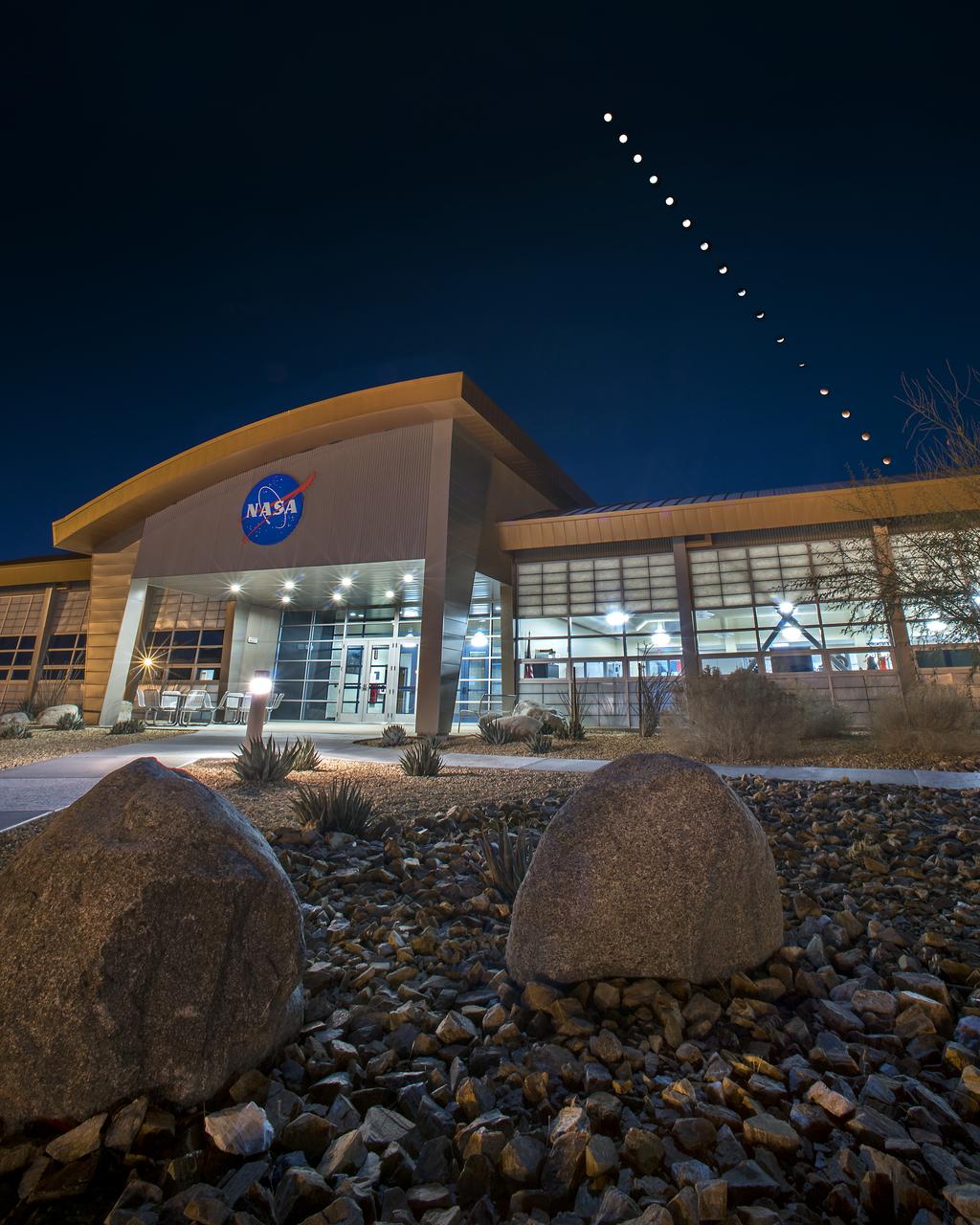

California’s NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center photographer Ken Ulbrich takes photos of Super Blue Blood Moon eclipse making a time-lapse composition of the event on January 31. The total lunar eclipse provided a rare opportunity to capture a supermoon, a blue moon and a lunar eclipse at the same time. A supermoon occurs when the Moon is closer to Earth in its orbit and appearing 14 percent brighter than usual. As the second full moon of the month, this moon is also commonly known as a blue moon, though it will not be blue in appearance. The super blue moon passed through Earth’s shadow and took on a reddish tint, known as a blood moon. This total lunar eclipse occurs when the Sun, Earth, and a full moon form a near-perfect lineup in space. The Moon passes directly behind the Earth into its umbra (shadow).
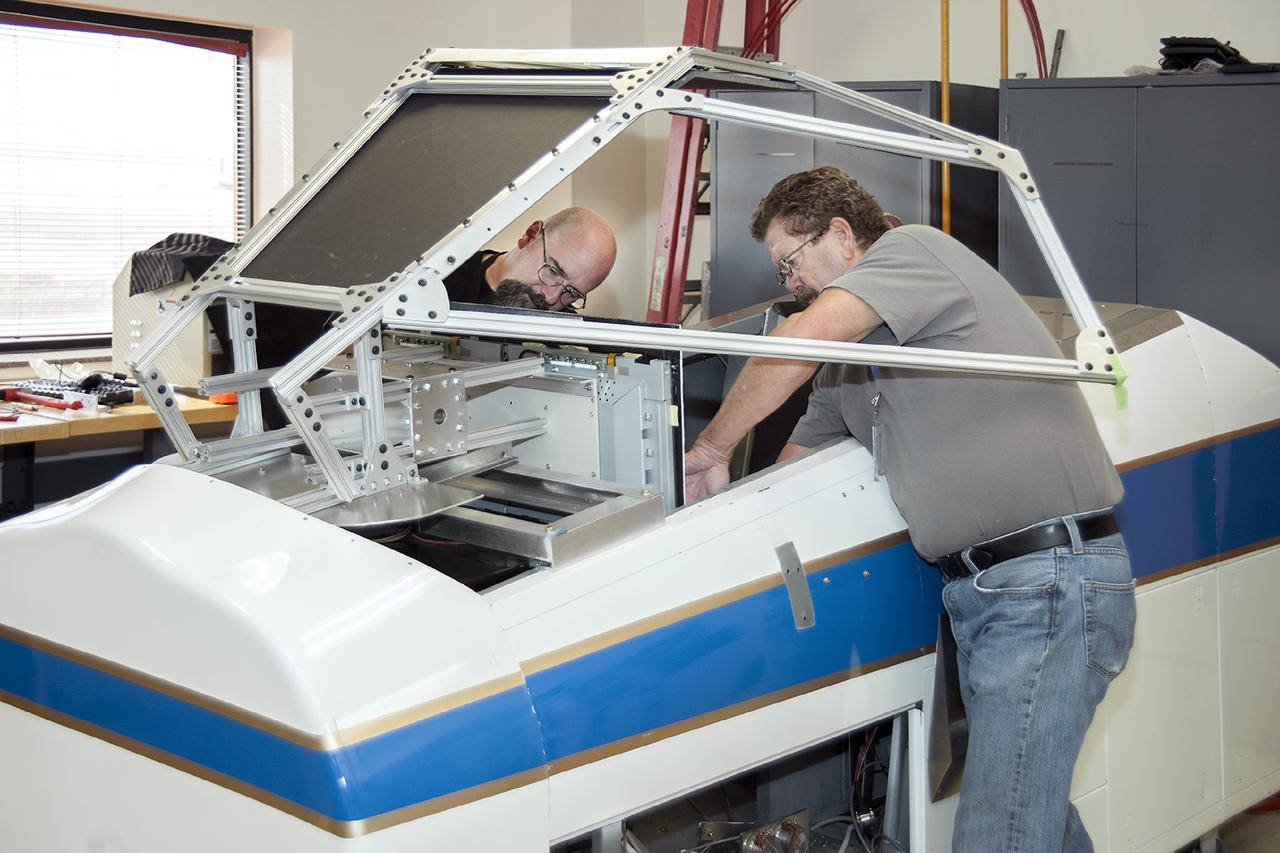

DRYDEN FLIGHT RESEARCH CENTER, Calif. - Simulation technicians Brent Bieber, left, and Dennis Pitts install a boilerplate Dream Chaser canopy structure over the cockpit of a flight simulator in the simulation laboratory at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California. The modification will give Dream Chaser pilot-astronauts a more representative view of the actual flight profiles the spacecraft would fly during piloted approach and landing tests. Sierra Nevada Corporation's Space Systems division is conducting uncrewed captive- and free-flight approach and landing tests of its Dream Chaser at Dryden during the summer and fall. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
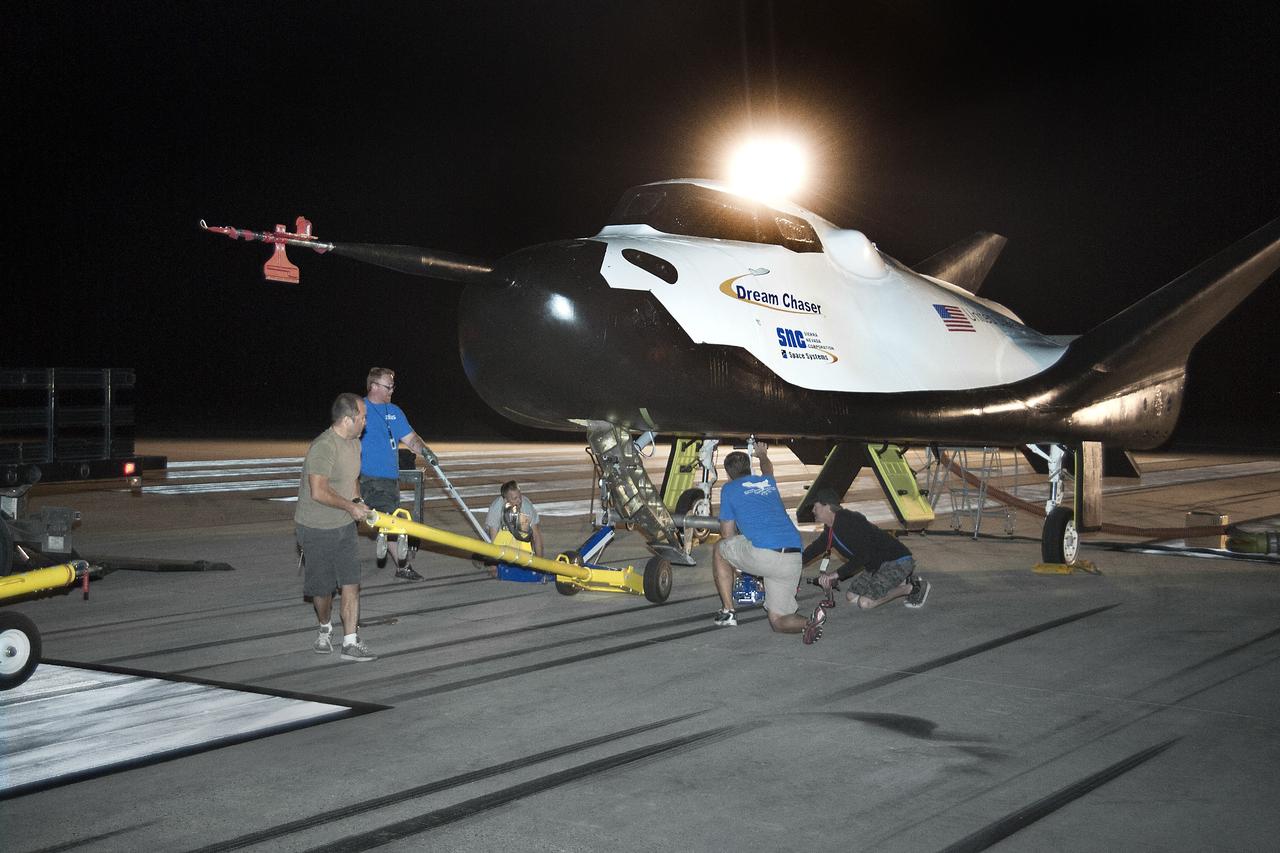

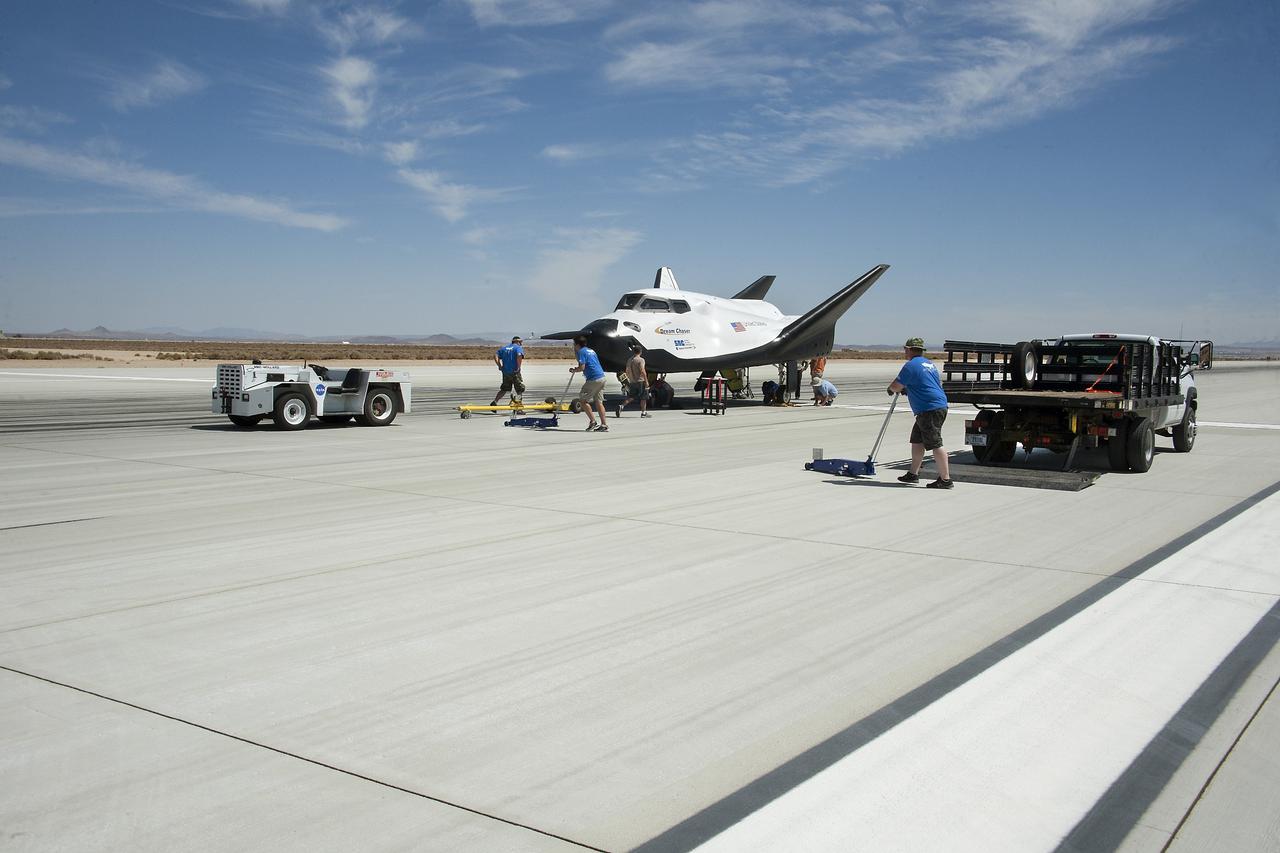
Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-013- Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, team members prepare for 60 mph tow tests of the company's Dream Chaser flight vehicle on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
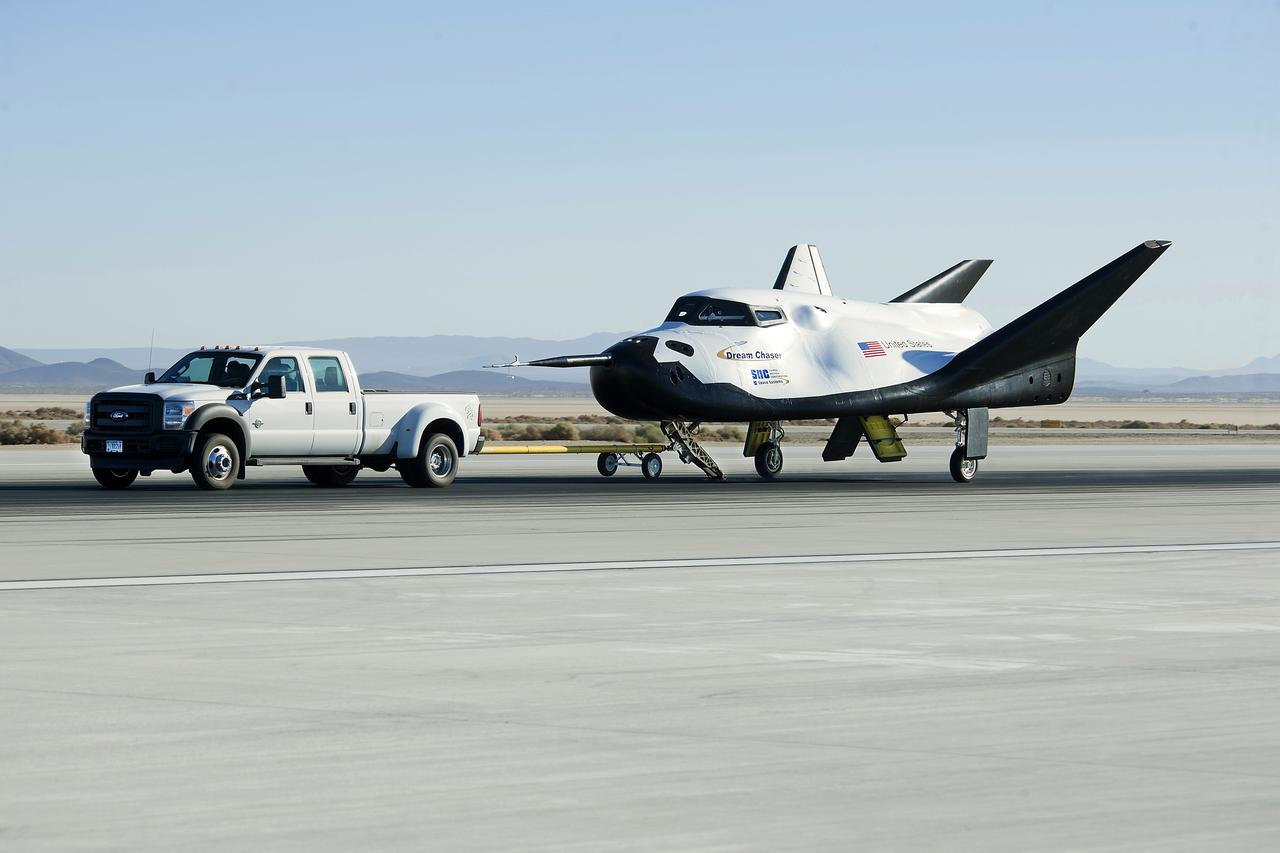

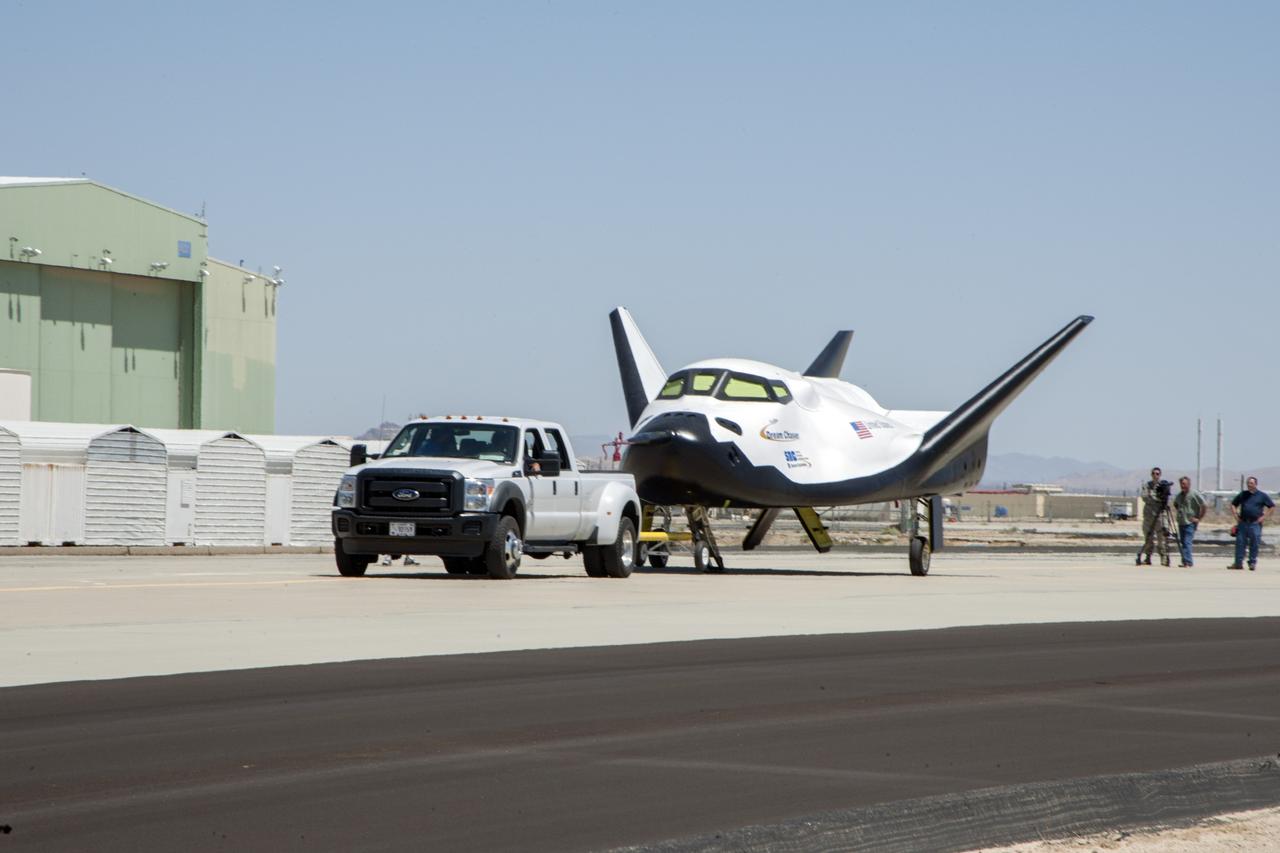
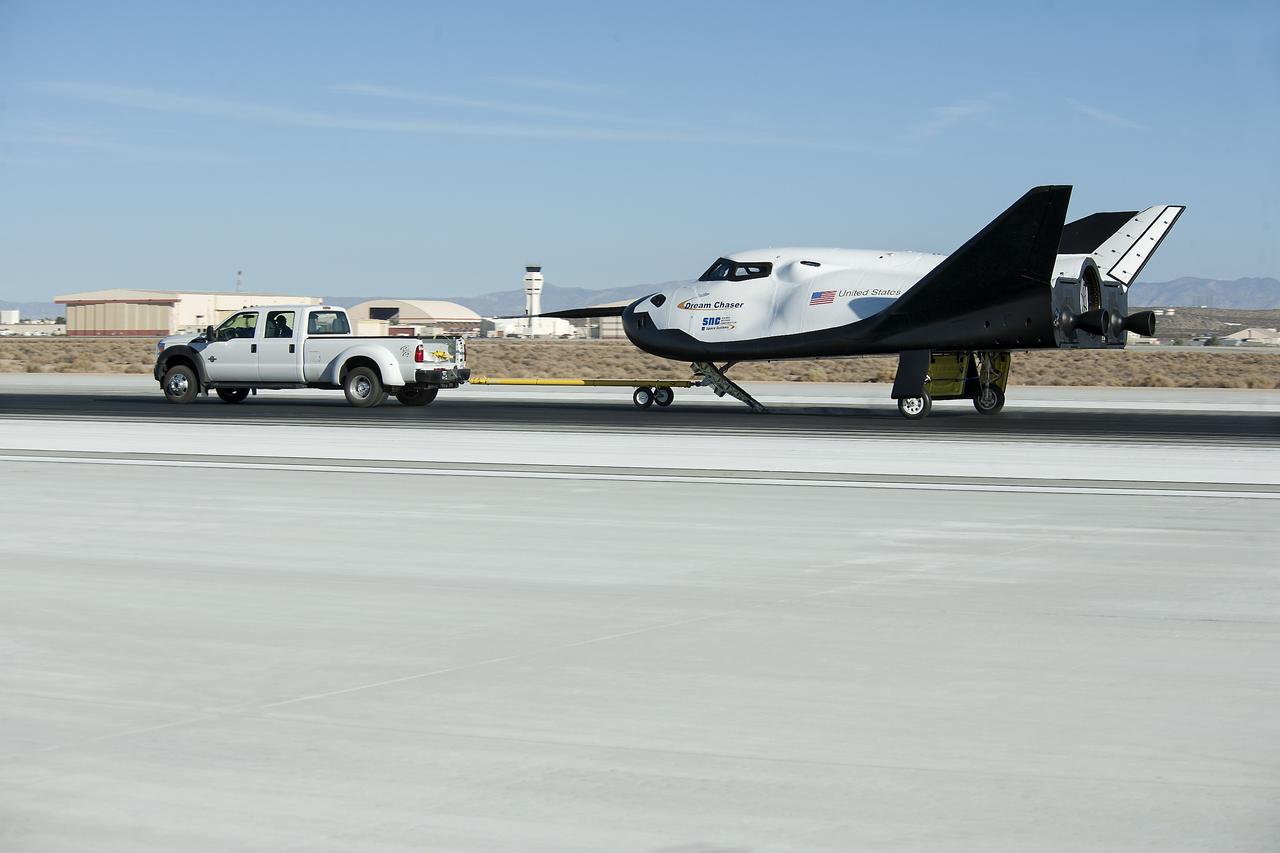
Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-047- A pickup truck pulls the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight vehicle through 60 mile per hour tow tests on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
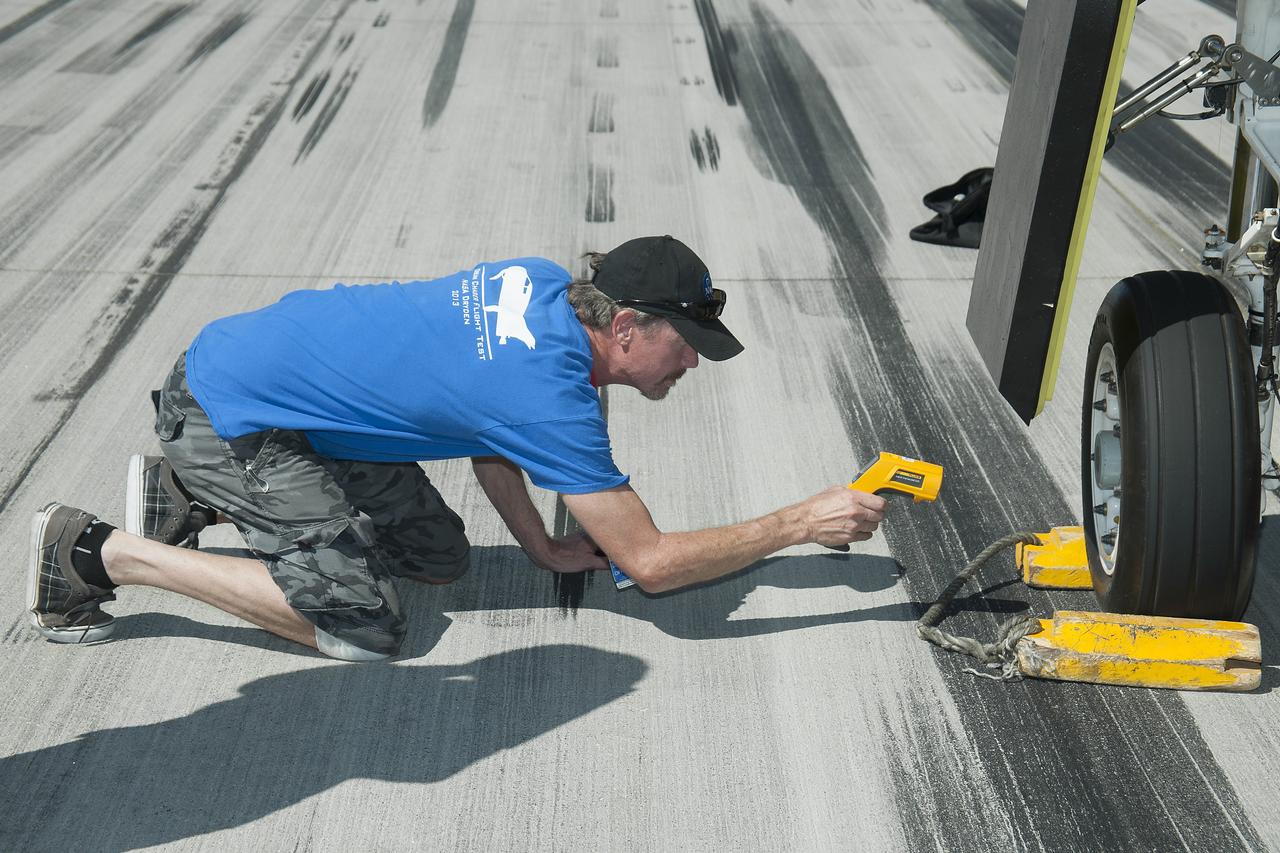

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-060- A Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, team member checks the company's Dream Chaser flight vehicle systems following a 60 mph tow test on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich

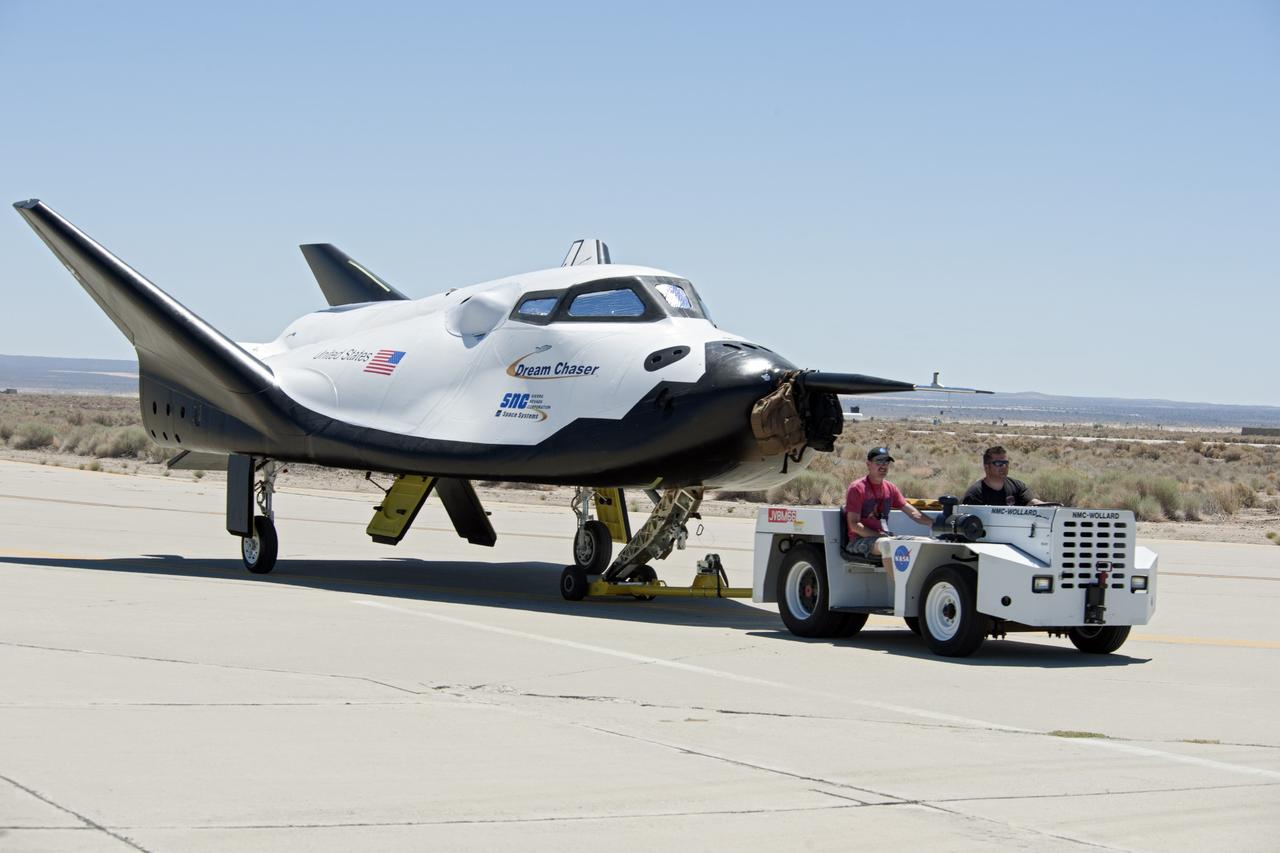
Edwards, Calif. – ED13-164-34 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle out to a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-007- The Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight vehicle is prepared for 60 mph tow tests on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-022- The Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight vehicle is prepared for 60 mile per hour tow tests on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
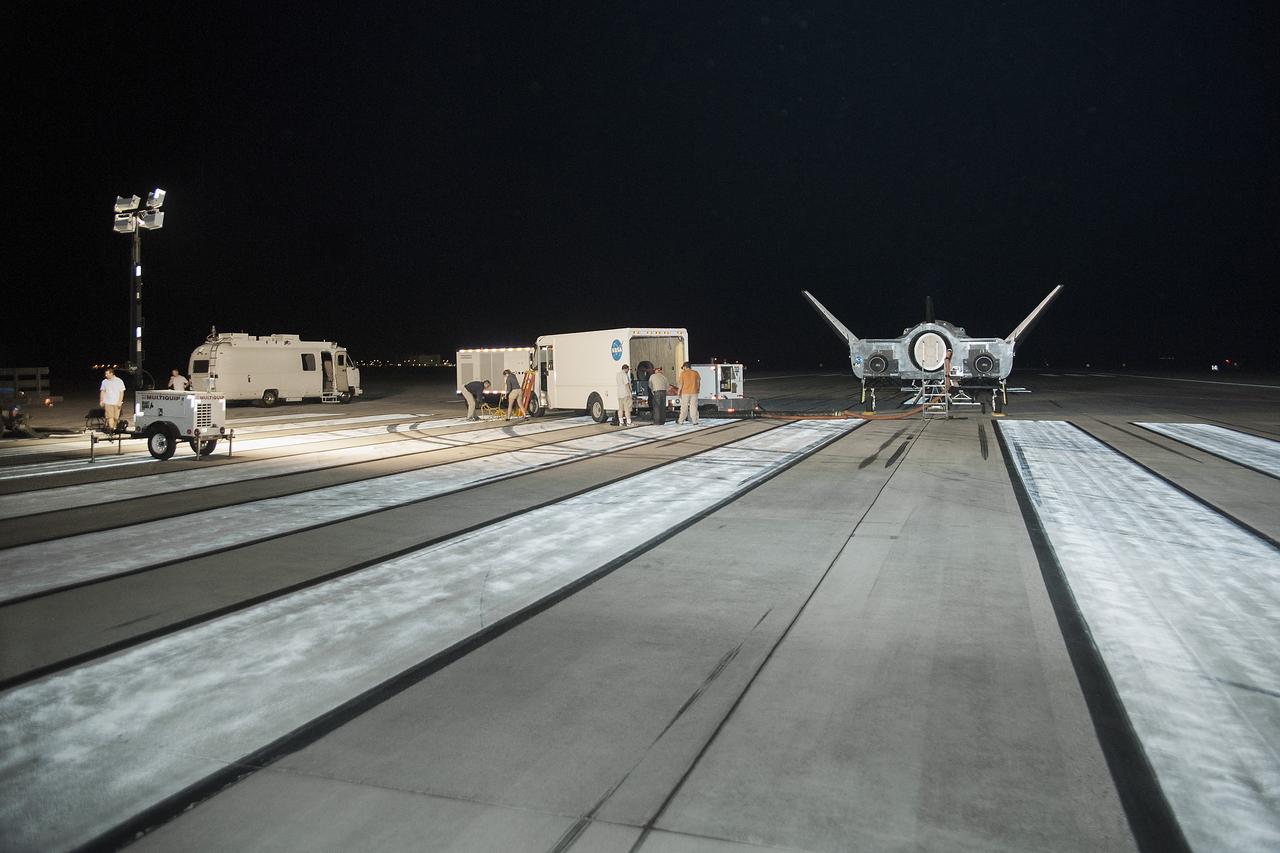

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-010- The Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight vehicle is prepared for 60 mph tow tests on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
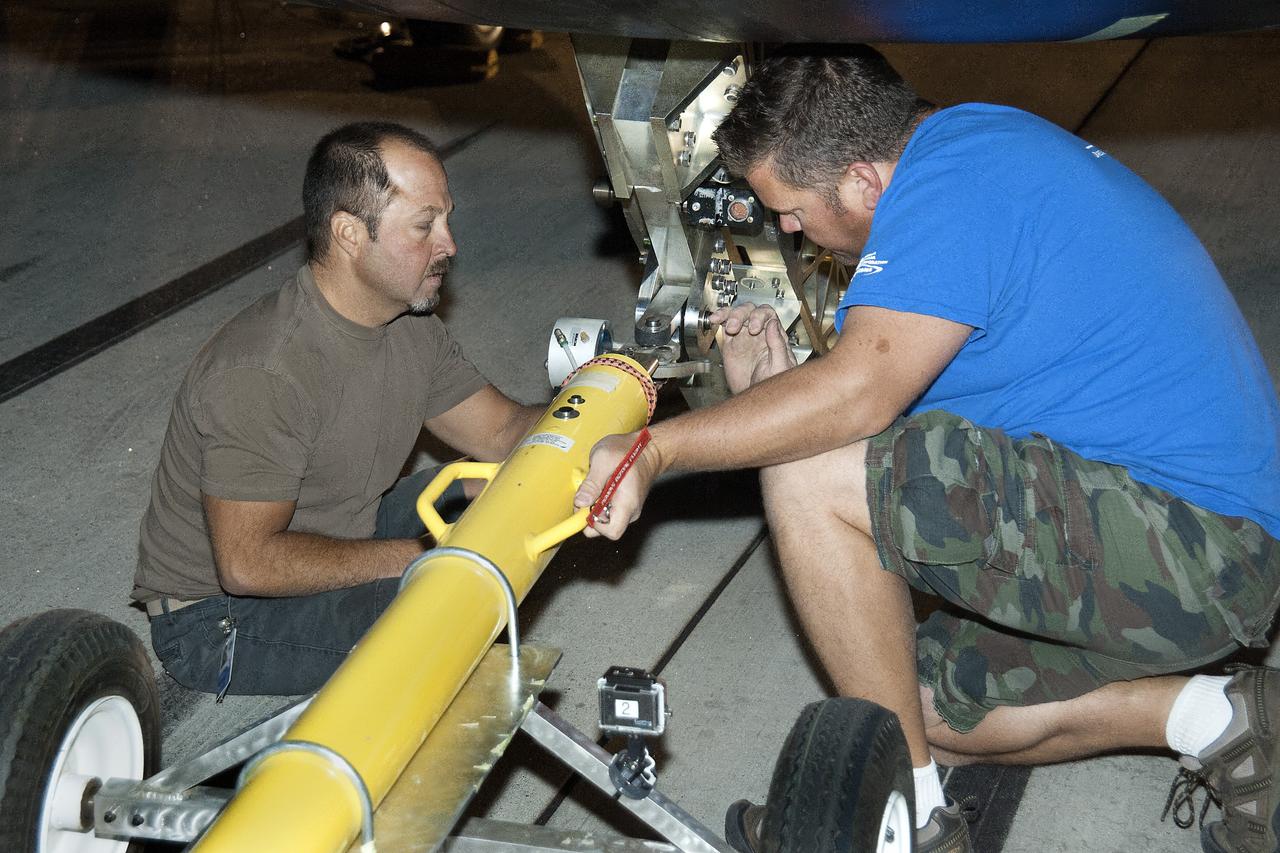

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-016- Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, team members prepare for 60 mph tow tests of the company's Dream Chaser flight vehicle on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-056- Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, team members monitor the company's Dream Chaser flight vehicle systems during 60 mph tow testing on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
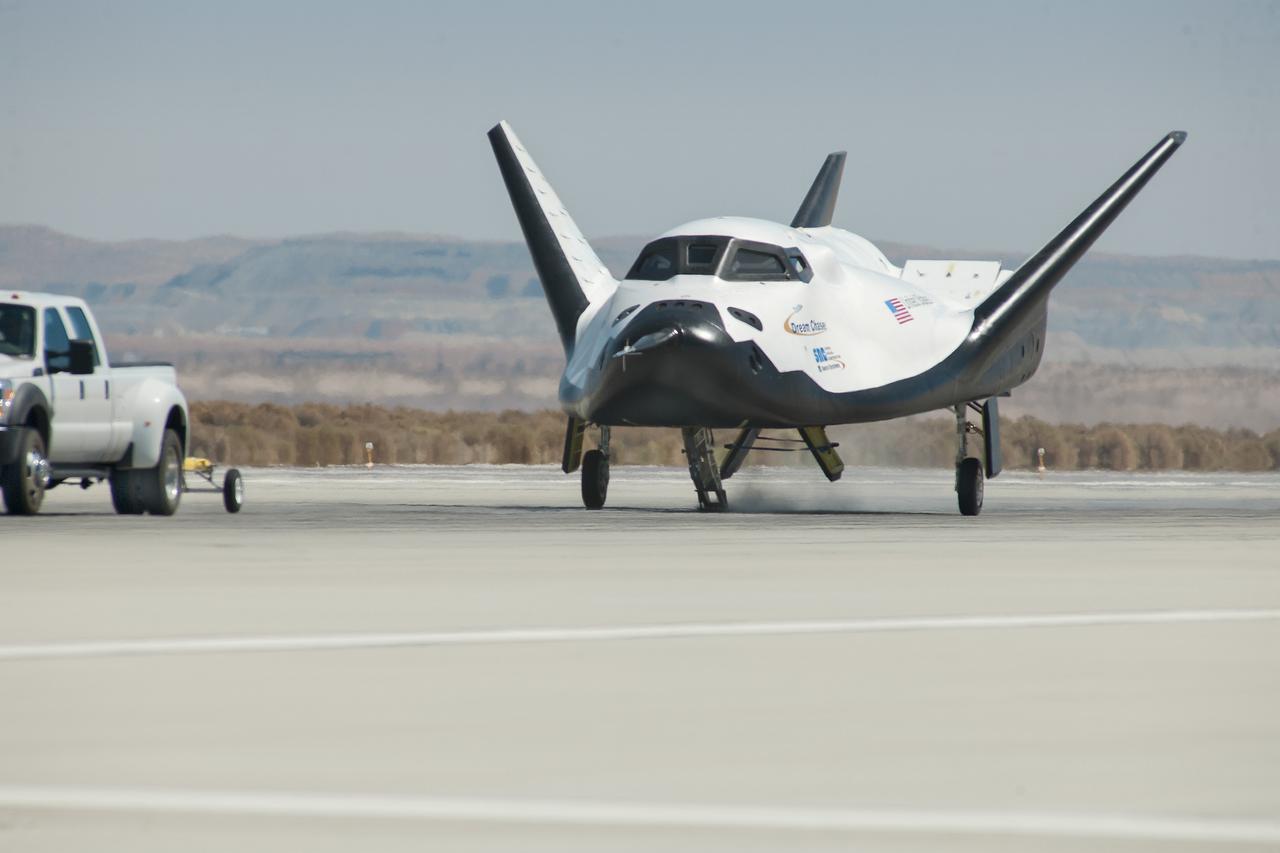

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-066- A pickup truck releases the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight vehicle during a 60 mile per hour tow test to validate the spacecraft's brakes on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
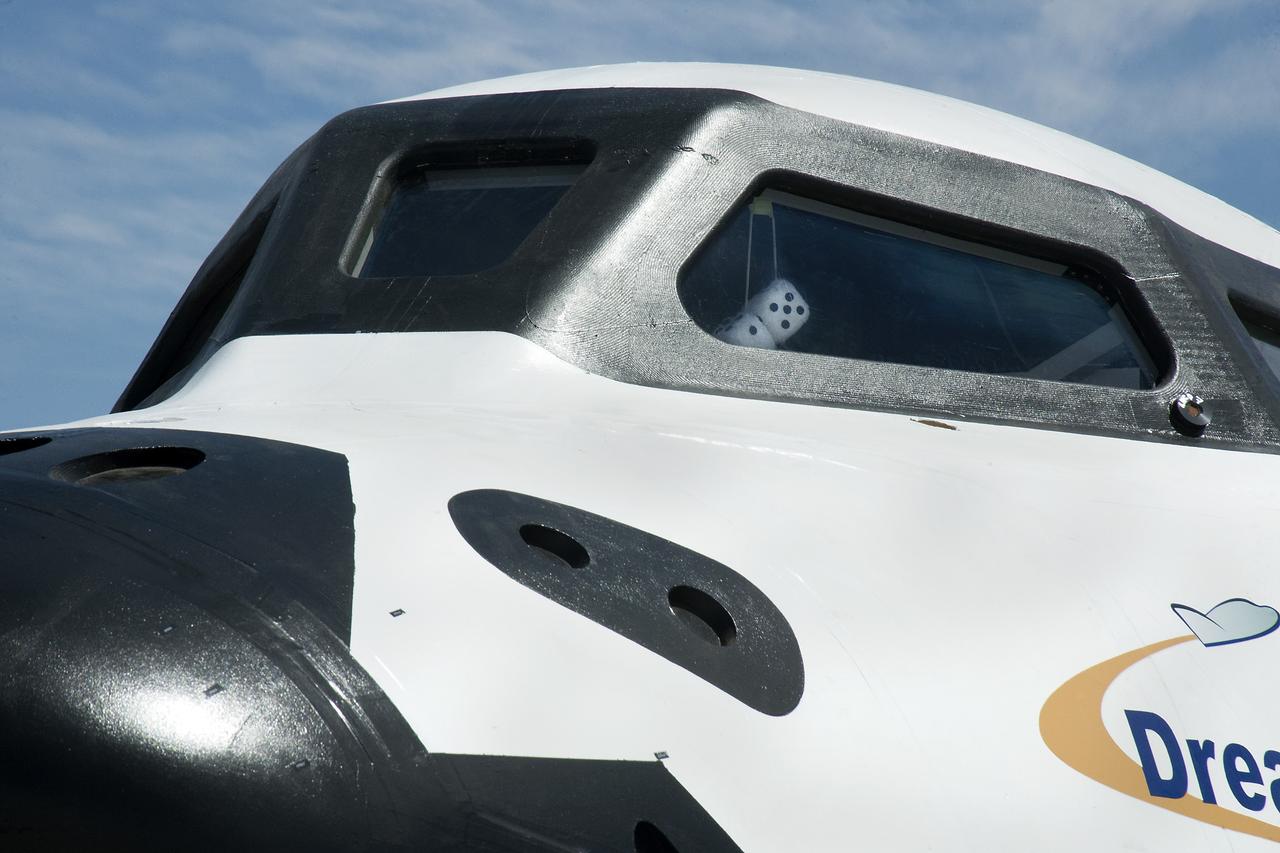

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-074- Sierra Nevada Corporation's, or SNC's, Dream Chaser flight vehicle sports a pair of fuzzy dice during 60 mph tow tests at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-069- Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, team members check the company's Dream Chaser flight vehicle systems following a 60 mph tow test on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-049- A pickup truck pulls the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight vehicle through 60 mile per hour tow tests on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-012- Technicians prepare for 60 mph tow tests of Sierra Nevada Corporation's, or SNC's, Dream Chaser flight vehicle on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
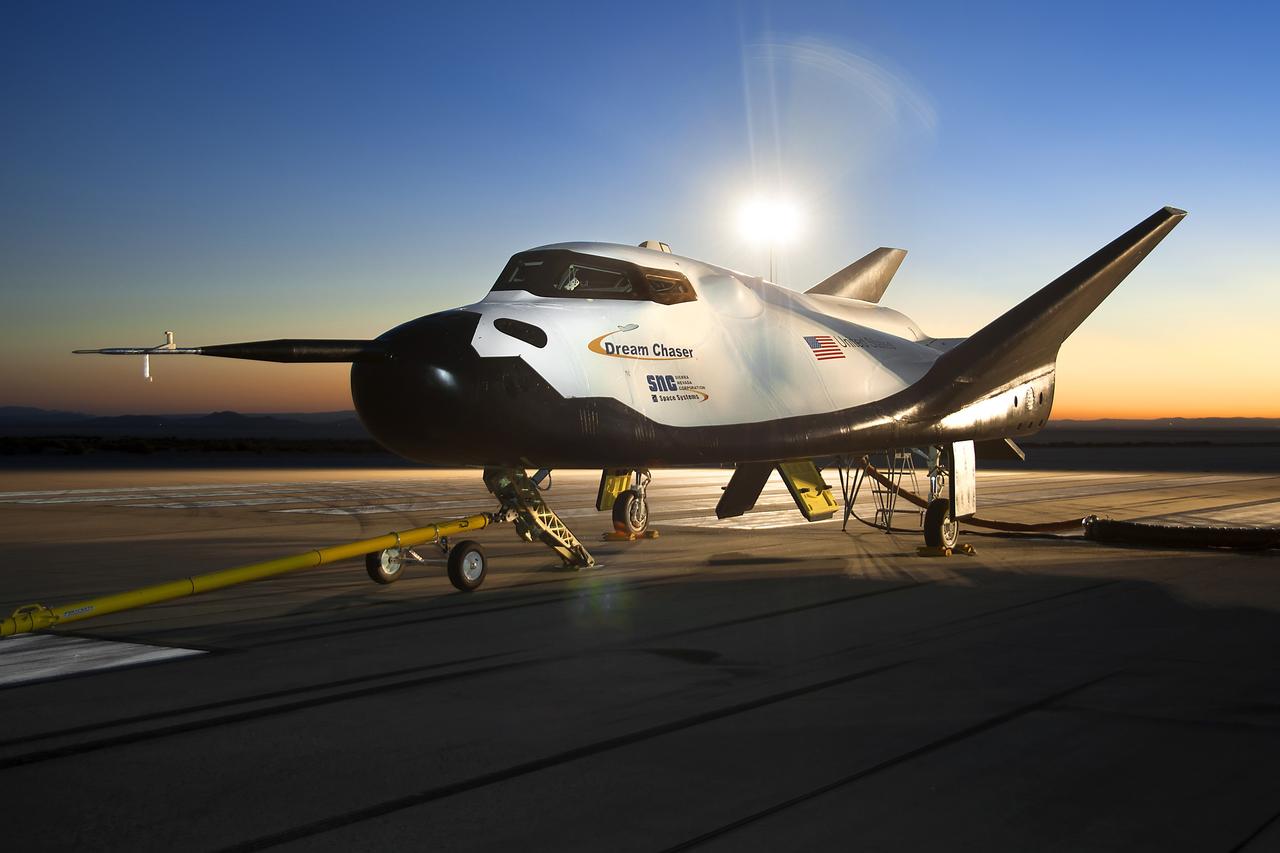

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-023- The Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight vehicle is prepared for 60 mile per hour tow tests on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
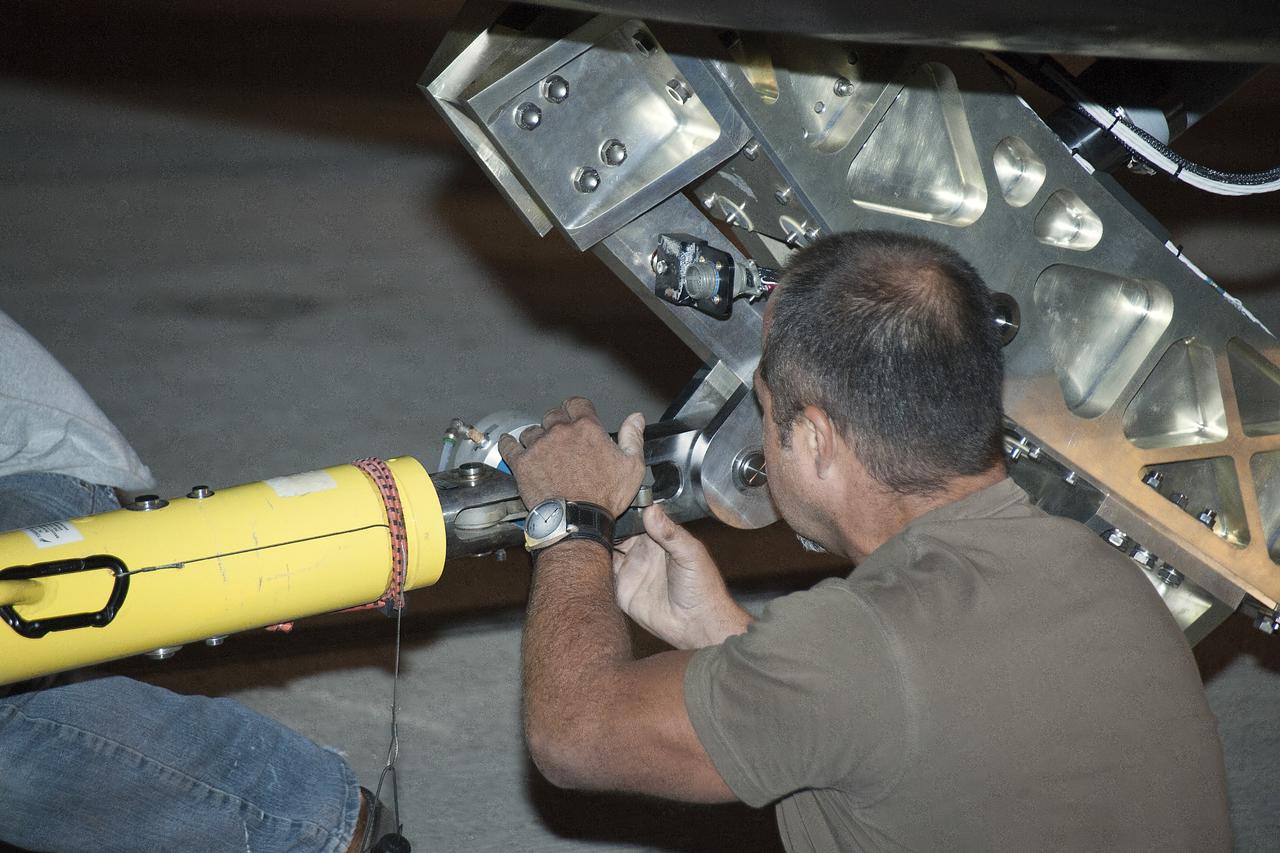

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-021- A Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, team member prepares for 60 mph tow tests of the company's Dream Chaser flight vehicle on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
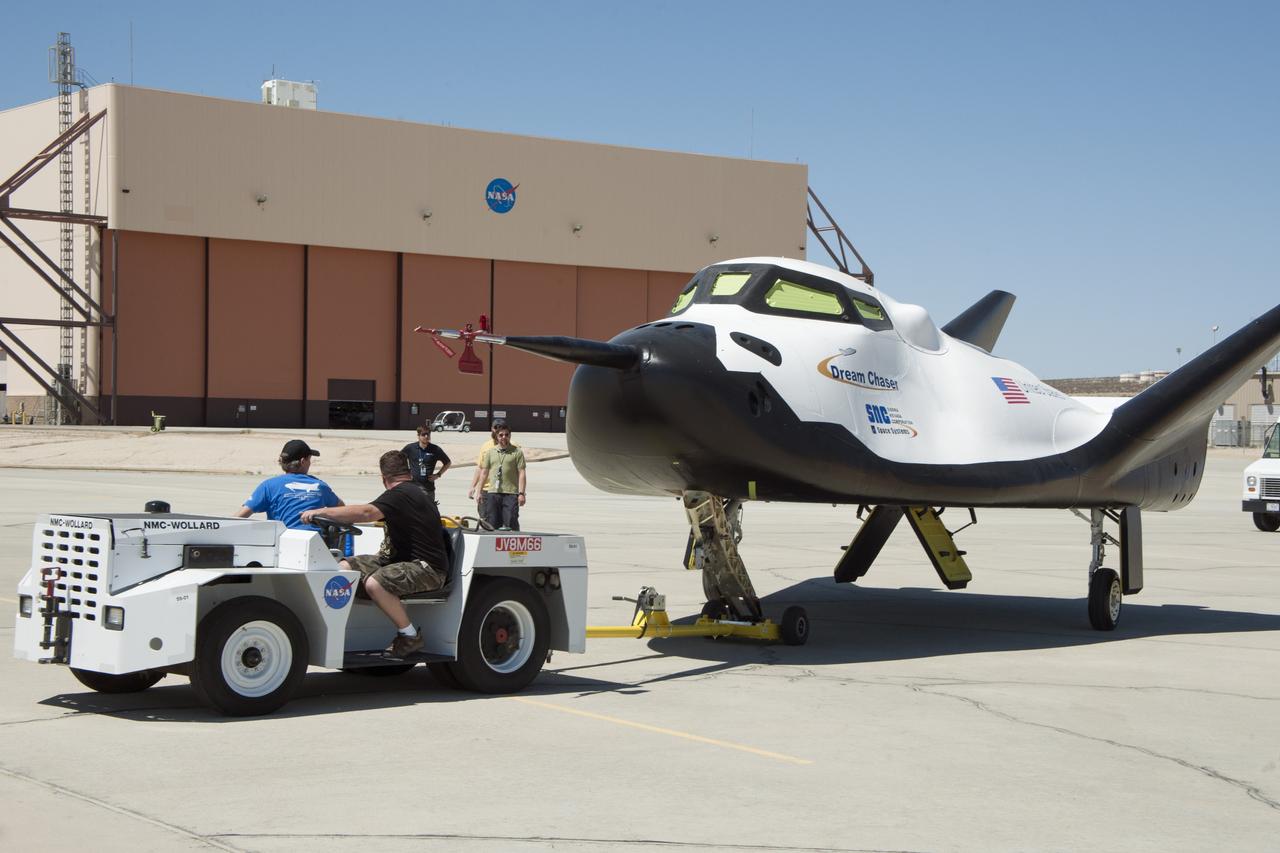

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-164-33 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle out to a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
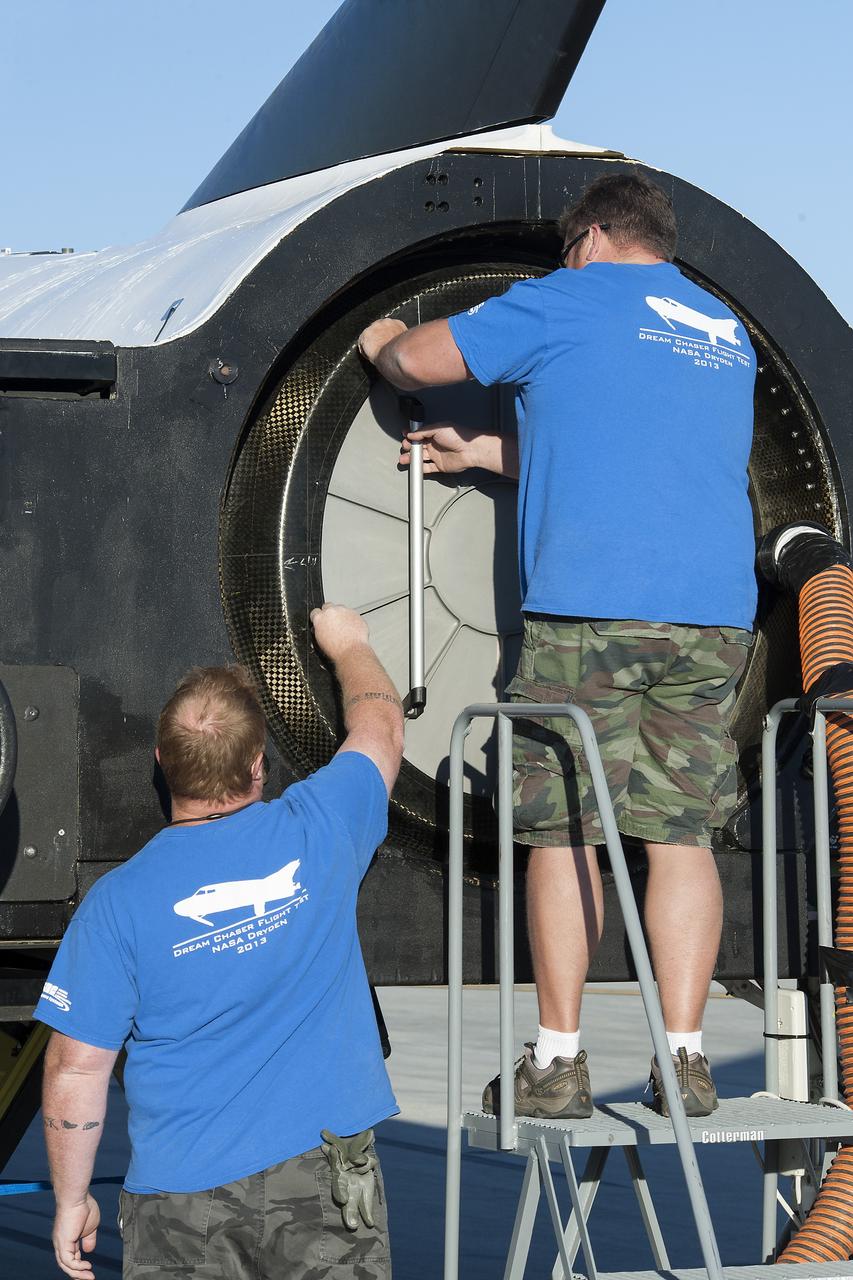

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-046- Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, team members prepare for 60 mph tow tests of the company's Dream Chaser flight vehicle on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
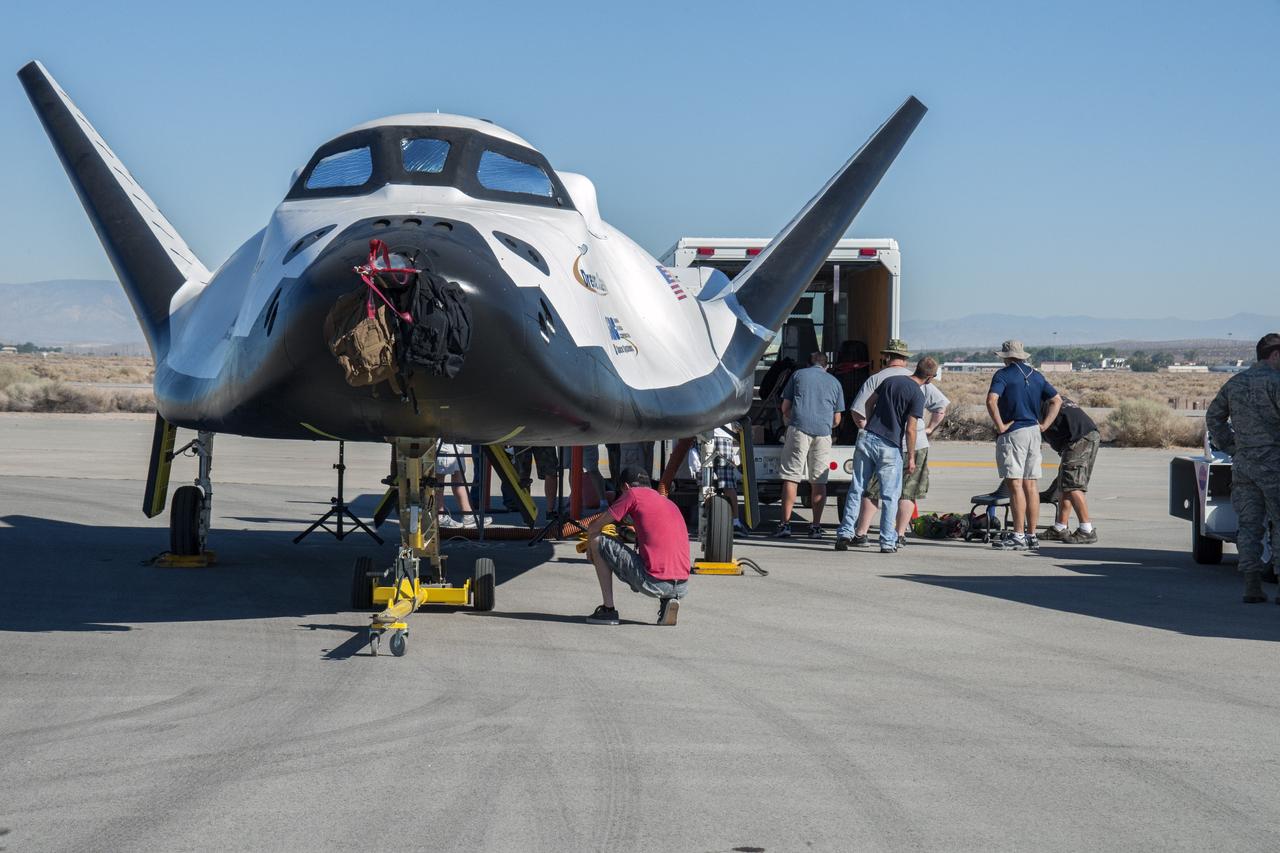

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0215-024 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members prepare to tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle along a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-070- Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, team members check the company's Dream Chaser flight vehicle systems following a 60 mph tow test on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
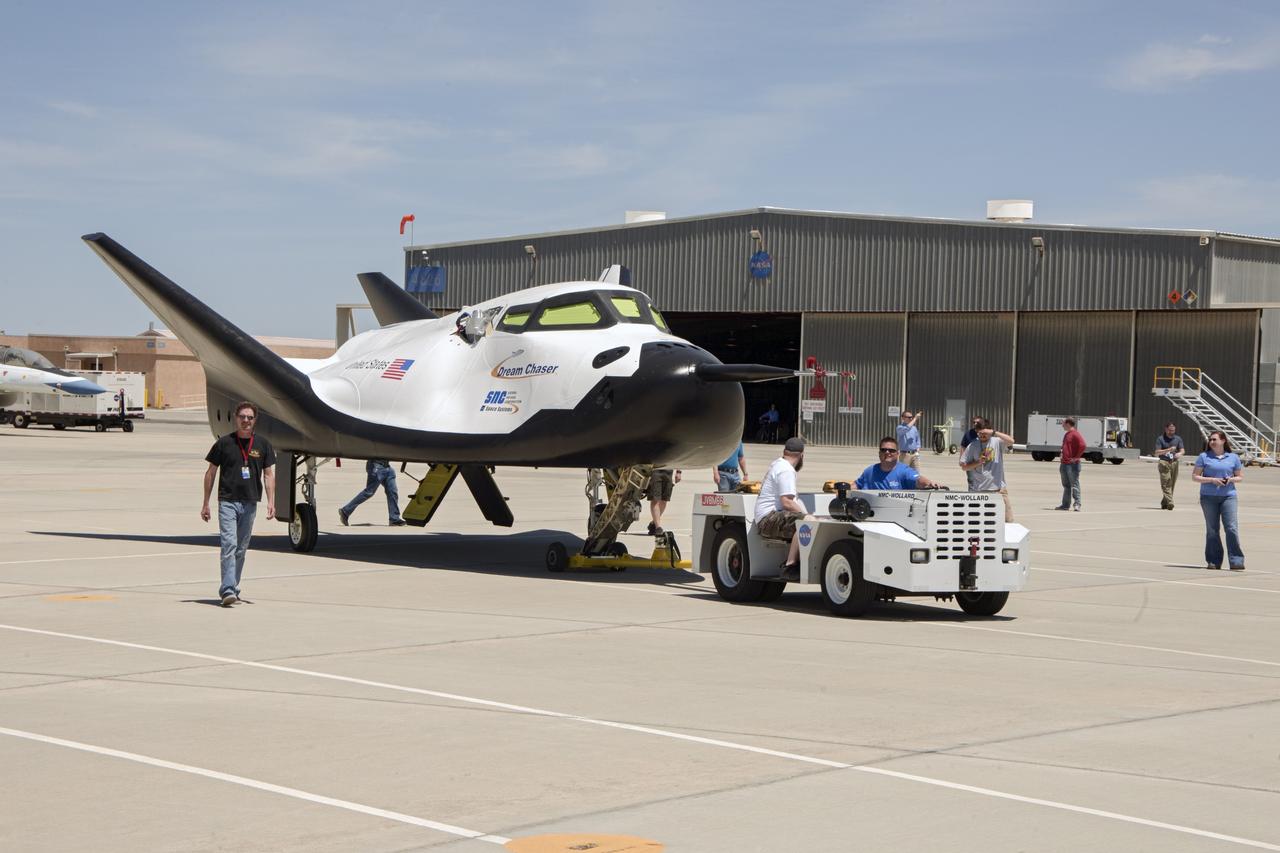

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-161-35 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle out to a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
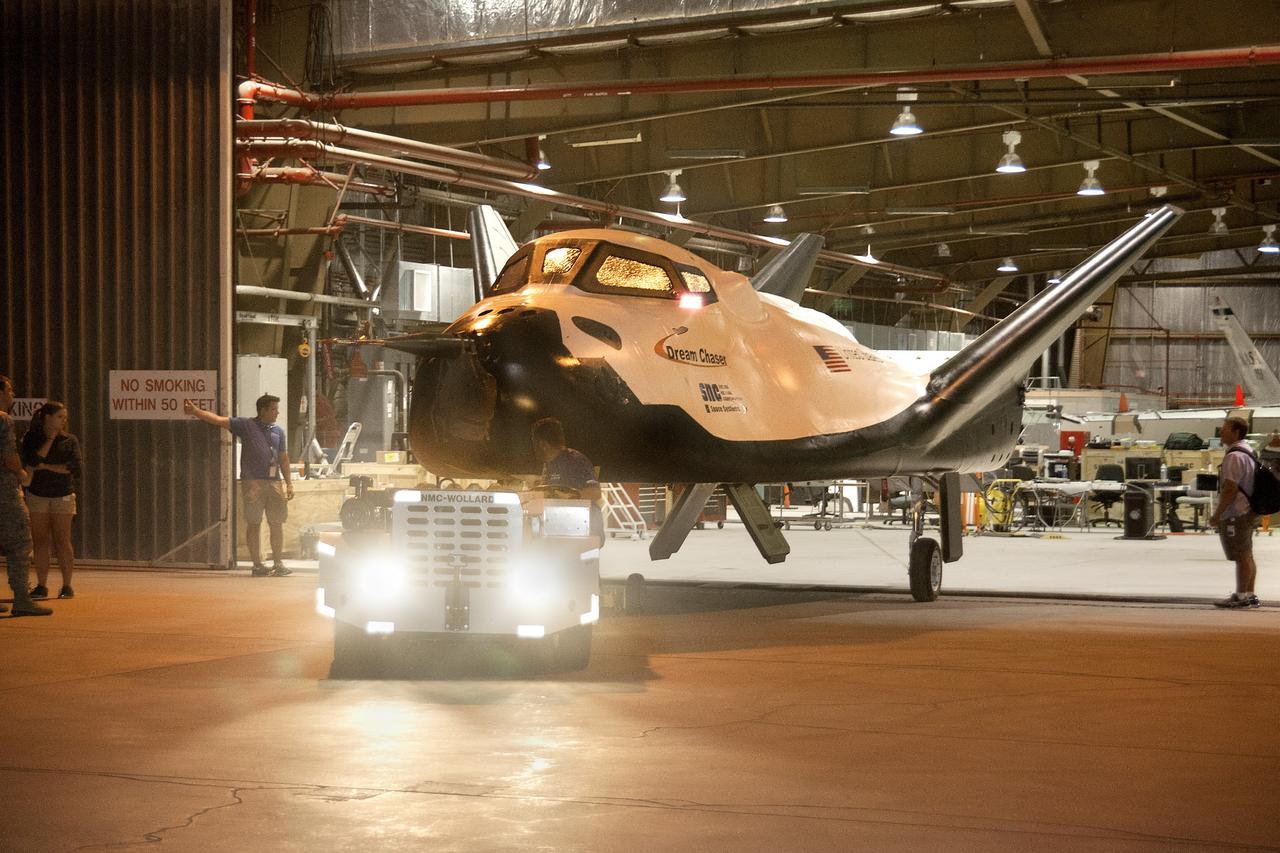

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-004- The Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight vehicle pulls out of a hangar at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California in preparation for tow tests. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
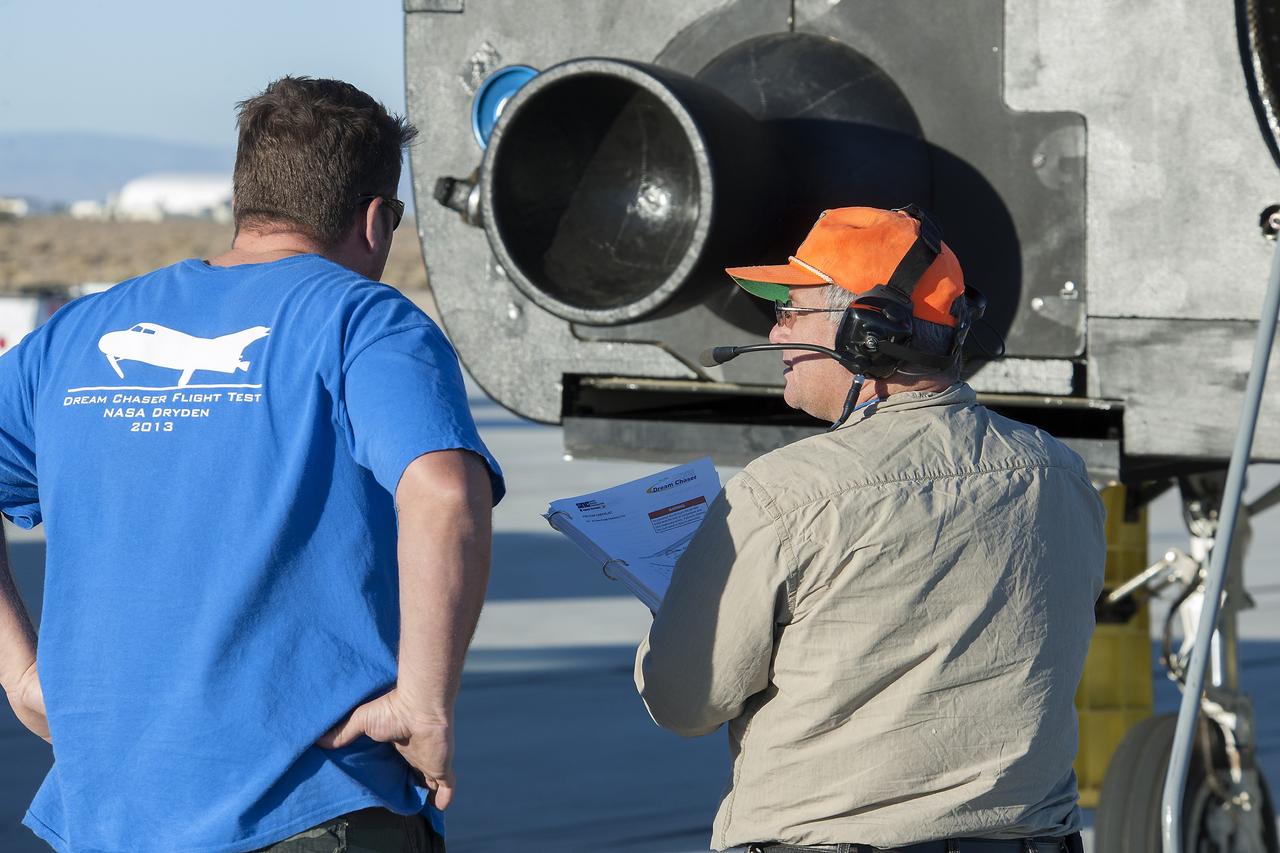

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-045- Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, team members prepare for 60 mph tow tests of the company's Dream Chaser flight vehicle on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich

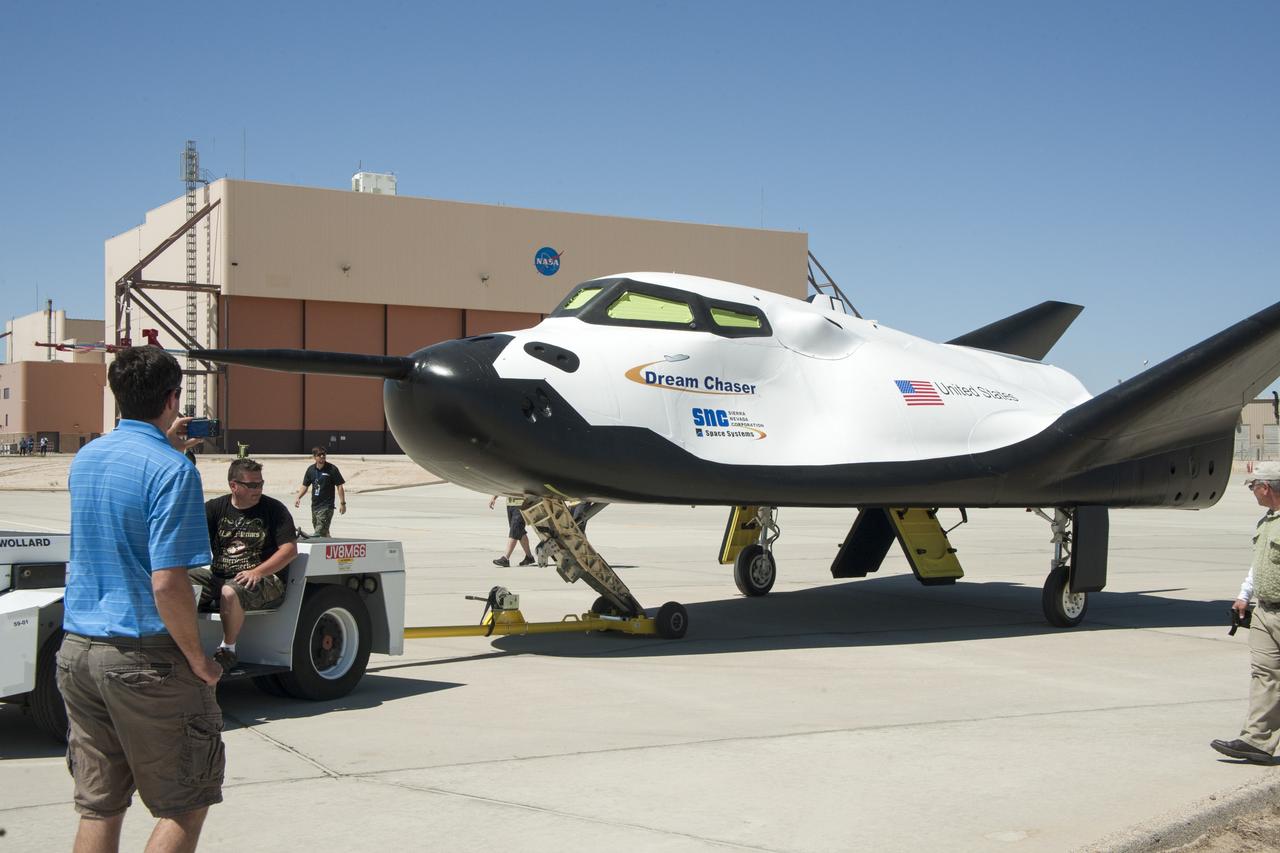
Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0215-072 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle along a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich

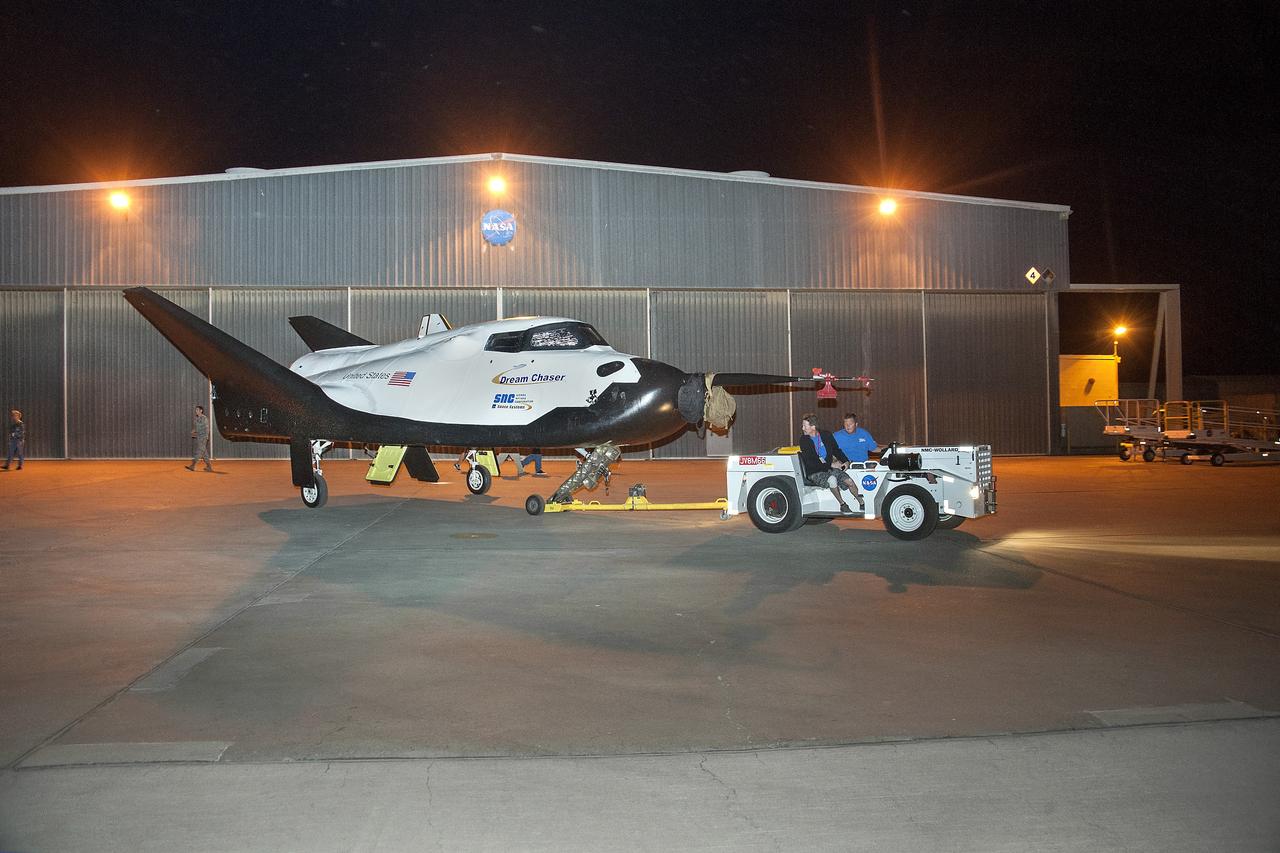
Edwards, Calif. – ED13-164-32 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle out to a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
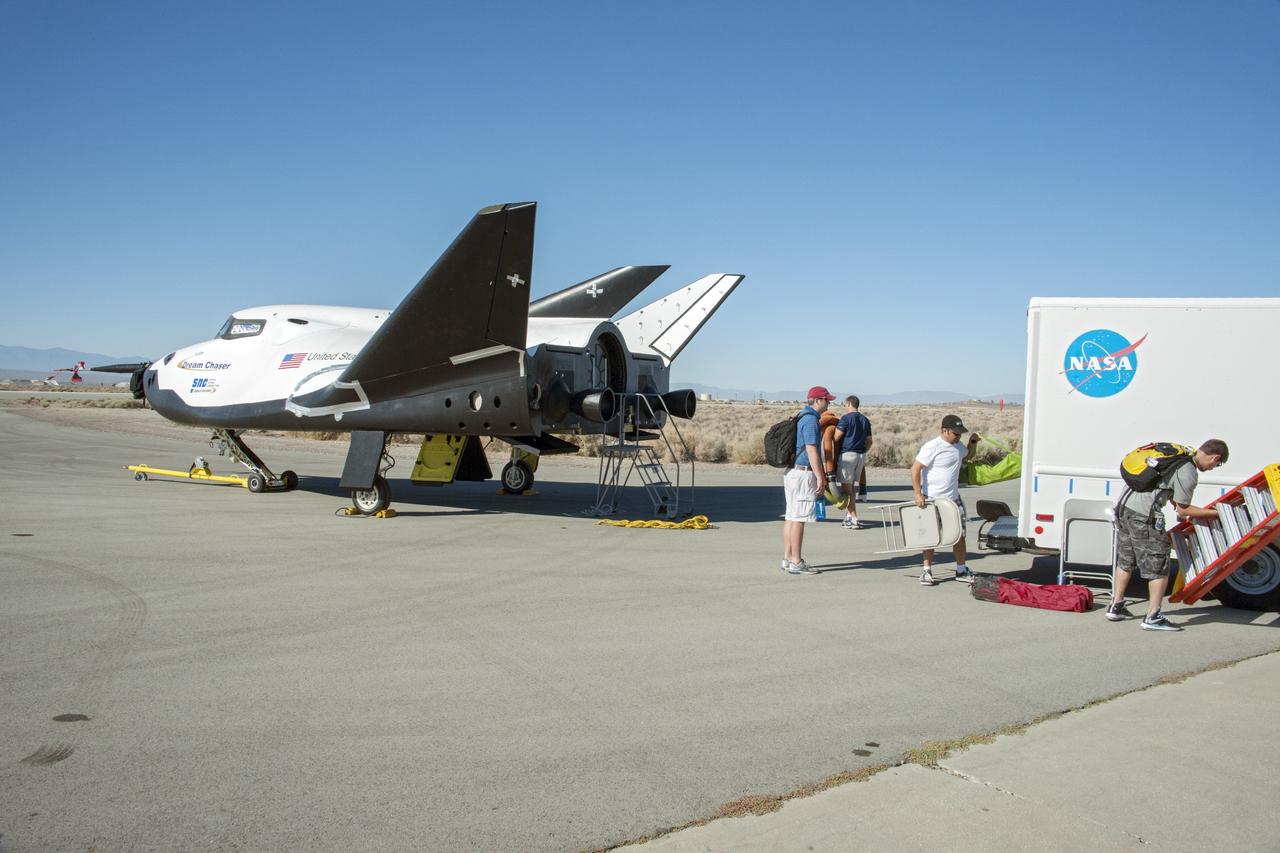

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0215-016 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members prepare to tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle along a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-008- The Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight vehicle is prepared for 60 mph tow tests on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
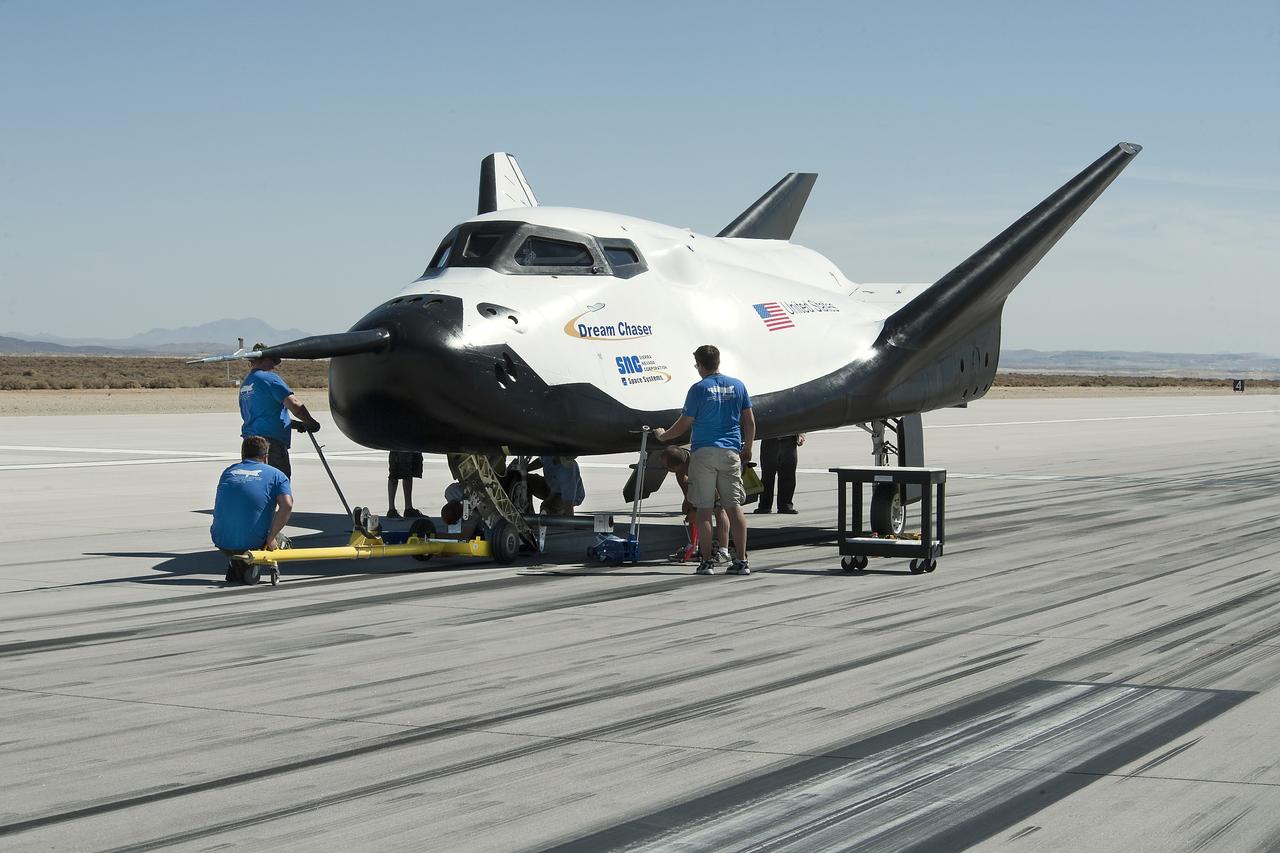

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-054- Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, team members check the company's Dream Chaser flight vehicle systems following a 60 mph tow test on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
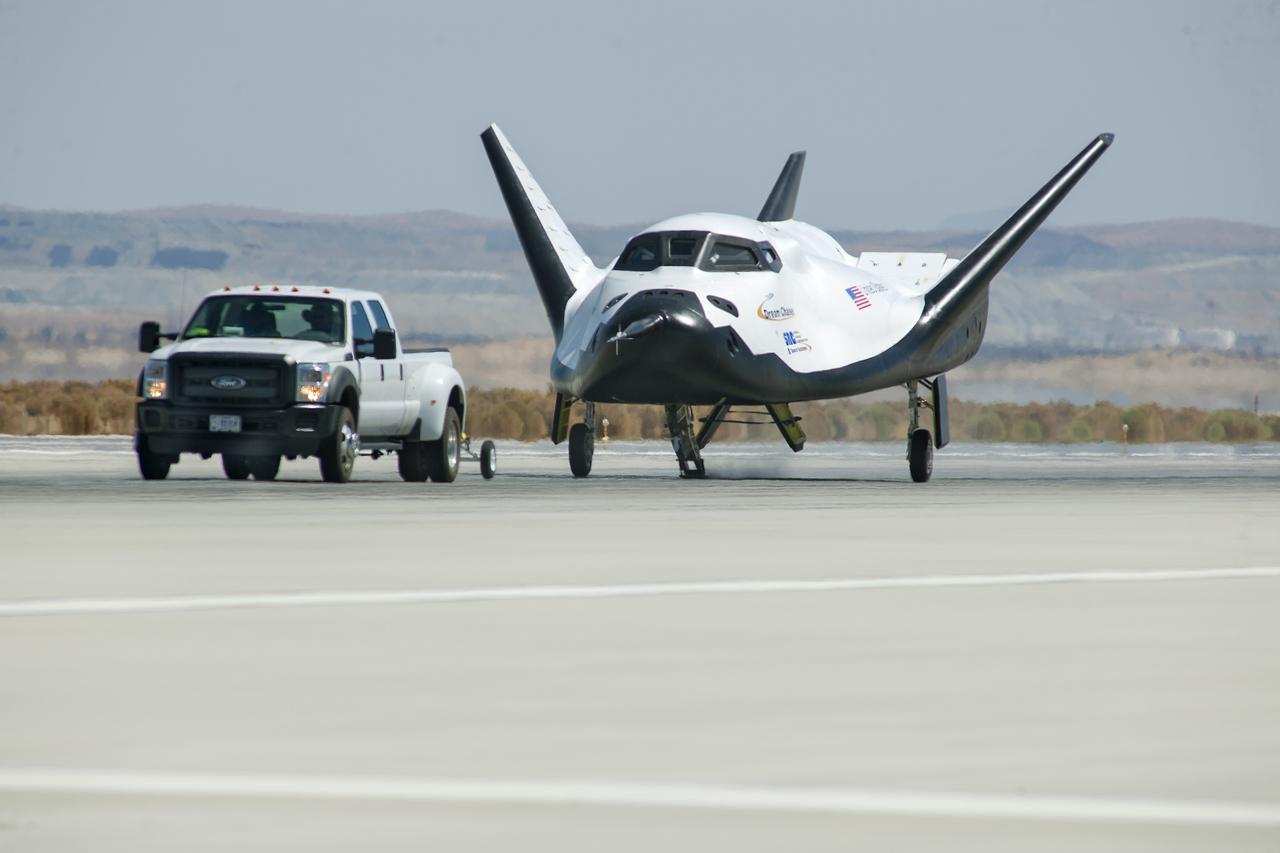

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-0266-047- A pickup truck pulls the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser flight vehicle through 60 mile per hour tow tests on taxi and runways at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Ground testing at 10, 20, 40 and 60 miles per hour is helping the company validate the performance of the spacecraft's braking and landing systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Development Round 2, or CCDev2, and Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, phases, which are intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
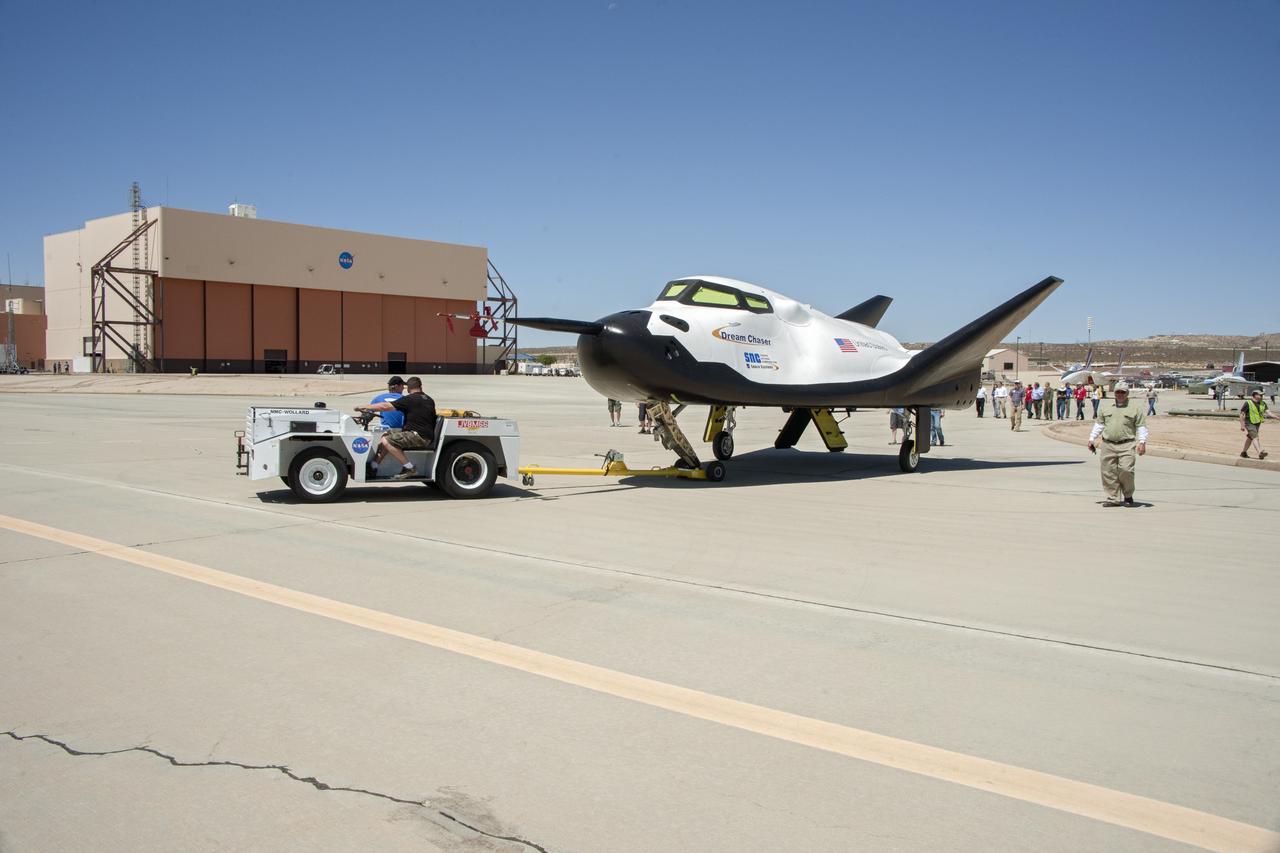

Edwards, Calif. – ED13-164-34 - Sierra Nevada Corporation SNC Space Systems' team members tow the Dream Chaser flight vehicle out to a concrete runway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California for range and taxi tow tests. The ground testing will validate the performance of the spacecraft's nose skid, brakes, tires and other systems prior to captive-carry and free-flight tests scheduled for later this year. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Ken Ulbrich
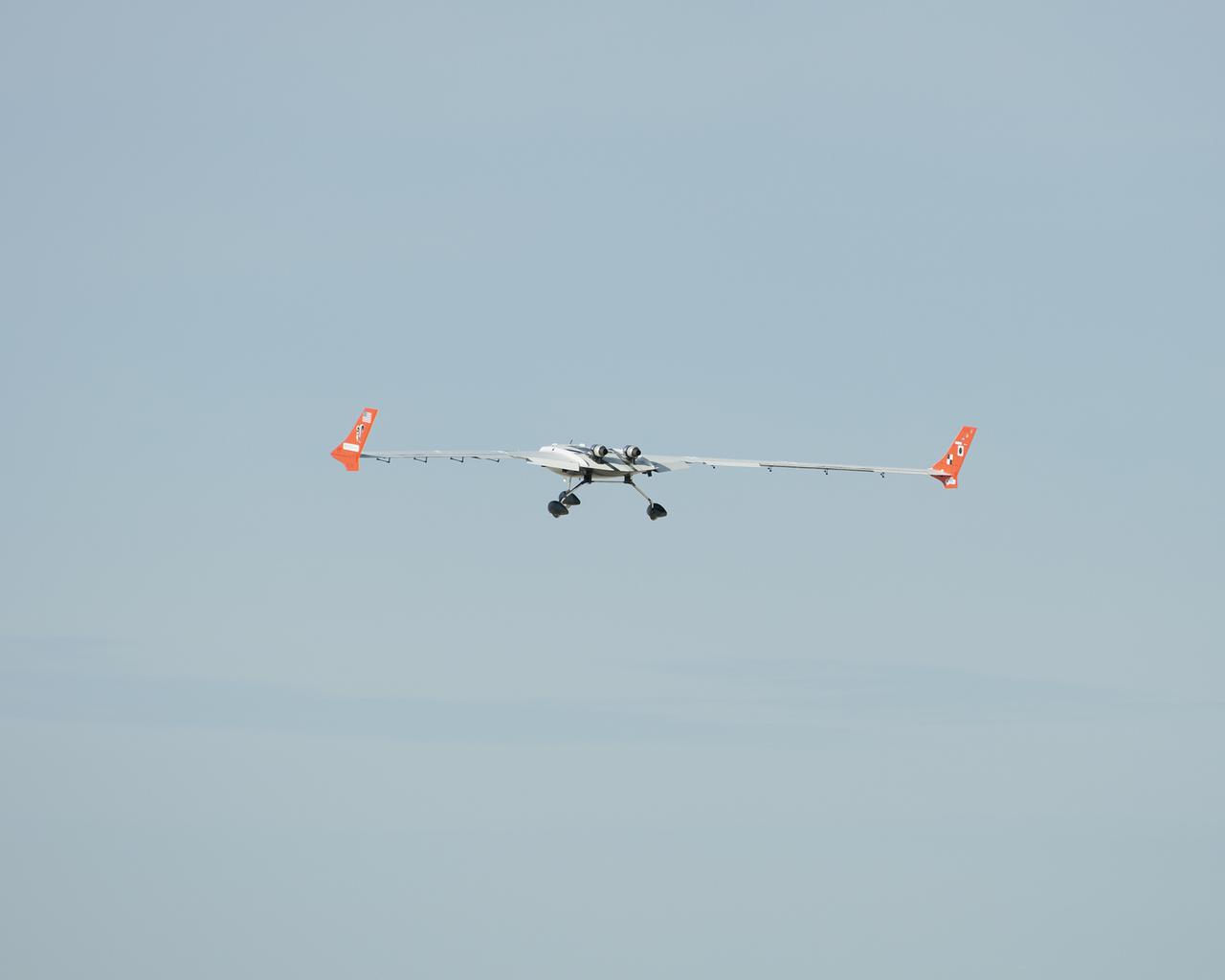

The X-56A takes off on its maiden flight from NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center, Edwards, California.
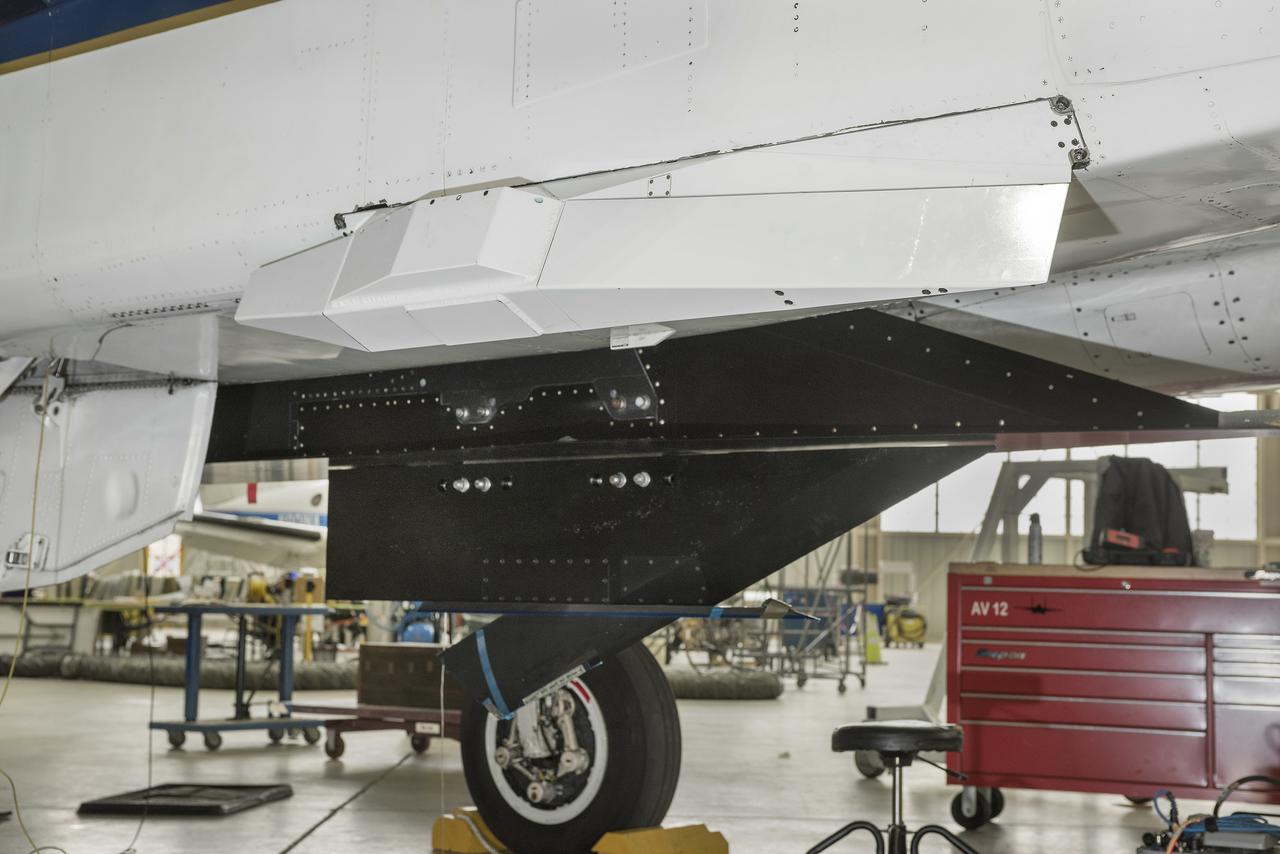

The Swept Wing Laminar Flow test article, integrated to the underside of a NASA F-15, will examine the effectiveness of different configurations of small dots, called distributed roughness elements, to extend smooth, laminar airflow over a wing’s depth, reducing friction drag.
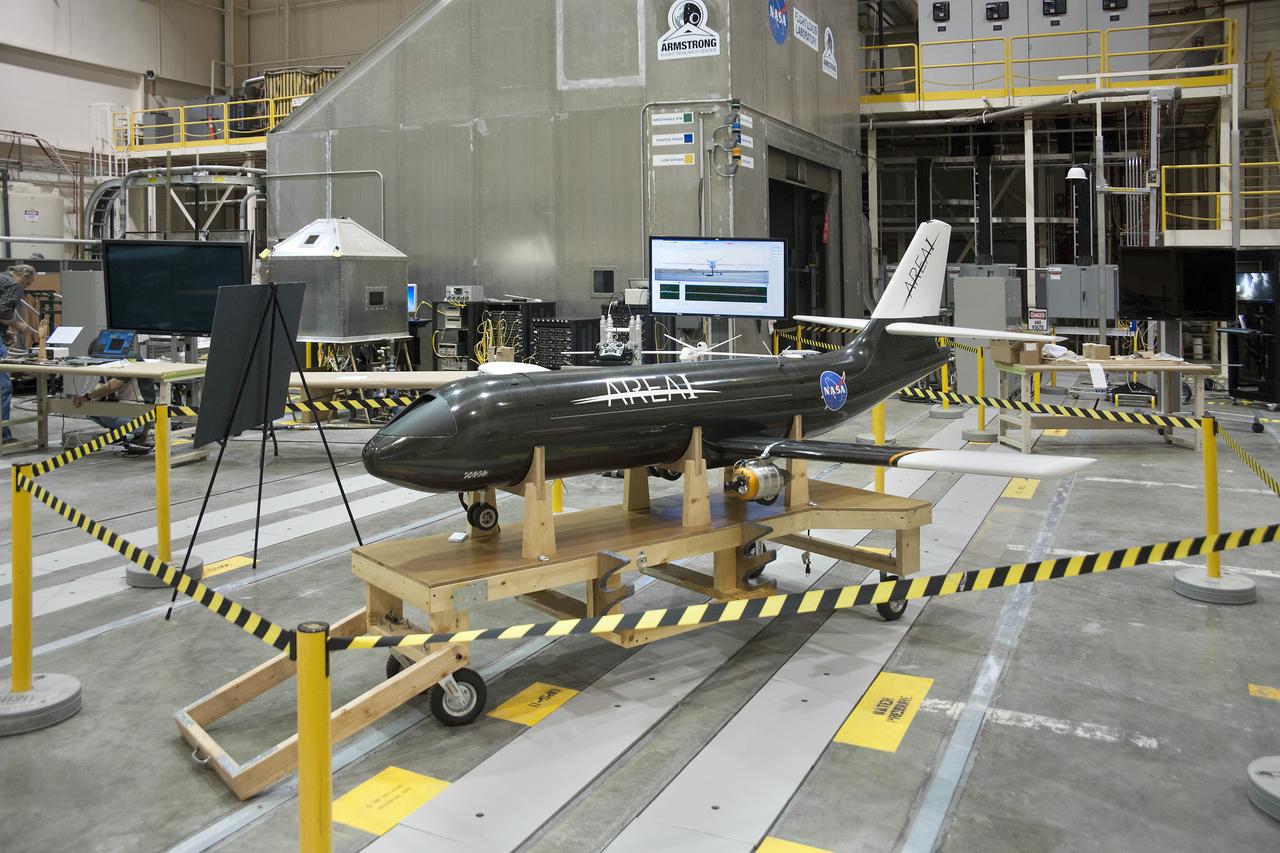

The objectives of testing on PTERA include the development of tools and vetting of system integration, evaluation of vehicle control law, and analysis of SAW airworthiness to examine benefits to in-flight efficiency.
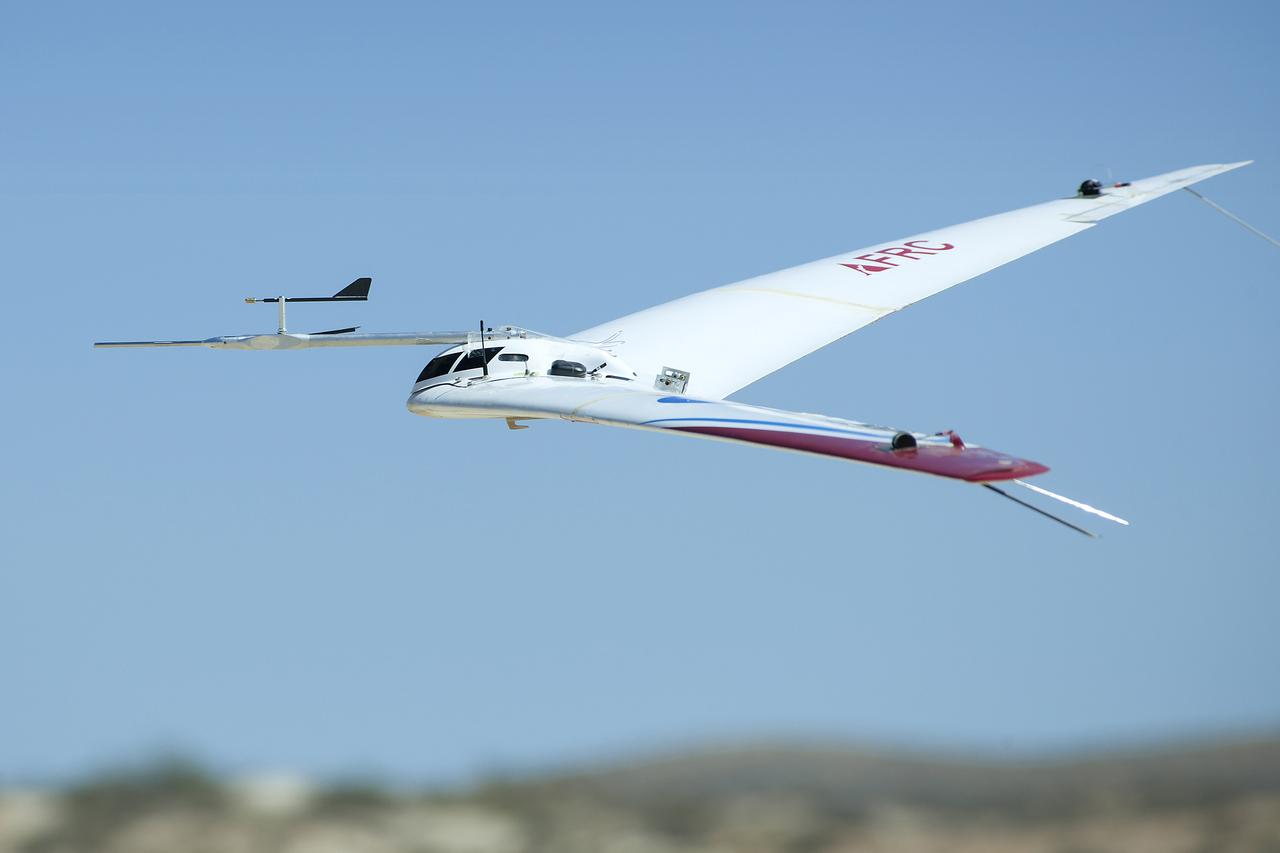

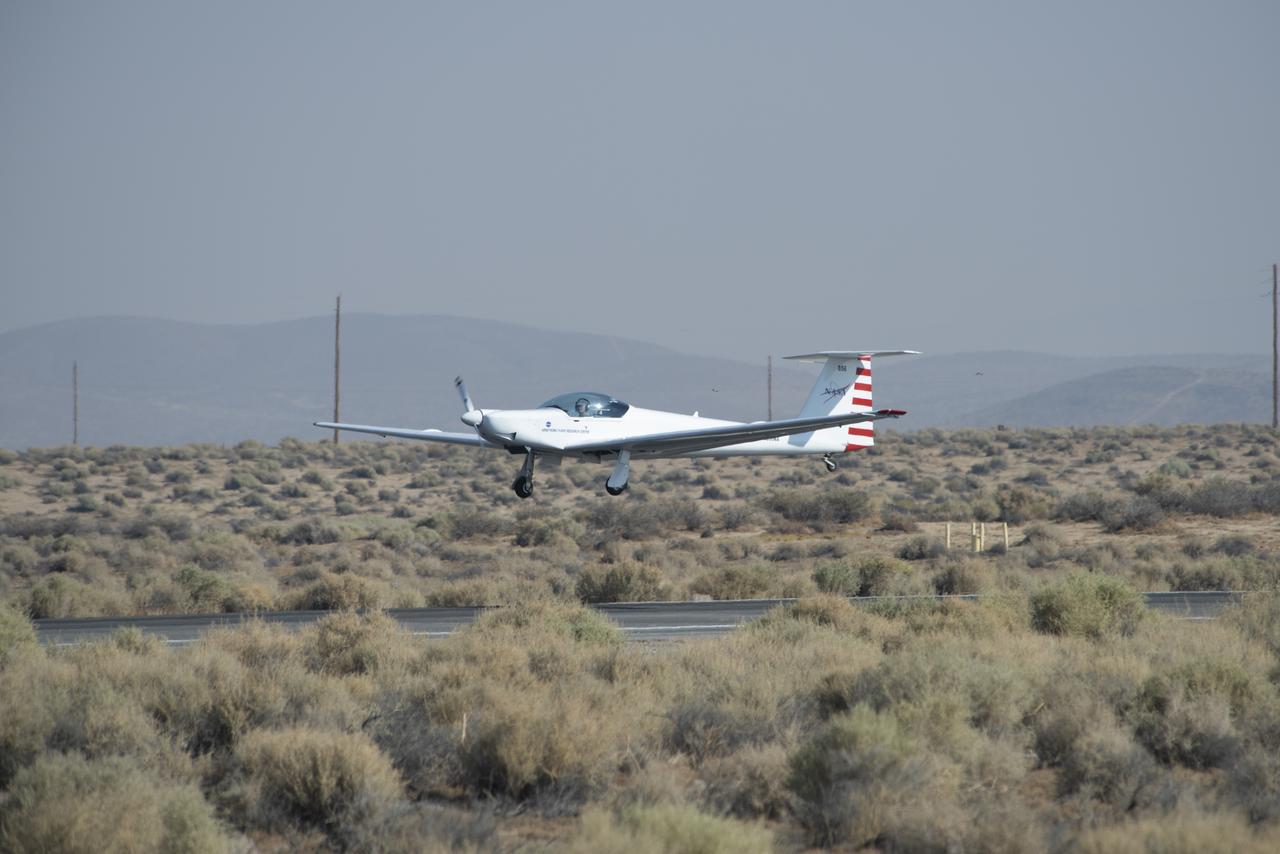
The proposed Prandtl-m is based on the Prandtl-d seen coming in for a landing during a flight test in June. The aerodynamics offer a solution that could lead to the first aircraft on Mars.
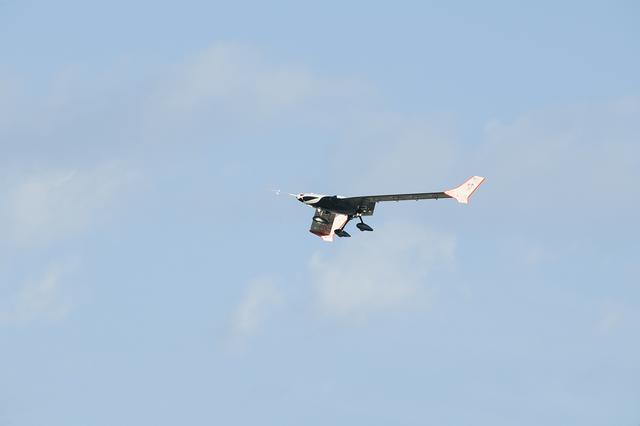

Long, thin, high-aspect-ratio wings are considered crucial to the design of future long-range aircraft, including fuel-efficient airliners and cargo transports. Unlike the short, stiff wings found on most aircraft today, slender, flexible airfoils are susceptible to uncontrollable vibrations, known as flutter, and may be stressed by bending forces from wind gusts and atmospheric turbulence. To improve ride quality, efficiency, safety, and the long-term health of flexible aircraft structures, NASA is using the X-56A Multi-Utility Technology Testbed (MUTT) to investigate key technologies for active flutter suppression and gust-load alleviation.
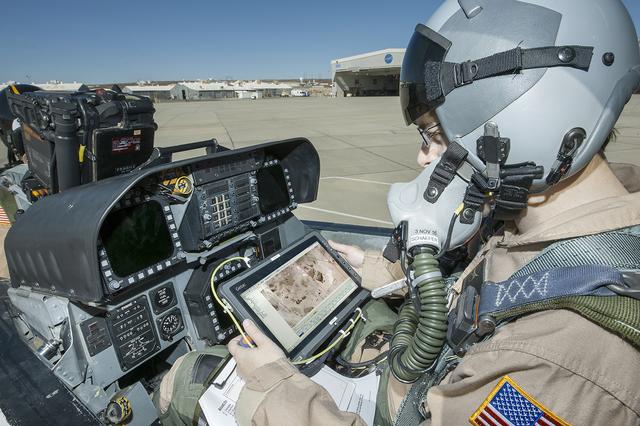

Flight Test Engineer Jacob Schaefer inspects the Cockpit Interactive Sonic Boom Display Avionics, or CISBoomDA, from the cockpit of his F-18 at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
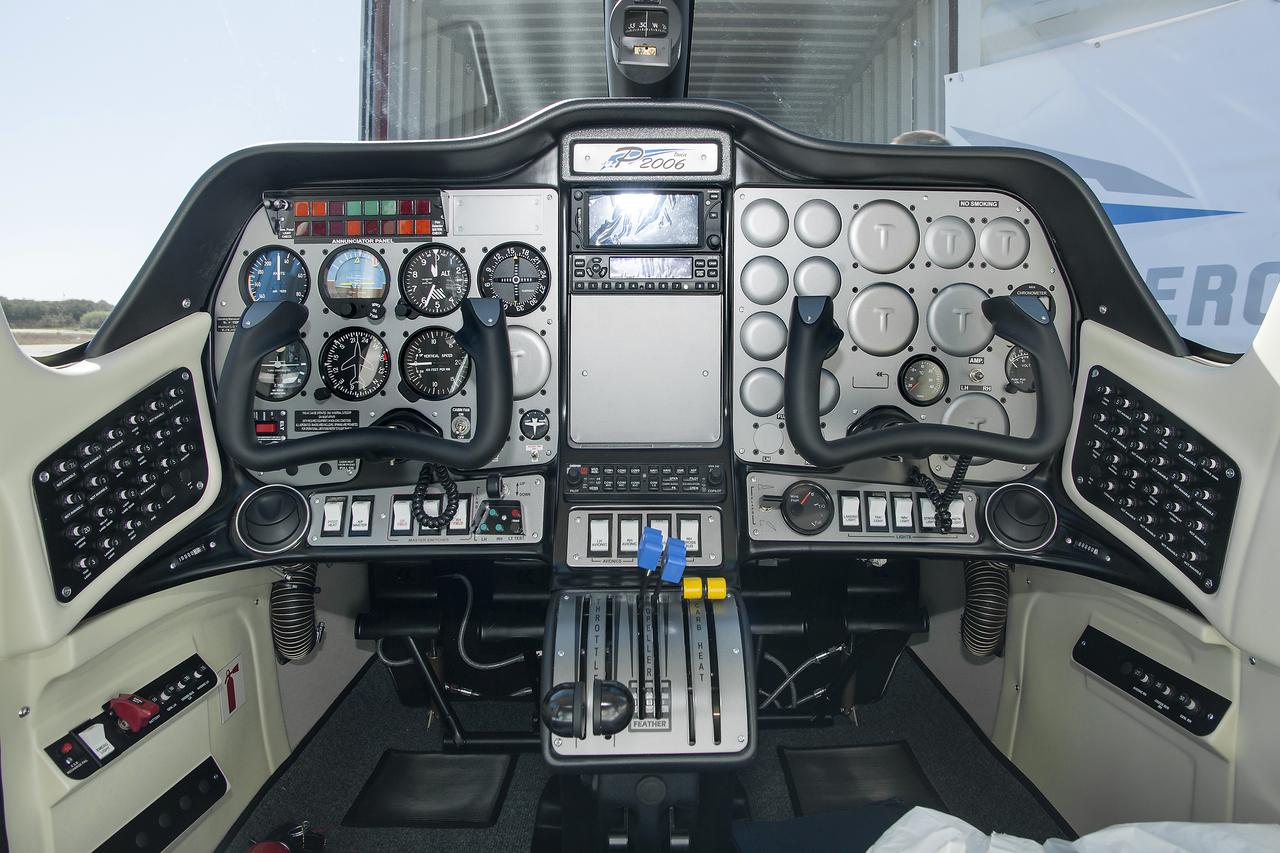

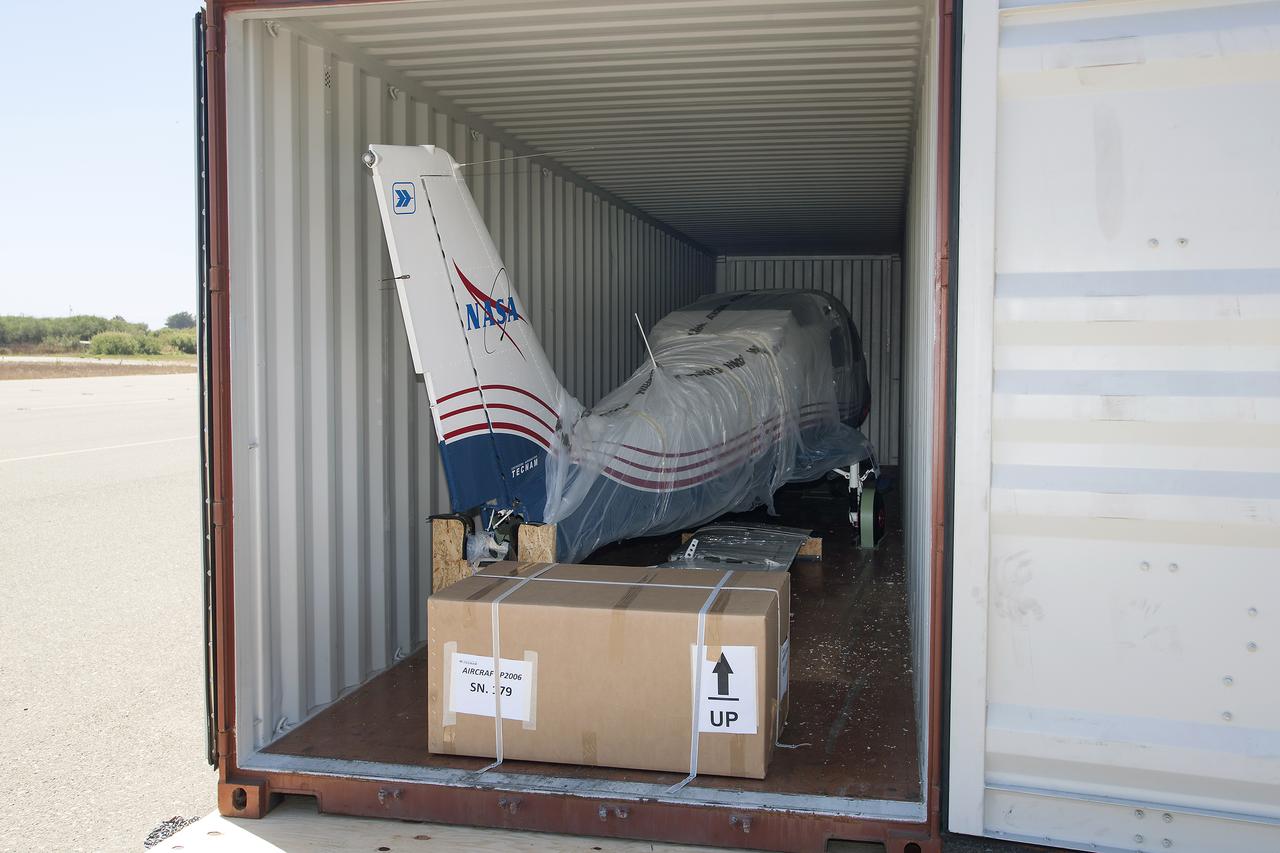
The Italian Tecnam aircraft fuselage, P2006T, arrived in California and will be integrated with the wing for electric propulsion becoming X-57, or Maxwell.
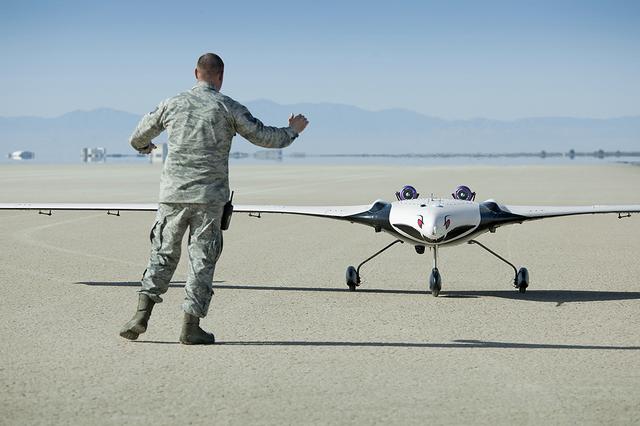

The X-56A Multi-Utility Technology Testbed (MUTT) is greeted on an Edwards Air Force Base runway by a U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) team member. NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center and the AFRL, along with participants from Langley Research Center and Glenn Research Center, and support from Lockheed Martin, are using the second X-56A (dubbed “Buckeye”) to check out aircraft systems, evaluate handling qualities, characterize and expand the airplane’s performance envelope, and verify pre-flight predictions regarding aircraft behavior. The 20-minute flight marked the beginning of a research effort designed to yield significant advances in aeroservoelastic technology using a low-cost, modular, remotely piloted aerial vehicle.
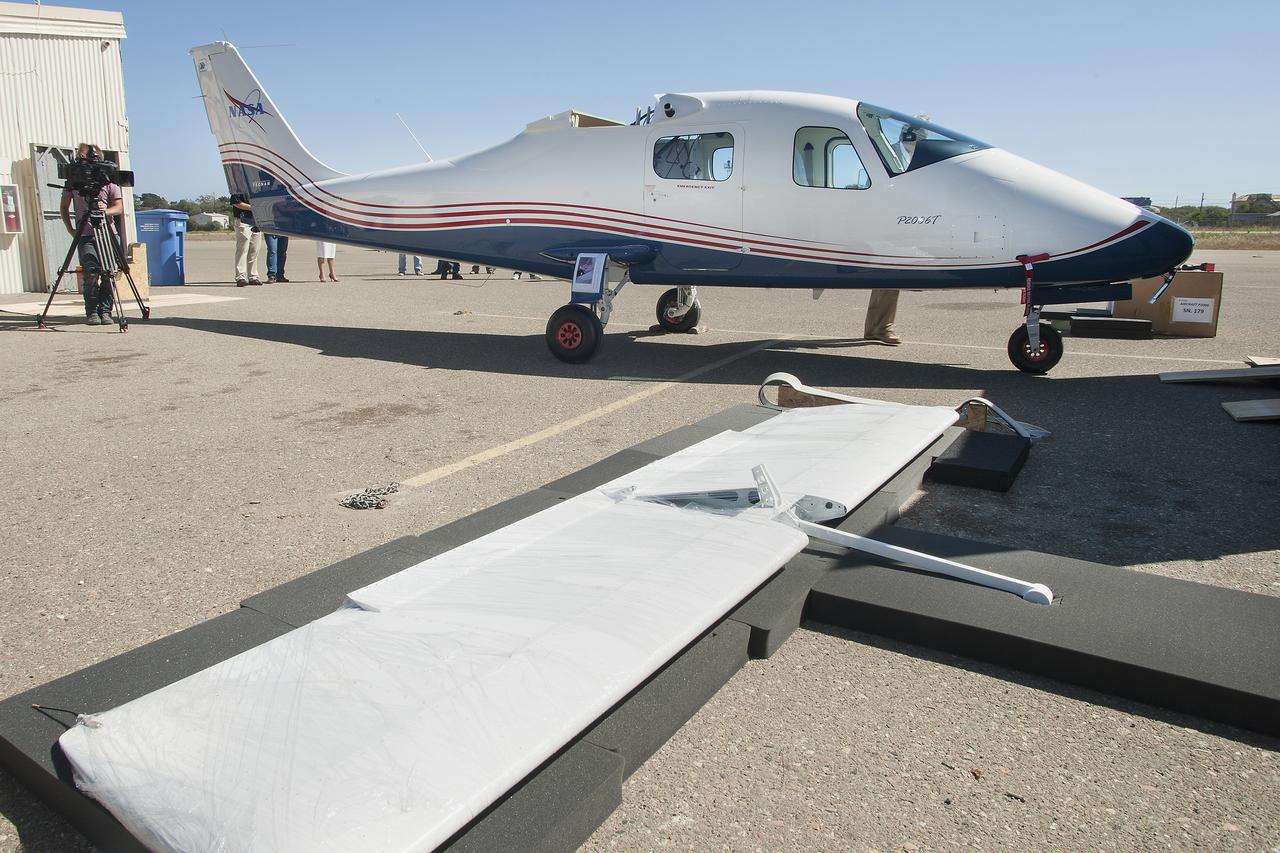

Preparations are underway to inspect, weigh and balance the Tecnam fuselage before it heads to Mojave, California, for wing integration.
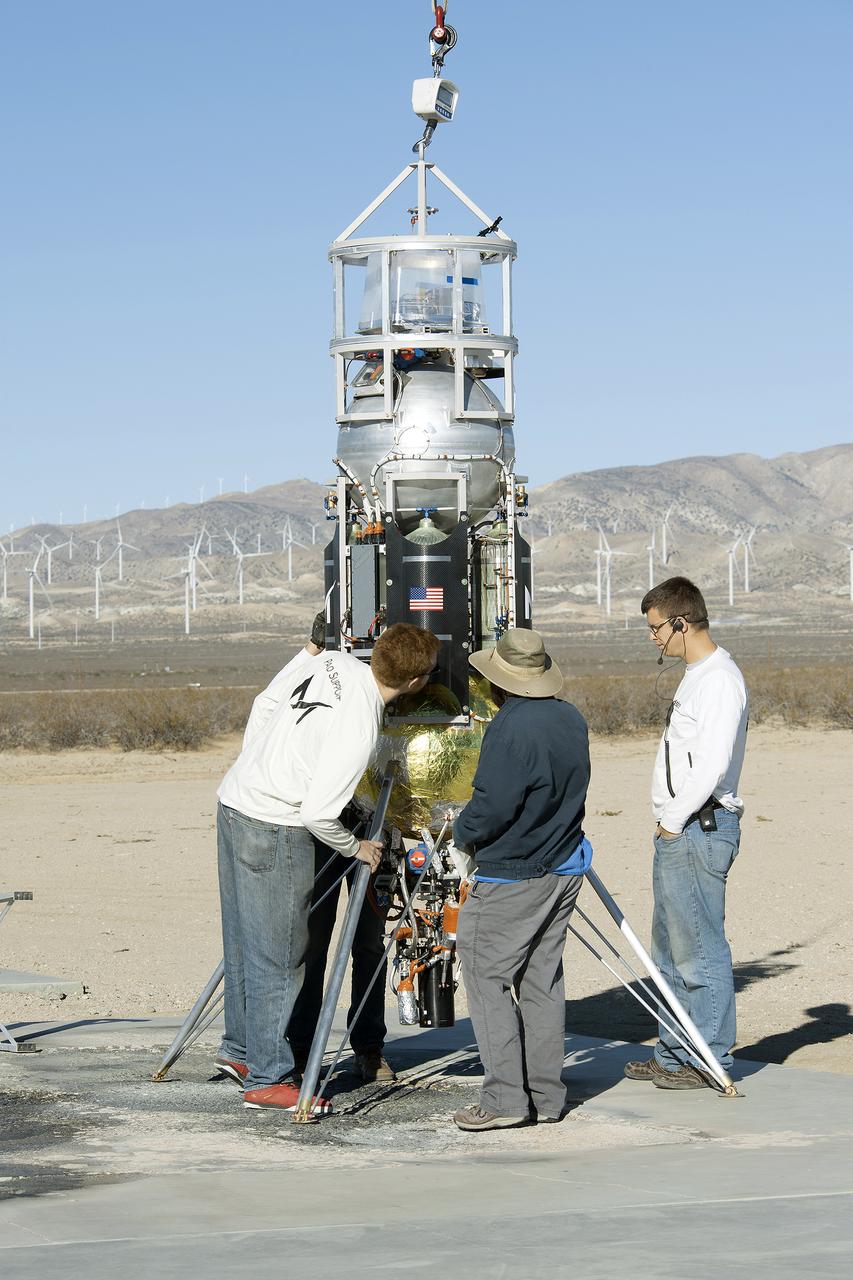

From left to right Masten employees, Luke Farrell, Richard Garcia and intern Alex Drozda employees prepare Xodiac rocket to flight test JHU APL technology.
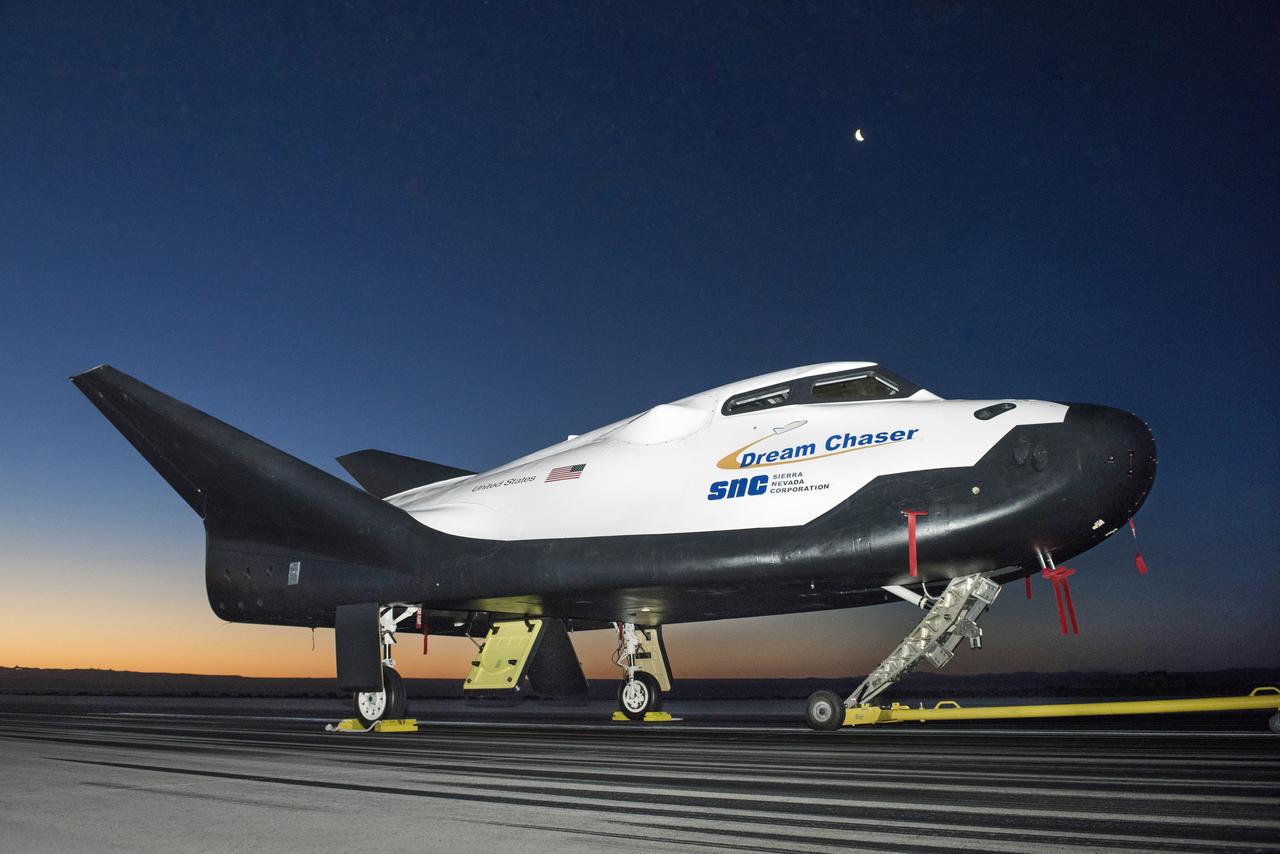

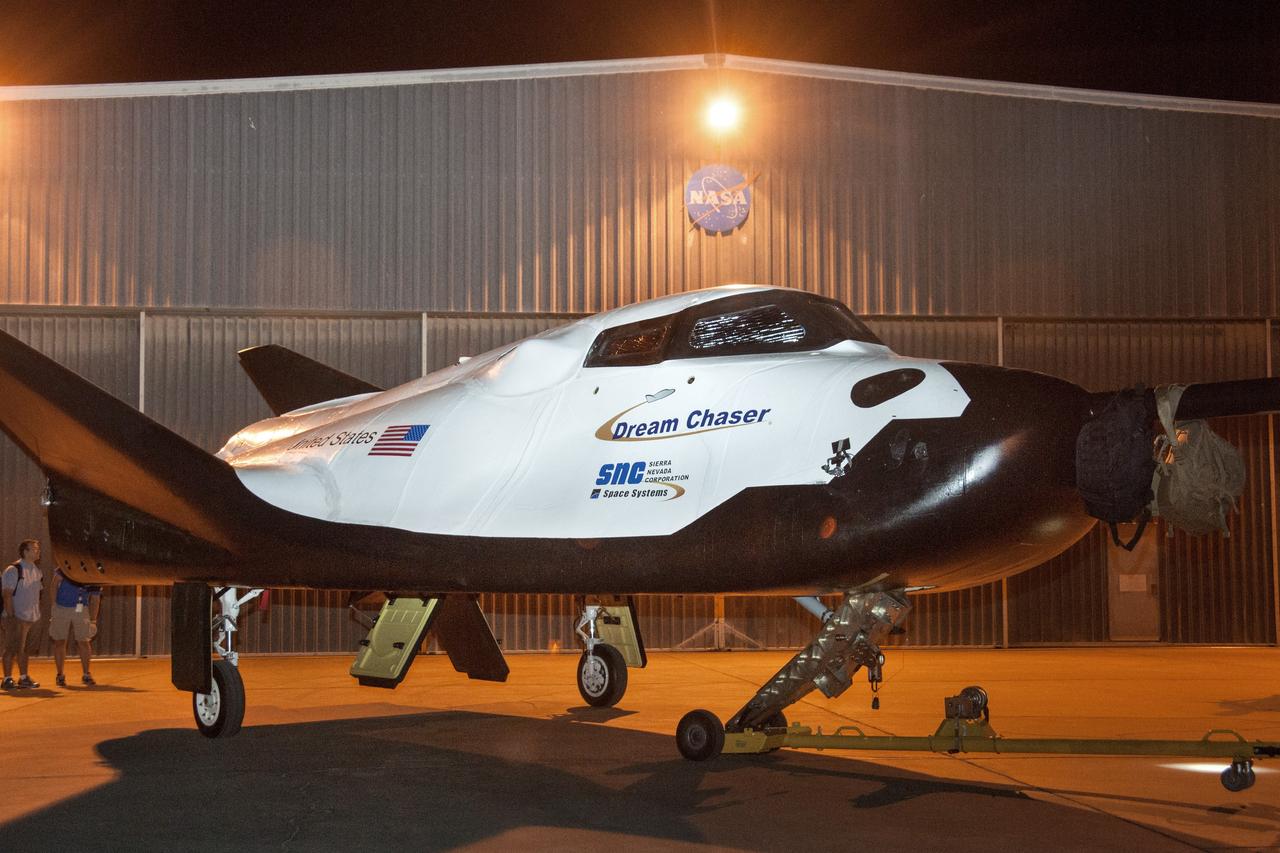
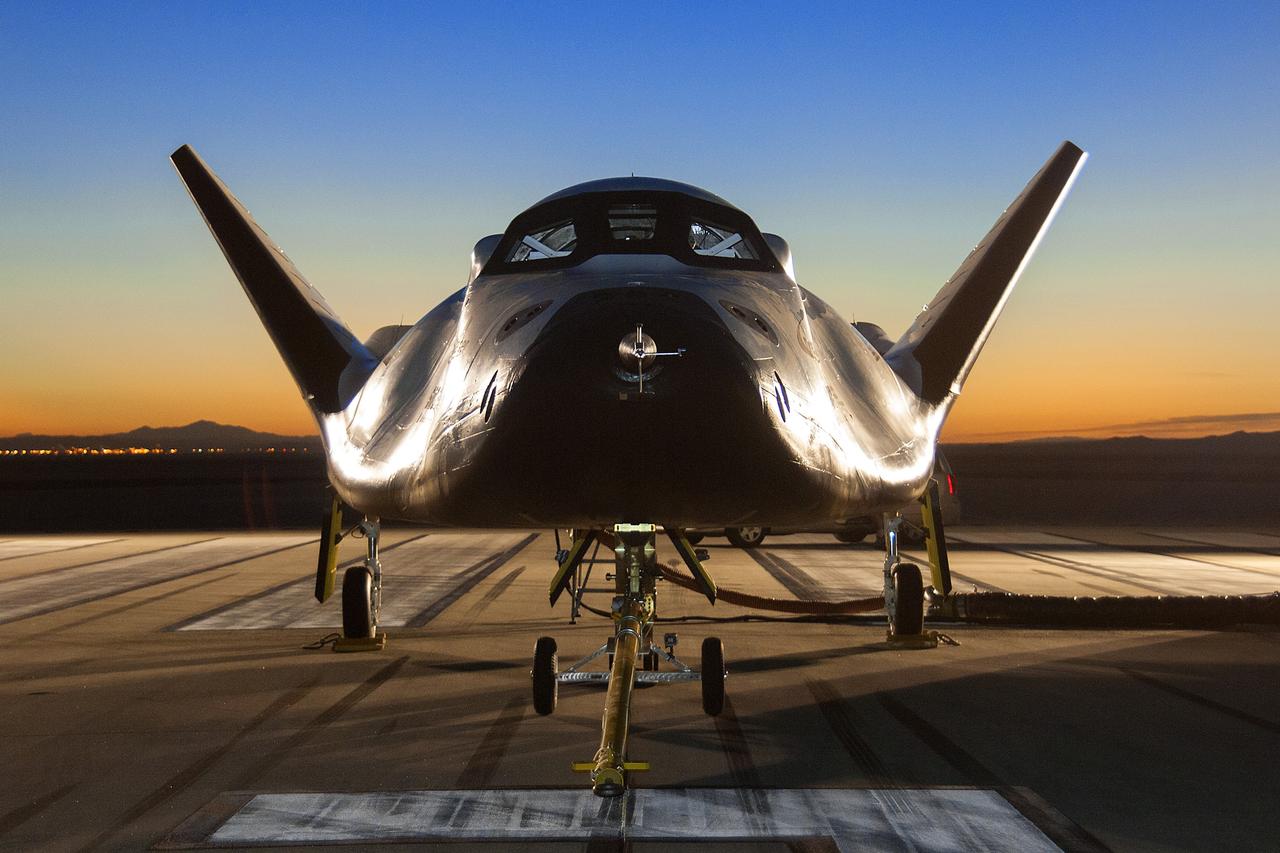
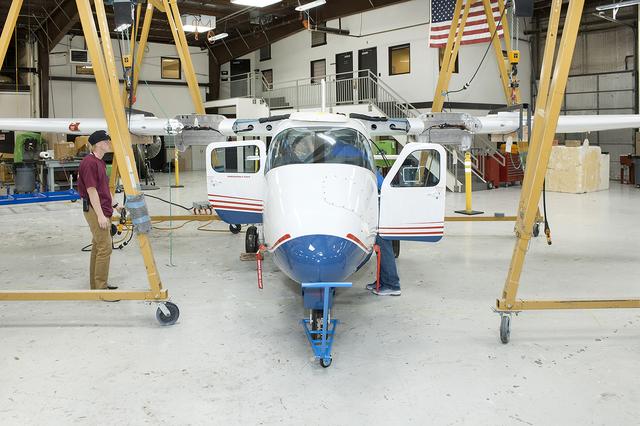
Sierra Nevada Corporation's (SNC) Dream Chaser® spacecraft shown on the runway at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center on May 20 preparing for a tow-test. The spacecraft is undergoing ground tests leading up to a free flight test later this year.
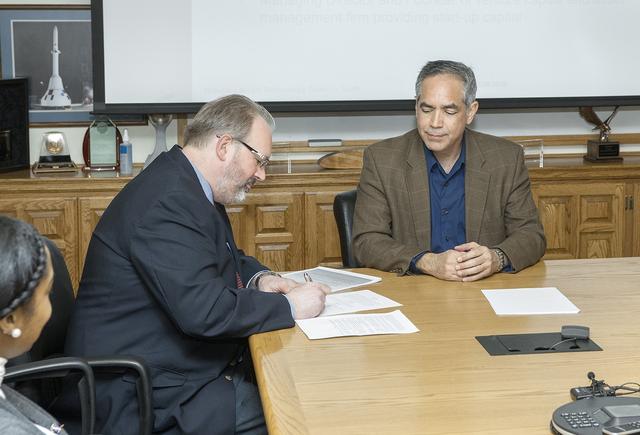

Vigilant Aerospace Systems CEO Kraettli Epperson, left, and NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center Director David McBride, sign the agreement for the company to commercialize a large drone communication system for the Federal Aviation Administration's aircraft tracking system called the Automatic Dependent Surveillance Broadcast. This communication system, which is to be mandated by the FAA for most aircraft in 2020, brings large, unmanned aircraft a step closer to flying in the National Airspace System.
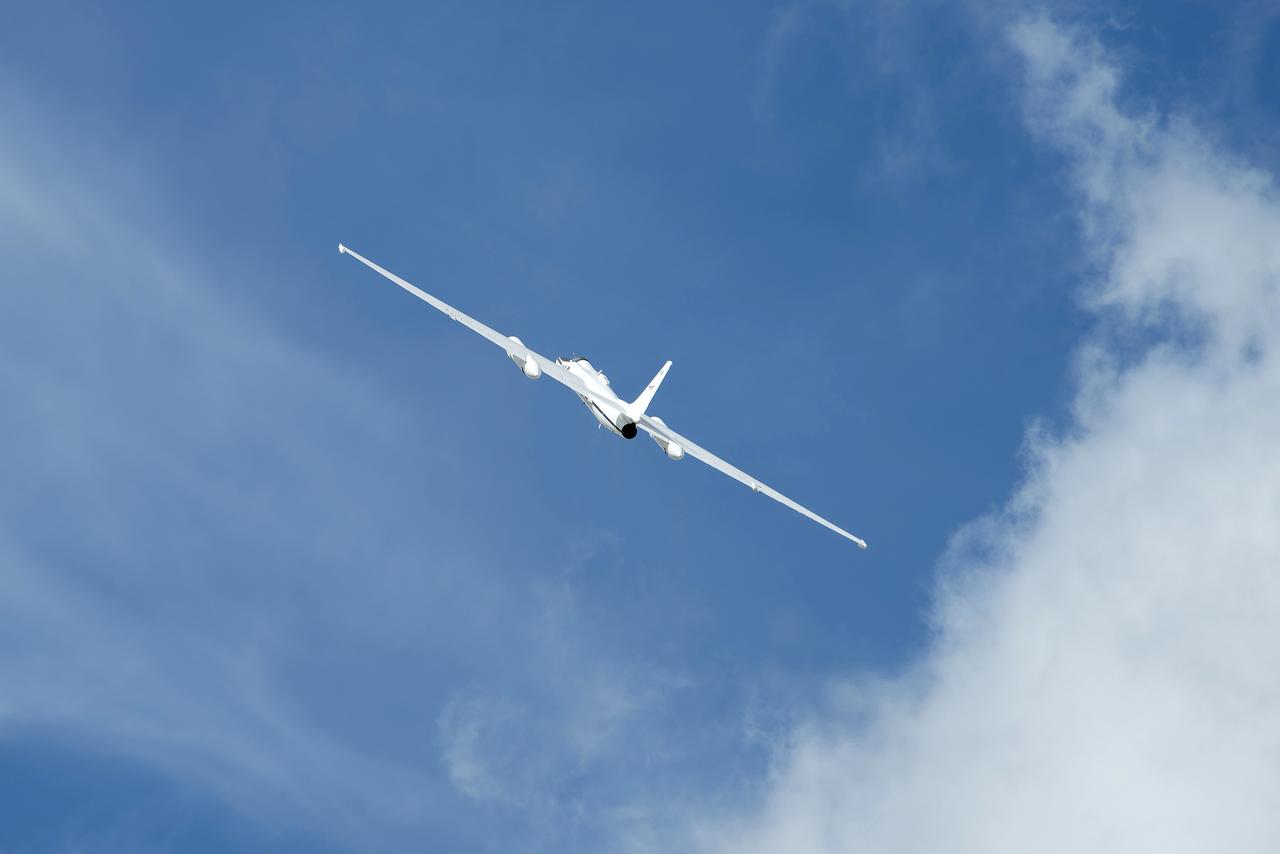

ER-2 flyover at L.A. County Airshow, March 25, 2017. NASA will be working with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) on their newest weather satellite, Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-R-series, or GOES-R, that launched into orbit Nov. 19. Now that it has reached its final designated orbit, GOES-R will be known operationally as GOES-16. The ER-2 will help NOAA calibrate sensors and validate data transmitted down from the satellite. The formal ER-2 science flights will take place between March and Mary of 2017 in two phases; during phase one, flights will be operated from the aircraft's normal base of operations at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s Building 703. Phase two flights will be based out of Warner Robbins Air Force Base in Georgia, where thunderstorm conditions can be more easily found and observed.
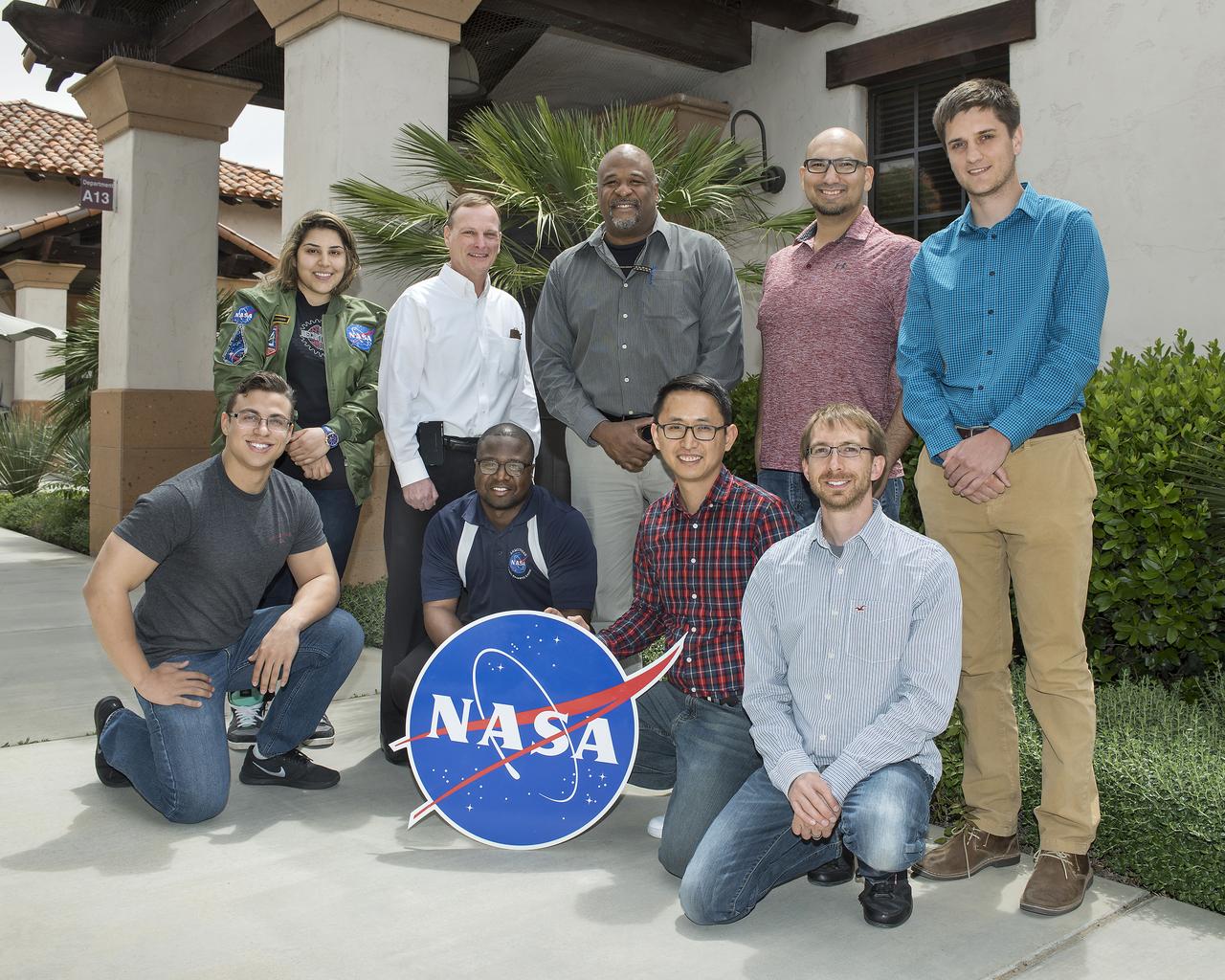

The Fiber Optic Sensing System team includes in the front from left Nick Finks, Ryan Warner, Patrick Chan and Paul Bean. In the back row from left are Shideh Naderi, Jeff Bauer, Allen Parker, Frank Pena and Nathan Perreau. Lance Richards, Anthony Piazza and Phil Hamory are current FOSS team members who are not pictured.

Charlie Lundquist, NASA Orion deputy program manager, right, presents an American flag flown aboard the Orion capsule during the Exploration Flight Test-1 mission to Armstrong Deputy Director Patrick Stoliker.
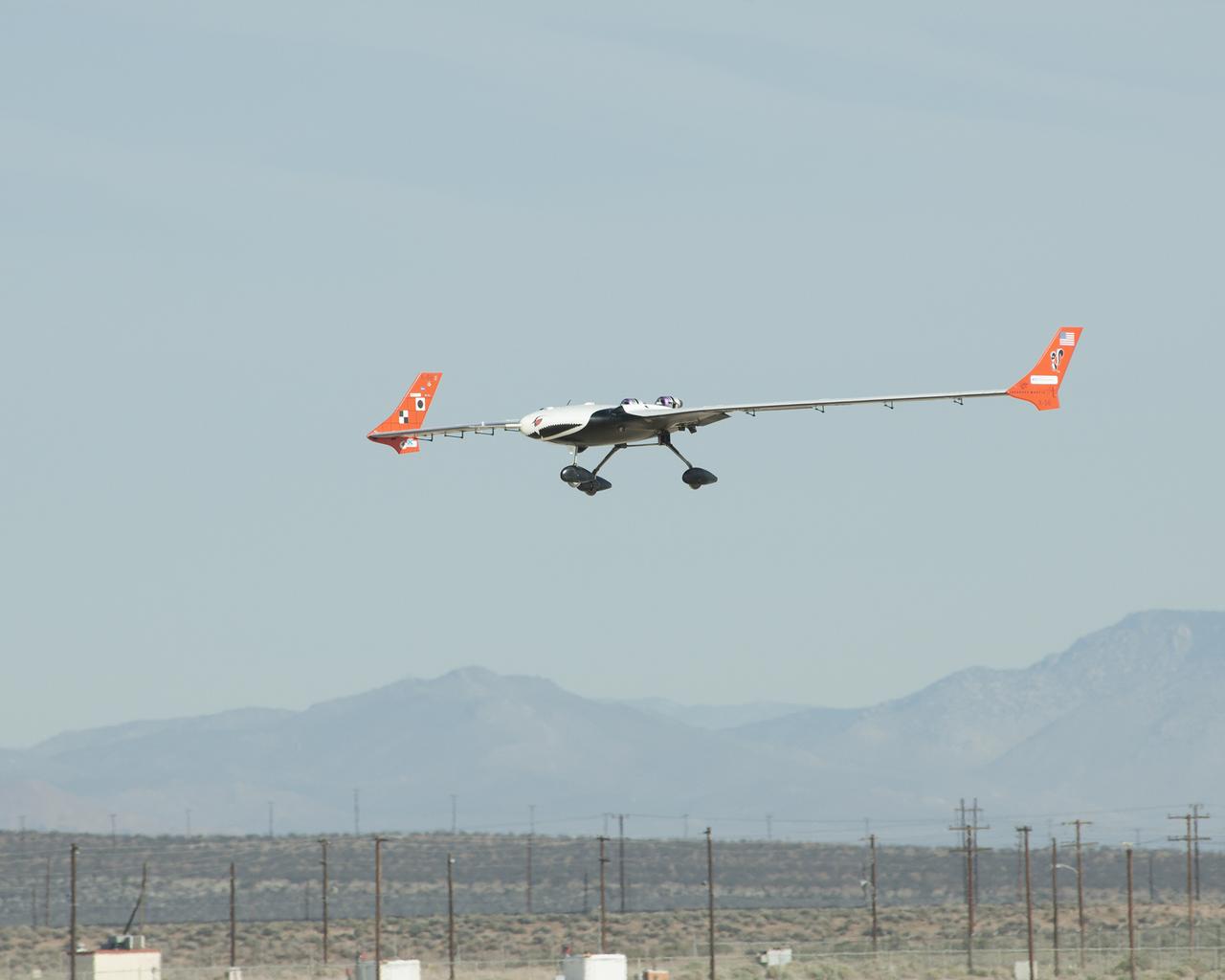

NASA researchers are using the X-56A, a low-cost, modular, remotely piloted aerial vehicle, to explore the behavior of lightweight, flexible aircraft structures.
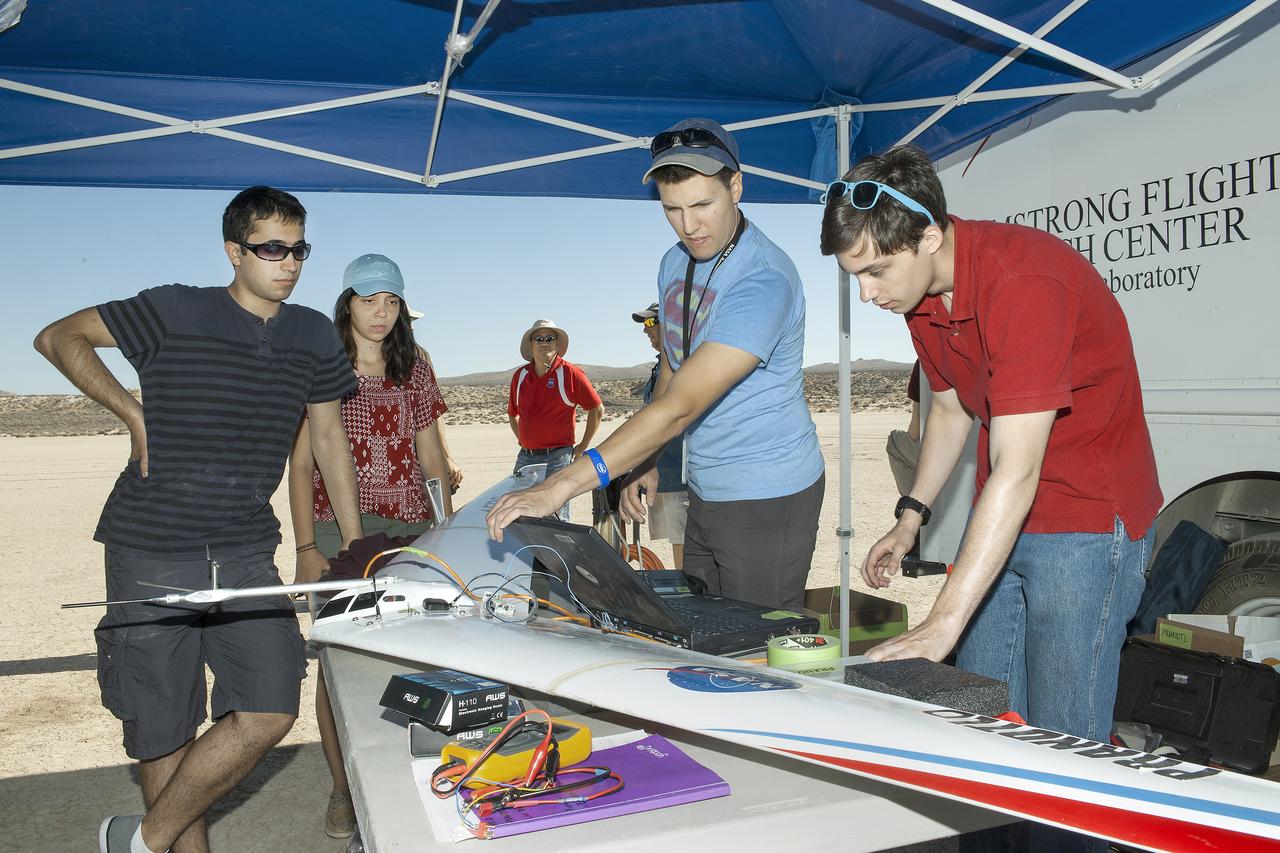

Jonathan Zur, from left, Alexandra Ocasio, Derek Abramson, Red Jensen, Etan Halberg and Keenan Albee wait for data to download from a Prandtl-d flight
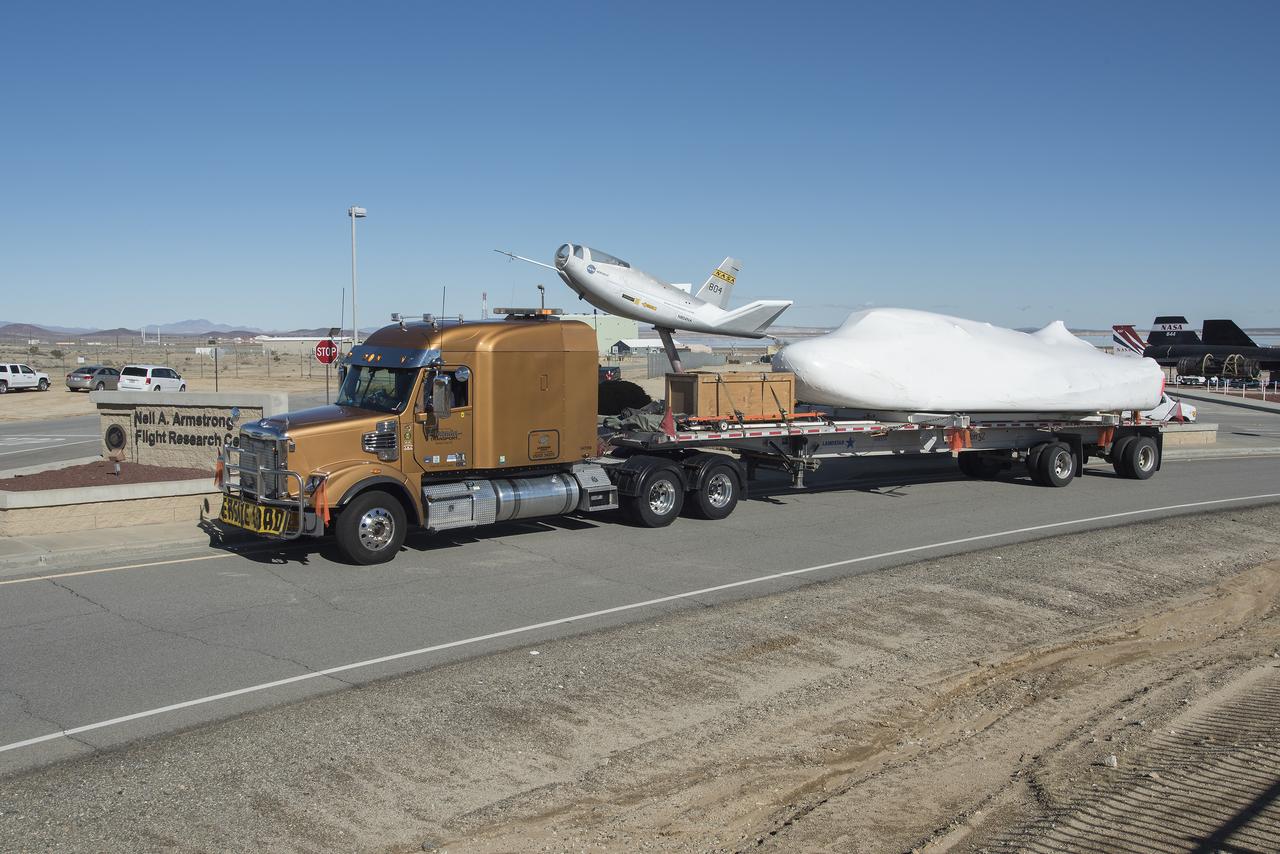

SNC delivers Dream Chaser to NASA Armstrong posing it with the HL-10 lifting body flown the 1960s.
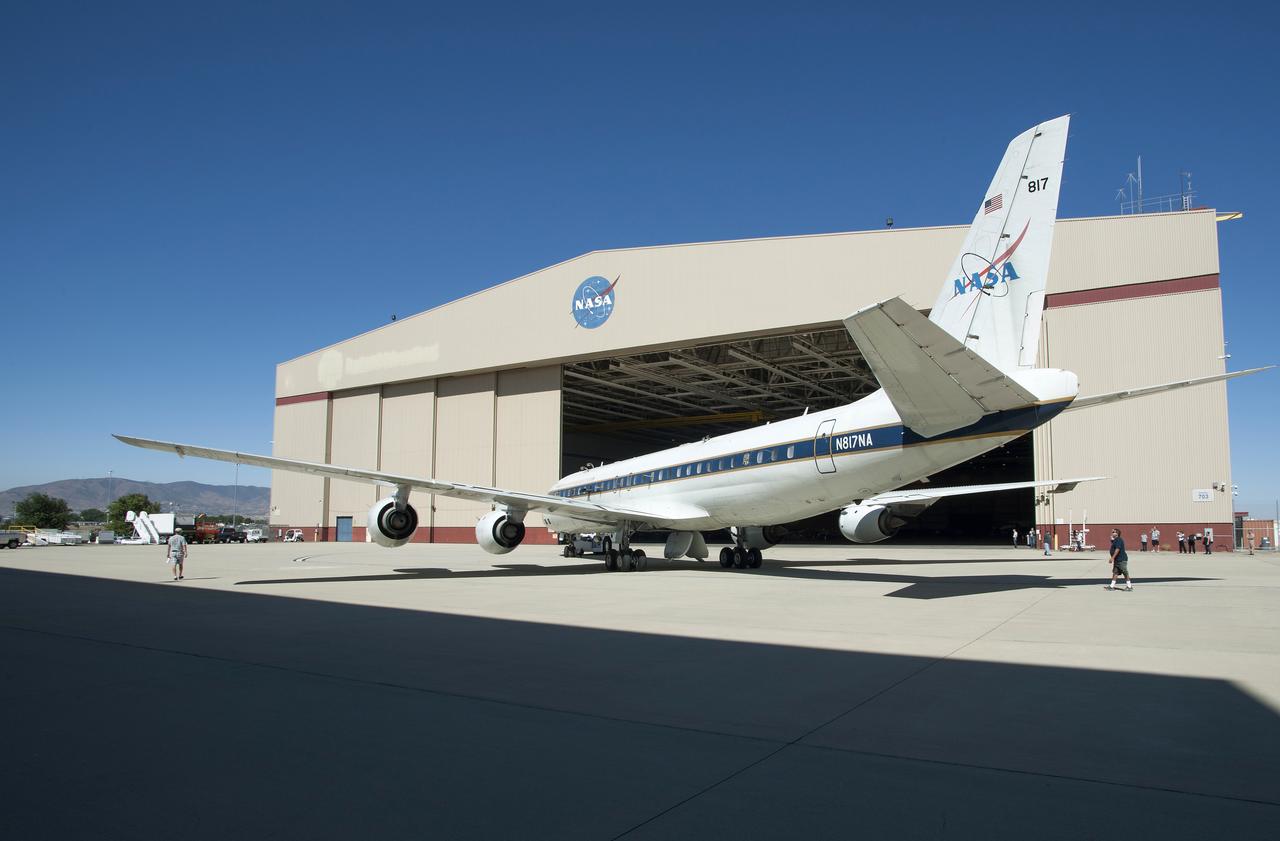

Media observe as ground crews tow NASA’s DC-8 airborne laboratory into its Palmdale, California hangar.
The CISBoomDA display allows the pilot of a supersonic aircraft to monitor the locations of any sonic booms produced, to prevent the aircraft from positioning booms in restricted area.
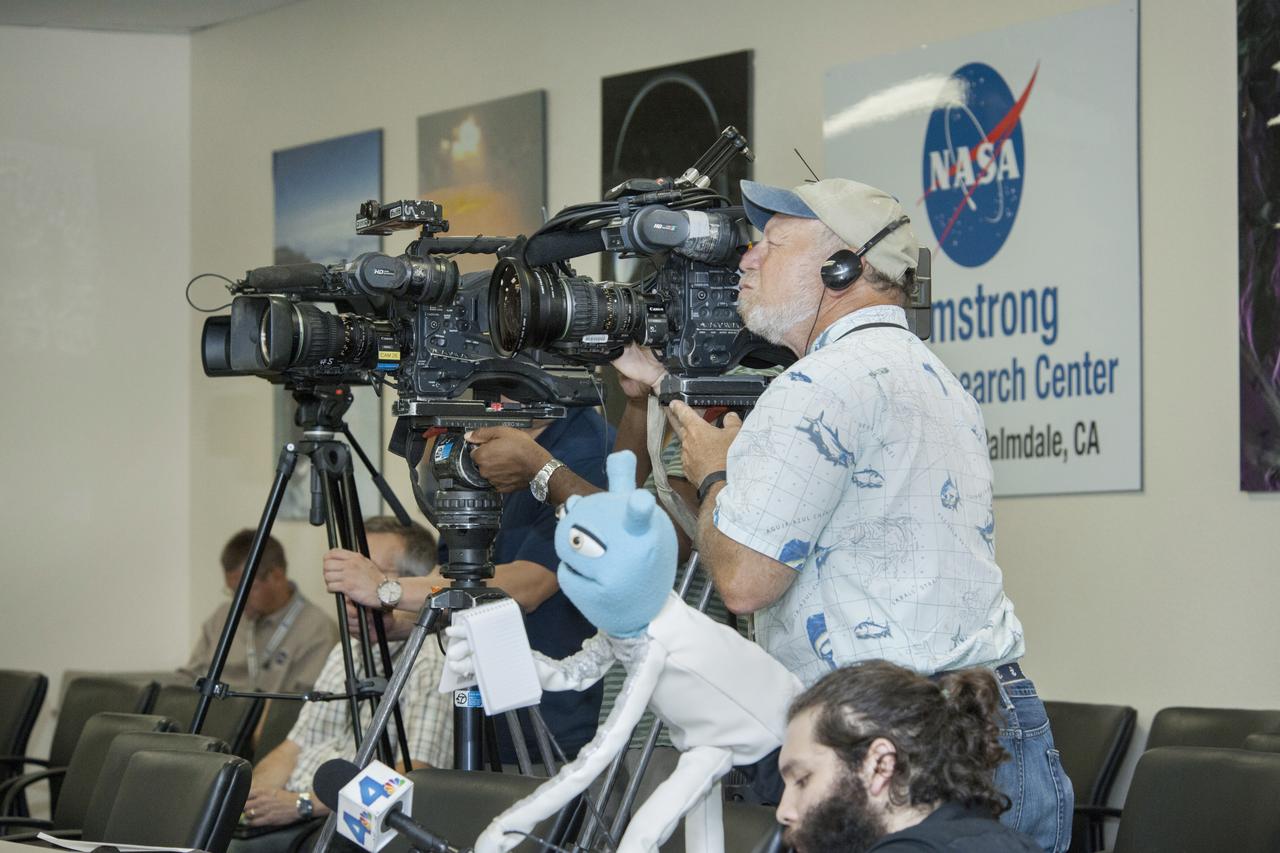

Media, including a puppeteer, participate in a press conference for the ATom airborne science mission which is studying the atmosphere.
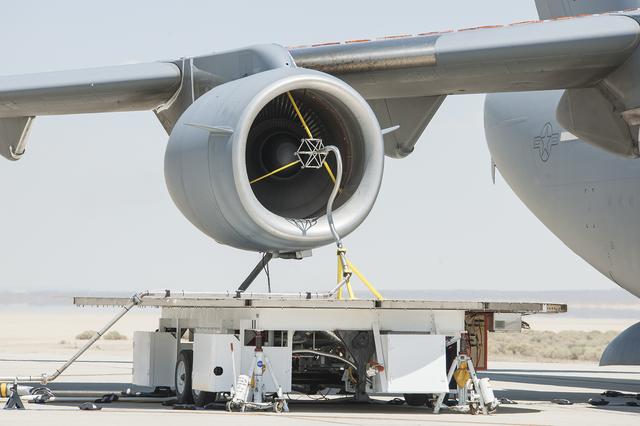

The volcanic ash distribution spider, shown here in the inlet of the engine while running, was used to send the ultra-fine particles of ash through the engine.
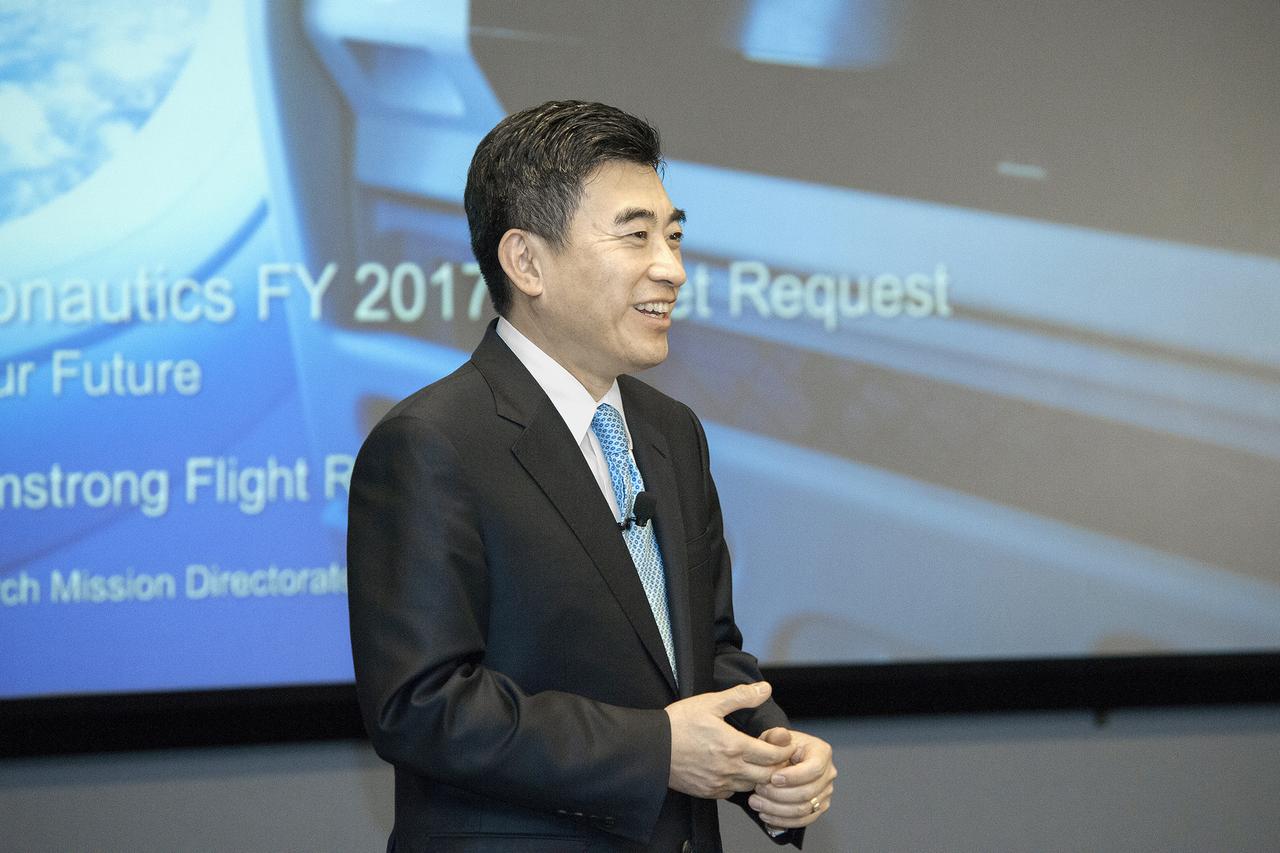

NASA Associate Administrator for Aeronautics Jaiwon Shin talked to staff and managers at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in California March 17 about the New Horizons initiative. The 10-year plan could substantially improve aviation and provide major economic benefits.

The Tecnam P2006T undergoes wing integration at Scaled Composites in Mojave, California, where the aircraft’s system will be converted to feature electric propulsion.

The TAMDAR Edge probe seen in the middle of the NASA Armstrong Ikhana is flying on a large remotely piloted aircraft for the first time.

Honeywell supplied a specially instrumented twin-engine King Air to serve as an intruder for NASA’s Ikhana UAS.
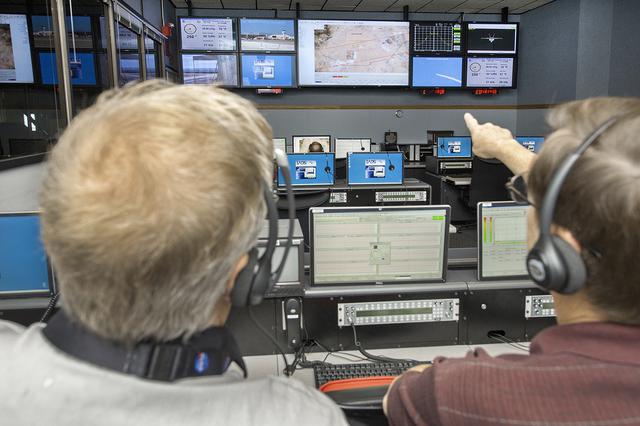

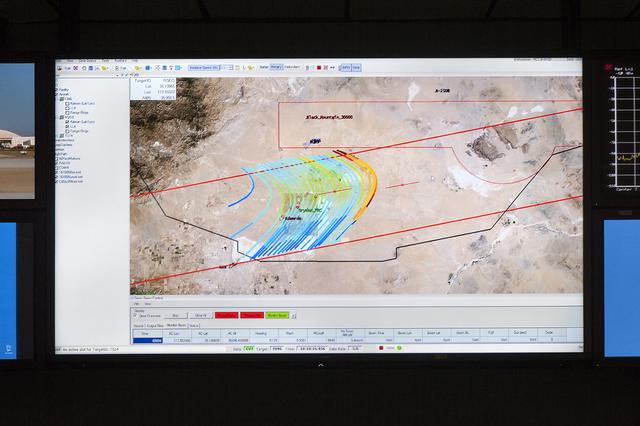
Engineers and researchers at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center monitored the flights, and were able to observe the mapping of the sonic boom carpet from the F-18, from the center’s Mission Control Center.

The TAMDAR Edge probe seen in the middle of the NASA Armstrong Ikhana is flying on a large remotely piloted aircraft for the first time.
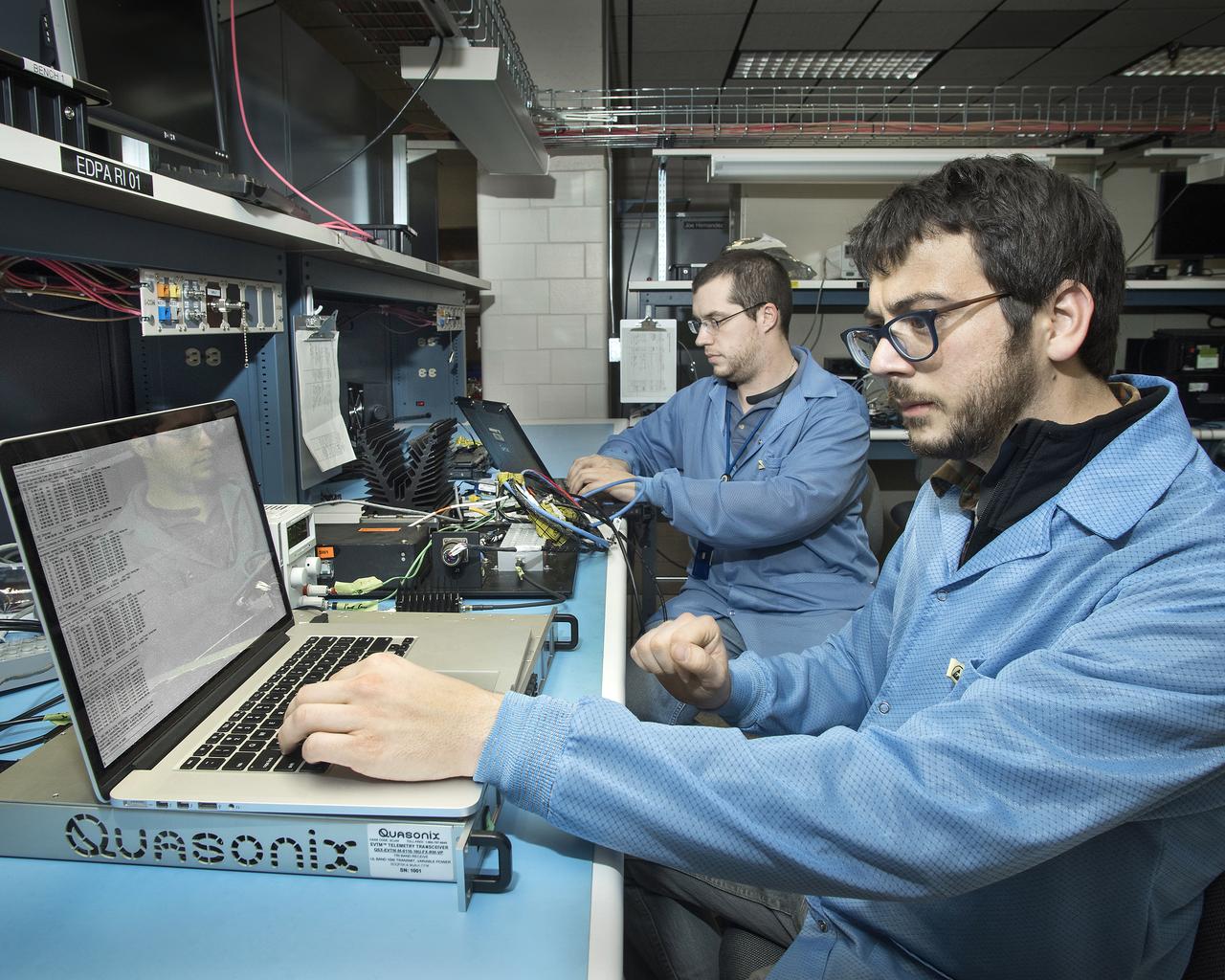

Otto Schnarr, front, and Matthew Waldersen check out the Advanced Data Acquisition and Telemetry System in an Armstrong laboratory.

Shideh Naderi works on designing the electronics for the next generation Fiber Optic Sensing System.

Initial flight-testing of the ACTE followed extensive wind tunnel experiments. For the first phase of ACTE flights, the experimental control surfaces were locked at a specified setting. Varied flap settings on subsequent tests are now demonstrating the capability of the flexible surfaces under actual flight conditions.

Patrick Chan demonstrates one way that the Fiber Optic Sensing System is used by bending a fiber with a 3D representation of the fiber’s shape as it bends.

NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden, a former pilot and astronaut who flew on four shuttle missions, appeared natural at the controls of the X-57 simulator cockpit, and flew a pair of simulations where he landed on the Edwards Air Force Base runway.

Otto Schnarr and Matthew Waldersen check out the Advanced Data Acquisition and Telemetry System in an Armstrong laboratory.
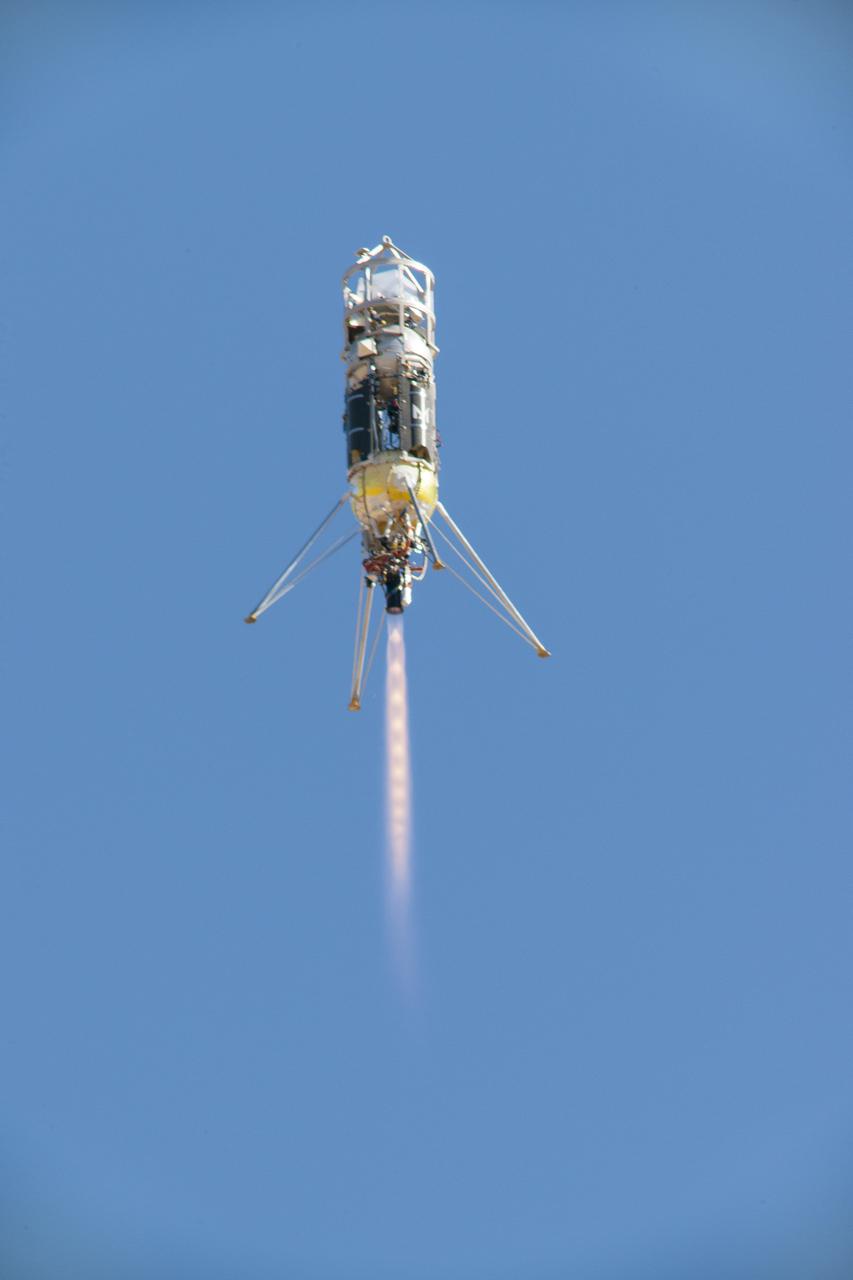

Masten rocket, Xodiac, launches out of Mojave Air and Space Port carrying JHU APL electromagnetic field measurement experiment.

The Tecnam P2006T cockpit for the X-57, or Maxwell, will be the first all electric propulsion aircraft once the plane and wing integration is complete.
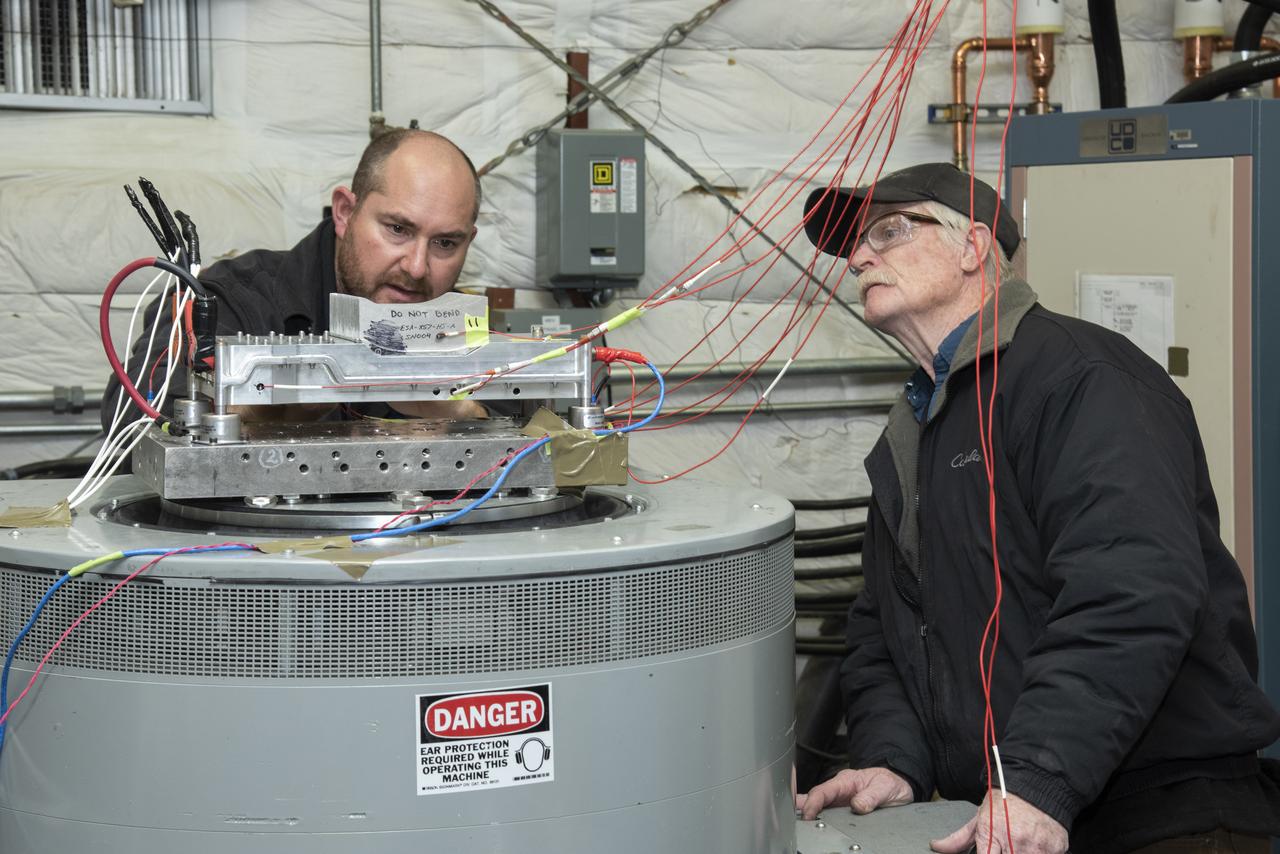

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASAs first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.
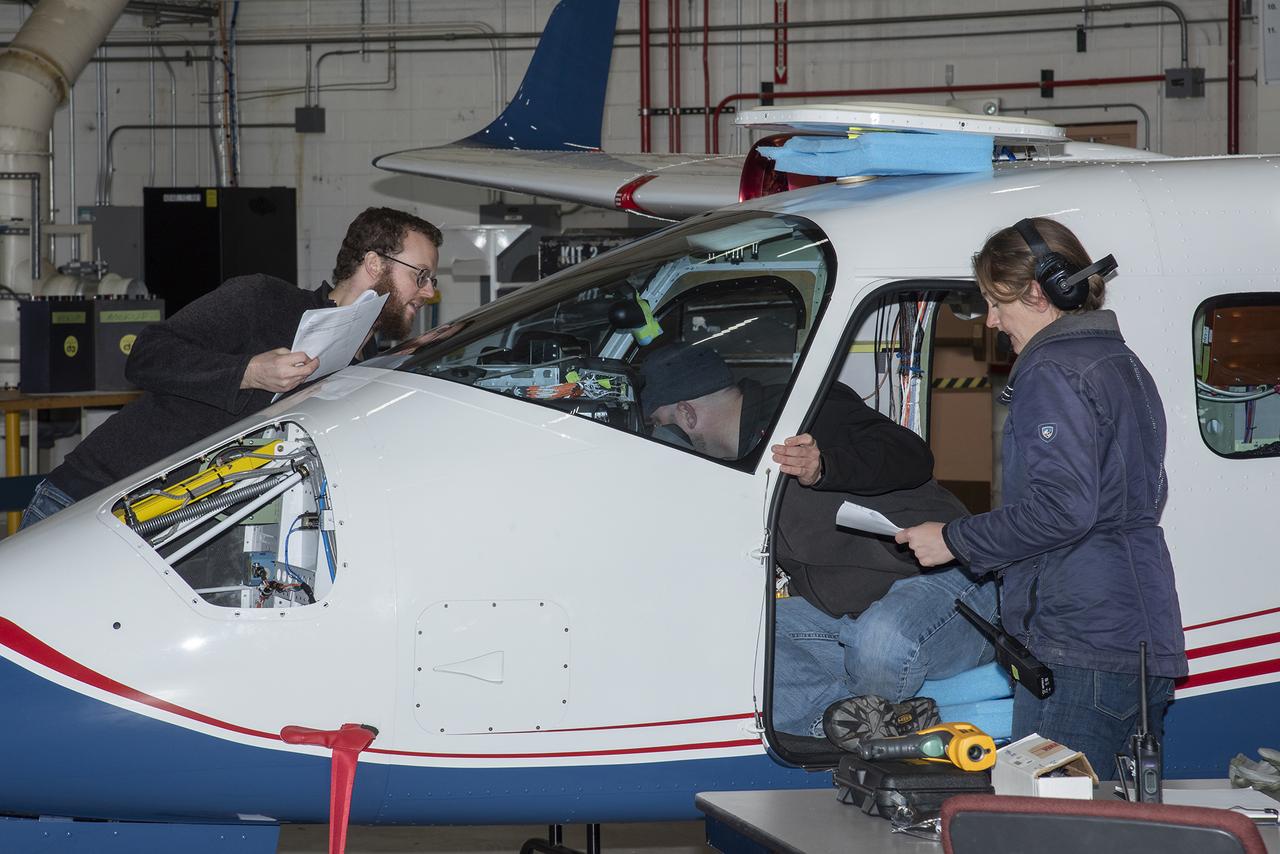

Telemetry testing begins on the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane, as the operations crew at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center records the results. Telemetry testing is a critical phase in X-57’s functional test series. In addition to confirming the ability of the X-57 aircraft to transmit speed, altitude, direction, and location to teams on the ground, telemetry testing also confirms the ability to transmit mission-critical-data, such as voltage, power consumption, and structural integrity. X-57’s goal is to help set certification standards for emerging electric aircraft markets.

The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project conducted connectivity and infrastructure flight tests with a NASA TG-14 glider aircraft at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center Sept. 30-Oct. 1, 2020. The flights were preparation for the NC Integrated Dry Run Test in December and allowed pilots to view the routes they will fly during the helicopter test.

Claudia Sales, NASA’s acting X-59 deputy chief engineer and airworthiness certification lead for the quiet supersonic research aircraft, supports ground testing for Acoustic Research Measurements (ARM) flights. The test campaign to evaluate technologies that reduce aircraft noise was conducted at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, in 2018.

The Navmar Applied Sciences Corporation’s TigerShark prepares for its final takeoff at Edwards Air Force Base for the Unmanned Aircraft Systems integration in the National Airspace Systems, Flight Test Series Six (FT6) project. FT6 flight tests took place at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California and focused on low size weight and power sensors for Detect and Avoid (DAA) operations in controlled airspace to inform the FAA through the RTCA Special Committee DAA Working Group on the phase 2 minimum operational performance standards for DAA and air-to-air radar.
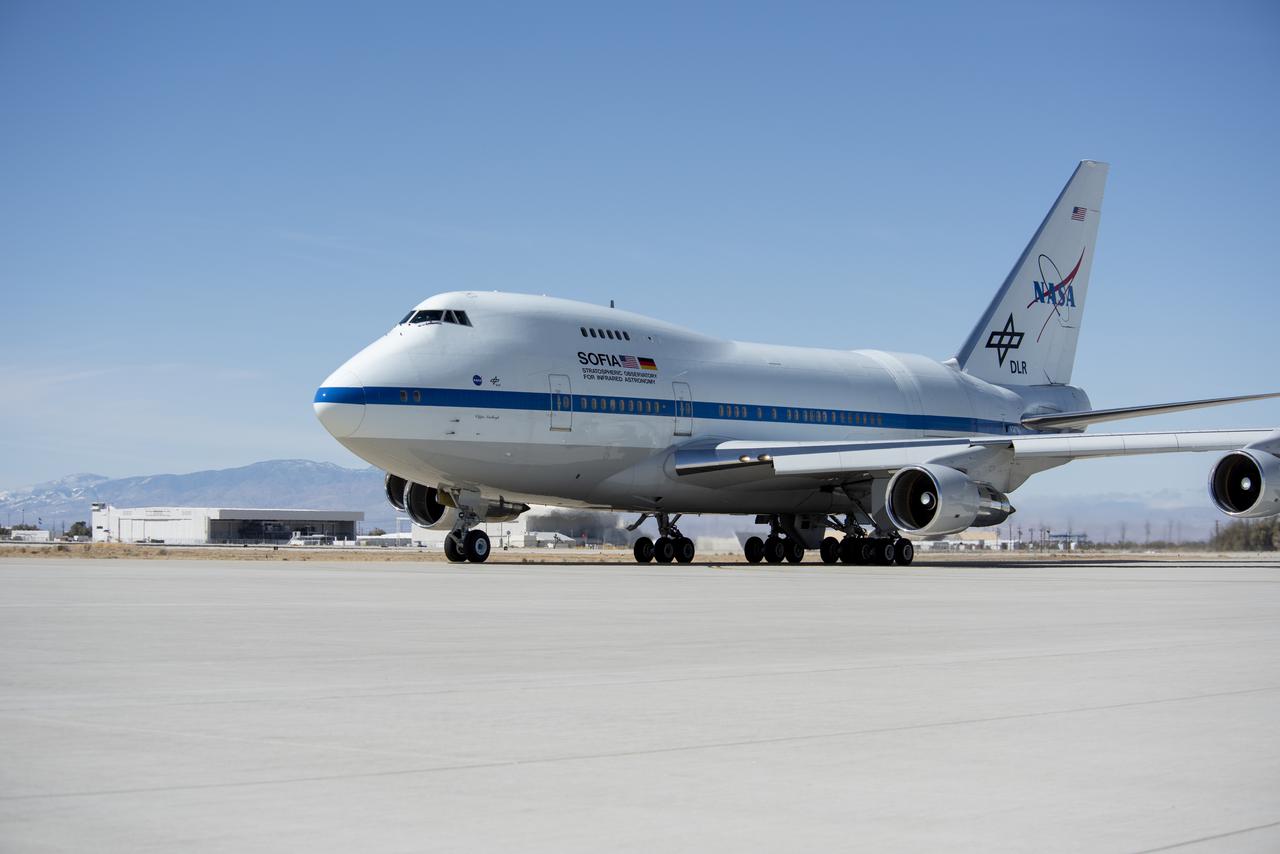

SOFIA Returns to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 Caption: SOFIA returns to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center building 703 in Palmdale, California on March 16, 2021 after spending six months in Germany conducting science observations.
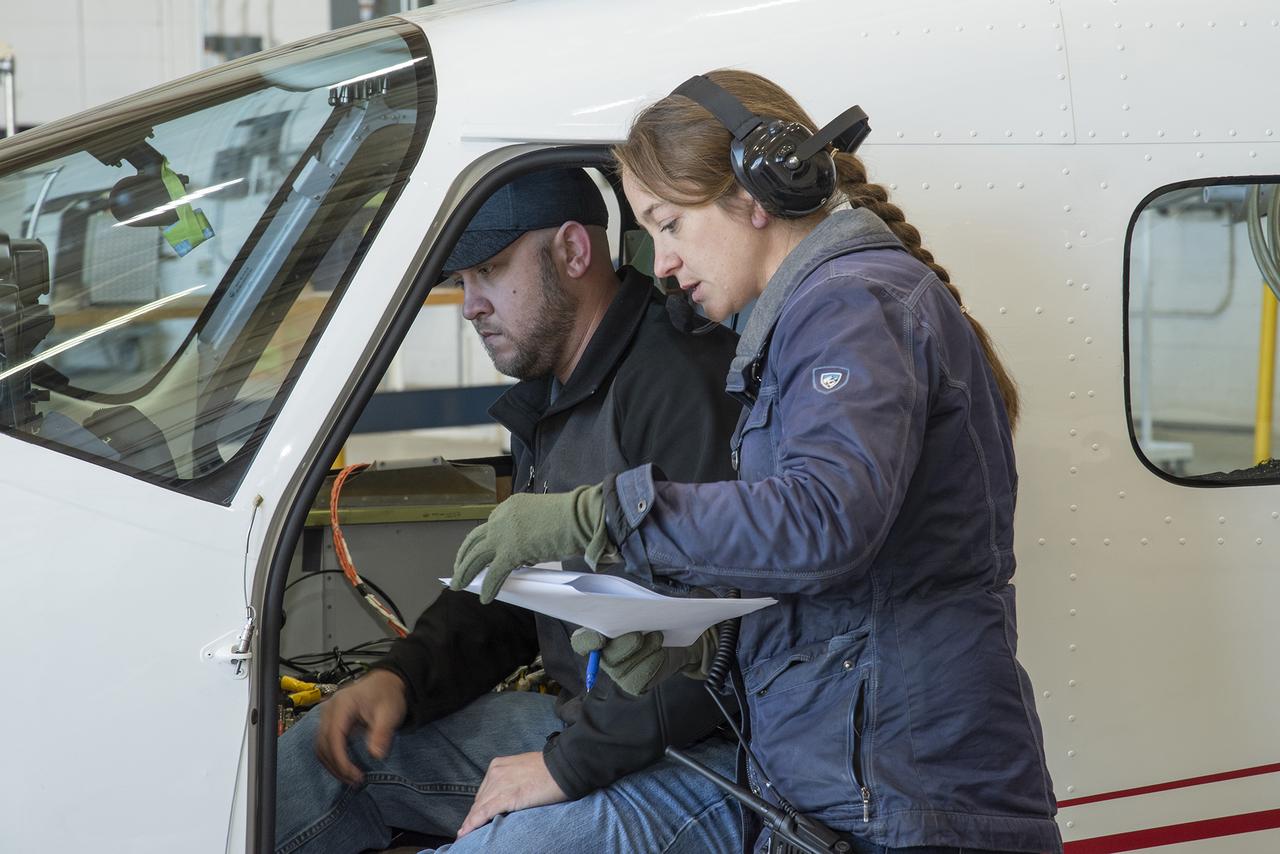

Telemetry testing begins on the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane, as the operations crew at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center records the results. Telemetry testing is a critical phase in X-57's functional test series. In addition to confirming the ability of the X-57 aircraft to transmit speed, altitude, direction, and location to teams on the ground, telemetry testing also confirms the ability to transmit mission-critical-data, such as voltage, power consumption, and structural integrity. X-57's goal is to help set certification standards for emerging electric aircraft markets.

NASA Administrator Bridenstine, former navy pilot, sits comfortably back in F-18 jet cockpit at Armstrong Flight Research Center.

The Navmar Applied Sciences Corporation’s TigerShark prepares for its final takeoff at Edwards Air Force Base for the Unmanned Aircraft Systems integration in the National Airspace Systems, Flight Test Series Six (FT6) project. FT6 flight tests took place at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California and focused on low size weight and power sensors for Detect and Avoid (DAA) operations in controlled airspace to inform the FAA through the RTCA Special Committee DAA Working Group on the phase 2 minimum operational performance standards for DAA and air-to-air radar.

A Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter provided by Flight Research Inc. in Mojave, California, sits on a helipad at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California the first week of December 2020. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project used the helicopter as a surrogate urban air mobility vehicle to develop and implement infrastructure, including the markings seen in the image, to support safe operations of these vehicles. Â
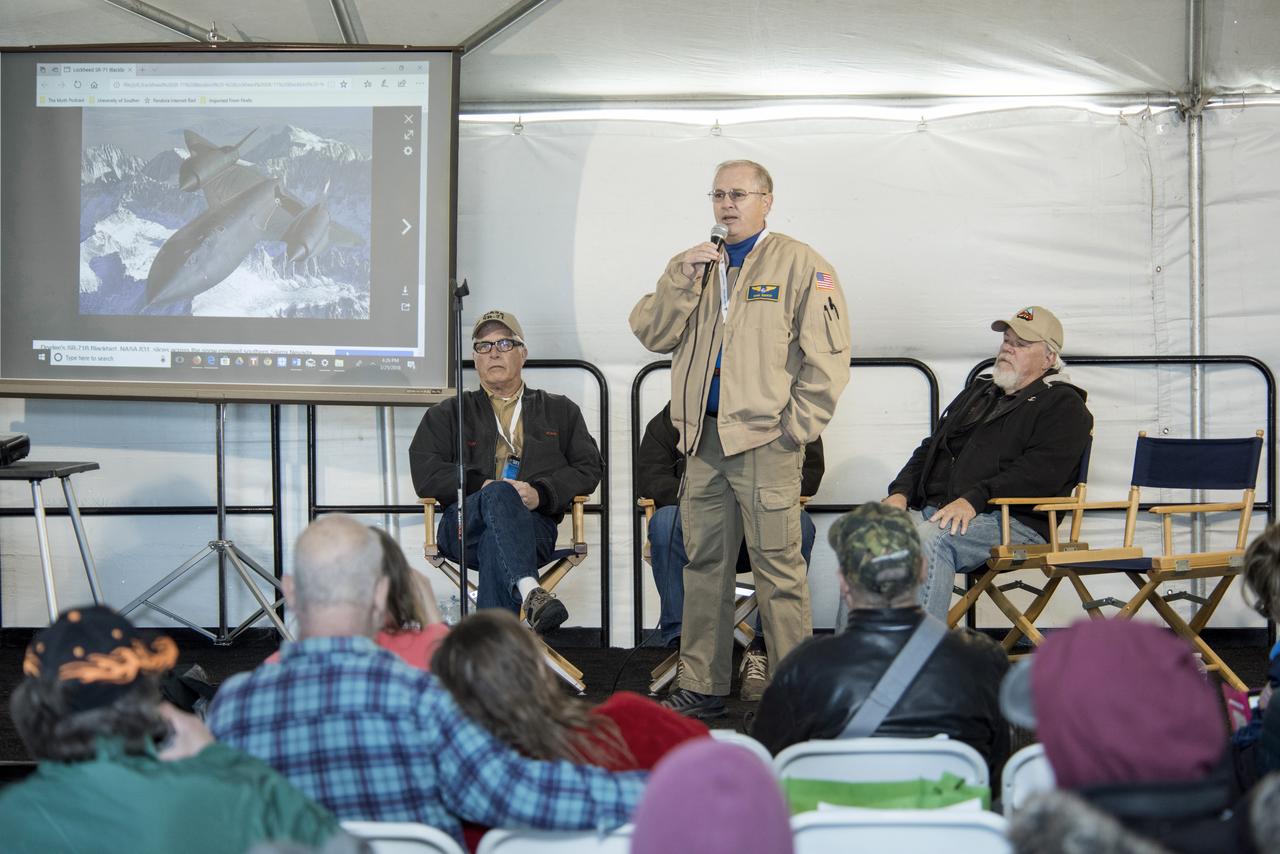

Dana Purifoy, NASA Armstrong director of Flight Operations, talking, and John McKay, former Armstrong SR-71 crew chief, participate on a panel discussion about the triple supersonic aircraft.
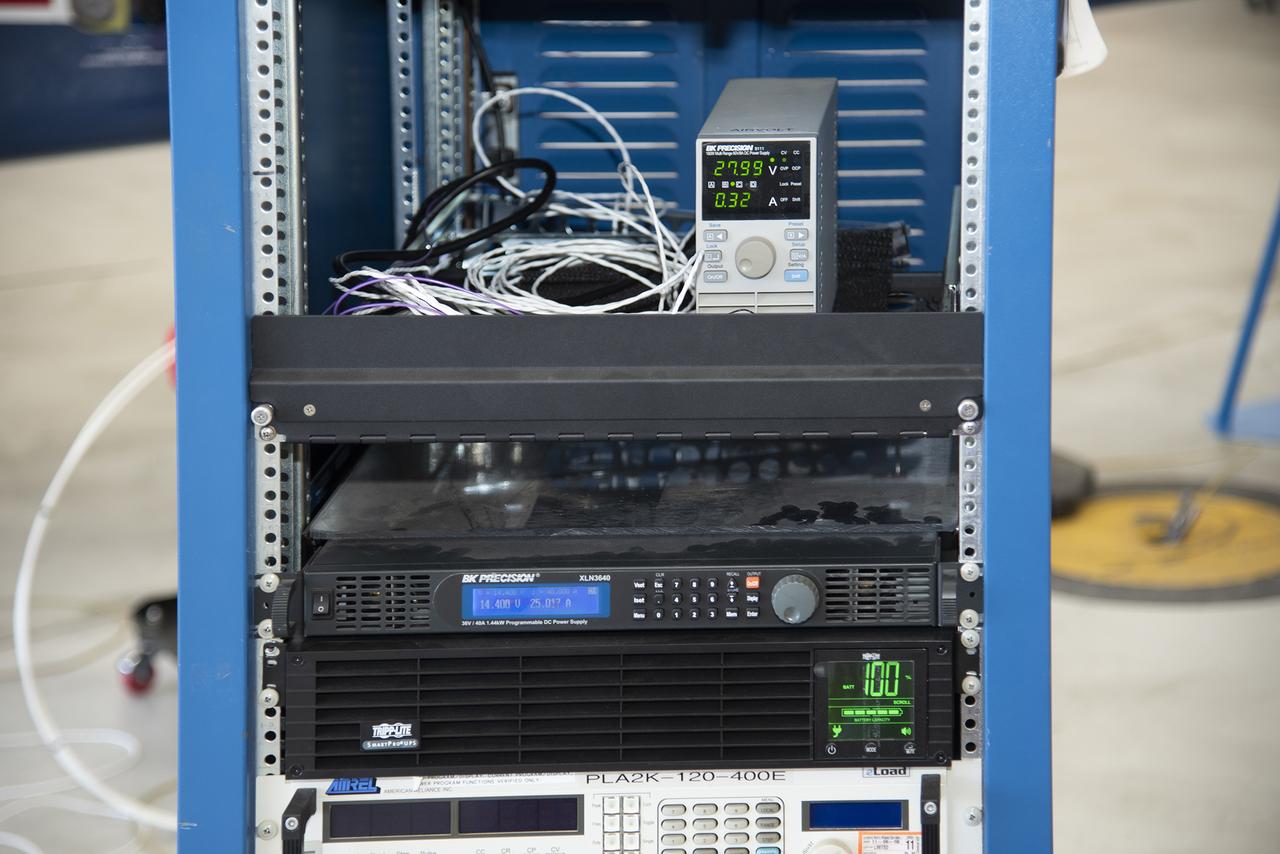

Telemetry testing begins on the X-57 Maxwell, NASA’s first all-electric X-plane, as the operations crew at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center records the results. Telemetry testing is a critical phase in X-57’s functional test series. In addition to confirming the ability of the X-57 aircraft to transmit speed, altitude, direction, and location to teams on the ground, telemetry testing also confirms the ability to transmit mission-critical-data, such as voltage, power consumption, and structural integrity. X-57’s goal is to help set certification standards for emerging electric aircraft markets.

Telemetry testing begins on the X-57 Maxwell, NASA's first all-electric X-plane, as the operations crew at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center records the results. Telemetry testing is a critical phase in X-57's functional test series. In addition to confirming the ability of the X-57 aircraft to transmit speed, altitude, direction, and location to teams on the ground, telemetry testing also confirms the ability to transmit mission-critical-data, such as voltage, power consumption, and structural integrity. X-57's goal is to help set certification standards for emerging electric aircraft markets.
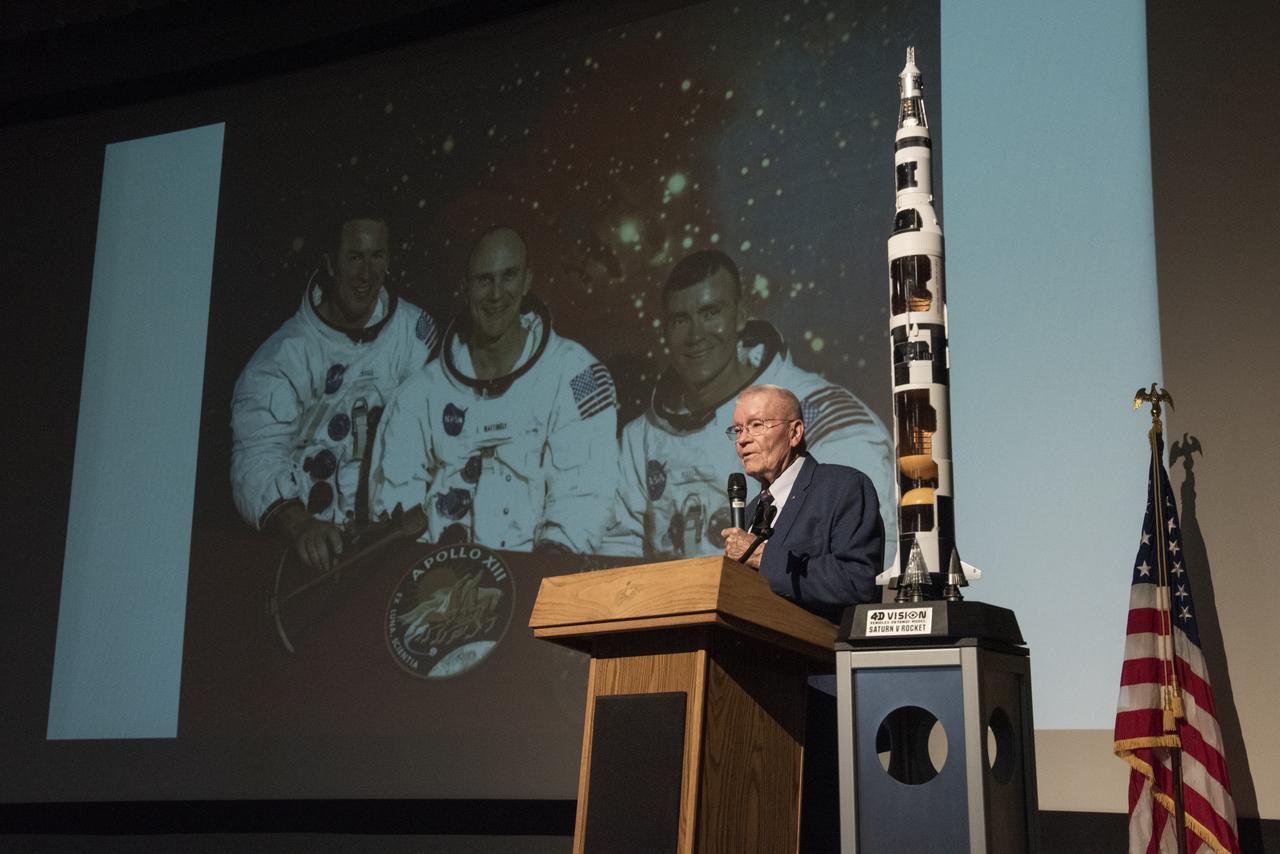

Apollo Astronaut Fred Haise speaks to a crowd of NASA and U.S Air Force employees at the Edwards Air Force Base theater about his career with NASA and as a military pilot. Haise stands on stage with a photo of former astronauts Jim Lovell and Jack Swigert who accompanied him on the Apollo 13 lunar mission in the background with a model of the Saturn V rocket.
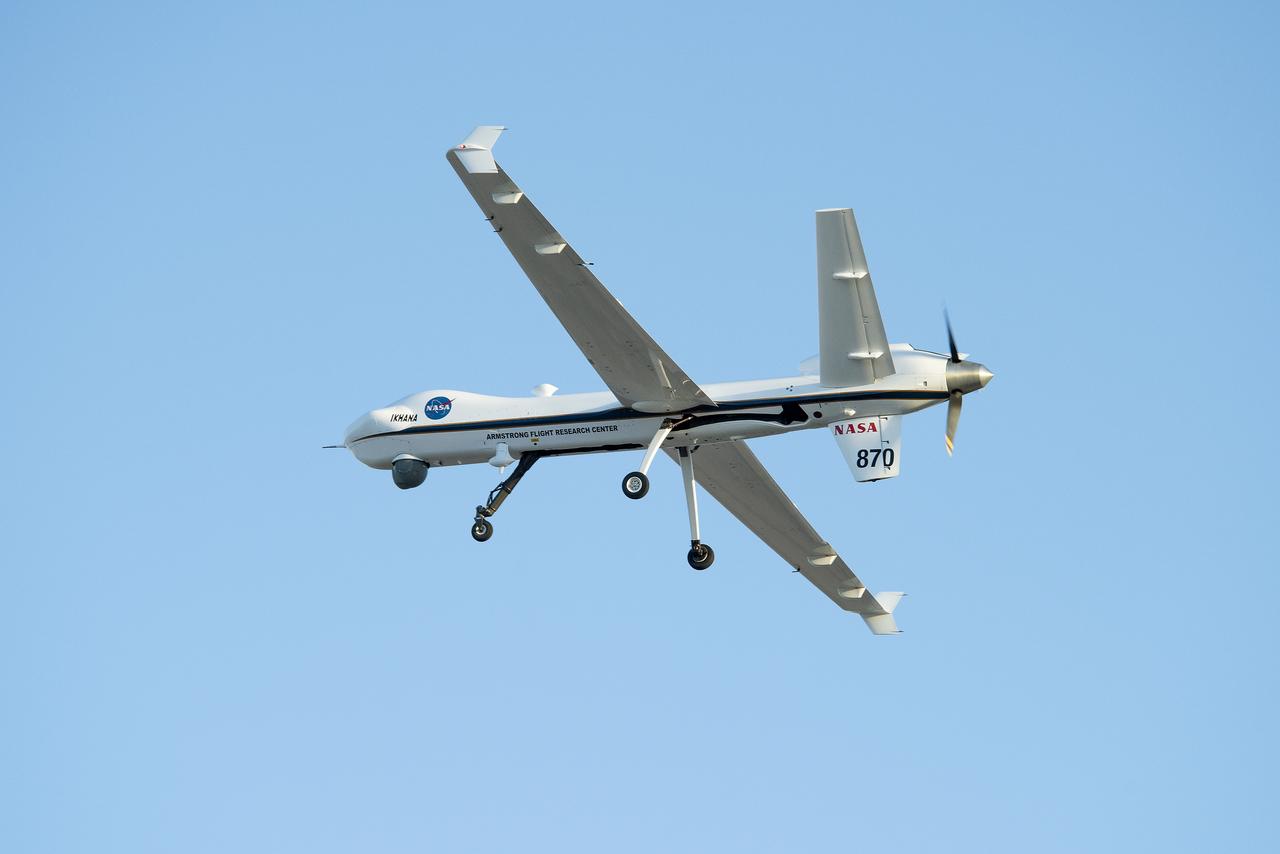

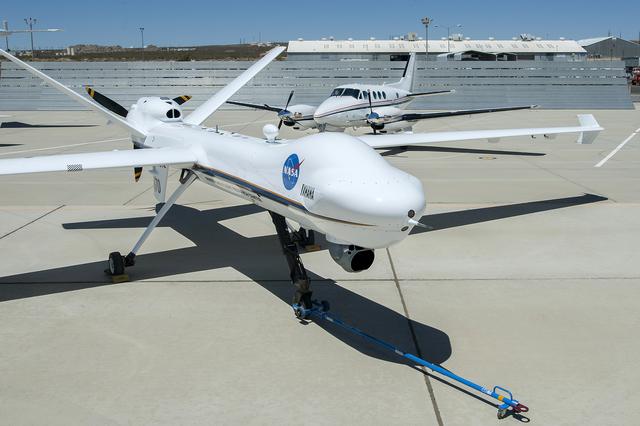
NASA’s Ikhana aircraft, based at the agency’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, flew for 2.5 hours on June 12 in the national airspace without a safety chase aircraft.
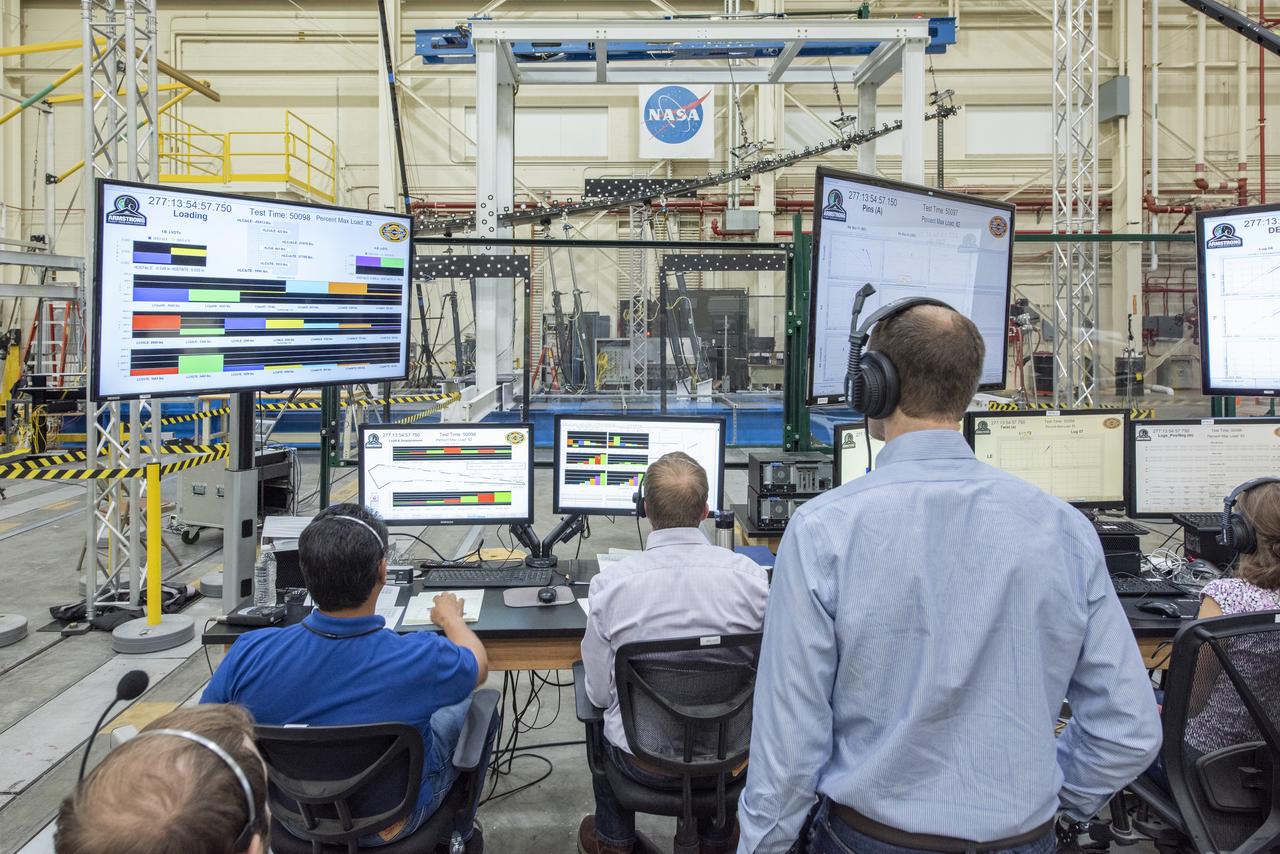

NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center and Langley Research Center staff members monitor a test of the Passive Aeroelastic Tailored (PAT) wing at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.

The Navmar Applied Sciences Corporation’s TigerShark prepares for its final takeoff at Edwards Air Force Base for the Unmanned Aircraft Systems integration in the National Airspace Systems, Flight Test Series Six (FT6) project. FT6 flight tests took place at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California and focused on low size weight and power sensors for Detect and Avoid (DAA) operations in controlled airspace to inform the FAA through the RTCA Special Committee DAA Working Group on the phase 2 minimum operational performance standards for DAA and air-to-air radar.

The Navmar Applied Sciences Corporation’s TigerShark prepares for its final takeoff at Edwards Air Force Base for the Unmanned Aircraft Systems integration in the National Airspace Systems, Flight Test Series Six (FT6) project. FT6 flight tests took place at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California and focused on low size weight and power sensors for Detect and Avoid (DAA) operations in controlled airspace to inform the FAA through the RTCA Special Committee DAA Working Group on the phase 2 minimum operational performance standards for DAA and air-to-air radar.
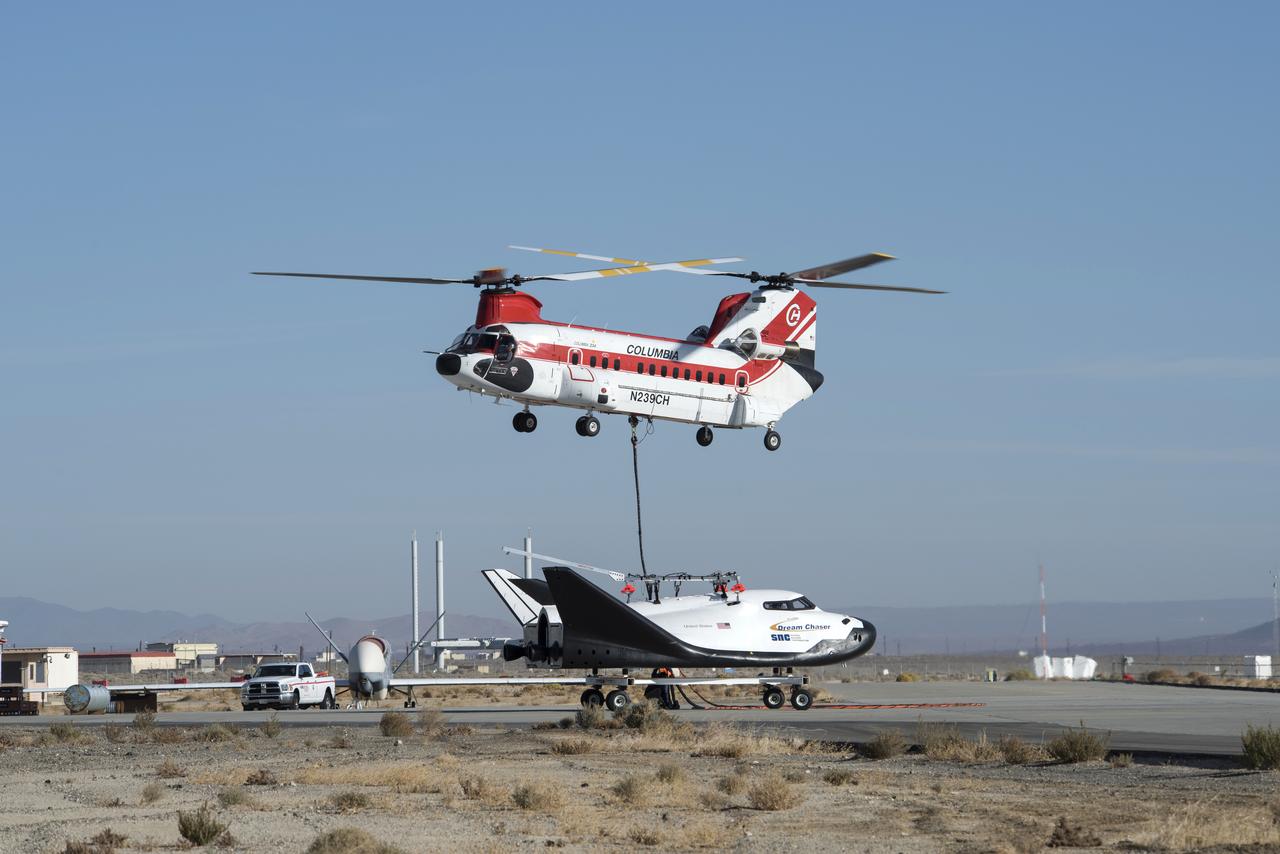

Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser was lifted by helicopter from the ramp at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, before its successful approach and landing flight test on Nov. 11, 2017.
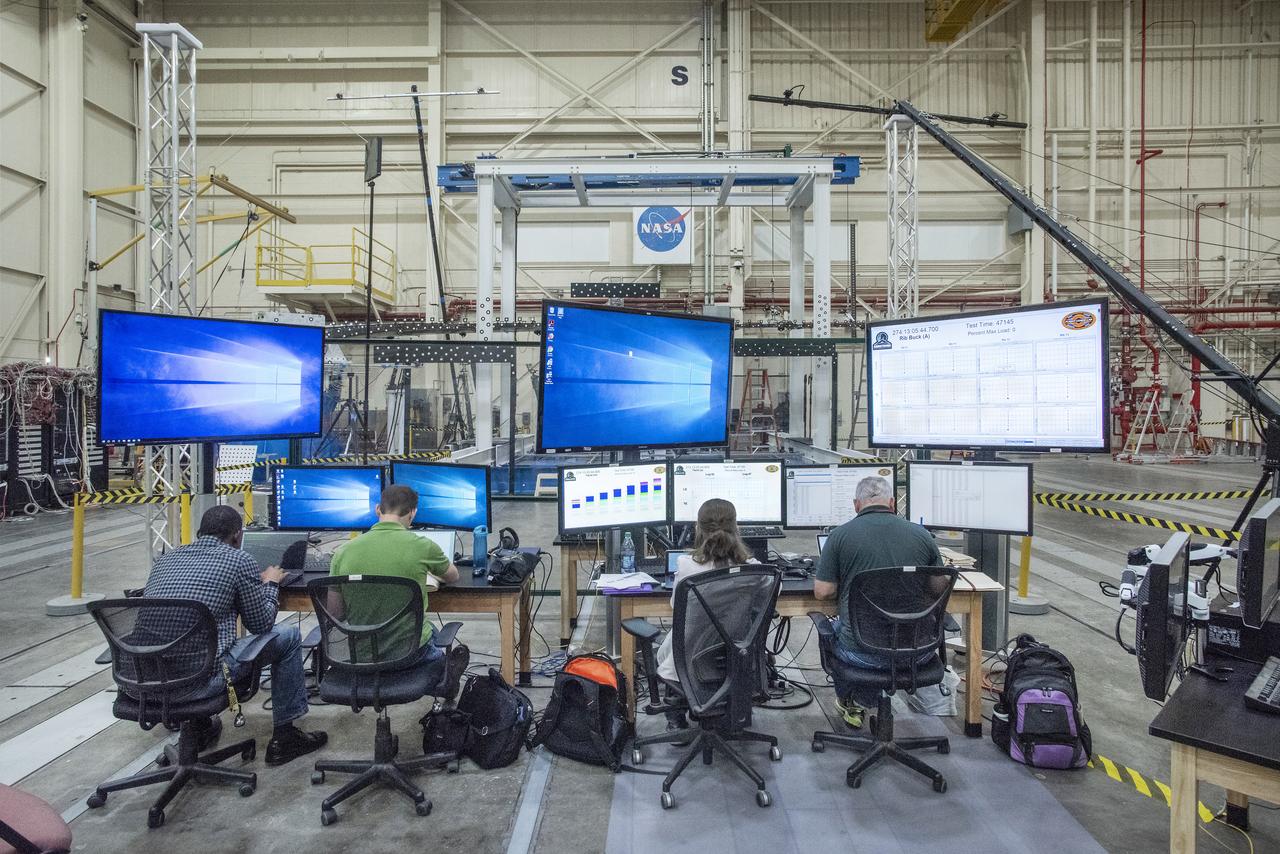

NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center and Langley Research Center staff members monitor a test of the Passive Aeroelastic Tailored (PAT) wing at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.

The first of three “new” F/A-18B Hornets arrived at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California Nov. 6.
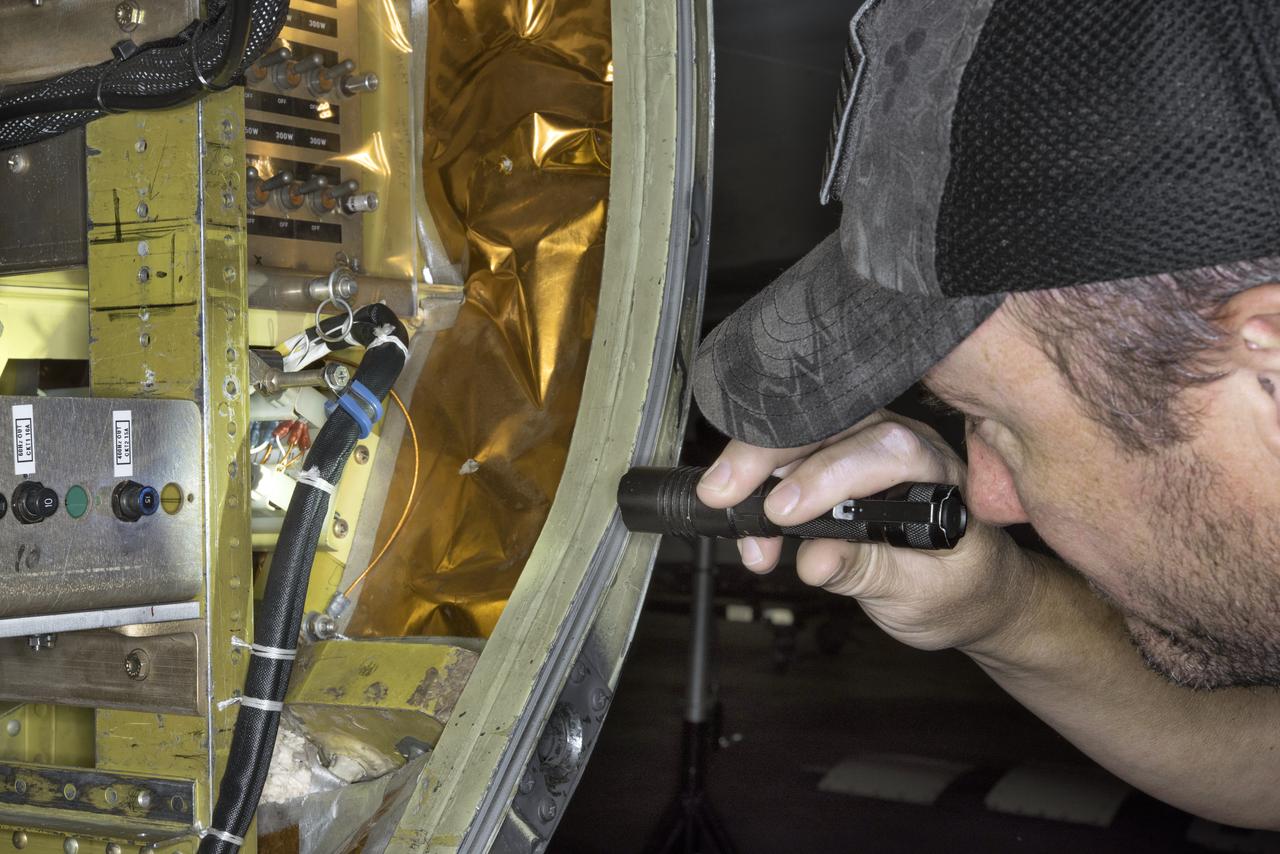

A ground crewman at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Palmdale, CA inspects the forward panel on the mid-body section of NASA’s ER2’s wingpod. The crew is preparing to fly the air-LUSI instrument aboard the ER2 to measure the Moon.
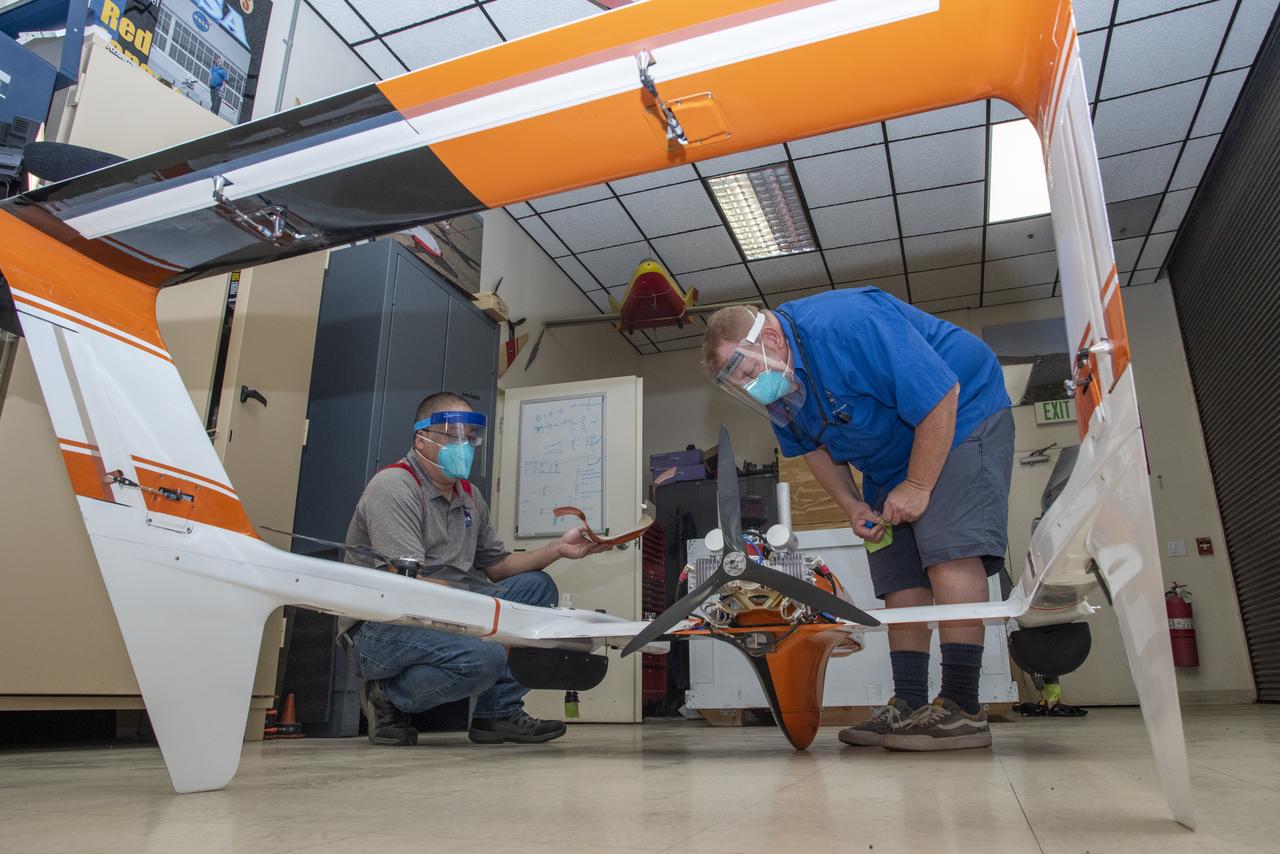

Derek Abramson and Robert Jensen assemble pieces of the Hybrid Quadrotor 90C (HQ-90) at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s Dale Reed Subscale Flight Research Lab in California on Oct. 1, 2020. This vertical lift and transition remotely piloted aircraft arrived in pieces packed in crates. It was reassembled for the Resilient Autonomy project to test software in flight.
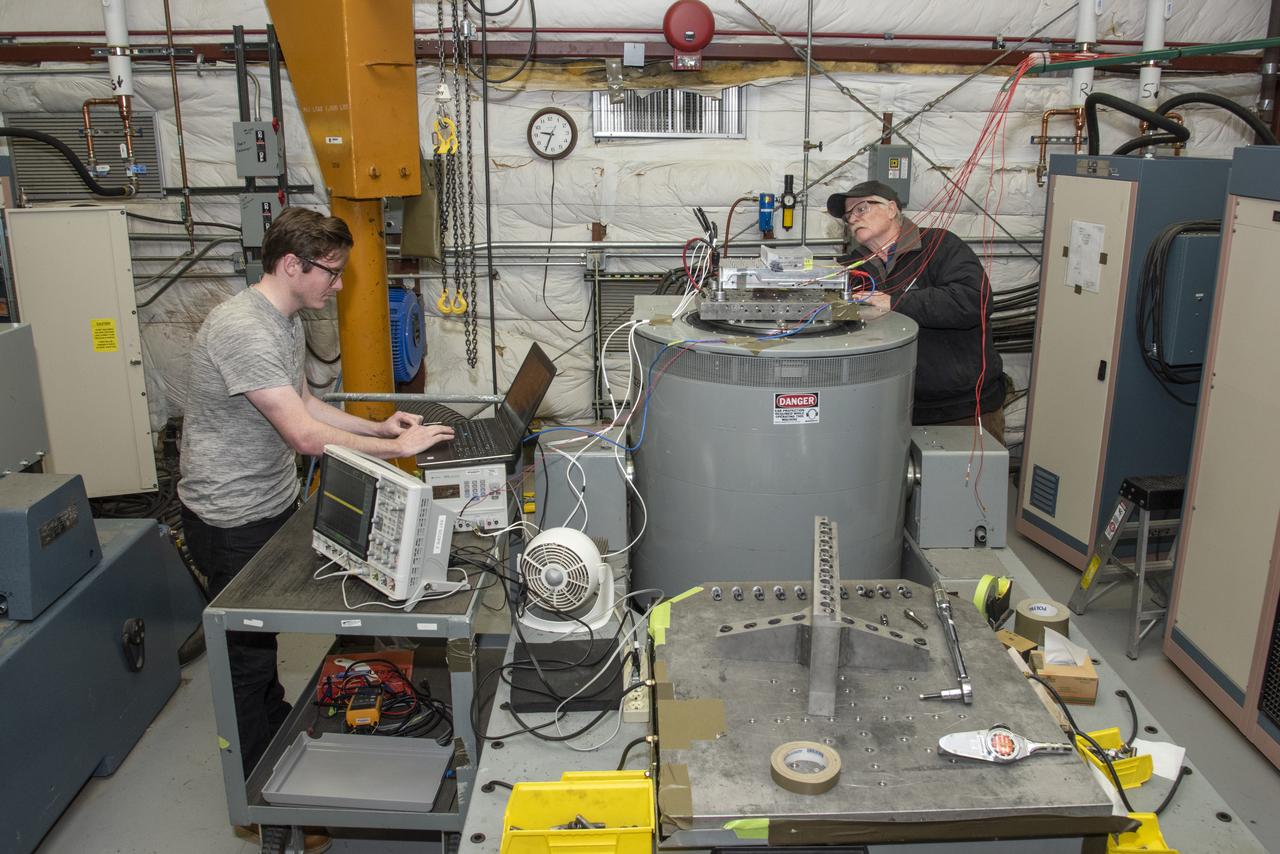

Engineers from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center and Empirical Systems Aerospace prepare a cruise motor controller, planned to be used on NASA's all-electric X-57 Maxwell, for vibration testing at Armstrong's environmental lab. Testing the cruise motor controller at various vibration levels, based on baseline flight testing in the project's first phase, helps ensure that the hardware will withstand similar vibration in flight conditions. X-57, NASA's first all-electric experimental aircraft, or X-plane, will fly in its first all-electric configuration in 2020.

In Armstrong auditorium, Bridenstine discusses the future of NASA under his administration then answered questions from employees
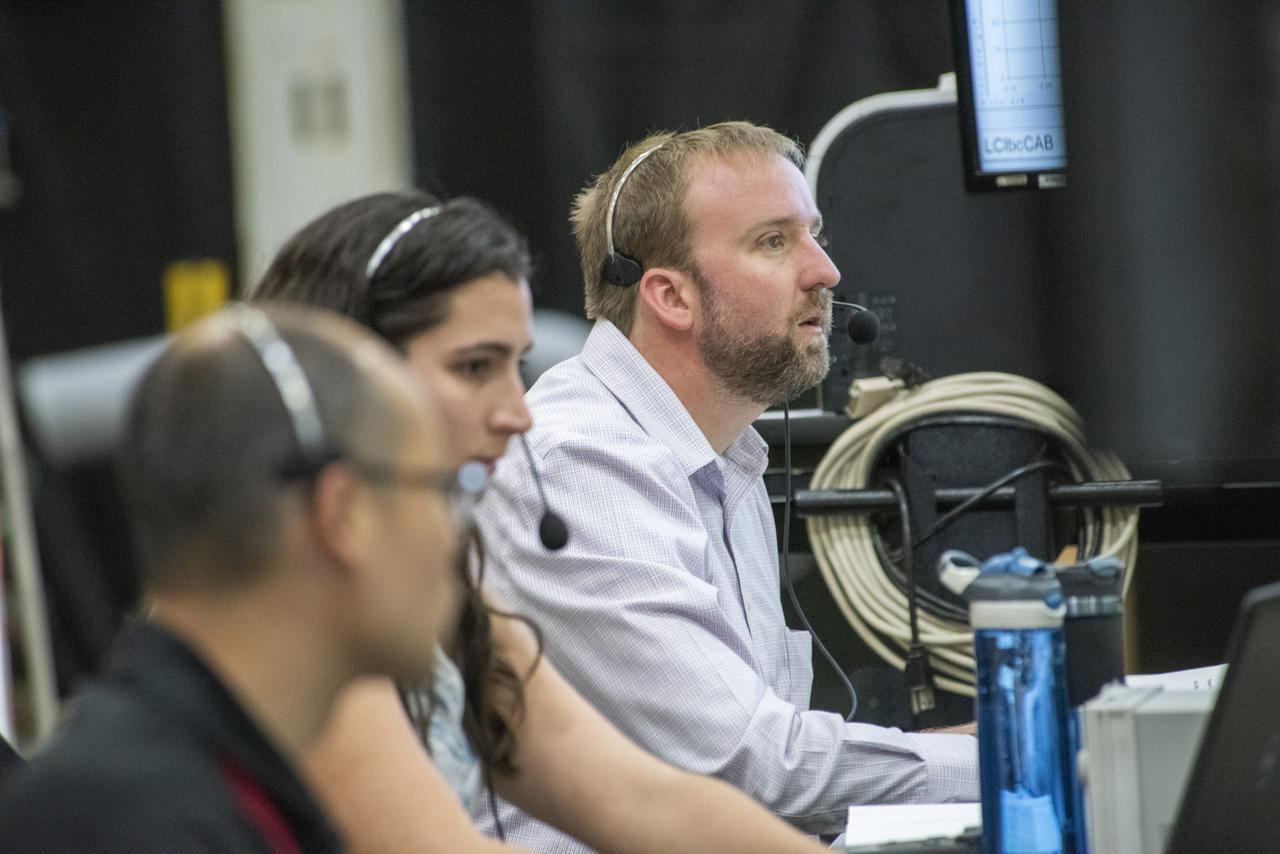

Wesley Li, Kirsten Boogaard and test conductor Eric Miller observe testing of the X-57 distributed electric aircraft wing at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. Tests increased confidence in the wing's durability and calibrated installed strain gauges for inflight load monitoring of the wing.
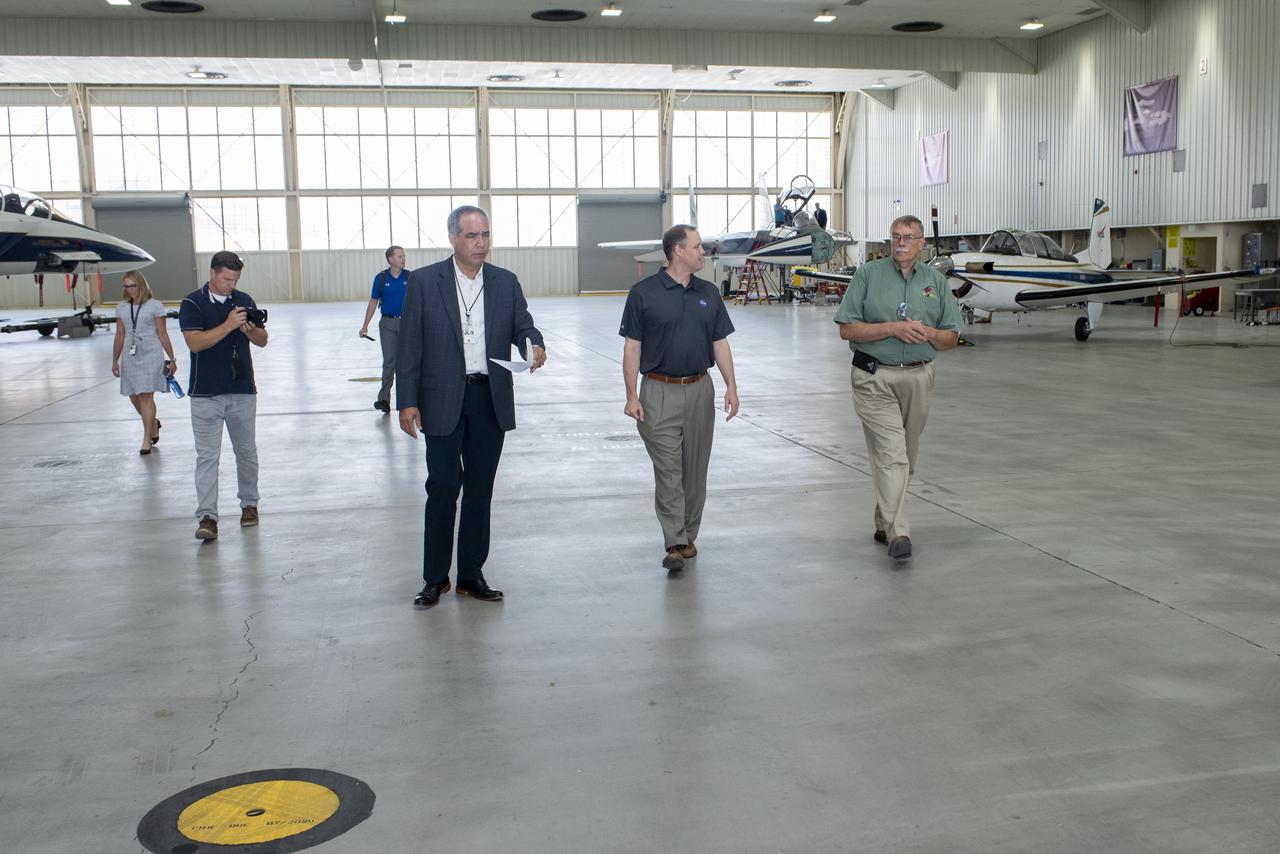

Bridenstine tours main Armstrong hangar that houses the center aircraft used for flight research and safety chase such as F/A-18, F-15B/D, King Air B-200, T-34C and TG-14 aircraft.
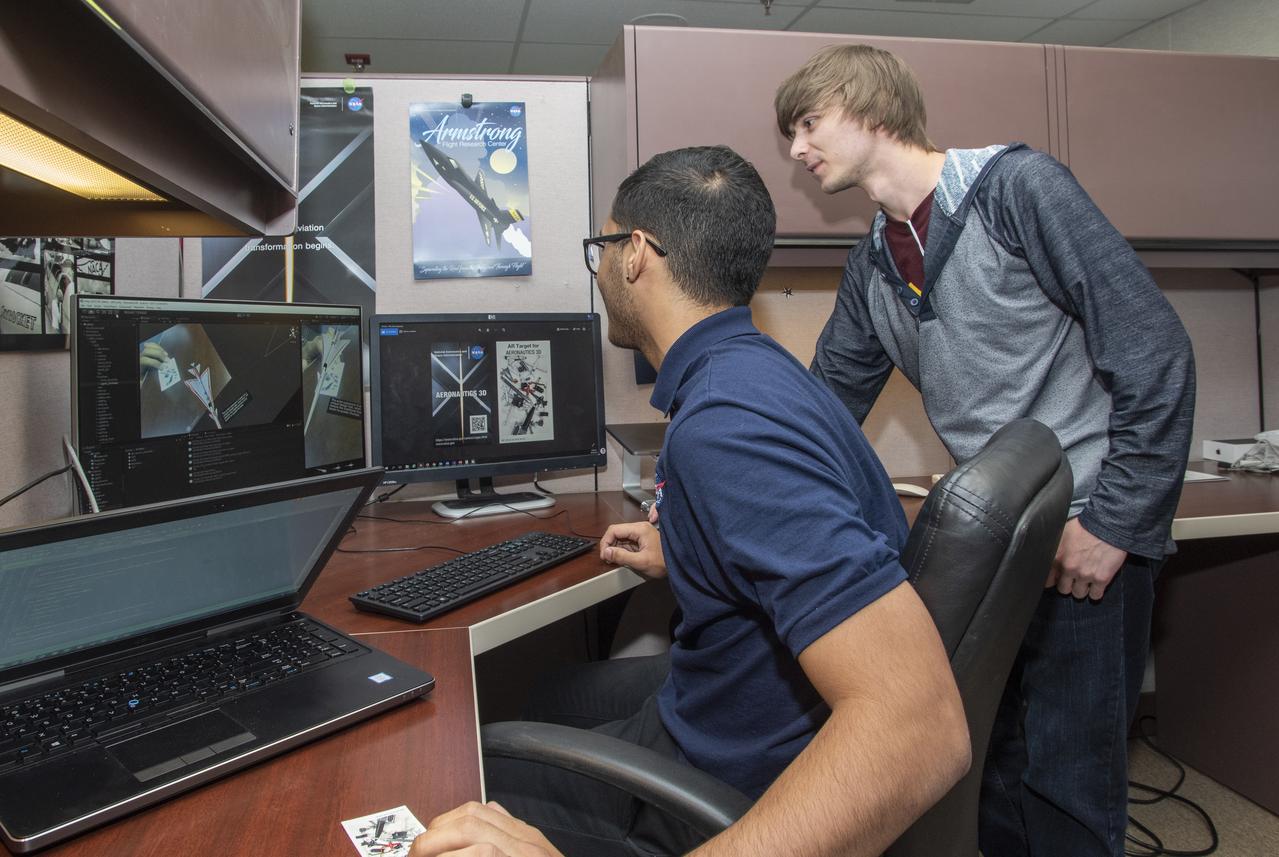

Kendrick Morales, left, and Alexander Passofaro, right, work together to transition the software for the Aeronautics AR app from being target image dependent to deleting the target image.
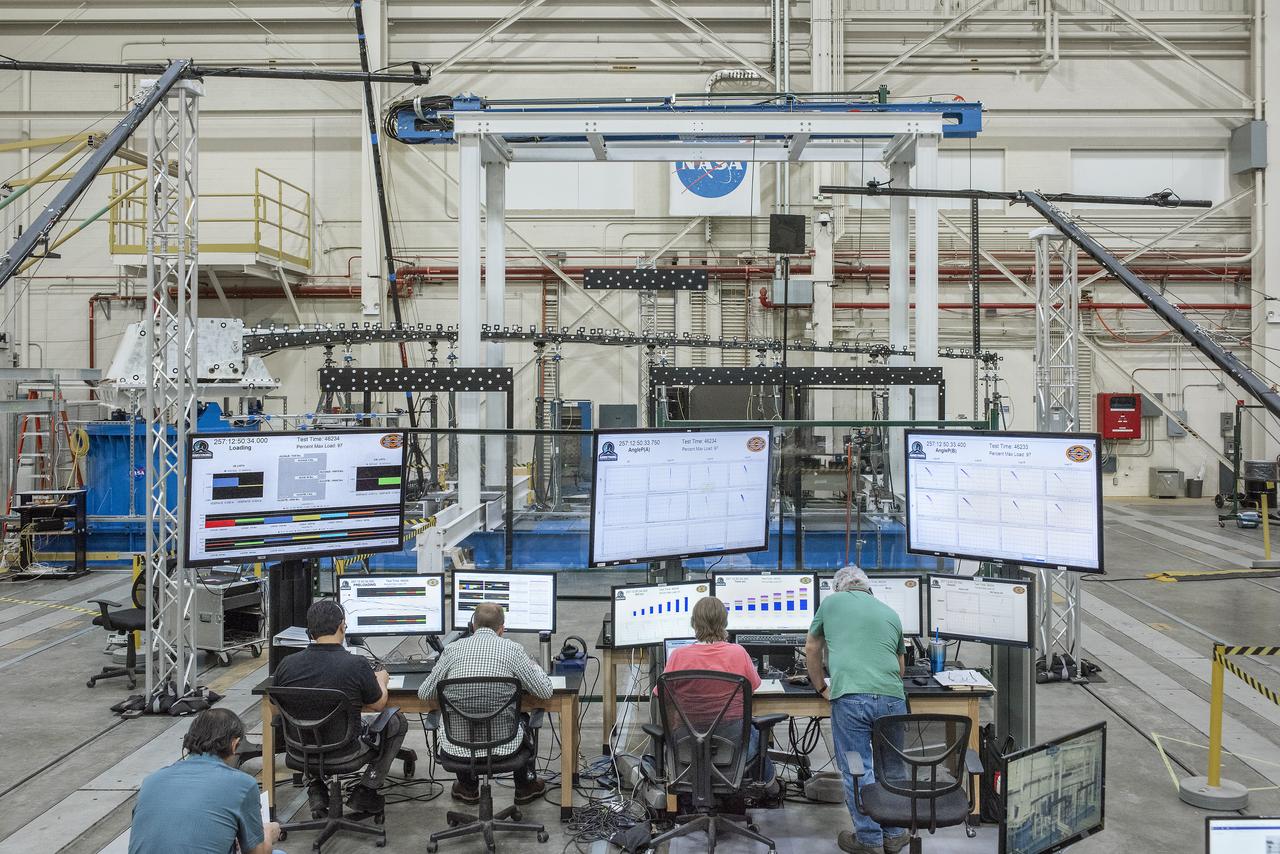

This broad view of the Flight Loads Laboratory at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California shows the test set up for the high-aspect ratio Passive Aeroelastic Tailored wing.
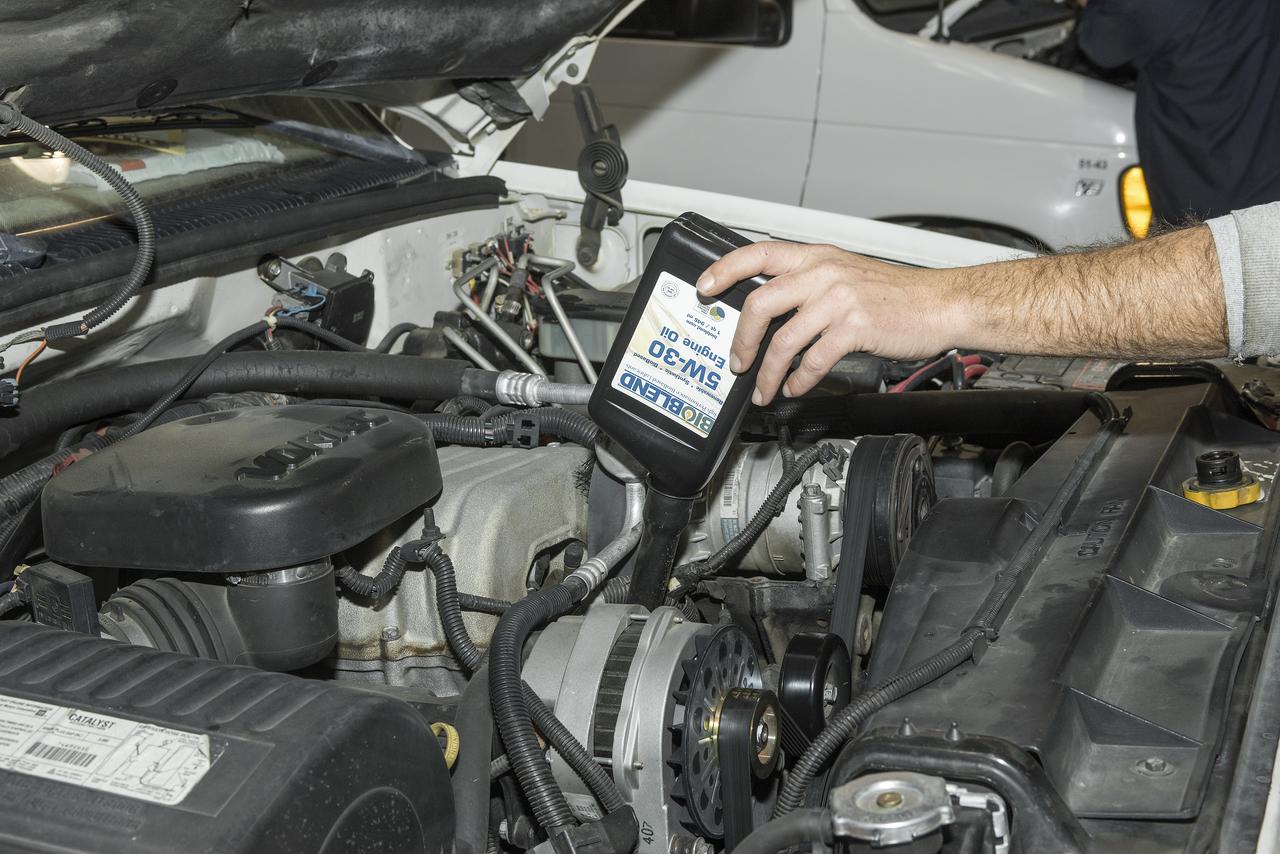

A new bio-based synthetic engine oil is added to one of the vehicles that Armstrong is using to assist in performance testing of the new product.
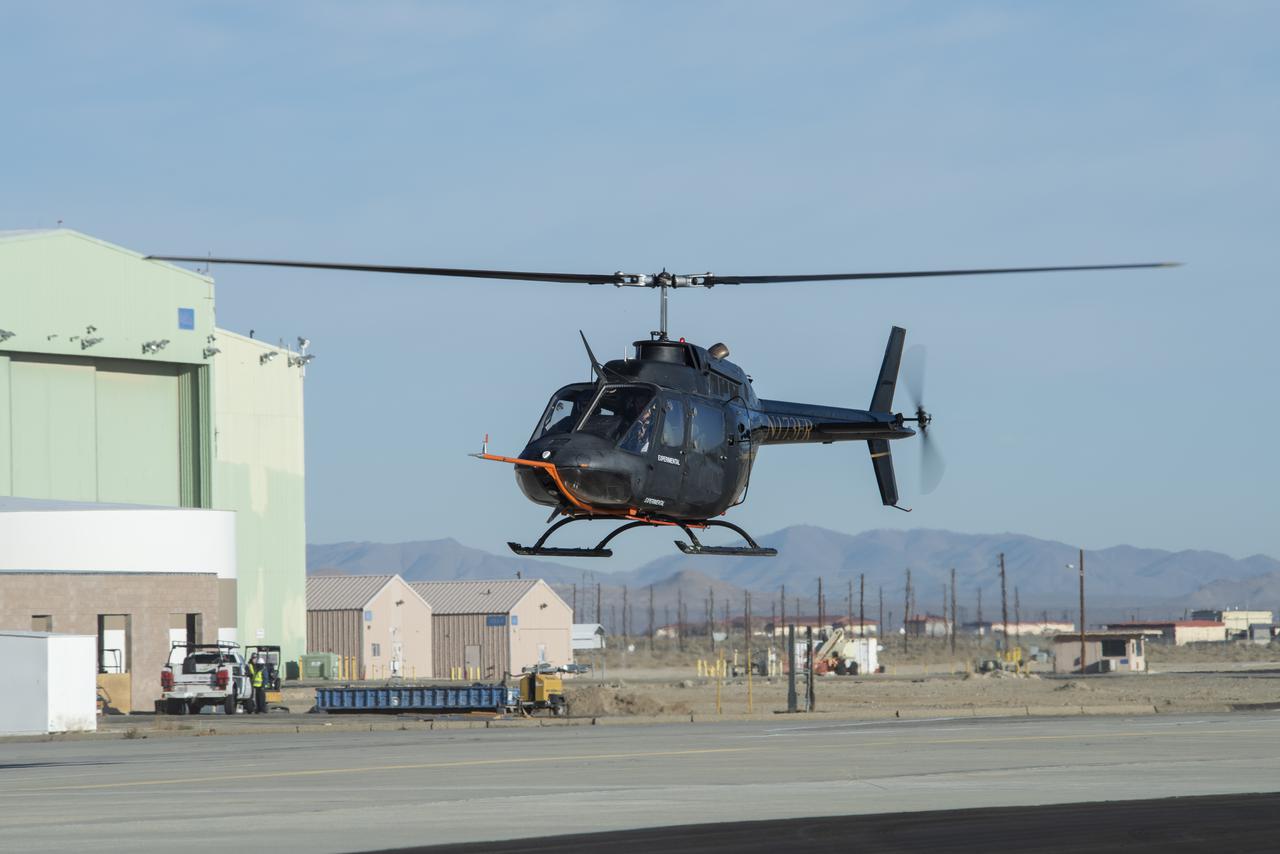

A Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter provided by Flight Research Inc. in Mojave, California, flies at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California the first week of December 2020. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project used the helicopter as a surrogate urban air mobility vehicle to develop a data baseline for future flight testing. Â
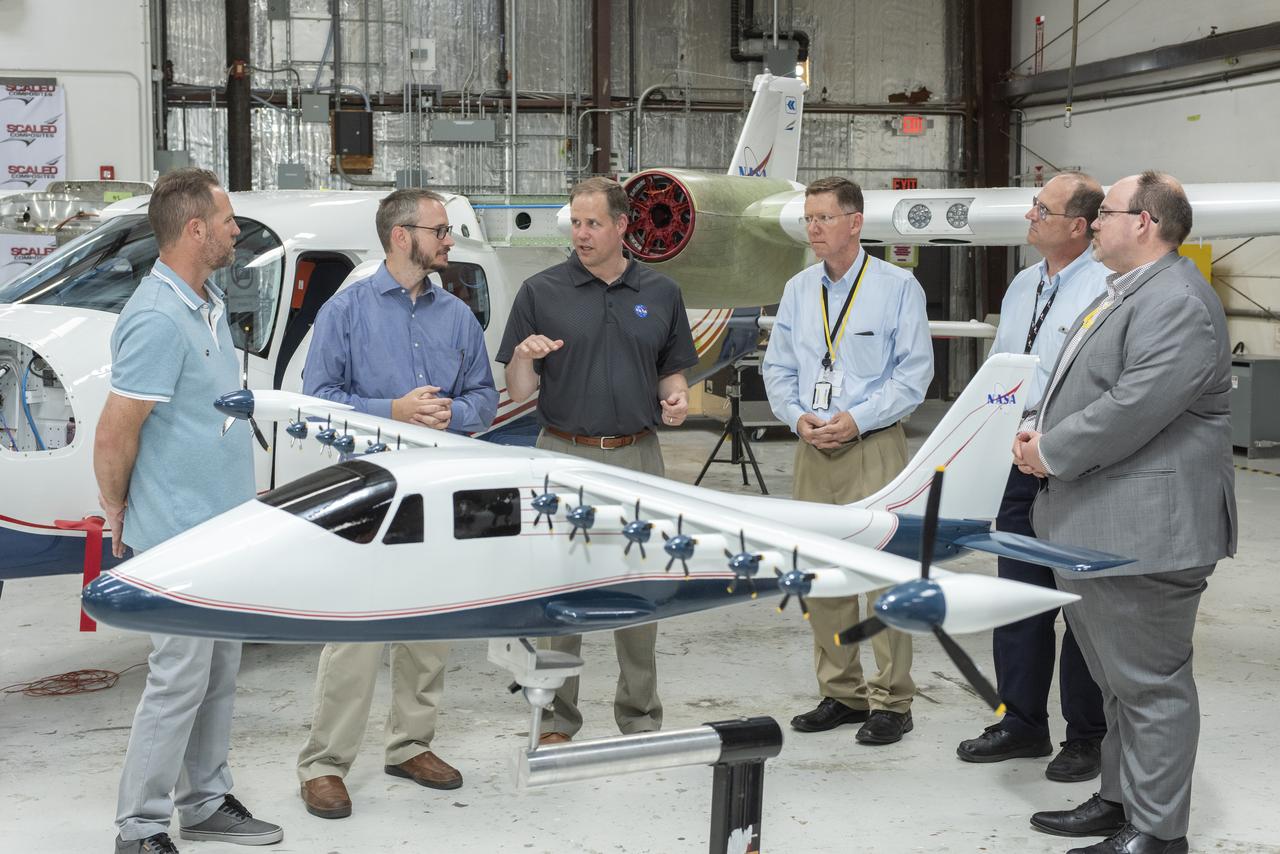

Administrator Bridenstine hears about the progress to modify the Tecnam P2006T from a combustion aircraft to an all-electric aircraft. Armstrong's X-57 team and ESAero, the prime contractor for the plane, are doing the briefing. The final configuration model of X-57 stands in front of group.