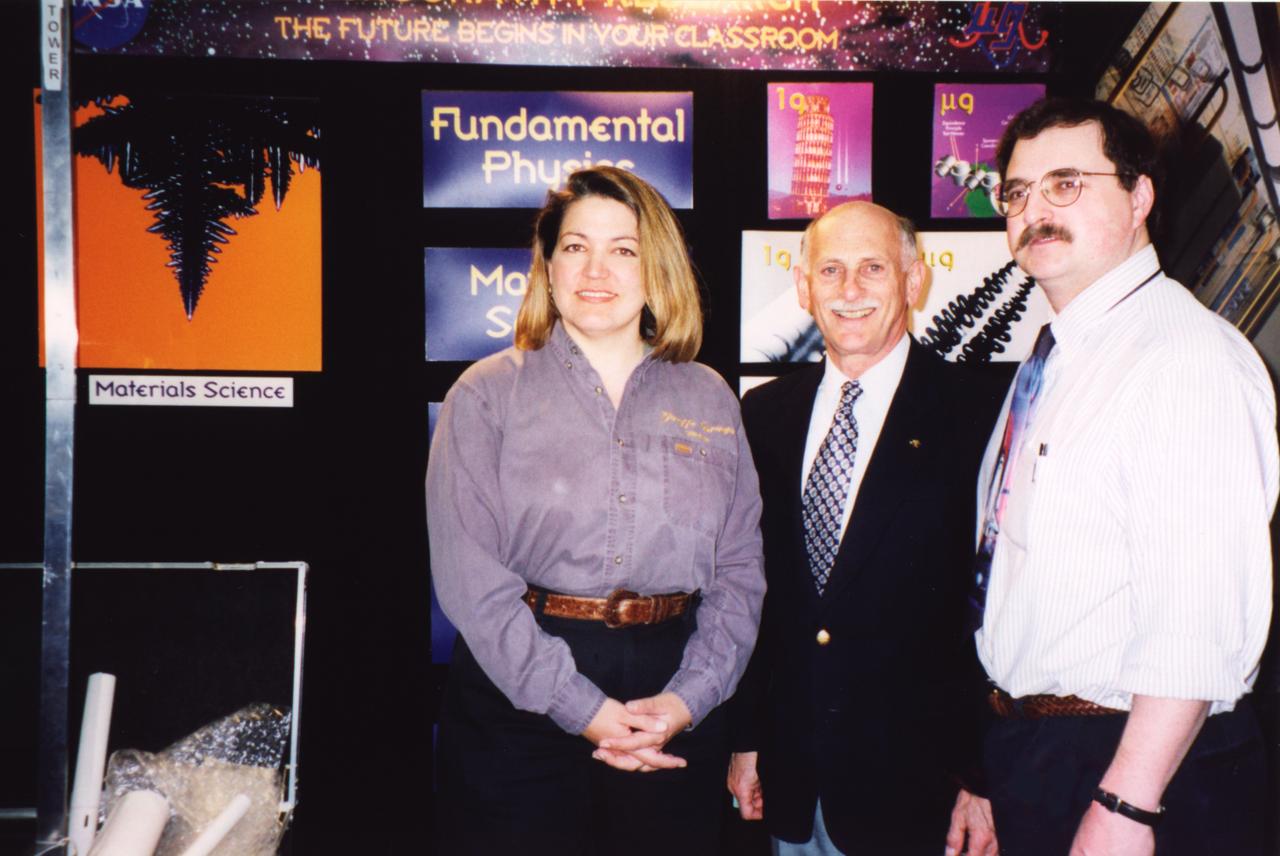

Representatives of NASA materials science experiments supported the NASA exhibit at the Rernselaer Polytechnic Institute's Space Week activities, April 5 through 11, 1999. From left to right are: Angie Jackman, project manager at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center for dendritic growth experiments; Dr. Martin Glicksman of Rennselaer Polytechnic Instutute, Troy, NY, principal investigator on the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) that flew three times on the Space Shuttle; and Dr. Matthew Koss of College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA, a co-investigator on the IDGE and now principal investigator on the Transient Dendritic Solidification Experiment being developed for the International Space Station (ISS). The image at far left is a dendrite grown in Glicksman's IDGE tests aboard the Shuttle. Glicksman is also principal investigator for the Evolution of Local Microstructures: Spatial Instabilities of Coarsening Clusters.
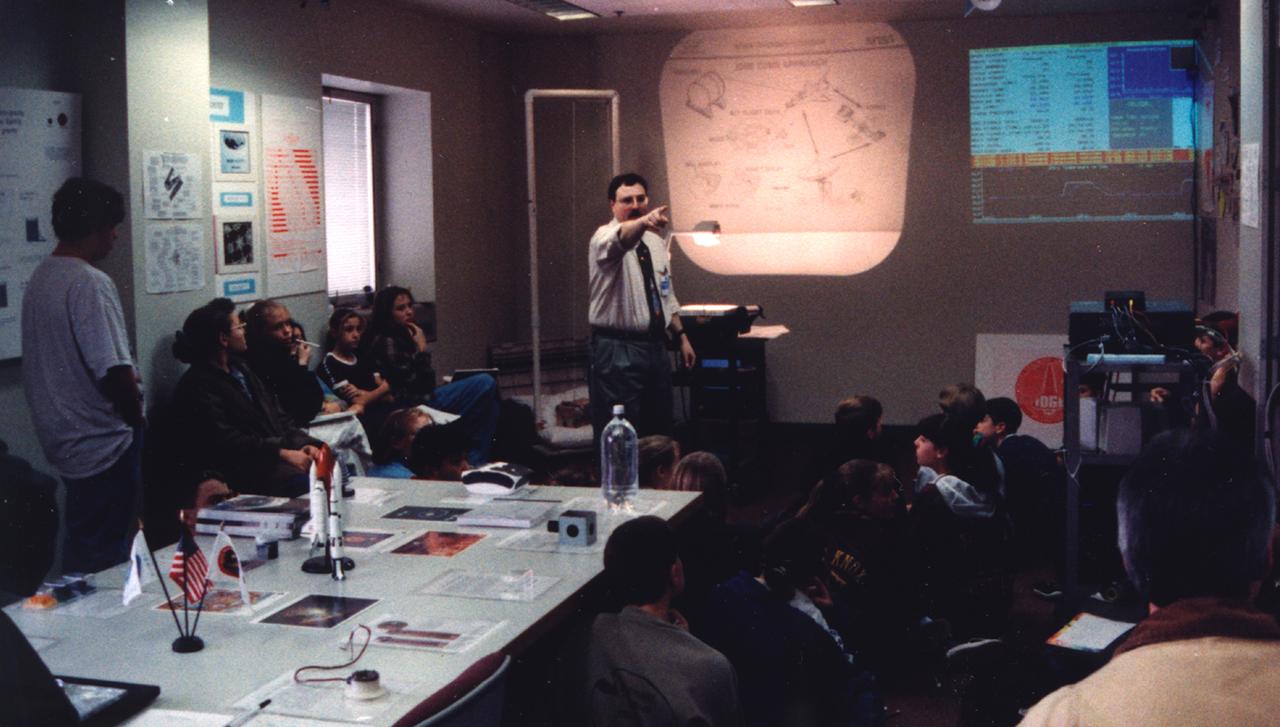

Matthew Koss lectures middle-school students about materials science research in space during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997) in the visitor's center set up by the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) team at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)in Troy, NY. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: RPI
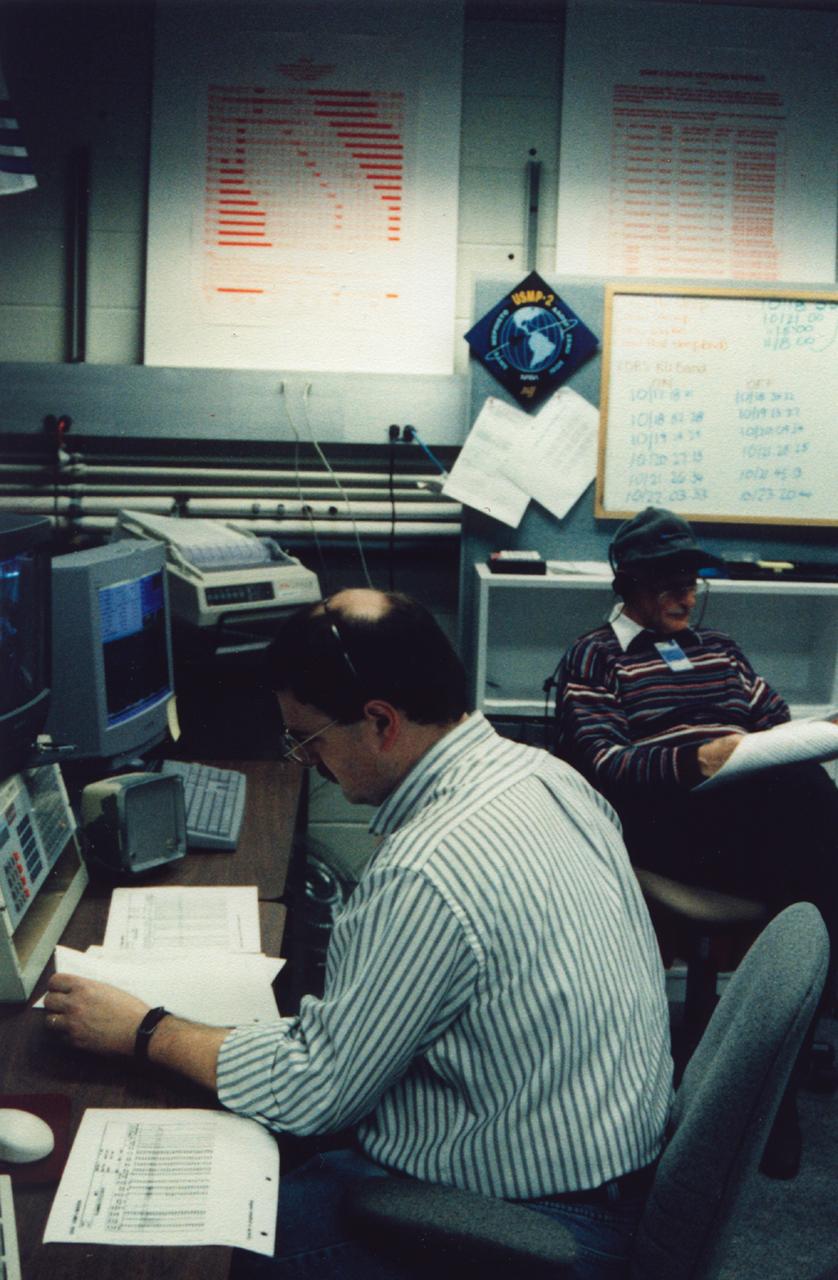

Matthew Koss (forground) and Martin Glicksman (rear), principal investigator and lead scientist (respectively), review plans for the next step in the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997). Remote Operations Control Center (ROCC) like this one, at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) in Troy, NY, will become more common during operations with the International Space Station. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relavent metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)

NASA Kennedy Space Center's Sam Ball, third from left, speaks during the Energy Action Day employee event held in NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. Part of Energy Awareness Month, the event featured subject matter experts in the area of solar energy, its connections to the space program and options for residential solar power. From left to right are Nick Murdock, energy and water program manager at Kennedy; Chuck Tatro of NASA's Launch Services Program; Ball; Anuj Chokshi of FPL; Bill McMullen of Southern Power; John Sherwin of the Florida Solar Energy Center in Cocoa; and Lorraine Koss of the Brevard County Solar Co-op.
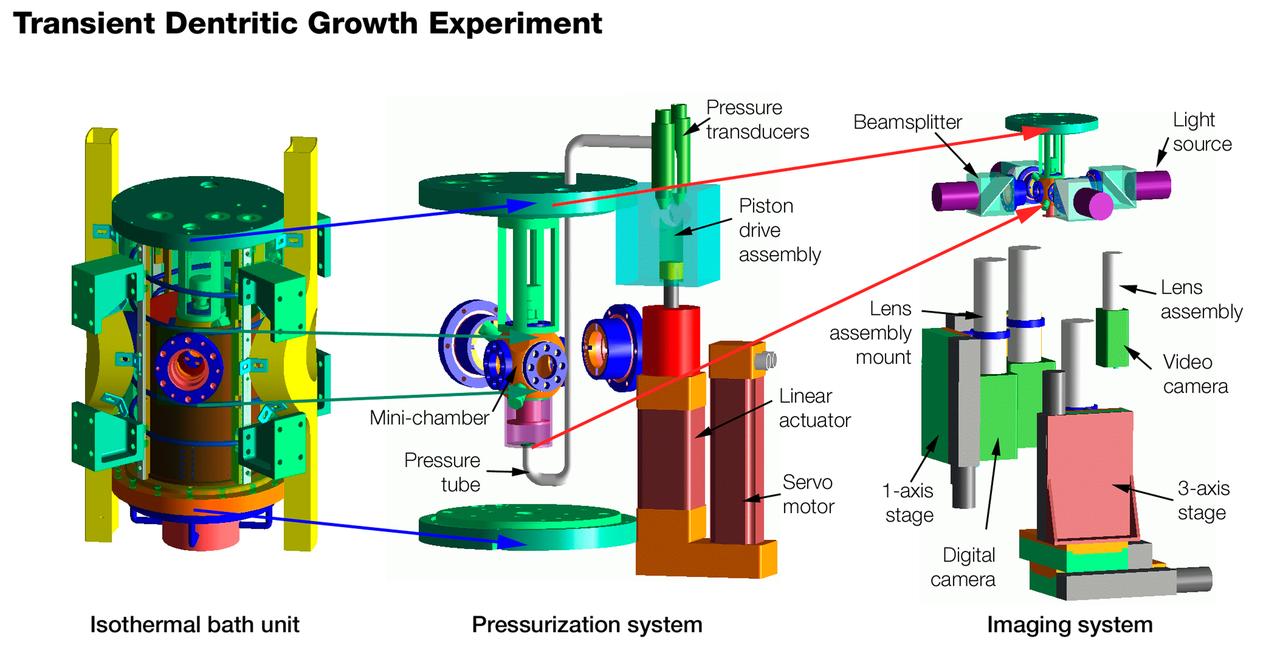
The Transient Dendritic Solidification Experiment (TDSE) is being developed as a candidate for flight aboard the International Space Station. TDSE will study the growth of dendrites (treelike crystalline structures) in a transparent material (succinonitrile or SCN) that mimics the behavior or widely used iron-based metals. Basic work by three Space Shuttle missions of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. The TDSE is similar to IDGE, but will maintain a constant temperature while varying pressure on the dendrites. Shown here is an exploded view of major elements of the TDSE. A similar view is availble without labels. The principal investigator is Matthew Koss of College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
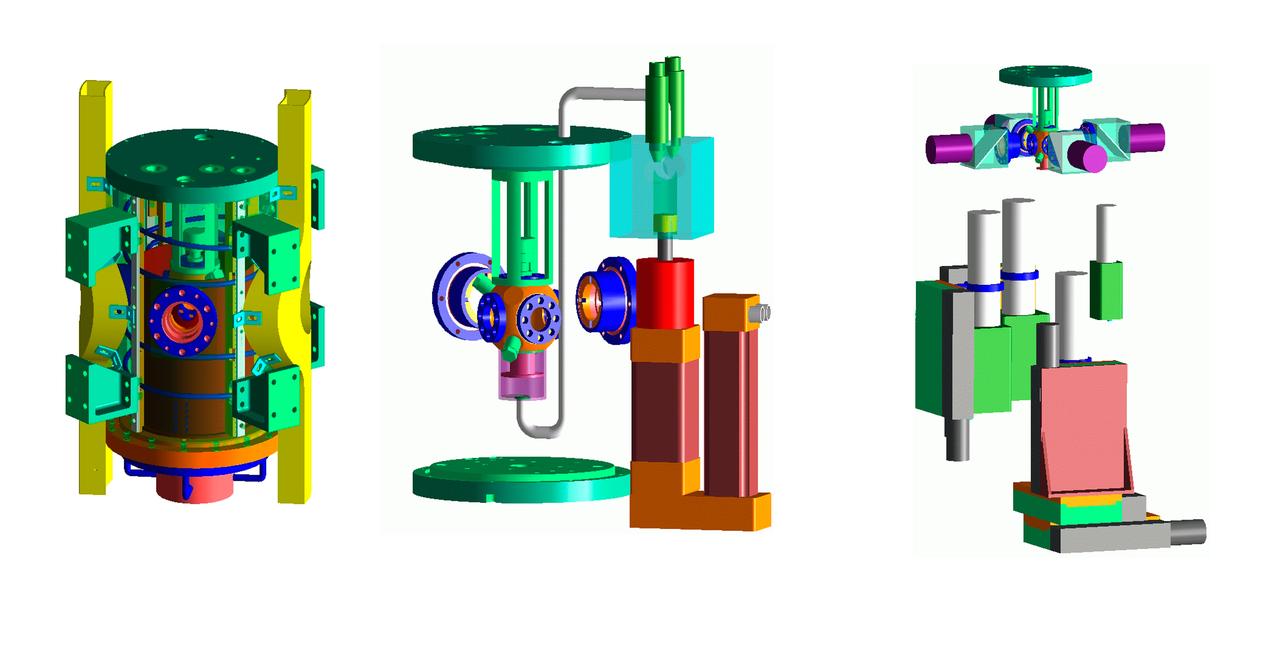
The Transient Dendritic Solidification Expepriment (TDSE) is being developed as a candidate for flight aboard the International Space Station. TDSE will study the growth of dendrites (treelike crystalline structures) in a transparent material (succinonitrile or SCN) that mimics the behavior of widely used iron-based metals. Basic work by three Space Shuttle missions of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Expepriment (IDGE) is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. The TDSE is similar to IDGE, but will maintain a constant temperature while varying pressure on the dendrites. Shown here is an exploded view of major elements of TDSE. A similar view is available with labels. The principal investigator is Matthew Koss of College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
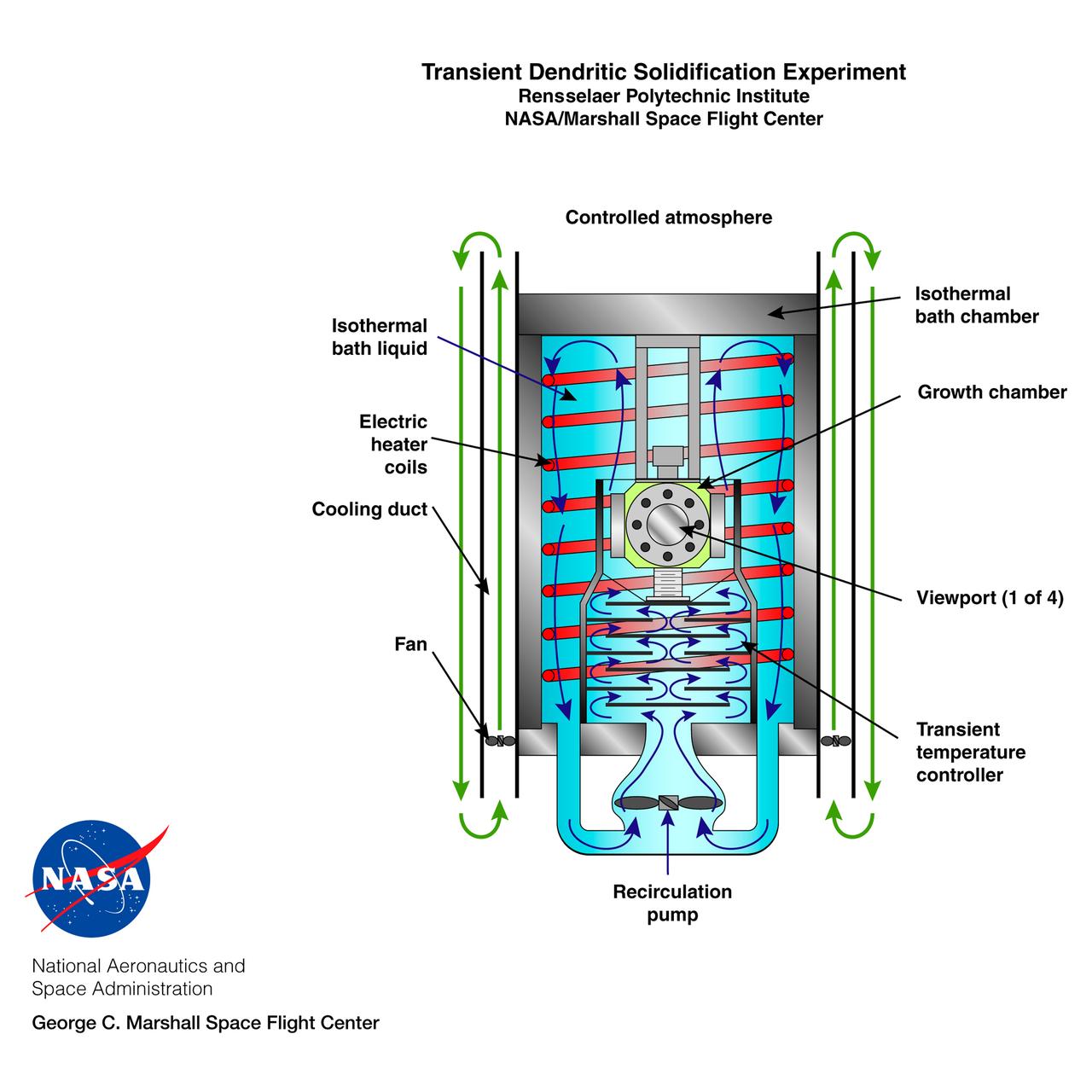
The Transient Dentritic Solidification Experiment (TDSE) is being developed as a candidate for flight aboard the International Space Station. TDSE will study the growth of dentrites (treelike crystalline structures) in a transparent material (succinonitrile or SCN) that mimics the behavior of widely used iron-based metals. Basic work by three Space Shuttle flights (STS-62, STS-75, and STS-87) of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. The TDSE is similar to IDGE, but will maintain a constant temperature while varying pressure on the dentrites. Shown here is a cutaway of the isothermal bath containing its growth cell at the heart of the TDSE. The principal investigator is Matthew Koss of College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA. Note: an Acrobat PDF version is available from http://microgravity.nasa.gov/gallery