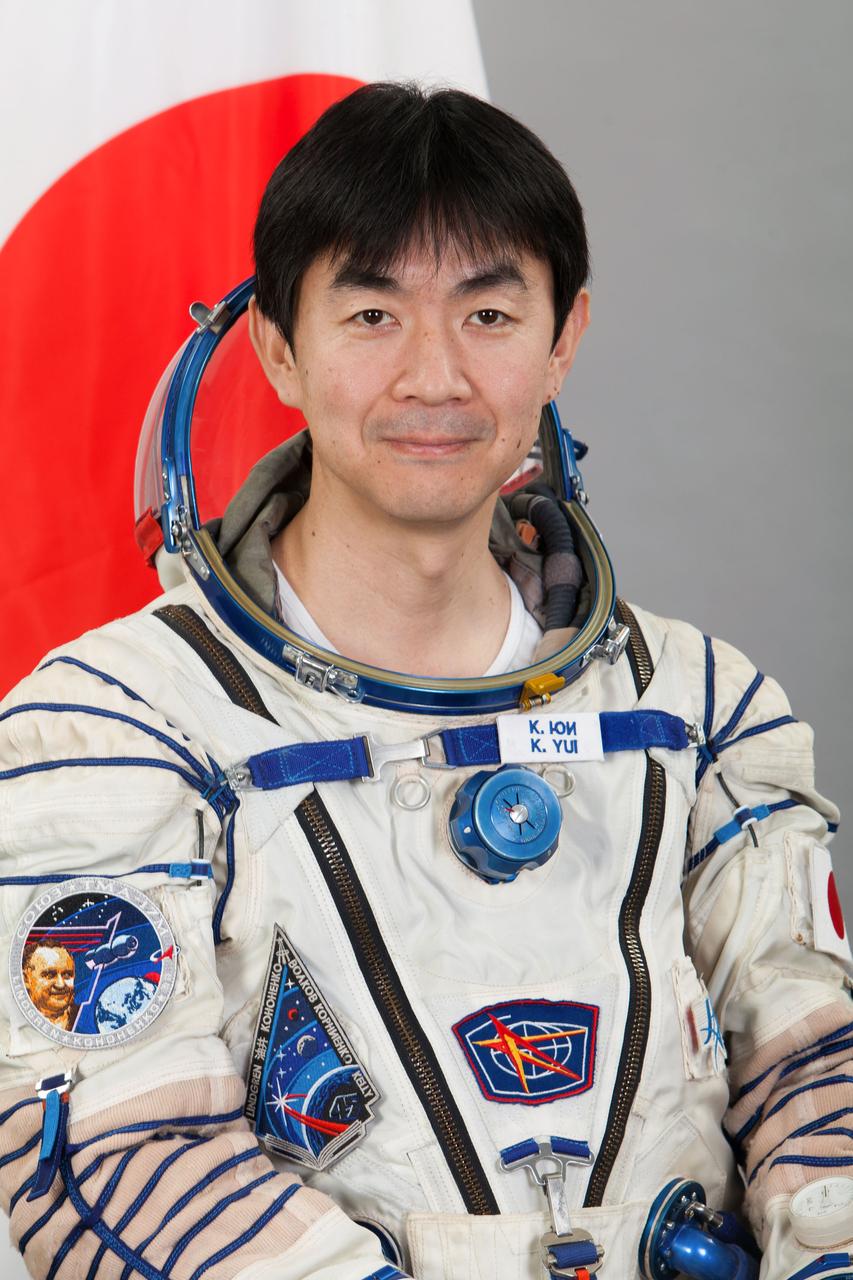

JSC2015E053681 (04/30/2015) --- Expedition 44 Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Kimiya Yui.
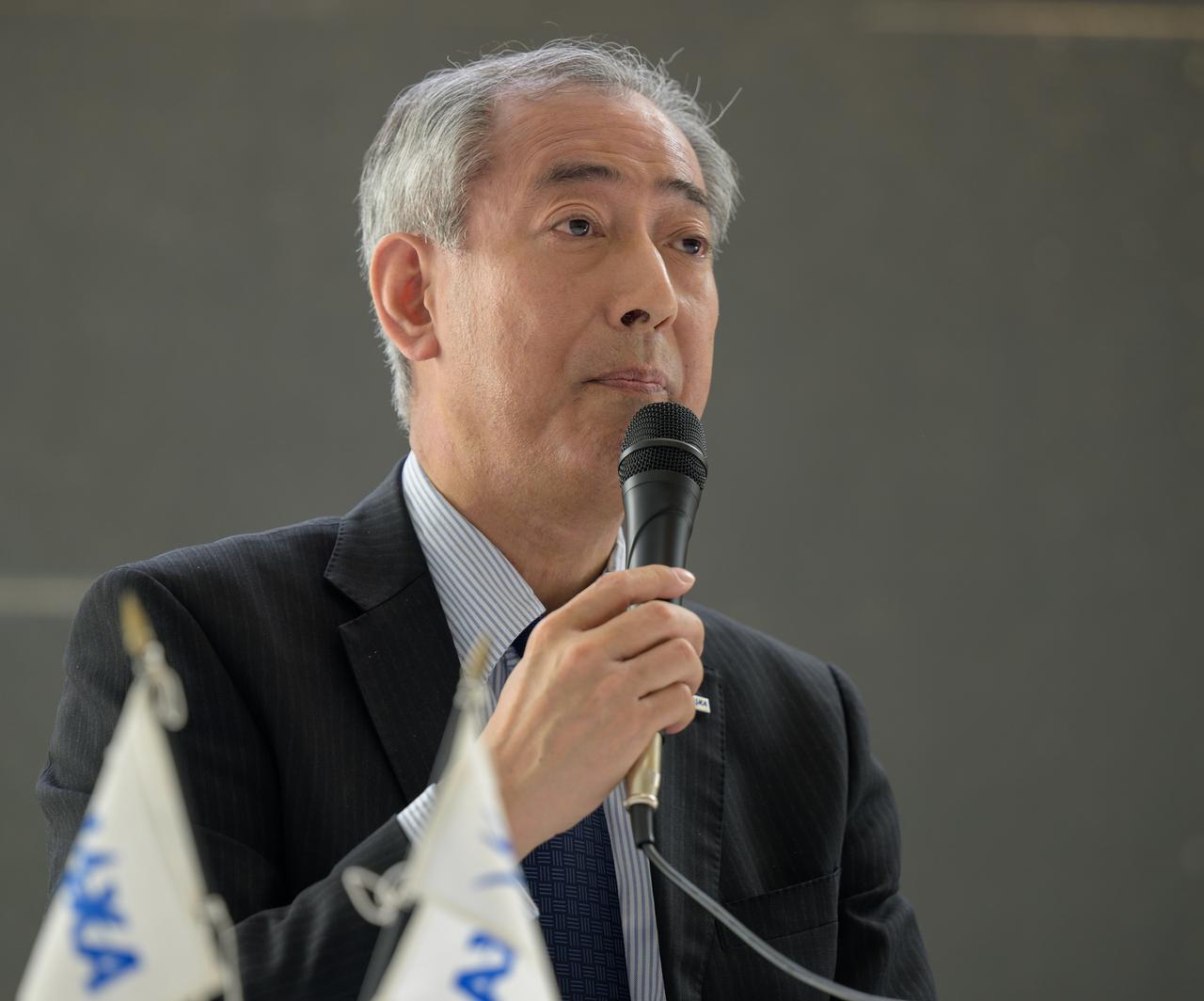

Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) President Hiroshi Yamakawa discusses the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
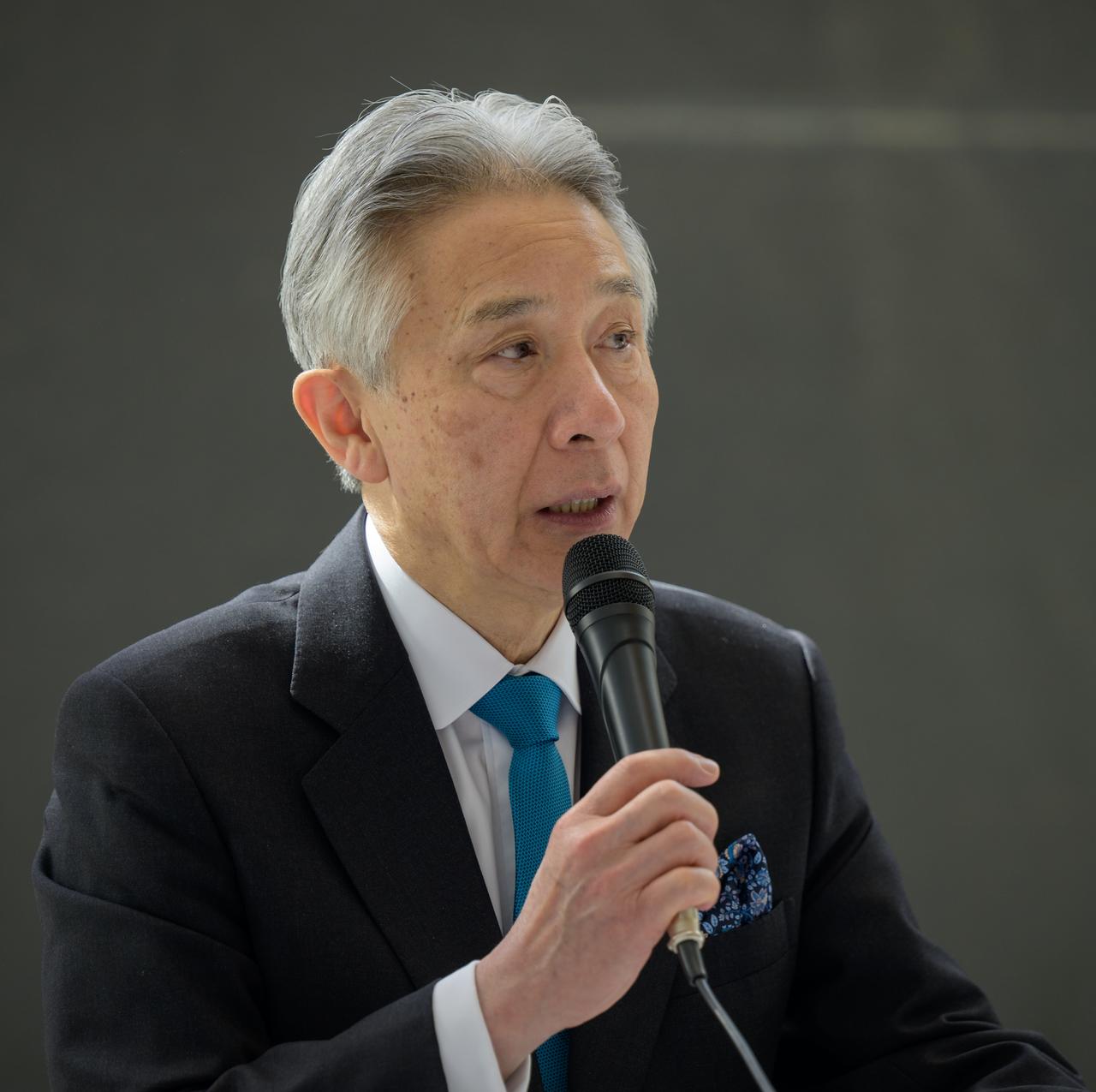

Japan’s Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology Masahito Moriyama discusses the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A model of the Pressurized lunar rover is seen during a briefing discussing the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A model of the Pressurized lunar rover is seen during a briefing discussing the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
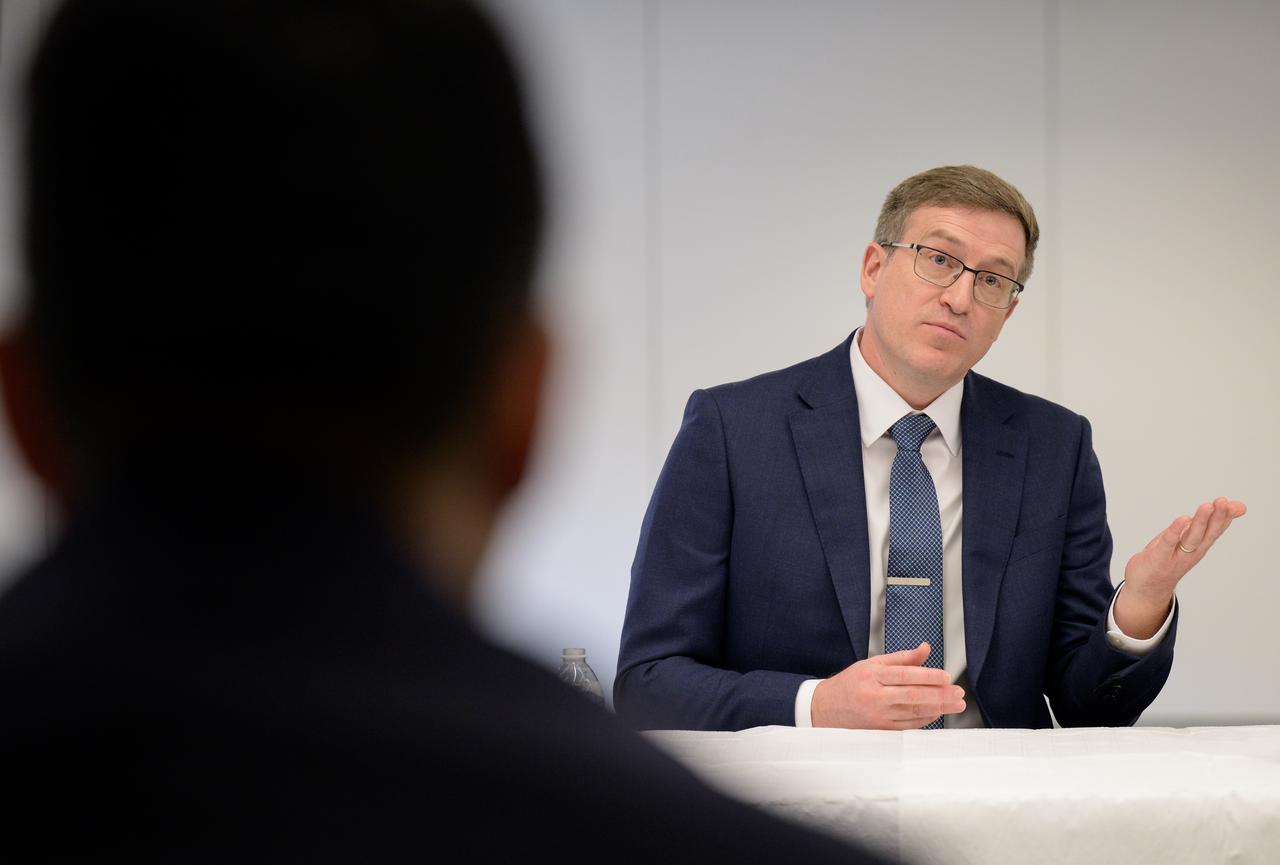

NASA Pressurized Rover Project Manager Danny Newswander discusses the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
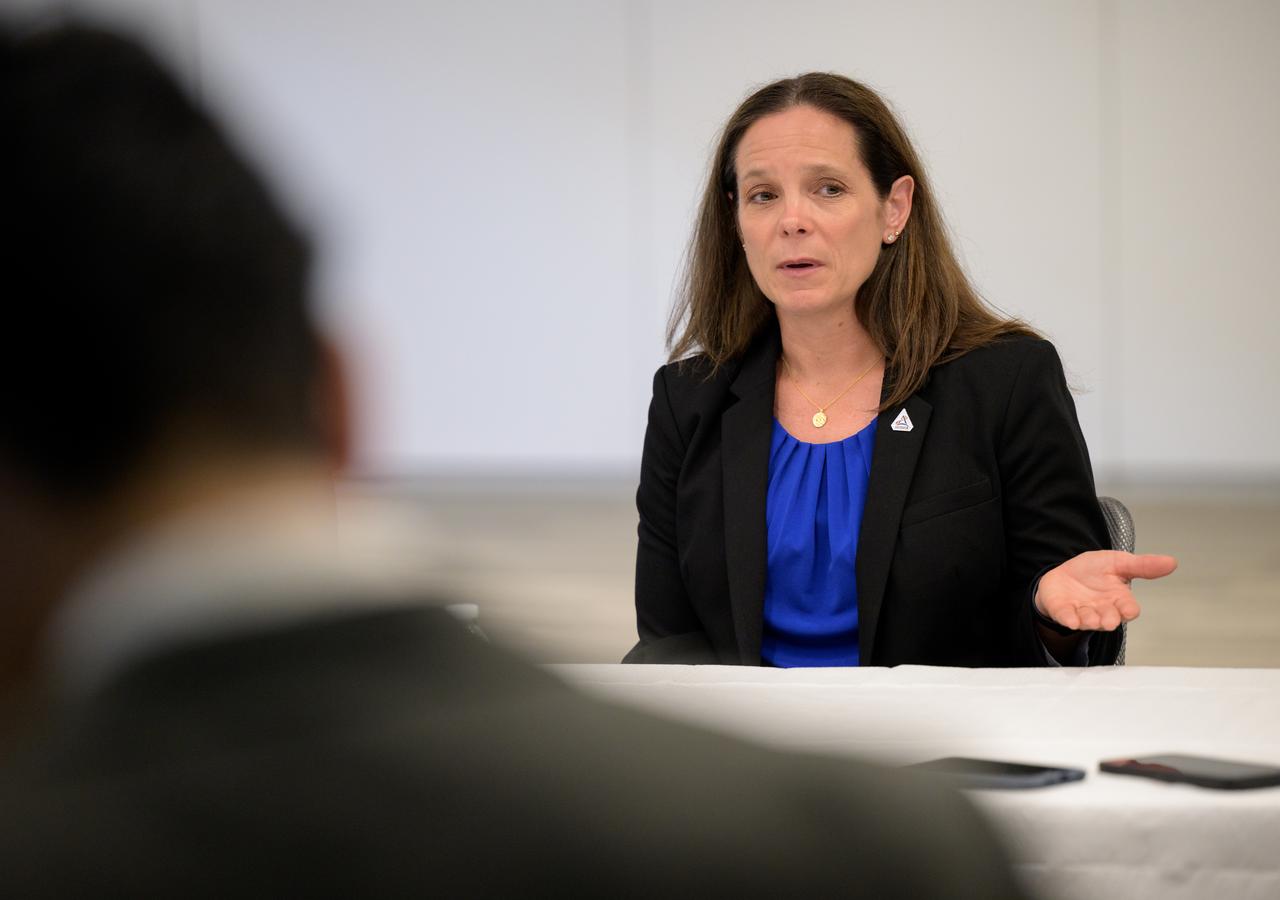

NASA Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Program Lara Kearney discusses the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
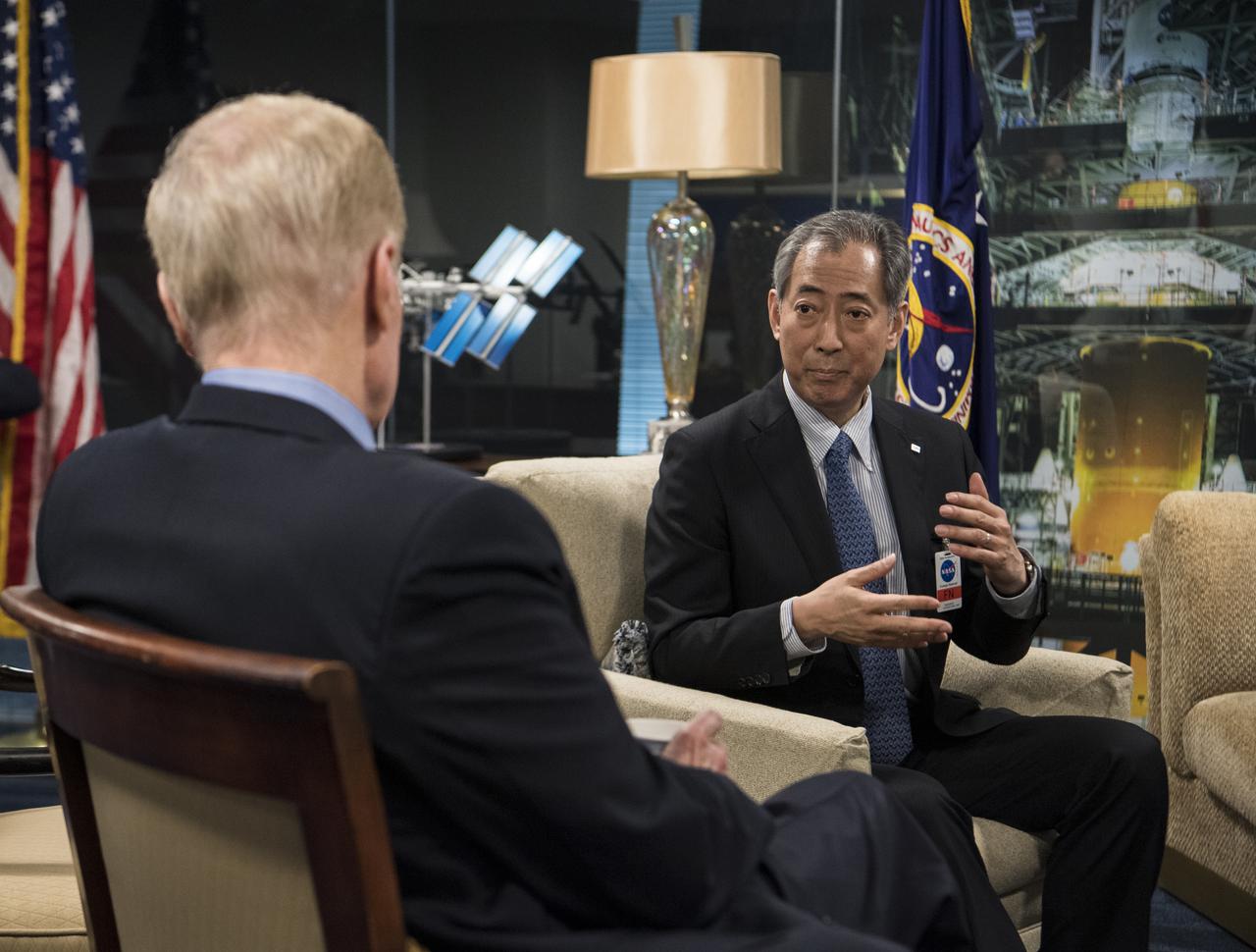

President of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Hiroshi Yamakawa speaks with NASA Administrator Bill Nelson during a meeting, Thursday, April 7, 2022, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
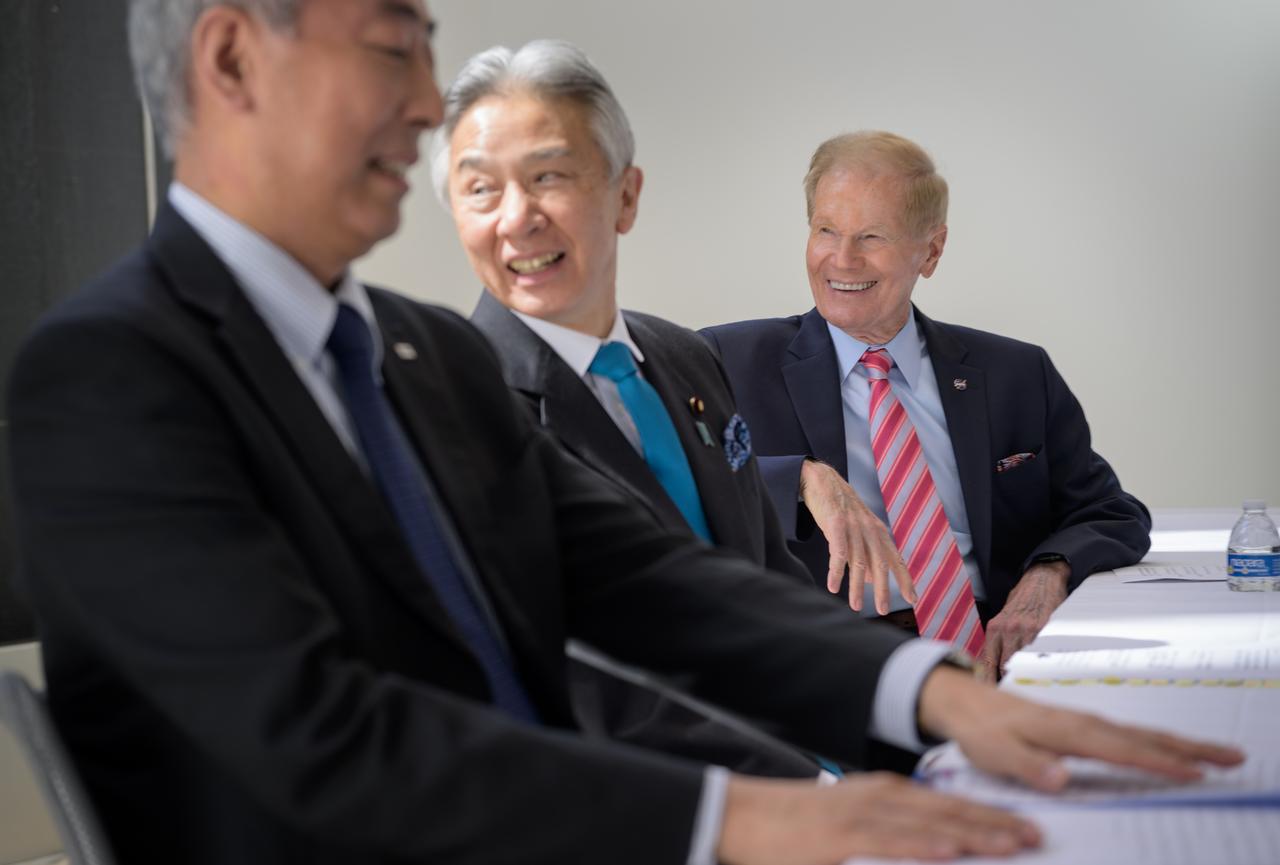

Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) President Hiroshi Yamakawa, left, Japan’s Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology Masahito Moriyama, and NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, are seen during a briefing where they discussed the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
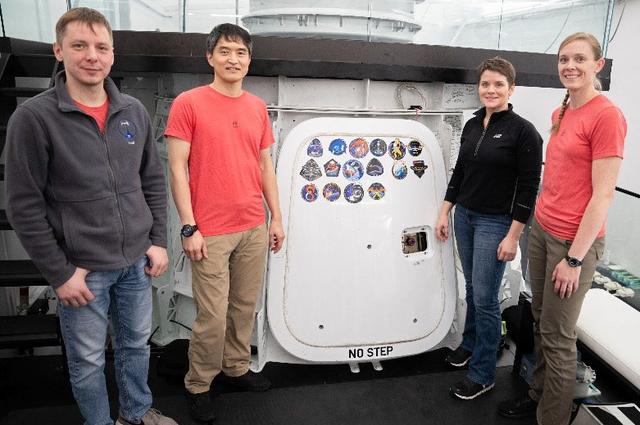

jsc2025e011333 (Feb. 24, 2025) --- NASA's SpaceX Crew-10 crewmembers pose for a portrait in front of the Crew-10 patch at the company’s facility in Hawthorne, California. From left are Mission Specialist Kirill Peskov of Roscosmos, Mission Specialist Takuya Onishi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), Commander Anne McClain of NASA, and Pilot Nichole Ayers of NASA. Credit: SpaceX
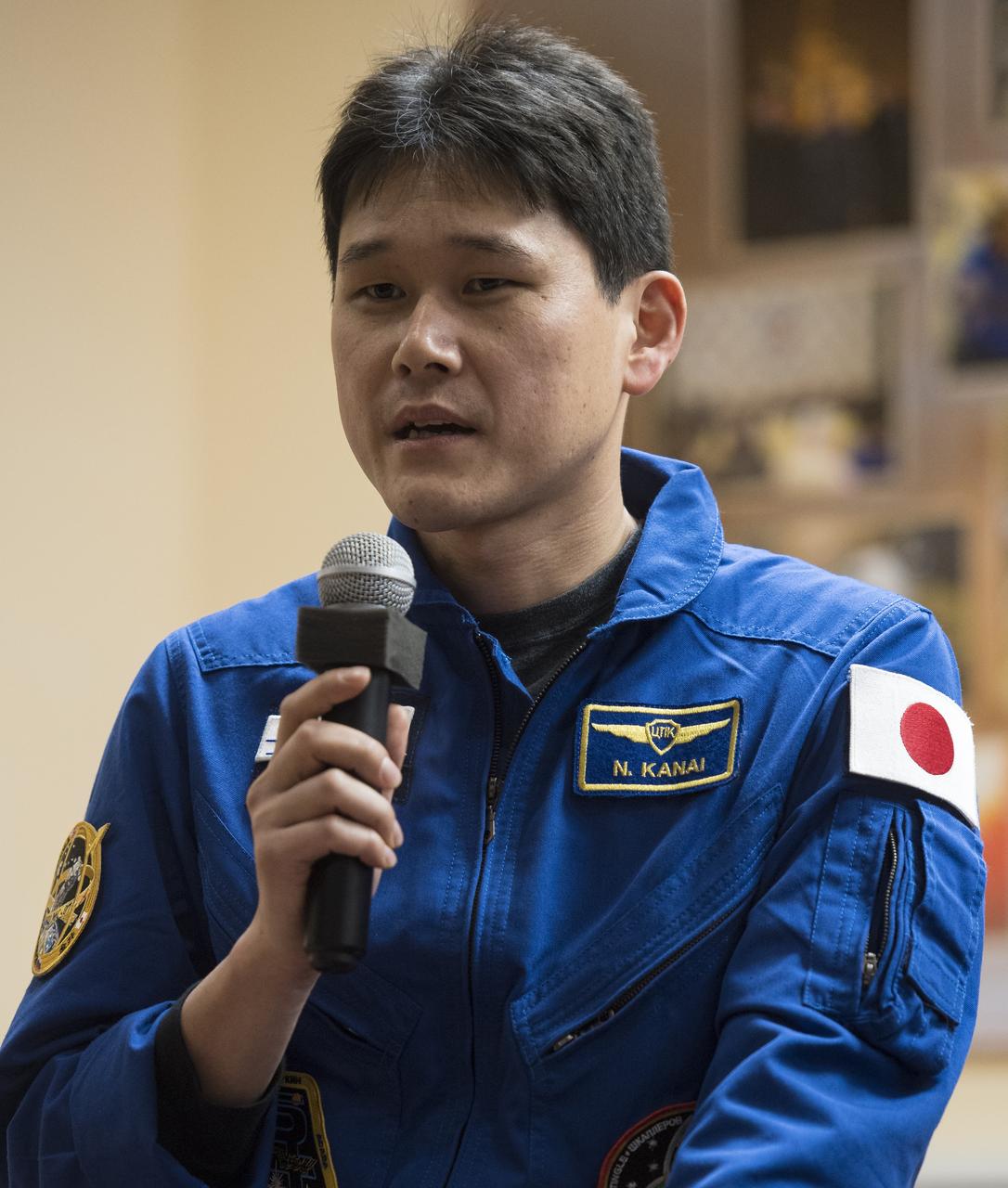

Expedition 54 flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) answers a question during a press conference, Saturday, Dec. 16, 2017 at the Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch to the International Space Station aboard the Soyuz spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on December 17. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
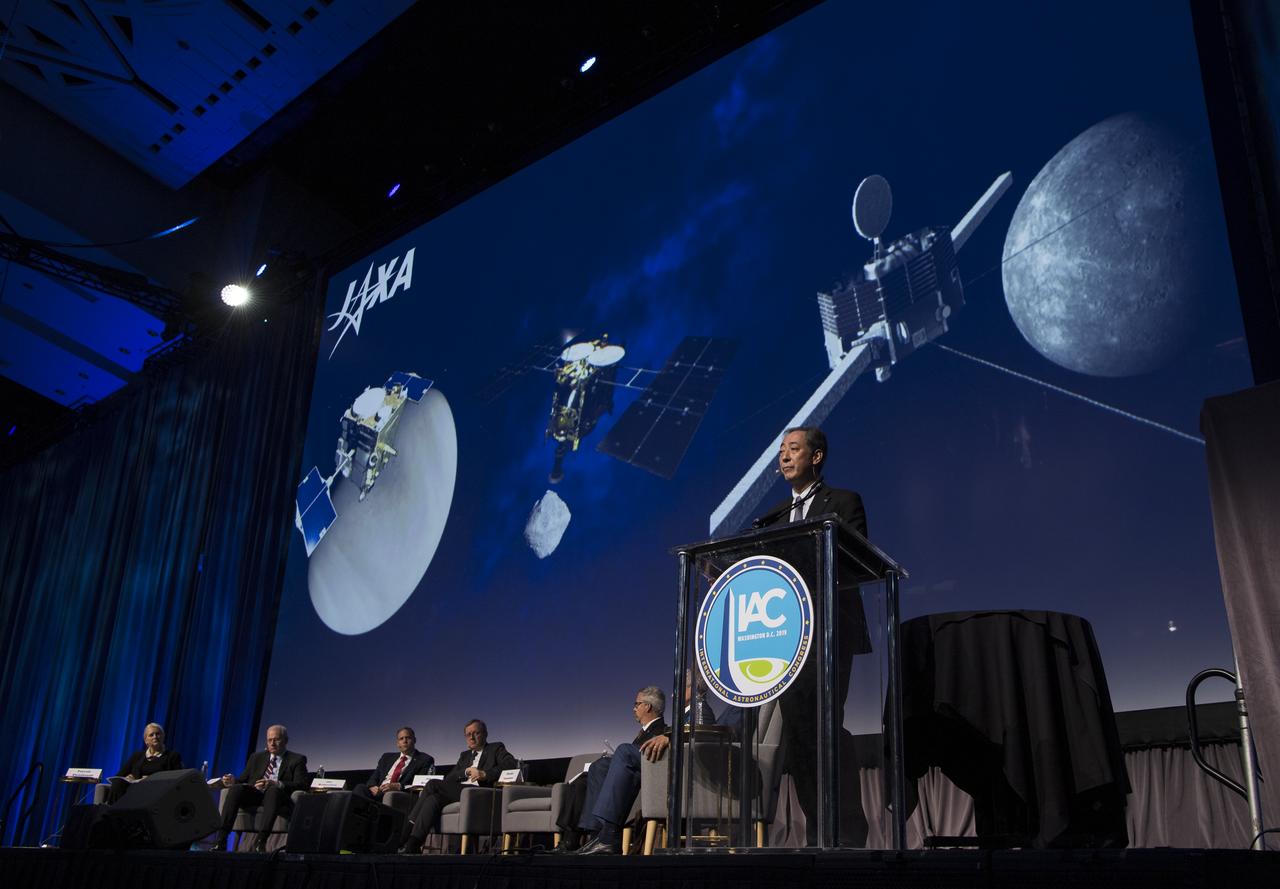

Hiroshi Yamakawa, President of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), speaks during the Heads of Agency Plenary of the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Monday, Oct. 21, 2019 at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
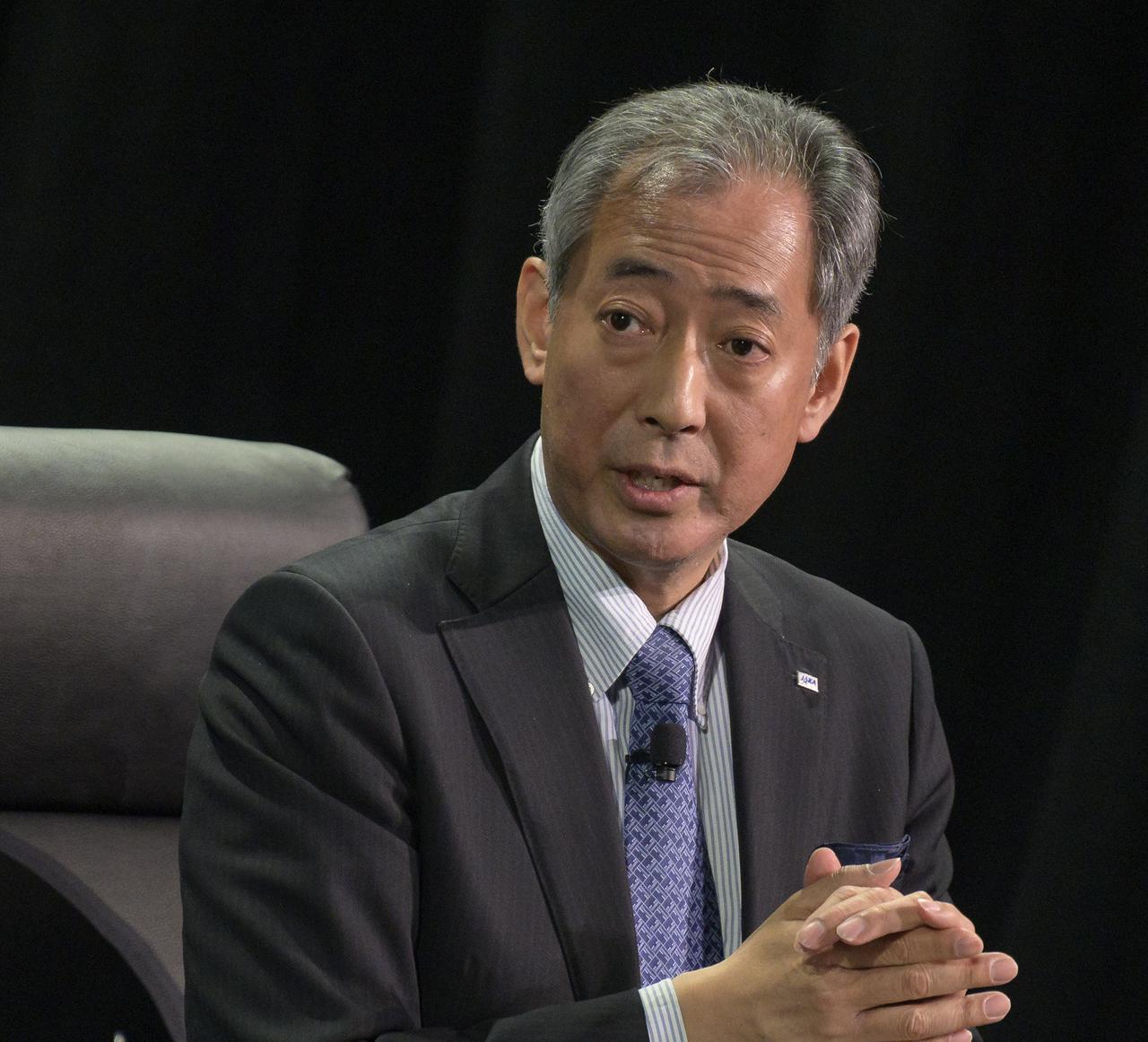

Dr. Hiroshi Yamakawa, President, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) speaks in a Heads of Agency panel during the 37th Space Symposium, Wednesday, April 6, 2022, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Kuniaki Shiraki, President of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), center, answers a reporter’s question during a Soyuz post-docking press conference at the Russian Mission Control Center in Korolev, Russia on Friday, June 10, 2011. The Soyuz TMA-02M docked to the International Space Station carrying Expedition 28 Soyuz Commander Sergei Volkov, NASA Flight Engineer Mike Fossum and JAXA (Japanase Aerospace Exploration Agency) Flight Engineer Satoshi Furukawa. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
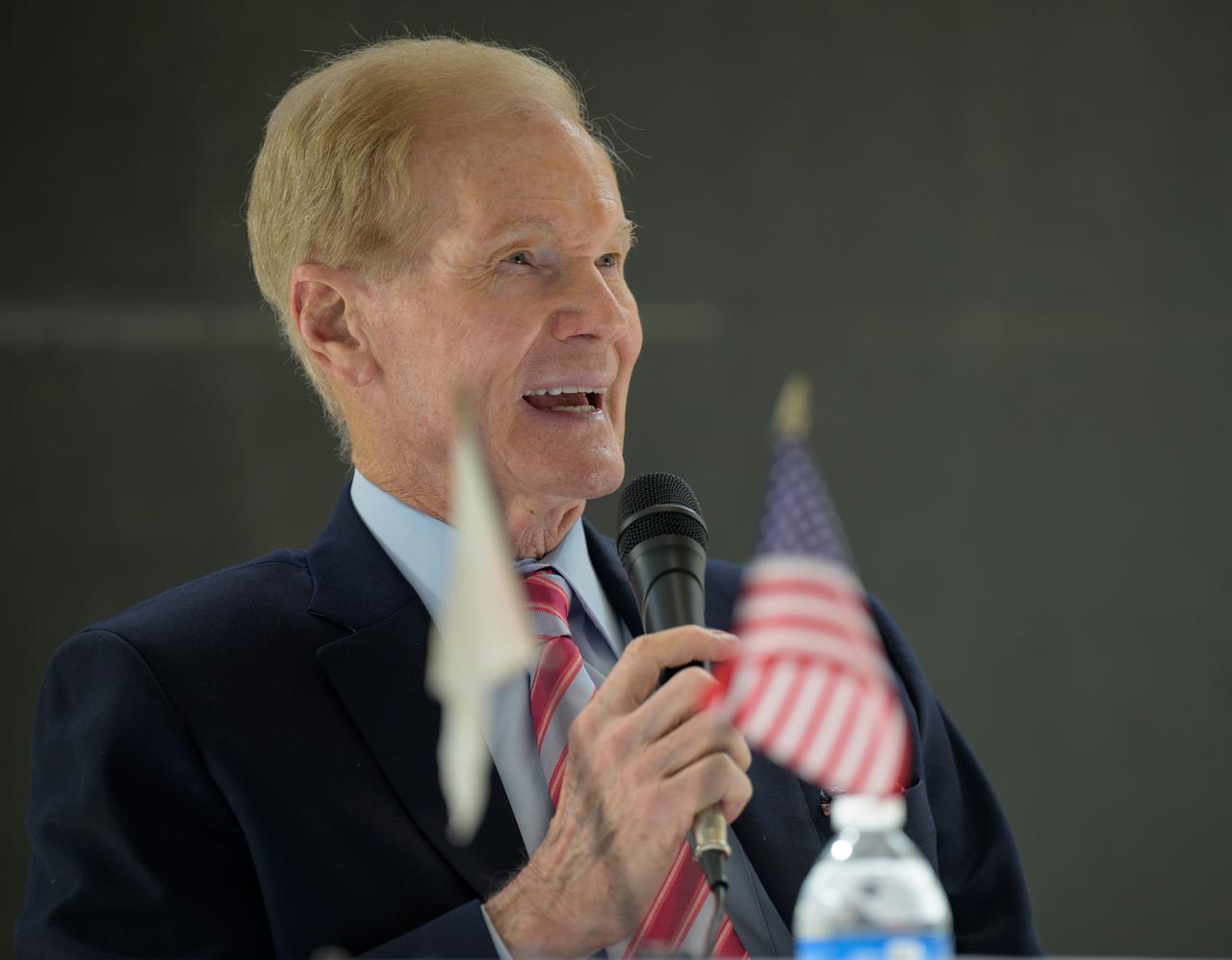

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson discusses the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
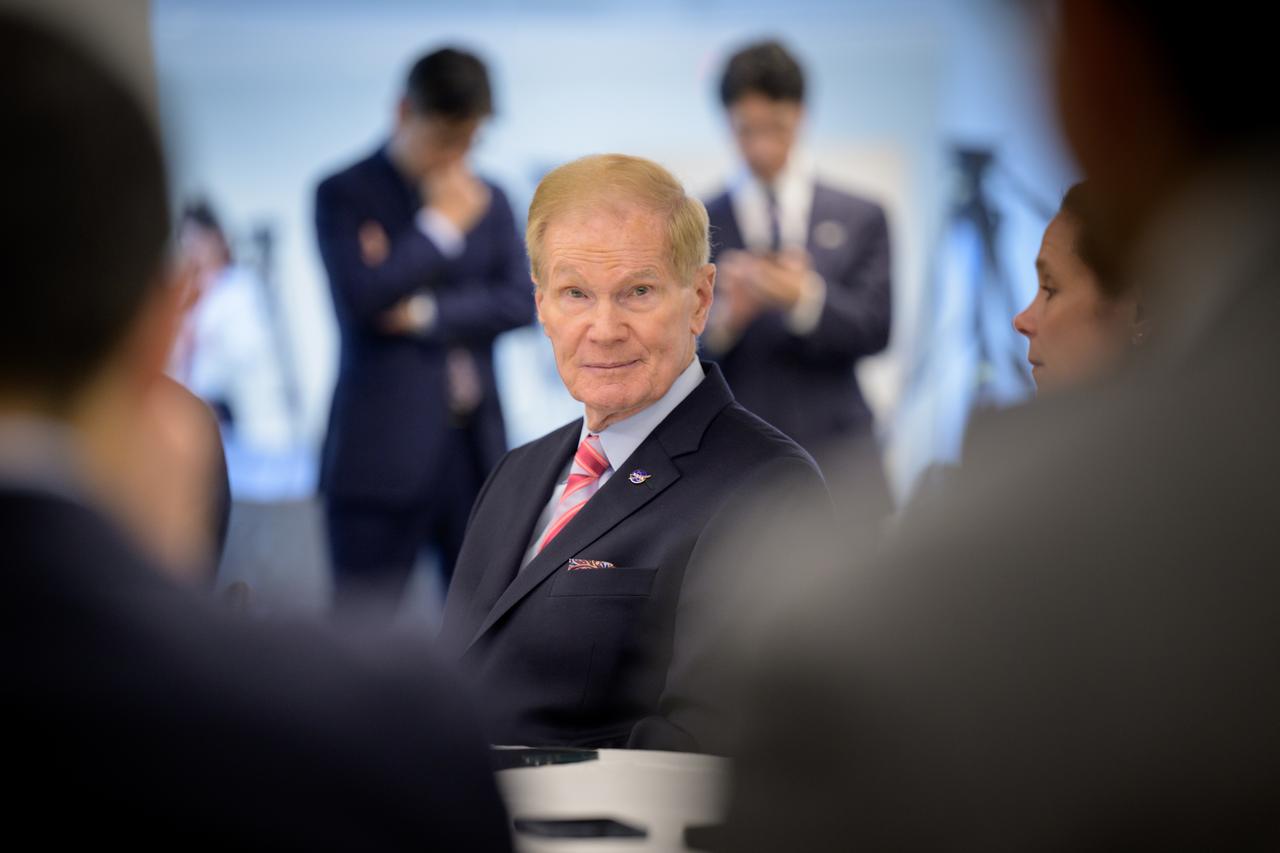

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson discusses the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
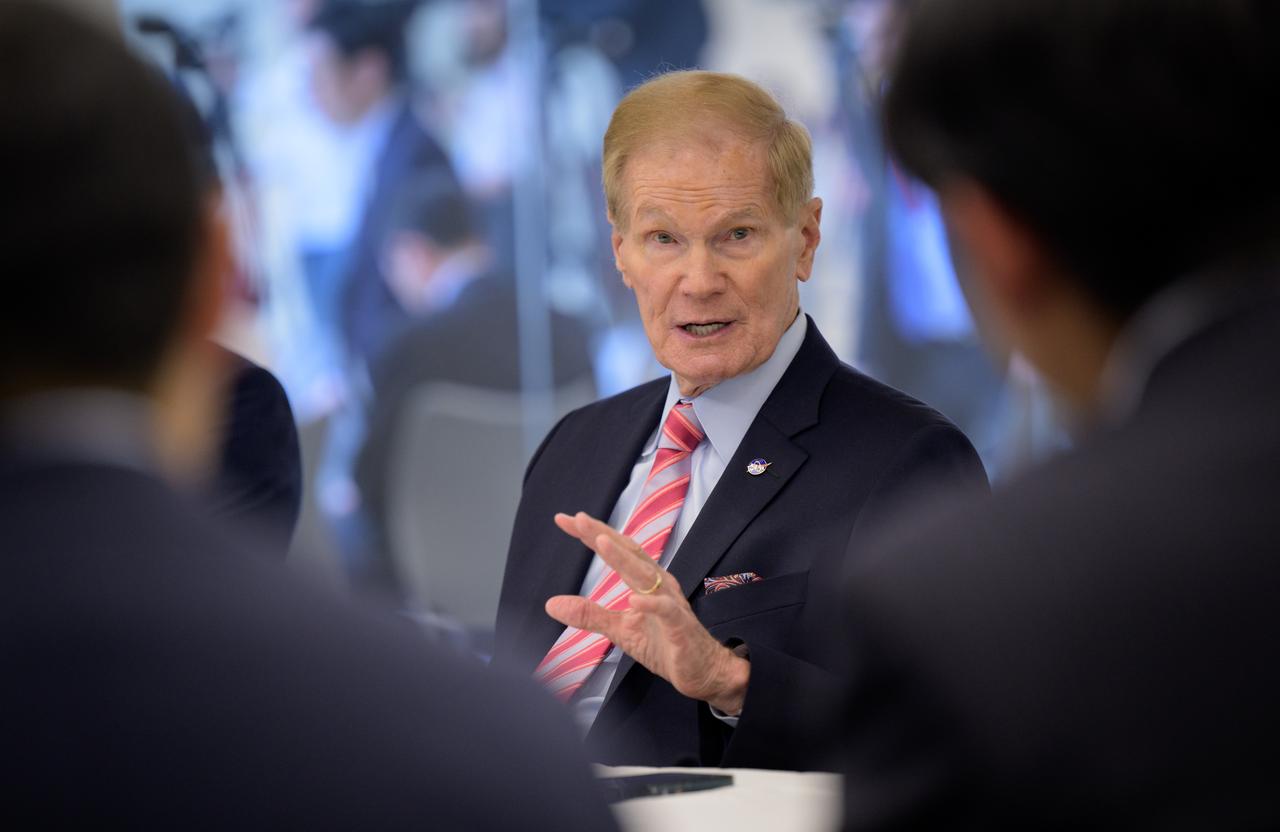

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson discusses the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson discusses the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
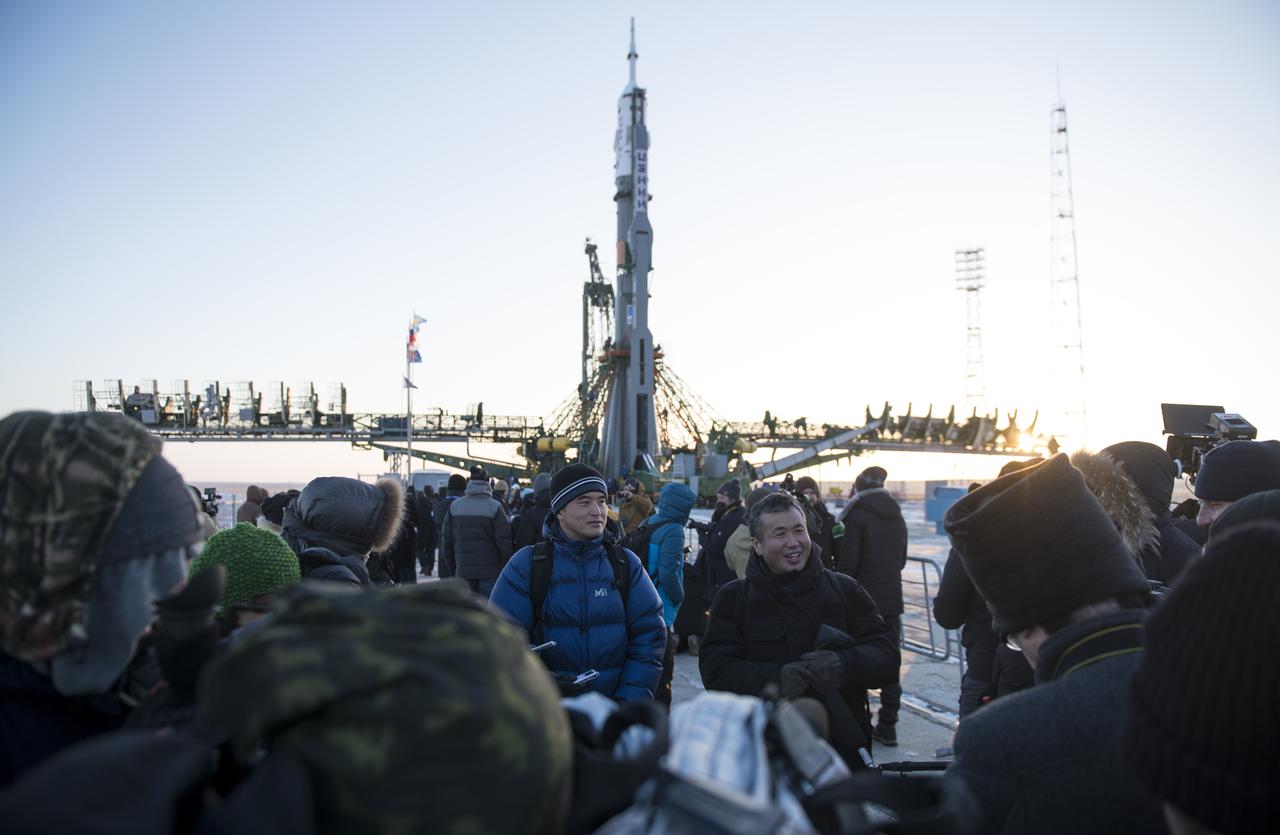

Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Takuya Onishi, left, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) International Space Station Program Manager Koichi Wakata, right, answers questions from the media, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017, after the Soyuz rocket was raised into a vertical position on the launch pad at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
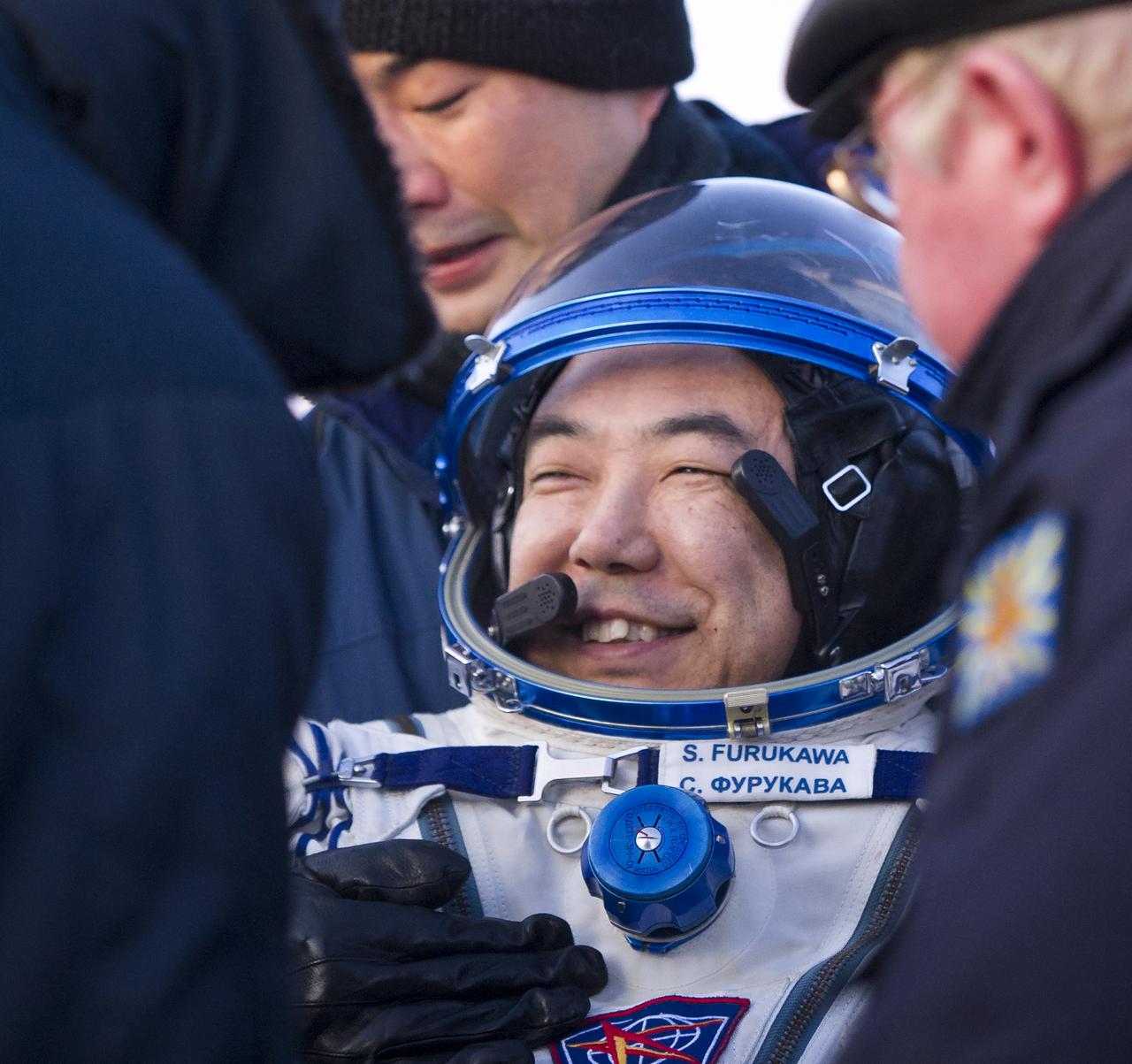

Expedition 29 Flight Engineer, JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Astronaut, Satoshi Furukawa smiles as he is helped to a chair outside the Soyuz TMA-02M Capsule just minutes after he and Expedition 29 Commander Mike Fossum and Flight Engineer Sergei Volkov landed in a remote area outside of the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan, on Tuesday, Nov. 22, 2011. NASA Astronaut Fossum, Russian Cosmonaut Volkov and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Astronaut Furukawa are returning from more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 28 and 29 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
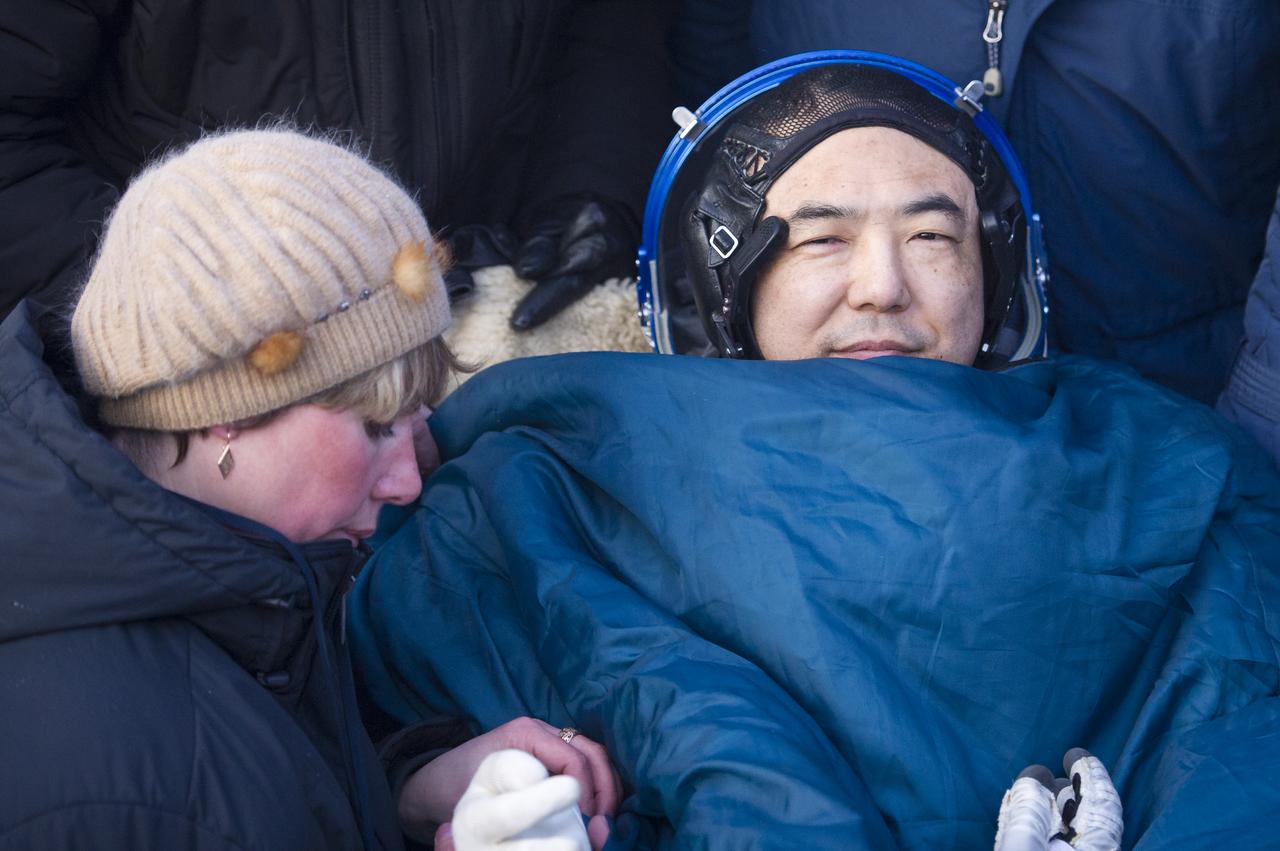

Expedition 29 Flight Engineer, JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Astronaut, Satoshi Furukawa smiles as he rest in a chair outside the Soyuz TMA-02M Capsule just minutes after he and Expedition 29 Commander Mike Fossum and Flight Engineer Sergei Volkov landed in a remote area outside of the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan, on Tuesday, Nov. 22, 2011. NASA Astronaut Fossum, Russian Cosmonaut Volkov and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Astronaut Furukawa are returning from more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 28 and 29 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
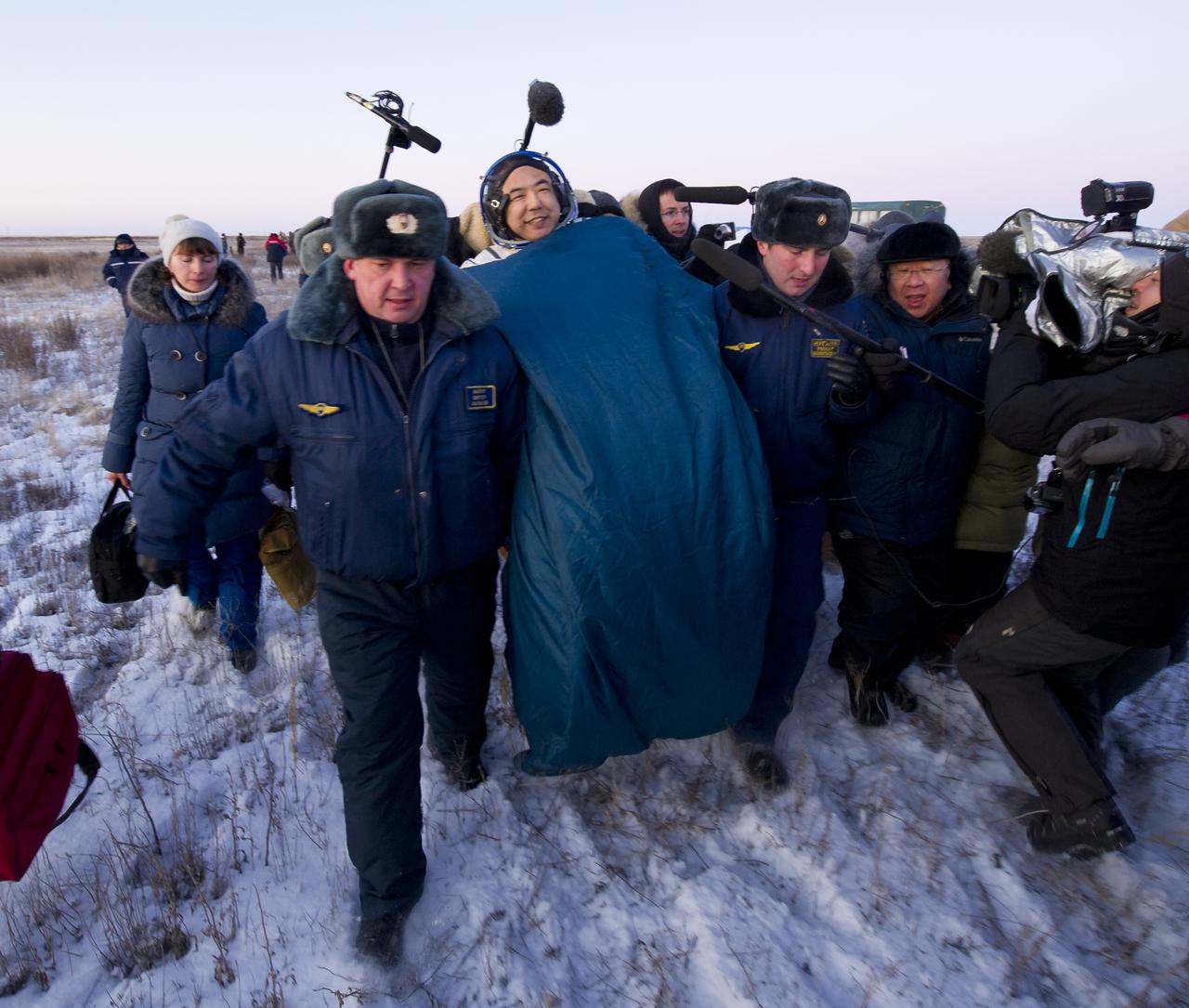

Expedition 29 Flight Engineer, JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Astronaut, Satoshi Furukawa smiles as he is carried in a chair to the medical tent just minutes after he and Expedition 29 Commander Mike Fossum and Flight Engineer Sergei Volkov landed in a remote area outside of the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan, on Tuesday, Nov. 22, 2011. NASA Astronaut Fossum, Russian Cosmonaut Volkov and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Astronaut Furukawa are returning from more than five months onboard the International Space Station where they served as members of the Expedition 28 and 29 crews. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
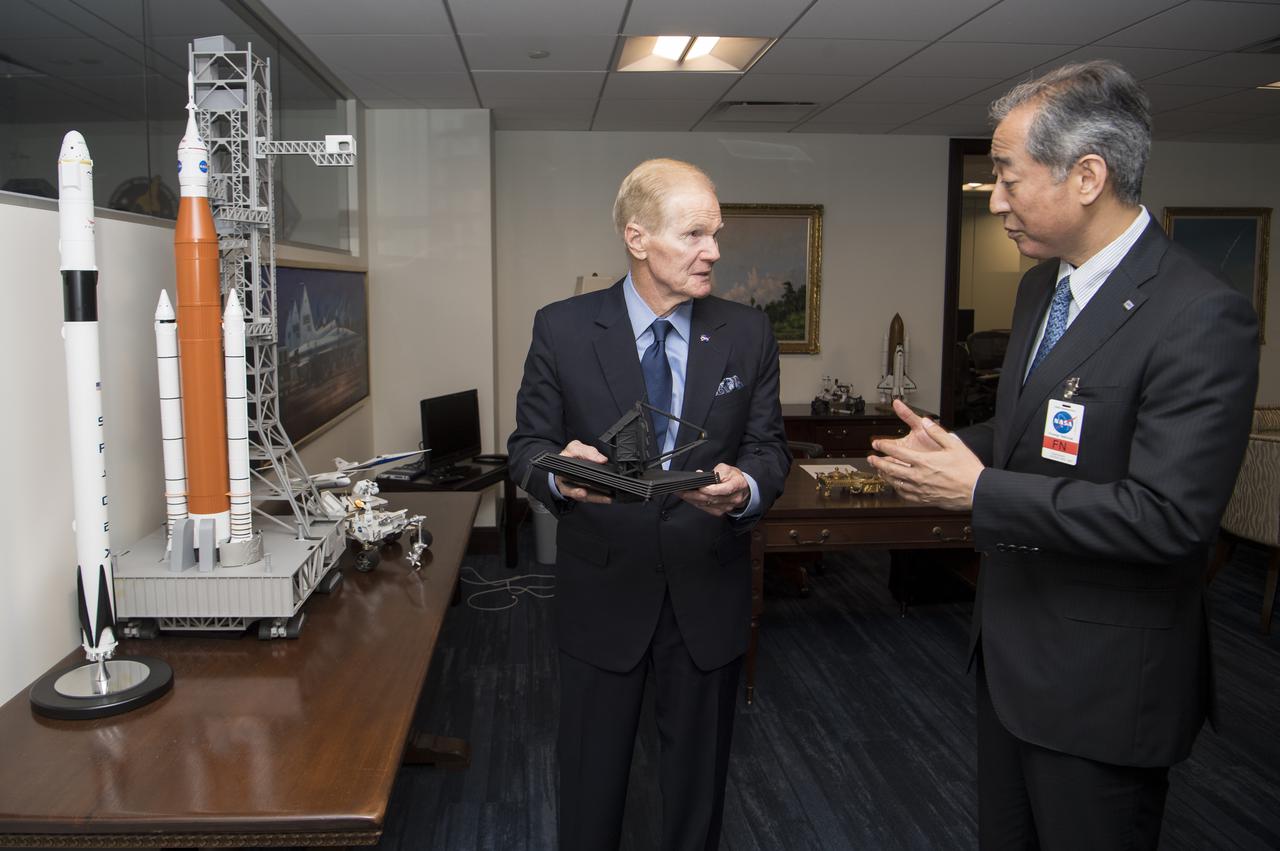

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, left, shows some of the models of spacecraft and satellites in his office, to President of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Hiroshi Yamakawa, during a meeting, Thursday, April 7, 2022, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
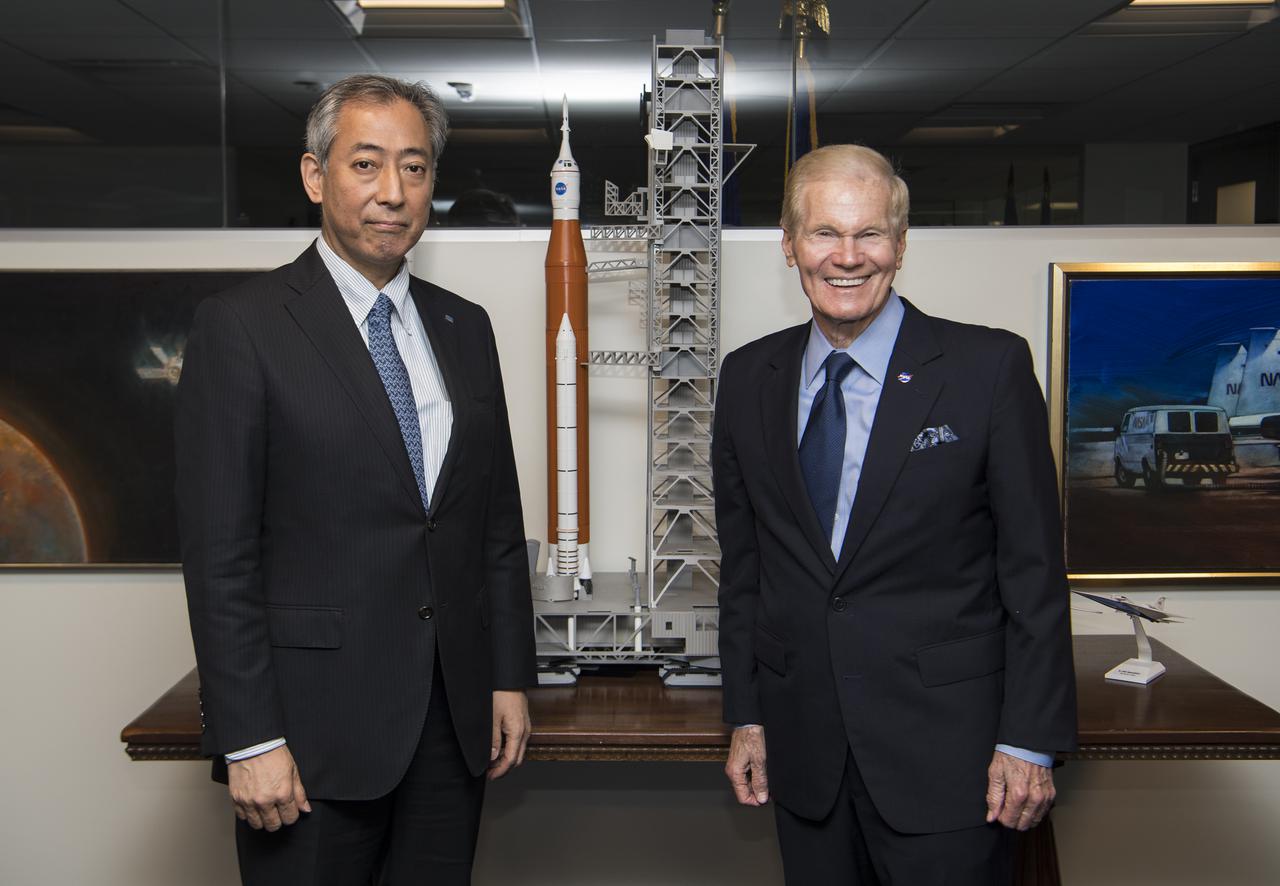
President of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Hiroshi Yamakawa, left, and NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, pose for a photo next to a model of the Space Launch System (SLS) during a meeting, Thursday, April 7, 2022, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
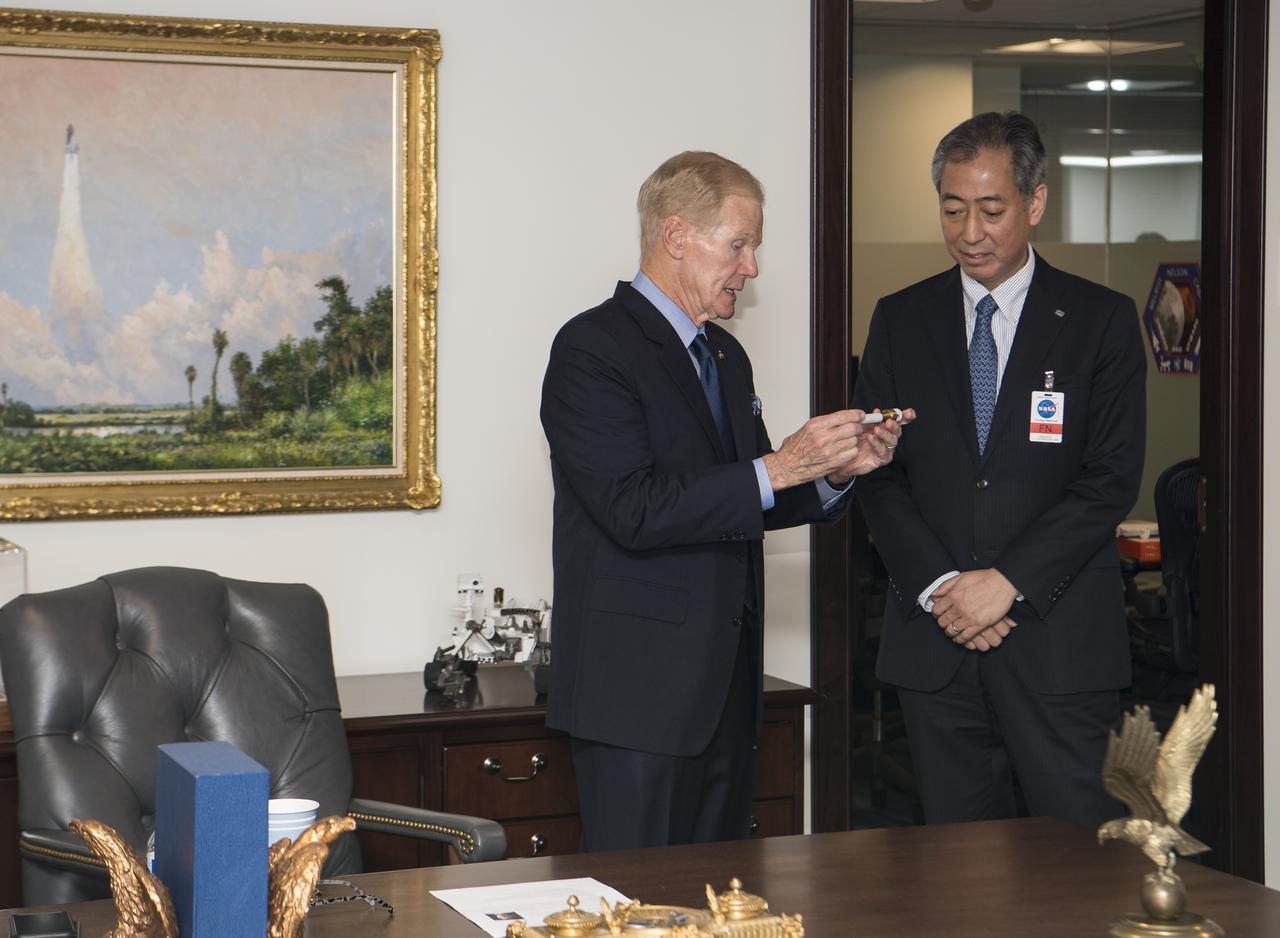

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, left, shows some of the models of spacecraft and satellites in his office, to President of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Hiroshi Yamakawa, during a meeting, Thursday, April 7, 2022, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
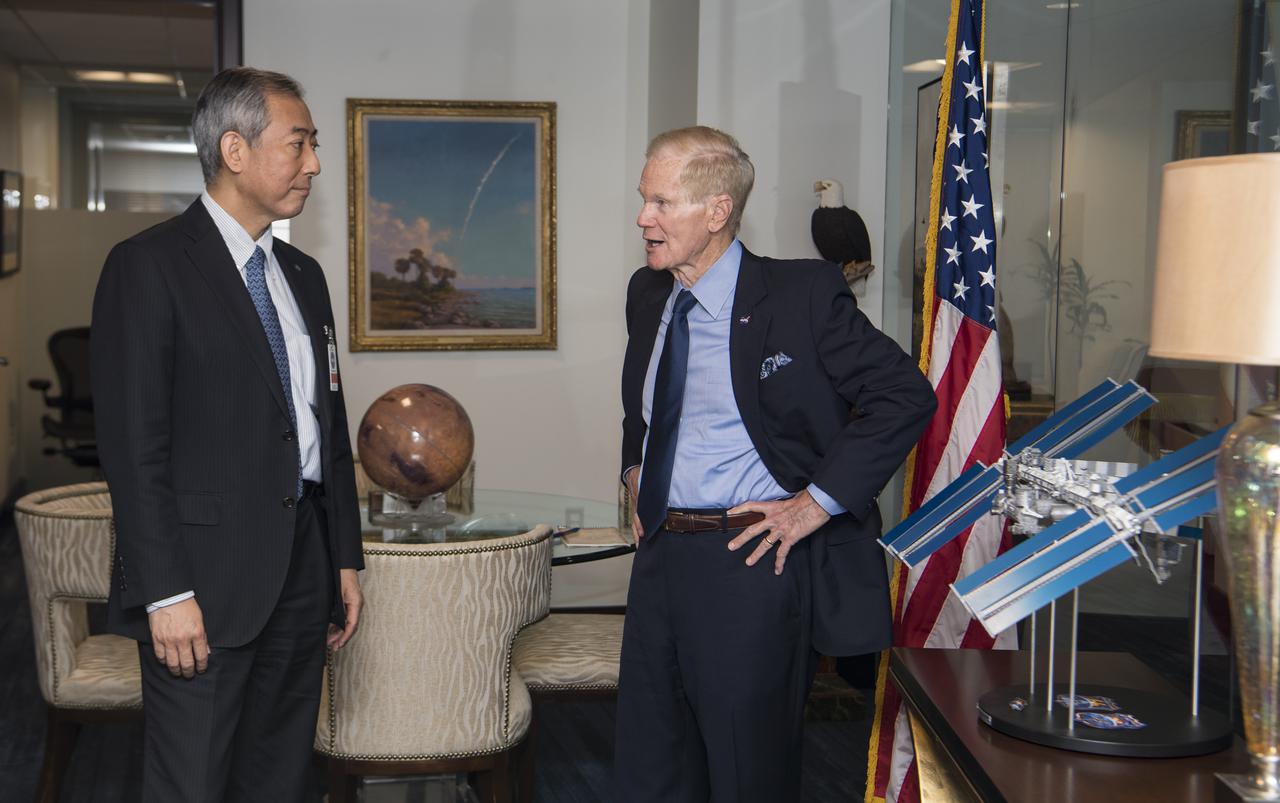

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, speaks with President of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Hiroshi Yamakawa, during a meeting, Thursday, April 7, 2022, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

A sign guides travelers to the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for Feb. 28, 2014 from the space center. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
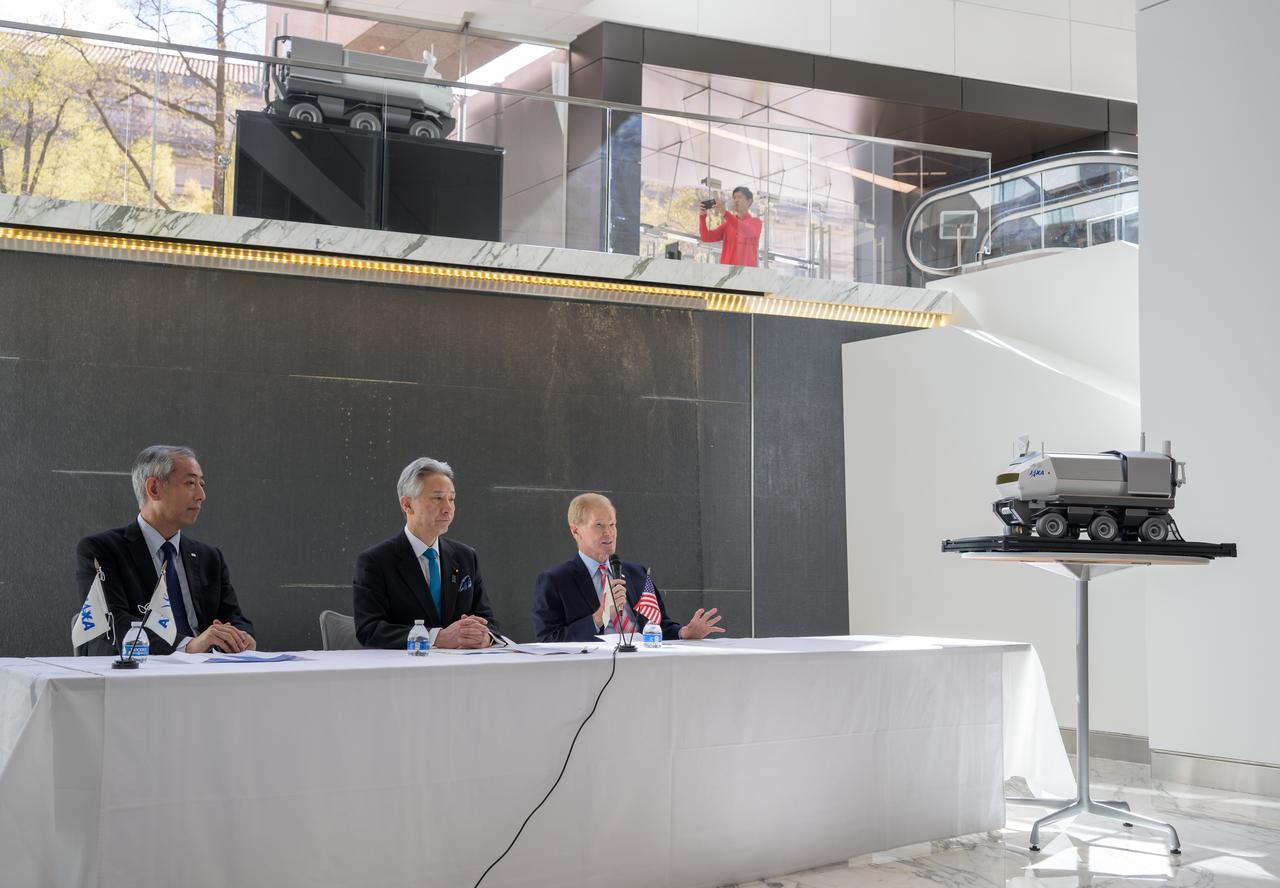

Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) President Hiroshi Yamakawa, left, Japan’s Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology Masahito Moriyama, and NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, are seen during a briefing where they discussed the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
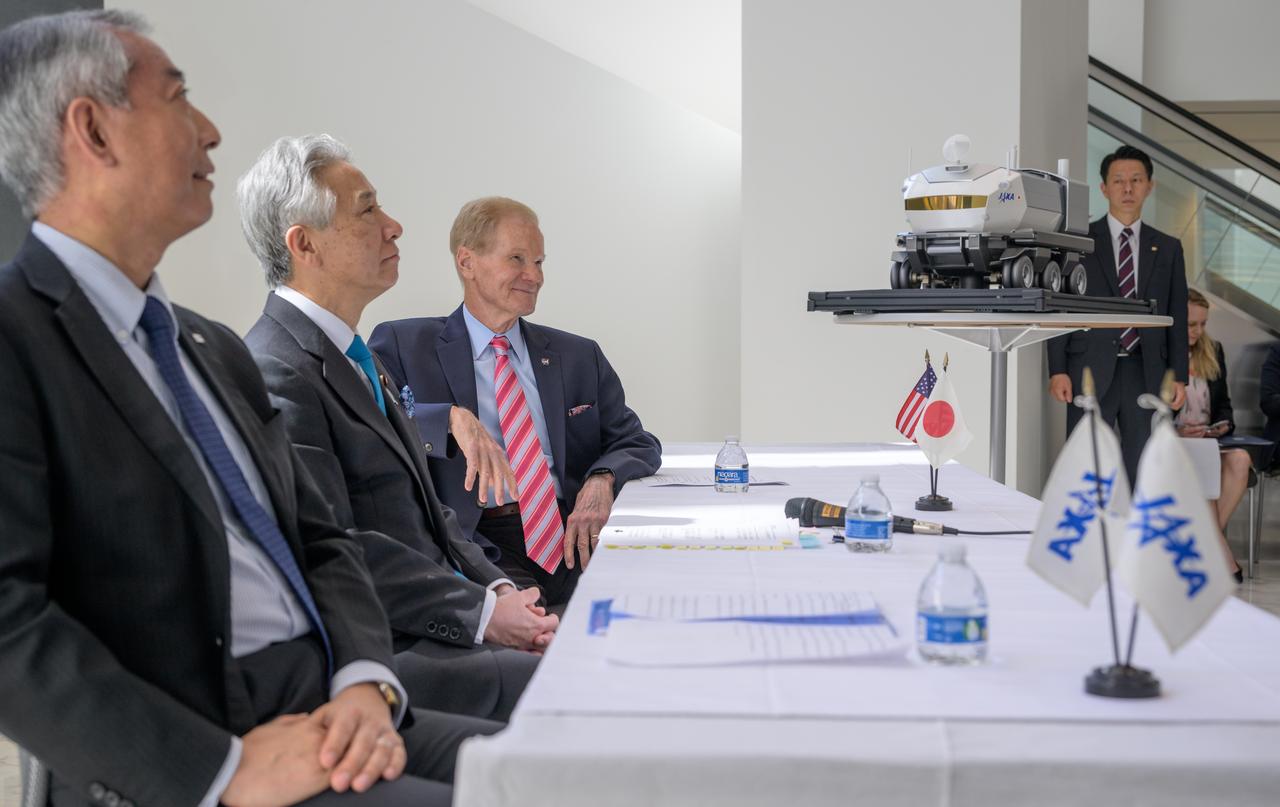
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) President Hiroshi Yamakawa, left, Japan’s Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology Masahito Moriyama, and NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, are seen during a briefing where they discussed the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
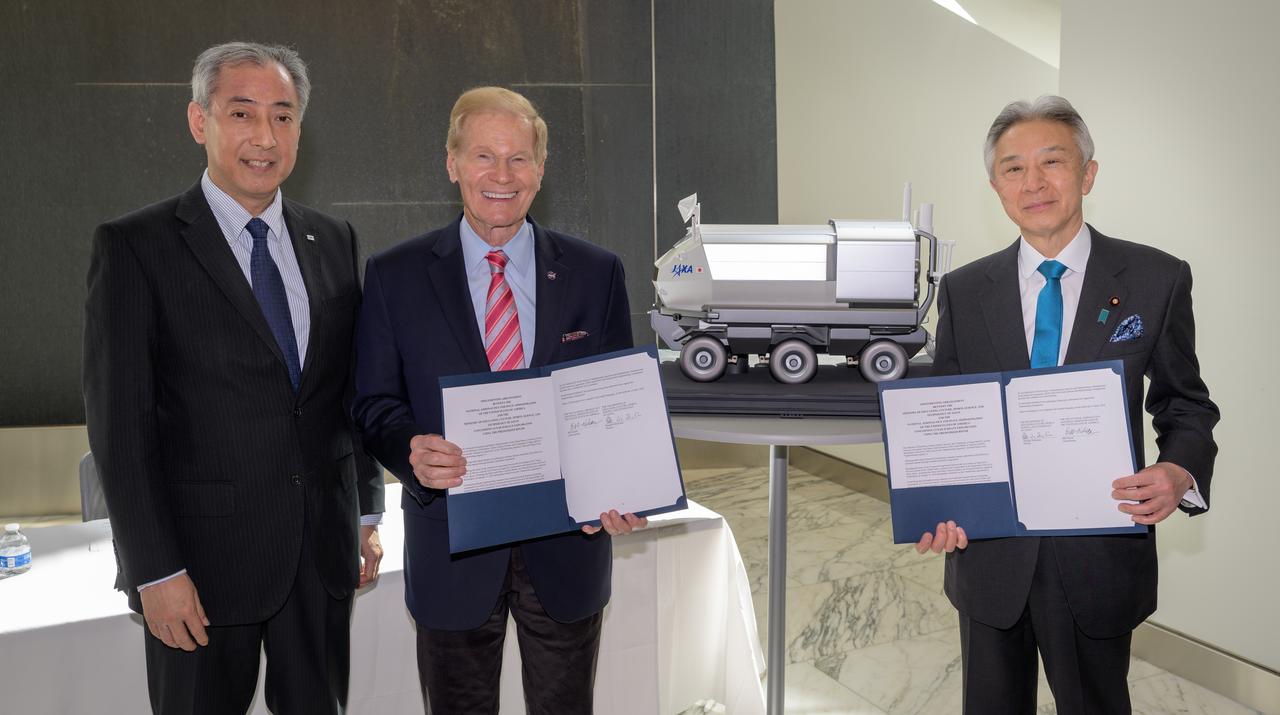
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) President Hiroshi Yamakawa, left, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, and Japan’s Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology Masahito Moriyama, right, pose for a group photograph holding the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
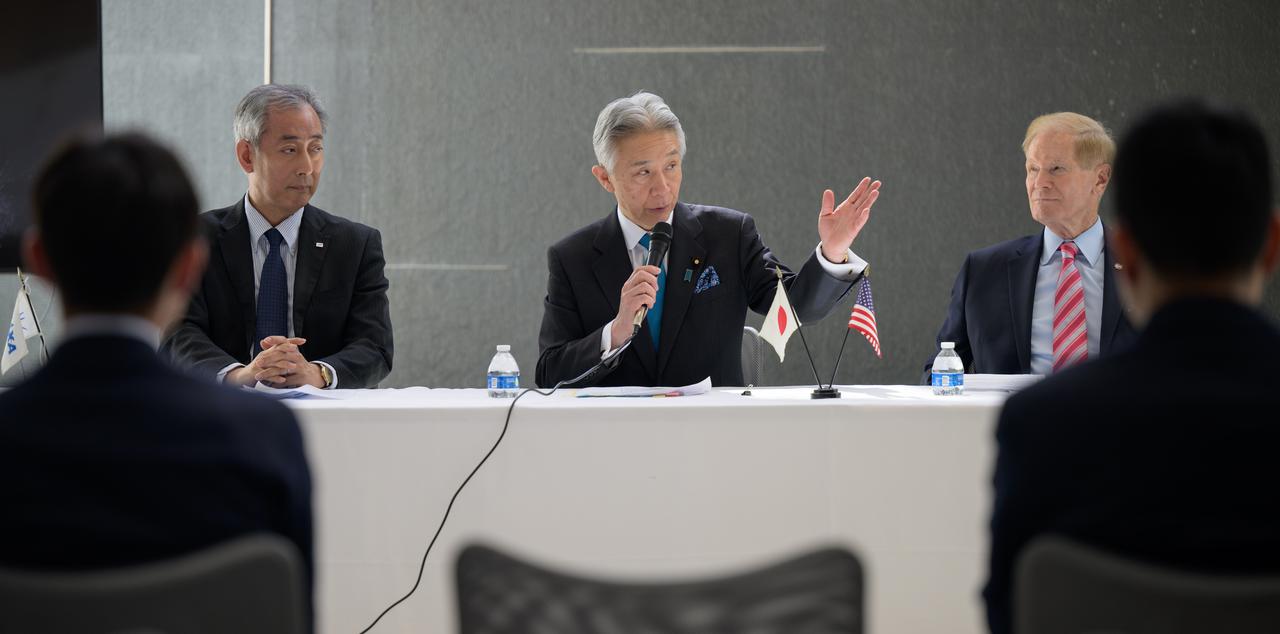

Japan’s Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology Masahito Moriyama, center, discusses the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
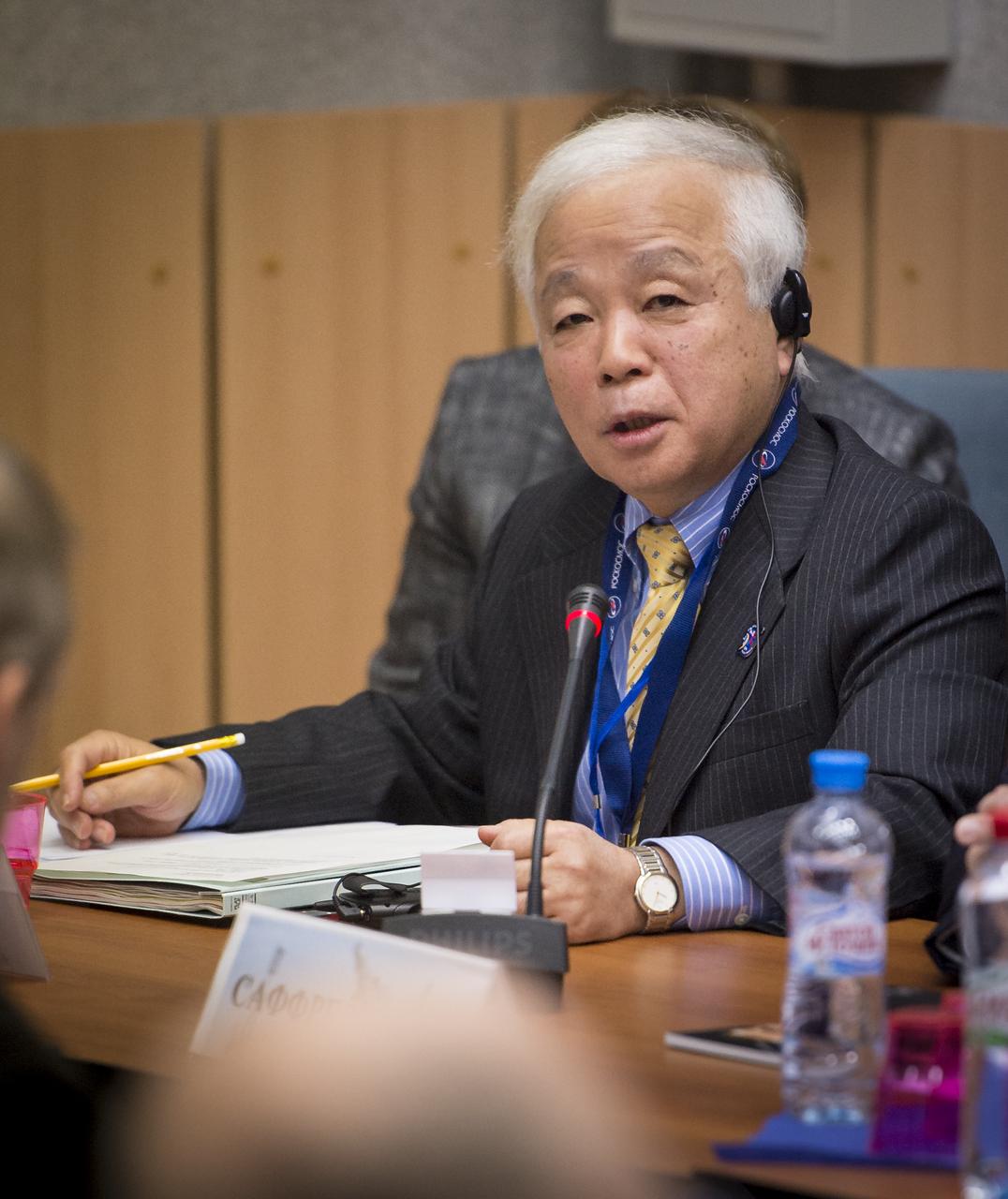

JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) President Naoki Okumura talks during the State Commission meeting to approve the Soyuz rocket launch of Expedition 38 Soyuz Commander Mikhail Tyurin of Roscosmos, Flight Engineer Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, and, Flight Engineer Rick Mastracchio of NASA for a six month mission aboard the International Space Station, Wednesday, Nov. 6, 2013 at the Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
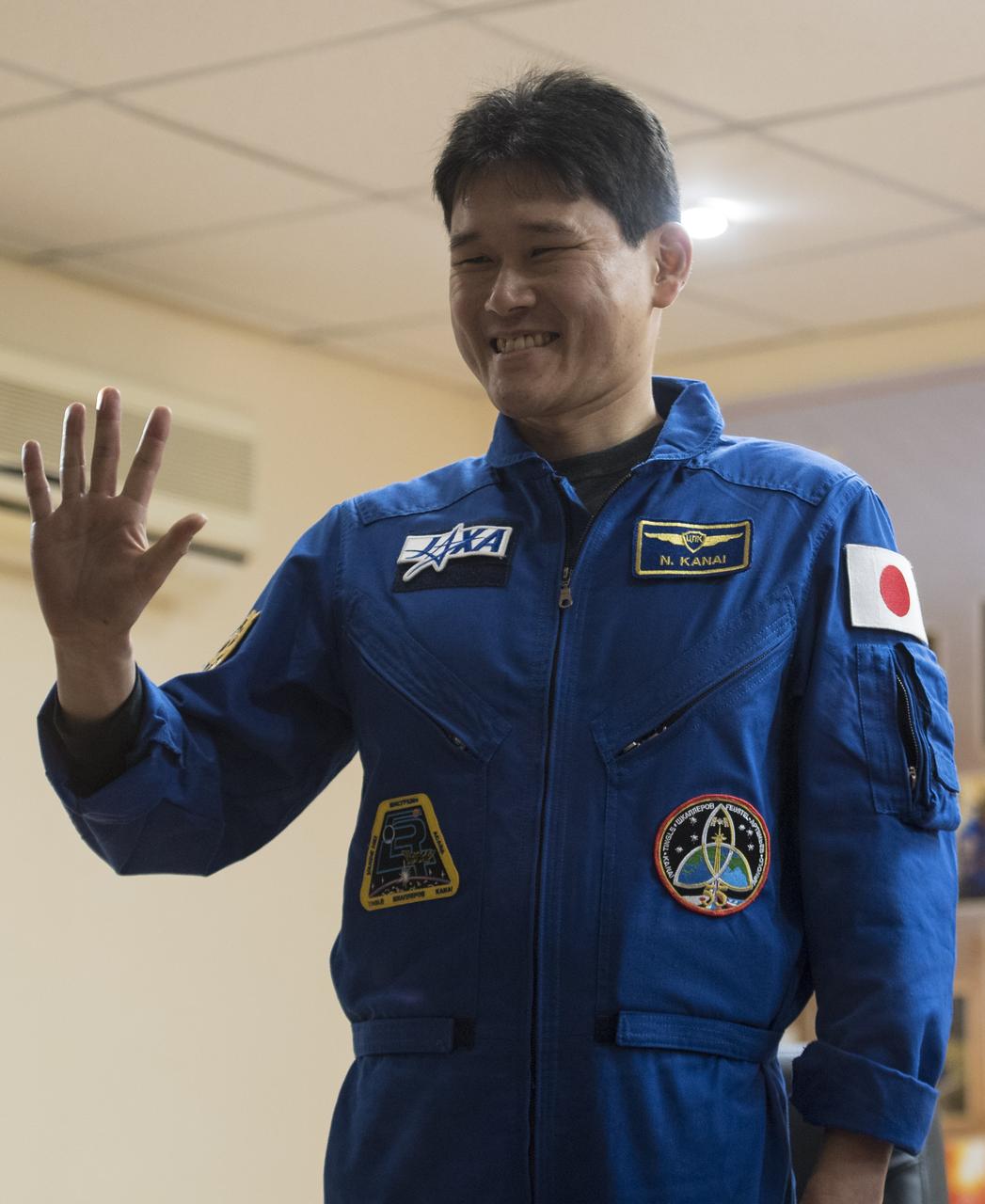

Expedition 54 flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) is seen in quarantine, behind glass, during a press conference, Saturday, Dec. 16, 2017 at the Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch to the International Space Station aboard the Soyuz spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on December 17. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Expedition 54 flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) is seen in quarantine, behind glass, during a press conference, Saturday, Dec. 16, 2017 at the Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch to the International Space Station aboard the Soyuz spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on December 17. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
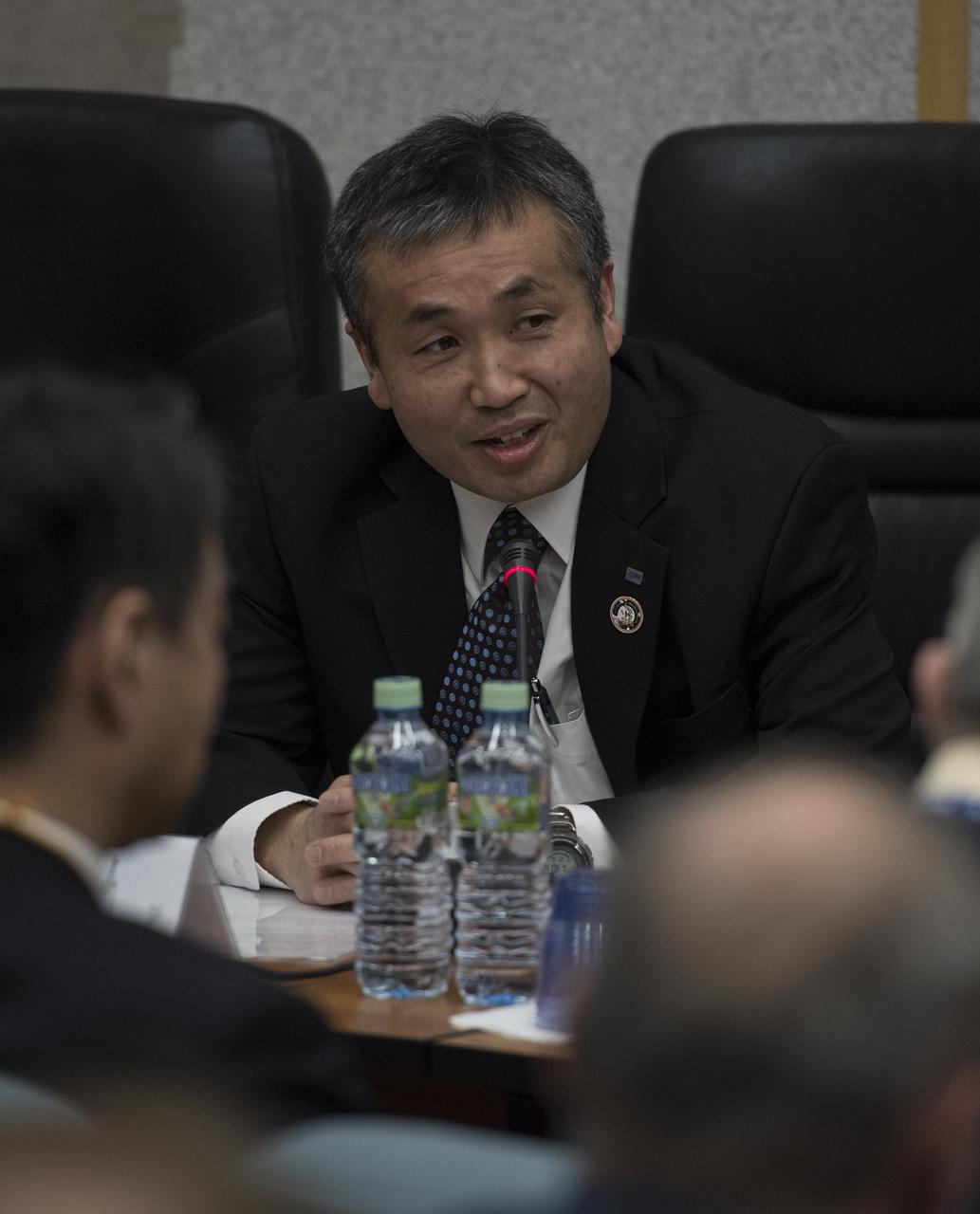

Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) International Space Station Program Manager Koichi Wakata is seen during the State Commission meeting to approve the Soyuz launch of Expedition 54 to the International Space Station, Saturday, Dec. 16, 2017 at the Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch to the International Space Station aboard the Soyuz spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on December 17. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
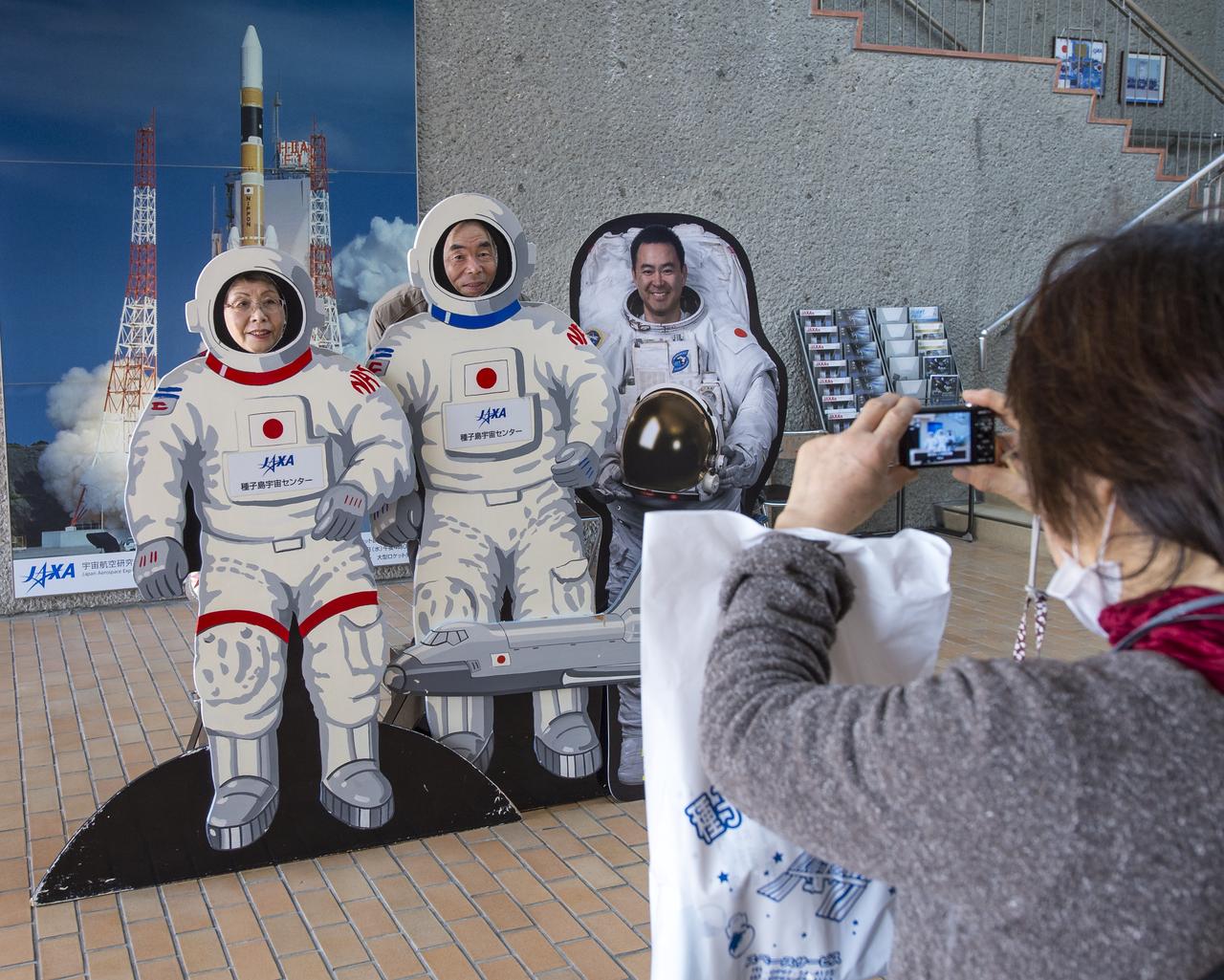

Tourist photograph themselves in astronaut space suites next to a cardboard cutout of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Astronaut Akihiko Hoshide at the visitor's center of the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
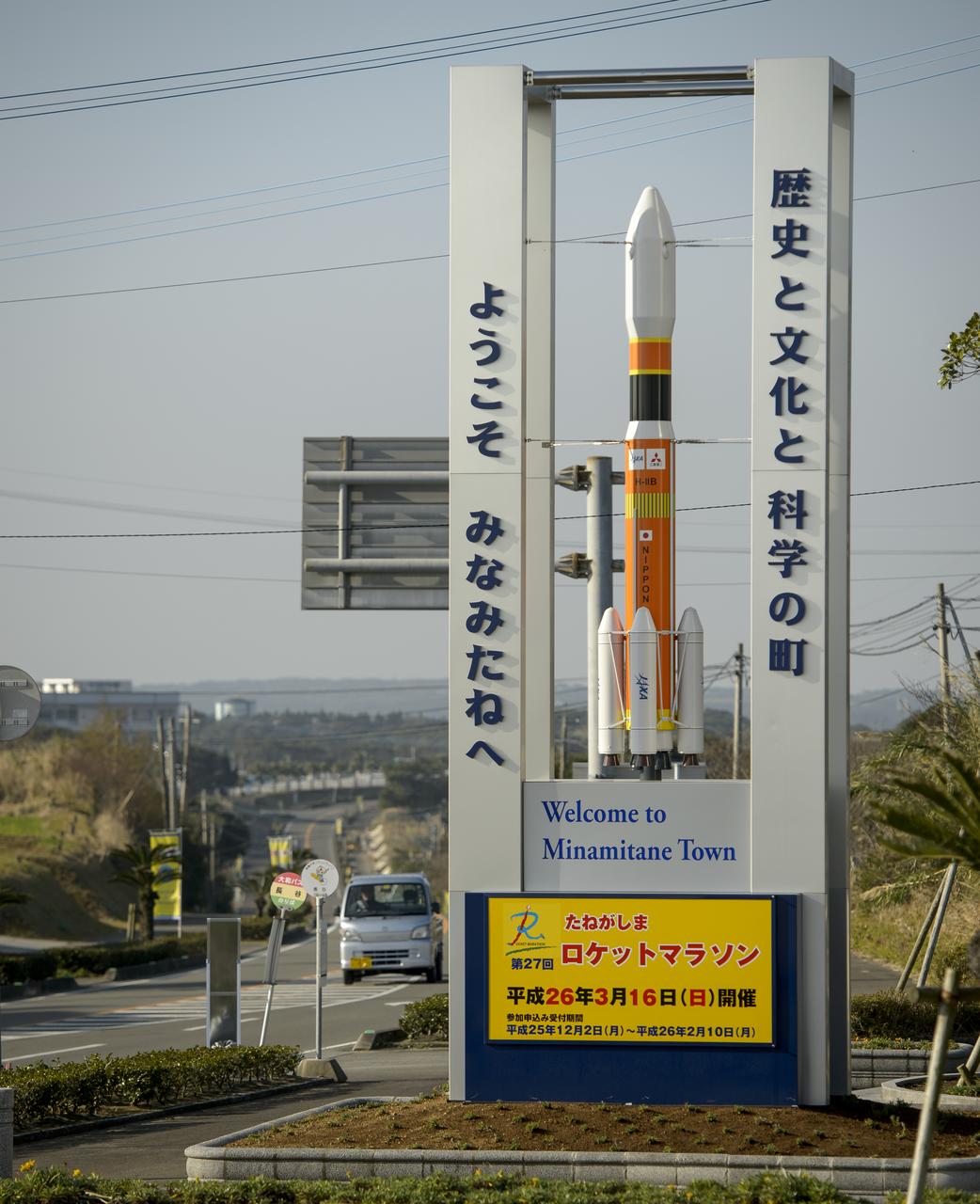

A sign with a model of the Japanese H-IIB rocket welcomes visitors to Minamitane Town, one of only a few small towns located outside of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), where the launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory will take place in the next week, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
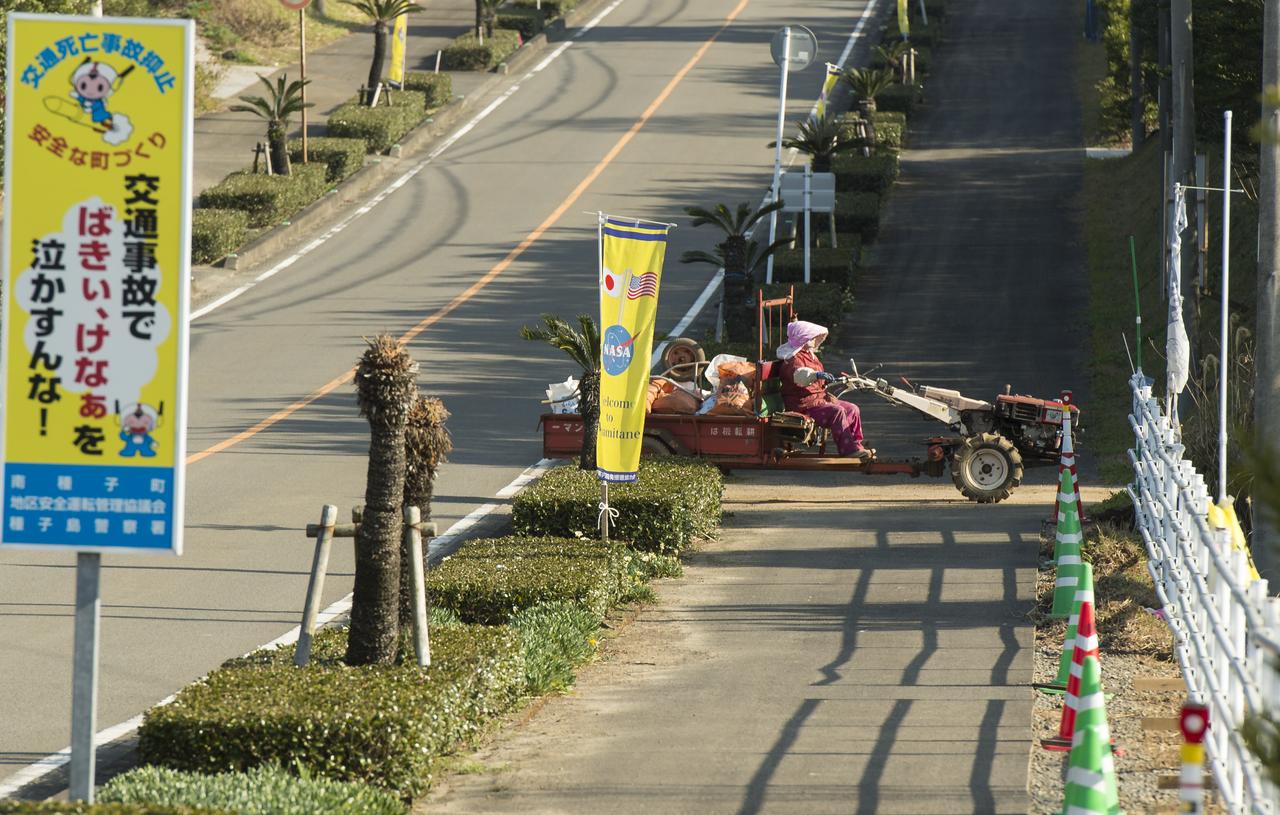

Roadside flags welcome the NASA team and visitors to Minamitame Town, one of only a few small towns located outside of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), where the launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory will take place in the next week, Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. The launch is planned for Feb. 28, 2014. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
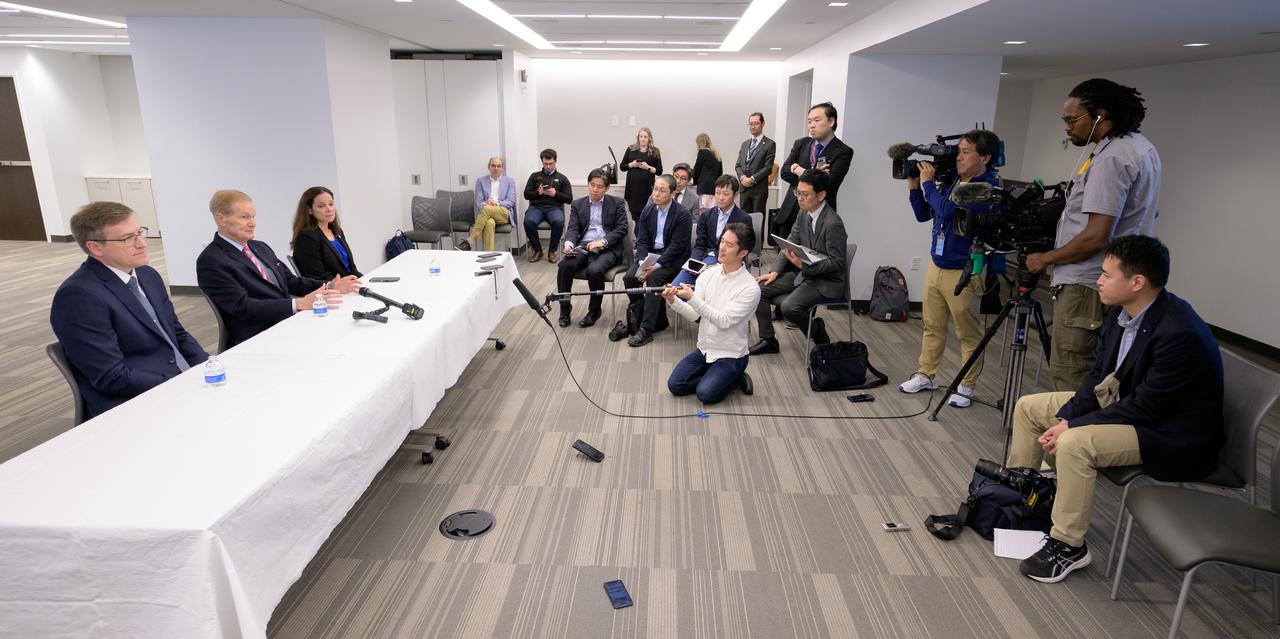

NASA Pressurized Rover Project Manager Danny Newswander, left, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, and NASA Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Program Lara Kearney, right, discuss the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Pressurized Rover Project Manager Danny Newswander, left, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, and NASA Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Program Lara Kearney, right, discuss the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
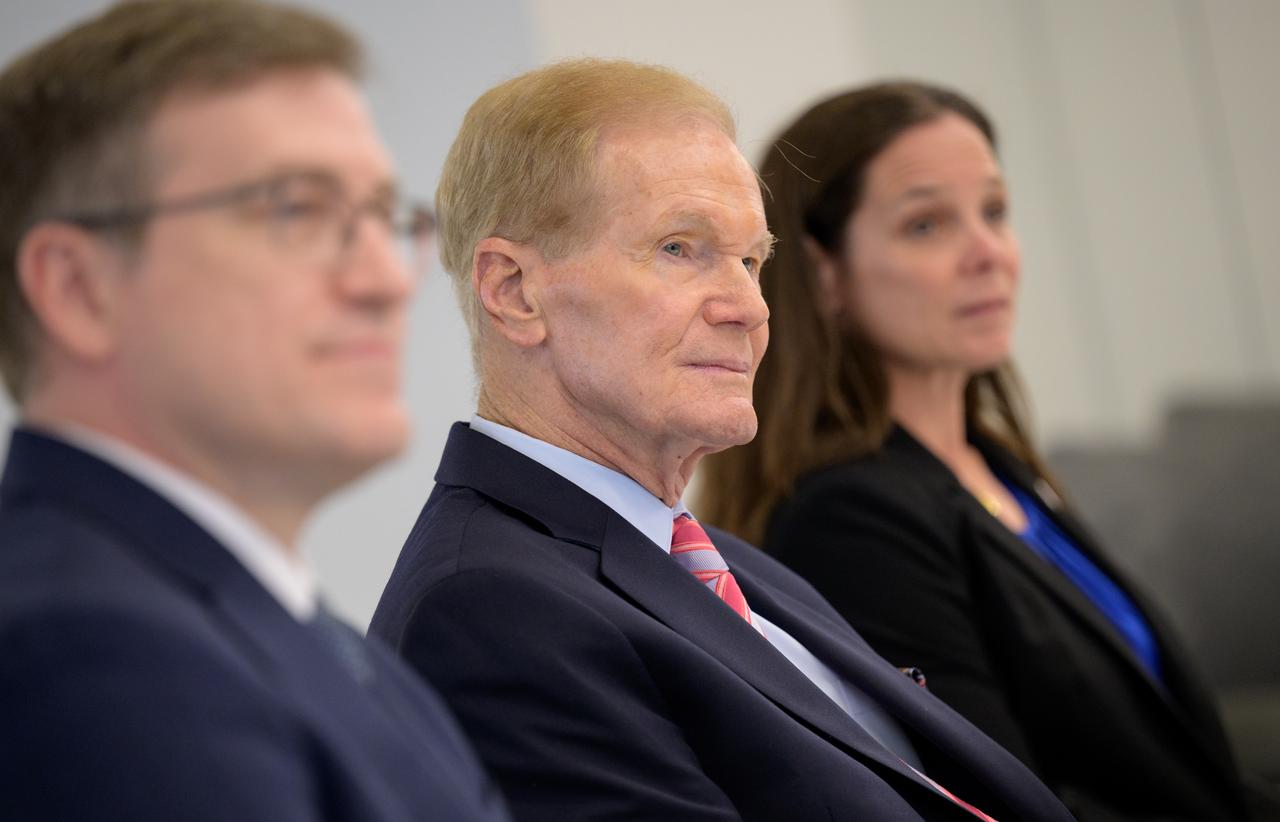

NASA Pressurized Rover Project Manager Danny Newswander, left, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, and NASA Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Program Lara Kearney, right, discuss the historic agreement signed April 9th at NASA Headquarters, between the United States and Japan to advance sustainable human exploration of the Moon, Wednesday, April 10, 2024, at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) offices in Washington. Under the agreement, Japan will design, develop, and operate a pressurized rover for crewed and uncrewed exploration on the Moon. NASA will provide the launch and delivery of the rover to the Moon as well as two Japanese astronaut missions to the lunar surface. Photo Credit: Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
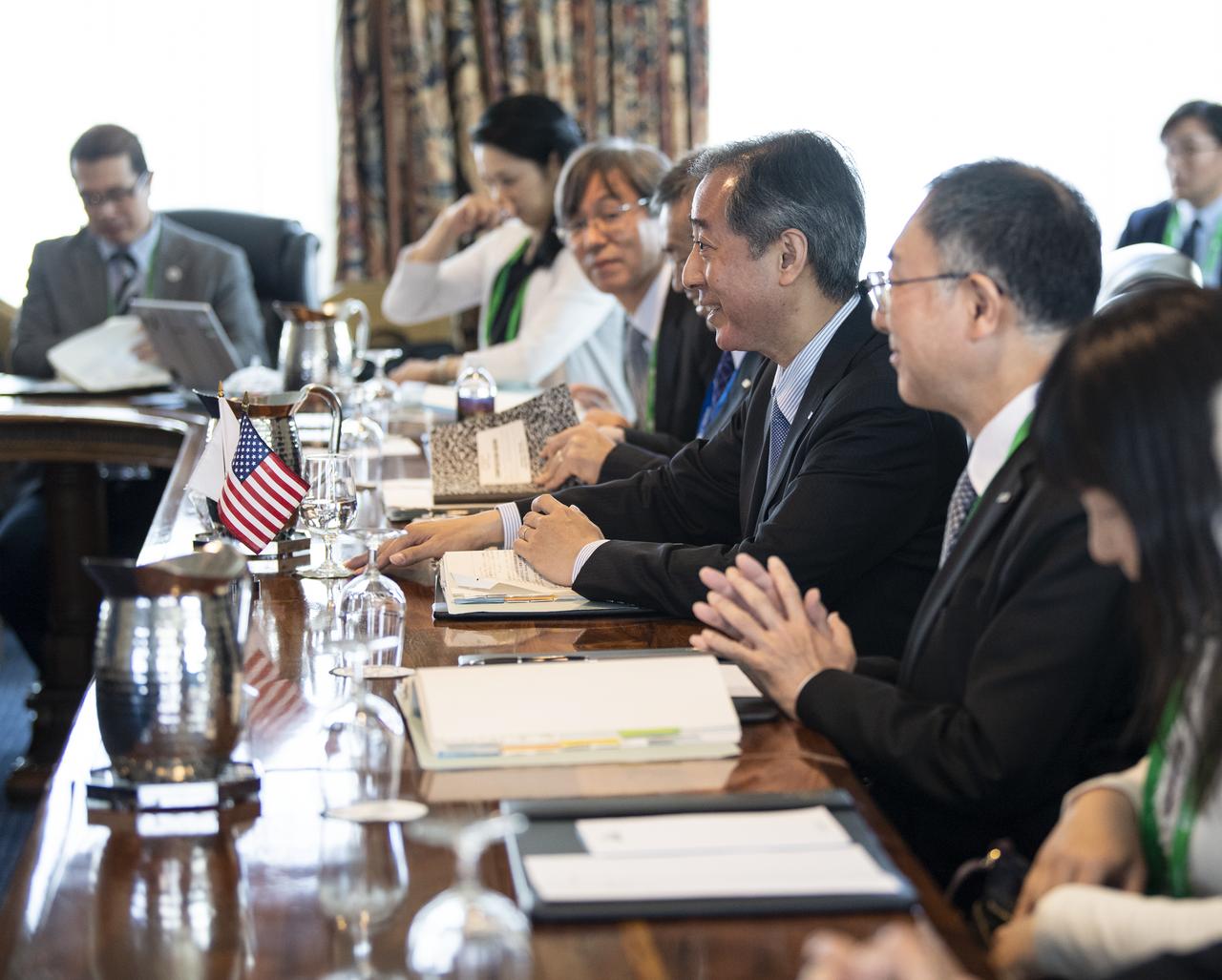

Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) President, Hiroshi Yamakawa, third from right, speaks about opportunities to work with NASA in human and robotic exploration at the lunar surface and around the Moon, at the Space Symposium, Monday, April 8, 2019 in Colorado Springs, Colorado. They also discussed the two agencies’ asteroid sample return missions, OSIRIS-REx AND Hayabusa-2, and how they are looking forward to sharing the data and results from those missions. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
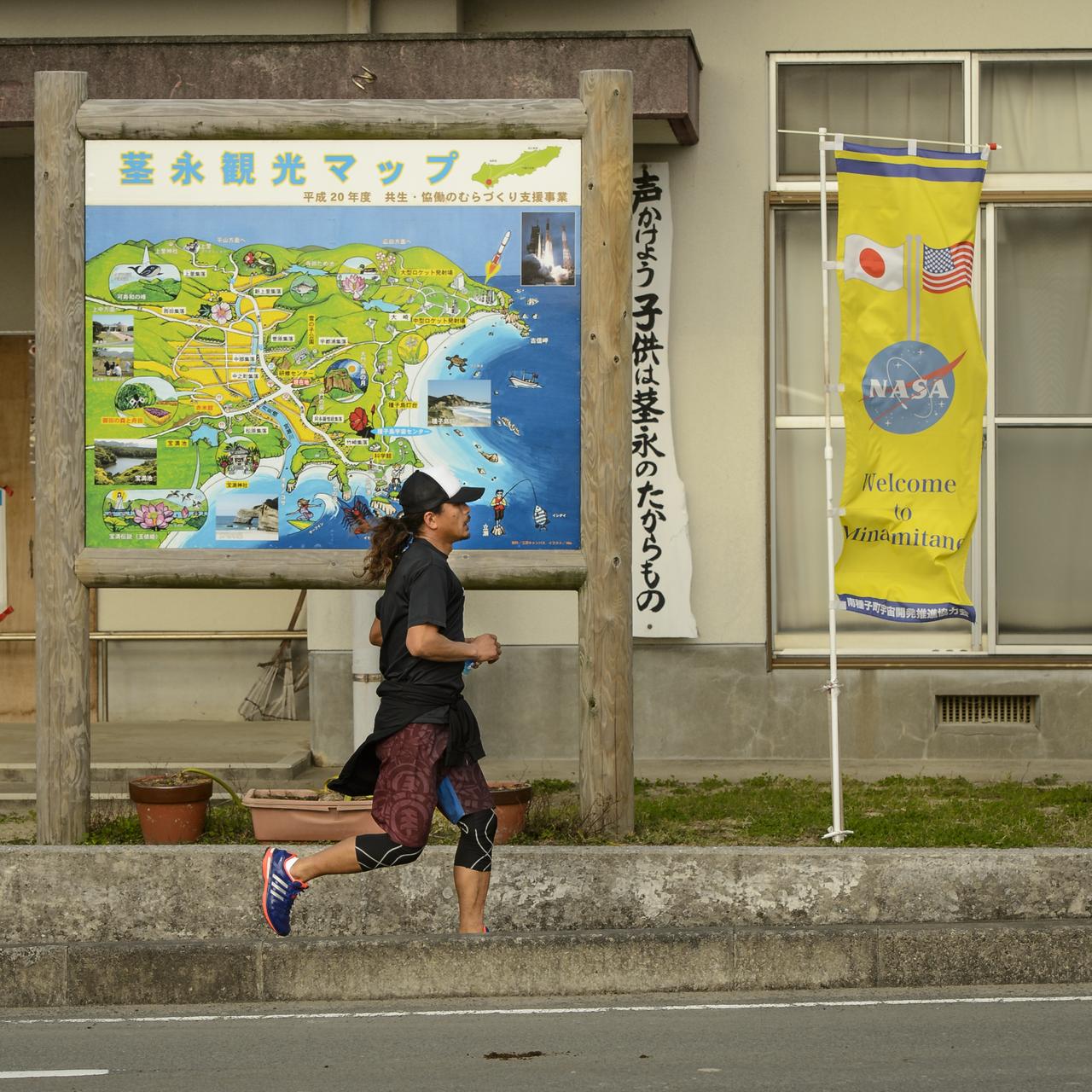

A jogger runs past a sign welcoming NASA and other visitors to Minamitane Town on Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Support and medical team members from NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), and Roscosmos wait to board the helicopter with NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli, ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Satoshi Furukawa, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Konstantin Borisov to return to Pensacola, Florida a few hours after landing in the Gulf of Mexico, Tuesday, March 12, 2024, onboard the SpaceX support ship MEGAN. Moghbeli, Mogensen, Furukawa, and Borisov are returning after nearly six-months in space as part of Expedition 70 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
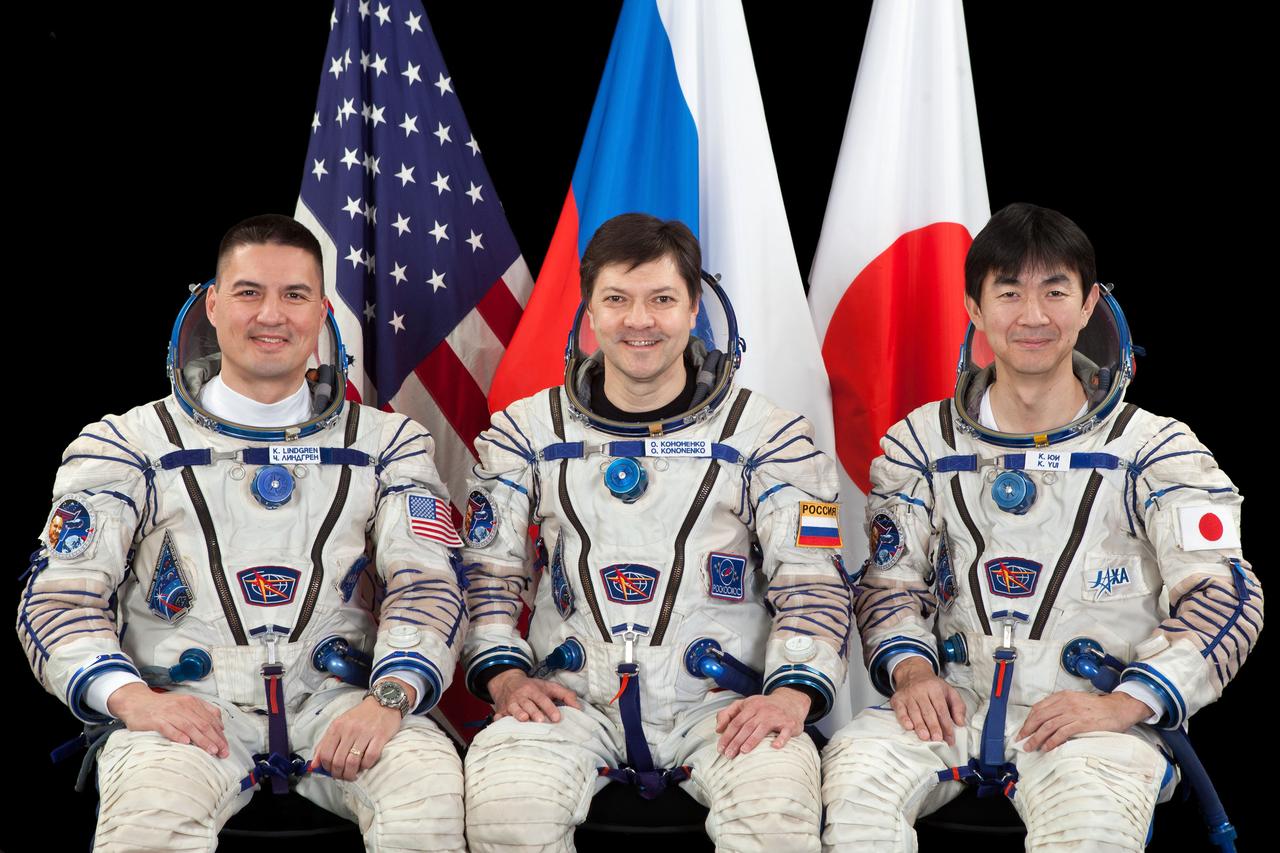

JSC2015E053687 (04/30/2015) --- Expedition 44 crew members NASA astronaut Kjell Lindgren (left), Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko (center) and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Kimiya Yui.
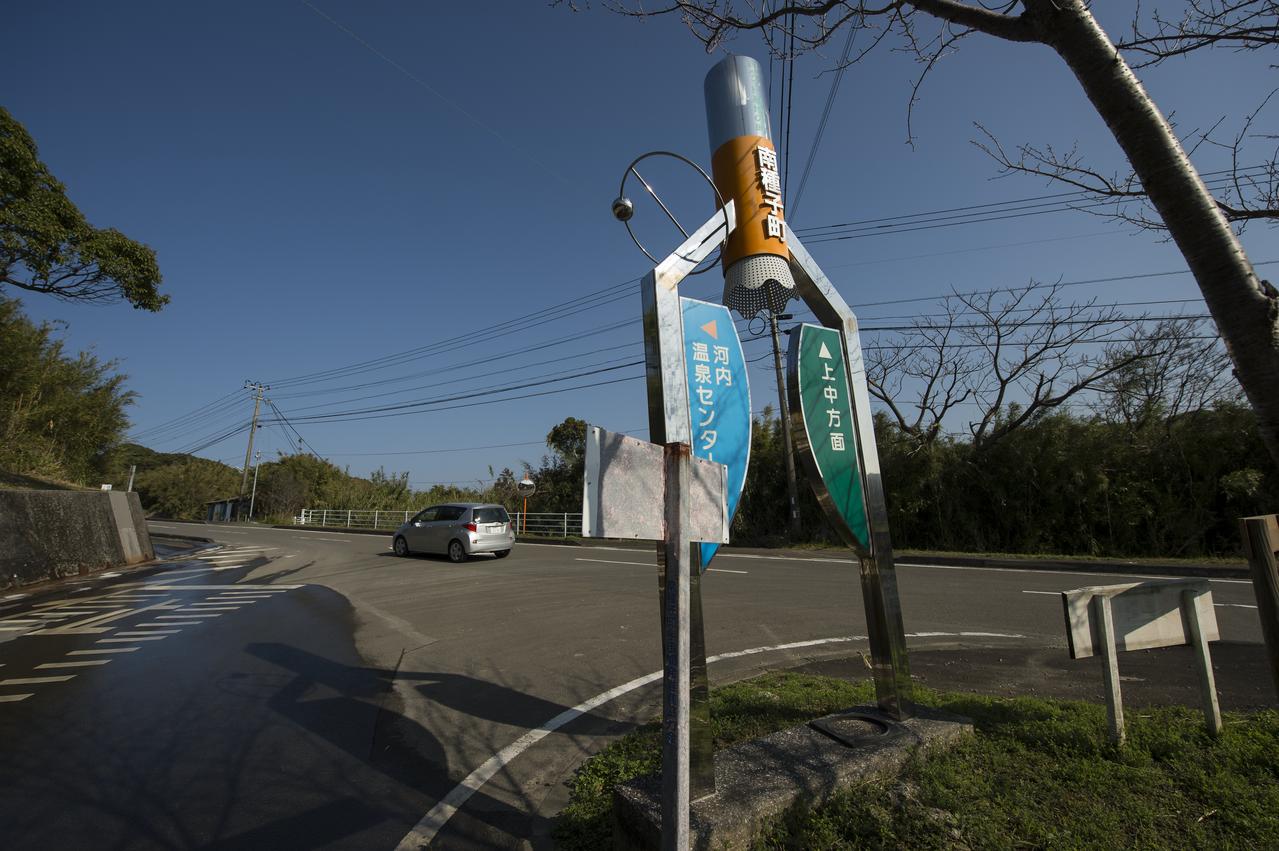

Space themed signs are seen along the roads to and from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC), Saturday, Feb. 22, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. A launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for Feb. 28, 2014 from the space center. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
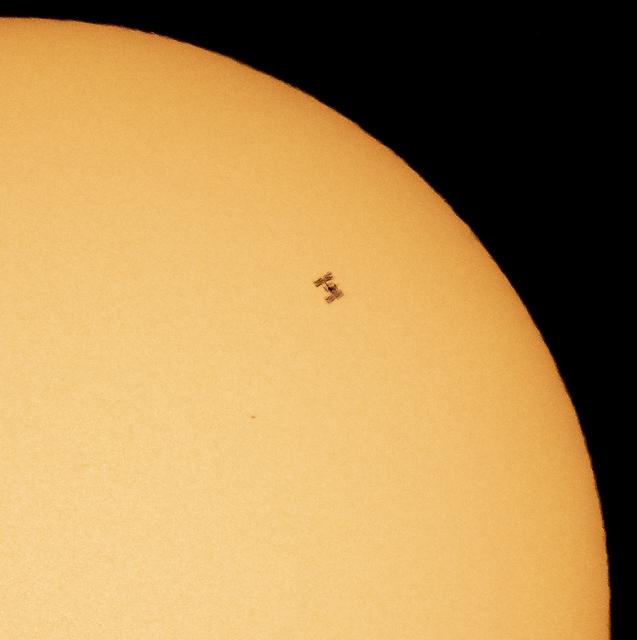

The International Space Station, with a crew of seven aboard, is seen in silhouette as it transits the sun at roughly five miles per second, Friday, April 23, 2021, as seen from Nottingham, Maryland. Aboard are: NASA astronauts Shannon Walker, Mike Hopkins, Victor Glover, Mark Vande Hei; Roscosmos cosmonauts Oleg Novitskiy, Pyotr Dubrov; and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi. Joining the crew aboard station tomorrow will be Crew-2 mission crew members: NASA astronauts Shane Kimbrough and Megan McArthur, JAXA astronaut Akihiko Hoshide, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Thomas Pesquet. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
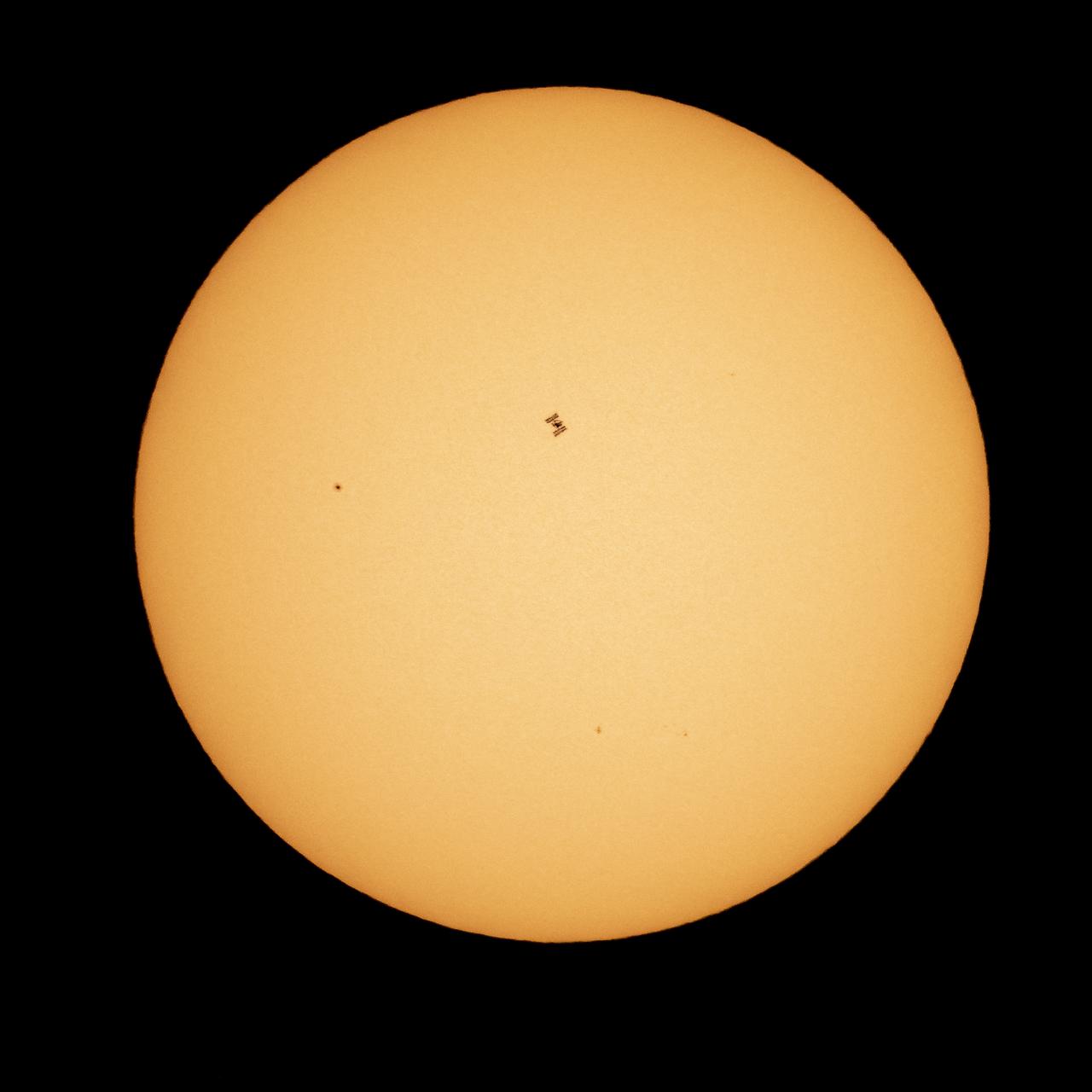

The International Space Station, with a crew of seven aboard, is seen in silhouette as it transits the sun at roughly five miles per second, Friday, April 23, 2021, as seen from Nottingham, Maryland. Aboard are: NASA astronauts Shannon Walker, Mike Hopkins, Victor Glover, Mark Vande Hei; Roscosmos cosmonauts Oleg Novitskiy, Pyotr Dubrov; and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi. Joining the crew aboard station tomorrow will be Crew-2 mission crew members: NASA astronauts Shane Kimbrough and Megan McArthur, JAXA astronaut Akihiko Hoshide, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Thomas Pesquet. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Expedition 52 backup crew member Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) is seen during a crew press conference at the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center (GCTC), Monday, July 10, 2017 in Star City, Russia. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
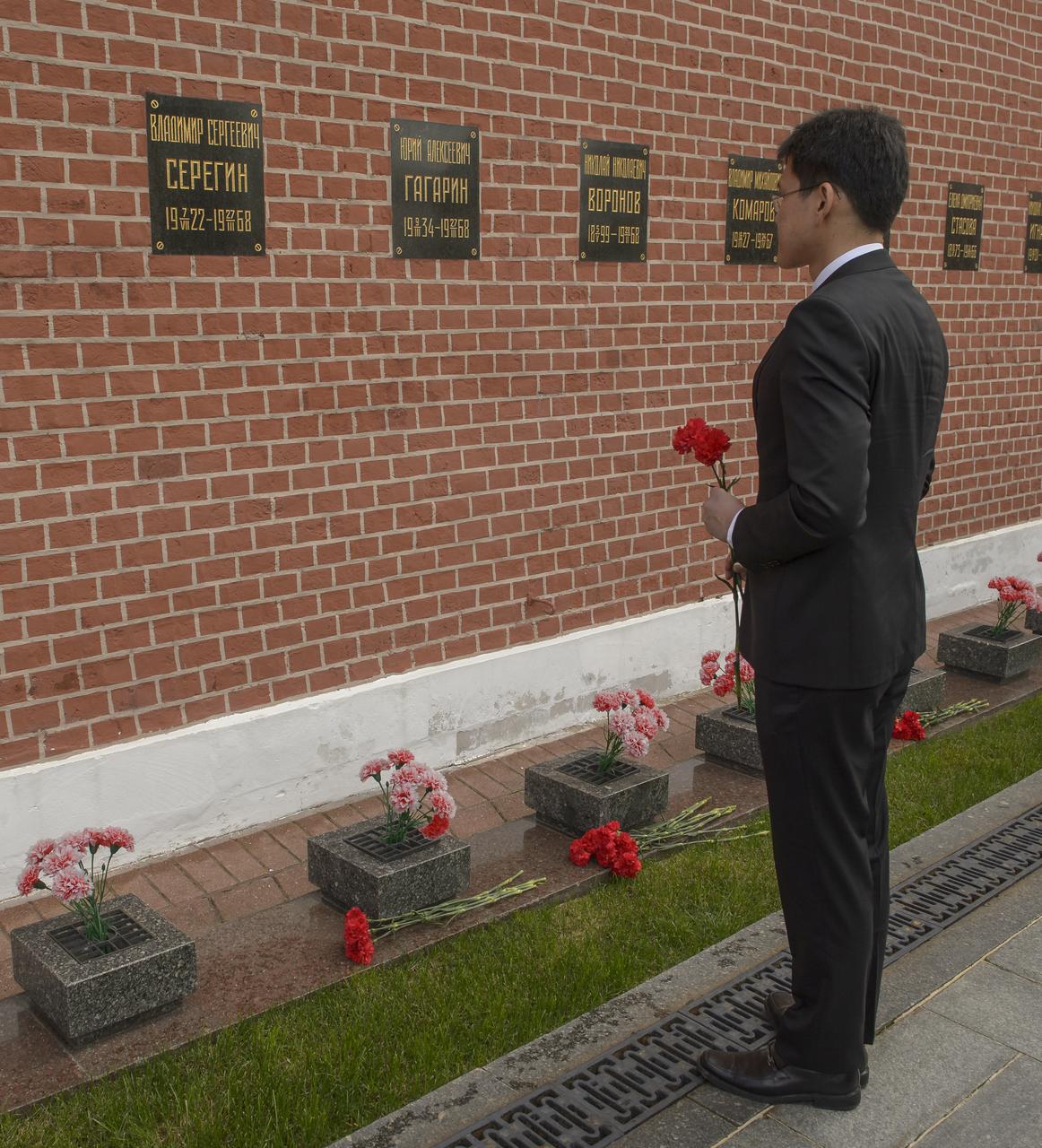

Expedition 52 backup crew member Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) lays roses at the site where Russian space icons are interred as part of traditional pre-launch ceremonies, Monday, July 10, 2017 in Moscow. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
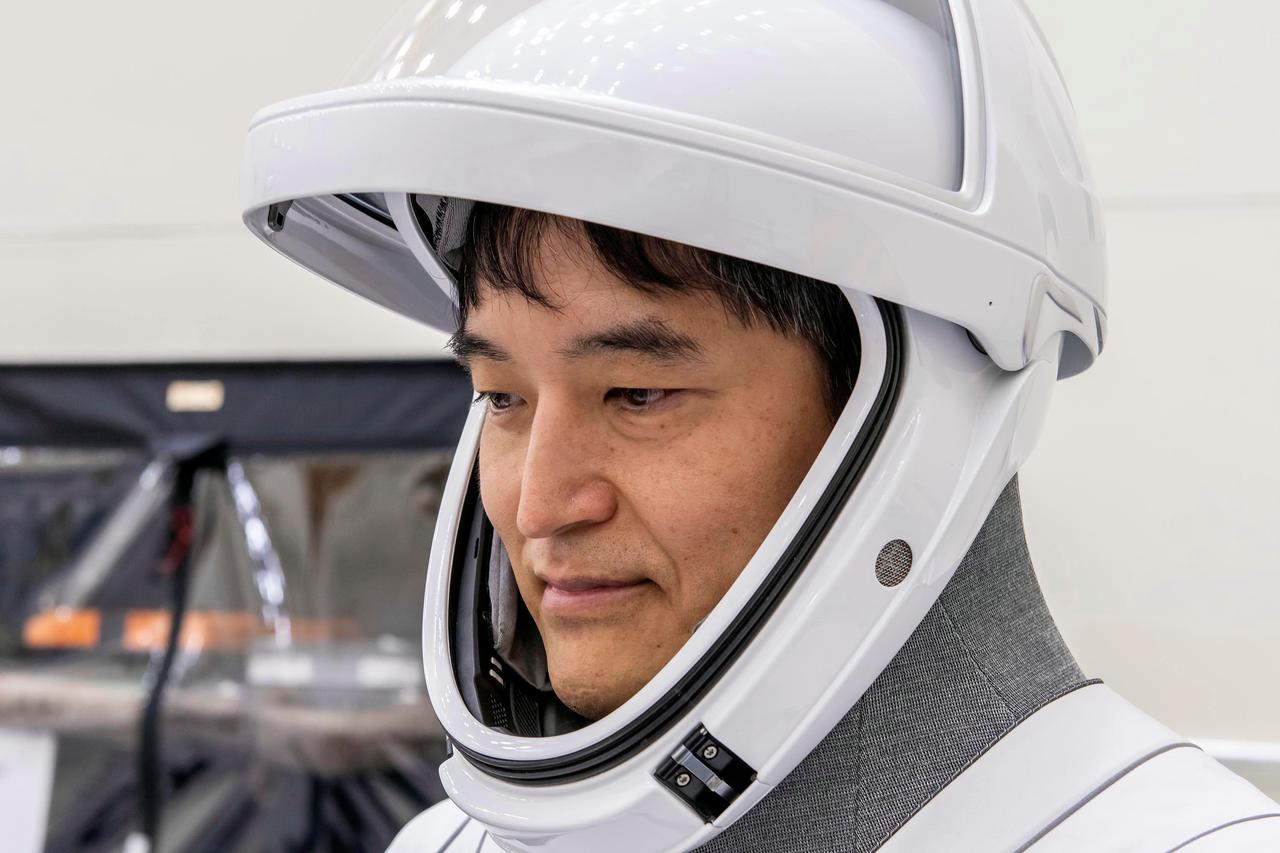

jsc2025e012273 - (February 17, 2025) --- SpaceX Crew-10 Mission Specialist Takuya Onishi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) in his flight suit at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

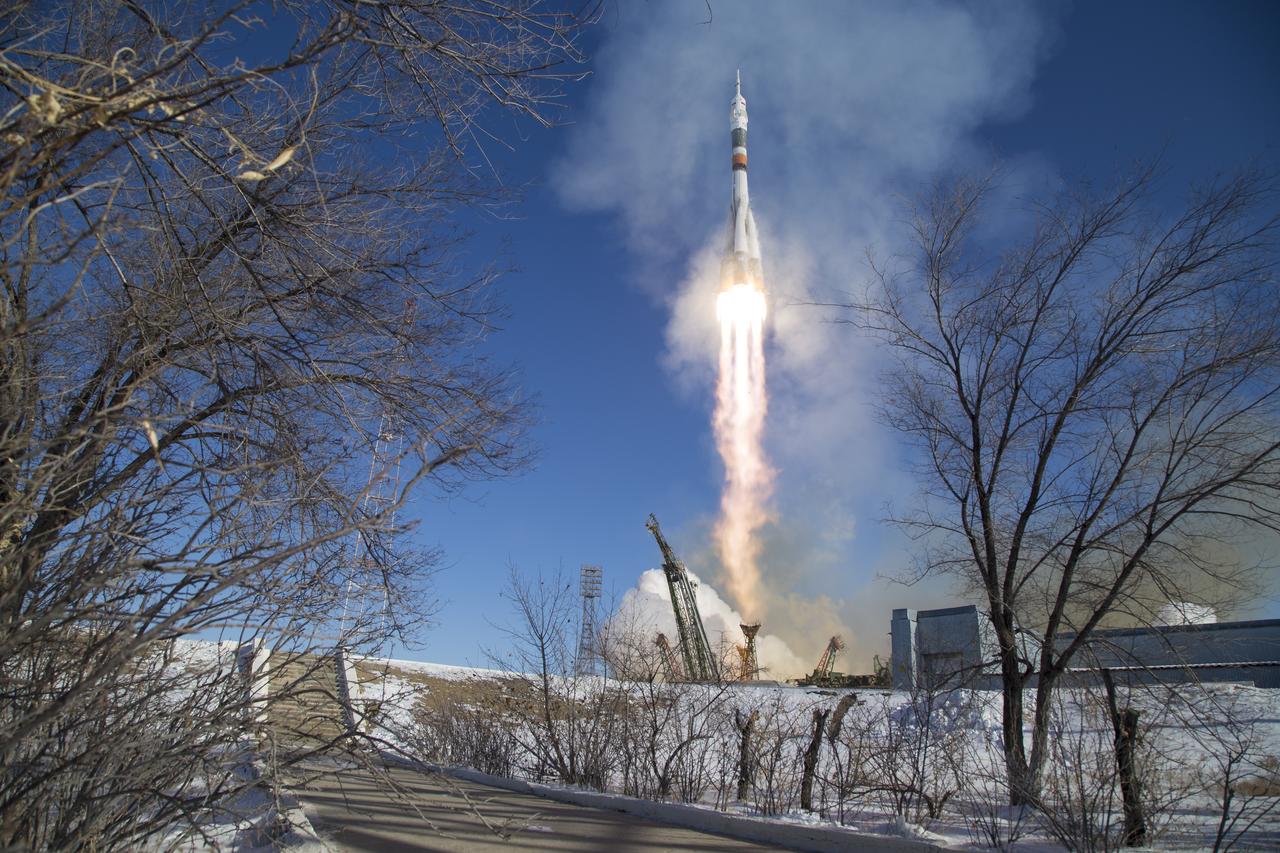
The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
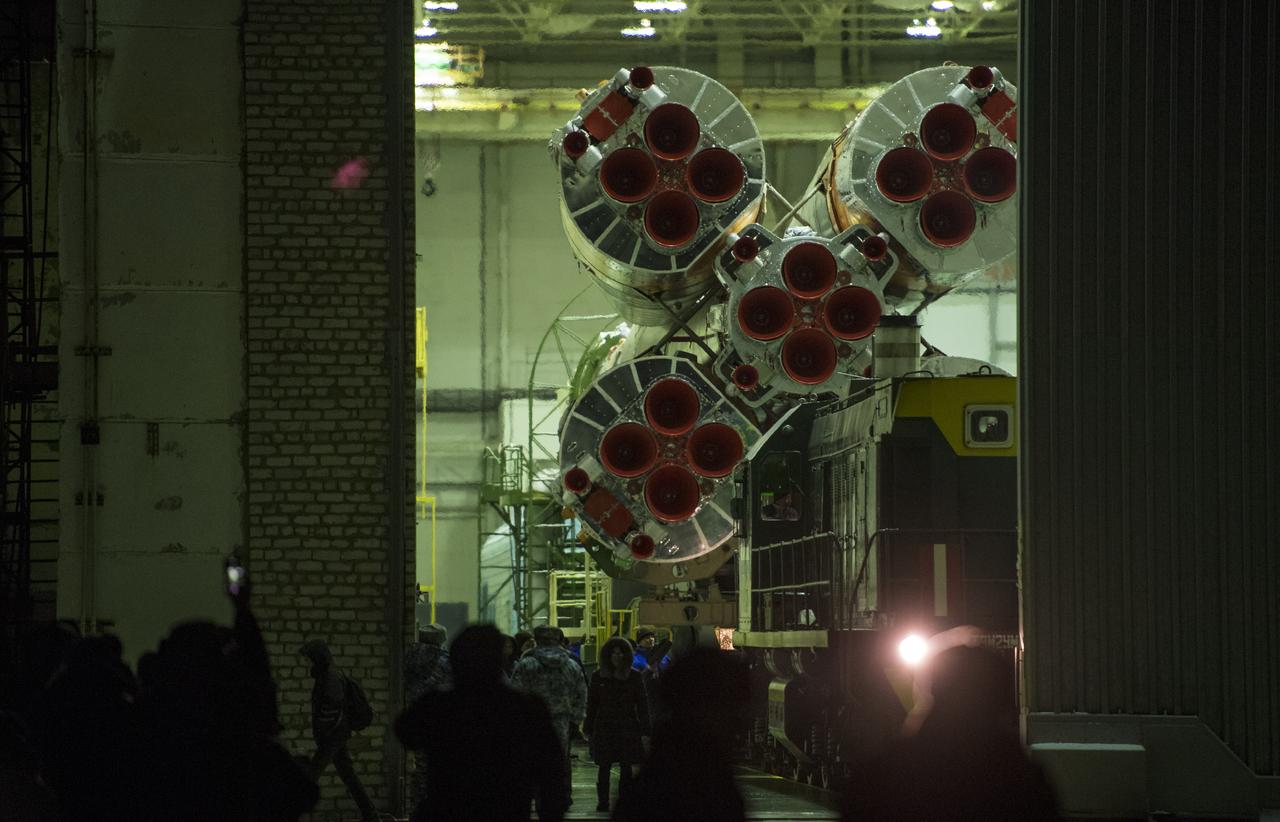

The Soyuz rocket is rolled out by train to the launch pad, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The Soyuz rocket is rolled out by train to the launch pad, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
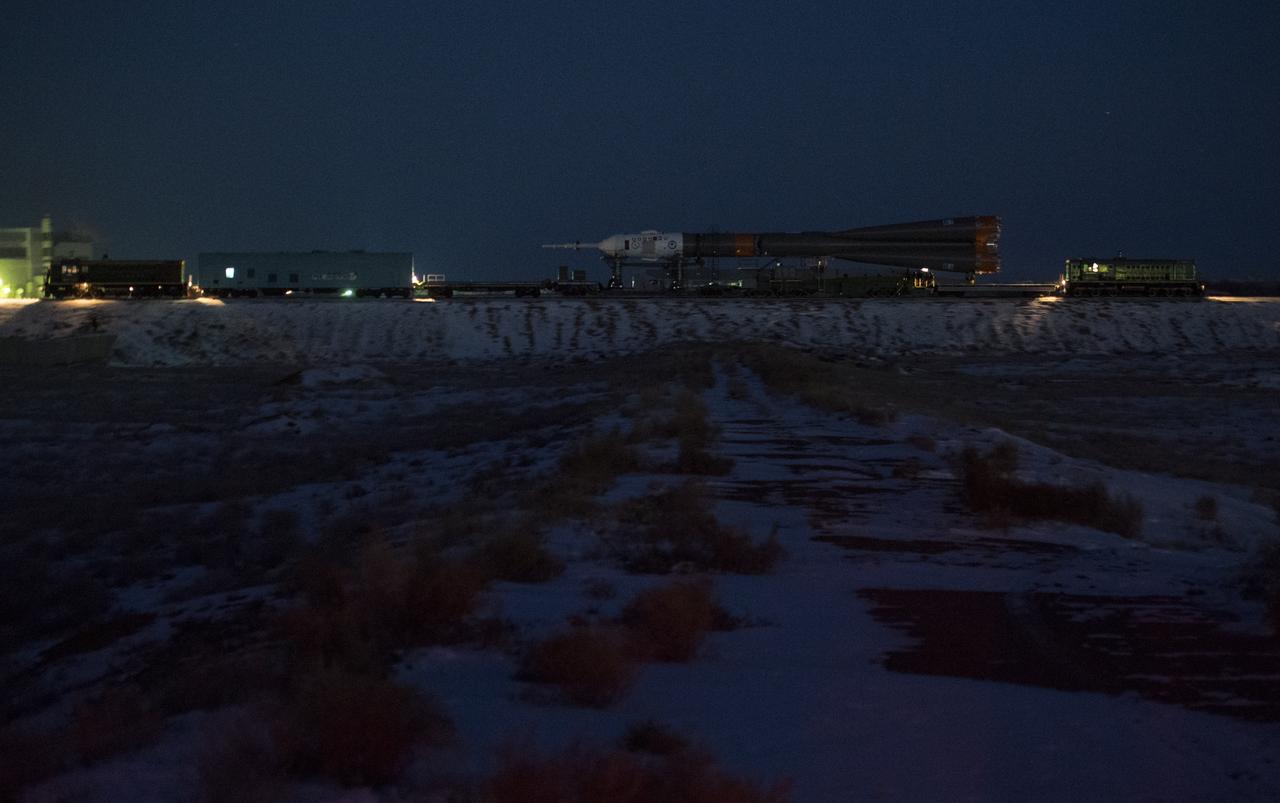

The Soyuz rocket is rolled out by train to the launch pad, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
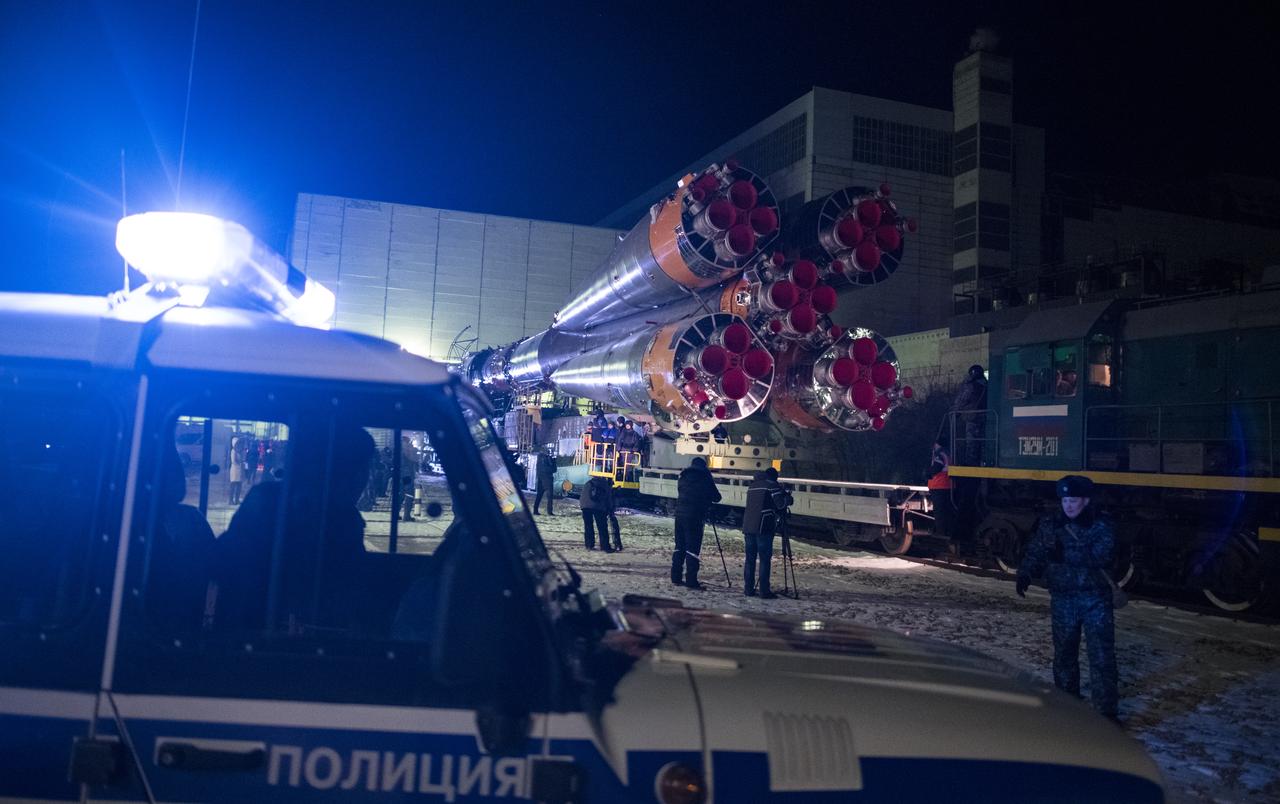

The Soyuz rocket is rolled out by train to the launch pad, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
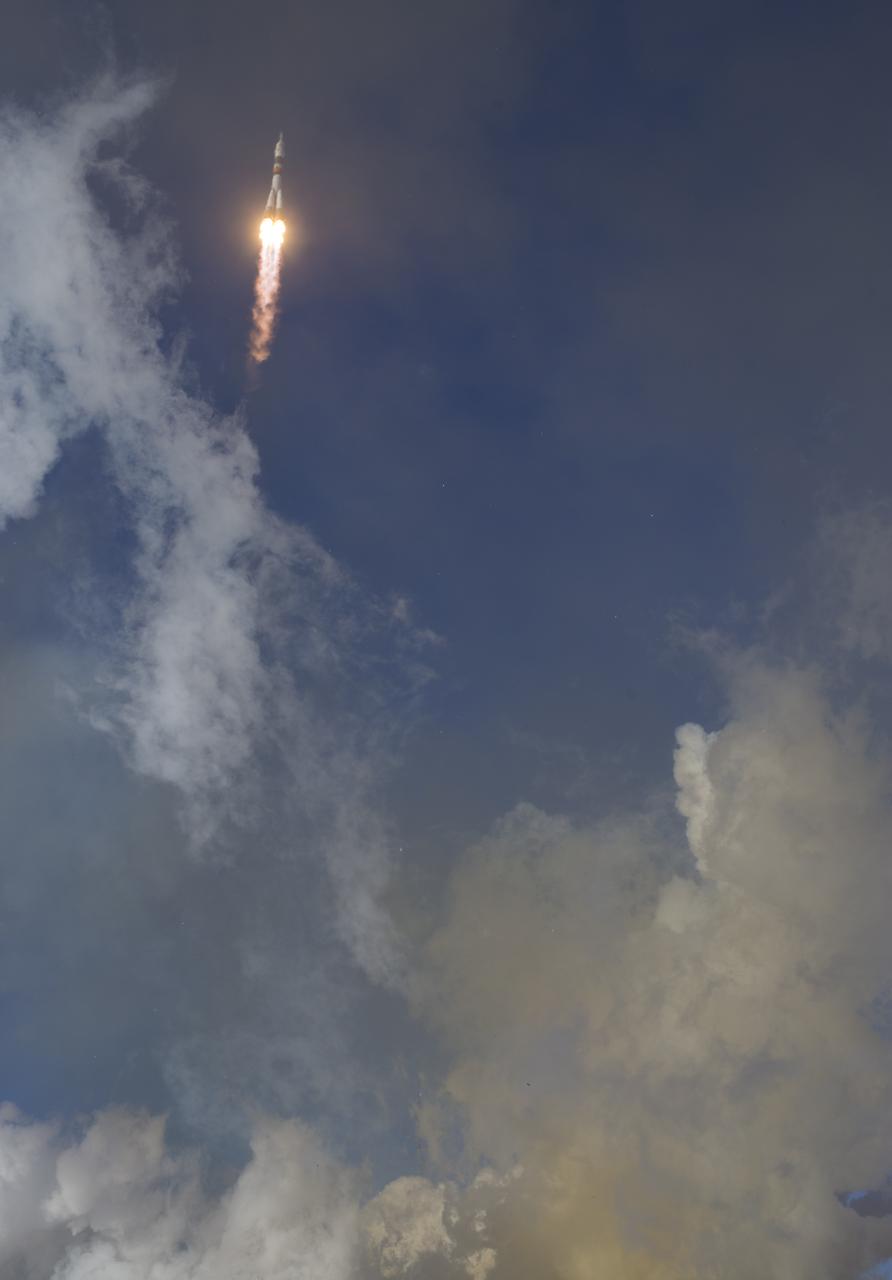

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
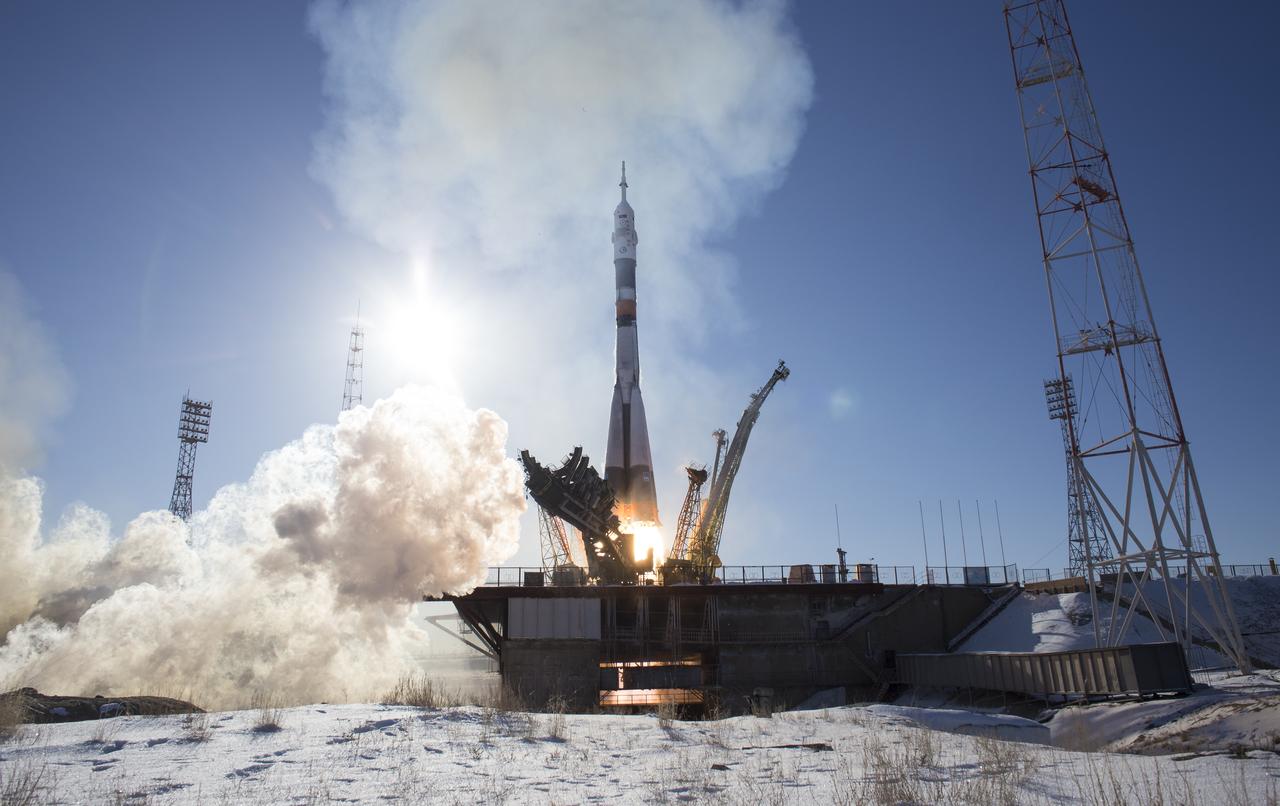

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
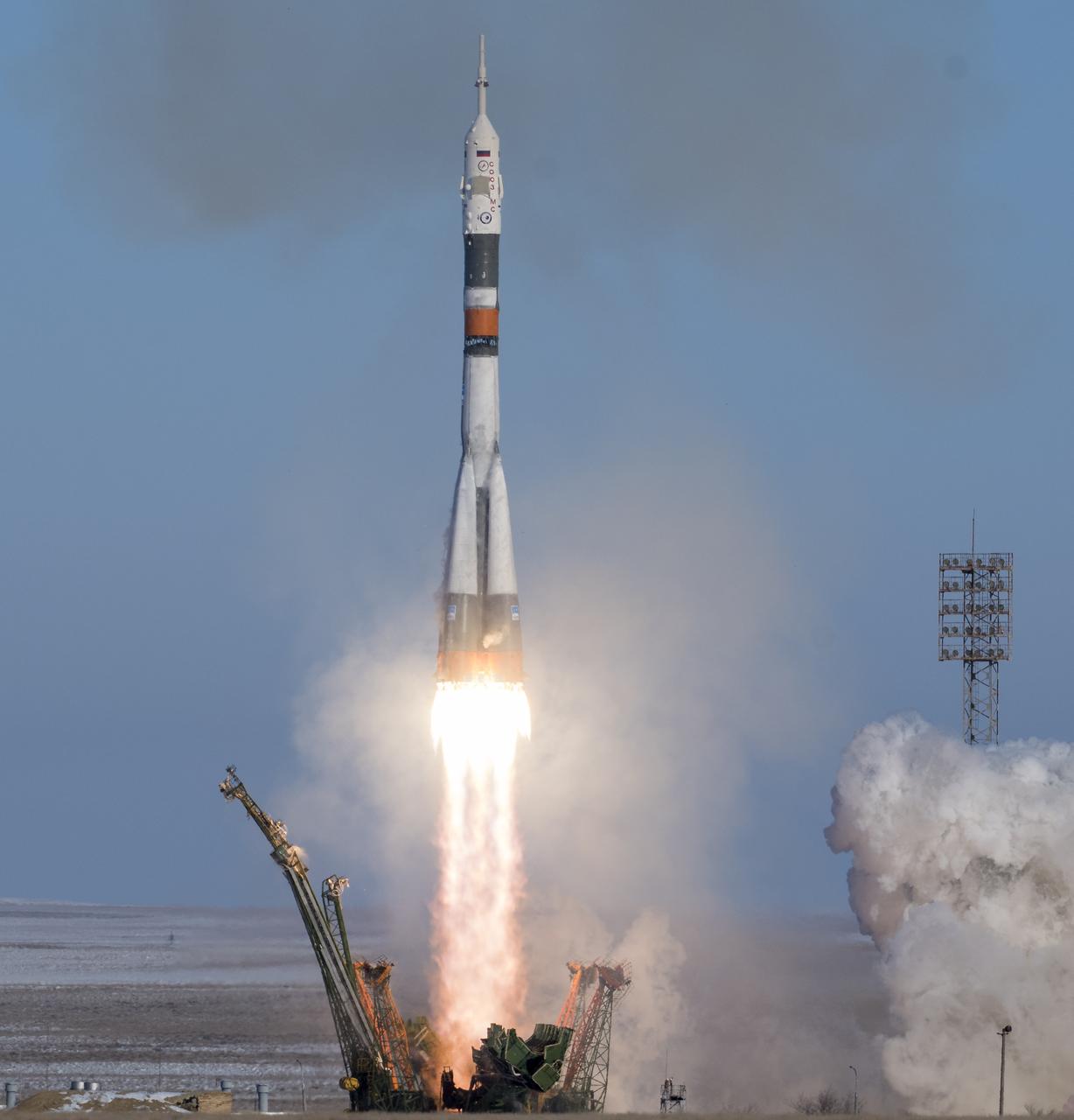

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
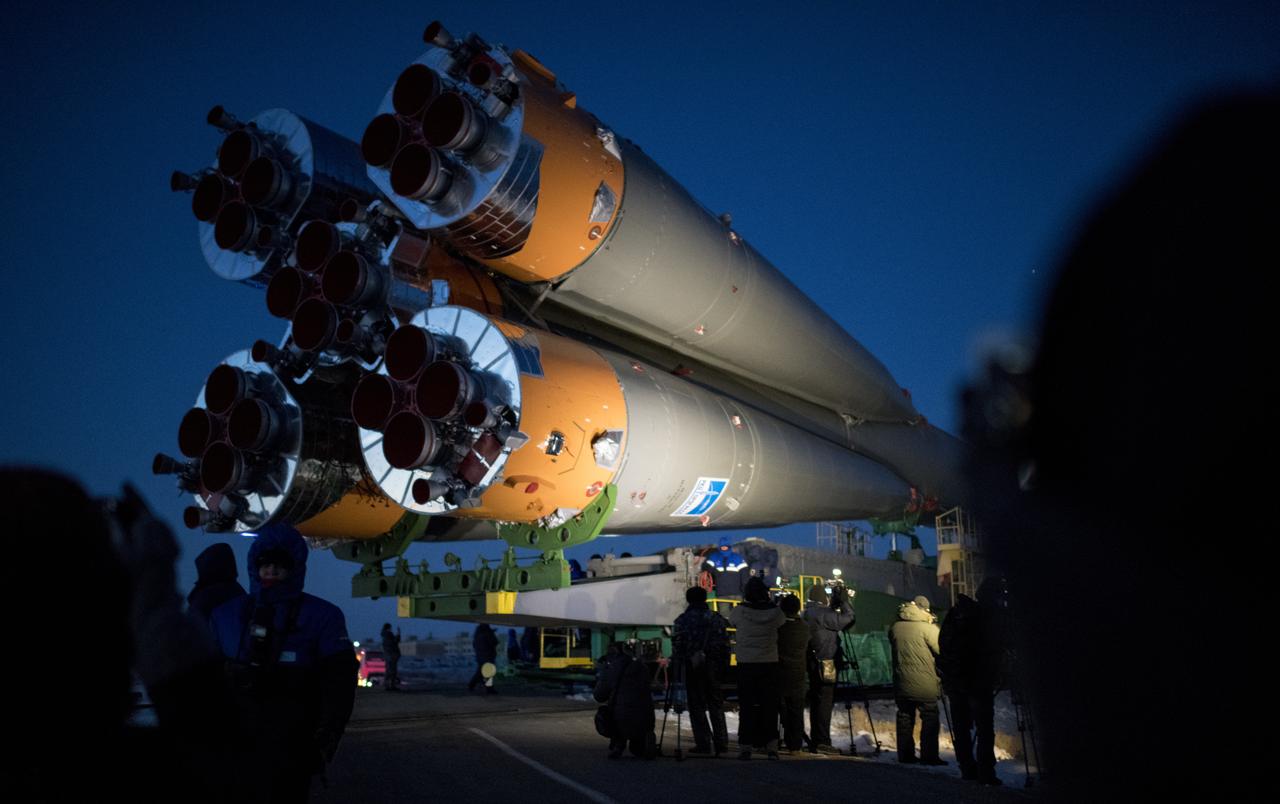

The Soyuz rocket is rolled out by train to the launch pad, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), (iptcdow}, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is seen on the launch pad at sunrise on, Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Norishige Kanai, of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), and flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA launched at 2:21 a.m. EST (1:21 p.m. Baikonur) and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
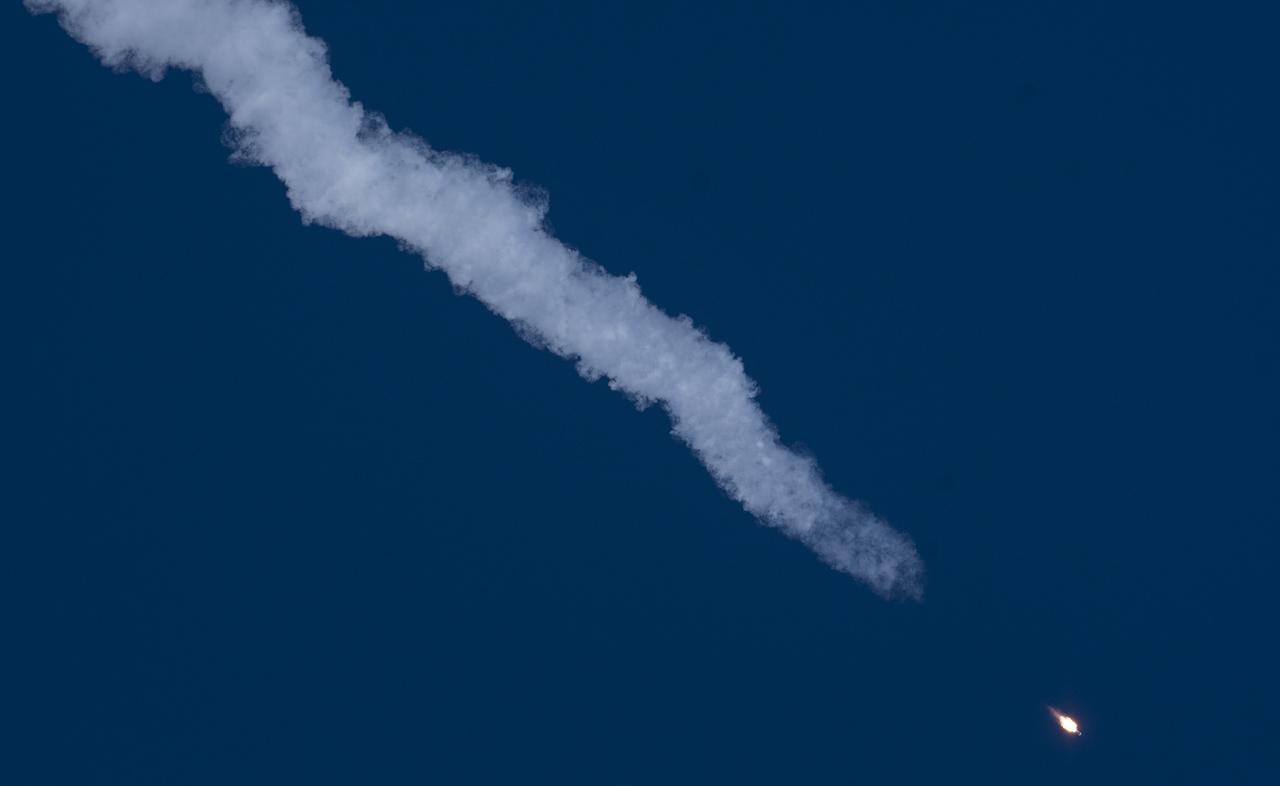

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The Soyuz rocket is rolled out by train to the launch pad, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
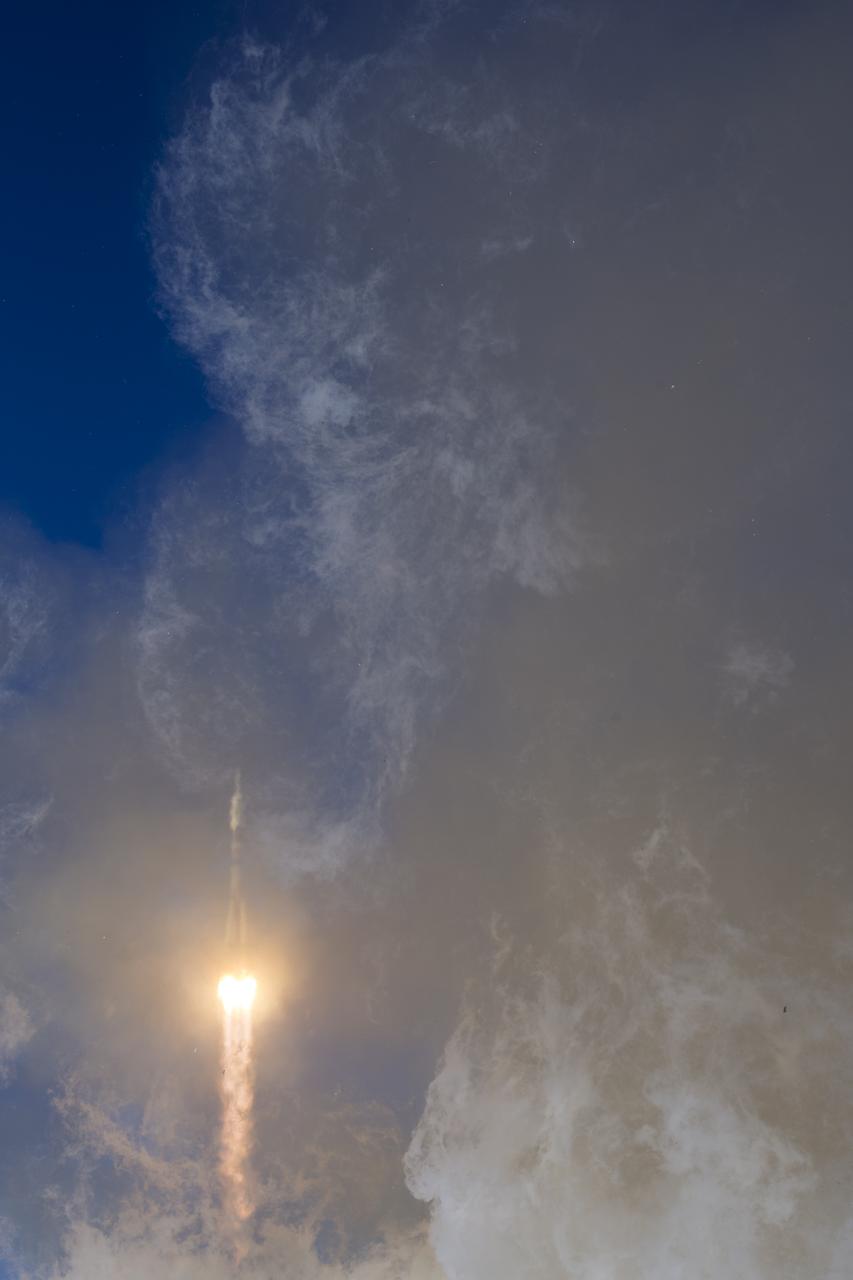

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
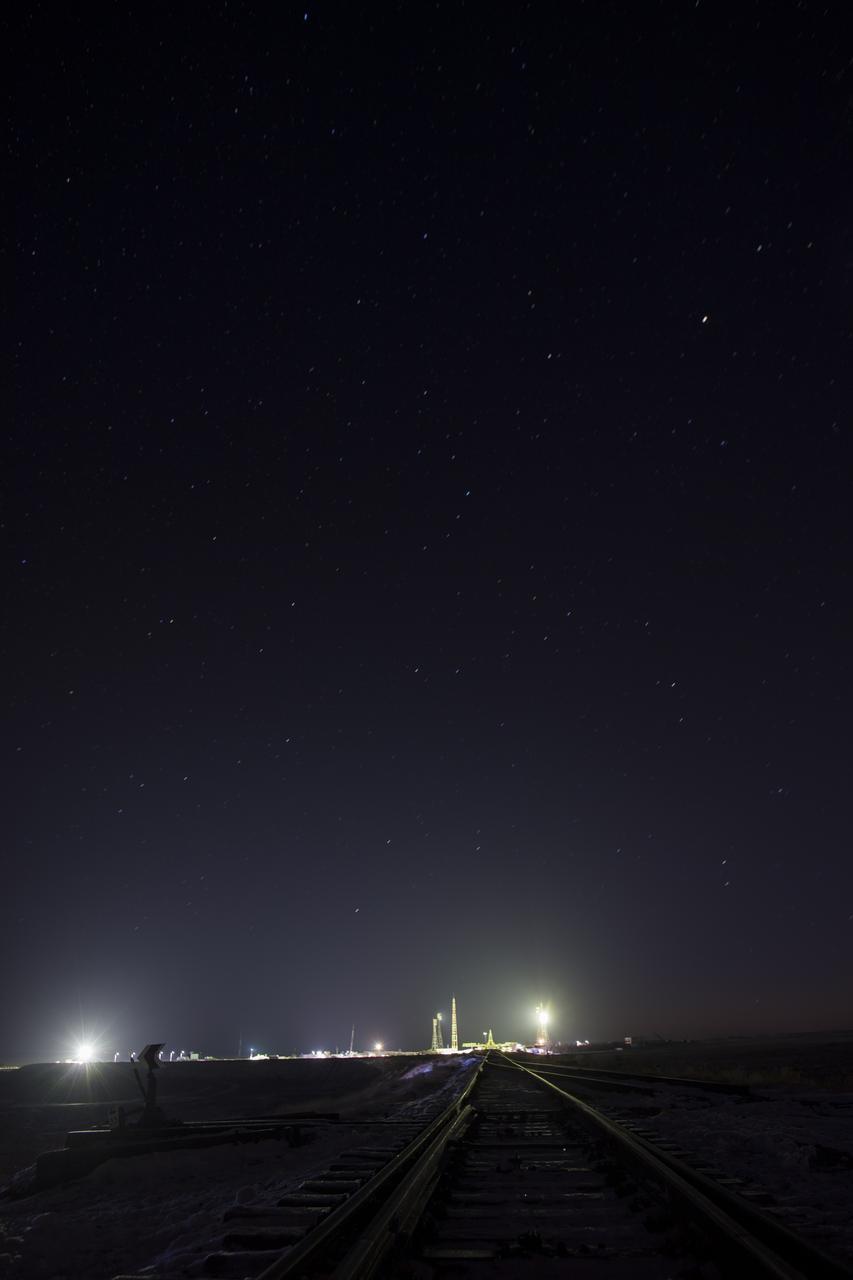

The launch pad is seen in this one minute exposure, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
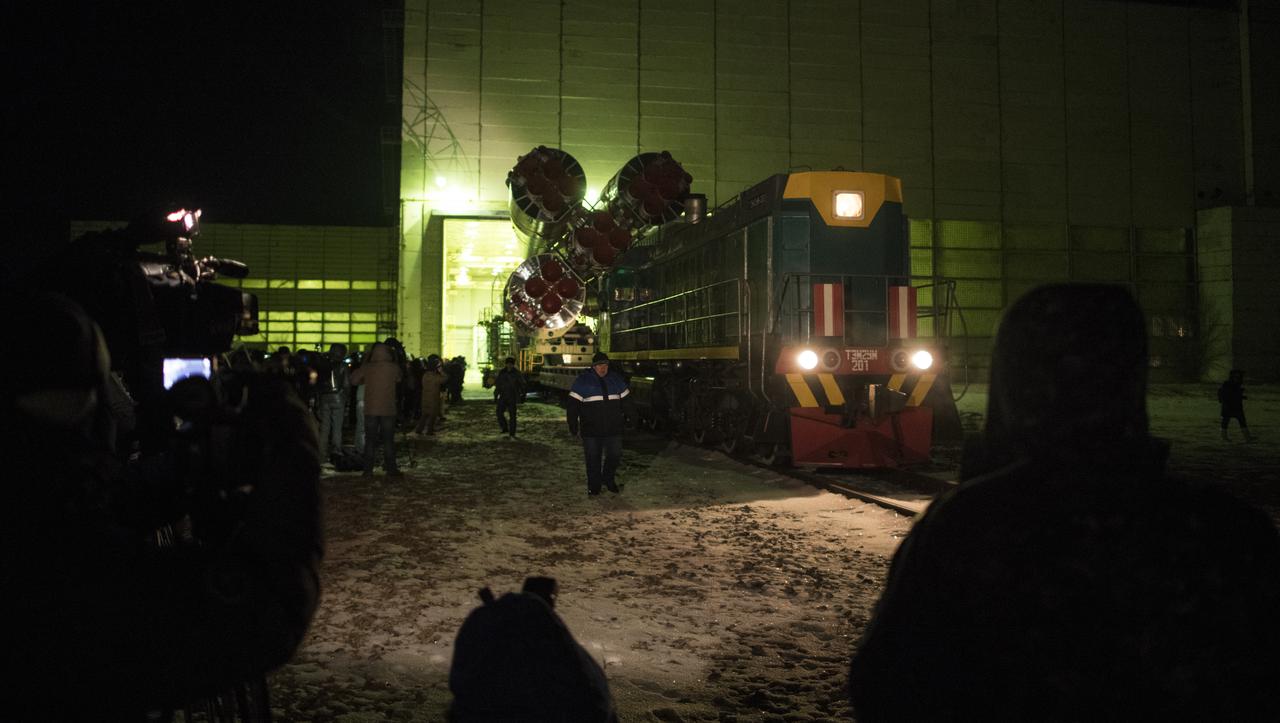

The Soyuz rocket is rolled out by train to the launch pad, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The Soyuz rocket is rolled out by train to the launch pad, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
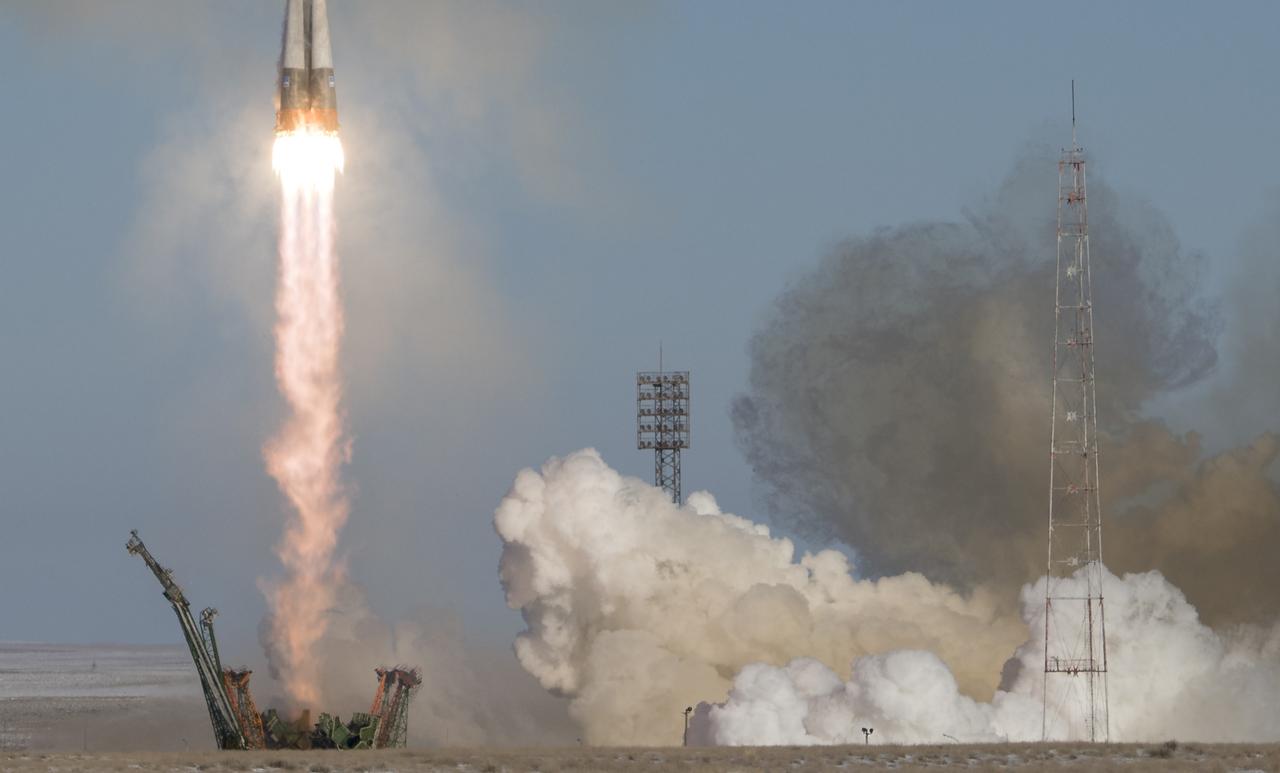

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
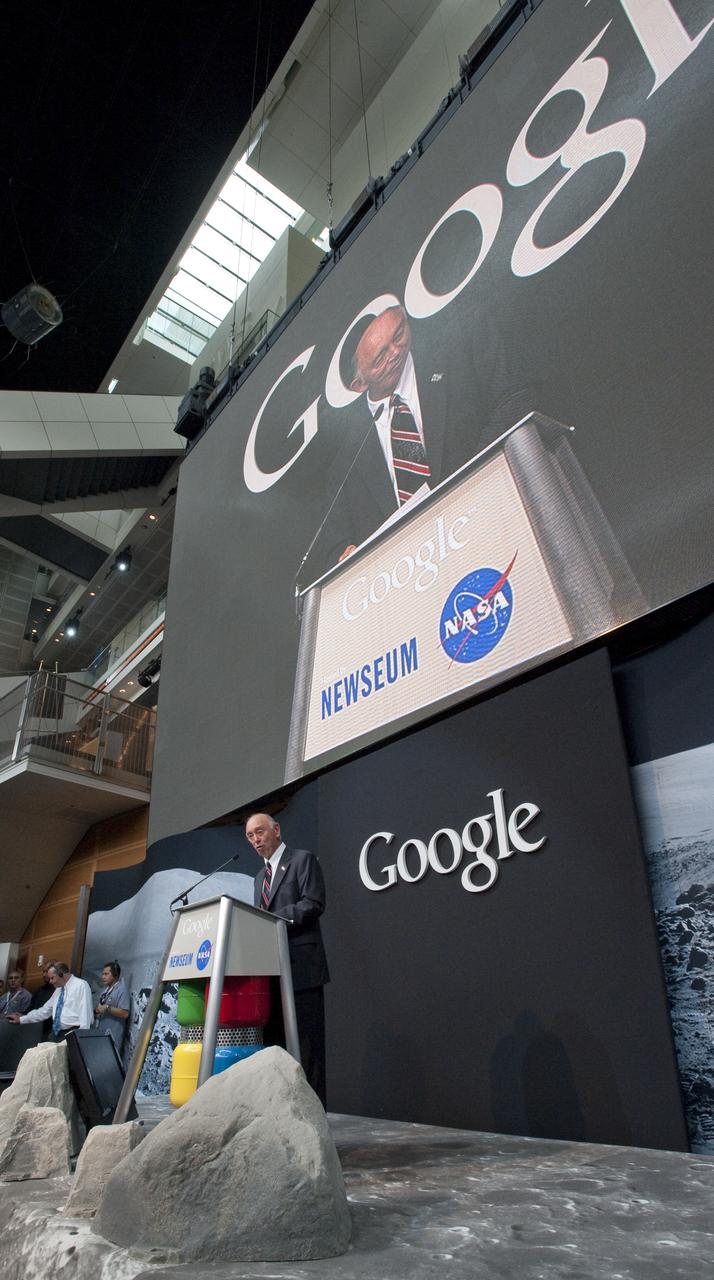

Yoshinori Yoshimura, a respresentative from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), speaks during a press conference, Monday, July 20, 2009, announcing the launch of Moon in Google Earth, an immersive 3D atlas of the Moon, accessible within Google Earth 5.0, Monday, July 20, 2009, at the Newseum in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
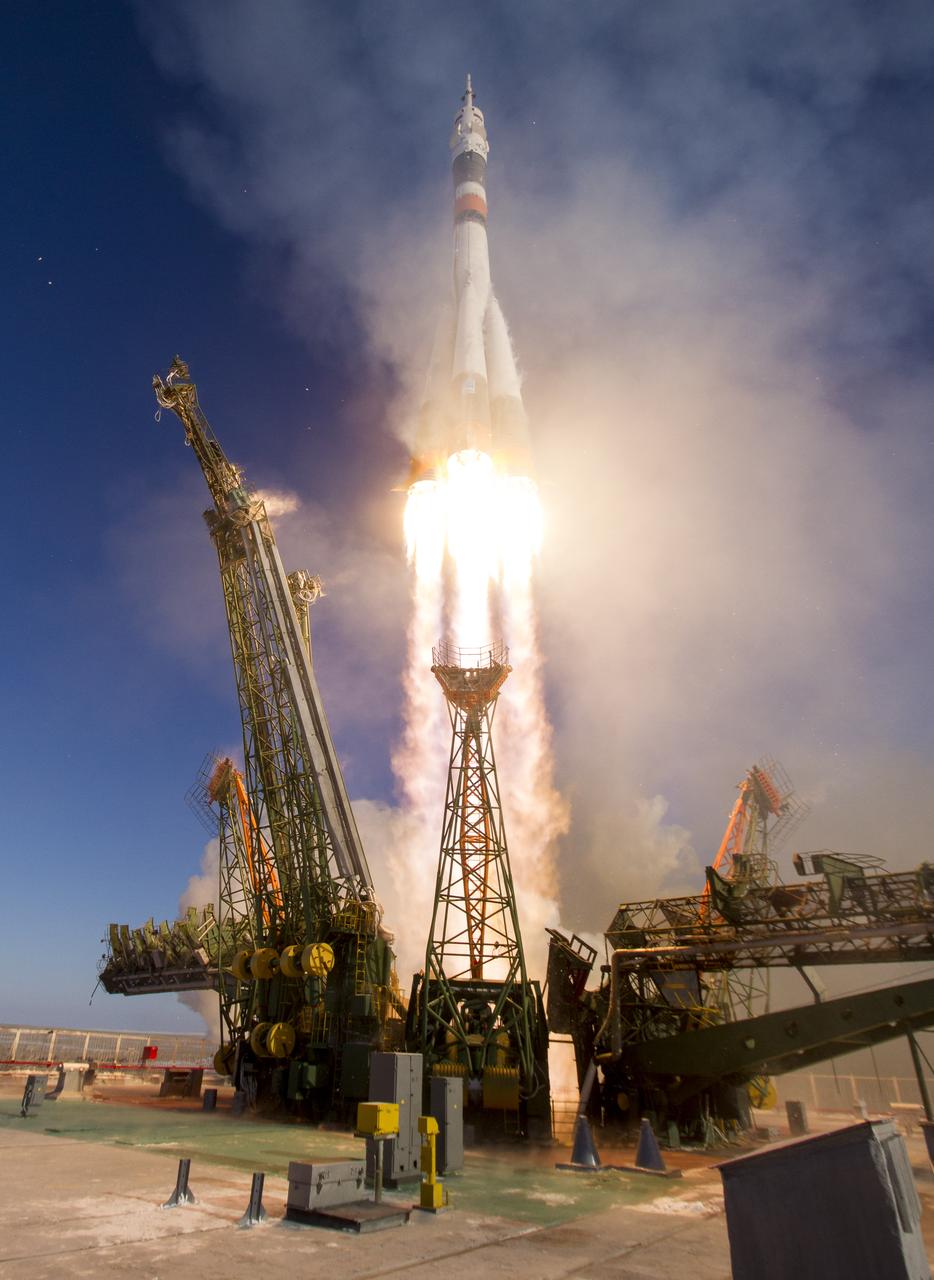

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
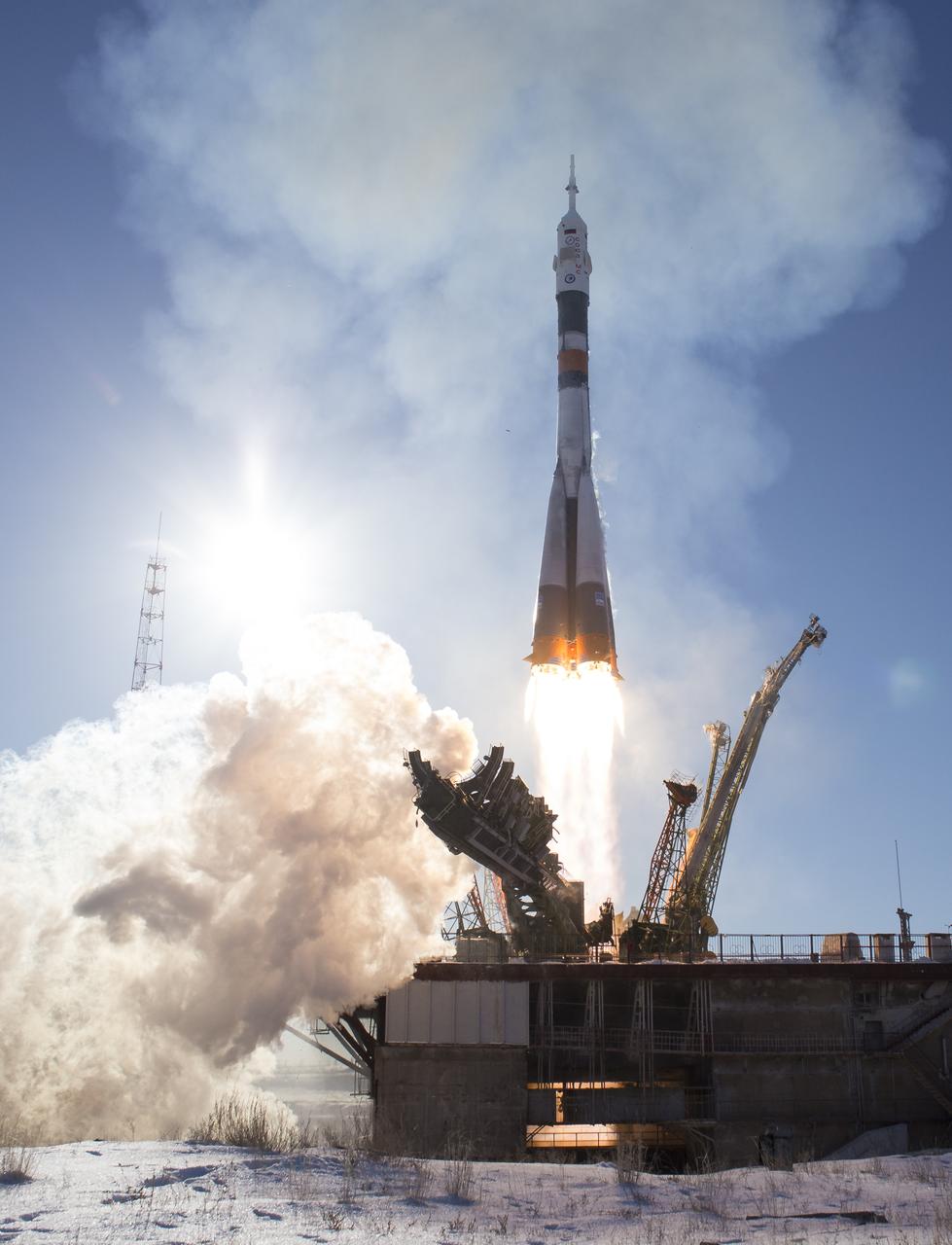

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
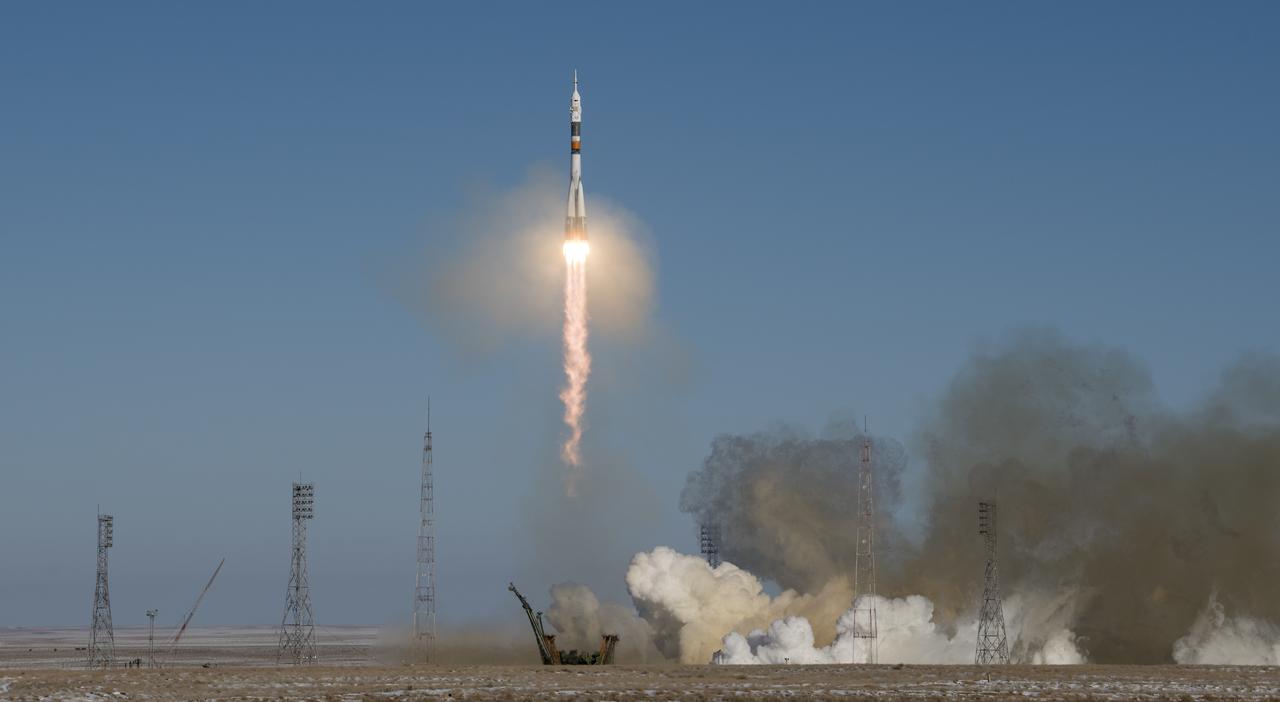

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The Soyuz rocket is rolled out by train to the launch pad, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The Soyuz rocket is rolled out by train to the launch pad, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
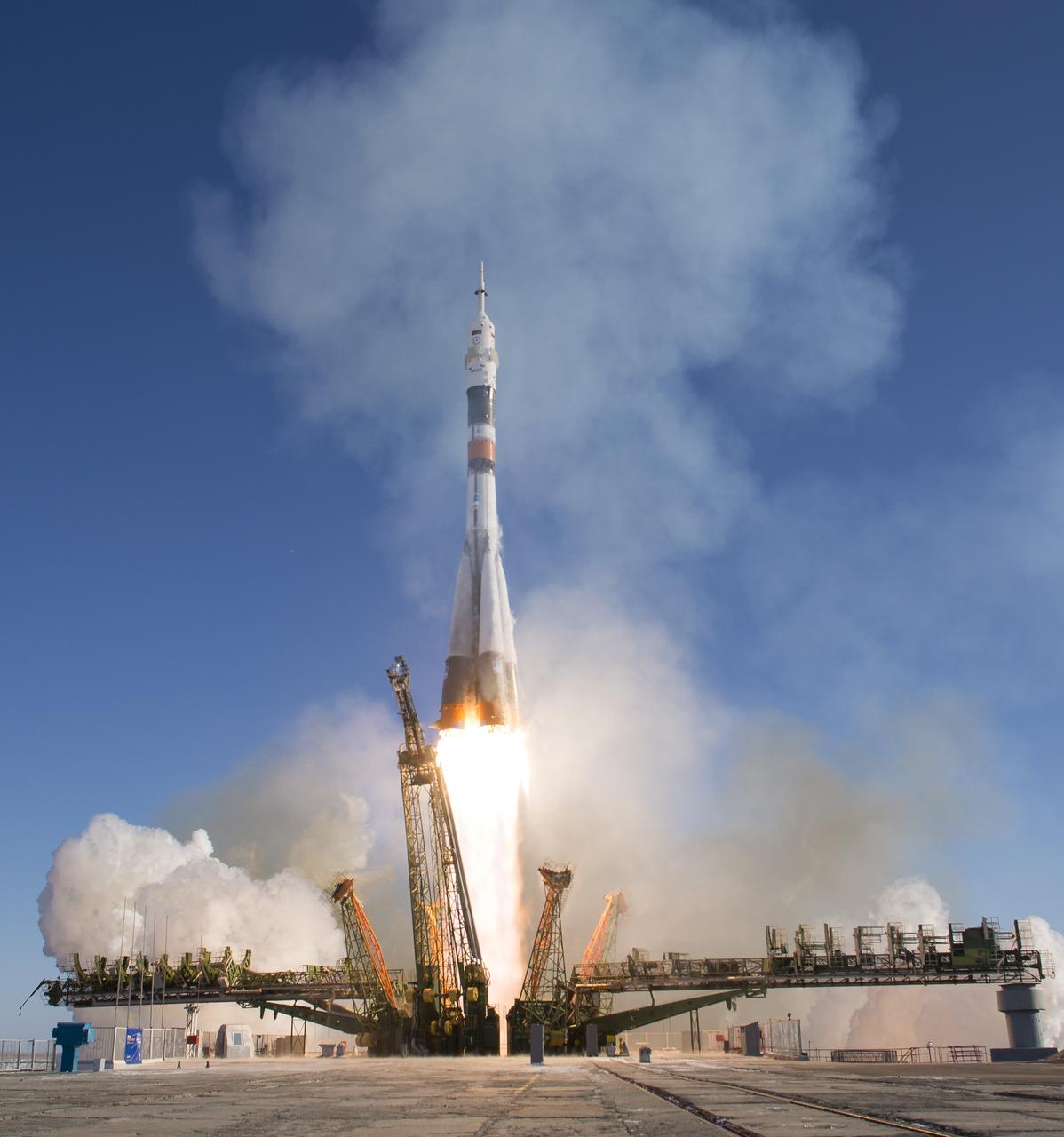

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
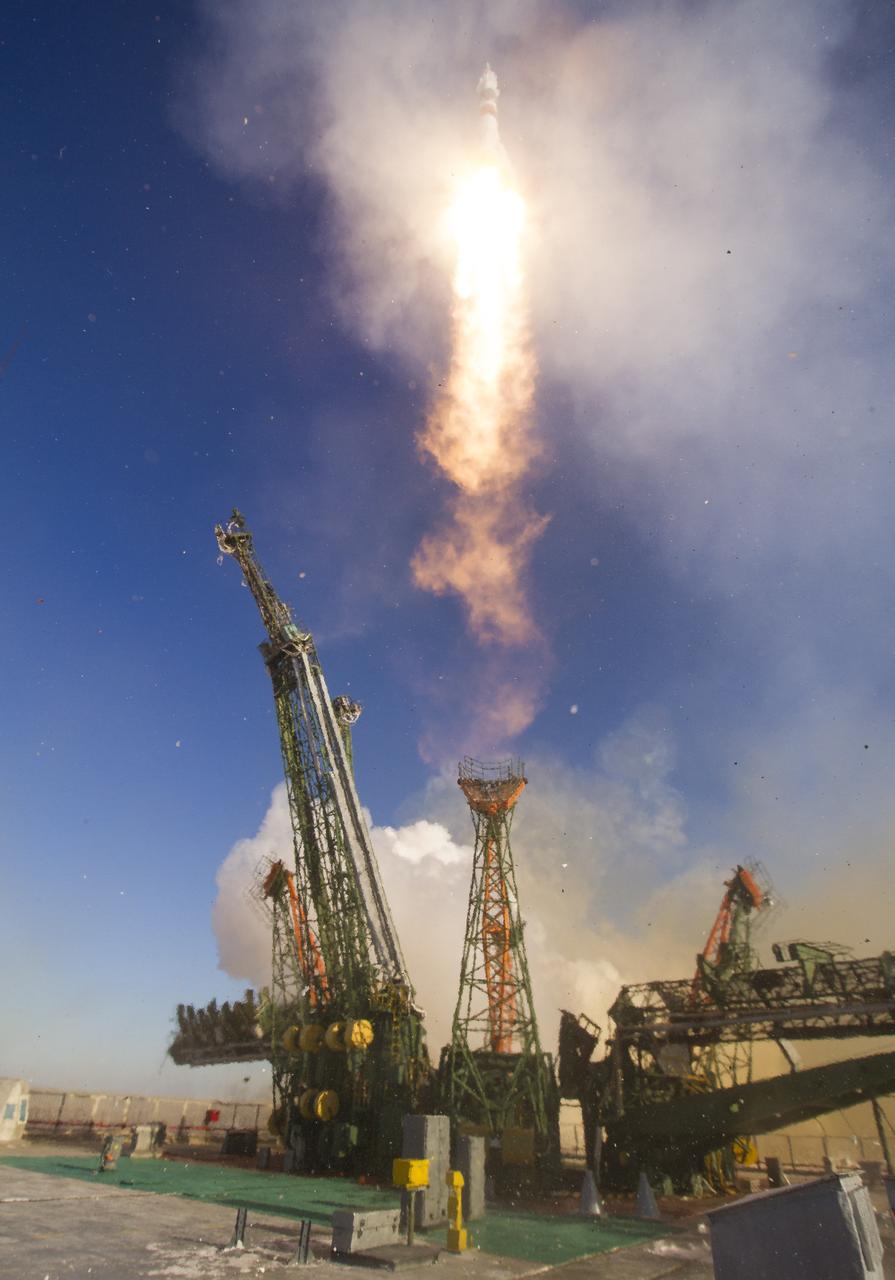

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), (iptcdow}, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
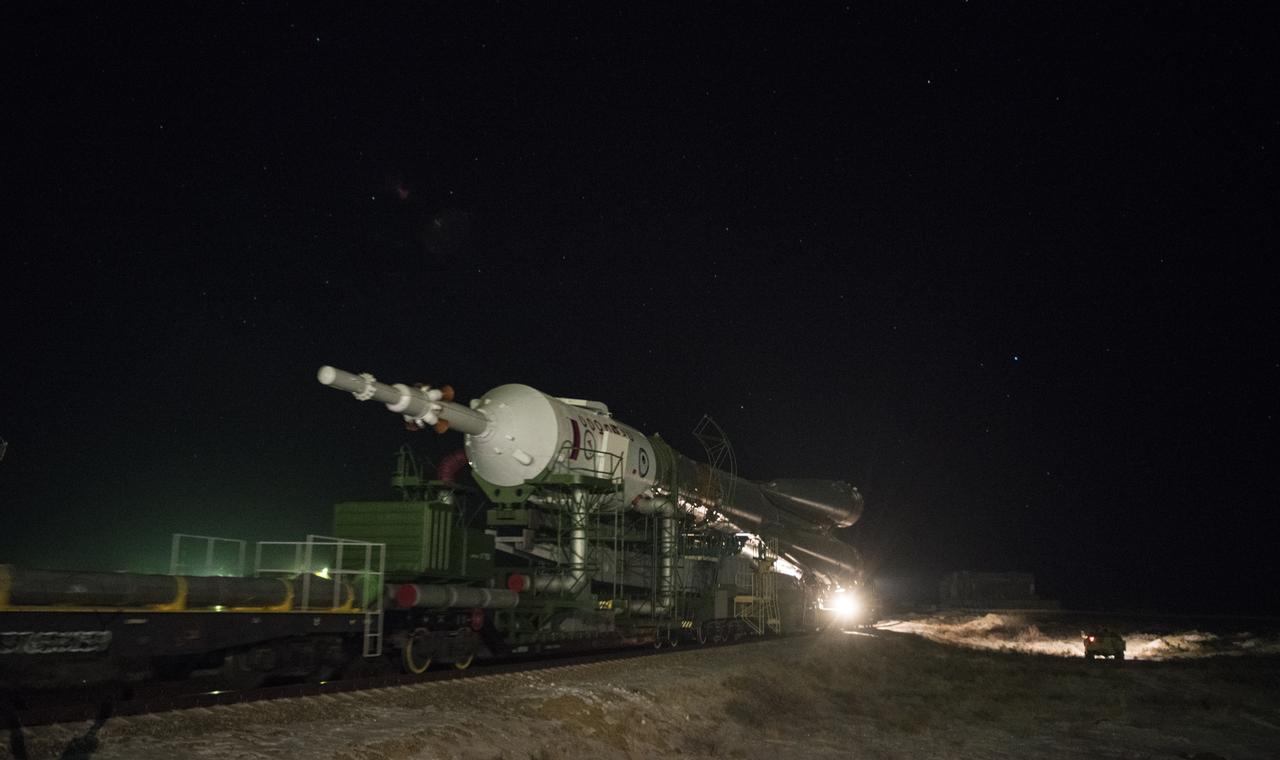

The Soyuz rocket is rolled out by train to the launch pad, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
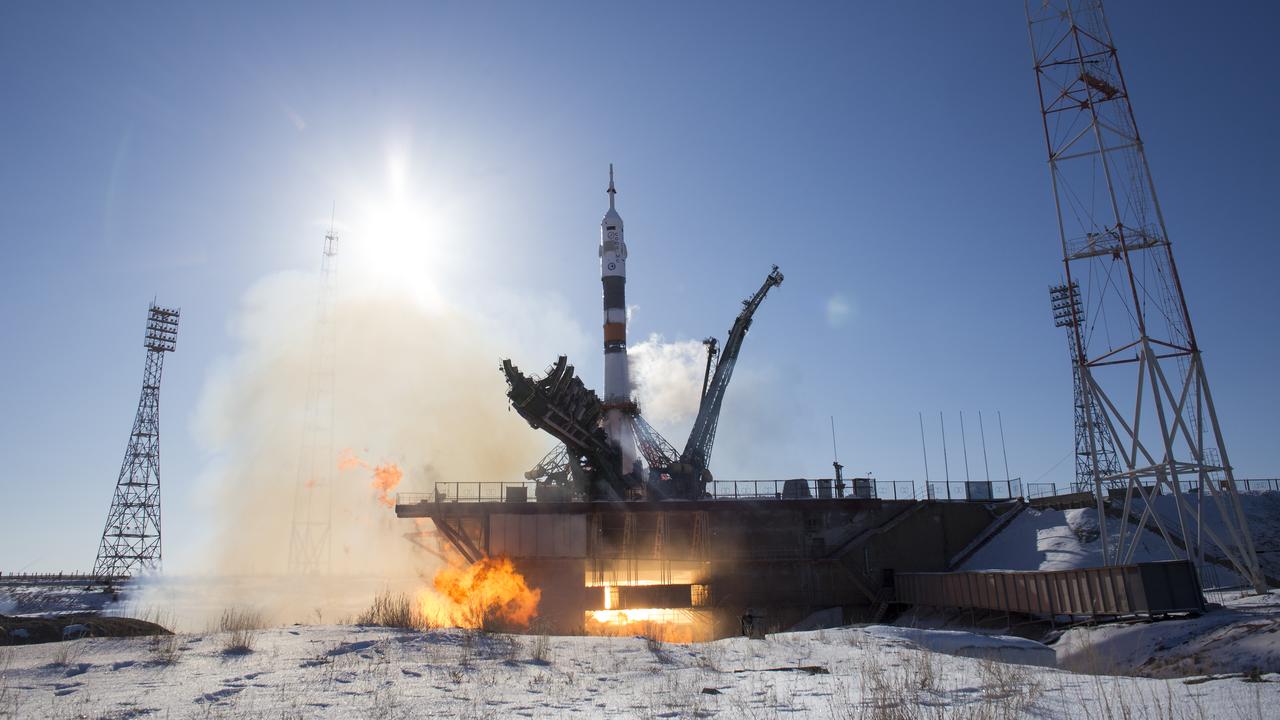

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
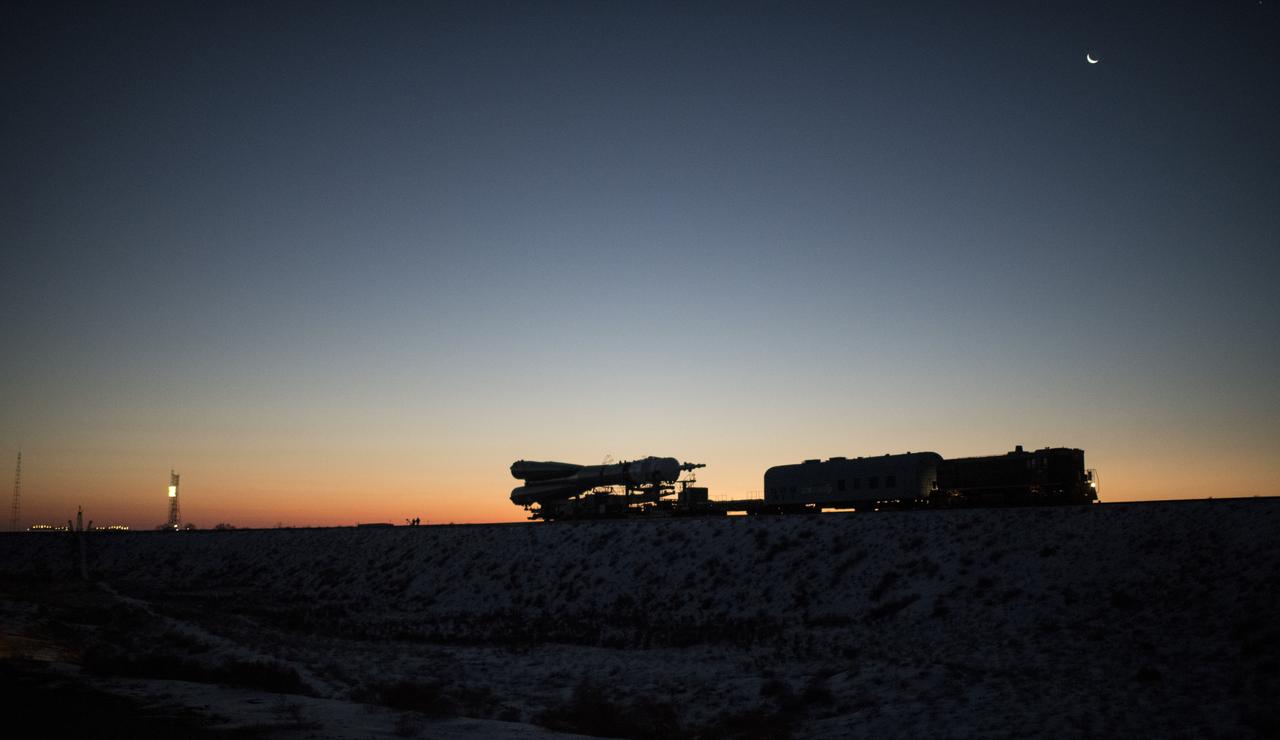

The Soyuz rocket is rolled out by train to the launch pad, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket boosters are seen being jettisoned during launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome, Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
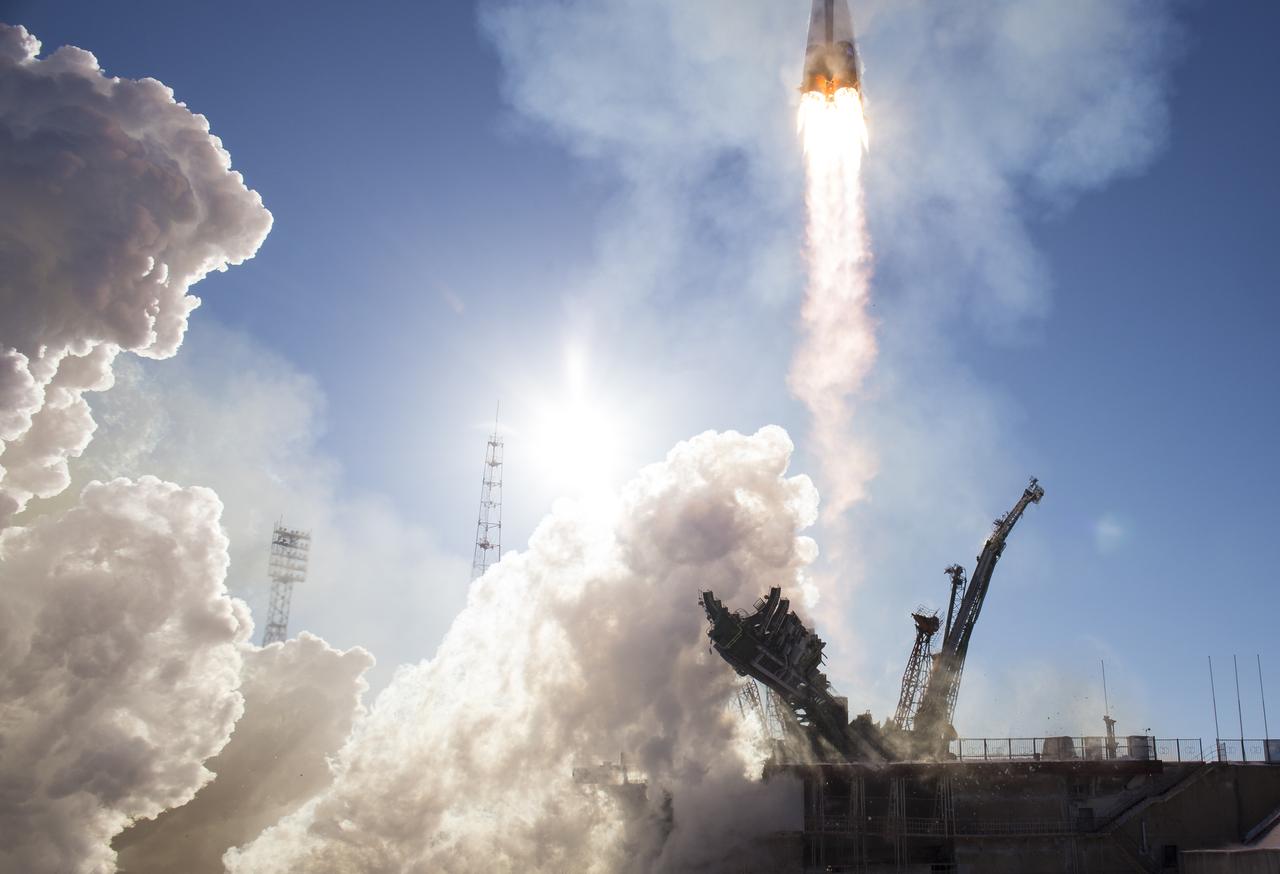

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket is launched with Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Shkaplerov, Tingle, and Kanai will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
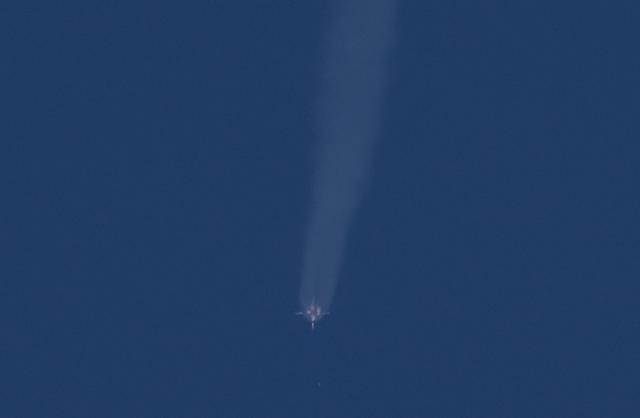

The Soyuz MS-07 rocket boosters are seen being jettisoned during launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome, Sunday, Dec. 17, 2017 in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
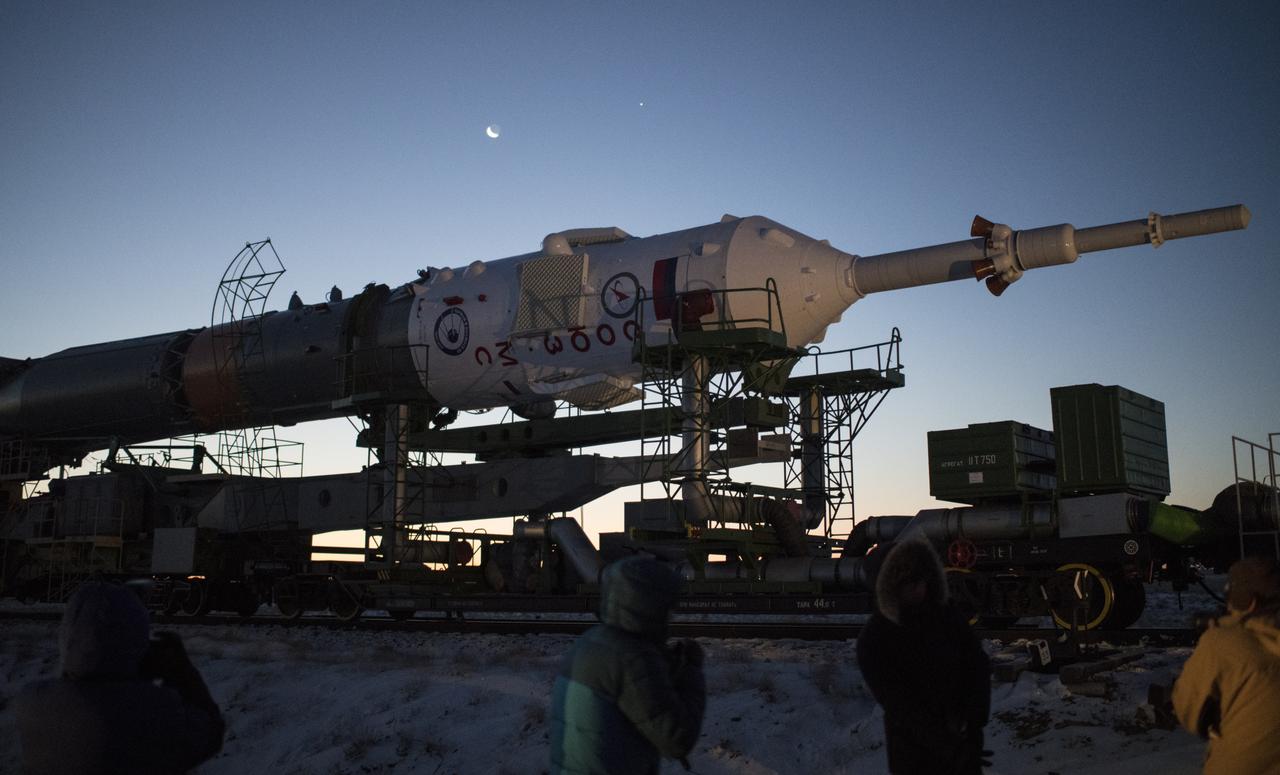

The Soyuz rocket is rolled out by train to the launch pad, Friday, Dec. 15, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch at 2:21 a.m. Eastern Time (1:21 p.m. Baikonur time) on Dec. 17 and will spend the next five months living and working aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
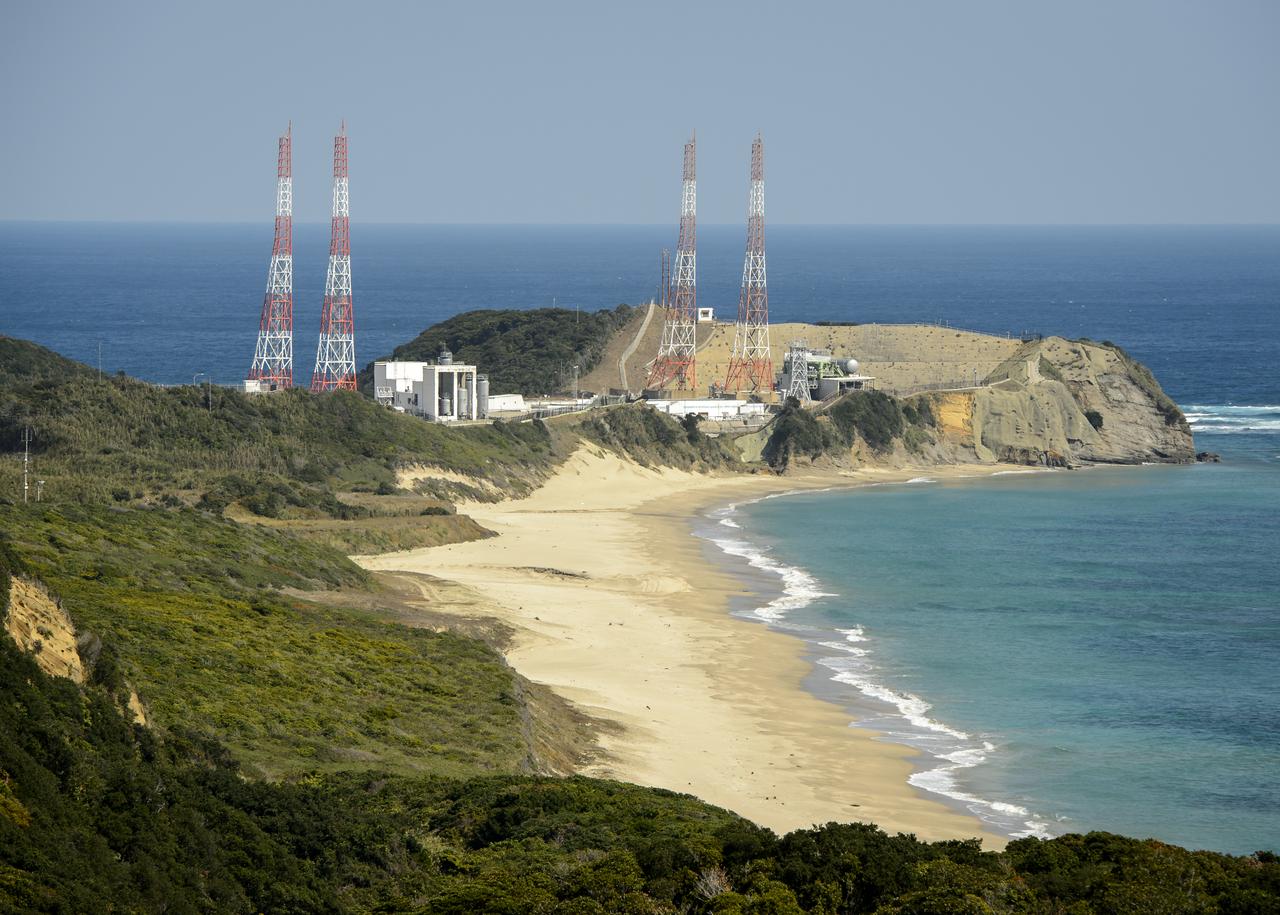

The launch pads at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center are seen a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
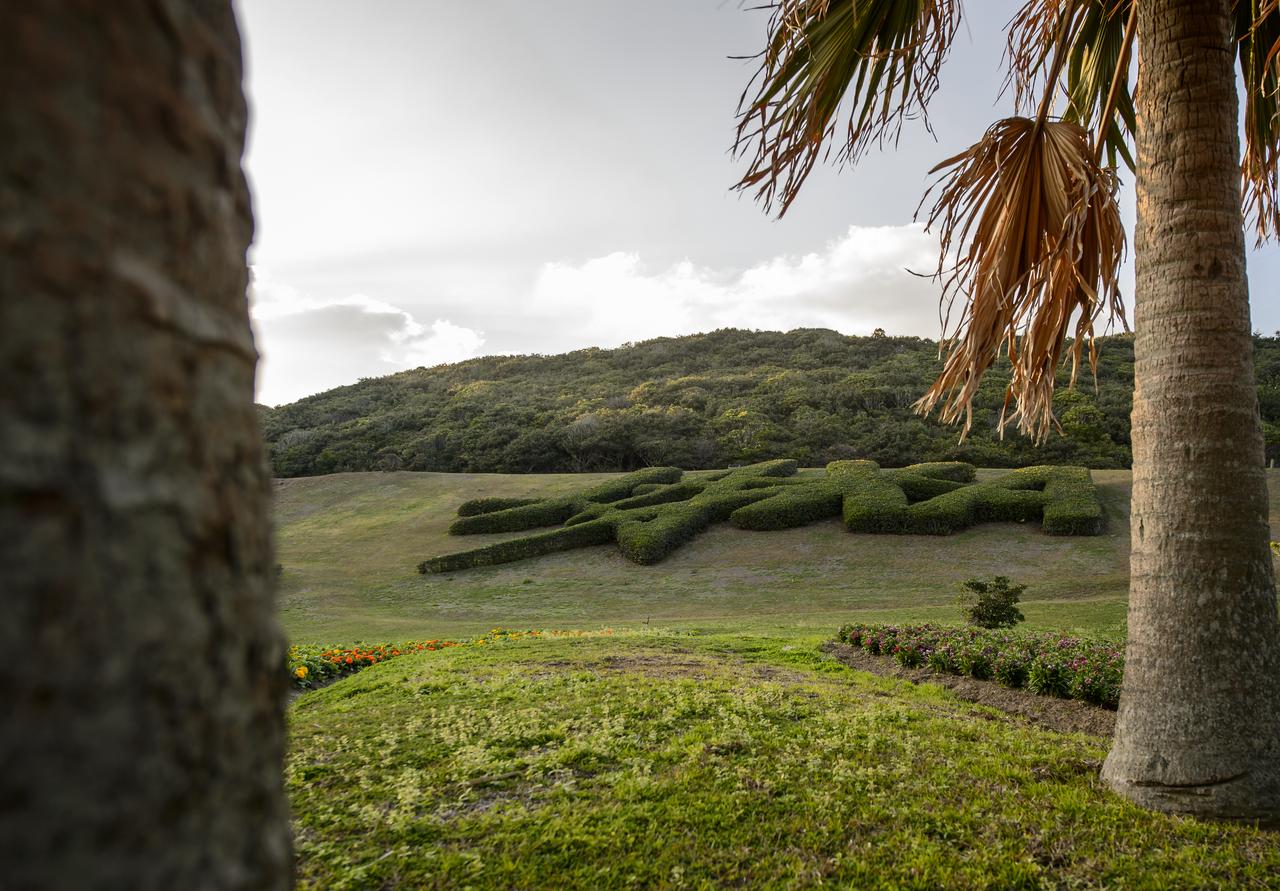

Topiary shaped into the logo of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) is seen at the Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
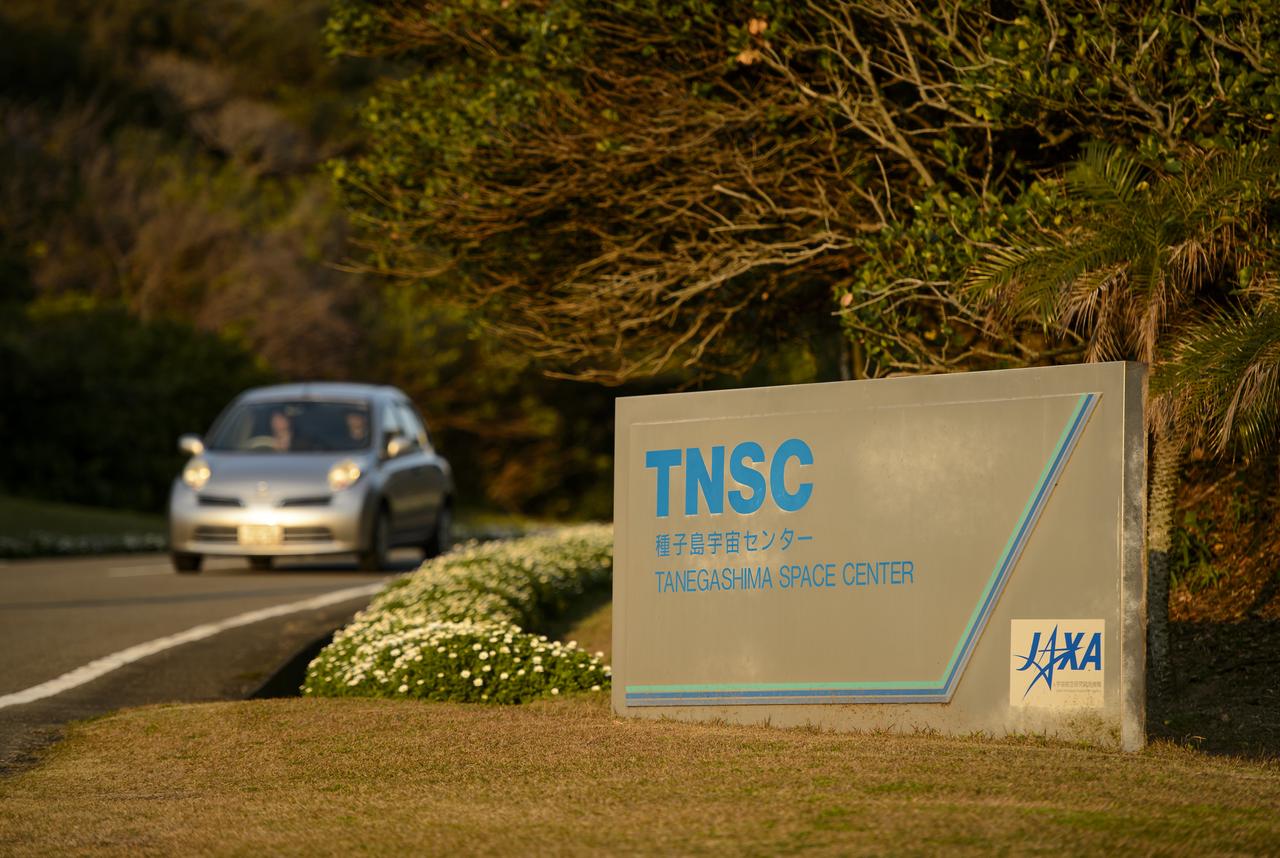

The entrance sign to the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) is seen a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
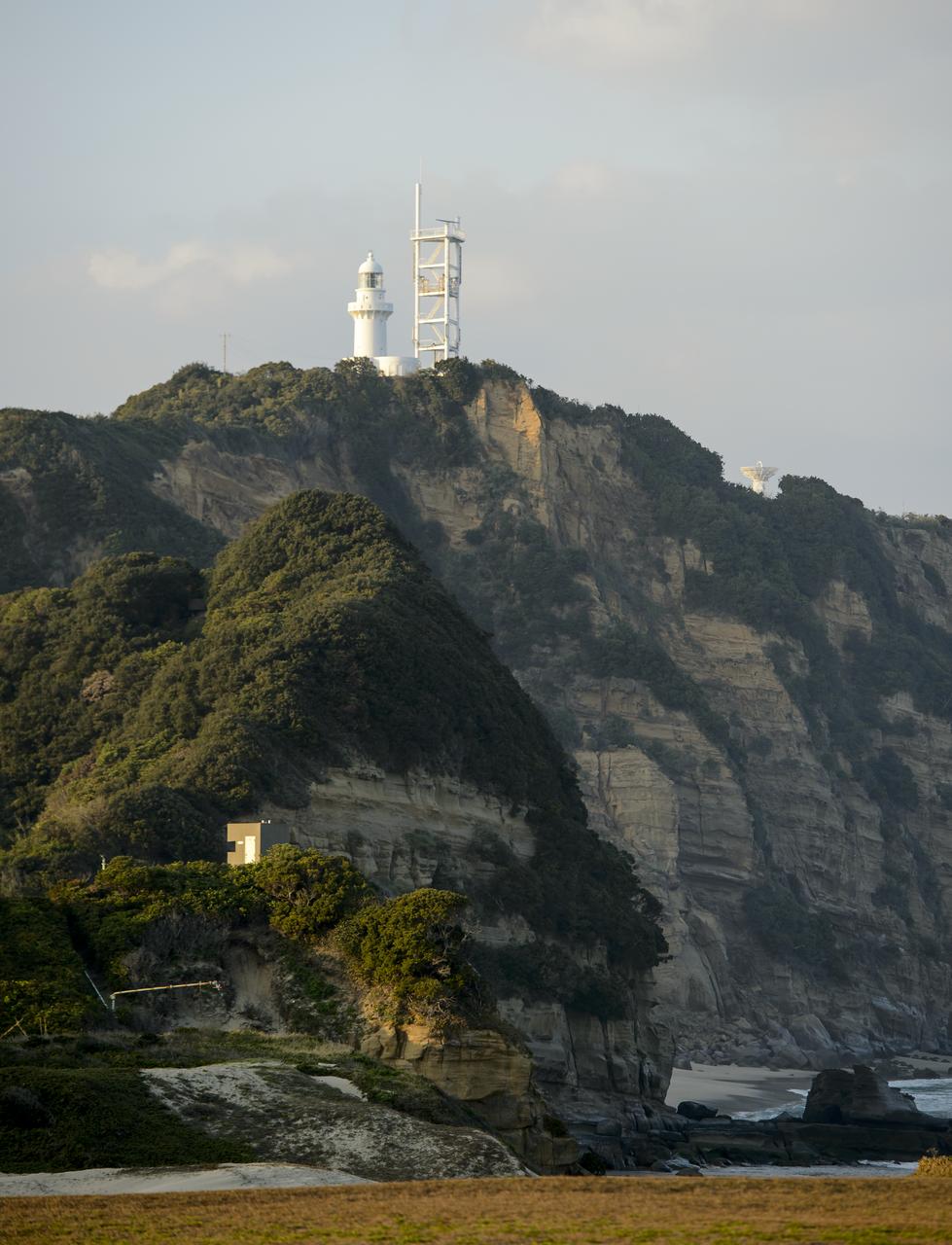

A light house and weather station is seen at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
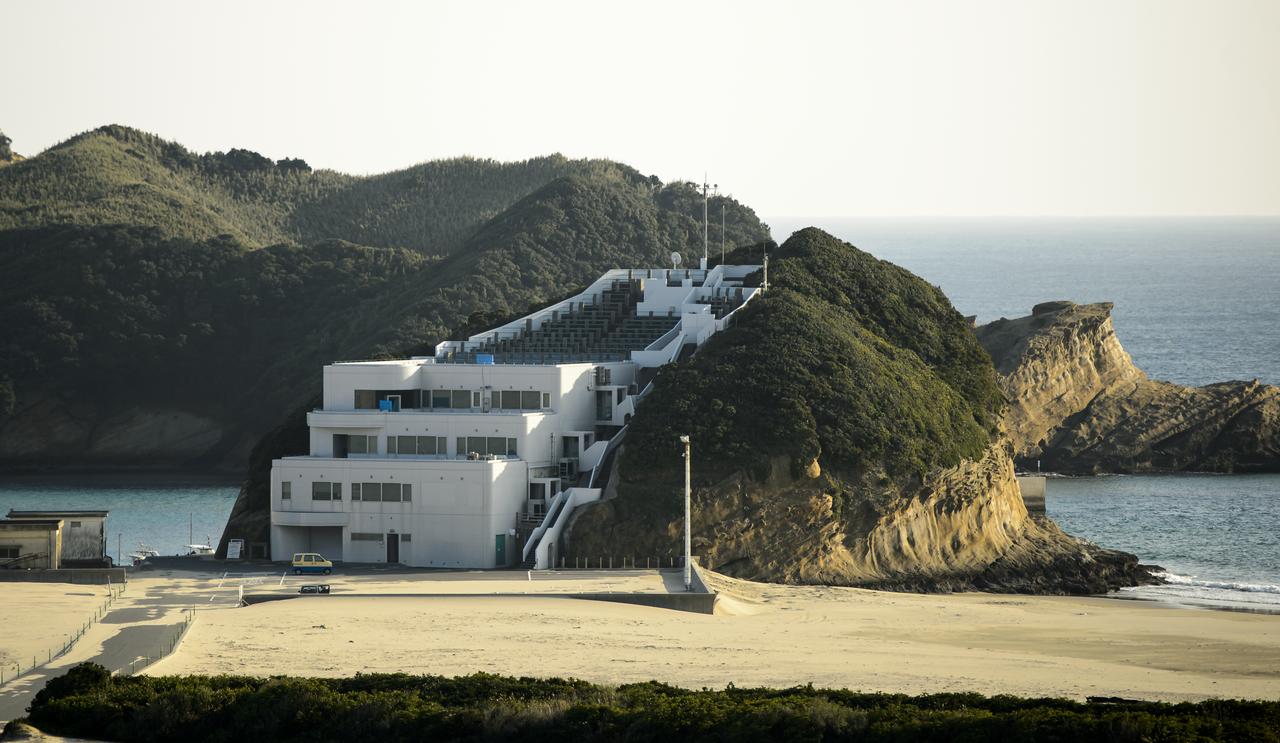

The Takesaki Observation Center is seen at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
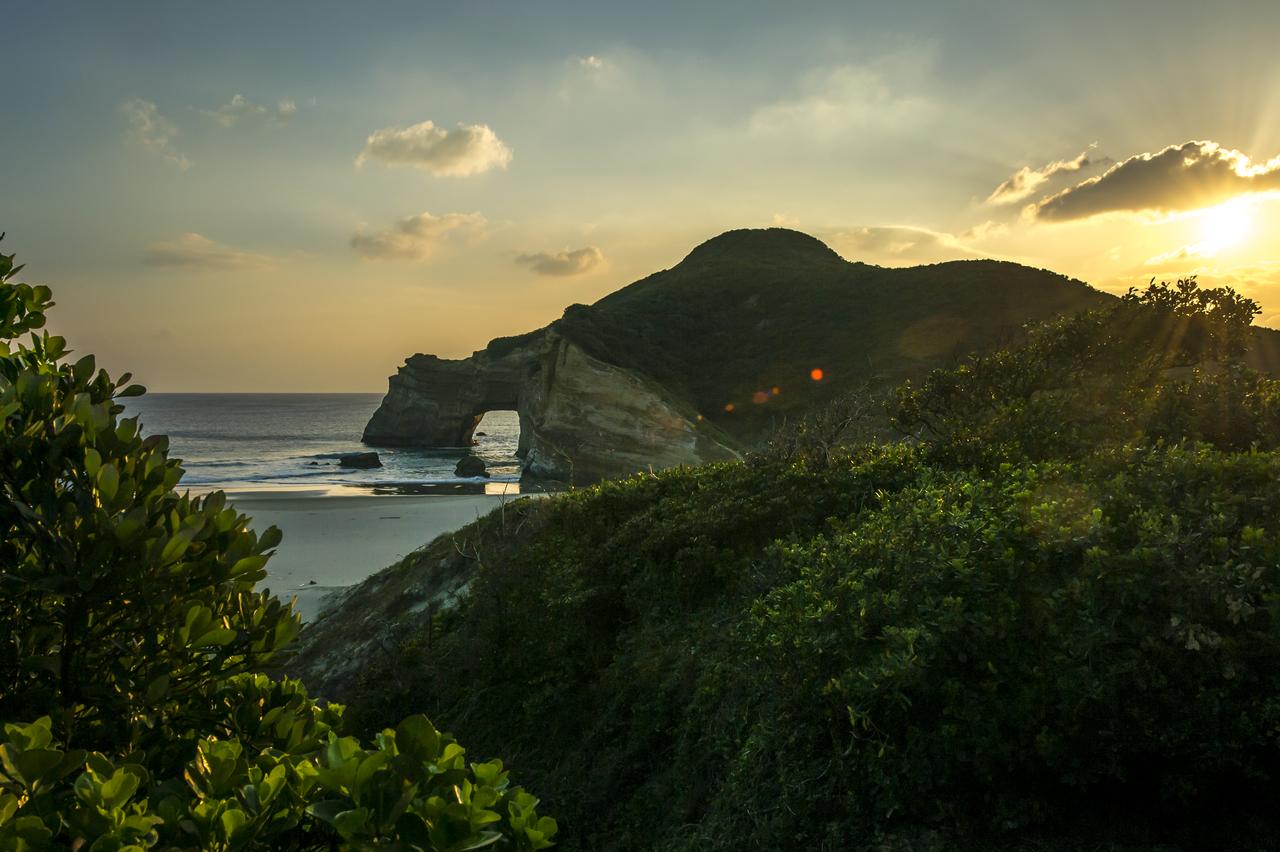

The sun sets just outside the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC) a week ahead of the planned launch of an H-IIA rocket carrying the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory, Friday, Feb. 21, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The NASA-JAXA GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
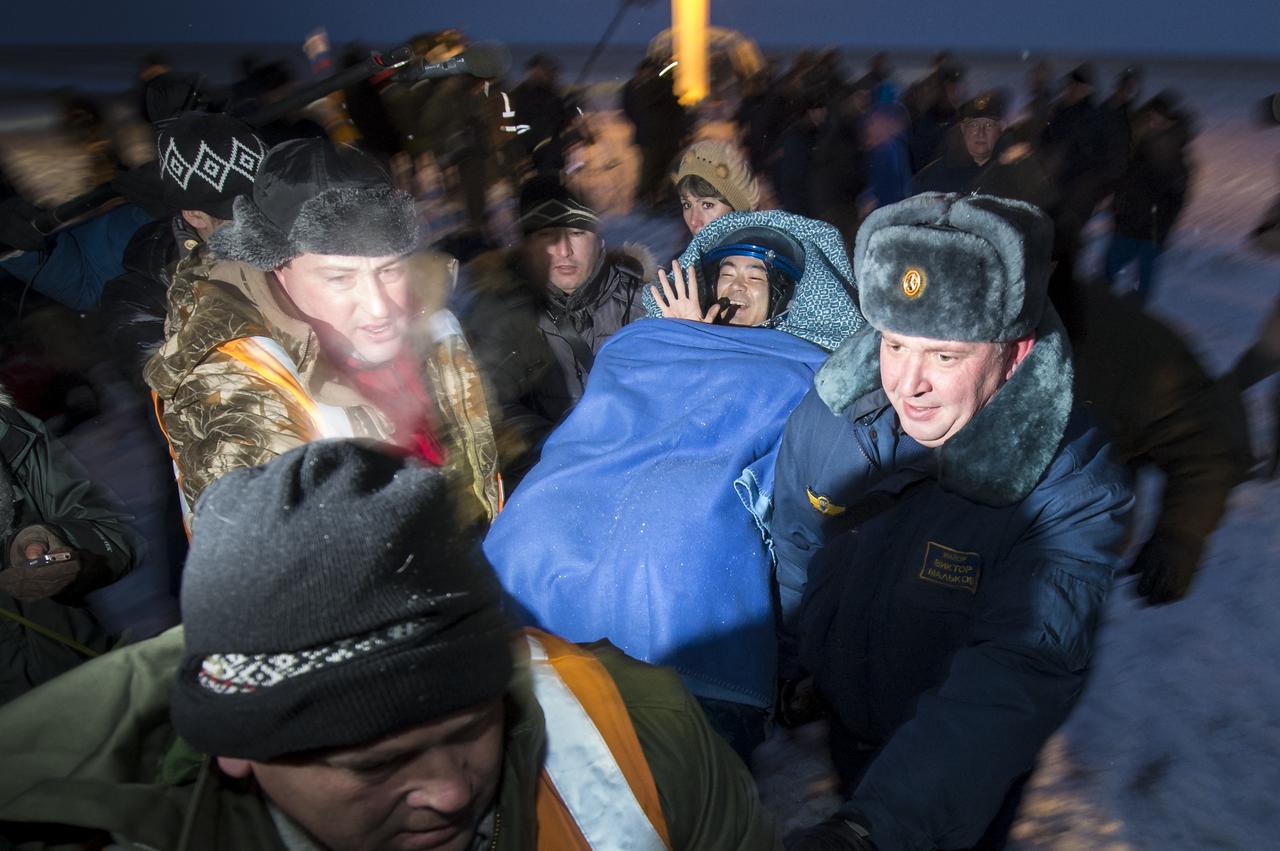

Expedition 33 Flight Engineer Akihiko Hoshide of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) is carried to a medical tent shortly after he and Commander Sunita Williams of NASA, and Flight Engineer Yuri Malenchenko of ROSCOSMOS (Russian Federal Space Agency), landed their Soyuz spacecraft in a remote area outside the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan, on Monday, Nov. 19, 2012. Williams, Hoshide and Malenchenko returned from four months onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
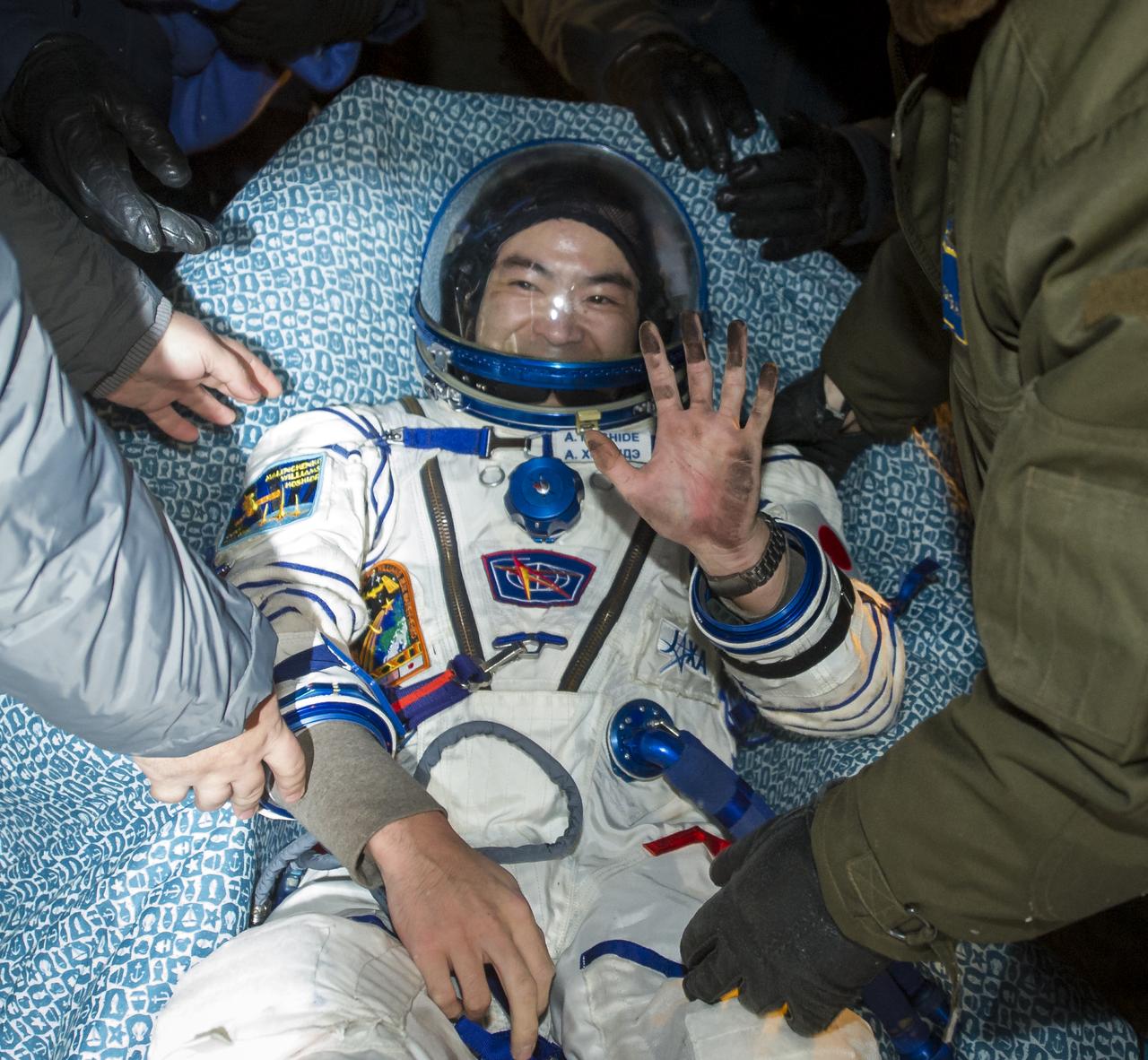

Expedition 33 Flight Engineer Akihiko Hoshide of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) waves hello in a chair outside the Soyuz Capsule after he and Commander Sunita Williams of NASA, and Flight Engineer Yuri Malenchenko of ROSCOSMOS (Russian Federal Space Agency), landed their Soyuz spacecraft in a remote area outside the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan, on Monday, Nov. 19, 2012. Williams, Hoshide and Malenchenko returned from four months onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
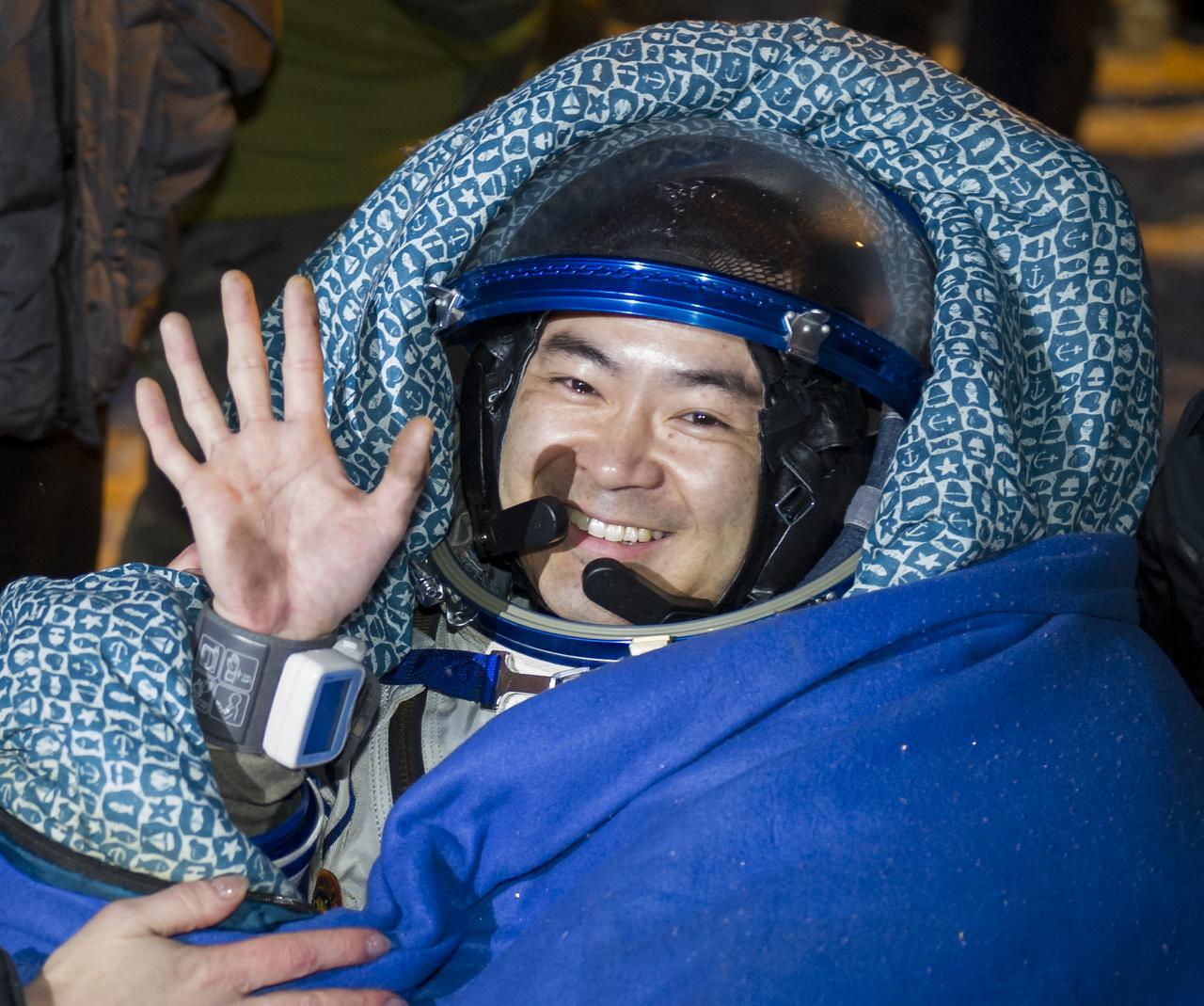

Expedition 33 Flight Engineer Akihiko Hoshide of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) waves hello in a chair outside the Soyuz Capsule after he and Commander Sunita Williams of NASA, and Flight Engineer Yuri Malenchenko of ROSCOSMOS (Russian Federal Space Agency), landed their Soyuz spacecraft in a remote area outside the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan, on Monday, Nov. 19, 2012. Williams, Hoshide and Malenchenko returned from four months onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
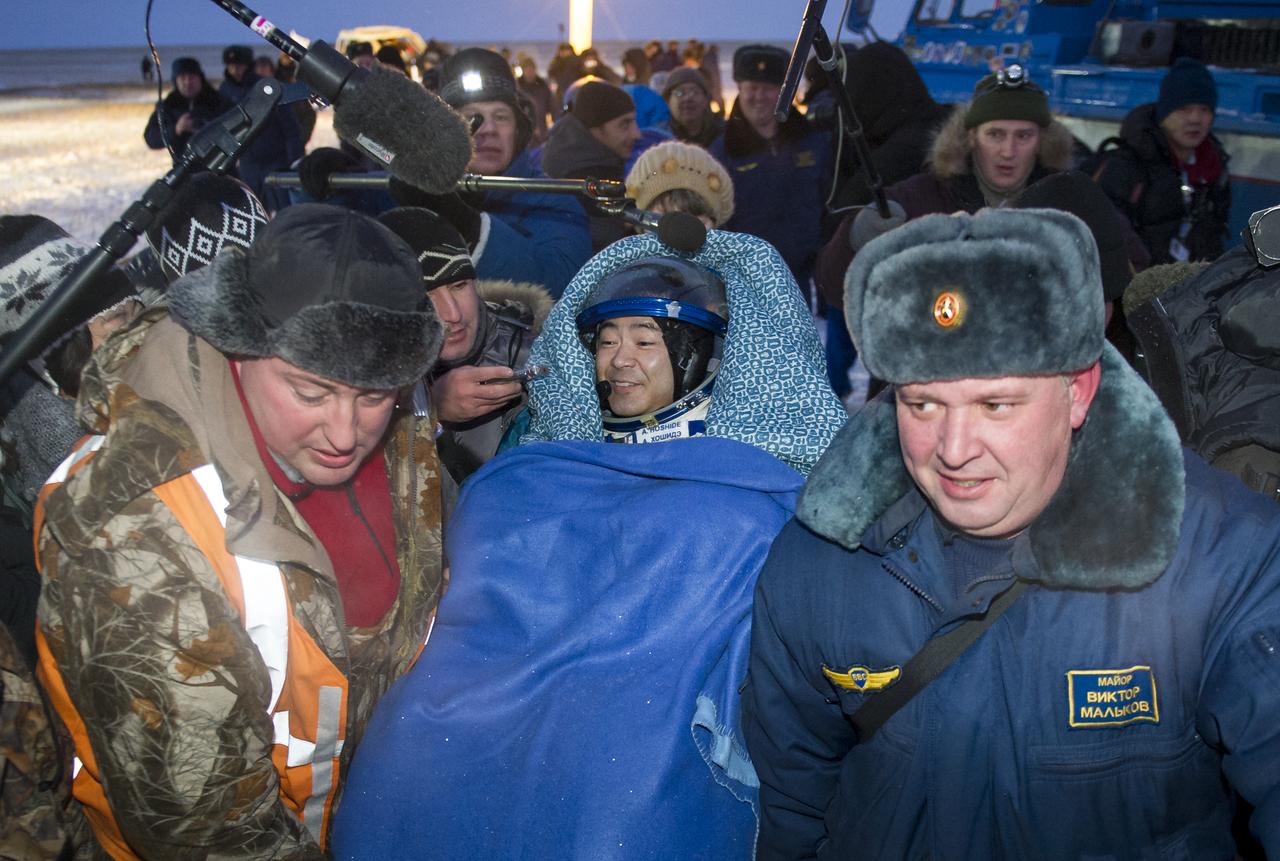

Expedition 33 Flight Engineer Akihiko Hoshide of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) is carried to a medical tent shortly after he and Commander Sunita Williams of NASA, and Flight Engineer Yuri Malenchenko of ROSCOSMOS (Russian Federal Space Agency), landed their Soyuz spacecraft in a remote area outside the town of Arkalyk, Kazakhstan, on Monday, Nov. 19, 2012. Williams, Hoshide and Malenchenko returned from four months onboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
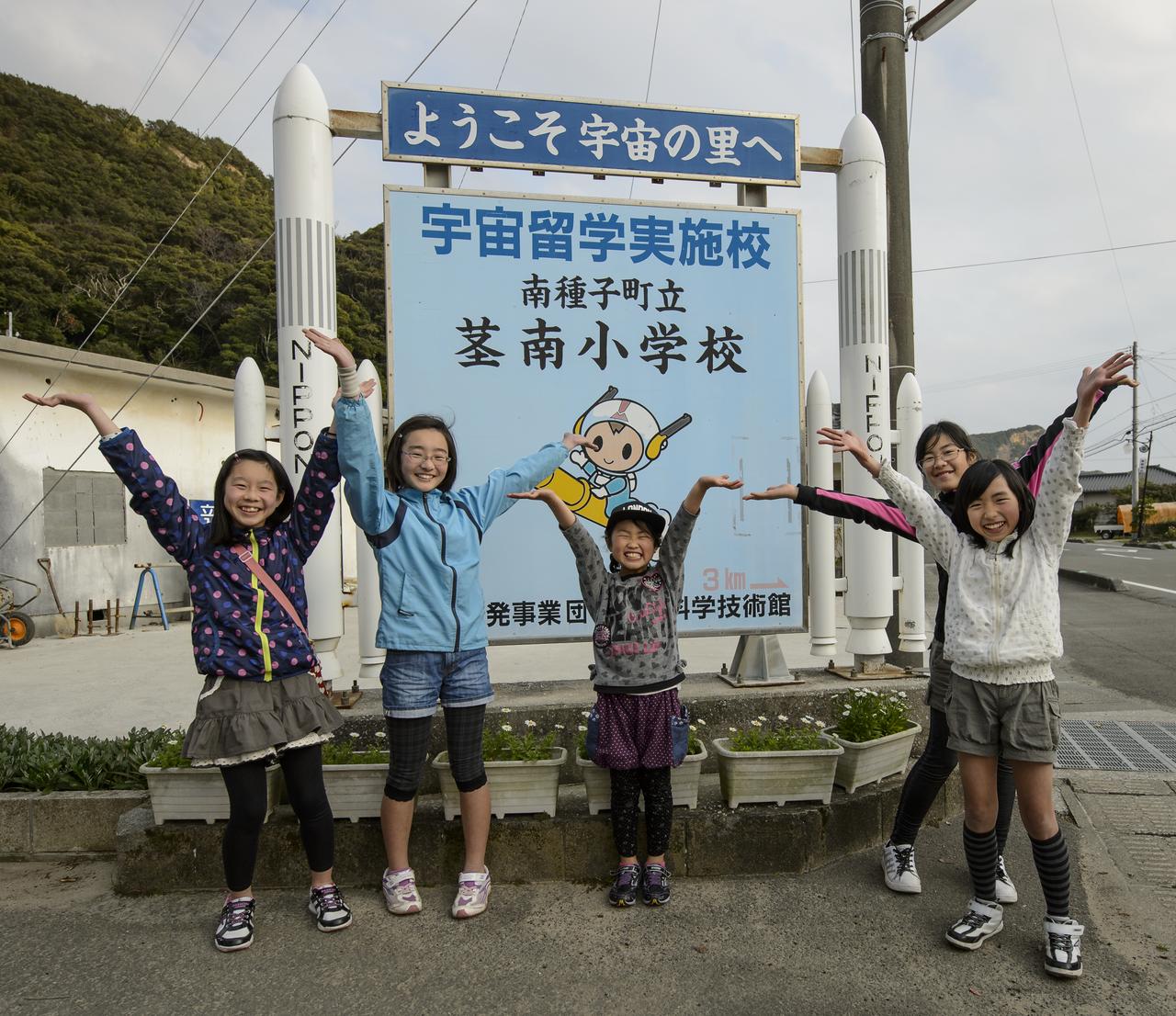

Minamitane elementary school girls pose for a photo in front of a sign featuring the town's mascot "Chuta-kun", Sunday, Feb. 23, 2014, Tanegashima Island, Japan. The Chuta-kun mascot rides a rocket and has guns on the side of his helmet to show the areas history as the site of the first known contact of Europe and the Japanese, in 1543 and the introduction of the gun. A Japanese H-IIA rocket carrying the NASA-Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory is planned for launch from the space center on Feb. 28, 2014. Once launched, the GPM spacecraft will collect information that unifies data from an international network of existing and future satellites to map global rainfall and snowfall every three hours. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
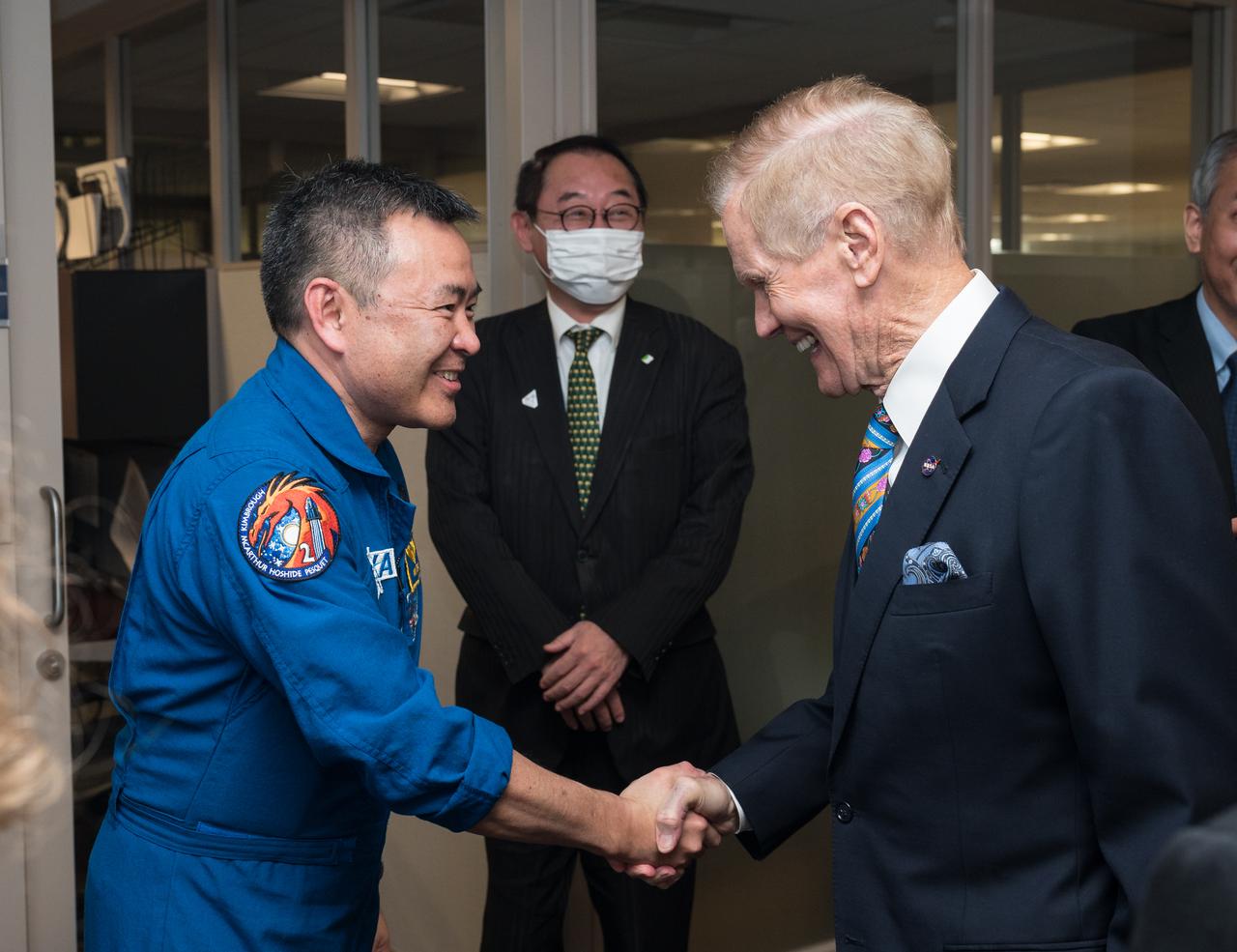
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, greets Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Hoshide Akihiko, before the signing of an agreement that builds on a long history of collaboration in space exploration between the U.S. and Japan, Friday, Jan. 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. “The Framework Agreement Between the Government of Japan and the Government of the United States of America for Cooperation in Space Exploration and Use of Outer Space, Including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies, For Peaceful Purposes” covers joint activities including space science, Earth science, space operations and exploration, aeronautical science and technology, space technology, space transportation, and safety and mission assurance, among others. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
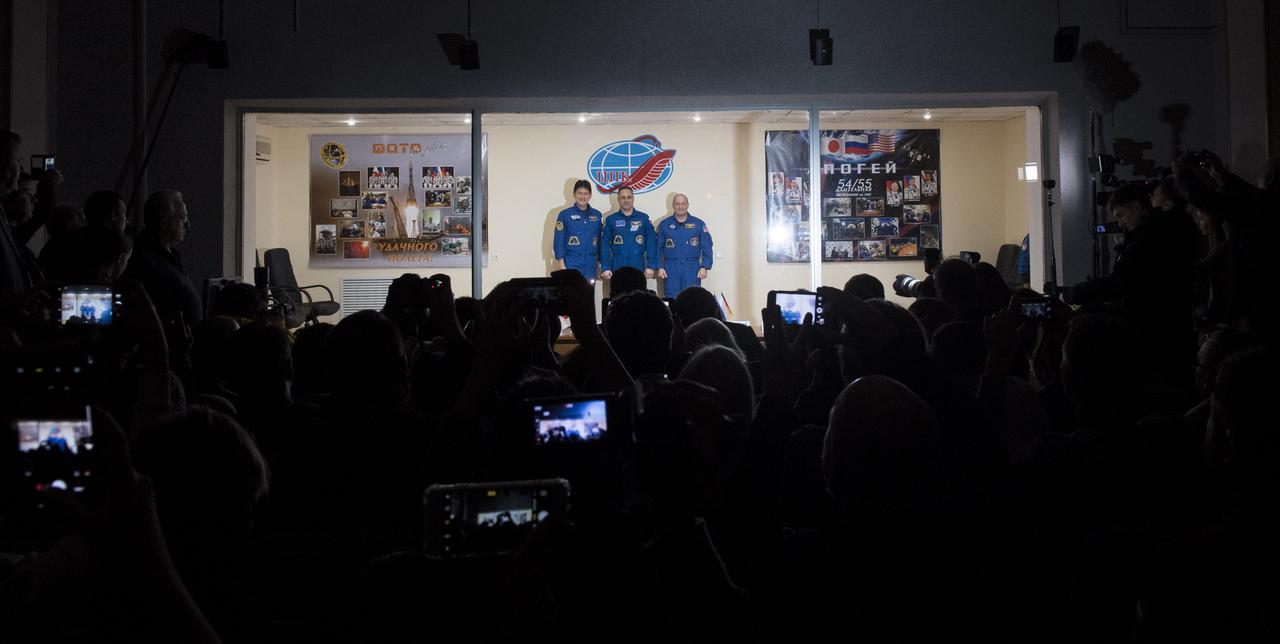

Expedition 54 prime crew members flight engineer Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), right, Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, center, and flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, right, pose for a picture at the conclusion of a press conference, Saturday, Dec. 16, 2017 at the Cosmonaut Hotel in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Expedition 54 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of Roscosmos, flight engineer Scott Tingle of NASA, and flight engineer Norishige Kanai of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) are scheduled to launch to the International Space Station aboard the Soyuz spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on December 17. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)