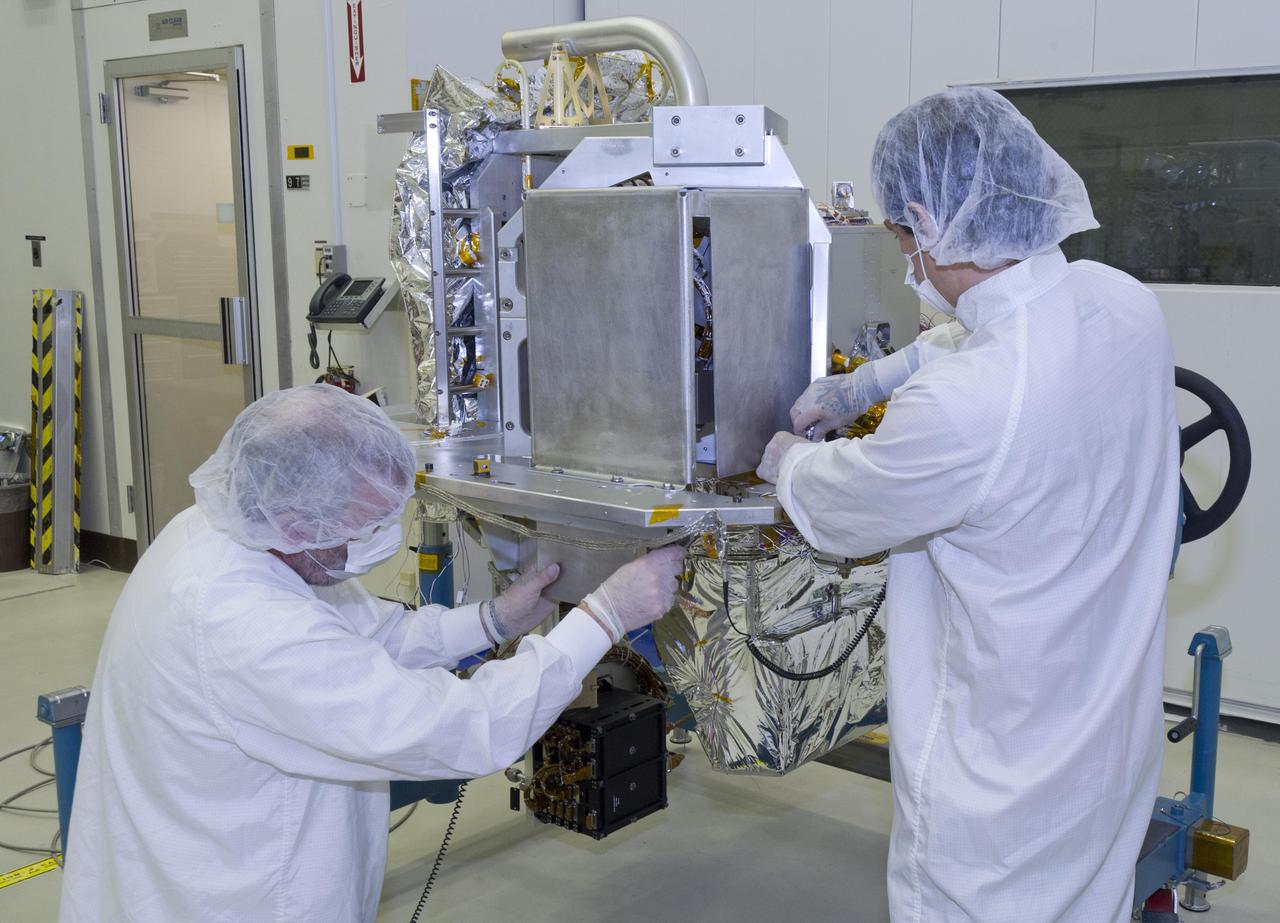

Technicians prep NASA OCO-2 instrument for shipping at Jet Propulsion Lab in Pasadena, Ca.

Technicians prep NASA OCO-2 instrument for shipping at Jet Propulsion Lab in Pasadena, Ca. Animation available in More Details.
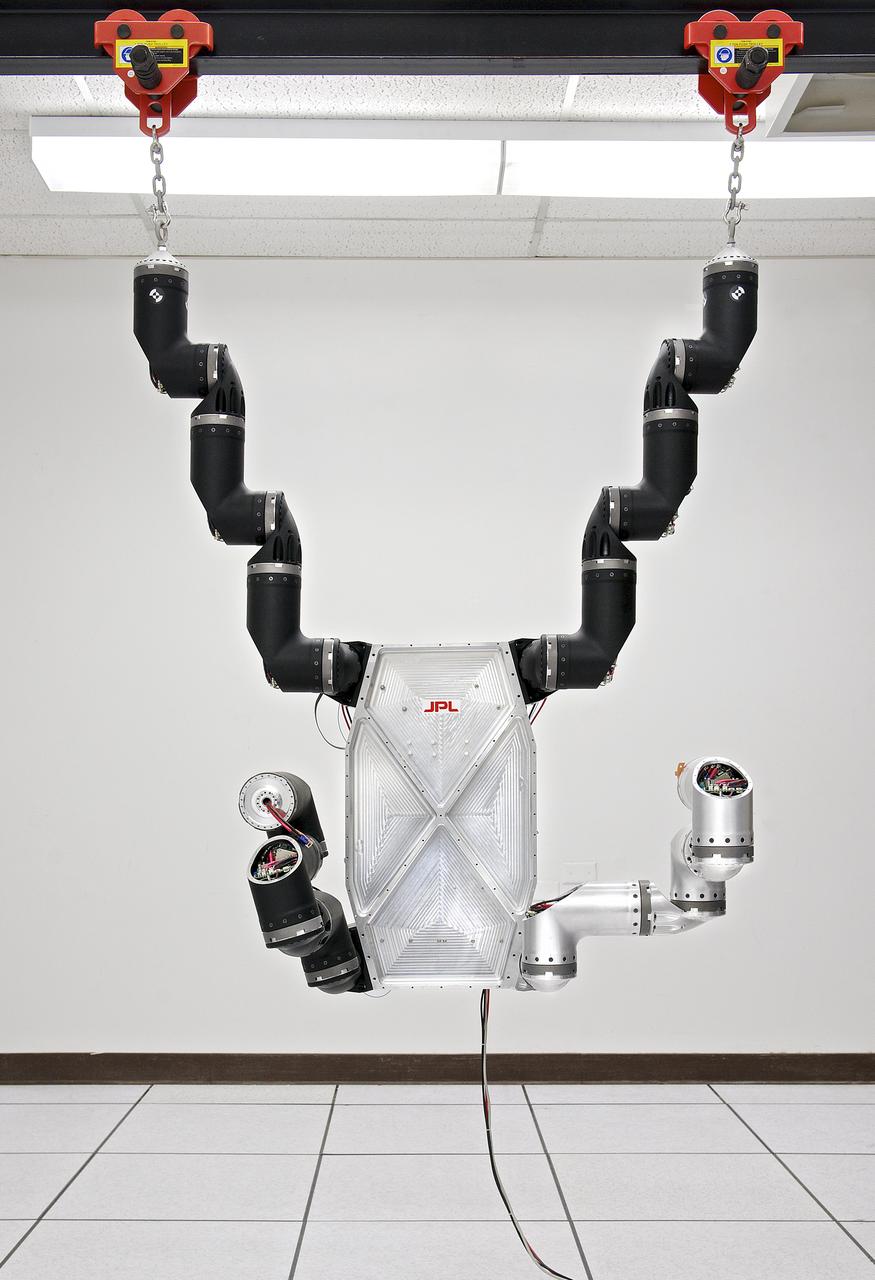

This photograph shows RoboSimian, a disaster-relief and -mitigation robot, under construction in a lab at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
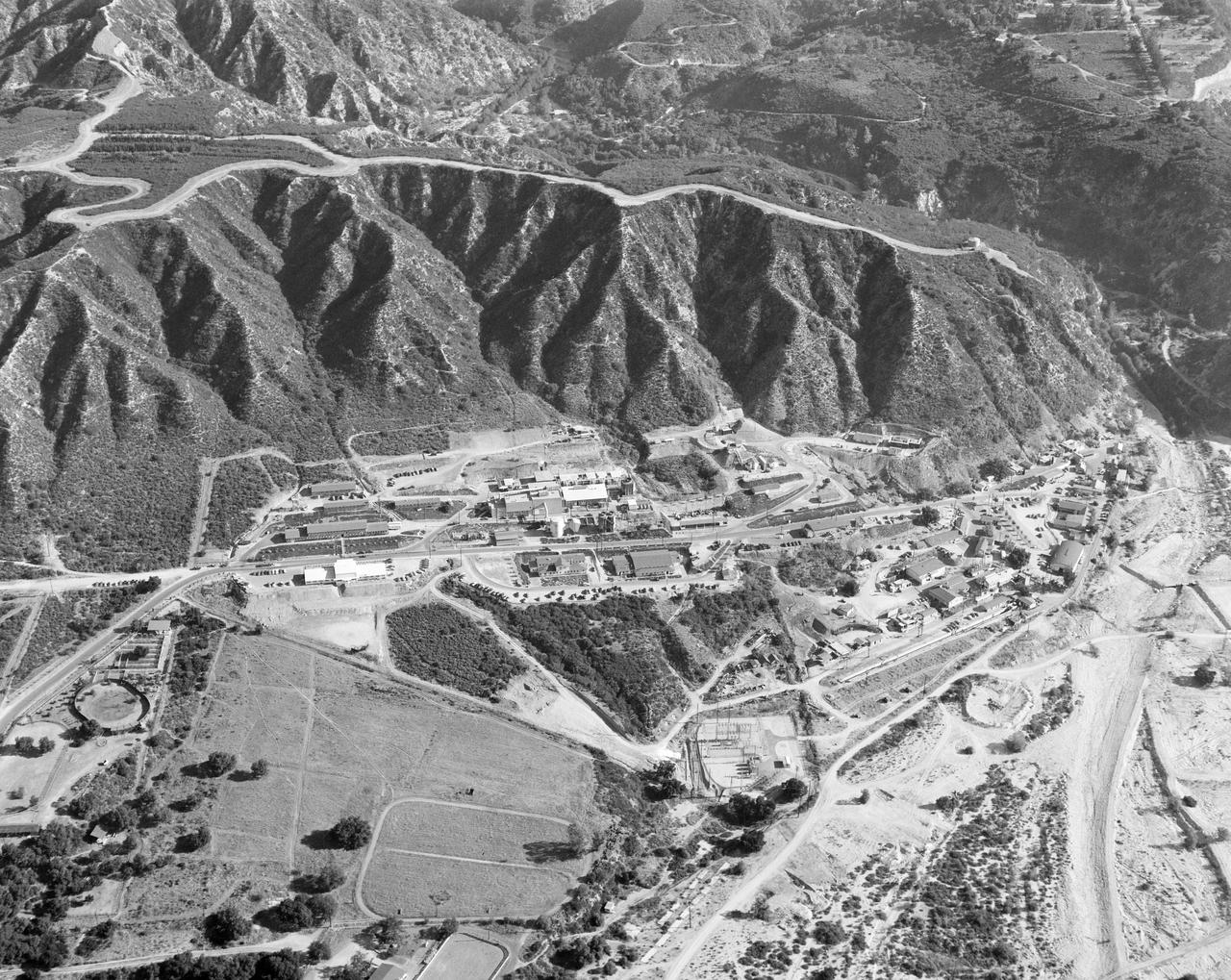

This archival image was released as part of a gallery comparing JPL's past and present, commemorating the 80th anniversary of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Oct. 31, 2016. This aerial image of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory was taken in September 1950, when the lab's main patron was the U.S. Army. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21116

This archival image was released as part of a gallery comparing JPL’s past and present, commemorating the 80th anniversary of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Oct. 31, 2016. This is what greeted visitors to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in December 1957, before NASA was created and the lab became one of its centers. There is no sign at this location today -- there is just a stairway that runs up the side of the main Administration Building (Building 180). The official lab sign has moved farther south, just as the lab itself has expanded farther south out from the base of the San Gabriel Mountains. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21115
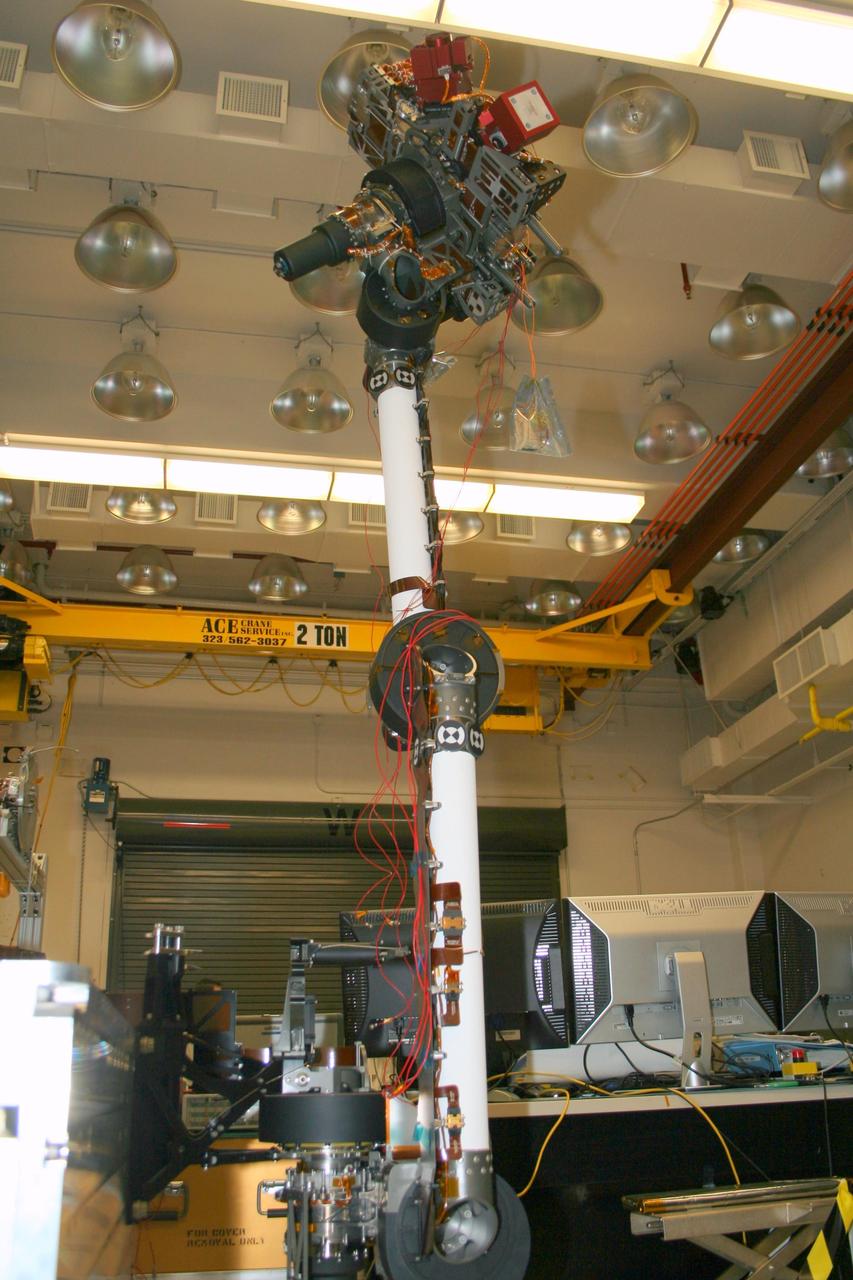

In the middle of this image taken at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the long robotic arm of NASA Mars Science Laboratory rises straight up toward the ceiling of the lab where it is being tested.
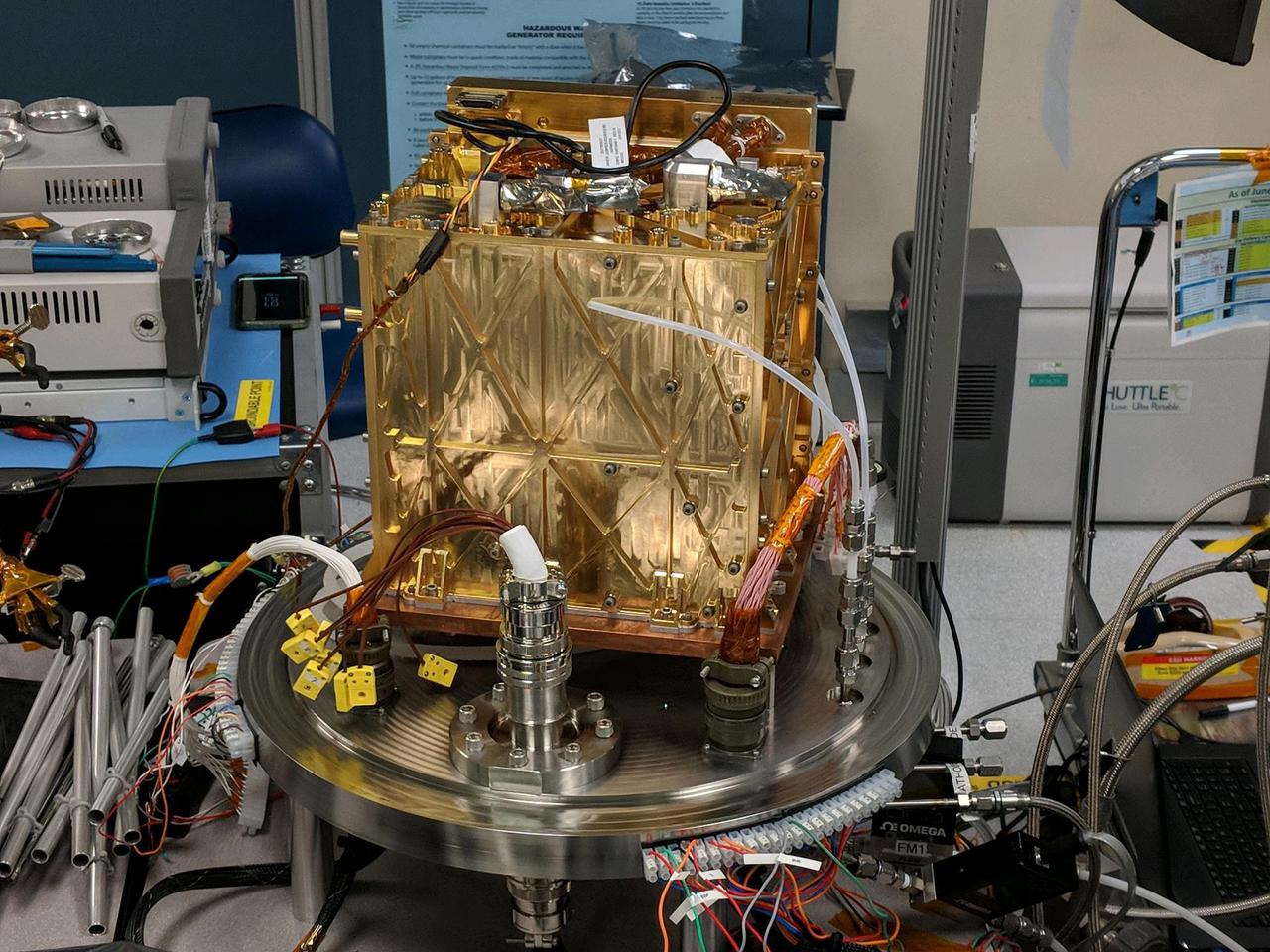

This engineering model of Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) instrument is about to undergo vibration testing in a lab at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Vibration tests demonstrate the ability of instruments to survive the extreme conditions of both a rocket launch from Earth and a landing on Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24202
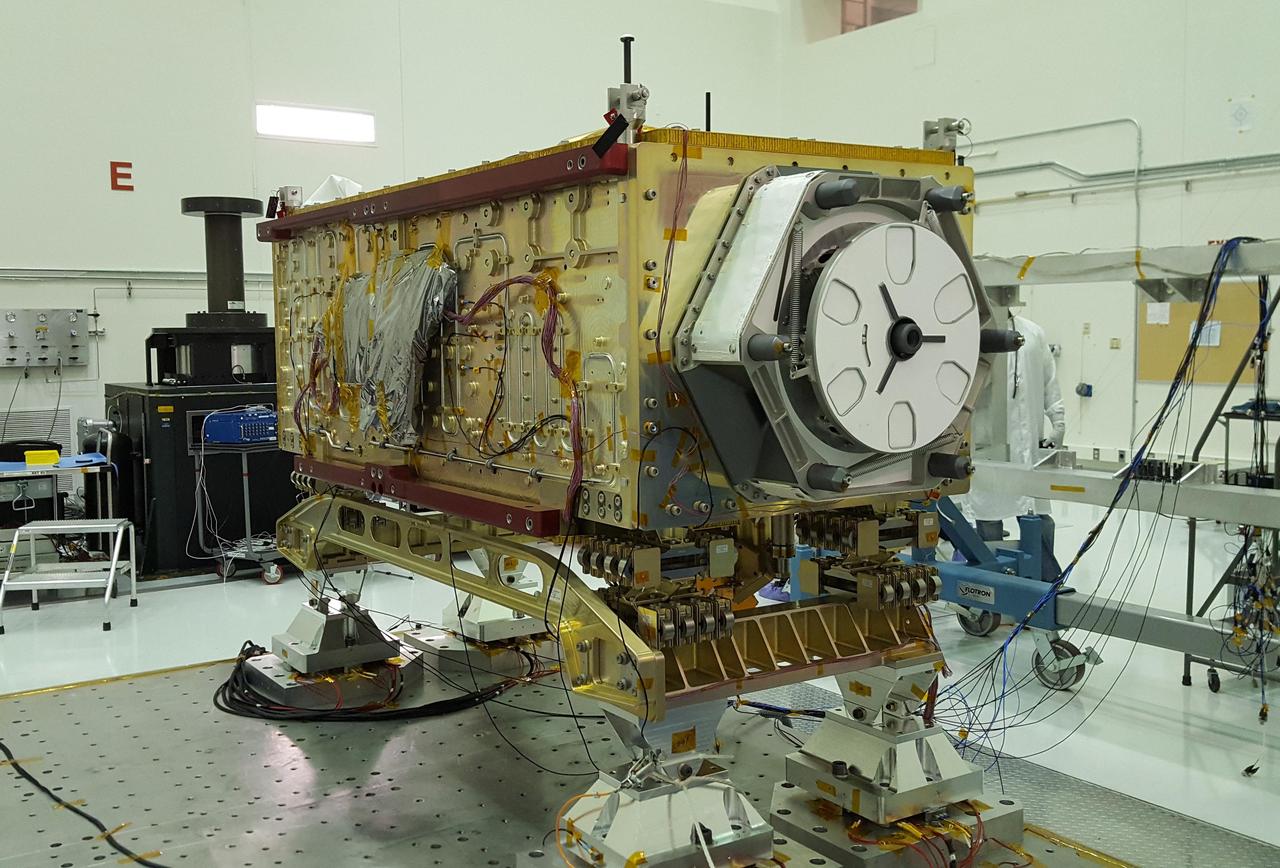

OCO-3 sits on the large vibration table (known as the "shaker") in the Environmental Test Lab at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The exposed wires lead to sensors used during dynamics and thermal-vacuum testing. Thermal blankets will be added to the instrument at Kennedy Space Center, where a Space-X Dragon capsule carrying OCO-3 will launch in on a Falcon 9 rocket to the space station on May 1, 2019. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23211

This view of Jupiter was taken by Voyager 1. This image was taken through color filters and recombined to produce the color image. This photo was assembled from three black and white negatives by the Image Processing Lab at Jet Propulsion Laboratory. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01384
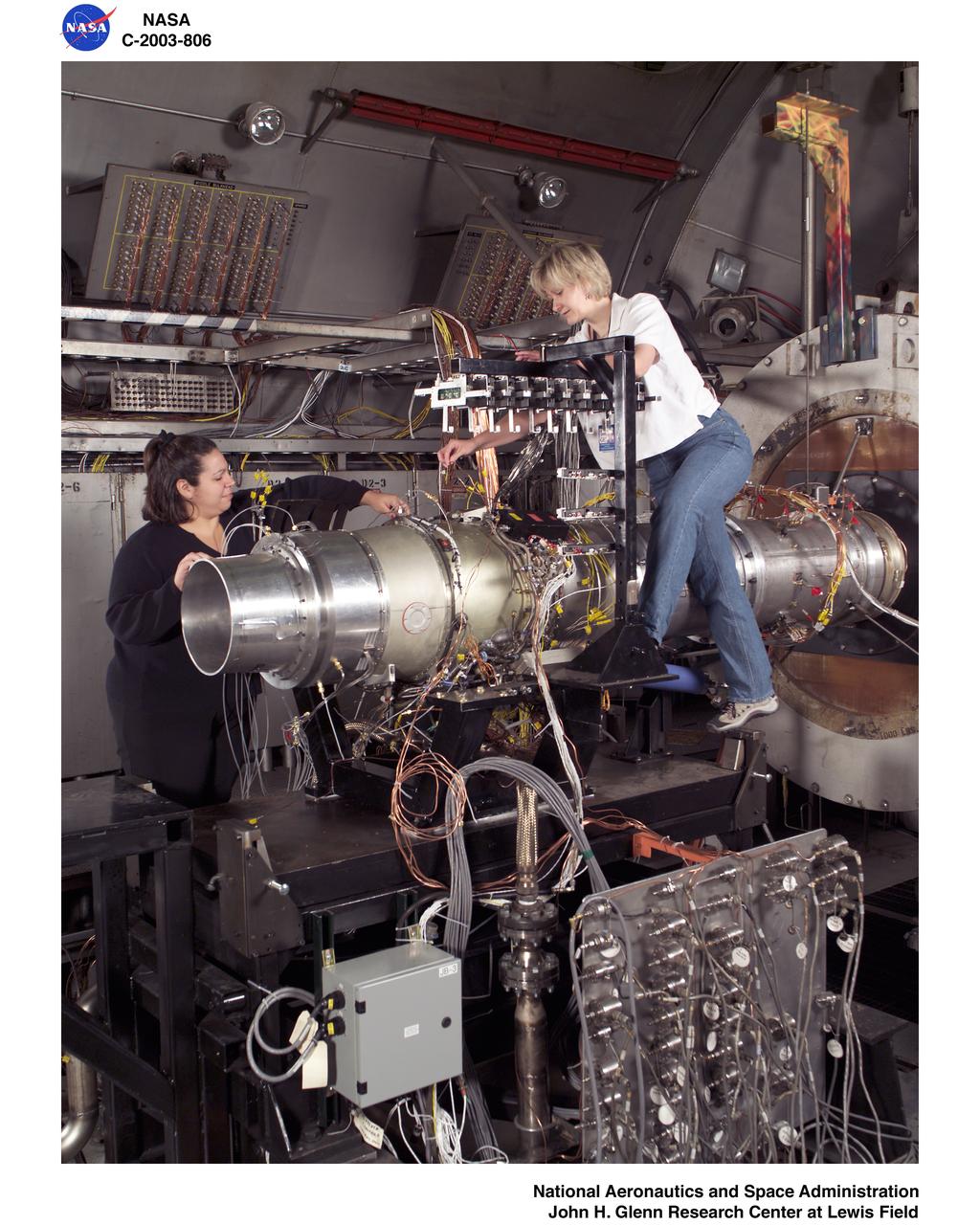
WILLIAMS INTERNATIONAL FJ33 TURBOFAN JET ENGINE TEST IN THE PROPULSION SYSTEMS LAB - PSL - CELL 4
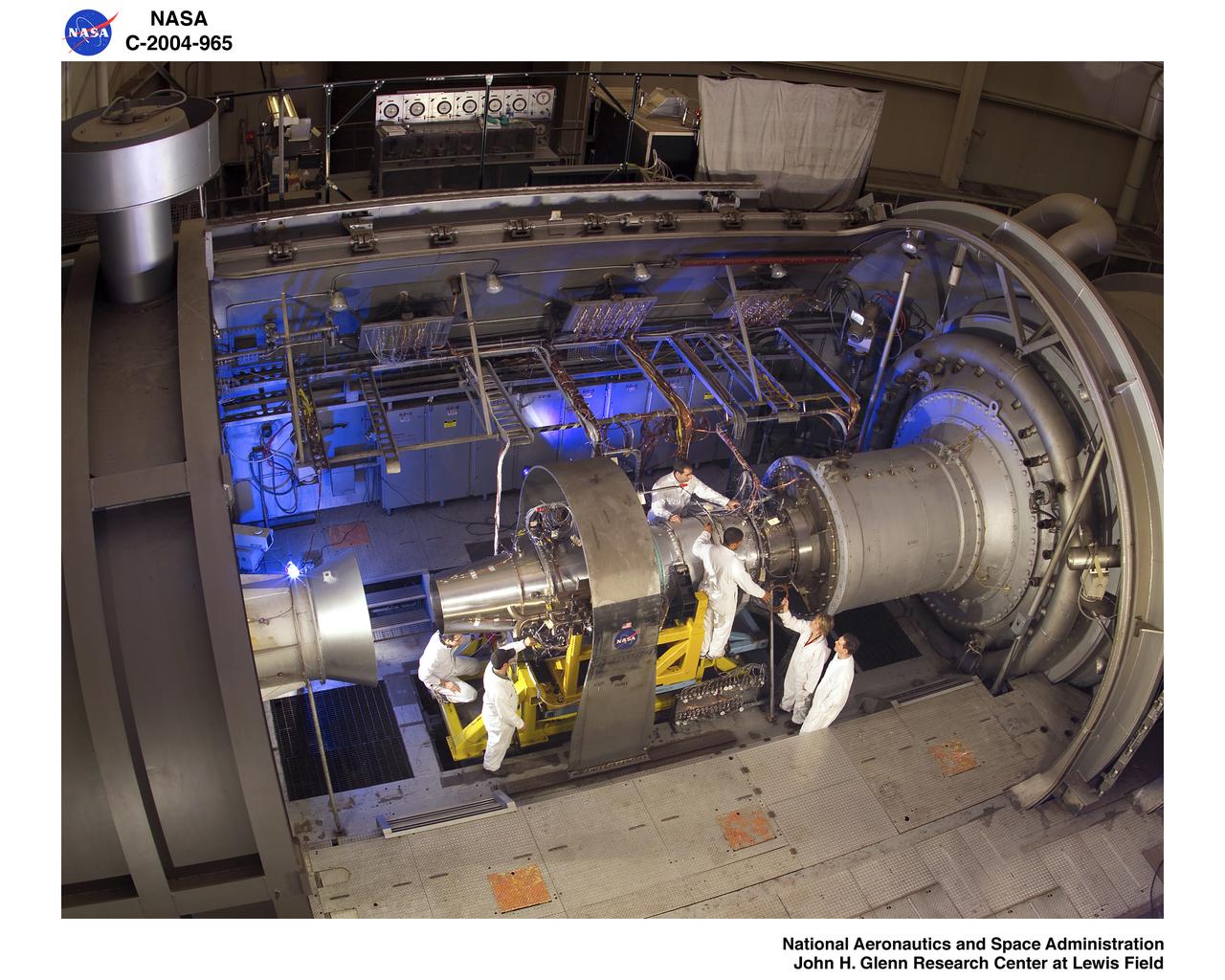
Jet engine being set up for testing with technicians from Propulsion System lab PSL
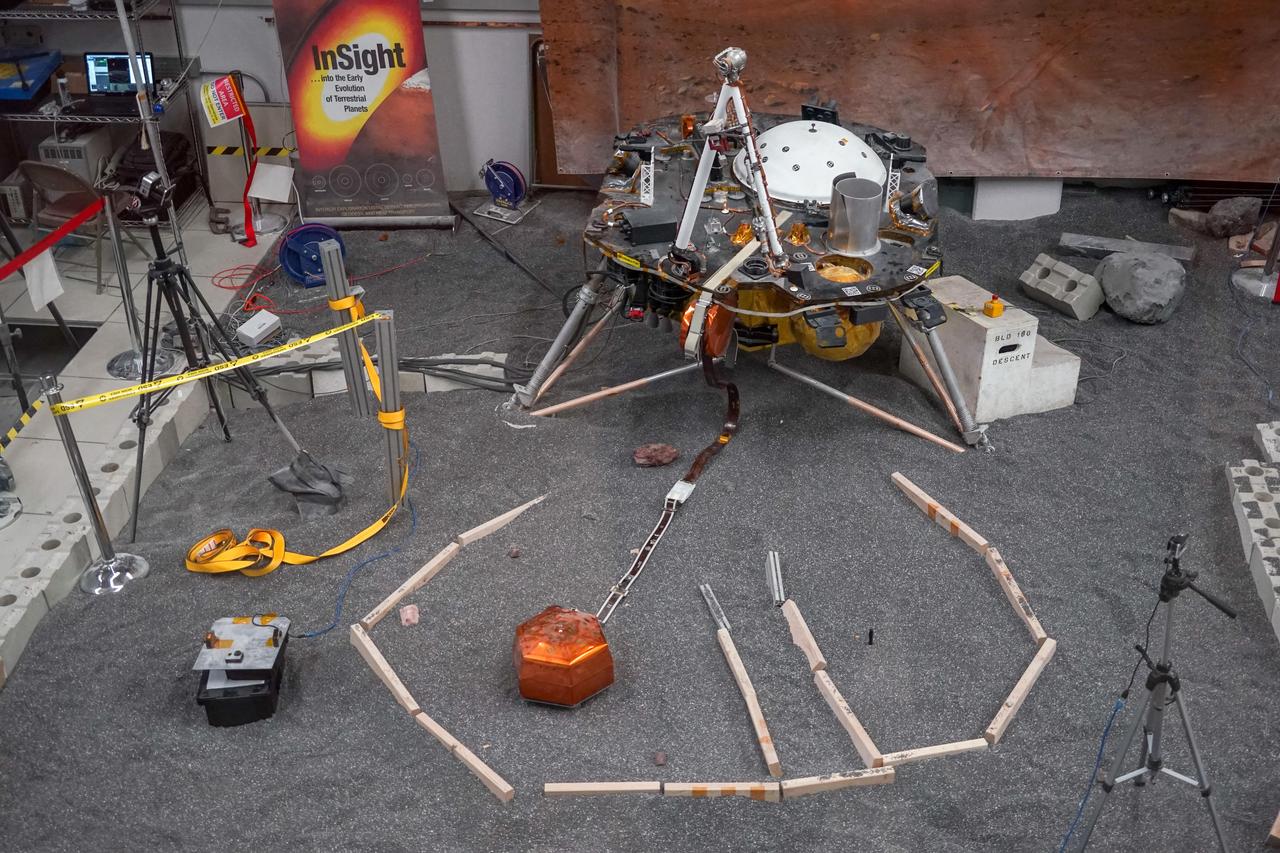

ForeSight, a fully functional, full-size model of NASA's InSight lander, sits in a lab space that has been sculpted to match terrain in front of the real lander on Mars. This work was done at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22953
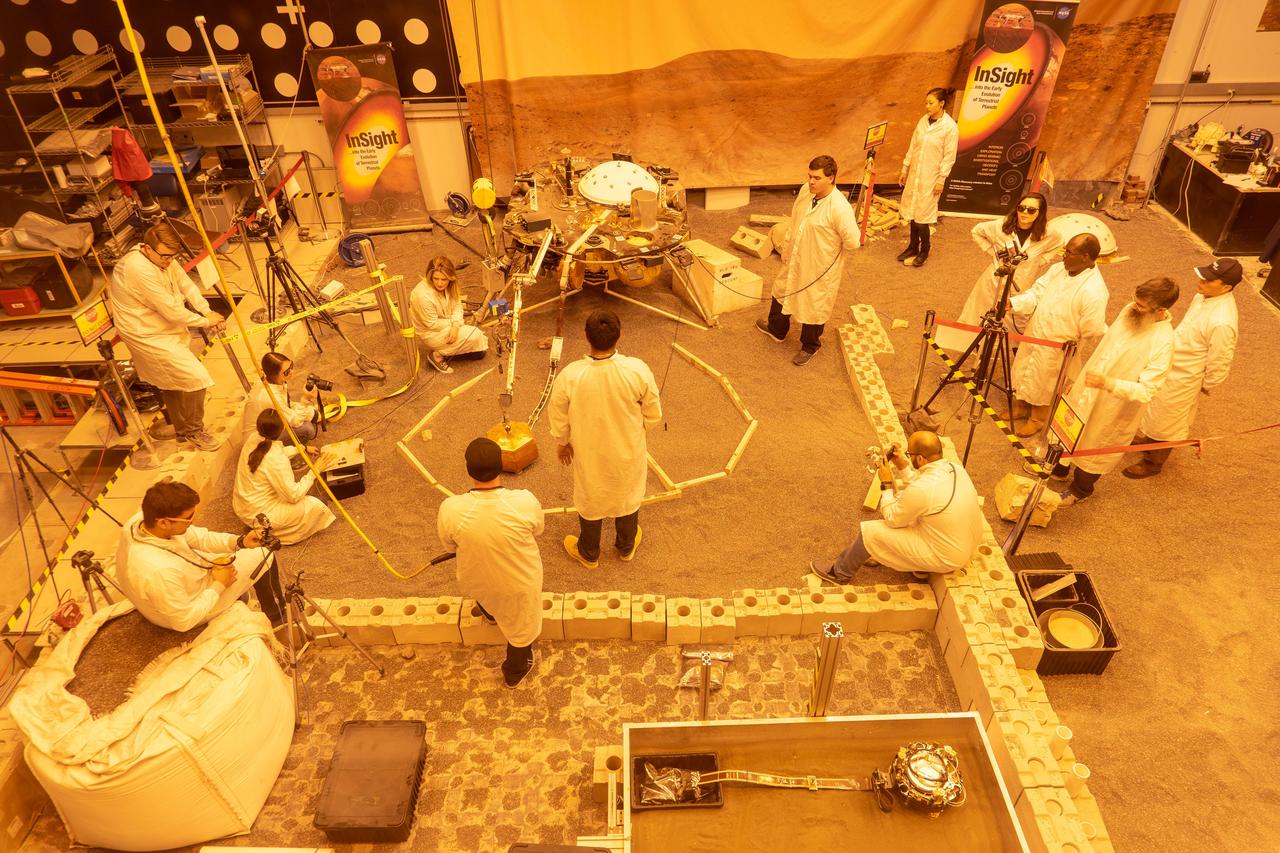

Engineers practice deploying InSight's instruments in a lab at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Several of them are wearing sunglasses to block the bright yellow lights in the test space, which mimic sunlight as it appears on Mars. The yellow lights are used to test cameras which are the same as those used by InSight on Mars. The entire lab space in the center of the image has been sculpted to mimic the terrain in front of the lander on Mars, creating more reliable test conditions. The area in the center of the image is the "workspace" where the lander's instruments can be set down; wood blocks have been laid down to mark the perimeter of these areas. Rocks have been chosen to match the size, shape and location of those in front of InSight on Mars. In the center of the image is a model of the lander's copper-colored seismometer; at the bottom-right is a second model of the seismometer used for a different kind of testing. In the lower left corner of the image is a bag of crushed granite, which is used in this lab to simulate Martian sand. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22744
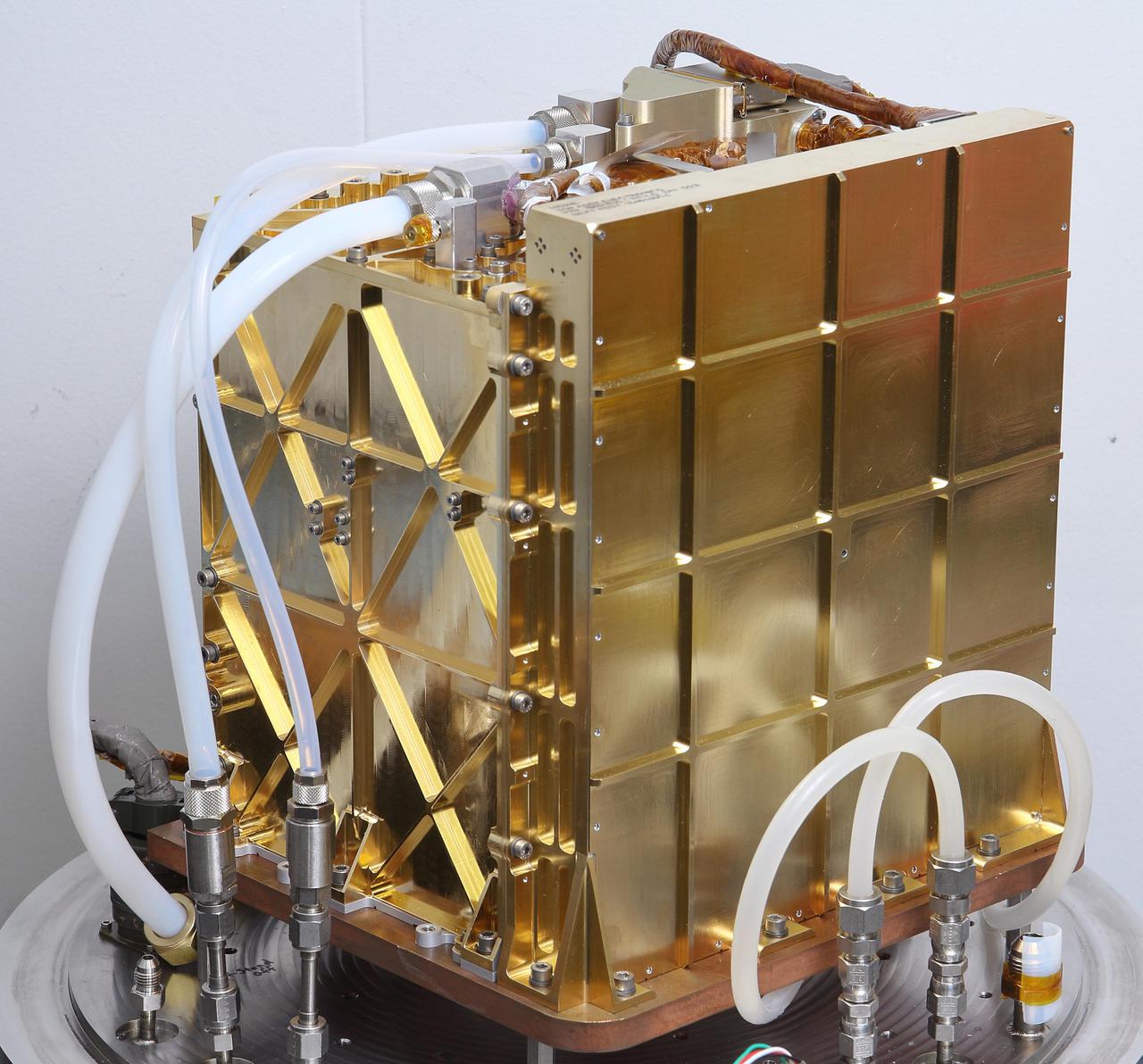
The engineering model (EM), an almost identical twin of MOXIE, is used for testing in the lab at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Inside this gold-plated aluminum box is the Solid Oxide Electrolysis unit, or SOXE, the heart of MOXIE. Using an electrochemical process called electrolysis, SOXE takes in the carbon dioxide gas and splits it into carbon monoxide and oxygen, which is measured for purity, filtered, and then released back into the Mars atmosphere. Tubes to take in the Mars atmosphere and vent oxygen and carbon monoxide produced by the EM are connected at the top of the EM. The electronics needed to run this complex machine are housed inside the larger sidewall seen on the right. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24201
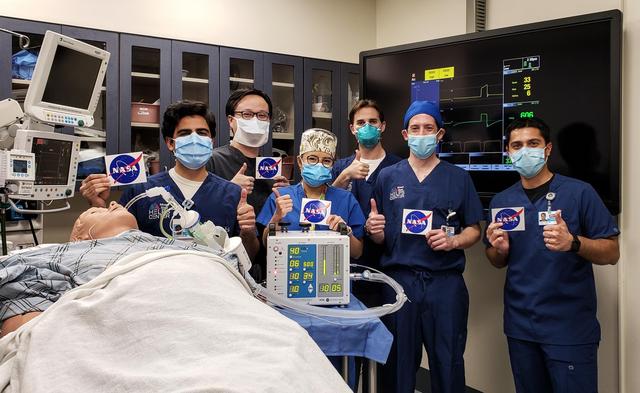
After testing a ventilator prototype developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, doctors in the Department of Anesthesiology and the Human Simulation Lab at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City give a thumbs up. Developed in response to the coronavirus outbreak, the device, called VITAL (Ventilator Intervention Technology Accessible Locally), requires far fewer parts than traditional ventilators, making it cheaper to build and ideal for rapid manufacture. Lying on the bed is a human patient simulator used to test the device. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23772
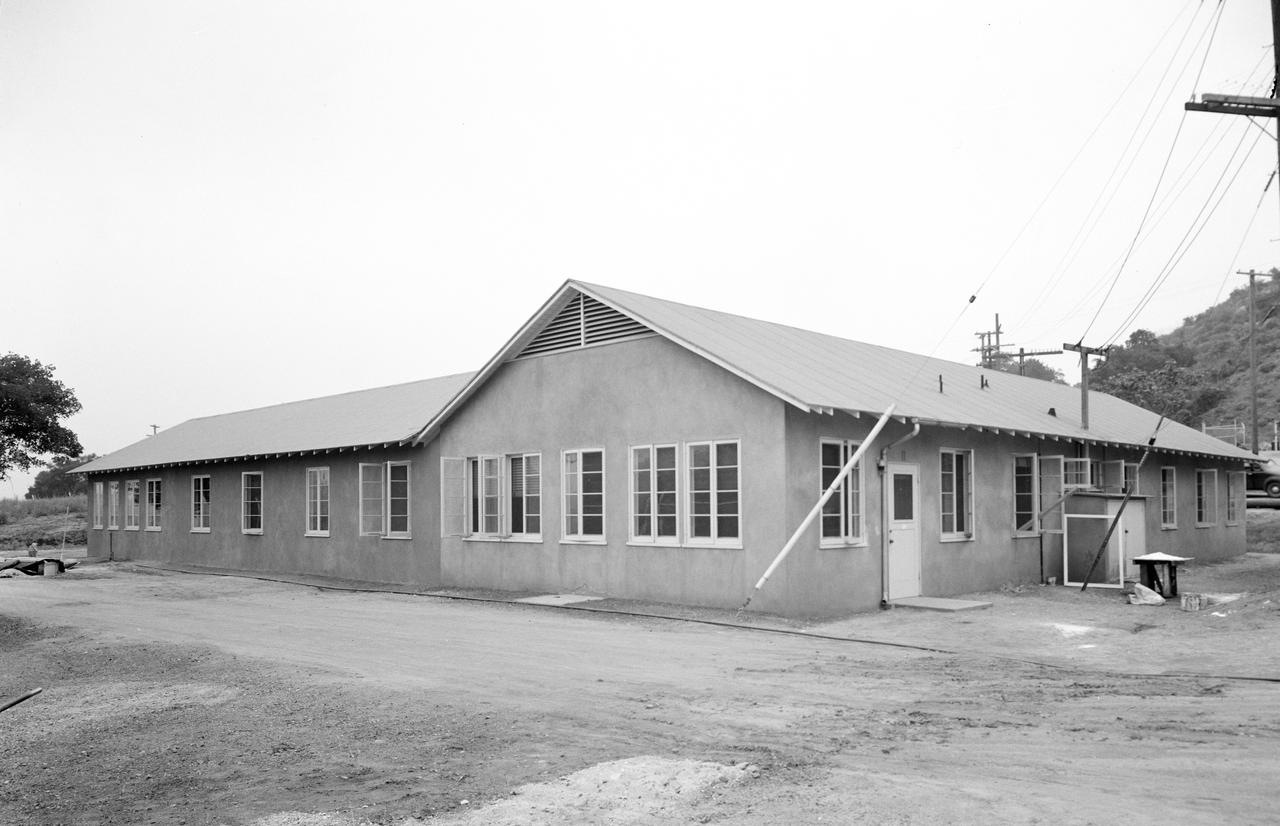

This archival image was released as part of a gallery comparing JPL's past and present, commemorating the 80th anniversary of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Oct. 31, 2016. Building 11, one of the oldest buildings on lab, was once JPL's central administration building. It is now the Space Sciences Laboratory. This picture dates back to May 1943. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21201
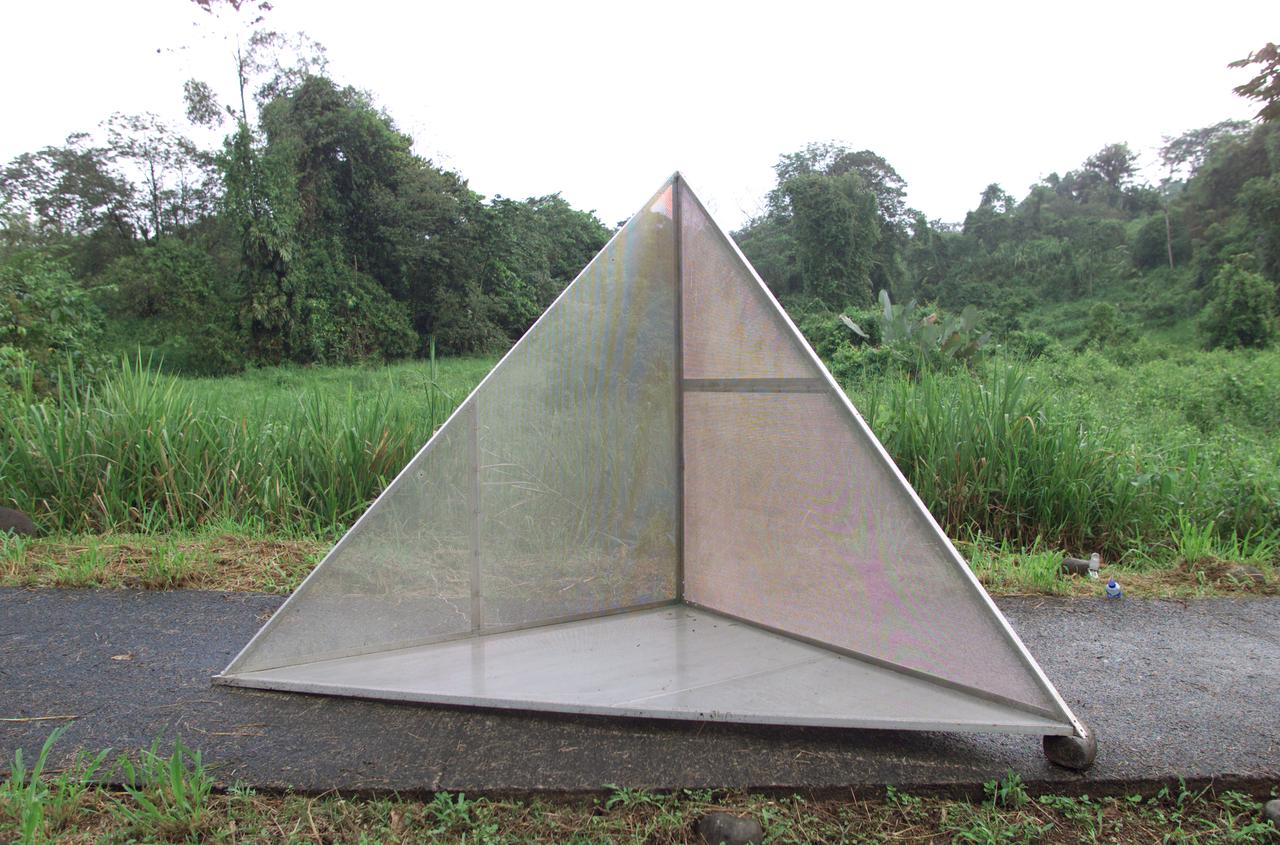

Reflectors setup in the La Selva region of the Costa Rican rain forest by scientist Paul Siqueira from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab. These reflectors are used by JPL scientists onboard Dryden's DC-8 aircraft to calibrate the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) system. Scientists place these reflectors at known points on the ground, allowing researchers onboard the aircraft to verify their data. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
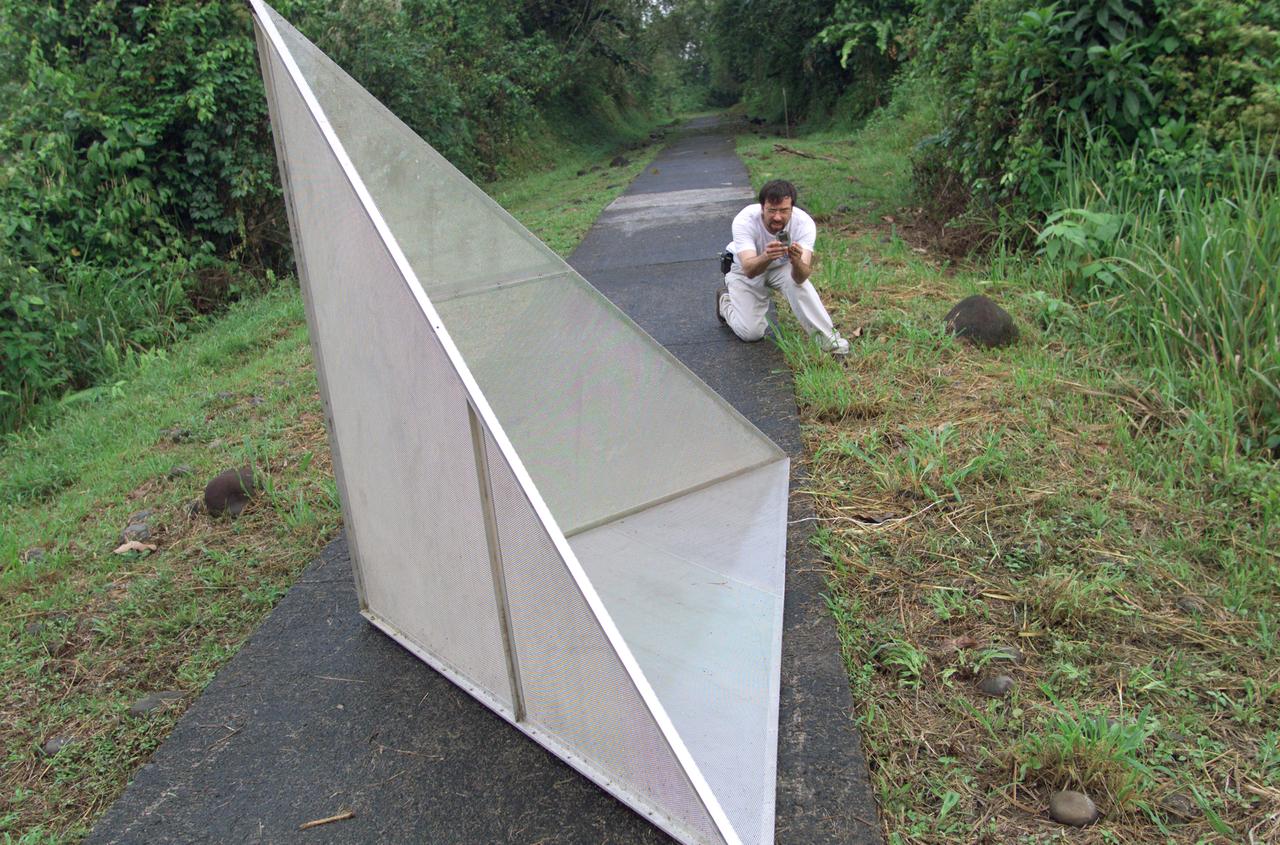

Reflectors setup in the La Selva region of the Costa Rican rain forest by scientist Paul Siqueira from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab. These reflectors are used by JPL scientists onboard Dryden's DC-8 aircraft to calibrate the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) system. Scientists place these reflectors at known points on the ground, allowing researchers onboard the aircraft to verify their data. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
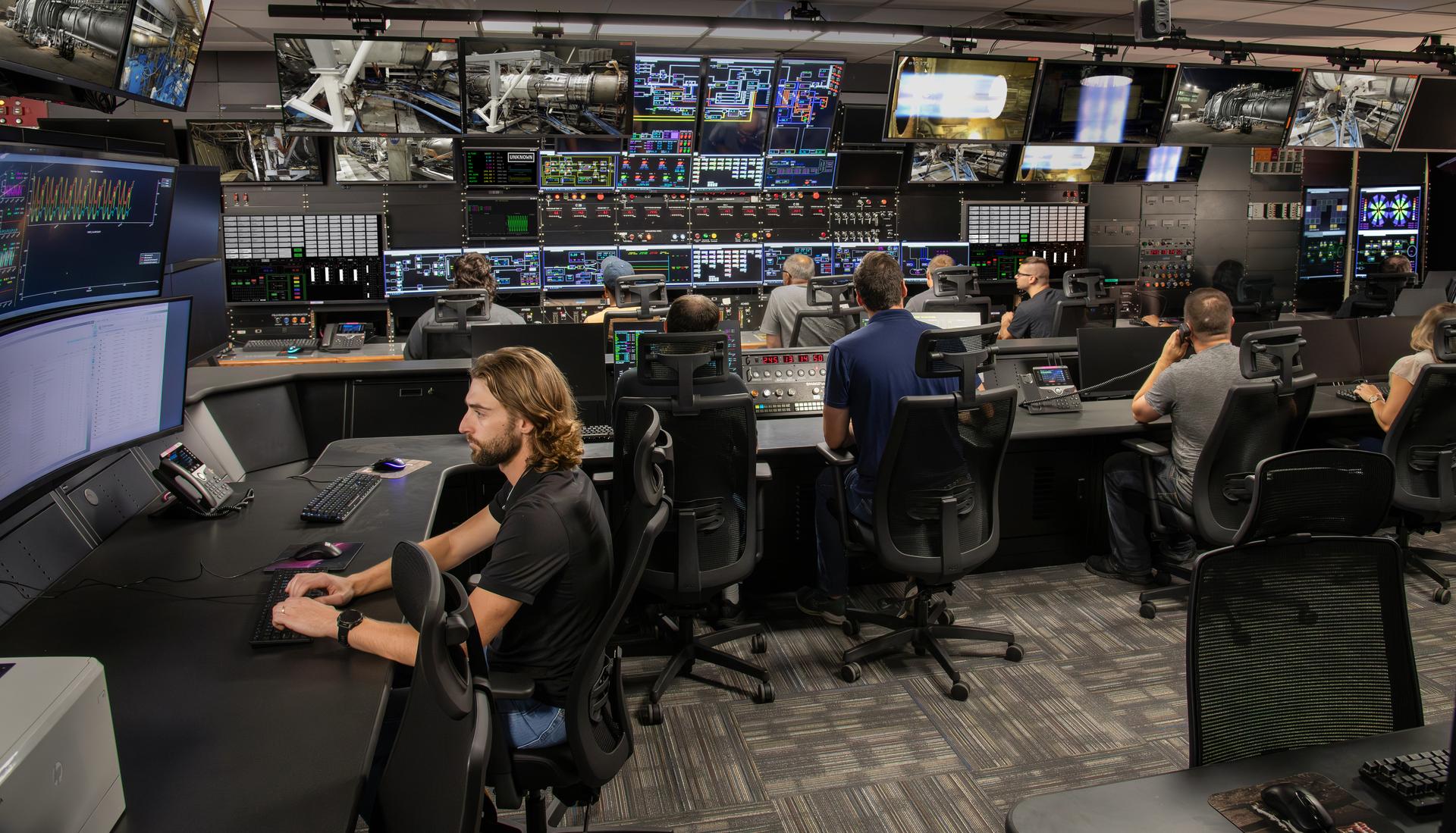

The NASA Glenn's Propulsion System Lab (PSL) recently remodeled control room. This is where jet and rocket engines are tested at GRC. This remodeled control room offers better test monitoring and work stations for test engineers and technicians.

The Carbon Mapper imaging spectrometer, which will measure the greenhouse gases methane and carbon dioxide from space, sits at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in August 2023, before its September shipment to Planet Labs PBC in San Francisco. The instrument will be integrated into a Tanager satellite. Designed and built by JPL, imaging spectrometer will be part of an effort led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper organization to collect data on greenhouse gas point-source emissions. The information will help locate and quantify "super-emitters" – the small percentage of individual sources responsible for a significant fraction of methane and carbon dioxide emissions around the world. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26092

This archival image was released as part of a gallery comparing JPL's past and present, commemorating the 80th anniversary of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Oct. 31, 2016. The Administration Building of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (Building 180) is pictured in January 1965. What appears as a parking lot in this photograph later becomes "The Mall", a landscaped open-air gathering place. A small security control post can be seen at the left of the 1965 image. And Building 167, one of the lab's cafeterias, is on the right. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21121
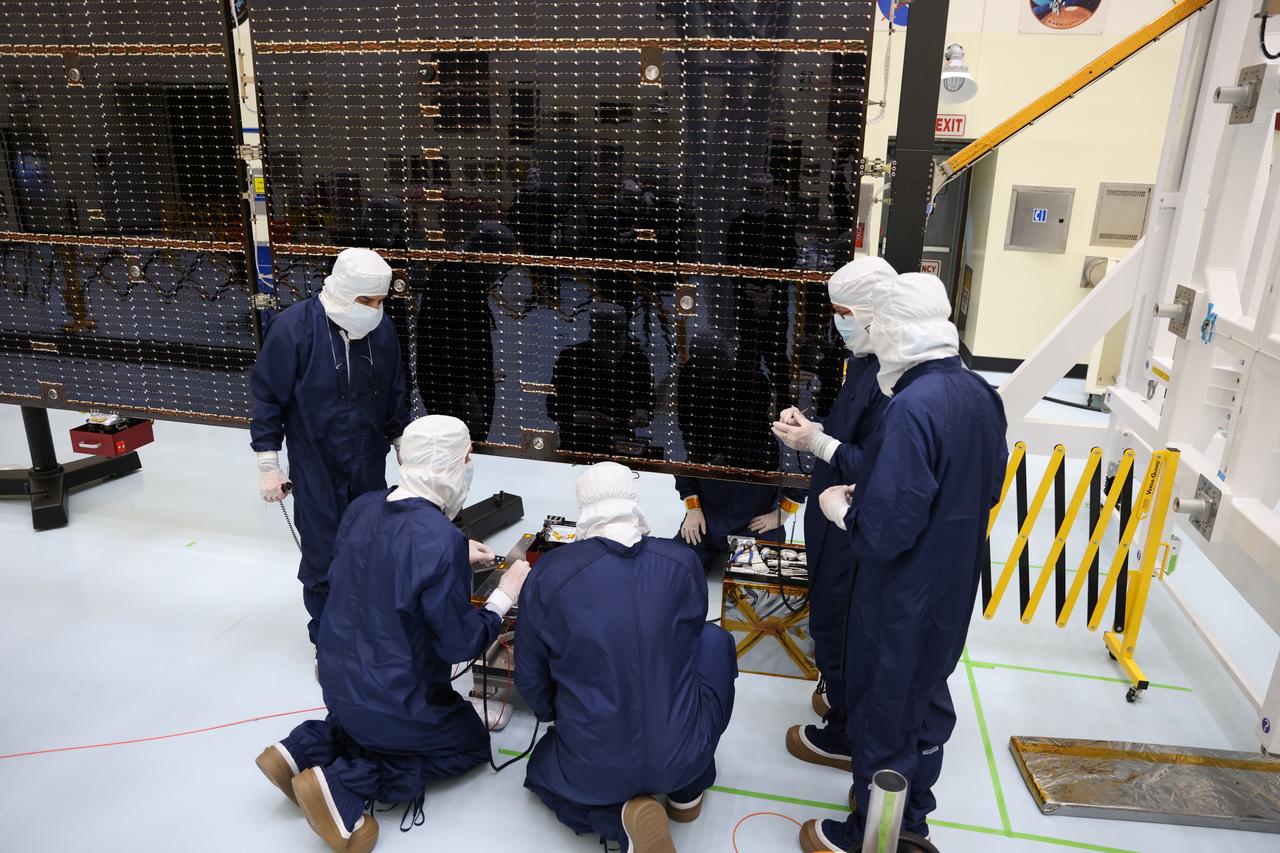

On March 20, technicians working inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida installed and began to test antennas on a solar array for NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft. The spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. Europa Clipper is the largest spacecraft NASA has ever developed for a planetary mission, and it will seek to determine whether there are places below the surface of Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, that could support life.
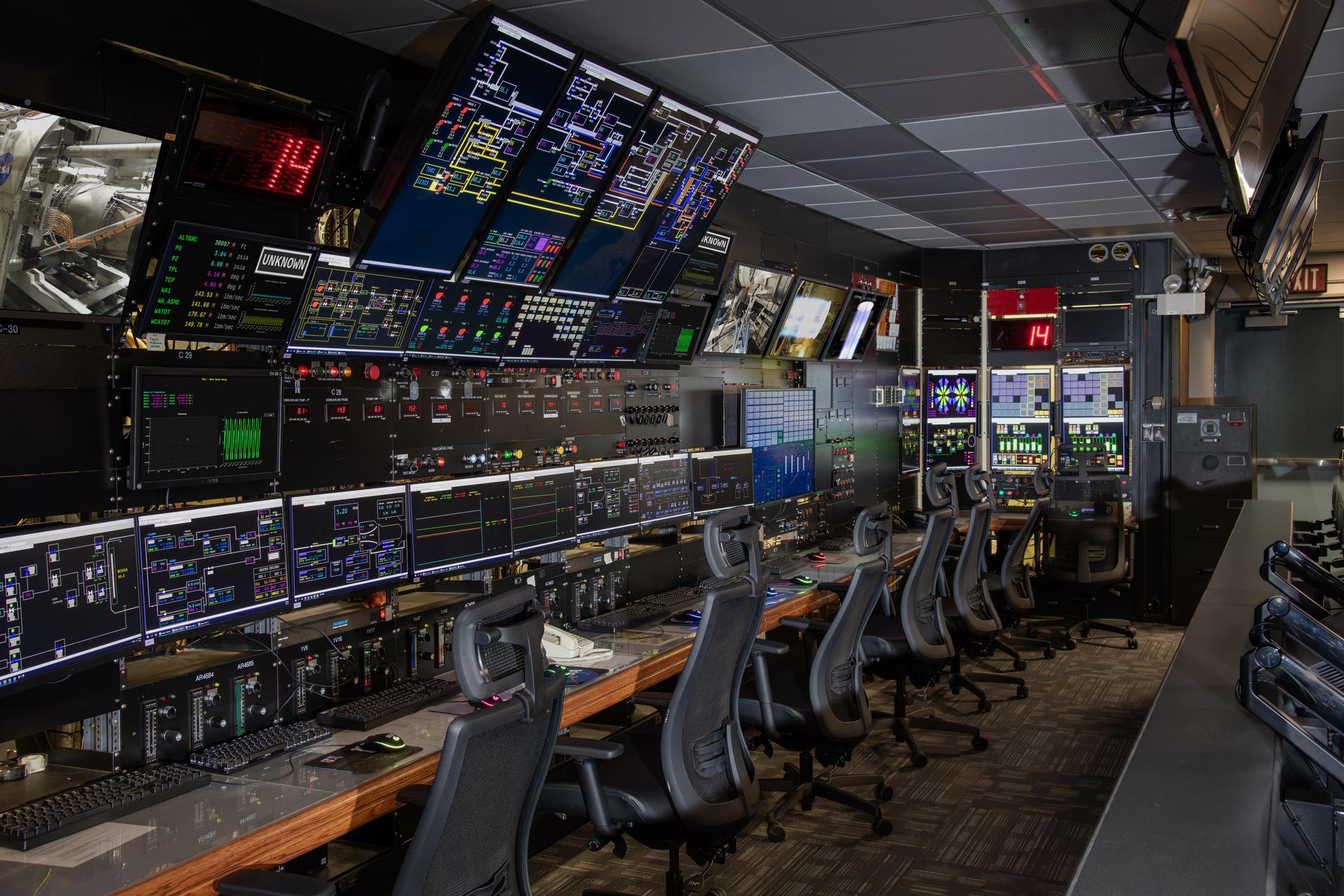

Gunnar Kadlic monitors the data system in the NASA Glenn's Propulsion System Lab (PSL) recently remodeled control room. This is where jet and rocket engines are tested at GRC. This re-modeled control room offers better test monitoring and work stations for test engineers and technicians.

This archival image was released as part of a gallery comparing JPL's past and present, commemorating the 80th anniversary of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Oct. 31, 2016. This photograph from 1949 shows the main entrance gate to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, after a snowstorm. To the left is JPL's administration building at the time (Building 67). Building 67 is the Materials Research Building today. The Space Flight Operations Facility (Building 230), which houses JPL's Mission Control, now stands over the parking area on the right. As the lab expanded, the main entrance gate moved farther south. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21118
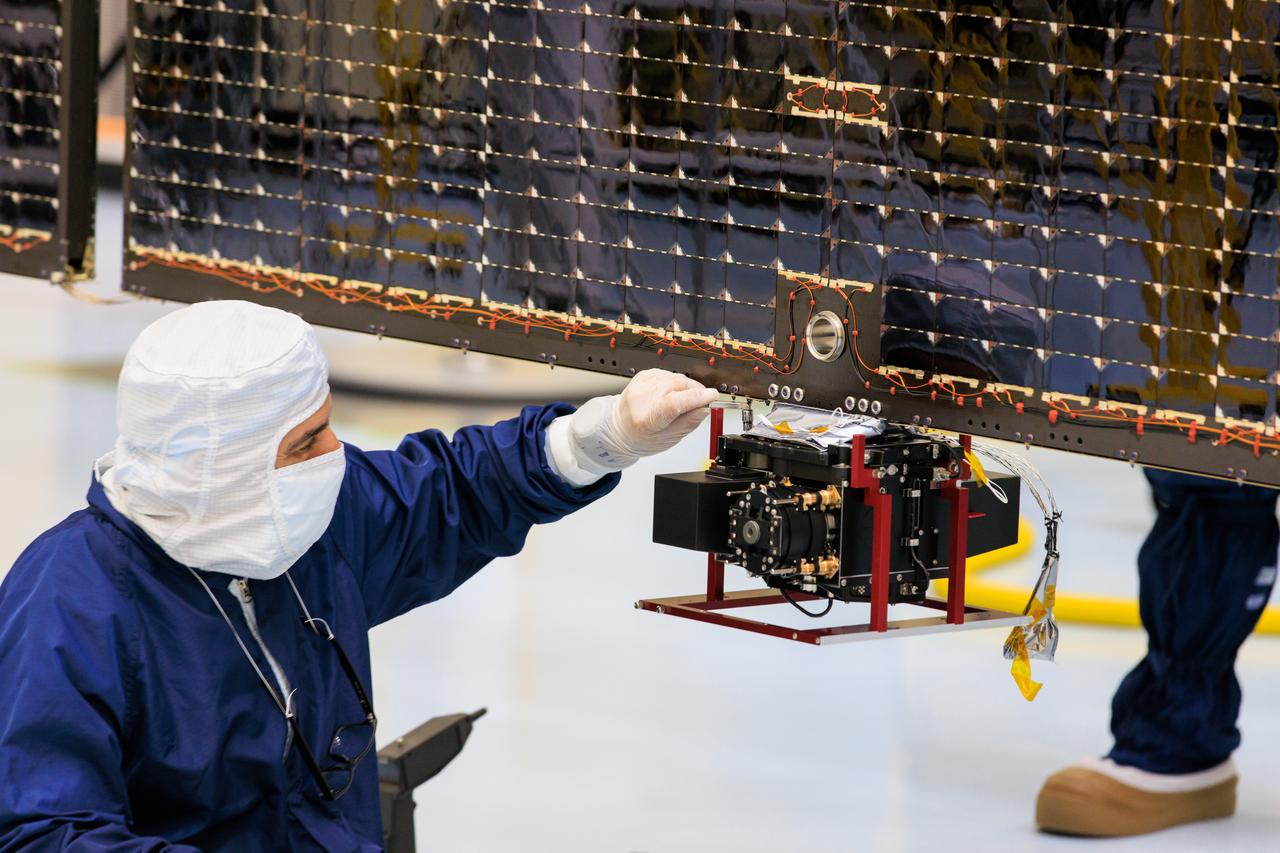
Technicians inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install and test antennas on a solar array on Wednesday, March 20, 2024, for the agency’s Europa Clipper spacecraft which will study Jupiter’s icy moon Europa to determine if the planet has conditions that could support life. The REASON, (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface) instrument will use the antennas to send both High Frequency (HF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) radio waves to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) deep and search the ocean, measure ice thickness, and study the topography, composition, and roughness of Europa’s surface. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A targeting October.
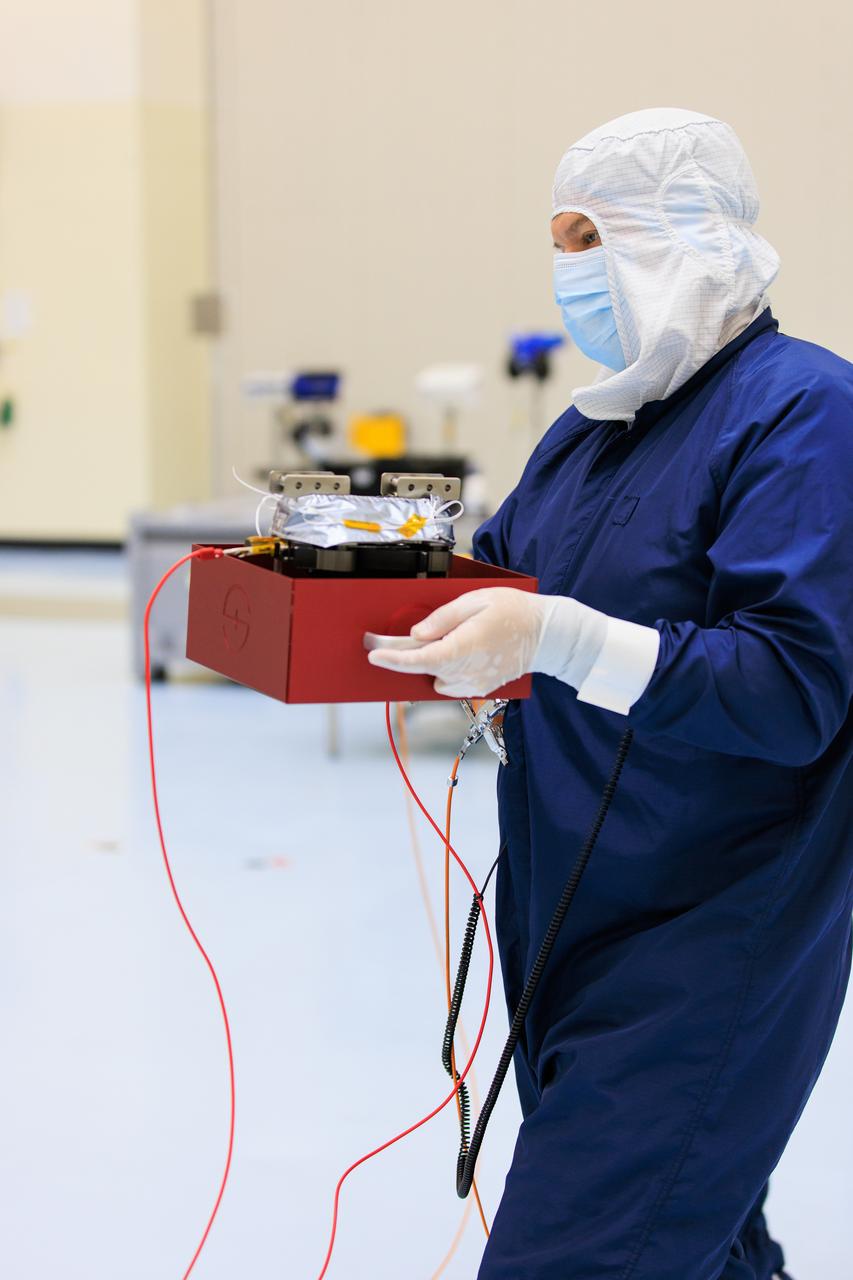

On Wednesday, March 20, 2024, a technician inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida carries an antenna that will attach to a solar array for the agency’s Europa Clipper spacecraft, which will study Jupiter’s icy moon Europa to determine if the planet has conditions that could support life. The REASON, (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface) instrument will use the antennas to send both High Frequency (HF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) radio waves to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) deep and search the ocean, measure ice thickness, and study the topography, composition, and roughness of Europa’s surface. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A targeting October 2024.
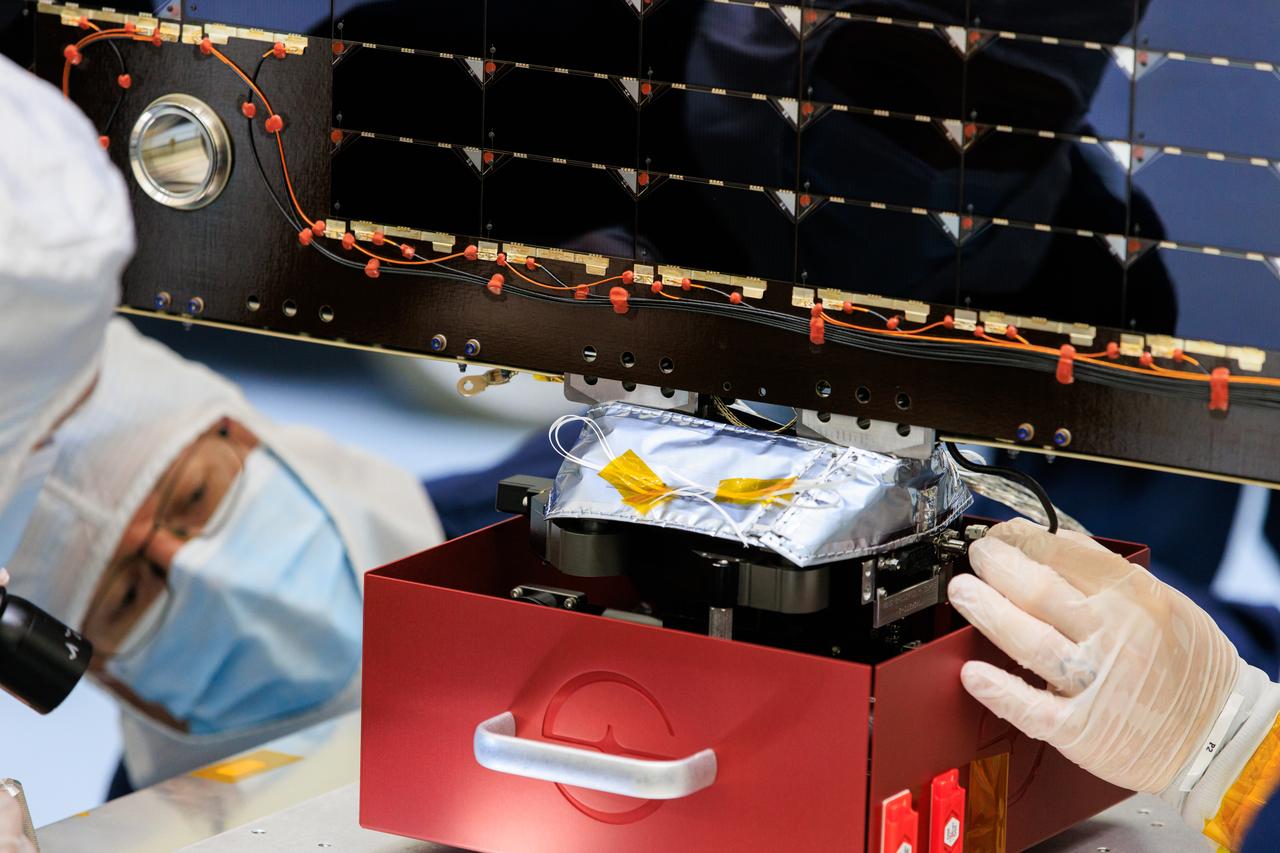

Technicians inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install and test one of several antennas on a solar array Wednesday, March 20, 2024, for the agency’s Europa Clipper spacecraft which will study Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, to determine if the planet can support life. REASON, (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface) instrument will use the antennas to send both very high frequency radio waves and high frequency to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) deep to search the ocean, measure ice thickness, and study the topography, composition, and roughness of Europa’s surface. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A targeting October 2024.
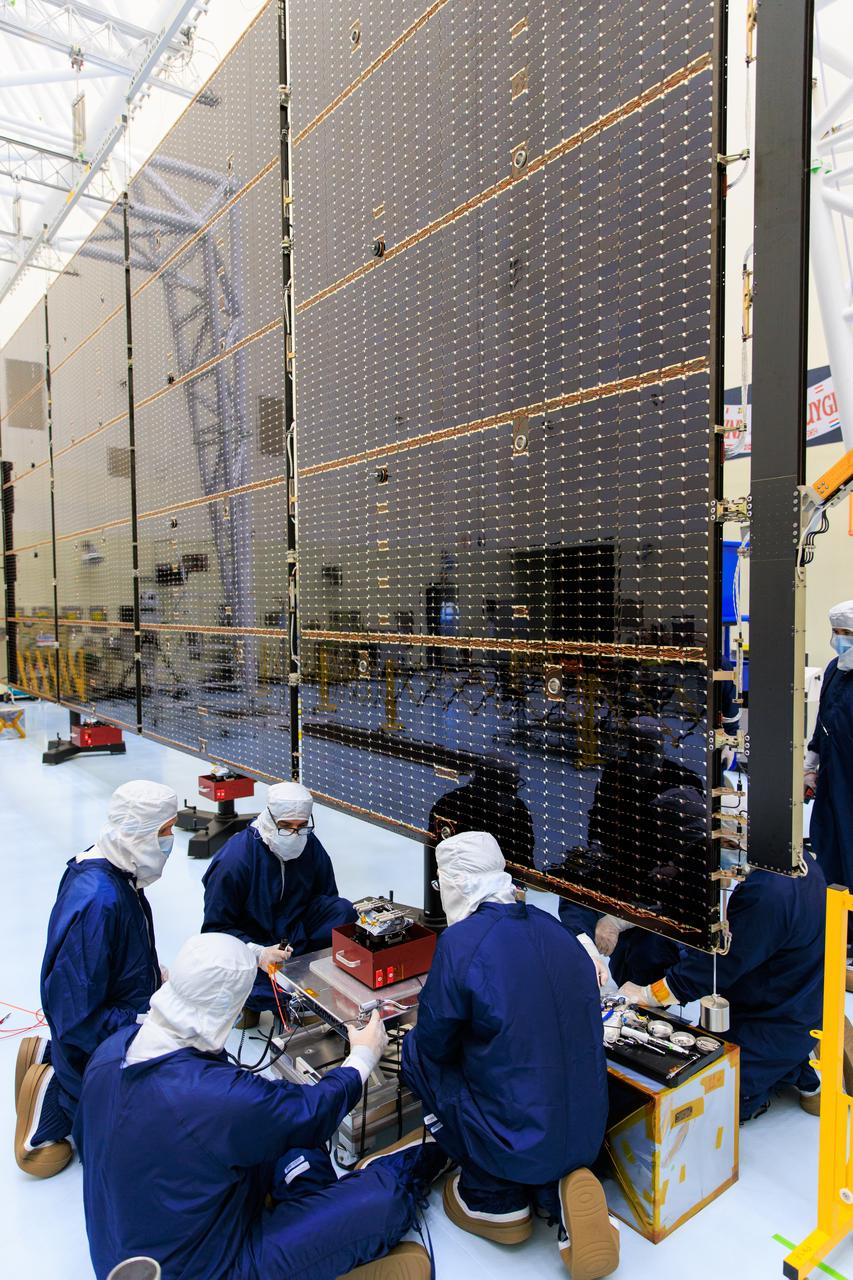

Technicians inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install and test one of several antennas on a solar array Wednesday, March 20, 2024, for the agency’s Europa Clipper spacecraft which will study Jupiter’s icy moon Europa to determine if the planet has conditions that could support life. REASON, (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface) instrument will use the antennas to send both High Frequency (HF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) radio waves to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) deep and search the ocean, measure ice thickness, and study the topography, composition, and roughness of Europa’s surface. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A targeting October 2024.
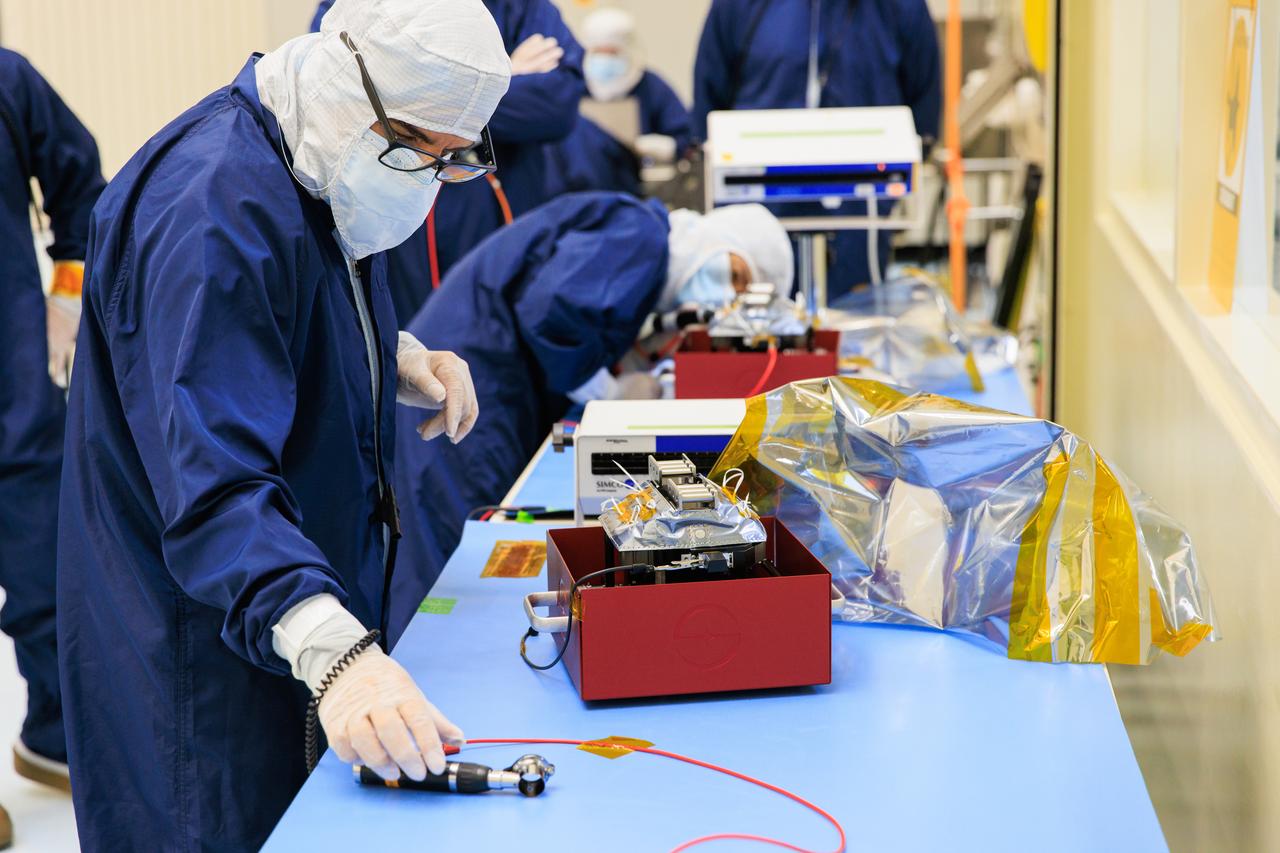

Technicians inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida test antennas on Wednesday, March 20, 2024, shortly before installing them on a solar array for the agency’s Europa Clipper spacecraft, which will study Jupiter’s icy moon Europa to determine if the planet has conditions that could support life. The REASON, (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface) instrument will use the antennas to send both High Frequency (HF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) deep and search the ocean, measure ice thickness, and study the topography, composition, and roughness of Europa’s surface. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A targeting October 2024.
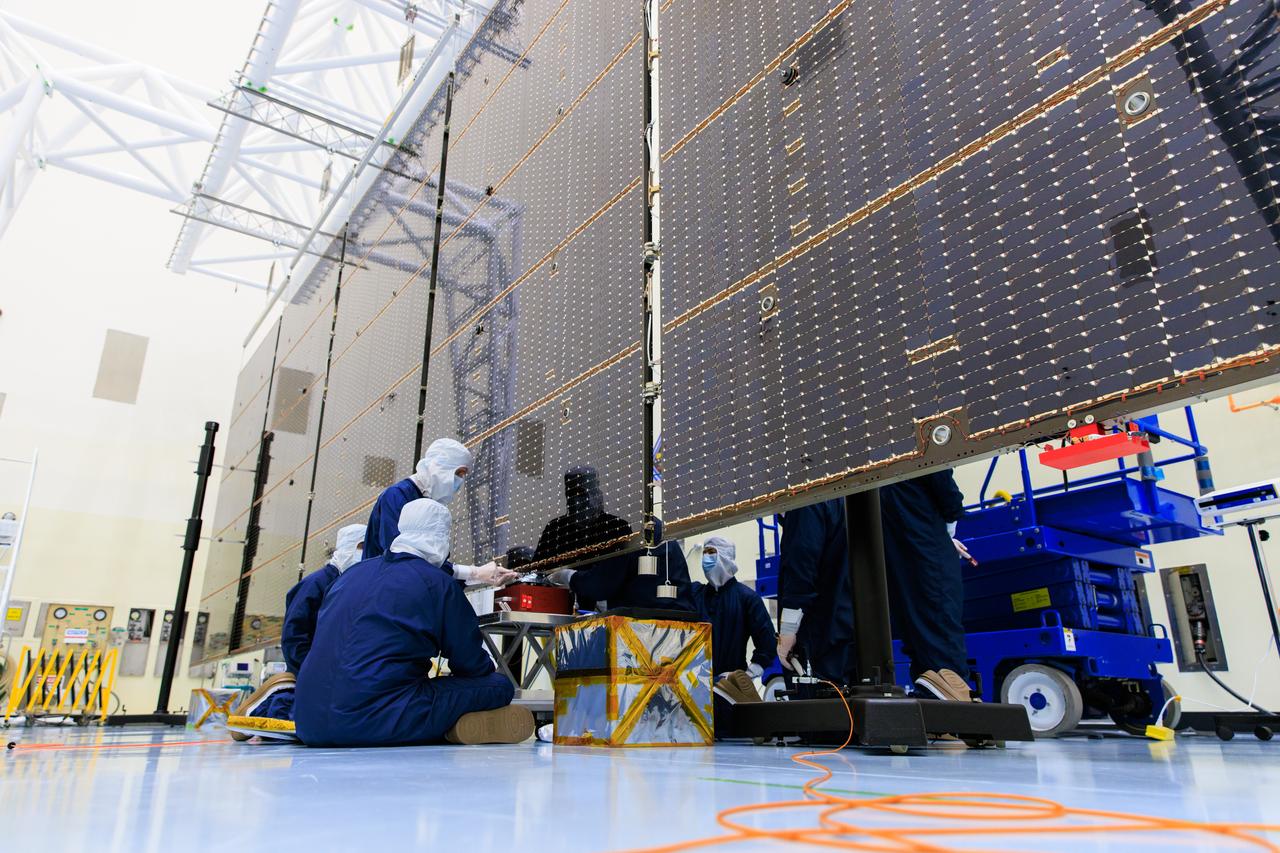

Technicians inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install and test one of several antennas on a solar array Wednesday, March 20, 2024, for the agency’s Europa Clipper spacecraft which will study Jupiter’s icy moon Europa to determine if the planet has conditions that could support life. REASON, (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface) instrument will use the antennas to send both High Frequency (HF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) radio waves to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) deep and search the ocean, measure ice thickness, and study the topography, composition, and roughness of Europa’s surface. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A targeting October 2024.
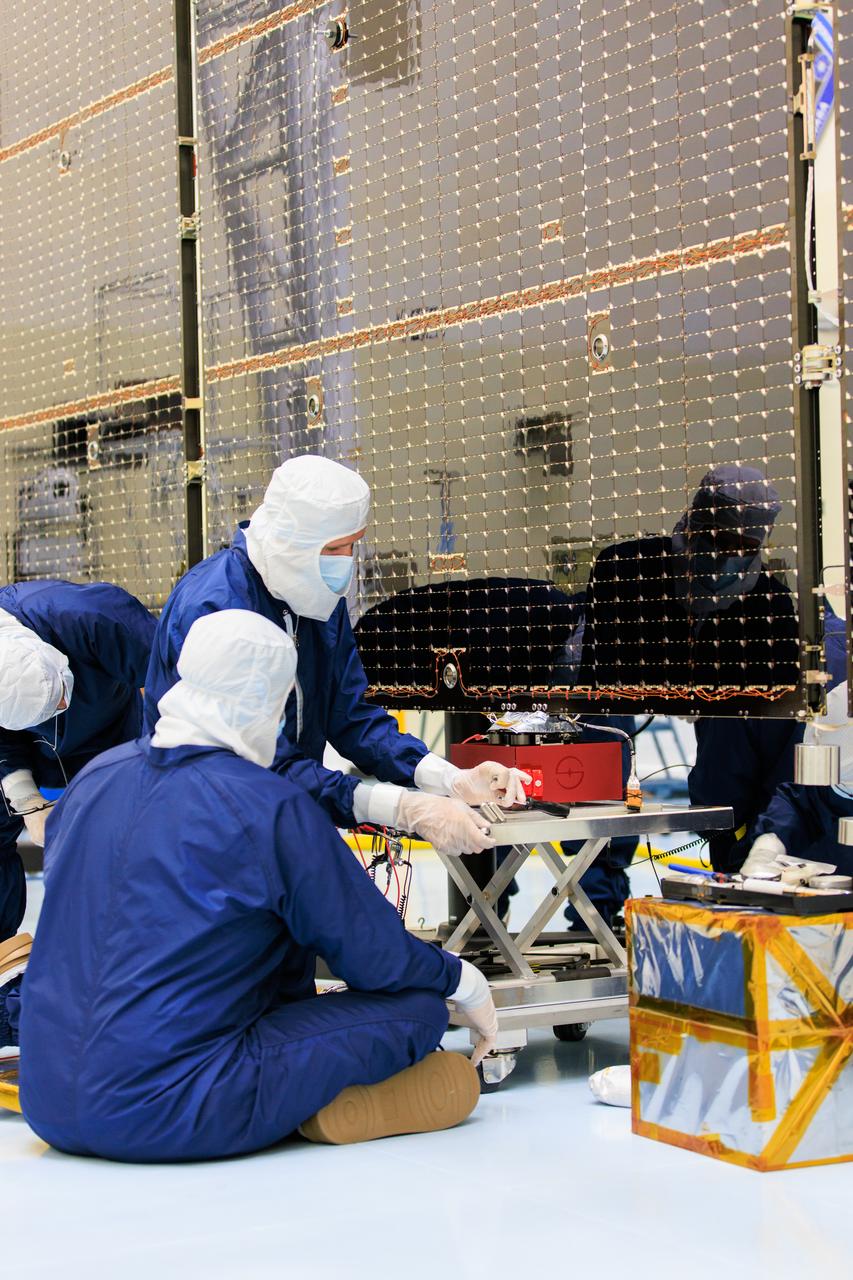

Technicians inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install and test one of several antennas on a solar array Wednesday, March 20, 2024, for the agency’s Europa Clipper spacecraft which will study Jupiter’s icy moon Europa to determine if the planet has conditions that could support life. REASON, (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface) instrument will use the antennas to send both High Frequency (HF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) radio waves to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) deep and search the ocean, measure ice thickness, and study the topography, composition, and roughness of Europa’s surface. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A targeting October 2024.
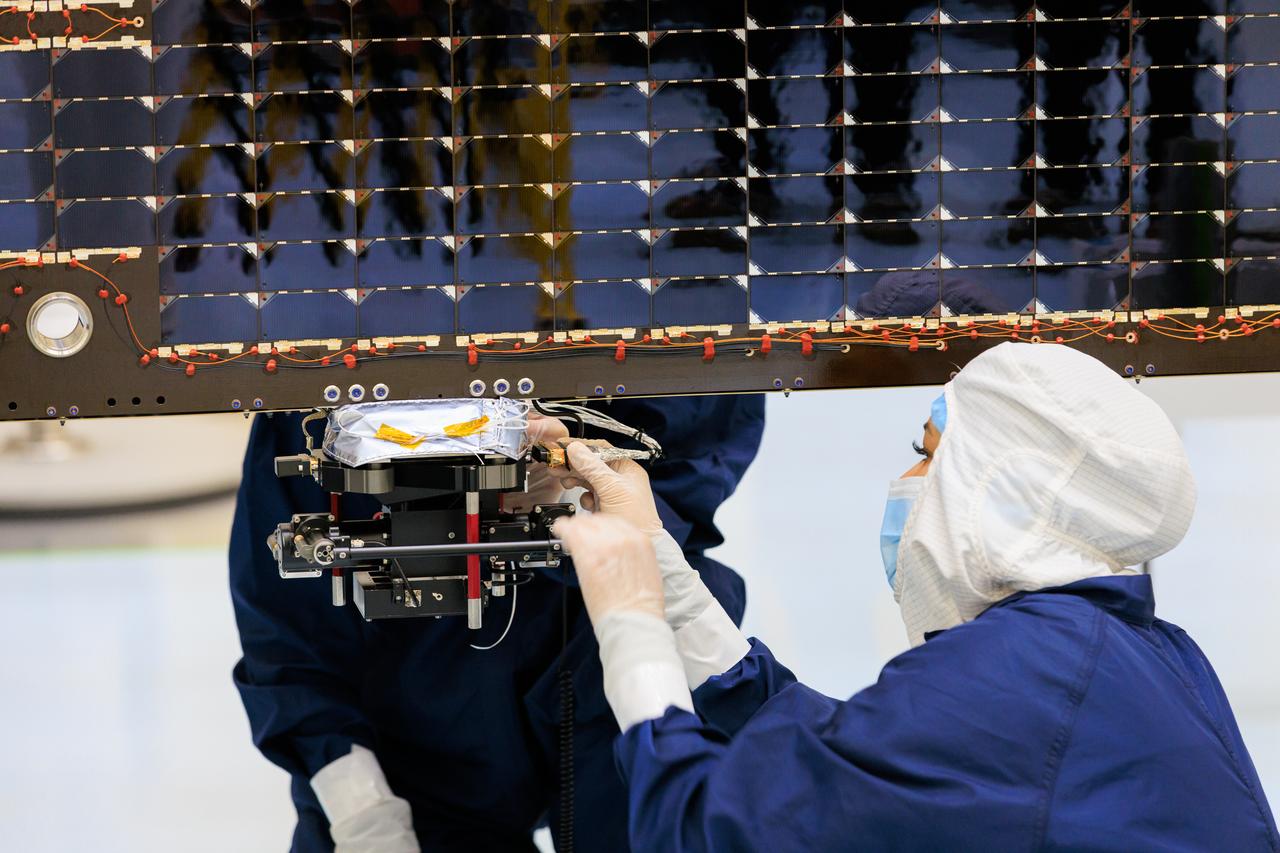

Technicians inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install and test antennas on a solar array on Wednesday, March 20, 2024, for the agency’s Europa Clipper spacecraft which will study Jupiter’s icy moon Europa to determine if the planet has conditions that could support life. The REASON, (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface) instrument will use the antennas to send both both High Frequency (HF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) radio waves to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) deep and search the ocean, measure ice thickness, and study the topography, composition, and roughness of Europa’s surface. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A targeting October.
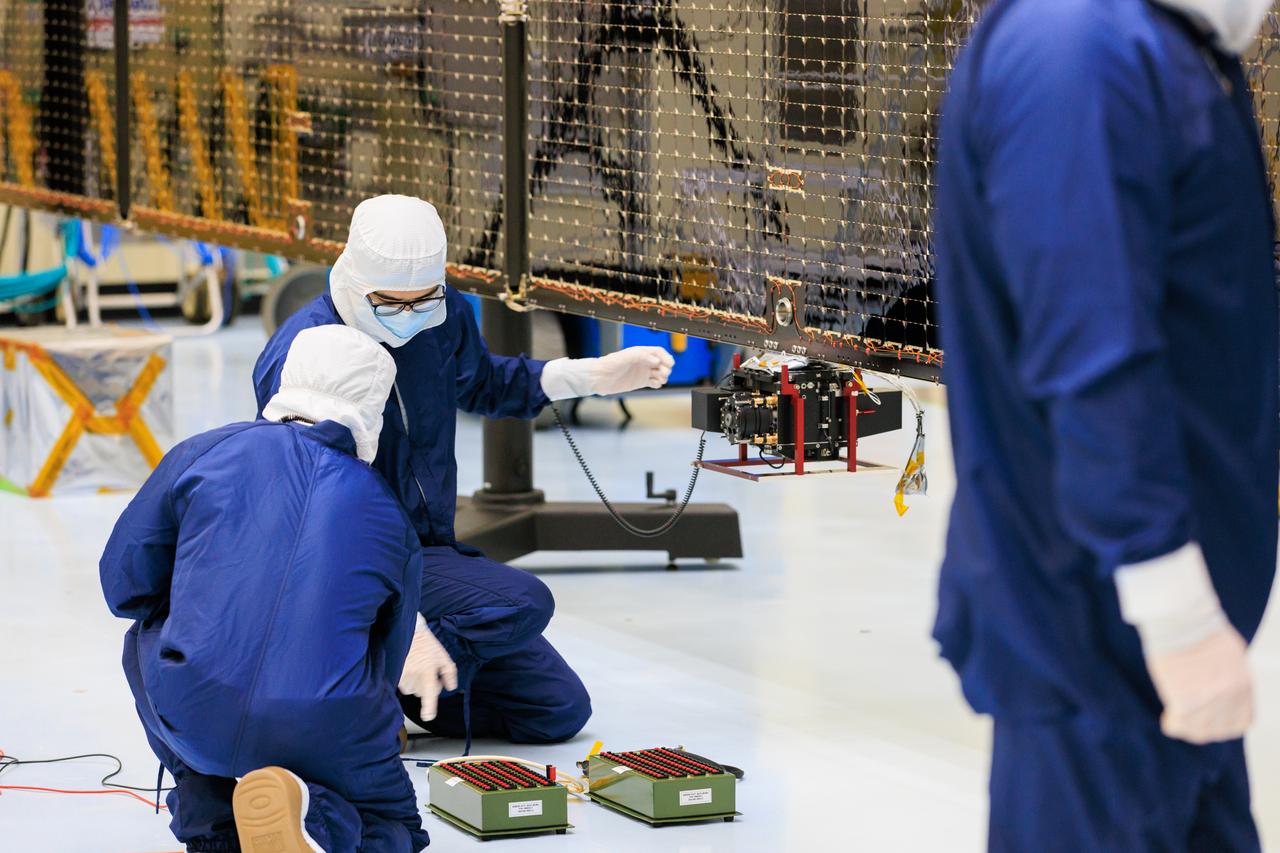

Technicians inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install and test antennas on a solar array on Wednesday, March 20, 2024, for the agency’s Europa Clipper spacecraft which will study Jupiter’s icy moon Europa to determine if the planet has conditions that could support life. The REASON, (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface) instrument will use the antennas to send both High Frequency (HF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) radio waves to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) deep and search the ocean, measure ice thickness, and study the topography, composition, and roughness of Europa’s surface. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A targeting October.
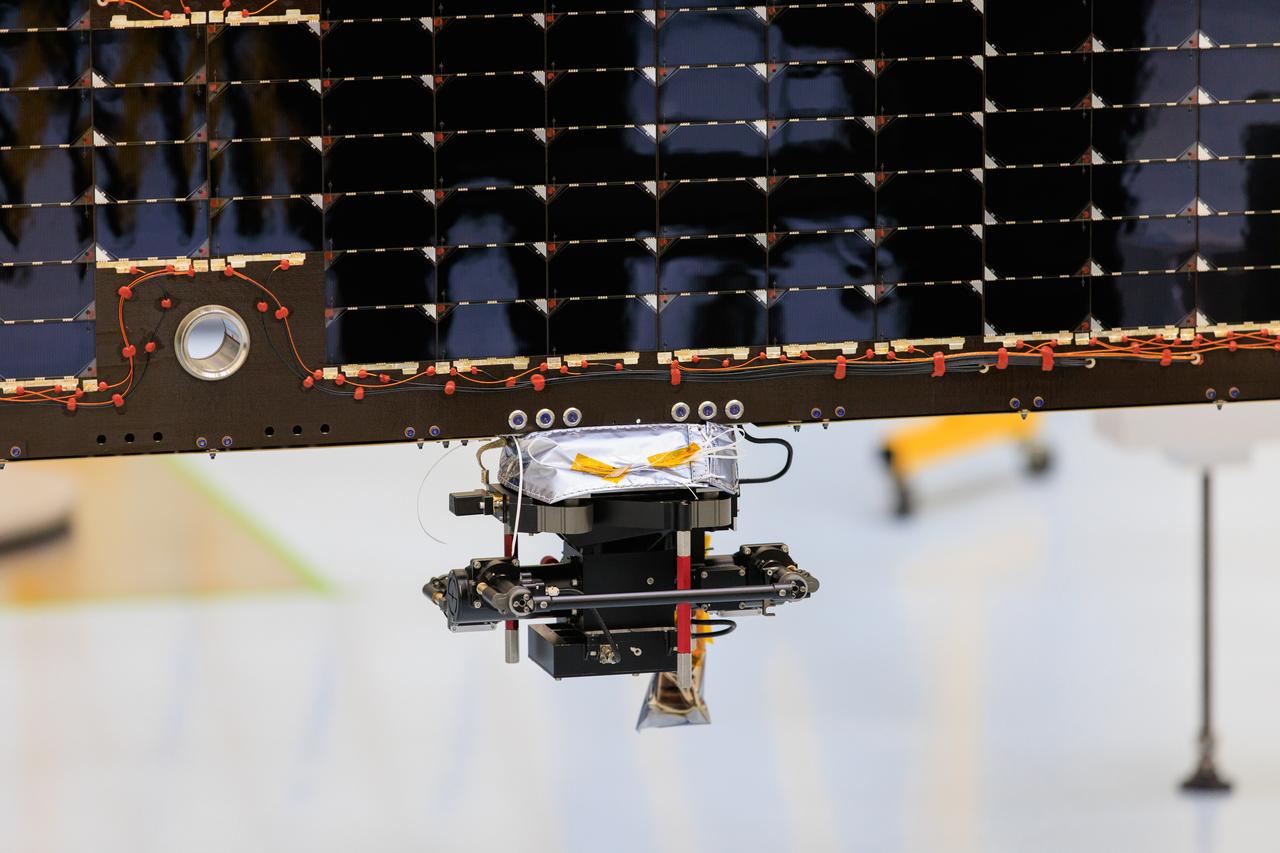
An antenna for the REASON, (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface) instrument attaches to a solar array for NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, March 20, 2024. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will study Jupiter’s icy moon Europa, and the REASON instrument will use the antennas to send both both High Frequency (HF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) radio waves to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) deep and search the ocean, measure ice thickness, and study the topography, composition, and roughness of Europa’s surface. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A, targeting October.
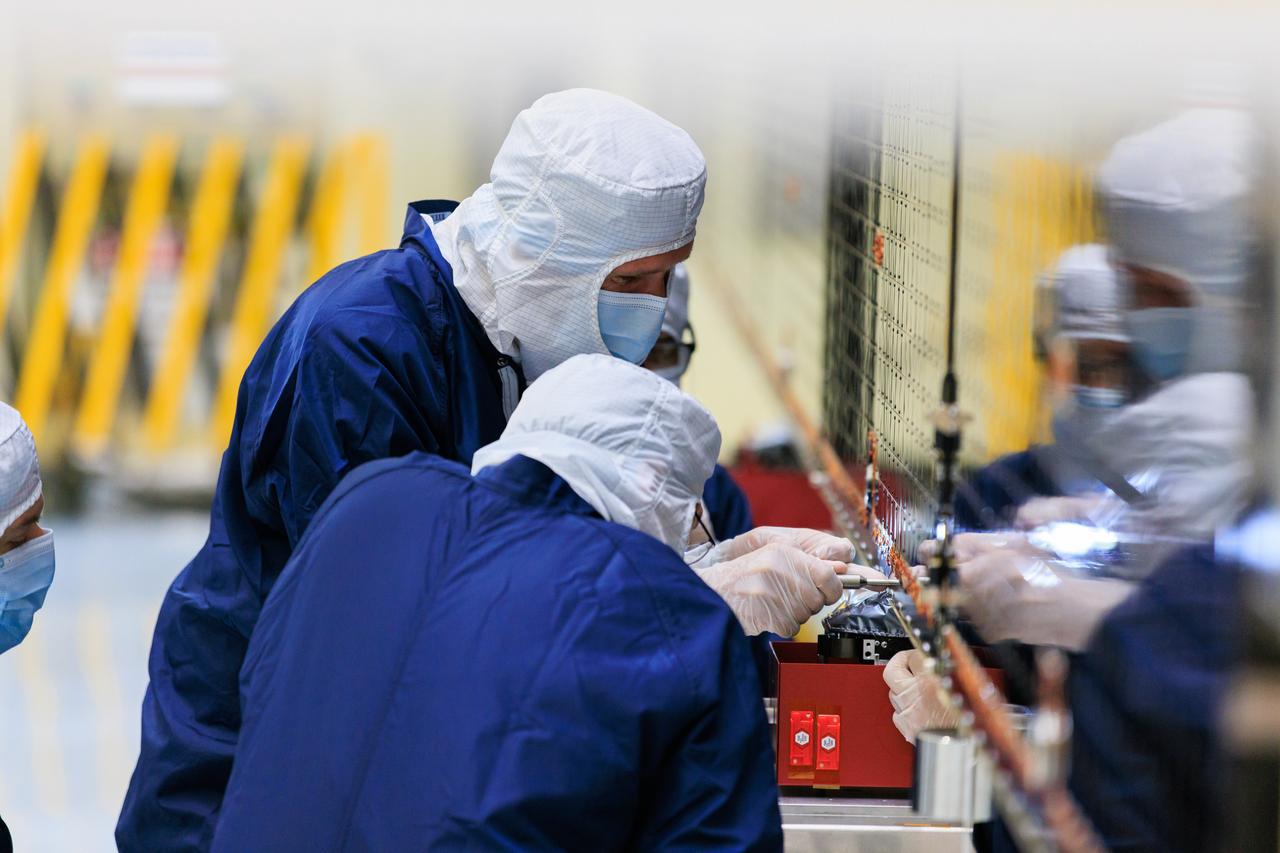

Technicians inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install and test one of several antennas on a solar array Wednesday, March 20, 2024, for the agency’s Europa Clipper spacecraft which will study Jupiter’s icy moon Europa to determine if the planet has conditions that could support life. REASON, (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface) instrument will use the antennas to send both High Frequency (HF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) radio waves to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) deep and search the ocean, measure ice thickness, and study the topography, composition, and roughness of Europa’s surface. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A targeting October 2024.
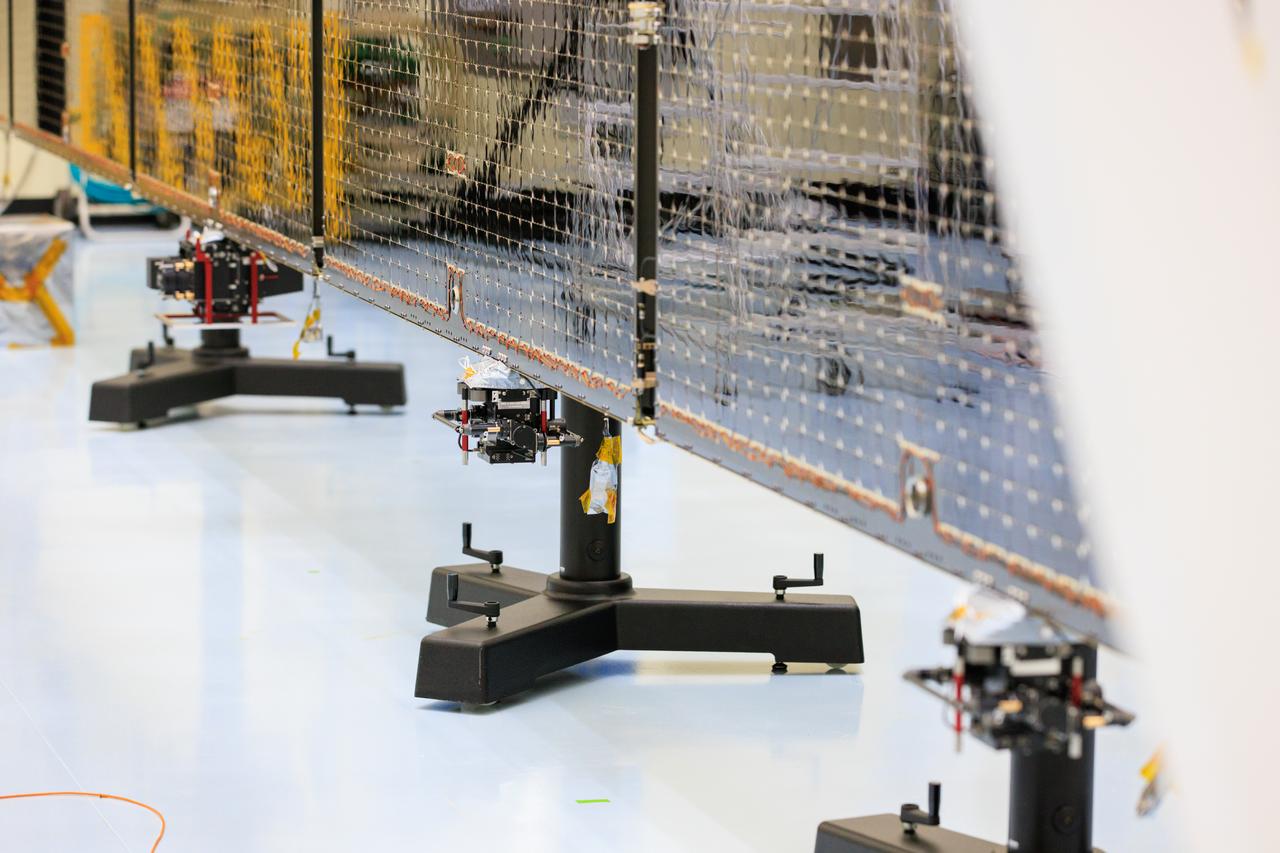

Technicians inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install and test antennas on a solar array on Wednesday, March 20, 2024, for the agency’s Europa Clipper spacecraft which will study Jupiter’s icy moon Europa to determine if the planet has conditions that could support life. The REASON, (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface) instrument will use the antennas to send both High Frequency (HF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) radio waves to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) deep and search the ocean, measure ice thickness, and study the topography, composition, and roughness of Europa’s surface. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A targeting October.
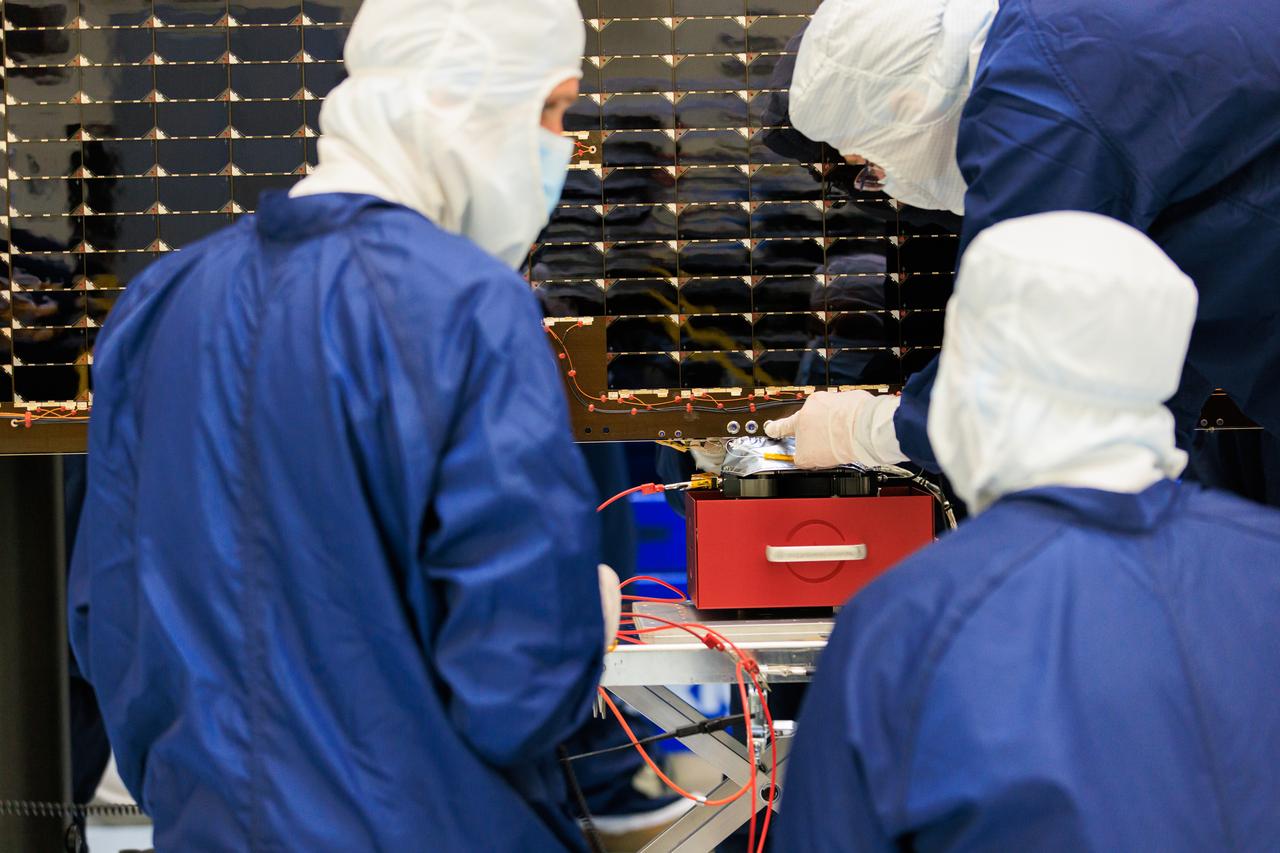

Technicians inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install and test one of several antennas on a solar array Wednesday, March 20, 2024, for the agency’s Europa Clipper spacecraft which will study Jupiter’s icy moon Europa to determine if the planet has conditions that could support life. REASON, (Radar for Europa Assessment and Sounding: Ocean to Near-surface) instrument will use the antennas to send both High Frequency (HF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) radio waves to penetrate up to 18 miles (30 kilometers) deep and search the ocean, measure ice thickness, and study the topography, composition, and roughness of Europa’s surface. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will ship to Florida later this year from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Southern California in preparation for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A targeting October 2024.
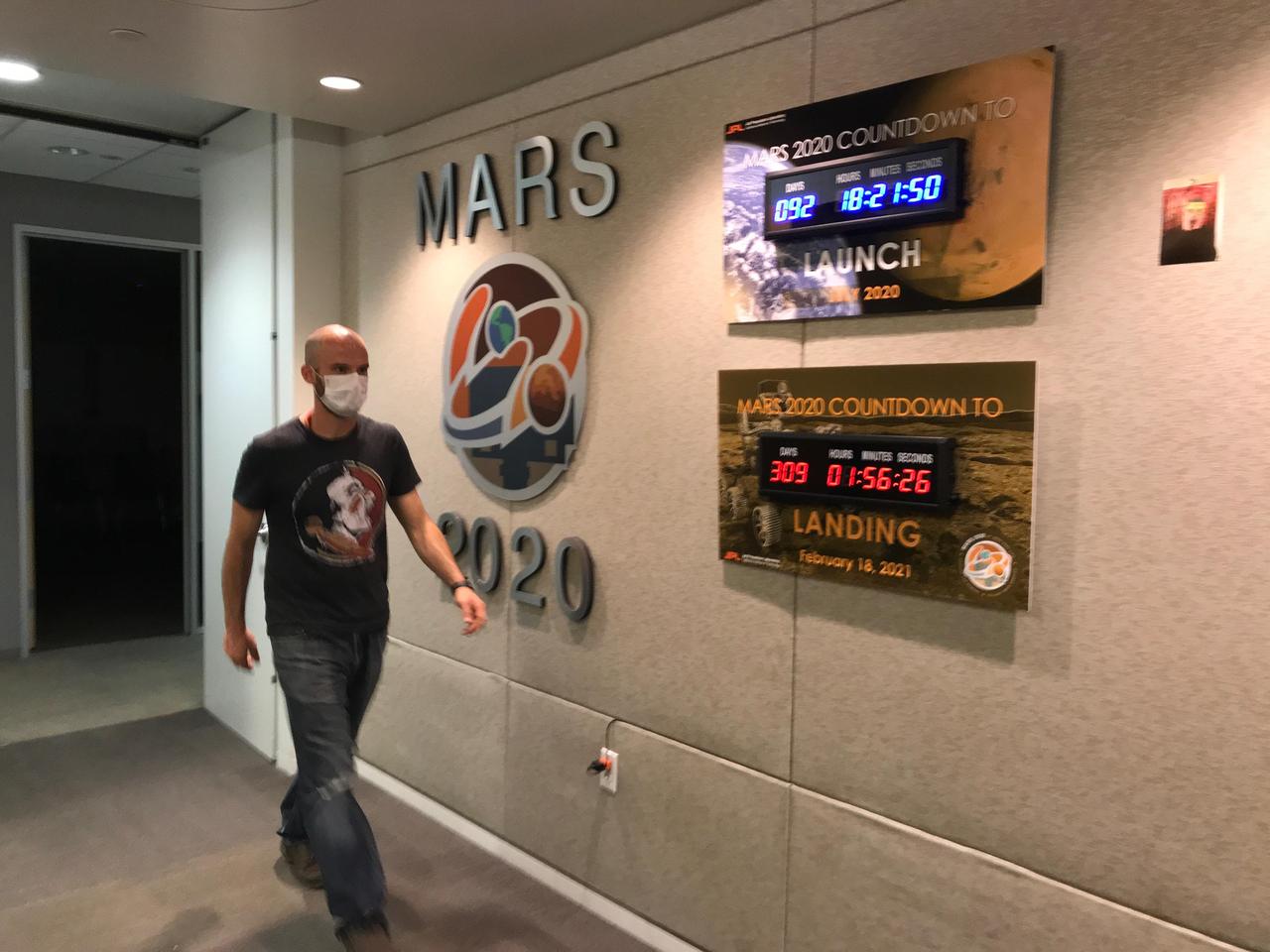

Ian Clark walks past mission countdown clocks in the Perseverance offices at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. The Lab instituted a suite of safe@work procedures — based on the guidance of occupational safety medical personnel — to ensure those working at JPL are social distancing, wearing protective equipment and have ready access to hand sanitizer and other cleaning supplies during the coronavirus pandemic. Clark is one of a small subset of project personnel whose mission-essential job required physical access to the facility. He was on-Lab to supervise the assembly and cleaning of the sample tubes that will hold Martian sediment and rock for return to Earth on a future mission. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23830
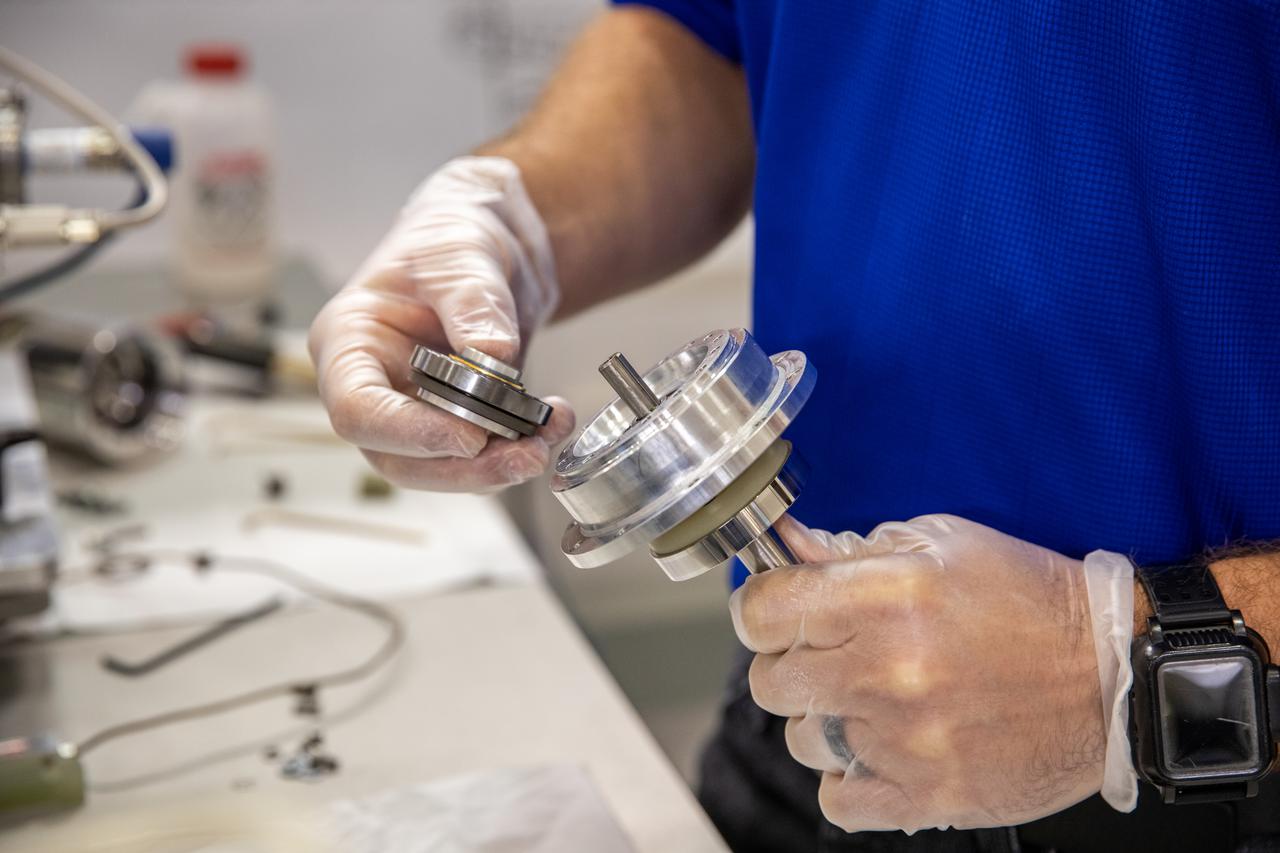

Drew Smith, a robotics engineer and lab manager with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, prepares a Bulk Metallic Glass Gear (BMGG) for ambient temperature tests in a vacuum inside a cryogenic cooler at Kennedy's Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations lab on June 17, 2021. Made from a custom bulk metallic glass alloy, BMGGs could be used in heater-free gearboxes at extremely low temperatures in locations such as the Moon, Mars, and Europa, one of Jupiter’s moons. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory is working with commercial partners to create the gears.

Drew Smith, a robotics engineer and lab manager with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, prepares a Bulk Metallic Glass Gear (BMGG) for ambient temperature tests in a vacuum inside a cryogenic cooler at Kennedy's Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations lab on June 17, 2021. Made from a custom bulk metallic glass alloy, BMGGs could be used in heater-free gearboxes at extremely low temperatures in locations such as the Moon, Mars, and Europa, one of Jupiter’s moons. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory is working with commercial partners to create the gears.
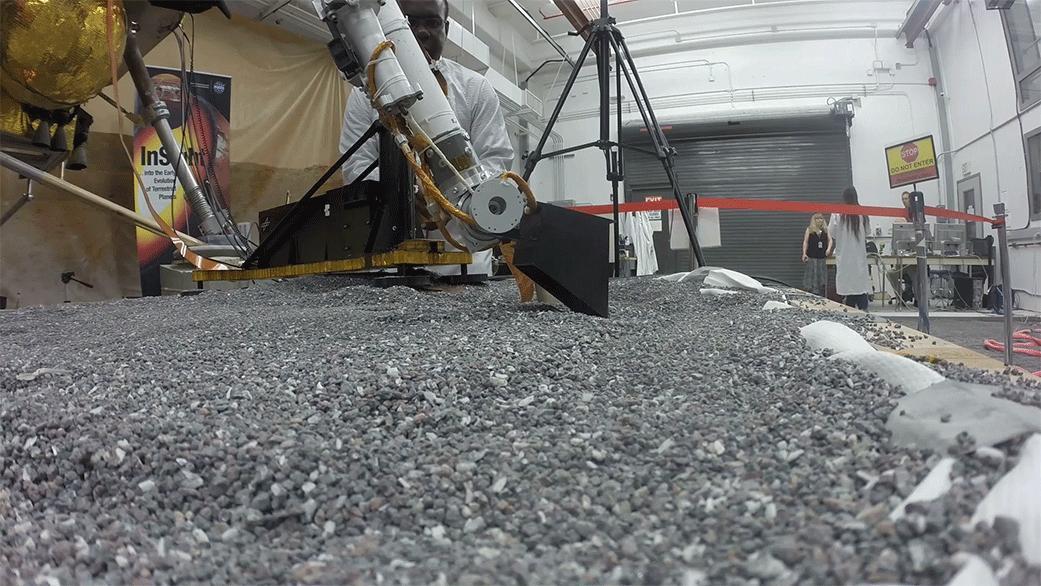

This footage from Aug. 19, 2019, shows a replica of InSight scraping soil with a scoop on the end of its robotic arm in a test lab at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. A replica of the "mole" — the lander's self-hammering heat probe — comes in to view as the scoop moves to the left. On Mars, InSight will use techniques practiced by engineers on Earth in order to scrape and tamp down soil on top of the mole to help it dig. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24099

In a laboratory simulating conditions on Jupiter's moon Europa at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, plain white table salt (sodium chloride) turned yellow (visible in a small well at the center of this photograph). The color is significant because scientists can now deduce that the yellow color previously observed on portions of the surface of Europa is actually sodium chloride. The JPL lab experiments matched temperature, pressure and electron radiation conditions at Europa's surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23273
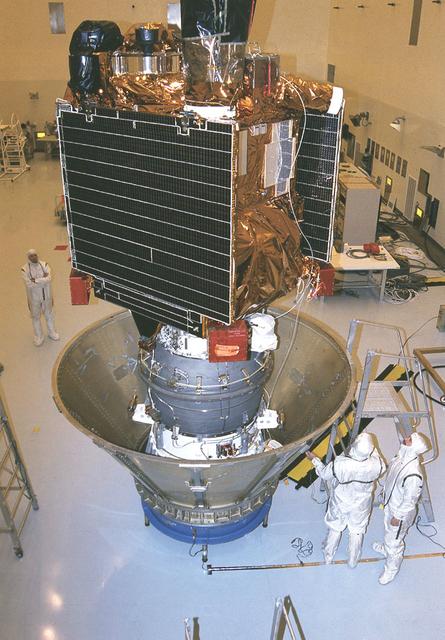

Workers at the Jet Propulsion Research Lab (JPL) in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) prepare the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft for transfer to the launch pad by placing it in a protective canister. The Surveyor spacecraft (upper) is already mated to its solid propellant upper stage booster (lower), which is actually the third stage of the Delta II expendable launch vehicle that will propel the spacecraft on its interplanetary journey to Mars.

In a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in October 2023, scientist Vanessa Bailey stands behind the Roman Coronagraph, which has been undergoing testing at the lab. Designed to block starlight and allow scientists to see the faint light from planets outside our solar system, the Coronagraph is a technology demonstration that will be part of NASA's Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26272
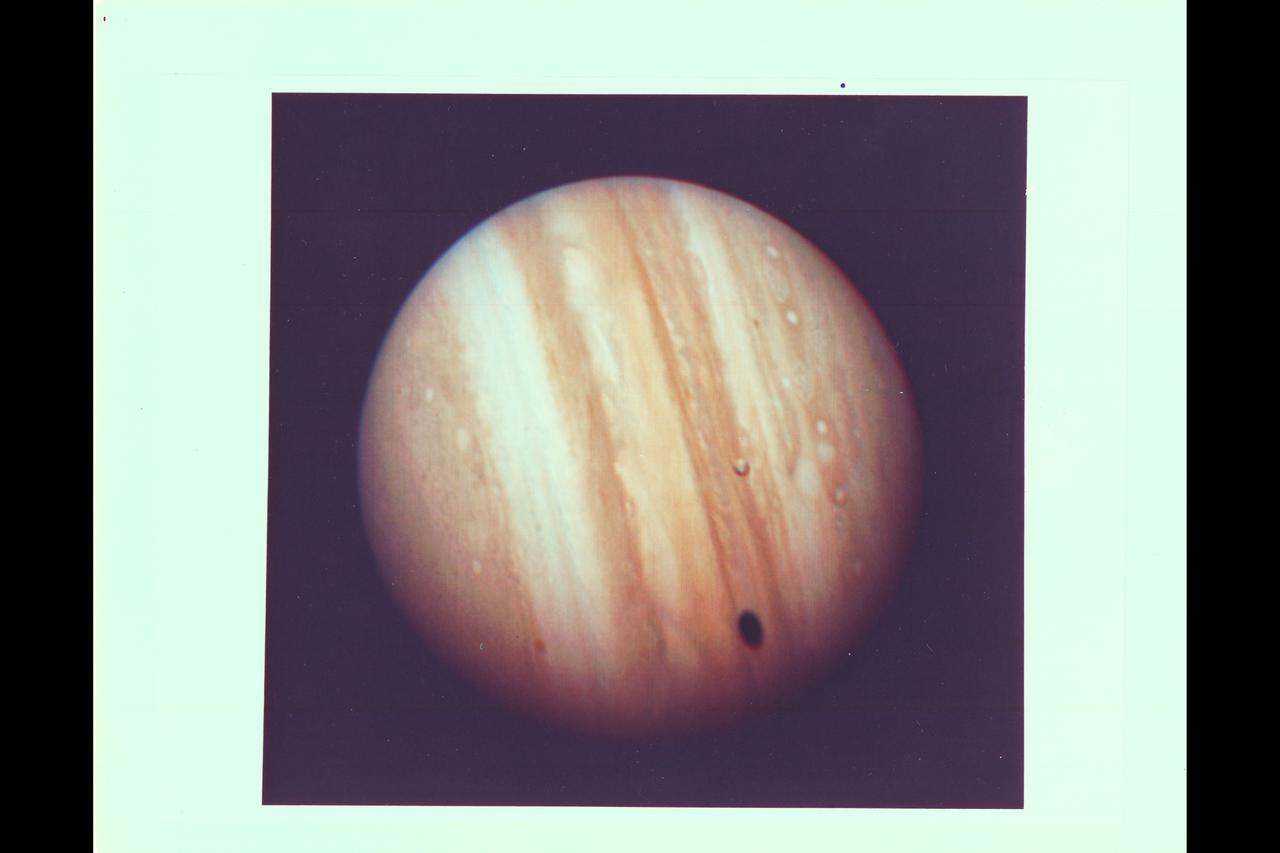

Photo by Voyager 1 Jupiter's satellite Io poses before the giant planet in this photo returned Jan 17, 1979 from a distance of 29 million miles (47 million kilometers). The satellite's shadow can be seen falling on the face of Jupiter at left. Io is traveling from left to right in its one-and-three-quarter-day orbit around Jupiter. Even from this great distance the image of Io shows dark poles and bright equatorial region. Voyager 1 will make its closest approach to Jupiter 174, 000 miles (280,000 kilometer) on March 5. It will then continue to Saturn in November 1980. This color photo was assembled at Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Image Processing Lab from three black and white images taken through filters. The Voyagers are managed for NASA's Office of Space Science by Jet Propulsion Laboratory. (JPL Ref: P-20946C)
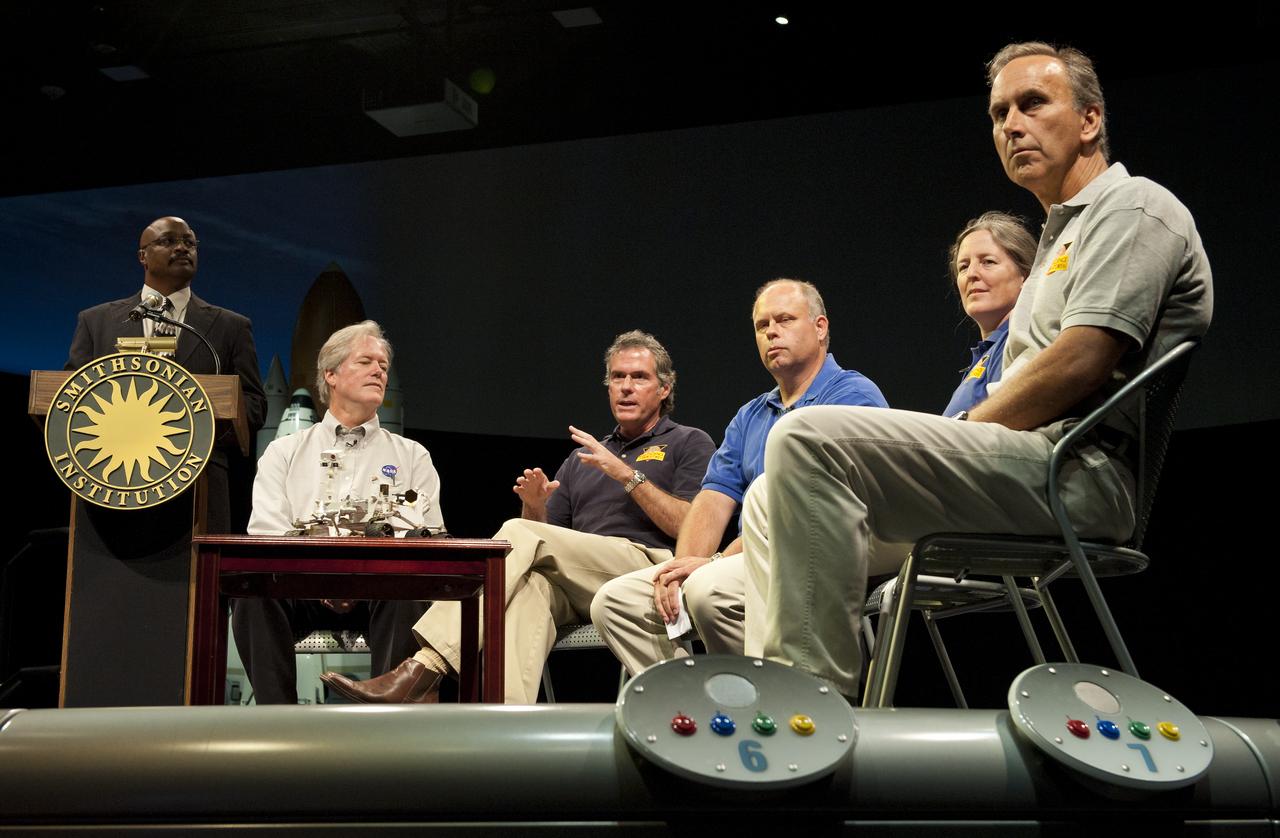

Michael Watkins (third from left), mission manager and project engineer, Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), Jet Propulsion Lab, Pasadena, Calif., speaks at a press conference at the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum on Friday, July 22, 2011 in Washington. From left to right, Watkins is joined by Dwayne Brown, NASA Headquarters public affairs officer; Michael Meyer, lead scientist Mars Exploration Program, NASA Headquarters; Watkins; John Grant, geologist, Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington; Dawn Sumner, geologist, University of California, Davis and John Grotzinger, MSL project scientist, JPL. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
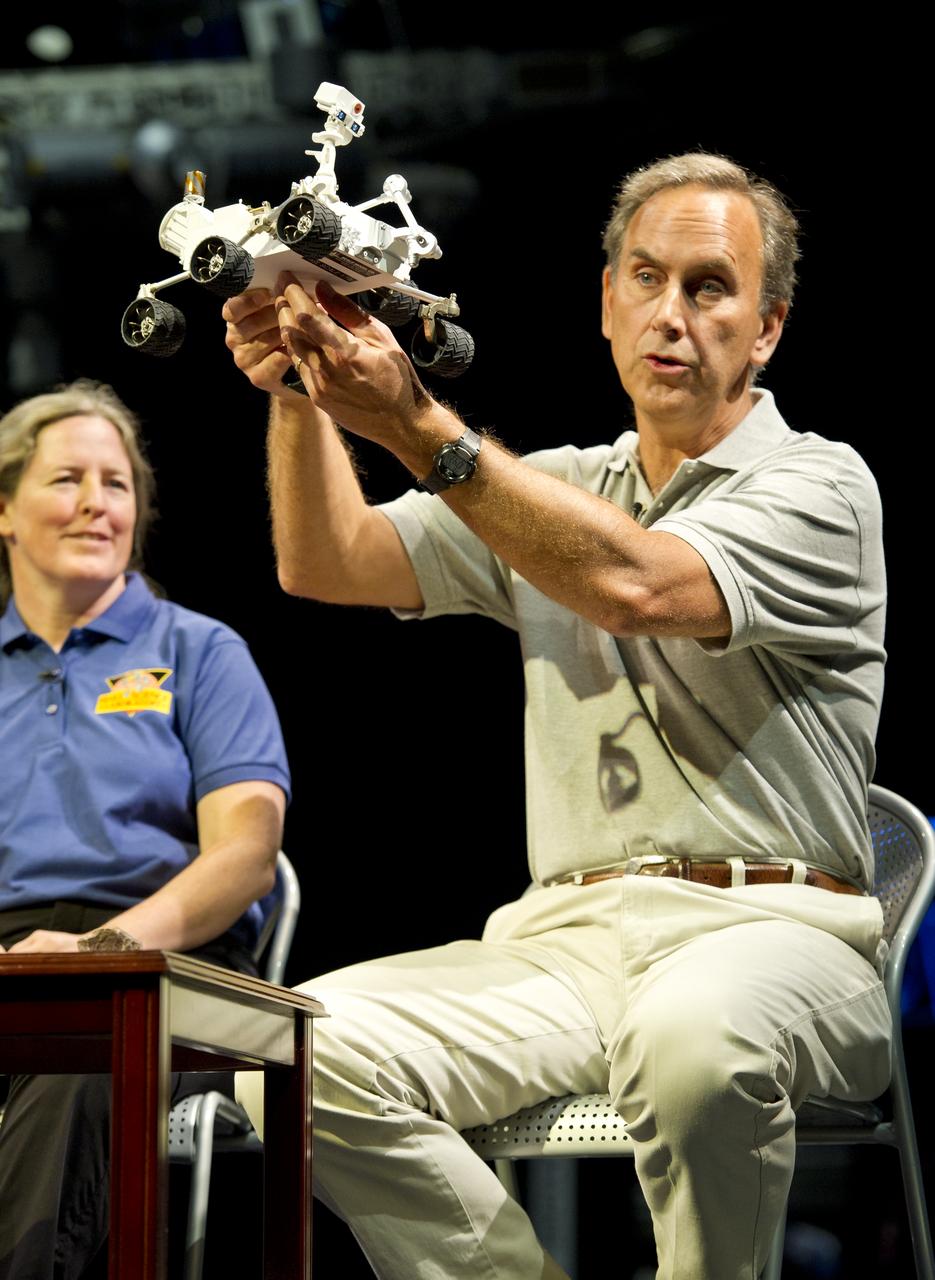

John Grotzinger, Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) project scientist, Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL), Pasadena, Calif., holds up a model of the MSL, or Curiosity, at a press conference at the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum on Friday, July 22, 2011 in Washington. The MSL is scheduled to launch late this year from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida and land in August 2012. Curiosity is twice as long and more than five times as heavy as previous Mars rovers. The rover will study whether the landing region at Gale crater had favorable environmental conditions for supporting microbial life and for preserving clues about whether life ever existed. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
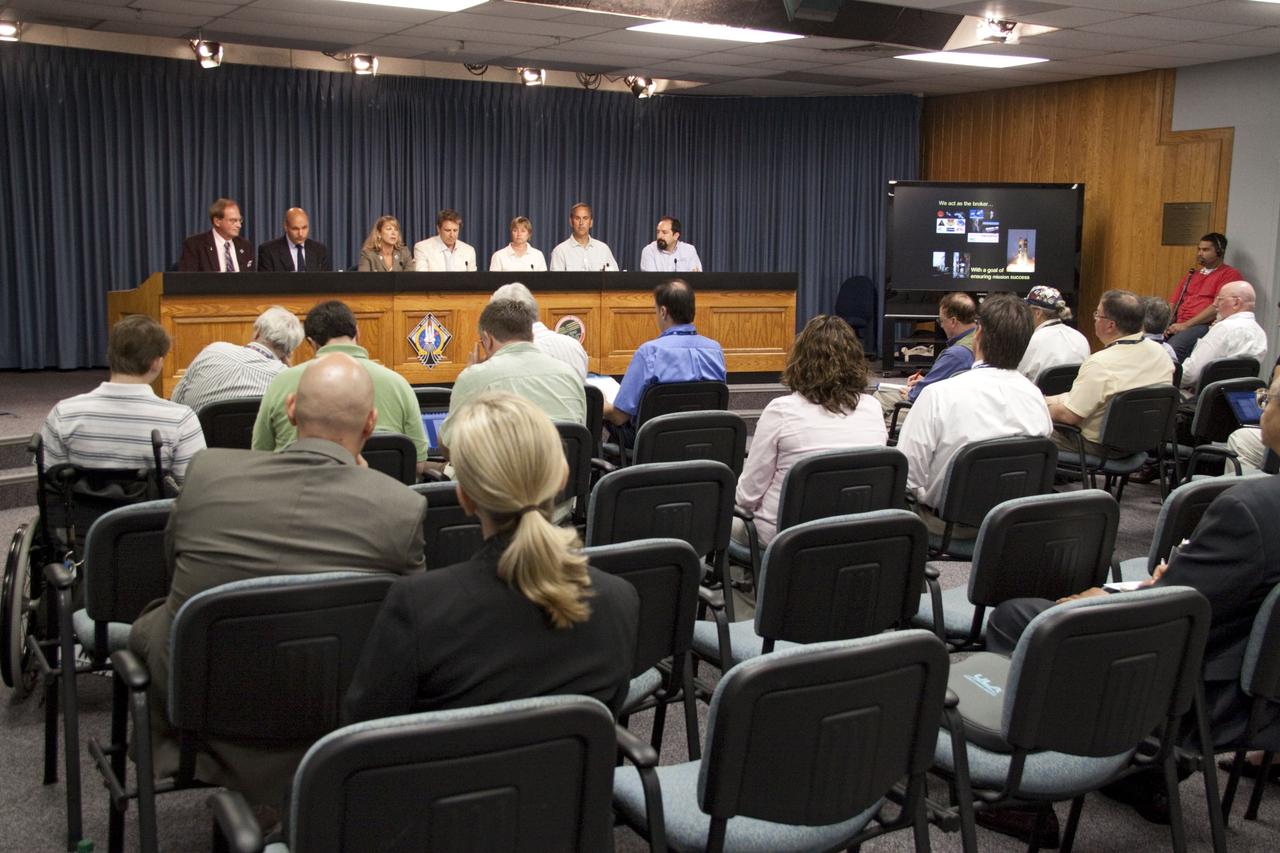

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, media were briefed about NASA's future science missions. Seen here are NASA Public Affairs Officer George Diller (left); Waleed Abdalati, NASA chief scientist; Amanda Mitskevich, NASA Launch Services Program manager; Scott Bolton, Juno principal investigator with the Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio; Maria Zuber, GRAIL principal investigator with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology; John Grotzinger, Mars Science Lab project scientist with the California Institute of Technology and Daniel Stern, NuStar project scientist with NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Calif. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
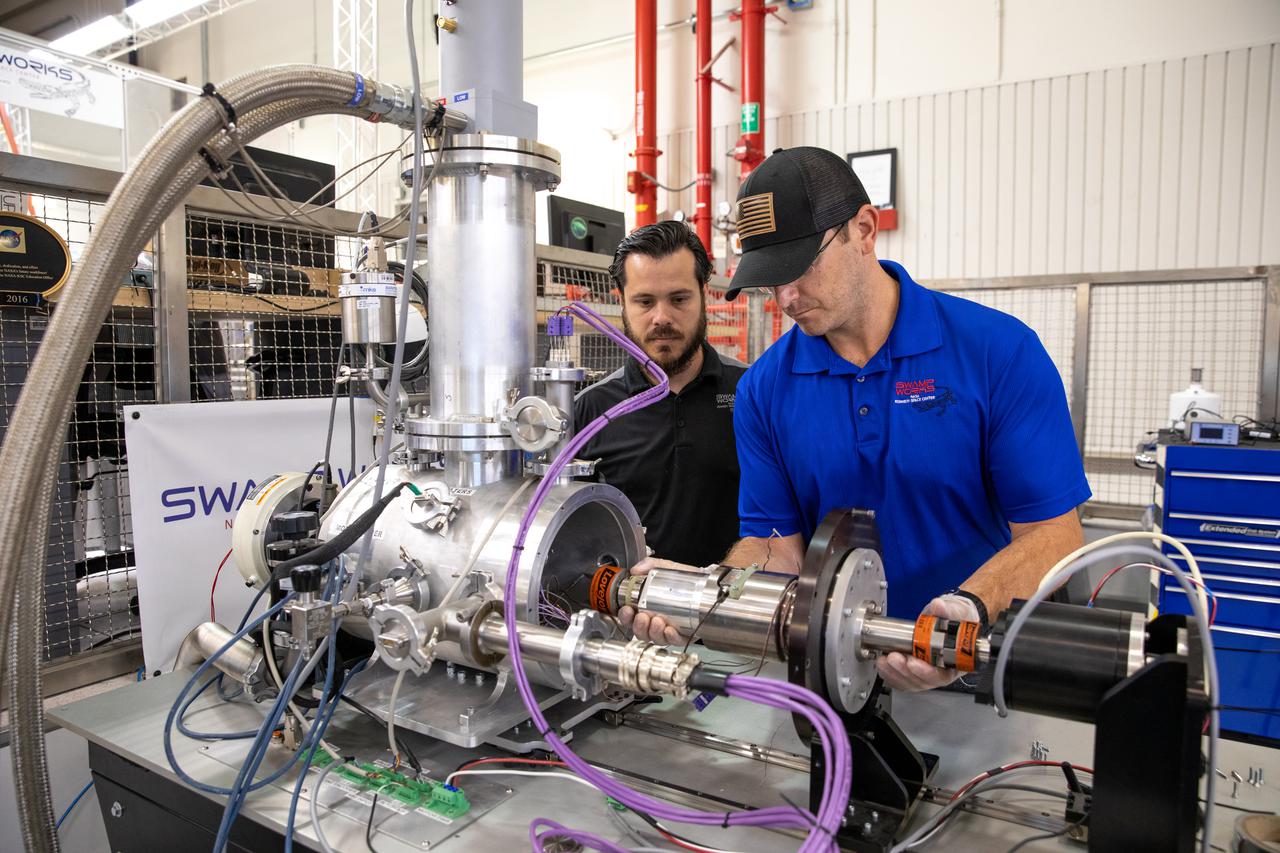

A.J. Nick, left, and Drew Smith, robotics engineers with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, test Bulk Metallic Glass Gears (BMGGs) in a vacuum inside a cryogenic cooler at Kennedy's Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations lab on June 17, 2021. Made from a custom bulk metallic glass alloy, BMGGs could be used in heater-free gearboxes at extremely low temperatures in locations such as the Moon, Mars, and Europa, one of Jupiter’s moons. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory is working with commercial partners to create the gears.
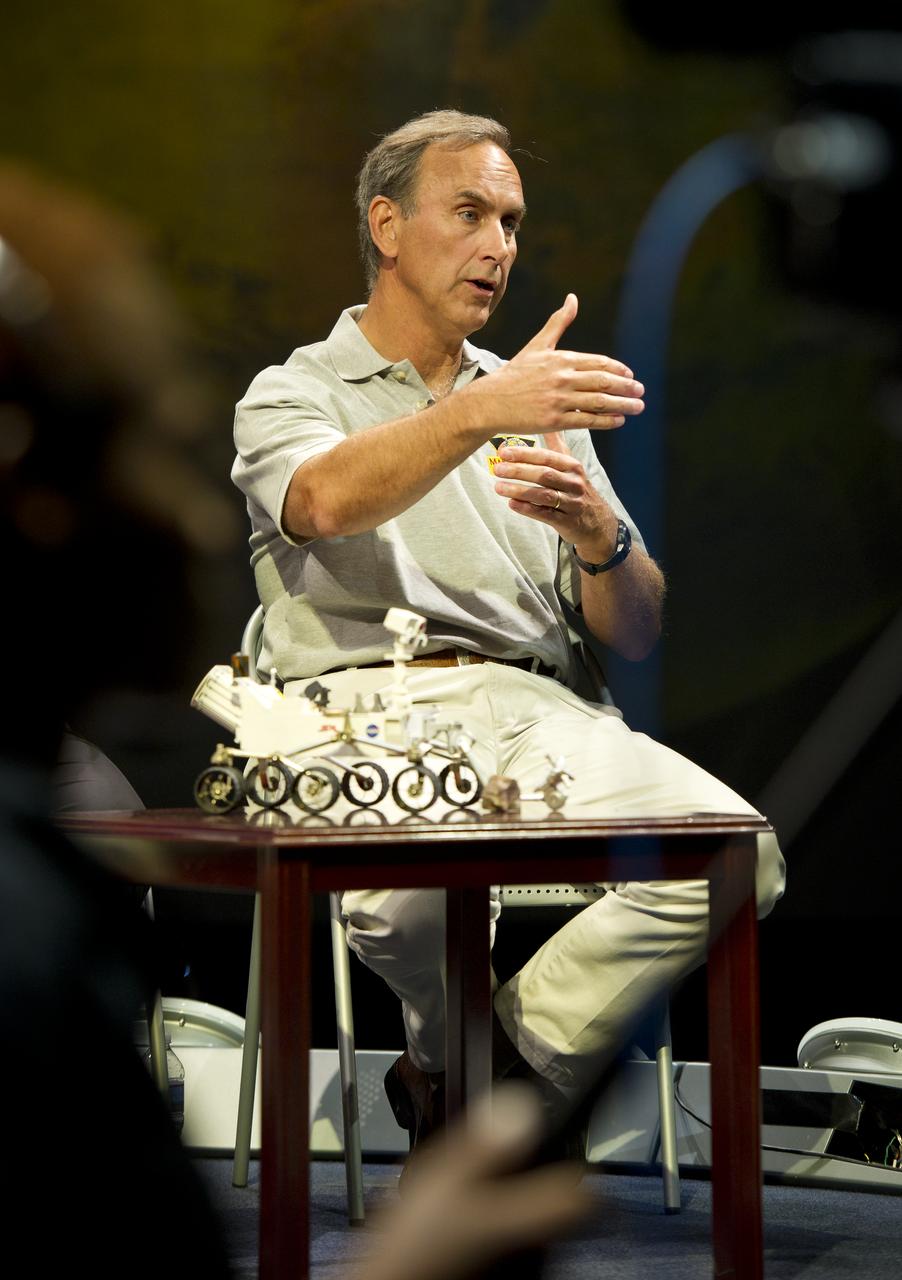

John Grotzinger, Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) project scientist, Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL), Pasadena, Calif., answers a reporter's question at a press conference at the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum on Friday, July 22, 2011 in Washington. The MSL is scheduled to launch late this year from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida and land in August 2012. Curiosity is twice as long and more than five times as heavy as previous Mars rovers. The rover will study whether the landing region at Gale crater had favorable environmental conditions for supporting microbial life and for preserving clues about whether life ever existed. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
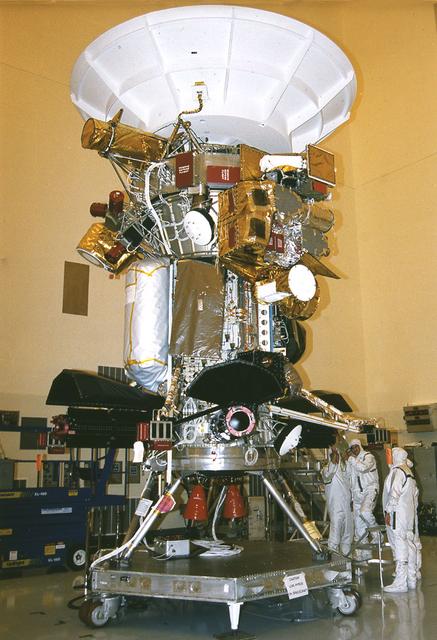

Jet Propulsion Research Lab (JPL) workers use a borescope to verify the pressure relief device bellow's integrity on a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) that has been installed on the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The activity is part of the mechanical and electrical verification testing of RTGs during prelaunch processing. RTGs use heat from the natural decay of plutonium to generate electrical power. The three RTGs on Cassini will enable the spacecraft to operate far from the Sun where solar power systems are not feasible. They will provide electrical power to Cassini on it seven year trip to the Saturnian system and during its four year mission at Saturn.
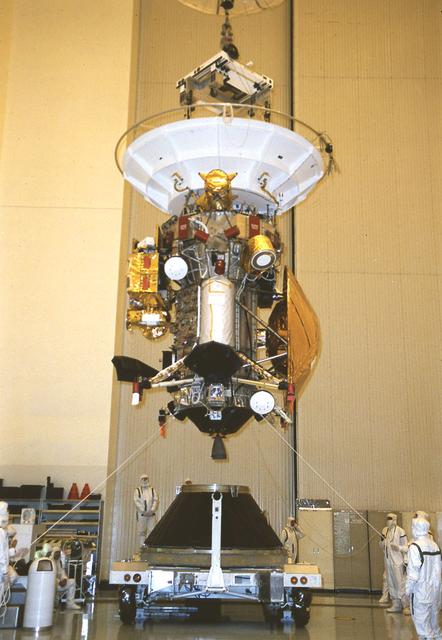

Jet Propulsion Research Lab (JPL) workers use a borescope to verify the pressure relief device bellow's integrity on a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) that has been installed on the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The activity is part of the mechanical and electrical verification testing of RTGs during prelaunch processing. RTGs use heat from the natural decay of plutonium to generate electrical power. The three RTGs on Cassini will enable the spacecraft to operate far from the Sun where solar power systems are not feasible. They will provide electrical power to Cassini on it seven year trip to the Saturnian system and during its four year mission at Saturn.
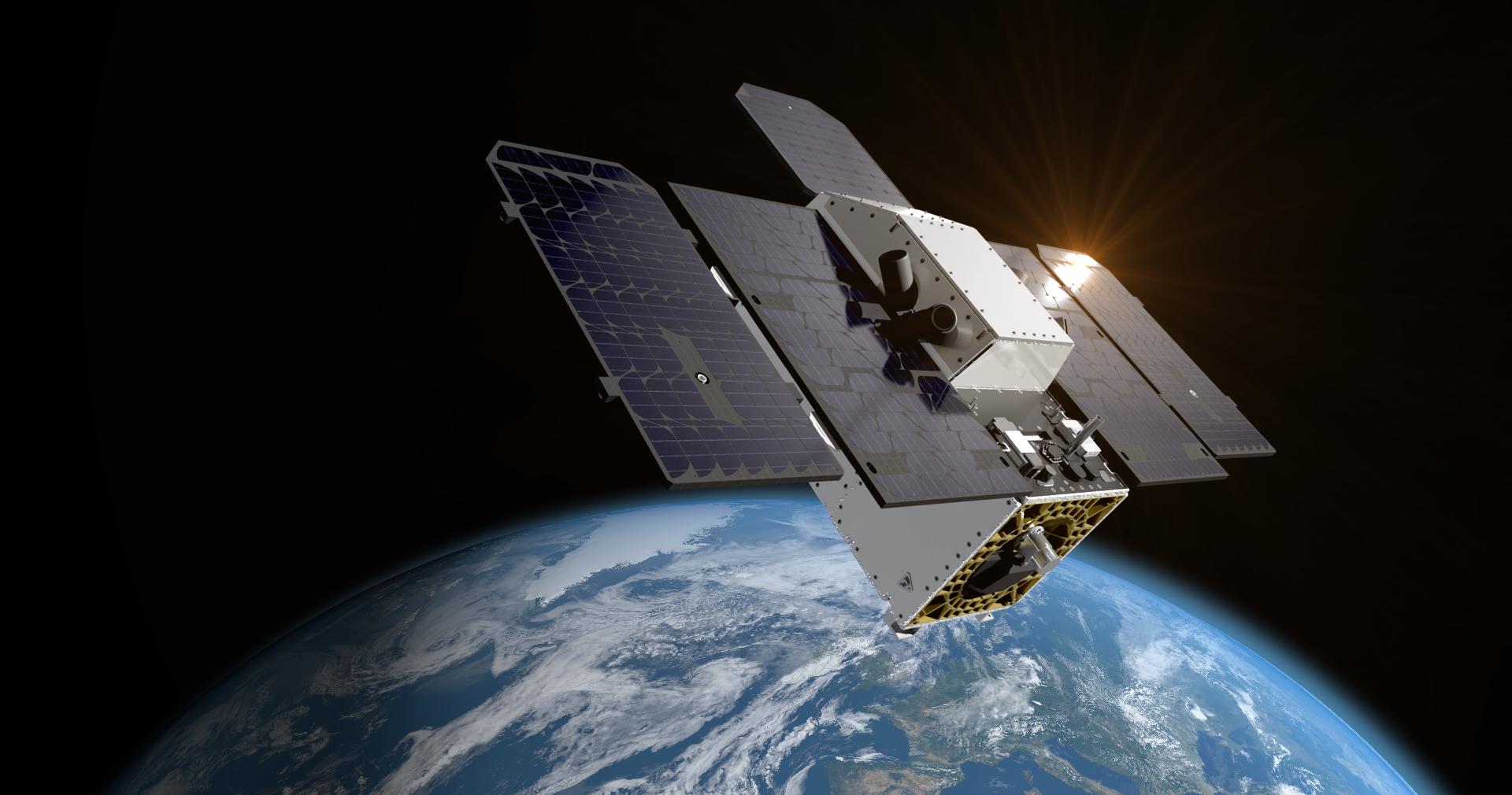

An artist's concept depicts one of the Carbon Mapper Coalition's Tanager satellites, which will use imaging spectrometer technology developed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California to measure methane and carbon dioxide point-source emissions, down to the level of individual facilities and equipment, on a global scale. The Tanager-1 satellite, launched from Vandenberg Space Force Based in California on Aug. 16, 2024, was developed as part of a philanthropically funded public-private coalition led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper. JPL and Planet Labs PBC, which built Tanager-1, are both members of the Carbon Mapper Coalition. The group plans to launch a second Tanager satellite, called Tanager-2, also being built by Planet Labs and equipped with a JPL-built imaging spectrometer. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26411
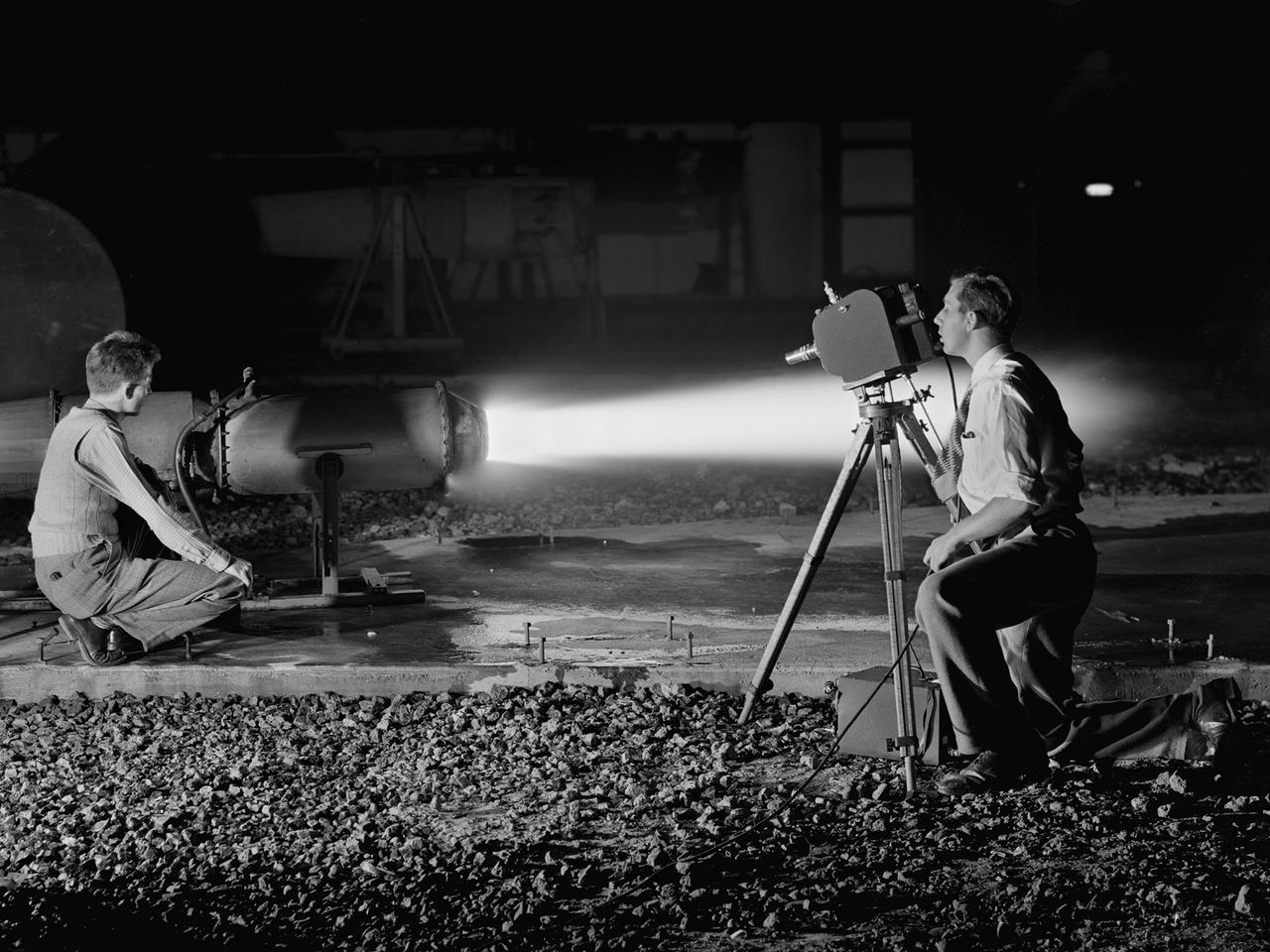

A National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) photographer films the test of a ramjet engine at the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The laboratory had an arsenal of facilities to test the engines and their components, and immersed itself in the study of turbojet and ramjet engines during the mid-1940s. Combustion, fuel injection, flameouts, and performance at high altitudes were of particular interest to researchers. They devised elaborate schemes to instrument the engines in order to record temperature, pressure, and other data. Many of the tests were also filmed so Lewis researchers could visually review the combustion performance along with the data. The photographer in this image was using high-speed film to document a thrust augmentation study at Lewis’ Jet Static Propulsion Laboratory. The ramjet in this photograph was equipped with a special afterburner as part of a general effort to improve engine performance. Lewis’ Photo Lab was established in 1942. The staff was expanded over the next few years as more test facilities became operational. The Photo Lab’s staff and specialized equipment have been key research tools for decades. They accompany pilots on test flights, use high-speed cameras to capture fleeting processes like combustion, and work with technology, such as the Schlieren camera, to capture supersonic aerodynamics. In addition, the group has documented construction projects, performed publicity work, created images for reports, and photographed data recording equipment.
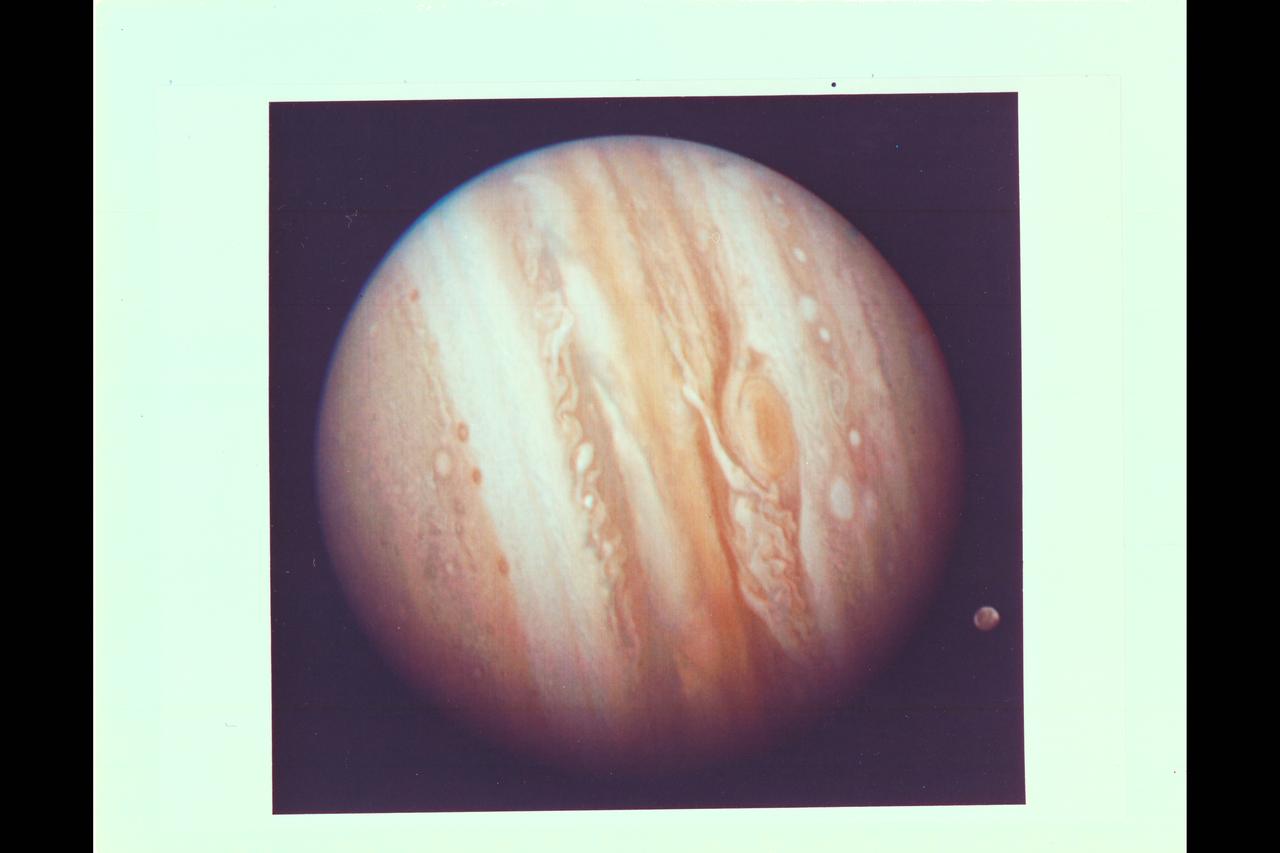

Photo by Voyager 1 (JPL) The spacecraft took this photo of the planet Jupiter on Jan 24, while still more than 25 million miles (40 million kilometers) away. As the spacecraft draws closer to the planet (about 1 million kilometers a day) more details are emergng in the turbulent clouds. The Great Red Spot shows prominently below center, surrounded by what scientists call a remarkably complex region of the giant planet's atmosphere. An elongated yellow cloud within the Great Red Spot is swirling around the spot's interior boundary in a counterclockwise direction with a period of a little less than six days, confirming the whirlpool-like circulation that astronomers have suspected from ground-based photographs. Ganymede, Jupiter's largest satellite, can be seen to the lower left of the planet. Ganymede is a planet-sized body larger than Mercury. This color photo was assembled at Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Image Processing Lab from there black and white images taken through filters. The Voyagers are managed for NASA's Office of Space Science by Jet Propulsion Laboratory. (ref: P-20945C Mission Image 1-9)
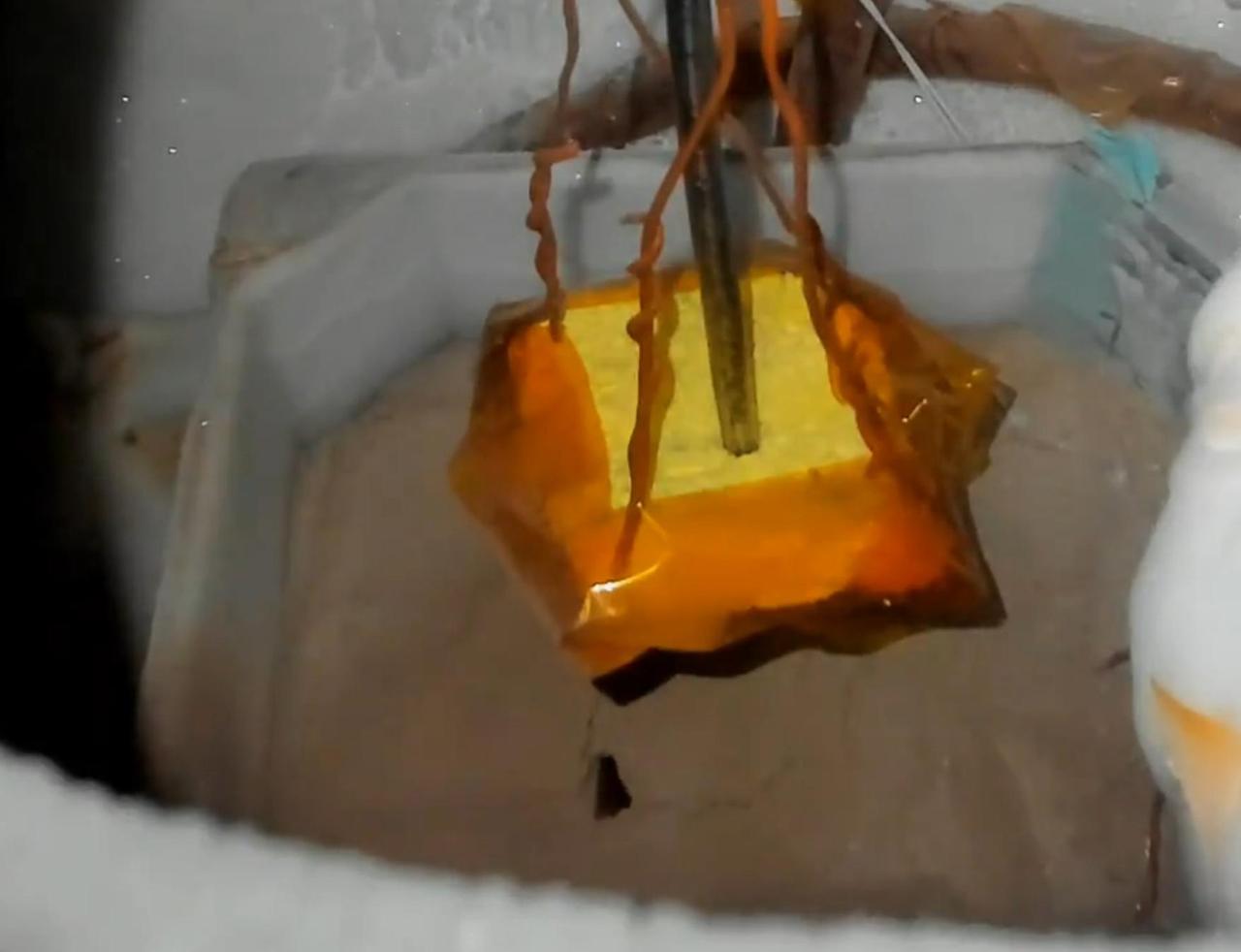

This image shows Martian soil simulant erupting in a plume during a lab experiment at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California that was designed to replicate the process believed to form Martian features called "spiders." In the experiment, researchers chilled Martian soil simulant in a container submerged within a liquid nitrogen bath. They placed it in JPL's Dirty Under-vacuum Simulation Testbed for Icy Environments (DUSTIE), where the air pressure was reduced to be similar to that of Mars' southern hemisphere. Carbon dioxide gas flowed into the chamber – diffused through the bright yellow sponge seen suspended over the simulant here – and condensed from gas to ice over the course of three to five hours. A heater inside the chamber then warmed the simulant from below, cracking the ice. After many tries, researchers saw a plume of carbon dioxide gas erupting from within the powdery simulant, as seen here. Video available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26404

Engineers and technicians prepare the Carbon Mapper imaging spectrometer, which will measure the greenhouse gases methane and carbon dioxide from space, for vibration testing at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in August 2023. This test is one of a series meant to ensure that the instrument can withstand the rigors of launch and the harsh conditions of space. Engineers subjected the spectrometer to intense vibrations similar to what it will endure atop a rocket blasting into orbit. The instrument was shipped from JPL to Planet Labs PBC in San Francisco on Sept. 12, 2023, where it will be integrated into a Tanager satellite. Designed and built by JPL, imaging spectrometer will be part of an effort led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper organization to collect data on greenhouse gas point-source emissions. The information will help locate and quantify "super-emitters" – the small percentage of individual sources responsible for a significant fraction of methane and carbon dioxide emissions around the world. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26093

The location where NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance rover will observe the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter's attempt at powered controlled flight at Mars is called "Van Zyl Overlook," after Jakob van Zyl. Van Zyl was the team's longtime colleague, mentor, and leader at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. He passed away unexpectedly in August 2020, about a month after the launch of Perseverance. Van Zyl joined JPL in 1986 and served in crucial roles at the Lab over a 33-year career, including as director for the Astronomy and Physics Directorate, associate director for project formulation and strategy, and finally director for the Solar System Exploration Directorate. As leader of solar system exploration at JPL, he oversaw successful operations of such NASA missions as Juno, Dawn, and Cassini, the implementation of the Mars InSight lander and MarCO CubeSats, as well as ongoing development of Europa Clipper, Psyche, and all of JPL's instruments and Ingenuity. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24435
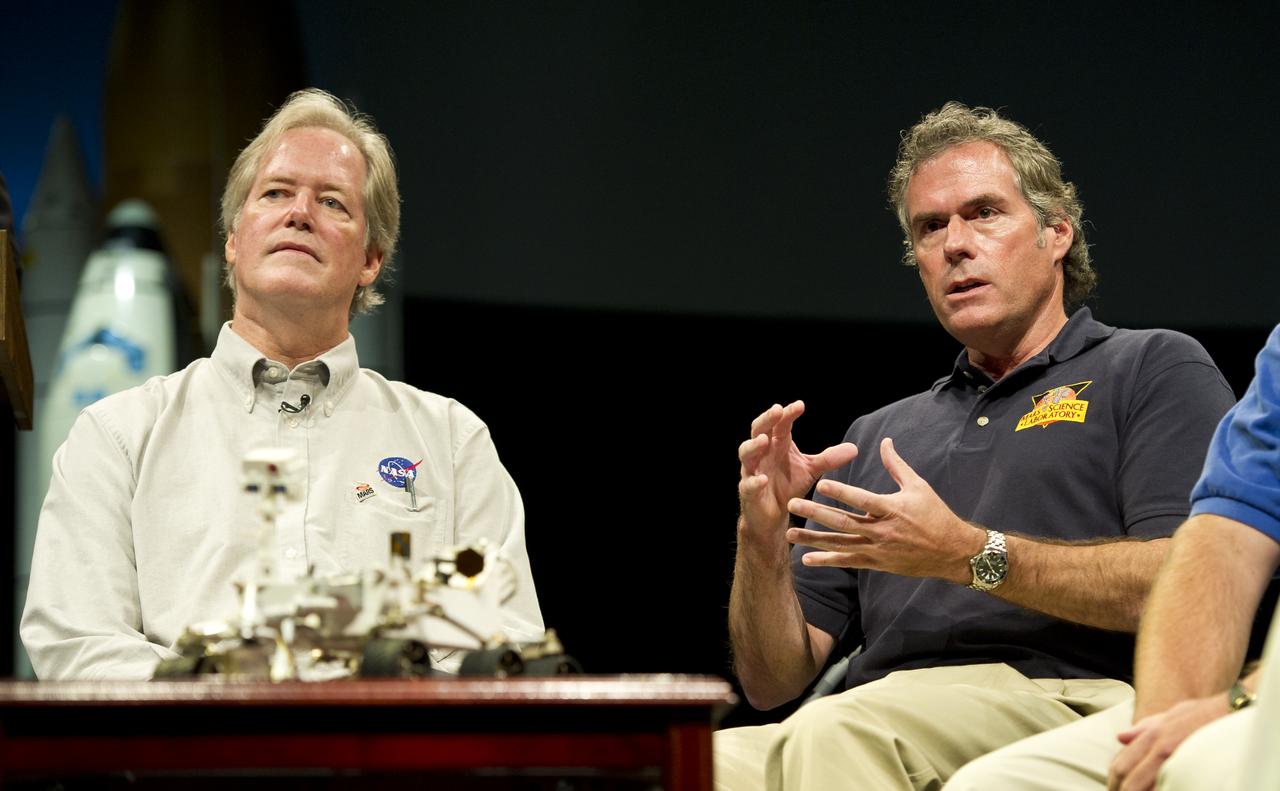

Michael Watkins (right), mission manager and Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) engineer, Jet Propulsion Lab, Pasadena, Calif., speaks at a press conference, as Michael Meyer, Mars Exploration Program lead scientist looks on, at the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum on Friday, July 22, 2011 in Washington. The MSL, or Curiosity, is scheduled to launch late this year from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida and land in August 2012. Curiosity is twice as long and more than five times as heavy as previous Mars rovers. The rover will study whether the landing region at Gale crater had favorable environmental conditions for supporting microbial life and for preserving clues about whether life ever existed. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
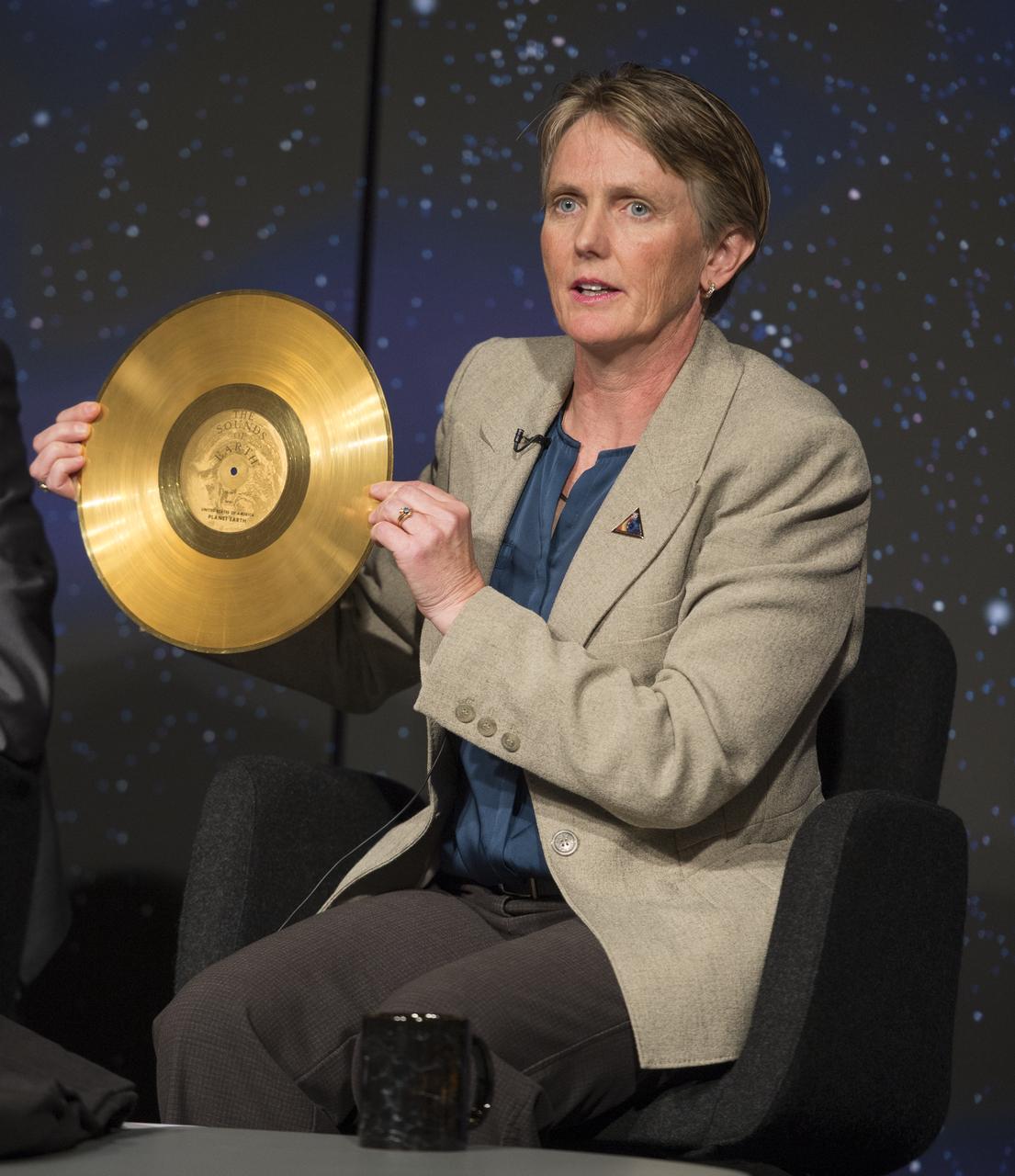

Suzanne Dodd, Voyager project manager, NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) holds a replica of the golden record carried on Voyager at a news conference on NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft, Thursday, Sept. 12, 2013 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The Golden Record was intended to communicate a story of our world to extraterrestrials. NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft officially is the first human-made object to venture into interstellar space. The 36-year-old probe is about 12 billion miles (19 billion kilometers) from our sun. New and unexpected data indicate Voyager 1 has been traveling for about one year through plasma, or ionized gas, present in the space between stars. A report on the analysis of this new data is published in Thursday's edition of the journal Science. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

An engineer prepares the Carbon Mapper imaging spectrometer, which will measure the greenhouse gases methane and carbon dioxide from space, for testing in a thermal vacuum chamber at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in July 2023. This test is one of a series meant to ensure that the instrument can withstand the rigors of launch and the harsh conditions of space. Engineers used the chamber to subject the spectrometer to the extreme temperatures it will encounter in the vacuum of space. The instrument was shipped from JPL to Planet Labs PBC in San Francisco on Sept. 12, 2023, where it will be integrated into a Tanager satellite. Designed and built by JPL, imaging spectrometer will be part of an effort led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper organization to collect data on greenhouse gas point-source emissions. The information will help locate and quantify "super-emitters" – the small percentage of individual sources responsible for a significant fraction of methane and carbon dioxide emissions around the world. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26094
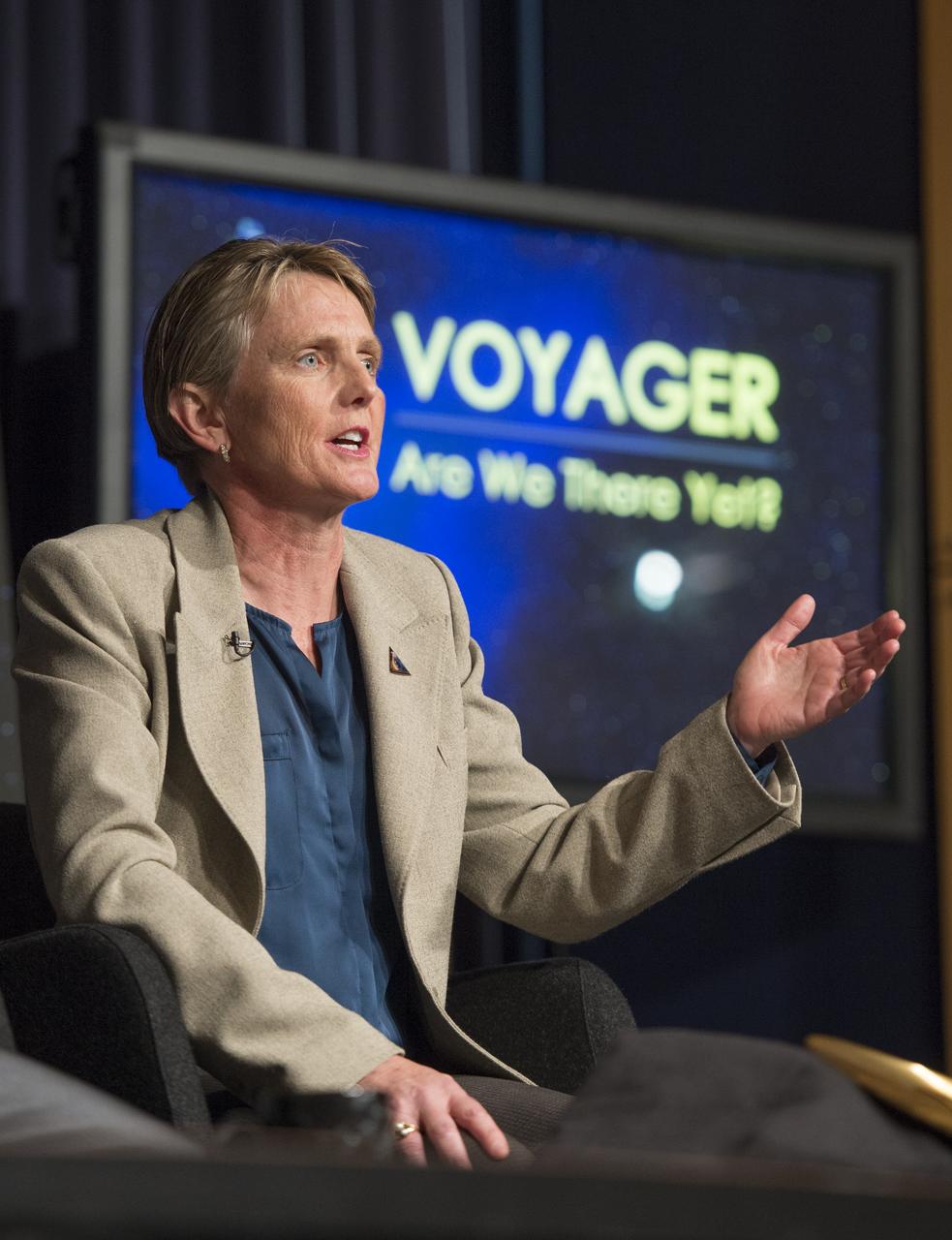

Suzanne Dodd, Voyager project manager, NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) speaks at a news conference on NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft, Thursday, Sept. 12, 2013 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft officially is the first human-made object to venture into interstellar space. The 36-year-old probe is about 12 billion miles (19 billion kilometers) from our sun. New and unexpected data indicate Voyager 1 has been traveling for about one year through plasma, or ionized gas, present in the space between stars. A report on the analysis of this new data is published in Thursday's edition of the journal Science. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
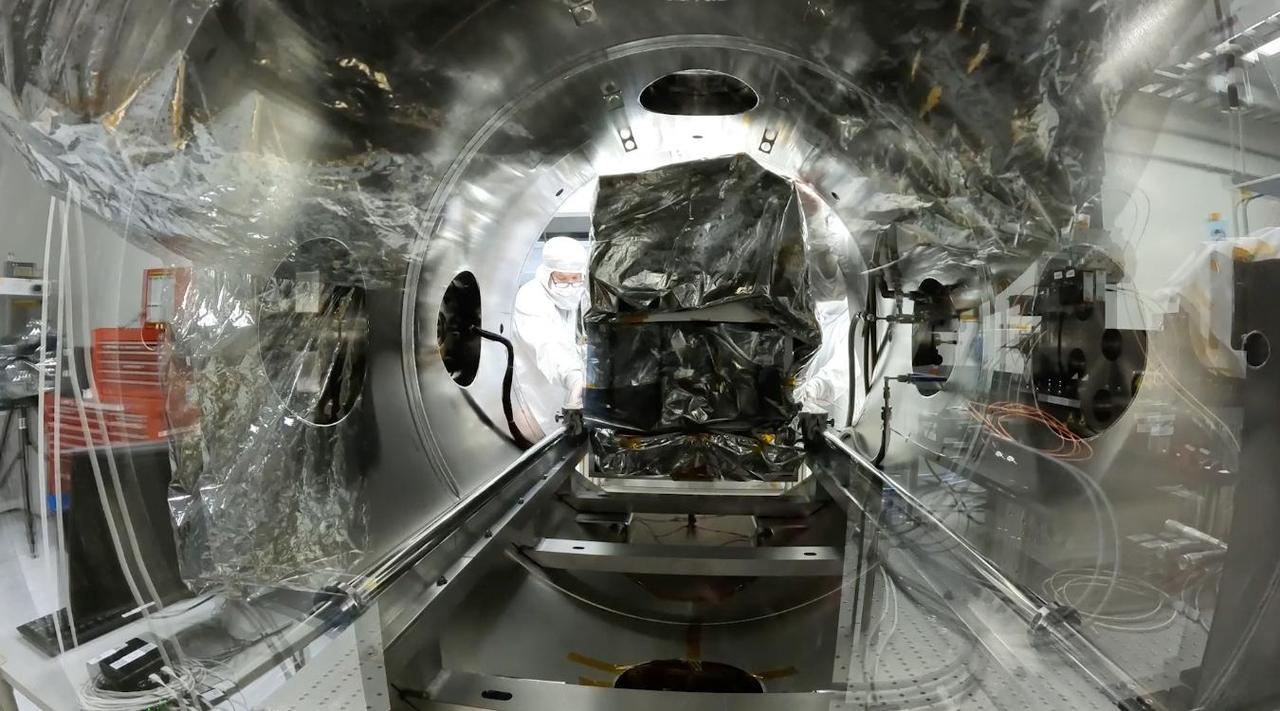

A technician slides an imaging spectrometer instrument, which will measure the greenhouse gases methane and carbon dioxide from space, into a thermal vacuum test chamber at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in July 2023. The thermal vacuum chamber test is one of a series meant to ensure that the instrument can withstand the rigors of launch and the harsh conditions of space. Engineers use the chamber to subject the spectrometer to the extreme temperatures it will encounter in the vacuum of space. The instrument shipped Sept. 12, 2023, from JPL to Planet Labs PBC in San Francisco, where it will be integrated into a Tanager satellite. Designed and built by JPL, imaging spectrometer will be part of an effort led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper organization to collect data on greenhouse gas point-source emissions. The information will help locate and quantify "super-emitters" – the small percentage of individual sources responsible for a significant fraction of methane and carbon dioxide emissions around the world. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26098
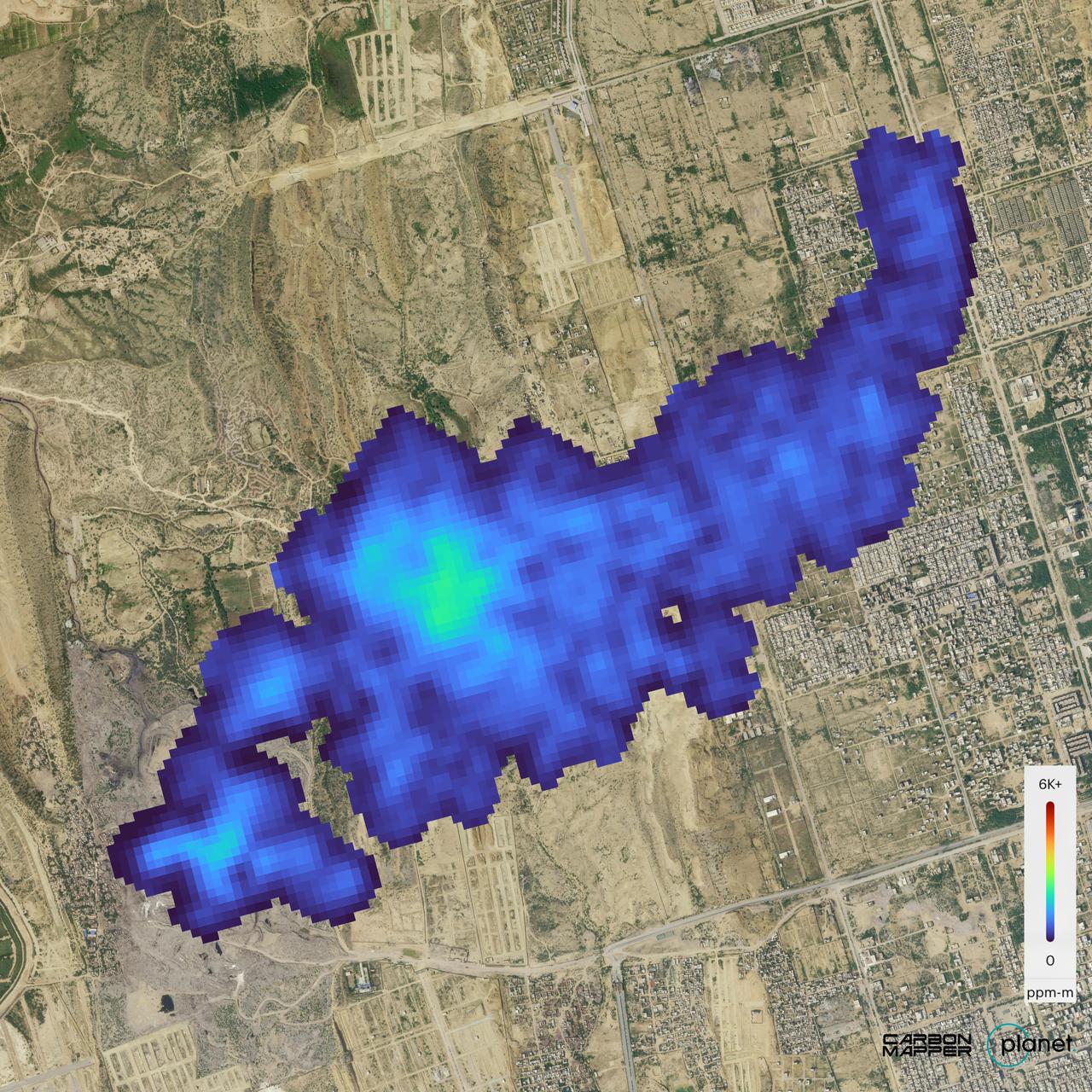
The Carbon Mapper Coalition's Tanager-1 satellite on Sept. 19, 2024, captured data over Karachi, Pakistan, showing the location and concentration of a methane plume measuring about 2½ miles (4 kilometers) long, emanating from a landfill. Enabled by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper and built by Planet Labs PBC, Tanager-1 uses an imaging spectrometer designed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Carbon Mapper's preliminary estimate of the source emissions rate is about 2,600 pounds (1,200 kilograms) of methane released per hour. Launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Aug. 16, 2024, Tanager-1 is part of a broader effort by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper to identify and measure greenhouse gas point-source emissions on a global scale. Both Planet and JPL are members of the philanthropically funded Carbon Mapper Coalition. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26416
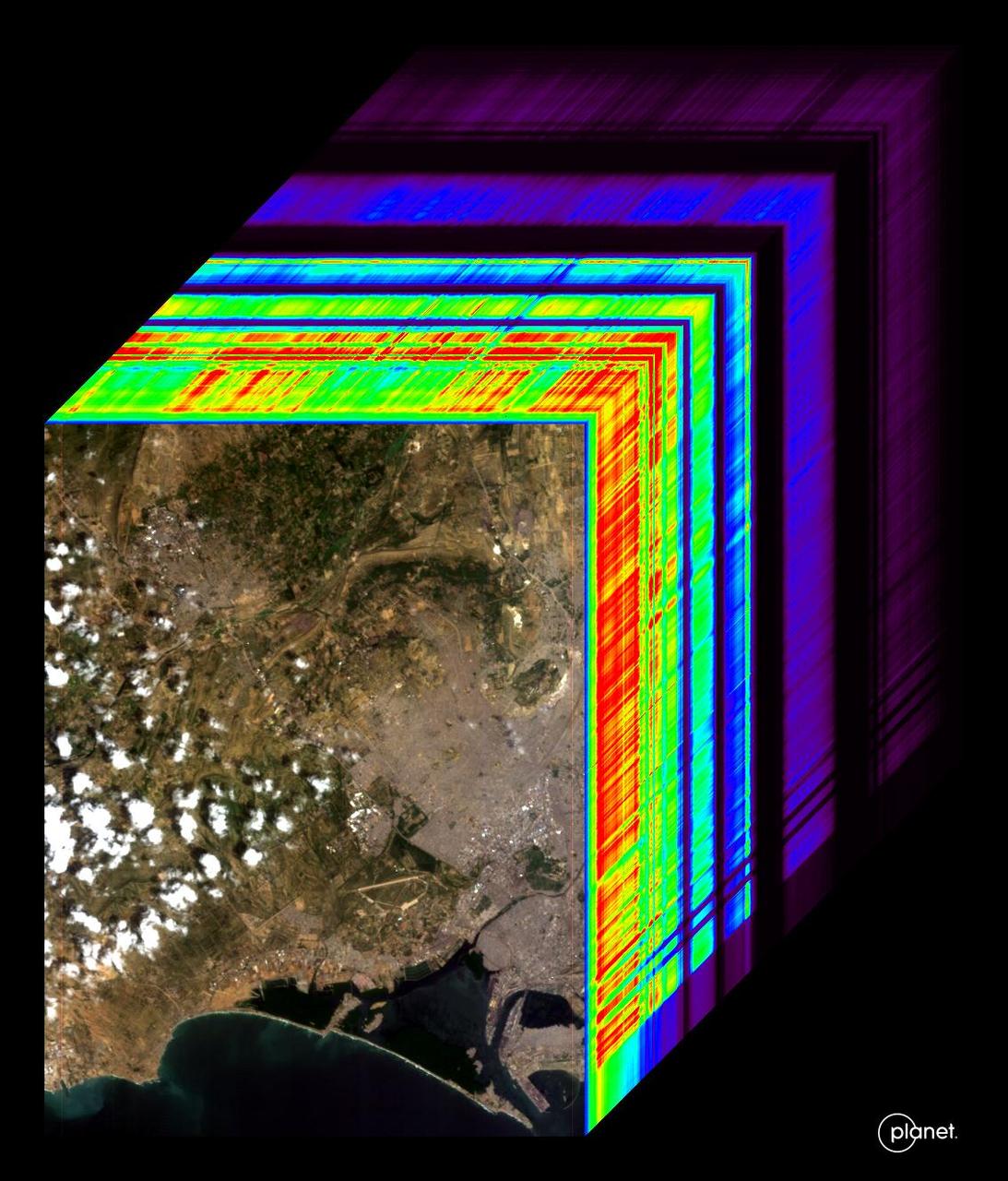
An imaging spectrometer designed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory captured its first data over Karachi, Pakistan, on Sept. 19, 2024. The instrument is aboard the Carbon Mapper Coalition's Tanager-1 satellite, which was built by Planet Labs PBC. An imaging spectrometer can measure hundreds of wavelengths of light that are reflected by Earth's surface. Different compounds in the planet's atmosphere and on the ground absorb different wavelengths of light, leaving spectral "fingerprints" that researchers can identify. The imaging spectrometer aboard Tanager-1 will enable the satellite to measure methane and carbon dioxide point-source emissions, down to the level of individual facilities and equipment, on a global scale. The image at the front of the cube shows a mix of information on land cover and water in the city and surrounding area, including exposed soil (brown), vegetation (green), and clouds. The rainbow colors extending through the main part of the cube are the wavelengths of light from corresponding spots in the front image. Tanager-1, which launched on Aug. 16, 2024, was developed as part of a philanthropically funded public-private coalition led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper. Planet Labs and JPL are both members of the Carbon Mapper Coalition. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26412
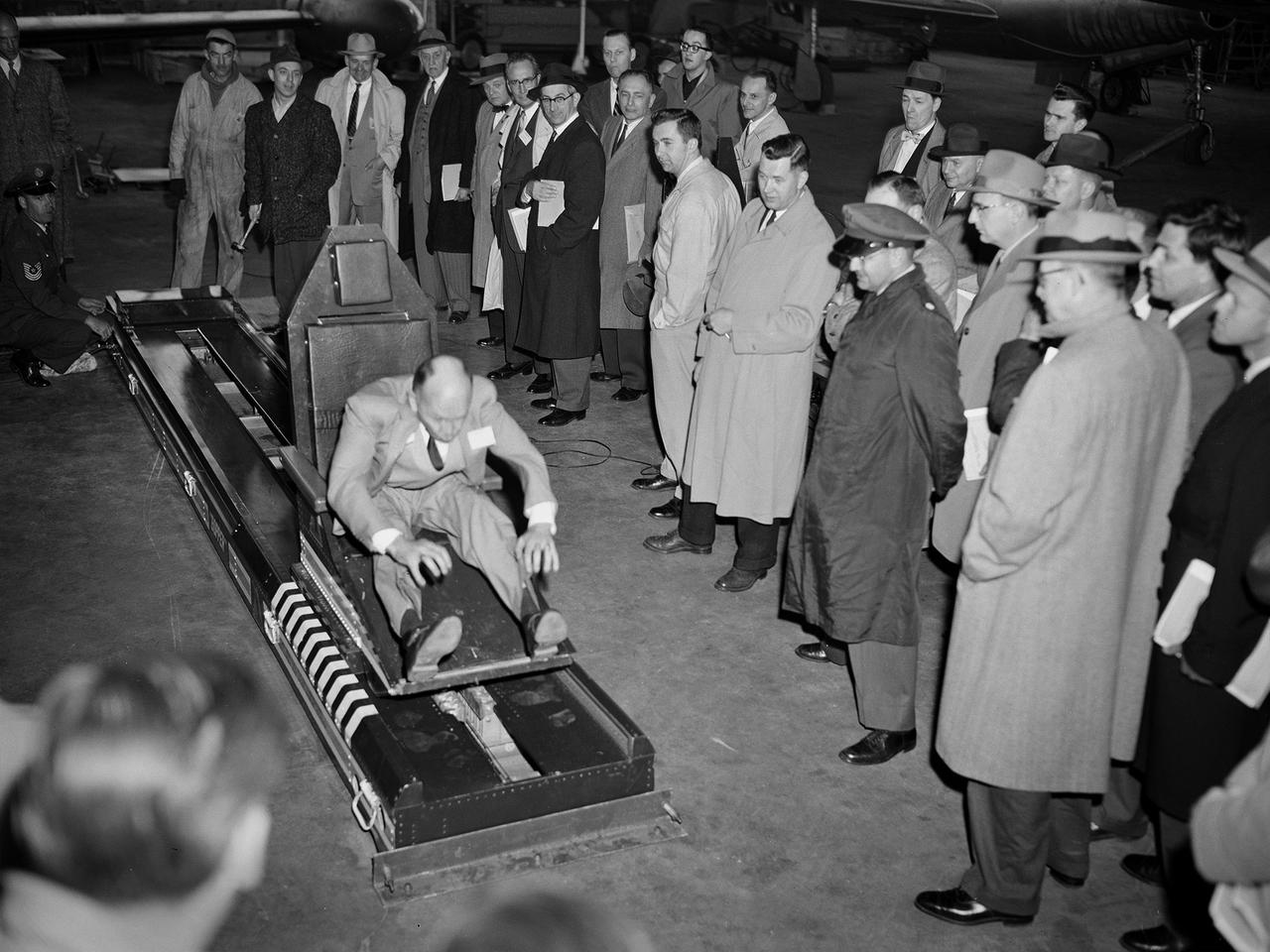

Howard Hasbrook volunteers for a demonstration of a scaled-down version of Lieutenant Colonel John Stapp’s rocket sled set up in the hangar at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. In 1945 Stapp, an Air Force medical doctor, volunteered to participate in a deceleration program to study the human body’s tolerance to aircraft crash forces. A 1500-pound sled powered by rockets was installed in 1947 on a section of railroad track in the California desert. Stapp participated in 29 experiments over the next seven years and broke land and deceleration records. These tests studied the effects of acceleration, G-force, deceleration, and wind blast on humans. Stapp suffered broken bones and retinal hemorrhages, but suffered no permanent damage. NACA Lewis was conducting a series of crash impact studies in the mid-1950s using dummies in actual aircraft. Irving Pinkel, the director of the program, and Stapp became friends through their mutual interest in this field. In April 1956 Stapp visited the Cleveland lab to give a talk to the local section of the American Rocket Society that discussed issues relating to the escape of pilots from the cockpit of supersonic jet aircraft. That same week, NACA Lewis’ Pinkel, Gerard Pesman, Merritt Preston, and Dugald Black received the annual Laura Taber Barbour Air Safety Award for their work on the Crash Fire Program. Black and Preston are visible in the crowd in this photograph.
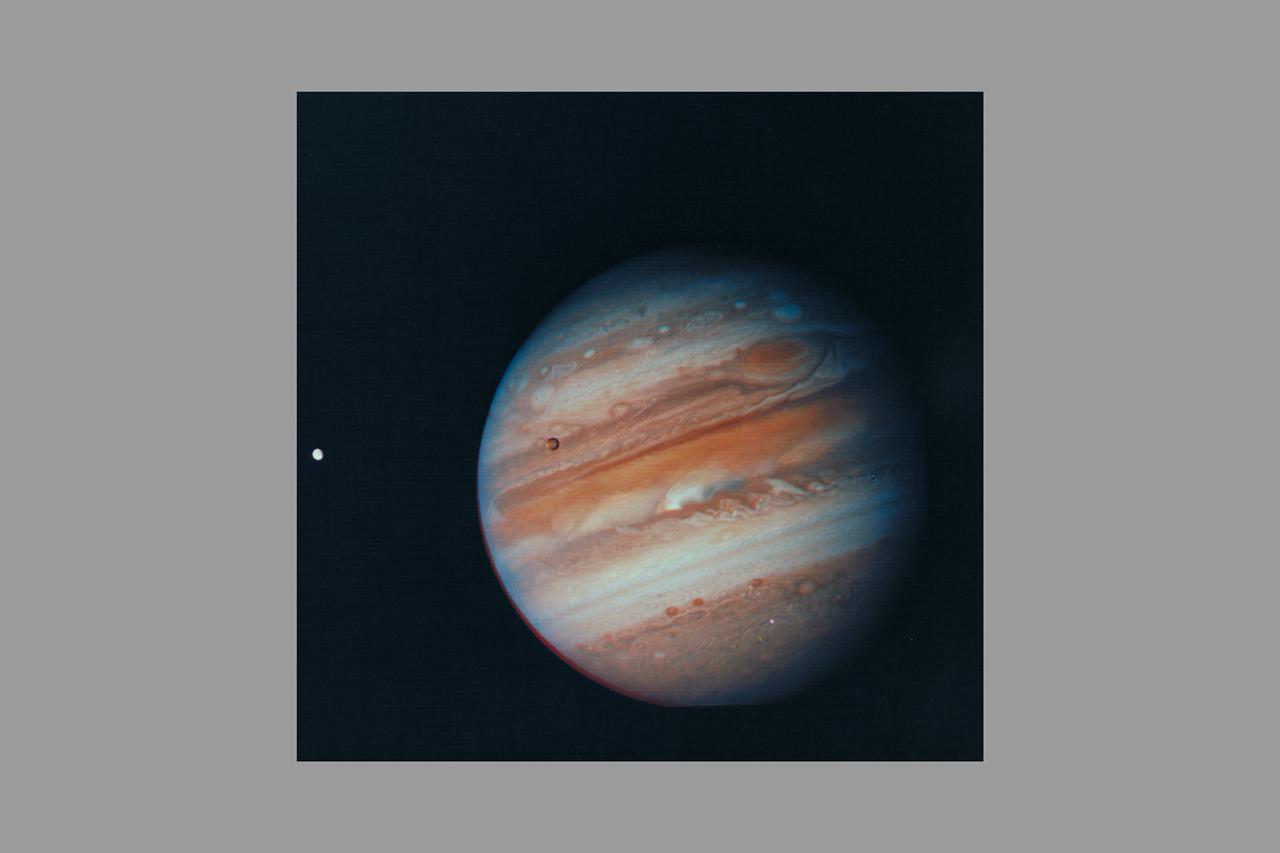

Photo by Voyager 1 (JPL) Jupiter, its Great Red Spot and three of its four largest satellites are visible in this photo taken Feb 5, 1979 by Voyager 1. The spacecraft was 28.4 million kilomters (17.5 million miles) from the planet at the time. The inner-most large satellite, Io, can be seen against Jupiter's disk. Io is distinguished by its bright, brown-yellow surface. To the right of Jupiter is the satellite Europa, also very bright but with fainter surface markings. The darkest satellite, Callisto (still nearly twice as bright as Earth's Moon), is barely visible at the bottom left of the picture. Callisto shows a bright patch in its northern hemisphere. All tThree orbit Jupiter in the equatorial plane, and appear in their present position because Voyageris above the plane. All three satellites show the same face to Jupiter always -- just as Earth's Moon always shows us the same face. In this photo we see the sides of the satellites that always face away from the planet. Jupiter's colorfully banded atmosphere displays complex patterns highlighted by the Great Red Spot, a large, circulating atmospheric disturbance. This photo was assembled from three black and white negatives by the Image Processing Lab at Jet Propulsion Laboratory. JPL manages and controls the Voyage Project for NASA's Office of Space Science. (ref: P-21083)
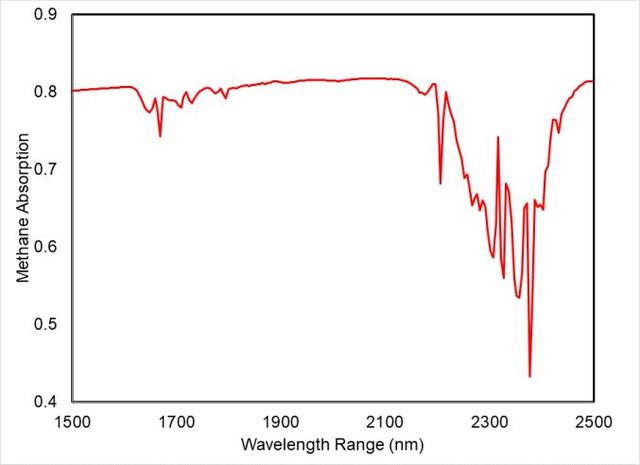
This spectral "fingerprint" of methane was produced from data taken during a September 2023 test at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California of a state-of-the-art imaging spectrometer that will measure the greenhouse gases methane and carbon dioxide from space. The instrument measures hundreds of wavelengths of light reflected by Earth's surface and absorbed by gases in the planet's atmosphere. Different compounds absorb different wavelengths of light, leaving a kind of spectral fingerprint that the imaging spectrometer can identify. These infrared fingerprints, invisible to the human eye, can pinpoint and quantify strong greenhouse gas emissions, and accelerate mitigation efforts. Before the imaging spectrometer was shipped from JPL to Planet Labs PBC in San Francisco, where it will be integrated into a Tanager satellite, there was a rare opportunity to use a sample of methane to test the completed instrument while it was in a vacuum chamber. The test was successful, and the imaging spectrometer produced this clear spectral fingerprint of methane (appearing as a red line in the graph). Designed and built by JPL, imaging spectrometer will be part of an effort led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper organization to collect data on greenhouse gas point-source emissions. The information will help locate and quantify "super-emitters" – the small percentage of individual sources responsible for a significant fraction of methane and carbon dioxide emissions around the world. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26095
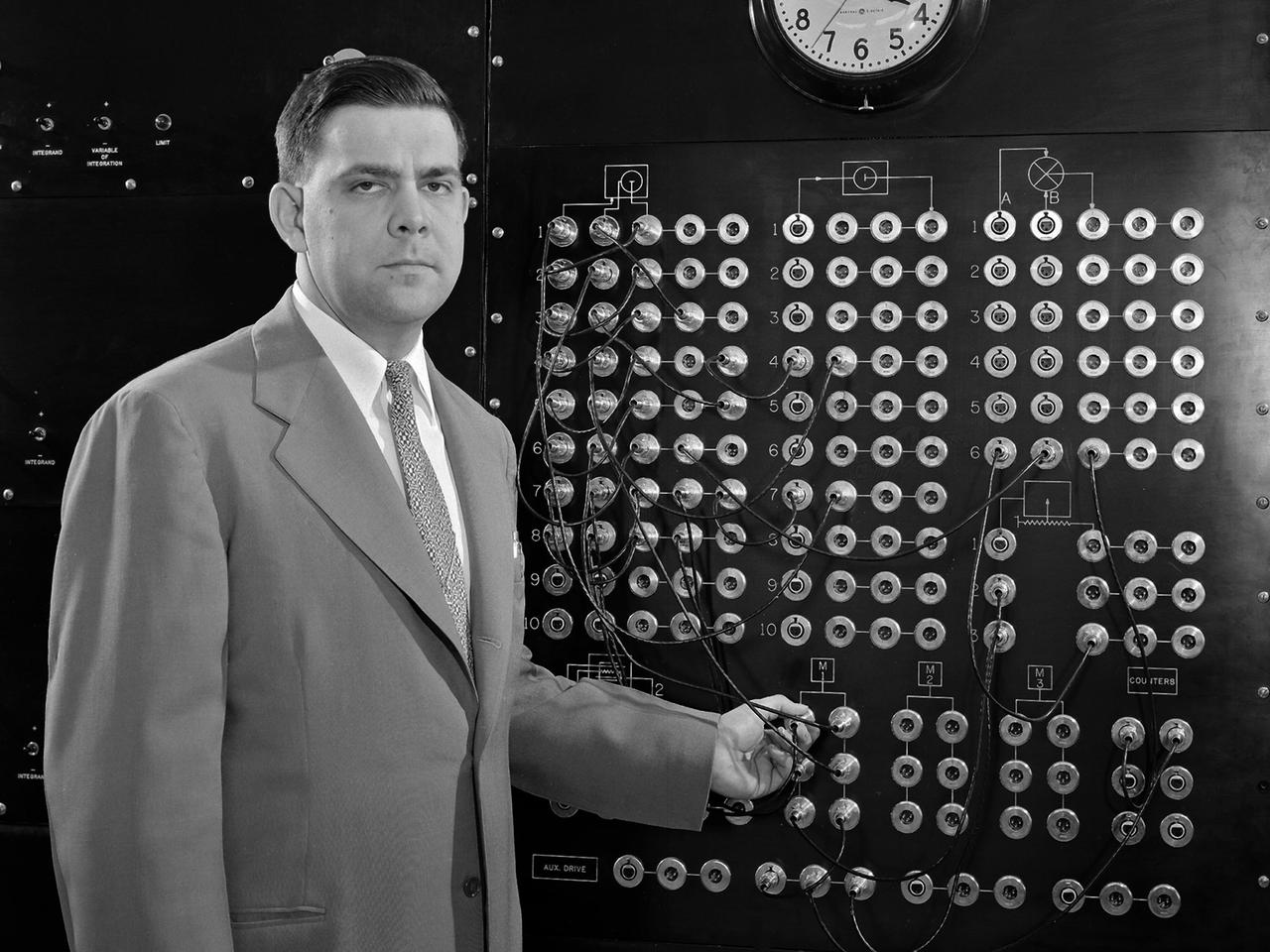

Harry Mergler stands at the control board of a differential analyzer in the new Instrument Research Laboratory at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The differential analyzer was a multi-variable analog computation machine devised in 1931 by Massachusetts Institute of Technology researcher and future NACA Committee member Vannevar Bush. The mechanical device could solve computations up to the sixth order, but had to be rewired before each new computation. Mergler modified Bush’s differential analyzer in the late 1940s to calculate droplet trajectories for Lewis’ icing research program. In four days Mergler’s machine could calculate what previously required weeks. NACA Lewis built the Instrument Research Laboratory in 1950 and 1951 to house the large analog computer equipment. The two-story structure also provided offices for the Mechanical Computational Analysis, and Flow Physics sections of the Physics Division. The division had previously operated from the lab’s hangar because of its icing research and flight operations activities. Mergler joined the Instrument Research Section of the Physics Division in 1948 after earning an undergraduate degree in Physics from the Case Institute of Technology. Mergler’s focus was on the synthesis of analog computers with the machine tools used to create compressor and turbine blades for jet engines.
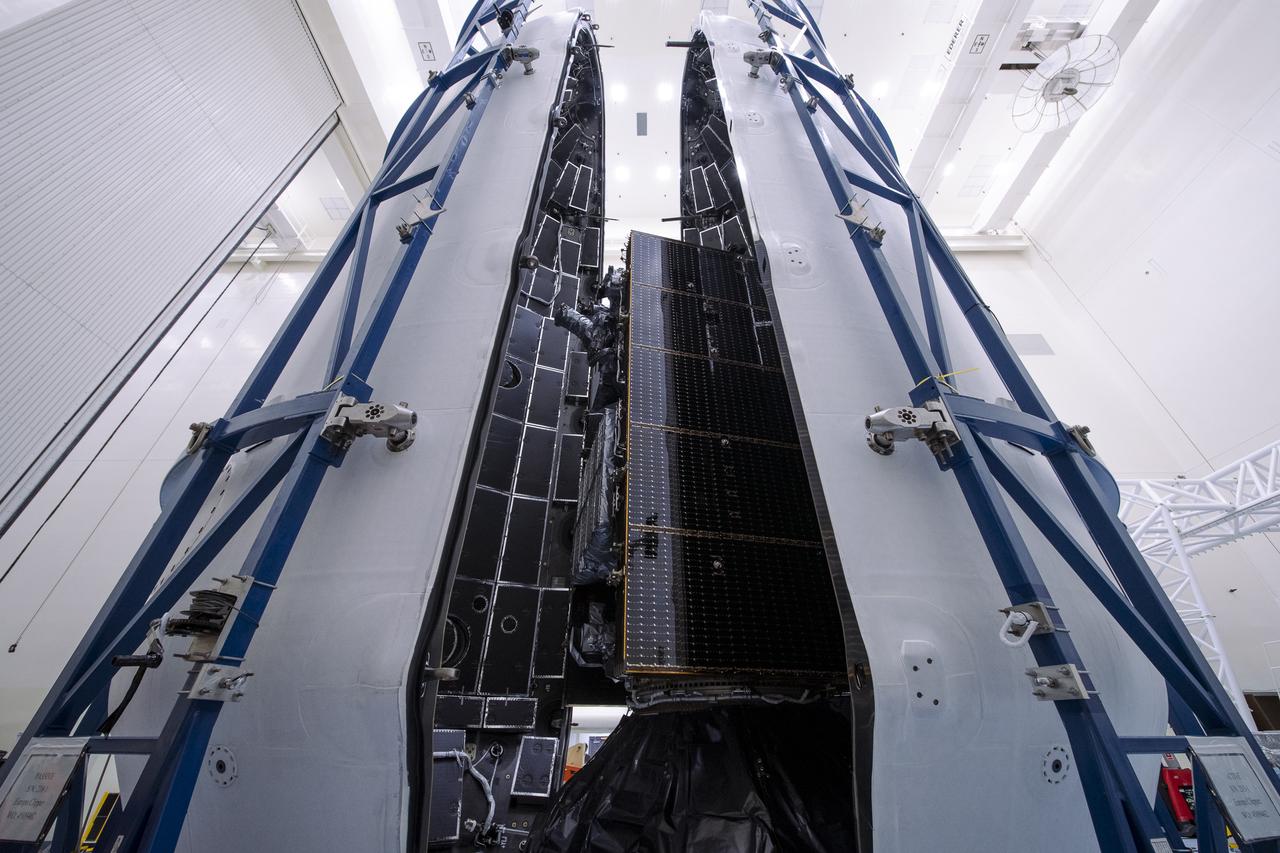

Technicians encapsulate NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft inside SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy payload fairing in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 2, 2024. The payload fairing will protect the spacecraft during liftoff from Launch Complex 39A on its journey to explore Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. The spacecraft will complete nearly 50 flybys of Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, to determine if there are conditions suitable for life beyond Earth.
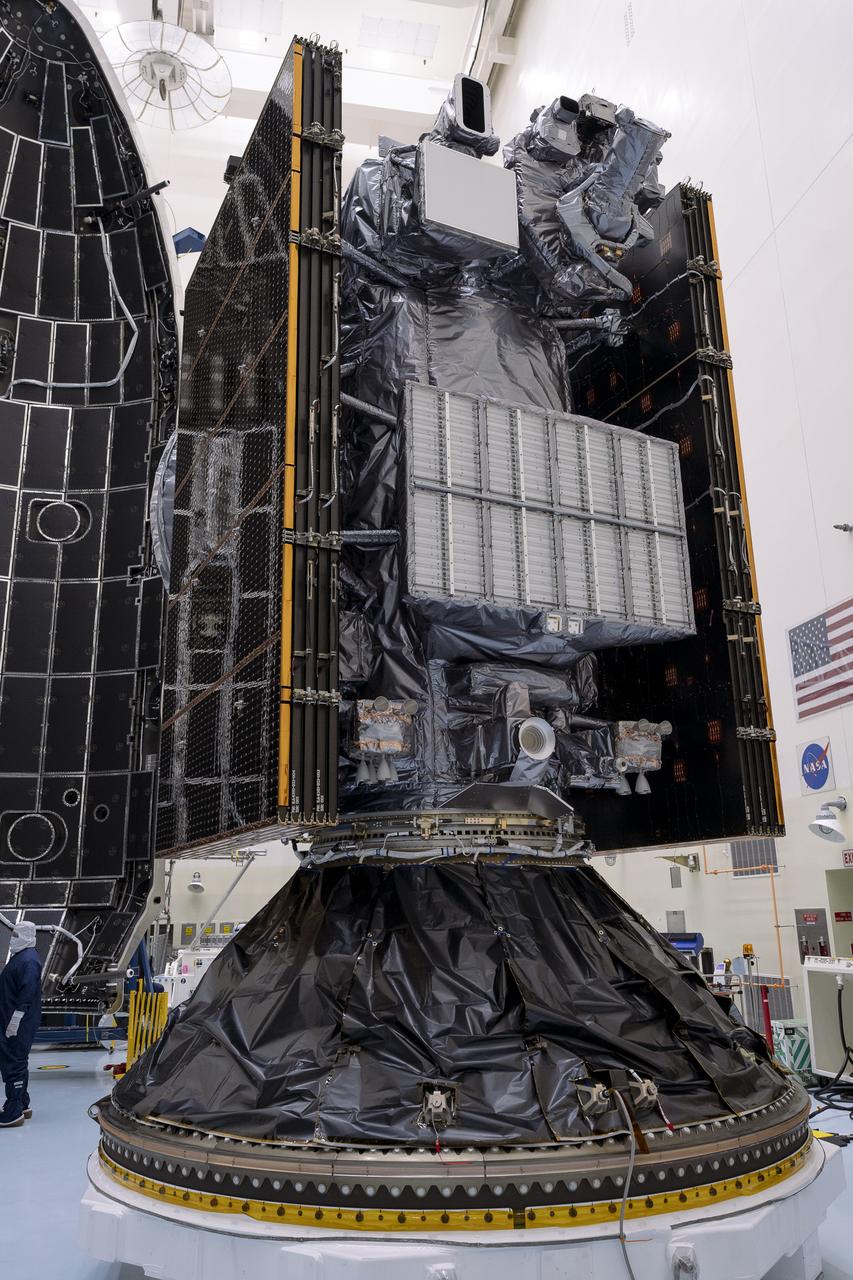

Technicians prepare to encapsulate NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft inside SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy payload fairing in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 2, 2024. The payload fairing will protect the spacecraft during liftoff from Launch Complex 39A on its journey to explore Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. The spacecraft will complete nearly 50 flybys of Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, to determine if there are conditions suitable for life beyond Earth.

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 12:06 p.m. EDT on Monday, Oct. 14, 2024. After launch, the spacecraft plans to fly by Mars in February 2025, then back by Earth in December 2026, using the gravity of each planet to increase its momentum. With help of these “gravity assists,” Europa Clipper will achieve the velocity needed to reach Jupiter in April 2030.
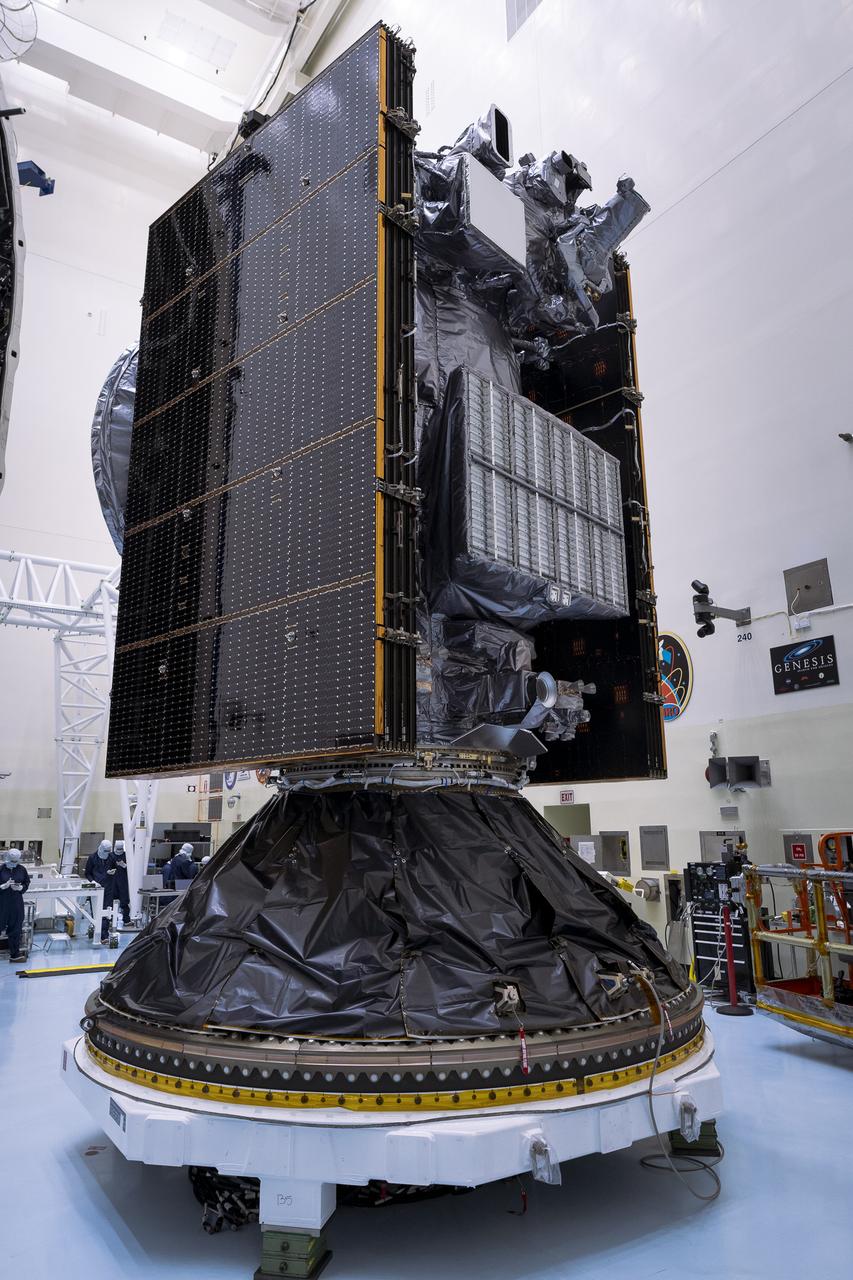

Technicians prepare to encapsulate NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft inside SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy payload fairing in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 2, 2024. The payload fairing will protect the spacecraft during liftoff from Launch Complex 39A on its journey to explore Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. The spacecraft will complete nearly 50 flybys of Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, to determine if there are conditions suitable for life beyond Earth.

Twin solar arrays for NASA’s Psyche spacecraft arrive by flatbed truck at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 15, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San Jose, in California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.
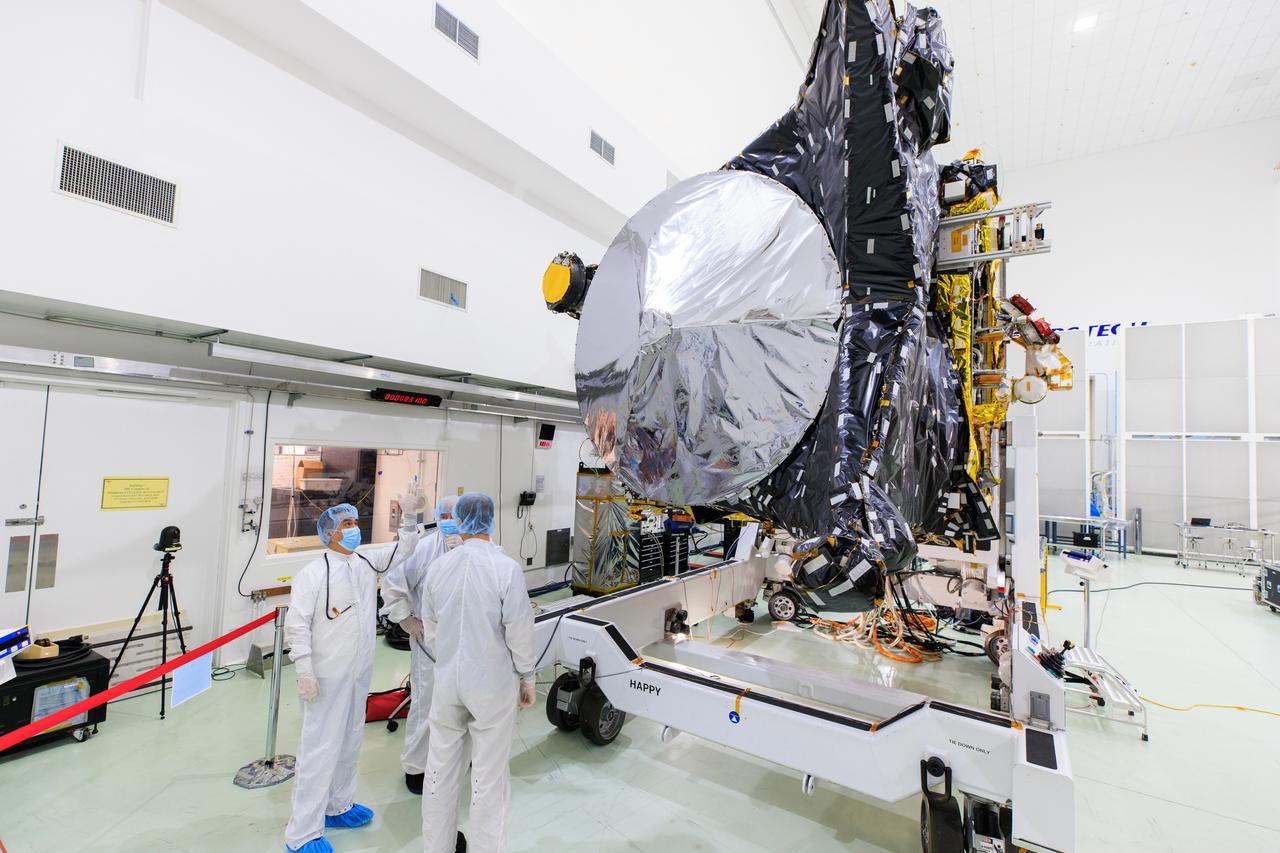

NASA's Psyche spacecraft is shown in a clean room on June 26, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Engineers and technicians from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California have begun final assembly, test, and launch operations on Psyche, with assembly of the spacecraft all but complete except for the installation of the solar arrays and the imagers. NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) technology demonstration, testing high-data-rate laser communications, remains integrated into the spacecraft. A final suite of tests will be run on the vehicle, after which it will be fueled and then mated onto a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket just prior to launch, targeted for October 2023.
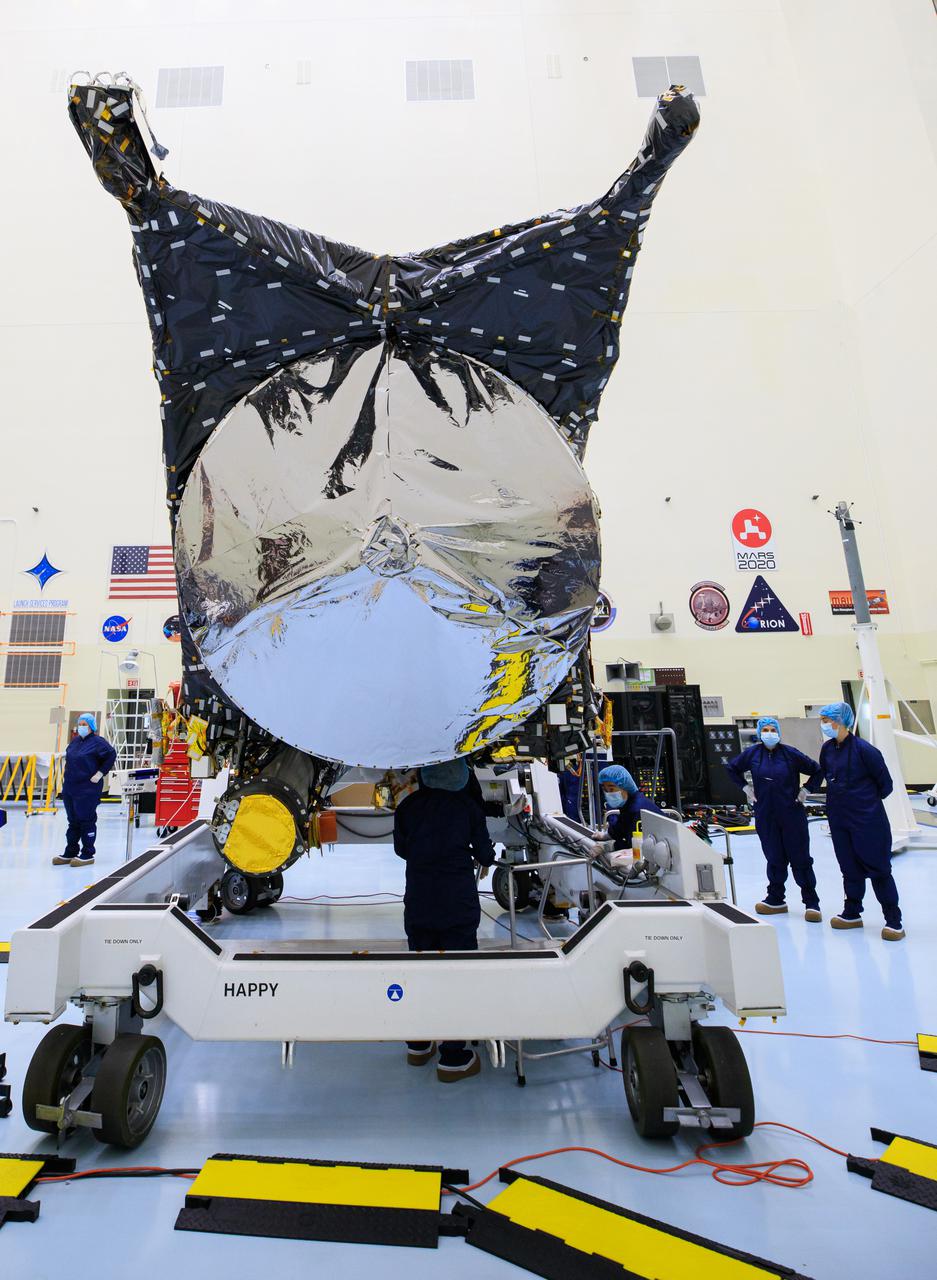

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida perform work on the agency’s Psyche spacecraft inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) on May 3, 2022. While inside the PHSF, the spacecraft will undergo routine processing and servicing ahead of launch. Psyche is targeting to lift off aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
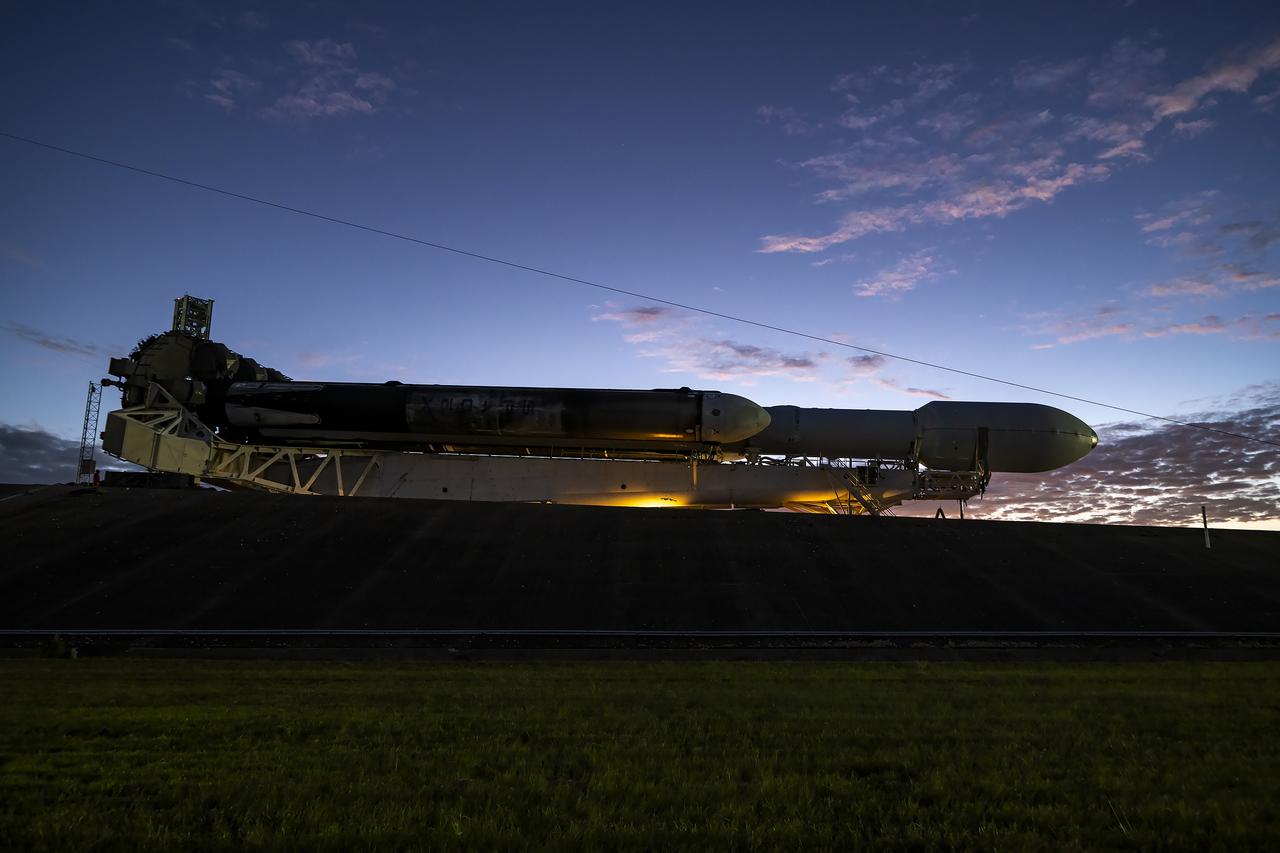

NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft attached to SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket, rolls to Launch Pad 39A on Saturday, Oct. 12, 2024, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of launch to Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. The spacecraft will complete nearly 50 flybys of Europa to determine if there are conditions suitable for life beyond Earth. NASA and SpaceX are targeting launch for Europa Clipper at 12:06 p.m. EDT on Monday, Oct. 14, from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
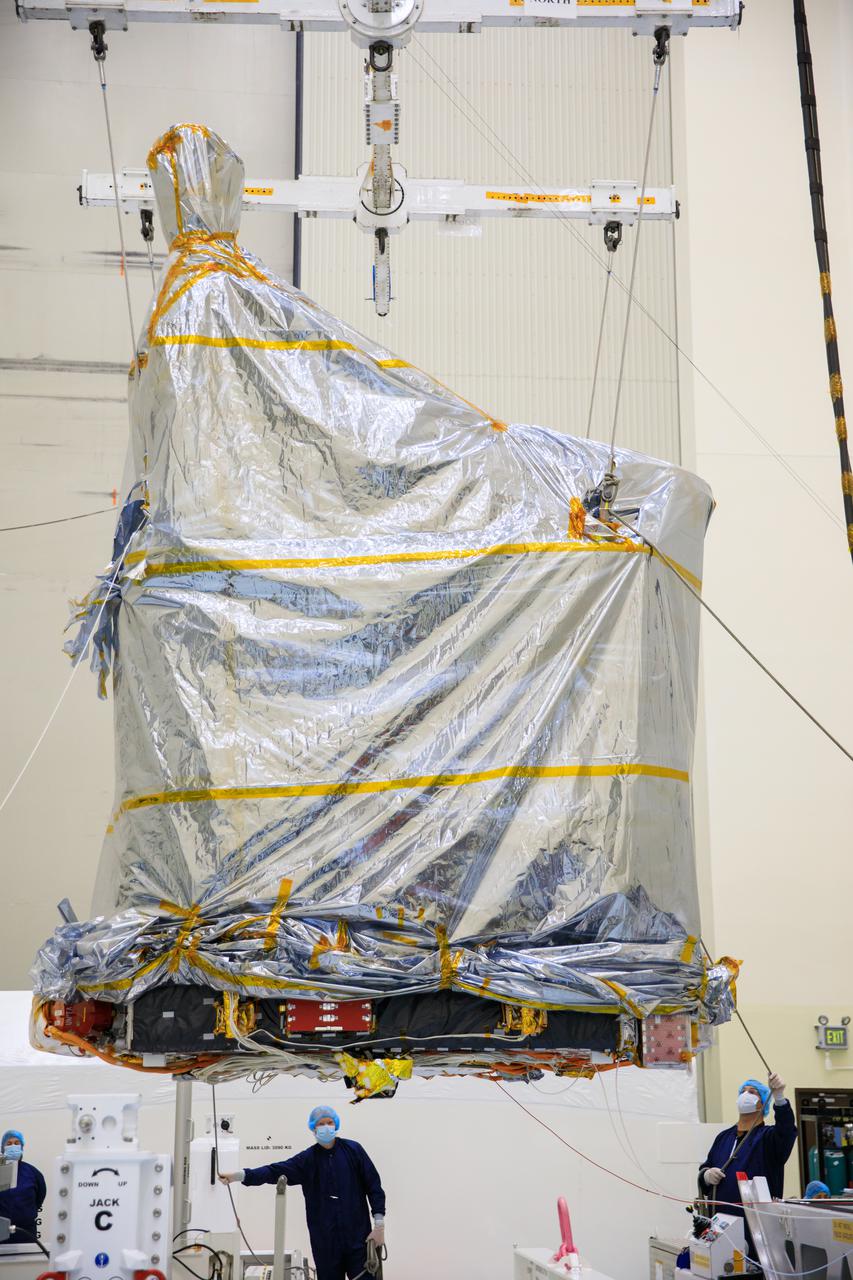

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the agency’s Psyche spacecraft – recently removed from its shipping container and inside a protective covering – is moved by crane to a work stand on Monday, May 2, 2022. Psyche is scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 12:06 p.m. EDT on Monday, Oct. 14, 2024. After launch, the spacecraft plans to fly by Mars in February 2025, then back by Earth in December 2026, using the gravity of each planet to increase its momentum. With help of these “gravity assists,” Europa Clipper will achieve the velocity needed to reach Jupiter in April 2030.
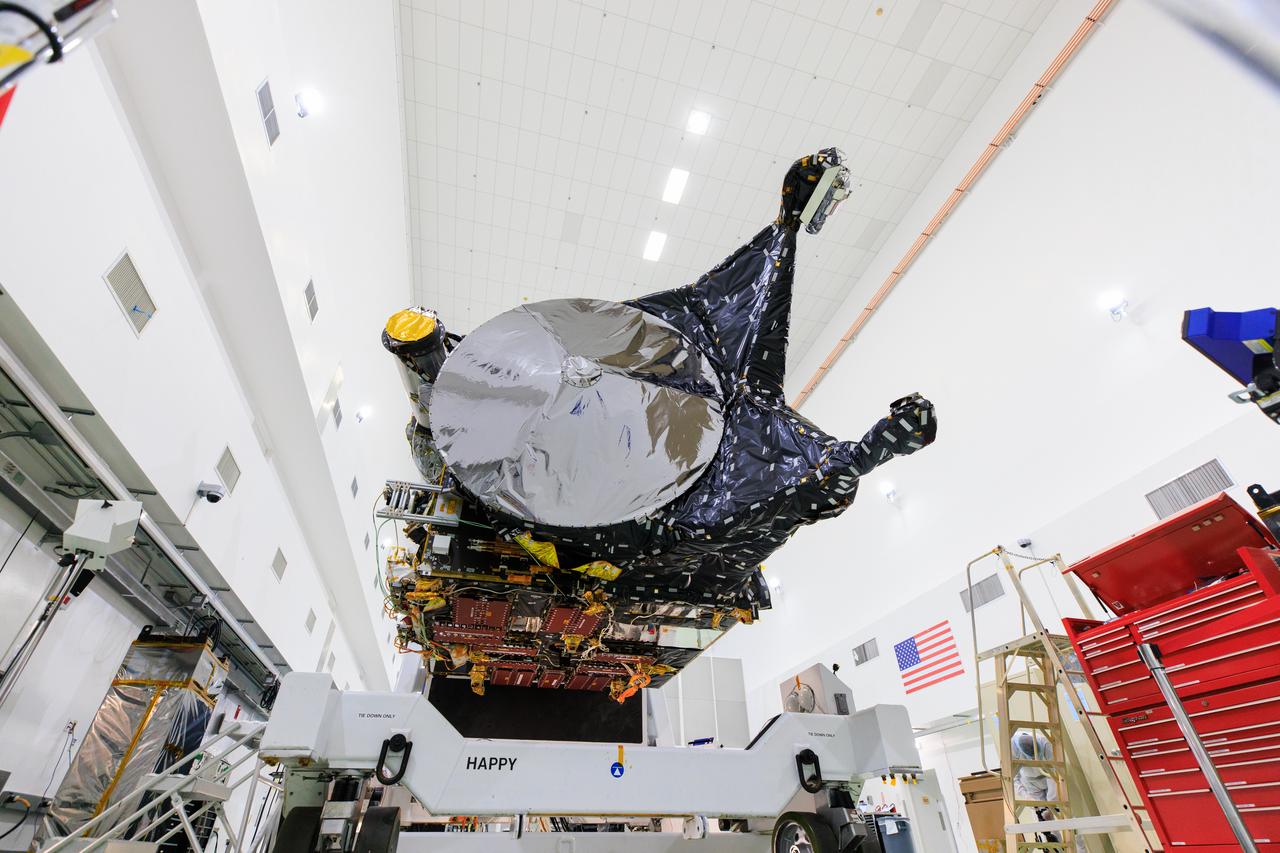

NASA's Psyche spacecraft is shown in a clean room on June 26, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Engineers and technicians from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California have begun final assembly, test, and launch operations on Psyche, with assembly of the spacecraft all but complete except for the installation of the solar arrays and the imagers. NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) technology demonstration, testing high-data-rate laser communications, remains integrated into the spacecraft. A final suite of tests will be run on the vehicle, after which it will be fueled and then mated onto a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket just prior to launch, targeted for October 2023.

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 12:06 p.m. EDT on Monday, Oct. 14, 2024. After launch, the spacecraft plans to fly by Mars in February 2025, then back by Earth in December 2026, using the gravity of each planet to increase its momentum. With help of these “gravity assists,” Europa Clipper will achieve the velocity needed to reach Jupiter in April 2030.
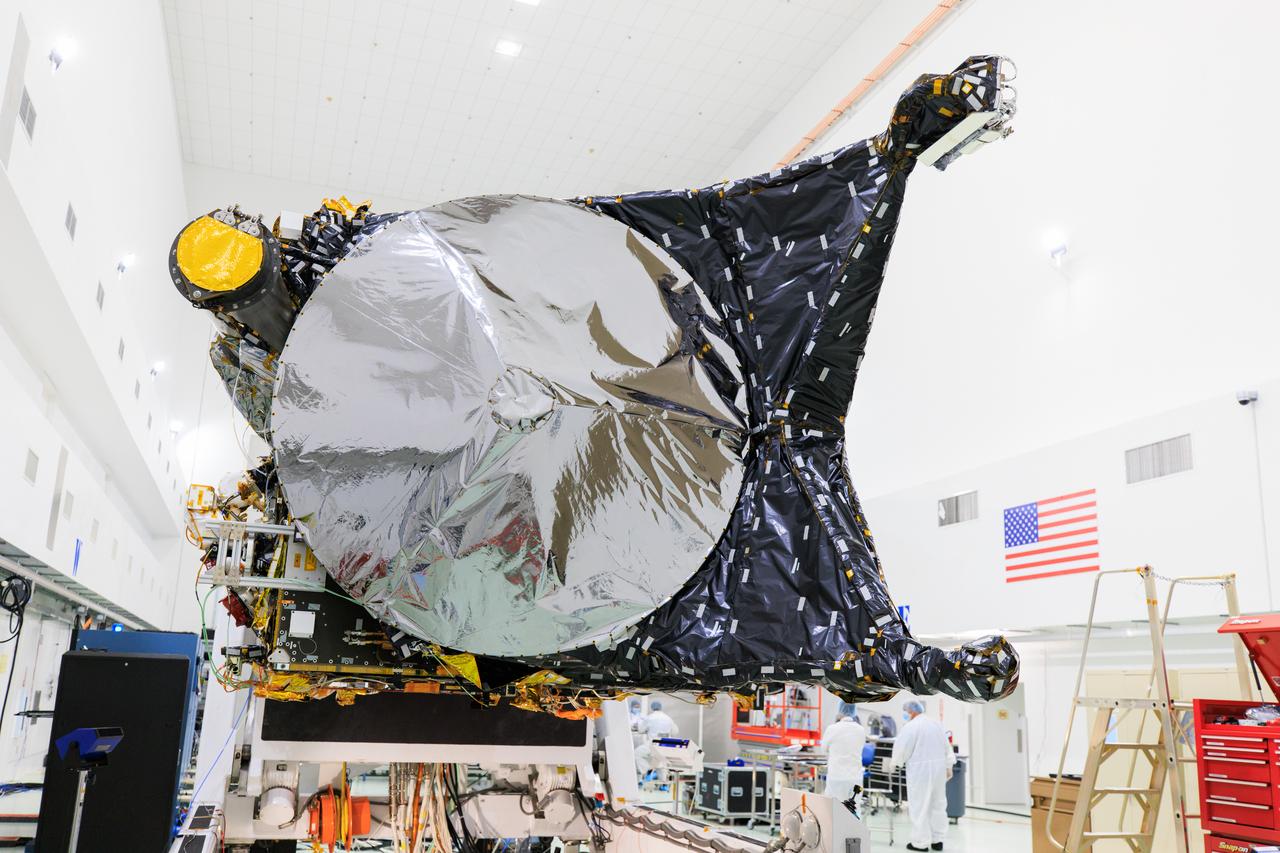

NASA's Psyche spacecraft is shown in a clean room on June 26, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Engineers and technicians from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California have begun final assembly, test, and launch operations on Psyche, with assembly of the spacecraft all but complete except for the installation of the solar arrays and the imagers. NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) technology demonstration, testing high-data-rate laser communications, remains integrated into the spacecraft. A final suite of tests will be run on the vehicle, after which it will be fueled and then mated onto a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket just prior to launch, targeted for October 2023.
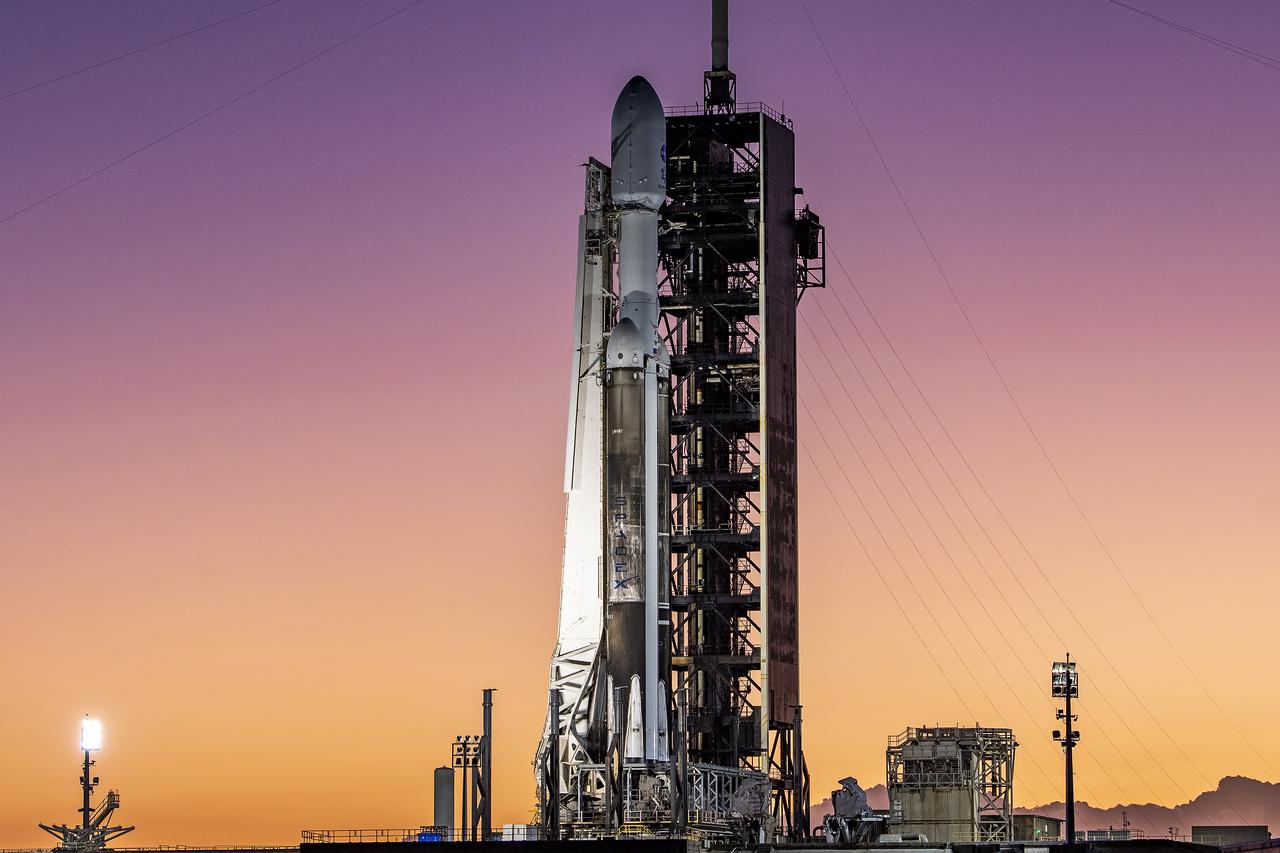

Europa Clipper spacecraft sits atop SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket at Launch Complex 39A on Sunday, Oct. 13, 2024, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of launch to Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. The spacecraft will complete nearly 50 flybys of Europa to determine if there are conditions suitable for life beyond Earth.
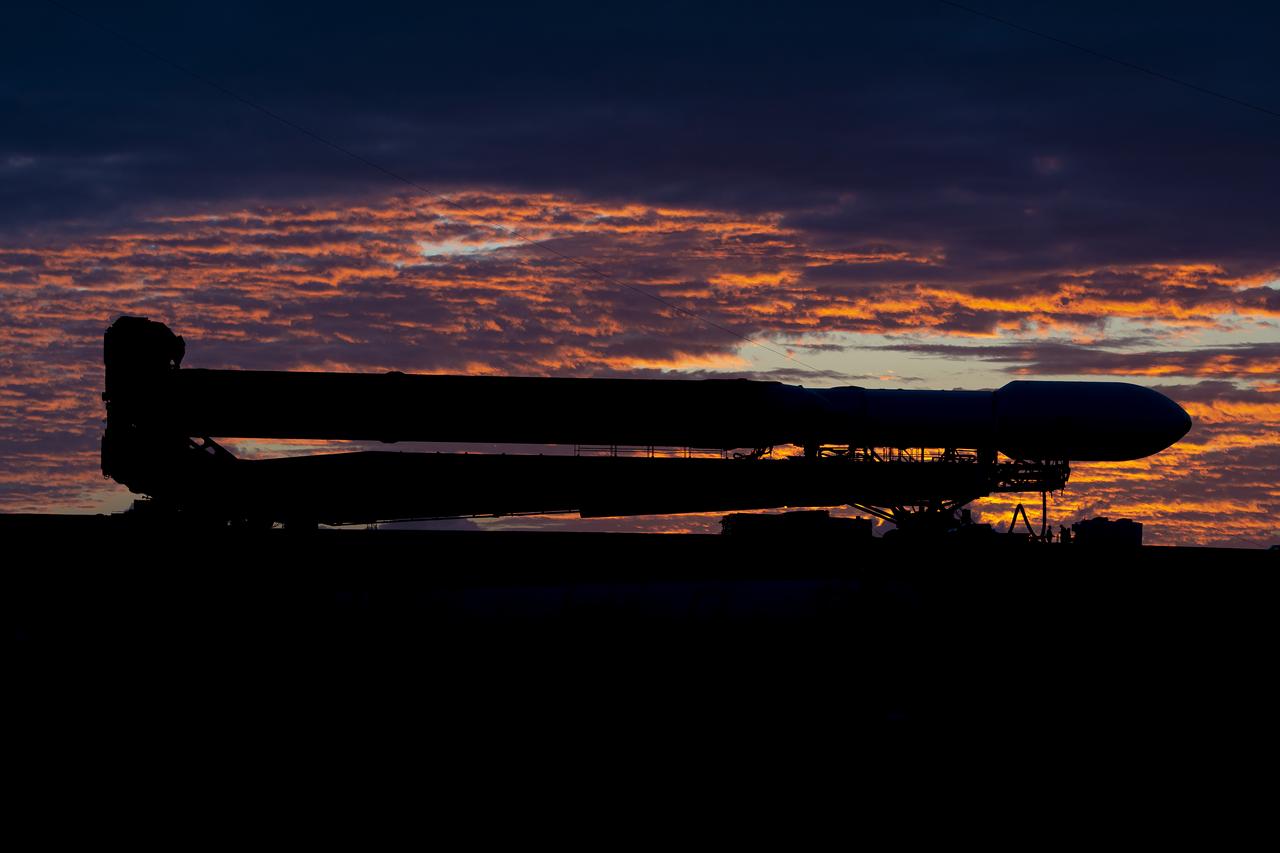

NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft attached to SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket, rolls to Launch Pad 39A on Saturday, Oct. 12, 2024, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of launch to Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. The spacecraft will complete nearly 50 flybys of Europa to determine if there are conditions suitable for life beyond Earth. NASA and SpaceX are targeting launch for Europa Clipper at 12:06 p.m. EDT on Monday, Oct. 14, from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
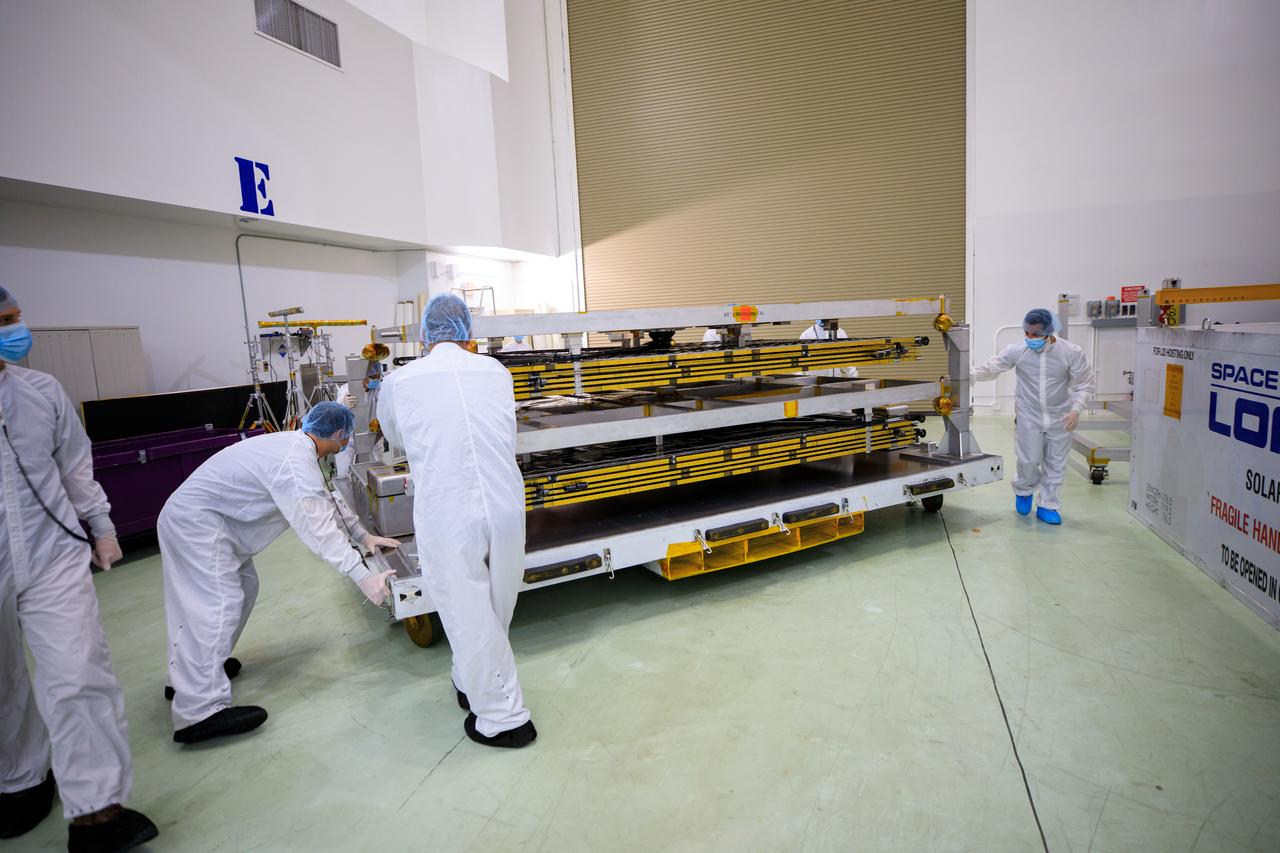

A NASA team uncrates the twin solar arrays for NASA’s Psyche spacecraft at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 18, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.
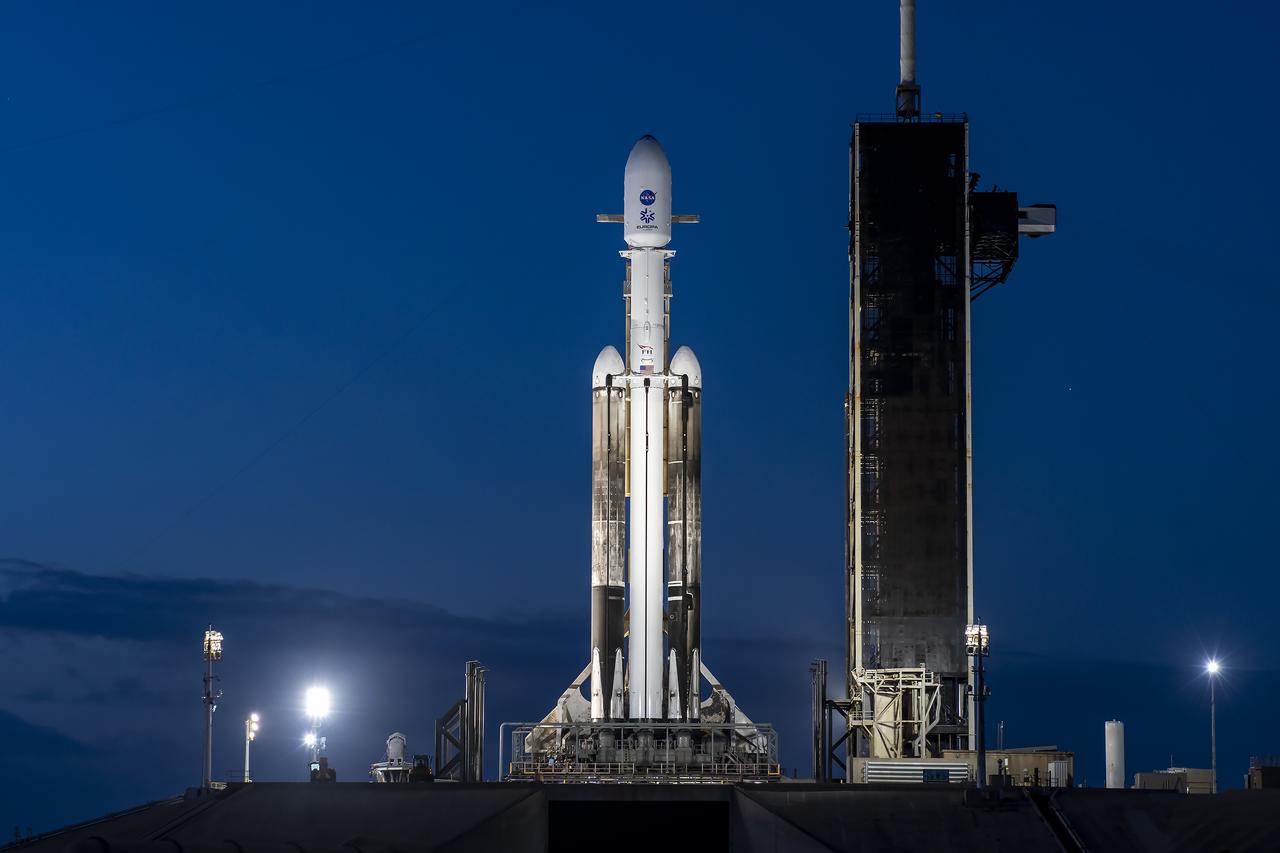

NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft and SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket are vertical at Launch Pad 39A on Sunday, Oct. 13, 2024, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of launch to Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. The spacecraft will complete nearly 50 flybys of Europa to determine if there are conditions suitable for life beyond Earth. Launch is targeting 12:06 p.m. EDT on Monday, Oct. 14, from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

A NASA team lifts the cover off the twin solar arrays for NASA’s Psyche spacecraft at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 18, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San Jose, in California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.
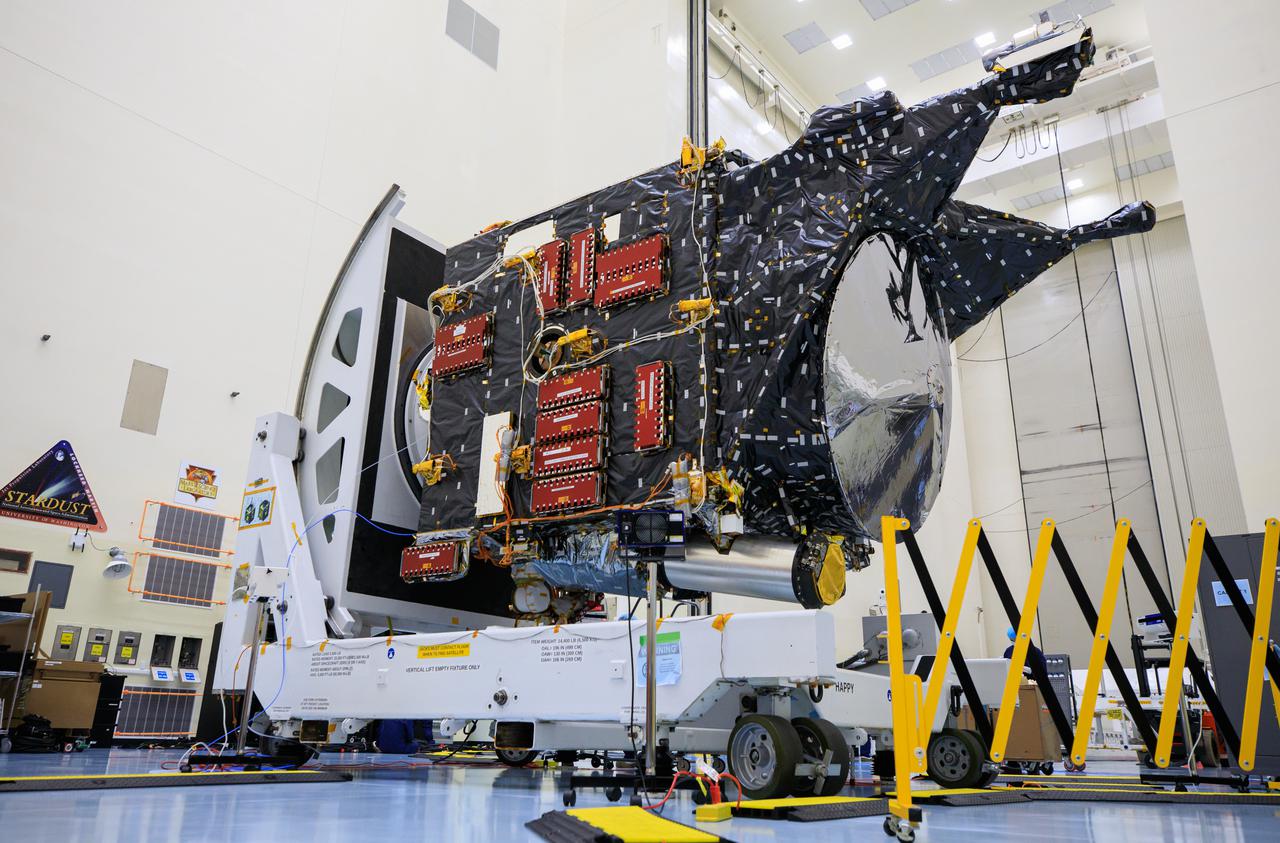

NASA’s Psyche spacecraft undergoes processing and servicing ahead of launch atop a work stand inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 3, 2022. Psyche is targeting to lift off aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
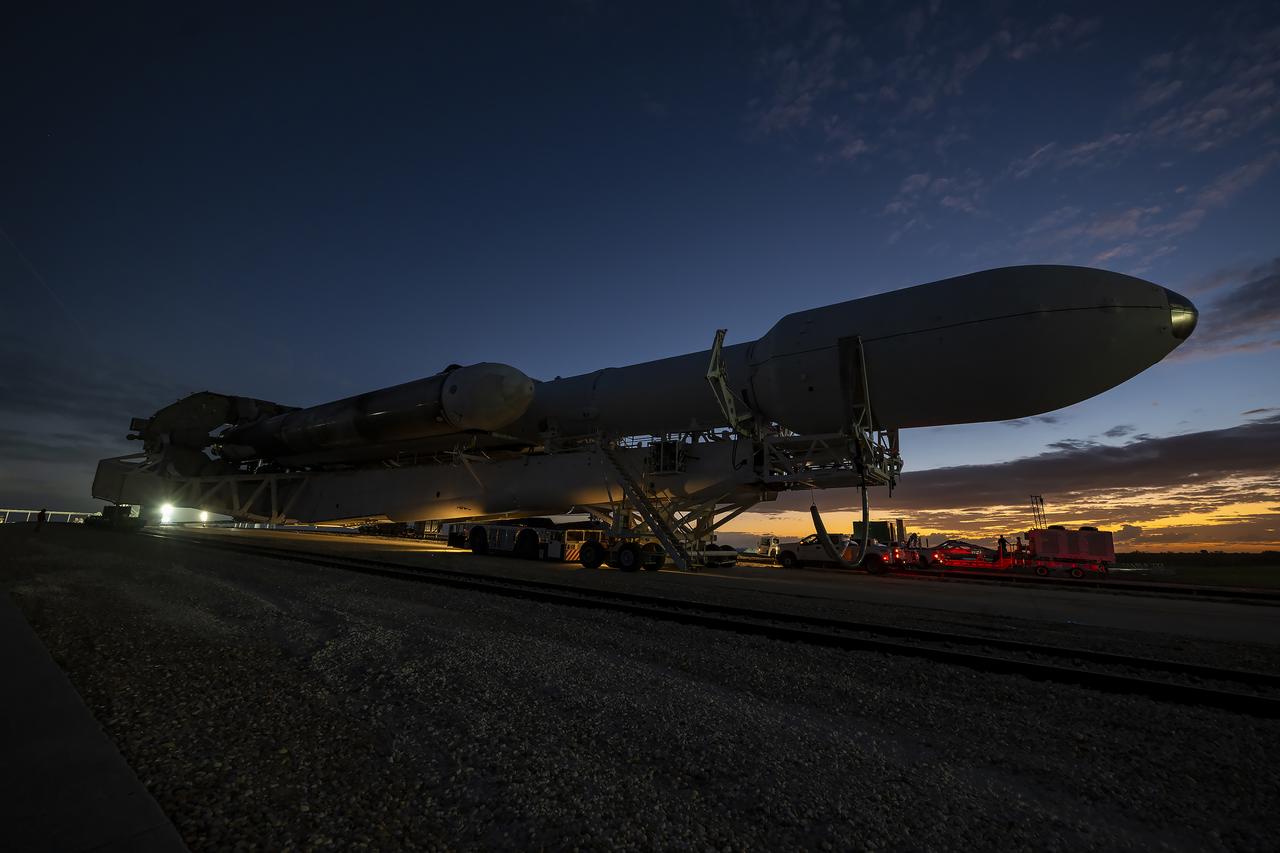

NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft attached to SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket, rolls to Launch Pad 39A on Saturday, Oct. 12, 2024, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of launch to Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. The spacecraft will complete nearly 50 flybys of Europa to determine if there are conditions suitable for life beyond Earth. NASA and SpaceX are targeting launch for Europa Clipper at 12:06 p.m. EDT on Monday, Oct. 14, from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
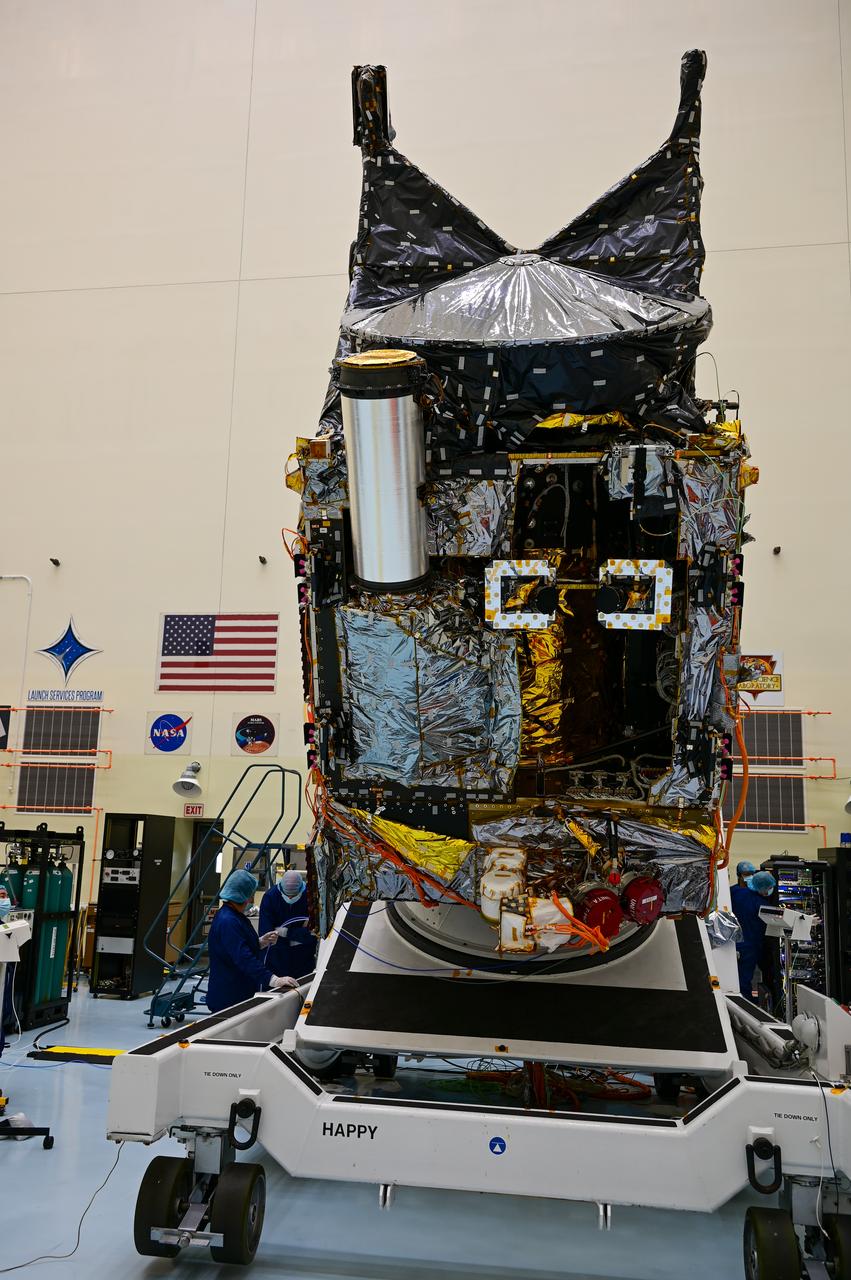

A team working on NASA’s Psyche spacecraft transitioning it from a vertical to horizontal test configuration during prelaunch processing inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 9, 2022. The mission is targeting an Aug. 1 launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 12:06 p.m. EDT on Monday, Oct. 14, 2024. After launch, the spacecraft plans to fly by Mars in February 2025, then back by Earth in December 2026, using the gravity of each planet to increase its momentum. With help of these “gravity assists,” Europa Clipper will achieve the velocity needed to reach Jupiter in April 2030.

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 12:06 p.m. EDT on Monday, Oct. 14, 2024. After launch, the spacecraft plans to fly by Mars in February 2025, then back by Earth in December 2026, using the gravity of each planet to increase its momentum. With help of these “gravity assists,” Europa Clipper will achieve the velocity needed to reach Jupiter in April 2030.
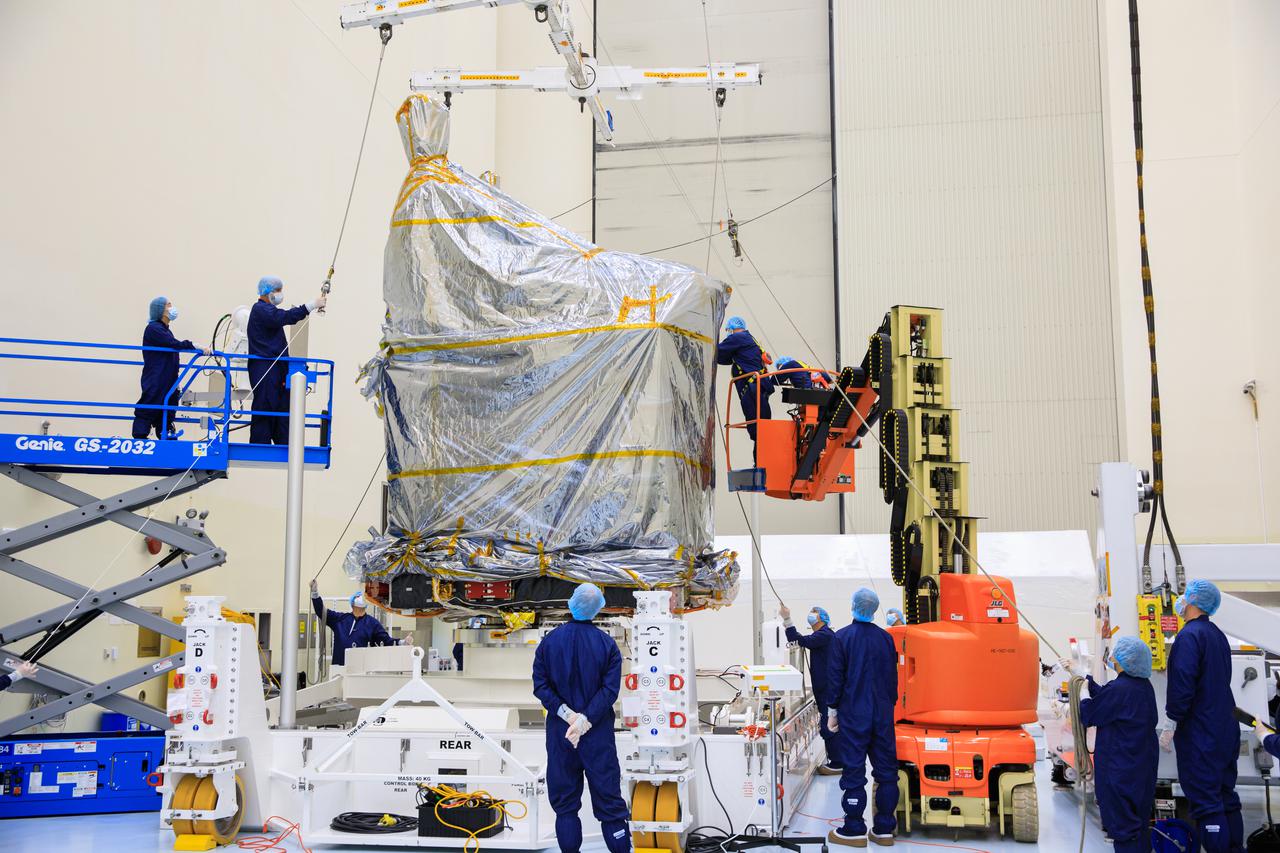

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the agency’s Psyche spacecraft – recently removed from its shipping container and inside a protective covering – is moved by crane to a work stand on Monday, May 2, 2022. Psyche is scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
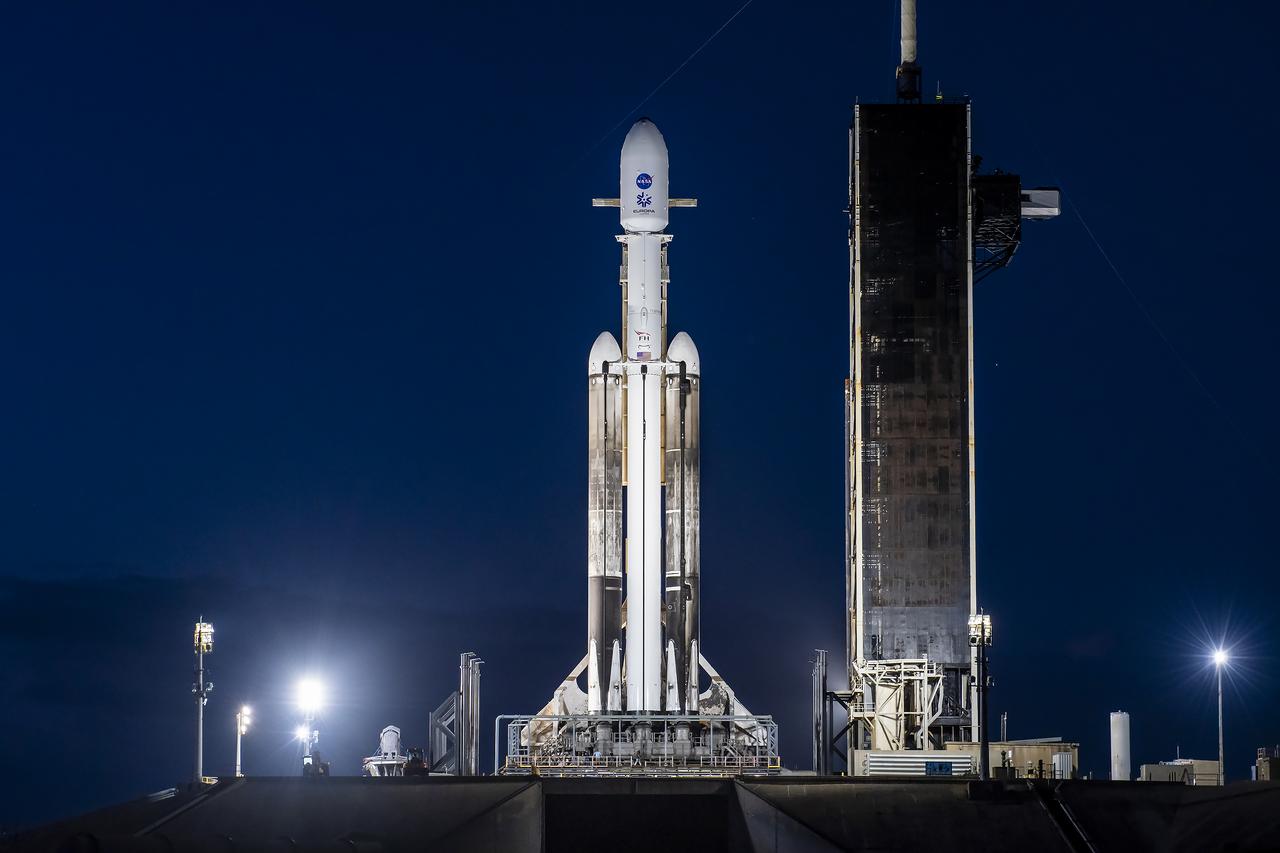

NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft and SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket stands at Launch Pad 39A on Sunday, Oct. 13, 2024, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of launch to Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. The spacecraft will complete nearly 50 flybys of Europa to determine if there are conditions suitable for life beyond Earth. NASA and SpaceX are targeting launch for Europa Clipper at 12:06 p.m. EDT on Monday, Oct. 14, from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
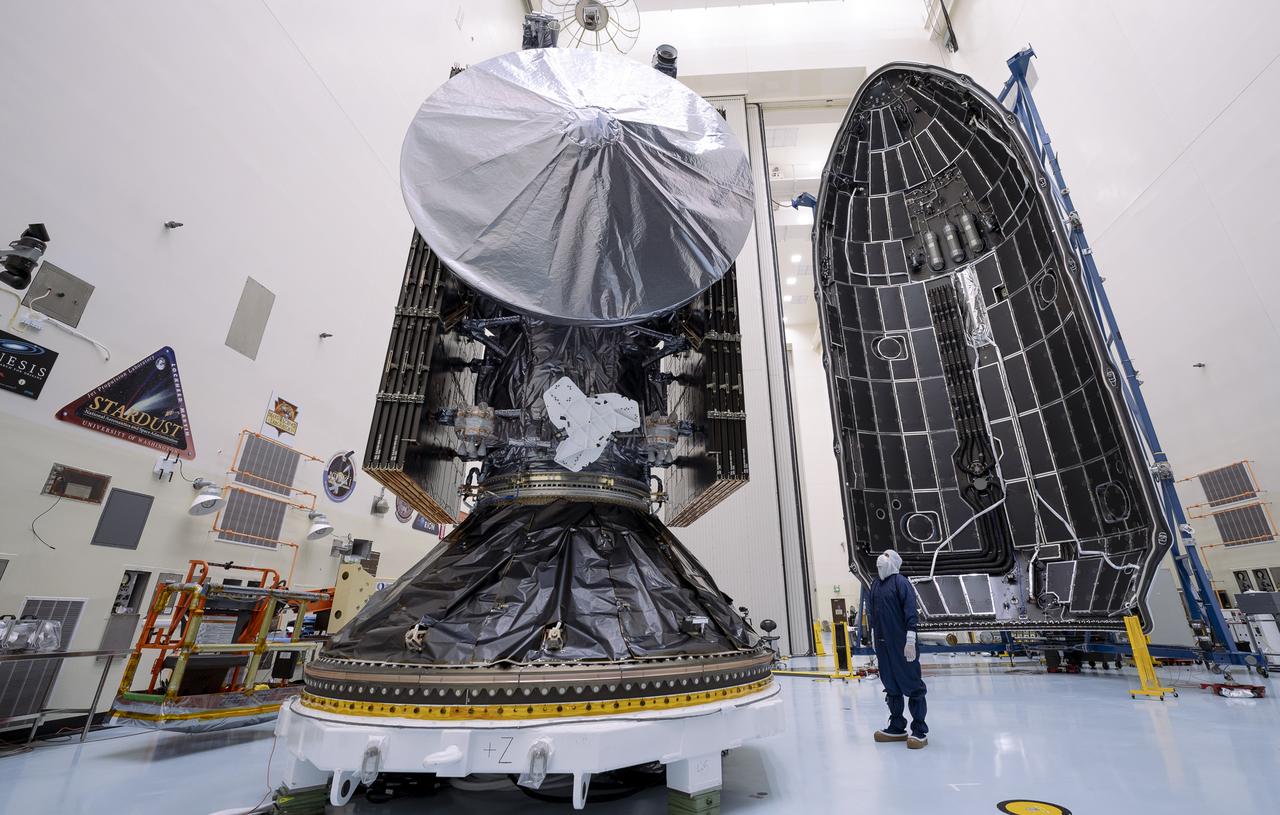

Technicians prepare to encapsulate NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft inside SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy payload fairing in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Oct. 2, 2024. The payload fairing will protect the spacecraft during liftoff from Launch Complex 39A on its journey to explore Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa. The spacecraft will complete nearly 50 flybys of Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, to determine if there are conditions suitable for life beyond Earth.
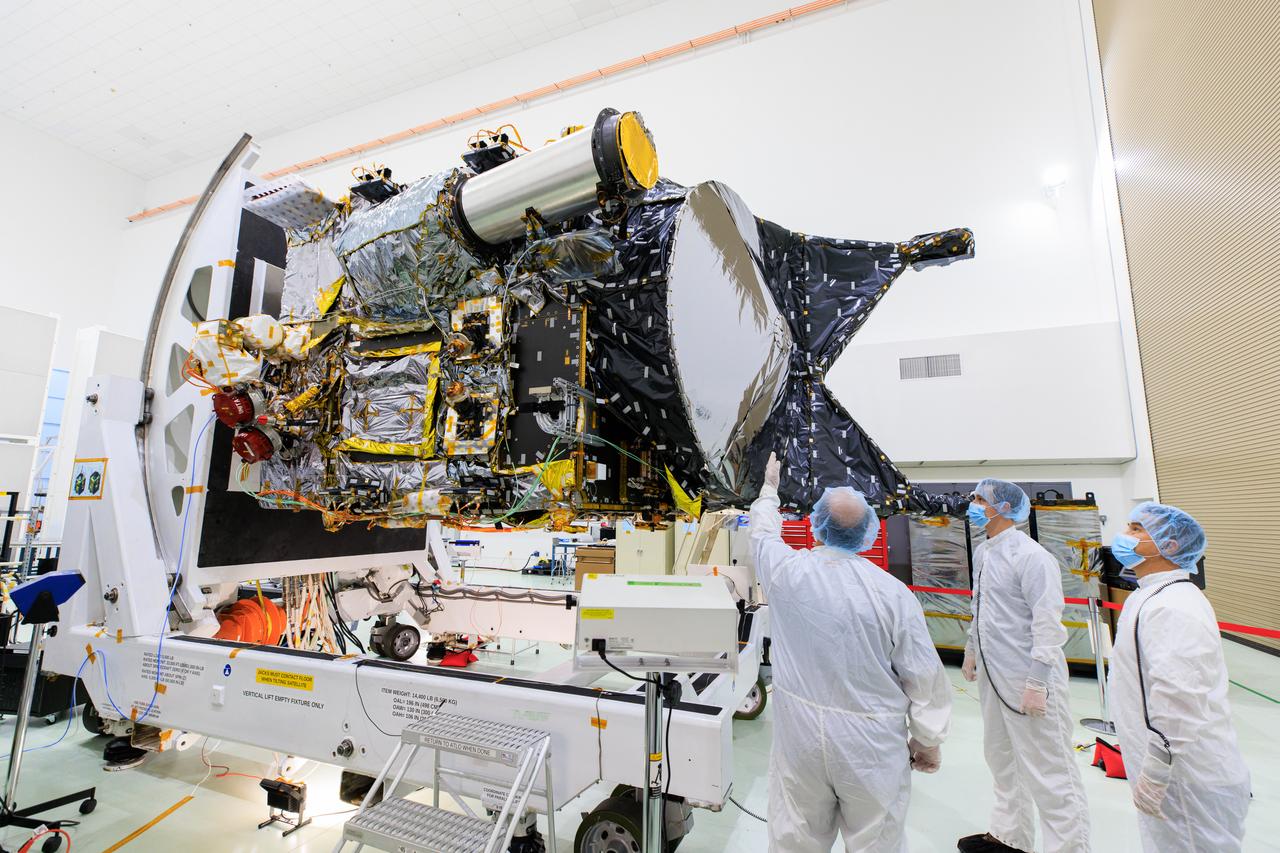

NASA's Psyche spacecraft is shown in a clean room on June 26, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Engineers and technicians from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California have begun final assembly, test, and launch operations on Psyche, with assembly of the spacecraft all but complete except for the installation of the solar arrays and the imagers. NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) technology demonstration, testing high-data-rate laser communications, remains integrated into the spacecraft. A final suite of tests will be run on the vehicle, after which it will be fueled and then mated onto a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket just prior to launch, targeted for October 2023.
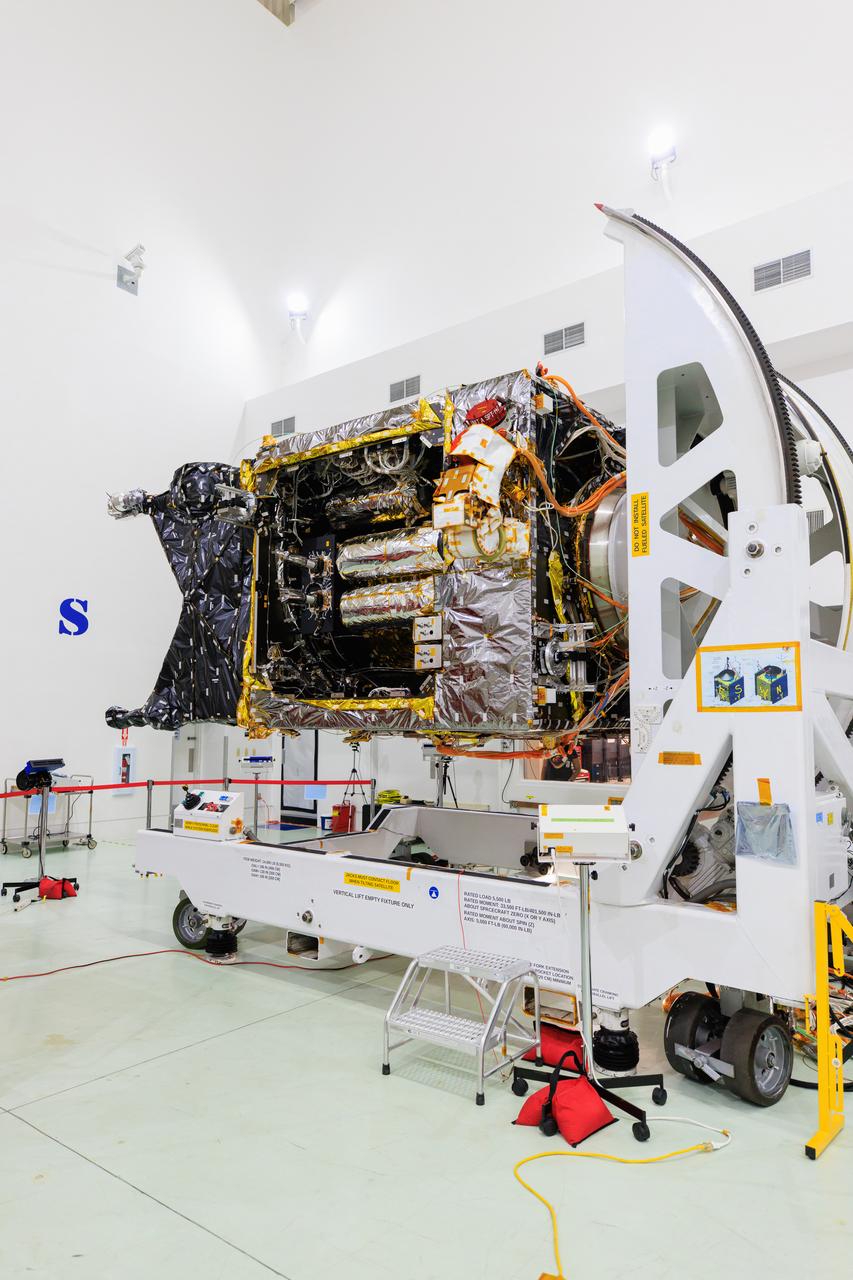

NASA's Psyche spacecraft is shown in a clean room on June 26, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Engineers and technicians from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California have begun final assembly, test, and launch operations on Psyche, with assembly of the spacecraft all but complete except for the installation of the solar arrays and the imagers. NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) technology demonstration, testing high-data-rate laser communications, remains integrated into the spacecraft. A final suite of tests will be run on the vehicle, after which it will be fueled and then mated onto a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket just prior to launch, targeted for October 2023.
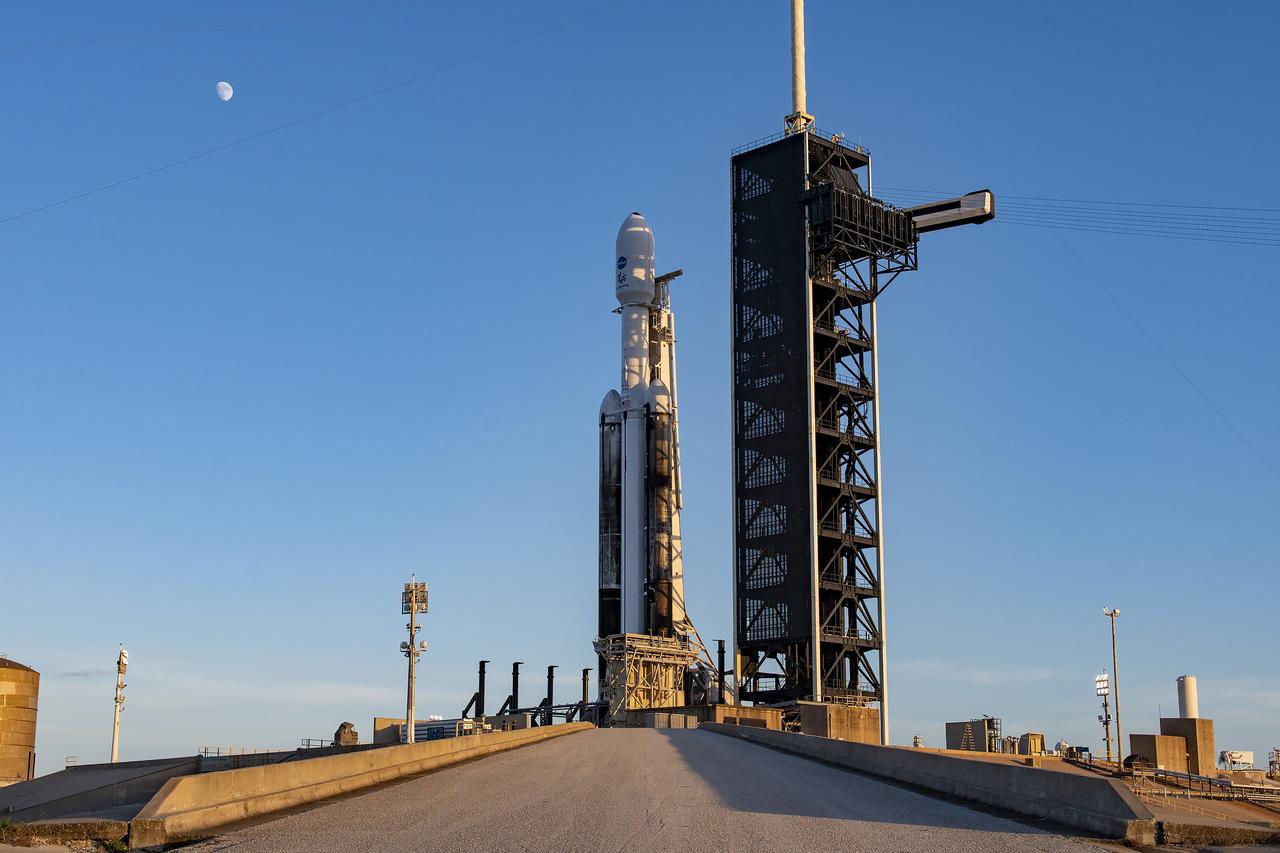

The Earth’s Moon appears with NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft encapsulated in a payload fairing atop SpaceX’s Heavy rocket at Launch Complex 39A on Sunday, Oct. 13, 2024, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will travel to Jupiter’s icy moon Europa to determine if there are conditions suitable for life beyond Earth.

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 12:06 p.m. EDT on Monday, Oct. 14, 2024. After launch, the spacecraft plans to fly by Mars in February 2025, then back by Earth in December 2026, using the gravity of each planet to increase its momentum. With help of these “gravity assists,” Europa Clipper will achieve the velocity needed to reach Jupiter in April 2030.
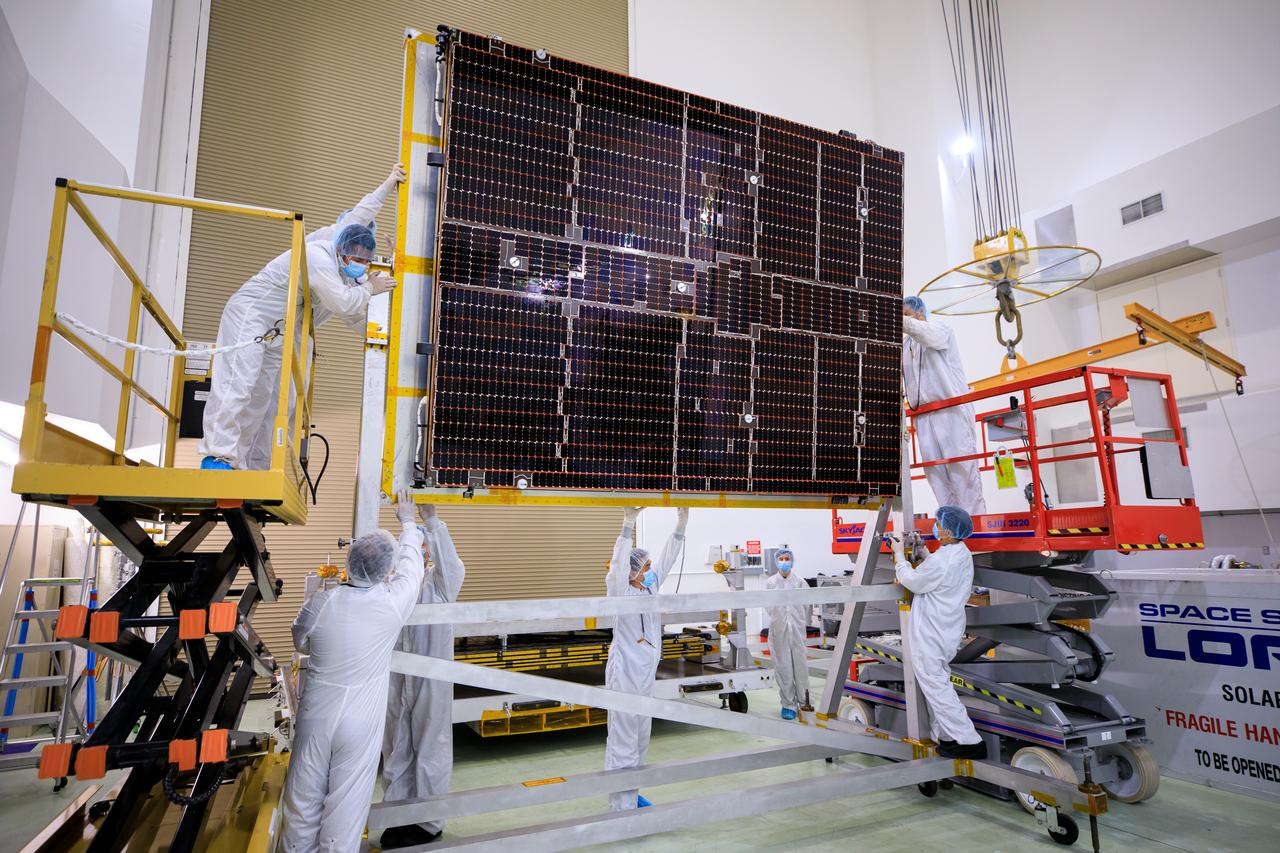

A NASA team helps attach solar arrays for the agency’s Psyche spacecraft onto a stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 18, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San, Jose, California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.