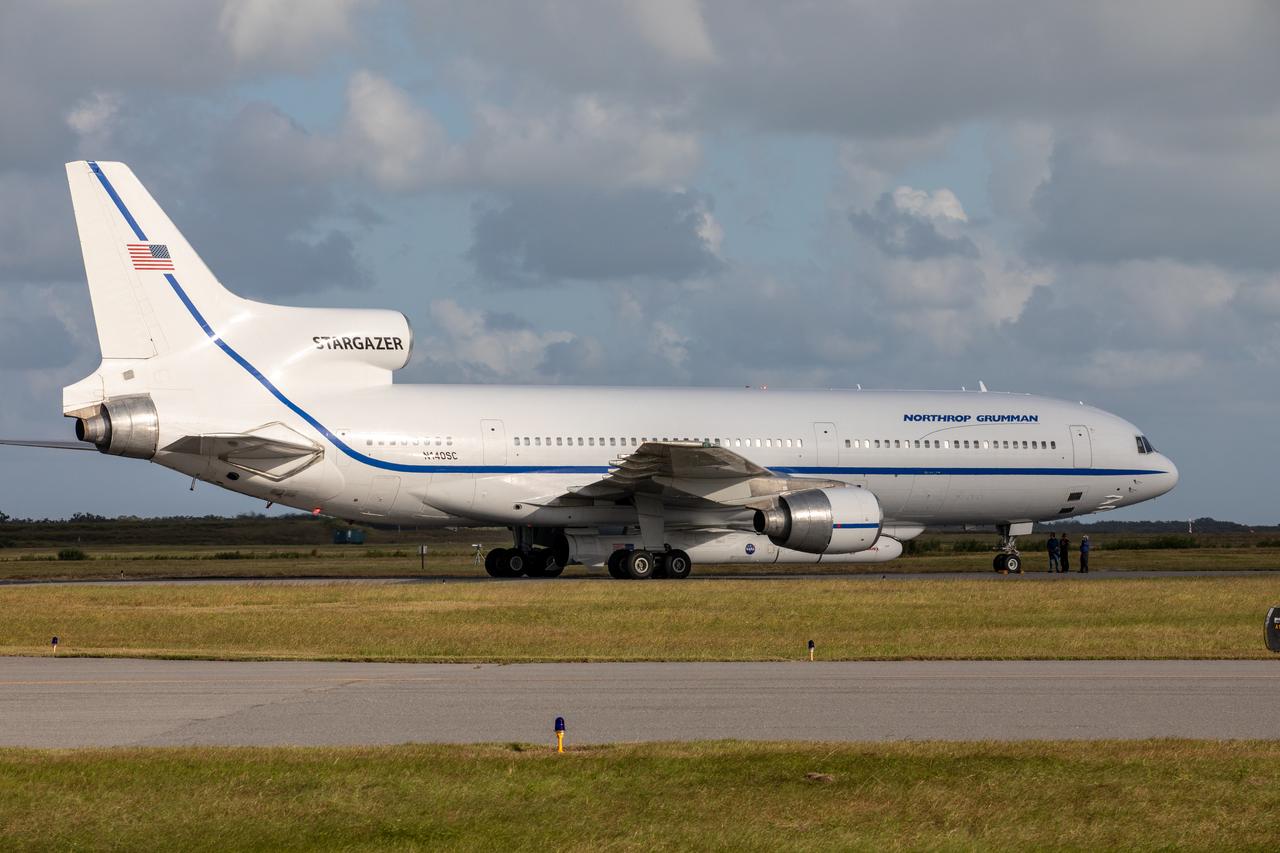

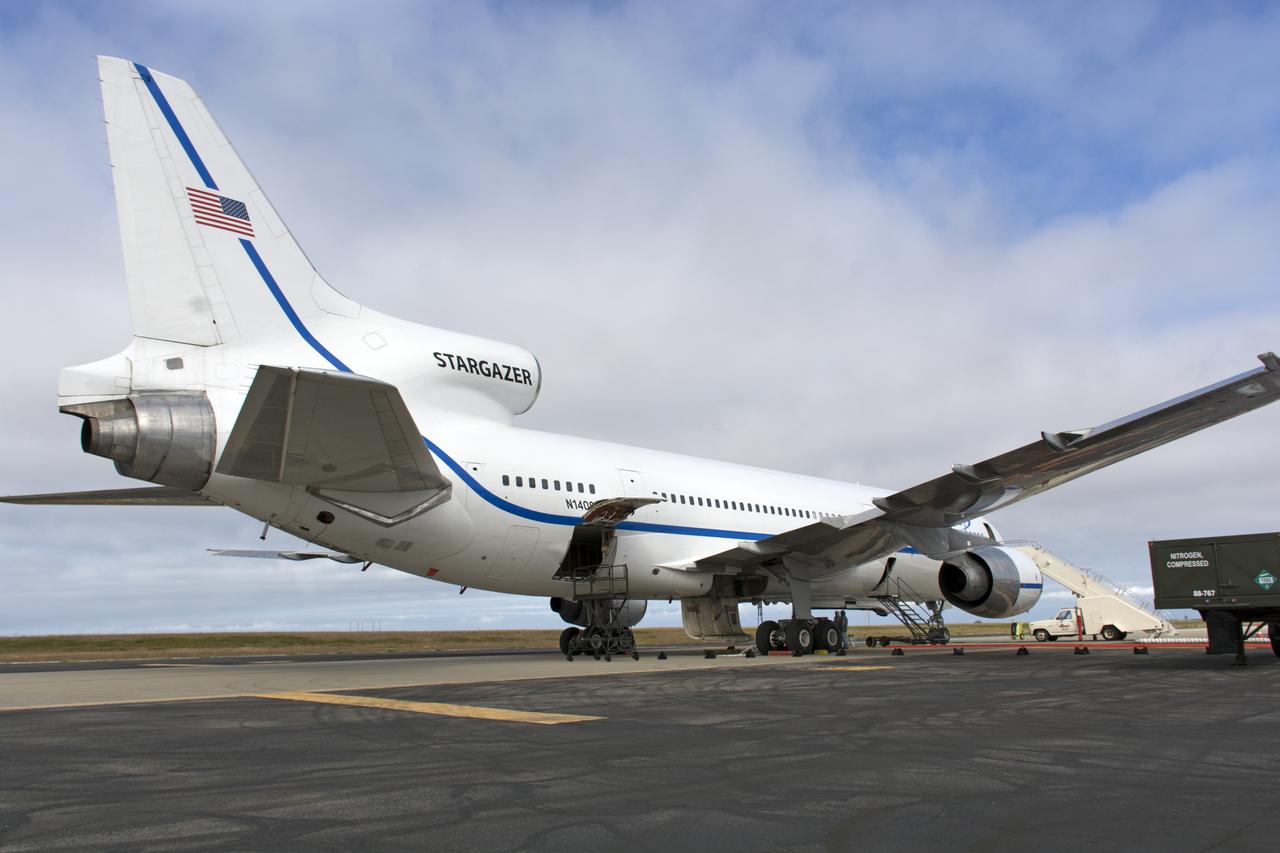
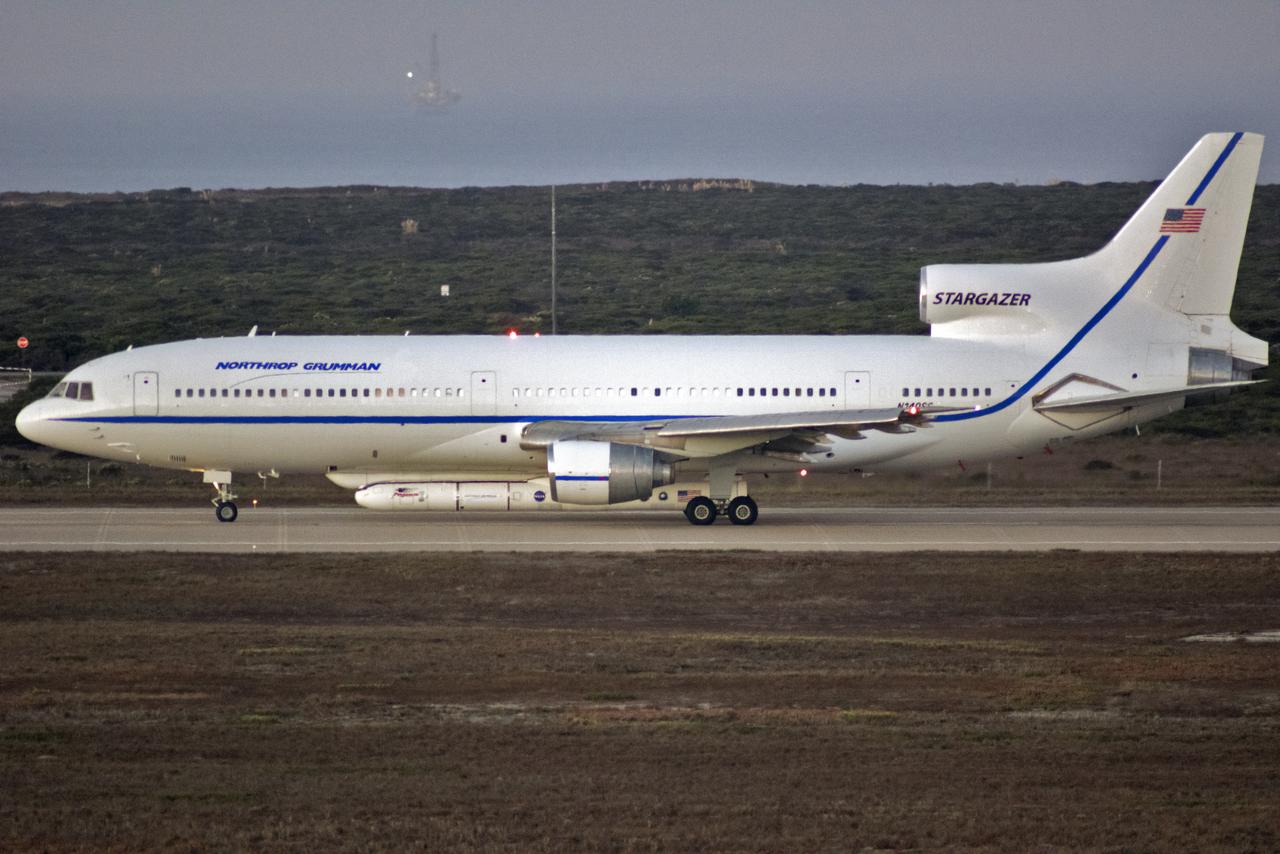
Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft has arrived at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 1, 2019. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
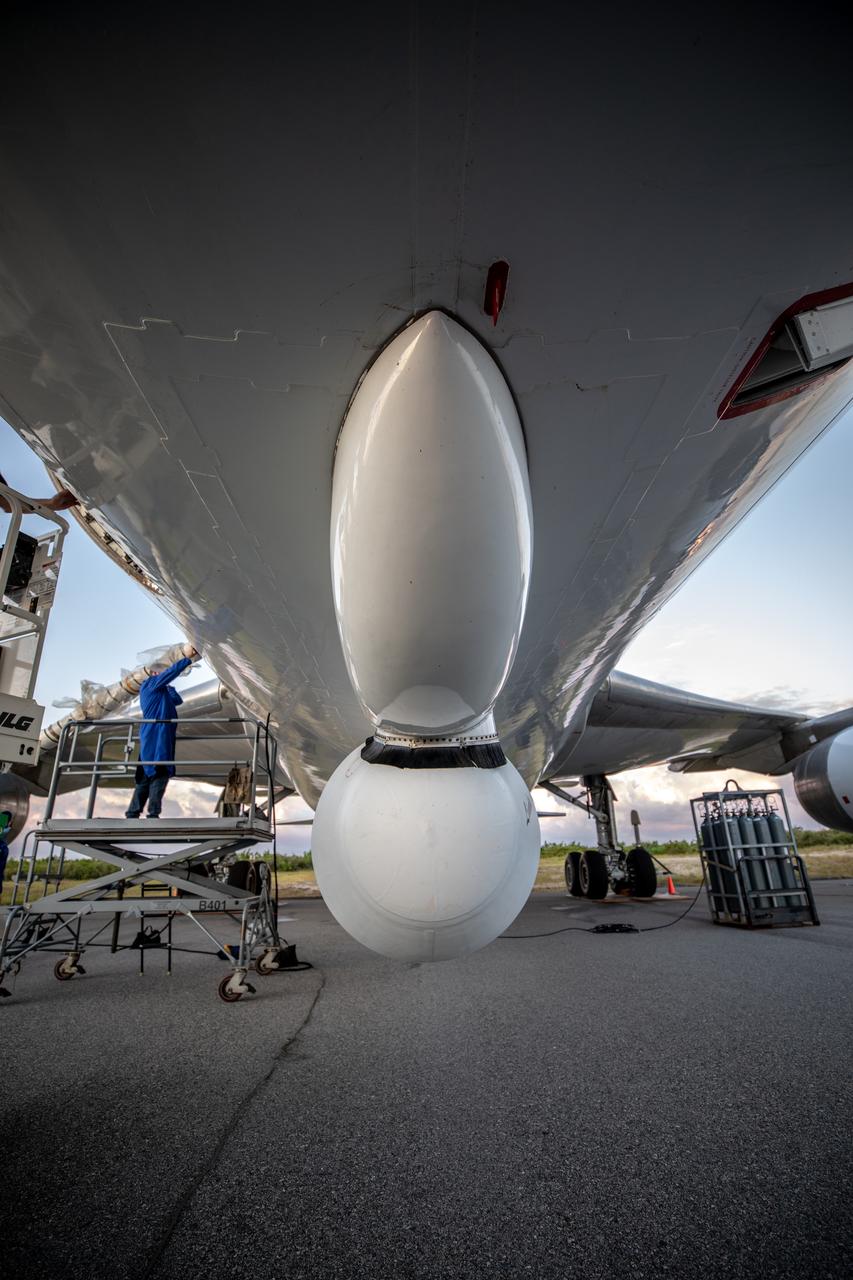

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, carrying NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), has arrived at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 1, 2019. The rocket is attached beneath the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
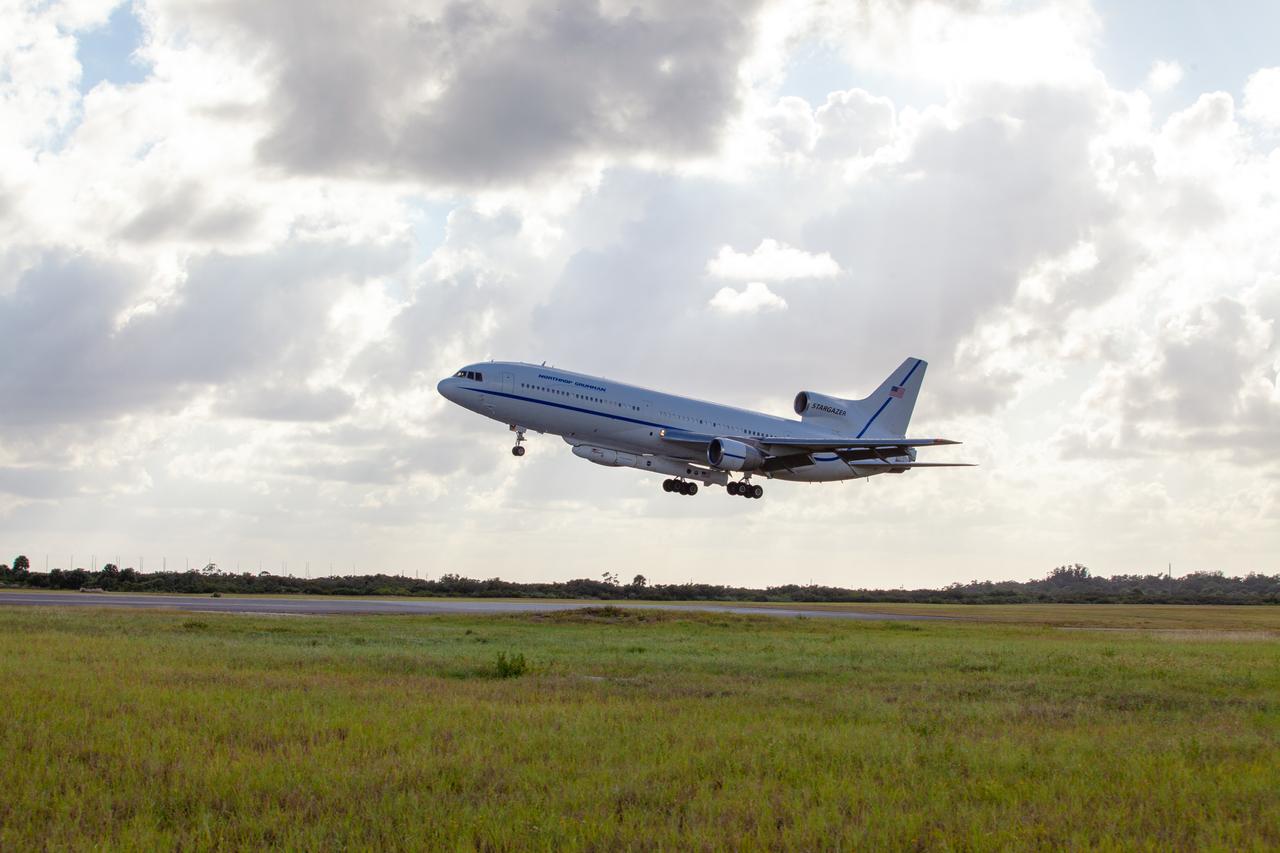

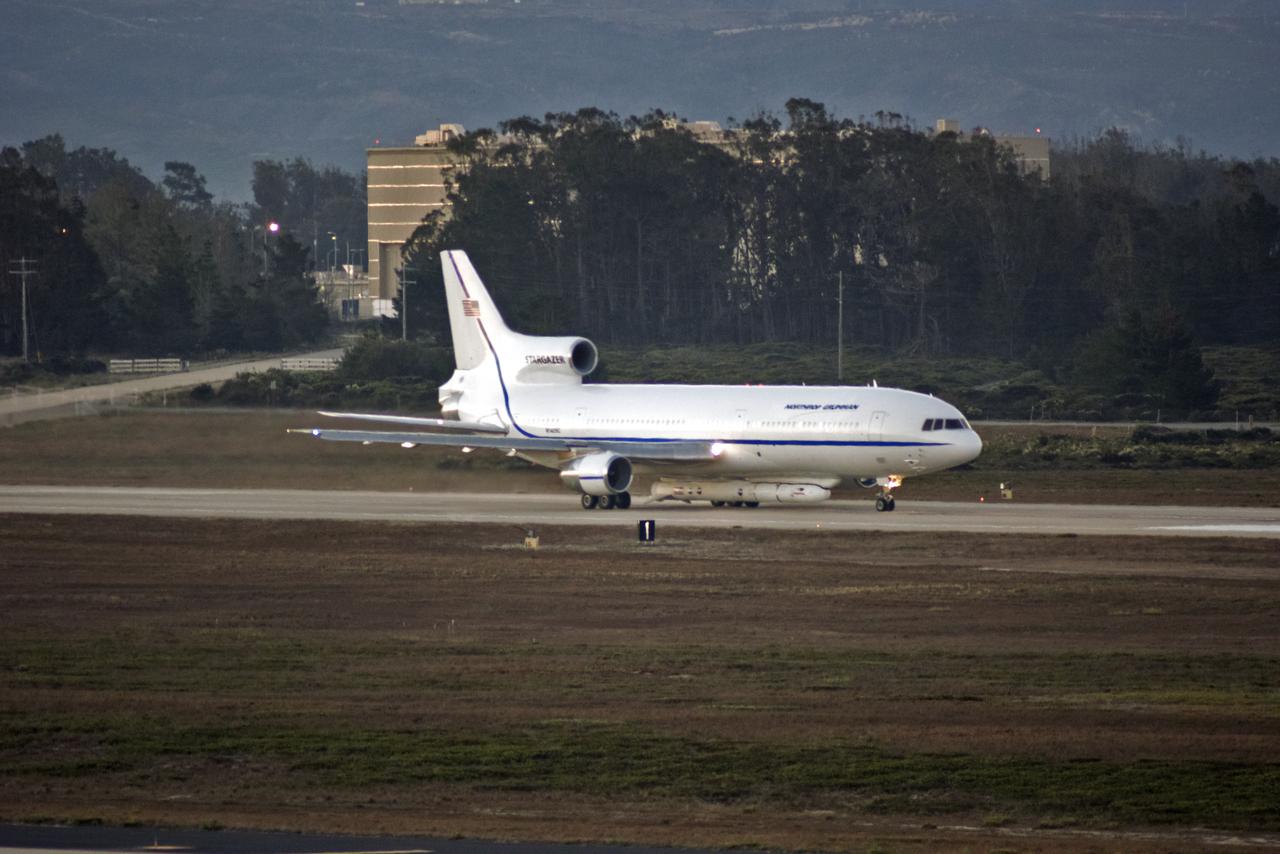
Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft descends toward the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 1, 2019. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
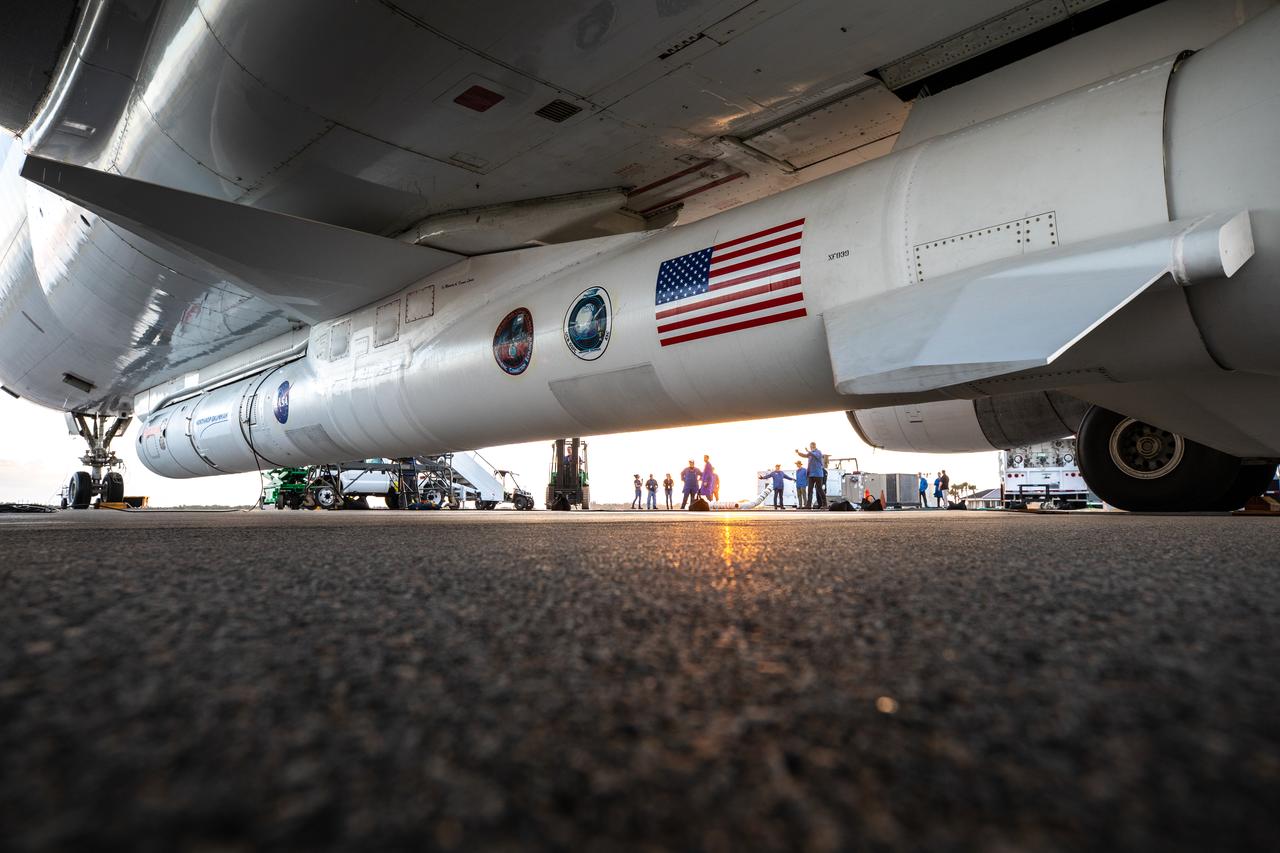

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, carrying NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), has arrived at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 1, 2019. The rocket is attached beneath the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
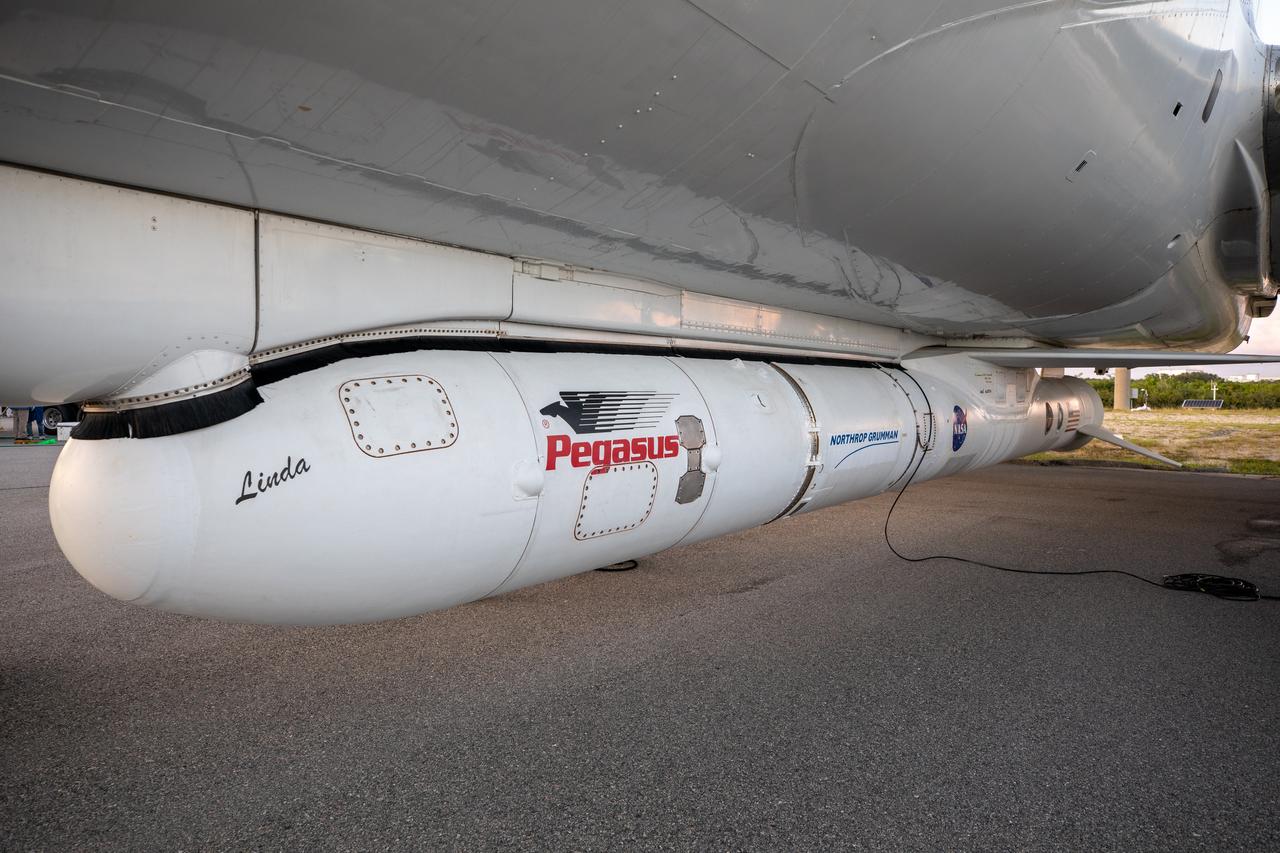

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, carrying NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), has arrived at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 1, 2019. The rocket is attached beneath the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
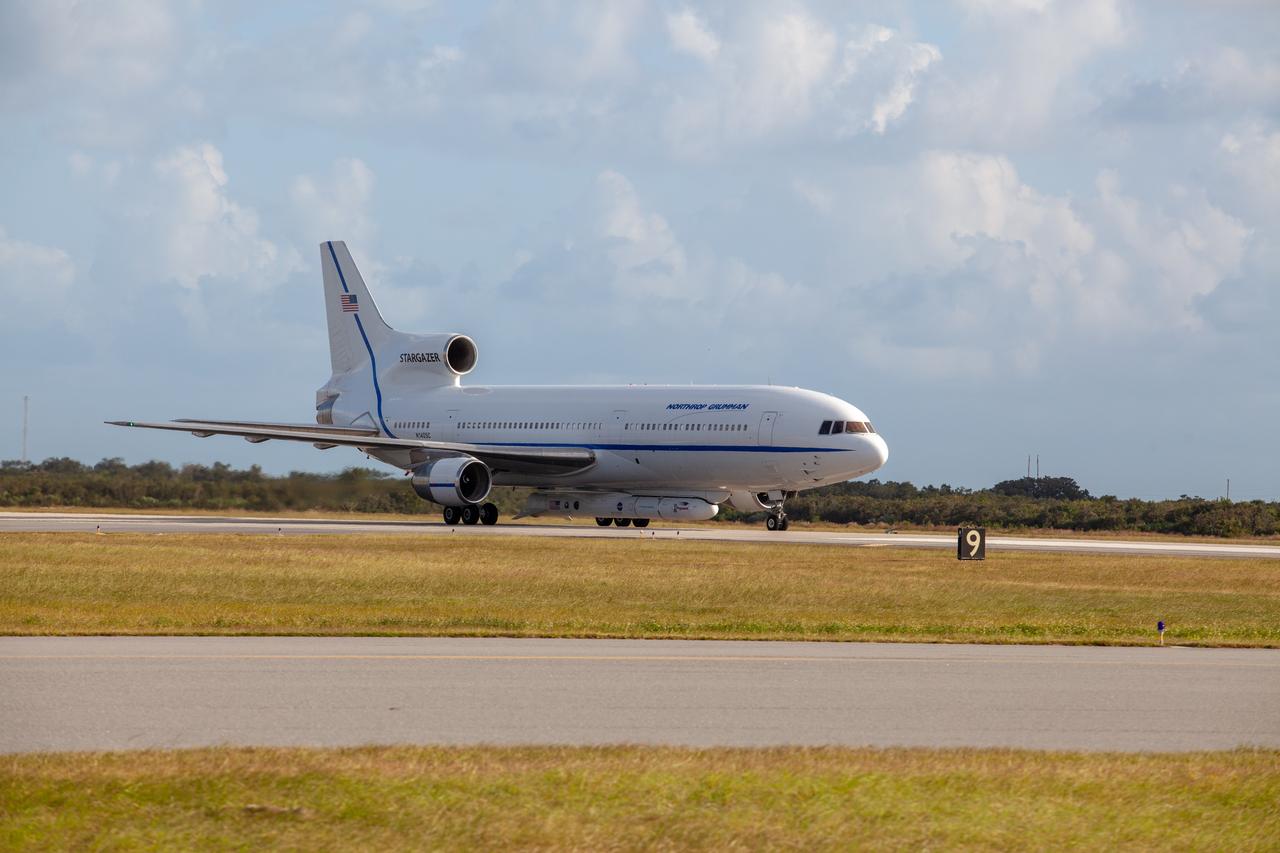

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft has arrived at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 1, 2019. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
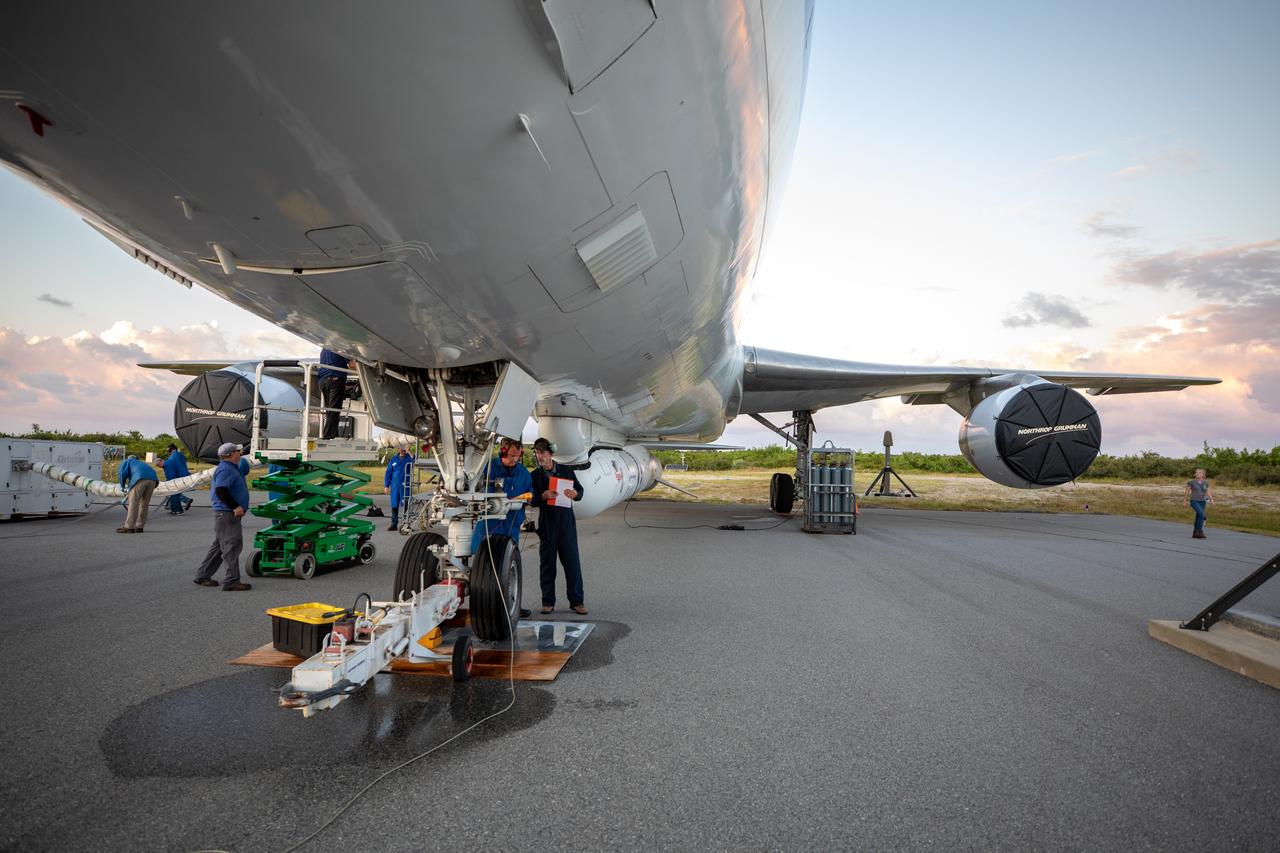

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft has arrived at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 1, 2019. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, carrying NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), has arrived at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 1, 2019. The rocket is attached beneath the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
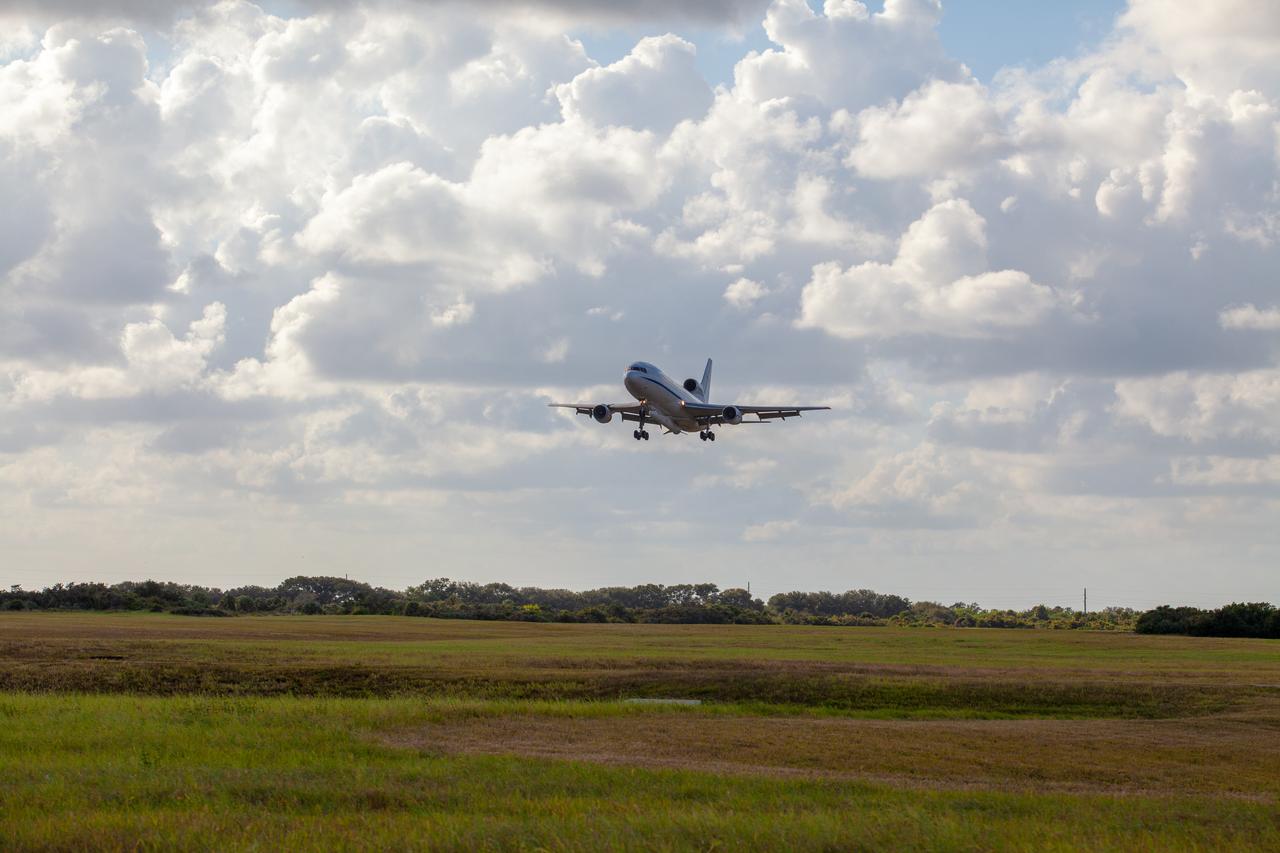

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft descends toward the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 1, 2019. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
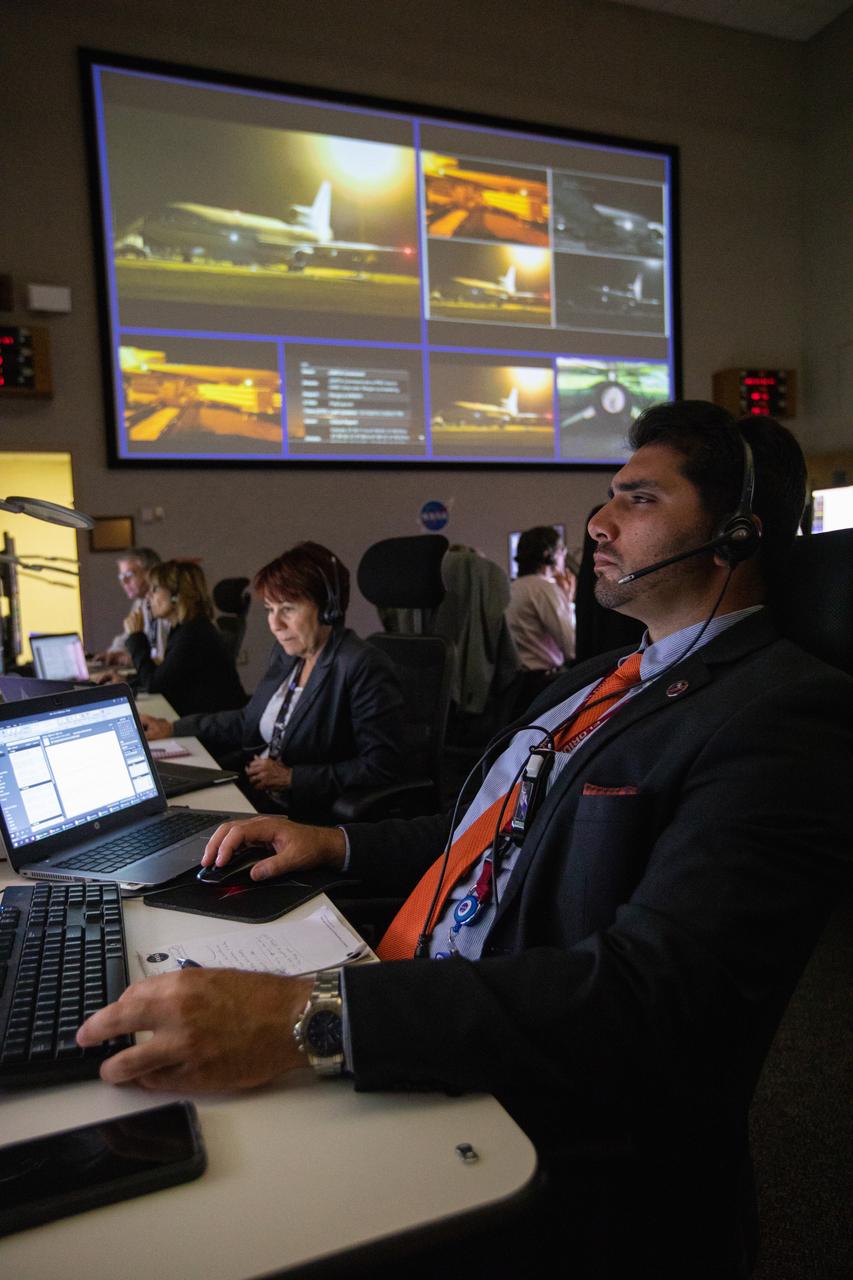

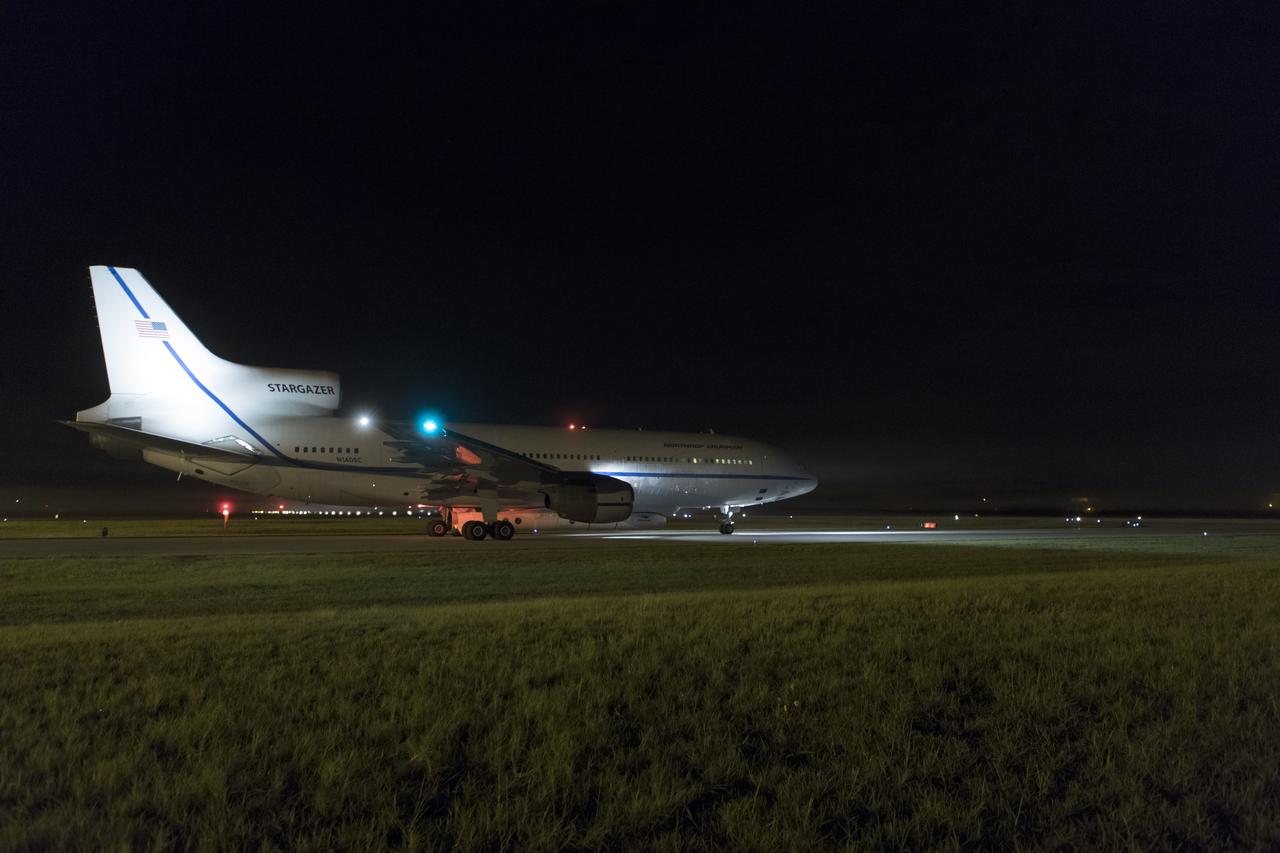
Members of the launch team monitor the launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.

Members of the launch team monitor the launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.

A member of the launch team monitors the launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.

Members of the launch team monitor the launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.

Members of the launch team monitor the launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.

Members of the launch team monitor the launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.

Members of the launch team monitor the launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.

Members of the launch team monitor the launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.

Members of the launch team monitor the launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.

Members of the launch team monitor the launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.
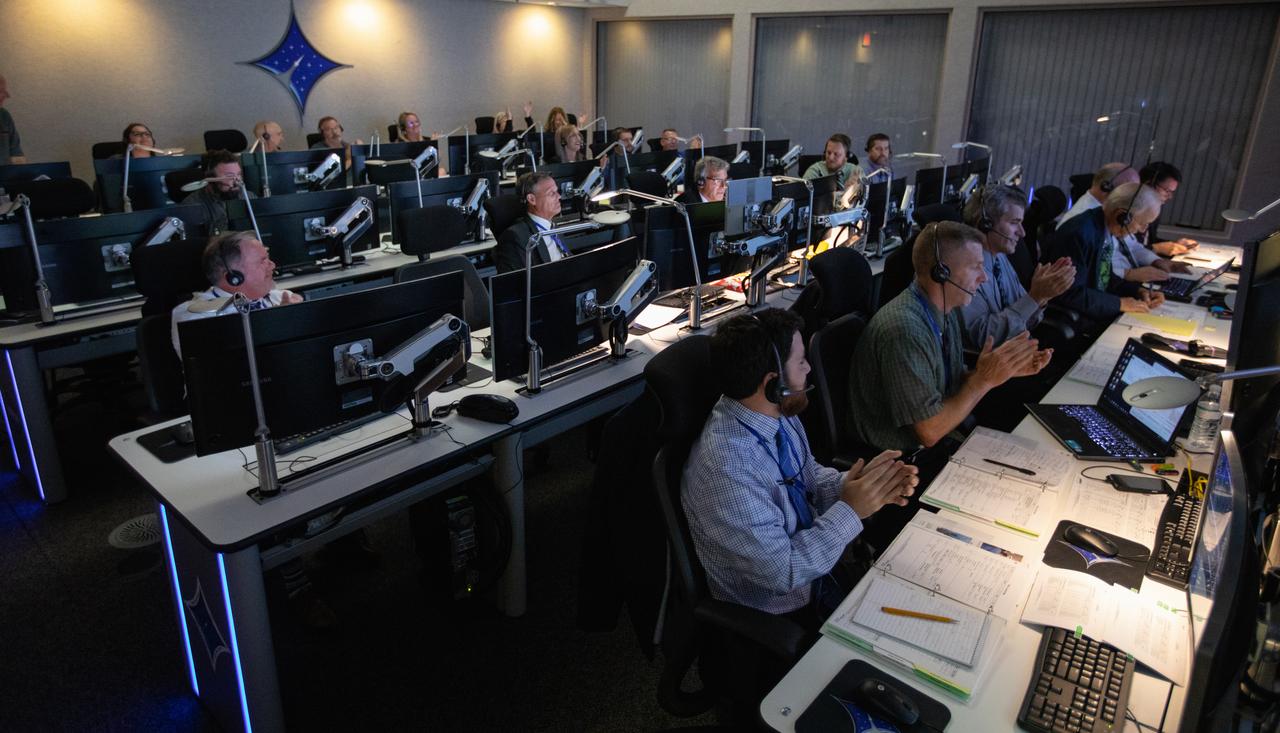

Inside Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), members of the launch team applaud the successful launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite on Oct. 10, 2019. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.

Members of the launch team monitor the launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.
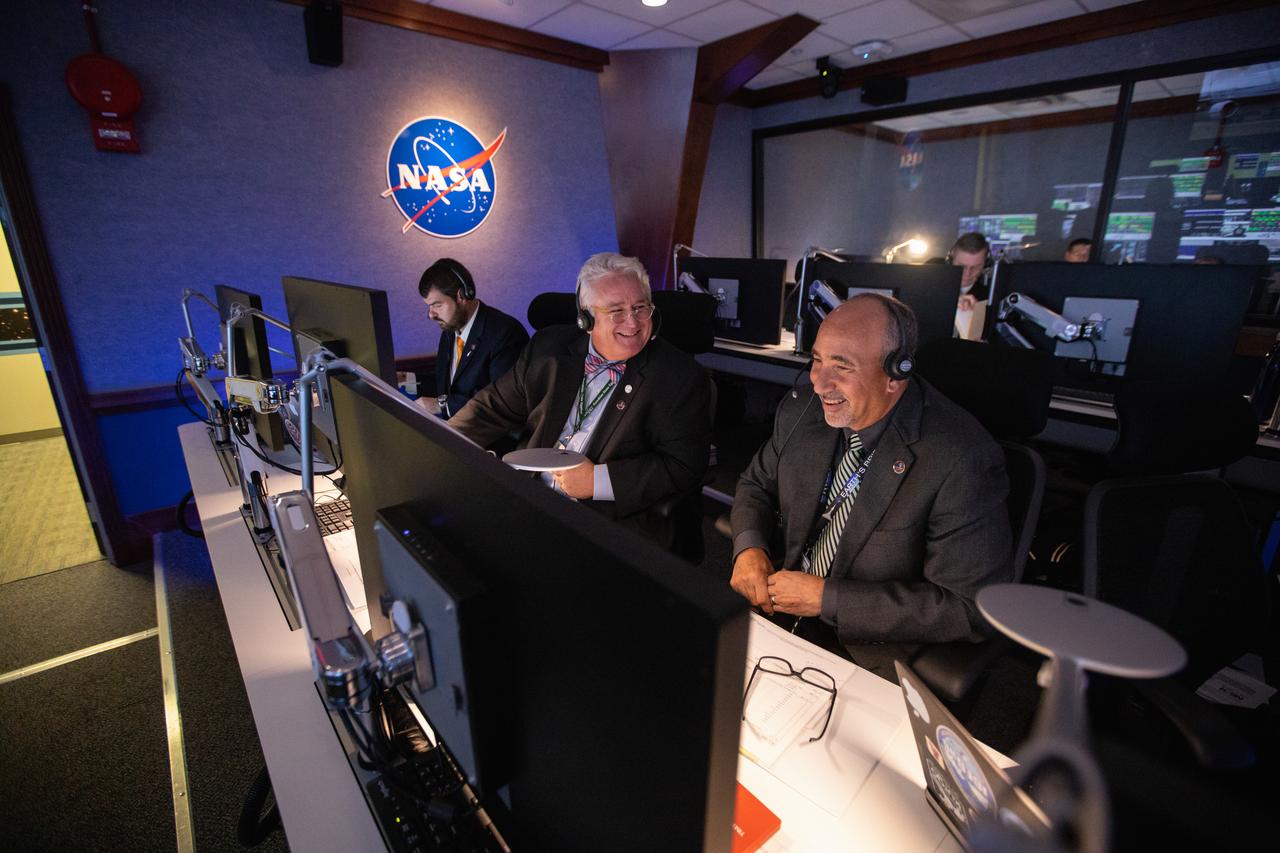

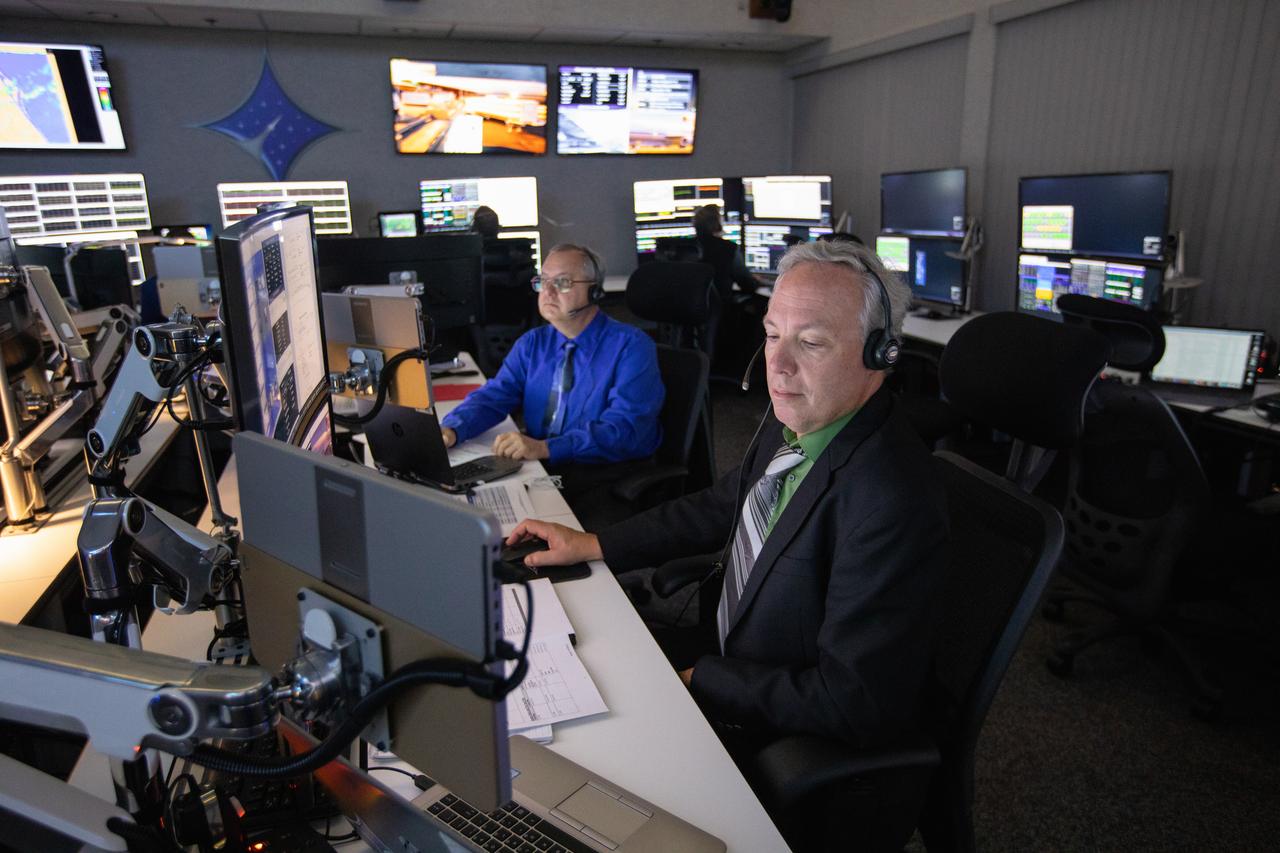
Albert Sierra (right), chief of NASA’s Launch Services Program’s (LSP) Flight Projects Office, and Garrett Lee Skrobot (second from right), senior mission manager, monitor the launch of the agency’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The ICON launch was managed by LSP.
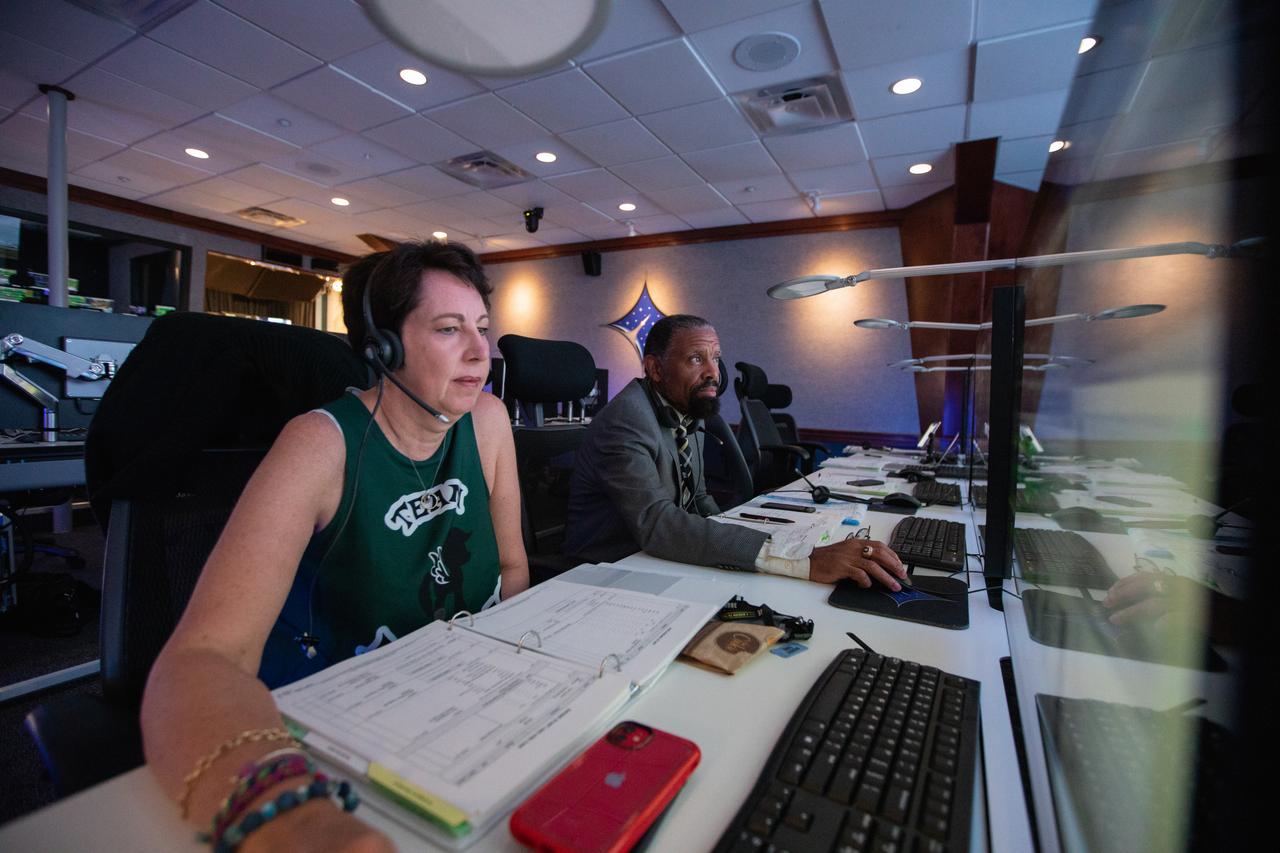

Inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), Nicola Fox, left, Heliophysics division director in NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, monitors the launch of the agency’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.
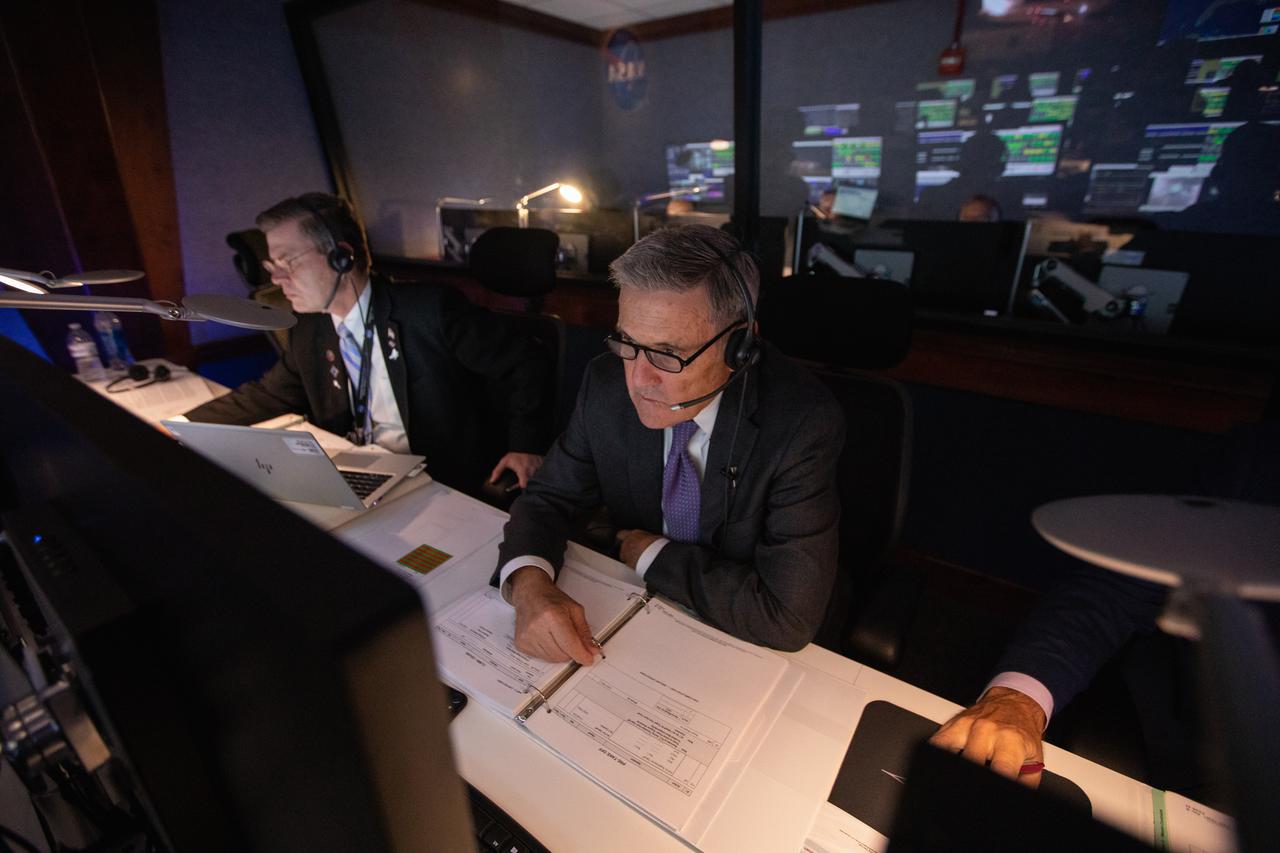

Inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana monitors the launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.
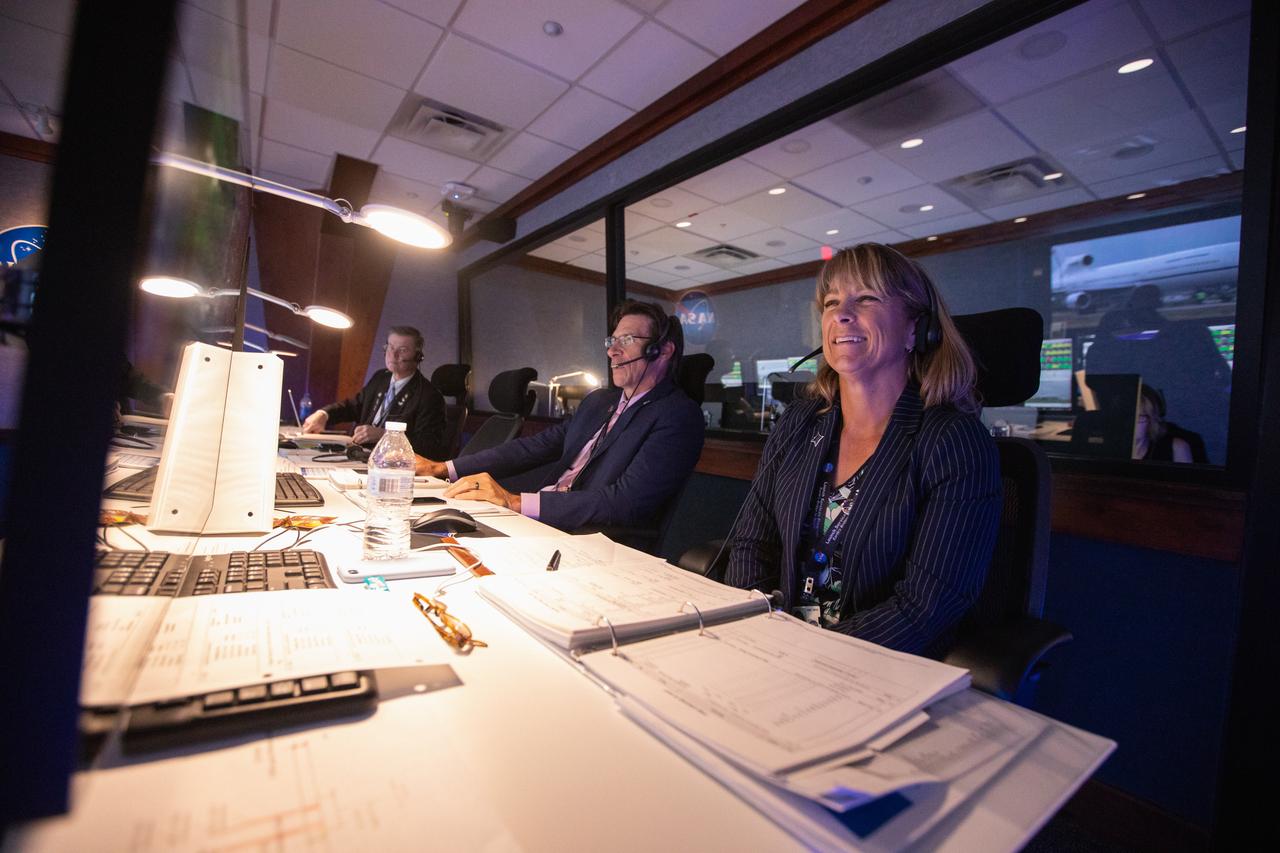

Inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), Amanda Mitskevich, right, program manager in NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), and Chuck Dovale, second from right, LSP deputy program manager, monitor the launch of the agency’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON). The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The ICON launch was managed by LSP.

Omar Baez, right, launch director in NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), monitors the launch of the agency’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The ICON launch was managed by LSP.
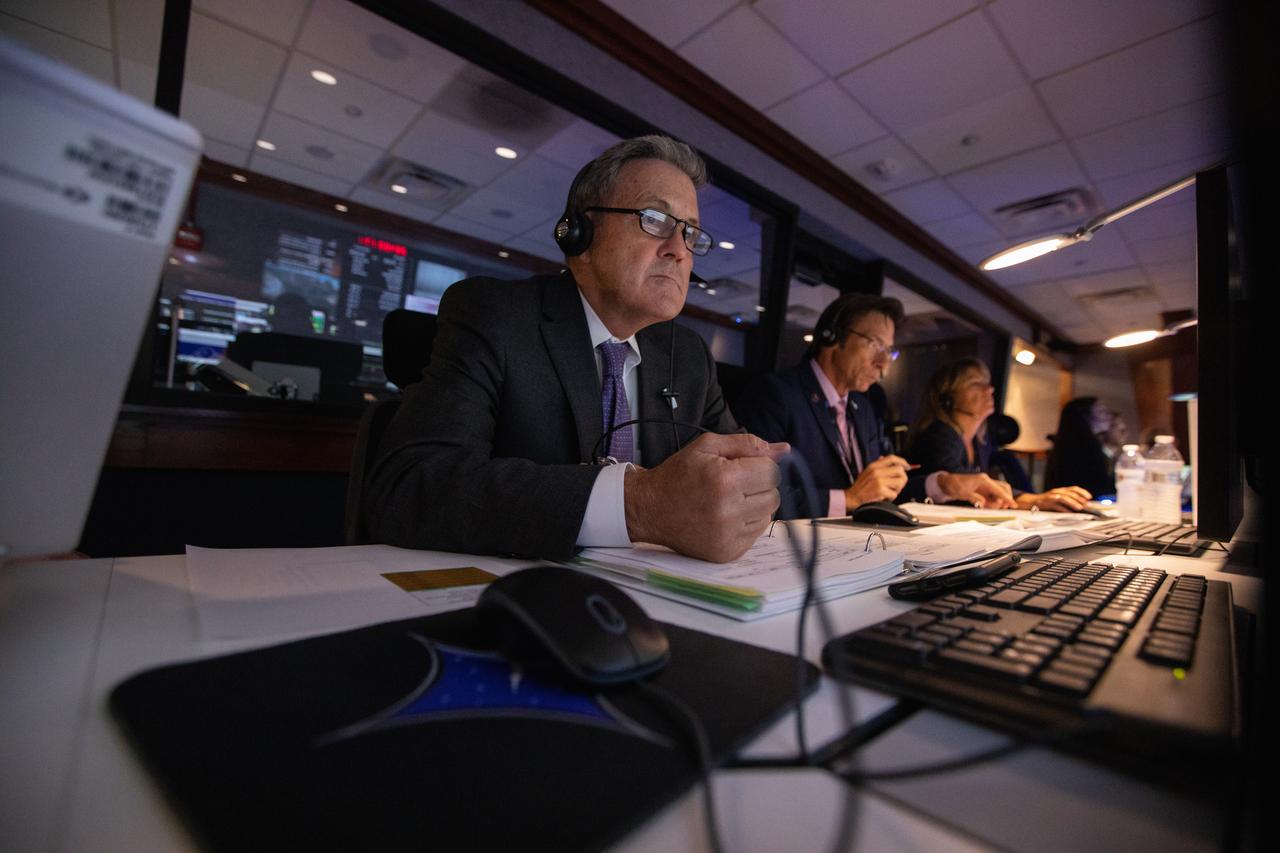

From left, Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Deputy Program Manager Chuck Dovale and LSP Program Manager Amanda Mitskevich monitor the launch of the agency’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The ICON launch was managed by LSP.
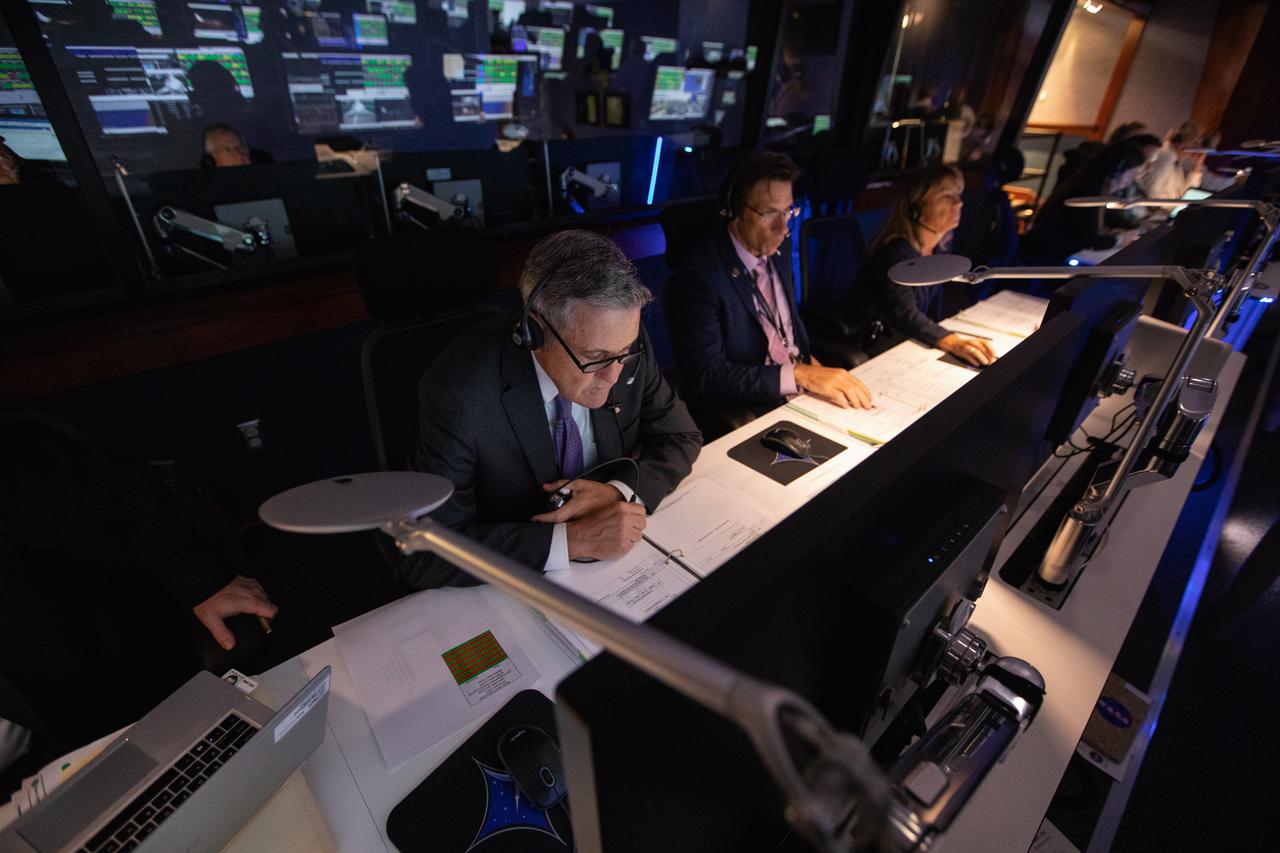

From left, Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Deputy Program Manager Chuck Dovale and LSP Program Manager Amanda Mitskevich monitor the launch of the agency’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The ICON launch was managed by LSP.
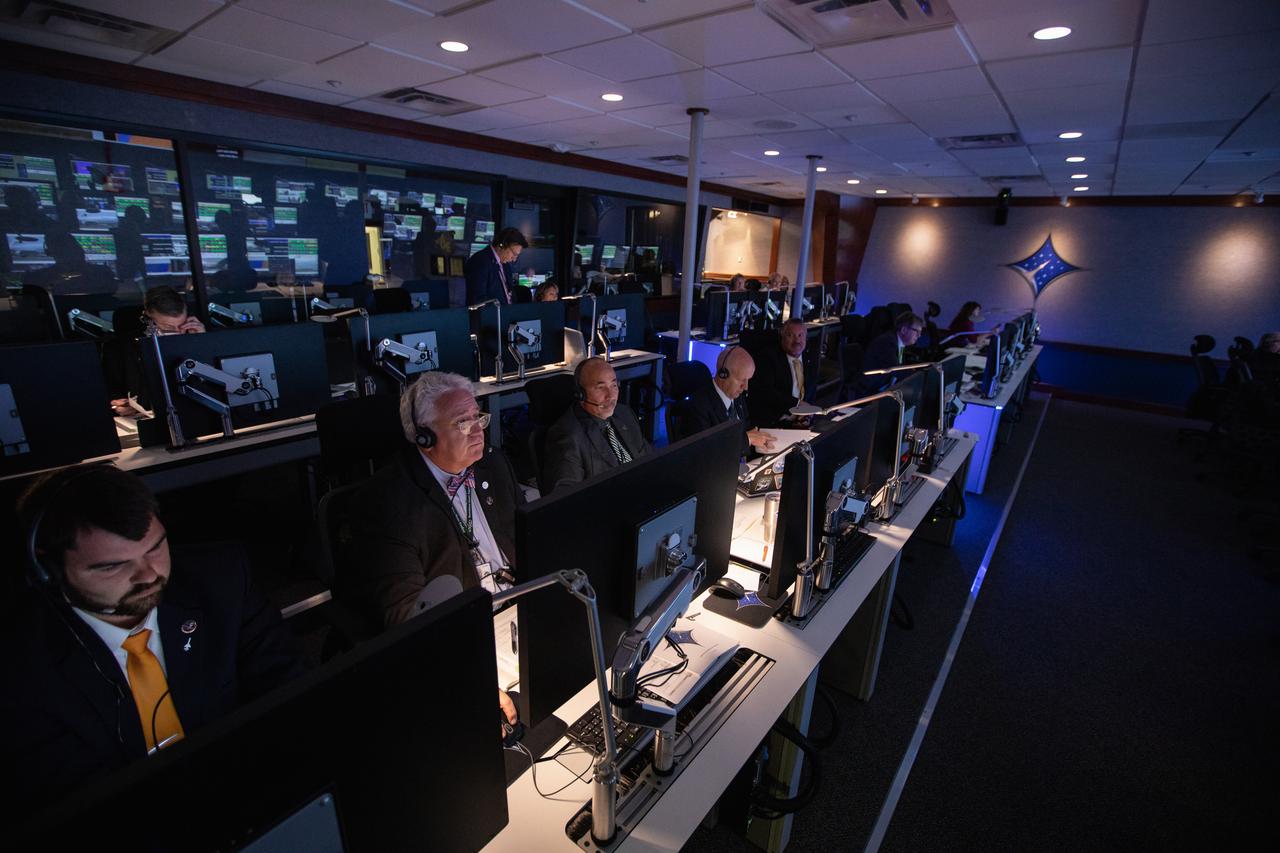

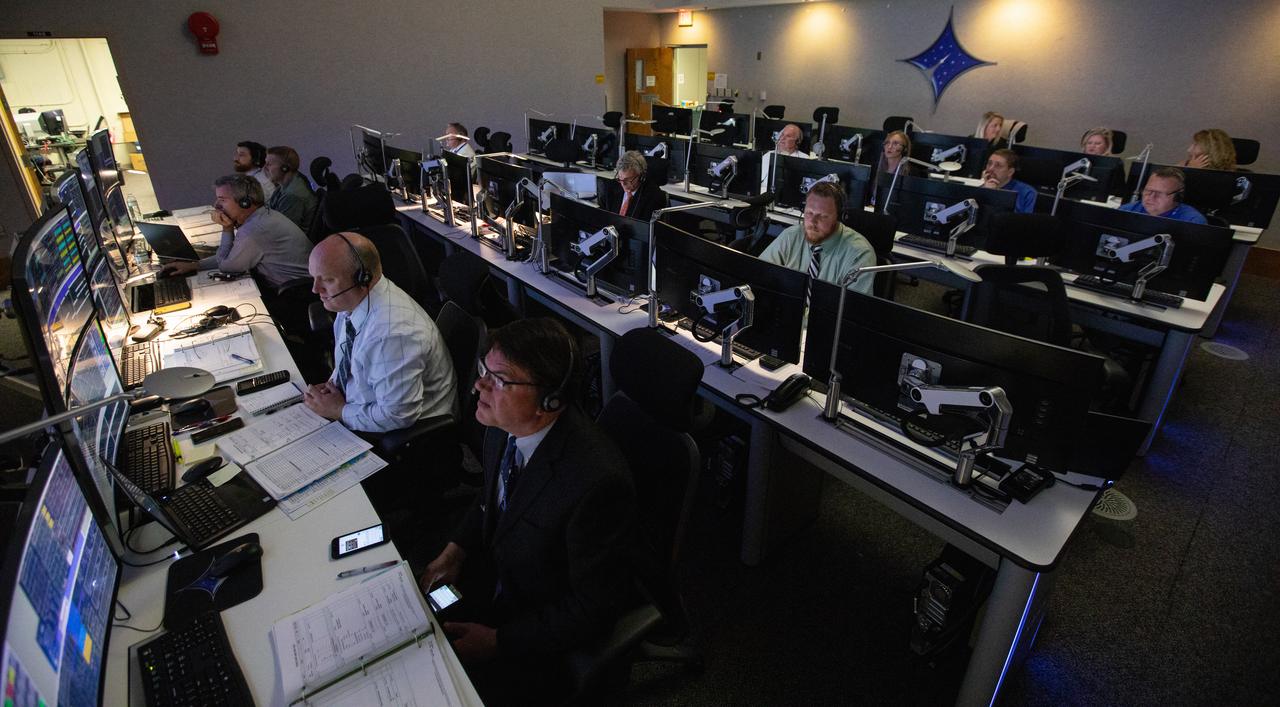
Inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), members of the launch team monitor the launch of NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.
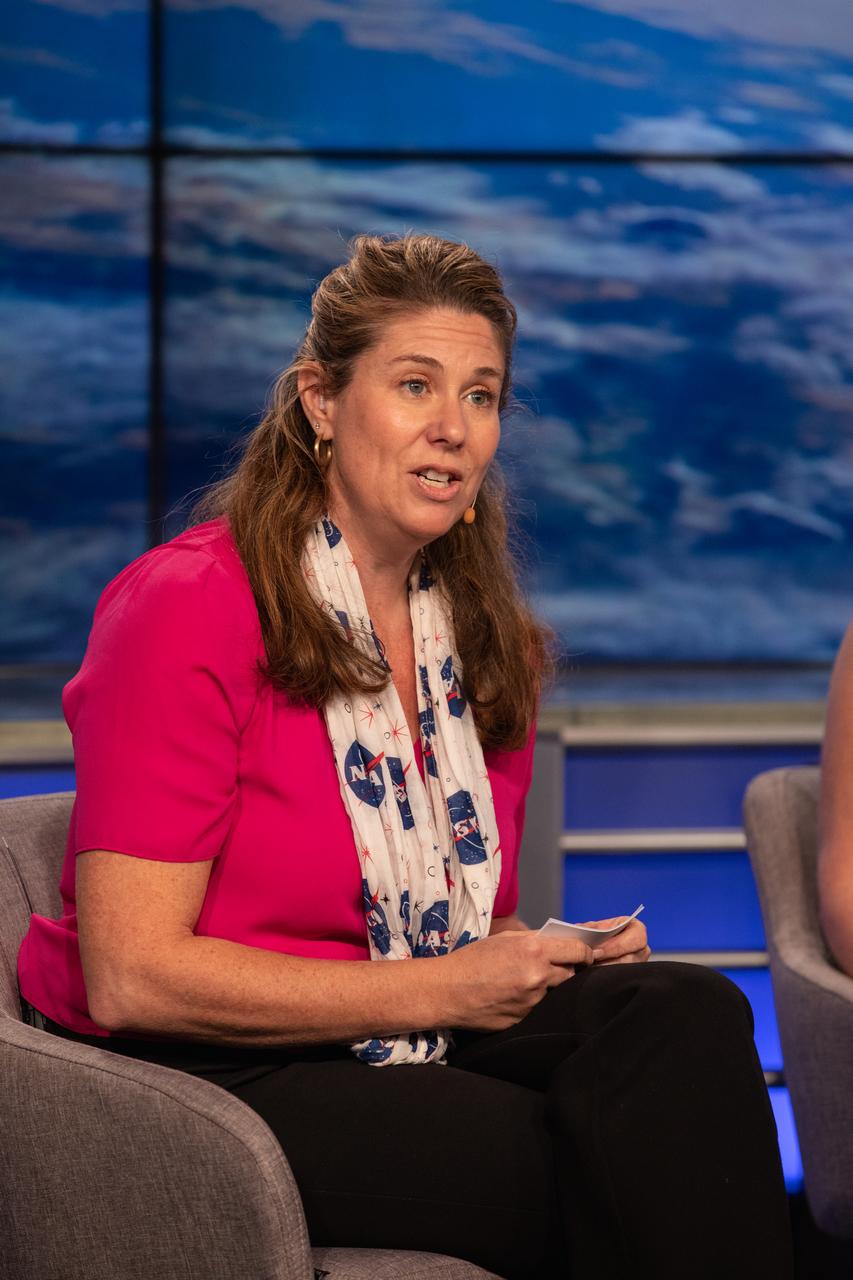

Karen Fox of NASA Communications moderates a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
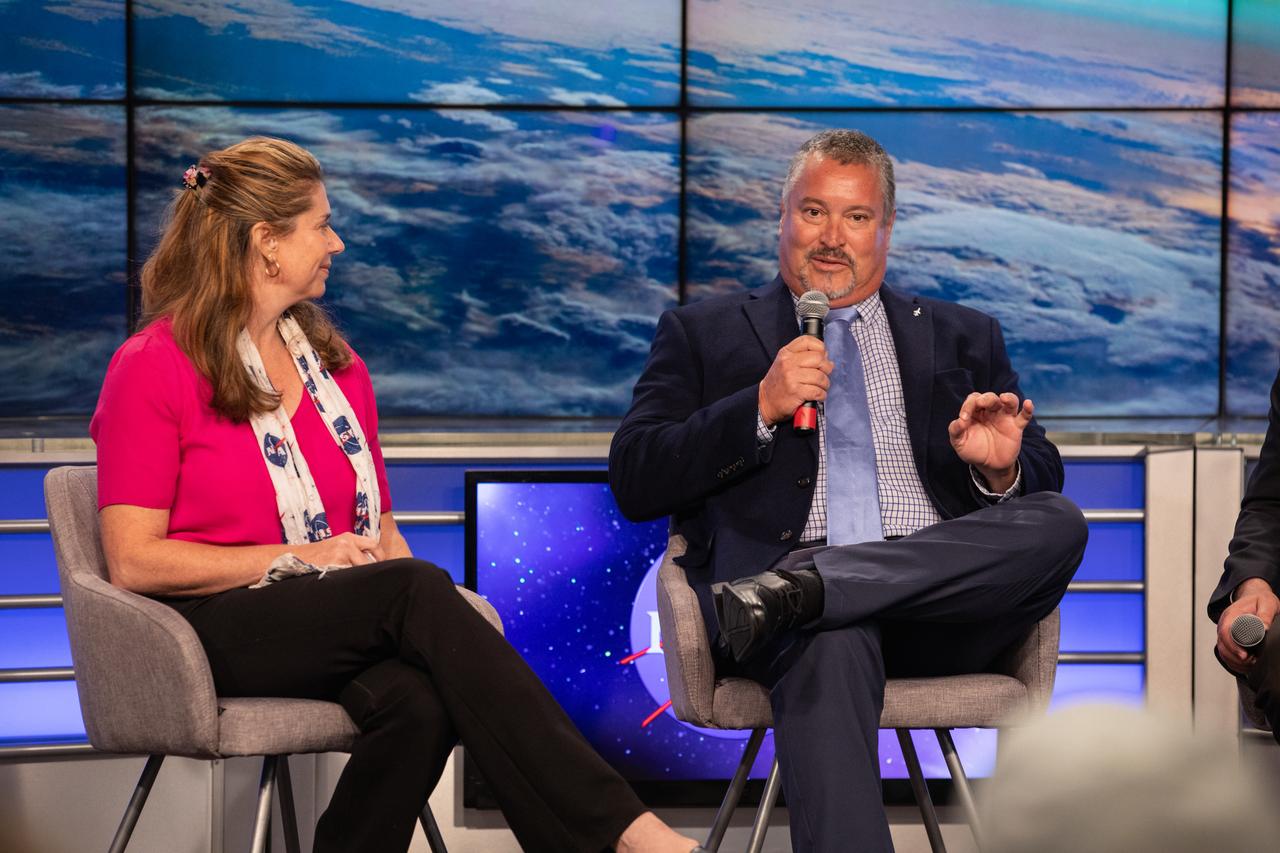

Omar Baez, launch director in NASA’s Launch Services Program, speaks to news media during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At left is Karen Fox of NASA Communications. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
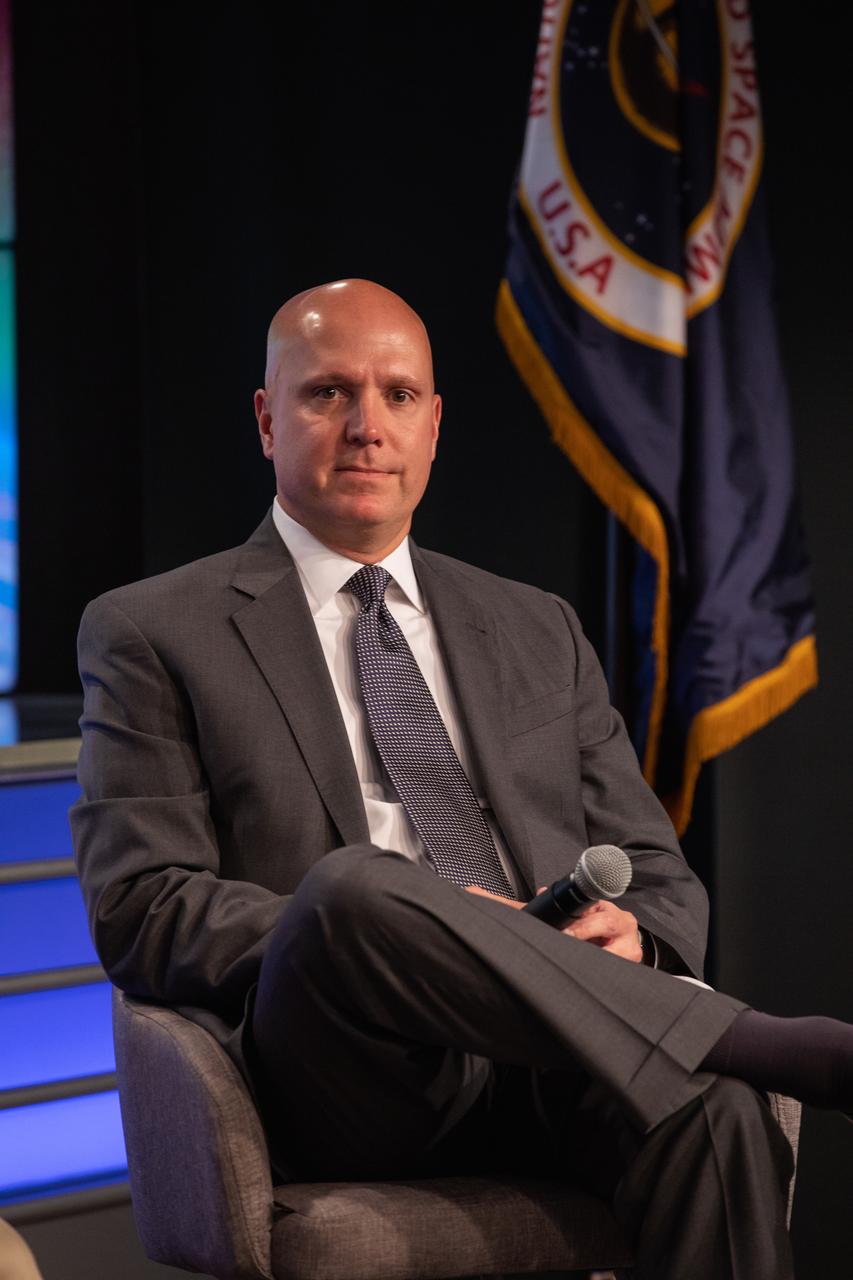

Steve Krein, vice president of civil and commercial space for Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems, speaks to news media during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
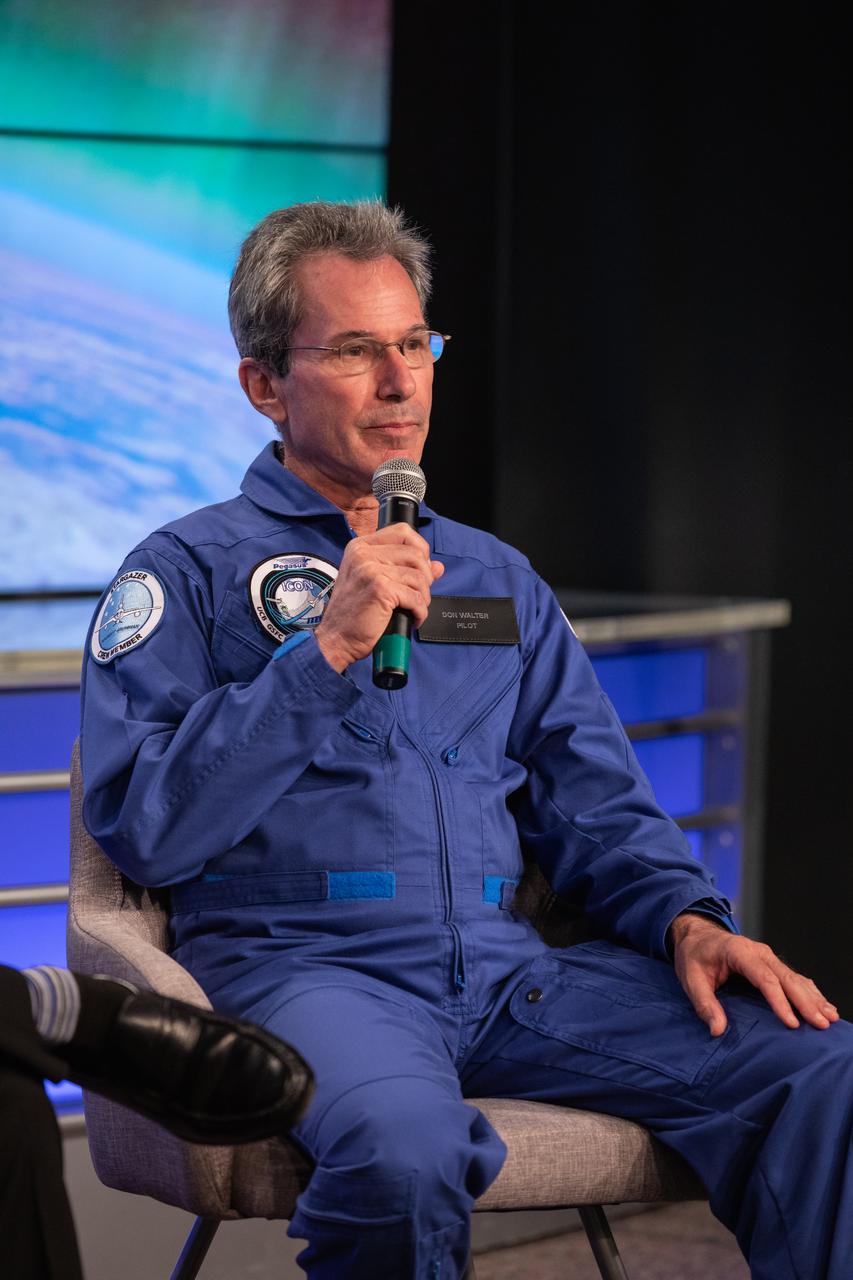

Don Walters, chief pilot of the L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems, speaks to news media during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
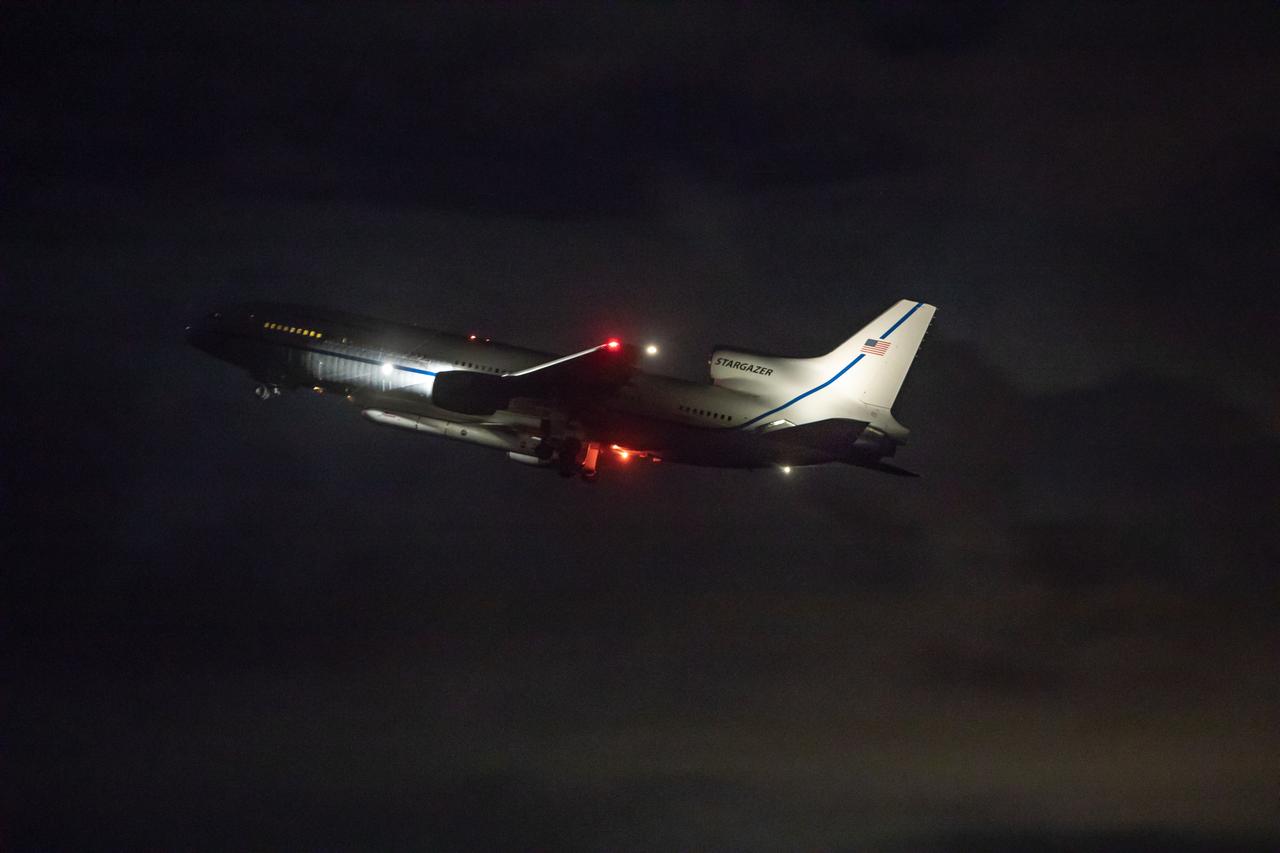

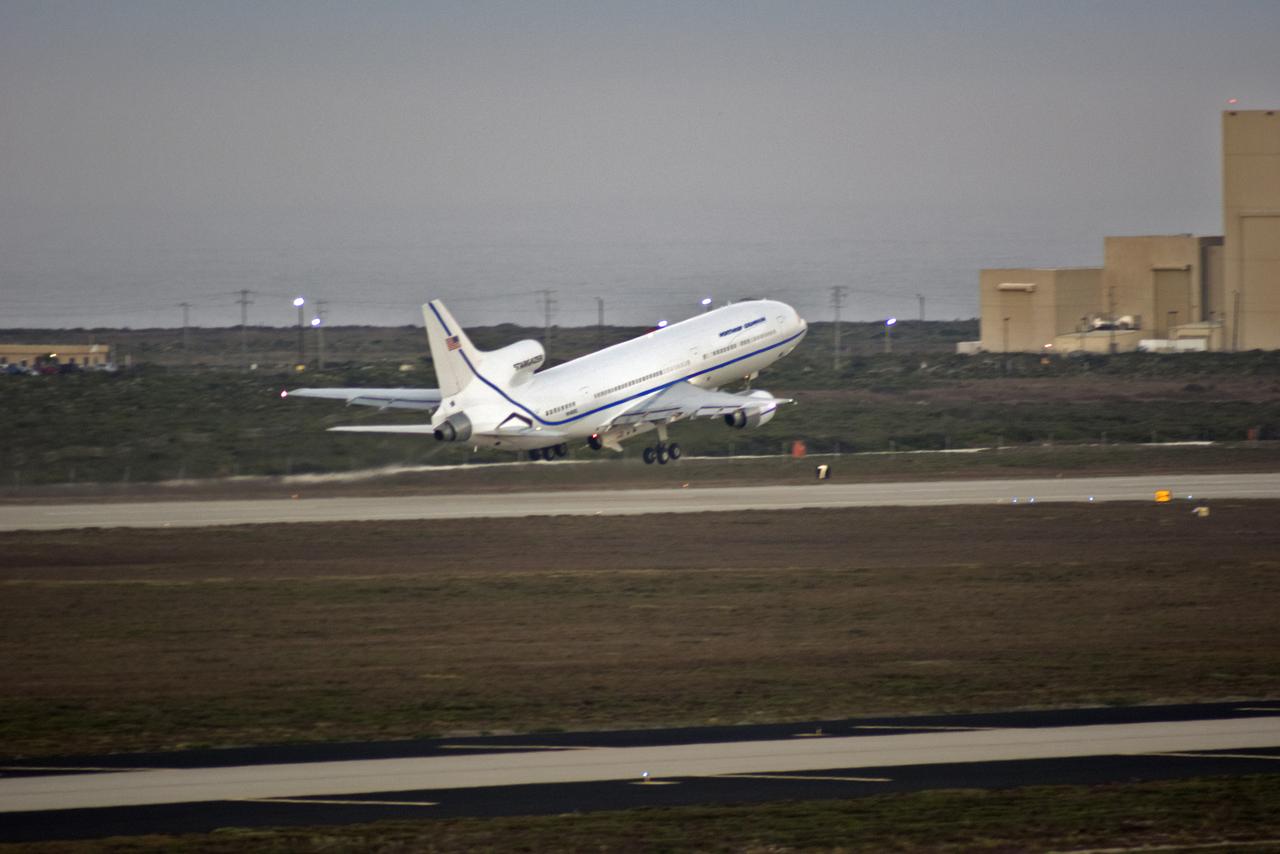
Northrop Grumman’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, with the company’s Pegasus XL rocket attached beneath, takes off from the Skid Strip runway at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 10, 2019. NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is secured inside the rocket's payload fairing. The air-launched Pegasus XL was released from the aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT to start ICON’s journey to space. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
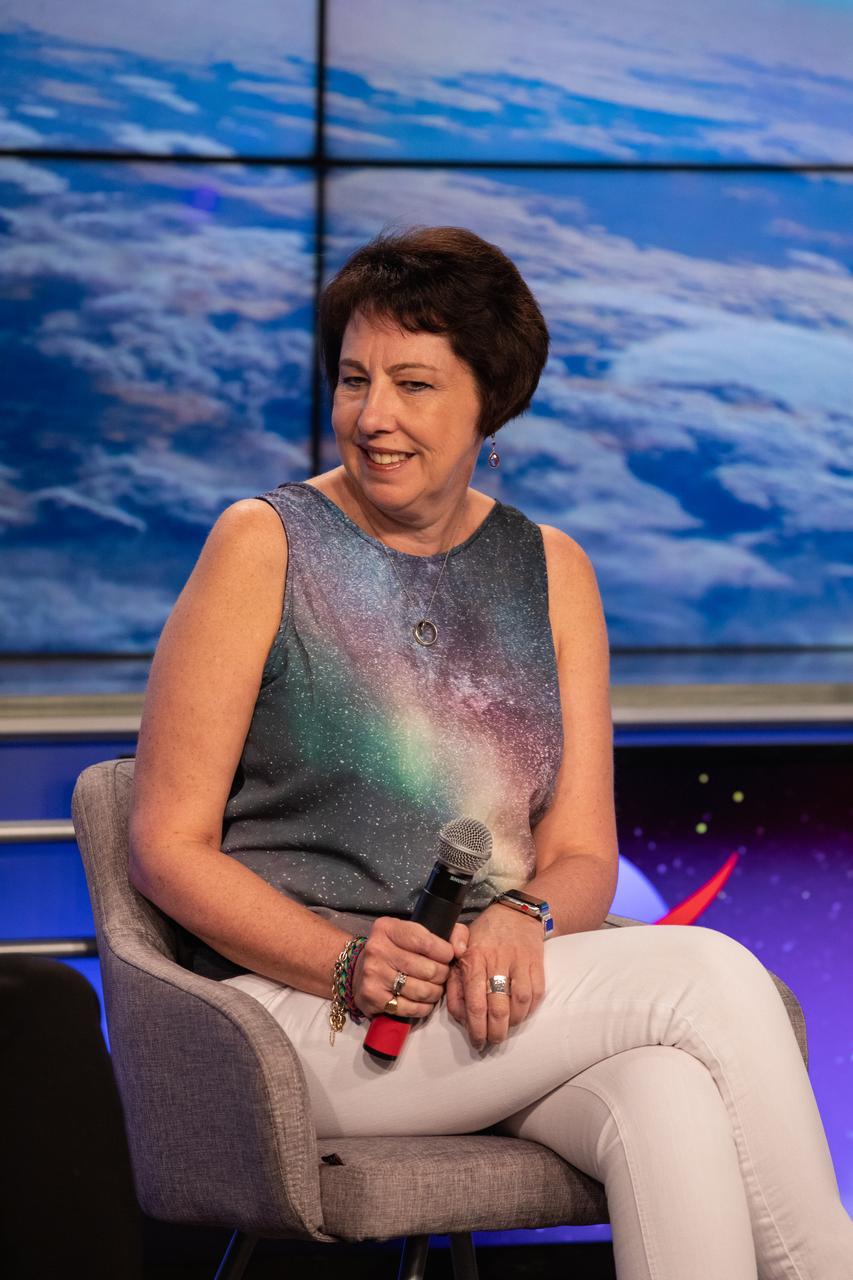

Nicola Fox, Heliophysics division director in NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, speaks to news media during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
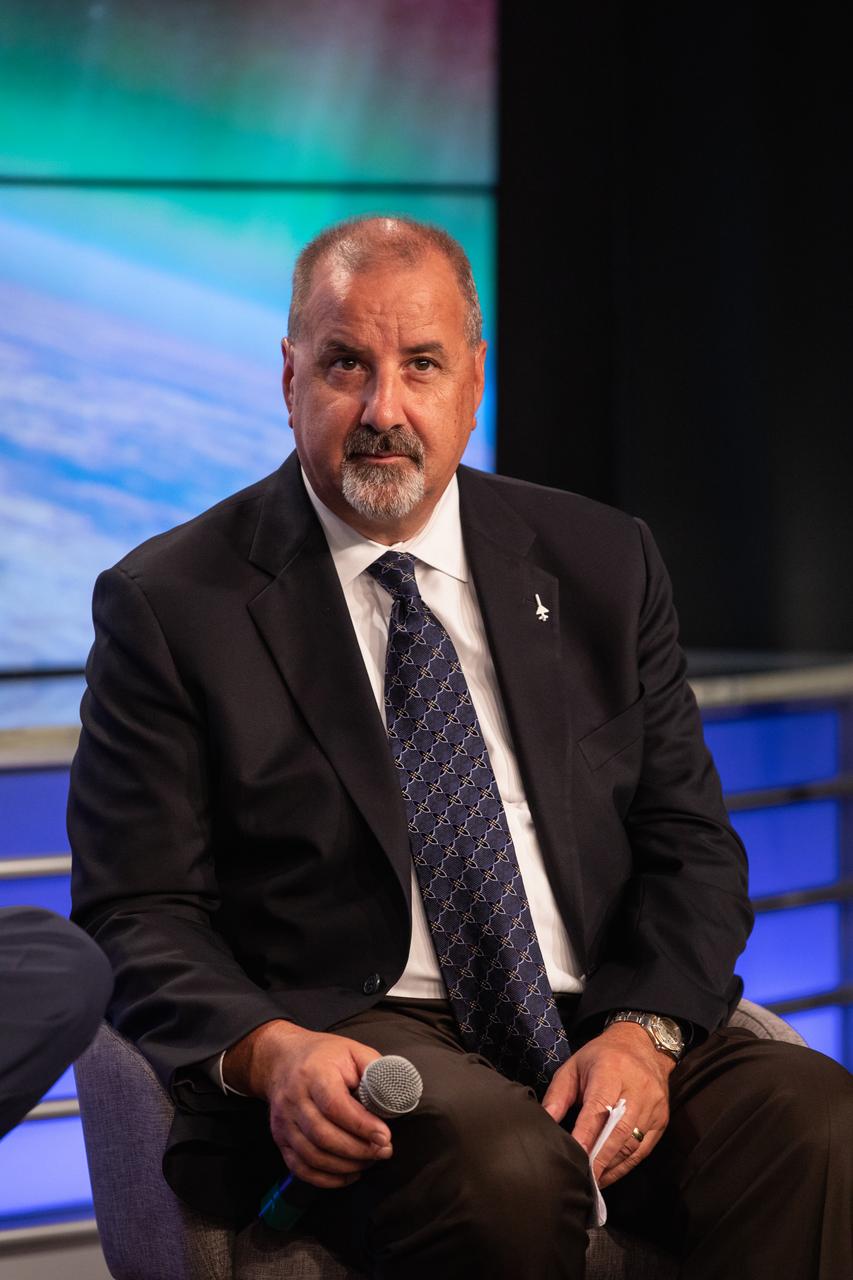

Phil Joyce, vice president of space launch programs for Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems, speaks to news media during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
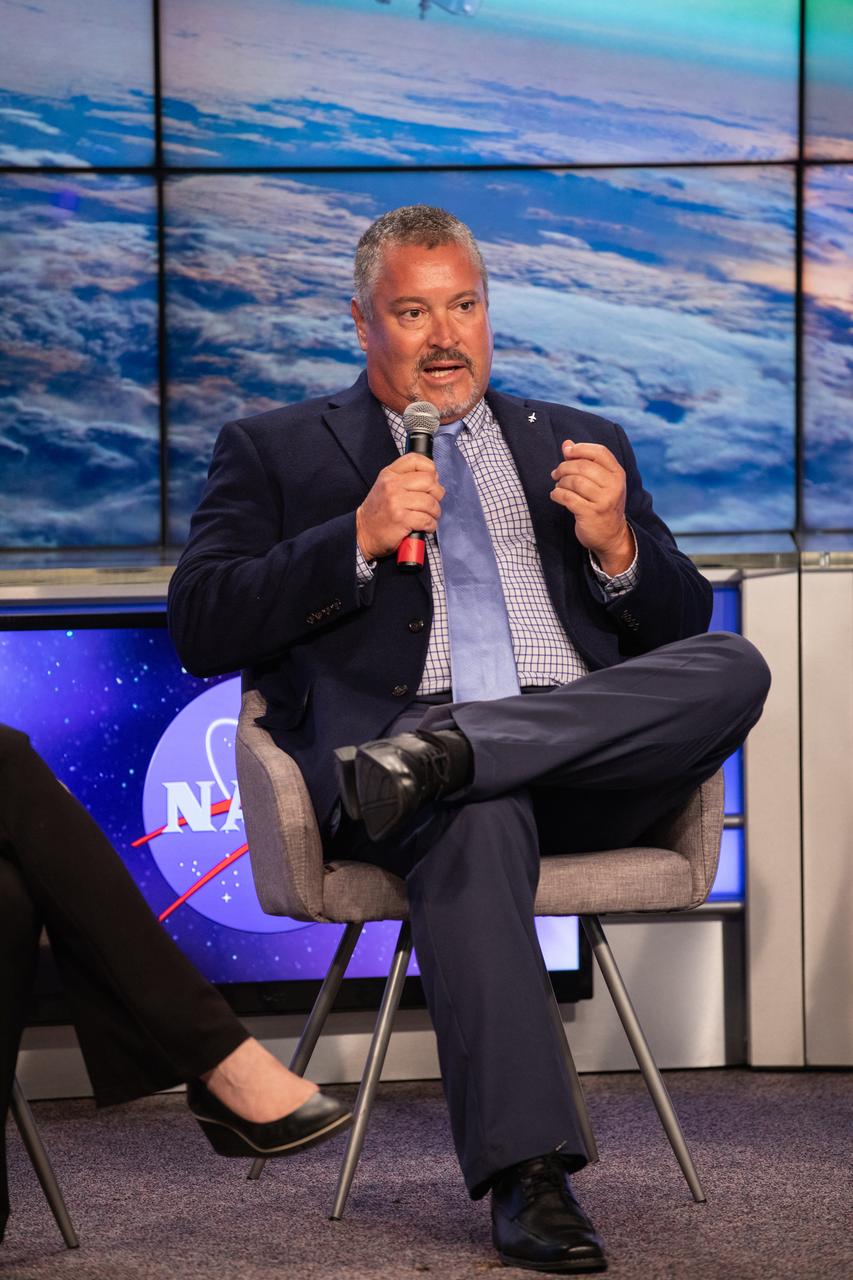

Omar Baez, launch director in NASA’s Launch Services Program, speaks to news media during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
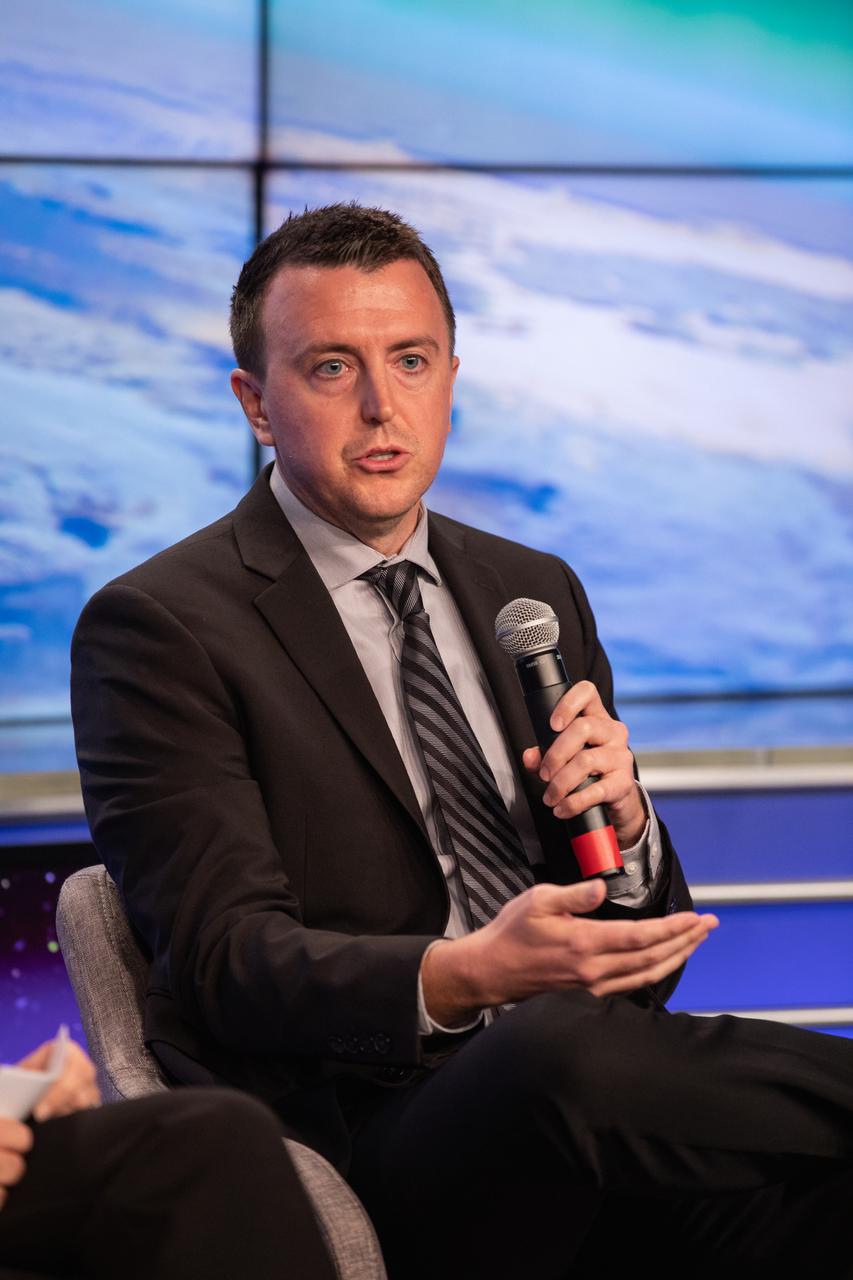

Will Ulrich, launch weather officer with the U.S. Air Force 45th Space Wing, speaks to news media during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
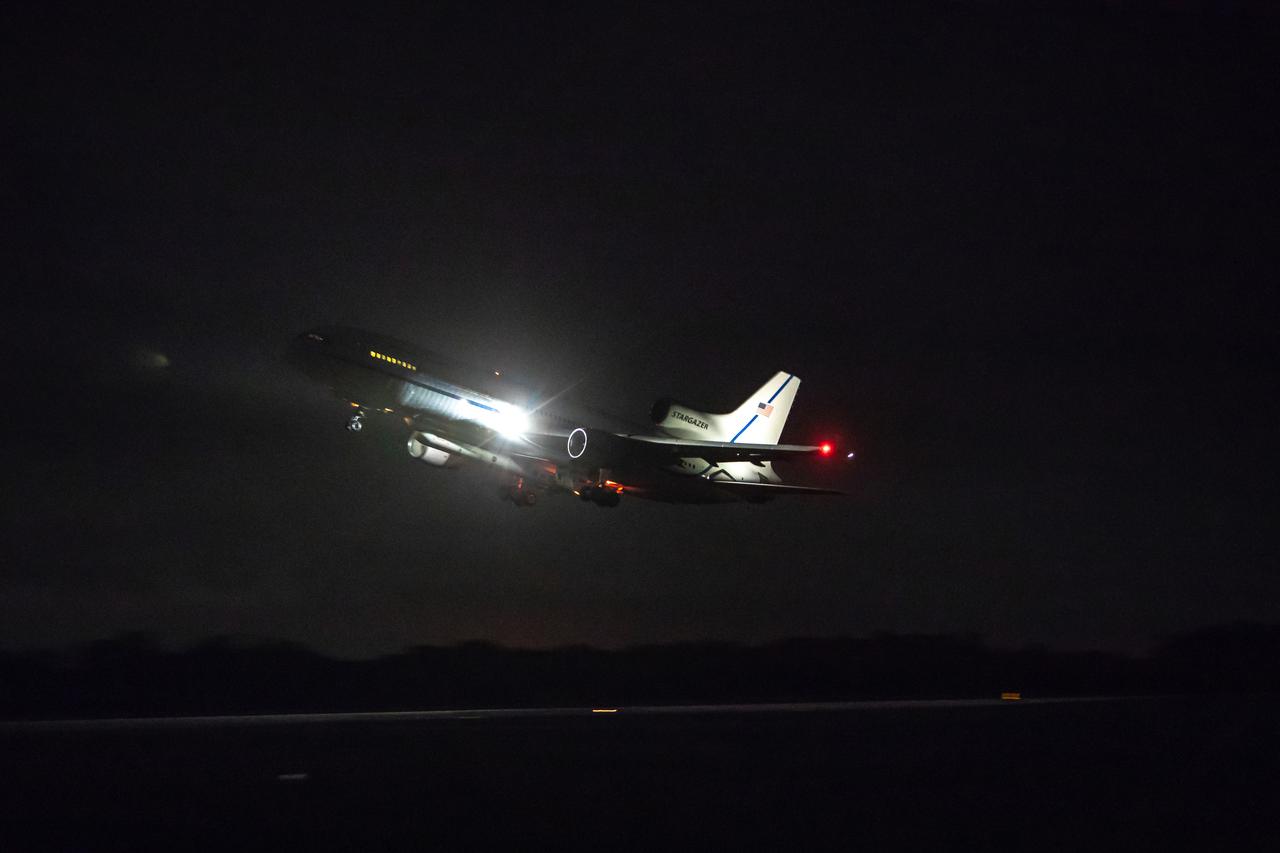

Northrop Grumman’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, with the company’s Pegasus XL rocket attached beneath, takes off from the Skid Strip runway at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 10, 2019. NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is secured inside the rocket's payload fairing. The air-launched Pegasus XL was released from the aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT to start ICON’s journey to space. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
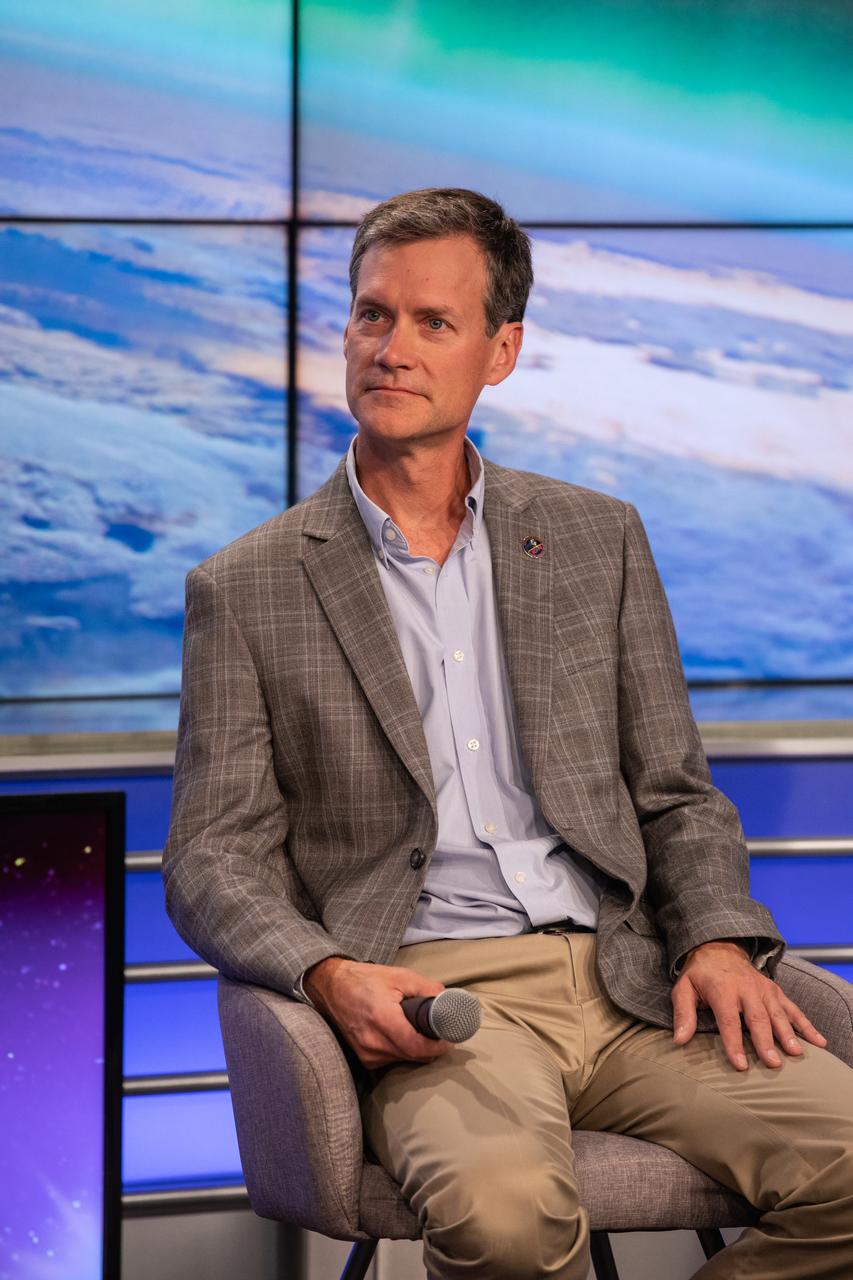

Thomas Immel of the Space Sciences Laboratory at the University of California Berkeley speaks to news media during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Immel is ICON’s principal investigator. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
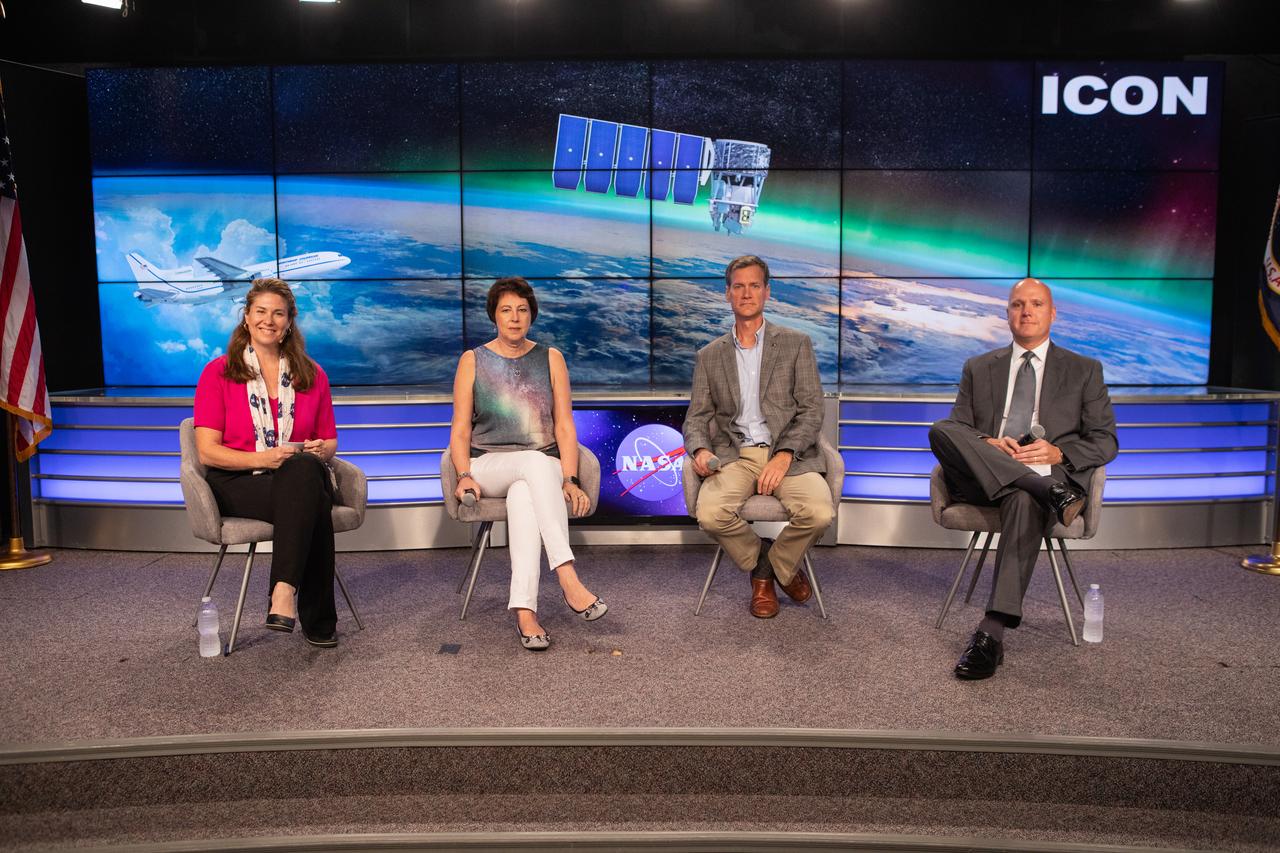

Launch and mission managers for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left to right are Karen Fox, NASA Communications; Nicola Fox, Heliophysics division director in NASA’s Science Mission Directorate; Thomas Immel, ICON principal investigator at the Space Sciences Laboratory at the University of California Berkeley; and Steve Krein, vice president of civil and commercial space for Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
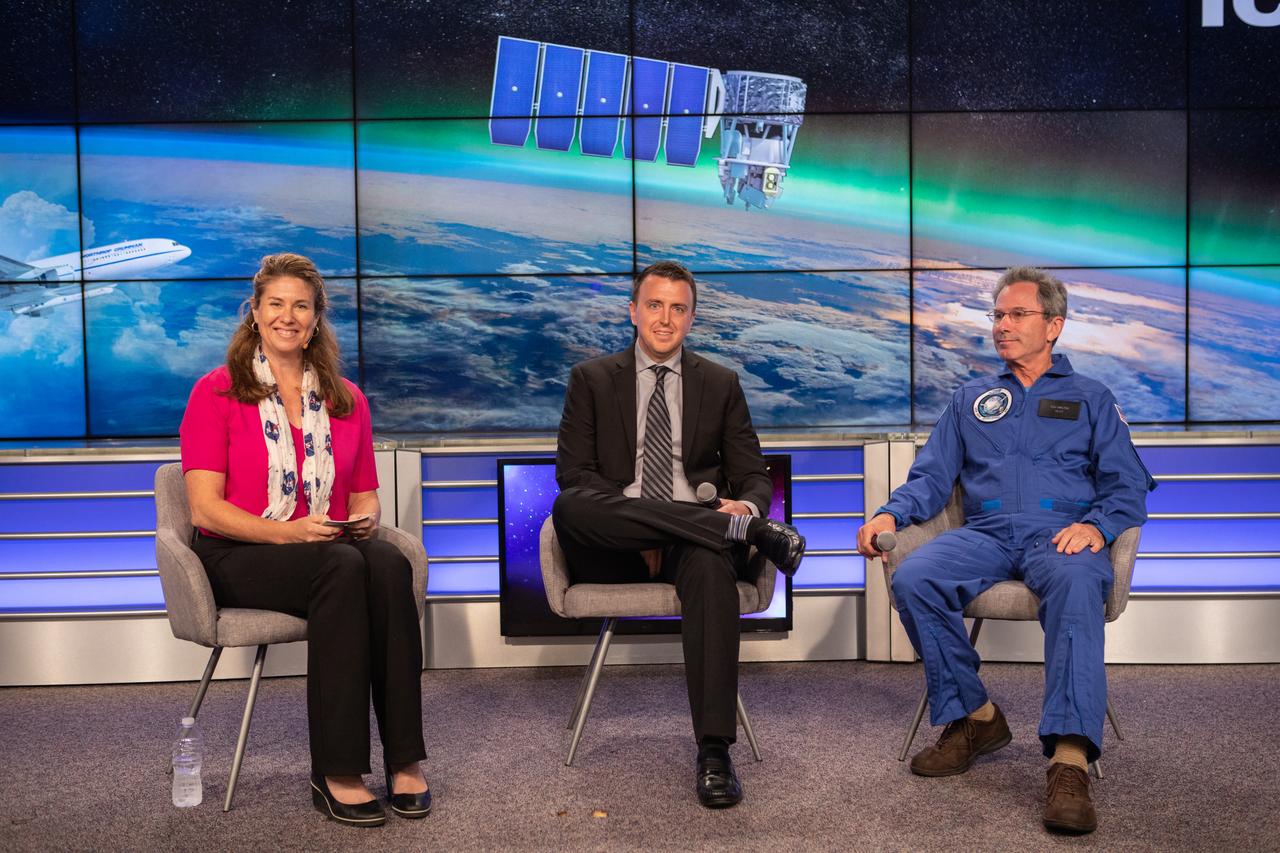

Launch and mission managers for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left to right are Karen Fox, NASA Communications; Will Ulrich, launch weather officer with the U.S. Air Force 45th Space Wing; and Don Walters, chief pilot of the L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
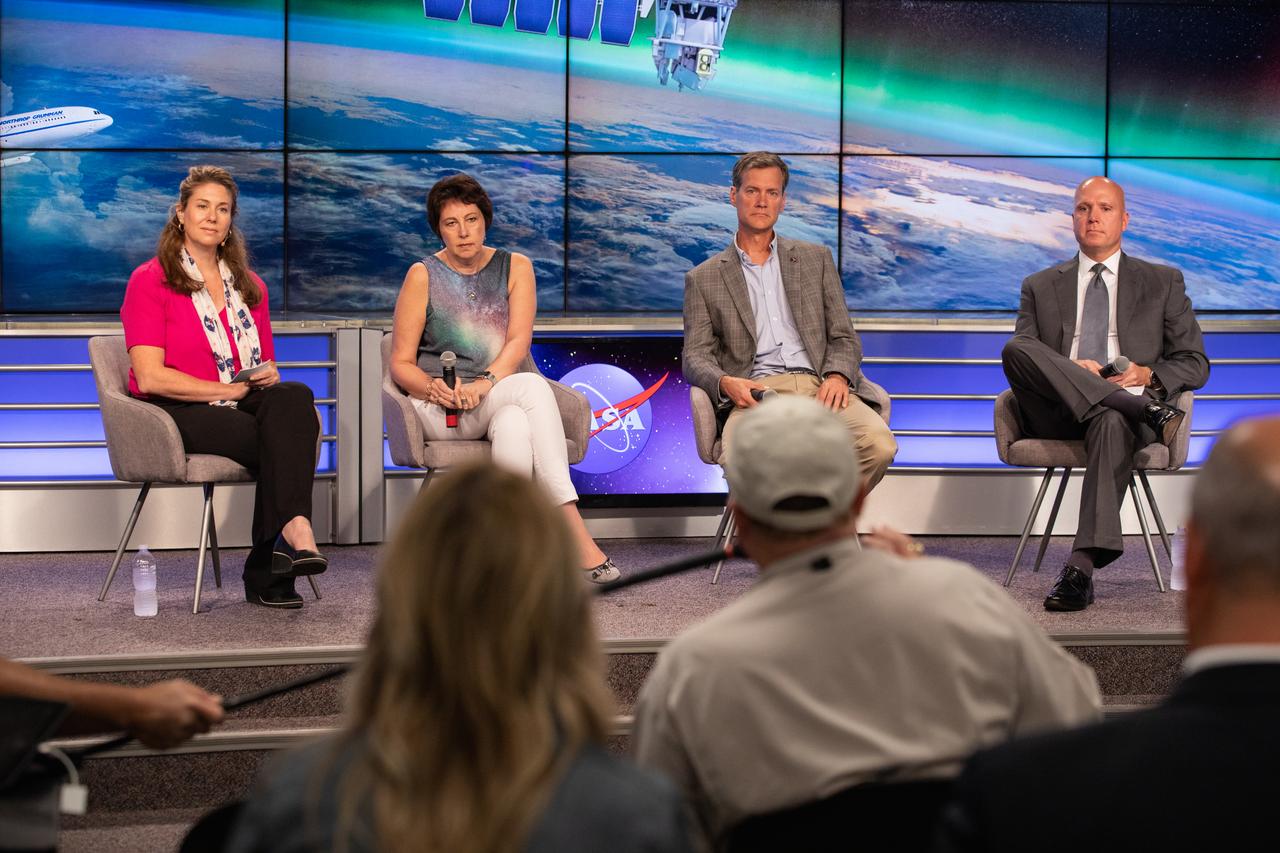

Launch and mission managers for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left to right are Karen Fox, NASA Communications; Nicola Fox, Heliophysics division director in NASA’s Science Mission Directorate; Thomas Immel, ICON principal investigator at the Space Sciences Laboratory at the University of California Berkeley; and Steve Krein, vice president of civil and commercial space for Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
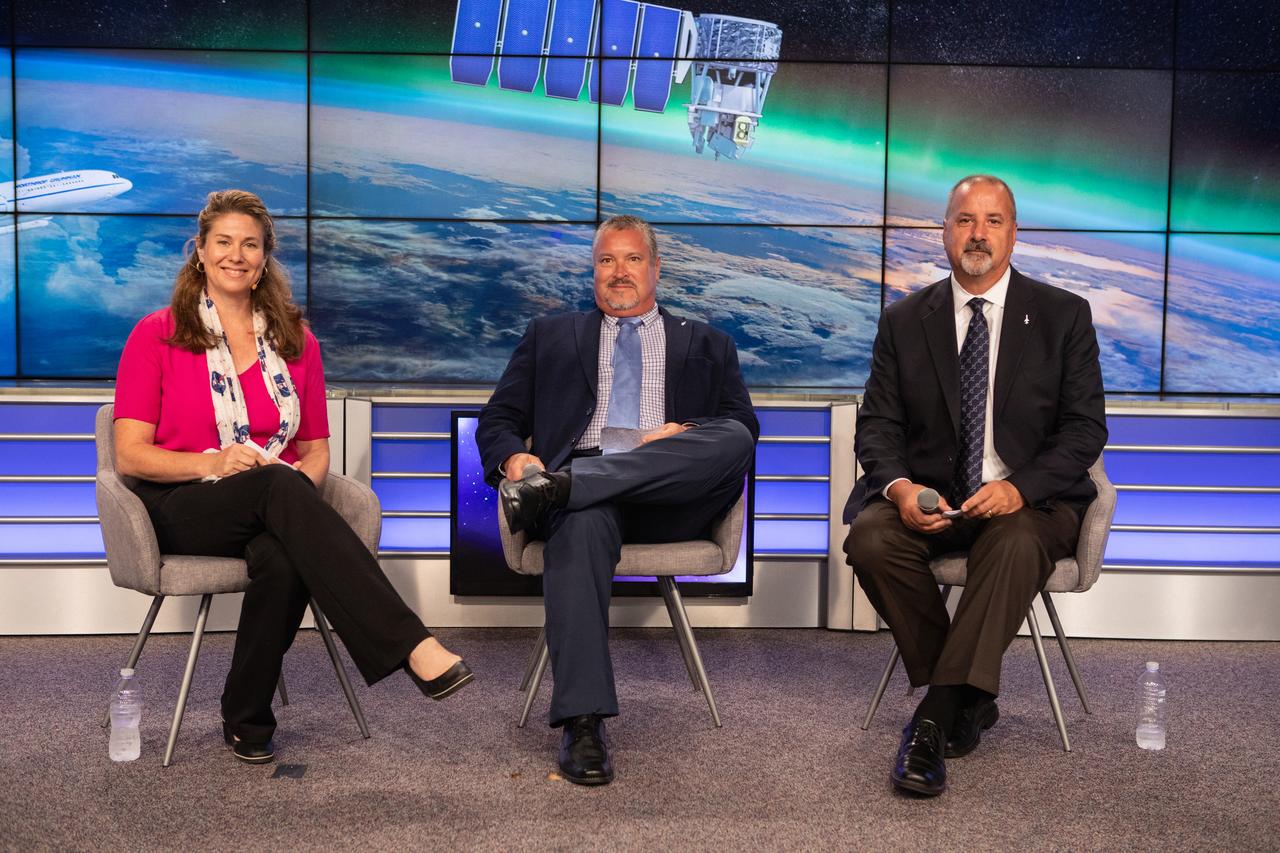

Launch and mission managers for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left to right are Karen Fox, NASA Communications; Omar Baez, launch director in NASA’s Launch Services Program; and Phil Joyce, vice president of space launch programs for Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
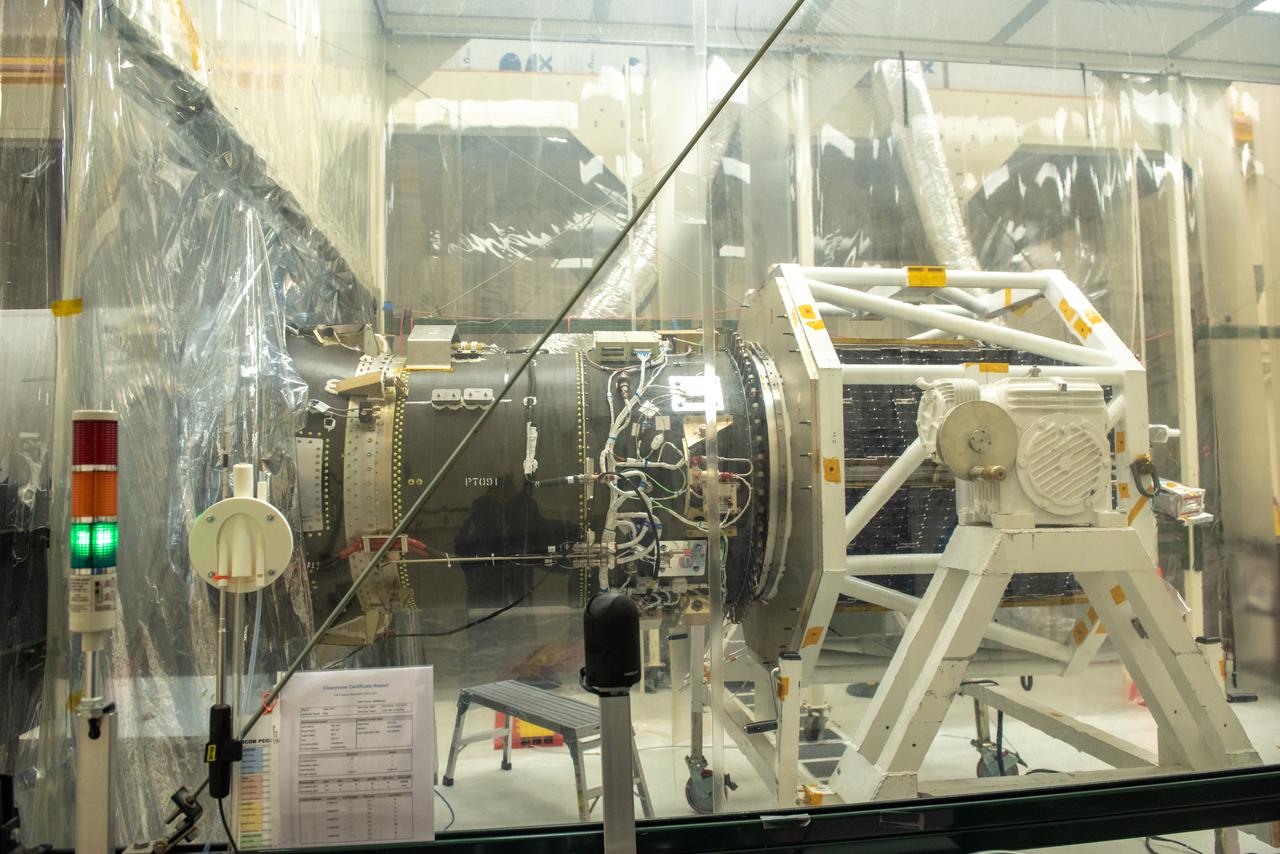
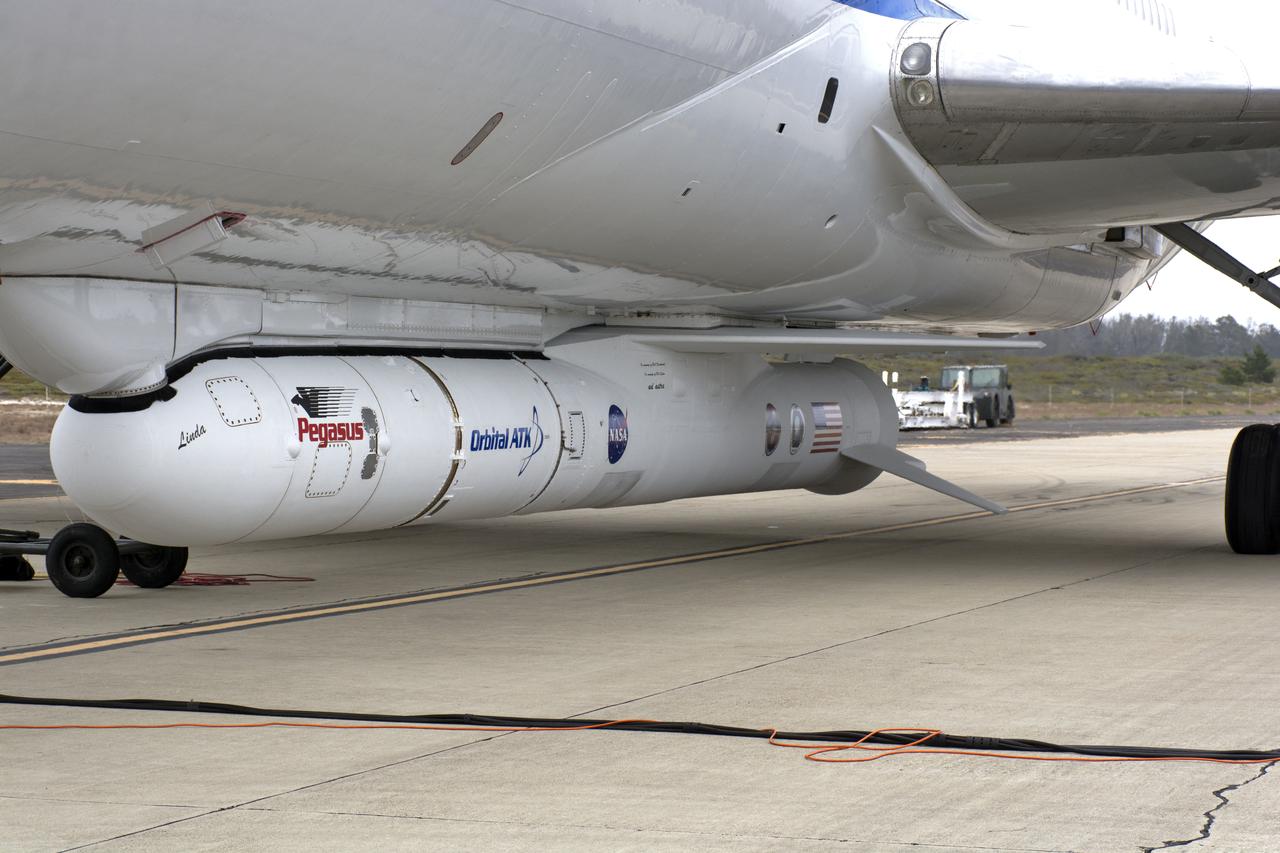
NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is attached to the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 10, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 9, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
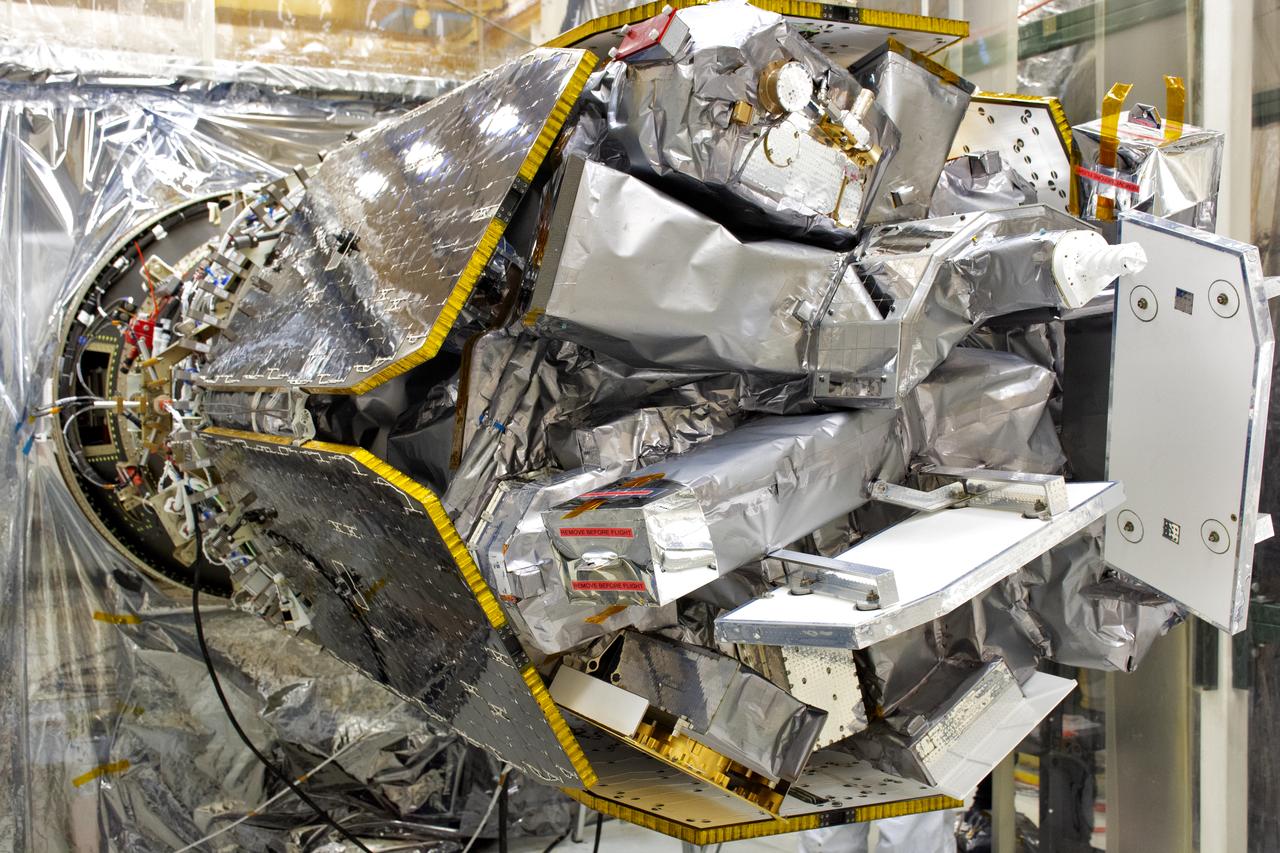

A stereographic view of NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) in a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Aug. 16, 2018. ICON will launch on a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL vehicle, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 26. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
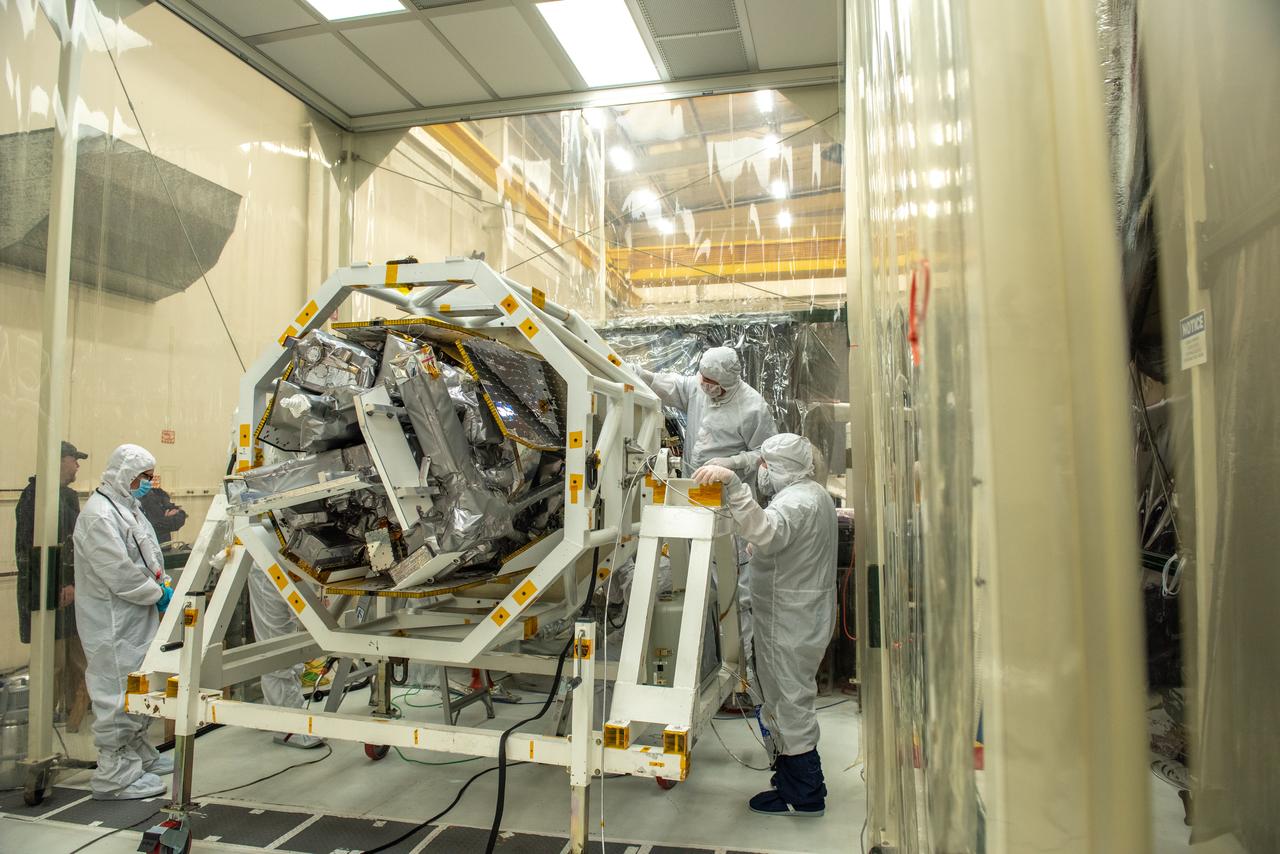

Technicians attach NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) to the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 10, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 9, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.

Technicians attach NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) to the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 10, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 9, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
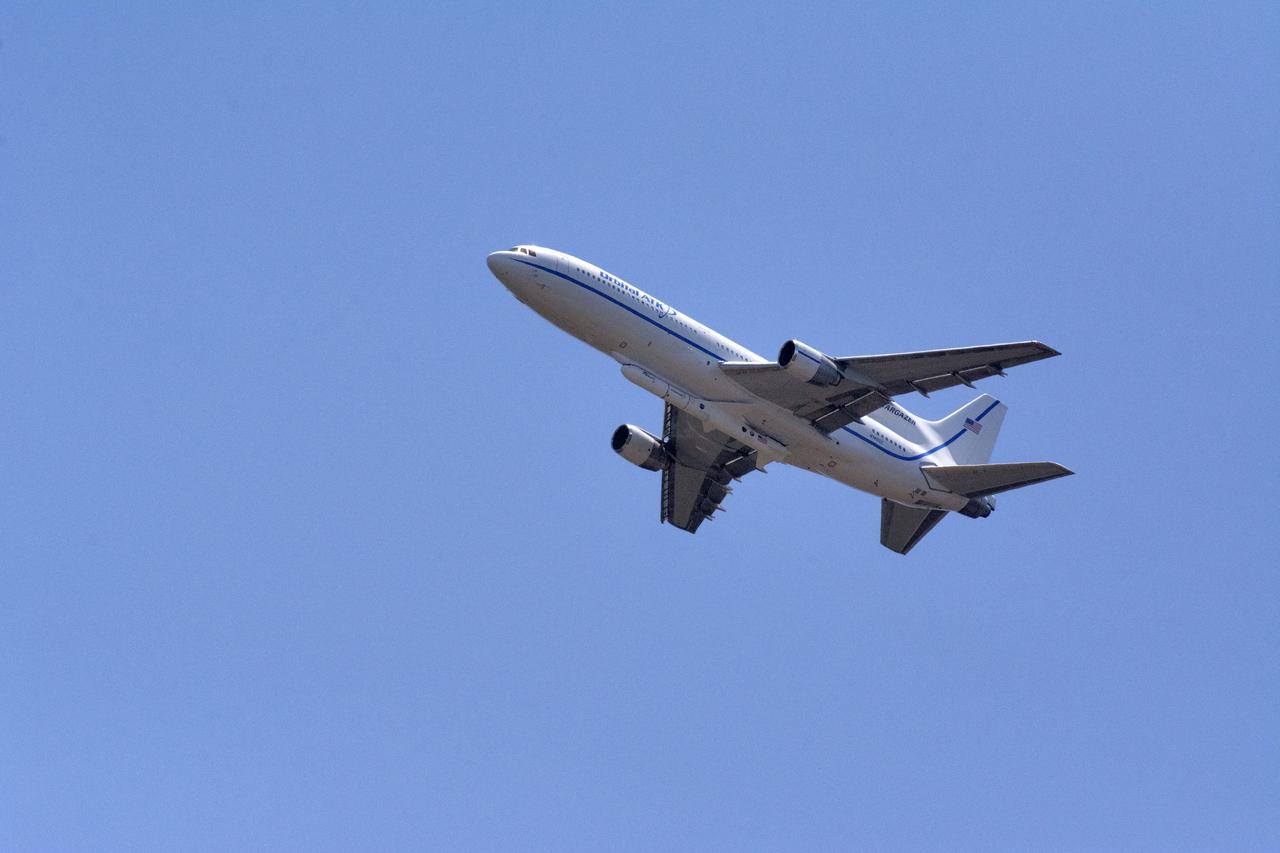

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer takes off from the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on June 6, 2018. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States). ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
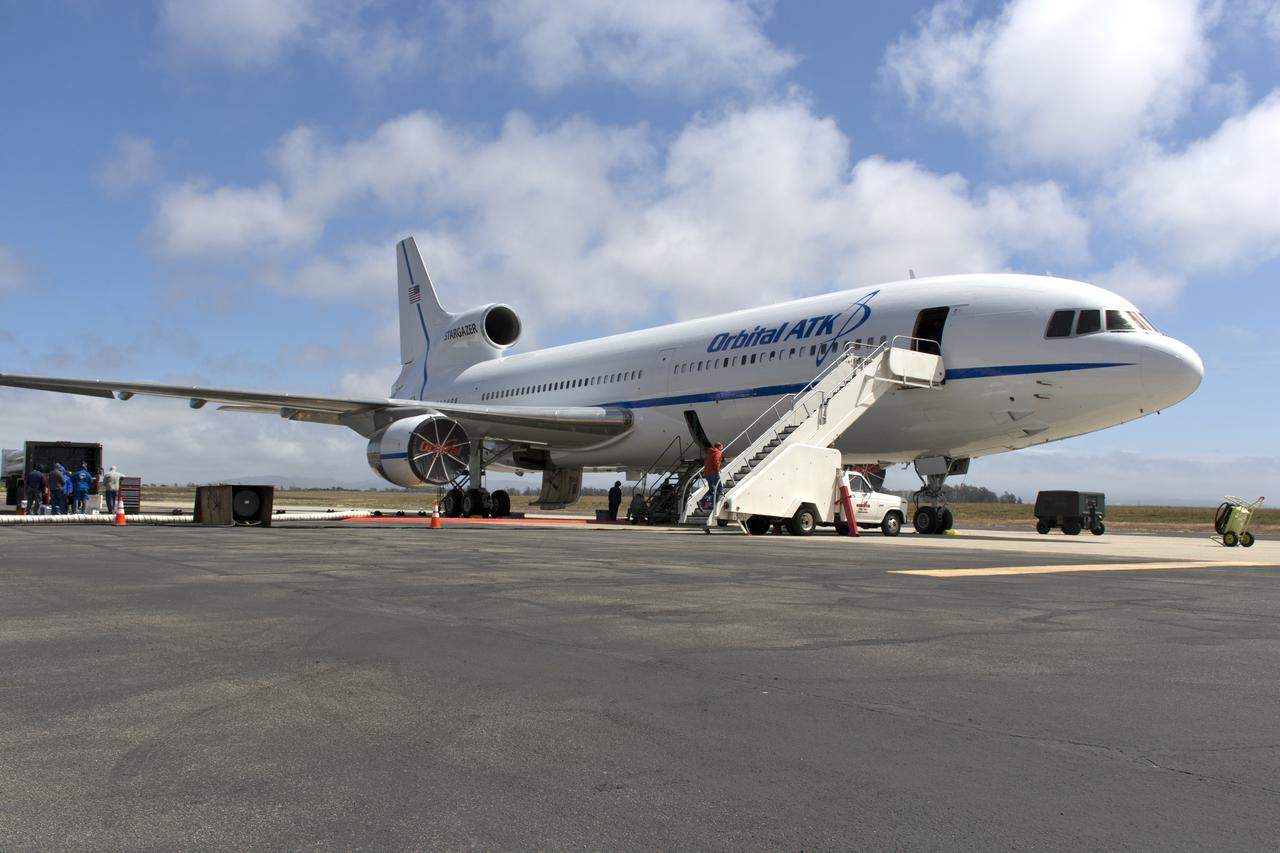

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft is at the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on May 26, 2018. Preparations are underway to attach the company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), beneath the aircraft. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States). ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
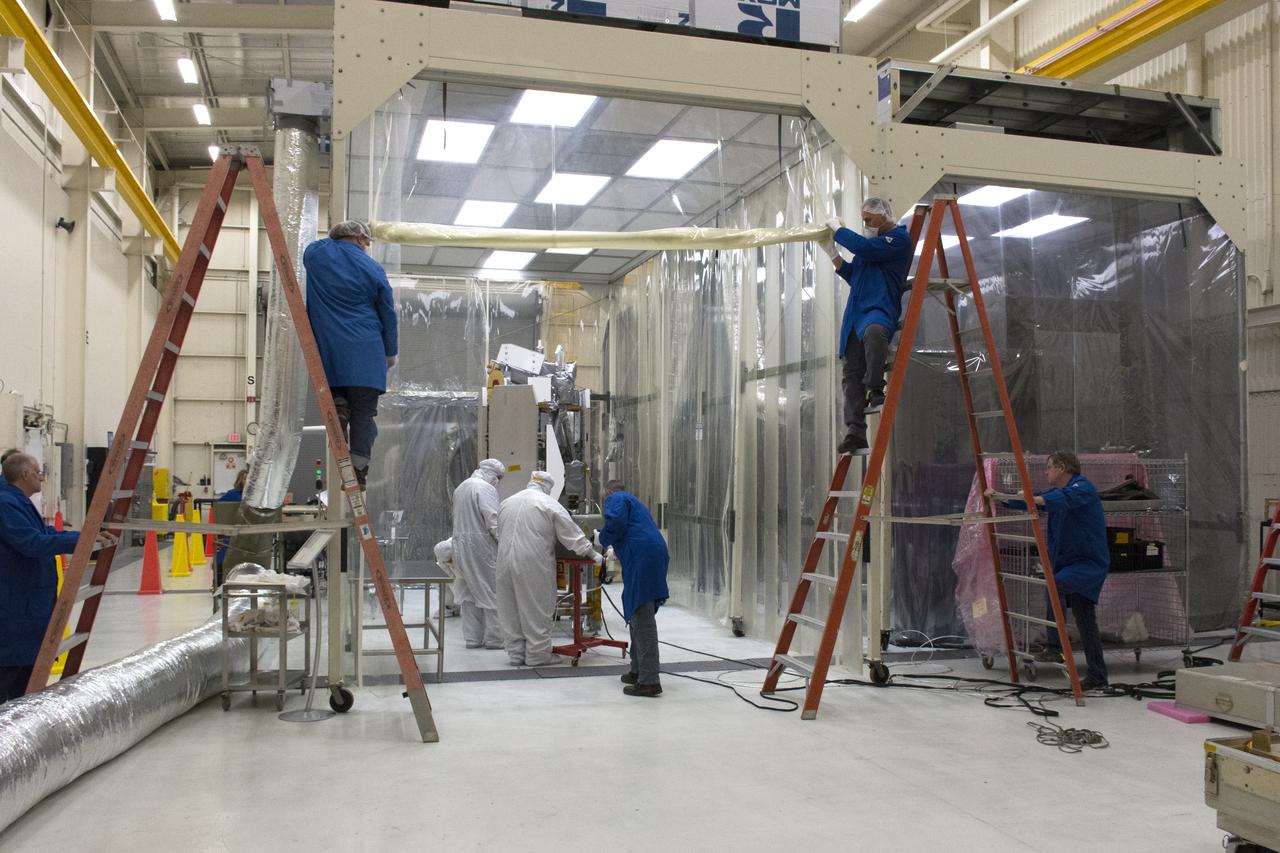

NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is moved to a clean room on May 4, 2018, inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on Orbital ATK's Pegasus XL rocket, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
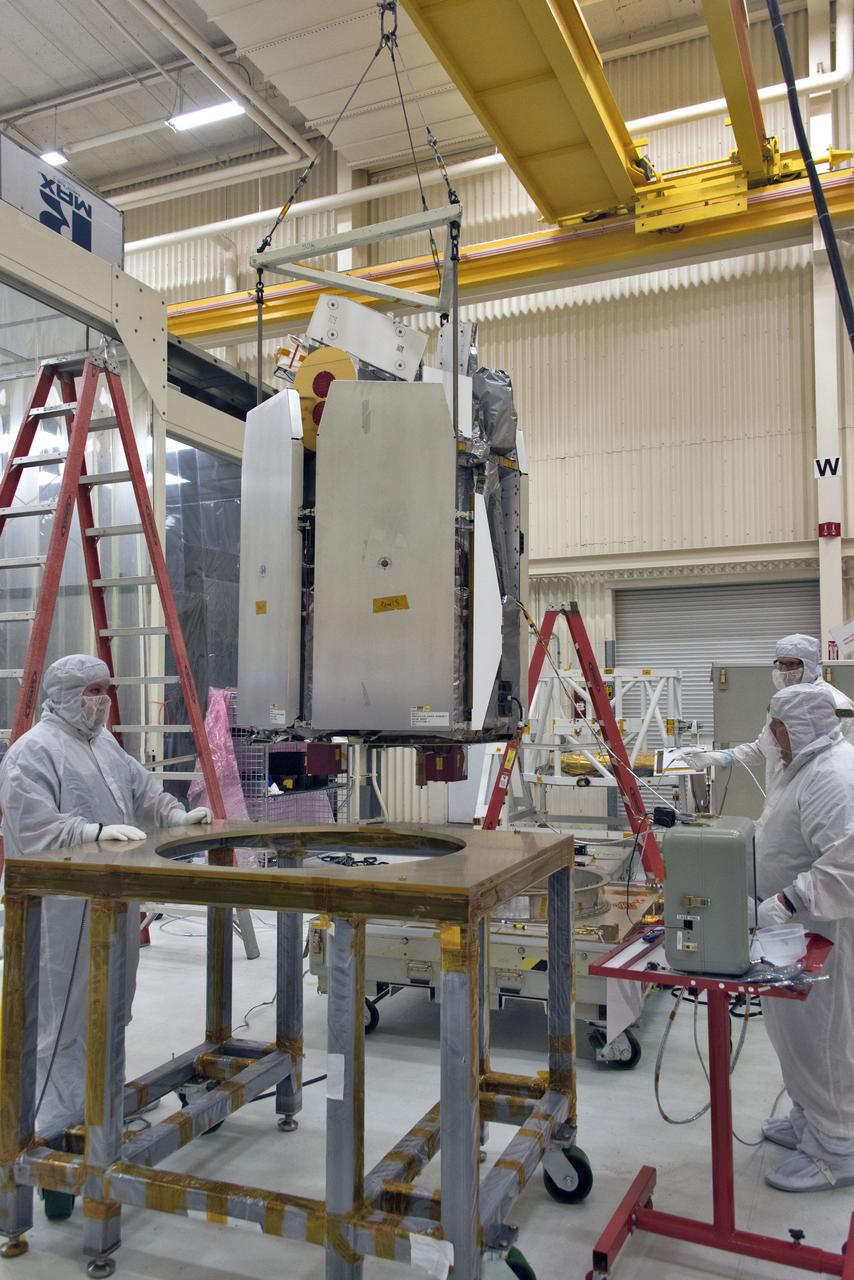

A crane lifts and moves NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) to a work stand on May 1, 2018, inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on Orbital ATK's Pegasus XL rocket, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
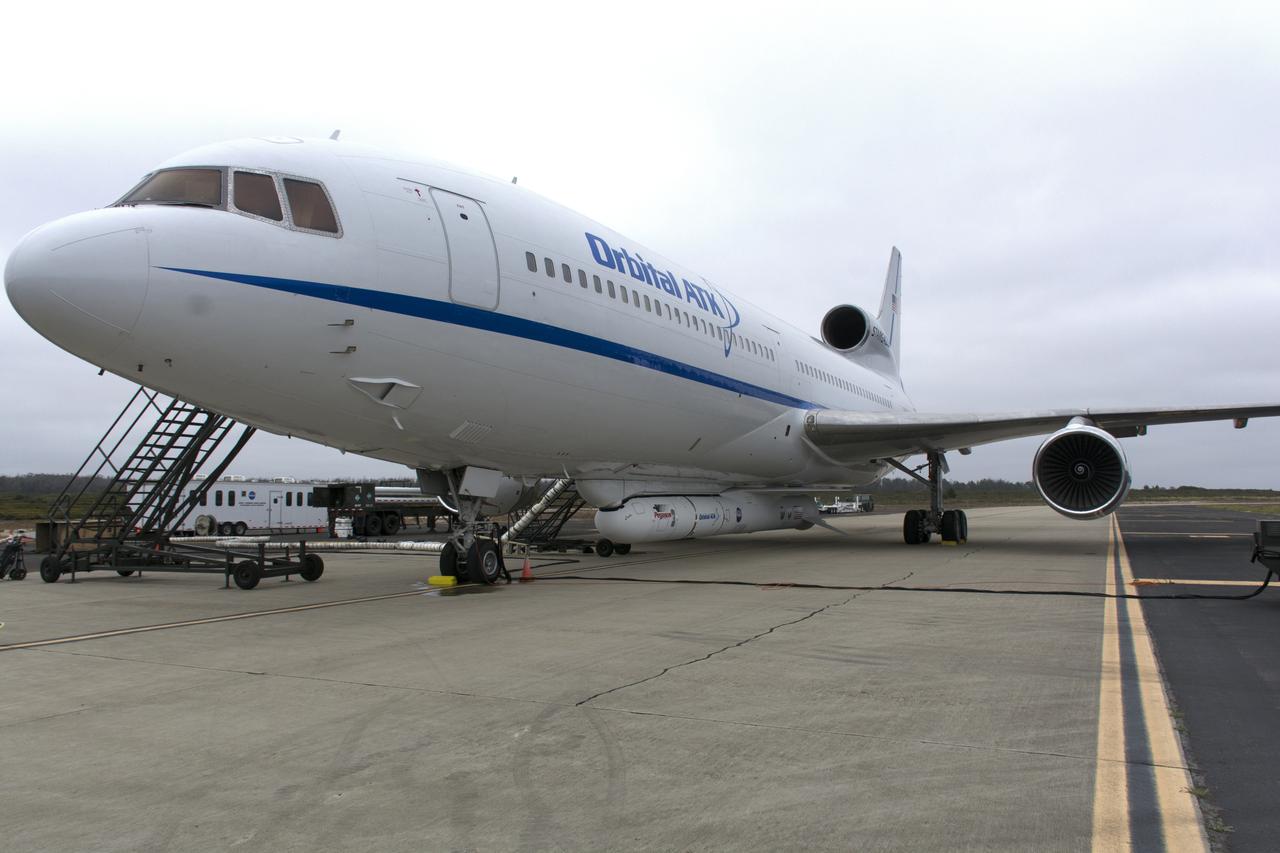

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer is being readied for takeoff June 6, 2018, from the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States). ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
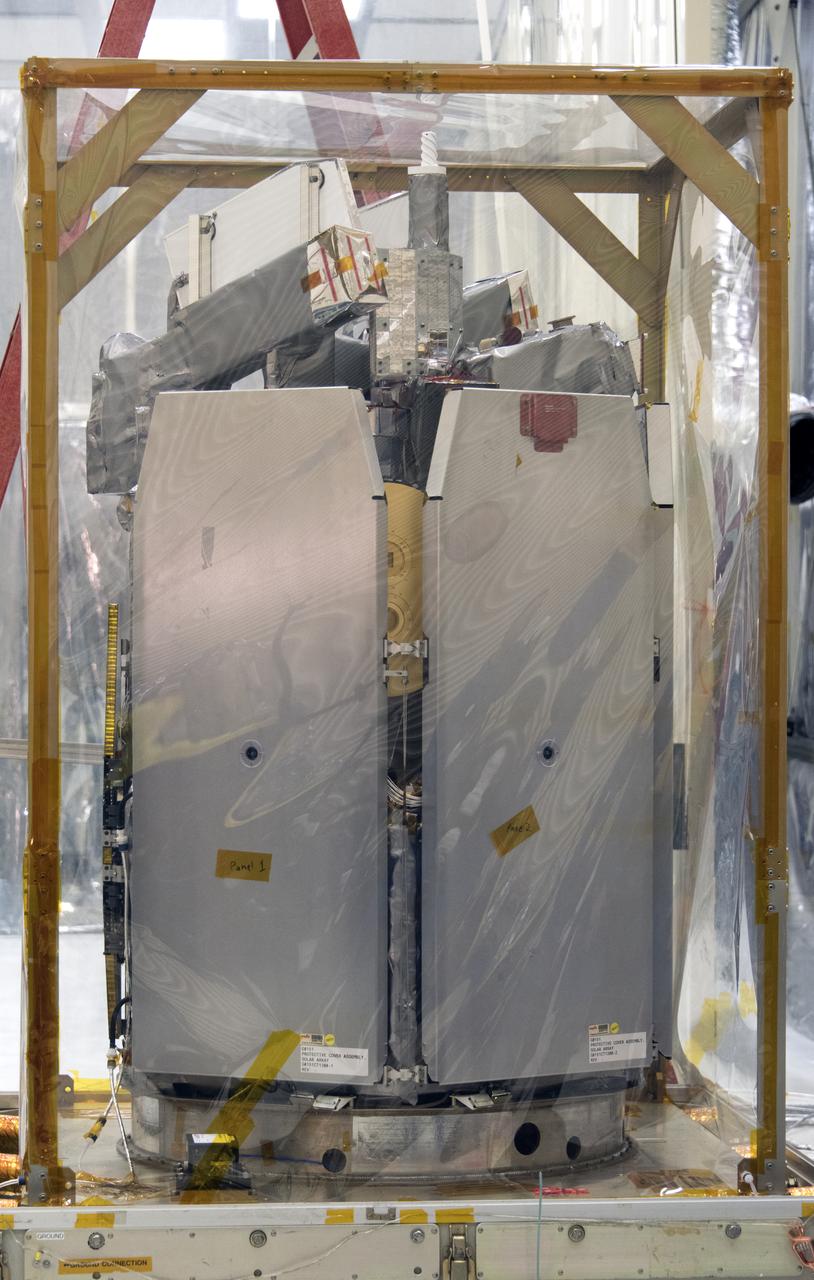

NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is uncrated from its shipping container on May 1, 2018, inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on Orbital ATK's Pegasus XL rocket, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer prepares for takeoff June 6, 2018, from the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States). ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
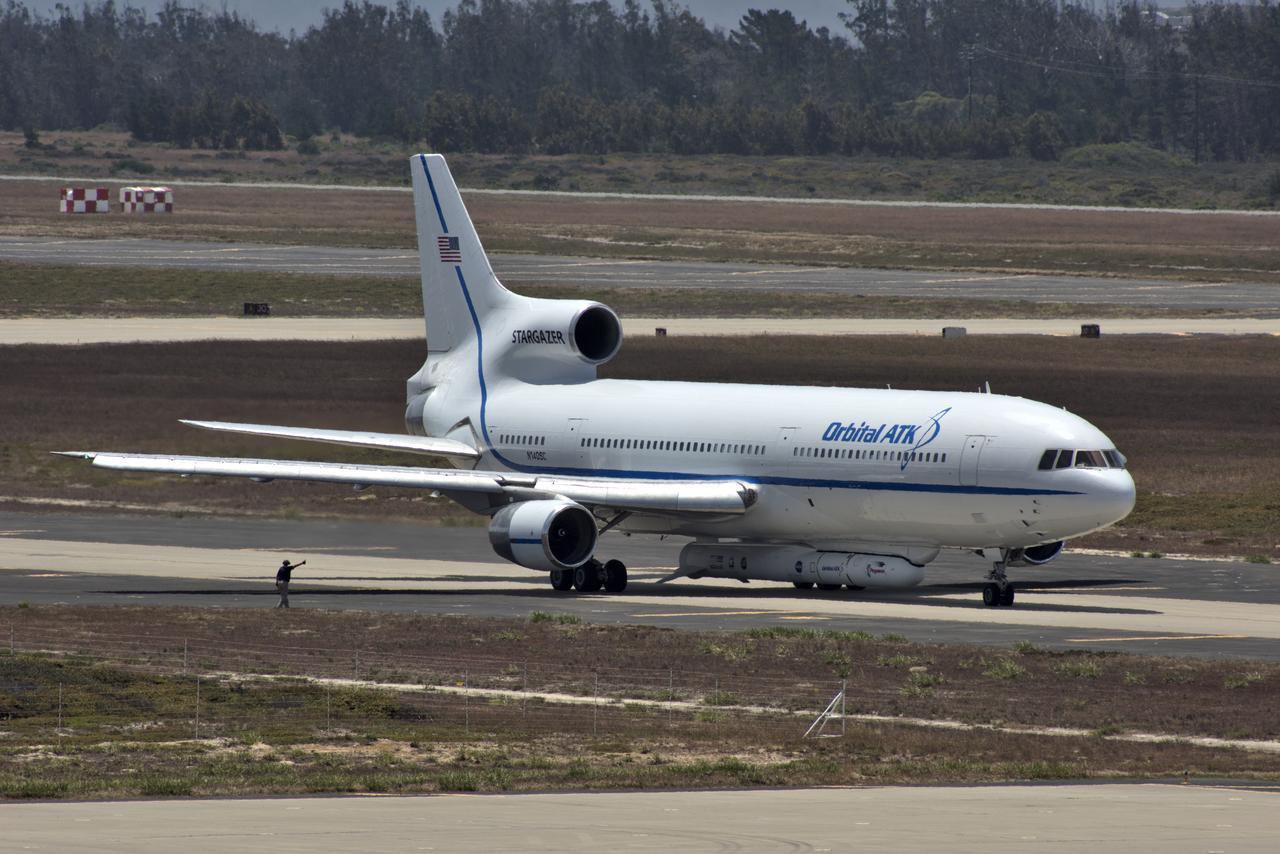

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer prepares for takeoff June 6, 2018, from the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States). ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
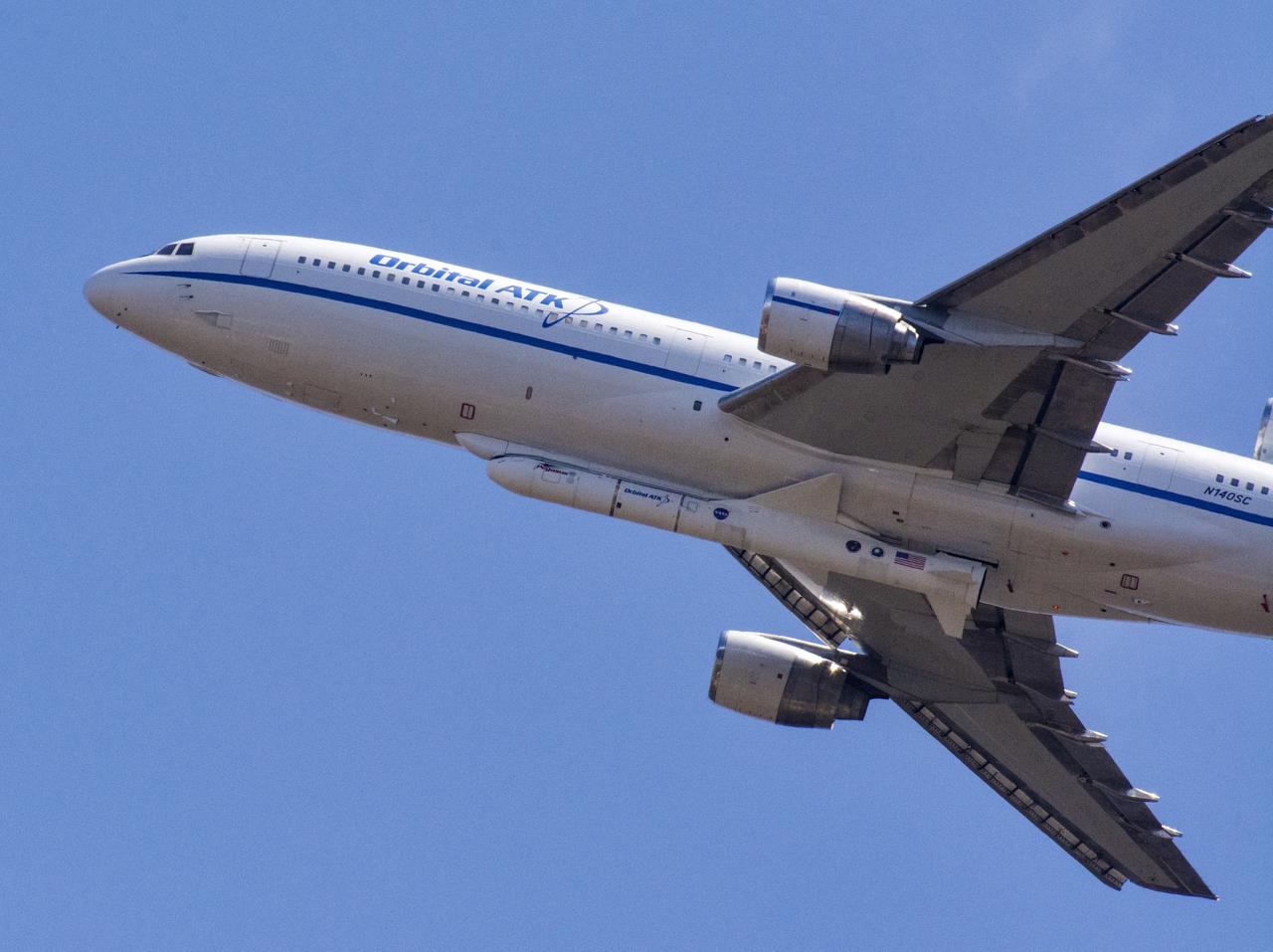

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer soars upward after takeoff from the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on June 6, 2018. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States). ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer is being readied for takeoff June 6, 2018, from the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States). ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft is at the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on May 26, 2018. Preparations are underway to attach the company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), beneath the aircraft. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States). ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
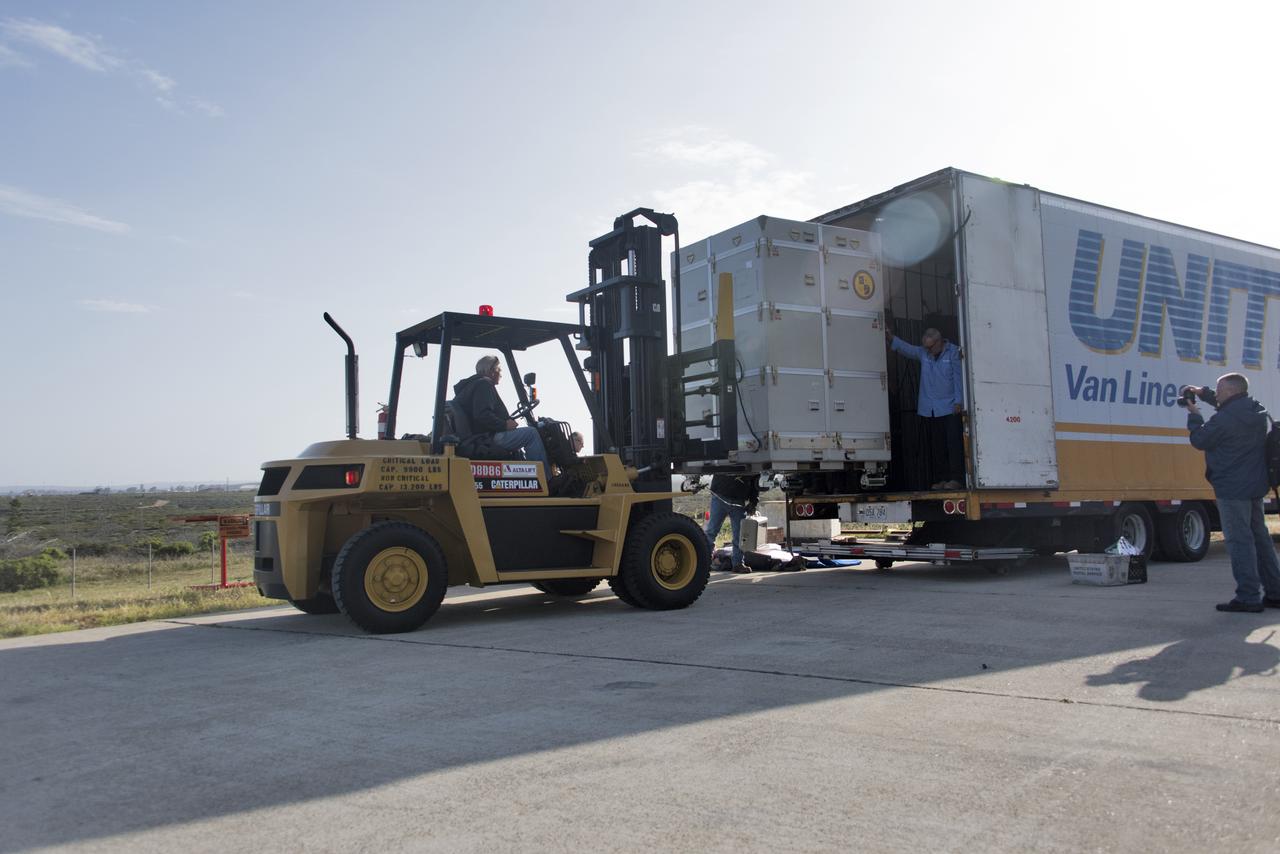

NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) arrives by truck on May 1, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ICON will be offloaded and transported to Building 1555. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on Orbital ATK's Pegasus XL rocket, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
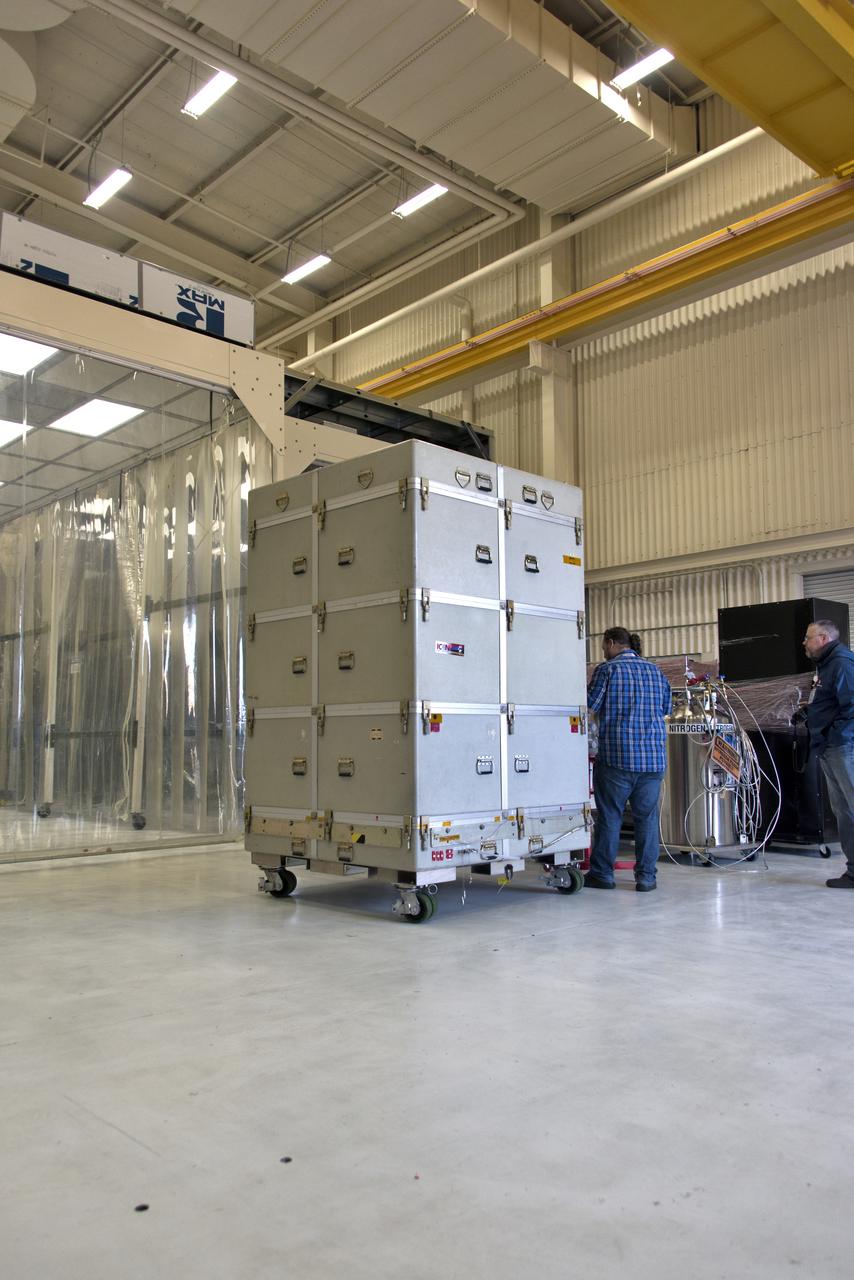

NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), inside its shipping container, is moved inside Building 1555 on May 1, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on Orbital ATK's Pegasus XL rocket, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.

A technician assists with connections as NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is attached to the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket May 14, 2018, inside a clean room in Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on the Pegasus XL rocket, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
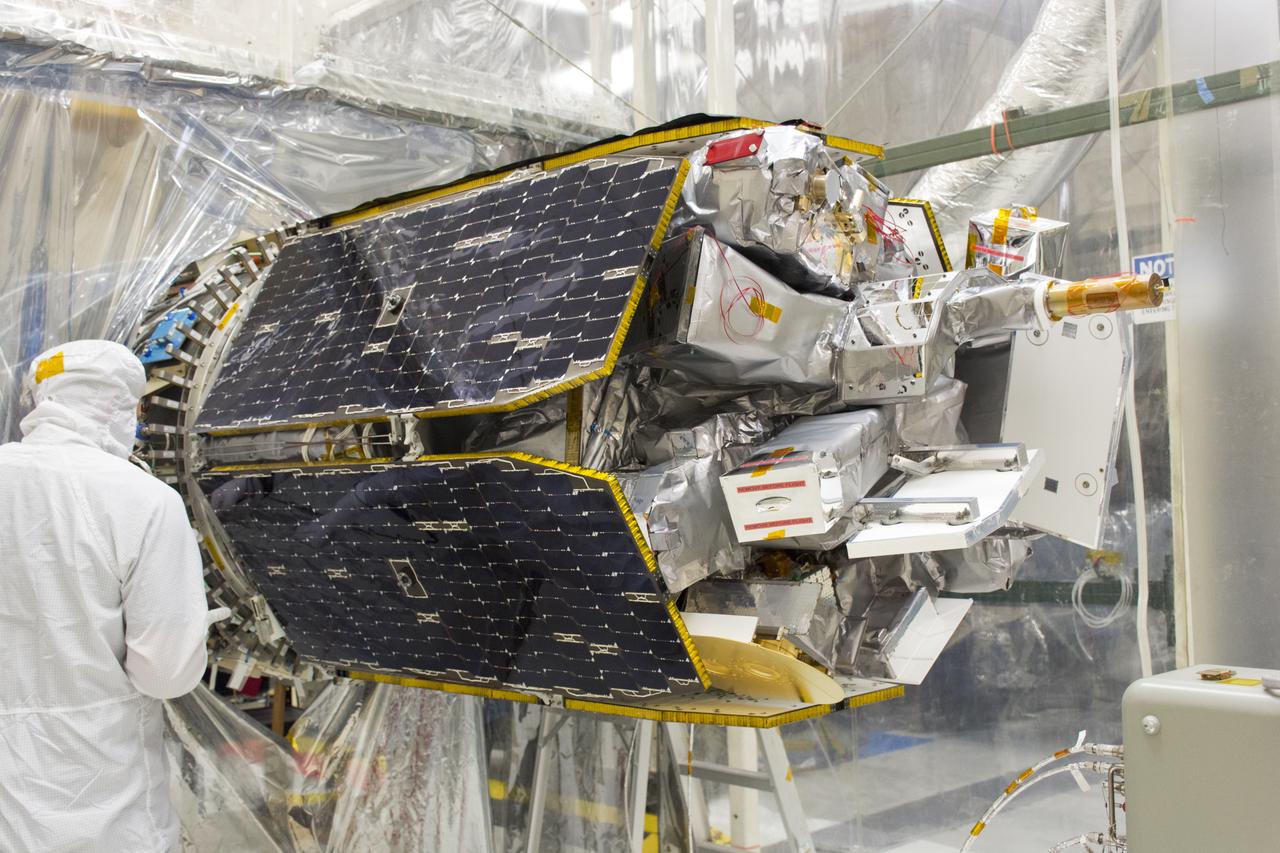
A technician assists with connections as NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is attached to the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket May 14, 2018, inside a clean room in Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on the Pegasus XL rocket, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
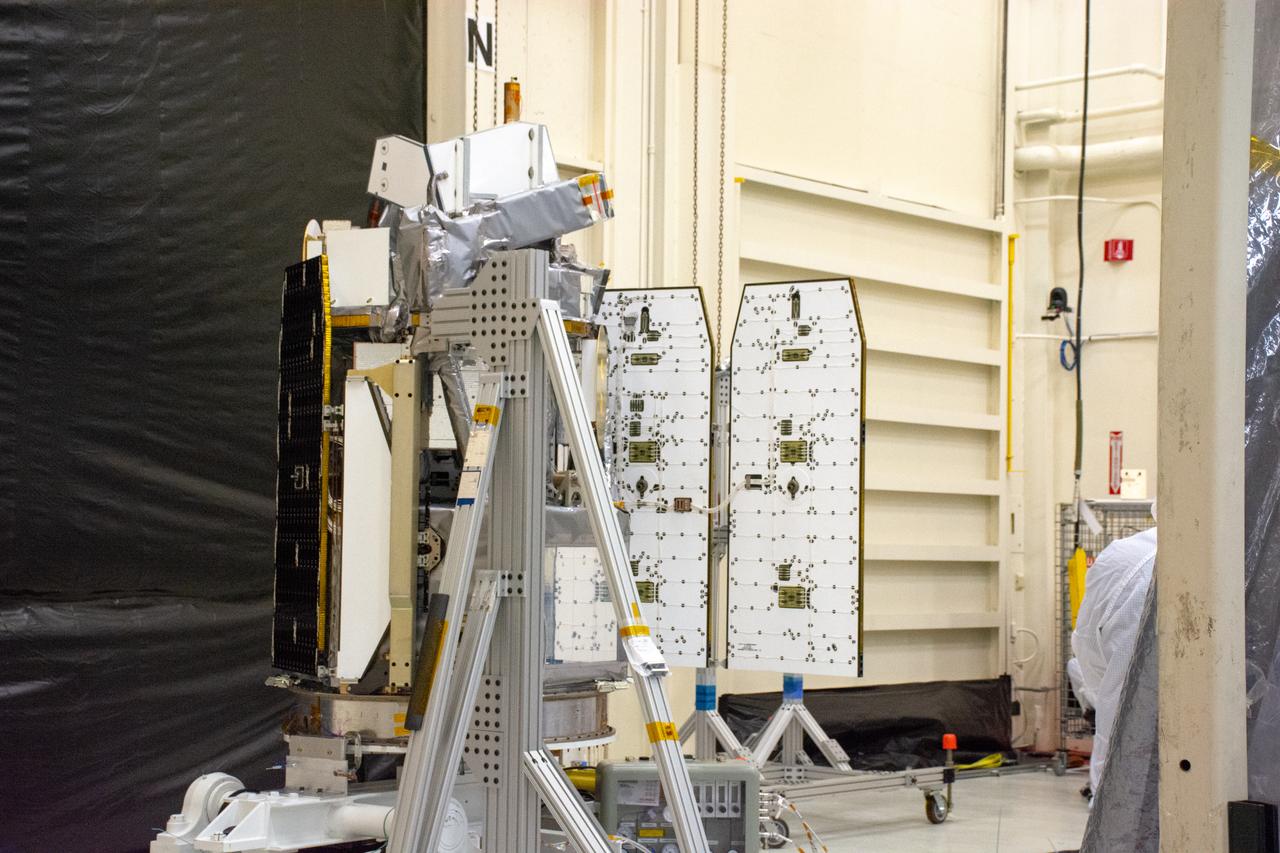

The solar panels on NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) are being deployed to test them inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 10, 2019. ICON will launch on a Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.

Technicians extend the solar array on NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) during a deployment test inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 10, 2019. ICON will launch on a Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
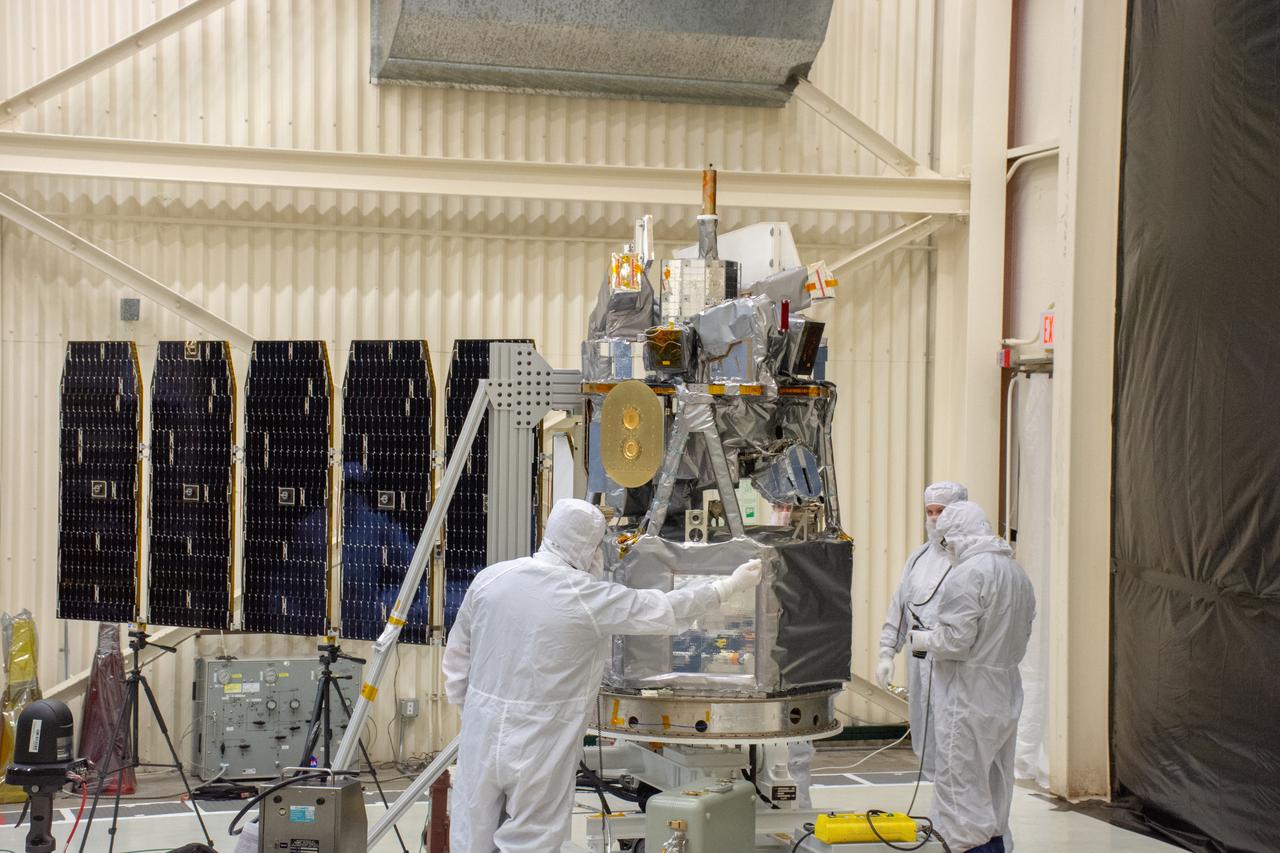

Technicians extend the solar array on NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) during a deployment test inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 10, 2019. ICON will launch on a Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
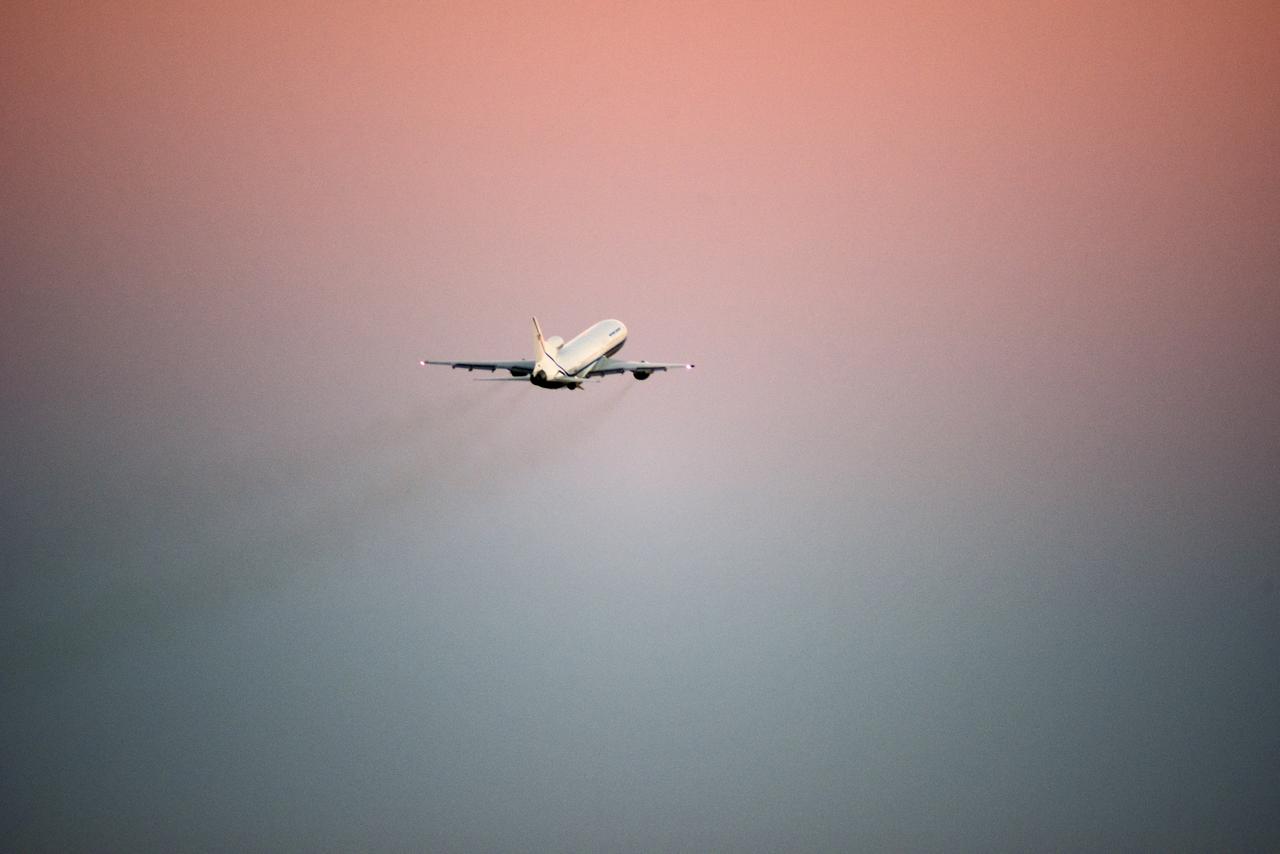

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer soars upward after takeoff from the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Oct. 19, 2018. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The Pegasus XL rocket will launch from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.

The Northrop Grumman L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, with the Pegasus XL rocket attached beneath, starts down the runway at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2018. NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is secured inside the rocket's payload fairing. The Pegasus XL rocket will be carried aloft by the Stargazer. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
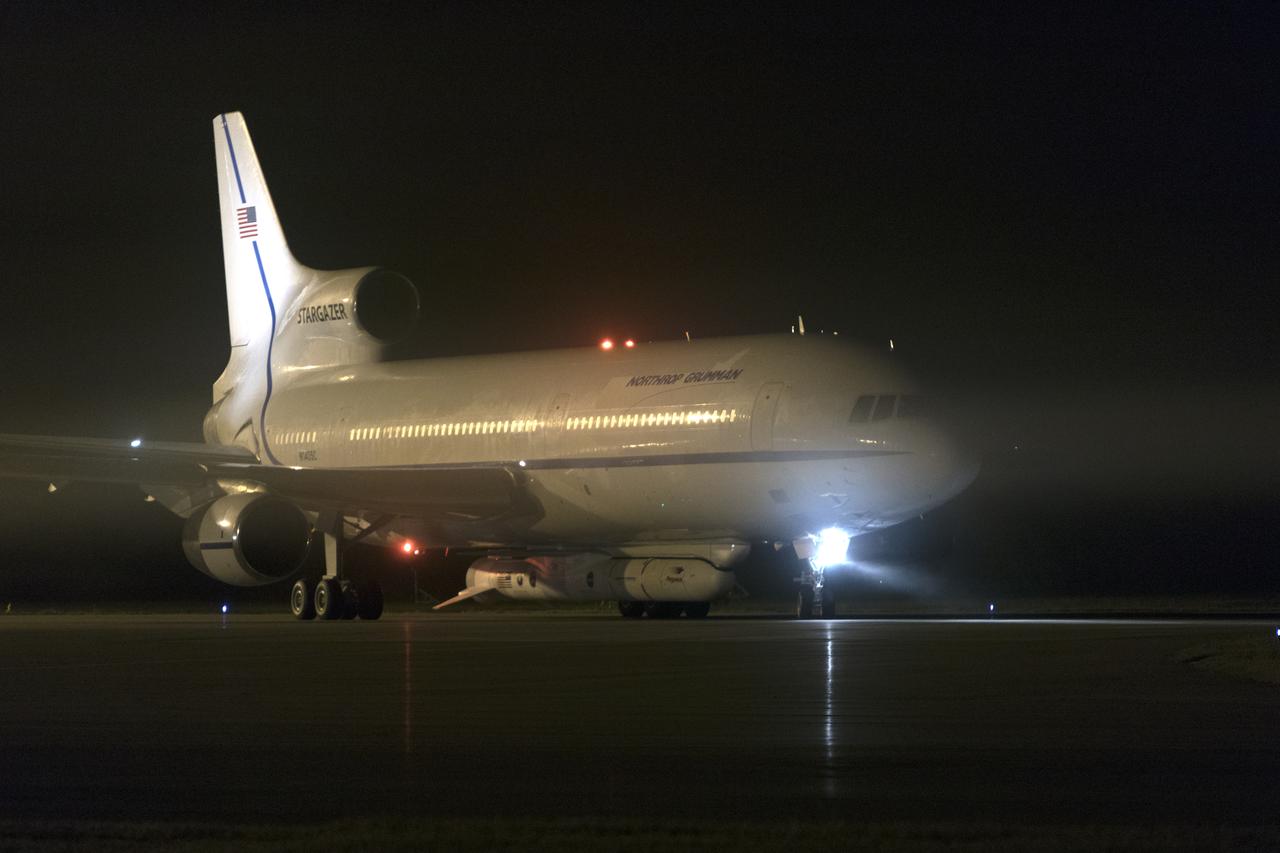

The Northrop Grumman L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, with the Pegasus XL rocket attached beneath, starts down the runway at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2018. NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is secured inside the rocket's payload fairing. The Pegasus XL rocket will be carried aloft by the Stargazer. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
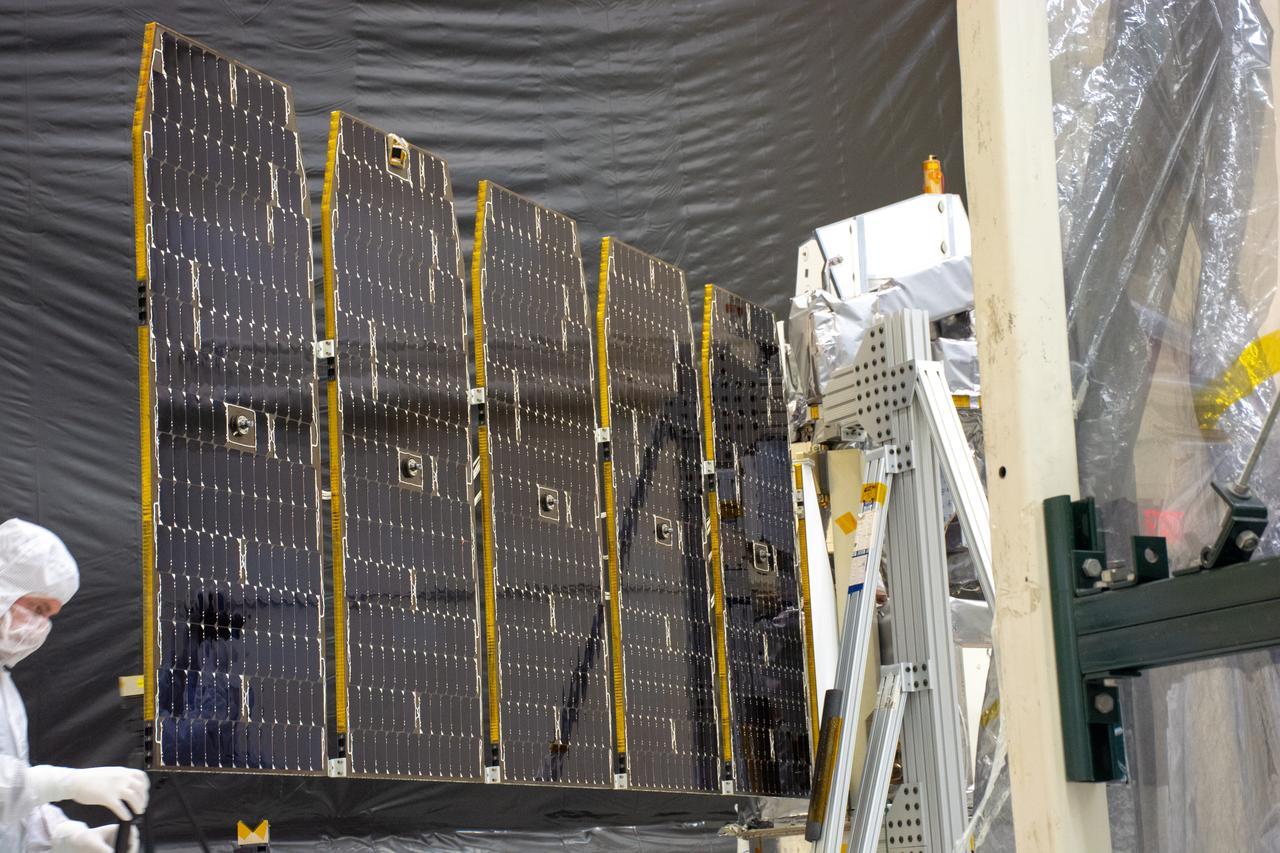

Technicians extend the solar array on NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) during a deployment test inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 10, 2019. ICON will launch on a Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
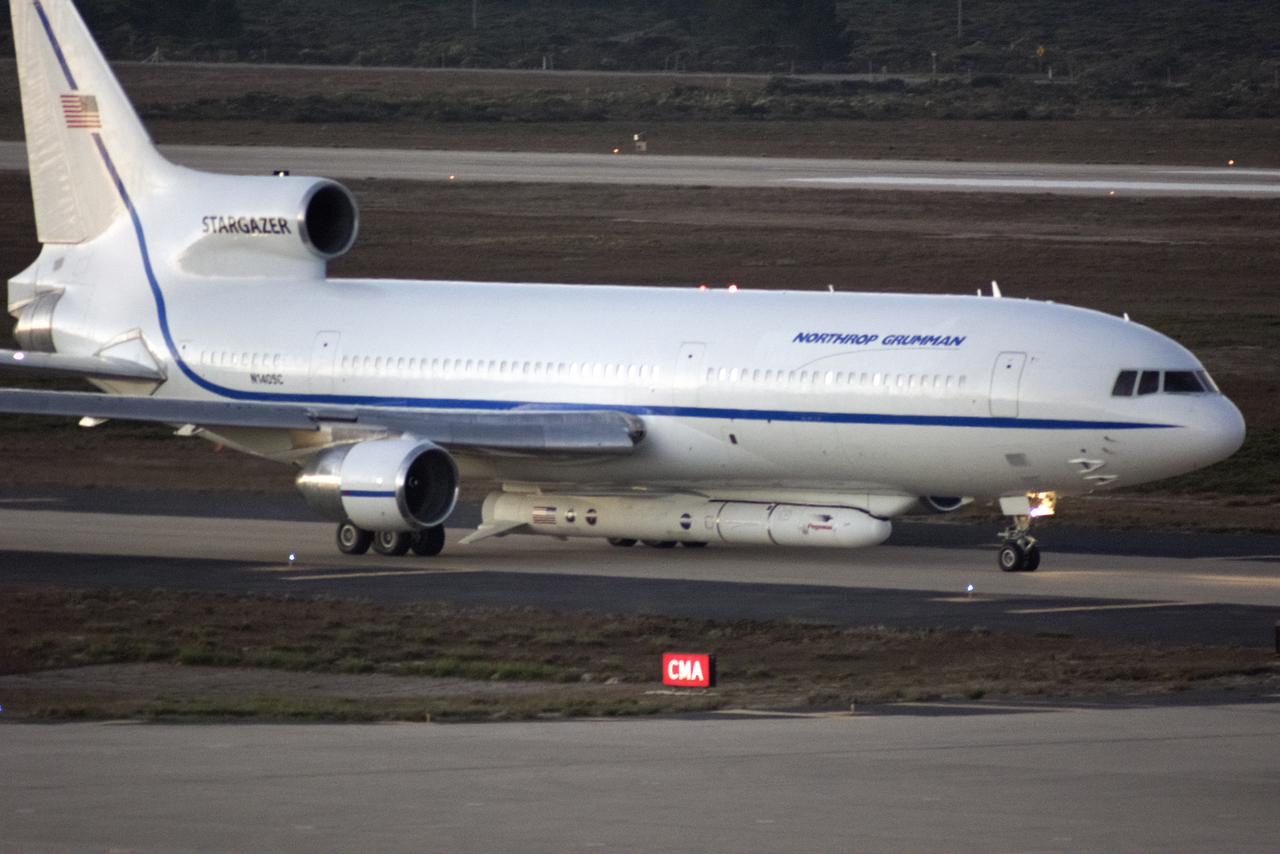

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer is being readied for takeoff Oct. 19, 2018, from the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The Pegasus XL rocket will launch from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
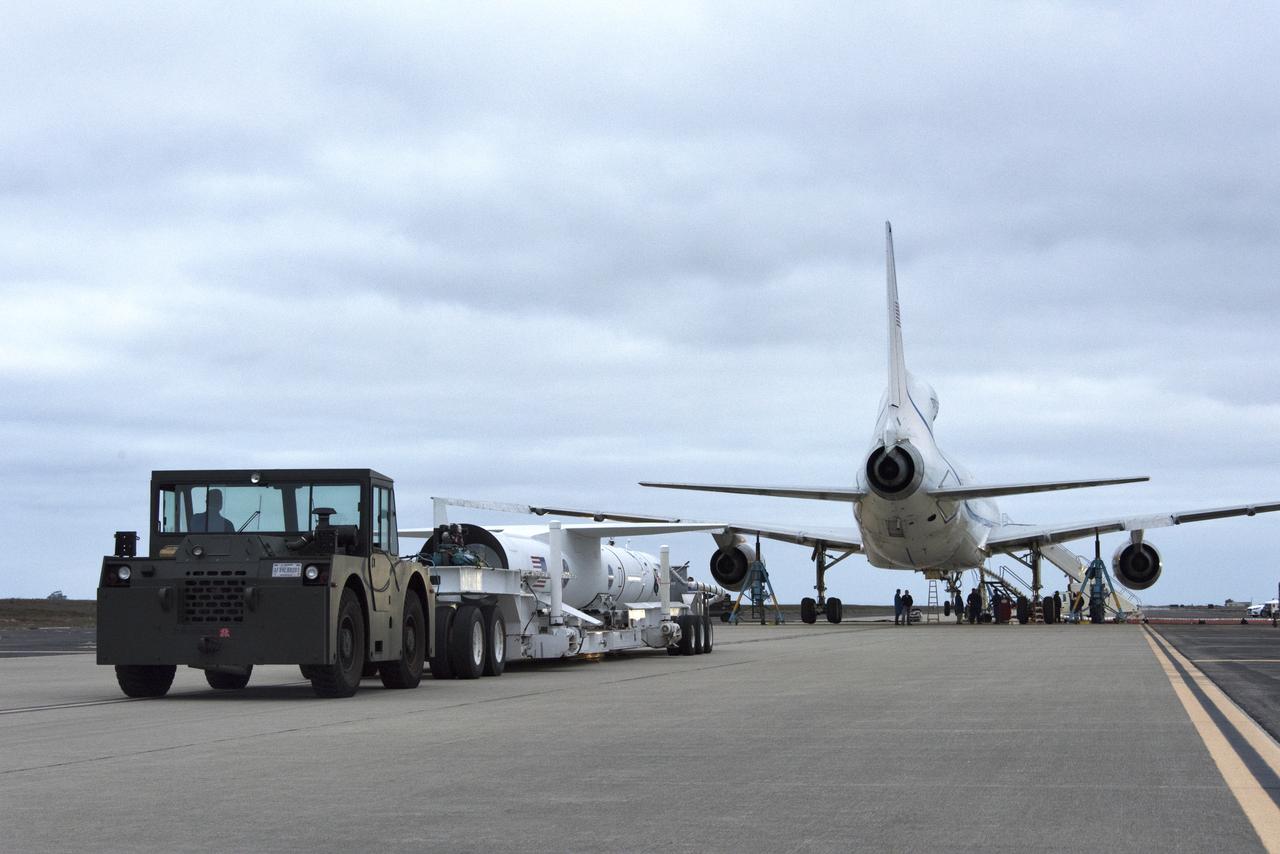

Northrop Grumman's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is transported to the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Oct. 14, 2018. Pegasus will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the trip to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Pegasus XL rocket will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at the Cape. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
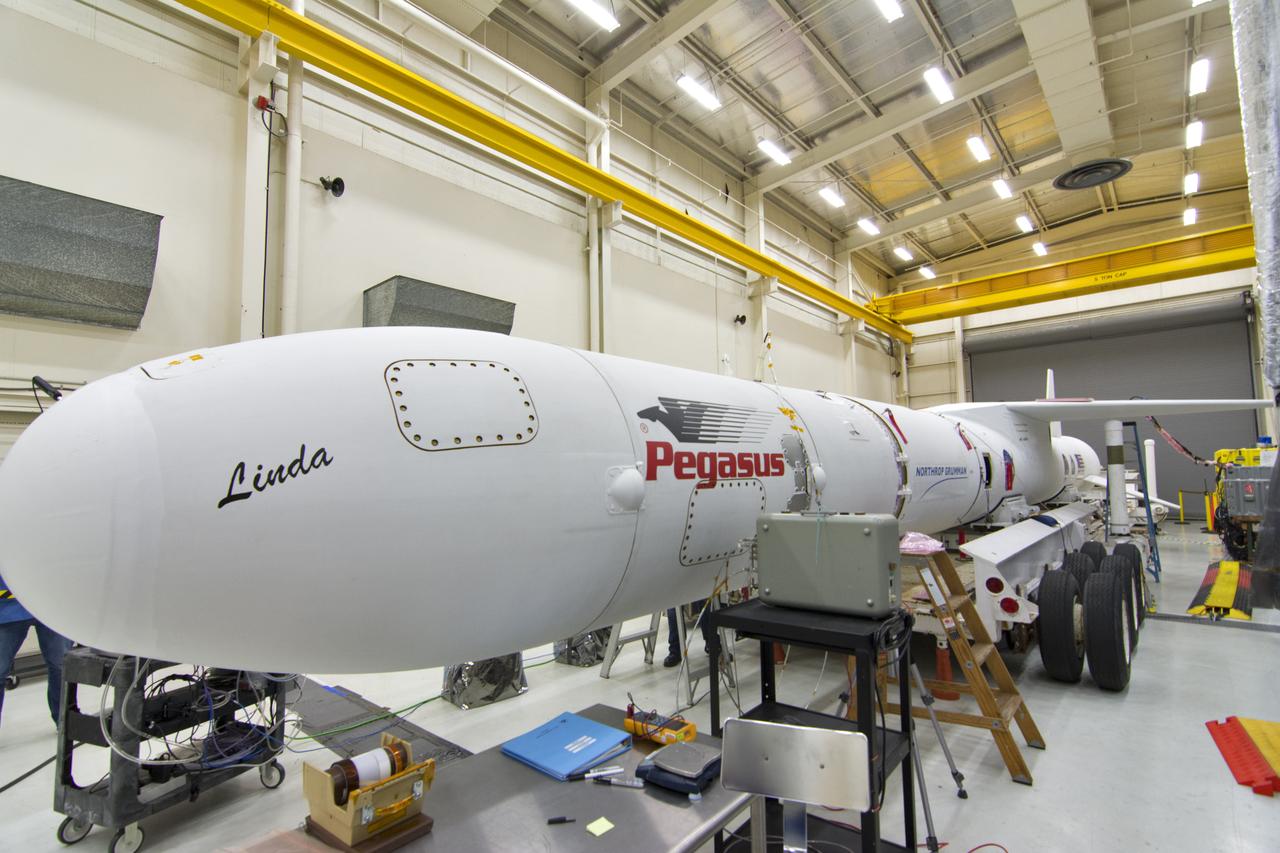

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL vehicle is inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Oct. 8, 2018. The payload fairing is installed around NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON). The Pegasus XL, attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 26. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
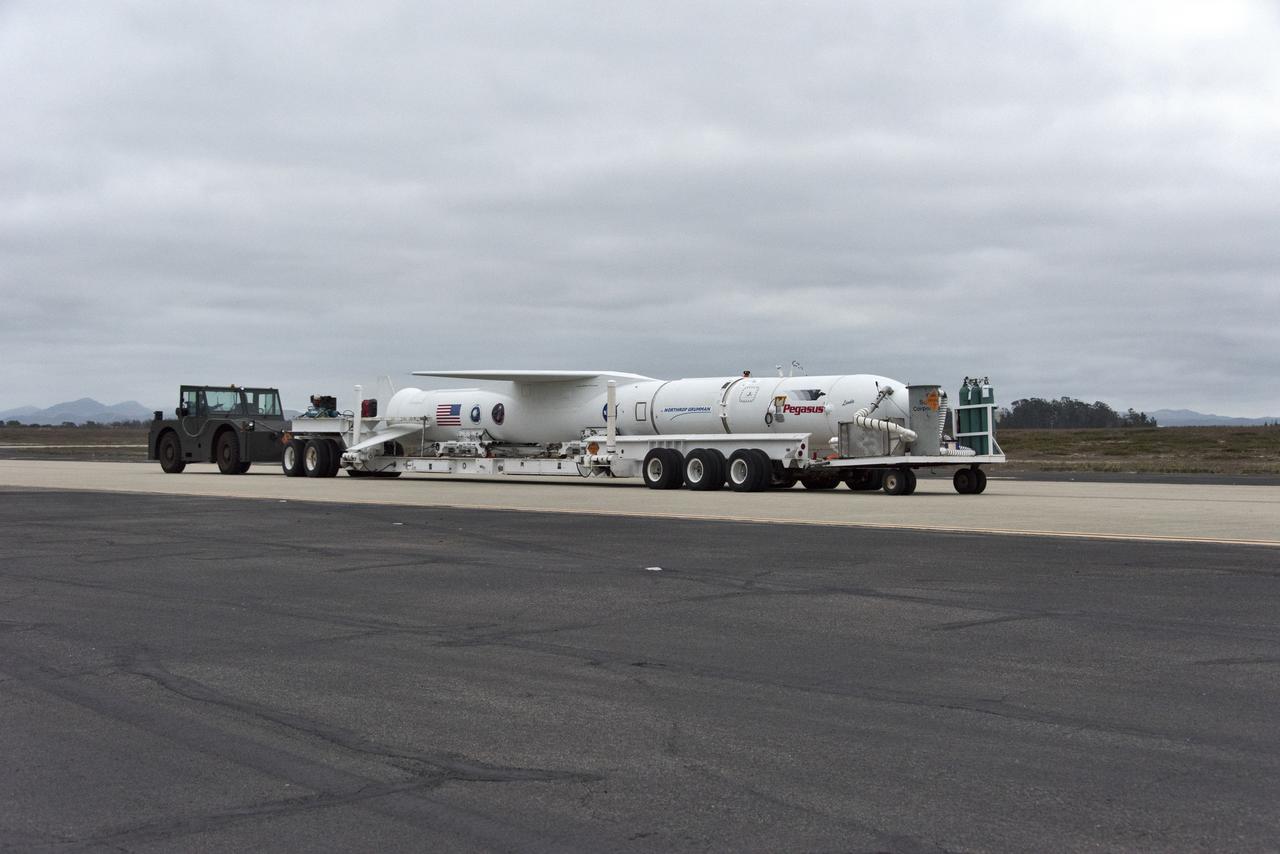

Northrop Grumman's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is transported to the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Oct. 14, 2018. Pegasus will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the trip to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Pegasus XL rocket will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at the Cape. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
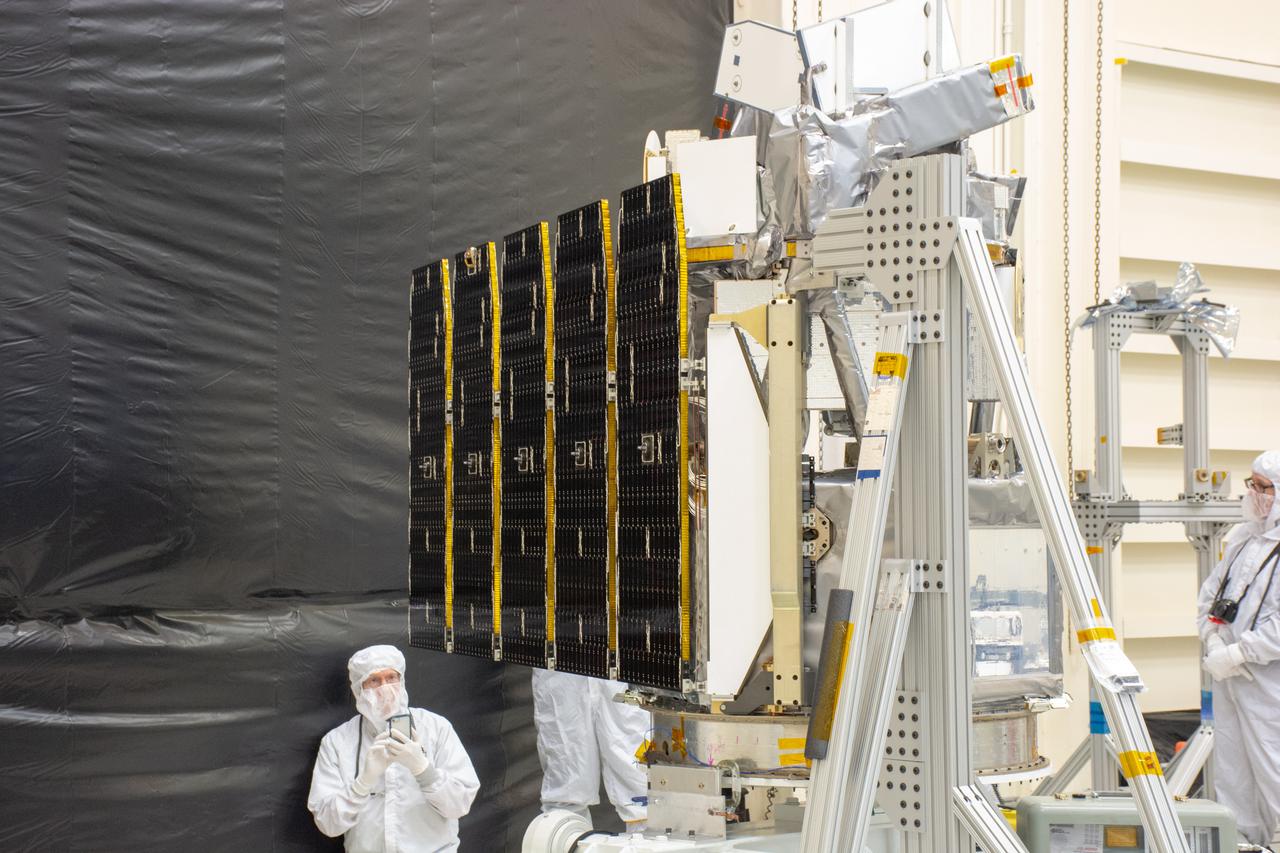

Technicians extend the solar array on NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) during a deployment test inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 10, 2019. ICON will launch on a Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
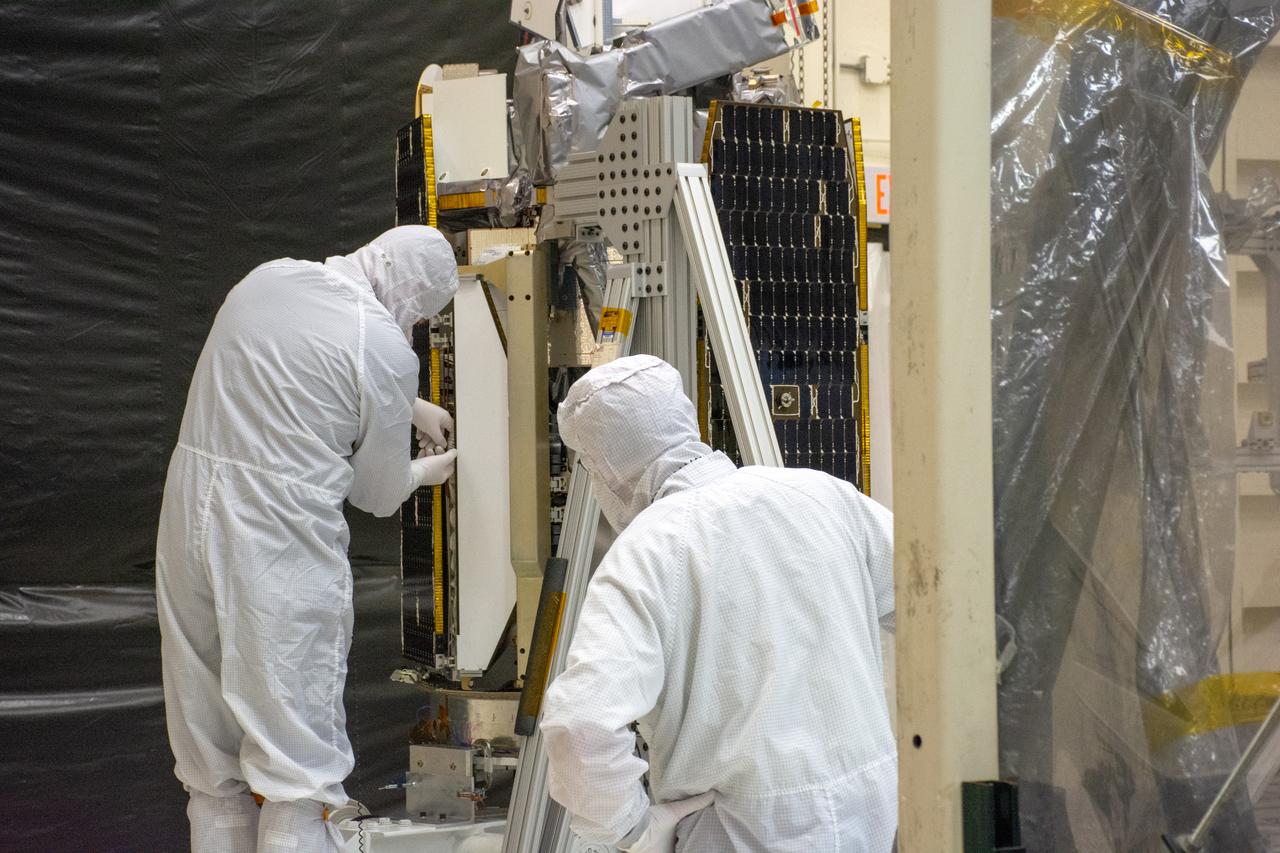

Technicians prepare NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) for a solar array deployment test inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 10, 2019. ICON will launch on a Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
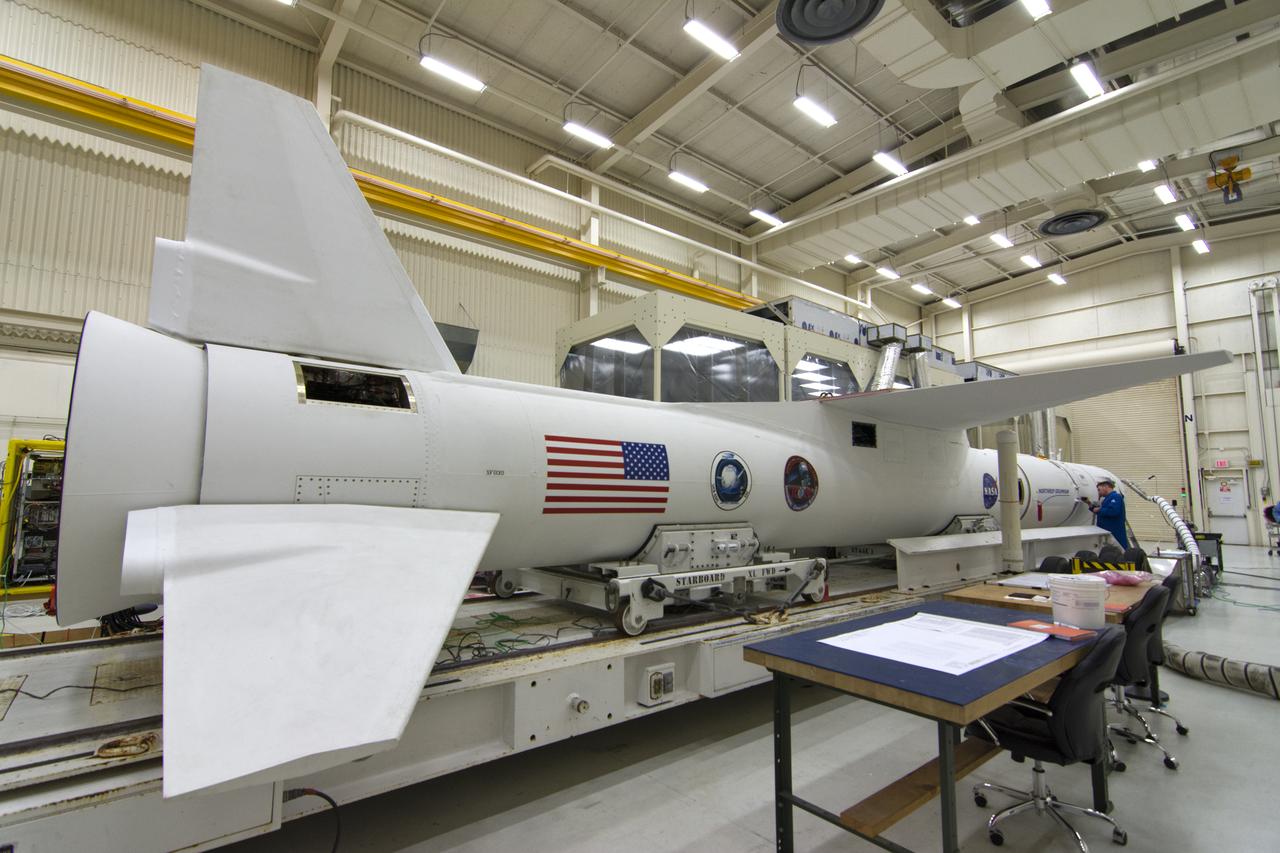

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL vehicle is inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Oct. 8, 2018. The payload fairing is installed around NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON). The Pegasus XL, attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 26. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
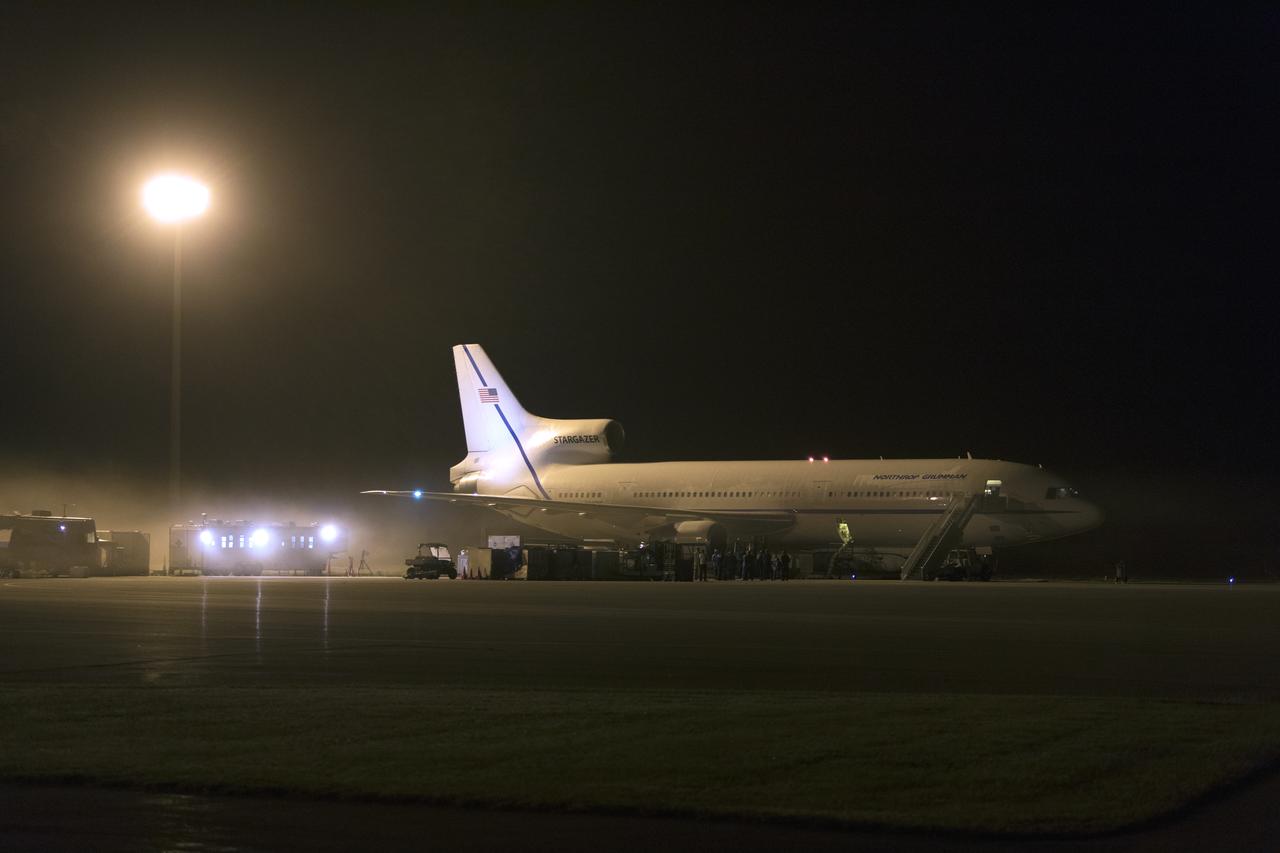

The Northrop Grumman L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, with the Pegasus XL rocket attached beneath, is being prepared for takeoff from the runway at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2018. NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite is secured inside the rocket's payload fairing. The Pegasus XL rocket will be carried aloft by the Stargazer. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
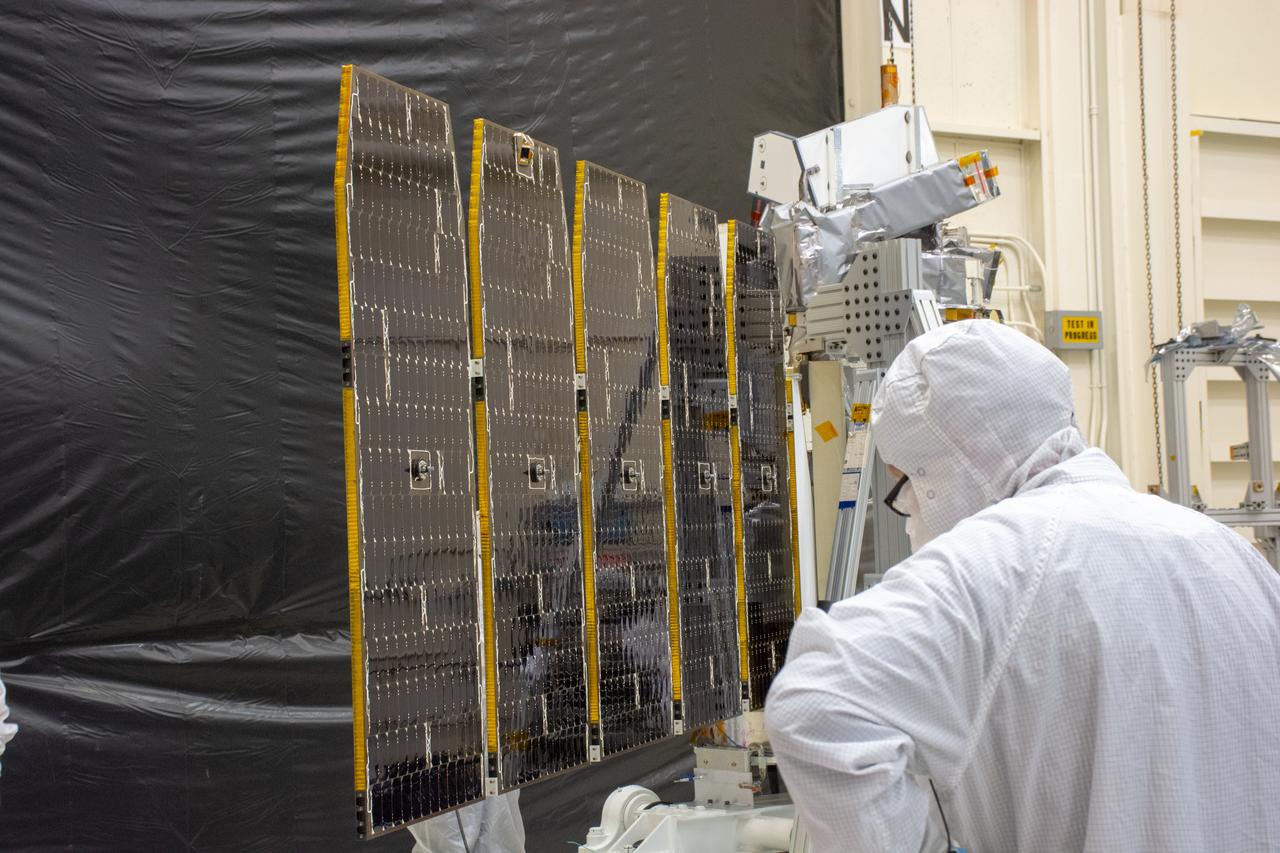

Technicians extend the solar array on NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) during a deployment test inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 10, 2019. ICON will launch on a Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
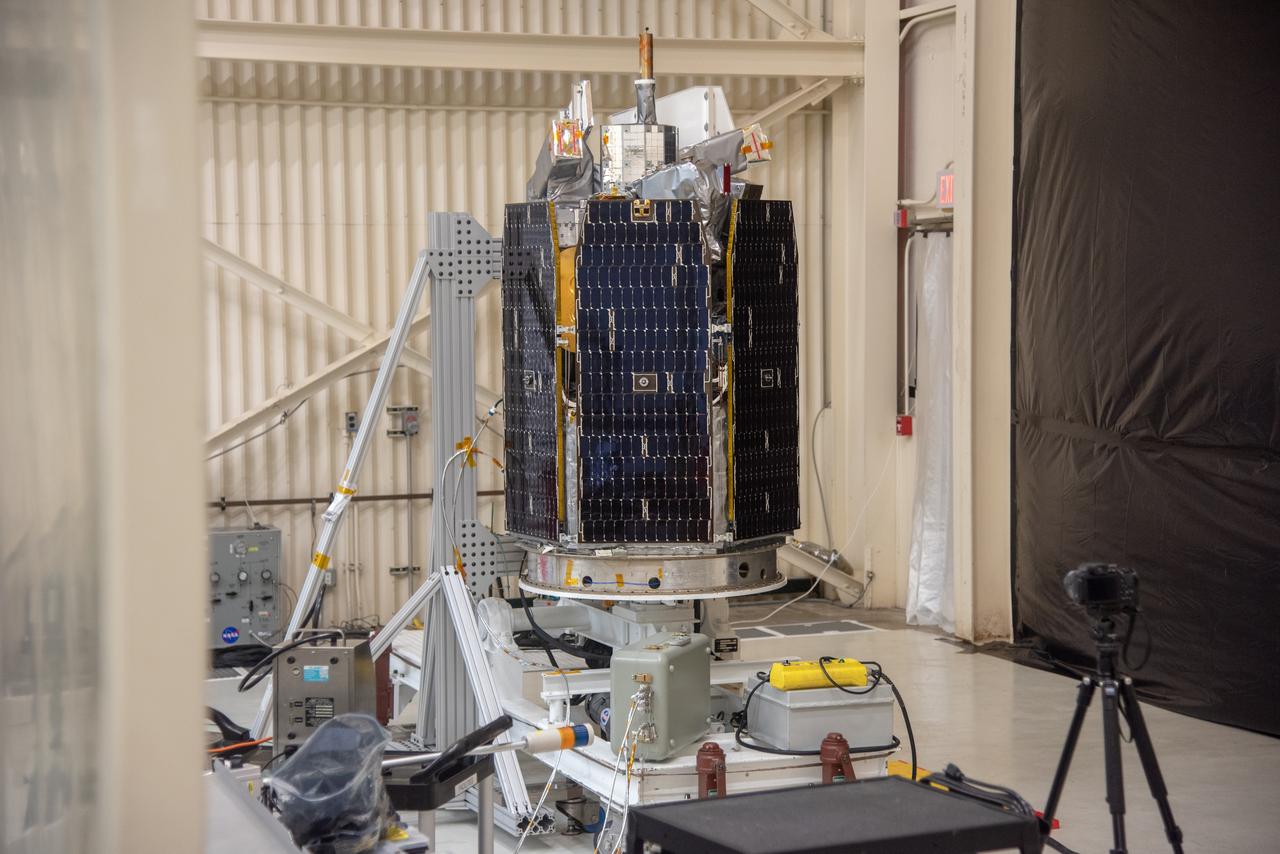

A solar array deployment test will begin on NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 10, 2019. ICON will launch on a Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
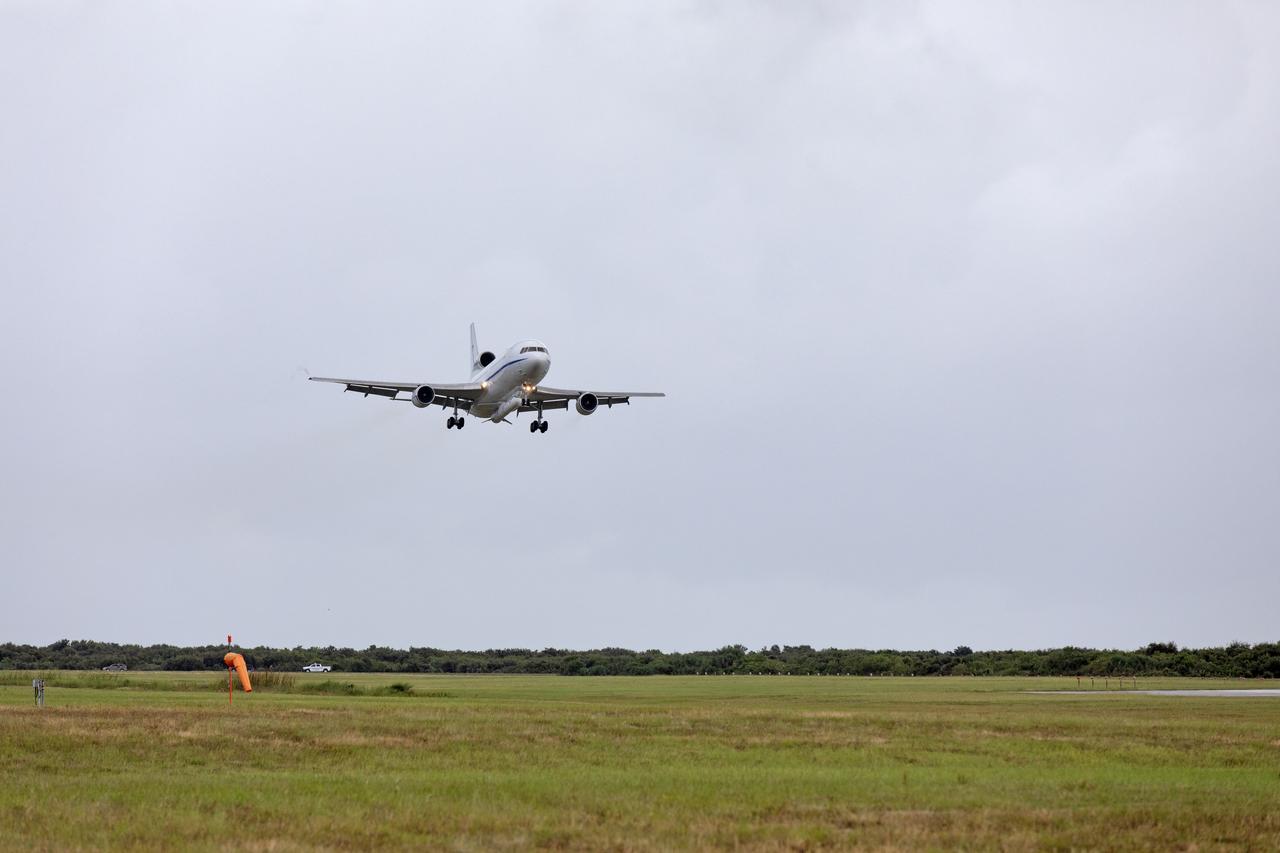

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer descends toward the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, on Oct. 19, 2018. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The Pegasus XL rocket will launch from the Skid Strip. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
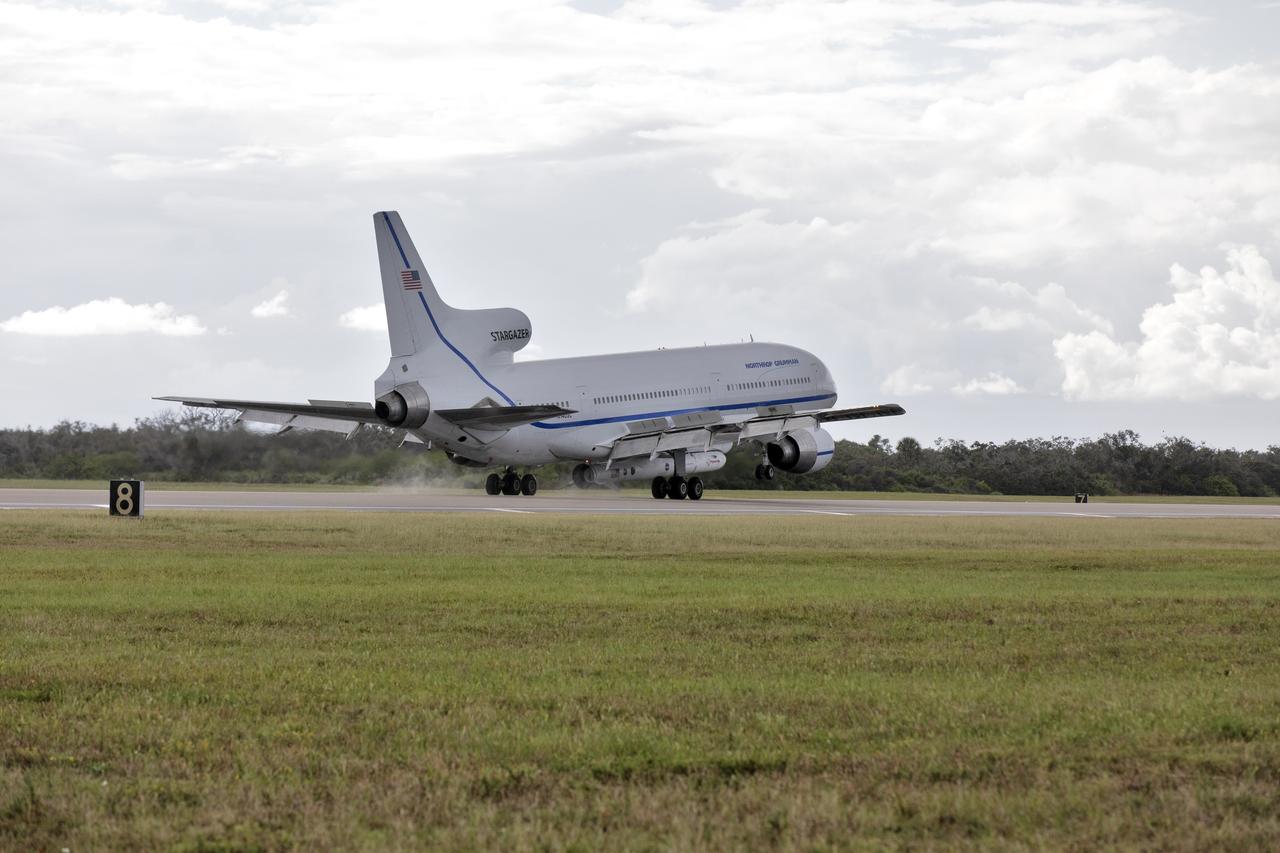

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer touches down at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, on Oct. 19, 2018. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The Pegasus XL rocket will launch from the Skid Strip. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 is on the tarmac after touching down at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, on Oct. 19, 2018. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The Pegasus XL rocket will launch from the Skid Strip. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.

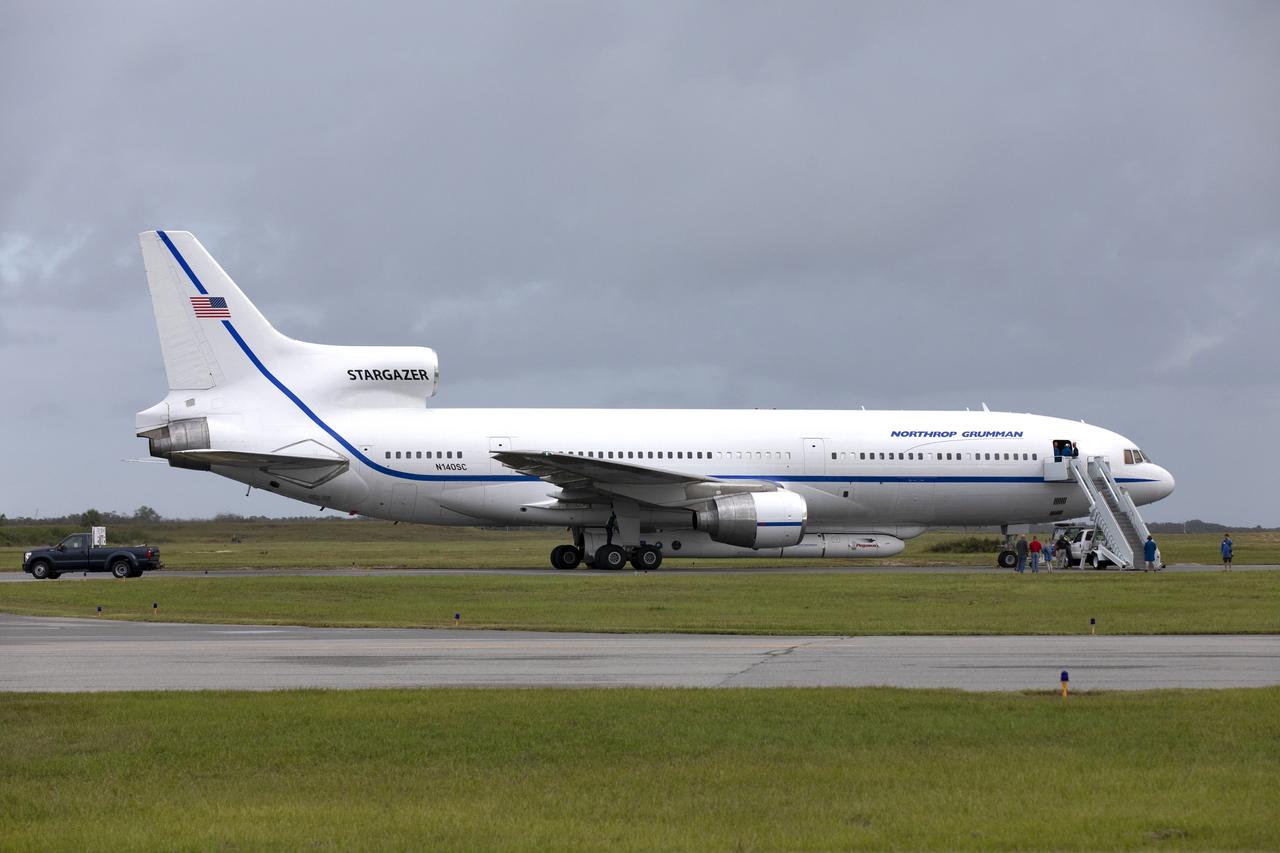
The Northrop Grumman L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, with the Pegasus XL rocket attached beneath, starts down the runway at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2018. NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is secured inside the rocket's payload fairing. The Pegasus XL rocket will be carried aloft by the Stargazer. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.

The Northrop Grumman L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, with the Pegasus XL rocket attached beneath, starts down the runway at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2018. NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is secured inside the rocket's payload fairing. The Pegasus XL rocket will be carried aloft by the Stargazer. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
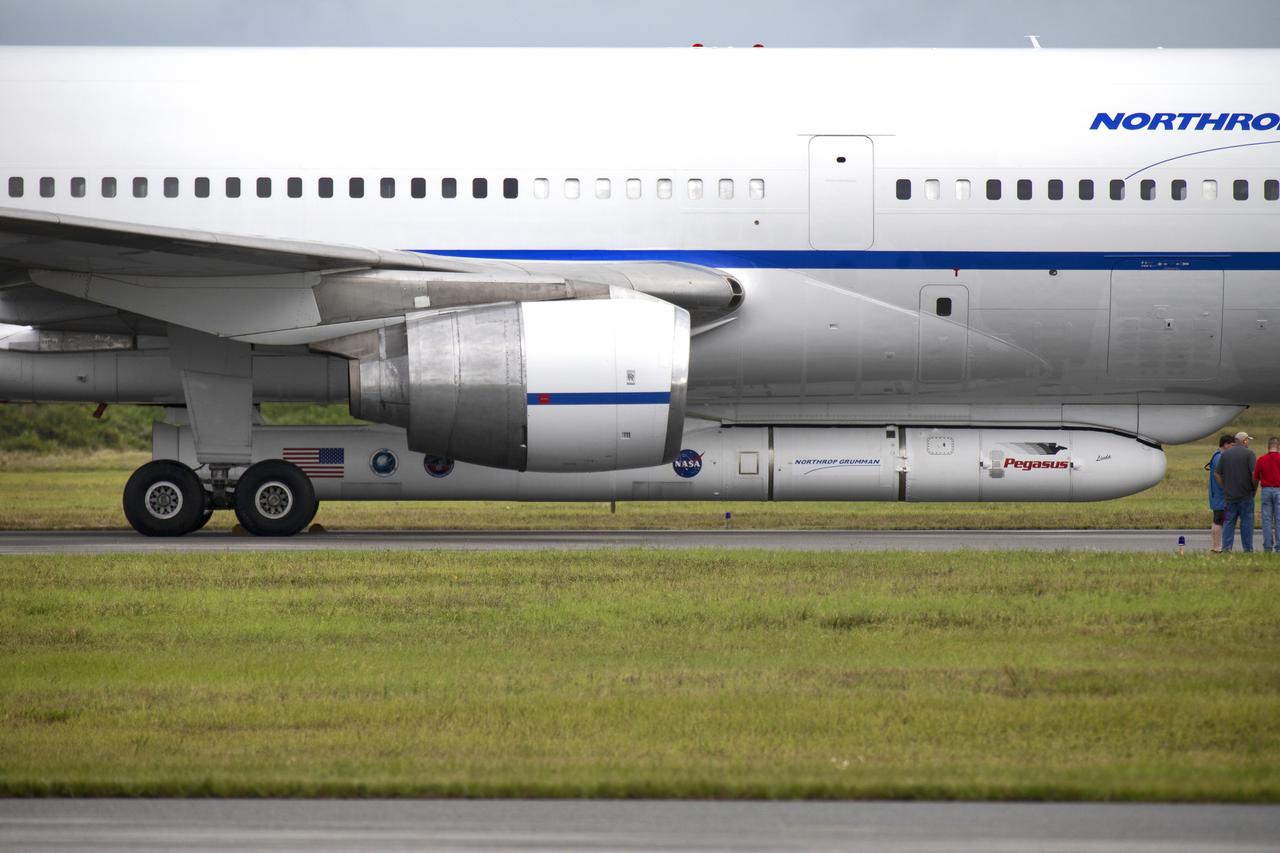

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 is on the tarmac after touching down at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, on Oct. 19, 2018. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is in view attached beneath the aircraft. The Pegasus XL rocket will launch from the Skid Strip. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer is ready for takeoff Oct. 19, 2018, from the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The Pegasus XL rocket will launch from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer takes off from the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Oct. 19, 2018. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The Pegasus XL rocket will launch from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.

The Northrop Grumman L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, with the Pegasus XL rocket attached beneath, starts down the runway at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 7, 2018. NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is secured inside the rocket's payload fairing. The Pegasus XL rocket will be carried aloft by the Stargazer. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer is ready for takeoff Oct. 19, 2018, from the hot pad at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The Pegasus XL rocket will launch from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
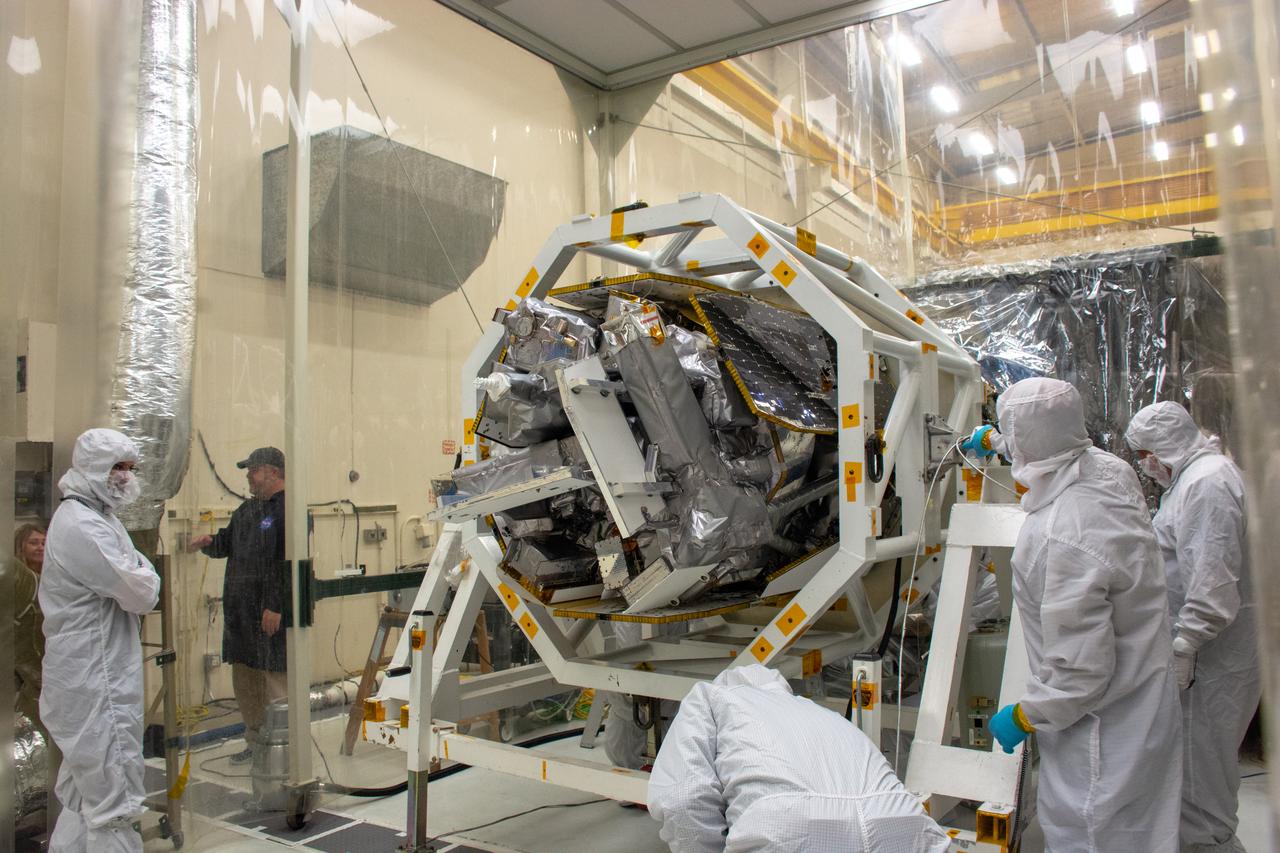

Technicians attach NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) to the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 10, 2019. Preparations are underway to perform a black light test on Pegasus before the port and starboard payload fairings are installed around ICON. The Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 9, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
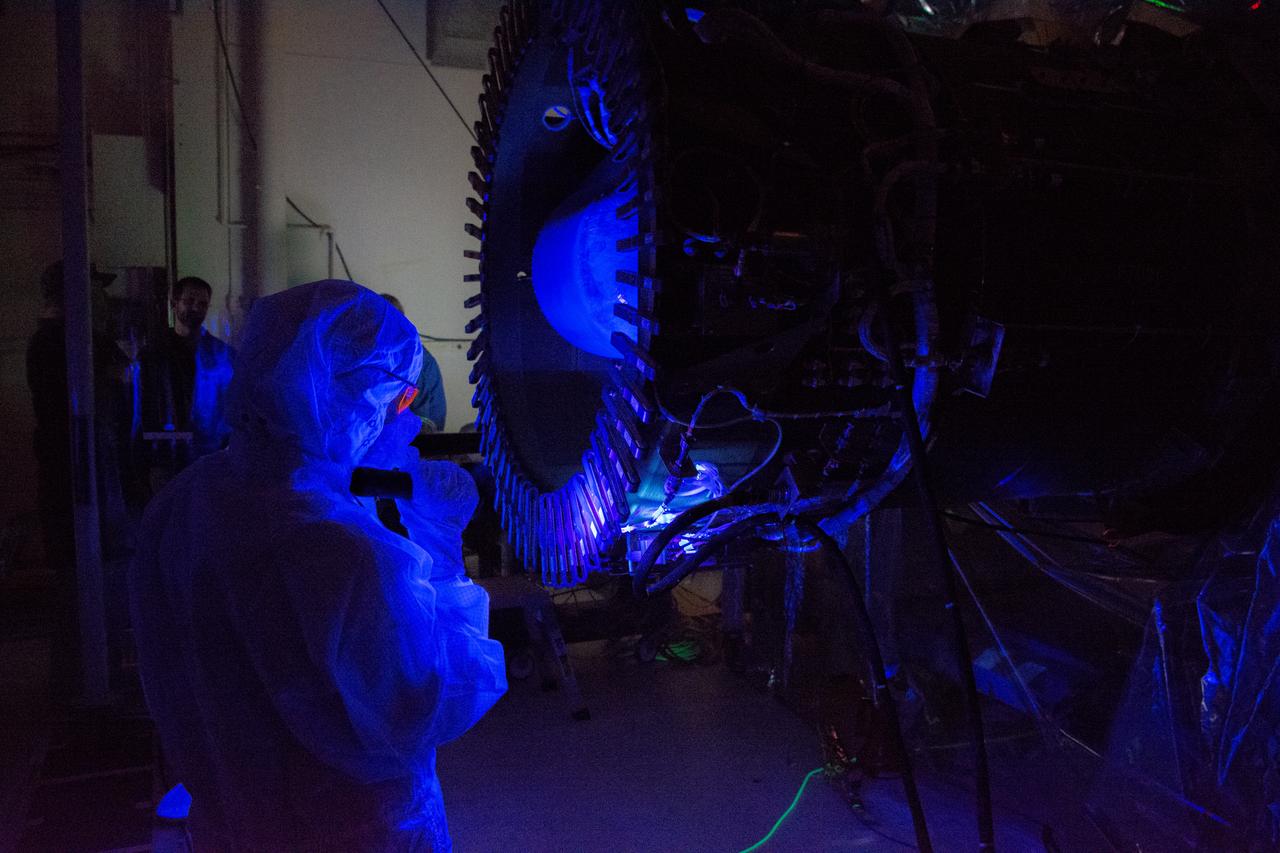
Technicians perform a black light inspection of the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 10, 2019, after NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) was attached to the rocket. The Pegasus port and starboard payload fairings will be installed around ICON. The Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 9, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
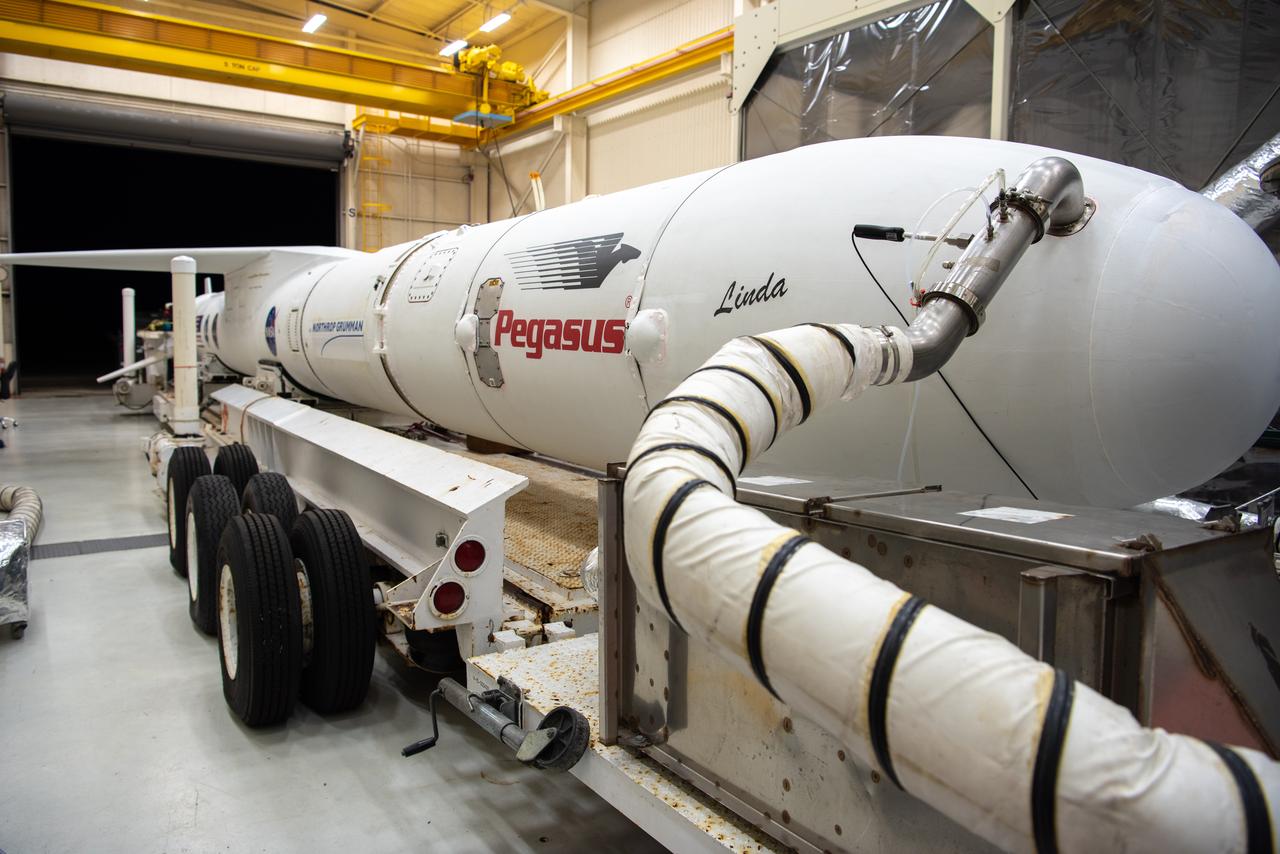

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) secured in its payload fairing, begins rollout from Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 25, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the flight to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. ICON will launch from the Skid Strip at CCAFS. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
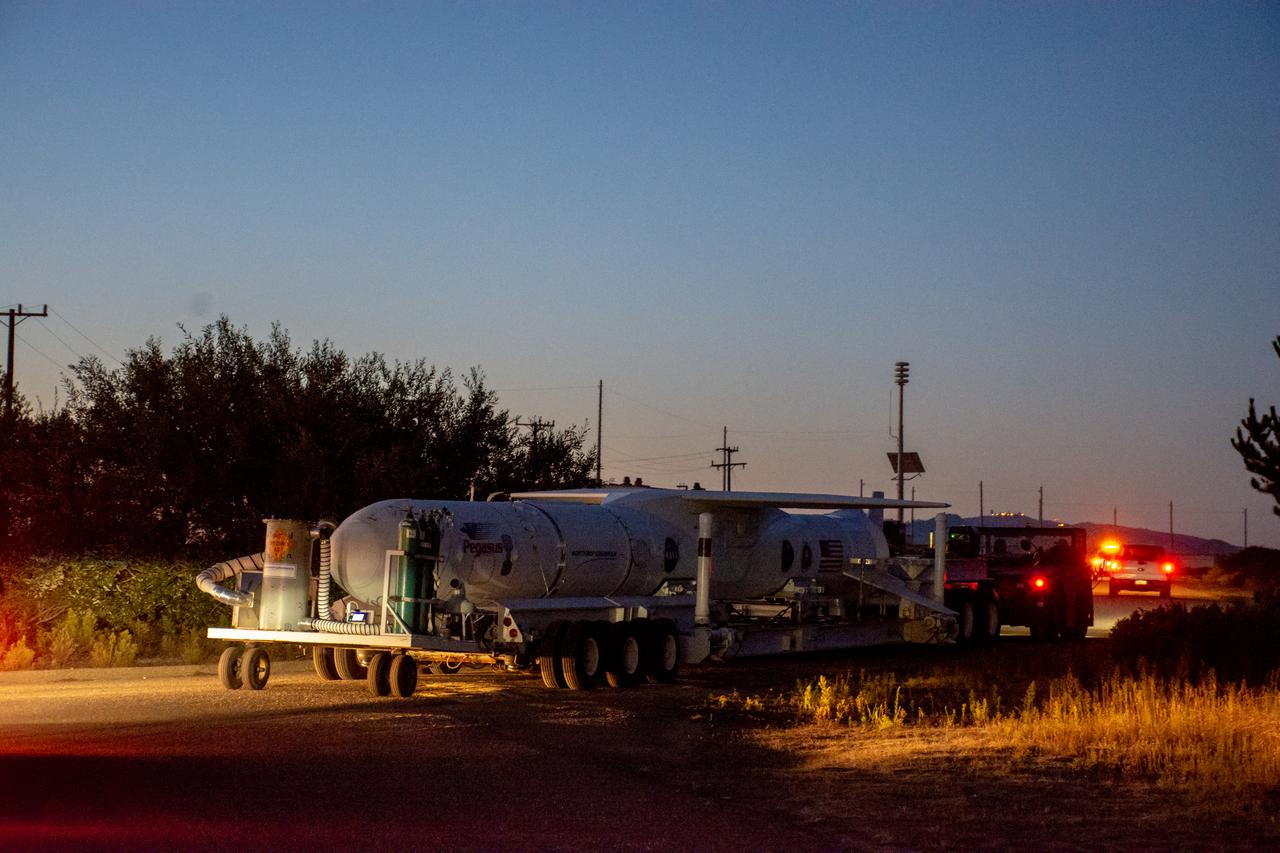

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) secured in its payload fairing, rolls out to the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 25, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the flight to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. ICON will launch from the Skid Strip at CCAFS. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
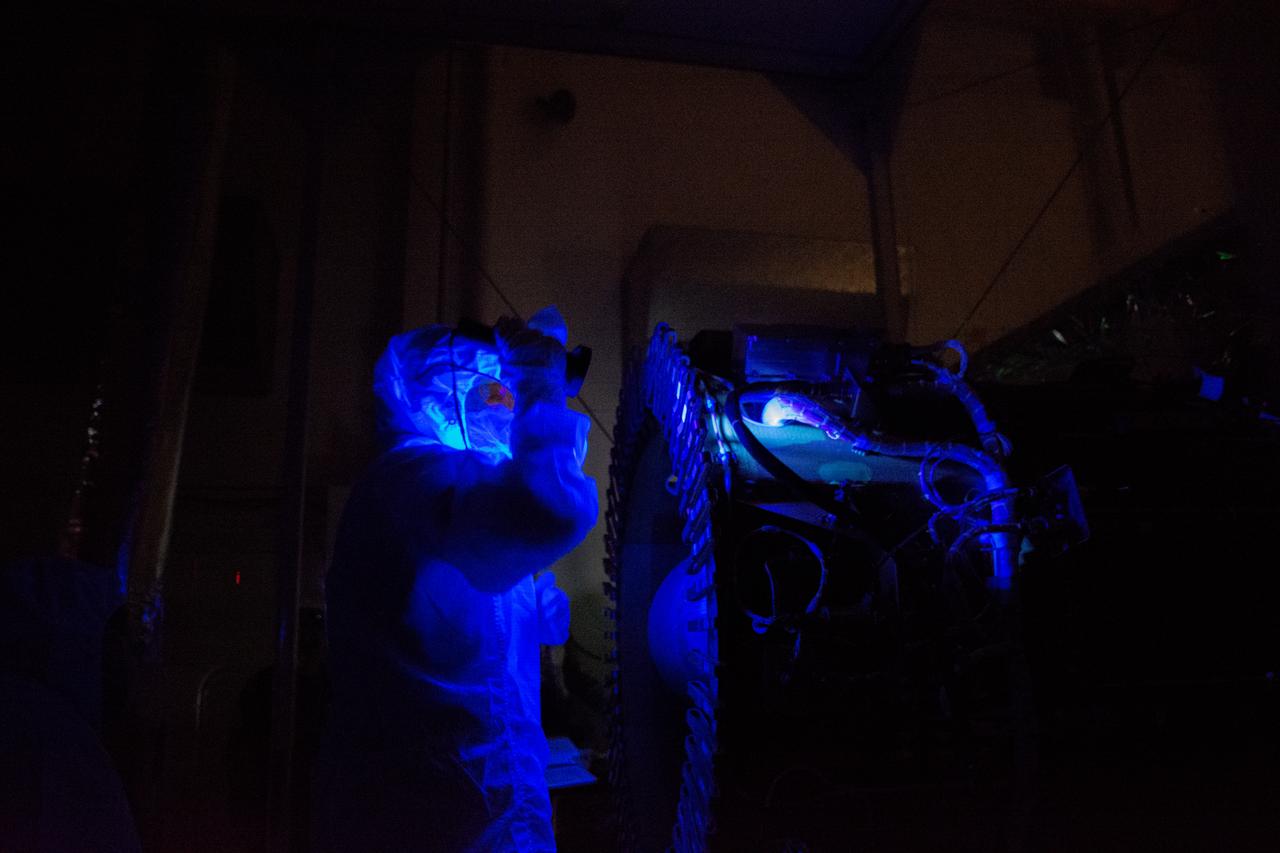

Technicians perform a black light inspection of the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 10, 2019, after NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) was attached to the rocket. The Pegasus port and starboard payload fairings will be installed around ICON. The Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 9, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
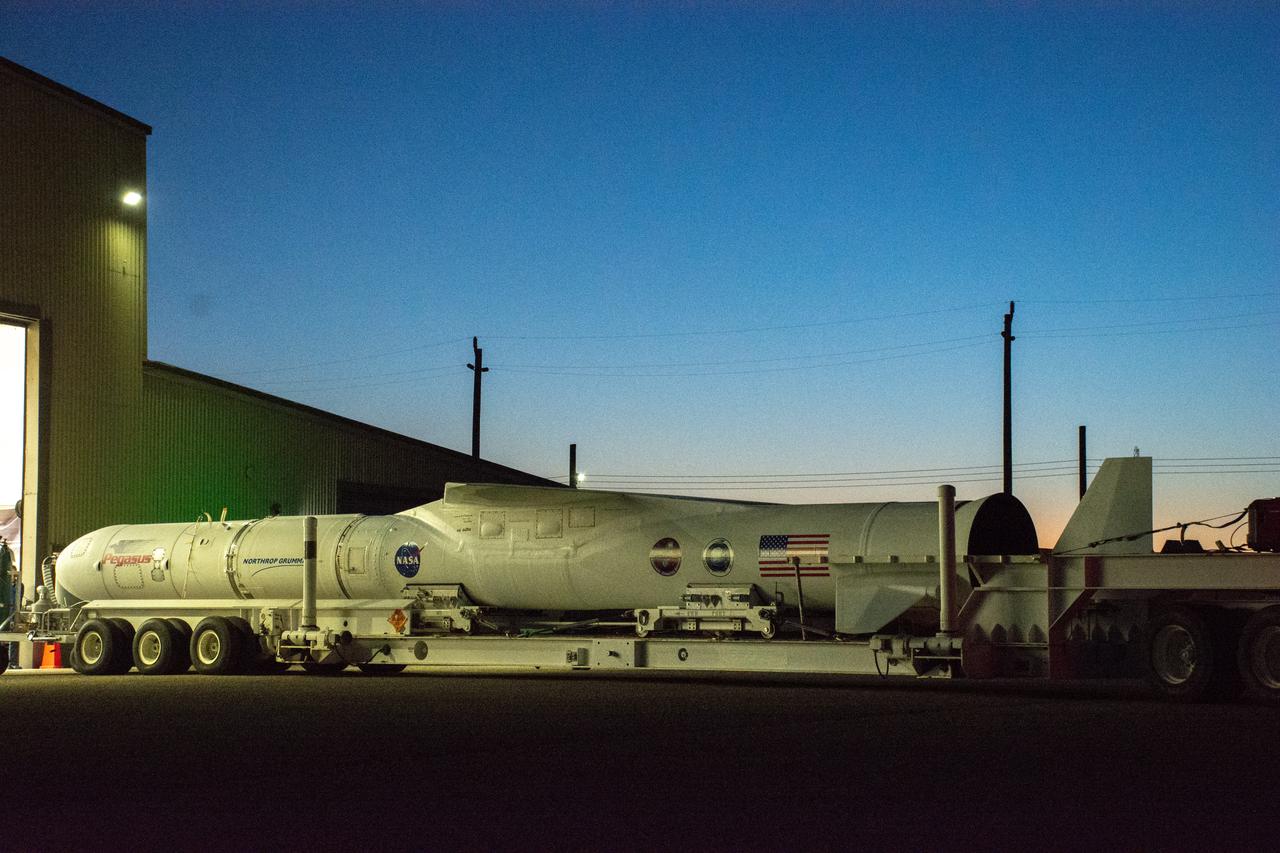

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) secured in its payload fairing, begins rollout from Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 25, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the flight to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. ICON will launch from the Skid Strip at CCAFS. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
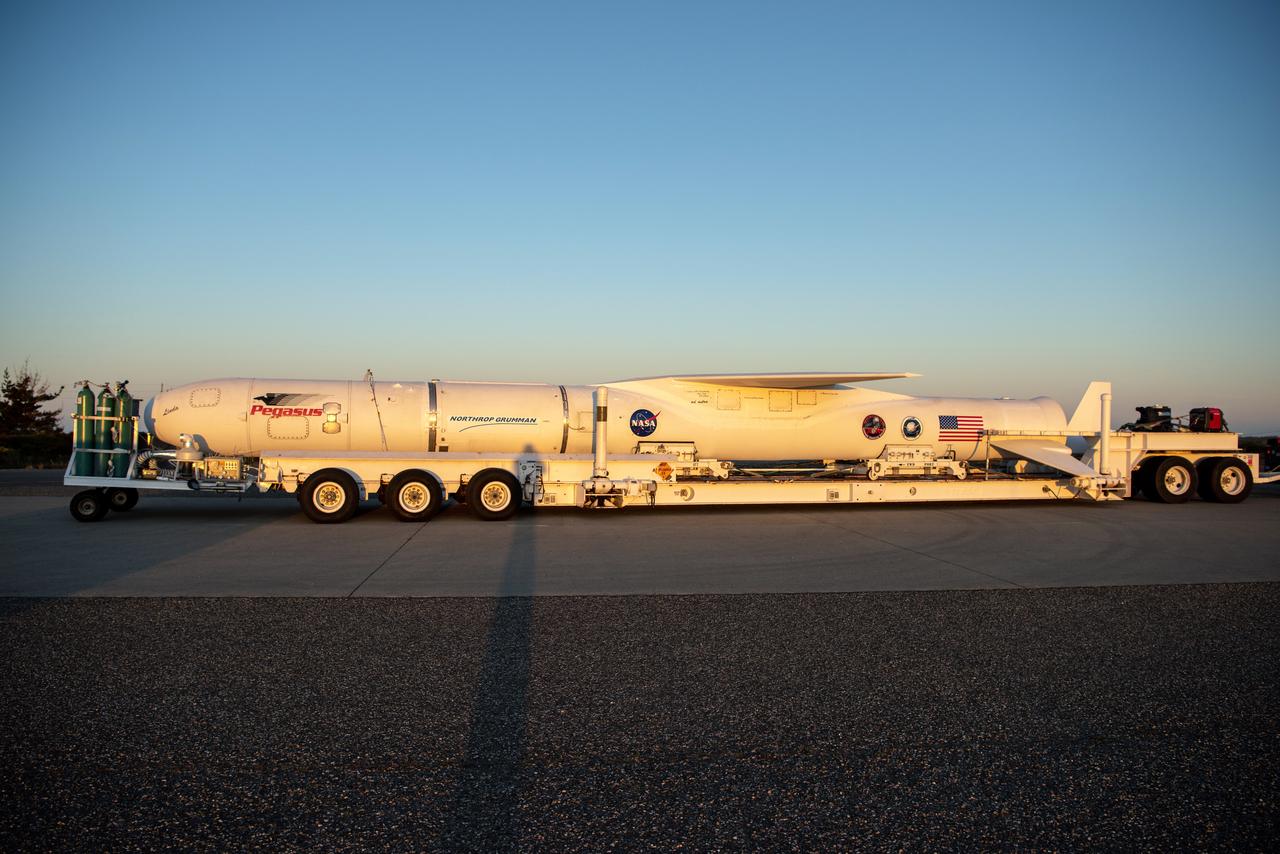

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) secured in its payload fairing, rolls out to the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 25, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the flight to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. ICON will launch from the Skid Strip at CCAFS. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
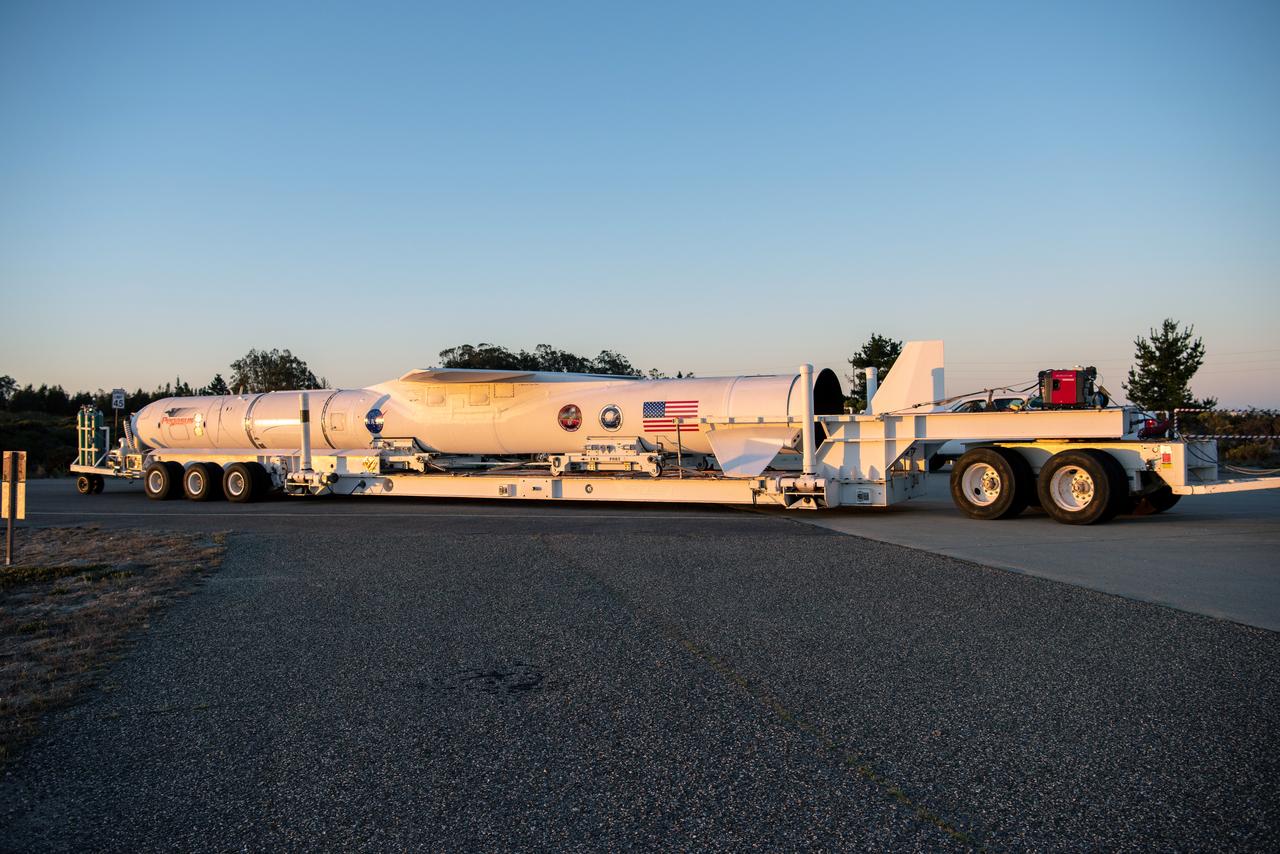

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) secured in its payload fairing, rolls out from Building 1555 to the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 25, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the flight to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. ICON will launch from the Skid Strip at CCAFS in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
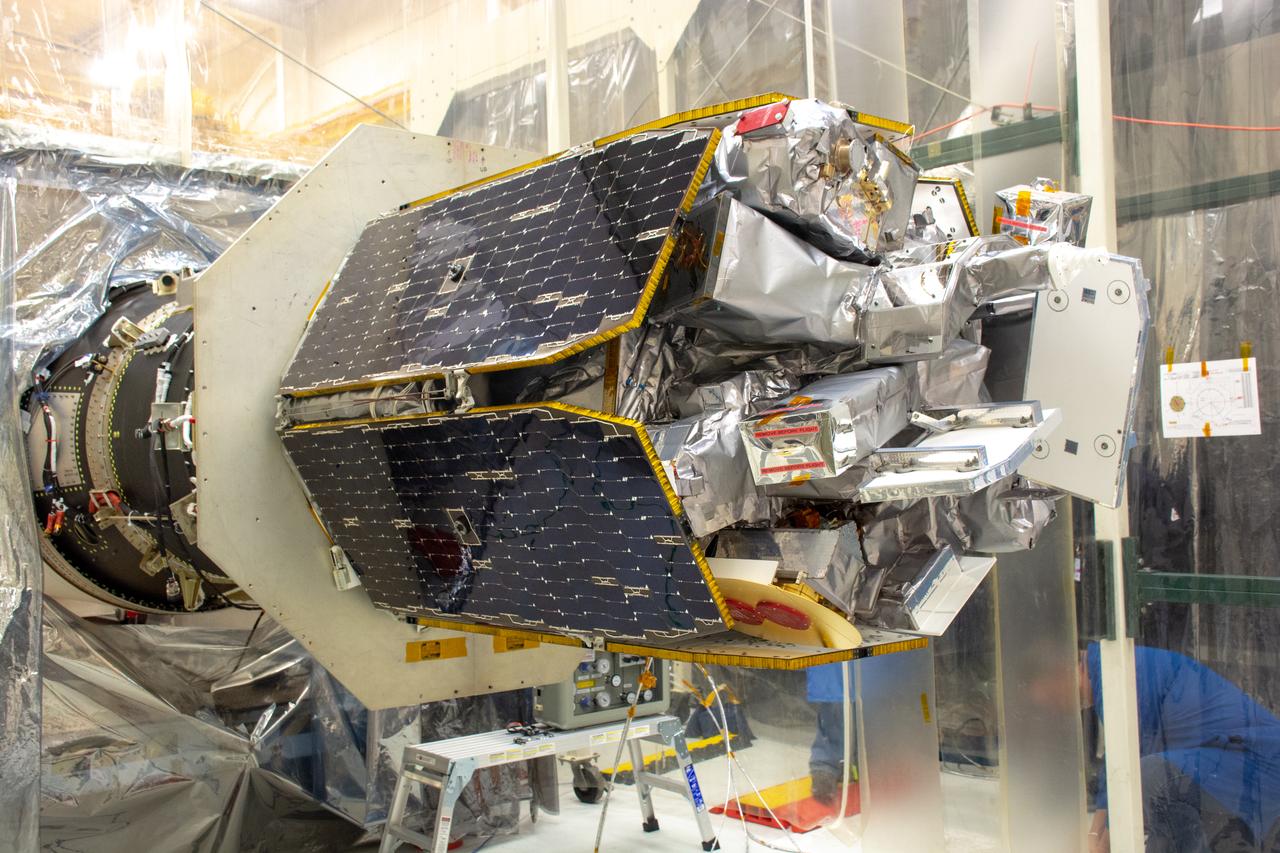

NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is attached to the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 10, 2019. Preparations are underway to perform a black light test on Pegasus before the port and starboard payload fairings are installed around ICON. The Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 9, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.

A technician performs a ultraviolet light inspection of the Orbital ATK Pegasus starboard on May 22, 2018, prior to fully mating NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) to Pegasus inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on the Pegasus XL, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.