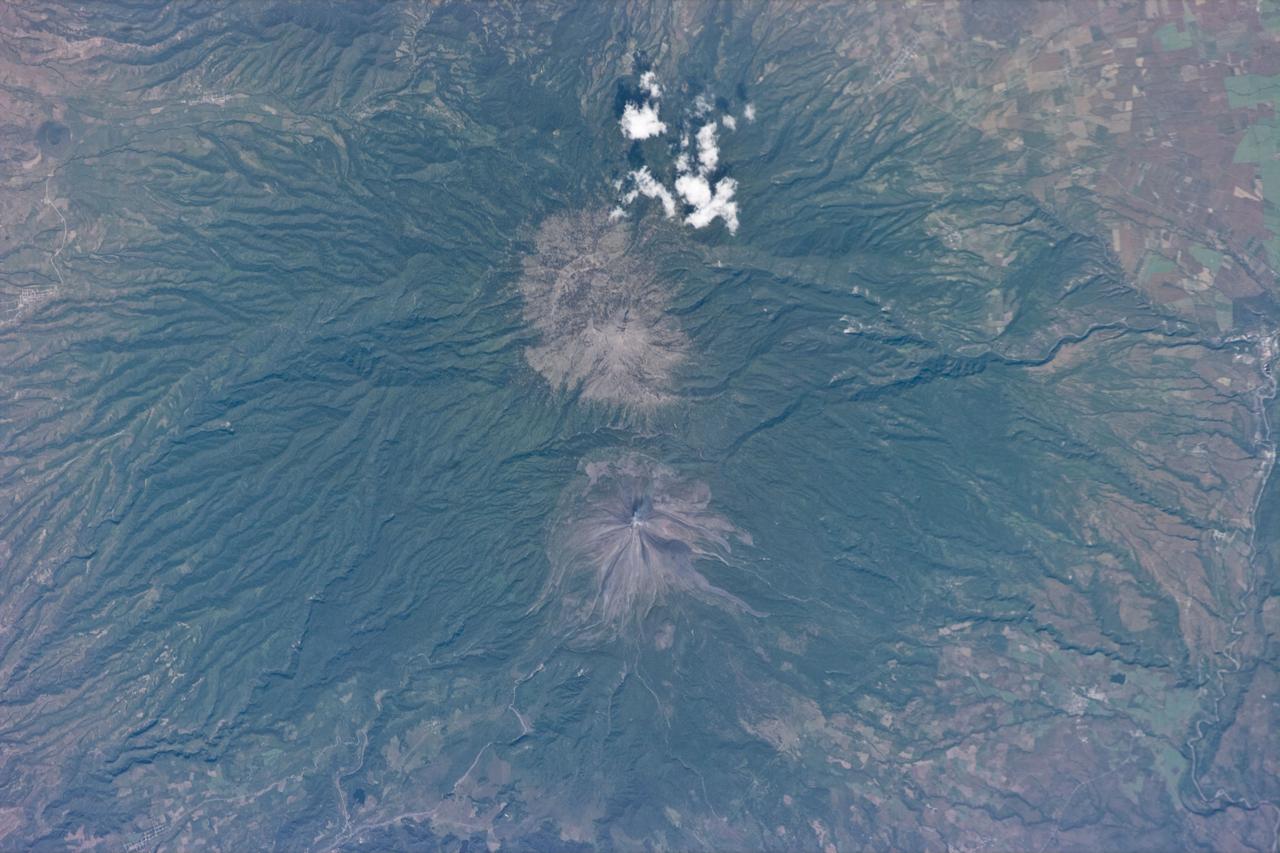

STS073-E-5274 (3 Nov. 1995) --- Colima was photographed with a color Electronic Still Camera (ESC) onboard the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Columbia. The volcano lies due south of Guadalajara and Lake Chapala. It is considered to be one of Mexico's most active and most dangerous volcanoes, lying not far from heavily populated areas.
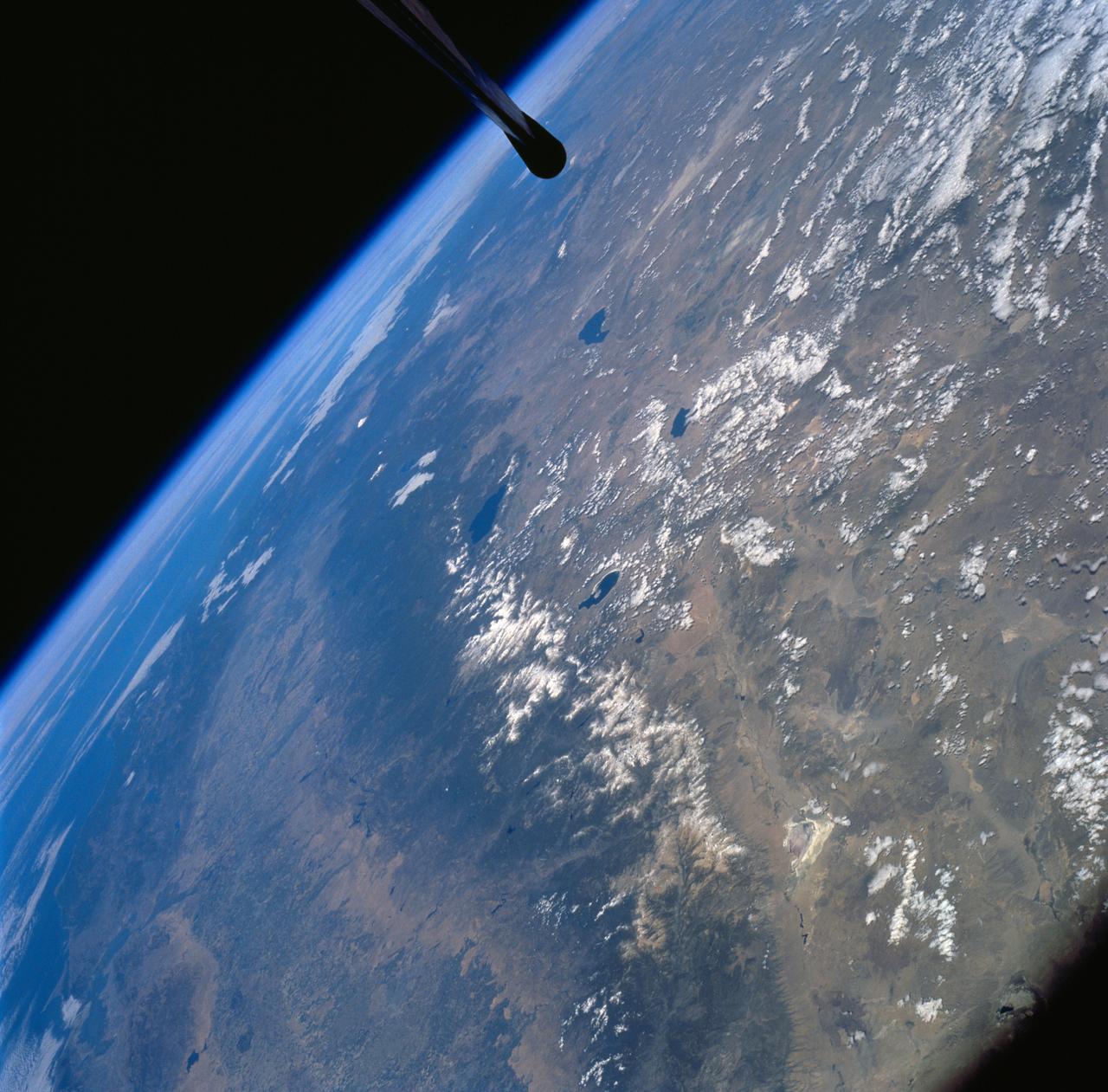

STS058-72-004 (18 Oct-1 Nov 1993) --- The Sierra Nevada Mountain Range can be seen in this north-looking high oblique view taken in October, 1993, by the STS-58 crew. Visible in the view to the west of the Sierra Nevada are the San Joaquin and Sacramento Valleys of central California. The San Francisco/Oakland Bay Area can be seen to the west of the valley at the extreme left of the photograph. To the east or right of the Sierra Nevada, the basin and Range Region of central and northern Nevada is visible. Mono Lake, Lake Tahoe and Pyramid Lake are also visible in this scene. The long northwest/southeast trending Walker Lane Shear Zone, which lies just to the east (right) of the Sierra Nevada is also visible. Near the top of the view (near the horizon), the snow covered volcanic peak Mount Shasta can be seen. Over 645 kilometers (400 miles) long and from 65 to 130 kilometers (40 to 80 miles) wide, the Sierra Nevada have many peaks in excess of 3,300 meters (11,000 feet) above sea level. A titled fault block in structure (the largest in the United States) and shaped by glaciers during the last ice age over 12,000 years ago, the Sierra Nevada eastern front rises sharply from the Great Basin of Nevada, while its western slope descends gradually to the hills bordering the Central Valley of California. Snow-fed streams supply much of the irrigation water to the Central Valley and to western Nevada and also generate hydroelectricity. Recent above normal precipitation (snowfall) of the last two years has helped in alleviating the drought conditions that had prevailed throughout most of California in the mid and late 1980's and early 1990's.

STS059-154-160 (9-20 April 1994) --- Orient with Mono Lake, California at the lower right; then the view is westward across the Sierra Nevada into the San Joaquin River drainage. A tiny network of ski trails can be seen on the Mono Lake side of the Sierras, on a line between Mono Lake and the snow-free San Joaquin headwaters. The ski trails mark Mammoth Mountain, where SRL investigators are studying microwave measurements of the water content of snowpacks. Linhof camera.

AS09-23-3586 (11 March 1969) --- Dallas, Ft. Worth, Sherman, Denison, Red River, and Lake Texoma, as photographed from the Apollo 9 spacecraft during its 122nd revolution of Earth.

AST-16-1132 (20 July 1975) --- A vertical view of the eastern portion of the state of South Australia in Australia, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The highlands area is the Flinders Range. The light-colored body of water is Lake Blanche. The lake to the south is Callabonna. This picture was taken at an altitude of 224 kilometers (139 statute miles) with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using high-definition aerial Ektachrome SO-242 type film.

STS058-105-016 (18 Oct-1 Nov 1993) --- This photograph includes much of the heart of New England, stretching from Boston and Boston Harbor (lower left) across New Hampshire and Vermont to Lake Champlain (upper left), and up to southern Maine (Portland is just off the photo at right center). The colors in this photograph are less vivid than those in STS-58-81-038, because the color changes on the deciduous trees in central and northern New England were past their peak when this photograph was taken. North of Boston flows the Merrimack River (which forms part of the state boundary between Massachusetts and New Hampshire). It is delineated by the small industrial towns (Concord, Manchester, Nashua, Lowell) which grew up on its banks. The White Mountains of New Hampshire are seen near the center, and Mt. Washington (6,288 feet) is capped with snow.
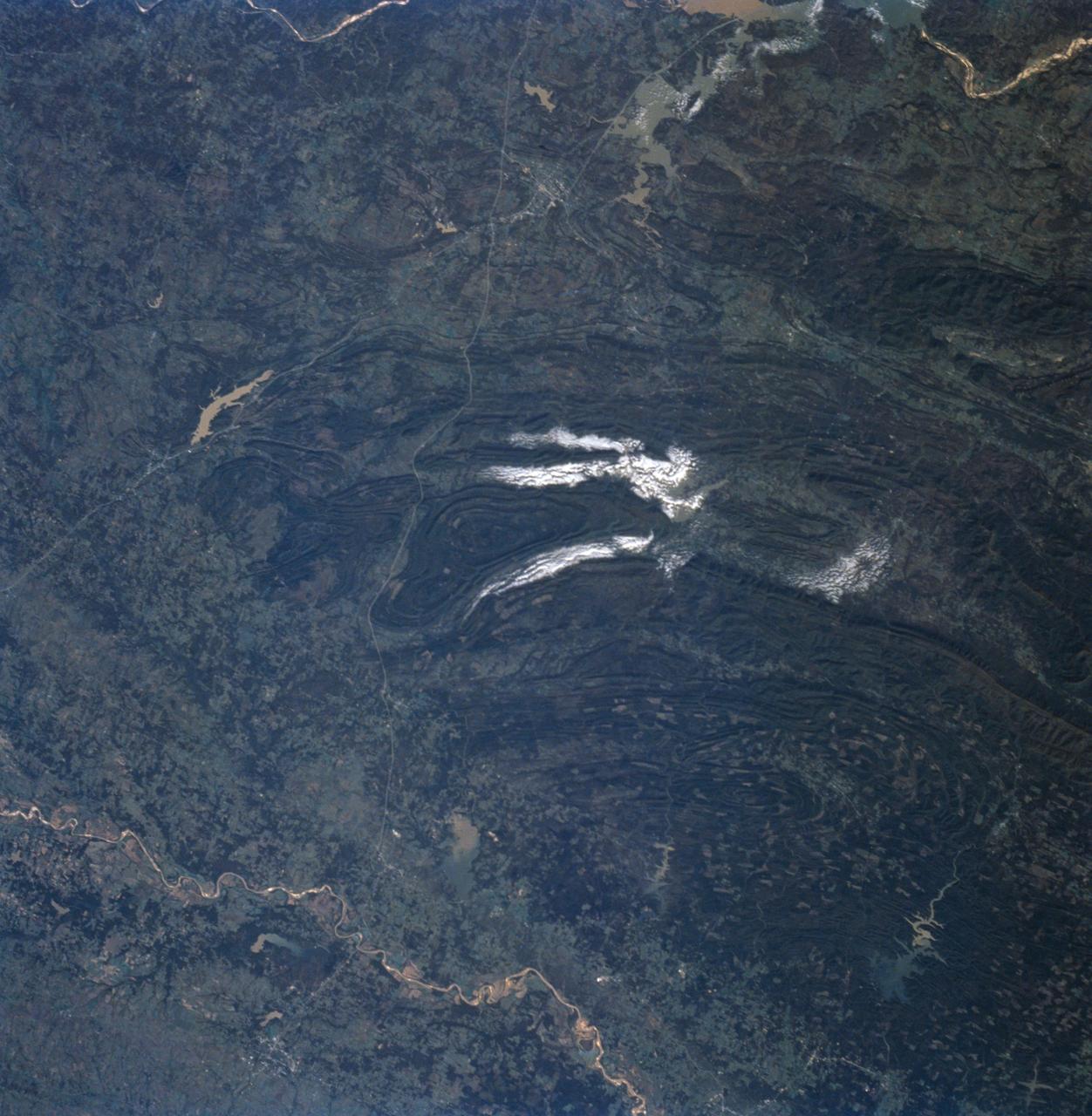

STS058-91-058 (18 Oct-1 Nov 1993) --- In this unusually clear view, the Ouachita Mountains of southeastern Oklahoma are framed on the north by Lake Eufaula on the South Canadian River, and on the south by the Red River. Sandstone, shale and chert (similar to flint) deposited in a sea several thousand feet deep were squeezed up to form the mountains about 250 million years ago. During the ensuing time, erosion of the western end of the Ouachita Mountains has emphasized linear ridges of resistant rock in the plunging anticlines and synclines, causing relief of 800 meters (2,600 feet) or more. Clouds formed by upslope winds border both the north and south sides of one of the most dramatic plunging synclines (in a syncline the rock layers dip toward the center of the structure). Toward the west, densely forested mountains give way to gently rolling, less rocky terrain and a drier climate which is better suited to farming. The mountains centered on Broken Bow, in the lower right corner of the scene, display abundant timber clearcuts that are being regenerated.

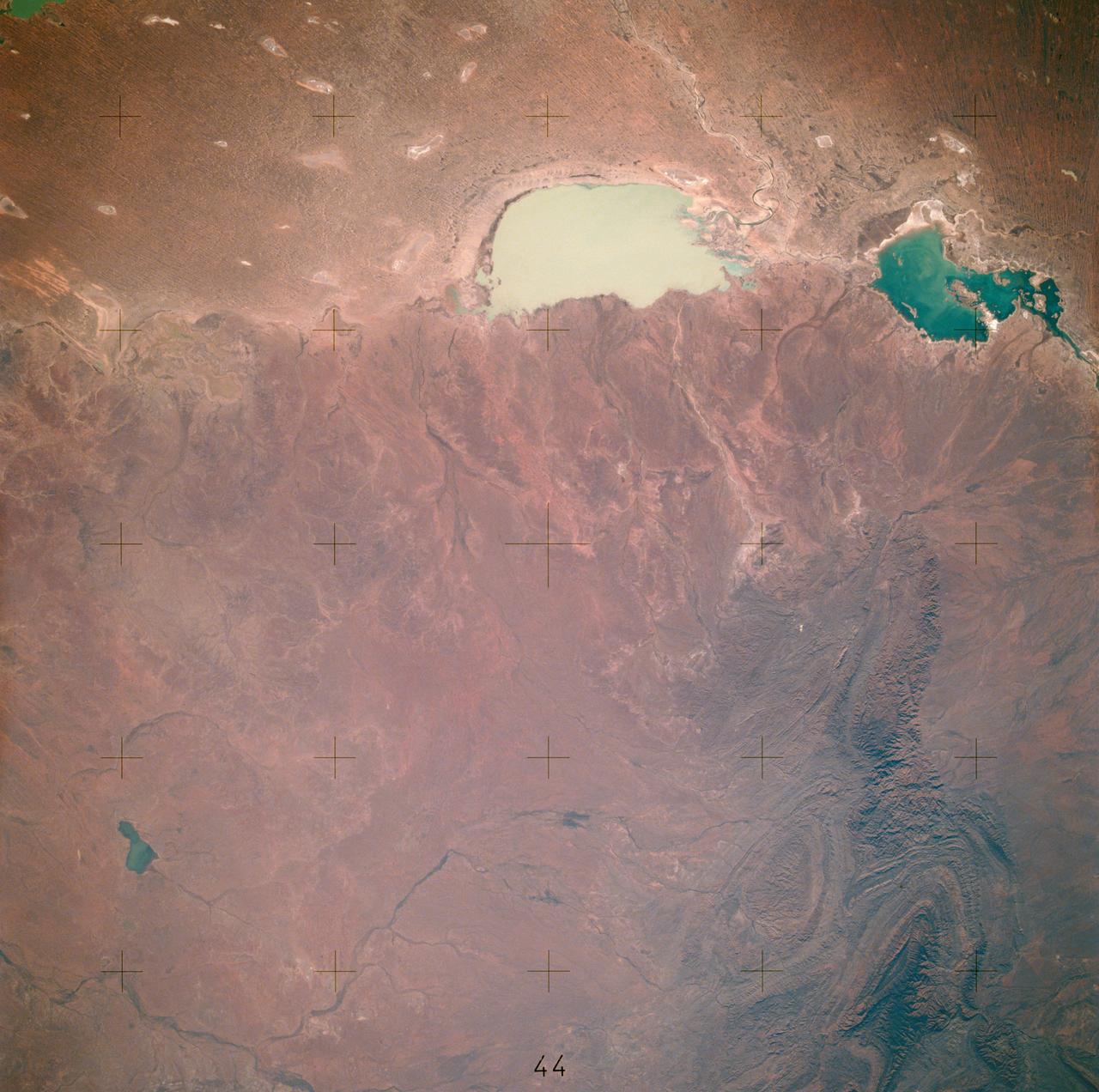
AST-19-1550 (24 July 1975) --- A vertical view of the Lake Eyre Basin area in the state of South Australia in Australia, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The picture was taken at an altitude of 241 kilometers (150 statute miles) with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using medium-speed Ektachrome QX-807 type film.
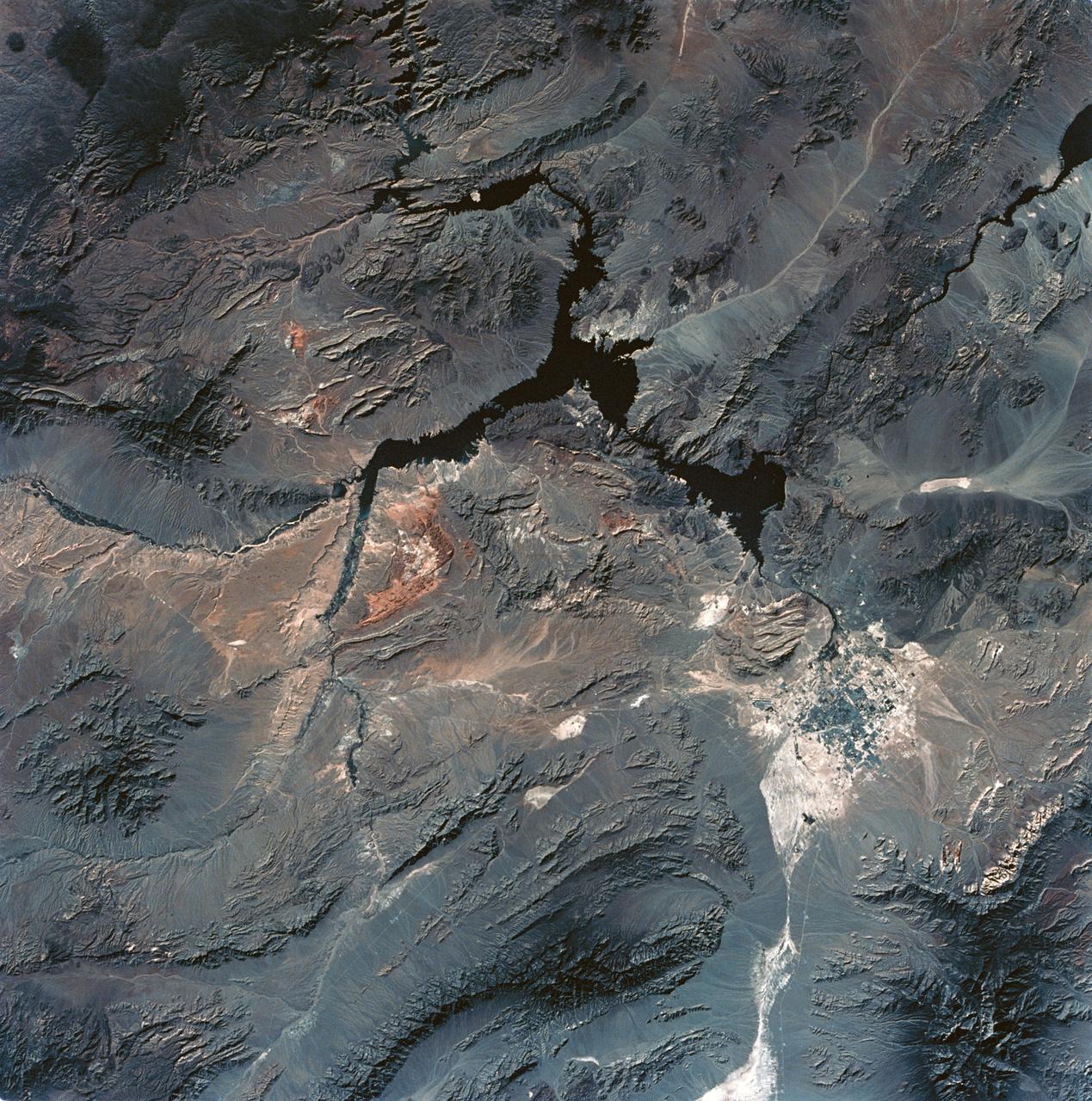

SL3-28-059 (July-September 1973) --- A vertical view of the Lake Mead and Las Vegas, Nevada area as photographed from Earth orbit by one of the six lenses of the Itek-furnished S190-A Multispectral Photographic Facility Experiment aboard the Skylab space station. Lake Mead is water of the Colorado River impounded by Hoover Dam. Most of the land in the picture is Nevada. However, a part of the northwest corner of Arizona can be seen. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA
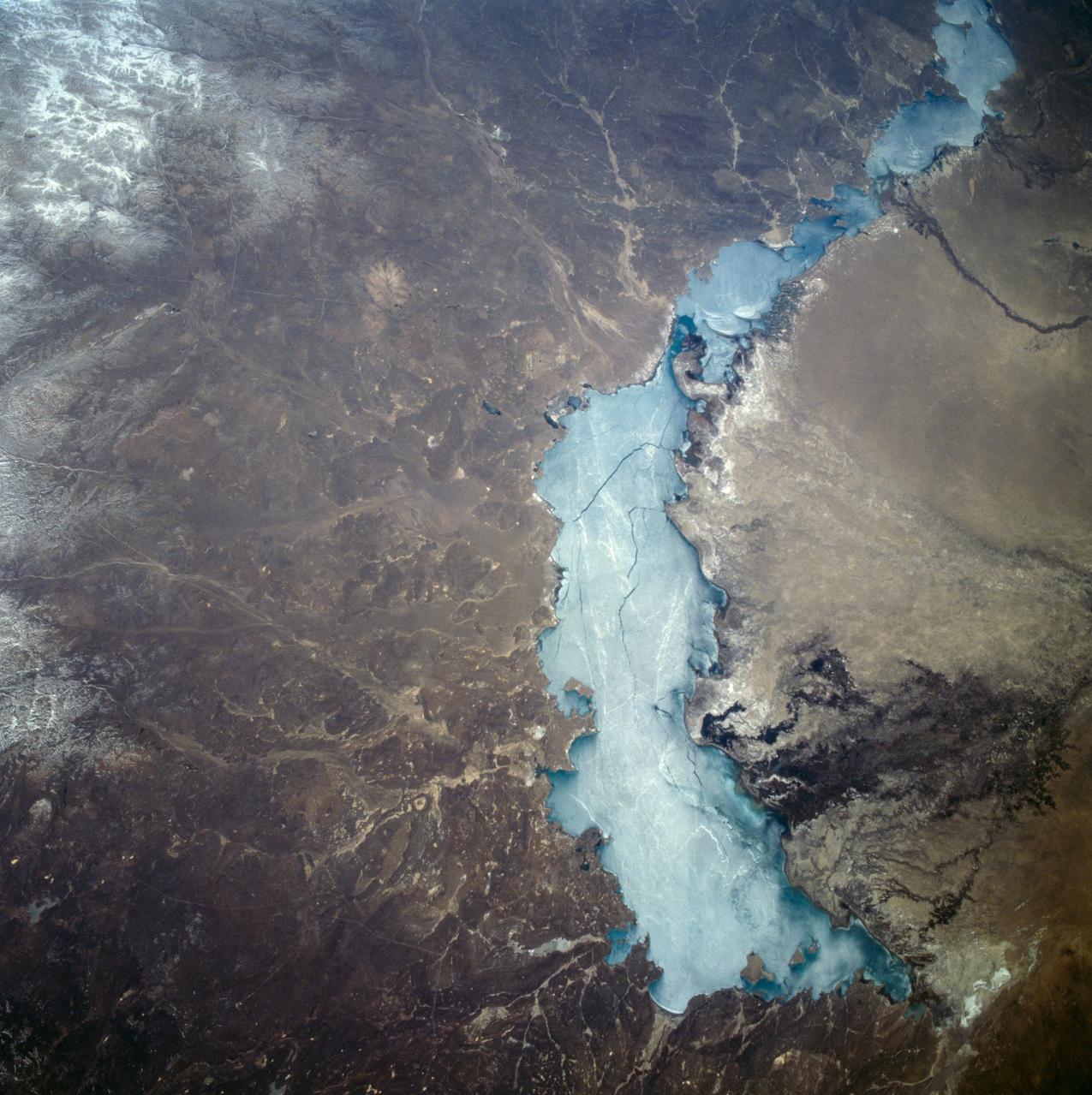

STS059-209-081 (9-20 April 1994) --- Lake Balkhash, in eastern Kazakhstan, is some 300 miles long. The lake, frozen in this scene, thawed noticeably during the mission. The shape of the lake is controlled by the delta of the Ili River, which flows from the Tien Shan Mountains in western China across this arid steppe. SRL scientists will use radar data to study the microwave effects of differences in soil moisture, and in freezing or thawing, on the deltaic sediments. Hasselblad camera.
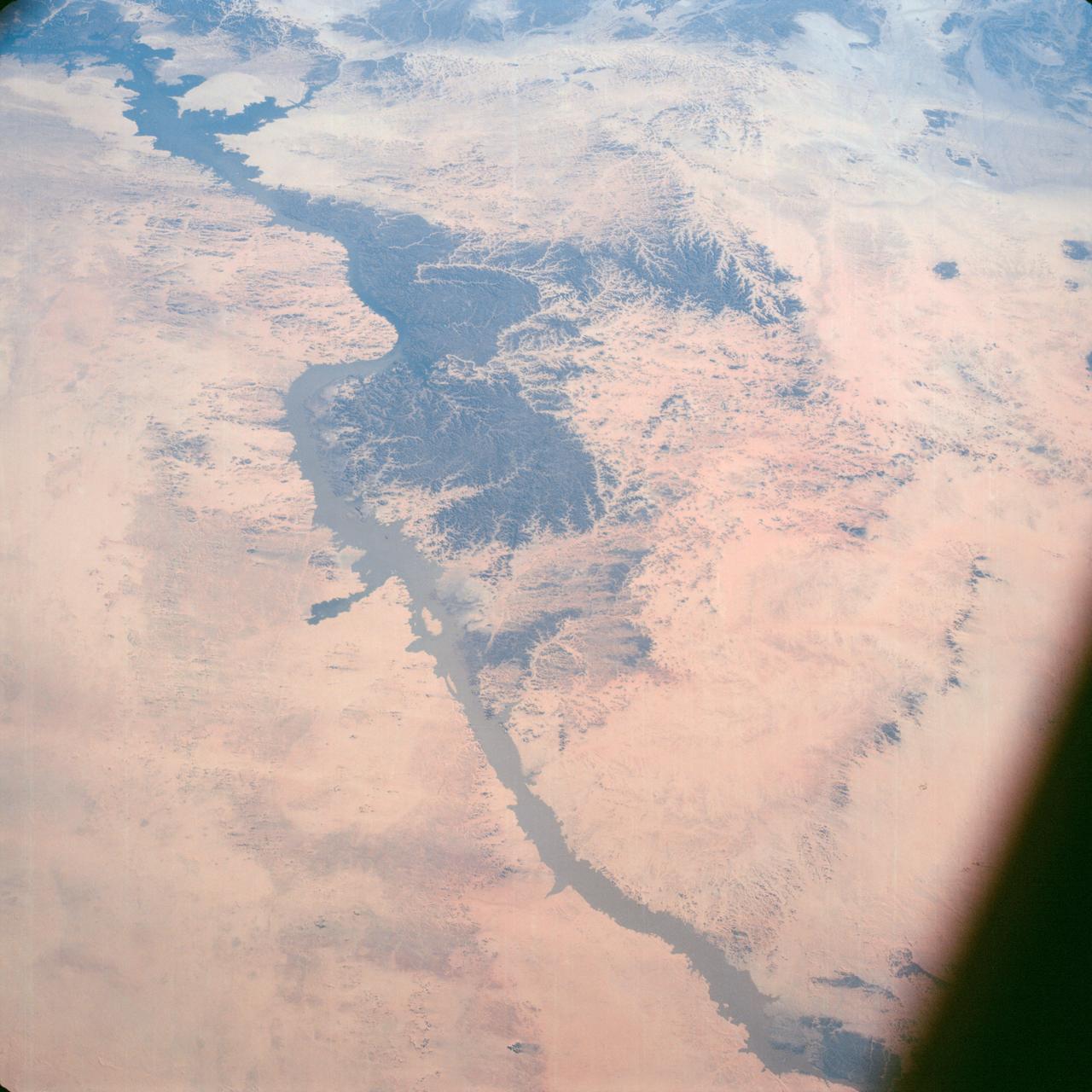

Lake Nasser on the Nile River in southeastern United Arab Republic (Egypt) as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 10th revolution of the earth. Photographed from an altitude of 130 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 14 hours and 56 minutes. Lake Nasser was created by the contruction of the Aswan Dam on the Nile.

STS058-91-074 (18 Oct-1 Nov 1993) --- The largest cityscape in the view is Nashville (top left), part of which is obscured under a band of clouds (the Cumberland River, on which Nashville lies, can not be seen under the cloud band). Close to the main cloud mass on the opposite side of the view, lies a small lake (Normandy Lake in sunglint (right center) 70 miles southeast of Nashville. Between these two features, in the center of the Nashville Basin, lies the city of Murfreesboro. The city appears here as a spider like pattern one third the distance from Nashville towards Normandy Lake. The Tennessee River can be seen bottom right and top right through holes in the cloud.
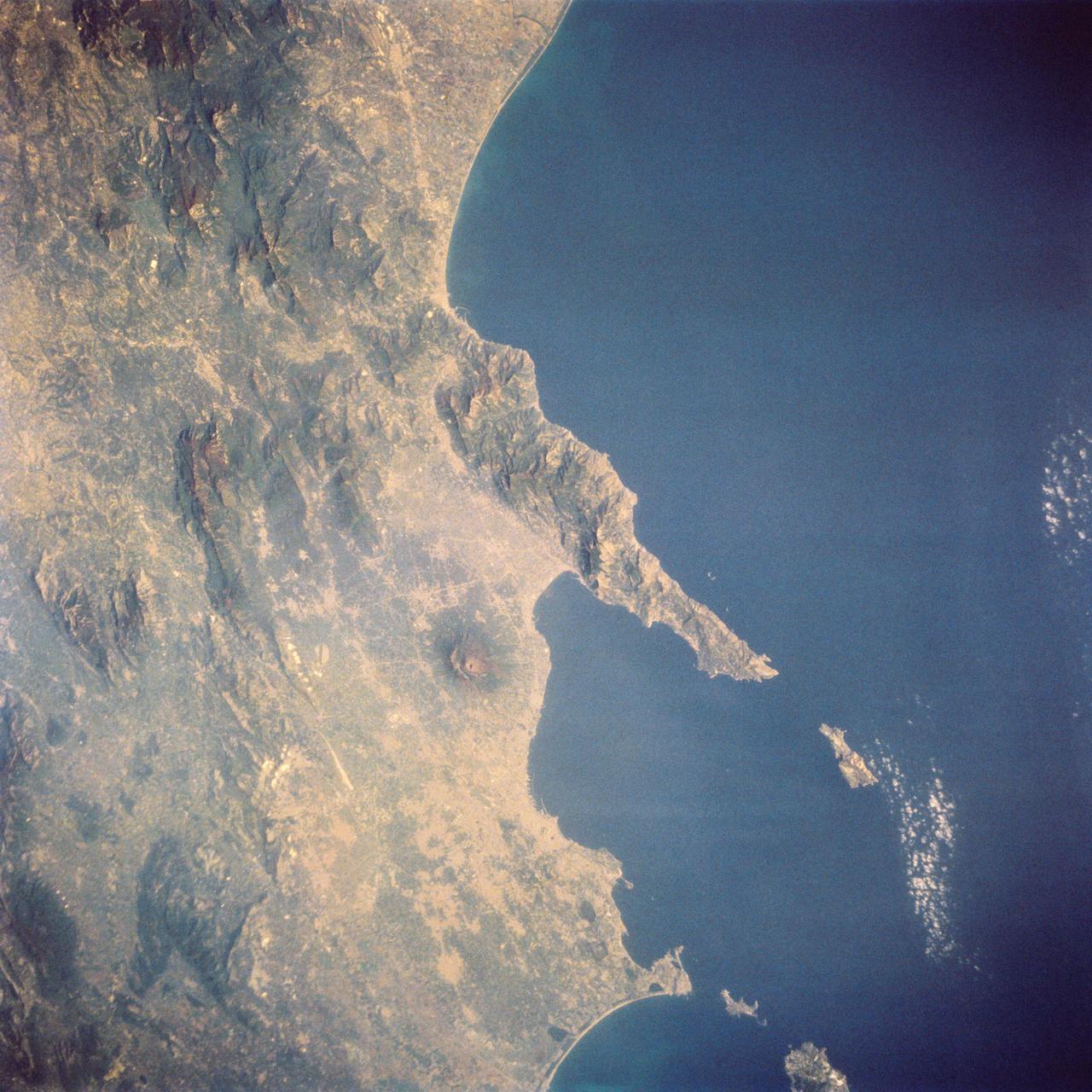

STS058-73-024 (18 Oct-1 Nov 1993) --- The ancient eruption of Vesuvius (the volcano near the center of the frame) destroyed the town of Pompeii located on its southeast flank. But the larger town of Naples, between Vesuvius (to the south) and the large, circular, lake-filled caldera of Campi Flegrei (to the west) also lives with the constant threat of volcanic hazards. In this view, Naples is the gray urban area with substantial coastal development just northwest of Vesuvius. Other landmarks marking the Italian coast include the small island of Capri, just off the west-pointing peninsula, and the city of Salerno on the coast just south of the same peninsula.

STS058-100-073 (18 Oct-1 Nov 1993) --- An unusually clear, northwestward view of central North Carolina shows the farms and timber of the inner coastal plain. The city of Fayetteville, and Fort Bragg to the west, is prominent at lower left center. The Research Triangle of Raleigh, Durham and Chapel Hill can be seen at upper right, upstream from Jordan Lake and Harris Lake on the New Hope River.

AST-30-2601 (20 July 1975) --- An area of the Cascade Mountains southeast of Seattle in the State of Washington, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The view includes Snoqualmie Pass, Cle Elum Lake, Kachess Lake and Keechelus Lake. The picture was taken at an altitude of 228 kilometers (141 statute miles) with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using medium-speed Ektachrome QX-807 type film.

SL3-27-180 (July-September 1973) --- A vertical view of the Snowy Mountains area of Australian Alps in the States of Victoria and New South Wales, Australia, as photographed from Earth orbit by one of the six lenses of the Itek-furnished S190-A Multispectral Photographic Facility Experiment aboard the Skylab space station. This picture was taken with type 2443 infrared color film. The lake near the center of the picture is the Eucumbene Reservoir. This area is located immediately south-southwest of the capital city of Canberra. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA

SL3-22-0214 (July-September 1973) --- A vertical view of southeastern Washington State as photographed from Earth orbit by one of the six lenses of the Itek-furnished S190-A Multispectral Photographic Facility Experiment aboard the Skylab space station. The Snake River flows into the Columbia River in the most southerly corner of the picture. The Wallula Lake is below the junction of the two rivers. The Yakima Valley is at the southwestern edge of the photograph. The Columbia Basin is in the center of the picture. The Cascade Range extends across the northwest corner of the photograph. This picture was taken with type SO-356 regular color film. The S190-A experiment is part of the Earth Resources Experiments Package. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA
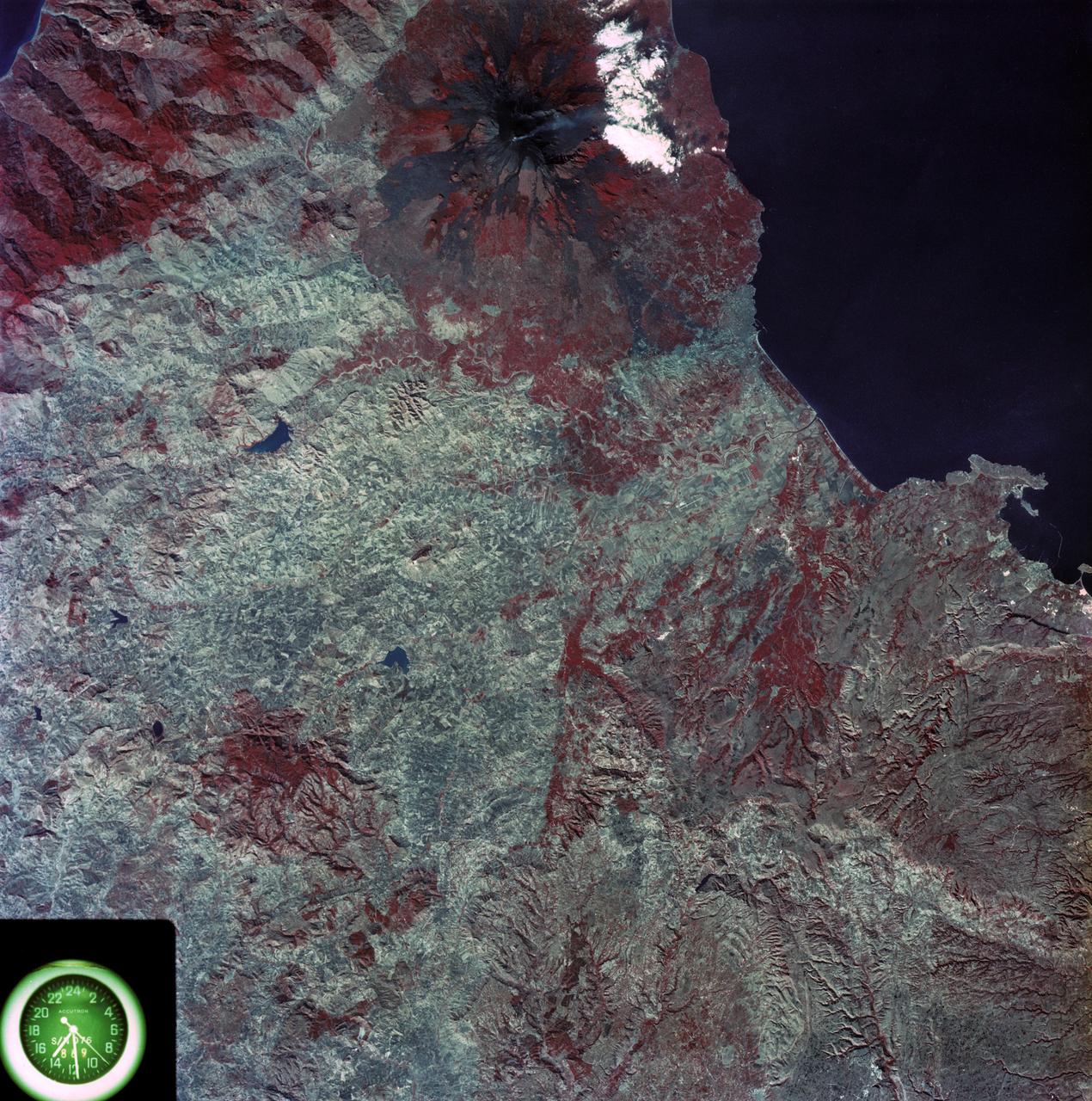
SL3-87-355 (July-September 1973) --- A vertical view of the eastern coast of Sicily area is seen in this Skylab 3 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch earth terrain camera) infrared photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. Mount Etna, the highest volcano in Europe (10,958 feet), is still active as evidenced by the thin plume of smoke emanating from its crest. (The altitude is approximate because the height of the volcano changes with each eruption). On the flanks of Etna recent lava flows appear black in contrast to the older flows and volcanic debris that are red. Numerous small, circular cinder cones on the flanks represent sites of previous eruptions. Catania, on the Mediterranean coast south of Etna, is the largest of several cities and villages which appear as light-gray patches on the lower slopes of the volcano. Plano de Catania, south of the city of Catania, is outlined by polygonal light and dark agricultural tracts. Several lakes, the largest of which is Lake Pozzillo, show up as dark blue in the photograph. The unusual colors in the picture are due to the use of color infrared film in which vegetation appears red. This is very evident on the slopes of Etna, in the Monti Nebrodi area at upper let, and in the local areas in the lower part of the picture. Studies of Mount Etna and related volcanic features will be undertaken by Professor Roberto Cassinis of Servizio Geologio d?Italia, Rome. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observation Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA
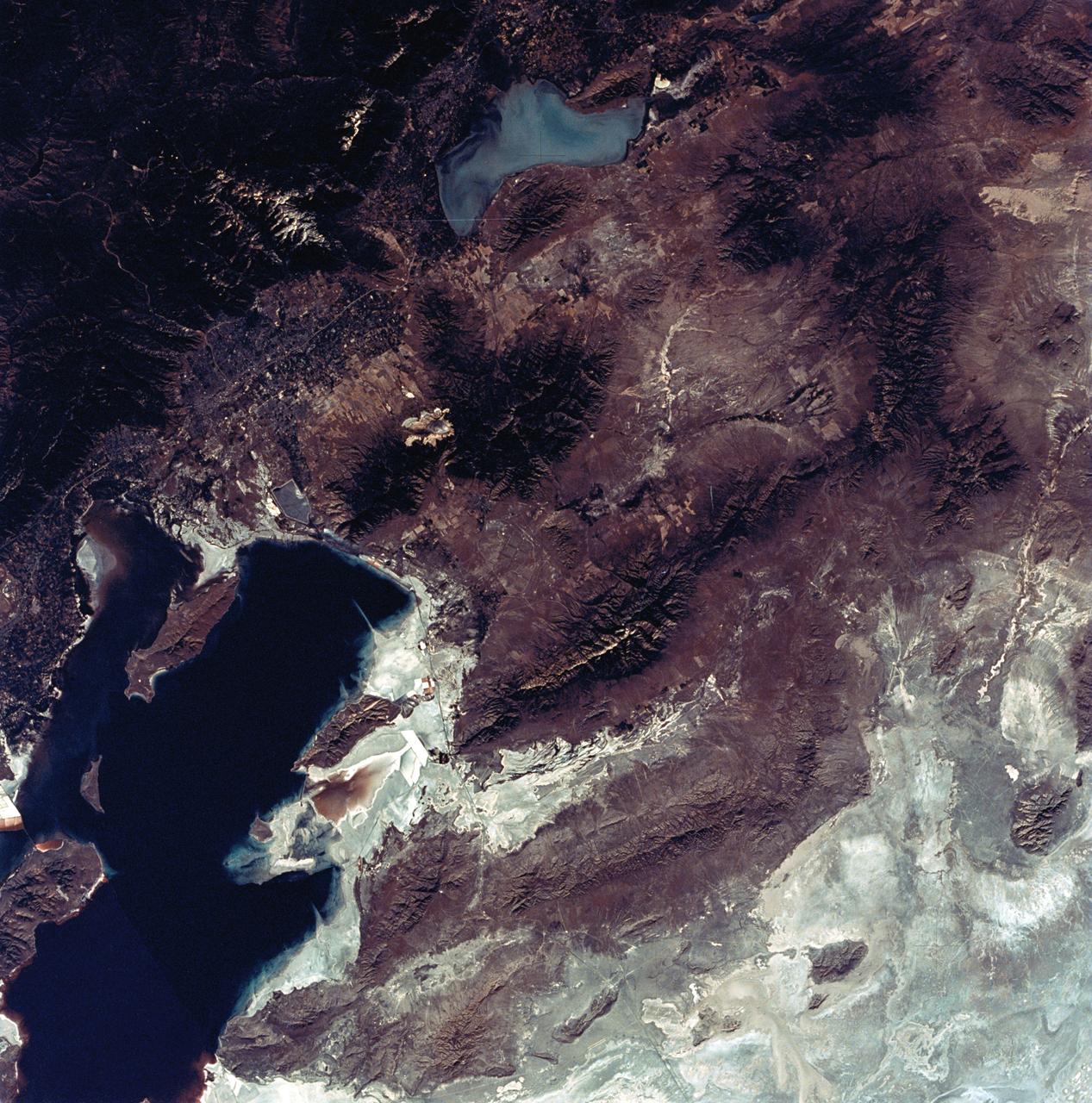

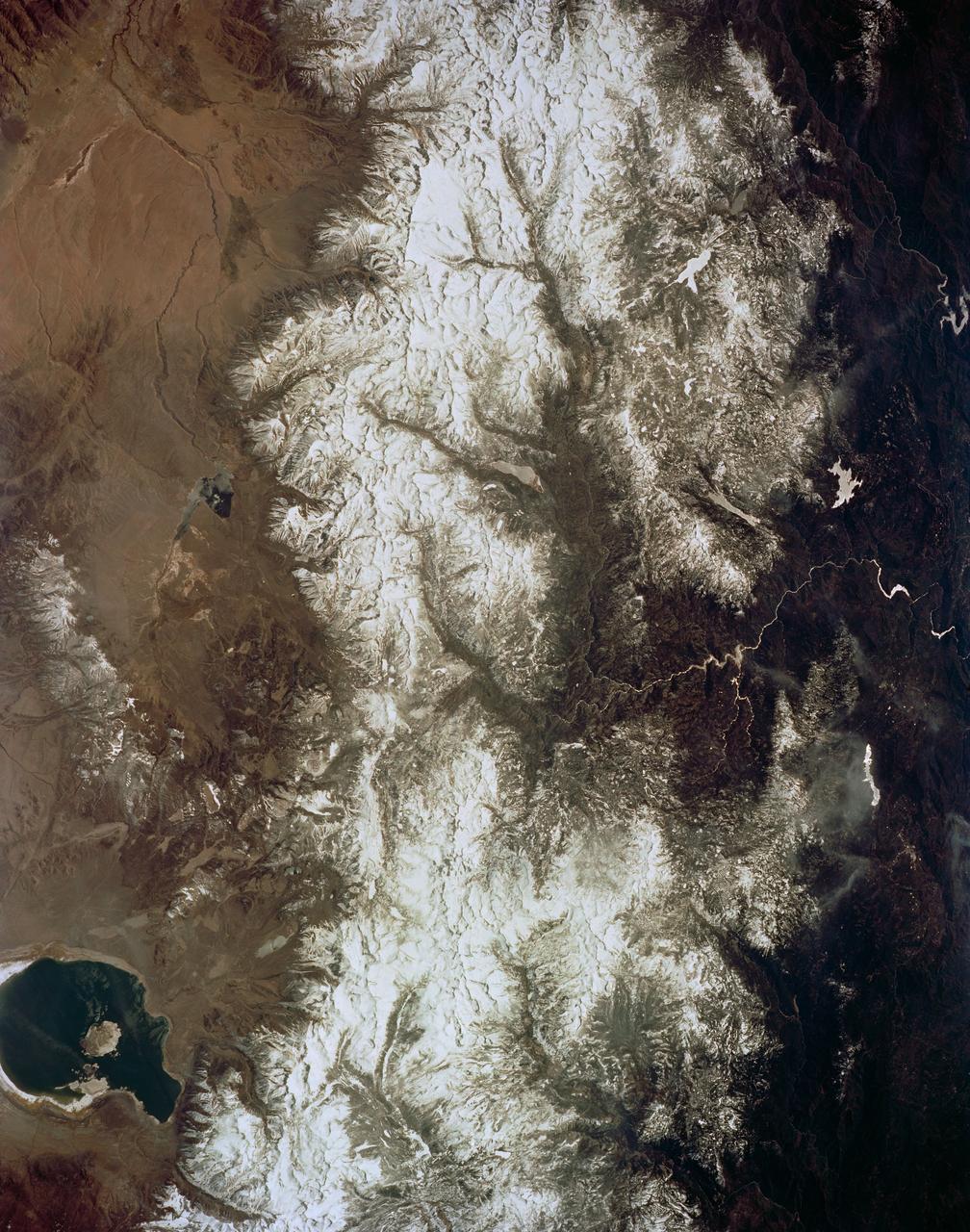
SL3-22-0322 (July-September 1973) --- An oblique view of the Salt Lake City, Utah area as photographed from Earth orbit by one of the six lenses of the Itek-furnished S190-A Multispectral Photographic Facility Experiment aboard the Skylab space station. Approximately two-thirds of the Great Salt Lake is in view. The smaller body of water south of Salt Lake City is Utah Lake. The Wasatch Range is on the east side of the Great Salt Lake. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA
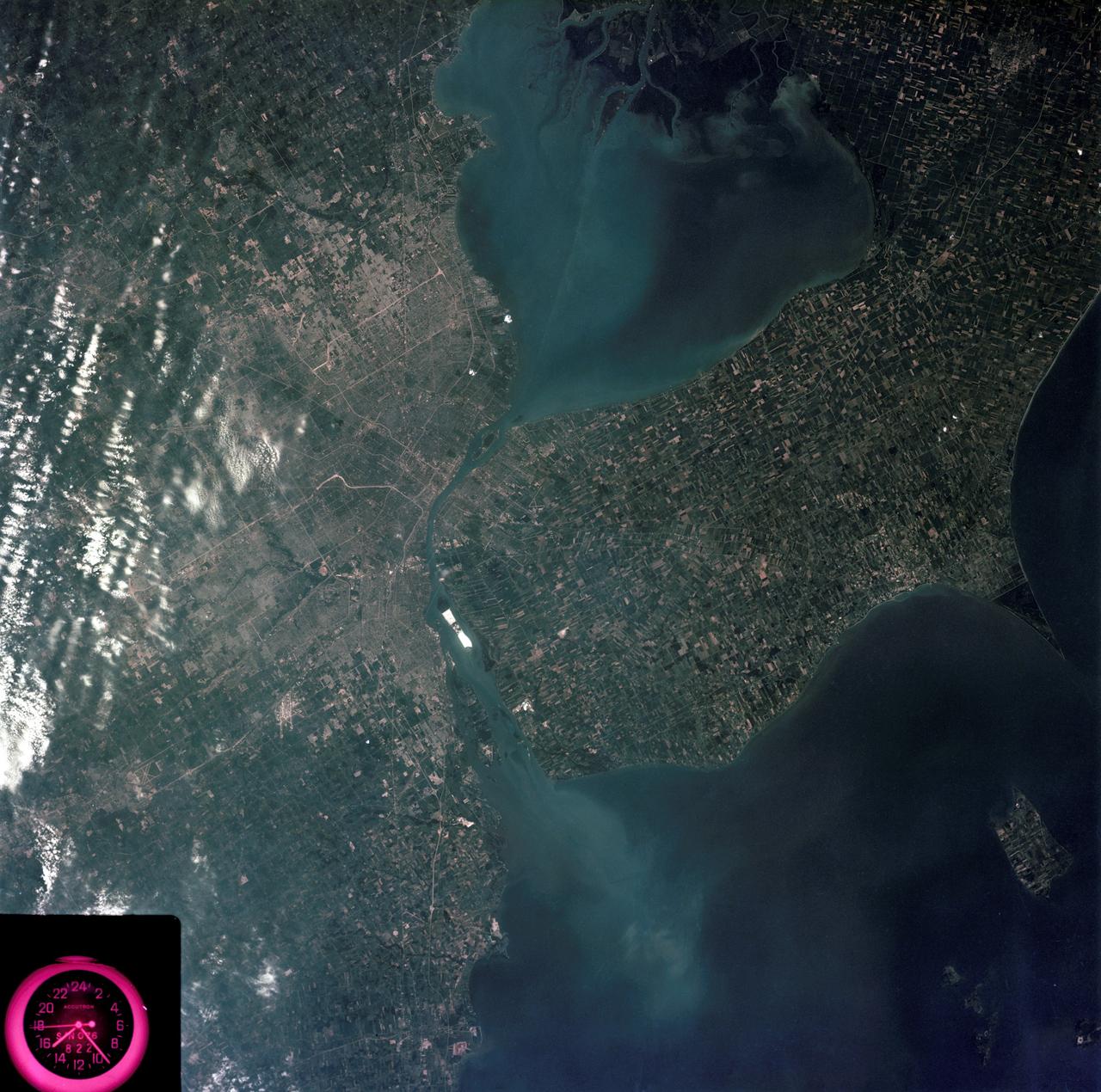

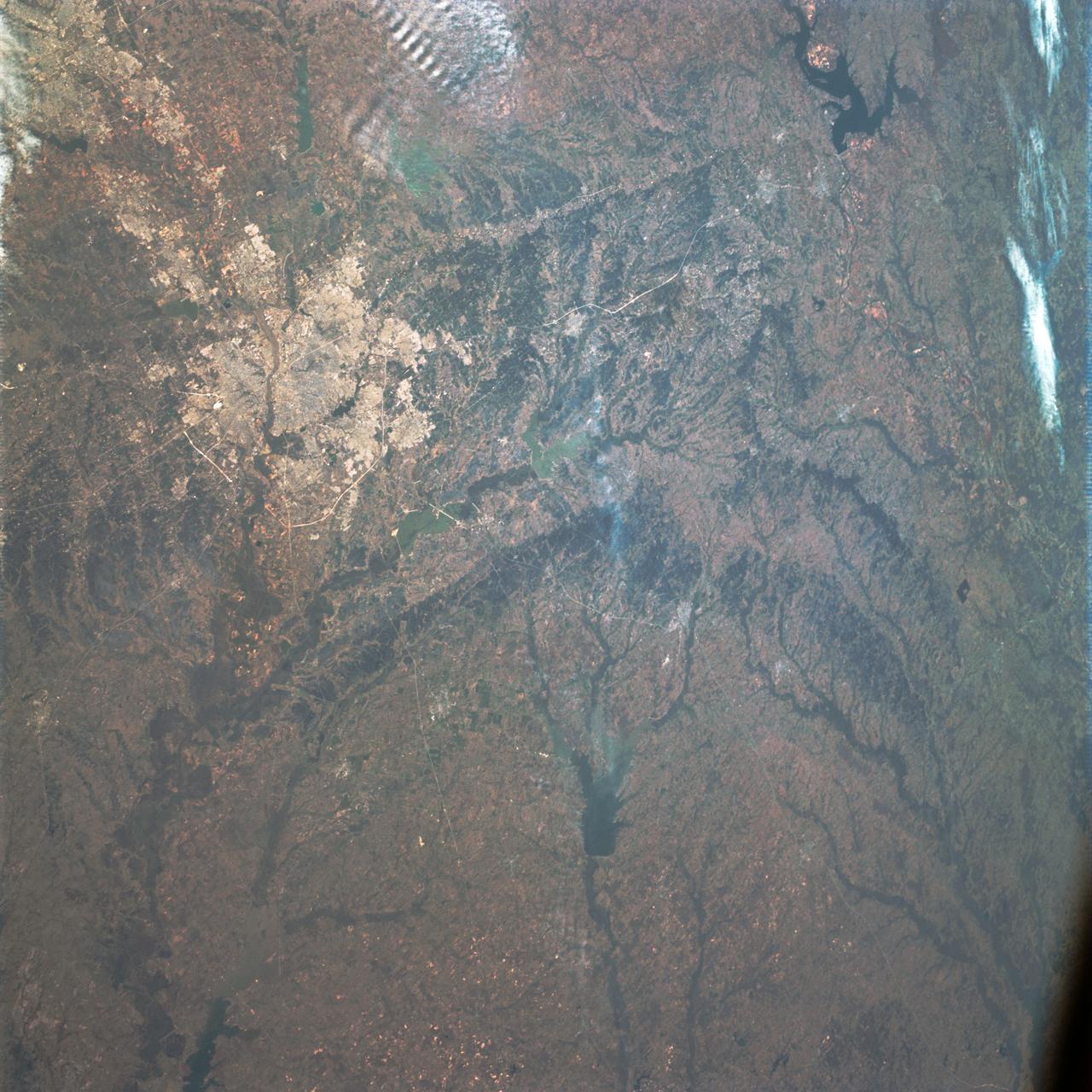
SL3-83-0152 (July-September 1973) --- A near vertical view of the metropolitan Detroit, Michigan area is seen in this Skylab 3 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch Earth terrain camera) photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The 25-mile long Detroit River drains the smaller body of water (Lake St. Clair) and flows southwestward separating Detroit from Windsor, Ontario, and empties into Lake Erie. The Detroit River handles a great deal of Great Lakes barge and ship traffic. Major streets and thoroughfares radiating from the city are clearly visible. Fighting Island is the highly reflective, white area located almost in the center of the picture. This high reflectivity is caused by the functional use of the island-disposal ponds for chemical salts. Sedimentation and/or pollution patterns in the area provide interesting visual phenomena for speculation and analysis. Distinct and rather unique cultivated field patterns can be observed south and east of Windsor, Ontario. This is a direct result of an English survey and land tenure system which was utilized when the area was settled. New areas of residential development are fairly easy to differentiate from older, established residential areas. Vegetation and extent of area coverage can be determined. The Oakland County Planning Commission and the Federal Bureau of Outdoor Recreation working closely with Irv Sattinger of the Environmental Research Institute of Michigan (University of Michigan) are presently processing and analyzing photographic and Multispectral scanner data to determine its usefulness for recreation and open space site studies for this area. Photo credit: NASA
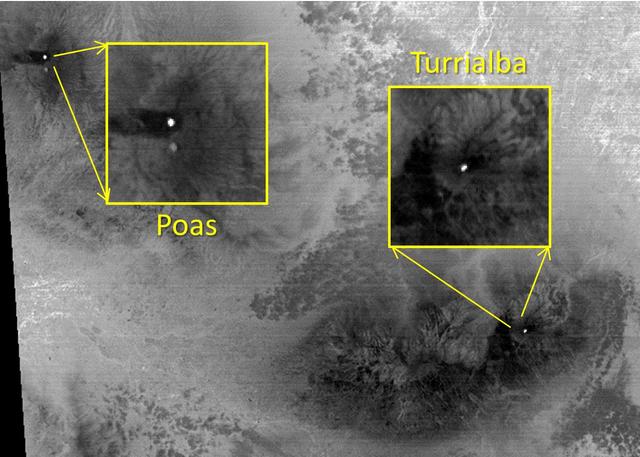
The March, 2015 eruption of Turrialba Volcano in Costa Rica caught everyone by surprise as seen in this image from the ASTER instrument onboard NASA Terra spacecraft. Activity had greatly diminished when the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument on NASA's Terra spacecraft acquired this nighttime thermal infrared image on April 2, 2015. The hot summit crater appears in white, indicating continued volcanic unrest. To the west, Poas Volcano's hot crater lake also appears white, though its temperature is considerably less than Turrialba's crater. The large image covers an area of 28 by 39 miles (45 by 63 kilometers); the insets 2 by 2 miles (3.1 by 3.1 kilometers). The image is centered at 10.1 degrees north, 84 degrees west. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19355
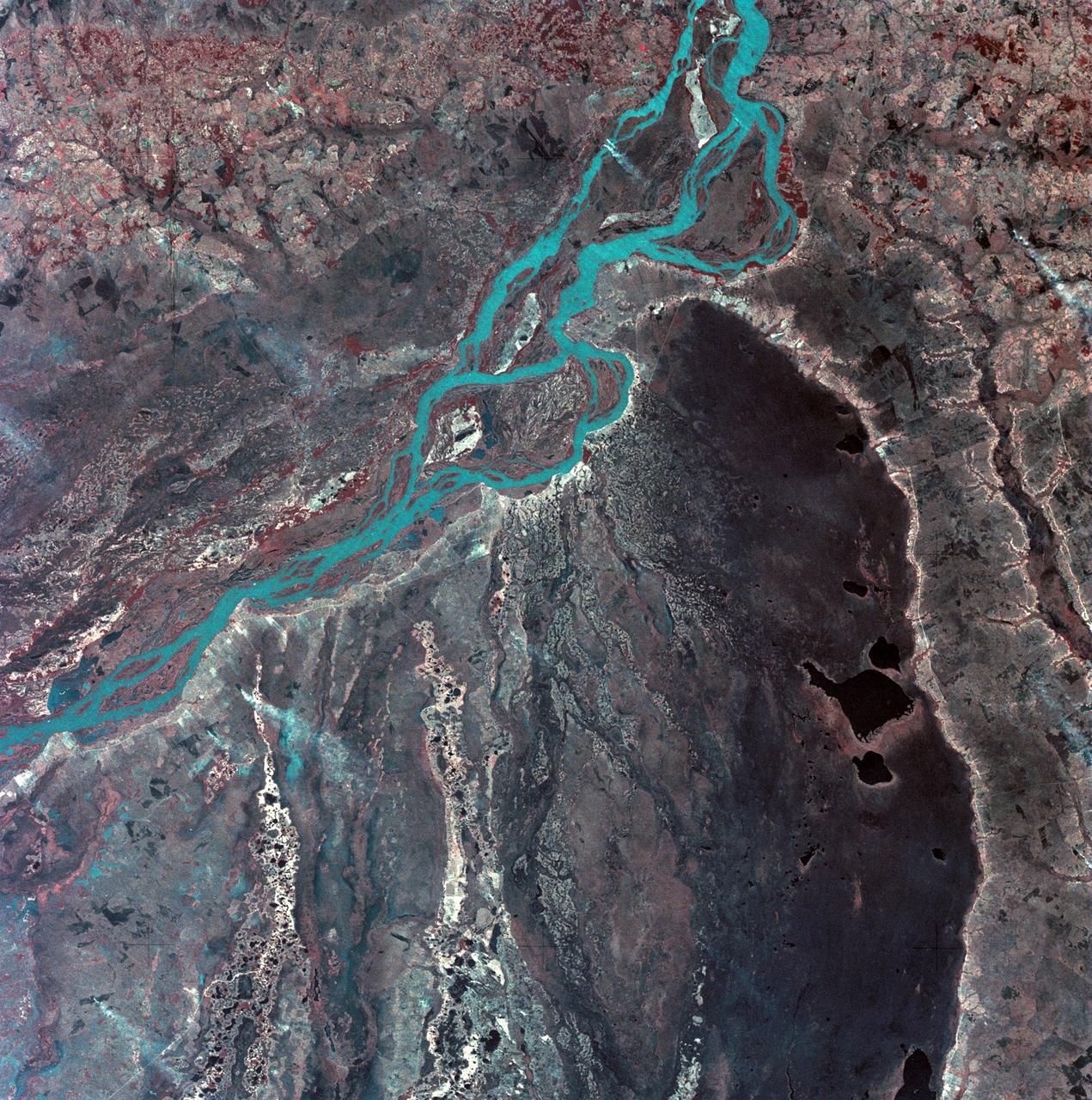

SL3-33-167 (July-September 1973) --- A vertical view of the Argentina-Paraguay border area of South America as photographed from Earth orbit by one of the six lenses of the Itek-furnished S190-A Multispectral Photographic Facility Experiment aboard the Skylab space station. This picture was taken with type 2443 infrared color film. The Parana River flows from east to west across the picture. This part of the Rio Parana is located between the towns of Posadas, Argentina, and Resistencia, Argentina. The major body of water in the large swamp area is Laguna Ibera. Note the several fires burning in this area. The largest land mass (Argentina) is south of the river. Paraguay is north of the river. Isla Apipe Grande is near the center of the photograph. The S190-A experiment is part of the Skylab Earth Resources Experiments Package. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA
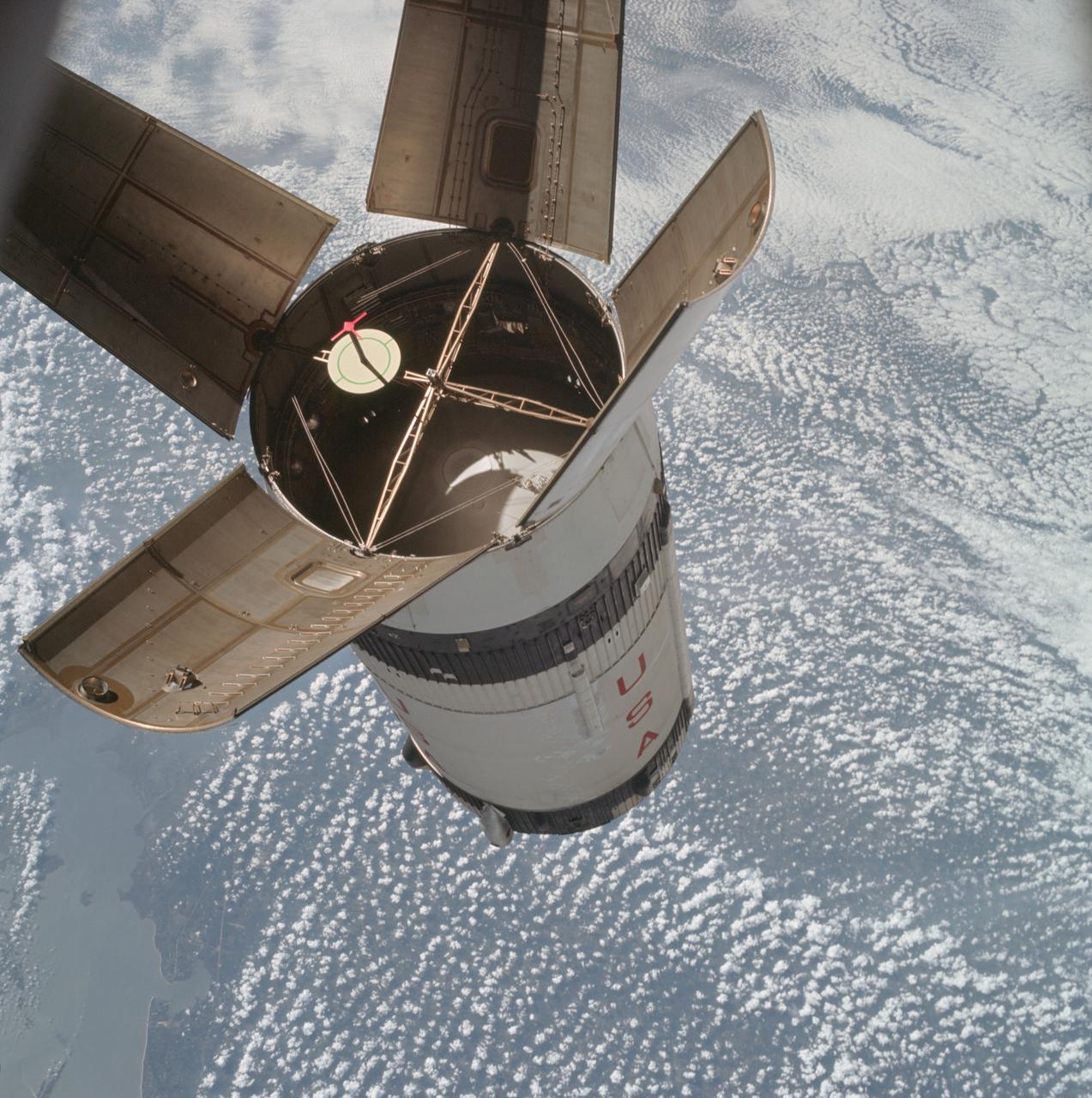

AS07-03-1541 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The expended Saturn IVB stage as photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during transposition and docking maneuvers. St. Louis Bay and Lake Borgne area just east of New Orleans is seen below. The round, white disc inside the open panels of the Saturn IVB is a simulated docking target similar to that used on the lunar module for docking during lunar missions.
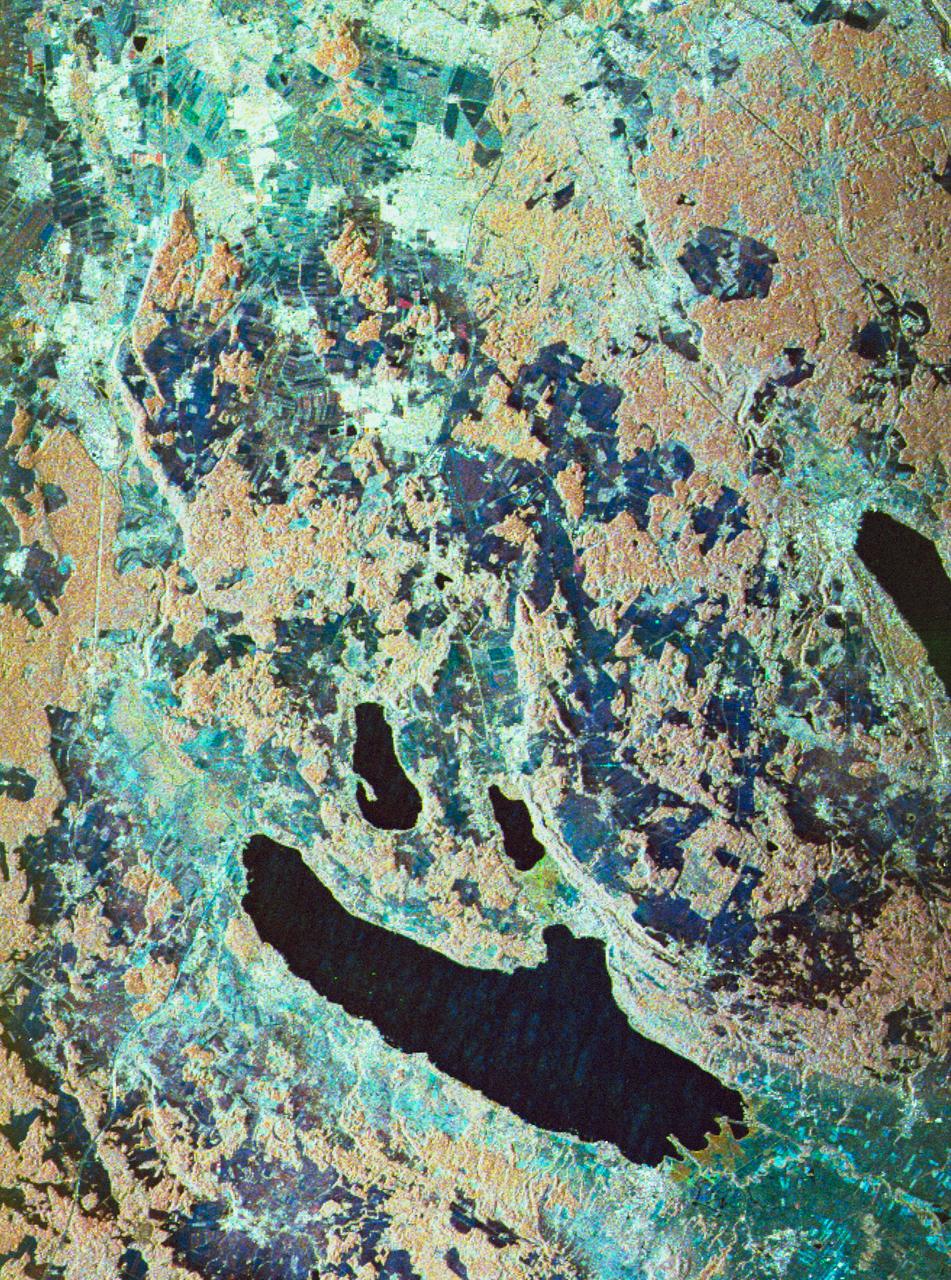
STS059-S-080 (18 April 1994) --- This is a false-color three frequency image of the Oberpfaffenhofen supersite, an area just south-west of Munich in southern Germany. The colors show the different conditions that the three radars (X-Band, C-Band and L-Band) can see on the ground. The image covers a 27 by 36 kilometer area. The center of the site is 48.09 degrees north and 11.29 degrees east. The image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) onboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on April 11, 1994. The dark area on the left is Lake Ammersee. The two smaller lakes are the Woerthsee and the Pilsensee. On the bottom is the tip of the Starnbergersee. The city of Munich is located just beyond the right of the image. The Oberpfaffenhofen supersite is the major test site for SIR-C/X-SAR calibration and scientific investigations concerning agriculture, forestry, hydrology and geology. This color composite image is a three frequency overlay. L-Band total power was assigned red, the C-Band total power is shown in green and the X-Band VV polarization appears blue. The colors on the image stress the differences between the L-Band, C-Band, X-Band images. If the three radar antennas were getting an equal response from objects on the ground, this image would appear in black and white. However, in this image, the blue areas corresponds to area for which the X-Band backscatter is relatively higher than the backscatter at L and C-Bands. This behavior is characteristic of grasslands, clear cuts and shorter vegetation. Similarly, the forested areas have a reddish tint (L-Band). The green areas seen near both the Ammersee and the Pilsensee lakes indicate marshy areas. The agricultural fields in the upper right hand corner appear mostly in blue and green (X-Band and C-Band). The white areas are mostly urban areas, while the smooth surfaces of the lakes appear very dark. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43930

This is a radar image of the central part of the island of Sumatra in Indonesia that shows how the tropical rainforest typical of this country is being impacted by human activity. Native forest appears in green in this image, while prominent pink areas represent places where the native forest has been cleared. The large rectangular areas have been cleared for palm oil plantations. The bright pink zones are areas that have been cleared since 1989, while the dark pink zones are areas that were cleared before 1989. These radar data were processed as part of an effort to assist oil and gas companies working in the area to assess the environmental impact of both their drilling operations and the activities of the local population. Radar images are useful in these areas because heavy cloud cover and the persistent smoke and haze associated with deforestation have prevented usable visible-light imagery from being acquired since 1989. The dark shapes in the upper right (northeast) corner of the image are a chain of lakes in flat coastal marshes. This image was acquired in October 1994 by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) onboard the space shuttle Endeavour. Environmental changes can be easily documented by comparing this image with visible-light data that were acquired in previous years by the Landsat satellite. The image is centered at 0.9 degrees north latitude and 101.3 degrees east longitude. The area shown is 50 kilometers by 100 kilometers (31 miles by 62 miles). The colors in the image are assigned to different frequencies and polarizations of the radar as follows: red is L-band horizontally transmitted, horizontally received; green is L-band horizontally transmitted, vertically received; blue is L-band vertically transmitted, vertically received. SIR-C/X-SAR, a joint mission of the German, Italian and United States space agencies, is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth program. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01797
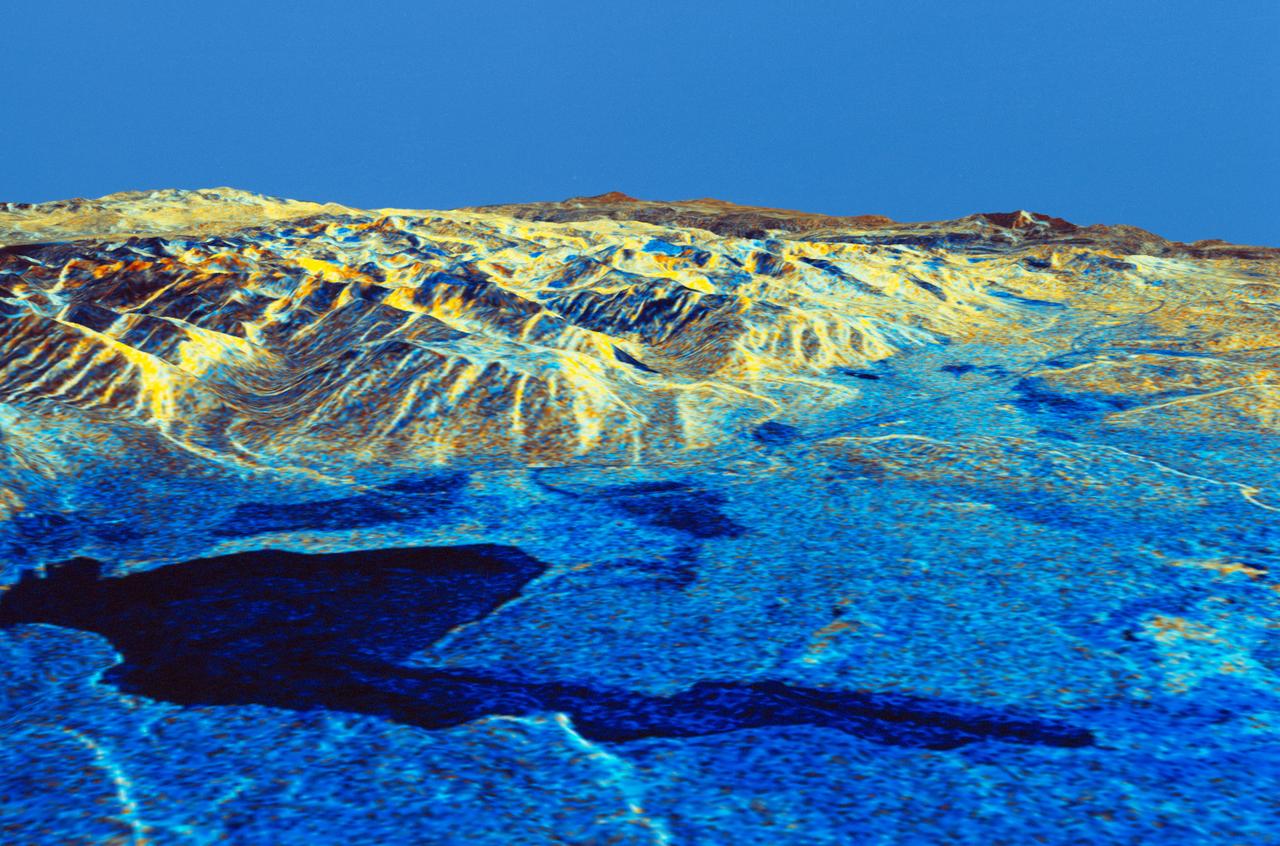
STS059-S-084 (17 April 1994) --- This is a three-dimensional perspective of Mammoth Mountain, California. This view was constructed by overlaying a SIR-C radar image on a U.S. Geological Survey digital elevation map. Vertical exaggeration is 2x. The image is centered at 37.6 degrees north, 119.0 degrees west. It was acquired from the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) onboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on its 67th orbit, April 13, 1994. In this color representation, red is C-Band HV-polarization, green is C-Band VV-polarization and blue is the ratio of C-Band VV to C-Band HV. Blue areas are smooth and yellow areas are rock outcrops with varying amounts of snow and vegetation. Crowley Lake is in the foreground and Highway 395 crosses in the middle of the image. Mammoth Mountain is shown in the upper right. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43933

Craig R. Bomben became a pilot in the Flight Crew Branch of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif., in June 2001. His flying duties include a variety of research and support activities while piloting the F/A-18, DC-8, T-34C and King Air aircraft. He has more than 17 years and 3,800 hours of military and civilian flight experience in over 50 different aircraft types. Bomben came to NASA Dryden from a U.S. Navy assignment to the Personnel Exchange Program, Canada. He served as a test pilot in the Canadian Armed Forces located in Cold Lake, Alberta. He participated in numerous developmental programs to include CT-133 airborne ejection seat testing, F/A-18 weapons flutter testing and F/A-18 night vision goggles integration. Bomben performed U.S. Navy fleet service in 1995 as a strike-fighter department head. He completed two overseas deployments onboard the USS George Washington and USS Stennis. As a combat strike leader, he headed numerous multi-national missions over Iraq in support of Operation Southern Watch. Bomben graduated from the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School in 1992 and was subsequently assigned to the Naval Weapons Test Squadron at Pt. Mugu, Calif. During this tour he developed the F-14D bombsight and worked on various other F-14D and F/A-18 weapon systems developmental programs. Bomben is a 1985 graduate of Washington State University with a bachelor of science degree in electrical engineering. He graduated from naval flight training in 1987 and was recognized as a Commodore List graduate. His first assignment was to Naval Air Station Pensacola, Fla., where he was an instructor in the T-2B Buckeye. When selected to fly the F/A-18 in 1989, he joined a fleet squadron and deployed aboard the USS Forrestal. Bomben is married to the former Aissa Asuncion. They live in Lancaster, Calif., with their 3 children.