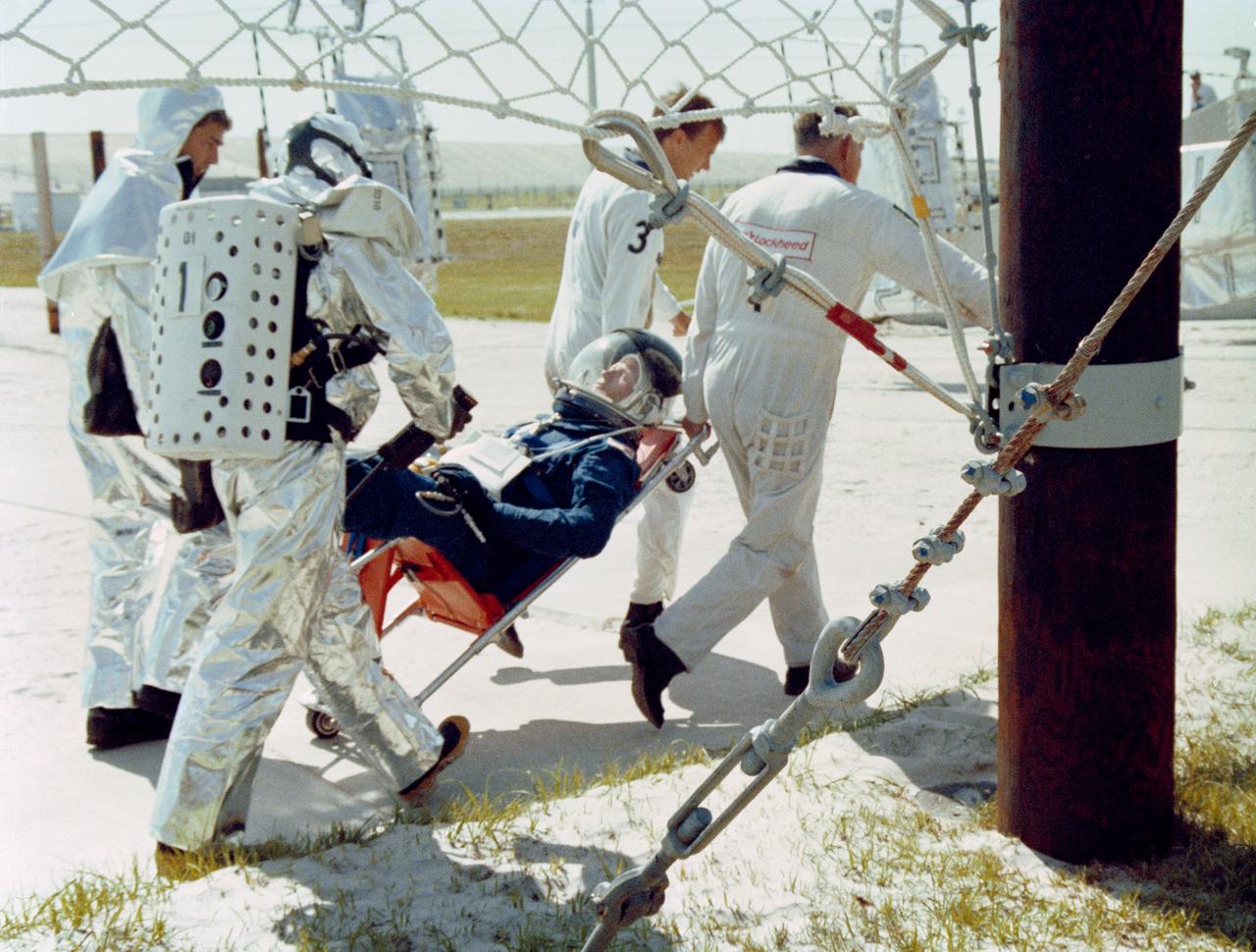

S88-40898 (4 May 1988) --- Astronauts, members of the orbiter close-out crew and fire and rescue personnel participate in a simulated emergency egress exercise near the slide wire termination point bunker at Launch Pad 39B. The simulated exercise was performed to familiarize personnel with evacuation routes as well as emergency equipment and procedures. Reasons for conducting the emergency exercises include the need to validate recent post-Challenger upgrades to the launch pad's emergency escape system and the new procedures developed in preparation for STS-26. (NOTE: The astronaut pictured and many of the others who participated in the exercises are not members of STS-26 prime crew).
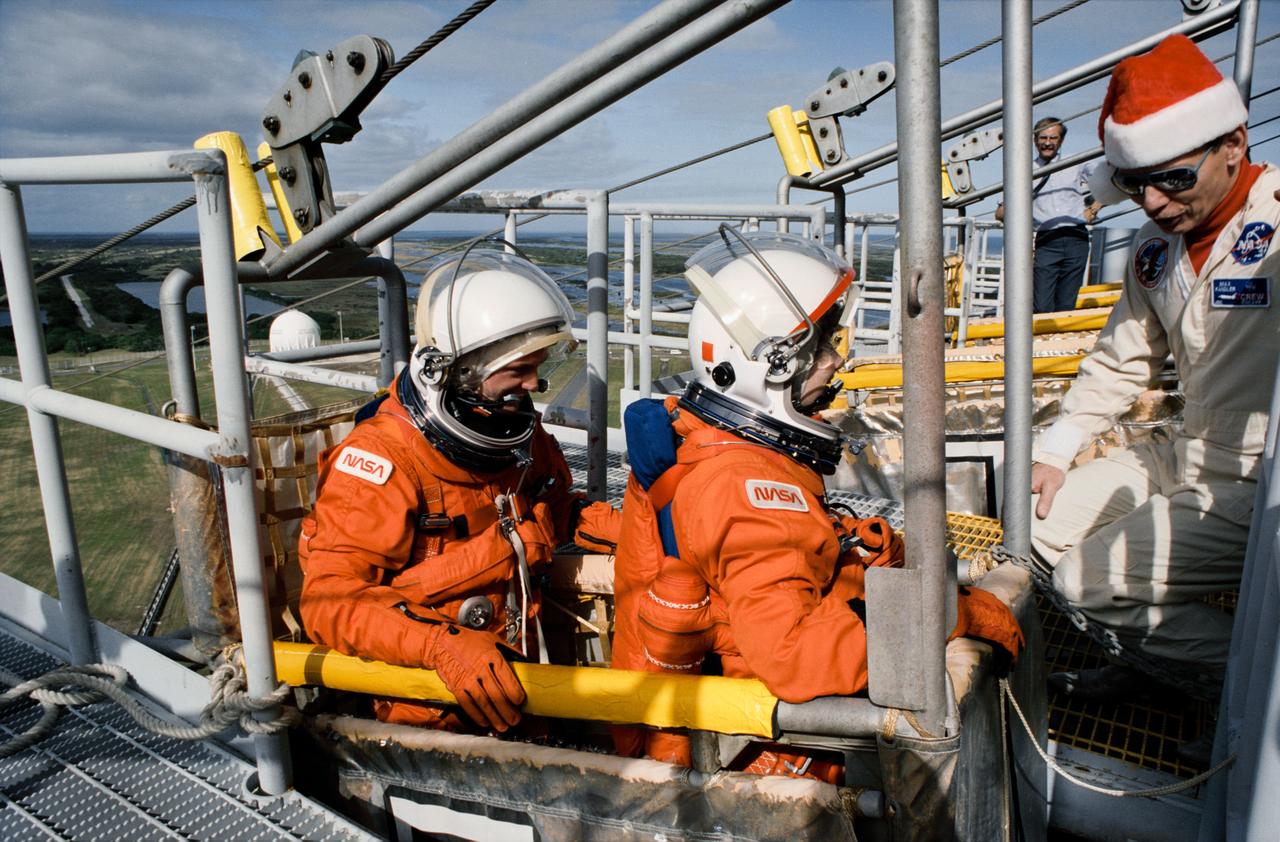

S93-25030 (15 Dec 1992) --- Two astronauts assigned to fly aboard Endeavour for the STS-54 mission are briefed on the slidewire escape system at the launch pad. Pictured in the slidewire litter are astronauts Gregory J. Harbaugh (left) and Susan J. Helms, mission specialists. They are assisted by Max Kandler of Lockheed, Houston. All five crewmembers are in Florida this week to participate in countdown demonstration tests.
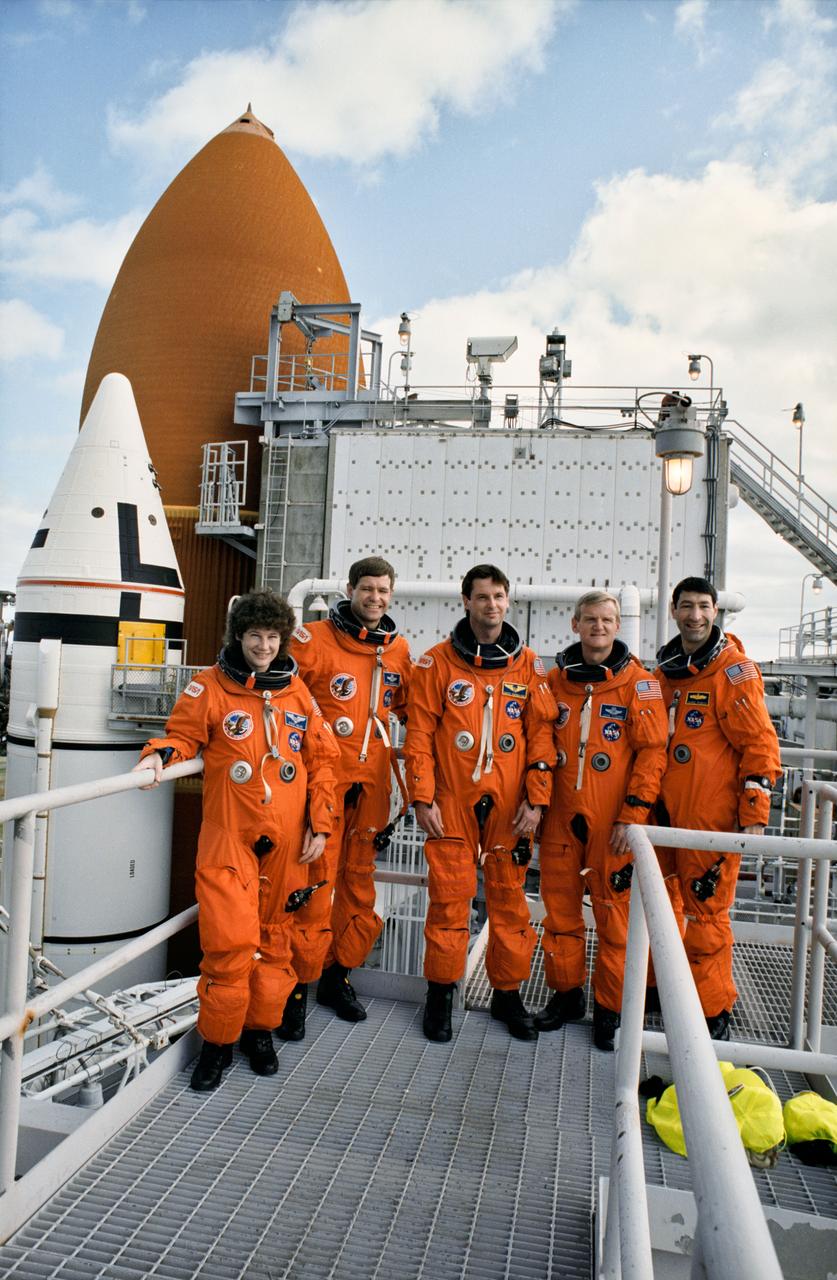

S93-25028 (15 Dec 1992) --- Astronauts assigned to fly aboard Endeavour pose near the Shuttle during a break in countdown demonstration tests. Left to right are Susan J. Helms, Donald R. McMonagle, Gregory J. Harbaugh, John H. Casper and Mario Runco Jr.
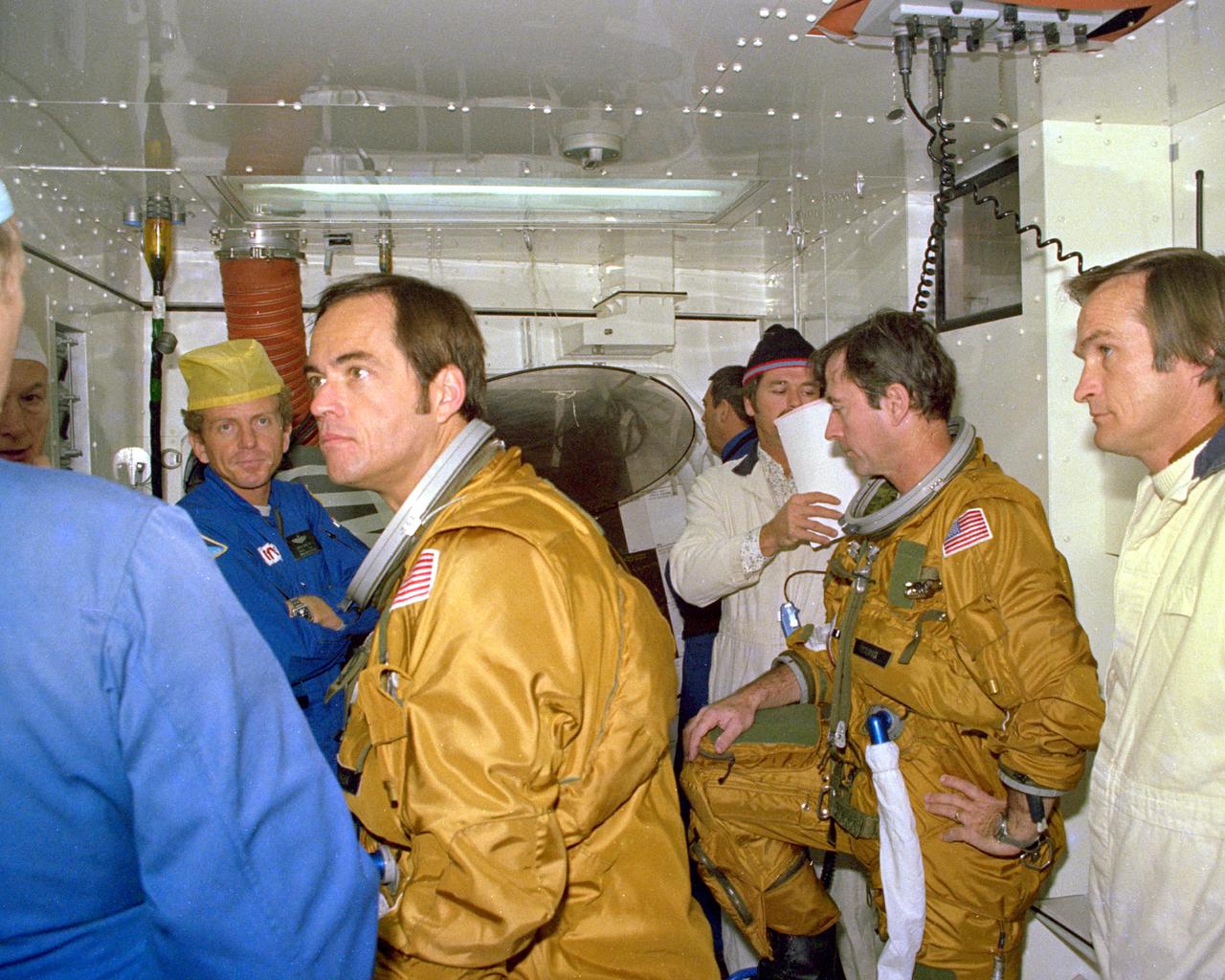

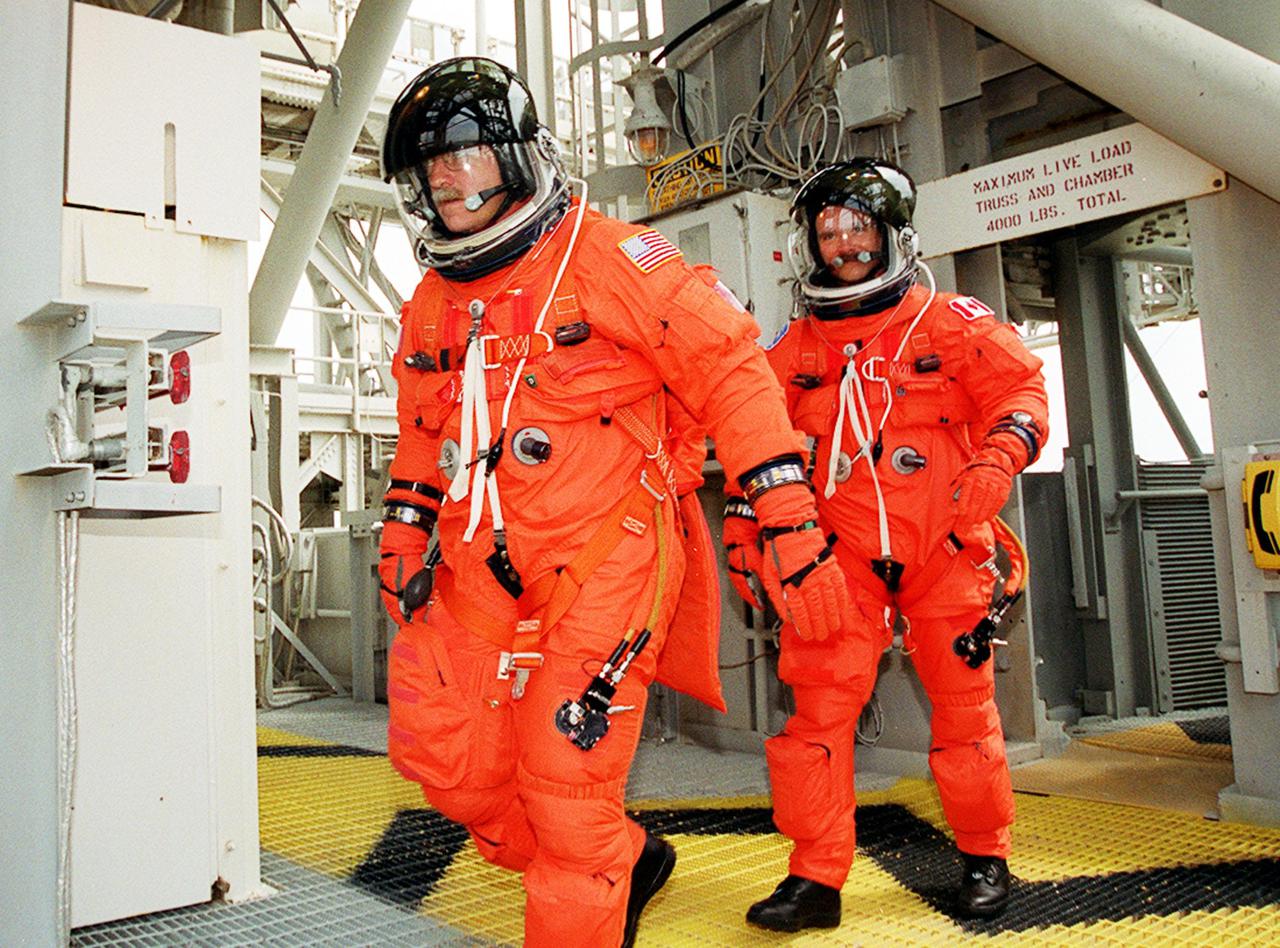
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shutle astronauts being briefed on the emergency pad escape system are (left to right) Loren Shriver (with hat), Prime Crew Pilot Bob Criippen and Commander John Young. The slidewire system provides a quick escape from upper launch pad platforms in case of a serious emergency. The flight crews wore the spacesuits and other equipment to be worn during a mission, but sandbags were used to duplicate the weight of riders in the slidewire baskets during the training.
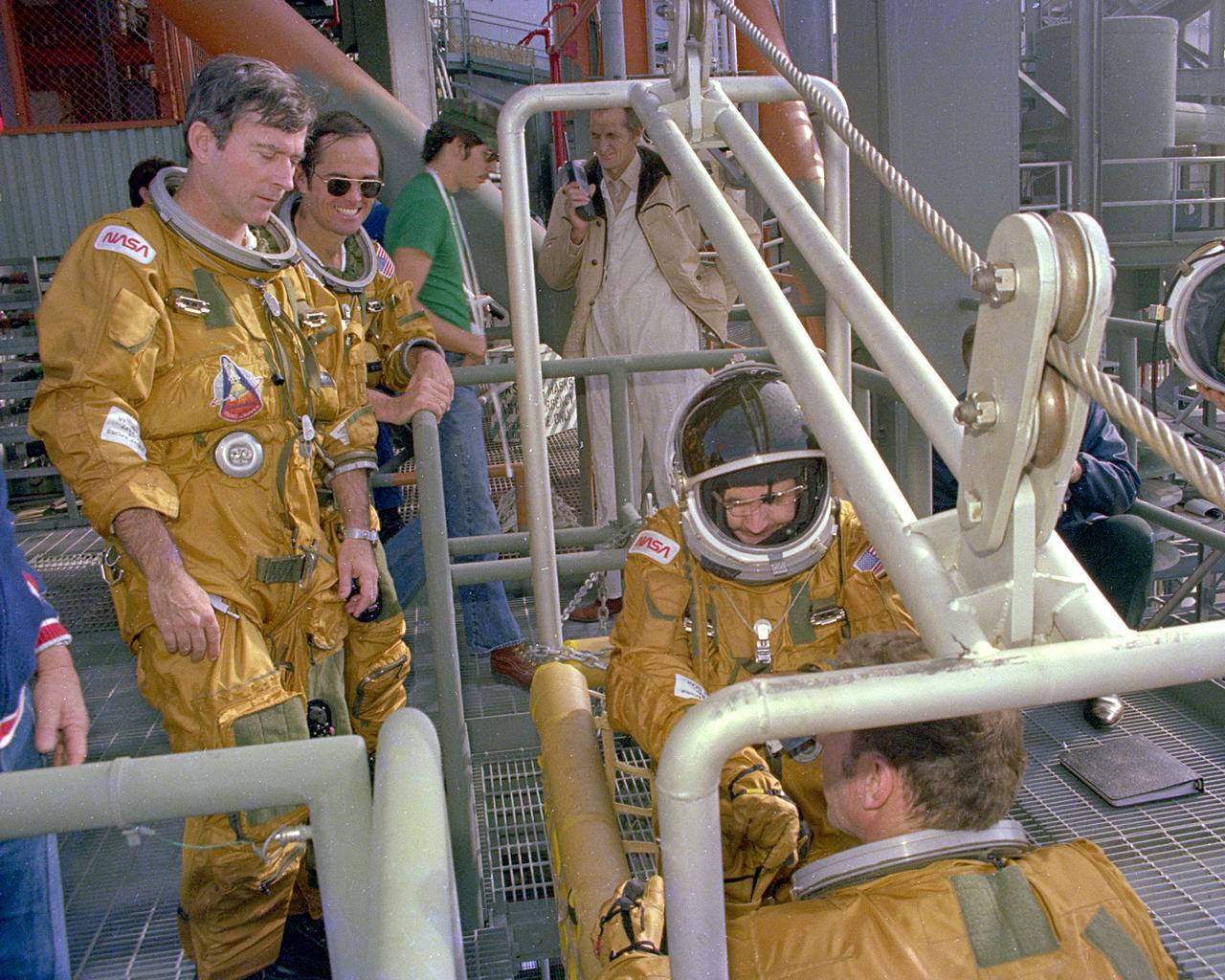

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle prime crew Commander John Young and Pilot Bob Crippen watch as backup crew members Richard Truly and Joe Engle board the emergency pad escape system known as the slidewire. The slidewire system provides a quick escape from upper launch pad platforms in case of a serious emergency. The flight crews wore the spacesuits and other equipment to be worn during a mission, but sandbags were used to duplicate the weight of riders in the slidewire baskeets during the training.
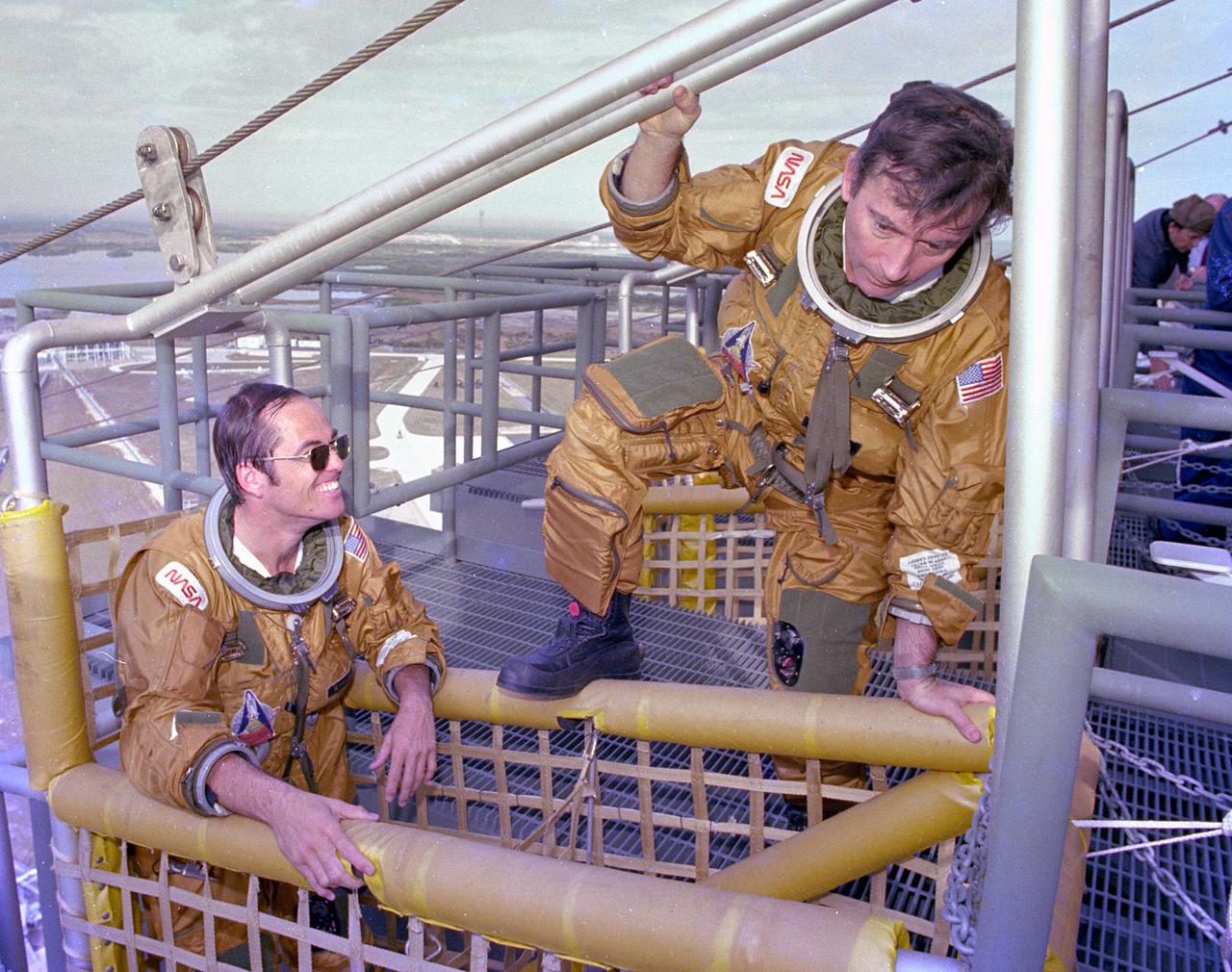

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle prime crew astronauts Bob Crippen (left) and John Young (center) board the emergency pad escape system known as the 'slidewire.' The slidewire system provides a quick escape from upper launch pad platforms in case of a serious emergency. The flight crews wore the spacesuits and other equipment to be worn during a mission, but sandbags were used to duplicate the weight of riders in the slidewire baskets during the training.
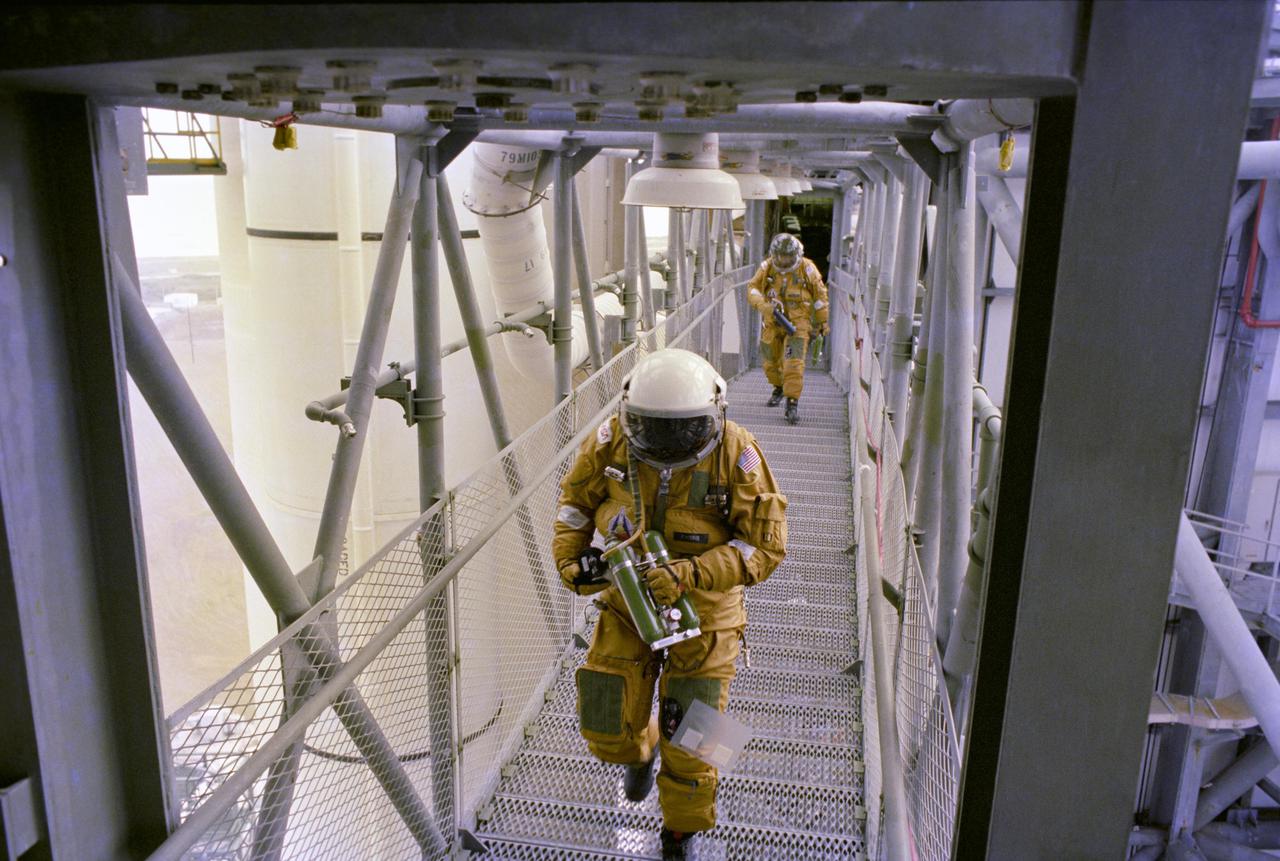

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On the Fixed Service Structure on Launch Complex 39A, space shuttle prime and backup astronaut crews plus other astronauts and ground personnel are given training on the use of the emergency pad escape system known as the “slidewire”. The slidewire system provides a quick escape from upper launch pad platforms in case of a serious emergency. The flight crews wear the spacesuits and other equipment to be worn during a mission, but sandbags are used to duplicate the weight of riders in the slidewire baskets during the training. The STS-1 mission, known as a shuttle systems test flight, will seek to demonstrate safe launch into orbit and safe return of the orbiter and crew and verify the combined performance of the entire shuttle vehicle -- orbiter, solid rocket boosters and external tank. STS-1 will be launched from Pad A at the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 no earlier than March 1981.
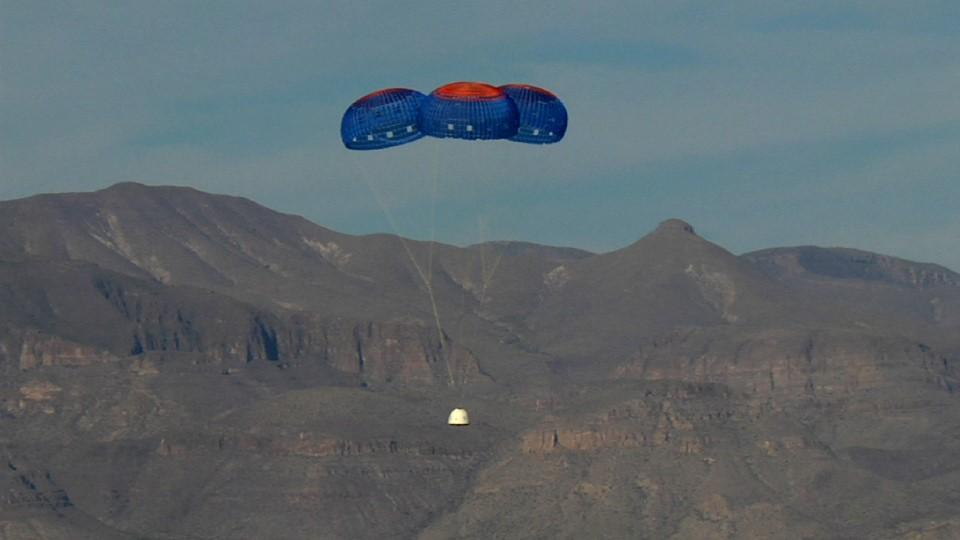

VAN HORN, Texas – Blue Origin’s New Shepard crew capsule escaped to an altitude of 2,307 feet before deploying parachutes for a safe return for a pad escape test at the company's West Texas launch site. The pusher escape system was designed and developed by Blue Origin to allow crew escape in the event of an emergency during any phase of ascent for its suborbital New Shepard system. As part of an incremental development program, the results of this test will shape the design of the escape system for the company's orbital biconic-shaped Space Vehicle. The system is expected to enable full reusability of the launch vehicle, which is different from NASA's previous launch escape systems that would pull a spacecraft away from its rocket before reaching orbit. The test was part of Blue Origin's work supporting its funded Space Act Agreement with NASA during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2). Through initiatives like CCDev2, NASA is fostering the development of a U.S. commercial crew space transportation capability with the goal of achieving safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from the International Space Station and low-Earth orbit. After the capability is matured and available to the government and other customers, NASA could contract to purchase commercial services to meet its station crew transportation needs. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Blue Origin
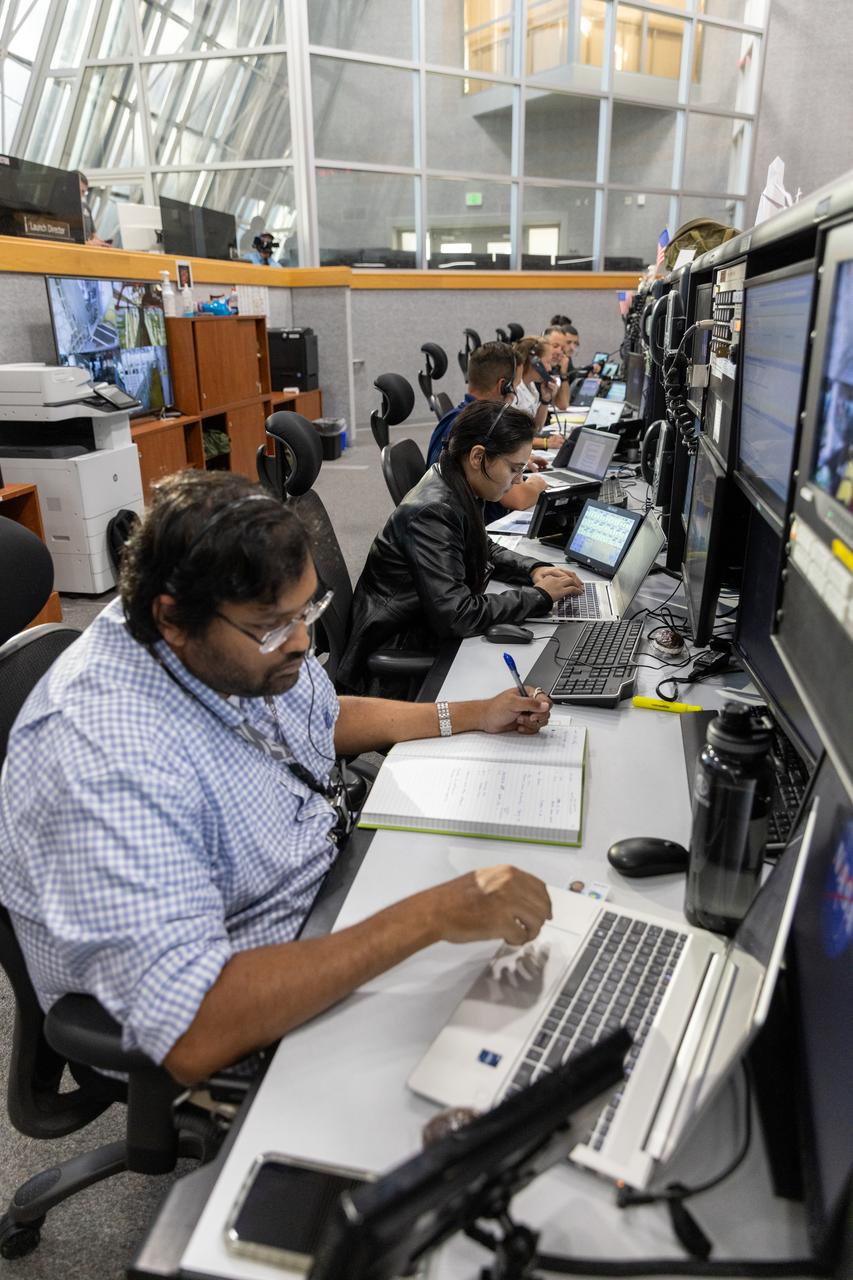

Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems participate in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
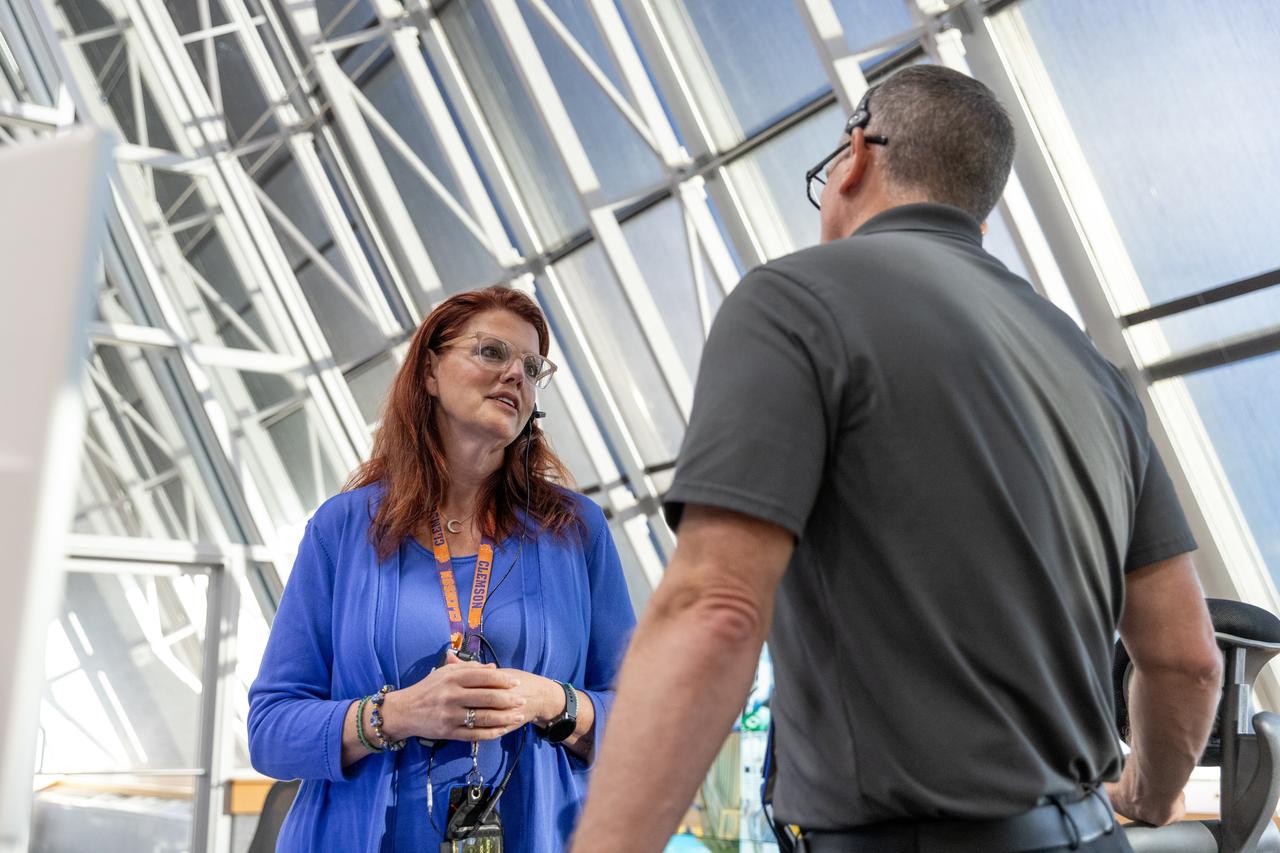

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director, Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
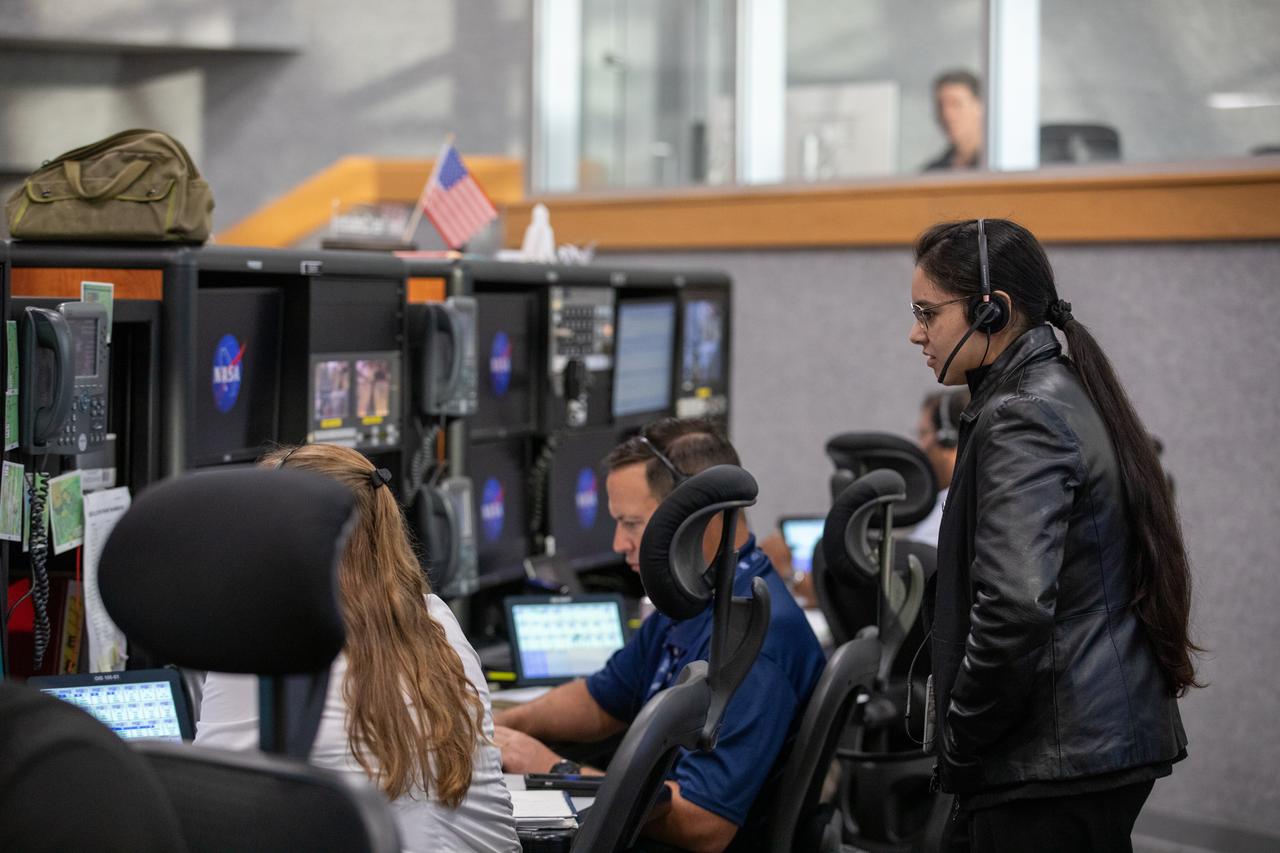

Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems participate in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
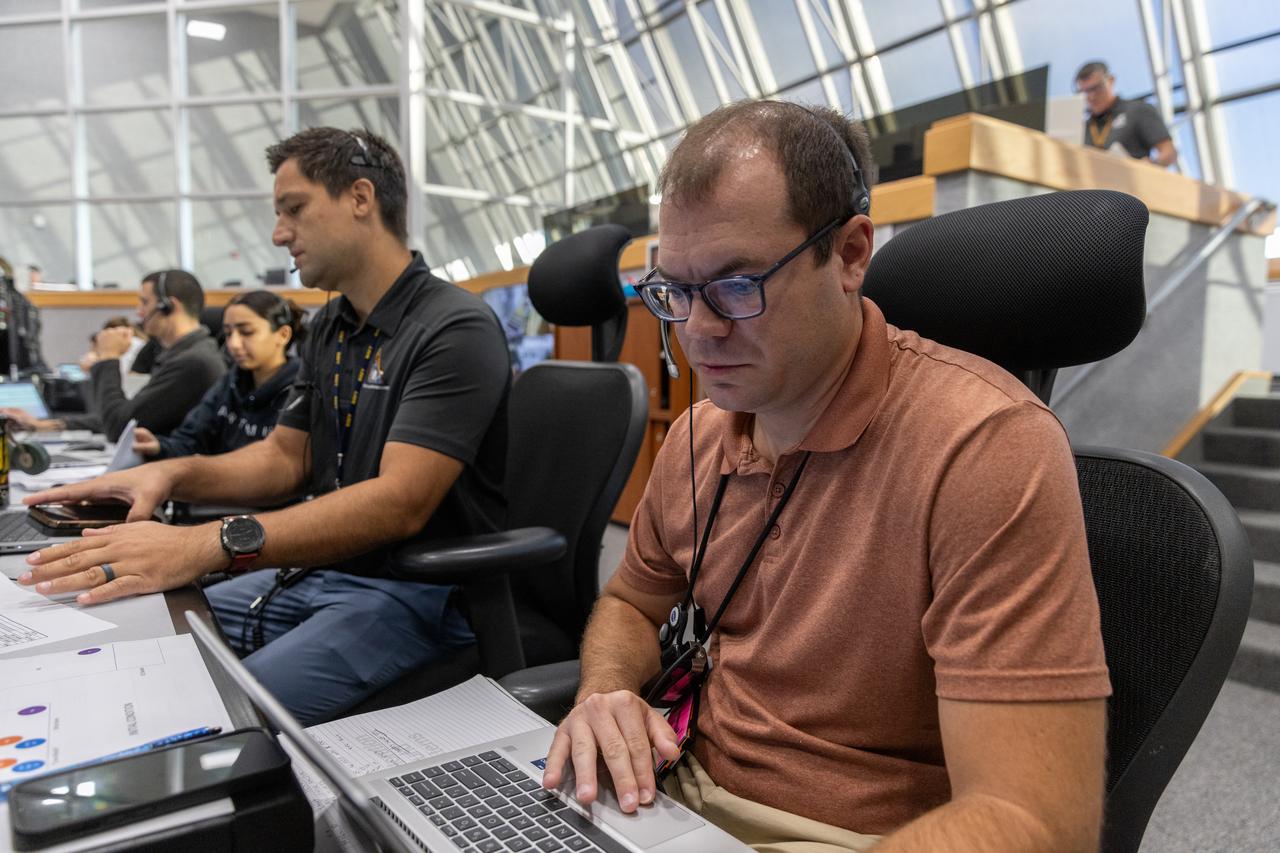

Jeremy Graeber, Artemis assistant launch director, Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
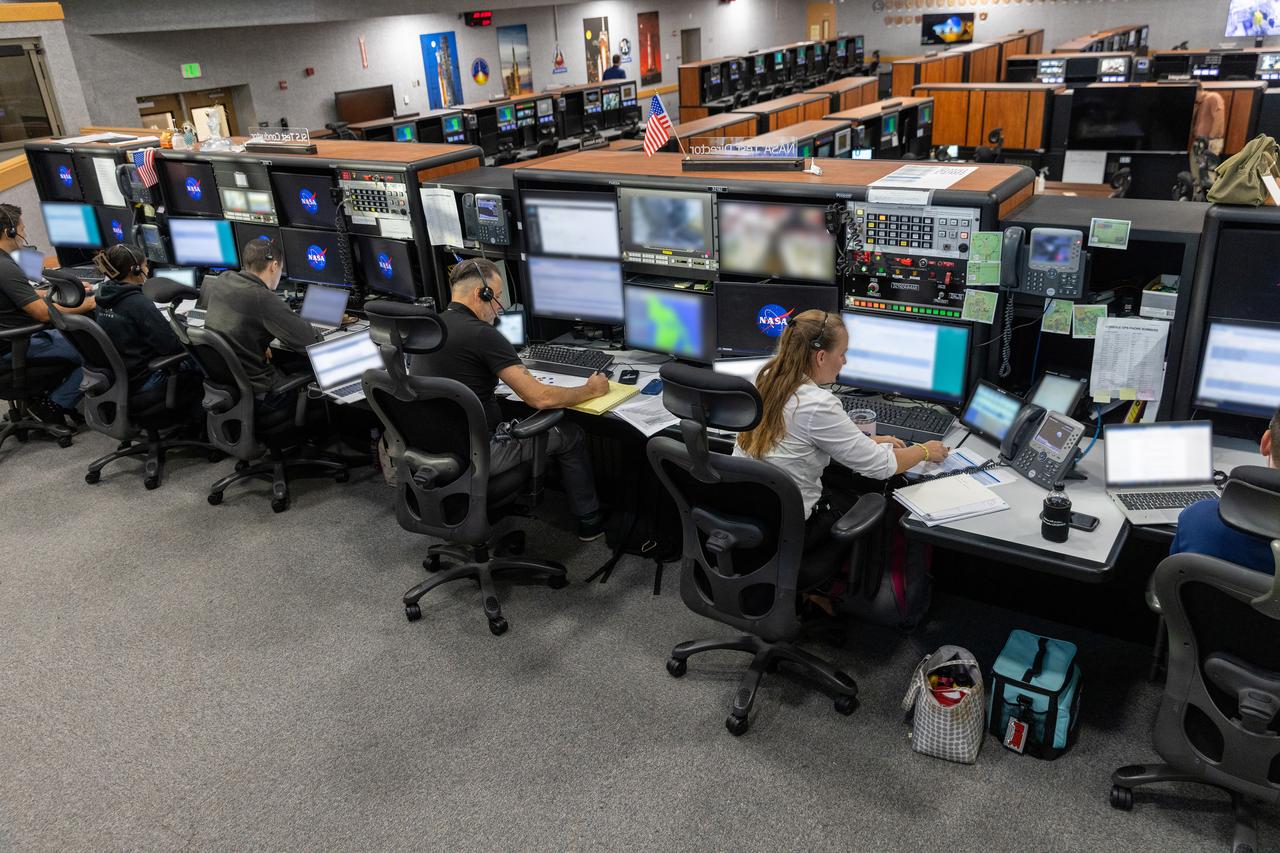

Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems participate in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
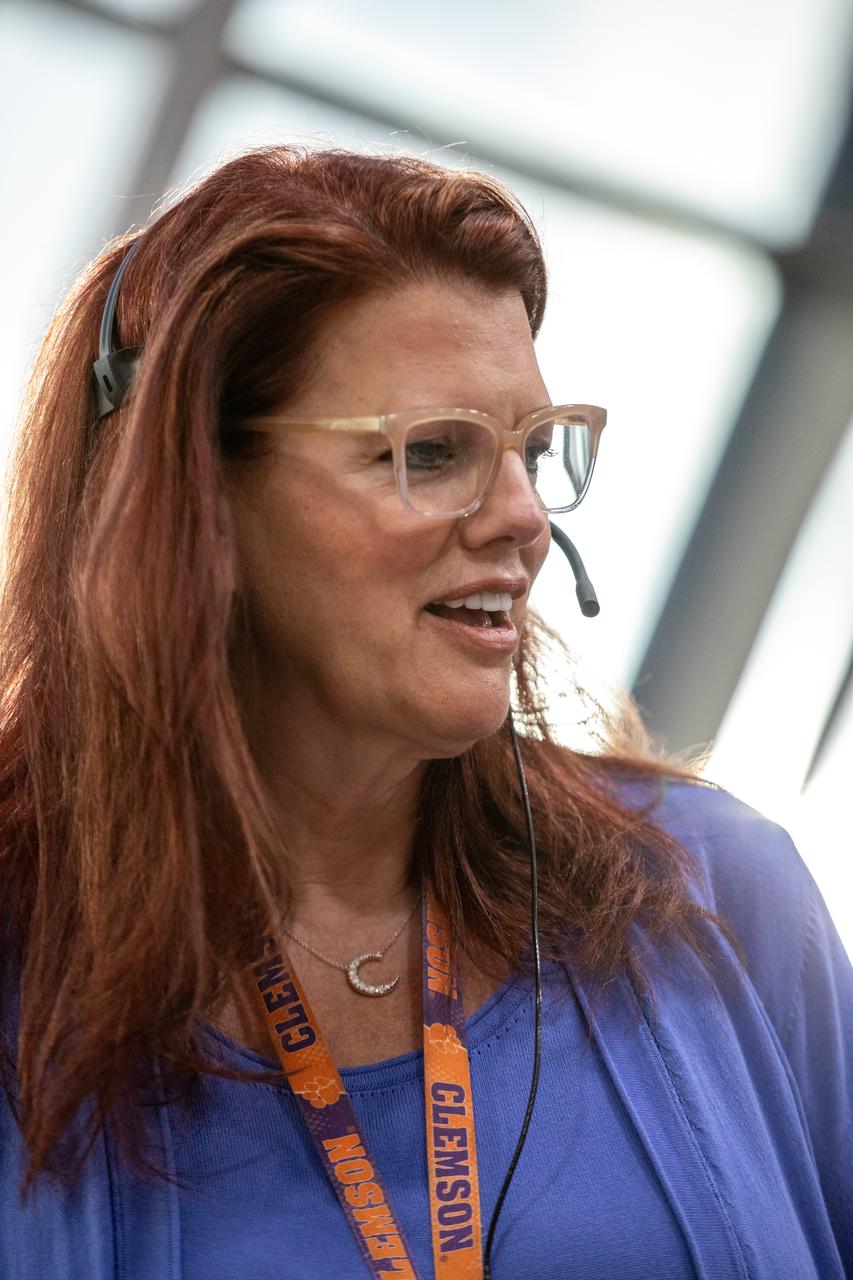

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director, Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
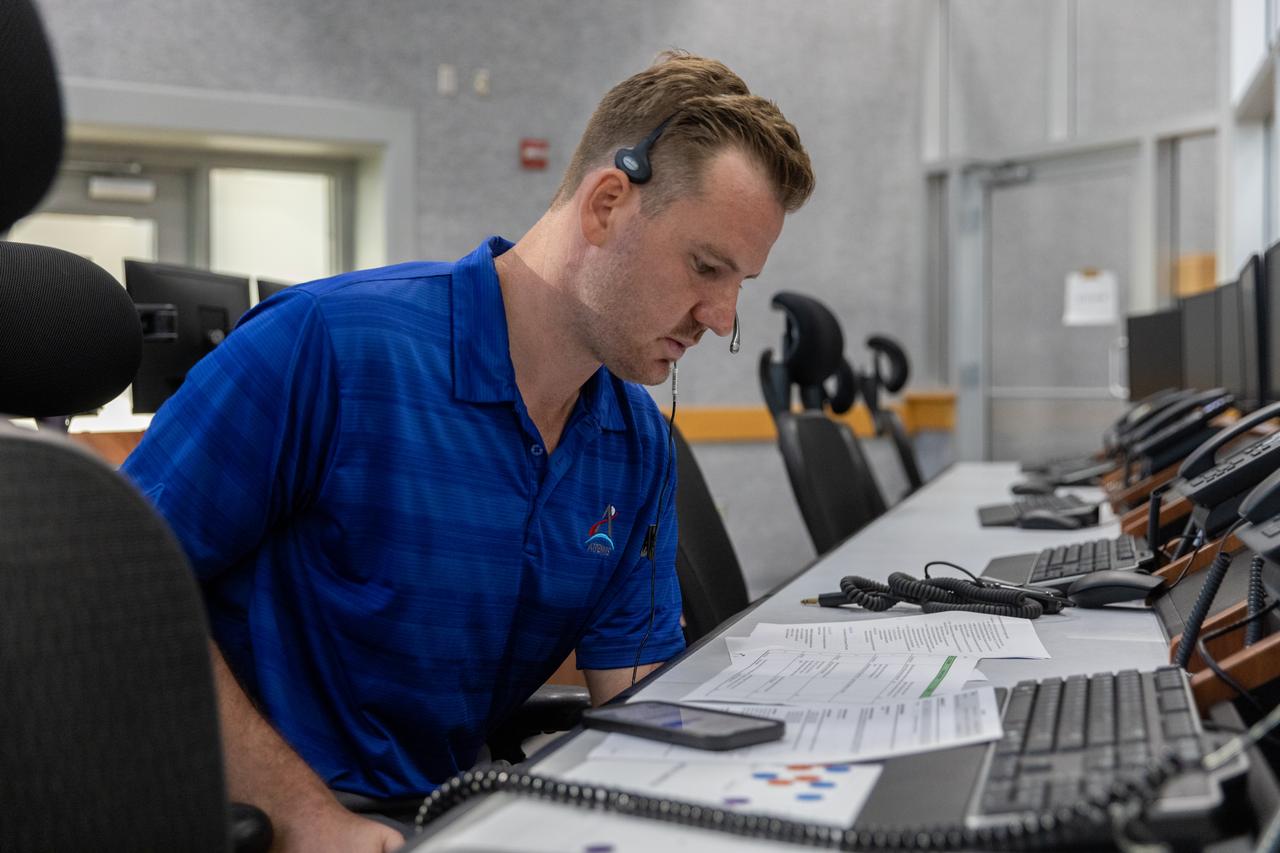

Joseph Pavicic, operations project engineer, Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
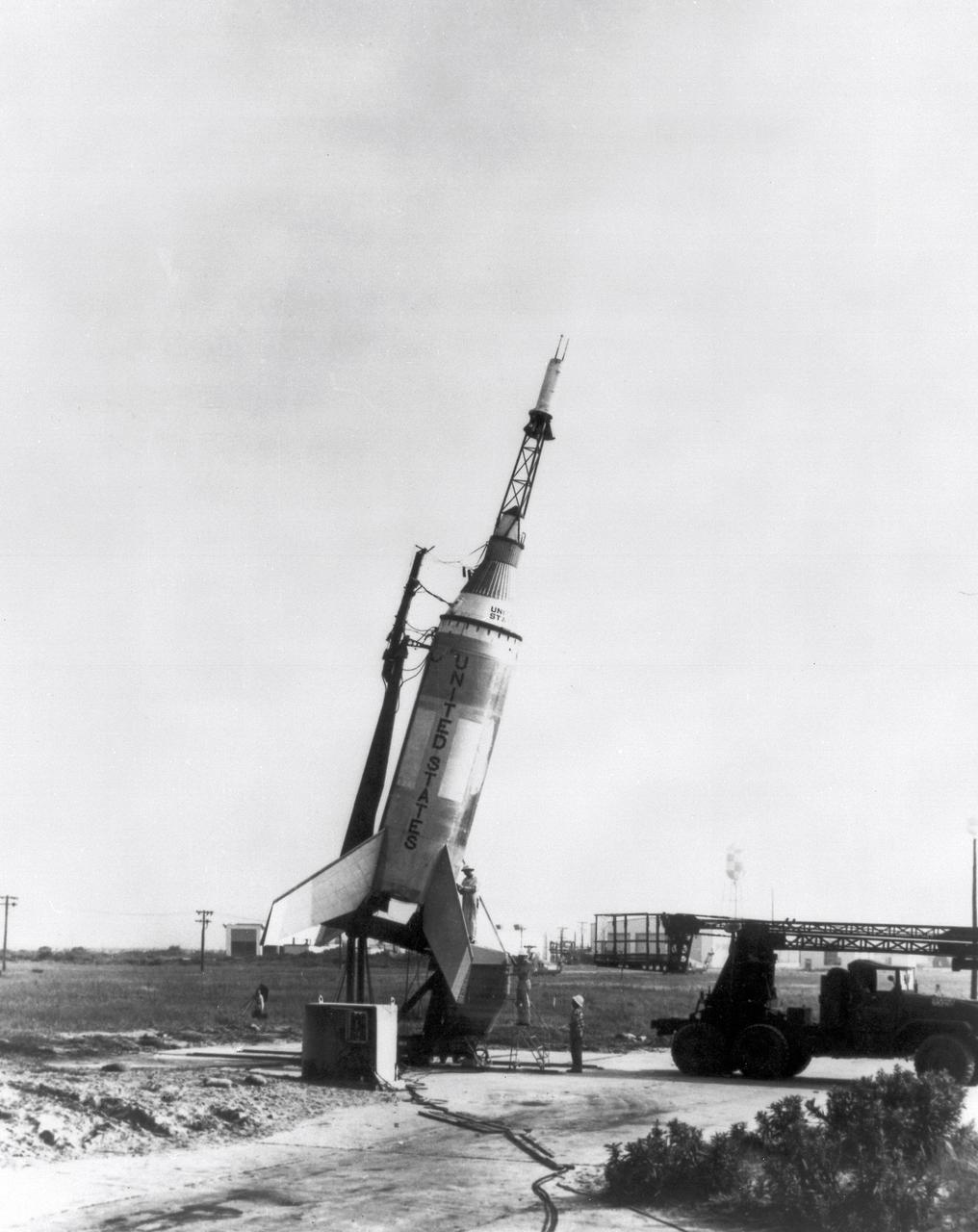

The Little Joe launch vehicle for the LJ1 mission on the launch pad at the wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Virginia, on January 21, 1960. This mission achieved the suborbital Mercury cupsule test, testing of the escape system, and biomedical tests by using a monkey, named Miss Sam.

The launch of the Little Joe booster for the LJ1B mission on the launch pad from the wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Virginia, on January 21, 1960. This mission achieved the suborbital Mercury capsule test, testing of the escape system, and biomedical tests by using a monkey, named Miss Sam.
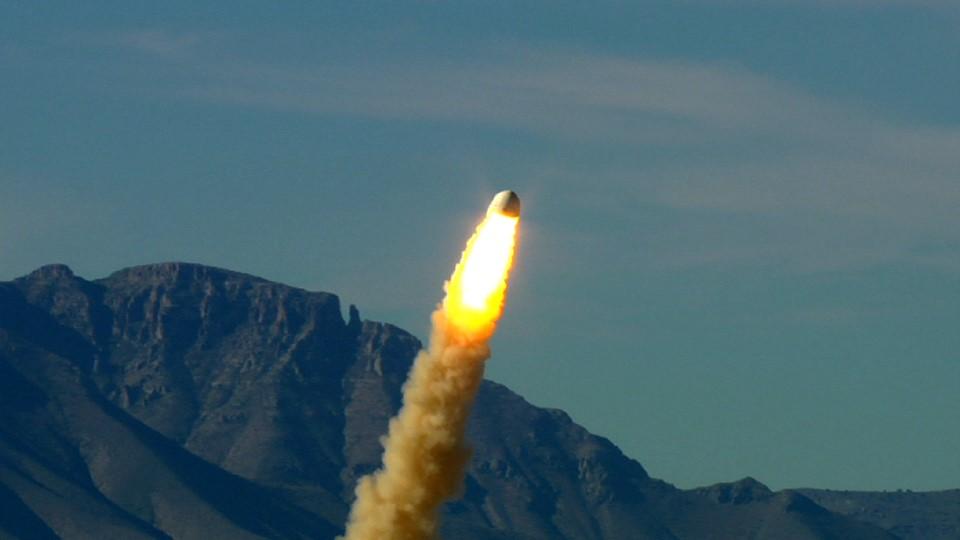

VAN HORN, Texas – Blue Origin’s pusher escape system rockets its New Shepard crew capsule away from a simulated propulsion module launch pad at the company's West Texas launch site, demonstrating a key safety system for both suborbital and orbital flights. The pad escape test took the company's suborbital crew capsule to an altitude of 2,307 feet during the flight test before descending safely by parachute to a soft landing 1,630 feet away. The pusher escape system was designed and developed by Blue Origin to allow crew escape in the event of an emergency during any phase of ascent for its suborbital New Shepard system. As part of an incremental development program, the results of this test will shape the design of the escape system for the company's orbital biconic-shaped Space Vehicle. The system is expected to enable full reusability of the launch vehicle, which is different from NASA's previous launch escape systems that would pull a spacecraft away from its rocket before reaching orbit. The test was part of Blue Origin's work supporting its funded Space Act Agreement with NASA during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2). Through initiatives like CCDev2, NASA is fostering the development of a U.S. commercial crew space transportation capability with the goal of achieving safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from the International Space Station and low-Earth orbit. After the capability is matured and available to the government and other customers, NASA could contract to purchase commercial services to meet its station crew transportation needs. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Blue Origin

Chris Ferguson, Boeing’s Director of Crew and Mission Operations for their Commercial Crew Program, is helped into his suit in preparation for a Boeing/United Launch Alliance emergency egress system demonstration on June 19, 2018. A veteran of three space shuttle missions, he commanded Atlantis in STS-135, the final mission of the Space Shuttle Program. The demonstration was held at Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The emergency egress system provides an escape route in the unlikely event of an emergency on the launch pad on launch day.
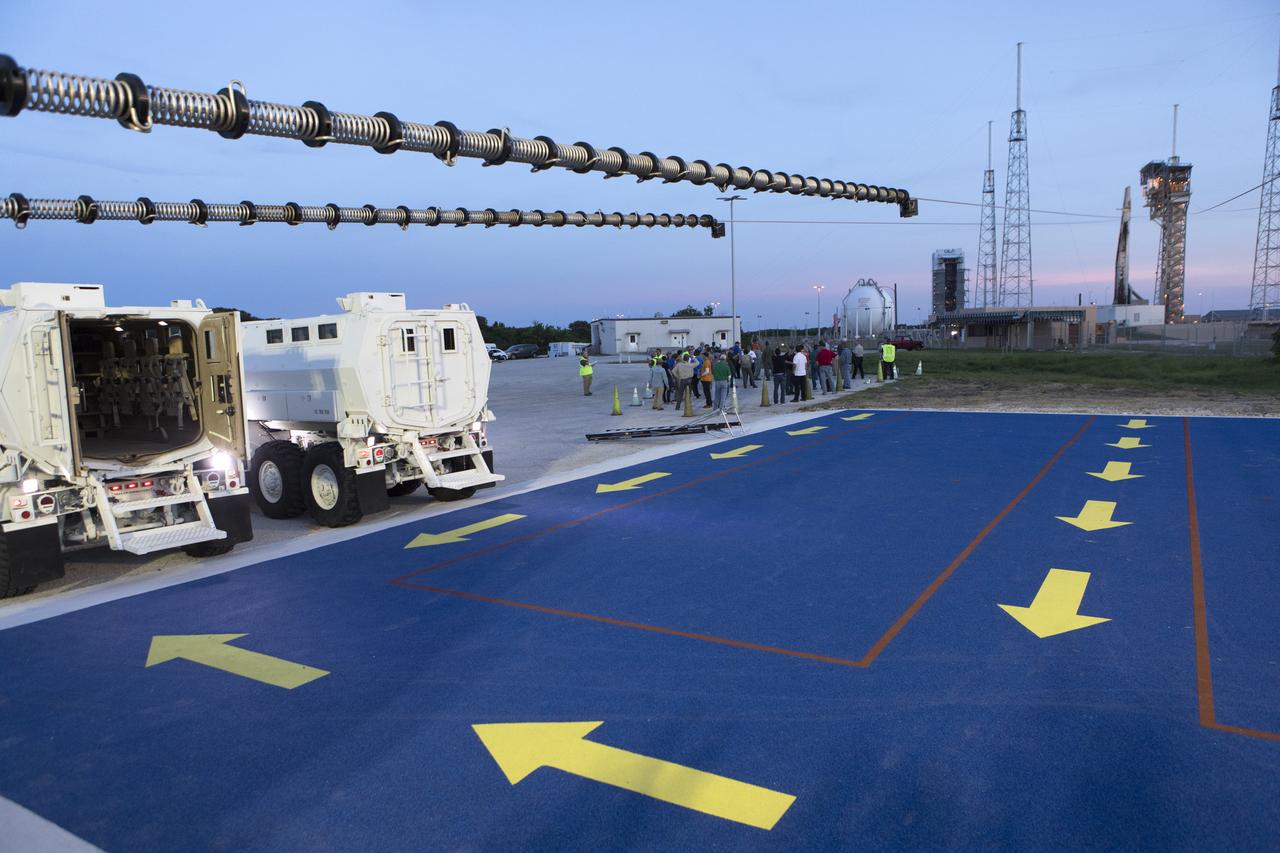

Two mine-resistant ambush protected vehicles, or MRAPs, sit ready to receive astronauts and ground crews during a Boeing/United Launch Alliance emergency egress system demonstration at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Launch Complex 41 in Florida on June 19, 2018. The emergency egress system will provide an escape route in the unlikely event of an emergency on the launch pad on launch day.
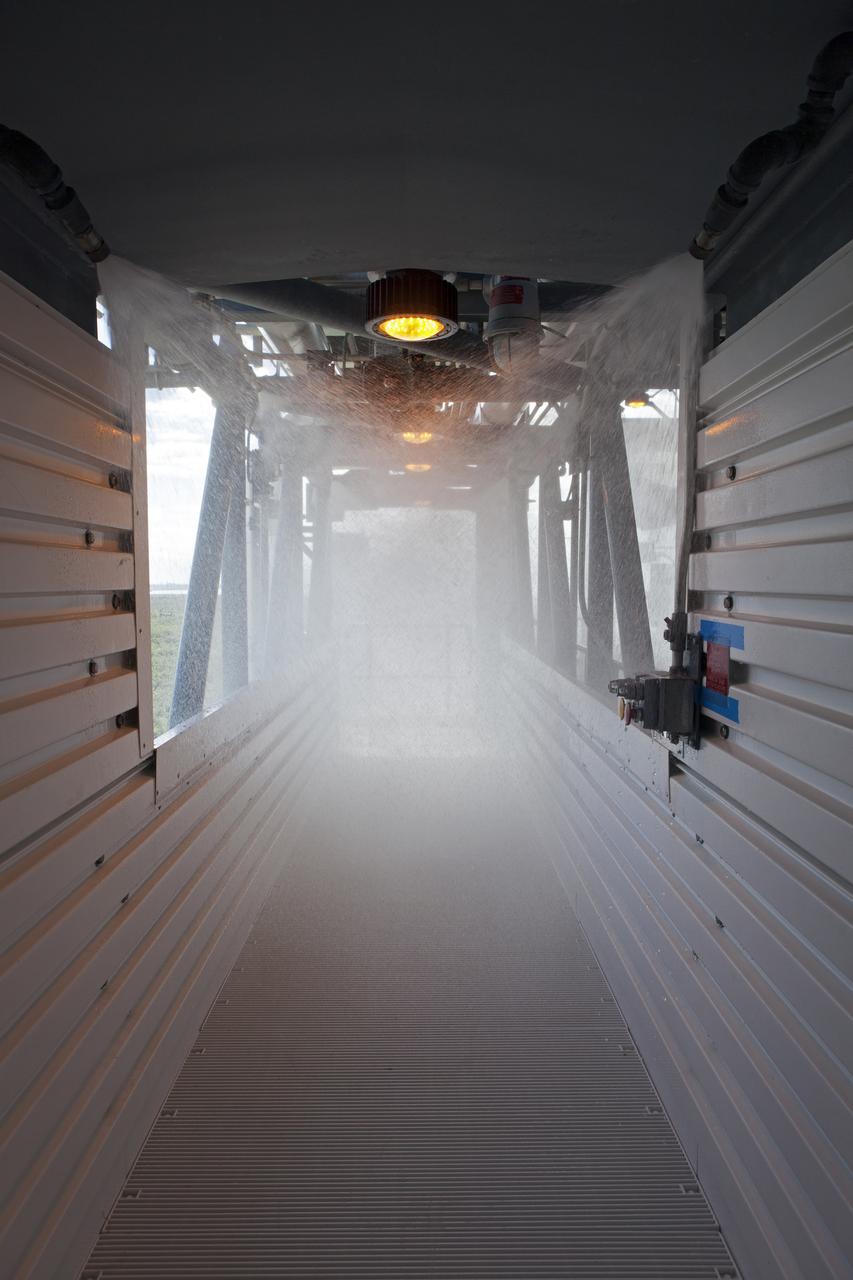

NASA, Boeing and United Launch Alliance personnel run a water deluge test on the Crew Access Tower at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The test gathered data on how launch site and astronaut crews would exit in the event of an emergency from the white room at the end of the crew access arm to the emergency escape system on the pad. Boeing’s Starliner will launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
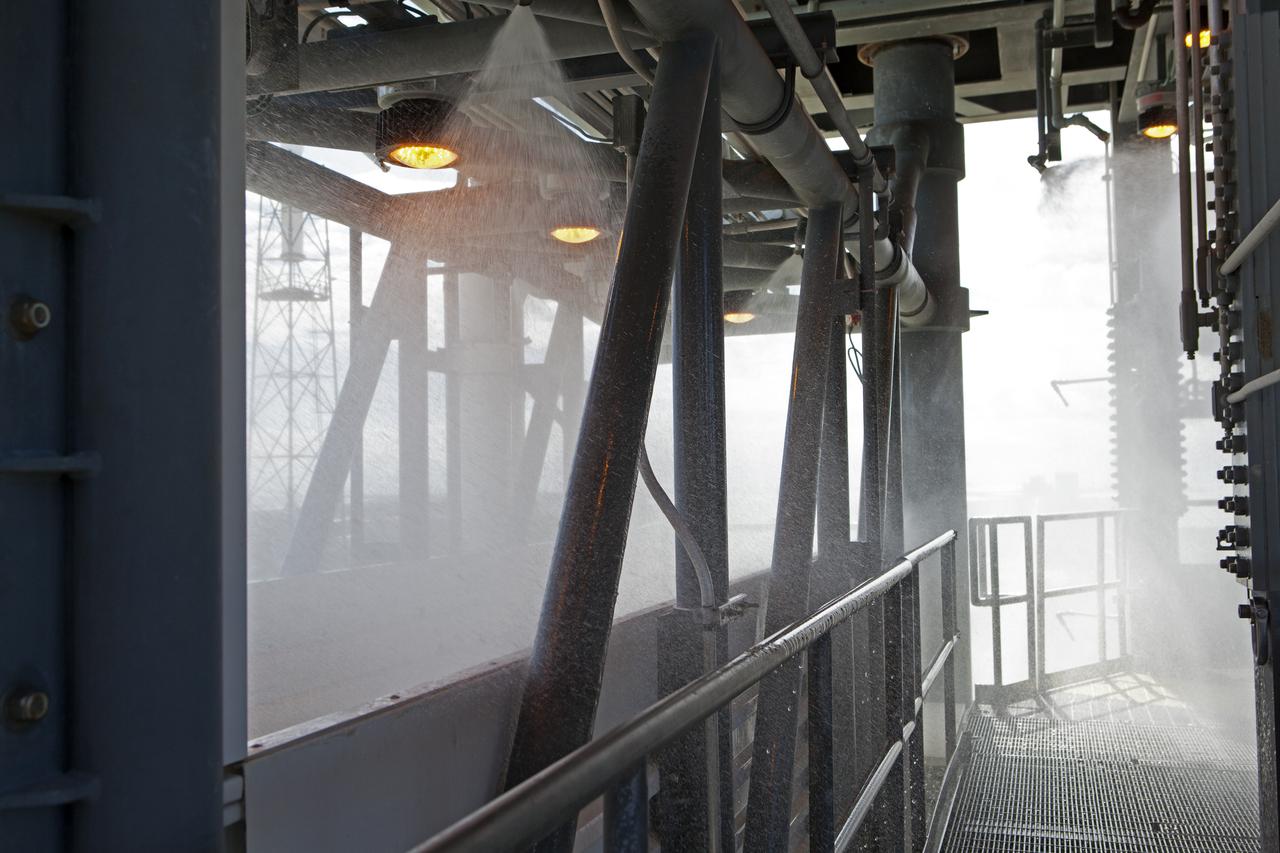

NASA, Boeing and United Launch Alliance personnel begin a water deluge test on the Crew Access Tower at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The test gathered data on how launch site and astronaut crews would exit in the event of an emergency from the white room at the end of the crew access arm to the emergency escape system on the pad. Boeing’s Starliner will launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-100 Mission Specialists Chris A. Hadfield (left) and John L. Phillips (right) settle in the slidewire basket at Launch Pad 39A. The basket is part of the emergency escape equipment on the pad. The crew is taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that also include a simulated launch countdown. The mission is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. The SSRMS is crucial to the continued assembly of the orbiting complex. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
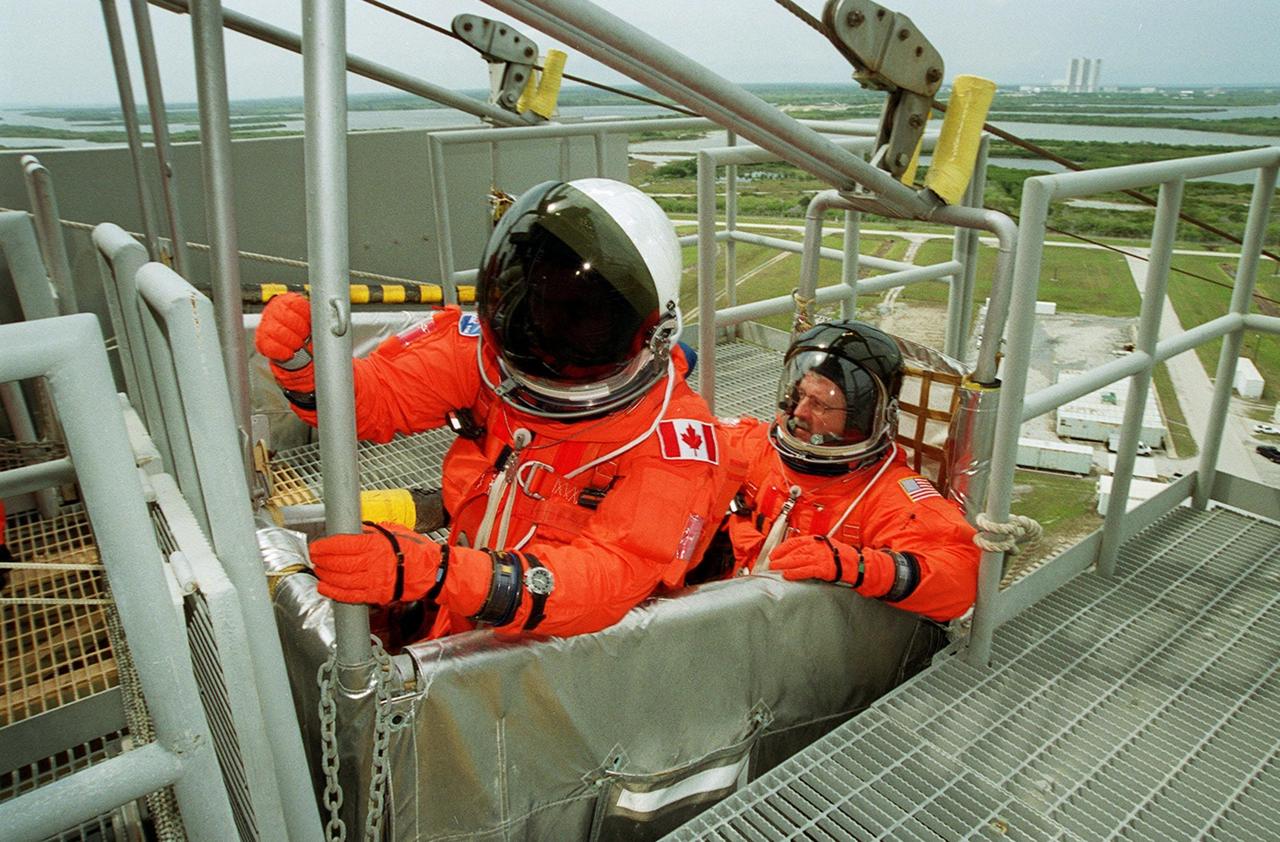

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-100 Mission Specialists Chris A. Hadfield (left) and John L. Phillips (right) settle in the slidewire basket at Launch Pad 39A. The basket is part of the emergency escape equipment on the pad. The crew is taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that also include a simulated launch countdown. The mission is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. The SSRMS is crucial to the continued assembly of the orbiting complex. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A

A Mercury capsule is mounted inside the Altitude Wind Tunnel for a test of its escape tower rockets at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. In October 1959 NASA’s Space Task Group allocated several Project Mercury assignments to Lewis. The Altitude Wind Tunnel was quickly modified so that its 51-foot diameter western leg could be used as a test chamber. The final round of tests in the Altitude Wind Tunnel sought to determine if the smoke plume from the capsule’s escape tower rockets would shroud or compromise the spacecraft. The escape tower, a 10-foot steel rig with three small rockets, was attached to the nose of the Mercury capsule. It could be used to jettison the astronaut and capsule to safety in the event of a launch vehicle malfunction on the pad or at any point prior to separation from the booster. Once actuated, the escape rockets would fire, and the capsule would be ejected away from the booster. After the capsule reached its apex of about 2,500 feet, the tower, heatshield, retropackage, and antenna would be ejected and a drogue parachute would be released. Flight tests of the escape system were performed at Wallops Island as part of the series of Little Joe launches. Although the escape rockets fired prematurely on Little Joe’s first attempt in August 1959, the January 1960 follow-up was successful.
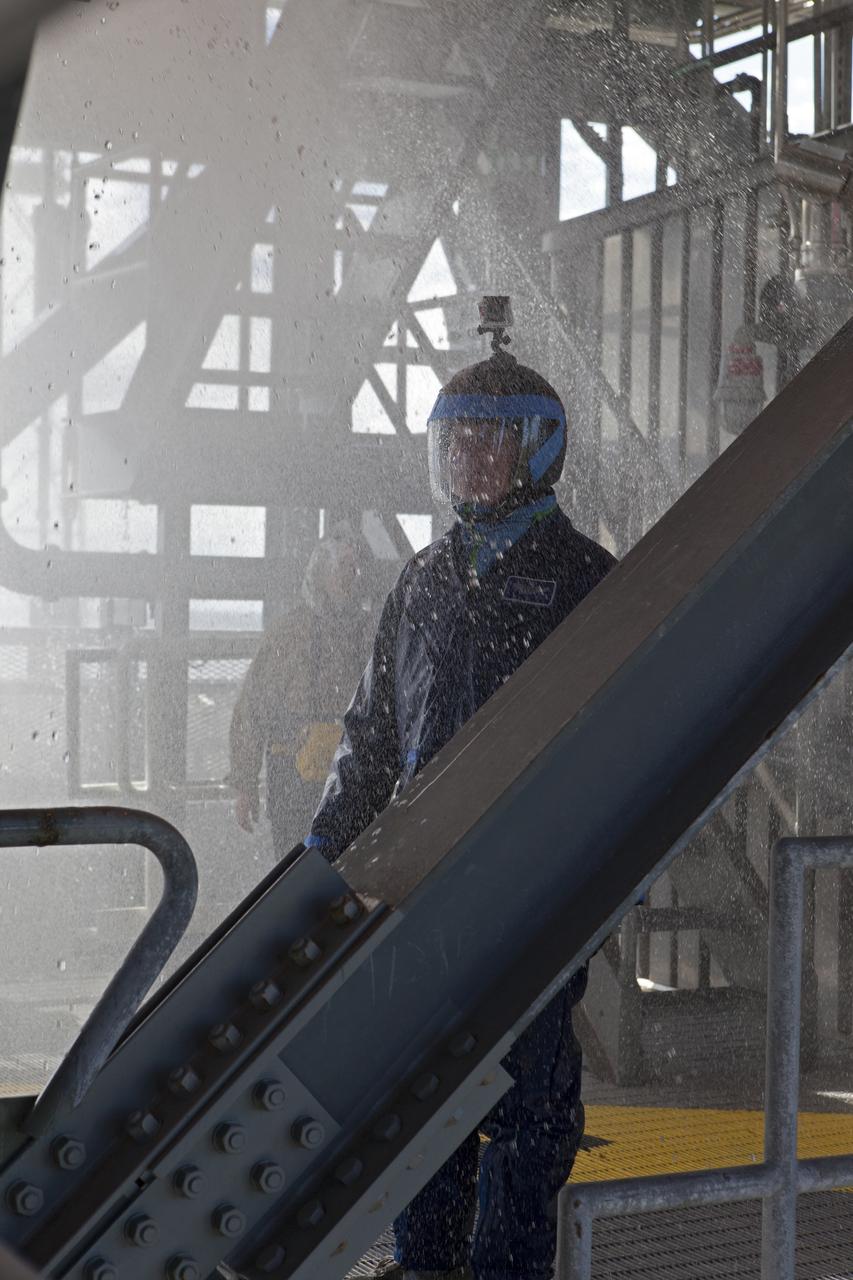

NASA and Boeing personnel experience conditions during a water deluge test on the Crew Access Tower at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The test gathered data on how launch site and astronaut crews would exit in the event of an emergency from the white room at the end of the crew access arm to the emergency escape system on the pad. Boeing’s Starliner will launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
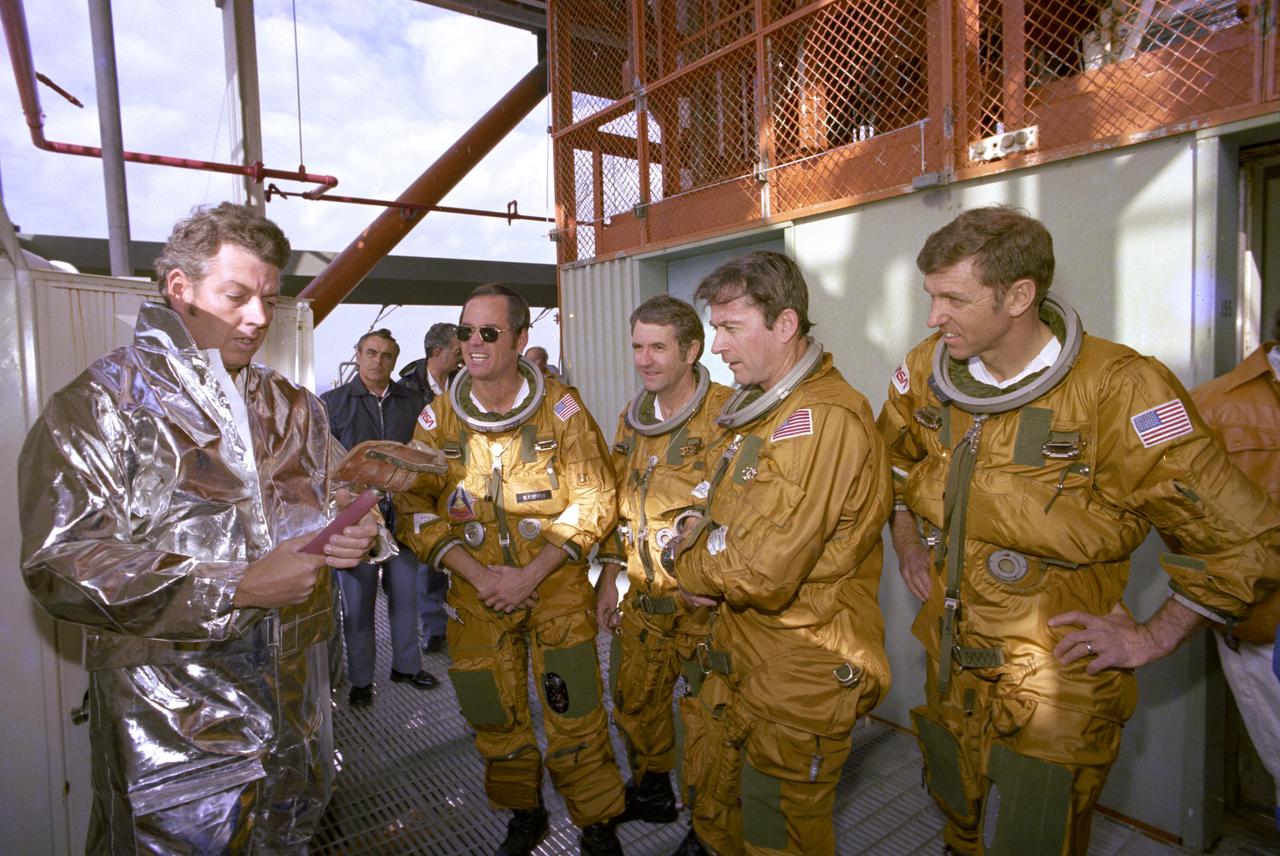

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On the Fixed Service Structure on Launch Complex 39A, space shuttle astronauts being briefed on the slidewire emergency pad escape system are (left to right) prime crew Pilot Bob Crippen, backup crew member Richard Truly, prime crew Commander John Young and backup crew member Joe Engle. The slidewire system provides a quick escape from upper launch pad platforms in case of a serious emergency. The flight crews wore the spacesuits and other equipment to be worn during a mission, but sandbags were used to duplicate the weight of riders in the slidewire baskets during the training. The STS-1 mission, known as a shuttle systems test flight, will seek to demonstrate safe launch into orbit and safe return of the orbiter and crew and verify the combined performance of the entire shuttle vehicle -- orbiter, solid rocket boosters and external tank. STS-1 will be launched from Pad A at the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 no earlier than March 1981.
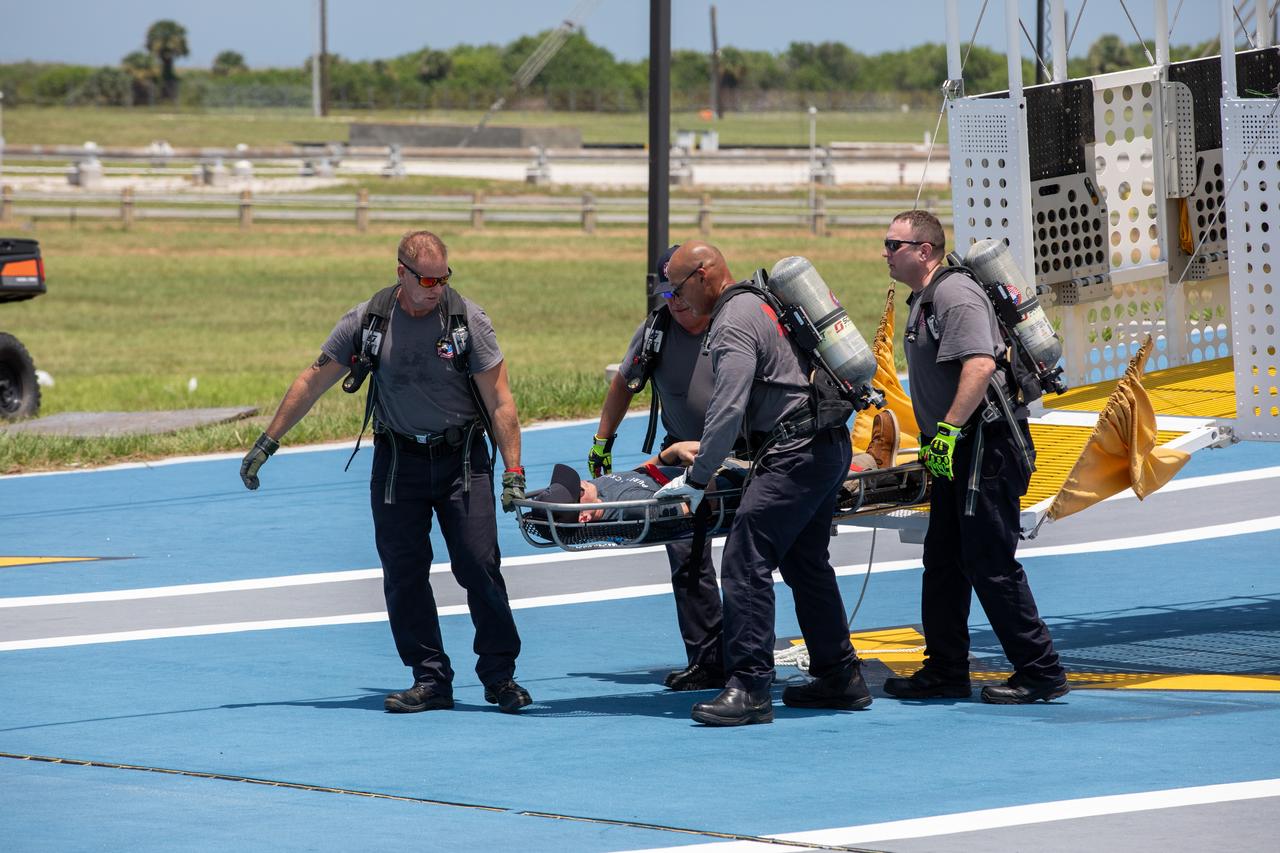

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Complex 39B on Friday, Aug. 9, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted several basket release demonstrations to validate the system.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Complex 39B on Friday, Aug. 9, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted several basket release demonstrations to validate the system.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Complex 39B on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Complex 39B on Friday, Aug. 9, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted several basket release demonstrations to validate the system.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Complex 39B on Friday, Aug. 9, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted several basket release demonstrations to validate the system.
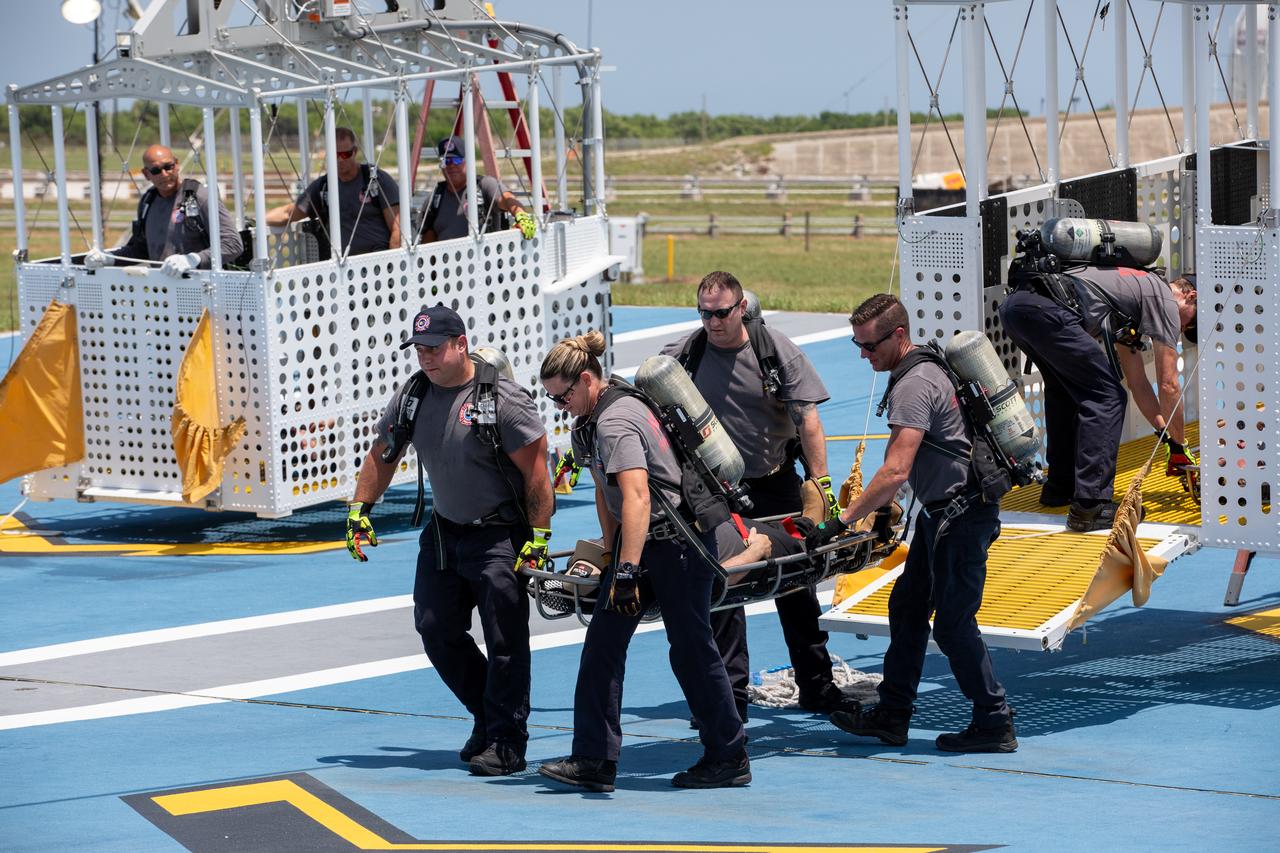

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Complex 39B on Friday, Aug. 9, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted several basket release demonstrations to validate the system.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Complex 39B on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.
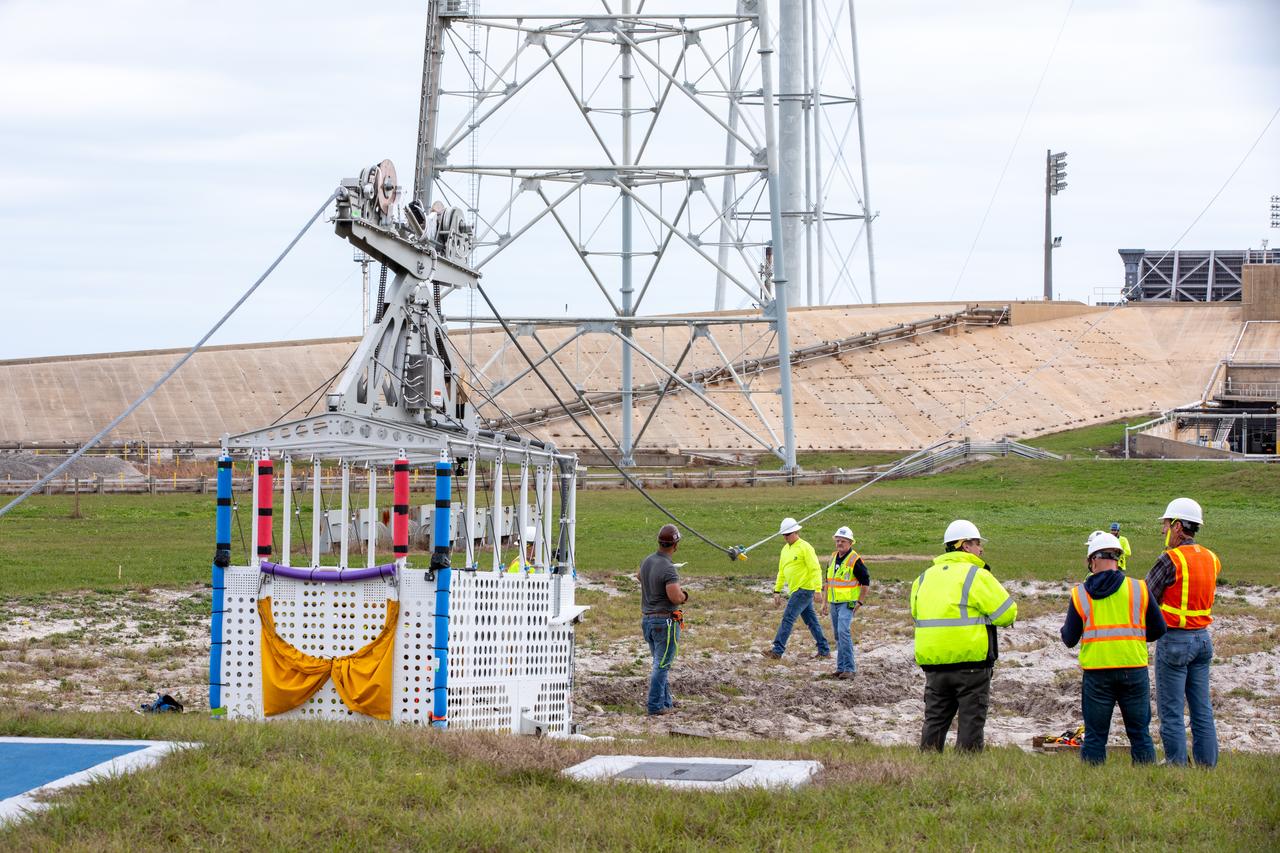

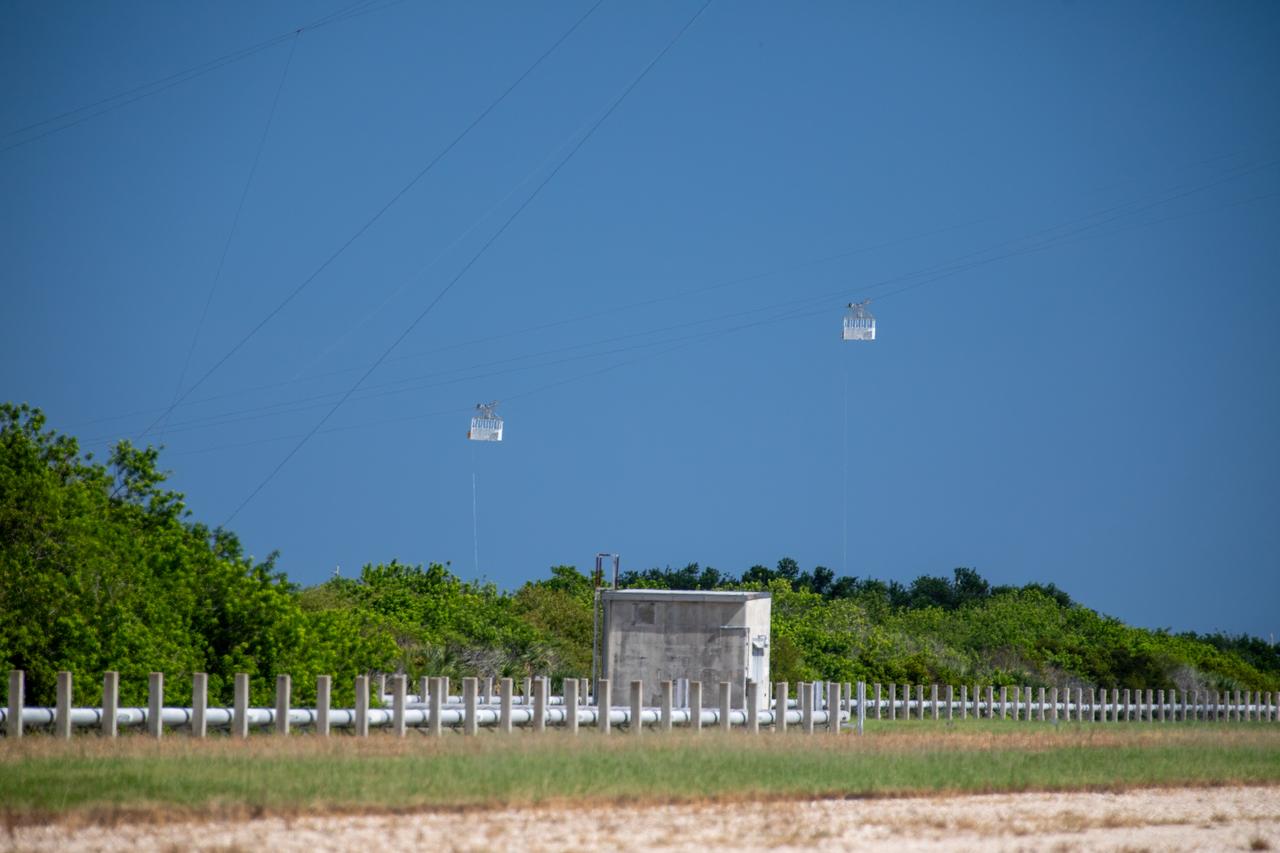
Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program, in preparation for the agency’s Artemis II crewed mission to the Moon, begin installation of four emergency egress baskets at Launch Complex 39B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Jan. 18, 2024. The baskets, similar to gondolas on ski lifts, are used in the case of a pad abort emergency to enable astronauts and other pad personnel a way to quickly escape away from the mobile launcher to the base of the pad and where waiting emergency transport vehicles will then drive them away.
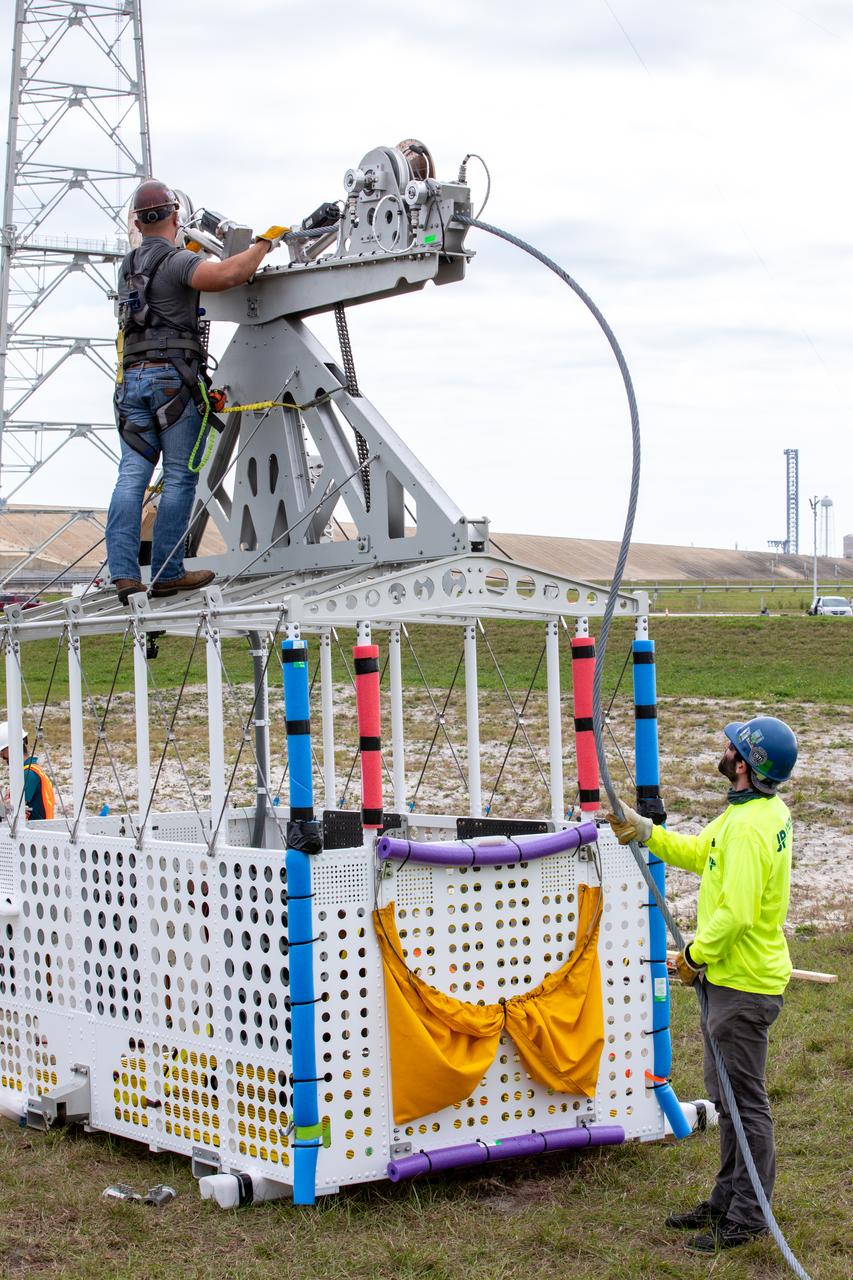

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program, in preparation for the agency’s Artemis II crewed mission to the Moon, begin installation of four emergency egress baskets at Launch Complex 39B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Jan. 18, 2024. The baskets, similar to gondolas on ski lifts, are used in the case of a pad abort emergency to enable astronauts and other pad personnel a way to quickly escape away from the mobile launcher to the base of the pad and where waiting emergency transport vehicles will then drive them away.
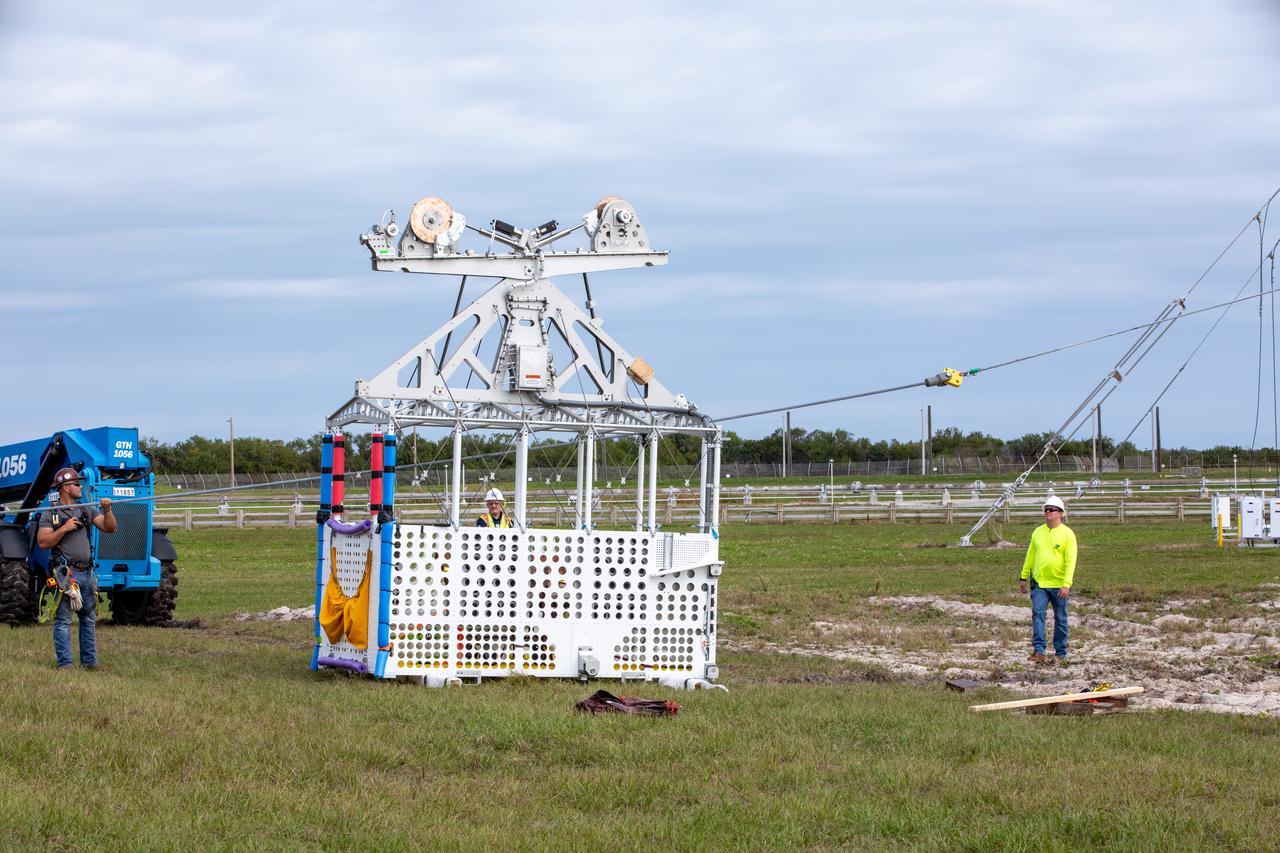

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program, in preparation for the agency’s Artemis II crewed mission to the Moon, begin installation of four emergency egress baskets at Launch Complex 39B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Jan. 18, 2024. The baskets, similar to gondolas on ski lifts, are used in the case of a pad abort emergency to enable astronauts and other pad personnel a way to quickly escape away from the mobile launcher to the base of the pad and where waiting emergency transport vehicles will then drive them away.
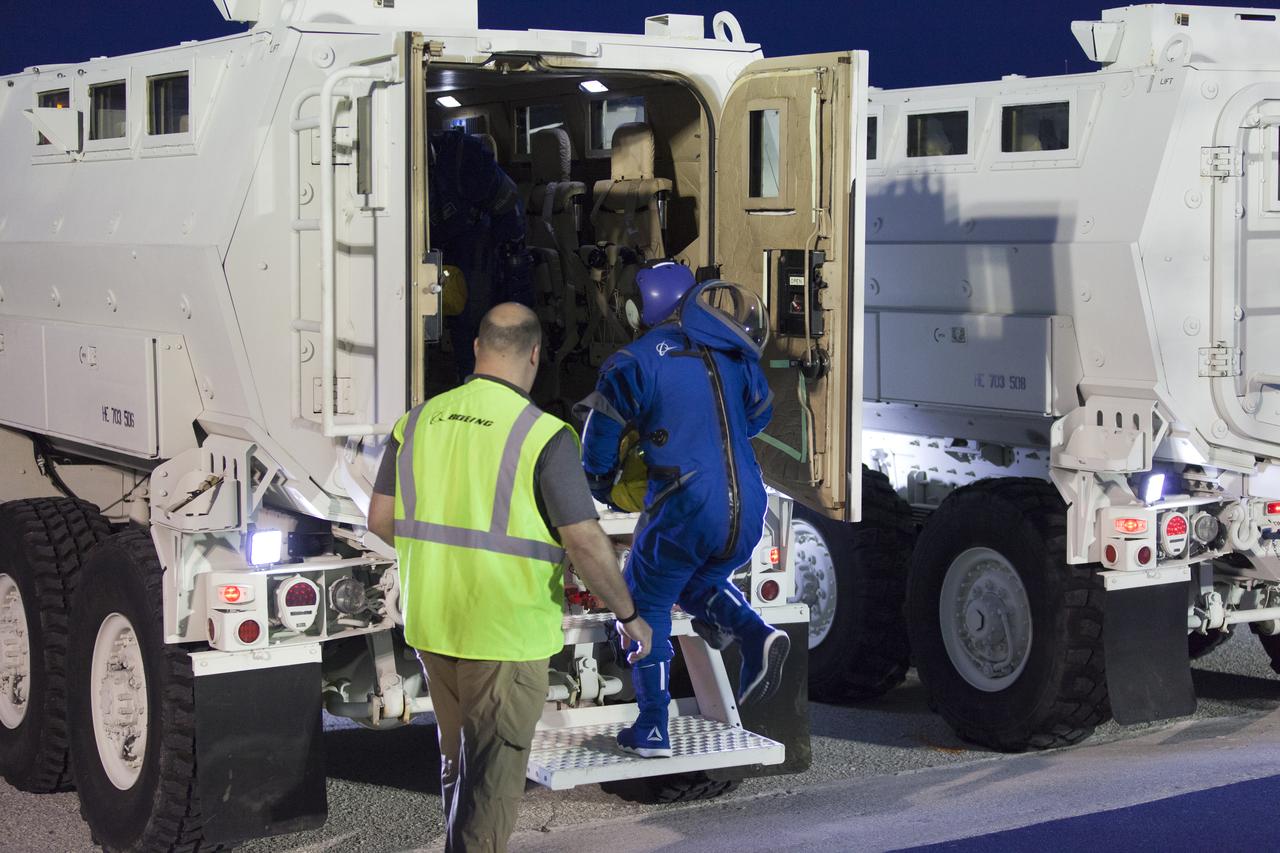

An astronaut heads into a mine-resistant ambush protected vehicle, or MRAP, during a Boeing/United Launch Alliance emergency egress system demonstration at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Launch Complex 41 in Florida on June 19, 2018. NASA’s MRAPs offer a mobile bunker for astronauts and ground crews, should they need to escape from the launch pad quickly in an emergency.
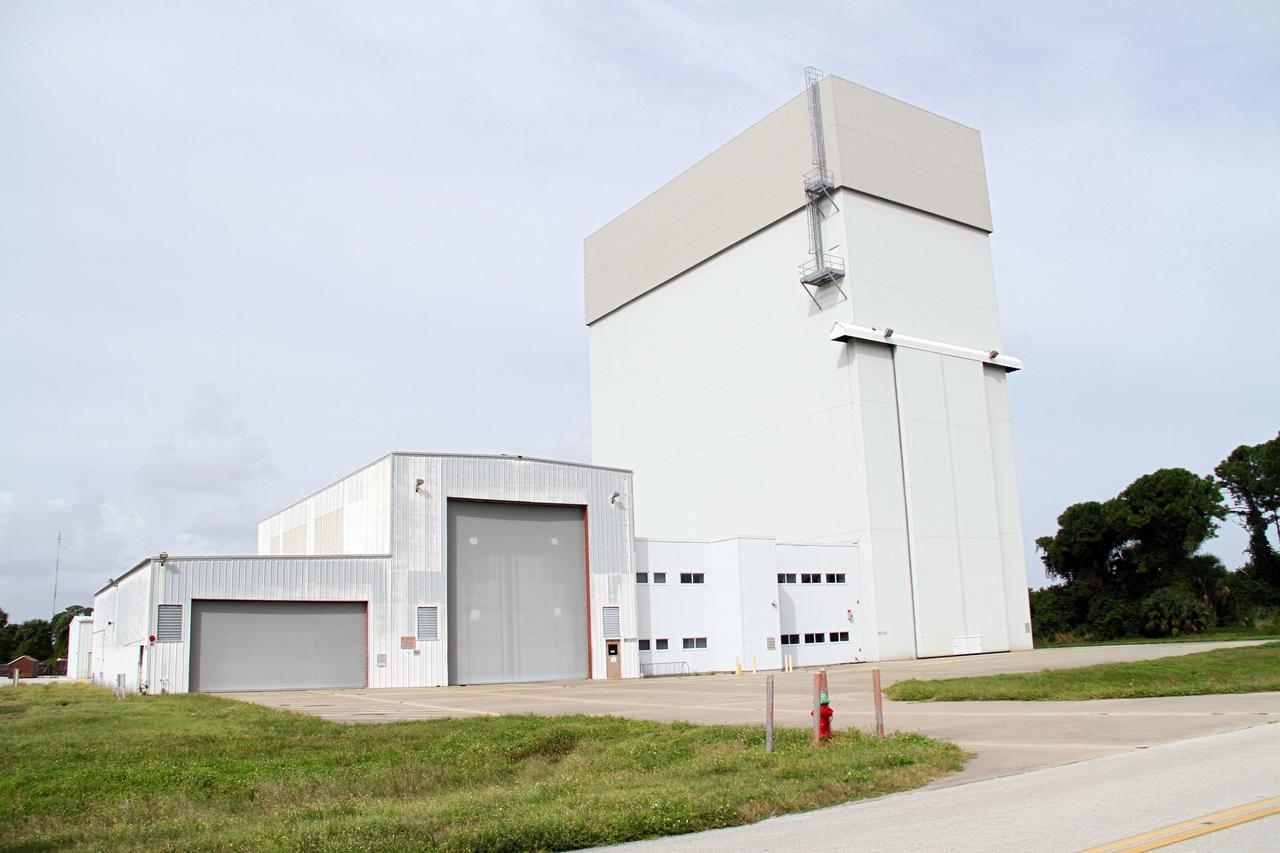

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –The Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, formerly known as the Canister Rotation Facility, is being outfitted and prepared for use by NASA's Orion Program to process the Launch Abort System, a multi-story rocket that will be positioned atop an Orion capsule to provide an escape system for astronauts during countdown and launch into orbit. The structure, the industrial area of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, served the Space Shuttle Program by standing the payload canister up so it could be taken to the launch pad and its contents transferred into the shuttle's cargo bay. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
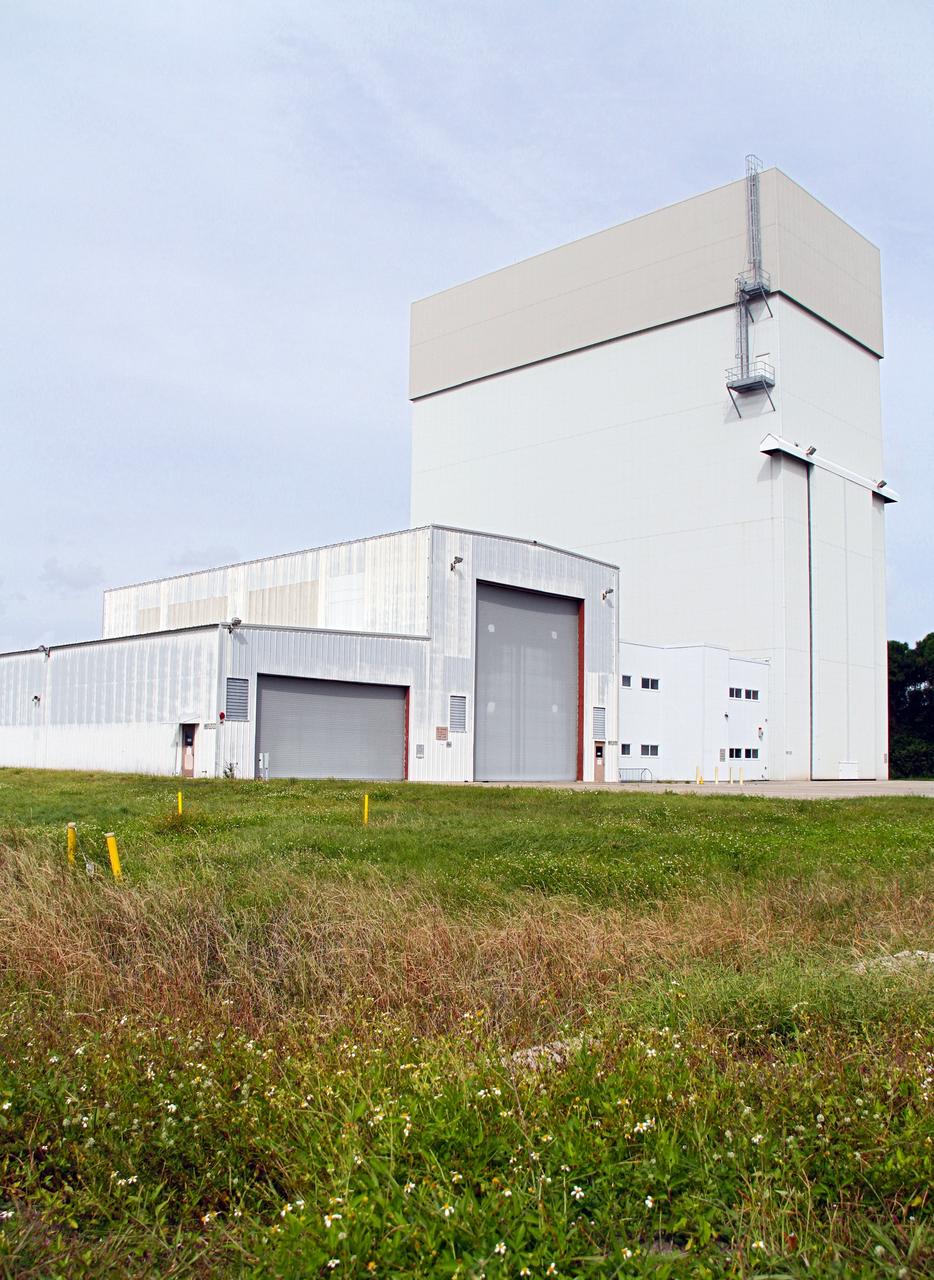

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –The Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, formerly known as the Canister Rotation Facility, is being outfitted and prepared for use by NASA's Orion Program to process the Launch Abort System, a multi-story rocket that will be positioned atop an Orion capsule to provide an escape system for astronauts during countdown and launch into orbit. The structure, the industrial area of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, served the Space Shuttle Program by standing the payload canister up so it could be taken to the launch pad and its contents transferred into the shuttle's cargo bay. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-100 Mission Specialists John L. Phillips (left) and Chris A. Hadfield (right) move quickly toward the slidewire baskets during emergency escape training at Launch Pad 39A. The training is part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that also include a simulated launch countdown. The mission is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. The SSRMS is crucial to the continued assembly of the orbiting complex. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-100 Mission Specialists John L. Phillips (left) and Chris A. Hadfield (right) move quickly toward the slidewire baskets during emergency escape training at Launch Pad 39A. The training is part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that also include a simulated launch countdown. The mission is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. The SSRMS is crucial to the continued assembly of the orbiting complex. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
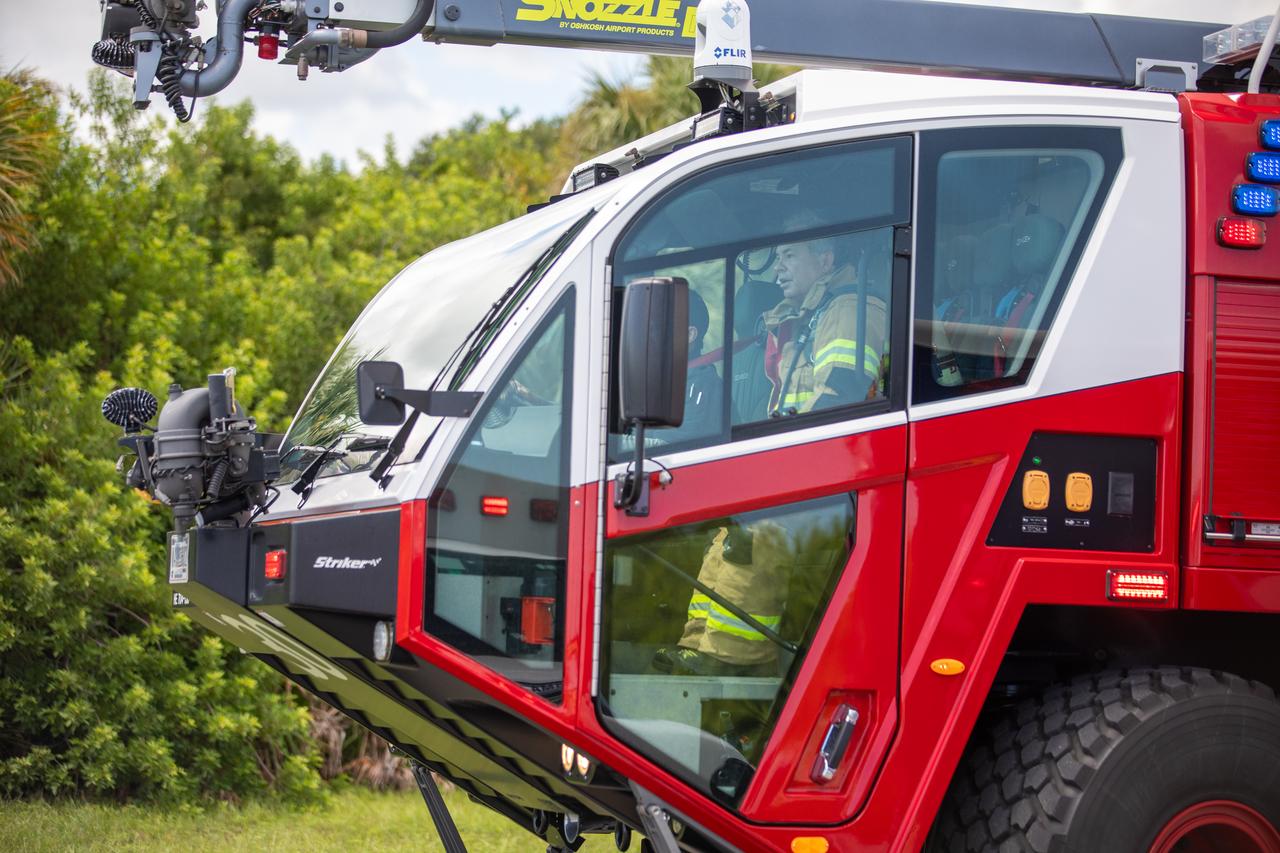

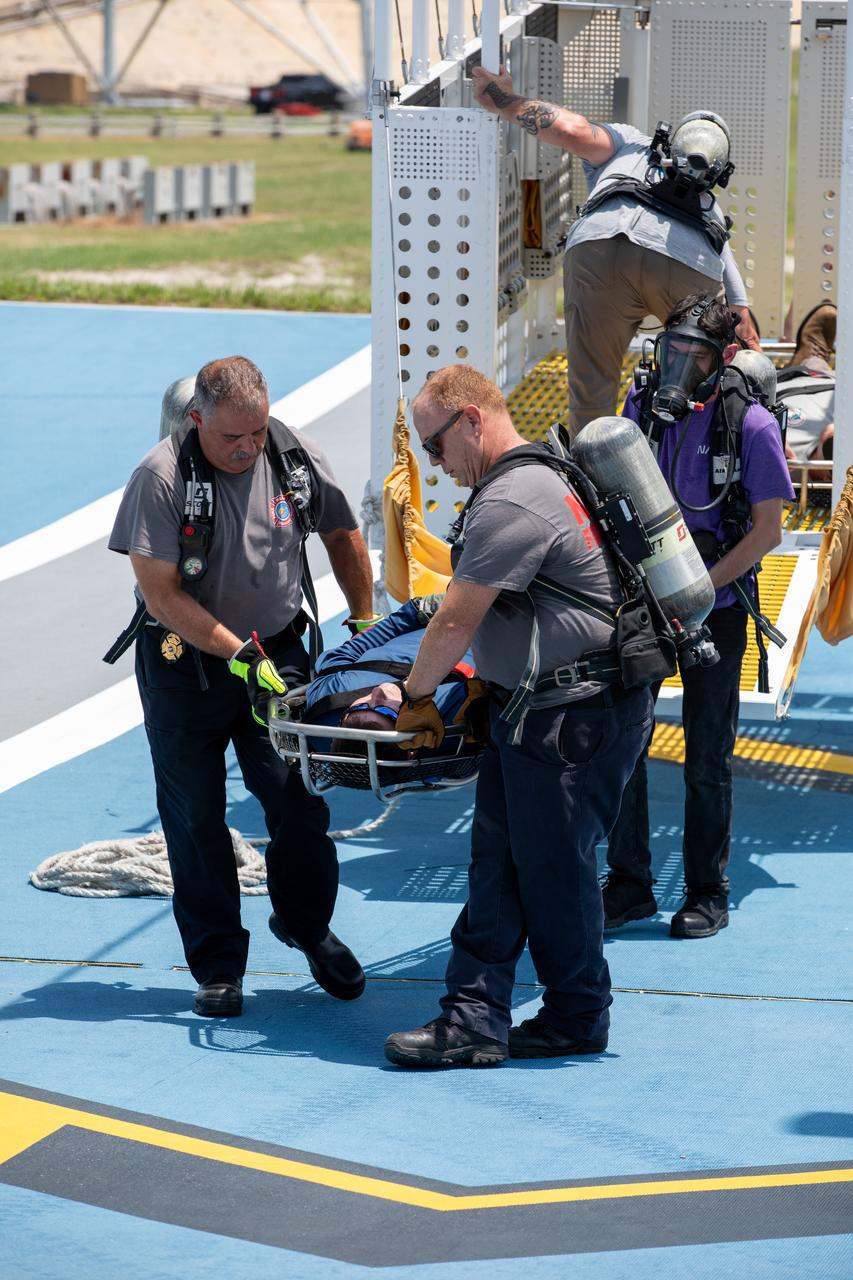
Medical and fire-rescue personnel participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.
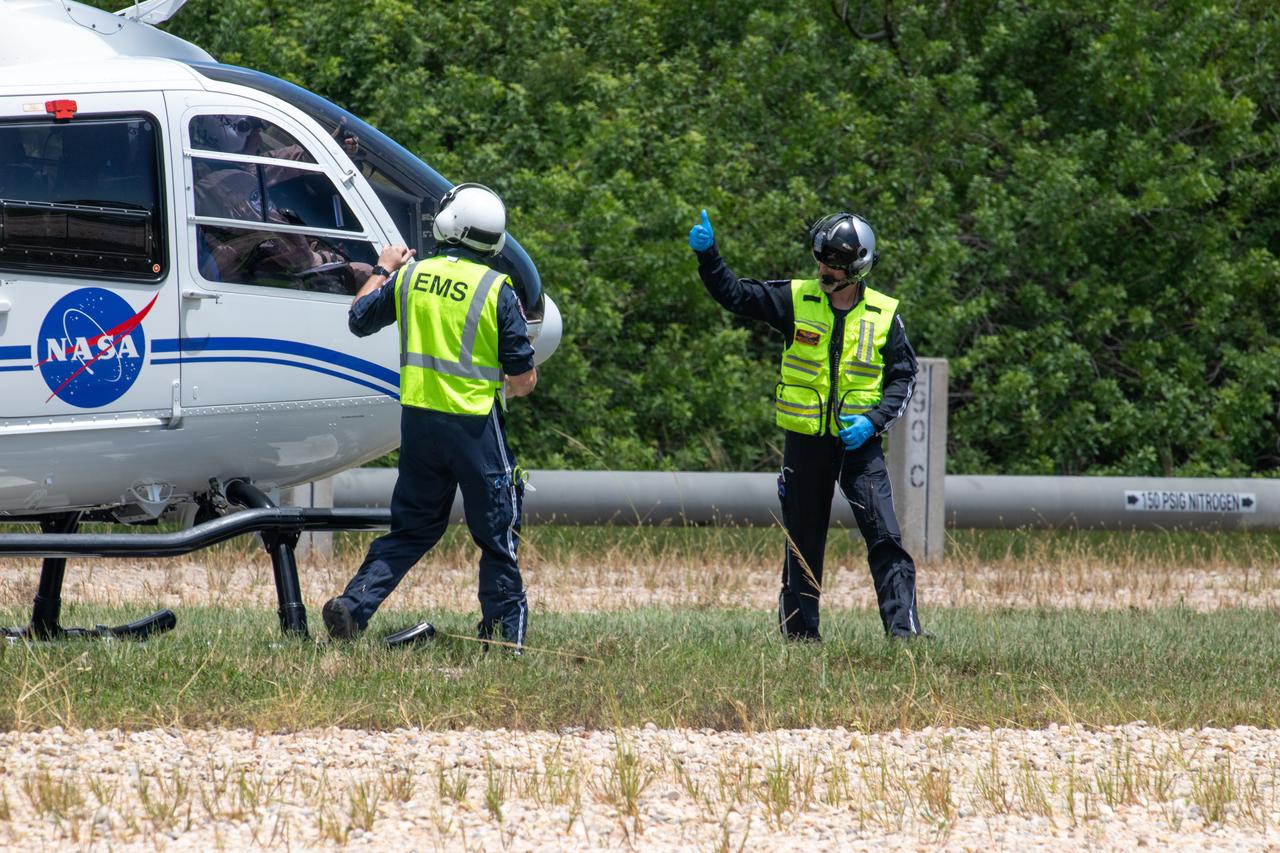

Medical and fire-rescue personnel participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.
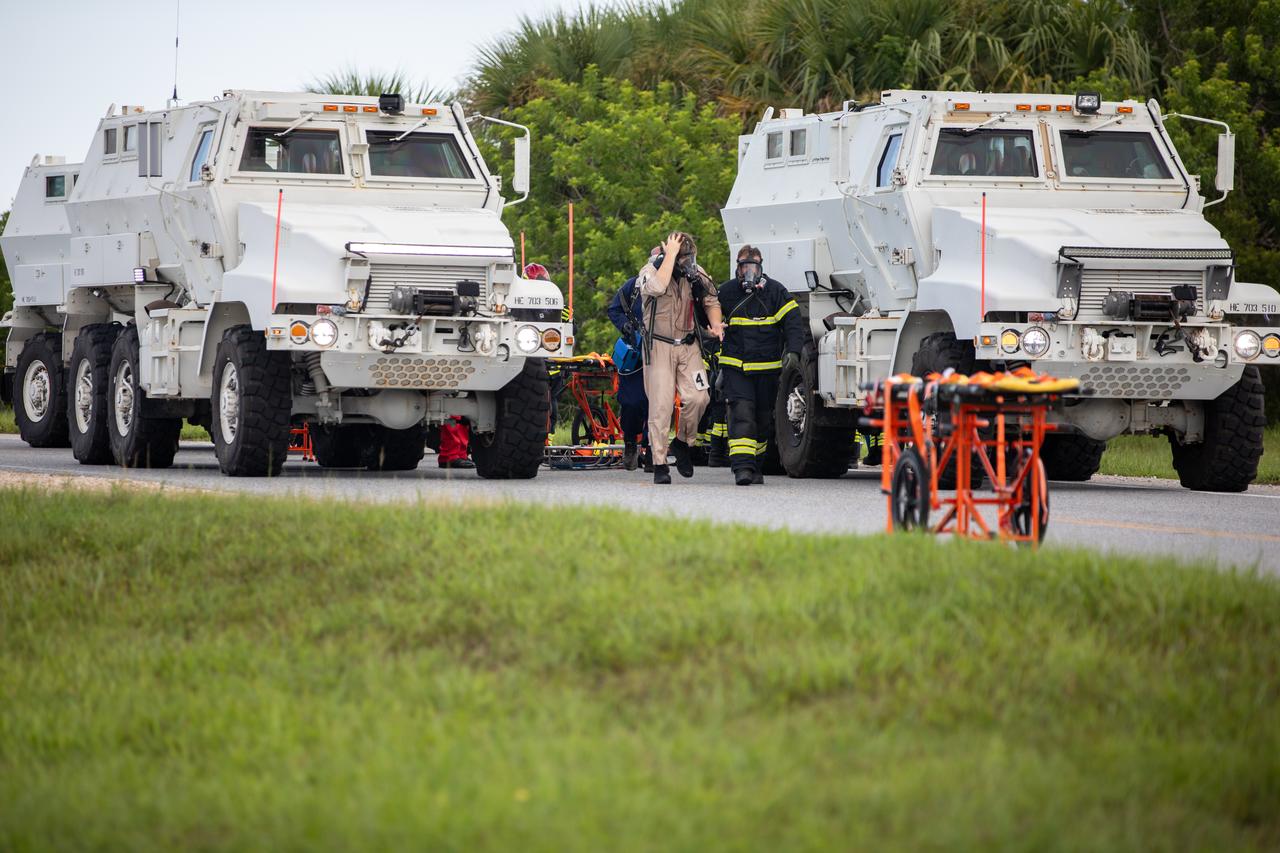

Medical and fire-rescue personnel participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.
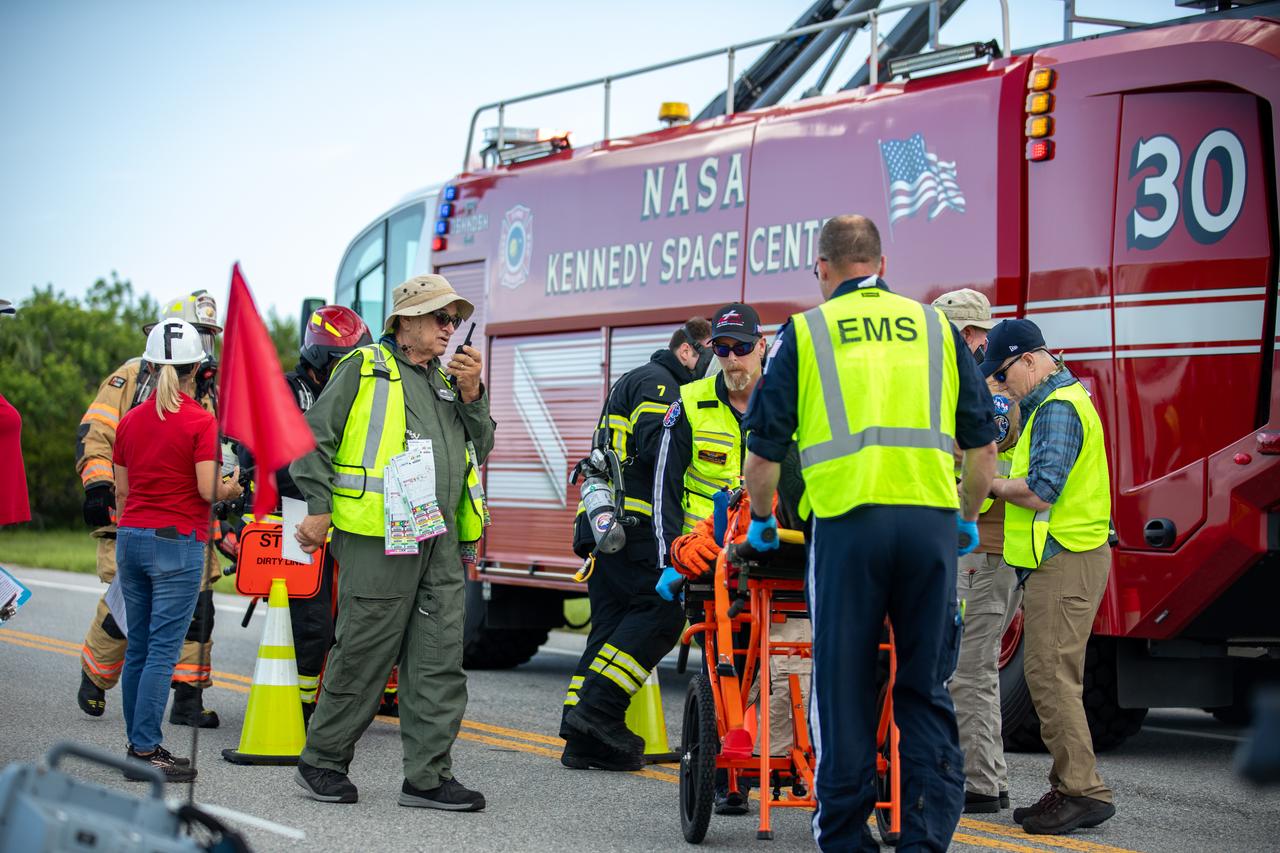

Medical and fire-rescue personnel participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.
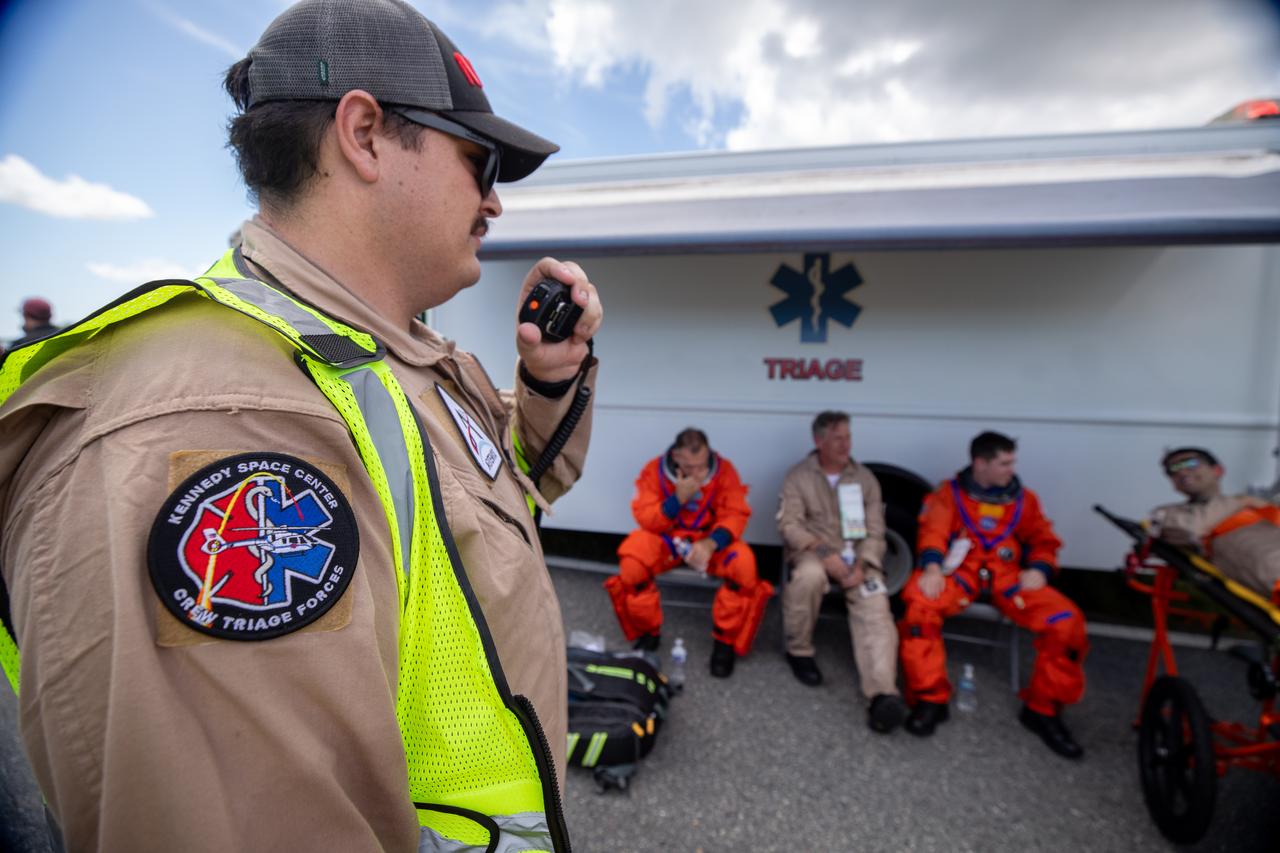

Medical and fire-rescue personnel participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.
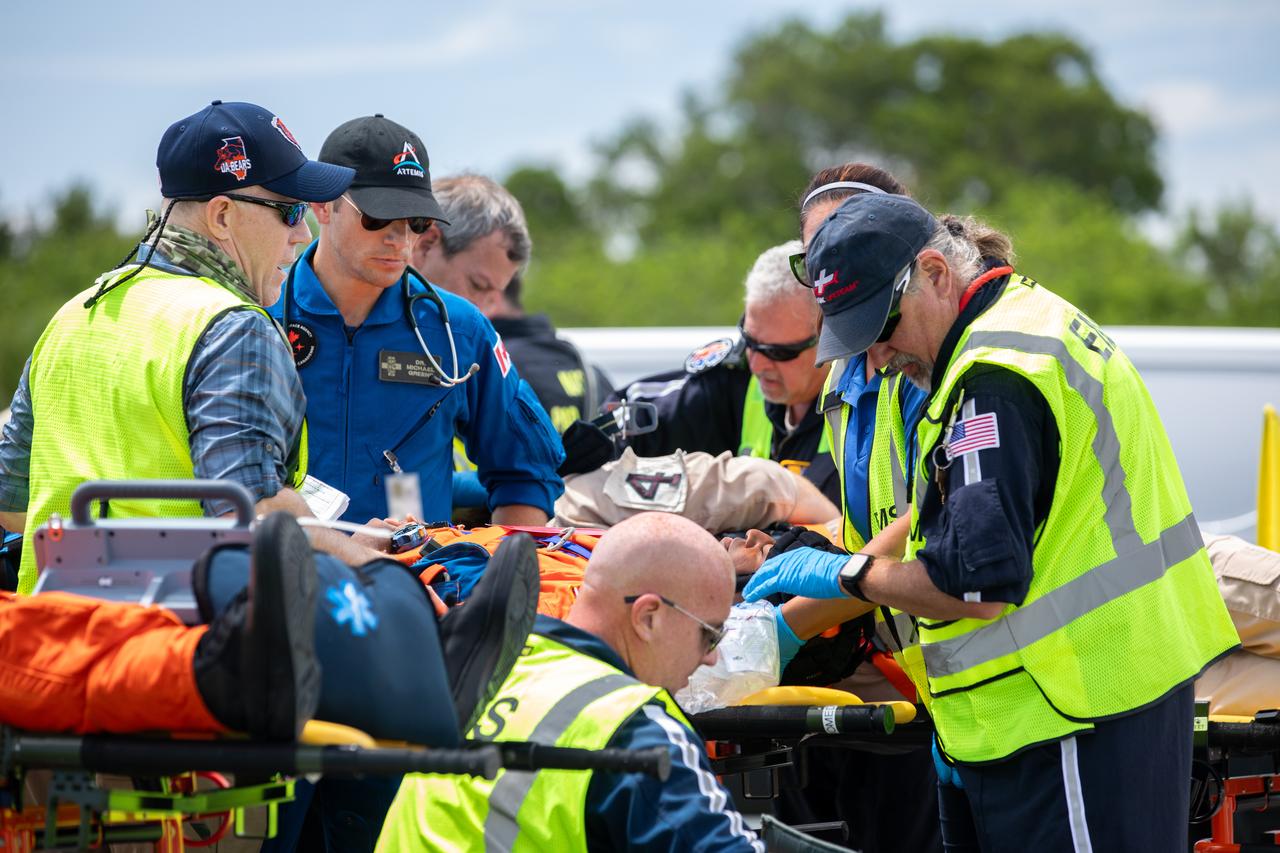

Medical, fire-rescue personnel, and simulated flight crew members participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.

Medical, fire-rescue personnel, and simulated flight crew members participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.

Medical and fire-rescue personnel participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.
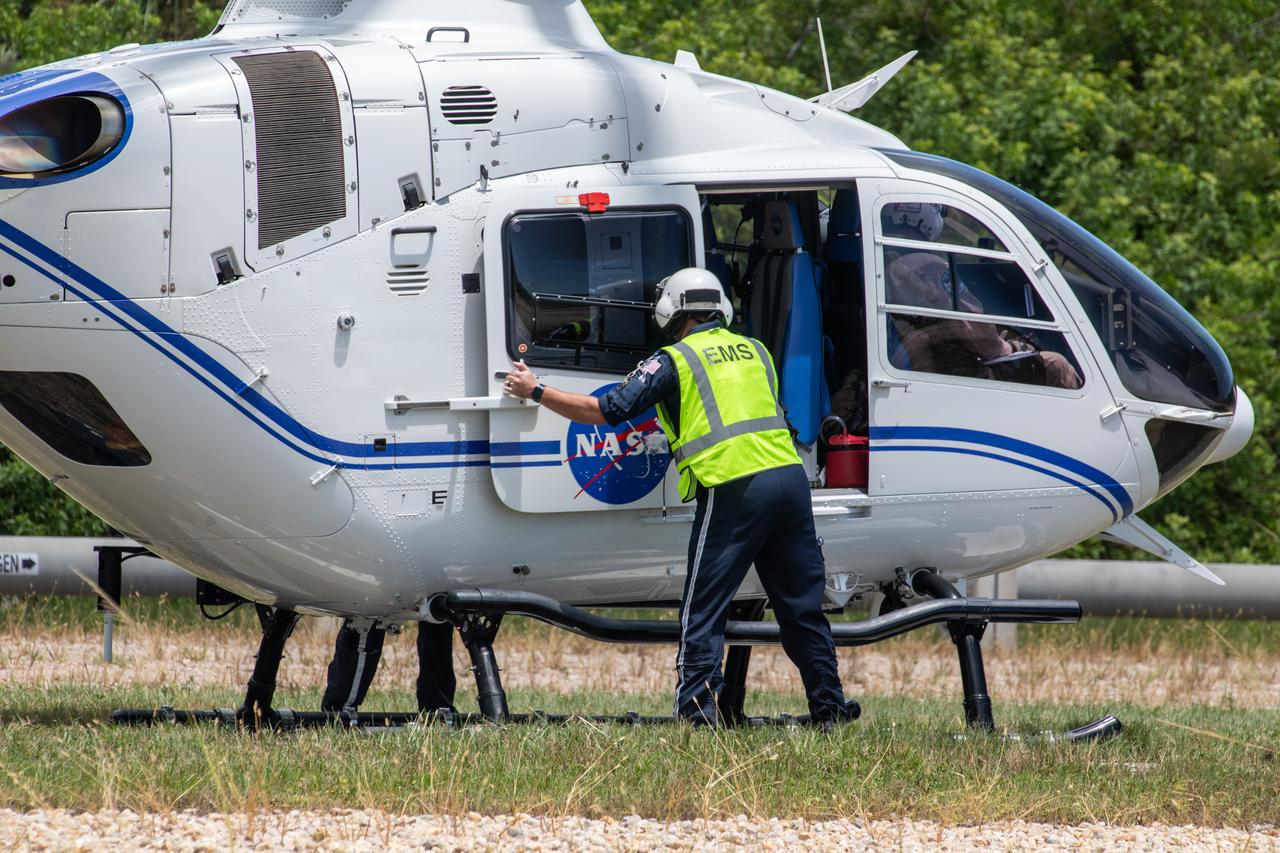

Medical and fire-rescue personnel participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.
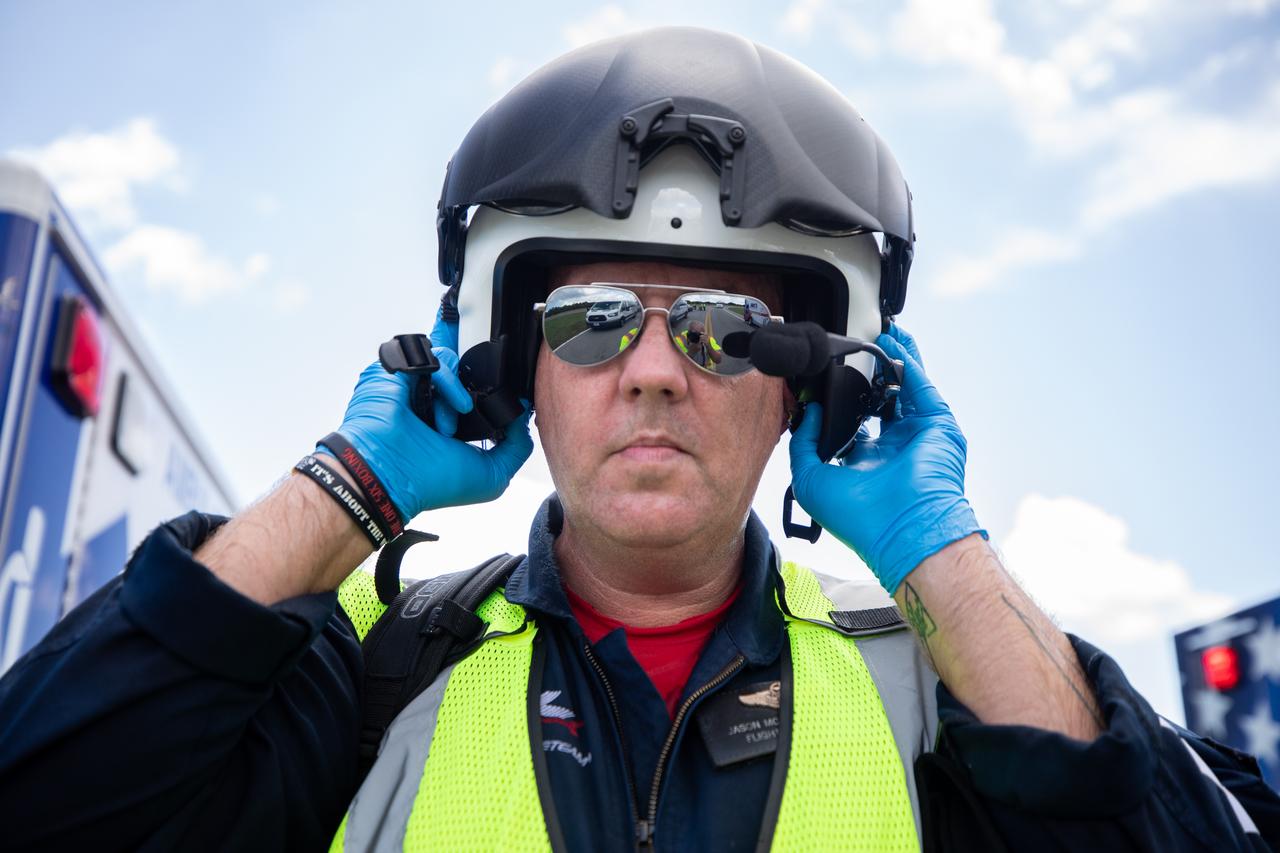

Medical and fire-rescue personnel participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.
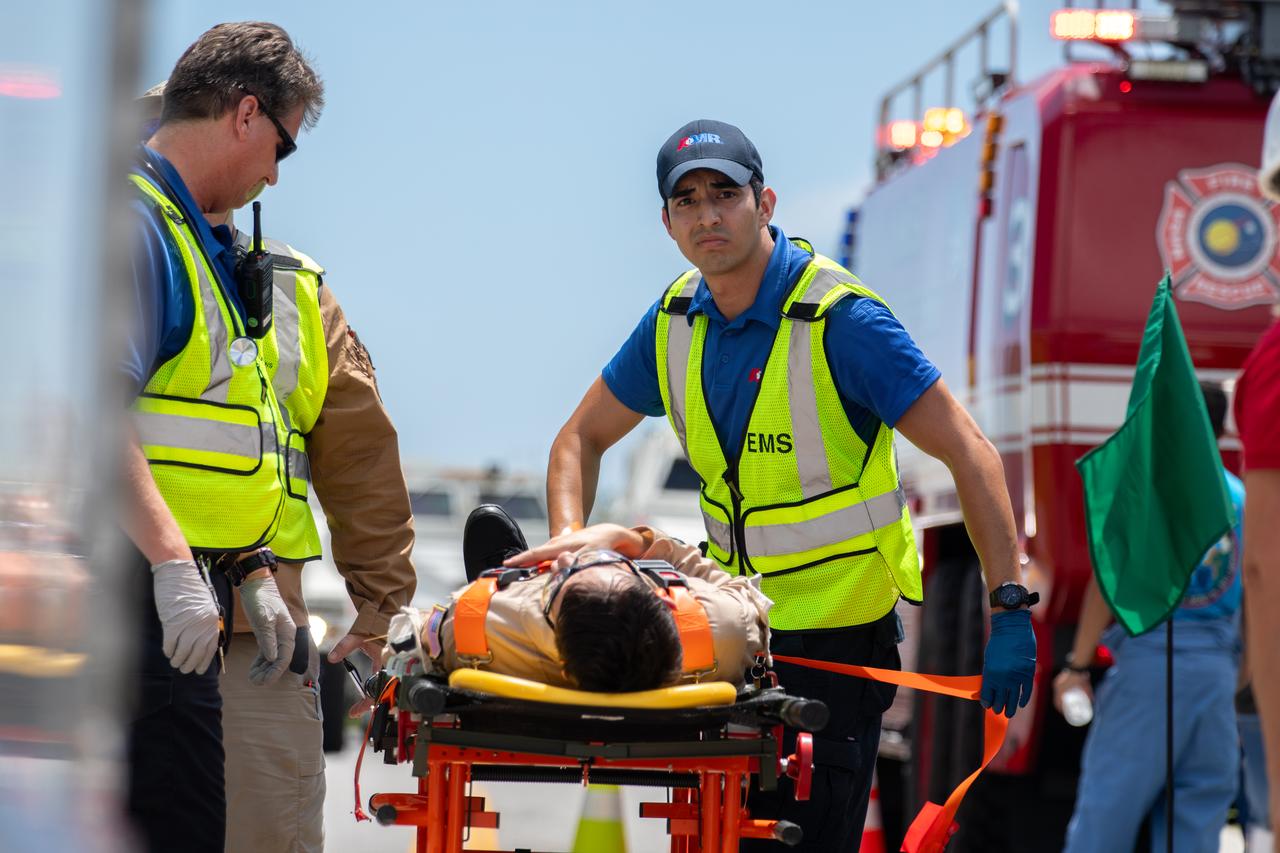

Medical and fire-rescue personnel participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.
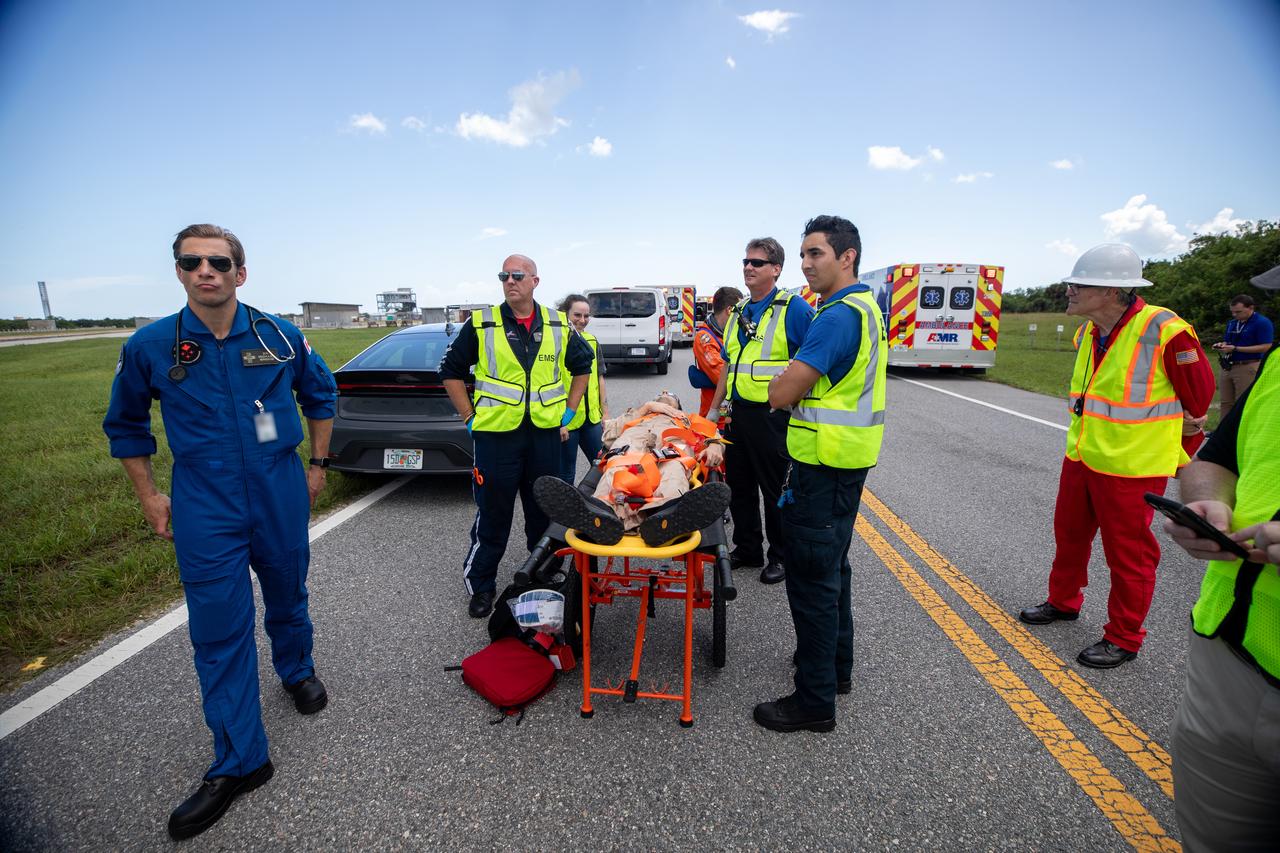

Medical, fire-rescue personnel, and simulated flight crew members participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.
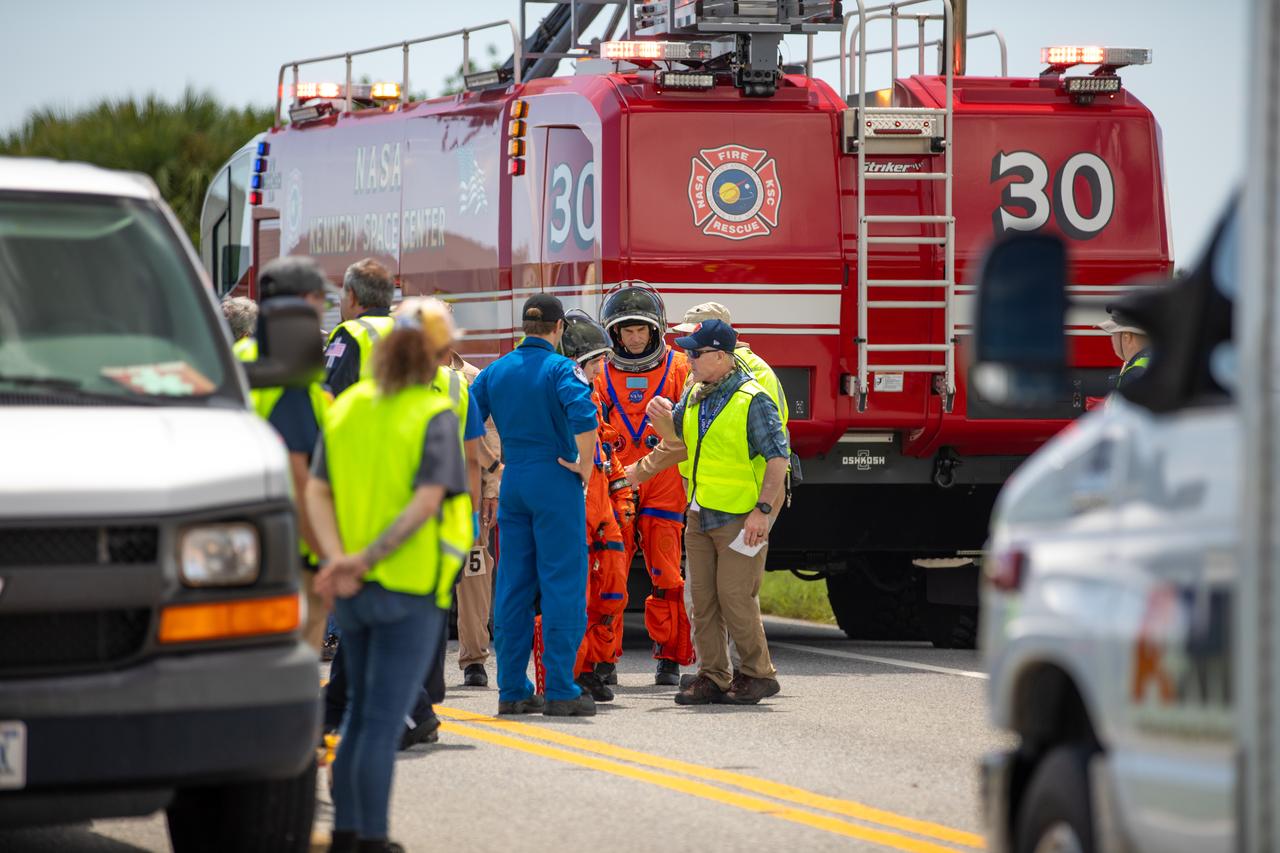

Medical, fire-rescue personnel, and simulated flight crew members participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.
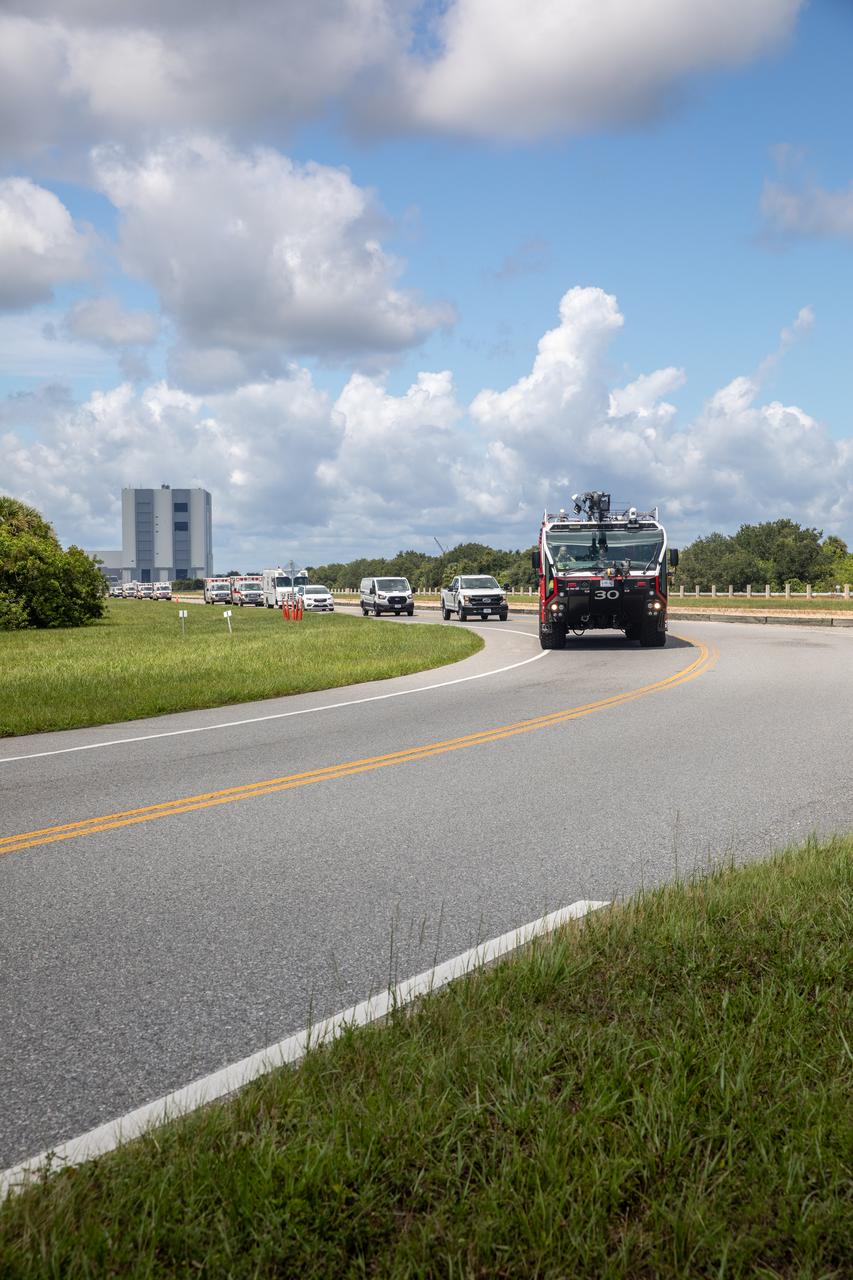

Medical and fire-rescue personnel participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.

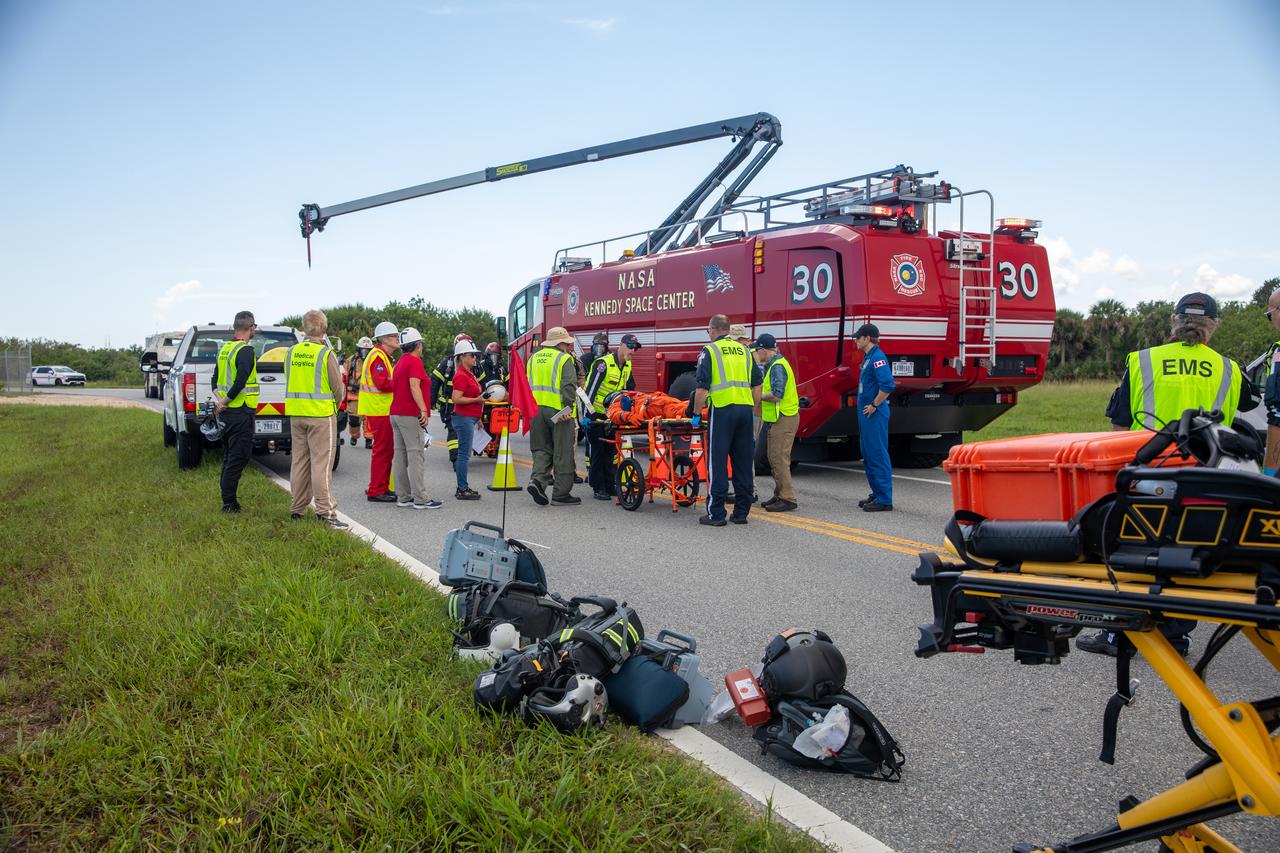
Medical and fire-rescue personnel participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.

Medical, fire-rescue personnel, and simulated flight crew members participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.

Medical and fire-rescue personnel participate in the Artemis II mission emergency escape or egress verification and validation tests near Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. During the multi-day tests, members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting in and out of the emergency egress baskets then down to the launch pad where they would be transported to emergency transport vehicles and driven to safety. Prior to this test and throughout the course of several months, teams conducted basket release demonstrations to validate the system.

VAN HORN, Texas – Blue Origin’s New Shepard crew capsule touched down 1,630 feet from the its simulated propulsion module launch pad at the company's West Texas launch site, completing a successful test of its New Shepard crew capsule escape system. The pusher escape system was designed and developed by Blue Origin to allow crew escape in the event of an emergency during any phase of ascent for its suborbital New Shepard system. As part of an incremental development program, the results of this test will shape the design of the escape system for the company's orbital biconic-shaped Space Vehicle. The system is expected to enable full reusability of the launch vehicle, which is different from NASA's previous launch escape systems that would pull a spacecraft away from its rocket before reaching orbit. The test was part of Blue Origin's work supporting its funded Space Act Agreement with NASA during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2). Through initiatives like CCDev2, NASA is fostering the development of a U.S. commercial crew space transportation capability with the goal of achieving safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from the International Space Station and low-Earth orbit. After the capability is matured and available to the government and other customers, NASA could contract to purchase commercial services to meet its station crew transportation needs. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Blue Origin
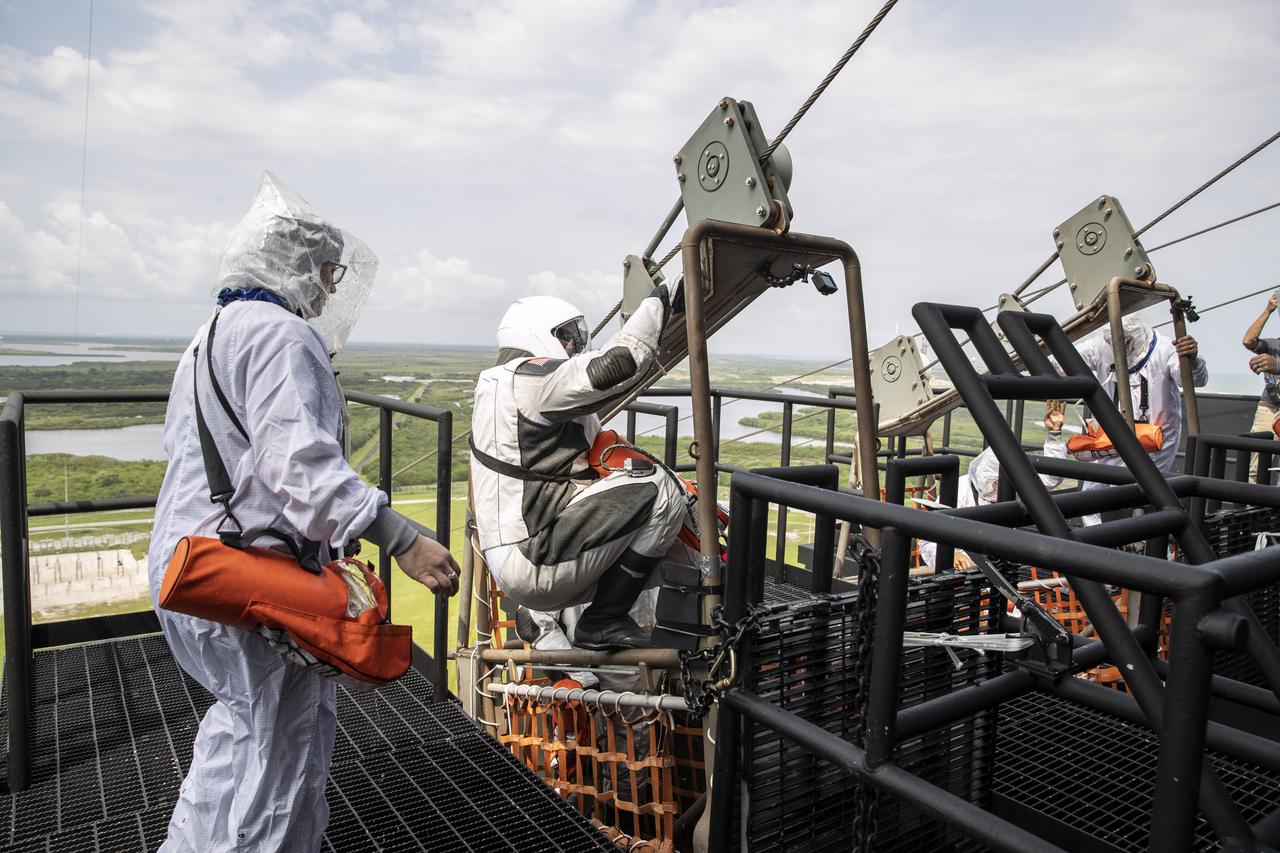

NASA and SpaceX conducted a formal verification of the company’s emergency escape system on Sept. 18, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida. NASA astronauts Shannon Walker and Bob Behnken participated in the exercise to verify the crew can safely and quickly evacuate from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency before liftoff of SpaceX’s first crewed flight test, called Demo-2. At tower level on the pad, Behnken practiced loading into a slidewire basket and simulating an emergency escape to ground level. As Boeing and SpaceX begin to make regular flights to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, the agency will continue to advance its mission to go beyond low-Earth orbit and establish a human presence on the Moon with the ultimate goal of sending astronauts to Mars.
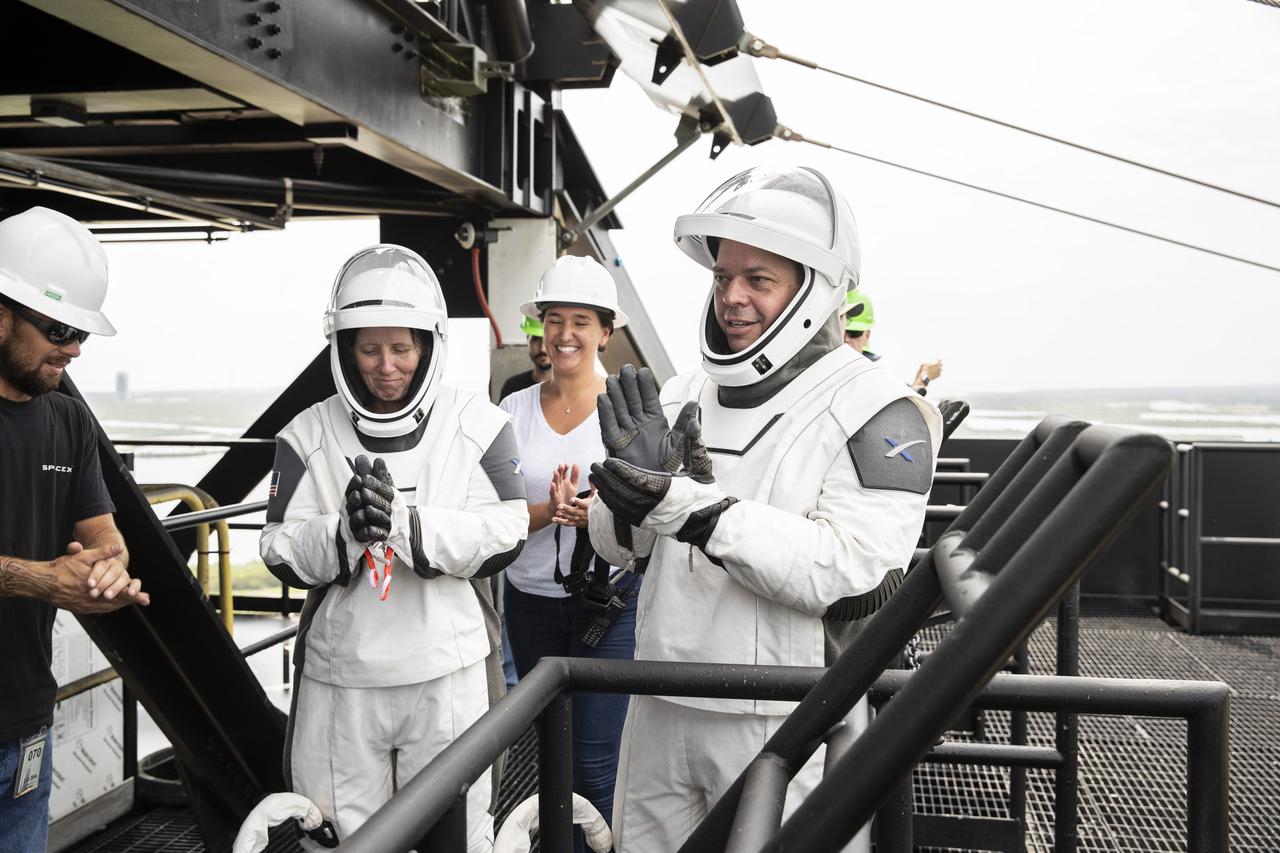

NASA and SpaceX conducted a formal verification of the company’s emergency escape system on Sept. 18, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida. From left, NASA astronauts Shannon Walker and Bob Behnken participated in the exercise to verify the crew can safely and quickly evacuate from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency before liftoff of SpaceX’s first crewed flight test, called Demo-2. At tower level on the pad, Walker and Behnken practiced loading into slidewire baskets and simulating an emergency escape to ground level. As Boeing and SpaceX begin to make regular flights to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, the agency will continue to advance its mission to go beyond low-Earth orbit and establish a human presence on the Moon with the ultimate goal of sending astronauts to Mars.
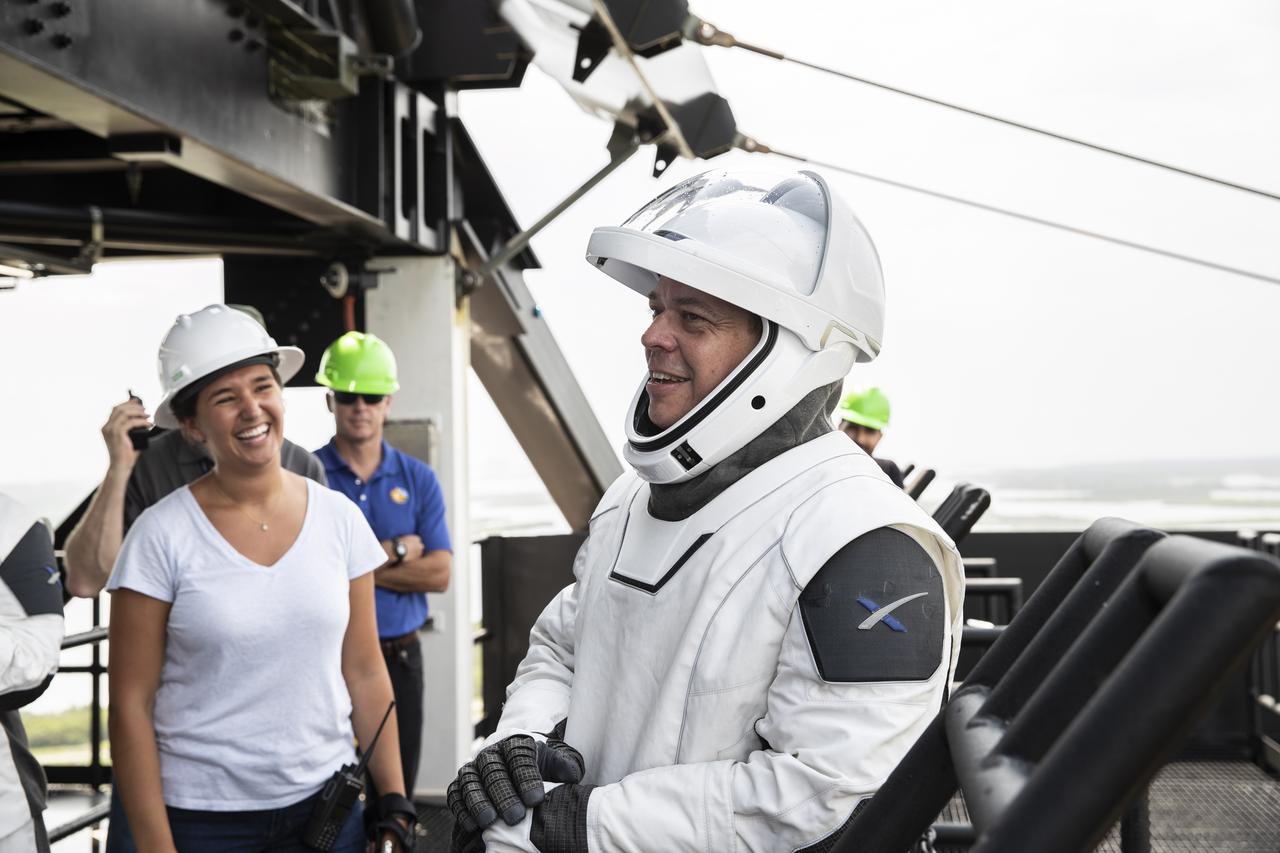

NASA and SpaceX conducted a formal verification of the company’s emergency escape system on Sept. 18, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida. NASA astronaut Bob Behnken participated in the exercise to verify the crew can safely and quickly evacuate from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency before liftoff of SpaceX’s first crewed flight test, called Demo-2. At tower level on the pad, Behnken practiced loading into a slidewire basket and simulating an emergency escape to ground level. As Boeing and SpaceX begin to make regular flights to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, the agency will continue to advance its mission to go beyond low-Earth orbit and establish a human presence on the Moon with the ultimate goal of sending astronauts to Mars.
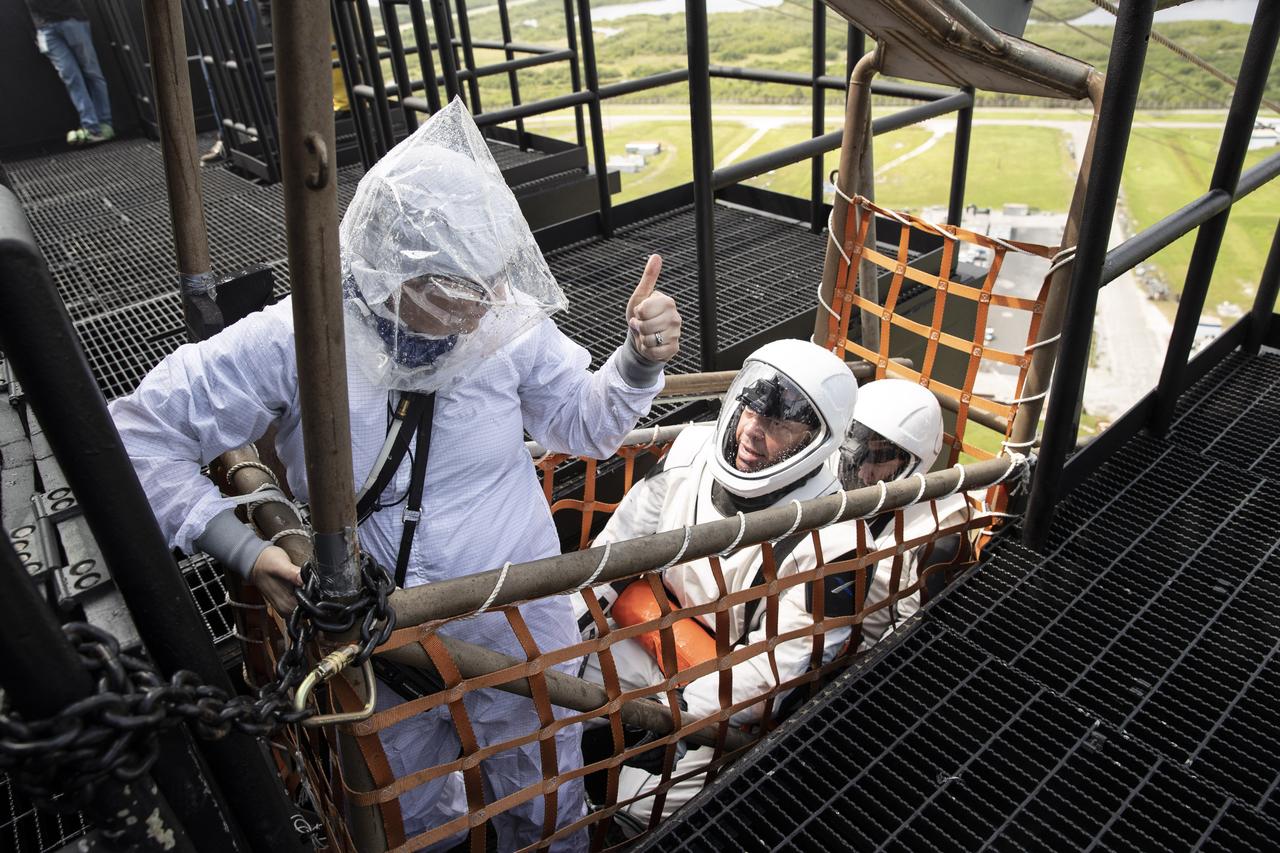

NASA and SpaceX conducted a formal verification of the company’s emergency escape system on Sept. 18, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida. From left, NASA astronauts Shannon Walker and Bob Behnken participated in the exercise to verify the crew can safely and quickly evacuate from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency before liftoff of SpaceX’s first crewed flight test, called Demo-2. At tower level on the pad, Walker and Behnken practiced loading into a slidewire basket and simulating an emergency escape to ground level. As Boeing and SpaceX begin to make regular flights to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, the agency will continue to advance its mission to go beyond low-Earth orbit and establish a human presence on the Moon with the ultimate goal of sending astronauts to Mars.
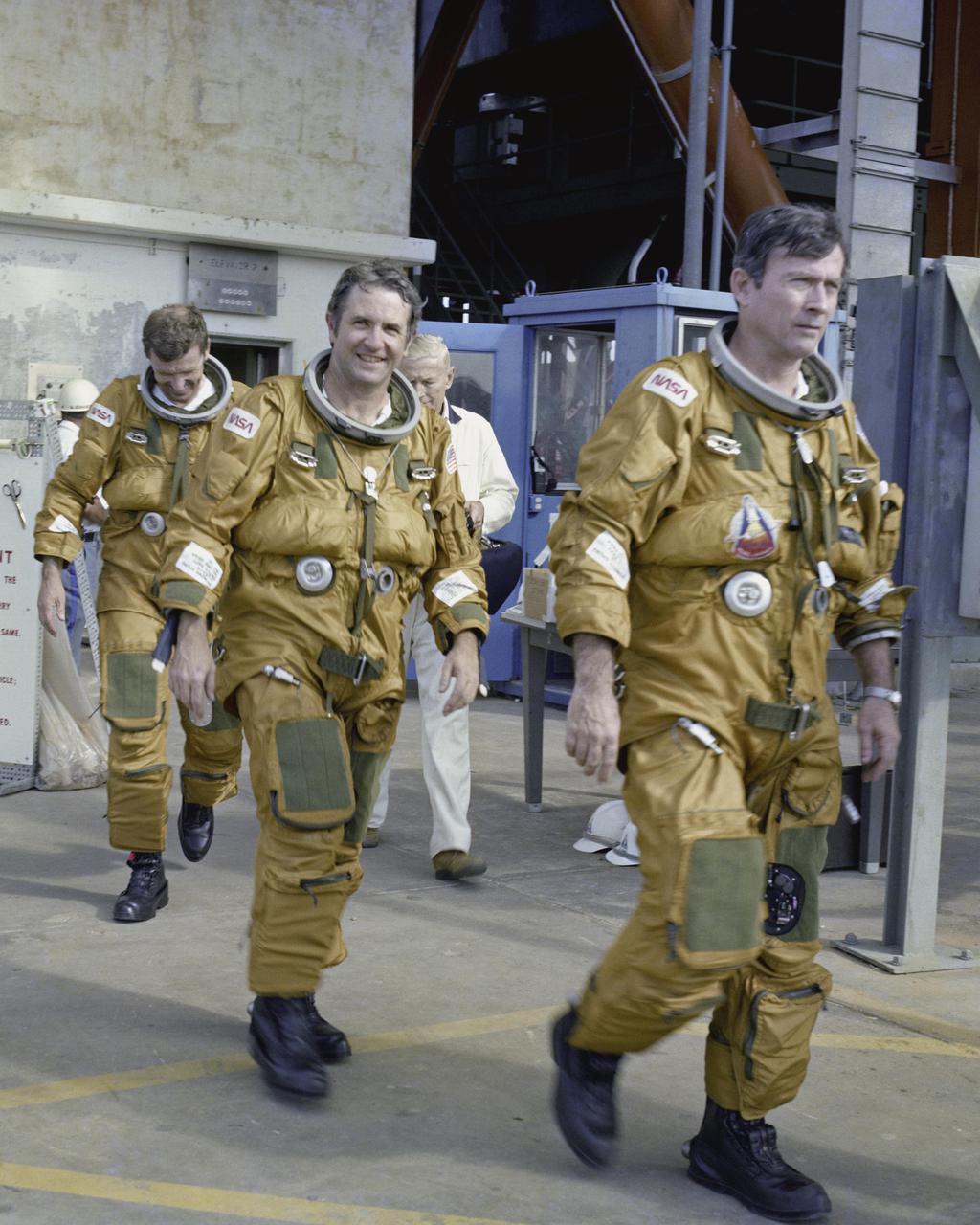

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Space Shuttle prime and backup astronaut crews are preparing to be briefed on the use of the emergency pad escape system, known as the “slidewire”. From left to right are backup astronauts Joe Engle and Richard Truly, and primary crew Commander John Young. Both the prime and backup crews wore the spacesuits and other equipment they will wear during a mission. The slidewire system provides a quick and sure escape from the upper pad platforms in case of a serious emergency. The flight crews wore the spacesuits and other equipment to be worn during a mission, but sandbags were used to duplicate the weight of riders in the slidewire baskets during the training. The STS-1 mission, known as a shuttle systems test flight, will seek to demonstrate safe launch into orbit and safe return of the orbiter and crew and verify the combined performance of the entire shuttle vehicle -- orbiter, solid rocket boosters and external tank. STS-1 will be launched from Pad A at the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 no earlier than March 1981.
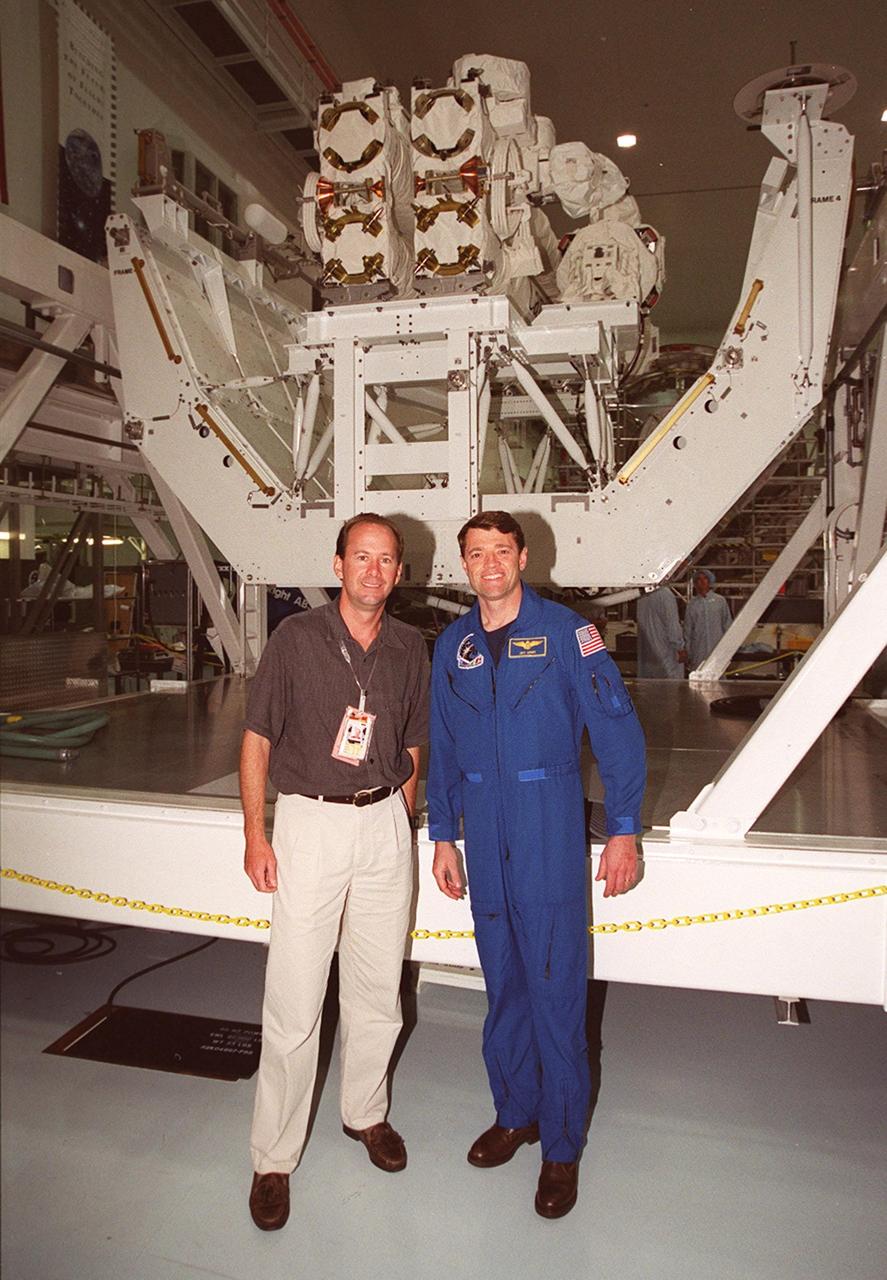
KSC’s PAO videographer, Glenn Benson (left) and STS-100 Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby pose in front of the Canadian robotic arm, SSRMS, in the Space Station Processing Facility. The STS-100 crew is at KSC for Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that include emergency escape training at the pad and a simulated launch countdown. The mission is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. The SSRMS is crucial to the continued assembly of the orbiting complex. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
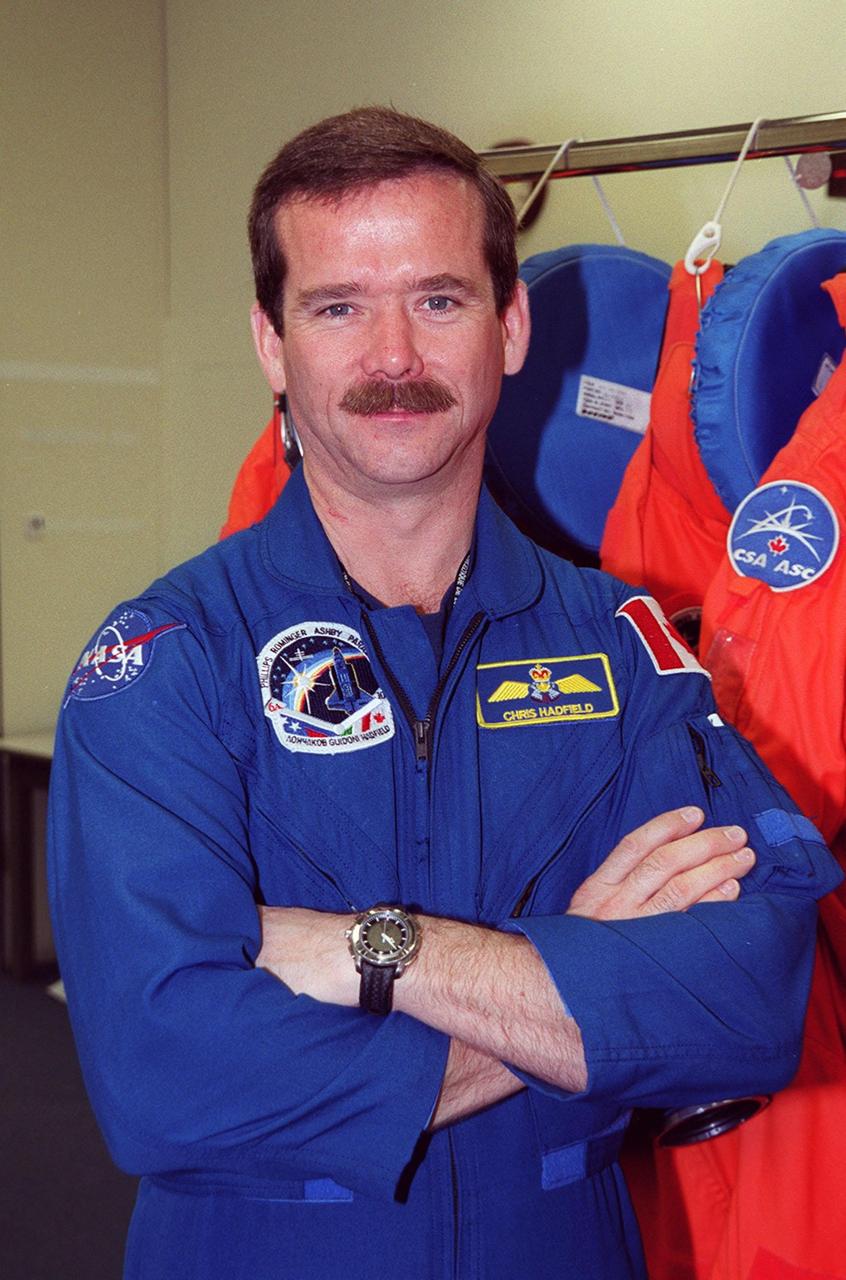

STS-100 Mission Specialist Chris Hadfield pauses for the camera during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that include emergency escape training at the pad and a simulated launch countdown. The mission is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the Canadian robotic arm, SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. The SSRMS is crucial to the continued assembly of the orbiting complex. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
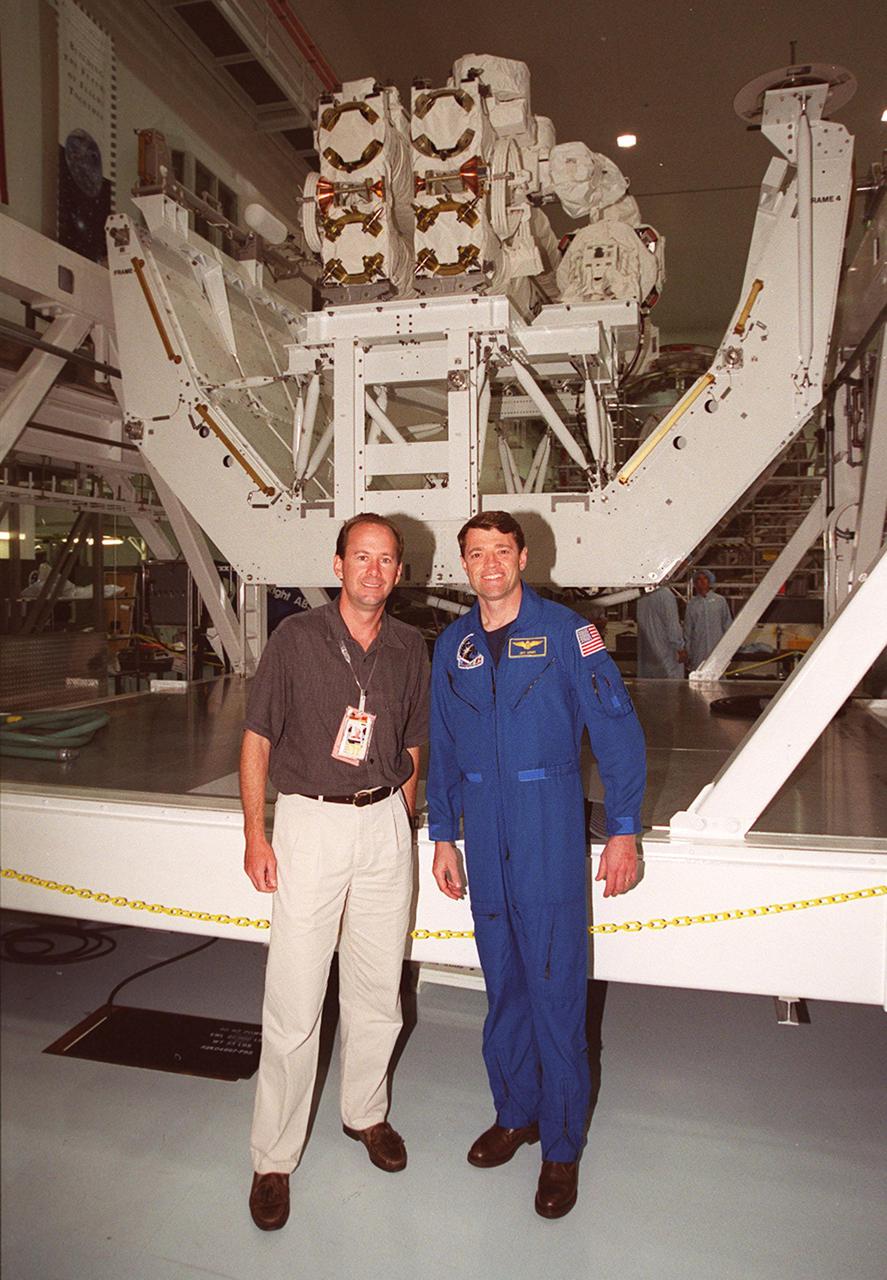
KSC’s PAO videographer, Glenn Benson (left) and STS-100 Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby pose in front of the Canadian robotic arm, SSRMS, in the Space Station Processing Facility. The STS-100 crew is at KSC for Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that include emergency escape training at the pad and a simulated launch countdown. The mission is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. The SSRMS is crucial to the continued assembly of the orbiting complex. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
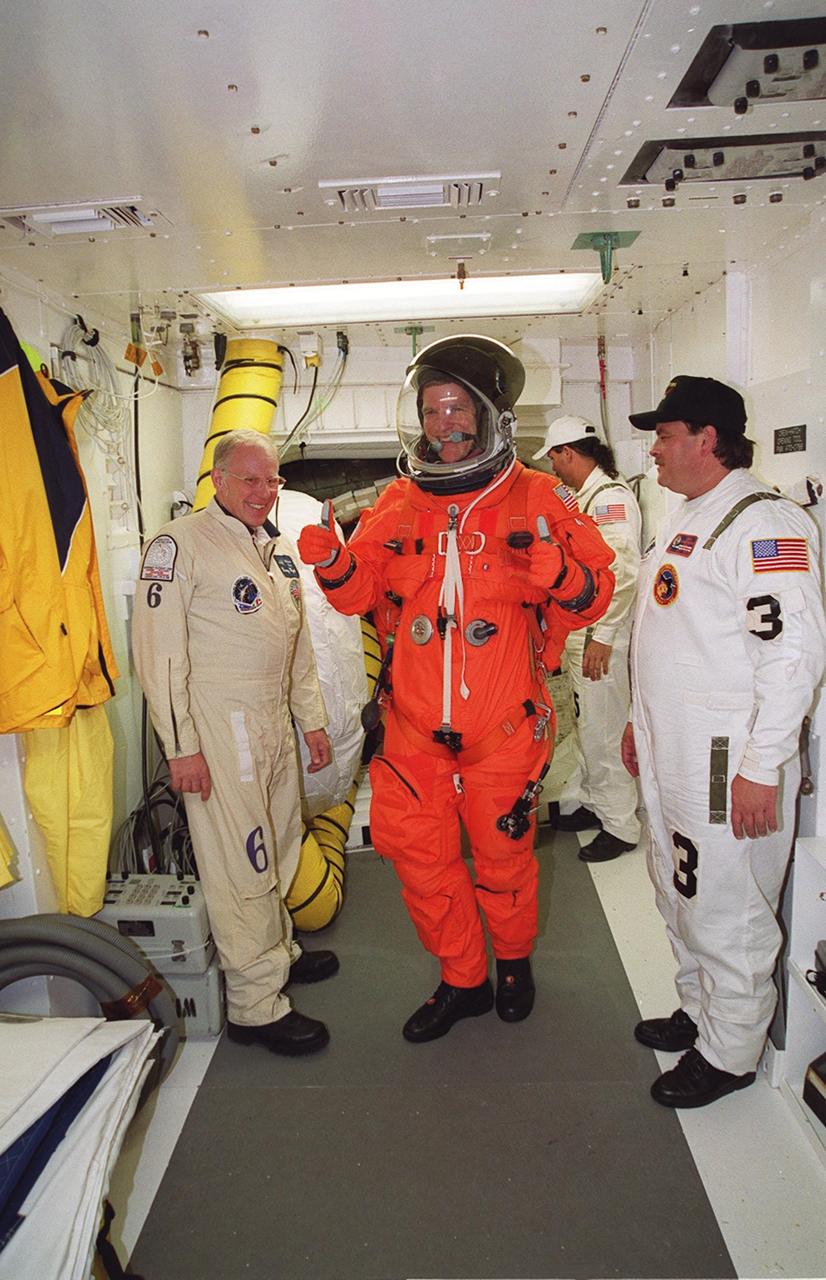

STS-100 Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski walks through the White Room after exiting Endeavour. He and the rest of the crew are taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that include emergency escape training at the pad and the simulated launch countdown. The mission is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. The SSRMS is crucial to the continued assembly of the orbiting complex. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A

In the White Room, Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski (left) and Umberto Guidoni (right) help Yuri V. Lonchakov exit Endeavour. They and the rest of the crew are taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that include emergency escape training at the pad and the simulated launch countdown. The mission is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. The SSRMS is crucial to the continued assembly of the orbiting complex. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
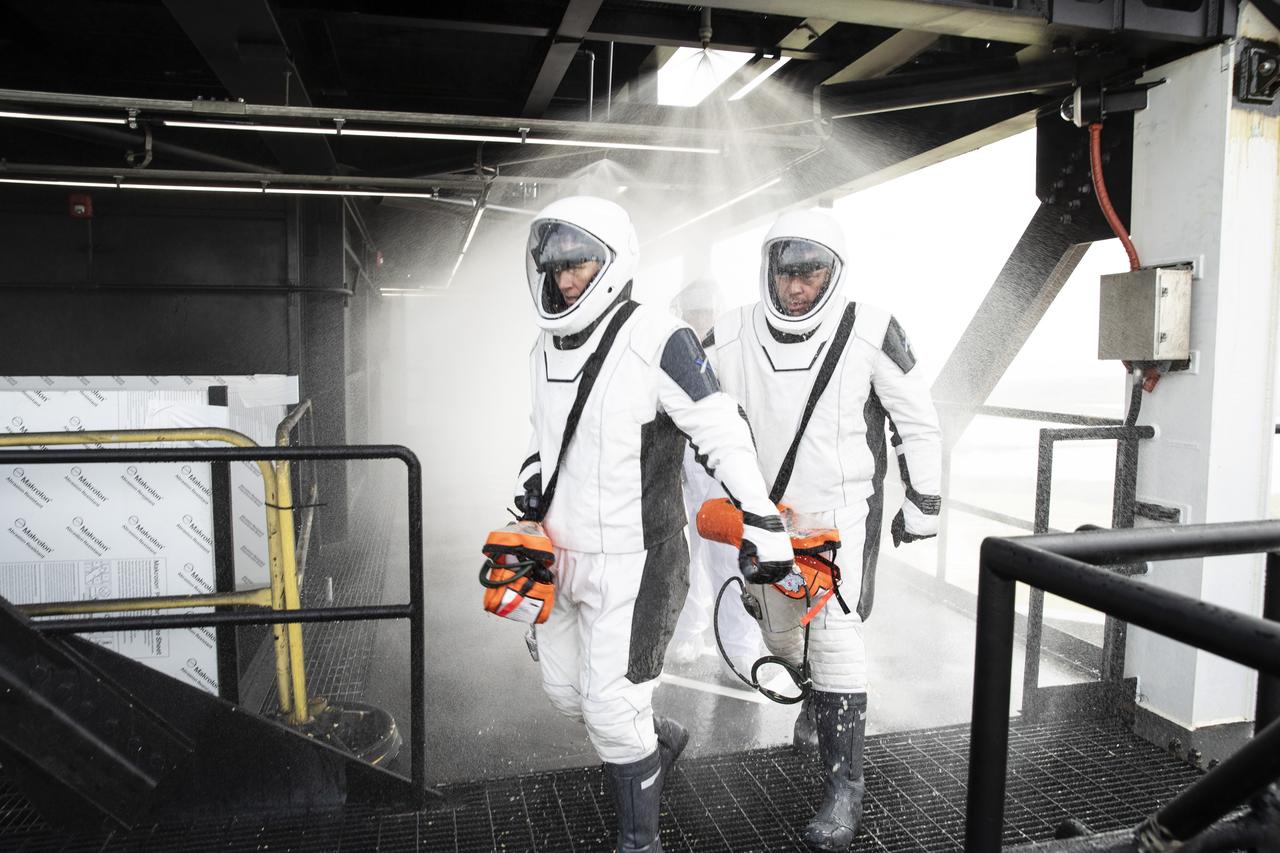

NASA and SpaceX conducted a formal verification of the company’s emergency escape system on Sept. 18, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida. NASA astronauts Shannon Walker, in front, and Bob Behnken participated in the exercise to verify the crew can safely and quickly evacuate from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency before liftoff of SpaceX’s first crewed flight test, called Demo-2. During the escape verification, Walker and Behnken pass through the water deluge system on the 265-foot level of the crew access tower. As Boeing and SpaceX begin to make regular flights to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, the agency will continue to advance its mission to go beyond low-Earth orbit and establish a human presence on the Moon with the ultimate goal of sending astronauts to Mars.
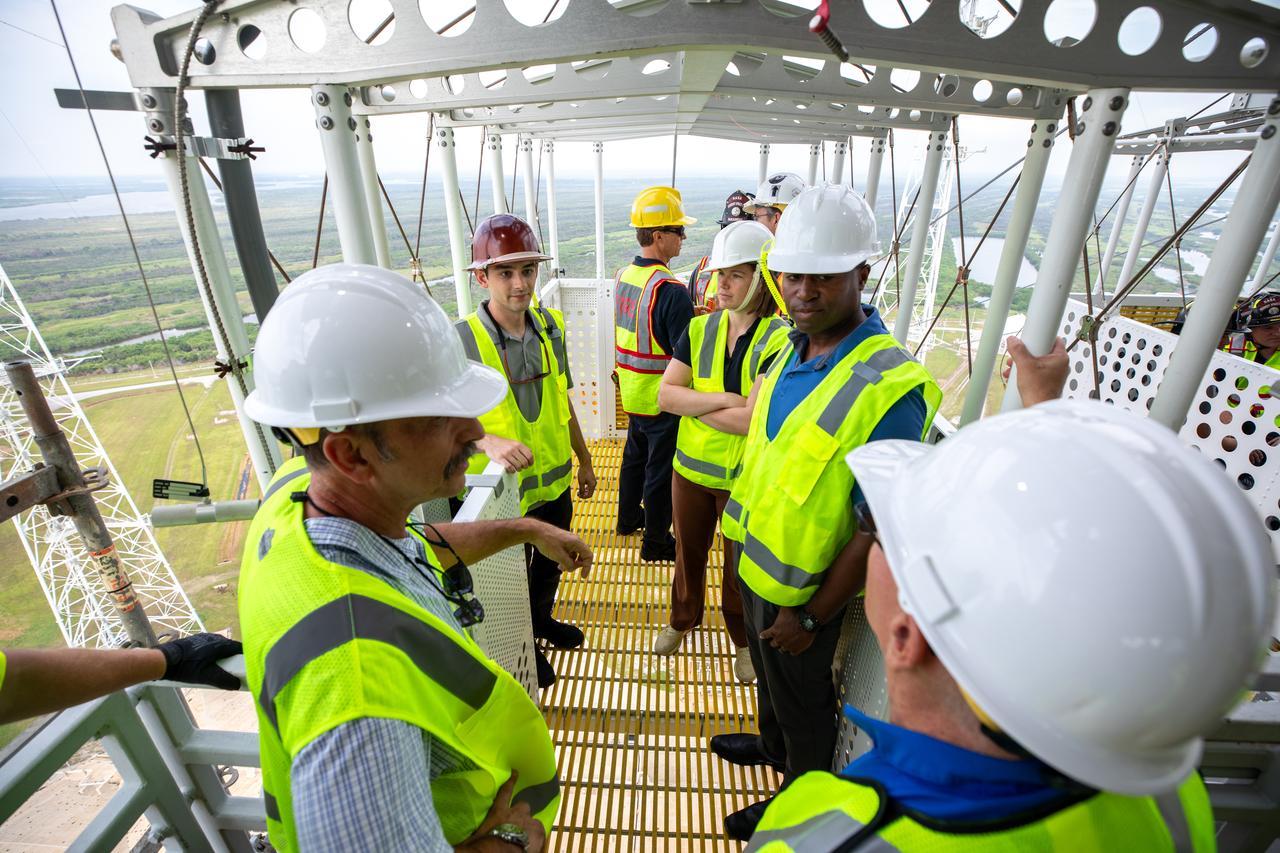

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program, as well as NASA’s pad rescue team, conduct training inside the Artemis emergency egress baskets at Launch Pad 39B as part of the Artemis emergency egress demonstration training at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 8, 2024. The baskets, similar to gondolas on ski lifts, are used in the case of a pad abort emergency to enable astronauts and other pad personnel a way to quickly escape away from the mobile launcher to the base of the pad and where waiting emergency transport vehicles will then drive them away.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program, as well as NASA’s pad rescue team, conduct training inside the Artemis emergency egress baskets at Launch Pad 39B as part of the Artemis emergency egress demonstration training at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 8, 2024. The baskets, similar to gondolas on ski lifts, are used in the case of a pad abort emergency to enable astronauts and other pad personnel a way to quickly escape away from the mobile launcher to the base of the pad and where waiting emergency transport vehicles will then drive them away.
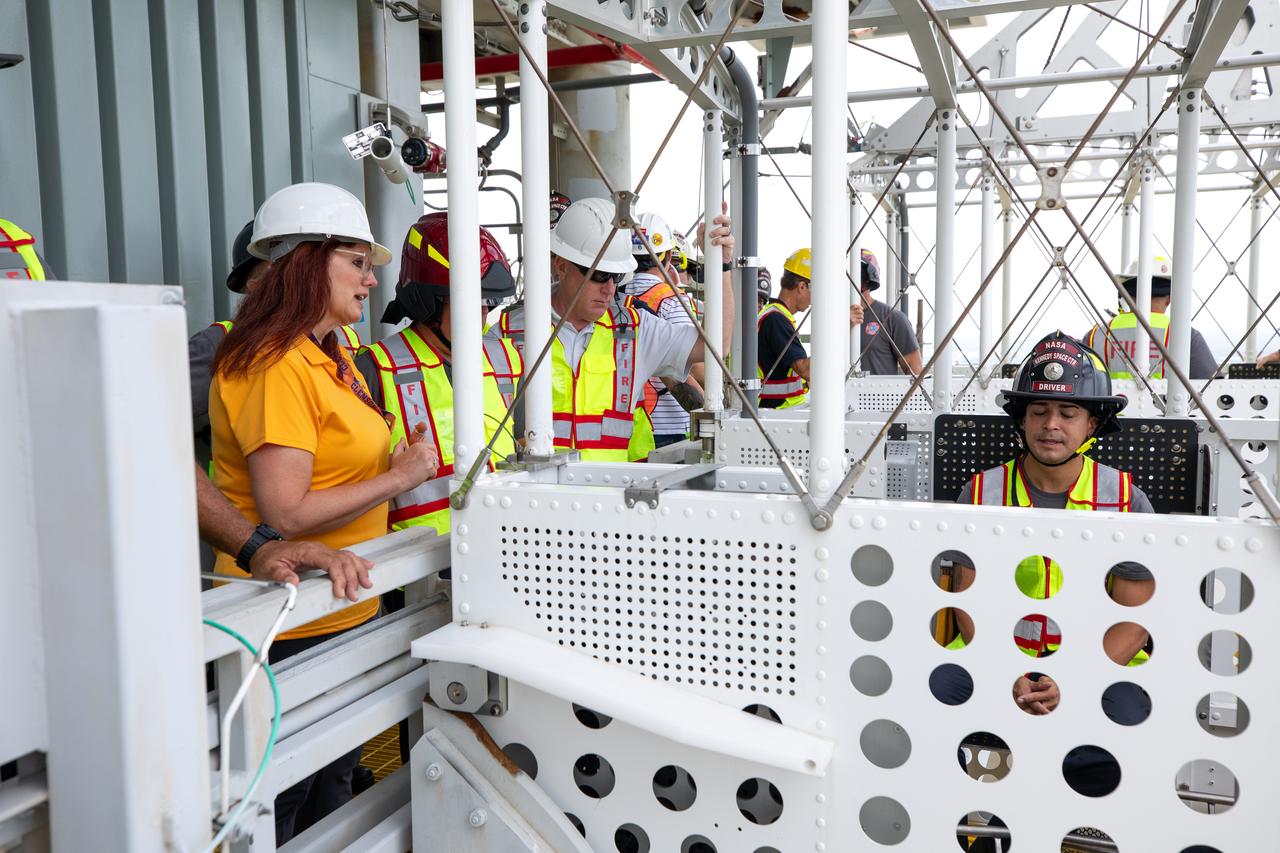

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program, as well as NASA’s pad rescue team, conduct training inside the Artemis emergency egress baskets at Launch Pad 39B as part of the Artemis emergency egress demonstration training at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 8, 2024. The baskets, similar to gondolas on ski lifts, are used in the case of a pad abort emergency to enable astronauts and other pad personnel a way to quickly escape away from the mobile launcher to the base of the pad and where waiting emergency transport vehicles will then drive them away.
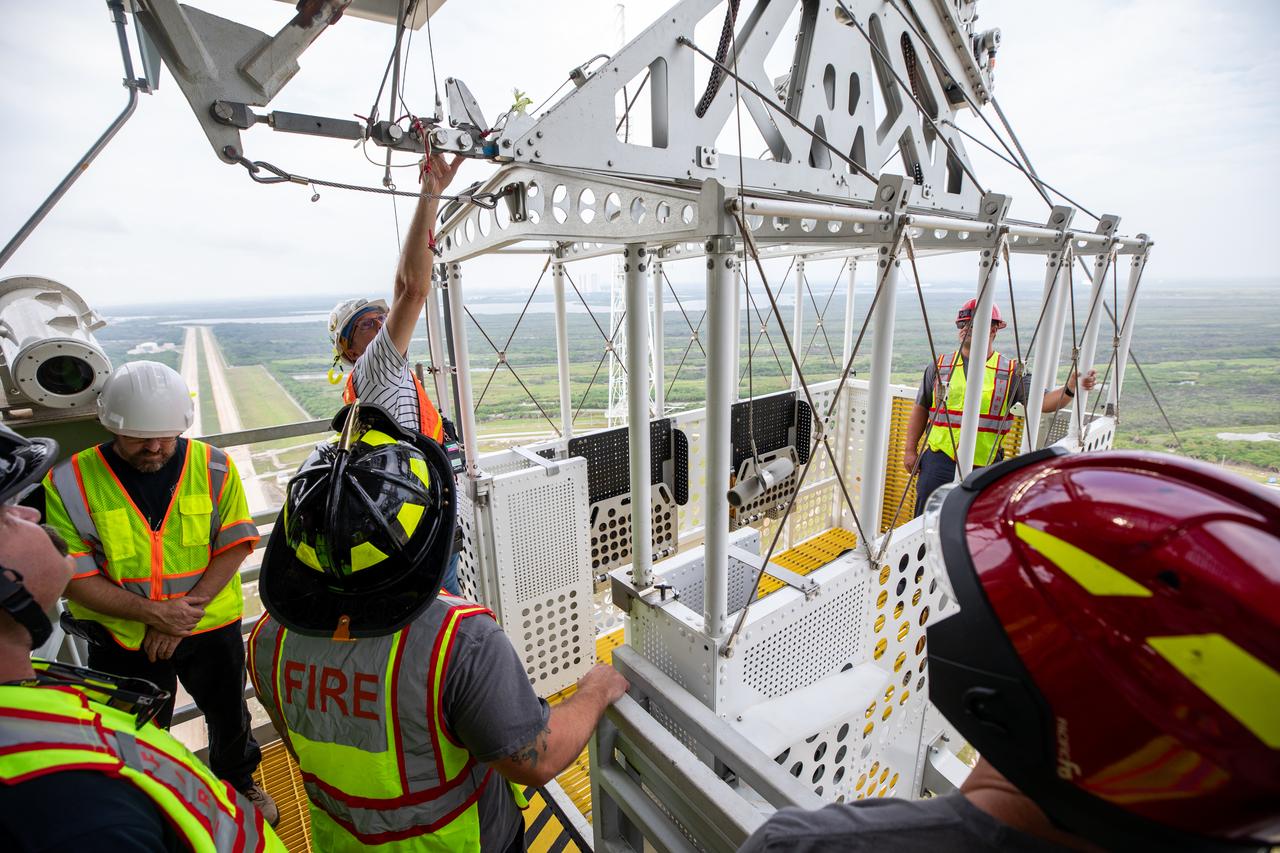

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program, as well as NASA’s pad rescue team, conduct training inside the Artemis emergency egress baskets at Launch Pad 39B as part of the Artemis emergency egress demonstration training at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 8, 2024. The baskets, similar to gondolas on ski lifts, are used in the case of a pad abort emergency to enable astronauts and other pad personnel a way to quickly escape away from the mobile launcher to the base of the pad and where waiting emergency transport vehicles will then drive them away.
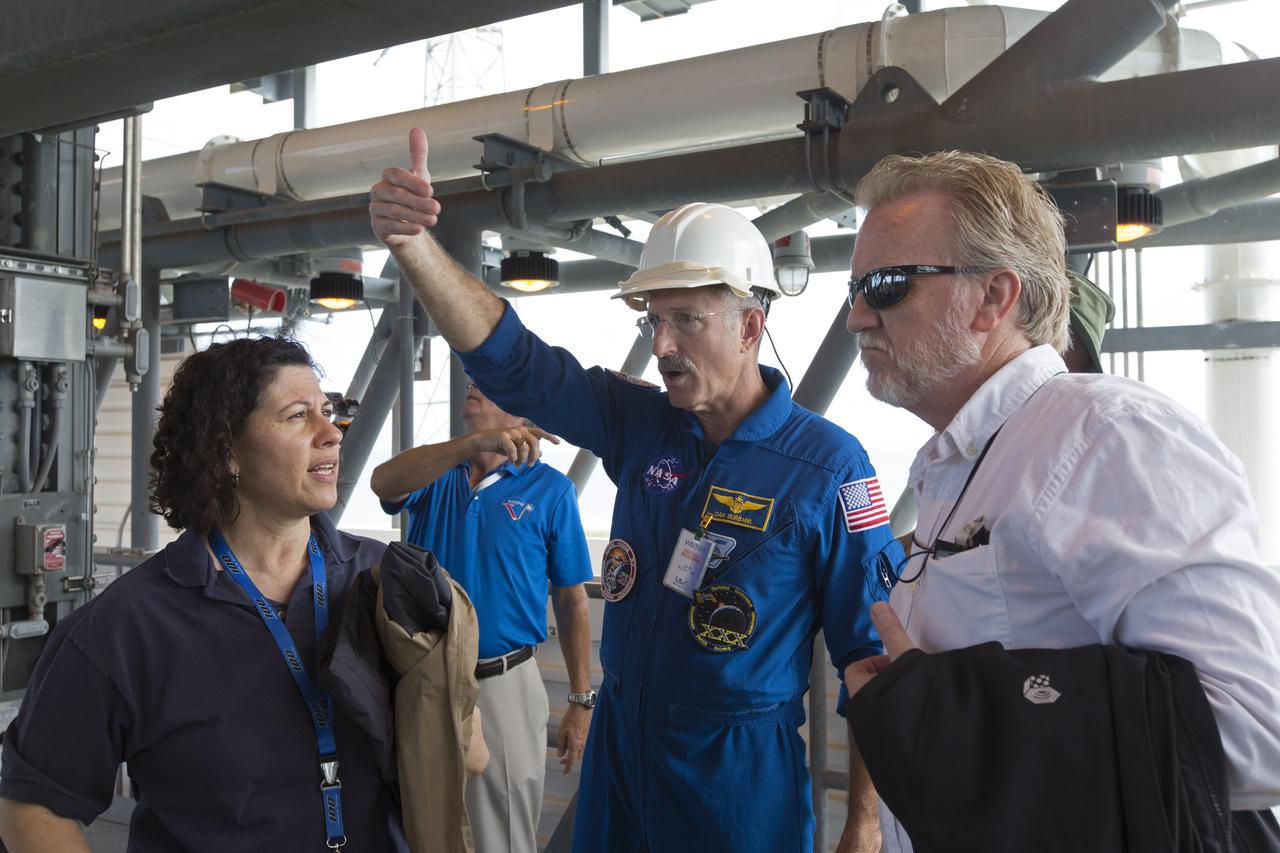

NASA, Boeing and United Launch Alliance personnel discuss procedures for an upcoming water deluge test on the Crew Access Tower at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The test gathered data on how launch site and astronaut crews would exit in the event of an emergency from the white room at the end of the crew access arm to the emergency escape system on the pad. Boeing’s Starliner will launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
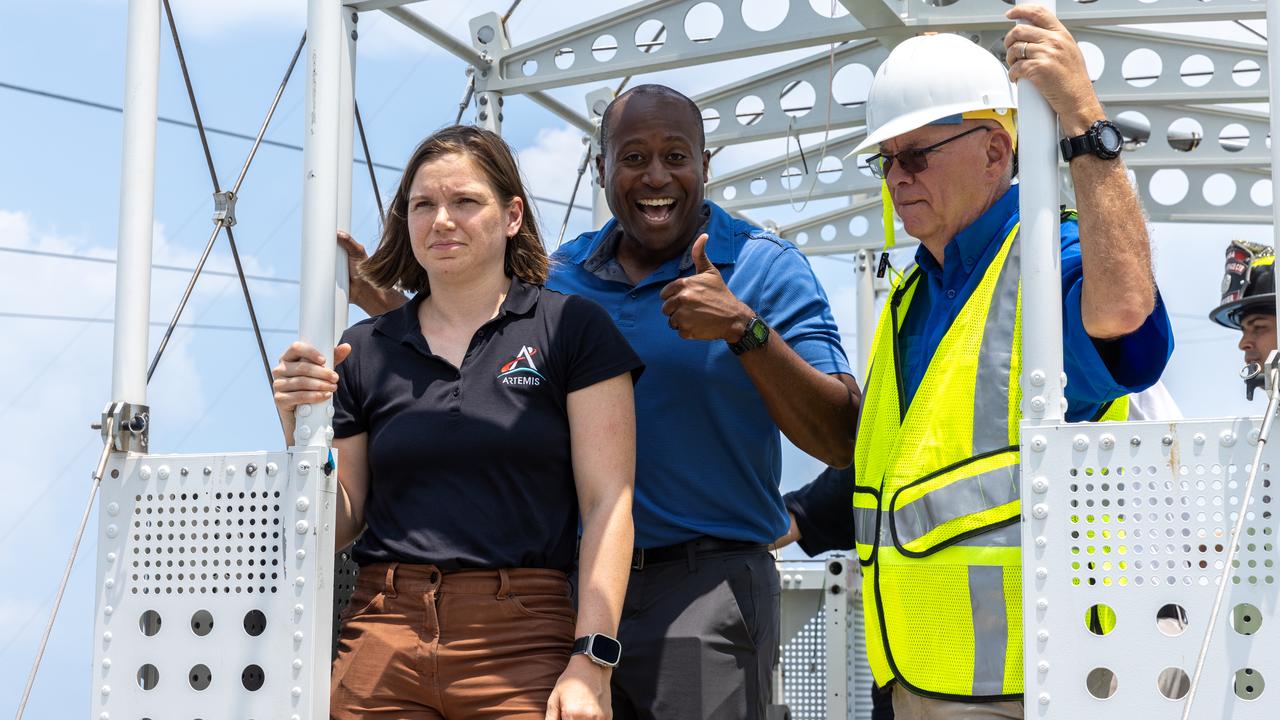

Artemis II backup crew members, CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jenni Gibbons and NASA astronaut Andre Douglas participate in one of a series of integrated system verification and validation tests inside the emergency egress baskets at Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 8, 2024. The baskets, similar to gondolas on ski lifts, are used in the case of a pad abort emergency to enable astronauts and other pad personnel a way to quickly escape away from the mobile launcher to the base of the pad and where waiting emergency transport vehicles will then drive them away.
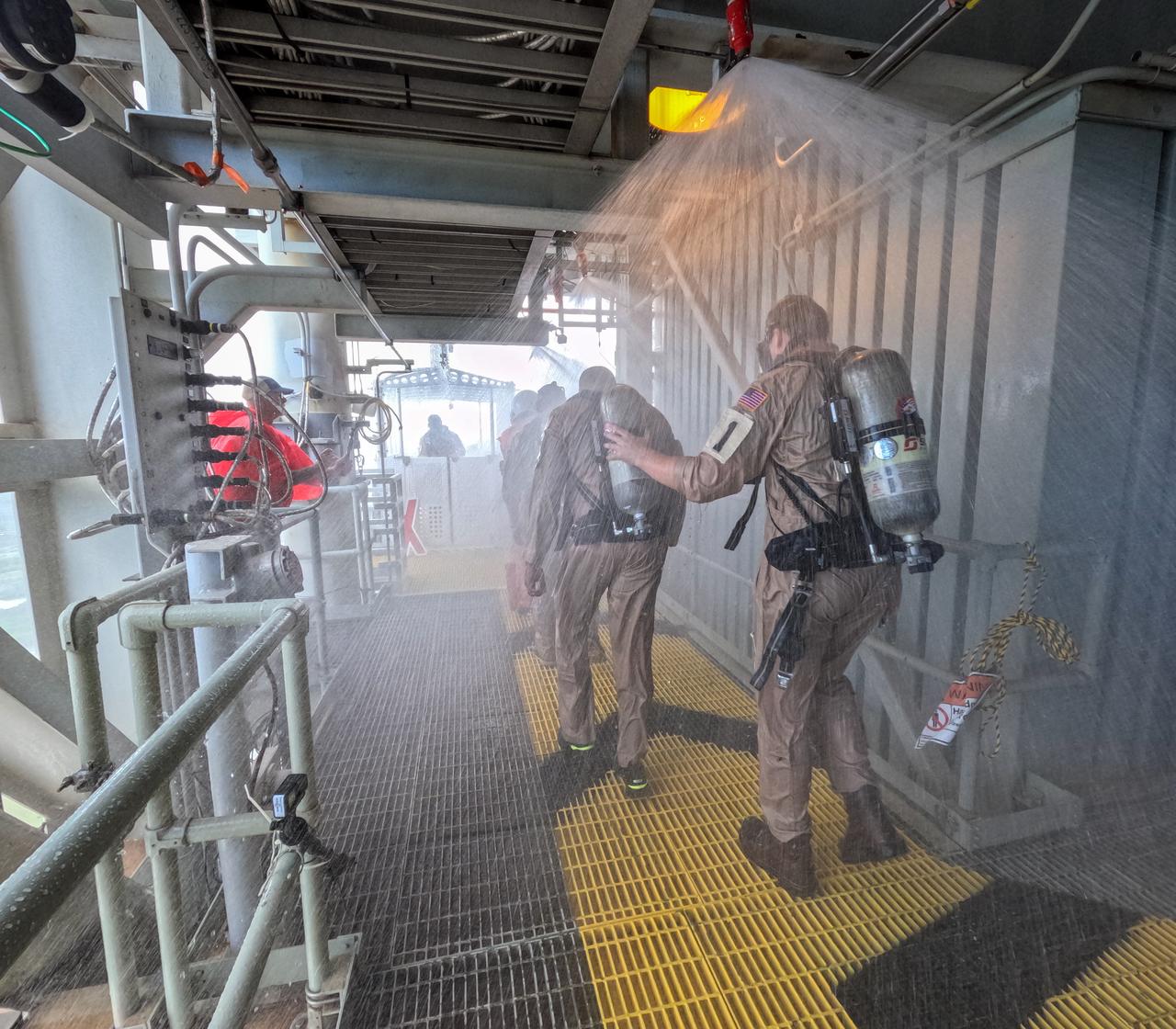

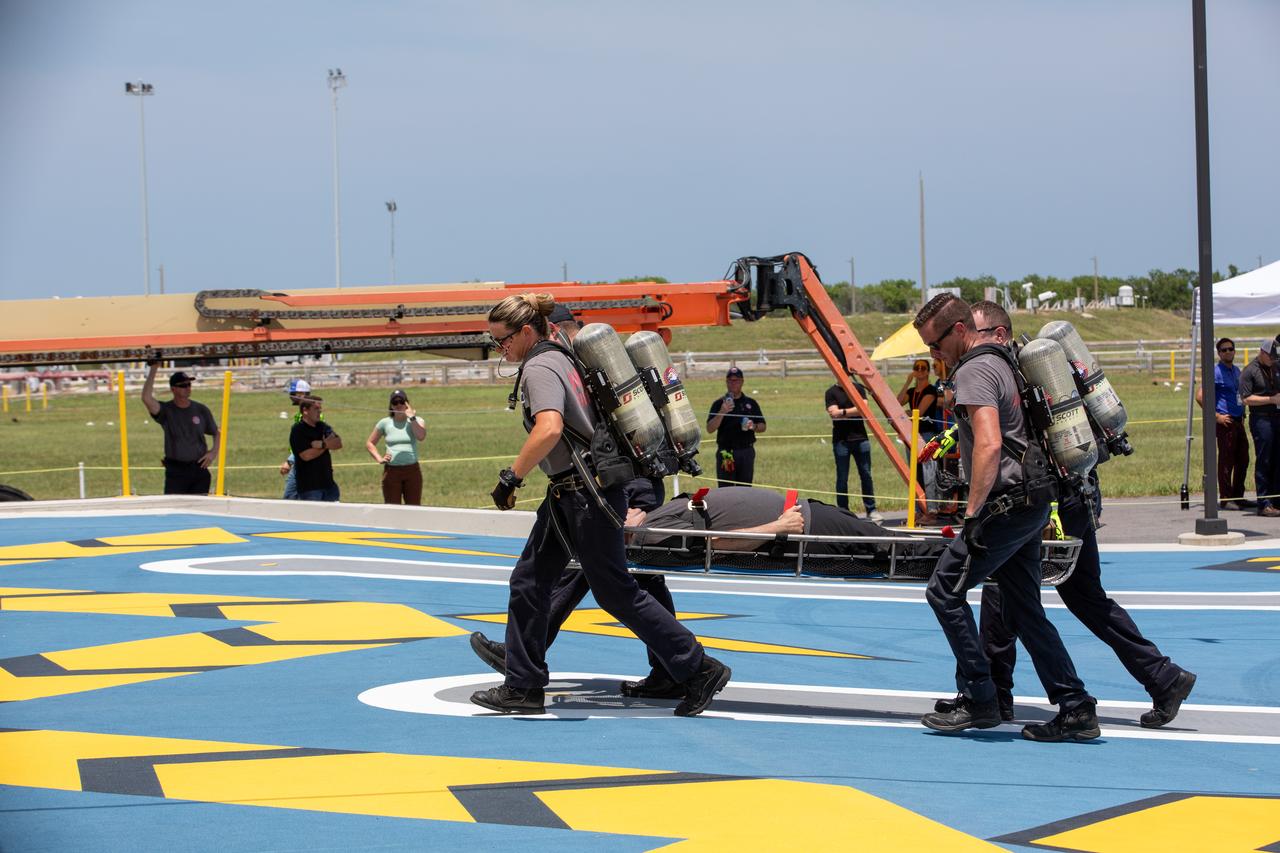
Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
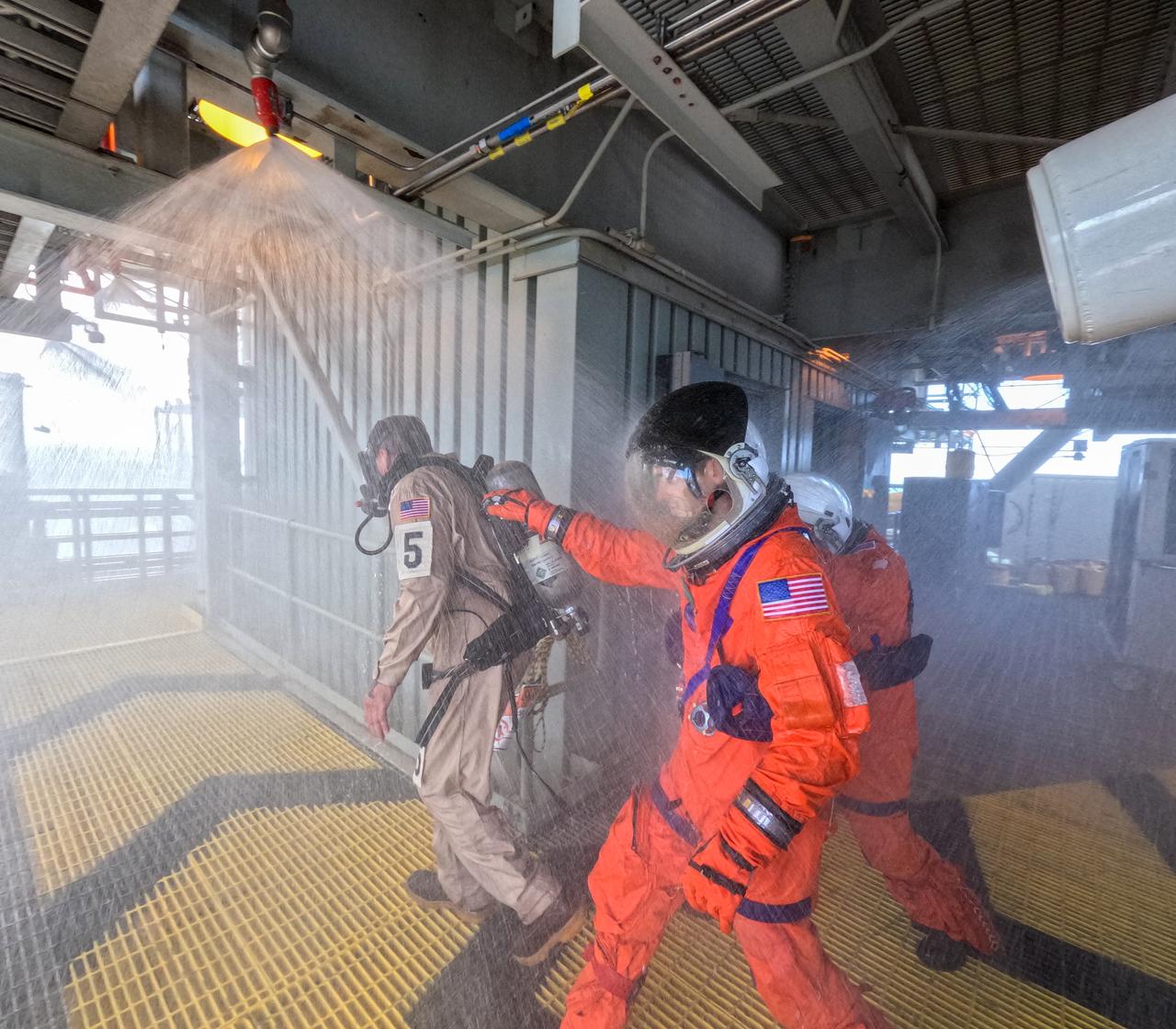

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
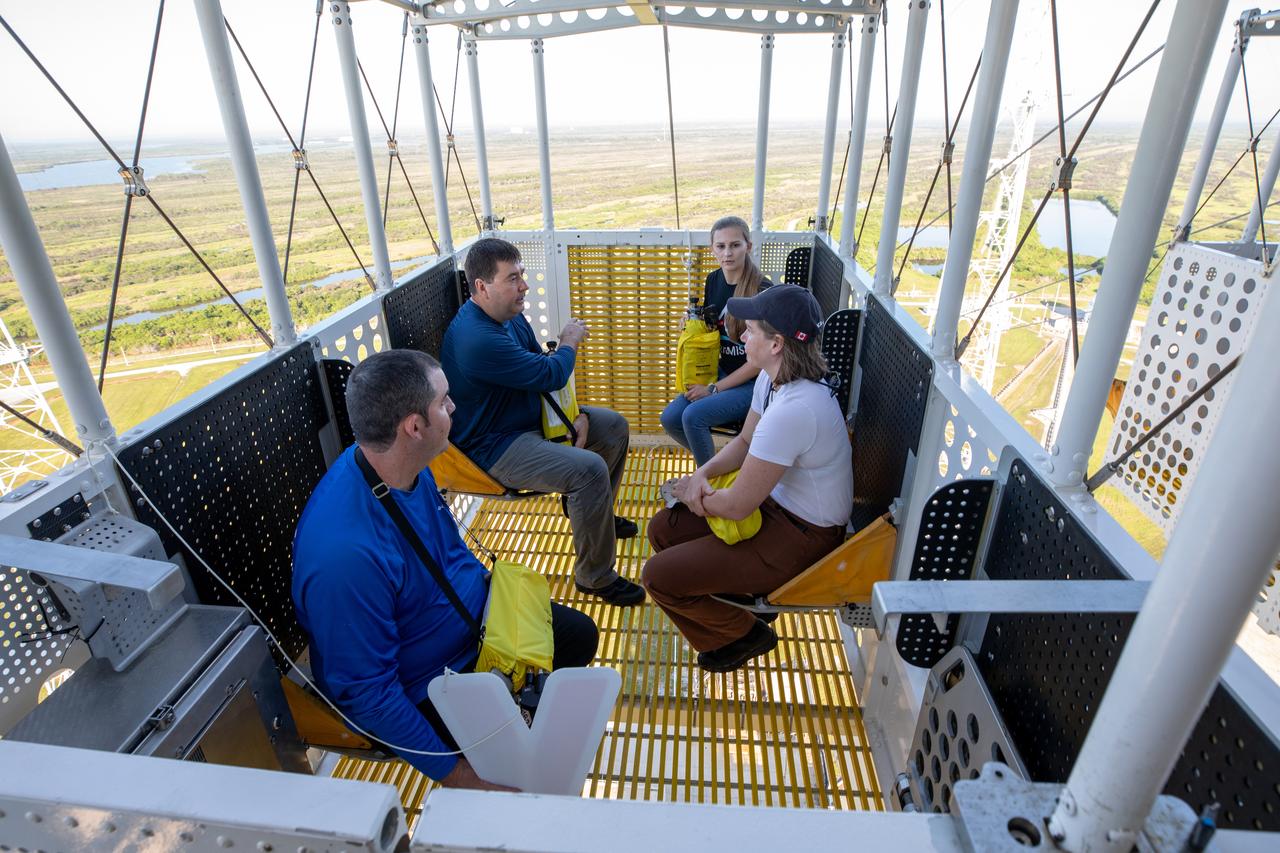

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
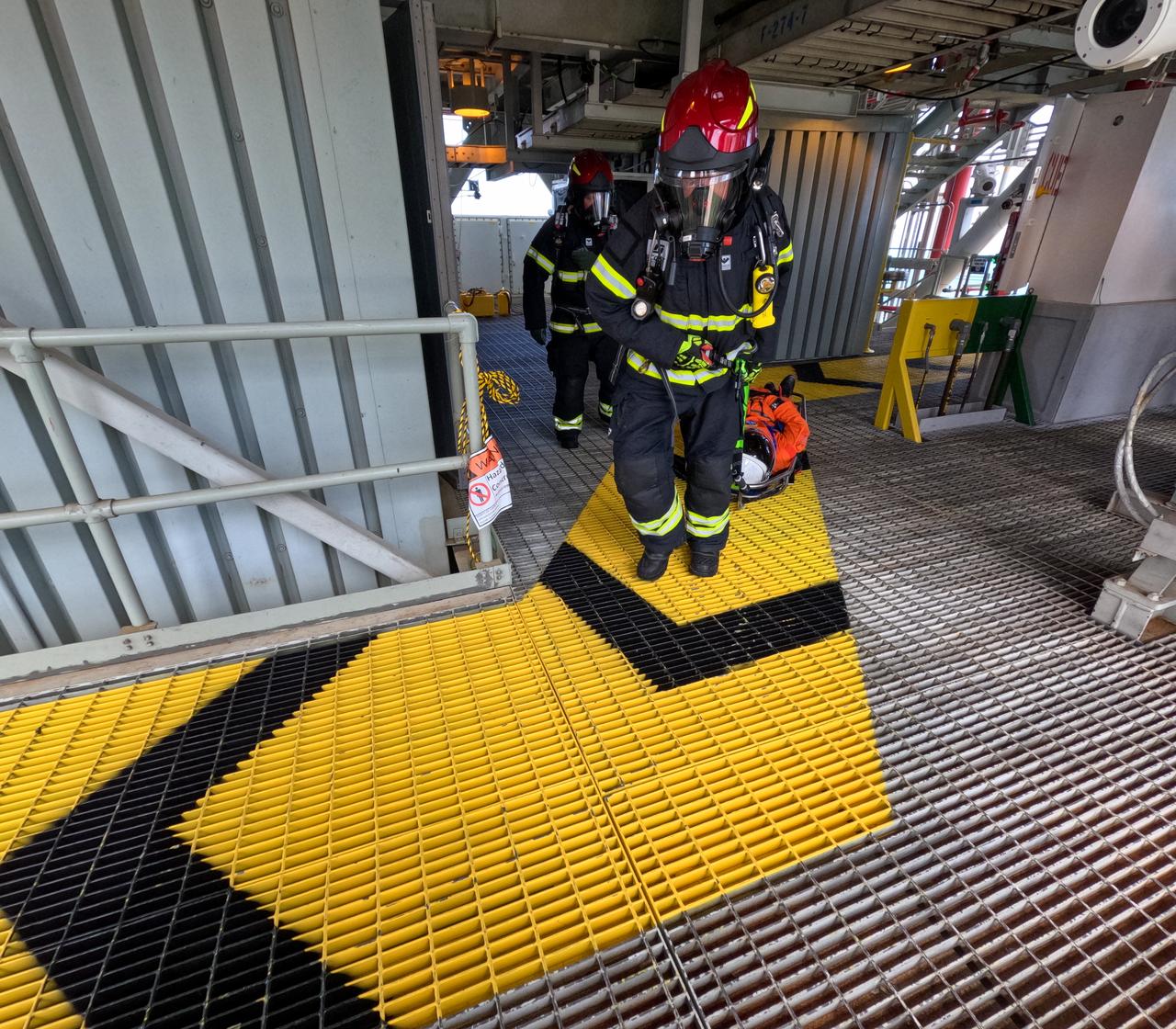

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
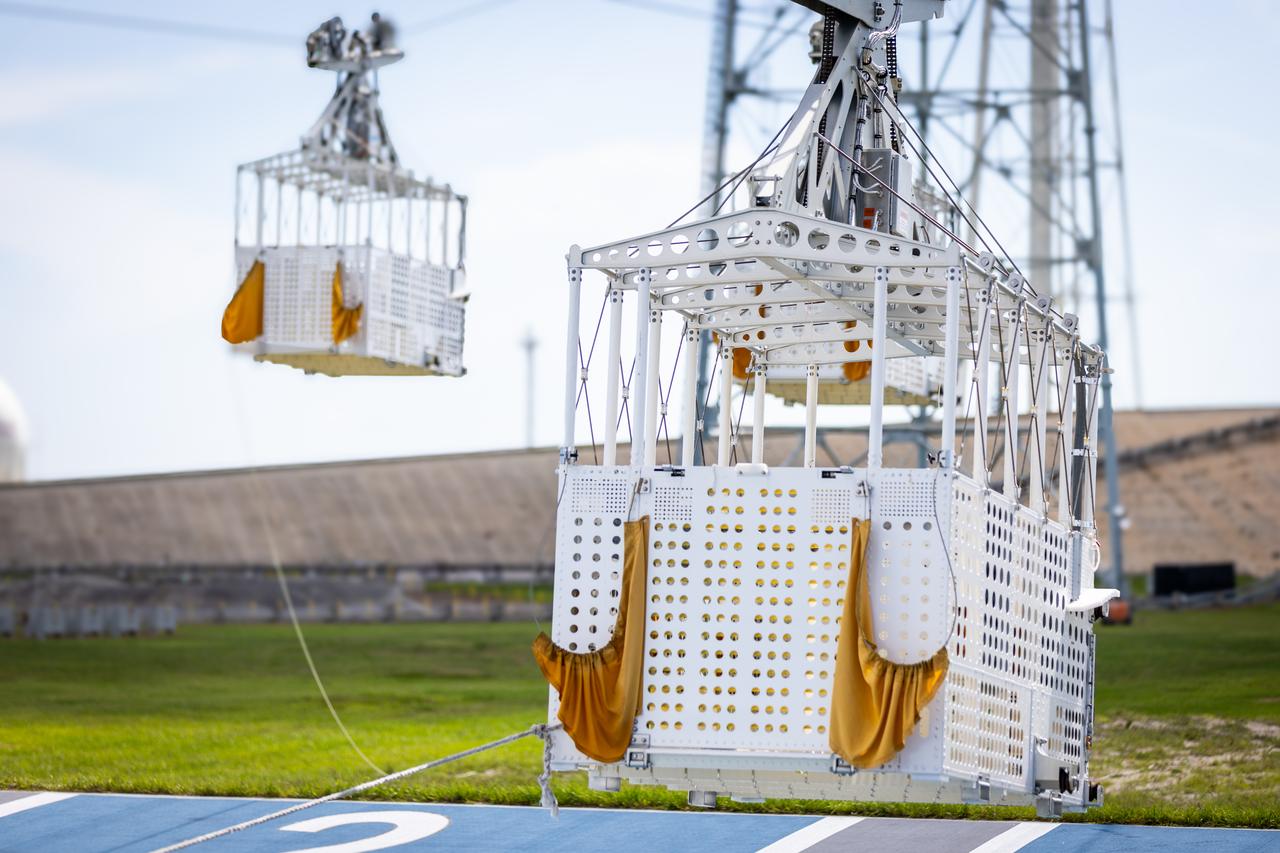

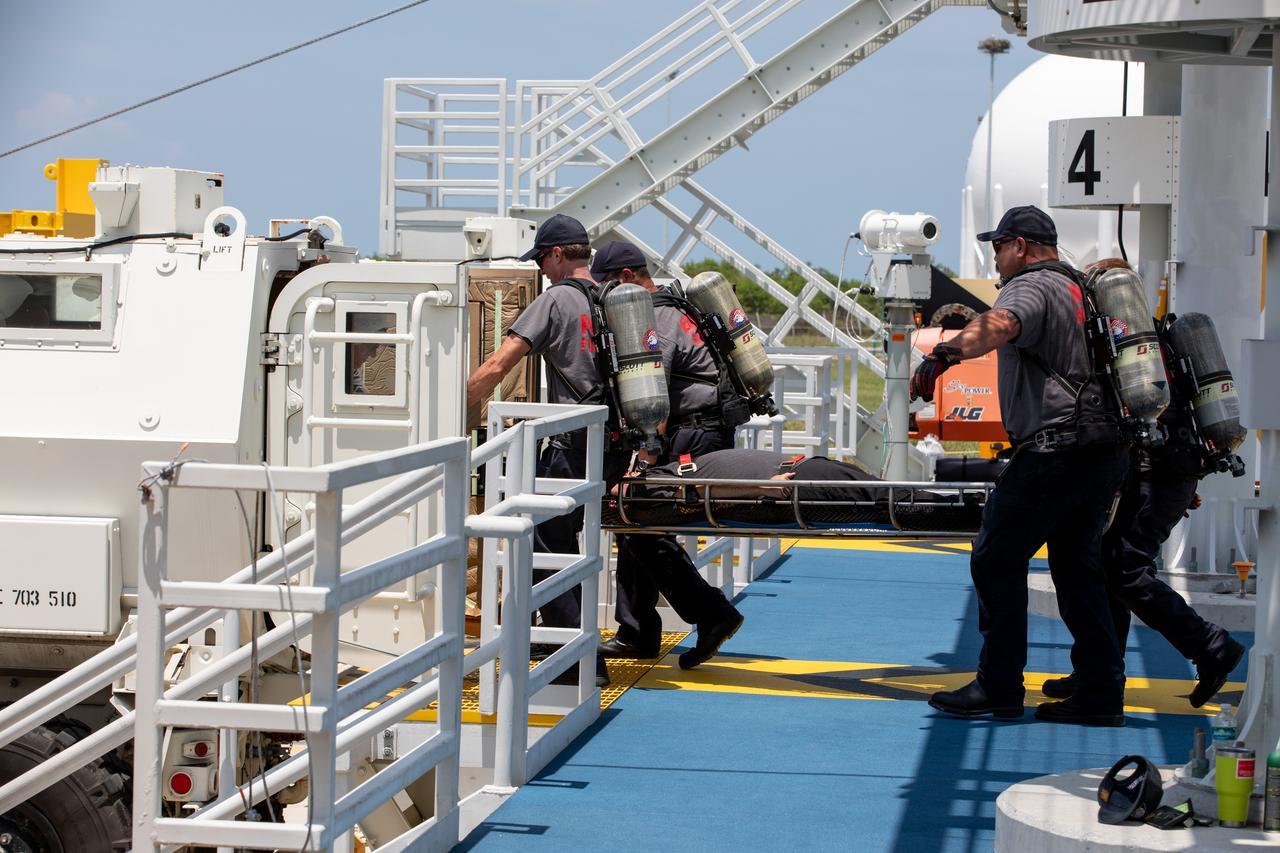
Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
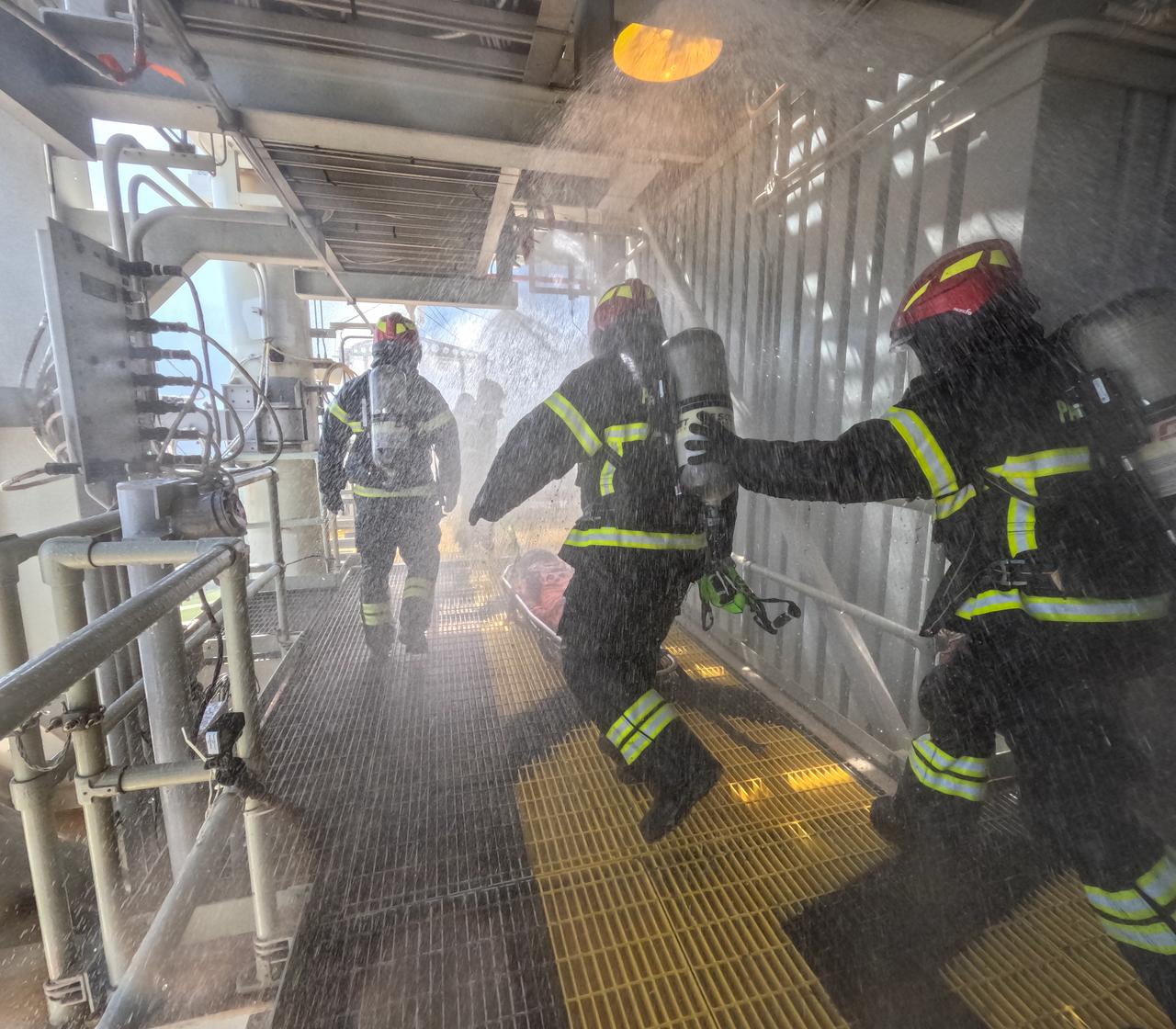

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
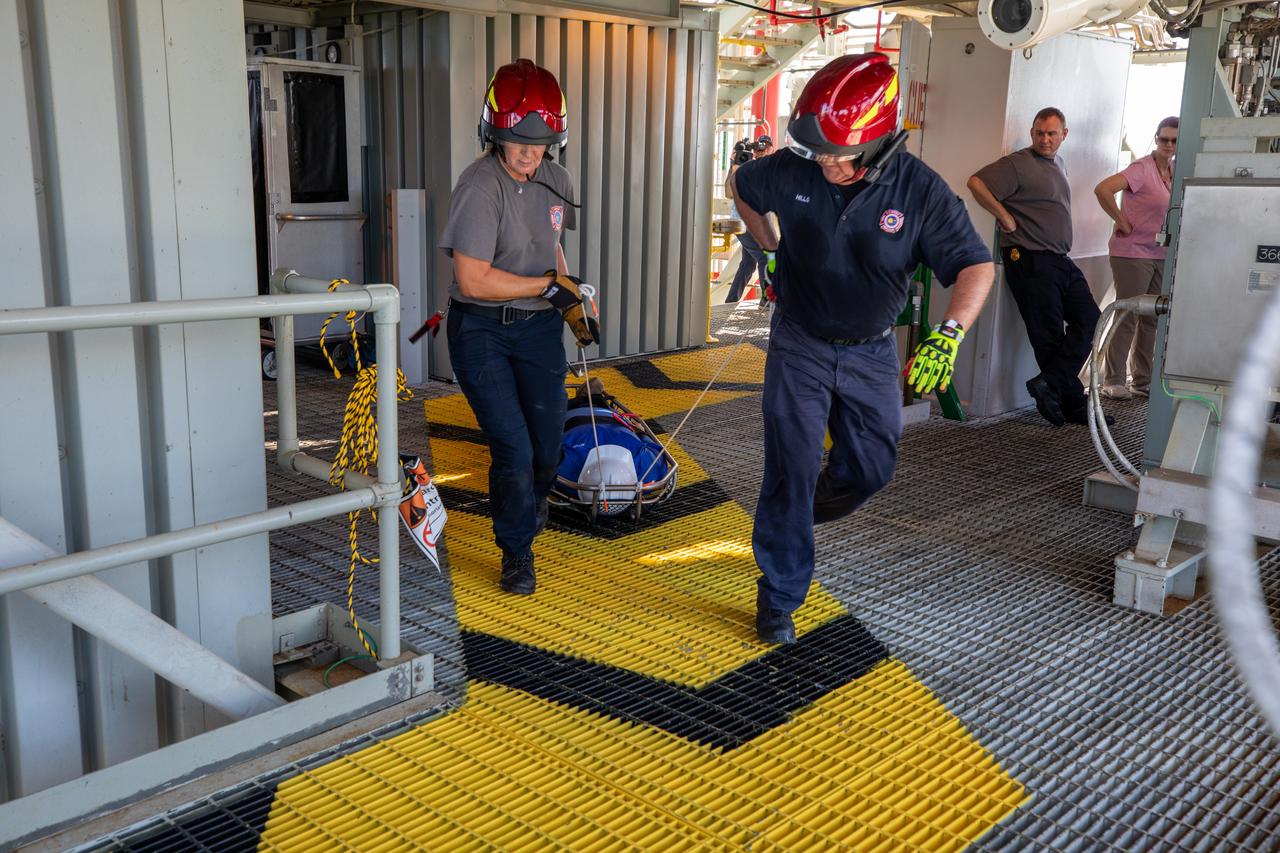

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
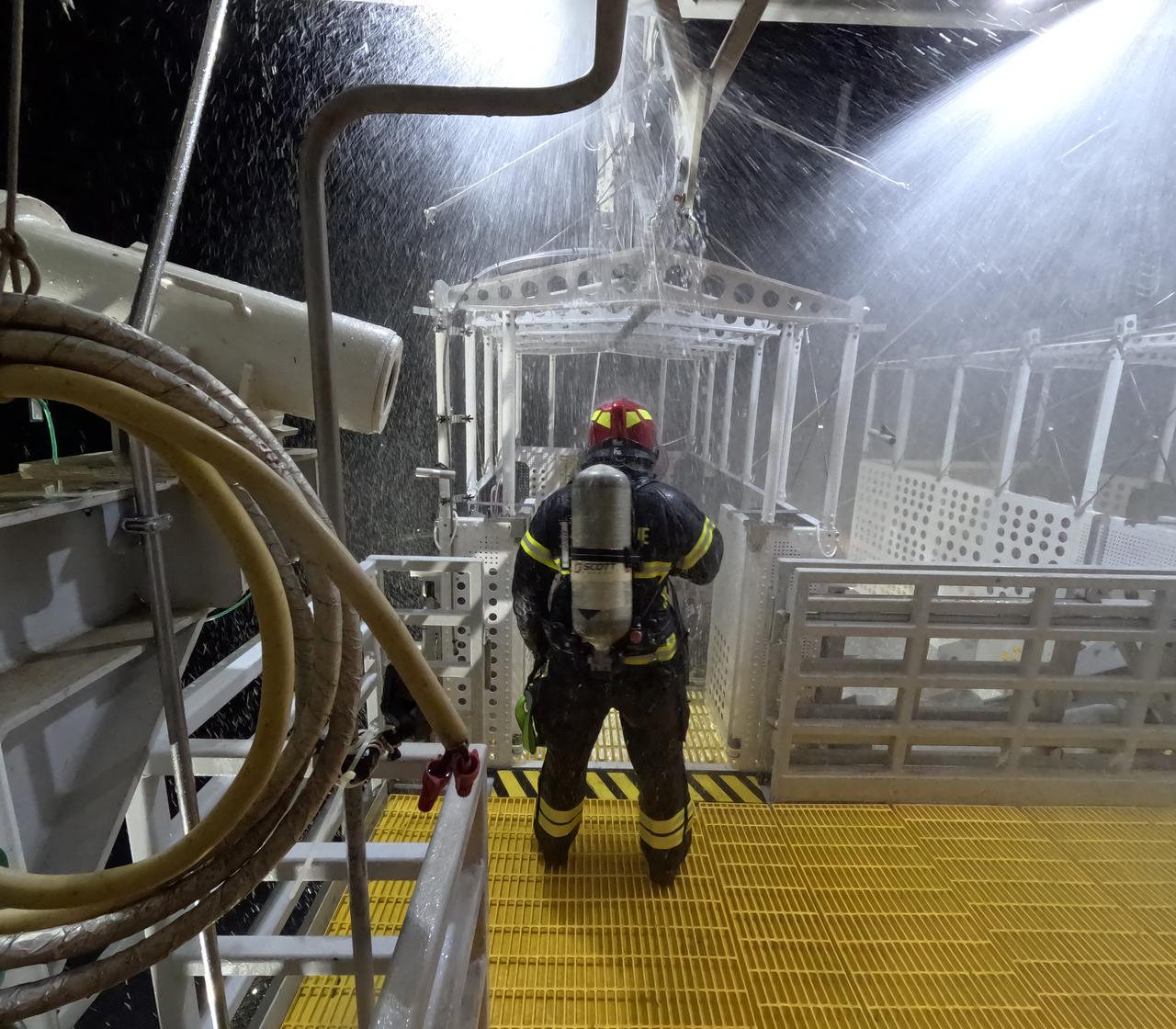

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Tuesday, Aug. 13, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program – who also suited up as astronauts – practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
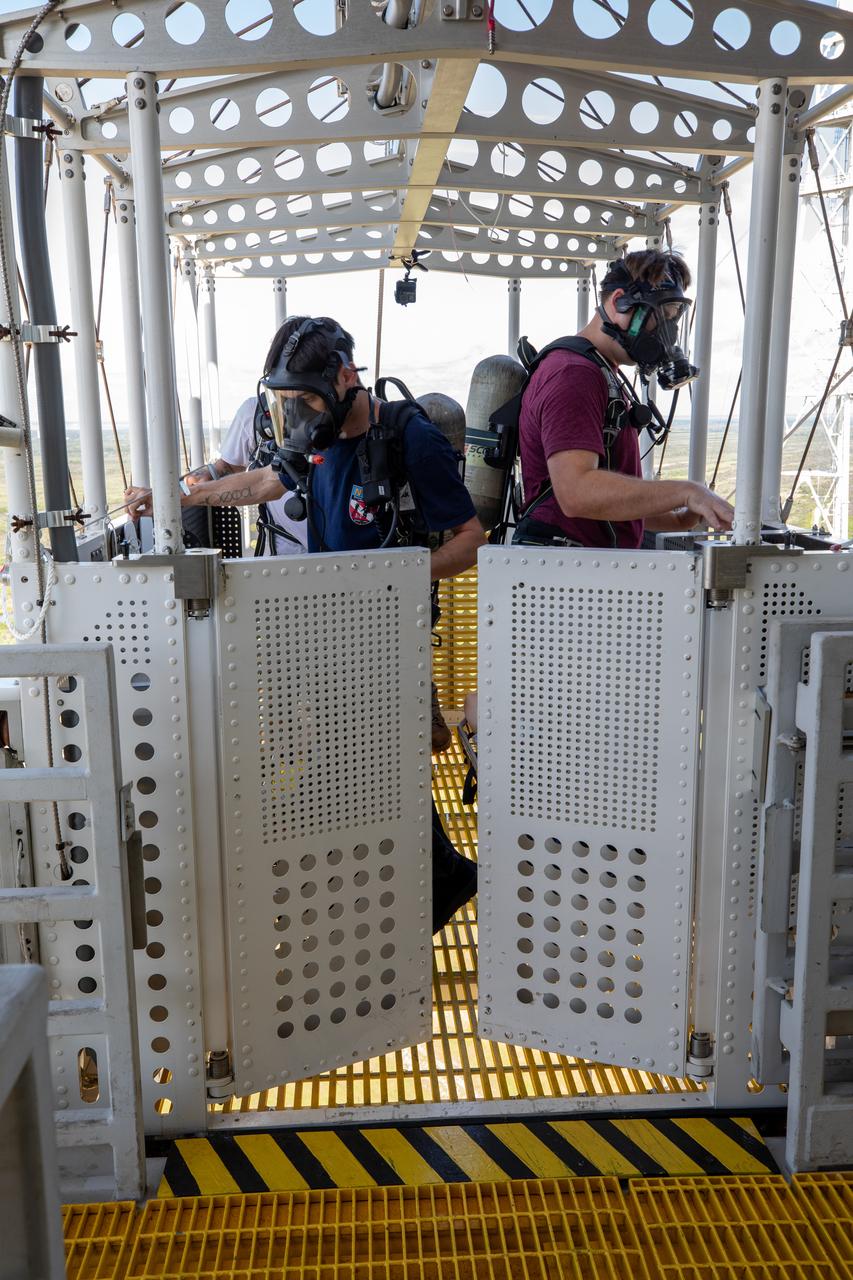

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
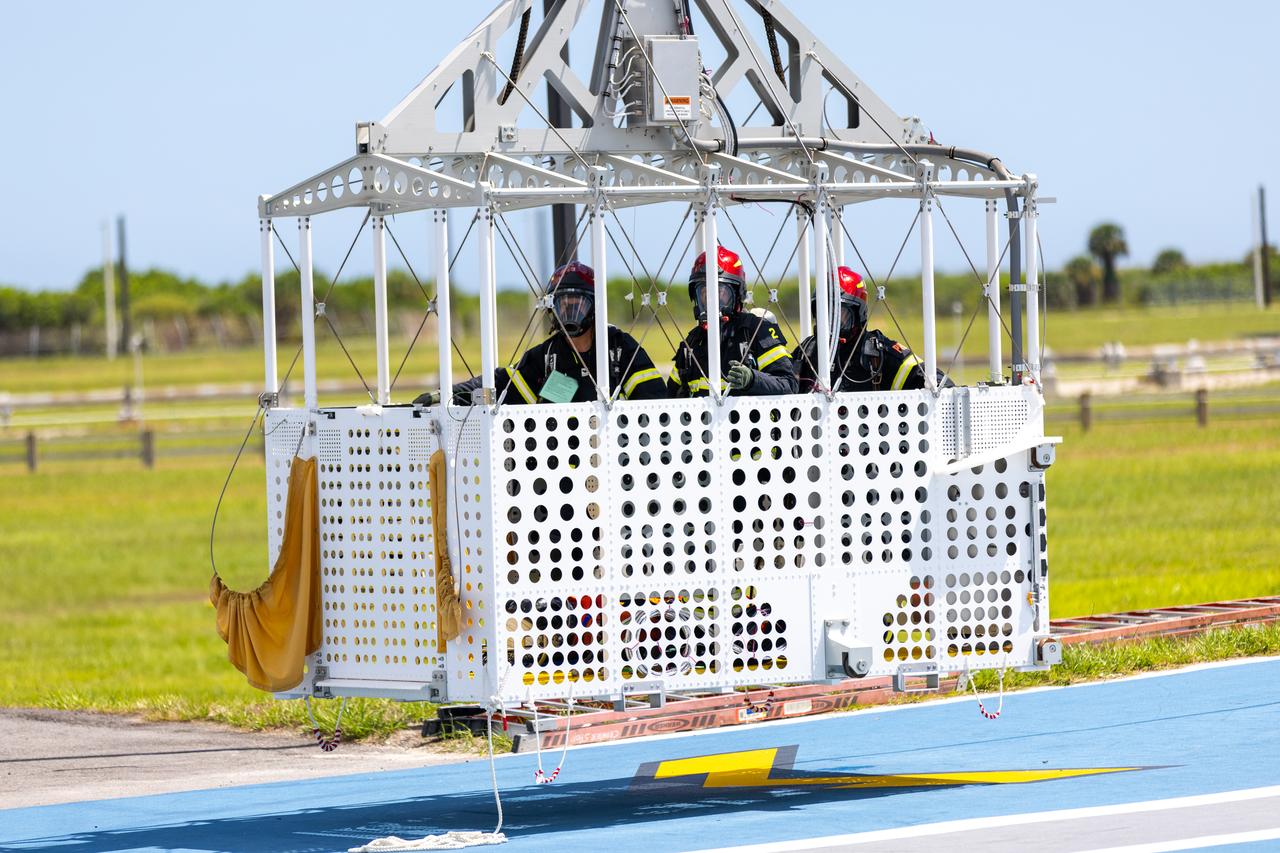

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
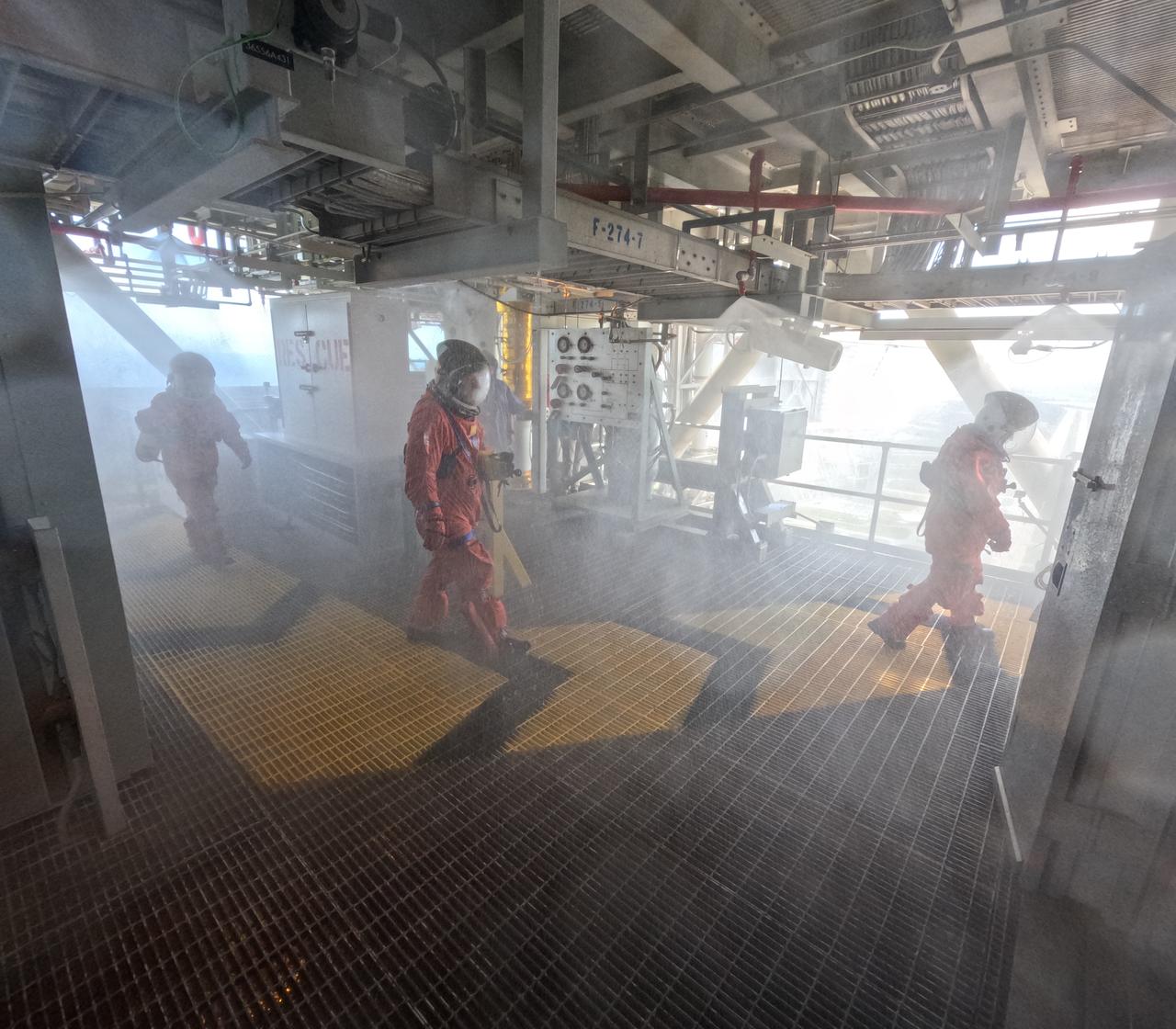

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
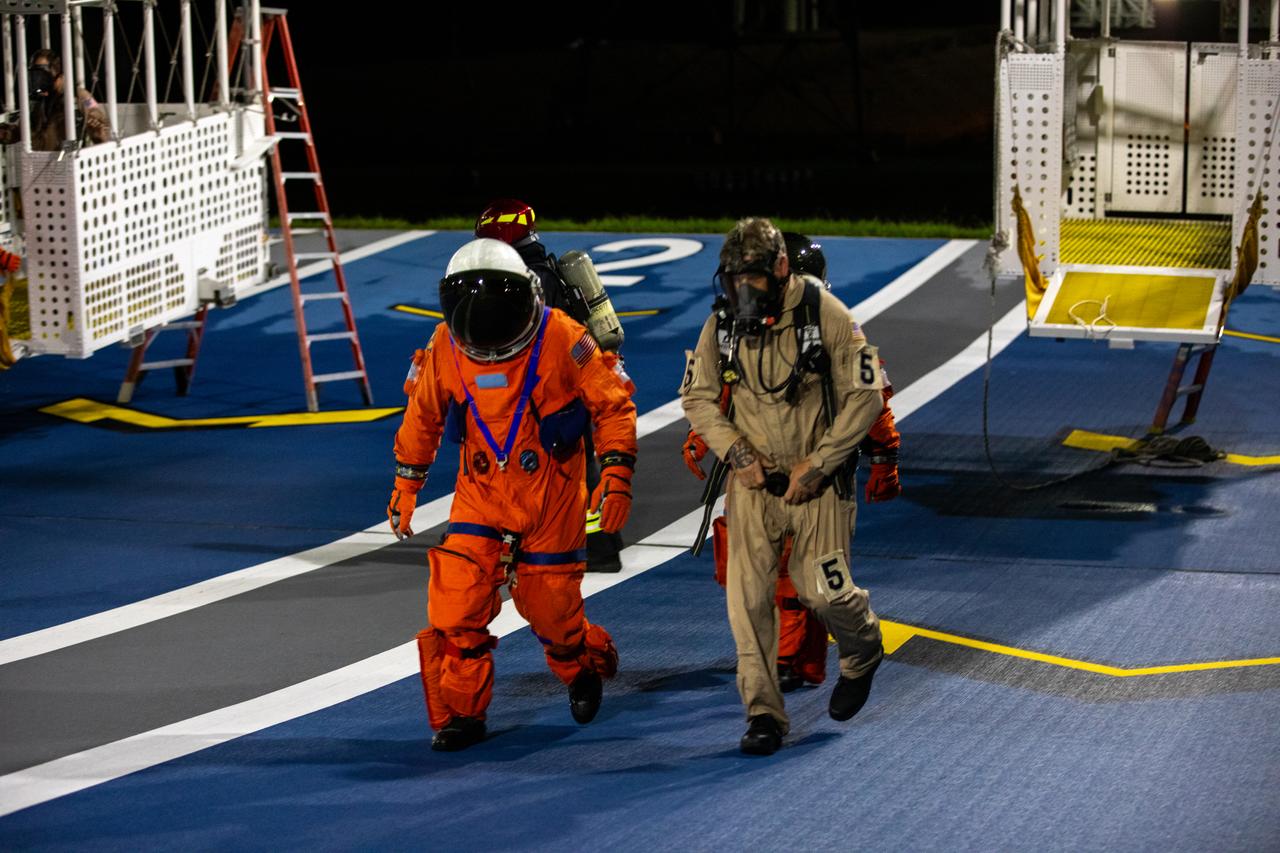

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Tuesday, Aug. 13, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
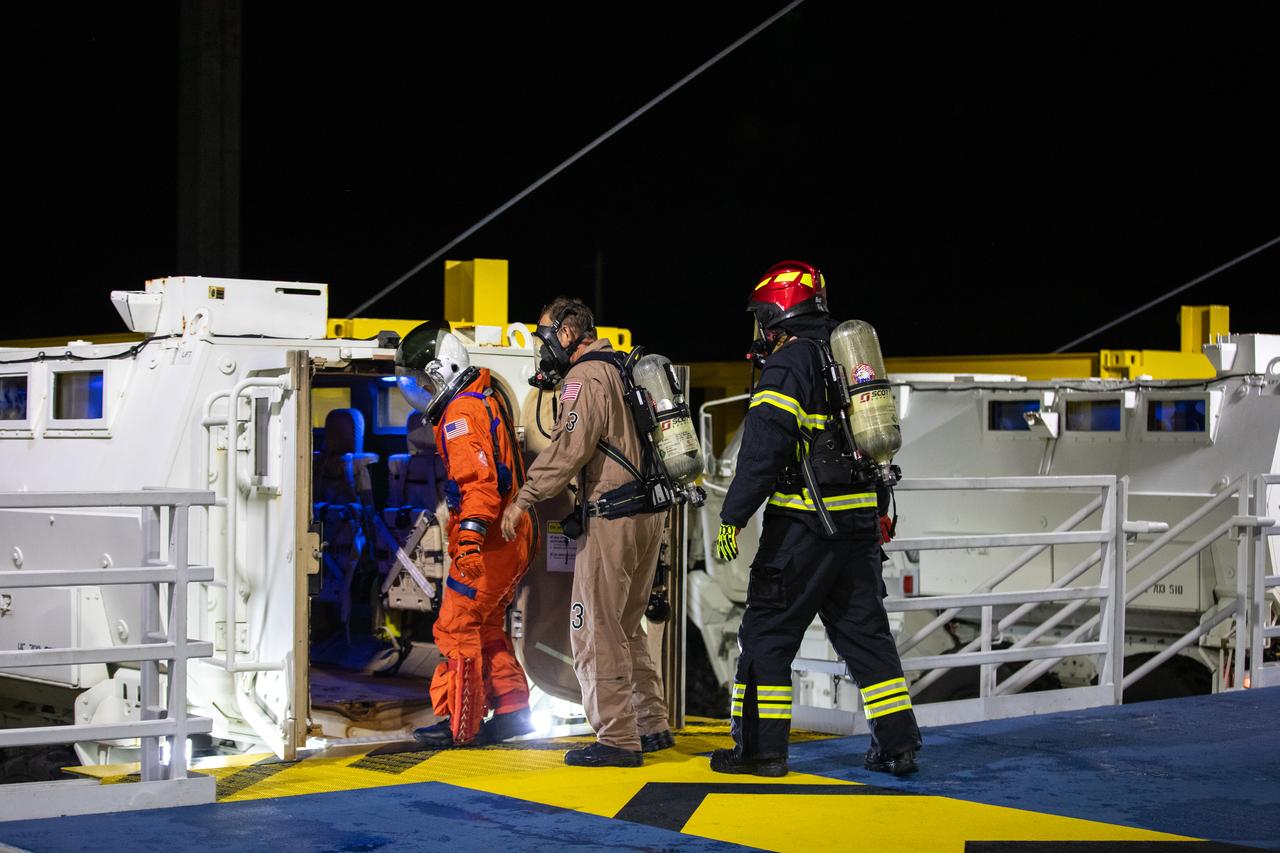

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Tuesday, Aug. 13, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
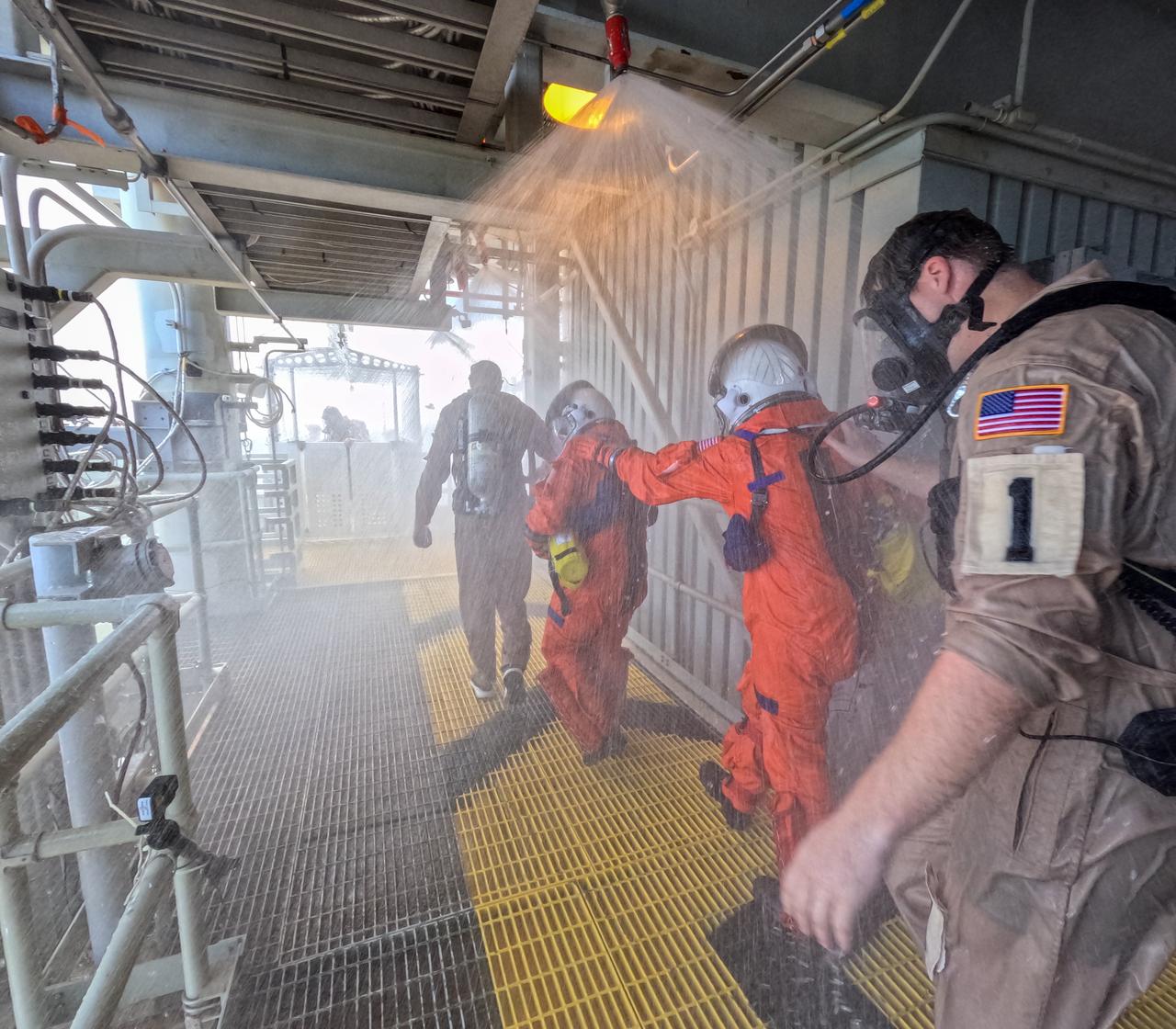

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
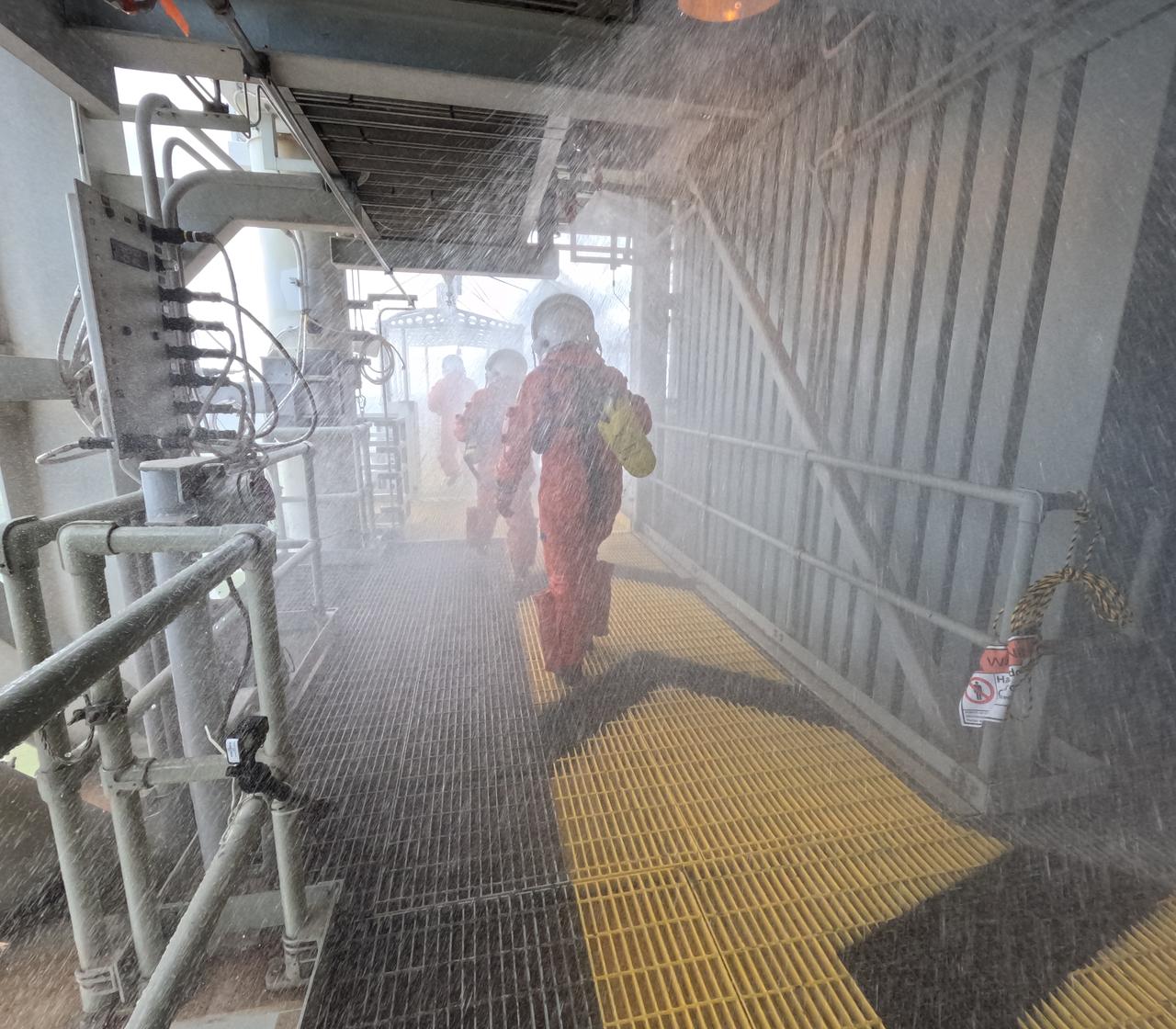

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
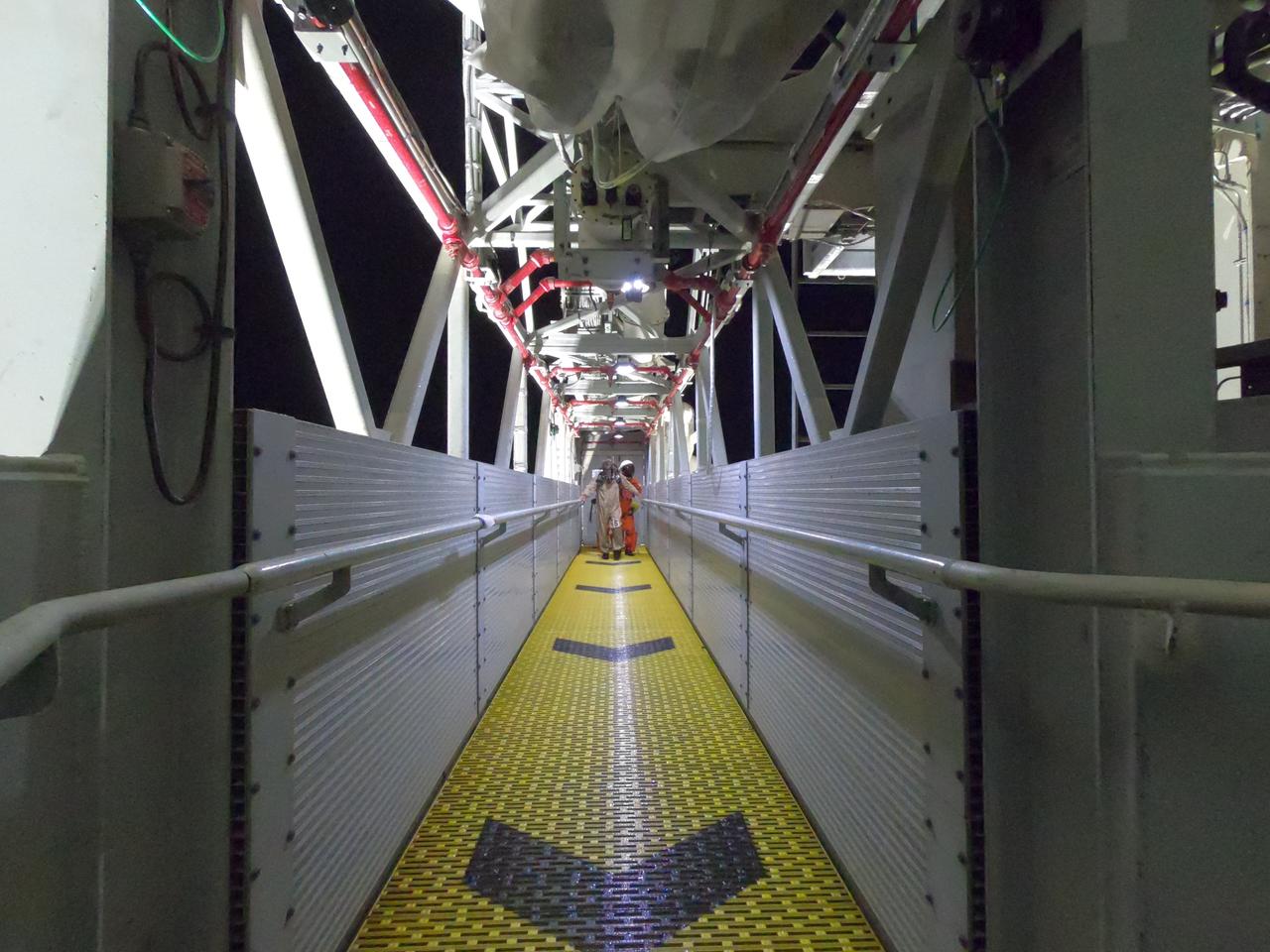

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Tuesday, Aug. 13, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program – who also suited up as astronauts – practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
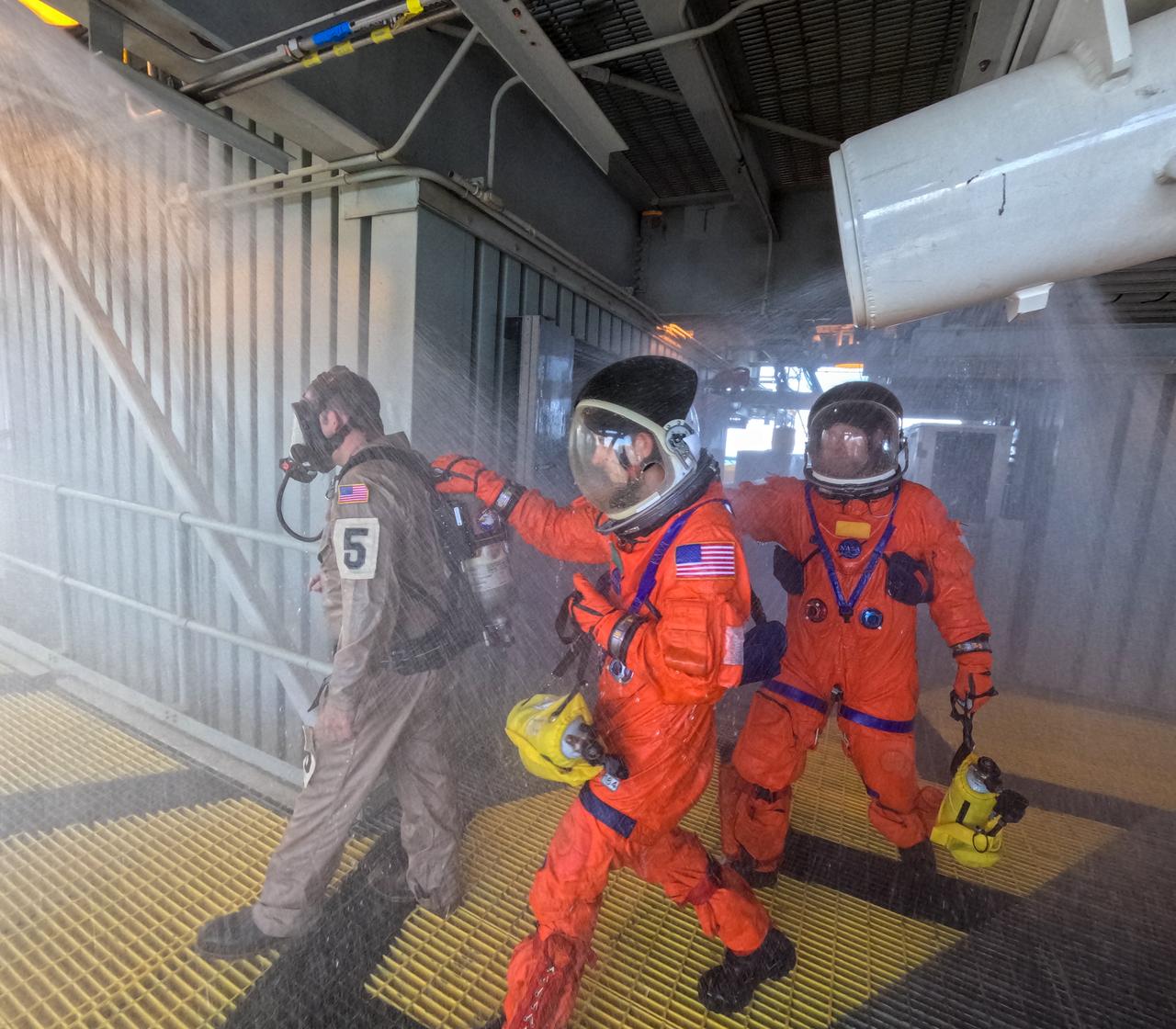

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, simulated flight crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Sunday, Aug. 11, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
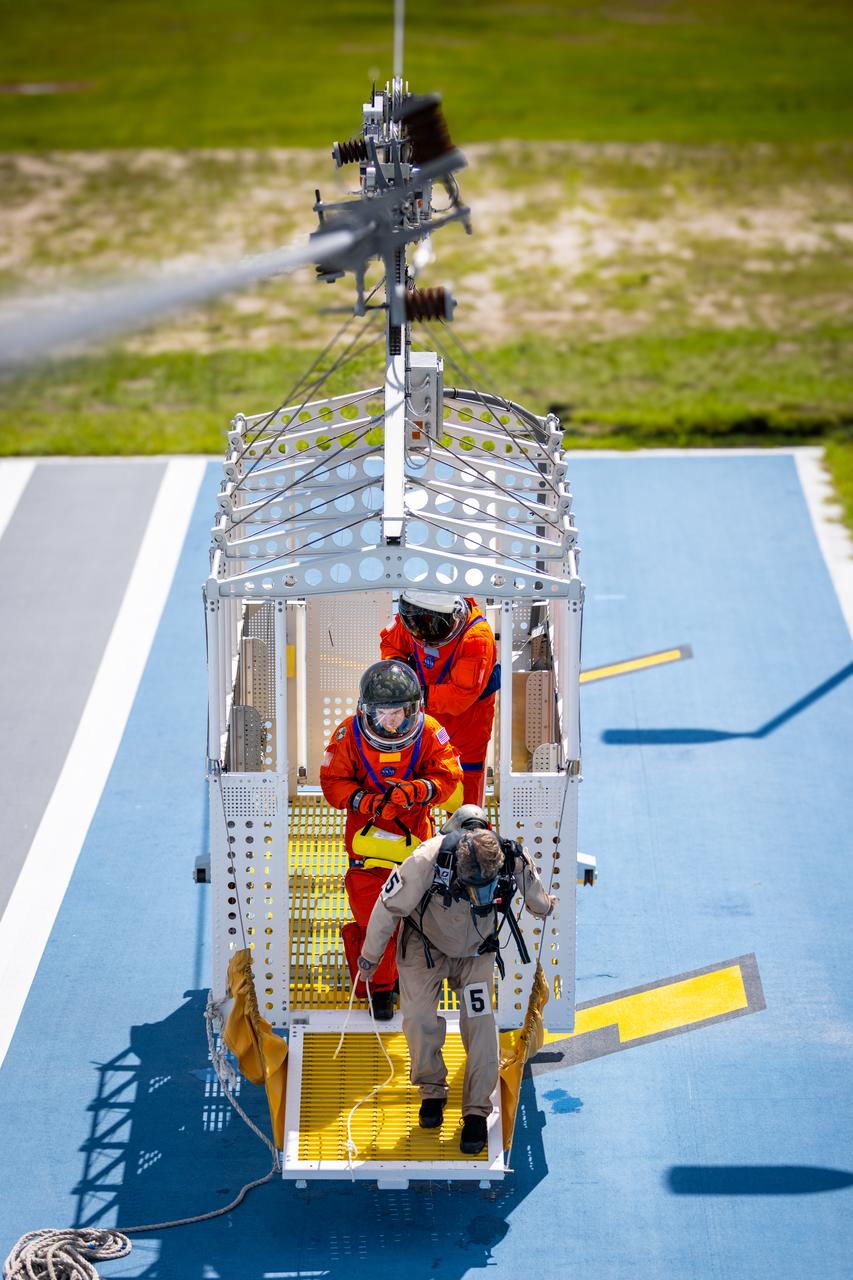

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
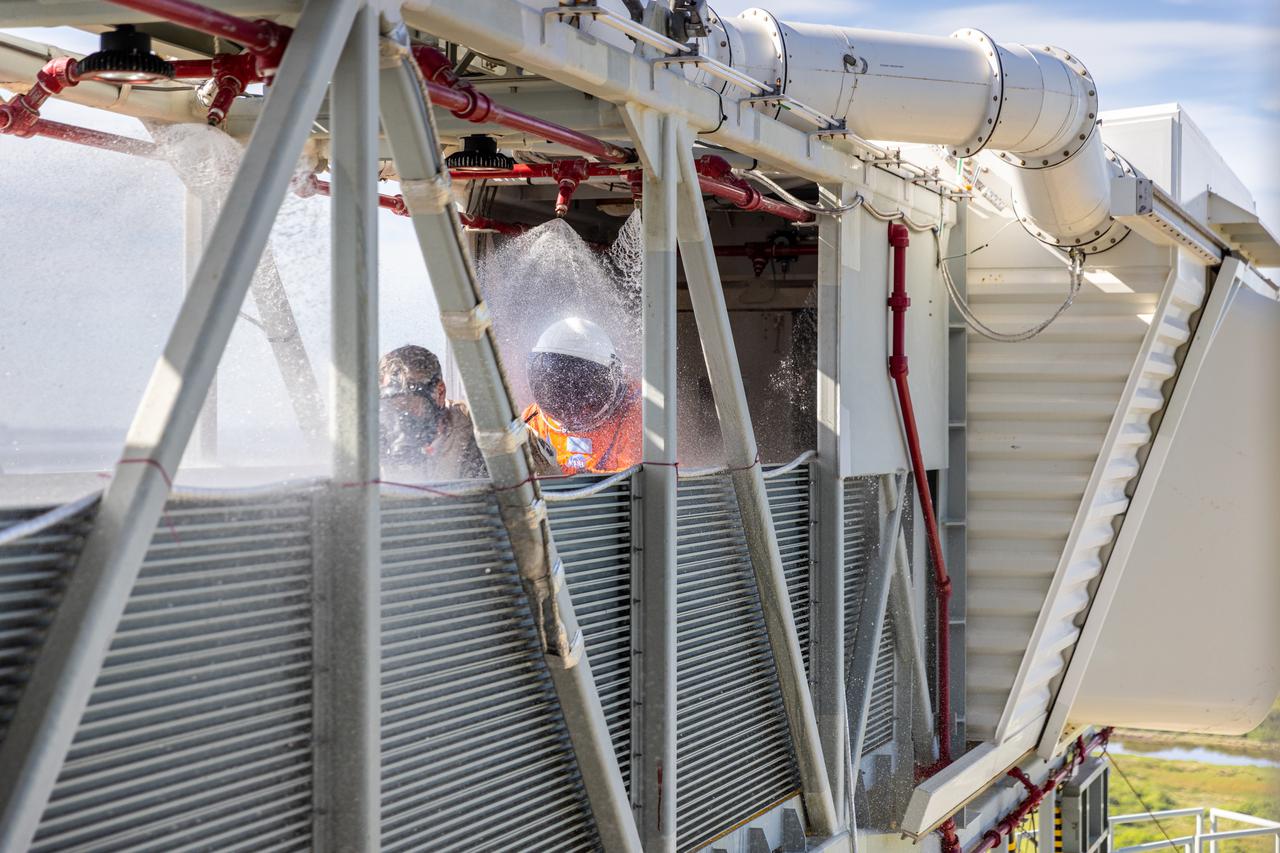

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.
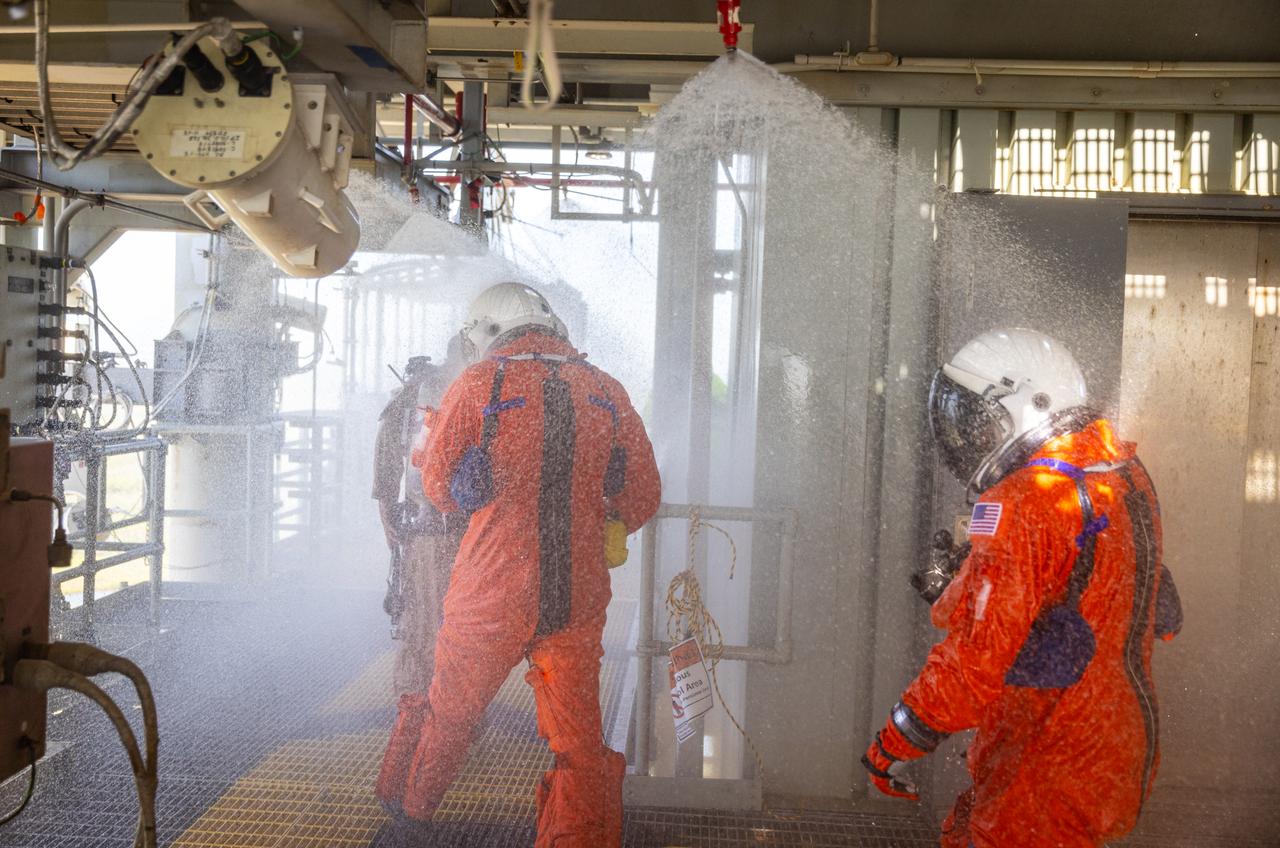

Teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida practice the Artemis mission emergency escape or egress procedures during a series of integrated system verification and validation tests at Launch Pad 39B on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team and the Exploration Ground Systems Program practiced the process of getting inside and out of the emergency egress baskets. While the crew and other personnel will ride the emergency egress baskets to the terminus area in a real emergency, no one rode the baskets for this test. Instead, teams tested the baskets during separate occasions by using water tanks filled to different levels to replicate simulate the weight of passengers.