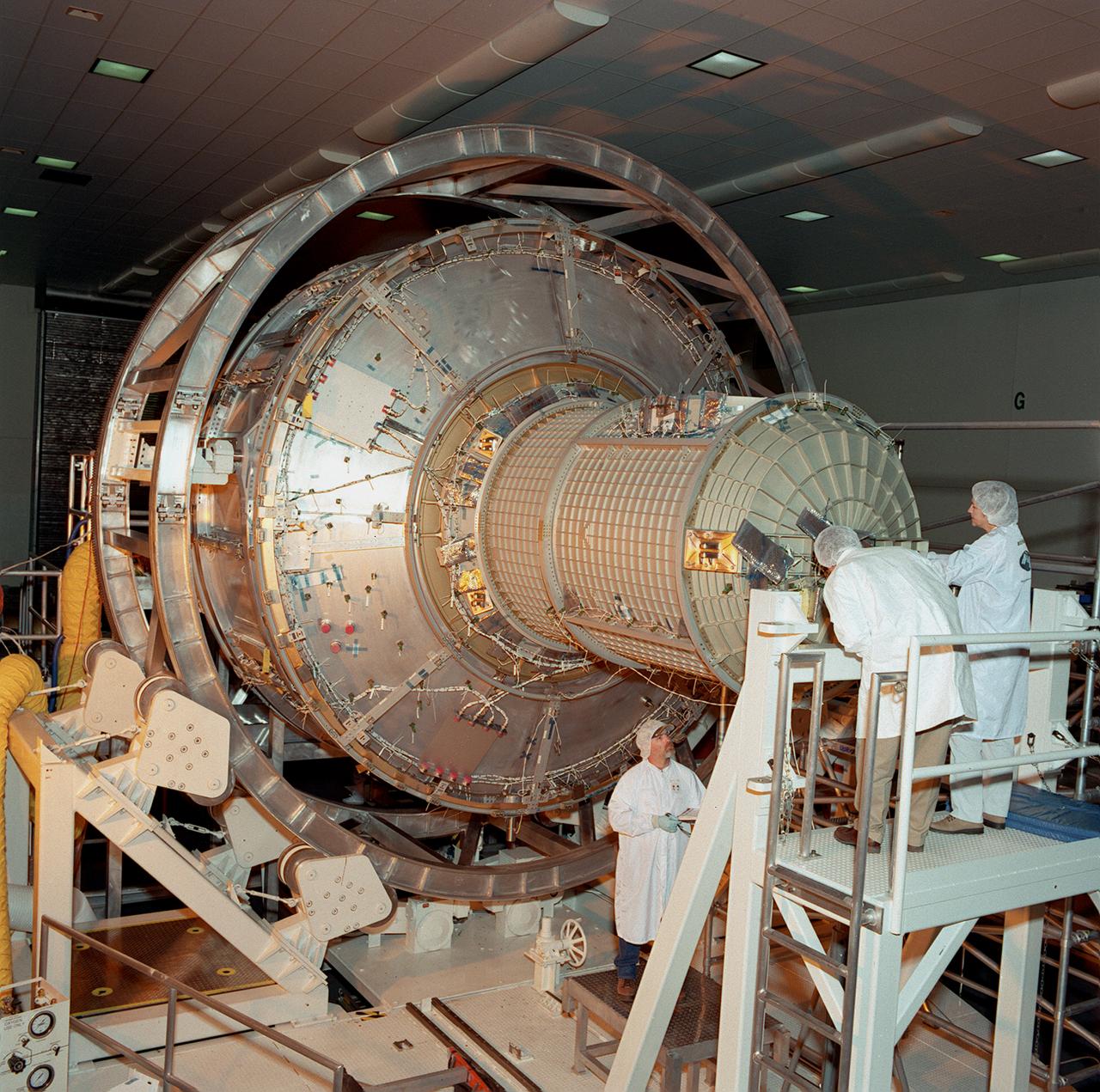

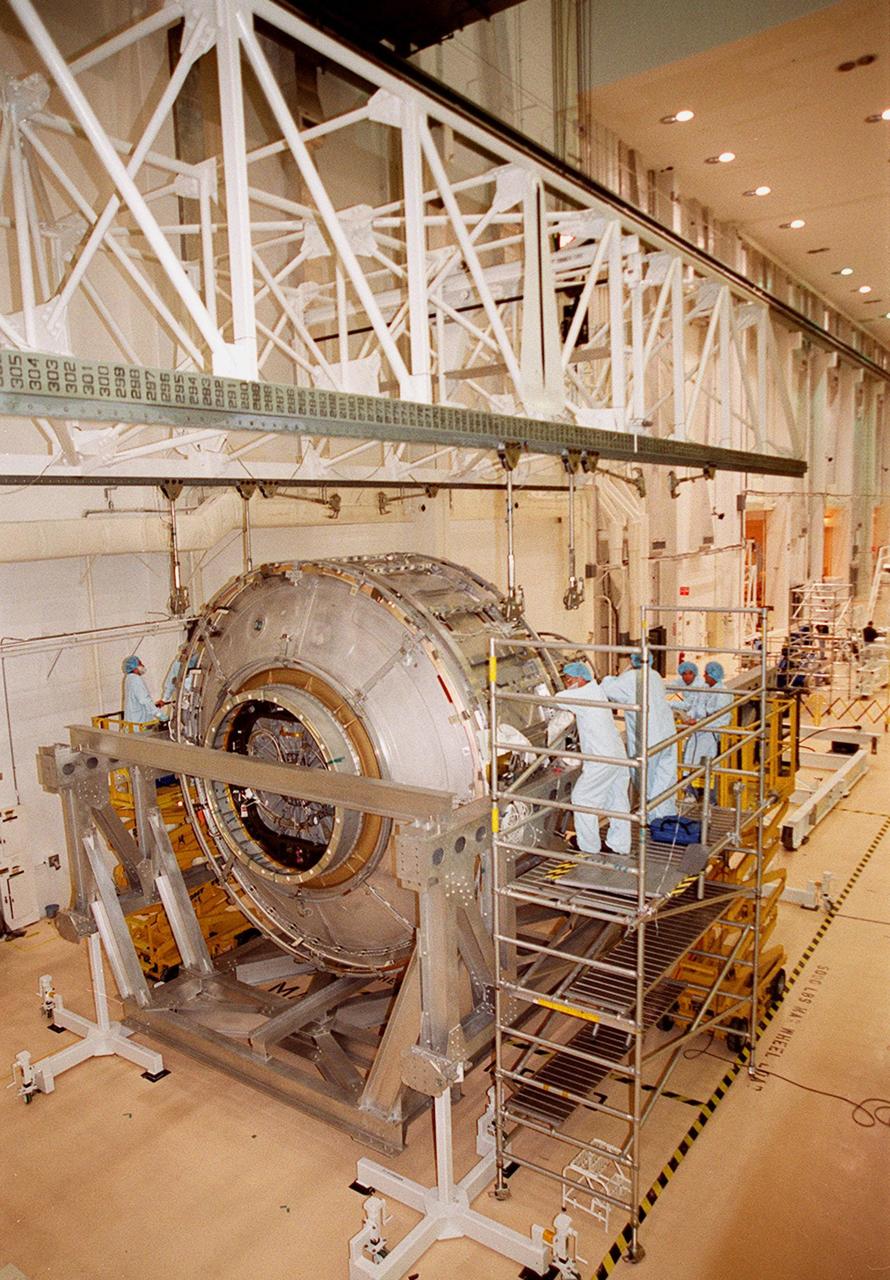
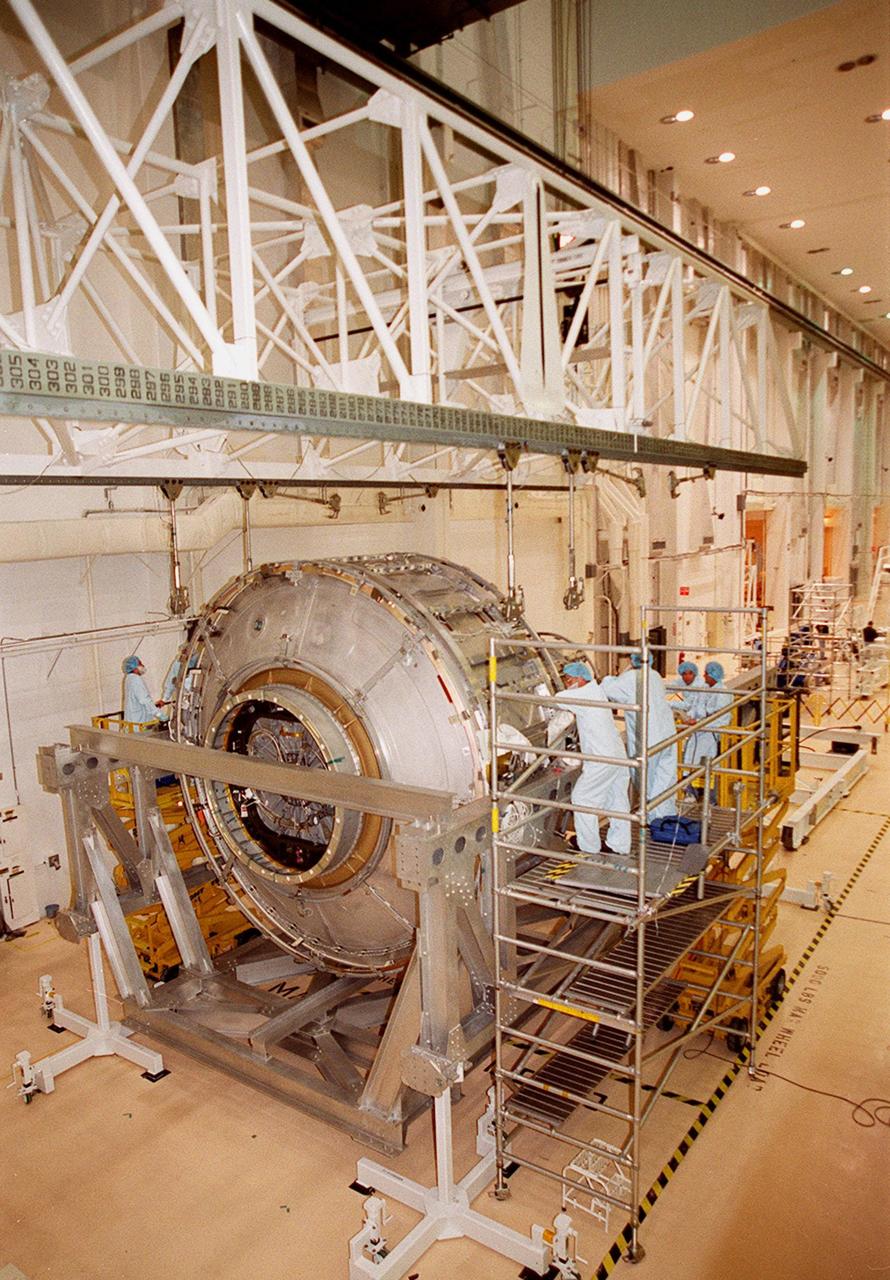
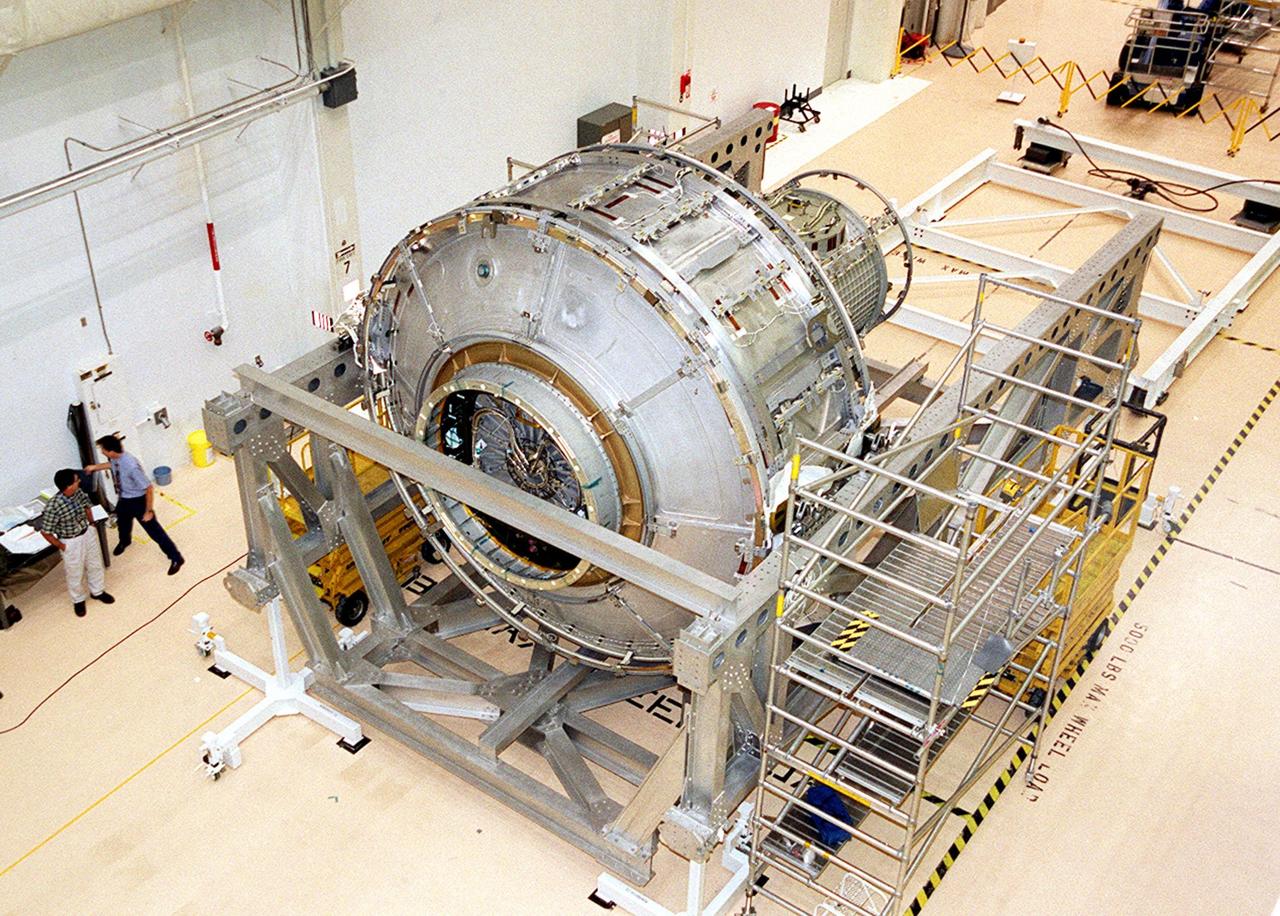
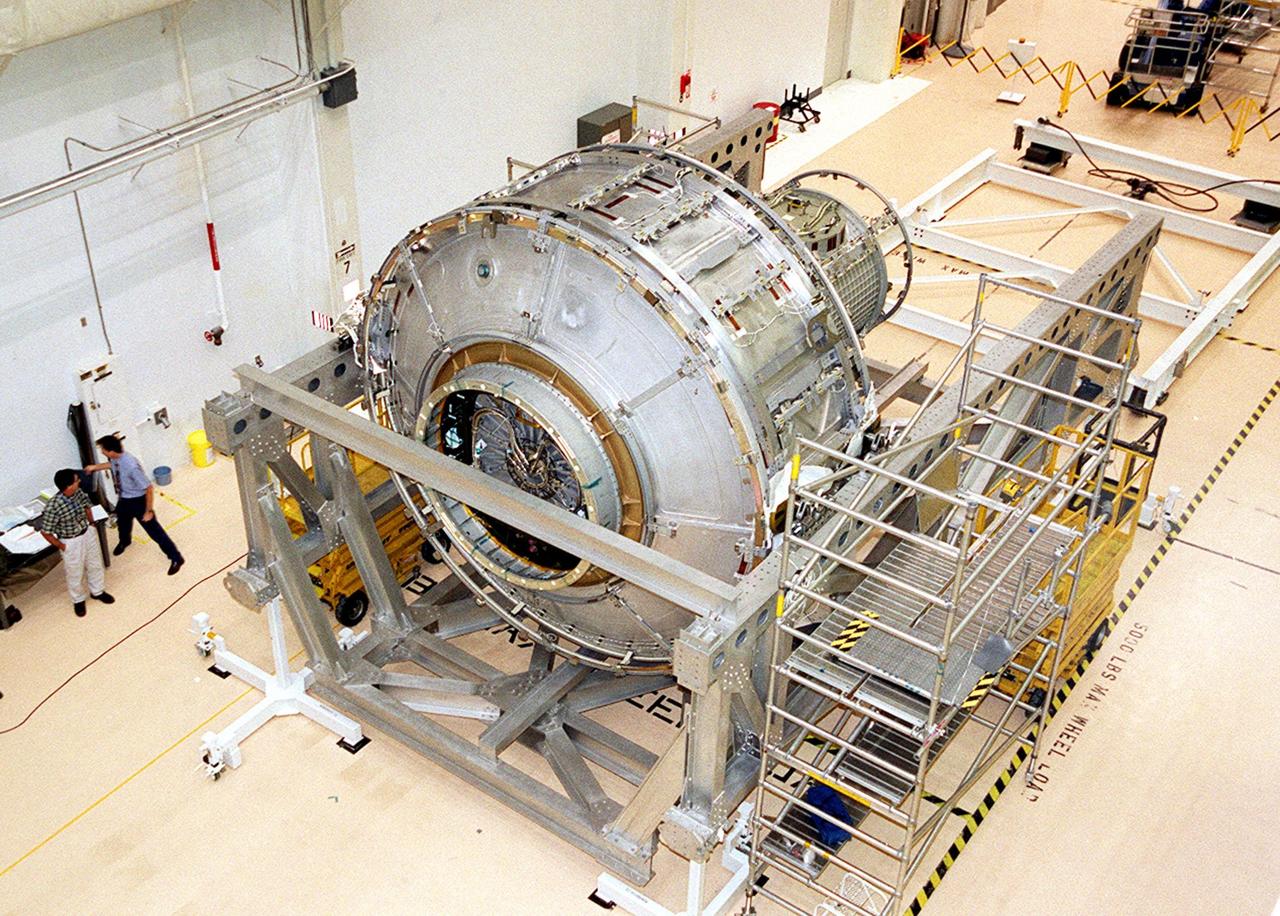
This photograph depicts the International Space Station's (ISS) Joint Airlock Module undergoing exhaustive structural and systems testing in the Space Station manufacturing facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) prior to shipment to the Kennedy Space Center. The Airlock includes two sections. The larger equipment lock, on the left, will store spacesuits and associated gear and the narrower crewlock is on the right, from which the astronauts will exit into space for extravehicular activity. The airlock is 18 feet long and has a mass of about 13,500 pounds. It was launched to the station aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Atlantis (STS-104 mission) on July 12, 2001. The MSFC is playing a primary role in NASA's development, manufacturing, and operations of the ISS.
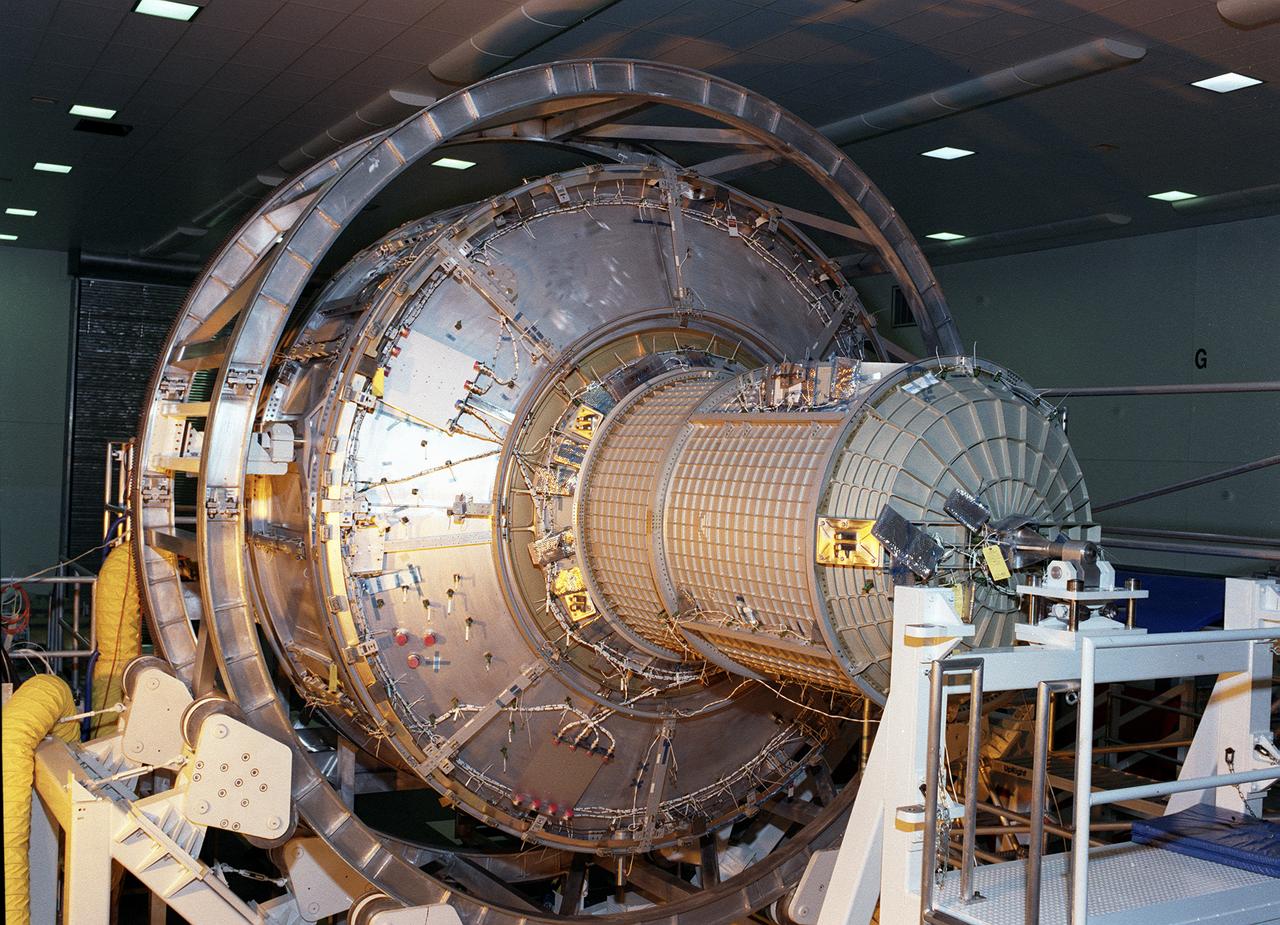
The Joint Airlock Module for the International Space Station (ISS) awaits shipment to the Kennedy Space Center in the Space Station manufacturing facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The Airlock includes two sections. The larger equipment lock on the left is where crews will change into and out of their spacesuits for extravehicular activities, and store spacesuits, batteries, power tools, and other supplies. The narrower crewlock from which the astronauts will exit into space for extravehicular activities, is on the right. The airlock is 18 feet long and has a mass of about 13,500 pounds. It was launched to the station aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Atlantis (STS-104 mission) on July 12, 2001. The MSFC is playing a primary role in NASA's development, manufacturing, and operations of the ISS.
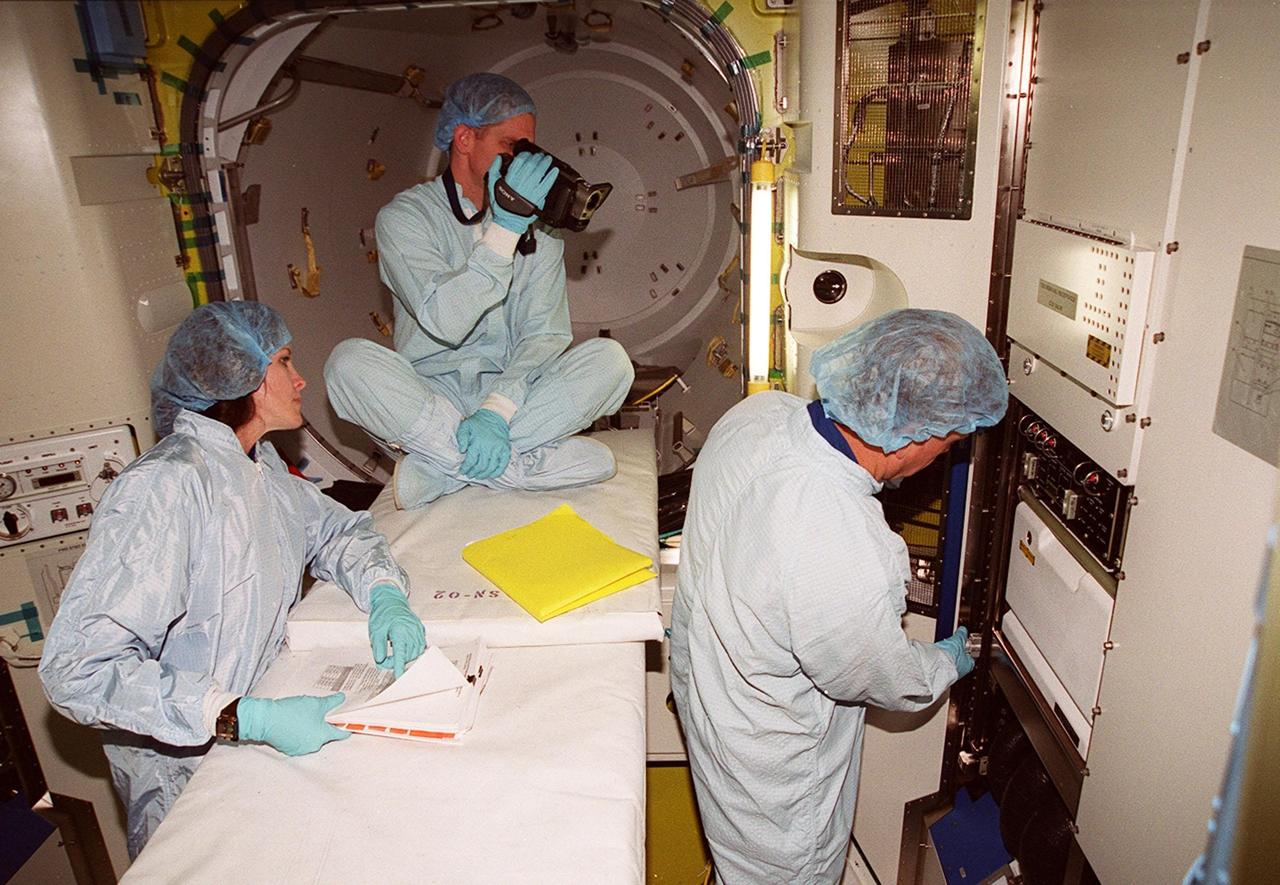
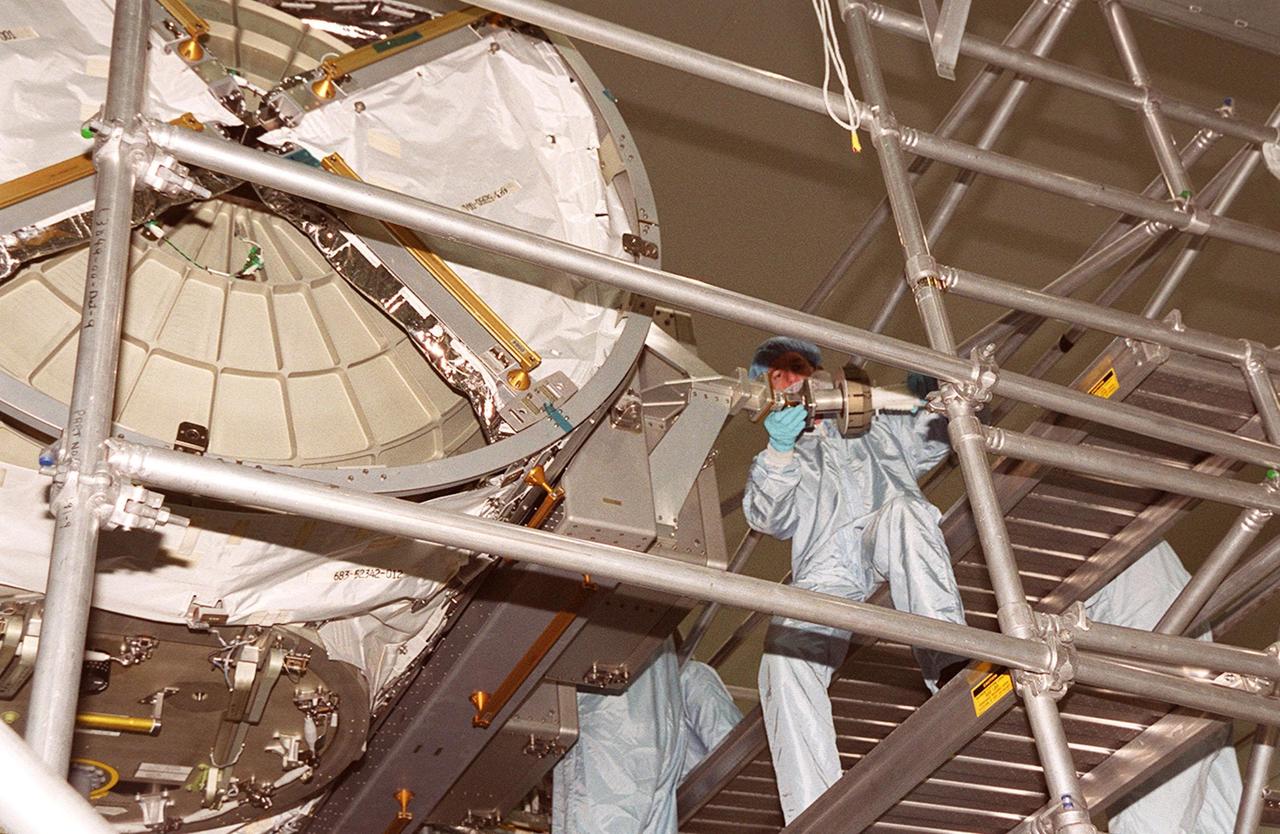
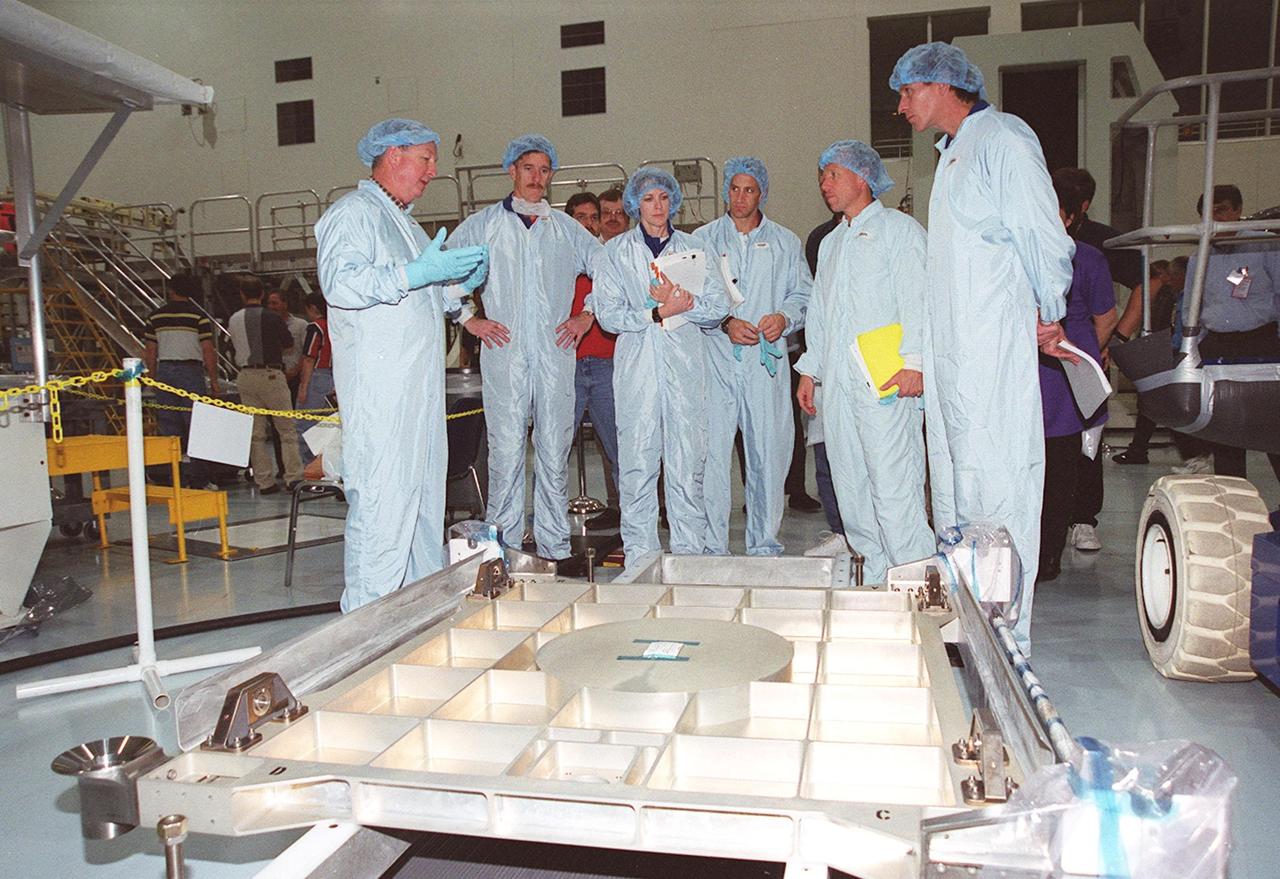
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-104 crew look over equipment inside the equipment lock component of the Joint Airlock Module. At left is Mission Specialist Janet L. Kavandi, and at right Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. The mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which also comprises a crew lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
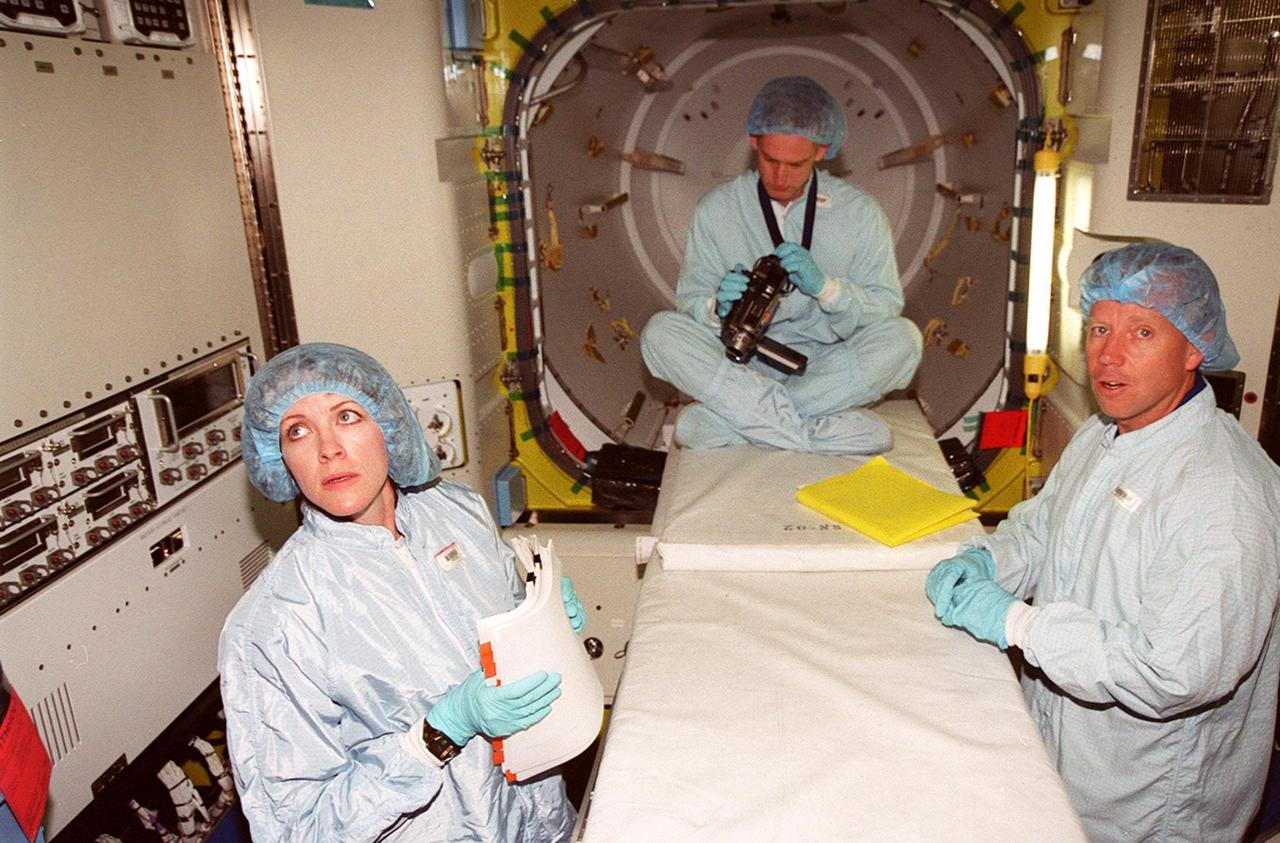
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-104 crew look over equipment inside the equipment lock component of the Joint Airlock Module. At left is Mission Specialist Janet L. Kavandi, and at right Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. The mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which also comprises a crew lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
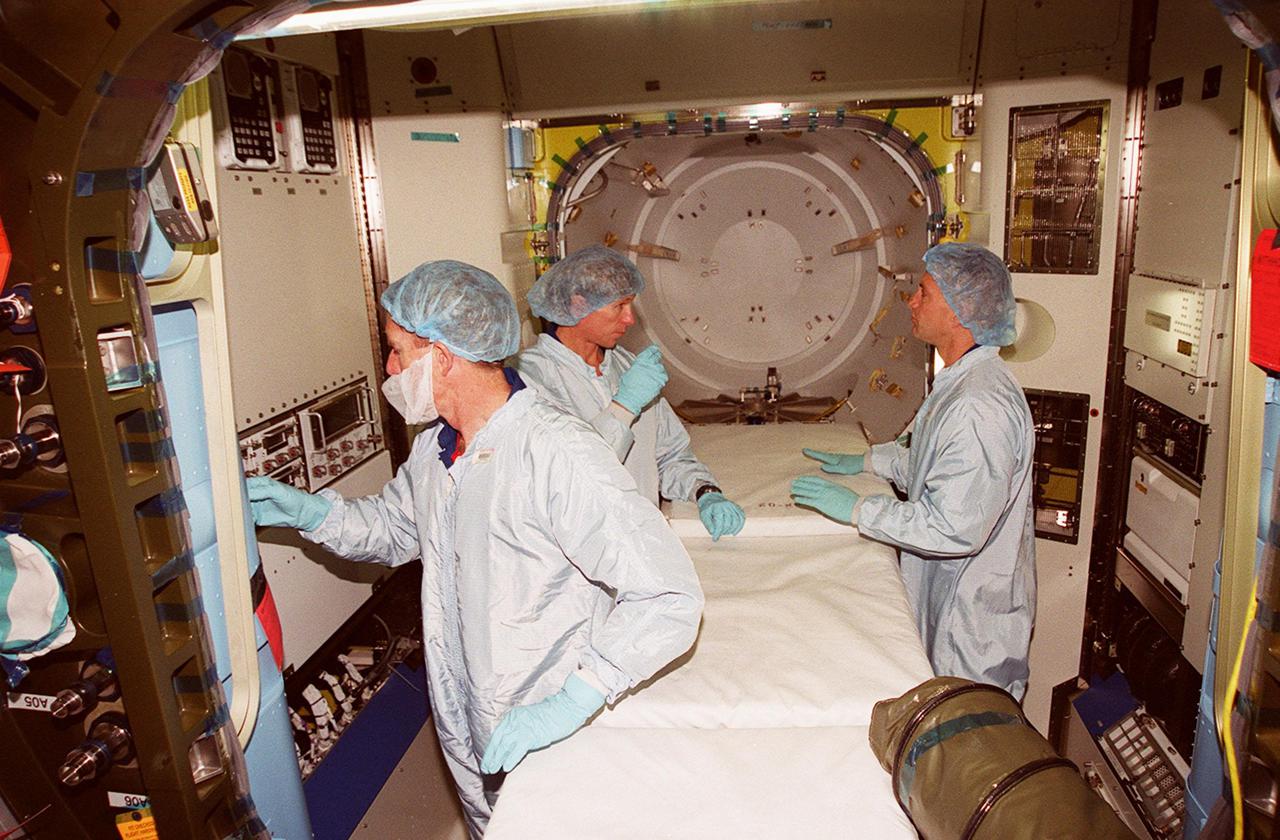

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-104 crew look over equipment inside the equipment lock component of the Joint Airlock Module. At left is Mission Specialist Janet L. Kavandi, and at right Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. The mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which also comprises a crew lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
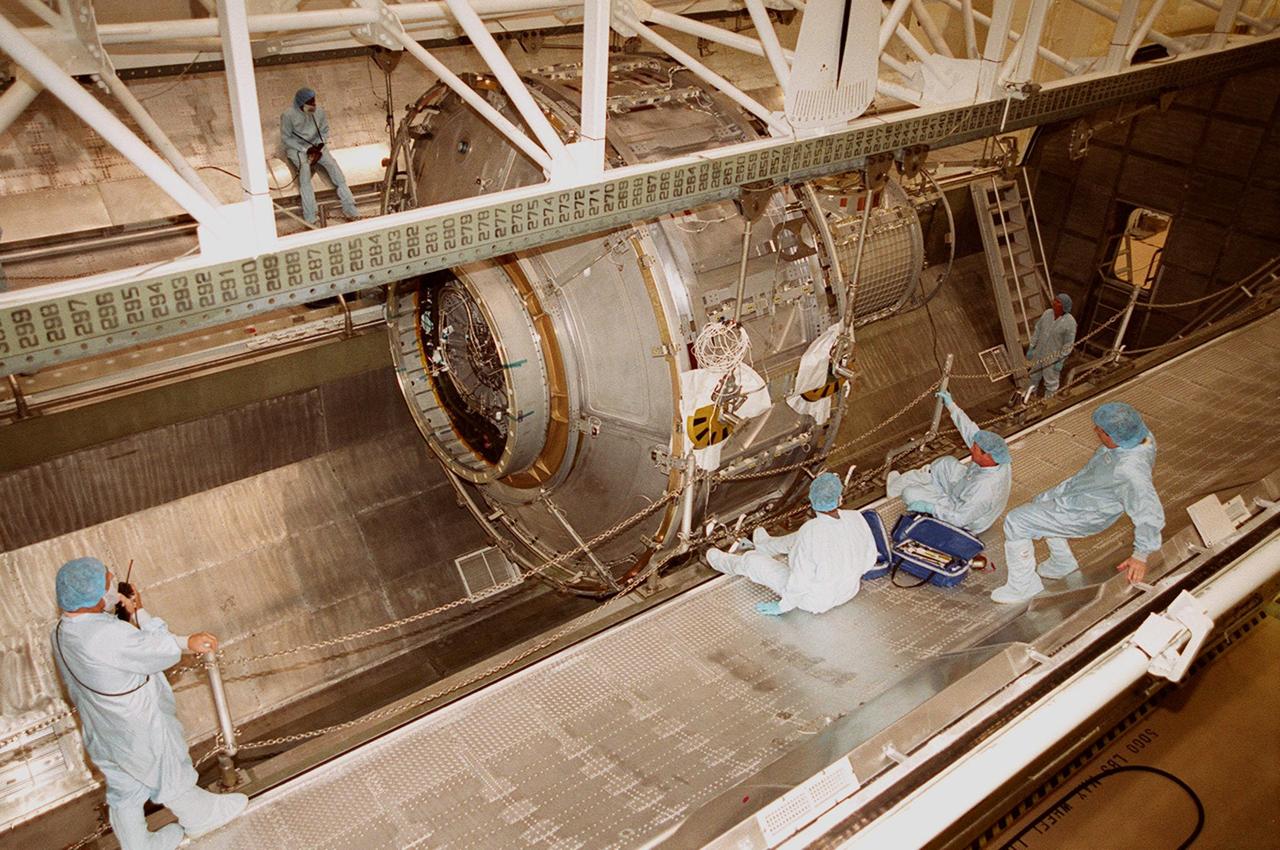
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers at right maneuver to their feet as the Joint Airlock Module is lowered into the payload canister. After being placed in the canister, the module will be transferred to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
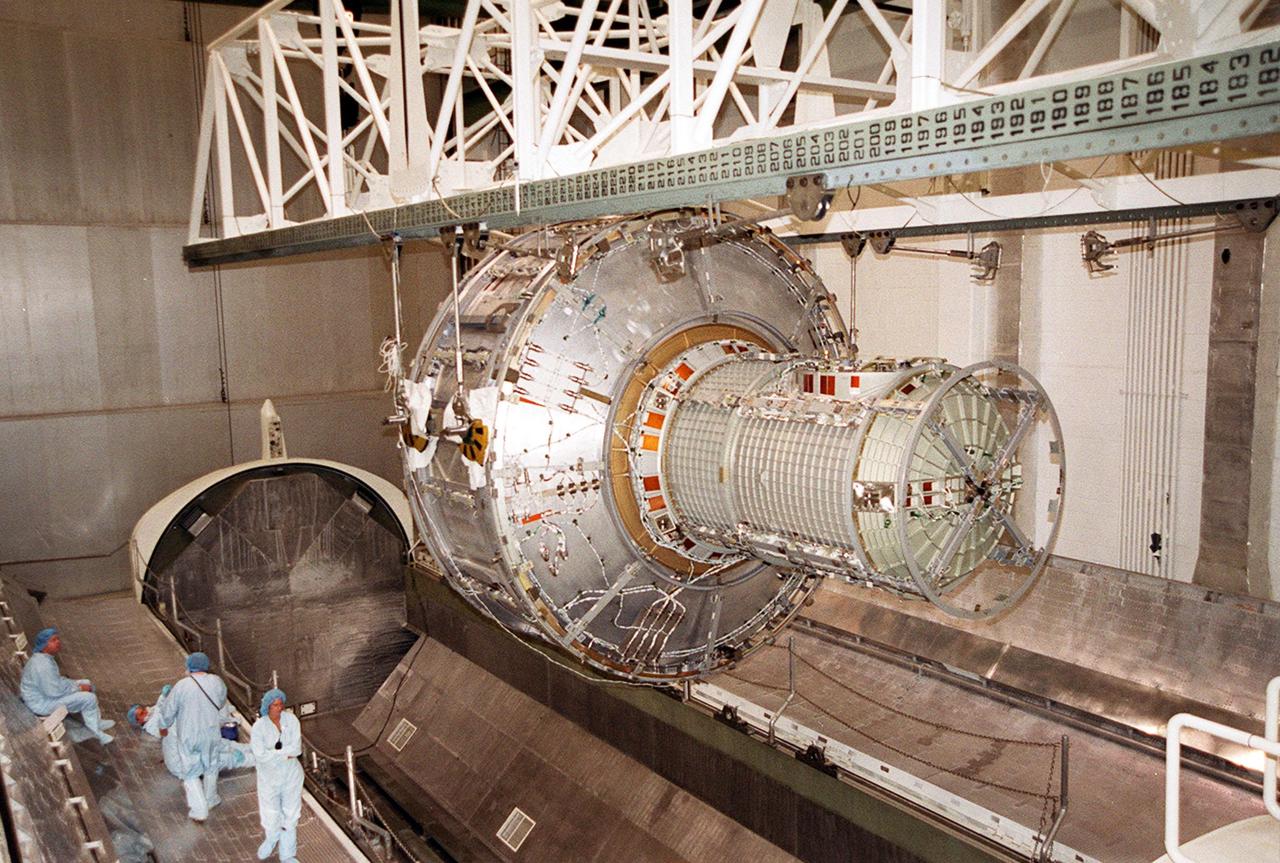
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Joint Airlock Module, suspended from an overhead crane, moves toward the payload canister below. After being placed in the canister, the module will be transferred to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
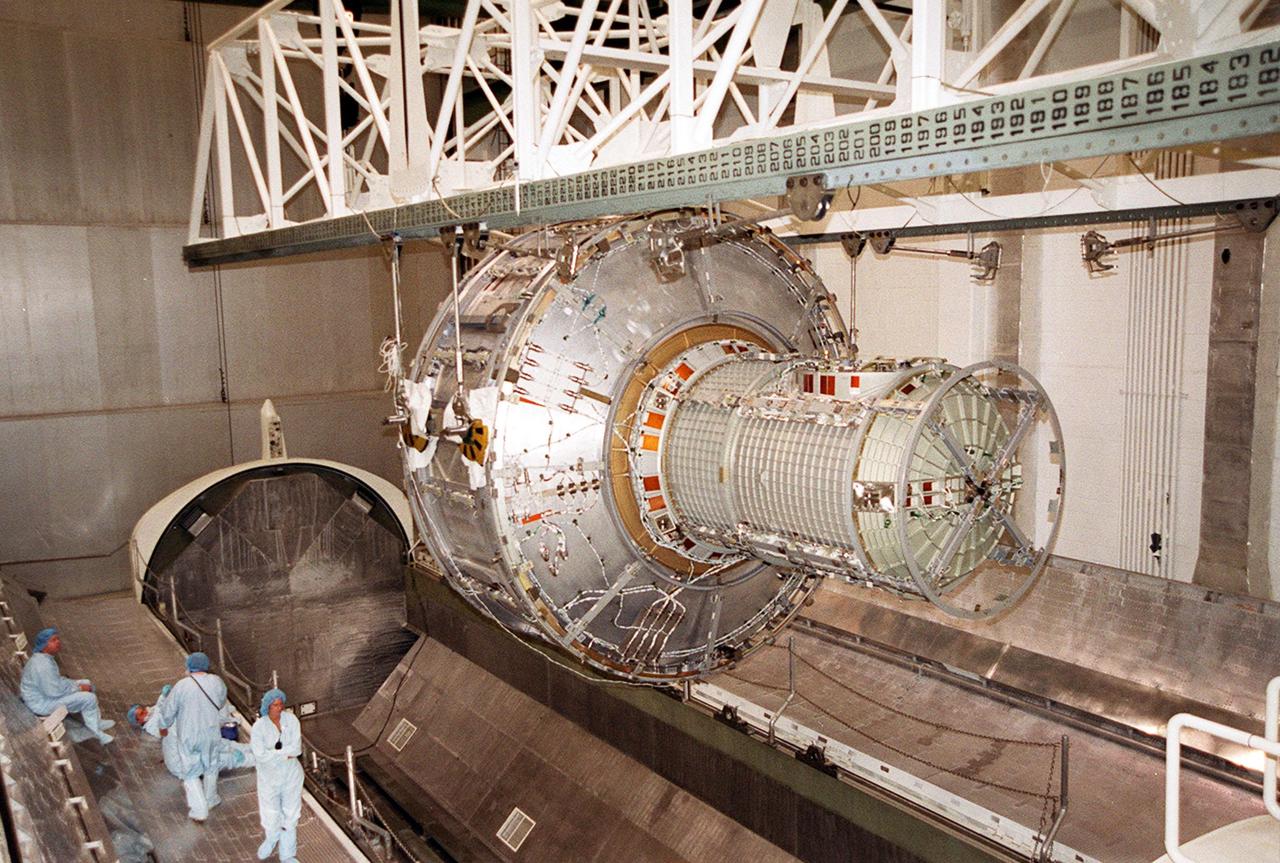
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Joint Airlock Module, suspended from an overhead crane, moves toward the payload canister below. After being placed in the canister, the module will be transferred to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
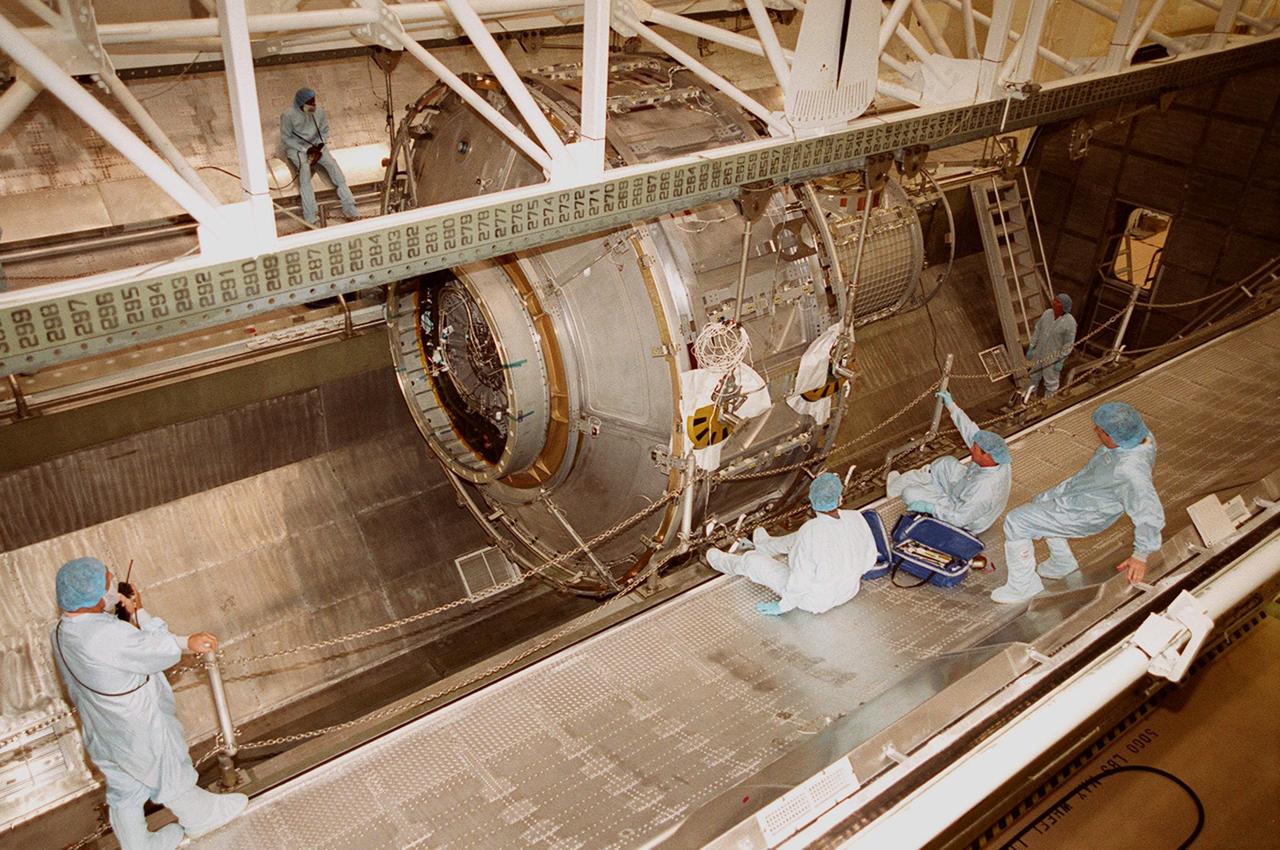
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers at right maneuver to their feet as the Joint Airlock Module is lowered into the payload canister. After being placed in the canister, the module will be transferred to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
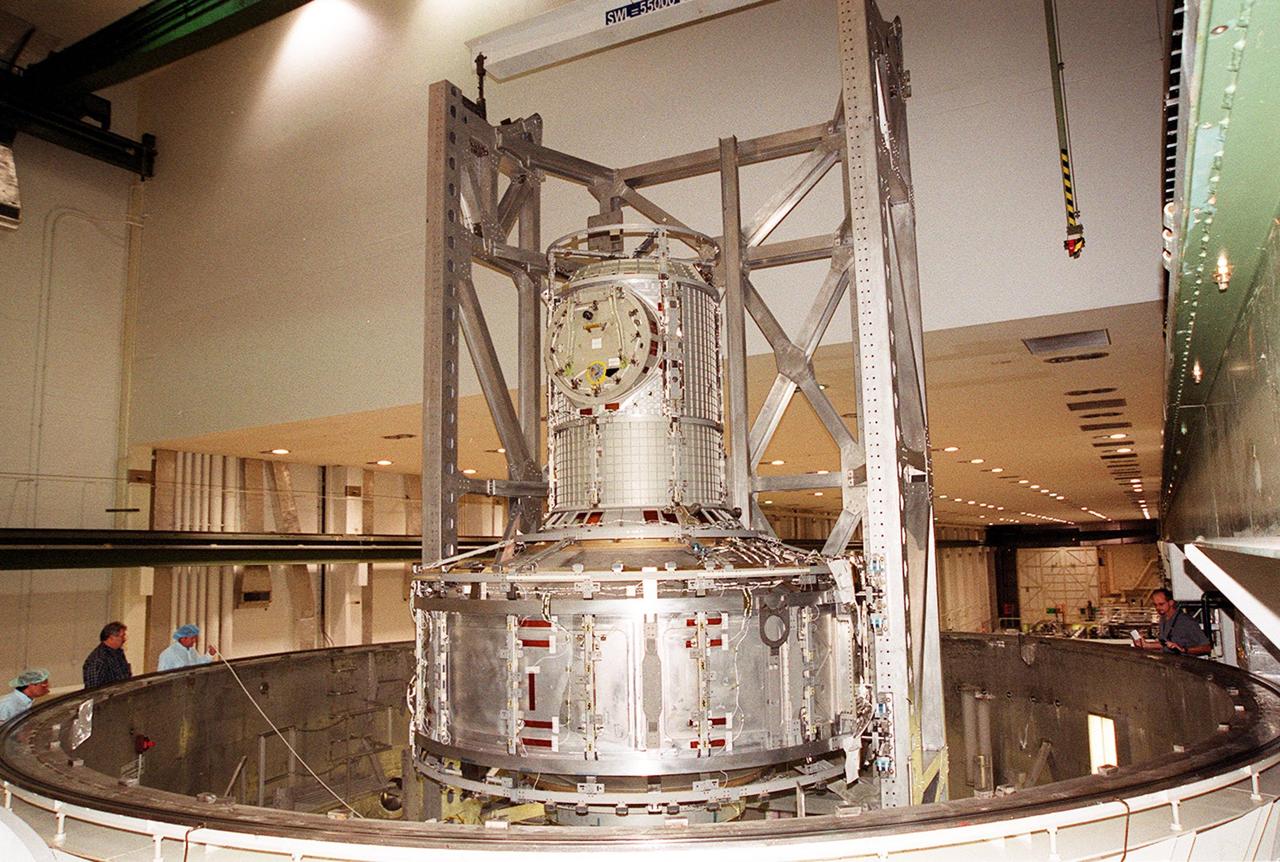

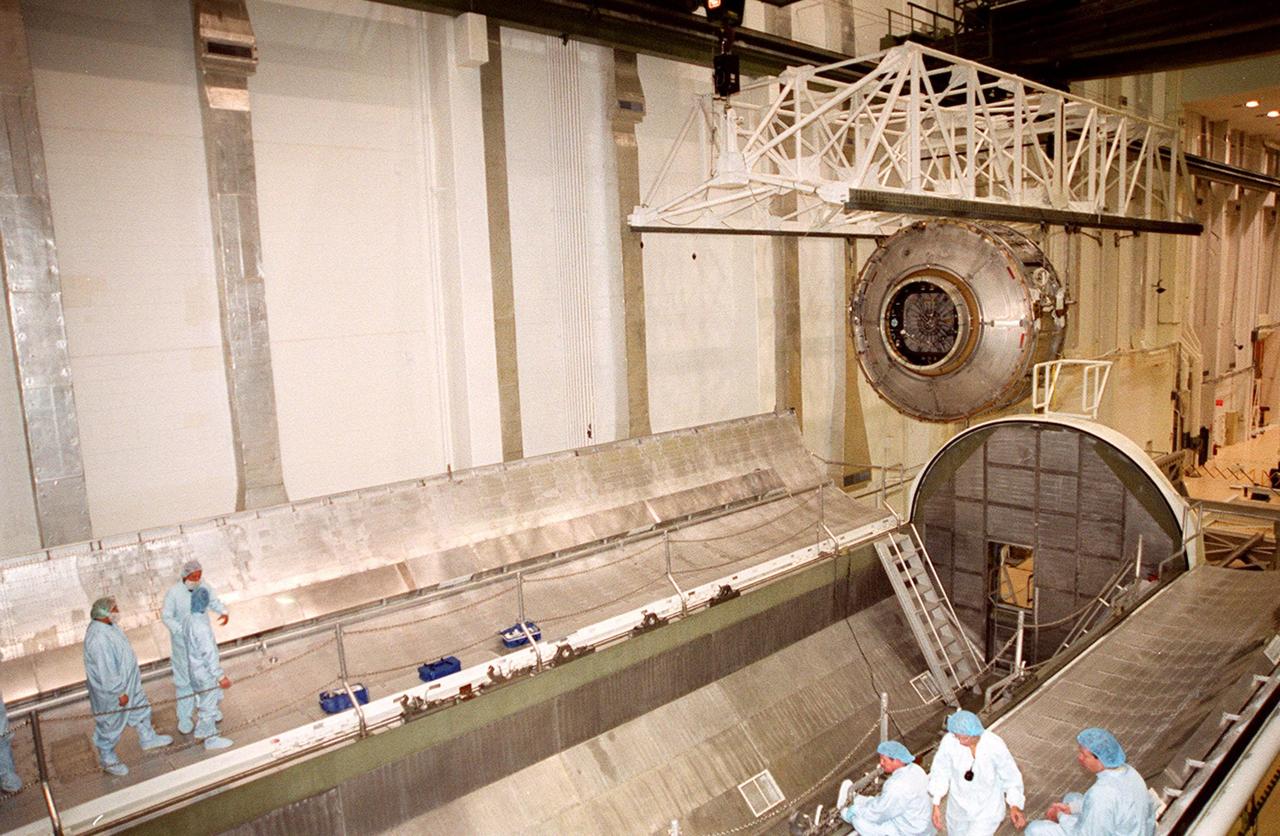
The overhead crane lowers the Joint Airlock Module inside the vacuum chamber in the Operations and Checkout Building. The airlock is being tested for leaks. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module provides a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
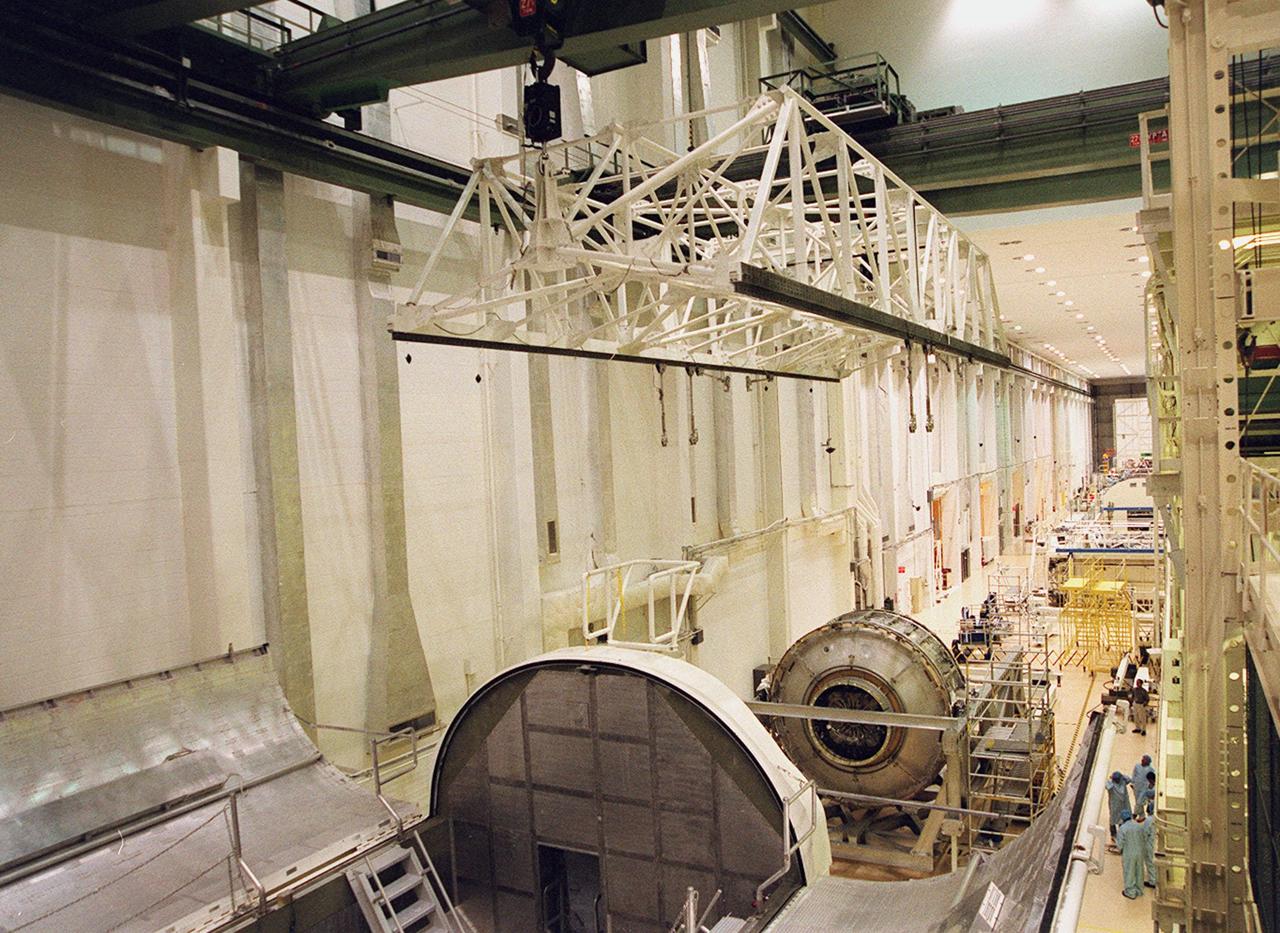
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An overhead crane in the Operations and Checkout Building hovers over the Joint Airlock Module (right) that it will lift and place in the payload canister in the foreground. The canister will transfer the module to the Space Station Processing Facility where it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
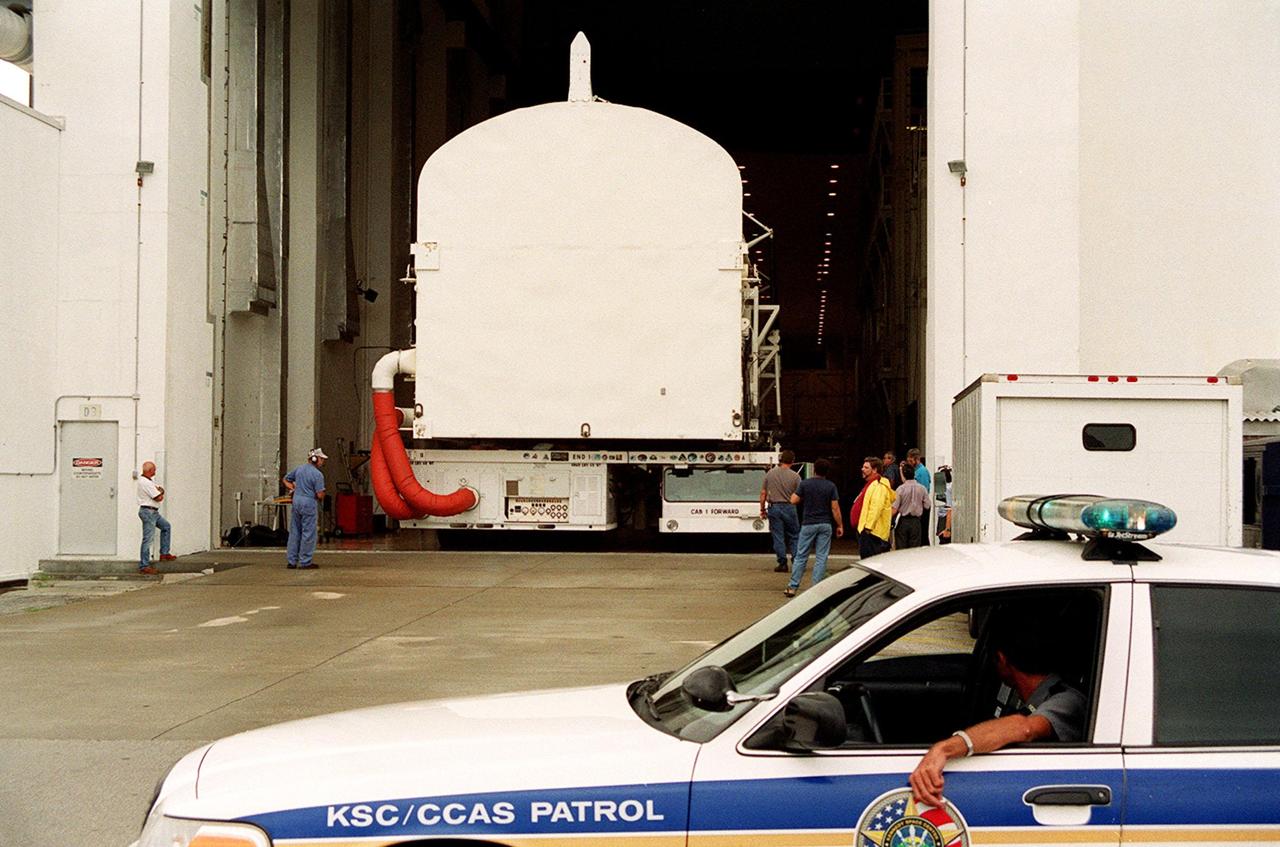

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The payload canister, with the Joint Airlock Module inside, backs out of the Operations and Checkout Building for a short trip to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The payload canister, with the Joint Airlock Module inside, backs out of the Operations and Checkout Building for a short trip to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
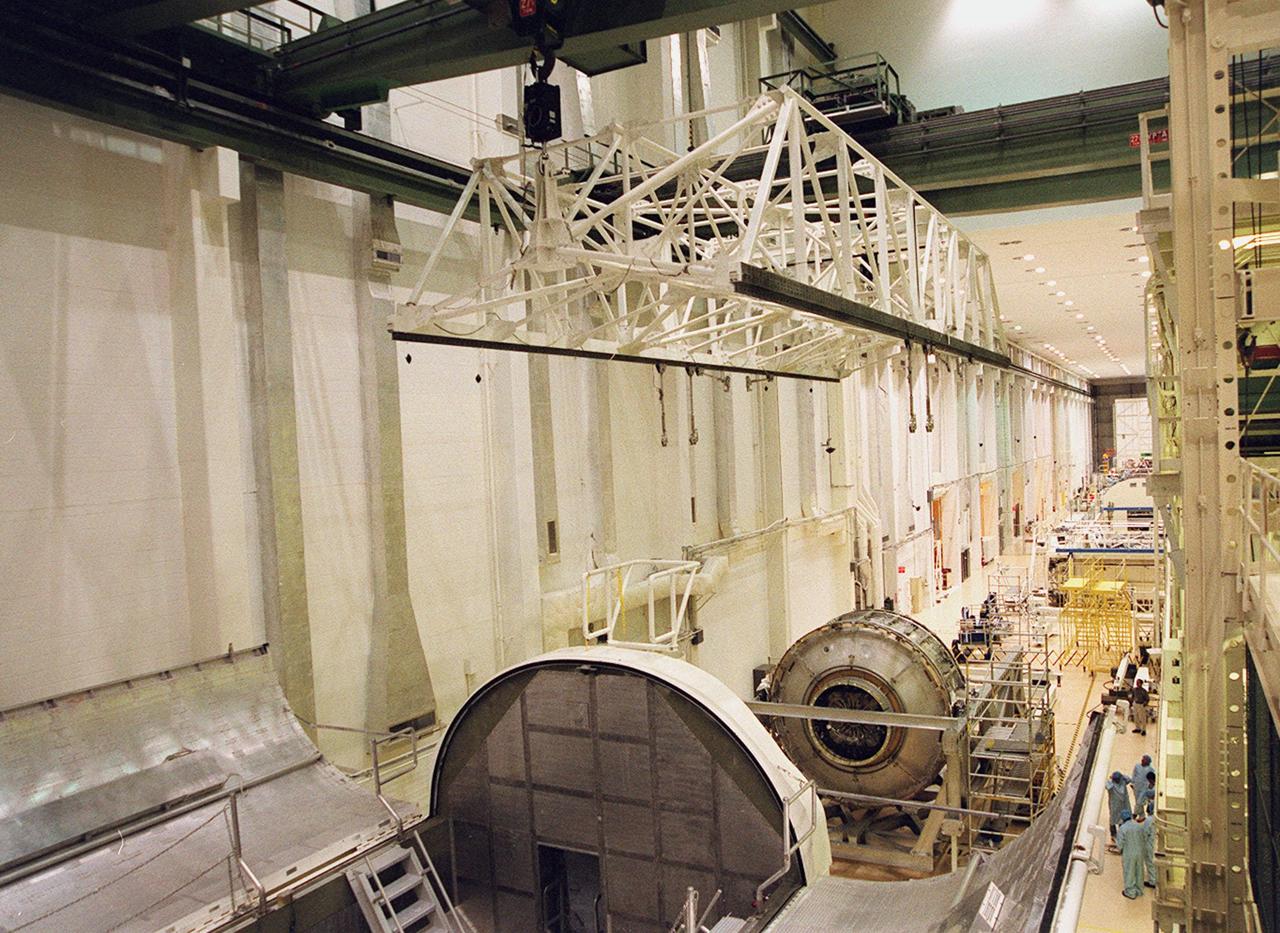
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An overhead crane in the Operations and Checkout Building hovers over the Joint Airlock Module (right) that it will lift and place in the payload canister in the foreground. The canister will transfer the module to the Space Station Processing Facility where it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Operations and Checkout Building keep watch as an overhead crane is lowered toward the Joint Airlock Module that it will lift and place in the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
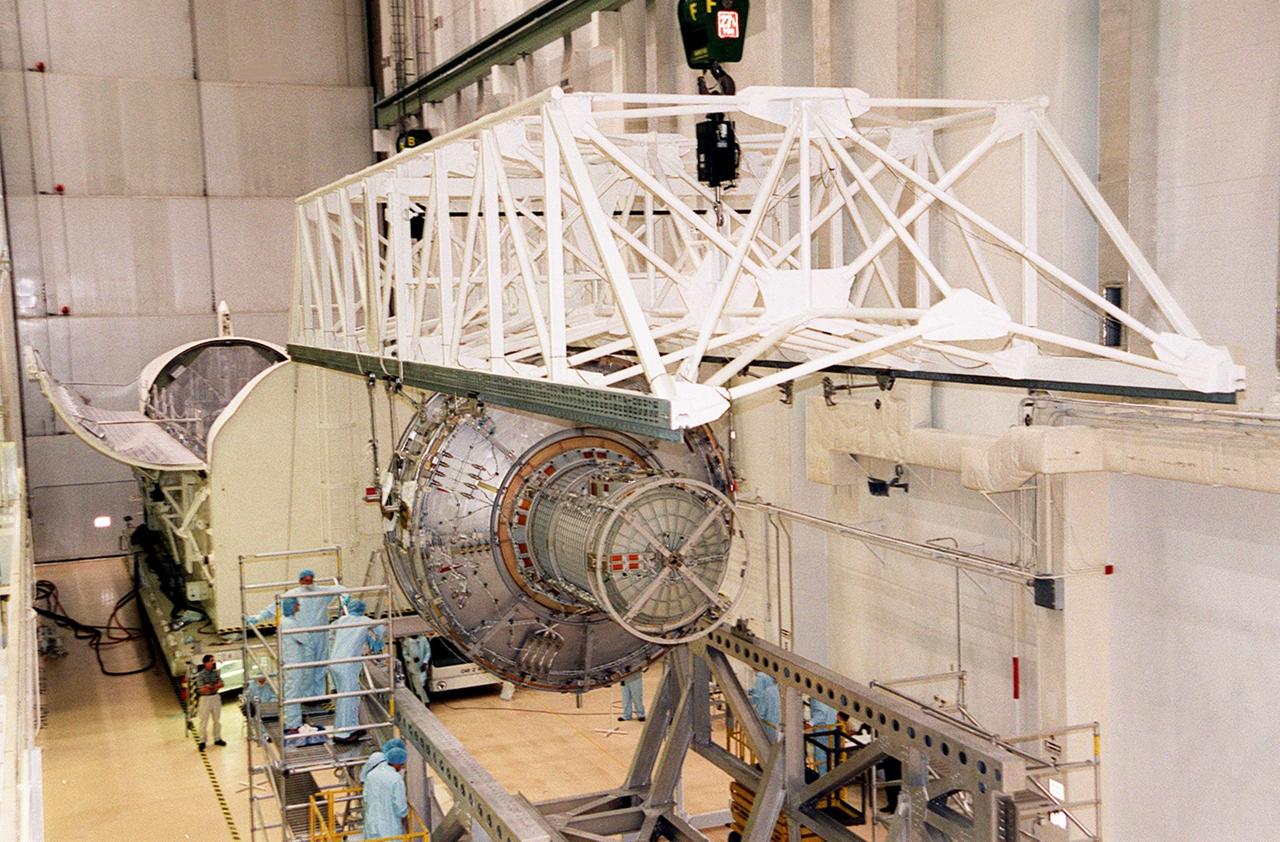
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, an overhead crane lifts the Joint Airlock Module to move and place it into the payload canister at left for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Operations and Checkout Building keep watch as an overhead crane is lowered toward the Joint Airlock Module that it will lift and place in the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
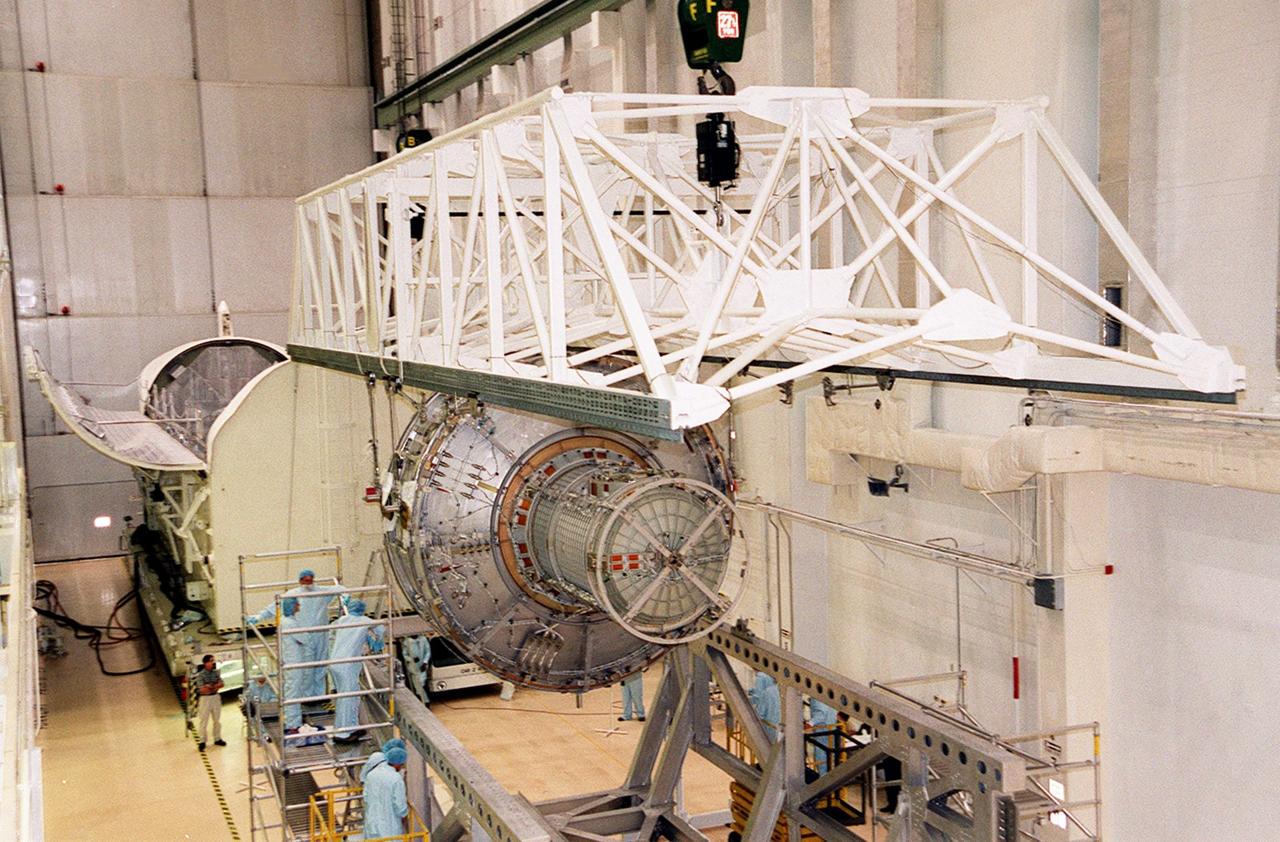
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, an overhead crane lifts the Joint Airlock Module to move and place it into the payload canister at left for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
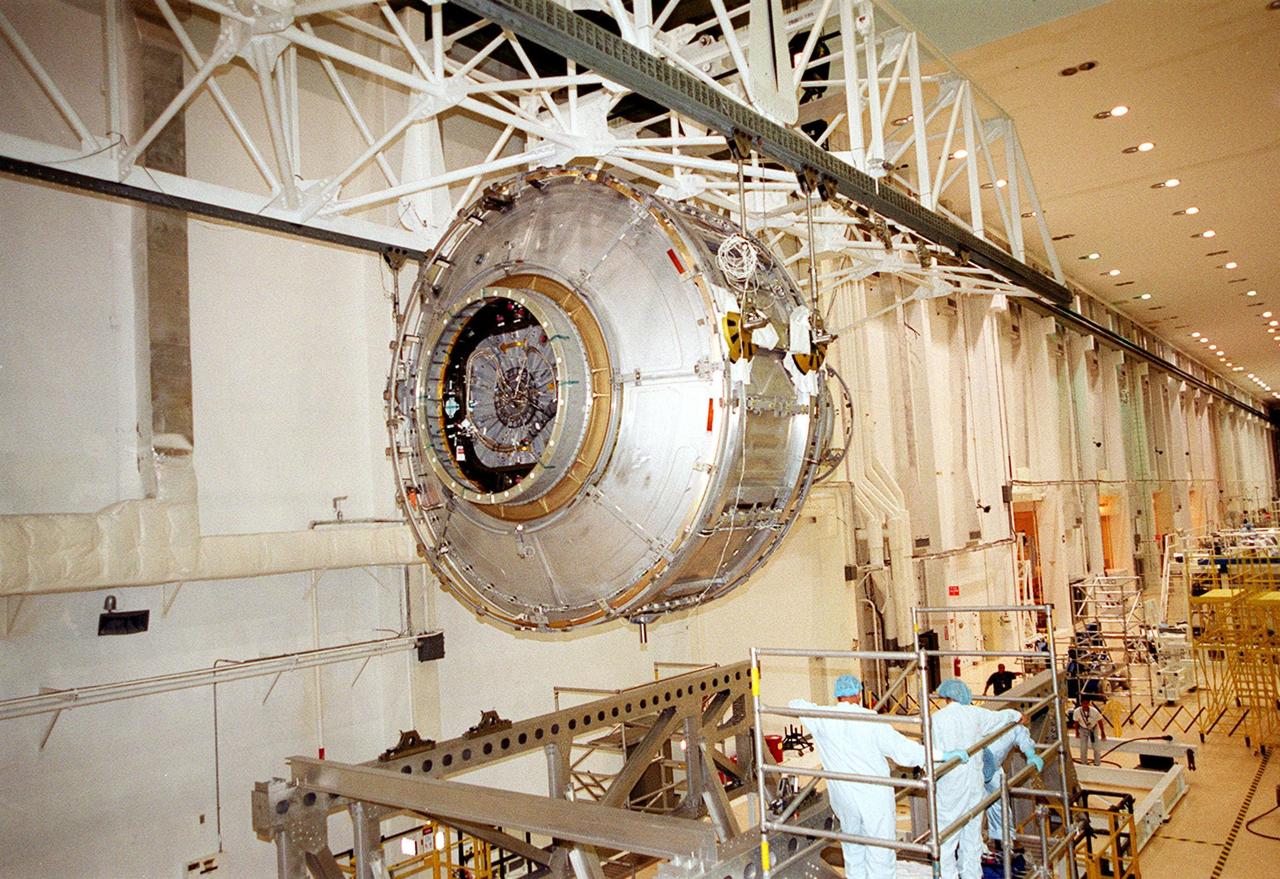
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Joint Airlock Module is suspended by an overhead crane in the Operations and Checkout Building before being moved and placed into the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
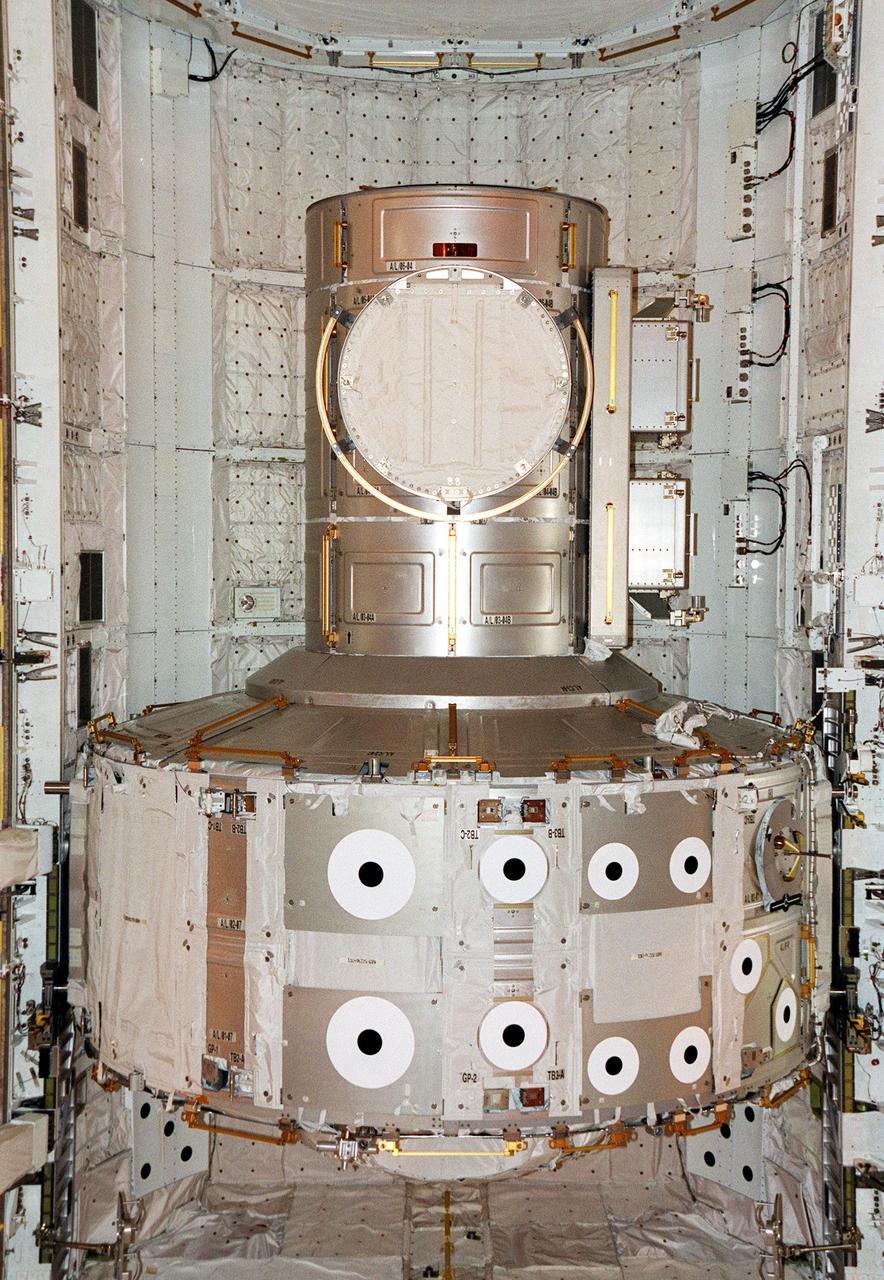
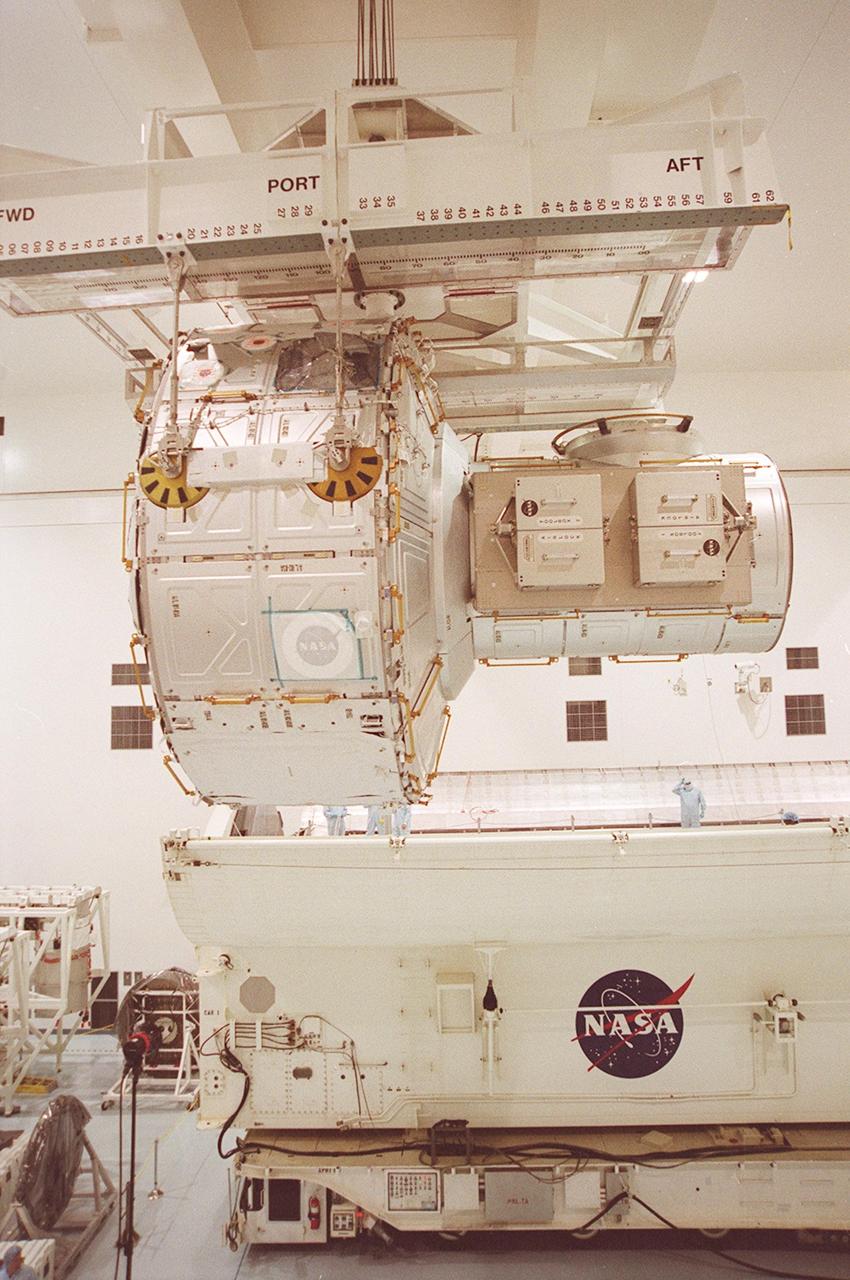
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Joint Airlock Module rests inside Atlantis’s payload bay. The module is the primary payload on mission STS-104, scheduled to be launched July 12 for the International Space Station. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Once installed and activated, the Airlock becomes the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity
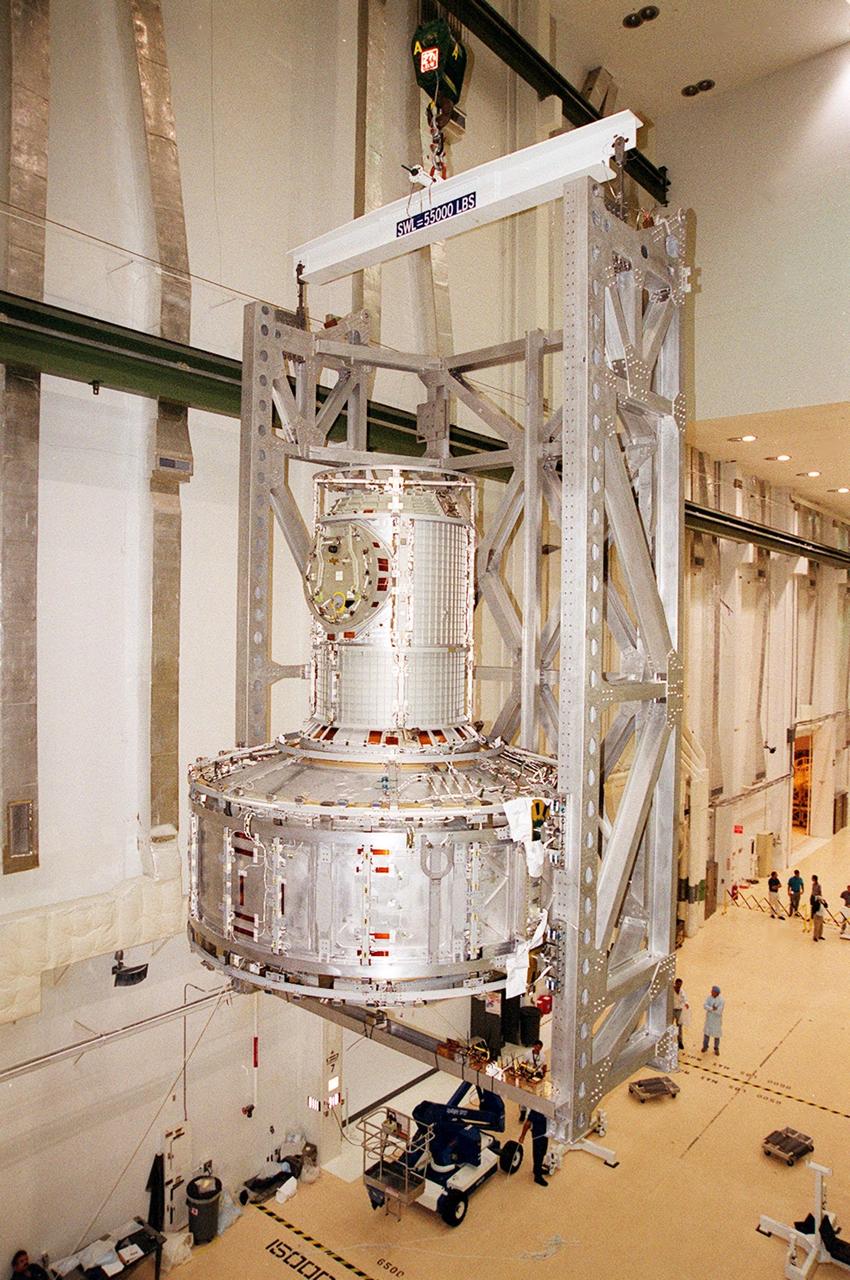
In the Operations and Checkout Building, an overhead crane lifts the Joint Airlock Module to move it to a vacuum chamber for testing. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module is specially designed to accommodate both suits, providing a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
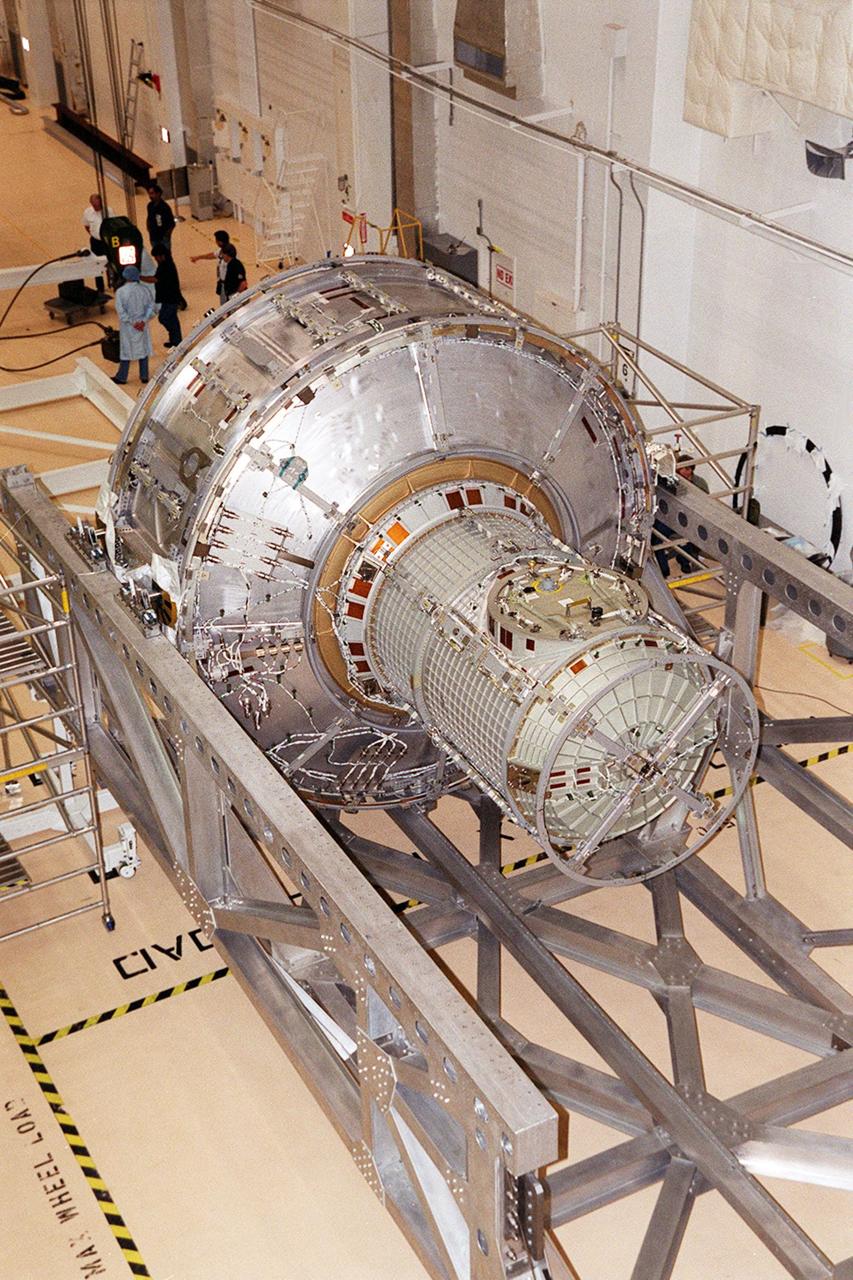
The Joint Airlock Module waits on a stand in the Operations and Checkout Building to be lifted and moved into a vacuum chamber for testing. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module is specially designed to accommodate both suits, providing a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
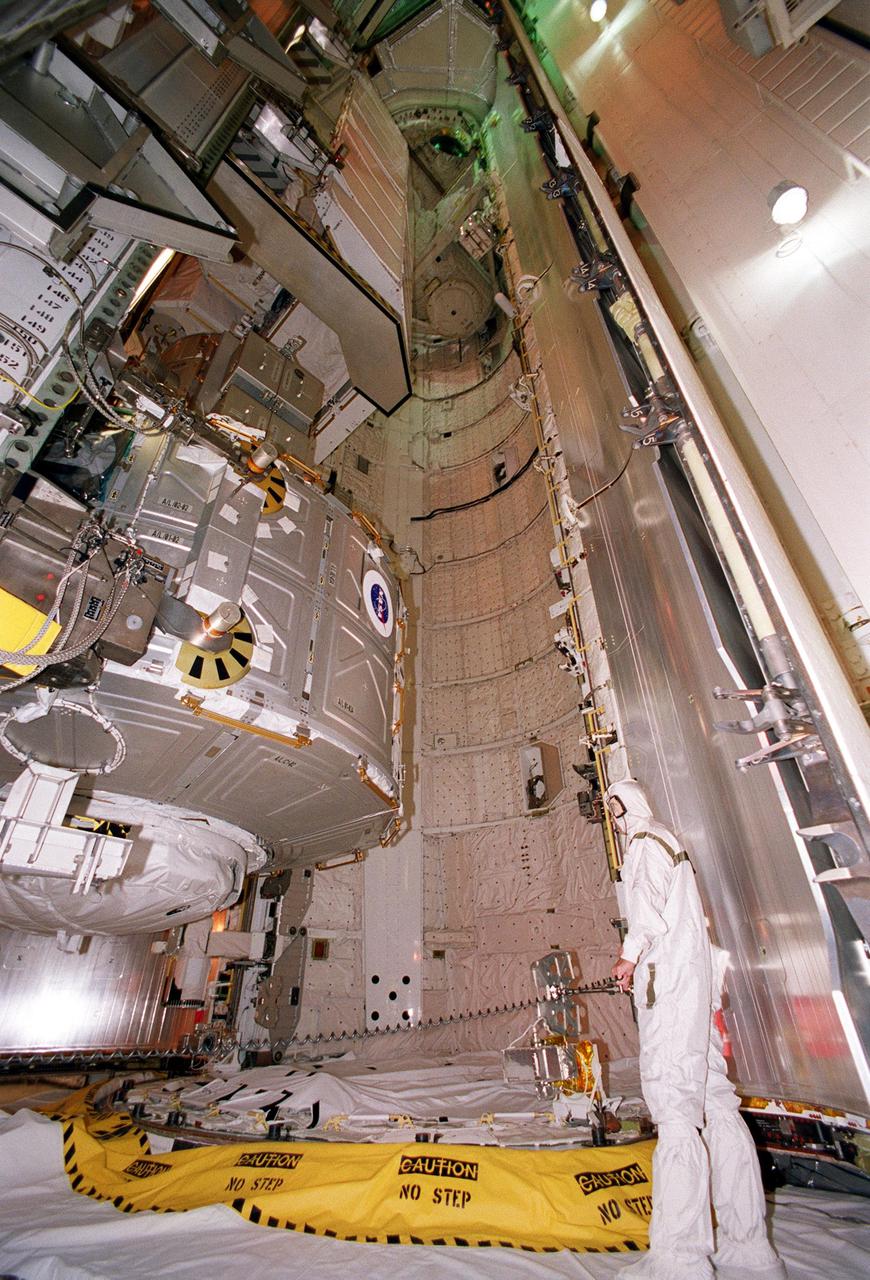
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Joint Airlock Module, sporting a NASA logo, is moved toward the payload bay of Space Shuttle Atlantis for mission STS-104. Once installed and activated, the airlock becomes the primary path for International Space Station spacewalk entry and departure using U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. Launch of Atlantis is scheduled no earlier than July 12 at 5:04 a.m. EDT
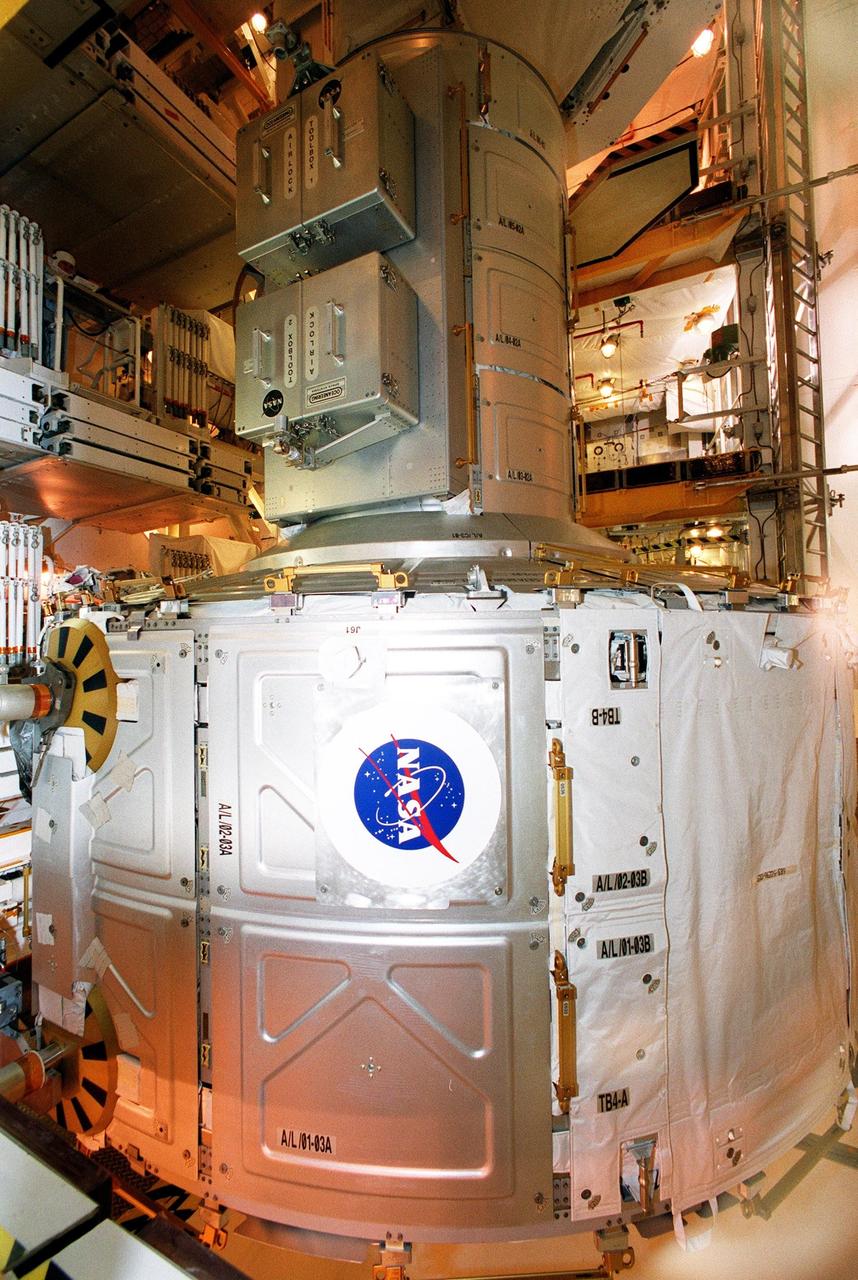

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Joint Airlock Module, sporting a NASA logo, is moved toward the payload bay of Space Shuttle Atlantis for mission STS-104. Once installed and activated, the airlock becomes the primary path for International Space Station spacewalk entry and departure using U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. Launch of Atlantis is scheduled no earlier than July 12 at 5:04 a.m. EDT
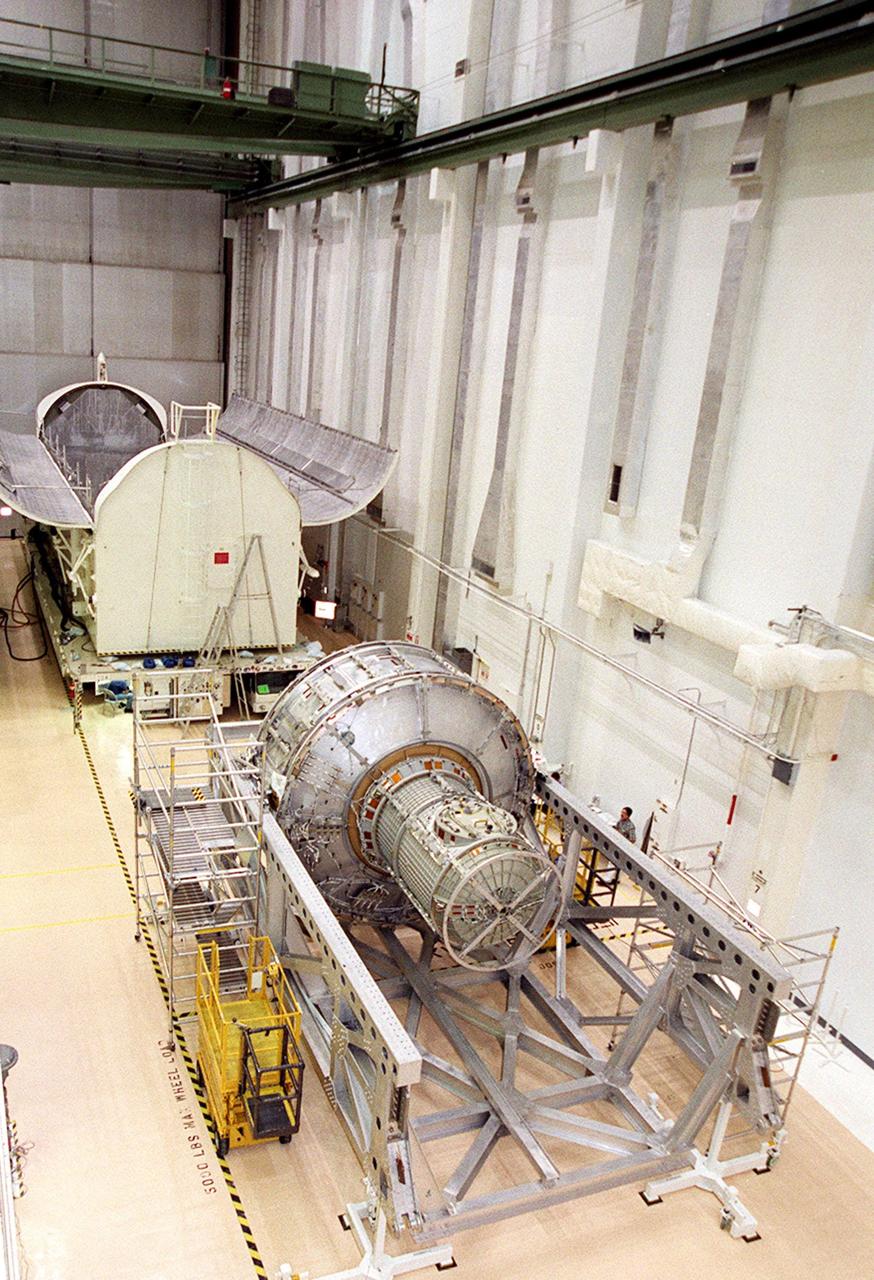

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module waits for transfer to the payload canister behind it after which it will be moved to the Space Station Processing Facility. There it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
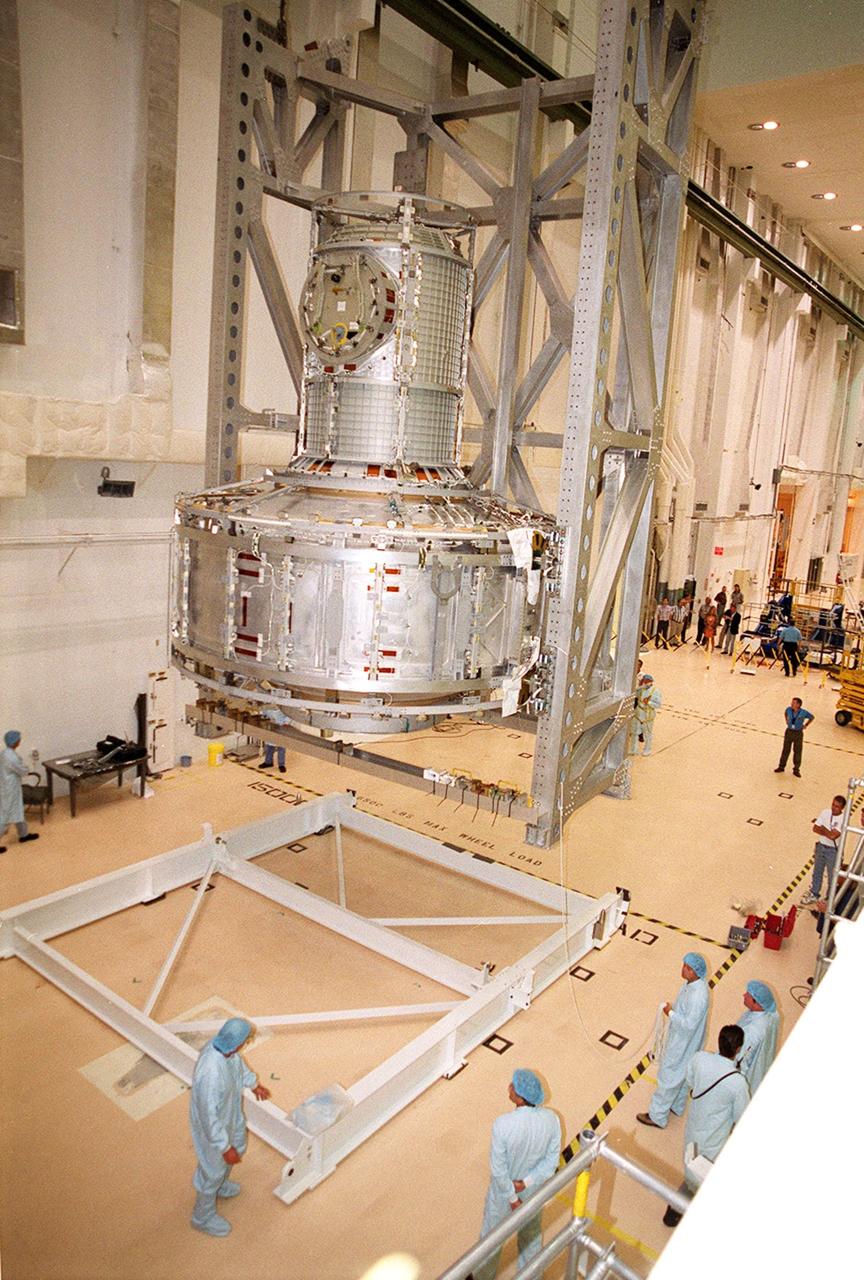
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module is lowered toward a stand on the floor where it will be moved to a horizontal position. Then it will be lifted into the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
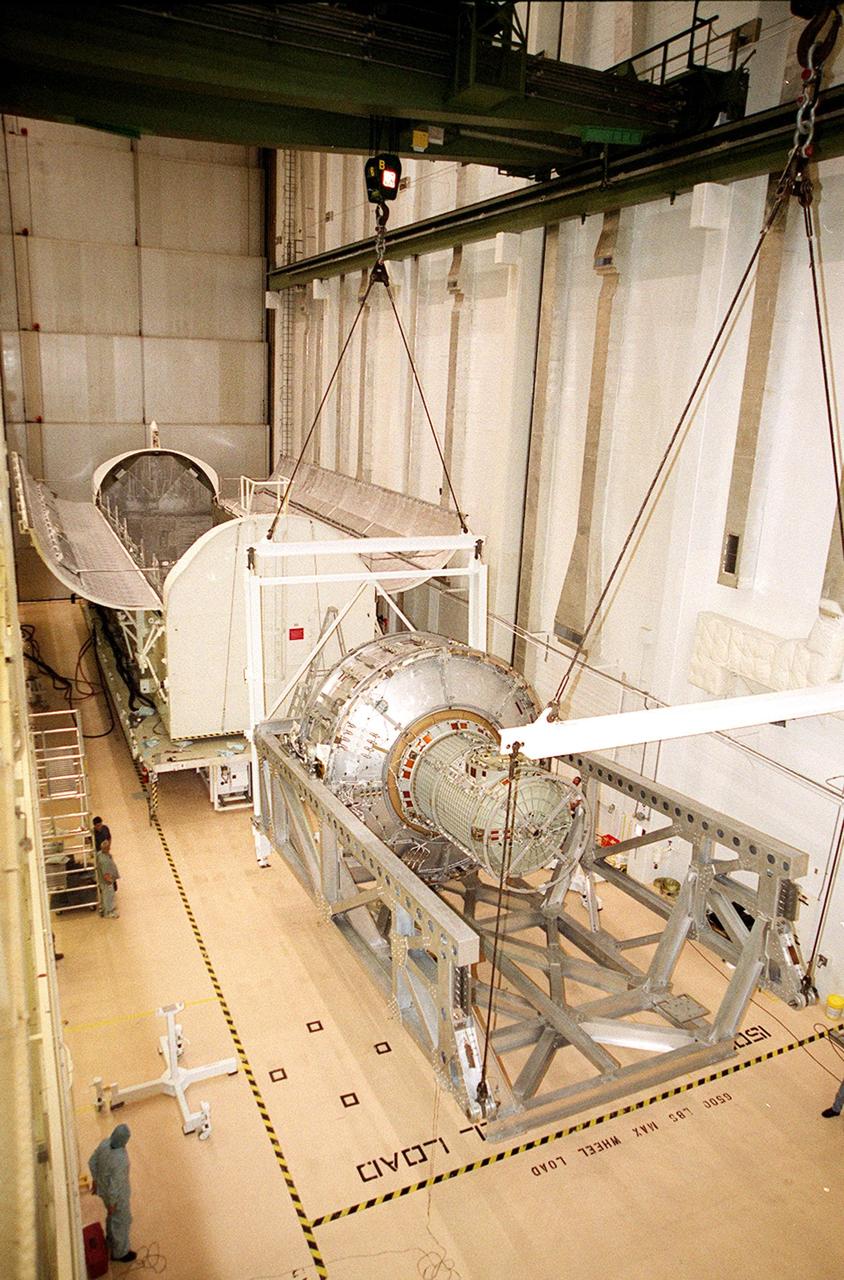

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module is placed in a horizontal position to be transferred to the payload canister behind it. Then it will be moved to the Space Station Processing Facility where it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
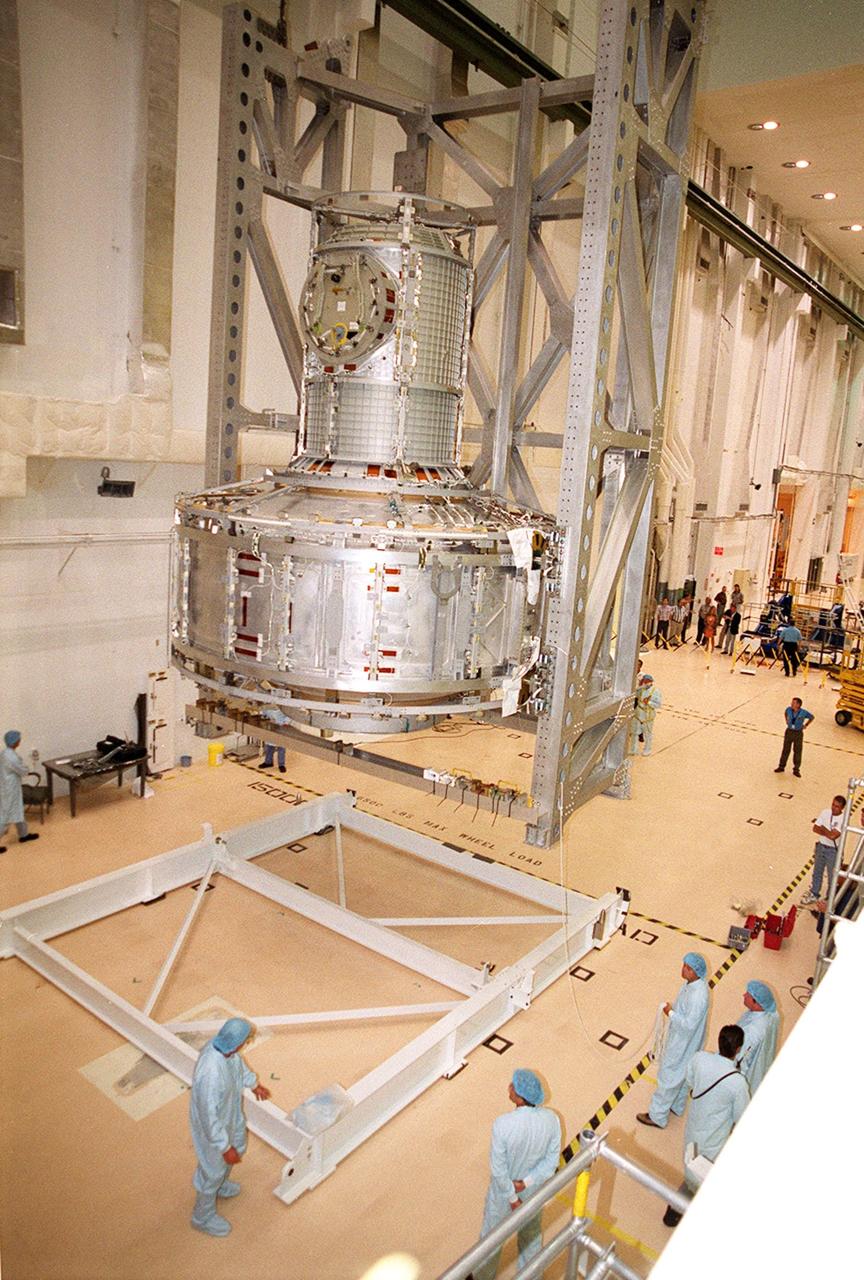
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module is lowered toward a stand on the floor where it will be moved to a horizontal position. Then it will be lifted into the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
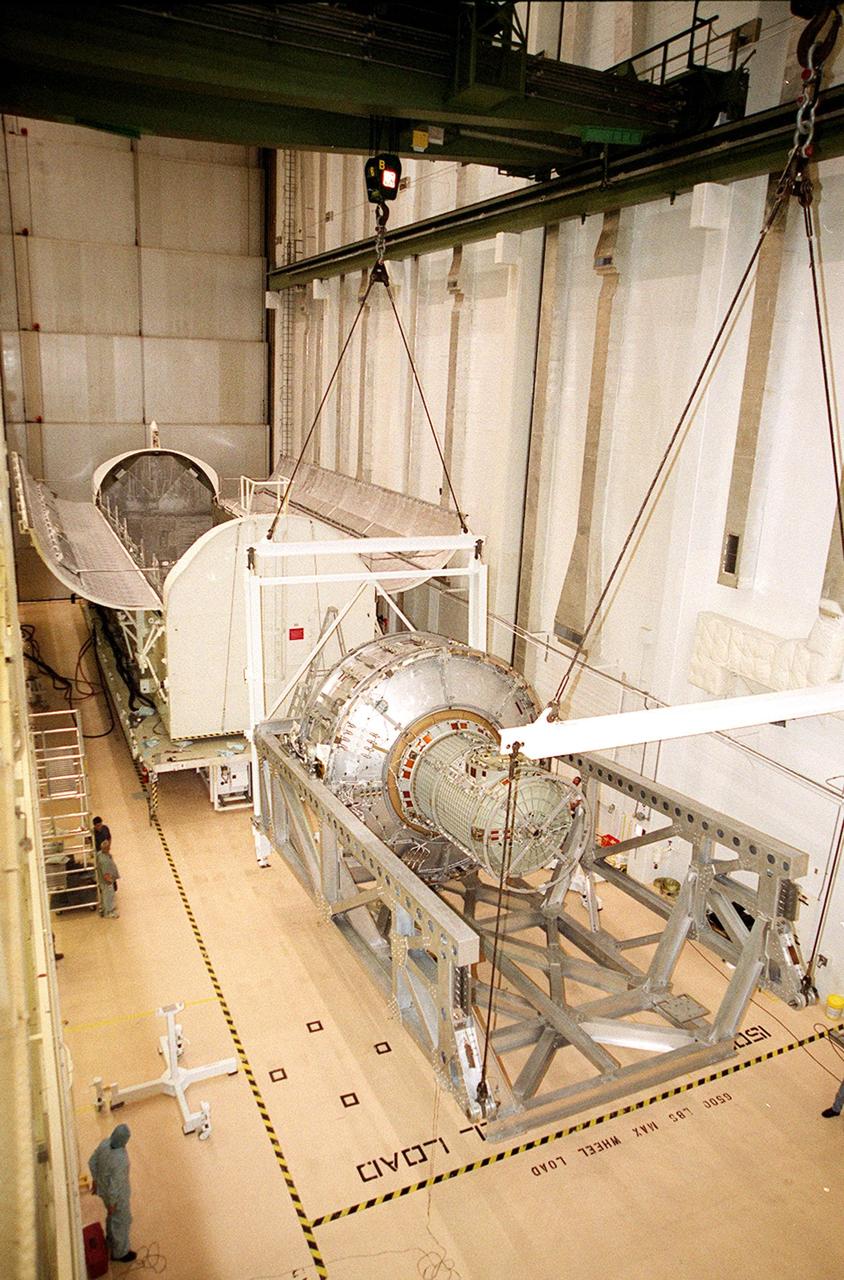

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module is placed in a horizontal position to be transferred to the payload canister behind it. Then it will be moved to the Space Station Processing Facility where it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module is ready to be lifted and placed in the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module is ready to be lifted and placed in the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the Joint Airlock Module is moved closer to the payload canister. The airlock will be installed in the payload bay of Atlantis for mission STS-104 to the International Space Station. The airlock is a pressurized flight element consisting of two cylindrical chambers attached end-to-end by a connecting bulkhead and hatch. Once installed and activated, the Airlock becomes the primary path for spacewalk entry to and departure from the Space Station for U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. STS-104 is scheduled for launch June 14 from Launch Pad 39B
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the foreground, standing or sitting on the doors of the payload canister, wait and watch as the Joint Airlock Module moves toward them. After being placed in the canister, the module will be transferred to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
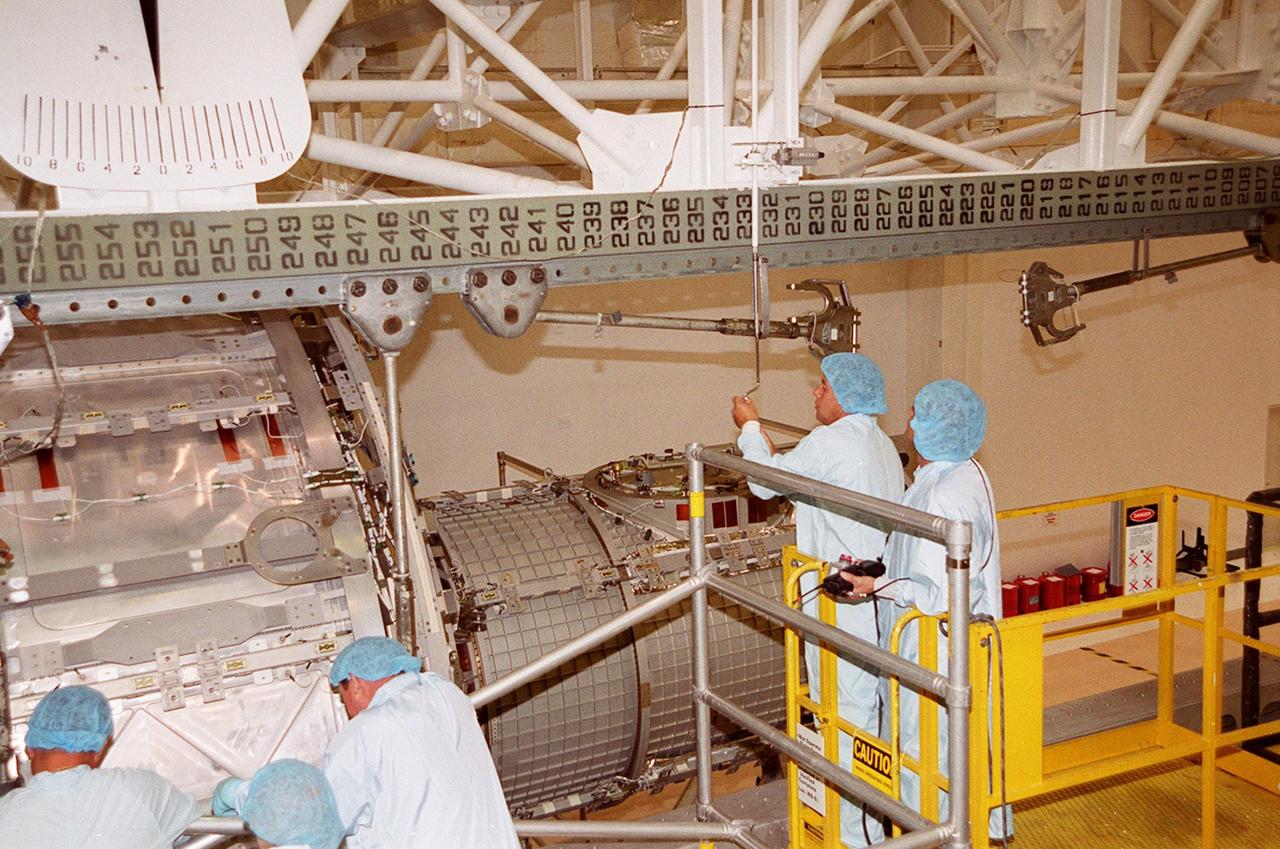
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker in the Operations and Checkout Building attaches the overhead crane to the Joint Airlock Module while another worker controls movement of the crane. The module will be lifted and placed in the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
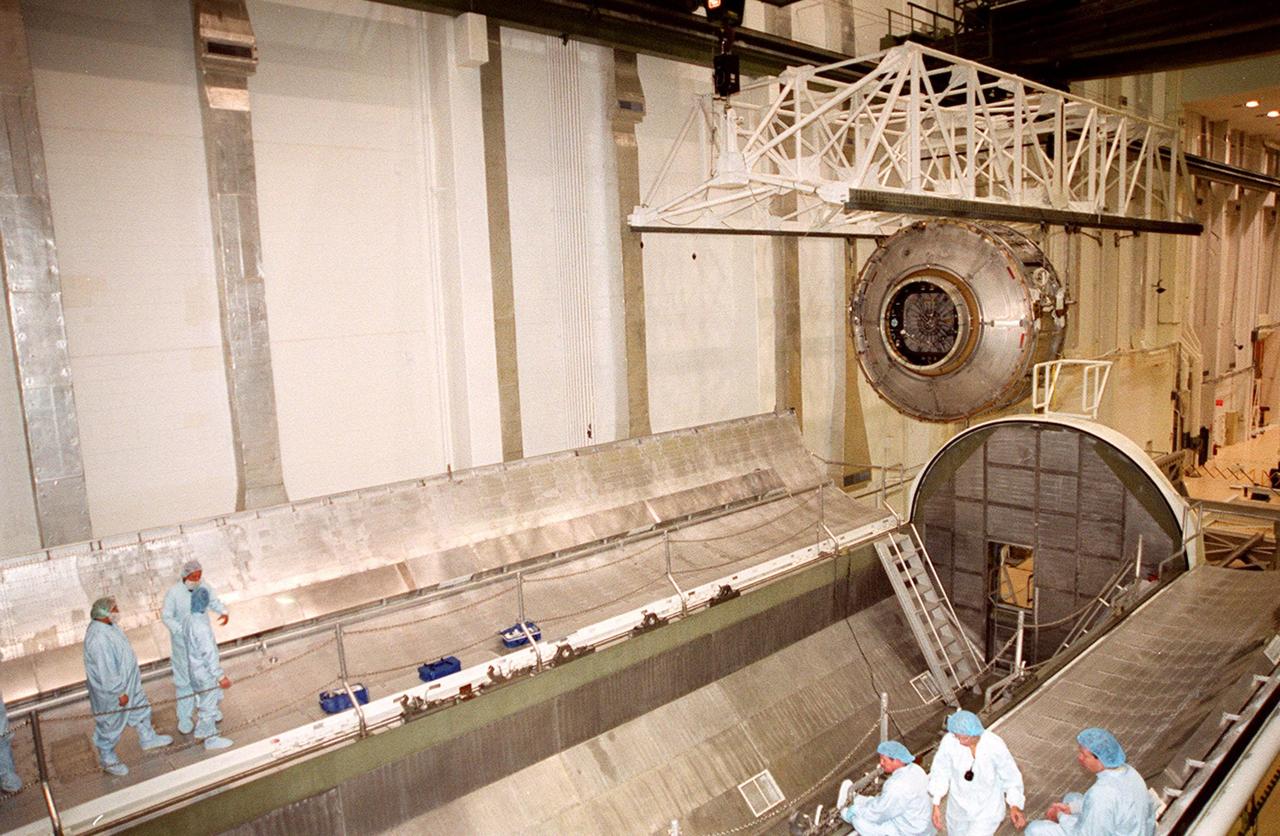
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the foreground, standing or sitting on the doors of the payload canister, wait and watch as the Joint Airlock Module moves toward them. After being placed in the canister, the module will be transferred to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
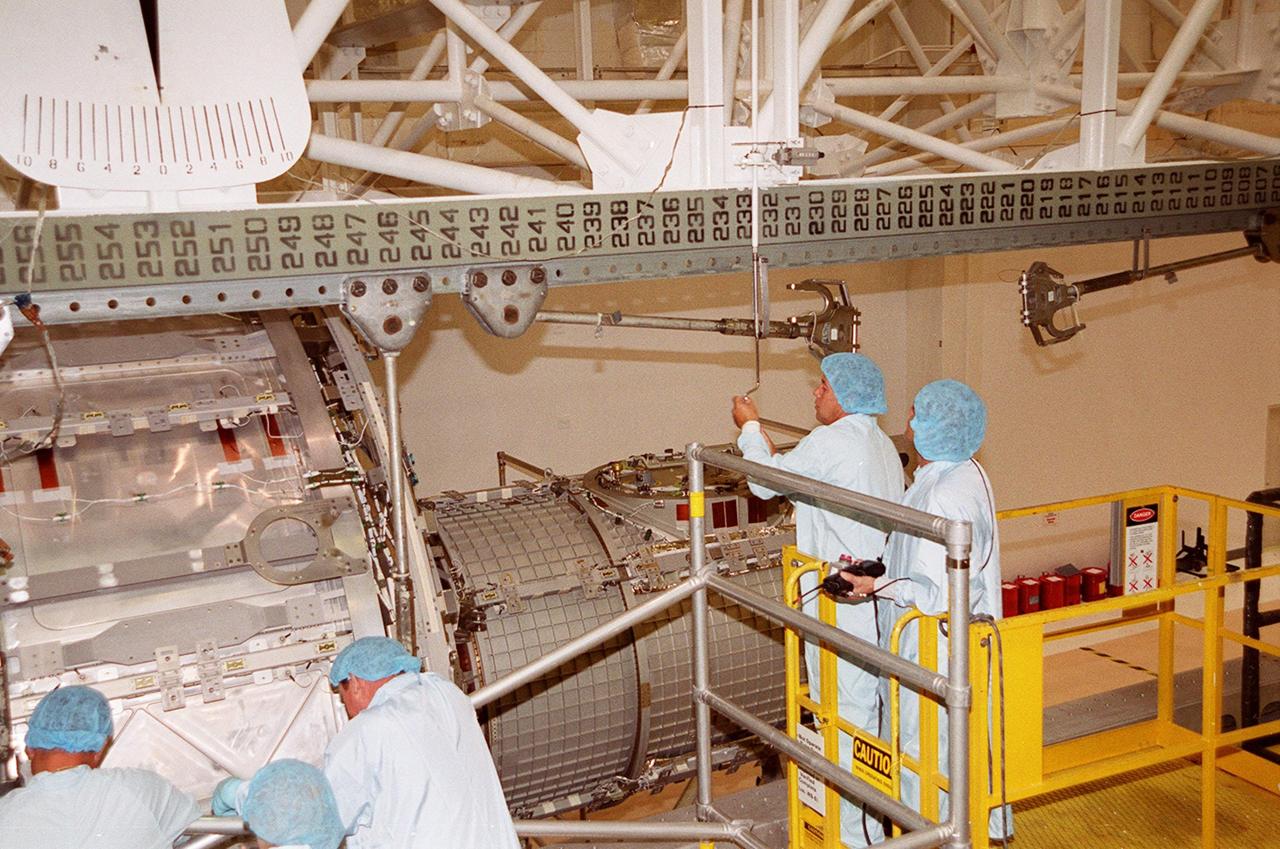
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker in the Operations and Checkout Building attaches the overhead crane to the Joint Airlock Module while another worker controls movement of the crane. The module will be lifted and placed in the payload canister for transfer to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
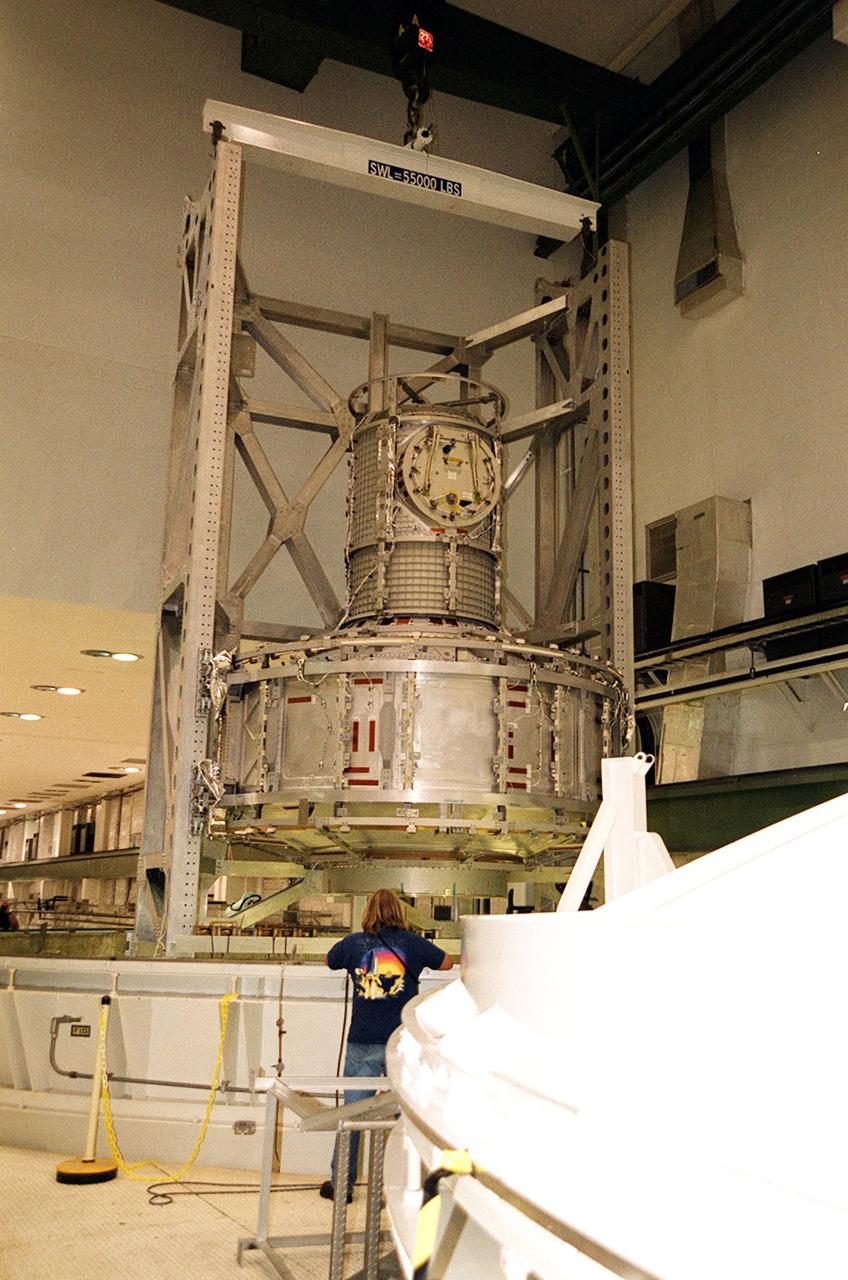

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module is suspended in air after being removed from the vacuum chamber where it was tested for leaks. The module was in a vacuum environment equivalent to 210,000 feet or 40 miles in altitude. It will be placed in a payload canister and taken to the Space Station Processing Facility. There it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
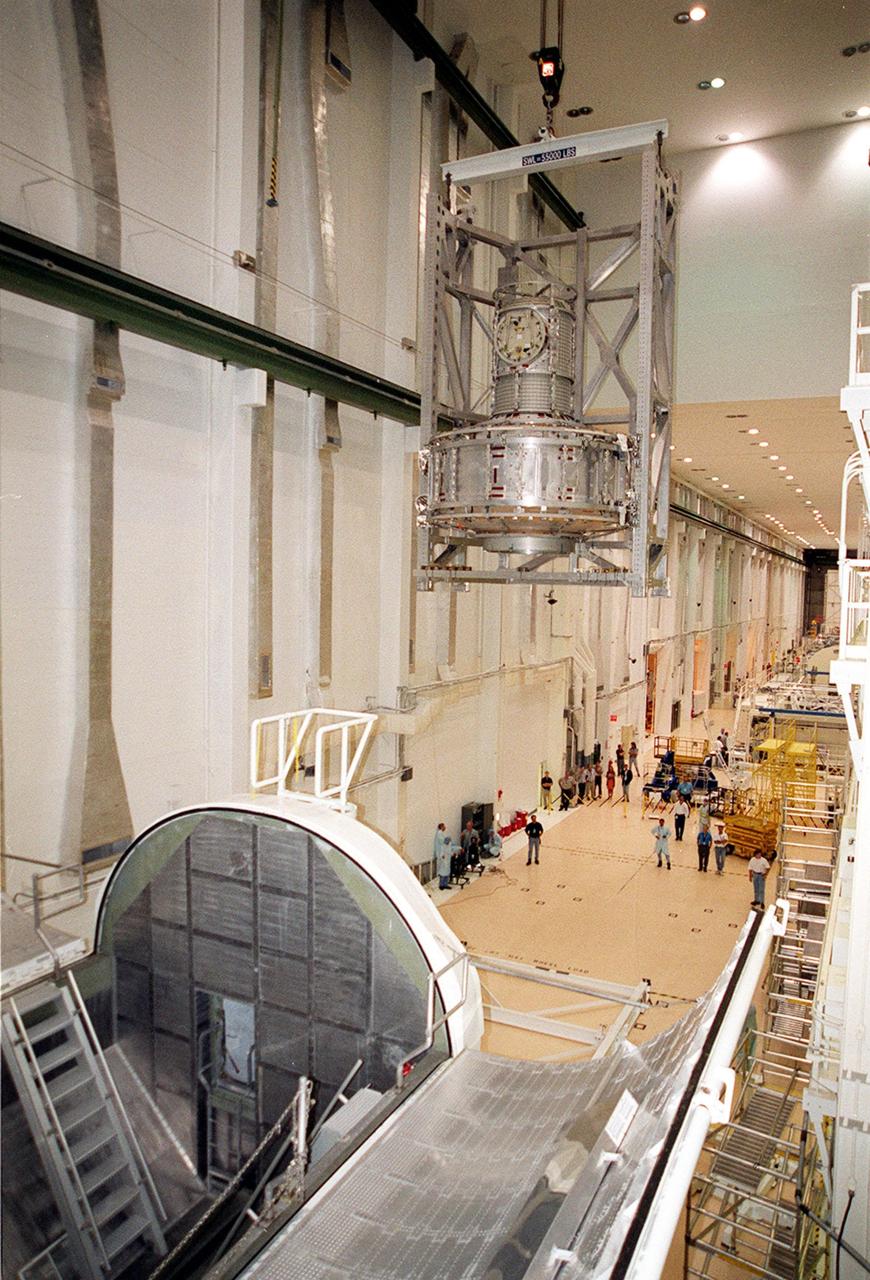

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module is carried across the Operations and Checkout Building toward a stand on the floor. The module will be moved to a horizontal position and placed in the payload canister at left. Then it will be taken to the Space Station Processing Facility where it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
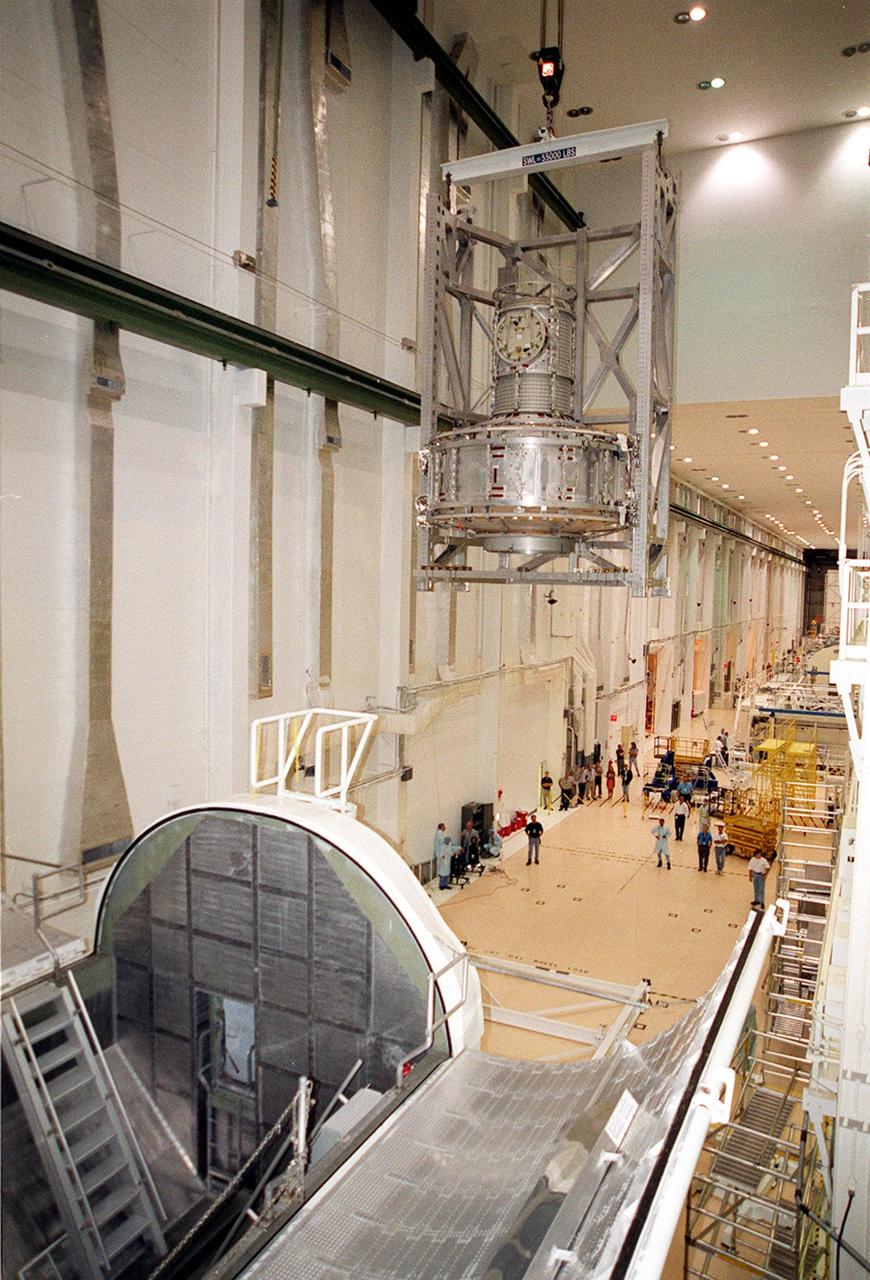

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module is carried across the Operations and Checkout Building toward a stand on the floor. The module will be moved to a horizontal position and placed in the payload canister at left. Then it will be taken to the Space Station Processing Facility where it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
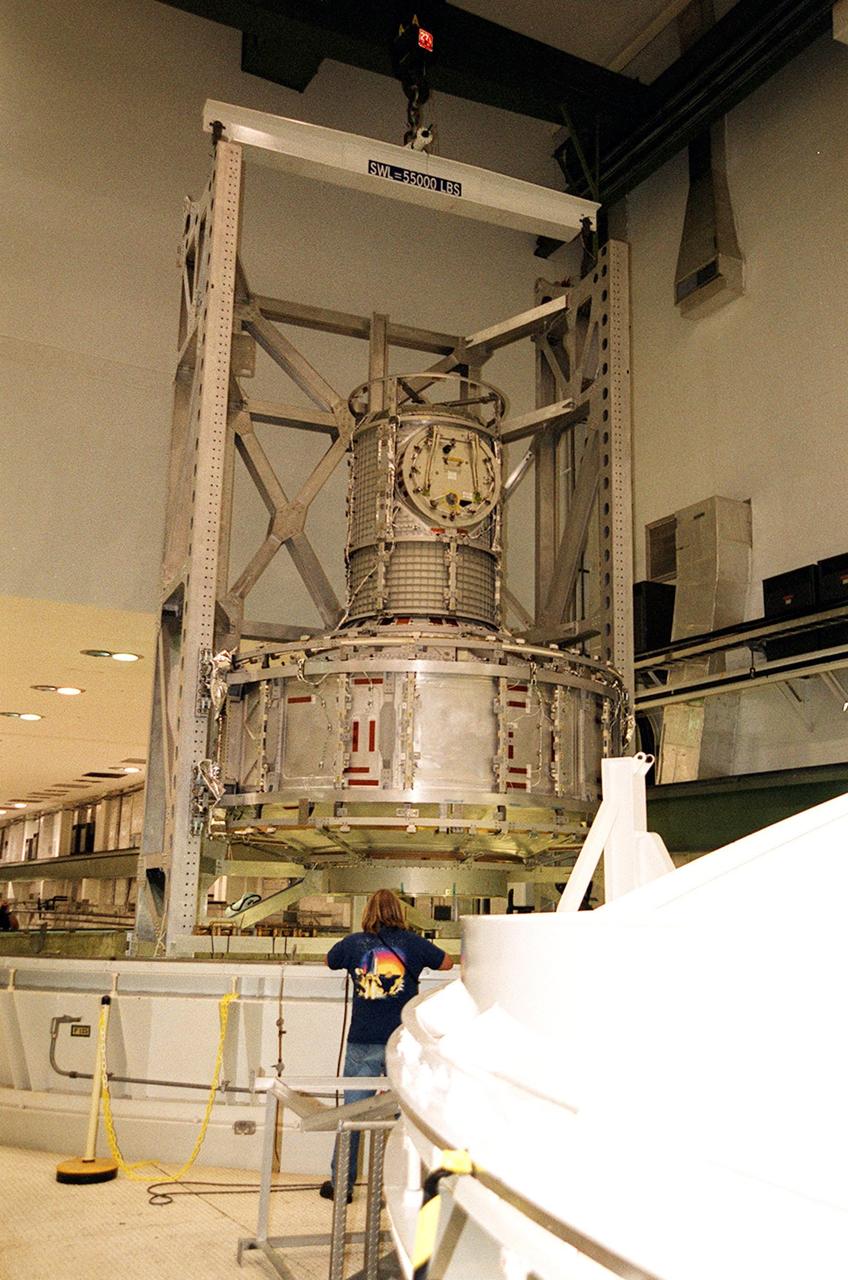

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module is suspended in air after being removed from the vacuum chamber where it was tested for leaks. The module was in a vacuum environment equivalent to 210,000 feet or 40 miles in altitude. It will be placed in a payload canister and taken to the Space Station Processing Facility. There it will continue to undergo preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001. The Joint Airlock Module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility
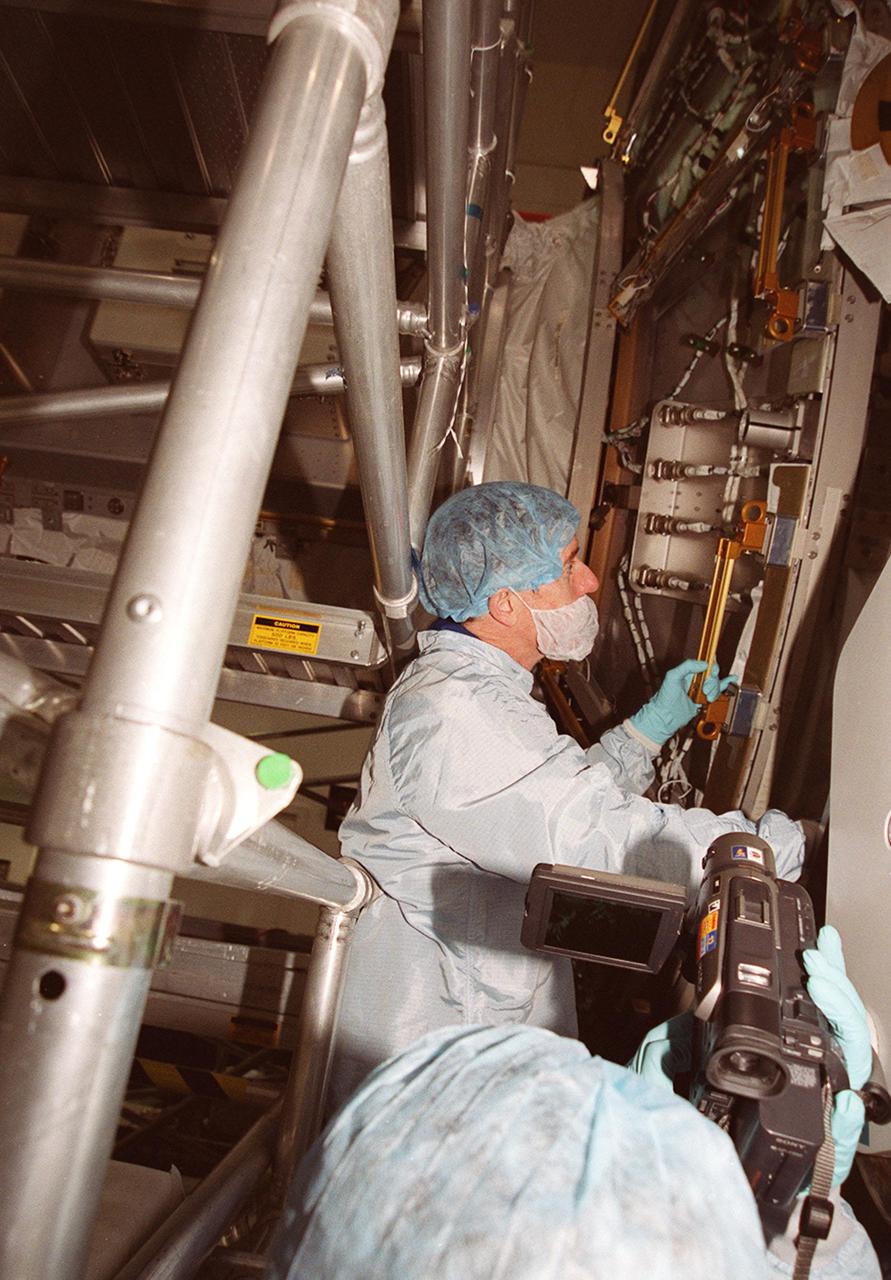

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-104 Mission Specialist James F. Reilly II checks out a piece of equipment. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. Reilly will perform three spacewalks during the mission, which will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus agument the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-104 Mission Specialist James F. Reilly II checks out a piece of equipment. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. Reilly will perform three spacewalks during the mission, which will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus agument the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-104 crew check out equipment. At left is Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt; and second from right is Mission Specialist James F. Reilly II. The crew is taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. The mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
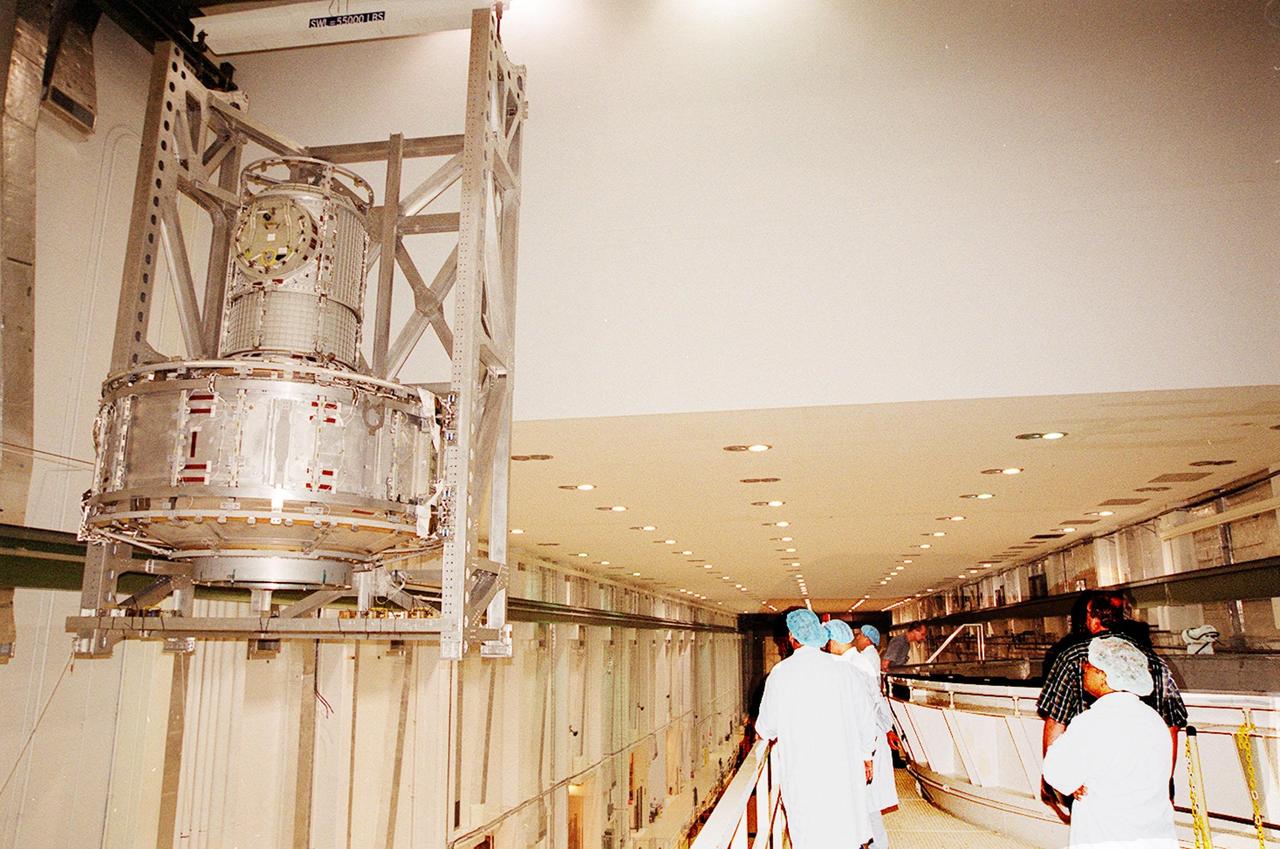

The Joint Airlock Module swings into position near the top of the Operations and Checkout Building to move toward the vacuum chamber at right. Workers alongside the chamber watch the airlock’s progress. The airlock is being tested for leaks. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module provides a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
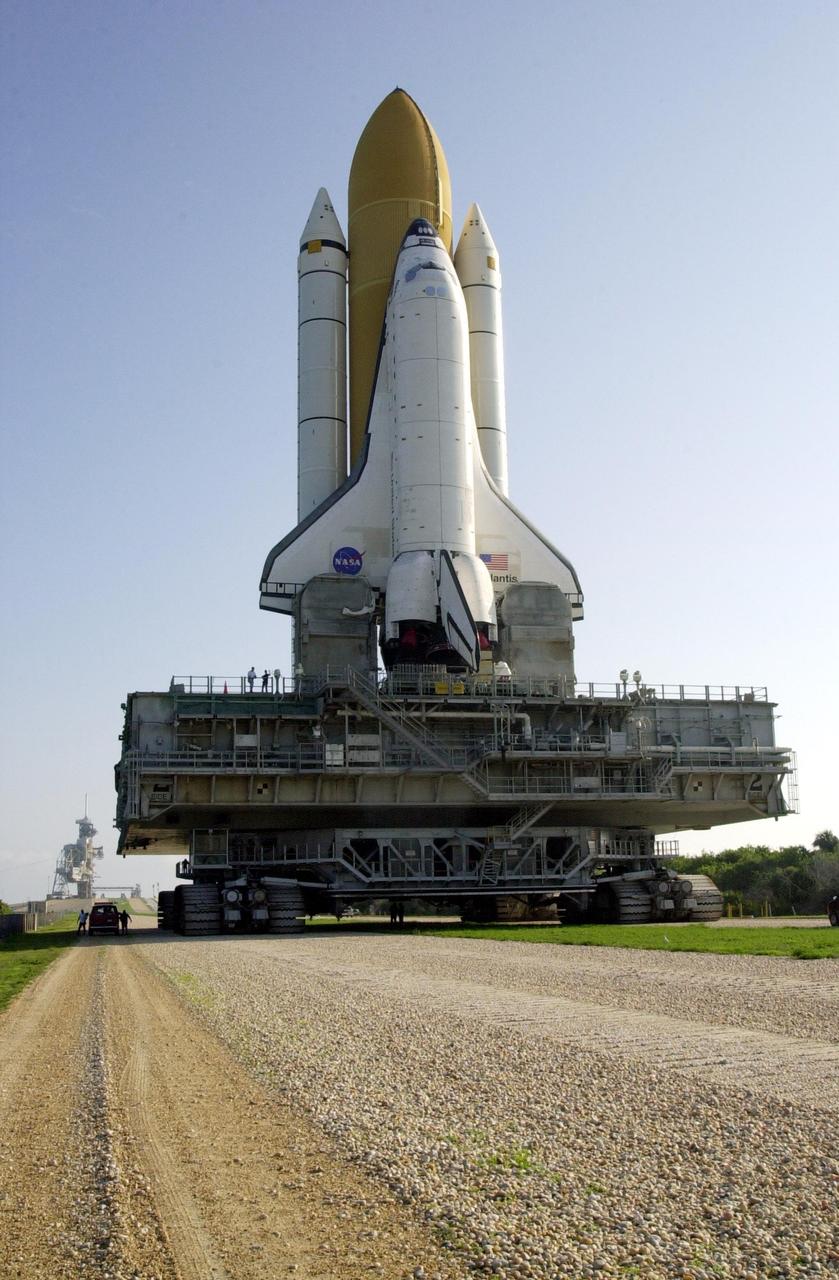

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Sitting atop the mobile launcher platform, Space Shuttle Atlantis wends its way to Launch Pad 39B. The Shuttle is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
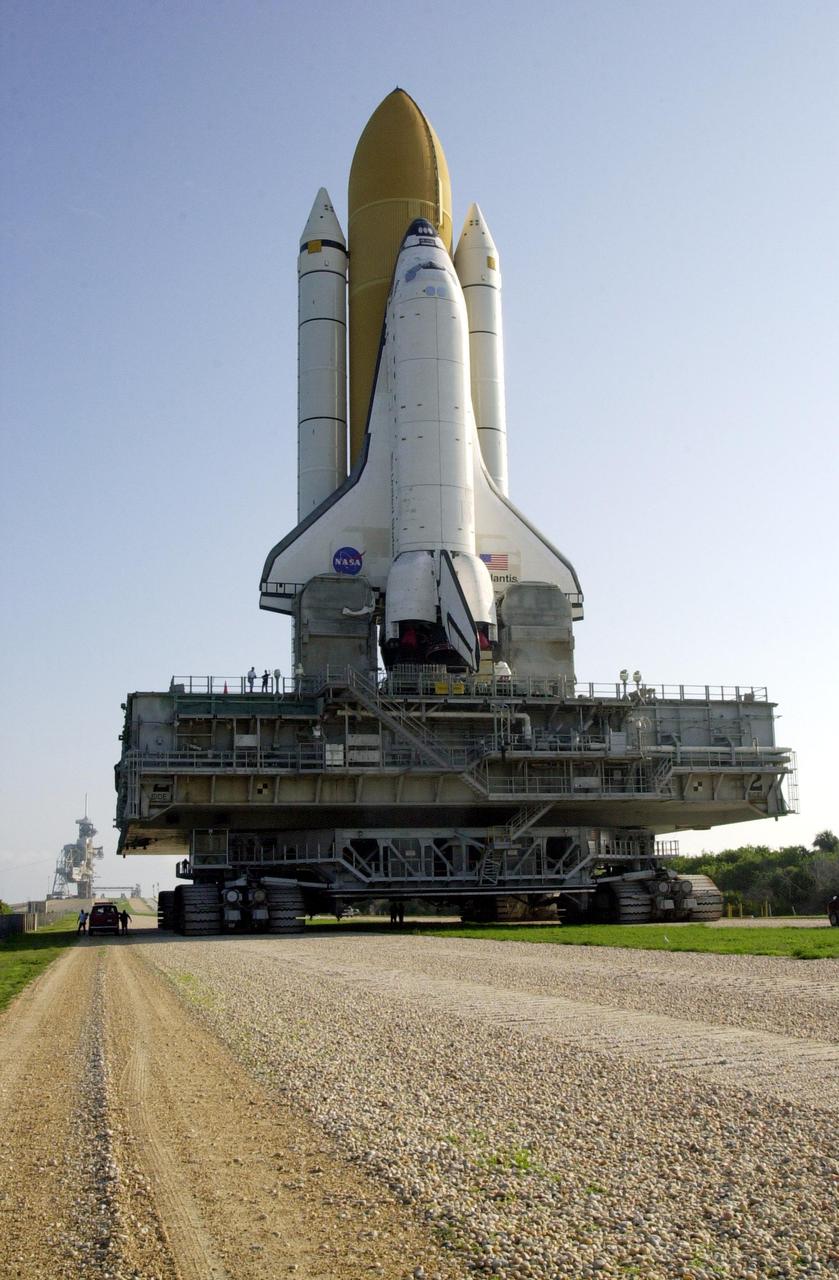

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Sitting atop the mobile launcher platform, Space Shuttle Atlantis wends its way to Launch Pad 39B. The Shuttle is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
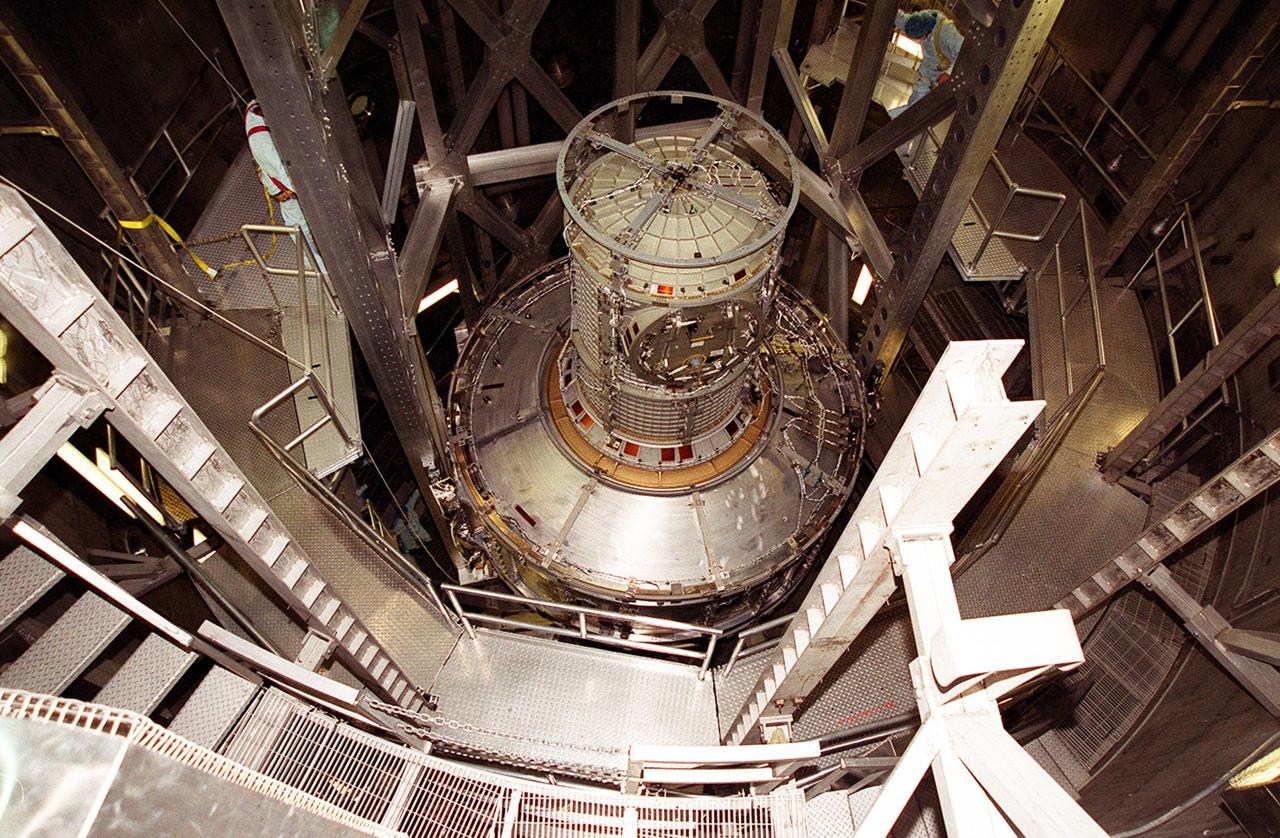
The Joint Airlock Module is fully lowered into the vacuum chamber inside the Operations and Checkout Building. Workers on either side check its position. The airlock is being tested for leaks. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module provides a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
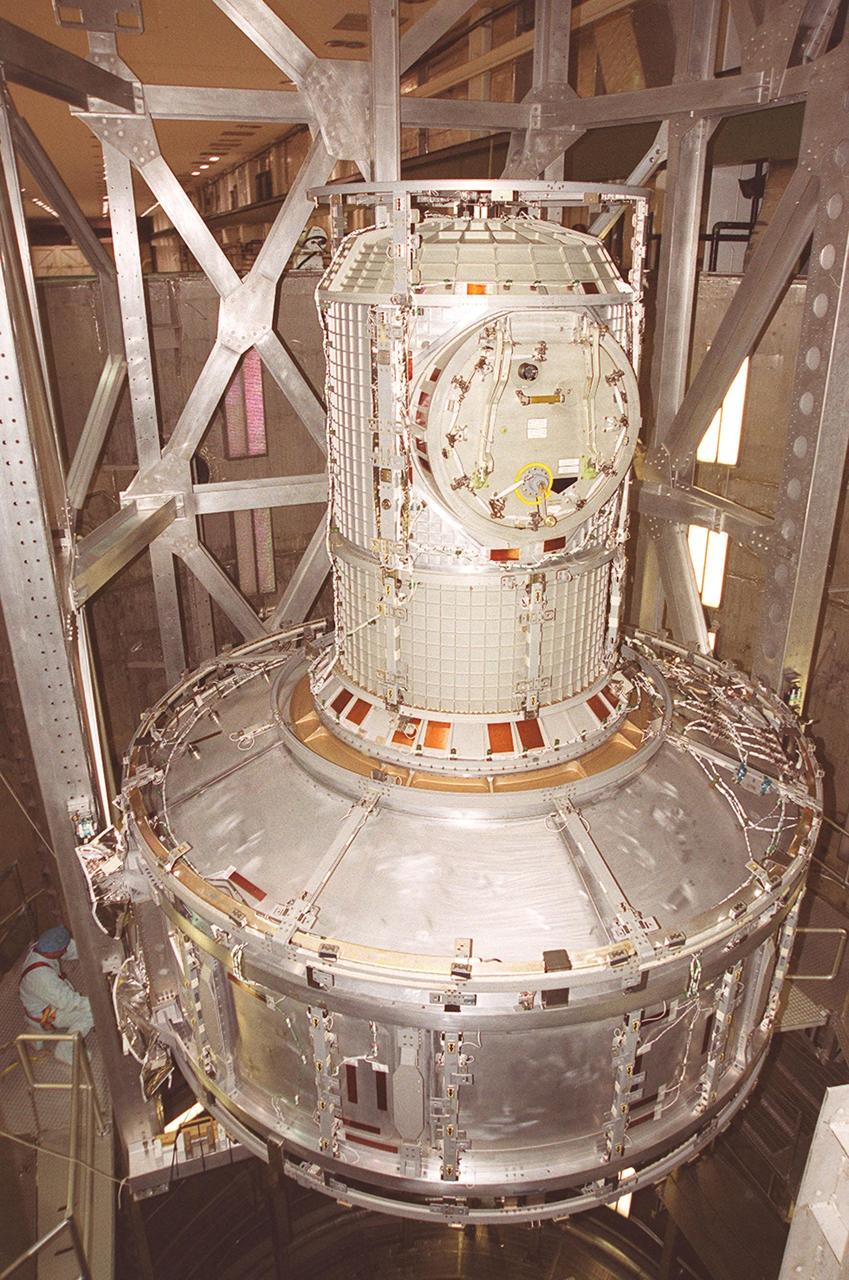
Workers inside the vacuum chamber in the Operations and Checkout Building watch as an overhead crane lowers the Joint Airlock Module inside. The airlock is being tested for leaks. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module provides a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
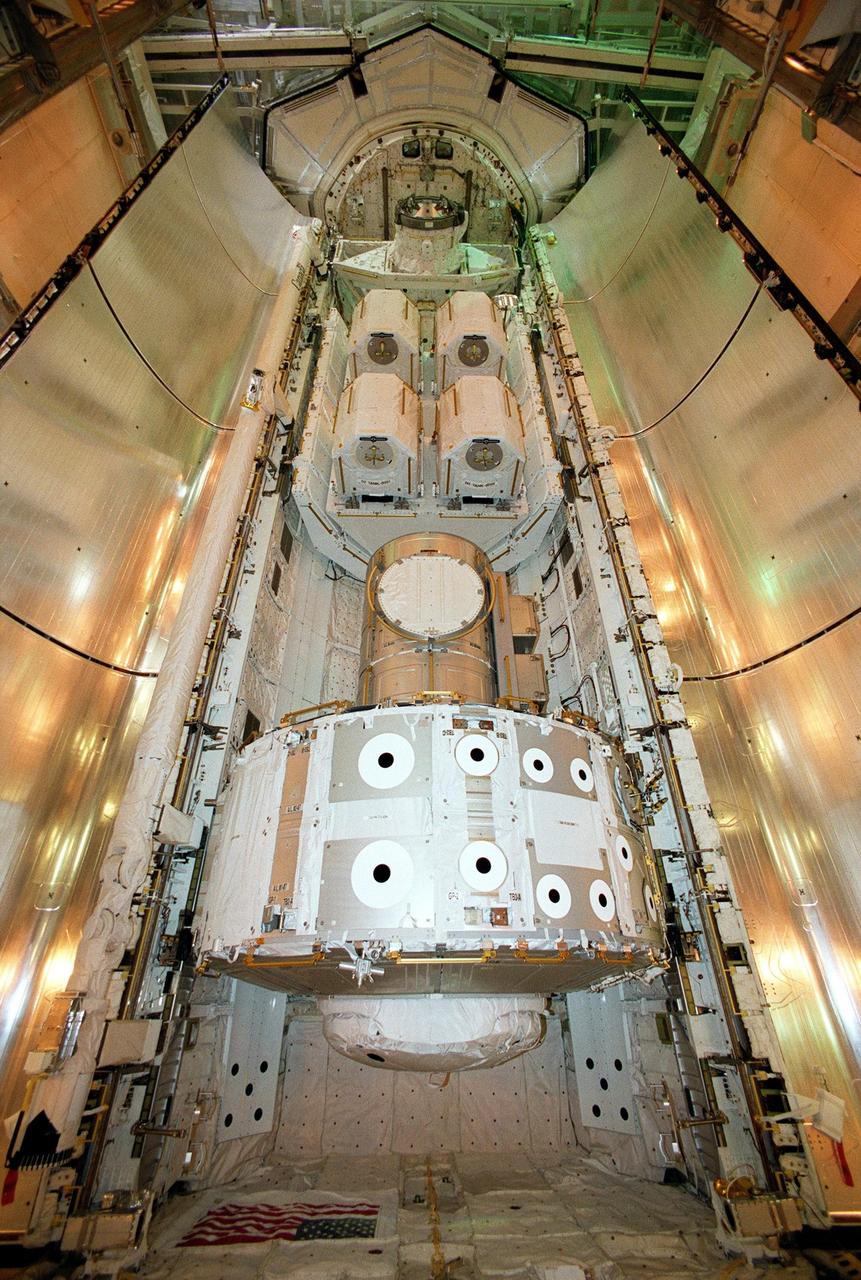

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Resting inside Atlantis’s payload bay are the Joint Airlock Module (bottom) and pallet containing the high pressure gas assembly (above). Both are heading for the International Space Station on mission STS-104, scheduled to be launched July 12. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Once installed and activated, the Airlock becomes the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. The high pressure gas assembly will support future spacewalk operations from the Space Station and augment the Service Module gas resupply system
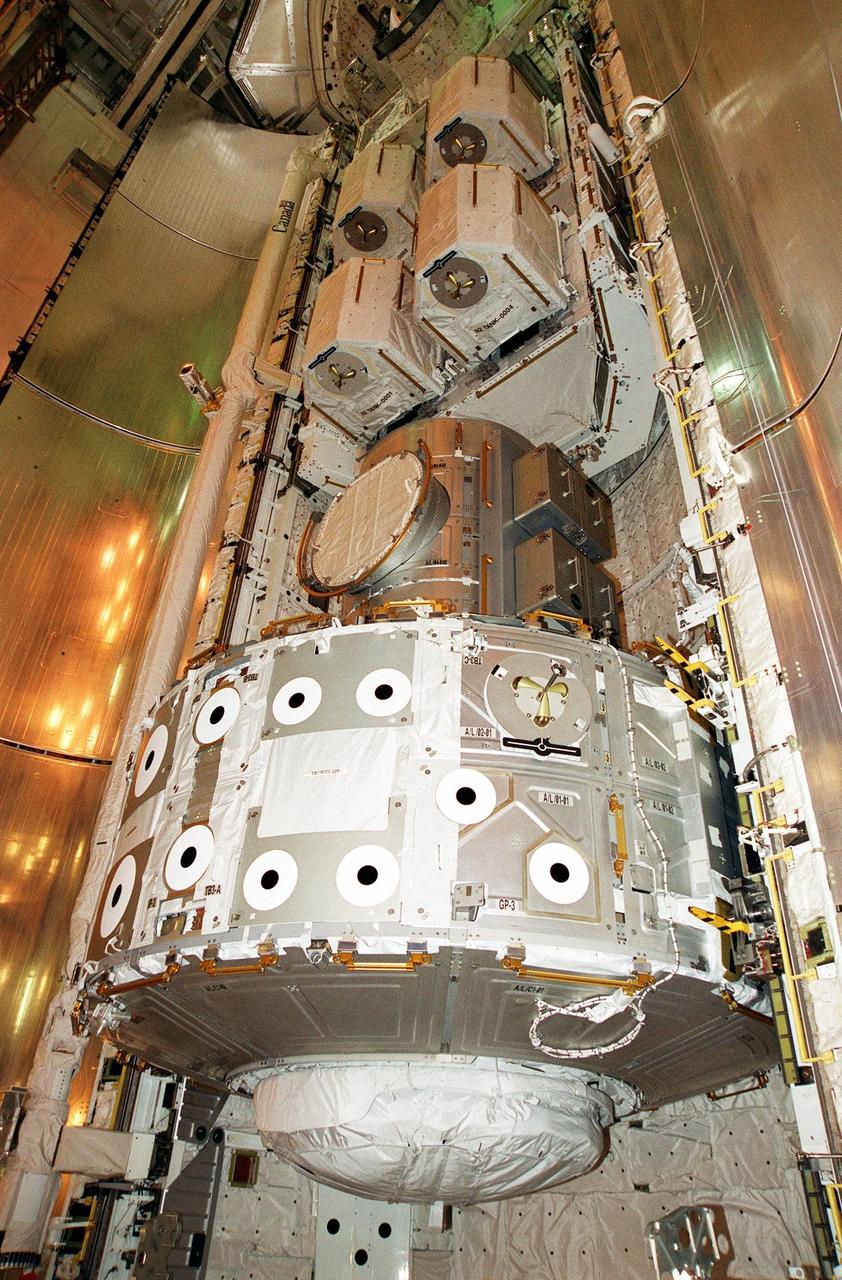
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Resting inside Atlantis’s payload bay are the Joint Airlock Module (bottom) and pallet containing the high pressure gas assembly (above). Both are heading for the International Space Station on mission STS-104, scheduled to be launched July 12. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Once installed and activated, the Airlock becomes the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. The high pressure gas assembly will support future spacewalk operations from the Space Station and augment the Service Module gas resupply system
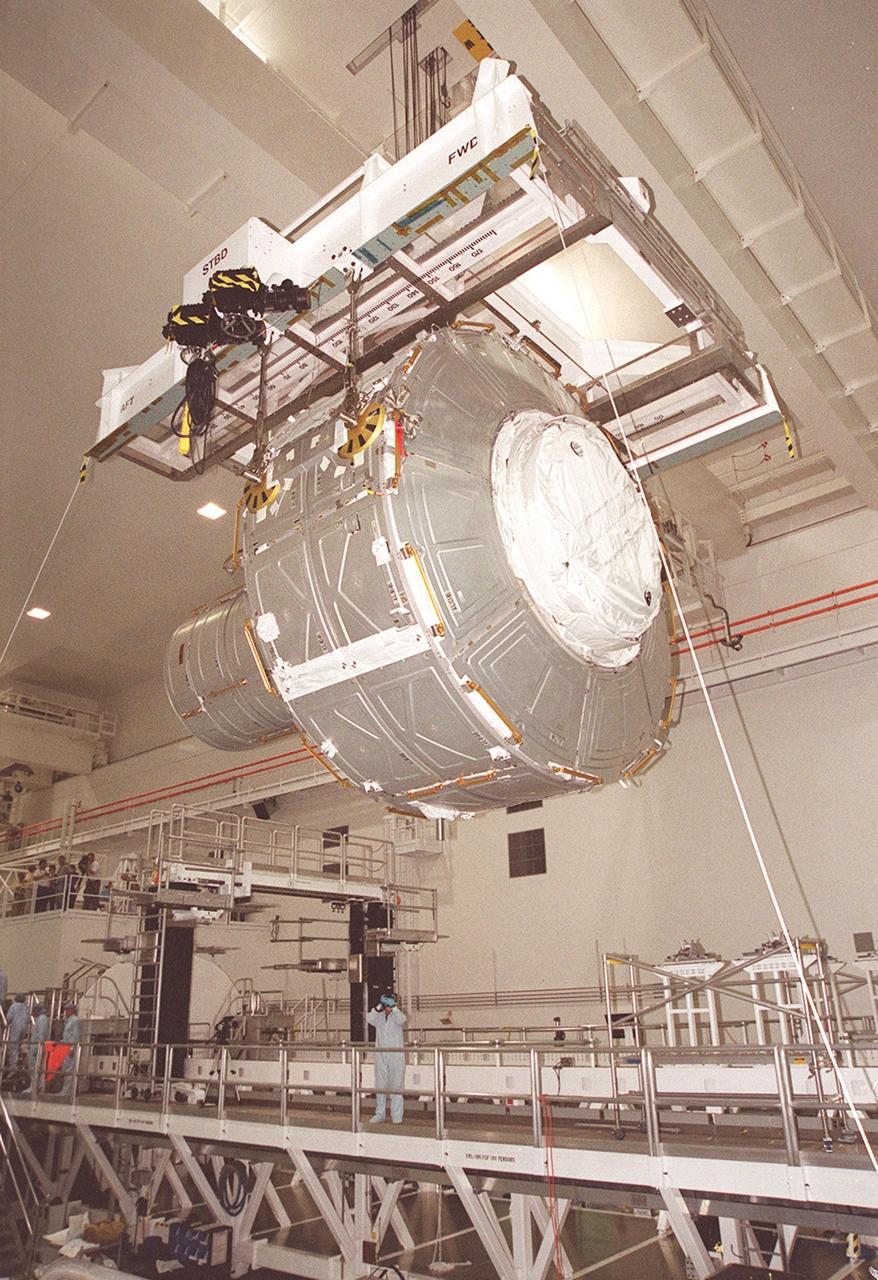

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the Joint Airlock Module is lifted from its workstand for a transfer to the payload canister. The airlock will be installed in the payload bay of Atlantis for mission STS-104 to the International Space Station. The airlock is a pressurized flight element consisting of two cylindrical chambers attached end-to-end by a connecting bulkhead and hatch. Once installed and activated, the airlock becomes the primary path for spacewalk entry to and departure from the Space Station for U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. STS-104 is scheduled for launch June 14 from Launch Pad 39B
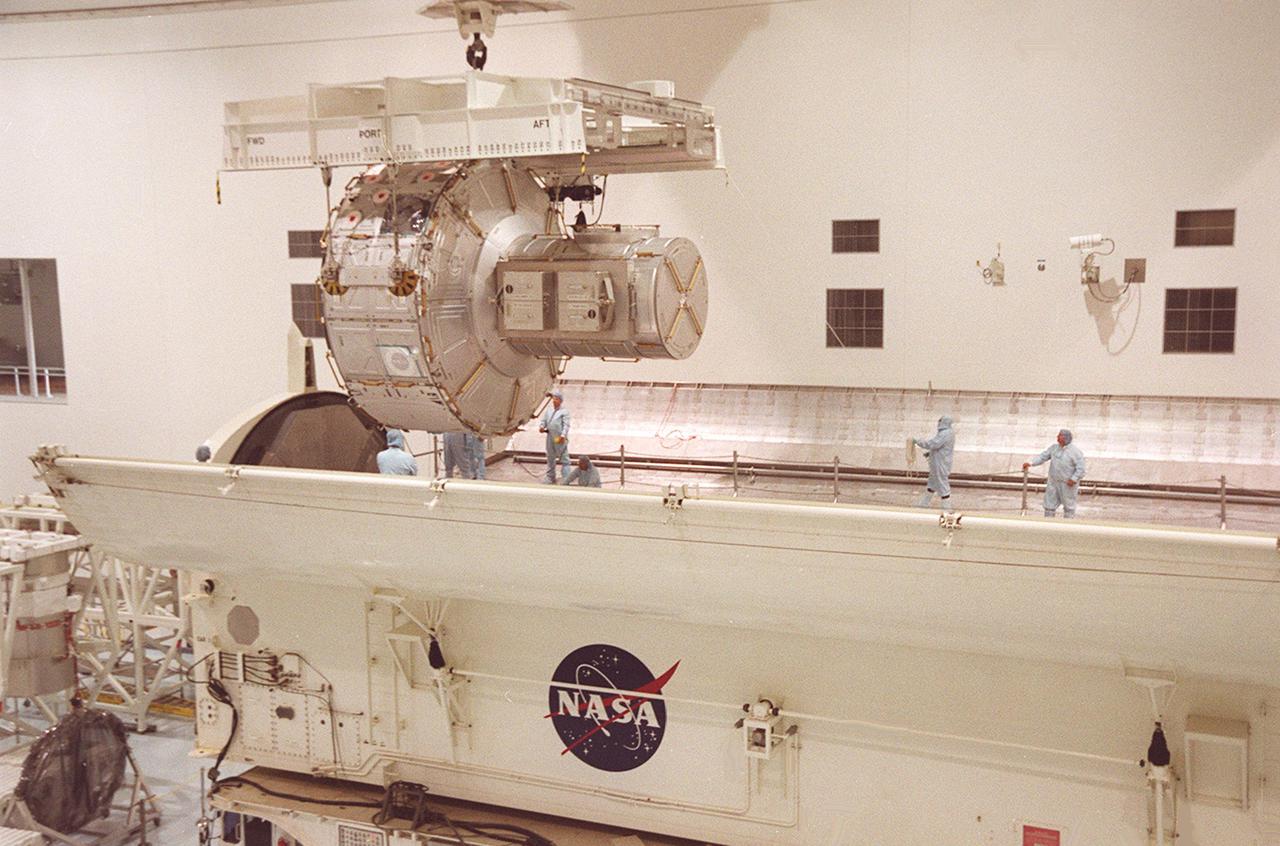
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers standing inside the payload canister help guide the Joint Airlock Module into place. The airlock will be installed in the payload bay of Atlantis for mission STS-104 to the International Space Station. The airlock is a pressurized flight element consisting of two cylindrical chambers attached end-to-end by a connecting bulkhead and hatch. Once installed and activated, the Airlock becomes the primary path for spacewalk entry to and departure from the Space Station for U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. STS-104 is scheduled for launch June 14 from Launch Pad 39B
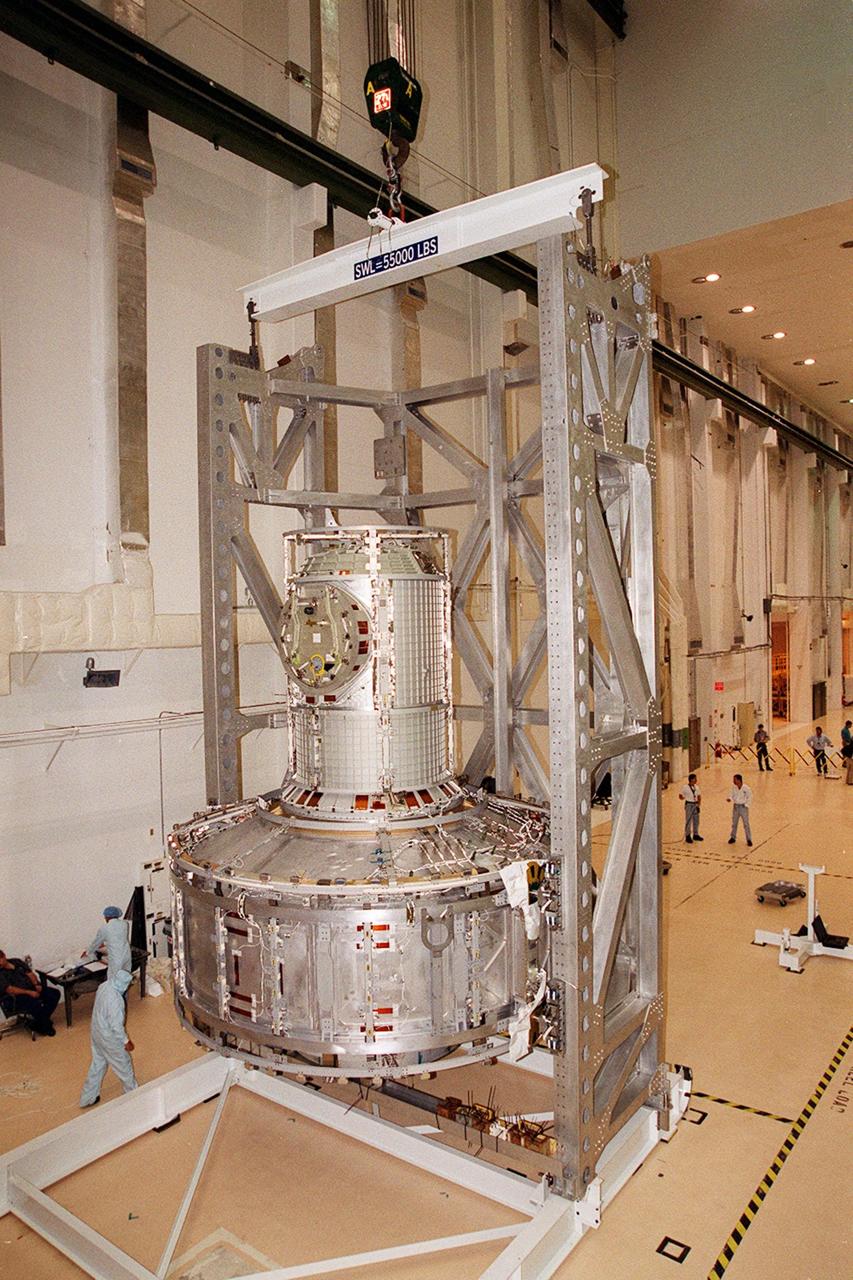

In the Operations and Checkout Building, the Joint Airlock Module, now in vertical position, is ready to be moved into a vacuum chamber for testing. The module is the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility. The airlock is a critical element of the ISS because of design differences between American and Russian spacesuits. The Joint Airlock Module is specially designed to accommodate both suits, providing a chamber where astronauts from every nation can suit up for space walks to conduct maintenance and construction work or to do science experiments outside the Station. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the 10th International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001. The Shuttle crew will secure the airlock to the right side of Unity, the American-built connecting node that currently comprises one-third of the current Space Station, along with the Russian modules Zarya and Zvezda
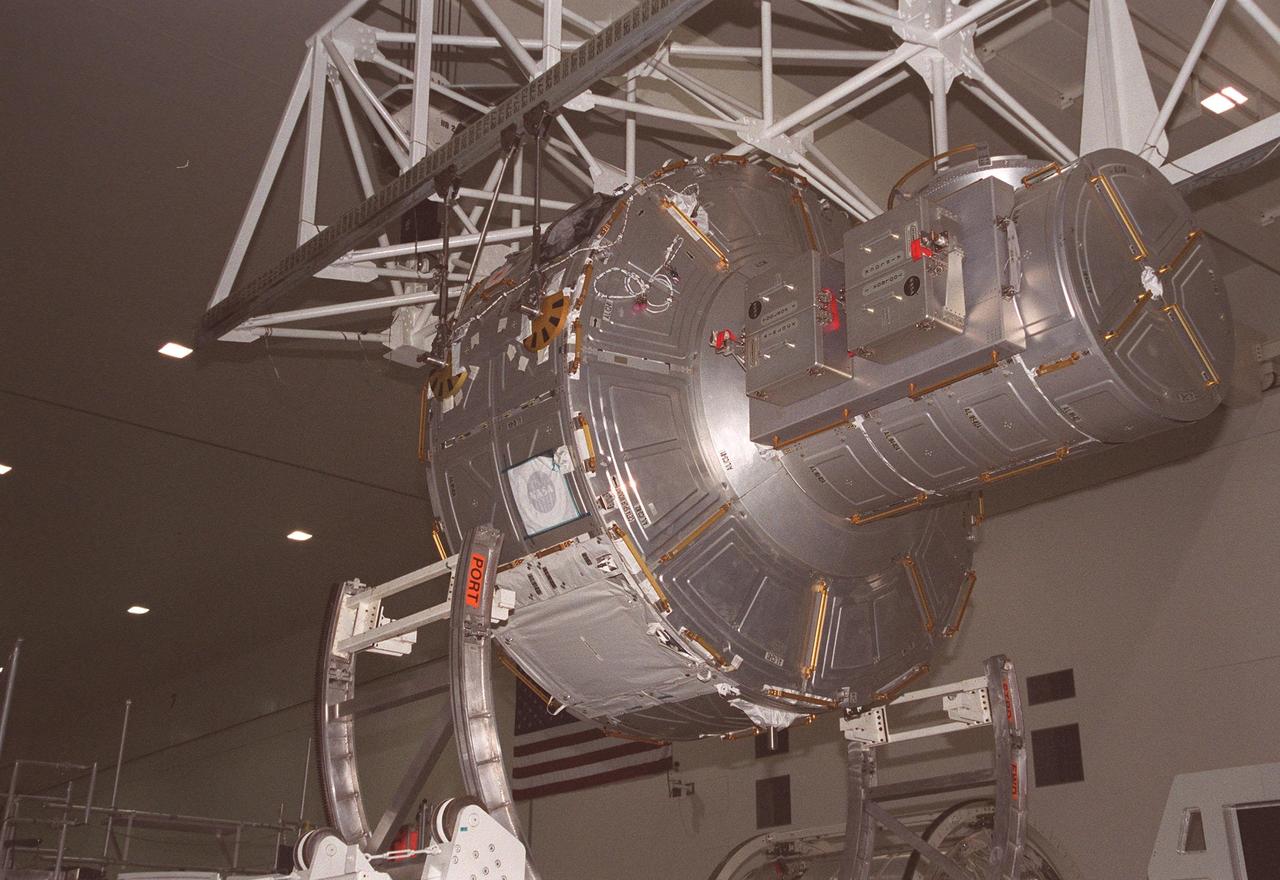
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An overhead crane in the Space Station Processing Facility lifts the Joint Airlock Module from its workstand to move it to the Launch Package Integration Stand. The LPIS provides personnel and equipment access to the flight element in its final launch configuration. The Airlock is the primary payload on mission STS-104 to the International Space Station. It is a pressurized flight element consisting of two cylindrical chambers attached end-to-end by a connecting bulkhead and hatch. Once installed and activated, the Airlock becomes the primary path for spacewalk entry to and departure from the Space Station for U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. STS-104 is scheduled for launch June 14 from Launch Pad 39B
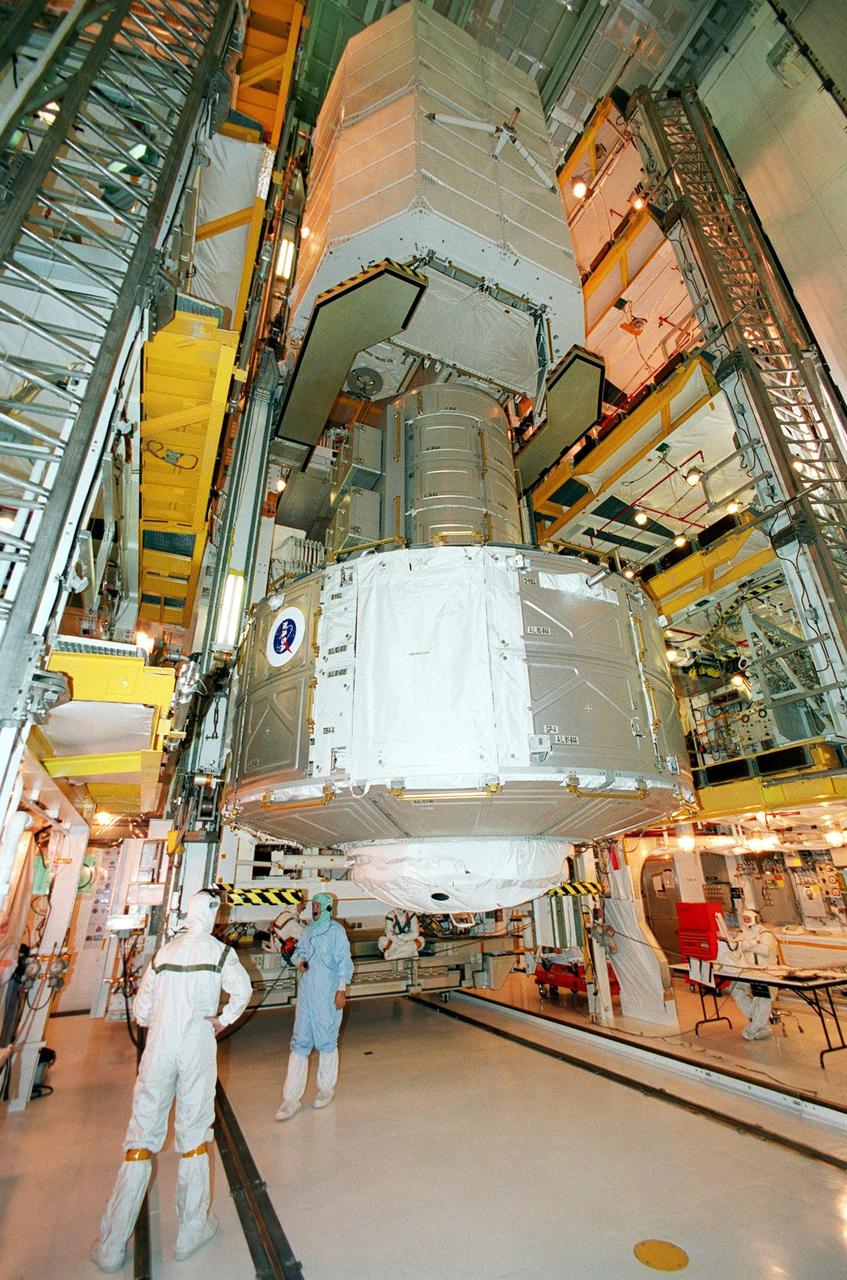

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Payload Changeout Room, Launch Pad 39B, the Joint Airlock Module (below) and Space Lab Double Pallet (above) are moved into the payload bay of Space Shuttle Atlantis for mission STS-104. The pallet contains two oxygen and two nitrogen High-Pressure Gas Tanks, which will be attached externally to the airlock during two of the STS-104 spacewalks. Once installed and activated, the airlock becomes the primary path for International Space Station spacewalk entry and departure using U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. Launch of Atlantis is scheduled no earlier than July 12 at 5:04 a.m. EDT
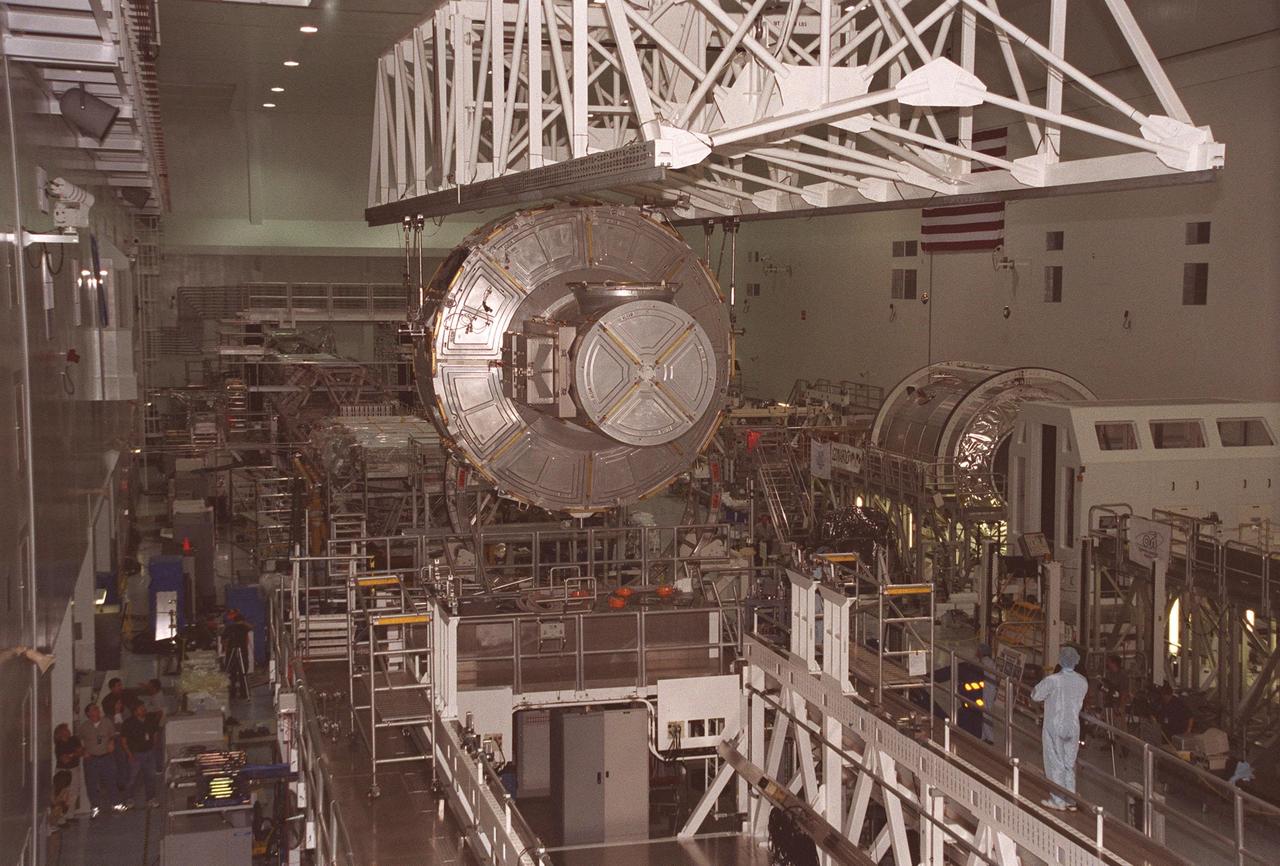
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the Joint Airlock Module is moved from a workstand to the Launch Package Integration Stand. The LPIS provides personnel and equipment access to the flight element in its final launch configuration. The Airlock is the primary payload on mission STS-104 to the International Space Station. It is a pressurized flight element consisting of two cylindrical chambers attached end-to-end by a connecting bulkhead and hatch. Once installed and activated, the Airlock becomes the primary path for spacewalk entry to and departure from the Space Station for U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. STS-104 is scheduled for launch June 14 from Launch Pad 39B
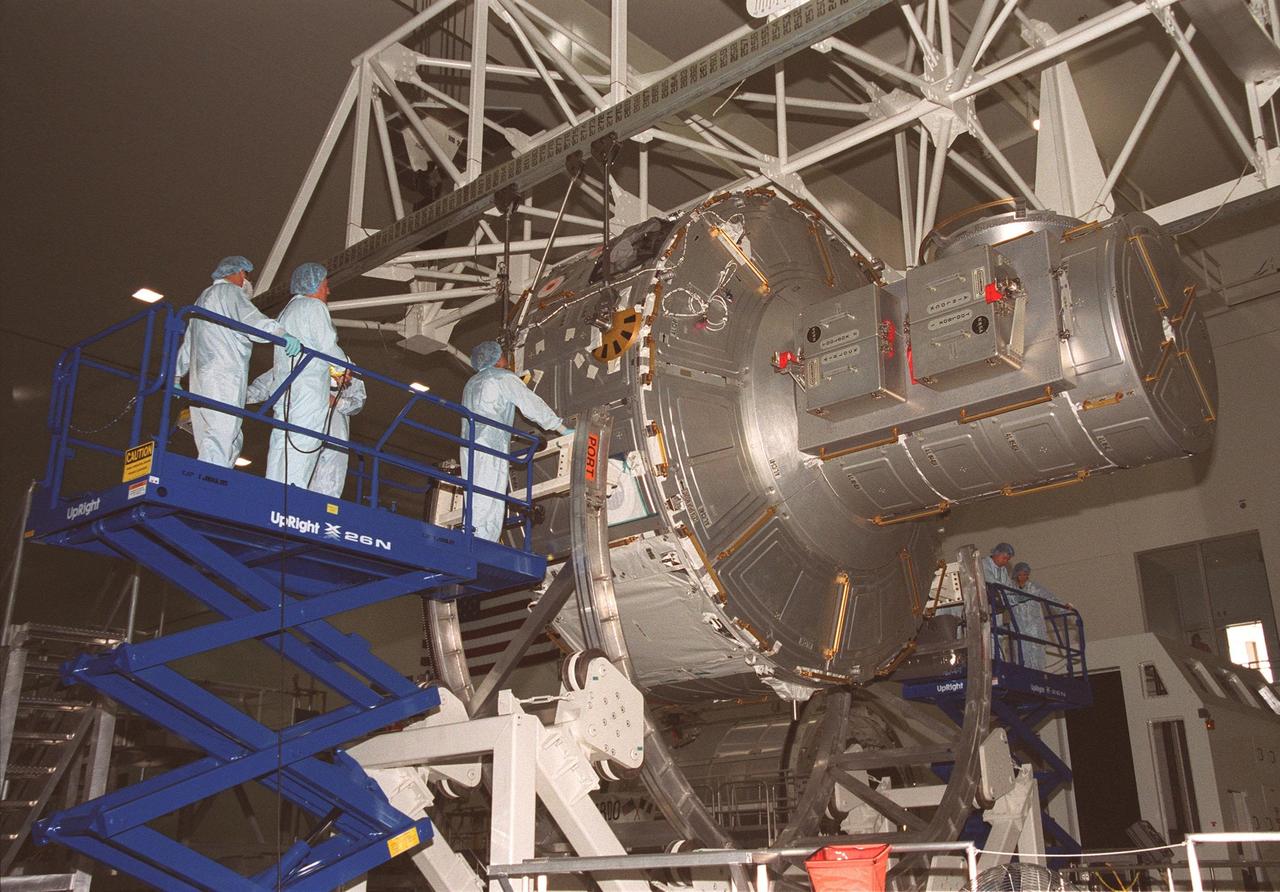

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the Joint Airlock Module is lowered toward the Launch Package Integration Stand. The LPIS provides personnel and equipment access to the flight element in its final launch configuration. The Airlock is the primary payload on mission STS-104 to the International Space Station. It is a pressurized flight element consisting of two cylindrical chambers attached end-to-end by a connecting bulkhead and hatch. Once installed and activated, the Airlock becomes the primary path for spacewalk entry to and departure from the Space Station for U.S. spacesuits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs. In addition, the Joint Airlock is designed to support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity. STS-104 is scheduled for launch June 14 from Launch Pad 39B
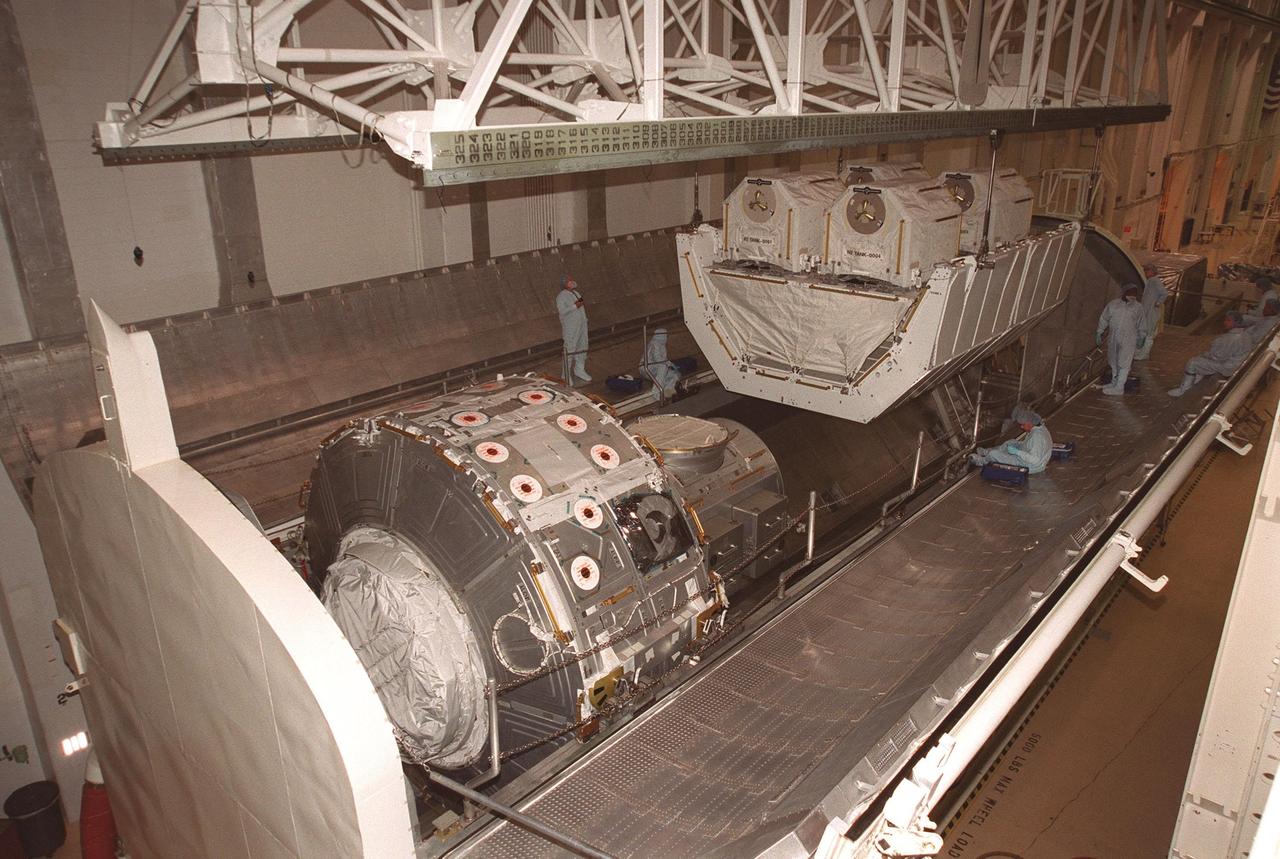

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With workers keeping a close watch, the overhead crane lowers the high pressure gas assembly two gaseous oxygen and two gaseous nitrogen storage tanks into the payload canister. The joint airlock module is already in the canister. The airlock and tanks are part of the payload on mission STS-104 and are being transferred to orbiter Atlantis’s payload bay. The storage tanks will be attached to the airlock during two spacewalks. The storage tanks will support future spacewalk operations from the Station and augment the Service Module gas resupply system. STS-104 is scheduled for launch June 14 from Launch Pad 39B
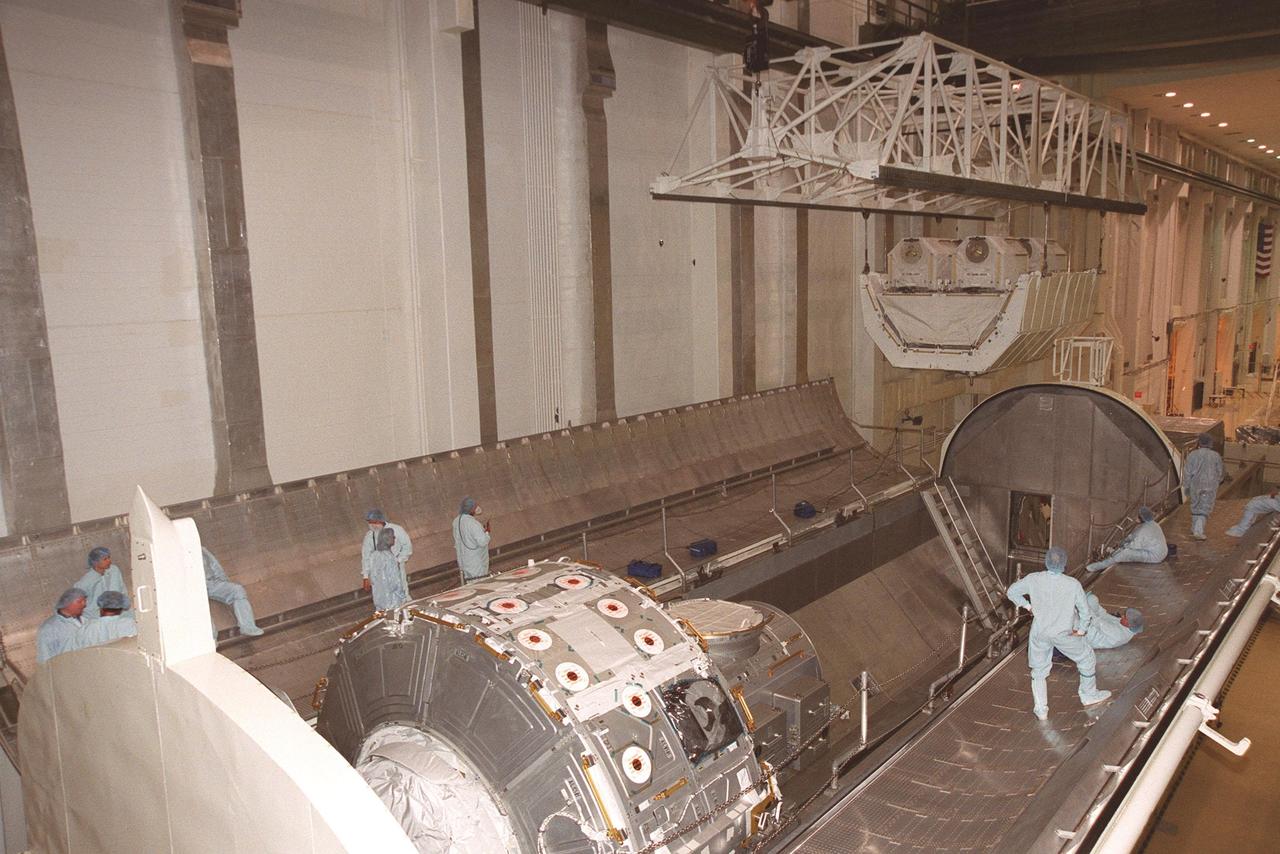
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, workers wait in the payload canister as an overhead crane moves the high pressure gas assembly two gaseous oxygen and two gaseous nitrogen storage tanks toward it. The joint airlock module is already in the canister. The airlock and tanks are part of the payload on mission STS-104 and are being transferred to orbiter Atlantis’s payload bay. The storage tanks will be attached to the airlock during two spacewalks. The storage tanks will support future spacewalk operations from the Station and augment the Service Module gas resupply system. STS-104 is scheduled for launch June 14 from Launch Pad 39B
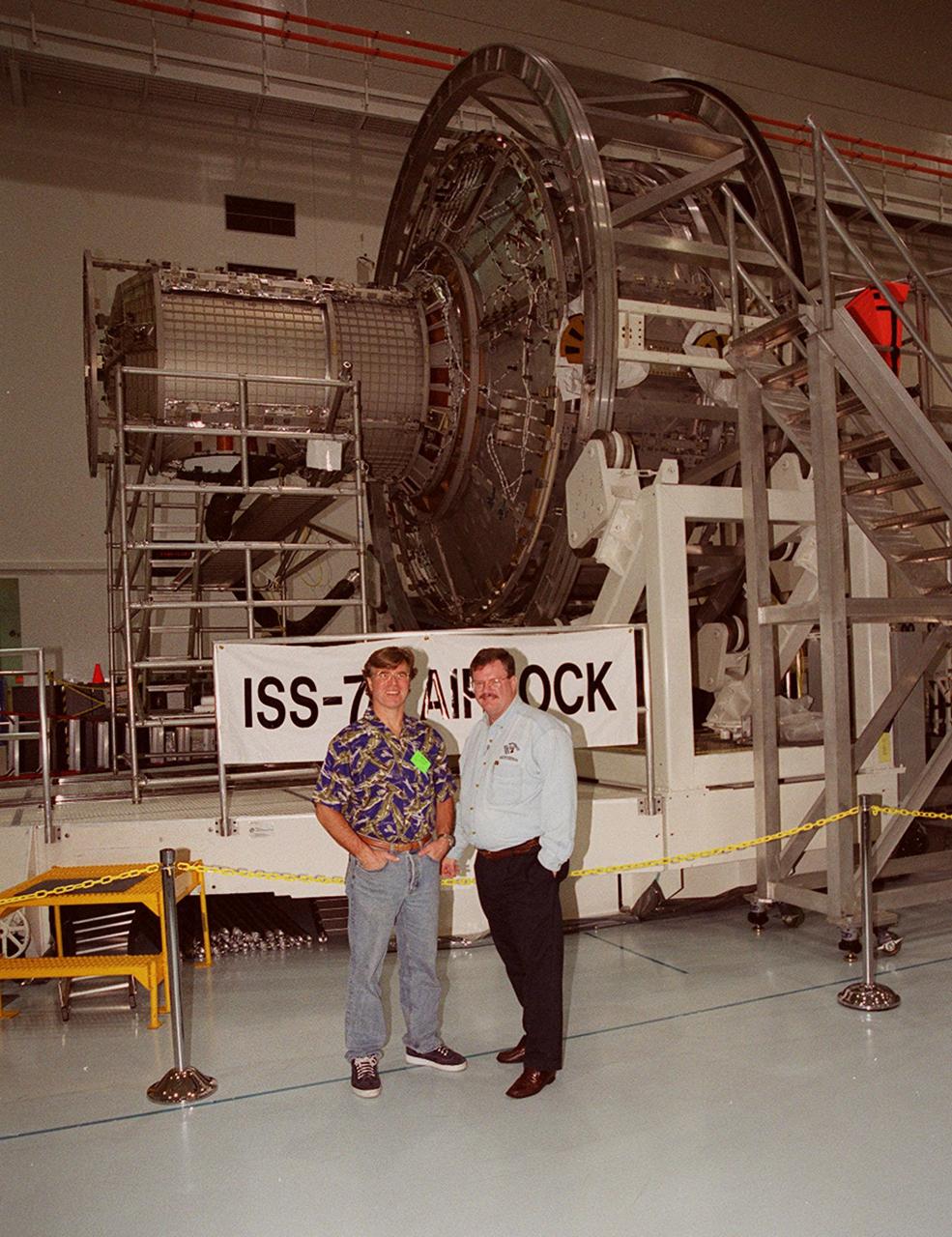
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, Steve Thomas (left), host of the television series "This Old House," poses in front of the Joint Airlock module. Thomas and Norm Abram, master carpenter with "This Old House," are at KSC to film an episode of the series
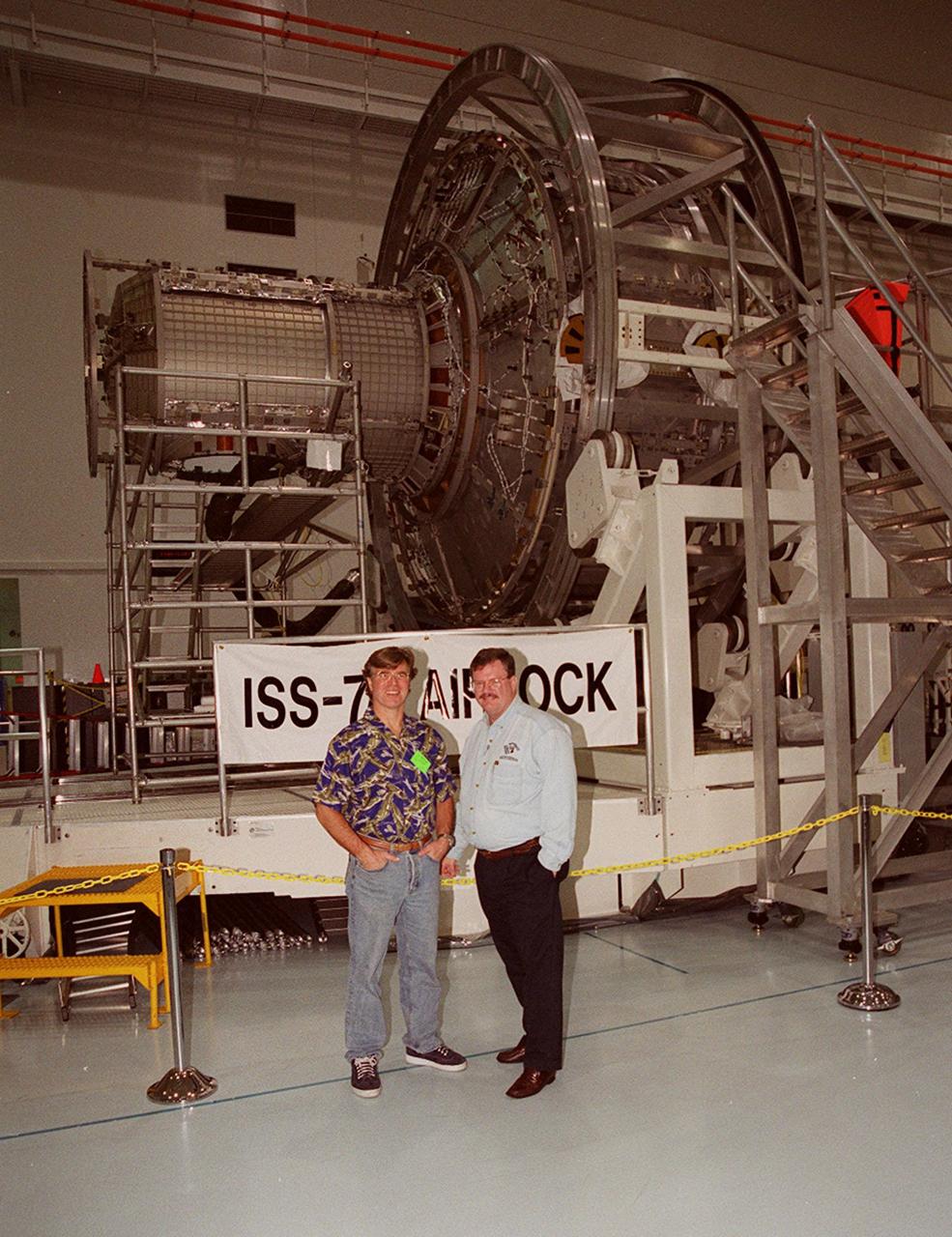
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, Steve Thomas (left), host of the television series "This Old House," poses in front of the Joint Airlock module. Thomas and Norm Abram, master carpenter with "This Old House," are at KSC to film an episode of the series
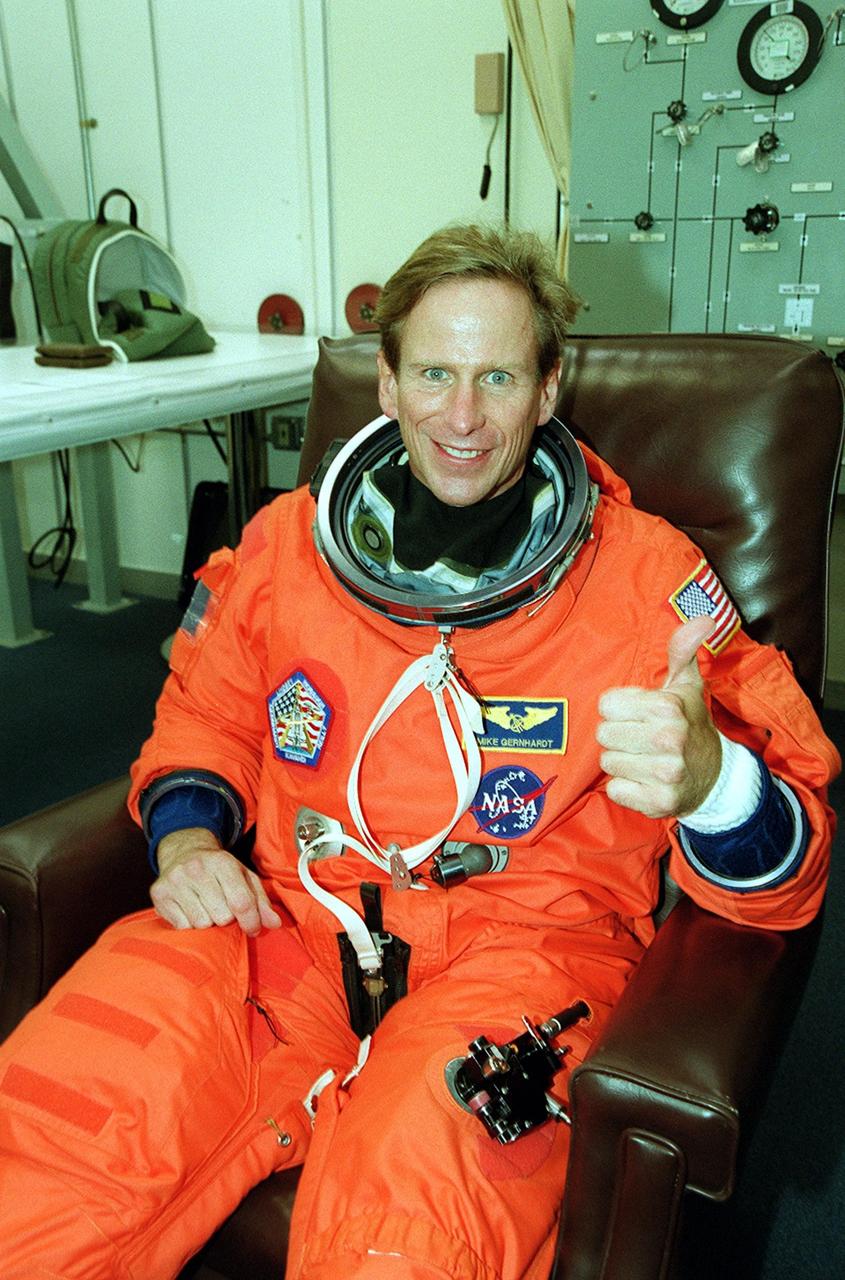

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-104 Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt signals he is ready for launch. This will be his fourth space flight. Liftoff of Space Shuttle Atlantis on mission STS-104 is targeted for 5:04 a.m., July 12, from Launch Pad 39B. The primary payload on the mission is the joint airlock module, which will be added to the International Space Station. The airlock will be the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, and will also support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity
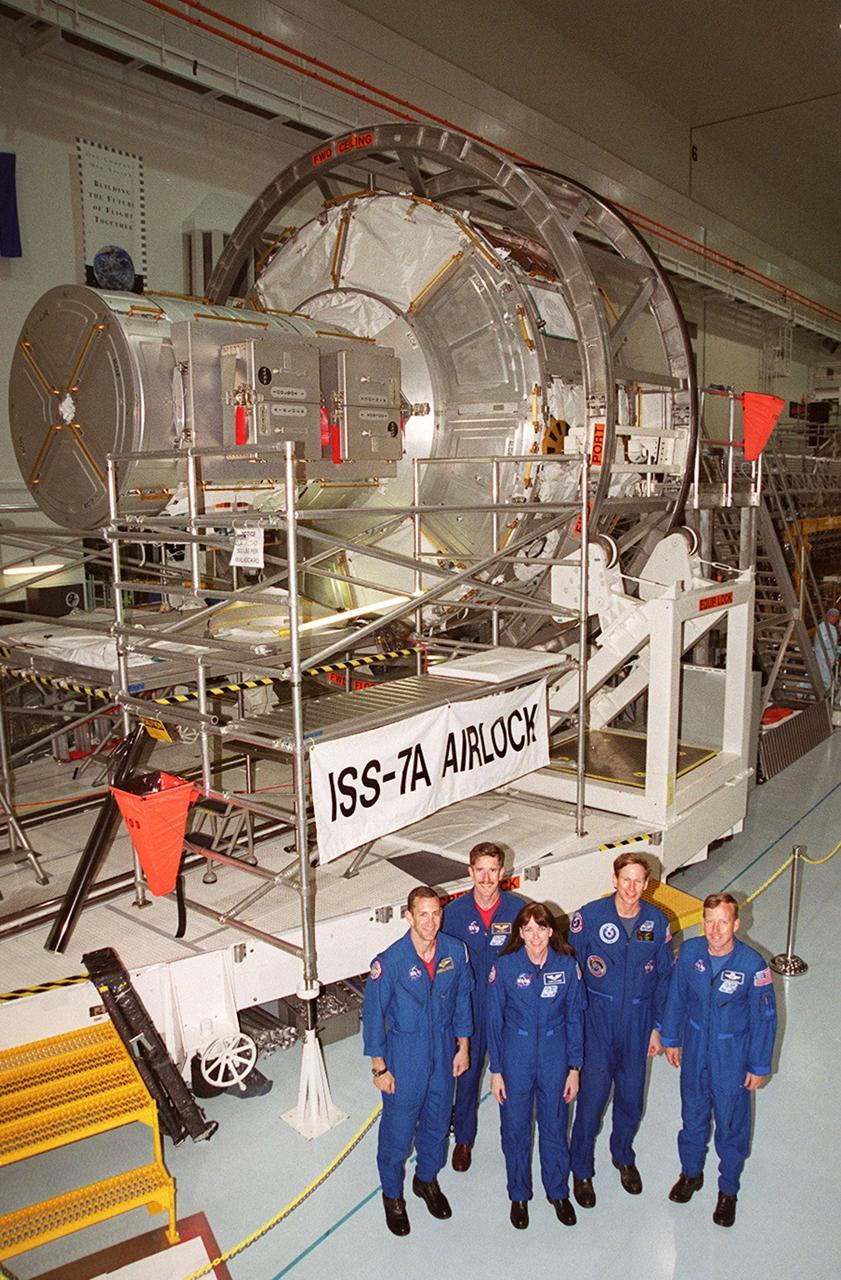

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-104 crew poses in front of the Joint Airlock Module in the Space Station Processing Facility. Standing, left to right, are Pilot Charles Hobaugh, Mission Specialists James Reillly, Janet Kavandi and Michael Gernhardt, and Commander Steven Lindsey. They are at KSC to continue Crew Equipment Interface Test activities such as payload familiarization. The airlock is the primary payload on their mission, scheduled to launch no earlier than June 14, 2001, from Launch Pad 39B

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Space Station Processing Facility, the STS-104 crew look over equipment as part of Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. Starting second from left are Mission Specialists James F. Reilly II, Janet L. Kavandi, Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh, Commander Steven Lindsey and Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt. The STS-104 mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus agument the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module

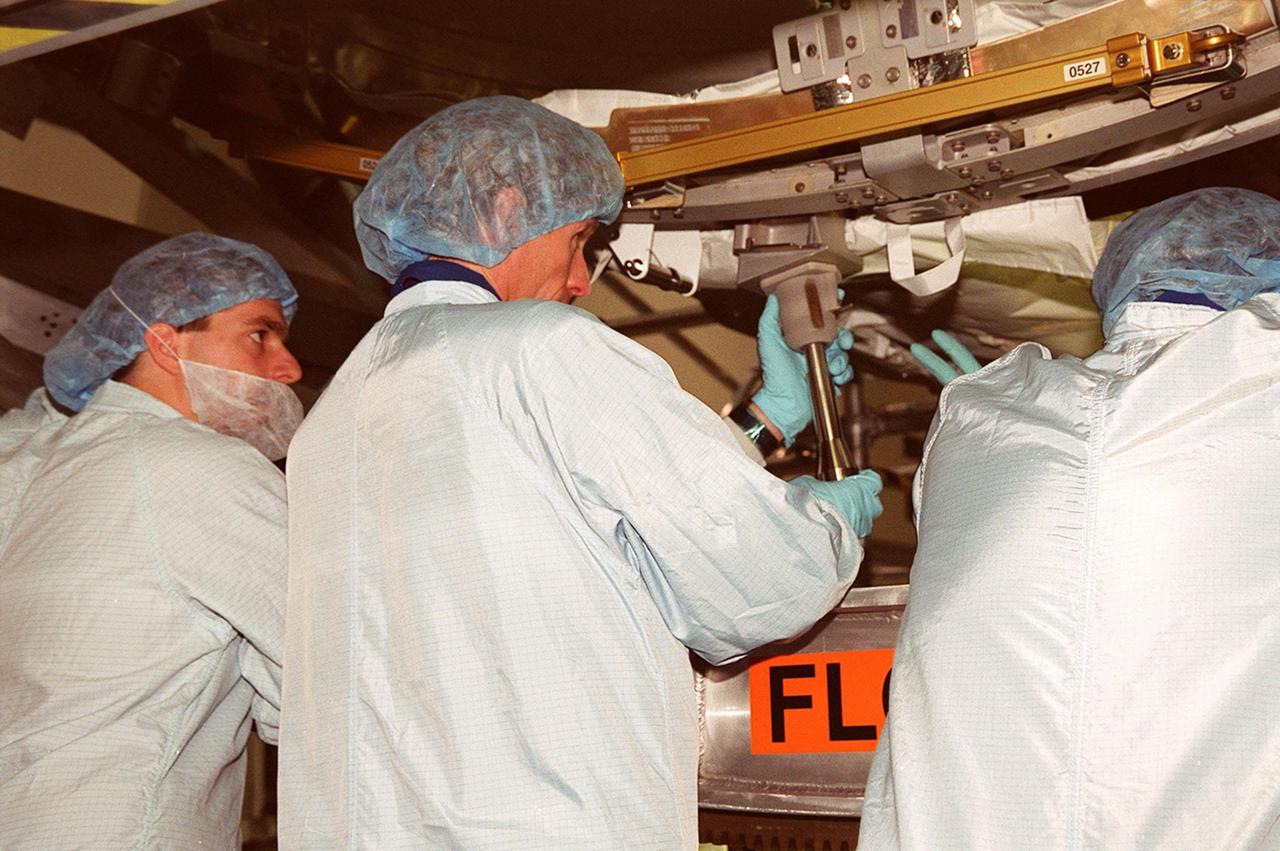
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-104 crew check out equipment at the Space Station Processing Facility as part of Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. Shown (from left) are Mission Specialist James F. Reilly II and Commander Steven W. Lindsey; (rear) Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh; (right) Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt. Not shown is Mission Specialist Janet L. Kavandi. ). The mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
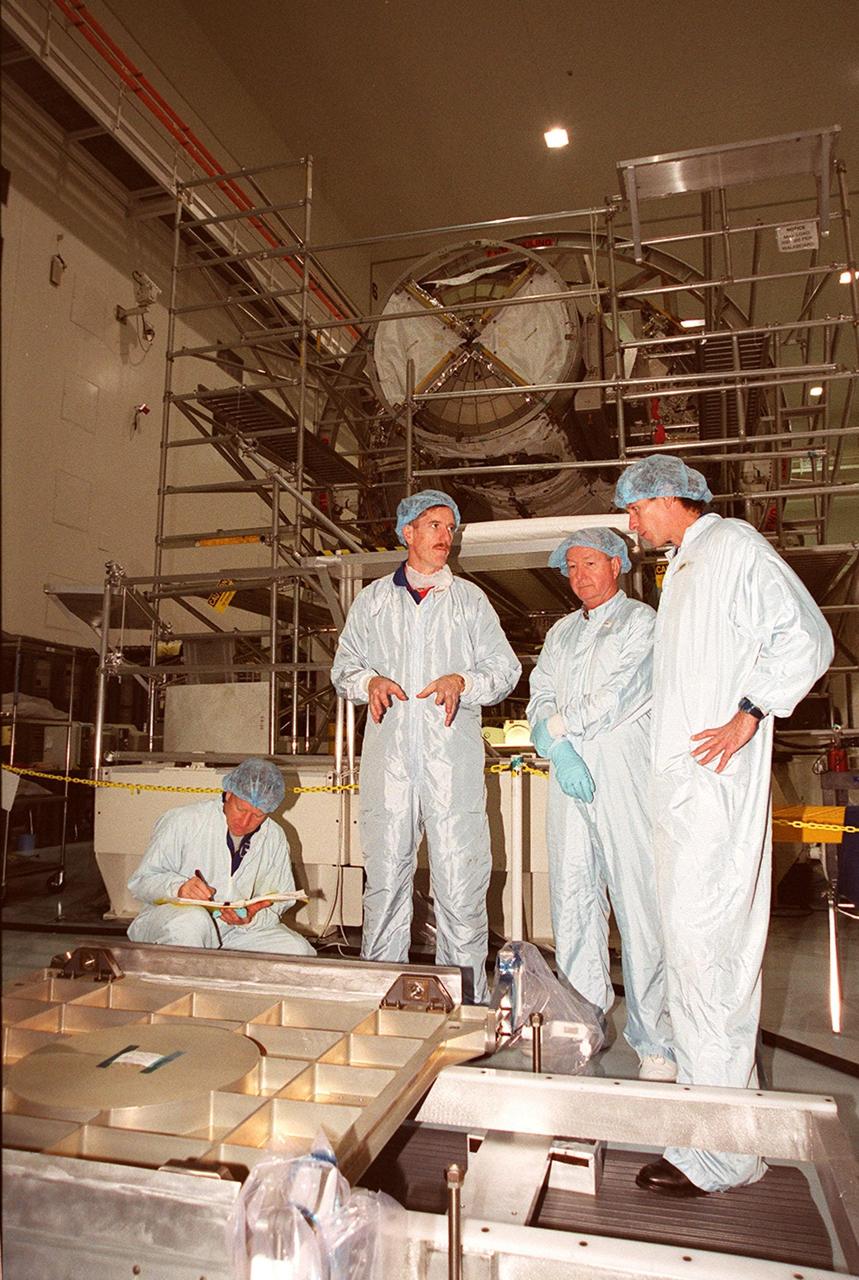

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the Space Station Processing Facility, the STS-104 crew look over equipment as part of Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. From left are Commander Steven Lindsey, Mission Specialist James F. Reilly II and Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt at far right. Not shown is Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh. The STS-104 mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus agument the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module

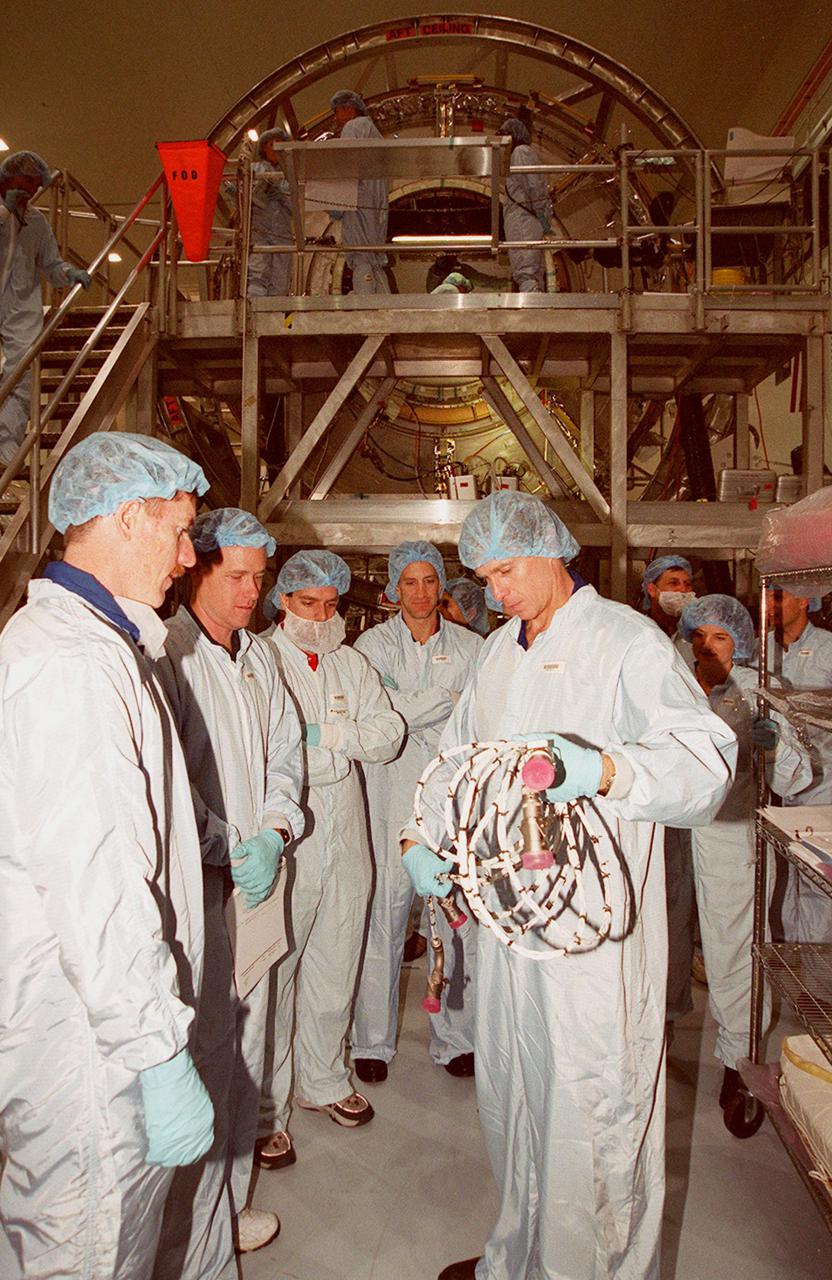
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-104 crew practice using tools they will work with on their mission. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. Seen are (from left) Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh and Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt. Also among the crew are Commander Steven W. Lindsey and Mission Specialists Janet L. Kavandi and James F. Reilly. The mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-104 crew check out equipment at the Space Station Processing Facility as part of Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. Shown are Mission Specialist James F. Reilly II (left), Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh (center) and Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt (right). The mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-104 crew check out equipment at the Space Station Processing Facility as part of Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. Seen are (from left) Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt, Commander Steven W. Lindsey, Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh and Mission Specialist James F. Reilly II. Not shown is Mission Specialist Janet L. Kavandi. The mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
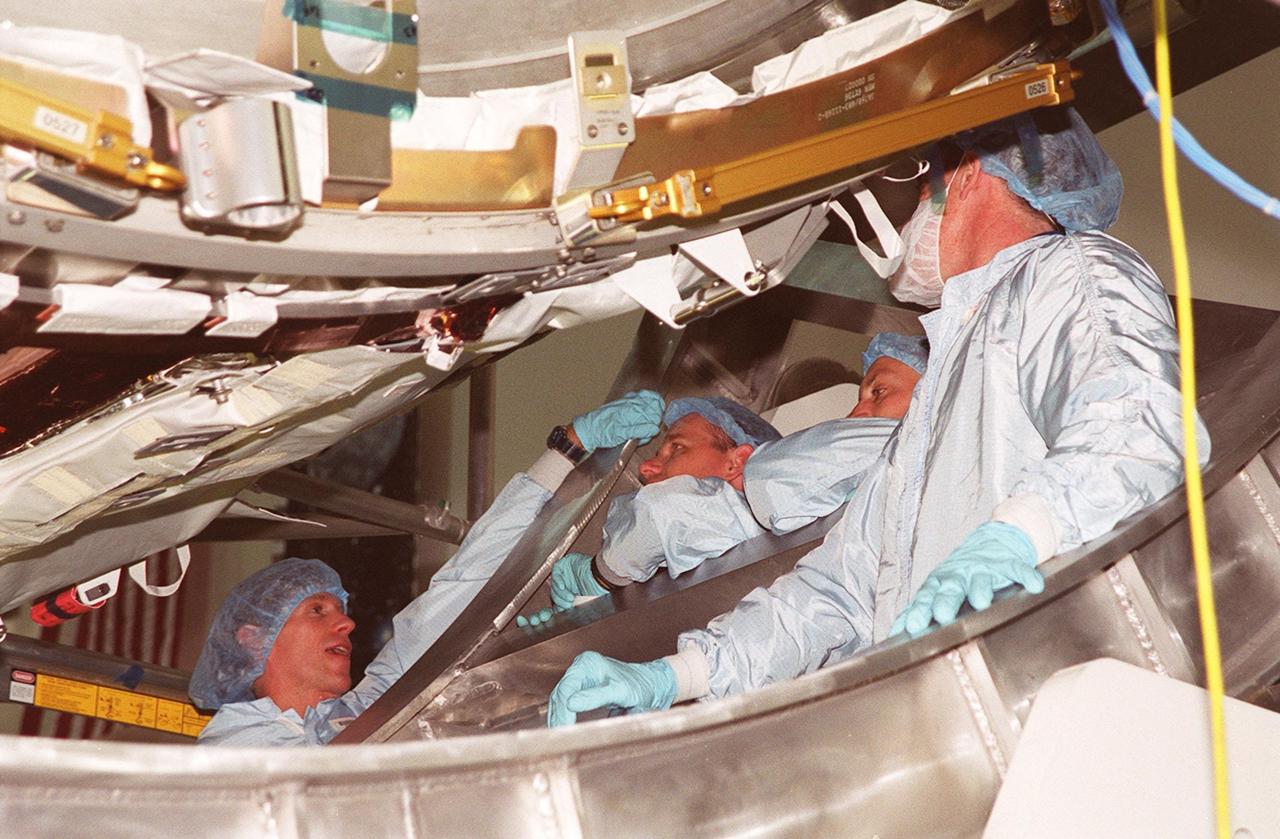

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-104 crew check out equipment at the Space Station Processing Facility as part of Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. Seen are (from left) Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt, Commander Steven W. Lindsey, Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh and Mission Specialist James F. Reilly II. Not shown is Mission Specialist Janet L. Kavandi. The mission will carry the Joint Airlock Module to the International Space Station. The U.S.-made module will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
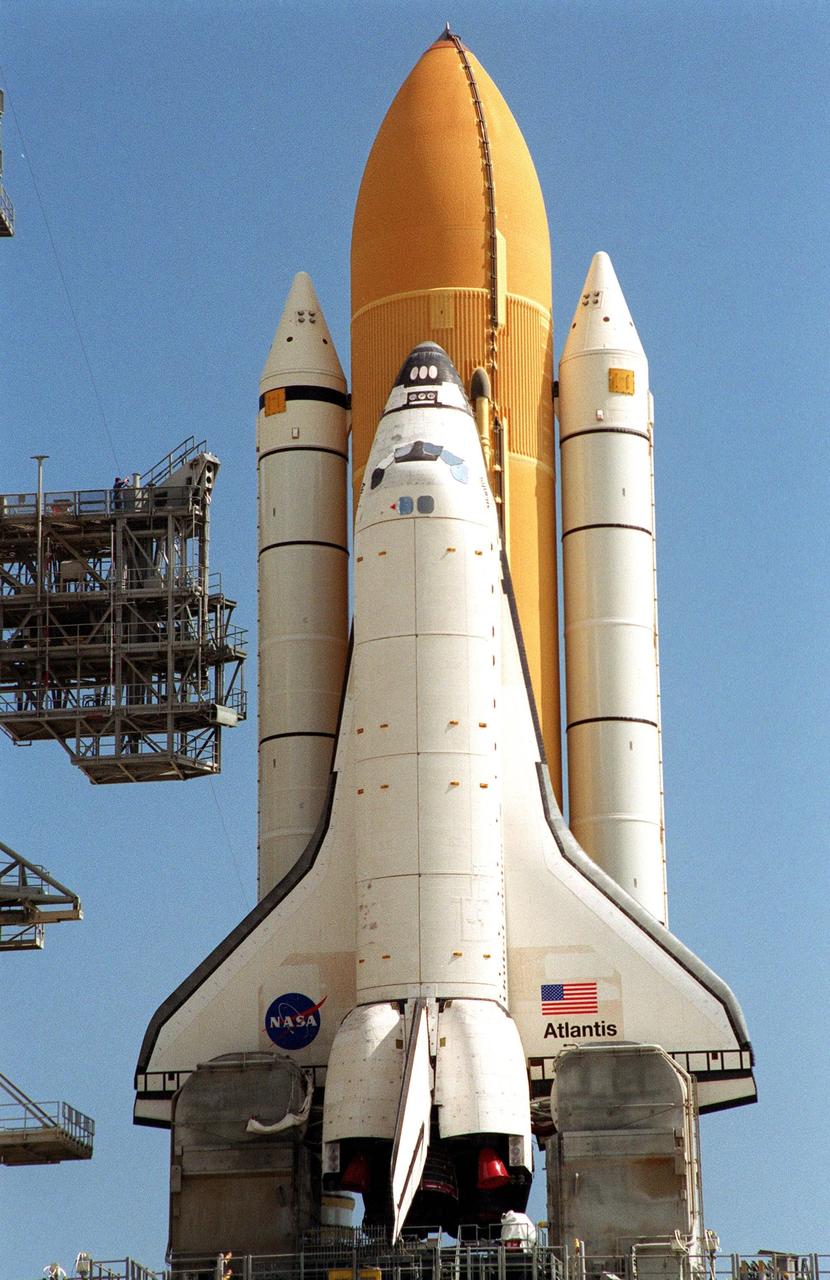

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Atop the mobile launcher platform, Space Shuttle Atlantis, with its orange external tank and white solid rocket boosters, sits on Launch Pad 39B after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. Seen on either side of the orbiter’s tail are the tail service masts. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals. The Shuttle is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
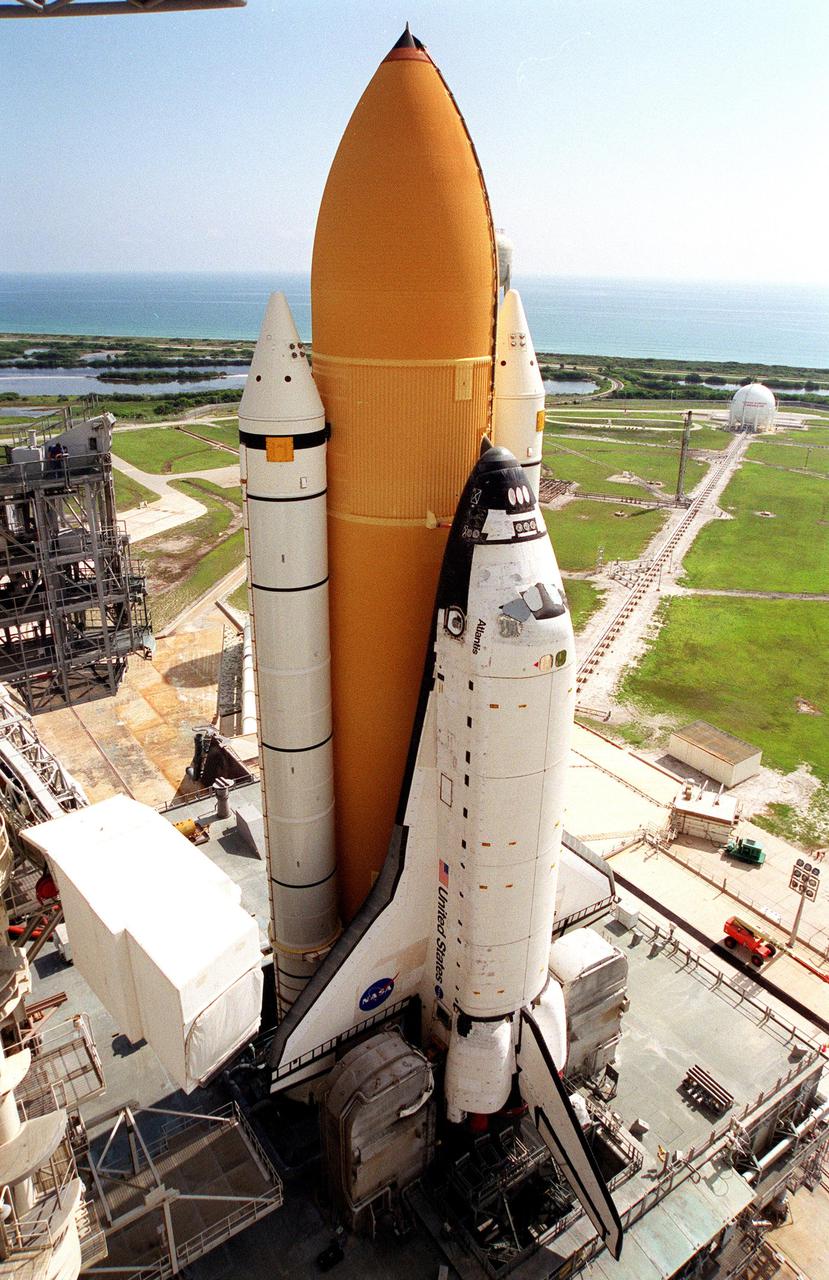

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Atop the mobile launcher platform, Space Shuttle Atlantis sits on Launch Pad 39B after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. Seen on either side of the orbiter’s tail are the tail service masts. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals. To the left of the orbiter is the white environmental chamber (white room) that mates with the orbiter and holds six persons. It provides access to the orbiter crew compartment. In the background is the Atlantic Ocean. The Shuttle is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
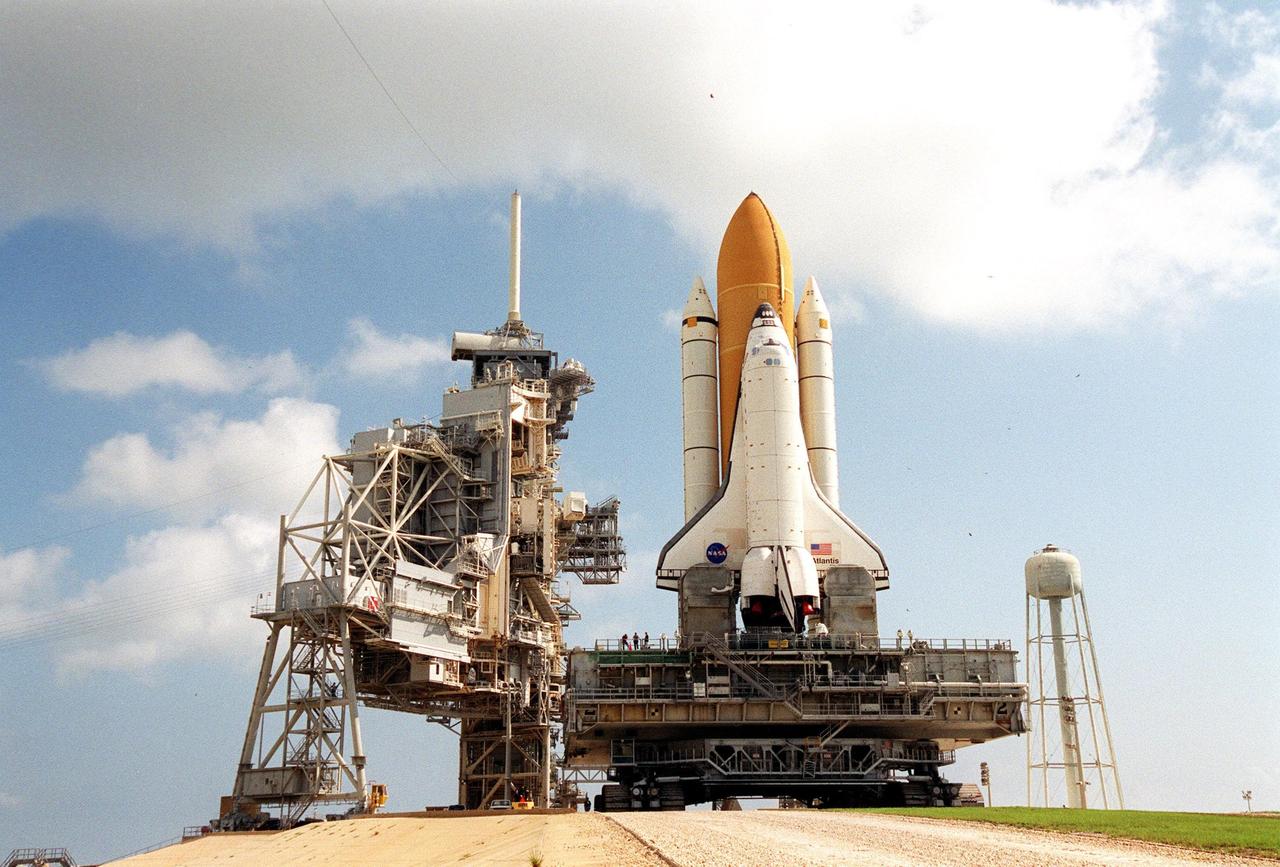

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Atop the mobile launcher platform, Space Shuttle Atlantis arrives on Launch Pad 39B after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. Seen on either side of the orbiter’s tail are the tail service masts. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals. The Shuttle is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
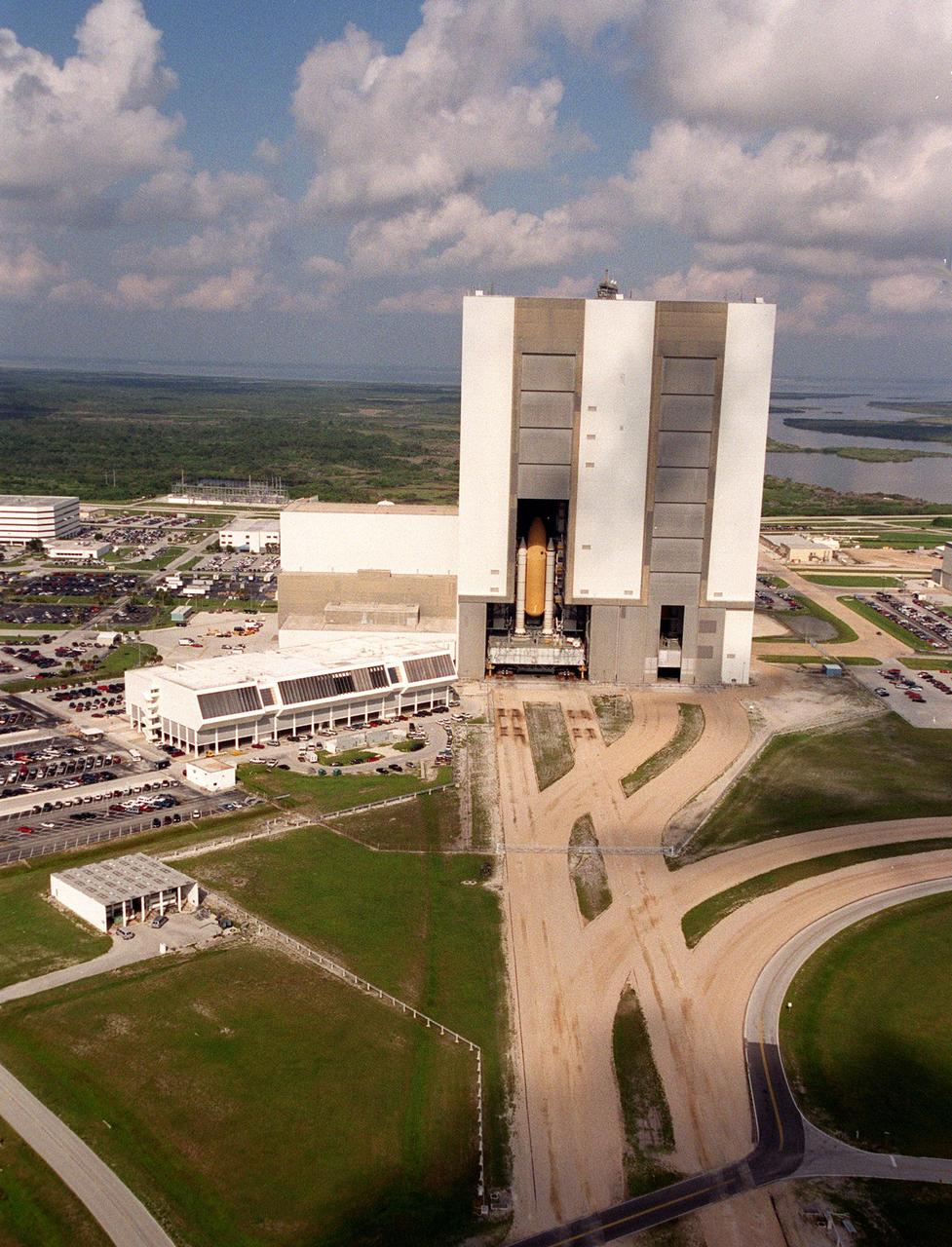

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Scattered clouds cast shadows as Space Shuttle Atlantis crawls back inside the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 1. After earlier starting its trek to Launch Pad 39B, Atlantis was returned to the VAB due to lightning in the area. To the left of the VAB is the Launch Control Center. The four-story building houses the firing rooms that are used to conduct Space Shuttle launches. Leading away from the VAB, in the foreground, is the crawlerway, the 130-foot-wide road specially constructed to transport the Shuttle, mobile launcher platform and crawler-transporter with a combined weight of about 17 million pounds. Space Shuttle Atlantis is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
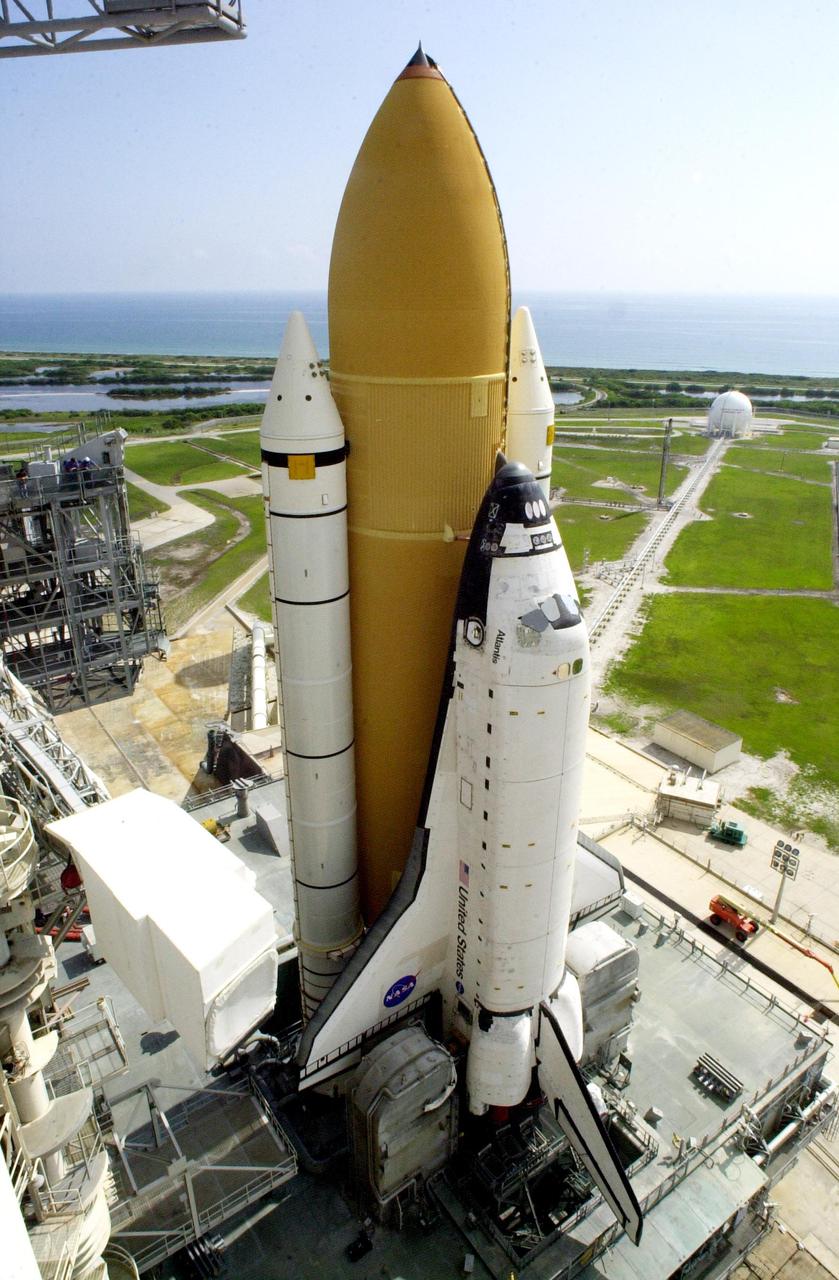

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Atop the mobile launcher platform, Space Shuttle Atlantis sits on Launch Pad 39B after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. Seen on either side of the orbiter’s tail are the tail service masts. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals. To the left of the orbiter is the white environmental chamber (white room) that mates with the orbiter and holds six persons. It provides access to the orbiter crew compartment. In the background is the Atlantic Ocean. The Shuttle is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module
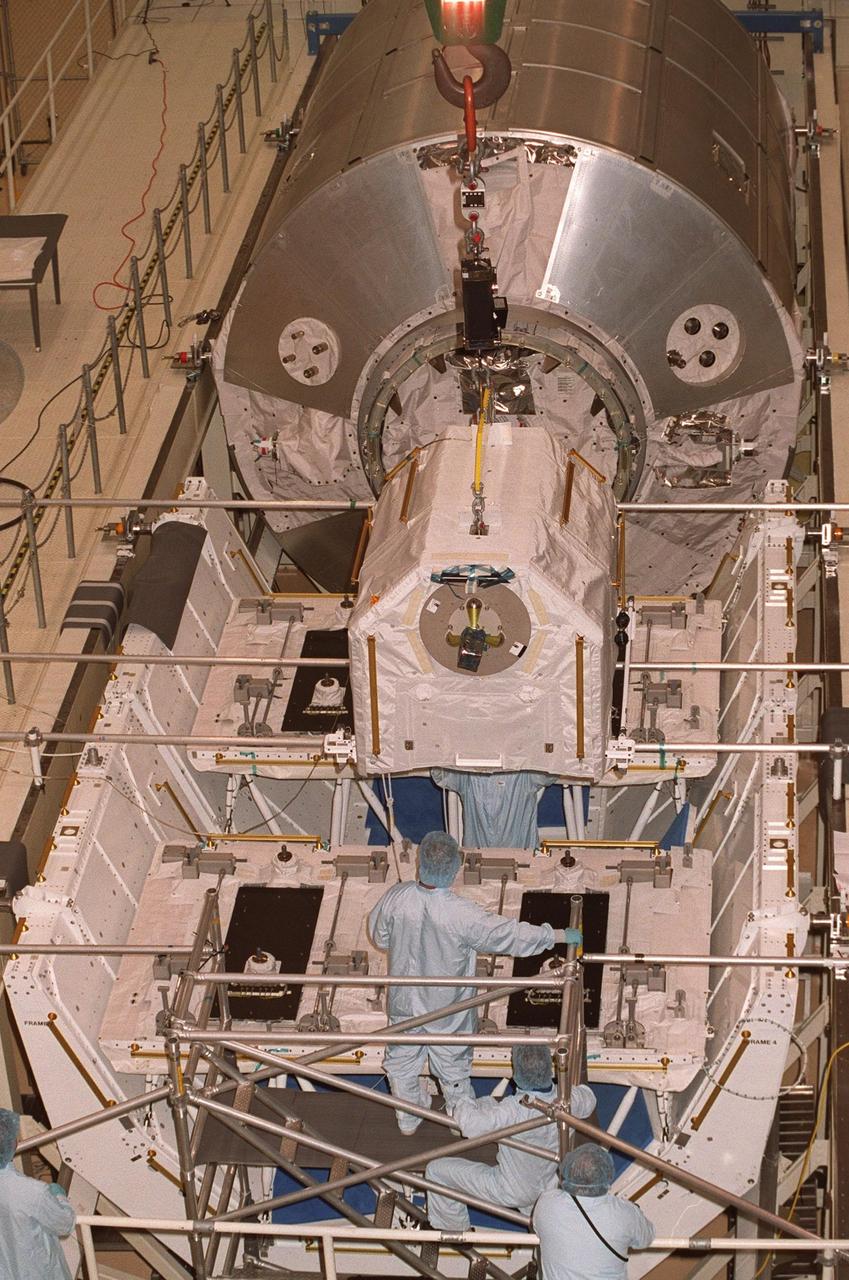

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An overhead crane in the Operations and Checkout Building lowers one of four gas tanks onto the Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet while workers help guide it. Part of the STS-104 payload, the storage tanks two gaseous oxygen and two gaseous nitrogen comprise the high pressure gas assembly that will be attached to the Joint Airlock Module during two spacewalks. The tanks will support future spacewalk operations from the Station and augment the Service Module gas resupply system
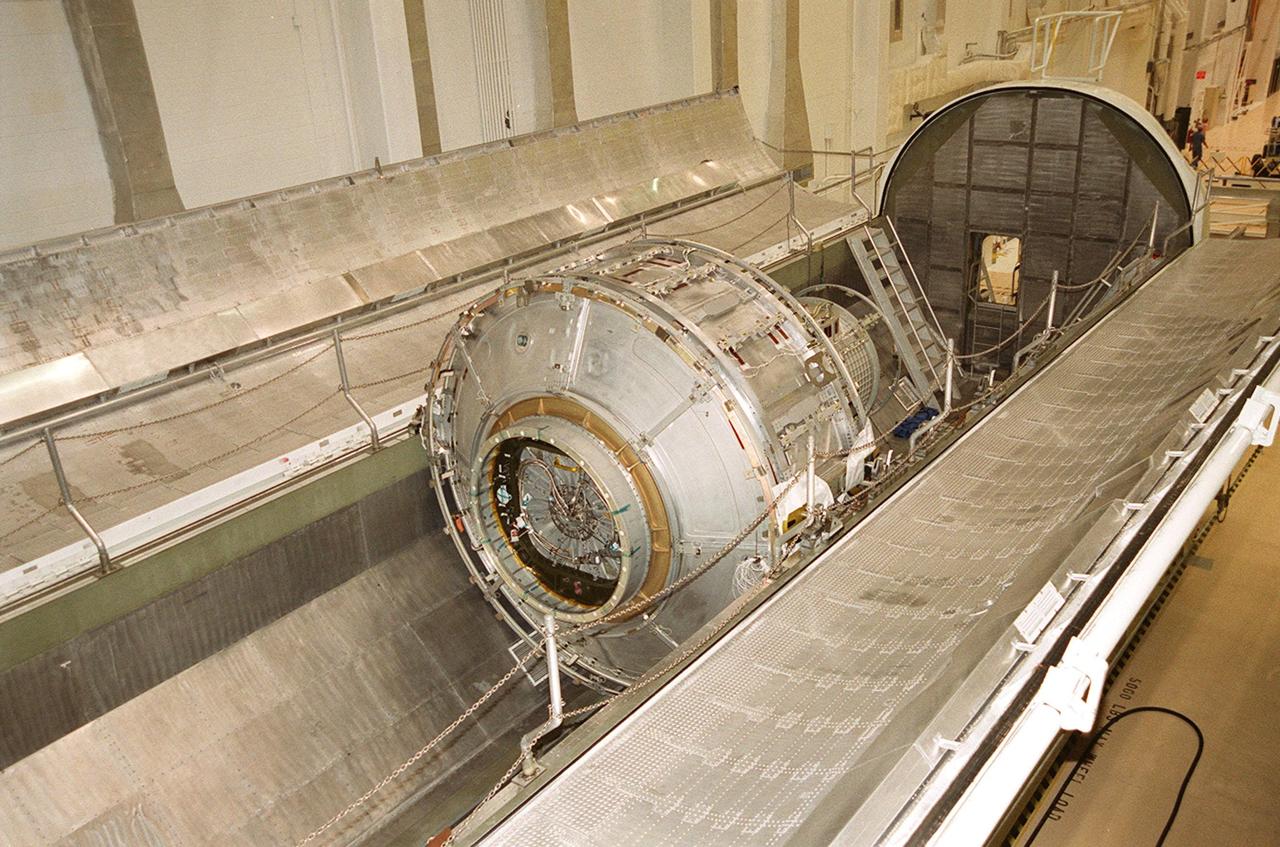
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Joint Airlock Module, the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility, rests in the payload canister that will take it to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001
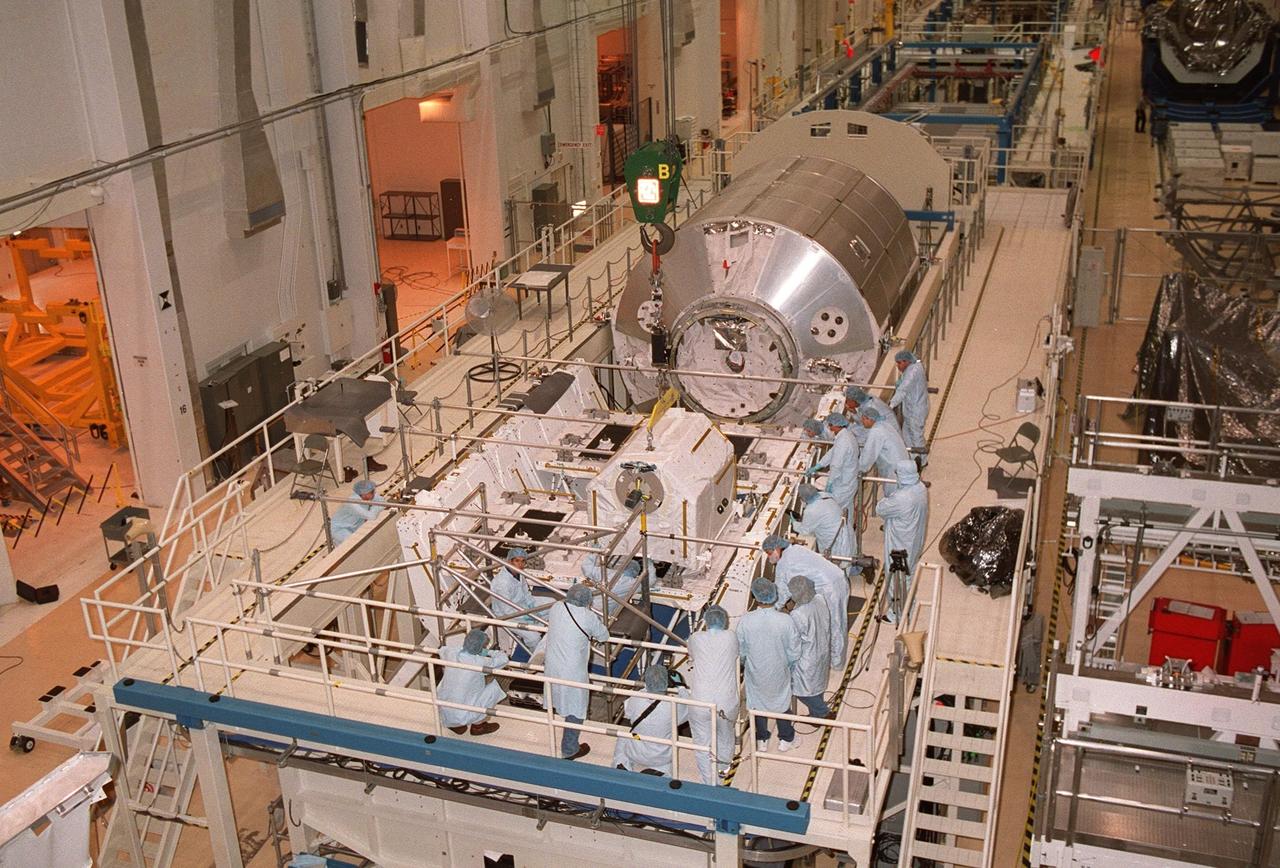
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, workers check out the placement of one of four gas tanks on the Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet. Part of the STS-104 payload, the storage tanks two gaseous oxygen and two gaseous nitrogen comprise the high pressure gas assembly that will be attached to the Joint Airlock Module during two spacewalks. The tanks will support future spacewalk operations from the Station and augment the Service Module gas resupply system
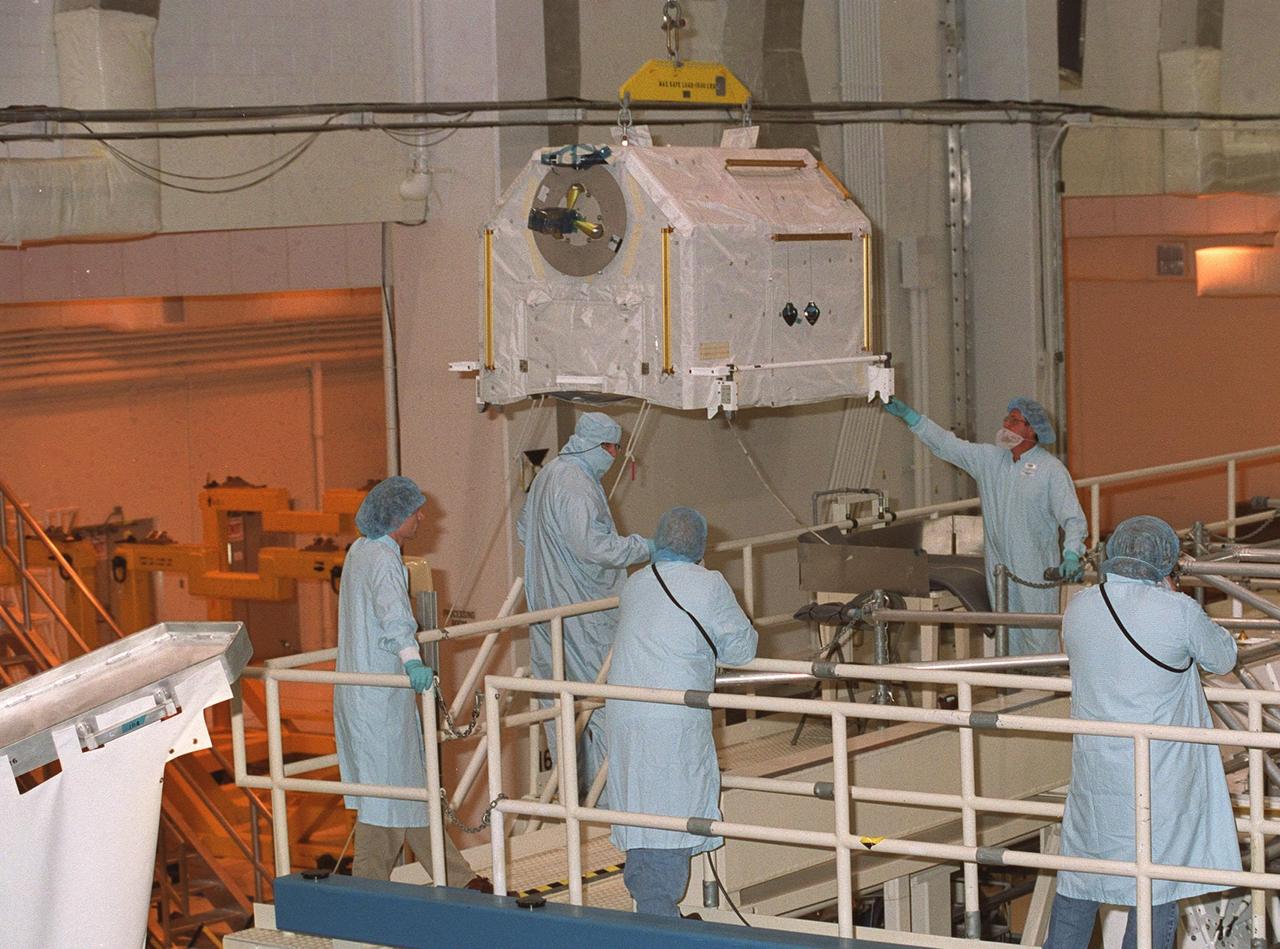

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Operations and Checkout Building stand by while one of four gas tanks is moved toward the Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet. Part of the STS-104 payload, the storage tanks two gaseous oxygen and two gaseous nitrogen comprise the high pressure gas assembly that will be attached to the Joint Airlock Module during two spacewalks. The tanks will support future spacewalk operations from the Station and augment the Service Module gas resupply system
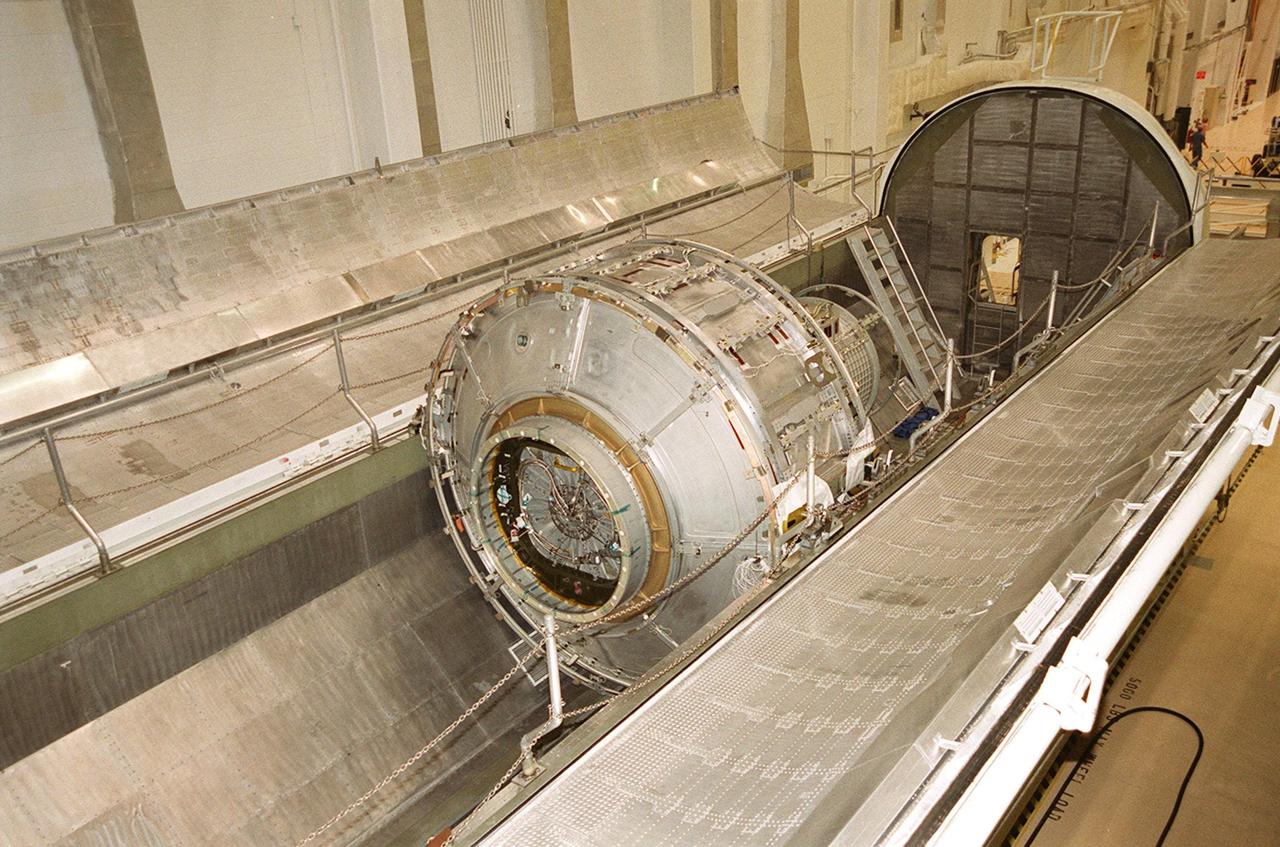
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Joint Airlock Module, the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility, rests in the payload canister that will take it to the Space Station Processing Facility. There the module will undergo more preflight processing for the STS-104 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis May 17, 2001
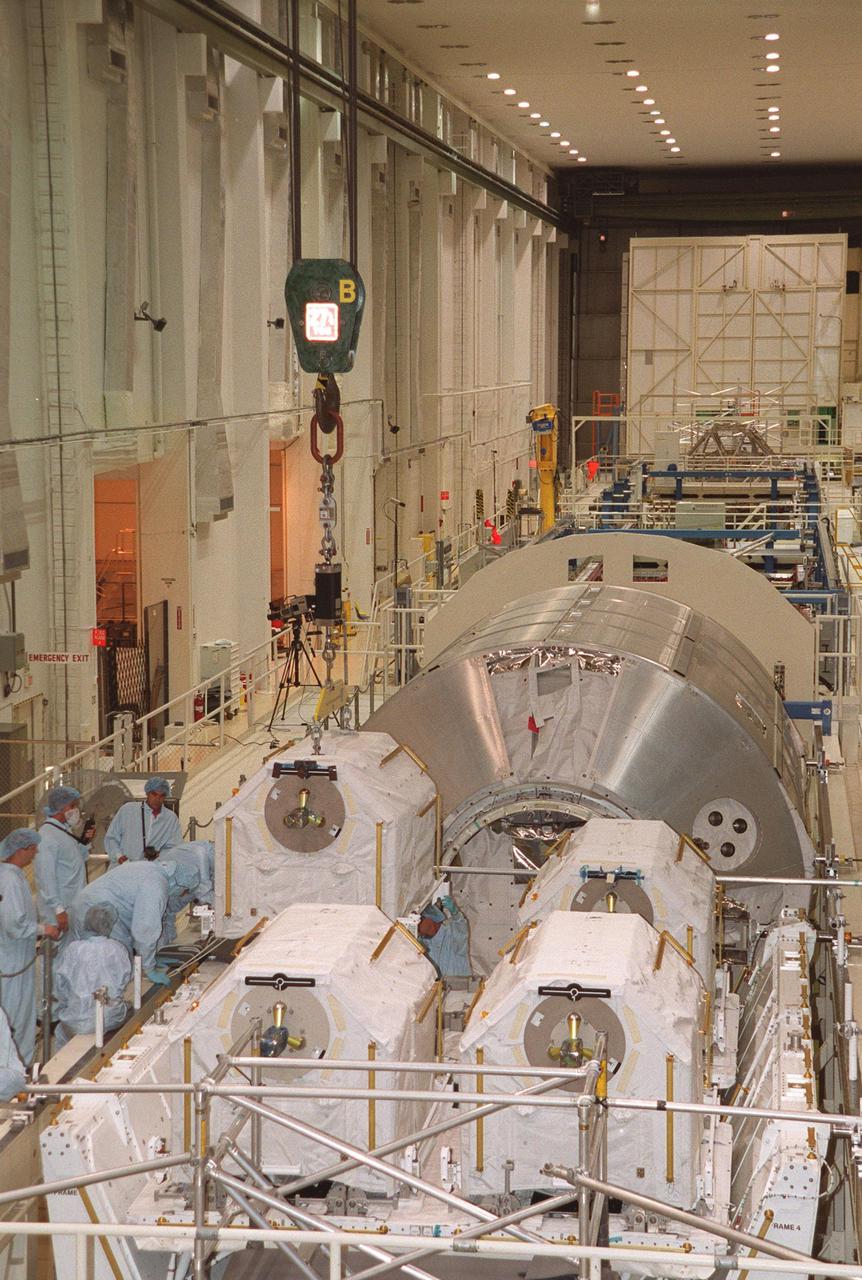

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, the last of four gas tanks is placed on the Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet. Part of the STS-104 payload, the storage tanks two gaseous oxygen and two gaseous nitrogen comprise the high pressure gas assembly that will be attached to the Joint Airlock Module during two spacewalks. The tanks will support future spacewalk operations from the Station and augment the Service Module gas resupply system
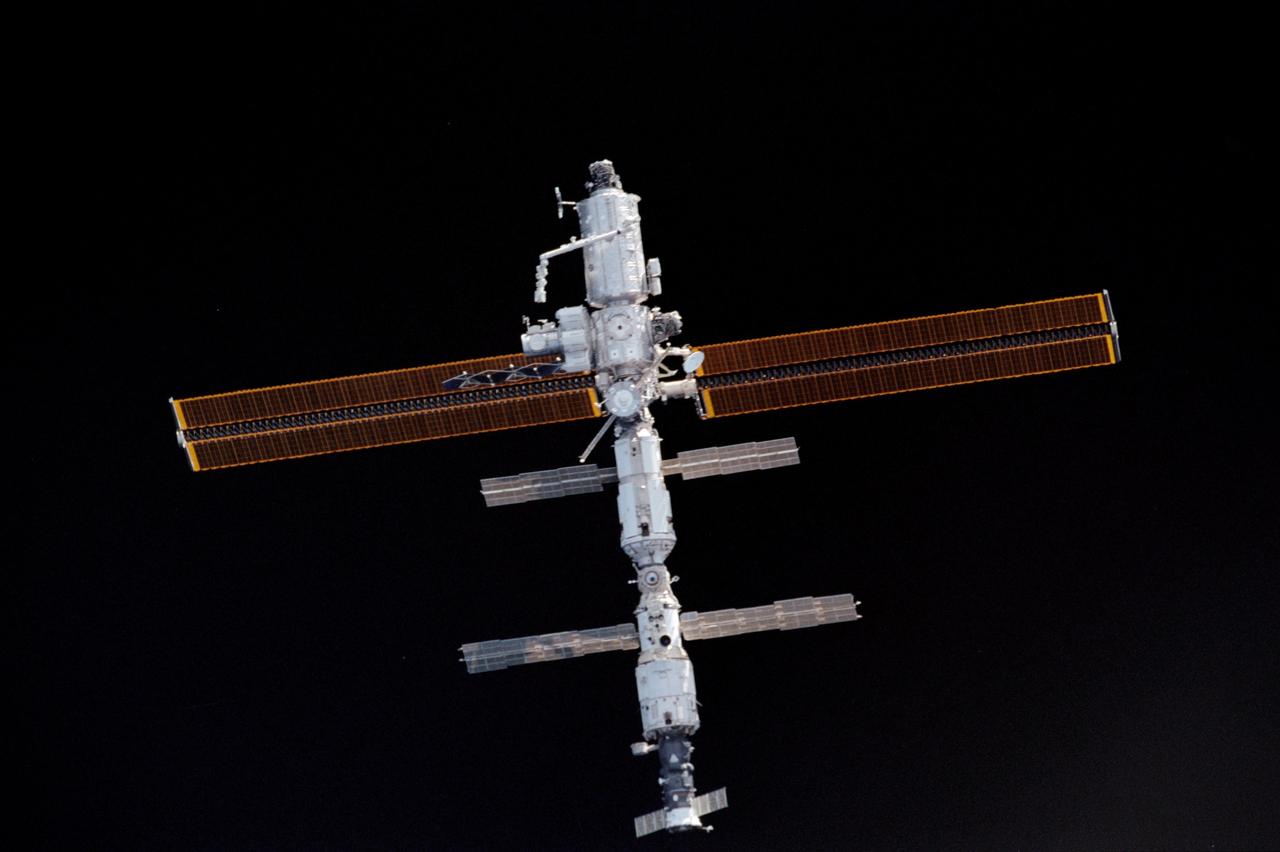

STS104-332-027 (21 July 2001) --- The International Space Station (ISS), just days after receiving the installment of the Quest airlock, was photographed by one the STS-104 astronauts during a fly-around of the orbital outpost. The survey occurred shortly after Atlantis' undocking. The Canadarm2 or Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS) appears to be pointed toward the new airlock on the station's starboard side. The STS-104 and Expedition Two crew's joint efforts in the past several days, in which the airlock was installed and other work was accomplished, marked the completion of the second phase of the station. Within the last year (beginning in July of 2000), 77 tons of hardware have been added to the complex, including the Zvezda module, the Z1 Truss Assembly, Pressurized Mating Adapter 3, the P6 Truss and its 240-foot long solar arrays, the U.S. laboratory Destiny, the Canadarm2 and finally the Quest airlock.
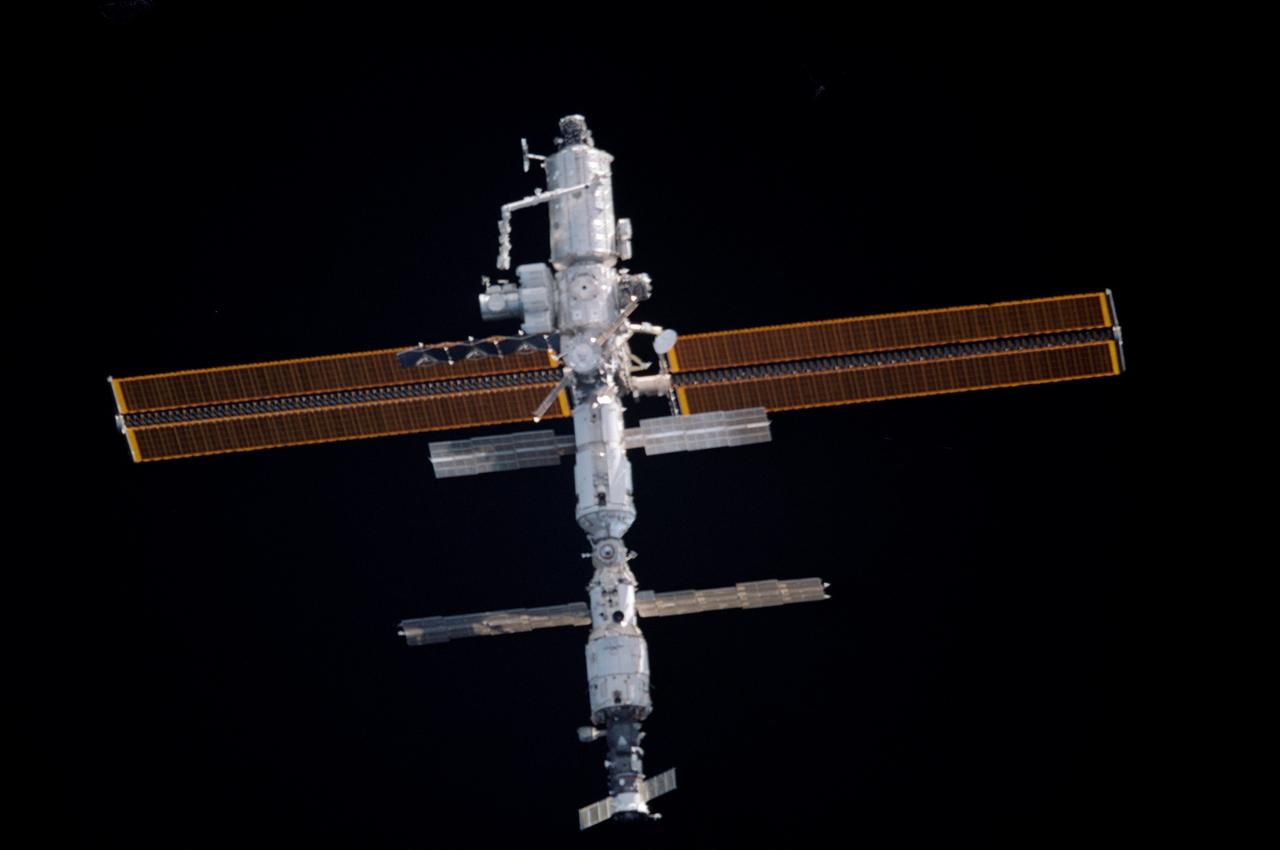

STS104-332-026 (21 July 2001) --- The International Space Station (ISS), just days after receiving the installment of the Quest airlock, was photographed by one the STS-104 astronauts during a fly-around of the orbital outpost. The survey occurred shortly after Atlantis' undocking. The Canadarm2 or Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS) appears to be pointed toward the new airlock on the station's starboard side. The STS-104 and Expedition Two crew's joint efforts in the past several days, in which the airlock was installed and other work was accomplished, marked the completion of the second phase of the station. Within the last year (beginning in July of 2000), 77 tons of hardware have been added to the complex, including the Zvezda module, the Z1 Truss Assembly, Pressurized Mating Adapter 3, the P6 Truss and its 240-foot long solar arrays, the U.S. laboratory Destiny, the Canadarm2 and finally the Quest airlock.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Billows of smoke and steam half frame Space Shuttle Atlantis as it roars into the still-black sky before dawn. At left can be seen the top of the lightning mast on Launch Pad 39B. Launch on mission STS-104 was on time at 5:03:59 a.m. EDT. The 10th assembly flight to the International Space Station, the mission is delivering the joint airlock module, which will require two spacewalks to attach it to the Space Station. The airlock will be the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, and will also support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity
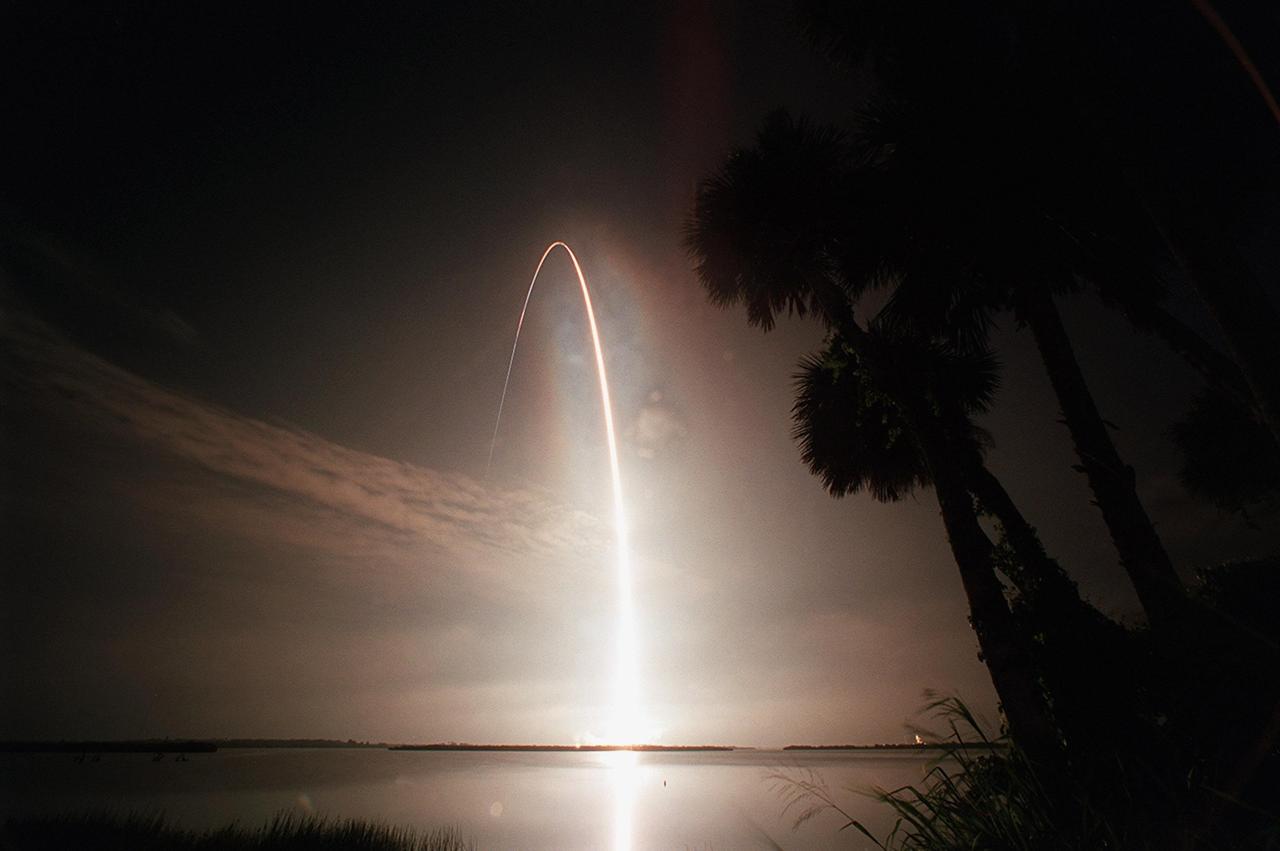

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Like a sun on a fast rise, Space Shuttle Atlantis arcs into the still-black sky over the Atlantic Ocean, casting a fiery glow on its way. Atlantis lifted off from Launch Pad 39B on time at 5:03:59 a.m. EDT. With a crew of five it is heading on the 10th assembly flight to the International Space Station. The primary payload on the mission is the joint airlock module, which will require two spacewalks to attach it to the Space Station. The airlock will be the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, and will also support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity
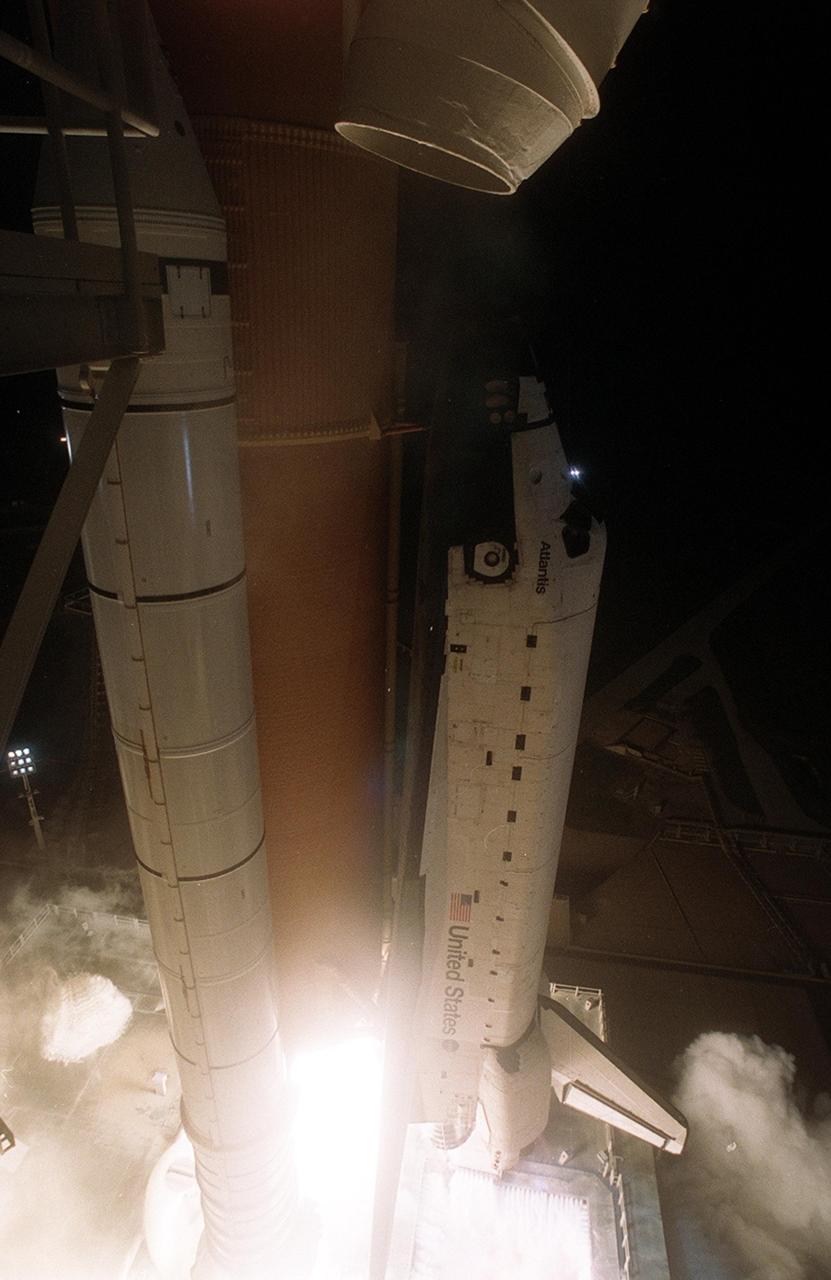
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis begins its trek to the International Space Station as it lifts off the pad with a crew of five on mission STS-104. Atlantis lifted off from Launch Pad 39B on time at 5:03:59 a.m. EDT. The 10th assembly flight to the International Space Station, the primary payload on the mission is the joint airlock module, which will require two spacewalks to attach it to the Space Station. The airlock will be the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, and will also support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity
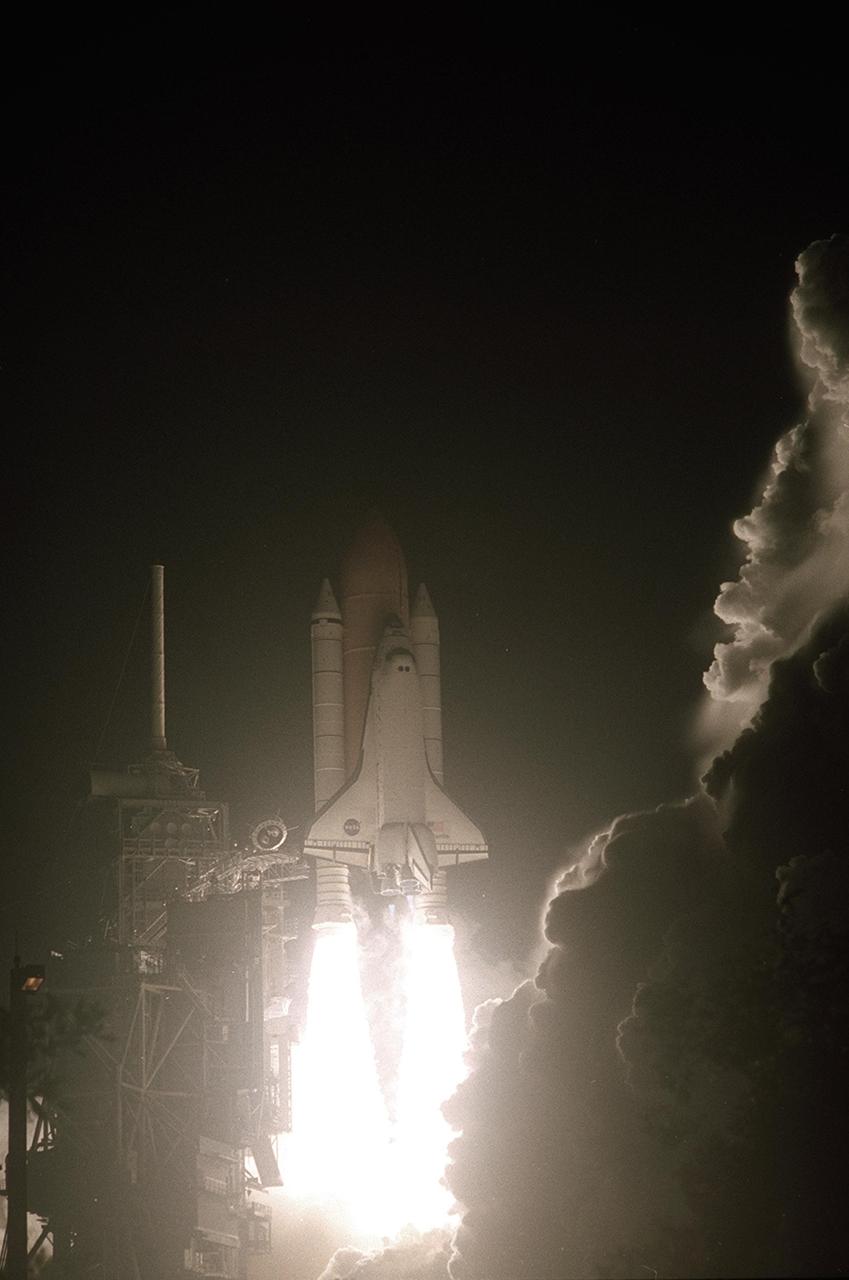

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis appears to leap from a fiery ball as it hurtles into the pre-dawn sky on mission STS-104. Atlantis lifted off from Launch Pad 39B on time at 5:03:59 a.m. EDT. With a crew of five, it is heading on the 10th assembly flight to the International Space Station. The primary payload on the mission is the joint airlock module, which will require two spacewalks to attach it to the Space Station. The airlock will be the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, and will also support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-104 Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh gets help donning his launch and entry suit before heading to the launch pad. This launch will be his first space flight. Liftoff of Space Shuttle Atlantis on mission STS-104 is targeted for 5:04 a.m., July 12, from Launch Pad 39B. The primary payload on the mission is the joint airlock module, which will be added to the International Space Station. The airlock will be the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, and will also support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity
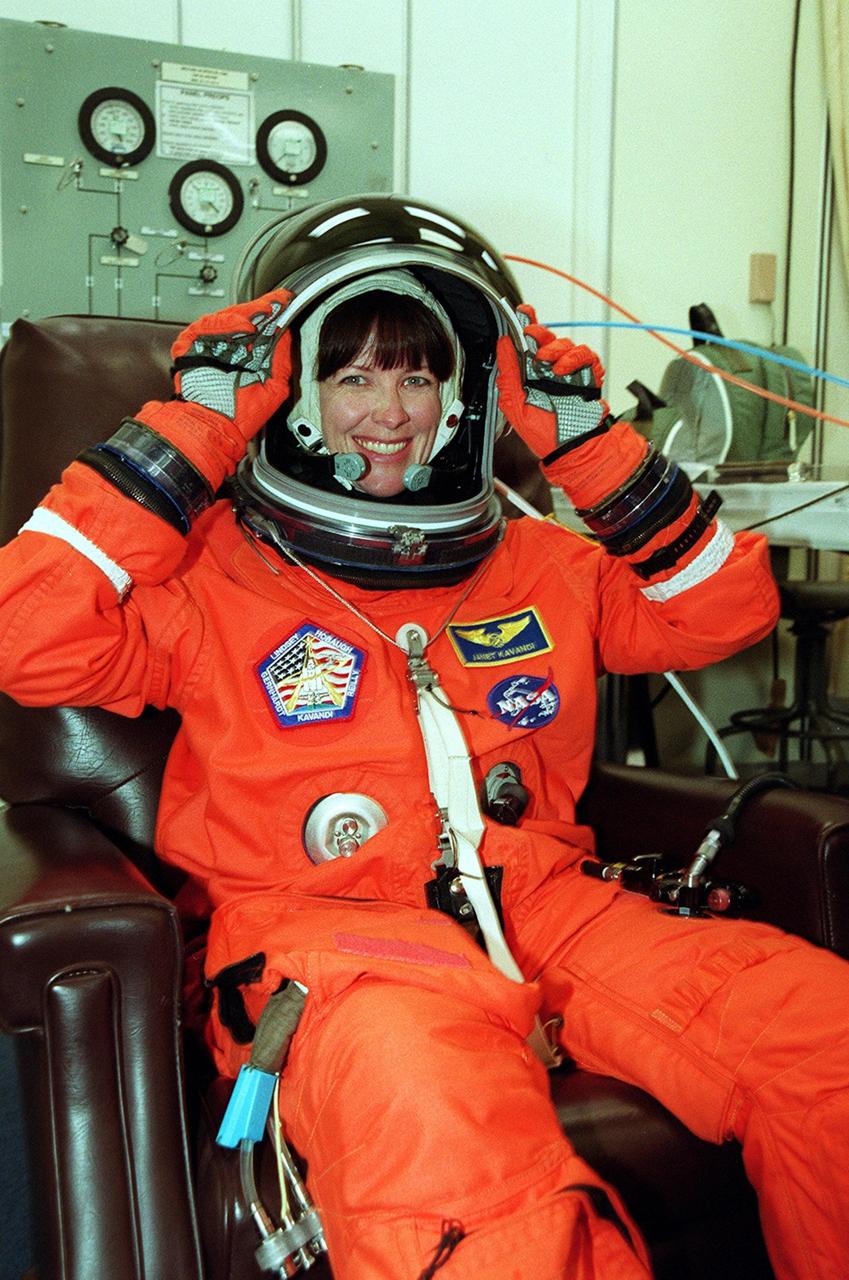

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-104 Mission Specialist Janet Lynn Kavandi adjusts her helmet as she dons her launch and entry suit before heading to the launch pad. This launch will be her third space flight. Liftoff of Space Shuttle Atlantis on mission STS-104 is targeted for 5:04 a.m., July 12, from Launch Pad 39B. The primary payload on the mission is the joint airlock module, which will be added to the International Space Station. The airlock will be the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, and will also support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity
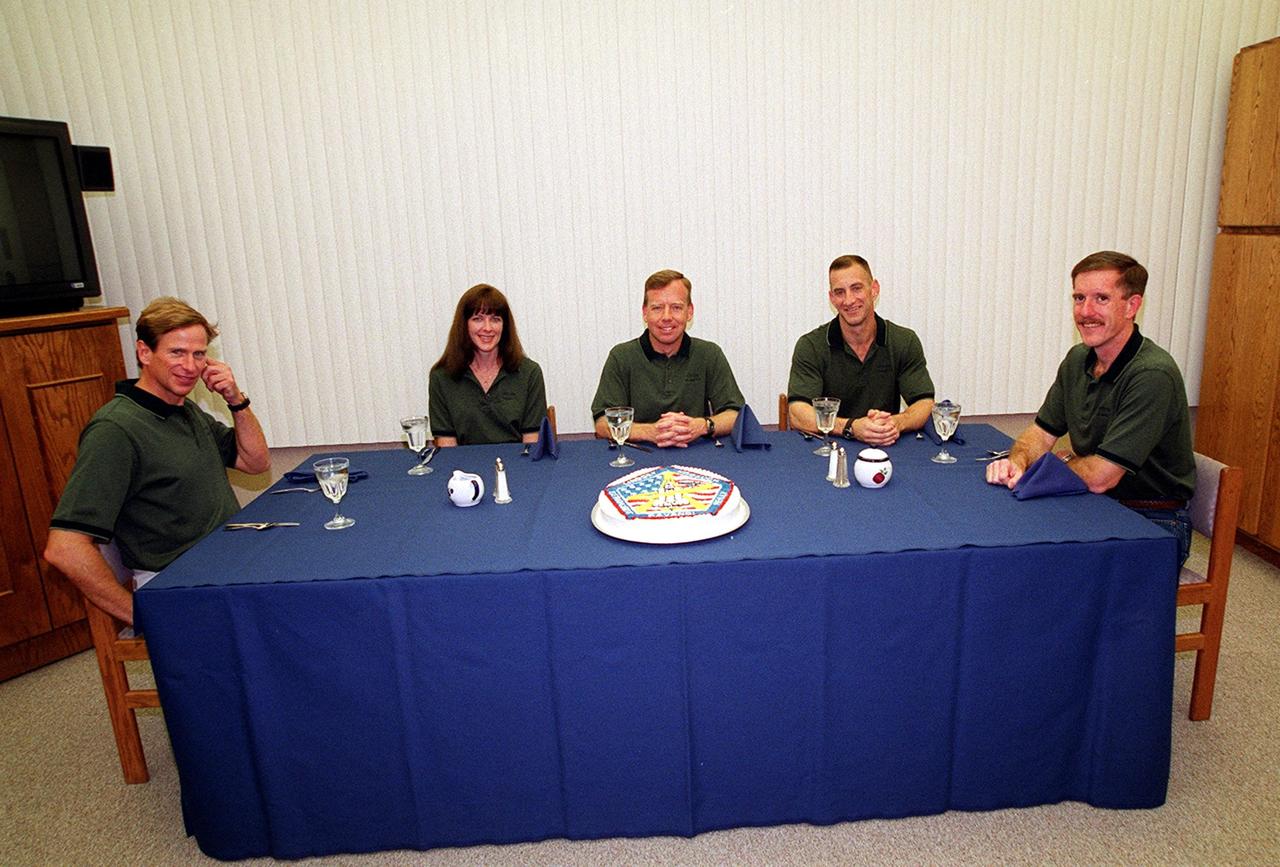

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-104 crew finish their final meal of the day before launch. Seated from left are Mission Specialists Michael L. Gernhardt and Janet Lynn Kavandi, Commander Steven W. Lindsey, Pilot Charles O. Hobaugh and Mission Specialist James F. Reilly. The launch of Space Shuttle Atlantis on mission STS-104 is targeted for 5:04 a.m., July 12, from Launch Pad 39B. The primary payload on the mission is the joint airlock module, which will be added to the International Space Station. The airlock will be the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, and will also support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity
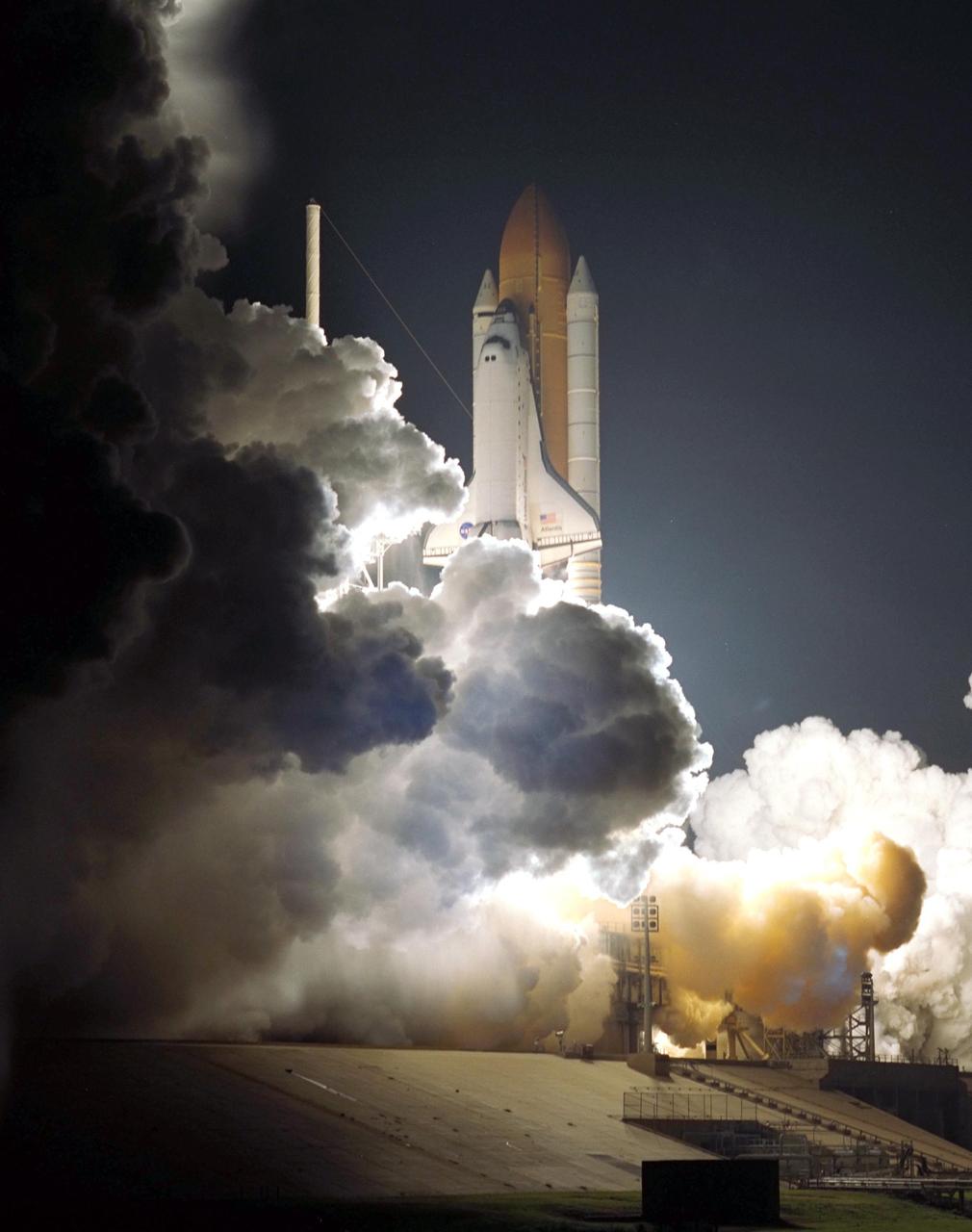

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Billows of smoke and steam surround Space Shuttle Atlantis as it blasts into the pre-dawn sky on mission STS-104. Atlantis lifted off from Launch Pad 39B on time at 5:03:59 a.m. EDT. The 10th assembly flight to the International Space Station, the mission is delivering the joint airlock module, which will require two spacewalks to attach it to the Space Station. The airlock will be the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, and will also support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity
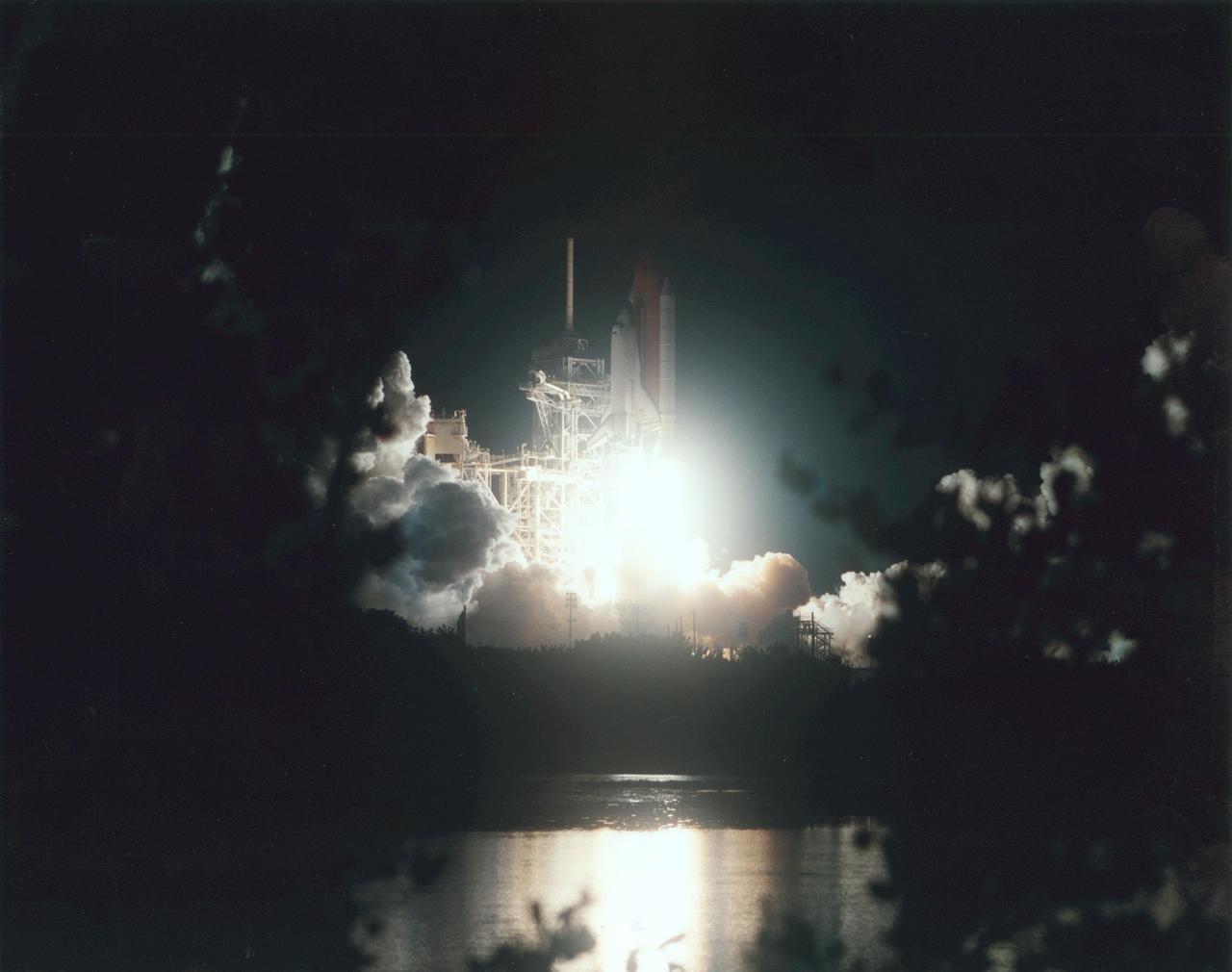

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis lifts off in a blaze of light that spotlights it against the still-black sky and reflects in the nearby waters. Launch of Atlantis on mission STS-104 from Pad 39B was on time at 5:03:59 a.m. EDT. The 10th assembly flight to the International Space Station, the mission is delivering the joint airlock module, which will require two spacewalks to attach it to the Space Station. The airlock will be the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, and will also support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity
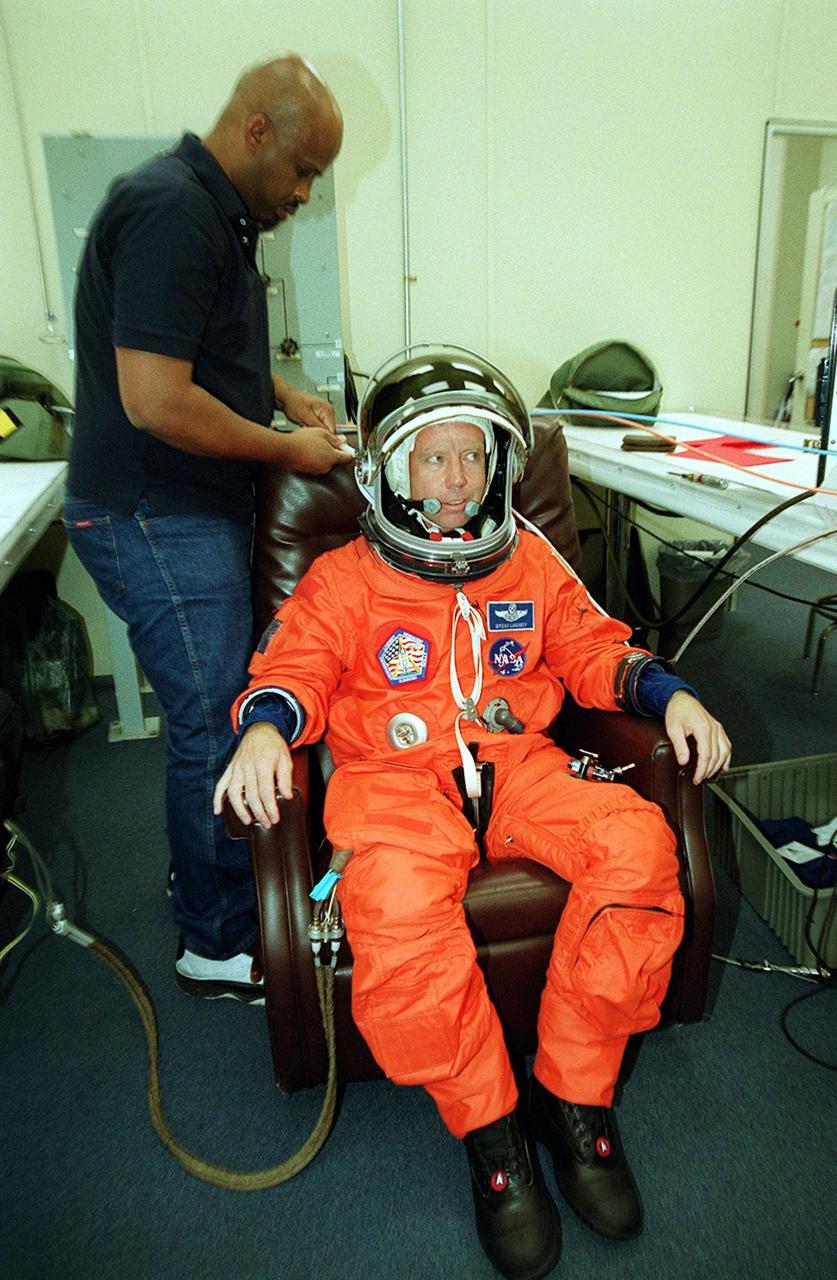

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-104 Commander Steven W. Lindsey gets help donning his launch and entry suit before heading to the launch pad. This launch will be his third space flight. Liftoff of Space Shuttle Atlantis on mission STS-104 is targeted for 5:04 a.m., July 12, from Launch Pad 39B. The primary payload on the mission is the joint airlock module, which will be added to the International Space Station. The airlock will be the primary path for Space Station spacewalk entry and departure for U.S. spacesuits, and will also support the Russian Orlan spacesuit for EVA activity
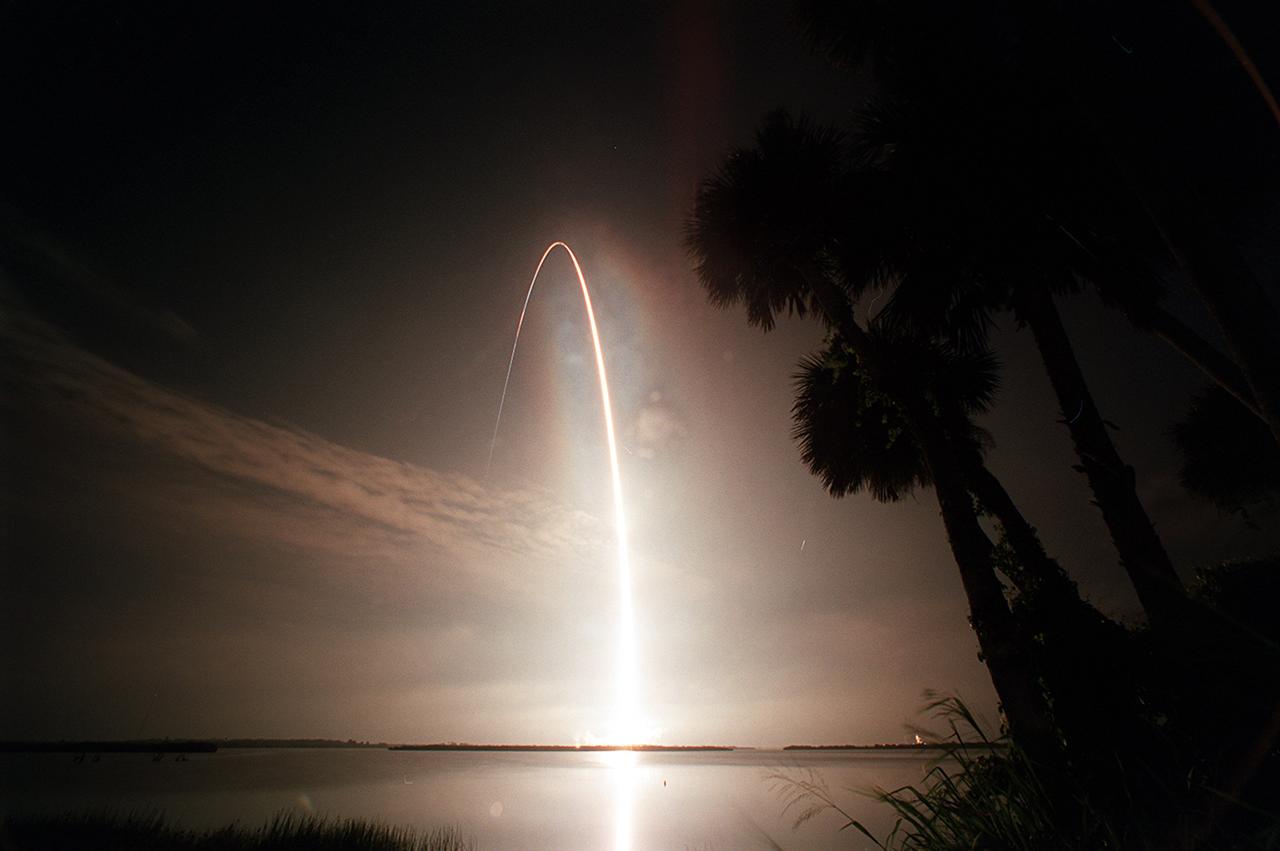

The Space Shuttle Atlantis arcs into the black sky over the Atlantic Ocean casting a fiery glow on its way. Atlantis STS-104 launched from Kennedy Launch Pad 39B at 5:03:59 am EDT, headed for the International Space Station (ISS). Its crew of five served as the 10th ISS assembly flight. The primary payload of the mission was the Joint Airlock module which was attached in two space walks. Once installed and activated, the ISS Airlock became the primary path for ISS space walk entry and departure for U.S. space suits, which are known as Extravehicular Mobility Units (EMUs). In addition, it is designed to support the Russian Orlan space suit. The Joint Airlock is 20-feet long, 13- feet in diameter and weighs 6.5 tons. The airlock includes two sections, the larger equipment lock on the left that will store space suits and associated gear, and the narrower crew lock on the right from which astronauts will exit into space for extravehicular activity. It was built at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) by the Space Station prime contractor Boeing.
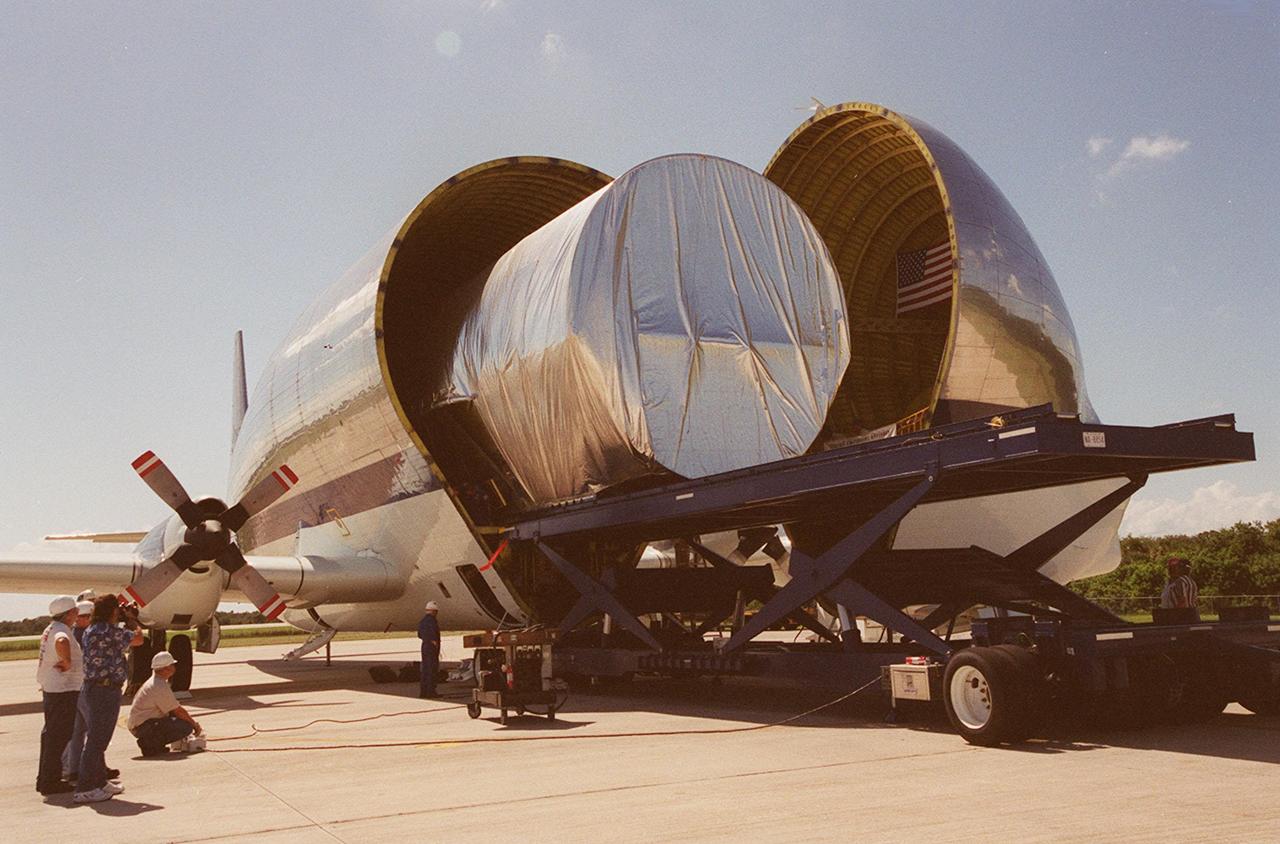

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Joint Airlock Module, the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility, rolls out of NASA's Super Guppy aircraft. It will be transferred to the Operations and Checkout Building in the KSC industrial area where it will undergo vacuum chamber testing. It will then be moved to the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) for further prelaunch preparation and checkout. The massive, spindle-shaped airlock is 20 feet long, has a diameter of 13 feet at its widest point, and weighs six and a half tons. It was manufactured at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center by the Huntsville division of The Boeing Company. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the tenth International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001
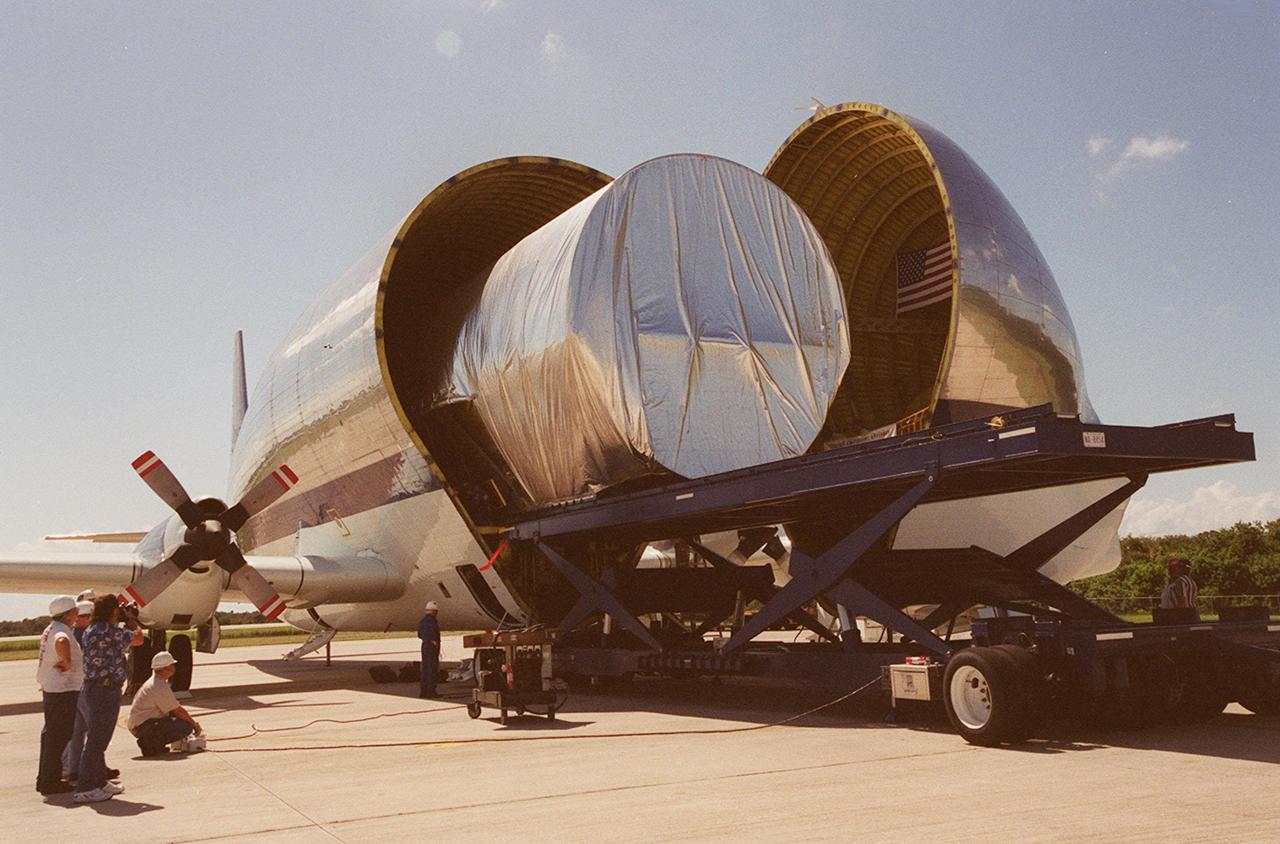

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Joint Airlock Module, the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility, rolls out of NASA's Super Guppy aircraft. It will be transferred to the Operations and Checkout Building in the KSC industrial area where it will undergo vacuum chamber testing. It will then be moved to the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) for further prelaunch preparation and checkout. The massive, spindle-shaped airlock is 20 feet long, has a diameter of 13 feet at its widest point, and weighs six and a half tons. It was manufactured at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center by the Huntsville division of The Boeing Company. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the tenth International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001
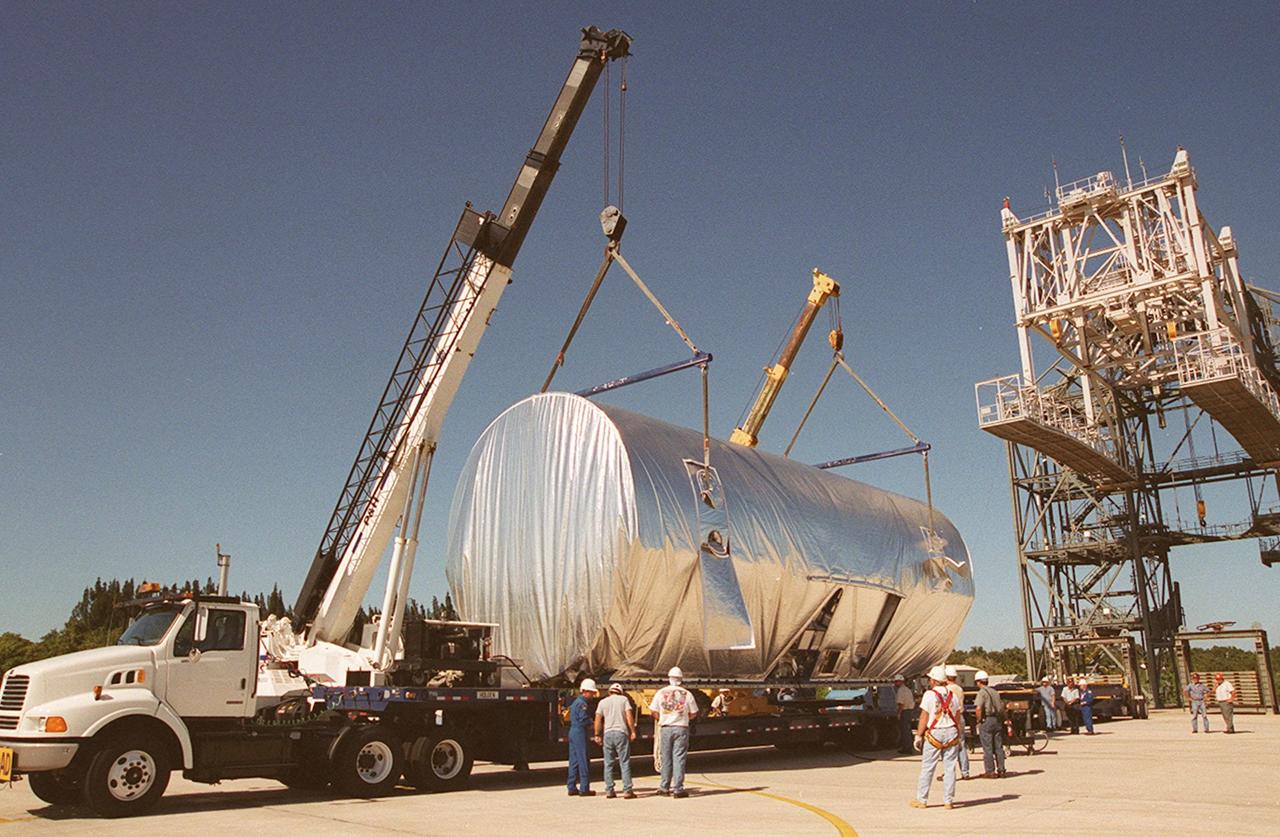

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, the Joint Airlock Module, the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility, is settled onto a flatbed trailer for transport to the Operations and Checkout Building in the KSC industrial area. There it will undergo vacuum chamber testing. It will then be moved to the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) for further prelaunch preparation and checkout. The massive, spindle-shaped airlock is 20 feet long, has a diameter of 13 feet at its widest point, and weighs six and a half tons. It was manufactured at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center by the Huntsville division of The Boeing Company. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the tenth International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001
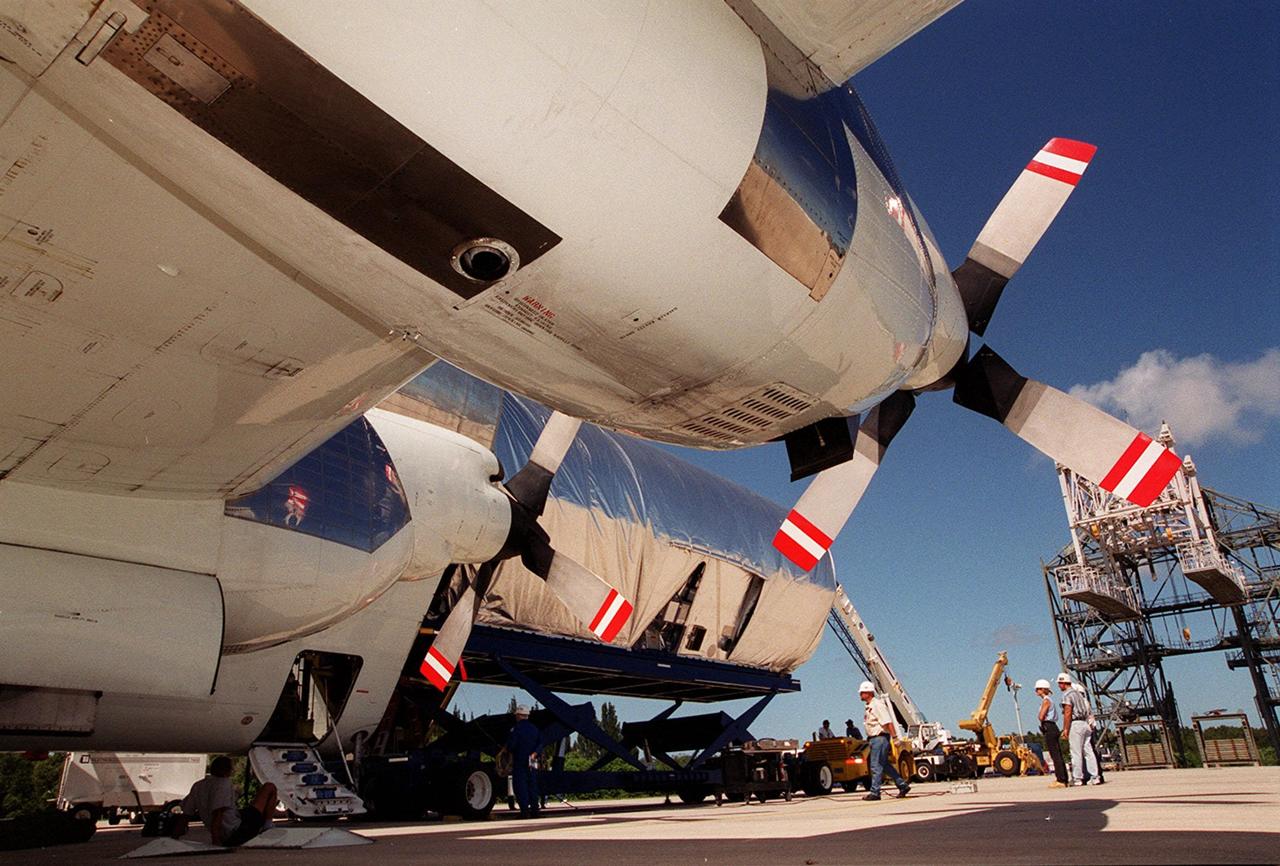

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Viewed from underneath the wing of NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, the Joint Airlock Module, the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility, rolls out of the aircraft. It will be transferred to the Operations and Checkout Building in the KSC industrial area where it will undergo vacuum chamber testing. Then it will be moved to the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) for further pre-launch preparation and checkout. The massive, spindle-shaped airlock is 20 feet long, has a diameter of 13 feet at its widest point, and weighs six and a half tons. It was manufactured at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center by the Huntsville division of The Boeing Company. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the tenth International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001
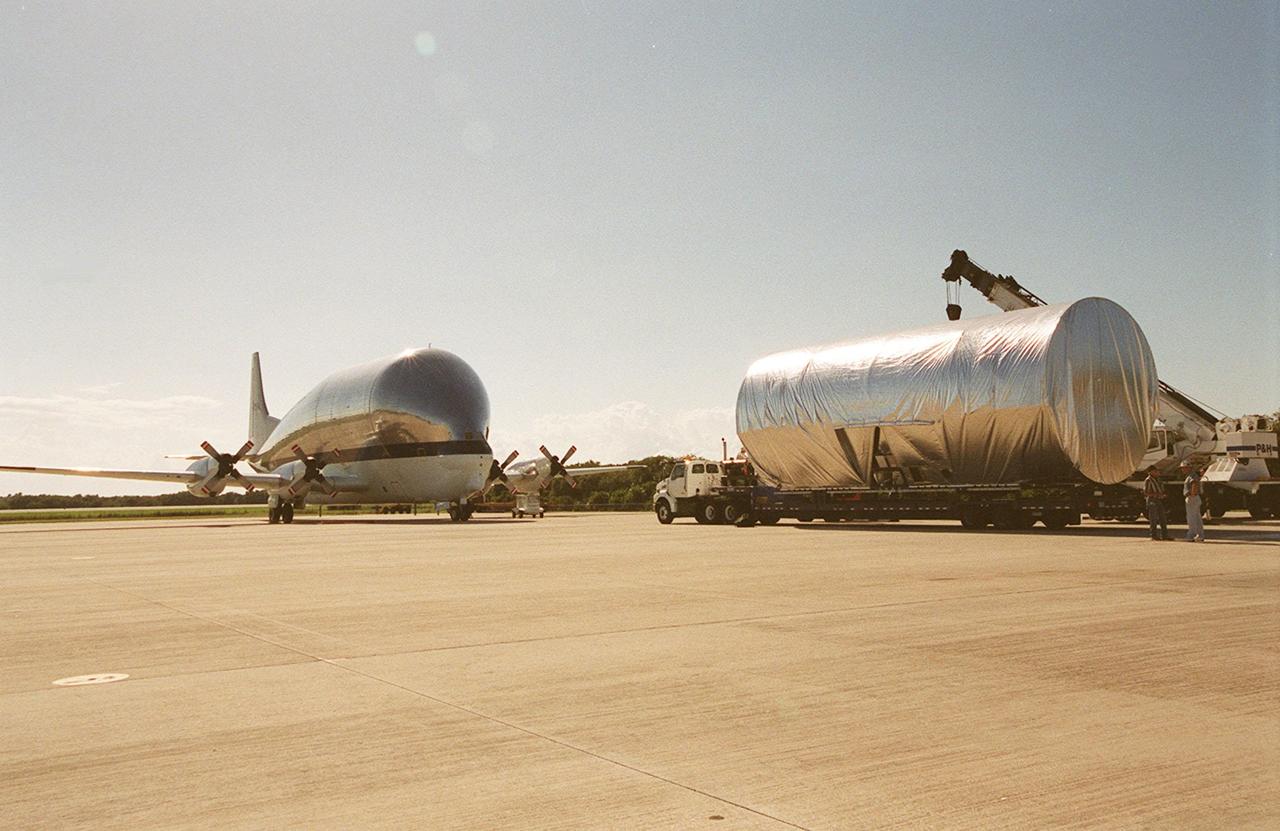

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility, the Joint Airlock Module, the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility, is ready for transport to the Operations and Checkout Building in the KSC industrial area. There it will undergo vacuum chamber testing. It will then be moved to the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) for further pre-launch preparation and checkout. The massive, spindle-shaped airlock is 20 feet long, has a diameter of 13 feet at its widest point, and weighs six and a half tons. It was manufactured at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center by the Huntsville division of The Boeing Company. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the tenth International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001
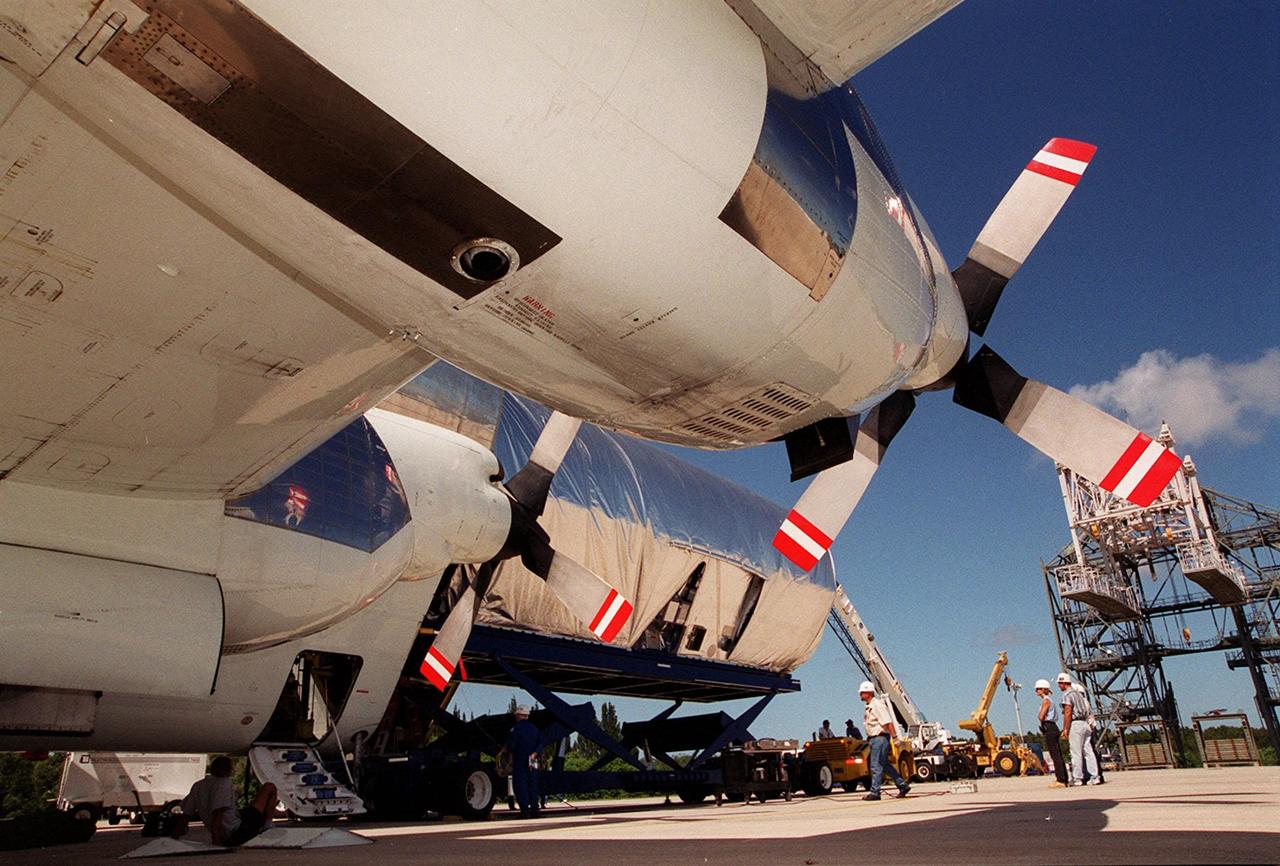

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Viewed from underneath the wing of NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, the Joint Airlock Module, the gateway from which crew members aboard the International Space Station (ISS) will enter and exit the 470-ton orbiting research facility, rolls out of the aircraft. It will be transferred to the Operations and Checkout Building in the KSC industrial area where it will undergo vacuum chamber testing. Then it will be moved to the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) for further pre-launch preparation and checkout. The massive, spindle-shaped airlock is 20 feet long, has a diameter of 13 feet at its widest point, and weighs six and a half tons. It was manufactured at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center by the Huntsville division of The Boeing Company. The Space Shuttle Atlantis will carry the airlock to orbit on mission STS-104, the tenth International Space Station flight, currently targeted for liftoff in May 2001