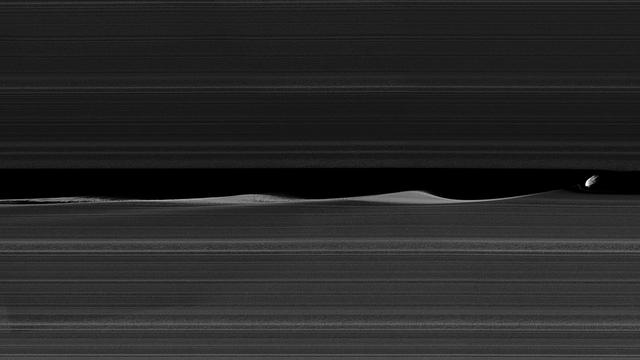
Daphnis, one of Saturn's ring-embedded moons, is featured in this view, kicking up waves as it orbits within the Keeler gap. The mosaic combines several images to show more waves in the gap edges. Daphnis is a small moon at 5 miles (8 kilometers) across, but its gravity is powerful enough to disrupt the tiny particles of the A ring that form the Keeler gap's edge. As the moon moves through the Keeler gap, wave-like features are created in both the horizontal and vertical plane. Images like this provide scientists with a close-up view of the complicated interactions between a moon and the rings, as well as the interactions between the ring particles themselves, in the wake of the moon's passage. Three wave crests of diminishing sizes trail Daphnis here. In each subsequent crest, the shape of the wave evolves, as the ring particles within the crests collide with one another. Close examination of Daphnis' immediate vicinity also reveals a faint, thin strand of ring material that almost appears to have been directly ripped out of the A ring by Daphnis. The images in this mosaic were taken in visible light, using the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera at a distance of approximately 17,000 miles (28,000 kilometers) from Daphnis and at a Sun-Daphnis-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 71 degrees. Image scale is 551 feet (168 meters) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA17212
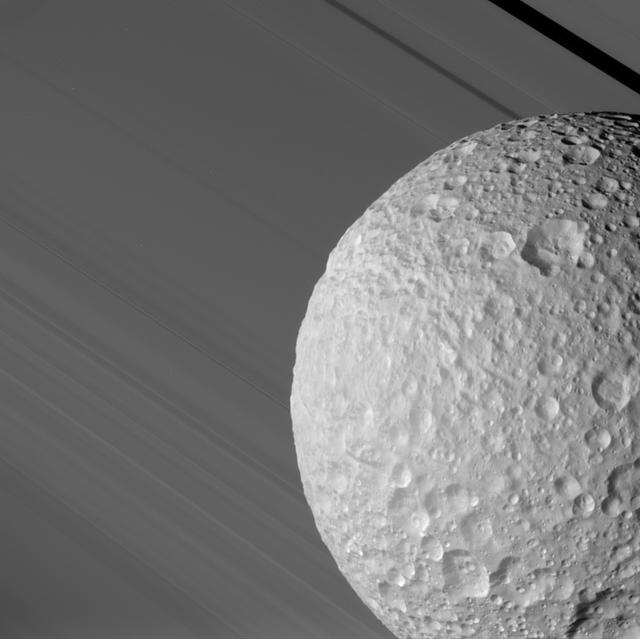

During its close flyby of Saturn's moon Mimas on Aug. 2, 2005, Cassini caught a glimpse of Mimas against the broad expanse of Saturn's rings. The Keeler Gap in the outer A ring, in which Cassini spied a never-before-seen small moon (see PIA06237), is at the upper right. The ancient, almost asteroid-like surface of Mimas is evident in its crater-upon-crater appearance. Even the material which has slumped down into the bottom of some of its craters bears the marks of later impacts. This image was taken through the clear filter of the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera at a distance of 68,000 kilometers (42,500 miles) from Mimas and very near closest approach. The smallest features seen on the moon are about 400 meters wide (440 yards); the Sun-Mimas-Cassini angle is 44 degrees. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06412
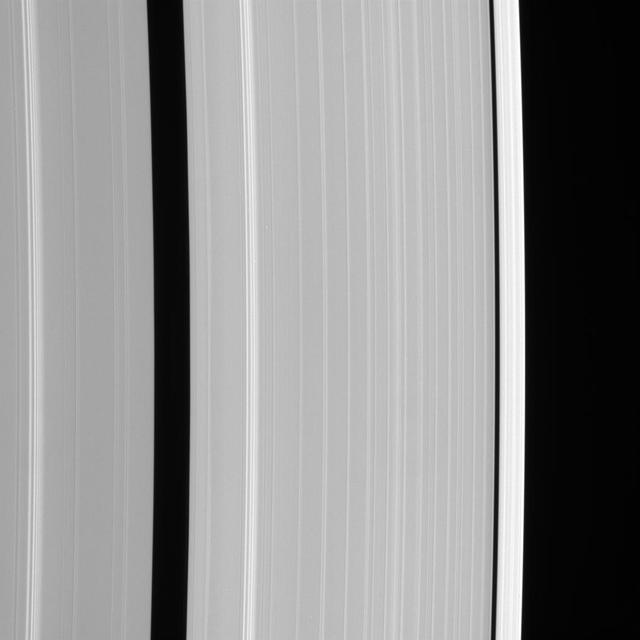

This Cassini spacecraft view shows details of Saturn outer A ring, including the Encke and Keeler gaps. The A ring brightens substantially outside the Keeler Gap
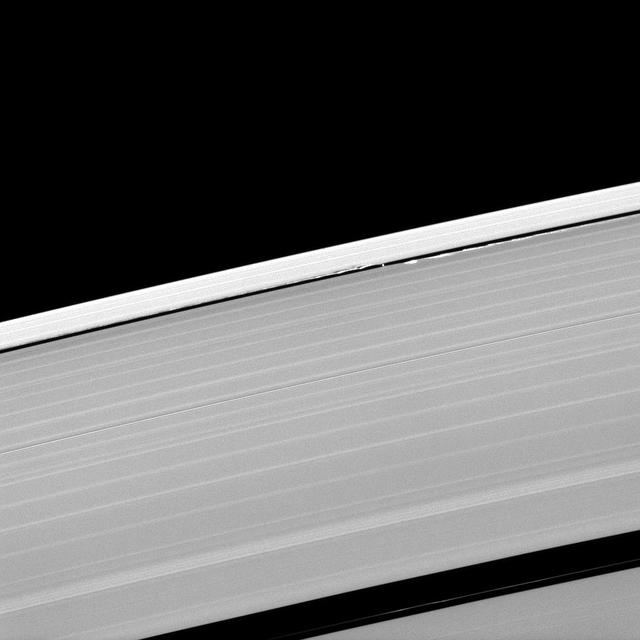

A scalloped look is created in the edges of the Keeler Gap in Saturn outer A ring as the moon Daphnis orbits in the gap.

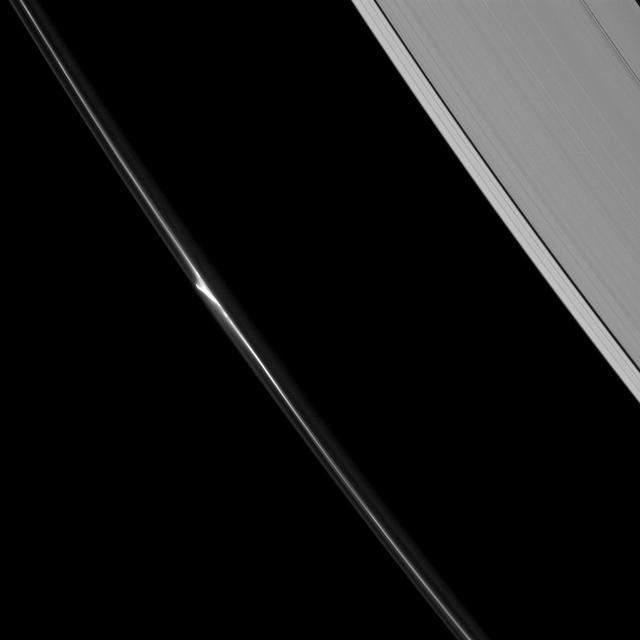
Daphnis drifts through the Keeler gap, at the center of its entourage of waves

The tiny wavemaker moon Daphnis is dwarfed by the very waves it creates on the edge of the Keeler gap as seen by NASA Cassini spacecraft.

Daphnis cruises through the Keeler Gap, raising edge waves in the ring material as it passes
The presence of the tiny ring moon Daphnis is betrayed by the edge waves it creates in the Keeler gap

This image, taken by NASA Cassini spacecraft, shows A beautiful mini-jet appearing in the dynamic F ring of Saturn. Saturn A ring including the Keeler gap and just a hint of the Encke gap at the upper-right also appears.
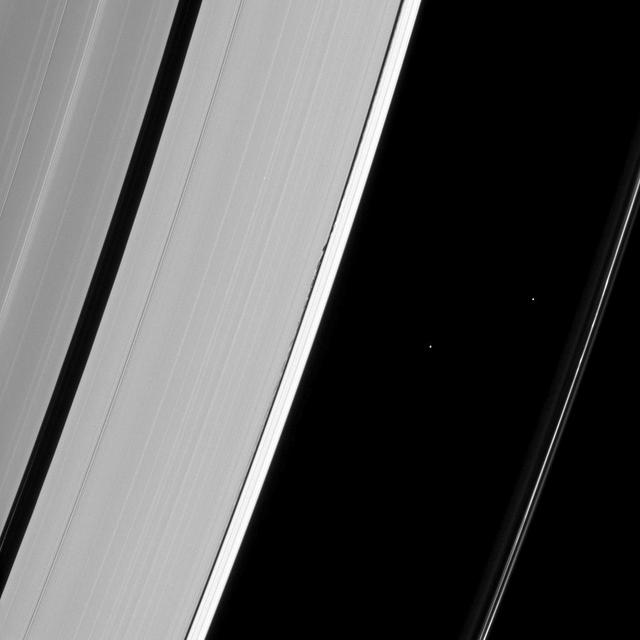
Saturn moons Daphnis and Pan demonstrate their effects on the planet rings in this view from NASA Cassini spacecraft. Daphnis, at left, orbits in the Keeler Gap of the A ring; Pan at right, orbits in the Encke Gap of the A ring.
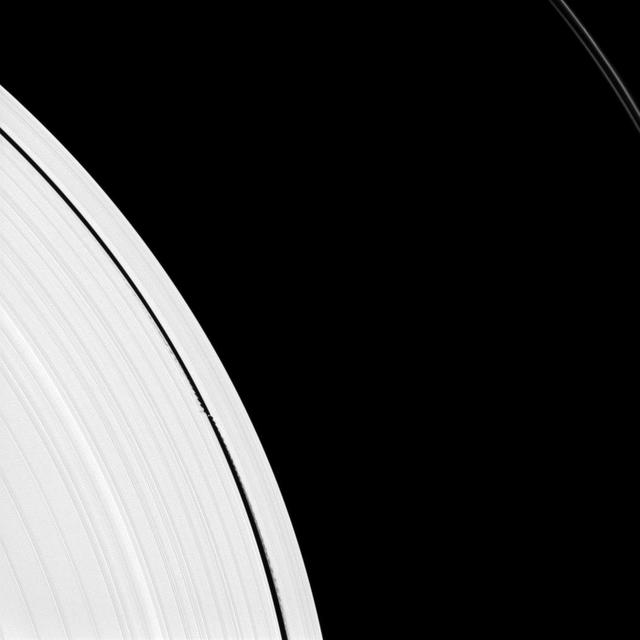

Saturn small moon Daphnis is caught in the act of raising waves on the edges of the Keeler gap, which is the thin dark band in the left half of the image. Waves like these allow scientists to locate small moons in gaps and measure their masses.
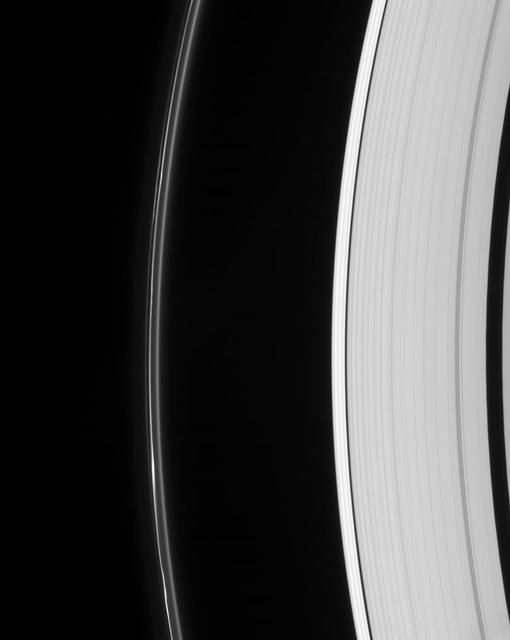

Saturn odd but ever-intriguing F ring displays multiple lanes and several bright clumps. The Keeler and Encke gaps are visible in the outer A ring, at right
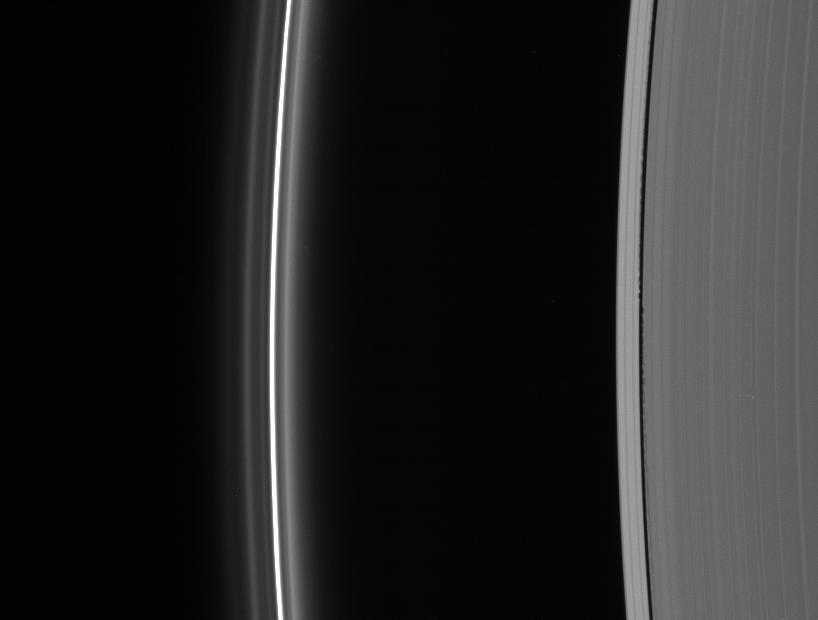
Edge waves in the Keeler Gap betray the presence of the embedded moon Daphnis. At left lies the brilliant F ring with its flanking strands
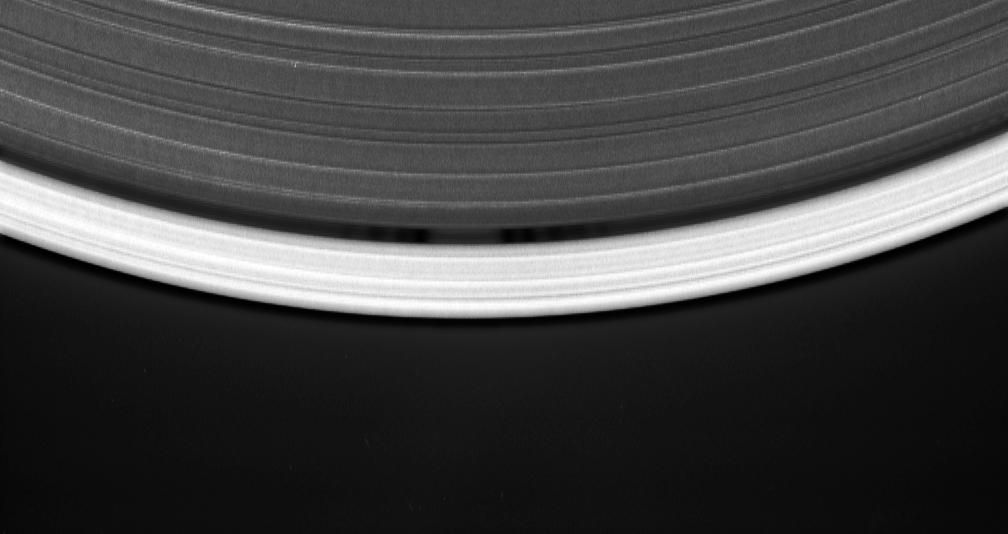

Cassini's celestial sleuthing has paid off with this time-lapse series of images which confirmed earlier suspicions that a small moon was orbiting within the narrow Keeler gap of Saturn's rings. The movie sequence, which consists of 12 images taken over 16 minutes while Cassini gazed down upon the sunlit side of the A ring, shows a tiny moon orbiting in the center of the Keeler gap, churning up waves in the gap edges as it goes. The pattern of waves travels with the moon in its orbit. The Keeler gap is located about 250 kilometers (155 miles) inside the outer edge of the A ring, which is also the outer edge of the bright main rings. The new object is about 7 kilometers across (4 miles) and reflects about 50 percent of the sunlight that falls upon it -- a brightness that is typical of particles in the nearby rings. The new body has been provisionally named S/2005 S1. Imaging scientists predicted the moon's presence and its orbital distance from Saturn after July 2004, when they saw a set of peculiar spiky and wispy features in the Keeler gap's outer edge. The similarities of the Keeler gap features to those noted in Saturn's F ring and the Encke gap led the scientists to conclude that a small body, a few kilometers across, was lurking in the center of the Keeler gap, awaiting discovery. Also included here is a view of the same scene created by combining six individual, unmagnified frames used in the movie sequence. This digital composite view improves the overall resolution of the scene compared to that available in any of the single images. The images in this movie sequence were obtained with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on May 1, 2005, at a distance of approximately 1.1 million kilometers (708,000 miles) from Saturn. Resolution in the original image was 8 kilometers (5 miles) per pixel. The images in the movie sequence have been magnified in (the vertical direction only) by a factor of two to aid visibility of features caused within the gap by the moonlet. An animation is available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06238
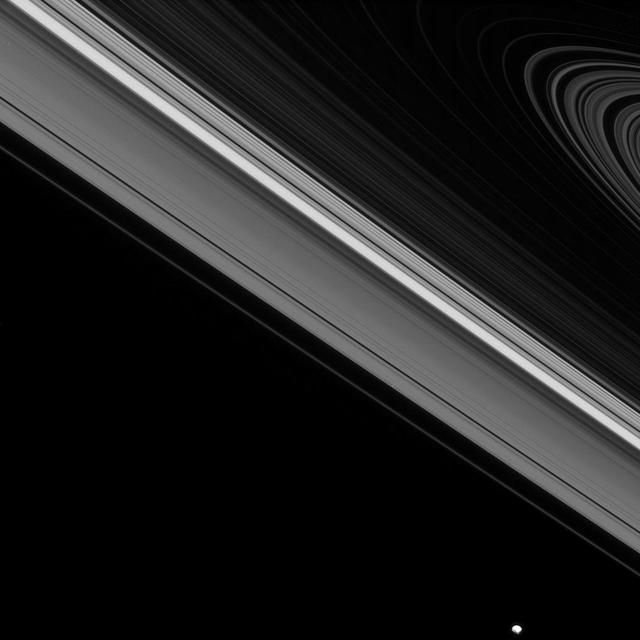

While the moon Epimetheus passes by, beyond the edge of Saturn main rings, the tiny moon Daphnis carries on its orbit within the Keeler gap of the A ring in this image from NASA Cassini spacecraft.
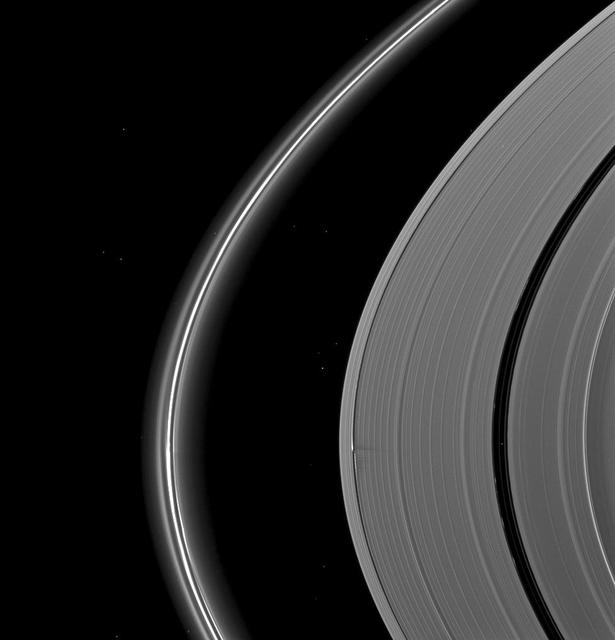
NASA Cassini spacecraft catches Saturn moon Daphnis making waves and casting shadows from the narrow Keeler Gap of the planet A ring in this view taken around the time of Saturn August 2009 equinox.
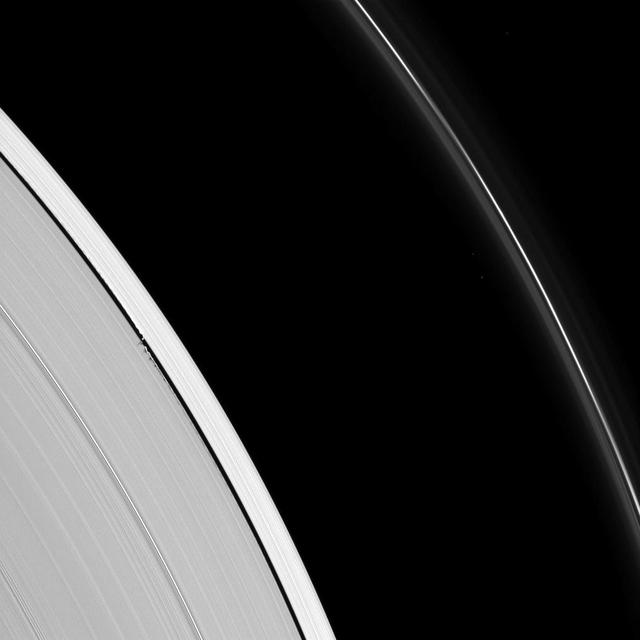

Tiny Daphnis appears as a bright dot in the Keeler Gap next to shadows cast by the moon and the edge waves it has created in the A ring in this image taken by NASA Cassini spacecraft before Saturn August 2009 equinox.
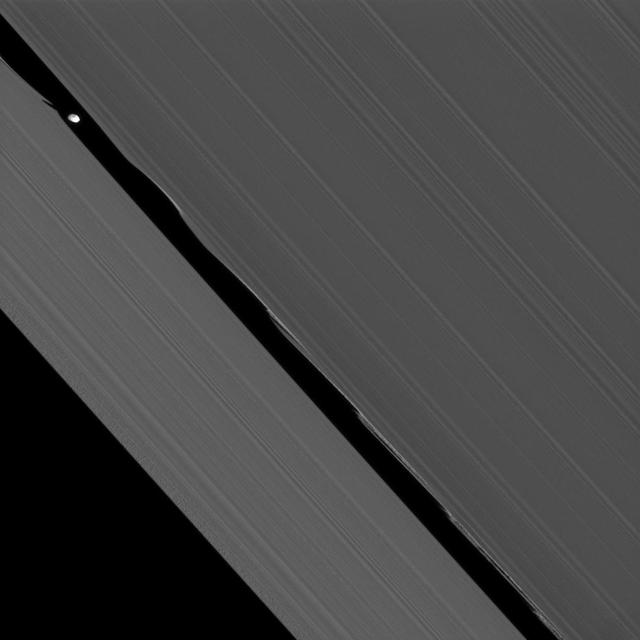

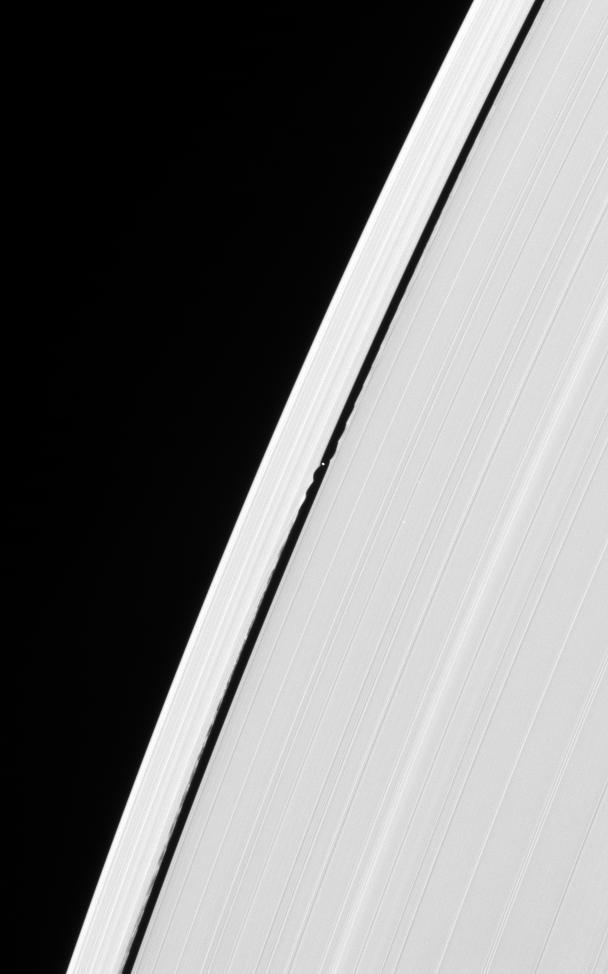
NASA Cassini spacecraft captures here one of its closest views of Saturn ring-embedded moon Daphnis. Seen at the upper left of this image, Daphnis appears in the Keeler Gap near the edge waves it has created in the A ring.
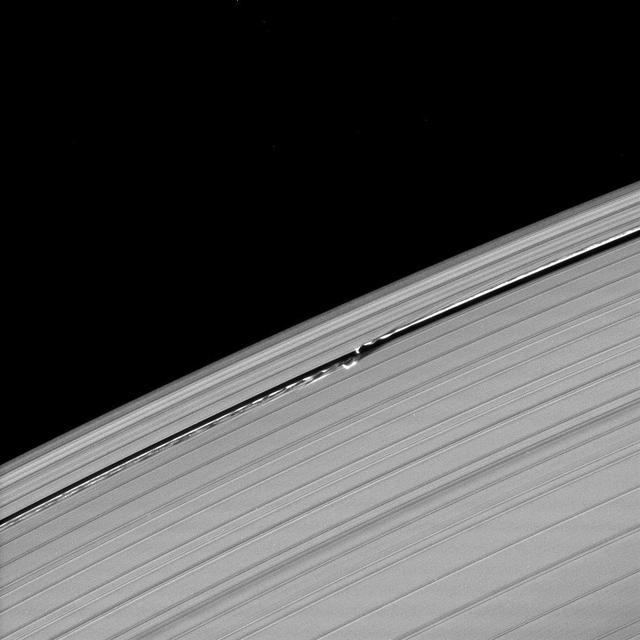

Waves in the edges of the Keeler gap in Saturn A ring, created by the embedded moon Daphnis, show considerable complexity in this image taken as Saturn approached its August 2009 equinox.
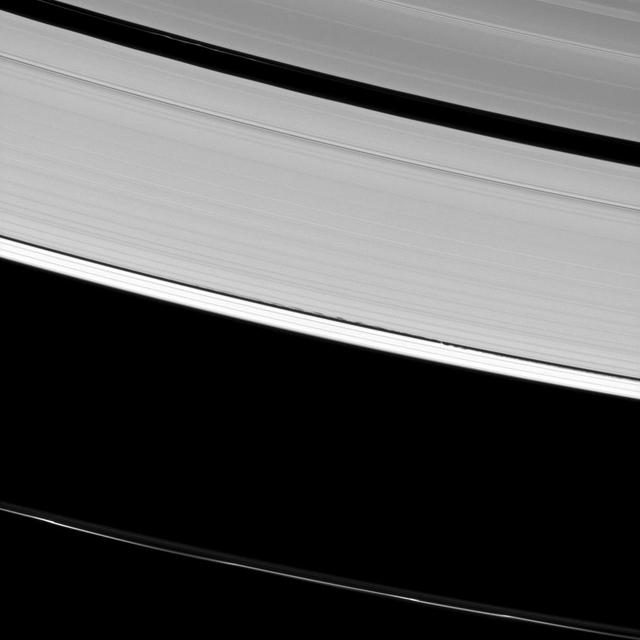

Saturn A ring is decorated with several kinds of waves. NASA Cassini spacecraft has captured a host of density waves, a bending wave, and the edge waves on the edge of the Keeler gap caused by the small moon Daphnis.
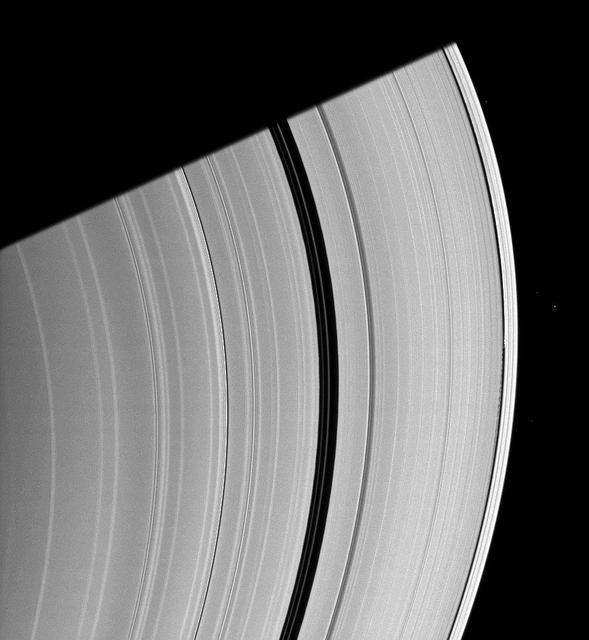

Saturn moon Daphnis, appearing as a tiny speck in the Keeler Gap of the A ring on the far right of this NASA Cassini spacecraft image, is almost lost among the moon attendant edge waves.
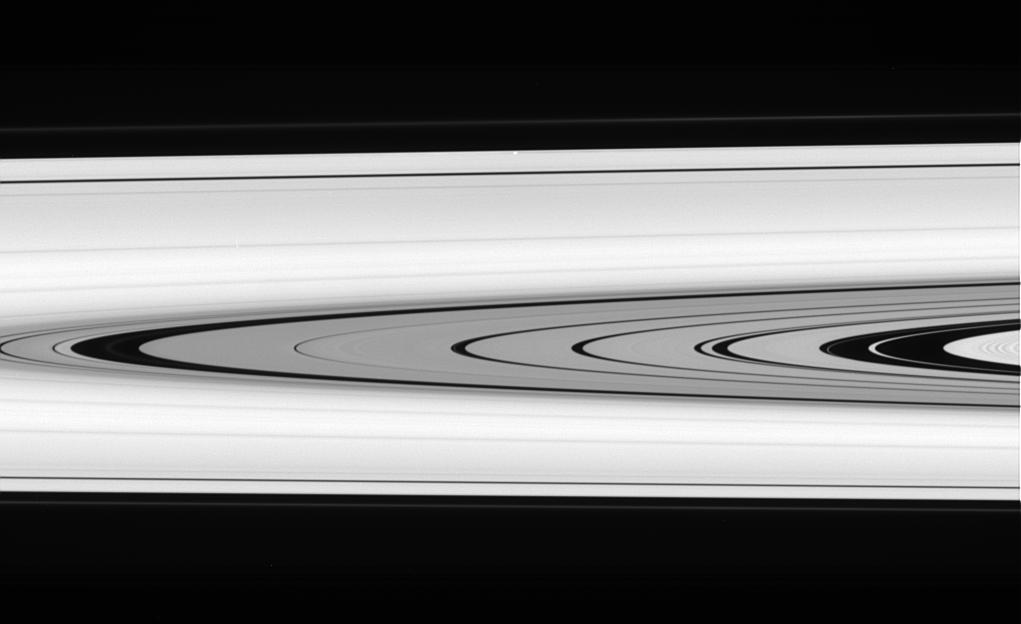

This splendid view offers a detailed look at the faint rings within the Cassini Division as well as a rare glimpse of the Keeler gap moon, Daphnis. The small, ring embedded moon is a bright unresolved speck above center, near outer edge of A ring
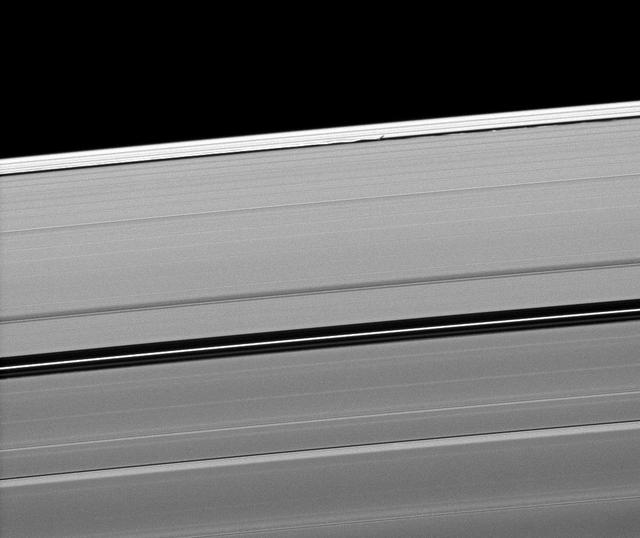

Saturn moon Daphnis casts a short shadow on the A ring in this image taken by NASA Cassini spacecraftabout six months after the planet August 2009 equinox. Daphnis appears as a tiny bright dot in the Keeler Gap of the A ring near the center top.
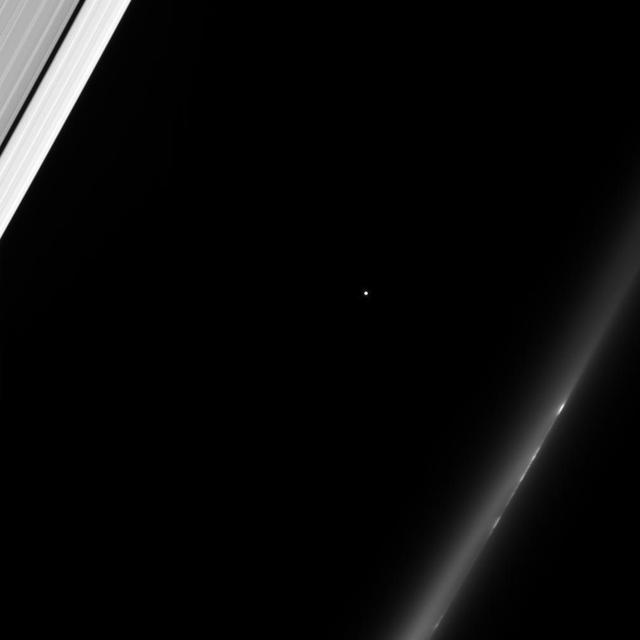

The Cassini spacecraft gazes toward a distant star as Saturn rings slip past in the foreground. At upper left is the outer A ring, with its dark Keeler Gap. At lower right, a train of bright clumps shuttles past in the wispy F ring
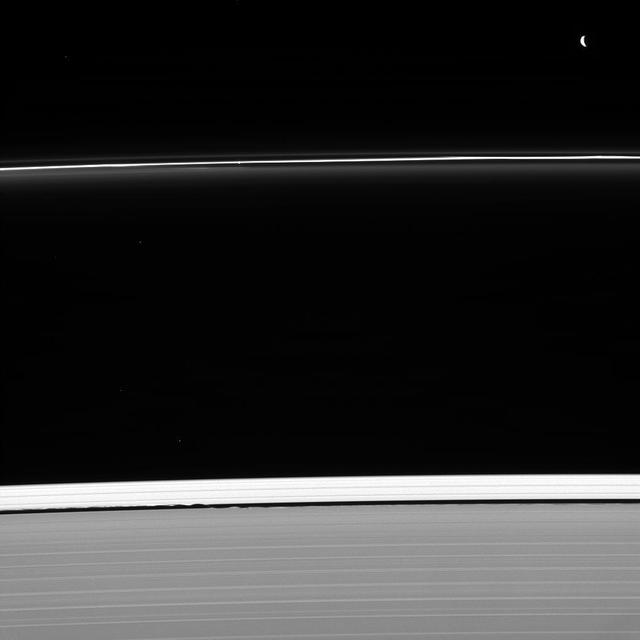

Two masters of their craft are caught at work shaping Saturn's rings. Pandora (upper right) sculpts the F ring, as does nearby Prometheus (not seen in this image). Meanwhile, Daphnis is busy holding open the Keeler gap (bottom center), its presence revealed here by the waves it raises on the gap's edge. The faint moon is located where the inner and outer waves appear to meet. Also captured in this image, shining through the F ring above the image center, is a single star. Although gravity is by its very nature an attractive force, moons can interact with ring particles in such a way that they effectively push ring particles away from themselves. Ring particles experience tiny gravitational "kicks" from these moons and subsequently collide with other ring particles, losing orbital momentum. The net effect is for moons like Pandora (50 miles or 81 kilometers across) and Daphnis (5 miles or 8 kilometers across) to push ring edges away from themselves. The Keeler gap is the result of just such an interaction. This view looks toward the unilluminated side of the rings from about 50 degrees below the ringplane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on Jan. 30, 2013. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18298
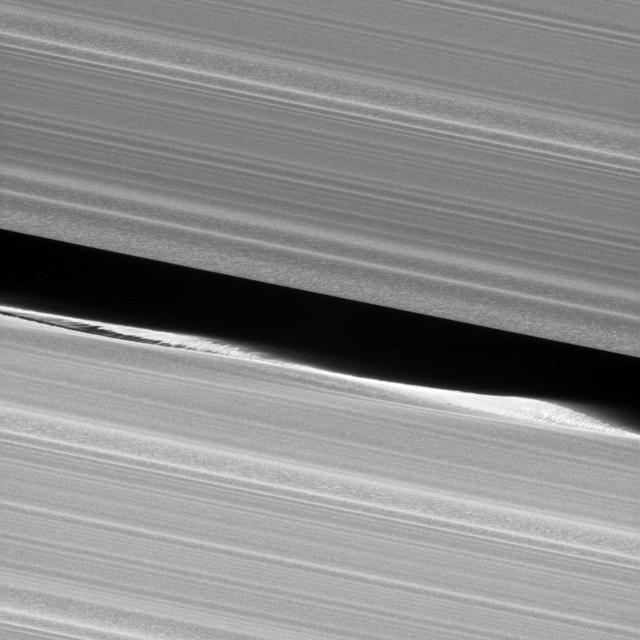

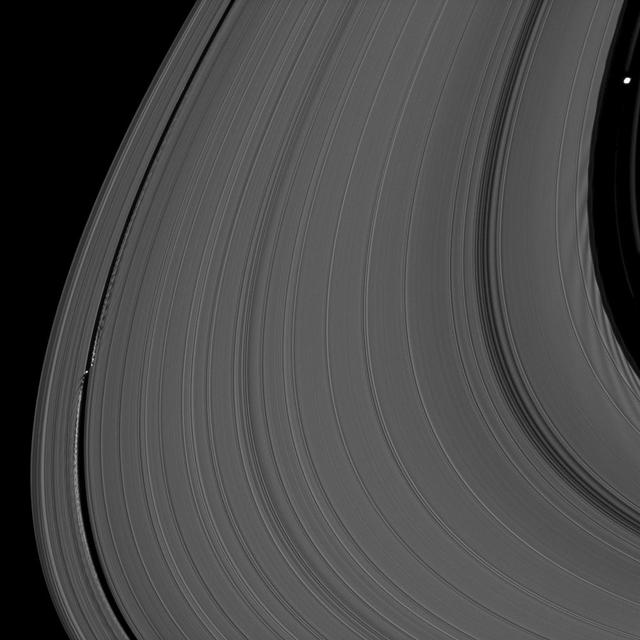
Before NASA's Cassini entered its Grand Finale orbits, it acquired unprecedented views of the outer edges of the main ring system. For example, this close-up view of the Keeler Gap, which is near the outer edge of Saturn's main rings, shows in great detail just how much the moon Daphnis affects the edges of the gap. Daphnis creates waves in the edges of the gap through its gravitational influence. Some clumping of ring particles can be seen in the perturbed edge, similar to what was seen on the edges of the Encke Gap back when Cassini arrived at Saturn in 2004. This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 3 degrees above the ring plane. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 18,000 miles (30,000 kilometers) from Daphnis and at a Sun-Daphnis-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 69 degrees. Image scale is 581 feet (177 meters) per pixel. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on Jan. 16, 2017. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21329
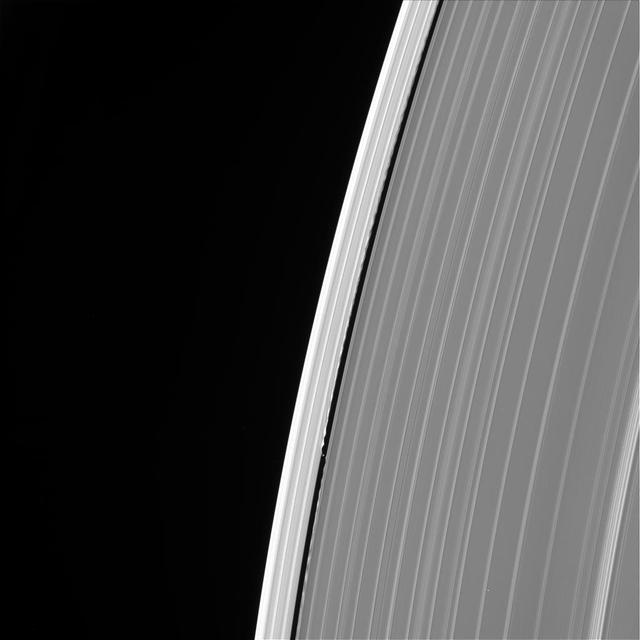
This image of Saturn's outer A ring features the small moon Daphnis and the waves it raises in the edges of the Keeler Gap. The image was taken by NASA's Cassini spacecraft on Sept. 13, 2017. It is among the last images Cassini sent back to Earth. The view was taken in visible light using the Cassini spacecraft wide-angle camera at a distance of 486,000 miles (782,000 kilometers) from Saturn. Image scale is 2.7 miles (4.3 kilometers). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21893
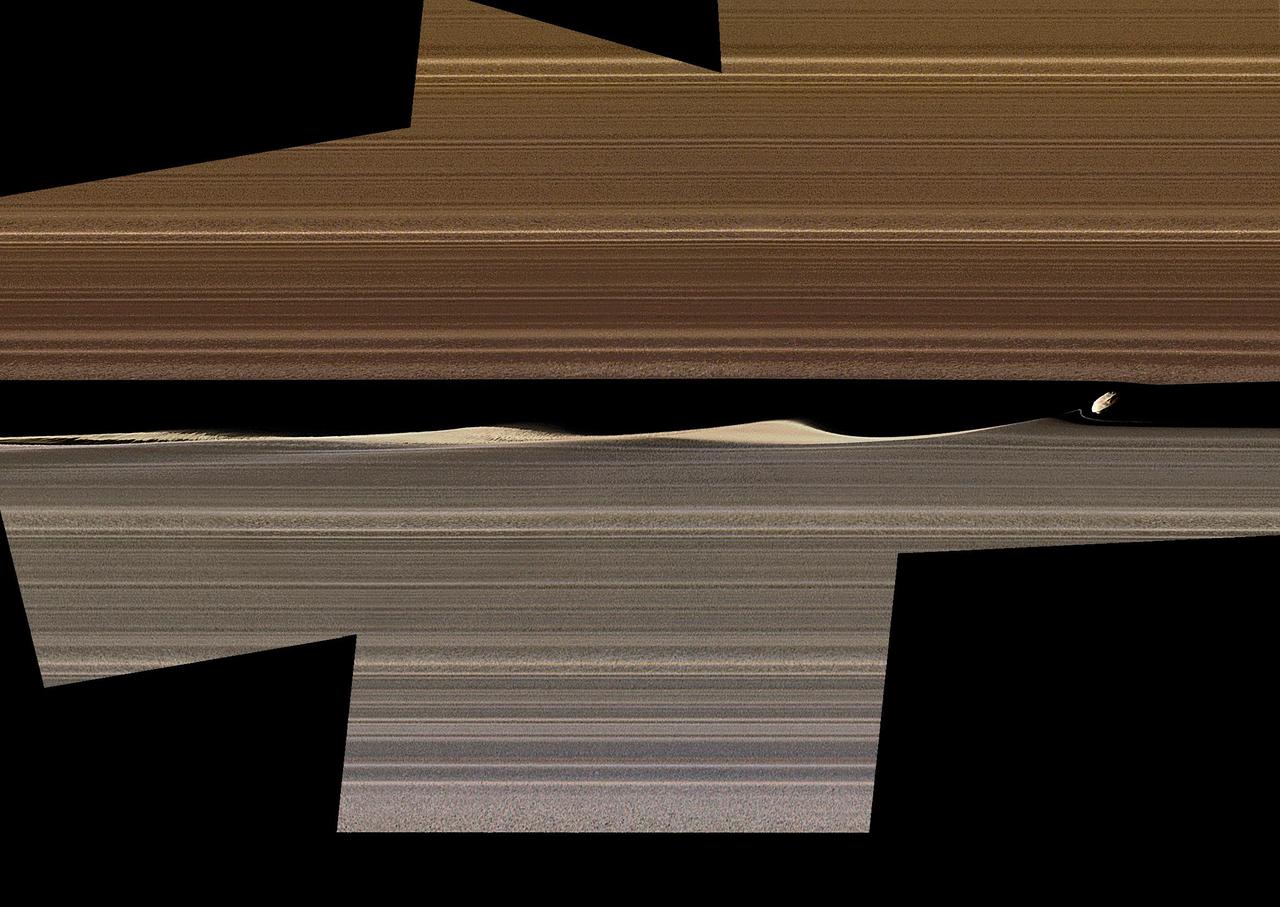

This enhanced-color image mosaic shows Daphnis, one of the moons embedded in Saturn's rings, in the Keeler gap on the sunlit side of the rings. Daphnis is seen kicking up three waves in the gap's outer edge. Three wave crests of diminishing sizes trail the moon. In each successive crest, the shape of the wave changes as the ring particles within the crest interact and collide with each other. A thin strand of ring material to the lower left of Daphnis is newly visible in this image, and there are intricate features that also hadn't been previously observed in the third wave crest downstream (see Figure 1). Cassini was at a very shallow angle above the rings (only about 15 degrees) when this image was taken. The resulting foreshortening makes it difficult to tell the difference in this image between features representing vertical structure and those representing radial, or outward from Saturn, structure within the ring plane. Nonetheless, Cassini imaging scientists have determined that the waves in the gap are largely vertical; compare this to the shadows that they were seen to cast during equinox (see PIA11547, PIA11653, PIA11655 and PIA11656). The thin strand of material is also probably vertical. Daphnis itself is actually five times smaller than the width of the gap, but it looks bigger here because of the foreshortening. The color in this image comes from using Imaging Science Subsystem images obtained by applying different filters to "paint" color onto the black-and-white version of this view previously released as PIA17212. The color of the ring region outward of the Keeler Gap (the "trans-Keeler region," in the lower portion of this image) is noticeably different from the color inward from the gap (upper portion of this image). In visible light, this color difference sharply coincides with the gap, while near-infrared Visible and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIMS) images show some bleeding of the trans-Keeler region into the region inward from the gap. The reasons for the sharp change in color are mysterious, but they probably have more to do with a change in particle sizes and other properties than with a change in composition. The images in this mosaic were taken in visible light, using the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera at a distance of approximately 17,000 miles (28,000 kilometers) from Daphnis and at a Sun-Daphnis-spacecraft angle, or phase angle, of 71 degrees (for the color images, 58 degrees). Image scale is 550 feet (170 meters) per pixel. The image was produced by Tilmann Denk at Freie Universität in Berlin. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23167
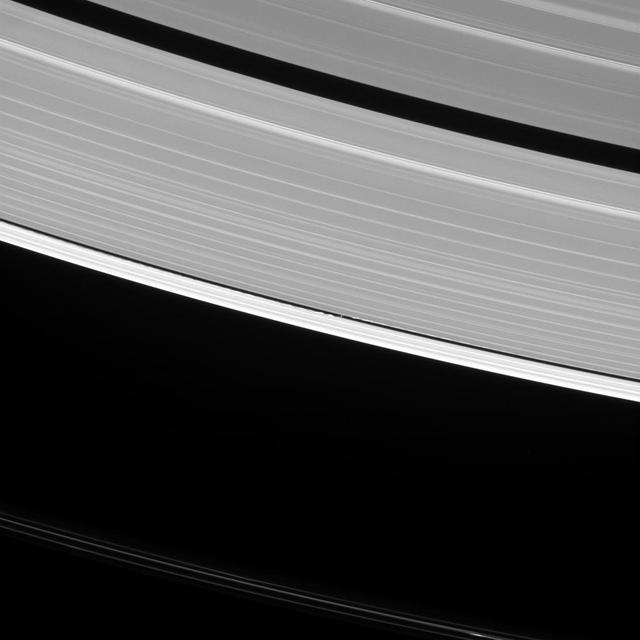

Saturn's moon Daphnis raises waves wherever it goes. In fact, such waves are one way that scientists search for undiscovered moons in the ring gaps. But they can tell researchers a lot of other things, as well. The waves that Daphnis (5 miles or 8 kilometers across) raises on the edges of the Keeler Gap can also be used to deduce the moon's mass and even some of its orbital behavior. Since the moon moves in and out of the ring-plane, and closer to and farther from the rings' edges as it orbits, the waves it makes change over time. Cassini has been observing these changes during its extended study of the Saturn system to help understand this interaction. This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 35 degrees above the ring plane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on Oct. 10, 2016. Daphnis has been brightened by a factor of two in this image to increase its visibility. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 810,000 miles (1.3 million kilometers) from Daphnis and at a Sun-Daphnis-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 96 degrees. Image scale is 5 miles (8 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20511
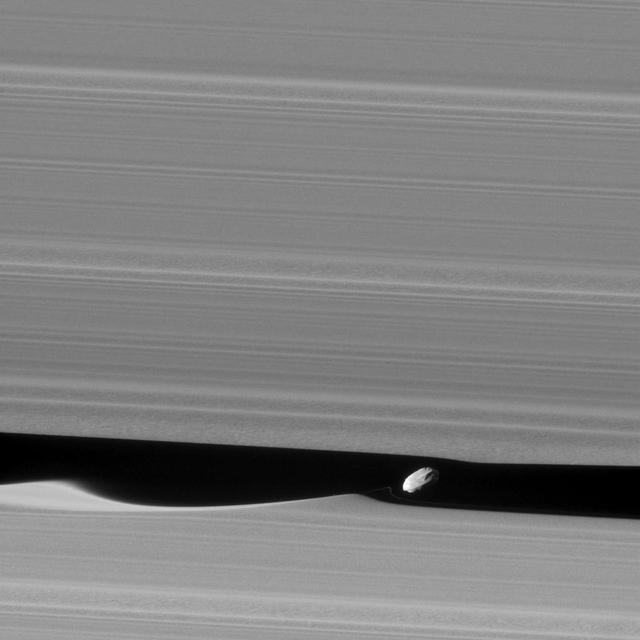

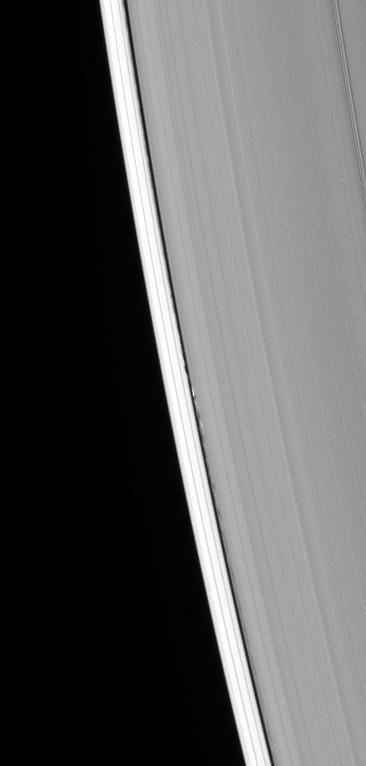
The wavemaker moon, Daphnis, is featured in this view, taken as NASA's Cassini spacecraft made one of its ring-grazing passes over the outer edges of Saturn's rings on Jan. 16, 2017. This is the closest view of the small moon obtained yet. Daphnis (5 miles or 8 kilometers across) orbits within the 42-kilometer (26-mile) wide Keeler Gap. Cassini's viewing angle causes the gap to appear narrower than it actually is, due to foreshortening. The little moon's gravity raises waves in the edges of the gap in both the horizontal and vertical directions. Cassini was able to observe the vertical structures in 2009, around the time of Saturn's equinox (see PIA11654). Like a couple of Saturn's other small ring moons, Atlas and Pan, Daphnis appears to have a narrow ridge around its equator and a fairly smooth mantle of material on its surface -- likely an accumulation of fine particles from the rings. A few craters are obvious at this resolution. An additional ridge can be seen further north that runs parallel to the equatorial band. Fine details in the rings are also on display in this image. In particular, a grainy texture is seen in several wide lanes which hints at structures where particles are clumping together. In comparison to the otherwise sharp edges of the Keeler Gap, the wave peak in the gap edge at left has a softened appearance. This is possibly due to the movement of fine ring particles being spread out into the gap following Daphnis' last close approach to that edge on a previous orbit. A faint, narrow tendril of ring material follows just behind Daphnis (to its left). This may have resulted from a moment when Daphnis drew a packet of material out of the ring, and now that packet is spreading itself out. The image was taken in visible (green) light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 17,000 miles (28,000 kilometers) from Daphnis and at a Sun-Daphnis-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 71 degrees. Image scale is 551 feet (168 meters) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21056
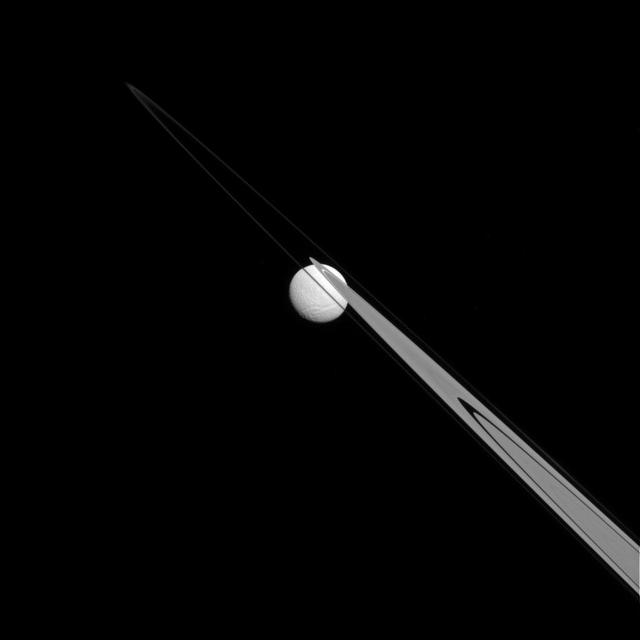

Like a drop of dew hanging on a leaf, Tethys appears to be stuck to the A and F rings from this perspective. Tethys (660 miles, or 1,062 kilometers across), like the ring particles, is composed primarily of ice. The gap in the A ring through which Tethys is visible is the Keeler gap, which is kept clear by the small moon Daphnis (not visible here). This view looks toward the Saturn-facing hemisphere of Tethys. North on Tethys is up and rotated 43 degrees to the right. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on July 14, 2014. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 1.1 million miles (1.8 million kilometers) from Tethys and at a Sun-Tethys-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 22 degrees. Image scale is 7 miles (11 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18284
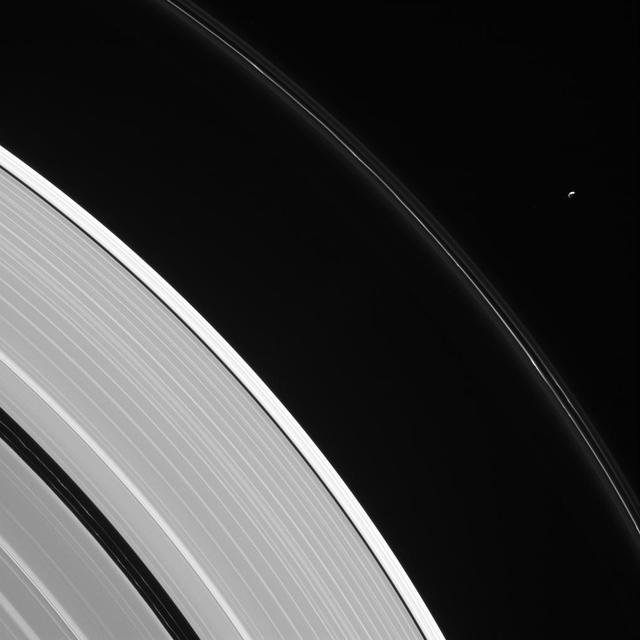

Pandora is seen here, in isolation beside Saturn's kinked and constantly changing F ring. Pandora (near upper right) is 50 miles (81 kilometers) wide. The moon has an elongated, potato-like shape (see PIA07632). Two faint ringlets are visible within the Encke Gap, near lower left. The gap is about 202 miles (325 kilometers) wide. The much narrower Keeler Gap, which lies outside the Encke Gap, is maintained by the diminutive moon Daphnis (not seen here). This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 23 degrees above the ring plane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on Aug. 12, 2016. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 907,000 miles (1.46 million kilometers) from Saturn and at a Sun-Saturn-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 113 degrees. Image scale is 6 miles (9 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20504
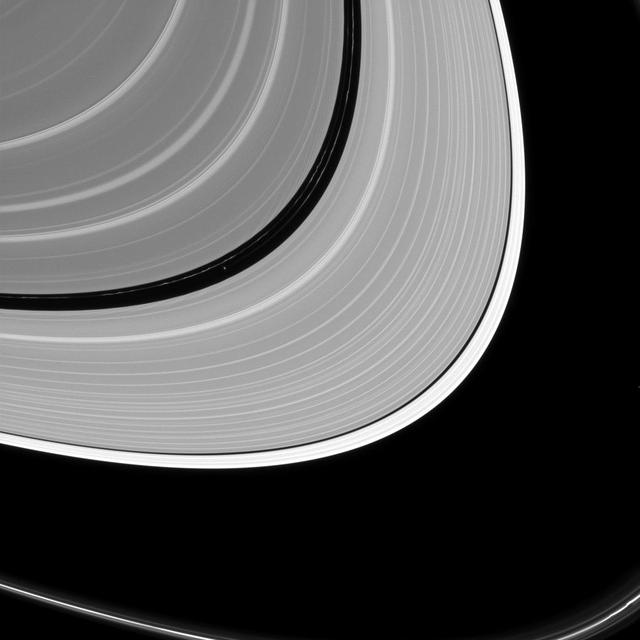

Pan may be small as satellites go, but like many of Saturn's ring moons, it has a has a very visible effect on the rings. Pan (17 miles or 28 kilometers across, left of center) holds open the Encke gap and shapes the ever-changing ringlets within the gap (some of which can be seen here). In addition to raising waves in the A and B rings, other moons help shape the F ring, the outer edge of the A ring and open the Keeler gap. This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 8 degrees above the ring plane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on July 2, 2016. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 840,000 miles (1.4 million kilometers) from Saturn and at a sun-Saturn-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 128 degrees. Image scale is 5 miles (8 kilometers) per pixel. Pan has been brightened by a factor of two to enhance its visibility. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20499
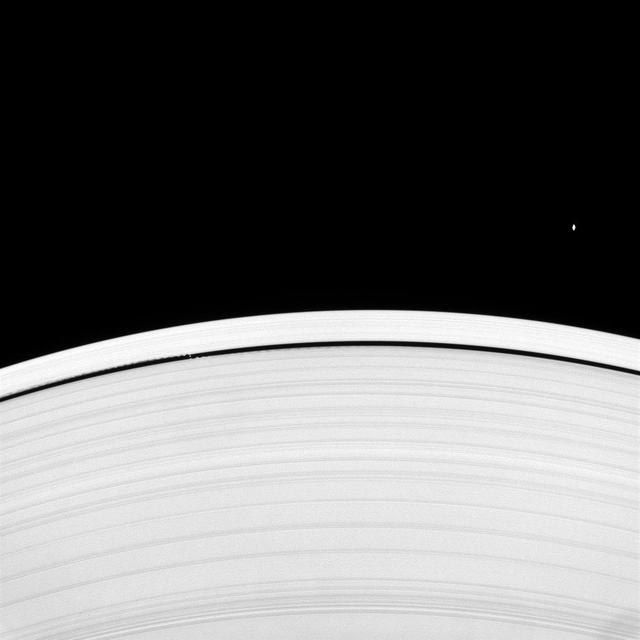

Looking upward from beneath the ringplane, the Cassini spacecraft spies Saturn's "wave maker" and "flying saucer" moons. Daphnis (8 kilometers, or 5 miles across at its widest point) and its gravitationally induced edge waves are seen at left within the Keeler Gap. The equatorial bulge on Atlas (30 kilometers, or 19 miles across at its widest point) is clearly visible here. See PIA06237 and PIA08405 for additional images and information about these two moons. This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 16 degrees below the ringplane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on April 22, 2008. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 898,000 kilometers (558,000 miles) from Saturn. Image scale is about 5 kilometers (3 miles) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA09907
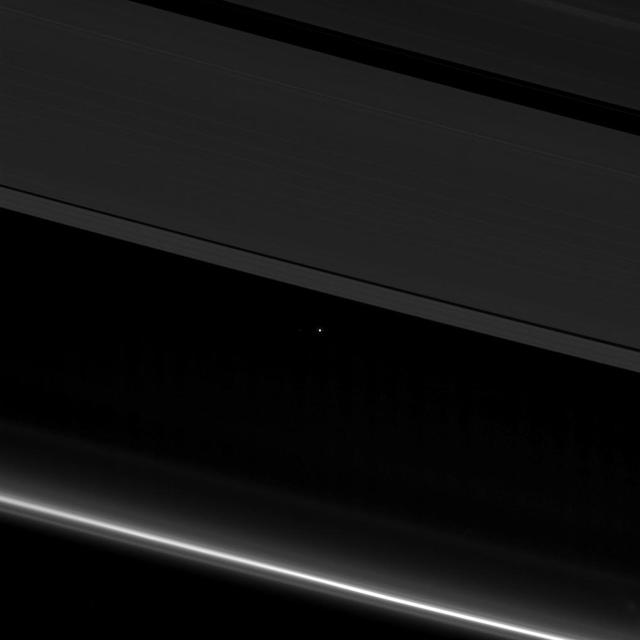

This view from NASA's Cassini spacecraft shows planet Earth as a point of light between the icy rings of Saturn. The spacecraft captured the view on April 12, 2017 at 10:41 p.m. PDT (1:41 a.m. EDT). Cassini was 870 million miles (1.4 billion kilometers) away from Earth when the image was taken. Although far too small to be visible in the image, the part of Earth facing toward Cassini at the time was the southern Atlantic Ocean. Earth's moon is also visible to the left of our planet in a cropped, zoomed-in version of the image (Figure 1). The rings visible here are the A ring (at top) with the Keeler and Encke gaps visible, and the F ring (at bottom). During this observation Cassini was looking toward the backlit rings, making a mosaic of multiple images, with the sun blocked by the disk of Saturn. Seen from Saturn, Earth and the other inner solar system planets are all close to the sun, and are easily captured in such images, although these opportunities have been somewhat rare during the mission. The F ring appears especially bright in this viewing geometry. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21445
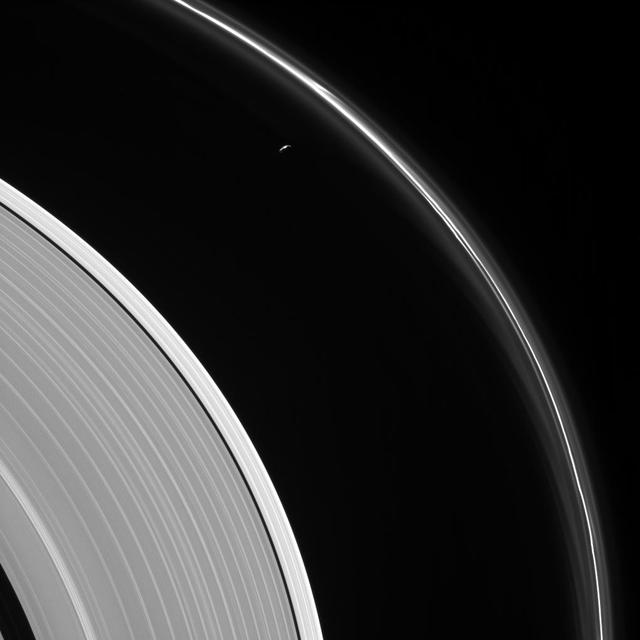

The thin sliver of Saturn's moon Prometheus lurks near ghostly structures in Saturn's narrow F ring in this view from NASA's Cassini spacecraft. Many of the narrow ring's faint and wispy features result from its gravitational interactions with Prometheus (86 kilometers, or 53 miles across). Most of the small moon's surface is in darkness due to the viewing geometry here. Cassini was positioned behind Saturn and Prometheus with respect to the sun, looking toward the moon's dark side and just a bit of the moon's sunlit northern hemisphere. Also visible here is a distinct difference in brightness between the outermost section of Saturn's A ring (left of center) and rest of the ring, interior to the Keeler Gap (lower left). This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 13 degrees above the ring plane. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on May 13, 2017. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 680,000 miles (1.1 million kilometers) from Saturn. Image scale is 4 miles (6 kilometers) per pixel. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21340