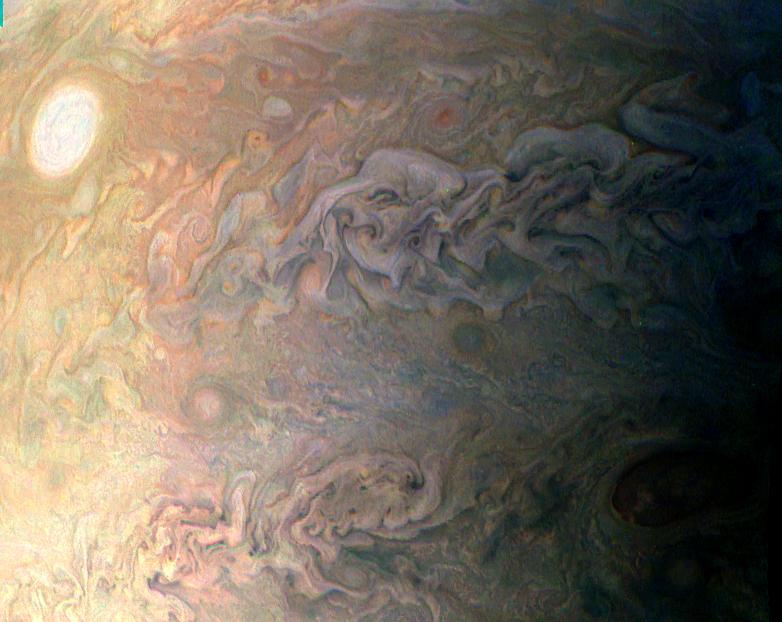

This amateur-processed image was taken on Dec. 11, 2016, at 9:27 a.m. PST (12:27 p.m. EST), as NASA's Juno spacecraft performed its third close flyby of Jupiter. At the time the image was taken, the spacecraft was about 15,200 miles (24,400 kilometers) from the gas giant planet. The citizen scientist (Eric Jorgensen) cropped the JunoCam image and enhanced the color to draw attention to Jupiter's swirling clouds southeast of the "pearl." The "pearl" is one of eight massive rotating storms at 40 degrees south latitude on Jupiter, known colloquially as the "string of pearls." The processing of this image highlights the turbulence of the clouds in the south temperate belt of the planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21377 . - Enhanced image by Eric Jorgensen based on images provided courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS

This image, taken by the JunoCam imager on NASA's Juno spacecraft, highlights the seventh of eight features forming a 'string of pearls' on Jupiter -- massive counterclockwise rotating storms that appear as white ovals in the gas giant's southern hemisphere. Since 1986, these white ovals have varied in number from six to nine. There are currently eight white ovals visible. Since 1986, these white ovals have varied in number from six to nine. There are currently eight white ovals visible. The image was taken on Dec. 11, 2016, at 9:27 a.m. PST (12:27 EST) as the Juno spacecraft performed its third close flyby of the planet. At the time the image was taken, the spacecraft was about 15,300 miles (24,600 kilometers) from Jupiter. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21219
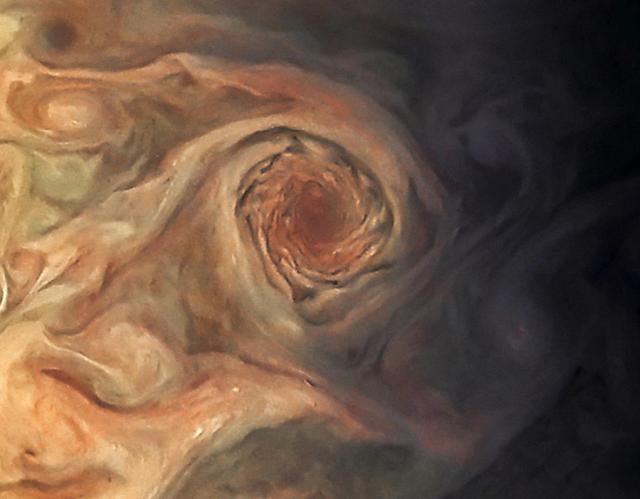

This image, taken by the JunoCam imager on NASA's Juno spacecraft, highlights a swirling storm just south of one of the white oval storms on Jupiter. The image was taken on March 27, 2017, at 2:12 a.m. PDT (5:12 a.m. EDT), as the Juno spacecraft performed a close flyby of Jupiter. At the time the image was taken, the spacecraft was about 12,400 miles (20,000 kilometers) from the planet. Citizen scientist Jason Major enhanced the color and contrast in this image, turning the picture into a Jovian work of art. He then cropped it to focus our attention on this beautiful example of Jupiter's spinning storms. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21387 . - Enhanced image by Jason Major (CC-BY) based on images provided courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS

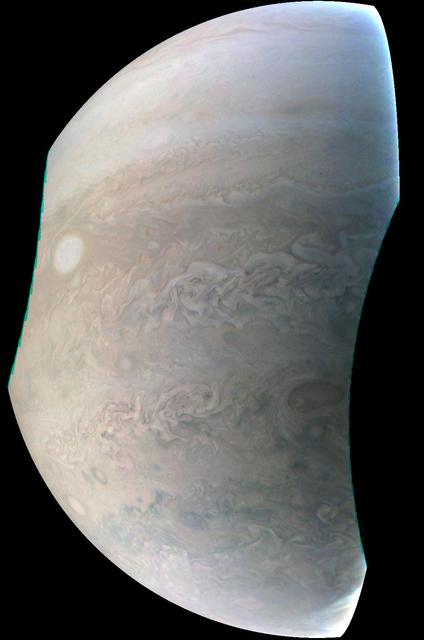
This enhanced color Jupiter image, taken by the JunoCam imager on NASA's Juno spacecraft, showcases several interesting features on the apparent edge (limb) of the planet. Prior to Juno's fifth flyby over Jupiter's mysterious cloud tops, members of the public voted on which targets JunoCam should image. This picture captures not only a fascinating variety of textures in Jupiter's atmosphere, it also features three specific points of interest: "String of Pearls," "Between the Pearls," and "An Interesting Band Point." Also visible is what's known as the STB Spectre, a feature in Jupiter's South Temperate Belt where multiple atmospheric conditions appear to collide. JunoCam images of Jupiter sometimes appear to have an odd shape. This is because the Juno spacecraft is so close to Jupiter that it cannot capture the entire illuminated area in one image -- the sides get cut off. Juno acquired this image on March 27, 2017, at 2:12 a.m. PDT (5:12 a.m. EDT), as the spacecraft performed a close flyby of Jupiter. When the image was taken, the spacecraft was about 12,400 miles (20,000 kilometers) from the planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21389. - Enhanced image by Björn Jónsson (CC-NC-SA) based on images provided courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS
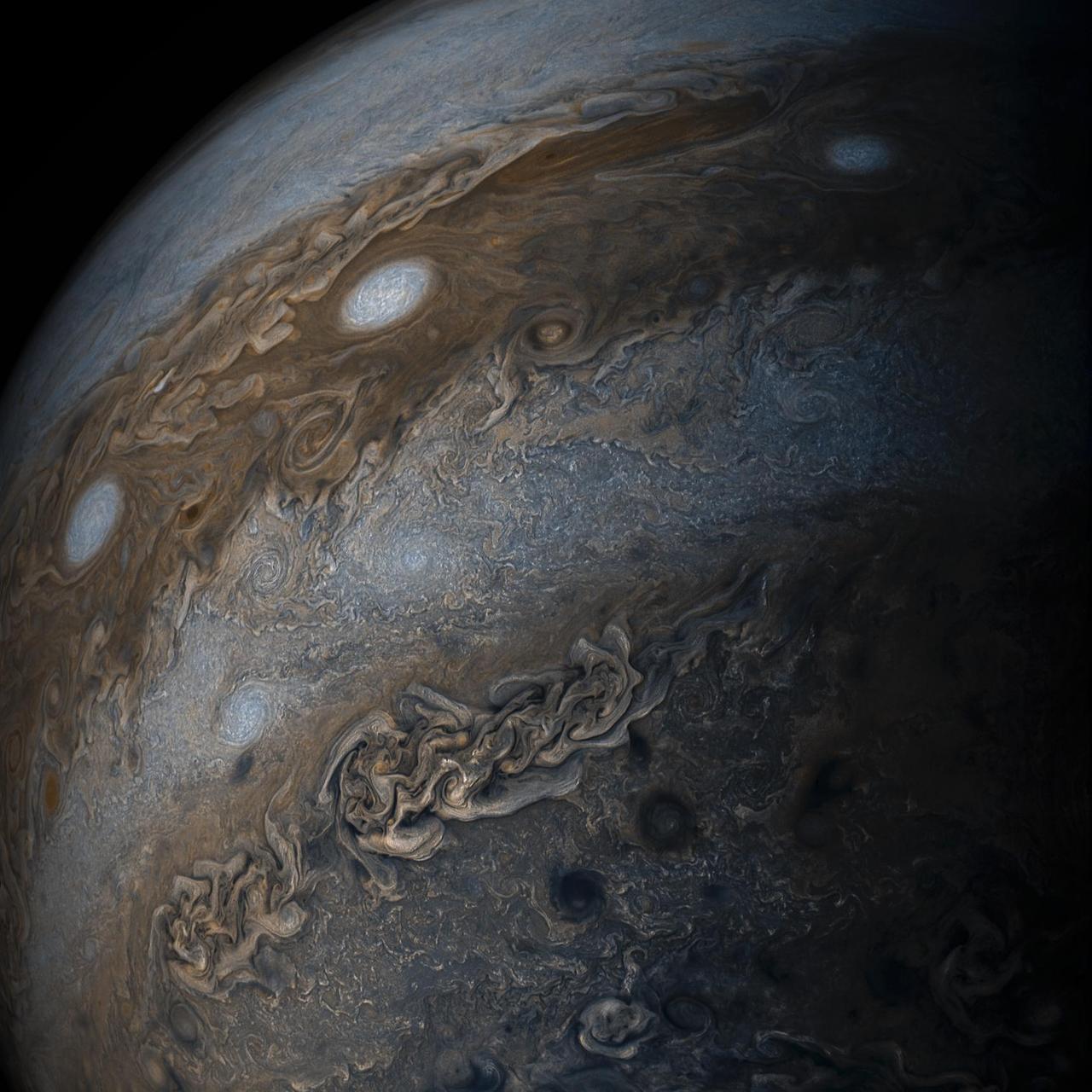

This enhanced-color image of Jupiter's bands of light and dark clouds was created by citizen scientists Gerald Eichstädt and Seán Doran using data from the JunoCam imager on NASA's Juno spacecraft. Three of the white oval storms known as the "String of Pearls" are visible near the top of the image. Each of the alternating light and dark atmospheric bands in this image is wider than Earth, and each rages around Jupiter at hundreds of miles (kilometers) per hour. The lighter areas are regions where gas is rising, and the darker bands are regions where gas is sinking. Juno acquired the image on May 19, 2017, at 11:30 a.m. PST (2:30 p.m. EST) from an altitude of about 20,800 miles (33,400 kilometers) above Jupiter's cloud tops. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21393
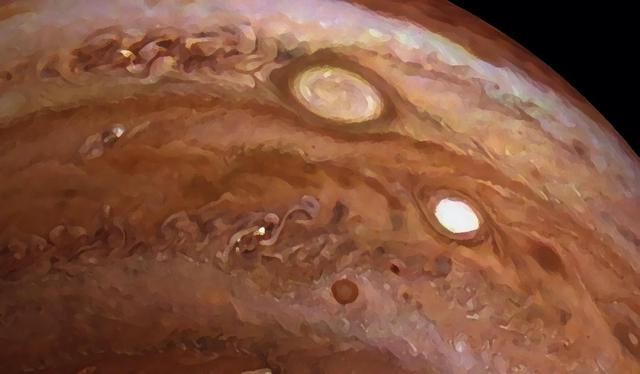
A JunoCam image of Jupiter's storm "Oval BA", taken on Juno's 26th perijove (PJ) pass, inspired this work of art, suitable for framing. Oval BA can be seen near the top of the image, a storm approximately the same size as Earth. The bright storm below and to the right of Oval BA is one of Jupiter's anticyclonic (counterclockwise-rotating) white ovals, common at this latitude, dubbed the string of pearls. The original JunoCam image artist Navaneeth Krishnan S used to produce this view was taken from from an altitude of 51,148 miles (82,315 kilometers) above Jupiter's cloud tops. Krishnan S processed the images to enhance the color and contrast, giving us the sense of this image being a painting. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24292
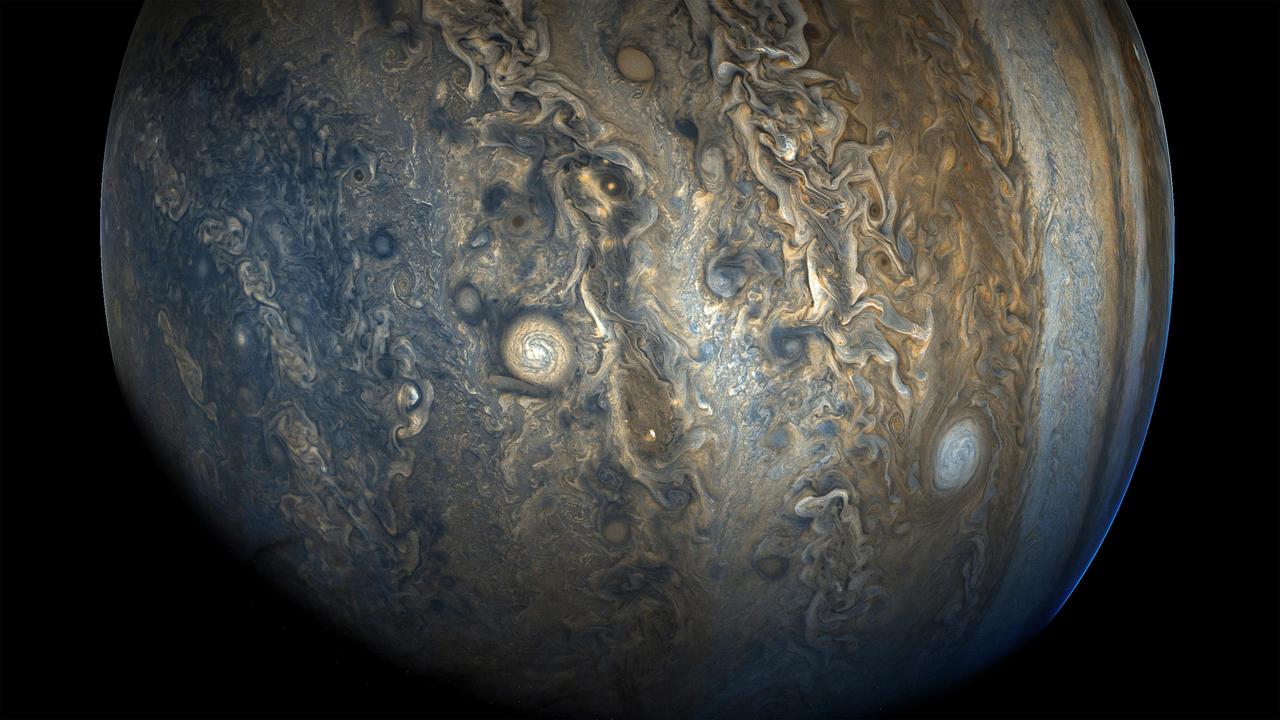

See Jupiter's southern hemisphere in beautiful detail in this new image taken by NASA's Juno spacecraft. The color-enhanced view captures one of the white ovals in the "String of Pearls," one of eight massive rotating storms at 40 degrees south latitude on the gas giant planet. The image was taken on Oct. 24, 2017 at 11:11 a.m. PDT (2:11 p.m. EDT), as Juno performed its ninth close flyby of Jupiter. At the time the image was taken, the spacecraft was 20,577 miles (33,115 kilometers) from the tops of the clouds of the planet at a latitude of minus 52.96 degrees. The spatial scale in this image is 13.86 miles/pixel (22.3 kilometers/pixel). Citizen scientists Gerald Eichstädt and Seán Doran processed this image using data from the JunoCam imager. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21970
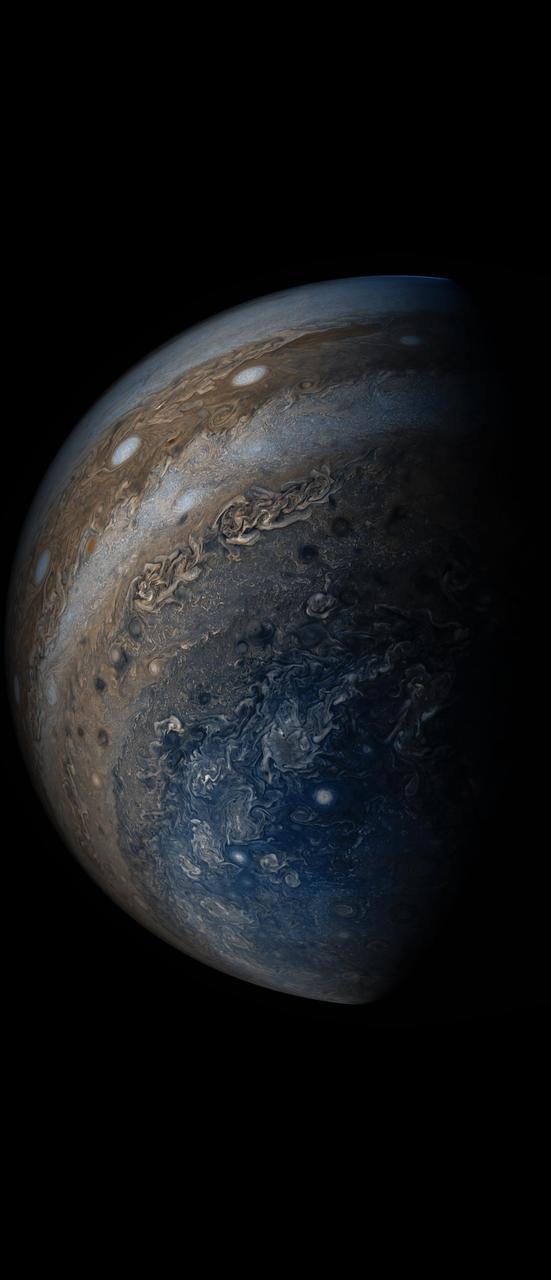

NASA's Juno spacecraft was racing away from Jupiter following its seventh close pass of the planet when JunoCam snapped this image on May 19, 2017, from about 29,100 miles (46,900 kilometers) above the cloud tops. The spacecraft was over 65.9 degrees south latitude, with a lovely view of the south polar region of the planet. This image was processed to enhance color differences, showing the amazing variety in Jupiter's stormy atmosphere. The result is a surreal world of vibrant color, clarity and contrast. Four of the white oval storms known as the "String of Pearls" are visible near the top of the image. Interestingly, one orange-colored storm can be seen at the belt-zone boundary, while other storms are more of a cream color. Citizen scientists Gerald Eichstädt and Seán Doran processed this image using data from the JunoCam imager. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21392
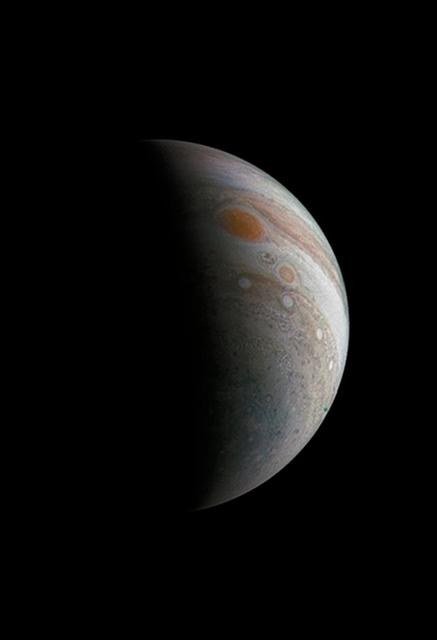

This image of a crescent Jupiter and the iconic Great Red Spot was created by a citizen scientist (Roman Tkachenko) using data from Juno's JunoCam instrument. You can also see a series of storms shaped like white ovals, known informally as the "string of pearls." Below the Great Red Spot a reddish long-lived storm known as Oval BA is visible. The image was taken on Dec. 11, 2016 at 2:30 p.m. PST (5:30 p.m. EST), as the Juno spacecraft performed its third close flyby of Jupiter. At the time the image was taken, the spacecraft was about 285,100 miles (458,800 kilometers) from the planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21376 . - Enhanced image by Roman Tkachenko (CC-BY) based on images provided courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS
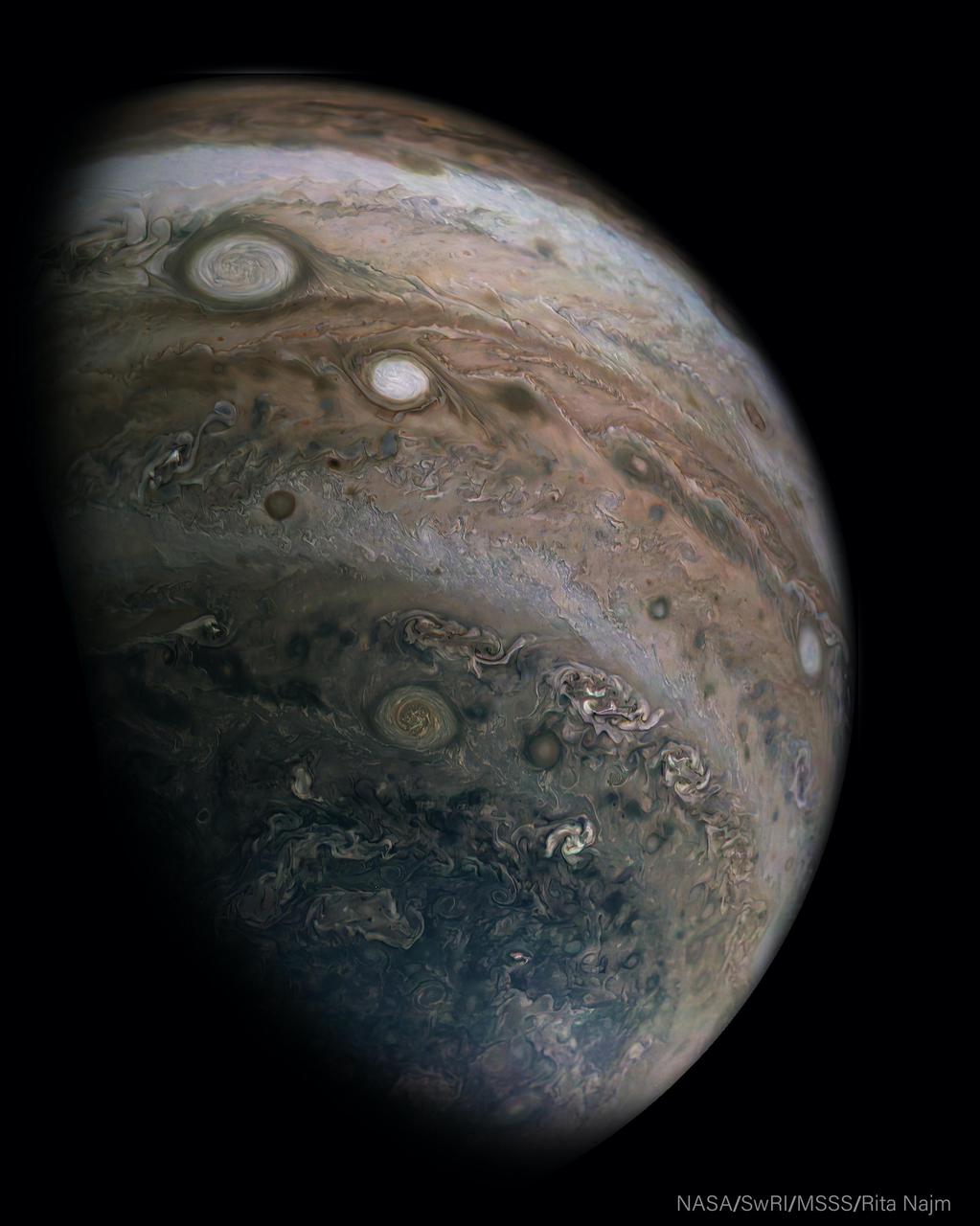

This image was captured by the JunoCam imager aboard NASA's Juno spacecraft on April 10, 2020, during the mission's 25th science pass of Jupiter. Oval BA, a large muddy circle of clouds near the upper-left of picture, is a storm approximately the same size as Earth. The bright storm below and to the right of Oval BA is one of Jupiter's "string of pearls" — massive counterclockwise rotating storms that appear as white ovals in the gas giant's southern hemisphere. The original JunoCam image used to produce this view was taken from an altitude of about 400,000 miles (64,500 kilometers) above Jupiter's cloud tops. Citizen scientist Rita Najm processed the images to enhance the color and contrast. Juno's elliptical orbit around Jupiter is evolving gradually as the perijove (closest approach) point moves farther north on each pass. Shorter closer views in the north are accompanied by a longer duration, more distant perspective, for viewing the southern hemisphere. These changes in perspective give us ever new views of this beautiful giant and its huge storms. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24234

This sequence of enhanced-color images shows how quickly the viewing geometry changes for NASA's Juno spacecraft as it swoops by Jupiter. The images were obtained by JunoCam. Once every 53 days the Juno spacecraft swings close to Jupiter, speeding over its clouds. In just two hours, the spacecraft travels from a perch over Jupiter's north pole through its closest approach (perijove), then passes over the south pole on its way back out. This sequence shows 14 enhanced-color images. The first image on the left shows the entire half-lit globe of Jupiter, with the north pole approximately in the center. As the spacecraft gets closer to Jupiter, the horizon moves in and the range of visible latitudes shrinks. The third and fourth images in this sequence show the north polar region rotating away from our view while a band of wavy clouds at northern mid-latitudes comes into view. By the fifth image of the sequence the band of turbulent clouds is nicely centered in the image. The seventh and eighth images were taken just before the spacecraft was at its closest point to Jupiter, near Jupiter's equator. Even though these two pictures were taken just four minutes apart, the view is changing quickly. As the spacecraft crossed into the southern hemisphere, the bright "south tropical zone" dominates the ninth, 10th and 11th images. The white ovals in a feature nicknamed Jupiter's "String of Pearls" are visible in the 12th and 13th images. In the 14th image Juno views Jupiter's south poles. Citizen scientists Gerald Eichstädt and Seán Doran created this image using data from the spacecraft's JunoCam imager. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21645