
As a result of the recommendations from President Nixon's Space Task Group, Marshall Space Flight Center engineers studied various ways to enhance commonality and integration in the American space program. This artist's concept from 1969 shows a possible spacecraft configuration for a marned Mars mission. In this mode, two planetary vehicles, each powered by a Nuclear Shuttle, are joined together during the flight and rotated to provide artificial gravity for crew members.
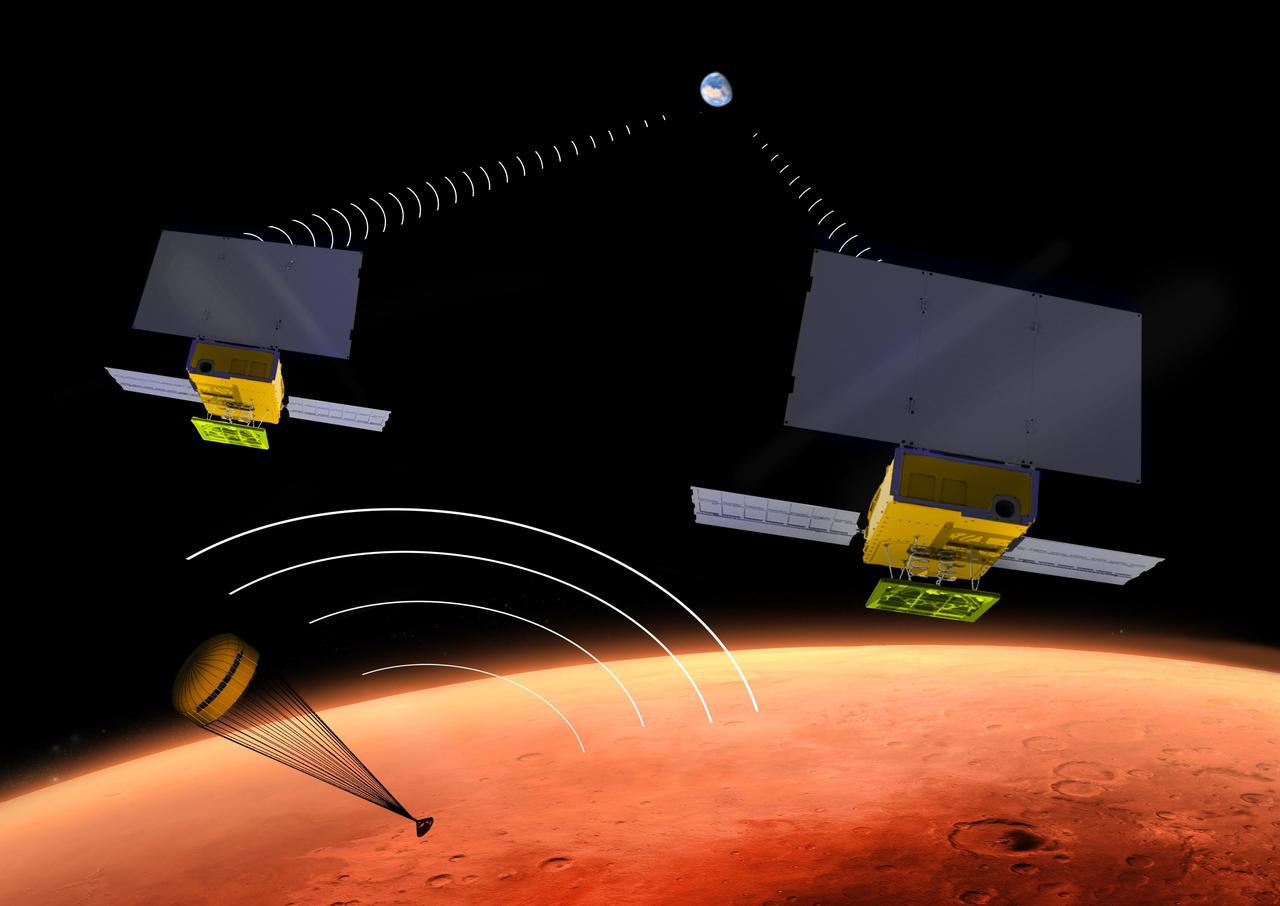

NASA's two MarCO CubeSats will be flying past Mars in September 2016 just as NASA's next Mars lander, InSight, is descending through the Martian atmosphere and landing on the surface. MarCO, for Mars Cube One, will provide an experimental communications relay to inform Earth quickly about the landing. This illustration depicts a moment during the lander's descent when it is transmitting data in the UHF radio band, and the twin MarCO craft are receiving those transmissions while simultaneously relaying the data to Earth in a different radio band. Each of the MarCO twins carries two solar panels for power, and both UHF-band and X-band radio antennas. As a technology demonstration, MarCO could lead to other "bring-your-own-relay" mission designs and also to use of miniature spacecraft for a wide diversity of interplanetary missions. MarCO is the first interplanetary use of CubeSat technologies for small spacecraft. CubeSats are a class of spacecraft based on a standardized small size and modular use of off-the-shelf technologies to streamline development. Many have been made by university students, and dozens have been launched into Earth orbit using extra payload mass available on launches of larger spacecraft. The two briefcase-size MarCO CubeSats will ride along with InSight on an Atlas V launch vehicle lifting off in March 2016 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. MarCO is a technology demonstration aspect of the InSight mission and not needed for that mission's success. InSight, an acronym for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, will investigate the deep interior of Mars to advance understanding of how rocky planets, including Earth, formed and evolved. After launch, the MarCO twins and InSight will be navigated separately to Mars. Note: After thorough examination, NASA managers have decided to suspend the planned March 2016 launch of the Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) mission. The decision follows unsuccessful attempts to repair a leak in a section of the prime instrument in the science payload. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19388
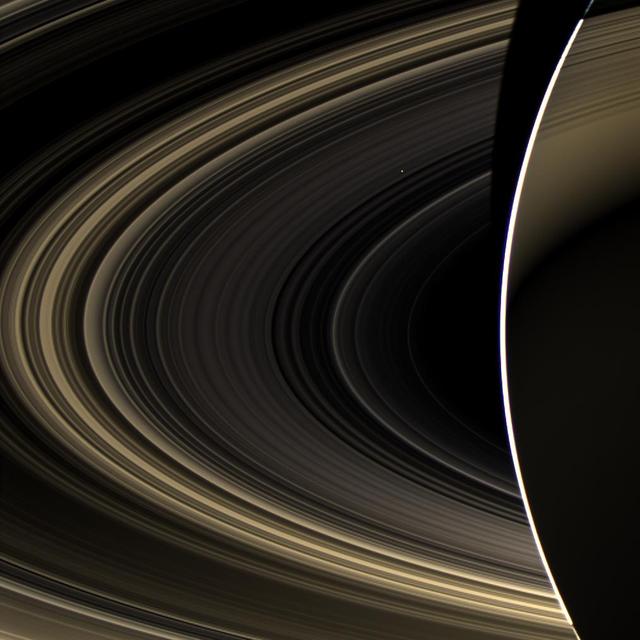

Peering over the shoulder of giant Saturn, through its rings, and across interplanetary space, NASA Cassini spacecraft spies the bright, cloudy terrestrial planet, Venus.
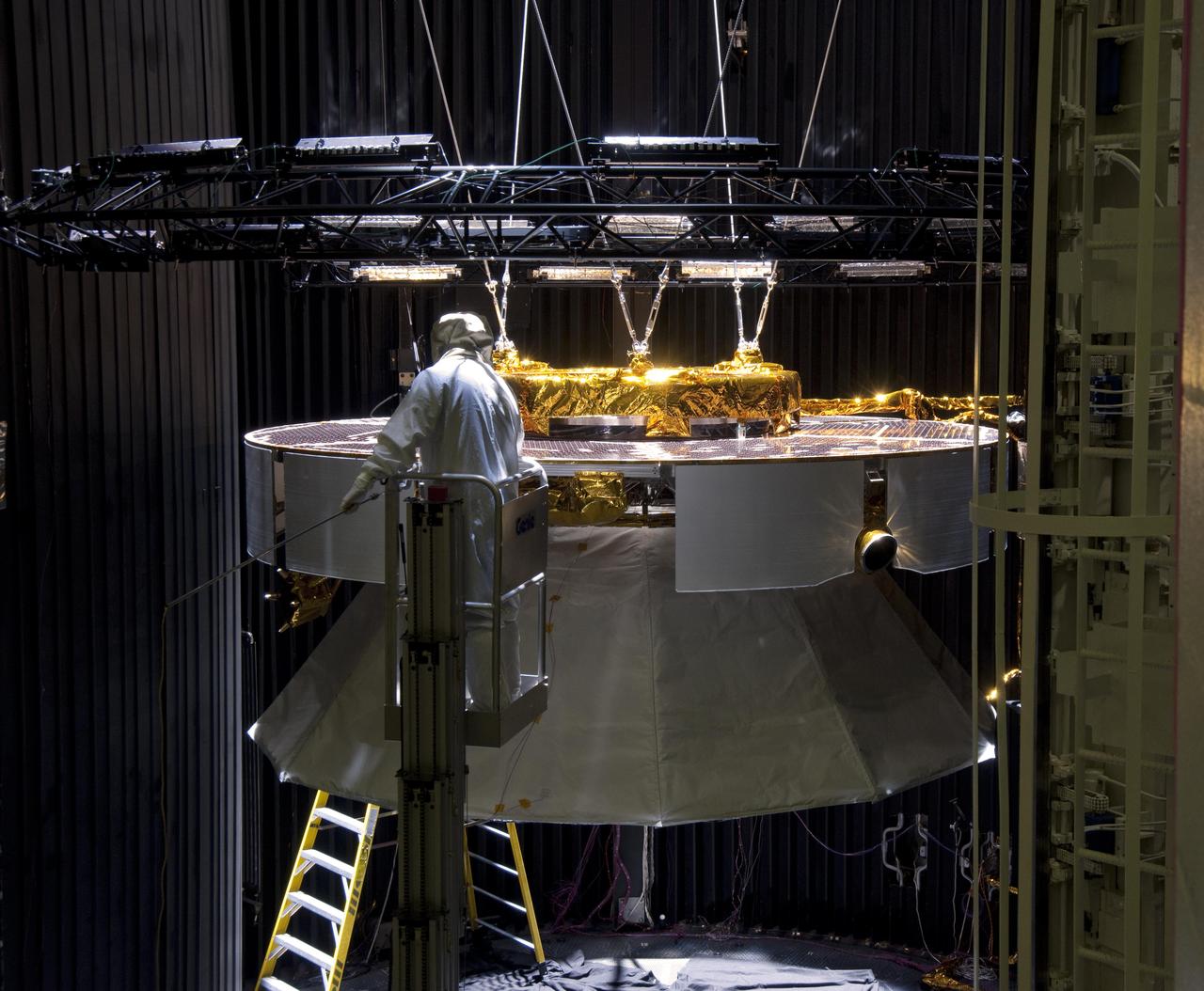

Testing of the cruise stage for NASA Mars Science Laboratory in August 2010 included a session in a facility that simulates the environment found in interplanetary space.
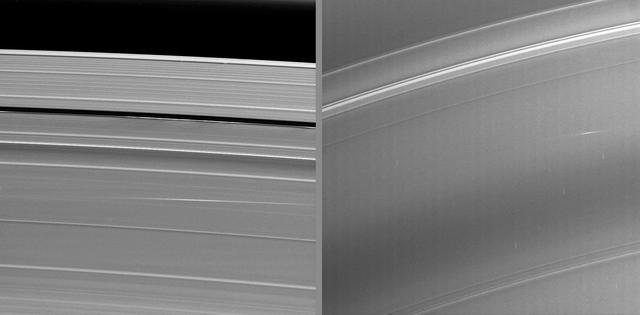
The bright streaks visible in these Cassini images taken during Saturn’s August 2009 equinox are exciting evidence of a constant rain of interplanetary projectiles onto the planet’s rings.
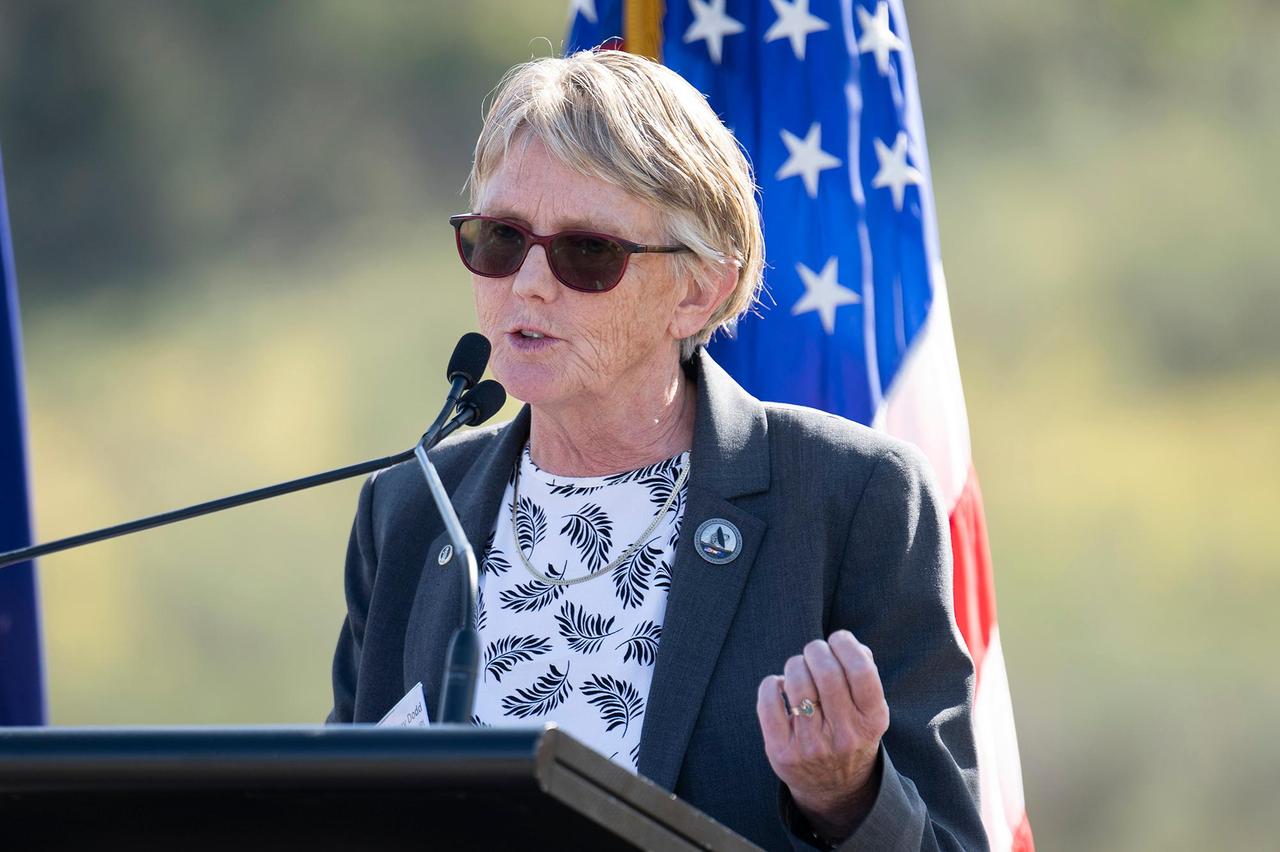

Suzanne Dodd, the director for the Interplanetary Network Directorate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, addresses an audience at the Deep Space Network's Canberra complex on March 19, 2025. That day marked 60 years since the Australian facility joined the network. JPL's Interplanetary Network Directorate oversees the Deep Space Network's three complexes in Canberra, Madrid, and Goldstone, near Barstow, California. JPL manages the Deep Space Network for the agency's Space Communications and Navigation program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26585

Dawn on Saturn is greeted across the vastness of interplanetary space by the morning star, Venus, in this image from NASA Cassini spacecraft. Venus appears just off the edge of the planet directly above the white streak of Saturn G ring.
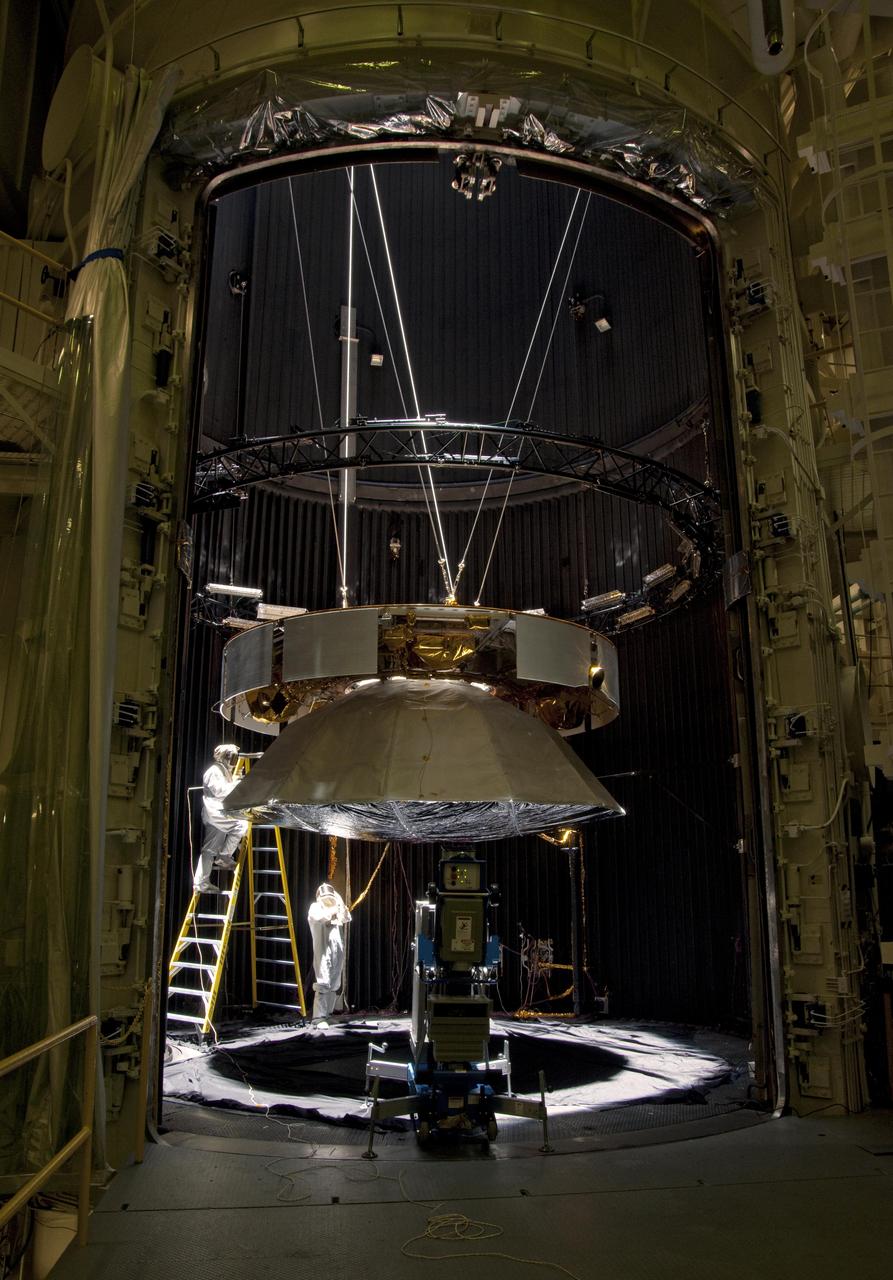

Testing of the cruise stage for NASA Mars Science Laboratory in August 2010 included a session in a facility that simulates the environment found in interplanetary space. Spacecraft technicians at JPL prepare a space-simulation test.
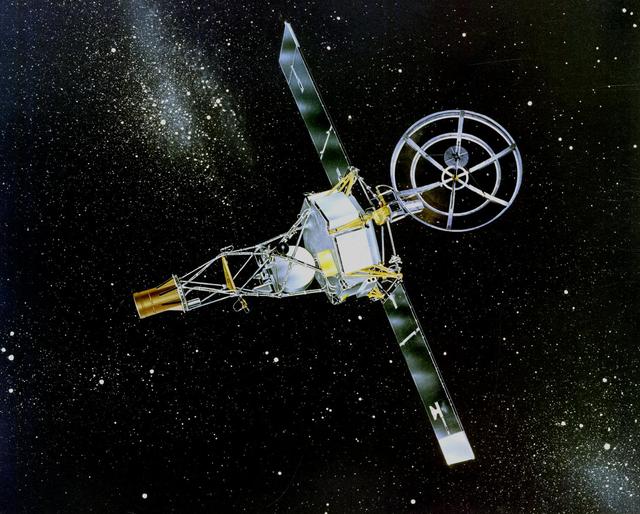

NASA Mariner 2 was the world first successful interplanetary spacecraft. Launched August 27, 1962, on an Atlas-Agena rocket, Mariner 2 passed within about 34,000 kilometers 21,000 miles of Venus.
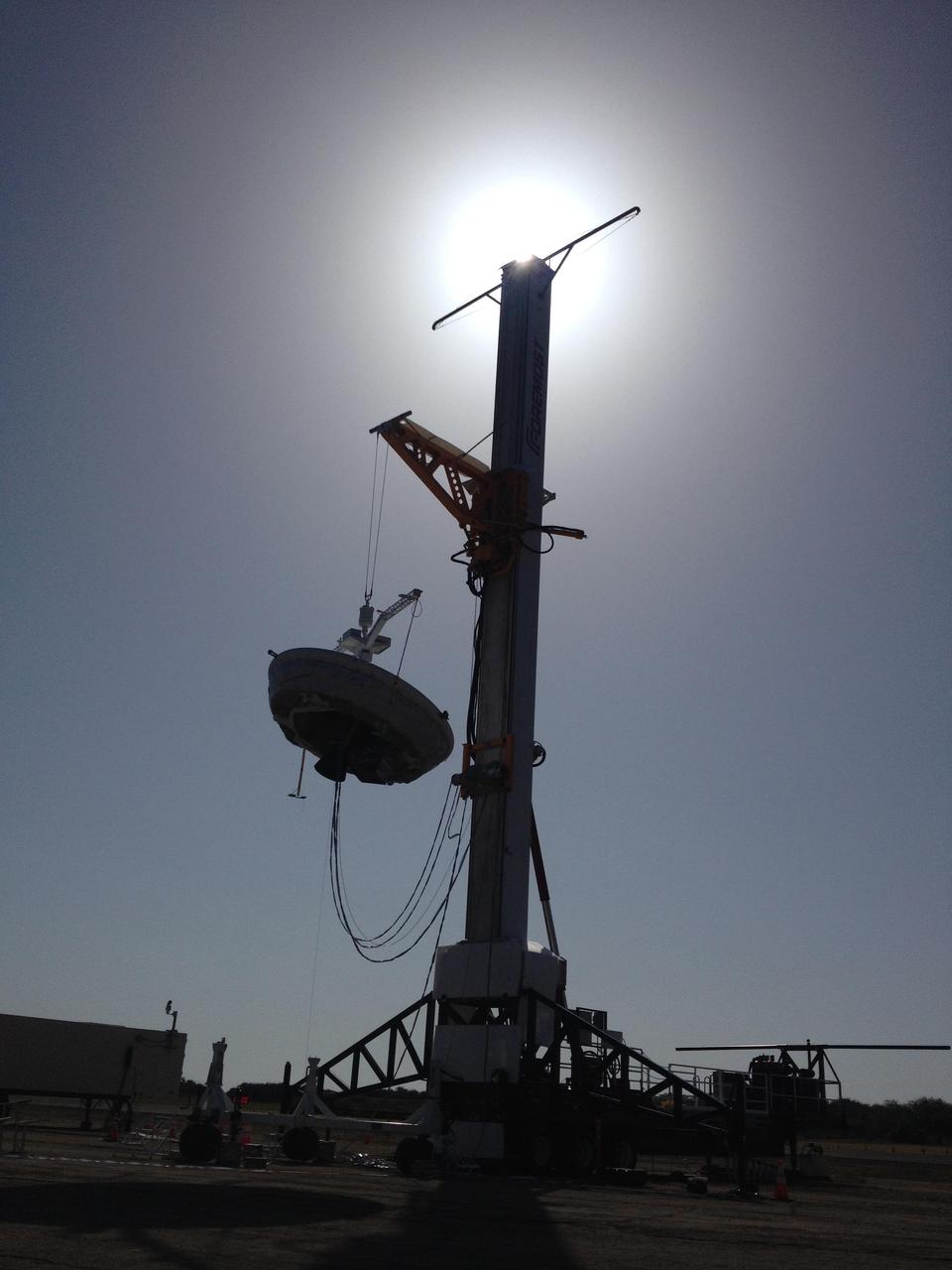

A saucer-shaped vehicle part of NASA Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator LDSD project designed to test interplanetary landing devices hangs on a tower in preparation for launch at the Pacific Missile Range Facility in Kauai, Hawaii.
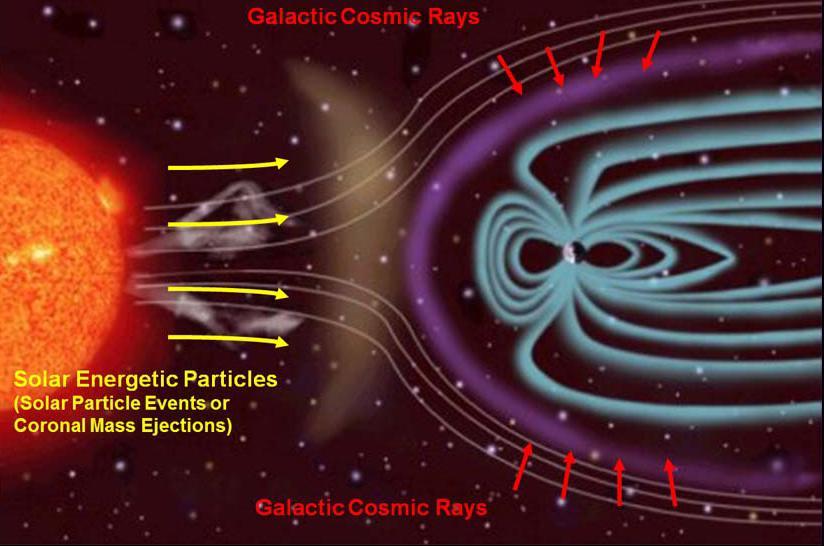
This illustration depicts the two main types of radiation that NASA Radiation Assessment Detector RAD onboard Curiosity monitors, and how the magnetic field around Earth affects the radiation in space near Earth.
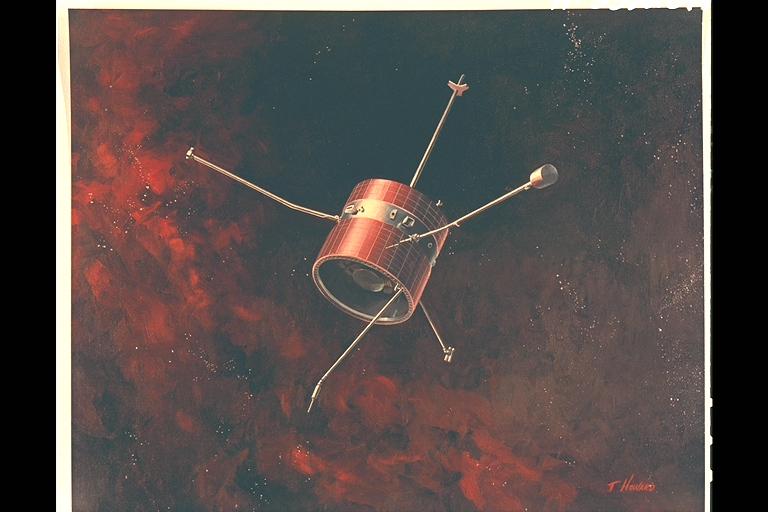

Artist: T Howard Interplanetary Pioneer 6 Spacecraft launched in 1965 to study the sun.
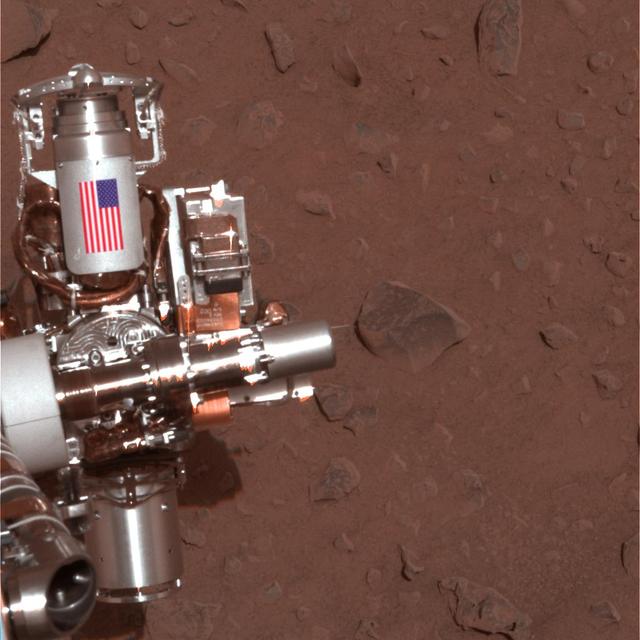

The piece of metal with the American flag on it in this image of a NASA rover on Mars is made of aluminum recovered from the site of the World Trade Center towers in the weeks after their destruction.
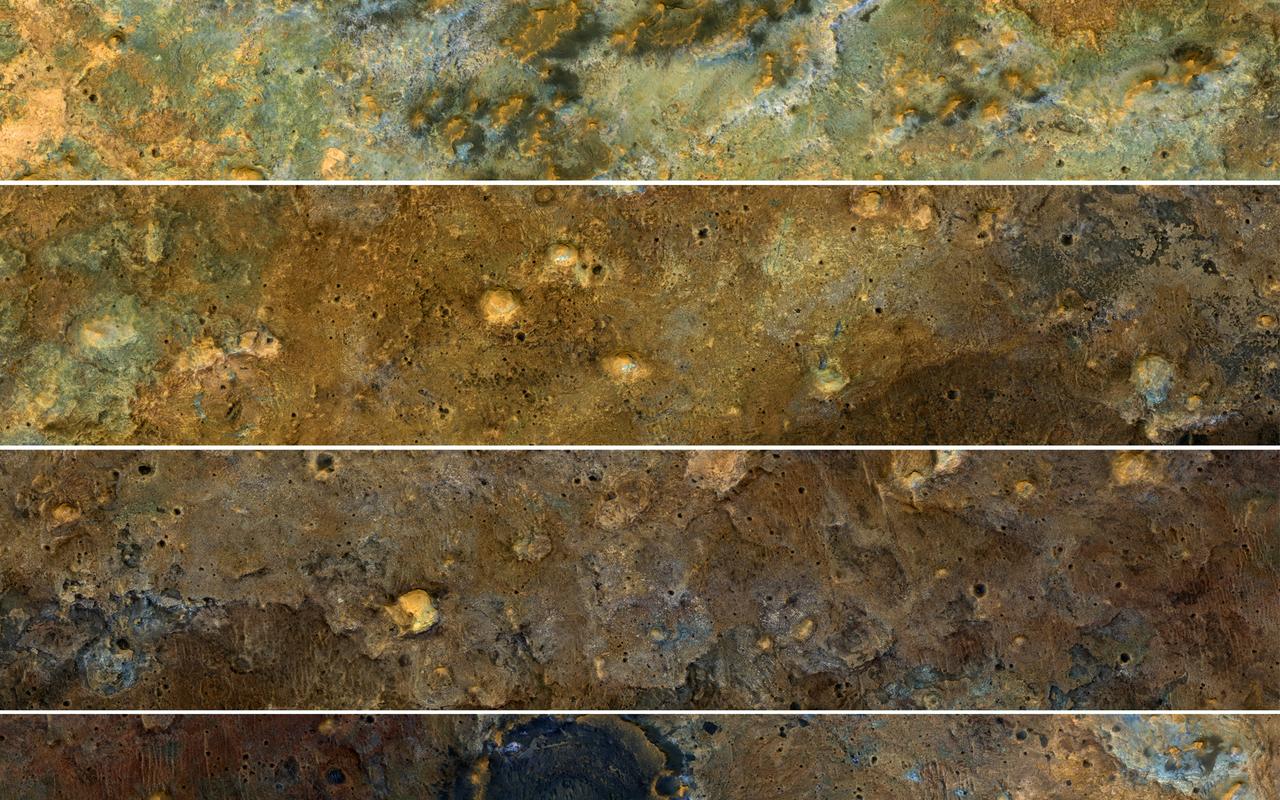
The clay-rich terrain surrounding Mawrth Vallis is one of the most scenic regions of Mars, a future interplanetary park, as seen by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Here, we cut a long, oblique view into strips to see the full color coverage in more compact form. The origin of these altered layers is the subject of continued debates, perhaps to be resolved by a future rover on the surface. We do know that these layers are very ancient, dating back to a time when the environment of Mars was wetter and more habitable, if there were any inhabitants. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21871
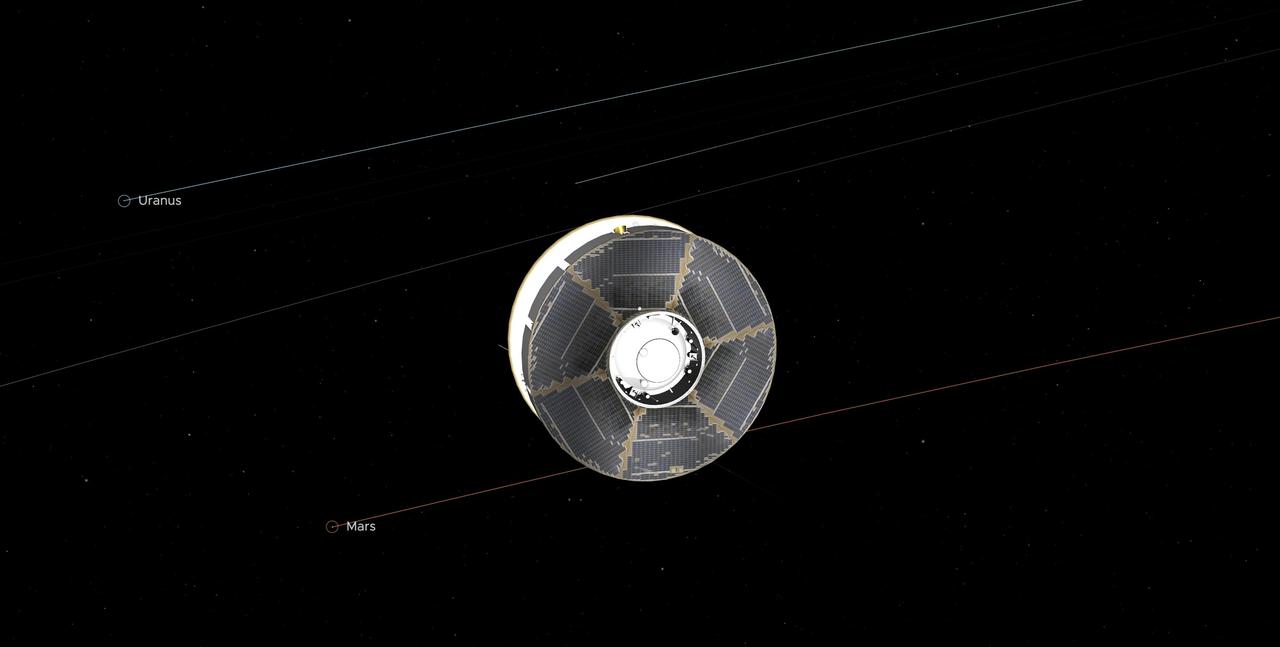

This illustration of the Mars 2020 spacecraft (the solar-panel-covered cruise stage most visible here along with a portion of the white back shell) in interplanetary space was generated using imagery from NASA's Eyes on the Solar System. The image is from the mission's midway point between Earth and Mars — 146.3 million miles (235.4 million kilometers) away from each. In straight-line distance, Earth is 26.6 million miles (42.7 million kilometers) behind Perseverance, and Mars is 17.9 million miles (28.8 million kilometers) in front. Visible in the graphic are the solar panels on the cruise stage surrounding the top of the aeroshell. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24231
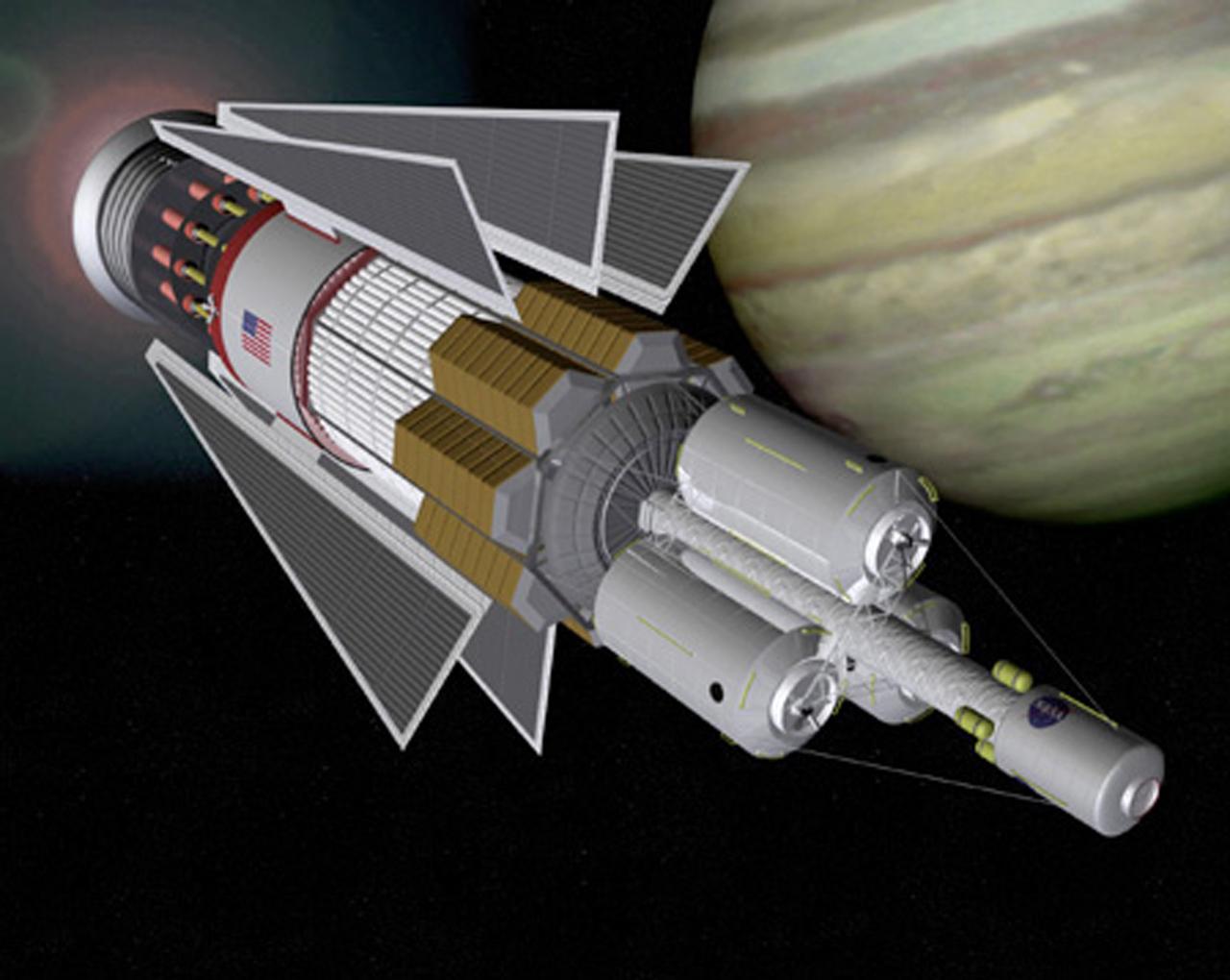
In the 1960's U.S. Government laboratories, under Project Orion, investigated a pulsed nuclear fission propulsion system. Based on Project Orion, an interplanetary vehicle using pulsed fission propulsion would incorporate modern technologies for momentum transfer, thermal management, and habitation design.

Andrew Klesh, a Mission Architect at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory is seen during a keynote titled “MarCO: Flight Results from the First Interplanetary CubeSat Mission” at the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Friday, Oct. 25, 2019, at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
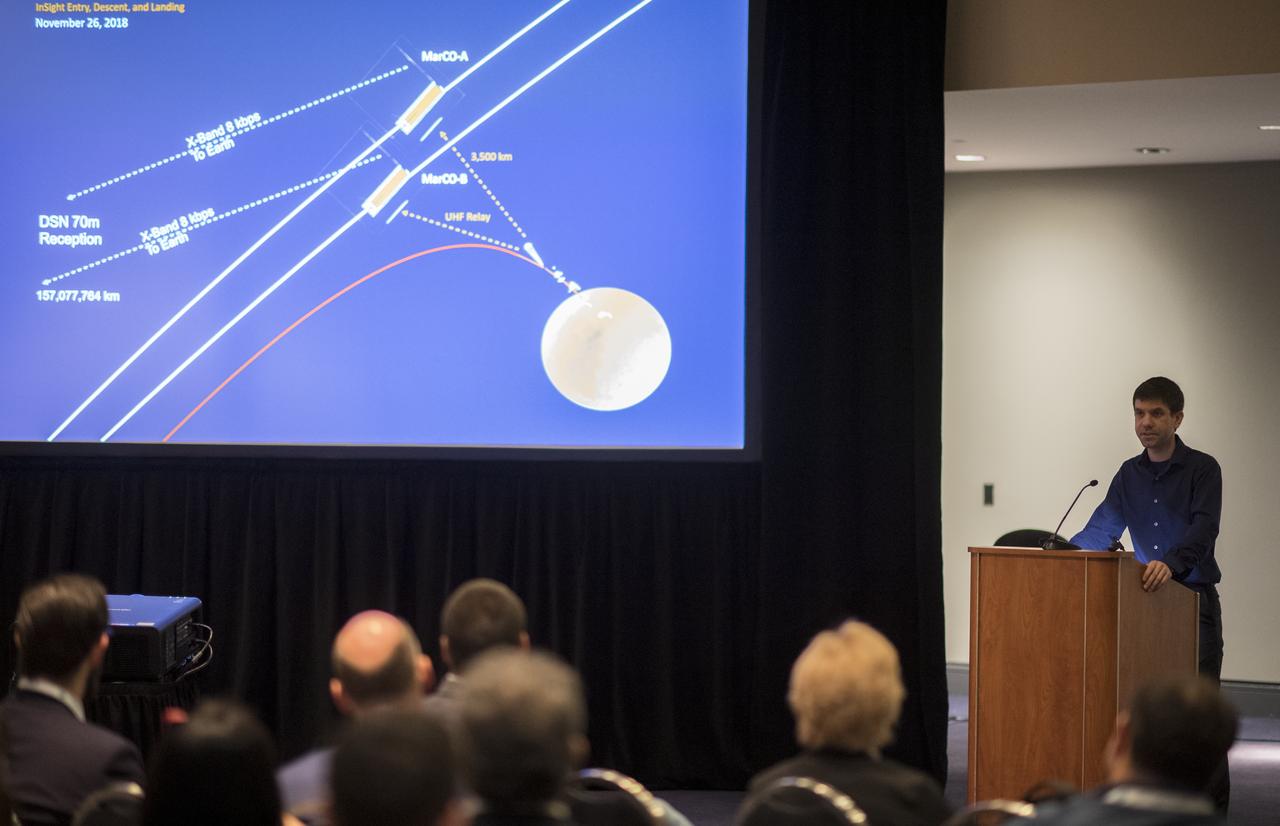

Andrew Klesh, a Mission Architect at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory is seen during a keynote titled “MarCO: Flight Results from the First Interplanetary CubeSat Mission” at the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Friday, Oct. 25, 2019, at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
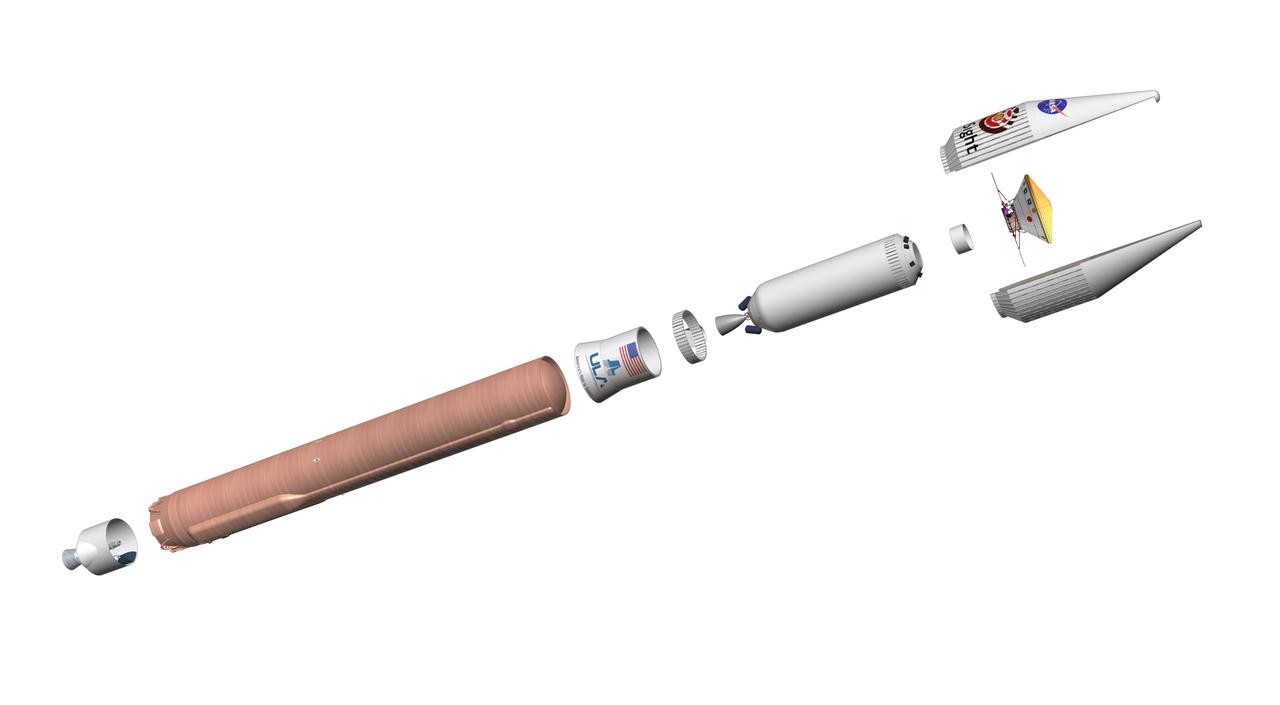
Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, is scheduled to launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base on California's Pacific coast between May 5 and June 8, 2018. The lander will launch to Mars aboard an Atlas V-401 launch vehicle, one of the biggest rockets available for interplanetary flight. It stands 188 feet (57.3 meters) tall, or about as tall as a 19-story building. Fully stacked, with the spacecraft, the Atlas V-401 weighs about 730,000 pounds (333,000 kilograms). That's about 14 big rigs, fully loaded with cargo! The three numbers in the 401 designation signify: 4: a payload fairing -- or nose cone -- that is about 13 feet (4 meters) in diameter 0: solid-rocket boosters supplementing the main booster 1: the upper stage, which has one engine https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22231

Russian Scientists from the Commission of Interplanetary Travel of the Soviet Academy of Science November 21,1959 Left to right: Front row: Yury S. Galkin, Anatoly A. Blagonravov, and Prof. Leonid I. Sedov (Chair of the Commission for Interplanetary Travel)-Soviet Academy of Science, Leninski Gory, Moscow, Russia Dr. H.J. E. Reid and Floyd L. Thompson Langley Research Center. Second row: Boris Kit Translator, Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. Eugene C. Draley and Laurence K. Loftin, Jr. -Langley Research Center Arnold W. Frutkin and Harold R. Lawrence NASA Headquarters. Back row: T.Melvin Butler-Langley Research Center John W. Townsend Goddard Space Flight Center, NASA, Washington D.C., and George M. Low NASA Headquarters.
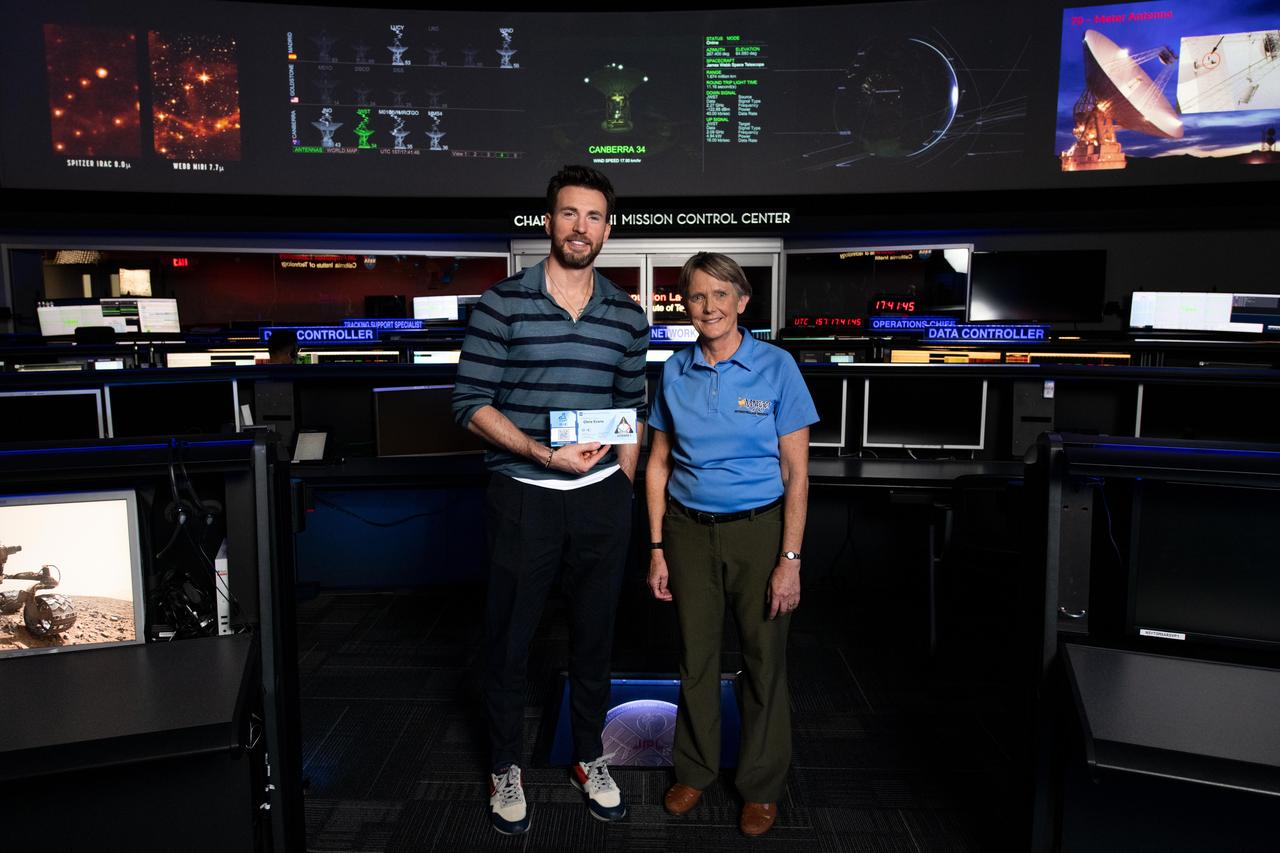

Actor Chris Evans (left) receives a "boarding pass" to the Moon from Suzanne Dodd, director of the Interplanetary Network Directorate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. The pair are seen in the Space Flight Operations Facility at JPL on June 6, 2022. Evans visited JPL to learn more about space missions after starring as the lead voice in the space-themed movie "Lightyear." More than 3 million names, including Evans', were submitted online and will be included on a flash drive that will fly on the Orion spacecraft during NASA's Artemis I mission to the Moon. Artemis I will be the first uncrewed flight test of the Space Launch System rocket and the Orion spacecraft launching from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA's Artemis program aims to establish a sustained human presence on the Moon that will serve as a launching pad for exploring Mars and beyond. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25311
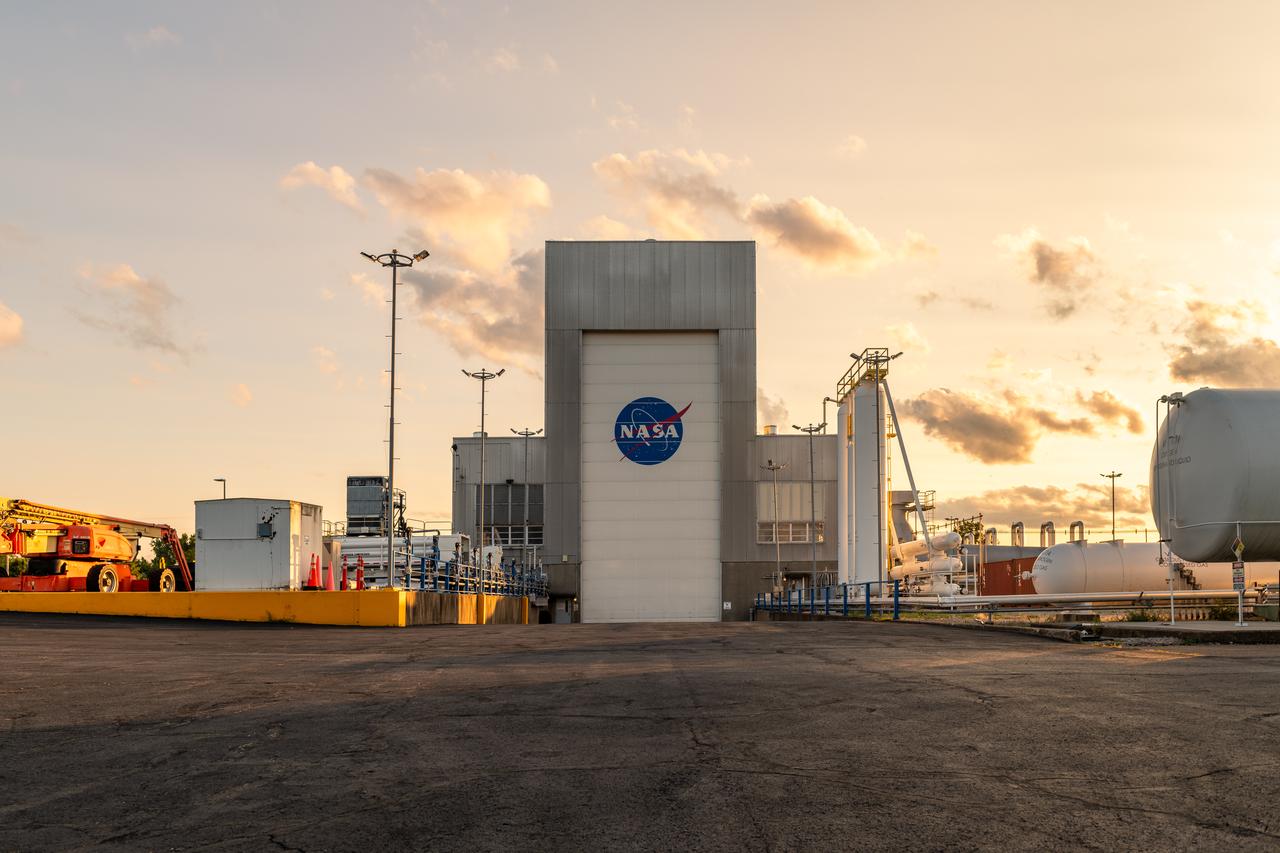

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
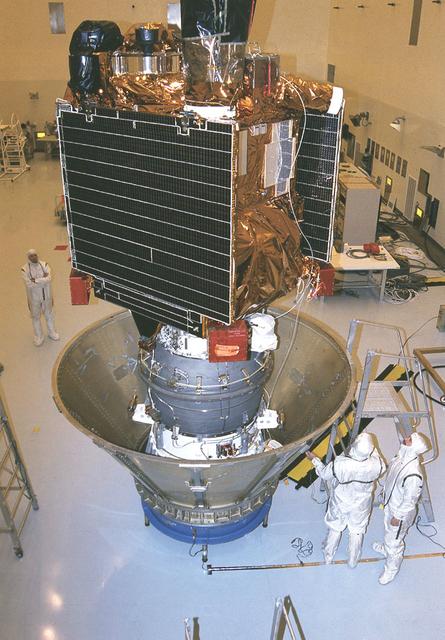

Workers at the Jet Propulsion Research Lab (JPL) in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) prepare the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft for transfer to the launch pad by placing it in a protective canister. The Surveyor spacecraft (upper) is already mated to its solid propellant upper stage booster (lower), which is actually the third stage of the Delta II expendable launch vehicle that will propel the spacecraft on its interplanetary journey to Mars.
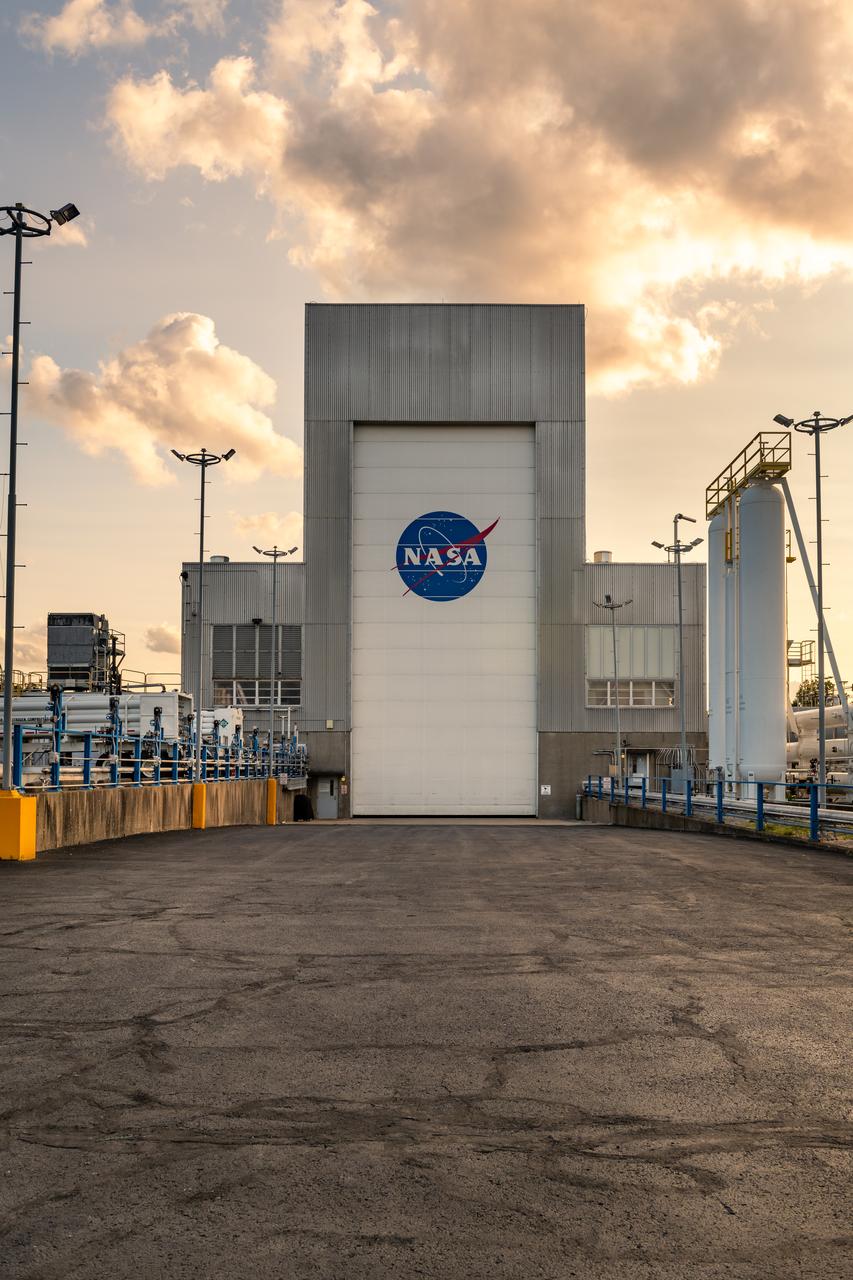

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
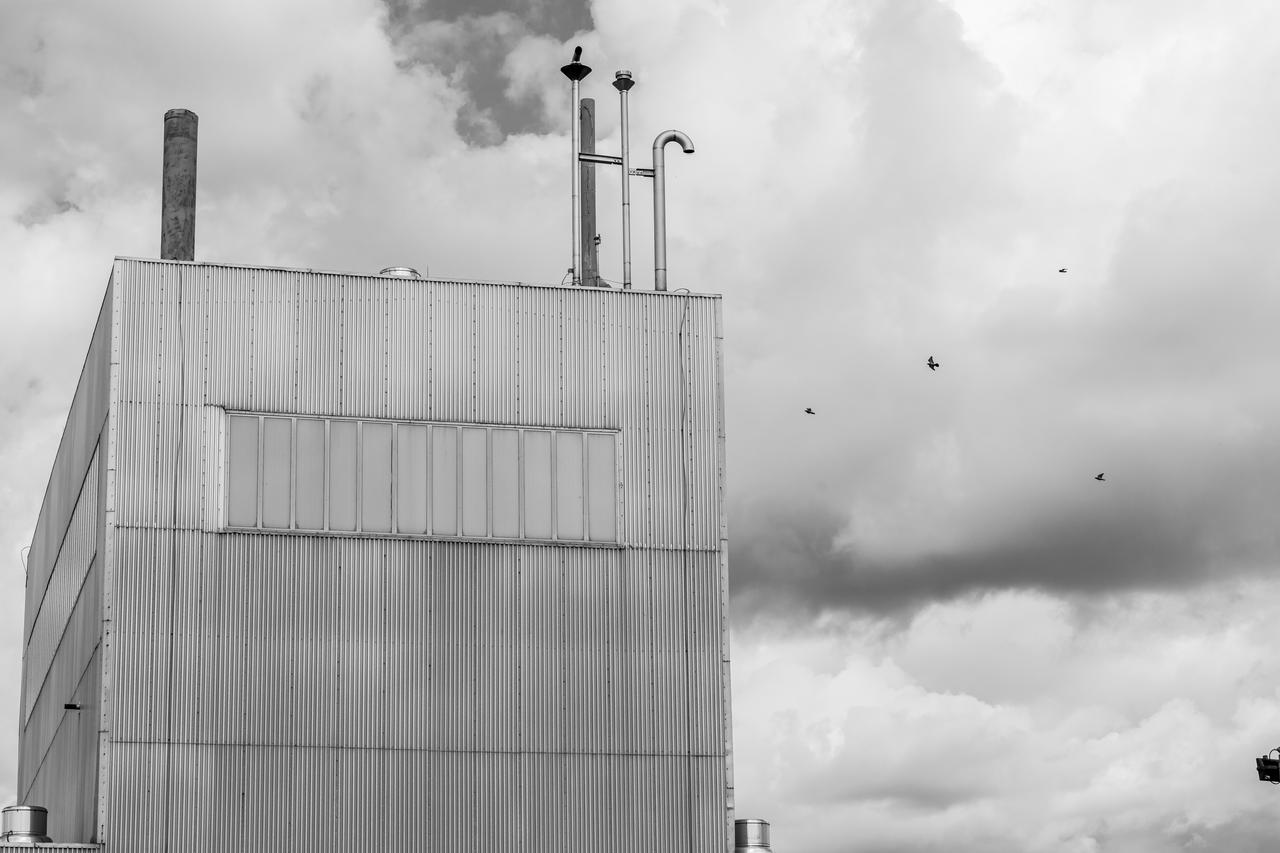

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
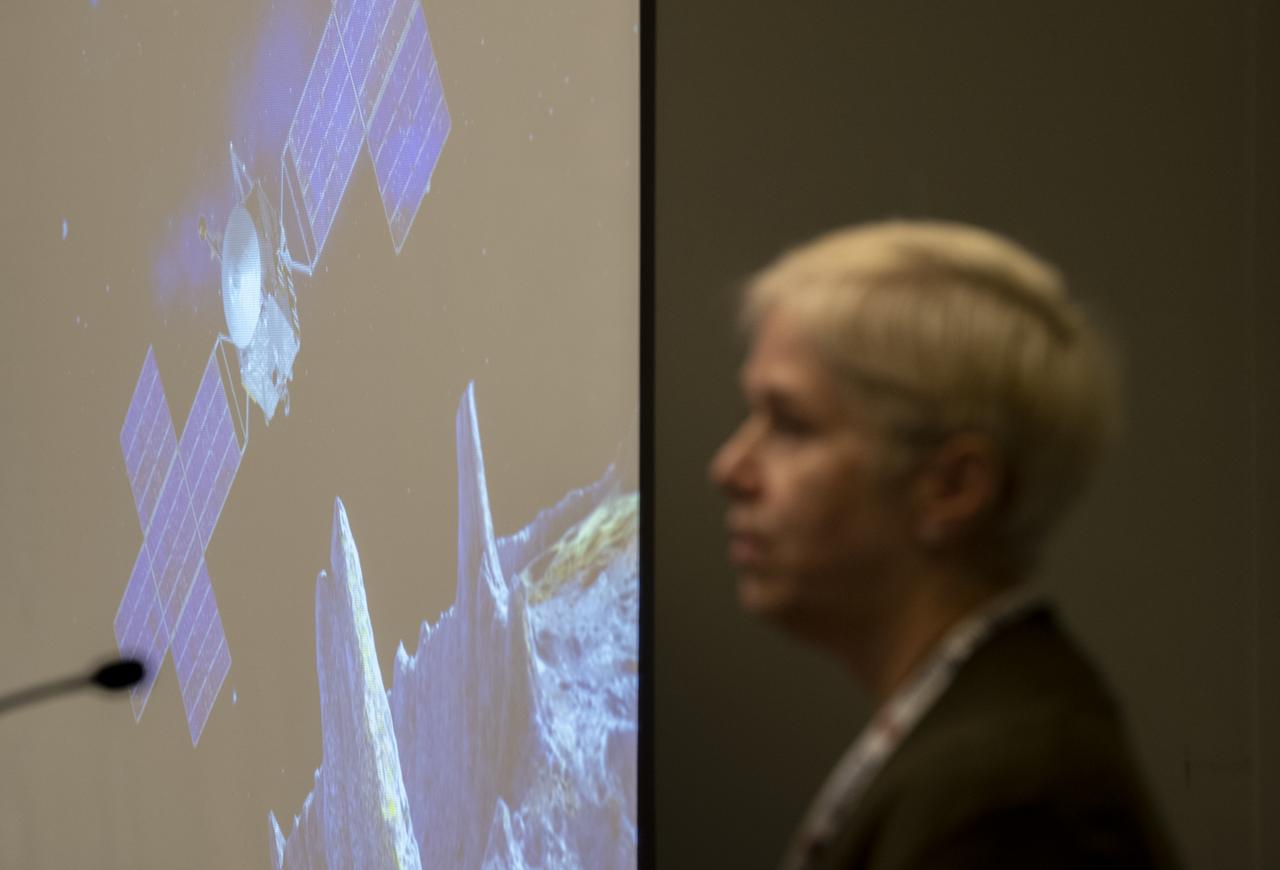

An artists rendition of the Psyche spacecraft is seen on scree as Linda Elkins-Tanton, Managing Director and Foundation Professor of Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration, is seen during a keynote titled “The ASU Interplanetary Initiative: Advancing Society Through ” at the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Tuesday, Oct. 22, 2019 at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Elkins-Tanton is the principle investigator of NASA’s upcoming Psyche mission which is scheduled to launch in 2022. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
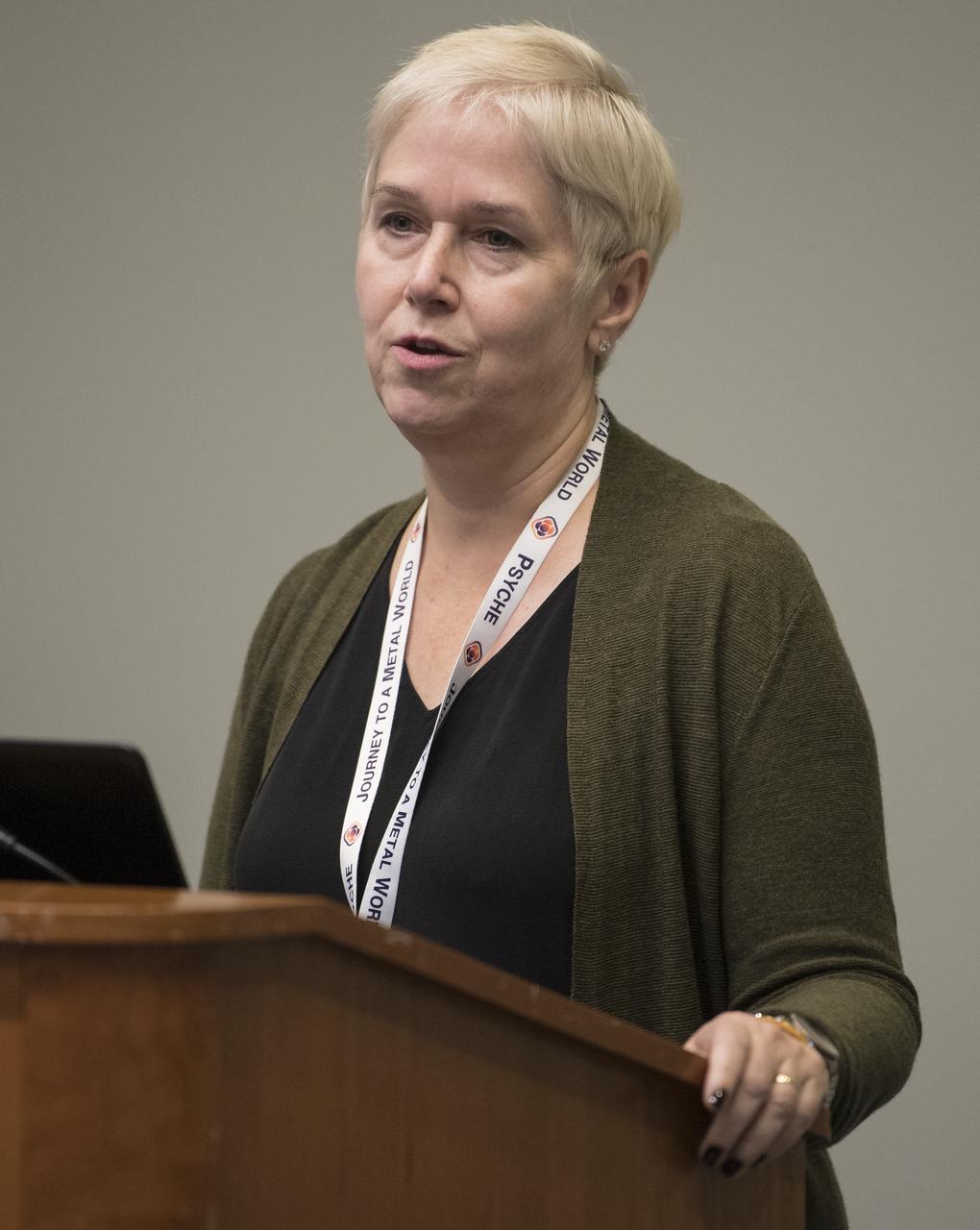

Linda Elkins-Tanton, Managing Director and Foundation Professor of Arizona State University’s School of Earth and Space Exploration, is seen during a keynote titled “The ASU Interplanetary Initiative: Advancing Society Through ” at the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Tuesday, Oct. 22, 2019 at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Elkins-Tanton is the principle investigator of NASA’s upcoming Psyche mission which is scheduled to launch in 2022. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
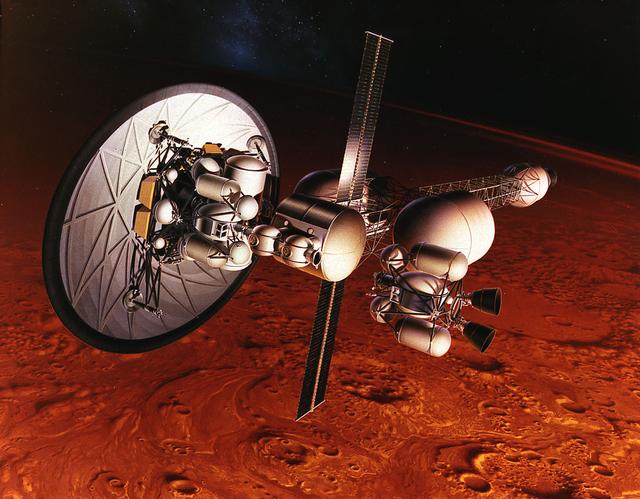
Originally investigated in the 1960's by Marshall Space Flight Center plarners as part of the Nuclear Energy for Rocket Vehicle Applications (NERVA) program, nuclear-thermal rocket propulsion has been more recently considered in spacecraft designs for interplanetary human exploration. This artist's concept illustrates a nuclear-thermal rocket with an aerobrake disk as it orbits Mars.
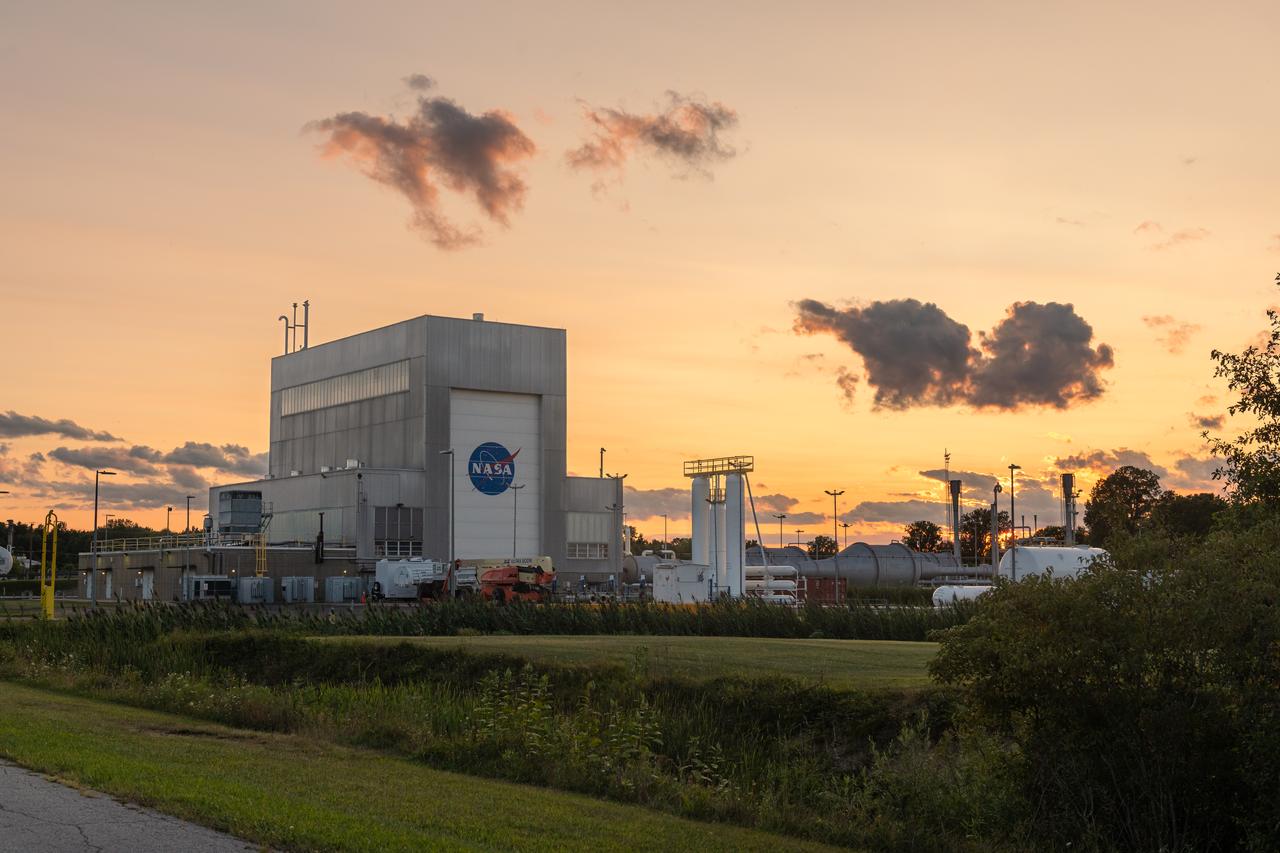

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
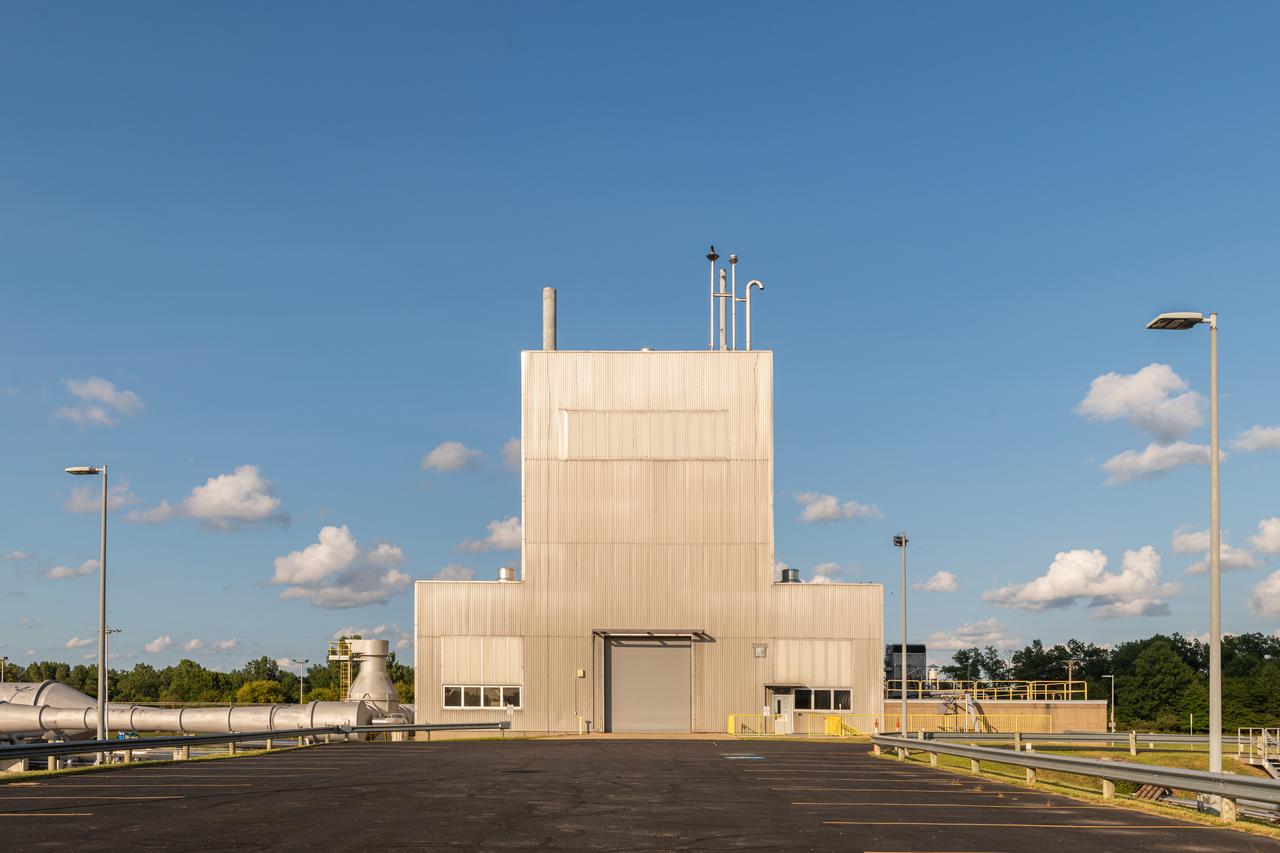

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
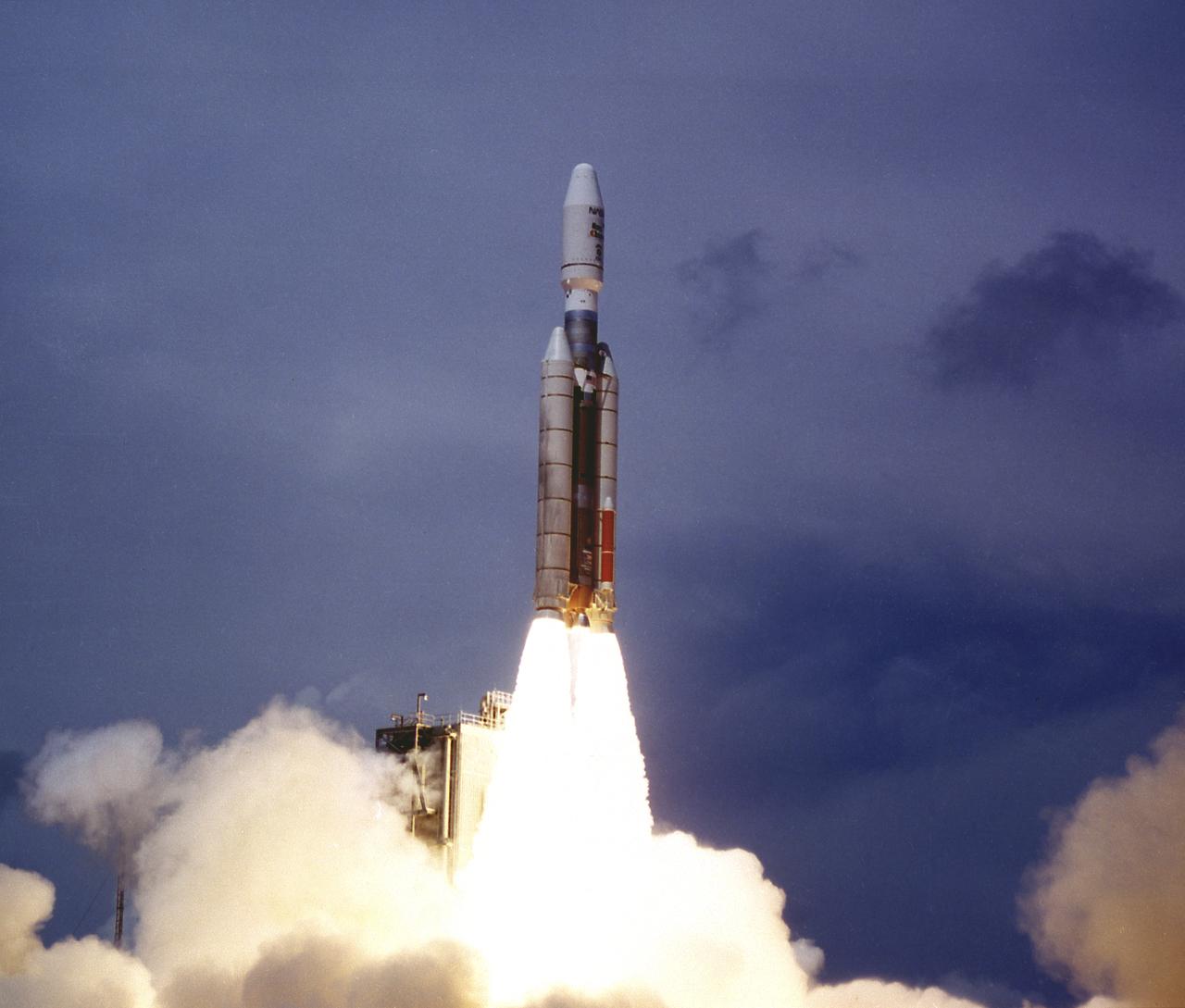

Titan III vehicle launched the Mars Observer spacecraft and the Transfer Orbit Stage (TOS) from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on September 25, 1992. Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), TOS will fire to send the Observer on an 11-month interplanetary journey to the Mars. The Observer failed to reach the Mars orbit in August 1993.
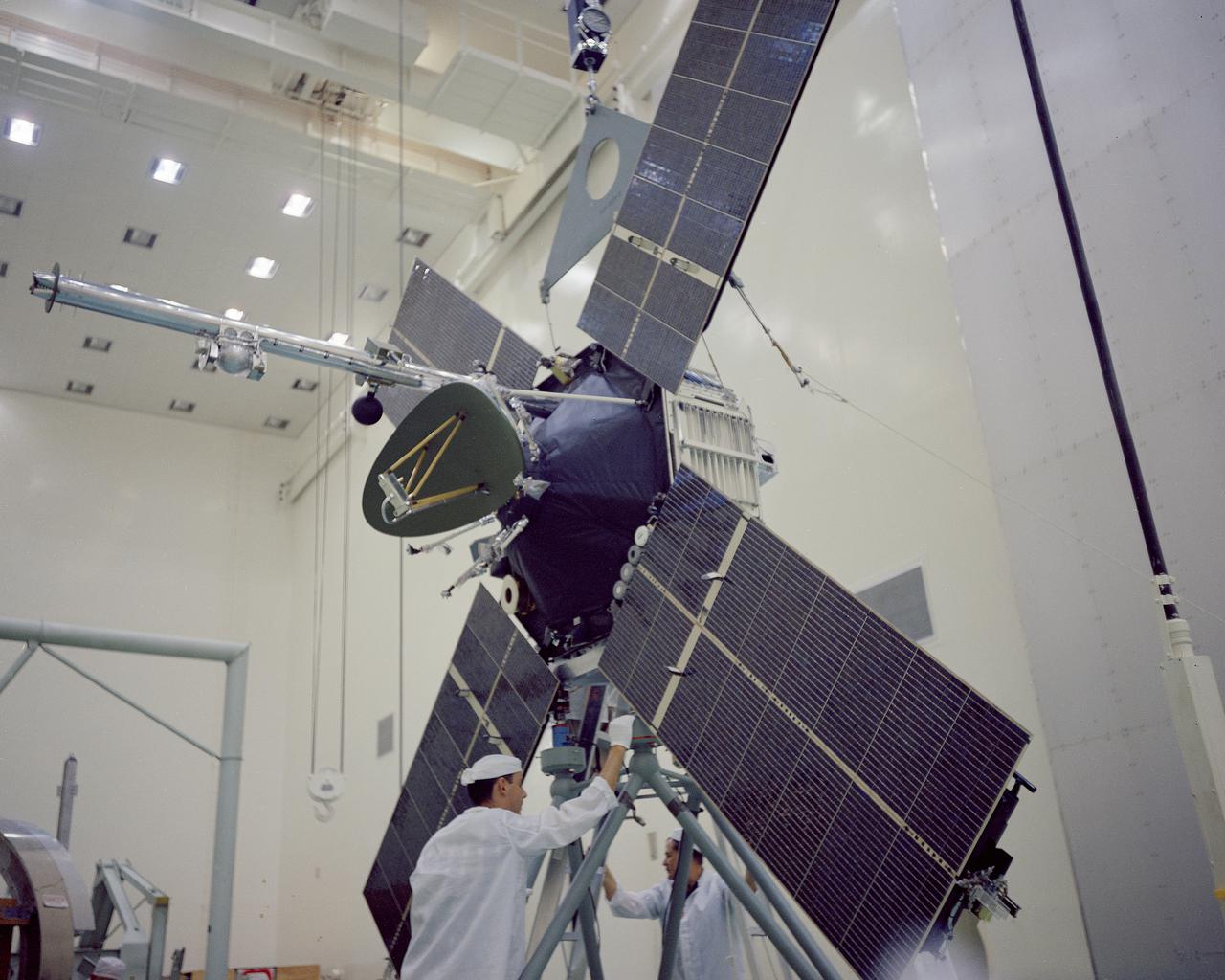

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- In the AO Building at Cape Kennedy Air Force Station in Florida, the Mariner 3 spacecraft is processed prior to mating with its payload faring. Mariner is one of two identical deep-space probes designed and built by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory for NASA's Mariner Mars 1964 project. Mariner 3 is intended to conduct close-up scientific observations of Mars and transmit information back to Earth on interplanetary space and the space surrounding the Red Planet. Photo Credit: NASA
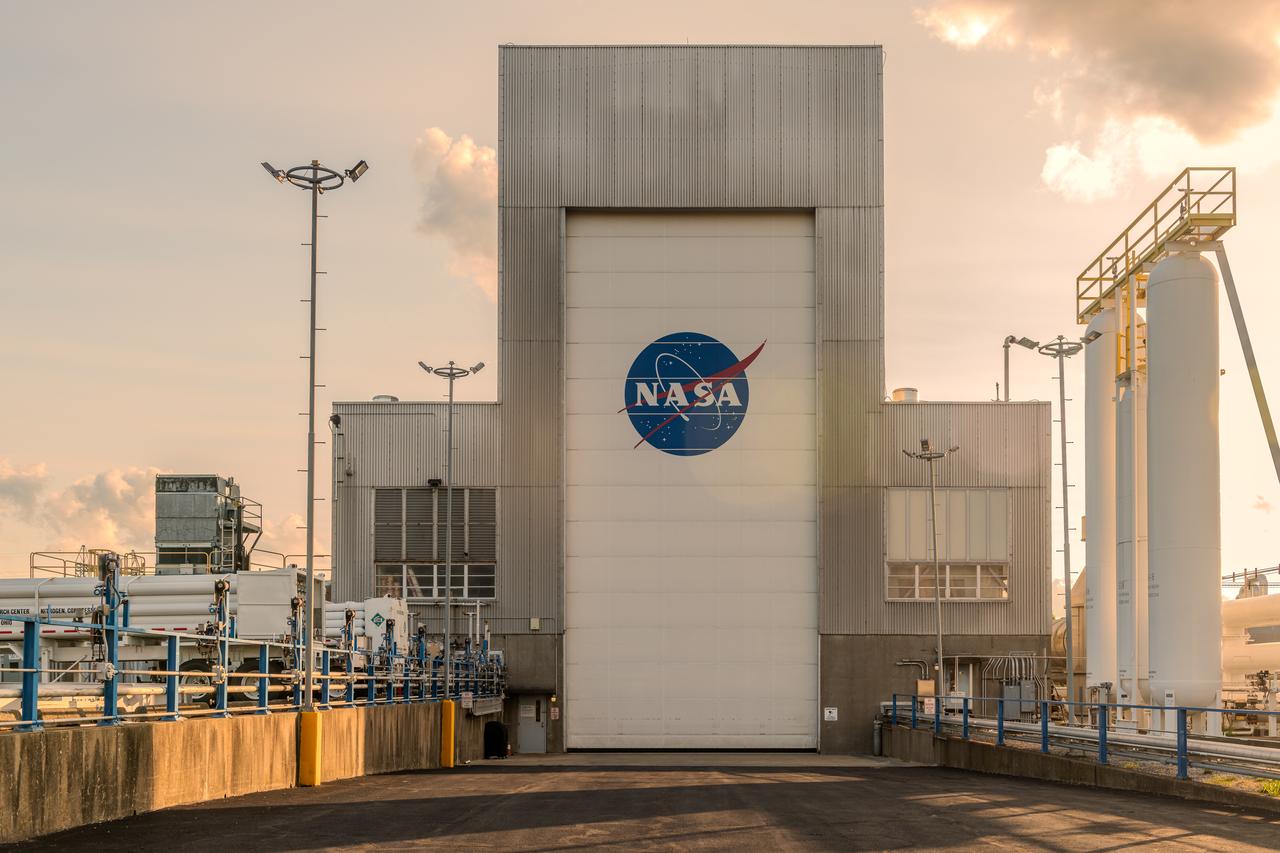

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
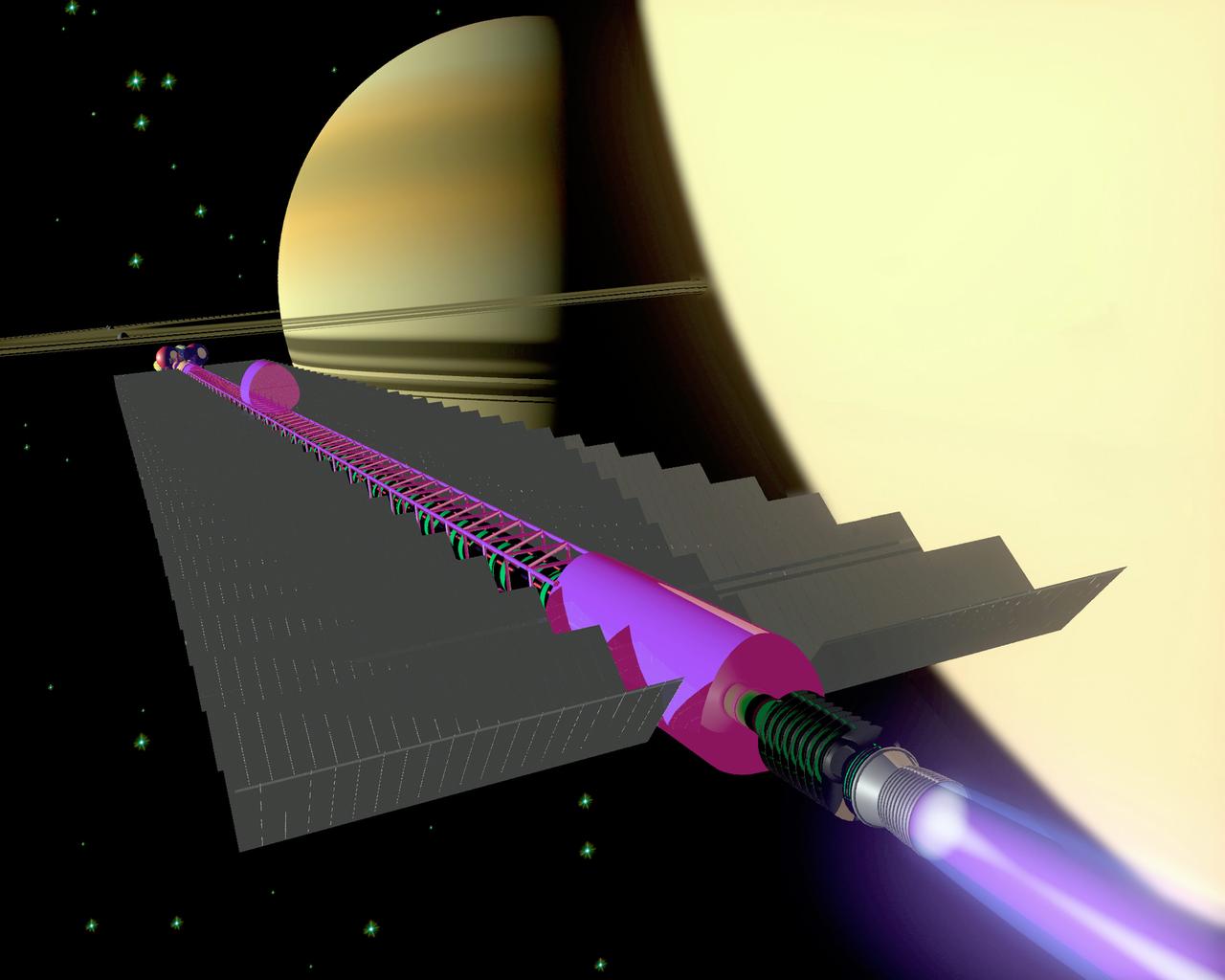
Travel to distant stars is a long-range goal of Marshall Space Flight Center's Advanced Concept Group. One of the many propulsion systems currently being studied is fusion power. The objective of this and many other alternative propulsion systems is to reduce the costs of space access and to reduce the travel time for planetary missions. One of the major factors is providing an alternate engery source for these missions. Pictured is an artist's concept of future interplanetary space flight using fusion power.
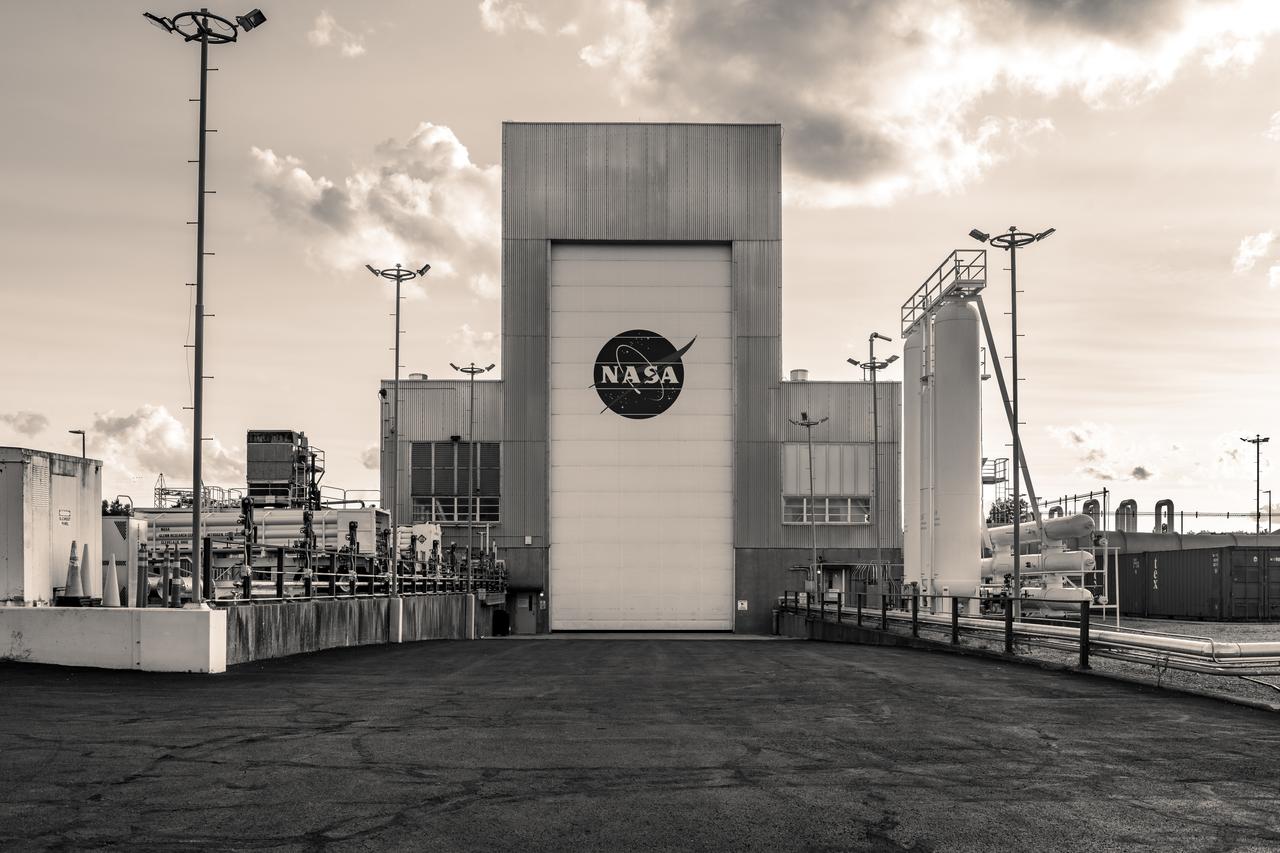

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
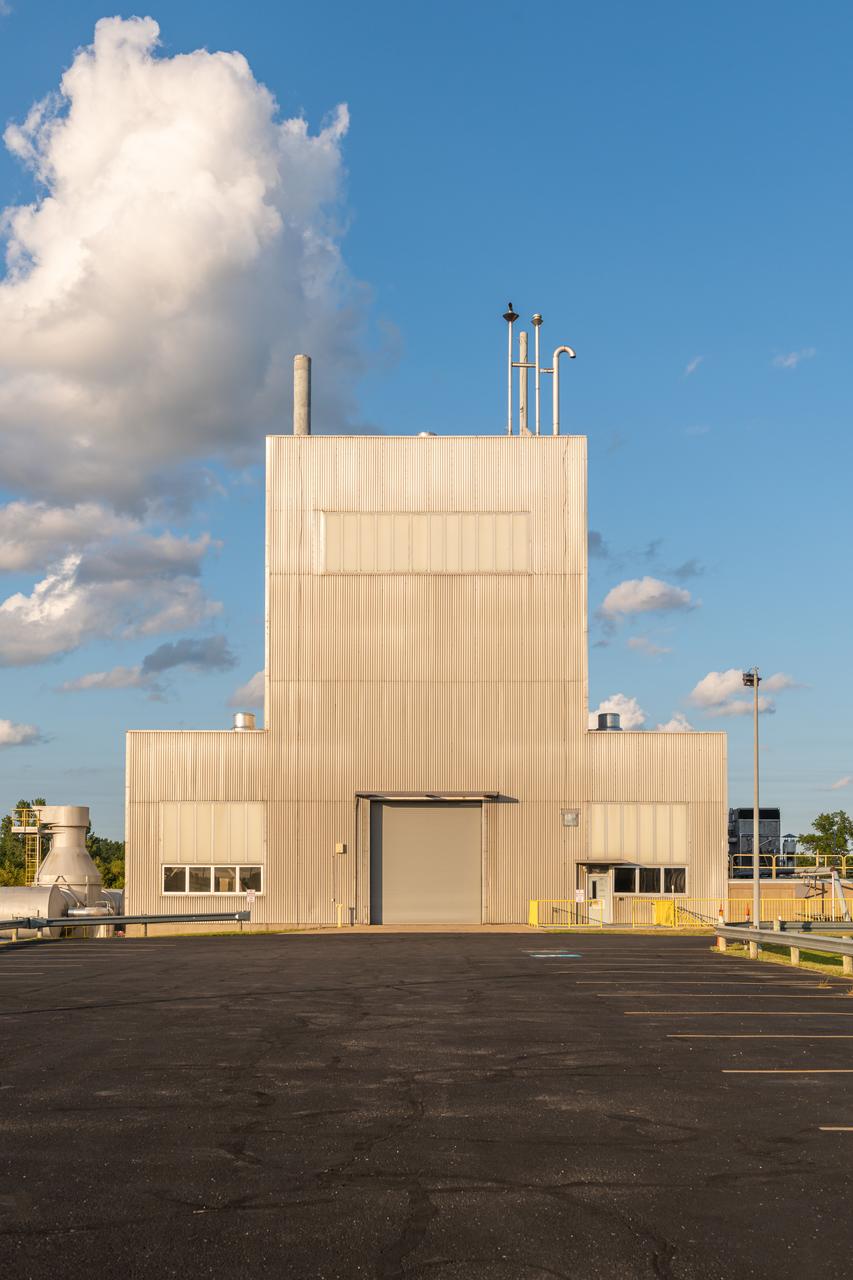

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
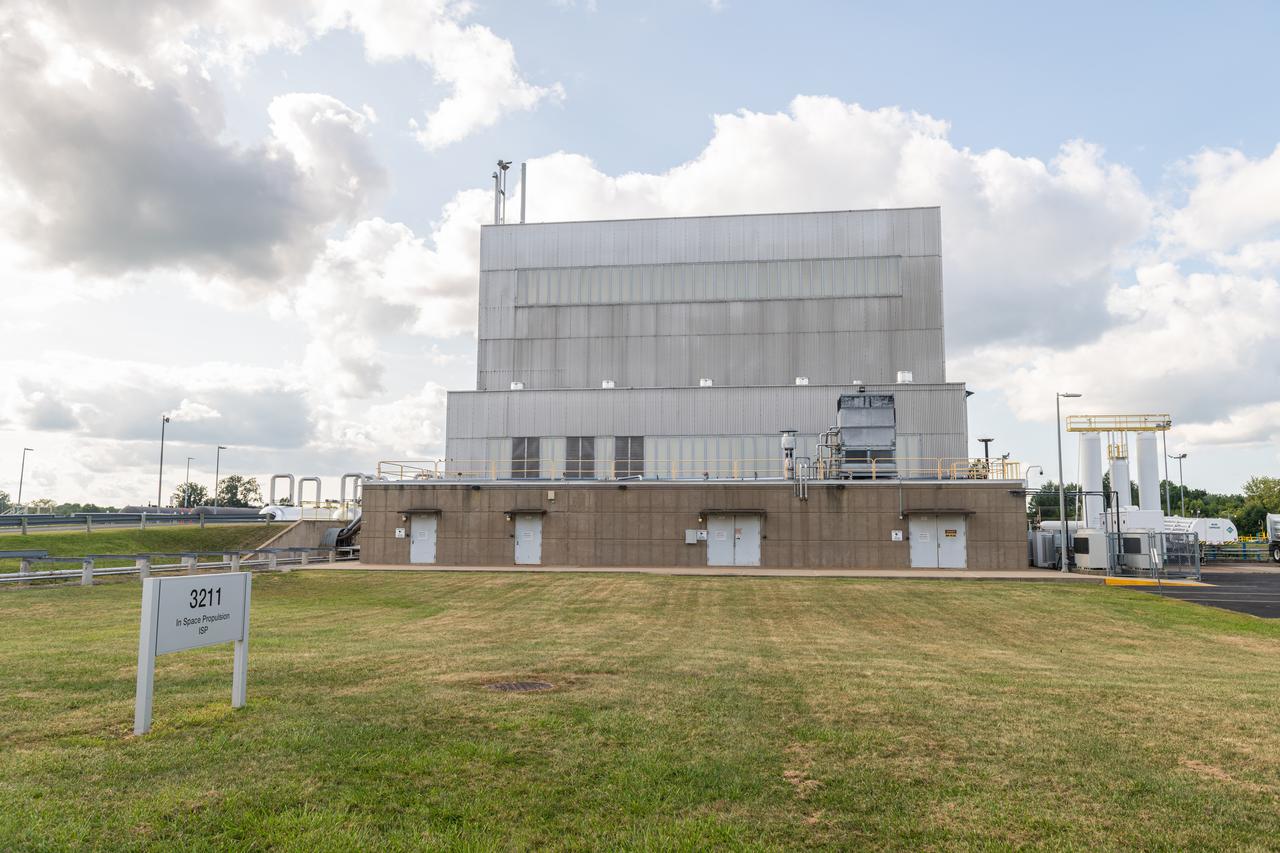

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
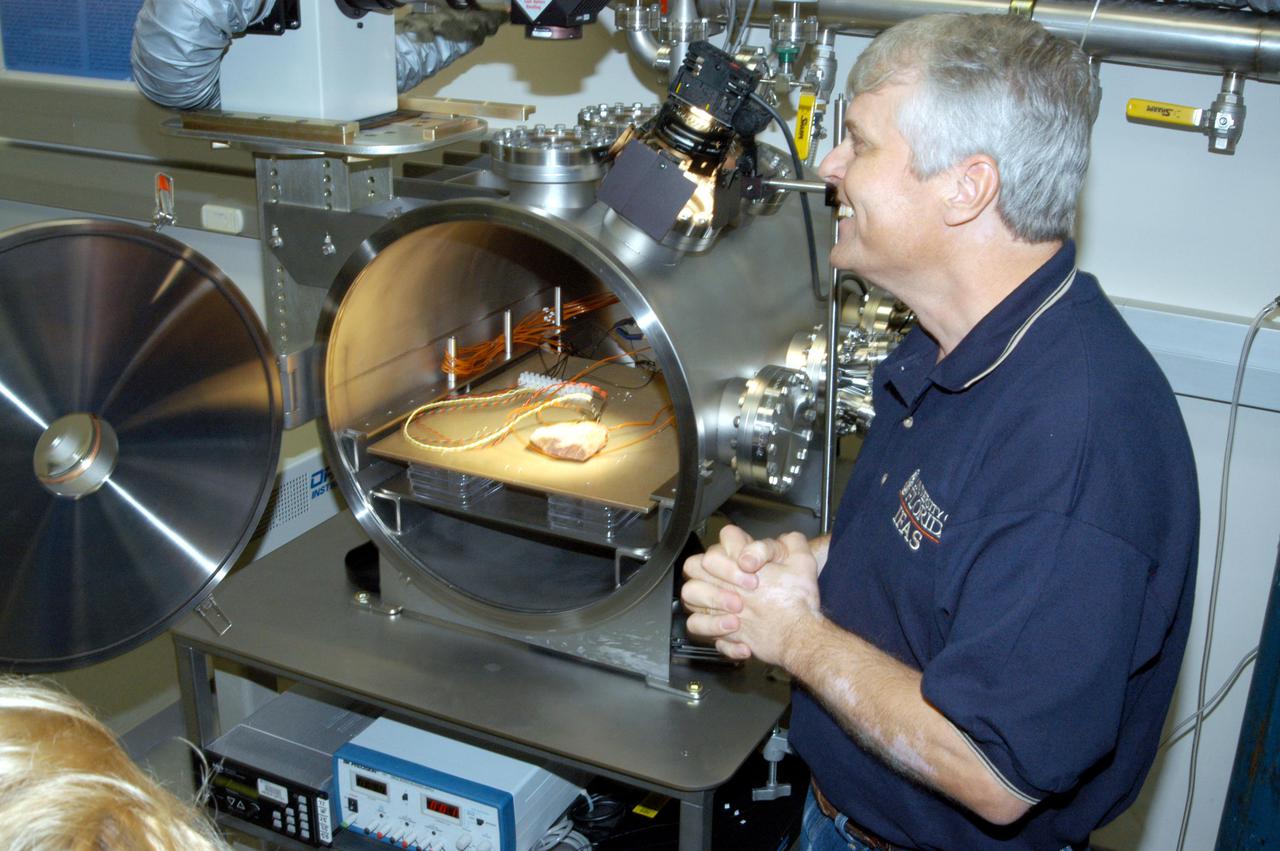

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Andy Schuerger, a research assistant professor with the University of Florida, demonstrates the Mars Simulation Chamber at the Space Life Sciences Lab during a tour of the facility for members of the news media. Schuerger is studying the effects of interplanetary space and Mars surface conditions on the survival, growth, and potential adaption of terrestrial microbes to the martian surface.
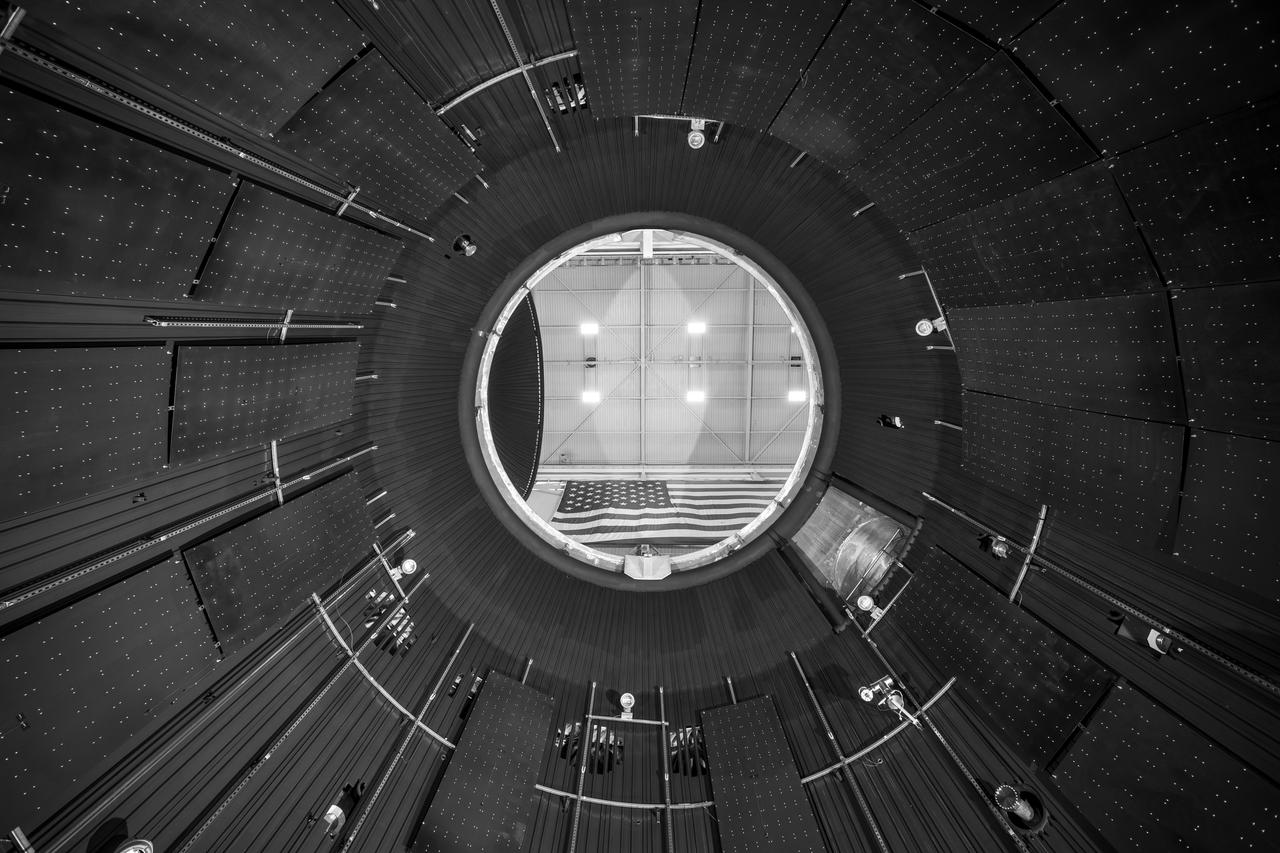

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. This is a view from inside the chamber looking up toward the American flag. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
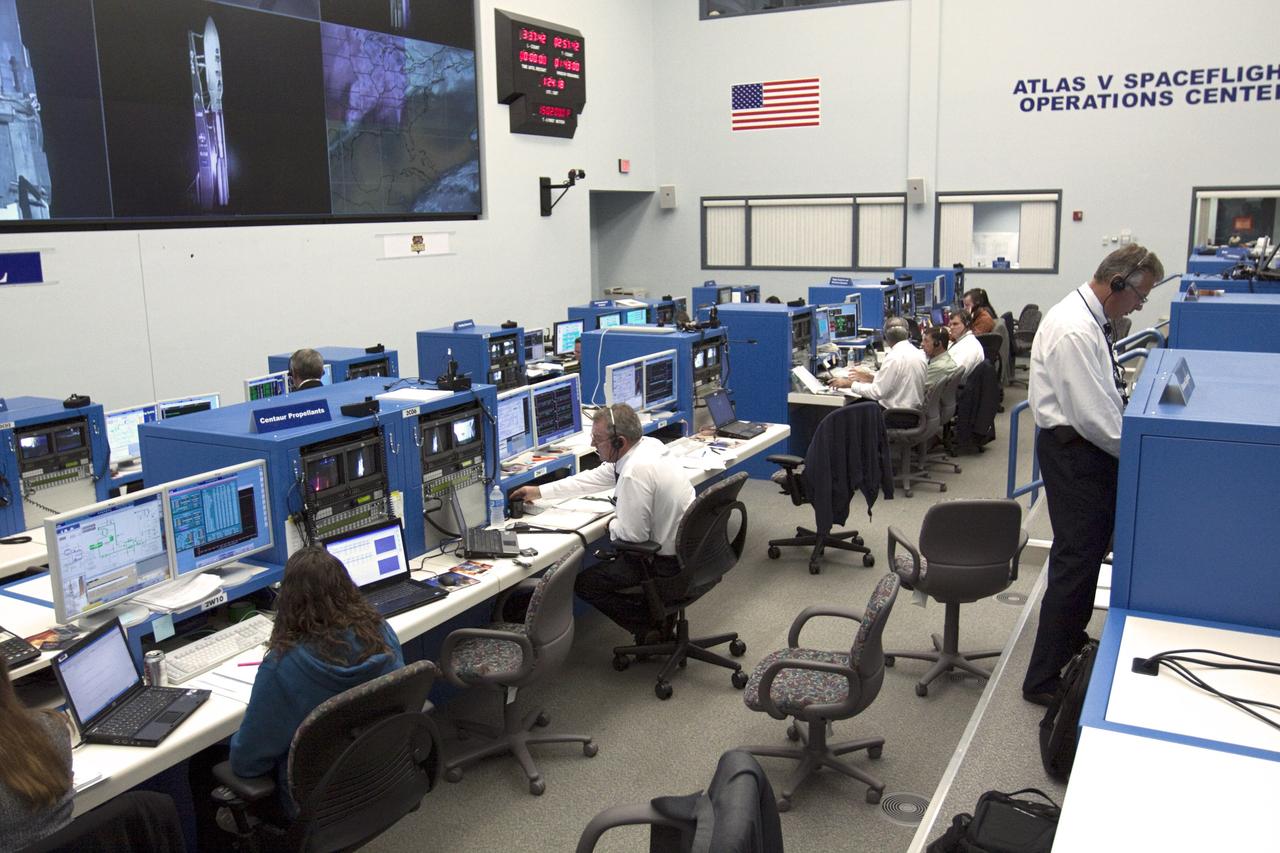

CAPE CANAVERAL – Launch controllers oversee the countdown in the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) before the launch of the Mars Science Laboratory on an Atlas V rocket. MSL lifted off at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26, beginning a 9-month interplanetary cruise to Mars. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
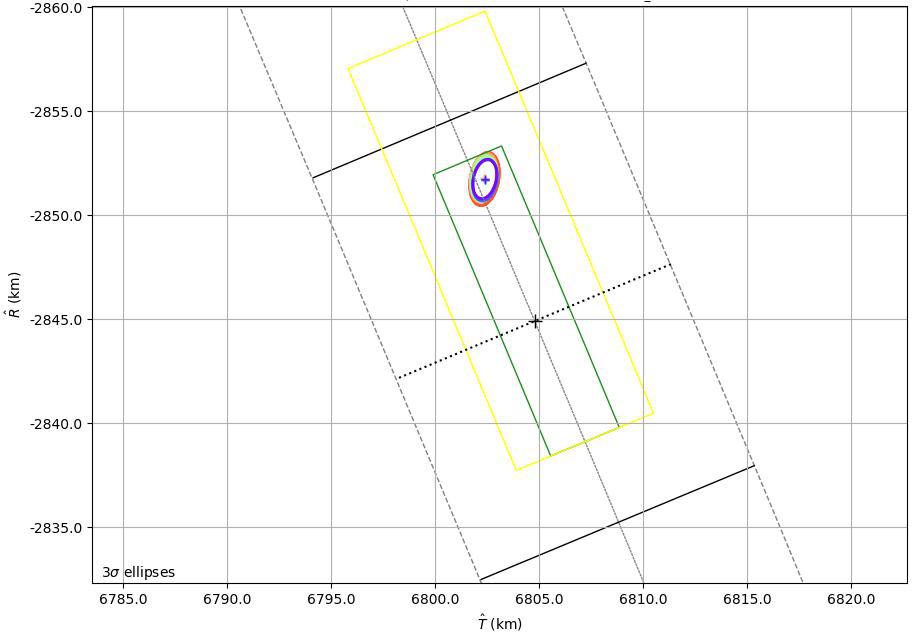
This graphic shows the B-Plane for NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance rover mission as of February 15, 2021. A B-Plane is a key performance metric that navigators for interplanetary missions use to determine the accuracy of their spacecraft's trajectory. The entry target on the lower right of the image (black cross) depicts the point where mission navigators are targeting the Mars 2020 spacecraft to enter the Red Planet's atmosphere. Higher up, the red, orange, green, and blue ovals depict the estimated "entry uncertainty ellipse" for the spacecraft as determined by previous navigation solutions. The inner-most ring (purple) depicts the most recent trajectory path. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24296
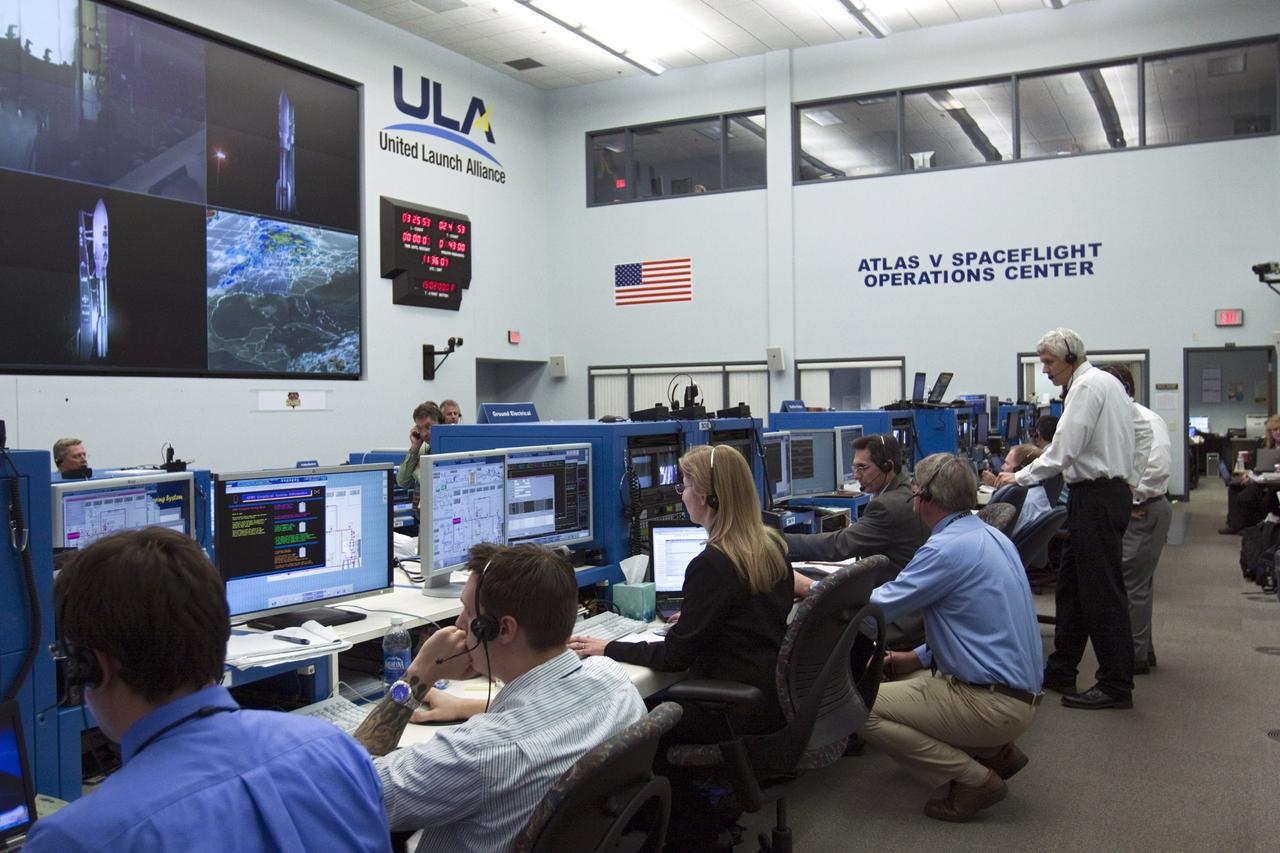

CAPE CANAVERAL – Launch controllers oversee the countdown in the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) before the launch of the Mars Science Laboratory on an Atlas V rocket. MSL lifted off at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26, beginning a 9-month interplanetary cruise to Mars. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
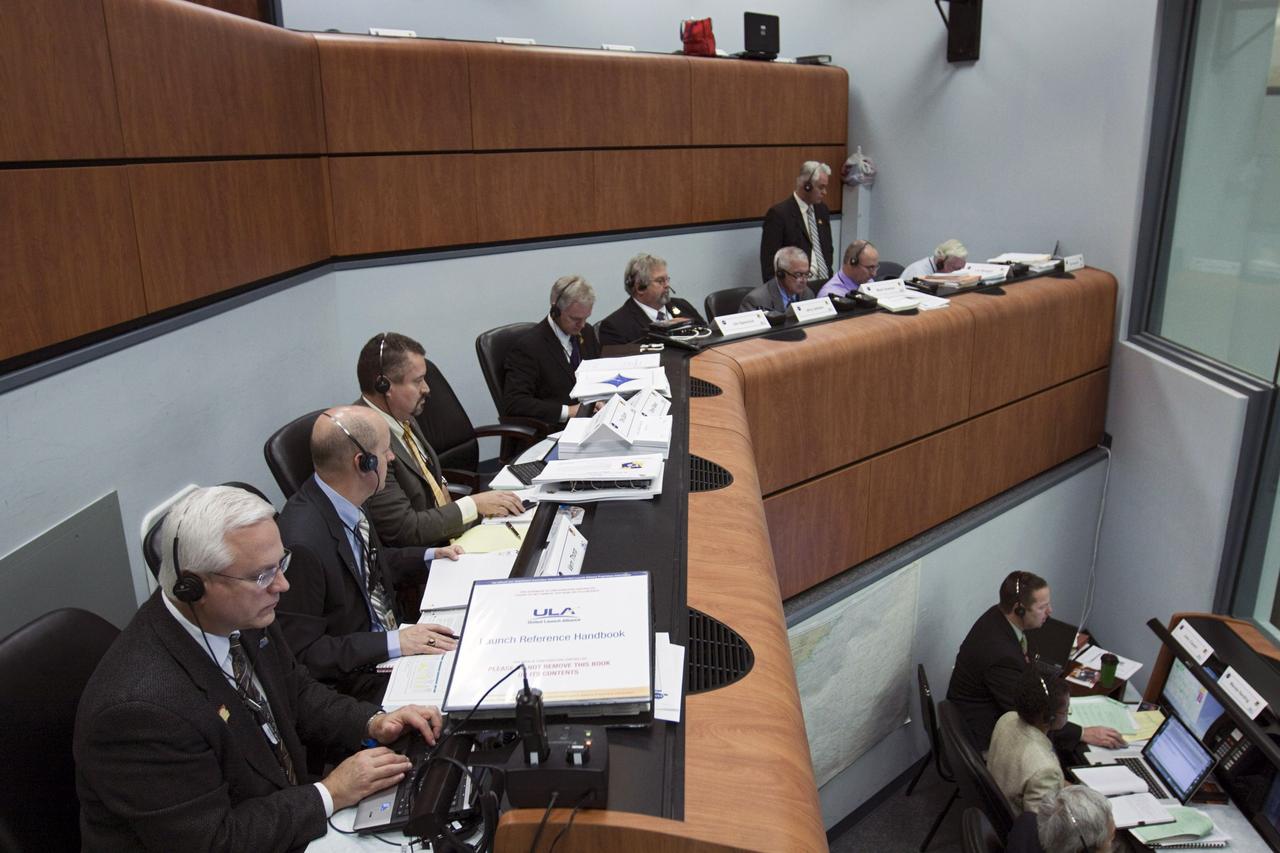

CAPE CANAVERAL – Launch managers from NASA and United Launch Alliance oversee the countdown in the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) before the launch of the Mars Science Laboratory on an Atlas V rocket. MSL lifted off at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26, beginning a 9-month interplanetary cruise to Mars. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Space Shuttle Payloads: Kennedy Space Center was the hub for the final preparation and launch of the space shuttle and its payloads. The shuttle carried a wide variety of payloads into Earth orbit. Not all payloads were installed in the shuttle's cargo bay. In-cabin payloads were carried in the shuttle's middeck. Cargo bay payloads were typically large payloads which did not require a pressurized environment, such as interplanetary space probes, earth-orbiting satellites, scientific laboratories and International Space Station trusses and components. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
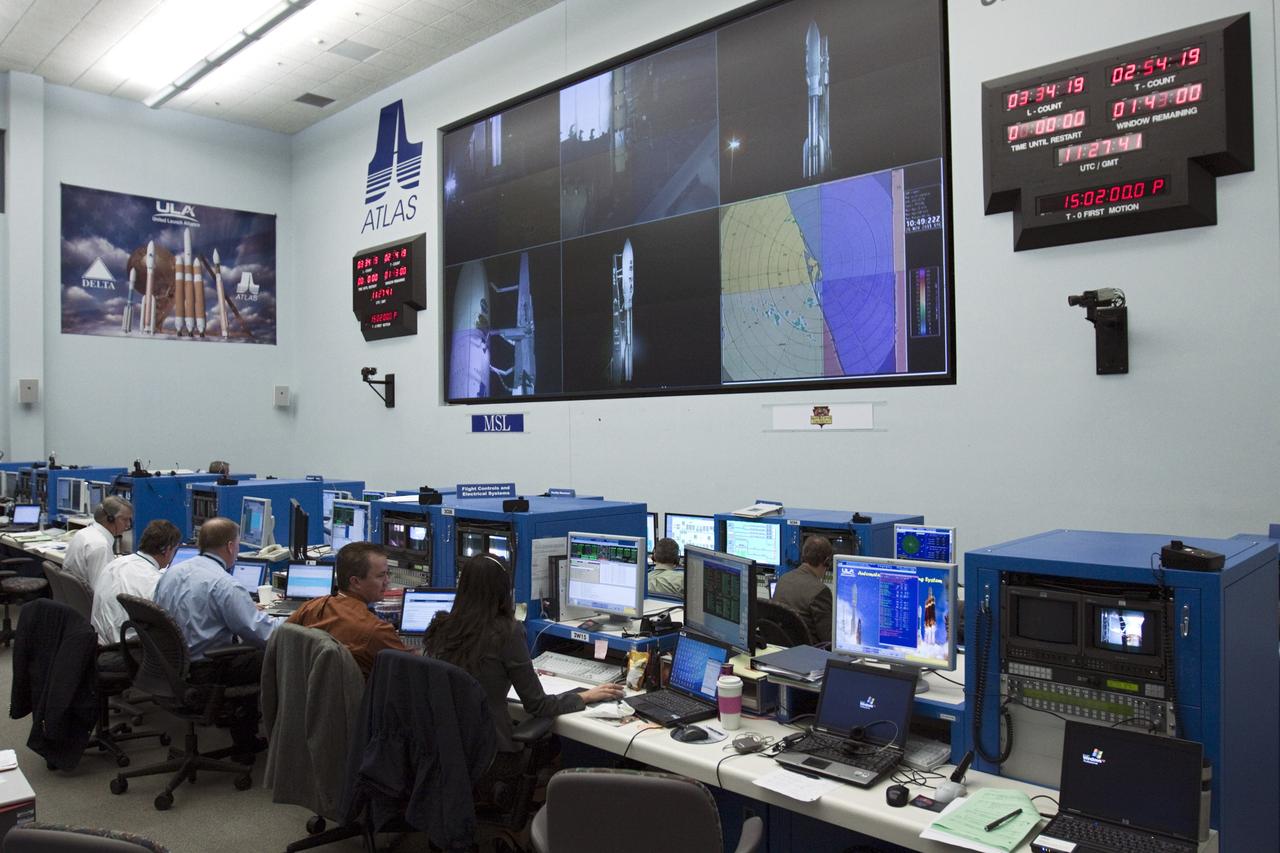

CAPE CANAVERAL – Launch controllers oversee the countdown in the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) before the launch of the Mars Science Laboratory on an Atlas V rocket. MSL lifted off at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26, beginning a 9-month interplanetary cruise to Mars. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
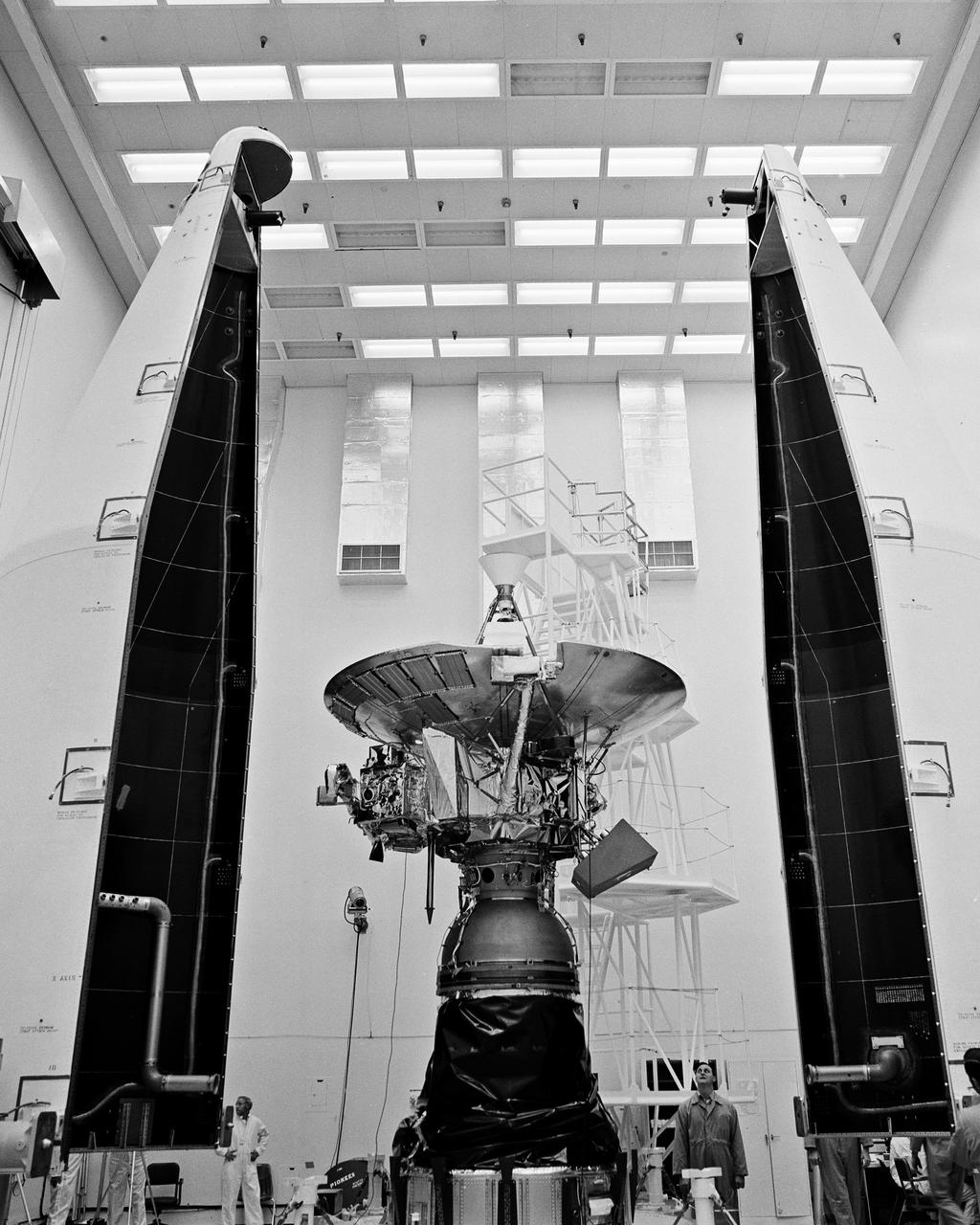

CAPE KENNEDY, Fla. -- In the AO Building at Cape Kennedy Air Force Station in Florida, the Pioneer G spacecraft awaits the installation of its protective payload fairing. The interplanetary space probe is scheduled for launch atop an Atlas Centaur rocket from Cape Kennedy April 5, 1973. Pioneer G's nearly two-year mission will take it on an investigation of the asteroid belt, then on to Jupiter, largest planet in our solar system. NASA's launch teams from the Kennedy Space Center will direct final testing and the launch itself. The mission is a project of the Ames Research Center. Photo Credit: NASA
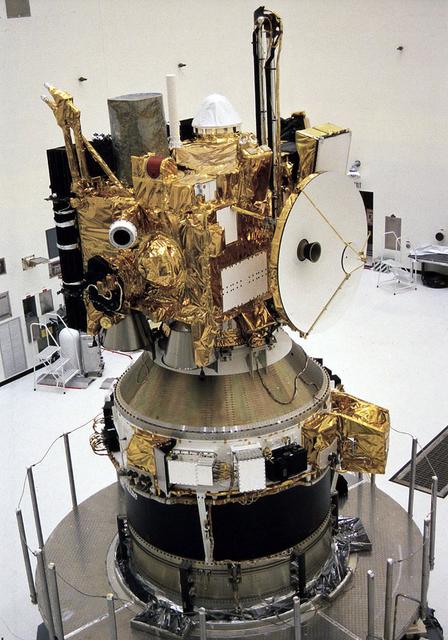

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, the integrated Mars Observer/Transfer Orbit Stage (TOS) payload is ready for encapsulation in the Titan III nose fairing. The TOS booster maiden flight was dedicated to Thomas O. Paine, a former NASA administrator who strongly supported interplanetary exploration and was an early backer of the TOS program. Launched September 25, 1992 from the Kennedy Space Flight Center aboard a Titan III rocket and the TOS, the Mars Observer spacecraft was to be the first U.S. spacecraft to study Mars since the Viking missions 18 years prior. Unfortunately, the Mars Observer spacecraft fell silent just 3 days prior to entering orbit around Mars.
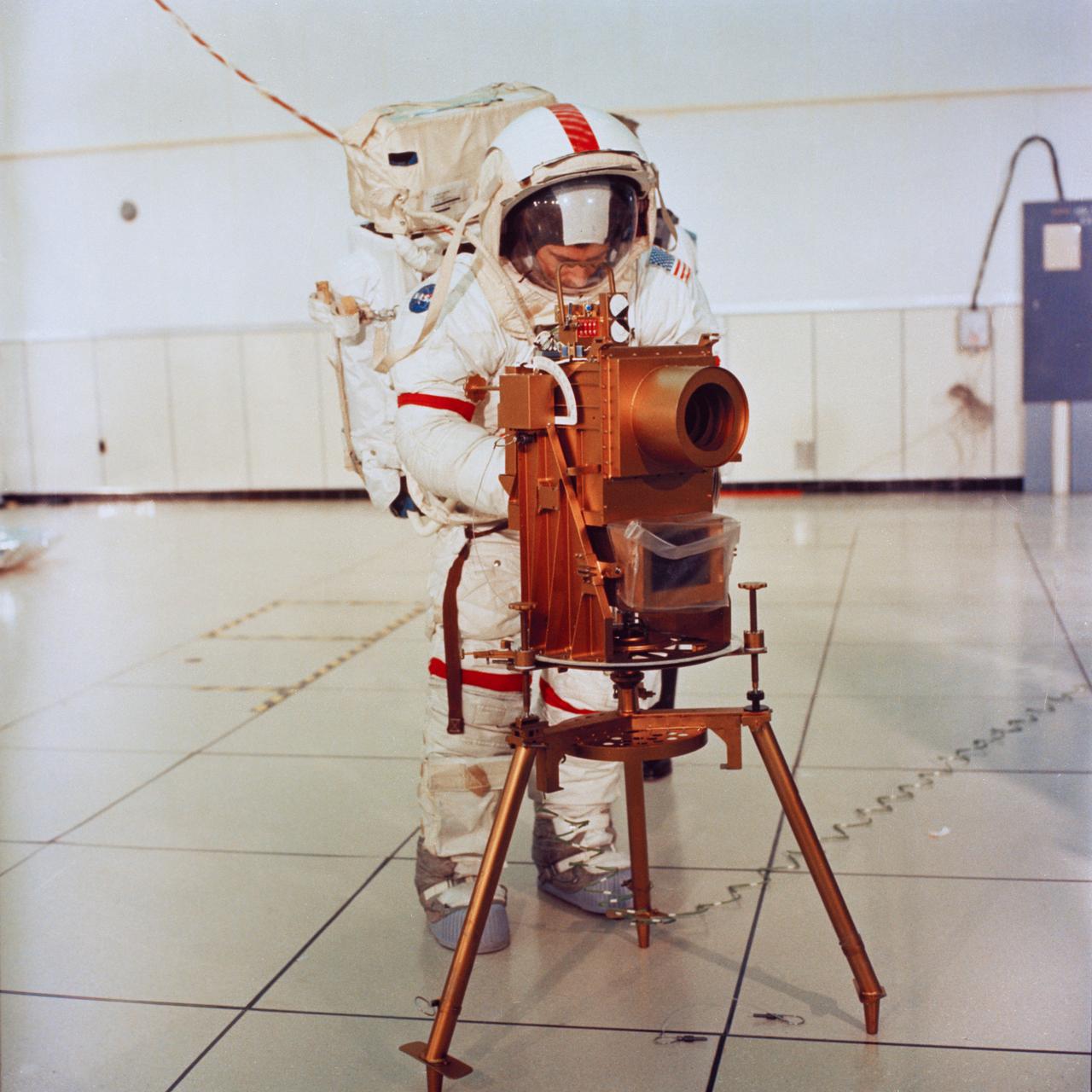

S72-19739 (22 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, participates in lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) training in the Flight Crew Training Building at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Young adjusts a training model of a Far Ultraviolet Camera/Spectroscope, an instrument which will be emplaced on the moon during the Apollo 16 EVA. Deep-space sources of hydrogen in interplanetary, interstellar and intergalactic regions will be mapped by this instrument which gathers both photographic images and spectroscope data in the far ultraviolet spectrum. This experiment will be the first such astronomical observation emplaced on the lunar surface.
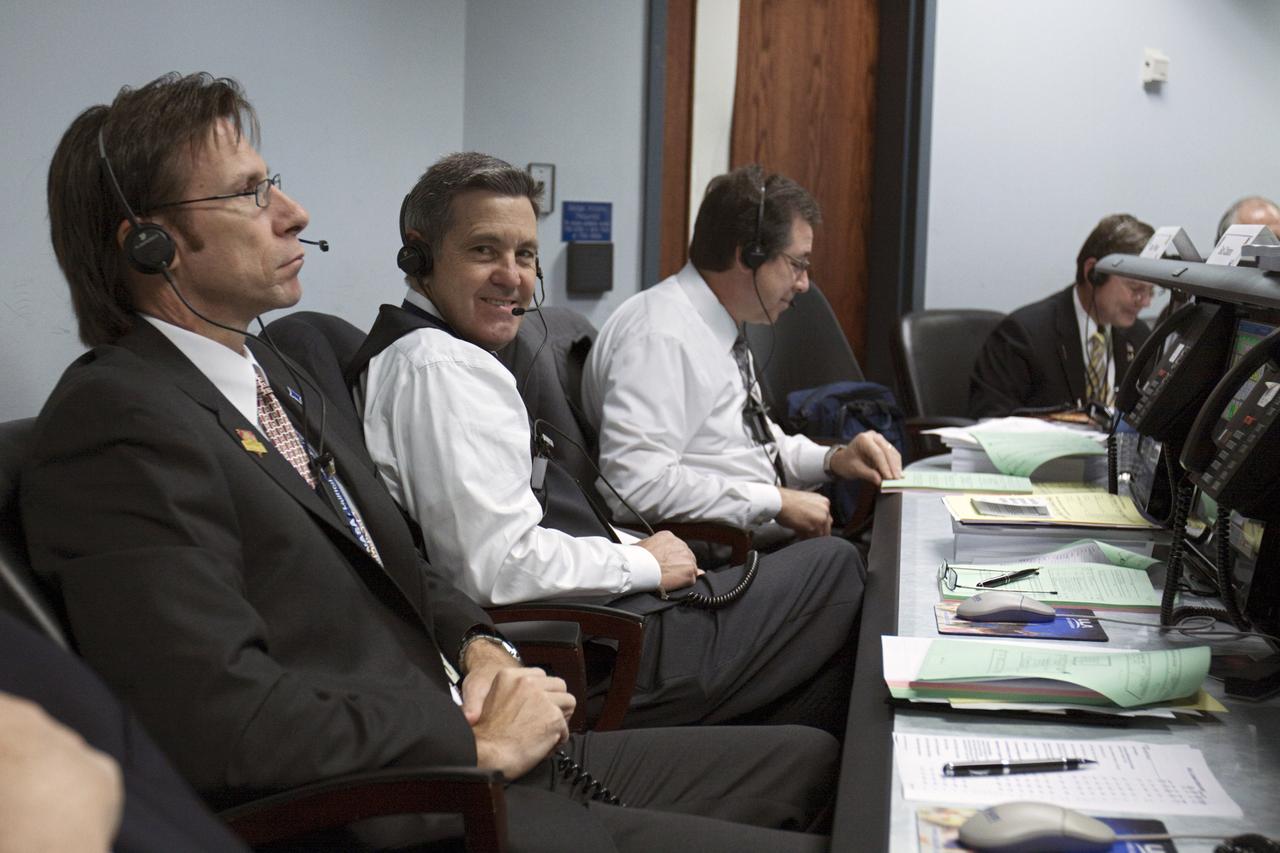

CAPE CANAVERAL – Chuck Duvale, deputy director of the Launch Services Program, left, and Bob Cabana, Kennedy Space Center director, oversee the countdown in the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) before the launch of the Mars Science Laboratory on an Atlas V rocket. MSL lifted off at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26, beginning a 9-month interplanetary cruise to Mars. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
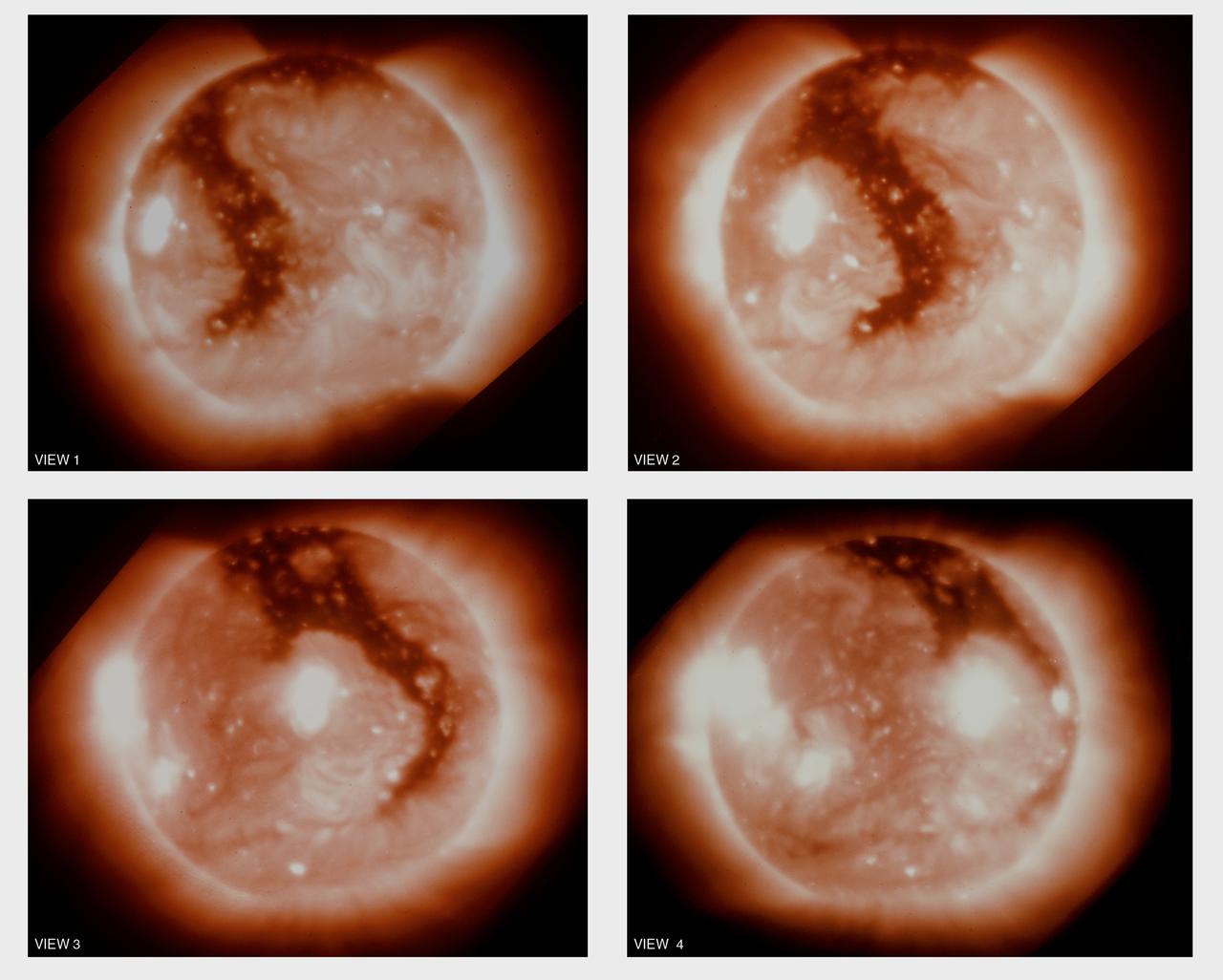
This montage is a sequence of soft x-ray photographs of the boot-shaped coronal hole rotating with the sun. The individual pictures were taken about 2 days apart by the Skylab telescope. Most of the apparent changes in this 6-day period resulted from a changing perspective. Skylab data helped demonstrate that coronal holes are sources of high-velocity streams in the solar wind. These high-velocity streams can be electrons, protons, and atomic nuclei that spray out from the Sun into interplanetary space. When the coronal hole is near the center of the Sun, as in view 2, the sprinkler is directed at Earth. These high-speed streams of solar wind distort Earth's magnetic field and disturb it's upper atmosphere.
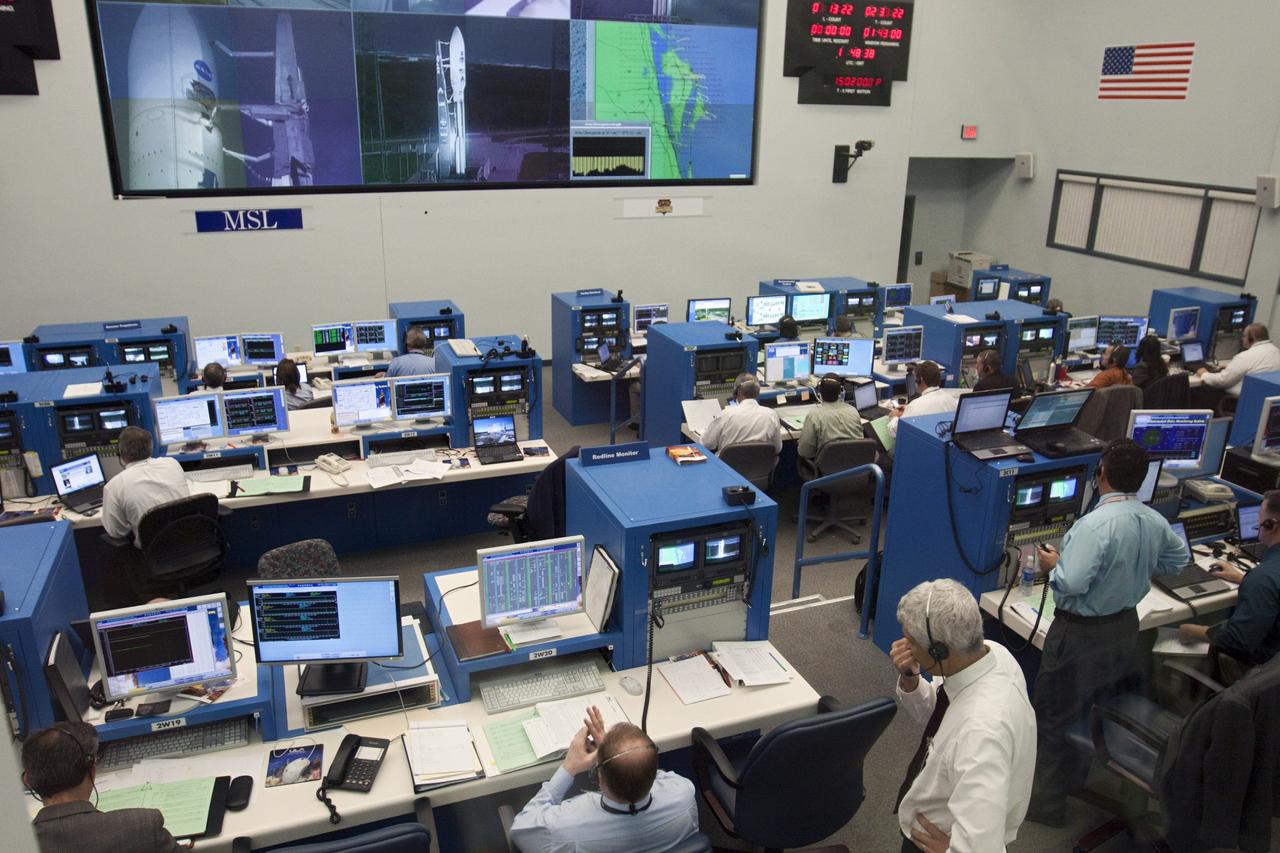

CAPE CANAVERAL – Launch controllers oversee the countdown in the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) before the launch of the Mars Science Laboratory on an Atlas V rocket. MSL lifted off at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26, beginning a 9-month interplanetary cruise to Mars. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., engineers move one of the two STEREO spacecraft to a workstand for installation of the solar arrays. Under black protective wrap on the left is the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
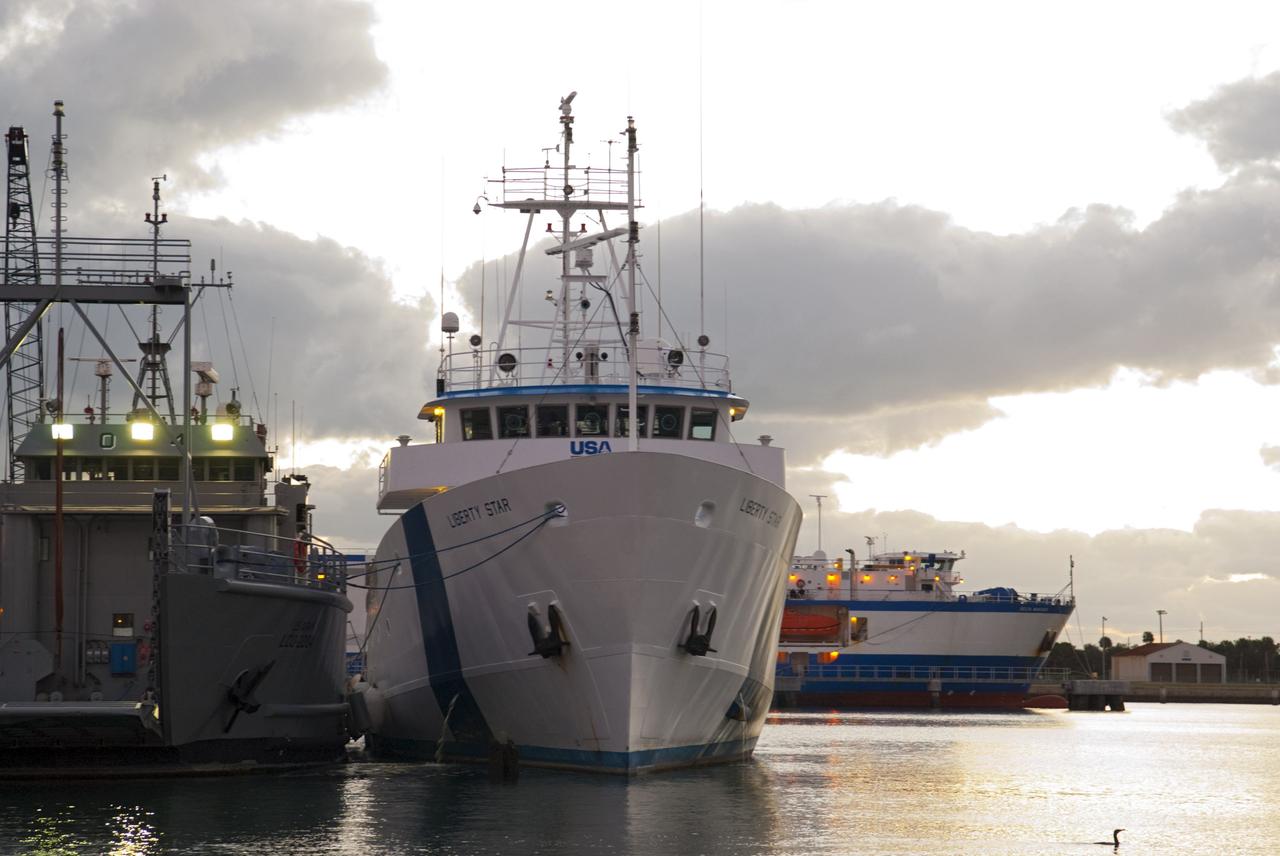

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Preparations are under way at Port Canaveral in Florida for the early-morning departure of NASA's Liberty Star ship. Liberty Star has been enlisted to support the Crew Module Recovery Attach Fitting Test (CRAFT) which began at-sea operations Nov. 29. Multiple attach clips are being evaluated against the current recovery cleat configuration by U.S. Air Force pararescue jumpers (PJs) and a U.S. Navy diver. The 21st Century Ground Systems Program will use data collected from the tests to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft being developed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
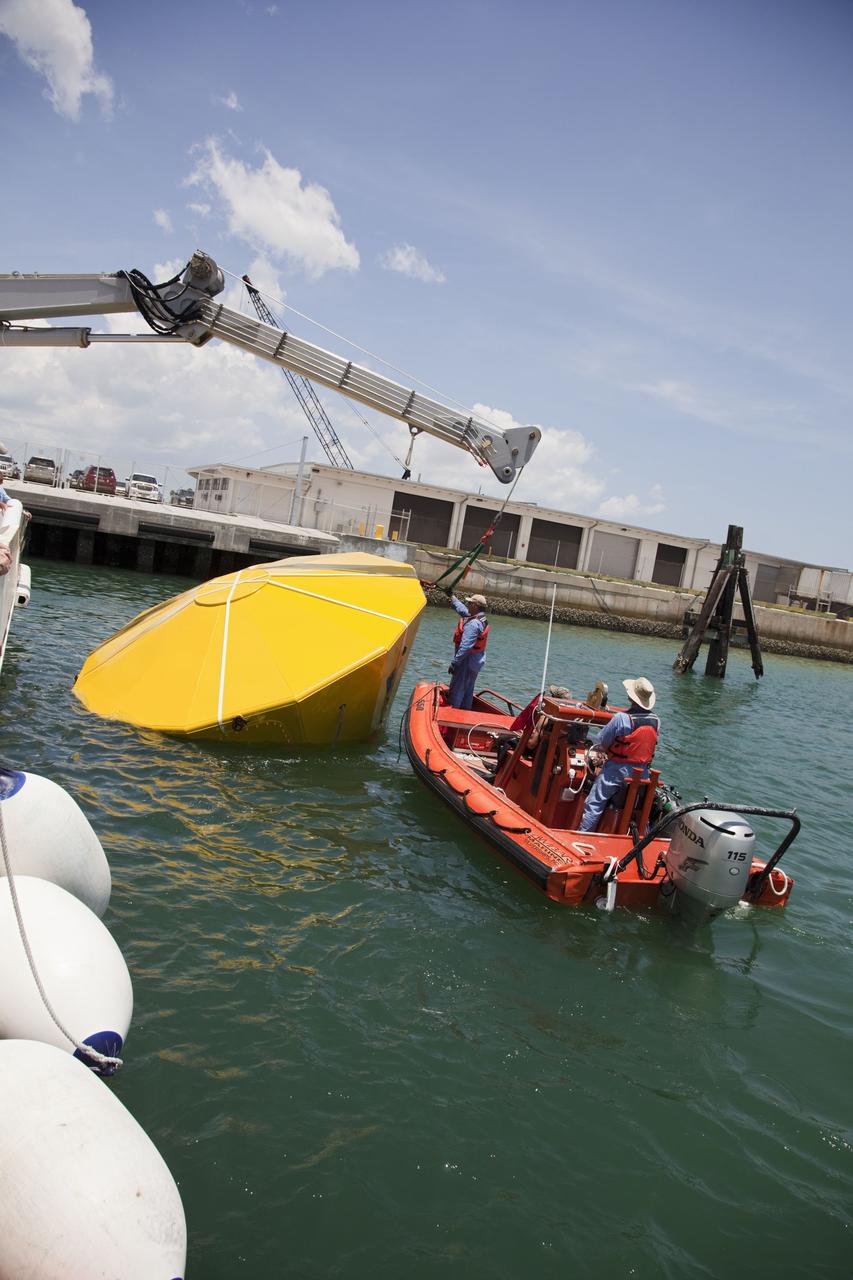

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Delta turn basin at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, United Space Alliance (USA) workers help orient an Orion test article to enable a ship's crane to rotate it. The uprighting tests are part of USA's research and development program to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to reorient and recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. USA is a major subcontractor to Lockheed Martin for the Orion spacecraft. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft designed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. Orion's first uncrewed orbital flight test is slated for 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/mpcv/. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
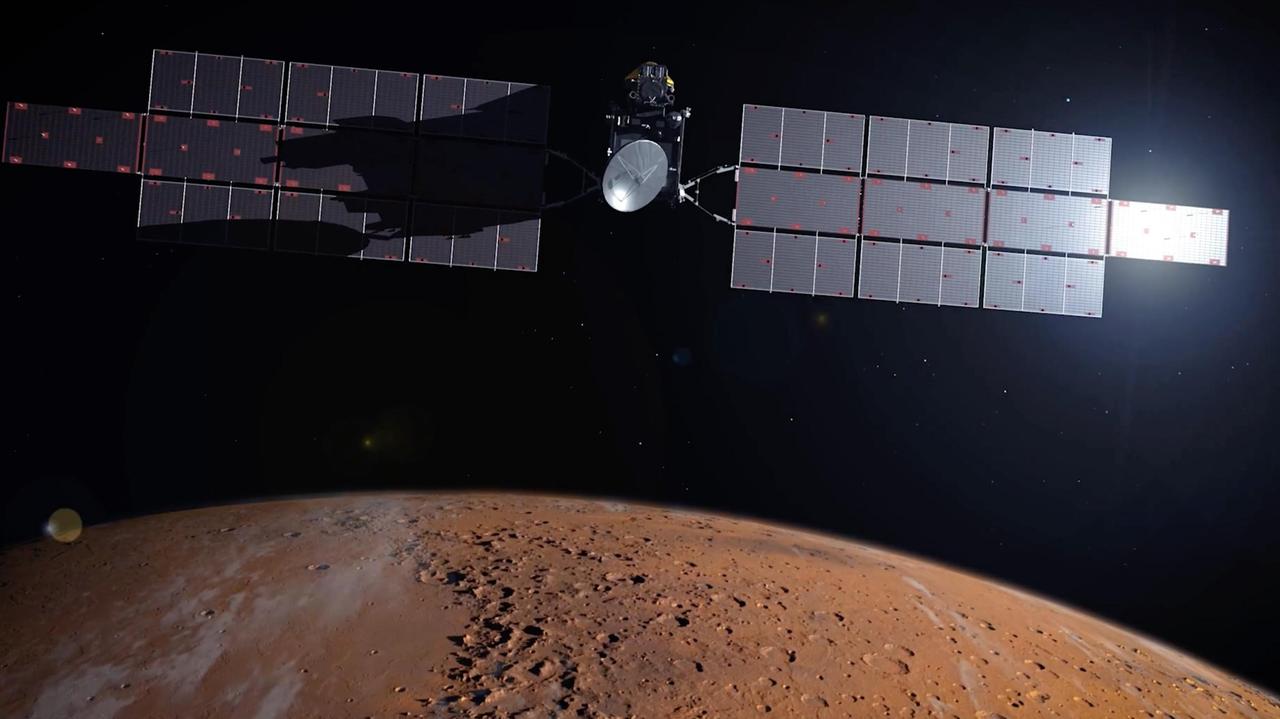

The Earth Return Orbiter (ERO) is one of the flight missions making up the Mars Sample Return campaign to bring martian rock and atmospheric samples back to Earth. This European Space Agency (ESA) orbiter would be the first interplanetary spacecraft to capture samples in orbit and make a return trip between Earth and Mars. ERO would also be the largest spacecraft to orbit the Red Planet. In addition to the rendezvous and return mission, ERO would provide critical Mars-Earth communications coverage for NASA's Perseverance rover and the Sample Retrieval Lander to deliver the martian samples. The Earth Return Orbiter is part of the multi-mission Mars Sample Return campaign being planned by NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25891
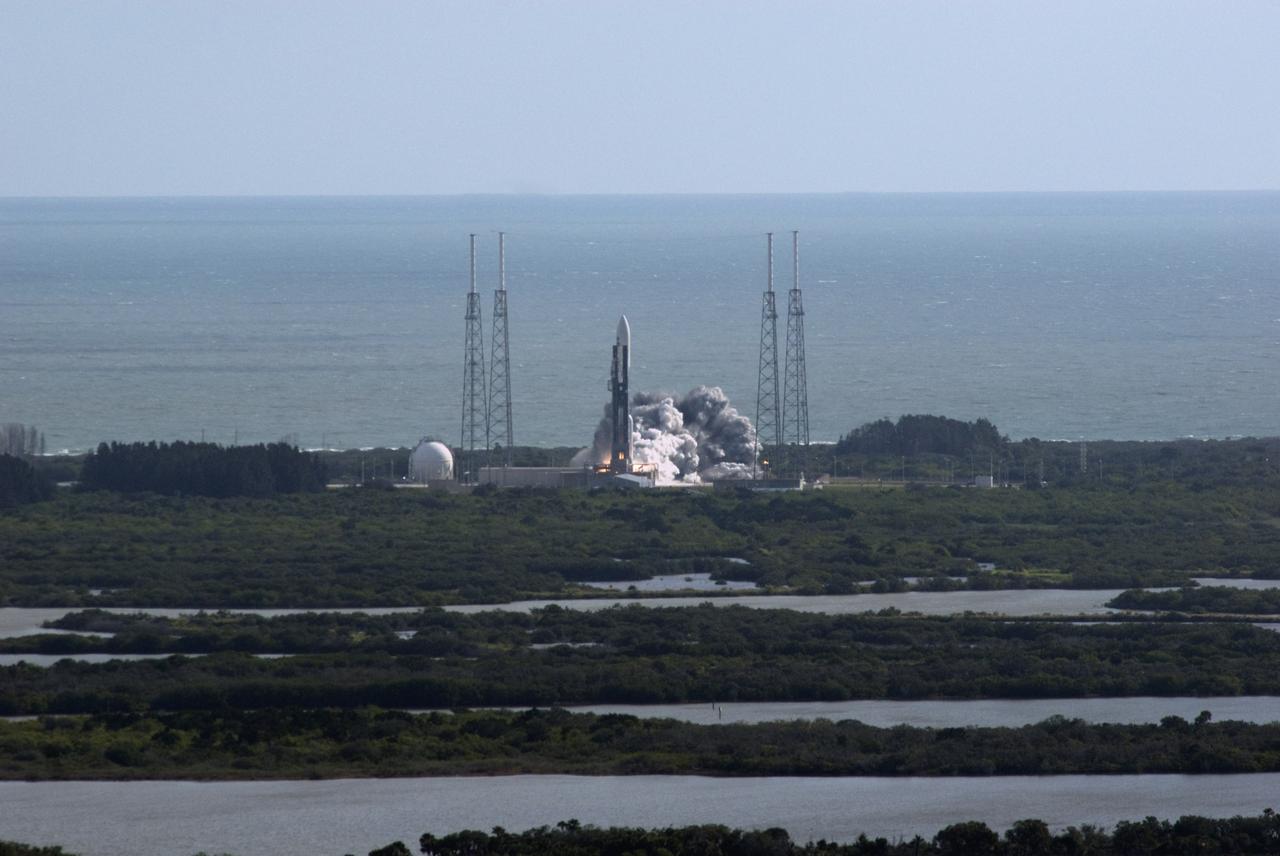

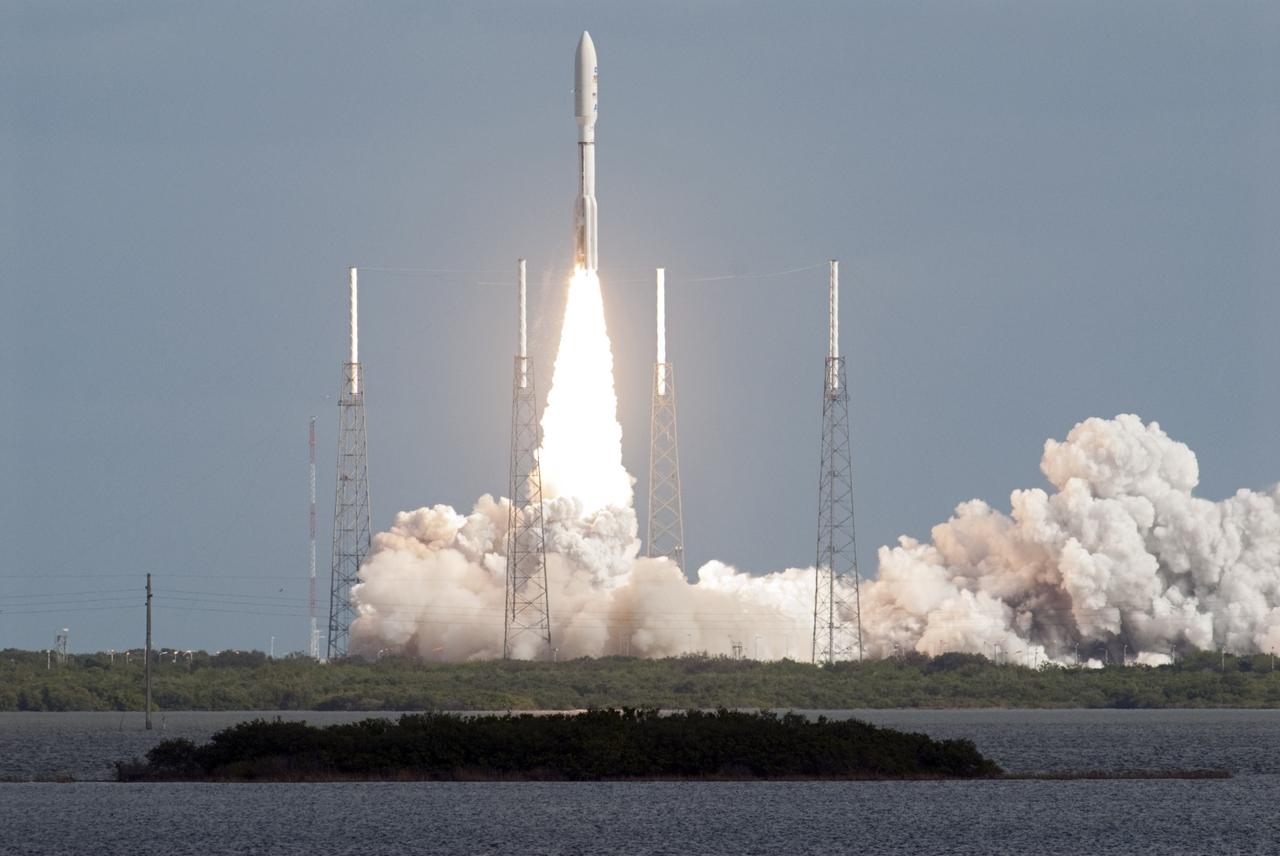
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Atlantic Ocean provides a backdrop as NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) spacecraft, sealed inside its payload fairing, launches atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. MSL lifted off from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26, beginning a 9-month interplanetary cruise to Mars. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Darrell L. McCall
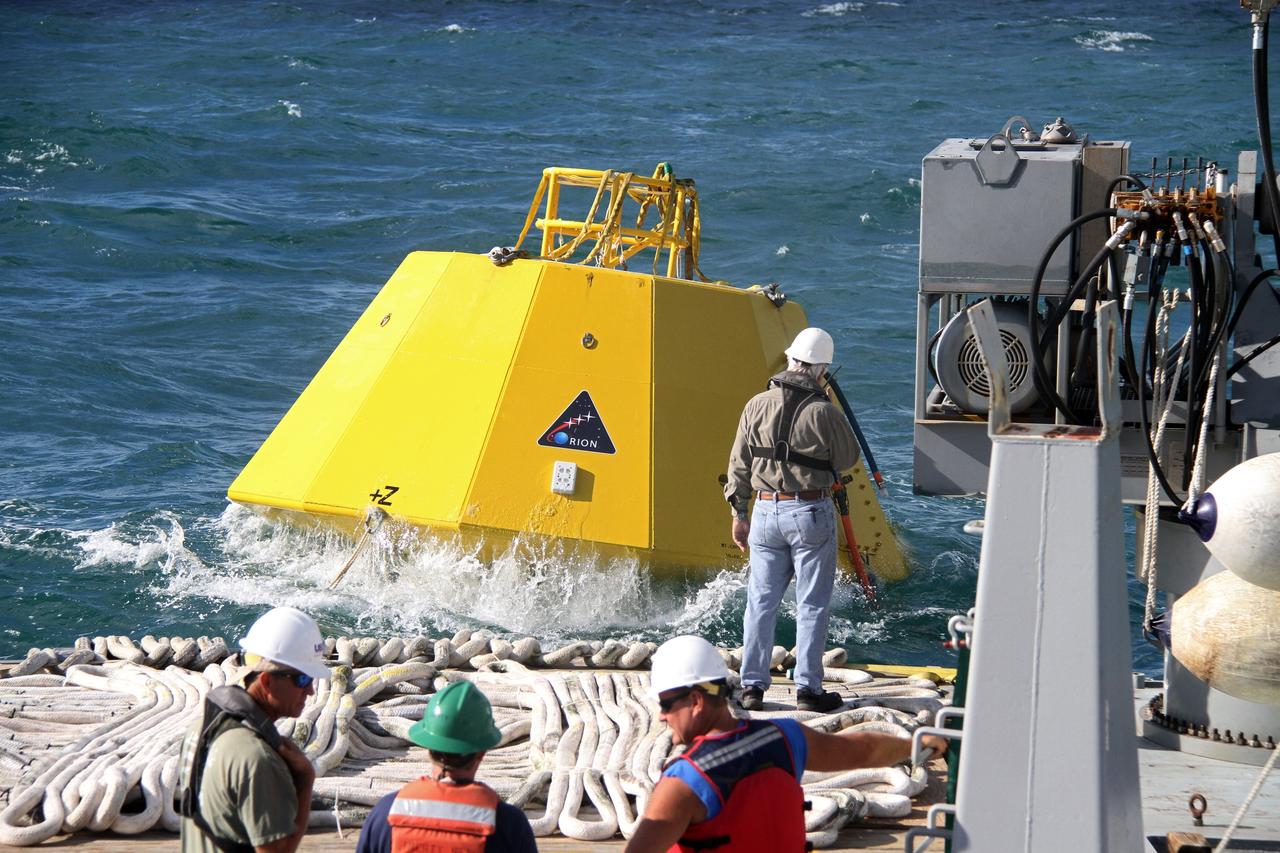

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An Orion flight test capsule makes a splash into the Atlantic Ocean as it slides from the deck of NASA's Liberty Star ship into the water. The Crew Module Recovery Attach Fitting Test (CRAFT) on the capsule, which began at-sea operations Nov. 29, is under way. Multiple attach clips are being evaluated against the current recovery cleat configuration by U.S. Air Force pararescue jumpers (PJs) and a U.S. Navy diver. The 21st Century Ground Systems Program will use data collected from the tests to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft being developed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
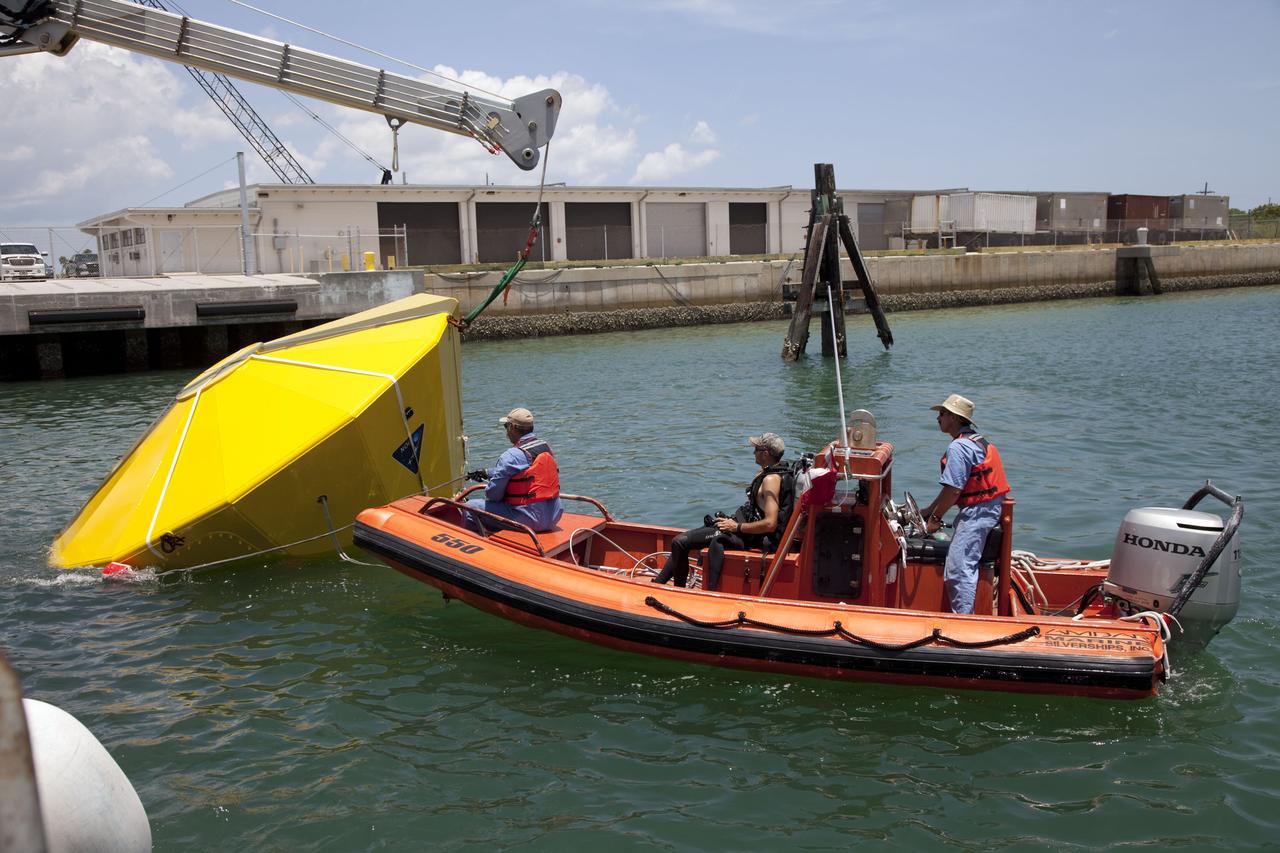

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Delta turn basin at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, United Space Alliance (USA) workers help orient an Orion test article to enable a ship's crane to rotate it. The uprighting tests are part of USA's research and development program to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to reorient and recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. USA is a major subcontractor to Lockheed Martin for the Orion spacecraft. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft designed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. Orion's first uncrewed orbital flight test is slated for 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/mpcv/. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
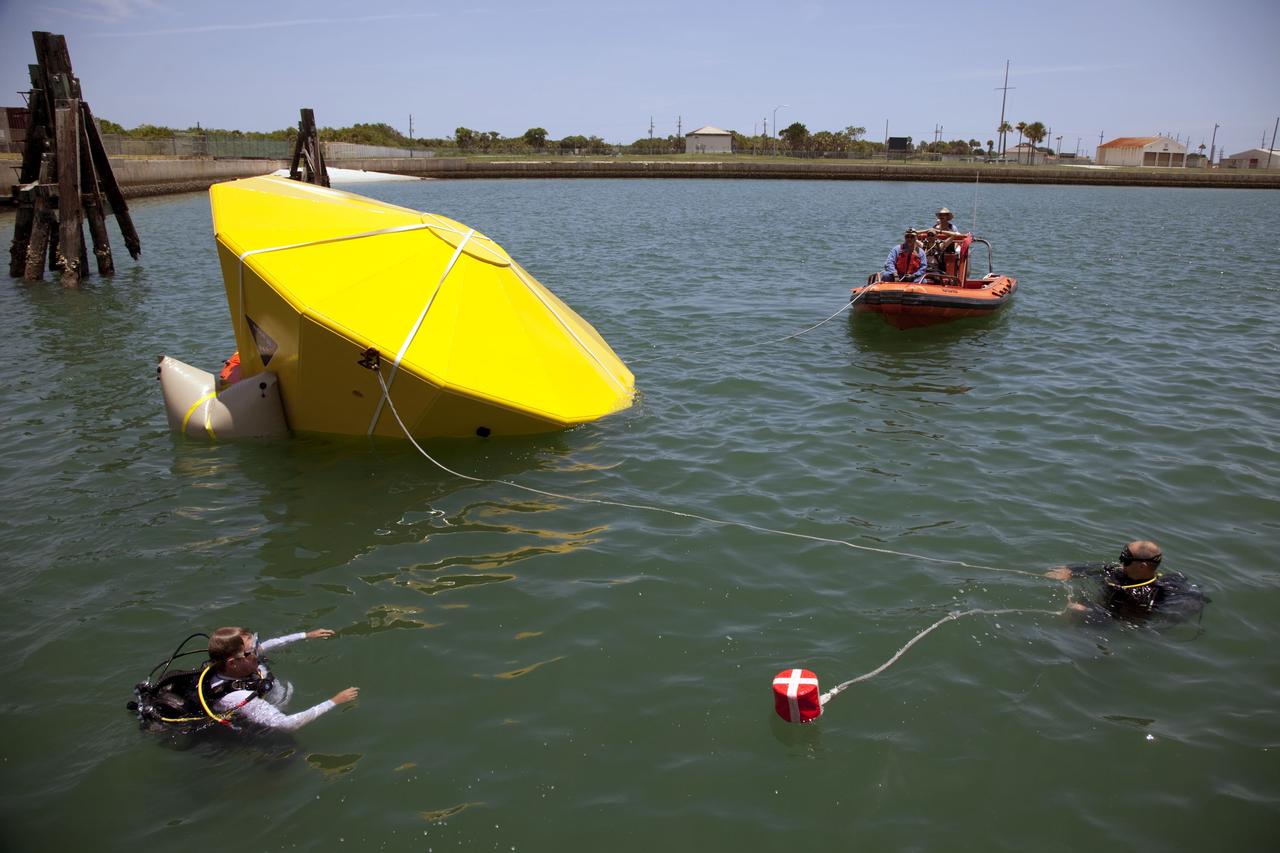

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Delta turn basin at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, United Space Alliance (USA) divers and boat crew monitor an Orion test article while waiting for its lift bags to inflate. The uprighting tests are part of USA's research and development program to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to reorient and recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. USA is a major subcontractor to Lockheed Martin for the Orion spacecraft. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft designed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. Orion's first uncrewed orbital flight test is slated for 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/mpcv/. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
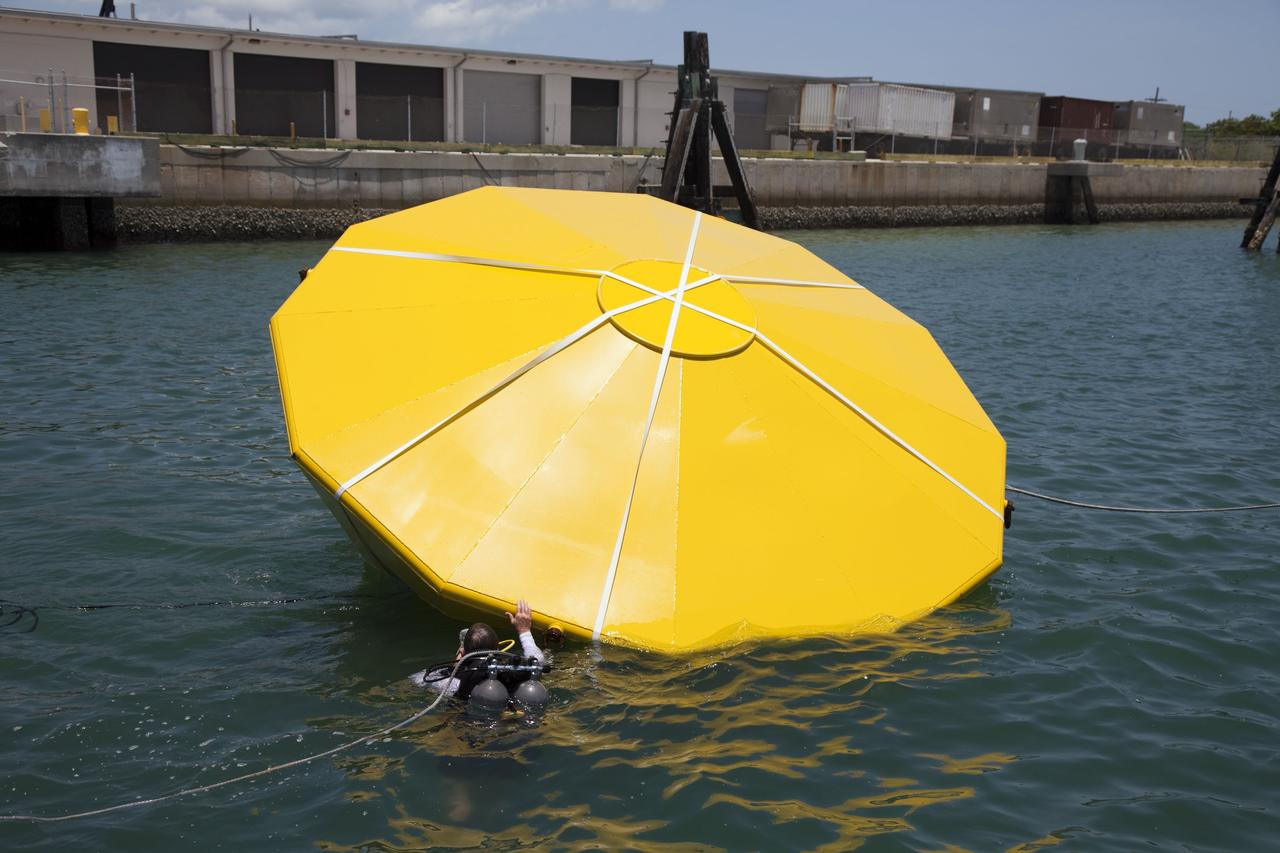

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Delta turn basin at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a United Space Alliance (USA) diver helps orient an Orion test article during a roll test. The uprighting tests are part of USA's research and development program to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to reorient and recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. USA is a major subcontractor to Lockheed Martin for the Orion spacecraft. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft designed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. Orion's first uncrewed orbital flight test is slated for 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/mpcv/. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
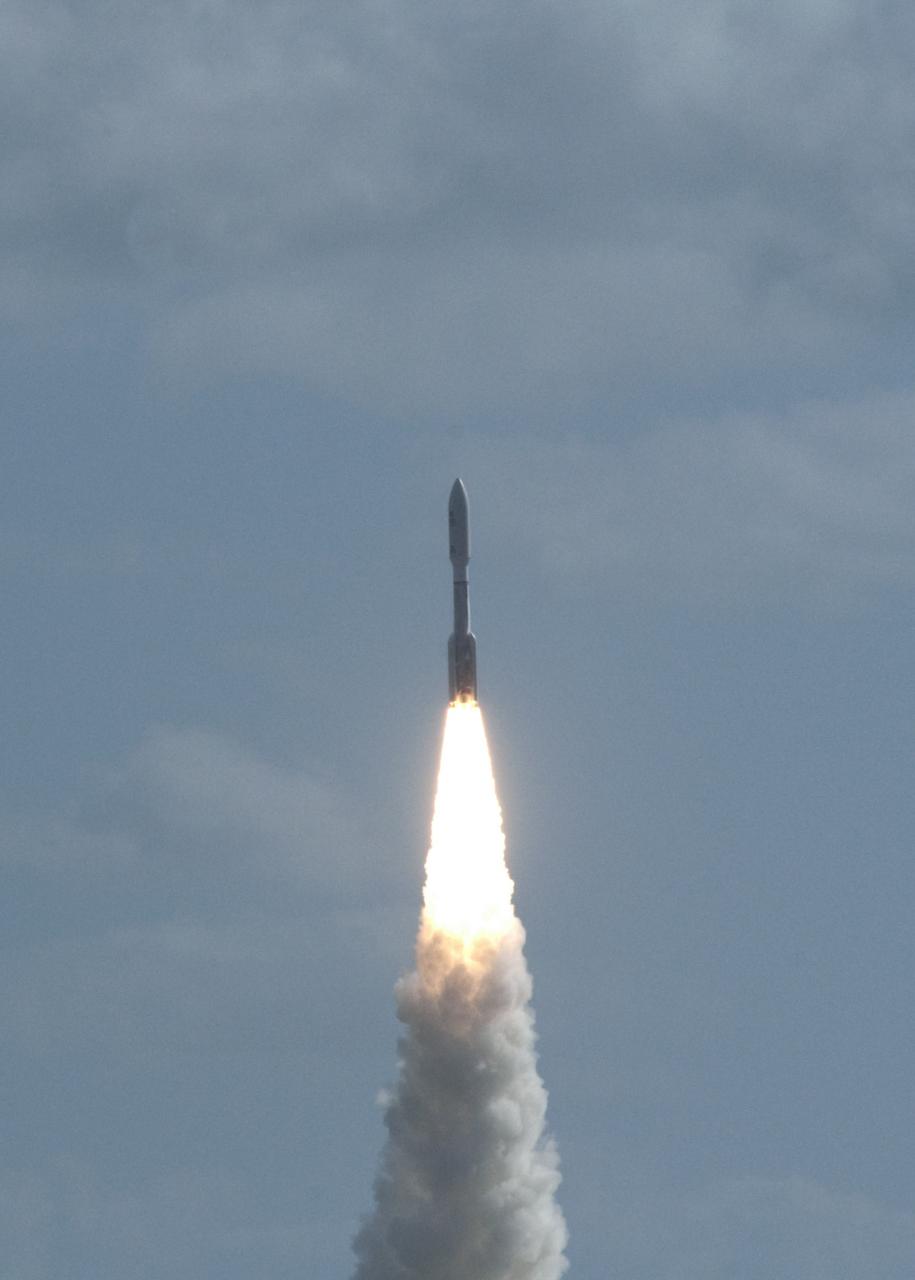

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) spacecraft, sealed inside its payload fairing atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket, blazes a trail into the skies above Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. MSL lifted off on the first opportunity at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26, beginning a 9-month interplanetary cruise to Mars. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Darrell L. McCall
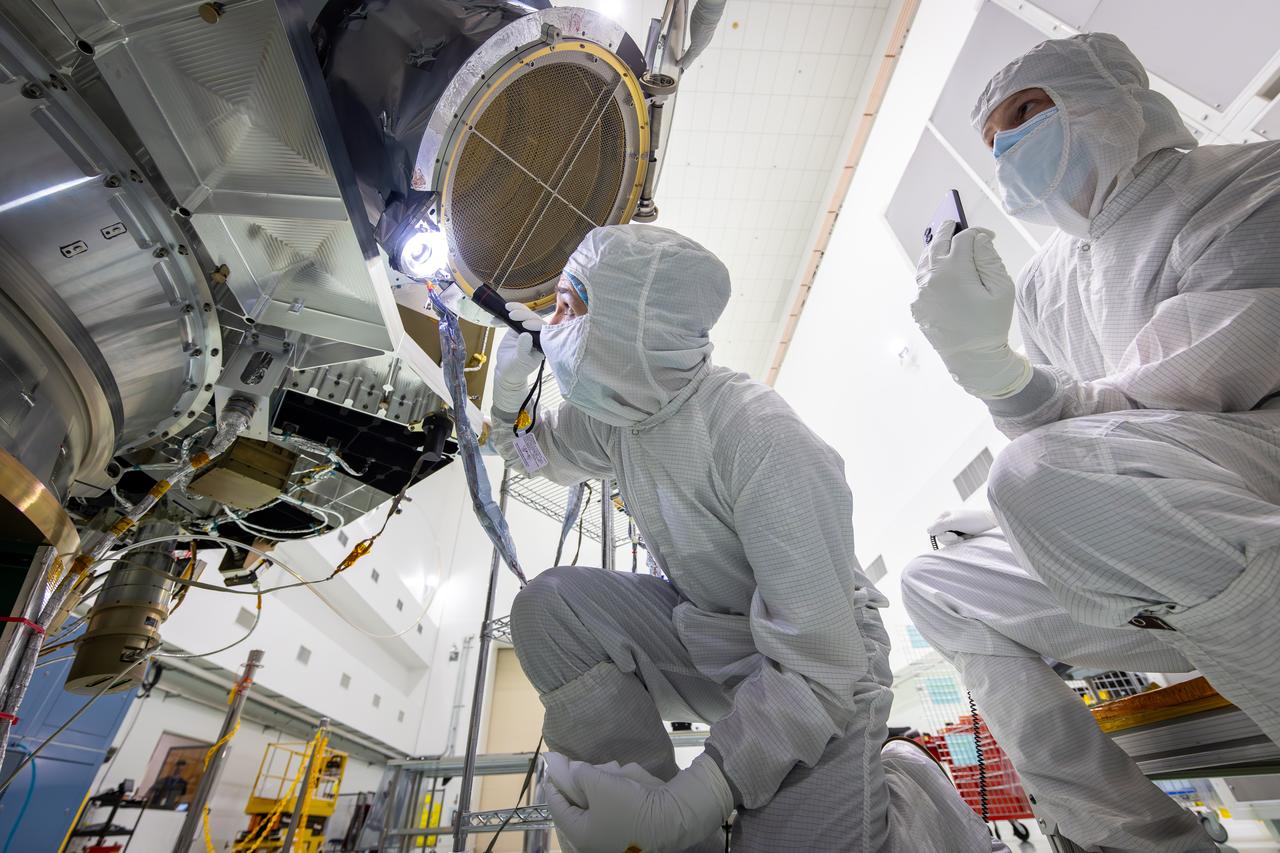

Technicians test the spring-activated door on the Interstellar Dust Experiment (IDEX) instrument of NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) observatory inside the high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The door will remain closed to protect IDEX from contamination during integration and launch. Once in space, the door will swing open permanently to allow interstellar and interplanetary dust to flow into the instrument for measurement. The IMAP observatory will study how the Sun shapes the boundaries of the heliosphere, the protective bubble around our solar system. Launch is targeted for no earlier than September 2025 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.

Technicians test the spring-activated door on the Interstellar Dust Experiment (IDEX) instrument of NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) observatory inside the high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The door will remain closed to protect IDEX from contamination during integration and launch. Once in space, the door will swing open permanently to allow interstellar and interplanetary dust to flow into the instrument for measurement. The IMAP observatory will study how the Sun shapes the boundaries of the heliosphere, the protective bubble around our solar system. Launch is targeted for no earlier than September 2025 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
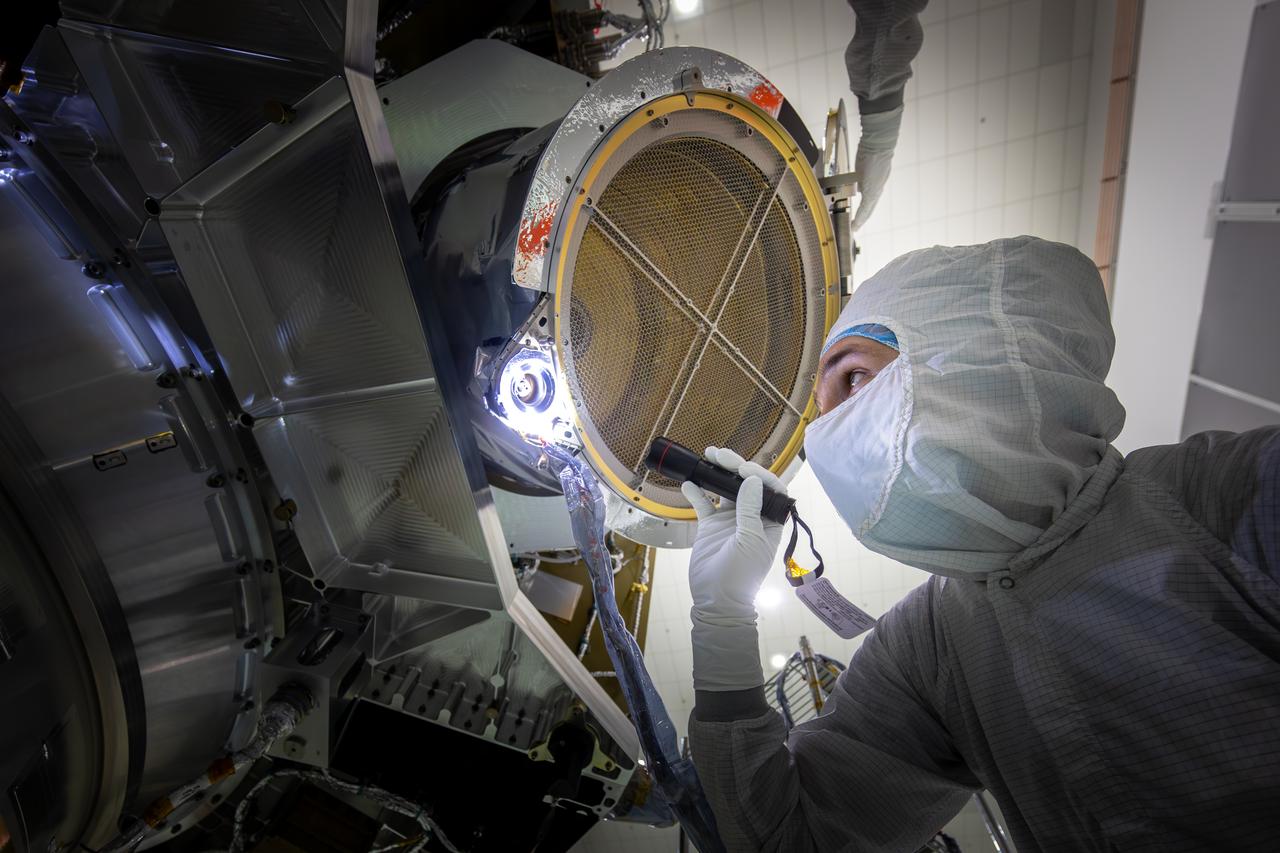

Technicians test the spring-activated door on the Interstellar Dust Experiment (IDEX) instrument of NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) observatory inside the high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The door will remain closed to protect IDEX from contamination during integration and launch. Once in space, the door will swing open permanently to allow interstellar and interplanetary dust to flow into the instrument for measurement. The IMAP observatory will study how the Sun shapes the boundaries of the heliosphere, the protective bubble around our solar system. Launch is targeted for no earlier than September 2025 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
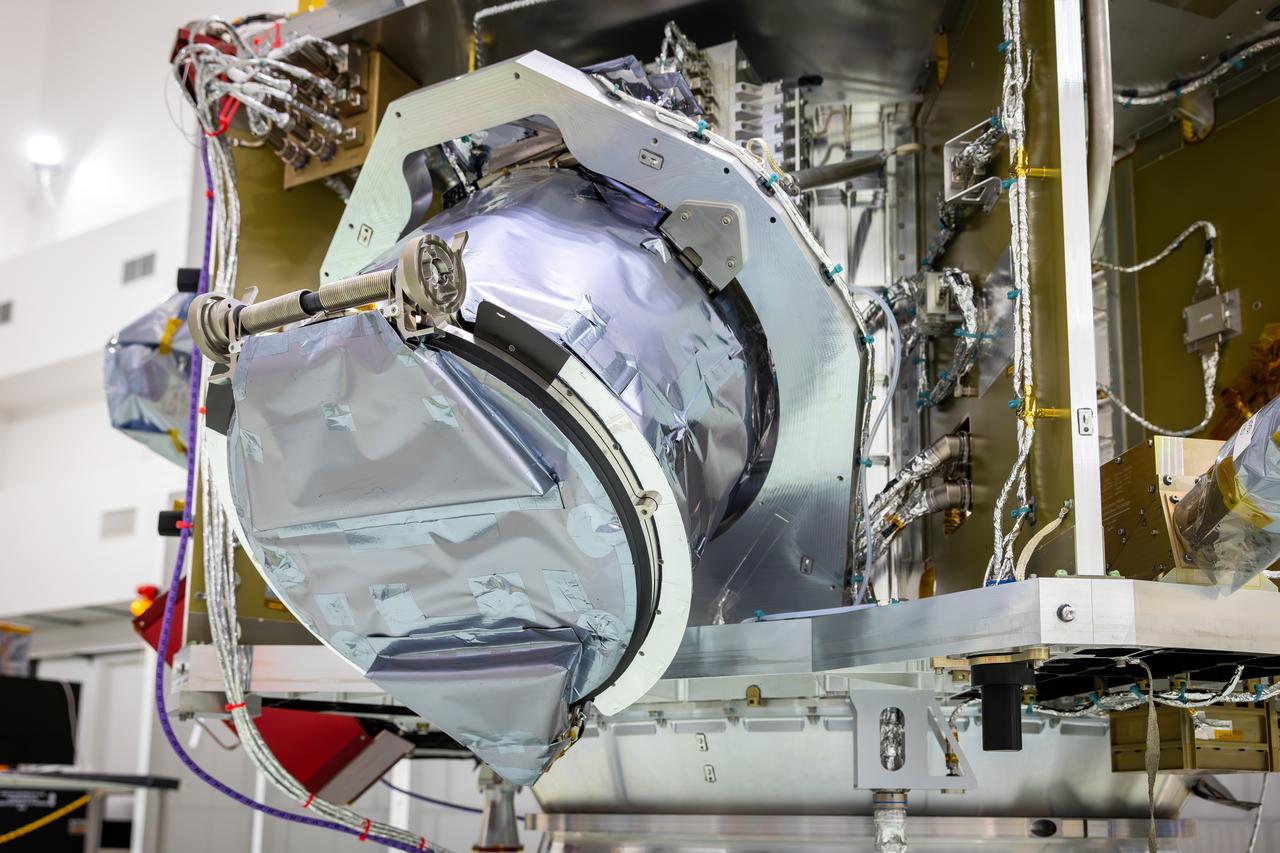
Technicians test the spring-activated door on the Interstellar Dust Experiment (IDEX) instrument of NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) observatory inside the high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The door will remain closed to protect IDEX from contamination during integration and launch. Once in space, the door will swing open permanently to allow interstellar and interplanetary dust to flow into the instrument for measurement. The IMAP observatory will study how the Sun shapes the boundaries of the heliosphere, the protective bubble around our solar system. Launch is targeted for no earlier than September 2025 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
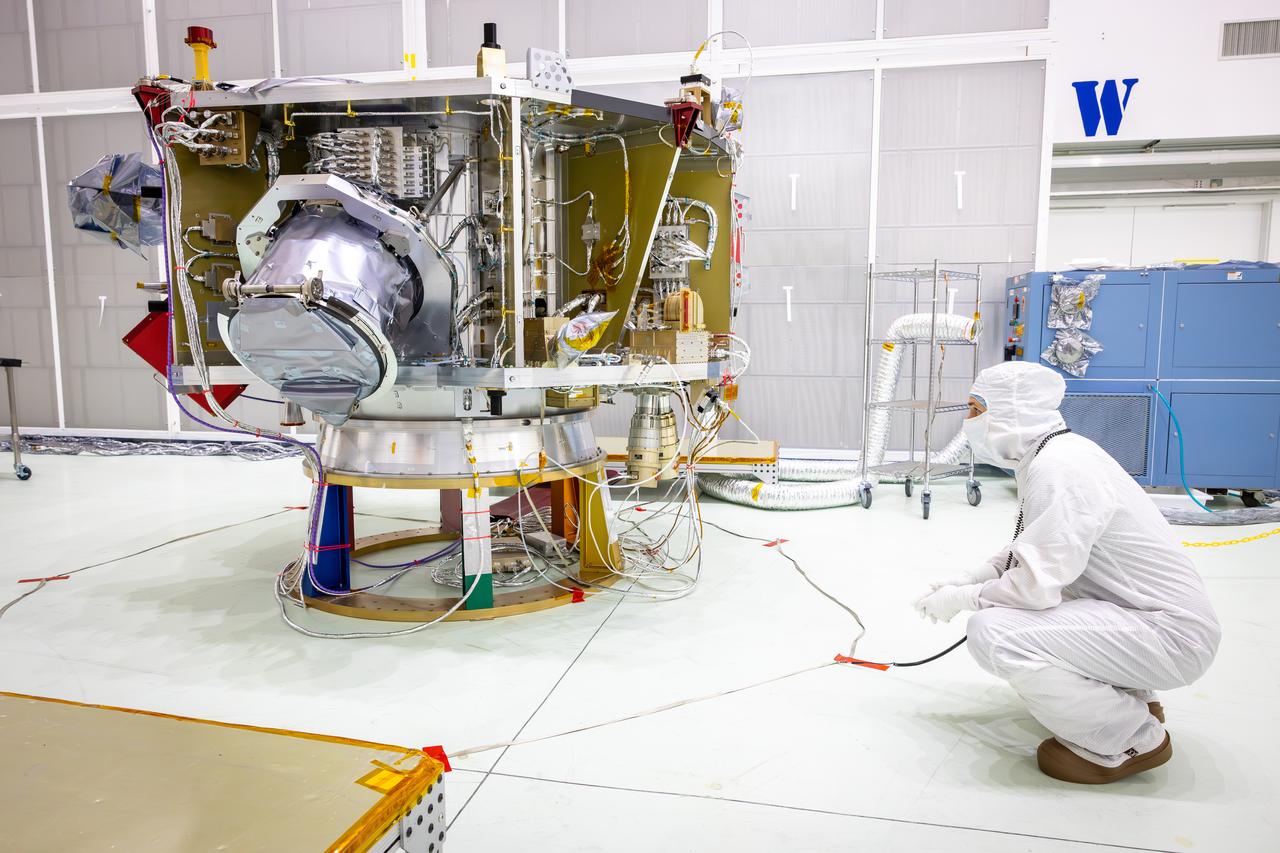

Technicians test the spring-activated door on the Interstellar Dust Experiment (IDEX) instrument of NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) observatory inside the high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The door will remain closed to protect IDEX from contamination during integration and launch. Once in space, the door will swing open permanently to allow interstellar and interplanetary dust to flow into the instrument for measurement. The IMAP observatory will study how the Sun shapes the boundaries of the heliosphere, the protective bubble around our solar system. Launch is targeted for no earlier than September 2025 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.

Technicians test the spring-activated door on the Interstellar Dust Experiment (IDEX) instrument of NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) observatory inside the high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The door will remain closed to protect IDEX from contamination during integration and launch. Once in space, the door will swing open permanently to allow interstellar and interplanetary dust to flow into the instrument for measurement. The IMAP observatory will study how the Sun shapes the boundaries of the heliosphere, the protective bubble around our solar system. Launch is targeted for no earlier than September 2025 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
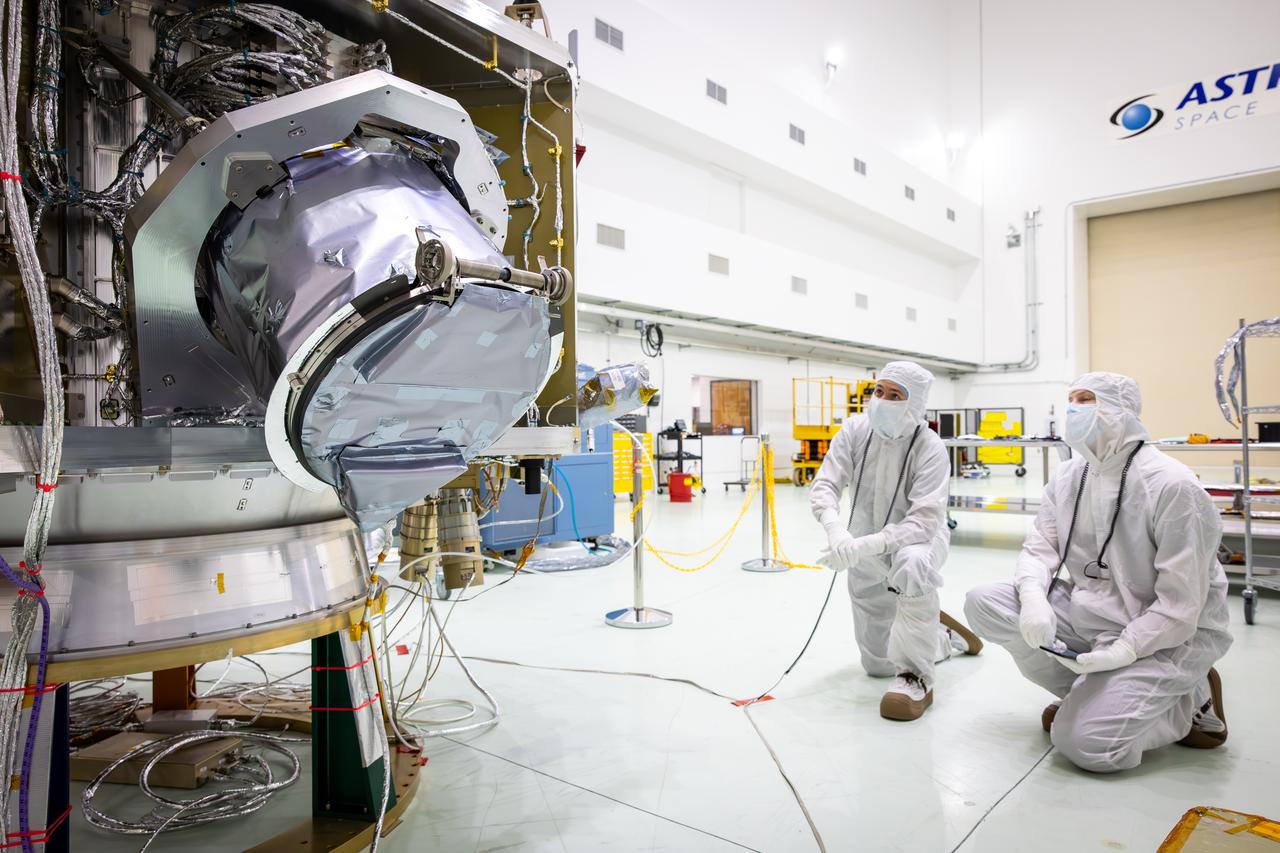

Technicians test the spring-activated door on the Interstellar Dust Experiment (IDEX) instrument of NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) observatory inside the high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 3, 2025. The door will remain closed to protect IDEX from contamination during integration and launch. Once in space, the door will swing open permanently to allow interstellar and interplanetary dust to flow into the instrument for measurement. The IMAP observatory will study how the Sun shapes the boundaries of the heliosphere, the protective bubble around our solar system. Launch is targeted for no earlier than September 2025 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
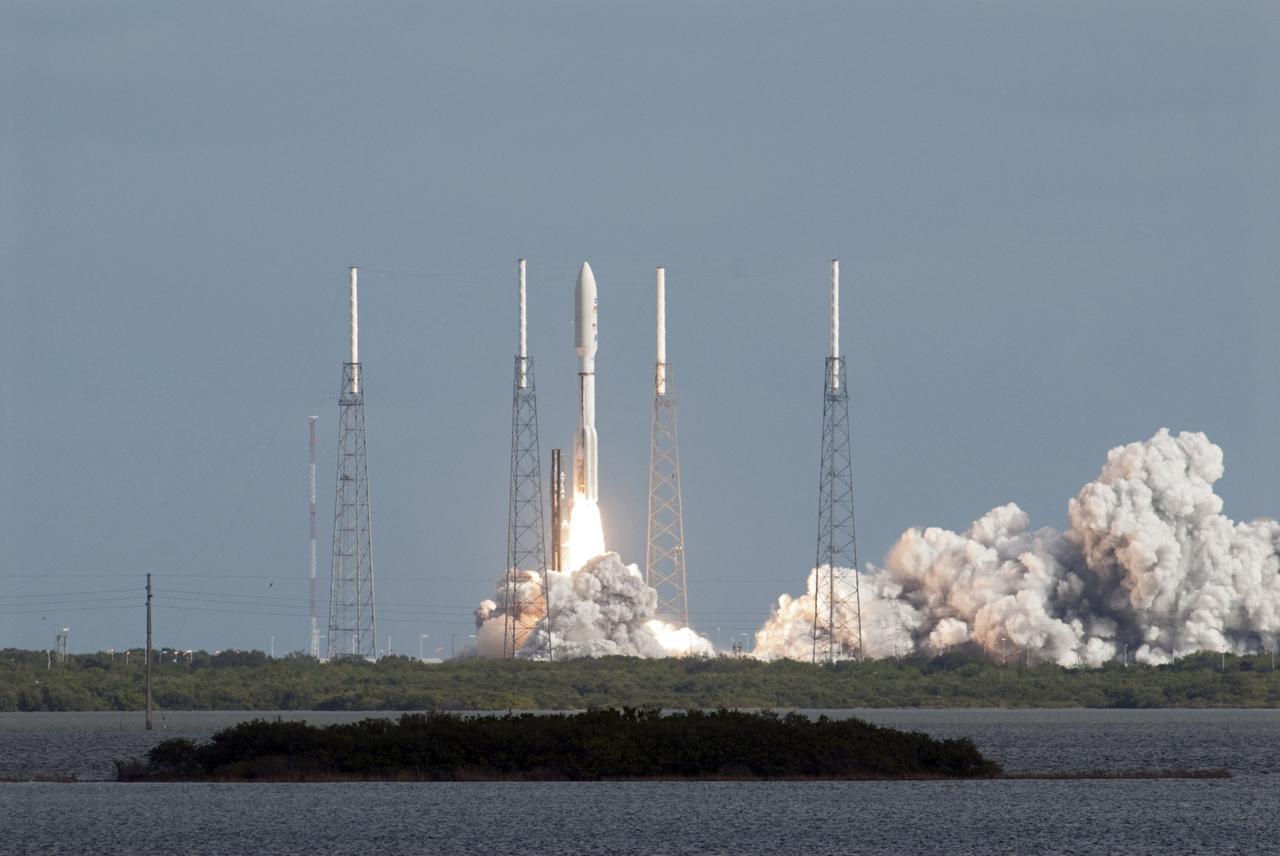

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) spacecraft, sealed inside its payload fairing, rises skyward aboard the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. MSL lifted off from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26, beginning a 9-month interplanetary cruise to Mars. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Bill White
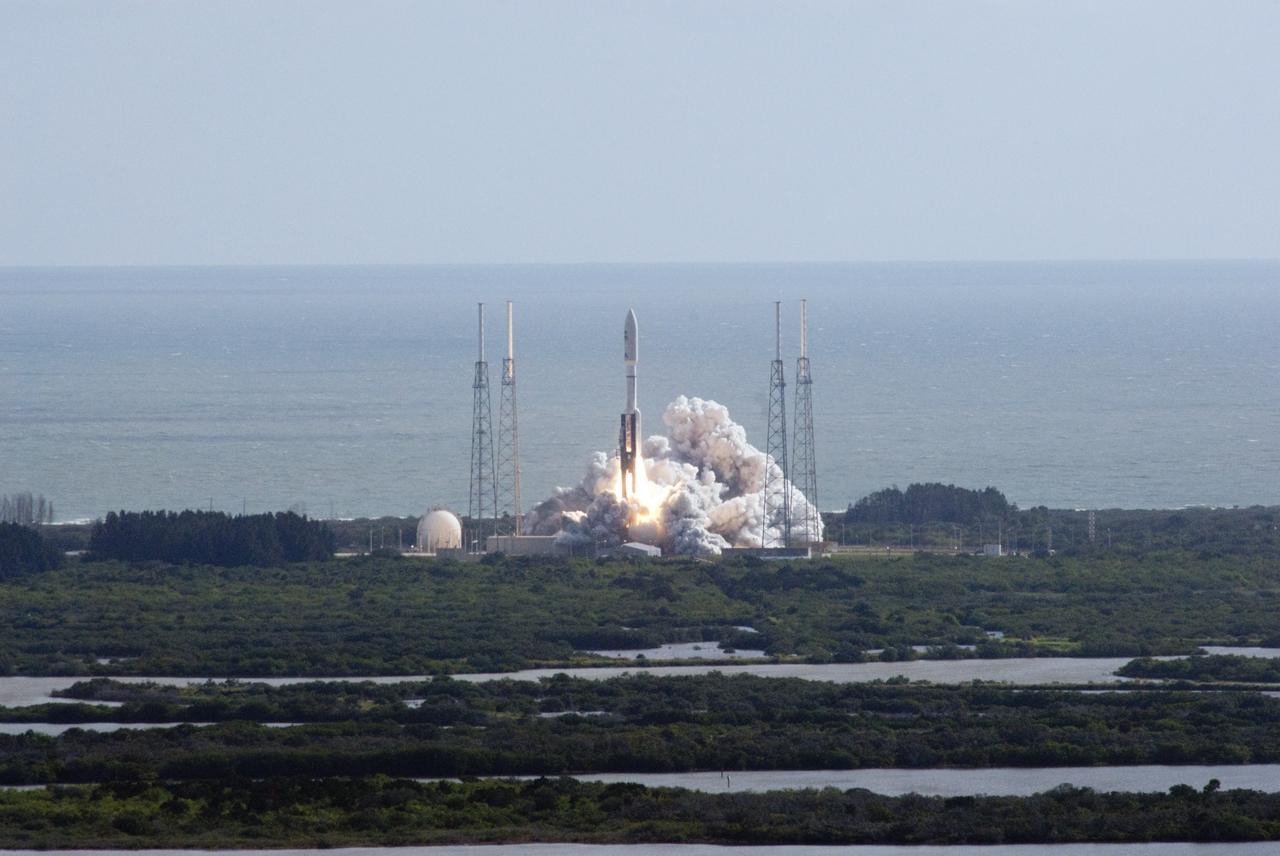

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Atlantic Ocean provides a backdrop as the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket clears the tower at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Sealed inside the rocket's protective payload fairing is NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) spacecraft, beginning a 9-month interplanetary cruise to Mars. Liftoff was at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Darrell L. McCall
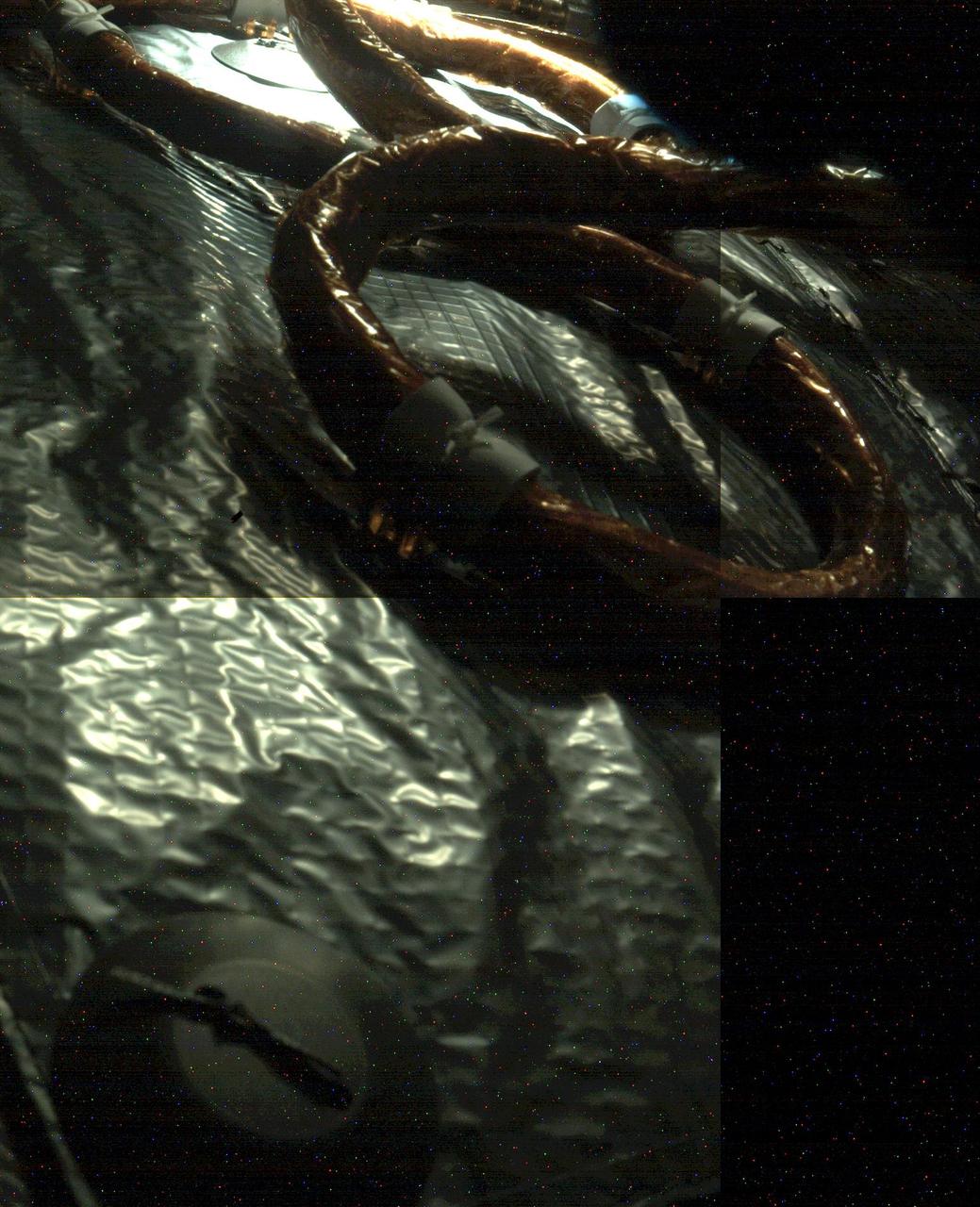

An electrical cable can be seen snaking its way along insulation material in this image of the interior of the Mars 2020 spacecraft at it cruises through interplanetary space to the Red Planet. The cable and insulation are tied to the inside of the spacecraft's heat shield, which will protect the spacecraft from the extreme temperatures generated by friction as it enters the Martian atmosphere on Feb 18, 2021. The light source is the Sun, which likely entered through a vent hole in the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) door. The picture was assembled from three images taken at different times by the Perseverance rover's rear left Hazcam during a systems check on Oct. 19, 2020. The colored pixels seen in the image are due to digital noise from the camera. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24233

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., final processing is underway on the STEREO spacecraft. Here, technicians perform final internal alignment verification of the Heliospheric Imager (HI) instrument prior to closing for flight. The HI is part of the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
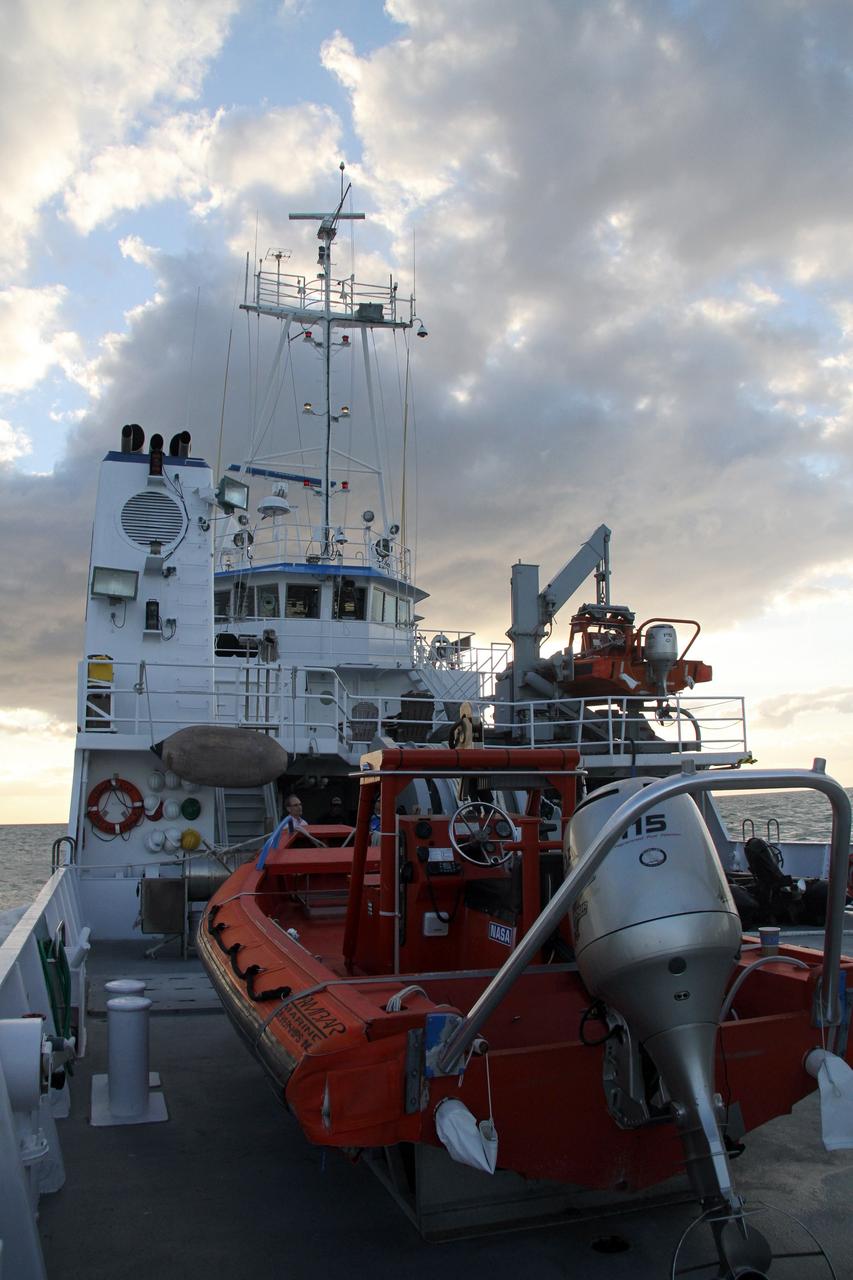

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's Liberty Star ship heads into the Atlantic Ocean where tests will be performed on an Orion flight test capsule. The Crew Module Recovery Attach Fitting Test (CRAFT) on the capsule, which began at-sea operations Nov. 29, is under way. Multiple attach clips are being evaluated against the current recovery cleat configuration by U.S. Air Force pararescue jumpers (PJs) and a U.S. Navy diver. The 21st Century Ground Systems Program will use data collected from the tests to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft being developed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL – Chuck Duvale, deputy director of the Launch Services Program, second from left, and Bob Cabana, Kennedy Space Center director, oversee the countdown in the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) before the launch of the Mars Science Laboratory on an Atlas V rocket. MSL lifted off at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26, beginning a 9-month interplanetary cruise to Mars. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., final processing is underway on the STEREO spacecraft. Here, technicians perform a final cleaning of the Heliospheric Imager (HI) instrument prior to closing for flight. The HI is part of the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
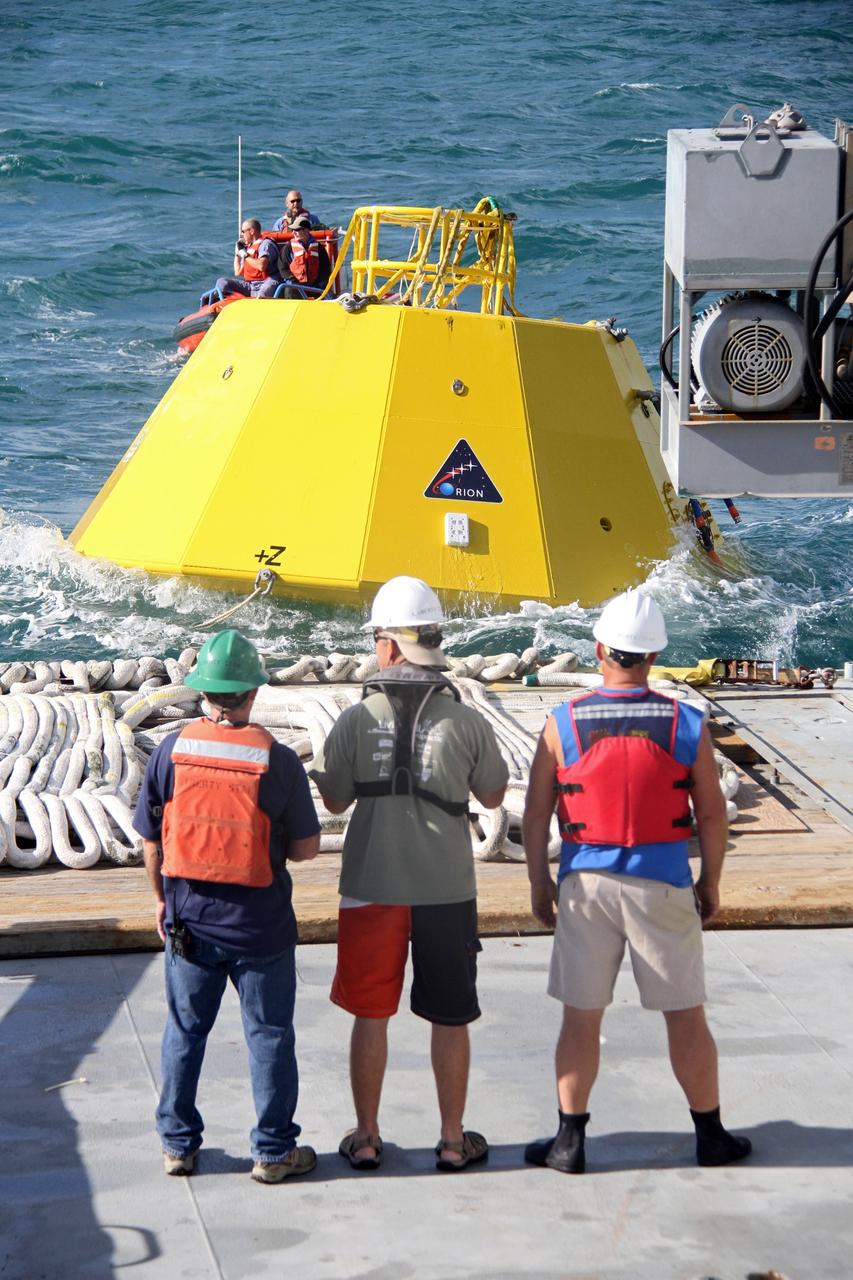

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers, on the deck of NASA's Liberty Star ship and in a boat in the Atlantic Ocean, prepare to begin testing of an Orion flight test capsule. The Crew Module Recovery Attach Fitting Test (CRAFT) on the capsule, which began at-sea operations Nov. 29, is under way. Multiple attach clips are being evaluated against the current recovery cleat configuration by U.S. Air Force pararescue jumpers (PJs) and a U.S. Navy diver. The 21st Century Ground Systems Program will use data collected from the tests to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft being developed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) spacecraft, sealed inside its payload fairing atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket, clears the tower at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. MSL lifted off from at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26, beginning a 9-month interplanetary cruise to Mars. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Bill White

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., final processing is underway on the STEREO spacecraft. Here, technicians close the door on the Heliospheric Imager (HI) assembly for flight. The top cover hinges open on-orbit. The HI is part of the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
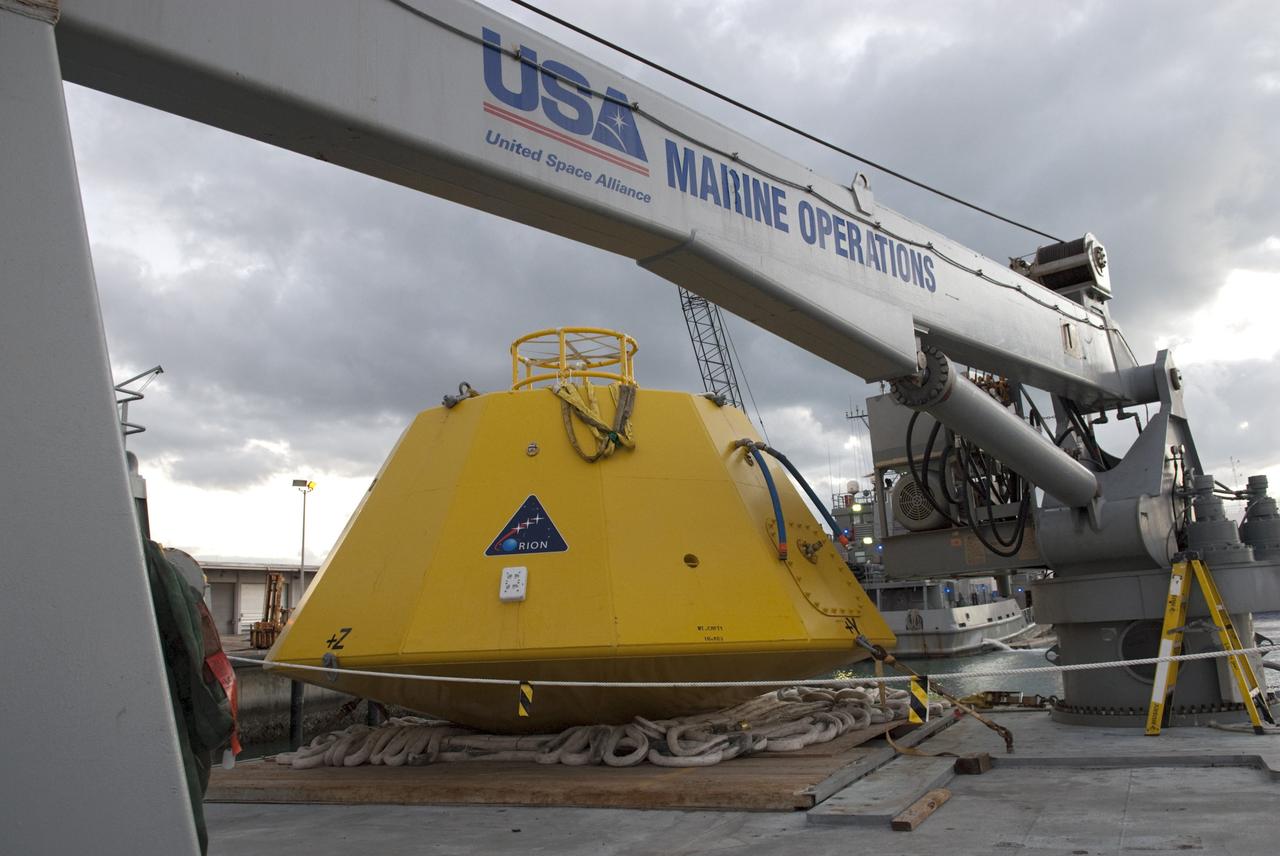

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Port Canaveral in Florida, an Orion flight test capsule is secured to the deck of NASA's Liberty Star ship. Liberty Star has been enlisted to support the Crew Module Recovery Attach Fitting Test (CRAFT) which began at-sea operations Nov. 29. Multiple attach clips are being evaluated against the current recovery cleat configuration by U.S. Air Force pararescue jumpers (PJs) and a U.S. Navy diver. The 21st Century Ground Systems Program will use data collected from the tests to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft being developed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., final processing is underway on the STEREO spacecraft. Here, technicians perform a final cleaning of the Heliospheric Imager (HI) instrument prior to closing for flight. The HI is part of the Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation (SECCHI) package of four instruments that will study the 3-D evolution of coronal mass ejections, from birth at the Sun's surface through the corona and interplanetary medium to its eventual impact at Earth. STEREO consists of two spacecraft whose mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-D. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. Preparations are under way for a liftoff aboard a Delta rocket no earlier than July 22. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
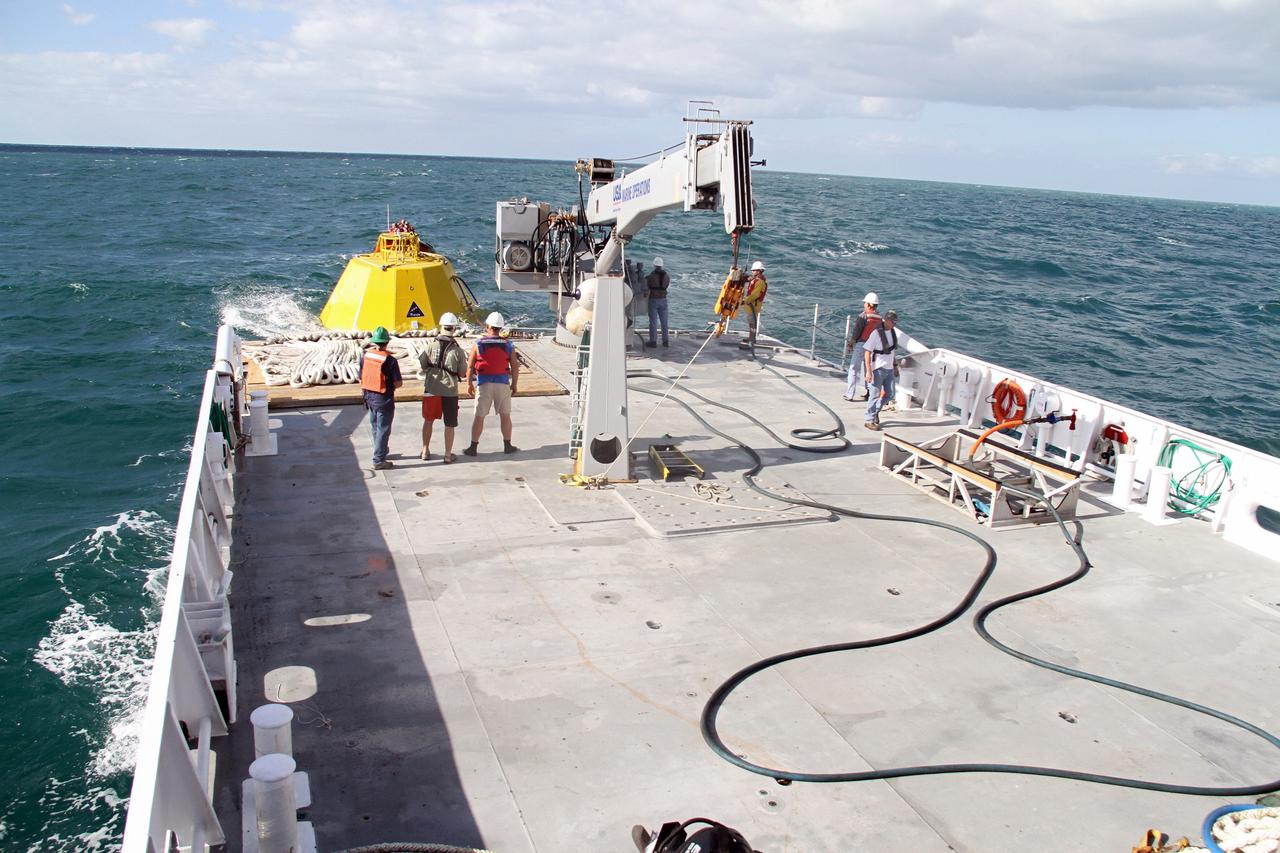
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers on the deck of NASA's Liberty Star ship prepare for testing in the Atlantic Ocean of an Orion flight test capsule to begin. The Crew Module Recovery Attach Fitting Test (CRAFT) on the capsule, which began at-sea operations Nov. 29, is under way. Multiple attach clips are being evaluated against the current recovery cleat configuration by U.S. Air Force pararescue jumpers (PJs) and a U.S. Navy diver. The 21st Century Ground Systems Program will use data collected from the tests to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft being developed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
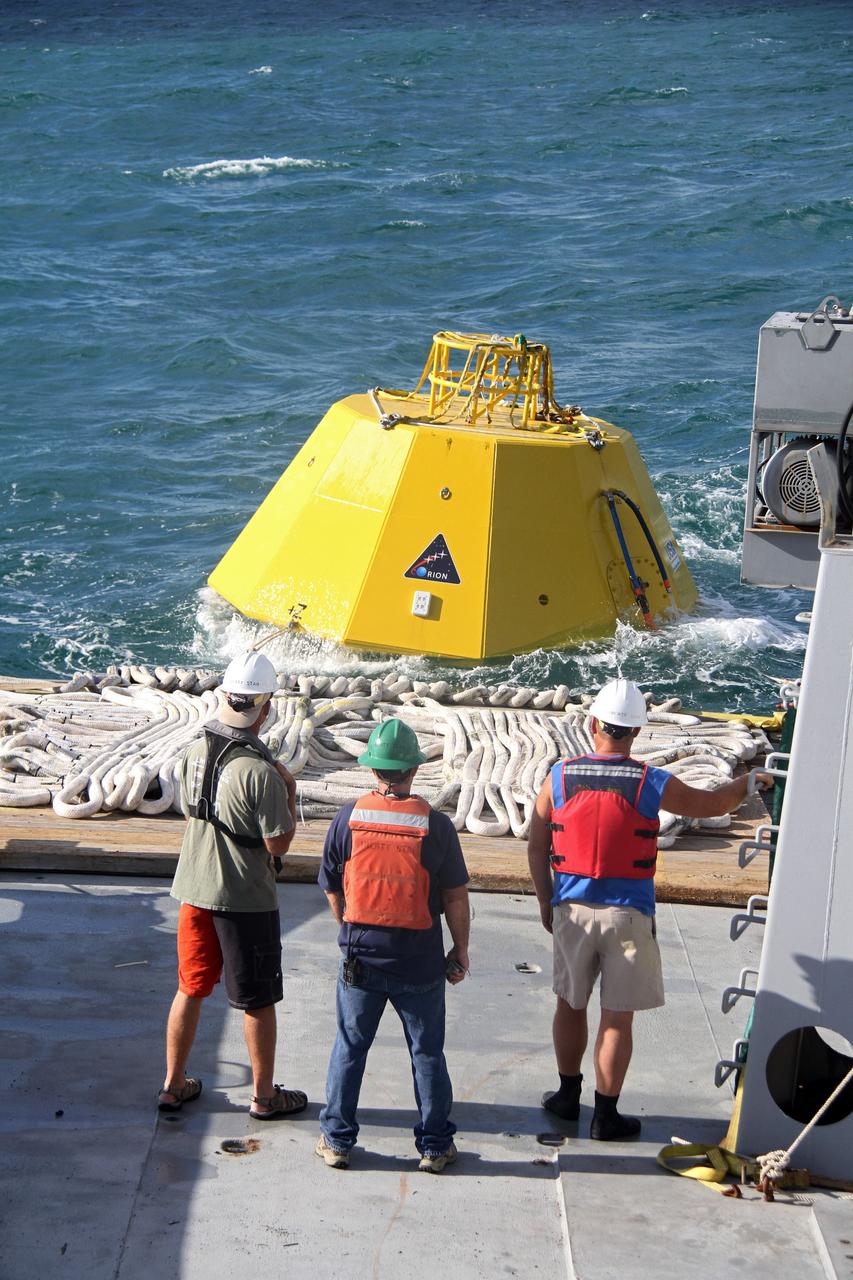

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers on the deck of NASA's Liberty Star ship prepare for testing in the Atlantic Ocean of an Orion flight test capsule to begin. The Crew Module Recovery Attach Fitting Test (CRAFT) on the capsule, which began at-sea operations Nov. 29, is under way. Multiple attach clips are being evaluated against the current recovery cleat configuration by U.S. Air Force pararescue jumpers (PJs) and a U.S. Navy diver. The 21st Century Ground Systems Program will use data collected from the tests to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft being developed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
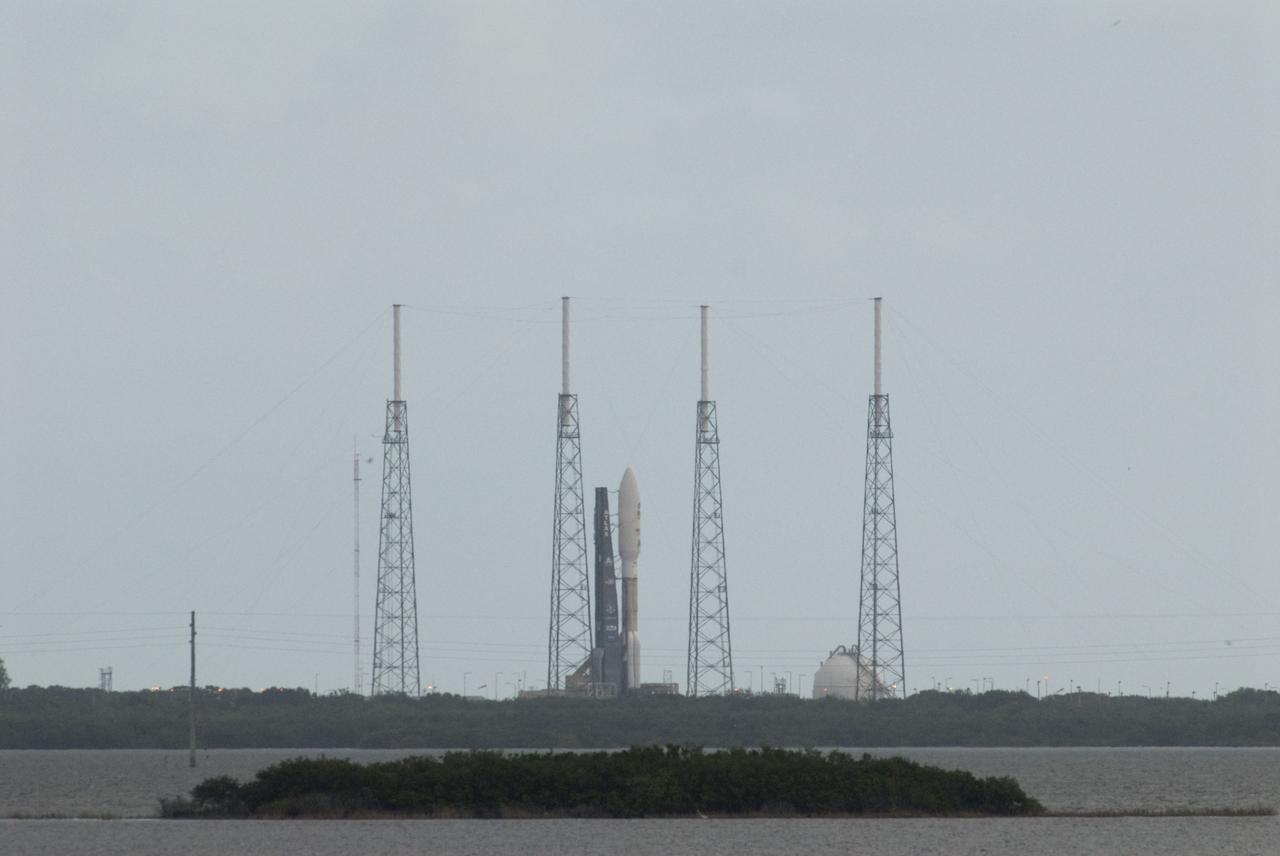

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Four towering lightning protection masts seem to stand guard as NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) spacecraft, sealed inside its payload fairing, awaits liftoff aboard the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. MSL lifted off from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26, beginning a 9-month interplanetary cruise to Mars. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Bill White
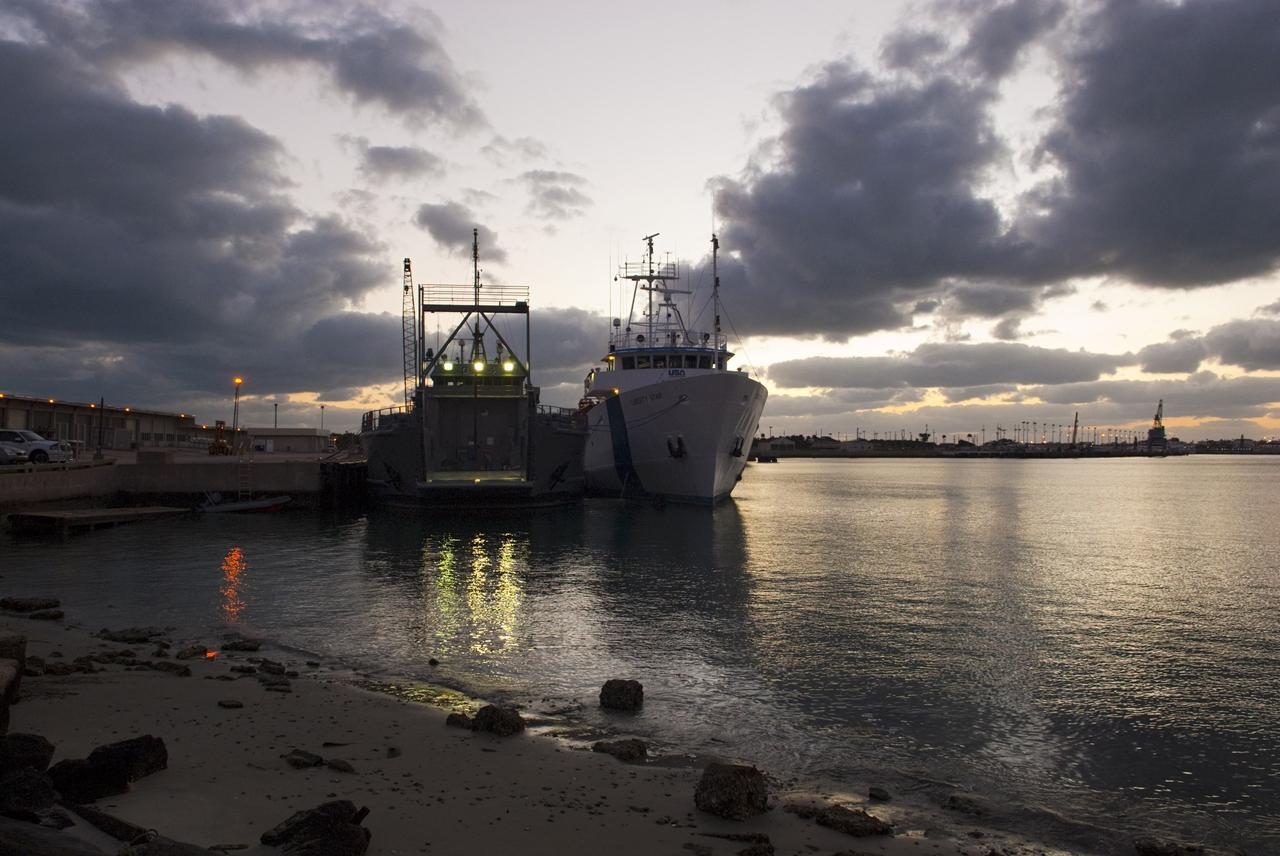

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Dawn at Port Canaveral in Florida finds preparations under way for the departure of NASA's Liberty Star ship. Liberty Star has been enlisted to support the Crew Module Recovery Attach Fitting Test (CRAFT) which began at-sea operations Nov. 29. Multiple attach clips are being evaluated against the current recovery cleat configuration by U.S. Air Force pararescue jumpers (PJs) and a U.S. Navy diver. The 21st Century Ground Systems Program will use data collected from the tests to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft being developed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
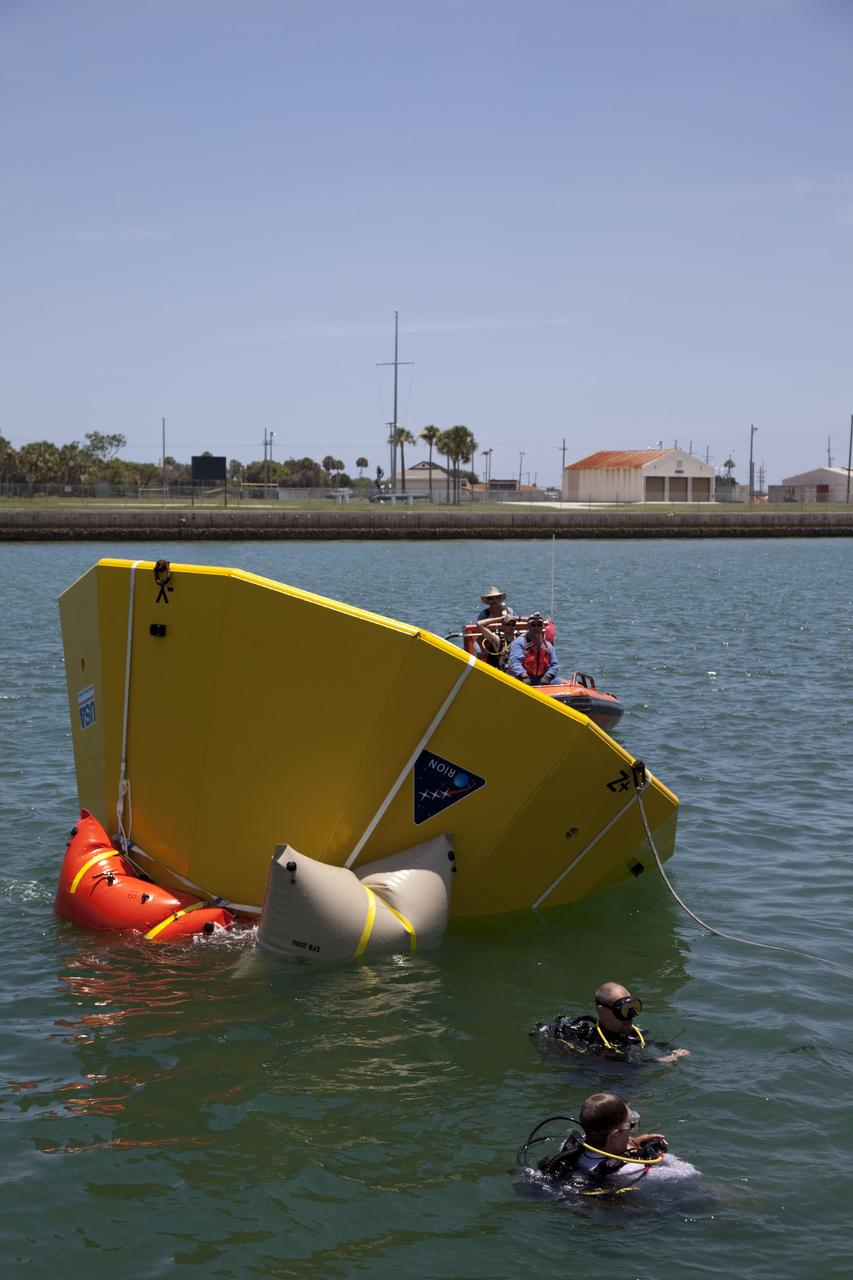

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Delta turn basin at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, United Space Alliance (USA) divers and boat crew tend an Orion test article while waiting for its lift bags to inflate. The uprighting tests are part of USA's research and development program to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to reorient and recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. USA is a major subcontractor to Lockheed Martin for the Orion spacecraft. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft designed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. Orion's first uncrewed orbital flight test is slated for 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/mpcv/. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
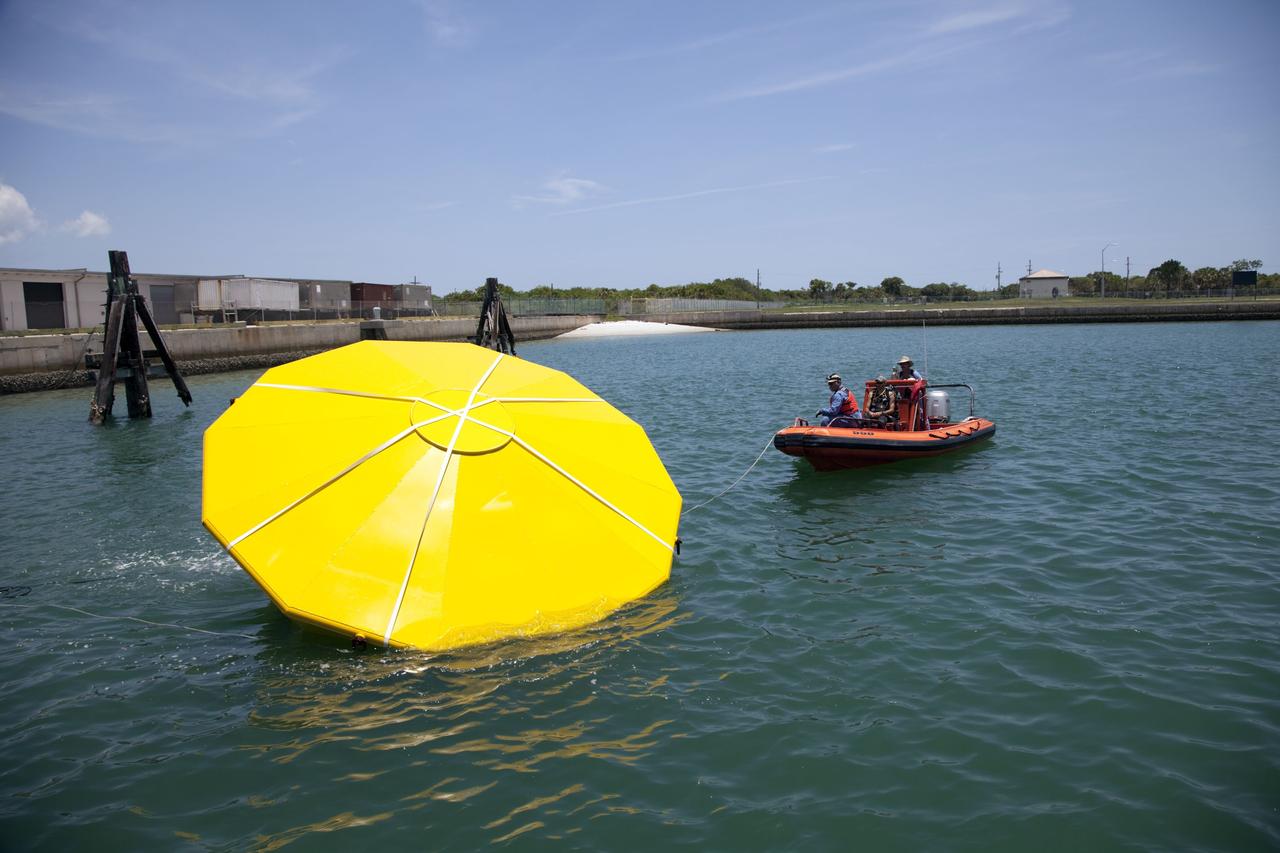

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Delta turn basin at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, United Space Alliance (USA) workers help orient an Orion test article during a roll test. The uprighting tests are part of USA's research and development program to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to reorient and recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. USA is a major subcontractor to Lockheed Martin for the Orion spacecraft. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft designed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. Orion's first uncrewed orbital flight test is slated for 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/mpcv/. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

A forklift carries the crated Mars Odyssey spacecraft from the Air Force C-17 cargo airplane that brought it from Denver, Colo.., location of the Lockheed Martin plant where the spacecraft was built. The crate will placed on a transport trailer to take it from KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2) located in the KSC Industrial Area. In the SAEF it will undergo final assembly and checkout. This includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. It will be fueled and then mated to an upper stage booster, the final activities before going to the launch pad. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. Mars Odyssey will be inserted into an interplanetary trajectory by a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A at Complex 17 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet's surface and measuring its environment
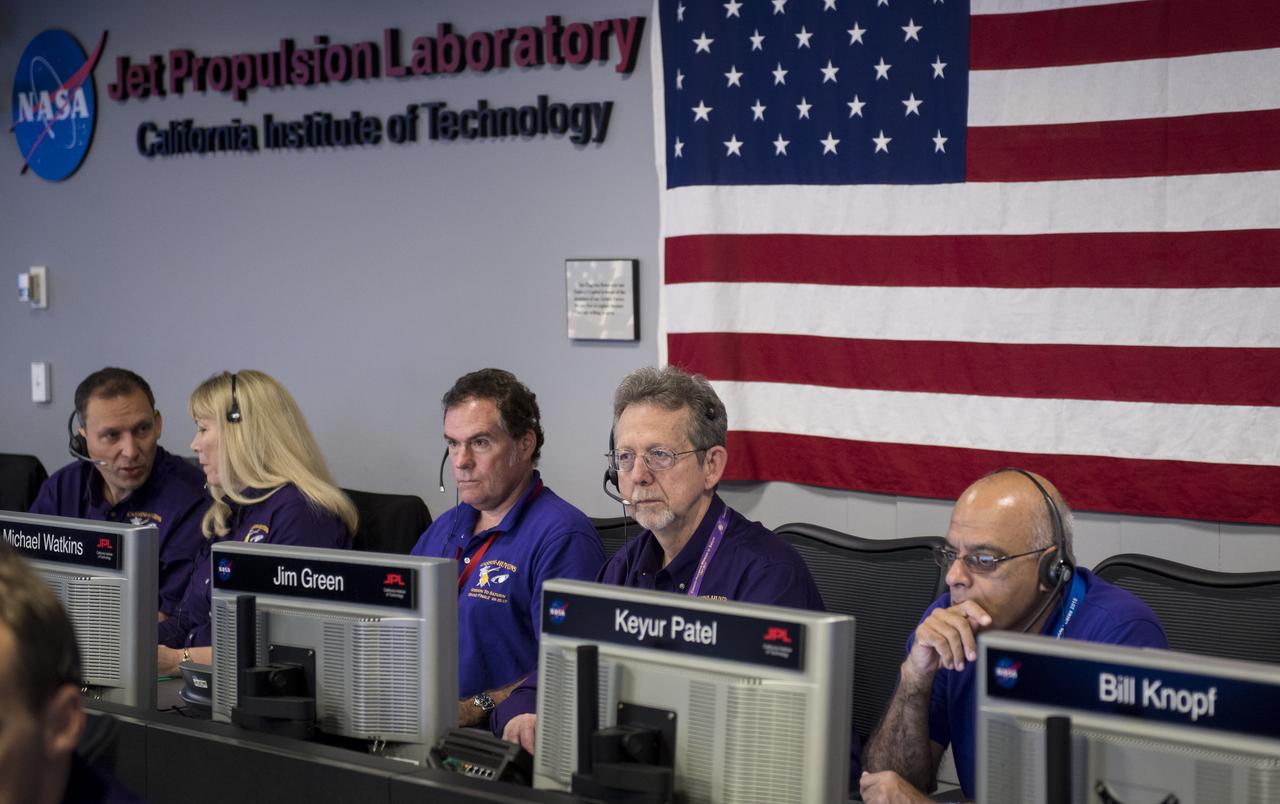

Associate administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen, left, Cassini project scientist at JPL, Linda Spilker, second from left, director of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Michael Watkins, center, director of NASA's Planetary Science Division, Jim Green, second from right, and director of the interplanetary network directorate at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Keyur Patel, left, are seen in mission control, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
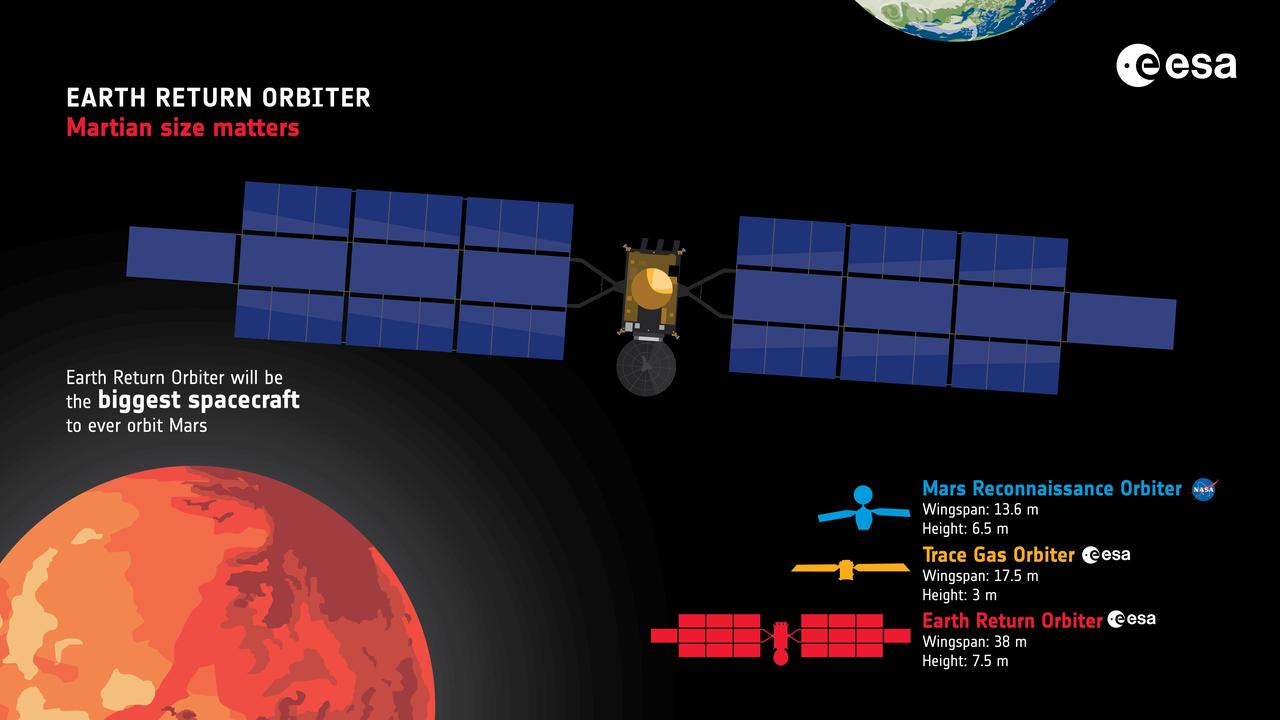
The European Space Agency's (ESA) Earth Return Orbiter (ERO) would be the biggest spacecraft to ever orbit Mars. The spacecraft would also be the first interplanetary spacecraft to rendezvous and capture hardware launched from another planet and return it to the Earth's surface, making a full round trip to Mars and back. ERO would be a multi-stage modular spacecraft equipped with both chemical and solar electric propulsion. The electric propulsion system would be the most powerful ever flown on any previous planetary mission. ERO would carry a radiation monitor to measure the total radiation dose experienced by the spacecraft throughout the entire mission, which in addition to monitoring the health of the ERO, should provide important information on how to design systems for future human explorers. Launch is planned in 2027, entering into Mars orbit in 2029. The Earth Return Orbiter is part of the multi-mission Mars Sample Return campaign being planned by NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25892

The Mars Odyssey spacecraft is removed from the Air Force C-17 cargo airplane that brought it from Denver, Colo.., location of the Lockheed Martin plant where the spacecraft was built. Mars Odyssey will be moved on a transport trailer from KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2) located in the KSC Industrial Area. In the SAEF it will undergo final assembly and checkout. This includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. It will be fueled and then mated to an upper stage booster, the final activities before going to the launch pad. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. Mars Odyssey will be inserted into an interplanetary trajectory by a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A at Complex 17 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet's surface and measuring its environment

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's Liberty Star ship, with an Orion flight test capsule secured to its deck, passes through the mouth of Port Canaveral in Florida into the Atlantic Ocean. Liberty Star has been enlisted to support the Crew Module Recovery Attach Fitting Test (CRAFT) which began at-sea operations Nov. 29. Multiple attach clips are being evaluated against the current recovery cleat configuration by U.S. Air Force pararescue jumpers (PJs) and a U.S. Navy diver. The 21st Century Ground Systems Program will use data collected from the tests to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft being developed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
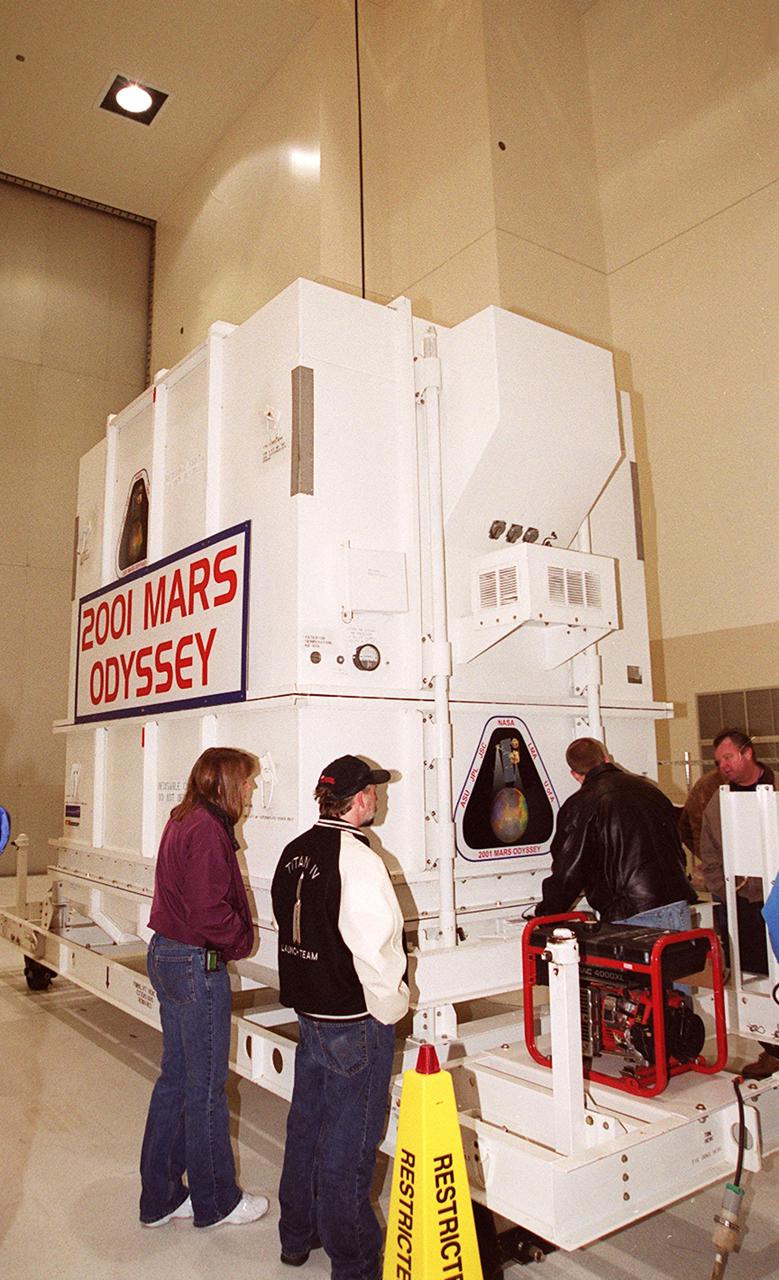

The crated 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft rests safely inside the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2) located in the KSC Industrial Area. The spacecraft arrived at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility aboard an Air Force C-17 cargo airplane that brought it from Denver, Colo.., location of the Lockheed Martin plant where the spacecraft was built. In the SAEF, Odyssey will undergo final assembly and checkout. This includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. It will be fueled and then mated to an upper stage booster, the final activities before going to the launch pad. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. Mars Odyssey will be inserted into an interplanetary trajectory by a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A at Complex 17 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet's surface and measuring its environment
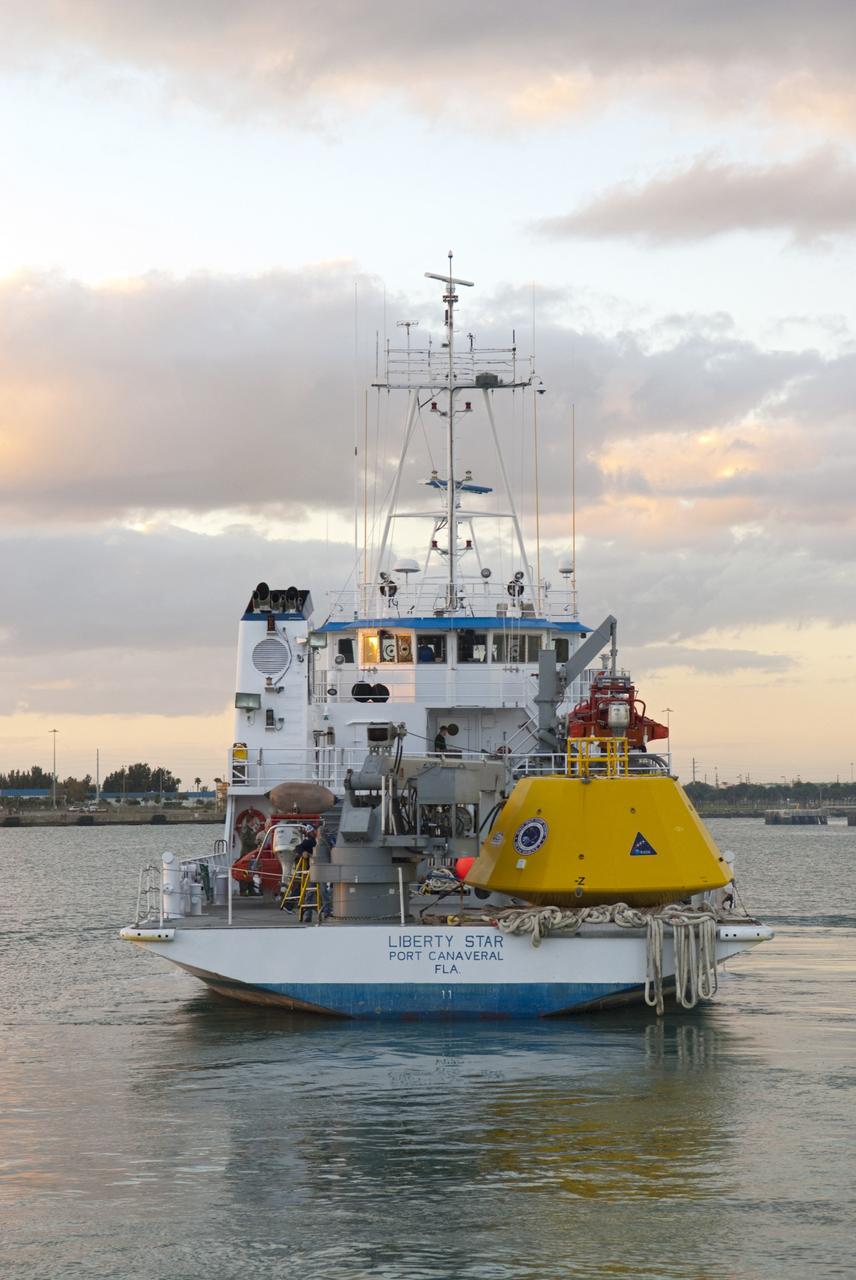

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's Liberty Star ship departs Port Canaveral in Florida with an Orion flight test capsule secured to its deck. Liberty Star has been enlisted to support the Crew Module Recovery Attach Fitting Test (CRAFT) which began at-sea operations Nov. 29. Multiple attach clips are being evaluated against the current recovery cleat configuration by U.S. Air Force pararescue jumpers (PJs) and a U.S. Navy diver. The 21st Century Ground Systems Program will use data collected from the tests to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft being developed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

The 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft arrives at the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2) located in the KSC Industrial Area. The spacecraft arrived at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility aboard an Air Force C-17 cargo airplane that brought it from Denver, Colo.., location of the Lockheed Martin plant where the spacecraft was built. In the SAEF, Odyssey will undergo final assembly and checkout. This includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. It will be fueled and then mated to an upper stage booster, the final activities before going to the launch pad. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. Mars Odyssey will be inserted into an interplanetary trajectory by a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A at Complex 17 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet's surface and measuring its environment
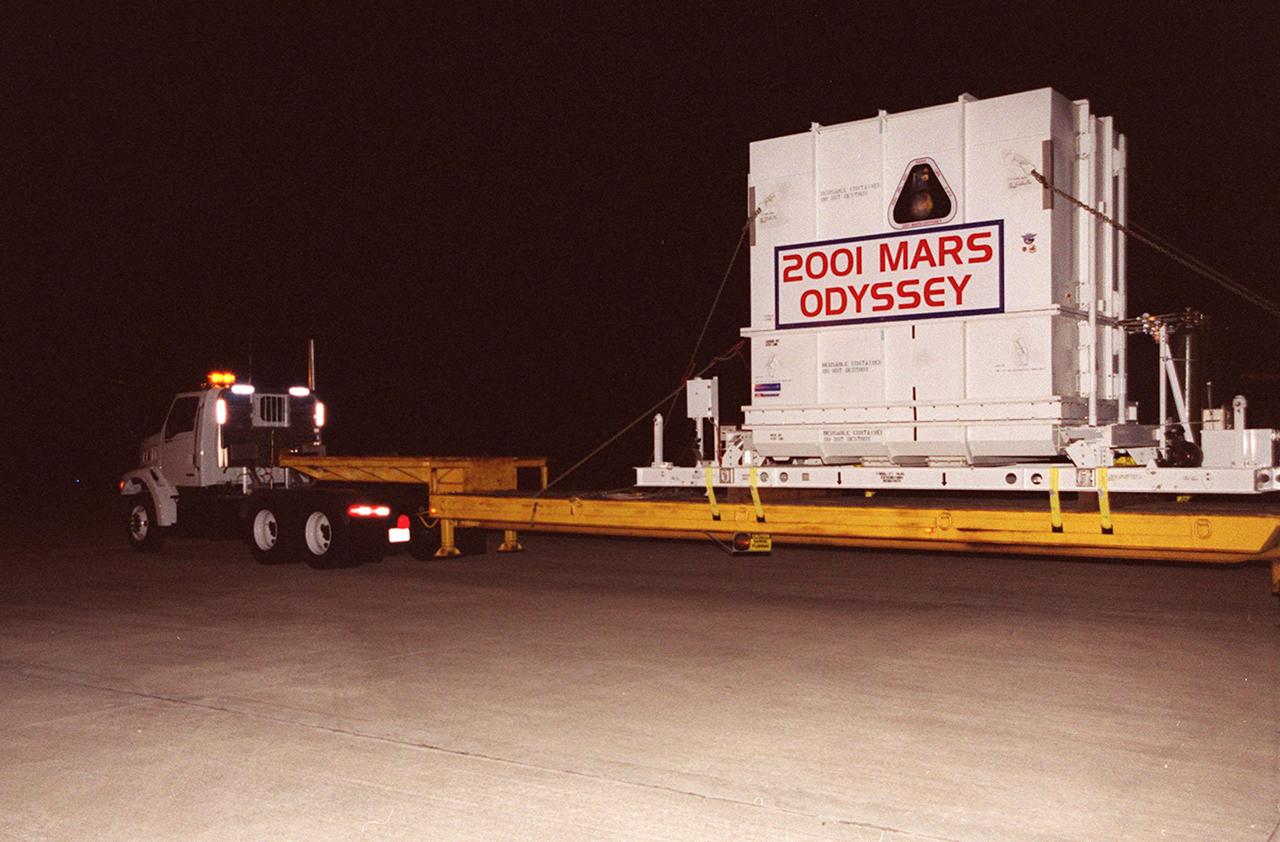

The 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft leaves the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility on the bed of a transport trailer. The spacecraft is being moved to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2) located in the KSC Industrial Area. The spacecraft arrived at the SLF aboard an Air Force C-17 cargo airplane that brought it from Denver, Colo.., location of the Lockheed Martin plant where the spacecraft was built. In the SAEF, Odyssey will undergo final assembly and checkout. This includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. It will be fueled and then mated to an upper stage booster, the final activities before going to the launch pad. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. Mars Odyssey will be inserted into an interplanetary trajectory by a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A at Complex 17 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet's surface and measuring its environment
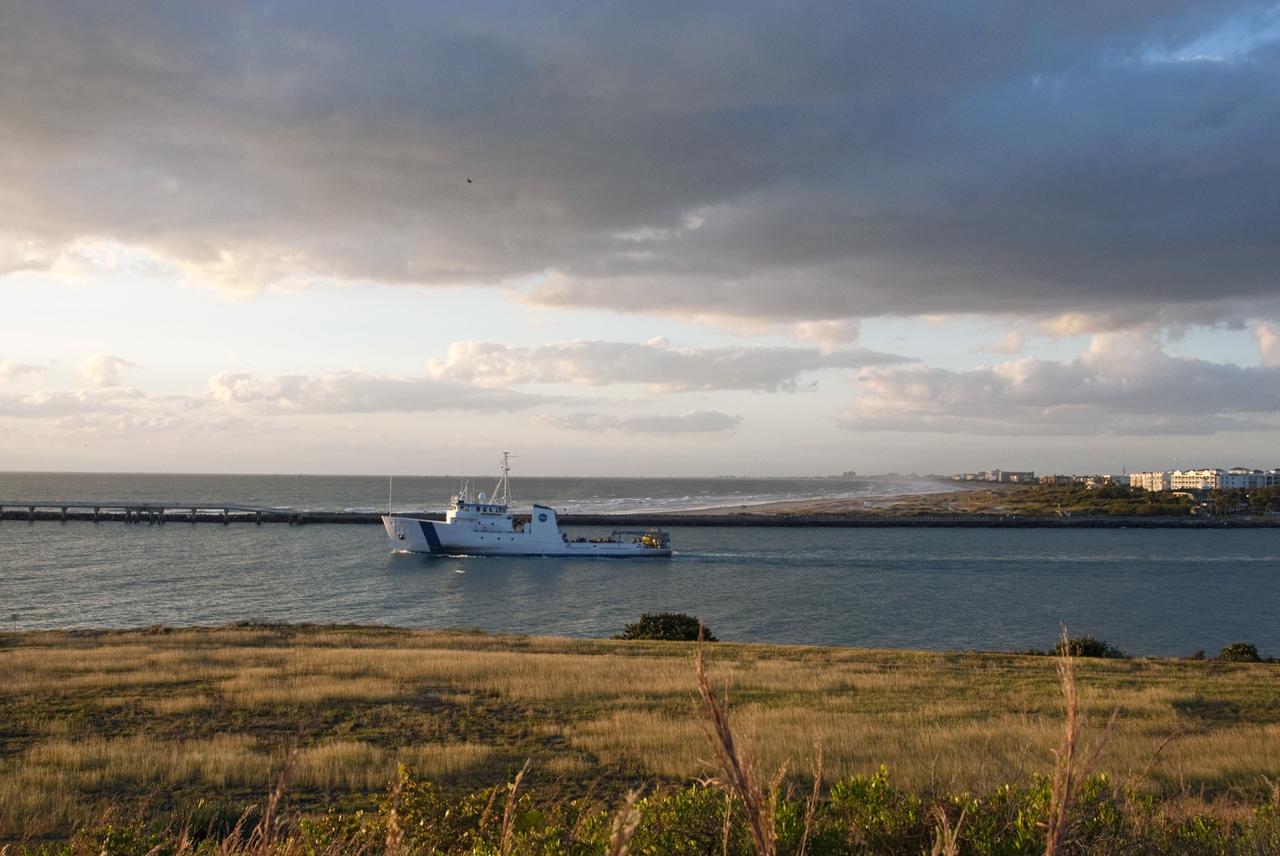

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's Liberty Star ship, with an Orion flight test capsule secured to its deck, passes through the mouth of Port Canaveral in Florida on its way to the Atlantic Ocean. Liberty Star has been enlisted to support the Crew Module Recovery Attach Fitting Test (CRAFT) which began at-sea operations Nov. 29. Multiple attach clips are being evaluated against the current recovery cleat configuration by U.S. Air Force pararescue jumpers (PJs) and a U.S. Navy diver. The 21st Century Ground Systems Program will use data collected from the tests to help develop ground operations support equipment that could be used to recover an uncrewed Orion flight test capsule after splashdown. The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle is NASA's next-generation spacecraft being developed for deep space missions to asteroids, moons and other interplanetary destinations throughout the solar system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

The Earth Return Orbiter (ERO) is one of the flight missions making up the Mars Sample Return campaign to bring martian rock and atmospheric samples back to Earth. The ESA orbiter would be the first interplanetary spacecraft to capture samples in orbit and make a return trip between Earth and Mars. The primary mission of the European spacecraft would be to find, fly to, and capture a volleyball-sized capsule called the Orbiting Sample (OS) container launched from the surface of Mars by NASA's Mars Ascent System and carrying a carefully selected set of samples previously collected on the surface of Mars by NASA's Perseverance rover. Having already spent three years to reach Mars and perform its rendezvous and capture mission, ERO would take a further two years to fly from its operational orbit around Mars up to escape altitude and make its way back to Earth. When ERO is about three days from Earth, the Earth Entry System (EES) carrying the OS would separate from the spacecraft and be placed on a precision trajectory for Earth entry and landing. The Earth Return Orbiter is part of the multi-mission Mars Sample Return campaign being planned by NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25893
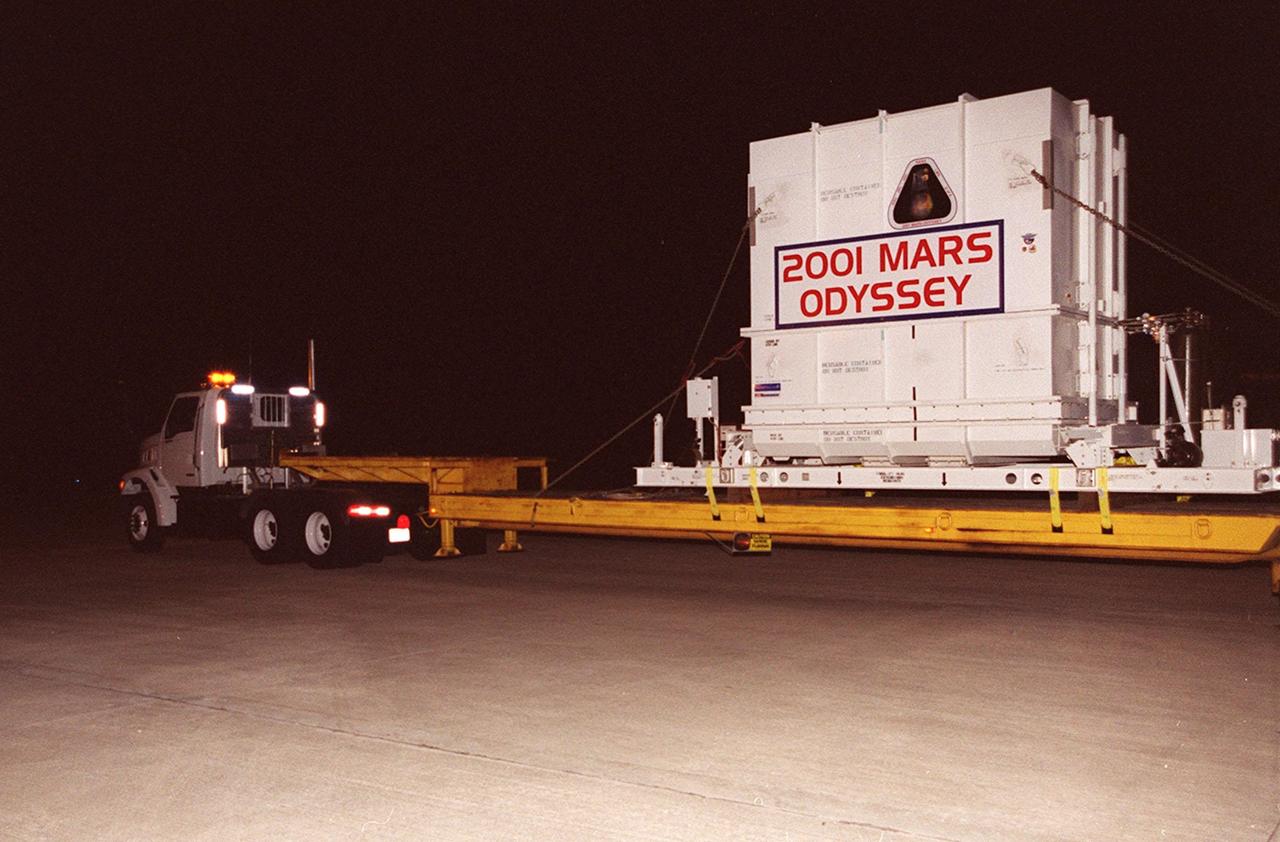

The 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft leaves the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility on the bed of a transport trailer. The spacecraft is being moved to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2) located in the KSC Industrial Area. The spacecraft arrived at the SLF aboard an Air Force C-17 cargo airplane that brought it from Denver, Colo.., location of the Lockheed Martin plant where the spacecraft was built. In the SAEF, Odyssey will undergo final assembly and checkout. This includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. It will be fueled and then mated to an upper stage booster, the final activities before going to the launch pad. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. Mars Odyssey will be inserted into an interplanetary trajectory by a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A at Complex 17 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet's surface and measuring its environment
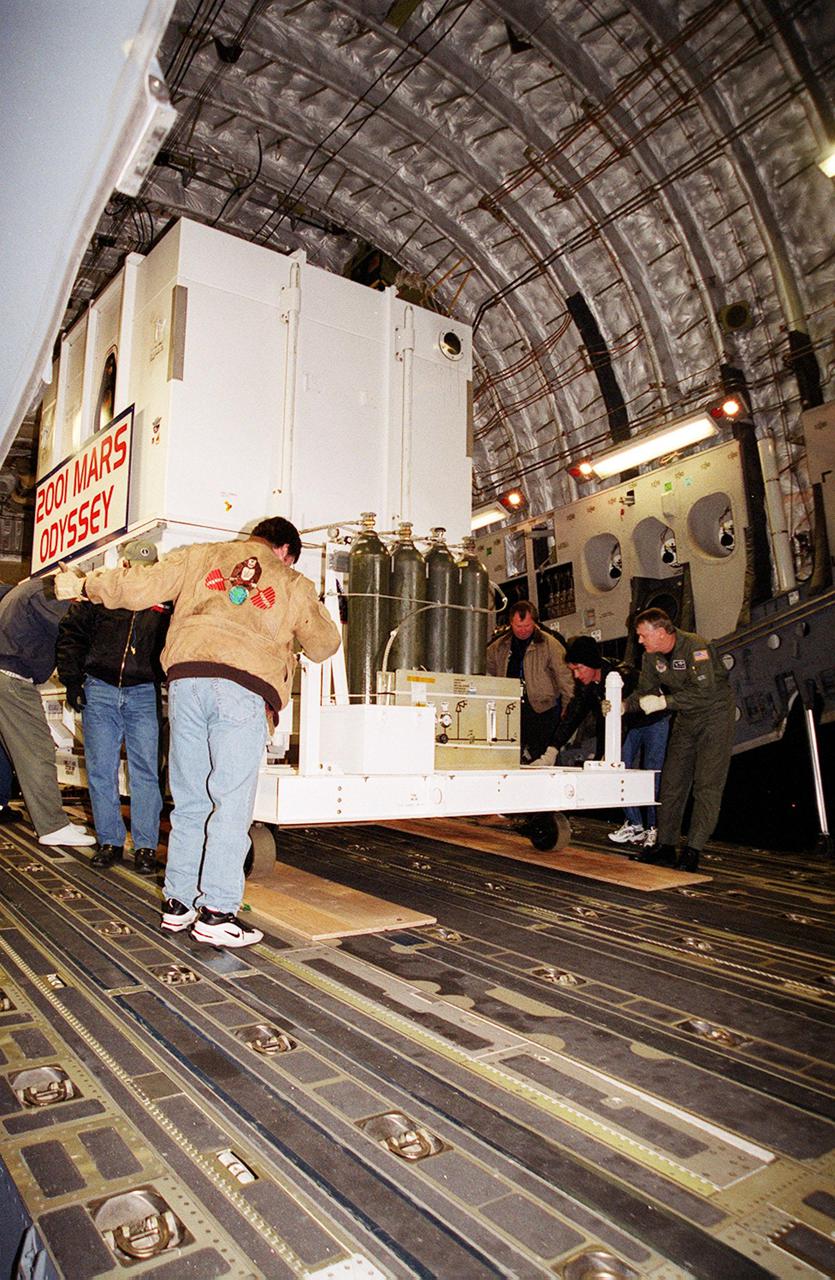

The Mars Odyssey spacecraft is maneuvered for removal from the Air Force C-17 cargo airplane that brought it from Denver, Colo.., location of the Lockheed Martin plant where the spacecraft was built. Mars Odyssey will be moved on a transport trailer from KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2 (SAEF-2) located in the KSC Industrial Area. In the SAEF it will undergo final assembly and checkout. This includes installation of two of the three science instruments, integration of the three-panel solar array, and a spacecraft functional test. It will be fueled and then mated to an upper stage booster, the final activities before going to the launch pad. Launch is planned for April 7, 2001 the first day of a 21-day planetary window. Mars Odyssey will be inserted into an interplanetary trajectory by a Boeing Delta II launch vehicle from Pad A at Complex 17 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The spacecraft will arrive at Mars on Oct. 20, 2001, for insertion into an initial elliptical capture orbit. Its final operational altitude will be a 250-mile-high, Sun-synchronous polar orbit. Mars Odyssey will spend two years mapping the planet's surface and measuring its environment