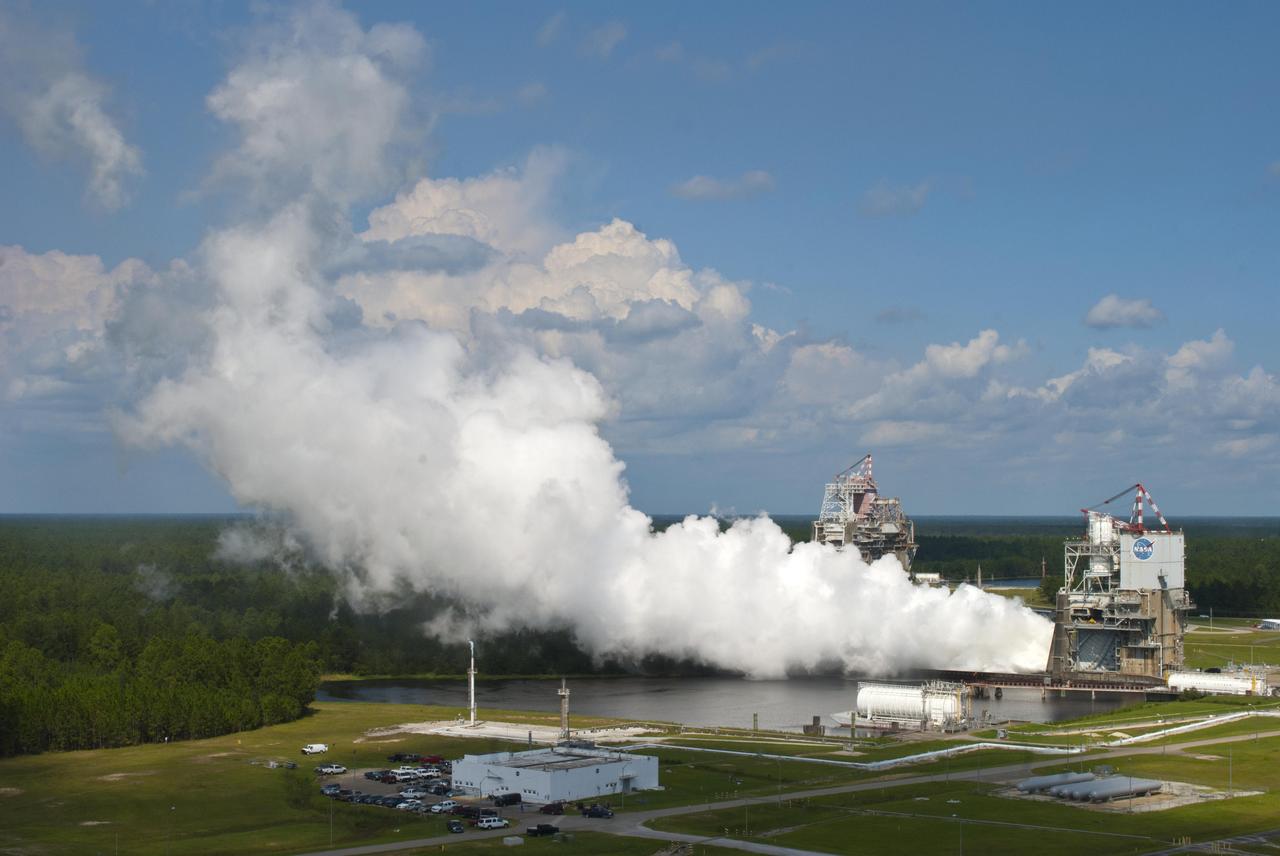

NASA engineers continued testing the next-generation J-2X rocket engine at Stennis Space Center with a 250-second test on Sept. 7. The test was the first conducted after the arrival of Hurricane Isaac forced closure of the Stennis facility for three days in late August. The est was conducted on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis. The facility's B-1/B-2 Test Stand can be seen in the left background.
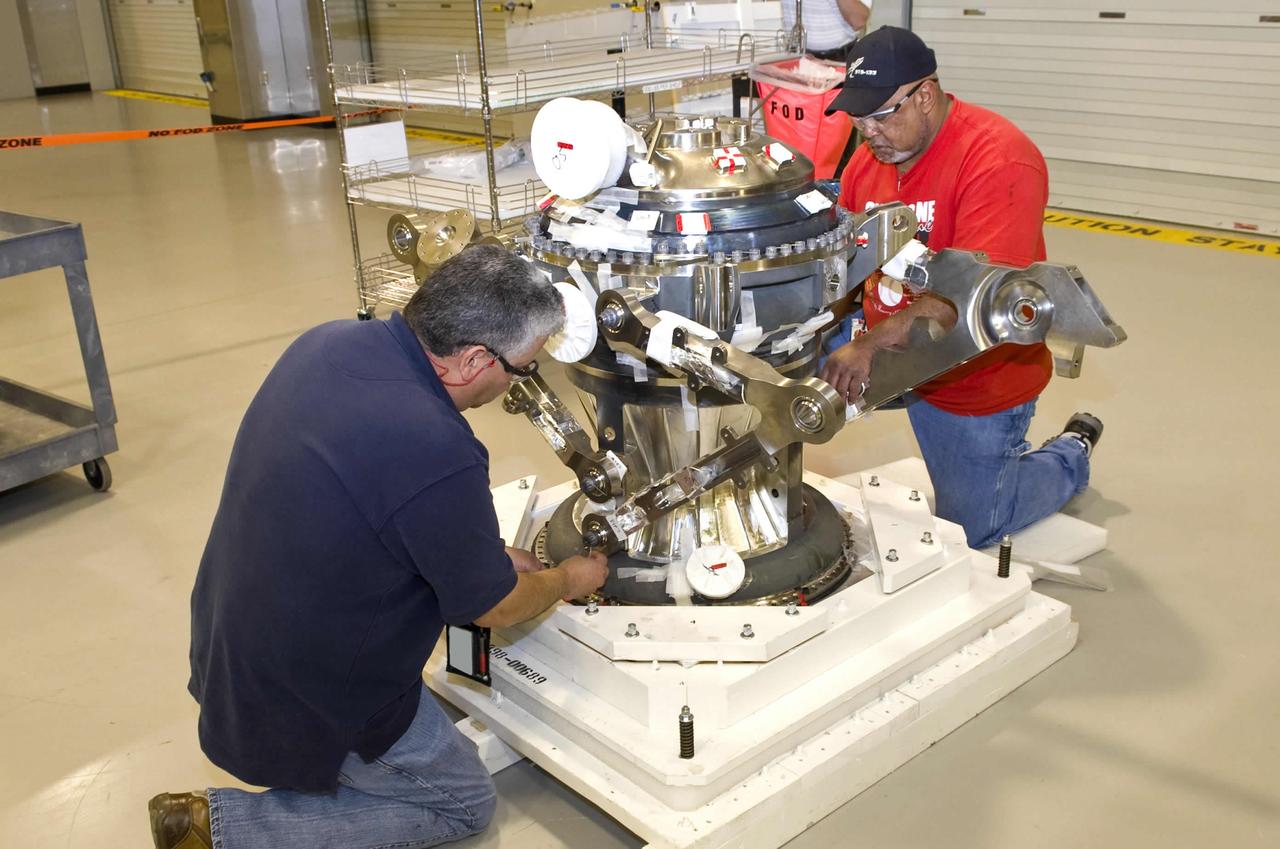

Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne employees Carlos Alfaro (l) and Oliver Swanier work on the main combustion element of the J-2X rocket engine at their John C. Stennis Space Center facility. Assembly of the J-2X rocket engine to be tested at the site is under way, with completion and delivery to the A-2 Test Stand set for June. The J-2X is being developed as a next-generation engine that can carry humans into deep space. Stennis Space Center is preparing a trio of stands to test the new engine.
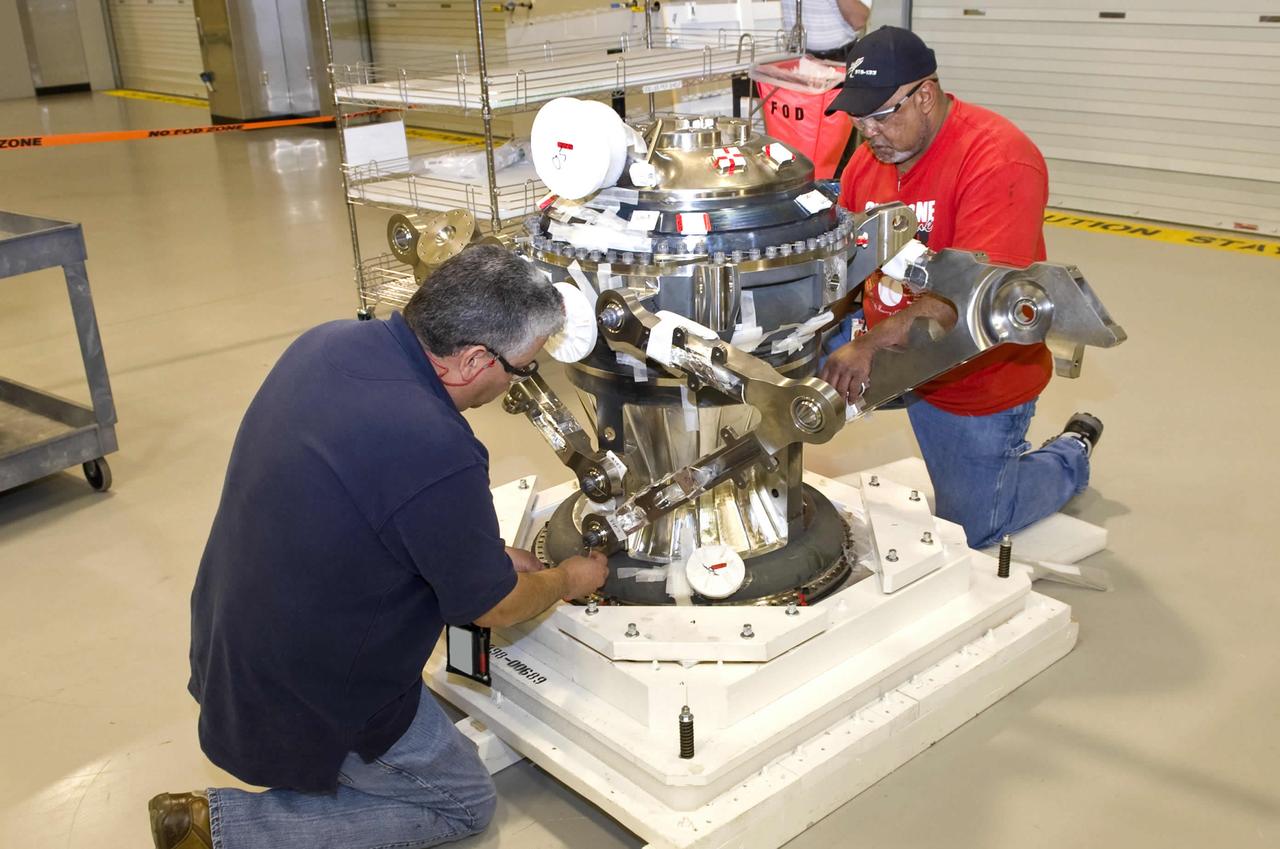

Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne employees Carlos Alfaro (l) and Oliver Swanier work on the main combustion element of the J-2X rocket engine at their John C. Stennis Space Center facility. Assembly of the J-2X rocket engine to be tested at the site is under way, with completion and delivery to the A-2 Test Stand set for June. The J-2X is being developed as a next-generation engine that can carry humans into deep space. Stennis Space Center is preparing a trio of stands to test the new engine.
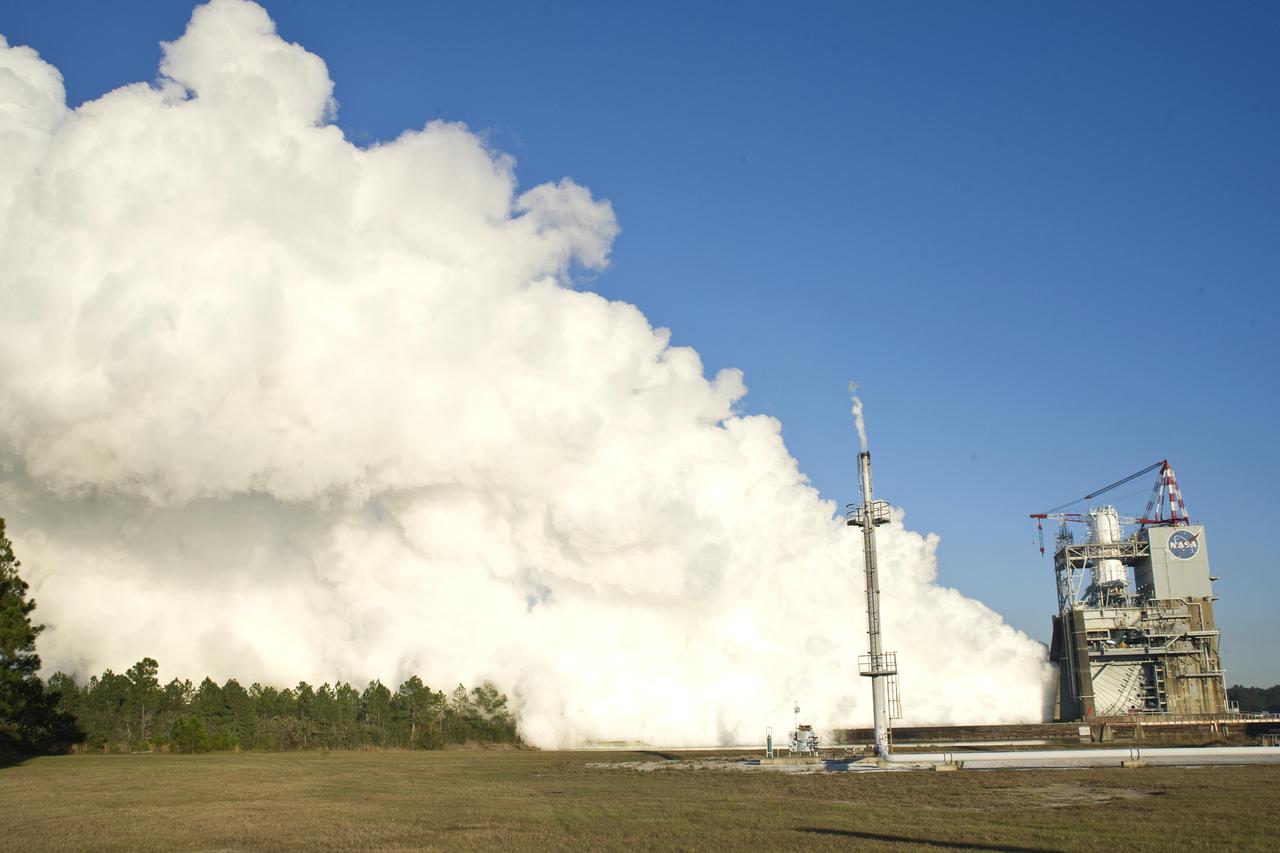

NASA conducted a key stability test firing of the J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Dec. 1, marking another step forward in development of the upper-stage engine that will carry humans deeper into space than ever before. The J-2X will provide upper-stage power for NASA's new Space Launch System.
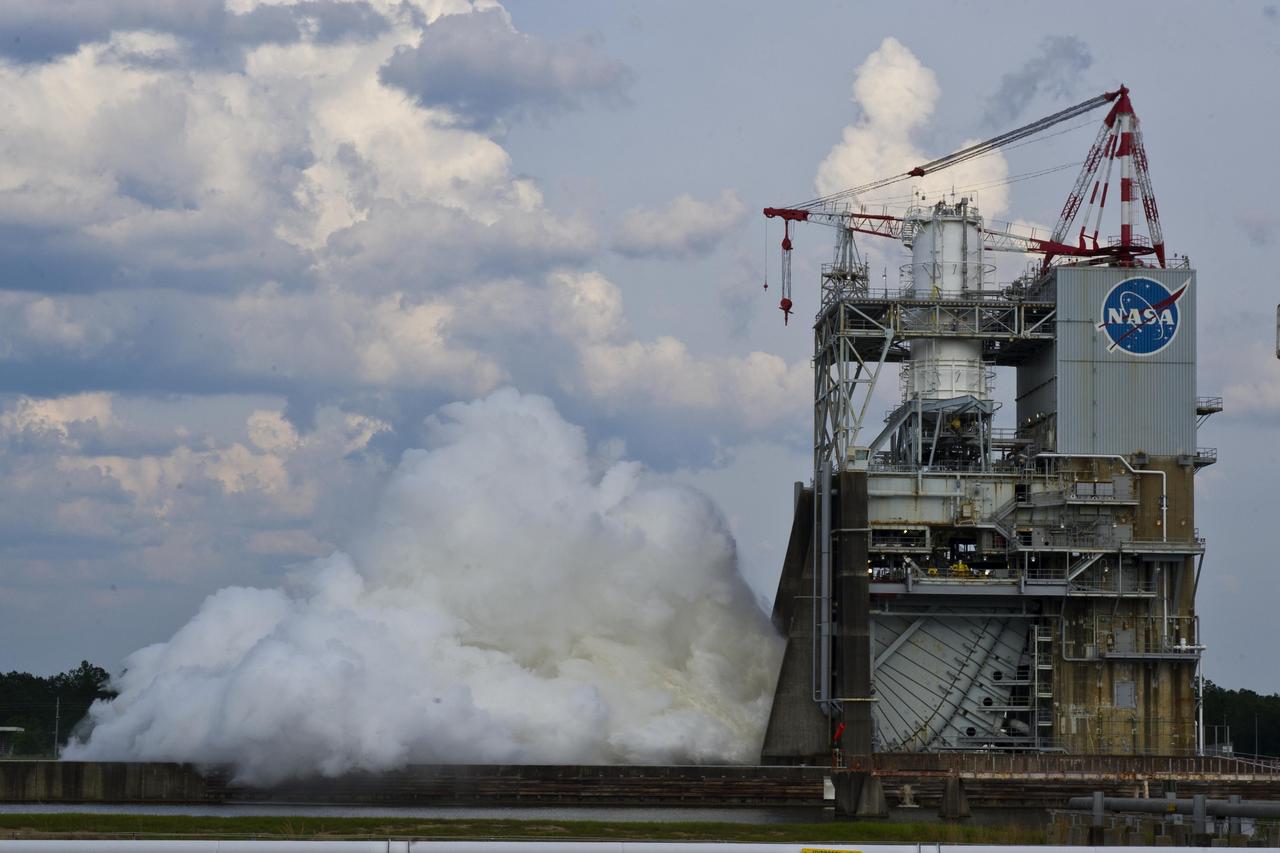

NASA conducted a successful seven-second test of the next-generation J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on May 16, 2012. The J-2X is being developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne.
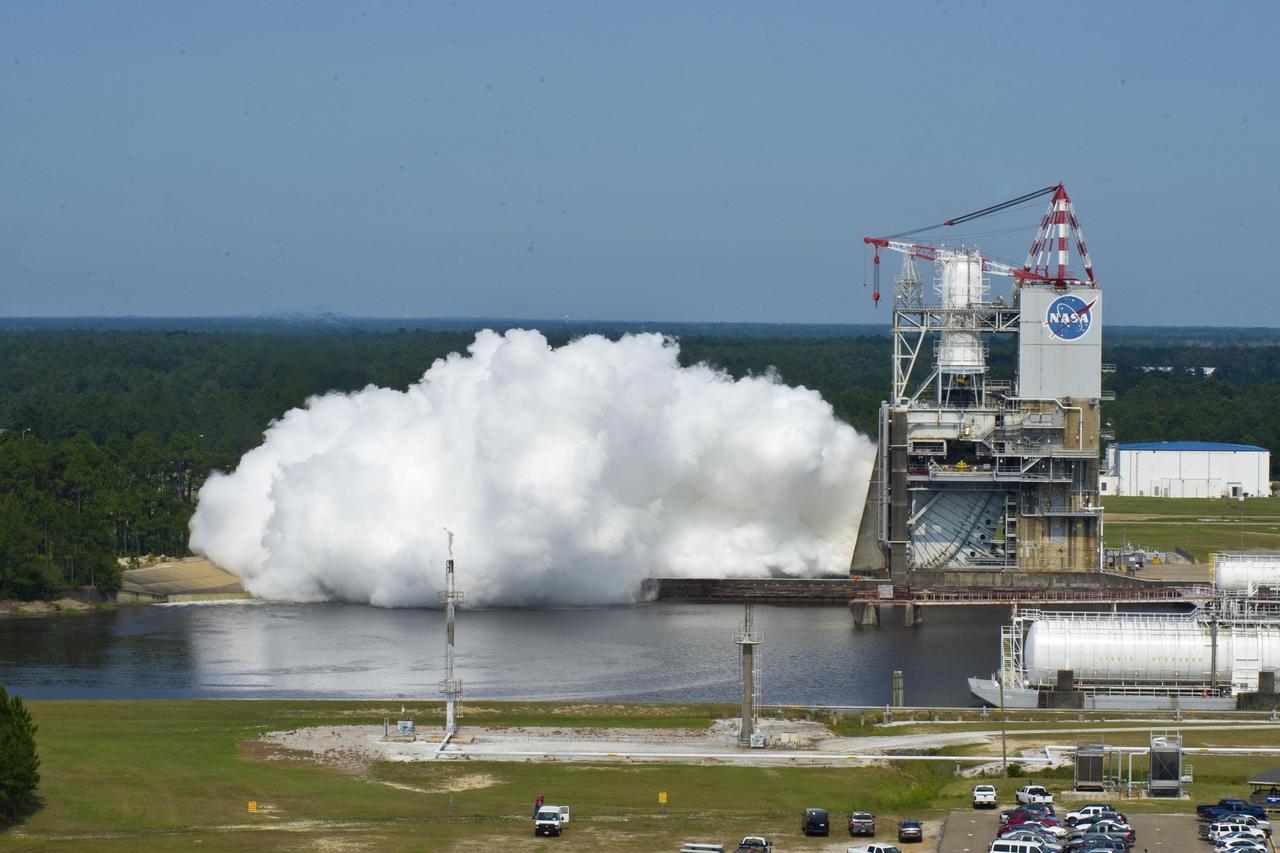

On May 25, 2012, NASA recorded another first during a 40-second test of the next-generation J-2X engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center. Test conductors fired the J-2X in both the secondary and primary modes of operation. Previous tests were run in one mode only; combining the two allowed operators to collect critical data on engine performance.
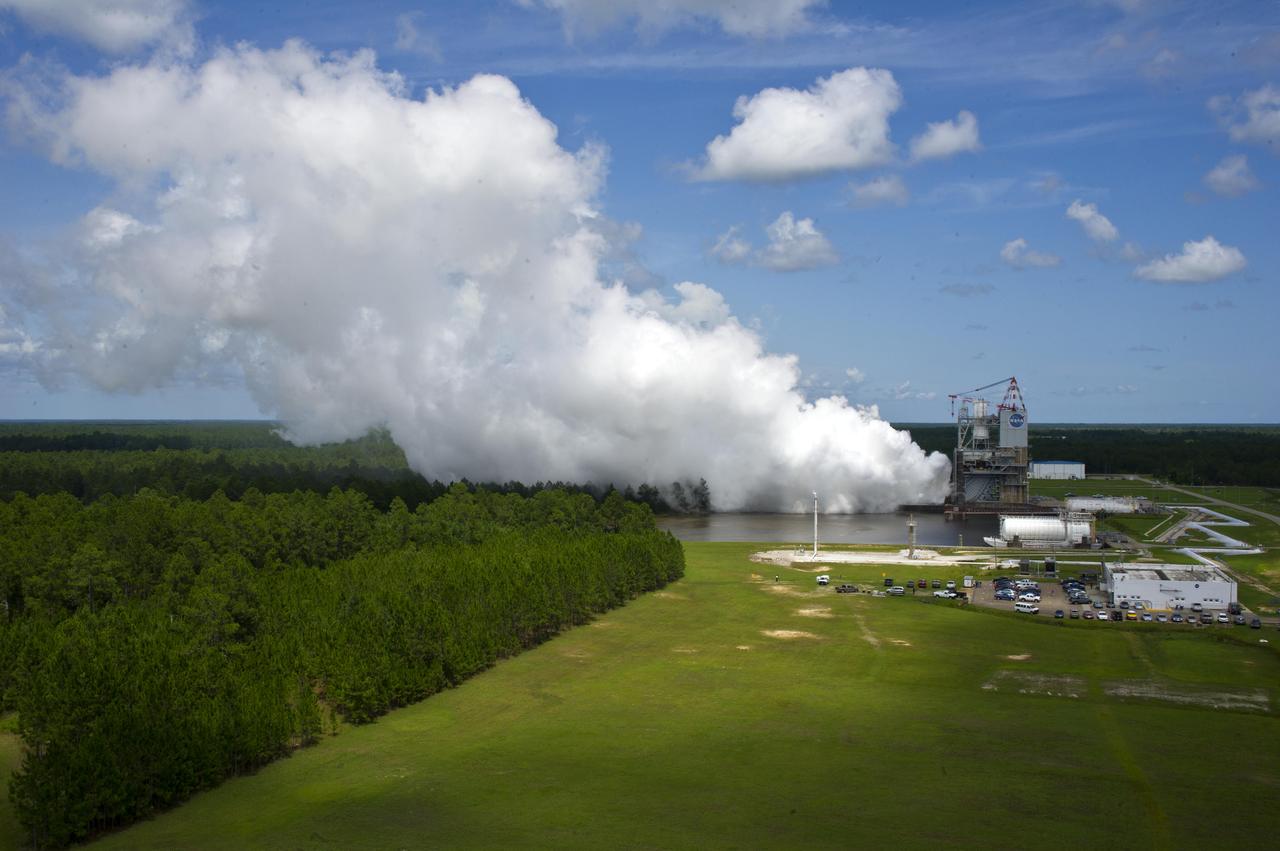

NASA's test of the J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on July 13 was picture perfect in more ways than one. Not only did the test provide a breathtaking view from atop the nearby A-1 Test Stand, and with the center's B-1/B-2 Test Stand in the background, but it achieved its target of 550 seconds. The test continued a series of firings to gather critical data for engine development.
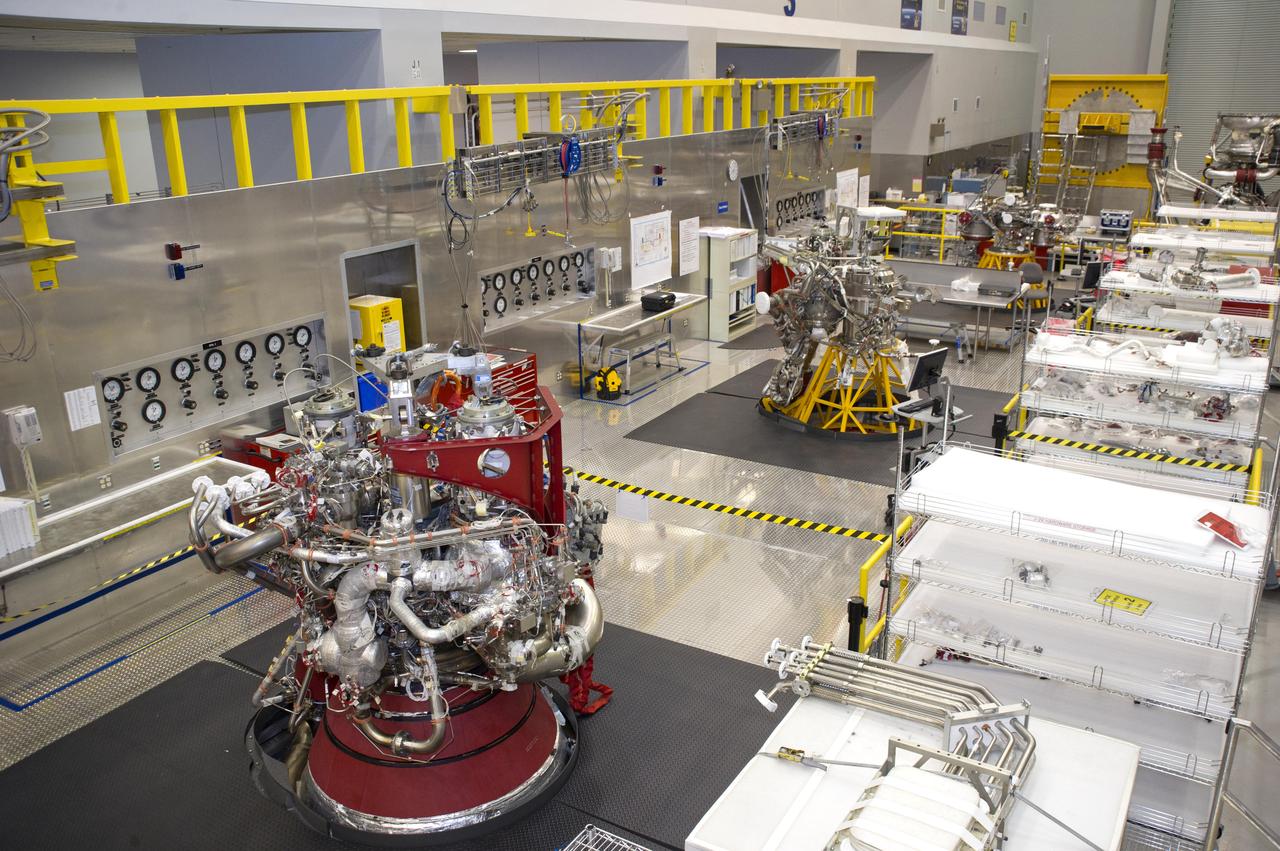
Two J-2X engines and a powerpack, developed for NASA by Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne, sit side-by-side Oct. 11 at Stennis Space Center as work continues on the Space Launch System. Engine 10001 (far left) has been removed from the A-2 Test Stand after being hot-fire tested 21 times, for a total of 2,697 seconds. The engine is now undergoing a series of post-test inspections. A J-2X powerpack (center) has been removed from the A-1 Test Stand to receive additional instrumentation. So far, the powerpack been hot-fire tested 10 times, for a total of 4,162 seconds. Meanwhile, assembly on the second J-2X engine, known as Engine 10002 and located to the far right, has begun in earnest, with engine completion scheduled for this November. Engine 10002 is about 15 percent complete.

NASA conducted a long-duration test of the J-2X powerpack, 1,261 seconds total, on the A-1 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Aug. 16, marking another step in development of the next-generation rocket engine. The powerpack is a system of components on the top portion of the J-2X engine, including the gas generator, oxygen and fuel turbopumps, and related ducts and valves.
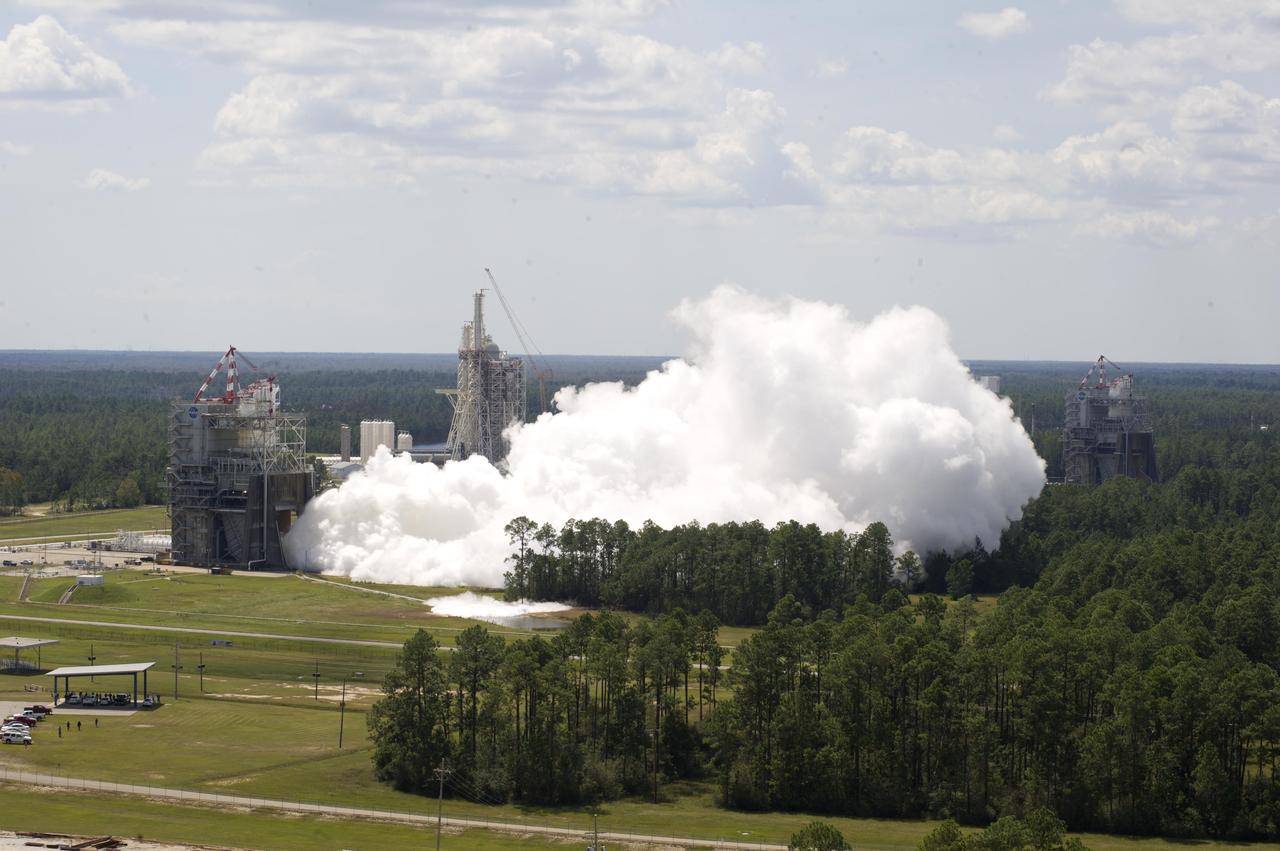

NASA engineers continued to collect test performance data on the new J-2X rocket engine at Stennis Space Center with a 250-second test Sept. 14. The test on the A-2 Test Stand was the 19th in a series of firings to gather critical data for continued development of the engine. The J-2X is being developed by Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne for NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. It is the first liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen rocket engine rated to carry humans into space to be developed in 40 years.
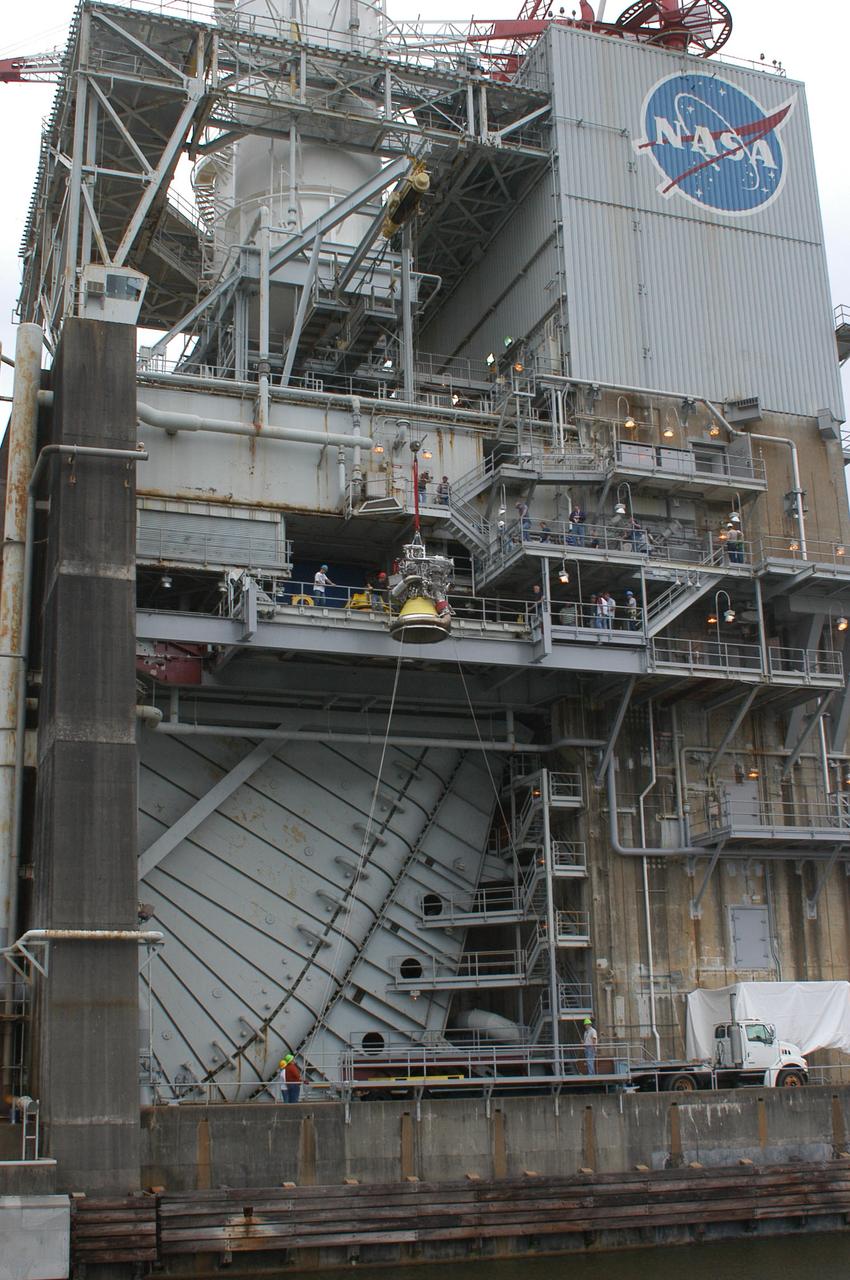

J-2X engine No. 10001 is returned March 8, 2012, to the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center for its second round of tests. The developmental engine underwent an initial series of tests last year. The J-2X engine is being built for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne.
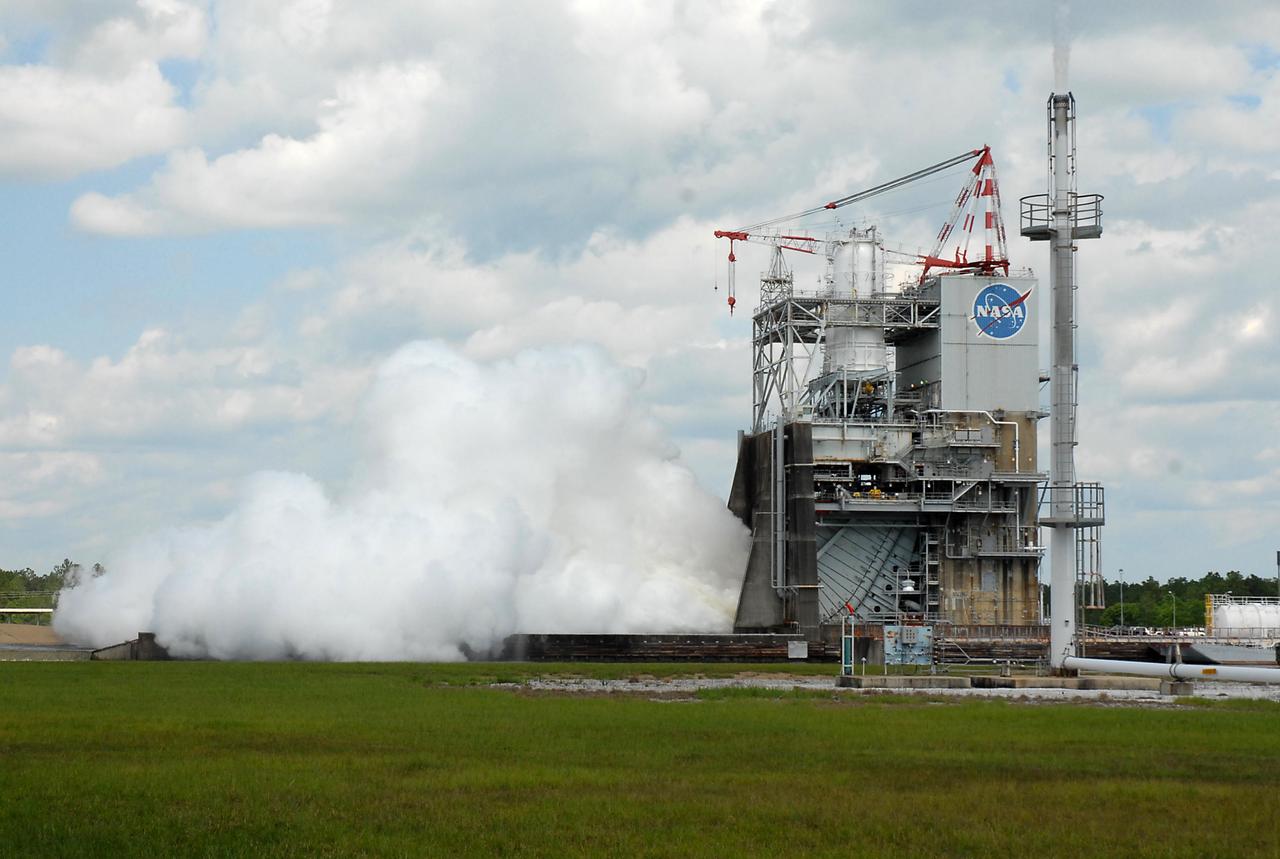

NASA engineers at Stennis Space Center conducted a 260-second test of the next-generation J-2X rocket engine June 13, 2012. As in a previous test, NASA engineers fired the engine at both secondary and primary modes to collect performance data.
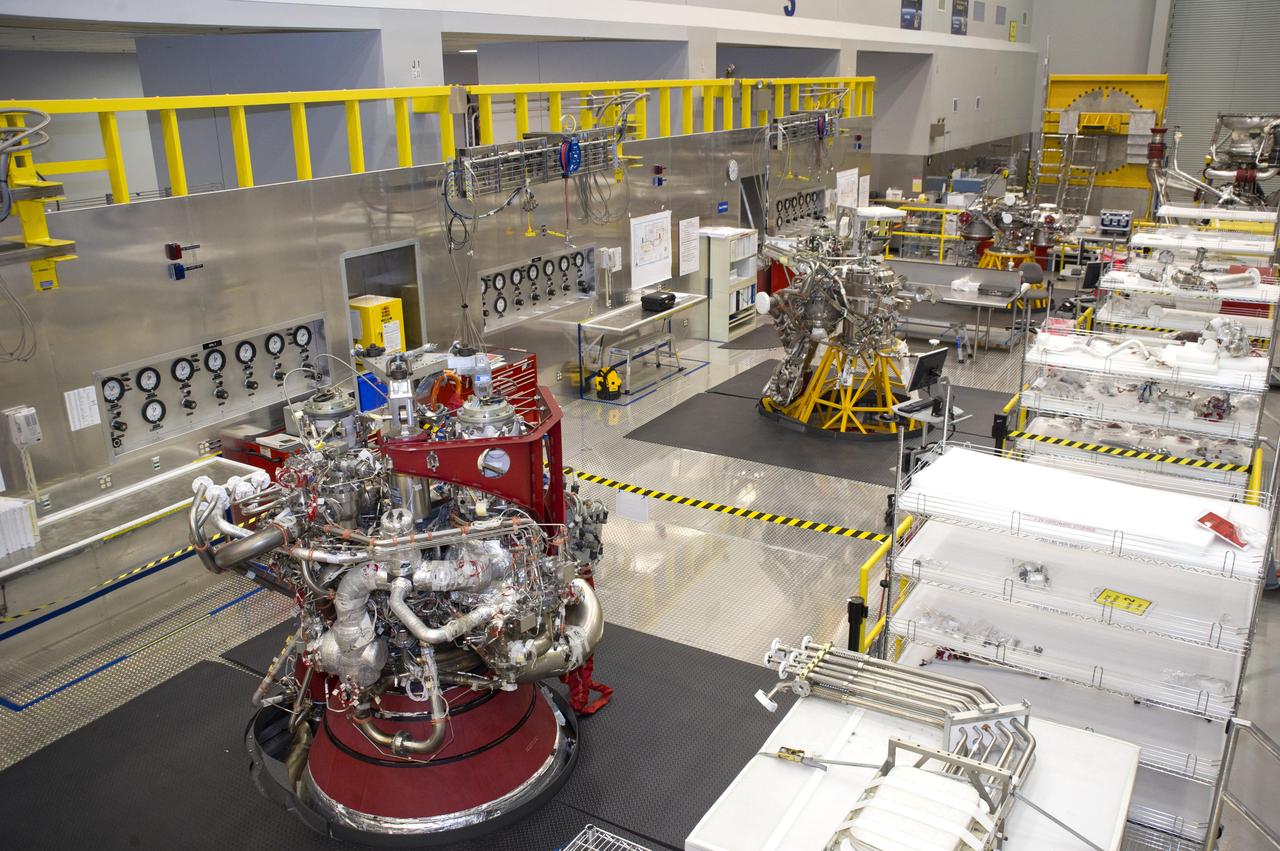
Two J-2X engines and a powerpack, developed for NASA by Pratt and Whitney Rocketdyne, sit side-by-side Oct. 11 at Stennis Space Center as work continues on the Space Launch System. Engine 10001 (far left) has been removed from the A-2 Test Stand after being hot-fire tested 21 times, for a total of 2,697 seconds. The engine is now undergoing a series of post-test inspections. A J-2X powerpack (center) has been removed from the A-1 Test Stand to receive additional instrumentation. So far, the powerpack been hot-fire tested 10 times, for a total of 4,162 seconds. Meanwhile, assembly on the second J-2X engine, known as Engine 10002 and located to the far right, has begun in earnest, with engine completion scheduled for this November. Engine 10002 is about 15 percent complete.
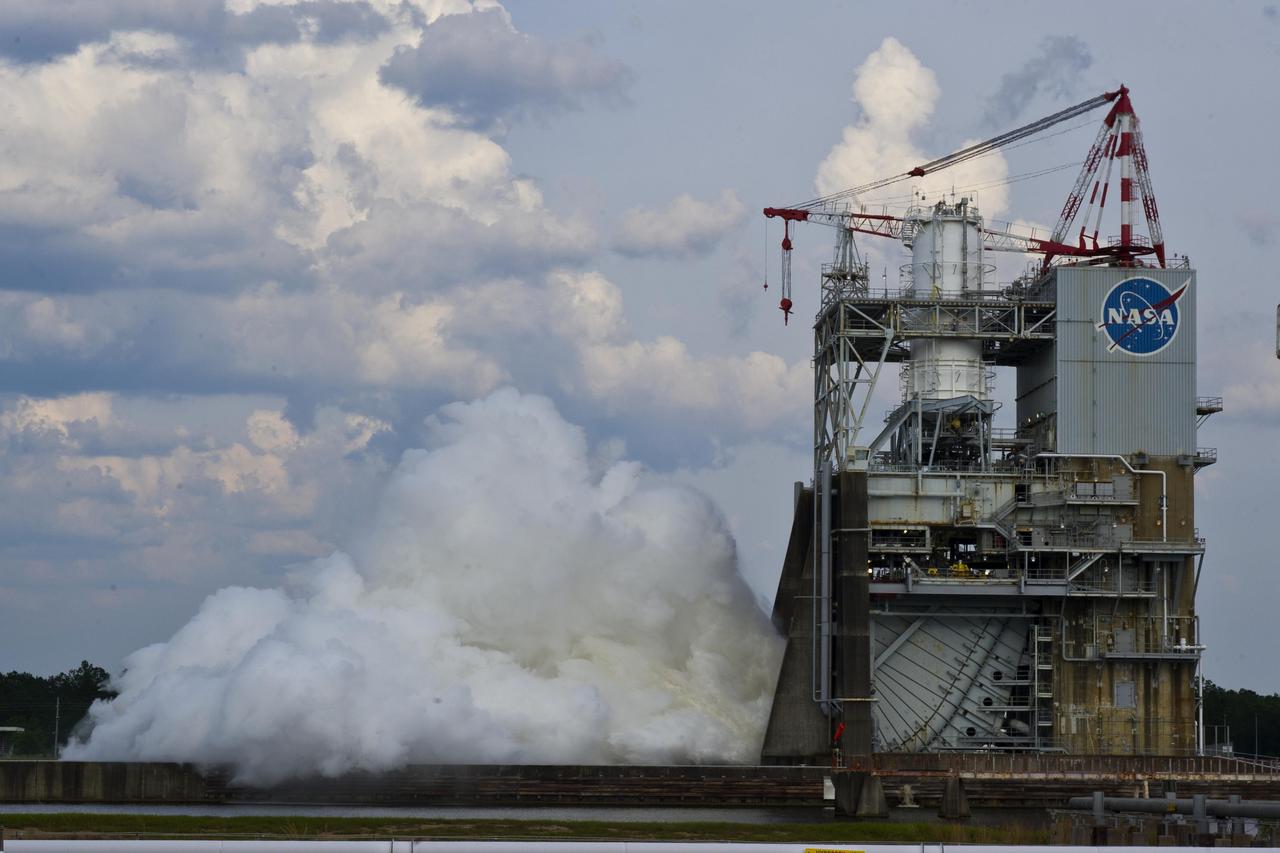

On May 16, 2012, engineers at Stennis Space Center conducted a test of the next-generation J-2X engine that will help power NASA's new Space Launch System, moving NASA even closer to a return to deep space.
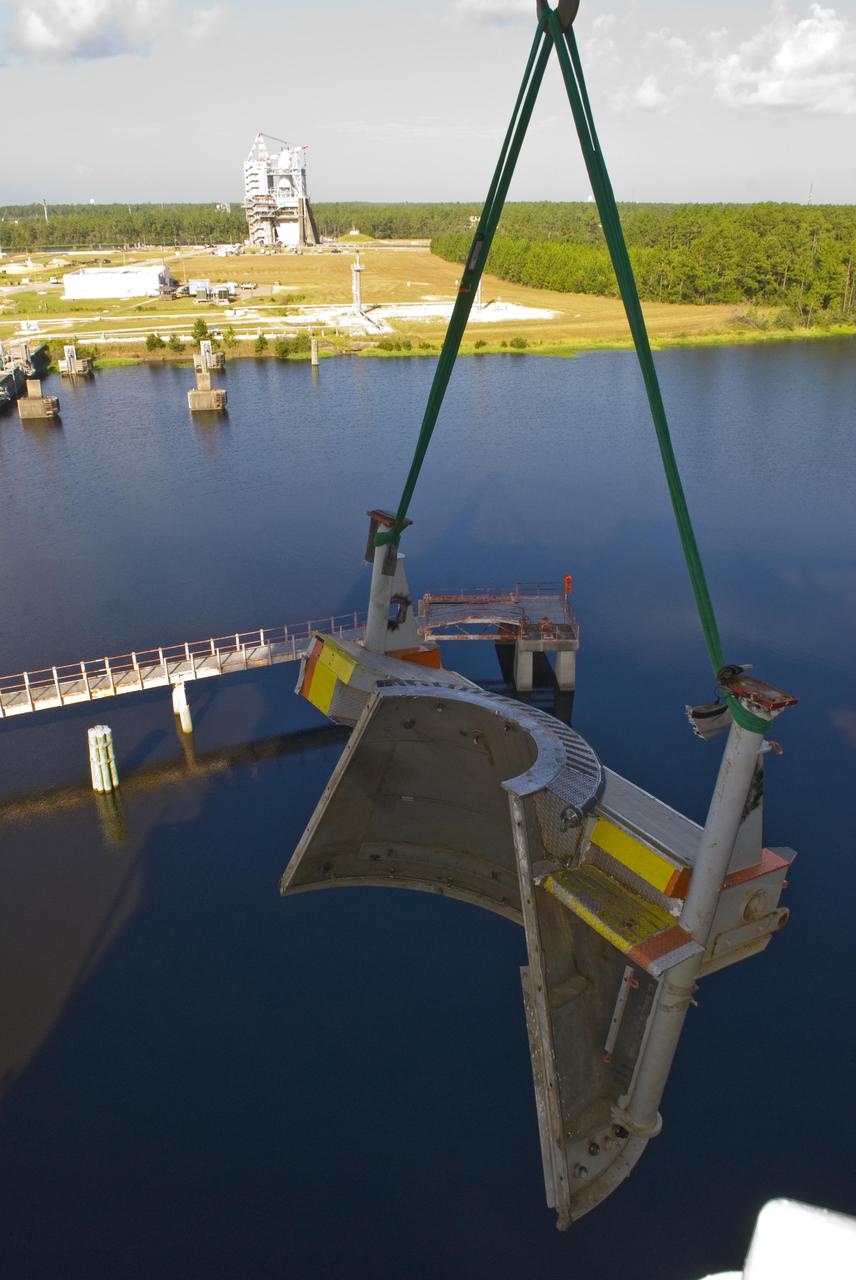

John C. Stennis Space Center employees remove one-half of the A-2 Test Stand clamshell used for testing space shuttle main engines. Space shuttle main engine testing concluded July 2009; the A-2 stand now is being prepared for testing the next-generation J-2X rocket engine in development. Testing of the J-2X engine is scheduled to begin in 2011.
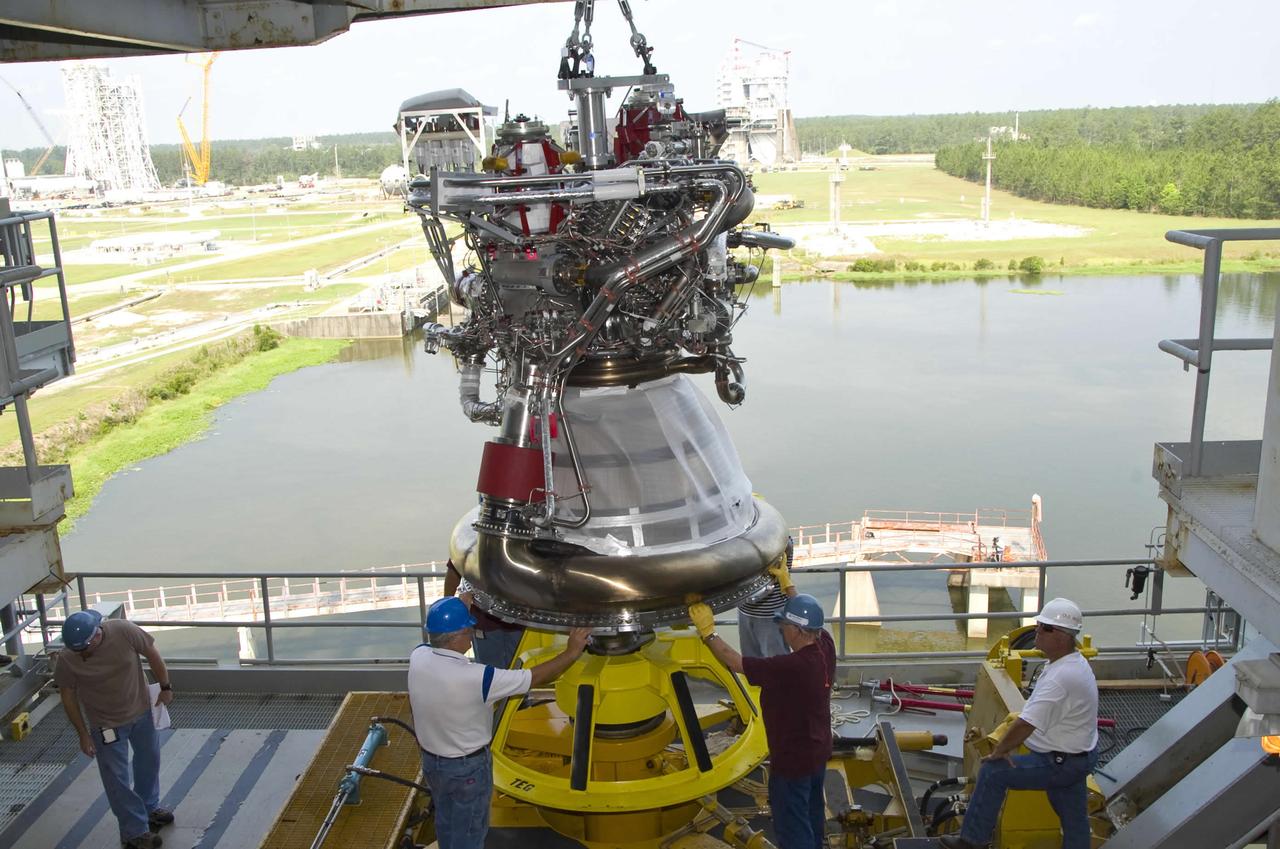

A J-2X next-generation rocket engine is lifted onto the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center. Testing of the engine began the following month. The engine is being developed for NASA by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne and could help carry humans beyond low-Earth orbit into deep space once more.
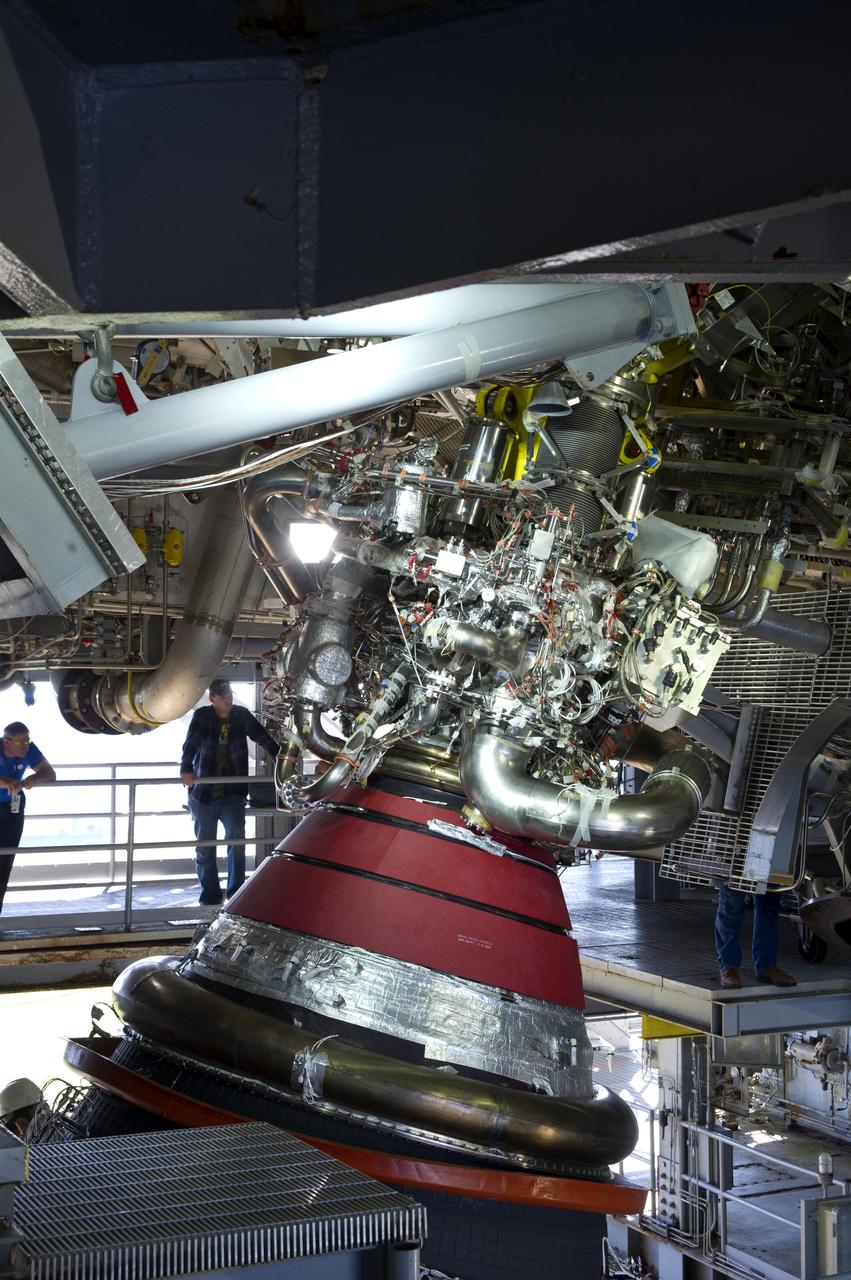
NASA removed J-2X engine No. 10001 from the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center in early October. Opening of the test stand clamshell flooring allowed a clear view of the next-generation engine and stub nozzle, which is being built to help power future deep-space missions. The engine is an upgrade from the heritage J-2 rocket engine, which helped power Apollo missions to the moon during the late 1960s and early 1970s.
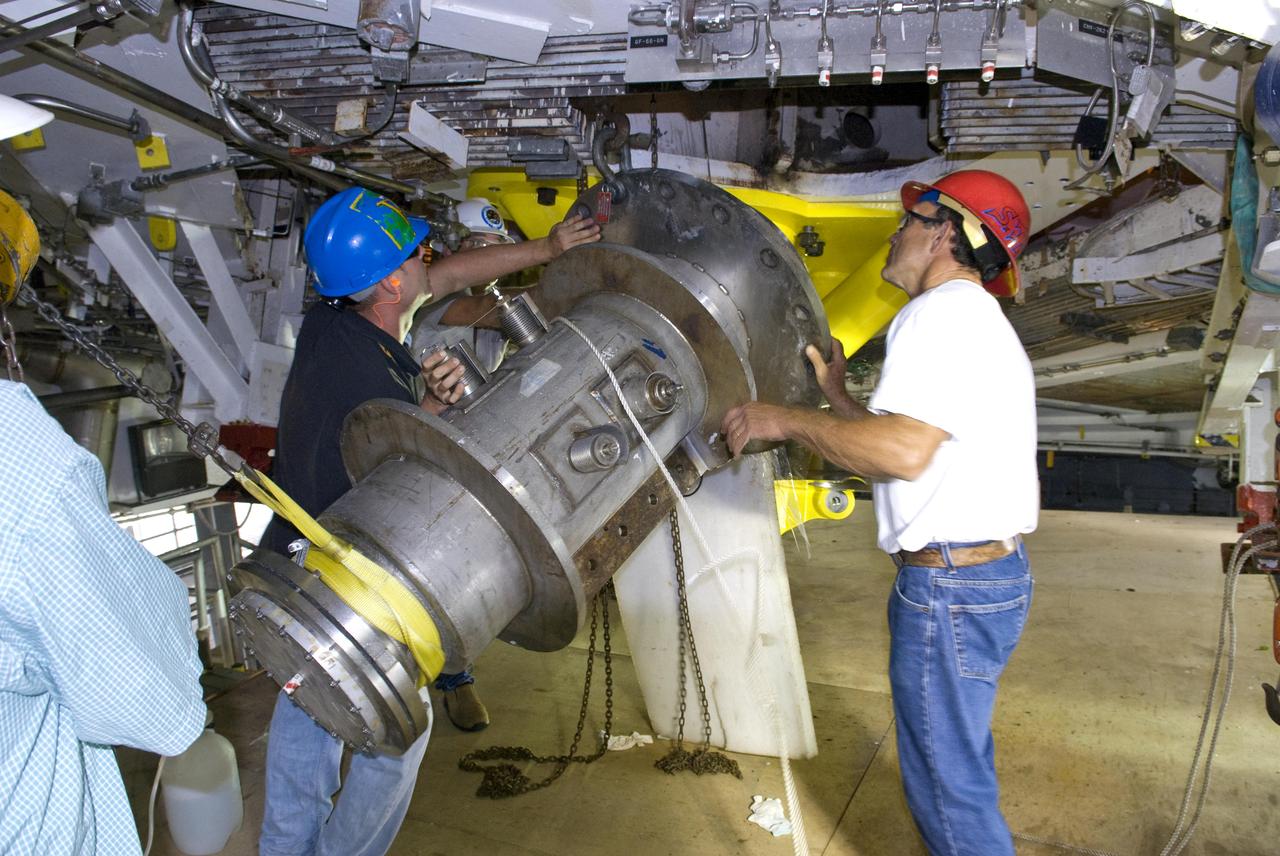

John C. Stennis Space Center employees remove space shuttle main engine run ducts from the A-2 Test Stand engine deck Oct. 25, 2010. Testing of space shuttle main engines concluded in July 2009. Stennis is preparing the A-2 Test Stand for testing the next-generation J-2X rocket engine being developed. Testing of the new engine is scheduled to begin in 2011.
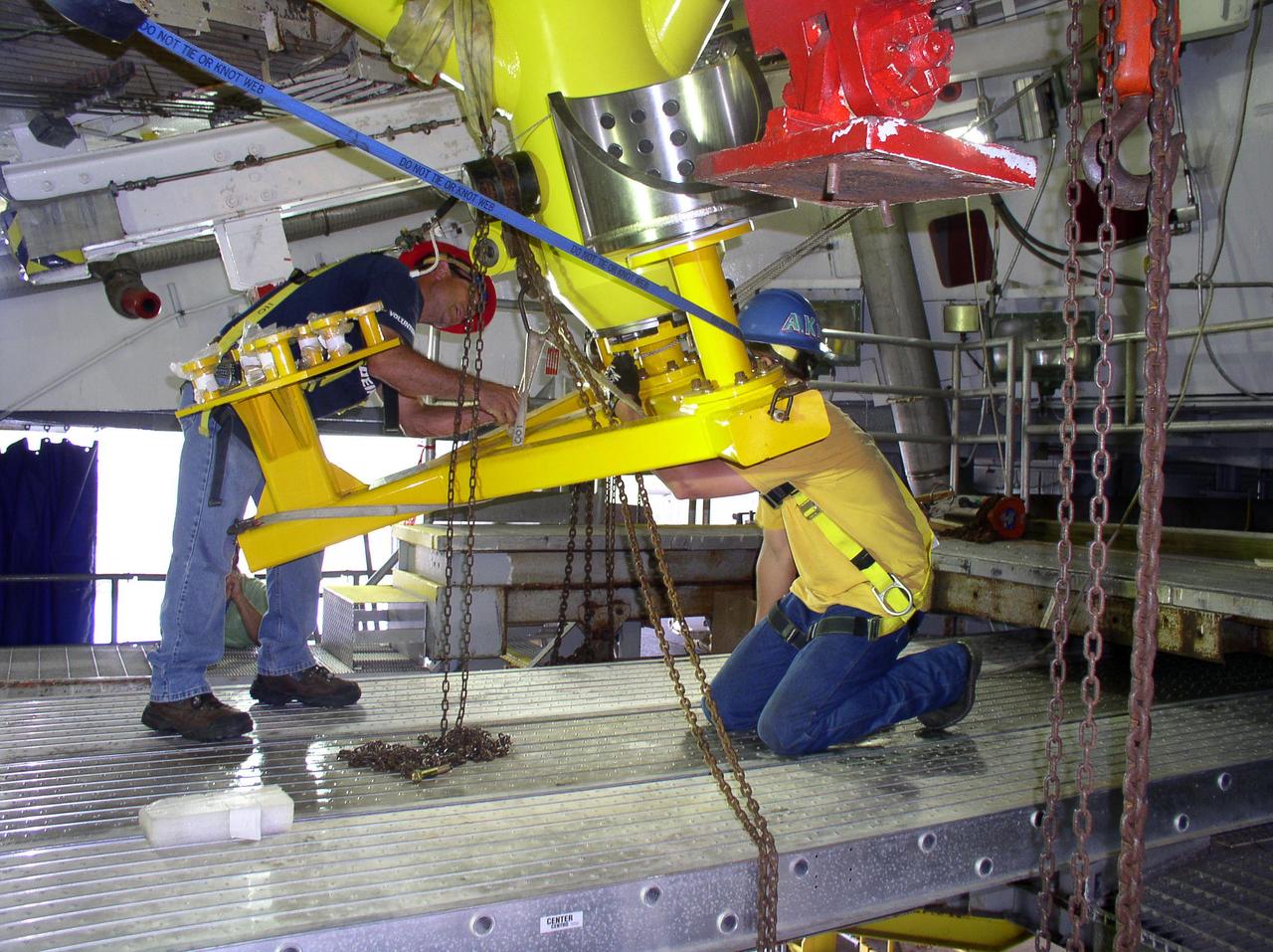

John C. Stennis Space Center employees install a new master interface tool on the A-2 Test Stand on Oct. 27, 2010. Until July 2009, the stand had been used for testing space shuttle main engines. With that test series complete, employees are preparing the stand for testing the next-generation J-2X rocket engine being developed. Testing of the new engine is scheduled to begin in 2011.
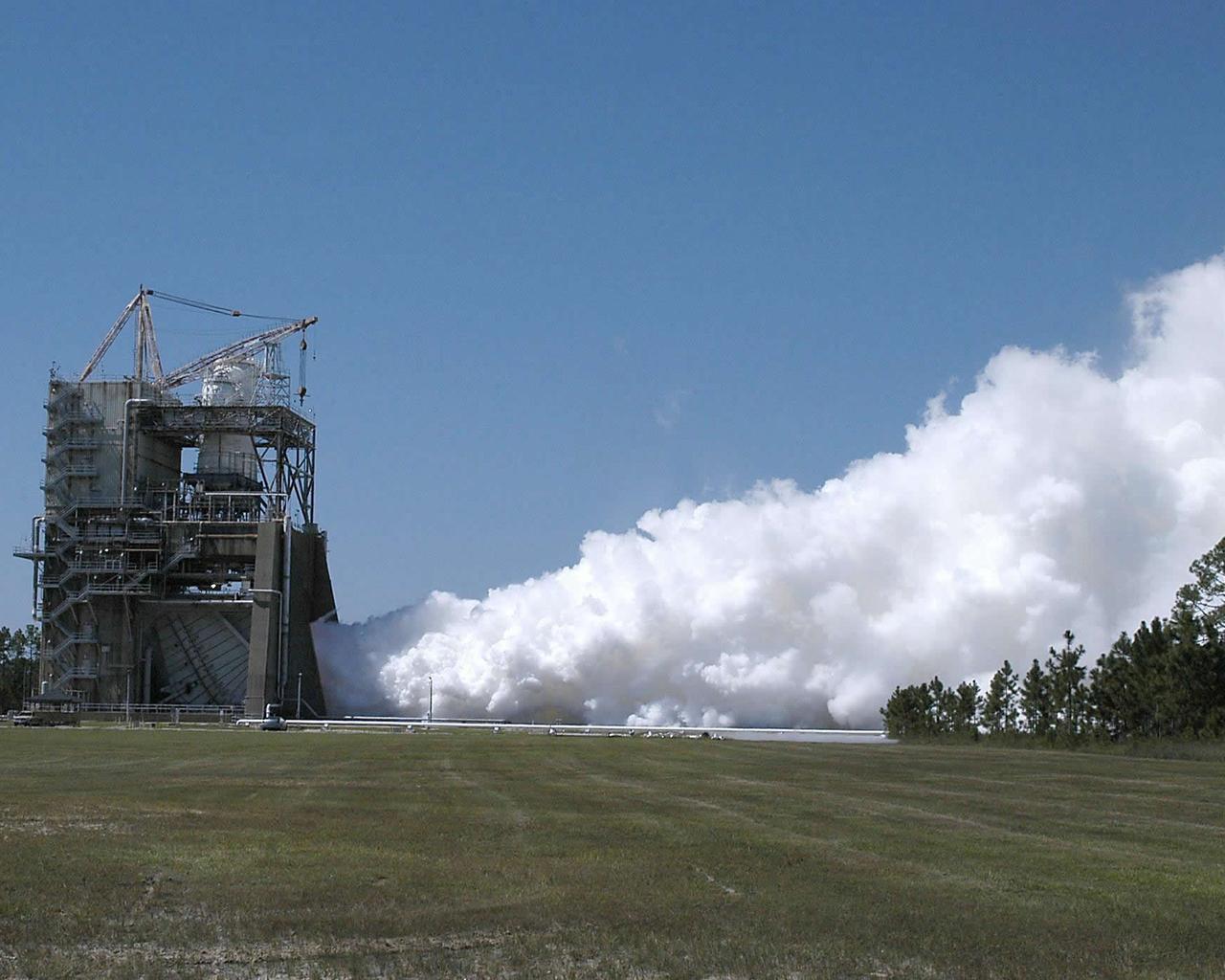

The Stennis Space Center conducted the final space shuttle main engine test on its A-1 Test Stand Friday. The A-1 Test Stand was the site of the first test on a shuttle main engine in 1975. Stennis will continue testing shuttle main engines on its A-2 Test Stand through the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2010. The A-1 stand begins a new chapter in its operational history in October. It will be temporarily decommissioned to convert it for testing the J-2X engine, which will power the upper stage of NASA's new crew launch vehicle, the Ares I. Although this ends the stand's work on the Space Shuttle Program, it will soon be used for the rocket that will carry America's next generation human spacecraft, Orion.