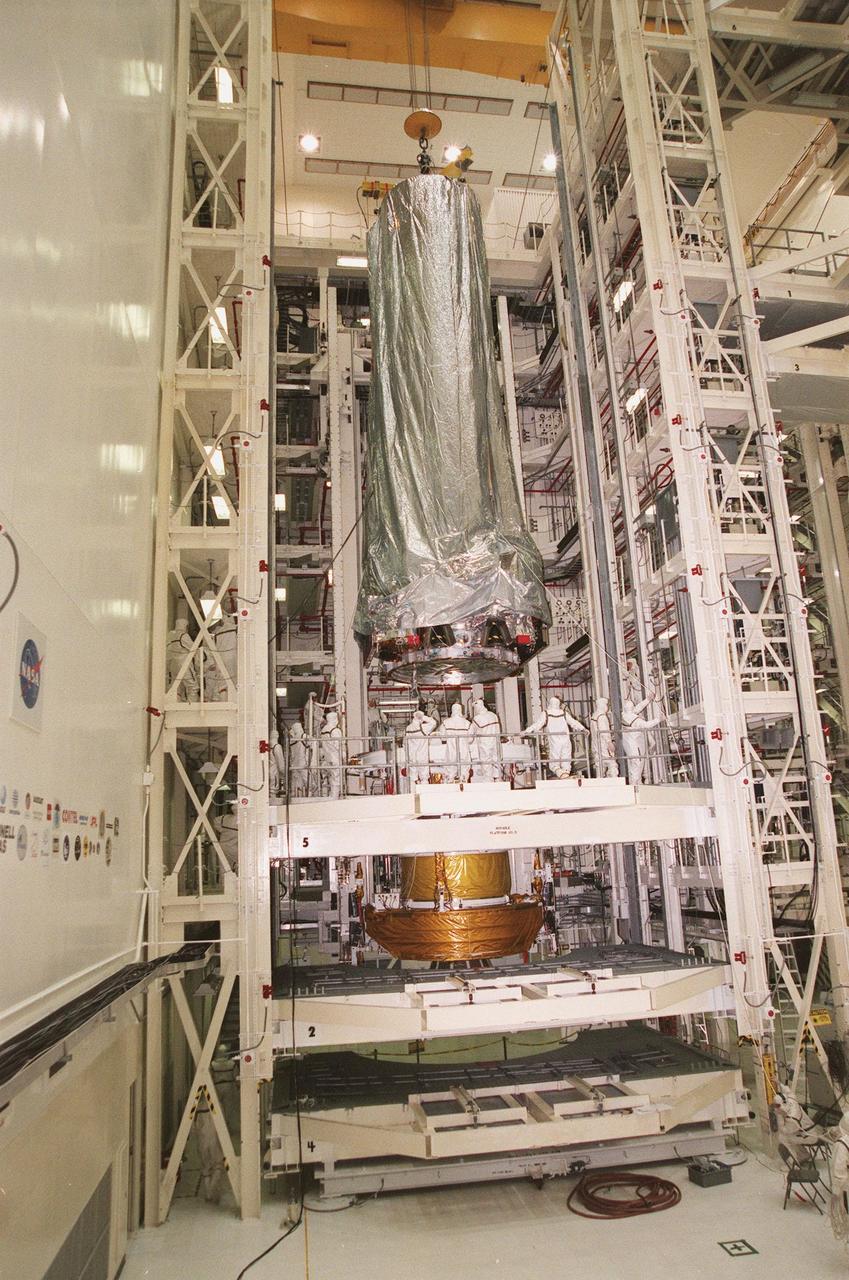

In the Vertical Processing Facility, the Chandra X-ray Observatory is lowered toward the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) in a workstand beneath it. There it will be mated with the IUS and then undergo testing to validate the IUS/Chandra connections and to check the orbiter avionics interfaces. Following that, an end-to-end test (ETE) will be conducted to verify the communications path to Chandra, commanding it as if it were in space. With the world's most powerful X-ray telescope, Chandra will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Chandra is scheduled for launch July 22 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia, on mission STS-93

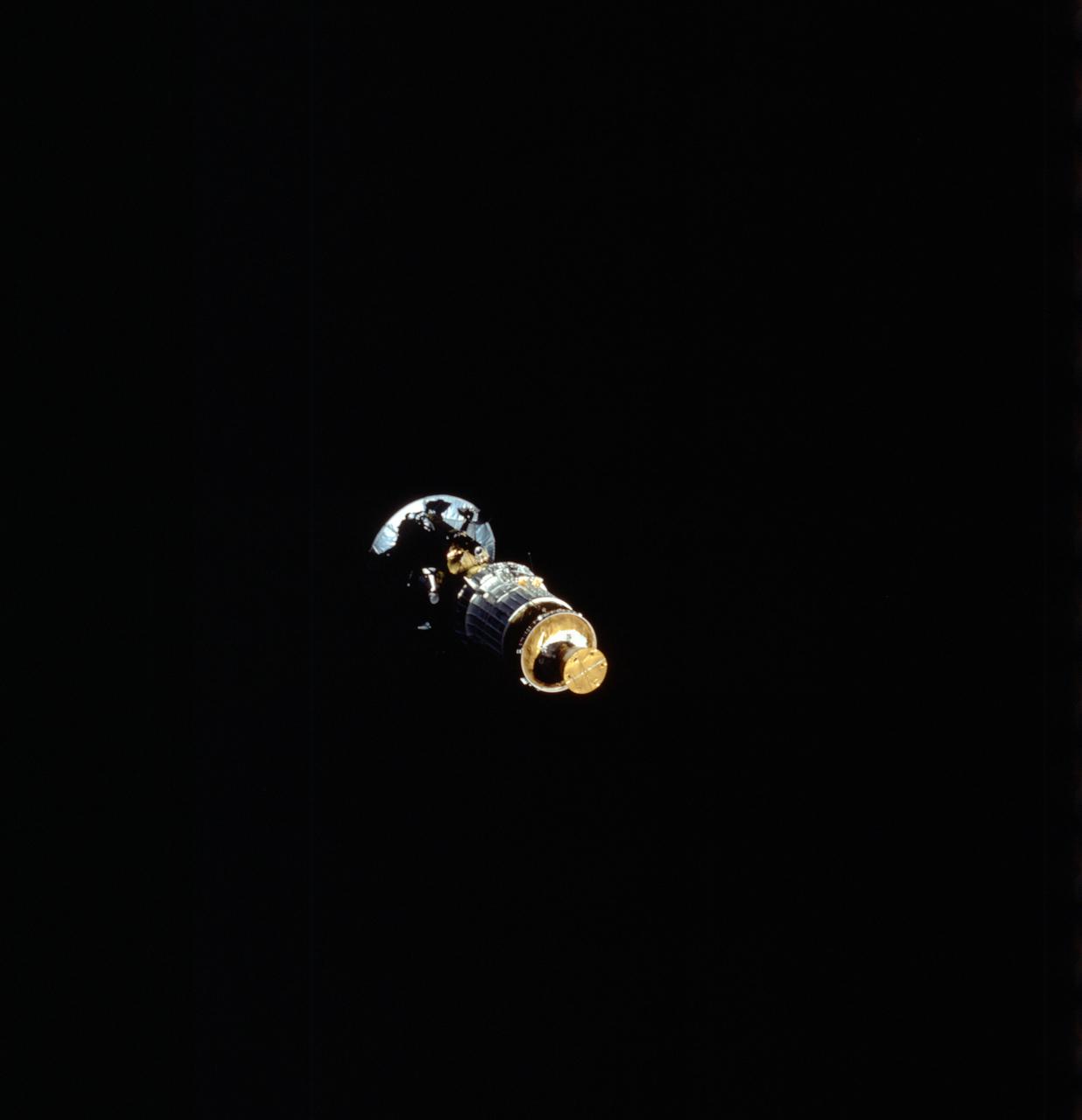
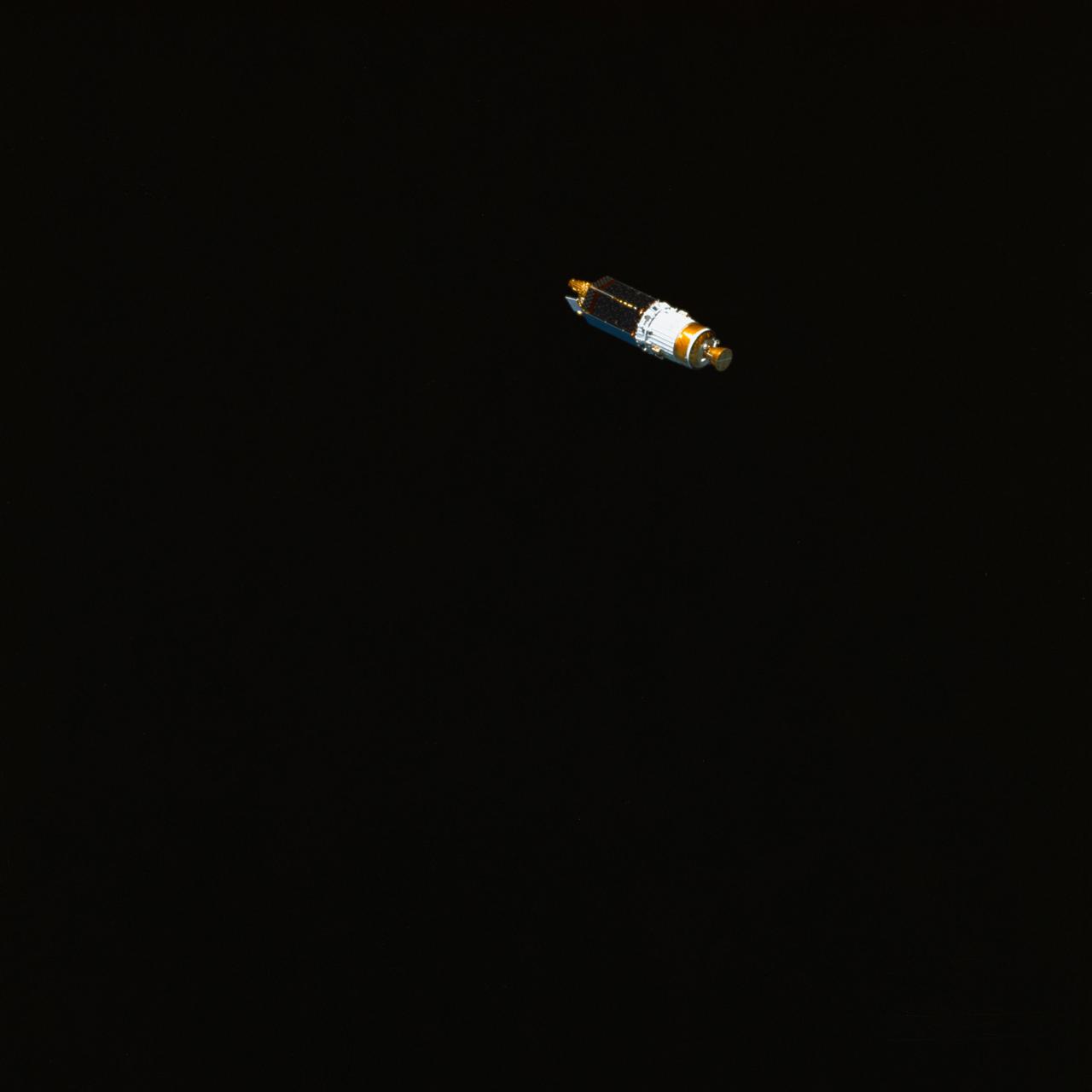
STS034-71-000AK (18 Oct 1989) --- Backdropped against the blackness of space, the Galileo spacecraft and its inertial upper stage (IUS) have just detached from a cradle-like device aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Atlantis to begin a six-year journey to Jupiter. The five-member STS-34 crew deployed the satellite within six hours of achieving Earth orbit on Oct. 18, 1989. The scene was exposed with a 70mm handheld Hasselblad camera. Earth's horizon and a thin line representing its airglow and atmosphere are visible on the left side of the frame.

STS029-78-019 (13 March 1989) --- Headed on its way to a much higher orbit is another Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-D), as photographed with a 70mm camera from inside Discovery's cabin. Moments earlier, the STS-29 crewmembers released the cylindrical form into space from Discovery's cargo bay. When at its final destination high above Earth, TDRS-D will no longer maintain its cylindrical form, having transformed into an operational satellite with antenna spanned out in various directions and its Interim Upper Stage (IUS), covered with gold foil and forward-most in this frame, discarded.

The THEMIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows the northern tip of Baetis Mensa. In false color images dark blue is often basaltic sands. In this image it is possible to trace the sands from the erosion of Beatis Mensa moving down the canyon gullies to the floor of Ophir Chasma. Orbit Number: 42247 Latitude: -4.17728 Longitude: 287.975 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2011-06-23 21:11 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20792

A crew member of the STS-93 mission took this photograph of the Chandra X-Ray Observatory, still attached to the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), backdropped against the darkness of space not long after its release from Orbiter Columbia. Two firings of an attached IUS rocket placed the Observatory into its working orbit. The primary duty of the crew of this mission was to deploy the 50,162-pound Observatory, the world's most powerful x-ray telescope.
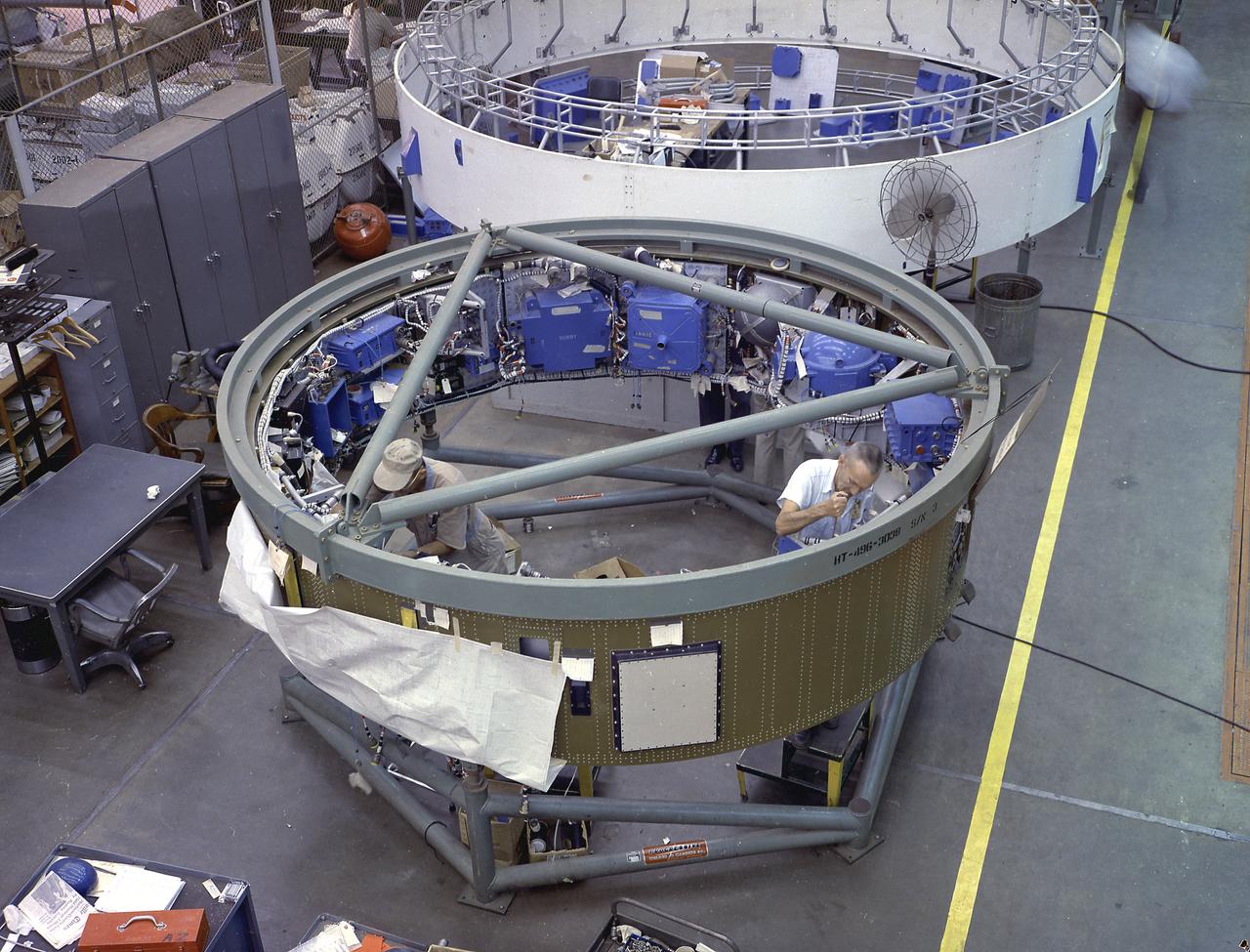
This image depicts a high angle view of technicians working on the instrument unit (IU) component assembly for the SA-8 mission in Marshall Space Flight Center's building 4705. A thin, circular structure, only 1-meter high and 7.6 meters in diameter, the IU was sandwiched between the S-IV and Apollo spacecraft. Packed inside were the computers, gyroscopes, and assorted black boxes necessary to keep the launch vehicle properly functioning and on its course.
S95-08962 (12 APRIL 1995) --- Members of the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Payload Processing Team hoist the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-G) into a work stand in the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF) for mating with its Inertial Upper Stage (IUS). After testing and final checkout, TDRS-G and the IUS will be transported to Launch Pad 39B and installed into the Space Shuttle Discovery's payload bay for launch on the STS-70 mission, scheduled for launch June 8, 1995.

The Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) booster (right) is lifted out of its container after arriving at Kennedy Space Center's Vertical Processing Facility. The IUS will be mated with the Chandra X-ray Observatory (at left) and then undergo testing to validate the IUS/Chandra connections and check the orbiter avionics interfaces. Following that, an end-to-end test (ETE) will be conducted to verify the communications path to Chandra, commanding it as if it were in space. With the world's most powerful X-ray telescope, Chandra will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Chandra is scheduled for launch July 22 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia, on mission STS-93
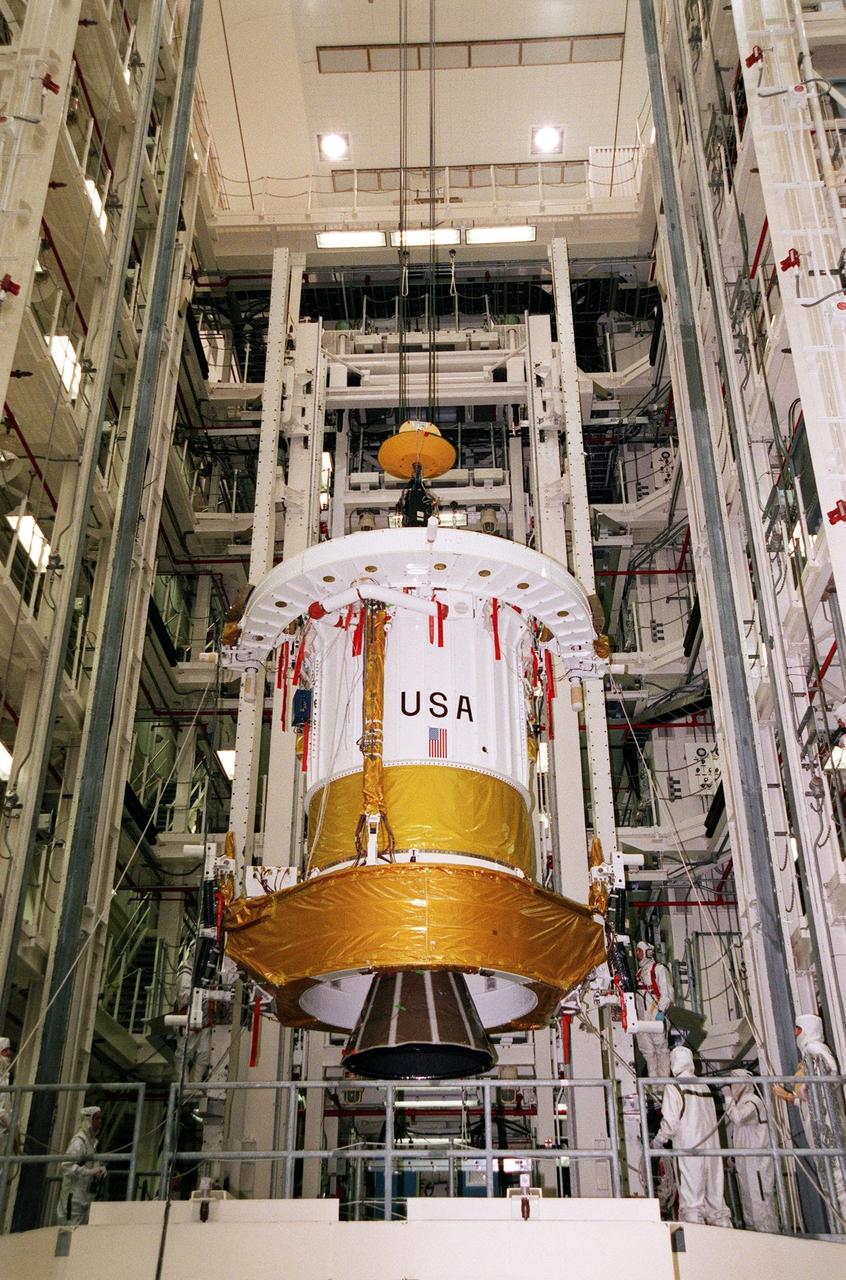

The Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) booster is lowered toward a workstand in Kennedy Space Center's Vertical Processing Facility. The IUS will be mated with the Chandra X-ray Observatory and then undergo testing to validate the IUS/Chandra connections and check the orbiter avionics interfaces. Following that, an end-to-end test (ETE) will be conducted to verify the communications path to Chandra, commanding it as if it were in space. With the world's most powerful X-ray telescope, Chandra will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Chandra is scheduled for launch July 22 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia, on mission STS-93
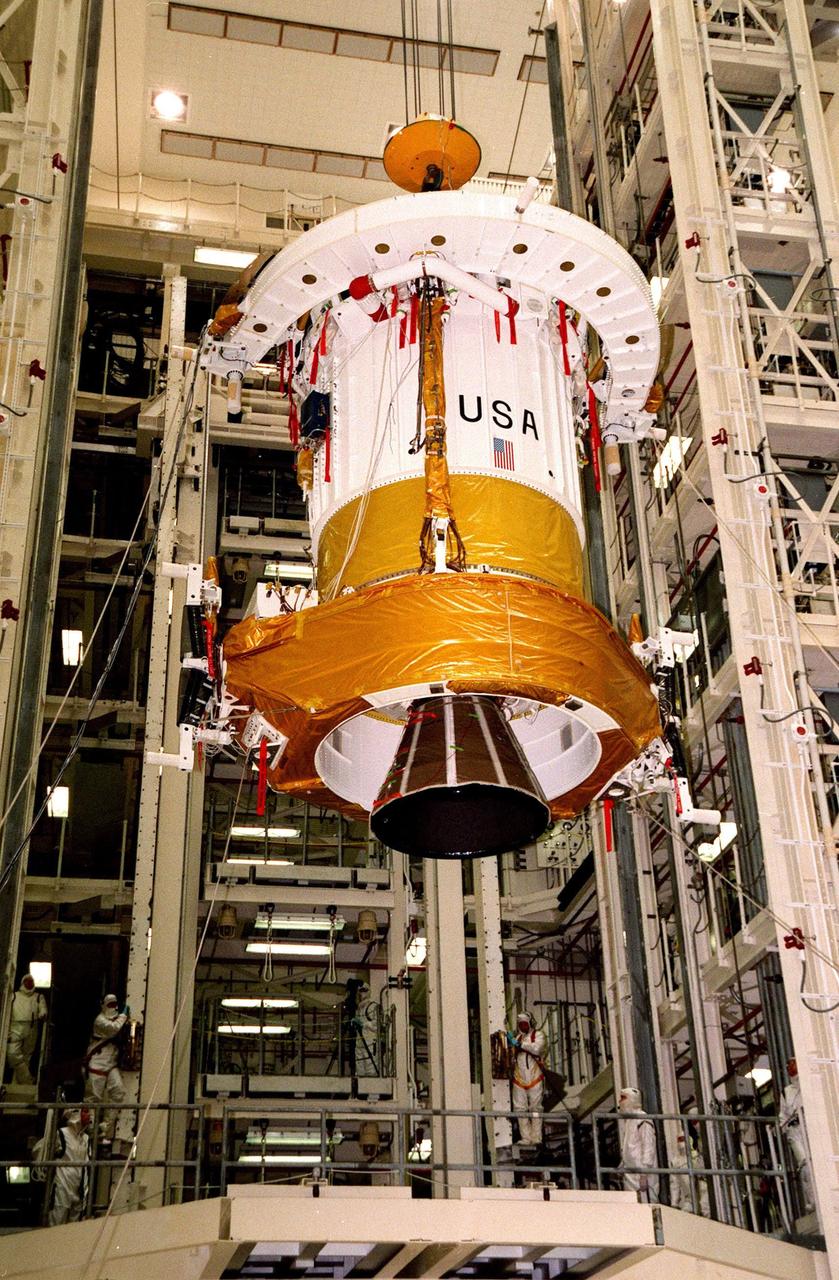

The Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) booster is moved toward a workstand in Kennedy Space Center's Vertical Processing Facility. The IUS will be mated with the Chandra X-ray Observatory and then undergo testing to validate the IUS/Chandra connections and check the orbiter avionics interfaces. Following that, an end-to-end test (ETE) will be conducted to verify the communications path to Chandra, commanding it as if it were in space. With the world's most powerful X-ray telescope, Chandra will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Chandra is scheduled for launch July 22 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia, on mission STS-93
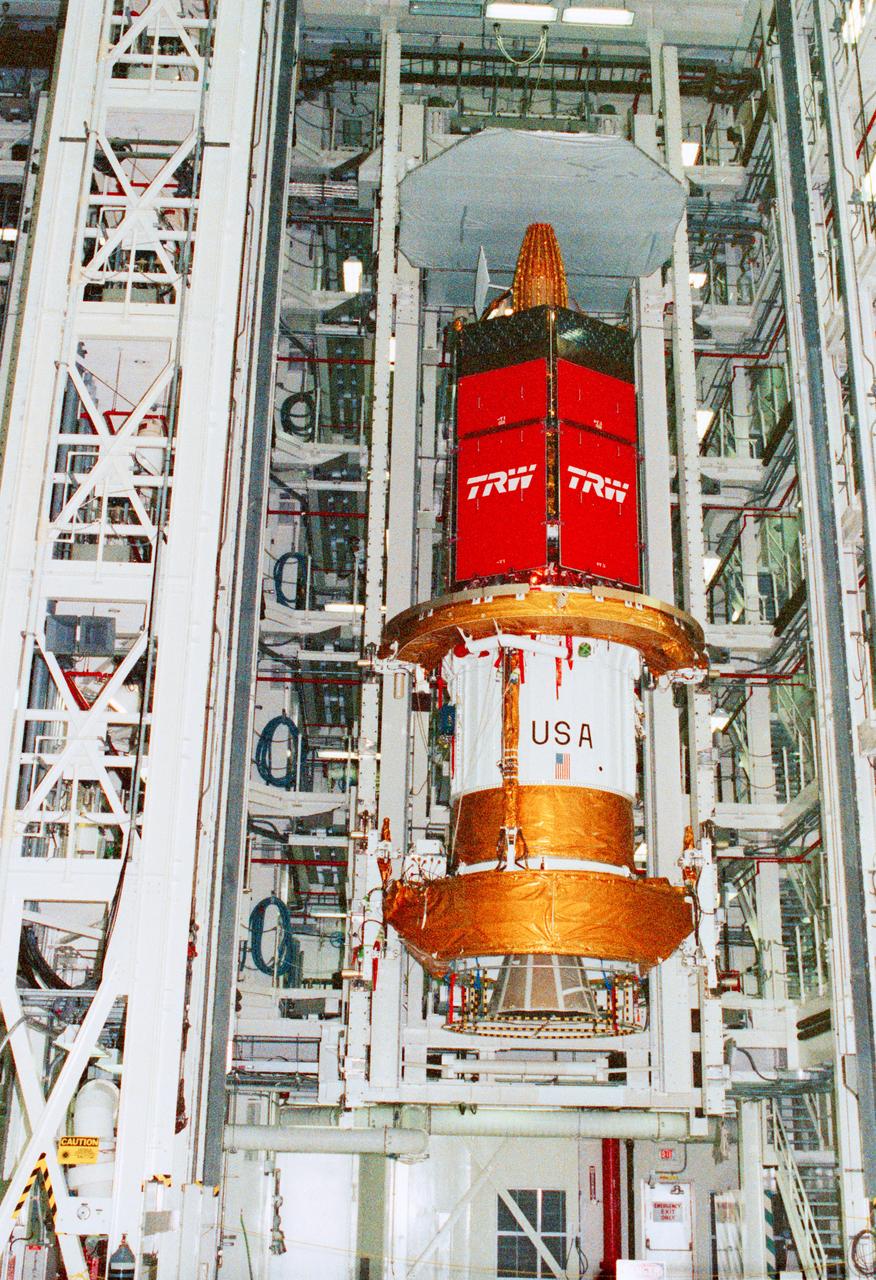
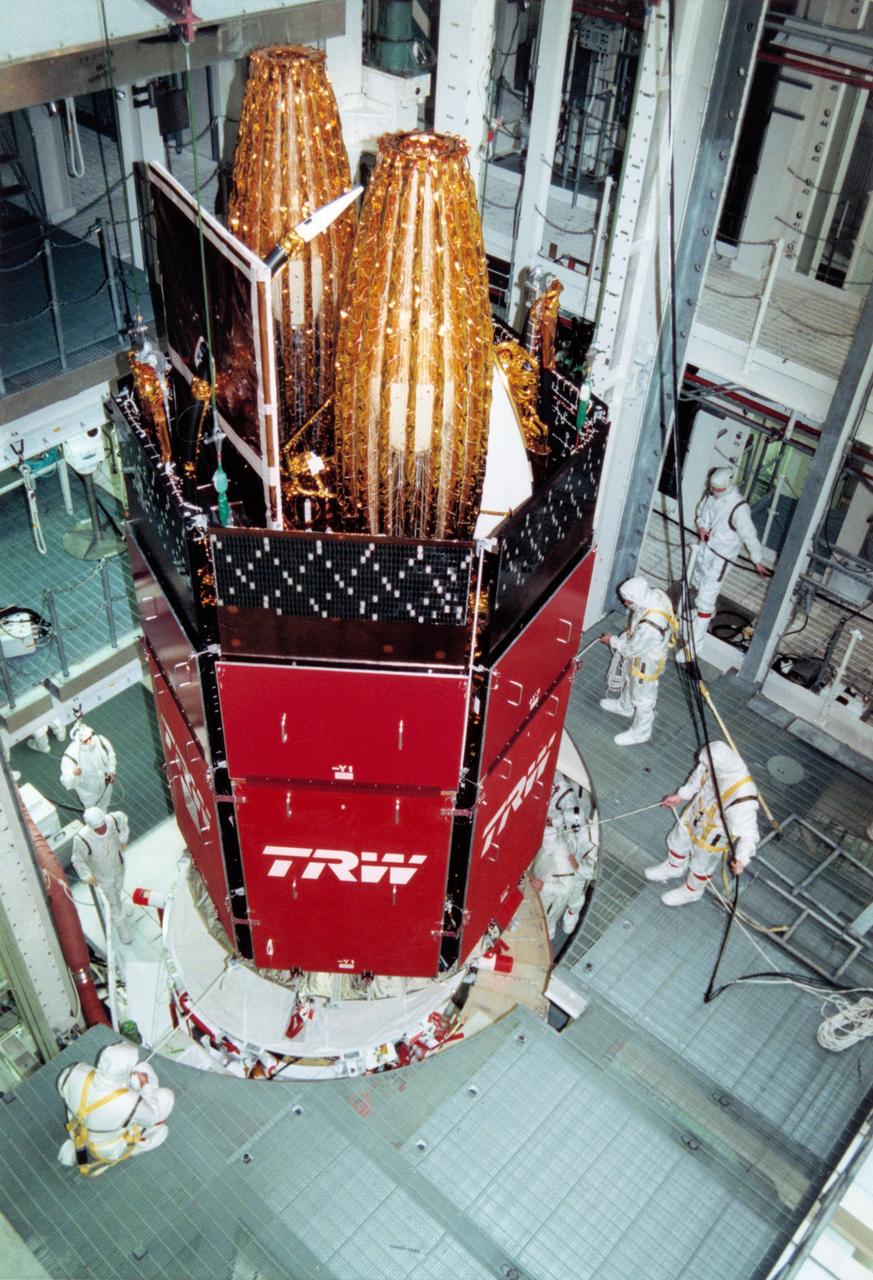
STS-43 Tracking and Data Relay Satellite E (TDRS-E) undergoes preflight processing in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC's) Vertical Processing Facility (VPF) before being loaded into a payload canister for transfer to the launch pad and eventually into Atlantis', Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104's, payload bay (PLB). This side of the TDRS-E will rest at the bottom of the PLB therefore the airborne support equipment (ASE) forward frame keel pin (at center of spacecraft) and the umbilical boom running between the two ASE frames are visible. The solar array panels are covered with protective TRW shields. Above the shields the stowed antenna and solar sail are visible. The inertial upper stage (IUS) booster is the white portion of the spacecraft and rests in the ASE forward frame and ASE aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) frame (at the bottom of the IUS). The IUS booster nozzle extends beyond the AFTA frame. View provided by KSC with alternate number KSC-91PC-1079.

S89-28093 (29 Dec 1988) --- In the clean room of the vertical processing facility, the TDRS-D satellite is hoisted, thus beginning the mating process with the inertial upper stage (IUS), located in an adjacent test cell.
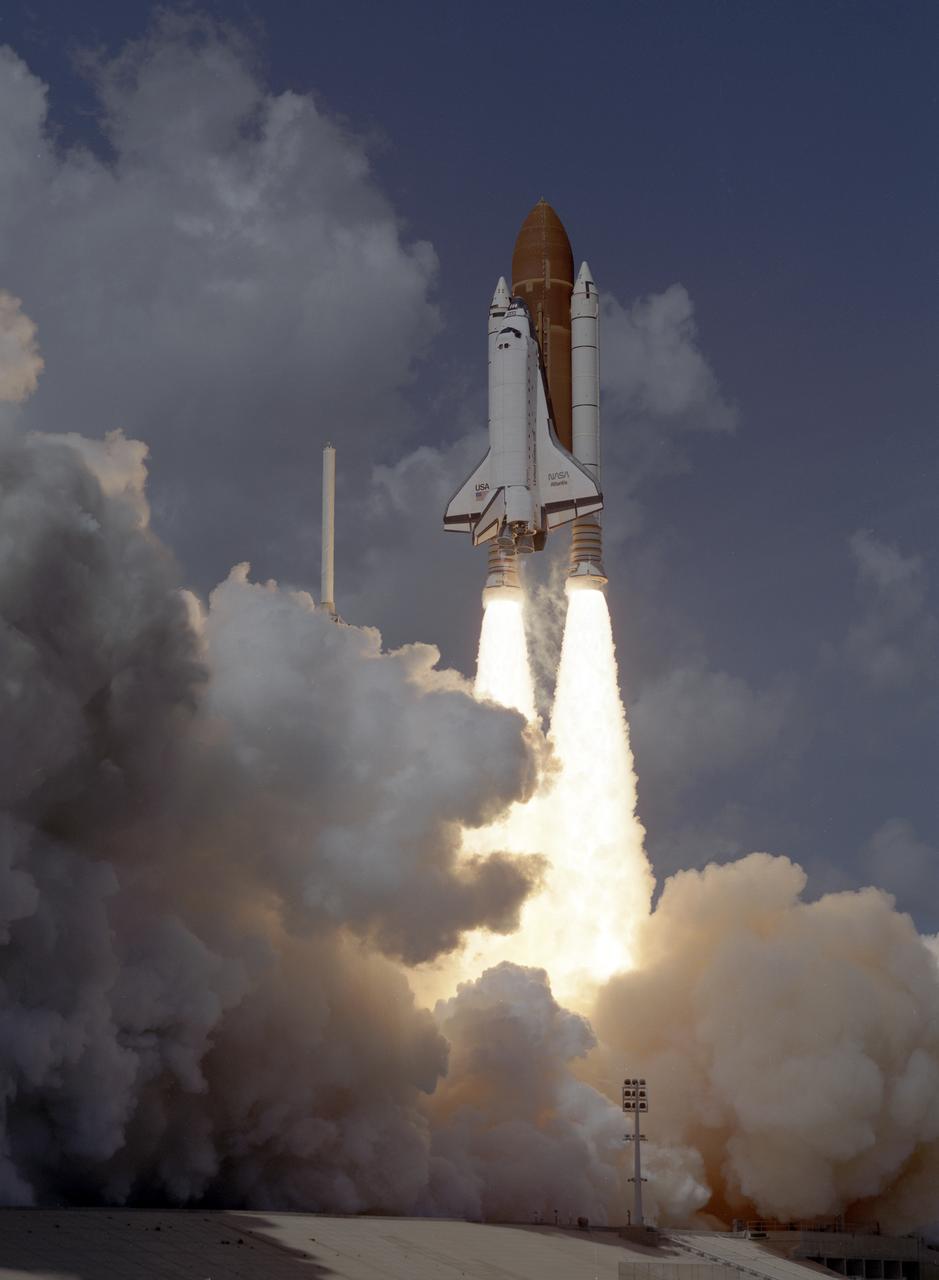

The STS-34 crew of five launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis on October 18, 1989 at 12:53:40pm (EDT). Crew members included commander Donald E. Williams, pilot Michael J. McCulley; and mission Specialists Shannon W. Lucid, Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, and Ellen S. Baker. The primary payload was the Galileo Jupiter Spacecraft and attached Inertial Upper Stage (IUS). Deployed 6 hours and 30 minutes into the flight, the IUS stages fired boosting Galileo on trajectory for a 6 year trip to Jupiter.
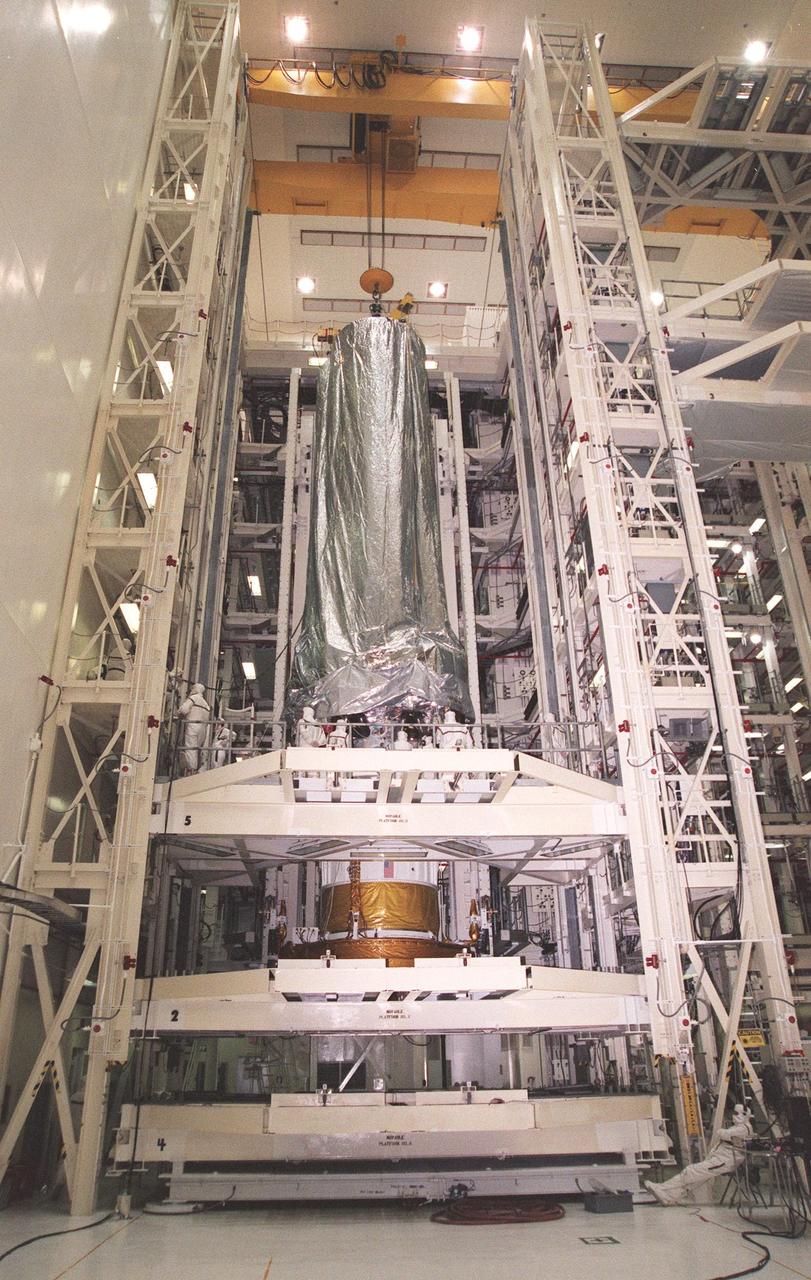

In the Vertical Processing Facility, the Chandra X-ray Observatory is lowered onto the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) beneath it. After the two components are mated, they will undergo testing to validate the IUS/Chandra connections and to check the orbiter avionics interfaces. Following that, an end-to-end test (ETE) will be conducted to verify the communications path to Chandra, commanding it as if it were in space. With the world's most powerful X-ray telescope, Chandra will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Chandra is scheduled for launch July 22 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia, on mission STS-93
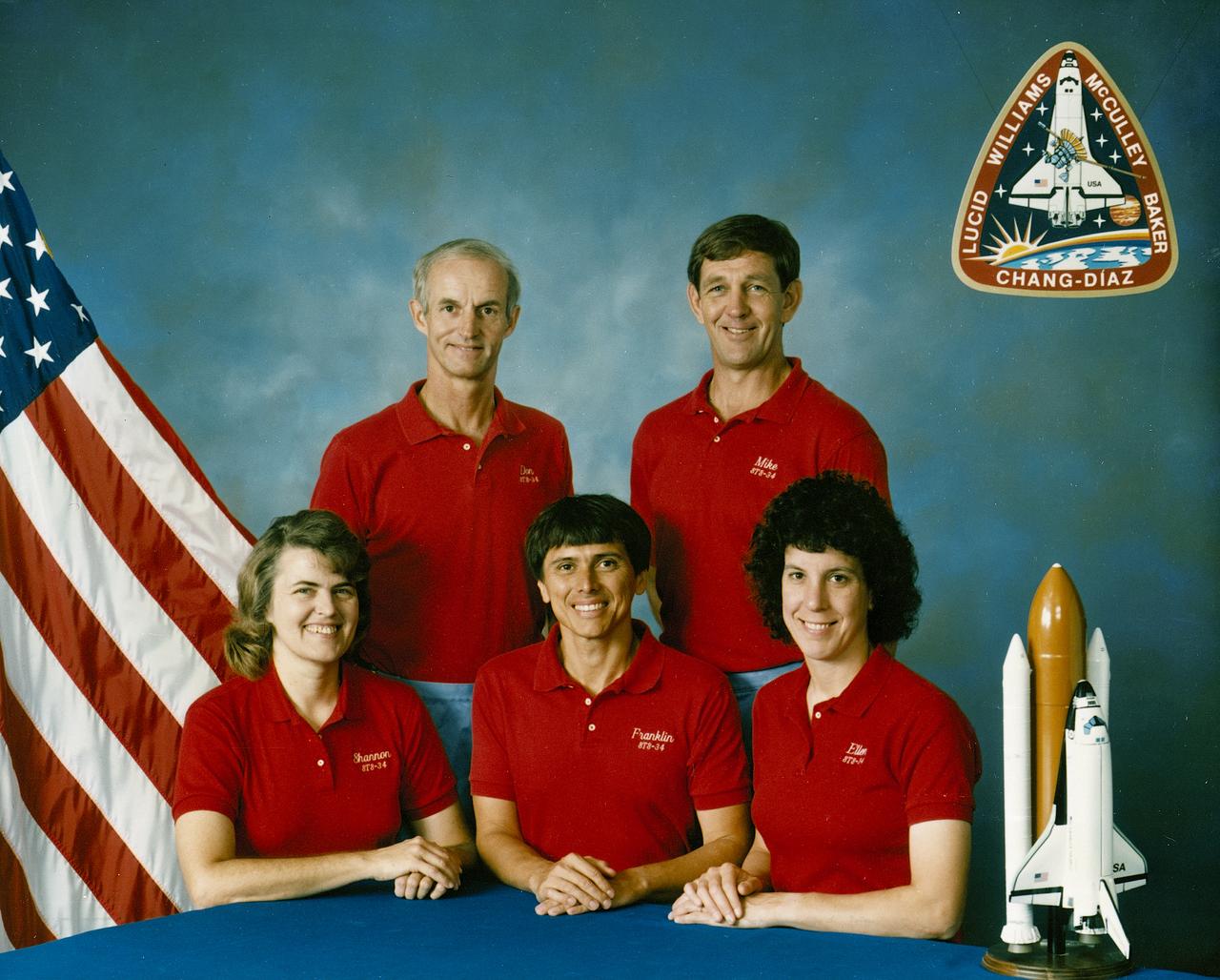

The STS-34 crew portrait includes 5 astronauts. Pictured left to right are Shannon W. Lucid, mission specialist; Donald E. Williams, commander; Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, mission specialist; Michael J. McCulley, pilot; and Ellen S. Baker, mission secialist. The crew of 5 launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis on October 18, 1989 at 12:53:40pm (EDT). The primary payload was the Galileo Jupiter Spacecraft and attached inertial upper stage (IUS). Deployed 6 hours and 30 minutes into the flight, the IUS stages fired, boosting Galileo on trajectory for a 6 year trip to Jupiter.

The STS-34 crew of five launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis on October 18, 1989 at 12:53:40pm (EDT). Crew members included commander Donald E. Williams, pilot Michael J. McCulley, and mission Specialists Shannon W. Lucid, Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, and Ellen S. Baker. The primary payload was the Galileo Jupiter Spacecraft and attached Inertial Upper Stage (IUS). Deployed 6 hours and 30 minutes into the flight, the IUS stages fired boosting Galileo on trajectory for a 6 year trip to Jupiter.
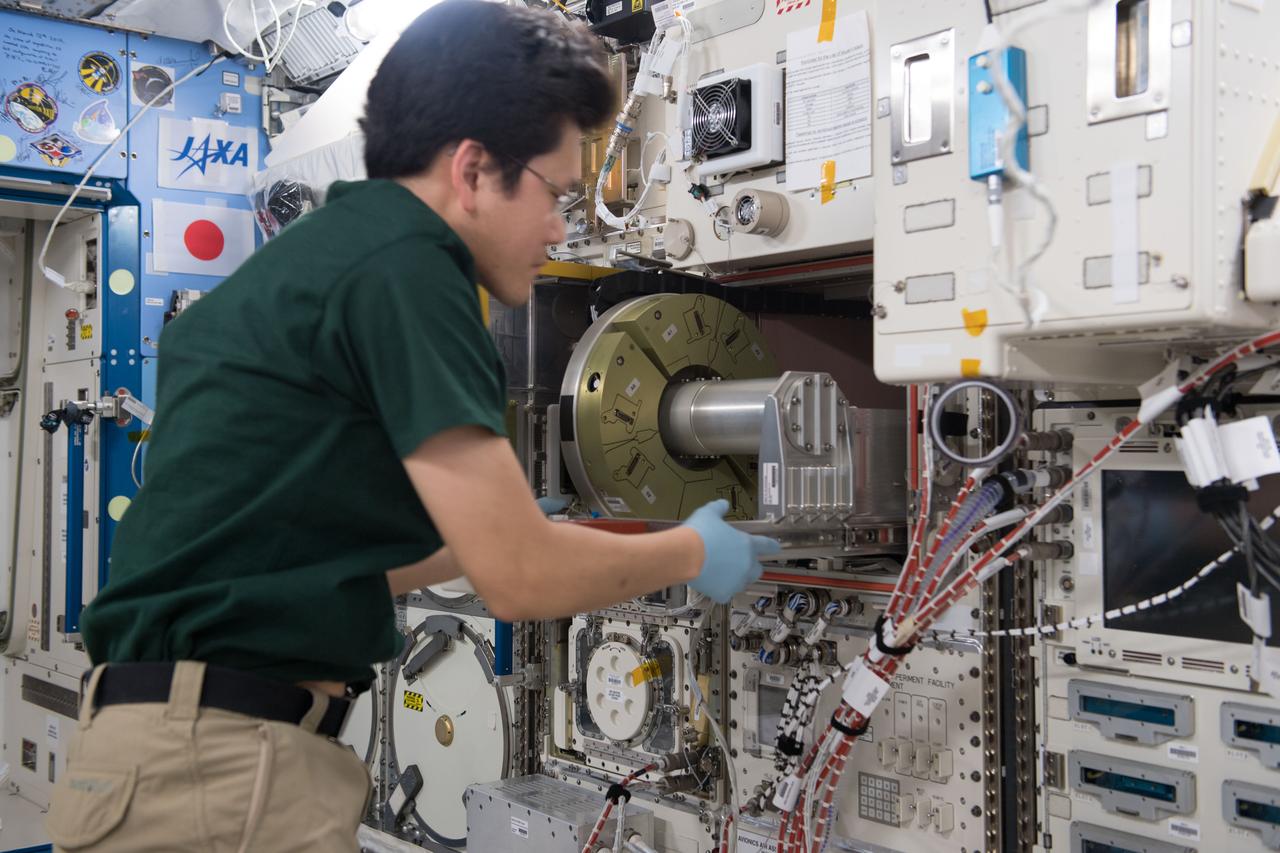

iss054e032753 (2/2/2018) --- A view of Japanese Aerospace Agency (JAXA) astronaut Norishige Kanai working to install Mouse Habitat Unit (MHU) Interface (I/F) Units in Cell Biology Experiment Facility (CBEF) Incubator Units (IUs). Photo was taken in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Pressurized Module (JPM).

S89-27381 (29 Dec 1988) --- Technicians and engineers in the Kennedy Space Center's Vertical Processing Facility clean room prepare to participate in the mating of the STS 29 tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS-D) with its inertial upper stage (IUS-9, out of frame).
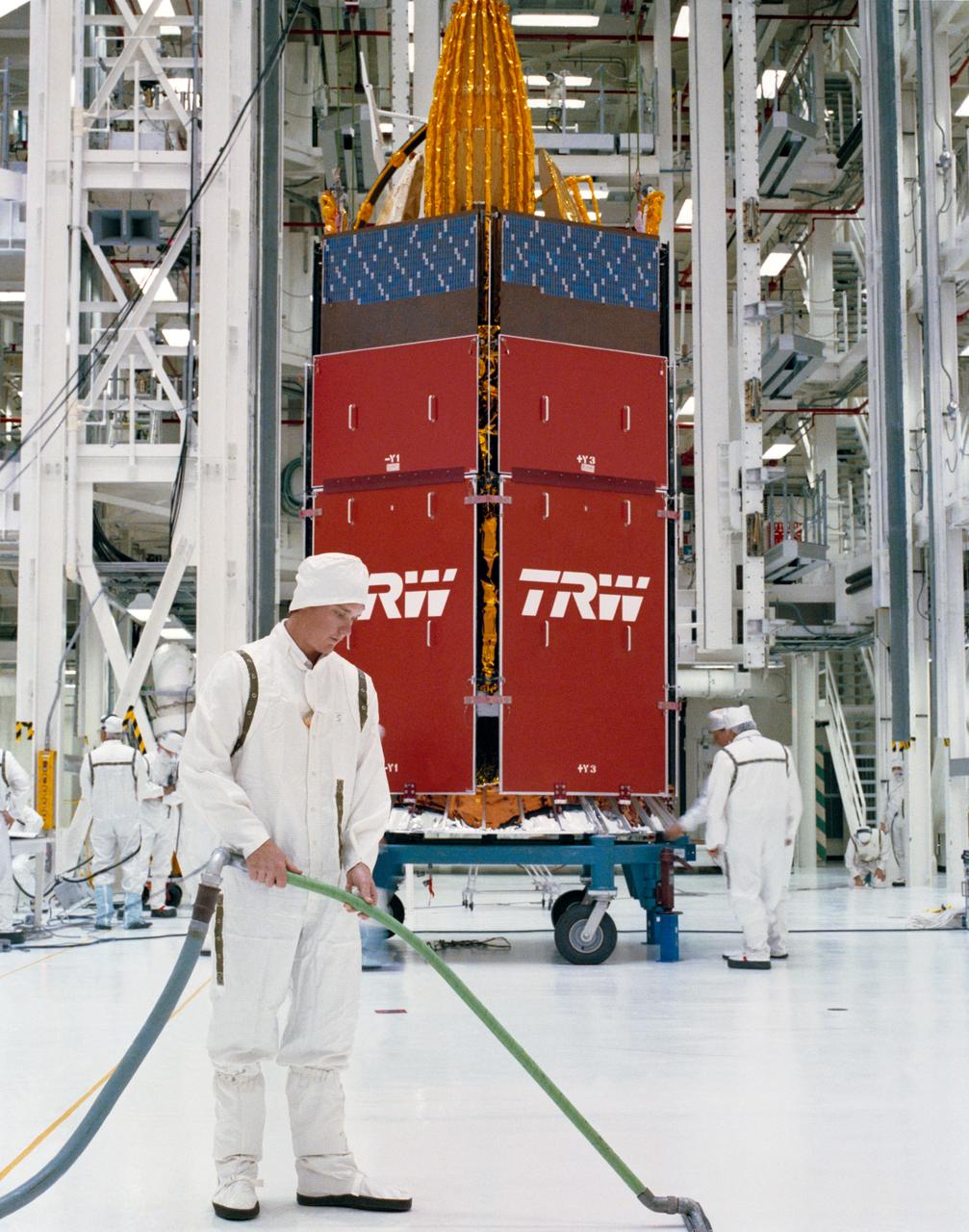

S89-27382 (29 Dec 1988) --- Technicians and engineers in the Kennedy Space Center's Vertical Processing Facility prepare to participate in the mating of the STS-29 tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS-D) with its inertial upper stage (IUS-9, out of frame).
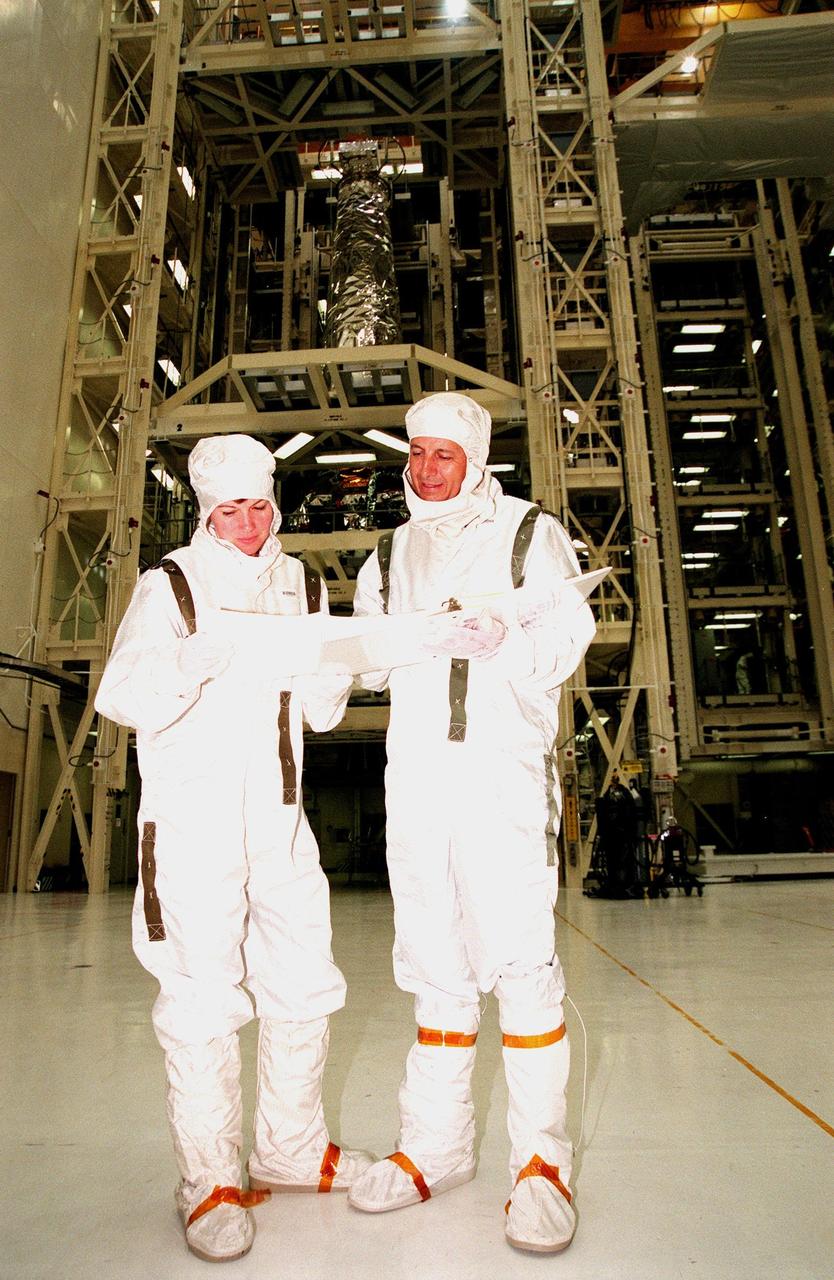

STS-93 Mission Specialists Catherine Coleman (left) and Michel Tognini of France (right), representing the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), look over material on the mission payload behind them, the Chandra X-ray Observatory. Chandra is being mated with the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) before testing to validate the IUS/Chandra connections and to check the orbiter avionics interfaces. Following that, an end-to-end test (ETE) will be conducted to verify the communications path to Chandra, commanding it as if it were in space. With the world's most powerful X-ray telescope, Chandra will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Chandra is scheduled for launch July 22 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia, on mission STS-93
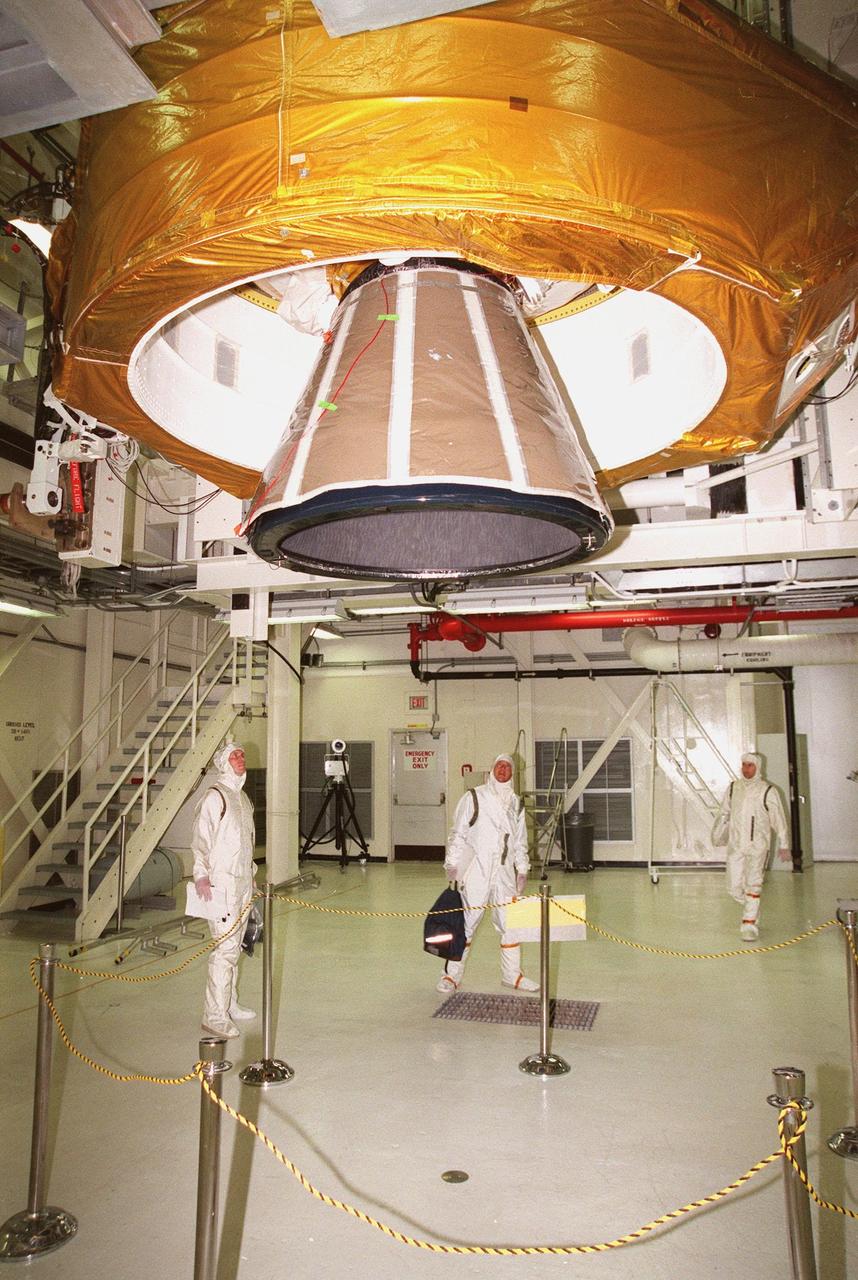

Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility observe the lower end of the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) that will be mated with the Chandra X-ray Observatory (out of sight above it). After the two components are mated, they will undergo testing to validate the IUS/Chandra connections and to check the orbiter avionics interfaces. Following that, an end-to-end test (ETE) will be conducted to verify the communications path to Chandra, commanding it as if it were in space. With the world's most powerful X-ray telescope, Chandra will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Chandra is scheduled for launch July 22 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia, on mission STS-93
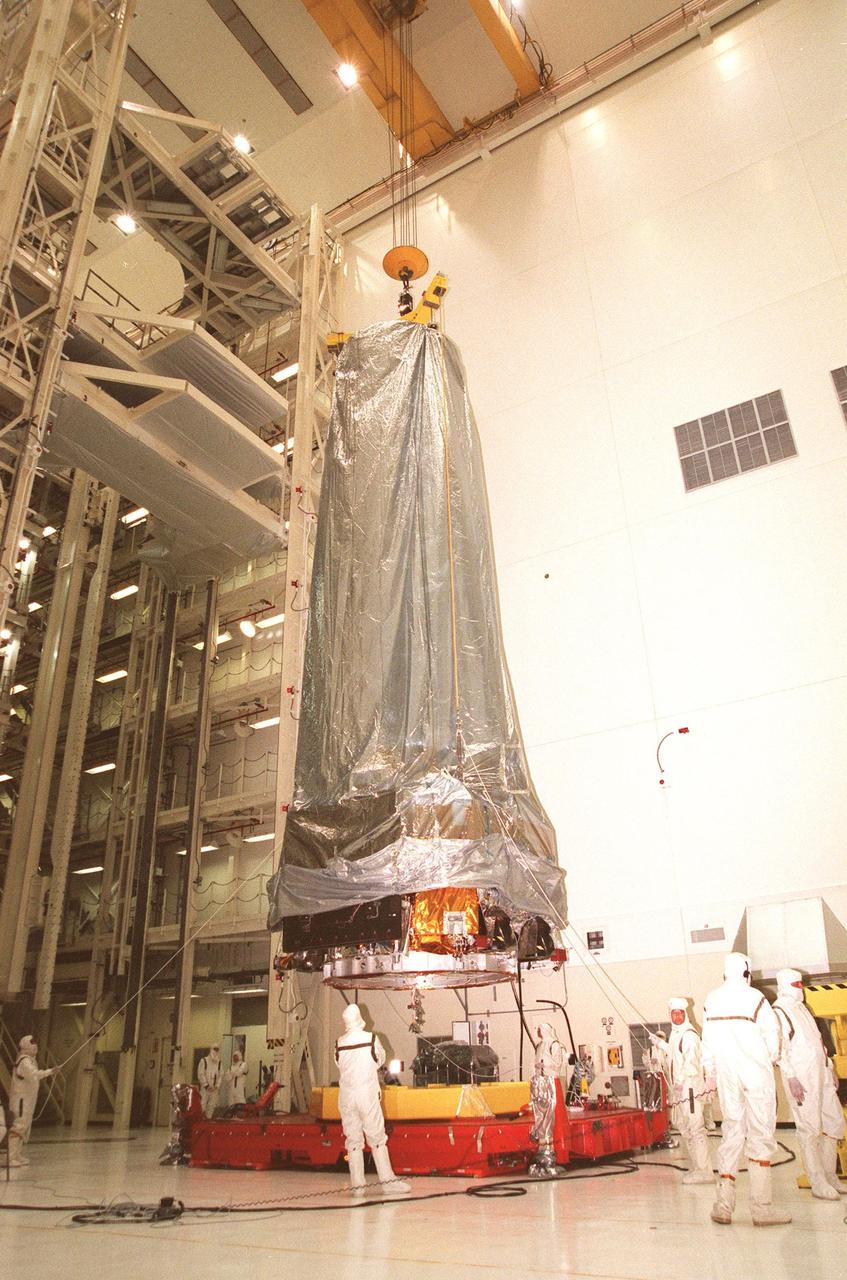

In the Vertical Processing Facility, the Chandra X-ray Observatory is lifted from its workstand in order to move it to the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) nearby. After being mated, the two components will then undergo testing to validate the IUS/Chandra connections and check the orbiter avionics interfaces. Following that, an end-to-end test (ETE) will be conducted to verify the communications path to Chandra, commanding it as if it were in space. With the world's most powerful X-ray telescope, Chandra will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe. Chandra is scheduled for launch July 22 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia, on mission STS-93