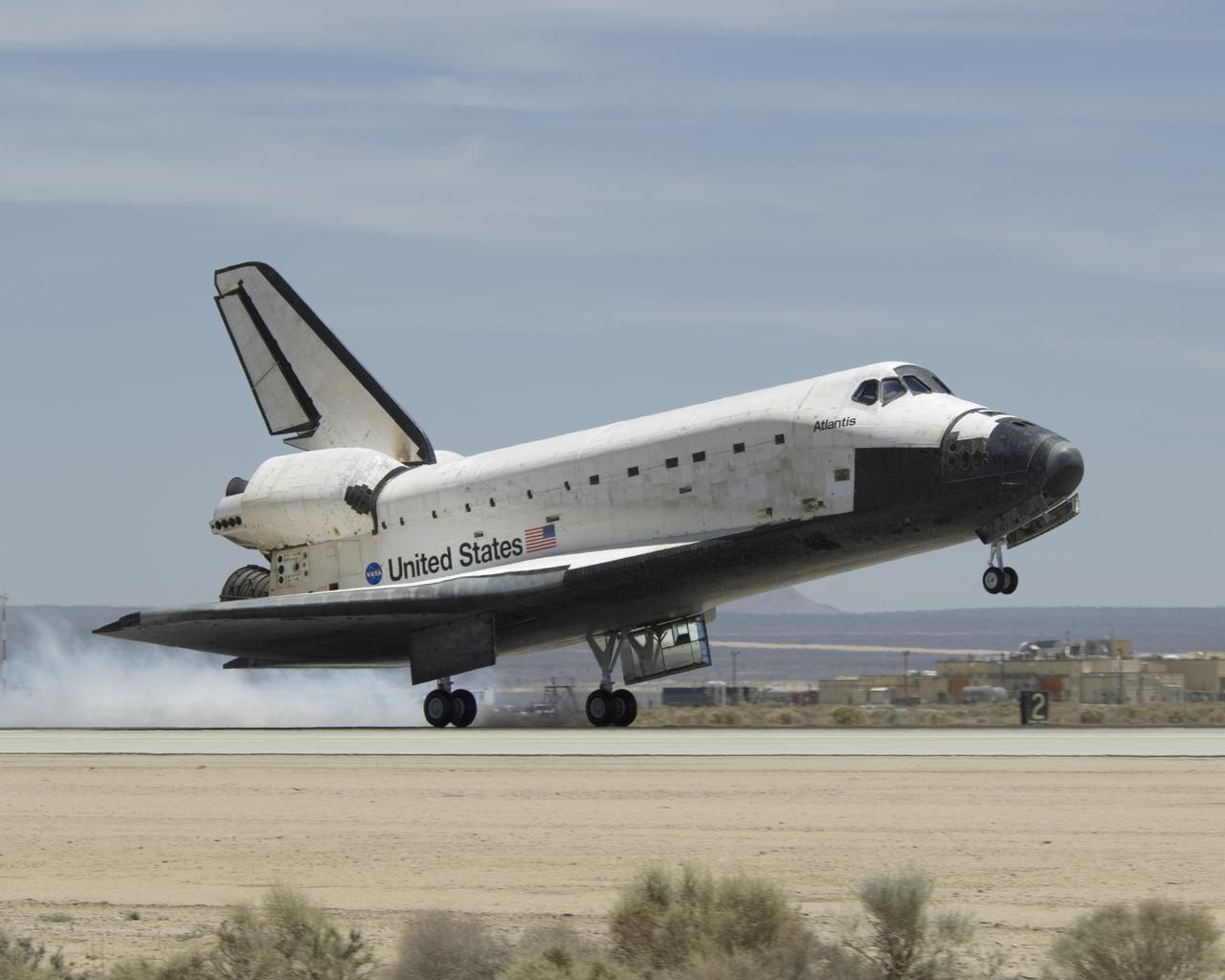

The Space Shuttle Atlantis touches down at Edwards AFB on June 22, 2007, to conclude International Space Station construction and supply mission STS-117.
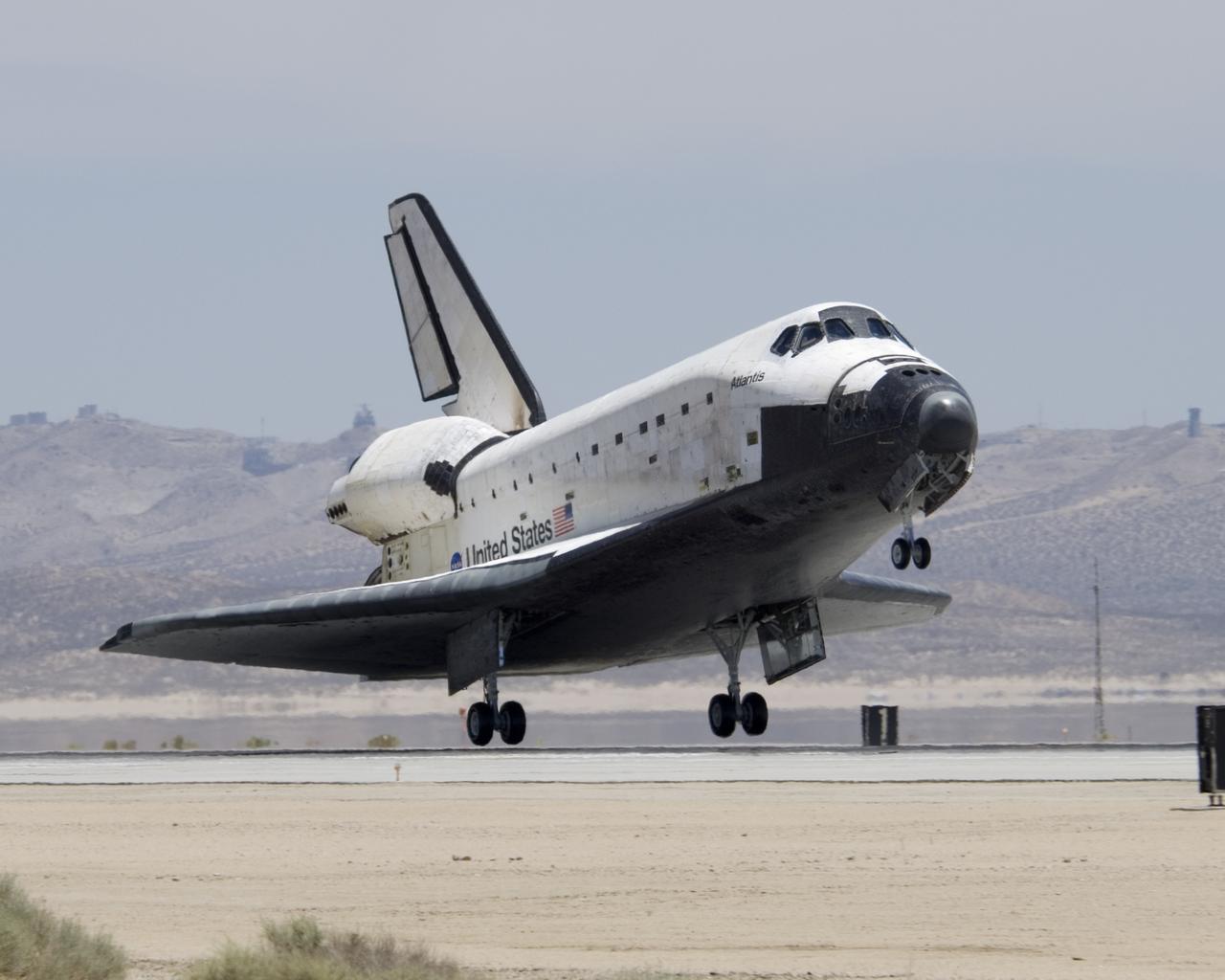

The Space Shuttle Atlantis touches down at Edwards AFB on June 22, 2007, to conclude International Space Station construction and supply mission STS-117.
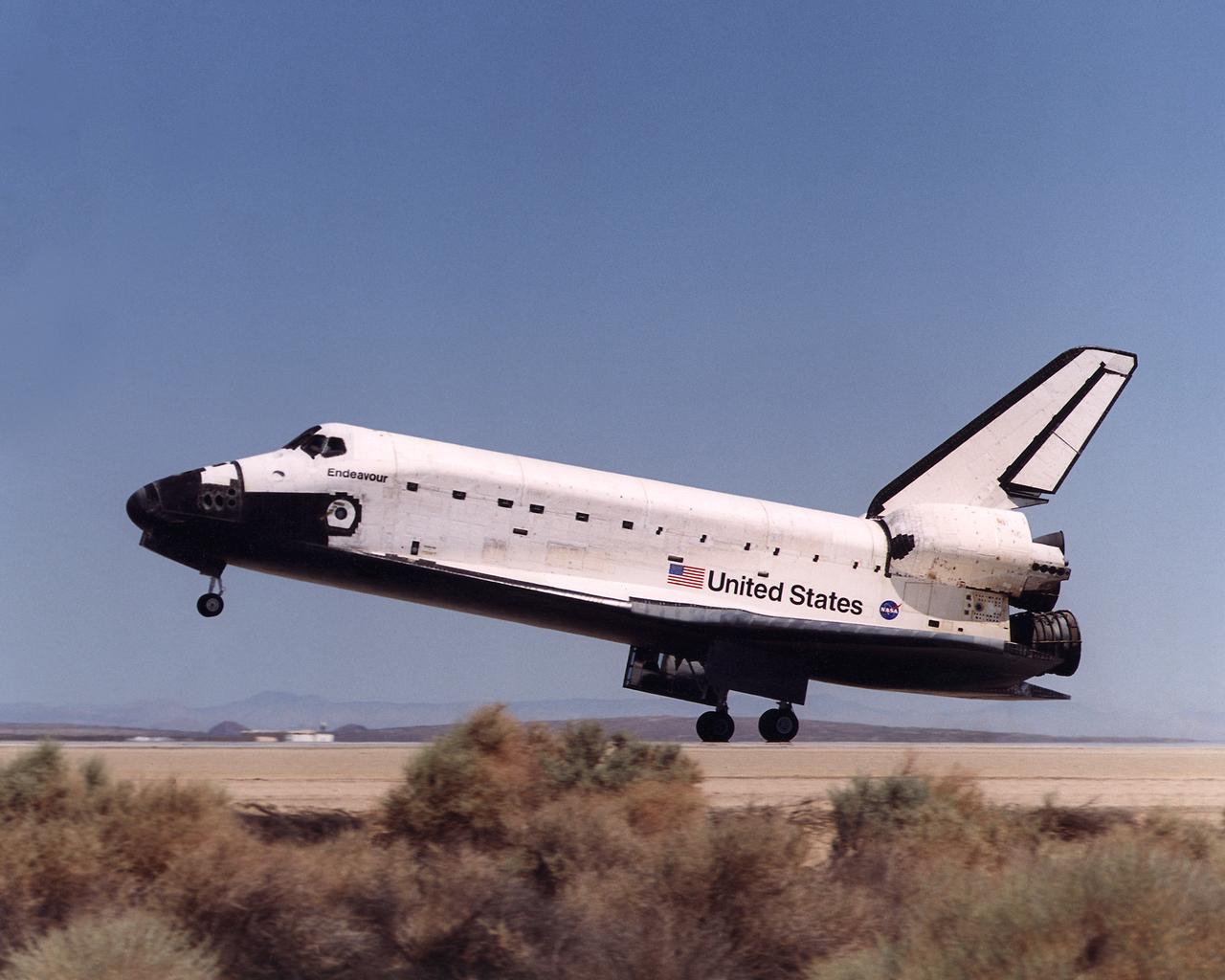

Space Shuttle Endeavour touches down on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, California to conclude International Space Station construction and supply mission STS-111.
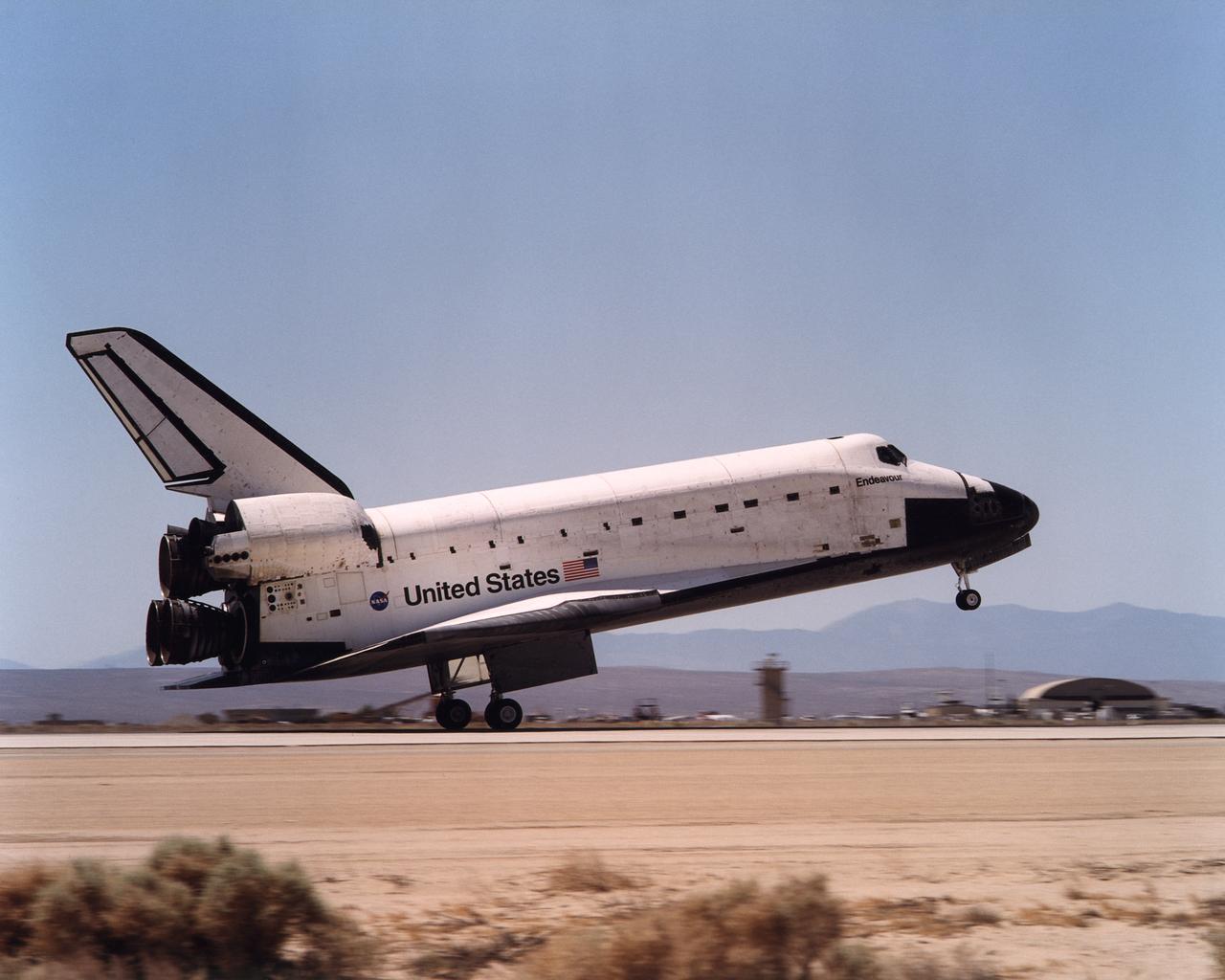

Space Shuttle Endeavour touches down on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, California to conclude International Space Station construction and supply mission STS-111.
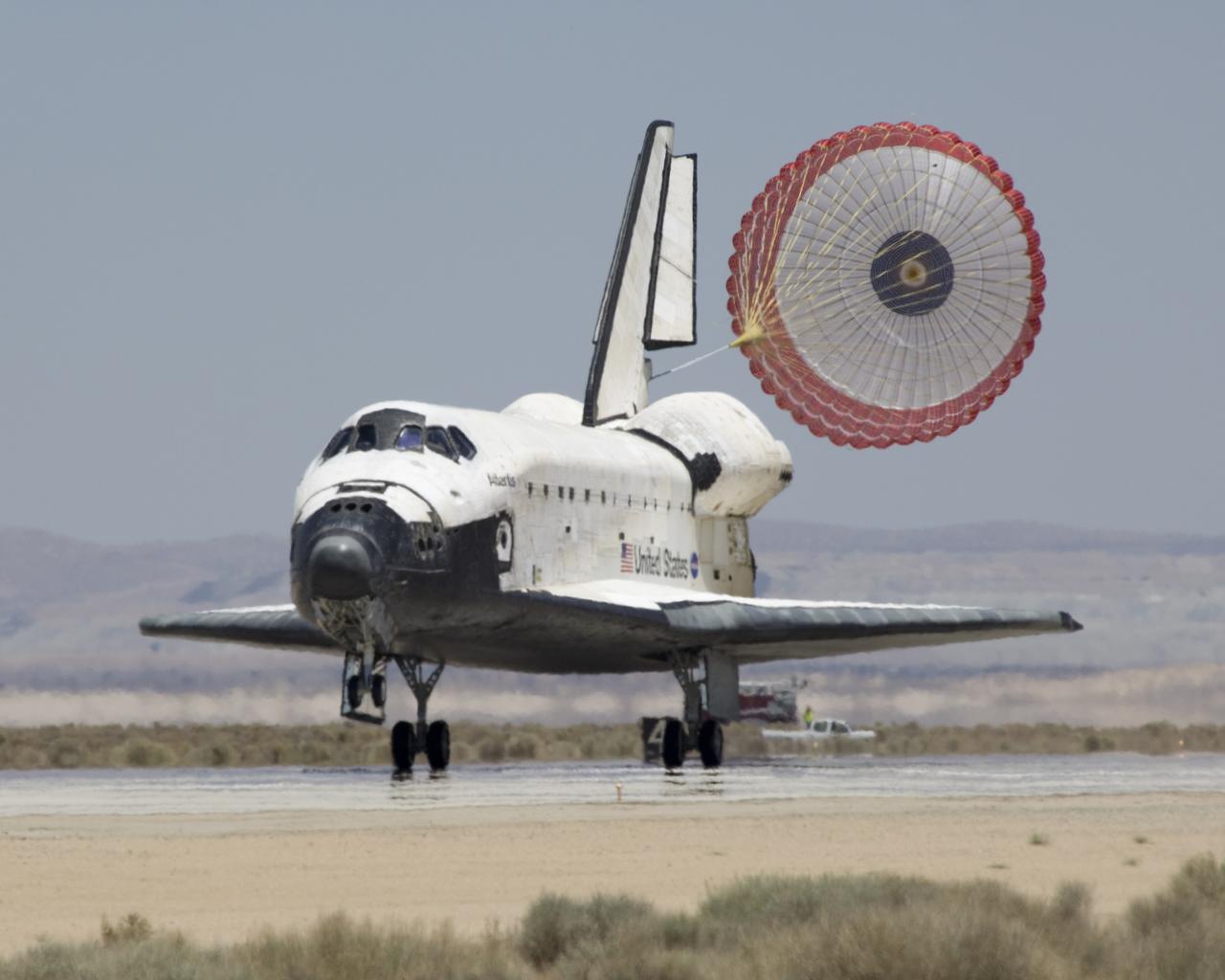

The Space Shuttle Atlantis' drag chute deploys as it rolls out on Runway 22 at Edwards AFB at the conclusion of its 13-day STS-117 mission to the ISS.
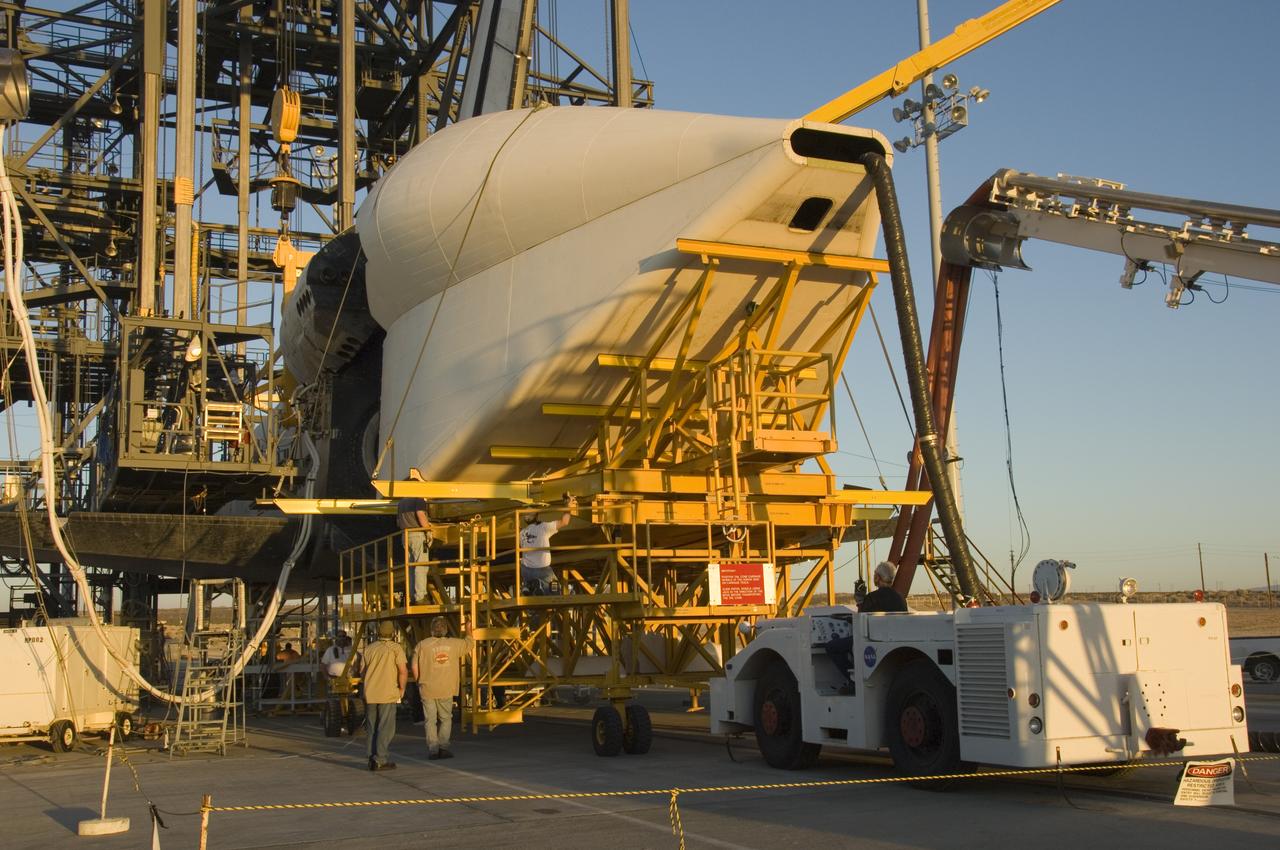

Technicians attach the tail cone, which helps reduce aerodynamic drag and turbulence during its ferry flight, to the Space Shuttle Atlantis in preparation for its return to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After the tail-cone is installed, Discovery will be mounted on NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, for the return flight.
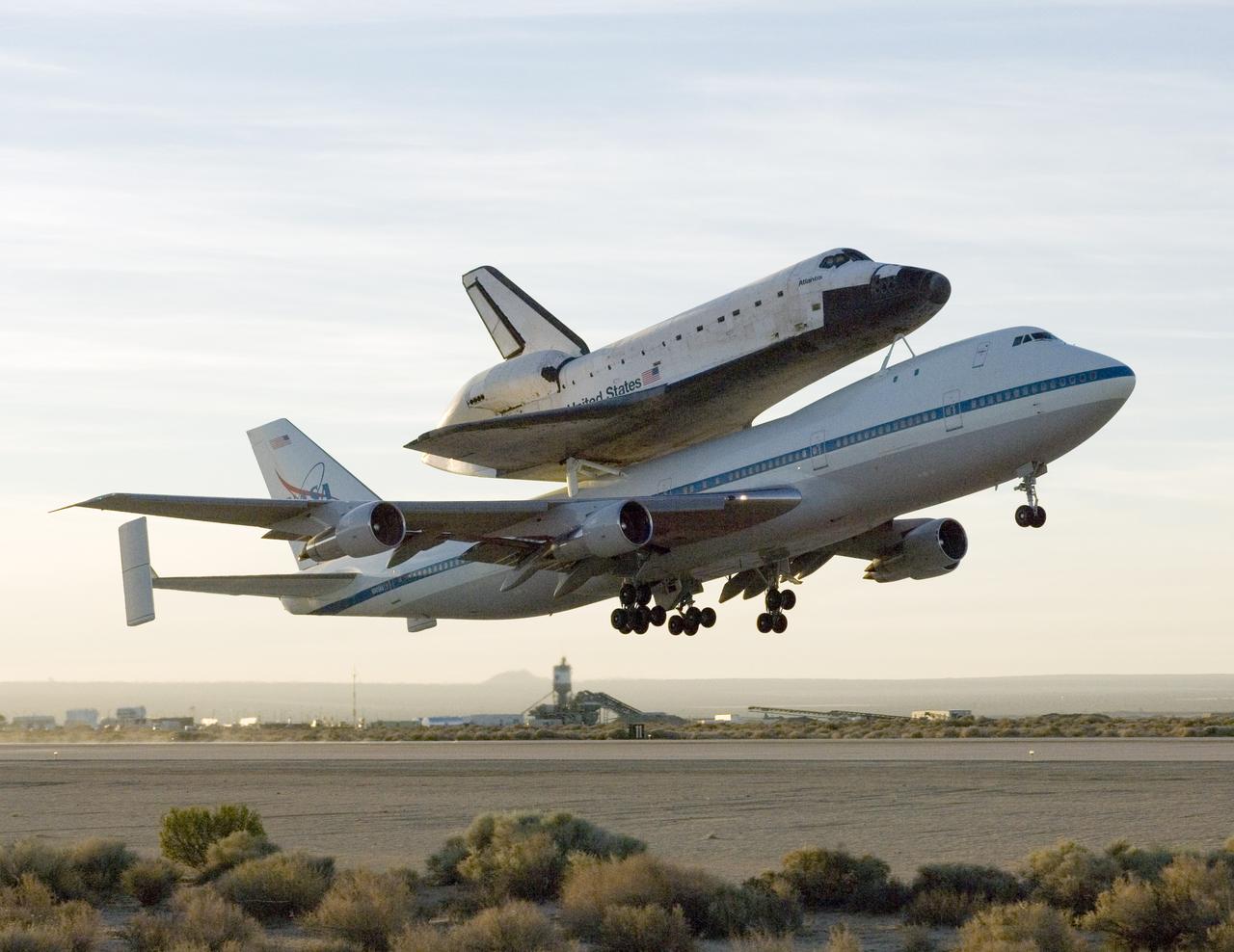

NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft with the Space Shuttle Atlantis on top lifts off from Edwards Air Force Base to begin its ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cross-country journey will take approximately two days, with stops at several intermediate points for refueling.
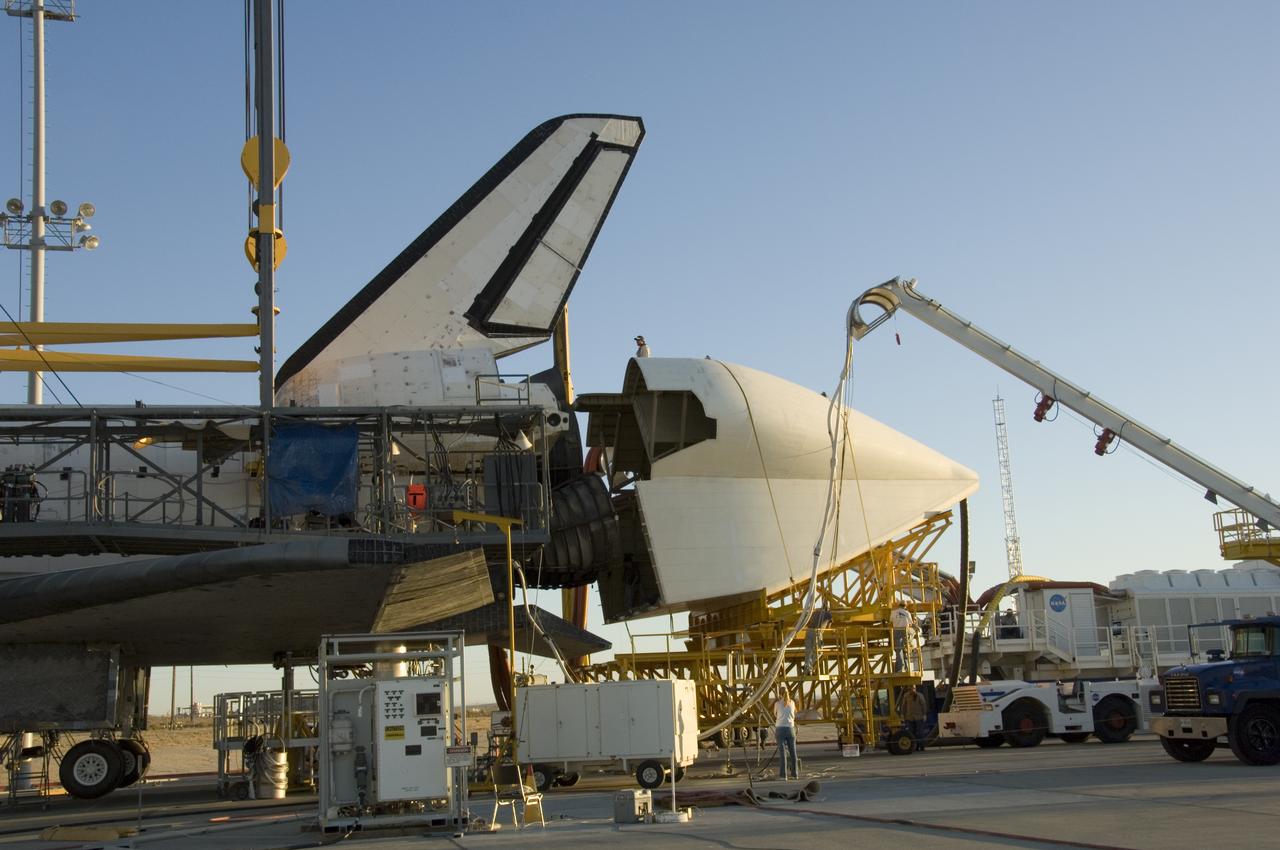

Technicians attach the tail cone, which helps reduce aerodynamic drag and turbulence during its ferry flight, to the Space Shuttle Atlantis in preparation for its return to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. After the tail-cone is installed, Discovery will be mounted on NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA, for the return flight.
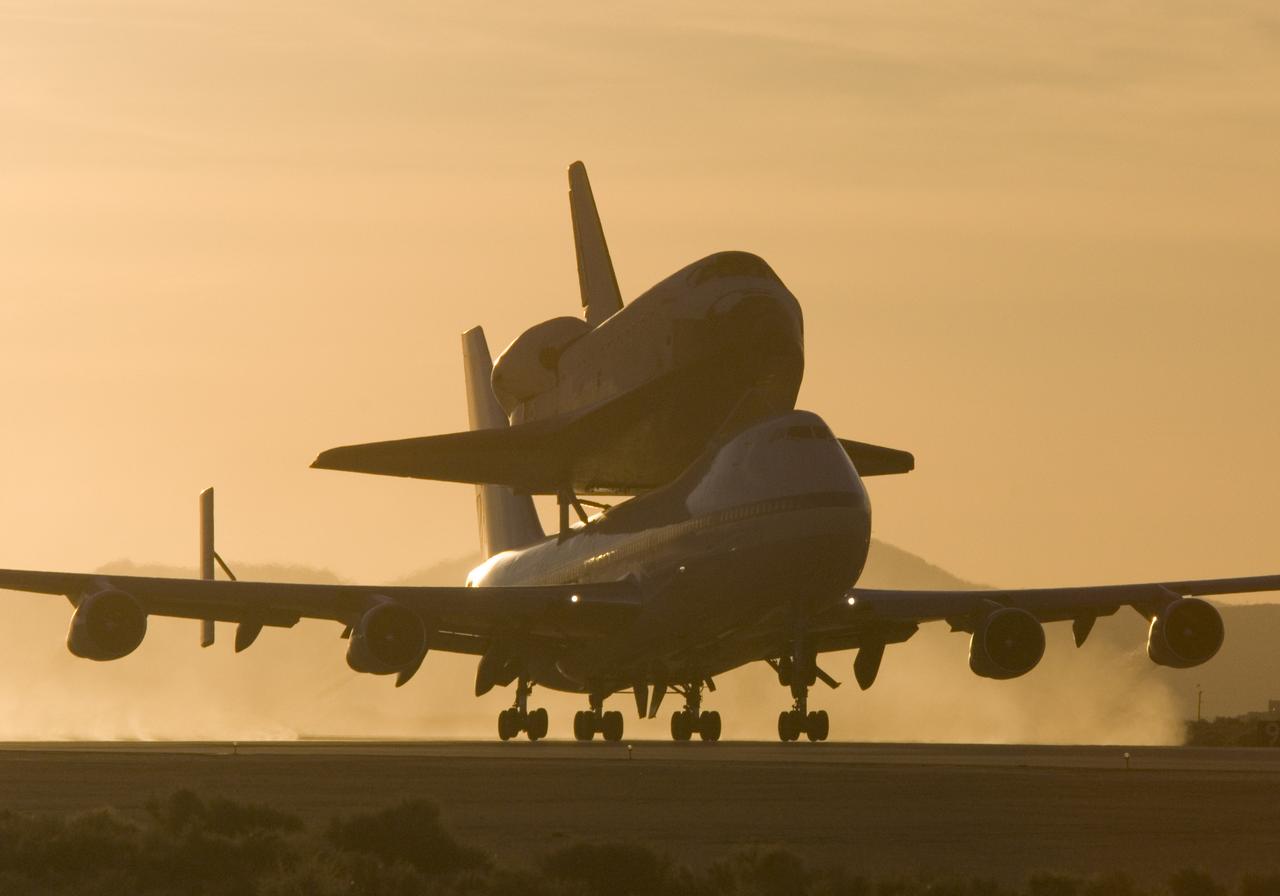

NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft with the Space Shuttle Atlantis on top lifts off from Edwards Air Force Base to begin its ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cross-country journey will take approximately two days, with stops at several intermediate points for refueling.

Lit by sunlight filtered through the smoke of a distant forest fire, the Space Shuttle Atlantis receives post-flight servicing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD), following its landing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft.
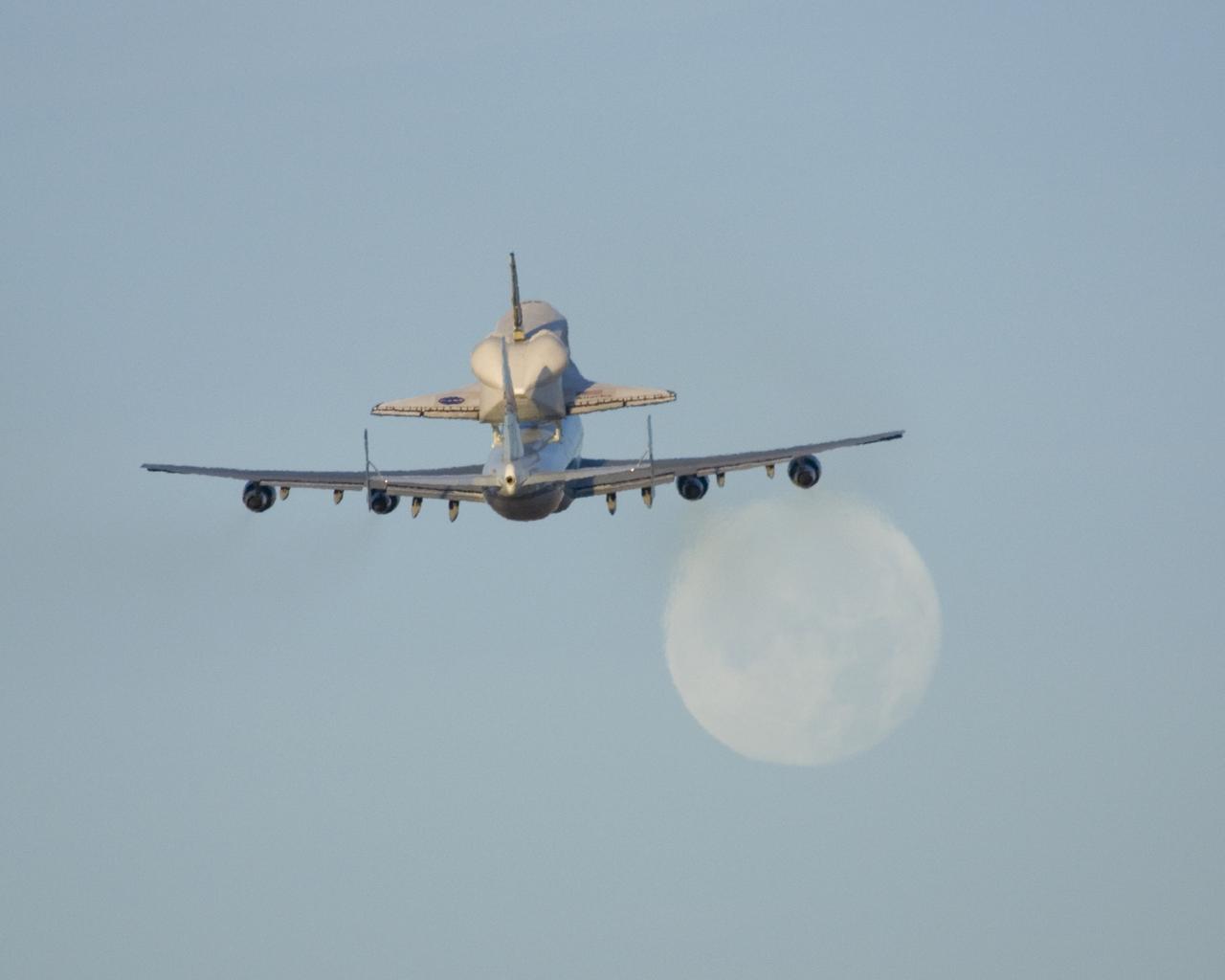

NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft with the Space Shuttle Atlantis on top lifts off from Edwards Air Force Base to begin its ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cross-country journey will take approximately two days, with stops at several intermediate points for refueling.
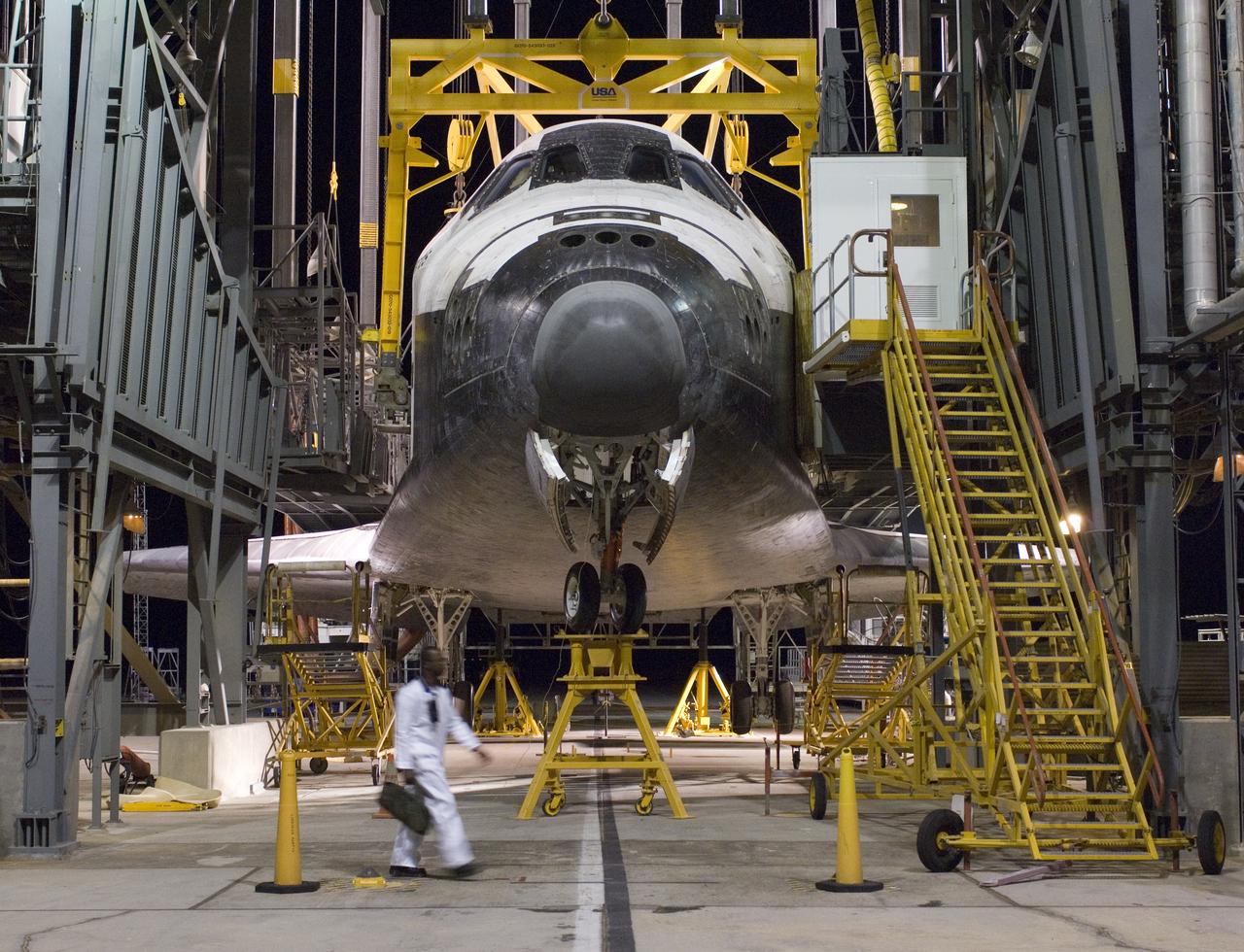

The Space Shuttle Atlantis receives post-flight servicing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD), following its landing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, June 22, 2007. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft.
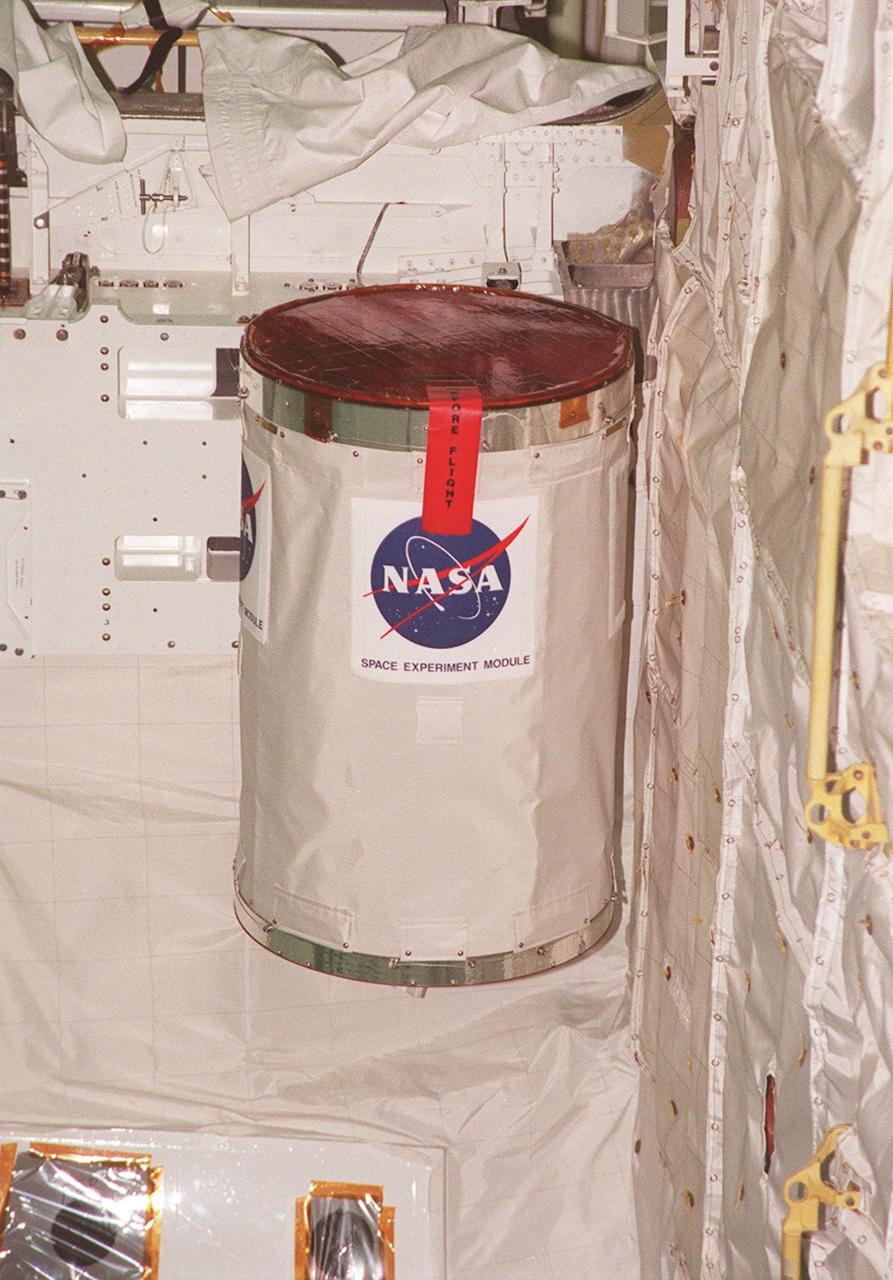

A GetAway Special canister (GAS can) filled with student experiments is installed in Discovery’s payload bay for mission STS-102. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
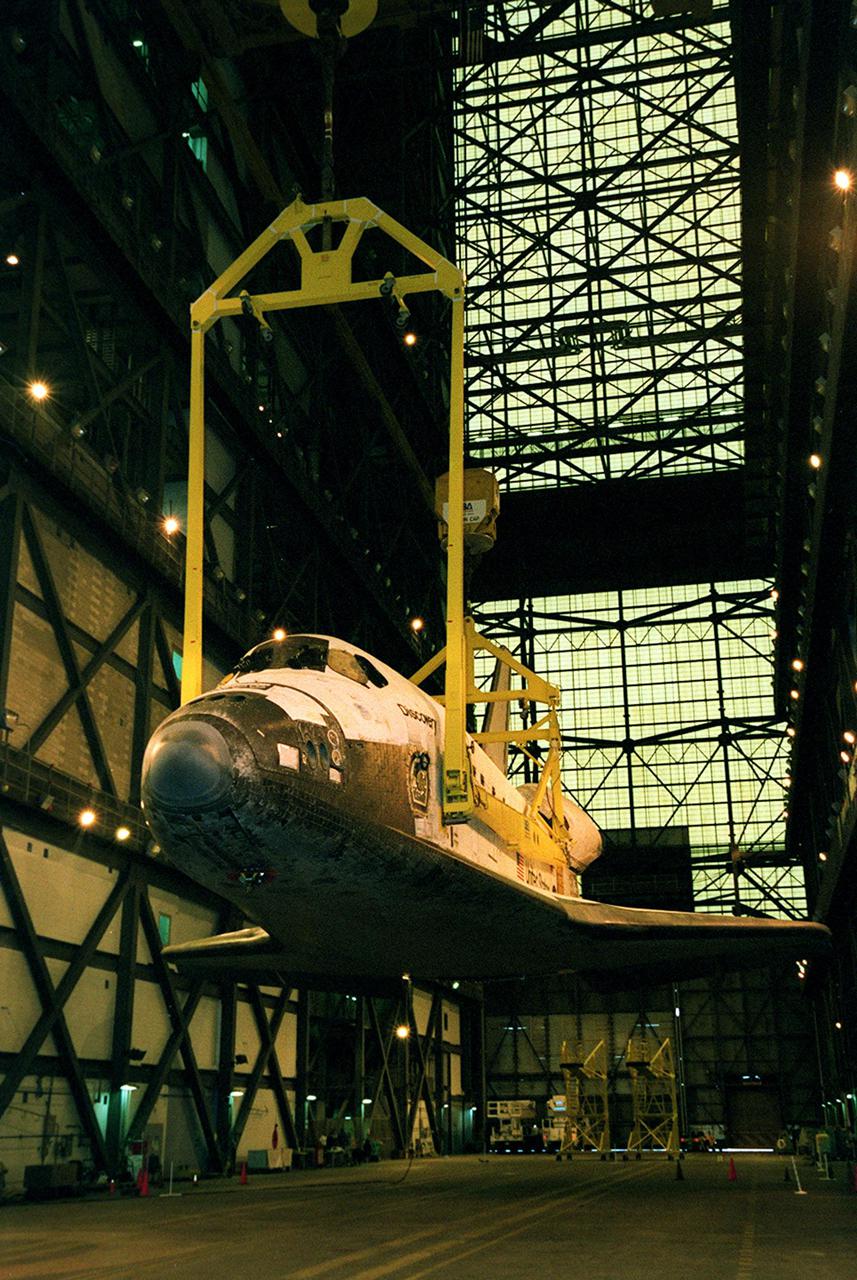

The orbiter Discovery is lifted by cranes in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building. It will next be lifted into a vertical position and into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to Earth

The orbiter Discovery is nearly vertical as overhead cranes lift it in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building. It will then be moved into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to earth
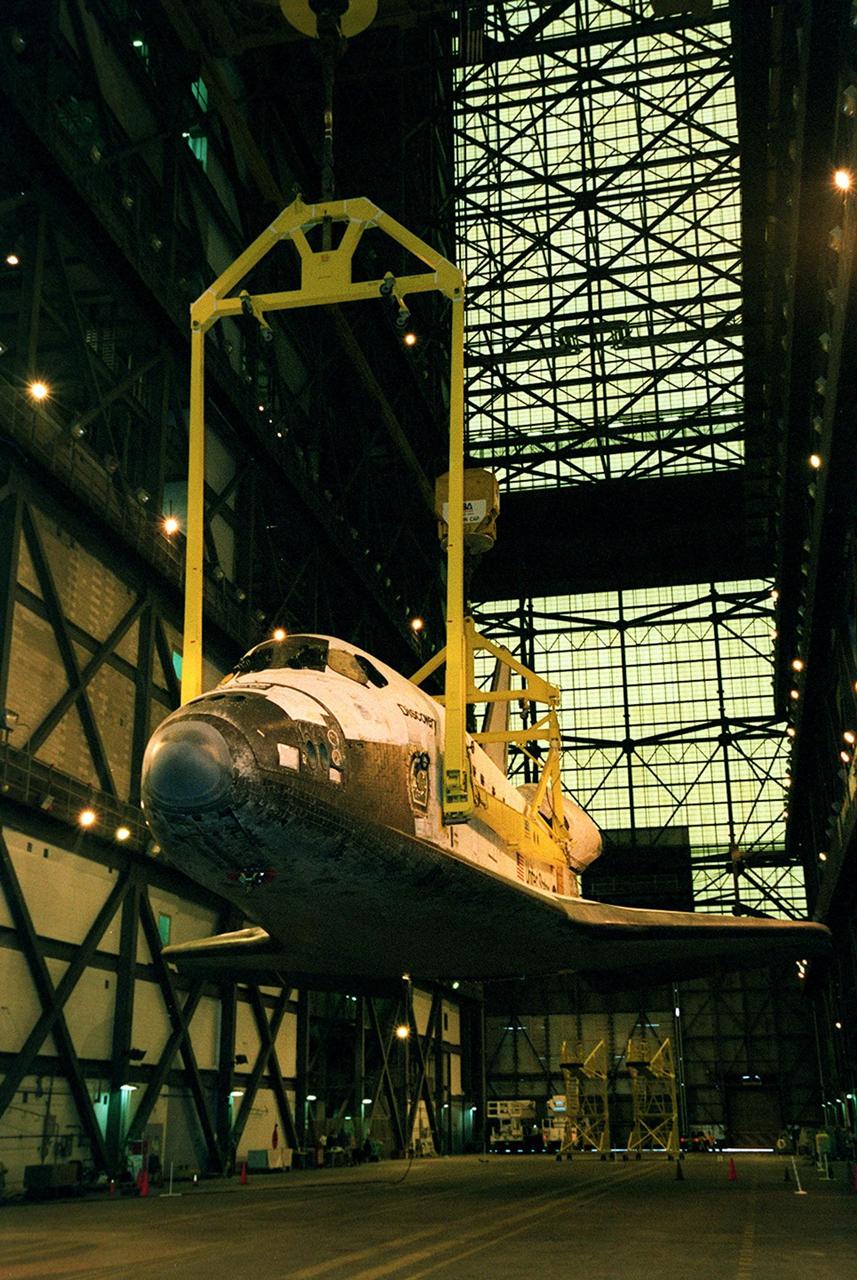

The orbiter Discovery is lifted by cranes in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building. It will next be lifted into a vertical position and into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to Earth
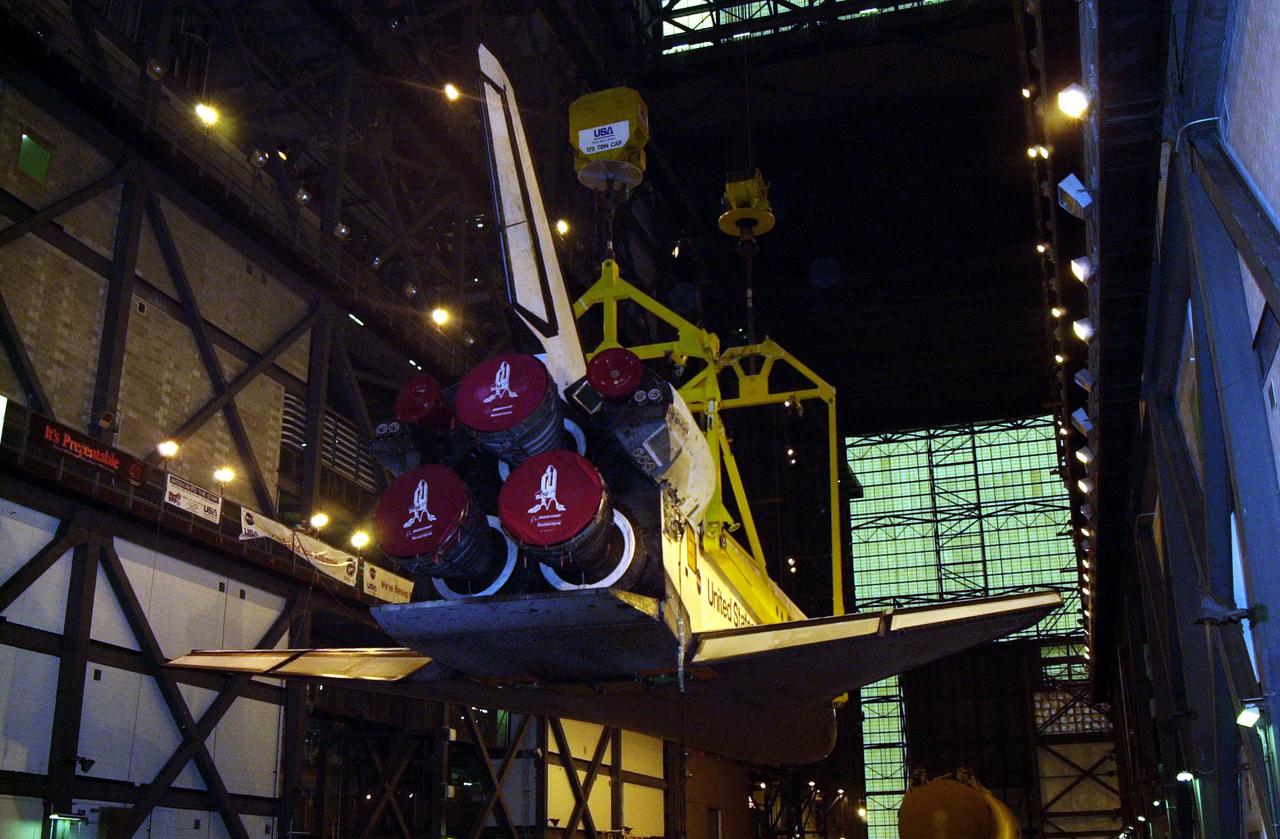

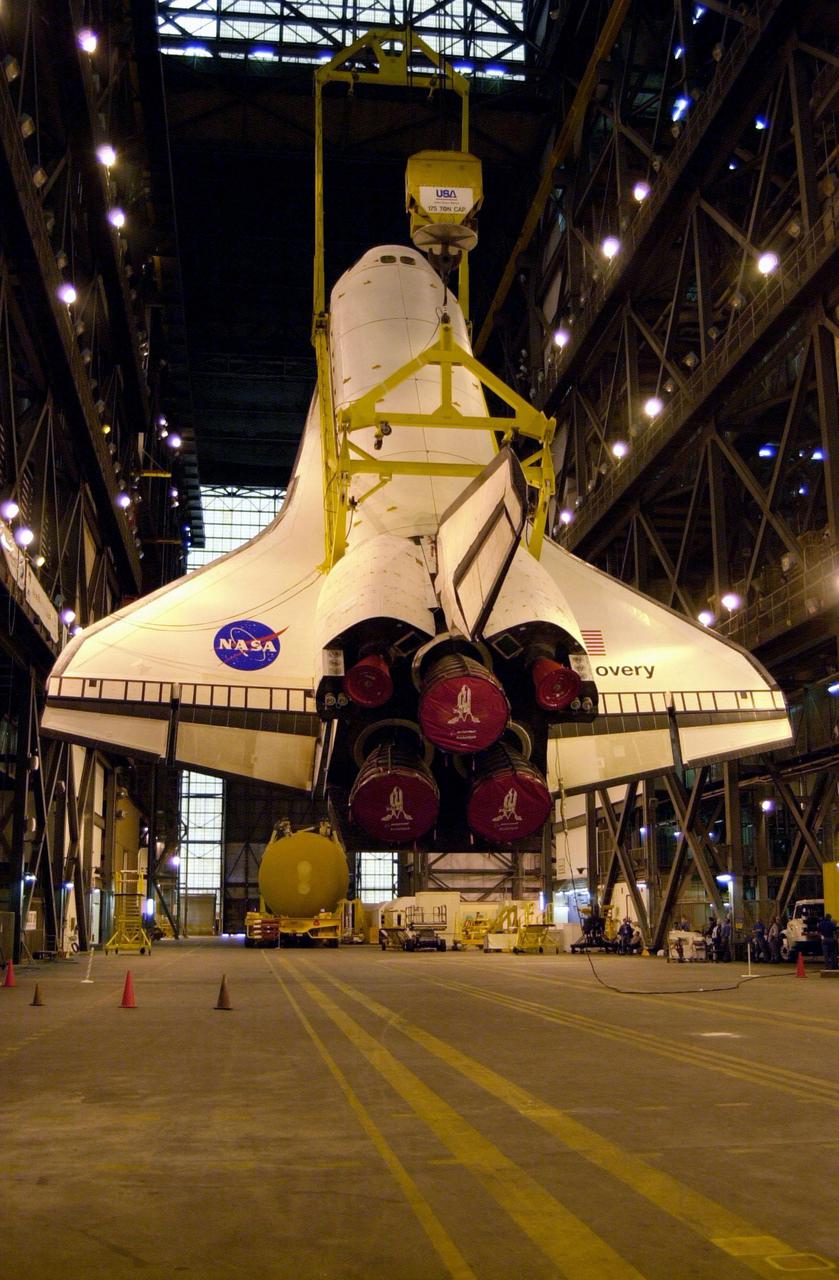
In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building, the orbiter Discovery (seen from the back) is lifted to vertical. It will then be lifted up and into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to earth
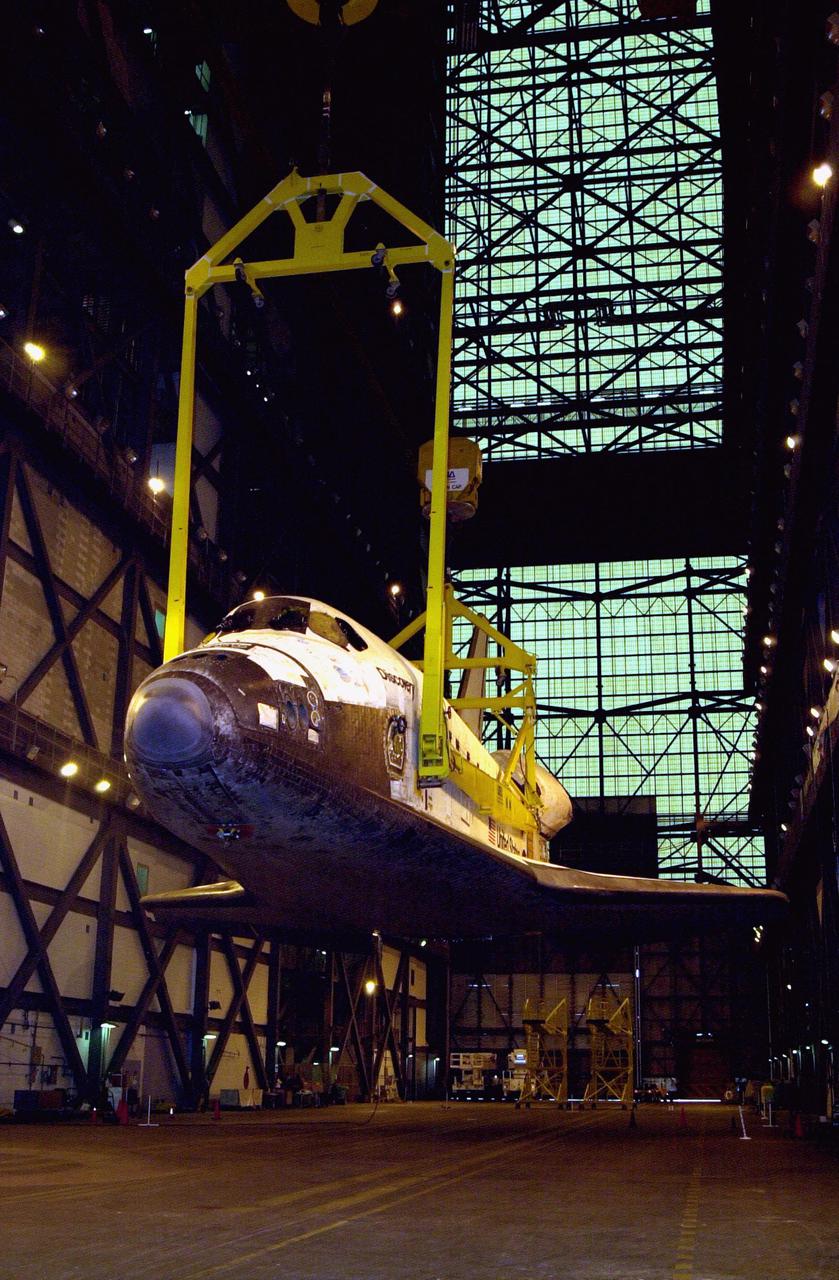

The orbiter Discovery (seen from the front) is lifted to vertical in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building. It will then be lifted up and into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to earth
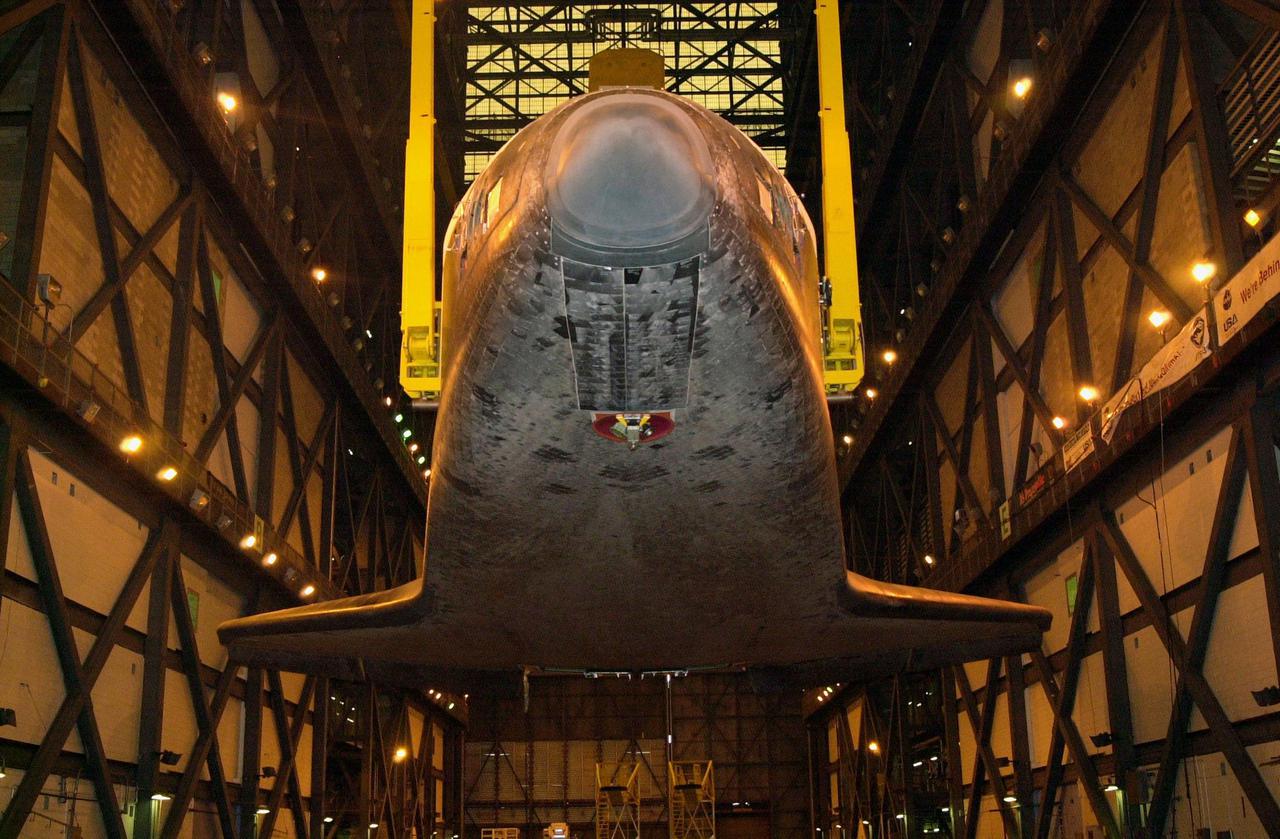

The underside of orbiter Discovery is seen as it is lifted to vertical in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building. It will then be lifted up and into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to earth
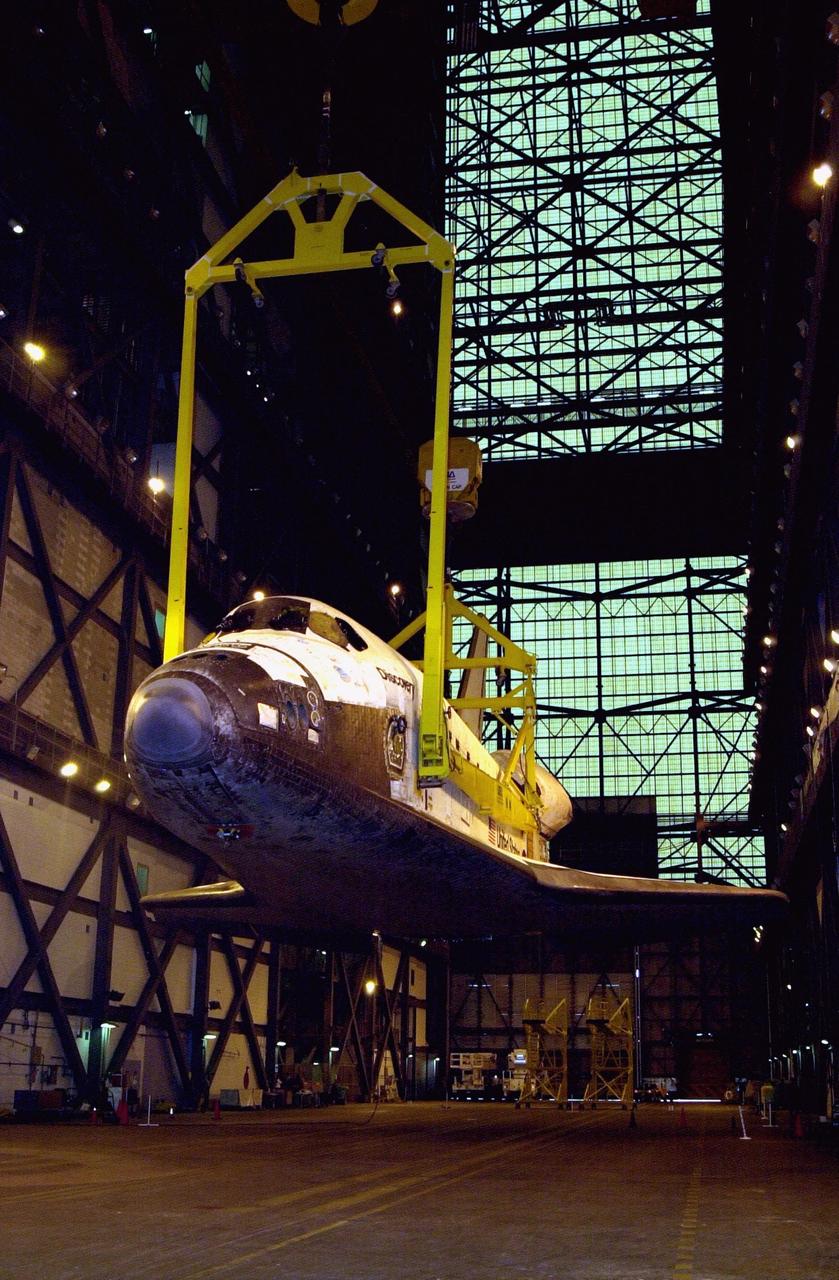

The orbiter Discovery (seen from the front) is lifted to vertical in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building. It will then be lifted up and into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to earth
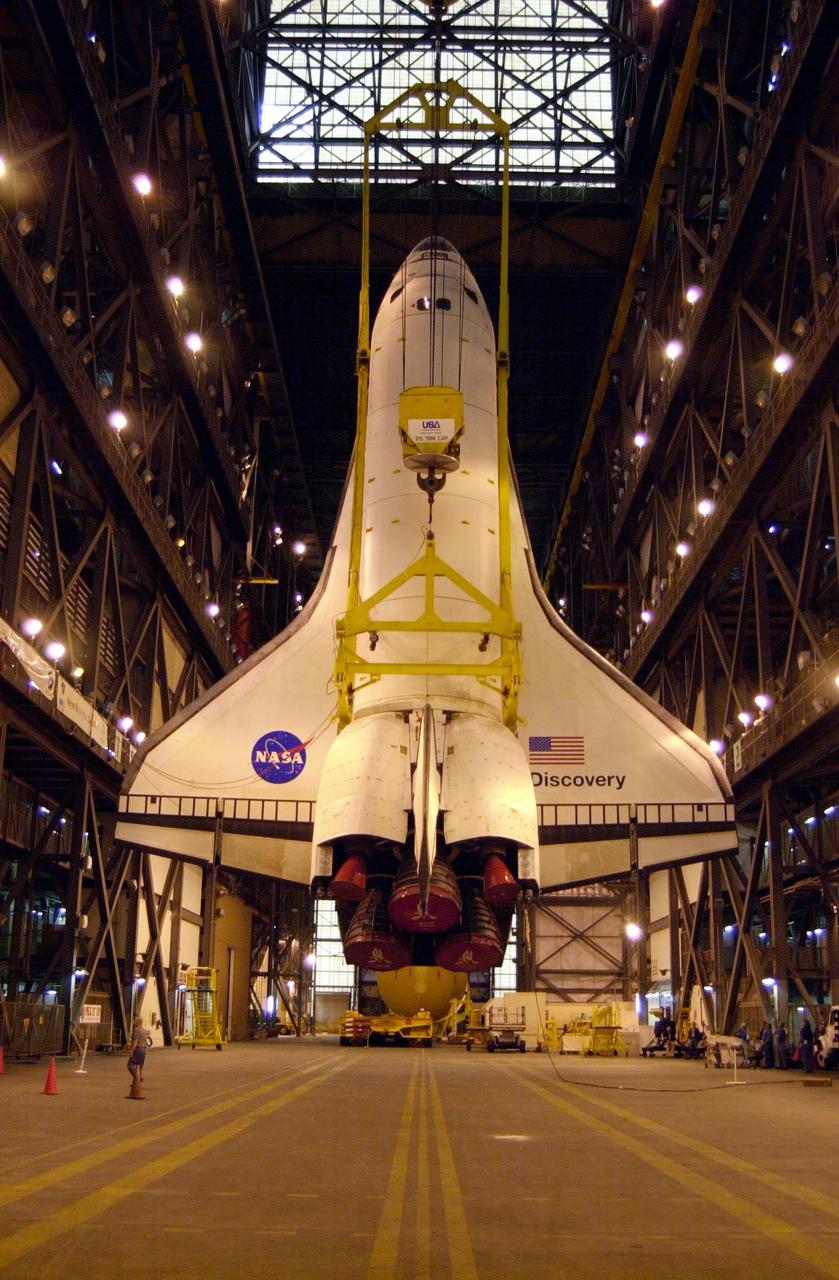

The orbiter Discovery is finally vertical and hangs suspended in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building. It will next be moved into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to earth
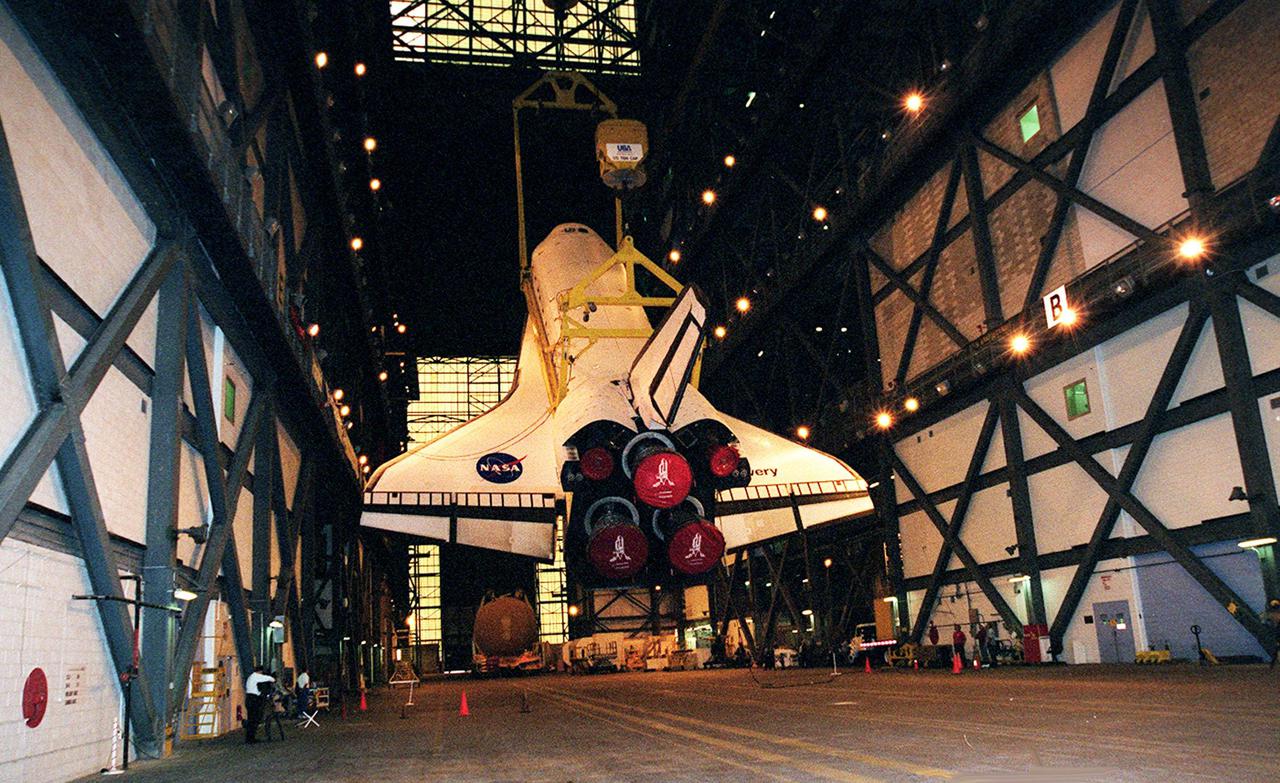

In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building the orbiter Discovery is suspended at an angle as it is lifted to a vertical position. It will next be lifted into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to Earth
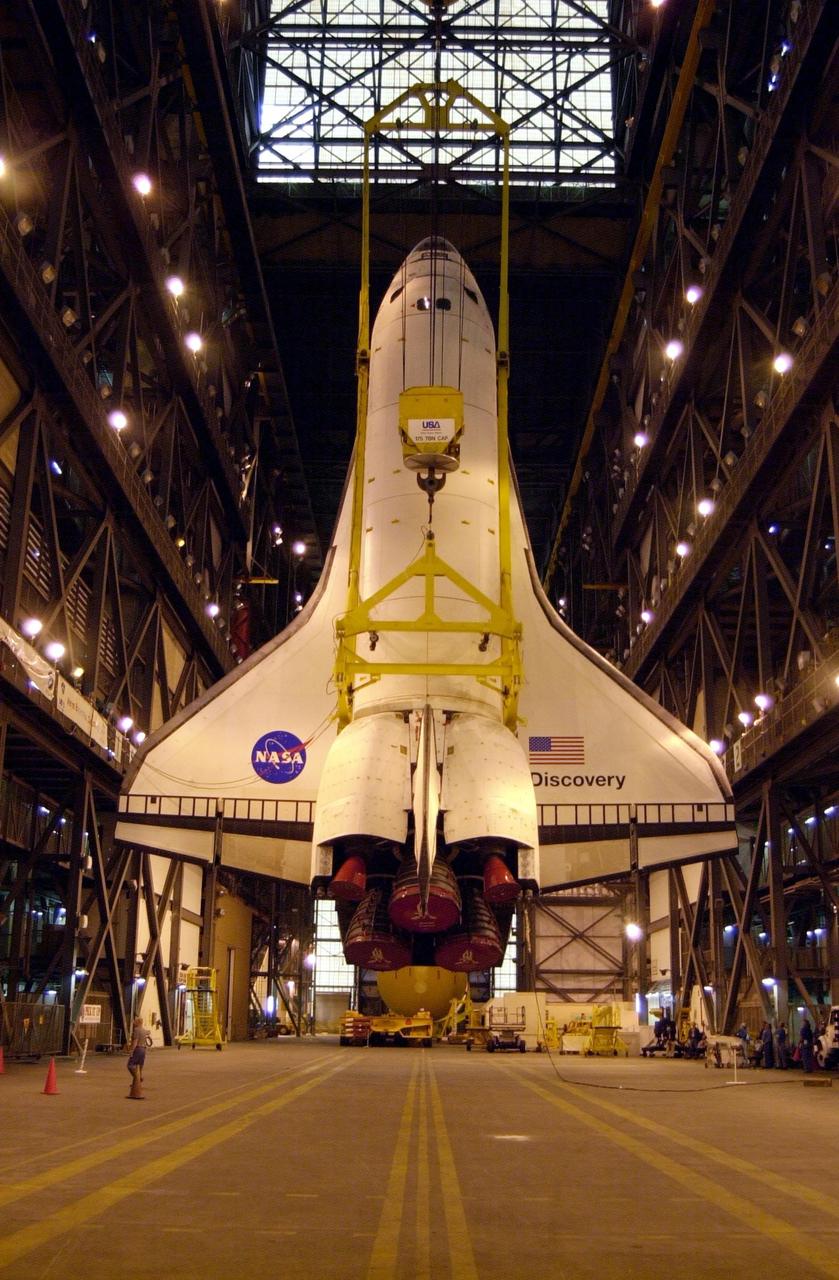

The orbiter Discovery is finally vertical and hangs suspended in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building. It will next be moved into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to earth
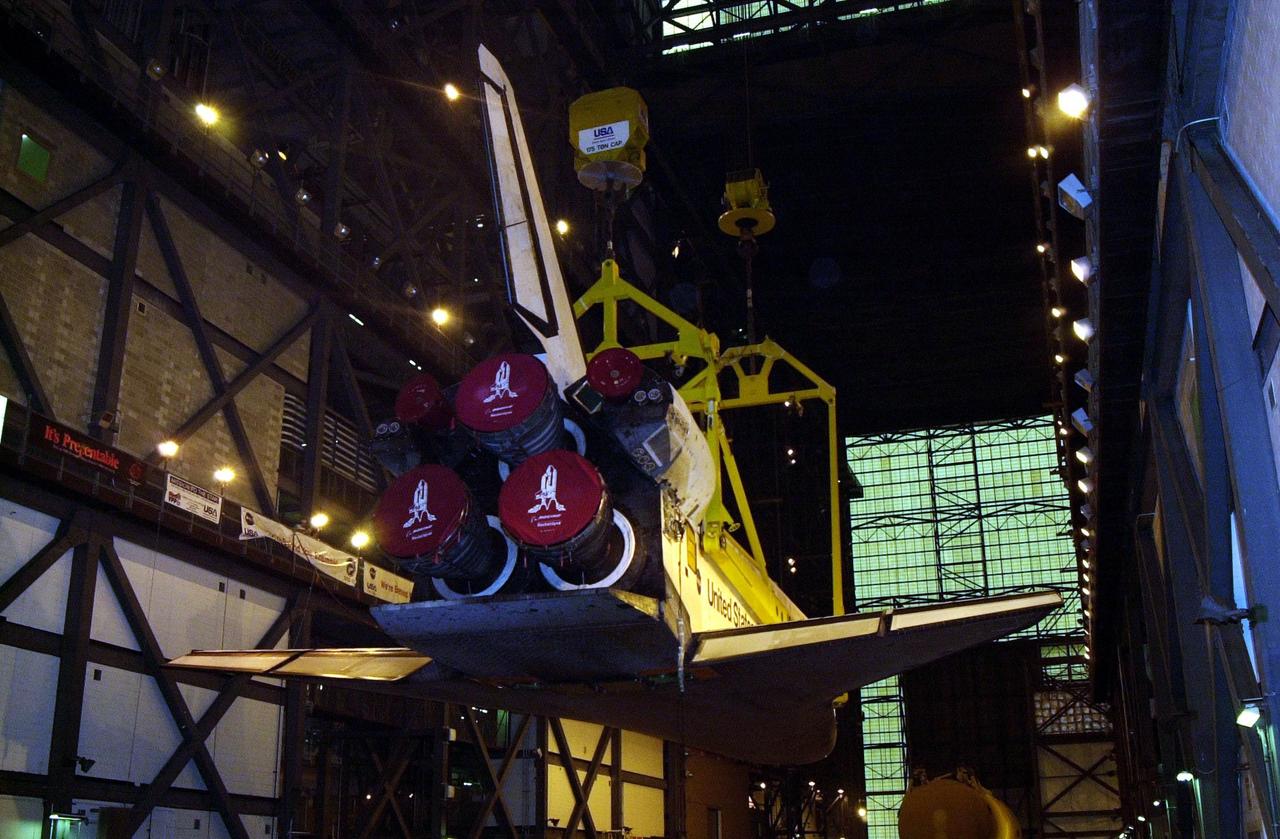

In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building, the orbiter Discovery (seen from the back) is lifted to vertical. It will then be lifted up and into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to earth
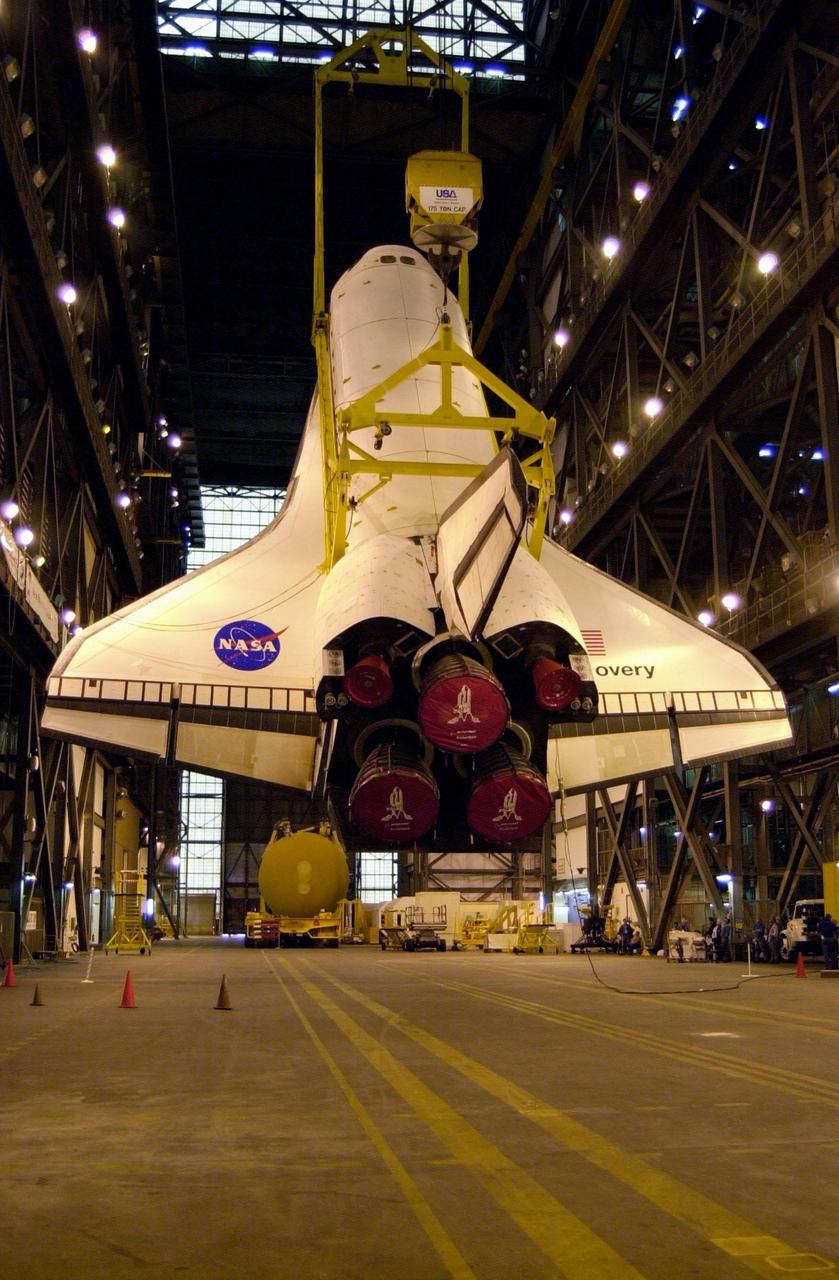

The orbiter Discovery is nearly vertical as overhead cranes lift it in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building. It will then be moved into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to earth
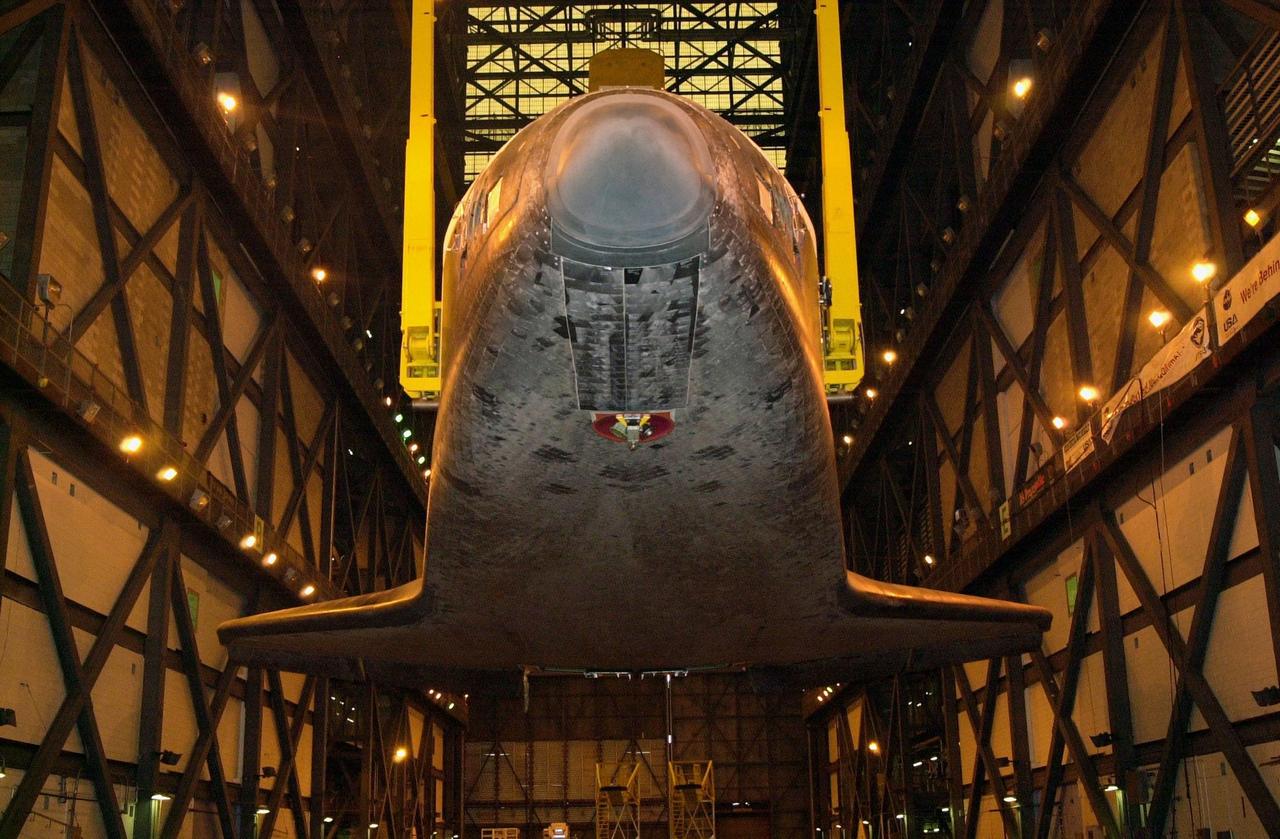

The underside of orbiter Discovery is seen as it is lifted to vertical in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building. It will then be lifted up and into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to earth
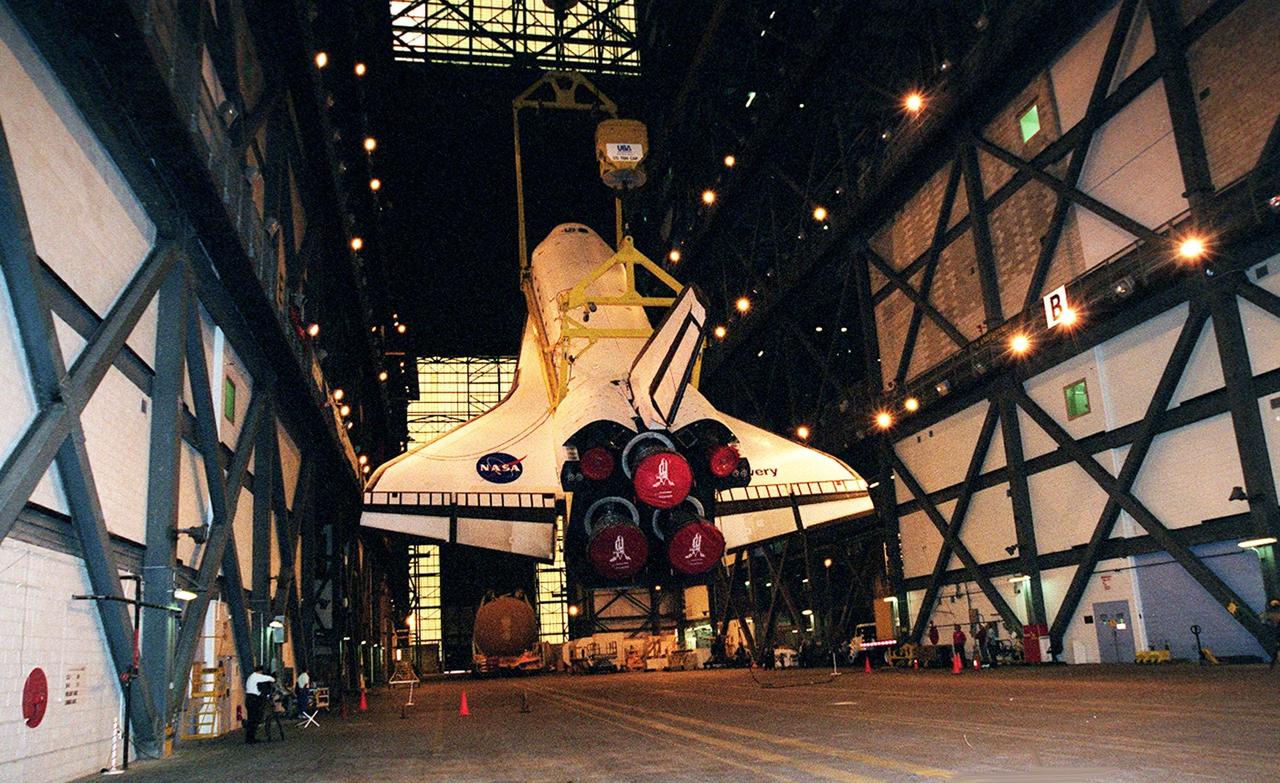

In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building the orbiter Discovery is suspended at an angle as it is lifted to a vertical position. It will next be lifted into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to Earth
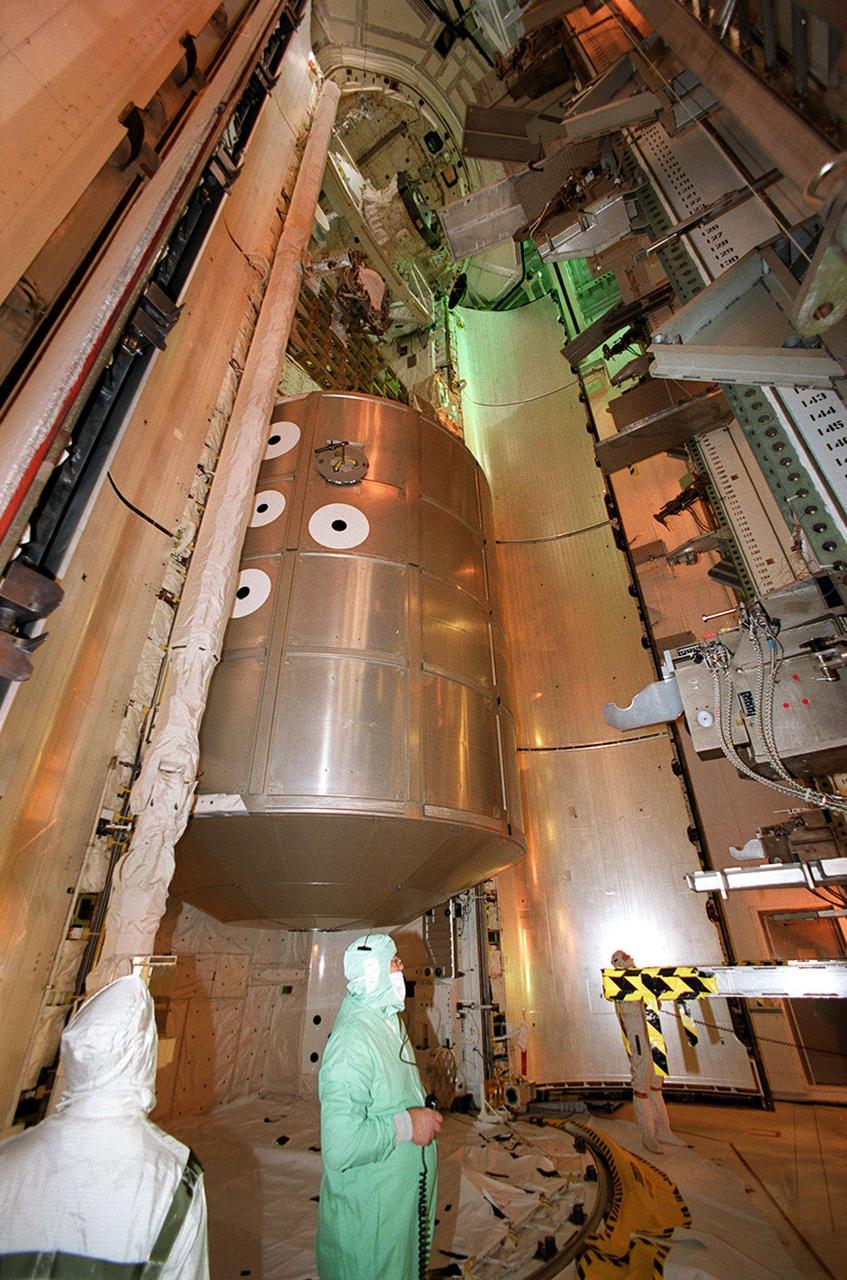

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo is moved into Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. The primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment, Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny. Discovery is scheduled to launch March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station
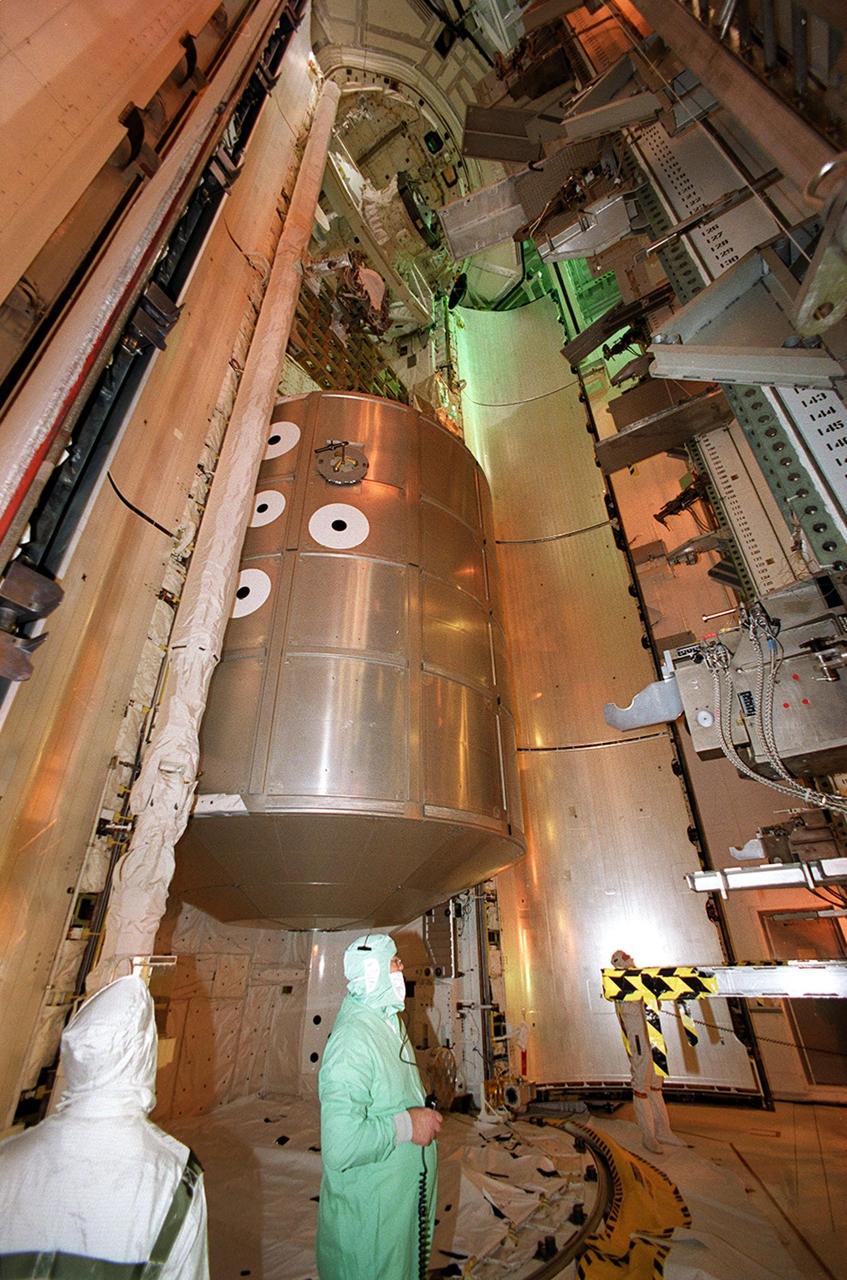

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo is moved into Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. The primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment, Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny. Discovery is scheduled to launch March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station
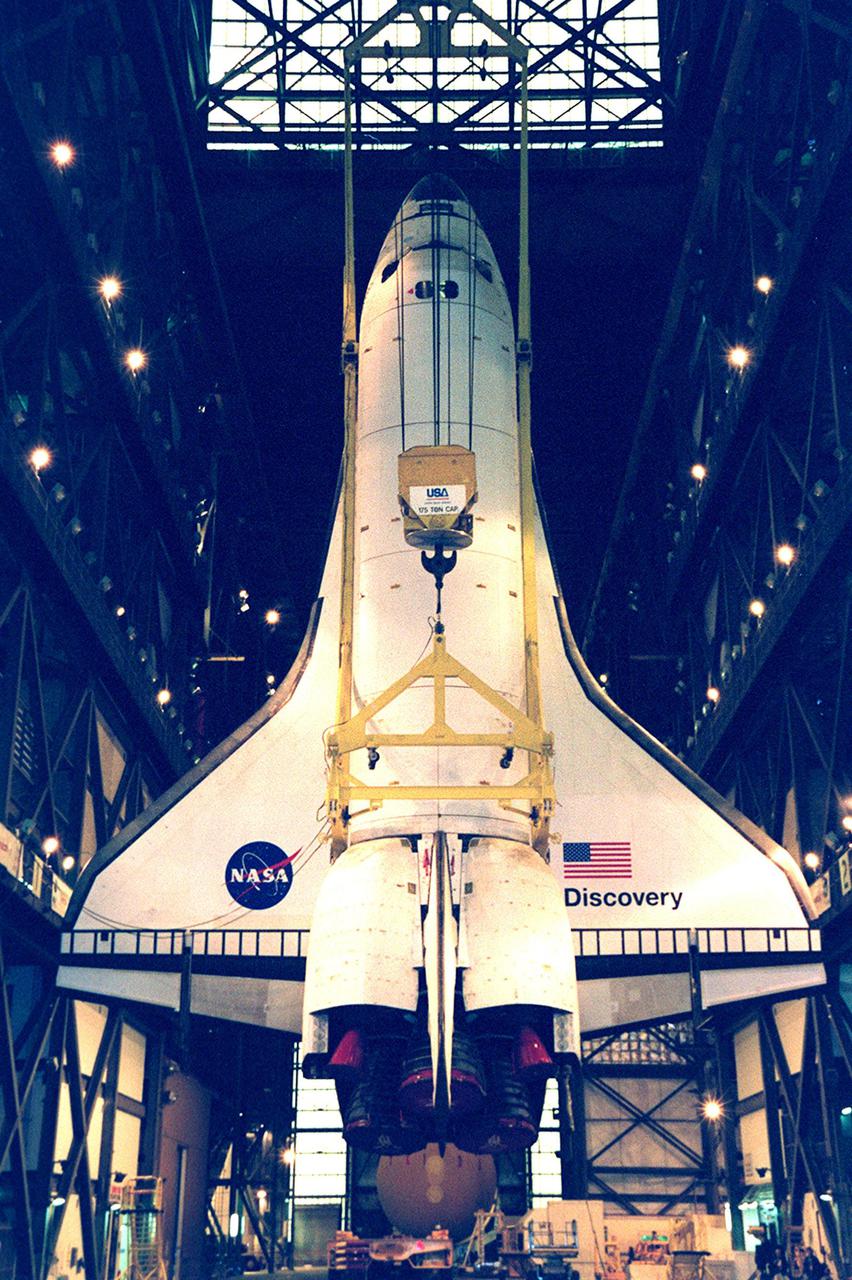

The orbiter Discovery finally hangs vertically, suspended from overhead cranes in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building. It will next be lifted into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to Earth
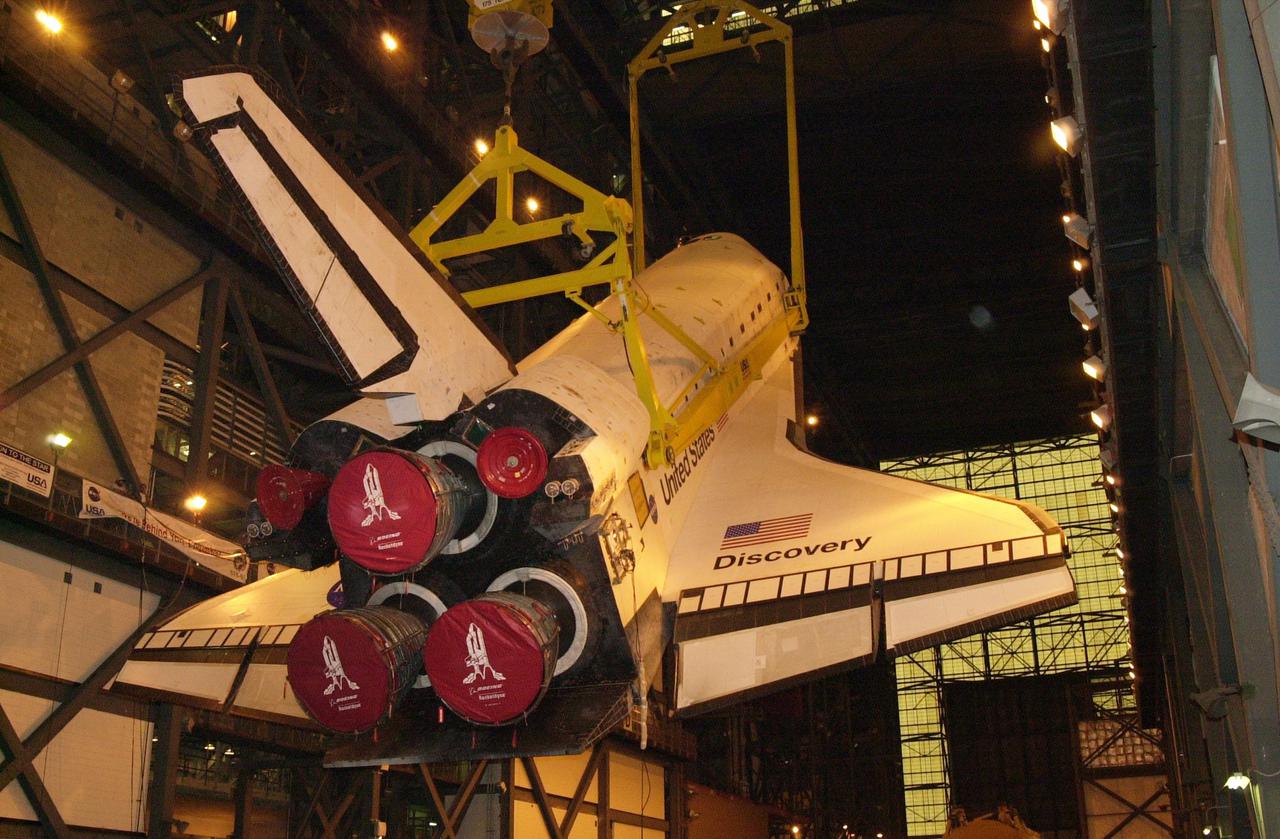

In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building, the orbiter Discovery is lifted for mating. It will be moved into high bay 1 and mated with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to earth
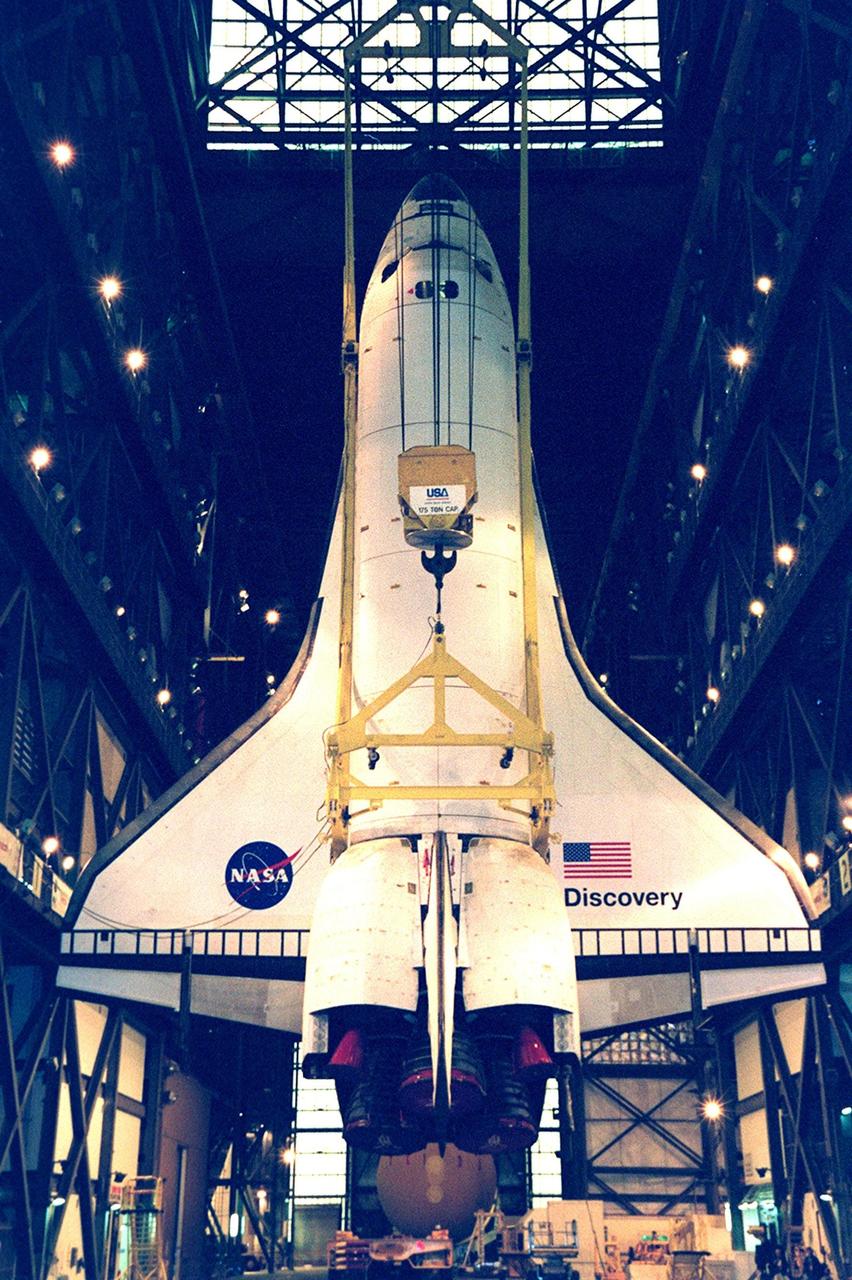

The orbiter Discovery finally hangs vertically, suspended from overhead cranes in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building. It will next be lifted into high bay 1 for mating with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Discovery will be launched March 8 on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The Shuttle will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the first of three pressurized modules provided by the Italian Space Agency to carry supplies and equipment to the Space Station and back to Earth
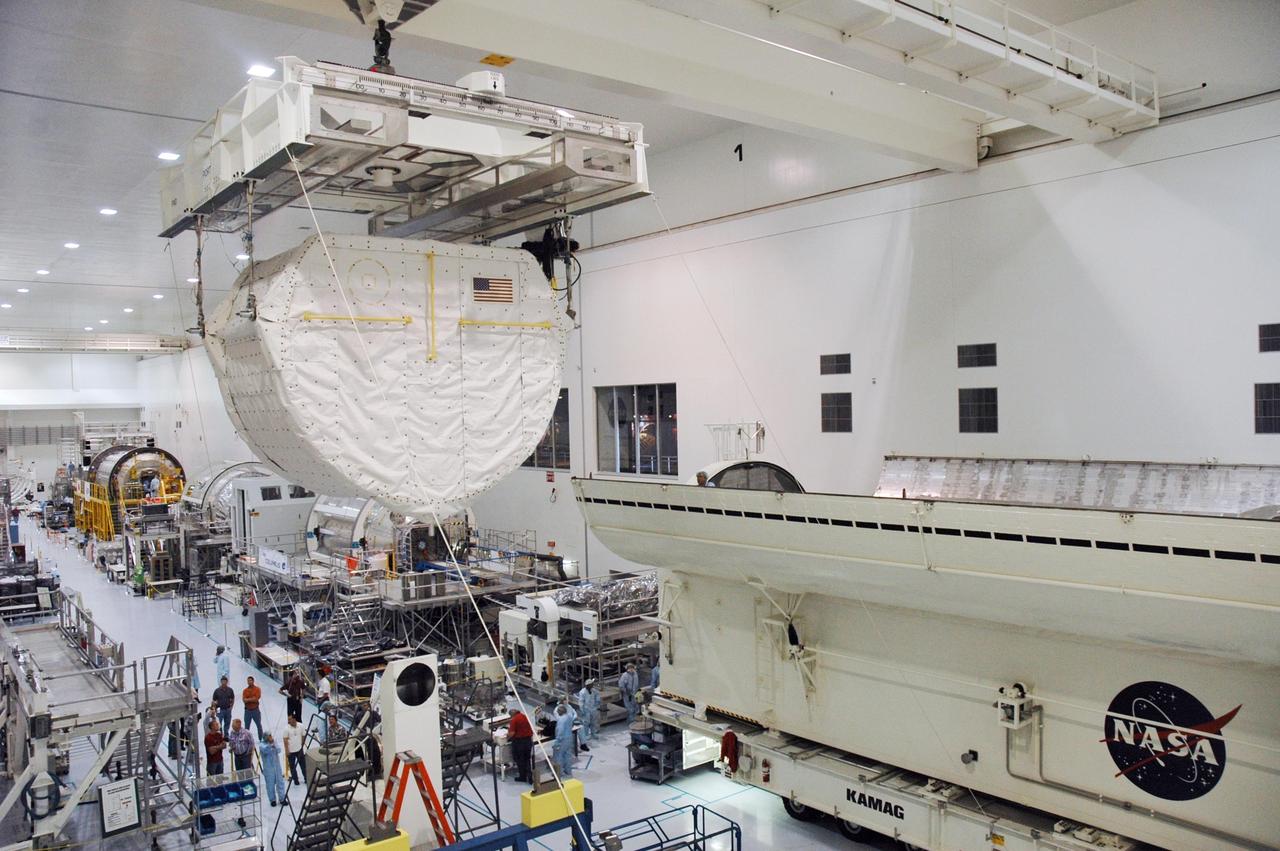

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane carries the SPACEHAB Module towards the Payload Canister. The SPACEHAB Module will carry racks of experiments, flight hardware, spacewalk equipment and supplies to support mission STS-116 to the International Space Station. STS-116 will be mission number 20 to the station and construction flight 12A.1. Along with SPACEHAB, the mission payload on Space Shuttle Discovery includes the P5 integrated truss structure and other key components. The launch window opens Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
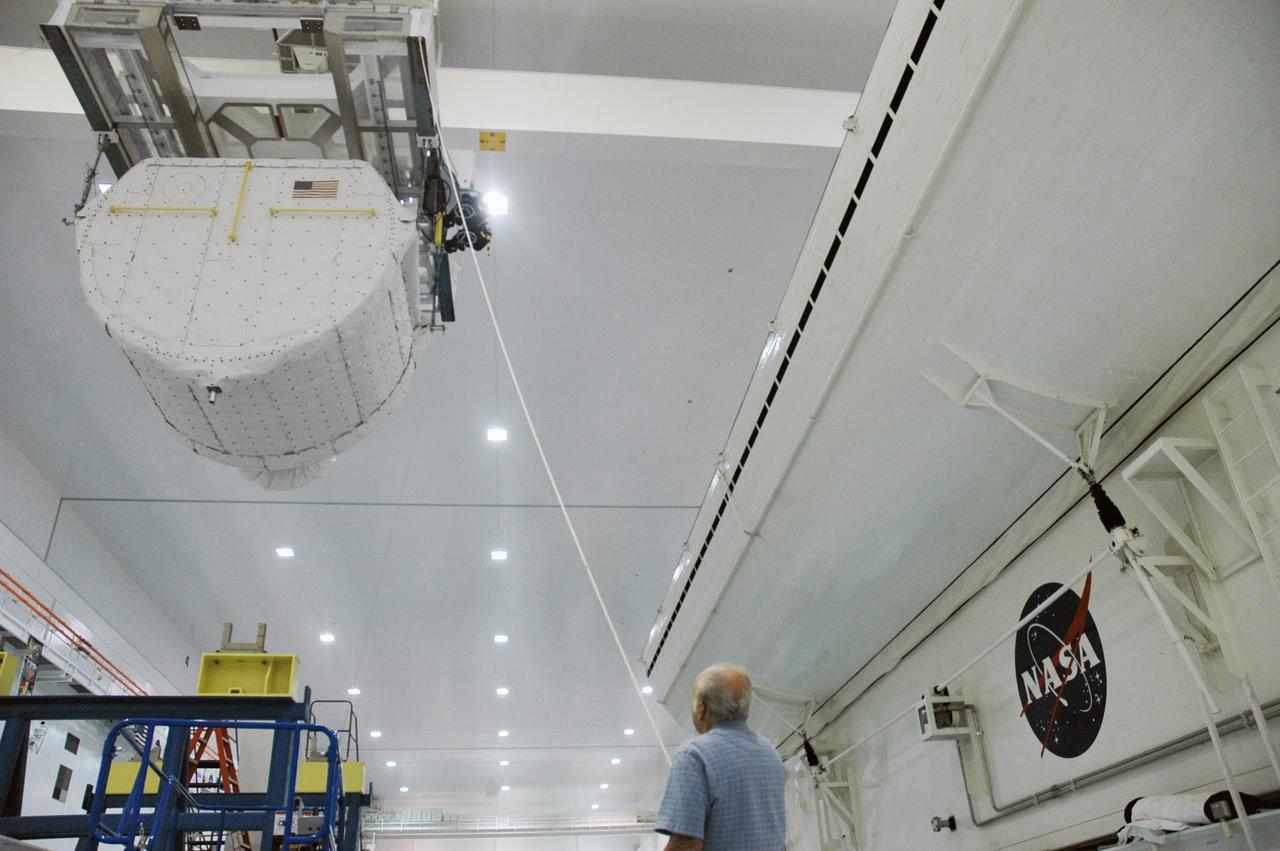

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane carries the SPACEHAB Module towards the Payload Canister. The SPACEHAB Module will carry racks of experiments, flight hardware, spacewalk equipment and supplies to support mission STS-116 to the International Space Station. STS-116 will be mission number 20 to the station and construction flight 12A.1. Along with SPACEHAB, the mission payload on Space Shuttle Discovery includes the P5 integrated truss structure and other key components. The launch window opens Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
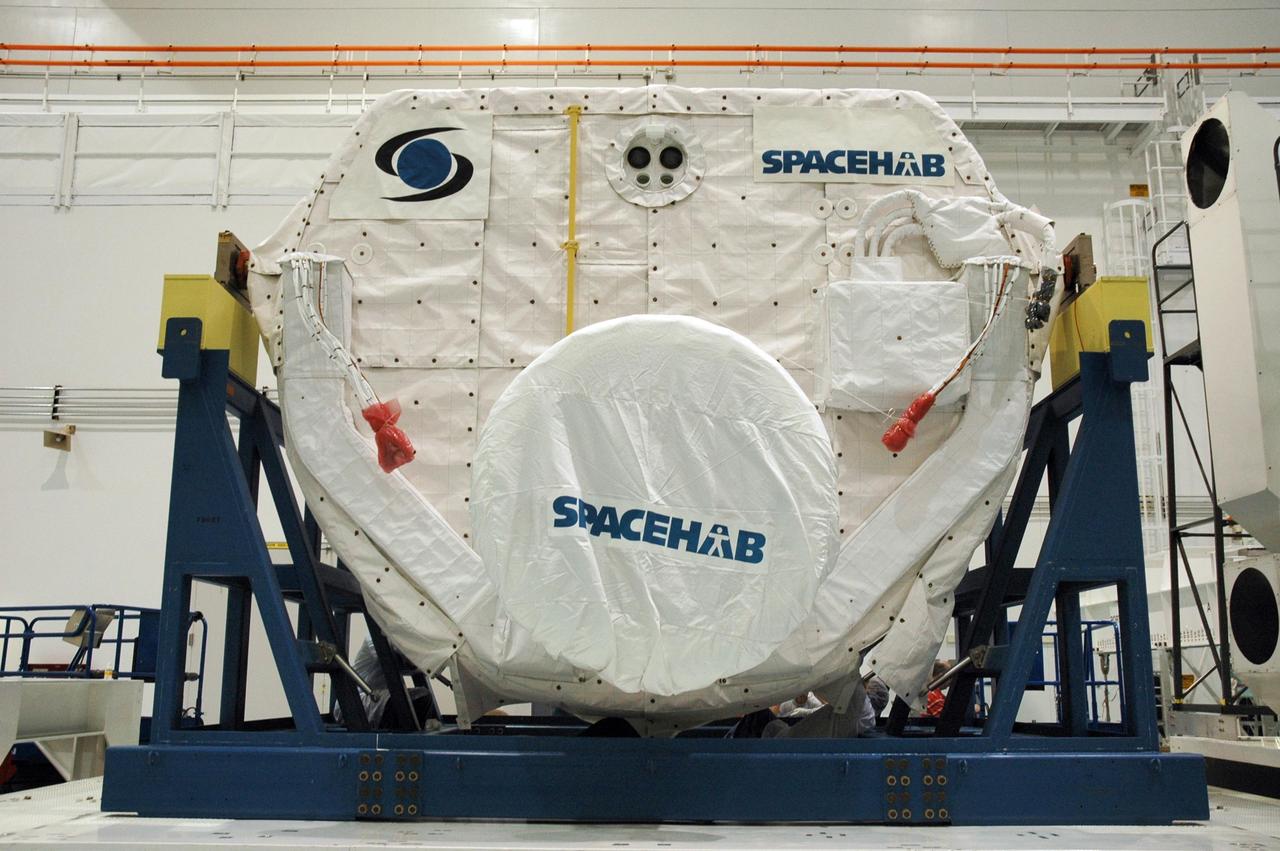

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility, technicians secure the protective coverings on the SPACEHAB Module before it is transferred to the Payload Canister. The SPACEHAB Module will carry racks of experiments, flight hardware, spacewalk equipment and supplies to support mission STS-116 to the International Space Station. STS-116 will be mission number 20 to the station and construction flight 12A.1. Along with SPACEHAB, the mission payload on Space Shuttle Discovery includes the P5 integrated truss structure and other key components. The launch window opens Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

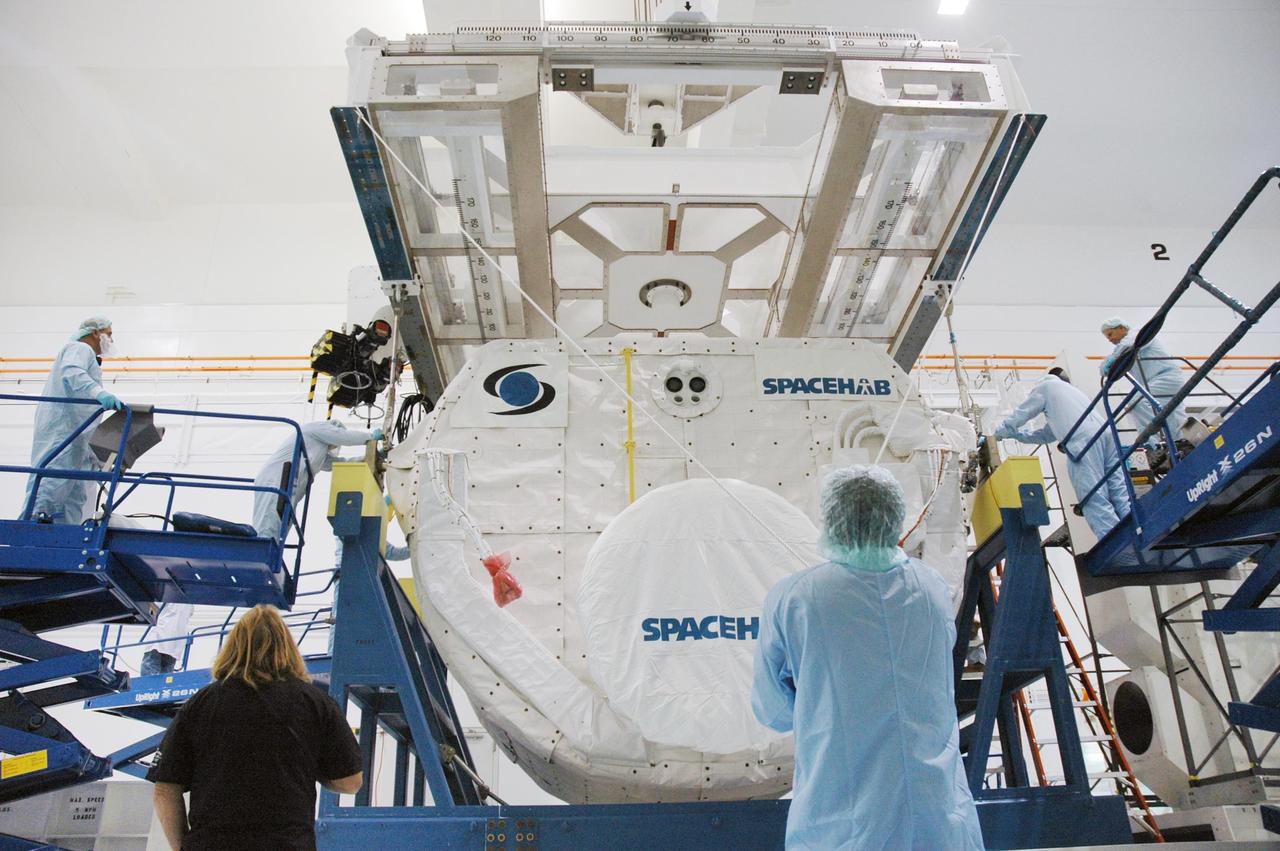
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane lowers the SPACEHAB Module into the Payload Canister. The SPACEHAB Module will carry racks of experiments, flight hardware, spacewalk equipment and supplies to support mission STS-116 to the International Space Station. STS-116 will be mission number 20 to the station and construction flight 12A.1. Along with SPACEHAB, the mission payload on Space Shuttle Discovery includes the P5 integrated truss structure and other key components. The launch window opens Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility, technicians secure the SPACEHAB Module to the overhead crane for transfer to the Payload Canister. The SPACEHAB Module will carry racks of experiments, flight hardware, spacewalk equipment and supplies to support mission STS-116 to the International Space Station. STS-116 will be mission number 20 to the station and construction flight 12A.1. Along with SPACEHAB, the mission payload on Space Shuttle Discovery includes the P5 integrated truss structure and other key components. The launch window opens Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
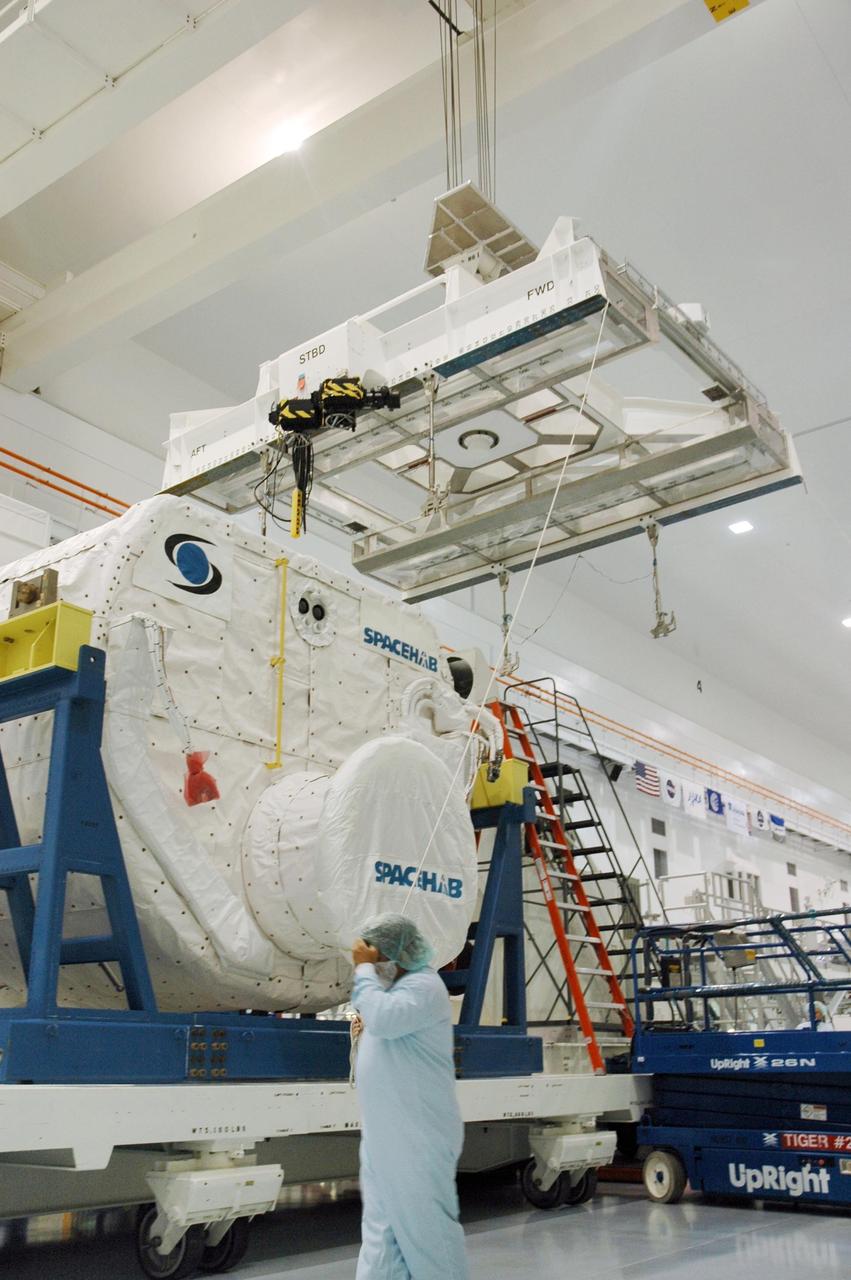

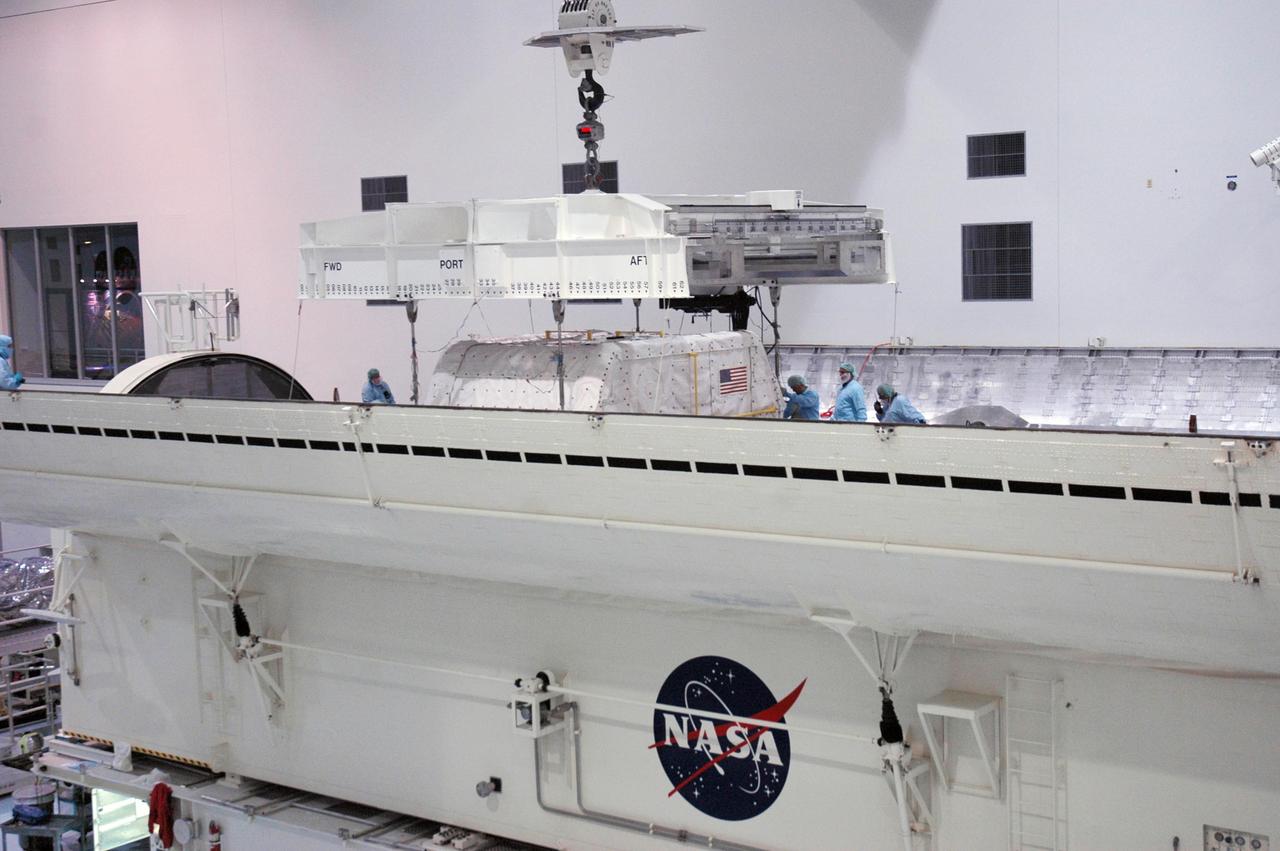
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane moves towards the SPACEHAB Module to transport in to the Payload Canister. The SPACEHAB Module will carry racks of experiments, flight hardware, spacewalk equipment and supplies to support mission STS-116 to the International Space Station. STS-116 will be mission number 20 to the station and construction flight 12A.1. Along with SPACEHAB, the mission payload on Space Shuttle Discovery includes the P5 integrated truss structure and other key components. The launch window opens Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
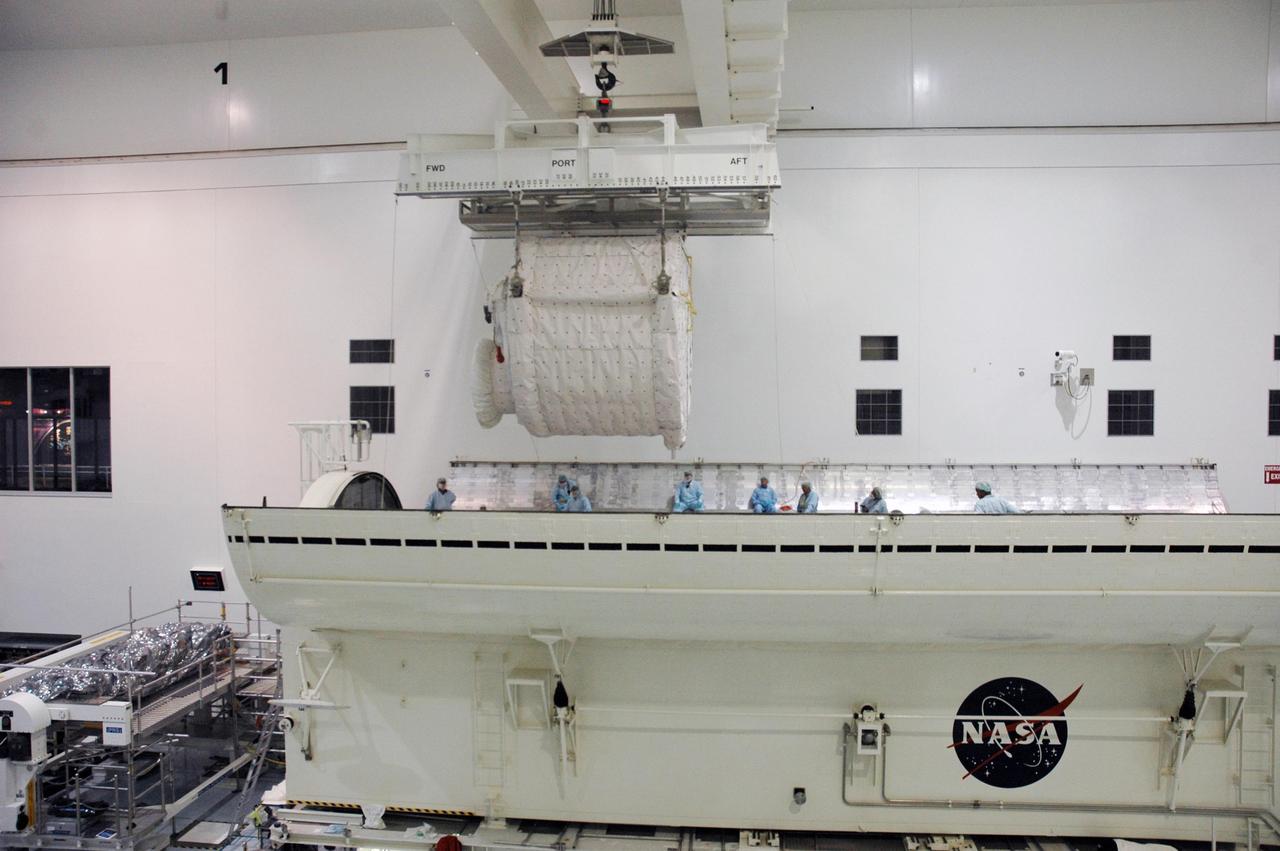

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane lowers the SPACEHAB Module into the Payload Canister. The SPACEHAB Module will carry racks of experiments, flight hardware, spacewalk equipment and supplies to support mission STS-116 to the International Space Station. STS-116 will be mission number 20 to the station and construction flight 12A.1. Along with SPACEHAB, the mission payload on Space Shuttle Discovery includes the P5 integrated truss structure and other key components. The launch window opens Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
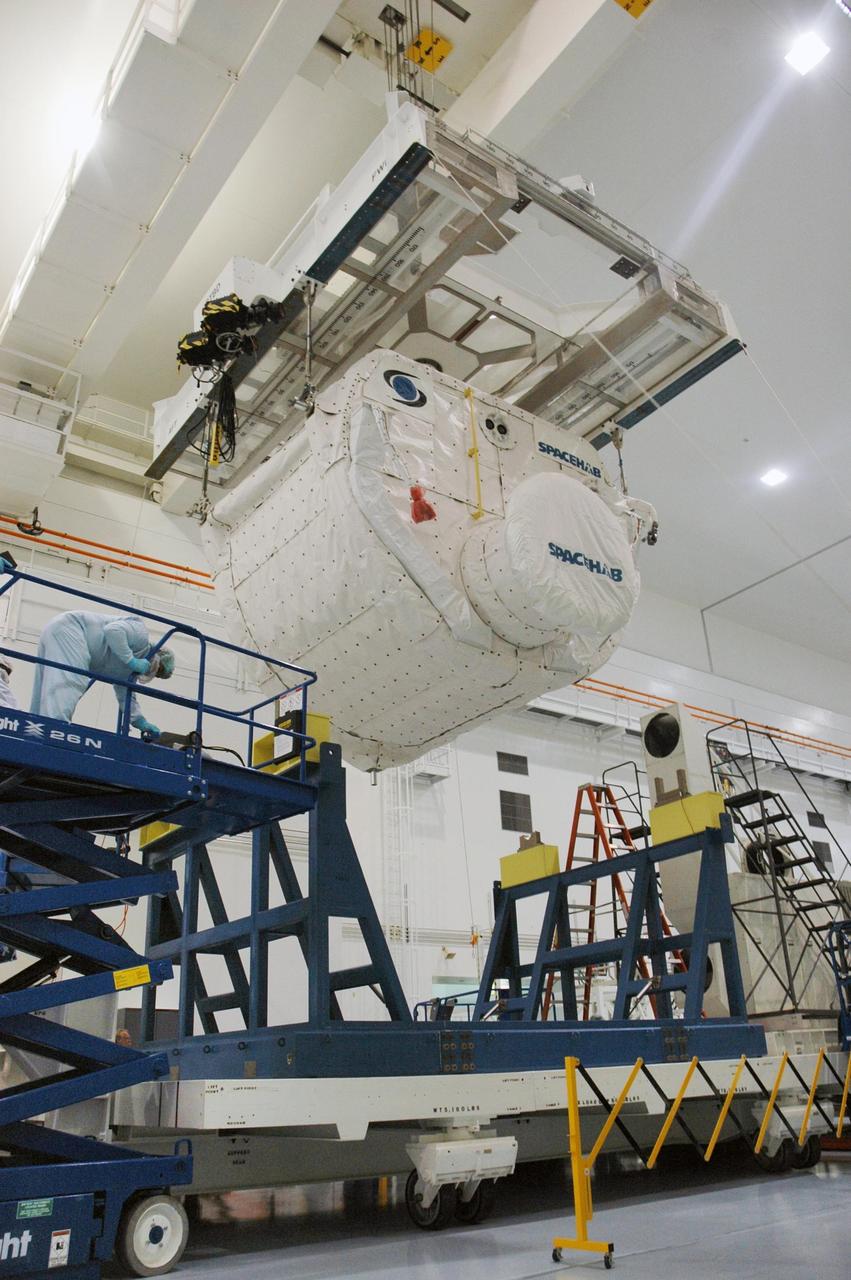

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane lifts the SPACEHAB Module from its stand for transfer to the Payload Canister. The SPACEHAB Module will carry racks of experiments, flight hardware, spacewalk equipment and supplies to support mission STS-116 to the International Space Station. STS-116 will be mission number 20 to the station and construction flight 12A.1. Along with SPACEHAB, the mission payload on Space Shuttle Discovery includes the P5 integrated truss structure and other key components. The launch window opens Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
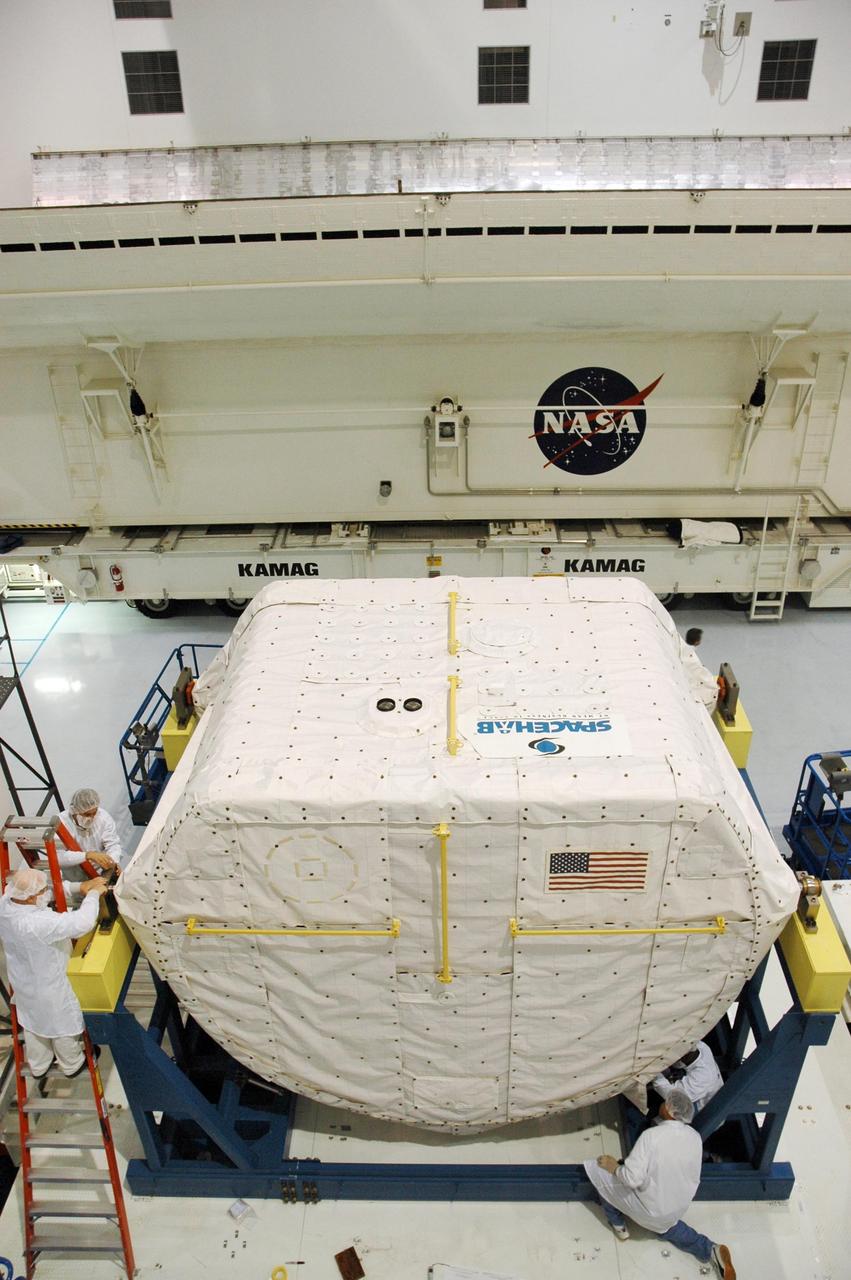

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility, technicians secure the protective coverings on the SPACEHAB Module before it is transferred to the Payload Canister. The SPACEHAB Module will carry racks of experiments, flight hardware, spacewalk equipment and supplies to support mission STS-116 to the International Space Station. STS-116 will be mission number 20 to the station and construction flight 12A.1. Along with SPACEHAB, the mission payload on Space Shuttle Discovery includes the P5 integrated truss structure and other key components. The launch window opens Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
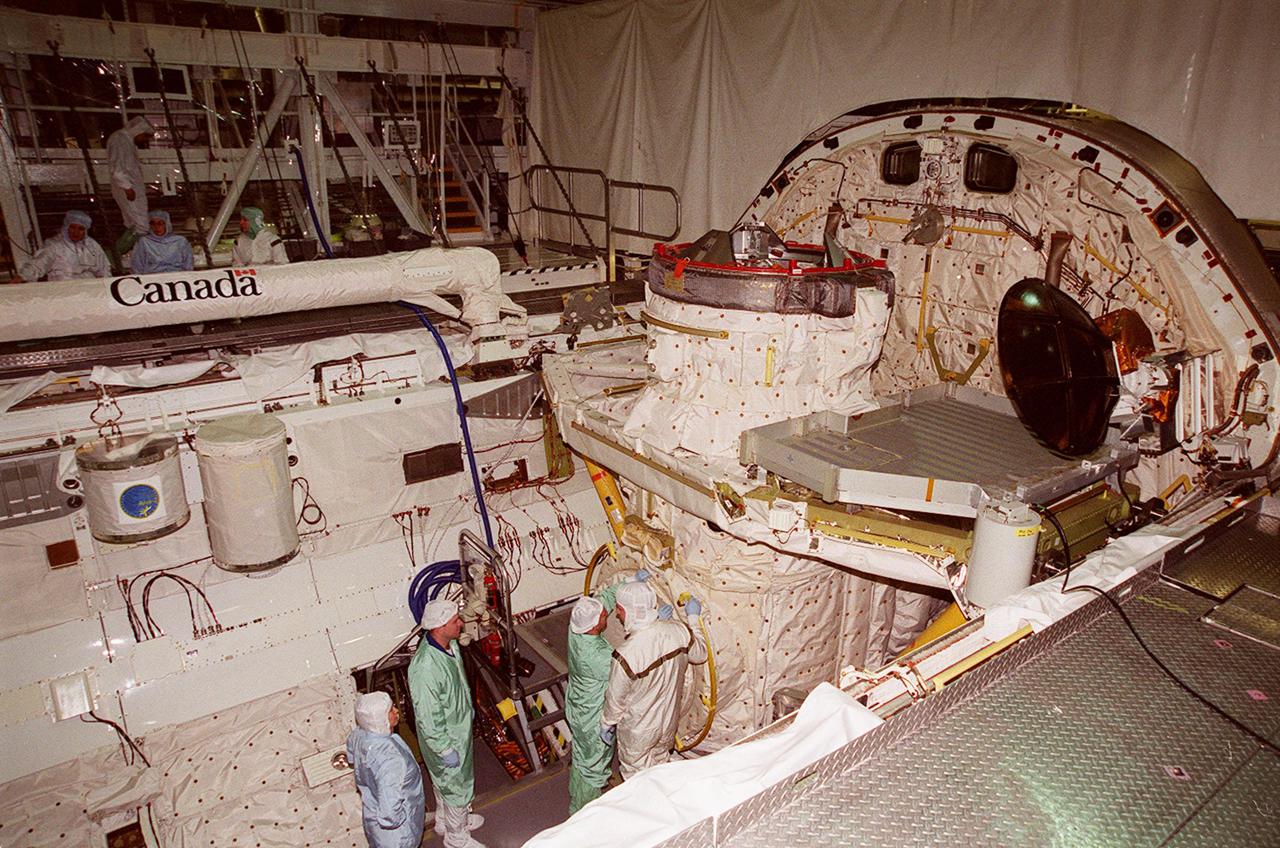

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, STS-102 Mission Specialist Paul W. Richards (left) looks on while Pilot James W. Kelly; checks out equipment in Discovery’s payload bay. Above them (left) are two GetAway Special canisters that contain experiments for the mission. Above them is the Canadian robotic arm, used to manipulate modules during the construction of the International Space Station. The crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
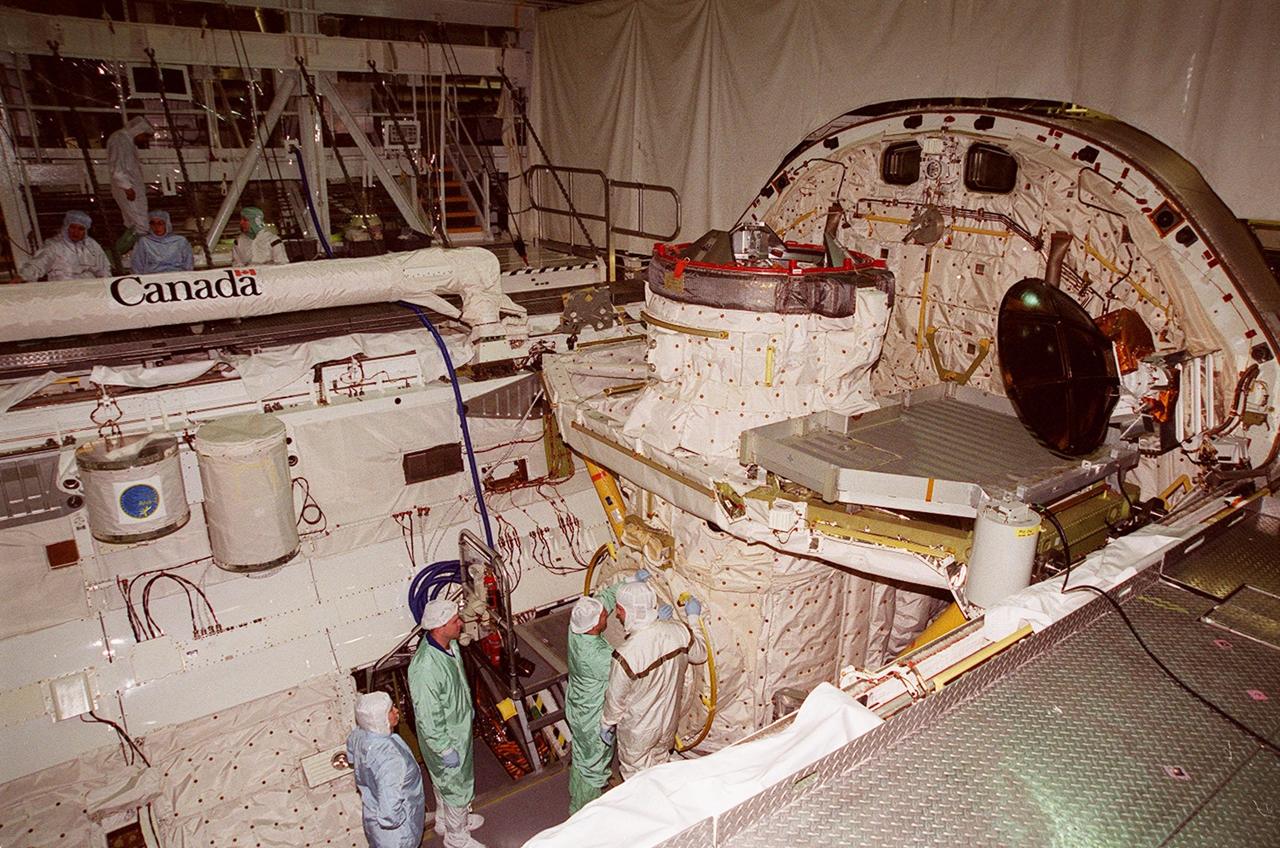

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, STS-102 Mission Specialist Paul W. Richards (left) looks on while Pilot James W. Kelly; checks out equipment in Discovery’s payload bay. Above them (left) are two GetAway Special canisters that contain experiments for the mission. Above them is the Canadian robotic arm, used to manipulate modules during the construction of the International Space Station. The crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
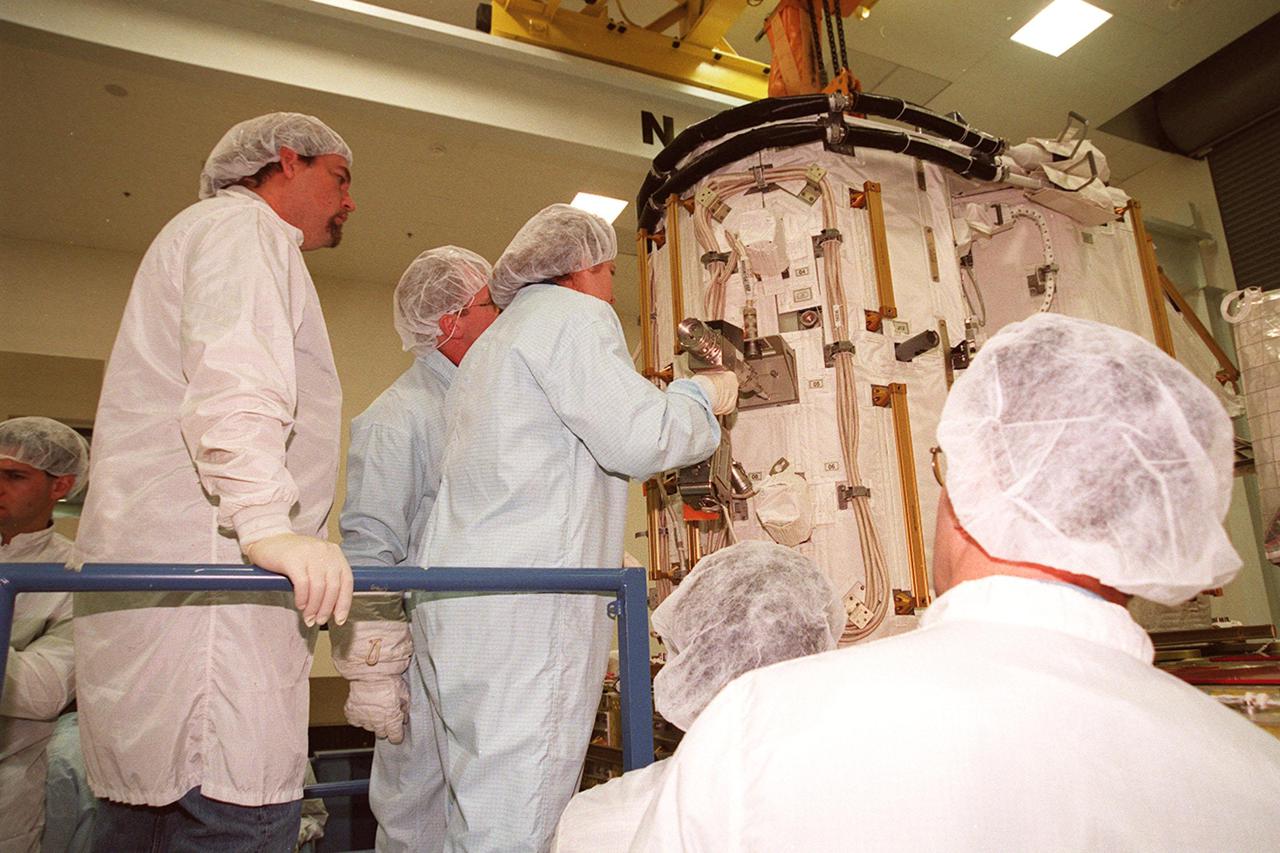

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, members of the STS-102 crew get acquainted with tools and equipment they will be using on their mission to the International Space Station. Susan Helms (center), who is part of the Expedition Two crew going to the International Space Station, practices with a tool on the Early Ammonia Servicer while Mission Specialist Andrew S.W. Thomas (next to her) looks on. The second spacewalk of the mission will require the crew to transfer the Early Ammonia Servicer to the P6 truss. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 8, 2001
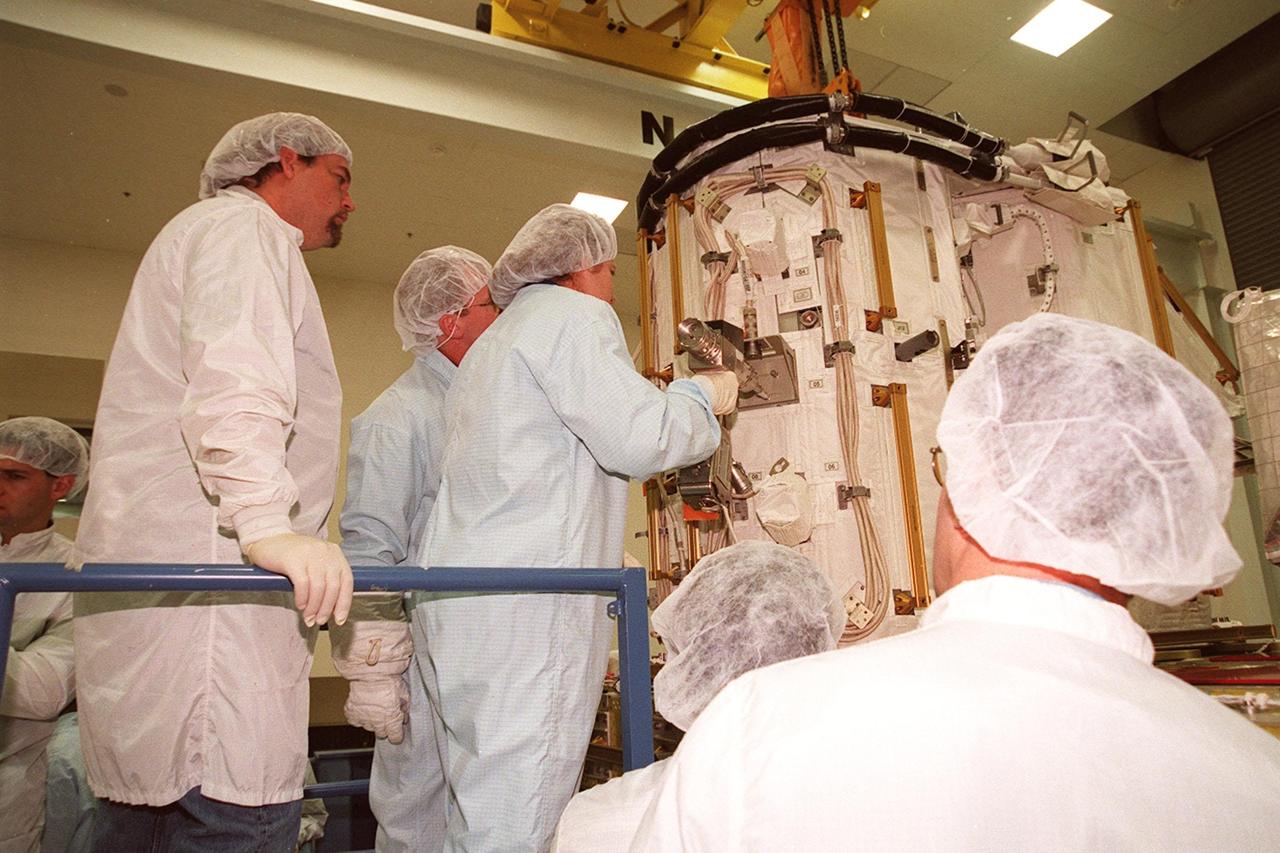

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, members of the STS-102 crew get acquainted with tools and equipment they will be using on their mission to the International Space Station. Susan Helms (center), who is part of the Expedition Two crew going to the International Space Station, practices with a tool on the Early Ammonia Servicer while Mission Specialist Andrew S.W. Thomas (next to her) looks on. The second spacewalk of the mission will require the crew to transfer the Early Ammonia Servicer to the P6 truss. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 8, 2001
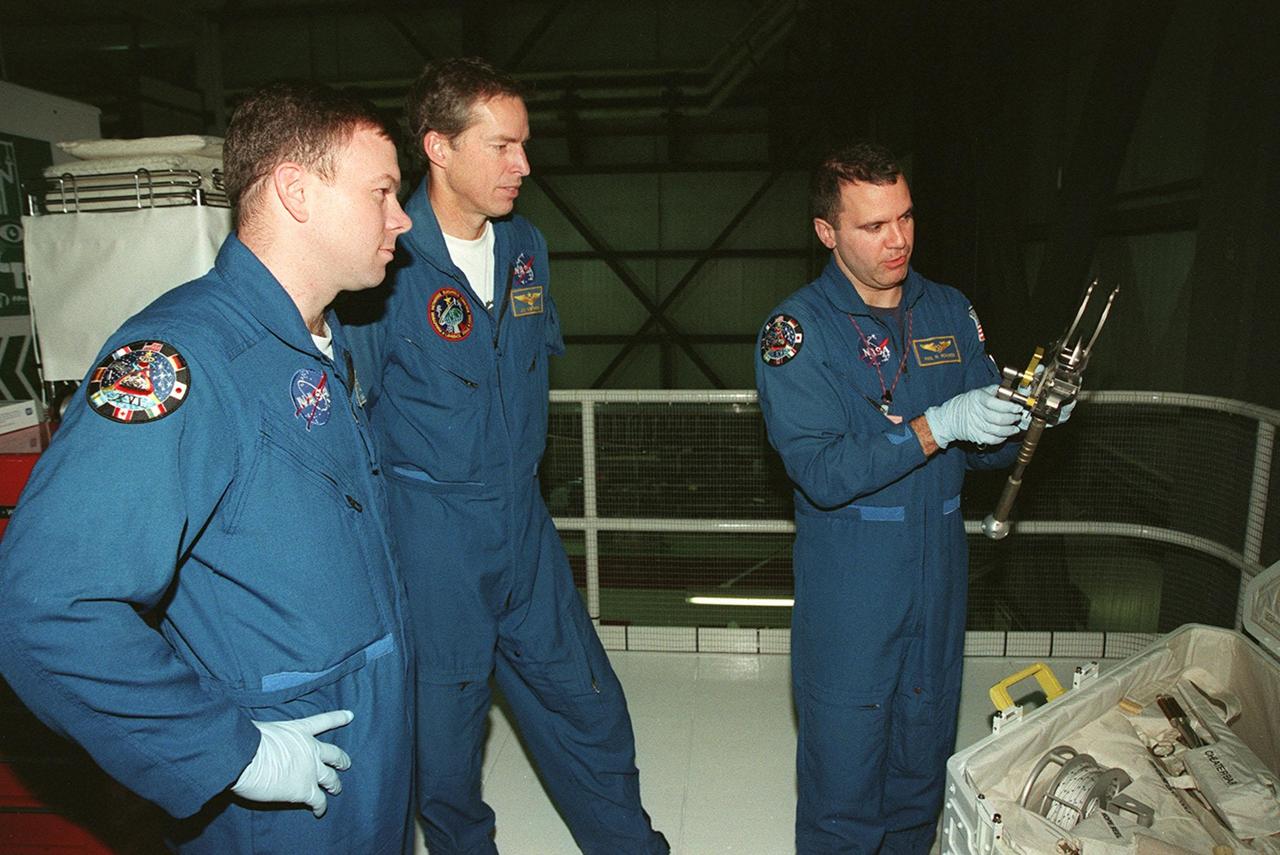

While STS-102 Pilot James W. Kelly and Commander James D. Wetherbee watch, Mission Specialist Paul W. Richards checks out a piece of equipment from the tool caddy below. The mission crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
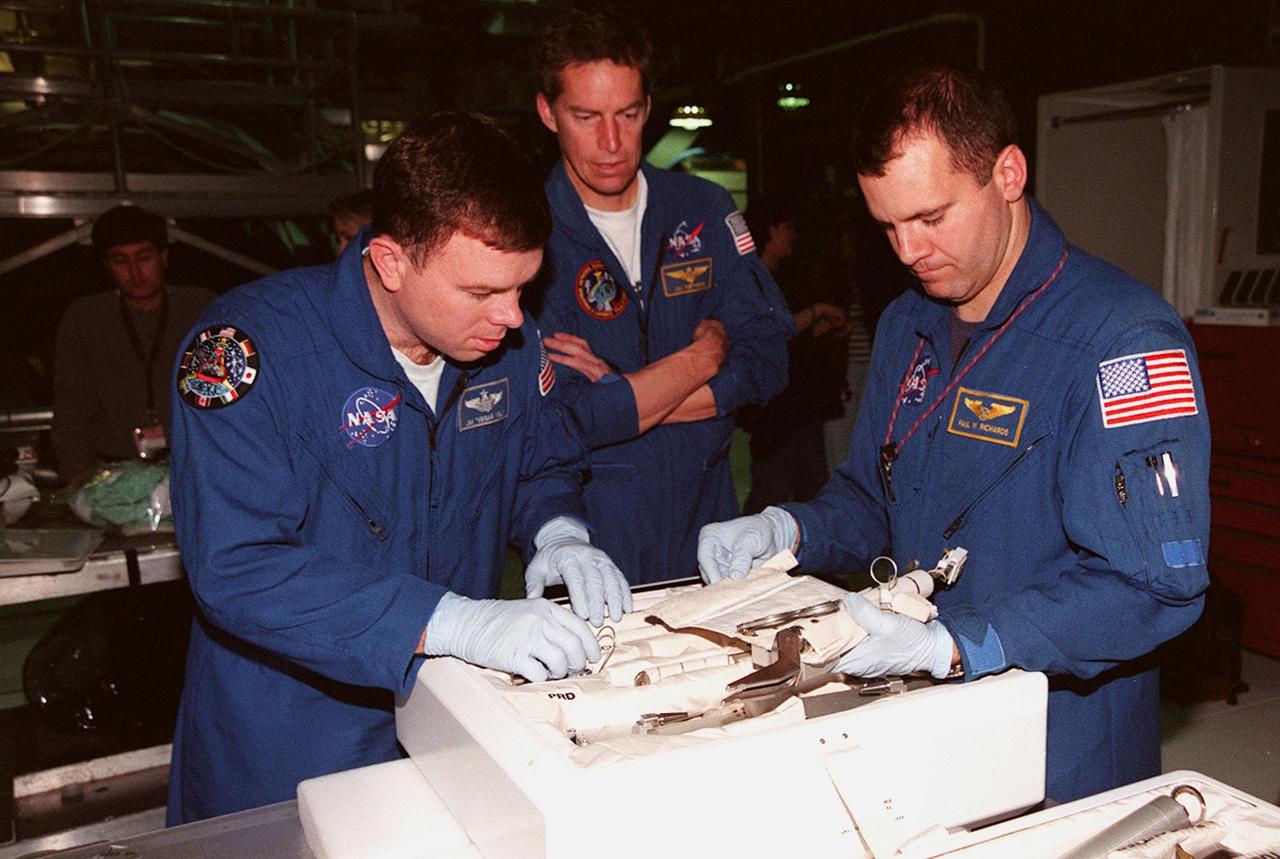

STS-102 Pilot James W. Kelly (left) and Mission Specialist Paul W. Richards look over equipment in the tool caddy that is carried on launches. Commander James D. Wetherbee (center) watches. The mission crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
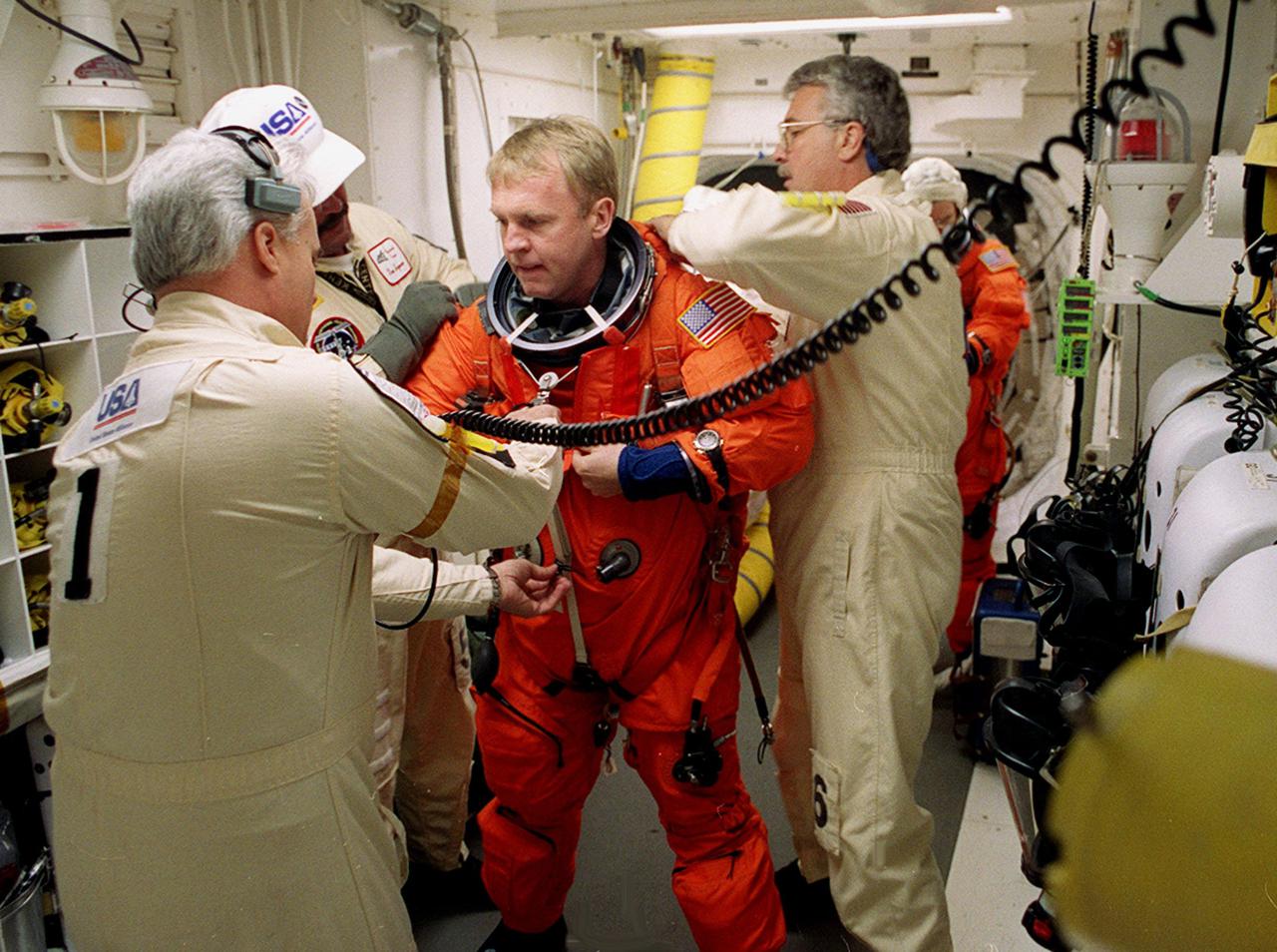

Before entering Space Shuttle Discovery, STS-102 Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas is helped with his launch and entry suit by technicians in the White Room. The mission is Thomas’s third Shuttle flight. Discovery is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo on the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment, Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny. Discovery is set to launch March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST. The 12-day mission is expected to end with a landing at KSC on March 20
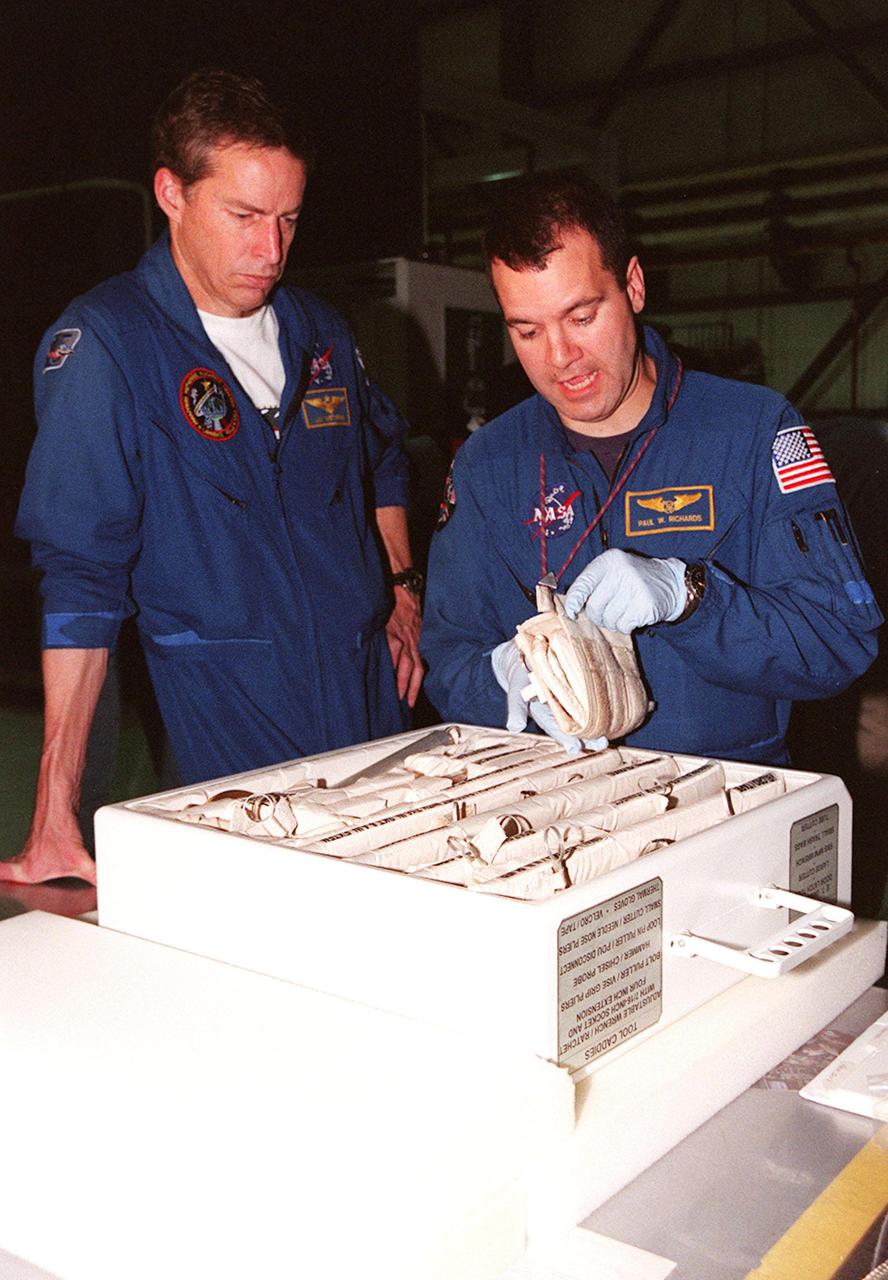

STS-102 Commander James D. Wetherbee watches as Mission Specialist Paul W. Richards handles some of the equipment inside the tool caddy that is carried on launches. The mission crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
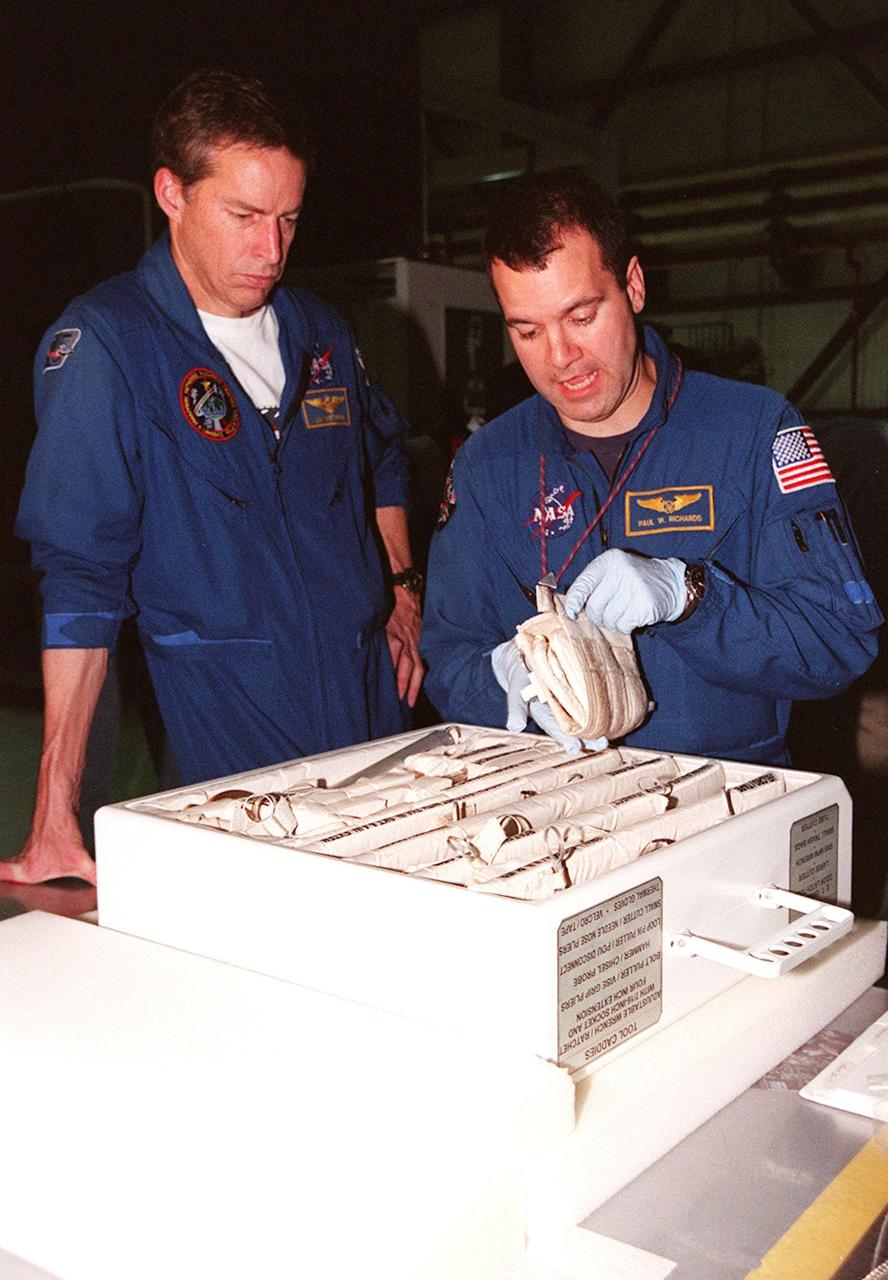

STS-102 Commander James D. Wetherbee watches as Mission Specialist Paul W. Richards handles some of the equipment inside the tool caddy that is carried on launches. The mission crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
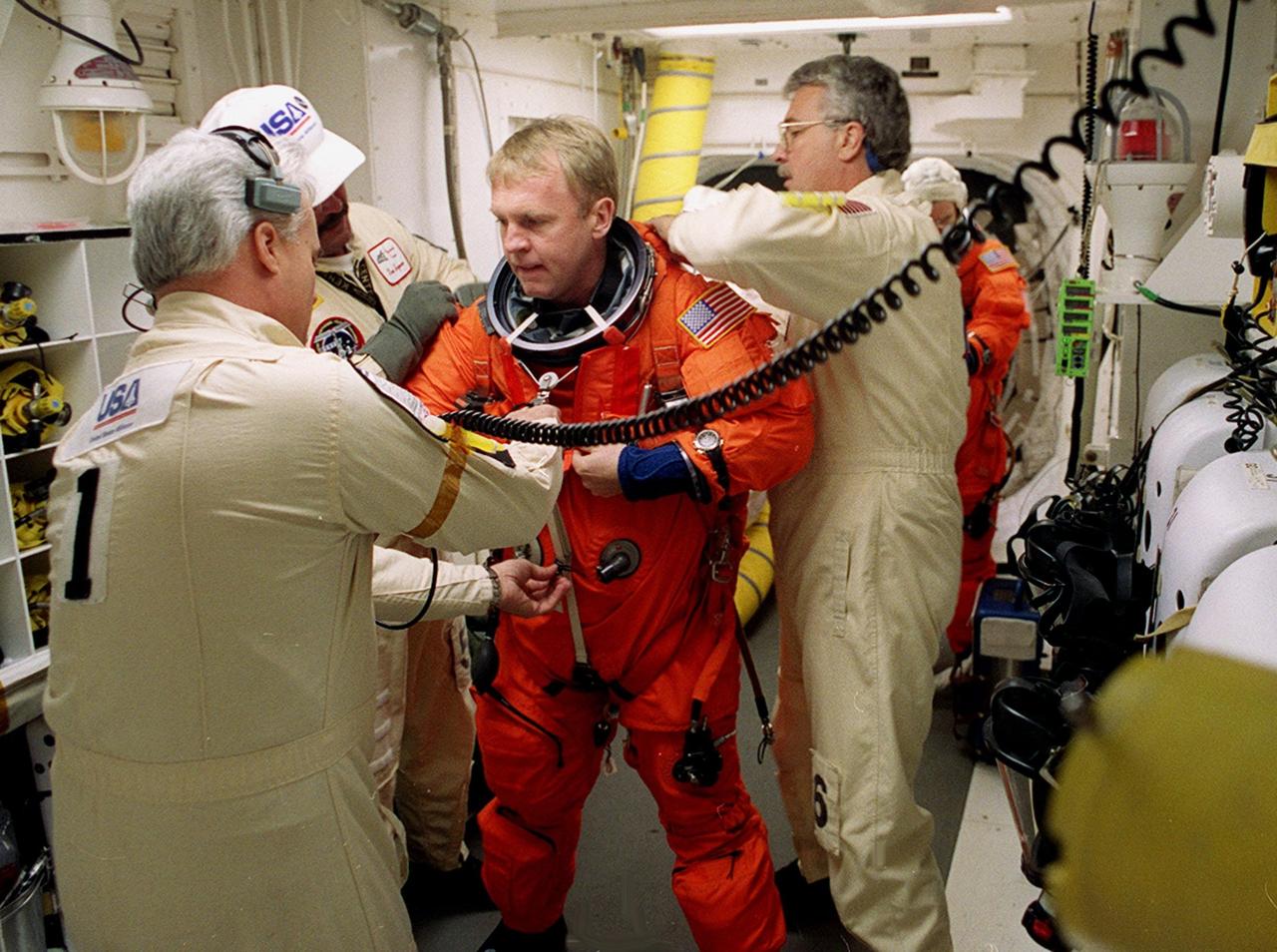

Before entering Space Shuttle Discovery, STS-102 Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas is helped with his launch and entry suit by technicians in the White Room. The mission is Thomas’s third Shuttle flight. Discovery is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo on the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment, Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny. Discovery is set to launch March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST. The 12-day mission is expected to end with a landing at KSC on March 20
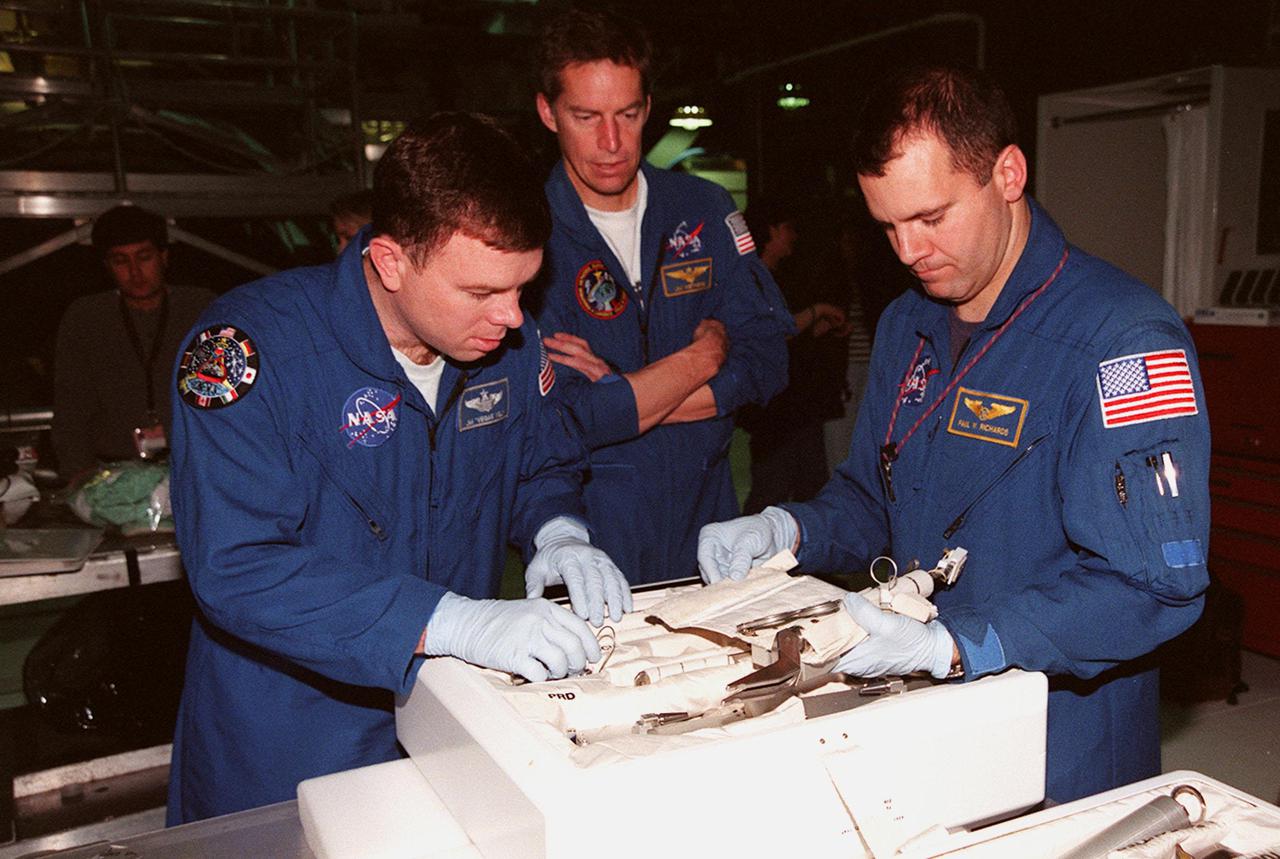

STS-102 Pilot James W. Kelly (left) and Mission Specialist Paul W. Richards look over equipment in the tool caddy that is carried on launches. Commander James D. Wetherbee (center) watches. The mission crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
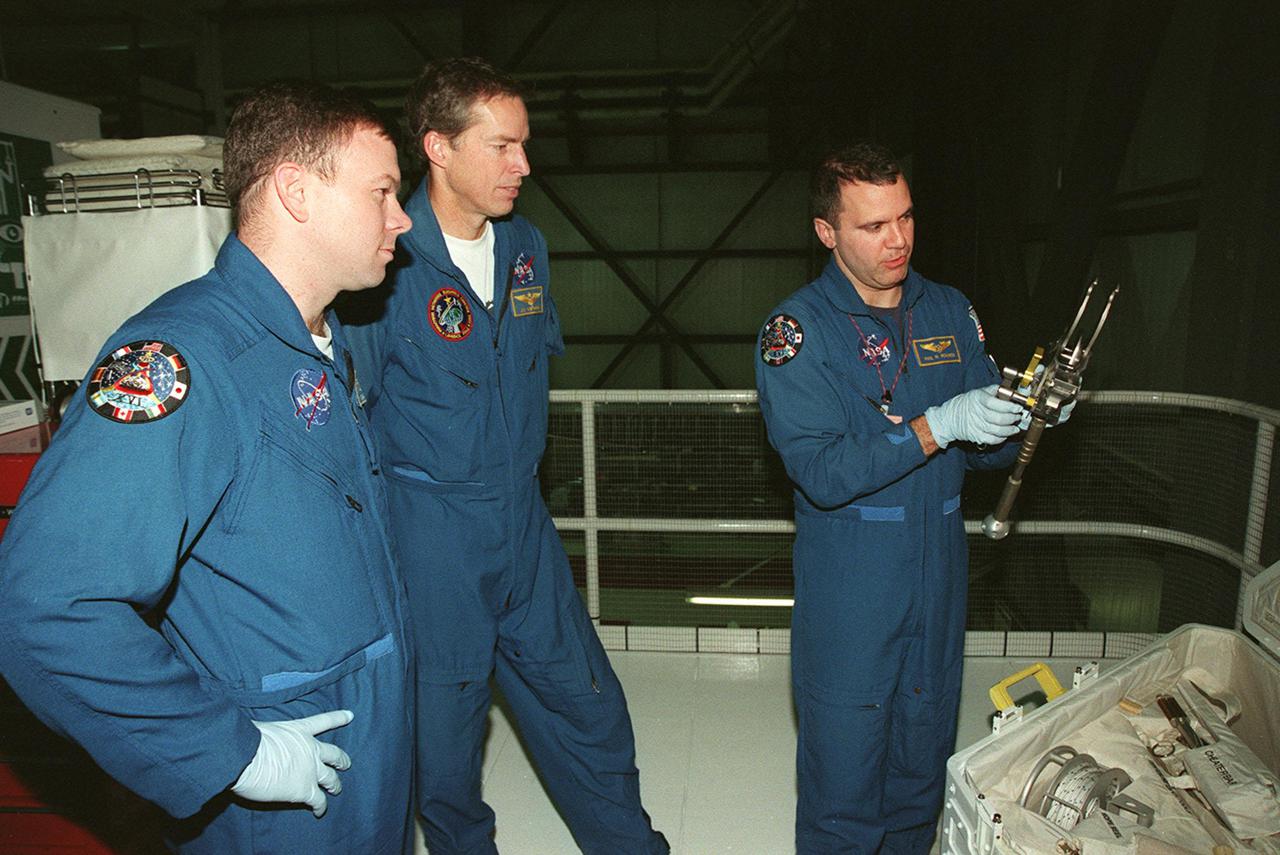

While STS-102 Pilot James W. Kelly and Commander James D. Wetherbee watch, Mission Specialist Paul W. Richards checks out a piece of equipment from the tool caddy below. The mission crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
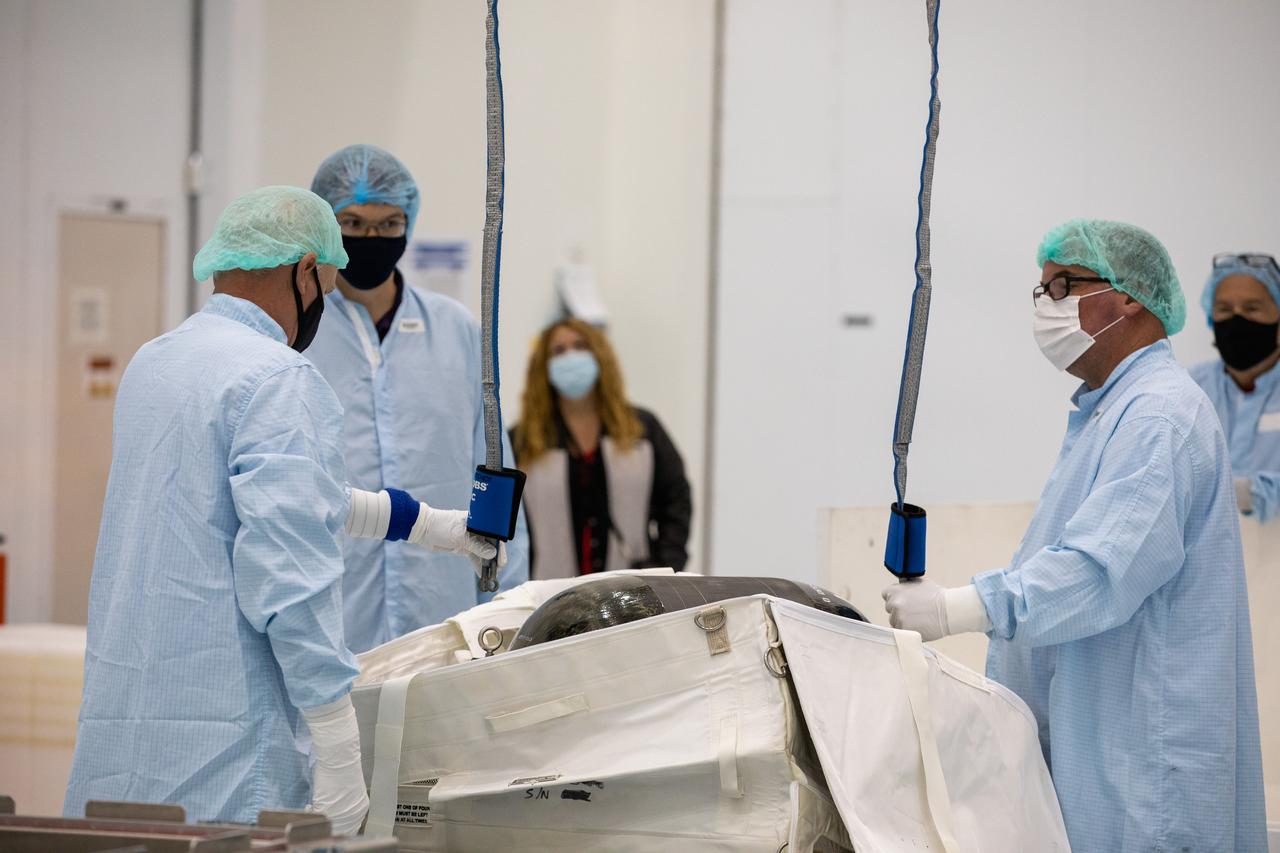

Technicians prepare to unpack and inspect a Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.
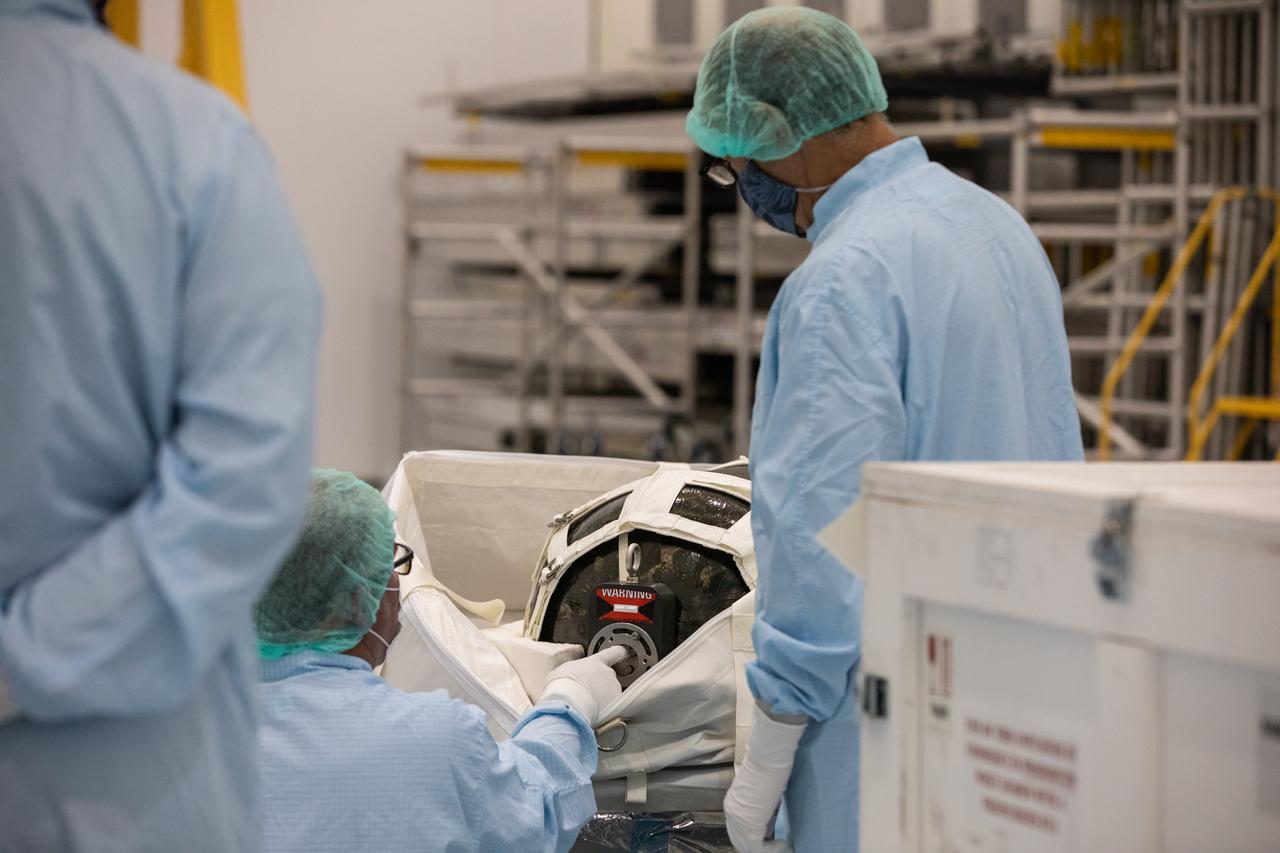

Technicians unpack and inspect a Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.
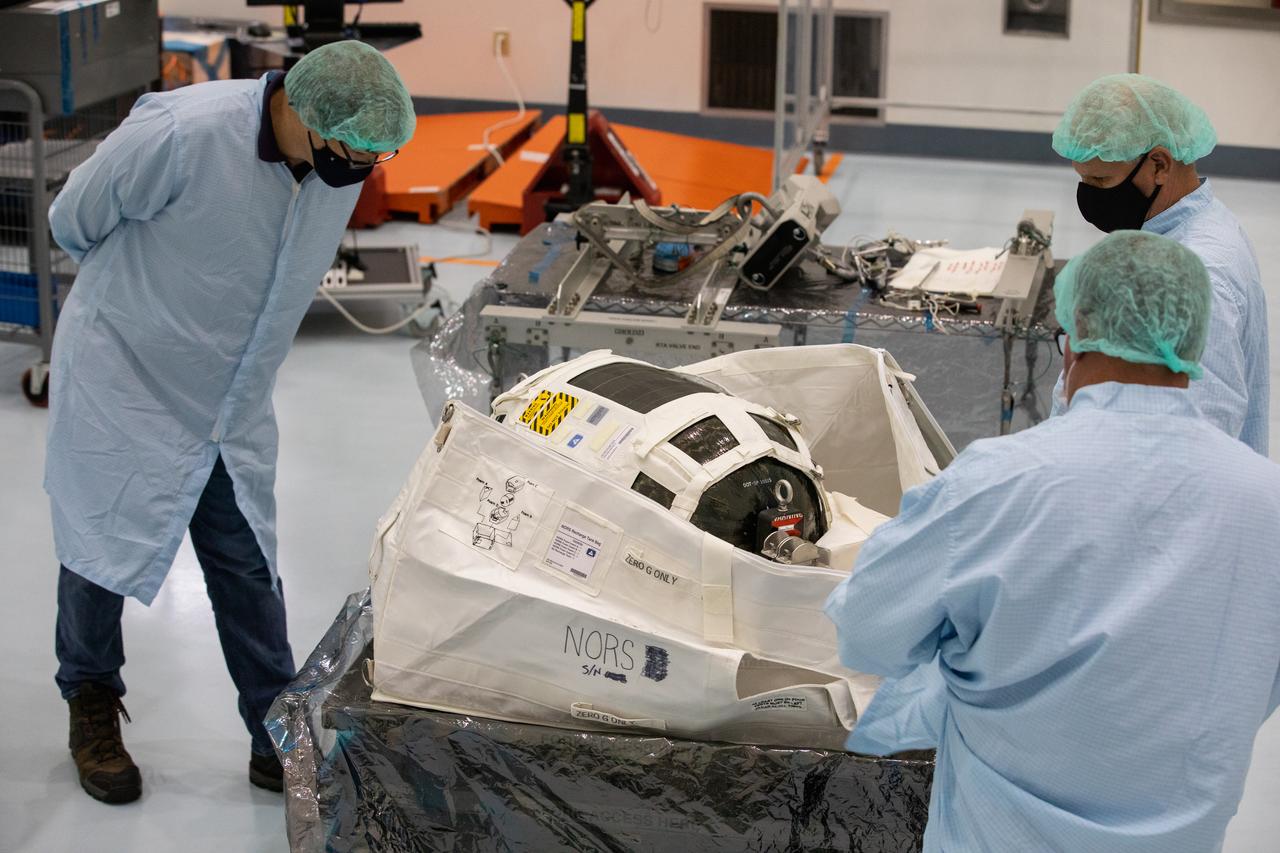

Technicians unpack and inspect a Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.
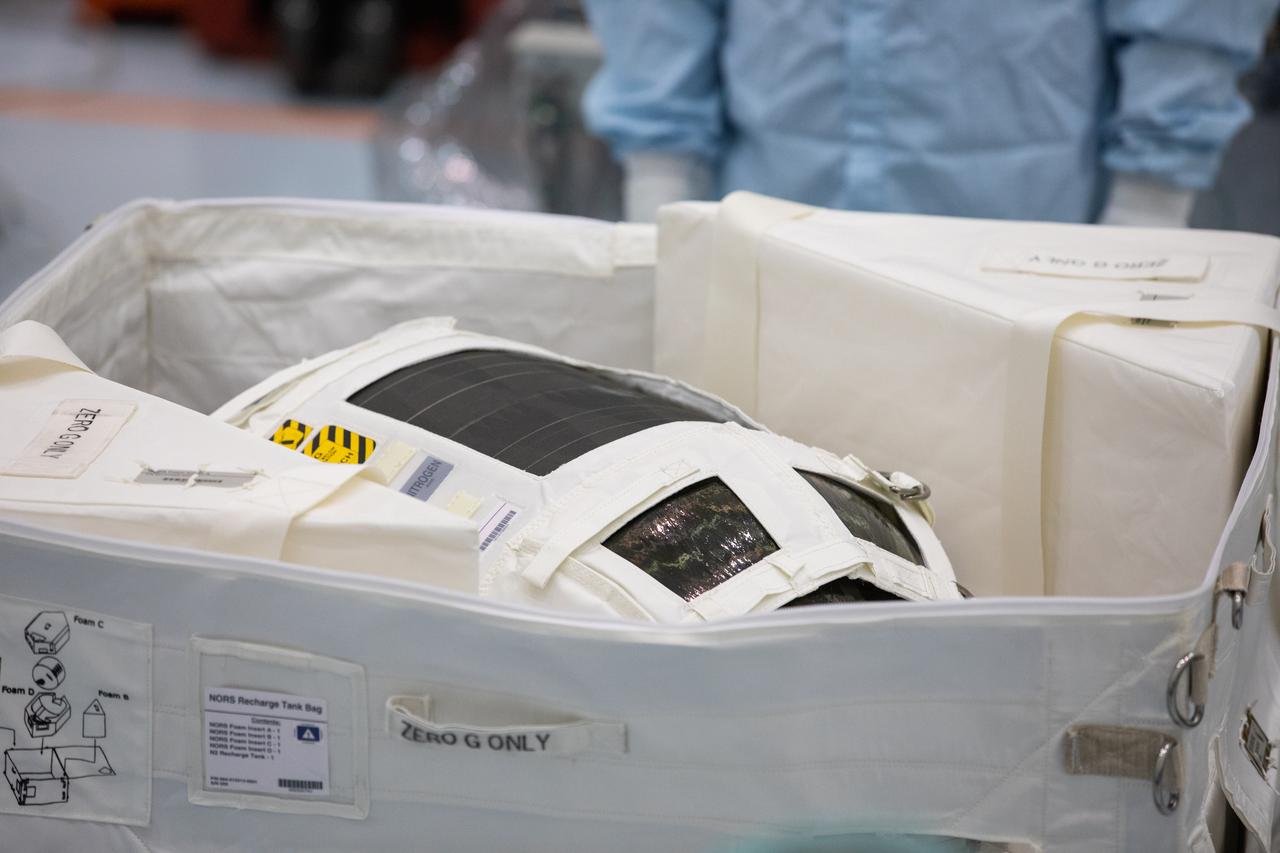
A Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank is unpacked and readied for inspection inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.
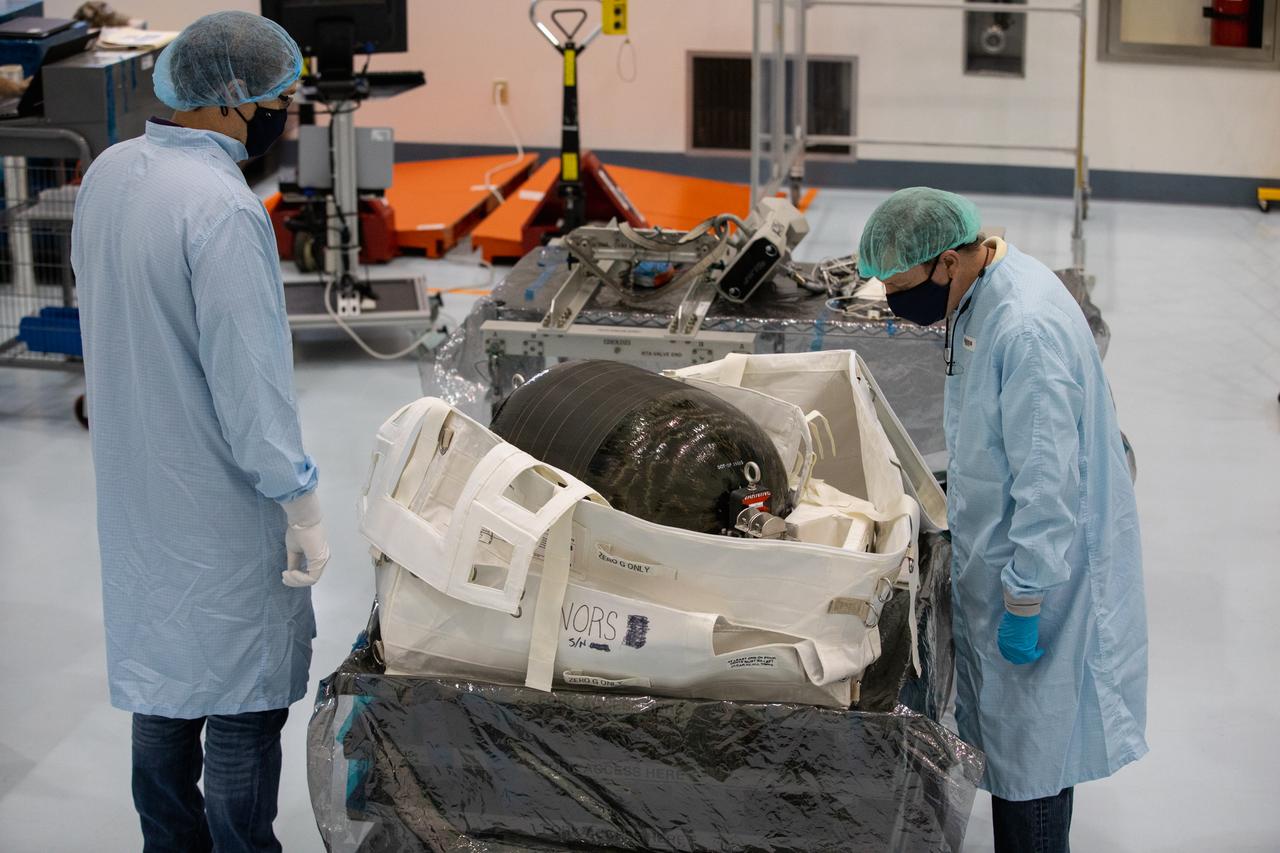

Technicians unpack and inspect a Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.
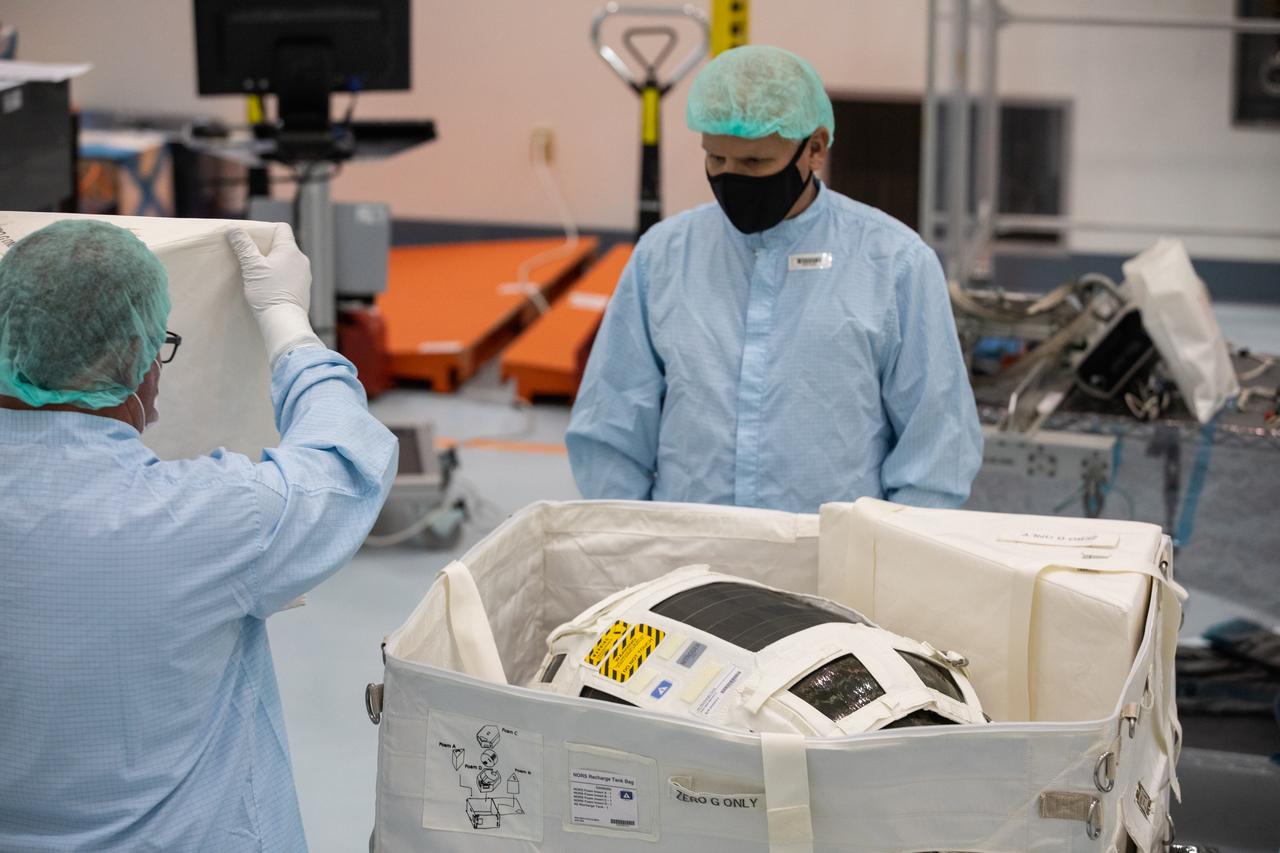

Technicians unpack and inspect a Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.
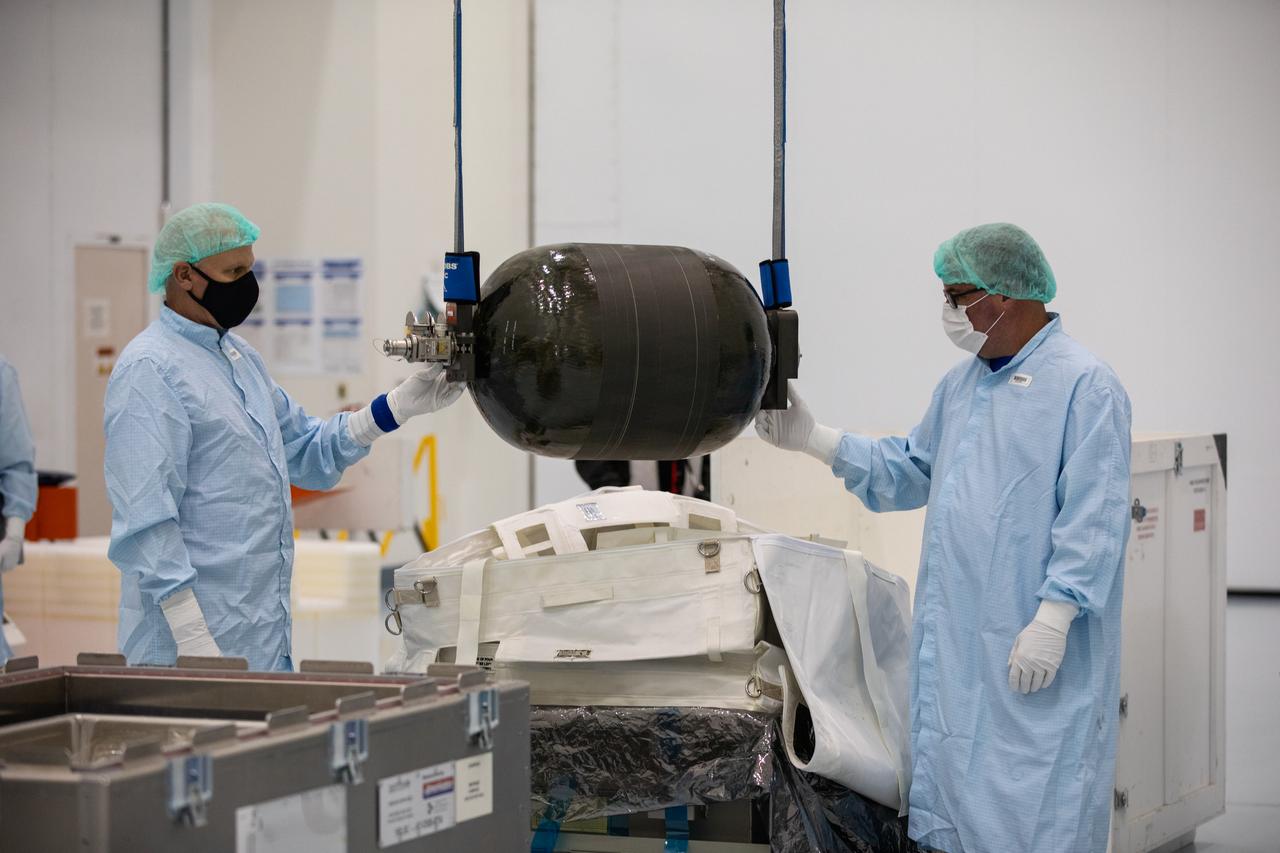

Technicians unpack and inspect a Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.
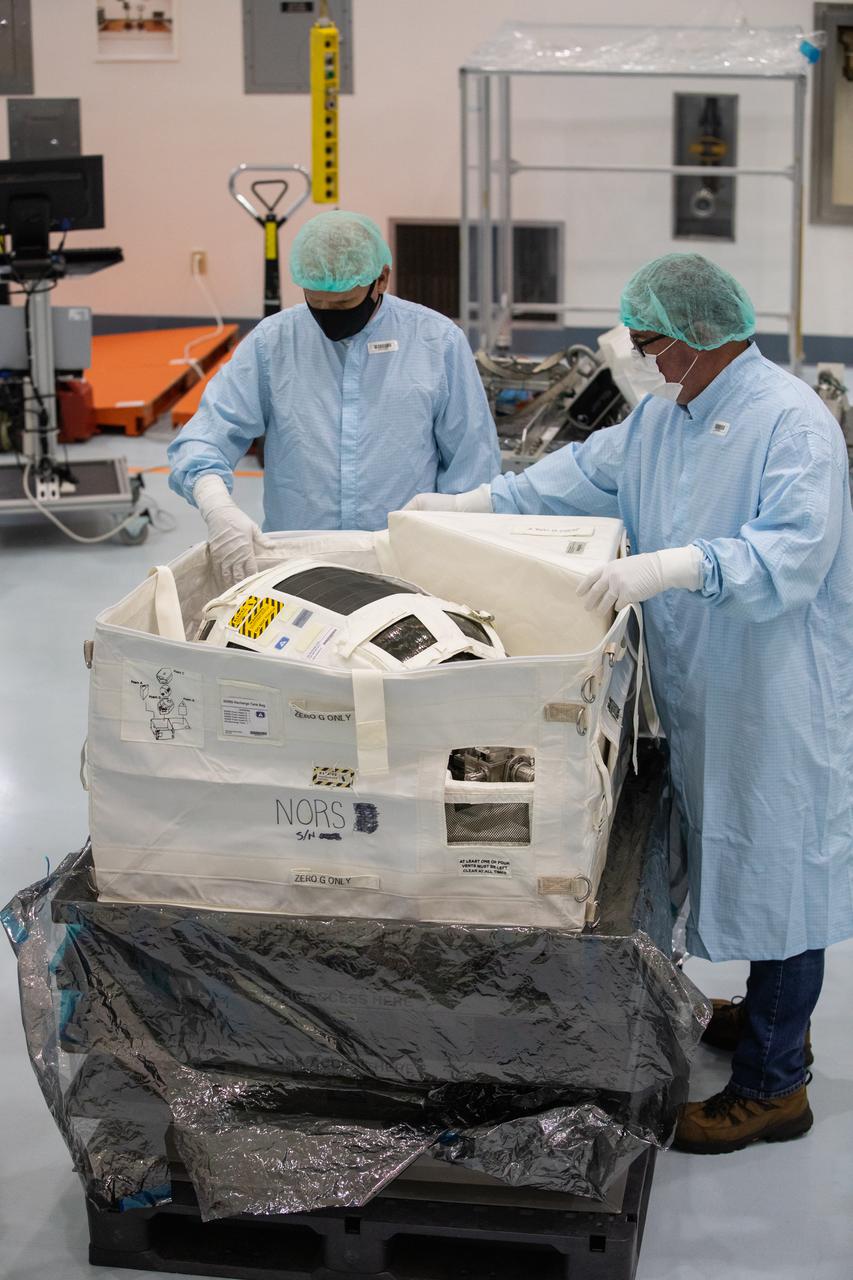

Technicians unpack and inspect a Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.

A technicians inspects a Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.
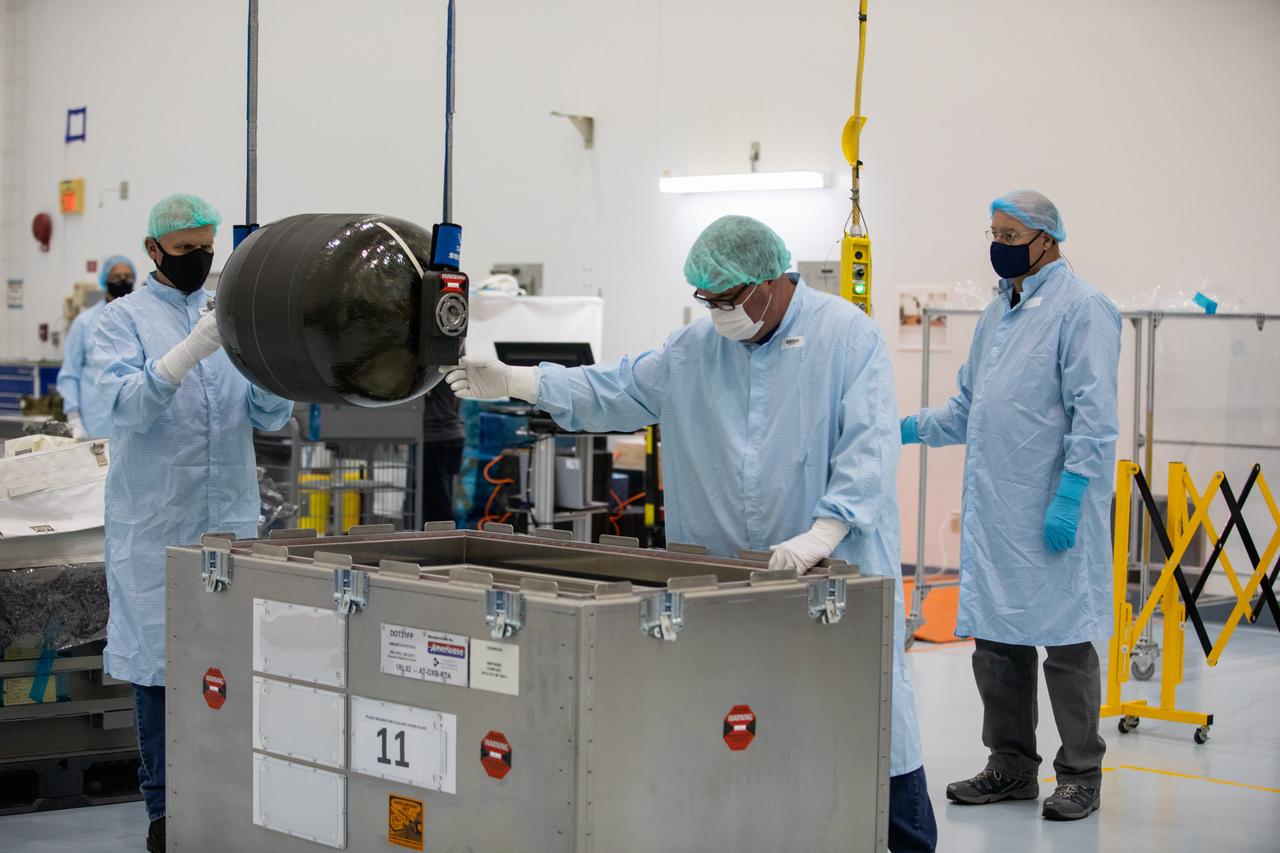

Technicians unpack and inspect a Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.
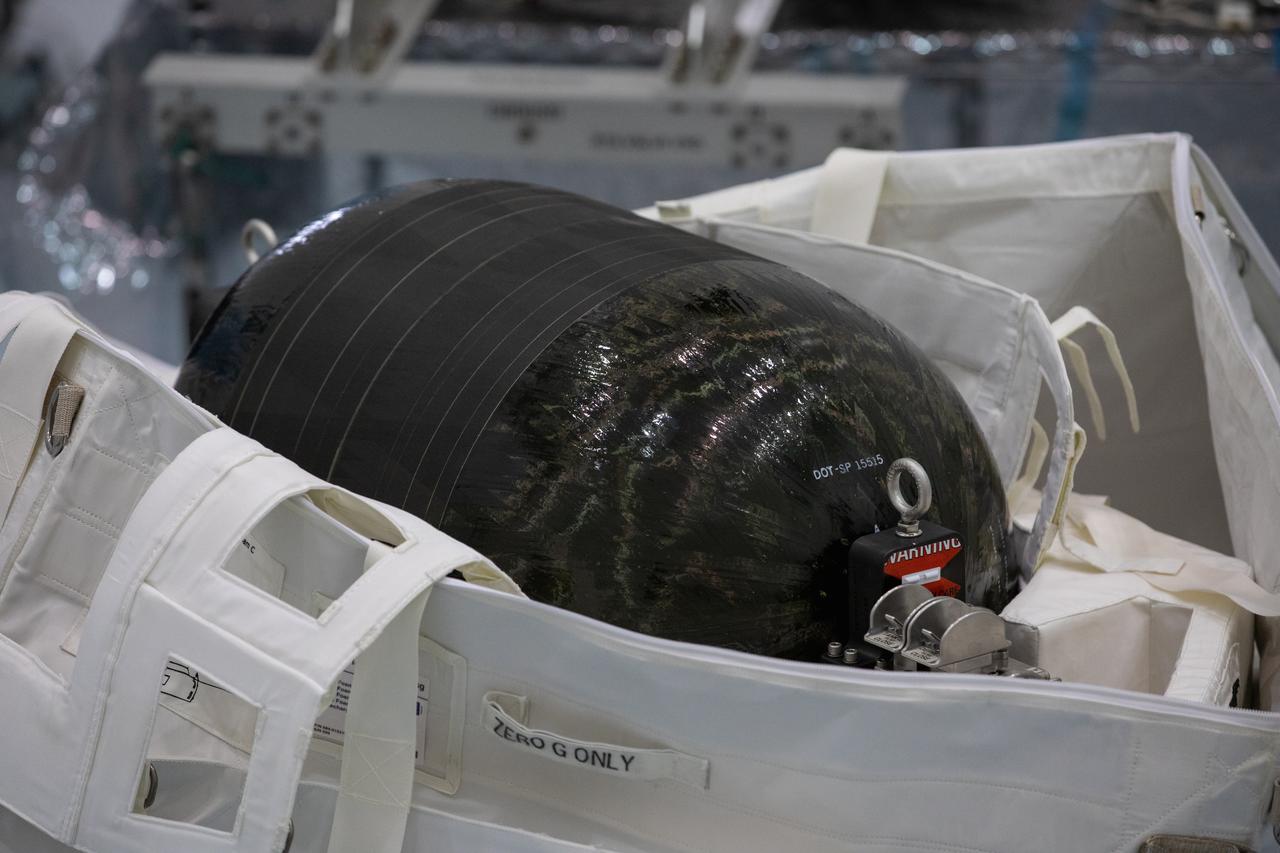

A Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank is unpacked and readied for inspection inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.
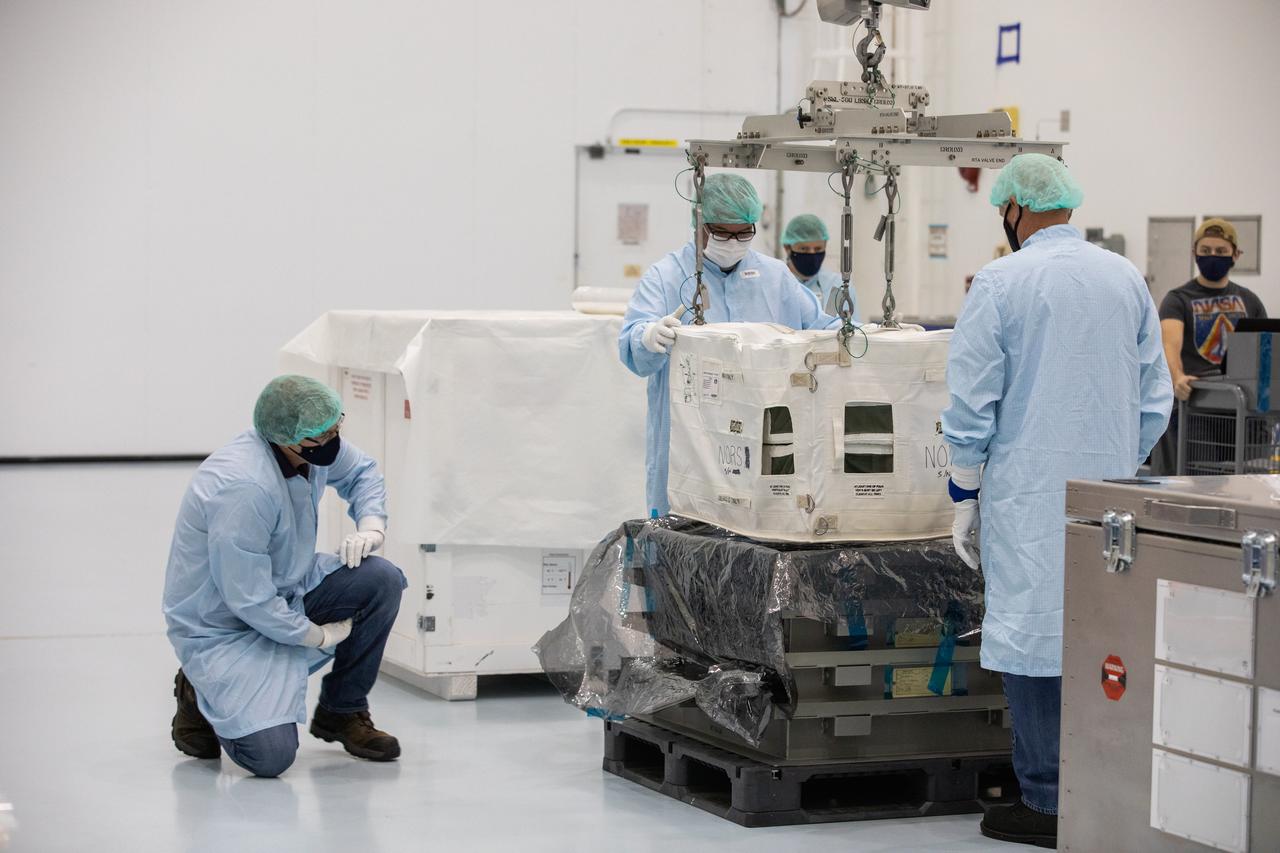

Technicians unpack and inspect a Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.

A Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank is unpacked and readied for inspection inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.
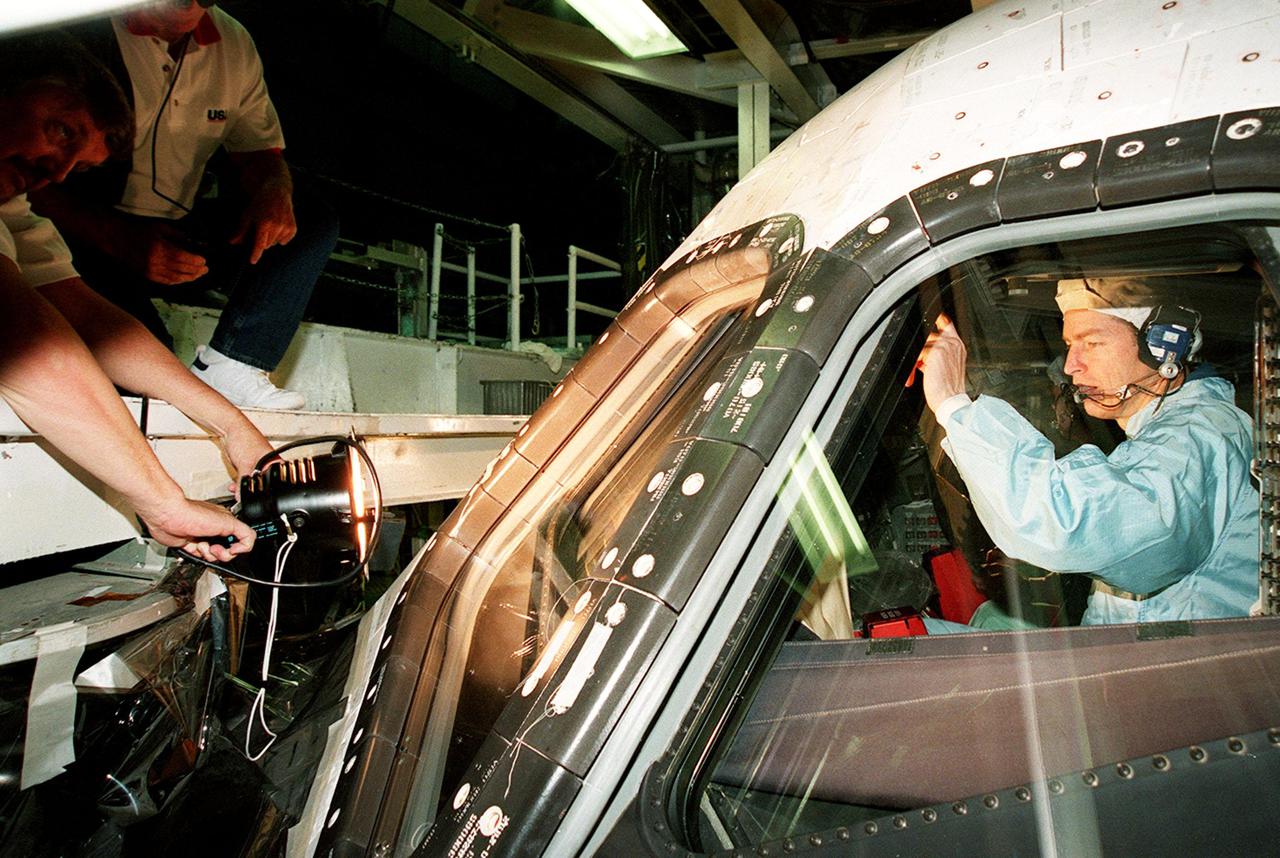

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, STS-102 Commander James D. Wetherbee checks out the window of Discovery from the inside while workers (left) check the outside.; The mission crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
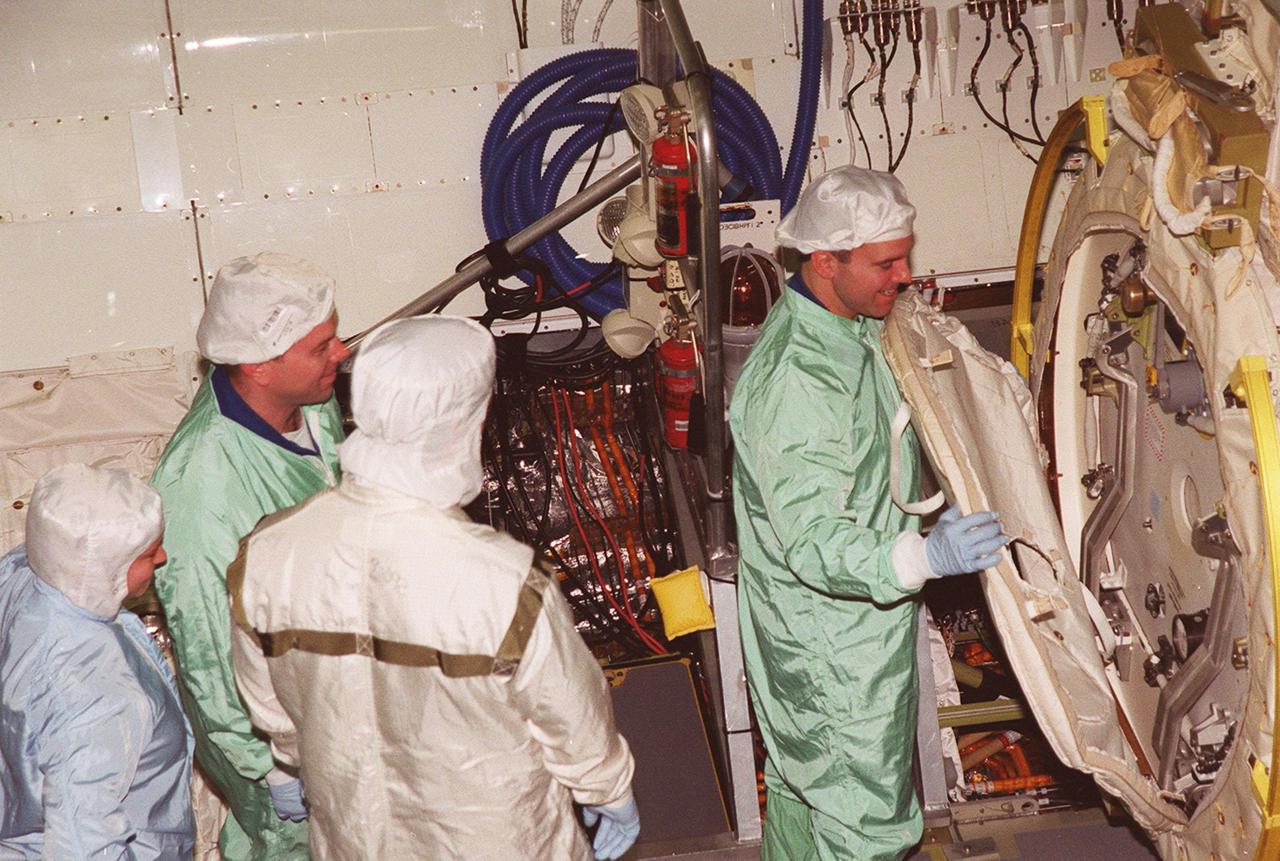

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, STS-102 Pilot James W. Kelly (left) looks on while Mission Specialist Paul W. Richards checks out equipment in Discovery’s payload bay. The crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
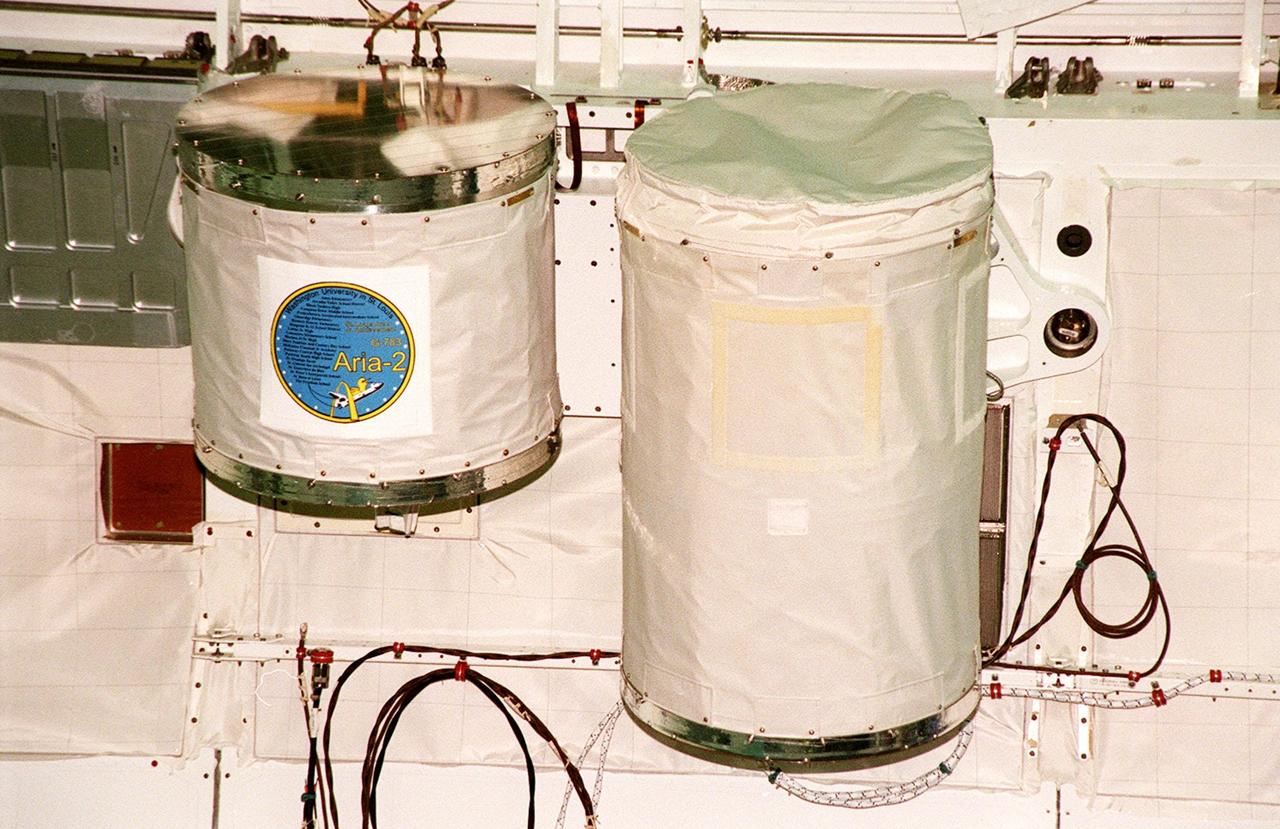

Two GetAway Special canisters (GAS can) are installed in Discovery’s payload bay for mission STS-102. The smaller one, left, is filled with student experiments from schools in St. Louis (hosted by Washington University at St. Louis). The larger, at right, is an experiment on Shuttle vibration force. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, STS-102 Pilot James W. Kelly (left) looks on while Mission Specialist Paul W. Richards checks out equipment in Discovery’s payload bay. The crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
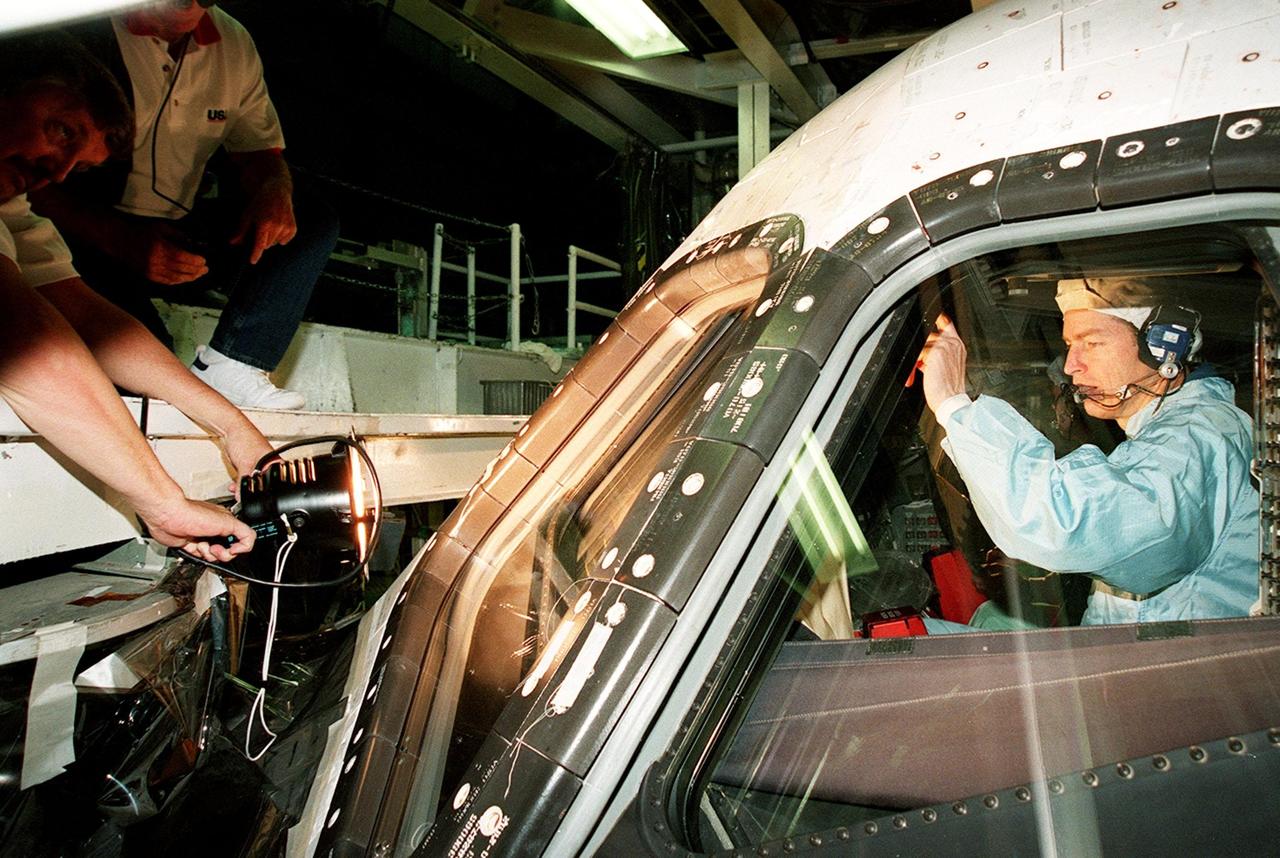

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, STS-102 Commander James D. Wetherbee checks out the window of Discovery from the inside while workers (left) check the outside.; The mission crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, STS-102 Mission Specialist Andrew S.W. Thomas practices using a tool on the Early Ammonia Servicer while Mission Specialist Paul W. Richards (left) looks on. Thomas, Richards and other crew members are at SPACEHAB to get acquainted with tools and equipment they will be using on their mission to the International Space Station. The second spacewalk of the mission will require the crew to transfer the Early Ammonia Servicer to the P6 truss. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 8, 2001
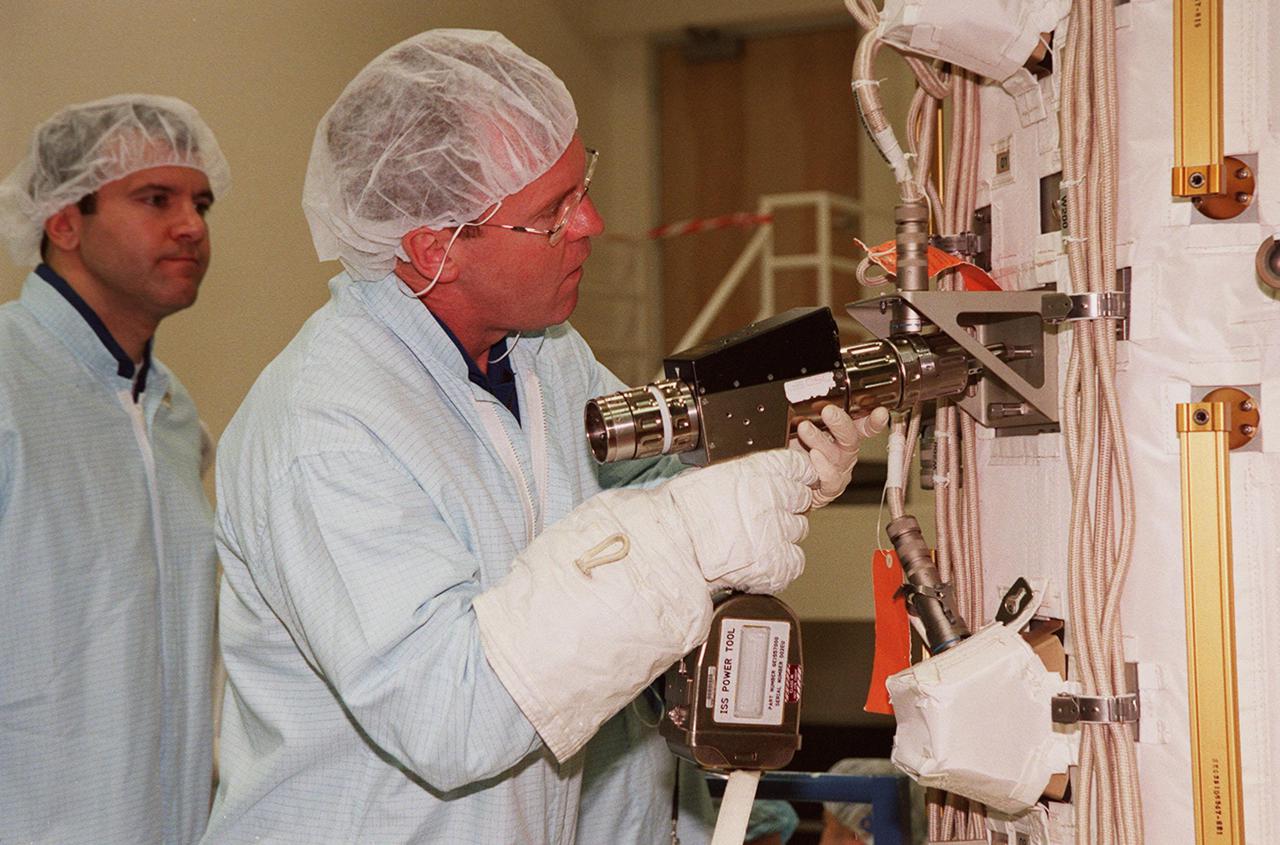

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, STS-102 Mission Specialist Andrew S.W. Thomas practices using a tool on the Early Ammonia Servicer while Mission Specialist Paul W. Richards (left) looks on. Thomas, Richards and other crew members are at SPACEHAB to get acquainted with tools and equipment they will be using on their mission to the International Space Station. The second spacewalk of the mission will require the crew to transfer the Early Ammonia Servicer to the P6 truss. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 8, 2001
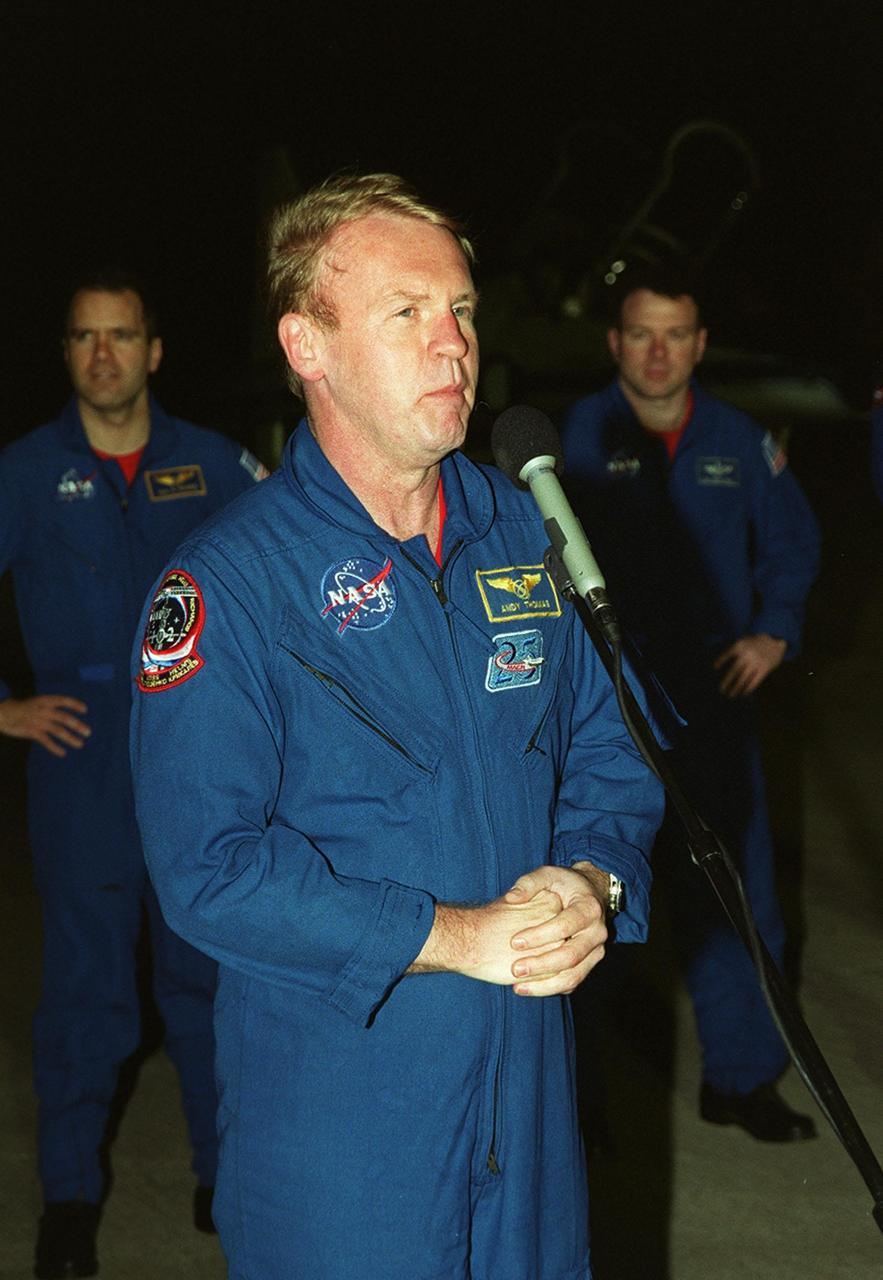

After arrival at the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-102 Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas addresses the media. Behind him are Mission Specialist Paul Richards (left) and Pilot James Kelly (right). The crew is making the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. STS-102 will be carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment. Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny. STS-102 is scheduled to launch March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST
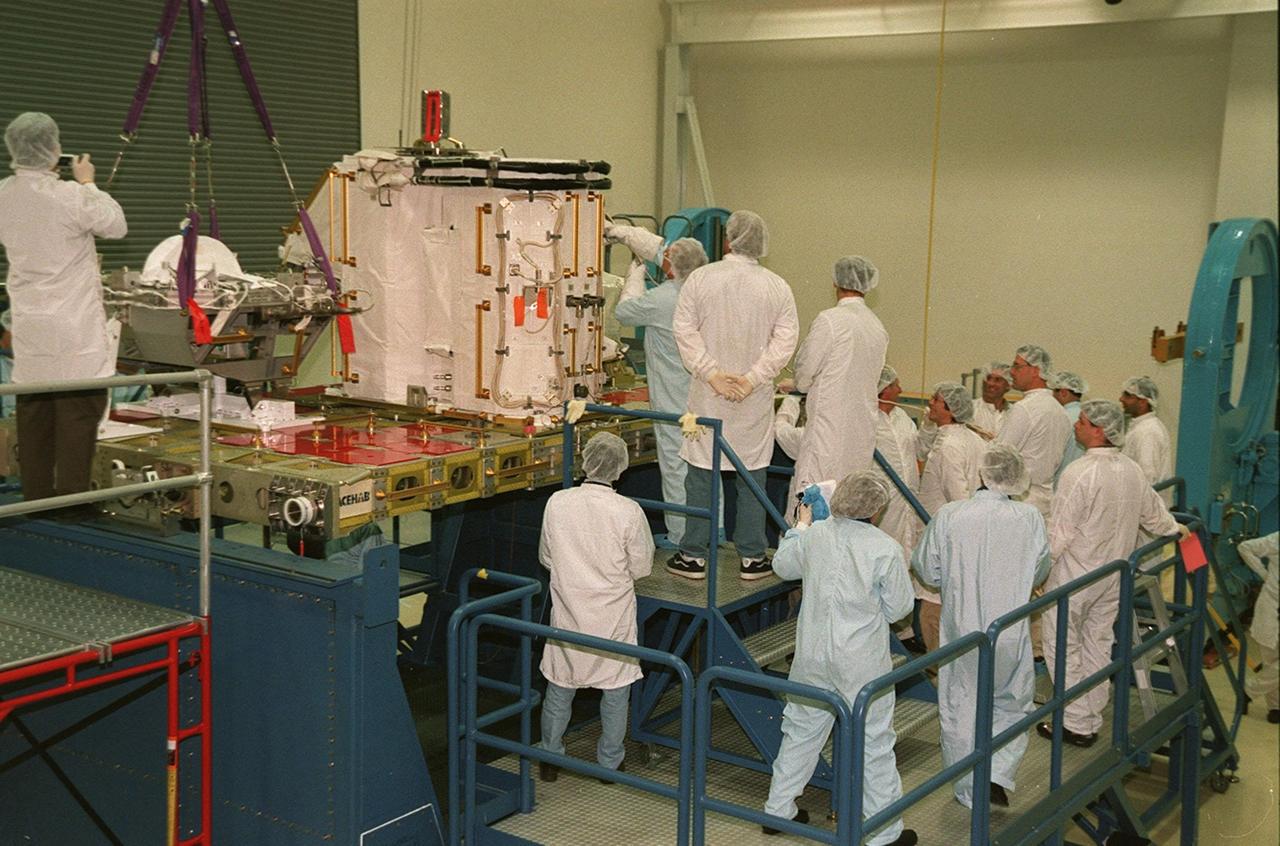

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers at SPACEHAB gather to watch STS-102 Mission Specialist Andrew S.W. Thomas work on the Early Ammonia Servicer. Thomas and other crew members are at SPACEHAB to get acquainted with tools and equipment they will be using on their mission to the International Space Station. The second spacewalk of the mission will require the crew to transfer the Early Ammonia Servicer to the P6 truss. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 8, 2001
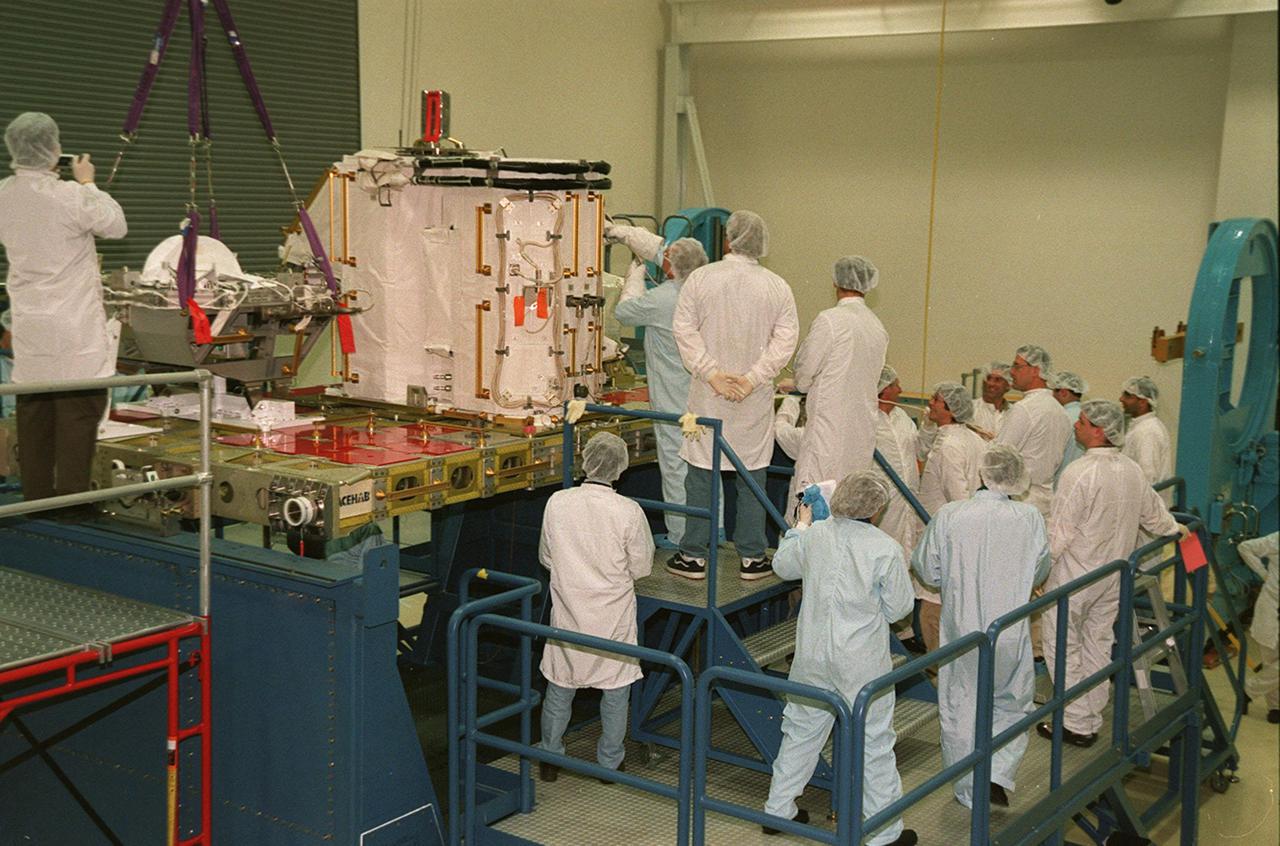

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers at SPACEHAB gather to watch STS-102 Mission Specialist Andrew S.W. Thomas work on the Early Ammonia Servicer. Thomas and other crew members are at SPACEHAB to get acquainted with tools and equipment they will be using on their mission to the International Space Station. The second spacewalk of the mission will require the crew to transfer the Early Ammonia Servicer to the P6 truss. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 8, 2001
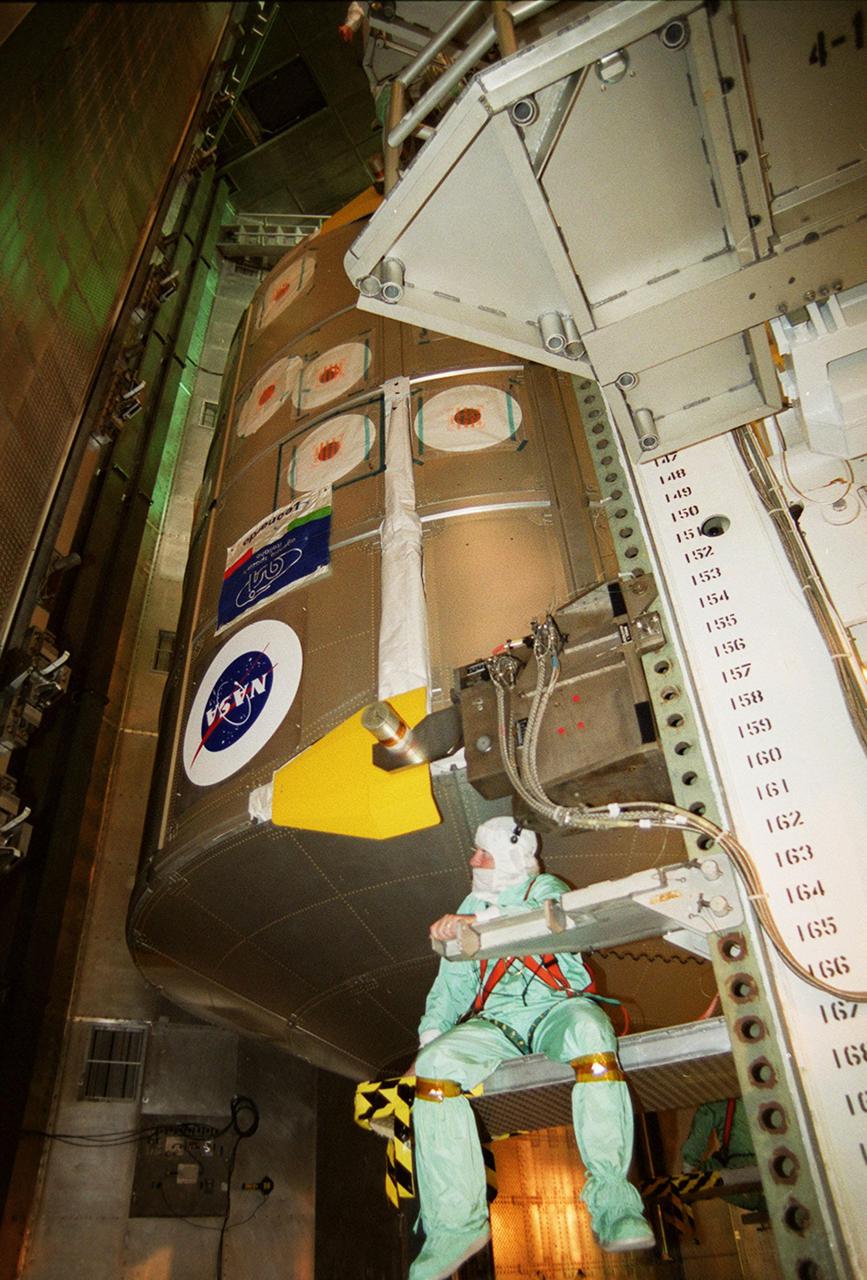

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Payload Changeout Room, Launch Pad 39B, the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo is ready to be transferred into Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. Discovery is scheduled to launch March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment, Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny
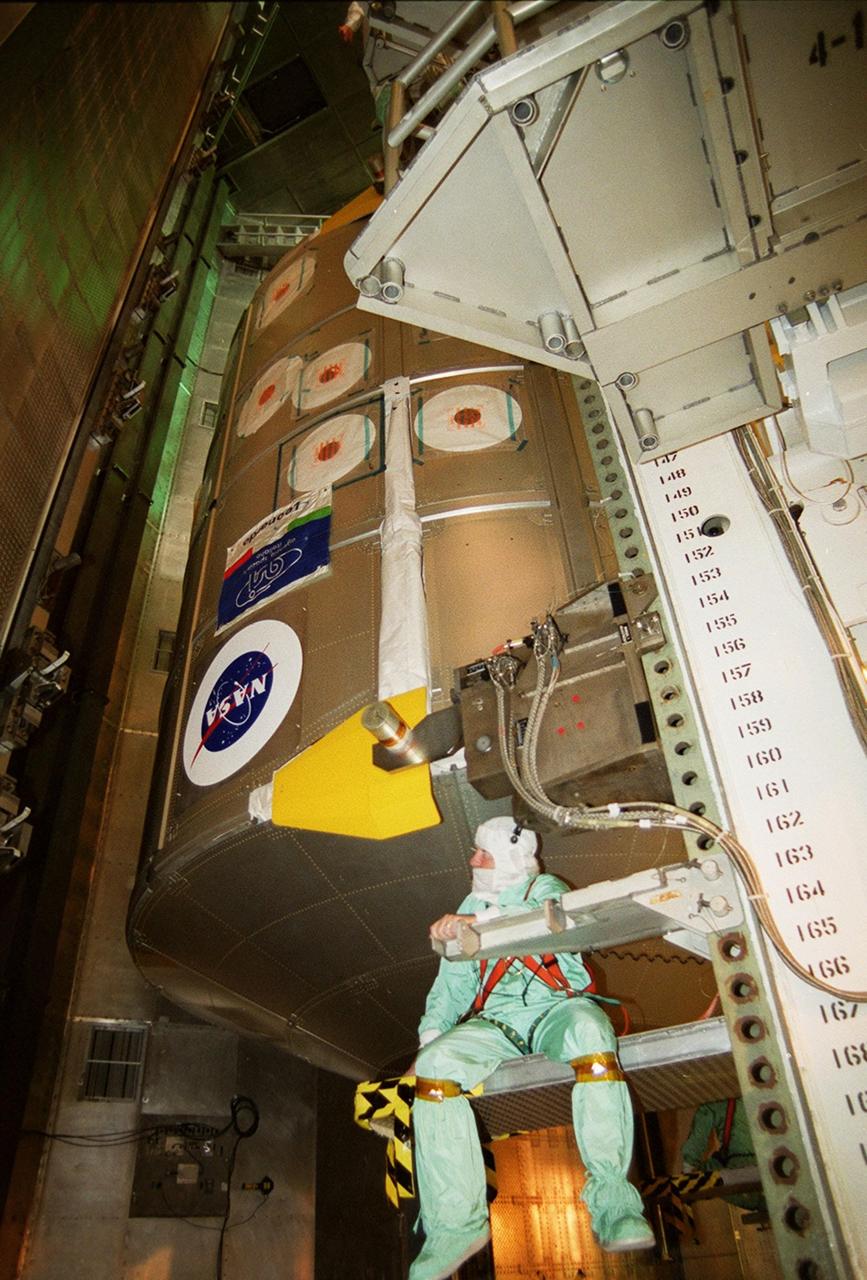

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Payload Changeout Room, Launch Pad 39B, the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo is ready to be transferred into Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. Discovery is scheduled to launch March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment, Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo rests in Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay after being transferred from the Payload Changeout Room, Launch Pad 39B. Behind it is the Integrated Cargo Carrier, holding several smaller payloads. Discovery is scheduled to launch March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment, Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny
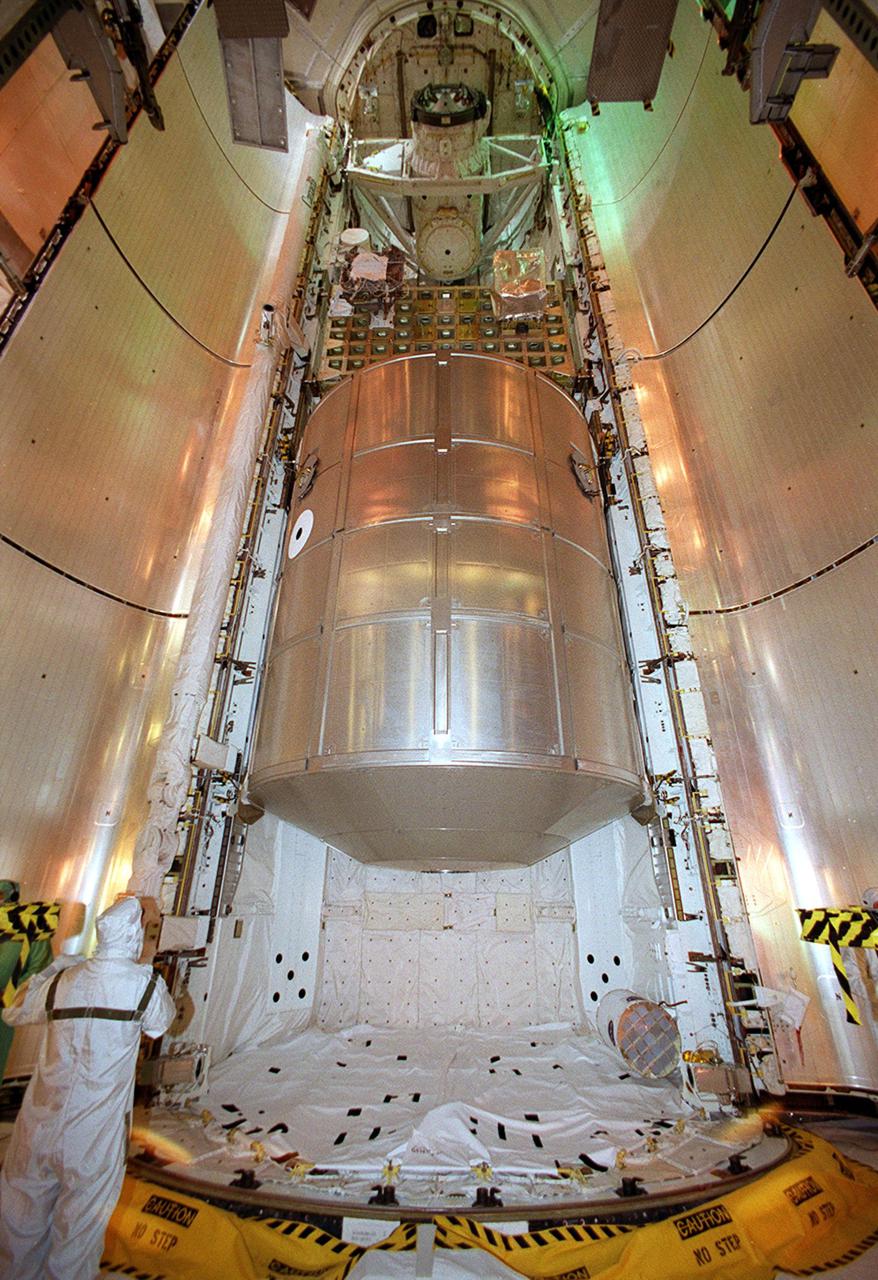

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo rests in Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay after being transferred from the Payload Changeout Room, Launch Pad 39B. Behind it is the Integrated Cargo Carrier, holding several smaller payloads. Discovery is scheduled to launch March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment, Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny
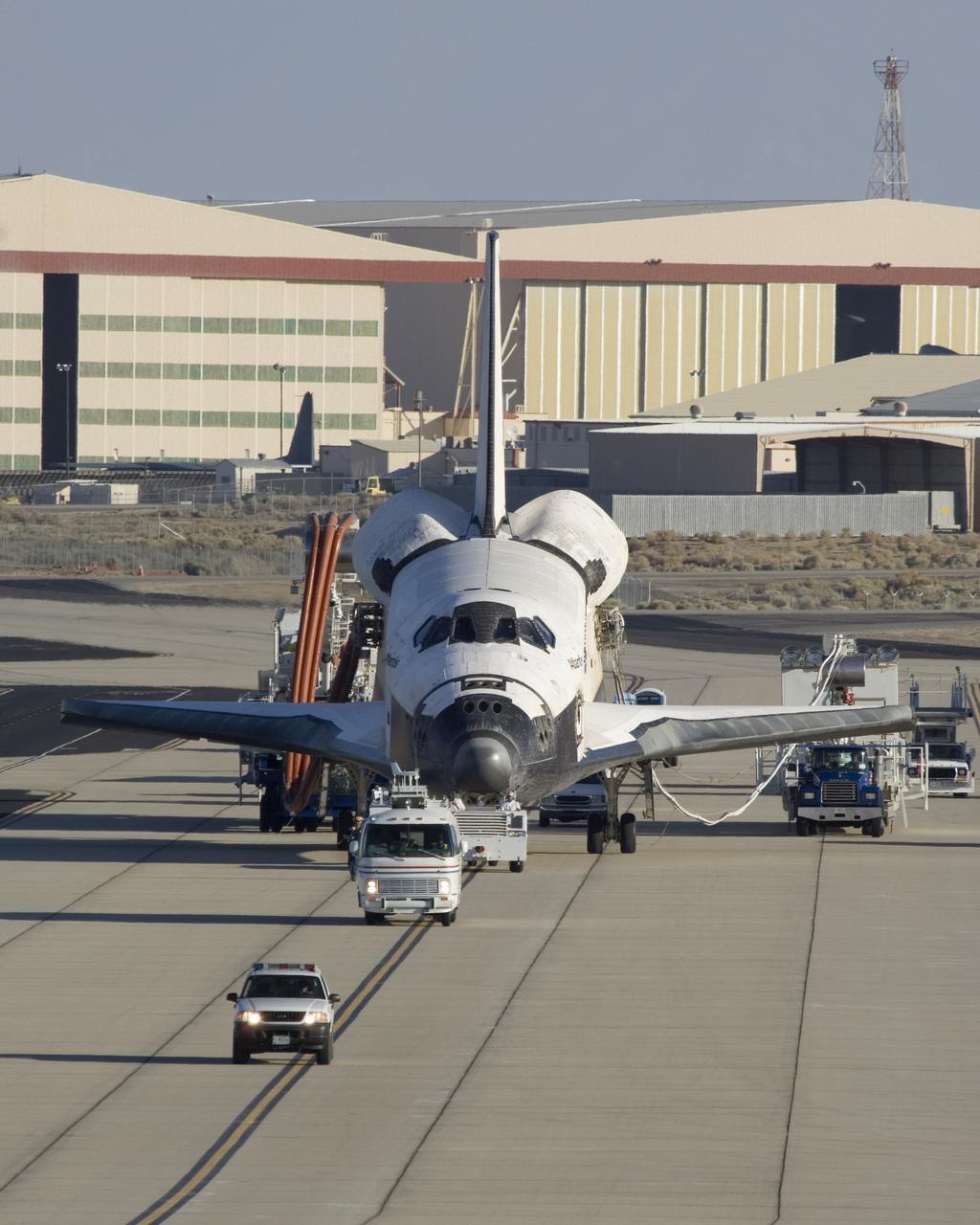

Space Shuttle Atlantis descended to a smooth landing at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., concluding a successful assembly mission to the International Space Station. With Commander Rick Sturckow and Pilot Lee Archambault at the controls, Atlantis landed at 12:49 p.m. PDT on June 22, 2007. Atlantis launched June 8, 2007, and arrived at the International Space Station on June 10. While at the orbital outpost, the crew installed the Starboard 3 and 4 truss segment and conducted four spacewalks to activate it. During the third spacewalk, the crew repaired an out of position thermal blanket on the left orbital maneuvering system pod. Atlantis also delivered a new station crew member, Flight Engineer Clayton Anderson. He replaced astronaut Suni Williams, who is the new record holder for a long-duration single spaceflight for a woman. She arrived at the station in December of 2006 with STS-116. STS-117 is the 118th shuttle mission and 21st mission to visit the space station.
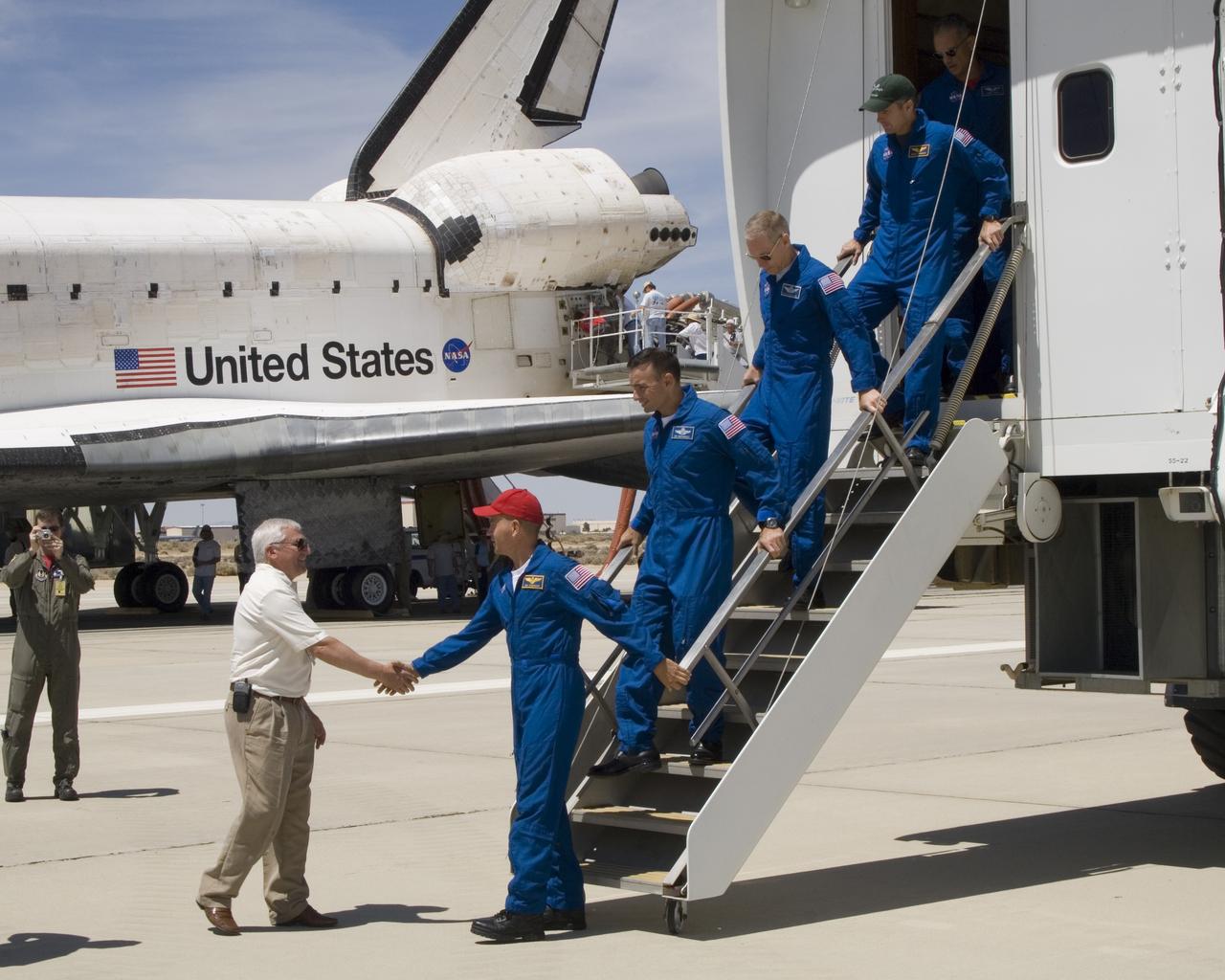

DFRC Center Director Kevin Petersen greets STS-117 Commander Frederick Sturckow and the crew of the Space Shuttle Atlantis at Edwards, AFB, Calif., on June 22, 2007. Left to right: DFRC Center Director Kevin Petersen, Commander Frederick Sturckow, Pilot Lee Archambault, and mission specialists Patrick Forrester, Steven Swanson and John D. Olivas.
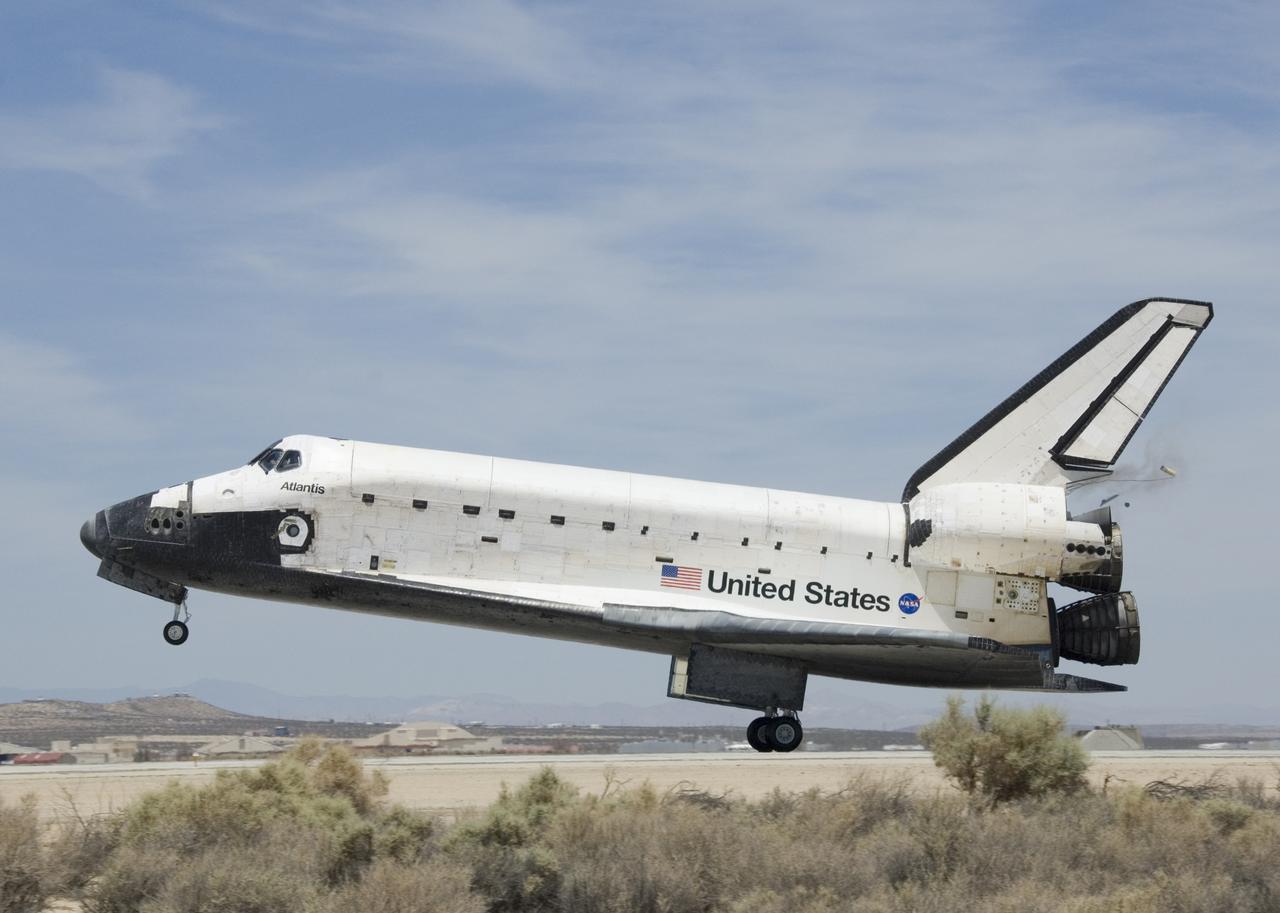

Space Shuttle Atlantis starts to deploy its braking parachute following touchdown at Edwards Air Force Base, California, on June 22, 2007.
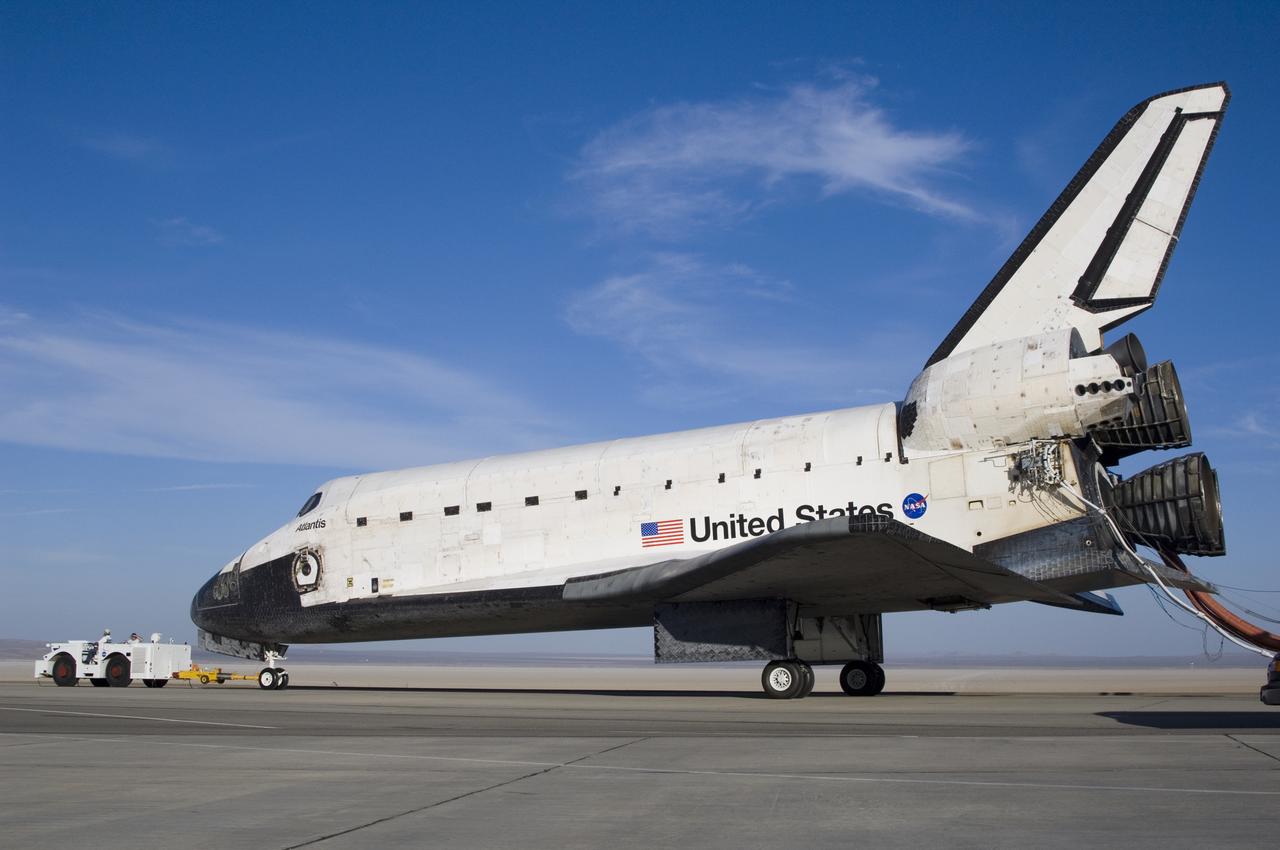

Following its landing on June 22, 2007, the Space Shuttle Atlantis is towed from the runway at Edwards Air Force Base to NASA Dryden's Mate-Demate Device (MDD) for post-flight processing in preparation for its return to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
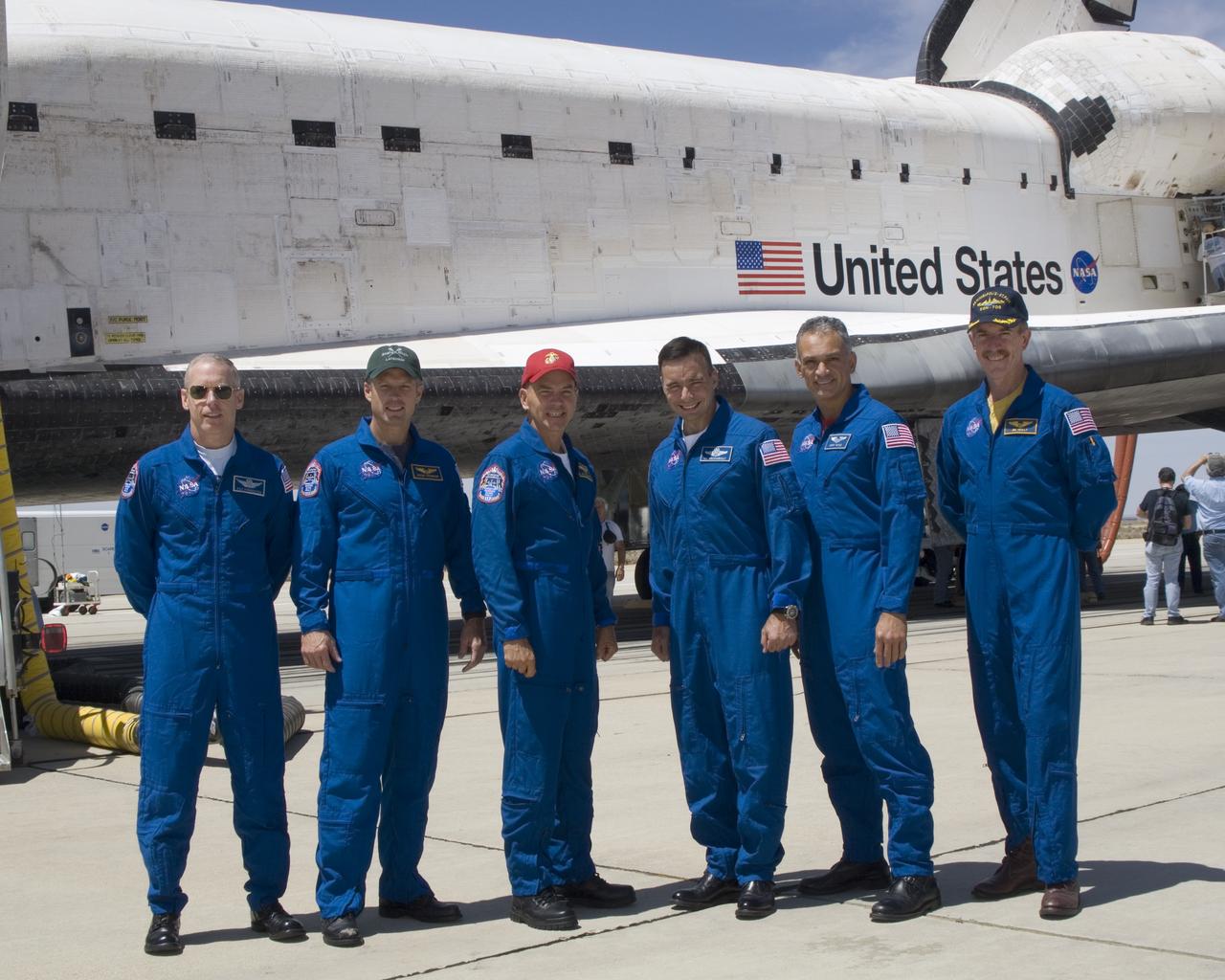

The crew of Space Shuttle mission STS-117 gathered in front of the shuttle Atlantis following landing at Edwards Air Force Base, California, June 22, 2007. From left to right: mission specialists Patrick Forrester and Steven Swanson, Commander Frederick Sturckow, Pilot Lee Archambault, and mission specialists John D. Olivas and James Reilly II.
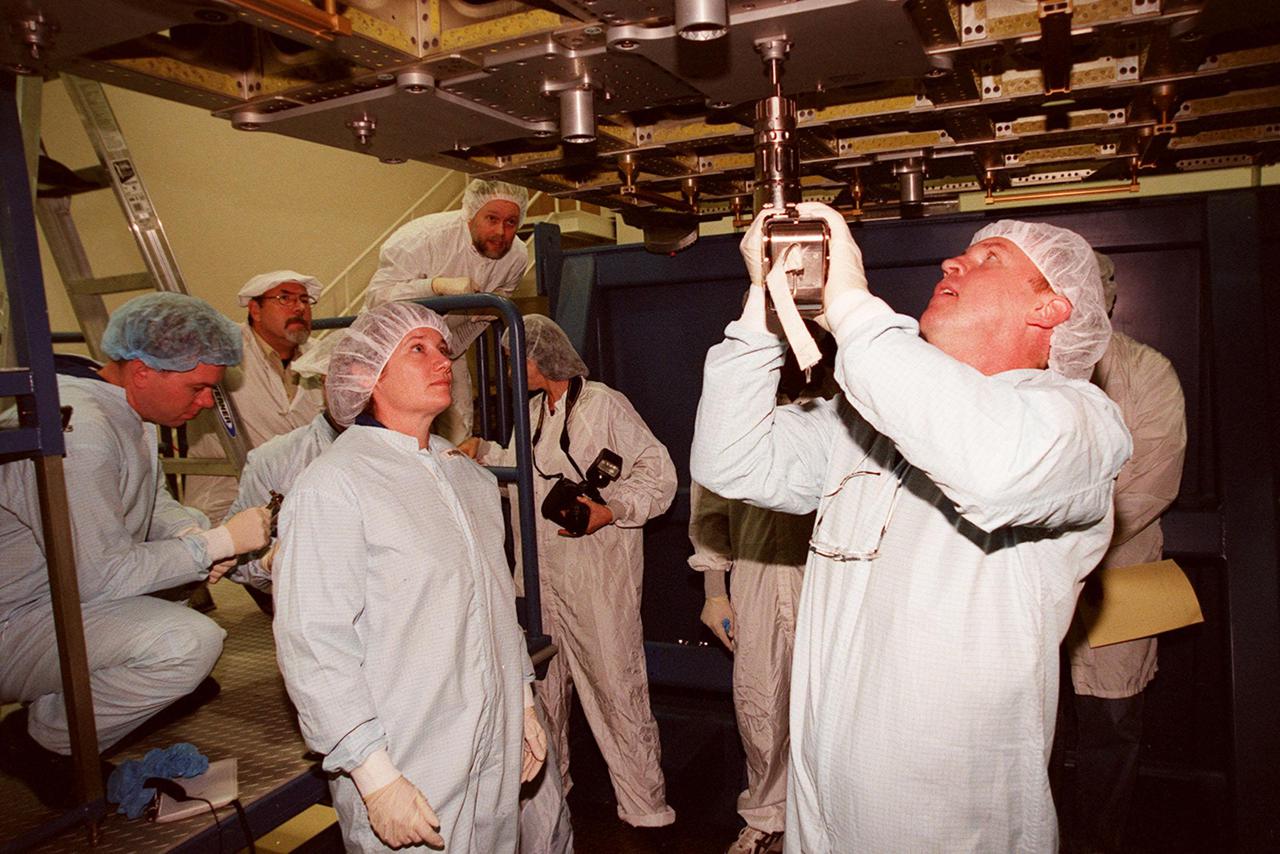

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, STS-102 Mission Specialist Andrew S.W. Thomas practices using a tool on the Integrated Cargo Carrier. Watching him, at left, is Susan Helms, part of the Expedition Two crew heading for the International Space Station on the flight. Behind Helms (at left) is Pilot James M. Kelly. They and other crew members are at SPACEHAB to get acquainted with tools and equipment they will be using on their mission. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 8, 2001
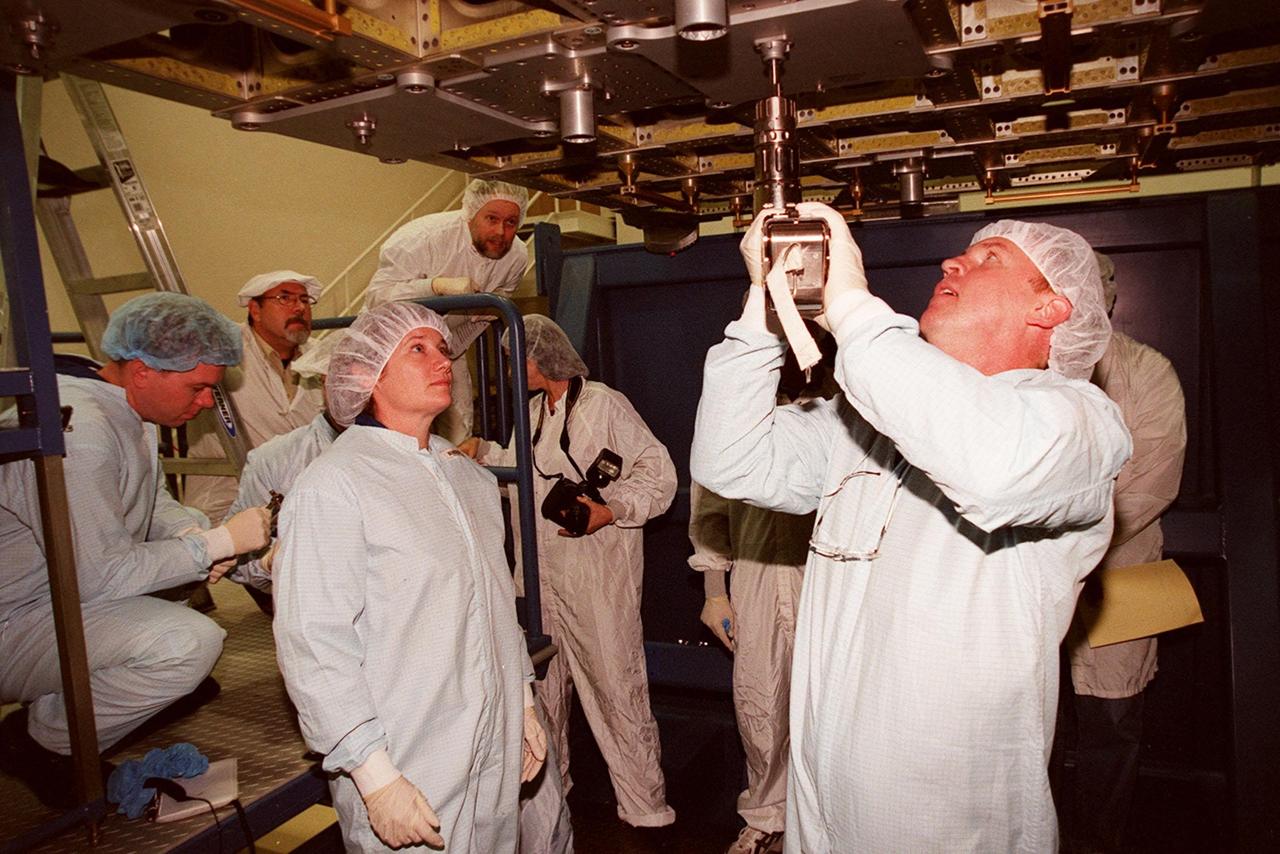

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, STS-102 Mission Specialist Andrew S.W. Thomas practices using a tool on the Integrated Cargo Carrier. Watching him, at left, is Susan Helms, part of the Expedition Two crew heading for the International Space Station on the flight. Behind Helms (at left) is Pilot James M. Kelly. They and other crew members are at SPACEHAB to get acquainted with tools and equipment they will be using on their mission. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 8, 2001
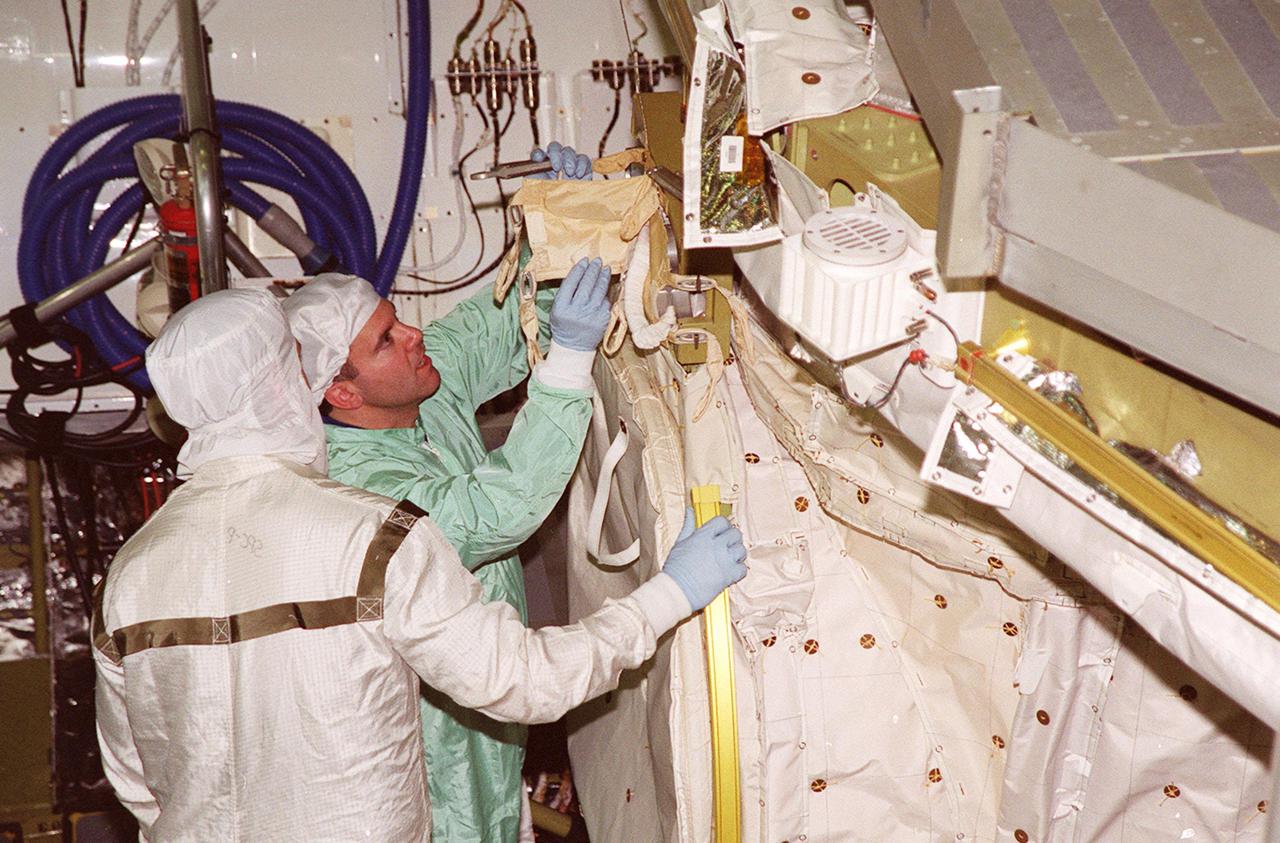

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, STS-102 Pilot James W. Kelly (right) checks out equipment in Discovery’s payload bay. The crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
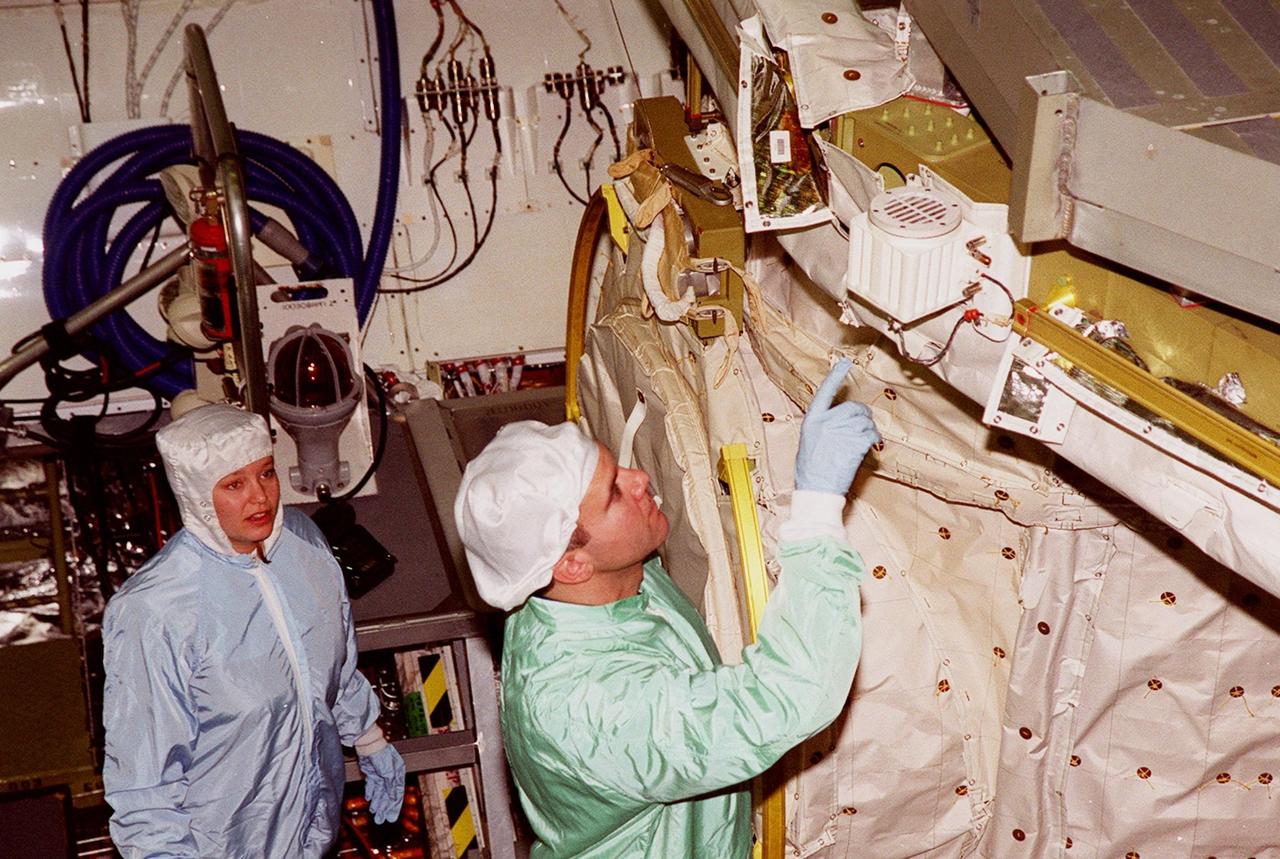

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, STS-102 Pilot James W. Kelly (right) points to a piece of equipment in Discovery’s payload bay. The crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
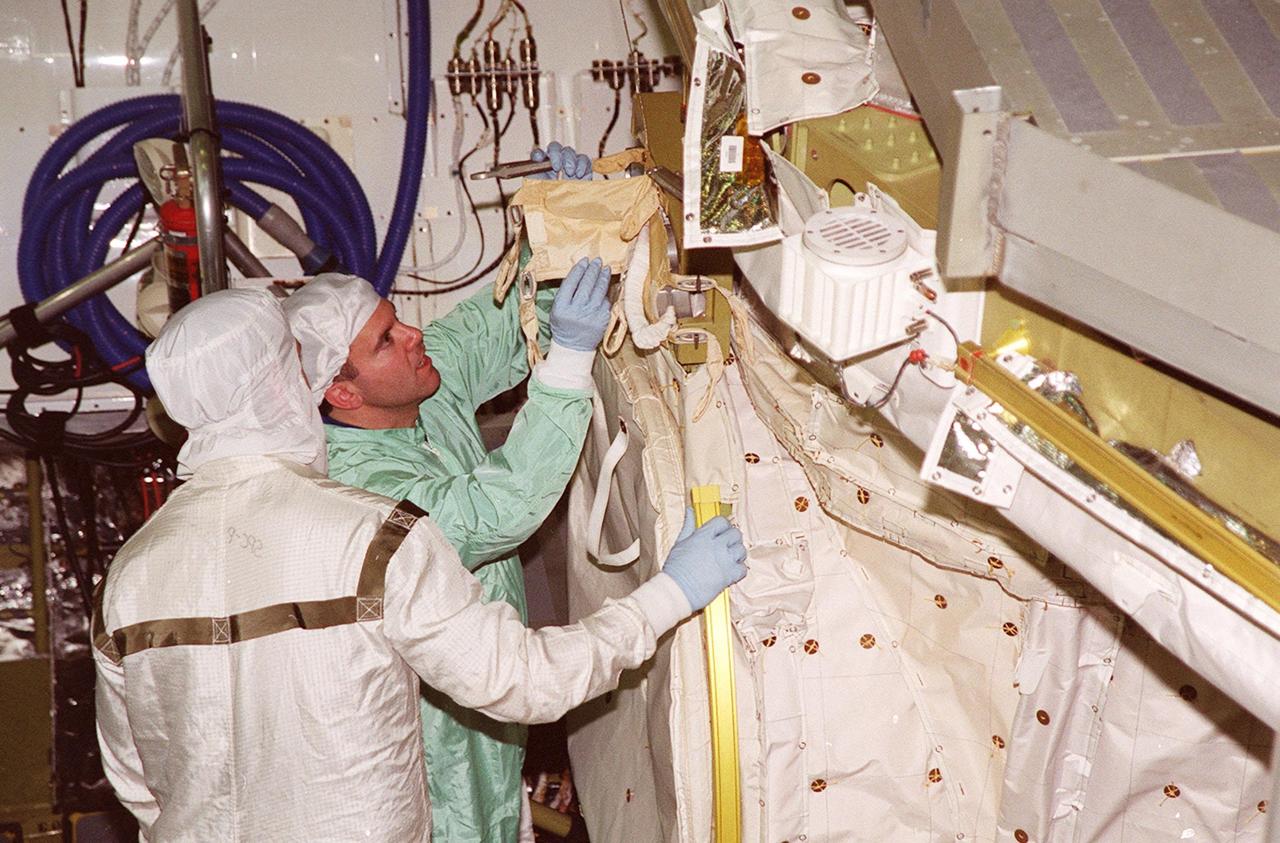

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, STS-102 Pilot James W. Kelly (right) checks out equipment in Discovery’s payload bay. The crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
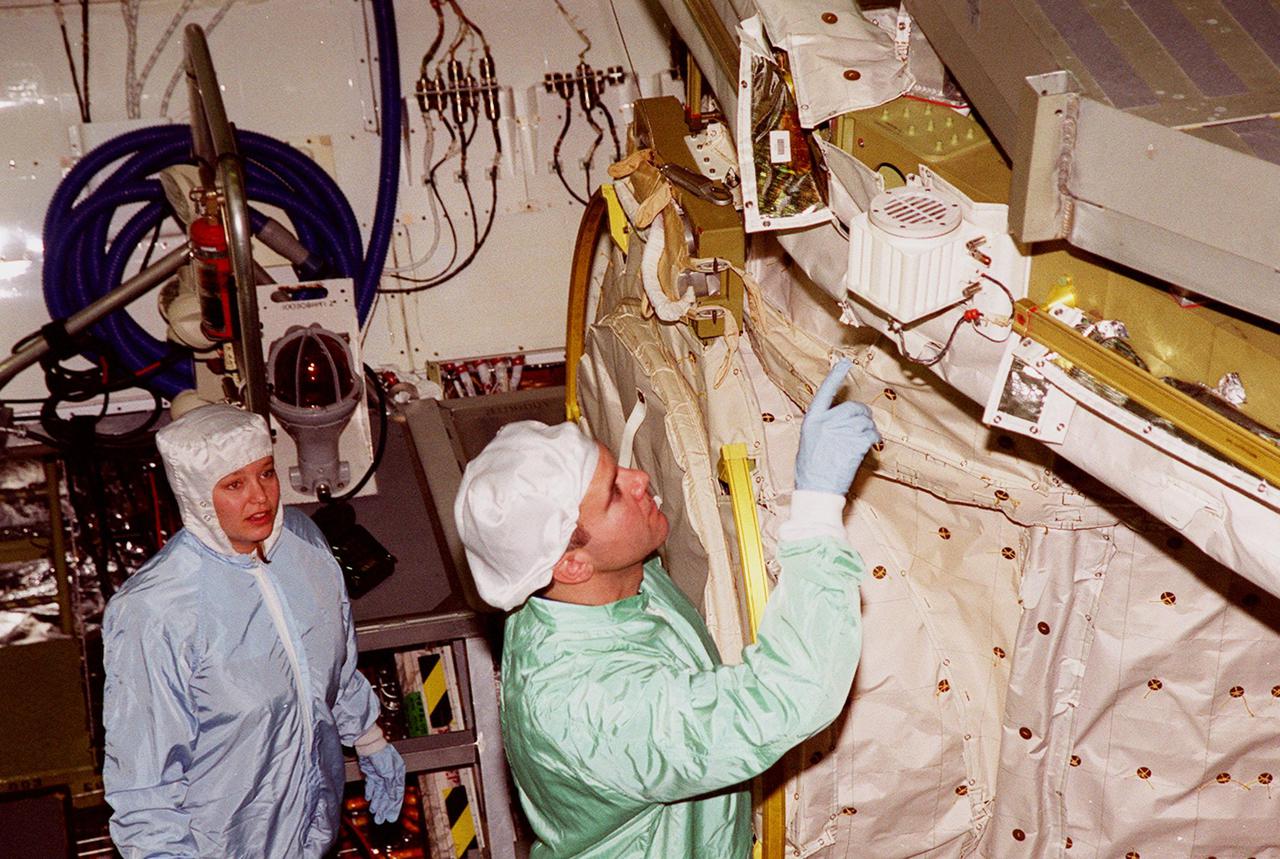

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1, STS-102 Pilot James W. Kelly (right) points to a piece of equipment in Discovery’s payload bay. The crew is at KSC for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the International Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 1, 2001. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery
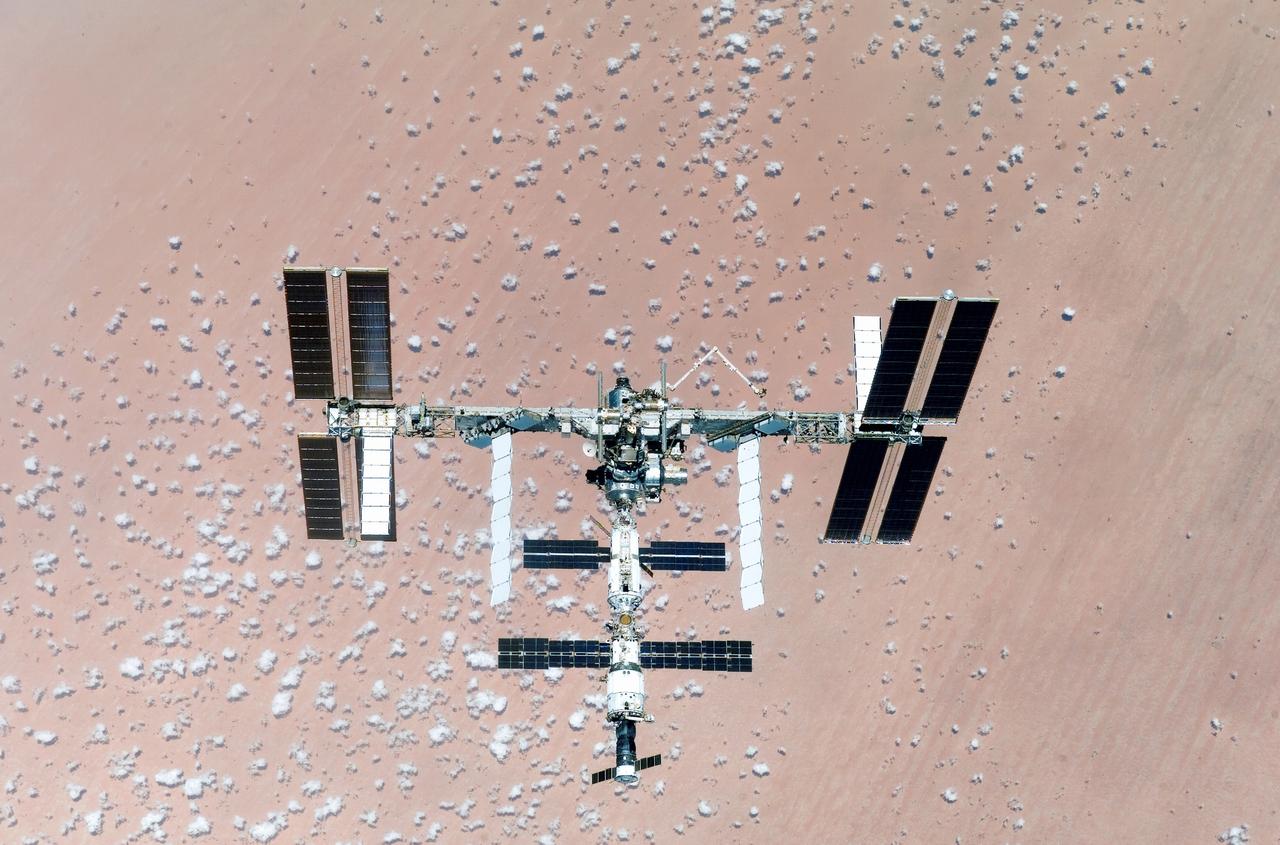

Back dropped by the colorful Earth, the International Space Station (ISS) boasts its newest configuration upon the departure of Space Shuttle Endeavor and STS-118 mission. Days earlier, construction resumed on the ISS as STS-118 mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the Starboard 5 (S-5) truss segment, removed a faulty Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG-3), installed a new CMG into the Z1 truss, relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1, retrieved the P6 transponder, and delivered roughly 5,000 pounds of supplies.
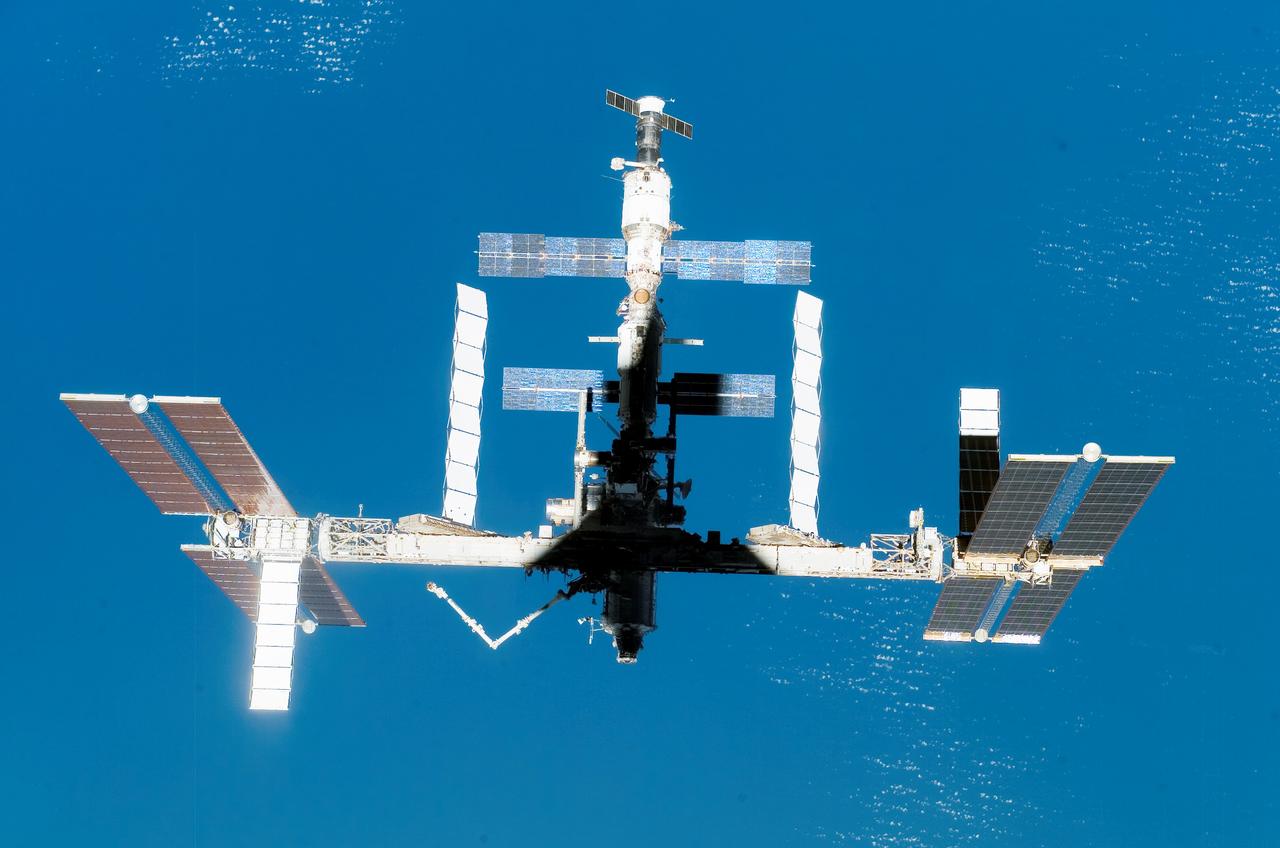

Back dropped by the blue Earth, the International Space Station (ISS) boasts its newest configuration upon the departure of Space Shuttle Endeavor and STS-118 mission. Days earlier, construction resumed on the ISS as STS-118 mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the Starboard 5 (S-5) truss segment, removed a faulty Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG-3), installed a new CMG into the Z1 truss, relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1, retrieved the P6 transponder, and delivered roughly 5,000 pounds of equipment and supplies.
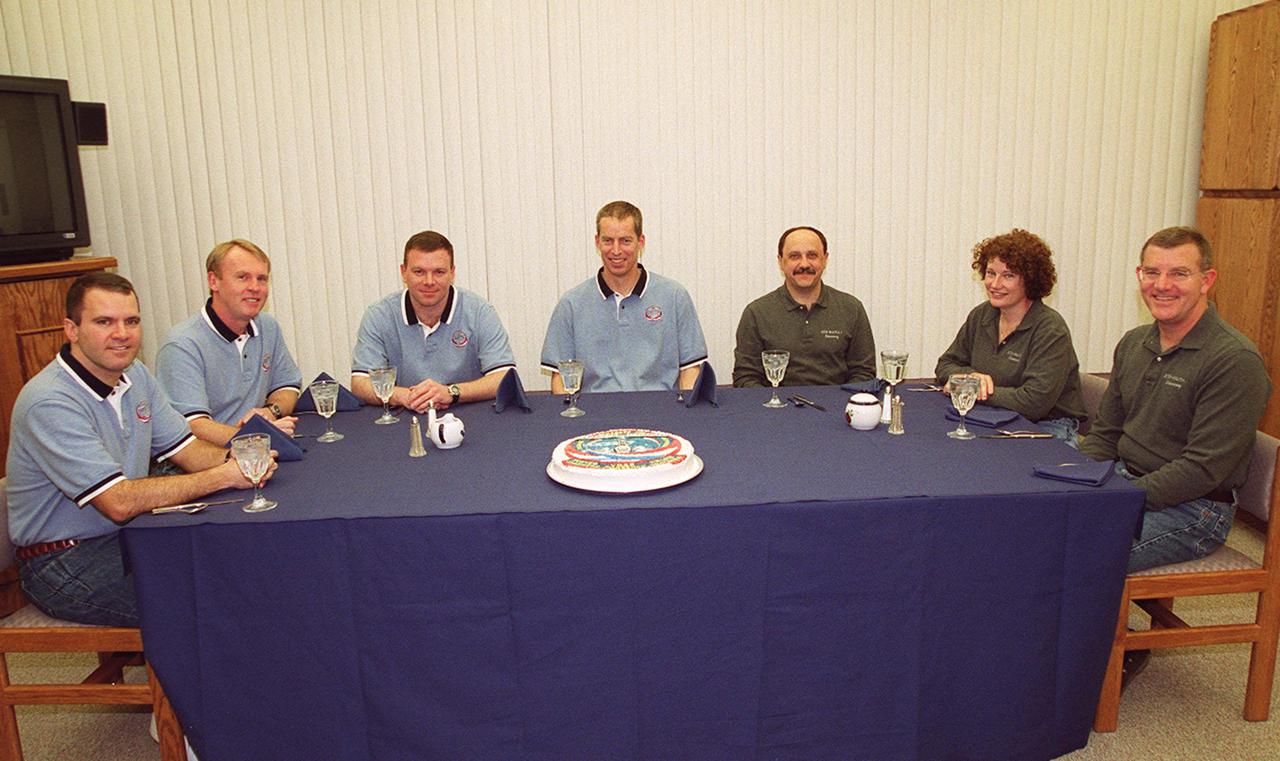

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-102 crew enjoys a snack before beginning suitup procedures for launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. From left, seated are Mission Specialists Paul Richards and Andrew Thomas, Pilot James Kelly and Commander James Wetherbee; Mission Specialists Yury Usachev, representing the Russian Aviation and Space Agency, Susan Helms and James Voss. Usachev, Helms and Voss are wearing different shirts because they also are the Expedition Two crew who will be replacing Expedition One on the International Space Station. Discovery is scheduled to launch March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST, carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. The primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment, Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny.
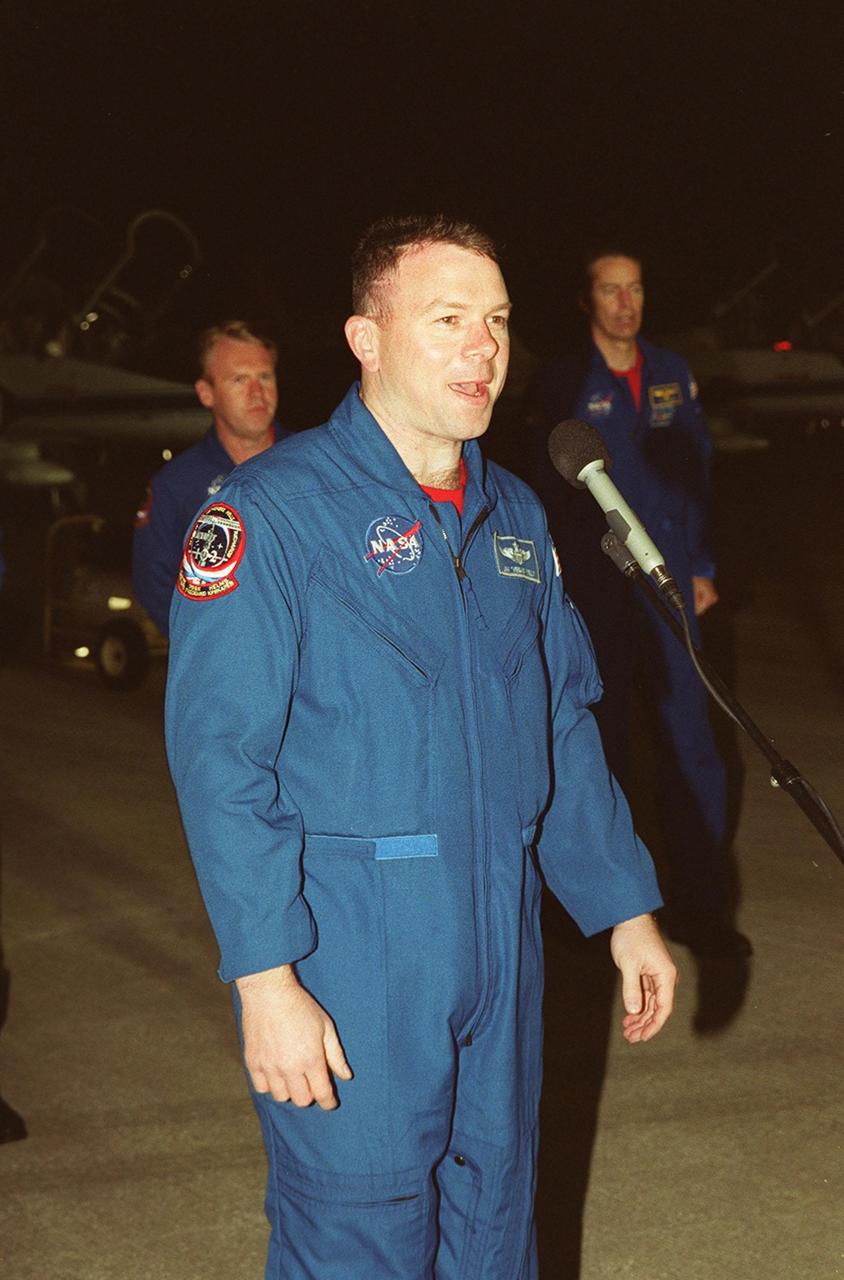

After arrival at the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-102 Pilot James Kelly addresses the media. Behind him are Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas (left) and Commander James Wetherbee (right). The crew is making the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. STS-102 will be carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment. Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny. STS-102 is scheduled to launch March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST
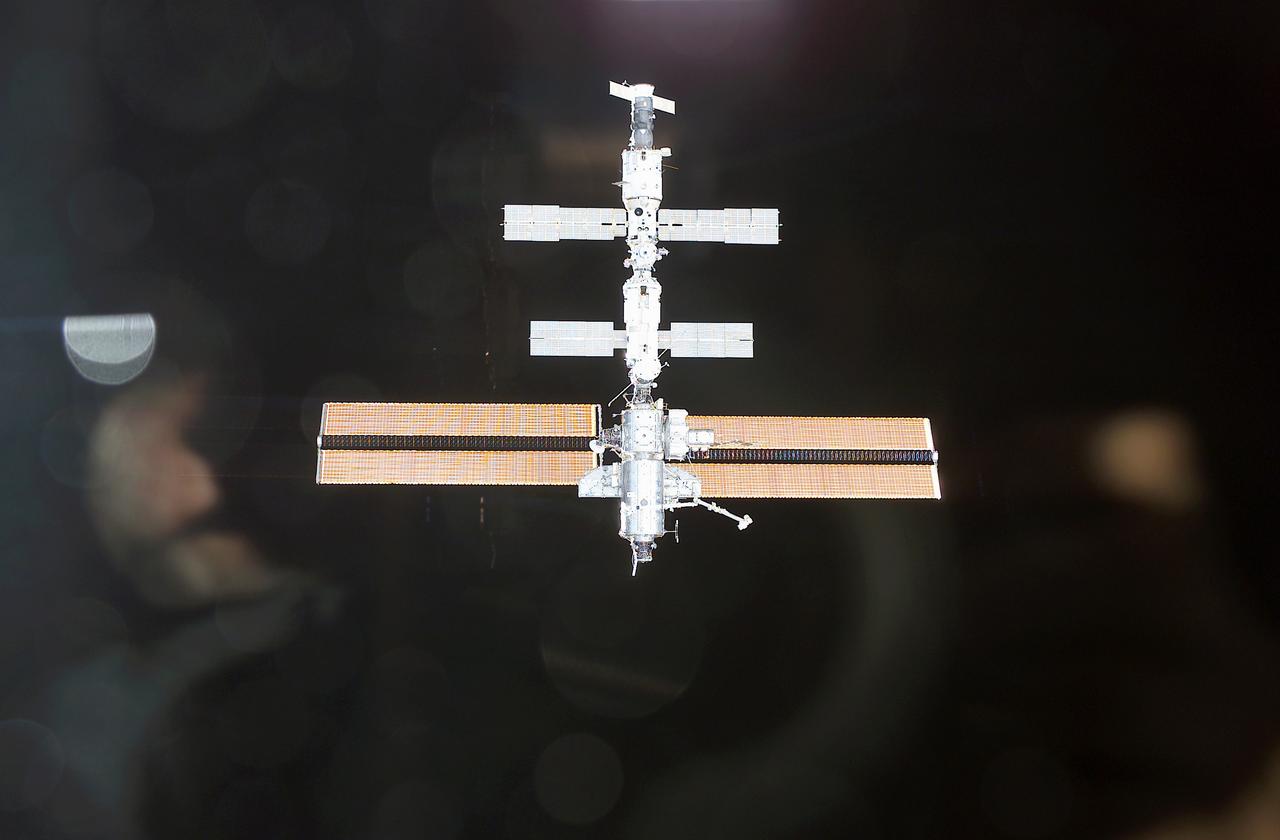
Backdropped against the blackness of space is the International Space Station (ISS), as viewed from the approching Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour, STS-111 mission, in June 2002. Expedition Five replaced Expedition Four crew after remaining a record-setting 196 days in space. Three spacewalks enabled the STS-111 crew to accomplish the delivery and installation of the Mobile Remote Servicer Base System (MBS), an important part of the Station's Mobile Servicing System that allows the robotic arm to travel the length of the Station, which is necessary for future construction tasks; the replacement of a wrist roll joint on the Station's robotic arm, and the task of unloading supplies and science experiments from the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module, which made its third trip to the orbital outpost. The STS-111 mission, the 14th Shuttle mission to visit the ISS, was launched on June 5, 2002 and landed June 19, 2002.
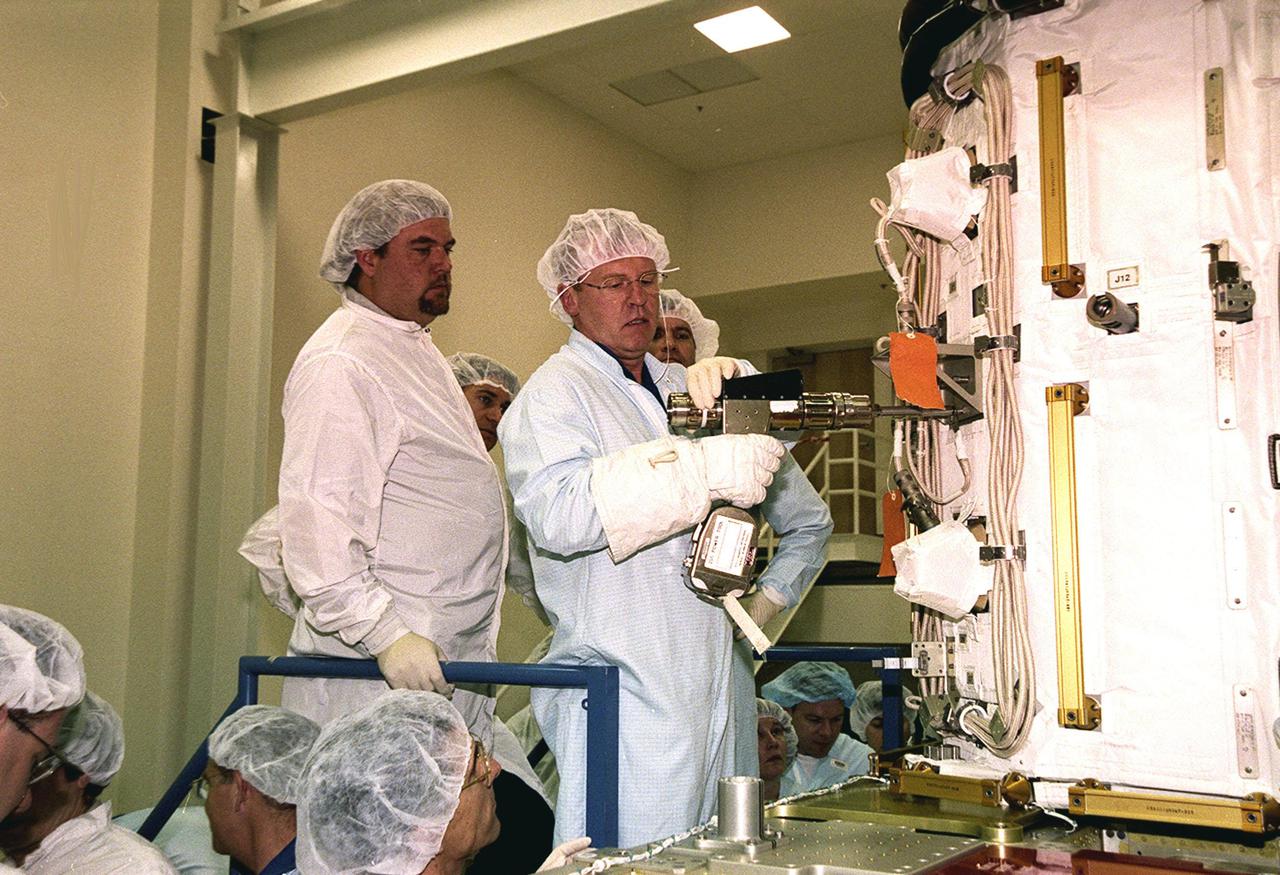

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, STS-102 Mission Specialist Andrew S.W. Thomas practices using a tool on the Early Ammonia Servicer under the watchful eyes of a technician. Thomas and other crew members are at SPACEHAB to get acquainted with tools and equipment they will be using on their mission to the International Space Station. The second spacewalk of the mission will require the crew to transfer the Early Ammonia Servicer to the P6 truss. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 8, 2001
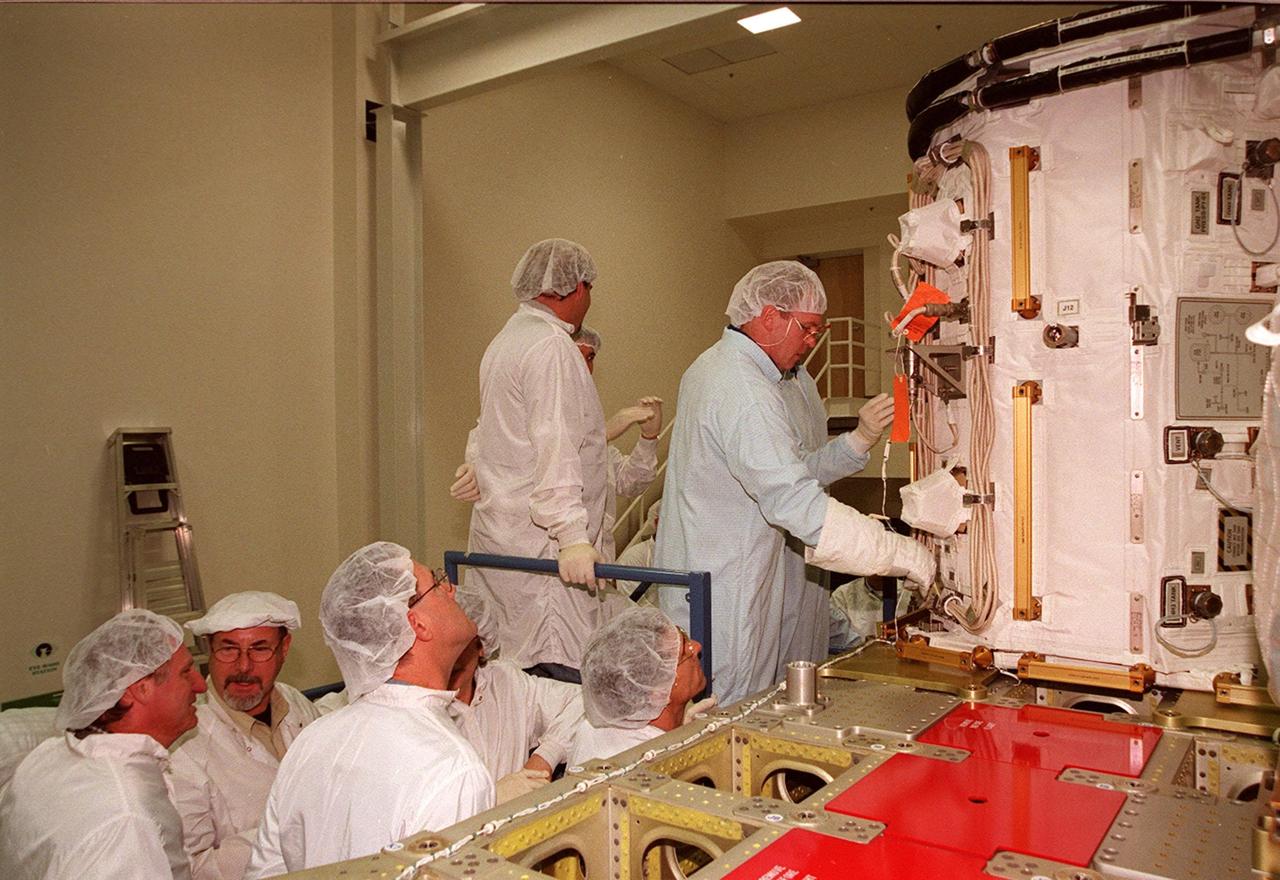

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, STS-102 Mission Specialist Andrew S.W. Thomas checks out the Early Ammonia Servicer under the watchful eyes of workers in the facility. Thomas and other crew members are at SPACEHAB to get acquainted with tools and equipment they will be using on their mission to the International Space Station. The second spacewalk of the mission will require the crew to transfer the Early Ammonia Servicer to the P6 truss. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 8, 2001
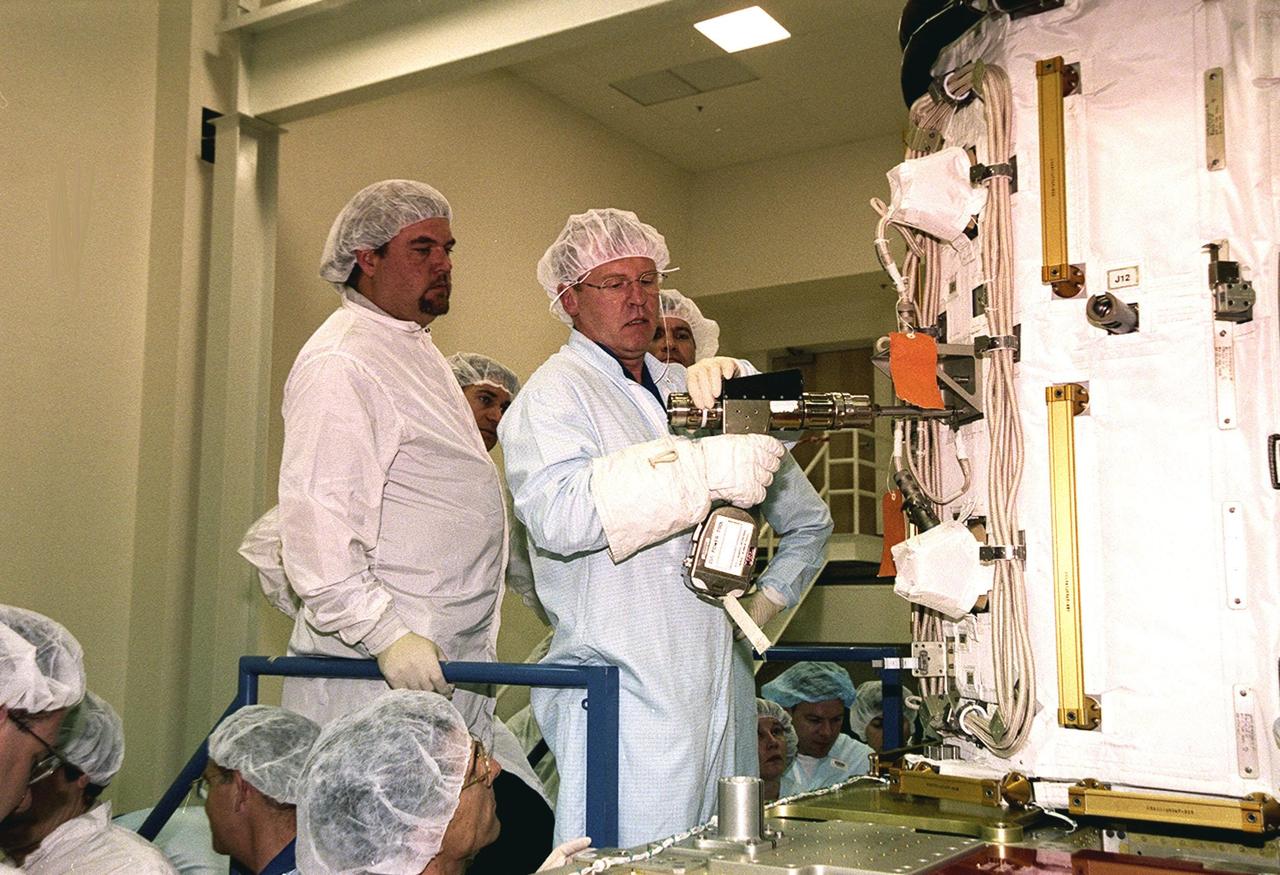

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, STS-102 Mission Specialist Andrew S.W. Thomas practices using a tool on the Early Ammonia Servicer under the watchful eyes of a technician. Thomas and other crew members are at SPACEHAB to get acquainted with tools and equipment they will be using on their mission to the International Space Station. The second spacewalk of the mission will require the crew to transfer the Early Ammonia Servicer to the P6 truss. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 8, 2001
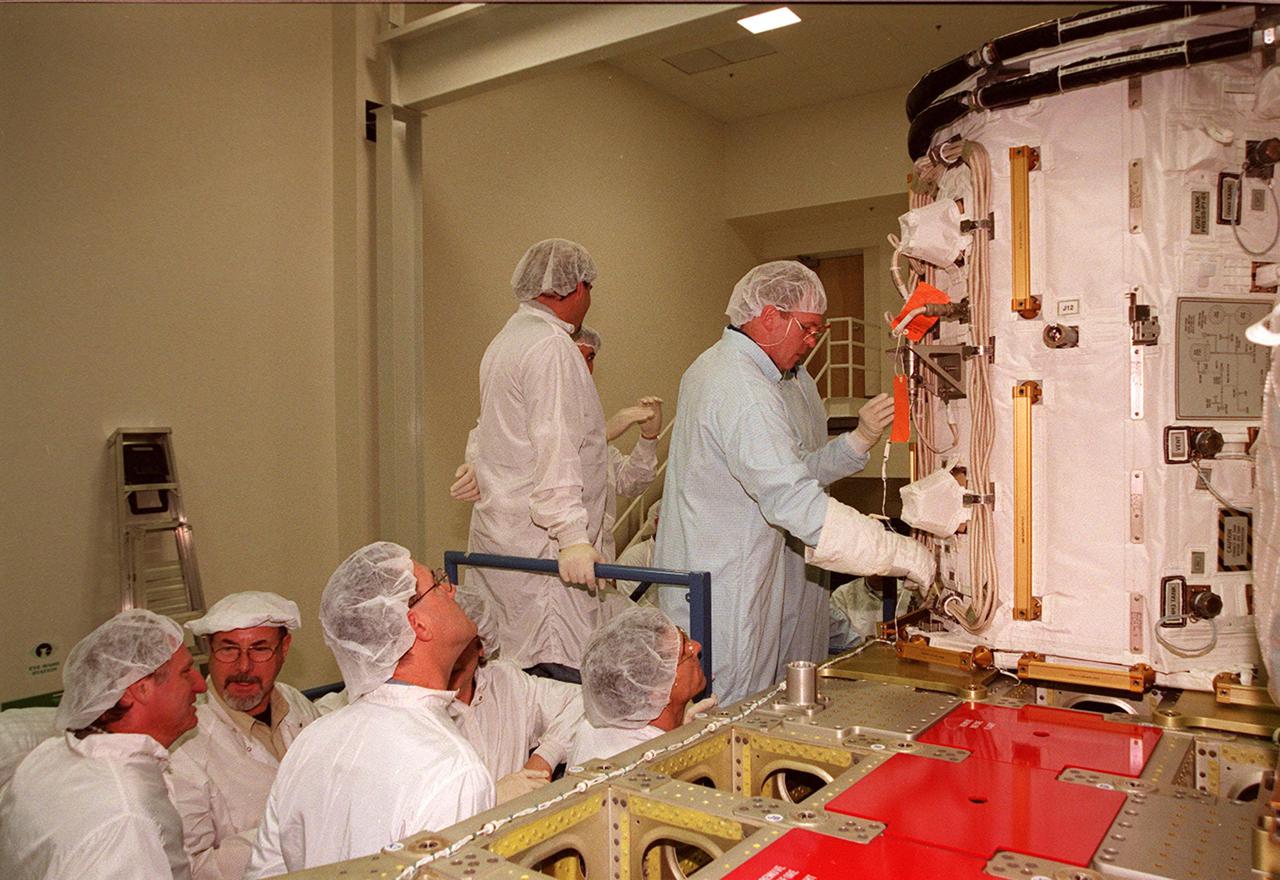

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, STS-102 Mission Specialist Andrew S.W. Thomas checks out the Early Ammonia Servicer under the watchful eyes of workers in the facility. Thomas and other crew members are at SPACEHAB to get acquainted with tools and equipment they will be using on their mission to the International Space Station. The second spacewalk of the mission will require the crew to transfer the Early Ammonia Servicer to the P6 truss. STS-102 is the 8th construction flight to the Space Station and will carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. On that flight, Leonardo will be filled with equipment and supplies to outfit the U.S. laboratory module Destiny. The mission will also be carrying the Expedition Two crew to the Space Station, replacing the Expedition One crew who will return on Shuttle Discovery. STS-102 is scheduled for launch March 8, 2001