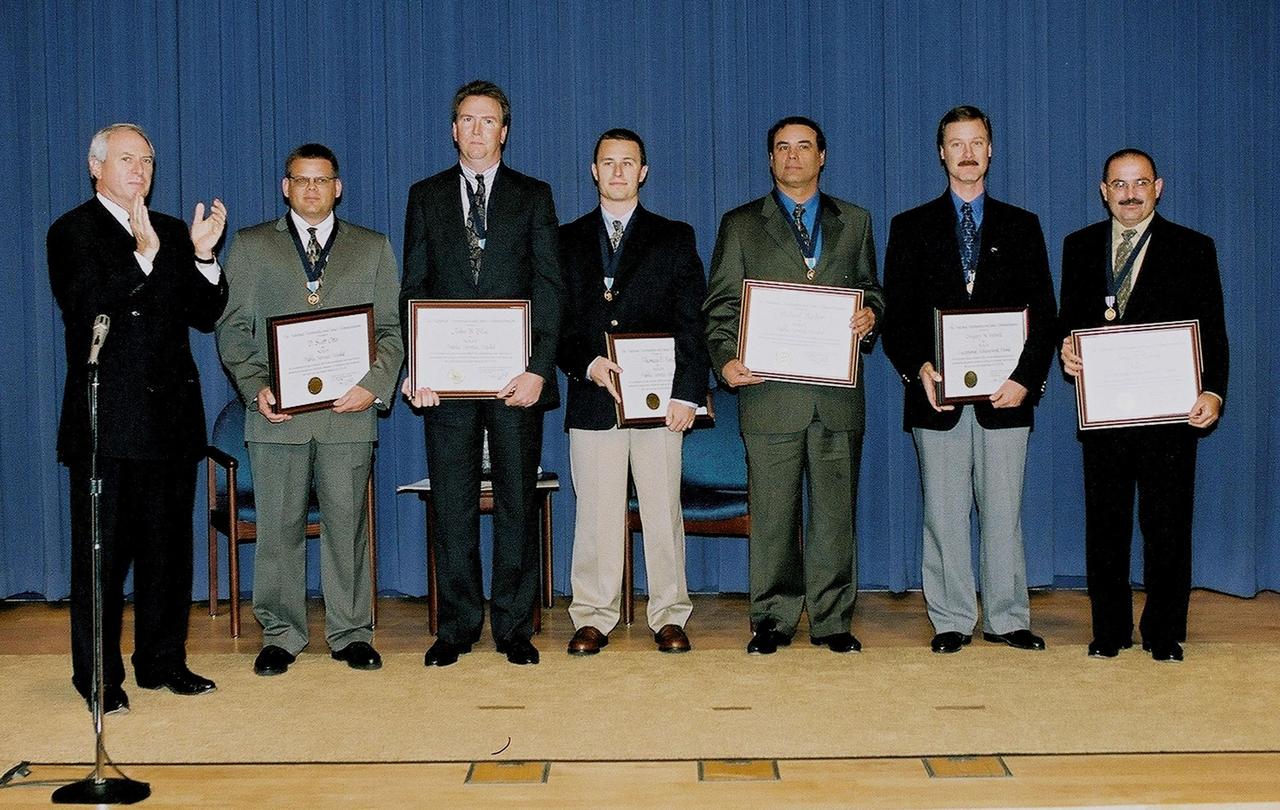

NASA Administrator Daniel Goldin (left) applauds the Space Shuttle ice and debris inspection team who were recognized for their keen safety observations prior to the launch of Space Shuttle Discovery. Standing next to Goldin are (left to right) D. Scott Otto, with Lockheed Martin Space Services Company; John B. Blue, Thomas F. Ford and Michael Barber, with United Space Alliance; Gregory N. Katnik and Jorge E. Rivera, with NASA. Katnick and Rivera received the agency’s Exceptional Achievement Medal; Barber, Blue, Ford and Otto received the NASA Public Service Medal. While scanning the launch pad before launch, the team found a stray 4-inch pin near the Shuttle’s external fuel tank that could have caused damage during launch. Discovery was safely launched the next day, on Oct. 11
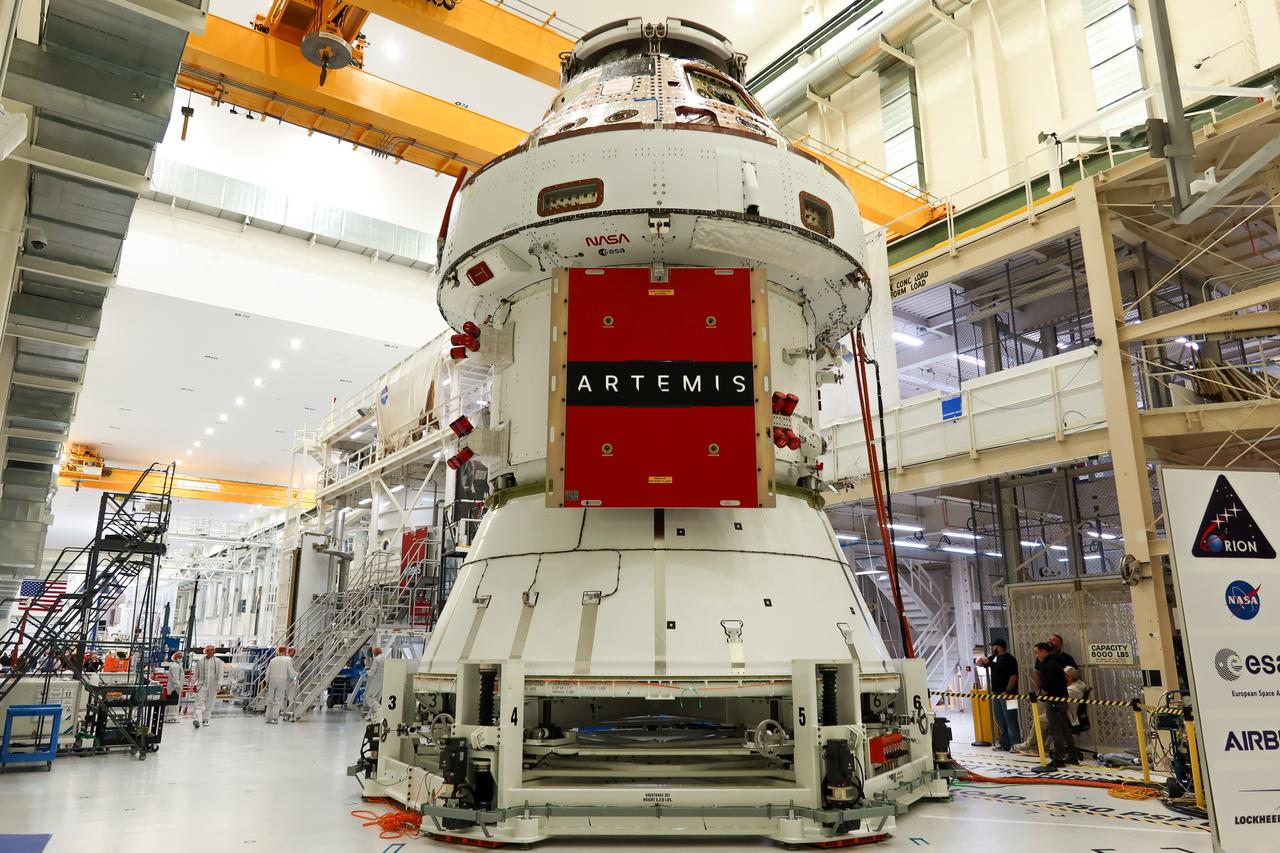

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.

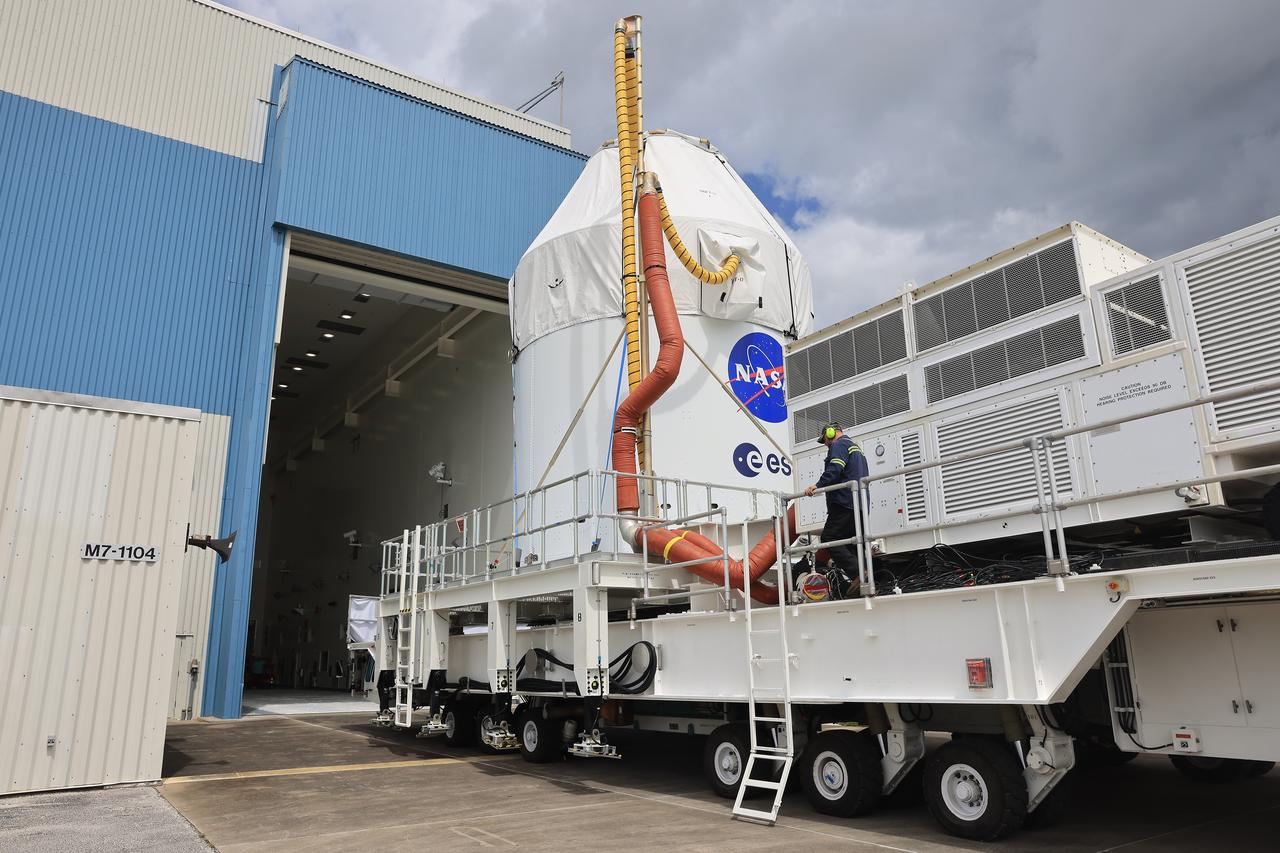
NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft arrives at the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, May 3, 2025, to undergo fueling and processing operations for prelaunch operations. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
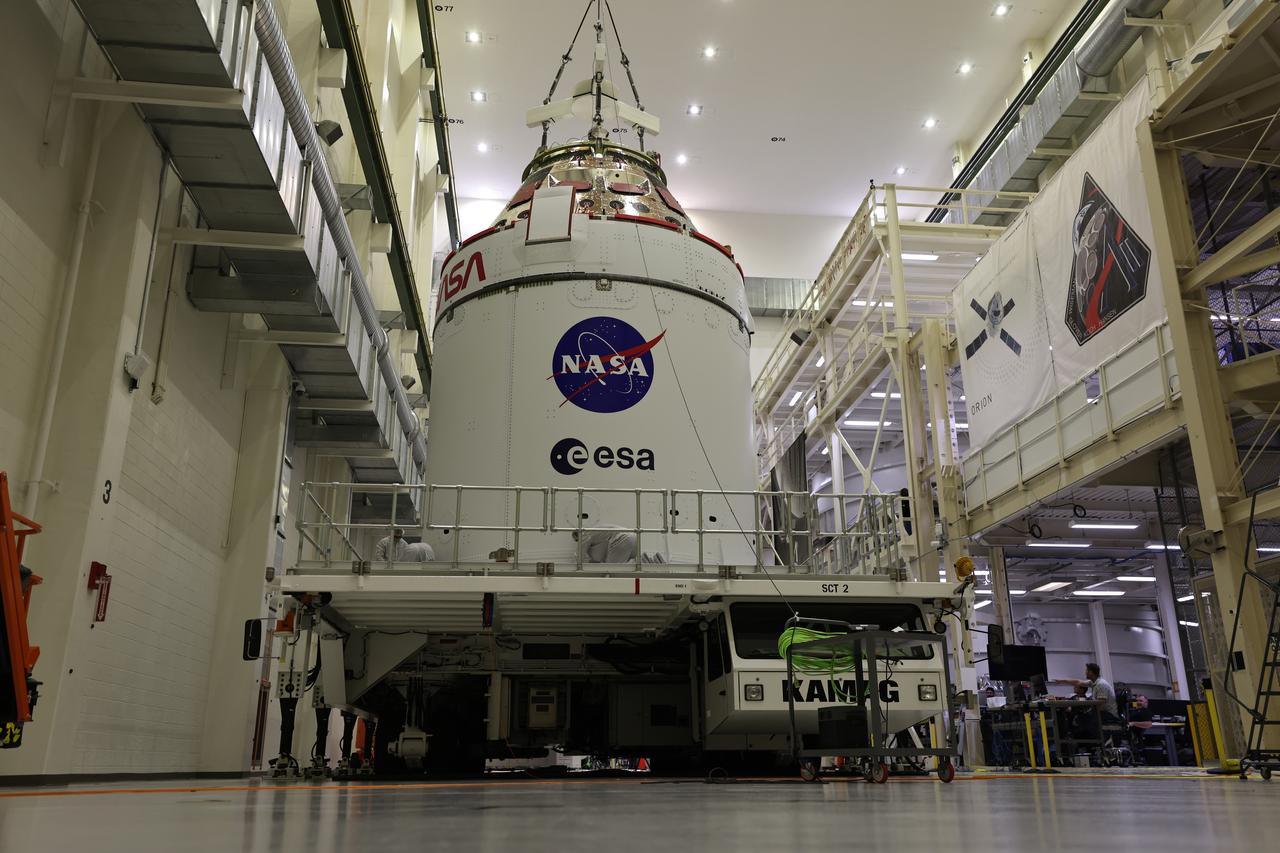

Crews use a massive crane to lift NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft onto the agency’s KAMAG transporter inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, May 1, 2025. The spacecraft will be transported to the Multi-Payload Processing Facility to undergo fueling and processing for prelaunch operations. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.

NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft arrives at the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, May 3, 2025, to undergo fueling and processing operations for prelaunch operations. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
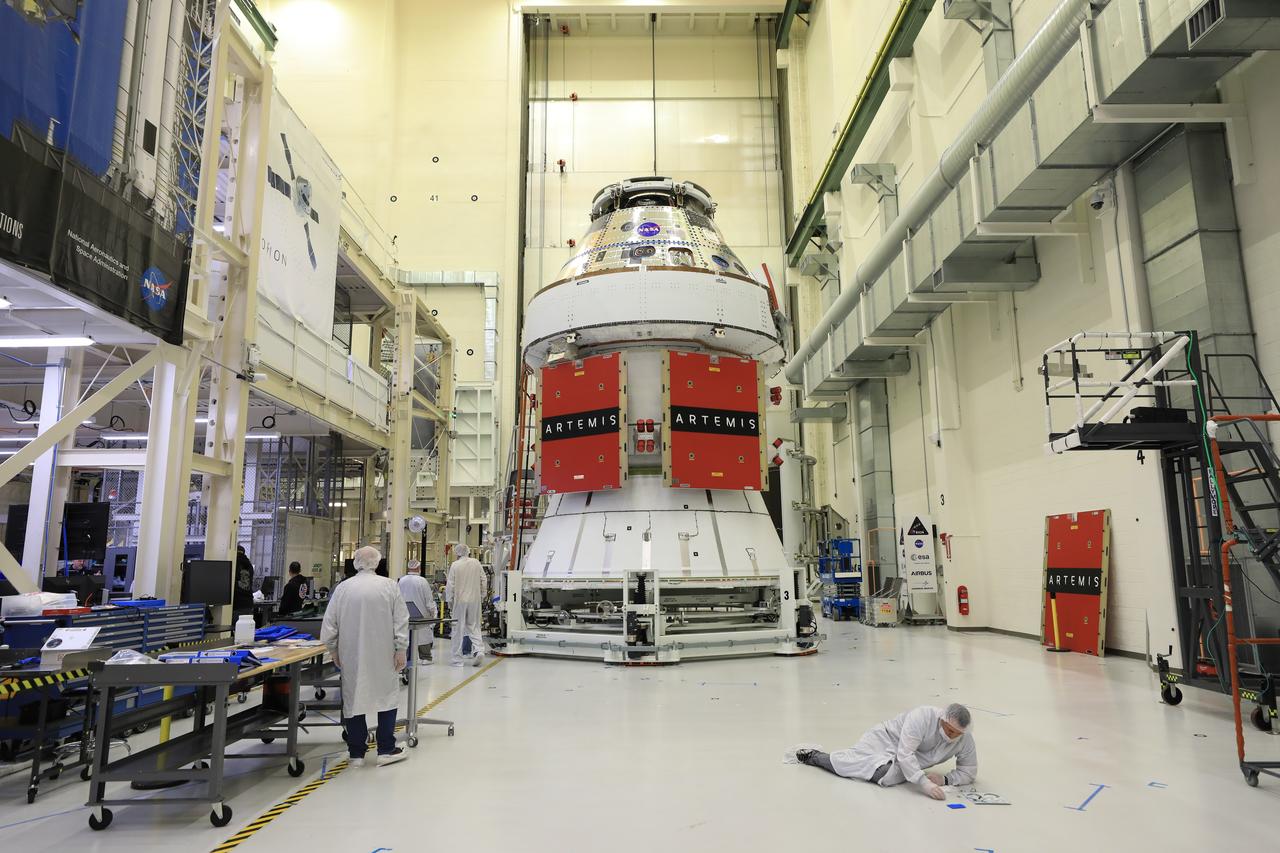

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
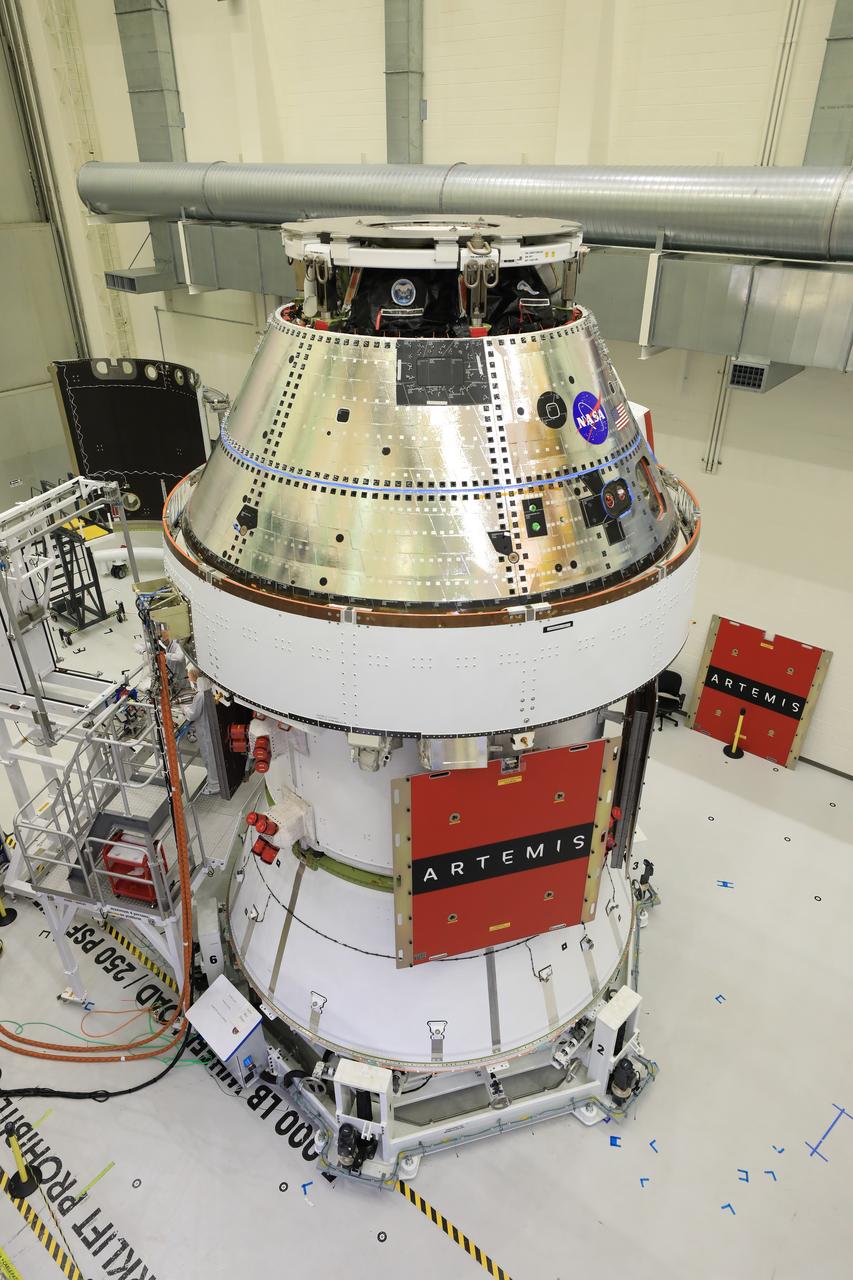

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
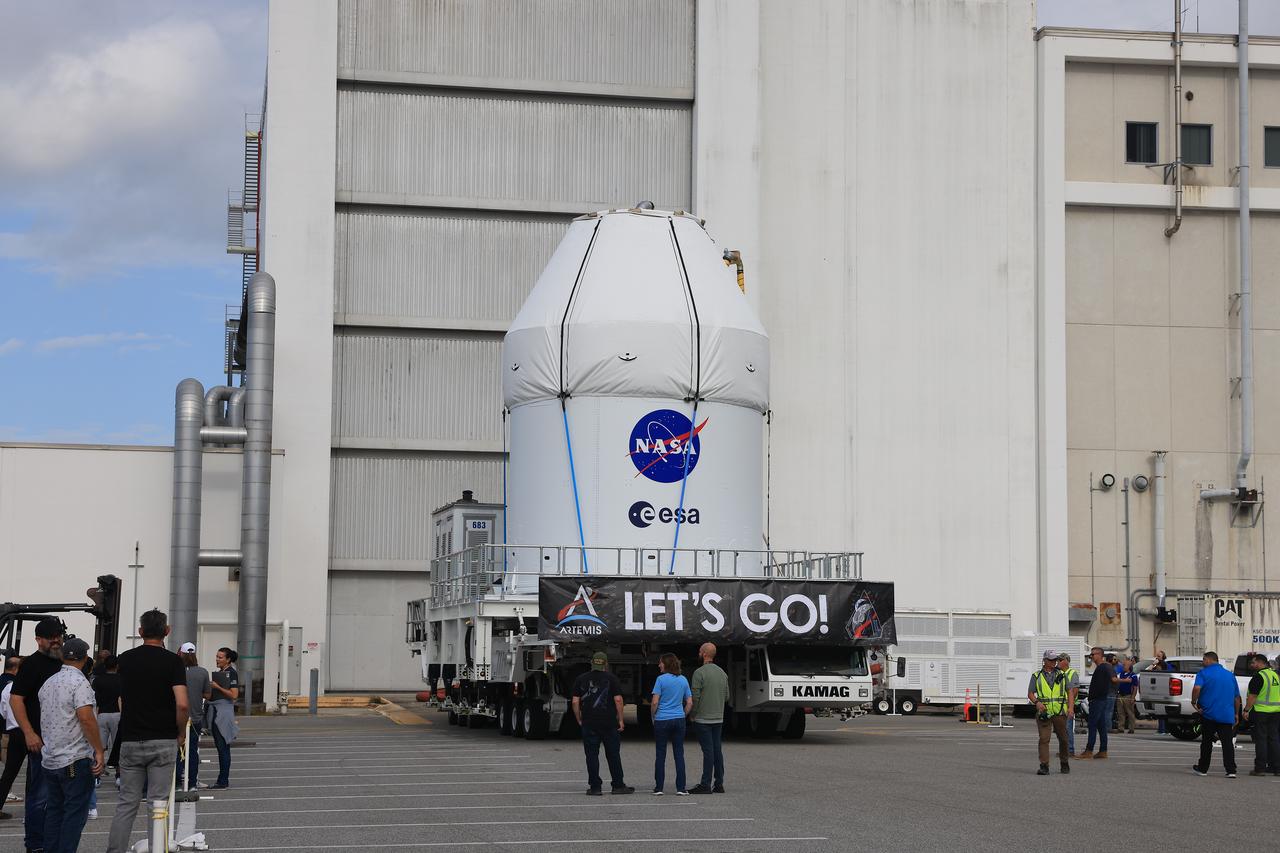

NASA’s KAMAG transporter carries the agency’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft from the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, May 3, 2025. The Orion spacecraft will undergo fueling and processing operations at the Multi-Function Facility. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program offload the agency’s Orion spacecraft from the KAMAG transporter to the servicing stand inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, May 4, 2025, to undergo fueling and processing operations for prelaunch operations. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
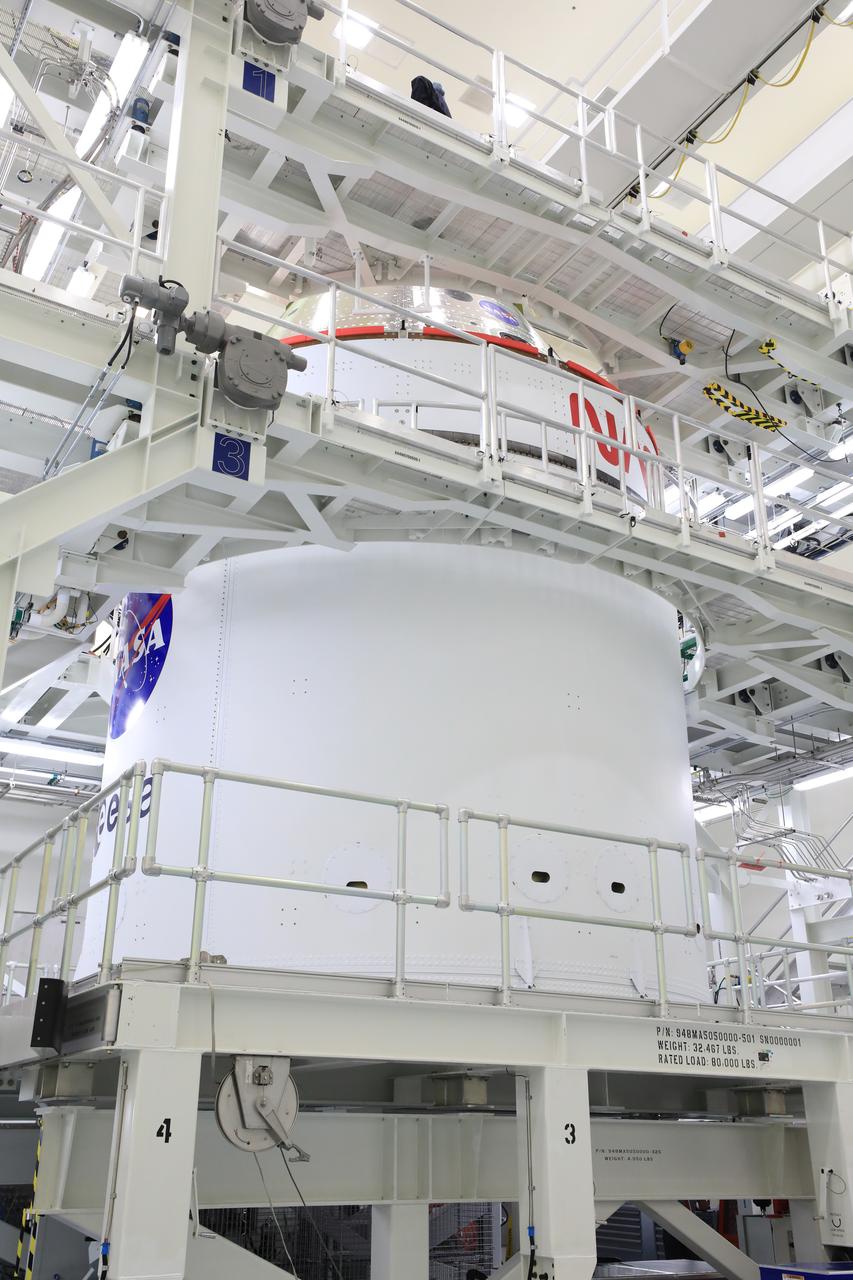

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program offload the agency’s Orion spacecraft from the KAMAG transporter to the servicing stand inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, May 4, 2025, to undergo fueling and processing operations for prelaunch operations. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.

NASA’s KAMAG transporter carries the agency’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft from the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, May 3, 2025. The Orion spacecraft will undergo fueling and processing operations at the Multi-Function Facility. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
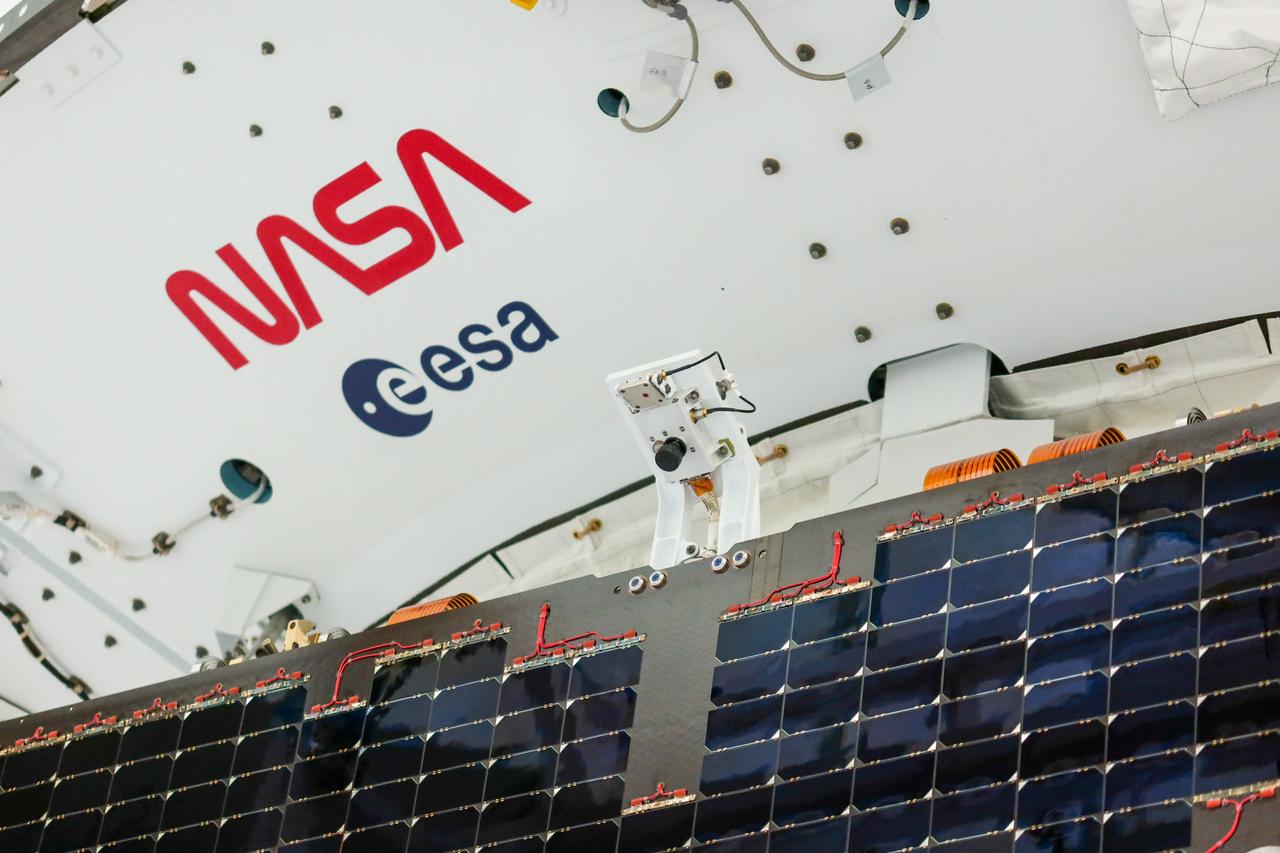

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
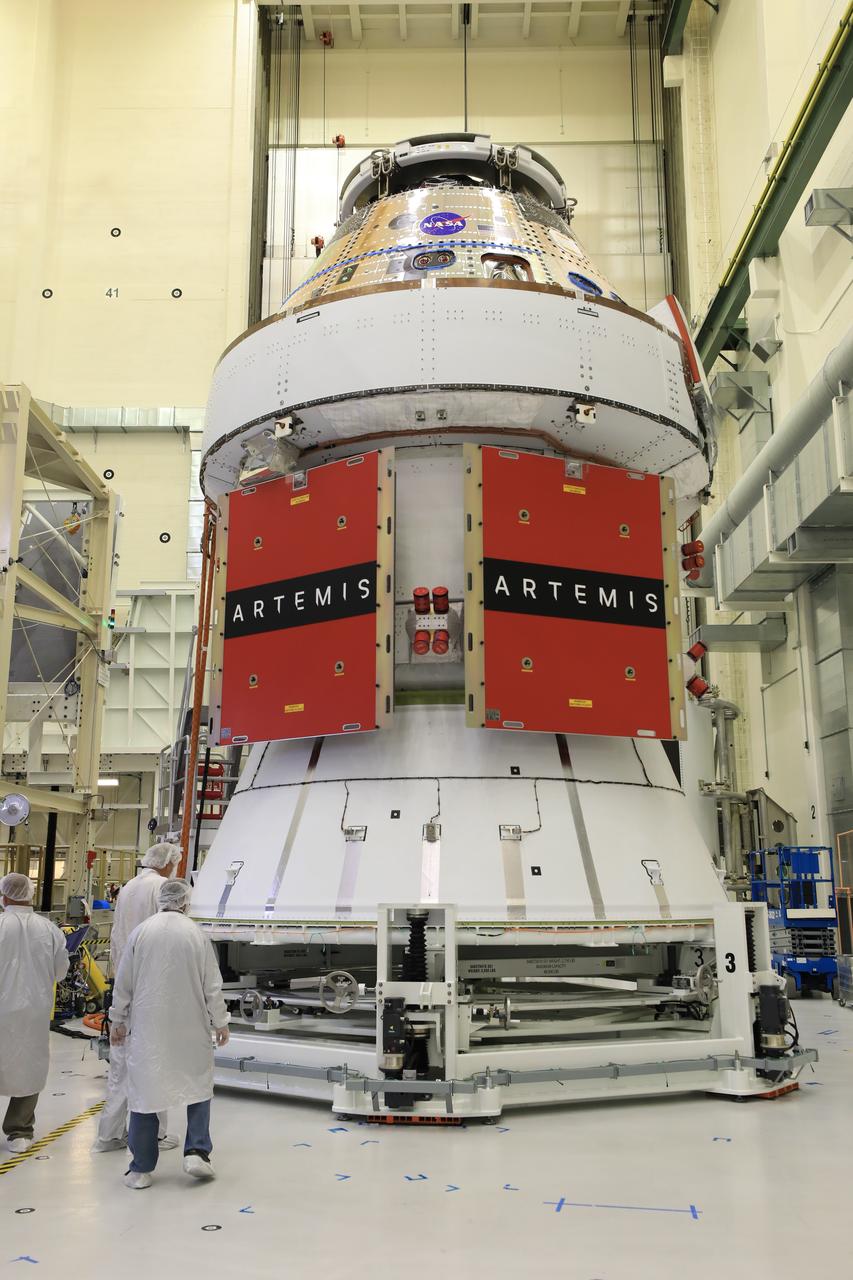

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
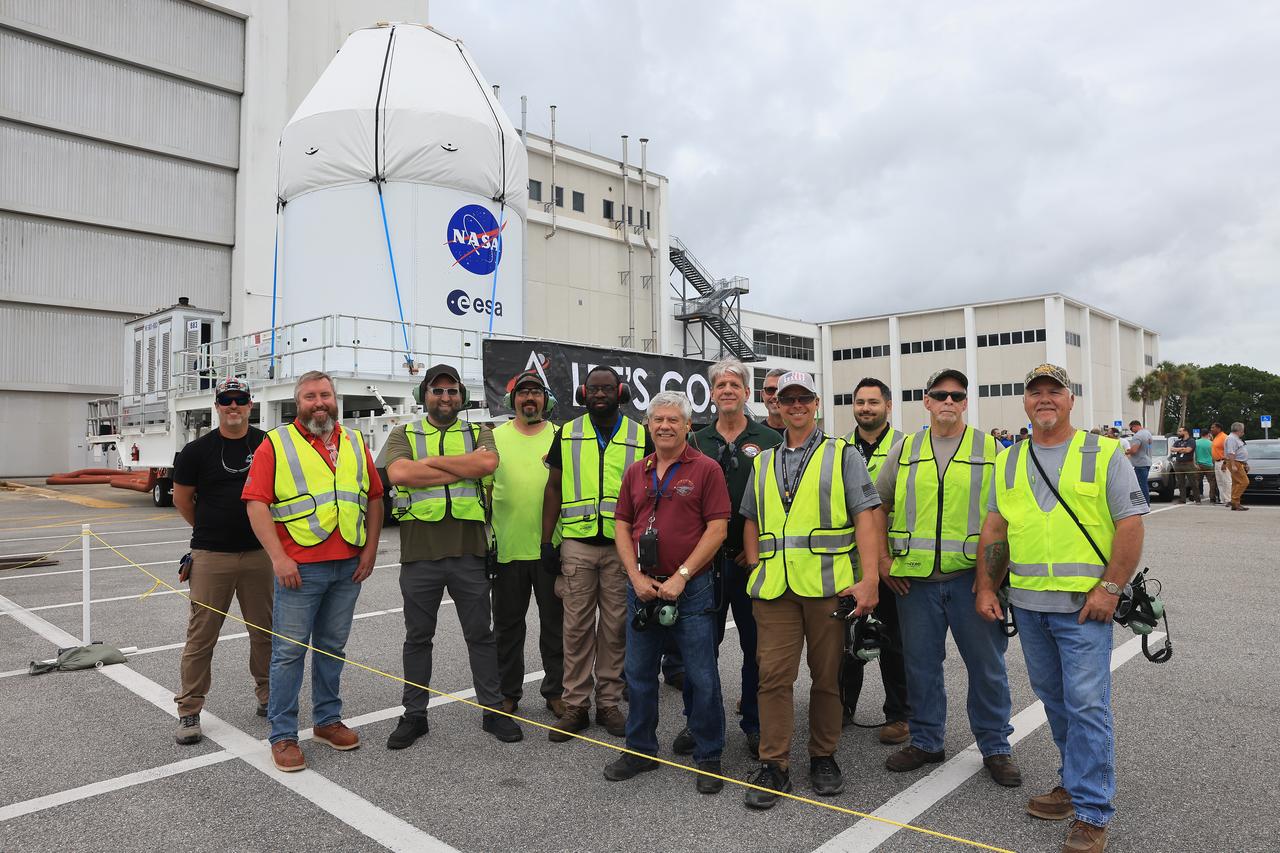

NASA’s KAMAG transporter carries the agency’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft from the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, May 3, 2025. The Orion spacecraft will undergo fueling and processing operations at the Multi-Function Facility. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
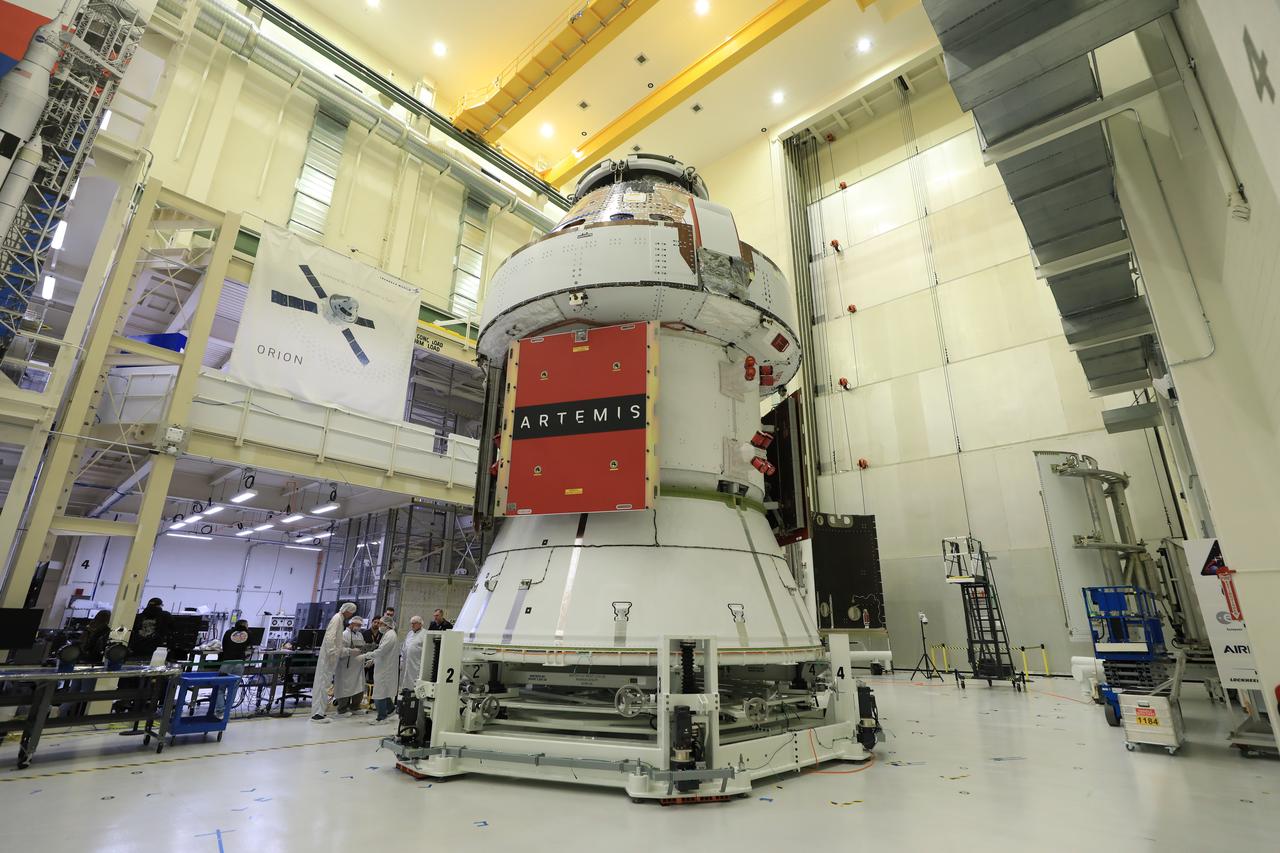

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.

NASA’s KAMAG transporter carries the agency’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft from the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, May 3, 2025. The Orion spacecraft will undergo fueling and processing operations at the Multi-Function Facility. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
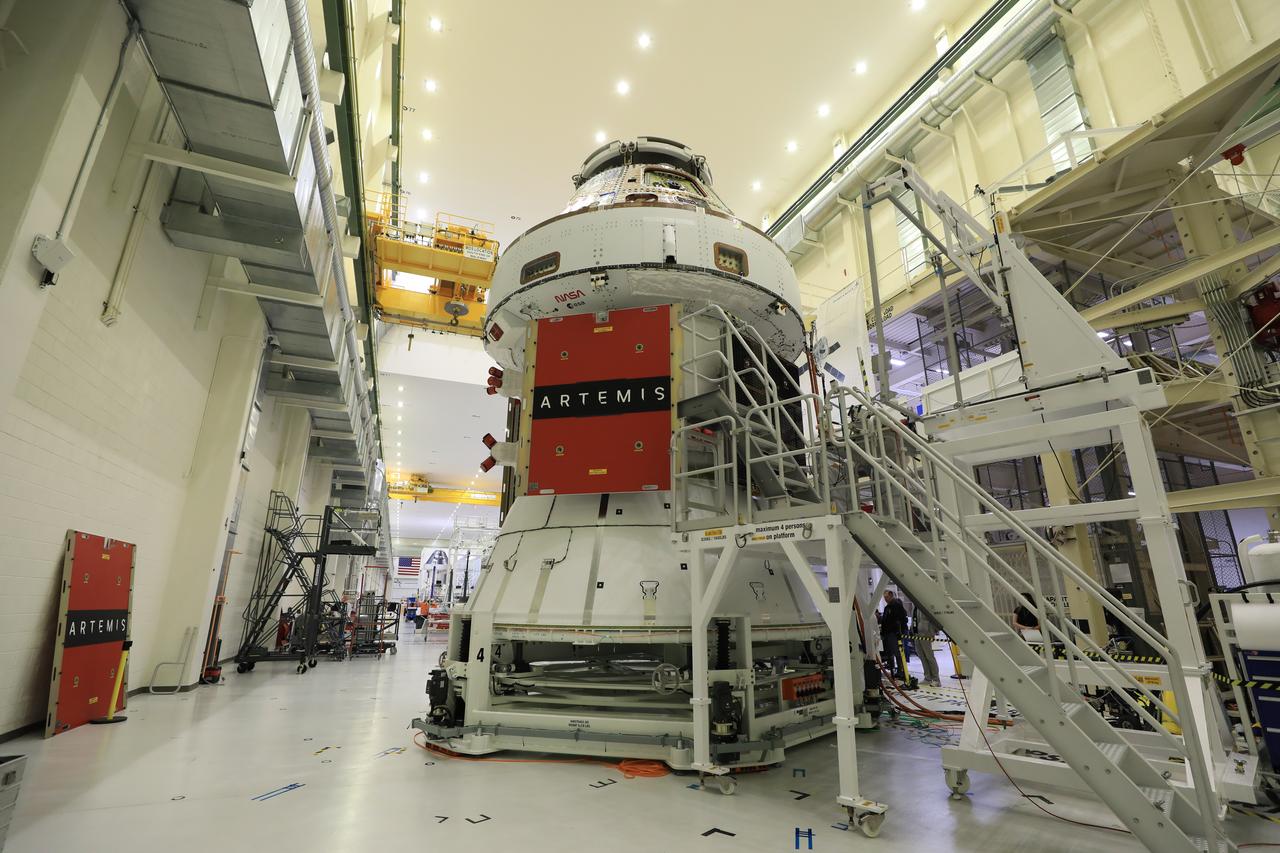

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
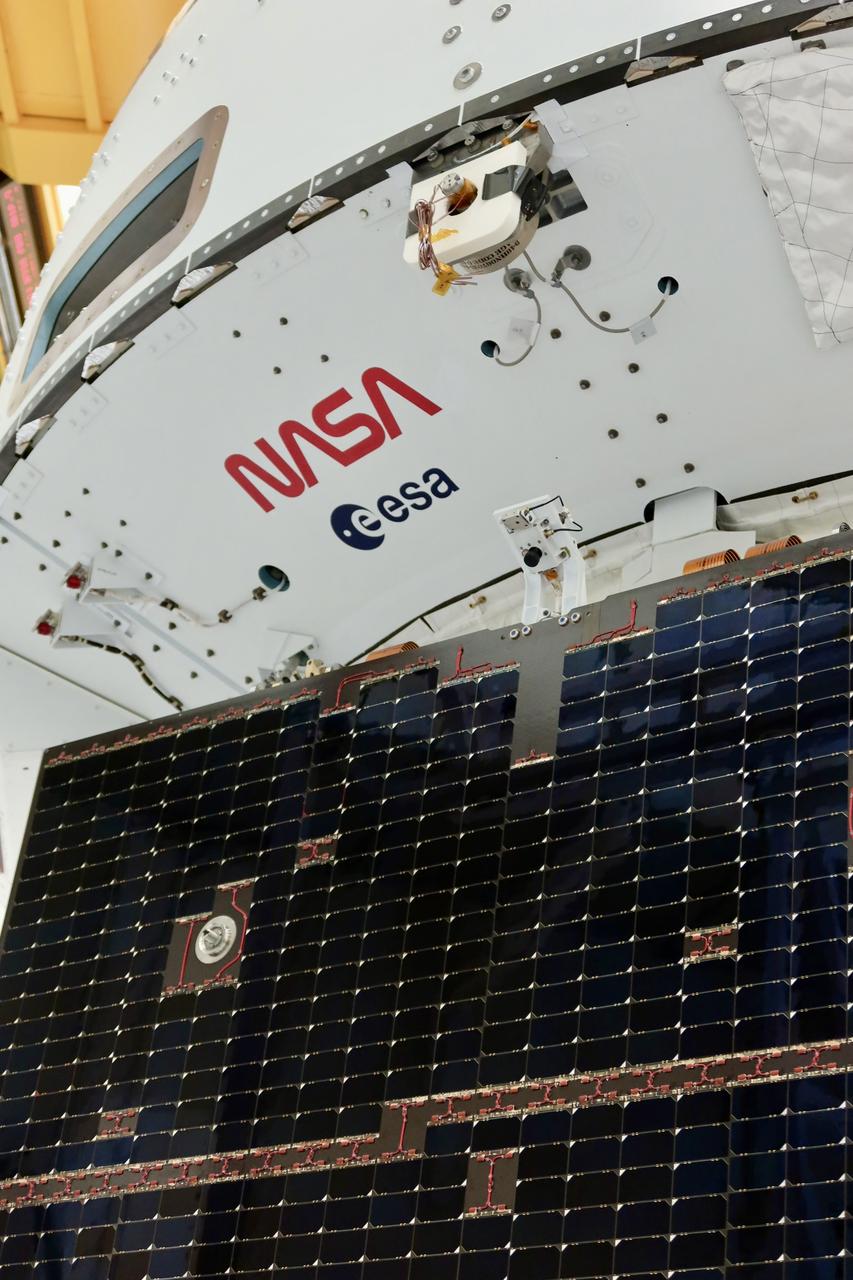

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
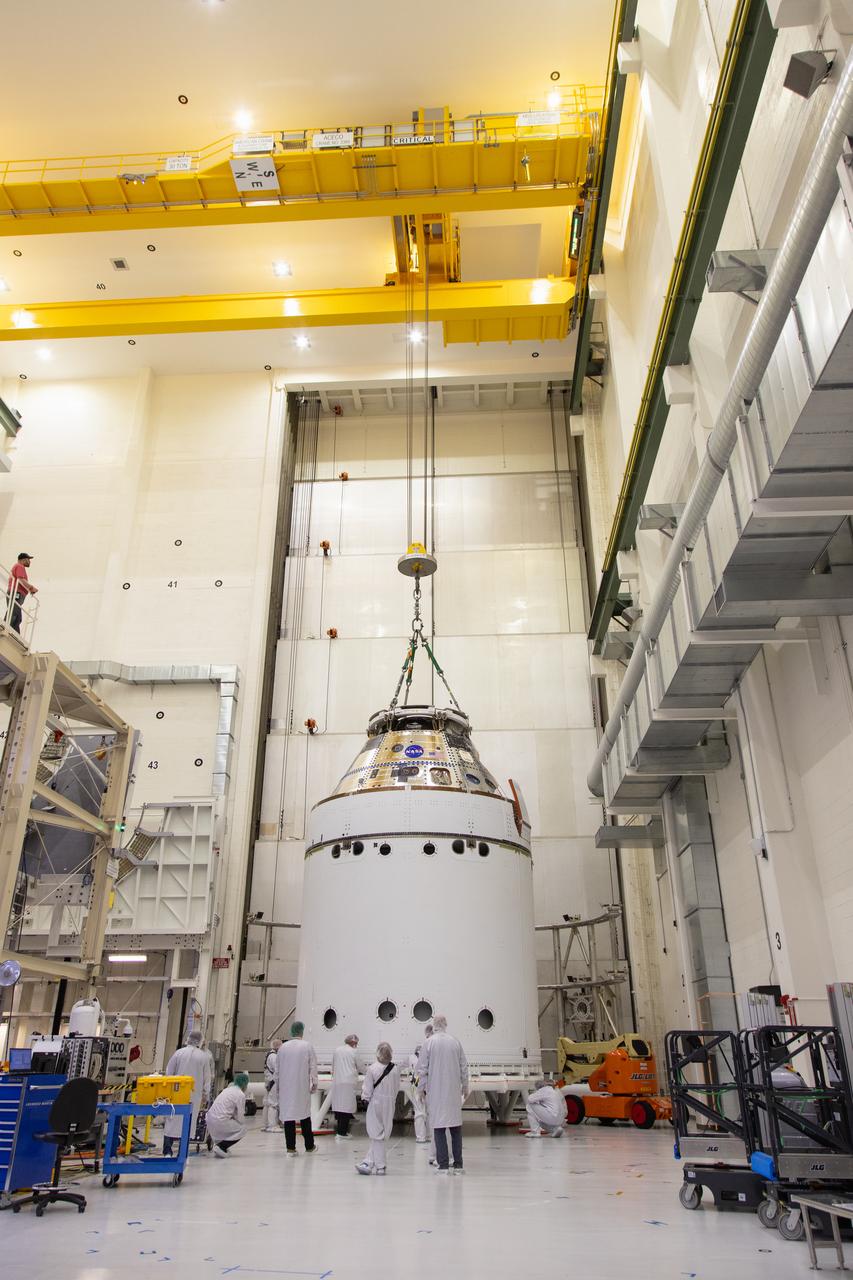

A crane returns NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft to the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) cell inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, March 21, 2025, following installation of four solar array winds and adapter jettison fairings. Once complete, the Orion spacecraft will be transported to other facilities for fueling and integration with its launch abort system before arriving at the Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be stacked atop the SLS (Space Launch System) by NASA’s Exploration Ground System team at the Vehicle Assembly Building in preparations for Artemis II launch operations.

NASA’s KAMAG transporter carries the agency’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft from the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, May 3, 2025. The Orion spacecraft will undergo fueling and processing operations at the Multi-Function Facility. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
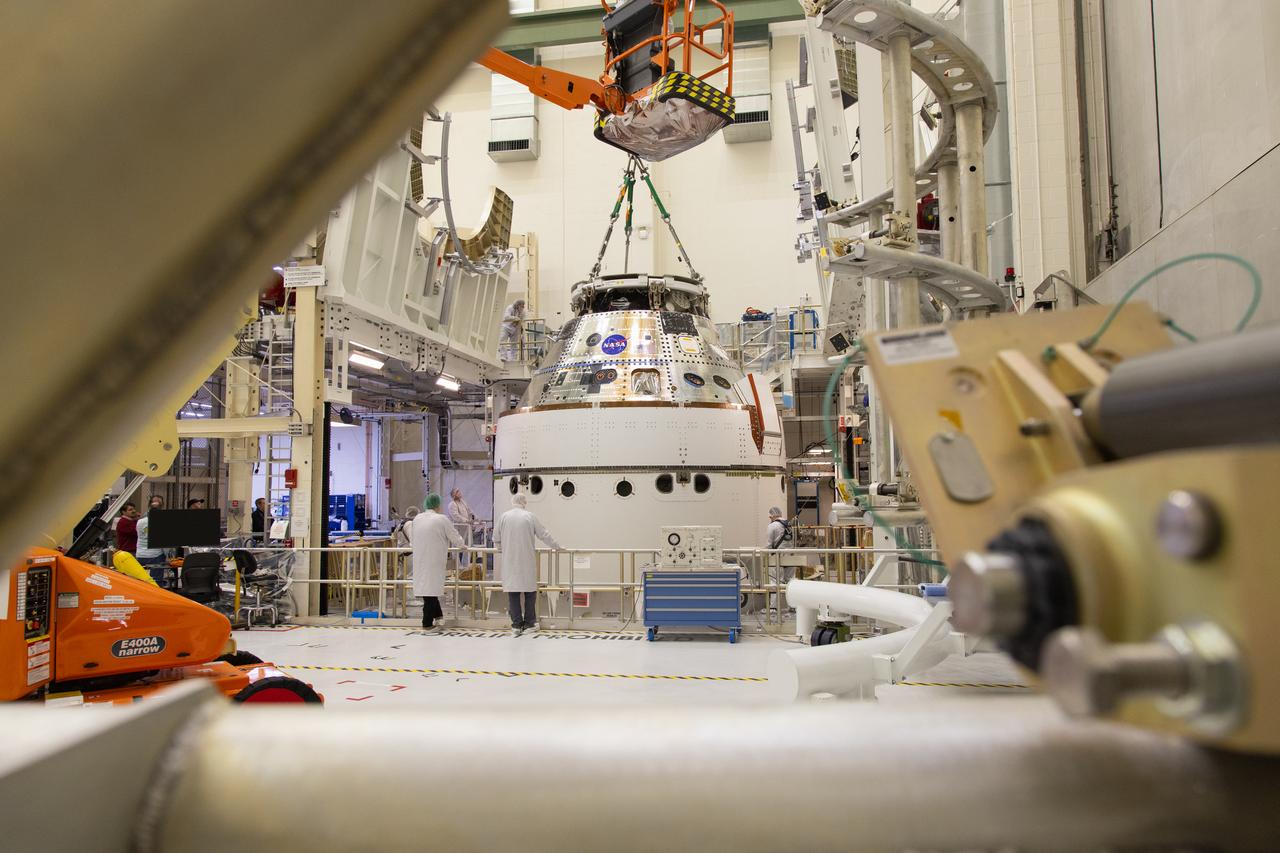
A crane returns NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft to the Final Assembly and System Testing (FAST) cell inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, March 21, 2025, following installation of four solar array winds and adapter jettison fairings. Once complete, the Orion spacecraft will be transported to other facilities for fueling and integration with its launch abort system before arriving at the Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be stacked atop the SLS (Space Launch System) by NASA’s Exploration Ground System team at the Vehicle Assembly Building in preparations for Artemis II launch operations.
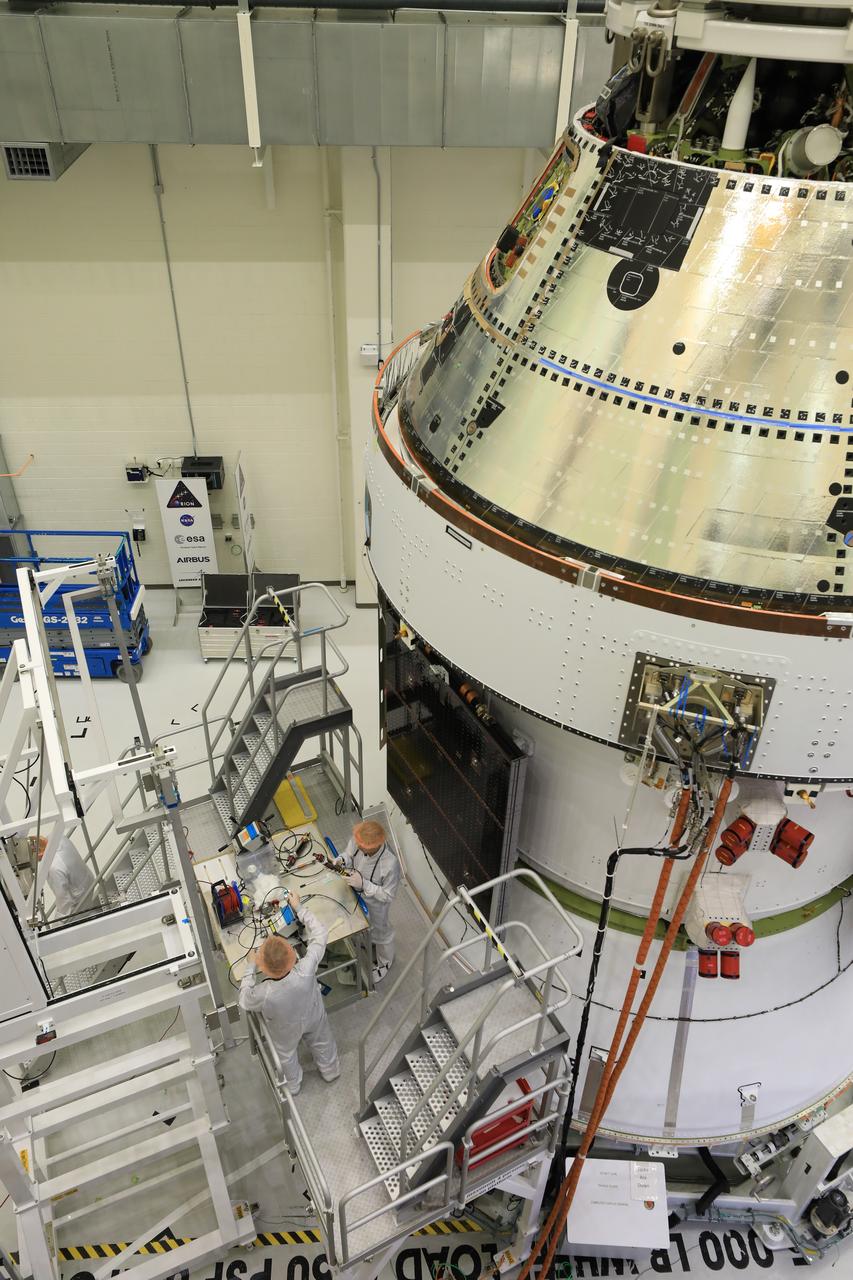

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
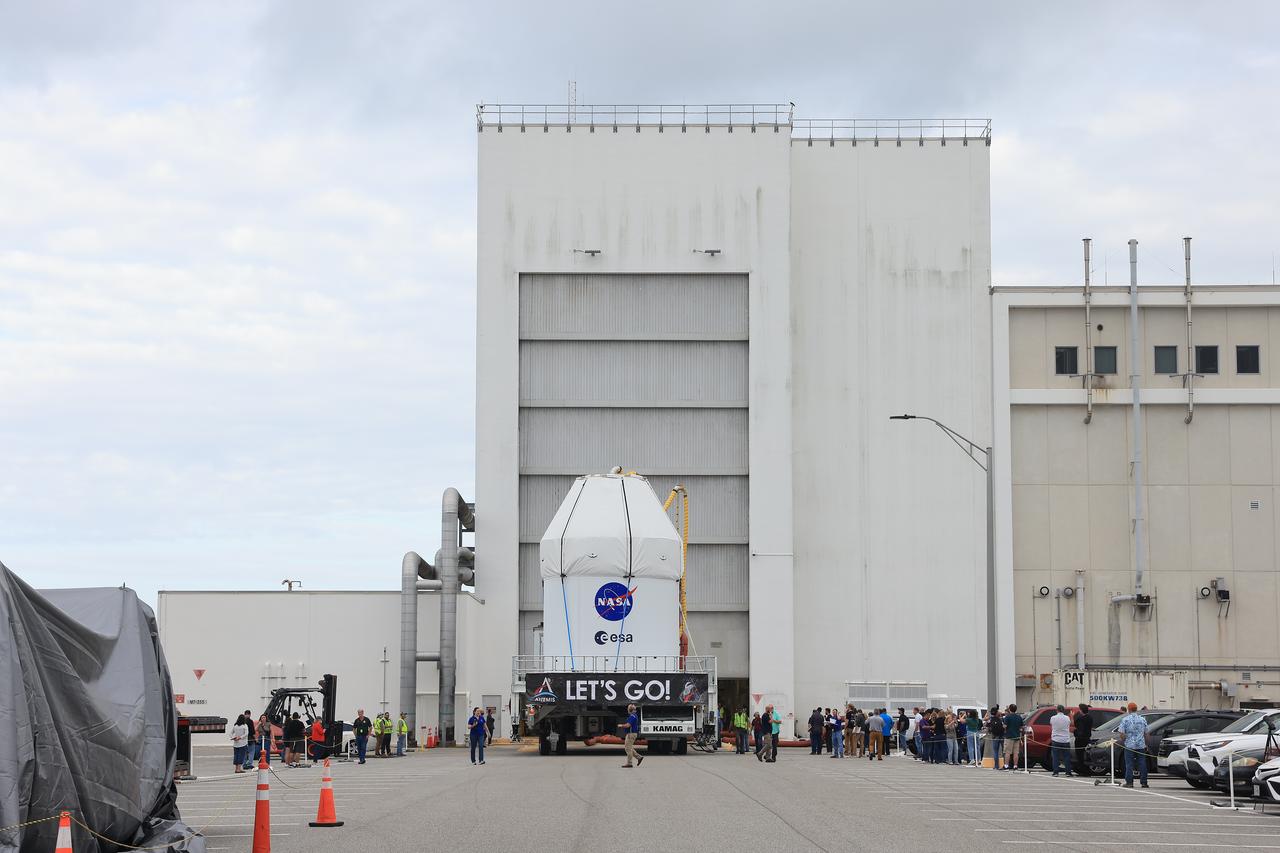

NASA’s KAMAG transporter carries the agency’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft from the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, May 3, 2025. The Orion spacecraft will undergo fueling and processing operations at the Multi-Function Facility. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
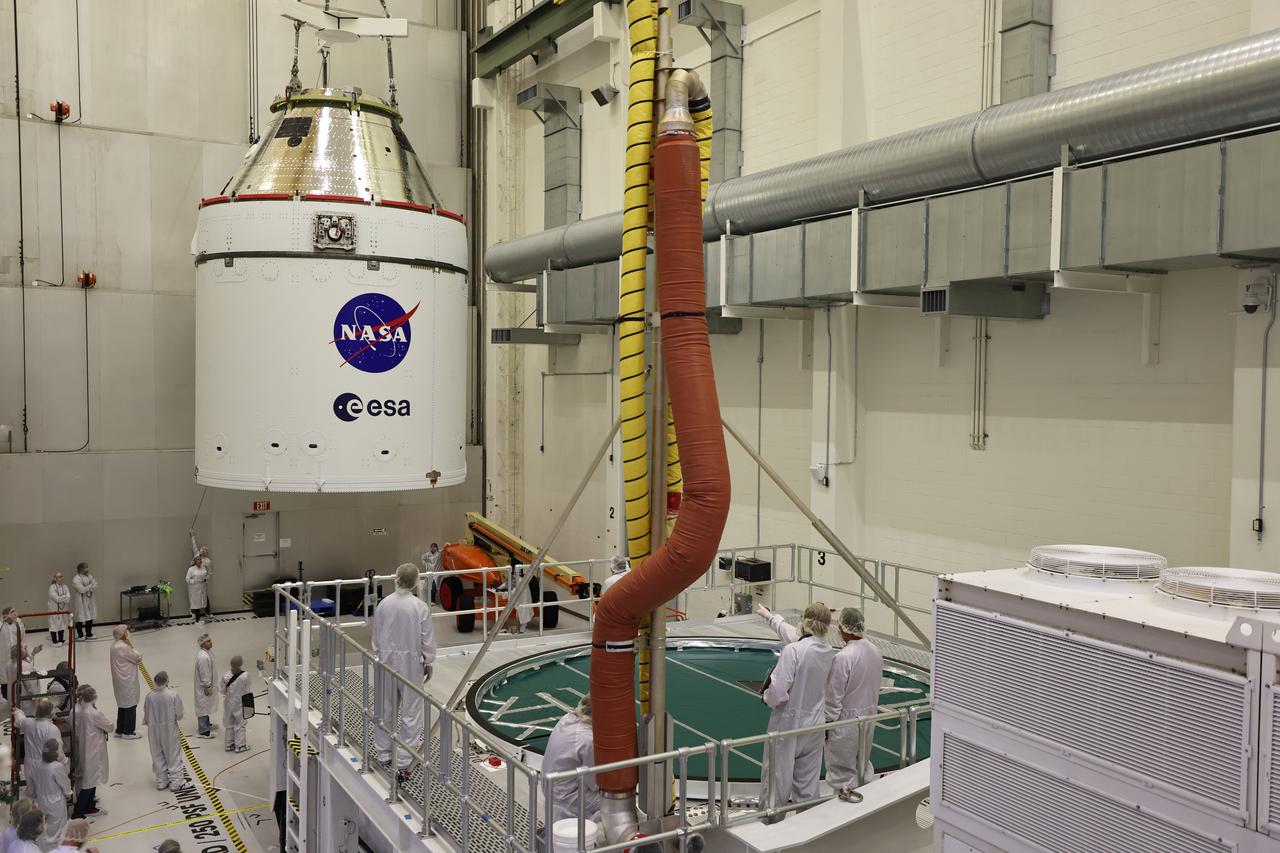

Crews use a massive crane to lift NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft onto the agency’s KAMAG transporter inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, May 1, 2025. The spacecraft will be transported to the Multi-Payload Processing Facility to undergo fueling and processing for prelaunch operations. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
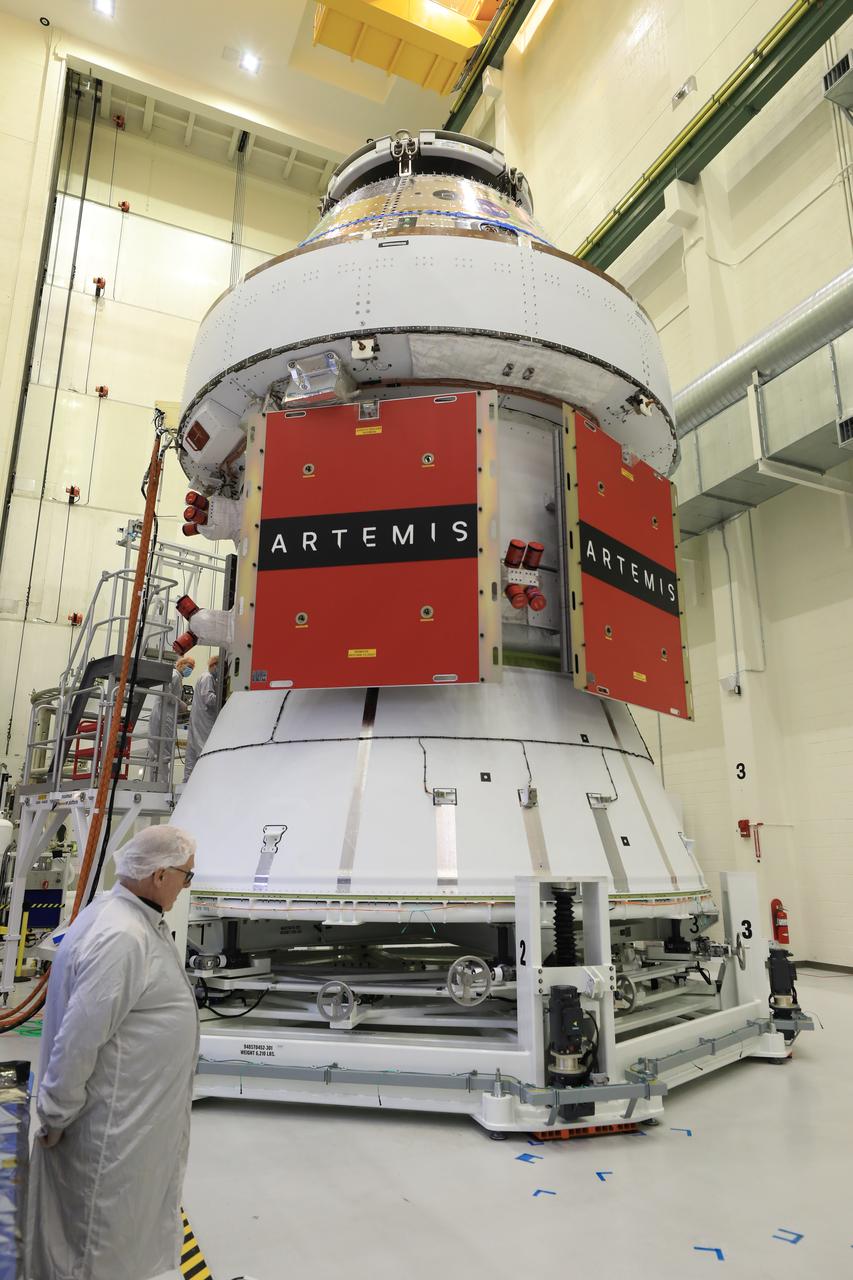

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
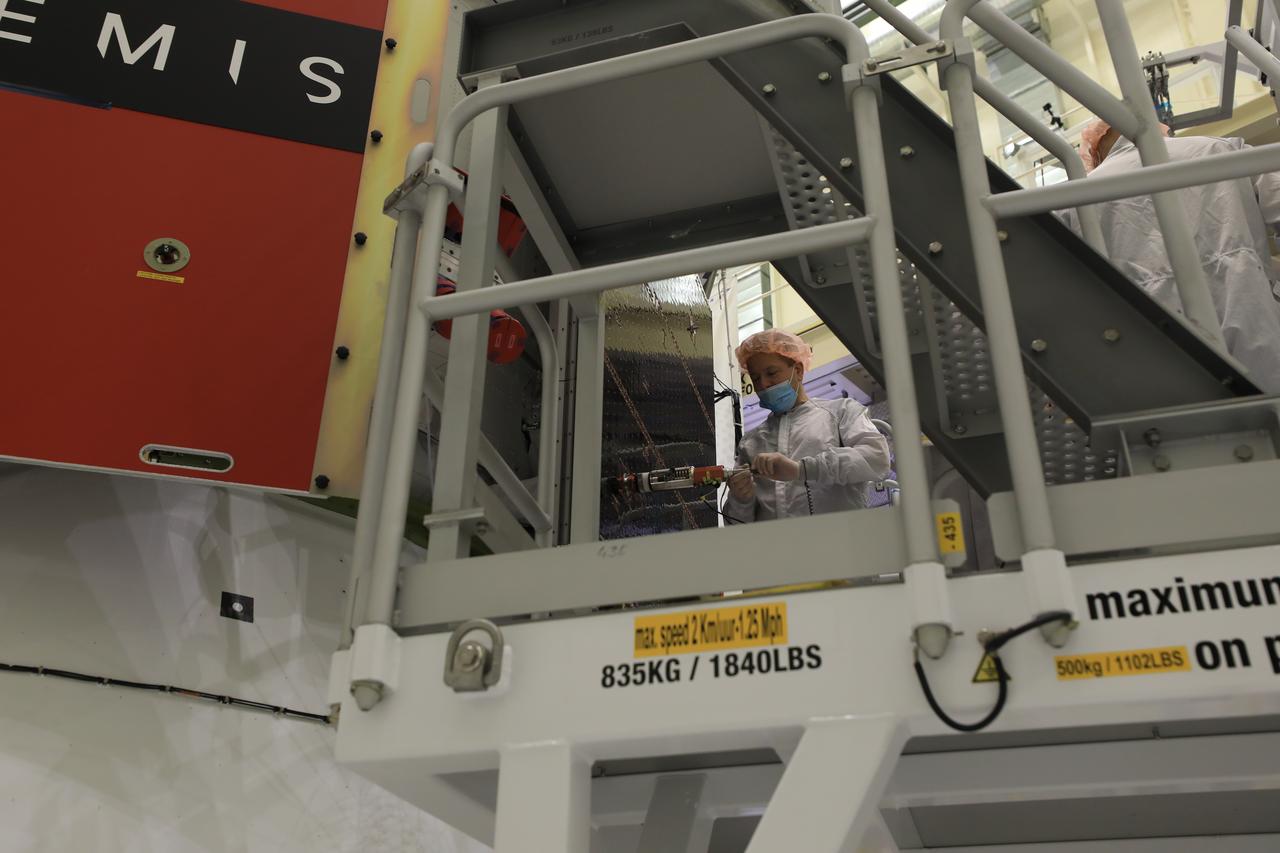

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
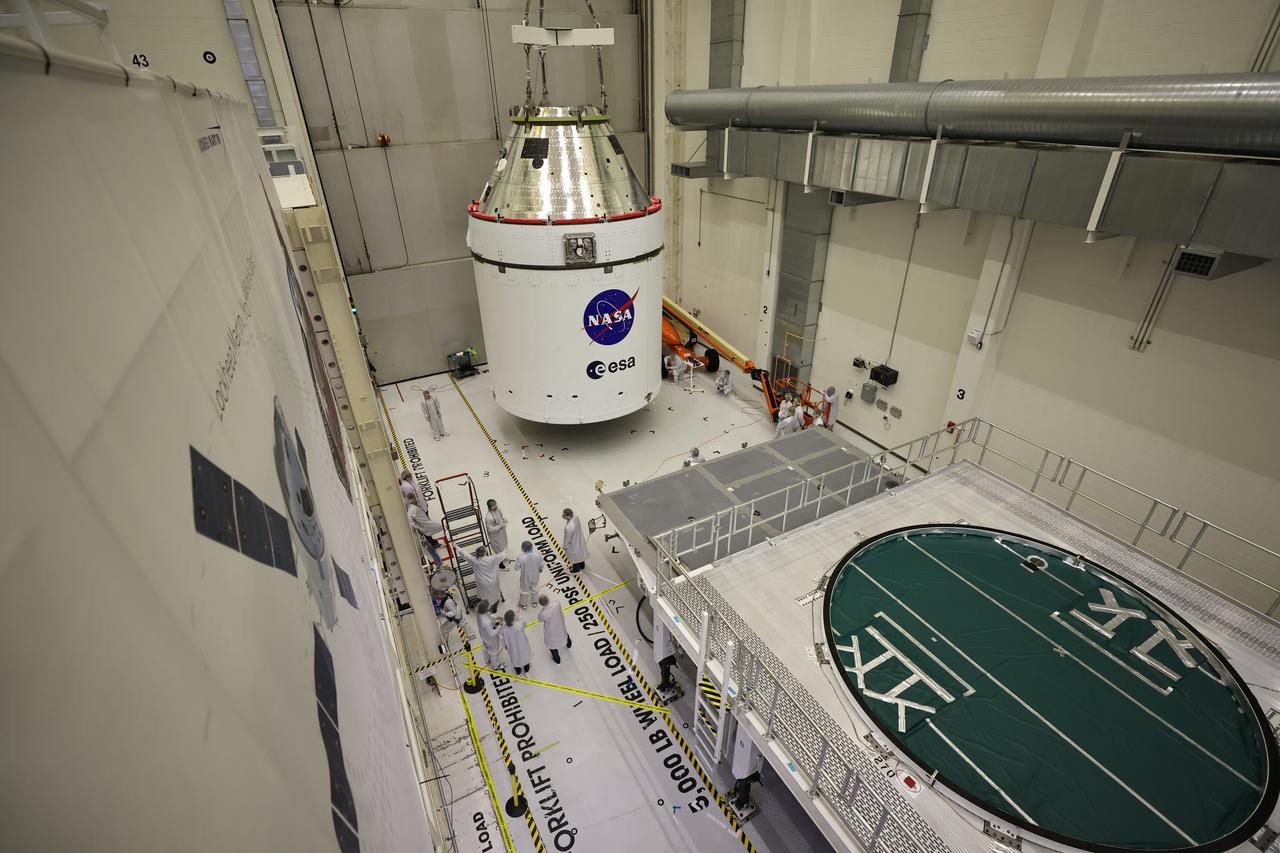

Crews use a massive crane to lift NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft onto the agency’s KAMAG transporter inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, May 1, 2025. The spacecraft will be transported to the Multi-Payload Processing Facility to undergo fueling and processing for prelaunch operations. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.

NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft arrives at the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, May 3, 2025, to undergo fueling and processing operations for prelaunch operations. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
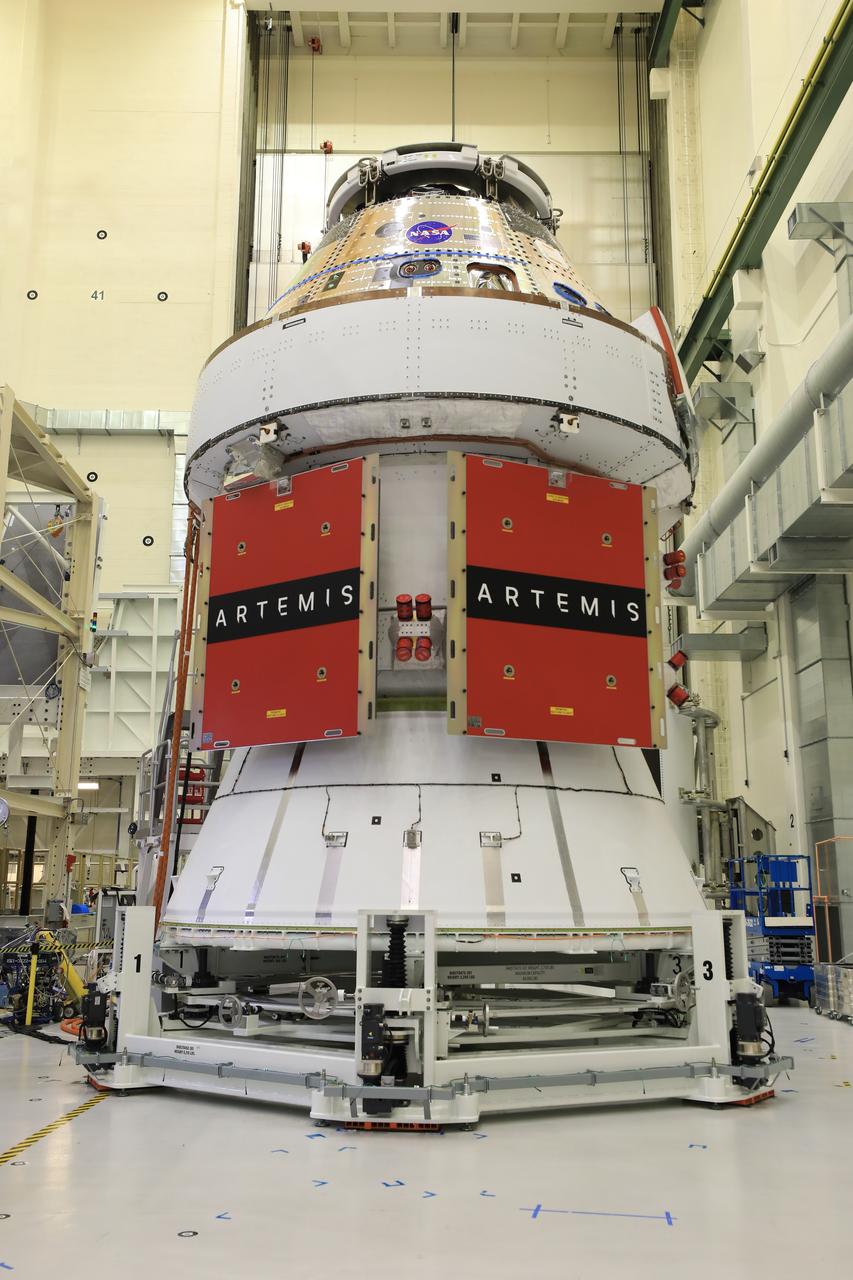

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.

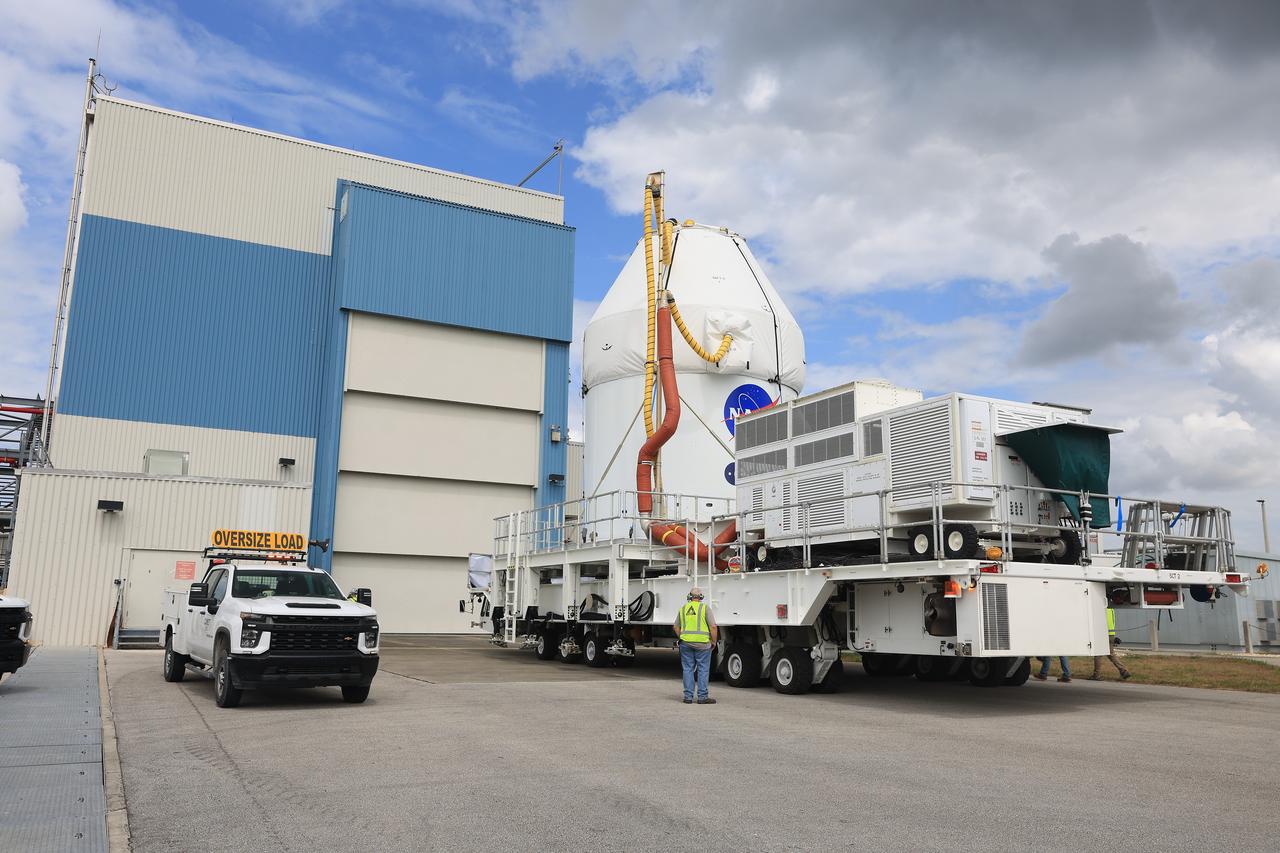
NASA’s KAMAG transporter carries the agency’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft from the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, May 3, 2025. The Orion spacecraft will undergo fueling and processing operations at the Multi-Function Facility. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
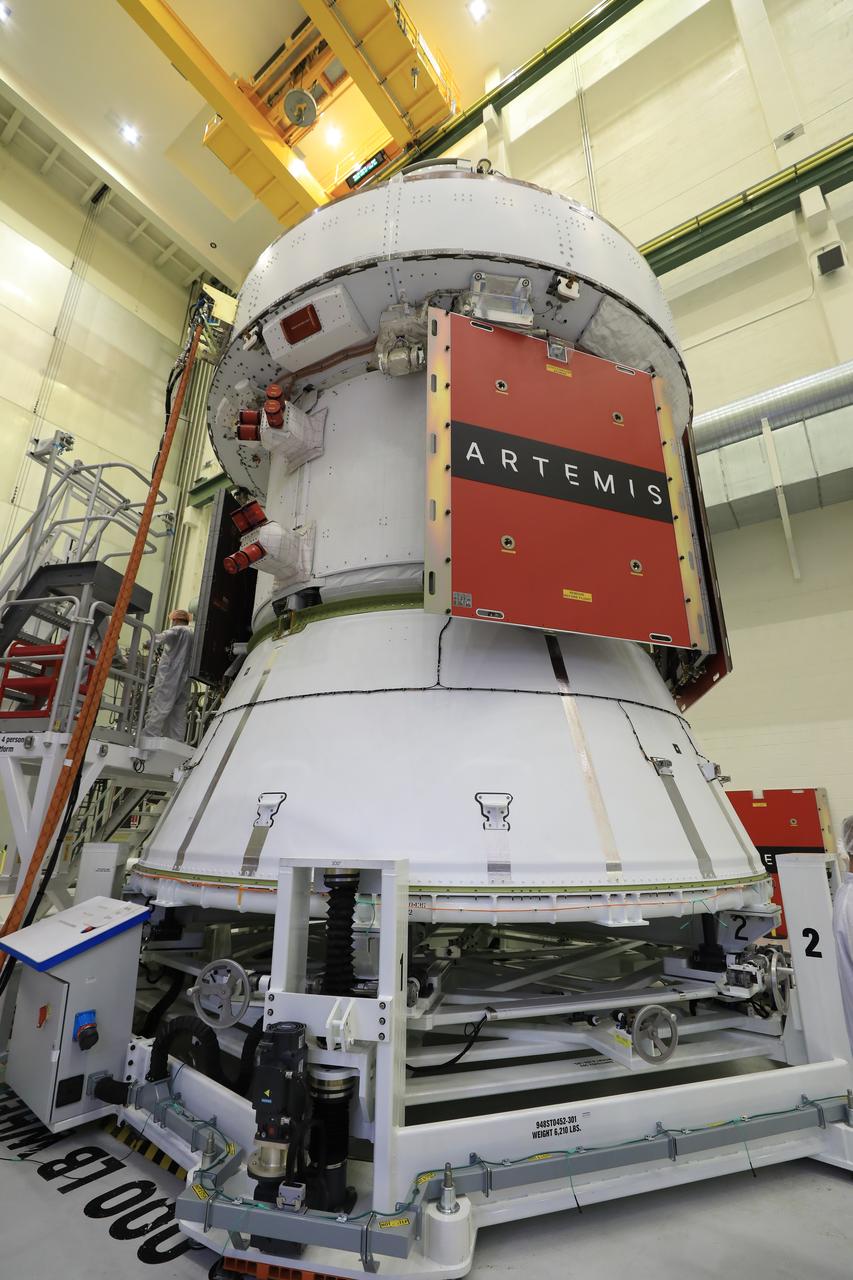

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
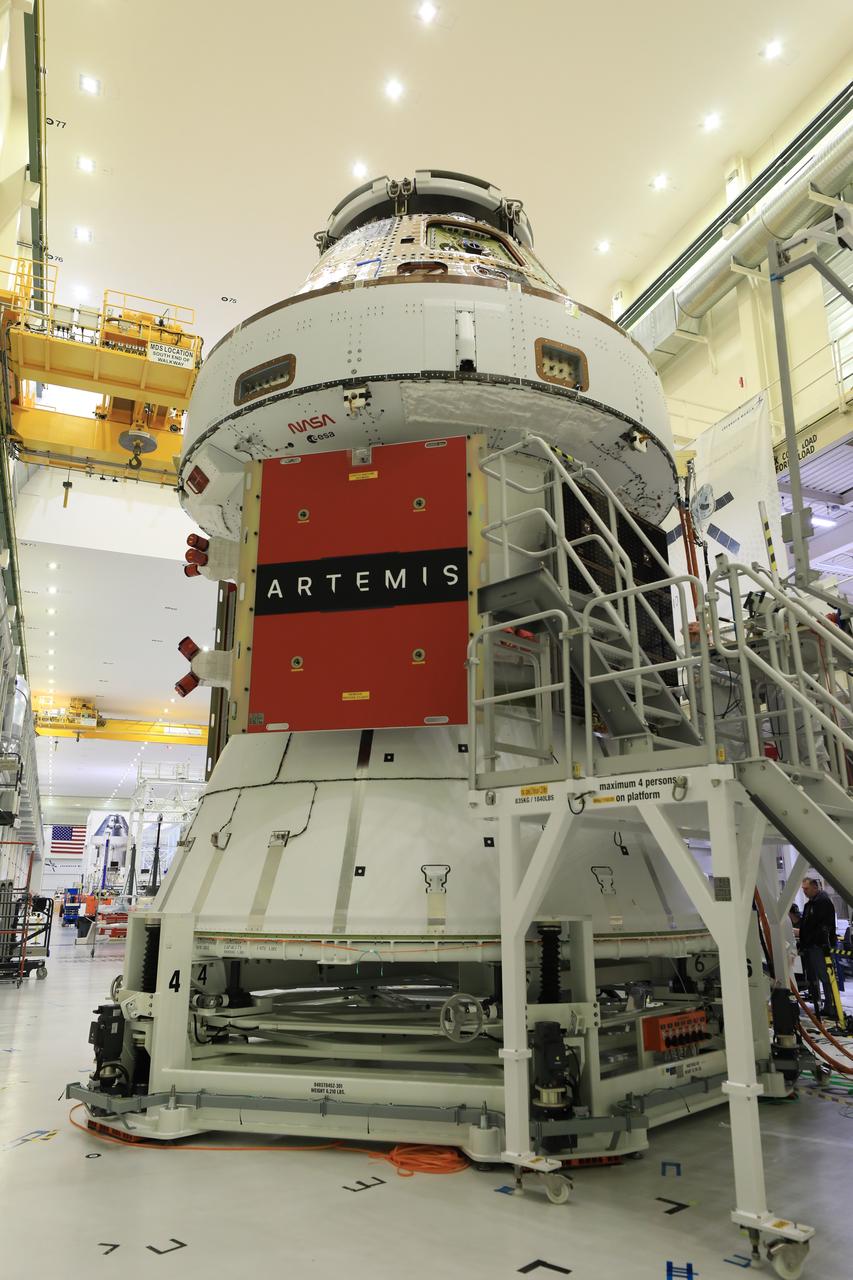

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
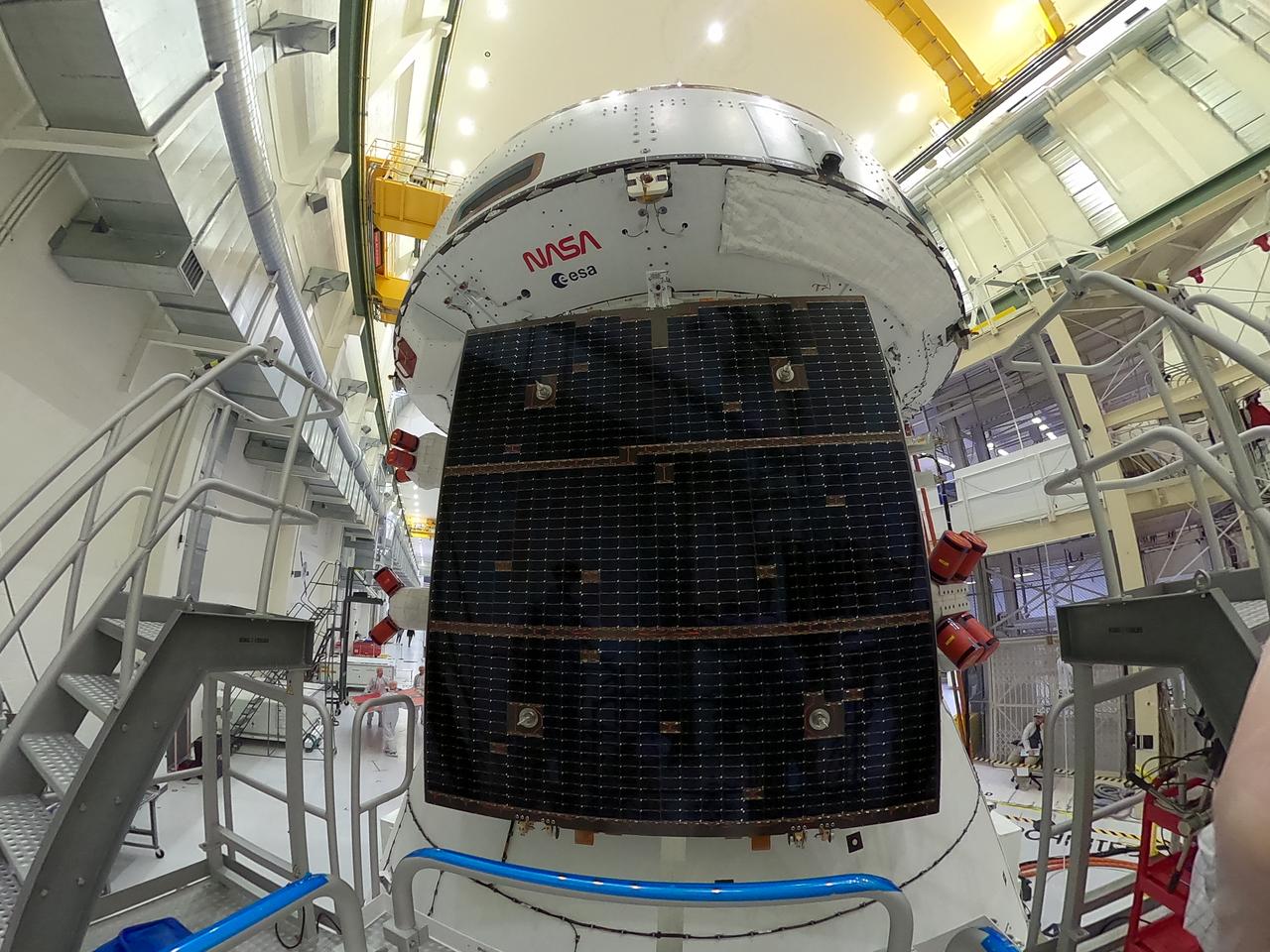

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
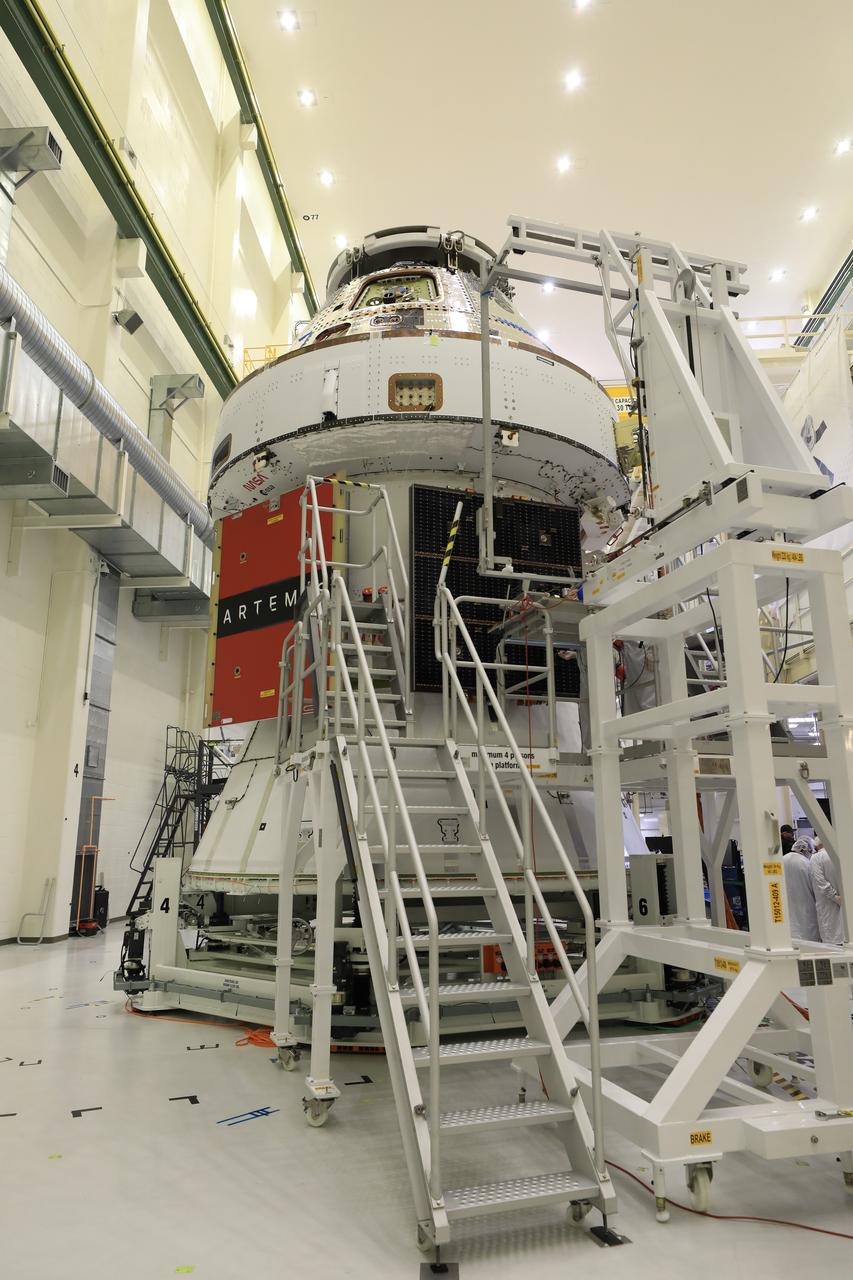

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
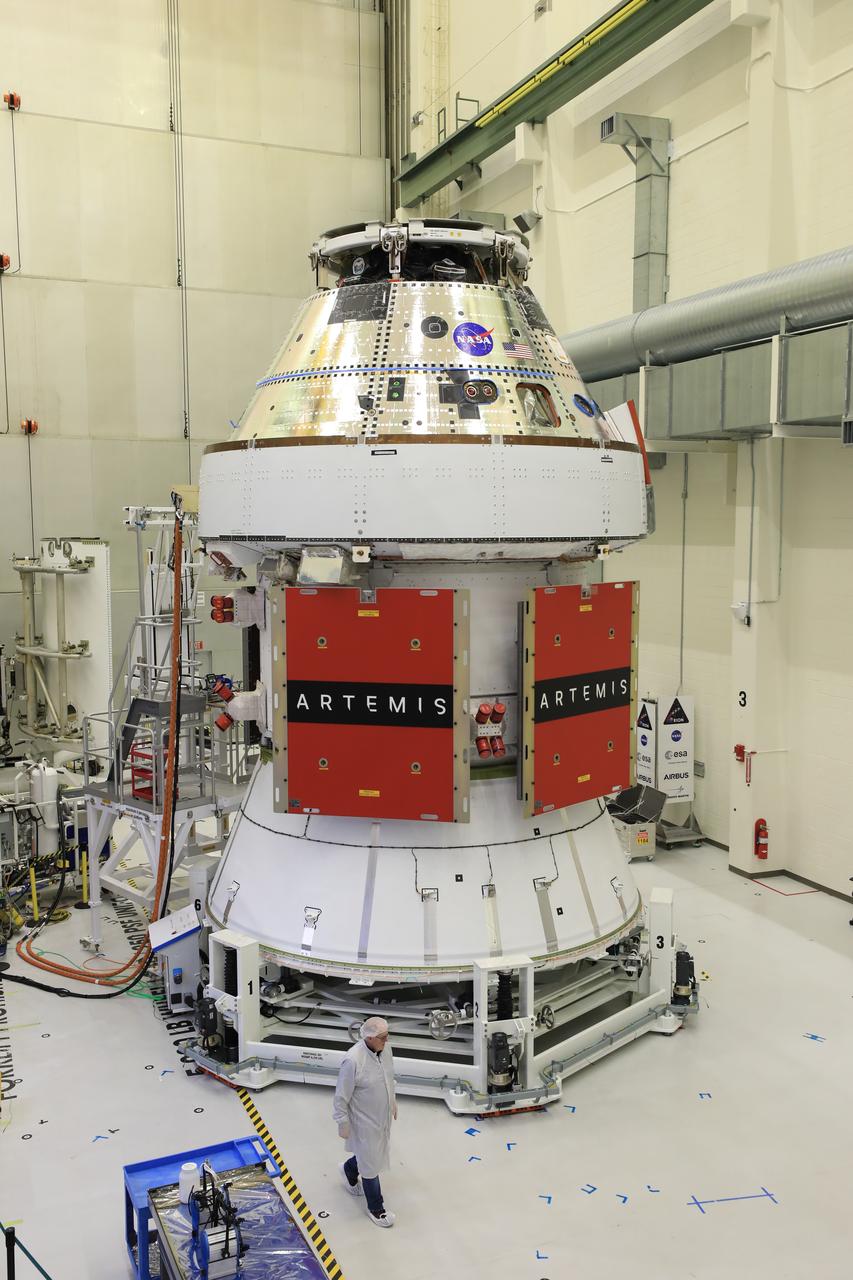

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.

NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft arrives at the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, May 3, 2025, to undergo fueling and processing operations for prelaunch operations. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
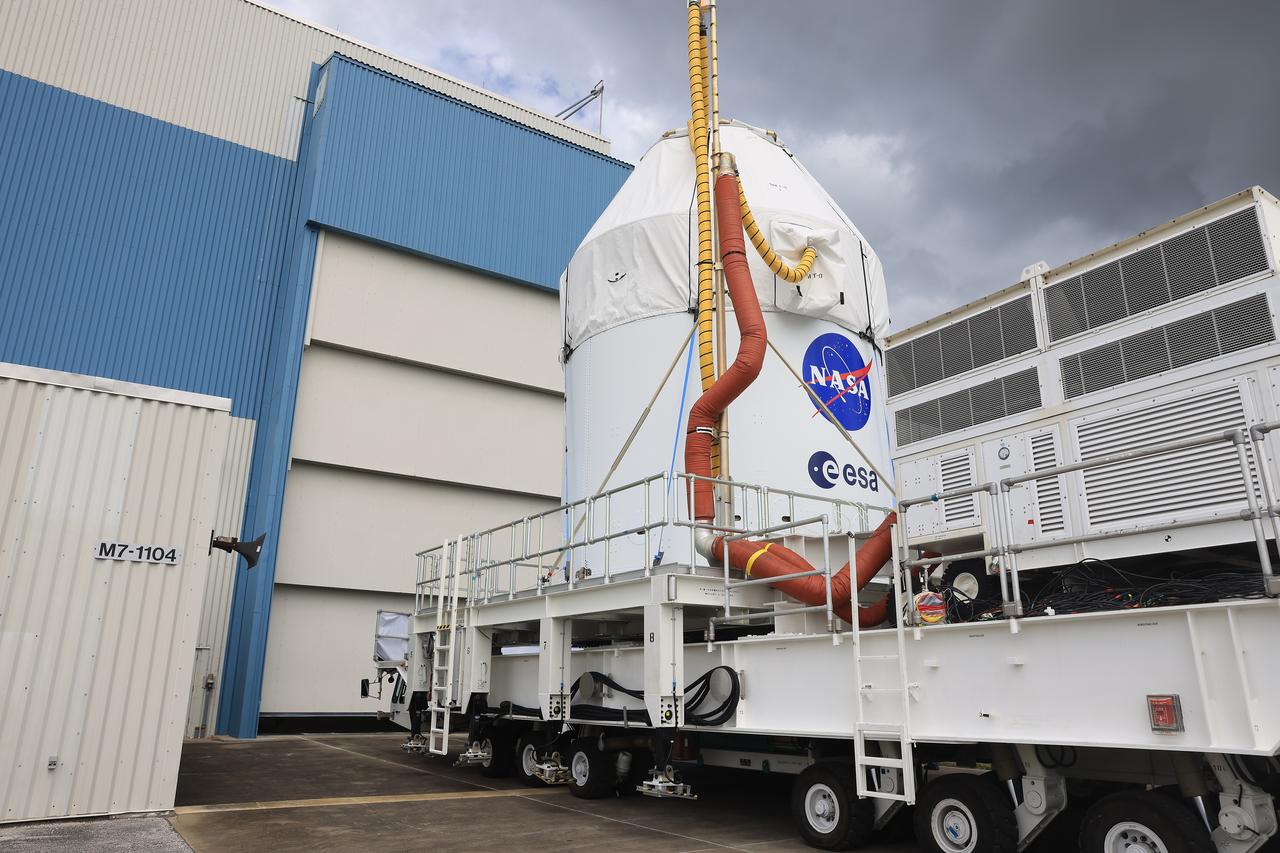

NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft arrives at the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, May 3, 2025, to undergo fueling and processing operations for prelaunch operations. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.

NASA’s KAMAG transporter carries the agency’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft from the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, May 3, 2025. The Orion spacecraft will undergo fueling and processing operations at the Multi-Function Facility. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
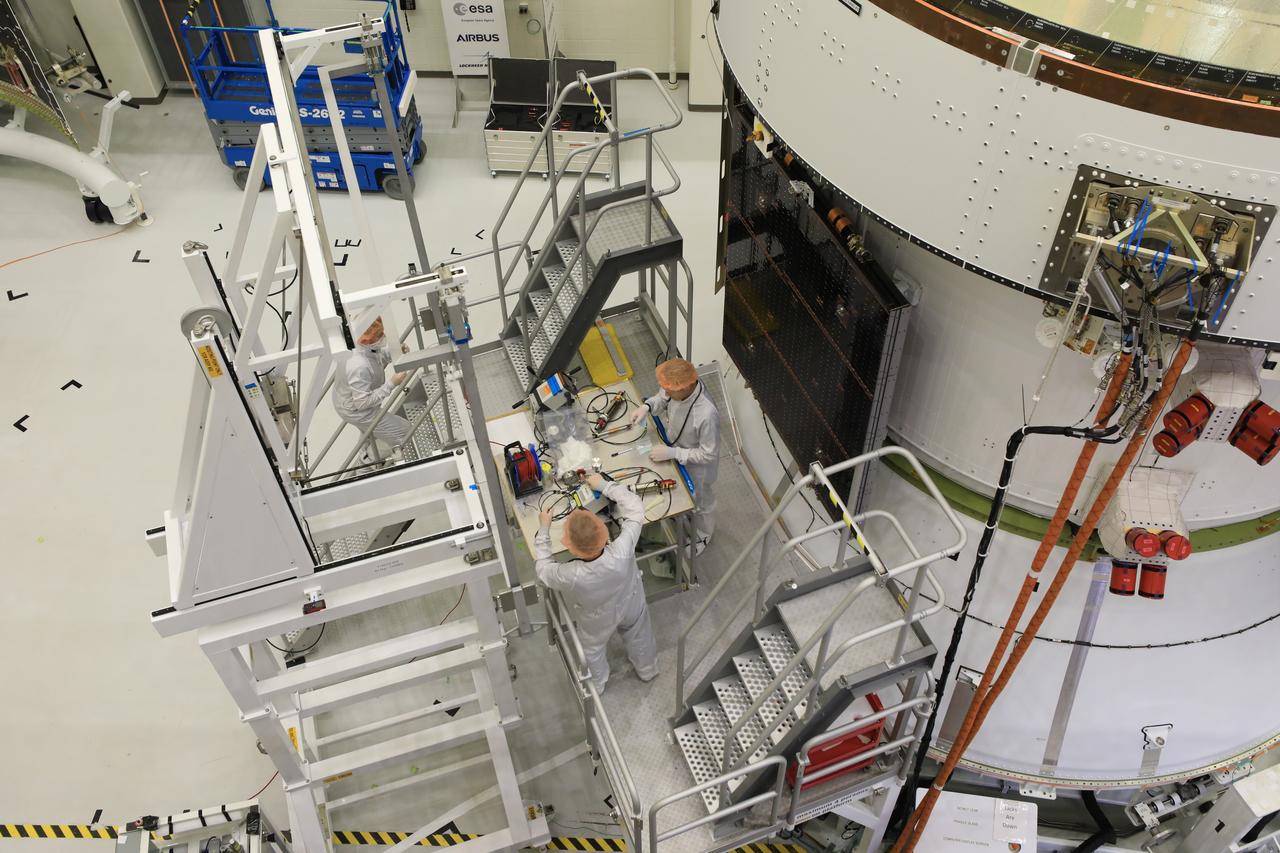

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
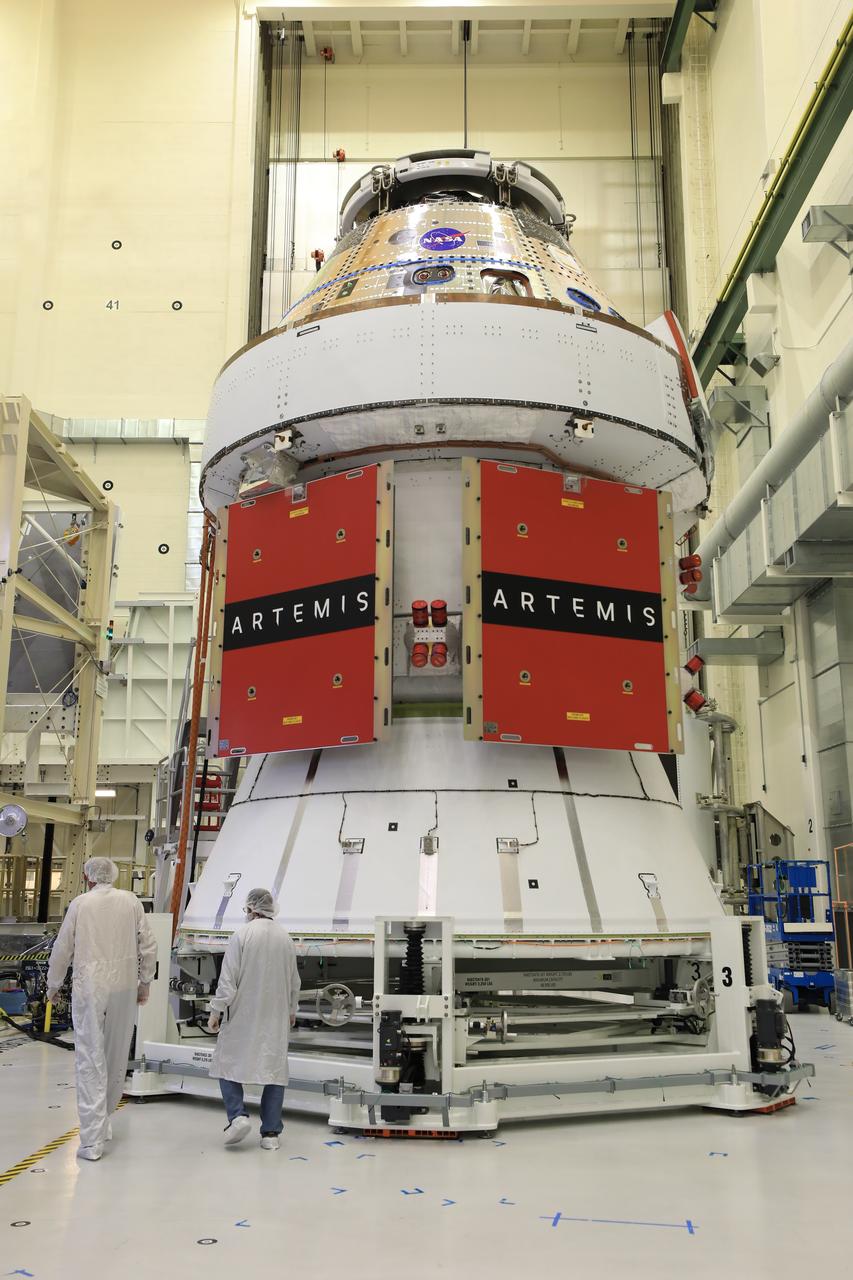

Technicians install four solar array wings on NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, March 3, 2025. Each solar array is nearly 23 feet long and can turn on two axes to remain aligned with the Sun for maximum power. Orion’s solar arrays, manufactured and installed by ESA (European Space Agency) and its contractor Airbus, will deliver power to the service module that provides propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power to the spacecraft, as well as air and water for the crew.
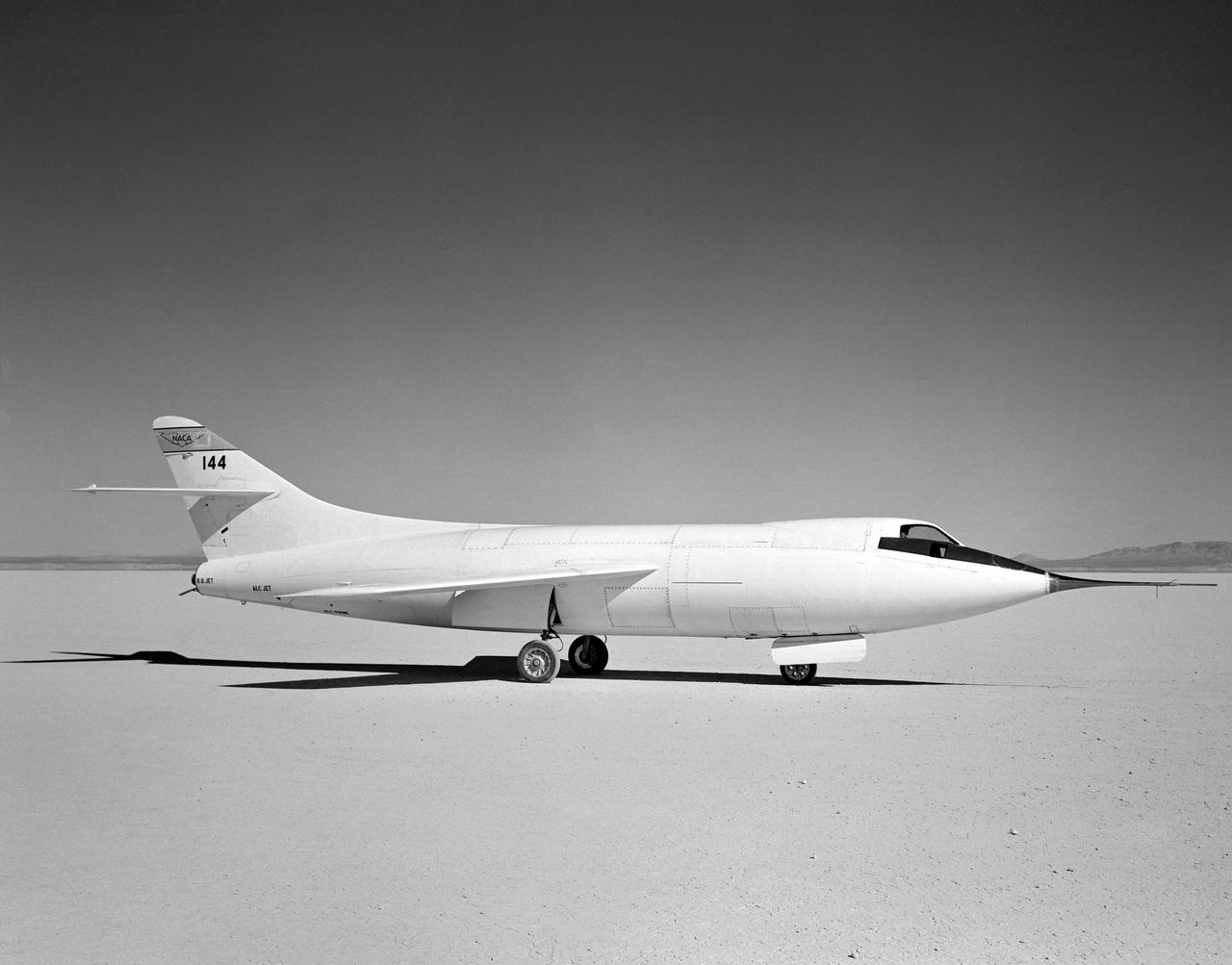

D-558-2 Aircraft on lakebed
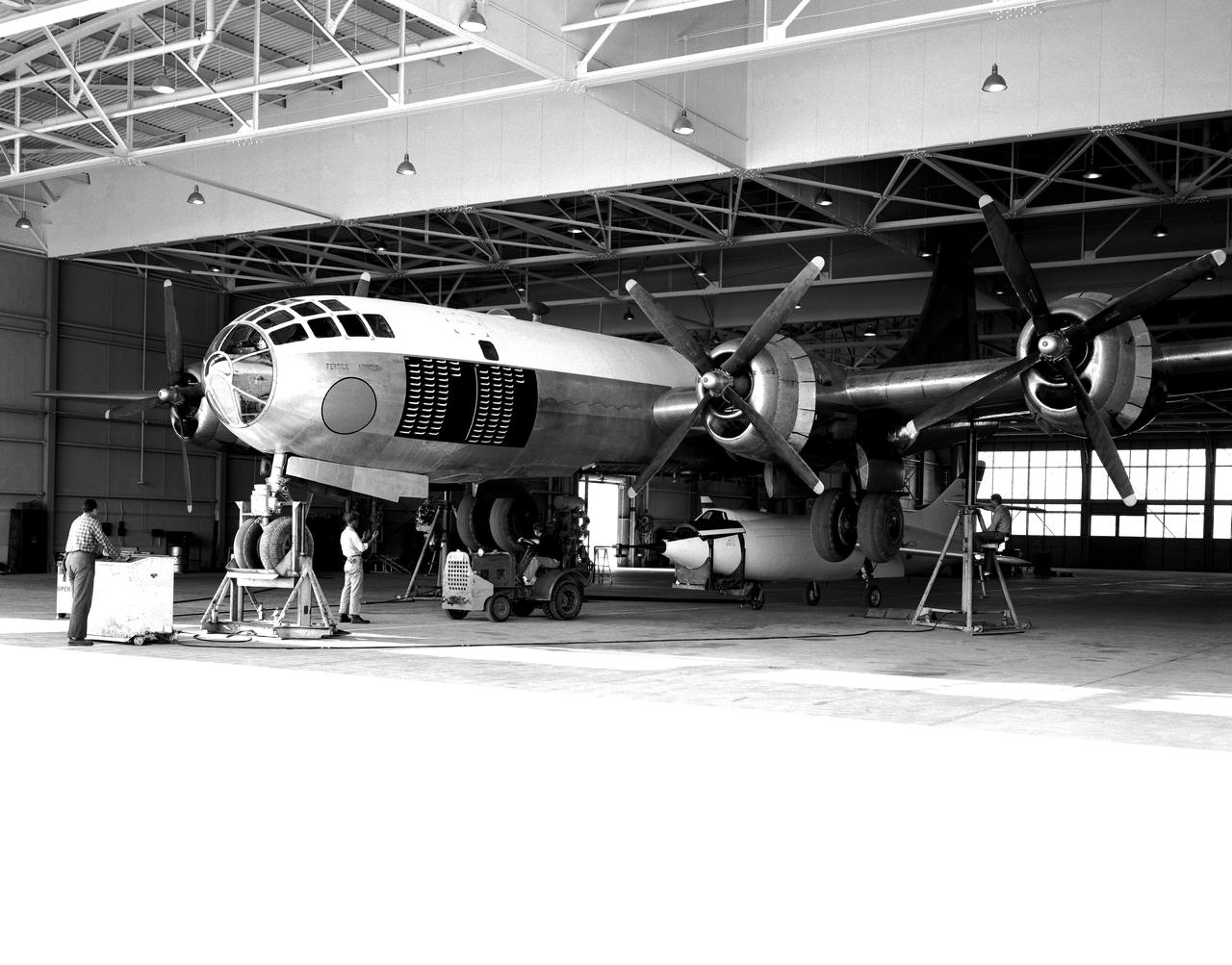

D-558-2 being mounted to P2B-1S launch aircraft in hangar.
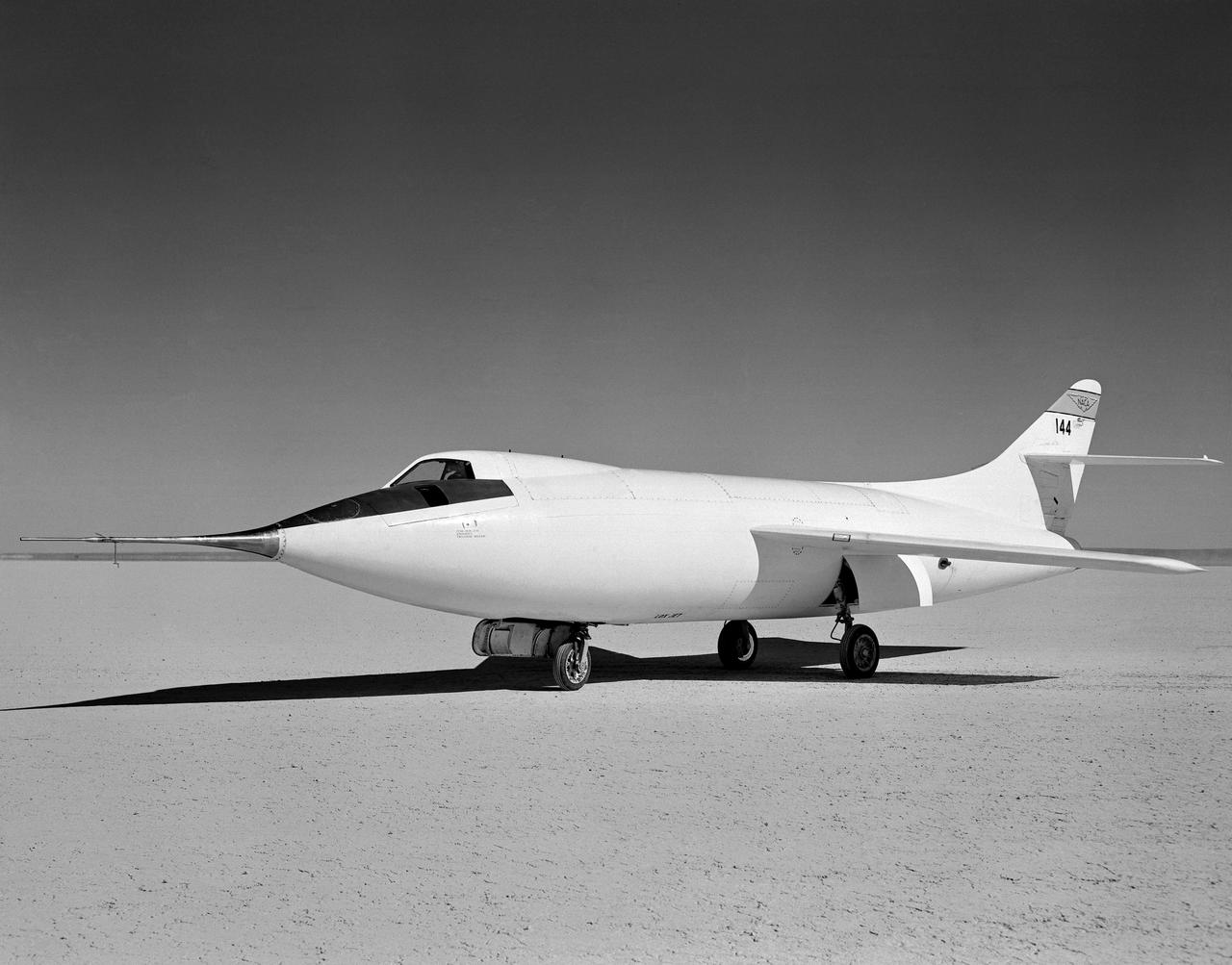

D-558-2 Aircraft on lakebed
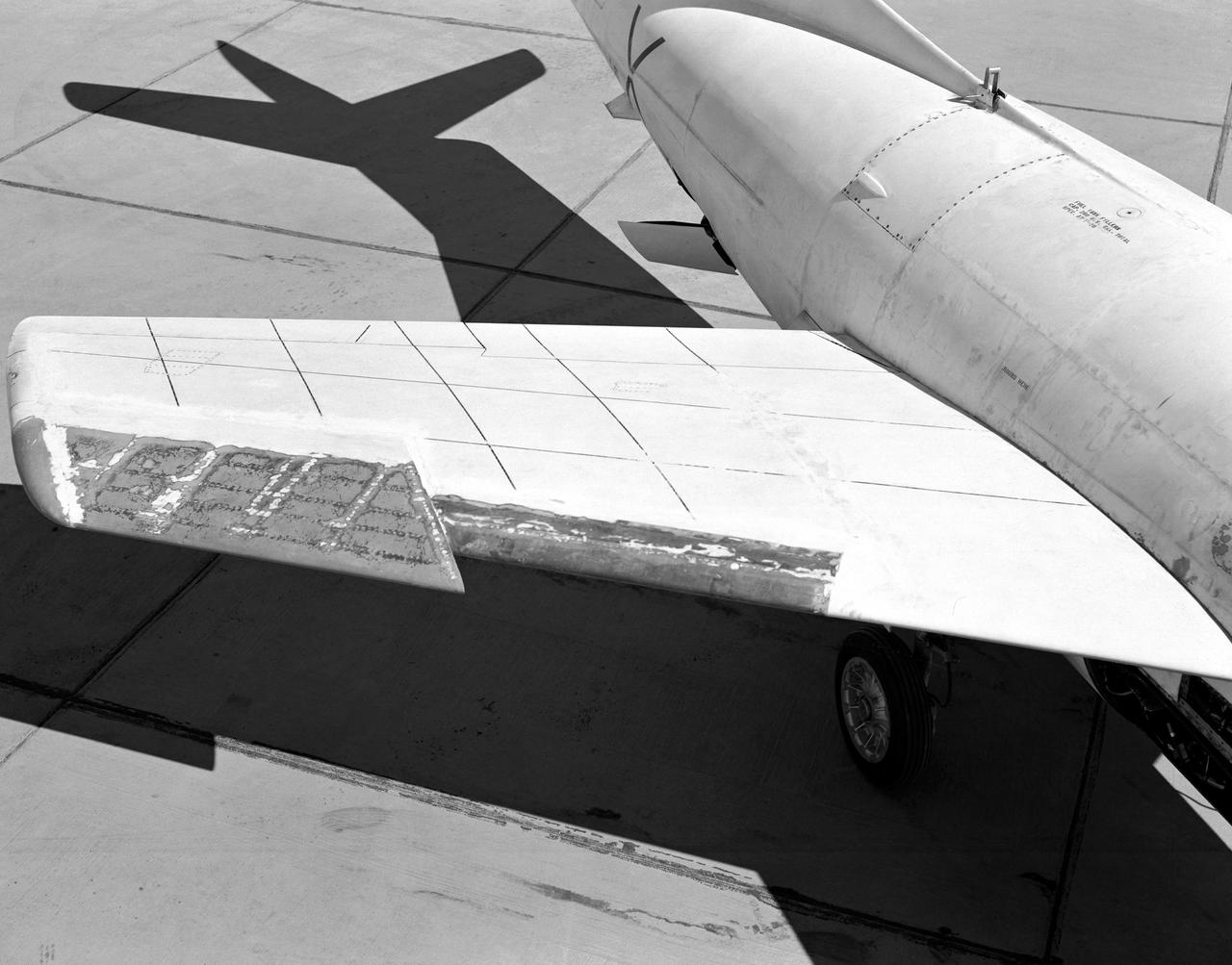

Wing chord extension on D-558-2
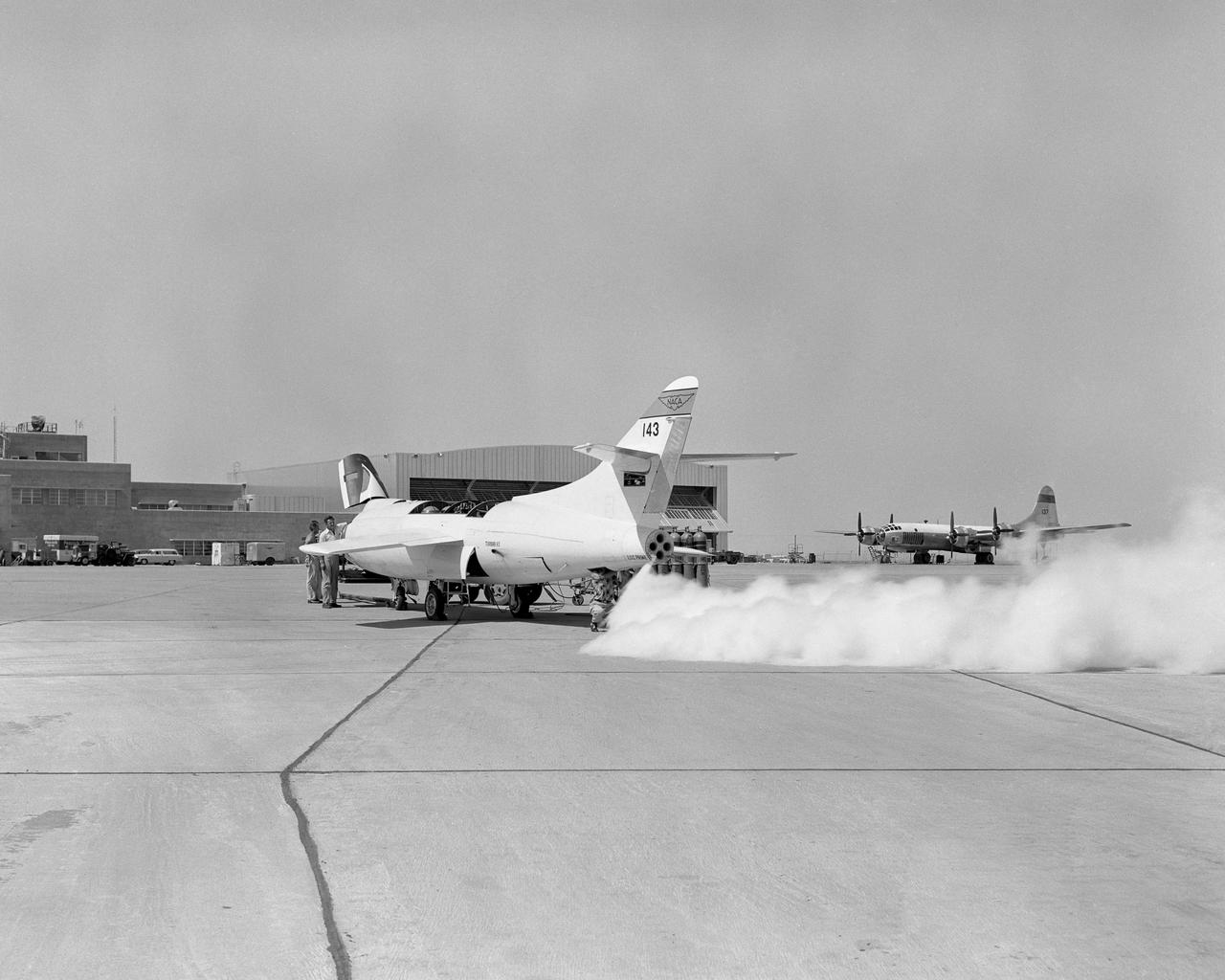

D558-2 #143 LOX jettison with P2BS in background
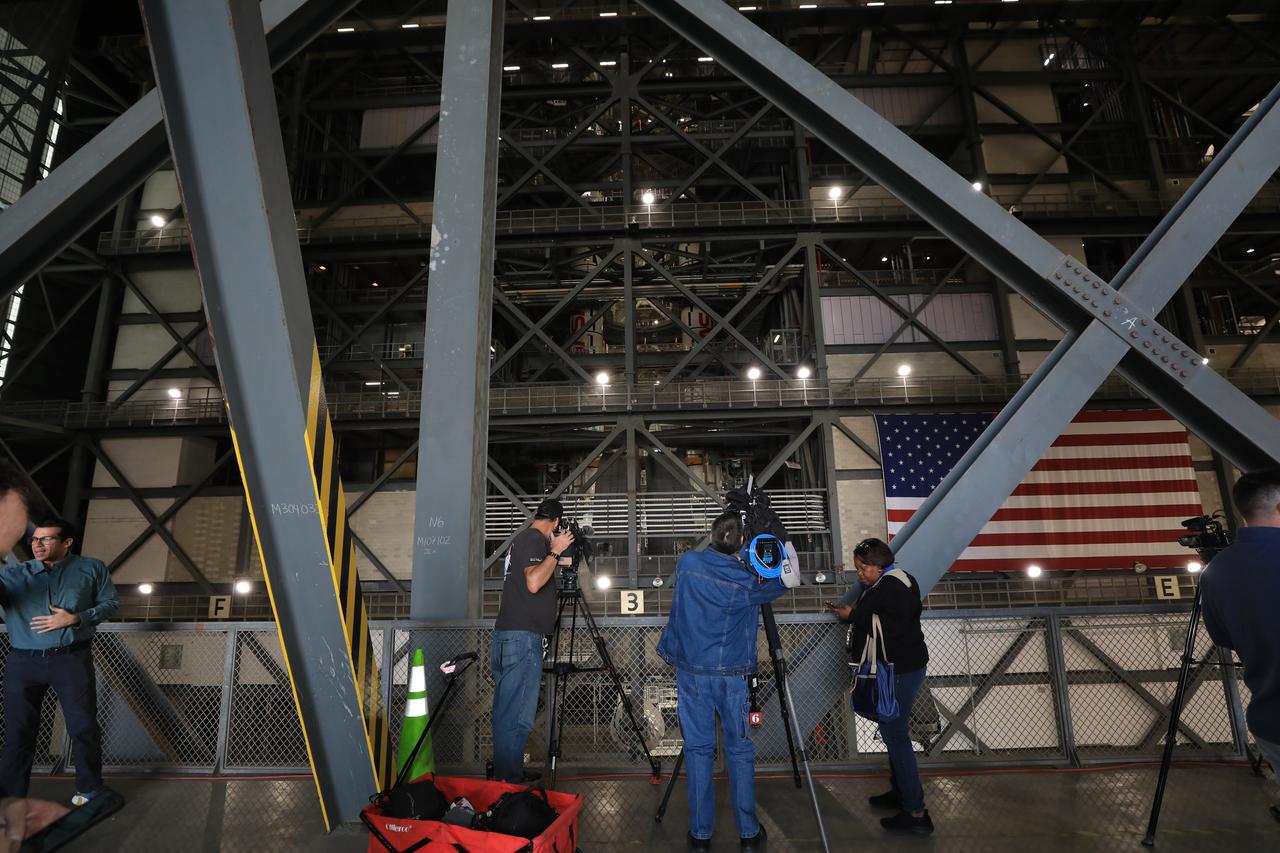

Members of the media get an up-close look at the integrated twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for Artemis II inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during Artemis Media Day on Friday, March 7, 2025. The twin solid boosters will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.

Members of the media get an up-close look at the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for Artemis II inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during Artemis Media Day on Friday, March 7, 2025. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II.
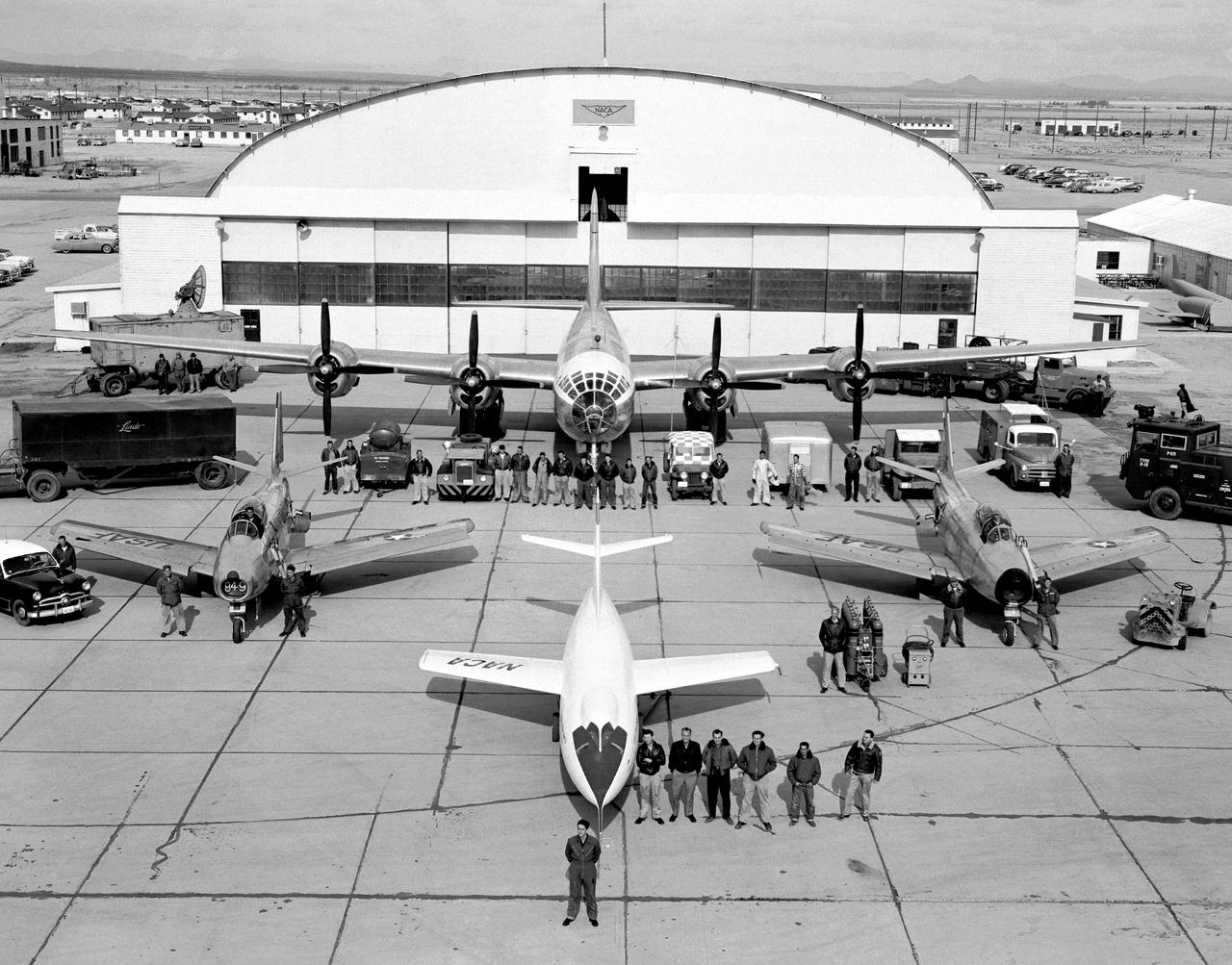

These people and this equipment supported the flight of the NACA D-558-2 Skyrocket at the High-Speed Flight Station at South Base, Edwards AFB. Note the two Sabre chase planes, the P2B-1S launch aircraft, and the profusion of ground support equipment, including communications, tracking, maintenance, and rescue vehicles. Research pilot A. Scott Crossfield stands in front of the Skyrocket.

Members of the media get an up-close look at the integrated twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for Artemis II inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during Artemis Media Day on Friday, March 7, 2025. The twin solid boosters will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.

Members of the media get an up-close look at the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for Artemis II inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during Artemis Media Day on Friday, March 7, 2025. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II.

Members of the media get an up-close look at the integrated twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for Artemis II inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during Artemis Media Day on Friday, March 7, 2025. The twin solid boosters will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.

Members of the media get an up-close look at the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for Artemis II inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during Artemis Media Day on Friday, March 7, 2025. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II.
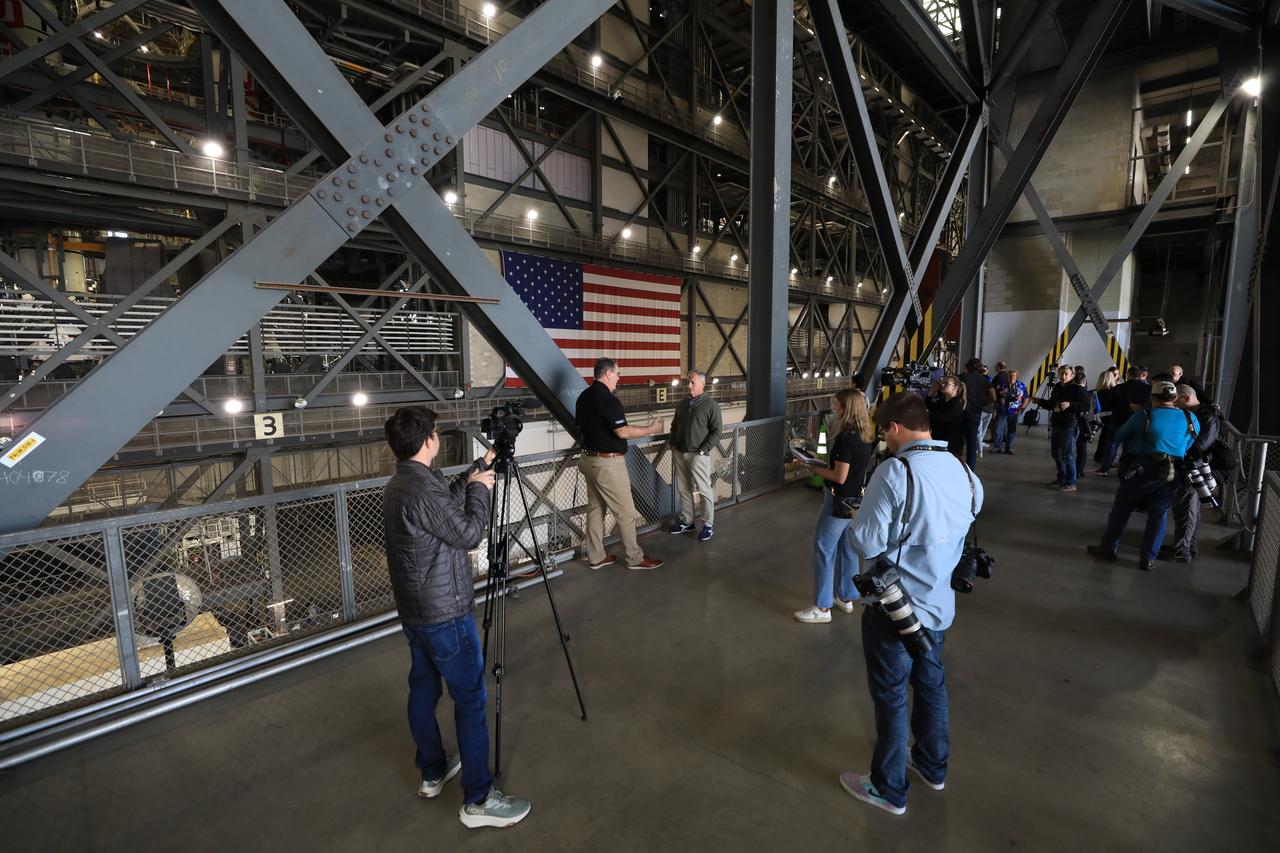

Members of the media get an up-close look at the integrated twin SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for Artemis II inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during Artemis Media Day on Friday, March 7, 2025. The twin solid boosters will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.