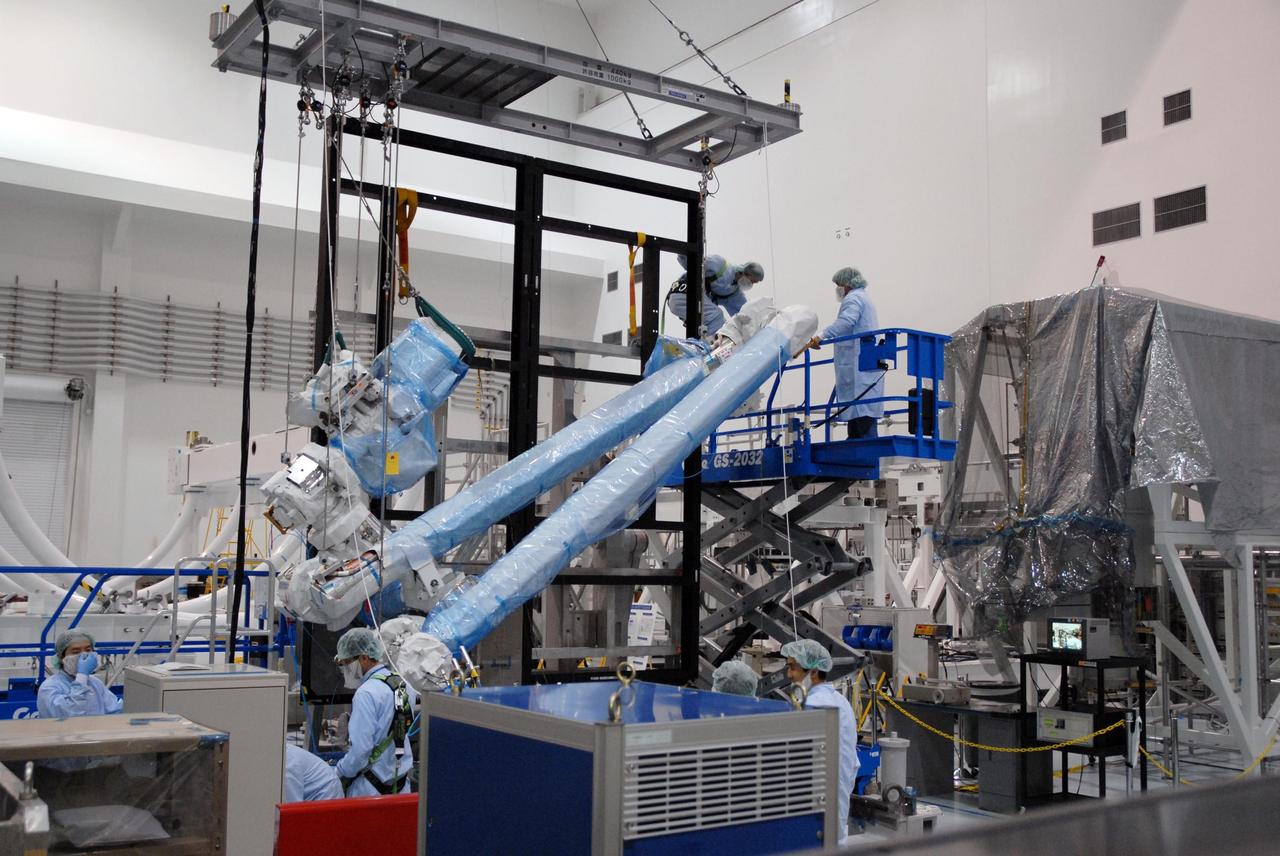

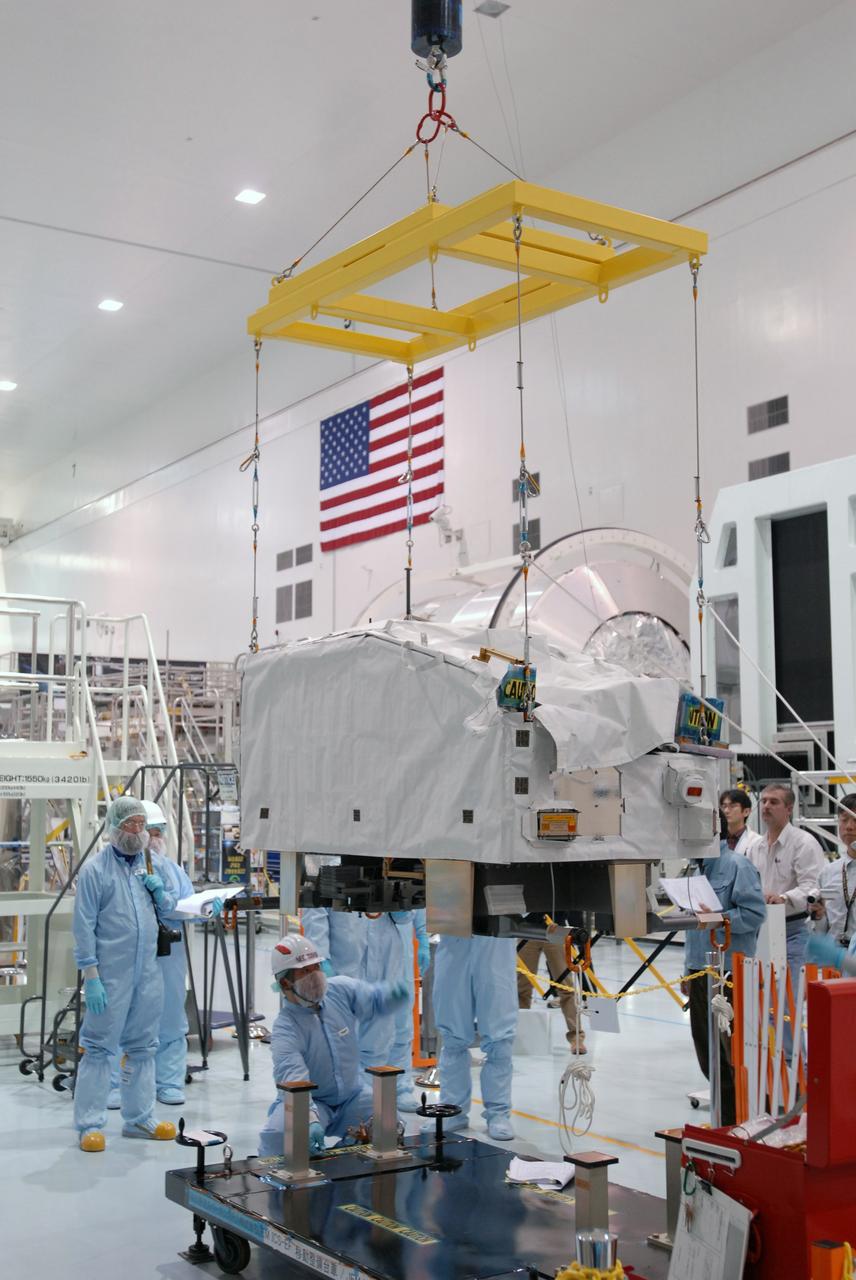
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers attach the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, to a hoisting device to prepare for installation to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
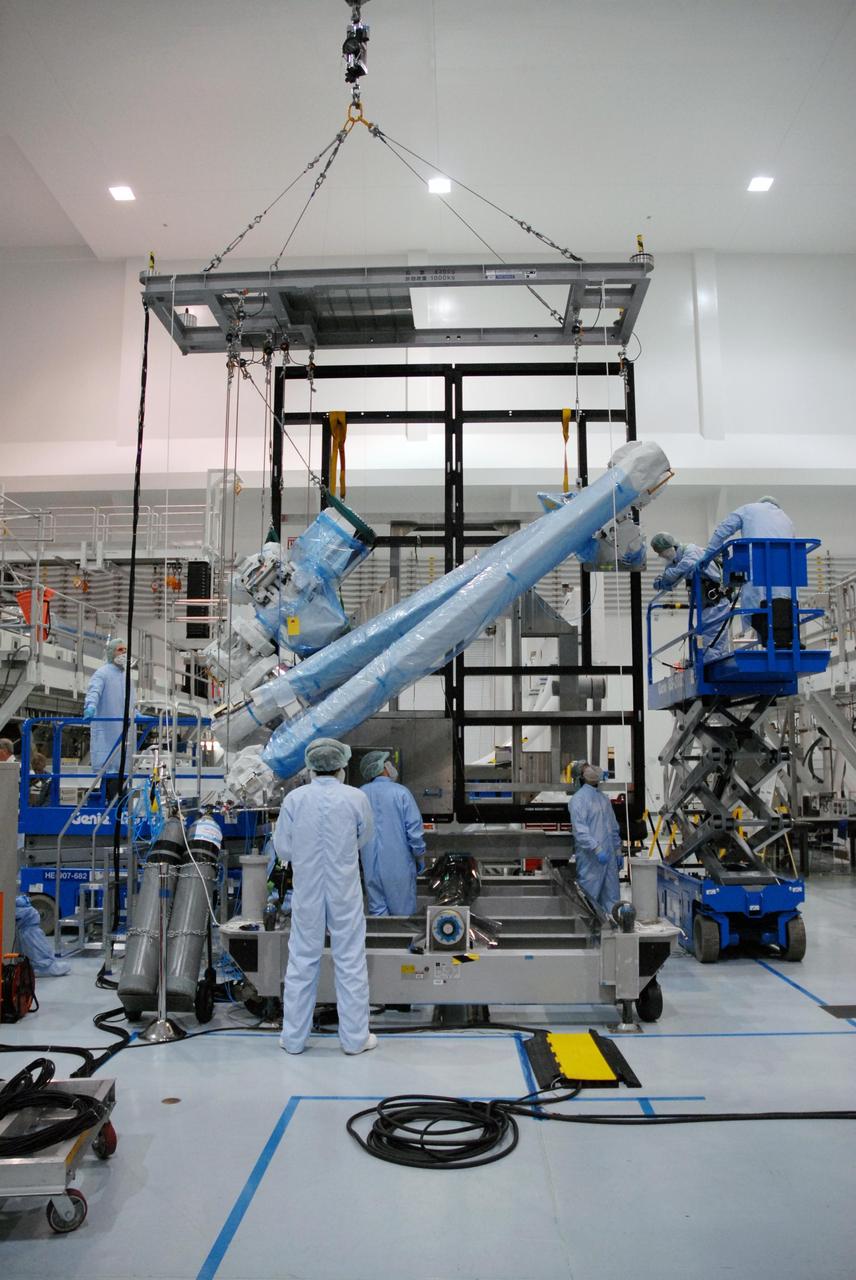

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers attach the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, to a hoisting device to prepare for installation to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers prepare the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, for installation on the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
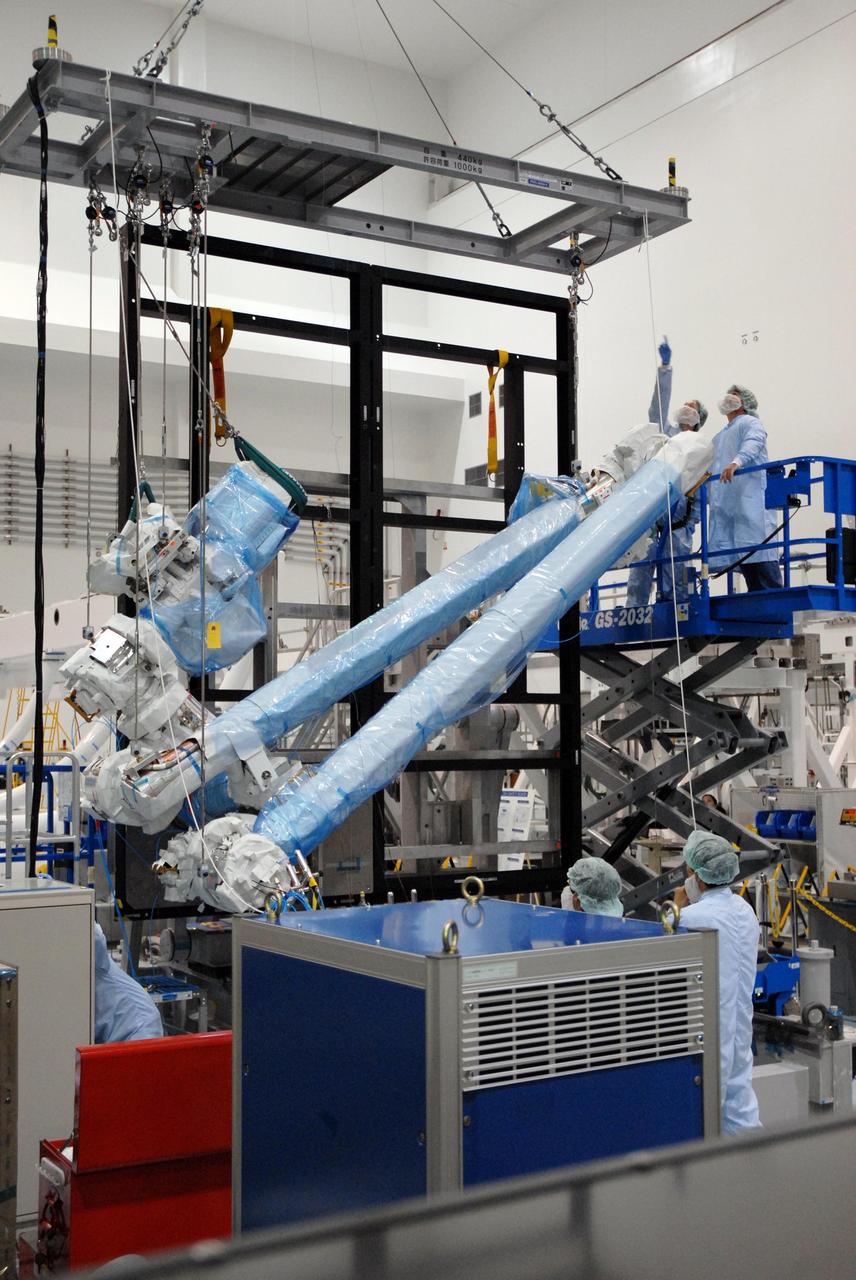
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers attach the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, to a hoisting device to prepare for installation to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
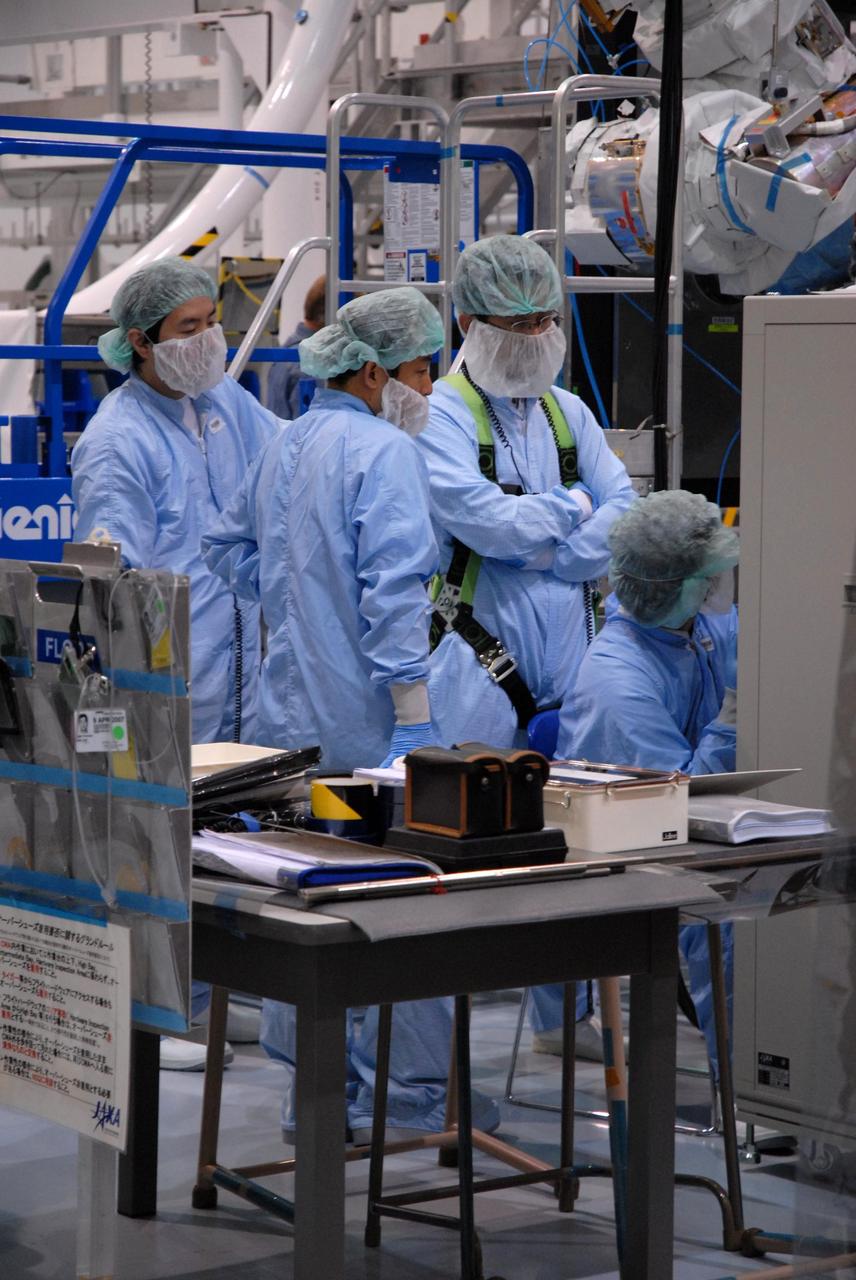

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency watch from a control area as the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, is attached to a hoisting device to prepare it for installation to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
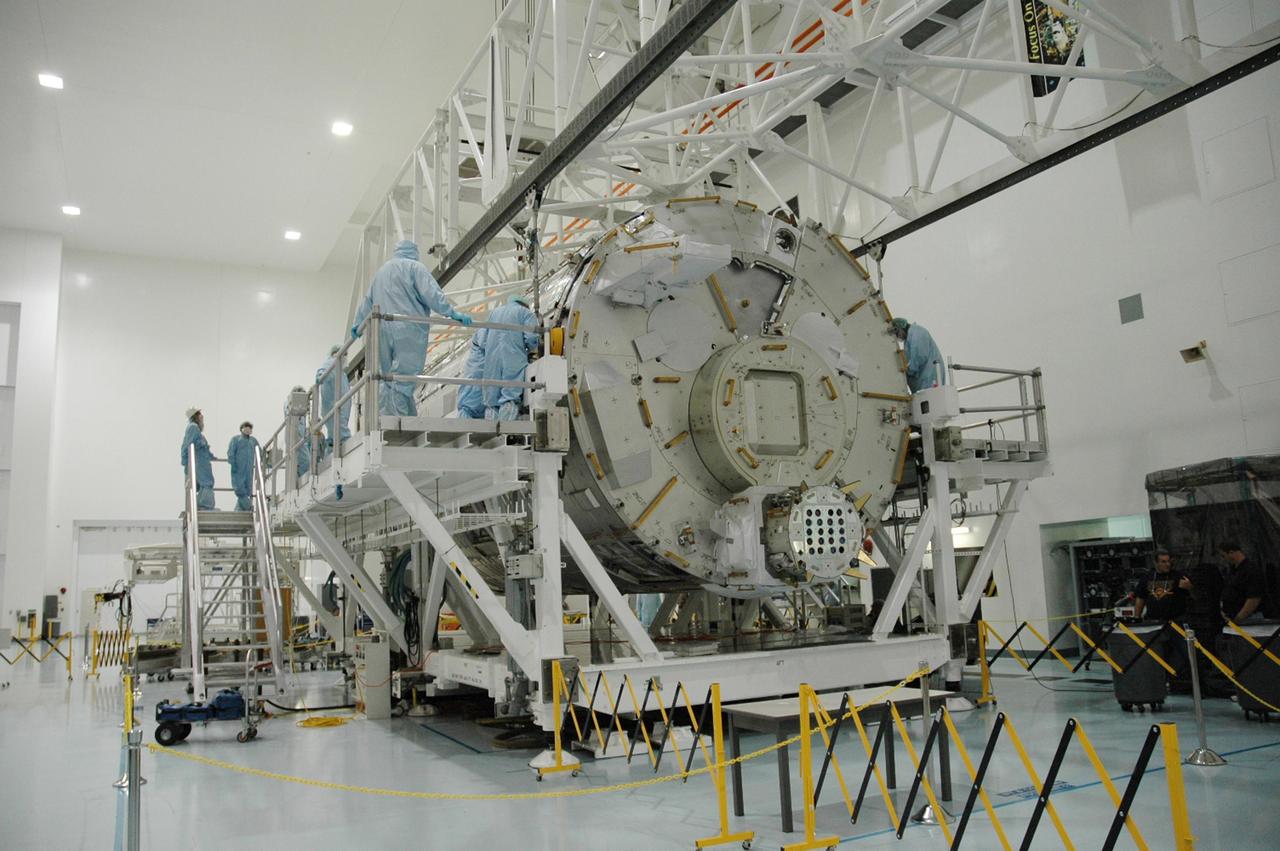

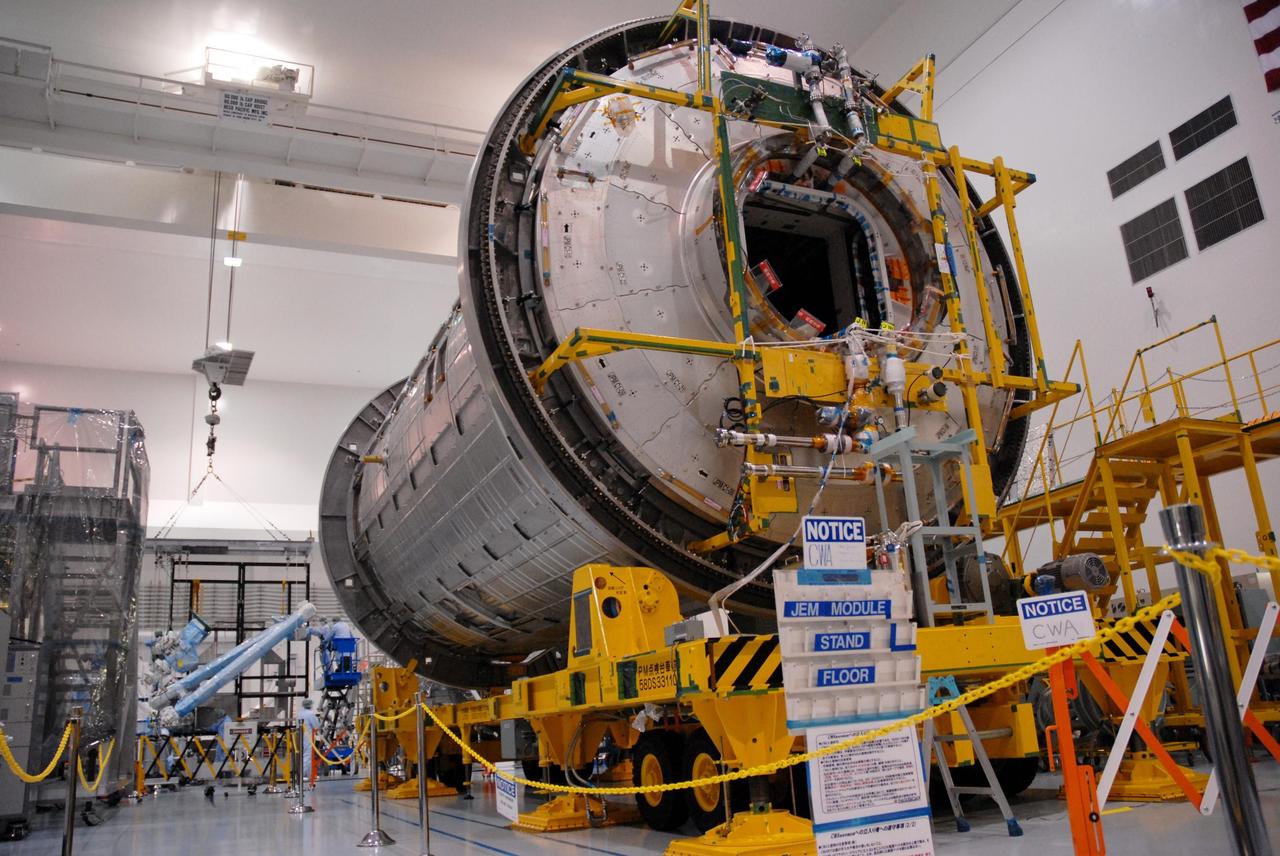
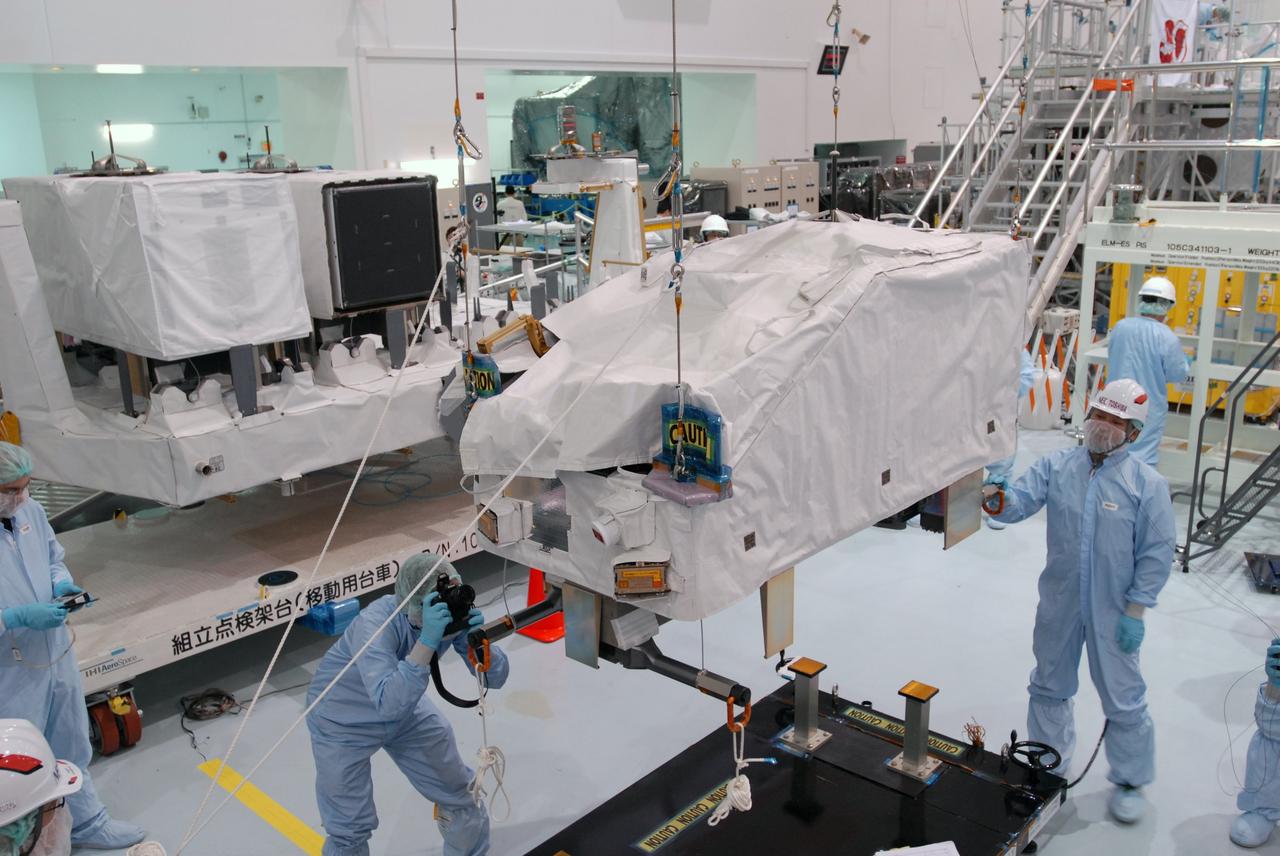
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers monitor the movement of the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) as it is lowered onto a weighing stand. The module will also be measured for its center of gravity. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency developed the laboratory at the Tsukuba Space Center near Tokyo. It is the first element, named "Kibo" (Hope), to be delivered to KSC. The JEM is Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station. It will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. The JEM is targeted for mission STS-124, to launch in early 2008. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
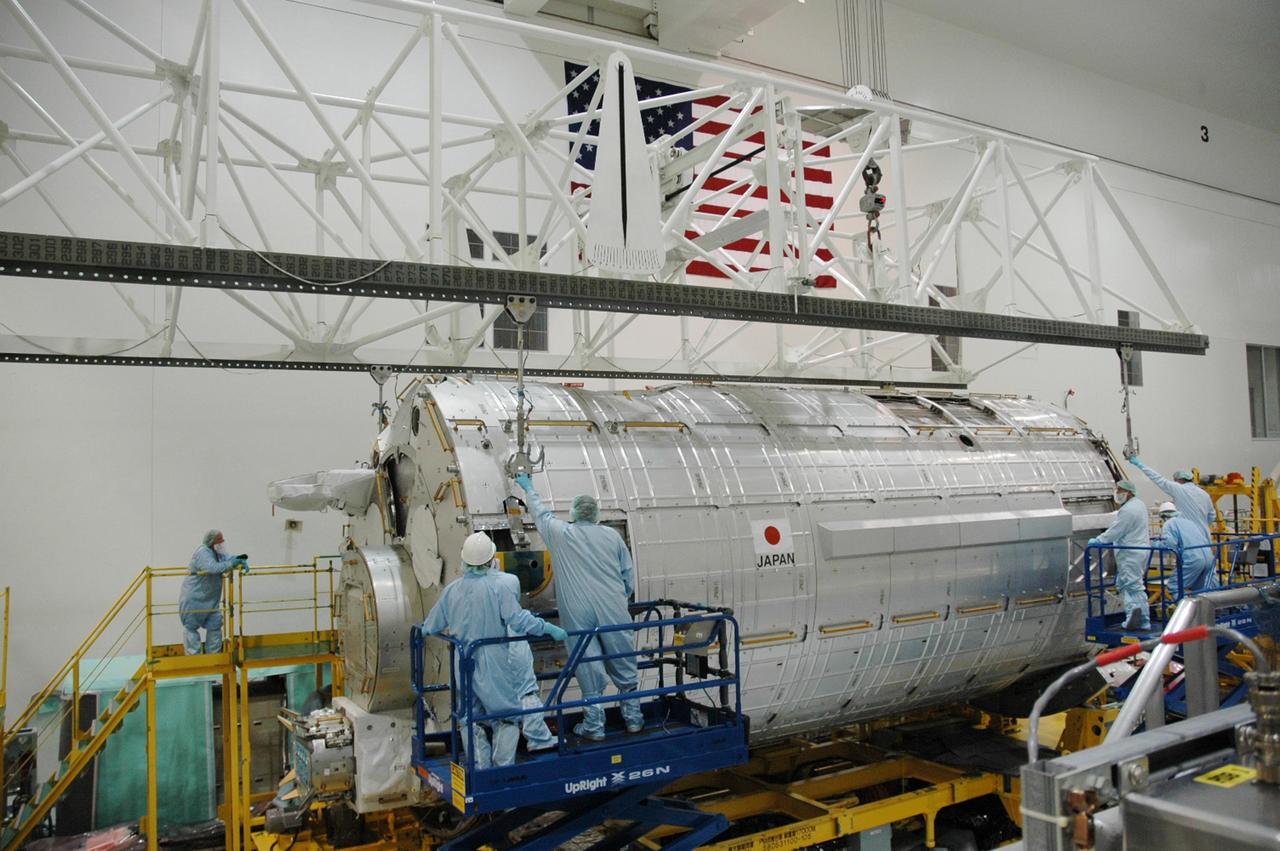

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers are attaching an overhead crane to the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) in order to lift it. The module is being moved to a stand where it will be weighed and measured for its center of gravity. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency developed the laboratory at the Tsukuba Space Center near Tokyo. It is the first element, named "Kibo" (Hope), to be delivered to KSC. The JEM is Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station. It will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. The JEM is targeted for mission STS-124, to launch in early 2008. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
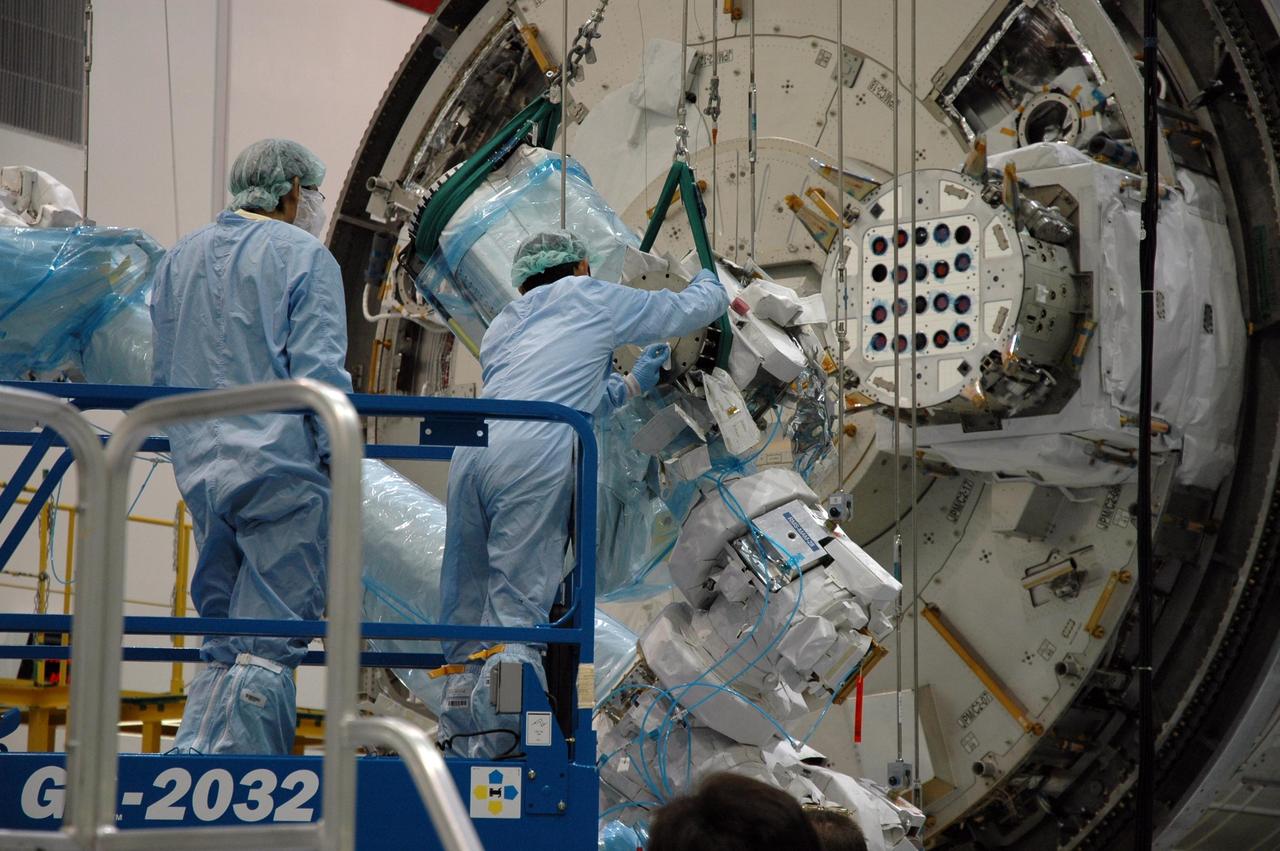

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers attach the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
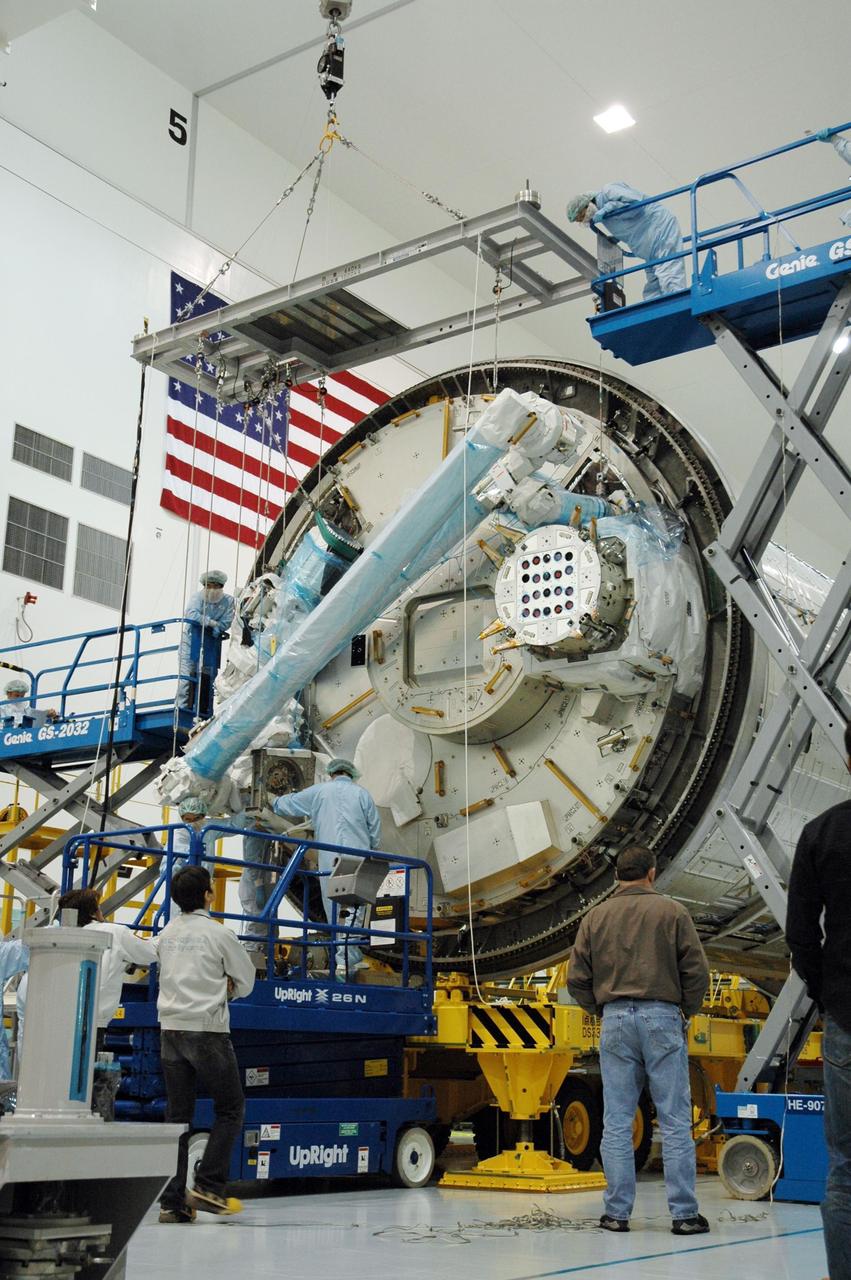

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers attach the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
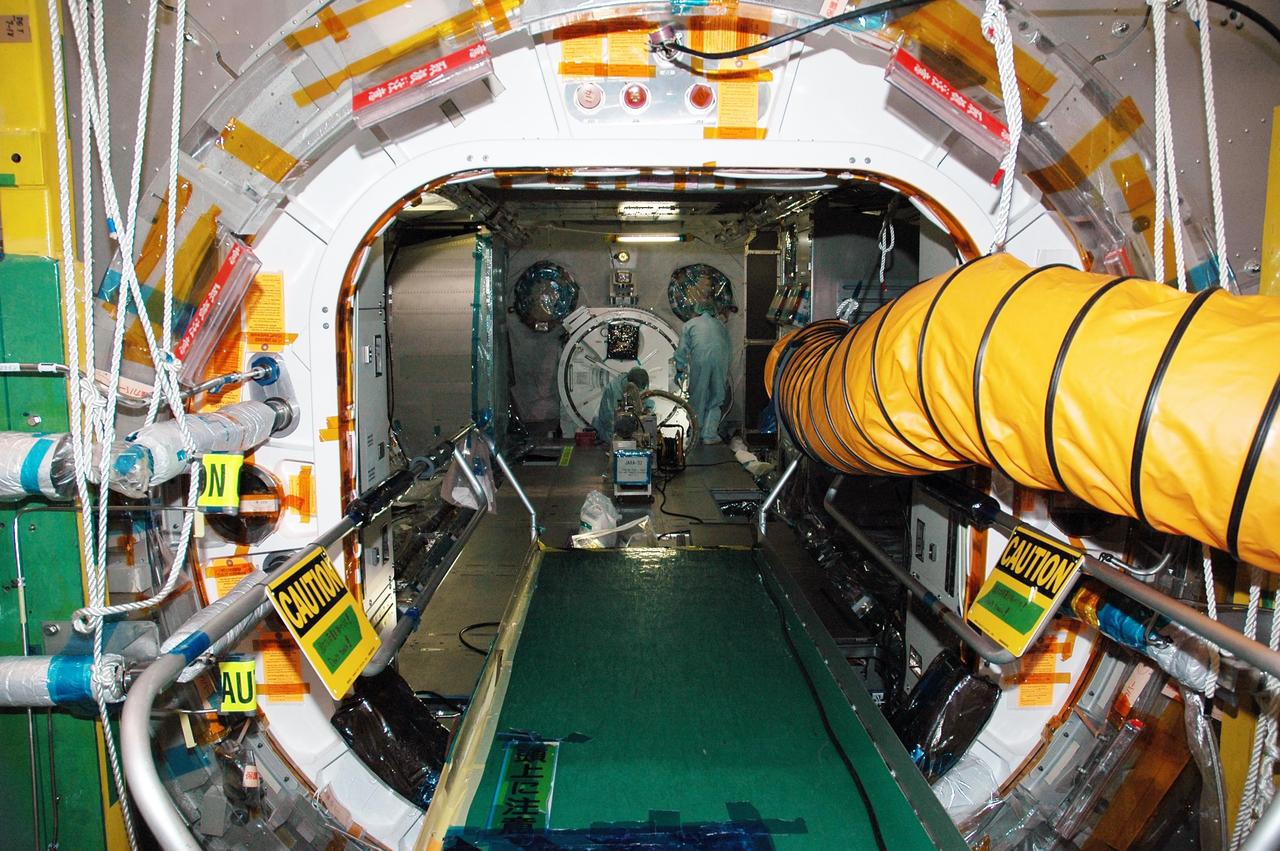

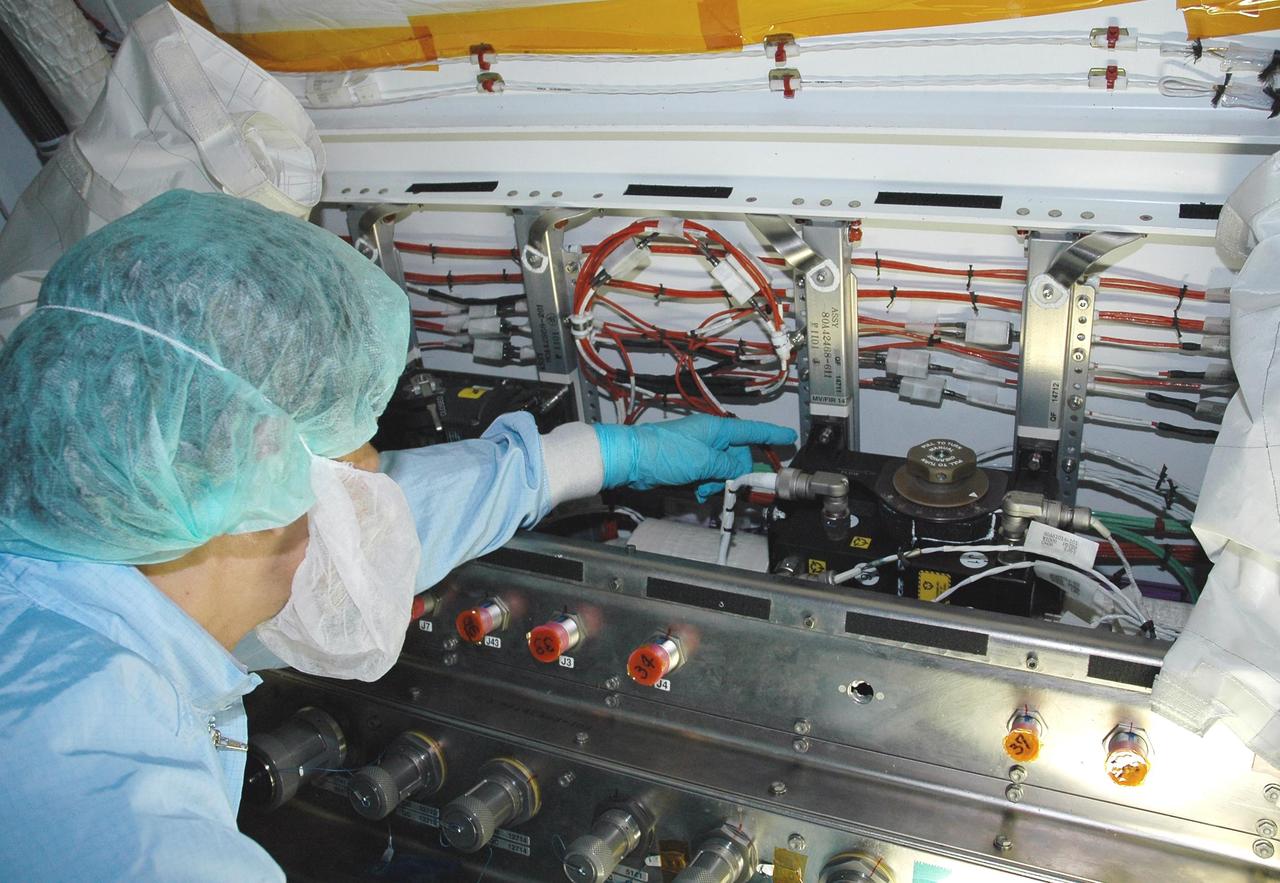
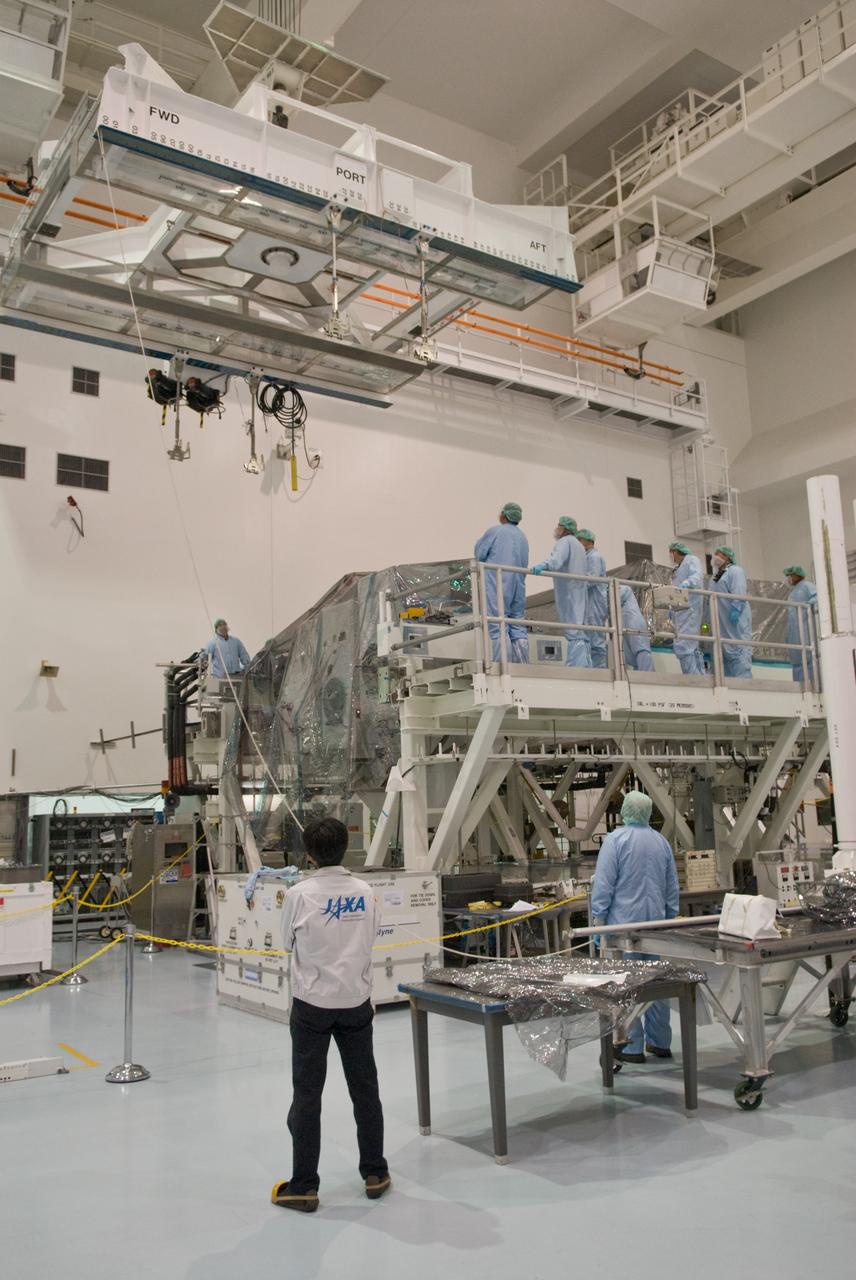
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) technicians install piping insulation on the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). The JEM, developed by JAXA for use on the International Space Station, is named Kibo -- which means "hope" in Japanese -- and will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. Research conducted in Kibo will focus on space medicine, biology, Earth observations, material production, biotechnology and communications. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
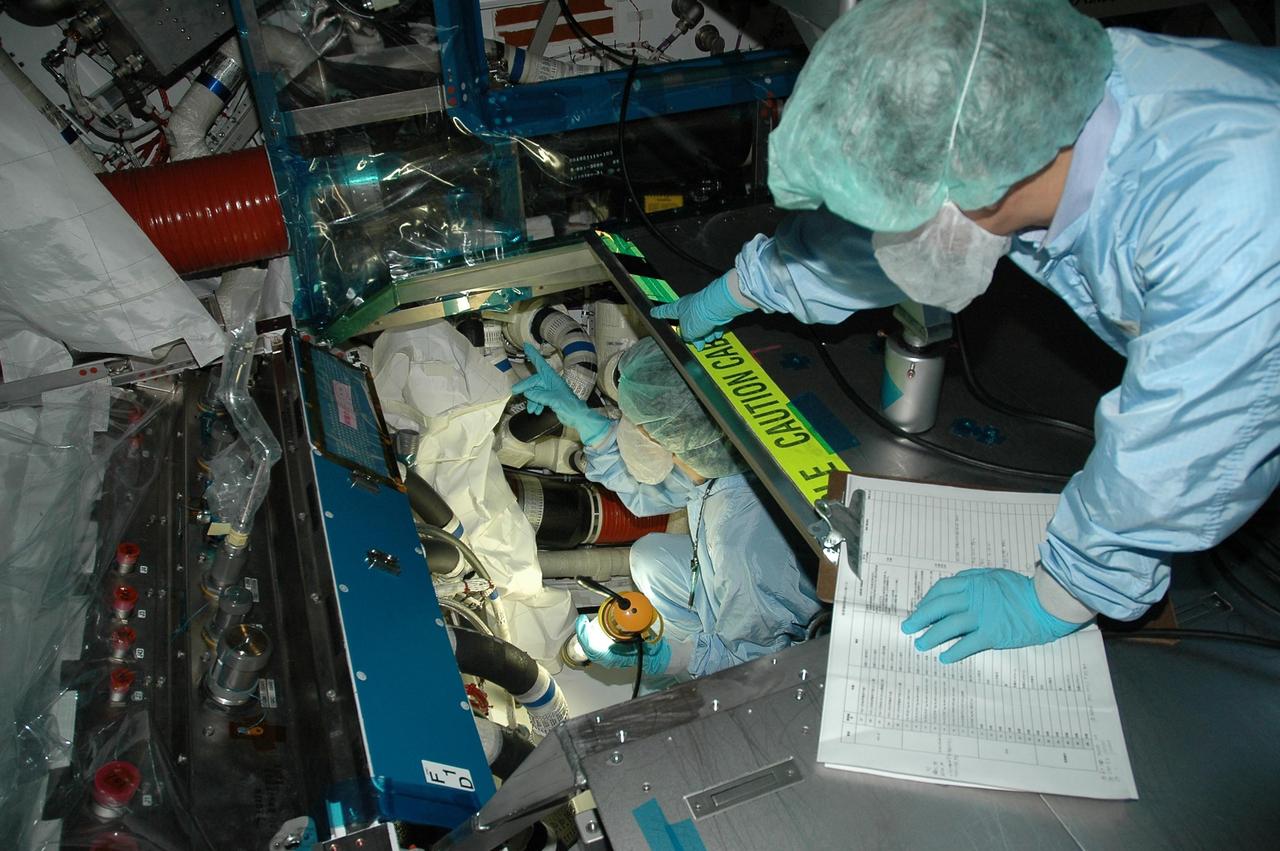

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) technician inspects the wiring on the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). The JEM, developed by JAXA for use on the International Space Station, is named Kibo -- which means "hope" in Japanese -- and will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. Research conducted in Kibo will focus on space medicine, biology, Earth observations, material production, biotechnology and communications. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
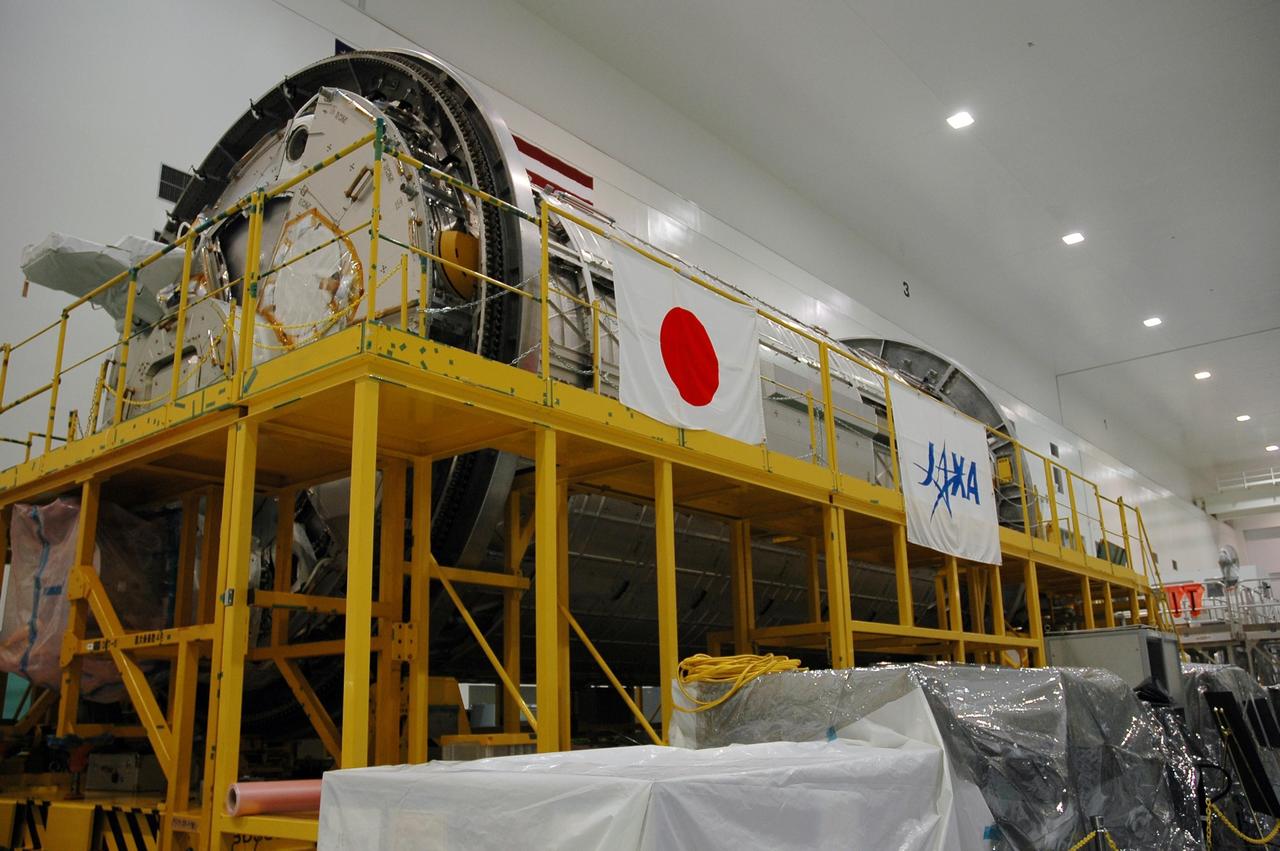

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) awaits its flight to the International Space Station (ISS). The JEM, developed by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) for installation on the ISS, is named Kibo -- which means "hope" in Japanese -- and will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. Research conducted in Kibo will focus on space medicine, biology, Earth observations, material production, biotechnology and communications. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
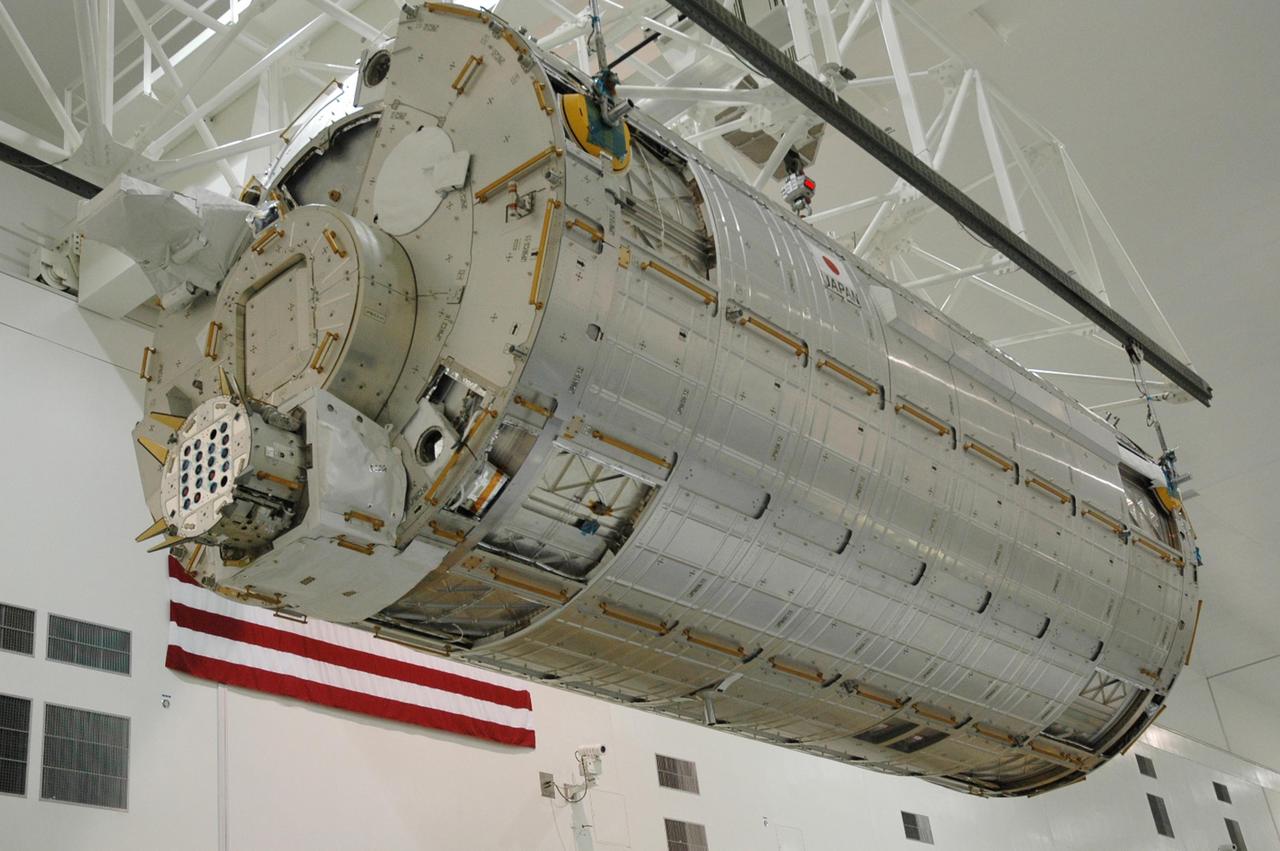

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), after being weighed, makes a return trip to its transporter. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency developed the laboratory at the Tsukuba Space Center near Tokyo. It is the first element, named "Kibo" (Hope), to be delivered to KSC. The JEM is Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station. It will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. The JEM is targeted for mission STS-124, to launch in early 2008. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
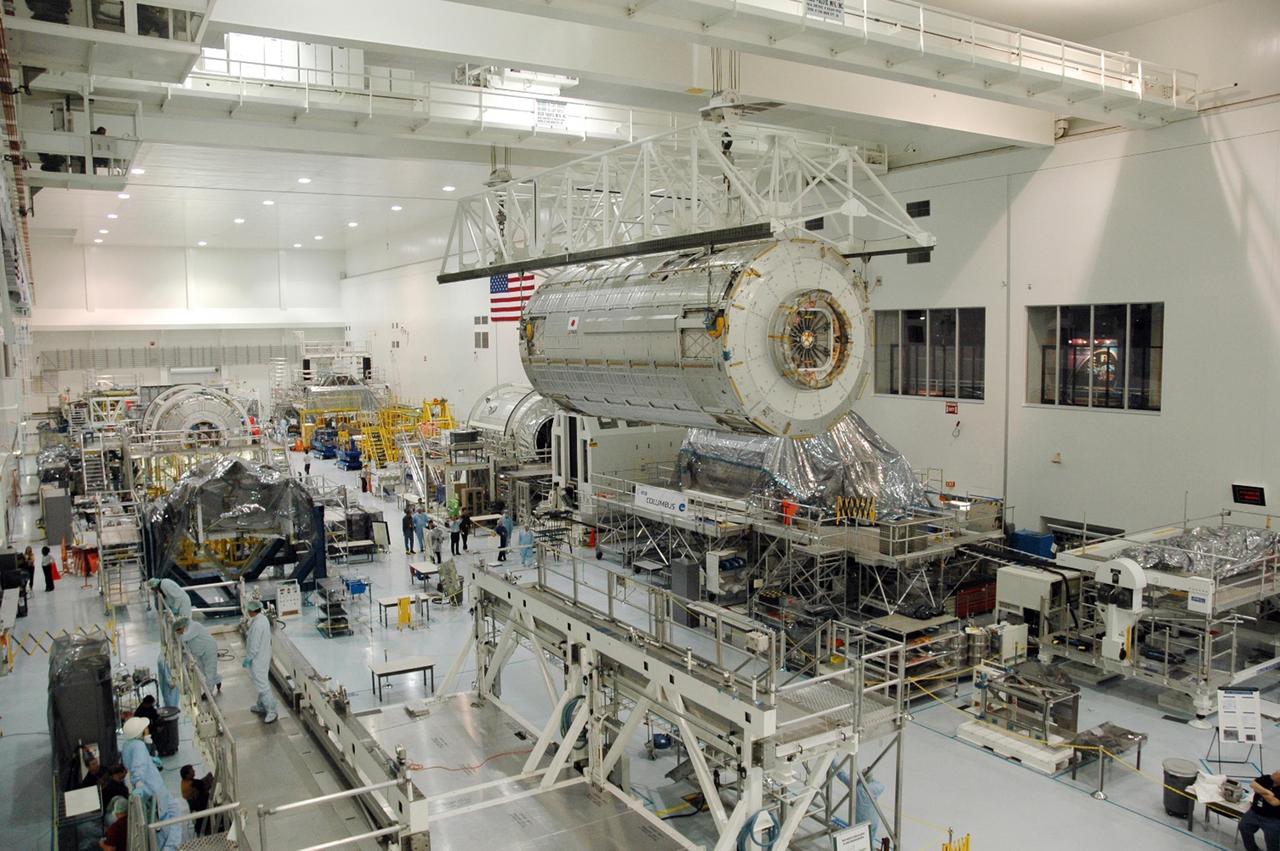

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane carries the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) across the facility. The module is being moved to another stand where it will be weighed and measured for its center of gravity. Other modules intended for the International Space Station are visible on other stands. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency developed the laboratory at the Tsukuba Space Center near Tokyo. It is the first element, named "Kibo" (Hope), to be delivered to KSC. The JEM is Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station. It will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. The JEM is targeted for mission STS-124, to launch in early 2008. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
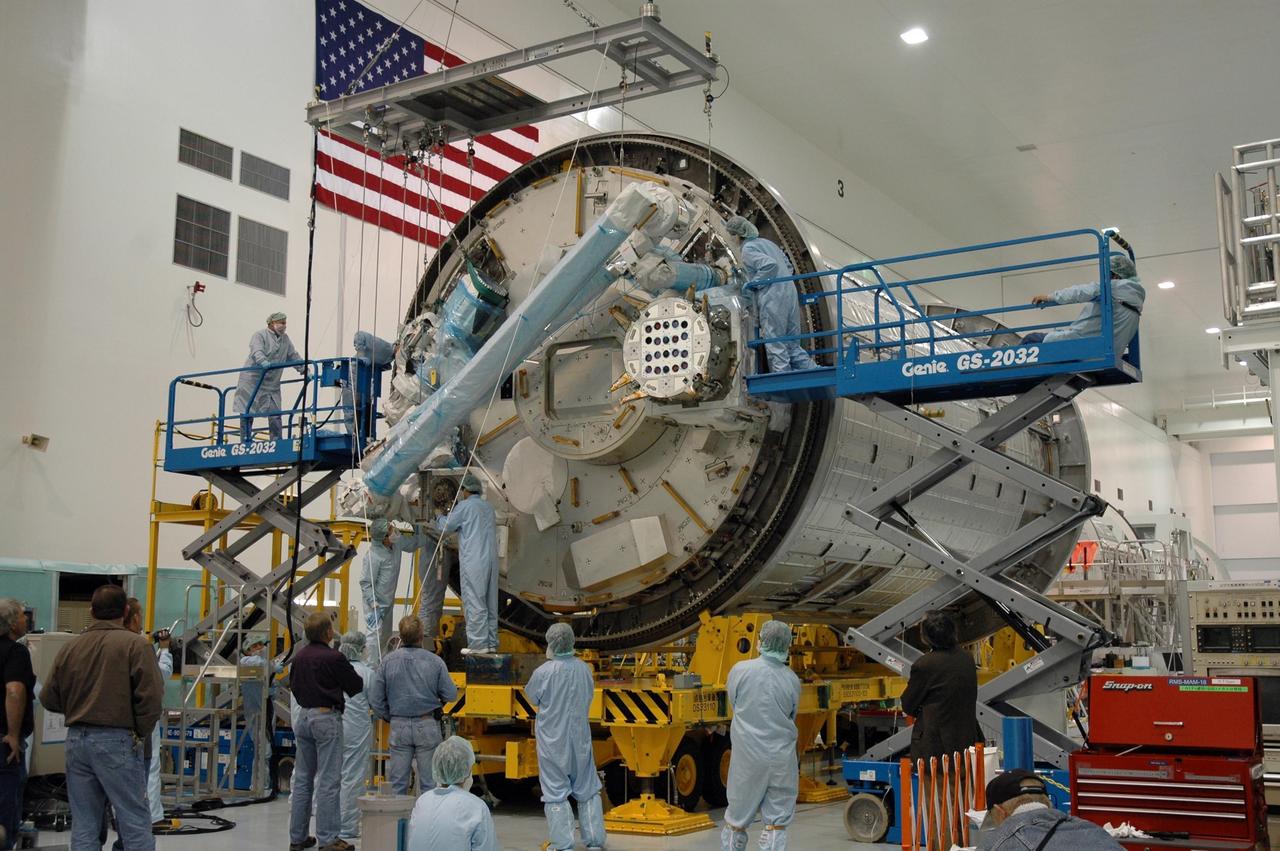

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers attach the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
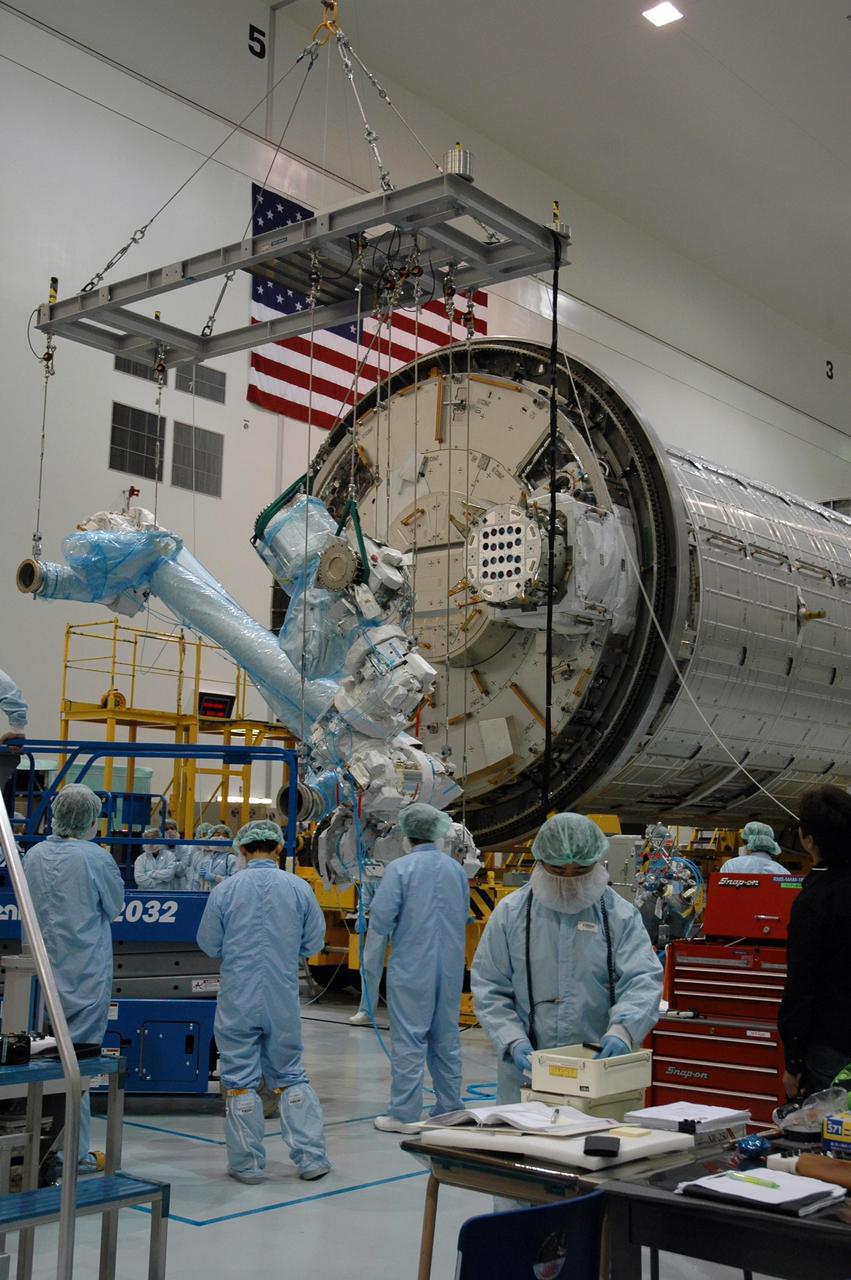

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers attach the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
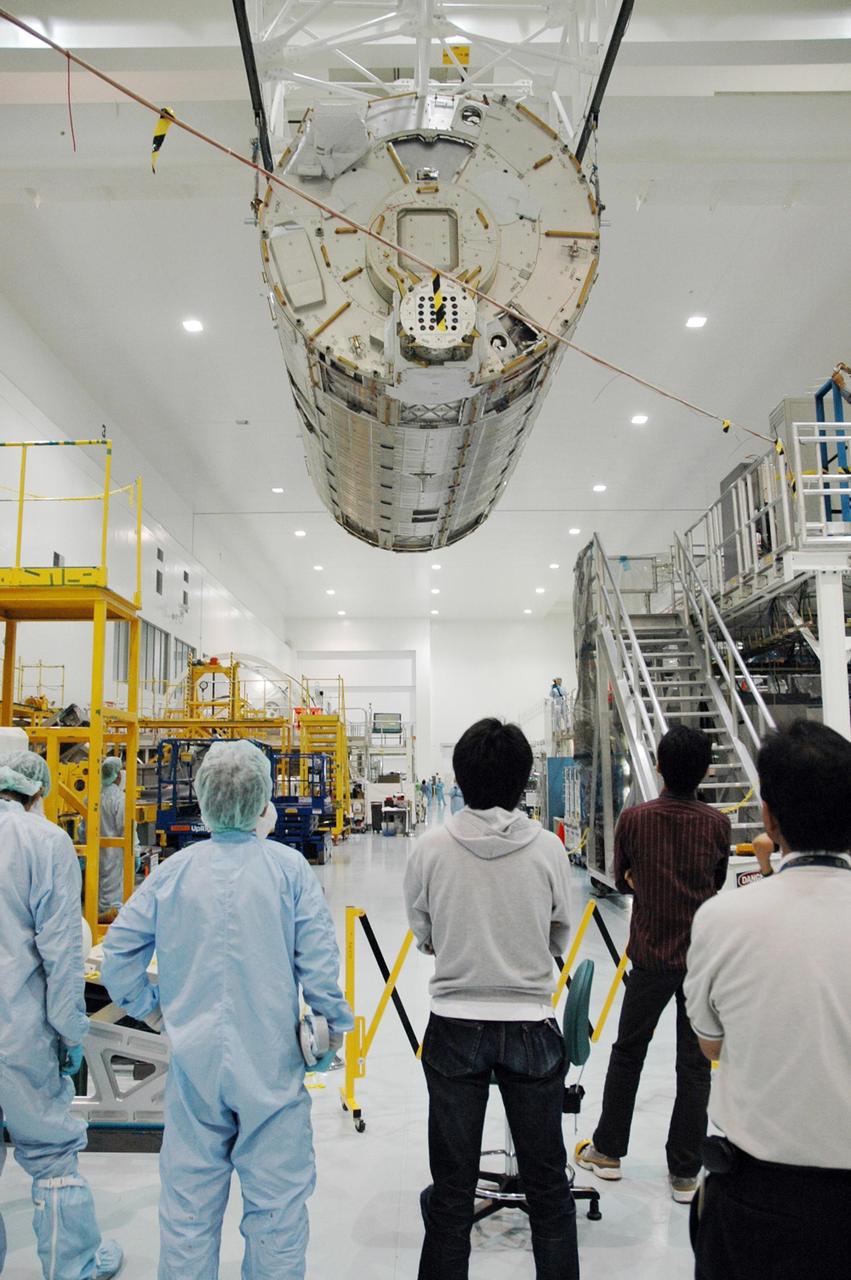

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers on the floor watch as an overhead crane moves the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) to a stand for weighing. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency developed the laboratory at the Tsukuba Space Center near Tokyo. It is the first element, named "Kibo" (Hope), to be delivered to KSC. The JEM is Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station. It will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. The JEM is targeted for mission STS-124, to launch in early 2008. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
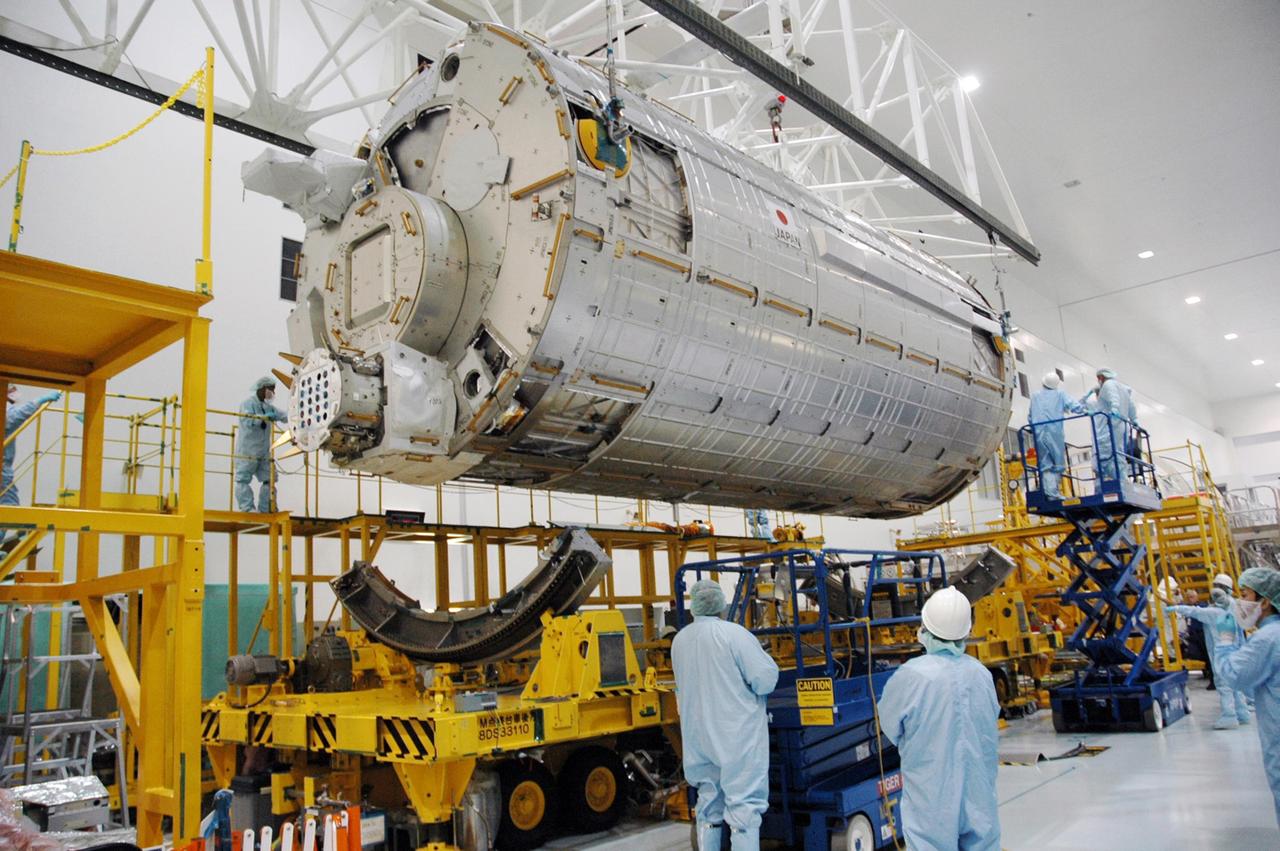

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), after being weighed, has been moved back across the facility and is lowered onto its transporter. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency developed the laboratory at the Tsukuba Space Center near Tokyo. It is the first element, named "Kibo" (Hope), to be delivered to KSC. The JEM is Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station. It will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. The JEM is targeted for mission STS-124, to launch in early 2008. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
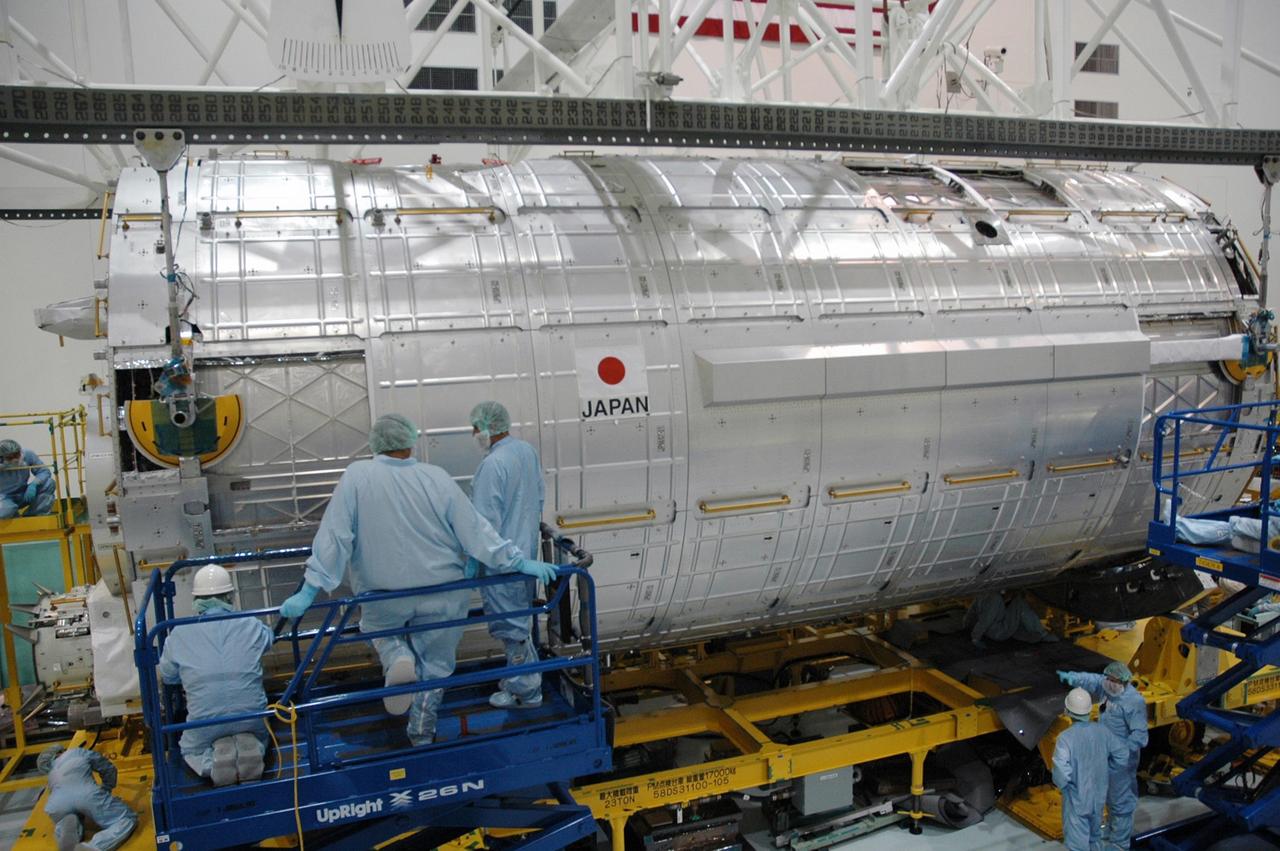

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers monitor the placement of the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) onto its transporter. The JEM was moved from the transporter for weighing and to measure its center of gravity. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency developed the laboratory at the Tsukuba Space Center near Tokyo. It is the first element, named "Kibo" (Hope), to be delivered to KSC. The JEM is Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station. It will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. The JEM is targeted for mission STS-124, to launch in early 2008. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
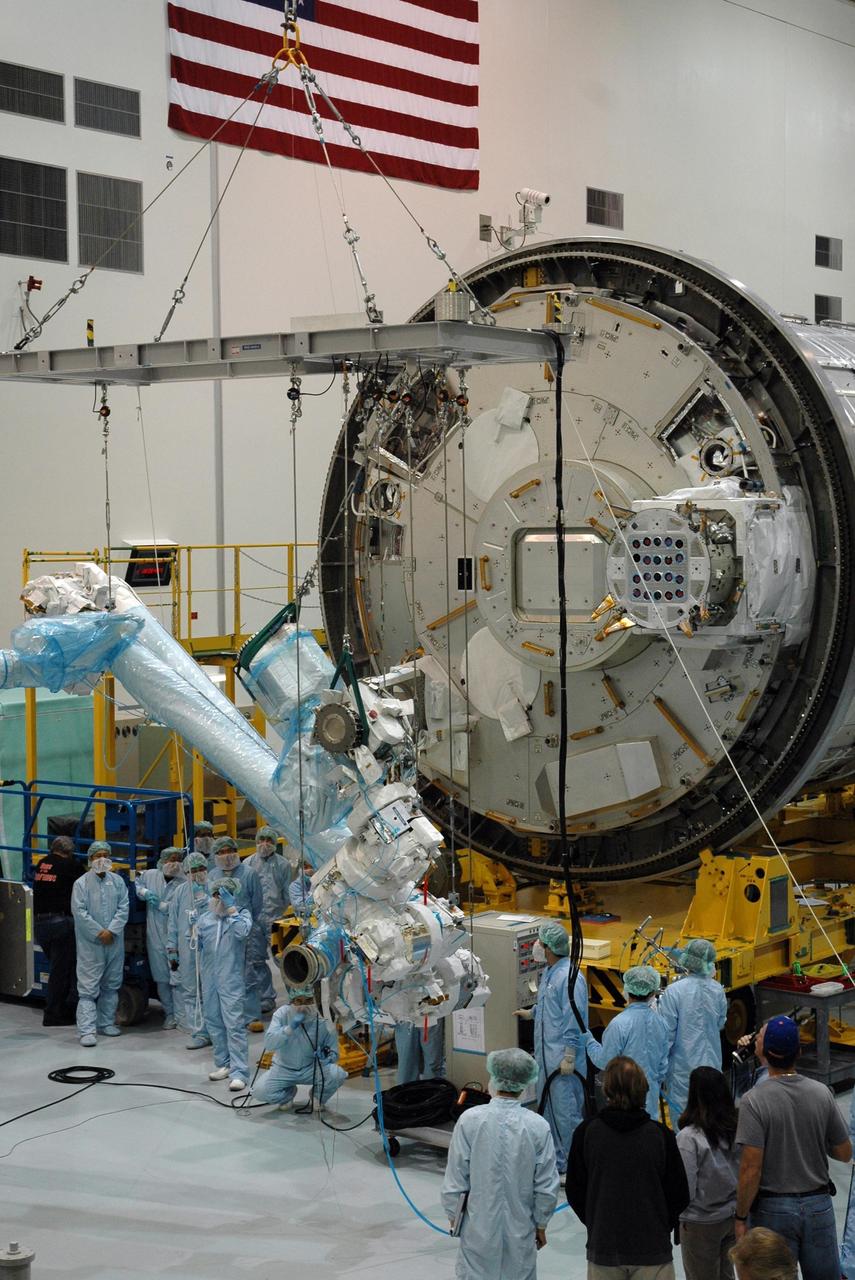

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers attach the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
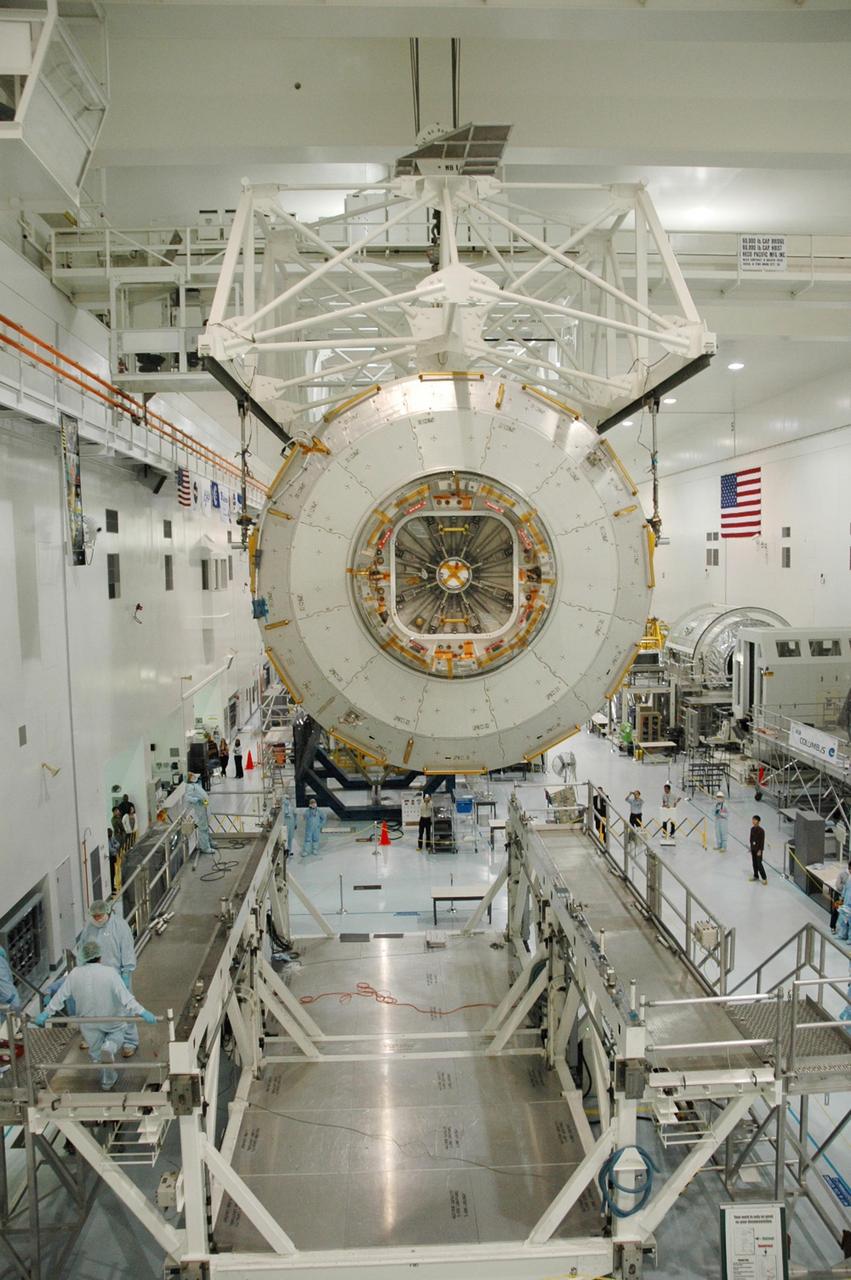

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane begins lowering the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) onto a weighing stand. The module will also be measured for its center of gravity. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency developed the laboratory at the Tsukuba Space Center near Tokyo. It is the first element, named "Kibo" (Hope), to be delivered to KSC. The JEM is Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station. It will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. The JEM is targeted for mission STS-124, to launch in early 2008. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
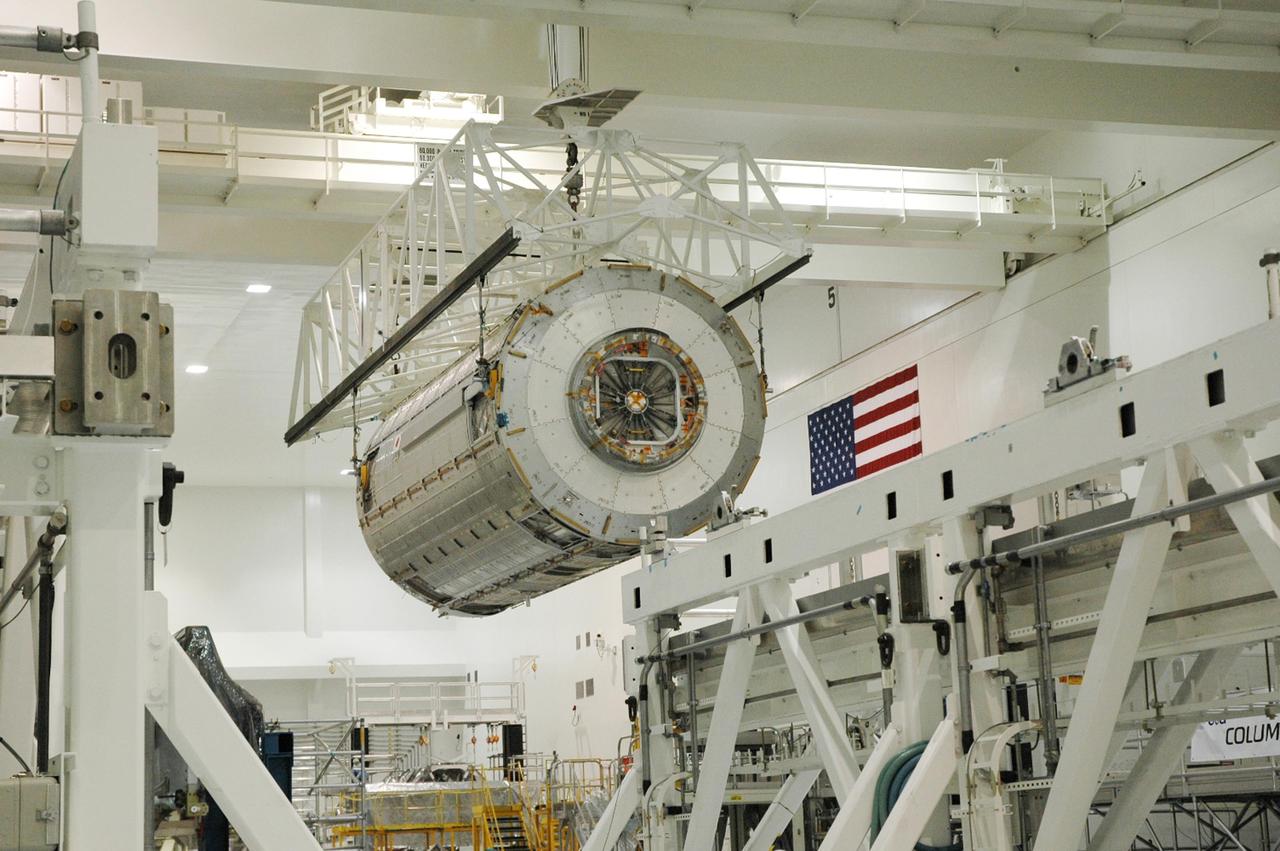

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane carries the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) across the facility. The module is being moved to another stand where it will be weighed and measured for its center of gravity. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency developed the laboratory at the Tsukuba Space Center near Tokyo. It is the first element, named "Kibo" (Hope), to be delivered to KSC. The JEM is Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station. It will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. The JEM is targeted for mission STS-124, to launch in early 2008. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
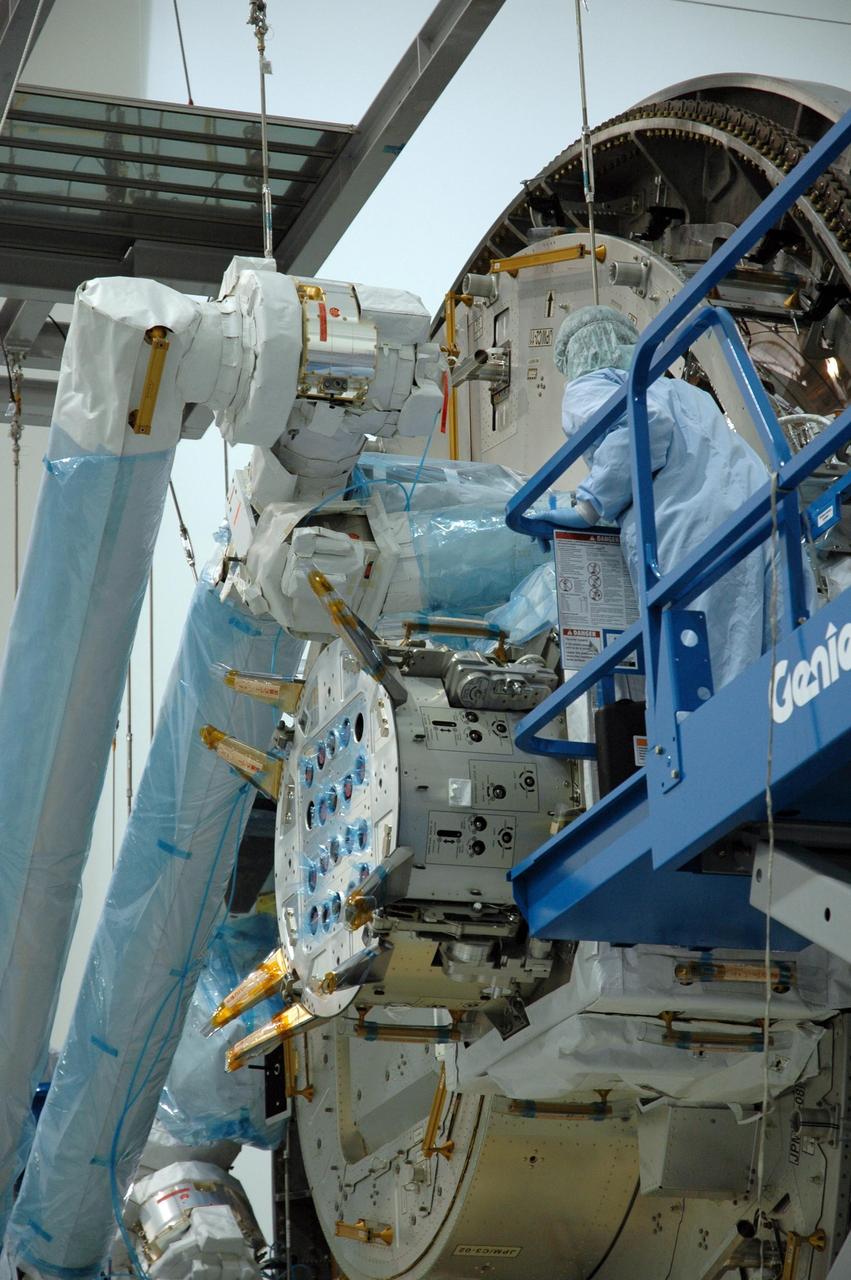
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, a worker helps to attach the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
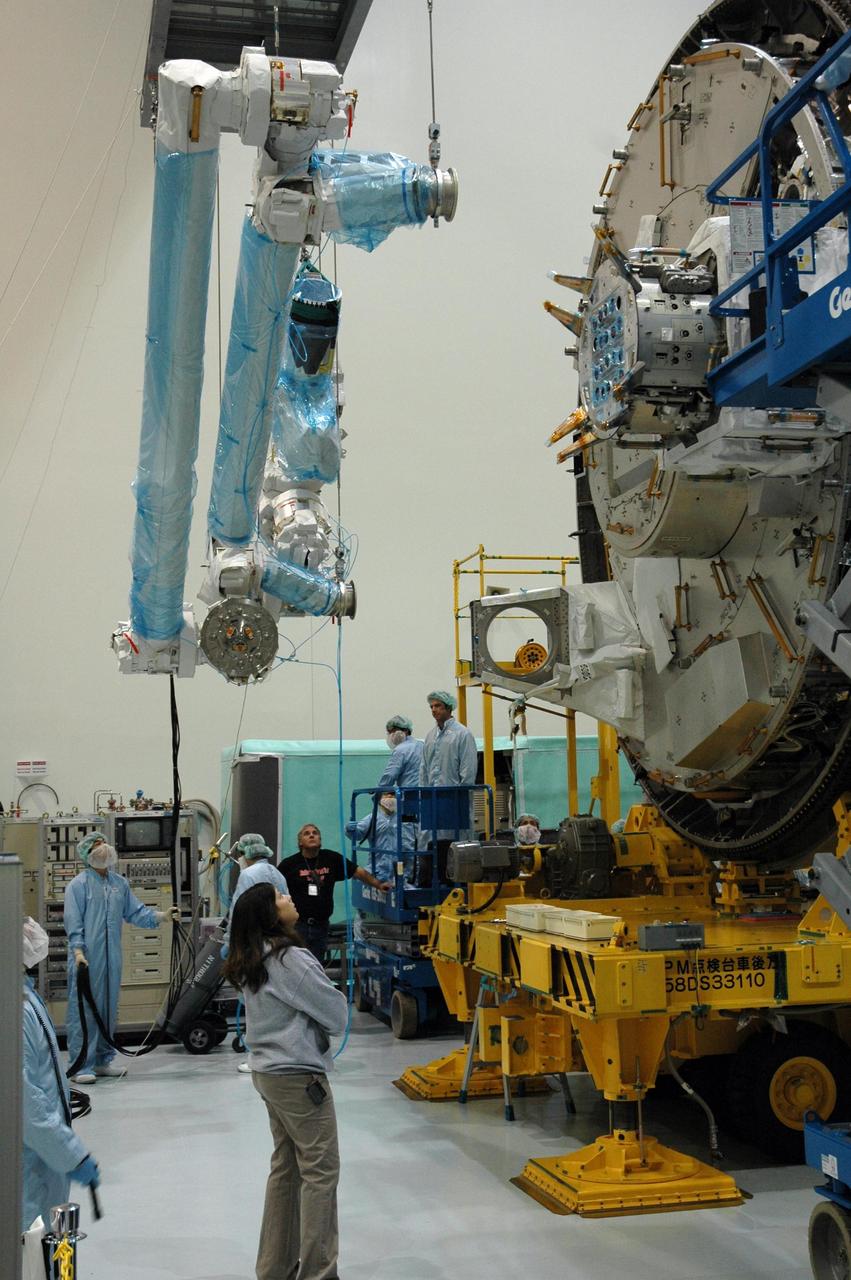

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers use a hoisting device to move the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, toward the Japanese Experiment Module for installation and testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008.The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
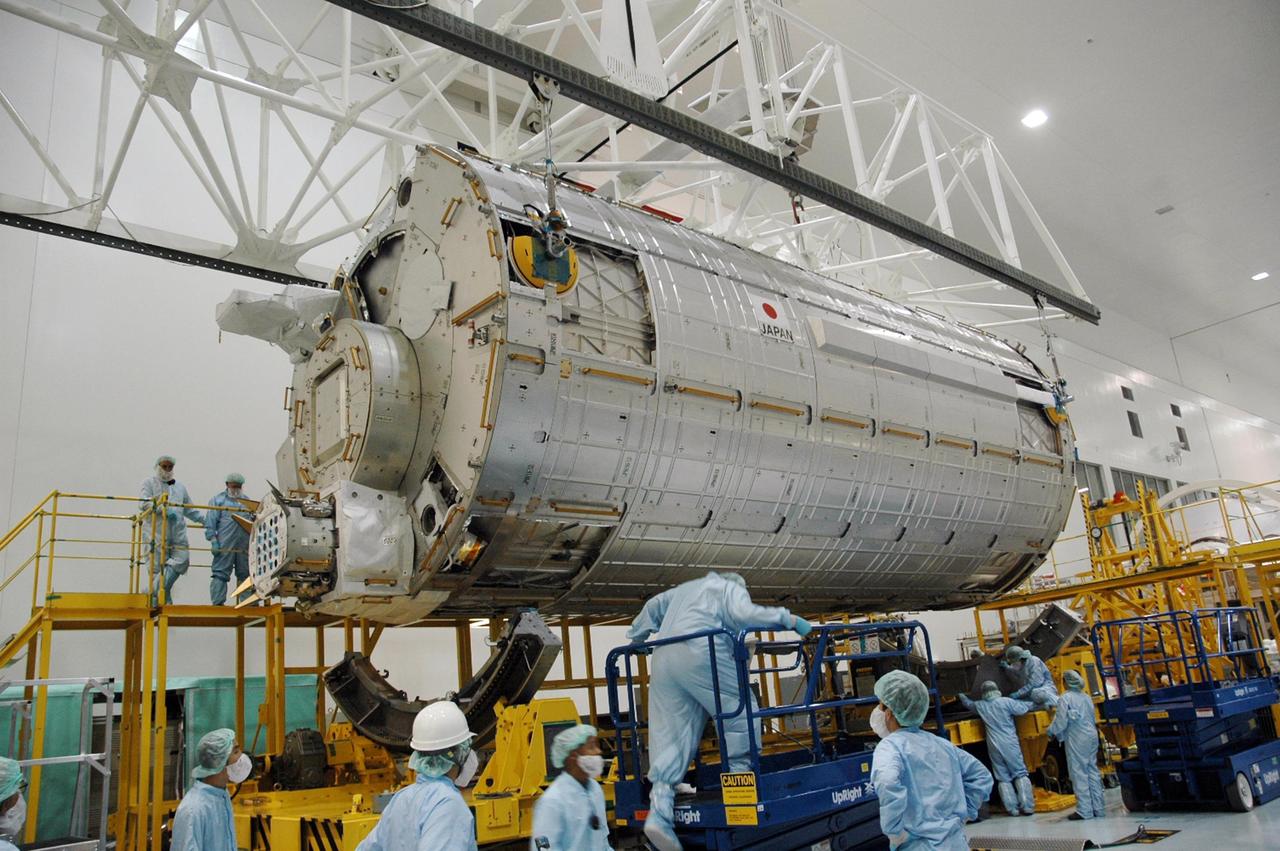

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, an overhead crane lifts the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) off of its transporter. The module is being moved to another stand where it will be weighed and measured for its center of gravity. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency developed the laboratory at the Tsukuba Space Center near Tokyo. It is the first element, named "Kibo" (Hope), to be delivered to KSC. The JEM is Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station. It will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. The JEM is targeted for mission STS-124, to launch in early 2008. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
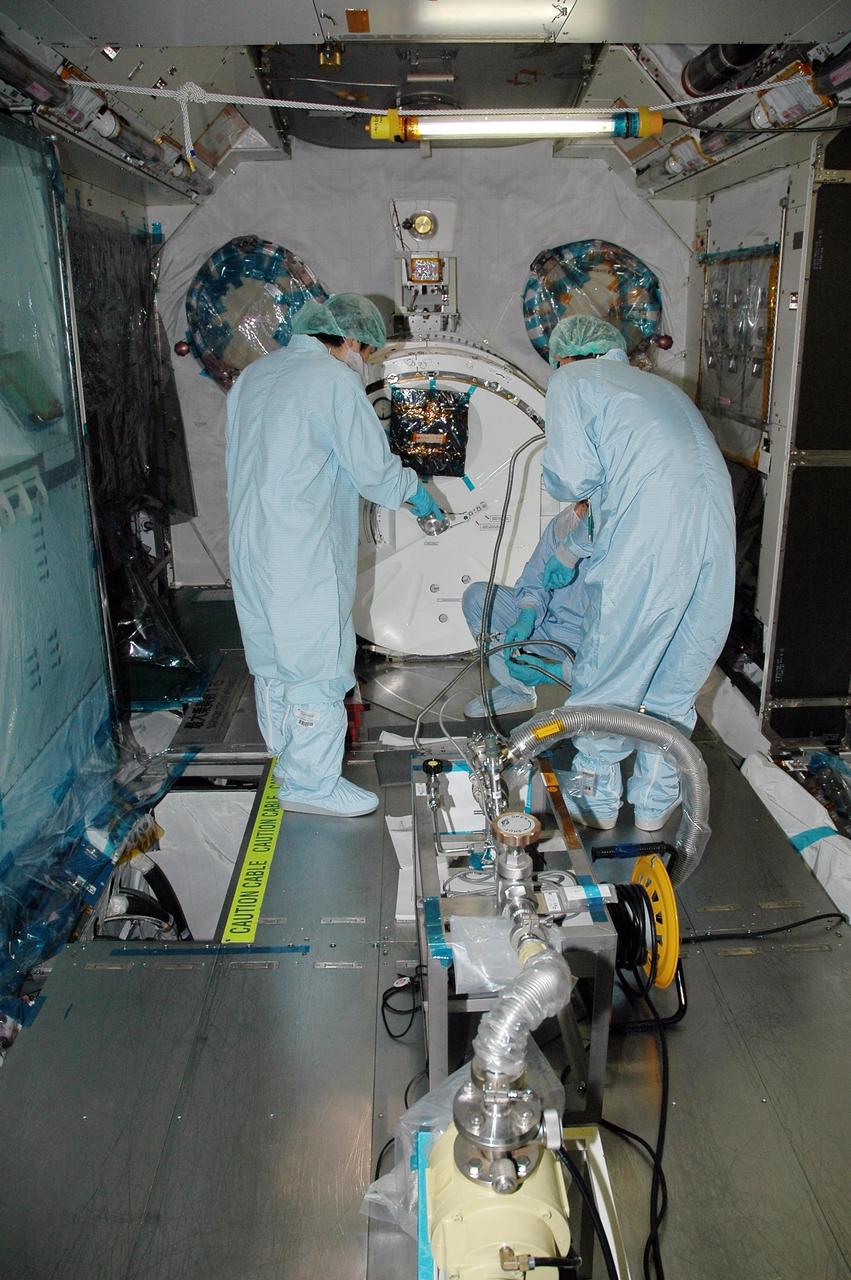

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) technicians install piping insulation on the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). The JEM, developed by JAXA for use on the International Space Station, is named Kibo -- which means "hope" in Japanese -- and will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. Research conducted in Kibo will focus on space medicine, biology, Earth observations, material production, biotechnology and communications. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
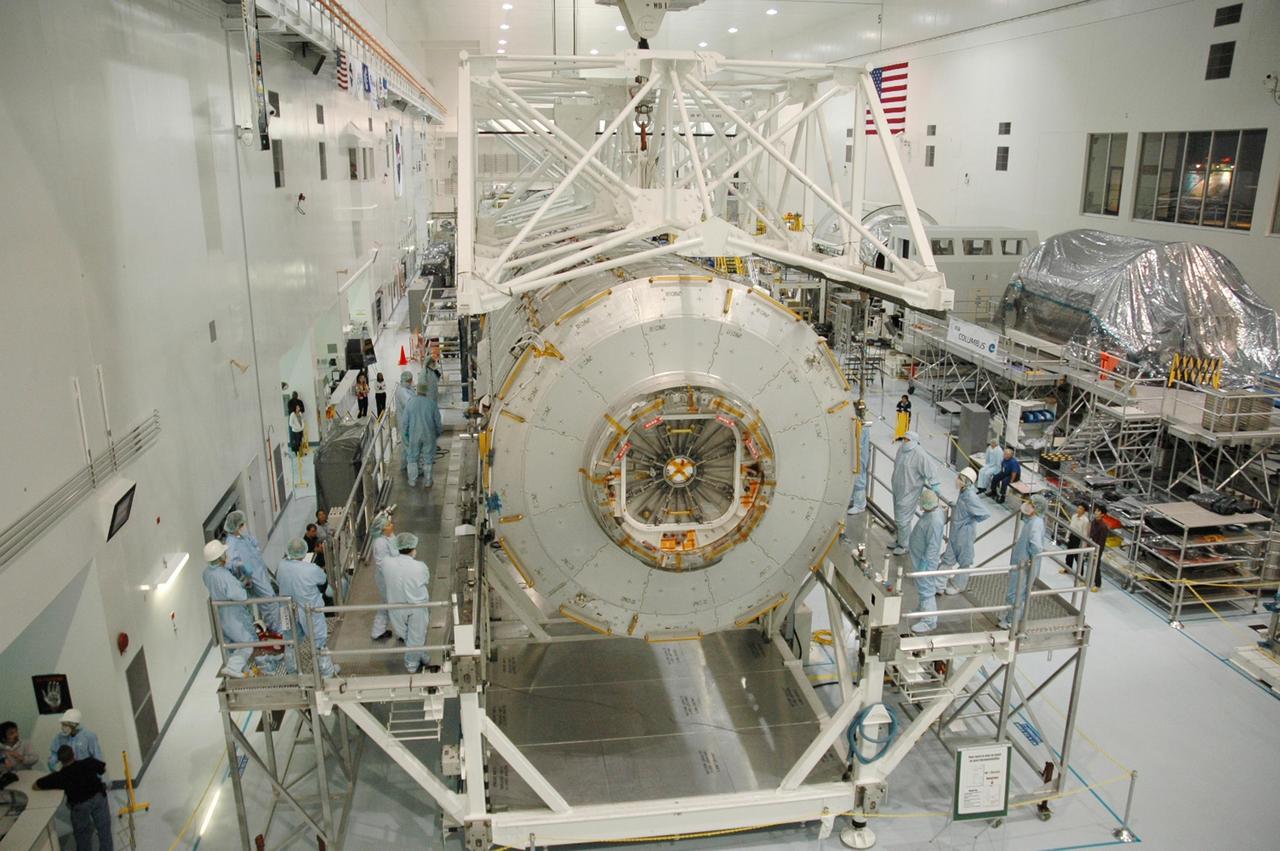

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers observe as an overhead crane lowers the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) onto a weighing stand. The module will also be measured for its center of gravity. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency developed the laboratory at the Tsukuba Space Center near Tokyo. It is the first element, named "Kibo" (Hope), to be delivered to KSC. The JEM is Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station. It will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. The JEM is targeted for mission STS-124, to launch in early 2008. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
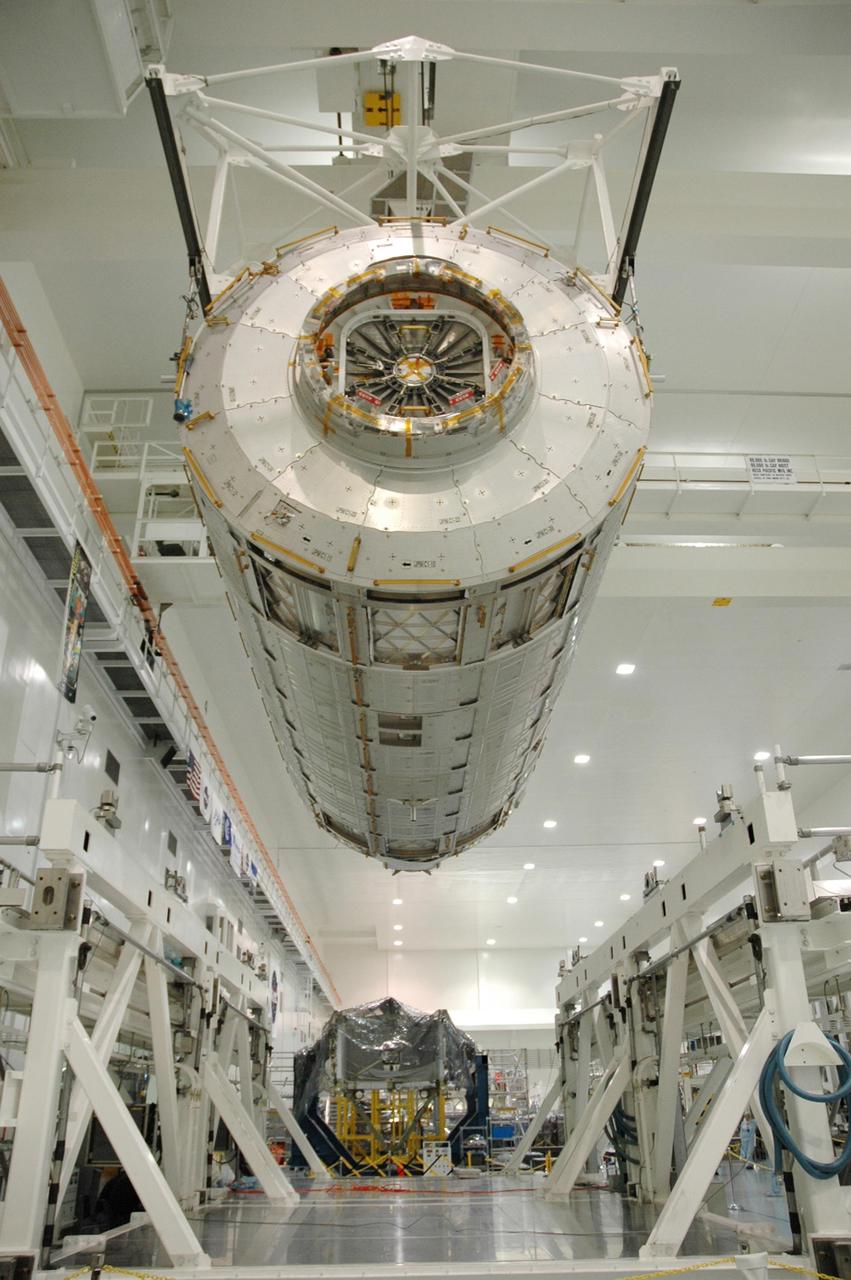

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), after being weighed, is lifted off the scale to be returned to its transporter. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency developed the laboratory at the Tsukuba Space Center near Tokyo. It is the first element, named "Kibo" (Hope), to be delivered to KSC. The JEM is Japan's primary contribution to the International Space Station. It will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. The JEM is targeted for mission STS-124, to launch in early 2008. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers attach the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, to the Japanese Experiment Module for testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008. The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
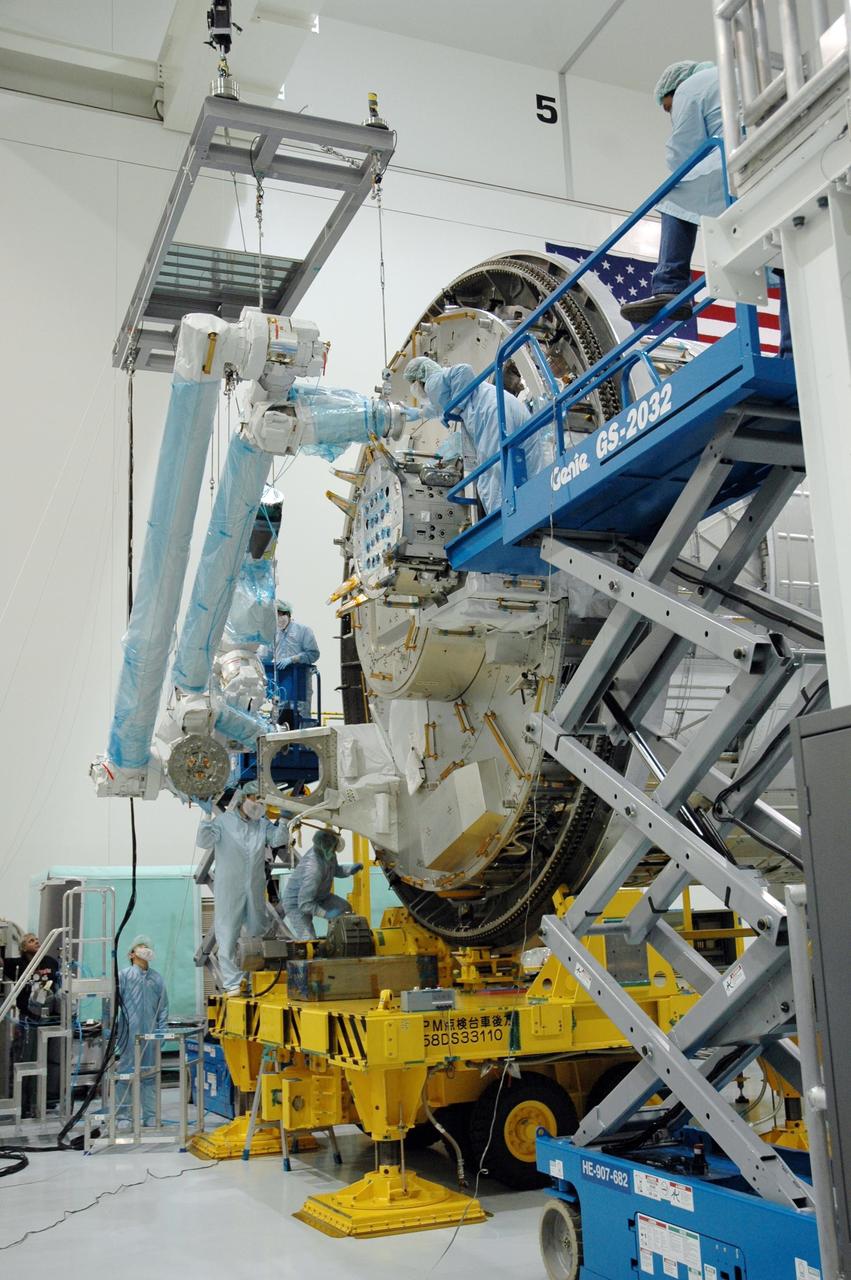
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center, workers use a hoisting device to move the Remote Manipulator System, or robotic arm, toward the Japanese Experiment Module for installation and testing. The RMS is one of the payloads scheduled to be delivered to the station on a future mission tentatively scheduled for 2008.The RMS is similar to the robotic arm already installed on the station's mobile base system. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) technicians inspect the wiring on the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). The JEM, developed by JAXA for use on the International Space Station, is named Kibo -- which means "hope" in Japanese -- and will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. Research conducted in Kibo will focus on space medicine, biology, Earth observations, material production, biotechnology and communications. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
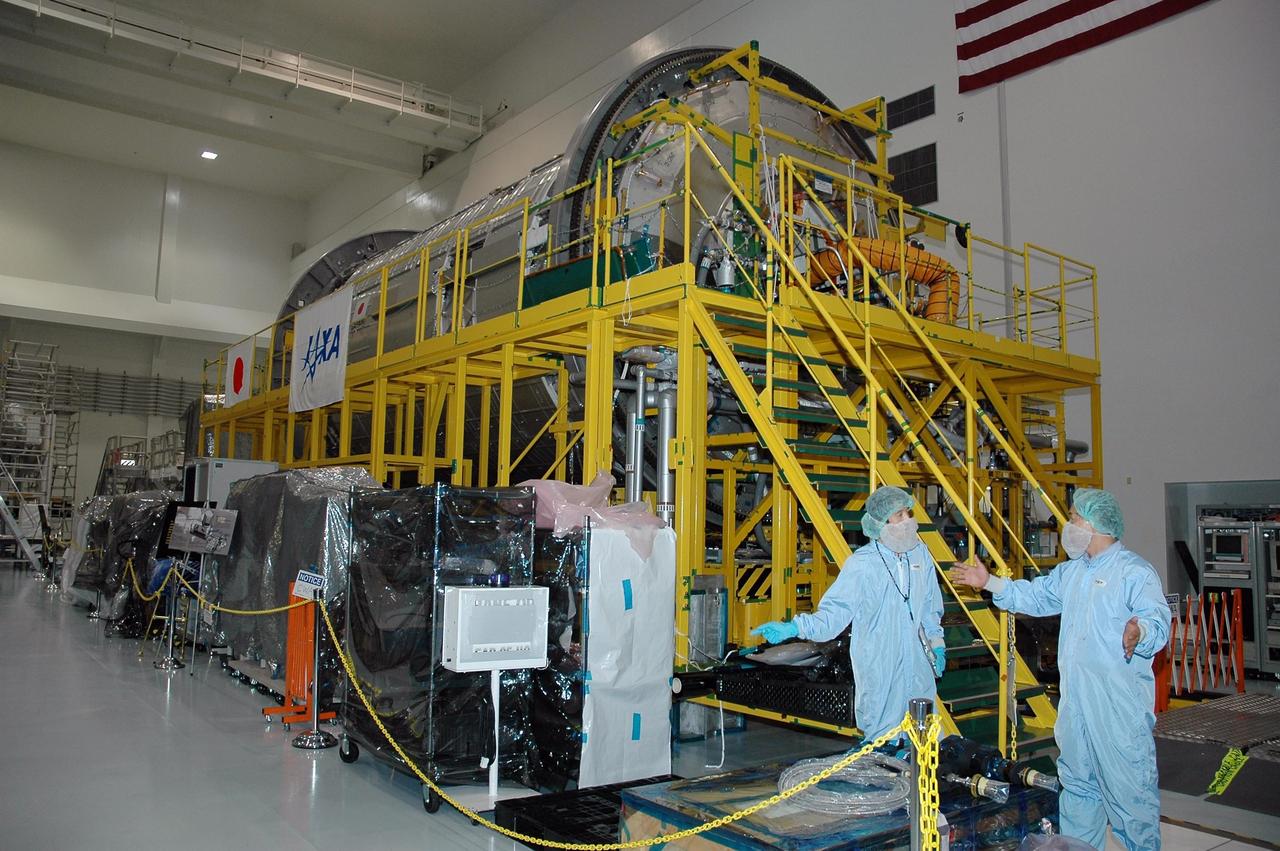

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, processing continues on the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) for its flight to the International Space Station (ISS). The JEM, developed by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) for installation on the ISS, is named Kibo -- which means "hope" in Japanese -- and will enhance the unique research capabilities of the orbiting complex by providing an additional environment for astronauts to conduct science experiments. Research conducted in Kibo will focus on space medicine, biology, Earth observations, material production, biotechnology and communications. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
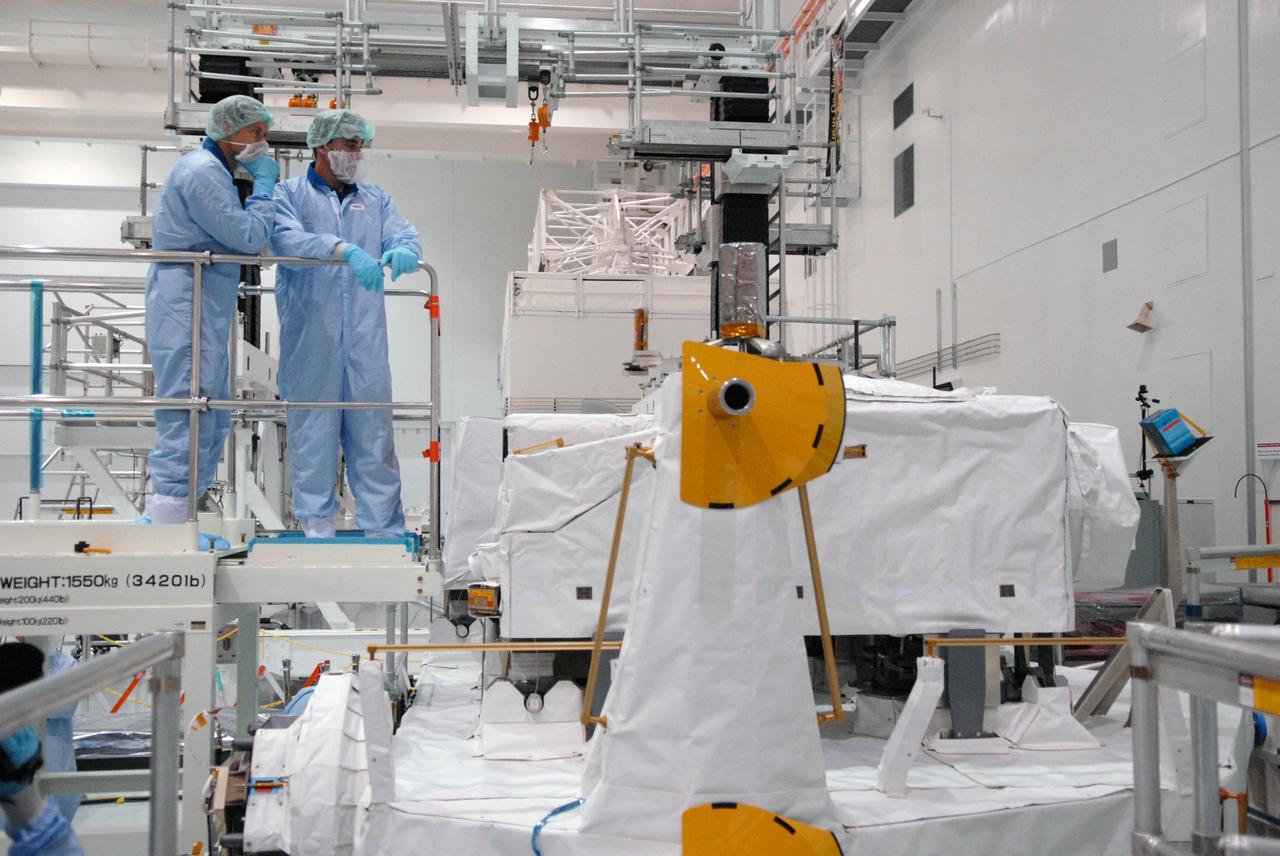

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the STS-127 crew look at some of the elements on the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES. The crew is Commander Mark Polansky, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Christopher Cassidy, Tom Marshburn, Dave Wolf, Julie Payette and Tim Kopra. They are at Kennedy for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, or CEIT, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware for the mission. The payload will be launched to the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitrios Gerondidakis
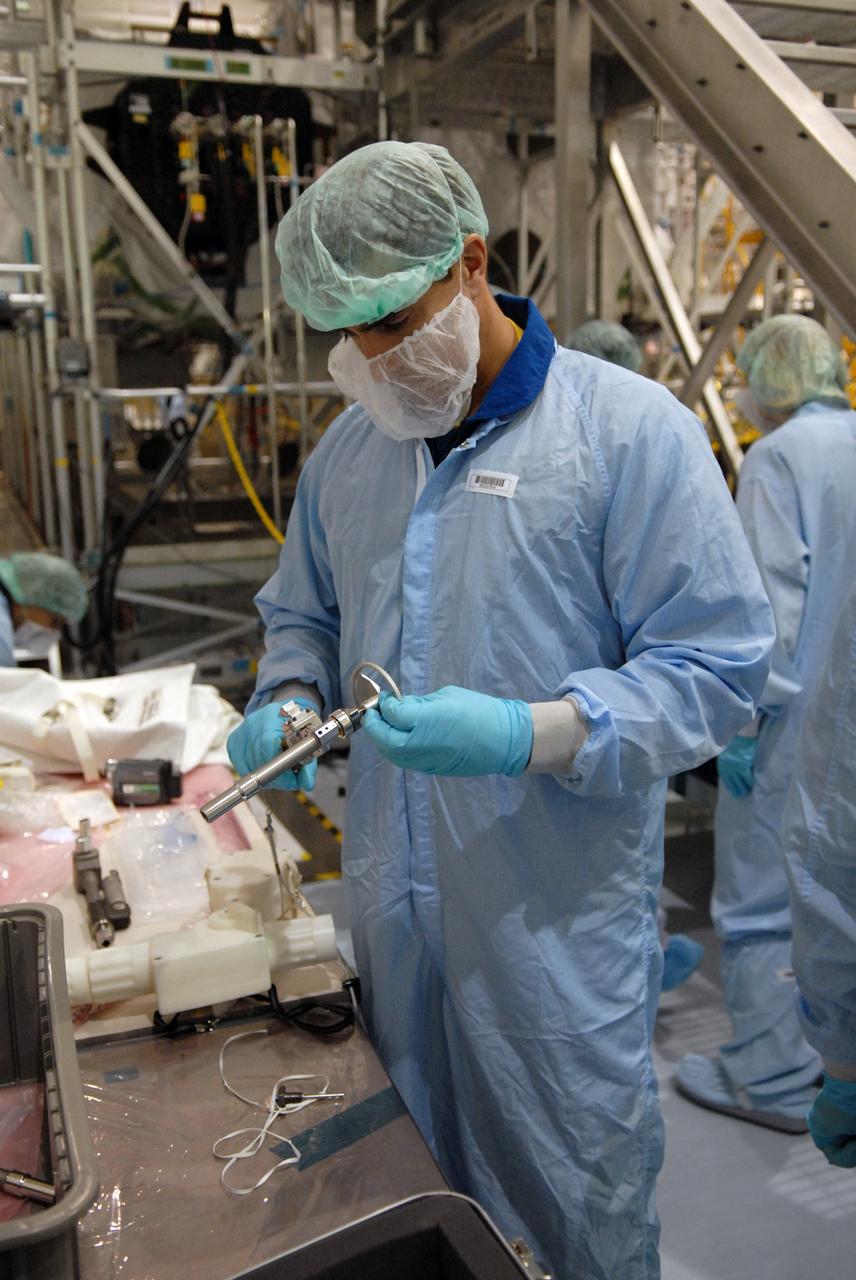

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the STS-127 Mission Specialist Chris Cassidy prepares the tools he will use on-orbit to set up the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, part of the payload on the mission. The crew members are at Kennedy for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, or CEIT, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware for the mission. The payload will be launched to the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitrios Gerondidakis
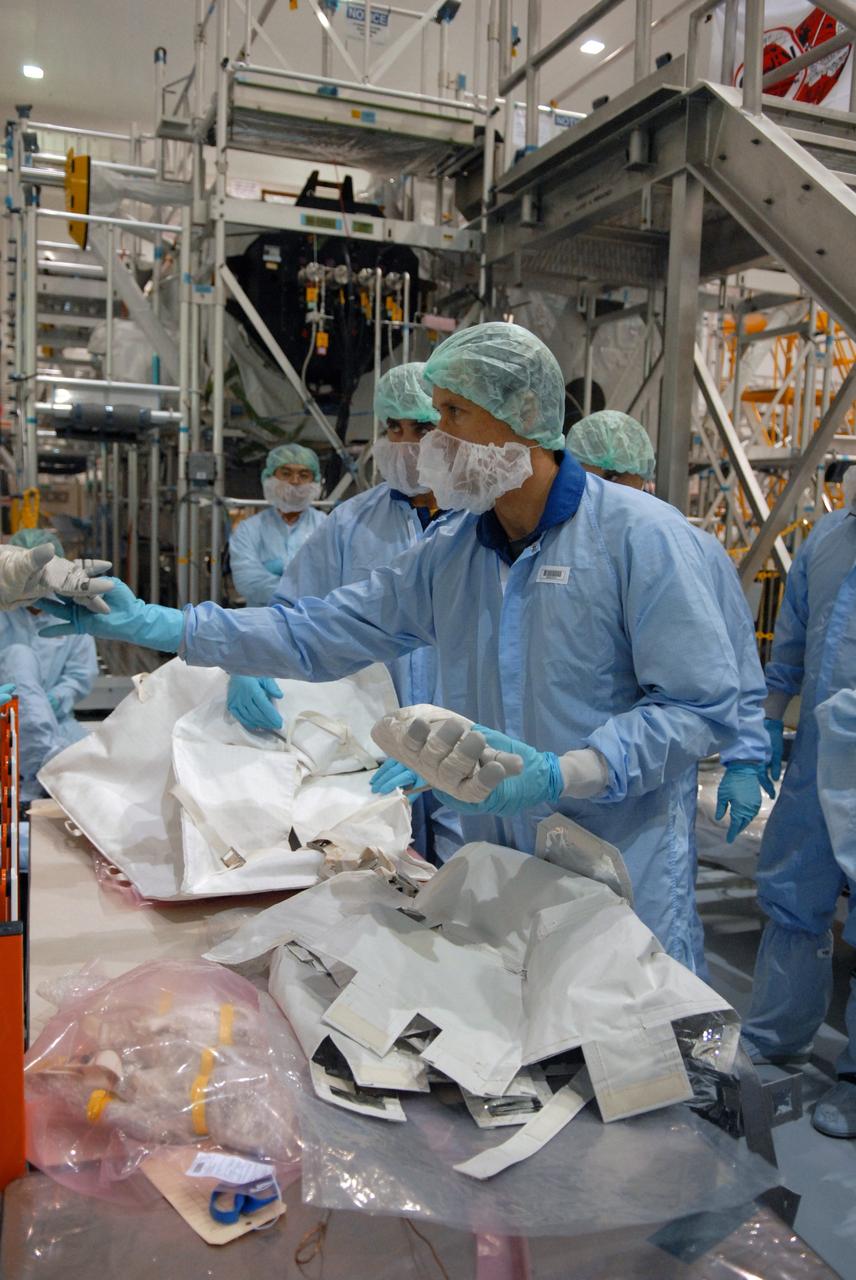

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the STS-127 crew check out equipment related to the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, part of the payload on the mission. The crew is Commander Mark Polansky, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Christopher Cassidy, Tom Marshburn, Dave Wolf, Julie Payette and Tim Kopra. They are at Kennedy for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, or CEIT, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware for the mission. The payload will be launched to the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitrios Gerondidakis
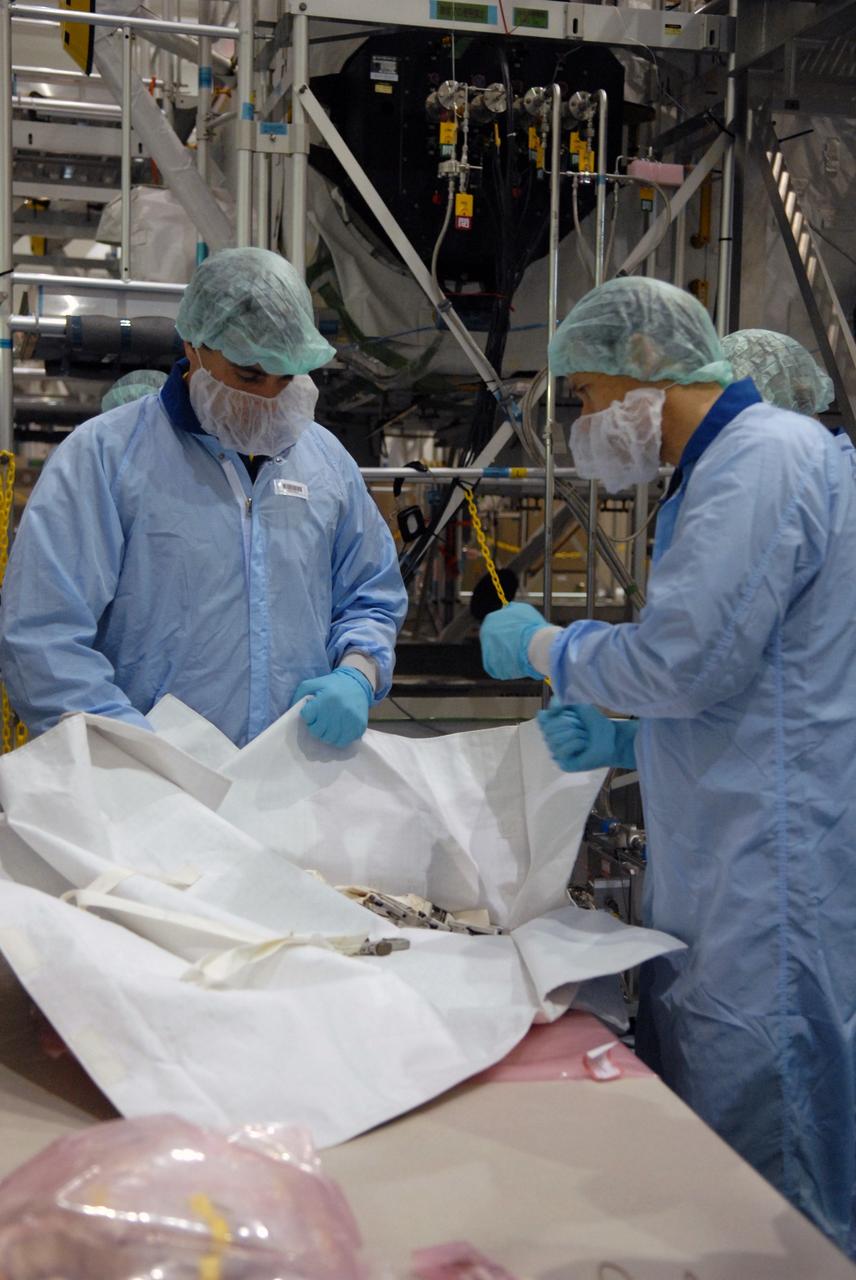

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the STS-127 Mission Specialists Chris Cassidy and Tom Marshburn review options of how they will stow the excess thermal blankets on the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, after they remove them on-orbit. The crew members are at Kennedy for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, or CEIT, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware for the mission. The payload will be launched to the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitrios Gerondidakis
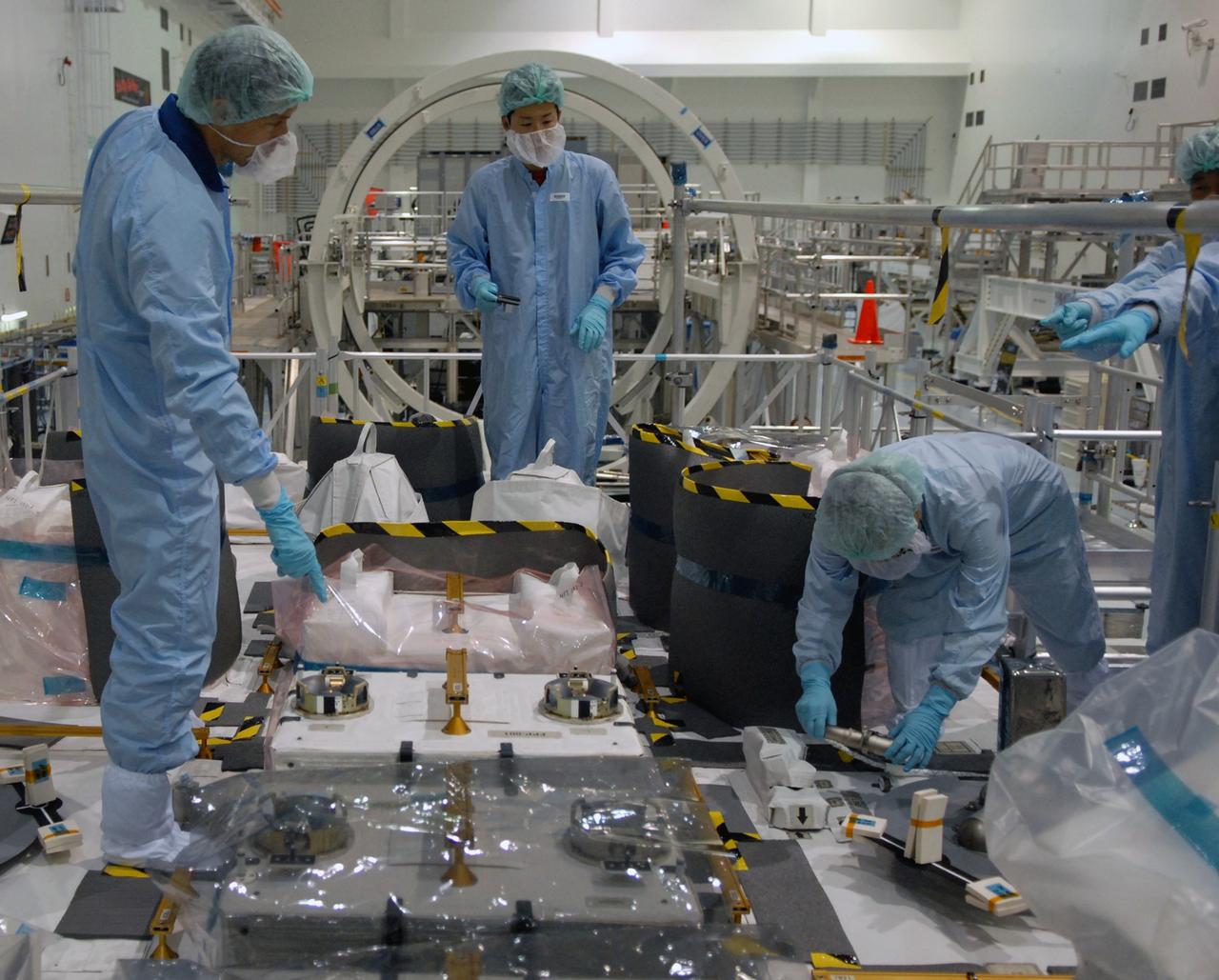

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the STS-127 crew check out equipment on the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, part of the payload on the mission. The crew is Commander Mark Polansky, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Christopher Cassidy, Tom Marshburn, Dave Wolf, Julie Payette and Tim Kopra. They are at Kennedy for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, or CEIT, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware for the mission. The payload will be launched to the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitrios Gerondidakis
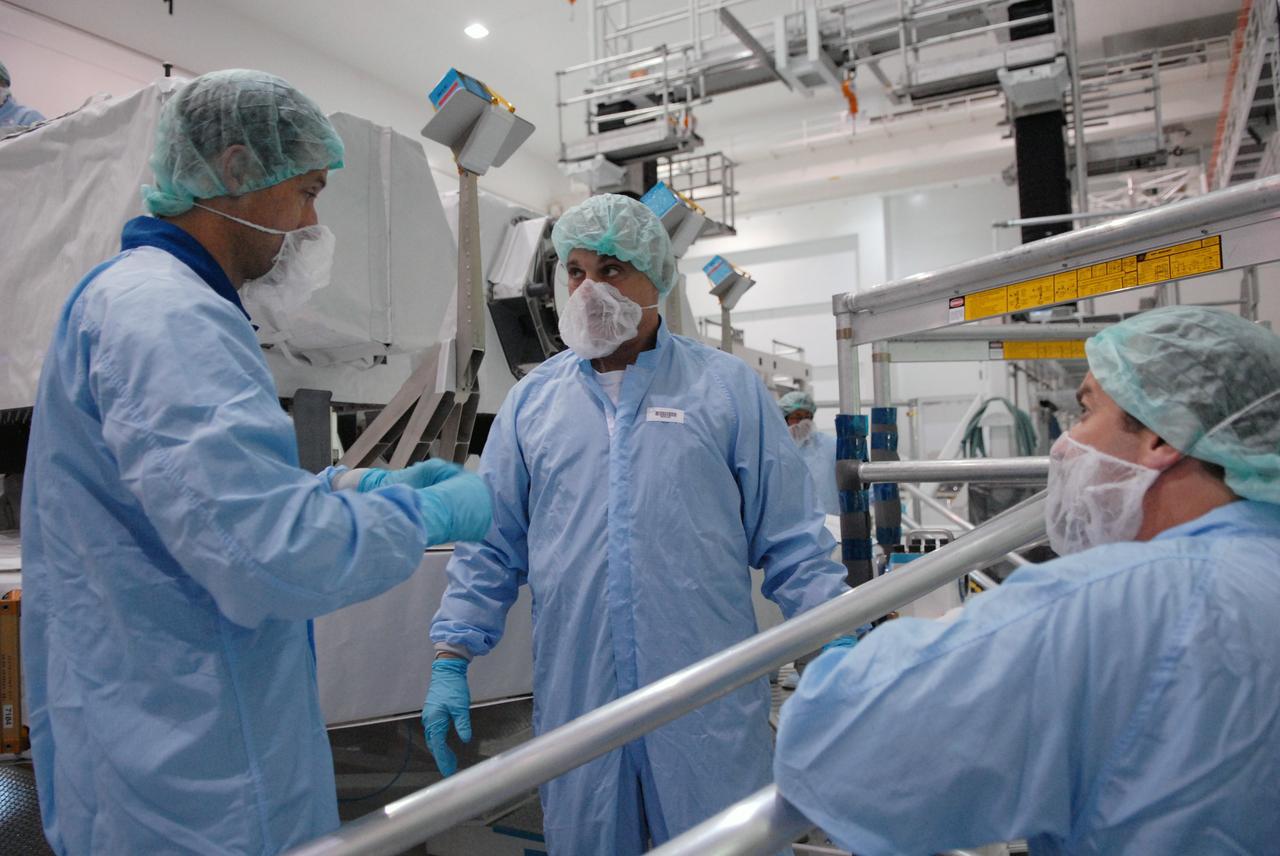

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Mission Specialists Tom Marshburn and Dave Wolf review their on-orbit task to install and make the JEM Exposed Facility operational. Other crew members are Commander Mark Polansky, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Christopher Cassidy, Julie Payette and Tim Kopra. They are at Kennedy for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, or CEIT, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware for the mission. The payload will be launched to the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitrios Gerondidakis
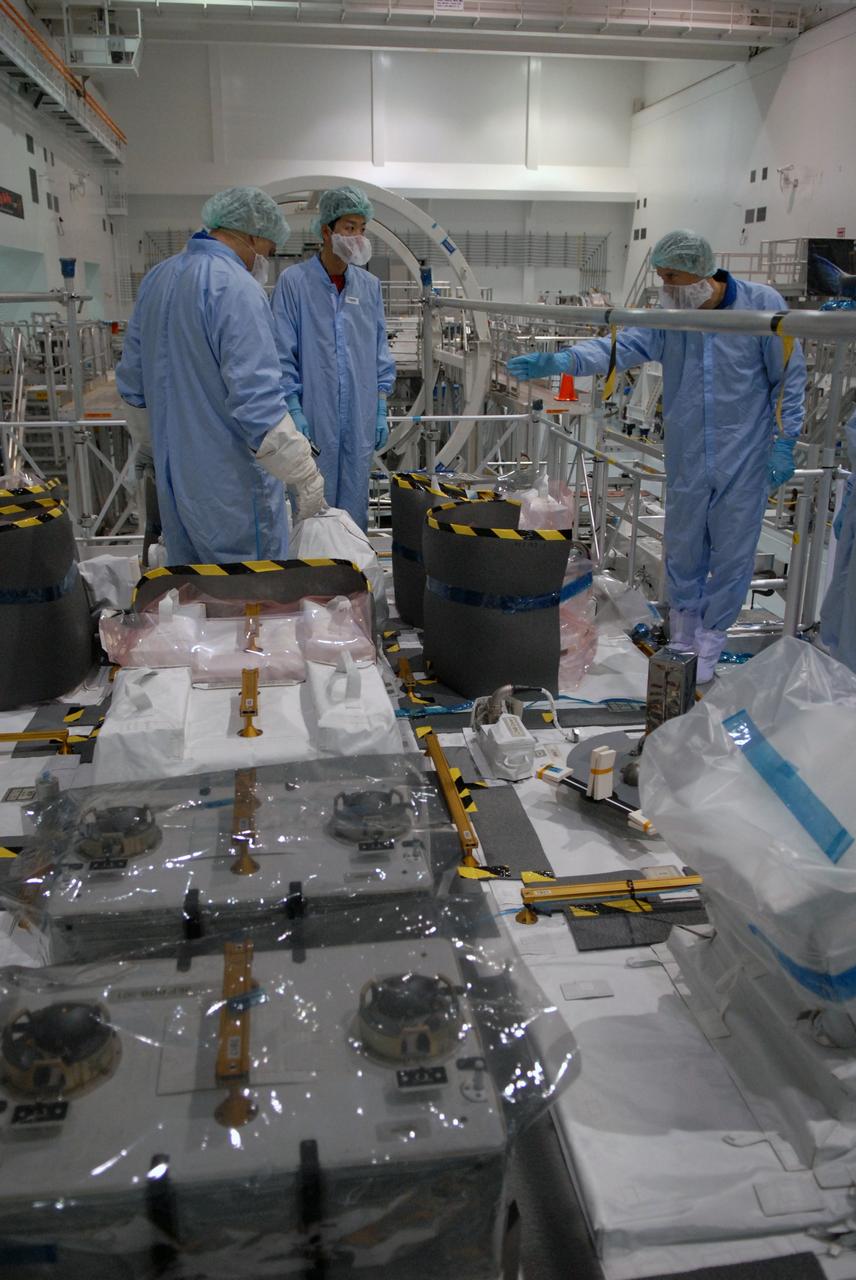

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the STS-127 crew look over equipment on the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, part of the payload on the mission. The crew is Commander Mark Polansky, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Christopher Cassidy, Tom Marshburn, Dave Wolf, Julie Payette and Tim Kopra. They are at Kennedy for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, or CEIT, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware for the mission. The payload will be launched to the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitrios Gerondidakis
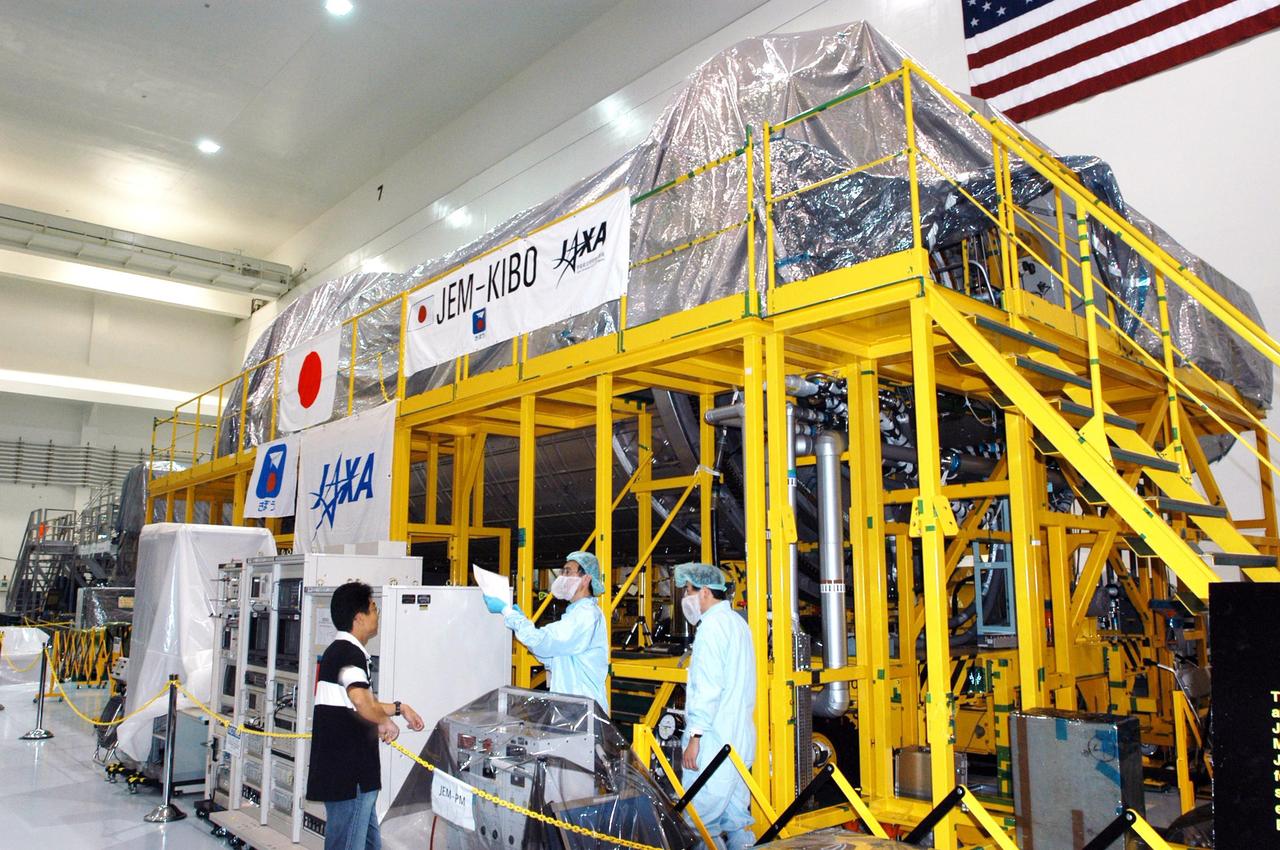

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) is dry and still covered following Hurricane Frances. The storm's path over Florida took it through Cape Canaveral and KSC property during Labor Day weekend. There was no damage to the Space Shuttle orbiters or to any other flight hardware.
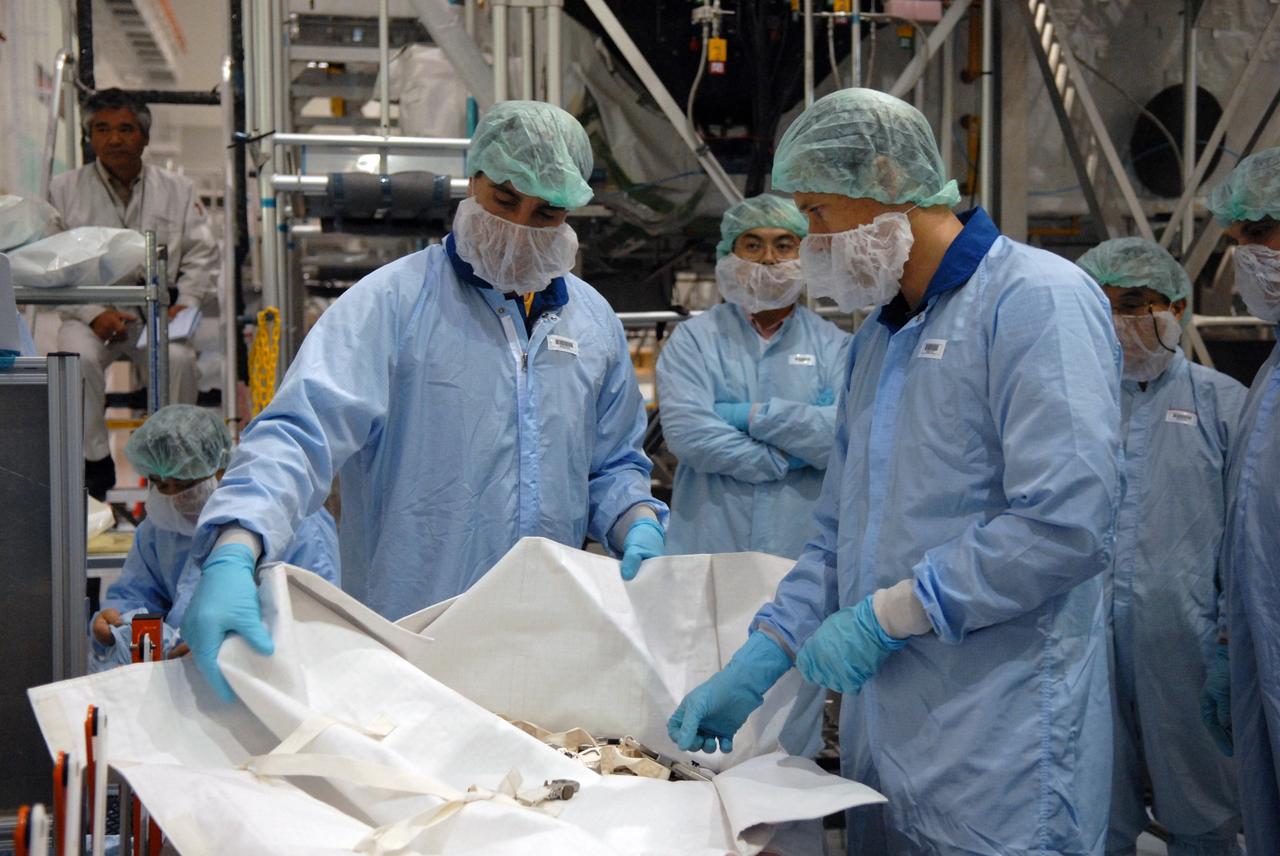

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the STS-127 Mission Specialists Chris Cassidy and Tom Marshburn review options of how they will stow the excess thermal blankets on the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, after they remove them on-orbit. The crew members are at Kennedy for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, or CEIT, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware for the mission. The payload will be launched to the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitrios Gerondidakis
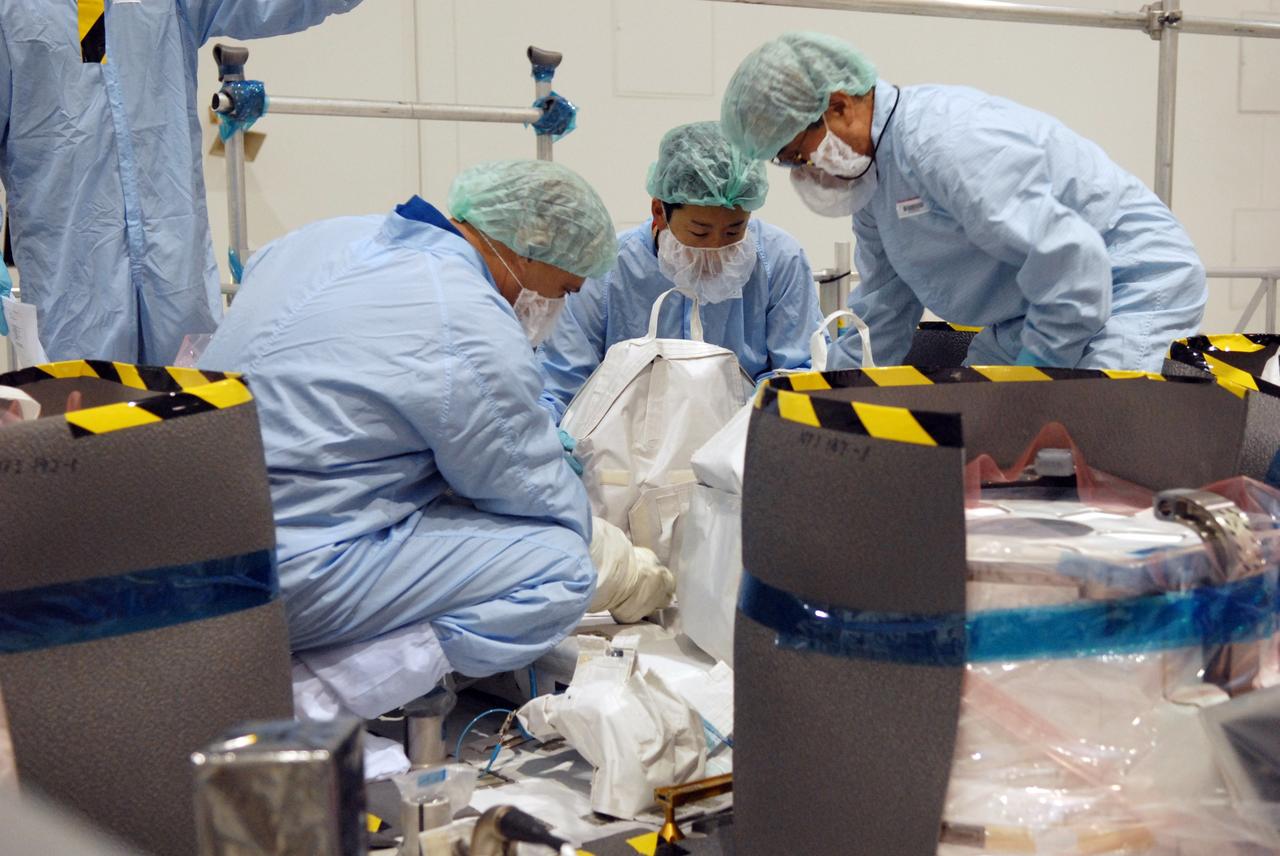

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the STS-127 crew check out equipment related to the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, part of the payload on the mission. The crew is Commander Mark Polansky, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Christopher Cassidy, Tom Marshburn, Dave Wolf, Julie Payette and Tim Kopra. They are at Kennedy for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, or CEIT, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware for the mission. The payload will be launched to the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitrios Gerondidakis
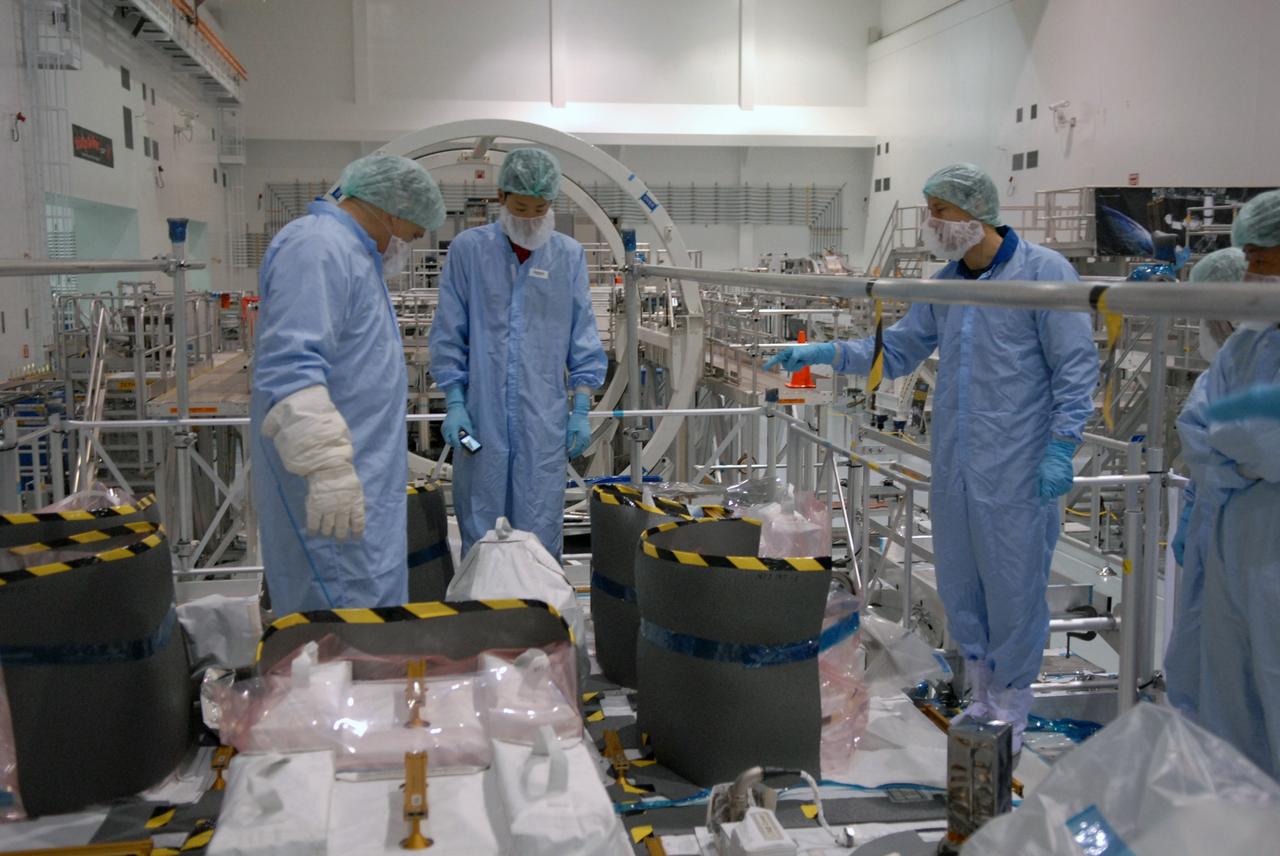

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the STS-127 crew look over equipment on the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, part of the payload on the mission. The crew is Commander Mark Polansky, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Christopher Cassidy, Tom Marshburn, Dave Wolf, Julie Payette and Tim Kopra. They are at Kennedy for Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, or CEIT, which provides experience handling tools, equipment and hardware for the mission. The payload will be launched to the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitrios Gerondidakis
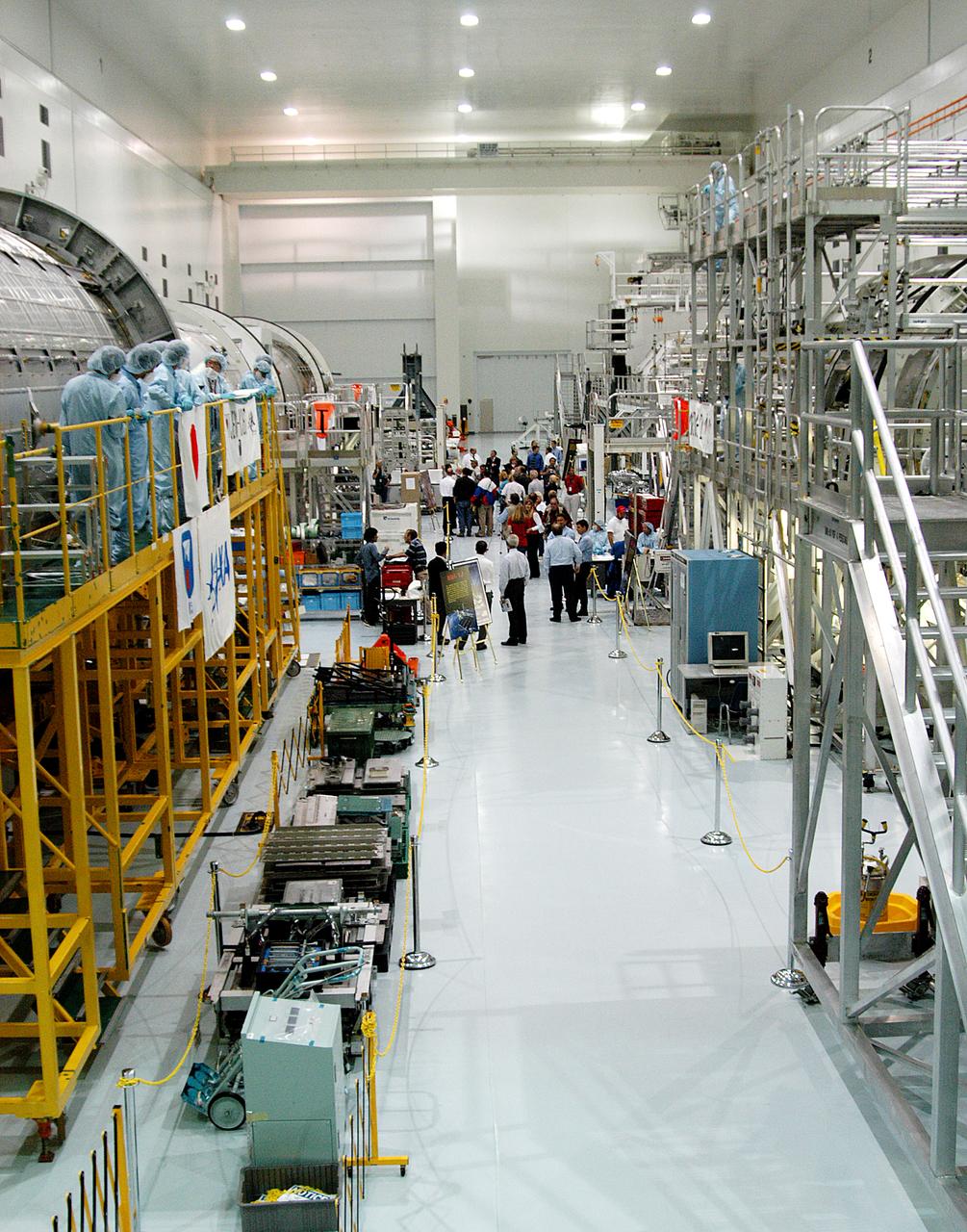

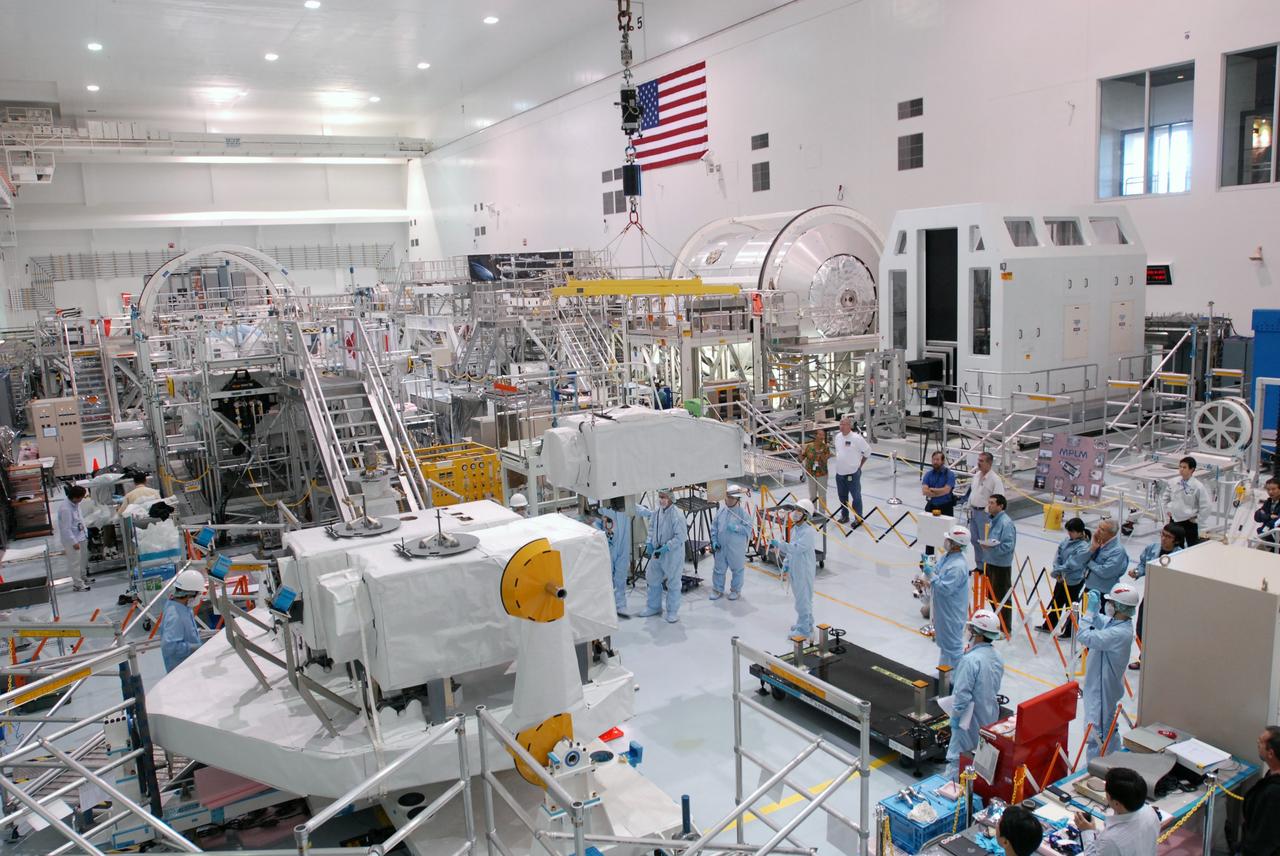
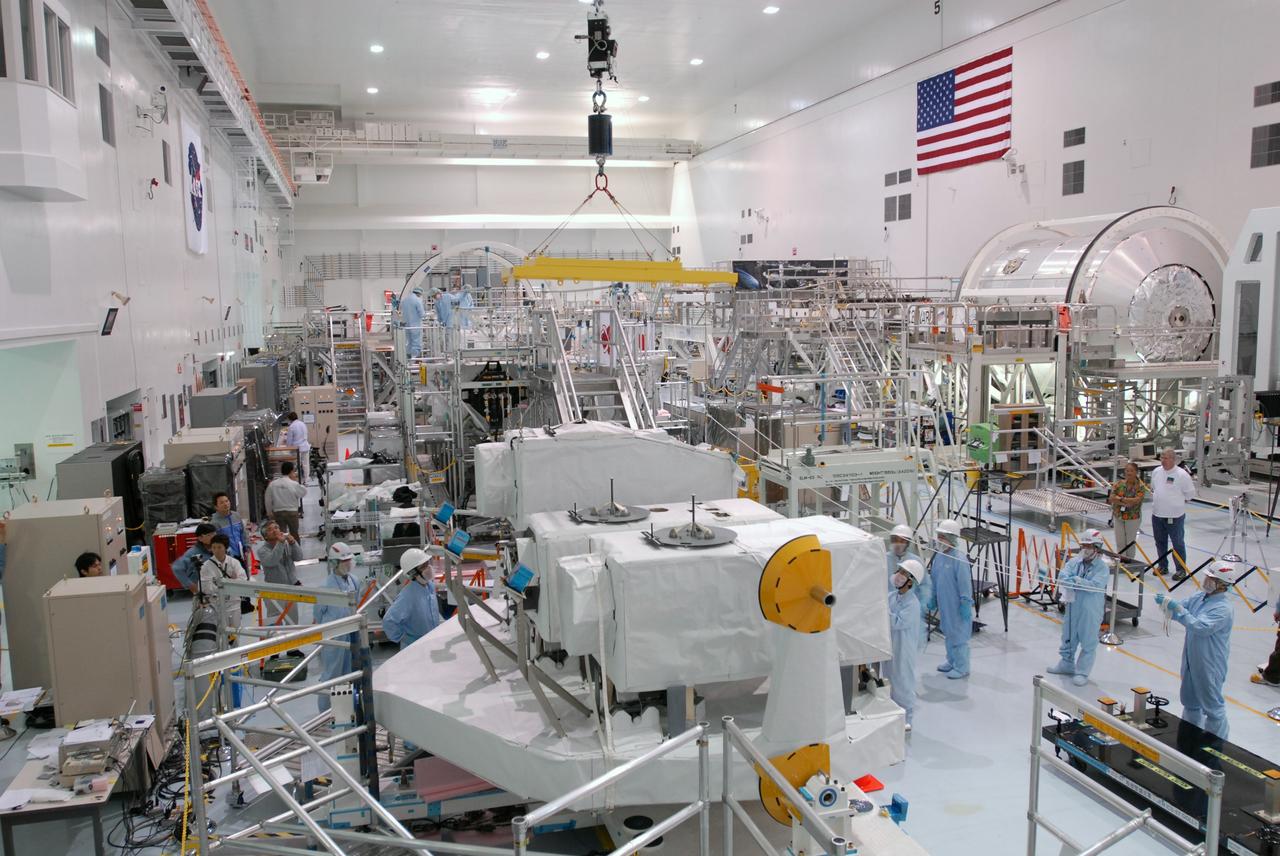
The Japanese Experiment Module or JEM (first element in left row), and other hardware undergoing processing for transport to the International Space Station, are made available for viewing by the media, assembling in the aisle of the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). Members of the media were invited to commemorate the fifth anniversary of the launch of the first element of the International Space Station by touring the SSPF. Reporters had the opportunity to see Space Station hardware that is being processed for deployment once the Space Shuttles return to flight, as well as talk with NASA and Boeing mission managers about the various hardware elements currently being processed for flight.
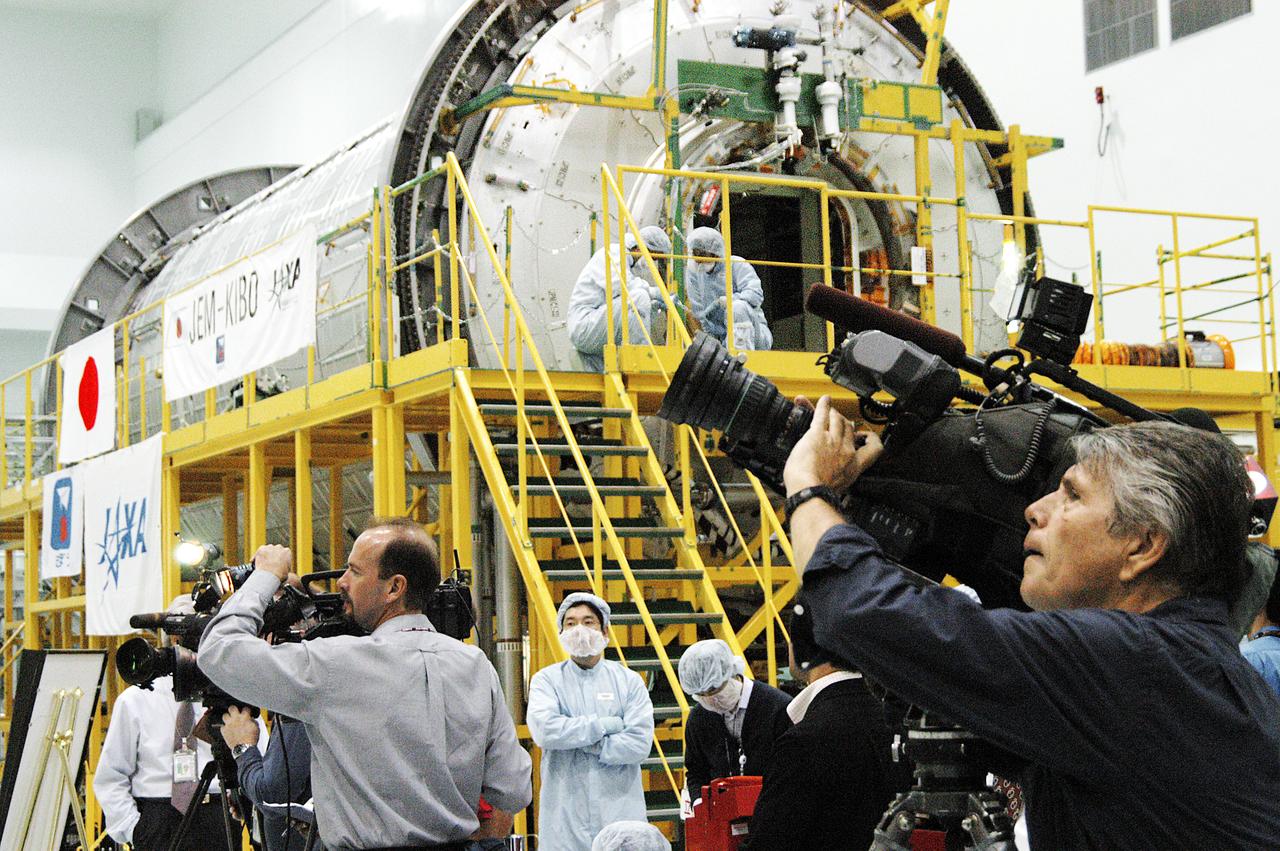

The Japanese Experiment Module or JEM (background) and other hardware undergoing processing for transport to the International Space Station are made available to photographers in the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). Members of the media were invited to commemorate the fifth anniversary of the launch of the first element of the International Space Station by touring the SSPF. Reporters had the opportunity to see Space Station hardware that is being processed for deployment once the Space Shuttles return to flight, as well as talk with NASA and Boeing mission managers about the various hardware elements currently being processed for flight.
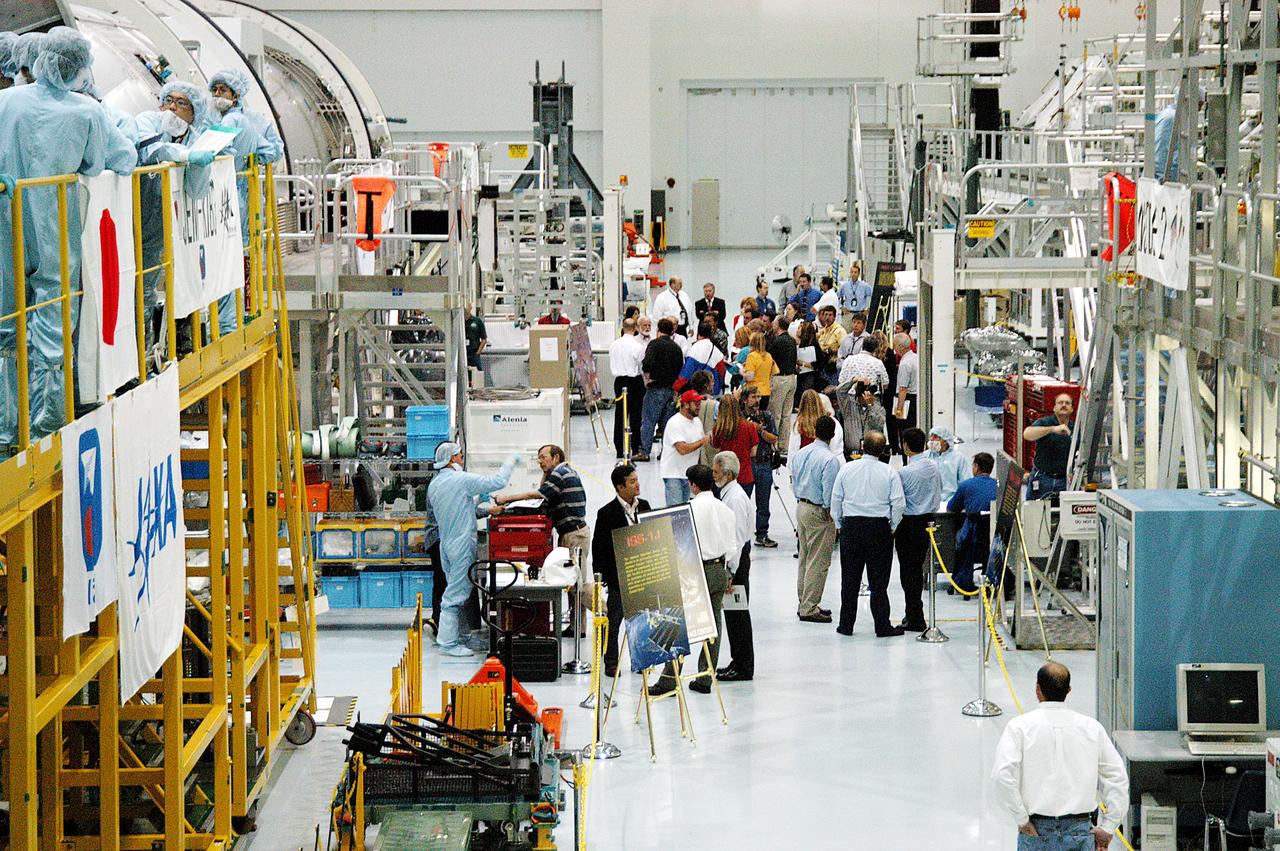

The Japanese Experiment Module or JEM (first element in left row), the Node 2 (first element in right row), and other hardware undergoing processing for transport to the International Space Station, are made available for viewing by the media, assembling in the aisle of the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). Members of the media were invited to commemorate the fifth anniversary of the launch of the first element of the International Space Station by touring the SSPF. Reporters had the opportunity to see Space Station hardware that is being processed for deployment once the Space Shuttles return to flight, as well as talk with NASA and Boeing mission managers about the various hardware elements currently being processed for flight.
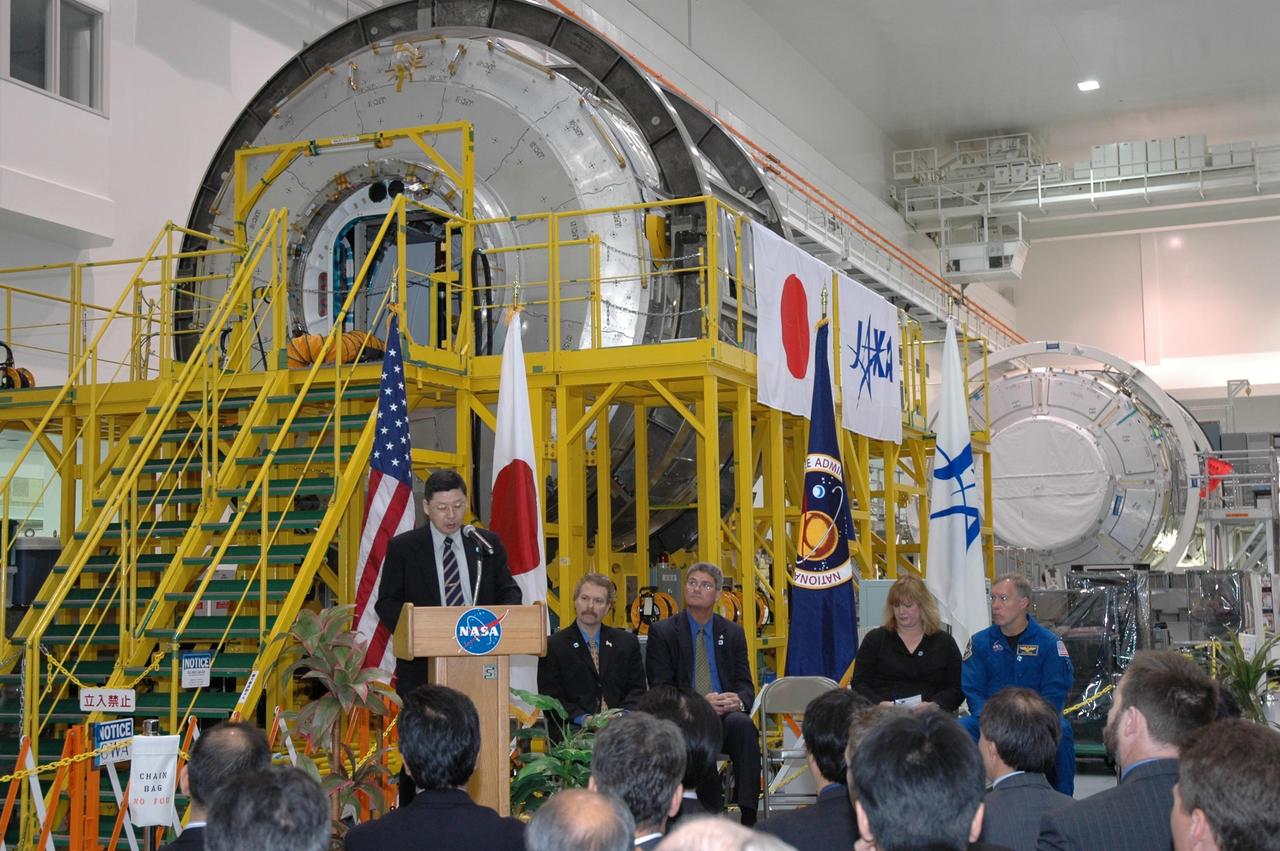

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcome the arrival of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, to the Kennedy Space Center. At the podium is Dr. Kichiro Imagawa, project manager of the JEM Development Project Team for JAXA. Seated at right are Russ Romanella, director of International Space Station and Spacecraft Processing; Bill Parsons, director of Kennedy Space Center; Melanie Saunders, associate manager of the International Space Station Program at Johnson Space Center; and Dominic Gorie, commander on mission STS-123 that will deliver the module to the space station. The logistics module will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
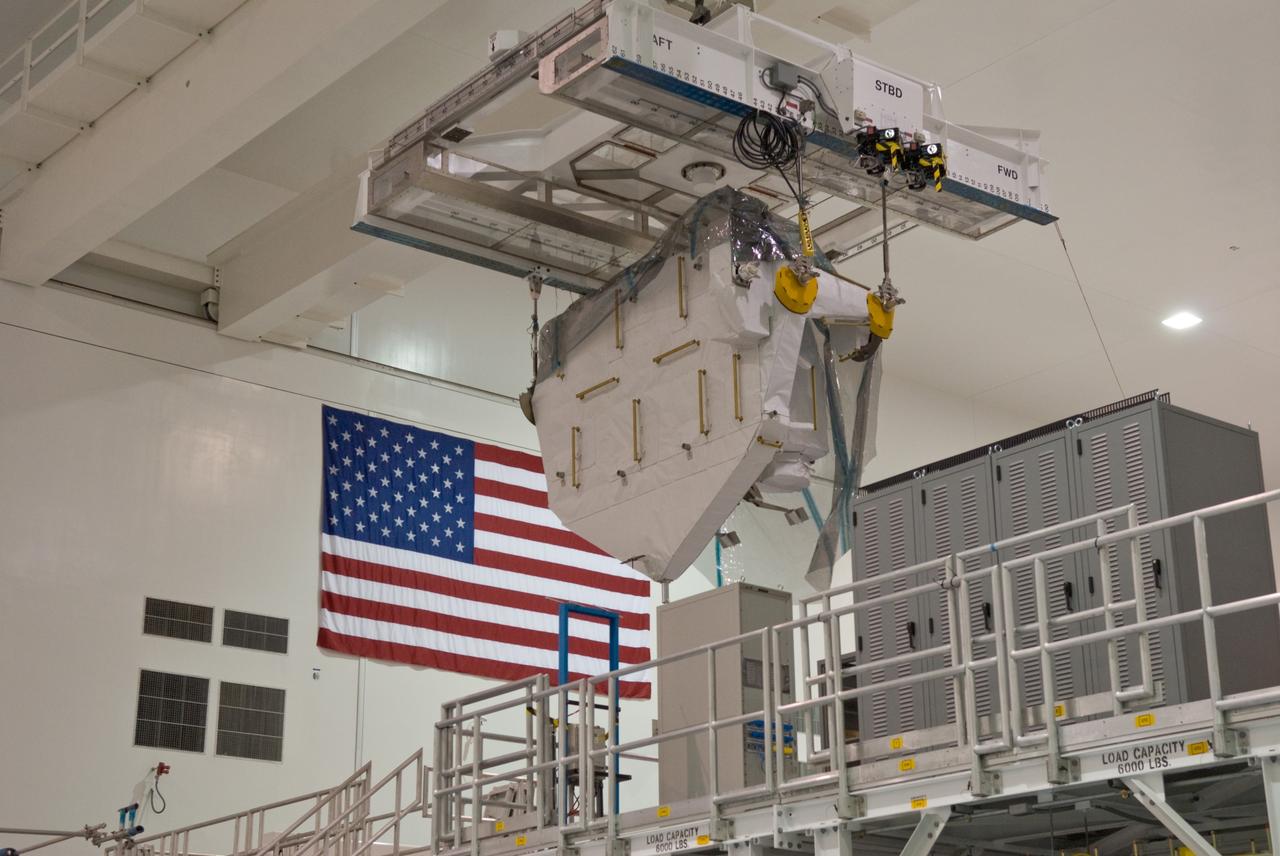

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Kibo Experiment Logistics Module Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, from its work stand to a payload canister. The canister will transport the payload to Launch Pad 39A. The ELM-ES is one of the final components of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory for the International Space Station. It can provide payload storage space and can carry up to three payloads at launch. The canister will deliver the ELM-ES and other elements to Launch Pad 39A for installation in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The STS-127 mission is targeted for launch June 13. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane is moved toward the Kibo Experiment Logistics Module Exposed Section, or ELM-ES. The crane will transfer the ES to the payload canister that will transport it to Launch Pad 39A. The ELM-ES is one of the final components of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory for the International Space Station. It can provide payload storage space and can carry up to three payloads at launch. The canister will deliver the ELM-ES and other elements to Launch Pad 39A for installation in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The STS-127 mission is targeted for launch June 13. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) sits on top of a stand in the Space Station Processing Facility. Earlier, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcomed the arrival of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section of the JEM, which will be delivered to the space station on mission STS-123. The JEM will fly on mission STS-124. The module will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
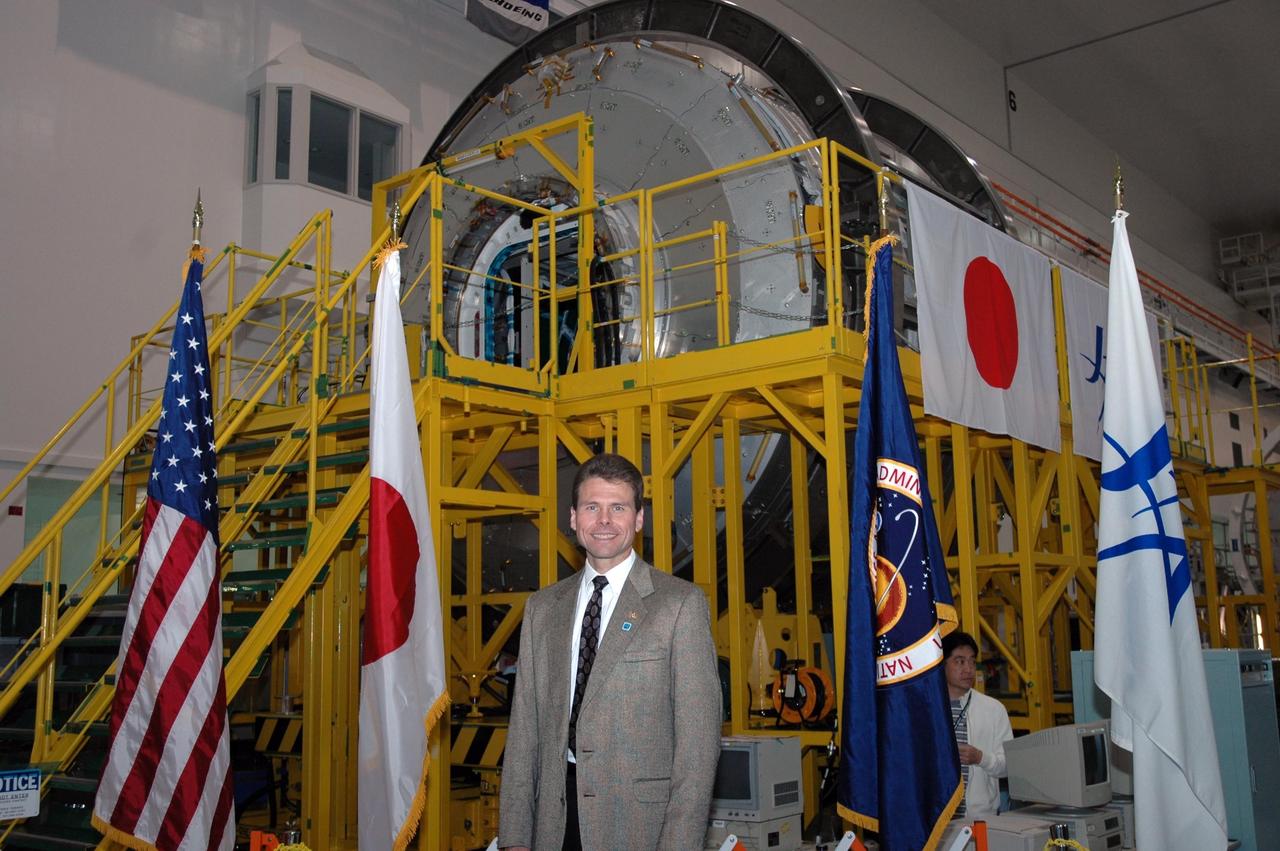

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, Scott Higginbotham, payload manager for the International Space Station, stands in front of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module. The module will be delivered to the space station on mission STS-123. Earlier, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcomed the arrival of the logistics module. The module will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
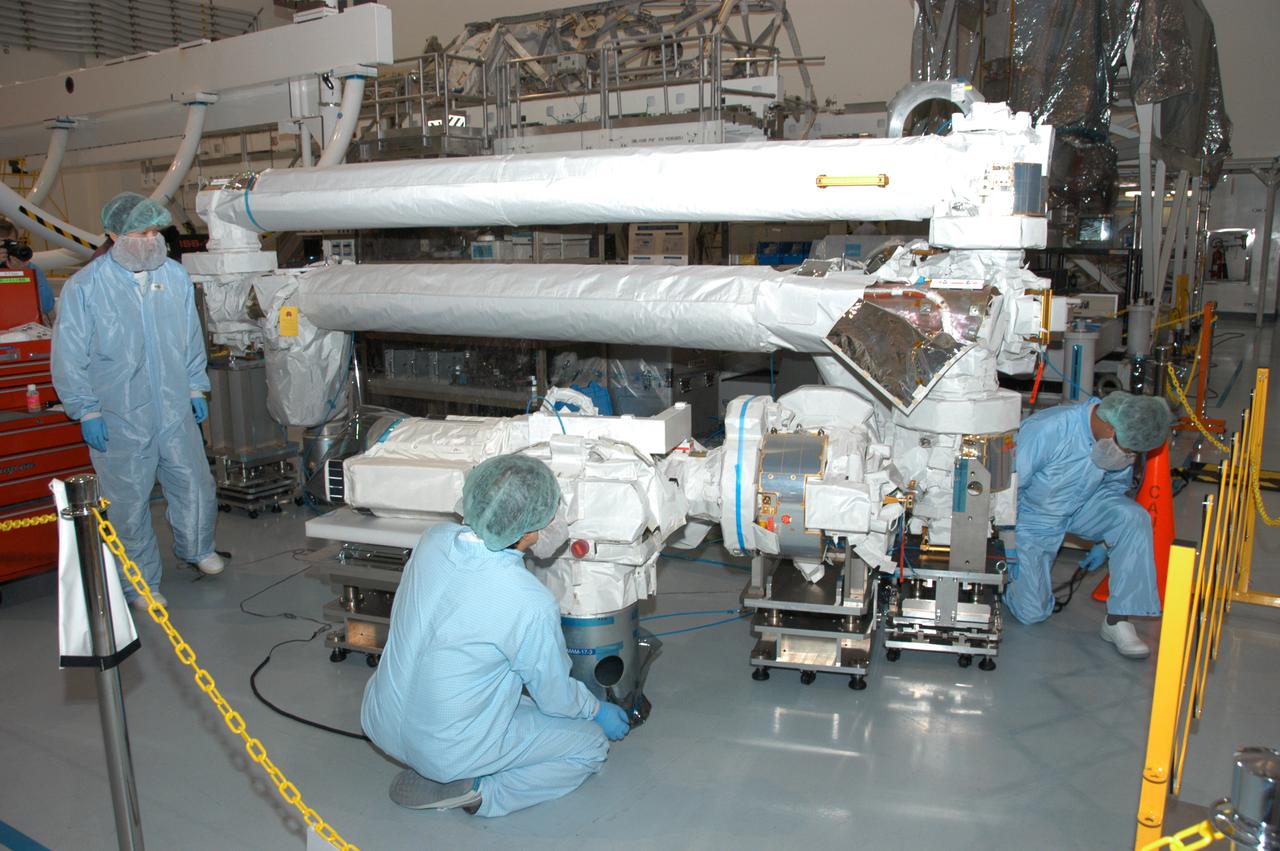

In the Space Station Processing Facility, technicians work on the Japanese remote manipulator system. It is scheduled to fly on a 2008 mission along with the Kibo Japanese Experiment Module Pressurized Module (JEM-PM).
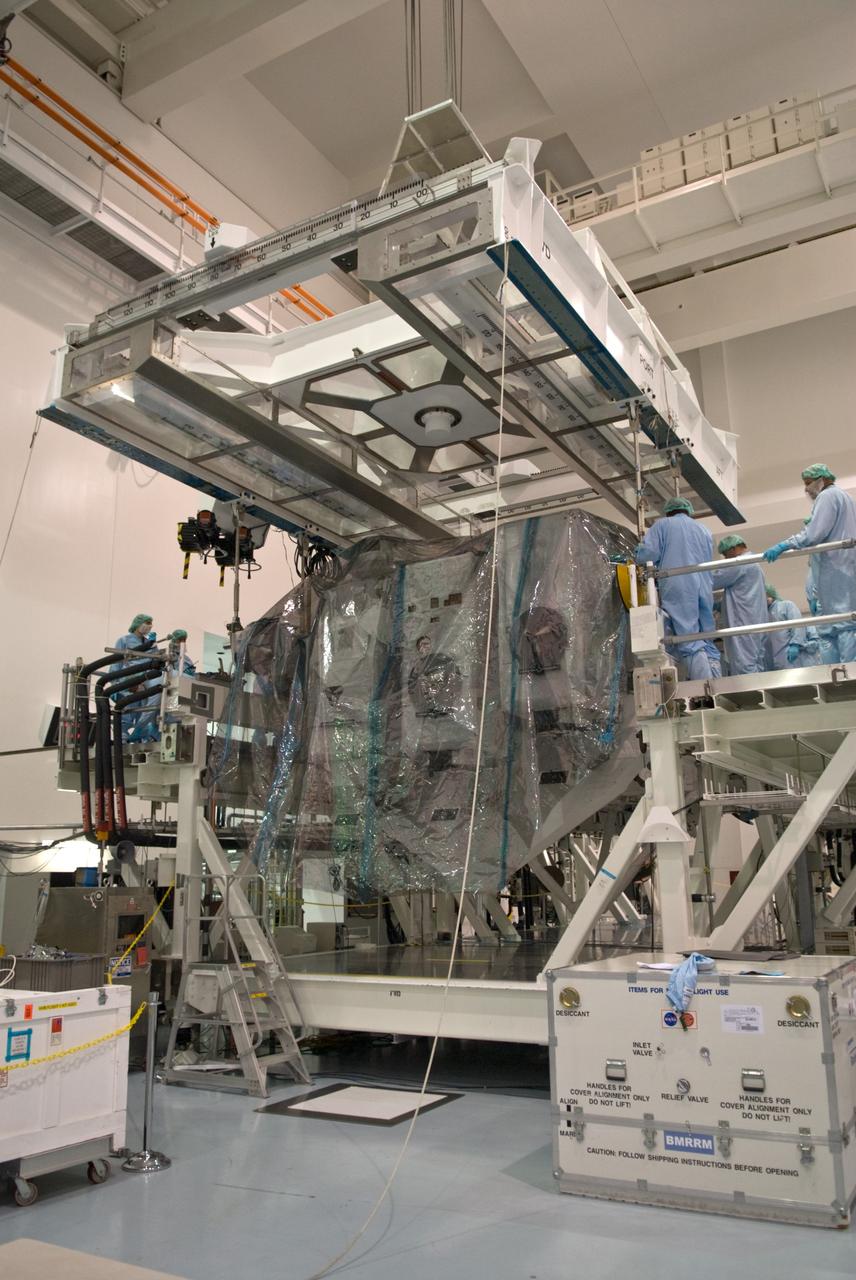

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane is lowered onto Kibo Experiment Logistics Module Exposed Section, or ELM-ES. The crane will transfer the ES to the payload canister that will transport it to Launch Pad 39A. The ELM-ES is one of the final components of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory for the International Space Station. It can provide payload storage space and can carry up to three payloads at launch. The canister will deliver the ELM-ES and other elements to Launch Pad 39A for installation in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The STS-127 mission is targeted for launch June 13. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
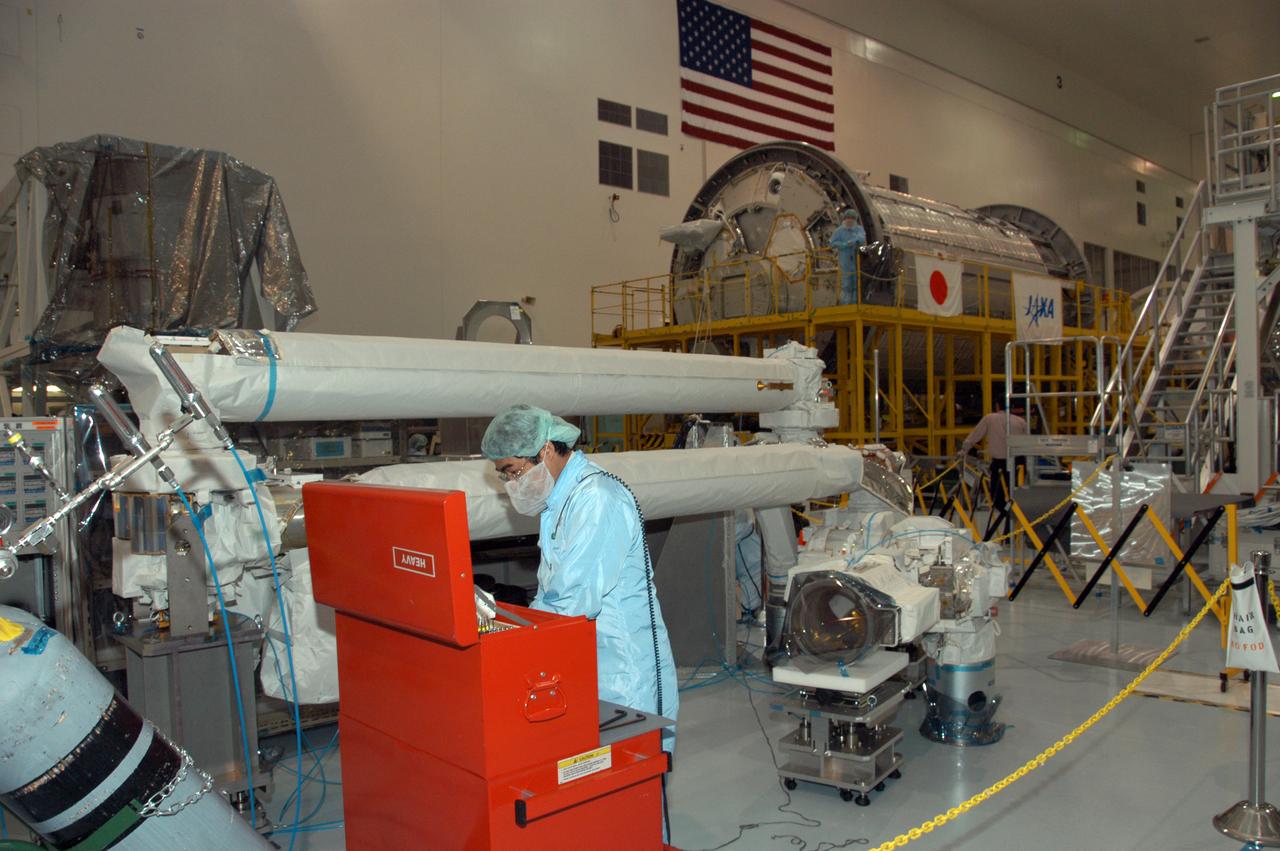

In the Space Station Processing Facility, technicians work on the Japanese remote manipulator system. It is scheduled to fly on a 2008 mission along with the Kibo Japanese Experiment Module Pressurized Module (JEM-PM).

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane carries the Kibo Experiment Logistics Module Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, the length of the room to a payload canister. The canister will transport the payload to Launch Pad 39A. The ELM-ES is one of the final components of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory for the International Space Station. It can provide payload storage space and can carry up to three payloads at launch. The canister will deliver the ELM-ES and other elements to Launch Pad 39A for installation in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The STS-127 mission is targeted for launch June 13. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
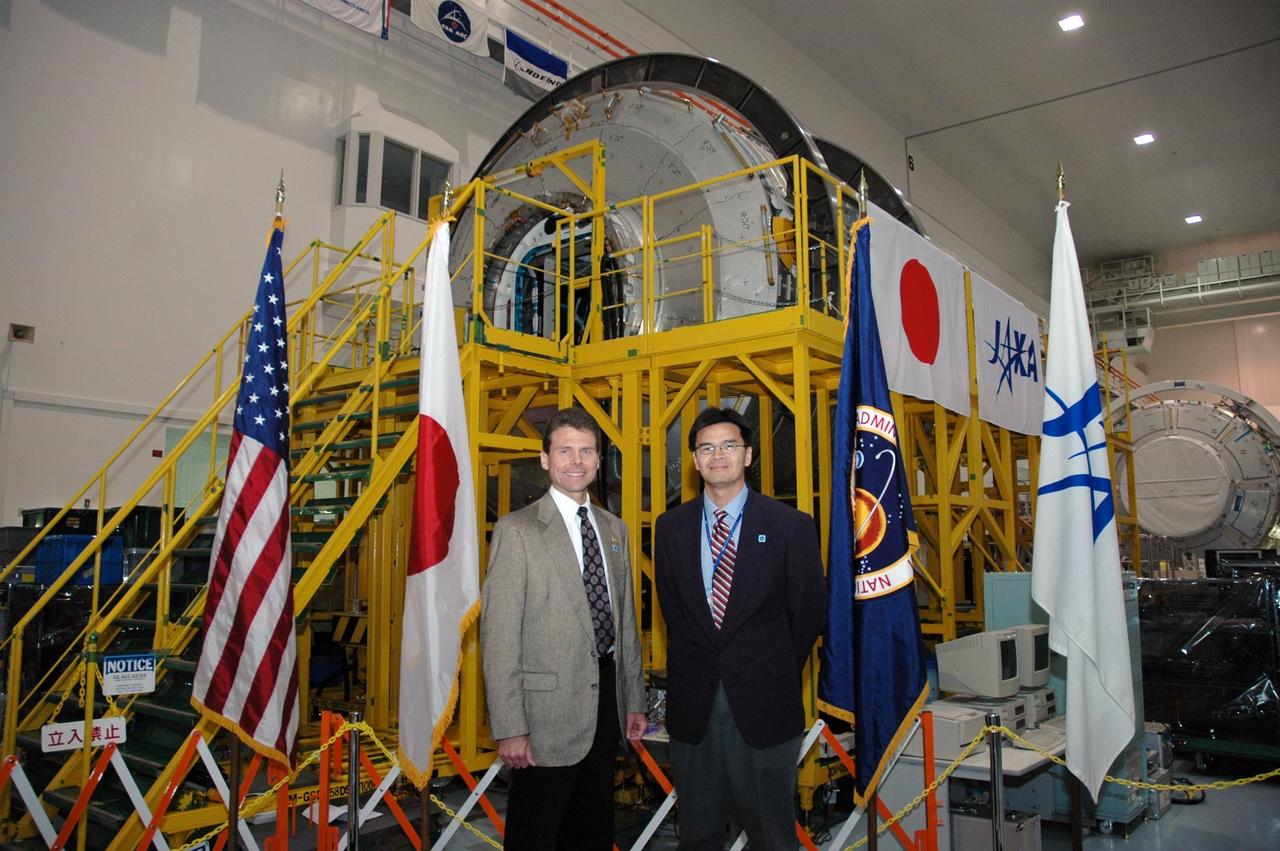

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, Scott Higginbotham and Chuong Nguyen, payload manager and deputy payload manager respectively for the International Space Station, stand in front of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module. Earlier, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcomed the arrival of the logistics module. The module will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
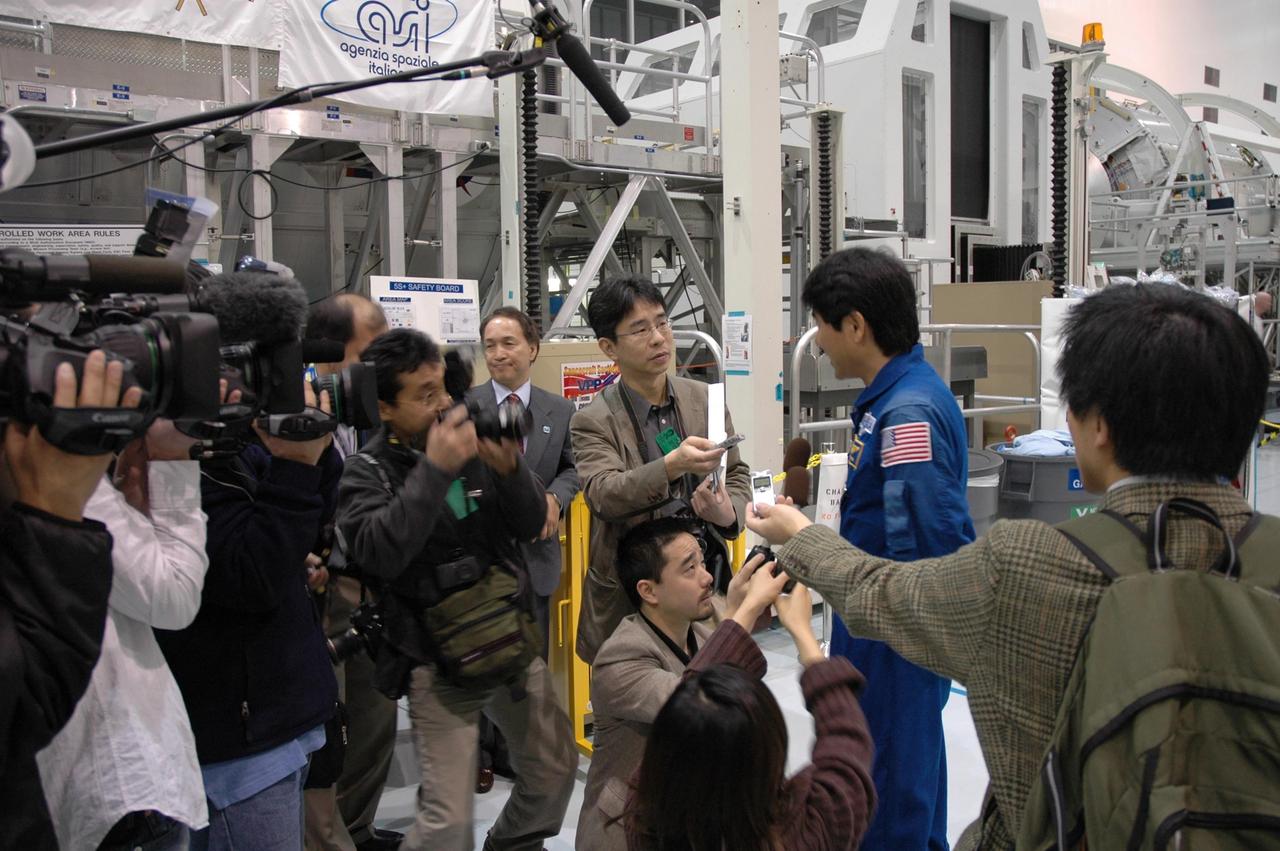

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, journalists and photographers ask Japanese astronaut Takao Doi about the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, that he will accompany on mission STS-123 to the International Space Station. Earlier, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcomed the arrival of the logistics module. The logistics module will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, astronaut Takao Doi (left) and Commander Dominic Gorie pose in front of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, that recently arrived at Kennedy. Doi and Gorie are crew members for mission STS-123 that will deliver the logistics module to the International Space Station. Earlier, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcomed the arrival of the module. The new International Space Station component arrived at Kennedy March 12 to begin preparations for its future launch on mission STS-123. It will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
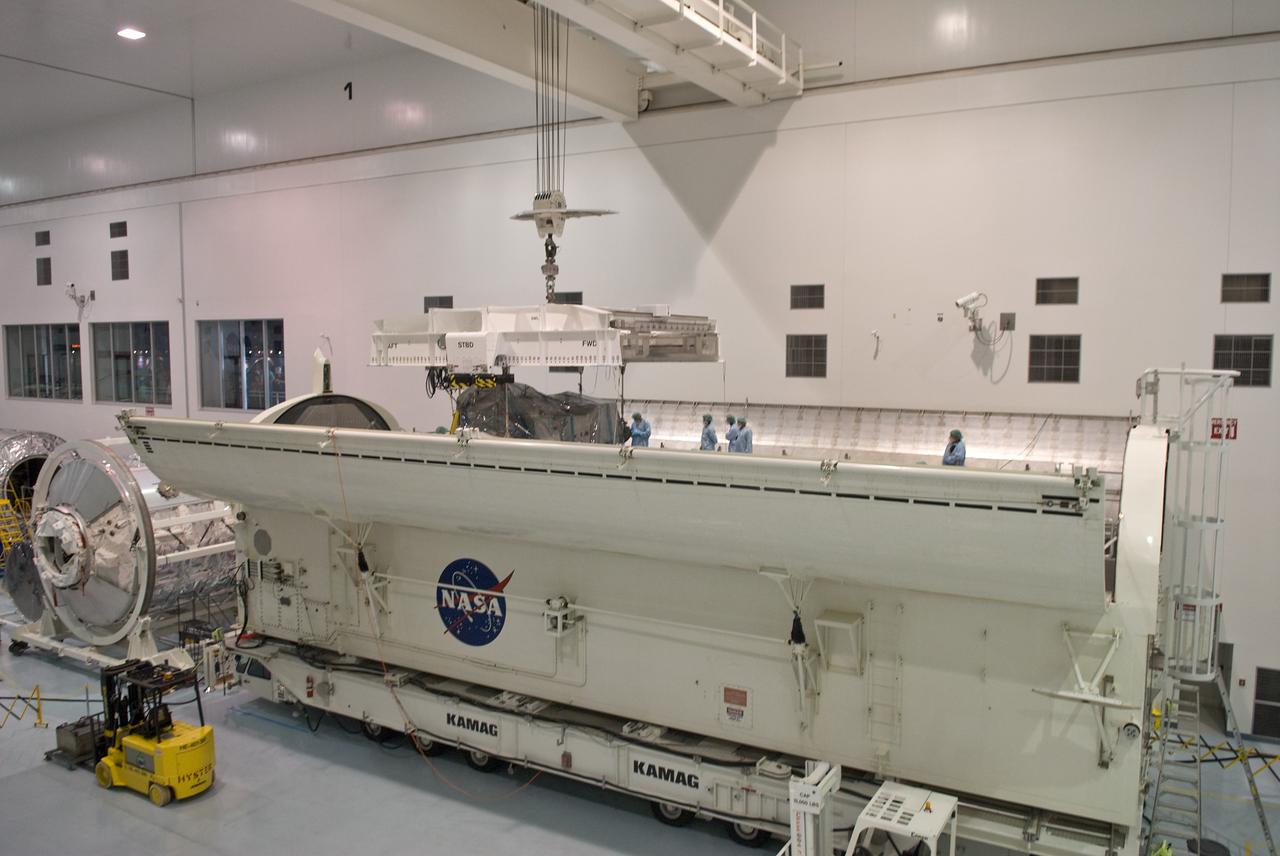

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Kibo Experiment Logistics Module Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, is lowered into the payload canister. The canister will transport the payload to Launch Pad 39A. The ES, along with the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo Exposed Facility, or EF, will be carried aboard space shuttle Endeavour on the STS-127 mission targeted for launch June 13. The ELM-ES is one of the final components of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory for the International Space Station. It can provide payload storage space and can carry up to three payloads at launch. The canister will deliver the ELM-ES and other elements to Launch Pad 39A for installation in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The STS-127 mission is targeted for launch June 13. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
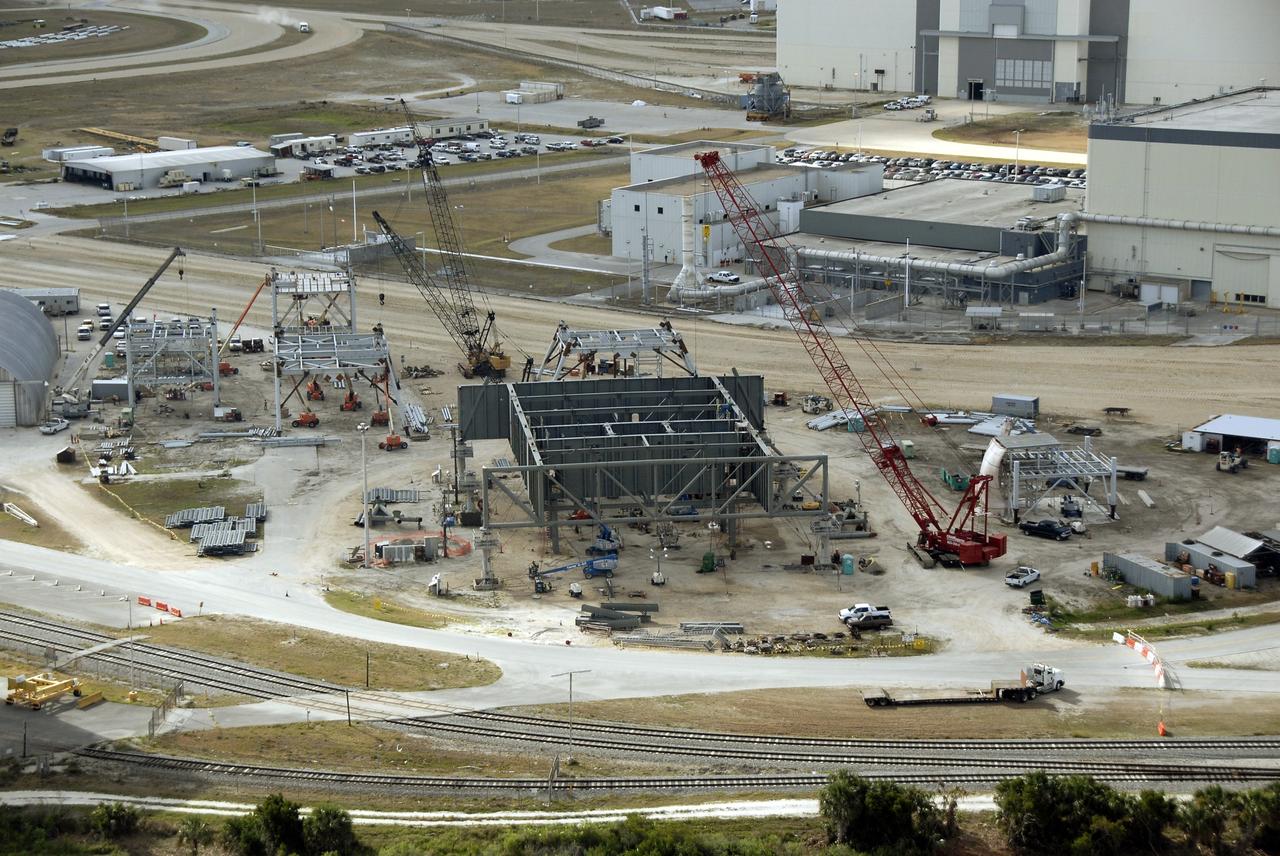

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the mobile launcher parking area behind the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the new mobile launcher, or ML, for the Ares rockets is under construction. The ML will be the base to launch the Orion crew exploration vehicle and the cargo vehicle. The base is being made lighter than space shuttle mobile launcher platforms so the crawler-transporter can pick up the added load of the 345-foot tower and taller rocket. When the structural portion of the new mobile launcher is complete, umbilicals, access arms, communications equipment and command/control equipment will be installed. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
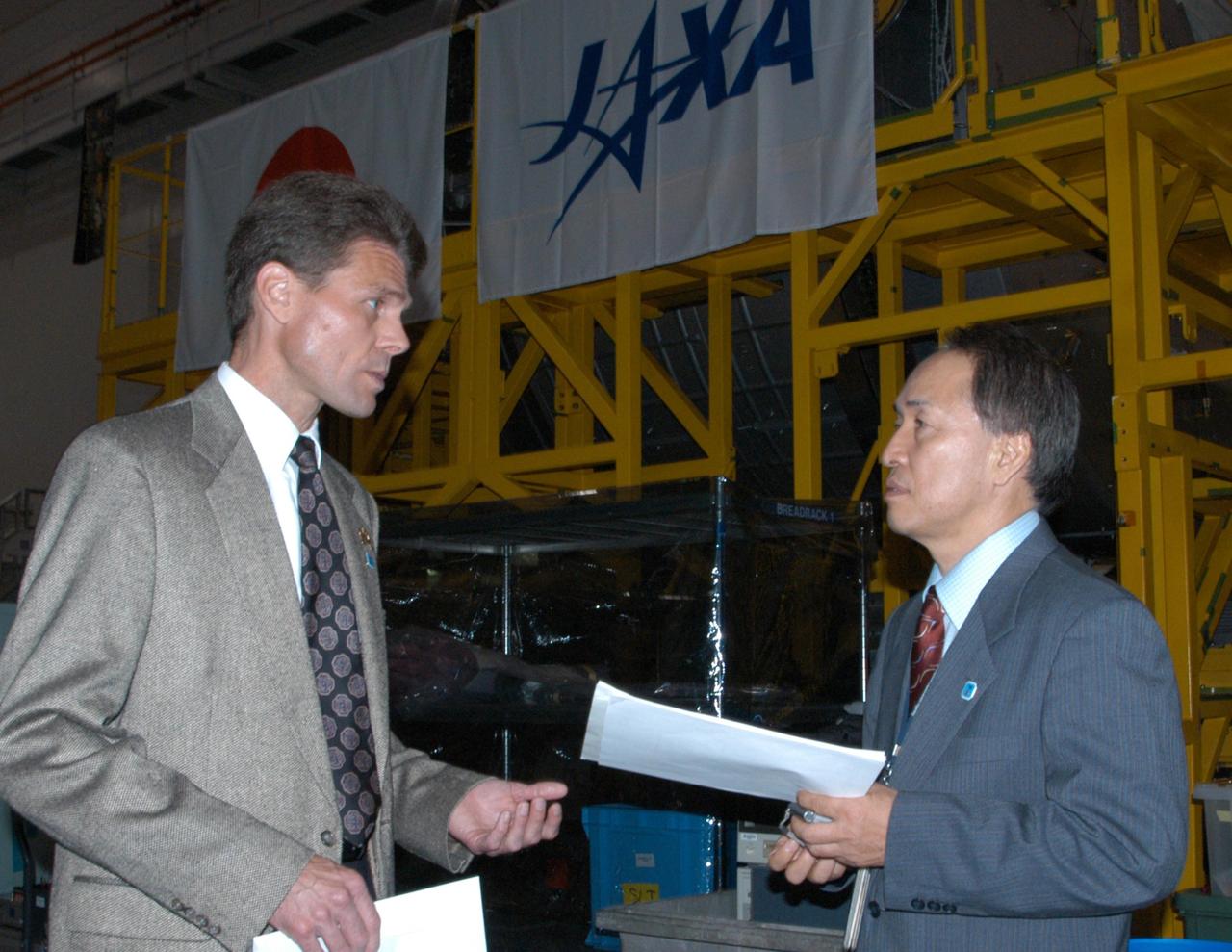

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, Scott Higginbotham, payload manager for the International Space Station, discusses the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), with Dr. Hidetaka Tanaka, the JEM Project Team resident manager at KSC for the Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA). Earlier, NASA and JAXA officials welcomed the arrival of the module. The new International Space Station component arrived at Kennedy March 12 to begin preparations for its future launch on mission STS-123. It will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
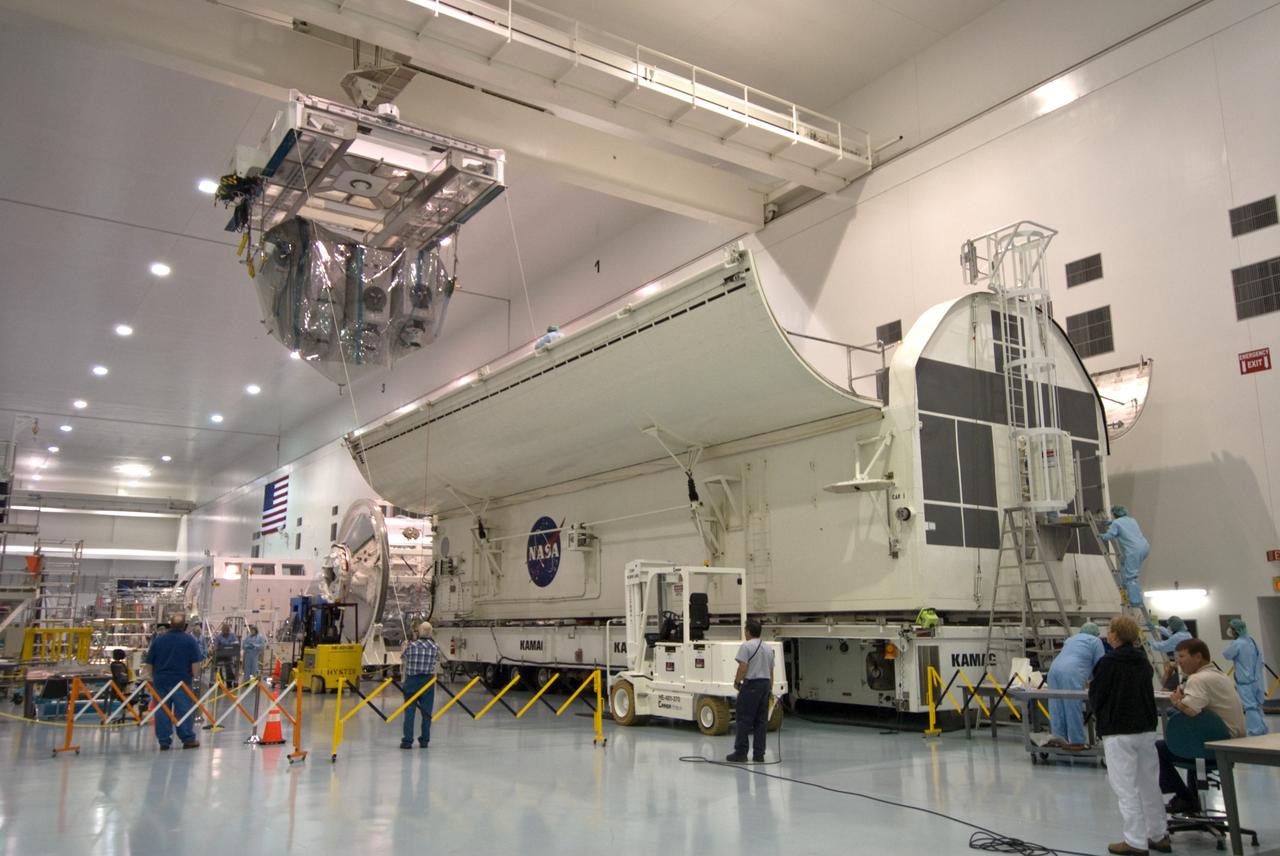

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane carries the Kibo Experiment Logistics Module Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, toward the payload canister, at right. The canister will transport the payload to Launch Pad 39A. The ELM-ES is one of the final components of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory for the International Space Station. It can provide payload storage space and can carry up to three payloads at launch. The canister will deliver the ELM-ES and other elements to Launch Pad 39A for installation in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The STS-127 mission is targeted for launch June 13. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcome the arrival of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, to the Kennedy Space Center. Seen here at right are JAXA representatives, including Japanese astronaut Takao Doi (center of front row), who is a crew member for mission STS-123 that will deliver the module to the space station. The new International Space Station component arrived at Kennedy March 12 to begin preparations for its future launch on mission STS-123. It will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
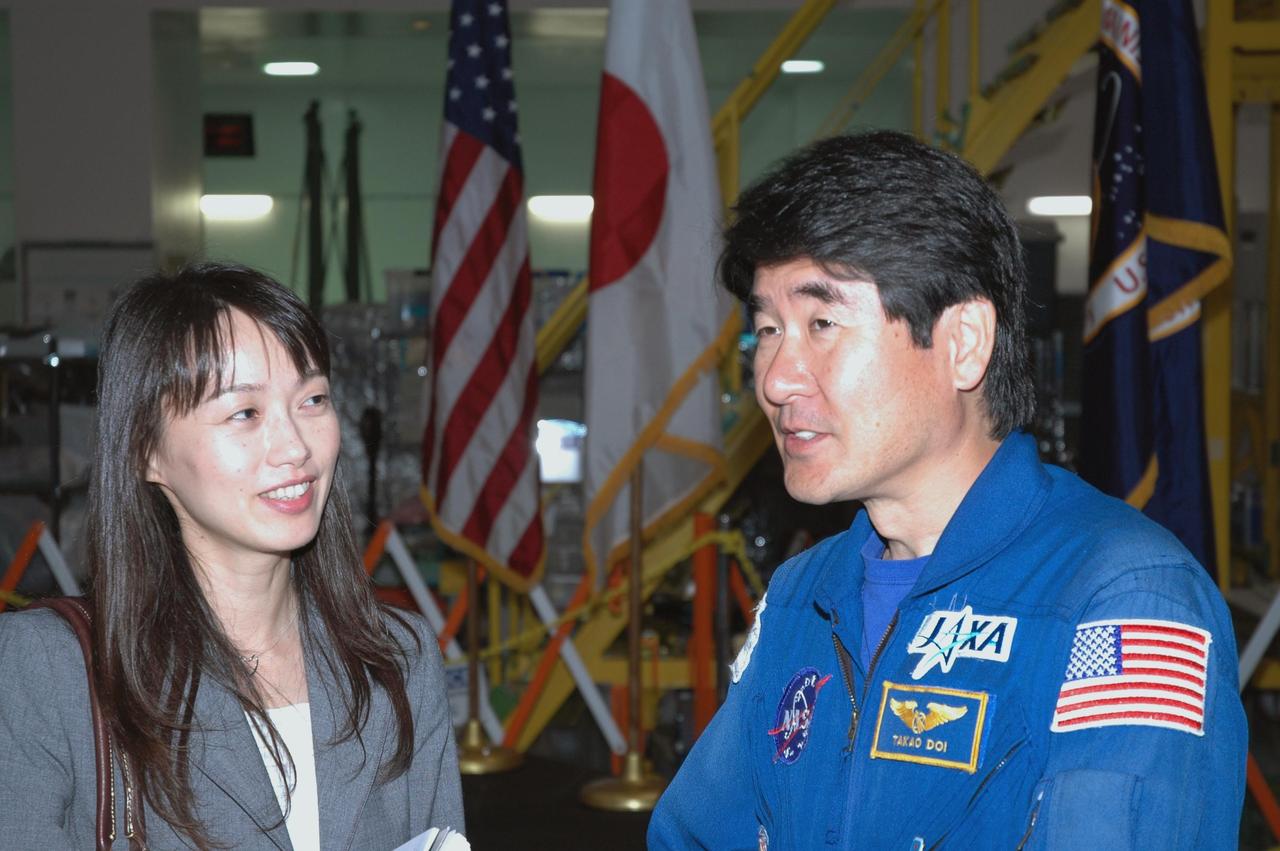

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After a welcoming ceremony for the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section of the Japanese Experiment Module, astronaut Takao Doi (right) talks with Kumiko Tanabe, a public affairs representative of the Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency. The logistics module will be delivered to the space station on mission STS-123. Doi is a crew member on that mission.The module will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section of the Japanese Experiment Module sits on top of a stand in the Space Station Processing Facility. Earlier, NASA and Japanese Space Agency (JAXA) officials welcomed the arrival of the logistics module, which will be delivered to the space station on mission STS-123. The module will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
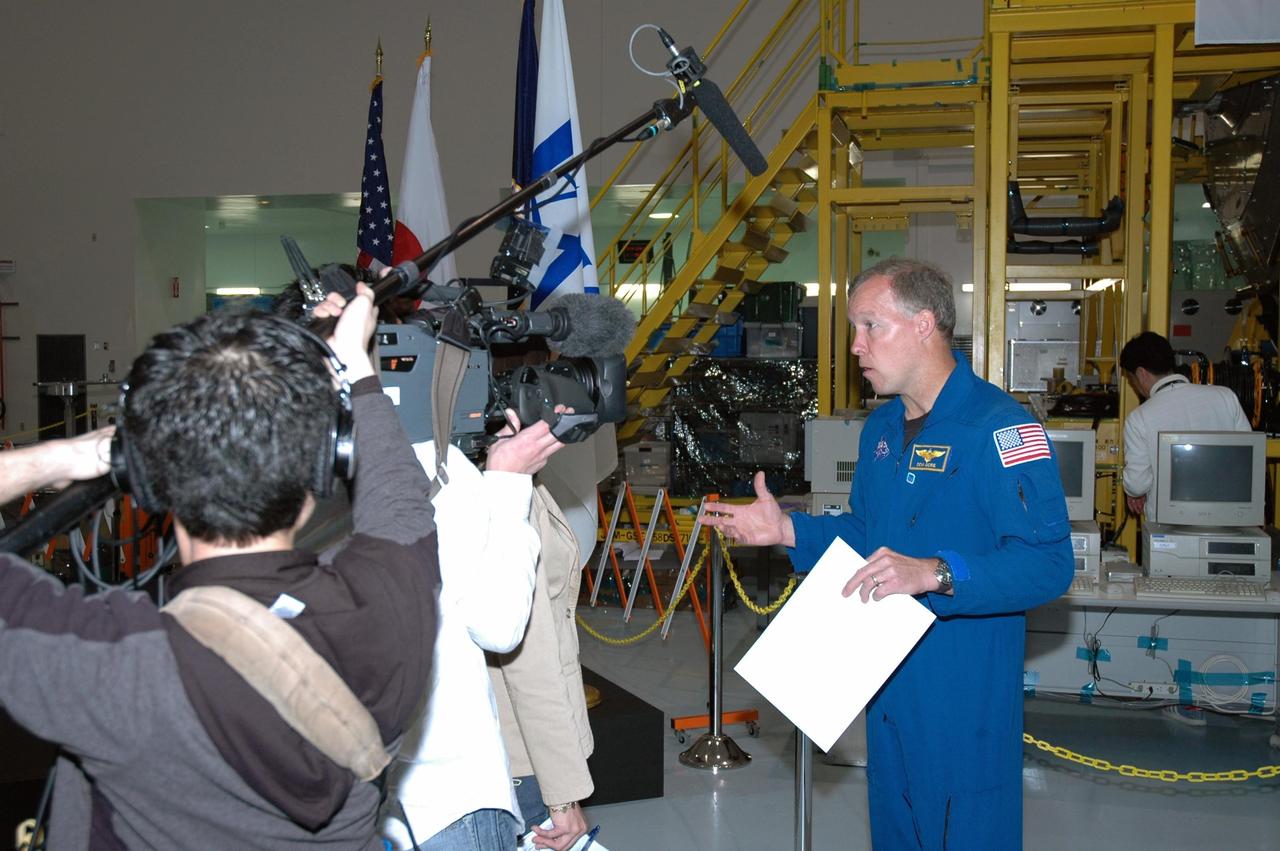

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After a welcoming ceremony for the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section of the Japanese Experiment Module, STS-123 Commander Dominic Gorie talks to the media. Earlier, NASA and Japanese Space Agency (JAXA) officials welcomed the arrival of the logistics module, which will be delivered to the space station on mission STS-123. The module will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
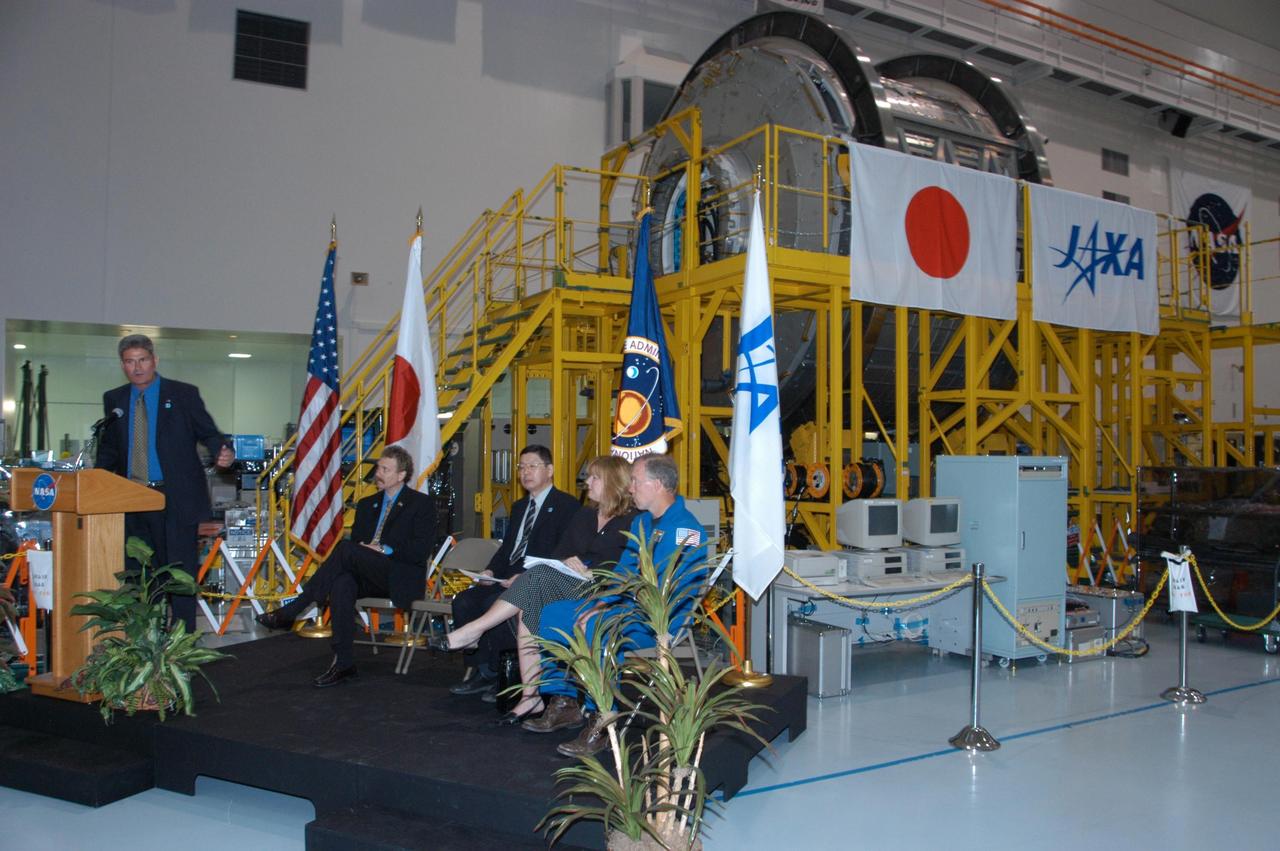

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcome the arrival of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, to the Kennedy Space Center. At the podium is Bill Parsons, director of Kennedy Space Center. Seated at right are Russ Romanella, director of International Space Station and Spacecraft Processing; Dr. Kichiro Imagawa, project manager of the JEM Development Project Team for JAXA; Melanie Saunders, associate manager of the International Space Station Program at Johnson Space Center; and Dominic Gorie, commander on mission STS-123 that will deliver the module to the space station. The new International Space Station component arrived at Kennedy March 12 to begin preparations for its future launch on mission STS-123. It will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
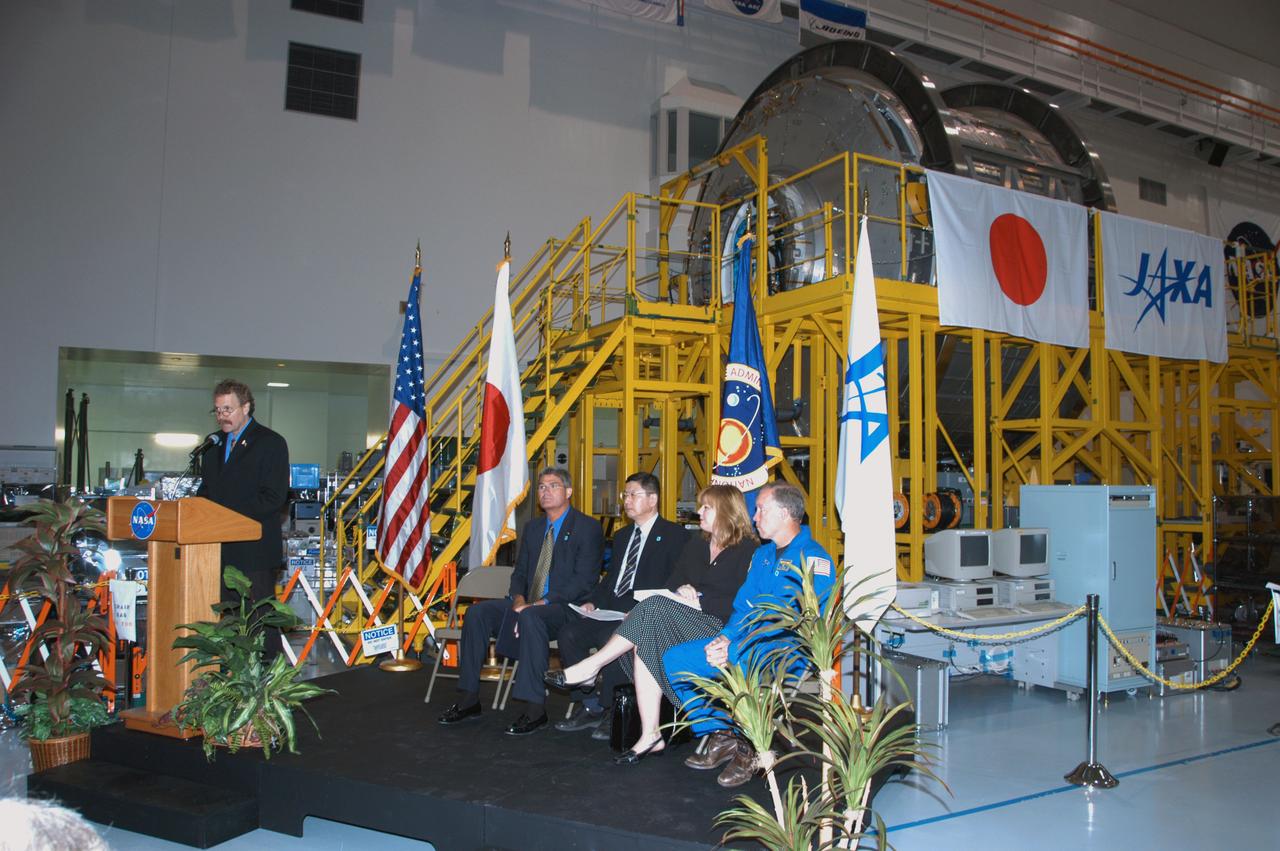

In the Space Station Processing Facility, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcome the arrival of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, to the Kennedy Space Center. At the podium is Russ Romanella, director of International Space Station and Spacecraft Processing. Seated at right are Bill Parsons, director of Kennedy Space Center; Dr. Kichiro Imagawa, project manager of the JEM Development Project Team for JAXA; Melanie Saunders, associate manager of the International Space Station Program at Johnson Space Center; and Dominic Gorie, commander on mission STS-123 that will deliver the module to the space station. The new International Space Station component arrived at Kennedy March 12 to begin preparations for its future launch on mission STS-123. It will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module.
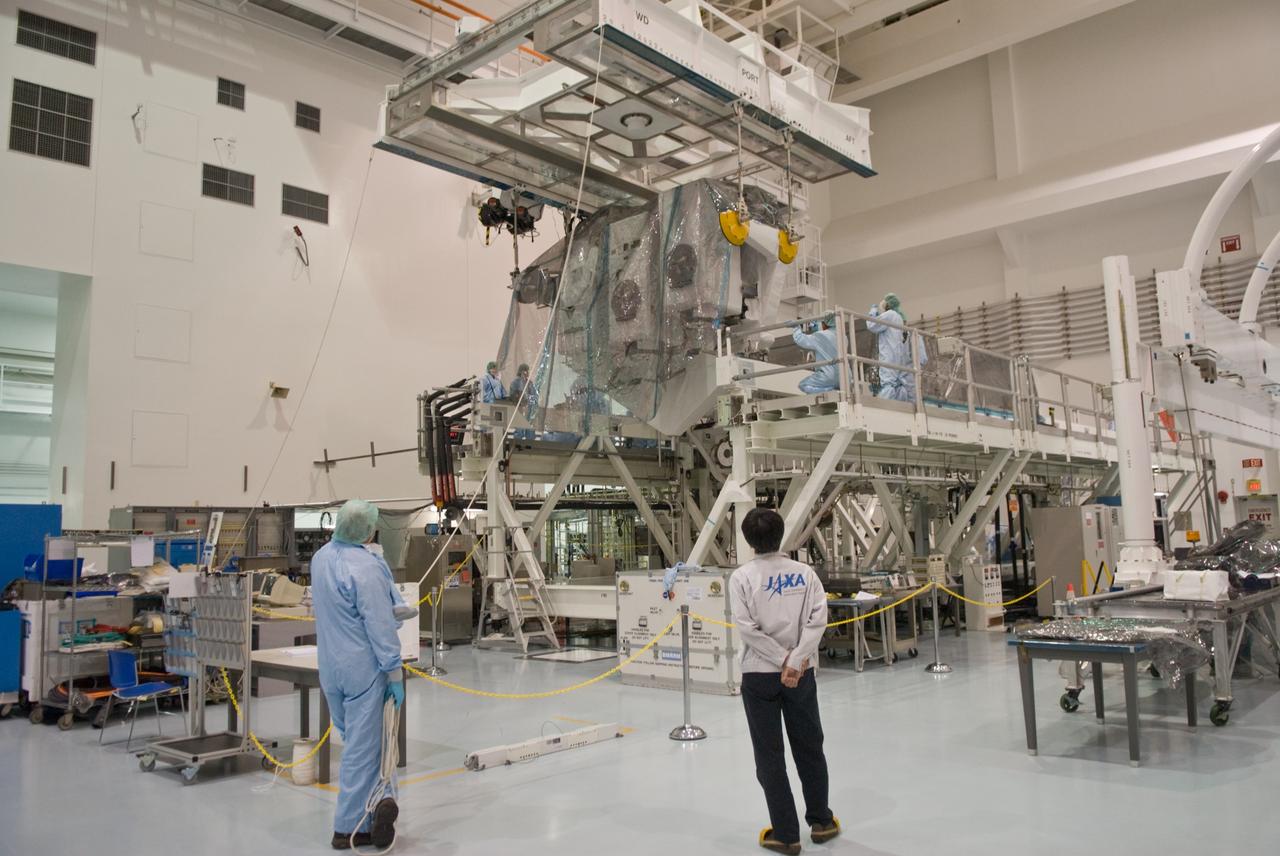

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane lifts Kibo Experiment Logistics Module Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, from its work stand. The crane will transfer the ES to the payload canister that will transport it to Launch Pad 39A. The ELM-ES is one of the final components of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory for the International Space Station. It can provide payload storage space and can carry up to three payloads at launch. The canister will deliver the ELM-ES and other elements to Launch Pad 39A for installation in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The STS-127 mission is targeted for launch June 13. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
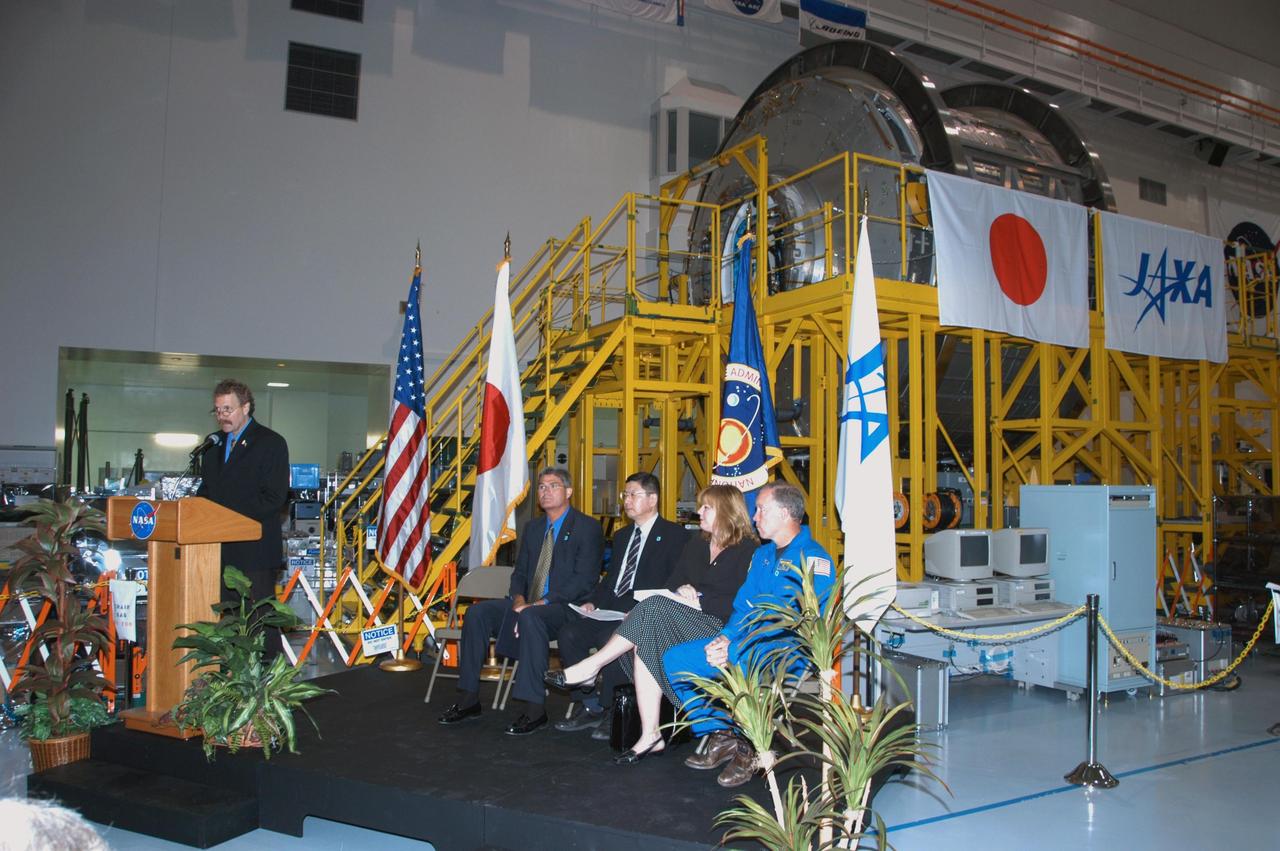

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcome the arrival of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, to the Kennedy Space Center. At the podium is Russ Romanella, director of International Space Station and Spacecraft Processing. Seated at right are Bill Parsons, director of Kennedy Space Center; Dr. Kichiro Imagawa, project manager of the JEM Development Project Team for JAXA; Melanie Saunders, associate manager of the International Space Station Program at Johnson Space Center; and Dominic Gorie, commander on mission STS-123 that will deliver the module to the space station. The new International Space Station component arrived at Kennedy March 12 to begin preparations for its future launch on mission STS-123. It will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
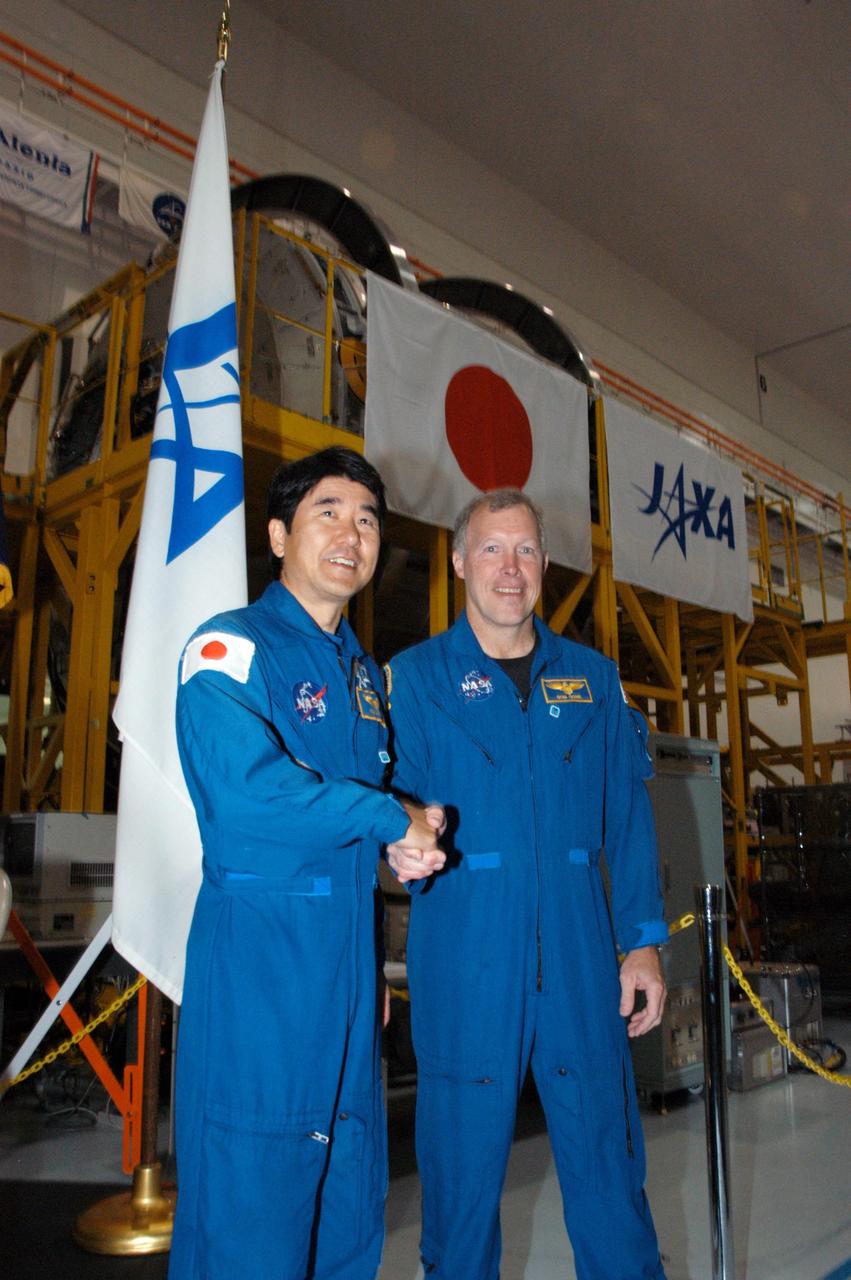

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, astronaut Takao Doi (left) and Commander Dominic Gorie pose in front of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, that recently arrived at Kennedy. Doi and Gorie are crew members for mission STS-123 that will deliver the logistics module to the International Space Station. Earlier, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcomed the arrival of the module. The new International Space Station component arrived at Kennedy March 12 to begin preparations for its future launch on mission STS-123. It will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

Members of the media were invited to commemorate the fifth anniversary of the launch of the first element of the International Space Station by touring the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at KSC. Here, Shimpei Takahashi (center), representative of the Japanese Air and Space Agency (JAXA), talks about the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) on camera. Reporters had the opportunity to see Space Station hardware that is being processed for deployment once the Space Shuttles return to flight, as well as talk with NASA and Boeing mission managers about the various hardware elements currently being processed for flight.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the ICS Exposed Facility, or ICS-EF, is lifted from its stand. It will be installed on the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES. The ICS-EF is composed of several components, including an antenna, pointing mechanism, frequency converters, high-power amplifier and various sensors including the Earth sensor, Sun sensor and inertial reference unit. The ICS-EF is part of space shuttle Endeavour's payload on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the ICS Exposed Facility, or ICS-EF, is moved across the floor to the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, where it will be installed alongside two other payloads, the SEDA-AP (Space Environment Data Acquisition Equipment-Attached Payload) and MAXI (Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image), already installed. The ICS-EF is composed of several components, including an antenna, pointing mechanism, frequency converters, high-power amplifier and various sensors including the Earth sensor, Sun sensor and inertial reference unit. The ICS-EF is part of space shuttle Endeavour's payload on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers examine the ICS Exposed Facility, or ICS-EF, after it is lifted from its stand. It will be installed on the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES. The ICS-EF is composed of several components, including an antenna, pointing mechanism, frequency converters, high-power amplifier and various sensors including the Earth sensor, Sun sensor and inertial reference unit. The ICS-EF is part of space shuttle Endeavour's payload on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
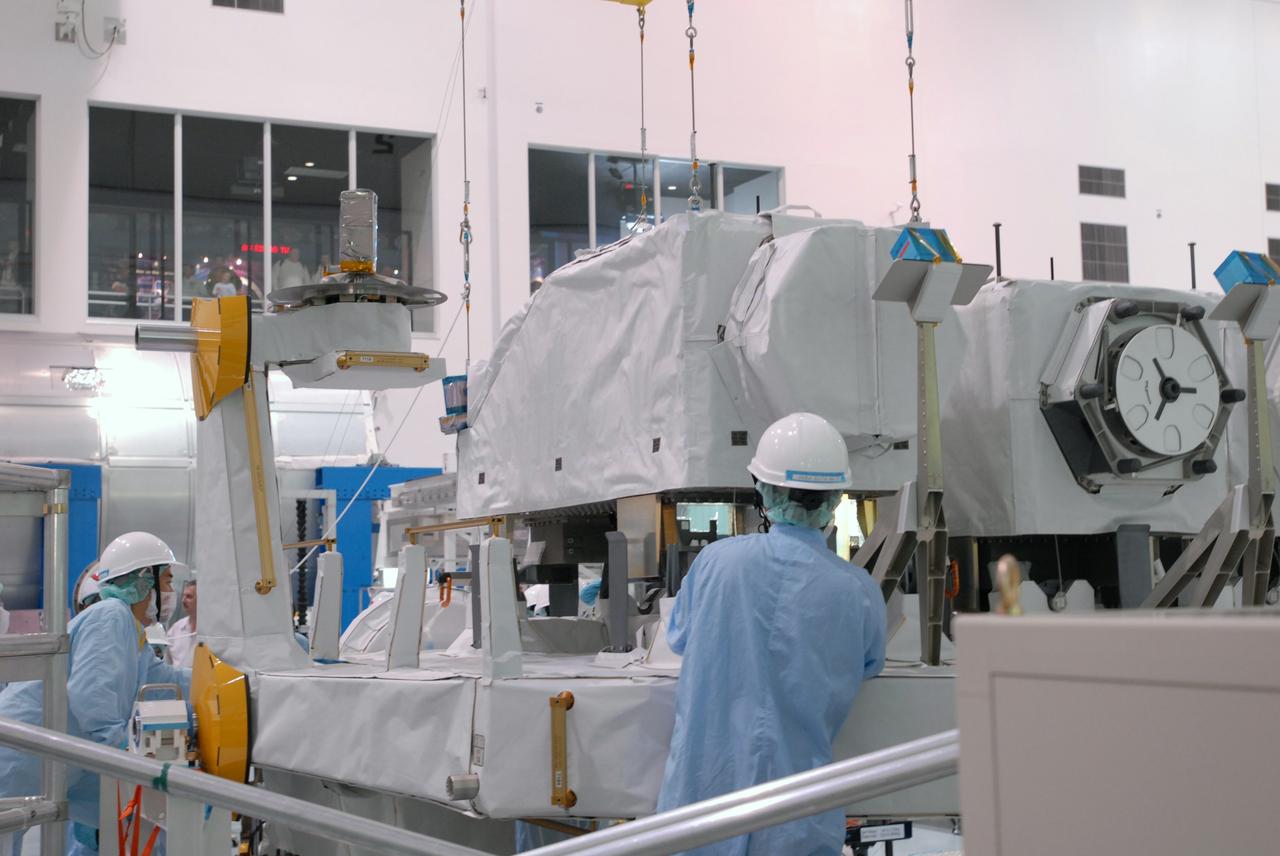

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane lowers the ICS Exposed Facility, or ICS-EF, onto the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, for installation. The ICS-EF is composed of several components, including an antenna, pointing mechanism, frequency converters, high-power amplifier and various sensors including the Earth sensor, Sun sensor and inertial reference unit. The ICS-EF is part of space shuttle Endeavour's payload on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
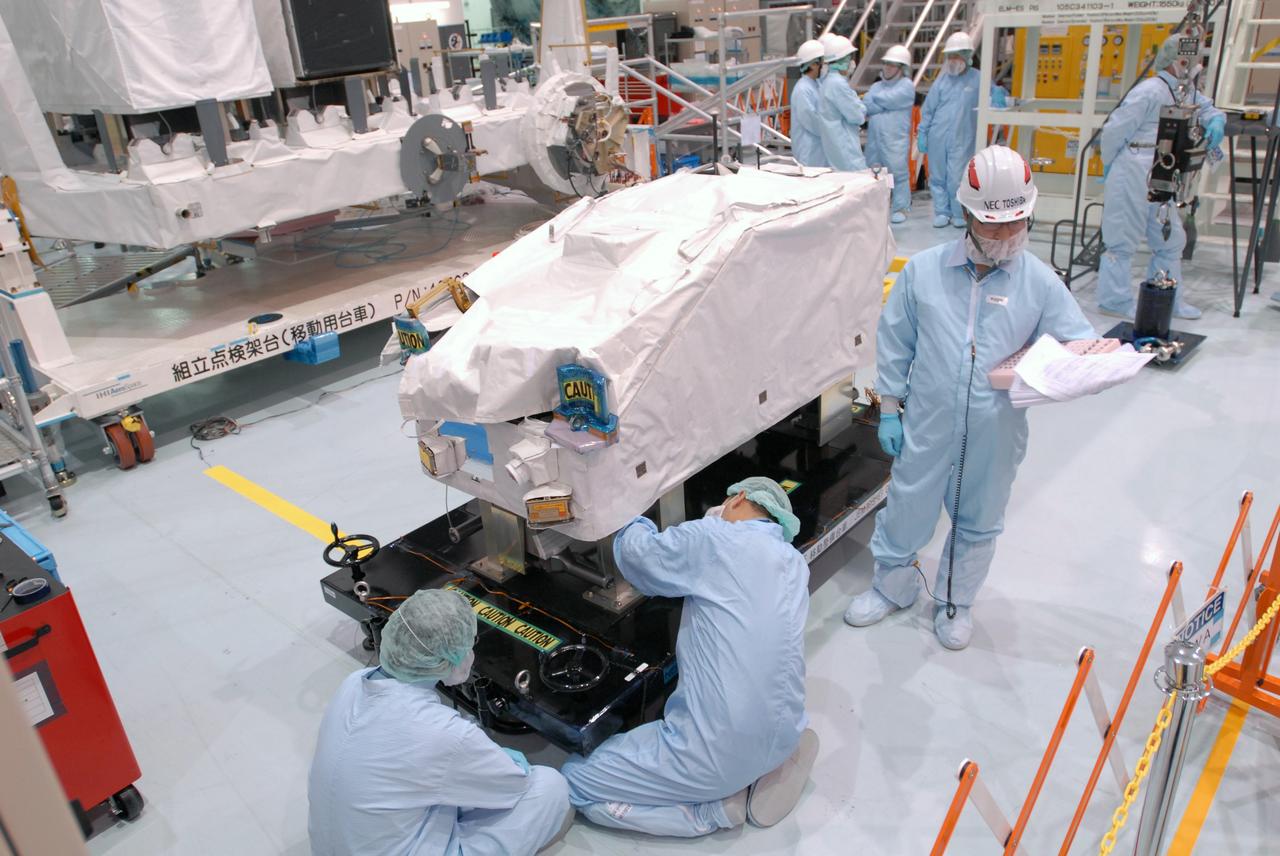

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers prepare the ICS Exposed Facility, ICS-EF, to be lifted and installed on the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES. The ICS-EF is composed of several components, including an antenna, pointing mechanism, frequency converters, high-power amplifier and various sensors including the Earth sensor, Sun sensor and inertial reference unit. The ICS-EF is part of space shuttle Endeavour's payload on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
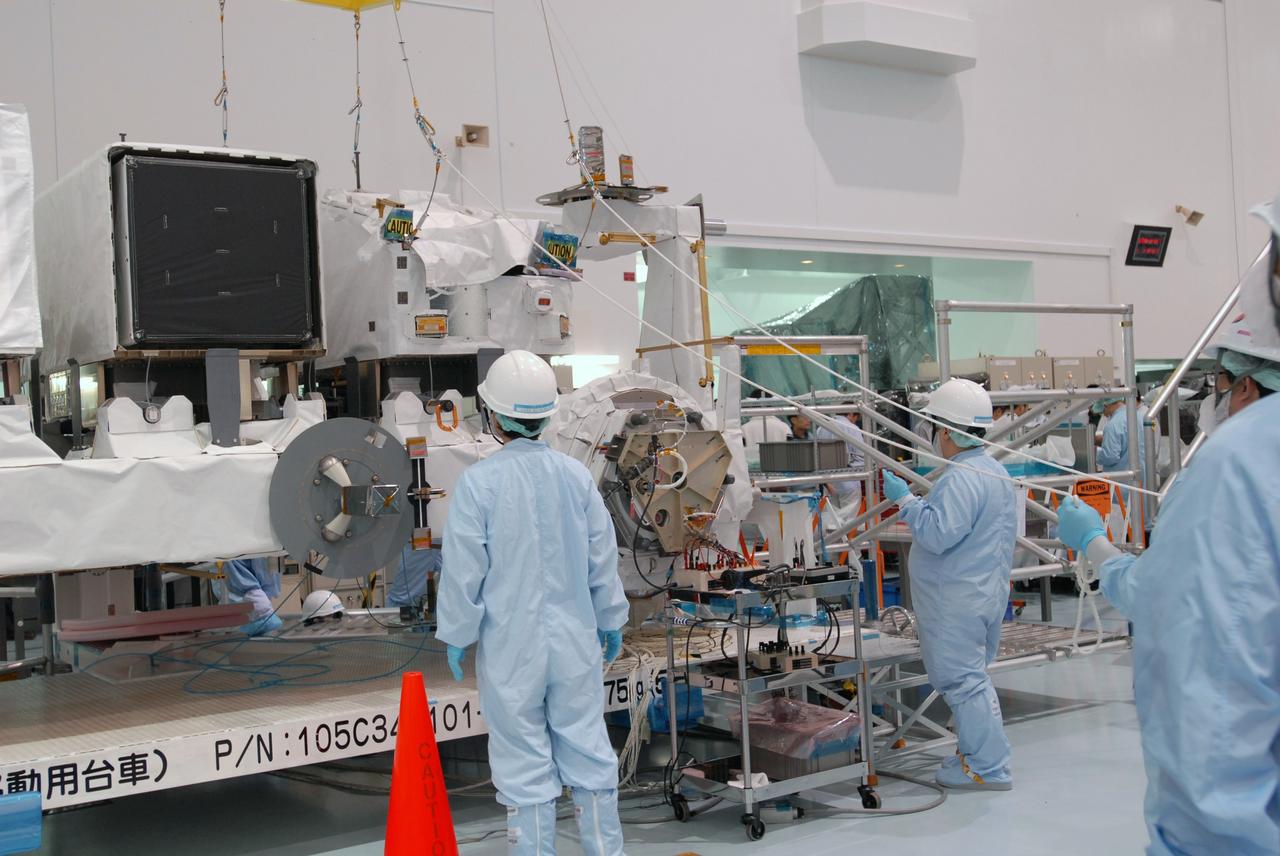

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane lowers the ICS Exposed Facility, or ICS-EF, onto the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, for installation. It is being placed next to two other payloads, the SEDA-AP (Space Environment Data Acquisition Equipment-Attached Payload) and MAXI (Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image). The ICS-EF is part of space shuttle Endeavour's payload on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
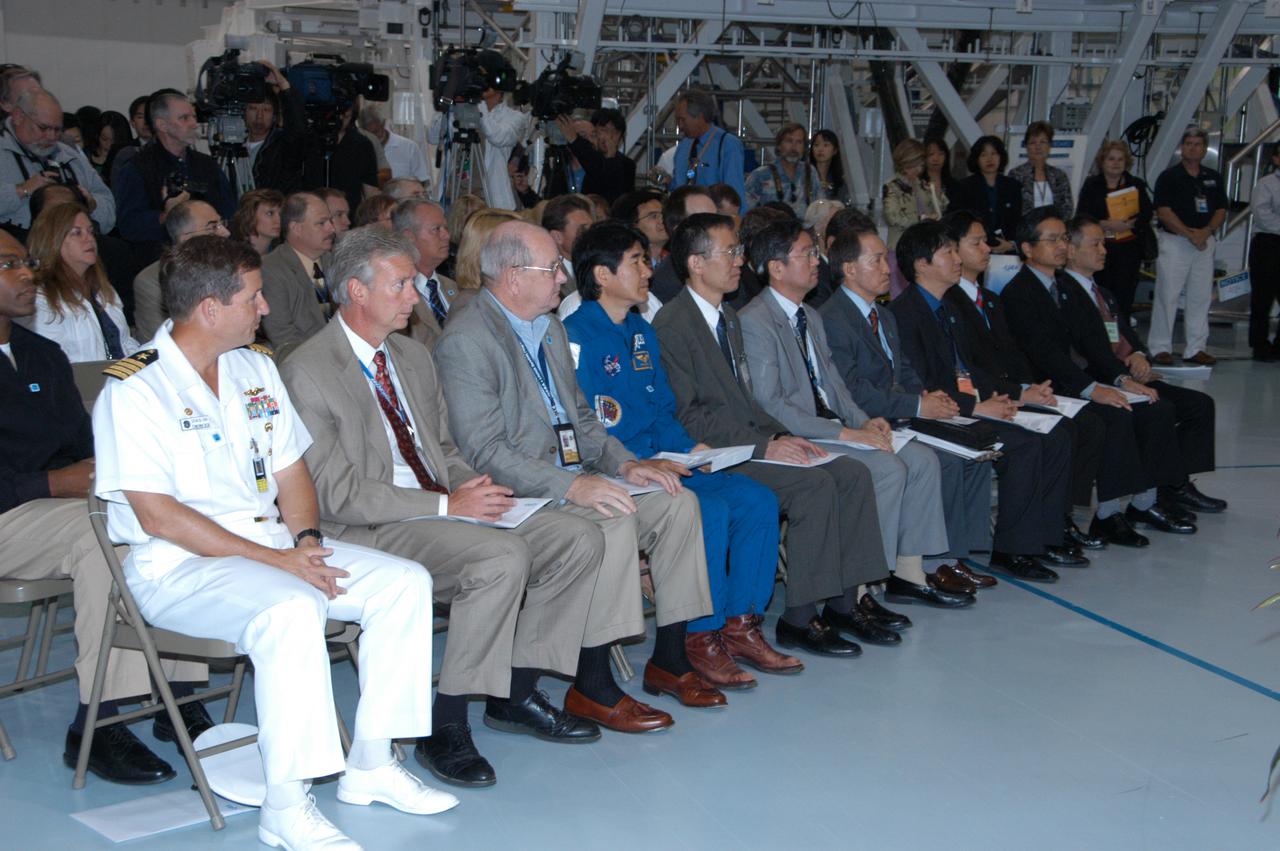

In the Space Station Processing Facility, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcome the arrival of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, to the Kennedy Space Center. Seen here at right are JAXA representatives, including Japanese astronaut Takao Doi (center of front row), who is a crew member for mission STS-123 that will deliver the module to the space station. The new International Space Station component arrived at Kennedy March 12 to begin preparations for its future launch on mission STS-123. It will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane lowers the ICS Exposed Facility, or ICS-EF, onto the Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, where it will be installed alongside two other payloads, the SEDA-AP (Space Environment Data Acquisition Equipment-Attached Payload) and MAXI (Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image). The ICS-EF is composed of several components, including an antenna, pointing mechanism, frequency converters, high-power amplifier and various sensors including the Earth sensor, Sun sensor and inertial reference unit. The ICS-EF is part of space shuttle Endeavour's payload on the STS-127 mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
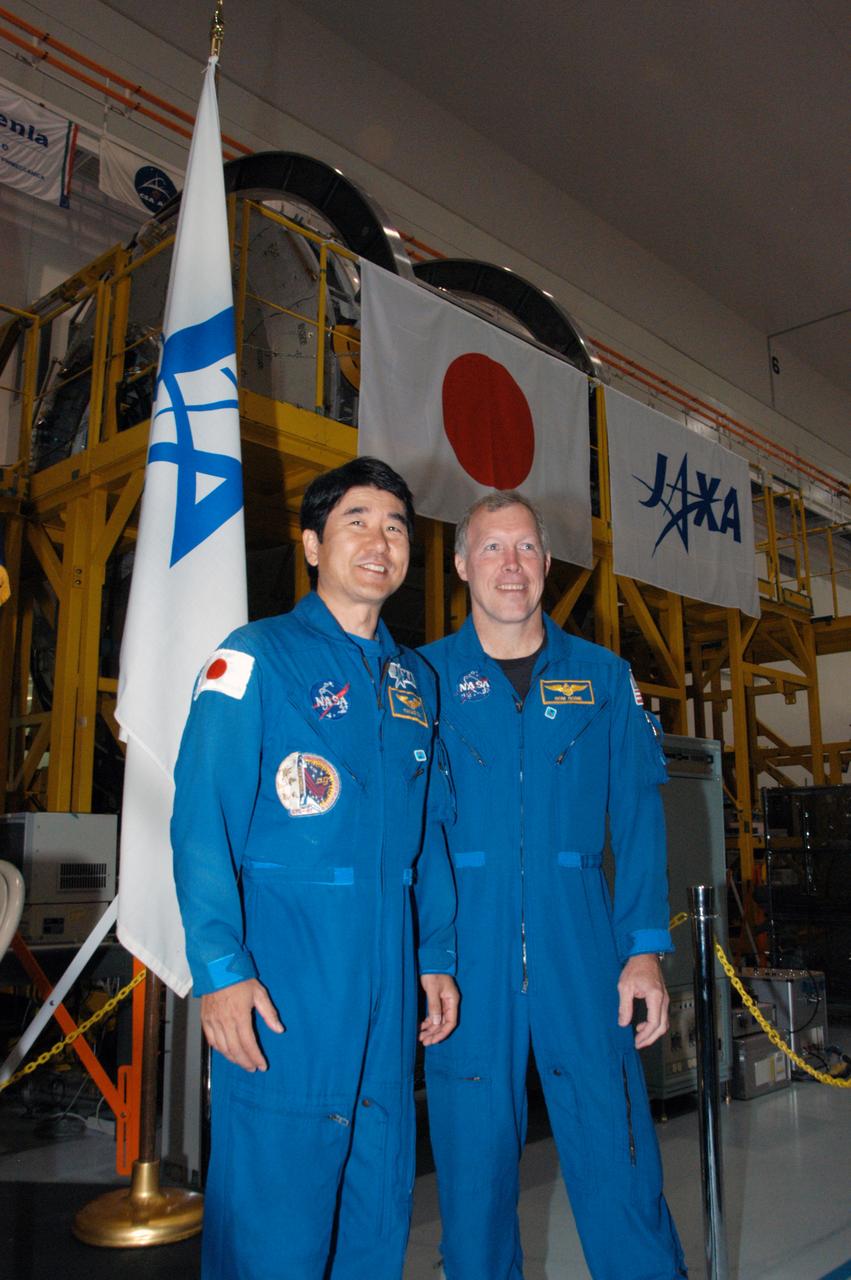

In the Space Station Processing Facility, astronaut Takao Doi (left) and Commander Dominic Gorie pose in front of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, that recently arrived at Kennedy. Doi and Gorie are crew members for mission STS-123 that will deliver the logistics module to the International Space Station. Earlier, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcomed the arrival of the module. The new International Space Station component arrived at Kennedy March 12 to begin preparations for its future launch on mission STS-123. It will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module.
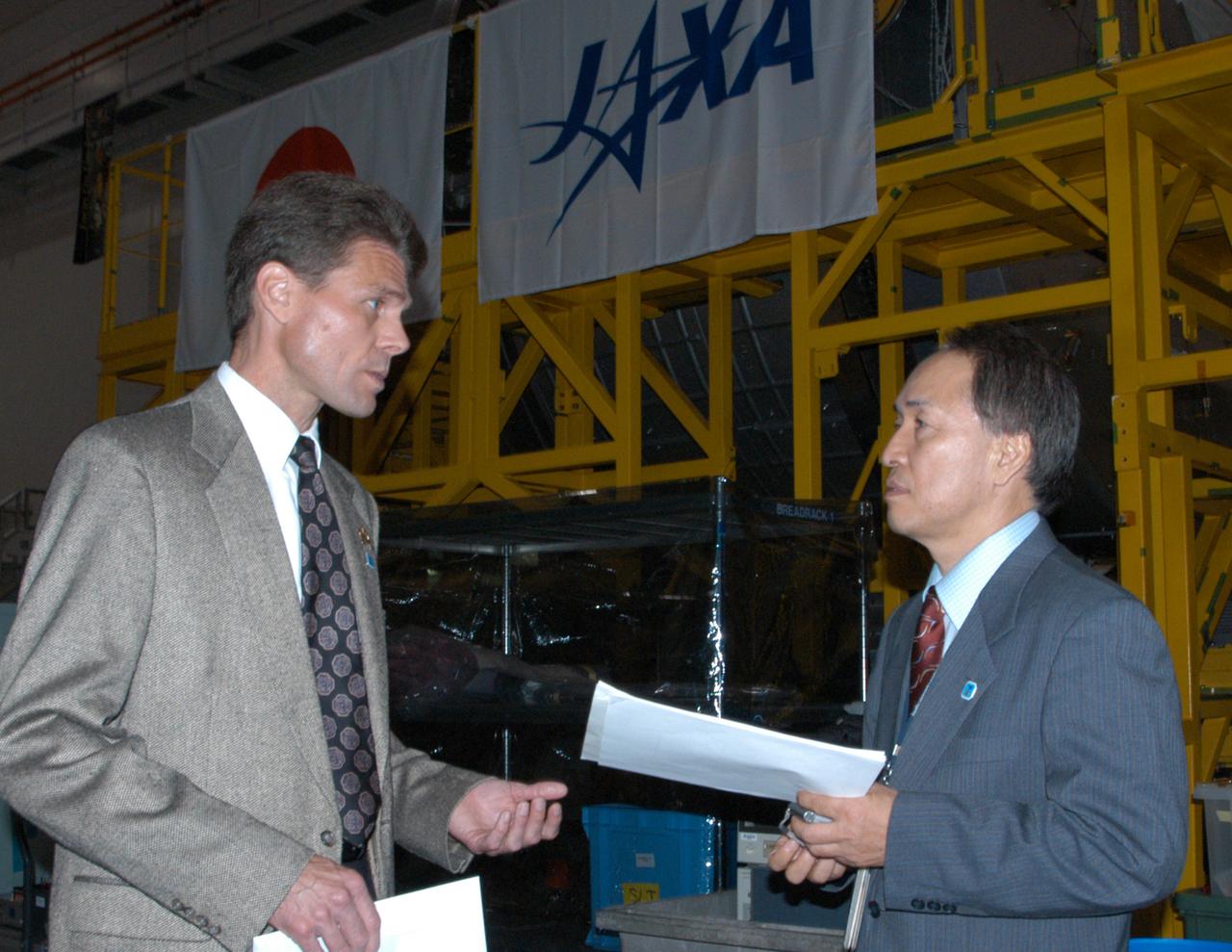

In the Space Station Processing Facility, Scott Higginbotham, payload manager for the International Space Station, discusses the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), with Dr. Hidetaka Tanaka, the JEM Project Team resident manager at KSC for the Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA). Earlier, NASA and JAXA officials welcomed the arrival of the module. The new International Space Station component arrived at Kennedy March 12 to begin preparations for its future launch on mission STS-123. It will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module.
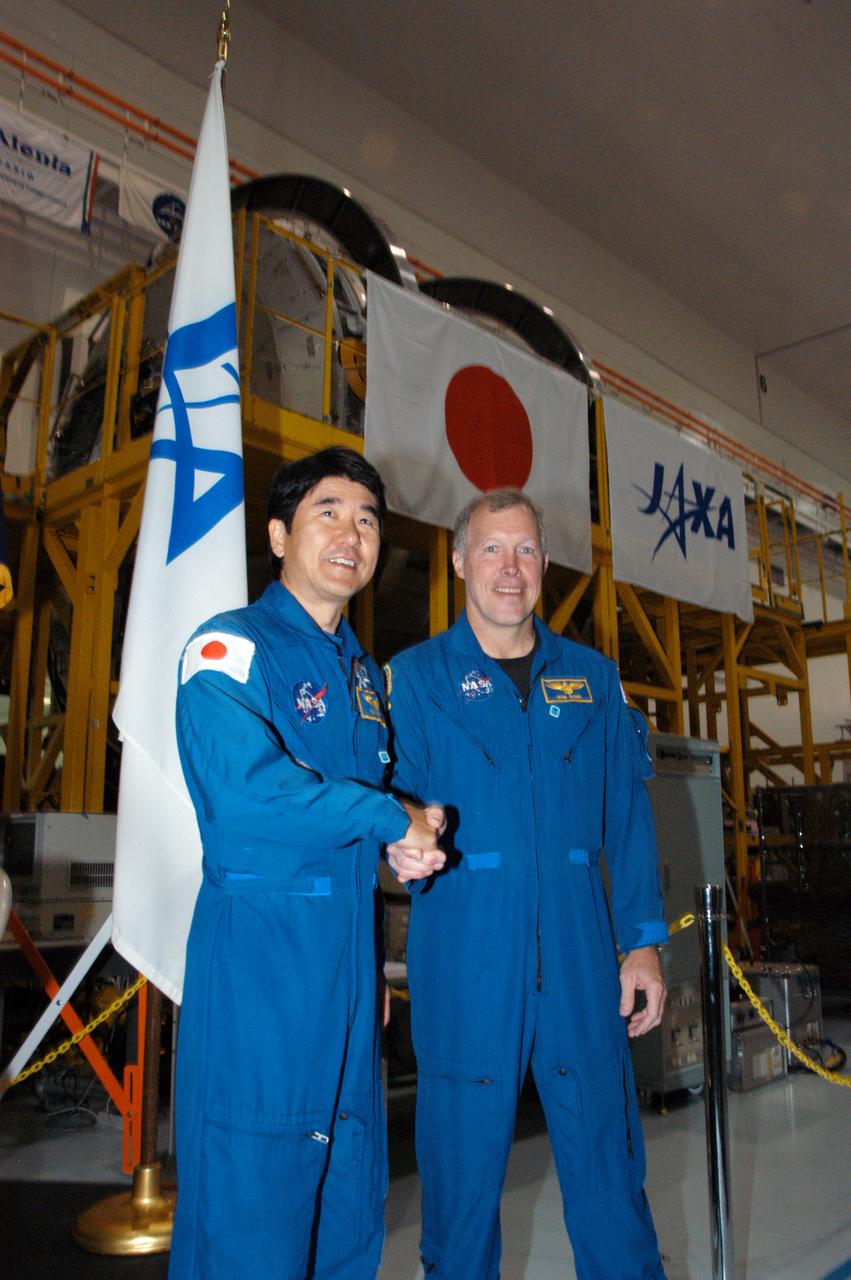

In the Space Station Processing Facility, astronaut Takao Doi (left) and Commander Dominic Gorie pose in front of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, that recently arrived at Kennedy. Doi and Gorie are crew members for mission STS-123 that will deliver the logistics module to the International Space Station. Earlier, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcomed the arrival of the module. The new International Space Station component arrived at Kennedy March 12 to begin preparations for its future launch on mission STS-123. It will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module.
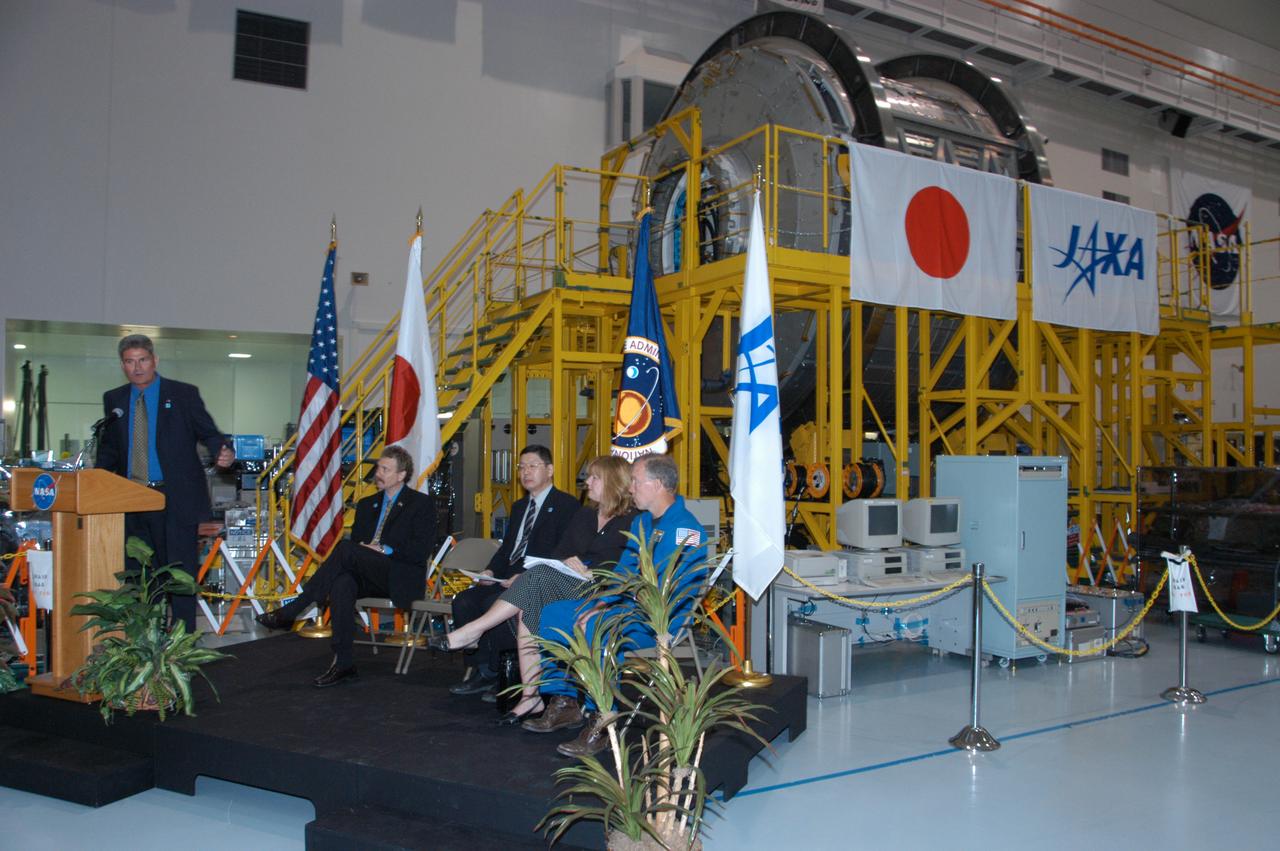

In the Space Station Processing Facility, NASA and Japanese Aerospace and Exploration Agency (JAXA) officials welcome the arrival of the Experiment Logistics Module Pressurized Section for the Japanese Experiment Module, or JEM, to the Kennedy Space Center. At the podium is Bill Parsons, director of Kennedy Space Center. Seated at right are Russ Romanella, director of International Space Station and Spacecraft Processing; Dr. Kichiro Imagawa, project manager of the JEM Development Project Team for JAXA; Melanie Saunders, associate manager of the International Space Station Program at Johnson Space Center; and Dominic Gorie, commander on mission STS-123 that will deliver the module to the space station. The new International Space Station component arrived at Kennedy March 12 to begin preparations for its future launch on mission STS-123. It will serve as an on-orbit storage area for materials, tools and supplies. It can hold up to eight experiment racks and will attach to the top of another larger pressurized module.