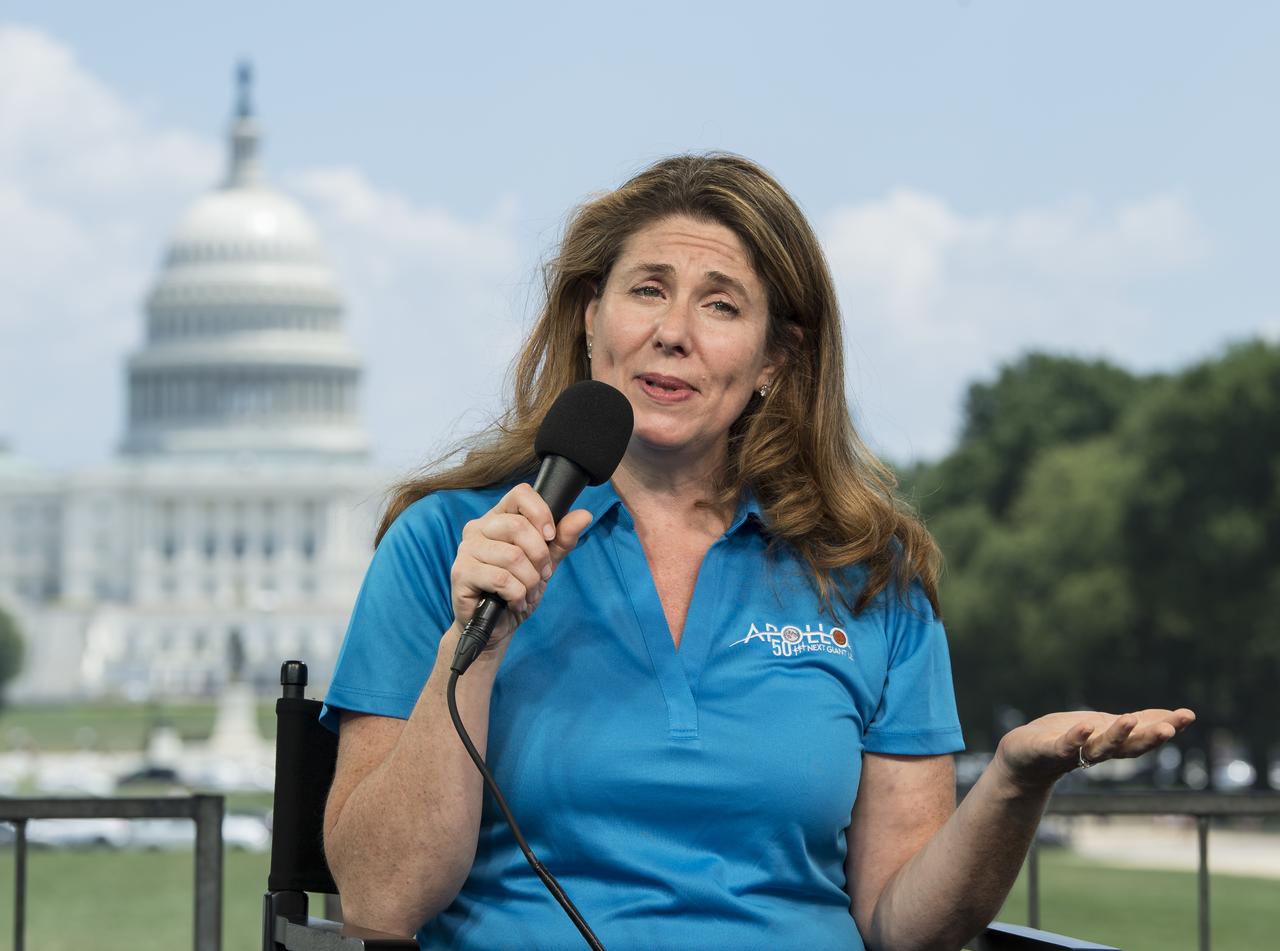

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics, Karen Fox, speaks during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 on the National Mall in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
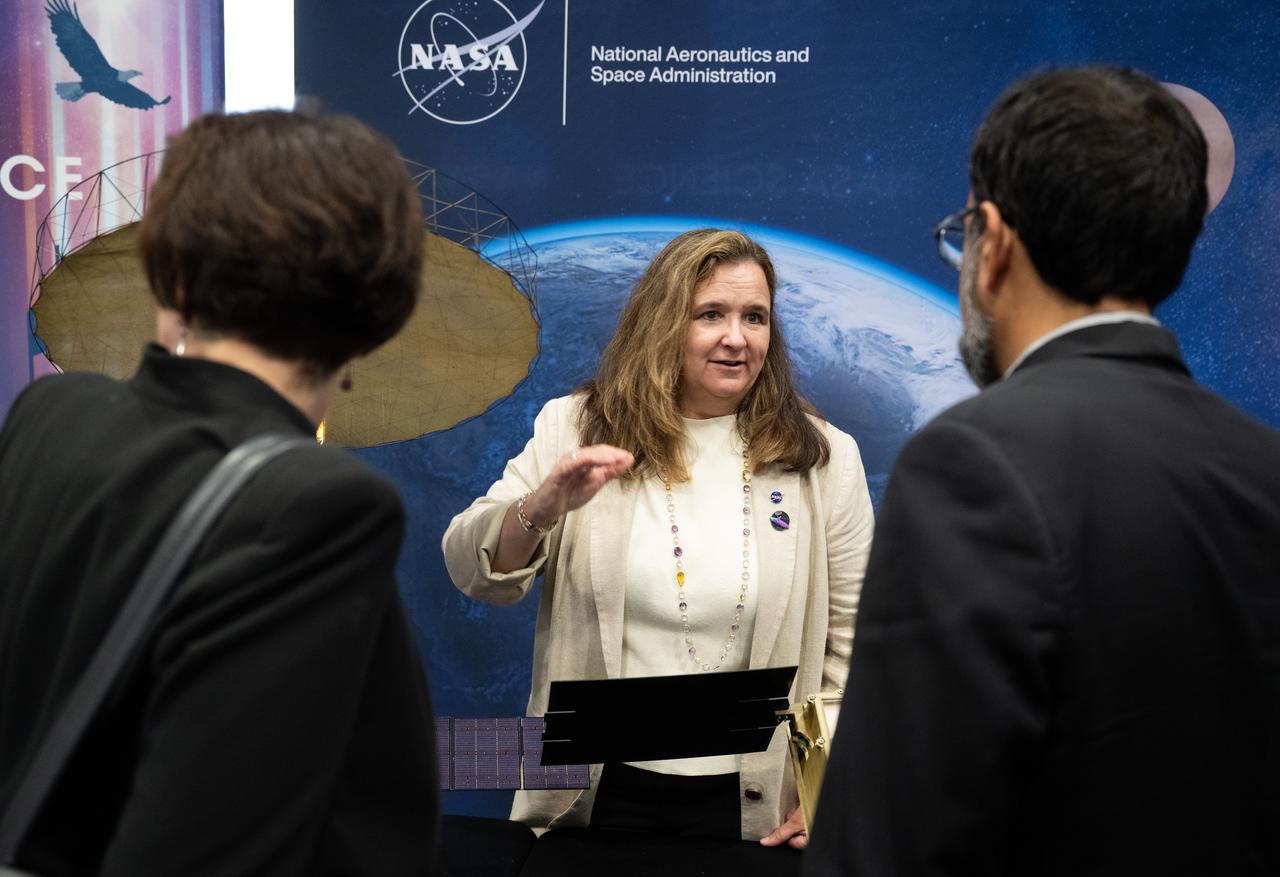

Karen St. Germain, director of the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, center, speaks with Nicola Fox, associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, left, and NASA Associate Administrator Amit Kshatriya during NASA’s Day on the Hill, Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, at the Hart Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
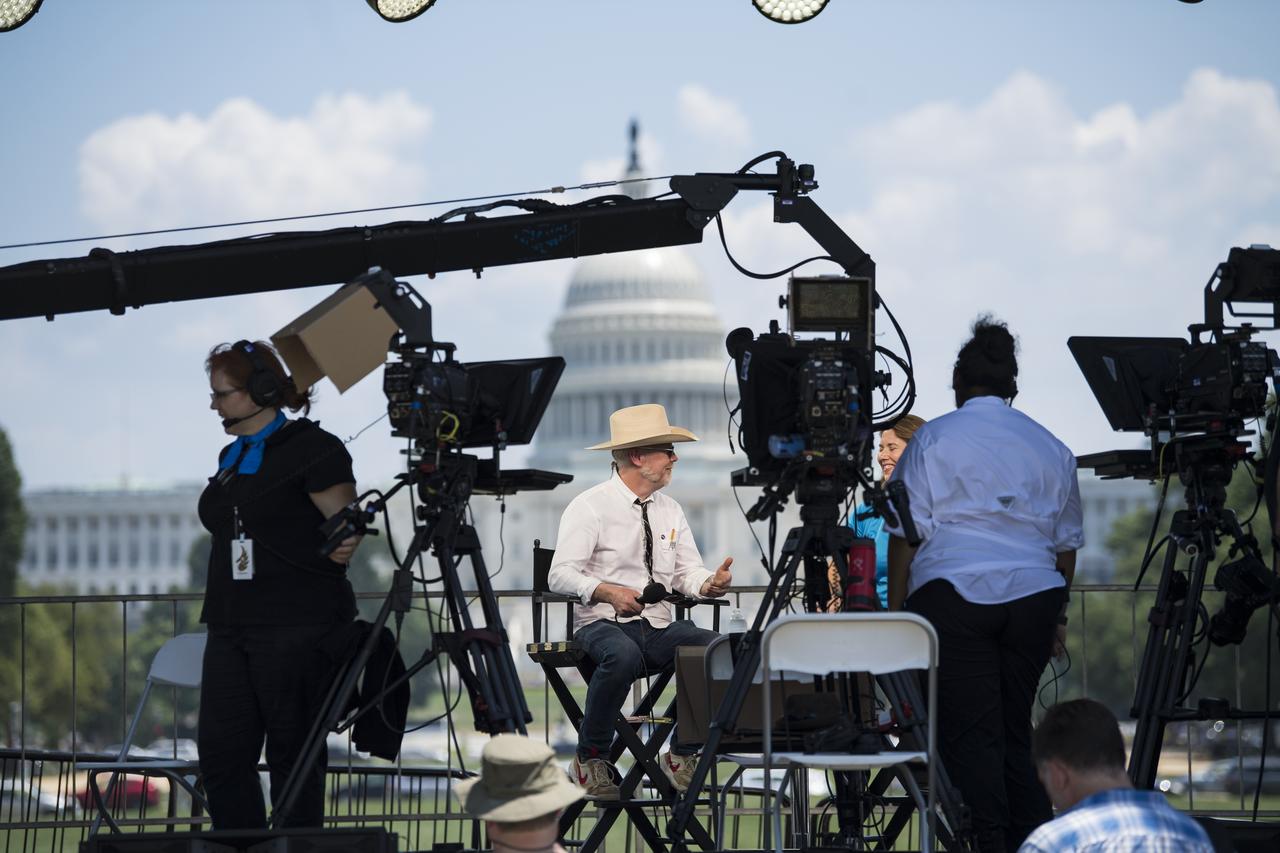

Adam Savage, maker and host of Savage Builds, left, speaks with NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics, Karen Fox, just before “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 on the National Mall in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
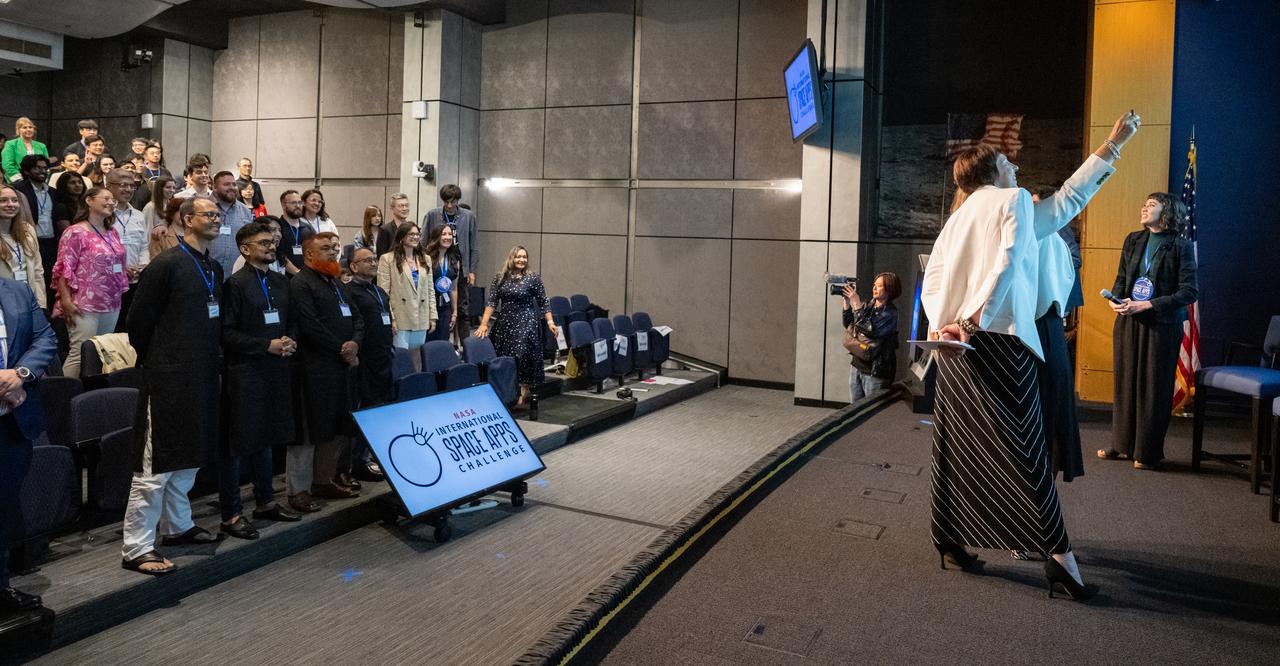

NASA Earth Science Division Director Karen St. Germain and NASA Earth Science Division Associate Administrator Nicola Fox pose for a selfie with guests during a gathering of NASA Space Apps Challenge Global Winners and Local Leads from around the world Wednesday, June 5, 2024, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
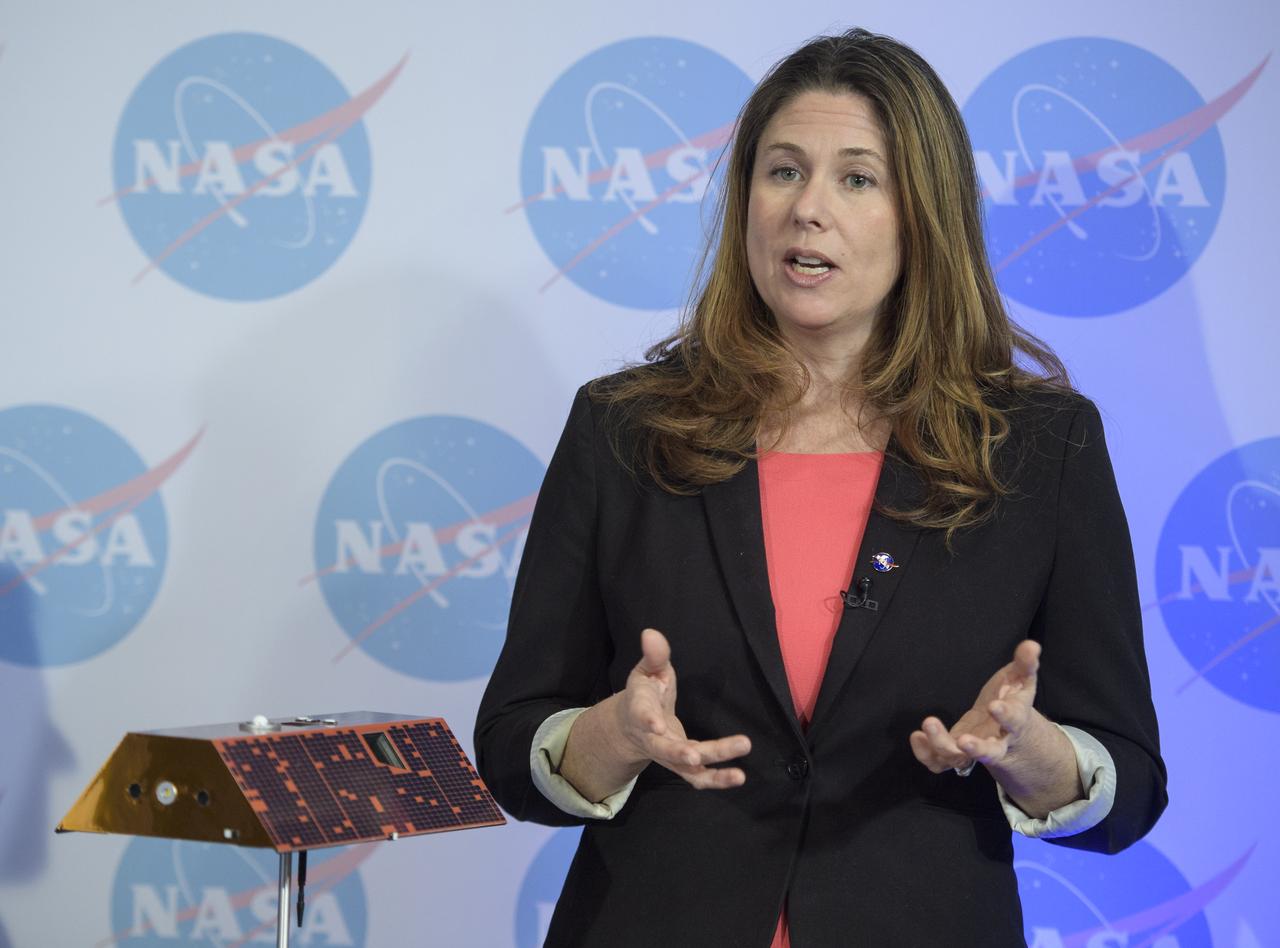

Karen Fox, of NASA's Office of Communications, introduces Michael Watkins, GRACE-FO science lead and director of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Frank Webb, GRACE-FO project scientist at JPL, during a briefing on the upcoming launch of the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-On (GRACE-FO) mission, Monday, April 30, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The twin GRACE-FO spacecraft will measure and monitor monthly changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
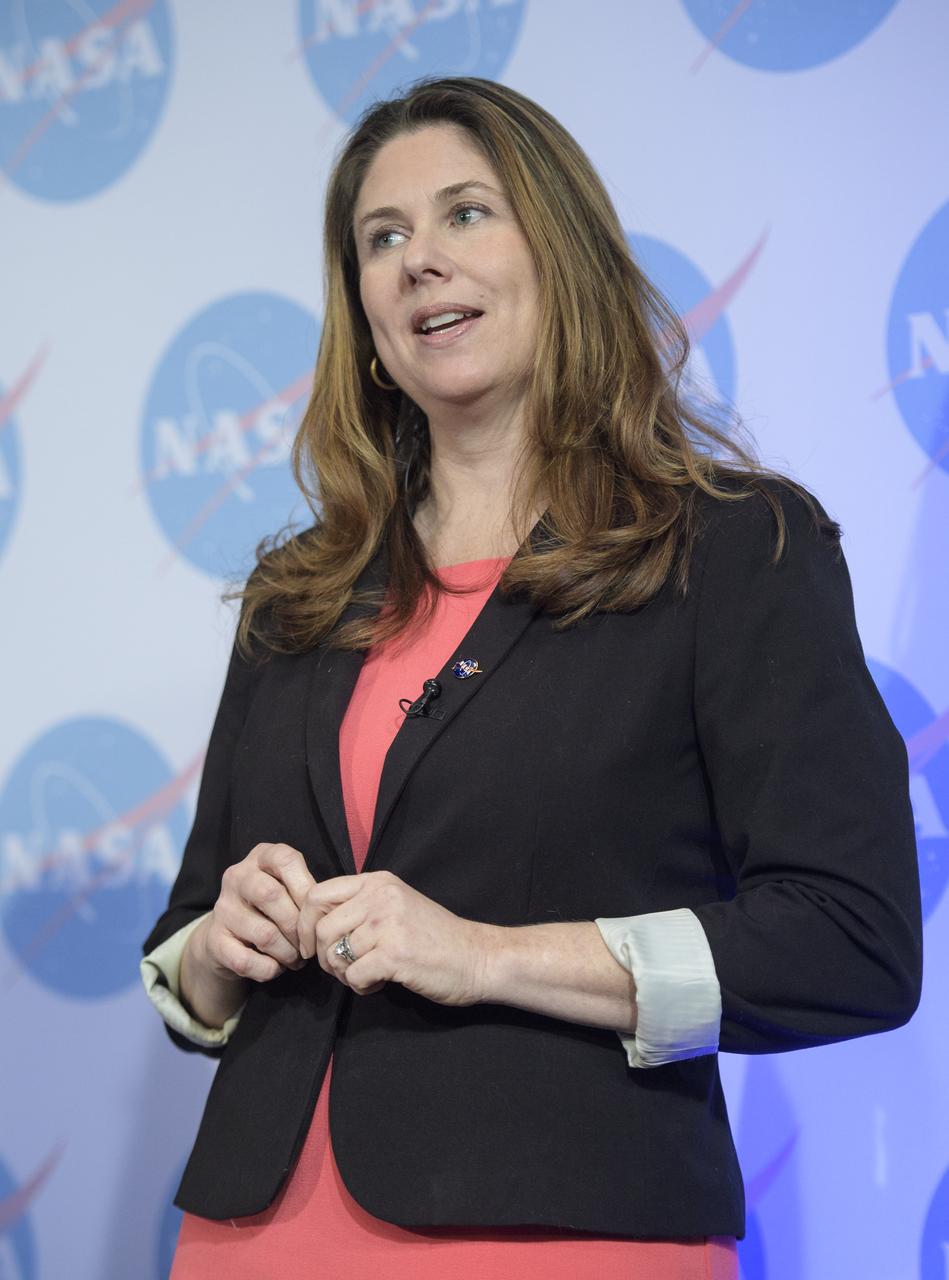

Karen Fox of NASA's Office of Communications, introduces David Jarrett, GRACE-FO program executive in the Earth Science Division at NASA Headquarters and Phil Morton, NASA GRACE-FO project manager at JPL, during a briefing on the upcoming launch of the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-On (GRACE-FO) mission, Monday, April 30, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The twin GRACE-FO spacecraft will measure and monitor monthly changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
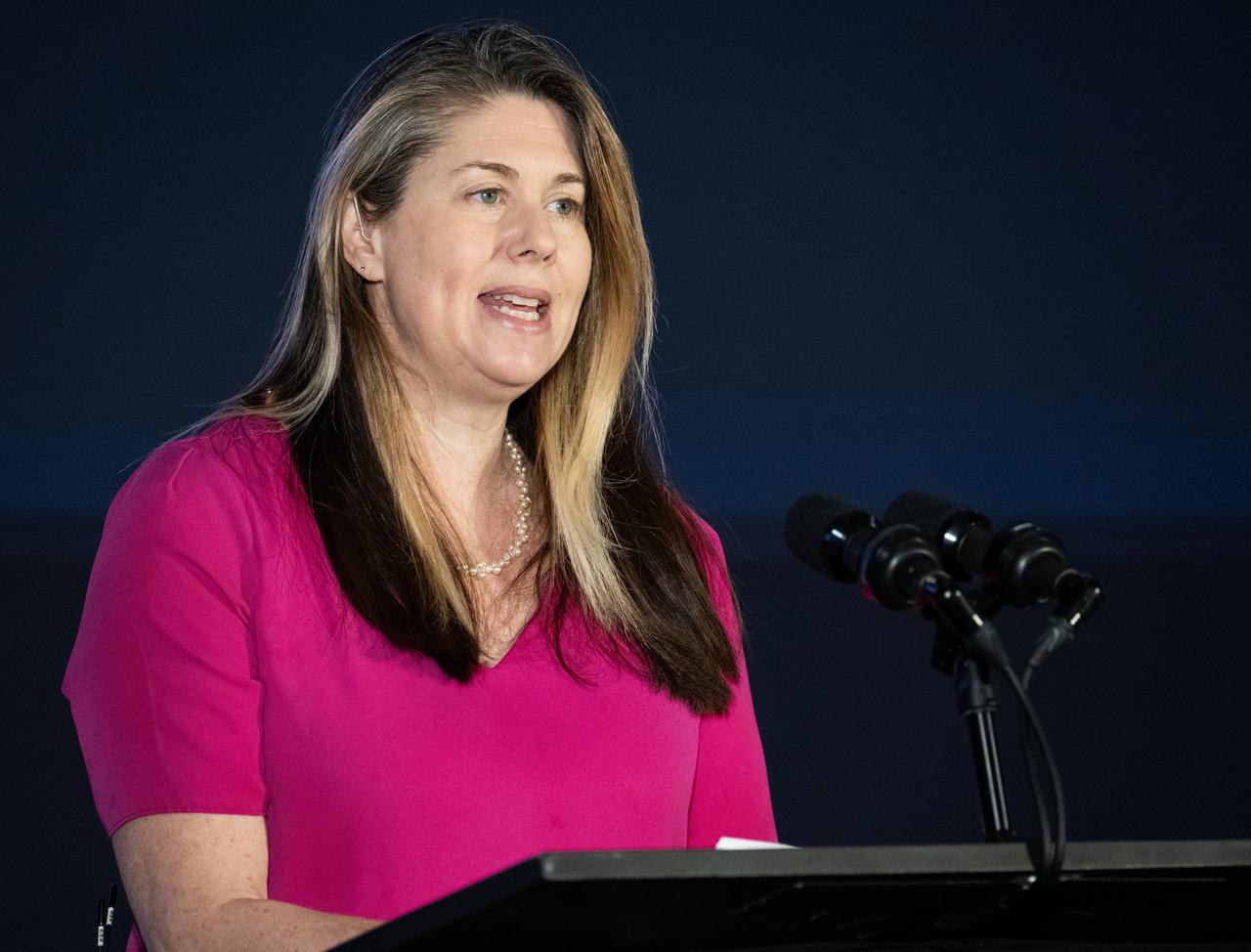

NASA Public Affairs Officer Karen Fox moderates a briefing on NASA’s TEMPO (Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution) instrument, Tuesday, March 14, 2023 at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA’s TEMPO instrument, the first Earth Venture Instrument mission, will measure air pollution across North America from Mexico City to the Canadian oil sands and from the Atlantic to the Pacific hourly and at a high spatial resolution. A partnership between NASA and the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, TEMPO will launch on a commercial satellite to geostationary orbit as early as April. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics Karen Fox, interviews, Apollo 11 astronaut Mike Collins during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics Karen Fox interviews Apollo 10 astronaut General Thomas Stafford during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
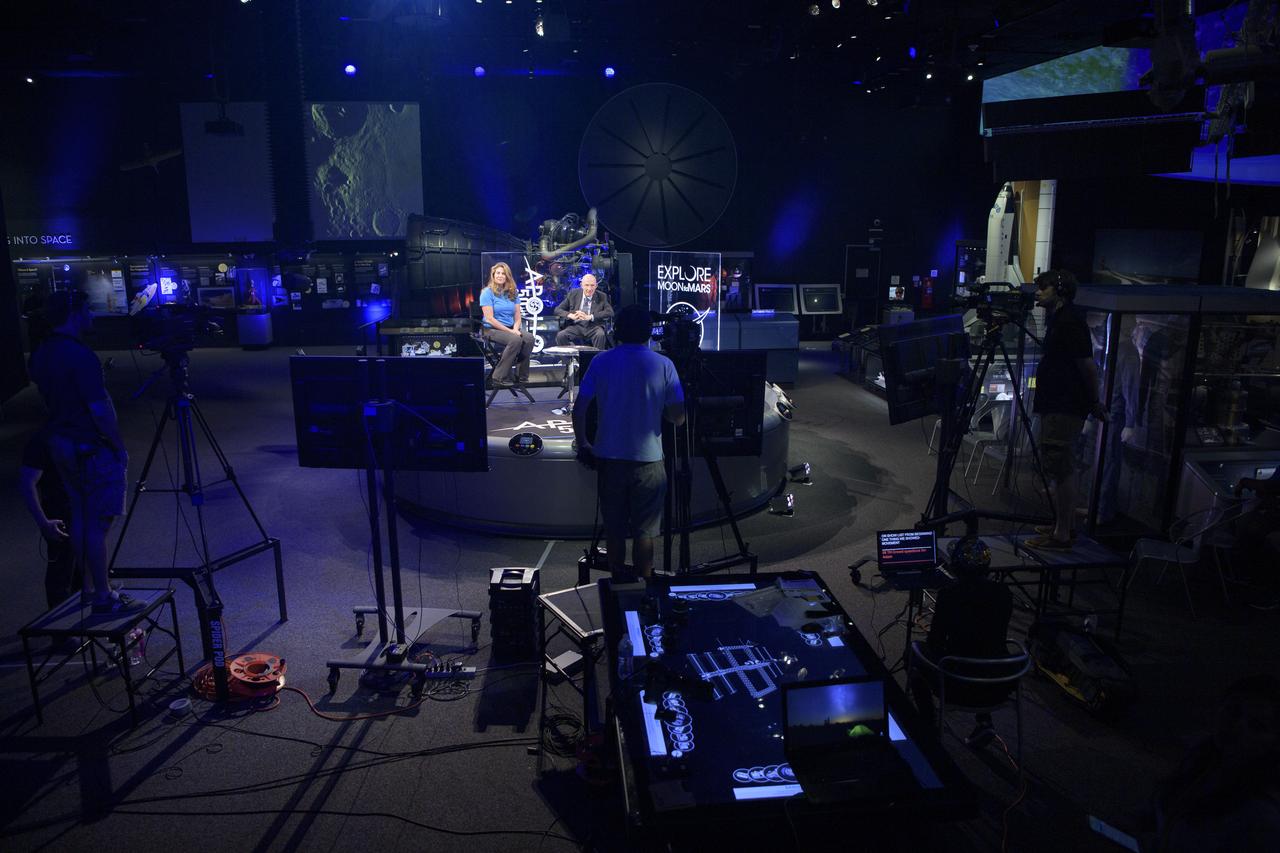

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics Karen Fox interviews Apollo 10 astronaut General Thomas Stafford during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics Karen Fox interviews Apollo 10 astronaut General Thomas Stafford during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
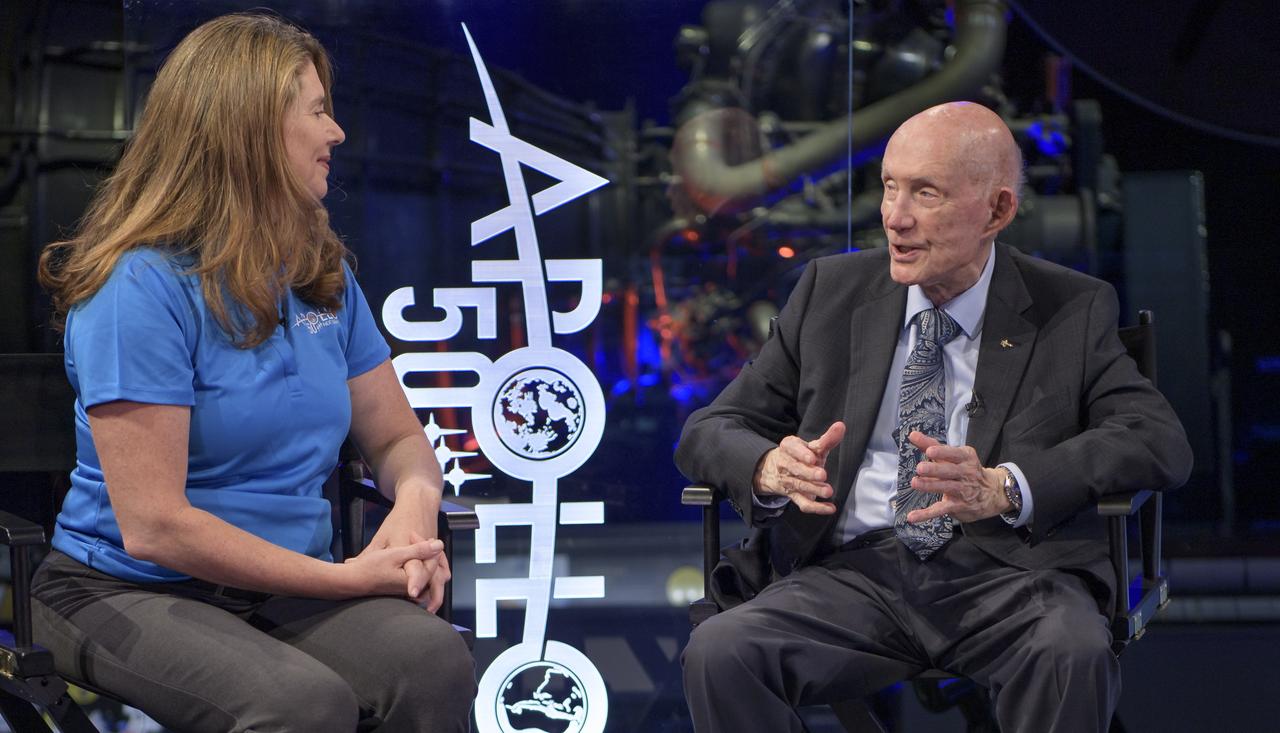

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics Karen Fox interviews Apollo 10 astronaut General Thomas Stafford during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics Karen Fox, interviews, Apollo 11 astronaut Mike Collins during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics Karen Fox interviews Apollo 10 astronaut General Thomas Stafford during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
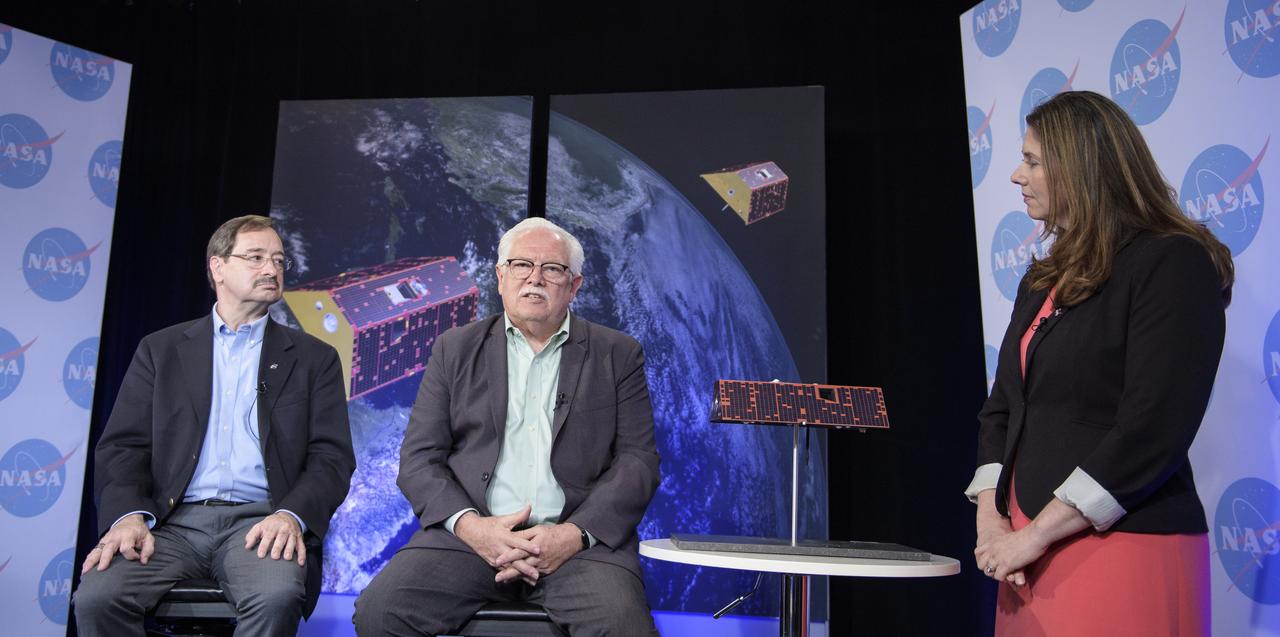

David Jarrett, GRACE-FO program executive in the Earth Science Division at NASA Headquarters, left, and Phil Morton, NASA GRACE-FO project manager at JPL, discuss the upcoming launch of the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-On (GRACE-FO) mission with Karen Fox of NASA's Office of Communications, Monday, April 30, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The twin GRACE-FO spacecraft will measure and monitor monthly changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics Karen Fox, left, interviews, Apollo 11 astronaut Mike Collins, and NASA astronaut candidate Zena Cardman during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics Karen Fox, left, interviews, Apollo 11 astronaut Mike Collins, and NASA astronaut candidate Zena Cardman during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
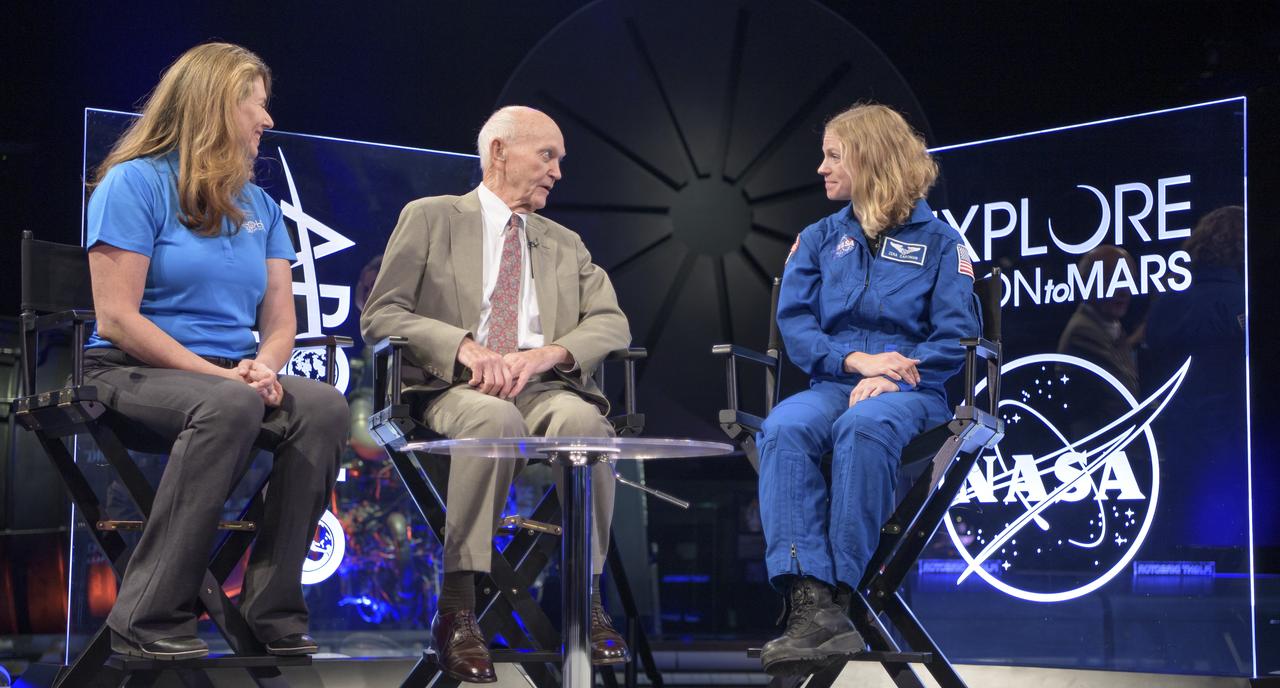

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics Karen Fox, left, interviews, Apollo 11 astronaut Mike Collins, and NASA astronaut candidate Zena Cardman during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics Karen Fox, left, interviews, Apollo 11 astronaut Mike Collins, and NASA astronaut candidate Zena Cardman during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
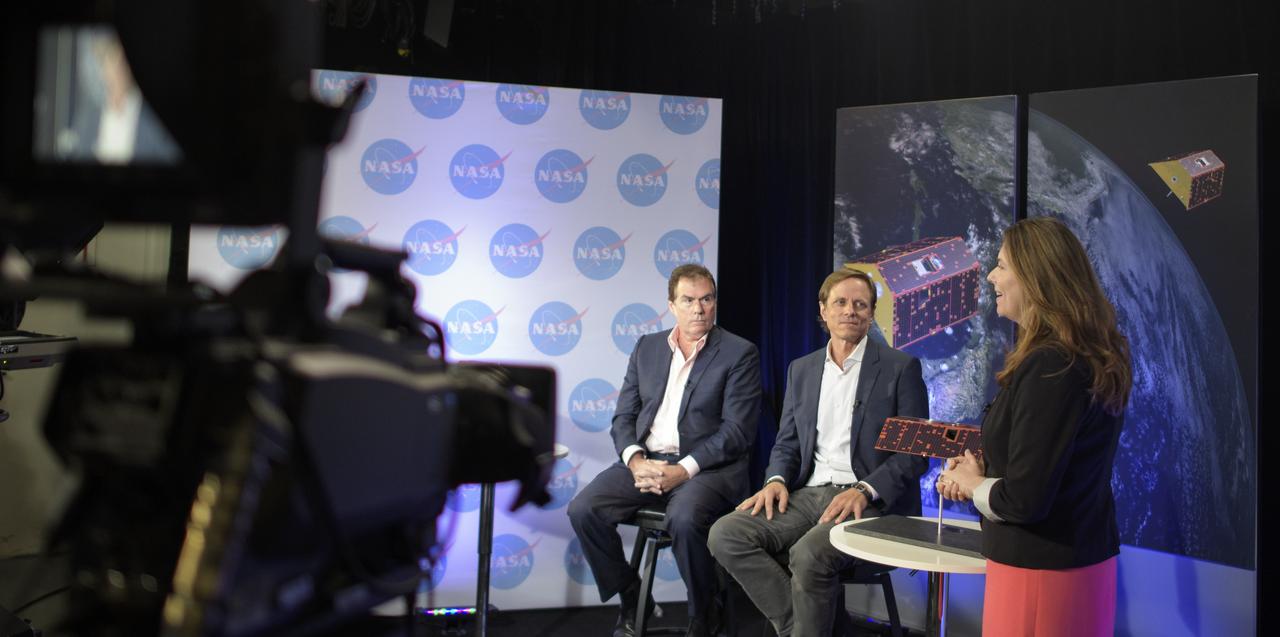

Karen Fox, of NASA's Office of Communications, right, discusses the upcoming launch of the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-On (GRACE-FO) mission with Michael Watkins, GRACE-FO science lead and director of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, left, and Frank Webb, GRACE-FO project scientist at JPL, Monday, April 30, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The twin GRACE-FO spacecraft will measure and monitor monthly changes in how mass is redistributed within and among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, land and ice sheets, as well as within Earth itself. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
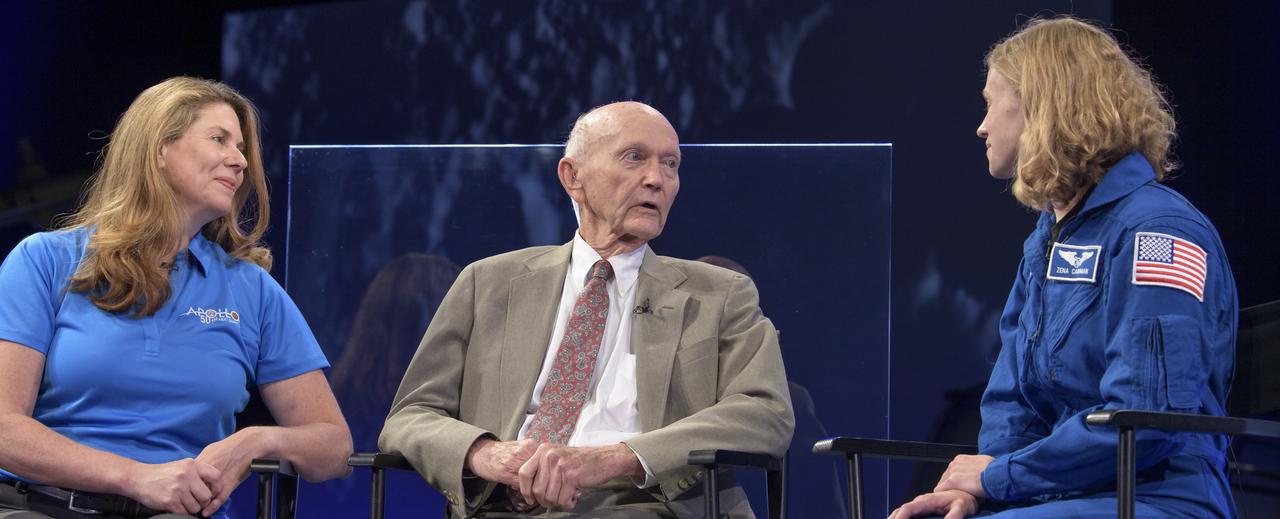

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics Karen Fox, left, interviews, Apollo 11 astronaut Mike Collins, and NASA astronaut candidate Zena Cardman during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Public Affairs Officer for Heliophysics Karen Fox, left, interviews, Apollo 11 astronaut Mike Collins, and NASA astronaut candidate Zena Cardman during “NASA’s Giant Leaps: Past and Future," a live television program on Friday, July 19, 2019 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA and the world are recognizing the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, in which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin crewed the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
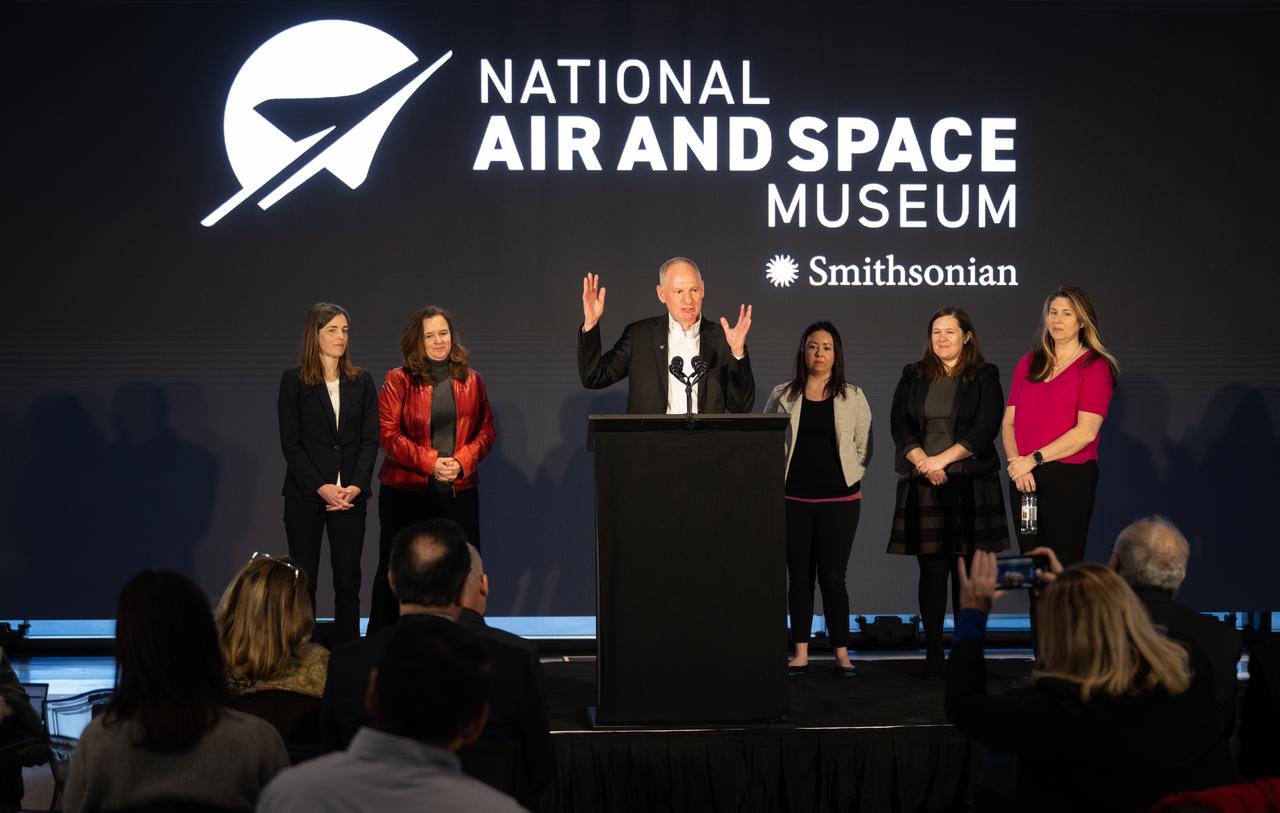

Barry Lefer, tropospheric composition program manager in the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, at podium, answers a question during a briefing on NASA’s TEMPO (Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution) instrument along with Caroline Nowlan, atmospheric physicist at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, left, Karen St. Germain, director of the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, second from left, Laura Judd, associate program manager for the Applied Sciences Health and Air Quality Applications in the Applied Sciences Program of NASA’s Earth Science Division, third from right, Erika Wright, education specialist at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, second from right, and Karen Fox, NASA Public Affairs Officer, right, Tuesday, March 14, 2023 at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA’s TEMPO instrument, the first Earth Venture Instrument mission, will measure air pollution across North America from Mexico City to the Canadian oil sands and from the Atlantic to the Pacific hourly and at a high spatial resolution. A partnership between NASA and the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, TEMPO will launch on a commercial satellite to geostationary orbit as early as April. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
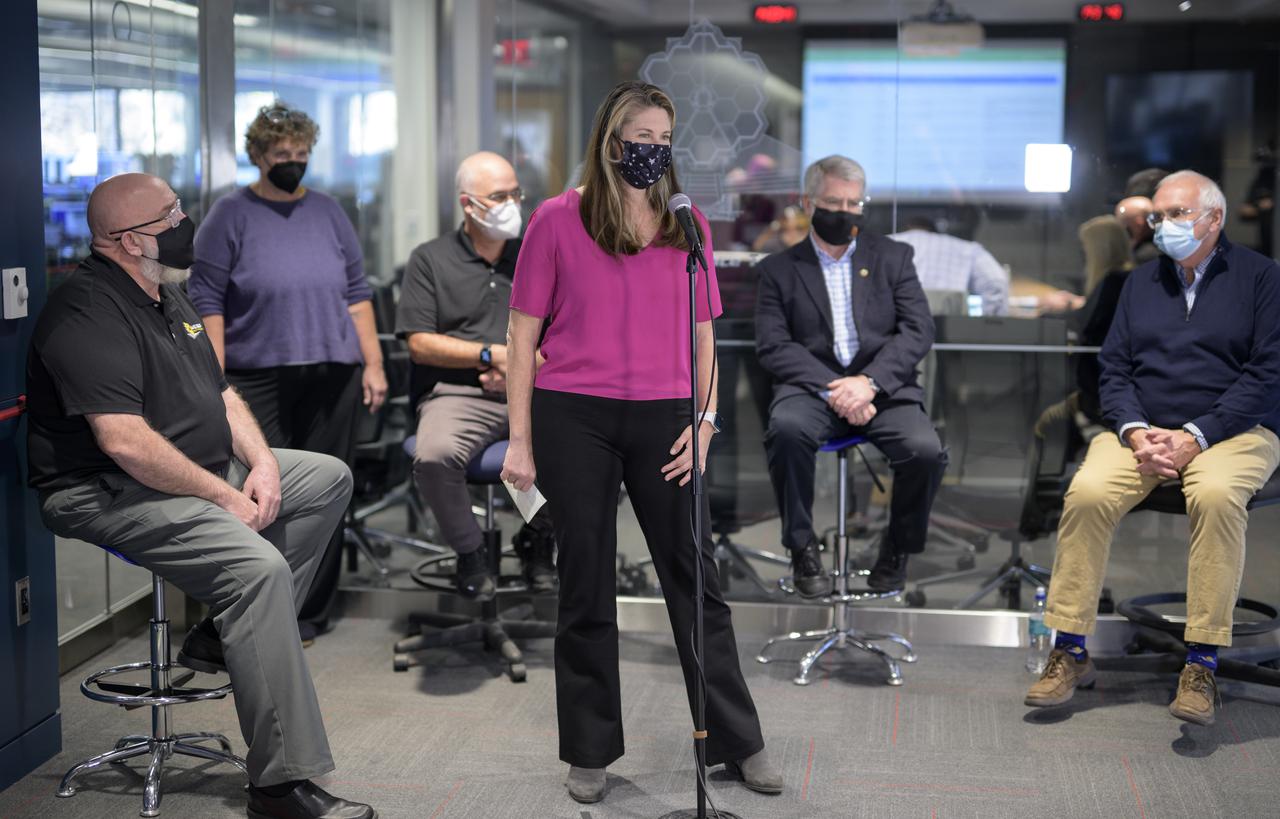

NASA Public Affairs Officer Karen Fox, center, moderates a briefing following the successful deployment of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope primary mirror, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from the Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. With Webb’s 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror fully deployed, the infrared observatory has completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Office of Communications Senior Science Communications Officer Karen Fox calls on reporters during an OSIRIS-REx sample return press conference, Sunday, Sept. 24, 2023, shortly after the capsule landed at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
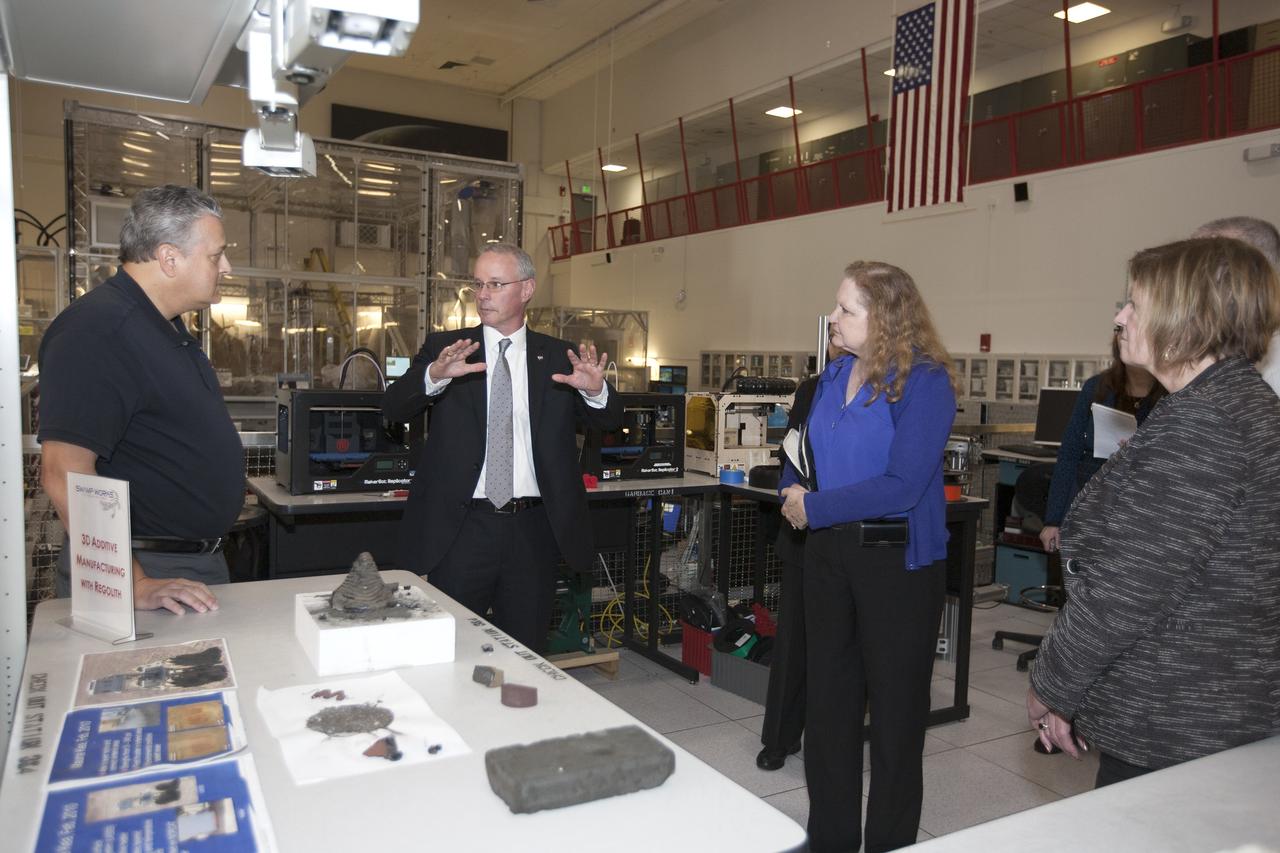

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During a visit to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Chief Technologist David Miller, second from left, tours laboratories inside the Swamp Works facility. Miller is briefed on technology developments in the lab by Jack Fox, chief of the Surface Systems Office in the Engineering and Technology Directorate. At right is Karen Thompson, Kennedy's chief technologist. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
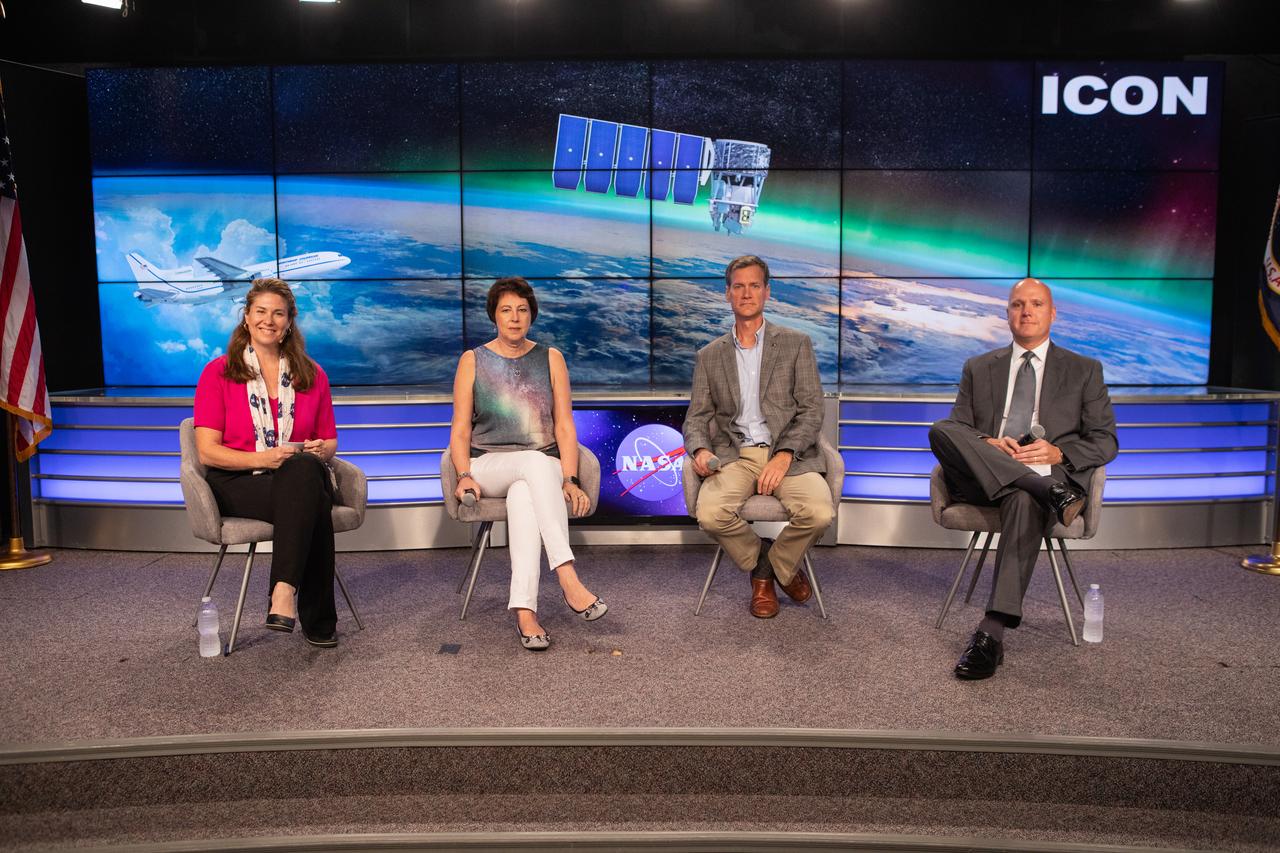

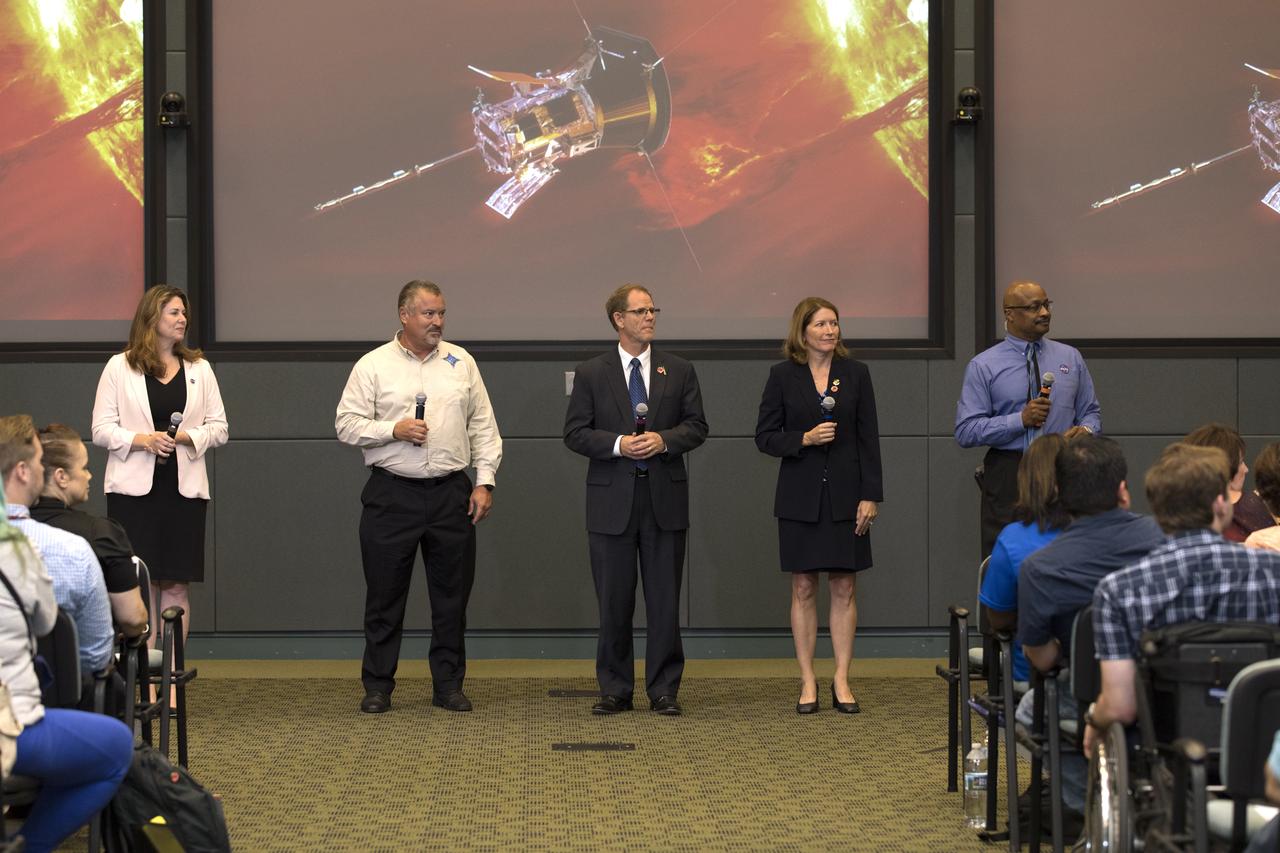
Launch and mission managers for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left to right are Karen Fox, NASA Communications; Nicola Fox, Heliophysics division director in NASA’s Science Mission Directorate; Thomas Immel, ICON principal investigator at the Space Sciences Laboratory at the University of California Berkeley; and Steve Krein, vice president of civil and commercial space for Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.

Launch and mission managers for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left to right are Karen Fox, NASA Communications; Nicola Fox, Heliophysics division director in NASA’s Science Mission Directorate; Thomas Immel, ICON principal investigator at the Space Sciences Laboratory at the University of California Berkeley; and Steve Krein, vice president of civil and commercial space for Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.

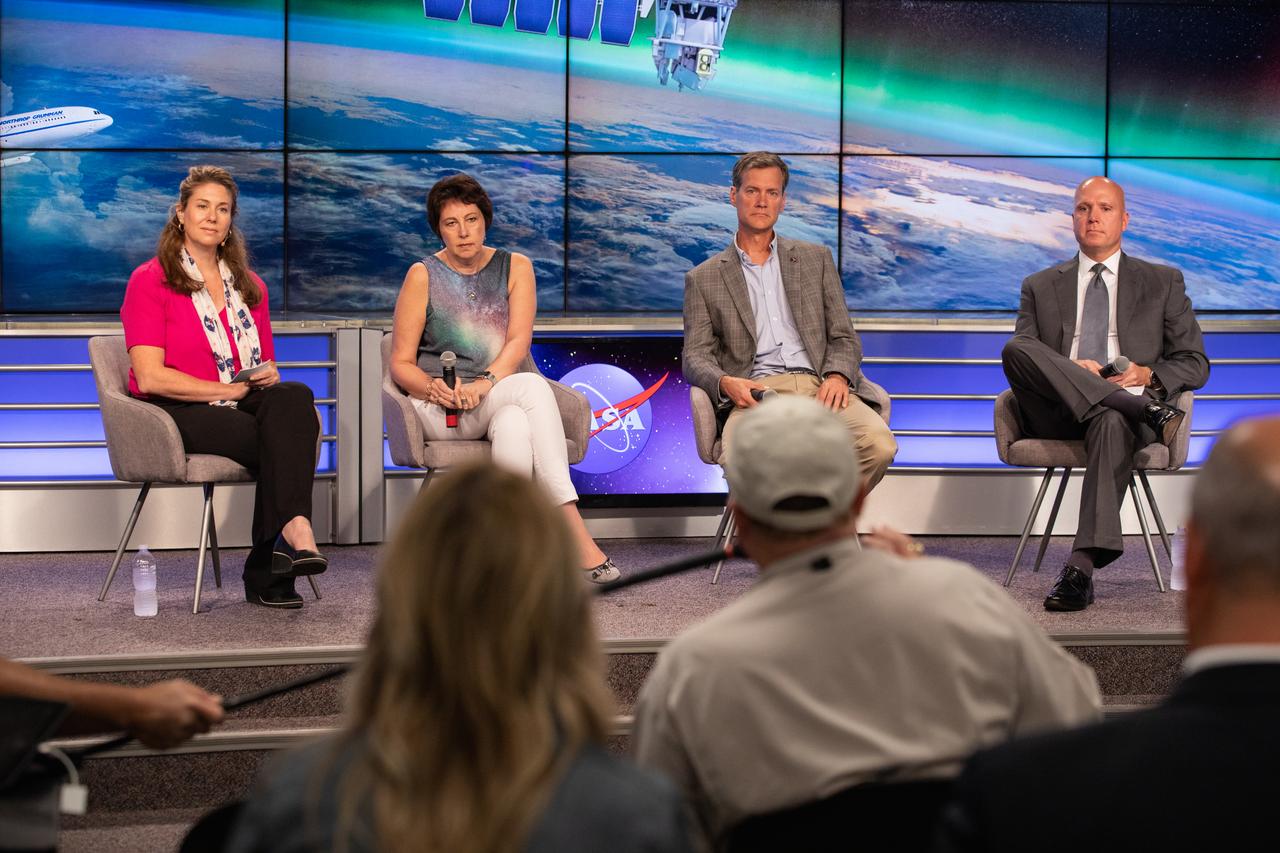
Karen Fox of NASA Communications moderates a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.

Omar Baez, launch director in NASA’s Launch Services Program, speaks to news media during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At left is Karen Fox of NASA Communications. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
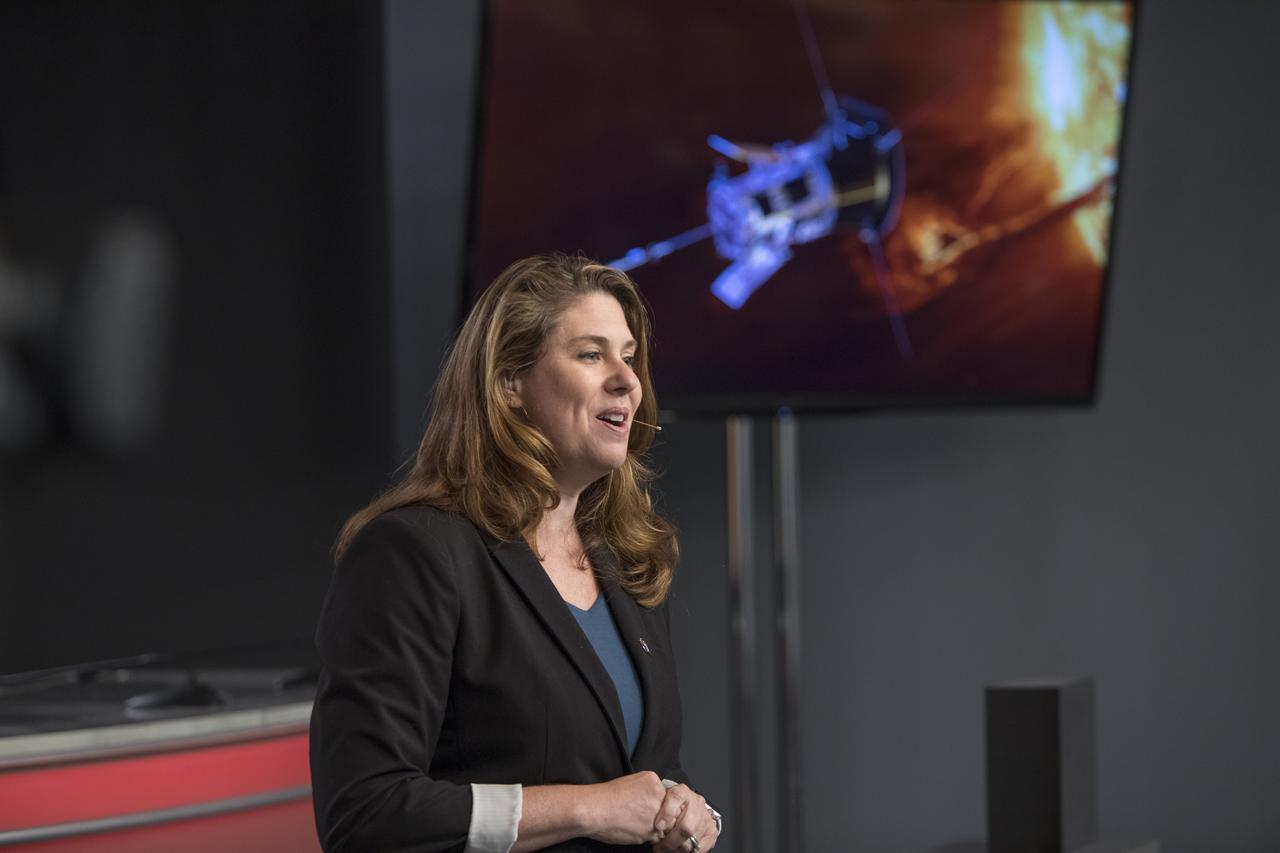

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, on Friday, July 20, 2018, Karen Fox of NASA Communications, speaks to members of the media during a prelaunch mission briefing for the Parker Solar Probe mission. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel in Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

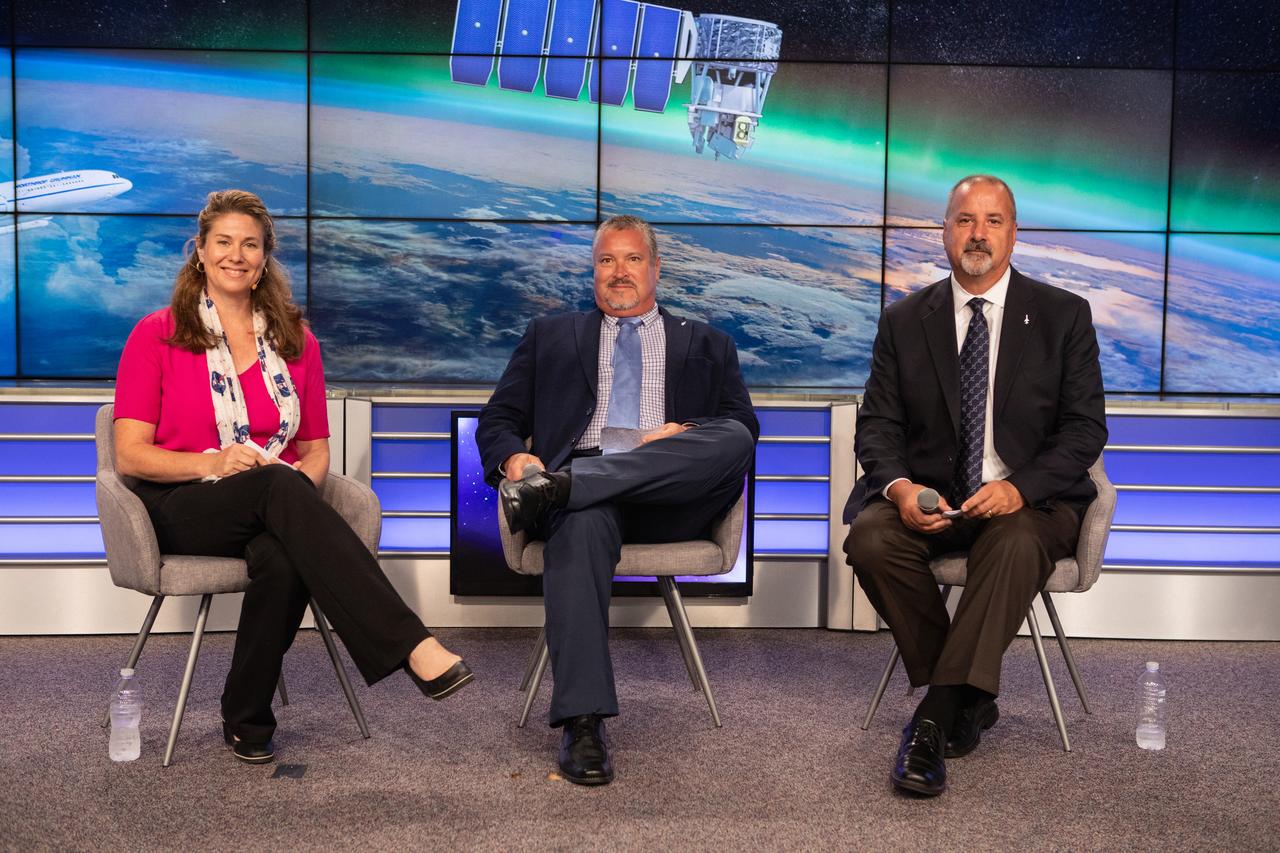
Karen Fox, with Goddard Space Flight Center, moderates a Solar Orbiter science press conference at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 7, 2020. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. The spacecraft was developed by Airbus Defence and Space. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Solar Orbiter will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Feb. 9, 2020, from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

Karen Fox, far left, with Goddard Space Flight Center, moderates a Solar Orbiter science press conference at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 7, 2020. Participants from left are Daniel Mueller, Solar Orbiter Project scientist, European Space Agency; Nicky Fox, director, NASA Heliophysics Division; Guenther Hasinger, director of science, European Space Agency; and Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator, NASA Science Mission Directorate. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. The spacecraft was developed by Airbus Defence and Space. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Solar Orbiter will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Feb. 9, 2020, from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

Karen Fox, far left, with Goddard Space Flight Center, moderates a Solar Orbiter science press conference at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 7, 2020. Participants from left are Daniel Mueller, Solar Orbiter Project scientist, European Space Agency; Nicky Fox, director, NASA Heliophysics Division; Guenther Hasinger, director of science, European Space Agency; and Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator, NASA Science Mission Directorate. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. The spacecraft was developed by Airbus Defence and Space. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Solar Orbiter will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Feb. 9, 2020, from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, on Friday, July 20, 2018, agency and mission leaders speak to members of the media during a prelaunch briefing for the Parker Solar Probe mission. From left are: Betsy Congdon, Thermal Protection System engineer with Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, Alex Young, solar scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Nicky Fox, project scientist with the Johns Hopkins University APL, and Karen Fox of NASA Communications. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel in Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Moderating the science briefing are Karen Fox, far left, Goddard Space Flight Center; and Dwaye Brown, far right, NASA Communications. Briefers are Andy Driesman, Parker Solar Probe project manager, Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory; Nicky Fox, Parker Solar Probe project scientist, Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory; and Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

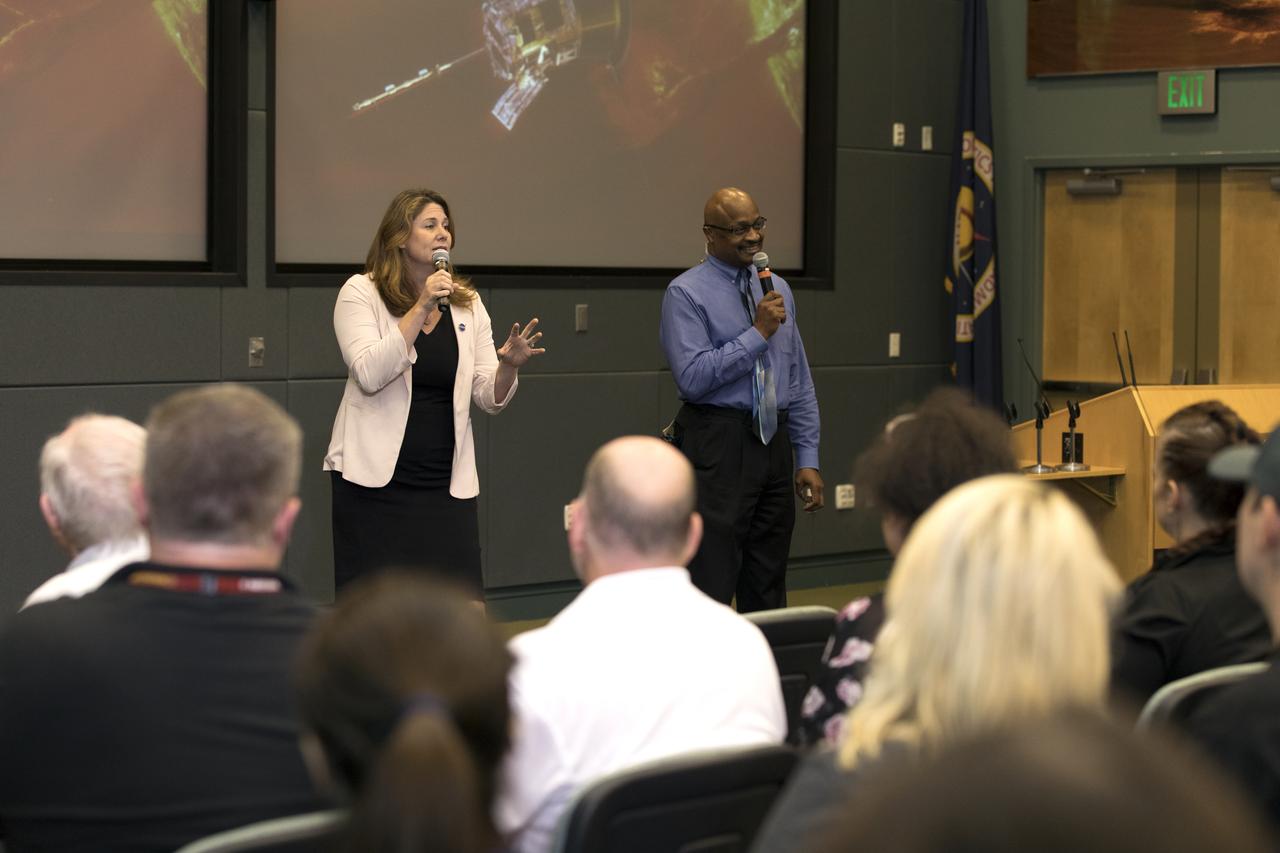
Karen Fox, NASA Communications, moderates a payload briefing for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Briefing moderators from left, are Karen Fox, Goddard Space Flight Center, and Dwayne Brown, NASA Communications. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Briefing moderators from left, are Karen Fox, Goddard Space Flight Center, and Dwayne Brown, NASA Communications. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
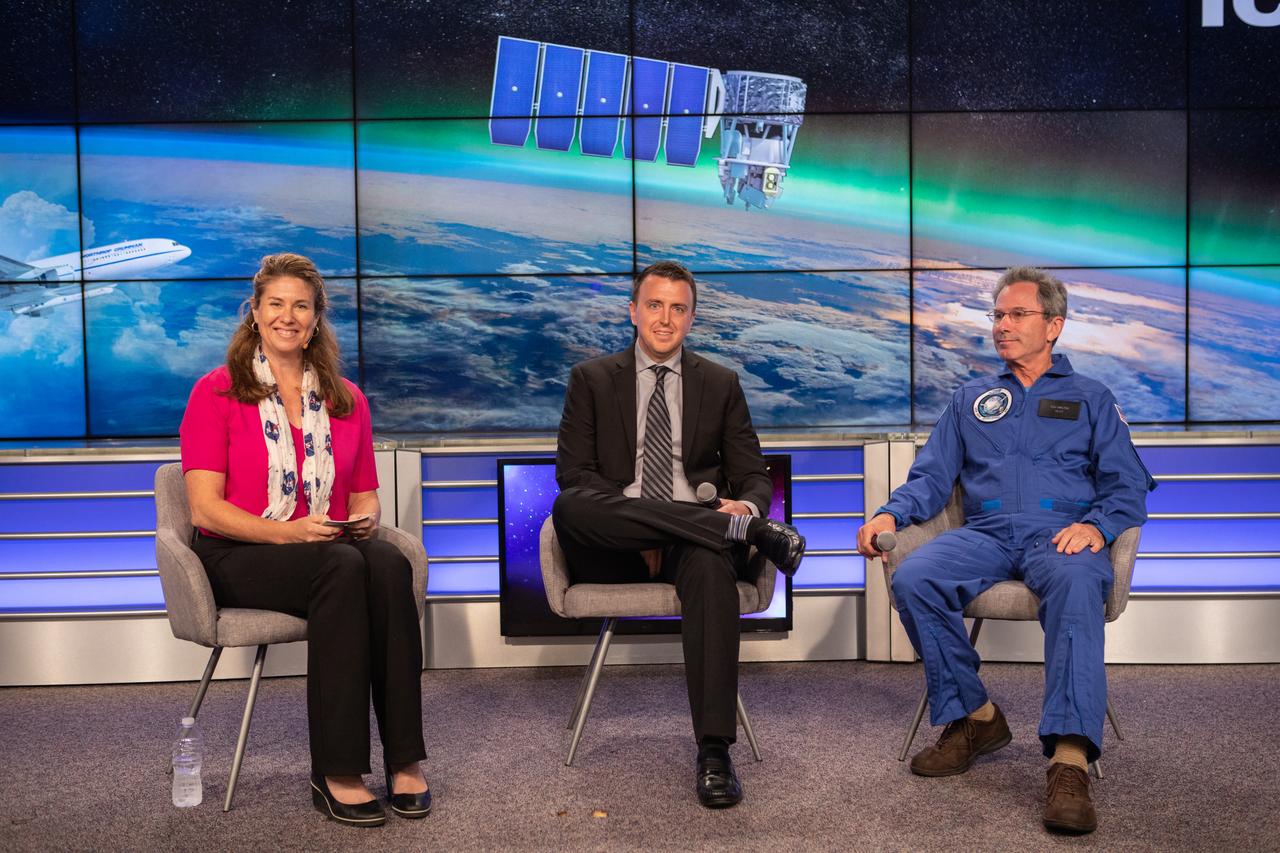

Launch and mission managers for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left to right are Karen Fox, NASA Communications; Will Ulrich, launch weather officer with the U.S. Air Force 45th Space Wing; and Don Walters, chief pilot of the L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
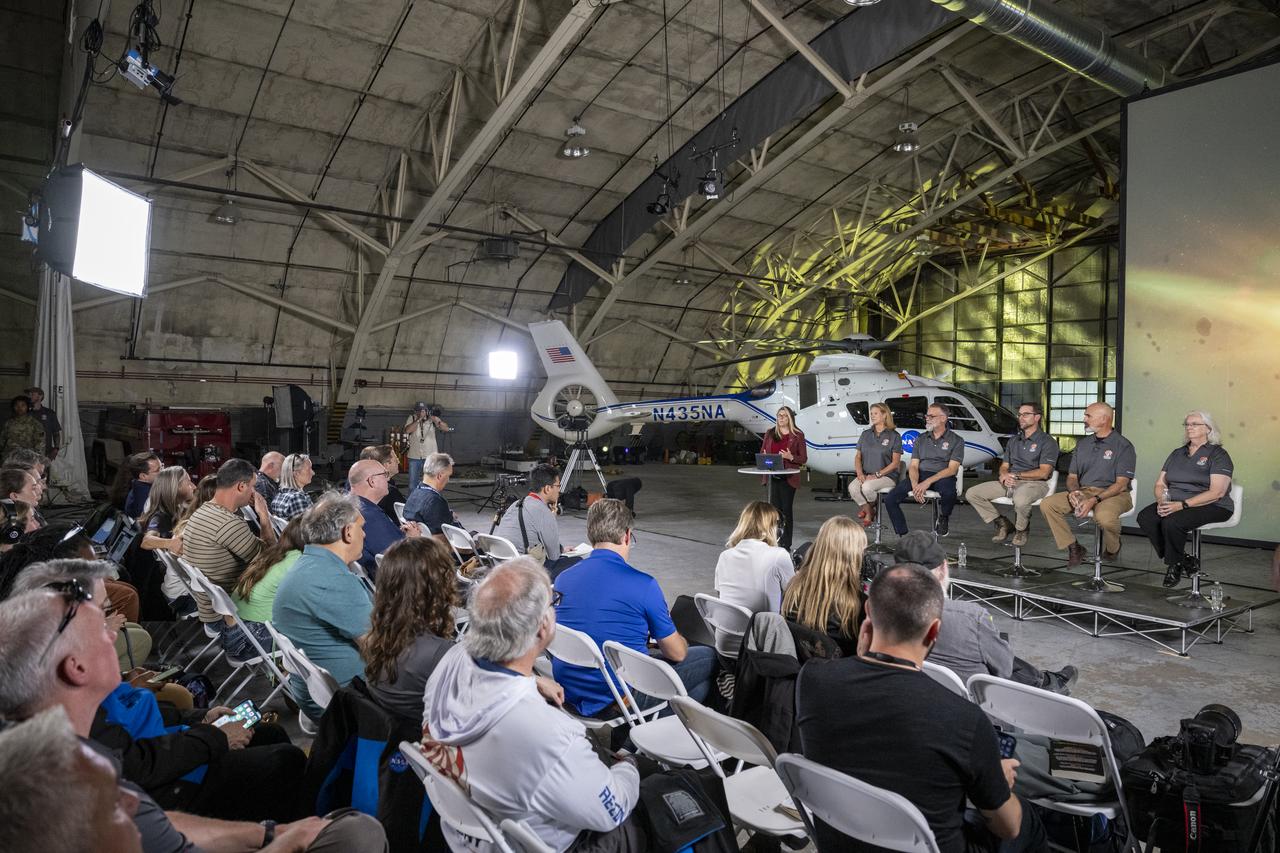

NASA Office of Communications Senior Science Communications Officer Karen Fox introduces, from left to right, NASA Planetary Science Division Director Lori Glaze, University of Arizona OSIRIS-REx Principal Investigator Dante Lauretta, NASA OSIRIS-REx Deputy Project Manager Mike Moreau, Lockheed Martin Deep Space Exploration Chief Engineer Tim Priser, and NASA Chief Scientist Eileen Stansbery during an OSIRIS-REx sample return press conference, Sunday, Sept. 24, 2023, shortly after the capsule landed at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

Launch and mission managers for NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on Oct. 8, 2019, in the News Center auditorium at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left to right are Karen Fox, NASA Communications; Omar Baez, launch director in NASA’s Launch Services Program; and Phil Joyce, vice president of space launch programs for Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems. ICON is targeted to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Oct. 9, 2019, aboard a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carried aloft by the company’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. The explorer will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.

A payload briefing for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft is held on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Participants from left are Karen Fox, moderator, NASA Communications; Brian Ramsey, deputy principal investigator, NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; Elisabetta Cavazzuti, ASI IXPE program manager, Italian Space Agency; Luca Baldini, Italian co-principal investigator, NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; and MacKenzie Ferrie, IXPE program manager, Ball Aerospace. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.

A payload briefing for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft is held on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Participants from left are Karen Fox, moderator, NASA Communications; Brian Ramsey, deputy principal investigator, NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; Elisabetta Cavazzuti, ASI IXPE program manager, Italian Space Agency; Luca Baldini, Italian co-principal investigator, NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; and MacKenzie Ferrie, IXPE program manager, Ball Aerospace. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Briefing moderators are Karen Fox, far left, Goddard Space Flight Center, and Dwayne Brown, far right, NASA Communications. Briefing participants are Omar Baez, launch director, NASA Kennedy Space Center; Scott Messer, program manager, NASA Programs, United Launch Alliance; and Kathy Rice, launch weather officer, 45th Weather Squadron, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
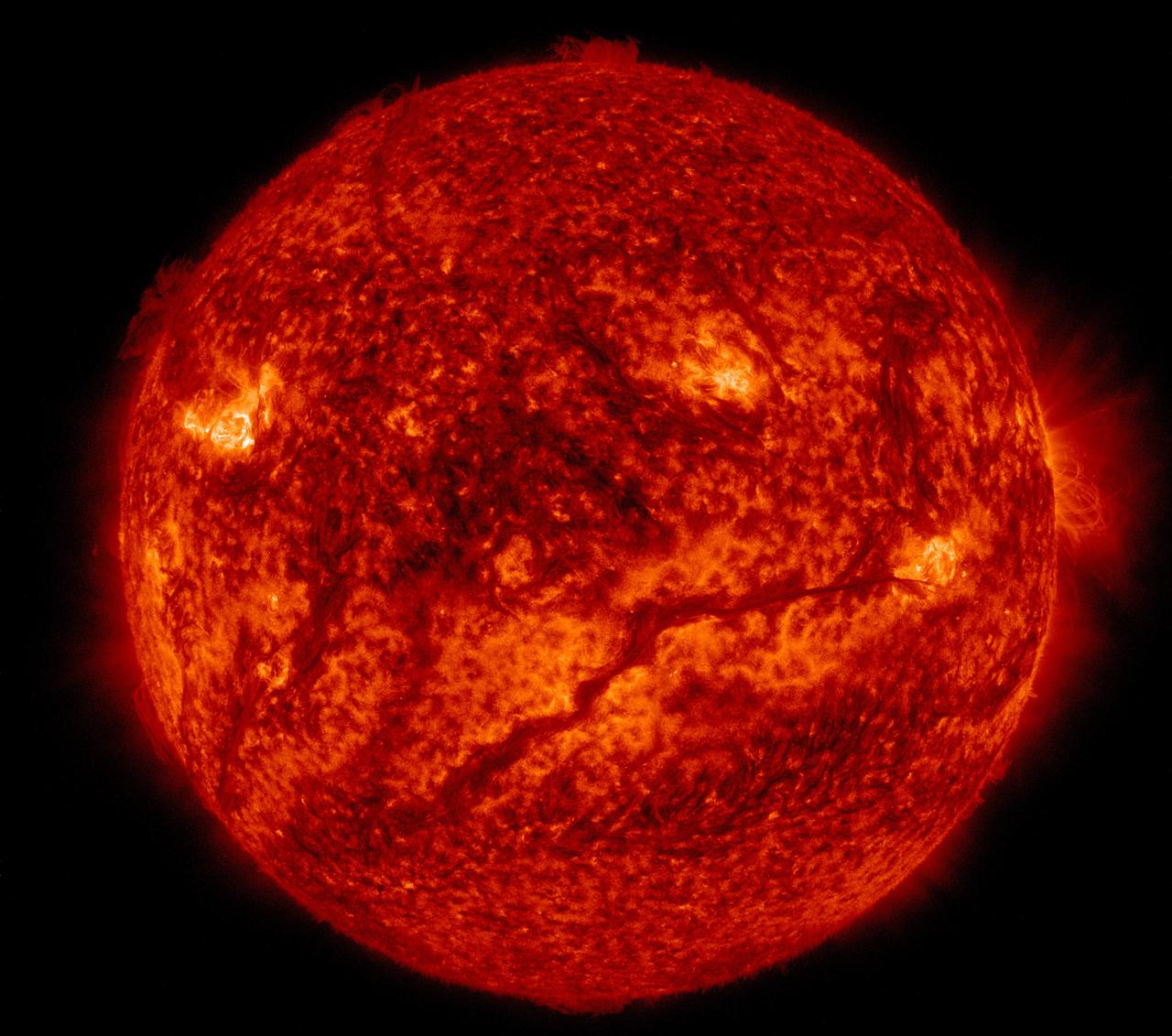
A dark line snaked across the lower half of the sun on Feb.10, 2015, as seen in this image from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. SDO shows colder material as dark and hotter material as light, so the line is, in fact, an enormous swatch of colder material hovering in the sun's atmosphere, the corona. Stretched out, that line – or solar filament as scientists call it – would be more than 533,000 miles long. That is longer than 67 Earths lined up in a row. Filaments can float sedately for days before disappearing. Sometimes they also erupt out into space, releasing solar material in a shower that either rains back down or escapes out into space, becoming a moving cloud known as a coronal mass ejection, or CME. SDO captured images of the filament in numerous wavelengths, each of which helps highlight material of different temperatures on the sun. By looking at such features in different wavelengths and temperatures, scientists learn more about what causes these structures, as well as what catalyzes their occasional eruptions. For more on SDO, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/sdo" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/sdo</a> Karen C. Fox NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland Credit: NASA/Goddard/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>