
Workmen inspect a J-2 engine at Rocketdyne's Canoga Park, California production facility. The J-2, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, was propelled by liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. A single J-2 engine was used in the S-IVB stage (the second stage of the Saturn IB and third stage for the Saturn V) and a cluster of five J-2 engines was used to propel the second stage of the Saturn V, the S-II. Initially rated at 200,000 pounds of thrust, the J-2 engine was later uprated in the Saturn V program to 230,000 pounds.

This figure is a line drawing of the J-2 engine with callouts of the major components and the engine characteristics.
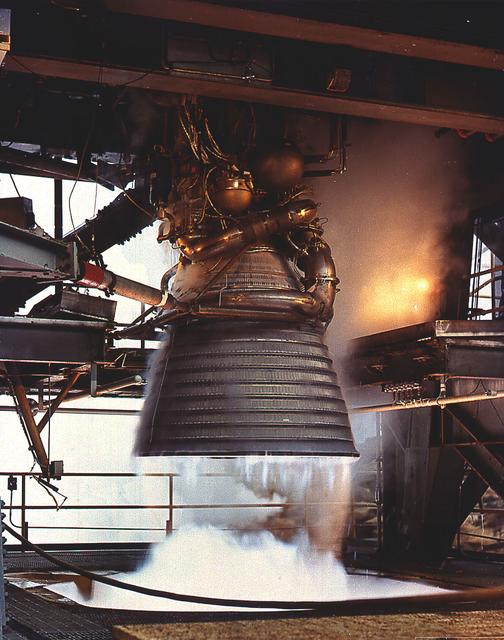
A J-2 engine undergoes static firing. The J-2, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, was propelled by liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. A single J-2 was utilized in the S-IVB stage (the second stage for the Saturn IB and third stage for the Saturn V) and in a cluster of five for the second stage (S-II) of the Saturn V. Initially rated at 200,000 pounds of thrust, the engine was later uprated in the Saturn V program to 230,000 pounds.
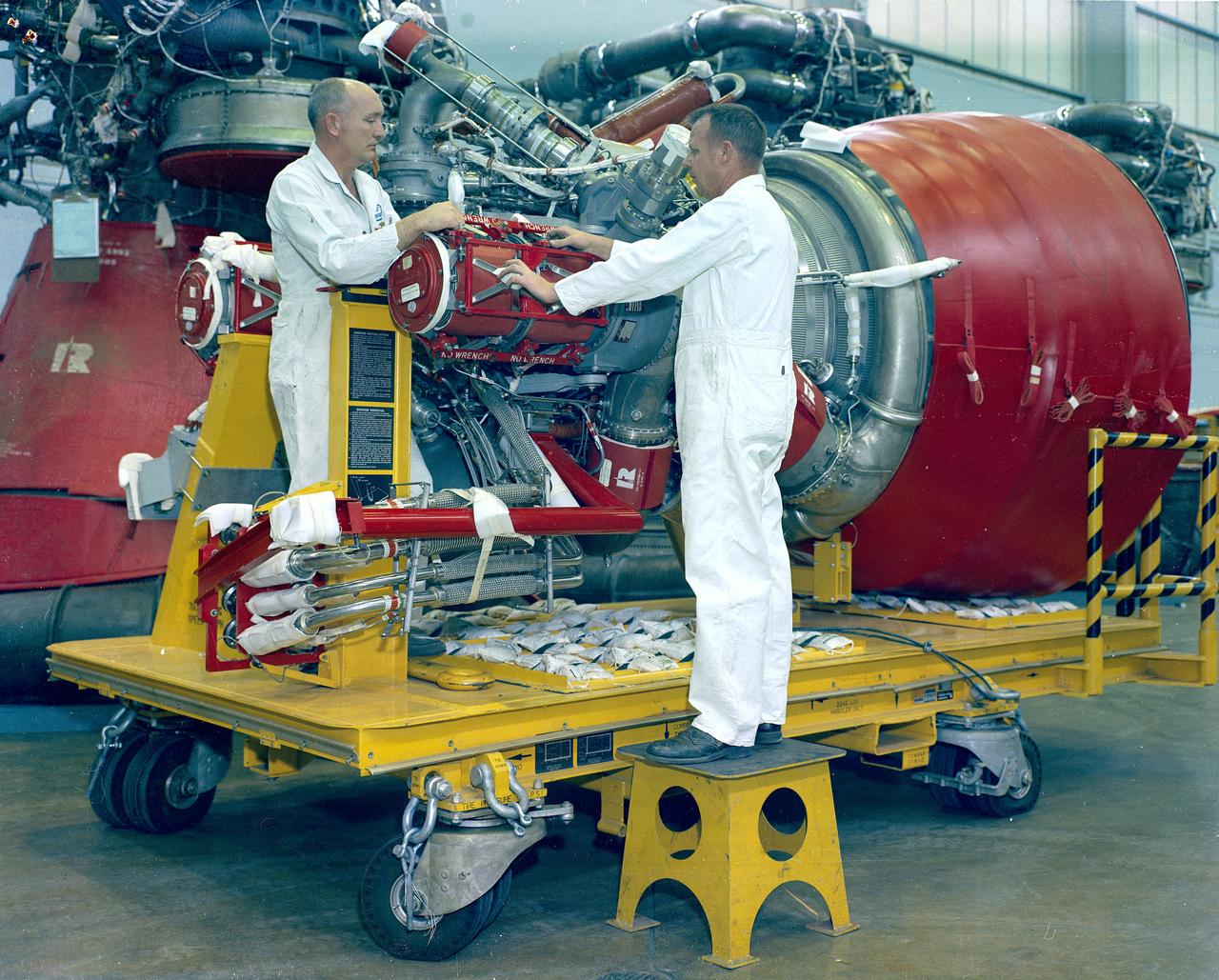

Pictured is a J-2 engine being processed at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). A single J-2 engine was utilized on the S-IVB stage, the second stage of the Saturn IB and the third stage of the Saturn V vehicles, while a cluster of five J-2 engines powered the second (S-II) stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle. The Saturn V was designed, developed, and tested by engineers at MSFC.

This image depicts the test firing of a J-2 engine in the S-IVB Test Stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The J-2, developed by Rocketdyne under the direction of MSFC, was propelled by liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. A single J-2 was utilized in the S-IVB stage (the second stage for the Saturn IB and third stage for the Saturn V) and in a cluster of five for the second stage (S-II) of the Saturn V. Initially rated at 200,000 pounds of thrust, the engine was later upgraded in the Saturn V program to 230,000 pounds.
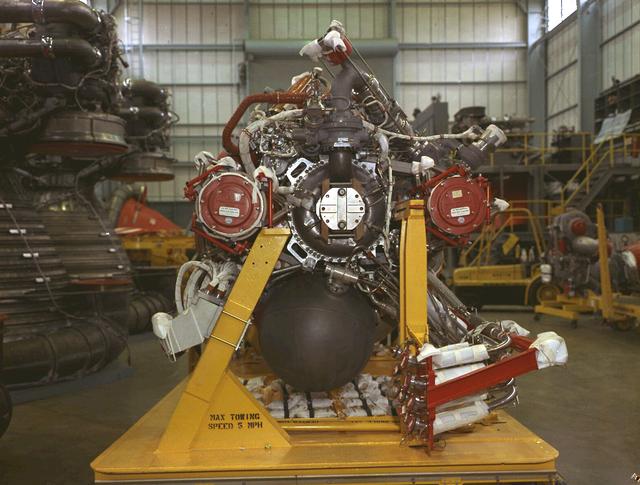

Pictured is a J-2 engine being processed at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). A single J-2 engine was utilized on the S-IVB stage, the second stage of the Saturn IB and the third stage of the Saturn V vehicles, while a cluster of five J-2 engines powered the second (S-II) stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle. The Saturn V was designed, developed, and tested by engineers at MSFC.
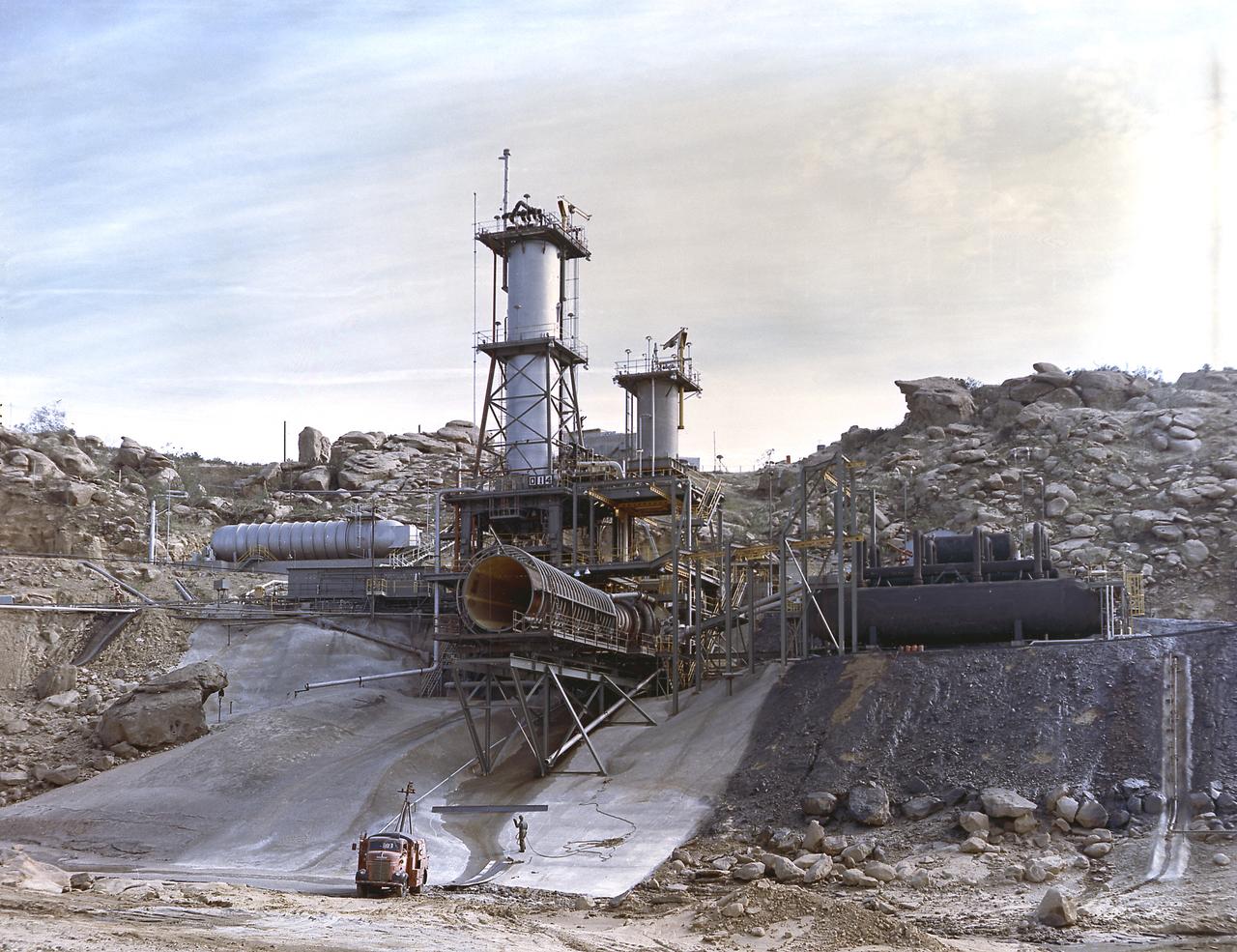

This image depicts an overall view of the vertical test stand for testing the J-2 engine at Rocketdyne's Propulsion Field Laboratory, in the Santa Susana Mountains, near Canoga Park, California. The J-2 engines were assembled and tested at Rocketdyne under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
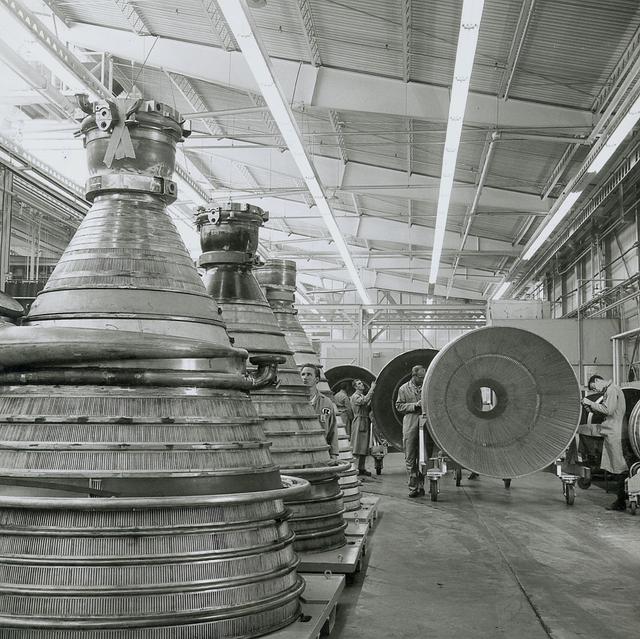

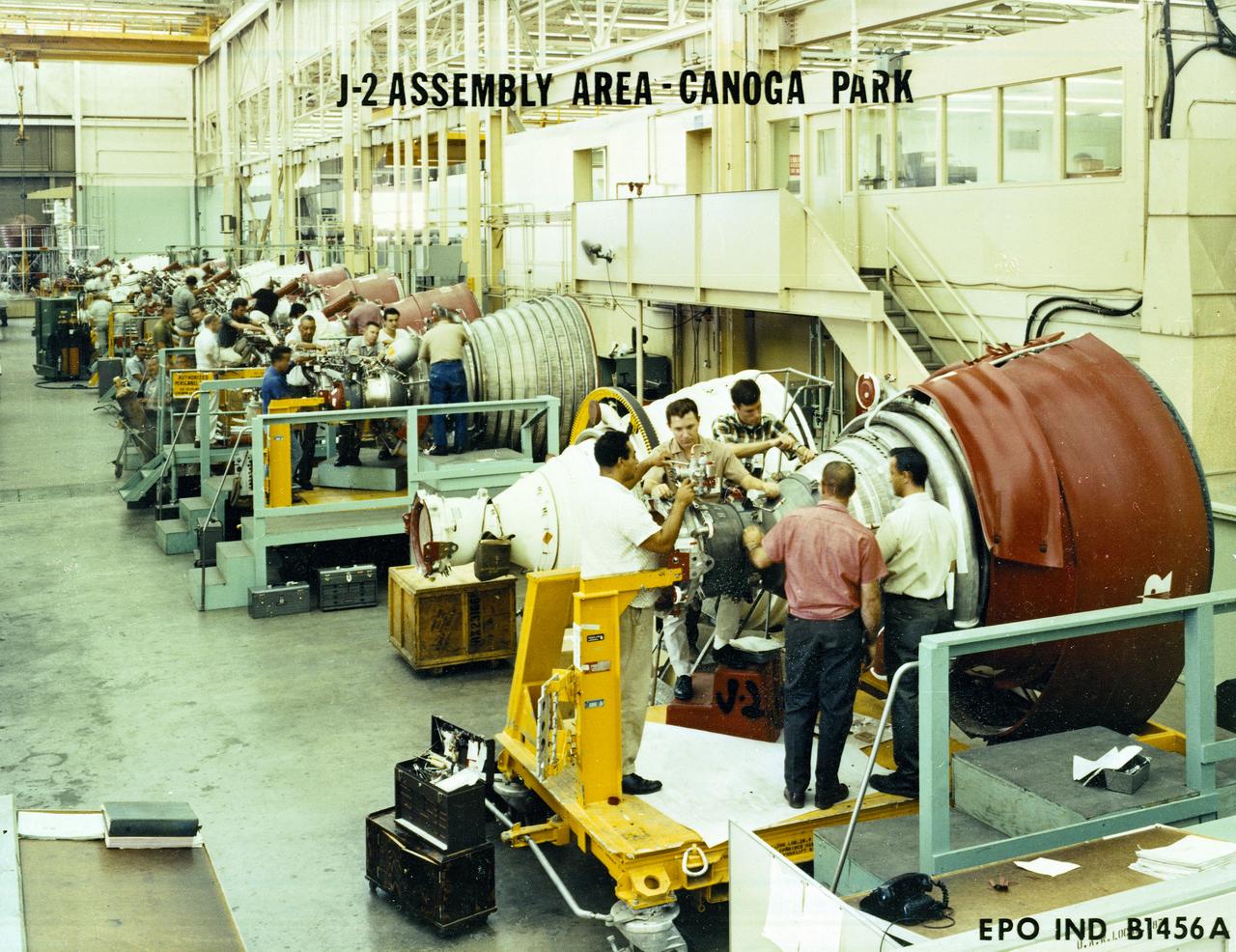
J-2 engines for the Saturn IB/Saturn V launch vehicles are lined up in the assembly area at Rocketdyne's manufacturing plant in Canoga Park, California. Five J-2 engines provided more than 1,000,000 pounds of thrust to accelerate the second stage toward a Moon trajectory.
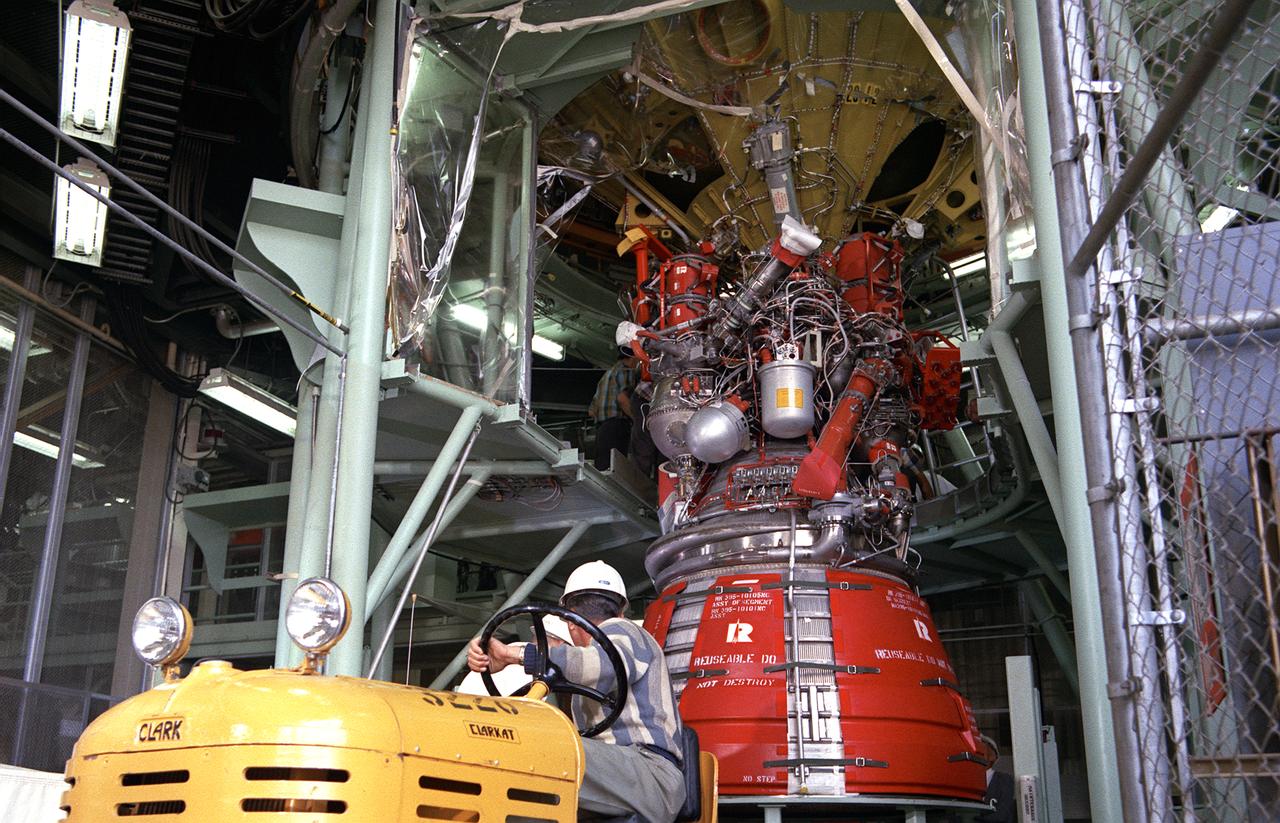

Workmen secure a J-2 engine onto the S-IVB (second) stage thrust structure. As part of Marshall Space Center's "building block" approach to the Saturn development, the S-IVB was utilized in the Saturn IBC launch vehicle as a second stage and the Saturn V launch vehicle as a third stage. The booster, built for NASA by McDornell Douglas Corporation, was powered by a single J-2 engine, initially capable of 200,000 pounds of thrust.

Smokeless flame juts from the diffuser of a unique vacuum chamber in which the upper stage rocket engine, the hydrogen fueled J-2, was tested at a simulated space altitude in excess of 60,000 feet. The smoke you see is actually steam. In operation, vacuum is established by injecting steam into the chamber and is maintained by the thrust of the engine firing through the diffuser. The engine was tested in this environment for start, stop, coast, restart, and full-duration operations. The chamber was located at Rocketdyne's Propulsion Field Laboratory, in the Santa Susana Mountains, near Canoga Park, California. The J-2 engine was developed by Rocketdyne for the Marshall Space Flight Center.
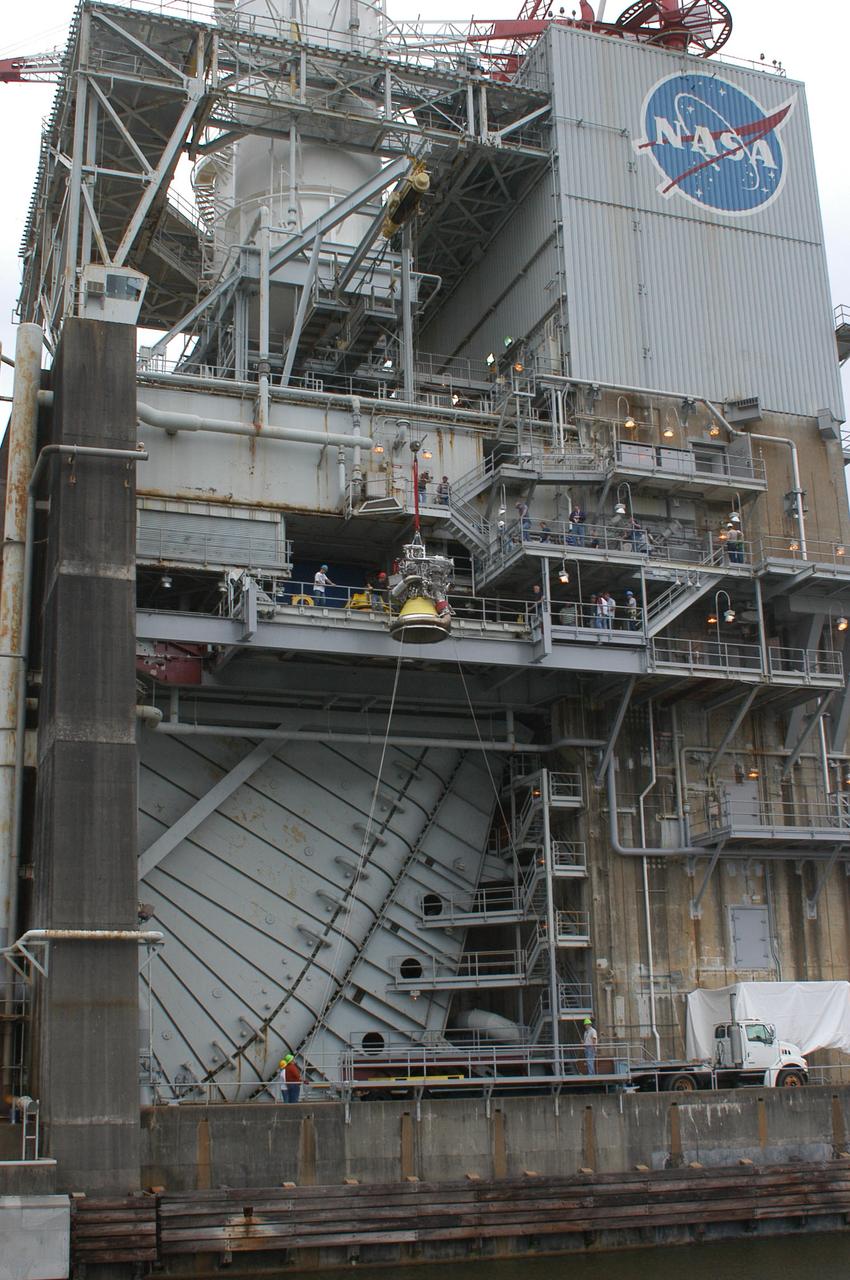

J-2X engine No. 10001 is returned March 8, 2012, to the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center for its second round of tests. The developmental engine underwent an initial series of tests last year. The J-2X engine is being built for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne.

A J-2 Gas Generator (GG) engine's duration test at Marshall's Test Stand-116.
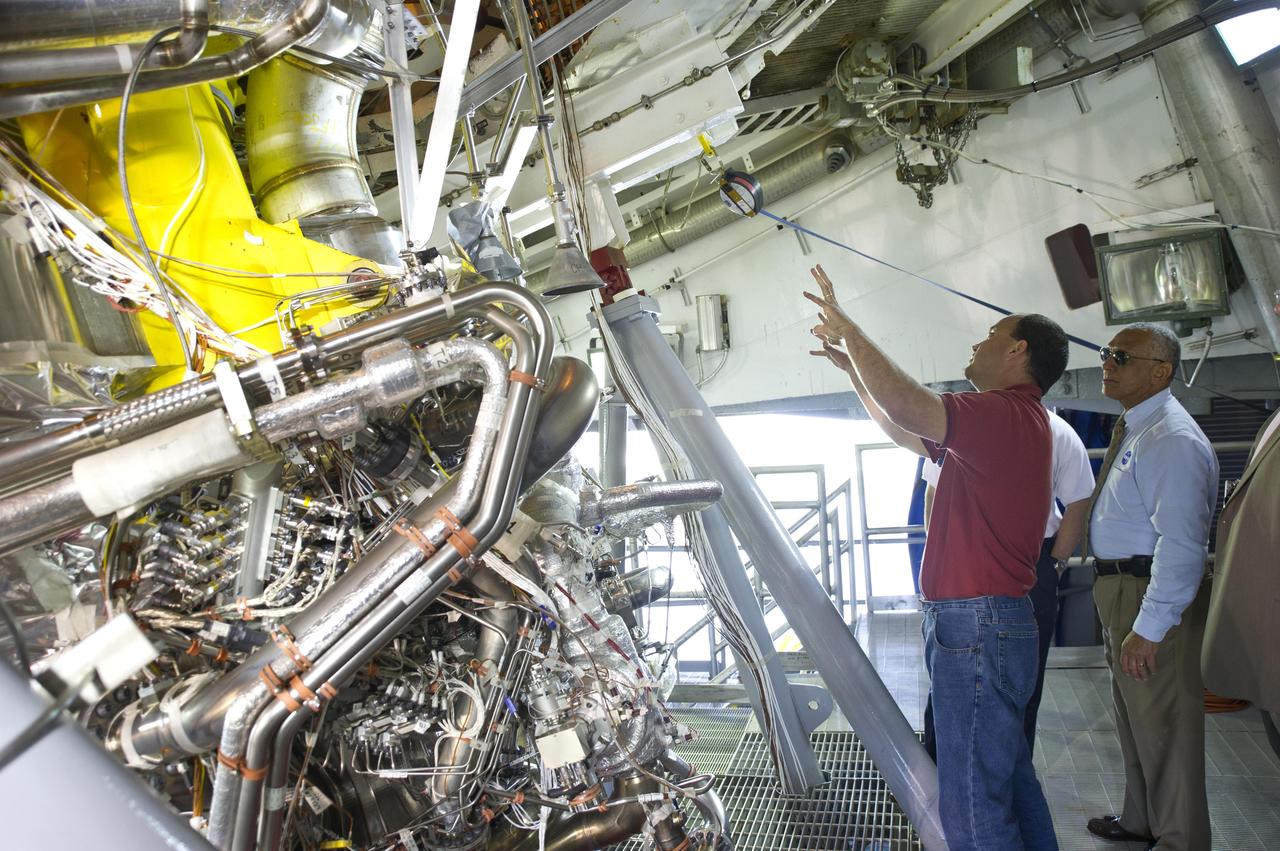
NASA Administrator Charles Bolden (r) takes an up-close look at the first development J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center during an April 20, 2012, visit. Pictured with Bolden is A-2 Test Stand Director Skip Roberts. The J-2X engine is being developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne.
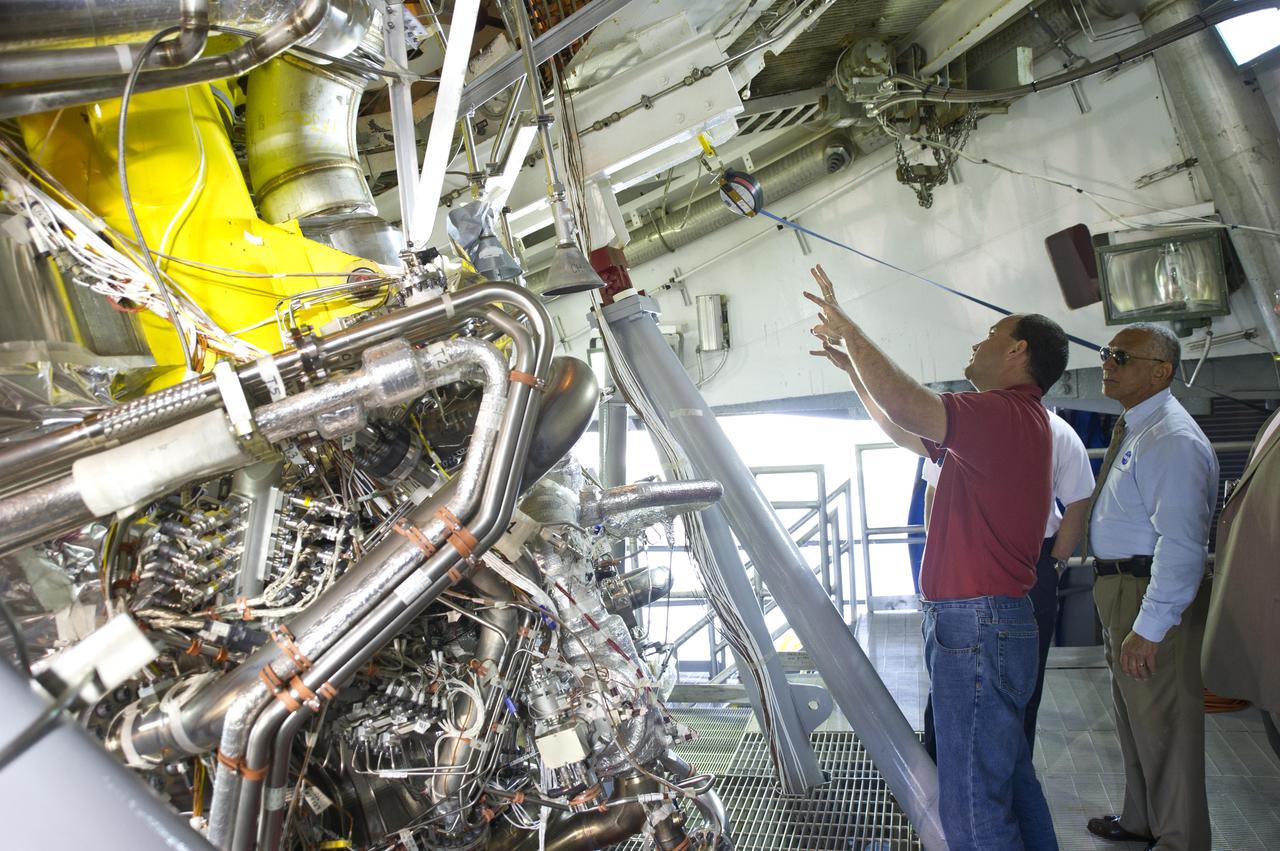
NASA Administrator Charles Bolden (r) takes an up-close look at the first development J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center during an April 20, 2012, visit. Pictured with Bolden is A-2 Test Stand Director Skip Roberts. The J-2X engine i s being developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne.
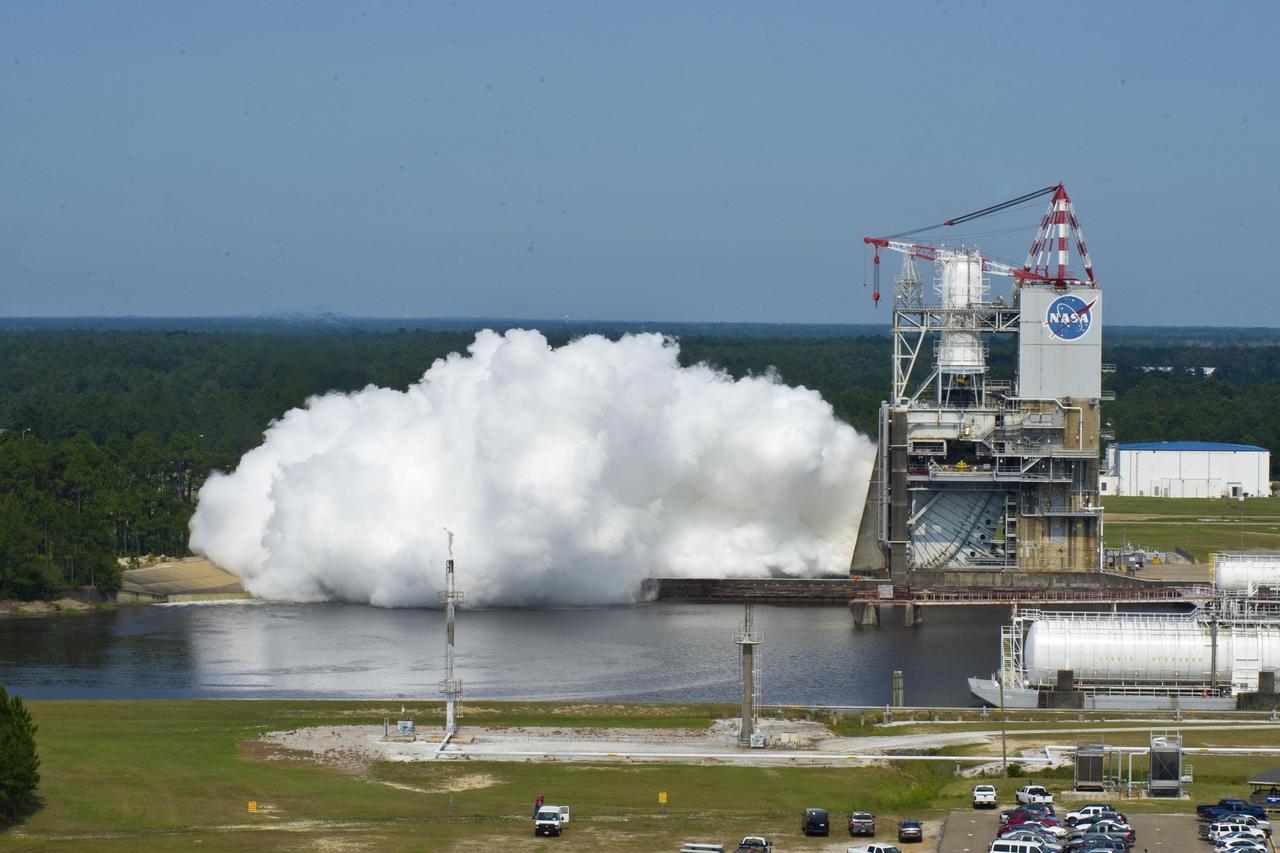

On May 25, 2012, NASA recorded another first during a 40-second test of the next-generation J-2X engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center. Test conductors fired the J-2X in both the secondary and primary modes of operation. Previous tests were run in one mode only; combining the two allowed operators to collect critical data on engine performance.
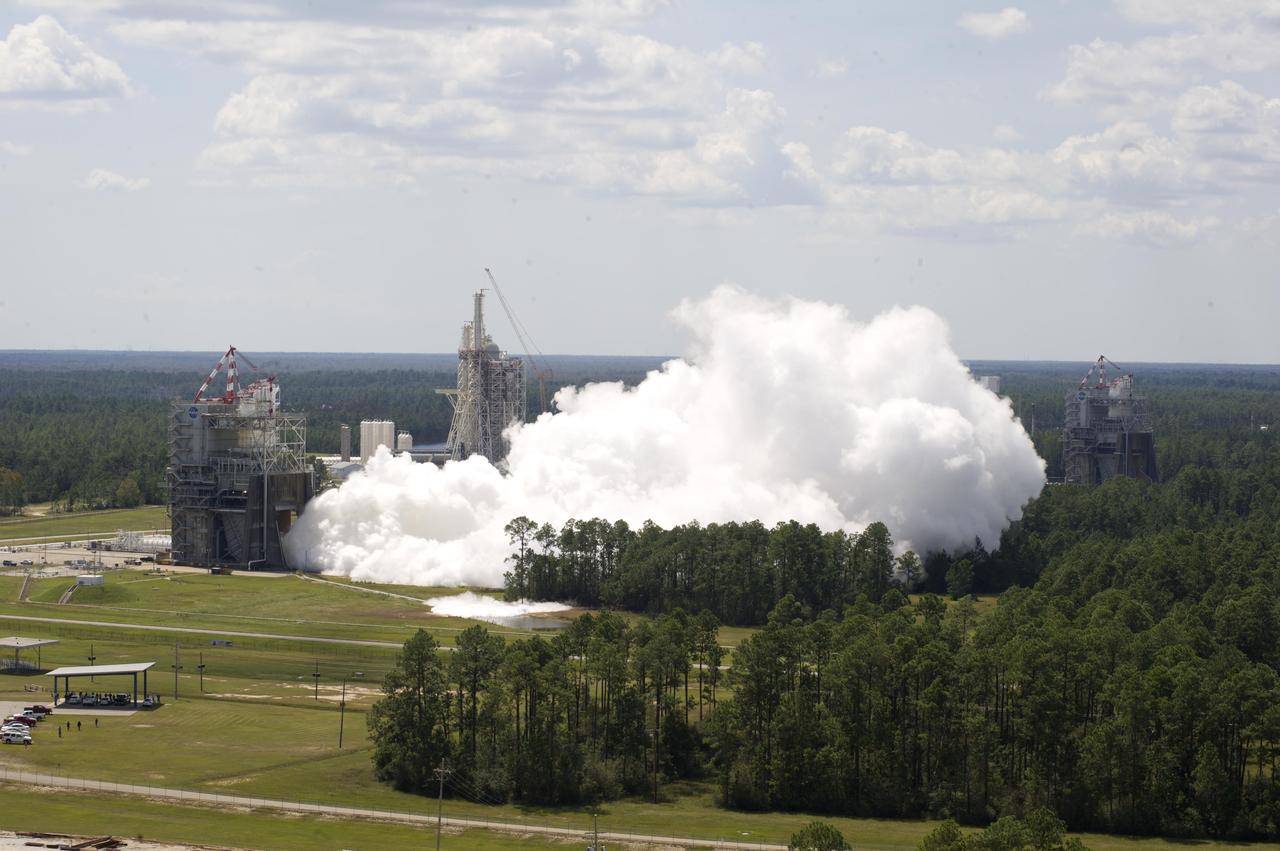

NASA engineers continued to collect test performance data on the new J-2X rocket engine at Stennis Space Center with a 250-second test Sept. 14. The test on the A-2 Test Stand was the 19th in a series of firings to gather critical data for continued development of the engine. The J-2X is being developed by Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne for NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. It is the first liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen rocket engine rated to carry humans into space to be developed in 40 years.
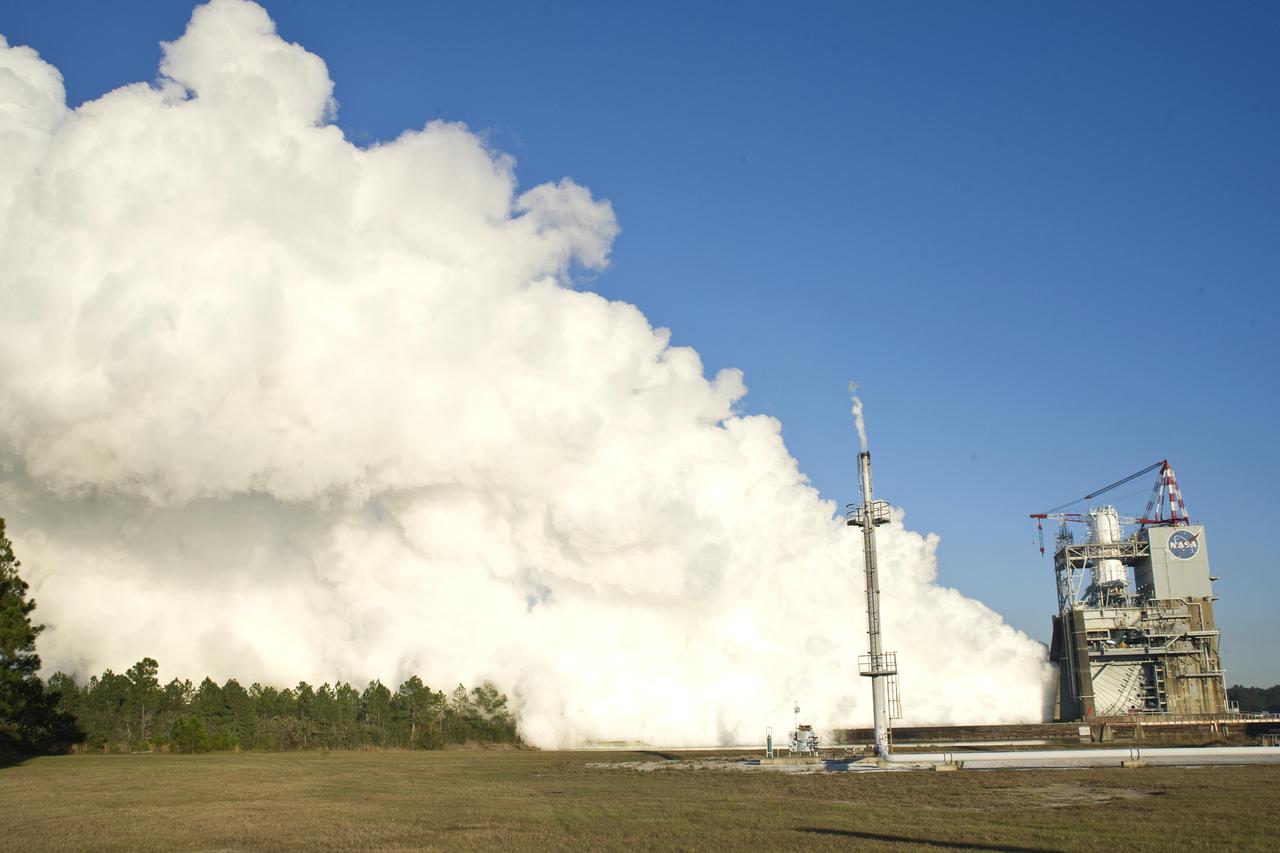

NASA conducted a key stability test firing of the J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Dec. 1, marking another step forward in development of the upper-stage engine that will carry humans deeper into space than ever before. The J-2X will provide upper-stage power for NASA's new Space Launch System.
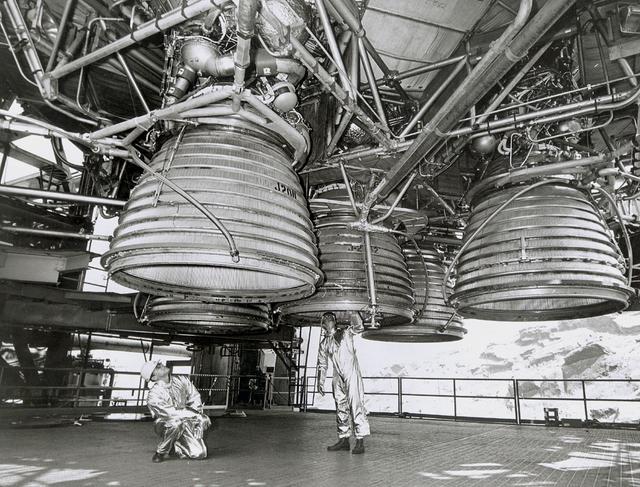

Two workers are dwarfed by the five J-2 engines of the Saturn V second stage (S-II) as they make final inspections prior to a static test firing by North American Space Division. These five hydrogen -fueled engines produced one million pounds of thrust, and placed the Apollo spacecraft into earth orbit before departing for the moon. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
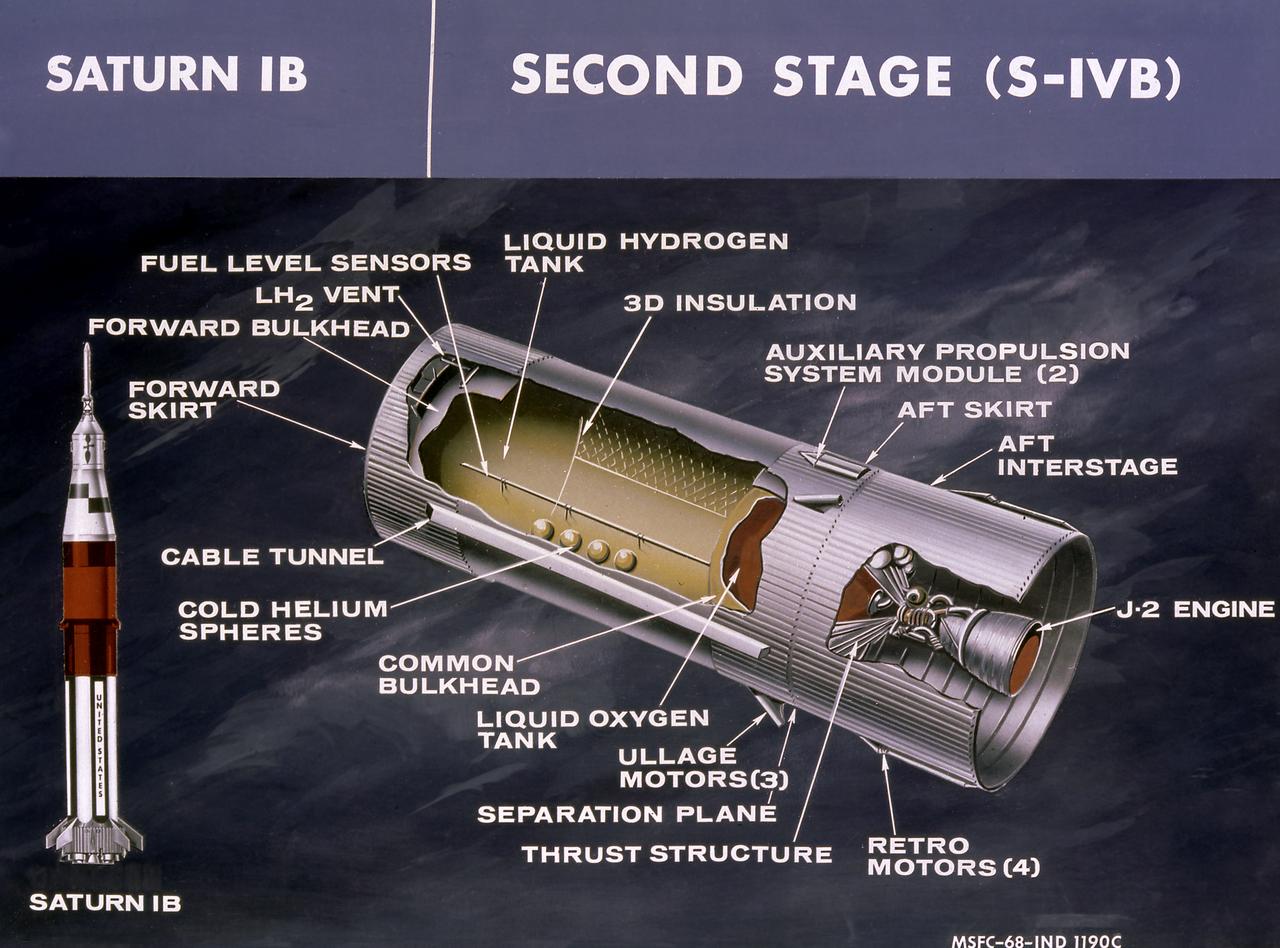
This cutaway drawing shows the S-IVB stage in its Saturn IB configuration. As a part of the Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) "building block" approach to the Saturn development, the S-IVB stage was utilized in the Saturn IB launch vehicle as a second stage and, later, the Saturn V launch vehicle as a third stage. The stage was powered by a single J-2 engine, initially capable of 200,000 pounds of thrust.
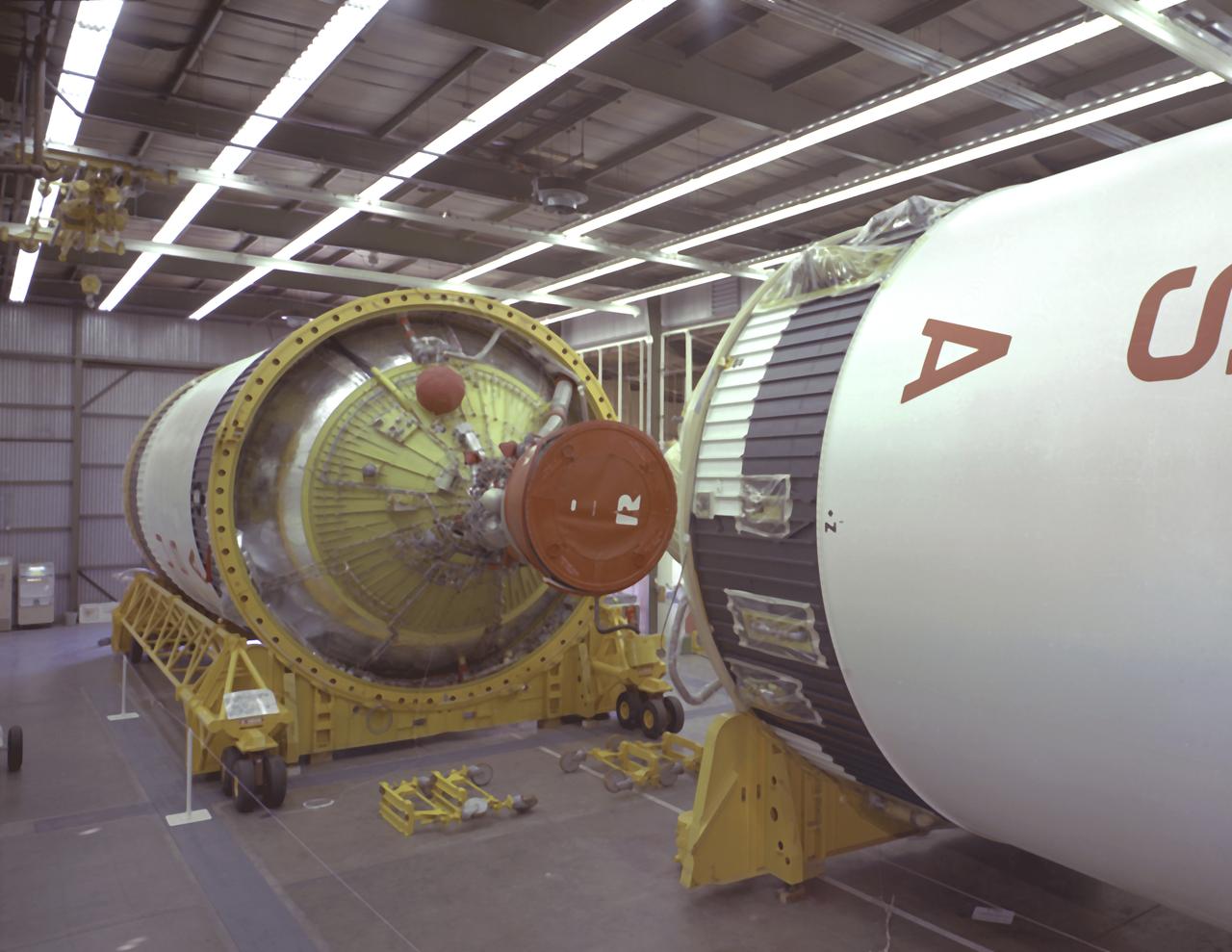

The Saturn IB S-IVB (second) stages in storage at the Douglas Aircraft Company's Sacramento Test Operations Facility (SACTO) in Sacramento, California. Designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and the Douglas Aircraft Company, the S-IVB stage was powered by a single J-2 engine, which produced 200,000 pounds of thrust, later uprated to 230,000 pounds for the Saturn V launch vehicle.
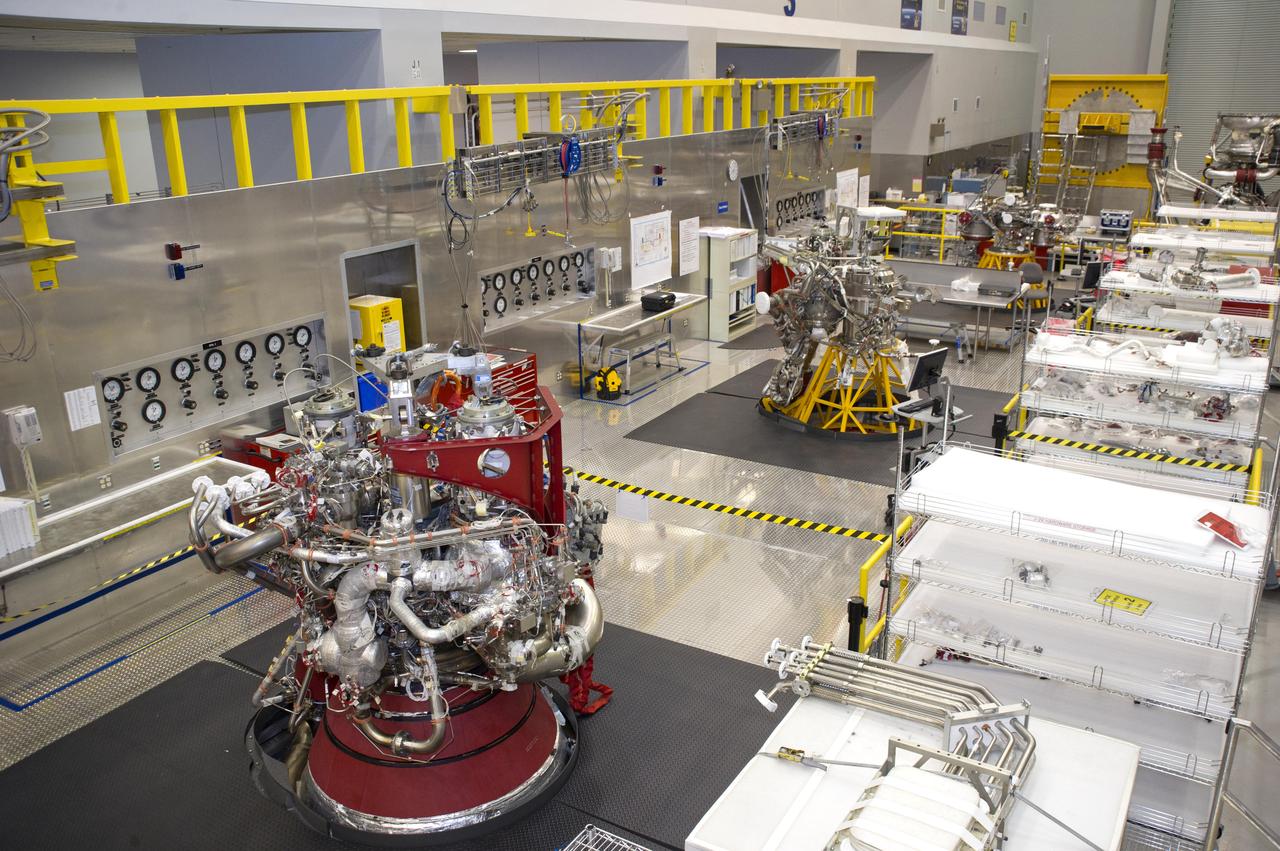
Two J-2X engines and a powerpack, developed for NASA by Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne, sit side-by-side Oct. 11 at Stennis Space Center as work continues on the Space Launch System. Engine 10001 (far left) has been removed from the A-2 Test Stand after being hot-fire tested 21 times, for a total of 2,697 seconds. The engine is now undergoing a series of post-test inspections. A J-2X powerpack (center) has been removed from the A-1 Test Stand to receive additional instrumentation. So far, the powerpack been hot-fire tested 10 times, for a total of 4,162 seconds. Meanwhile, assembly on the second J-2X engine, known as Engine 10002 and located to the far right, has begun in earnest, with engine completion scheduled for this November. Engine 10002 is about 15 percent complete.
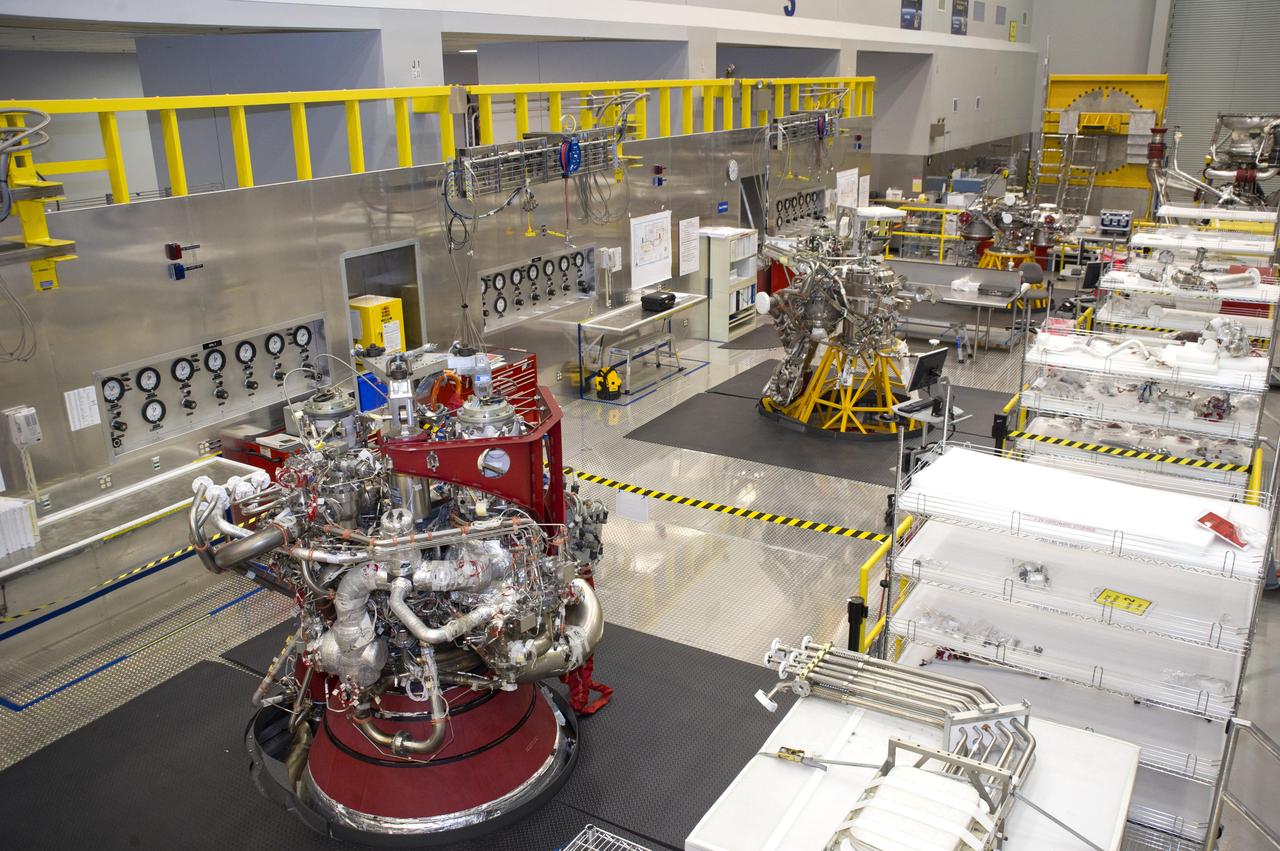
Two J-2X engines and a powerpack, developed for NASA by Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne, sit side-by-side Oct. 11 at Stennis Space Center as work continues on the Space Launch System. Engine 10001 (far left) has been removed from the A-2 Test Stand after being hot-fire tested 21 times, for a total of 2,697 seconds. The engine is now undergoing a series of post-test inspections. A J-2X powerpack (center) has been removed from the A-1 Test Stand to receive additional instrumentation. So far, the powerpack been hot-fire tested 10 times, for a total of 4,162 seconds. Meanwhile, assembly on the second J-2X engine, known as Engine 10002 and located to the far right, has begun in earnest, with engine completion scheduled for this November. Engine 10002 is about 15 percent complete.
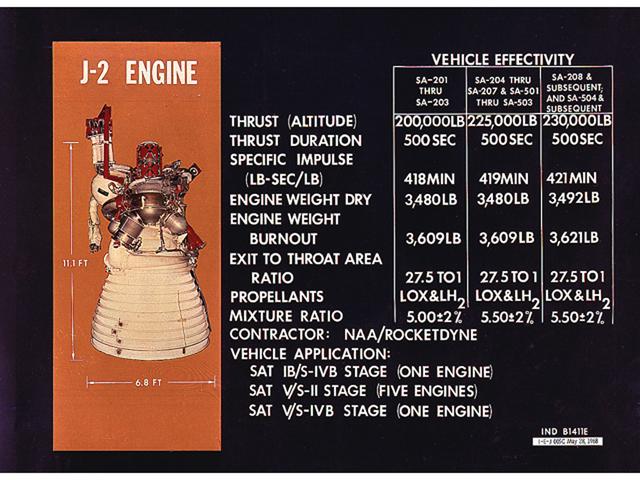
This chart is an illustration of J-2 Engine characteristics. A cluster of five J-2 engines powered the Saturn V S-II (second) stage with each engine providing a thrust of 200,000 pounds. A single J-2 engine powered the S-IVB stage, the Saturn IB second stage, and the Saturn V third stage. The engine was uprated to provide 230,000 pounds of thrust for the fourth Apollo Saturn V flight and subsequent missions. Burning liquid hydrogen as fuel and using liquid oxygen as the oxidizer, the cluster of five J-2 engines for the S-II stage burned over one ton of propellant per second, during about 6 1/2 minutes of operation, to take the vehicle to an altitude of about 108 miles and a speed of near orbital velocity, about 17,400 miles per hour.
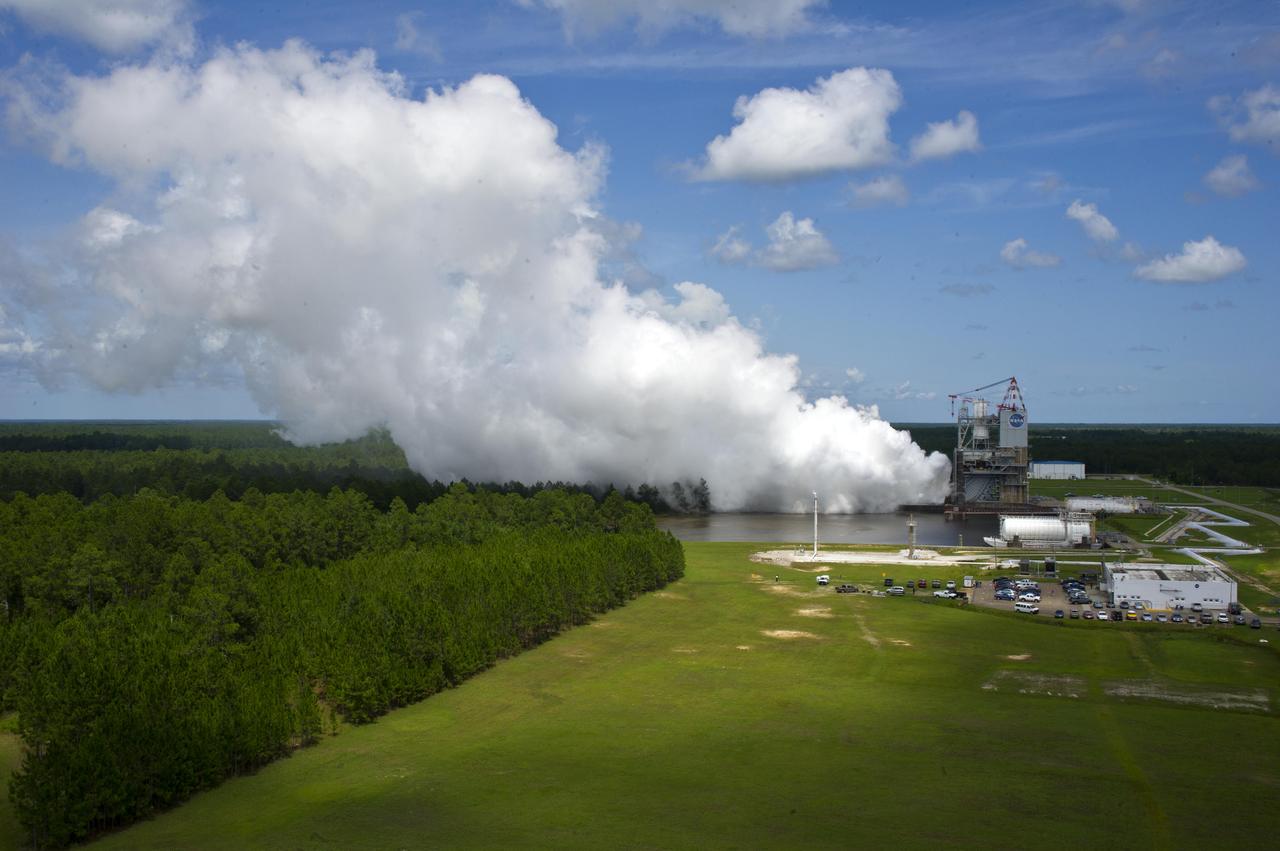

NASA's test of the J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on July 13 was picture perfect in more ways than one. Not only did the test provide a breathtaking view from atop the nearby A-1 Test Stand, and with the center's B-1/B-2 Test Stand in the background, but it achieved its target of 550 seconds. The test continued a series of firings to gather critical data for engine development.
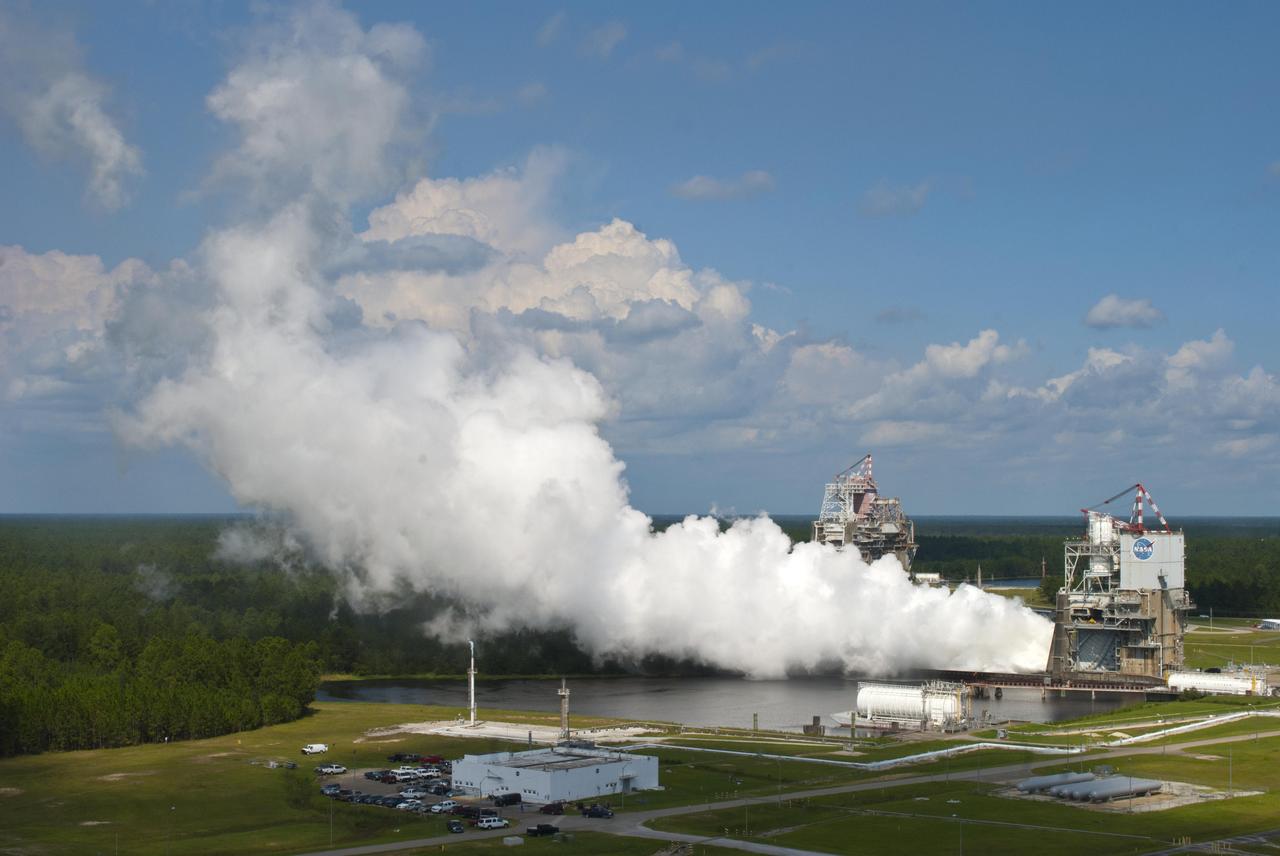

NASA engineers continued testing the next-generation J-2X rocket engine at Stennis Space Center with a 250-second test on Sept. 7. The test was the first conducted after the arrival of Hurricane Isaac forced closure of the Stennis facility for three days in late August. The est was conducted on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis. The facility's B-1/B-2 Test Stand can be seen in the left background.

The J-2 engine for Saturn V S-IVB (third) stage blasted from the test stand at Douglas Aircraft Co., Sacramento Test Operation (SACTO) facility in California. This third stage was used on the unmarned Saturn V flight of Apollo 6 in April 1968.
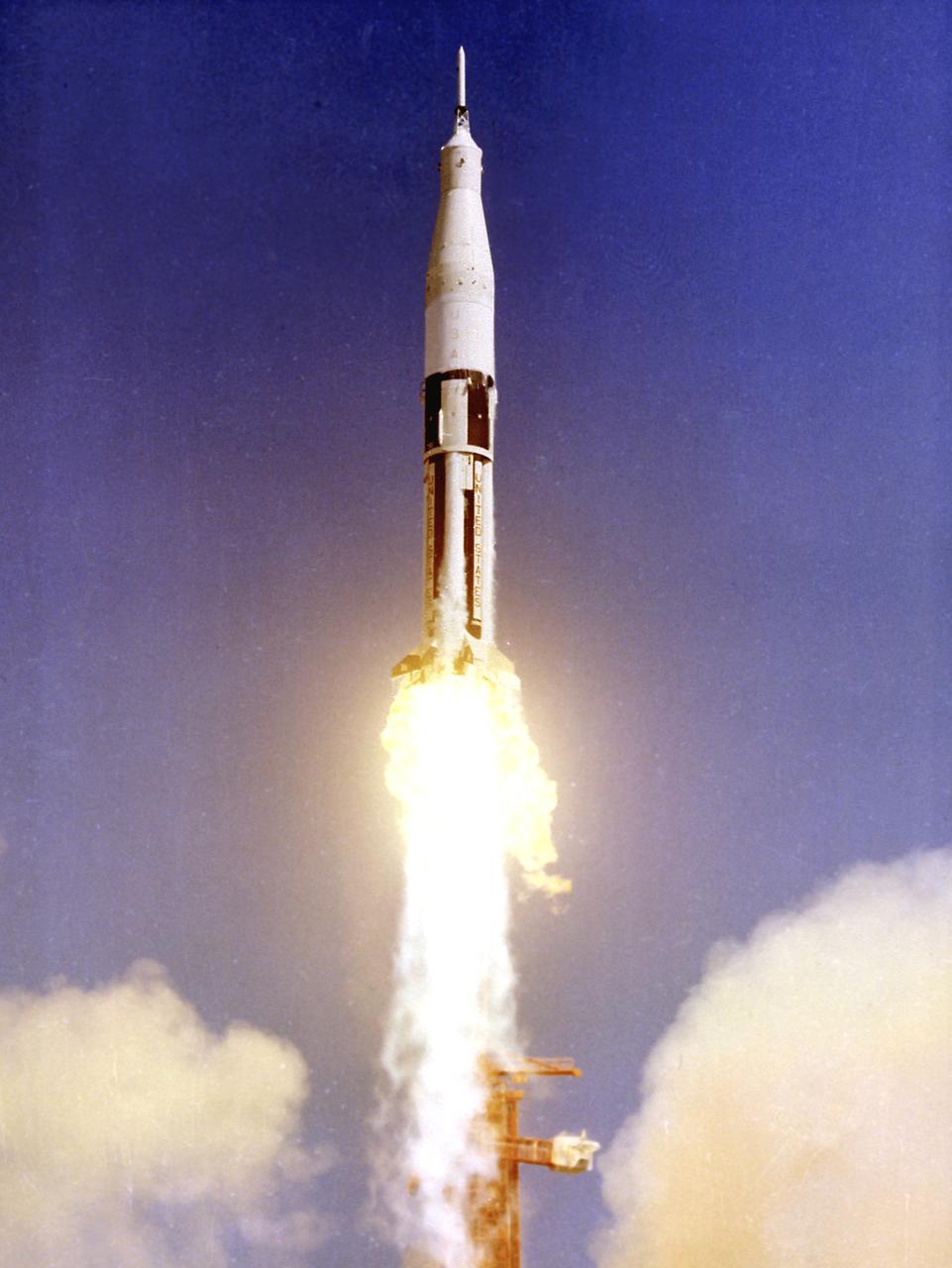

AS-201, the first Saturn IB launch vehicle developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), lifts off from Cape Canaveral, Florida, February 26, 1966. This was the first flight of the S-IB and S-IVB stages, including the first flight test of the liquid-hydrogen/liquid oxygen-propelled J-2 engine in the S-IVB stage. During the thirty-seven minute flight, the vehicle reached an altitude of 303 miles and traveled 5,264 miles downrange. In all, nine Saturn IB flights were made, ending with the Apollo Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) in July 1975.
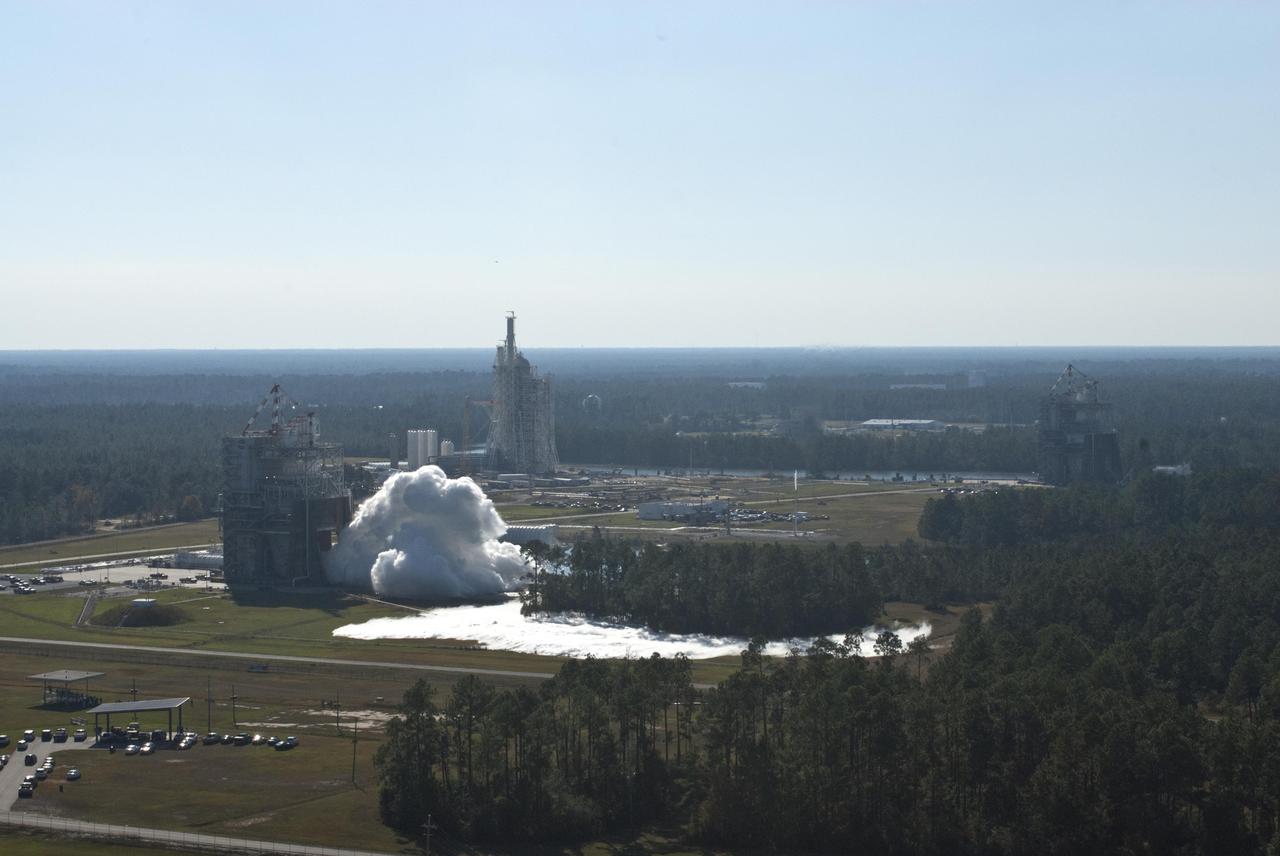

A photograph of a J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand from atop the B Test Stand at Stennis Space Center offers a panoramic view of the A Test Complex. The J-2X engine is being developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne to carry humans deeper into space than ever before.
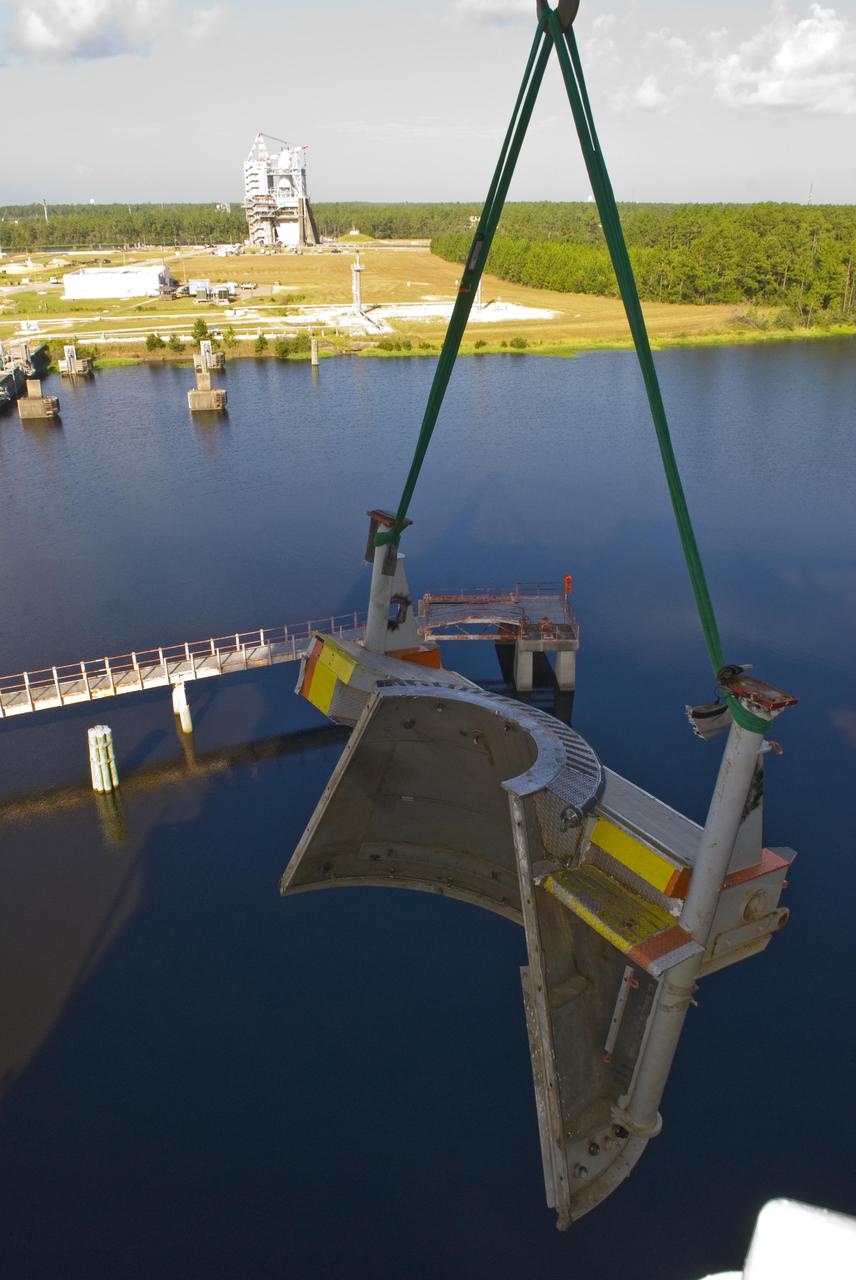

John C. Stennis Space Center employees remove one-half of the A-2 Test Stand clamshell used for testing space shuttle main engines. Space shuttle main engine testing concluded July 2009; the A-2 stand now is being prepared for testing the next-generation J-2X rocket engine in development. Testing of the J-2X engine is scheduled to begin in 2011.
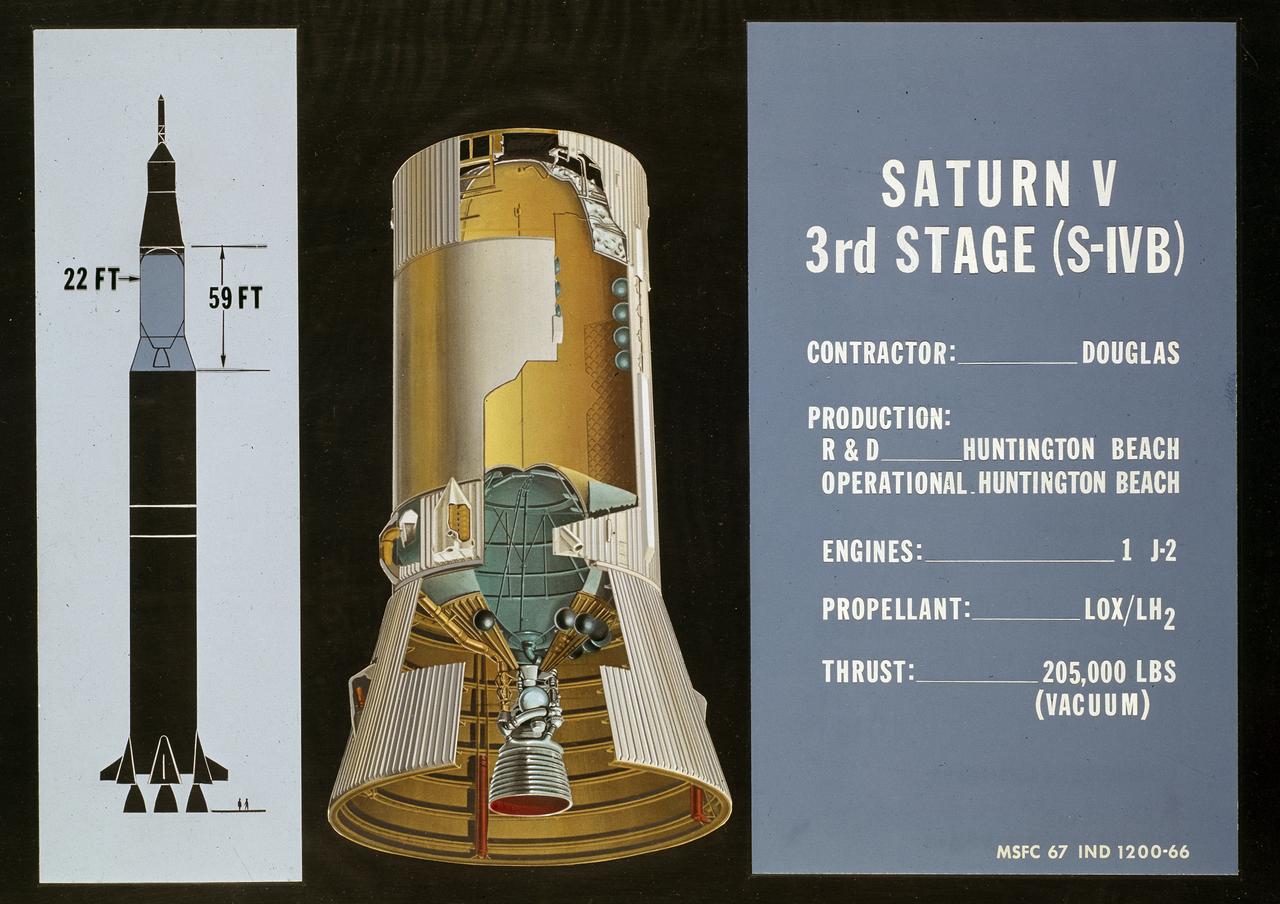
This cutaway drawing shows the S-IVB (third stage) of the Saturn V launch vehicle. As a part of the Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC) “building block” approach to the Saturn development, the S-IVB stage was utilized in the Saturn IB launch vehicle as a second stage and, later, the Saturn V launch vehicle as a third stage. The 59 foot long and 22 feet diameter stage was powered by a single J-2 engine, initially capable of 200,000 pounds of thrust.
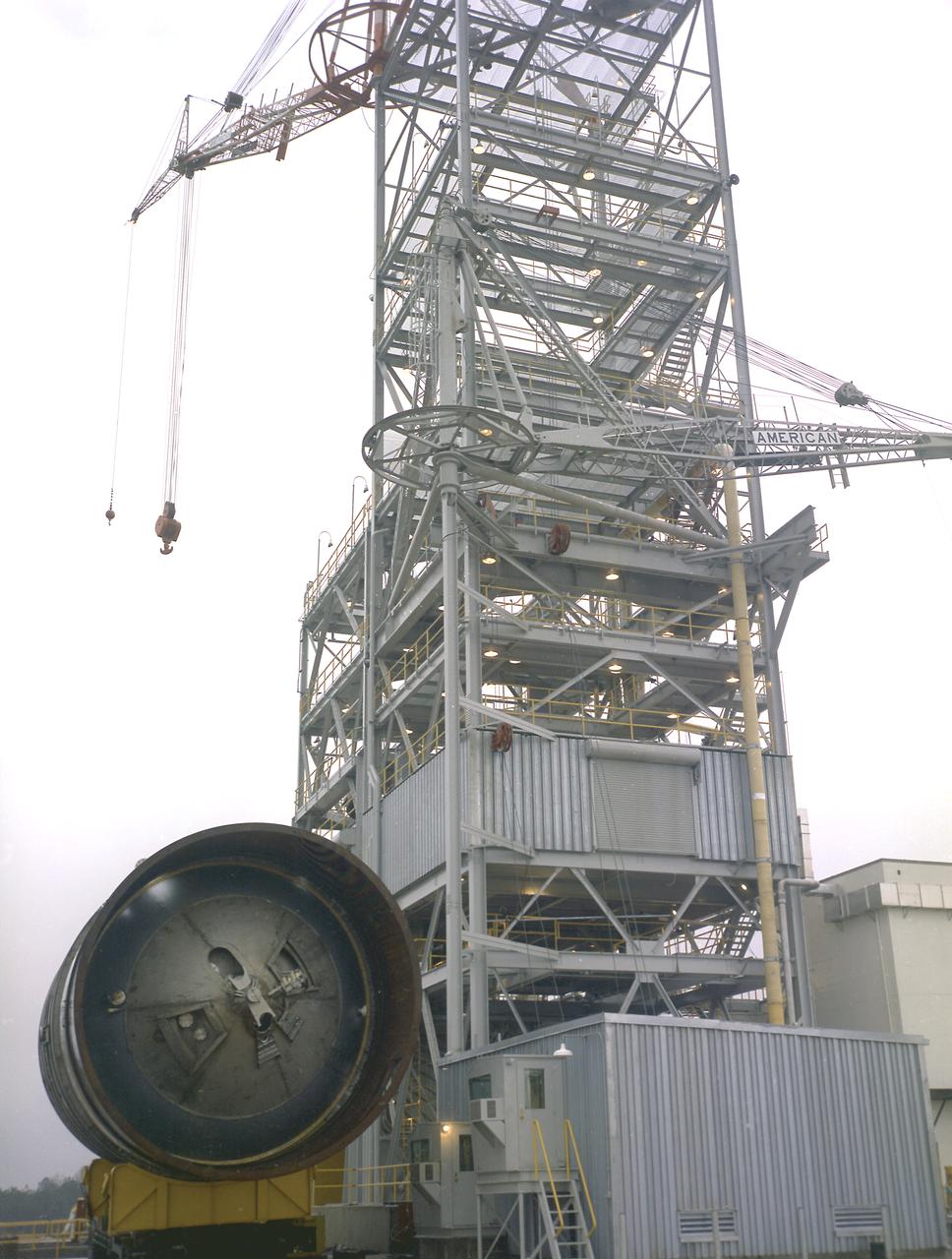

Workers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) move a facility test version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's second stage, the S-IVB, to the J-2 test stand on February 10, 1965. Also known as a "battleship" because of its heavy, rugged construction, the non-flight, stainless-steel model was used to check out testing facilities at MSFC.
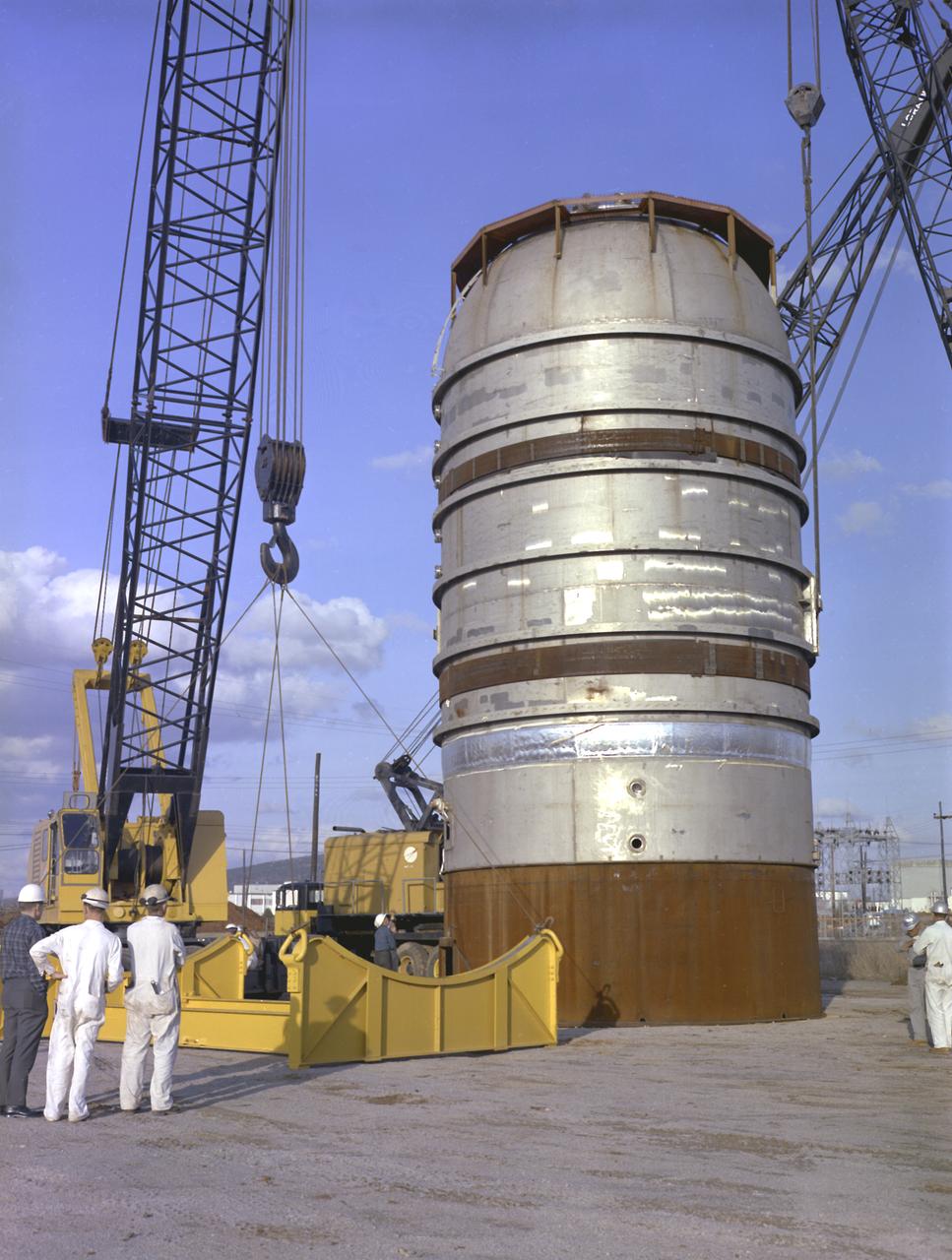

Workers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) move a facility test version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's second stage, the S-IVB, to the J-2 test stand on February 10, 1965. Also known as a "battleship" because of its heavy, rugged construction, the non-flight, stainless-steel model was used to check out testing facilities at MSFC.
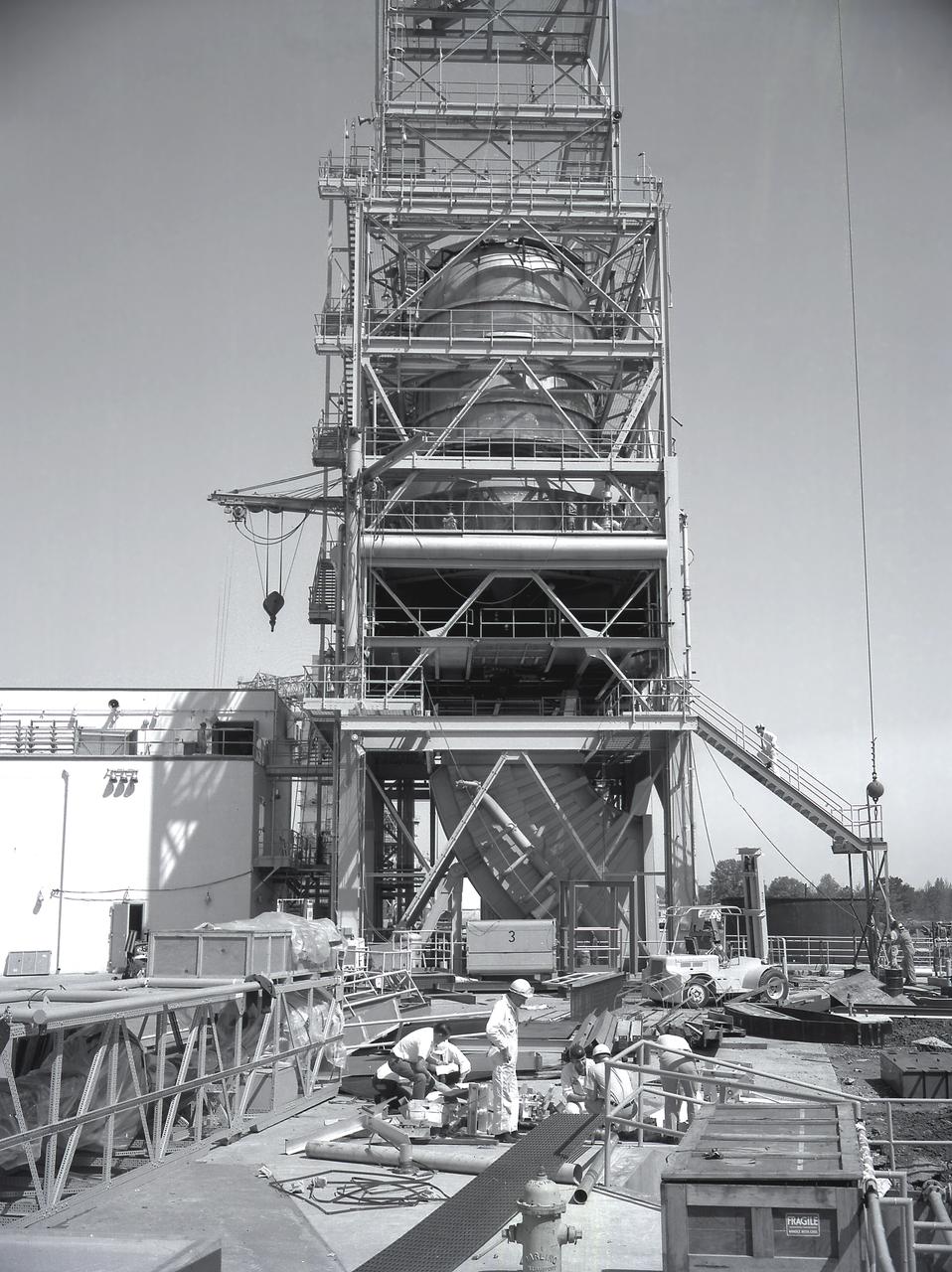

A facility test version of the S-IVB, the second stage of the Saturn IB launch vehicle, sits in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) J-2 test stand on February 10, 1965. Also known as a "battleship" because of its heavy, rugged construction, the non-flight, stainless-steel model was used to check out testing facilities at MSFC.

This drawing clearly shows the comparative sizes of the rocket engines used to launch the Saturn vehicles. The RL-10 and the H-1 engines were used to launch the Saturn I rockets. The J-2 engine was used on the second stage of Saturn IB and the second and third stages of Saturn V. The F-1 engine was used on the first stage of the Saturn V.
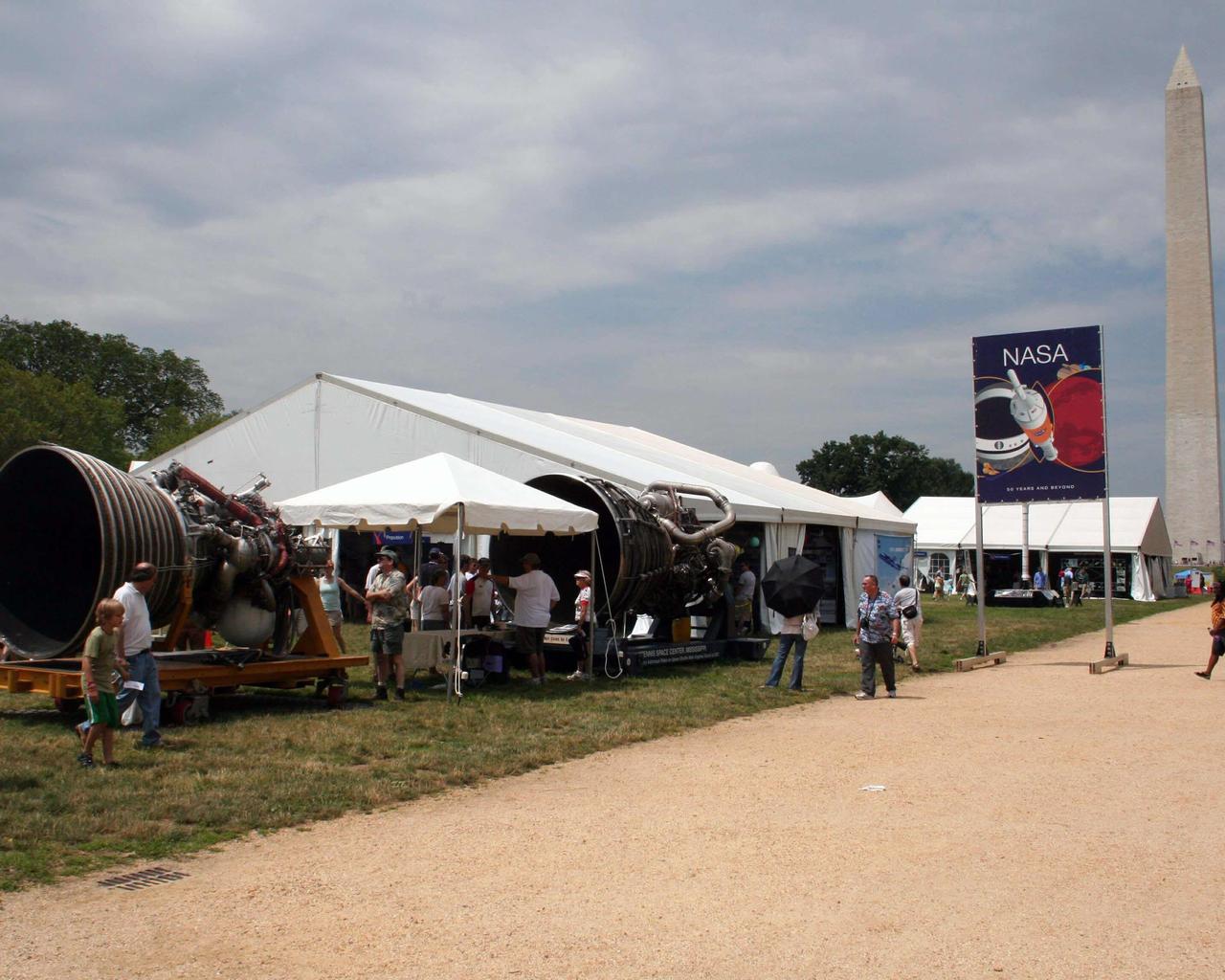

With the Washington Monument as a stirring background, a space shuttle main engine and J-2 engine from Stennis Space Center offer Washington Mall visitors a close-up look at the power of spaceflight
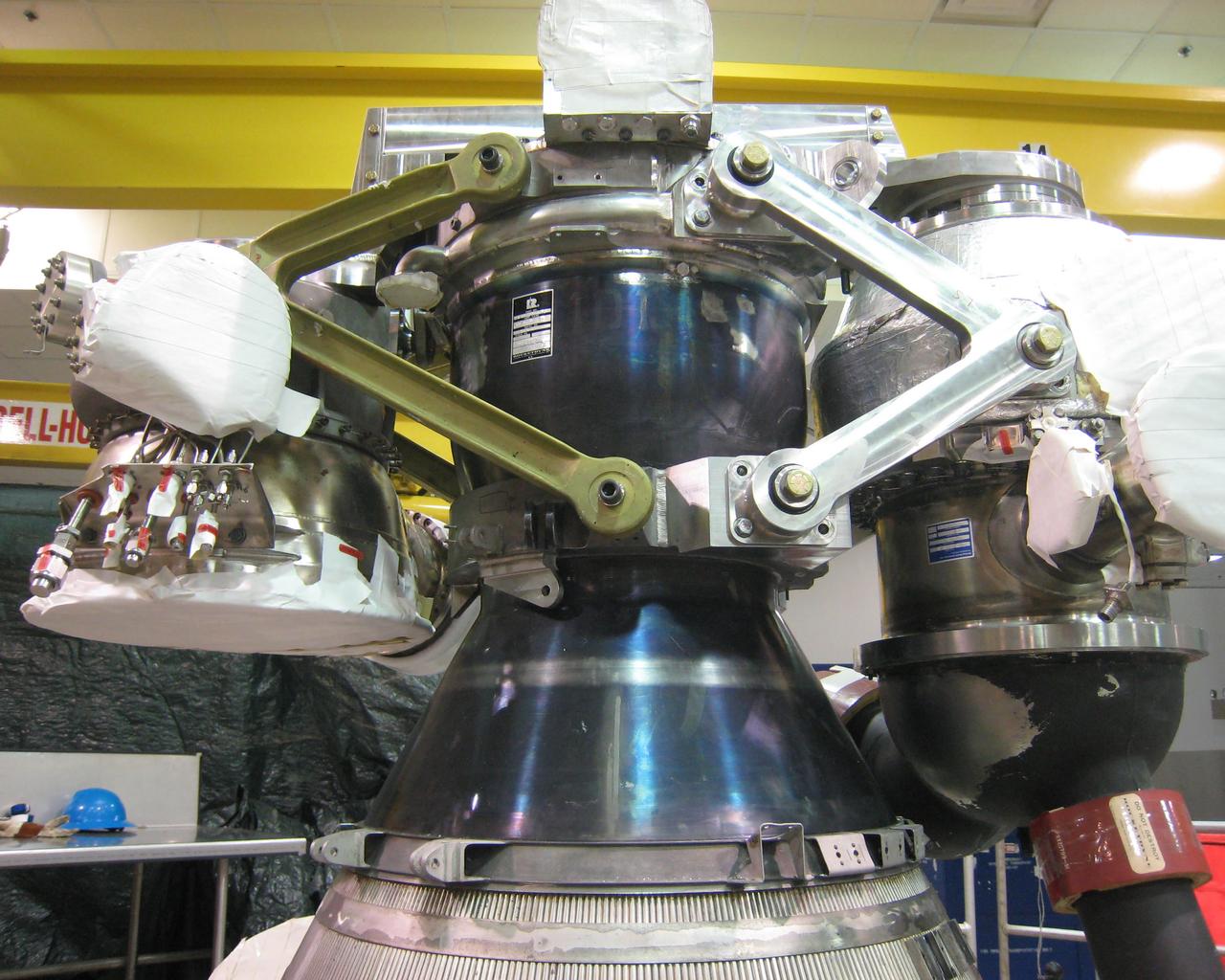

A vintage 1960 J-2 thrust chamber is fitted with brackets and pumps recently at the Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne assembly facility in Stennis Space Center's Building 9101. Together, the parts comprise the J-2X Powerpack 1A test article. Mississippi Space Services machined the new bracket (the V-shaped arm on the right), making this the first time parts for an engine test article were machined, welded and assembled on site at SSC.
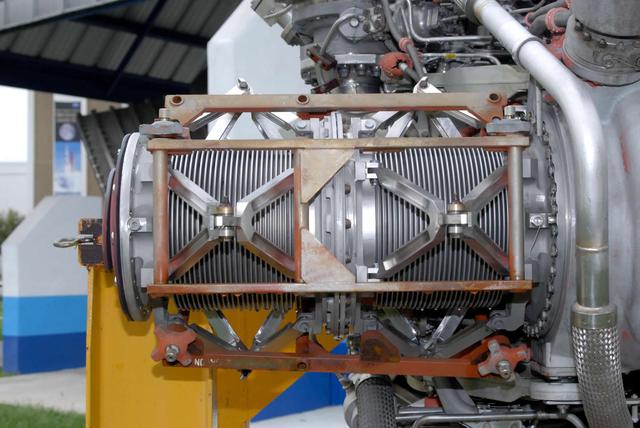

Stennis Space Center engineers are preparing to conduct water tests on an updated version of the scissors duct component of the J-2X engine. Measuring about 2 feet long and about 8 inches in diameter, the duct on the J-2X predecessor, the J-2, connected its fuel turbo pumps to the flight vehicle's upper stage run tanks. According to NASA's J-2X project manager at SSC, Gary Benton, the water tests should establish the limits of the duct's ability to withstand vibration.

S73-18667 (January 1973) --- Astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot for the Skylab 2 first manned mission, is suited up for Skylab training activity in the mission simulation and training facility at the Manned Spacecraft Center. Photo credit: NASA
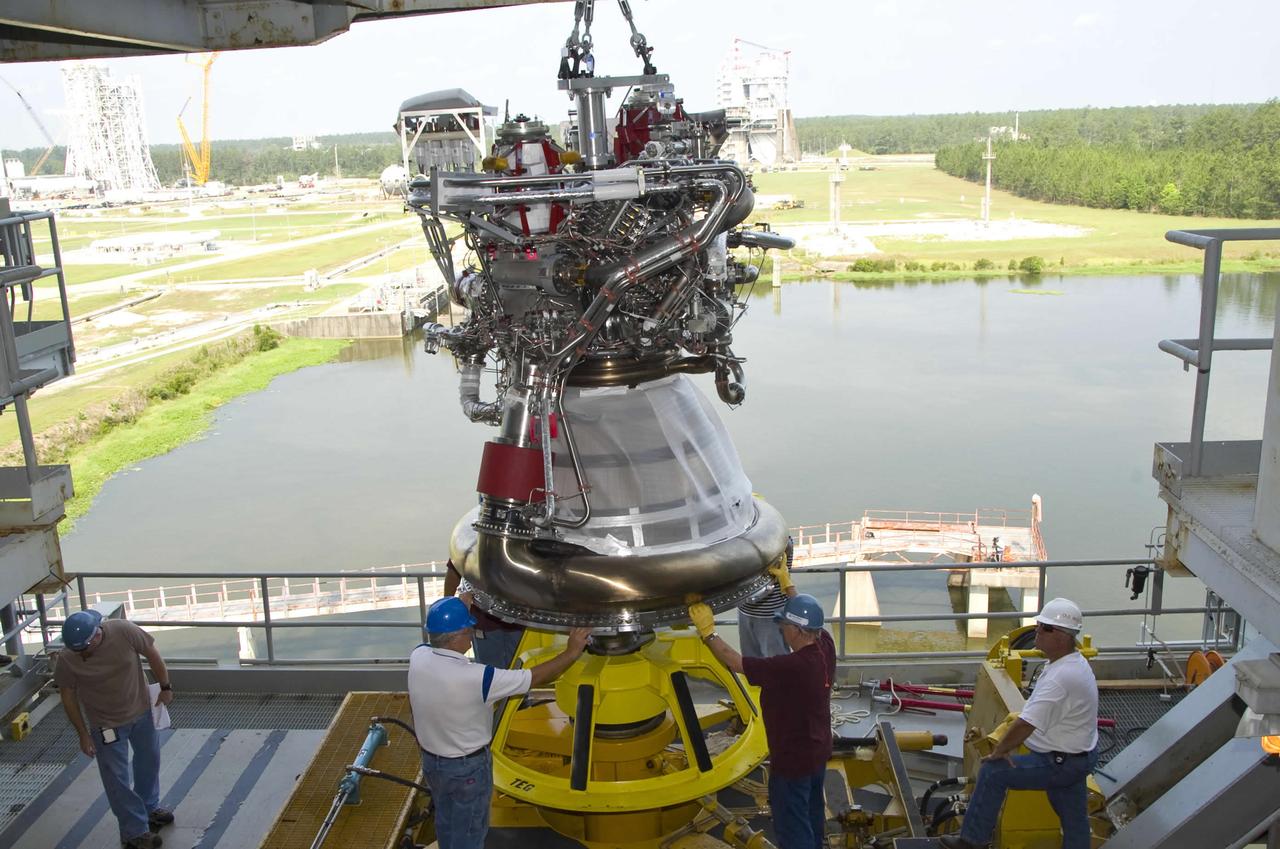

A J-2X next-generation rocket engine is lifted onto the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center. Testing of the engine began the following month. The engine is being developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne and could help carry humans beyond low-Earth orbit into deep space once more.
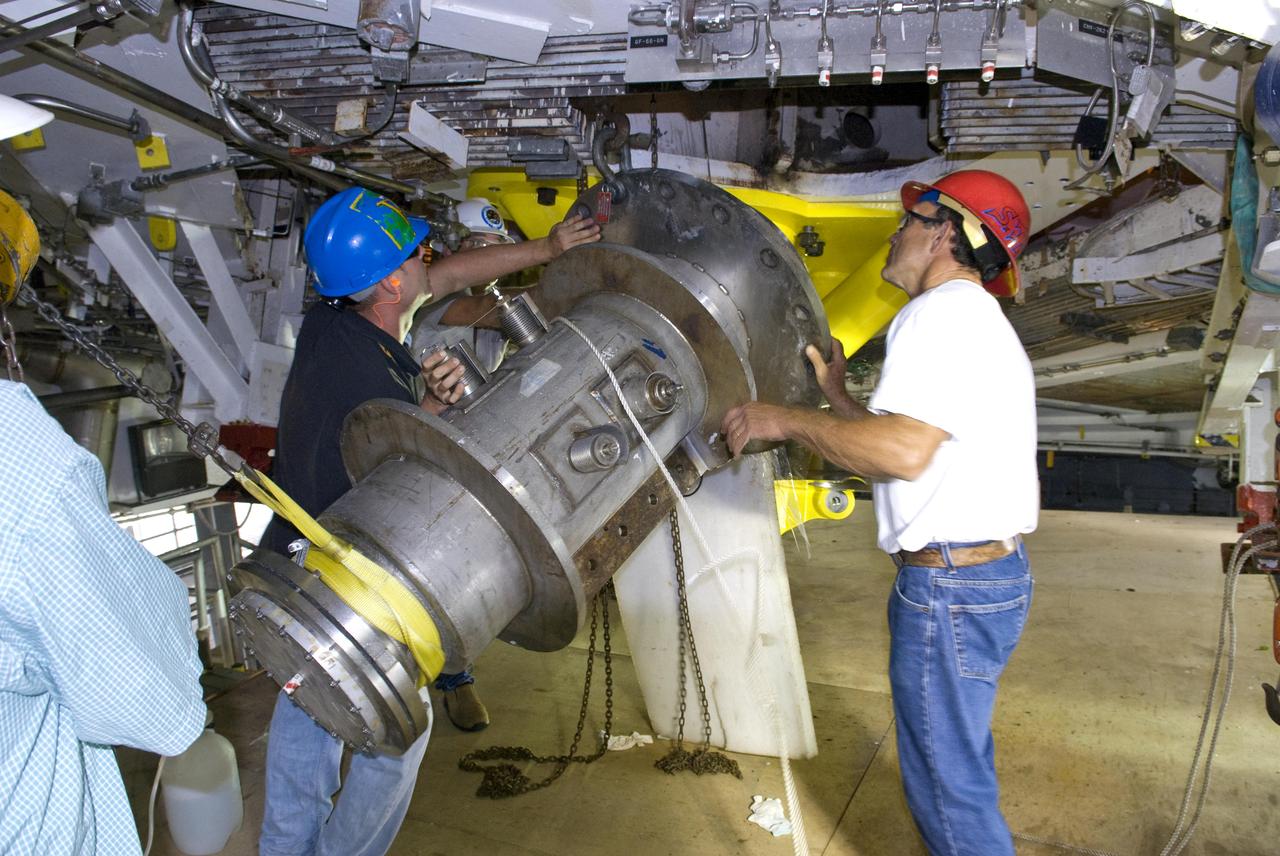

John C. Stennis Space Center employees remove space shuttle main engine run ducts from the A-2 Test Stand engine deck Oct. 25, 2010. Testing of space shuttle main engines concluded in July 2009. Stennis is preparing the A-2 Test Stand for testing the next-generation J-2X rocket engine being developed. Testing of the new engine is scheduled to begin in 2011.
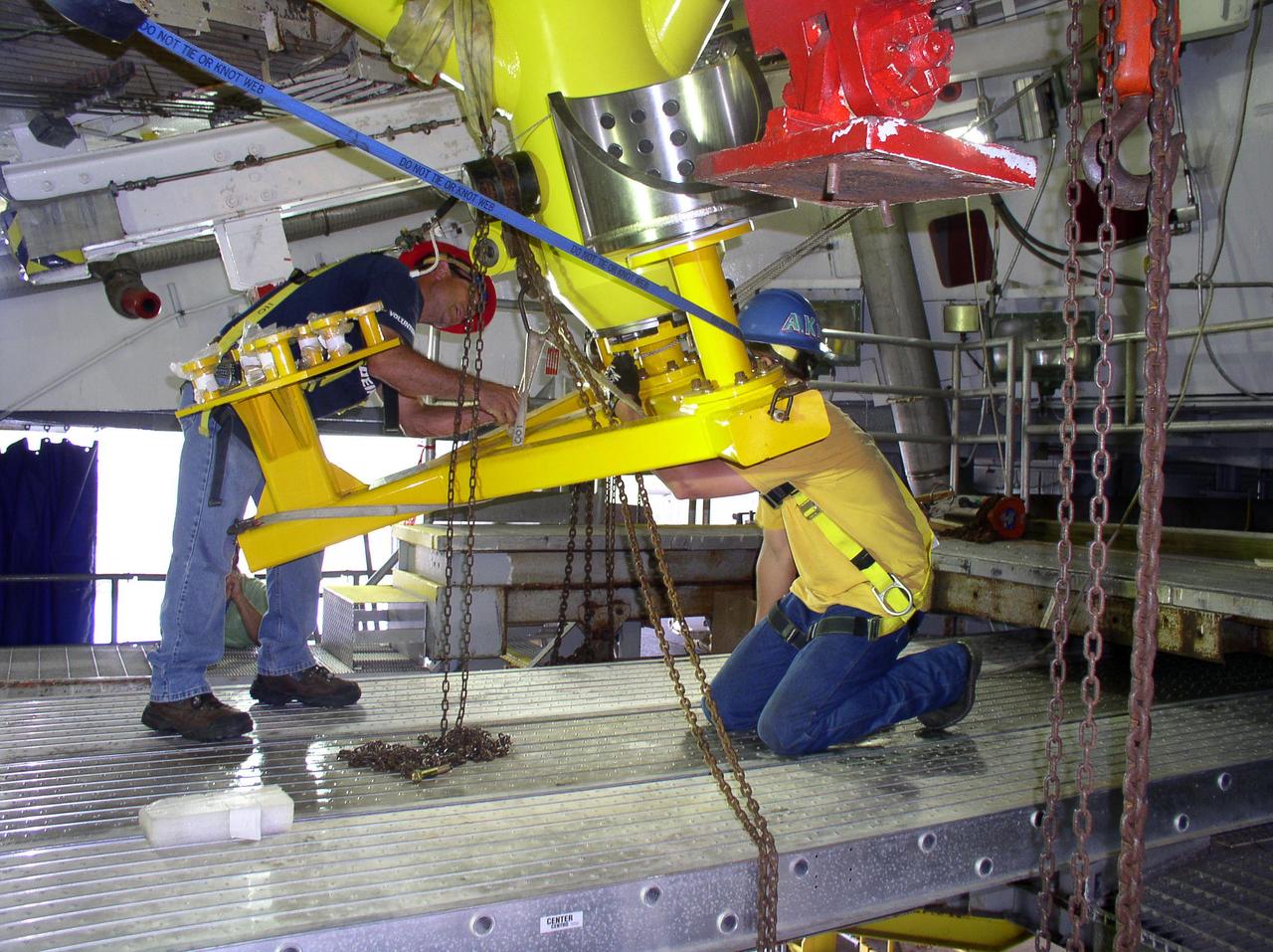

John C. Stennis Space Center employees install a new master interface tool on the A-2 Test Stand on Oct. 27, 2010. Until July 2009, the stand had been used for testing space shuttle main engines. With that test series complete, employees are preparing the stand for testing the next-generation J-2X rocket engine being developed. Testing of the new engine is scheduled to begin in 2011.

S85-45499 (2 Dec 1985) --- Payload specialist Robert J. Cenker.

NASA conducted a long-duration test of the J-2X powerpack, 1,261 seconds total, on the A-1 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Aug. 16, marking another step in development of the next-generation rocket engine. The powerpack is a system of components on the top portion of the J-2X engine, including the gas generator, oxygen and fuel turbopumps, and related ducts and valves.
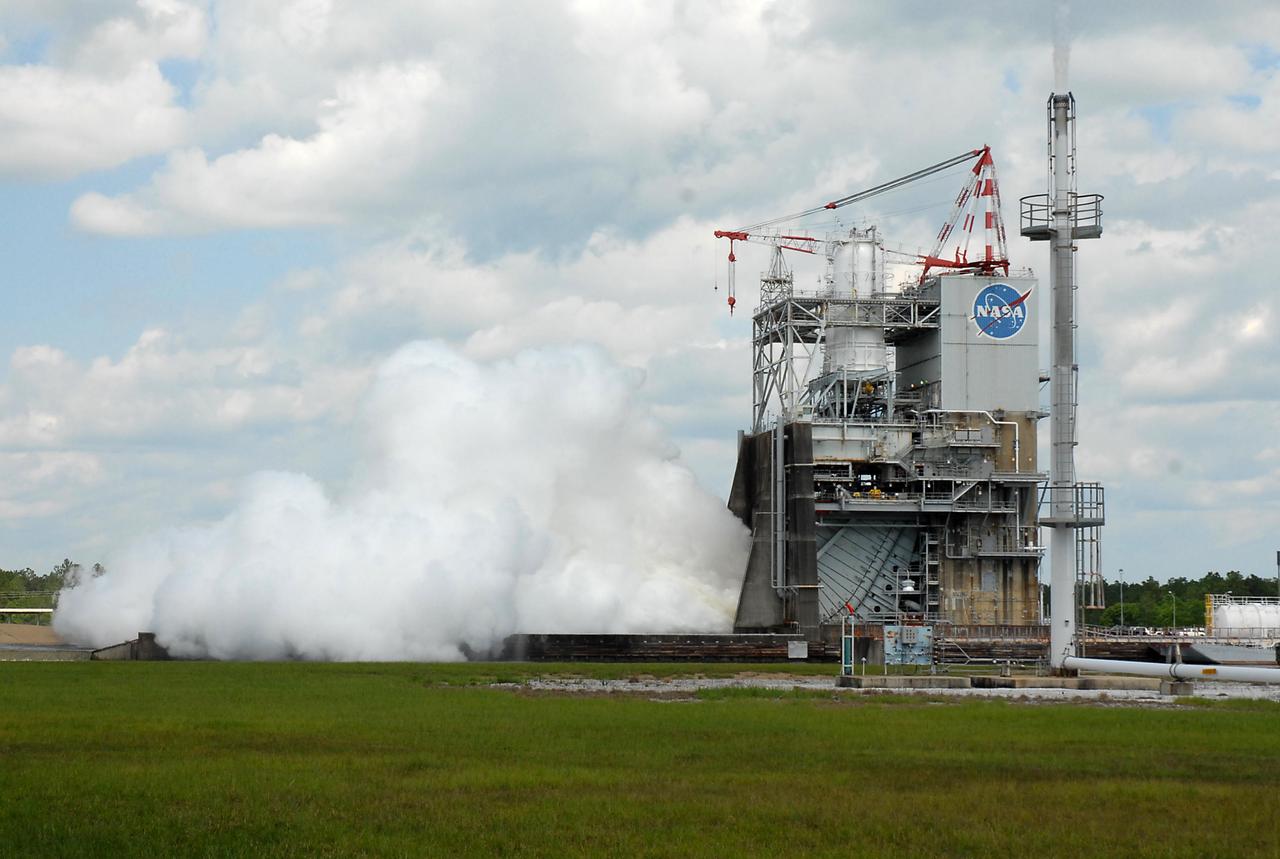

NASA engineers at Stennis Space Center conducted a 260-second test of the next-generation J-2X rocket engine June 13, 2012. As in a previous test, NASA engineers fired the engine at both secondary and primary modes to collect performance data.
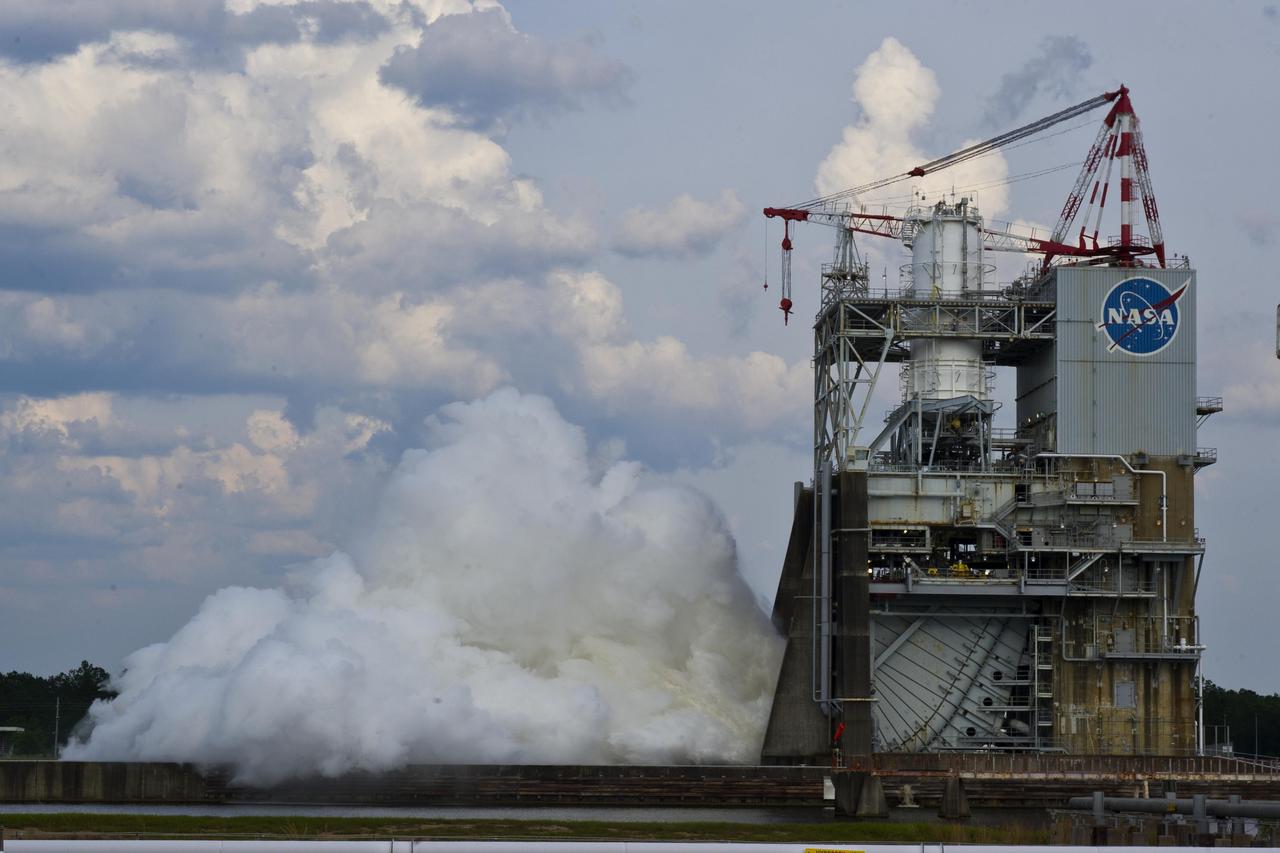

On May 16, 2012, engineers at Stennis Space Center conducted a test of the next-generation J-2X engine that will help power NASA's new Space Launch System, moving NASA even closer to a return to deep space.
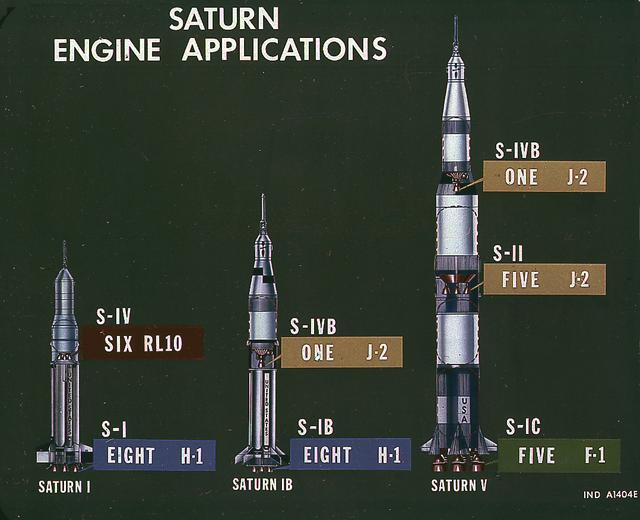
This image illustrates the basic differences between the three Saturn launch vehicles developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The Saturn I, consisted of two stages, the S-I (eight H-1 engines) and the S-IV (six RL-10 engines). The Saturn IB (center) also consisted of two stages, the S-IB (eight H-1 engines) and the S-IVB (one J-2 engine). The Saturn V consisted of three stages, the S-IC (five F-1 engines), the S-II (five J-2 engines), and the S-IVB (one J-2 engine).
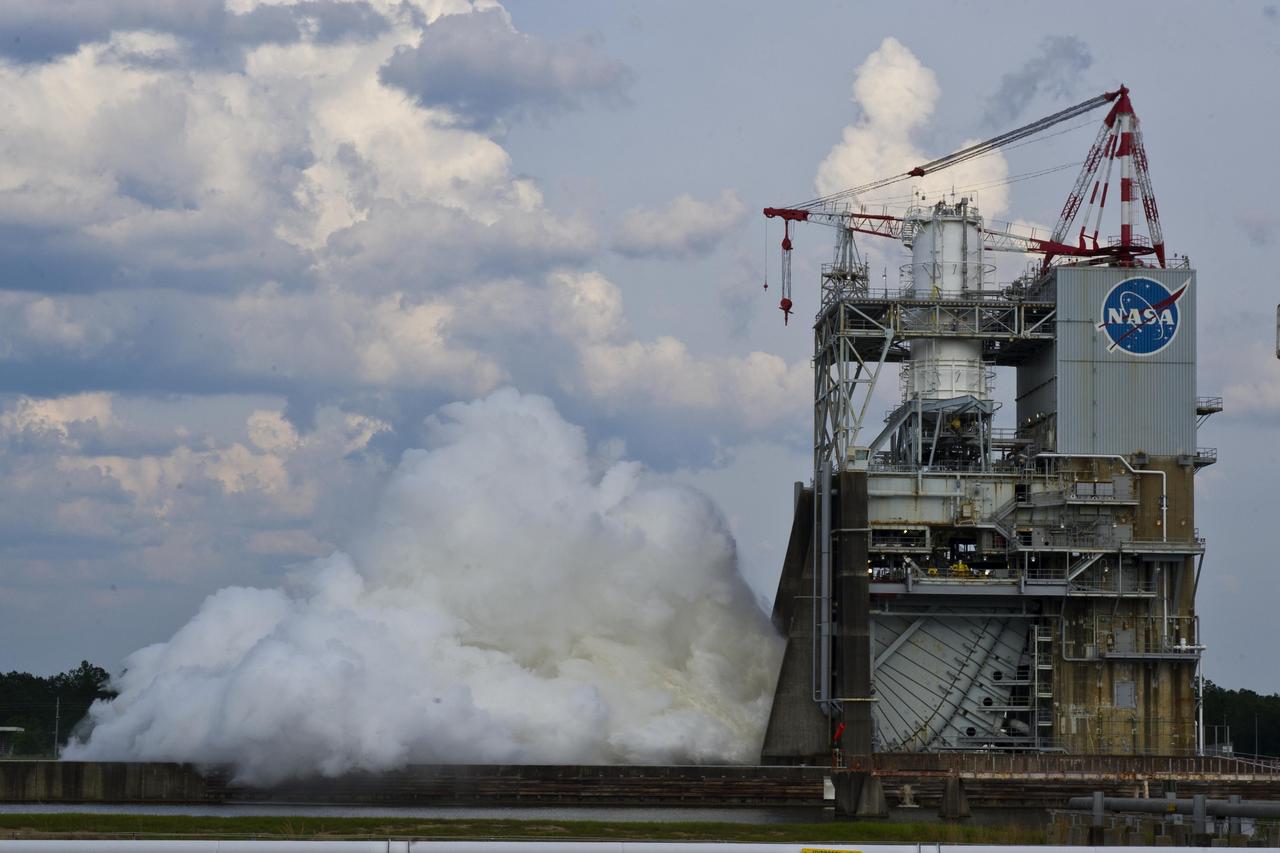

NASA conducted a successful seven-second test of the next-generation J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on May 16, 2012. The J-2X is being developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne.
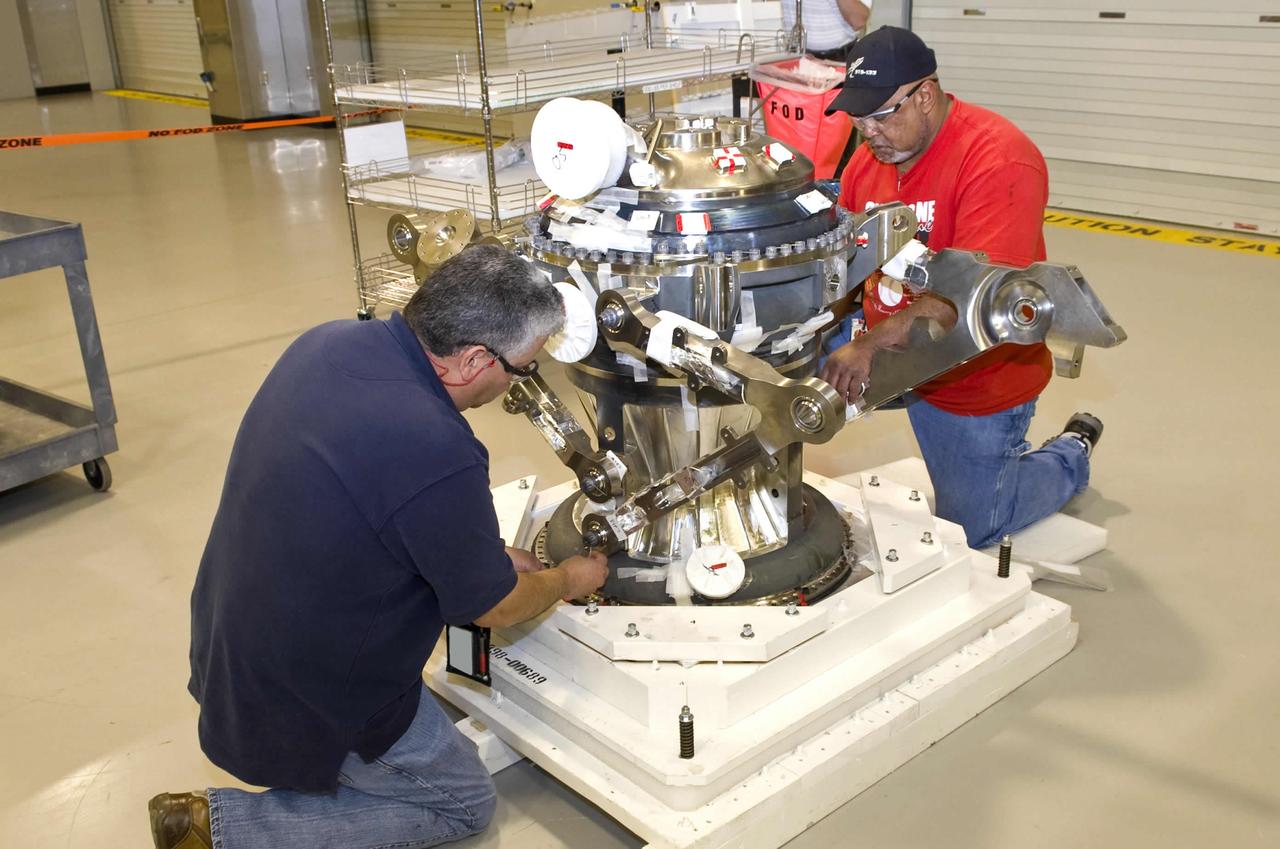

Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne employees Carlos Alfaro (l) and Oliver Swanier work on the main combustion element of the J-2X rocket engine at their John C. Stennis Space Center facility. Assembly of the J-2X rocket engine to be tested at the site is under way, with completion and delivery to the A-2 Test Stand set for June. The J-2X is being developed as a next-generation engine that can carry humans into deep space. Stennis Space Center is preparing a trio of stands to test the new engine.
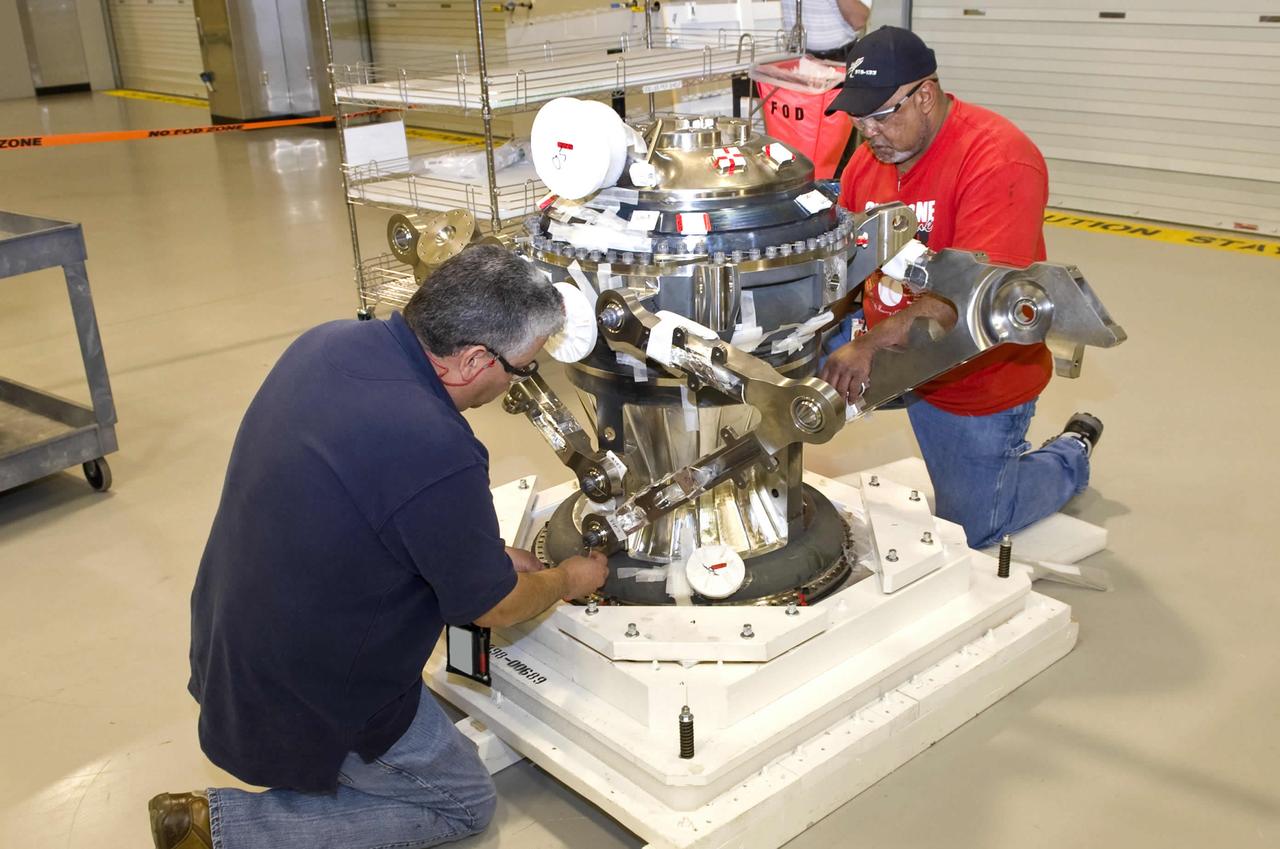

Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne employees Carlos Alfaro (l) and Oliver Swanier work on the main combustion element of the J-2X rocket engine at their John C. Stennis Space Center facility. Assembly of the J-2X rocket engine to be tested at the site is under way, with completion and delivery to the A-2 Test Stand set for June. The J-2X is being developed as a next-generation engine that can carry humans into deep space. Stennis Space Center is preparing a trio of stands to test the new engine.
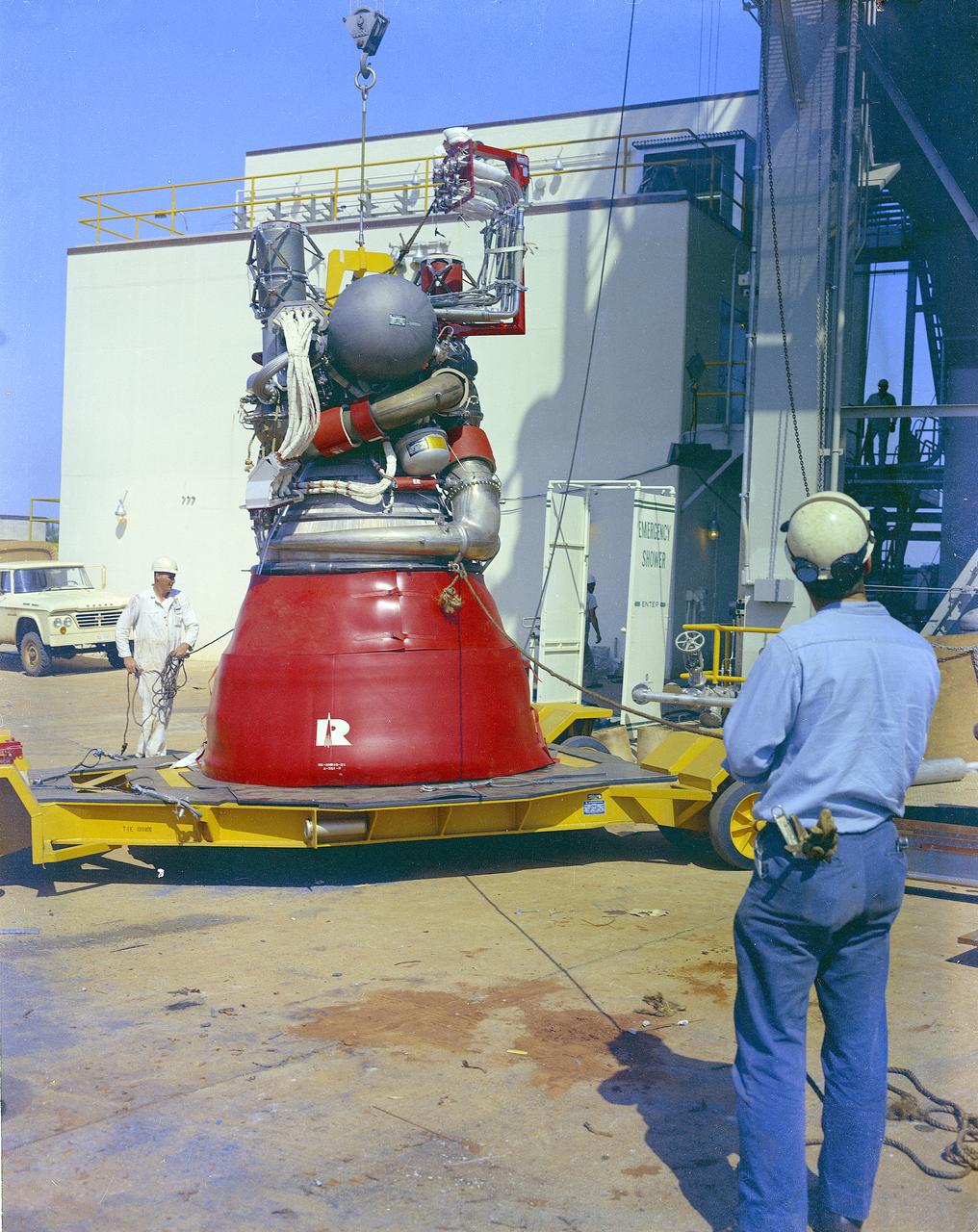

Two technicians watch carefully as cables prepare to lift a J-2 engine into a test stand. The J-2 powered the second stage and the third stage of the Saturn V moon rocket. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
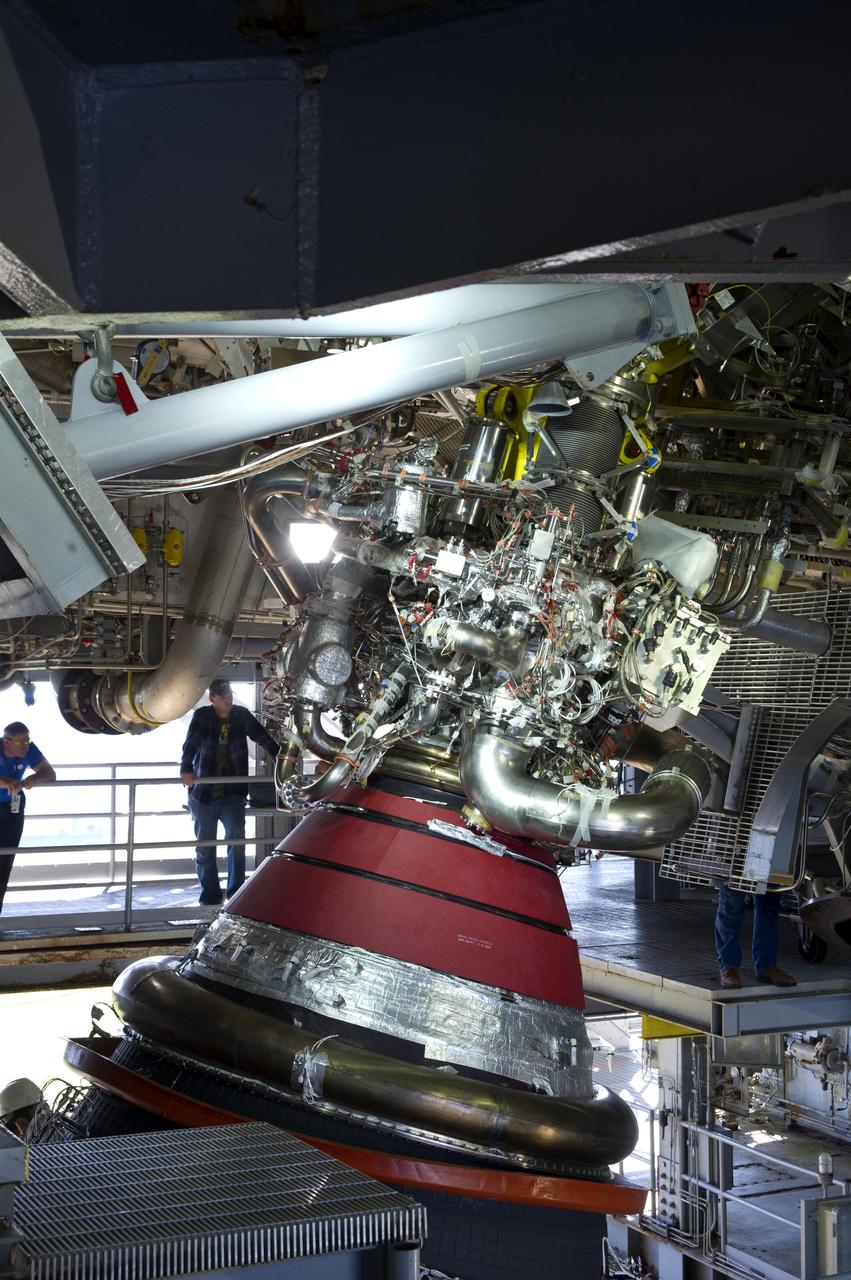
NASA removed J-2X engine No. 10001 from the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center in early October. Opening of the test stand clamshell flooring allowed a clear view of the next-generation engine and stub nozzle, which is being built to help power future deep-space missions. The engine is an upgrade from the heritage J-2 rocket engine, which helped power Apollo missions to the moon during the late 1960s and early 1970s.
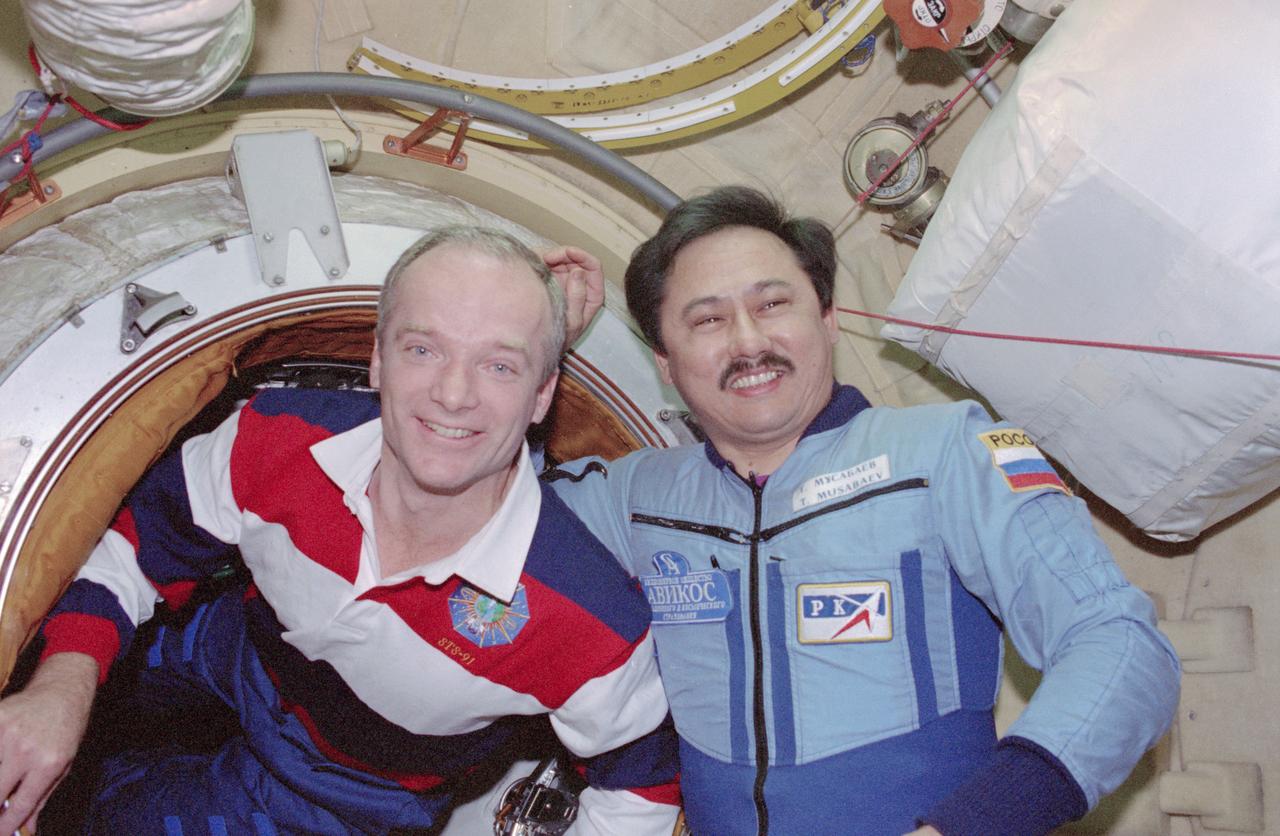

STS091-370-035 (2-12 June 1998) --- Astronaut Charles J. Precourt (left), STS-91 mission commander; and Talgat A. Musabayev, Mir-25 commander, reunite following hatch opening.
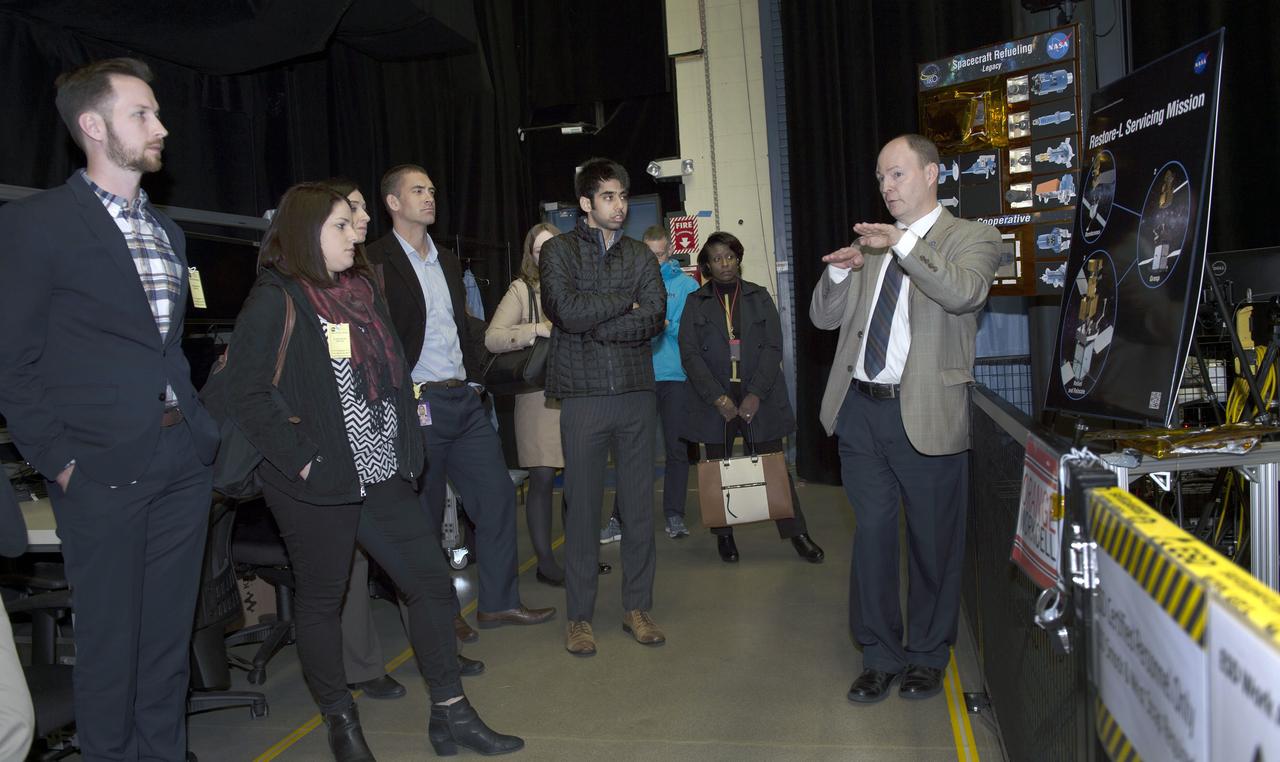

Congressional staff visited Goddard on March 10, 2017. They toured Science on a Sphere J. Garvin, B33 talk on ICESat-2 Dr. Kelly Brunt, Robotic Operations Center - Ben Reed, and JWST-Bill Ochs
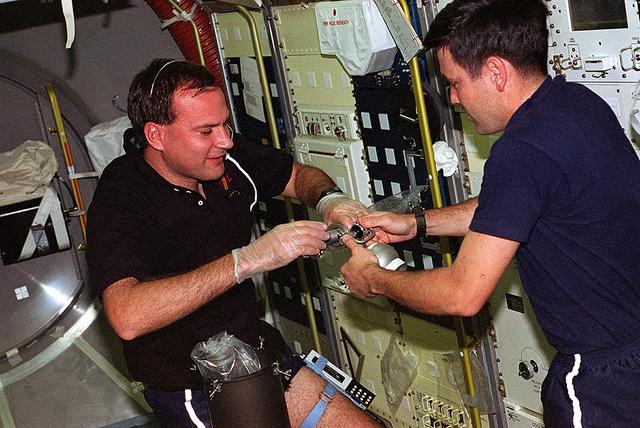

Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-65) onboard photo of Payload specialist Richard J. Hieb (right) and Shuttle Pilot James D. Halsell Jr. working on experiments in the Spacelab in the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2).
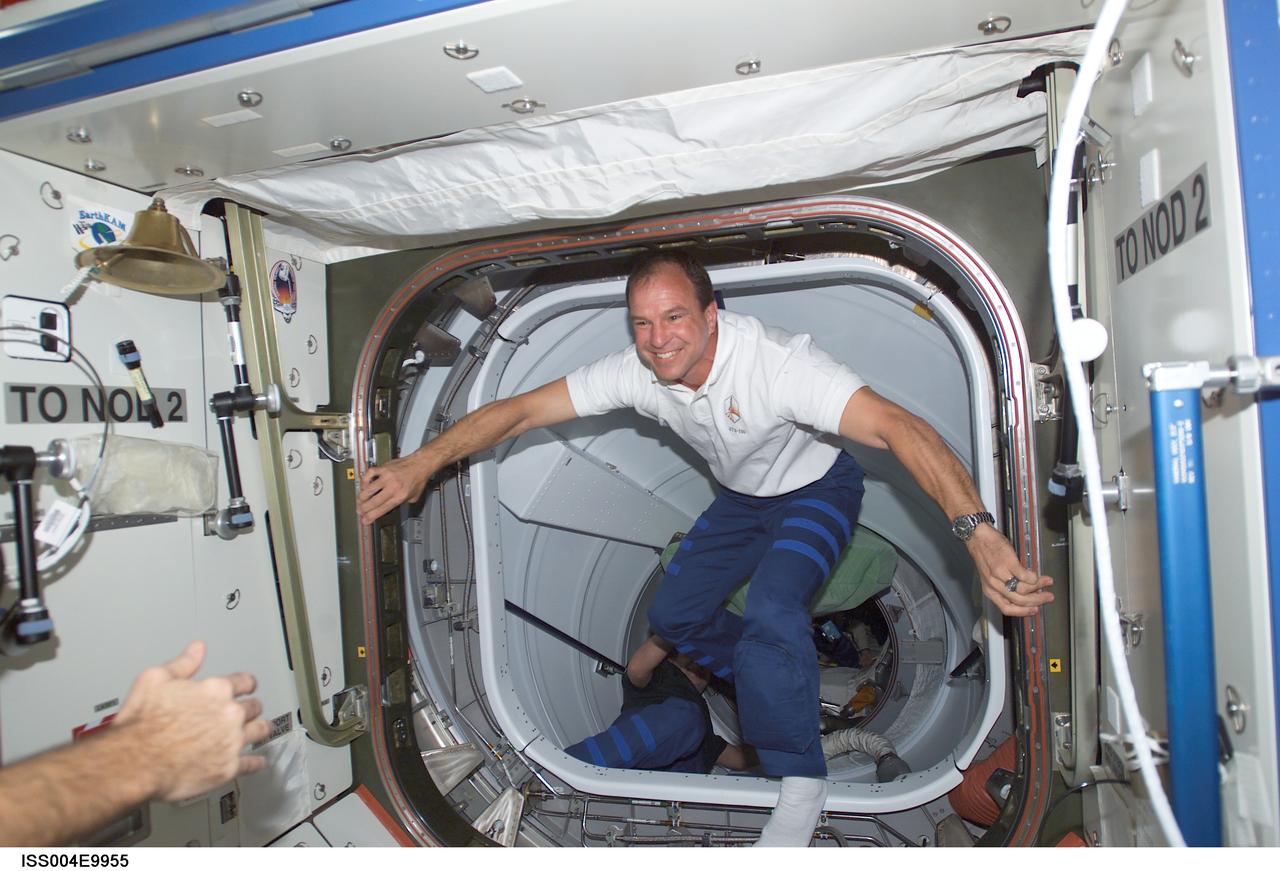

ISS004-E-9955 (10 April 2002) --- Astronaut Michael J. Bloomfield, STS-110 mission commander, steps into the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS) through the Pressurized Mating Adapter 2 (PMA-2) upon docking of the Space Shuttle Atlantis and the station.
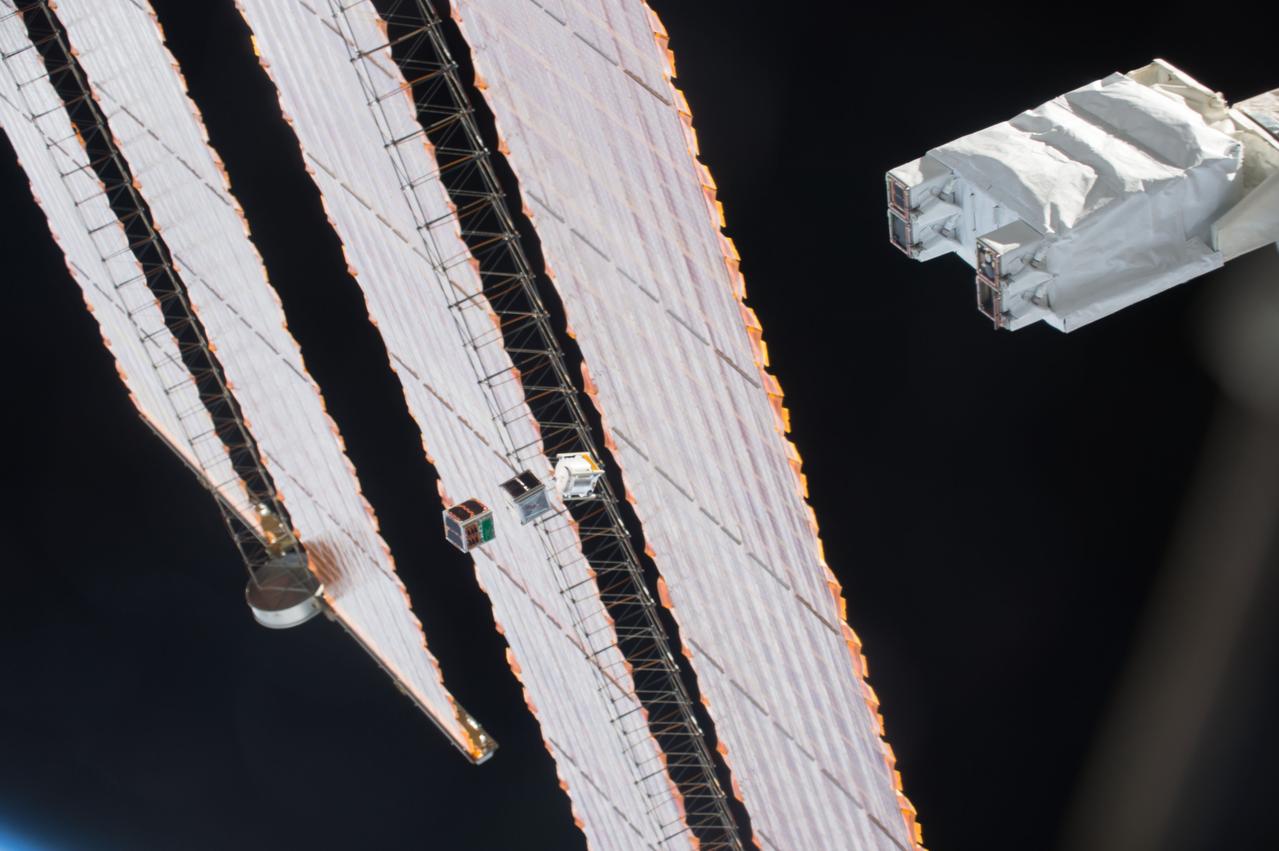

iss050e031207 (1/6/2017) --- A view during the Japanese-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer-6 (J-SSOD-6) deployment of the following satellites: Freedom (1U), Waseda-SAT3, ITF-2 (1U), Egg (3U), AOBA-Velox-III (U), TuPOD (3U). J-SSOD is a unique satellite launcher, handled by the Japanese Experiment Module Remote Manipulator System (JEMRMS), which provides containment and deployment mechanisms for several individual small satellites. Once the J-SSOD including satellite install cases with small satellites are installed on the Multi-Purpose Experiment Platform (MPEP) by crewmembers, it is passed through the JEM airlock for retrieval, positioning and deployment by the JEMRMS.
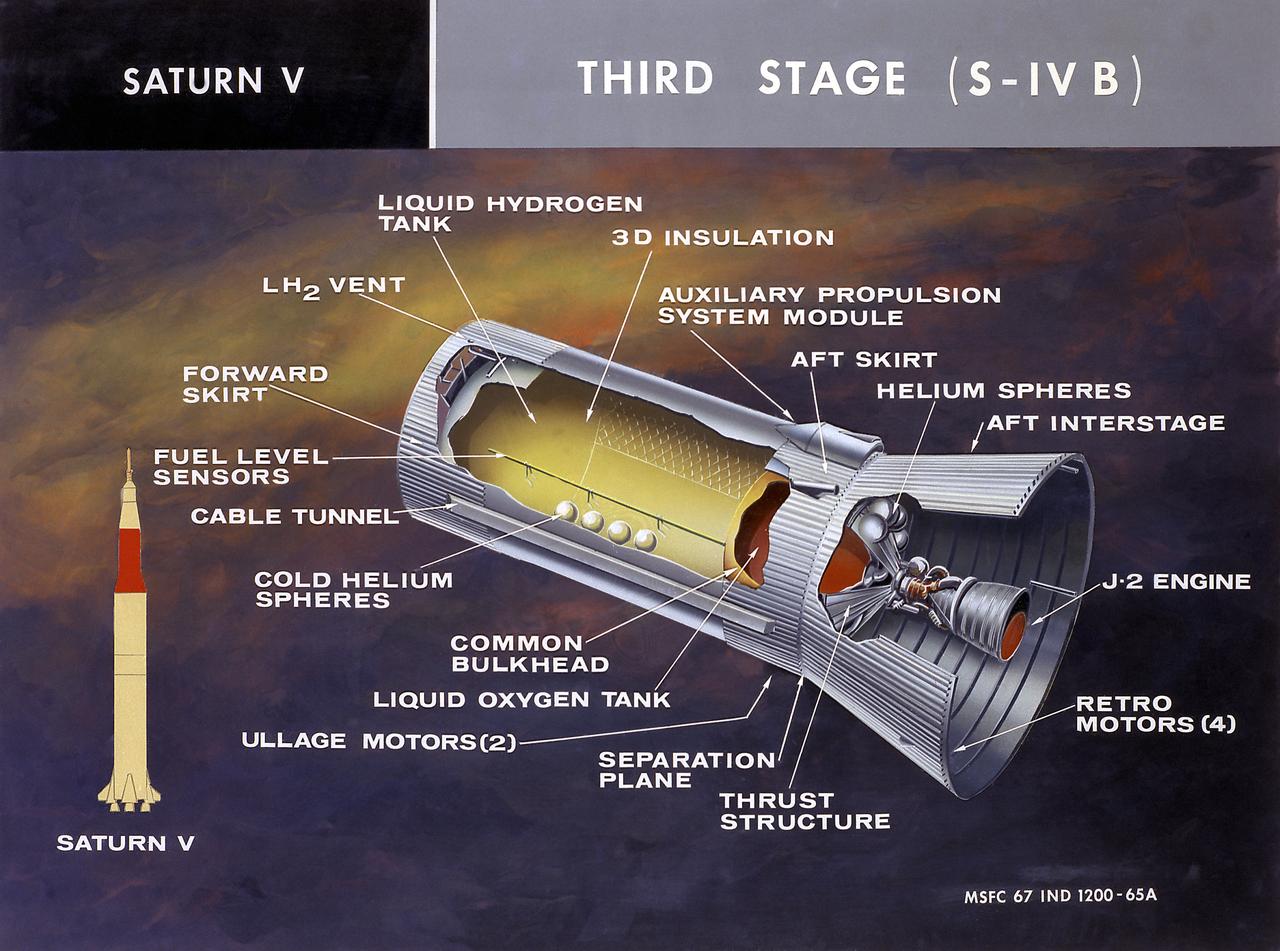
This cutaway illustration shows the Saturn V S-IVB (third) stage with the callouts of its major components. When the S-II (second) stage of the powerful Saturn V rocket burnt out and was separated the remaining units approached orbit around the Earth. Injection into the desired orbit was attaineded as the S-IVB (third stage) was ignited and burnt. The S-IVB stage was powered by a single 200,000-pound thrust J-2 engine and had a re-start capability built in for its J-2 engine. The S-IVB restarted to speed the Apollo spacecraft to escape velocity injecting it and the astronauts into a moon trajectory.
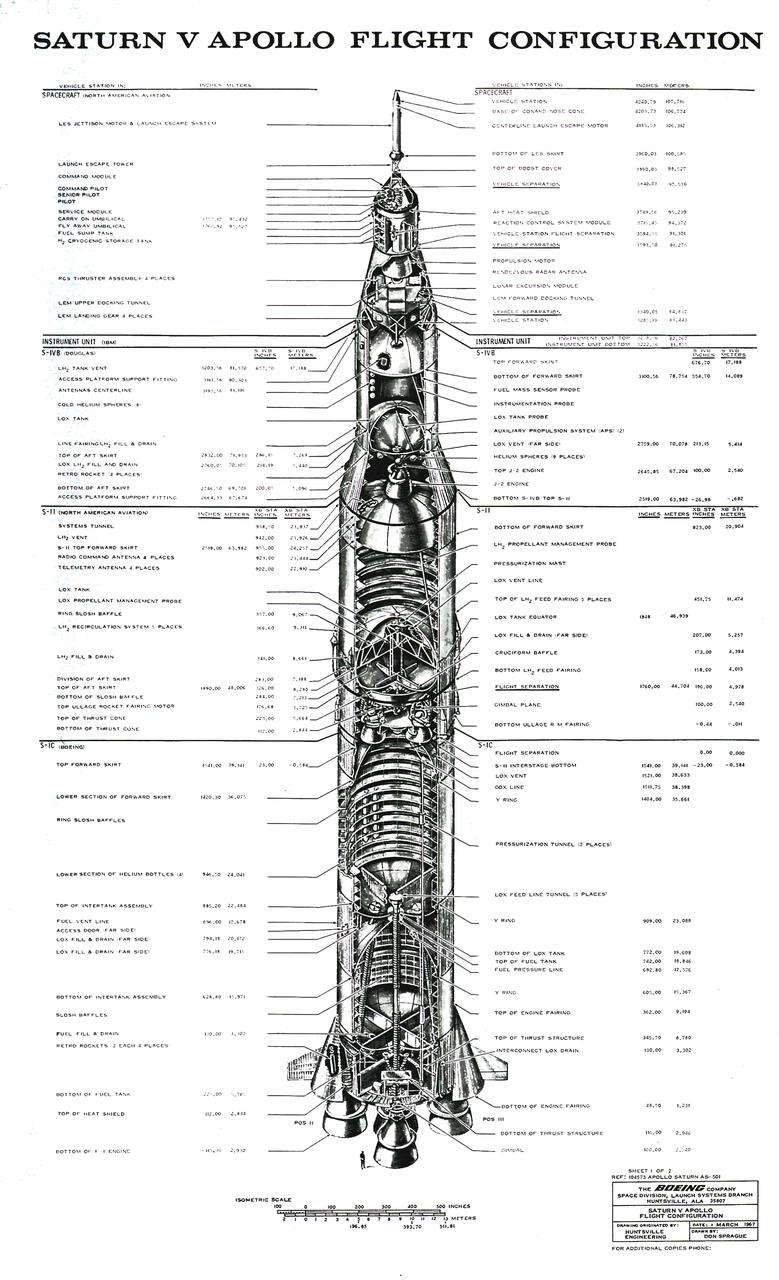
The Saturn V configuration is shown in inches and meters as illustrated by the Boeing Company. The Saturn V vehicle consisted of three stages: the S-IC (first) stage powered by five F-1 engines, the S-II (second) stage powered by five J-2 engines, the S-IVB (third) stage powered by one J-2 engine. A top for the first three stages was designed to contain the instrument unit, the guidance system, the Apollo spacecraft, and the escape system. The Apollo spacecraft consisted of the lunar module, the service module, and the command module. The Saturn V was designed perform lunar and planetary missions and it was capable of placing 280,000 pounds into Earth orbit.

JSC2008-E-031808 (2 April 2008) --- Astronauts John M. Grunsfeld (right), Andrew J. Feustel, Michael T. Good and Michael J. Massimino (second left), all STS-125 mission specialists, participate in an extravehicular activity (EVA) hardware training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center. Tomas Gonzalez-Torres (left) assisted the crewmembers.

JSC2008-E-031816 (2 April 2008) --- Astronauts John M. Grunsfeld (right), Michael J. Massimino, Andrew J. Feustel and Michael T. Good, all STS-125 mission specialists, participate in an extravehicular activity (EVA) hardware training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center. Tomas Gonzalez-Torres (left) assisted the crewmembers.
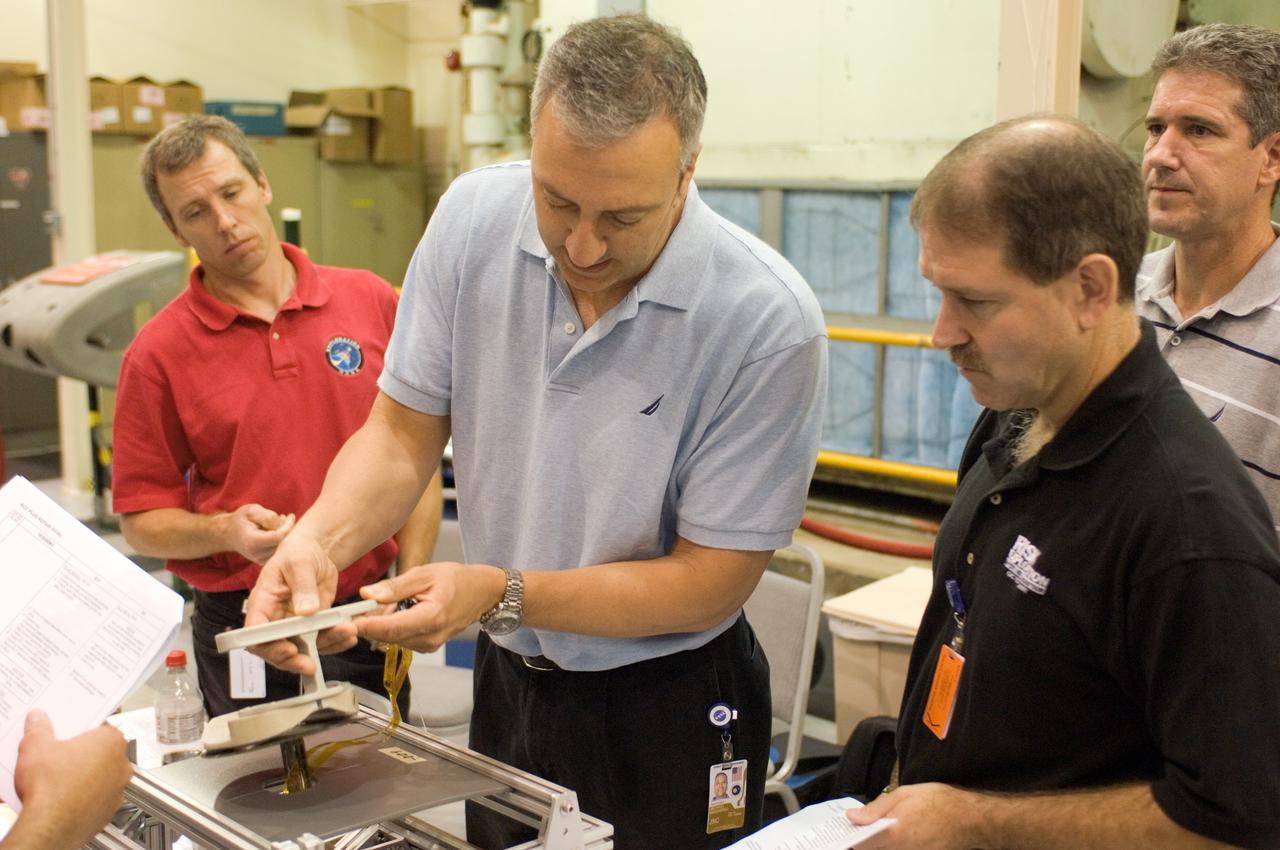

JSC2008-E-031815 (2 April 2008) --- Astronauts Michael J. Massimino (center), John M. Grunsfeld (right), Michael T. Good (right background) and Andrew J. Feustel, all STS-125 mission specialists, participate in an extravehicular activity (EVA) hardware training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center.
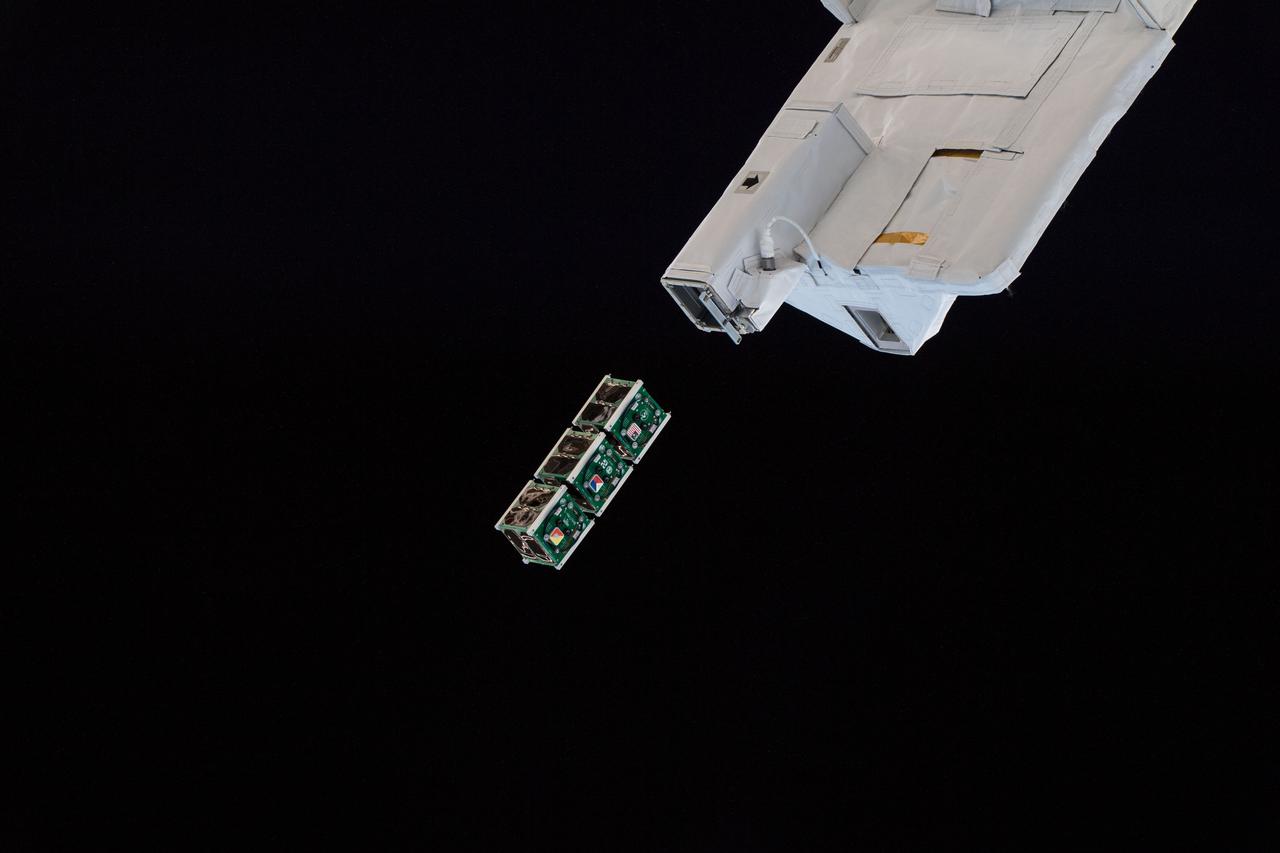
iss056e130478 (8/10/2018) --- A view of the BIRDS-2 Satellite Deployment during JSSOD-9 operations. The JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD) provides a novel, safe, small satellite launching capability to the International Space Station (ISS). Once the J-SSOD including satellite install cases with small satellites are installed on the Multi-Purpose Experiment Platform (MPEP) by crewmembers, it is passed through the JEM airlock for retrieval, positioning and deployment by the JEMRMS.
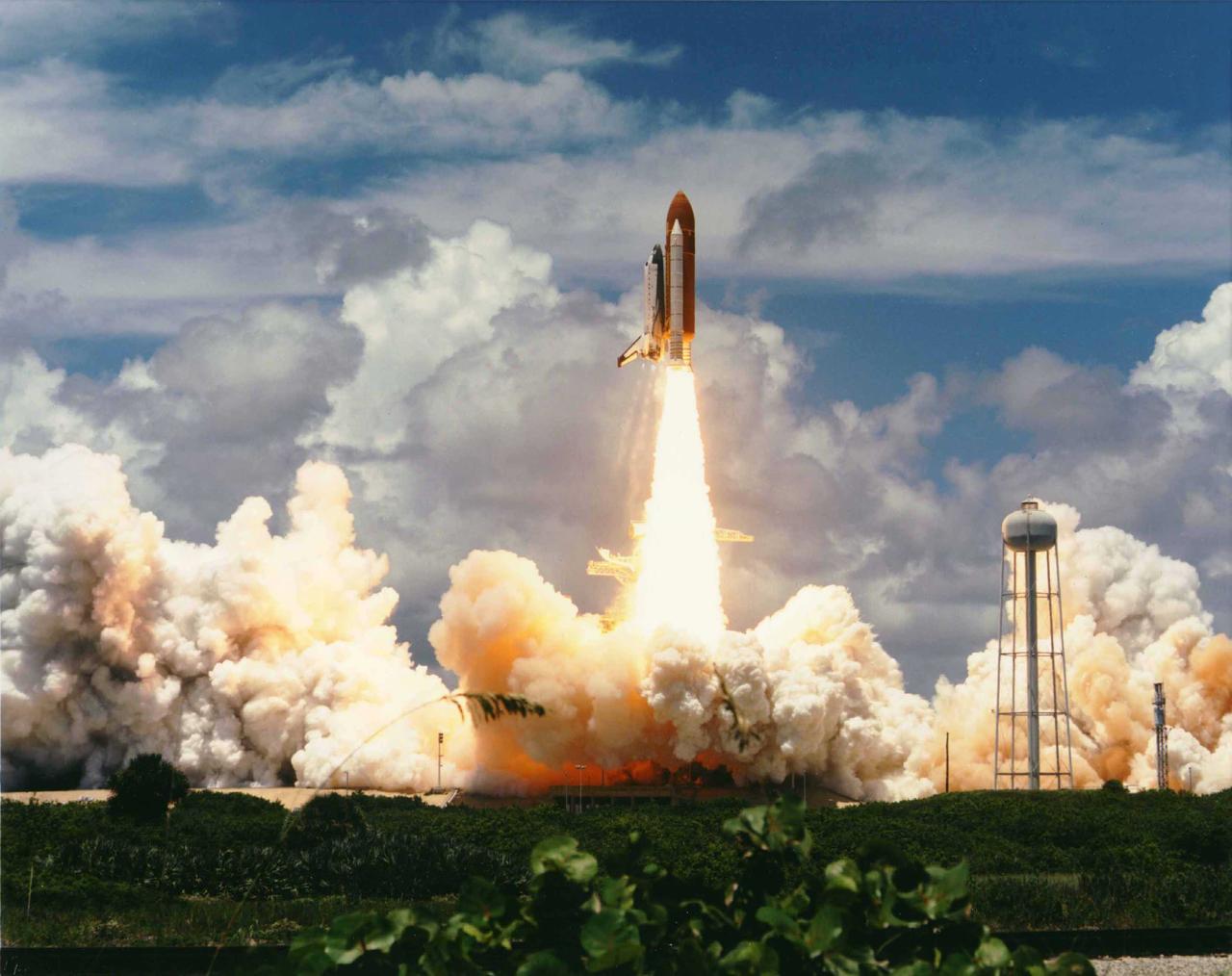

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The second International Microgravity Laboratory-2 (IML-2) is off to an ontime start as the Space Shuttle Columbia lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at 12:43:00 p.m. EDT. On board are a crew of seven and more than 80 investigations developed by more than 200 scientists from 13 countries. The IML-2 complement includes materials science, bioprocessing, space and radiation biology, and human physiology experiments that will be carried out over the course of the 14-day flight. The commander of Space Shuttle Mission STS-65 is Robert D. Cabana. James D. Halsell Jr. is the pilot; the payload commander is Richard J. Hieb; the three mission specialists are Carl E. Walz, Leroy Chiao and Donald A. Thomas. Dr. Chiaki Mukai, representing NASDA, the National Space Development Agency of Japan, is the payload specialist. Mukai becomes the first Japanese woman to fly into space.
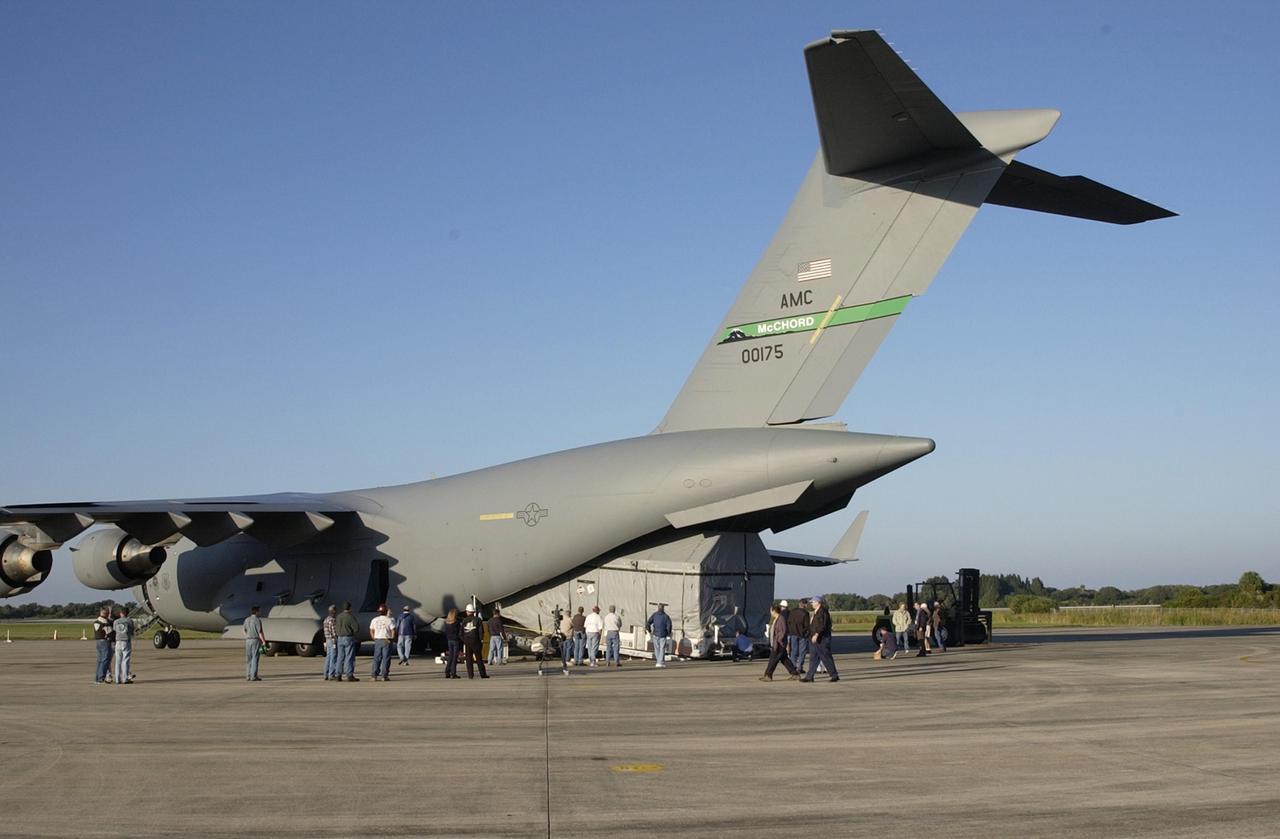

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-J (TDRS-J) is offloaded at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility from an Air Force C-17 air cargo plane. It will be transferred to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2). TDRS-J weighs 3,338 pounds, but at launch will weigh 7,031 pounds when fully fueled with its propellants consisting of monomethylhydrazine fuel and nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer. The solar arrays, when deployed, will supply the spacecraft with up to 2,200 watts of power. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
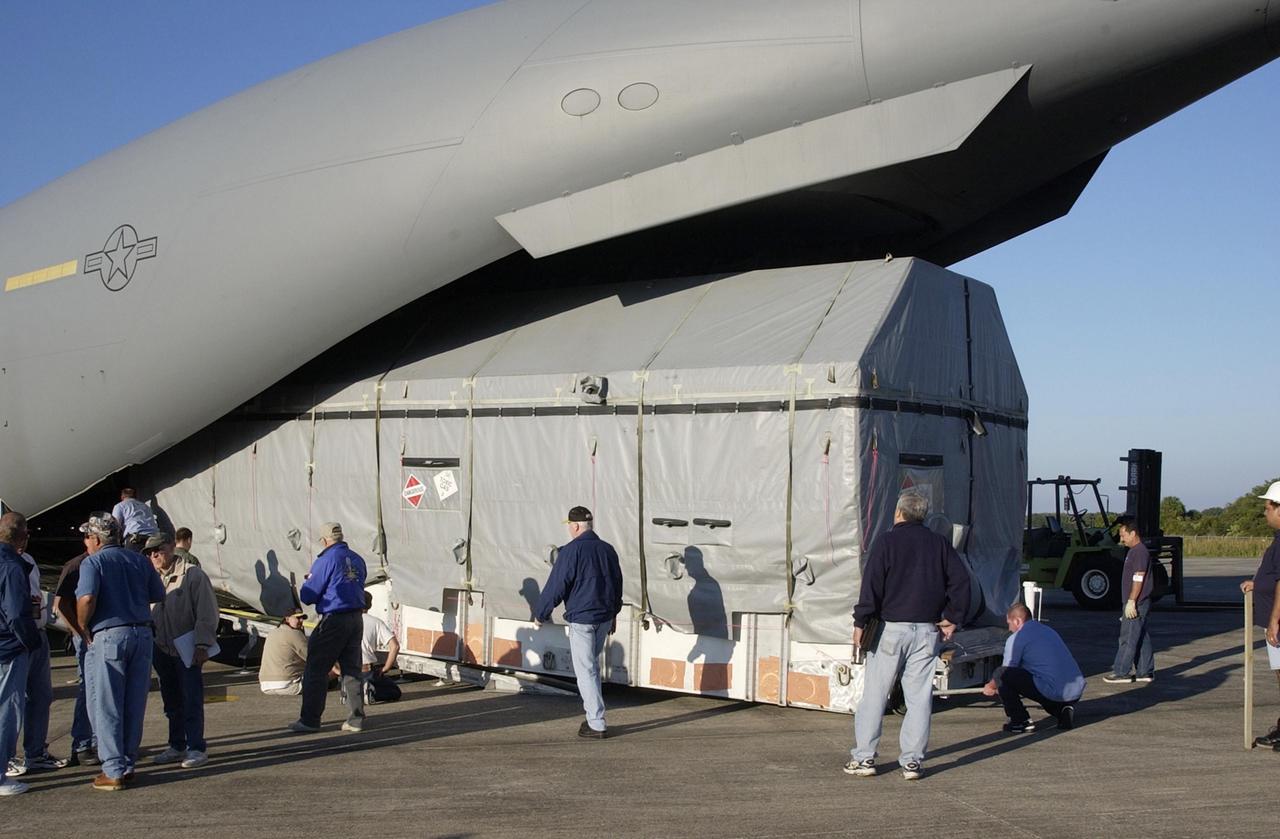

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-J (TDRS-J) is being offloaded at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility from an Air Force C-17 air cargo plane. It will be transferred to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2). TDRS-J weighs 3,338 pounds, but at launch will weigh 7,031 pounds when fully fueled with its propellants consisting of monomethylhydrazine fuel and nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer. The solar arrays, when deployed, will supply the spacecraft with up to 2,200 watts of power. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
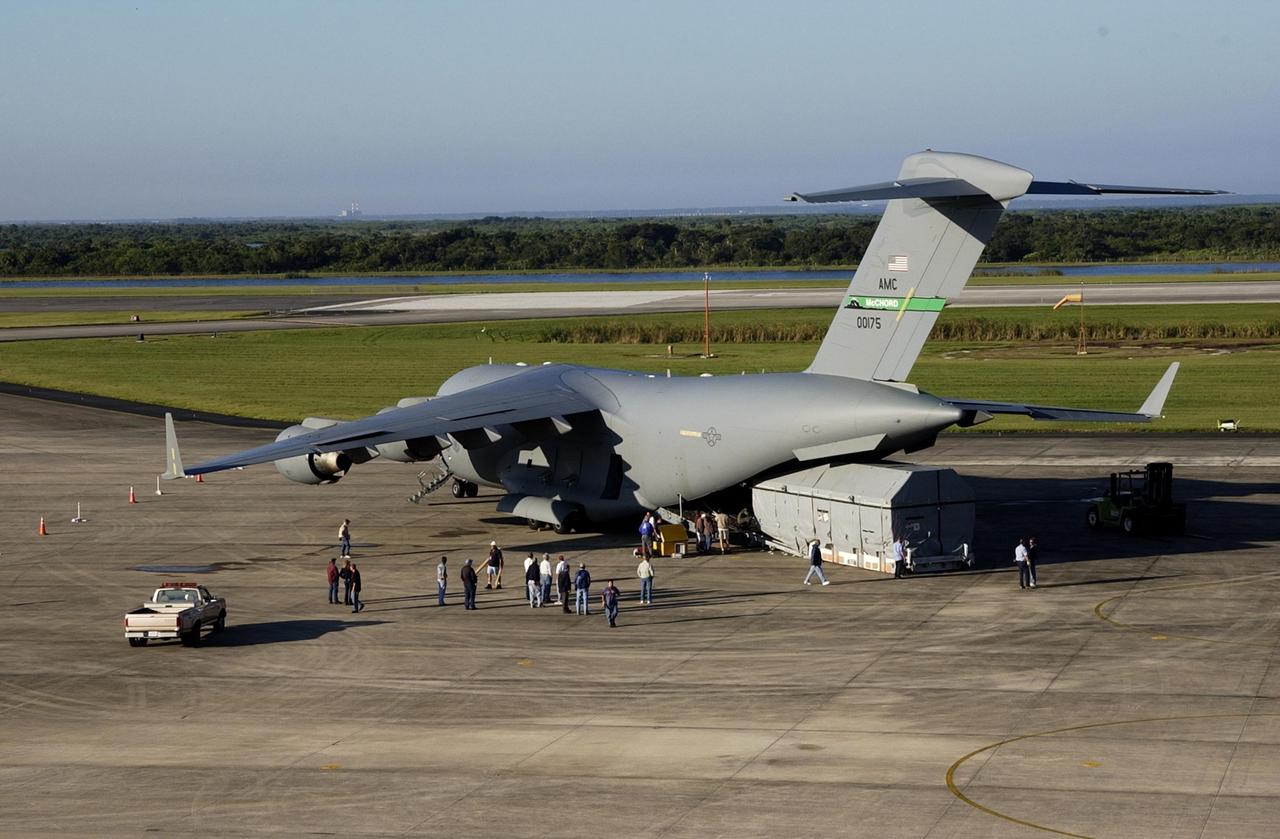

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-J (TDRS-J) has been offloaded at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility from an Air Force C-17 air cargo plane. It will be transferred to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2). TDRS-J weighs 3,338 pounds, but at launch will weigh 7,031 pounds when fully fueled with its propellants consisting of monomethylhydrazine fuel and nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer. The solar arrays, when deployed, will supply the spacecraft with up to 2,200 watts of power. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
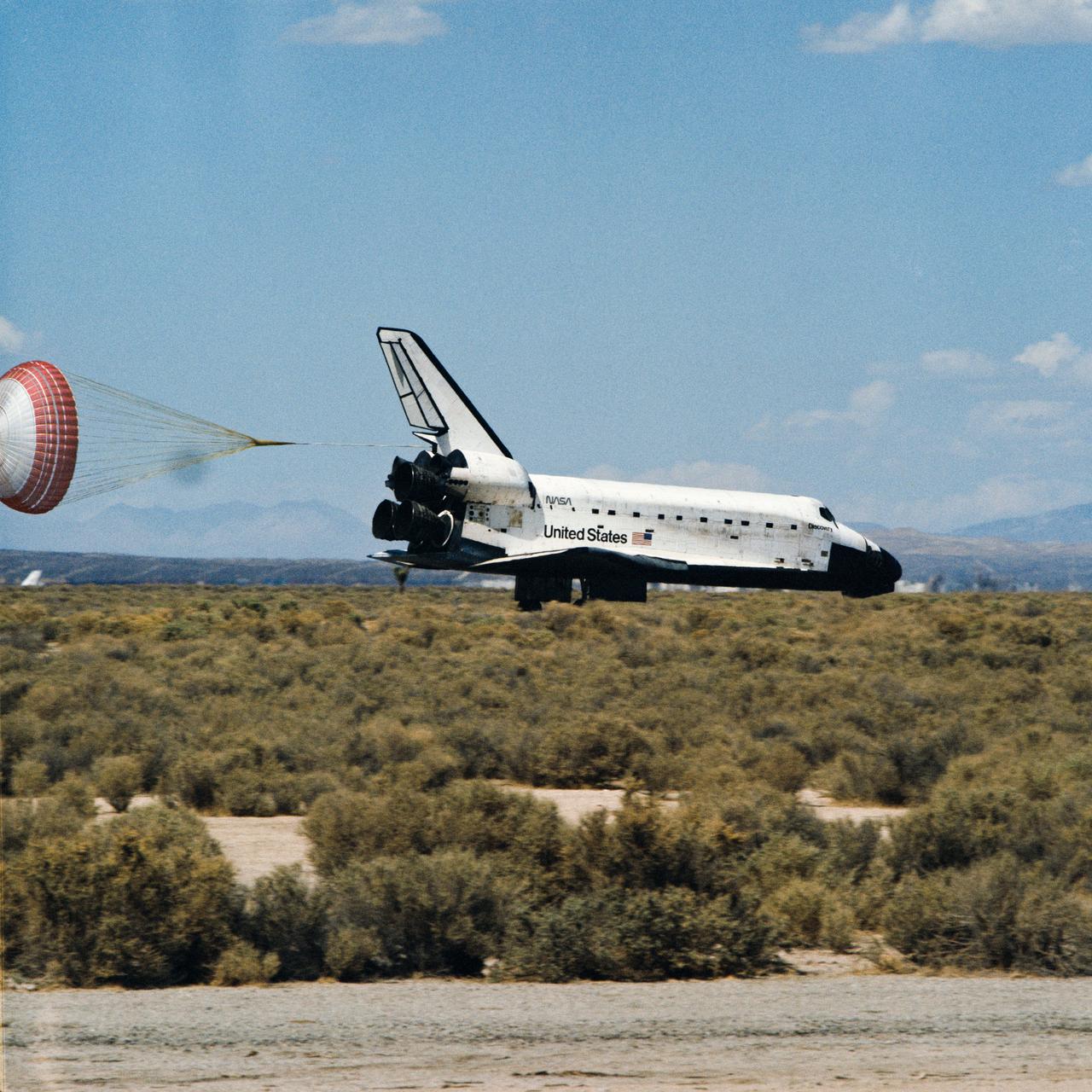

STS64-S-073 (20 Sept. 1994) --- The drag chute for the space shuttle Discovery is deployed as NASA's most-heavily flown spacecraft completes a 10-day, 22-hour and 50-minute mission. Discovery, with a crew of six NASA astronauts aboard, fired its de-orbit engine at 1:14 p.m. (PDT), Sept. 20, 1994. Touchdown was at 2:12:59 p.m. and the nose wheel touched down at 2:13:03 p.m., with wheel stop at 2:13:52 p.m. Bad weather in Florida called for an "eleventh hour" shift to the California landing site. Onboard for the flight, whose mission was to study Earth's atmosphere and to test tools and procedures for the International Space Station (ISS), were astronauts Richard N. Richards, L. Blaine Hammond, Mark C. Lee, Carl J. Meade, Susan J. Helms and Jerry M. Linenger. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
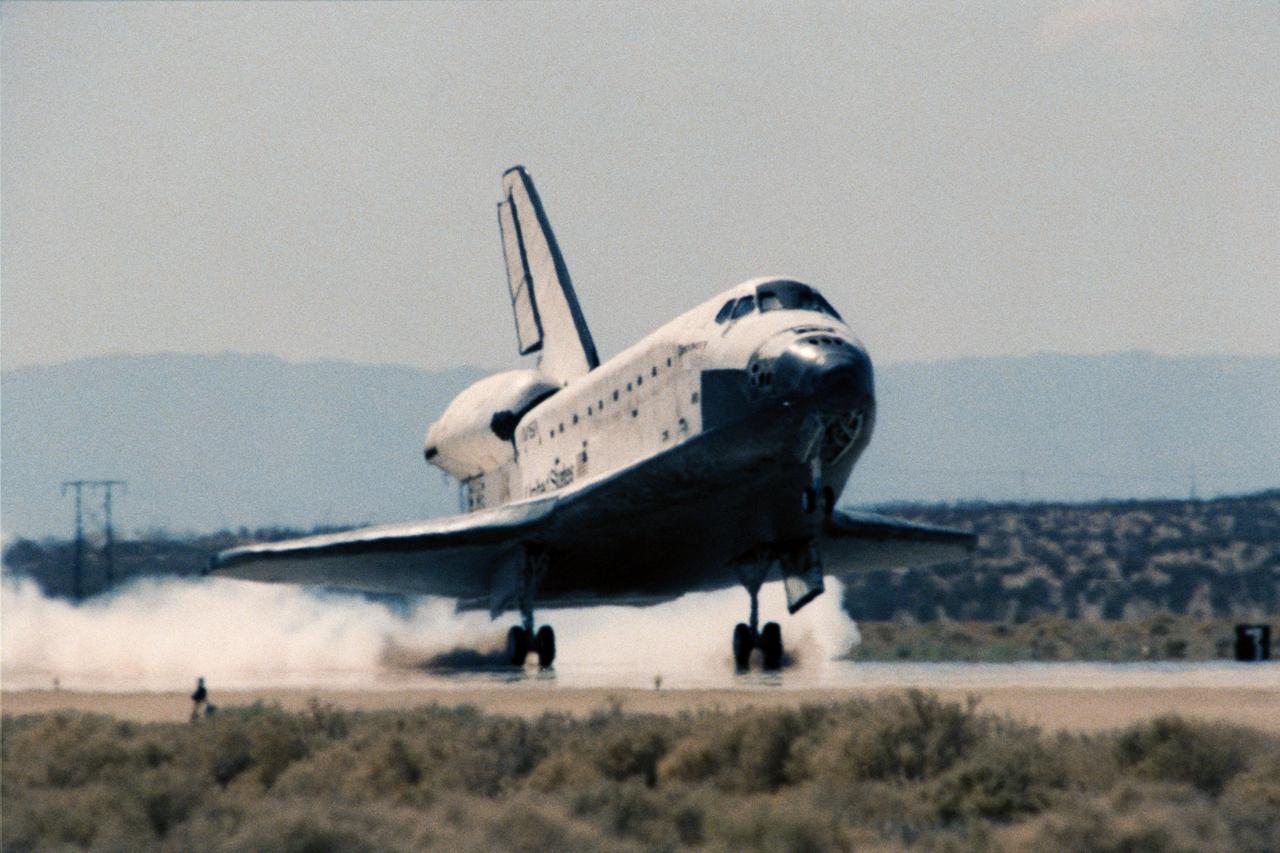

STS64-S-094 (20 Sept. 1994) --- The space shuttle Discovery, with a crew of six NASA astronauts aboard, touches down on Runway 04 at Edwards Air Force Base (EAFB), completing a 10-day, 22-hour and 50-minute mission. Following a de-orbit engine firing at 1:14 p.m. (PDT), Sept. 20, 1994. Touchdown was at 2:12:59 p.m., and the nose wheel touched down at 2:13:03 p.m., with wheel stop at 2:13:52 p.m. Bad weather in Florida called for an "eleventh hour" shift to the California landing site. Onboard for the flight, whose mission was to study Earth's atmosphere and to test tools and procedures for the International Space Station, were astronauts Richard N. Richards, L. Blaine Hammond Jr., Mark C. Lee, Carl J. Meade, Susan J. Helms and Jerry M. Linenger. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
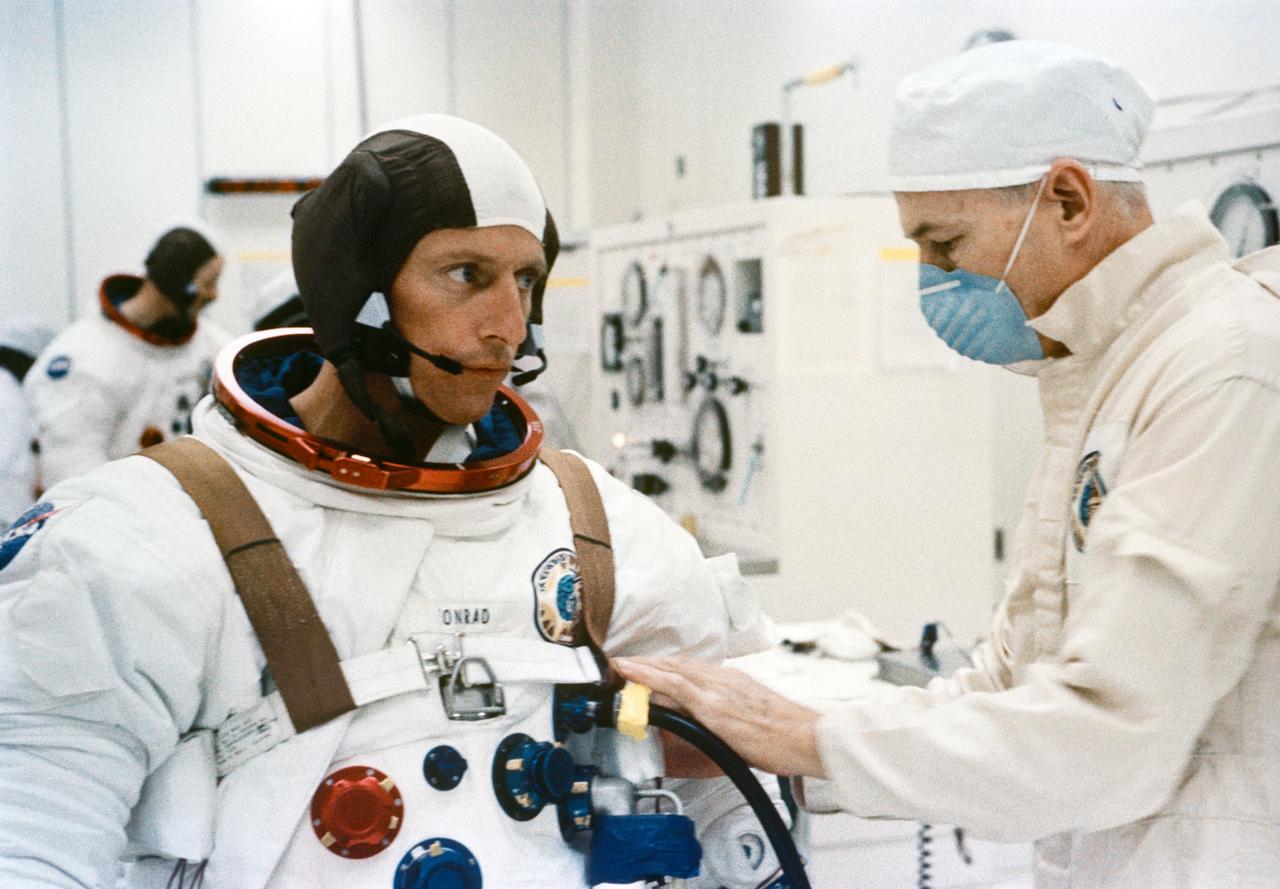
S73-25901 (25 May 1973) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the Skylab 2 mission, is suited up in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building at the Kennedy Space Center during Skylab 2 prelaunch preparations. Skylab 2, with astronauts Conrad, Joseph P. Kerwin and Paul J. Weitz aboard, was launched from KSC's Pad B, Launch Complex 39, at 9:00 a.m. (EDT), May 25, 1973. Photo credit: NASA
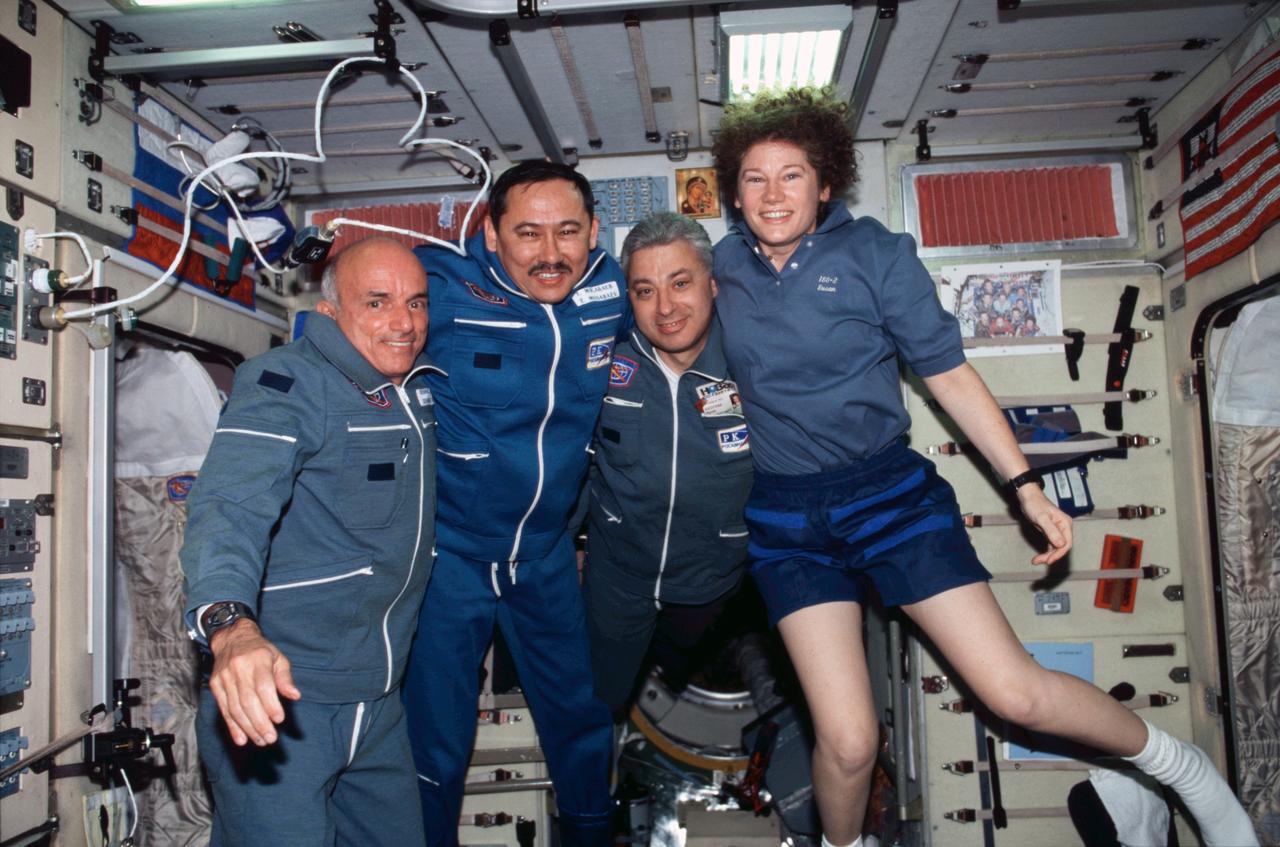

ISS002-356-013 (30 April ; 5 May 2001) --- The Soyuz 2 crewmembers and astronaut Susan J. Helms (right), Expedition 2 flight engineer, pose for a group photo in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). From the left are American businessman Dennis Tito; and cosmonauts Talgat Musabayev and Yuri Baturin, Soyuz 2 commander and flight engineer, respectively, representing Rosaviakosmos.
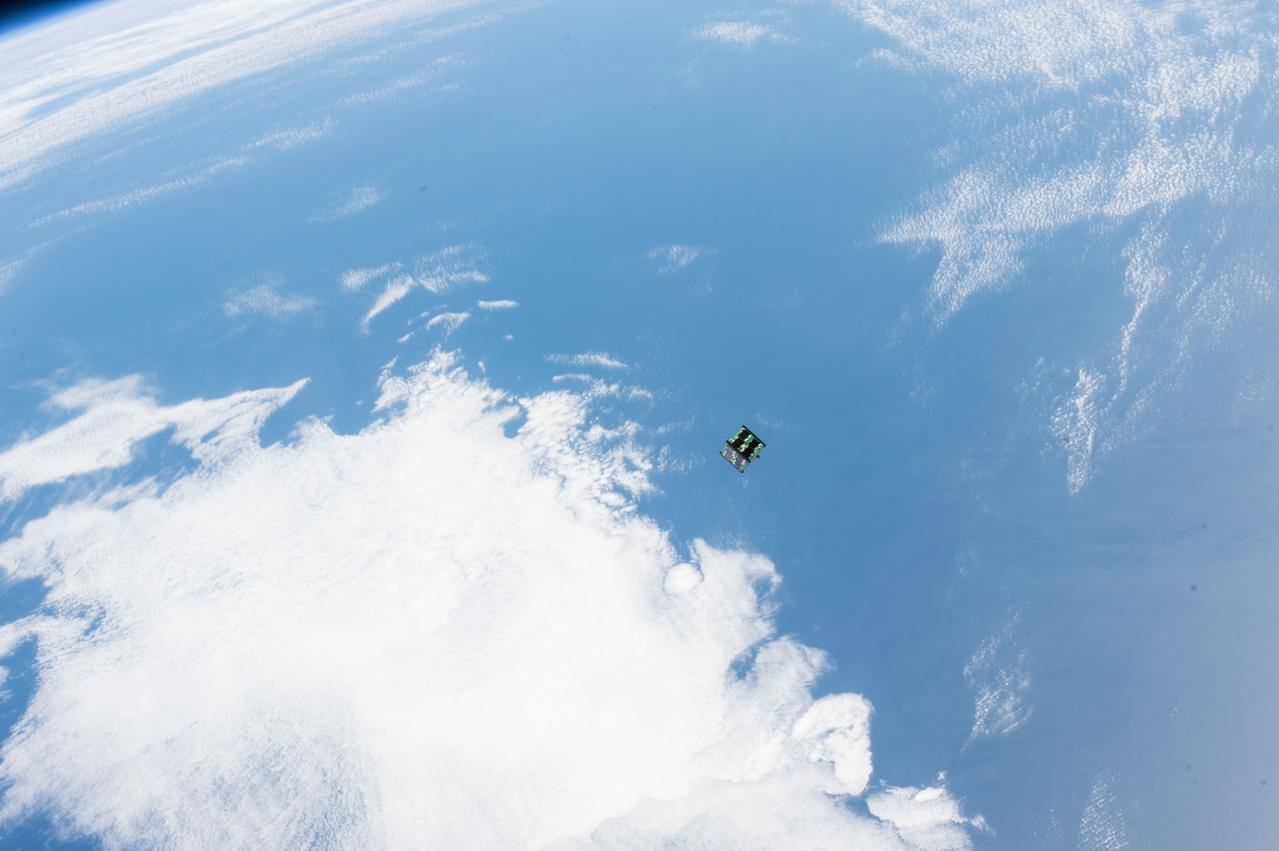

iss042e222241 (2/5/2015) --- Photographic documentation of the JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer-3 (J-SSOD-3) mission deploy of the CubeSat AESP-14 from Kibo. The satellite was developed by the Technological Institute of Aeronautics (ITA), with support from the Brazilian Space Agency (AEB), and the National Institute for Space Research (INPE).
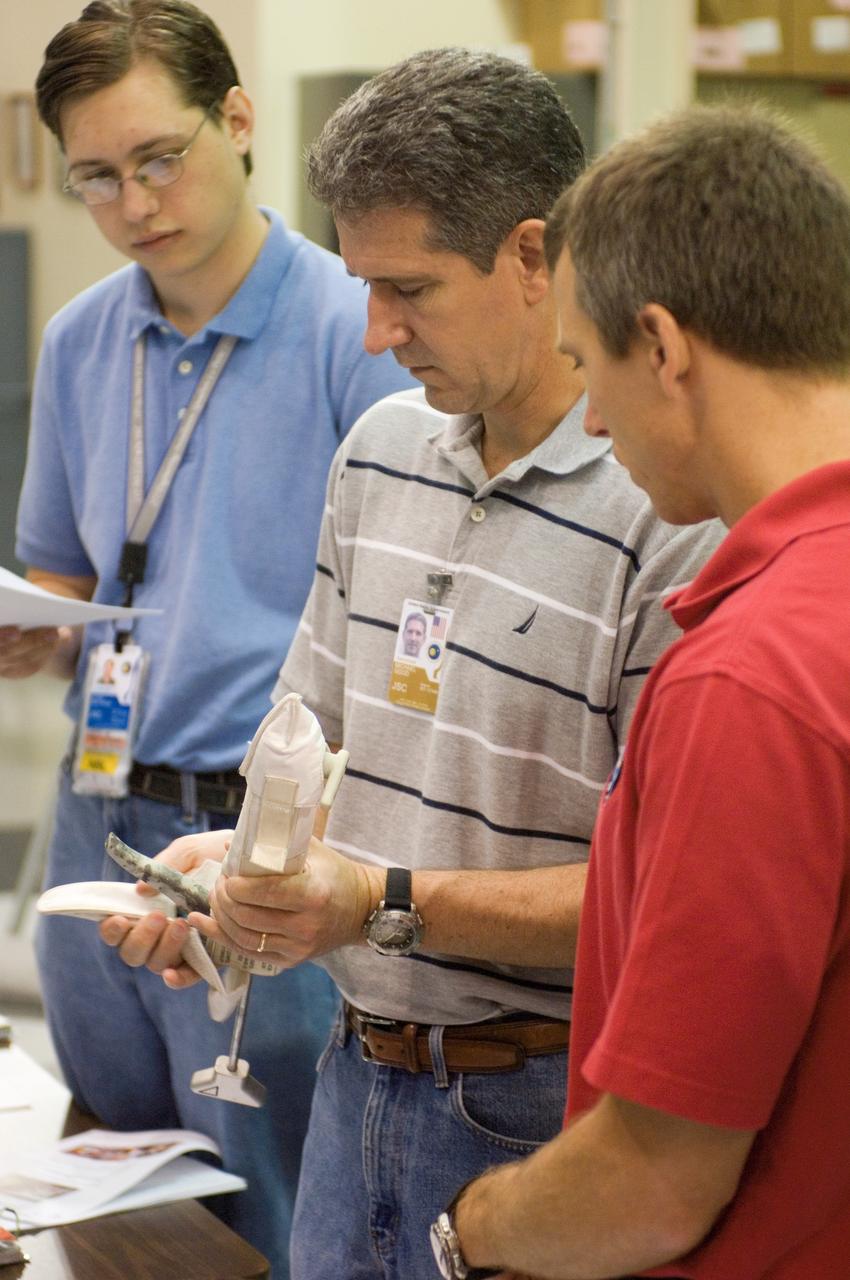

JSC2008-E-031809 (2 April 2008) --- Astronauts Andrew J. Feustel (right) and Michael T. Good, both STS-125 mission specialists, participate in an extravehicular activity (EVA) hardware training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center.
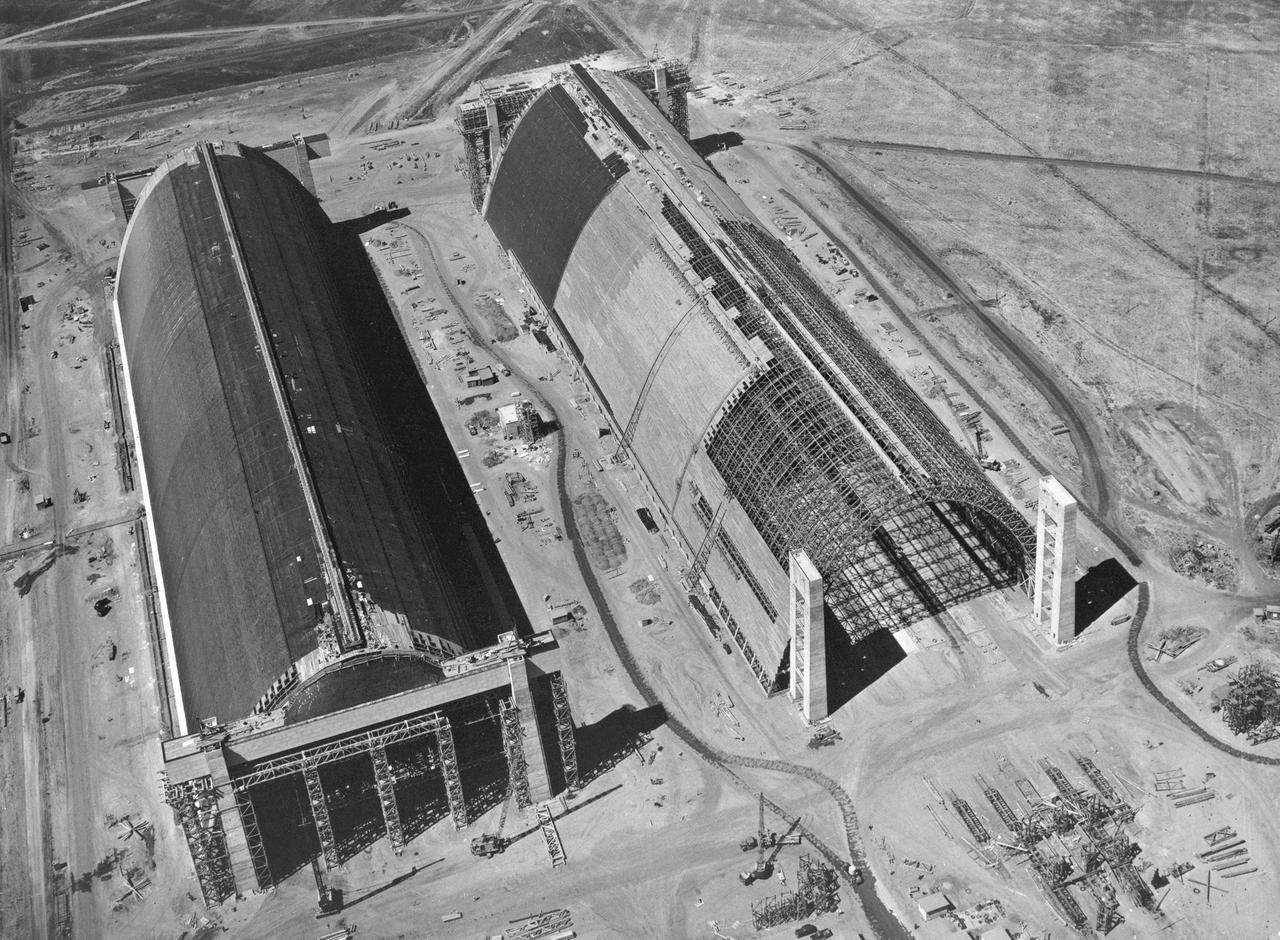

Navy (Contract NOy-5604 SNVL 1691) NAS Air station Moffett Field, overhead view of Hangar 2 and 3 from North West Corner Moffett Field Public Works Serial 1621 - Earl W. Heple & J. H. Pomeroy Contractors

Navy (Contract NOY-5604 SNVL 1689) NAS Airstation Moffett Field, broadside view of Hangar 2 from middle of landing mat. Moffett Field Public Works Serial 1621 - Earl W. Heple & J. H. Pomeroy Contractors
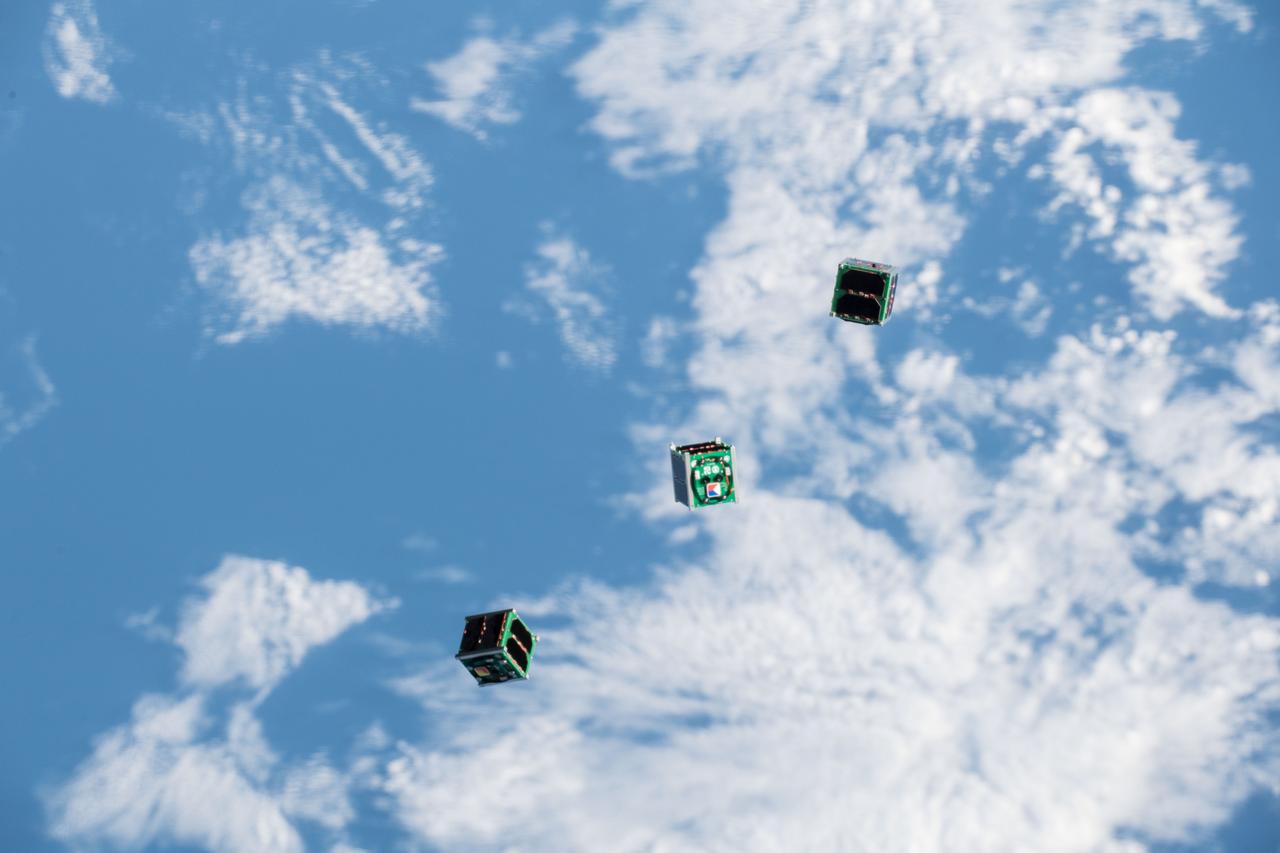

iss056e130515 (8/10/2018) --- A view of the BIRDS-2 Satellite Deployment during JSSOD-9 operations. The JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD) provides a novel, safe, small satellite launching capability to the International Space Station (ISS).
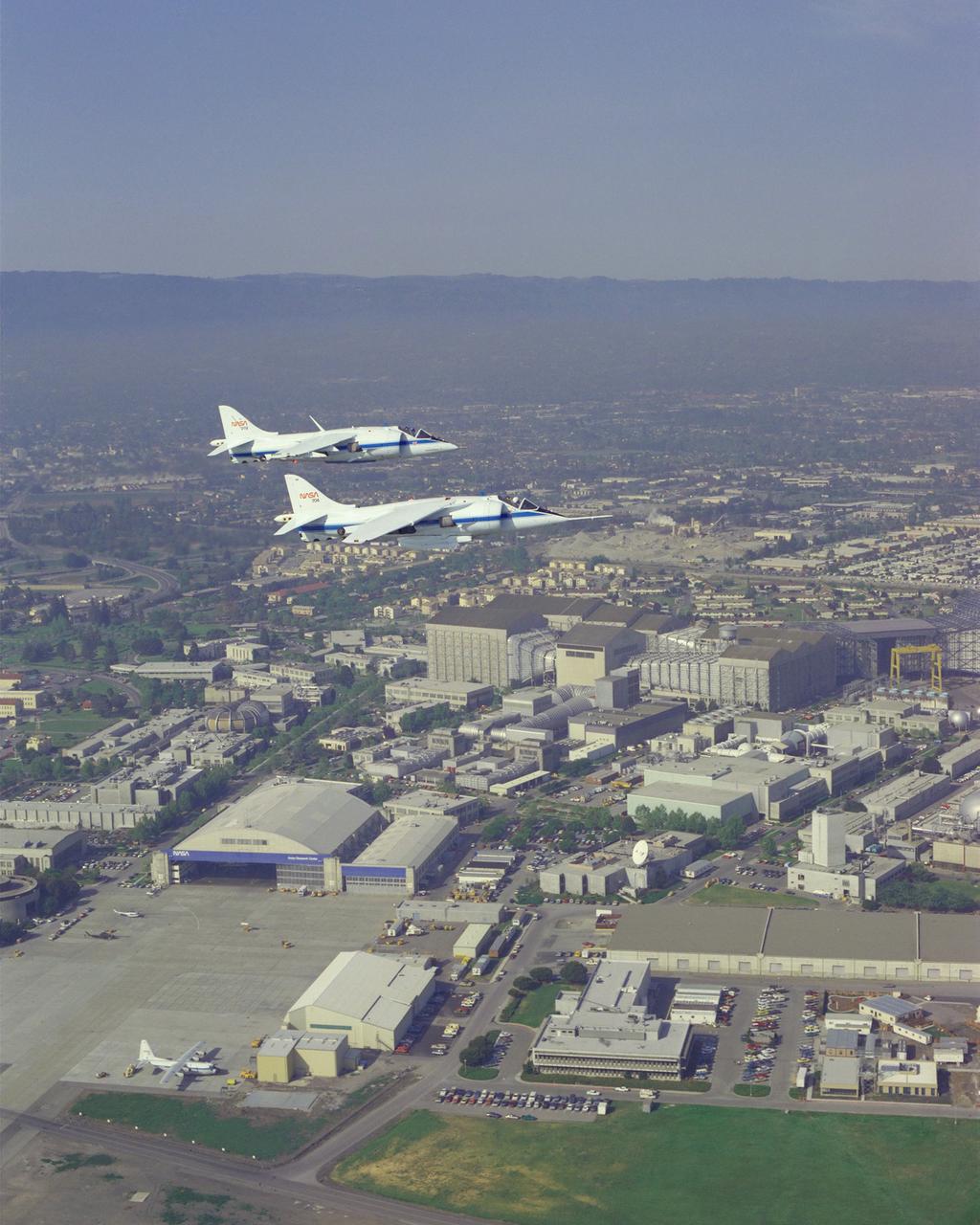

AV-8B (NASA-719) and AV-8C (NASA-704) air to air formation flight with T-38, U-2 (NASA-708) with pilots G. Hardy and J. Martin over NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field.
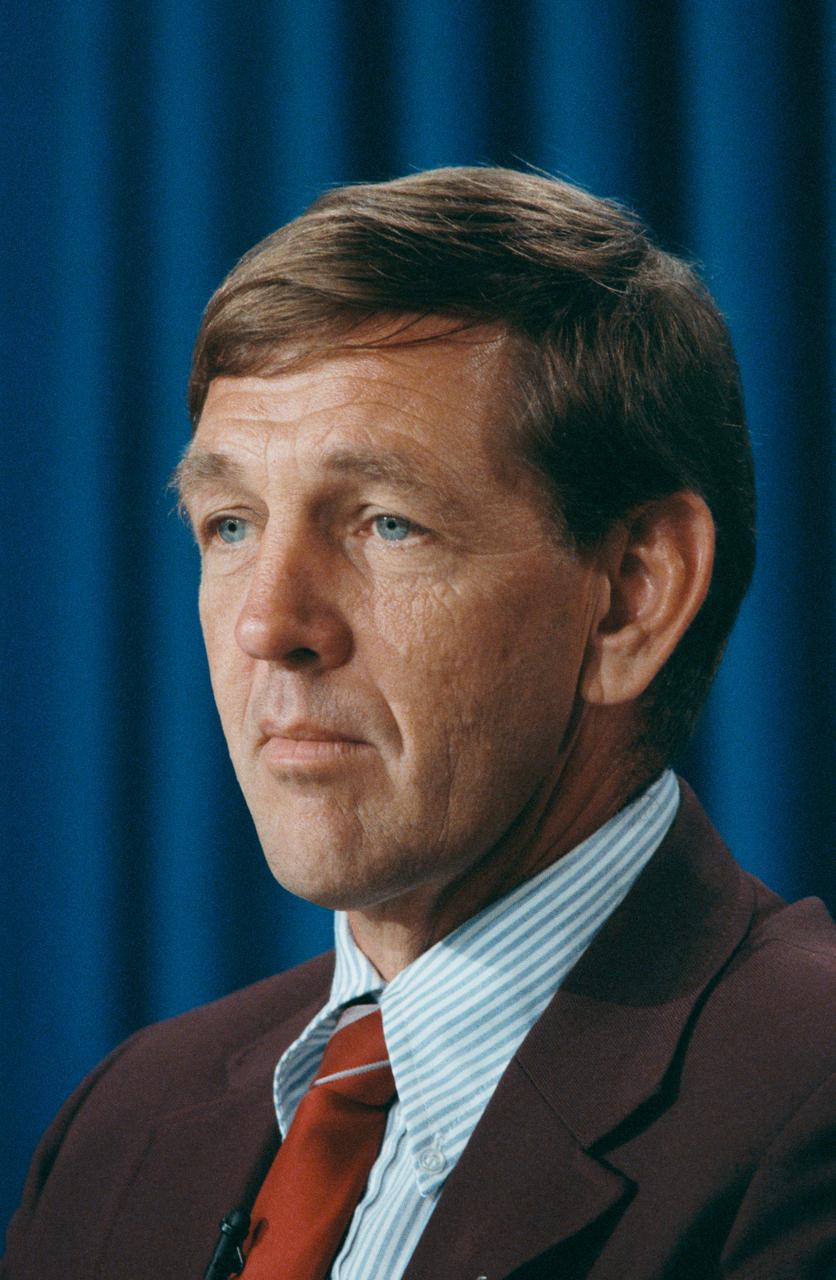

STS-34 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, Pilot Michael J. McCulley reflects on a question during the thirty days before launch (T-30) press briefing in the JSC Auditorium and Public Affairs Facility Bldg 2 briefing room.
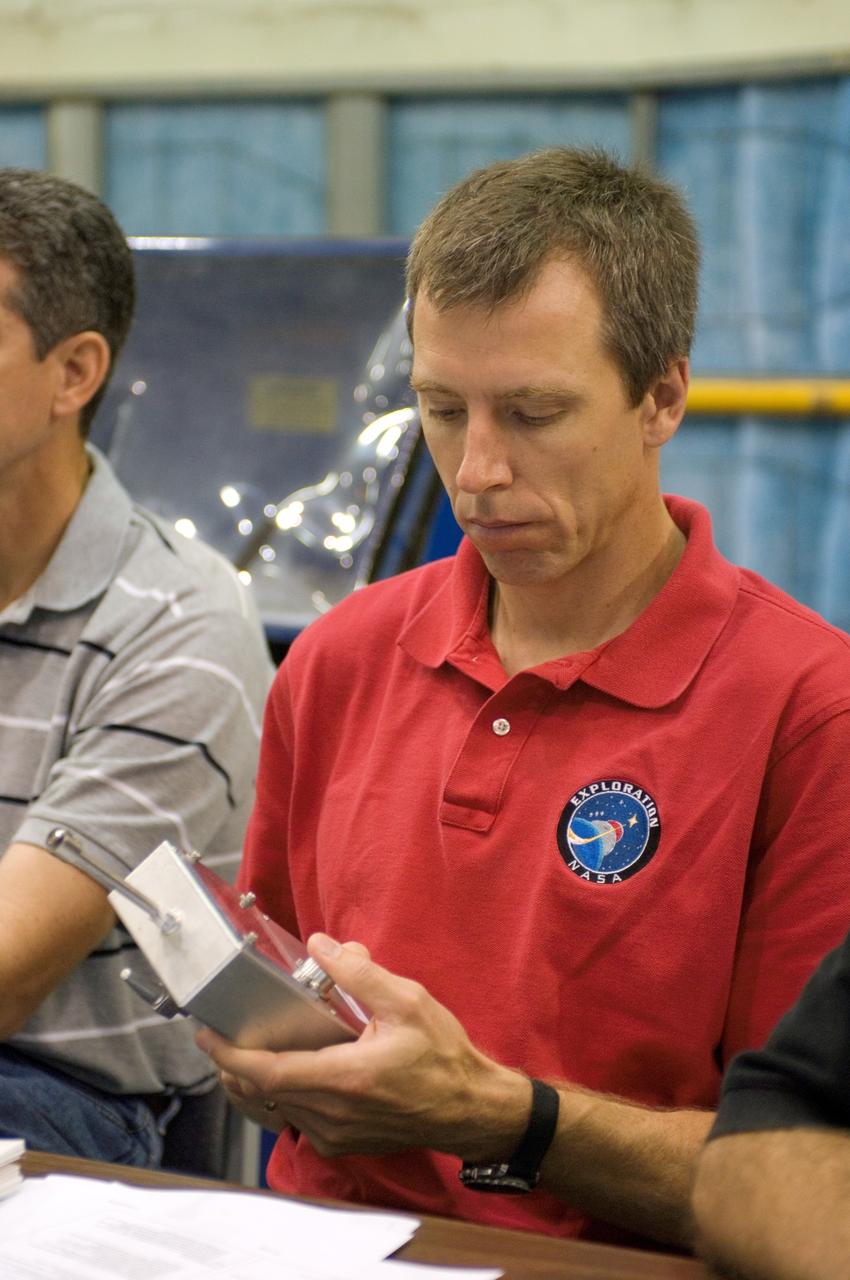

JSC2008-E-031806 (2 April 2008) --- Astronaut Andrew J. Feustel, STS-125 mission specialist, participates in an extravehicular activity (EVA) hardware training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center.
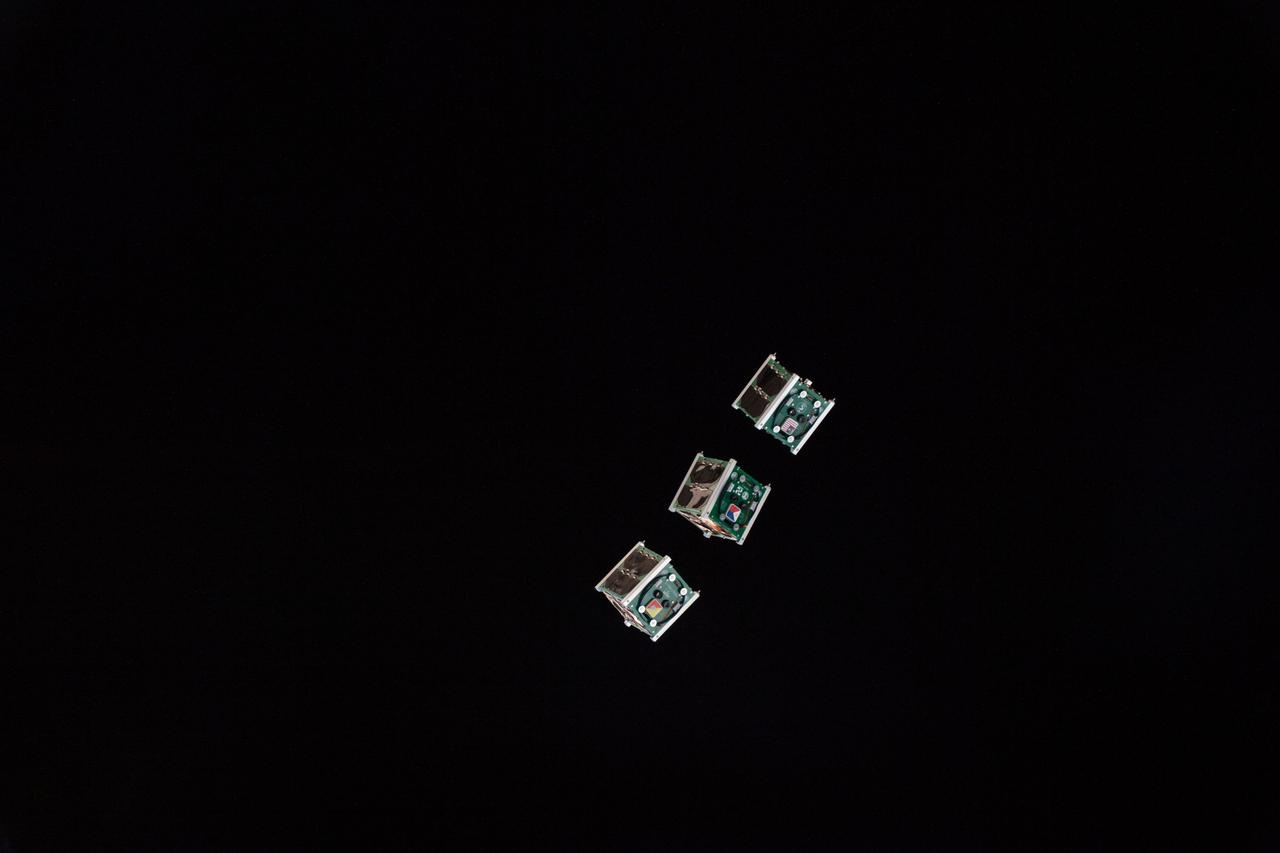

iss056e130490(8/10/2018) --- A view of the BIRDS-2 Satellite Deployment during JSSOD-9 operations. The JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD) provides a novel, safe, small satellite launching capability to the International Space Station (ISS).
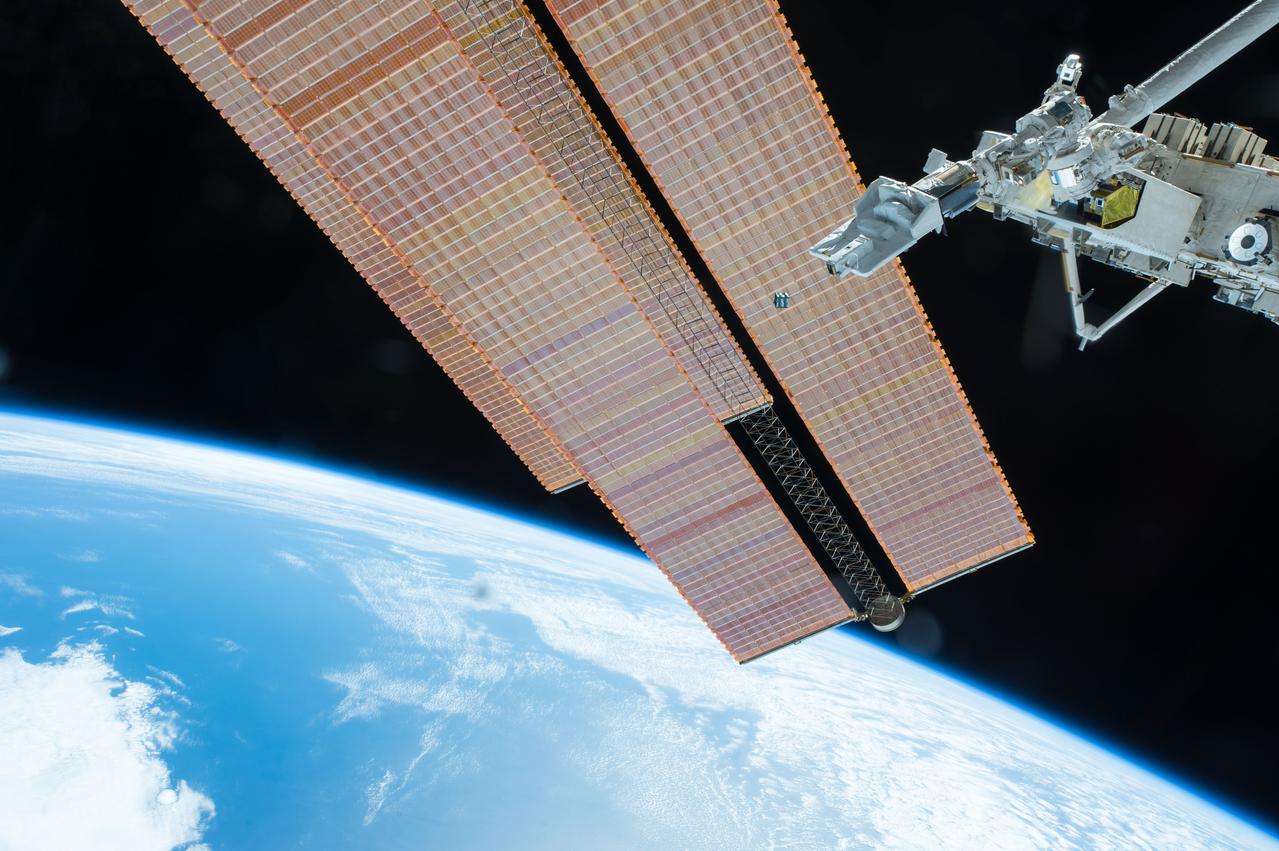

iss042e224107 (2/5/2015) --- Photographic documentation of the JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer-3 (J-SSOD-3) mission deploy of the CubeSat AESP-14 from Kibo. The satellite was developed by the Technological Institute of Aeronautics (ITA), with support from the Brazilian Space Agency (AEB), and the National Institute for Space Research (INPE).
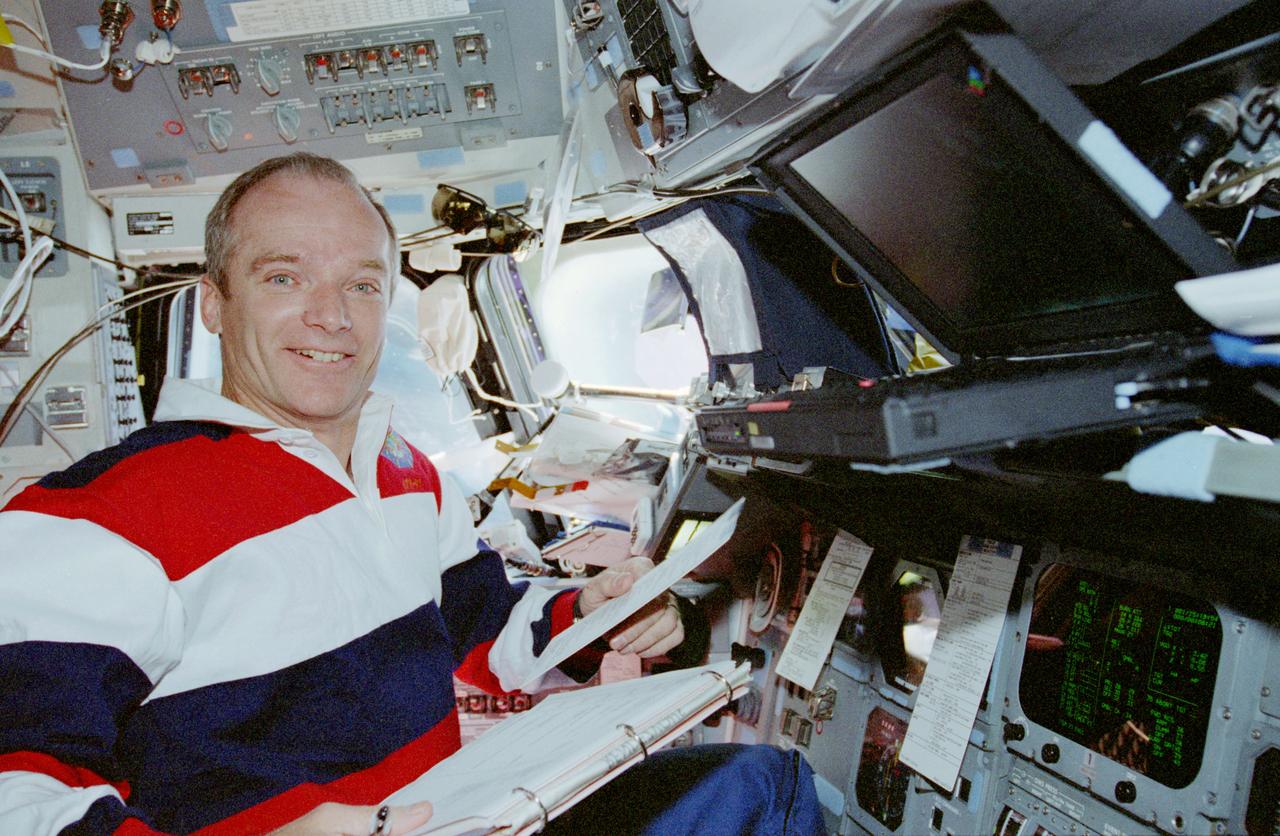

STS091-360-014 (2-12 June 1998) --- Astronaut Charles J. Precourt mans the commander's station on the flight deck of the Space Shuttle Discovery during NASA's scheduled final rendezvous operations with Russia's Mir space station. The veteran astronaut holds checklists related to the rendezvous activities.
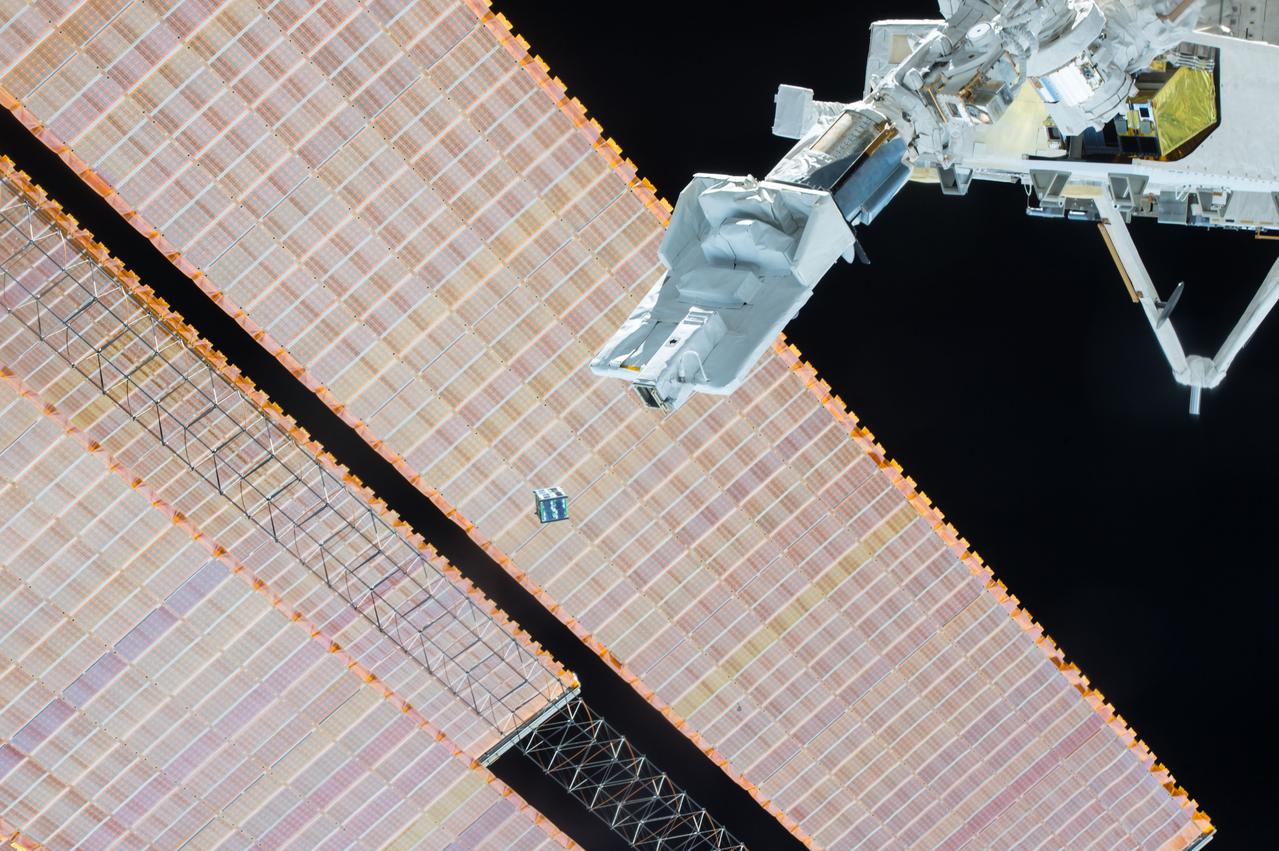
iss042e222236 (2/5/2015) --- Photographic documentation of the JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer-3 (J-SSOD-3) mission deploy of the CubeSat AESP-14 from Kibo. The satellite was developed by the Technological Institute of Aeronautics (ITA), with support from the Brazilian Space Agency (AEB), and the National Institute for Space Research (INPE).
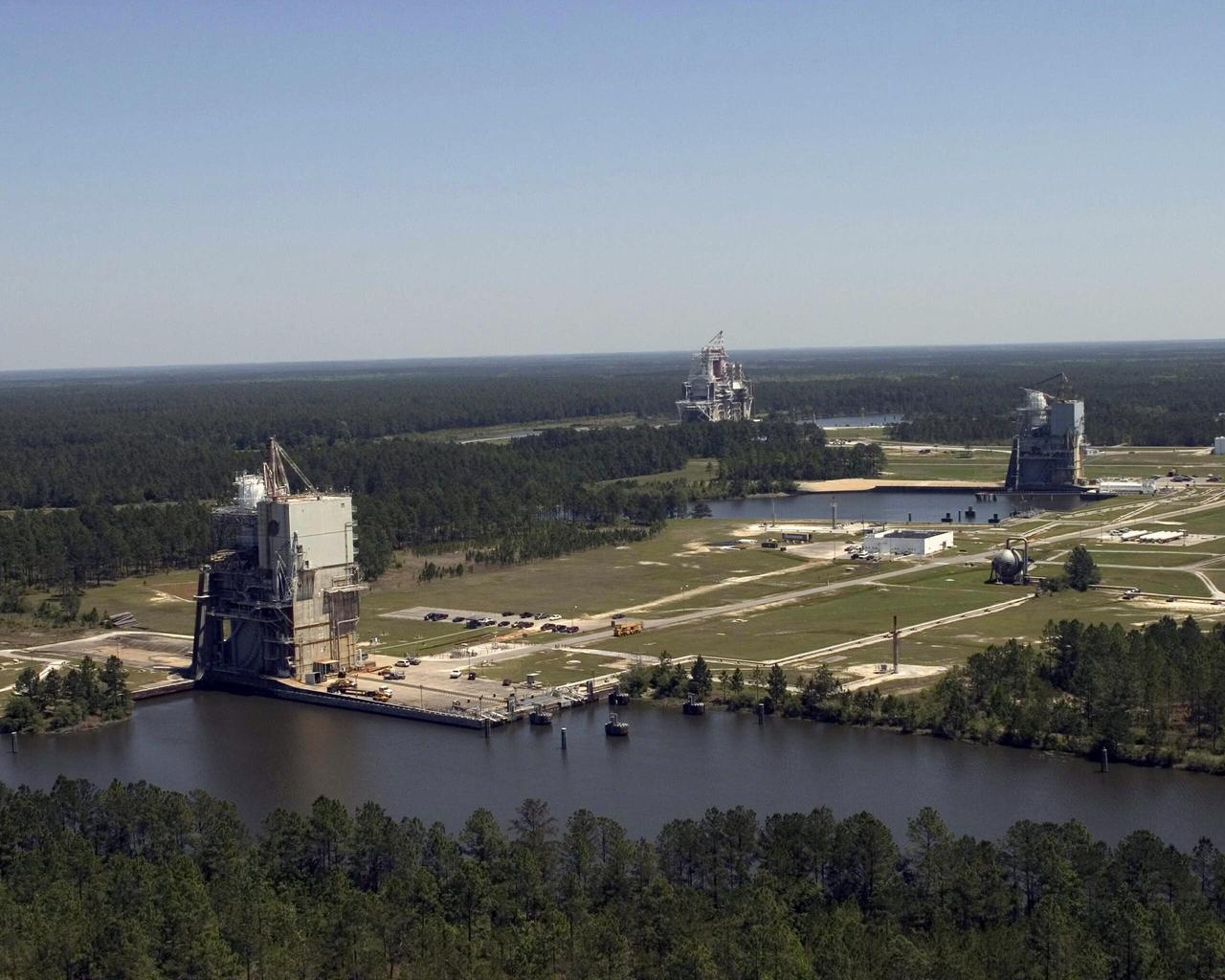

SSC's A-1, A-2 and B test stands were built in the early 1960s to test the first and second stages of the Apollo Saturn V rocket that safely transported Americans to the moon. The A-1 Stand (foreground) will soon test the J-2X engines that will power the rockets to take Americans back to the moon.
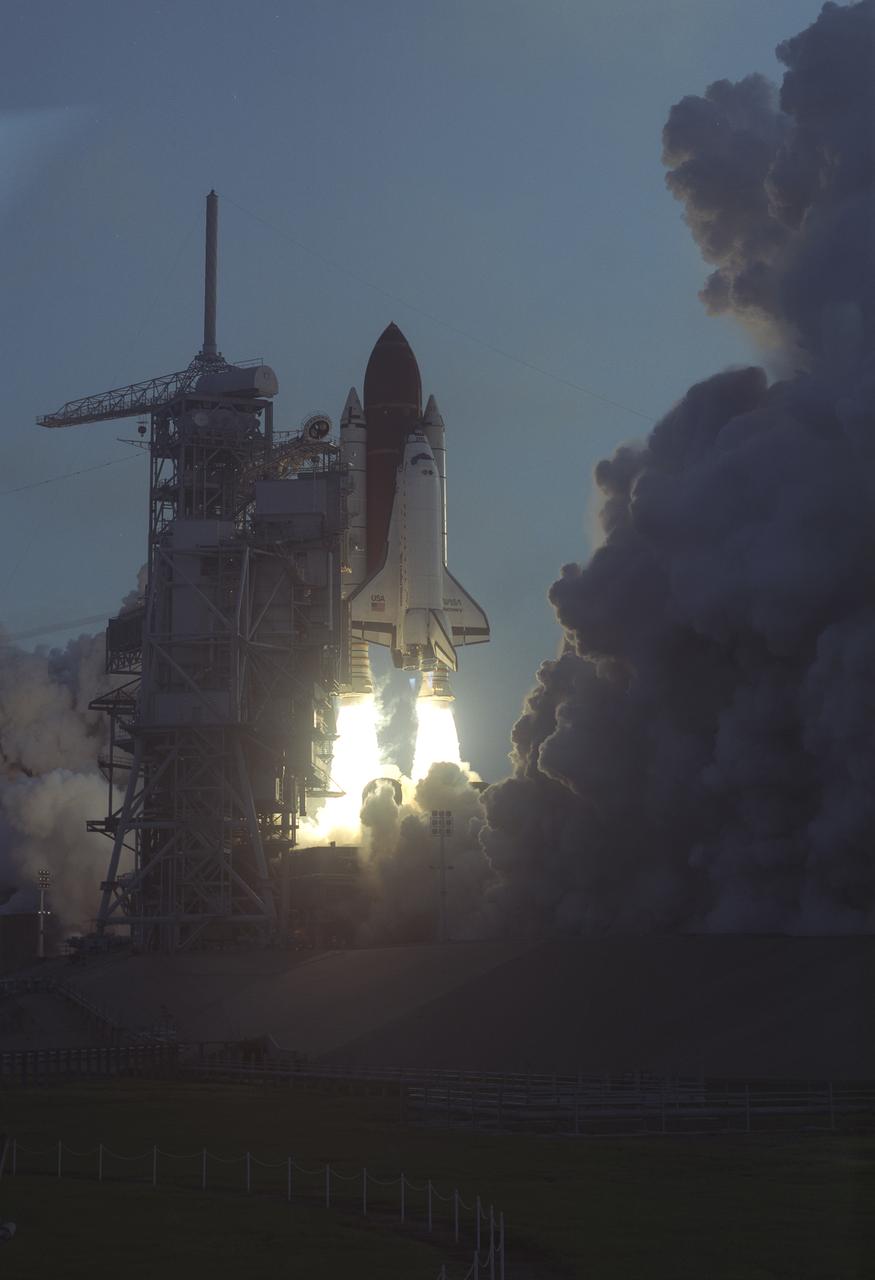

Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on April 28, 1991 at 7:33:14 am (EDT), STS-39 was a Department of Defense (DOD) mission. The crew included seven astronauts: Michael L. Coats, commander; L. Blaine Hammond, pilot; Guion S. Buford, Jr., mission specialist 1; Gregory J. Harbaugh, mission specialist 2; Richard J. Hieb, mission specialist 3; Donald R. McMonagle, mission specialist 4; and Charles L. Veach, mission specialist 5. The primary unclassified payload included the Air Force Program 675 (AFP-675), the Infrared Background Signature Survey (IBSS), and the Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (SPAS II).
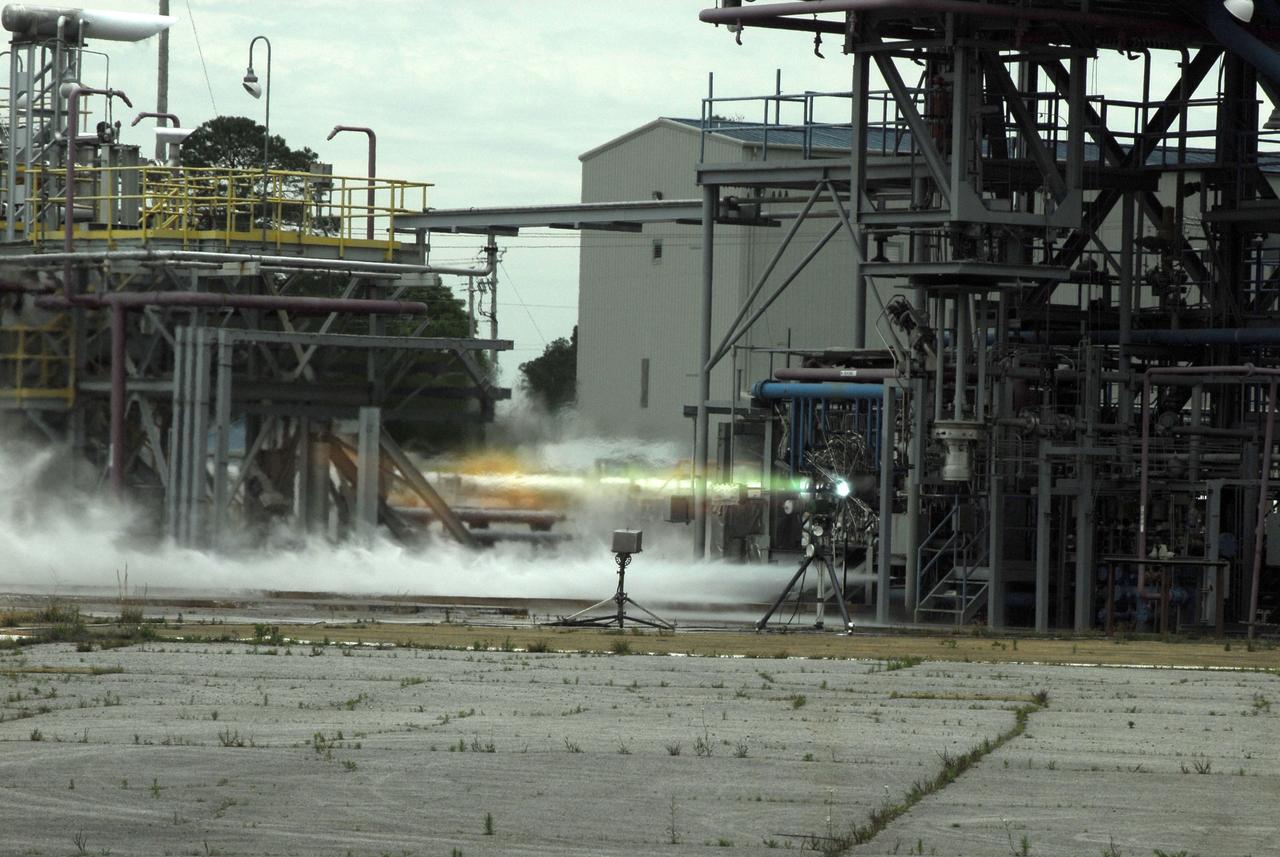

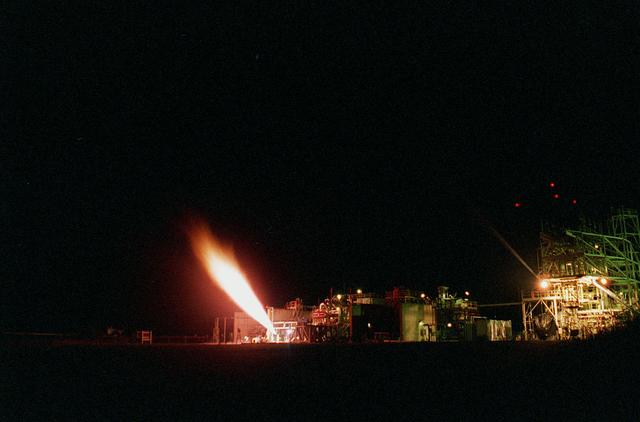
Chosen to power the upper stages of the new Ares I Crew Launch Vehicle (CLV) and the Ares V cargo segment, the J-2X engine is a stepped up version of the hydrogen/oxygen-fuelled Apollo-era J-2 engine. It was developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne (PWR), a business unit of United Technologies Corporation of Canoga Park, California. As seen in this photograph, the engine underwent a series of hot fire tests, performed on sub scale main injector hardware in the Test Stand 116 at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The injector is a major component of the engine that injects and mixes propellants in the combustion chamber, where they are ignited and burned to produce thrust.

Mission Control Activities during the STS-3 Mission, Day-4 with: Maj. Gen. James A. Abrahamson, Associate Administrator of the Space Transportation System (STS), NASA Hdqs., conversing with Dr. Kraft; Glynn S. Lunney, Manager, Space Shuttle Program Office, JSC, Aaron Cohen, Manager, Space Shuttle Orbiter Project Office; and, J. E. Conner, Ford Aerospace Engineer at the Instrumentation and Communications Officer (INCO) Console position. 1. Glynn S. Lunney 2. Major General James A. Abrahamson 3. Aaron Cohen 4. J. E. Conner 5. Dr. Christopher Kraft JSC, Houston, TX
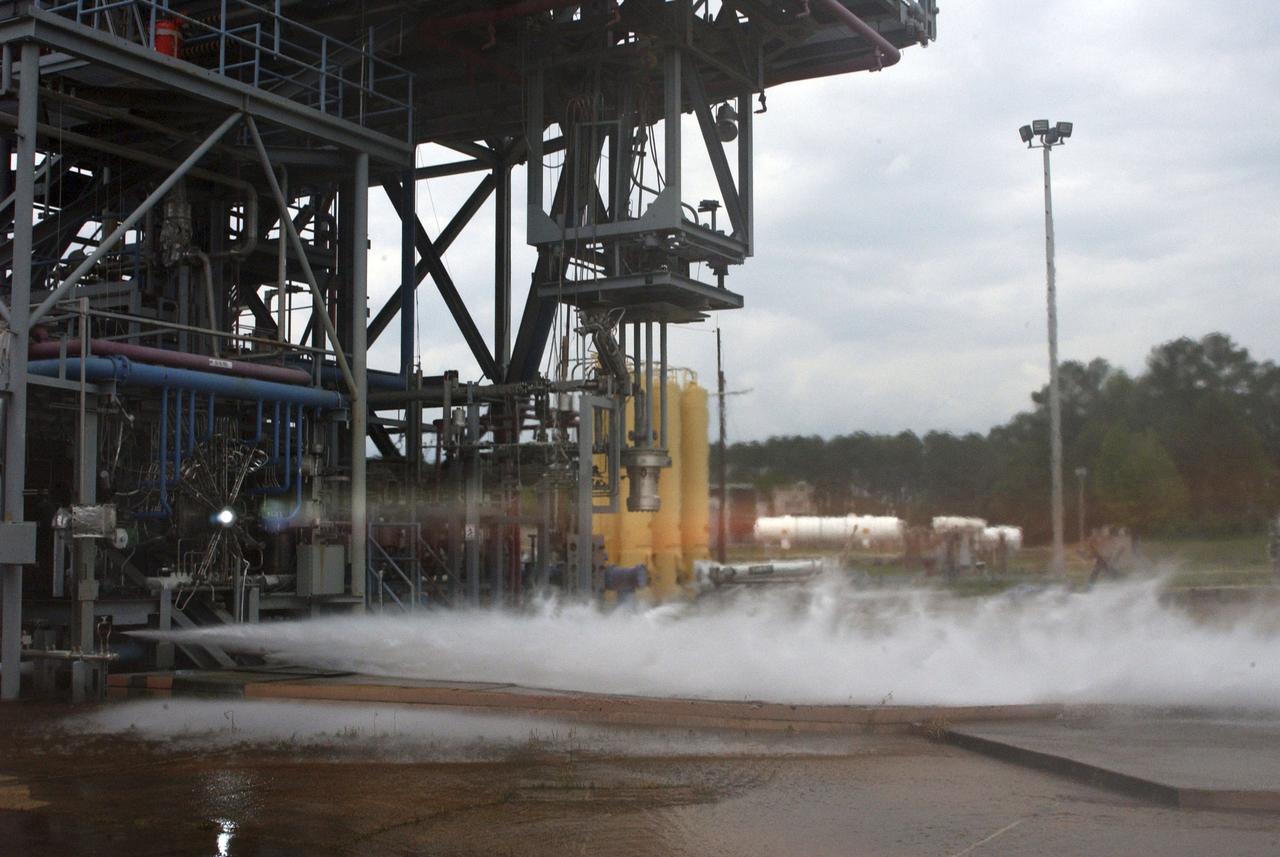

Chosen to power the upper stages of the new Ares I Crew Launch Vehicle (CLV) and the Ares V cargo segment, the J-2X engine is a stepped up version of the hydrogen/oxygen-fuelled Apollo-era J-2 engine. It was developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne (PWR), a business unit of United Technologies Corporation of Canoga Park, California. As seen in this photograph, the engine underwent a series of hot fire tests, performed on sub scale main injector hardware in the Test Stand 116 at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The injector is a major component of the engine that injects and mixes propellants in the combustion chamber, where they are ignited and burned to produce thrust.
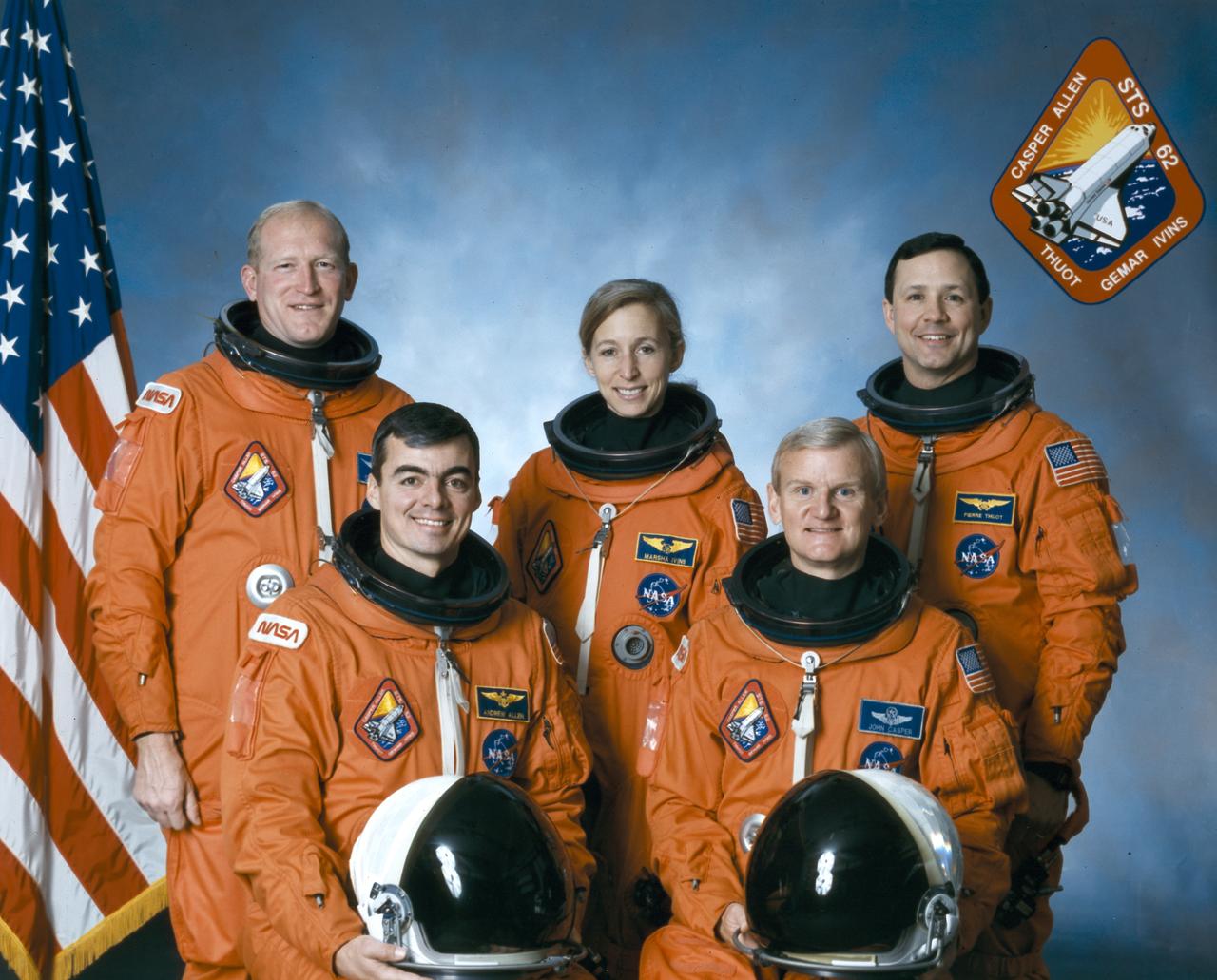

Astronauts included in the STS-62 crew portrait include (standing left to right) mission specialists Charles D. Gemar, Marsha S. Ivins, and Pierre J. Thuot. Seated left to right are Andrew M. Allen, pilot; and John H. Casper, commander. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on March 4, 1994 at 8:53:00 am (EST), the STS-62 mission carried two primary payloads; the U.S Microgravity Payload-2 (USMP-2) and the Office of Aeronautics and Space Technology-2 (OAST-2).
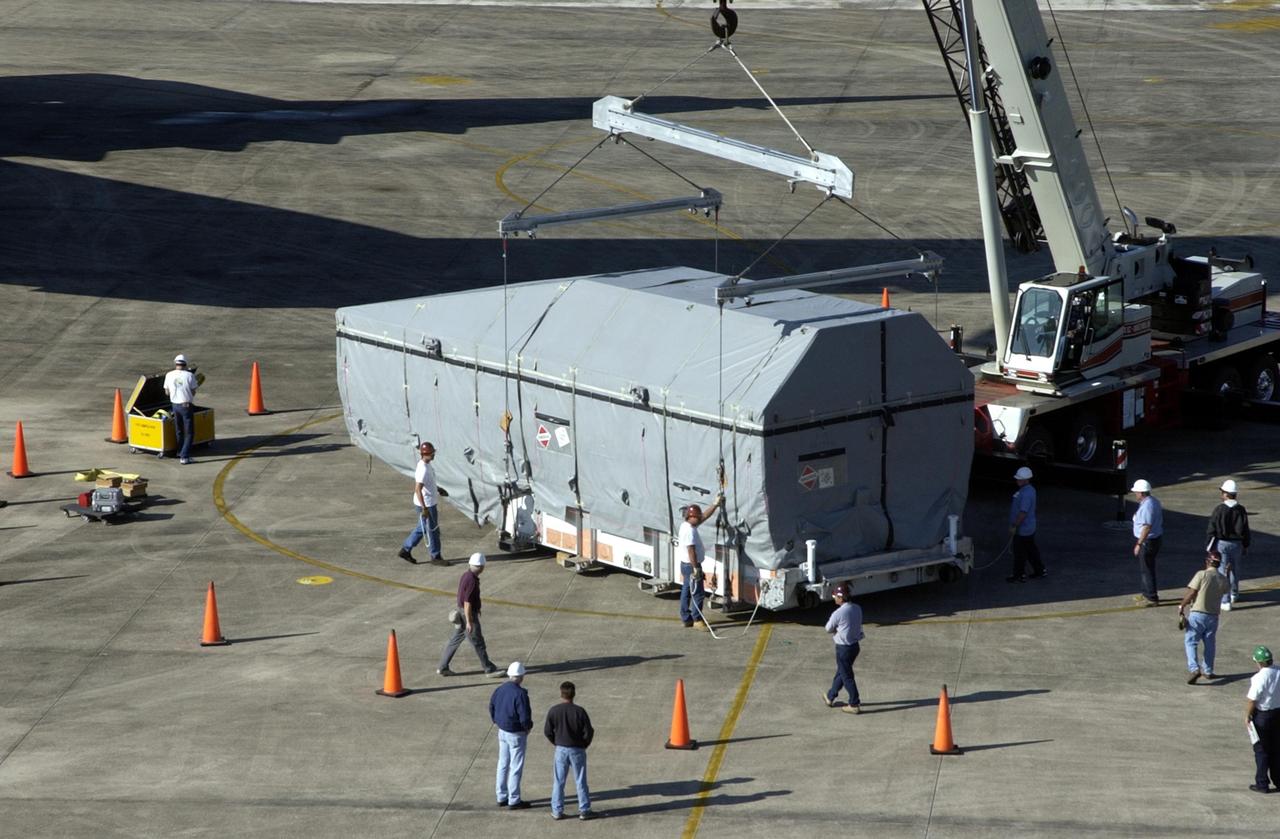

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers attach the container with the TDRS-J spacecraft inside to an overhead crane. The container will be placed on a transporter and taken to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2). TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
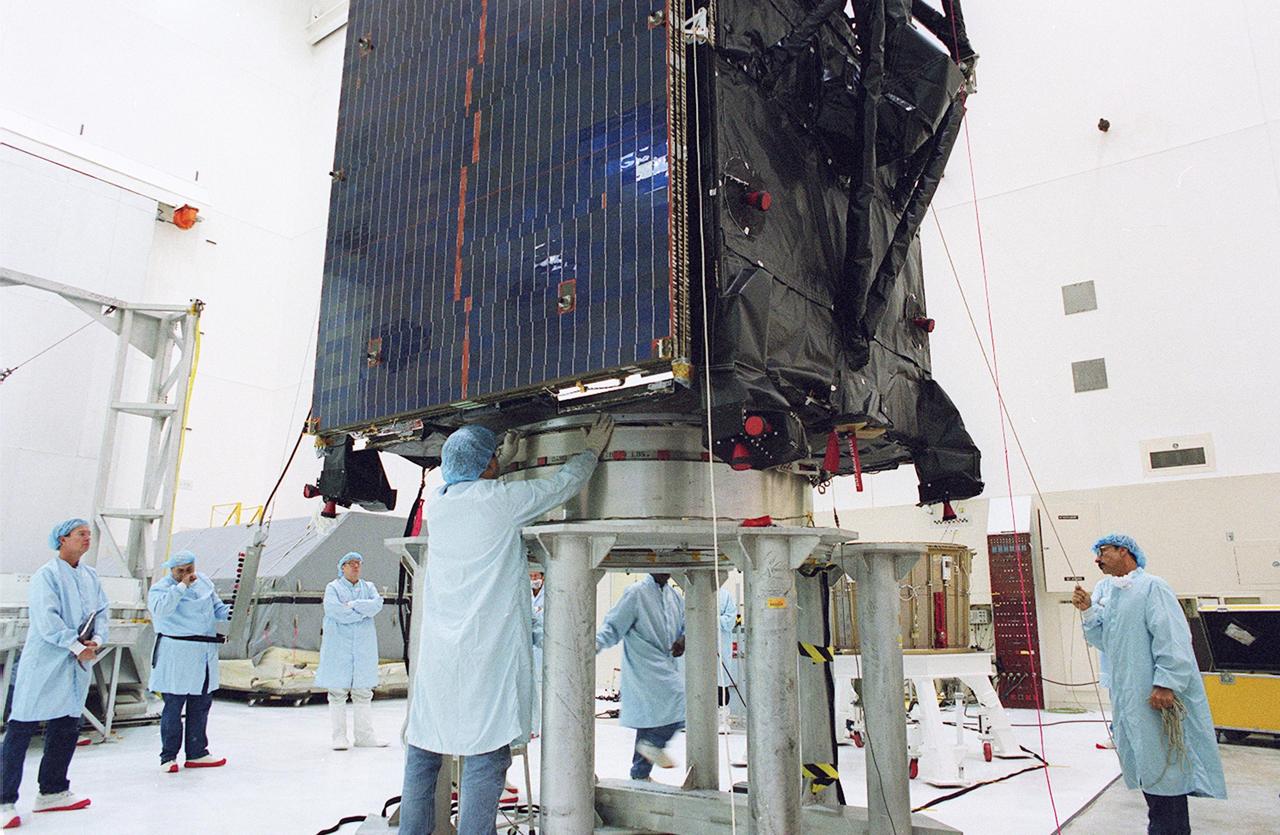

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers inspect the placement of the TDRS-J spacecraft on a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2) for final checkout and processing before launch, currently targeted for Nov. 20. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
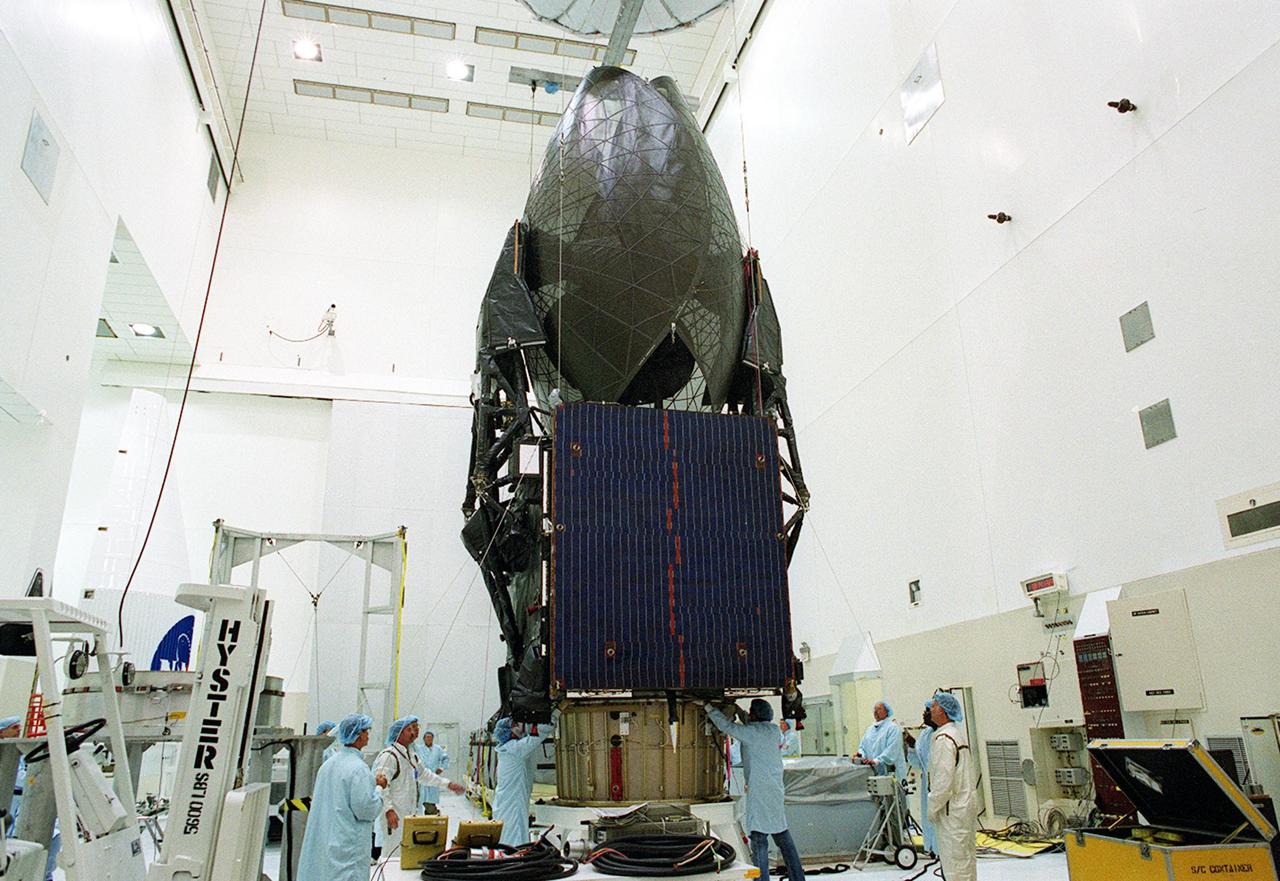

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers supervise the placement of the TDRS-J spacecraft onto a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2) for final checkout and processing before launch, currently targeted for Nov. 20. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
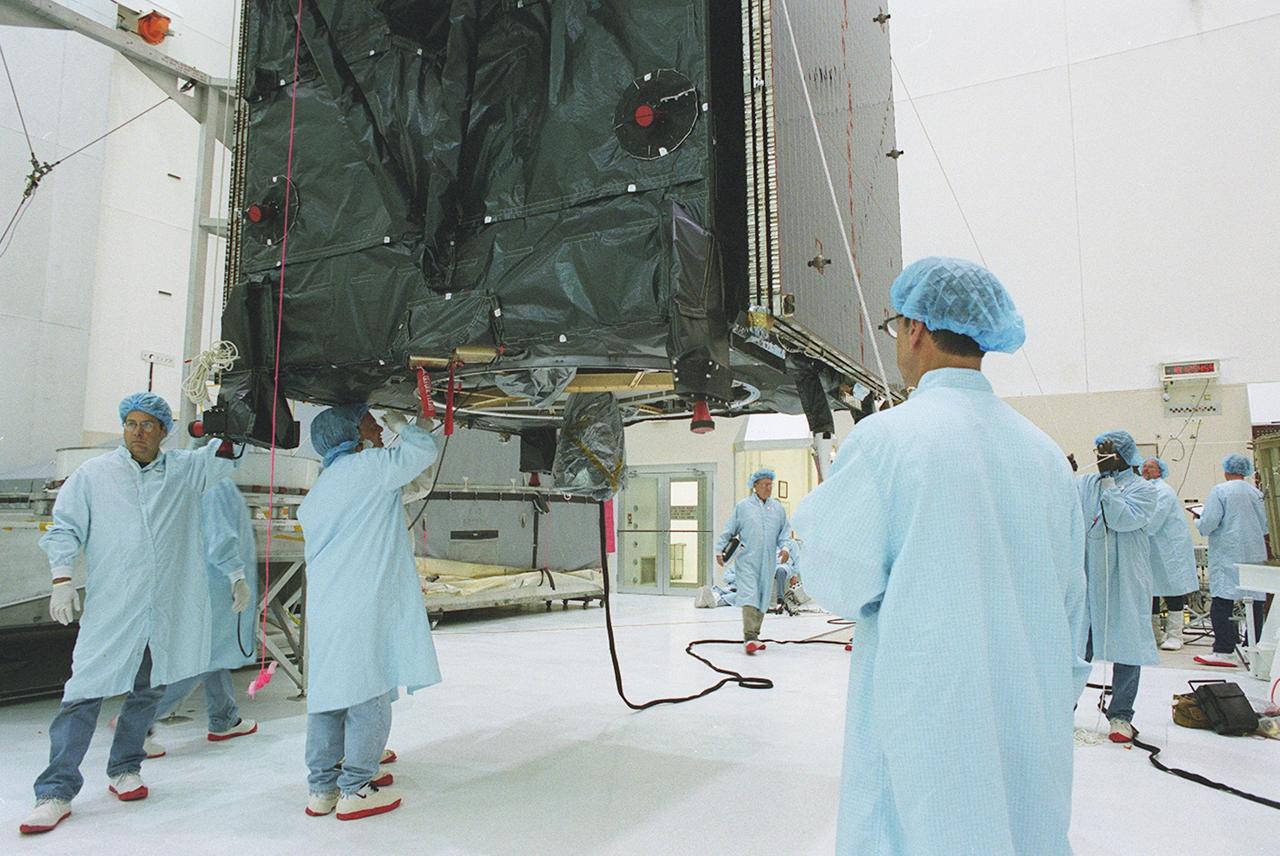

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers move the suspended TDRS-J spacecraft towards a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2) for final checkout and processing before launch, currently targeted for Nov. 20. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
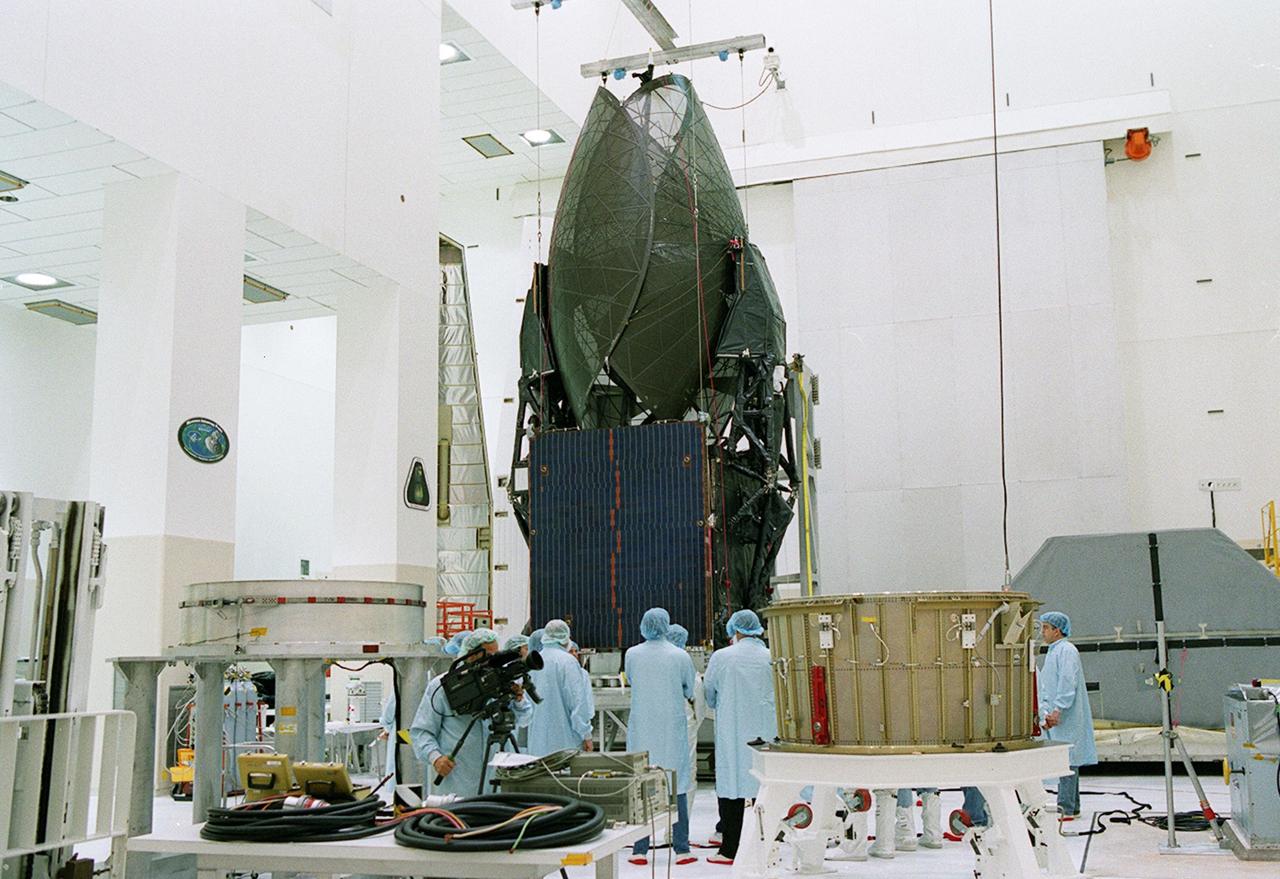

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The TDRS-J spacecraft is unpacked and prepared to be moved to a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2) for final checkout and processing before launch, currently targeted for Nov. 20. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
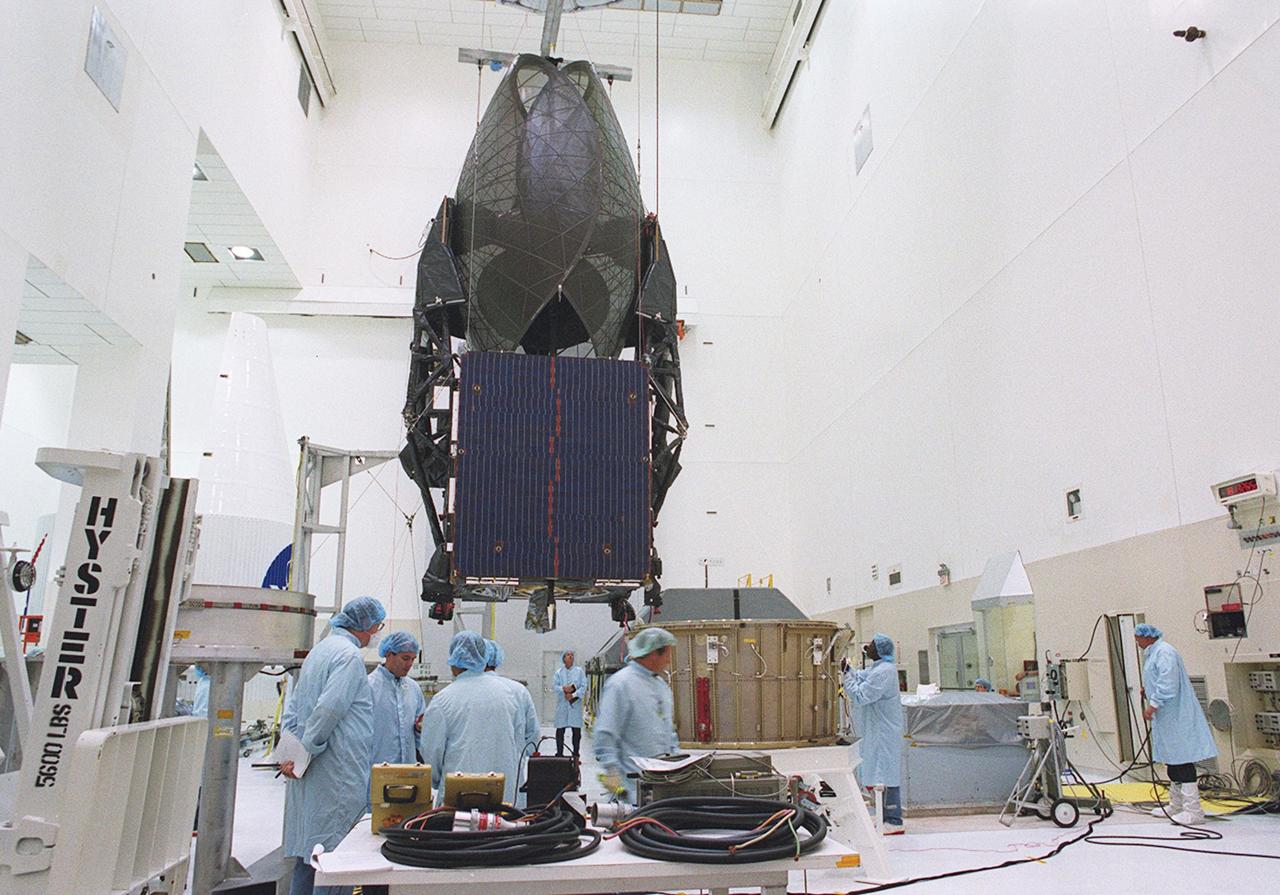

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers supervise the move of the suspended TDRS-J spacecraft towards a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2) for final checkout and processing before launch, currently targeted for Nov. 20. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
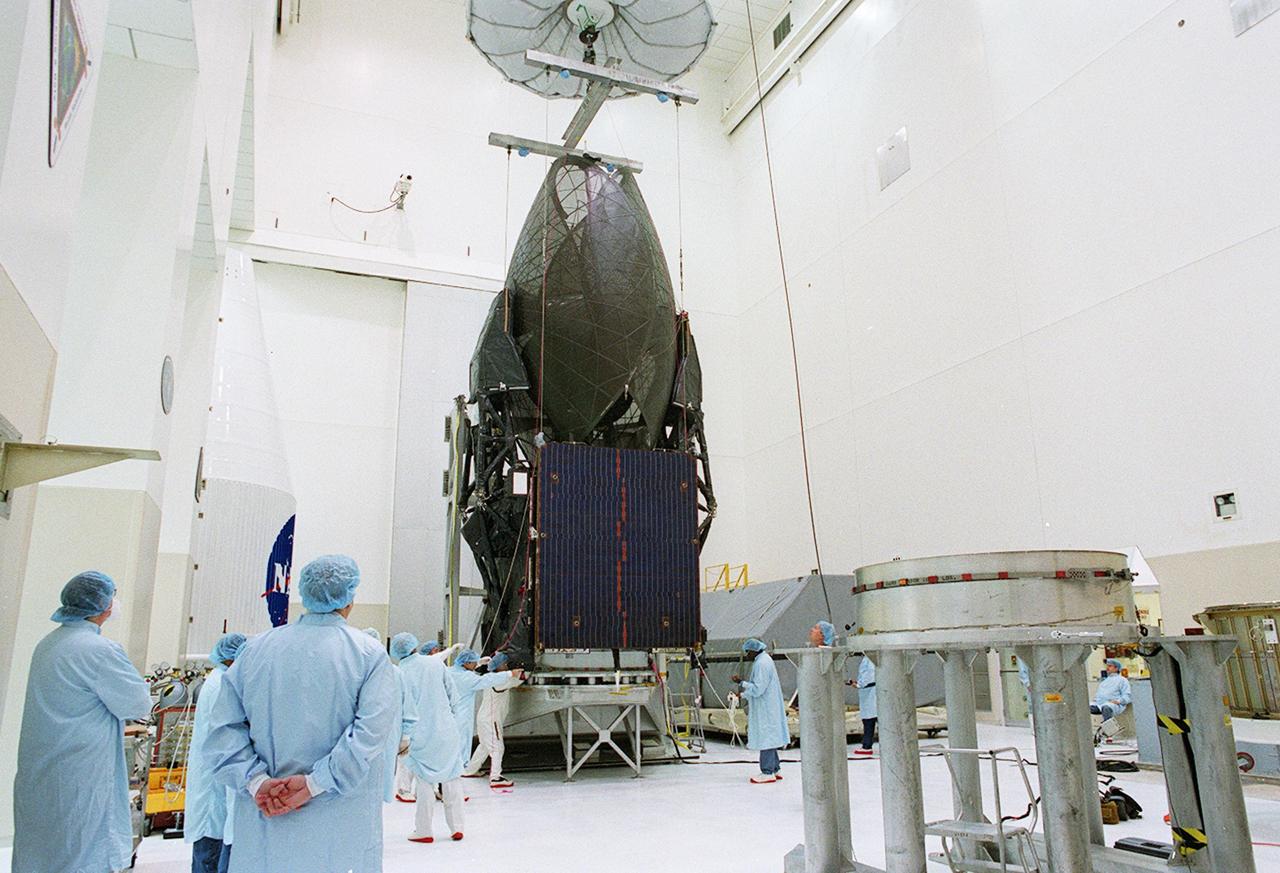

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers prepare to lift the TDRS-J spacecraft for its move to a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2) for final checkout and processing before launch, currently targeted for Nov. 20. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
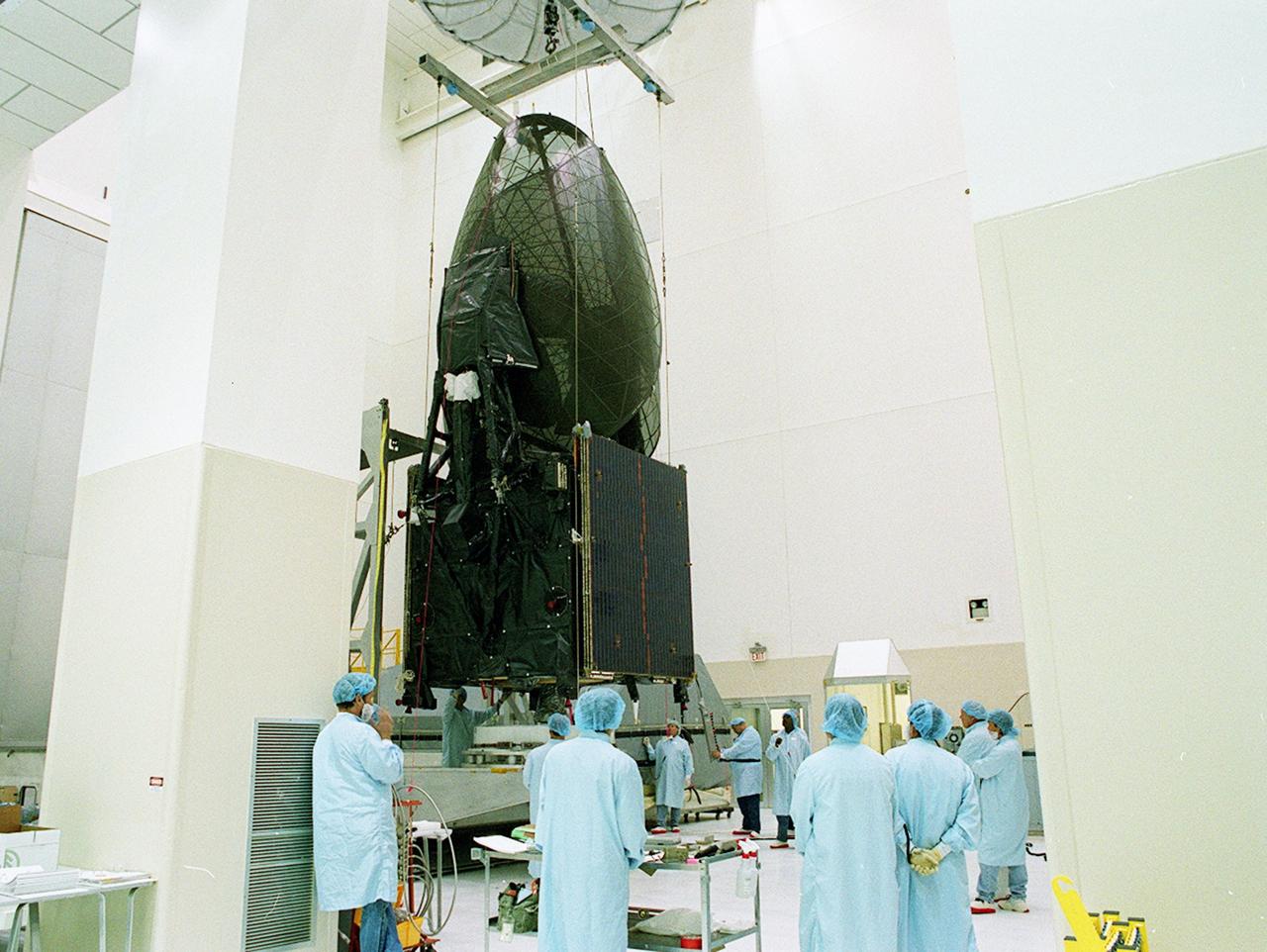

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers lift the TDRS-J spacecraft for its move to a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2) for final checkout and processing before launch, currently targeted for Nov. 20. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers lower the suspended TDRS-J spacecraft onto a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2) for final checkout and processing before launch, currently targeted for Nov. 20. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
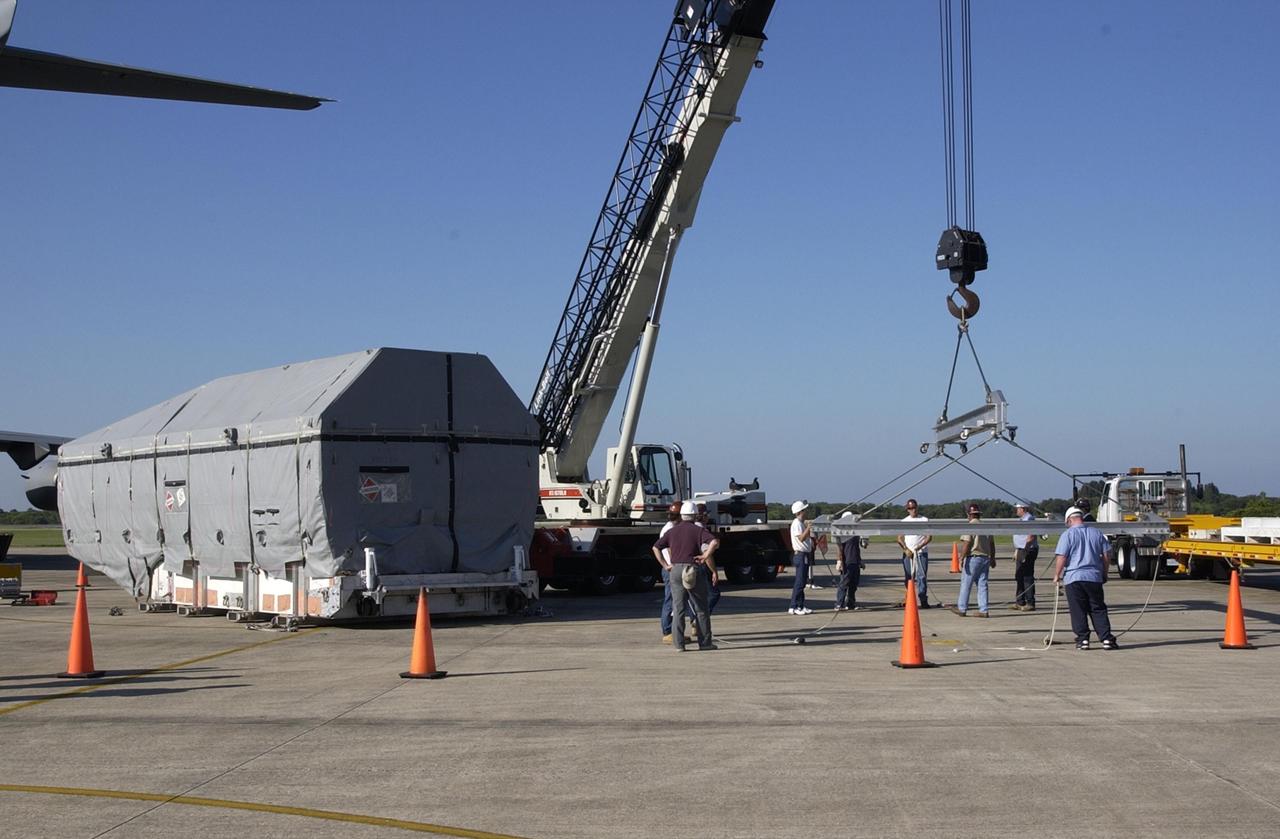

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A crane is lifted from the SLF to attach to the container with the TDRS-J spacecraft inside (at left). The container will be placed on a transporter and taken to the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2). TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The TDRS-J spacecraft is unpacked in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2) for final checkout and processing before launch, currently targeted for Nov. 20. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
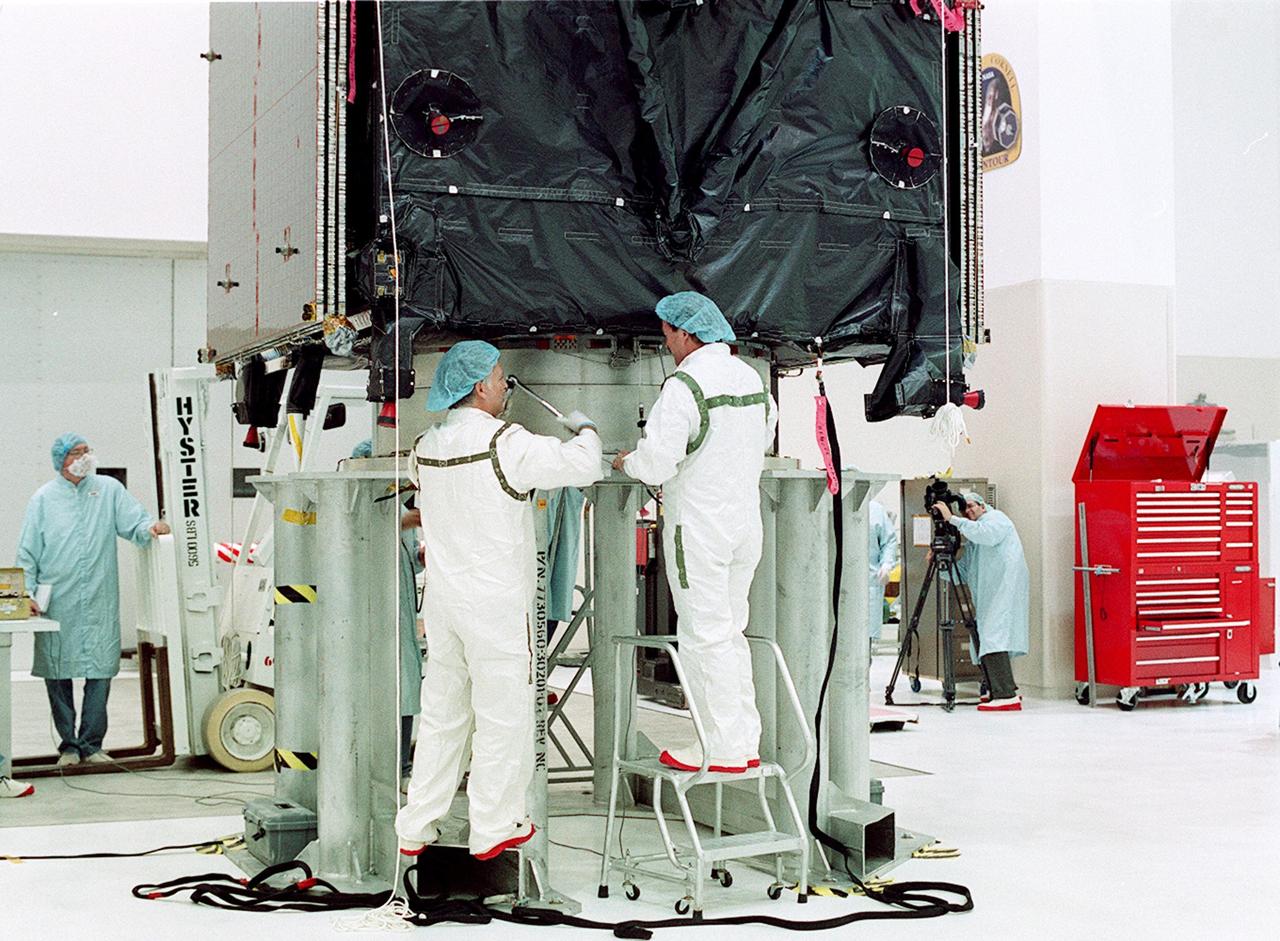
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers secure the TDRS-J spacecraft to a workstand in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2) for final checkout and processing before launch, currently targeted for Nov. 20. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.