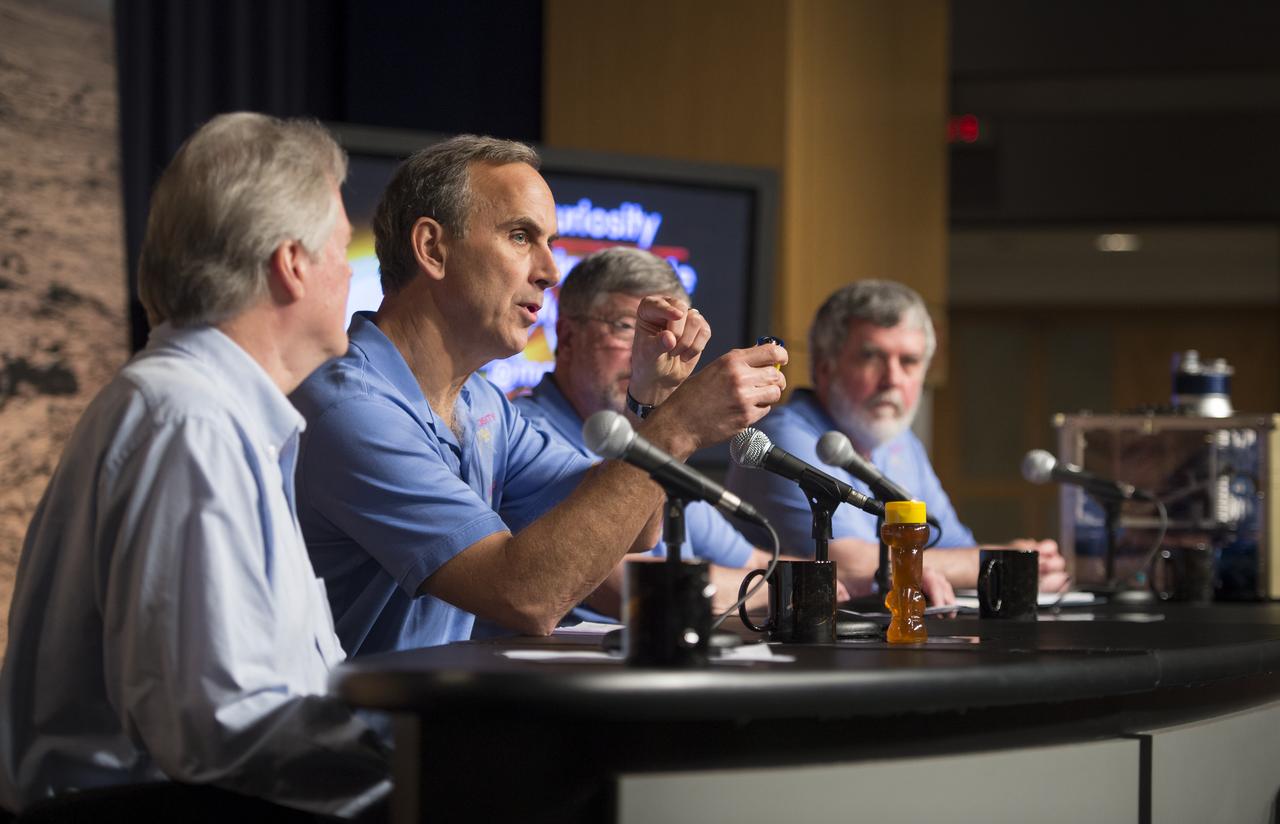

John Grotzinger (second from left), Curiosity project scientist, California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, speaks at a news conference presenting findings of the Curiosity rover's analysis of the first sample of rock powder collected on Mars, Tuesday, March 12, 2013 in Washington. The rock sample collected shows ancient Mars could have supported living microbes. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Michael Meyer (left), lead scientist, Mars Exploration Program at NASA Headquarters, speaks at a news conference presenting findings of the Curiosity rover's analysis of the first sample of rock powder collected on Mars, Tuesday, March 12, 2013 in Washington. The rock sample collected shows ancient Mars could have supported living microbes. John Grotzinger, Curiosity project scientist, California Institute of Technology is seen on the right. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
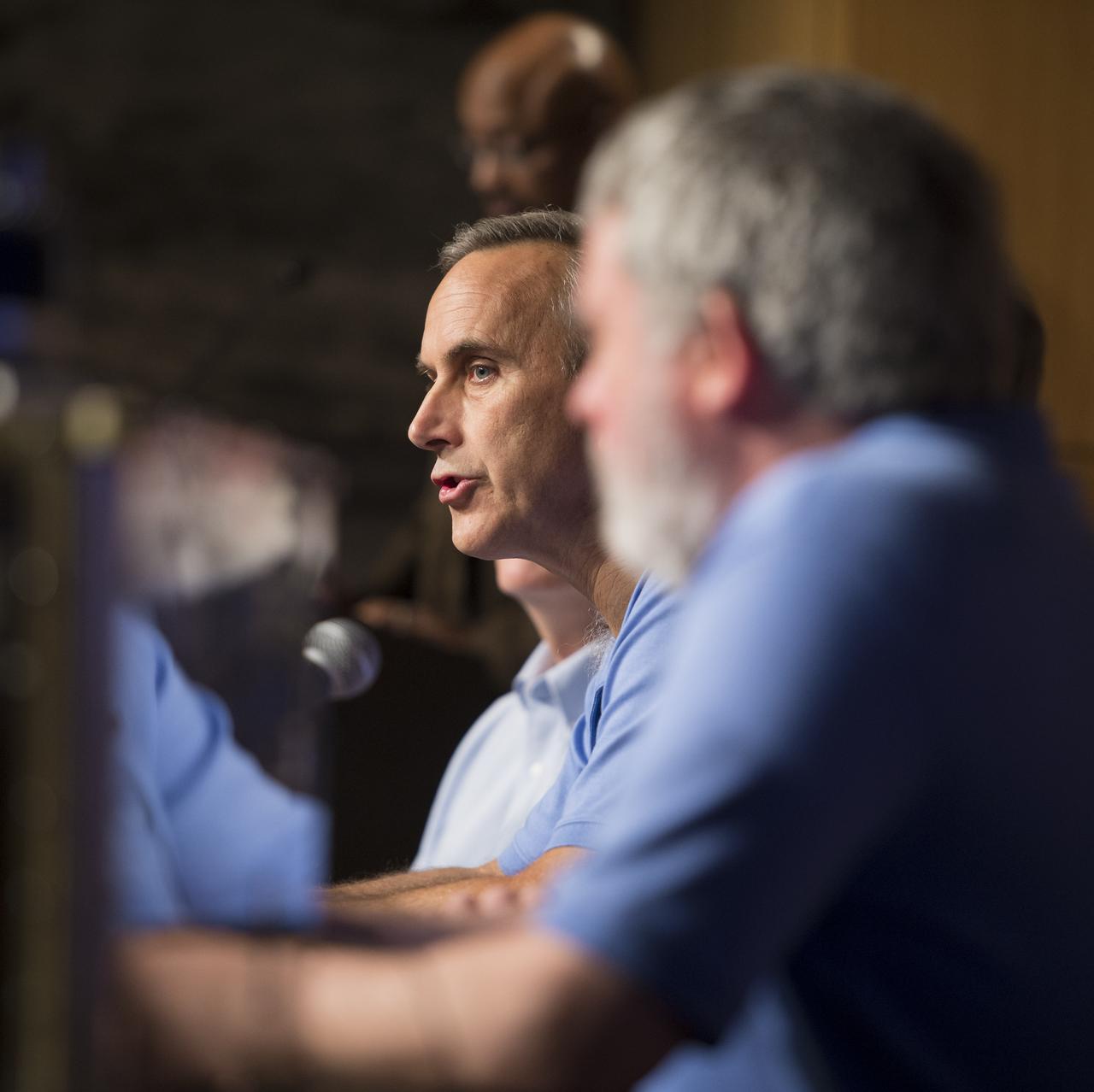

John Grotzinger (center), Curiosity project scientist, California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, speaks at a news conference presenting findings of the Curiosity rover's analysis of the first sample of rock powder collected on Mars, Tuesday, March 12, 2013 in Washington. The rock sample collected shows ancient Mars could have supported living microbes. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

John Grotzinger, Curiosity project scientist, California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, answers a reporter's question at a news conference where findings of the Curiosity rover's analysis of the first sample of rock powder collected on Mars were presented, Tuesday, March 12, 2013 in Washington. The rock sample collected shows ancient Mars could have supported living microbes. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
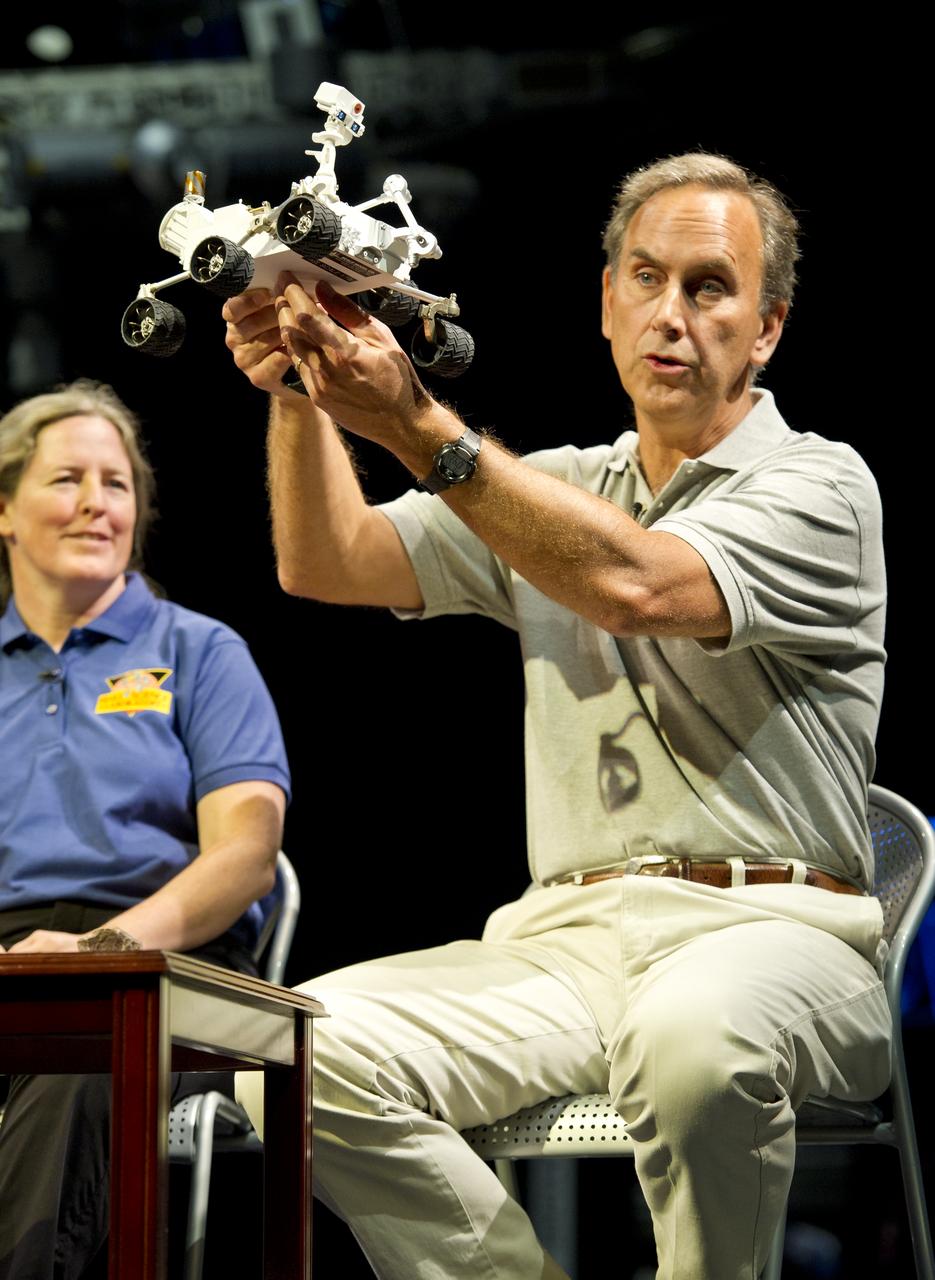

John Grotzinger, Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) project scientist, Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL), Pasadena, Calif., holds up a model of the MSL, or Curiosity, at a press conference at the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum on Friday, July 22, 2011 in Washington. The MSL is scheduled to launch late this year from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida and land in August 2012. Curiosity is twice as long and more than five times as heavy as previous Mars rovers. The rover will study whether the landing region at Gale crater had favorable environmental conditions for supporting microbial life and for preserving clues about whether life ever existed. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
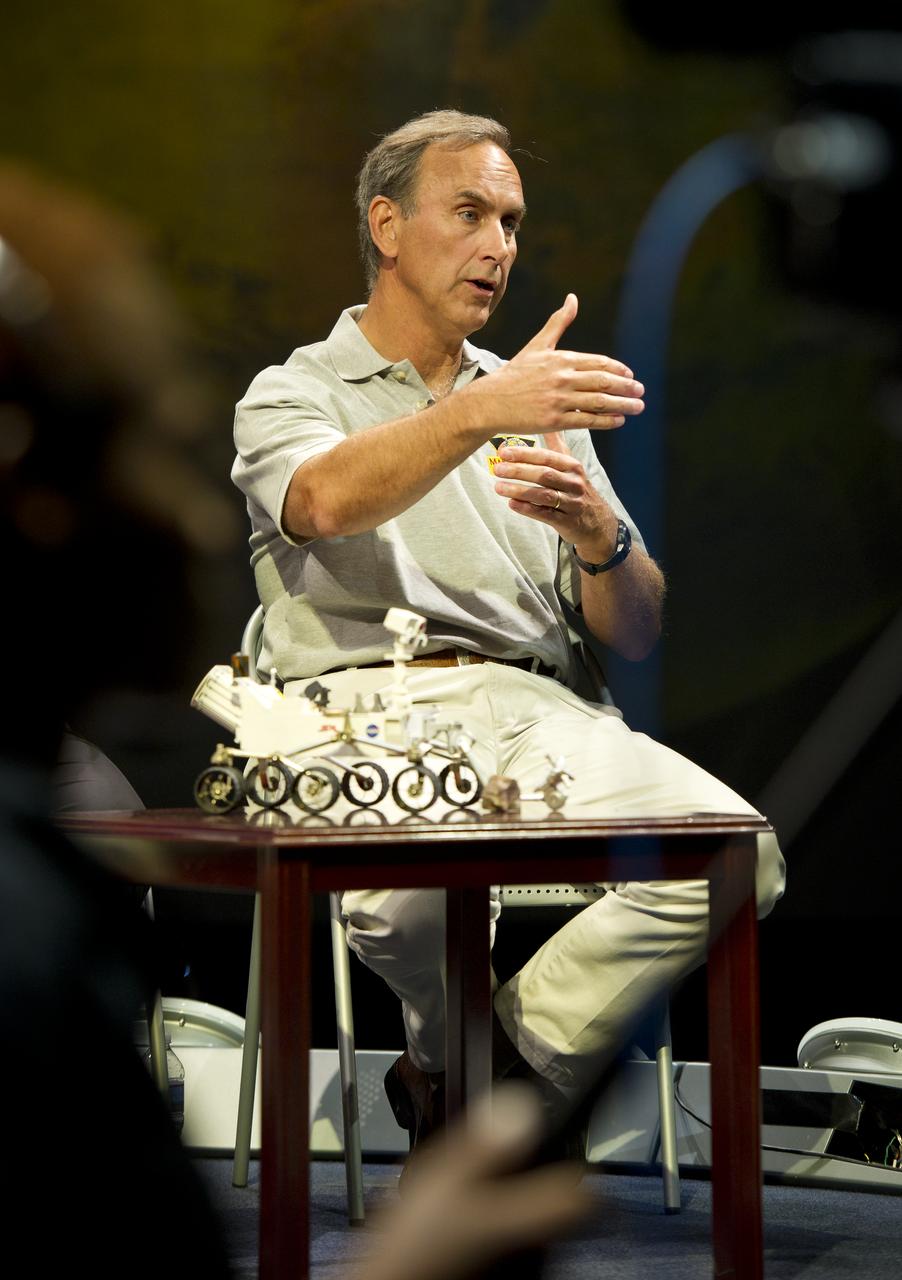

John Grotzinger, Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) project scientist, Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL), Pasadena, Calif., answers a reporter's question at a press conference at the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum on Friday, July 22, 2011 in Washington. The MSL is scheduled to launch late this year from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida and land in August 2012. Curiosity is twice as long and more than five times as heavy as previous Mars rovers. The rover will study whether the landing region at Gale crater had favorable environmental conditions for supporting microbial life and for preserving clues about whether life ever existed. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
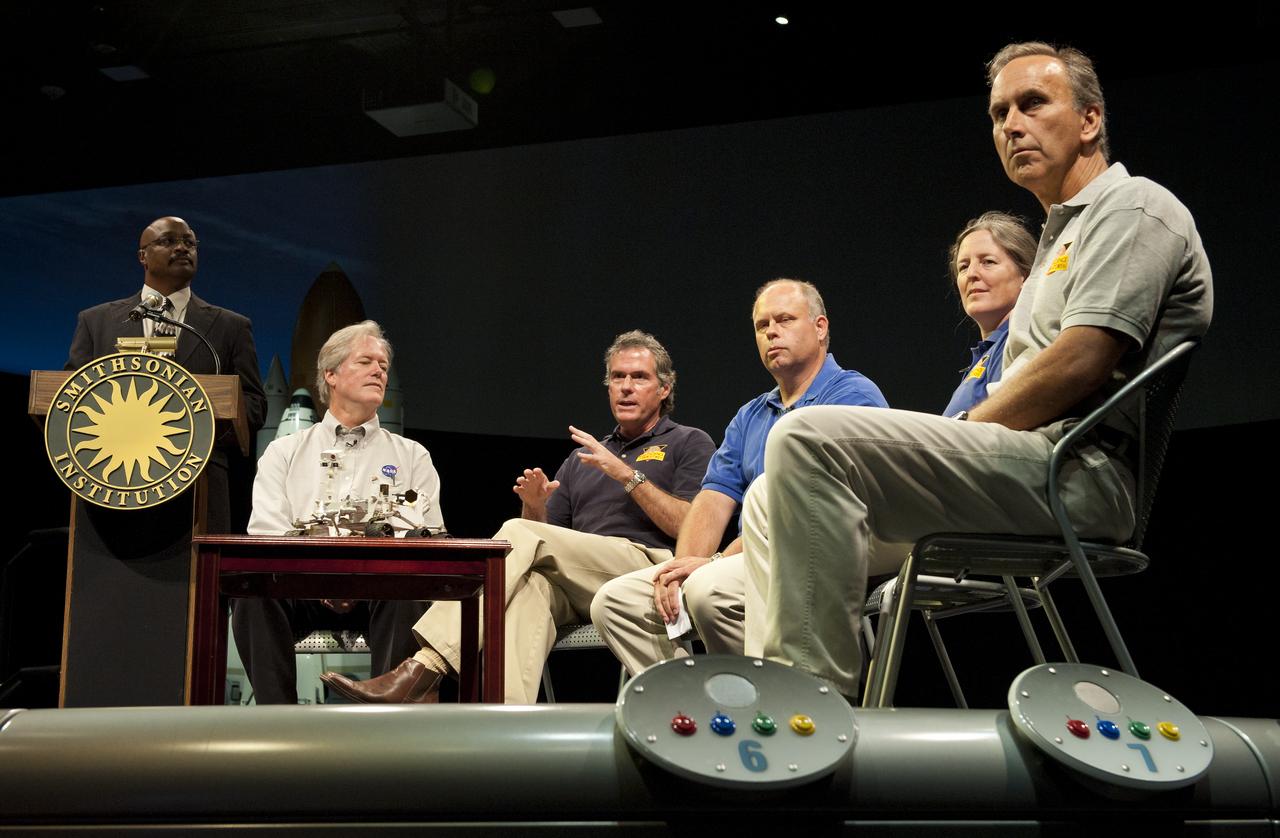

Michael Watkins (third from left), mission manager and project engineer, Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), Jet Propulsion Lab, Pasadena, Calif., speaks at a press conference at the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum on Friday, July 22, 2011 in Washington. From left to right, Watkins is joined by Dwayne Brown, NASA Headquarters public affairs officer; Michael Meyer, lead scientist Mars Exploration Program, NASA Headquarters; Watkins; John Grant, geologist, Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington; Dawn Sumner, geologist, University of California, Davis and John Grotzinger, MSL project scientist, JPL. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

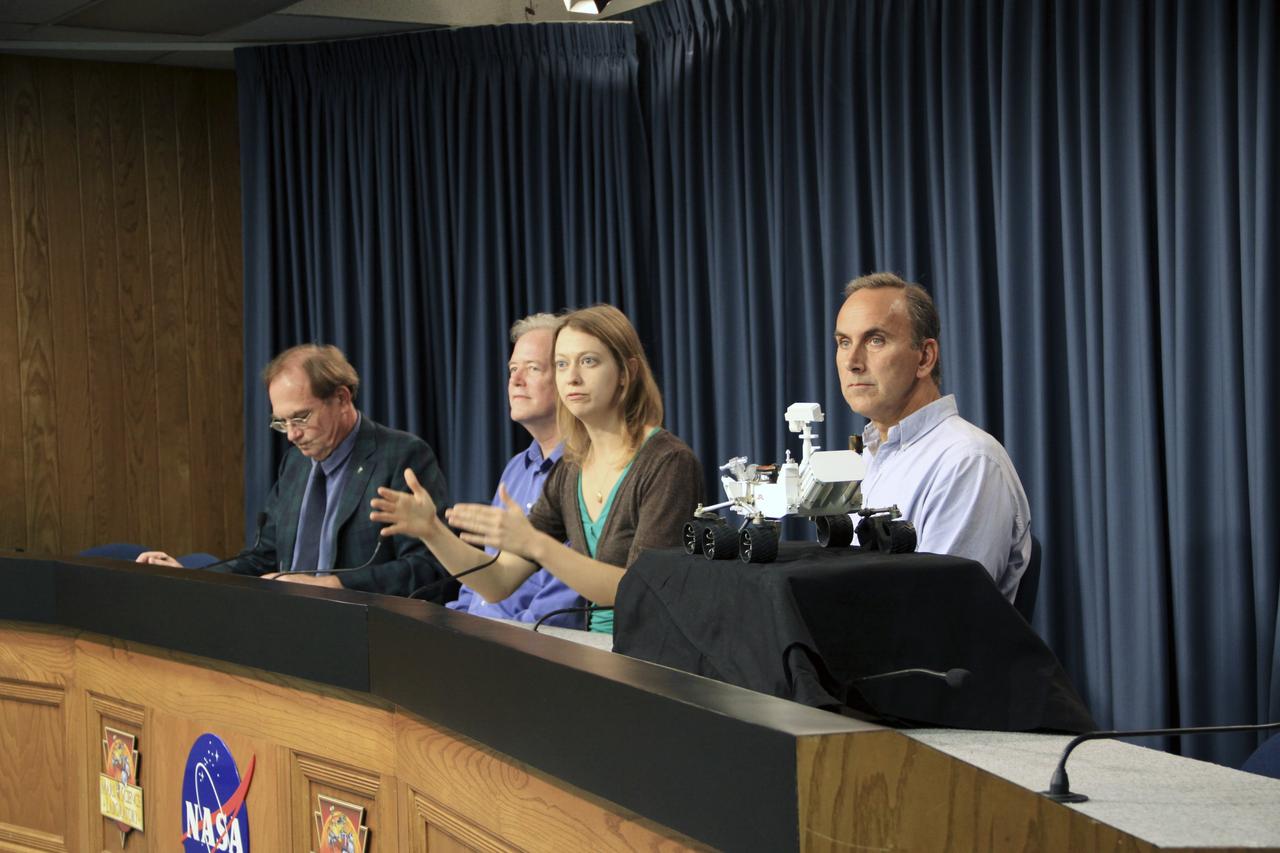
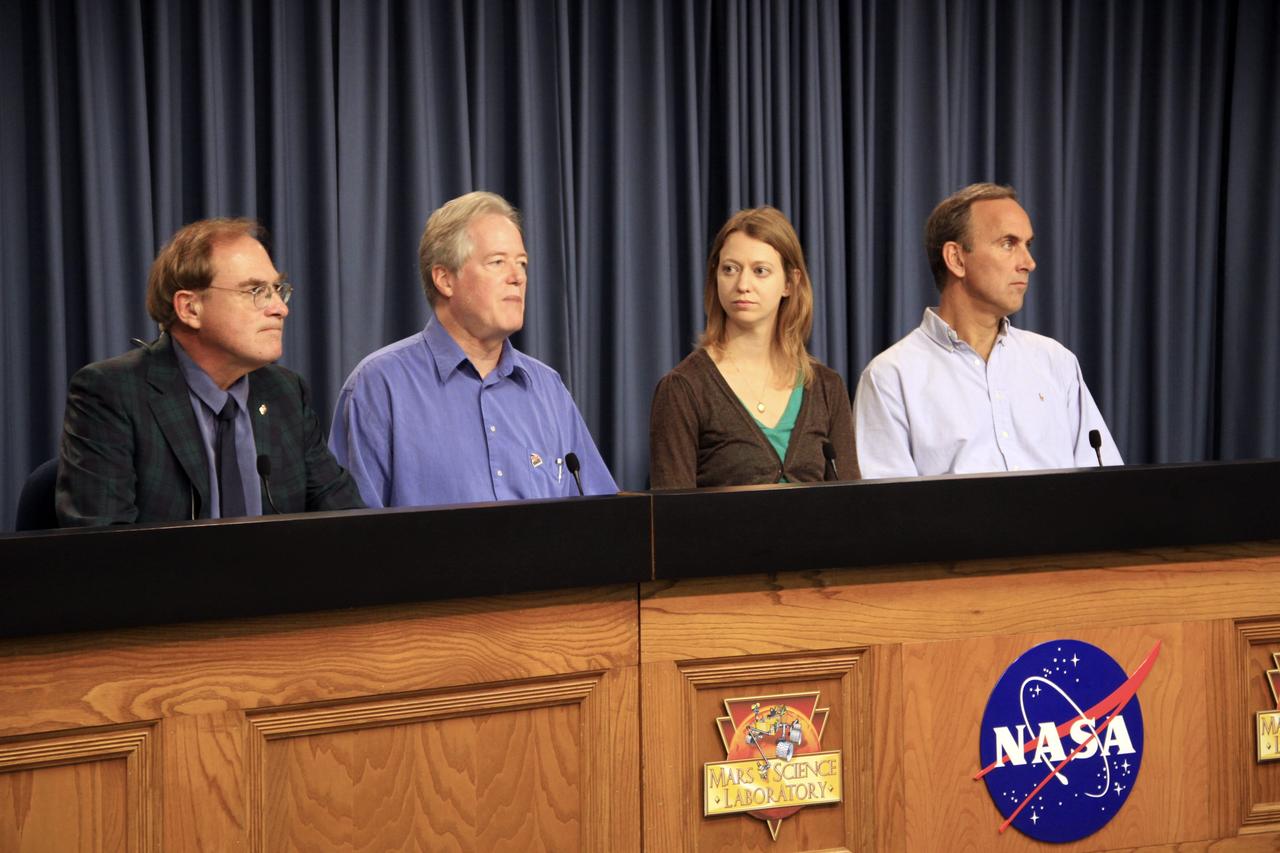
Participants at a news conference discussing findings of the analysis of a rock sample from Mars are seen, Tuesday, March 12, 2013 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. From left to right are seen: Michael Meyer, lead scientist, Mars Exploration Program at NASA Headquarters; John Grotzinger, Curiosity project scientist, California Institute of Technology in Pasadena; David Blake, principal investigator for Curiosity's Chemistry and Mineralogy investigation at NASA's Ames Research Center in Calif.; and Paul Mahaffy, principal investigator for Curiosity's Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) investigation at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

John Grunsfeld (at podium), Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, asks one last question of the Mars Curiosity rover panel, Tuesday, March 12, 2013 in Washington. The news conference covered the findings that the analysis of the rock sample collected shows ancient Mars could have supported living microbes. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
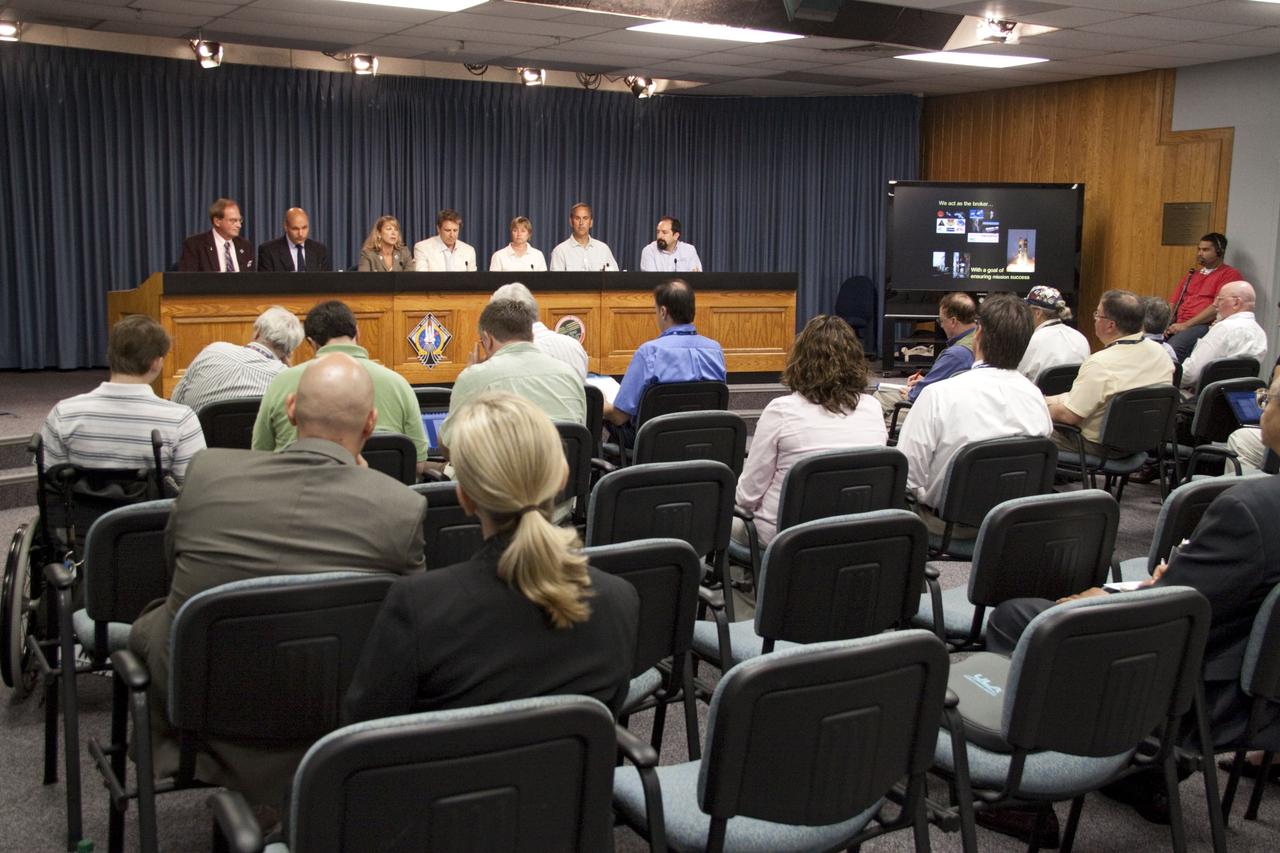

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, media were briefed about NASA's future science missions. Seen here are NASA Public Affairs Officer George Diller (left); Waleed Abdalati, NASA chief scientist; Amanda Mitskevich, NASA Launch Services Program manager; Scott Bolton, Juno principal investigator with the Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio; Maria Zuber, GRAIL principal investigator with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology; John Grotzinger, Mars Science Lab project scientist with the California Institute of Technology and Daniel Stern, NuStar project scientist with NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Calif. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
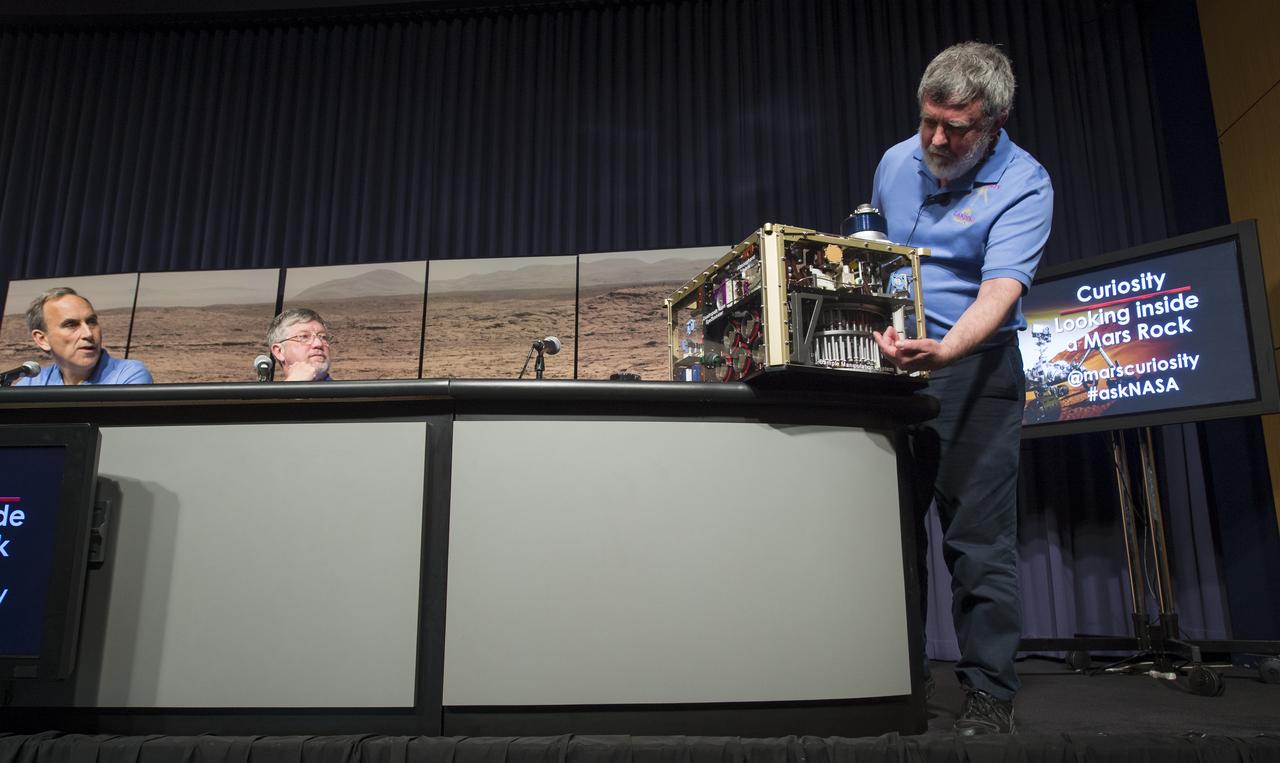

Paul Mahaffy (right), principal investigator for Curiosity's Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) investigation at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland, demonstrates how the SAM instrument drilled and captured rock samples on the surface of Mars at a news conference, Tuesday, March 12, 2013 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The analysis of the rock sample collected shows ancient Mars could have supported living microbes. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
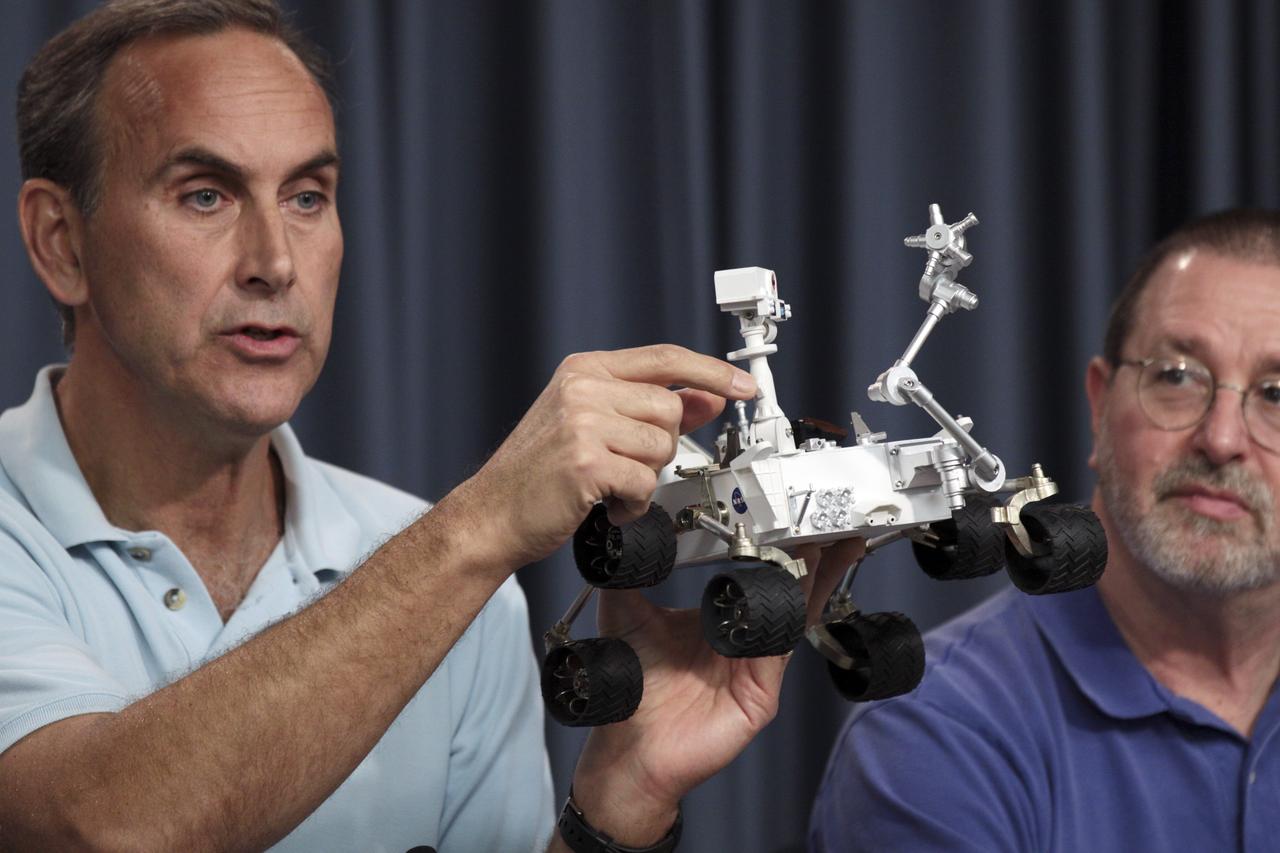

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – John Grotzinger, project scientist for Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, Calif., demonstrates the operation of MSL's rover, Curiosity, during a science briefing at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, part of preflight activities for the MSL mission. Michael Malin, principal investigator for the Mast Camera and Mars Descent Imager investigations on Curiosity from Malin Space Science Systems, looks on at right. MSL’s components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Scientist and Assistant Professor Bethany Ehlmann with the California Institute of Technology and Jet Propulsion Laboratory, answers a question from the media during a “What Do We Know About Mars” news conference, Nov. 21. The press conference was part of preflight activities for the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. NASA Public Affairs Officer George Diller, at left, moderates the conference that also features Lead Scientist Michael Meyer, Mars Exploration Program and Mars Science Laboratory Project Scientist John Grotzinger from the California Institute of Technology. MSL’s components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
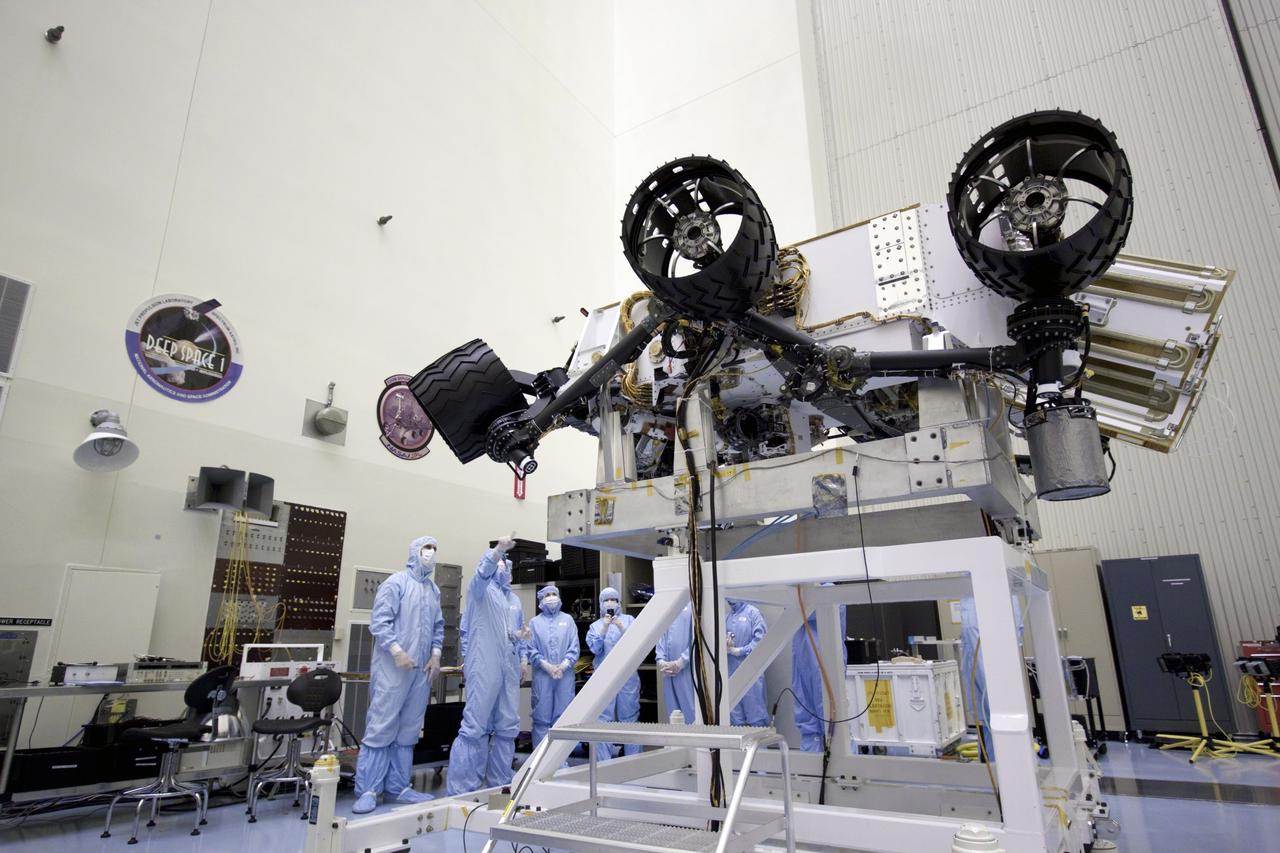

Cape Canaveral, Fla. - At the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, John Grotzinger, project scientist for NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover known as Curiosity, points out components of the rover to NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver, to his right. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida Nov. 25 with a window extending to Dec. 18 and arrival at Mars Aug. 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is host to a “What Do We Know About Mars” news conference, Nov. 21, as part of preflight activities for the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. NASA Public Affairs Officer George Diller, at left, moderates the conference featuring Lead Scientist Michael Meyer, Mars Exploration Program; Scientist and Assistant Professor Bethany Ehlmann with the California Institute of Technology and Jet Propulsion Laboratory; and Mars Science Laboratory Project Scientist John Grotzinger from the California Institute of Technology. MSL’s components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
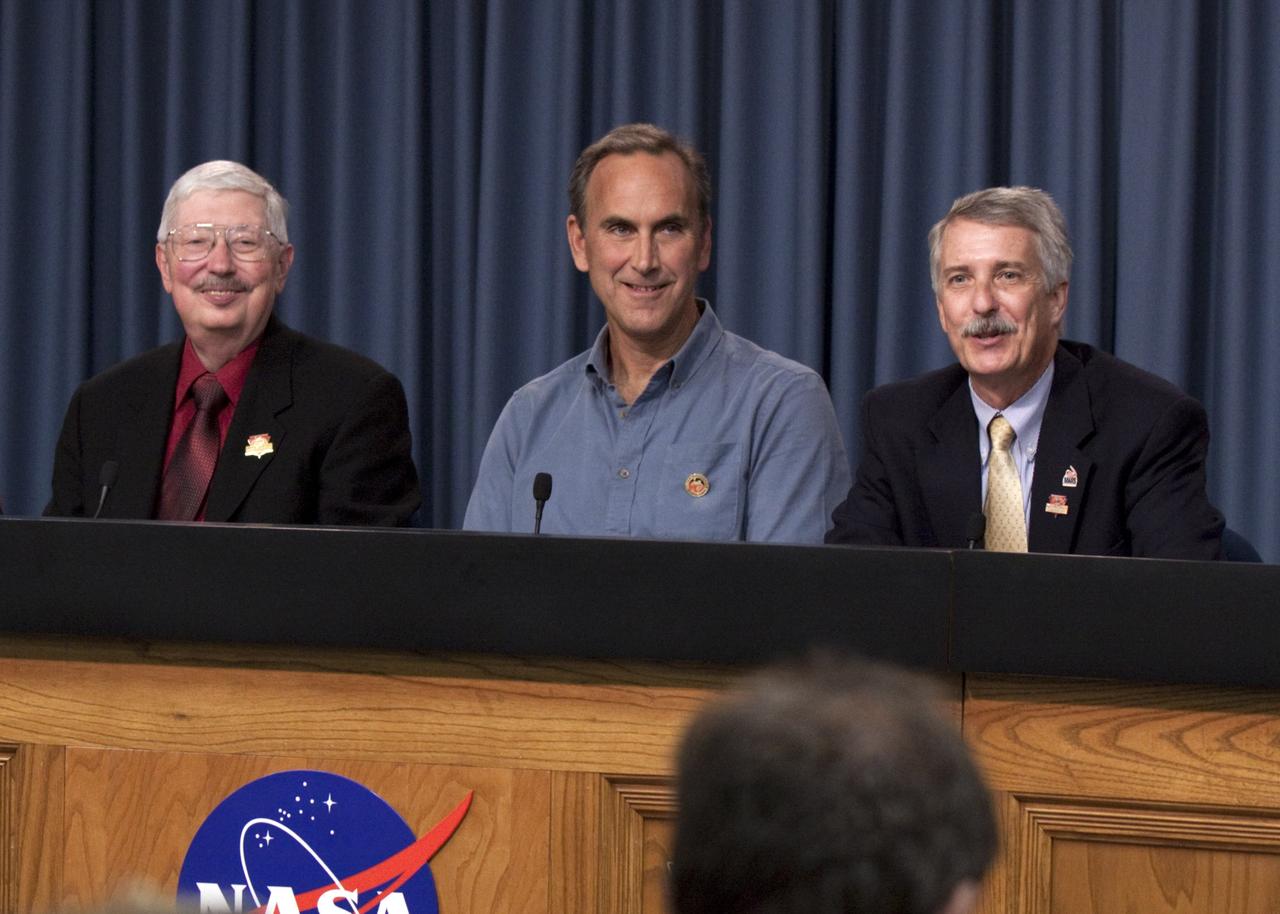

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A trio of panelists awaits the start of a post-launch news conference at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the successful launch of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. From left are Pete Theisinger, MSL project manager at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif.; John Grotzinger, MSL project scientist at the California Institute of Technology, also in Pasadena; and Doug McCuisition, director of the Mars Exploration Program at NASA Headquarters. MSL lifted off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 10:02 a.m. EST Nov. 26. MSL's components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
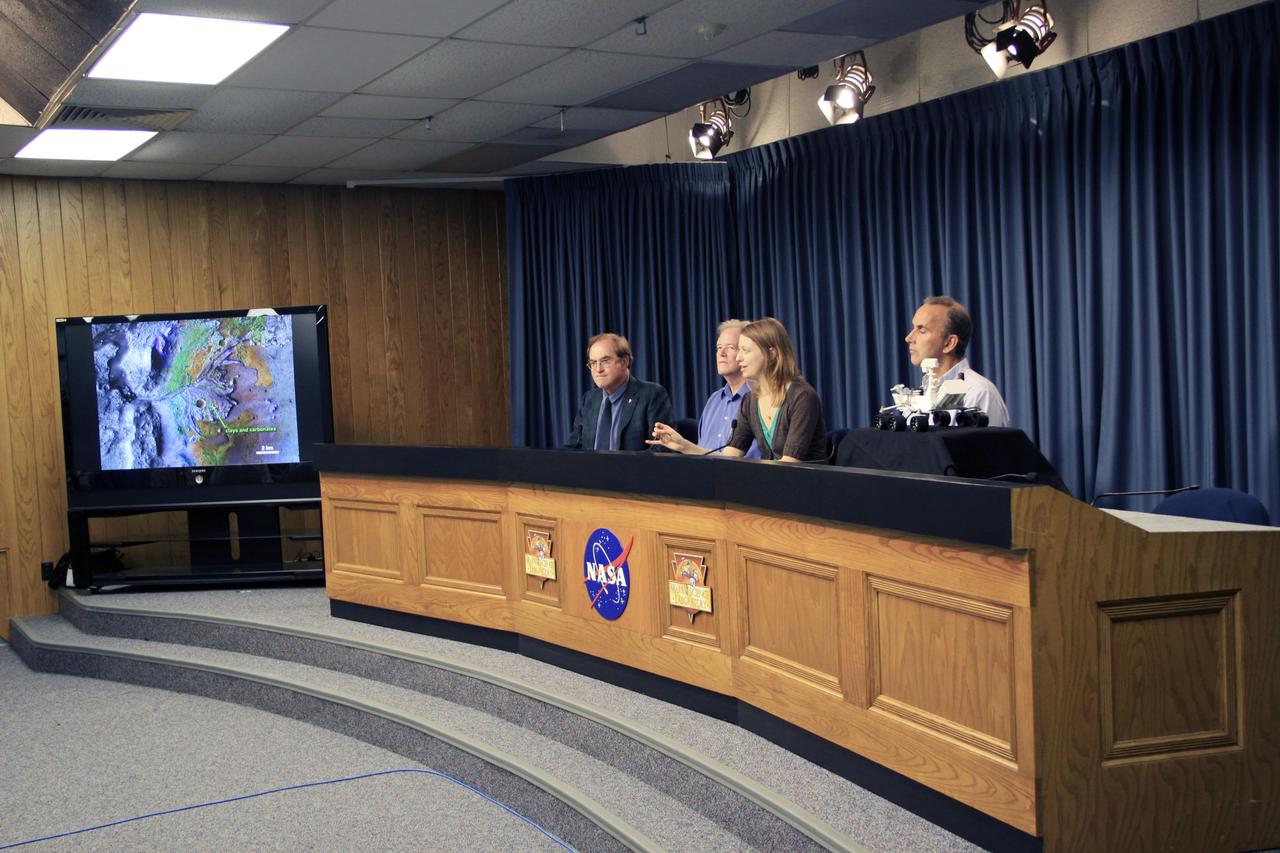

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Scientist and Assistant Professor Bethany Ehlmann with the California Institute of Technology and Jet Propulsion Laboratory, answers a question from the media during a “What Do We Know About Mars” news conference, Nov. 21. The press conference was part of preflight activities for the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. NASA Public Affairs Officer George Diller, at left, moderates the conference that also features Lead Scientist Michael Meyer, Mars Exploration Program and Mars Science Laboratory Project Scientist John Grotzinger from the California Institute of Technology. MSL’s components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
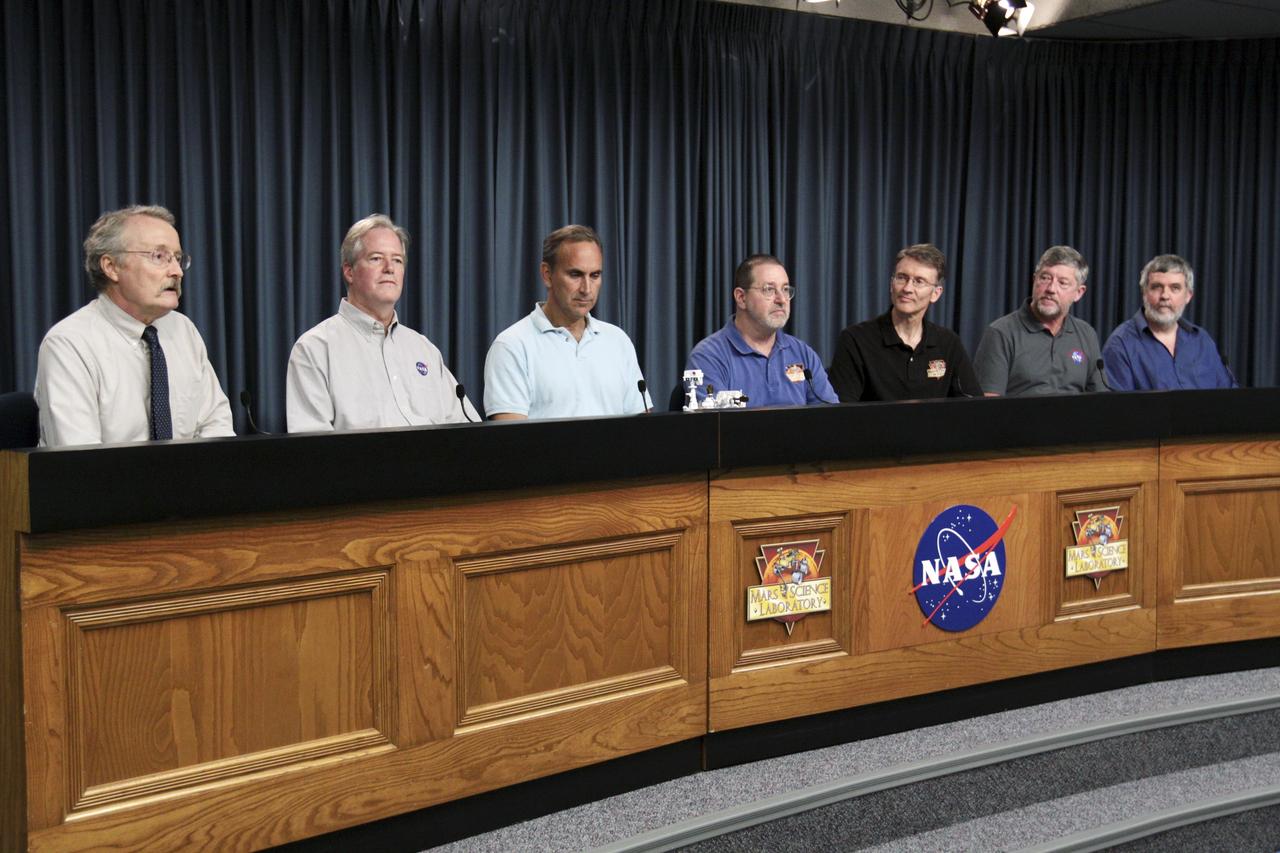

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is host to a Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) science briefing as part of preflight activities for the MSL mission. From left, NASA Public Affairs Officer Guy Webster moderates the conference featuring Michael Meyer, lead scientist for NASA Mars Exploration Program; John Grotzinger, project scientist for Mars Science Laboratory California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, Calif.; Michael Malin, principal investigator for the Mast Camera and Mars Descent Imager investigations on Curiosity, Malin Space Science Systems; Roger Wiens, principal investigator for Chemistry and Camera investigation on Curiosity, Los Alamos National Laboratory; David Blake, NASA principal investigator for Chemistry and Mineralogy investigation on Curiosity, NASA Ames Research Center; and Paul Mahaffy, NASA principal investigator for Sample Analysis at Mars investigation on Curiosity, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. MSL’s components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
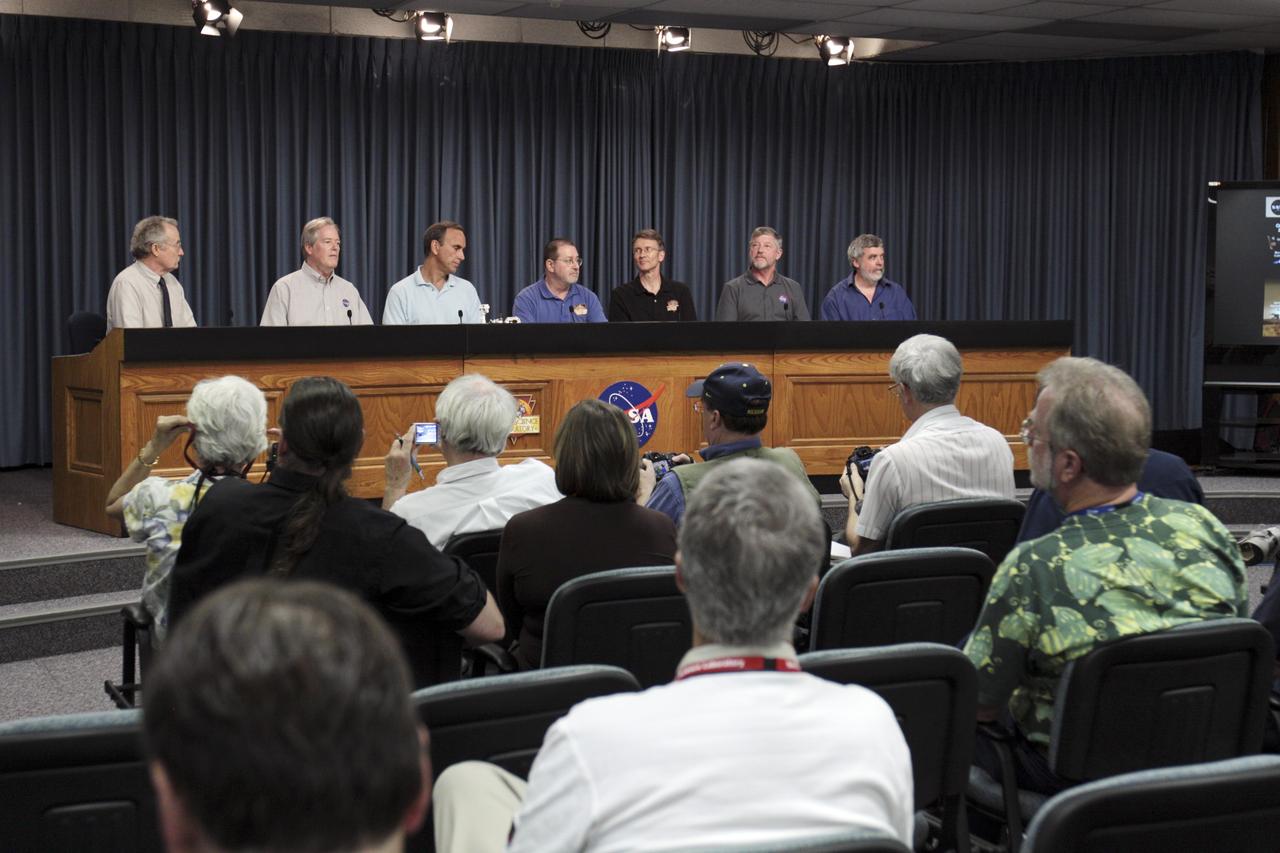

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is host to a Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) science briefing as part of preflight activities for the MSL mission. From left, NASA Public Affairs Officer Guy Webster moderates the conference featuring Michael Meyer, lead scientist for NASA Mars Exploration Program; John Grotzinger, project scientist for Mars Science Laboratory California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, Calif.; Michael Malin, principal investigator for the Mast Camera and Mars Descent Imager investigations on Curiosity, Malin Space Science Systems; Roger Wiens, principal investigator for Chemistry and Camera investigation on Curiosity, Los Alamos National Laboratory; David Blake, NASA principal investigator for Chemistry and Mineralogy investigation on Curiosity, NASA Ames Research Center; and Paul Mahaffy, NASA principal investigator for Sample Analysis at Mars investigation on Curiosity, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. MSL’s components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
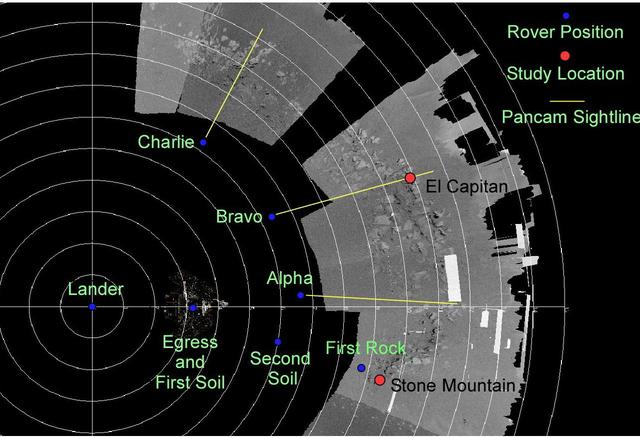
Opportunity Path