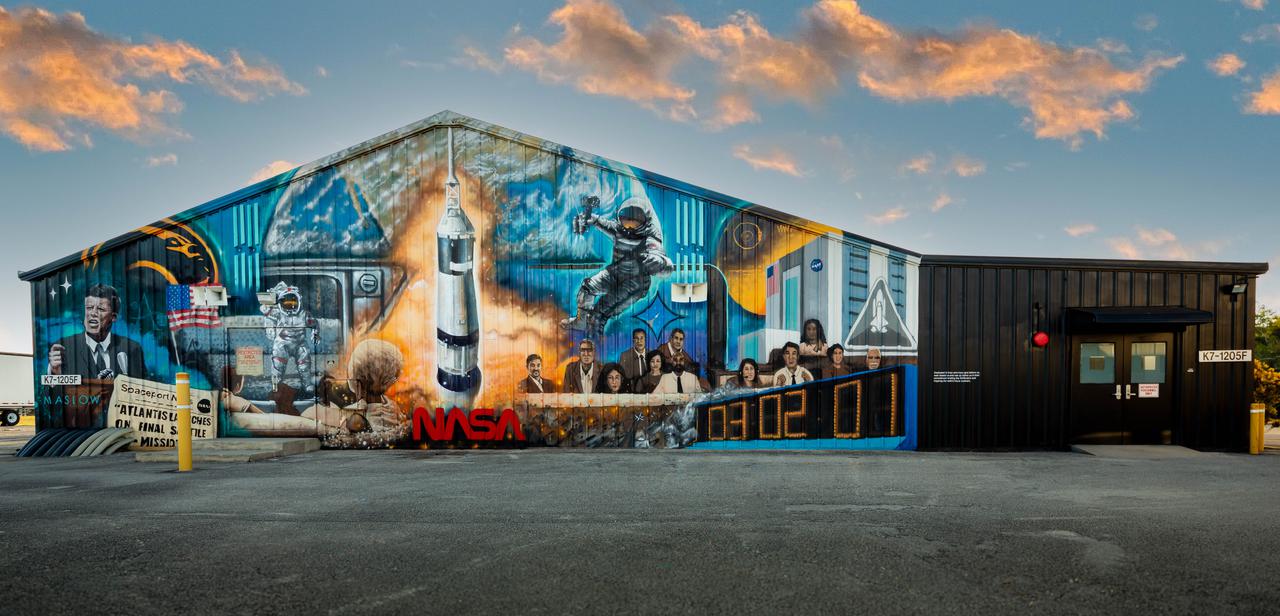

A mural painted by Florida artist Christopher Maslow adorns the northwest exterior wall of the Press Site News Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 10, 2022. Completed by the artist over the course of several months during 2021, the largescale artwork depicts notable landmarks, missions, and milestones from the history of NASA and its world-famous spaceport. The Press Site News Facility is the hub of launch broadcasts and home to the center’s TV auditorium. Along with the nearby NASA News Center, for decades Kennedy’s Press Site has been where reporters from television, radio, print, and online media outlets have monitored countless launches, landings, and other space events in order to deliver the news to the world.

A dedication to those who tell the NASA story is part of a mural painted by Florida artist Christopher Maslow on the northwest exterior wall of the Press Site News Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, photographed on Jan. 10, 2022. Completed by the artist over the course of several months during 2021, the largescale artwork depicts notable landmarks, missions, and milestones from the history of NASA and its world-famous spaceport. The Press Site News Facility is the hub of launch broadcasts and home to the center’s TV auditorium. Along with the nearby NASA News Center, for decades Kennedy’s Press Site has been where reporters from television, radio, print, and online media outlets have monitored countless launches, landings, and other space events in order to deliver the news to the world.
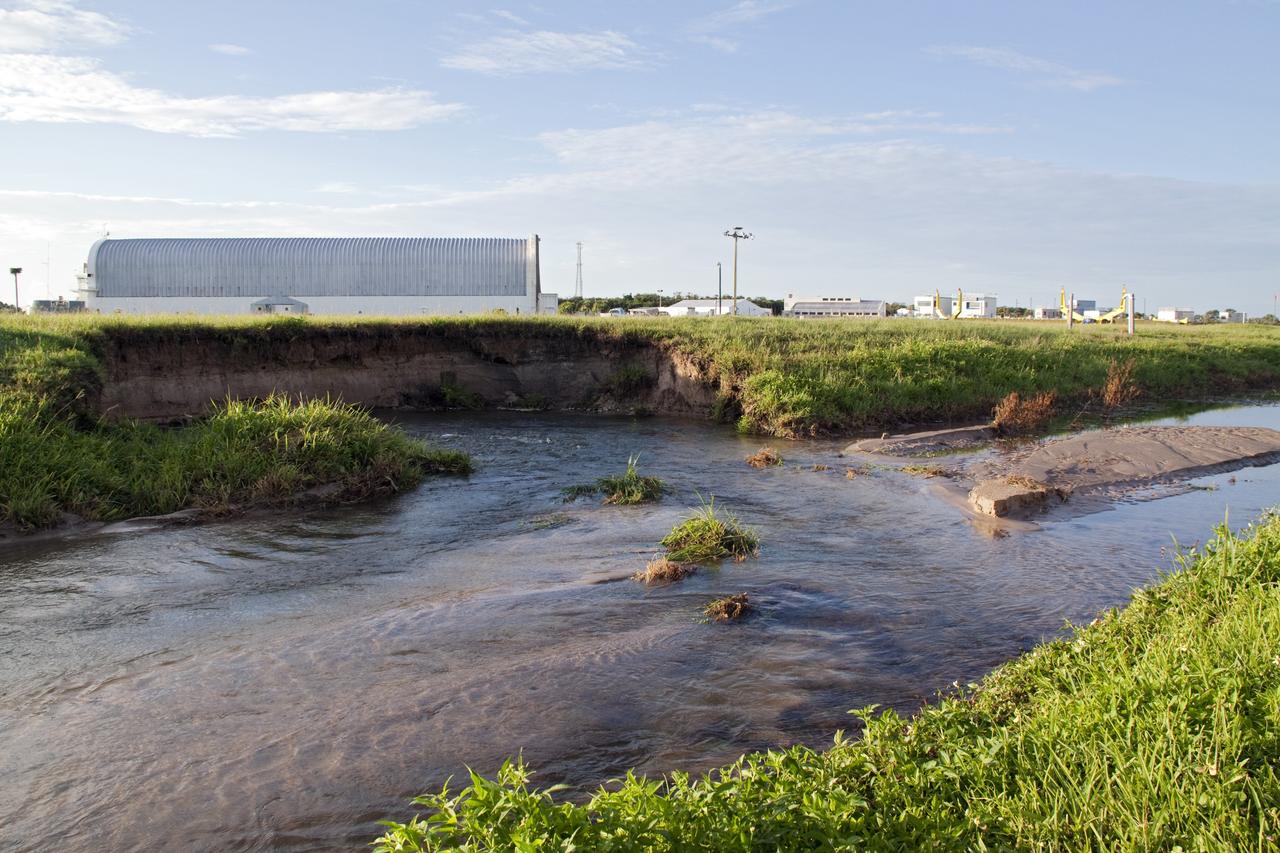

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the LC-39 Complex Turn Basin area across from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a major water main leak in a 24-inch pipe caused soil to wash away near the Press Site. The center was closed for the morning while workers assessed and repaired the break. In the background is the Pegasus barge docked at the Turn Basin which is used to deliver the space shuttle external fuel tank. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
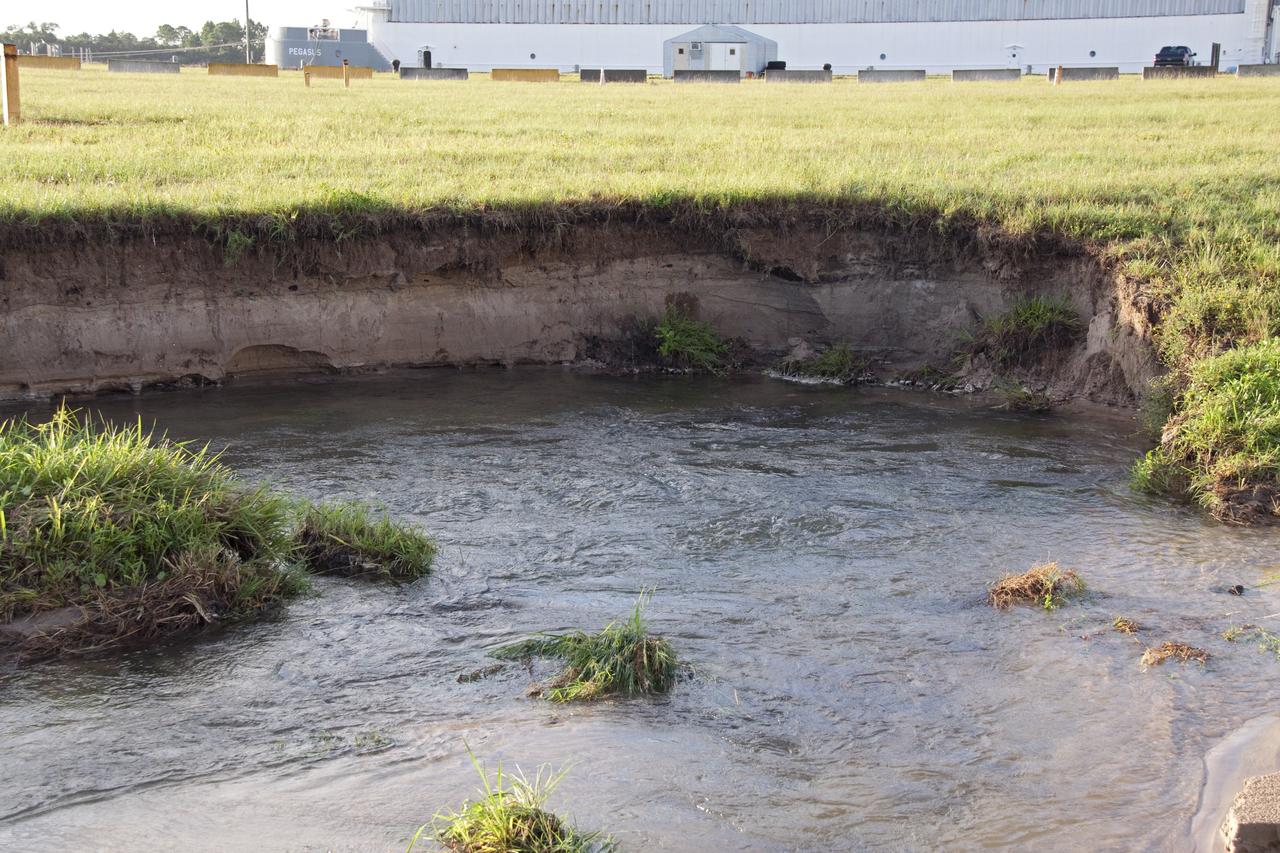

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the LC-39 Complex Turn Basin area across from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a major water main leak in a 24-inch pipe caused soil to wash away near the Press Site. The center was closed for the morning while workers assessed and repaired the break. In the background is the Pegasus barge docked at the Turn Basin which is used to deliver the space shuttle external fuel tank. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
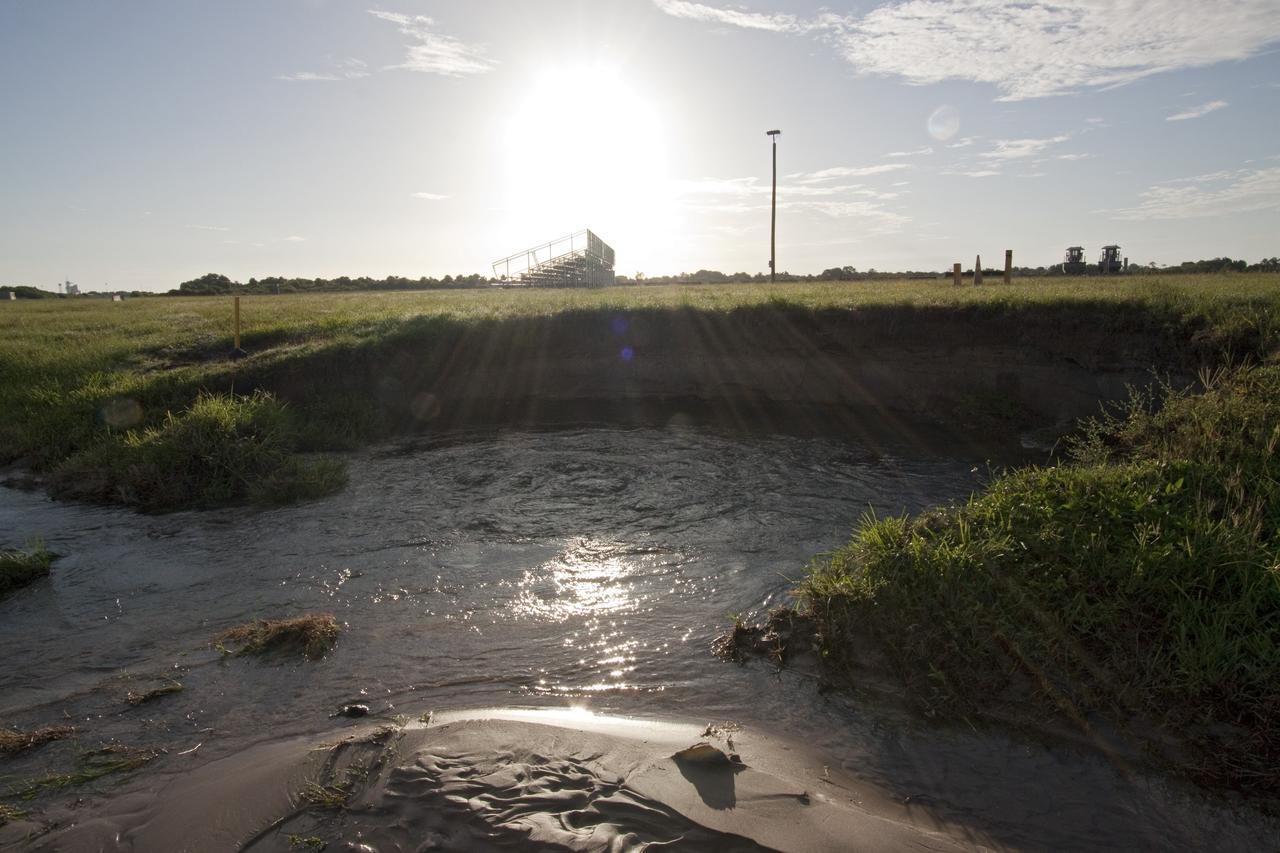

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Looking towards a shuttle launch viewing stand is the result of a major water main leak in a 24-inch pipe that caused soil to wash away near the Press Site in the LC-39 Complex Turn Basin area across from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center was closed for the morning while workers assessed and repaired the break. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
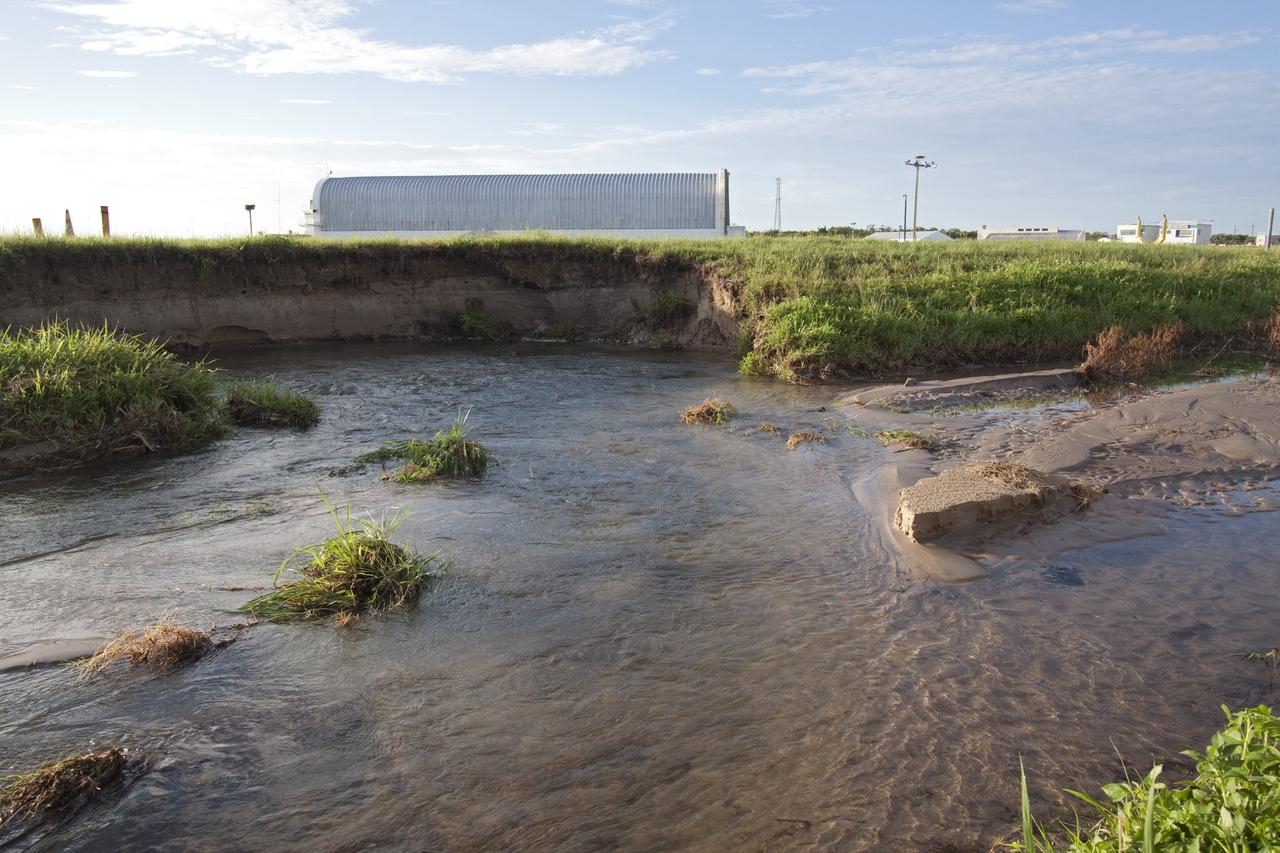

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the LC-39 Complex Turn Basin area across from the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a major water main leak in a 24-inch pipe caused soil to wash away near the Press Site. The center was closed for the morning while workers assessed and repaired the break. In the background is the Pegasus barge docked at the Turn Basin which is used to deliver the space shuttle external fuel tank. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
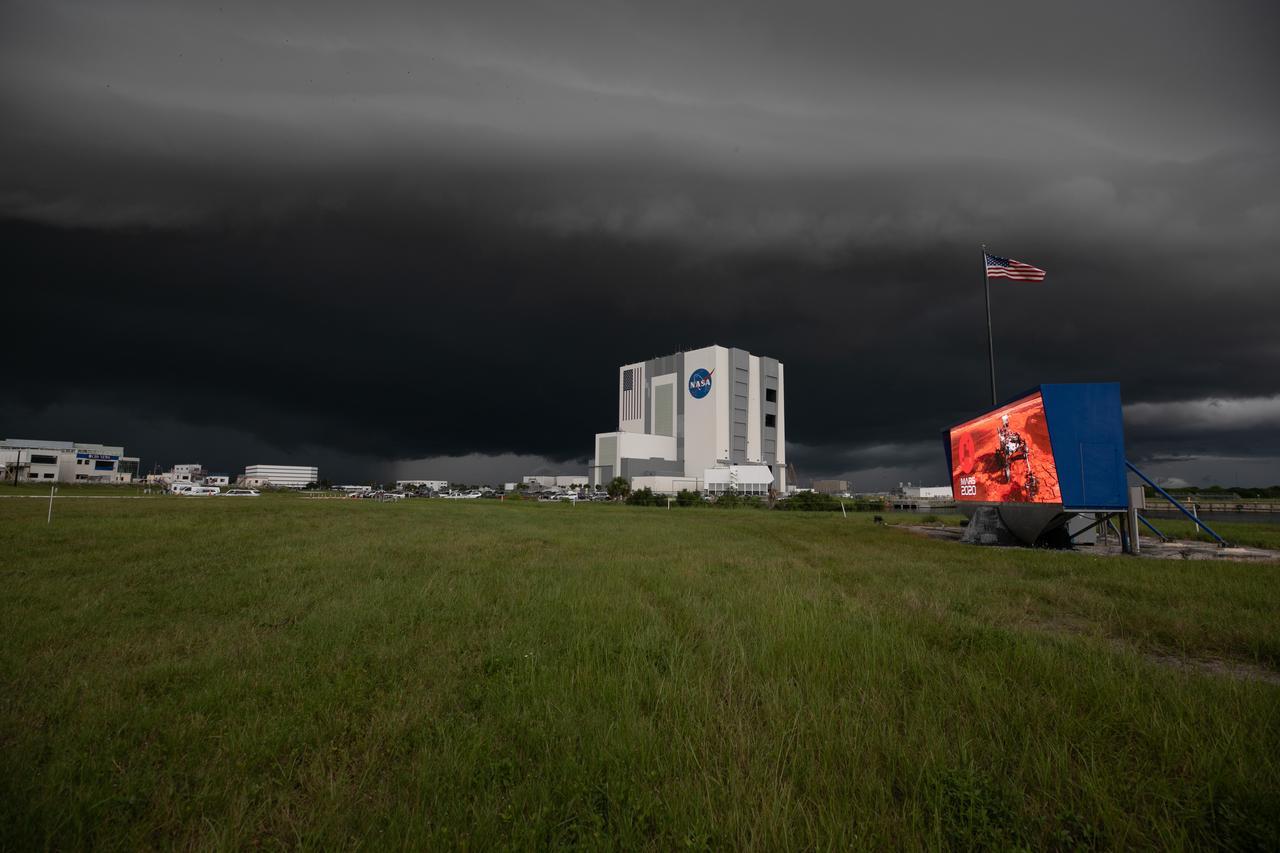

From NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site lawn near the iconic countdown clock, storm clouds can be seen rolling in over the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on July 28, 2020. Standing at 525 feet tall, this facility is capable of hosting multiple varieties of rockets and spacecraft at the same time. Currently, the VAB is being utilized to process and assemble the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond to Mars. Artemis I – the first launch under the agency’s Artemis Program – will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
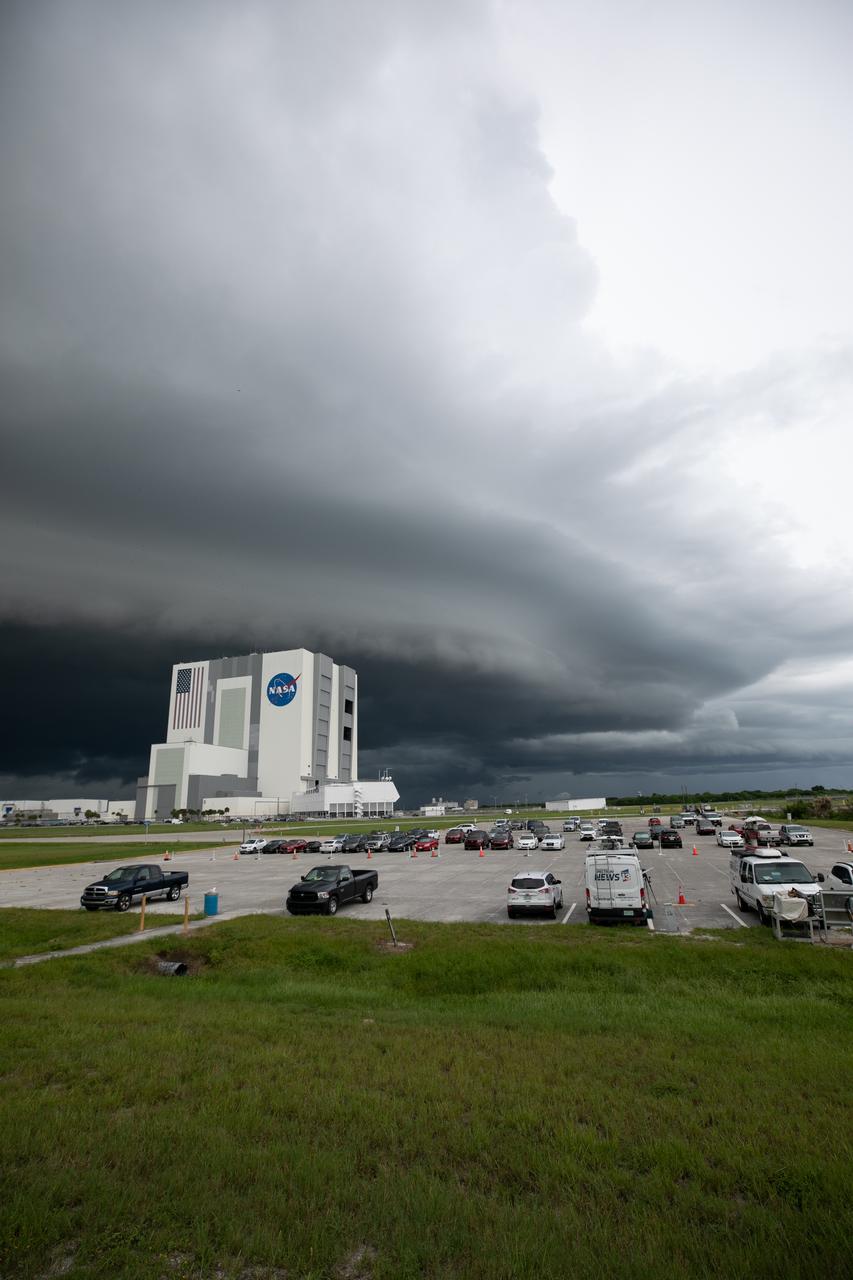

Storm clouds roll in over the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2020. Standing at 525 feet tall, this iconic landmark at Kennedy is capable of hosting multiple varieties of rockets and spacecraft at the same time. Currently, the VAB is being utilized to process and assemble the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond to Mars. Artemis I – the first launch under the agency’s Artemis Program – will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

From NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site lawn near the iconic countdown clock, storm clouds can be seen rolling in over the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on July 28, 2020. Standing at 525 feet tall, this facility is capable of hosting multiple varieties of rockets and spacecraft at the same time. Currently, the VAB is being utilized to process and assemble the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond to Mars. Artemis I – the first launch under the agency’s Artemis Program – will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
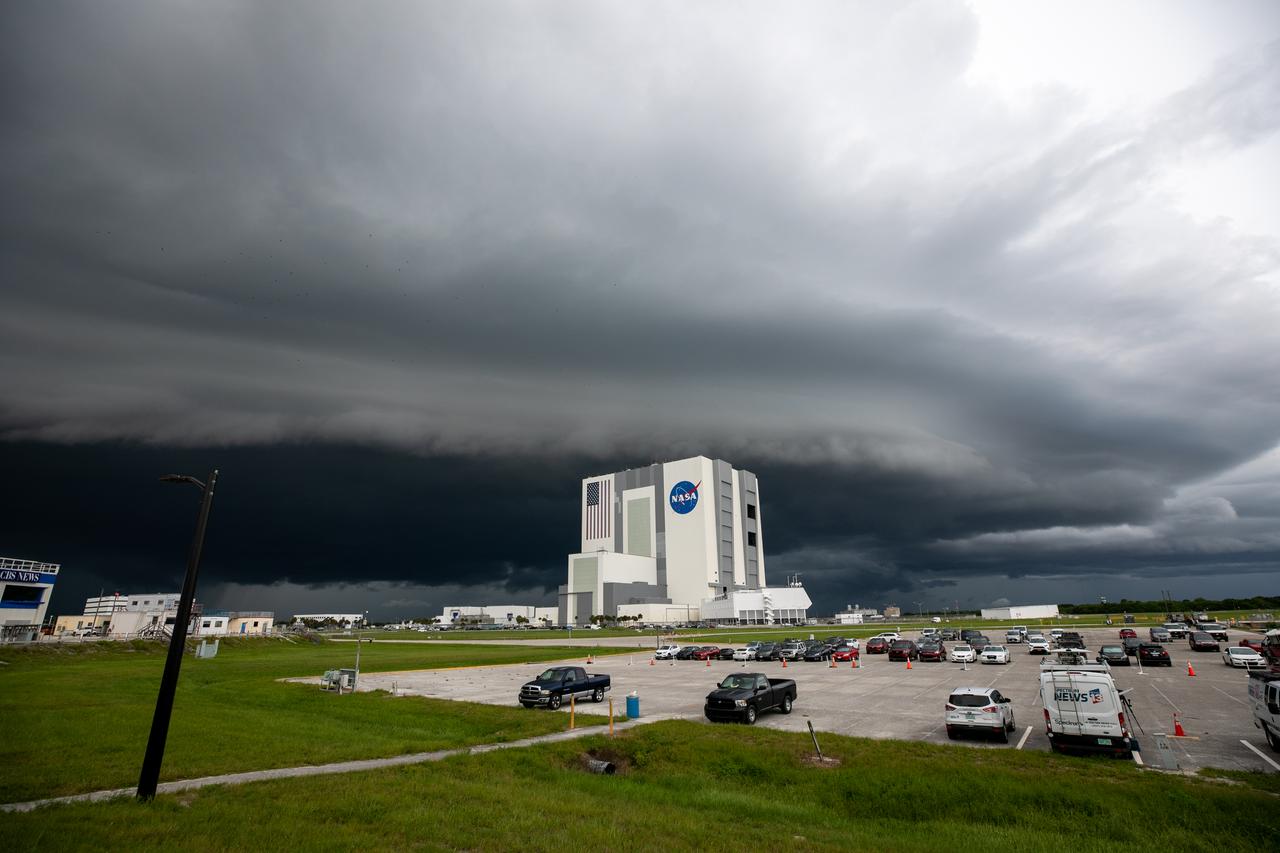

Storm clouds roll in over the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2020. Standing at 525 feet tall, this iconic landmark at Kennedy is capable of hosting multiple varieties of rockets and spacecraft at the same time. Currently, the VAB is being utilized to process and assemble the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond to Mars. Artemis I – the first launch under the agency’s Artemis Program – will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
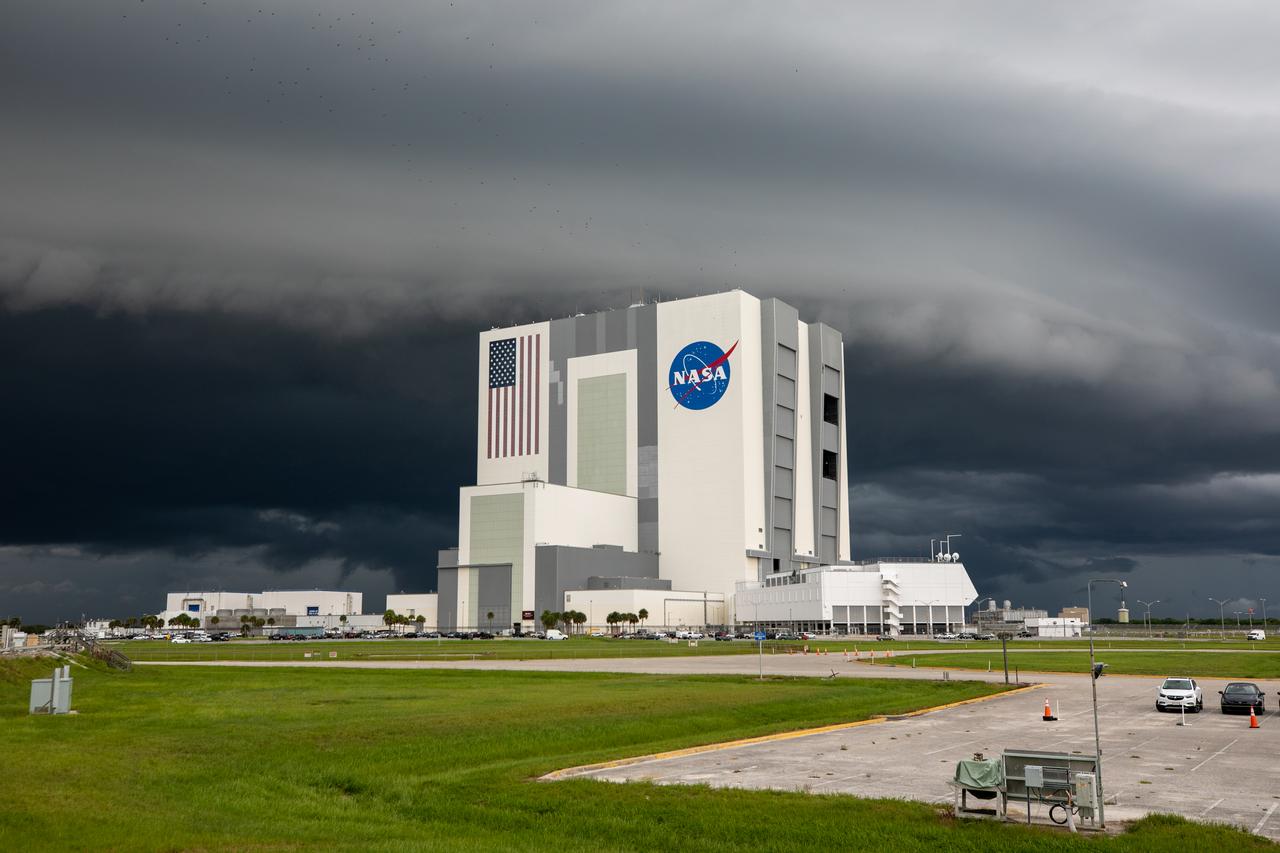

Storm clouds roll in over the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 28, 2020. Standing at 525 feet tall, this iconic landmark at Kennedy is capable of hosting multiple varieties of rockets and spacecraft at the same time. Currently, the VAB is being utilized to process and assemble the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond to Mars. Artemis I – the first launch under the agency’s Artemis Program – will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
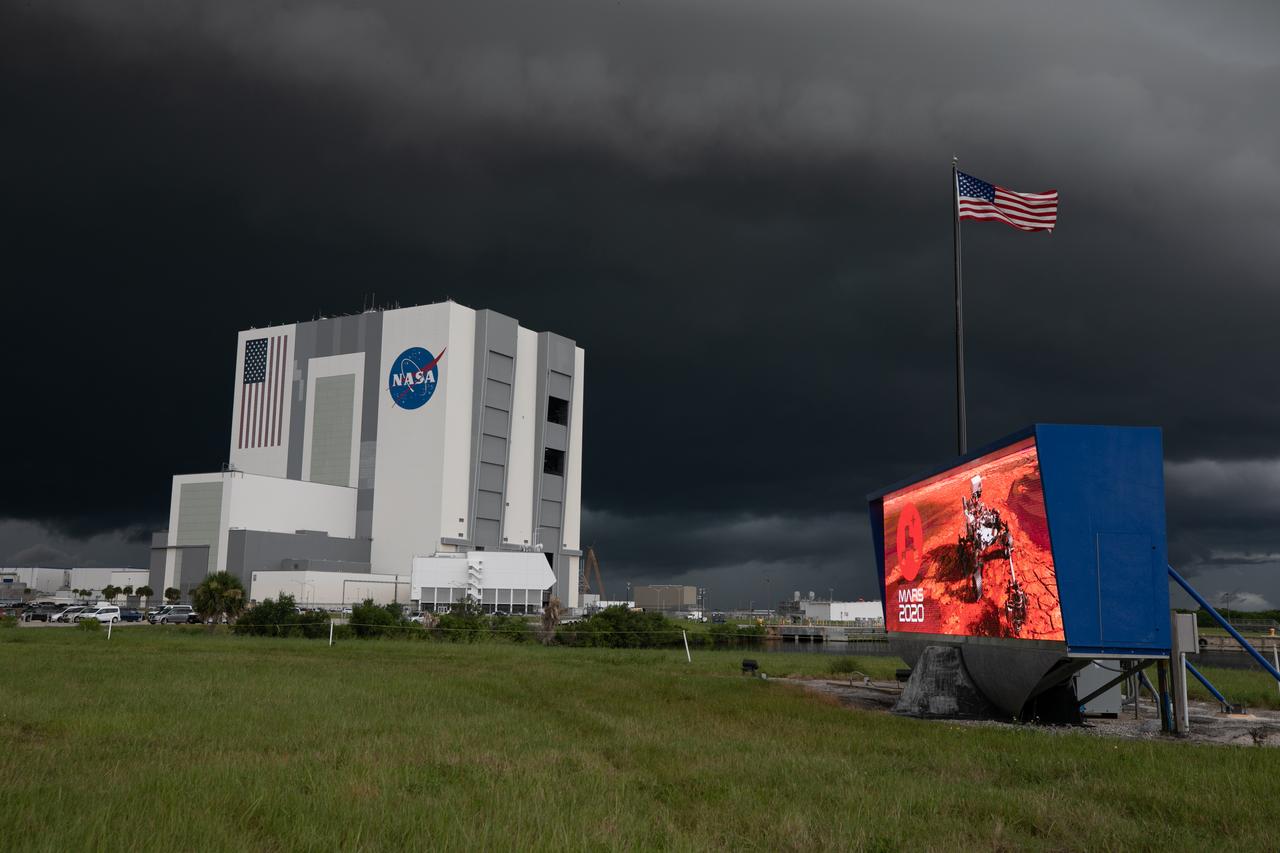

From NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site lawn near the iconic countdown clock, storm clouds can be seen rolling in over the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on July 28, 2020. Standing at 525 feet tall, this facility is capable of hosting multiple varieties of rockets and spacecraft at the same time. Currently, the VAB is being utilized to process and assemble the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket for Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond to Mars. Artemis I – the first launch under the agency’s Artemis Program – will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
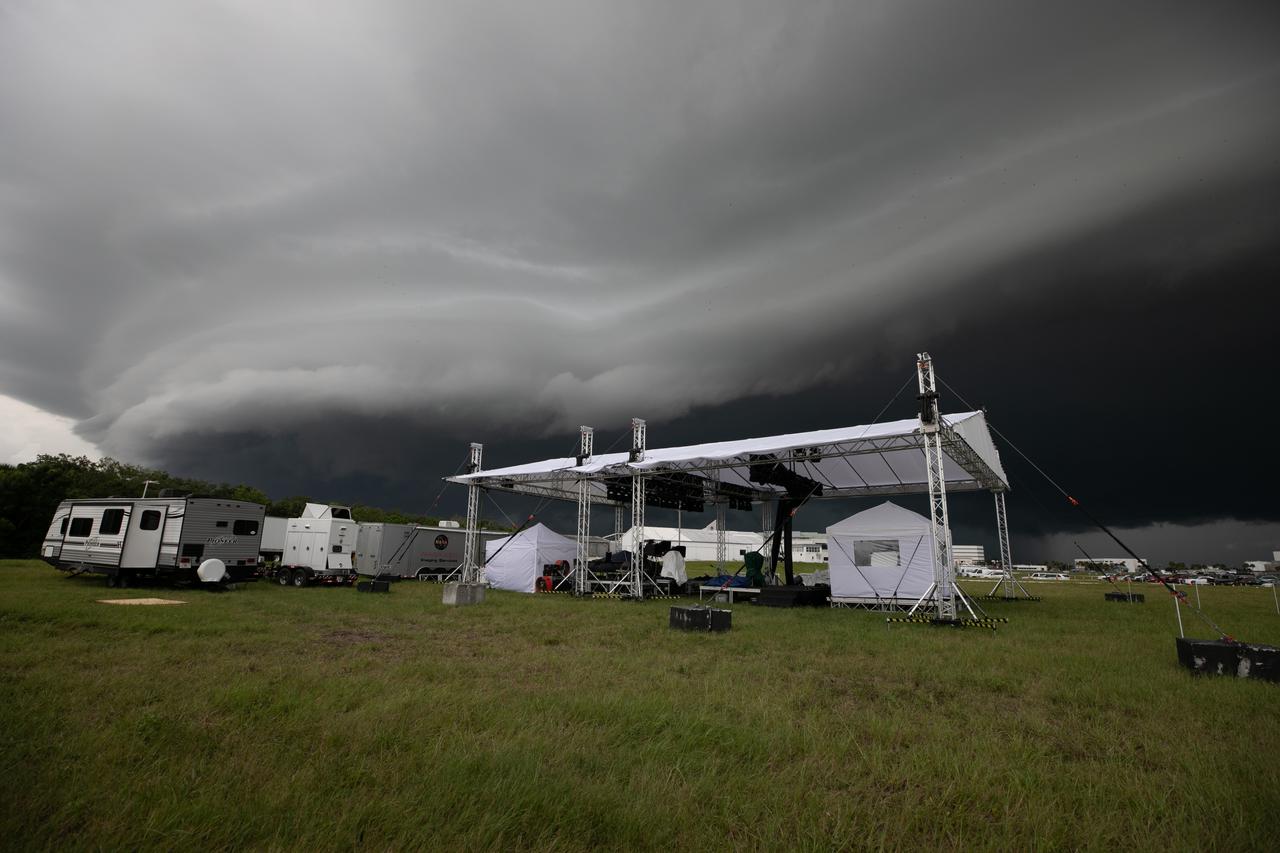

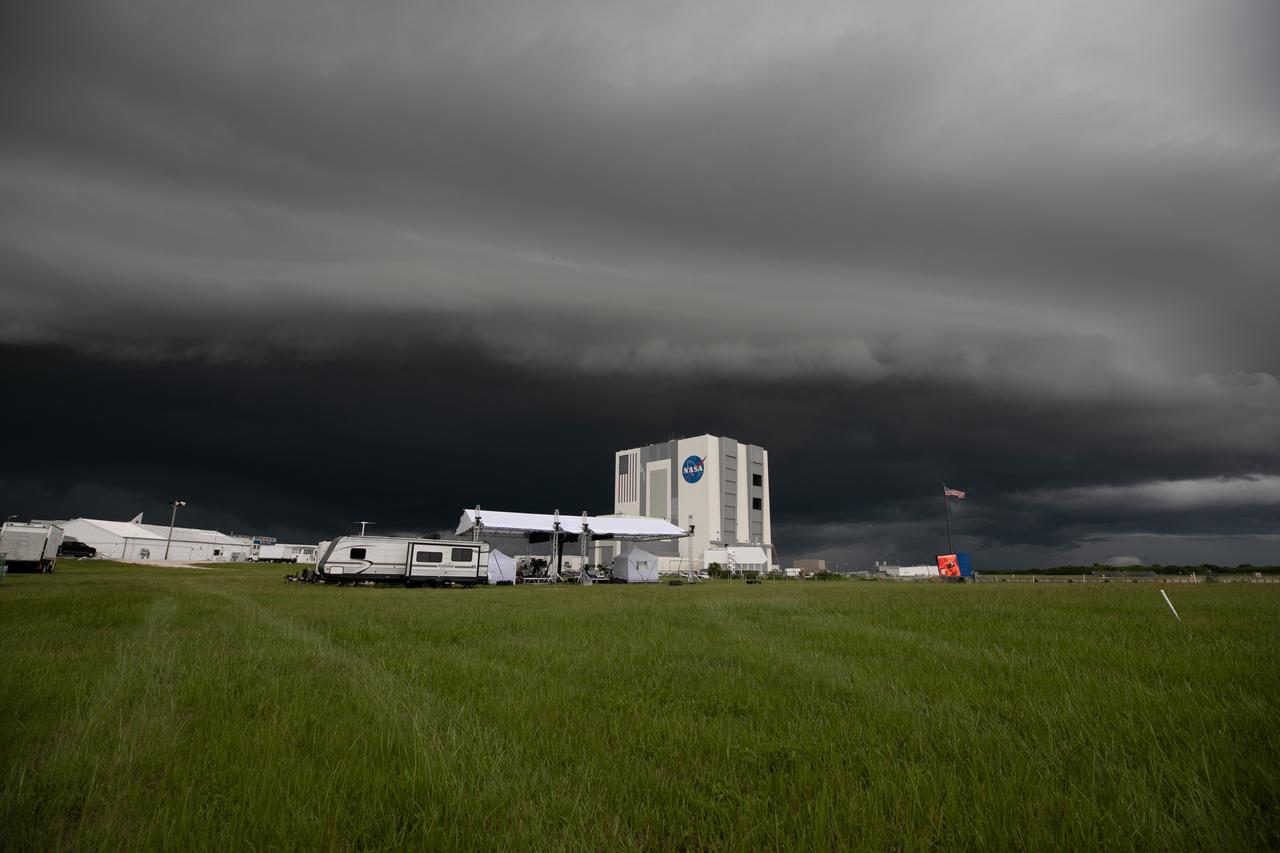
On July 28, 2020, storm clouds roll in over the Press Site lawn, where an exterior host set is being constructed in preparation for NASA’s Mars 2020 launch broadcast at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket, with the Mars Perseverance rover aboard, lifted off from nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on July 30 at 7:50 a.m. EDT. Once it arrives at the Red Planet, the rover will search for signs of ancient microbial life on Mars.

In this aerial view looking south can be seen Launch Complex (LC) 39 area, where assembly, checkout and launch of the Space Shuttle Orbiter and its External Tank and twin Solid Rocket Boosters take place. Central to the complex is the tallest building at the center, the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). To the immediate left, from top to bottom, are the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) High Bay 3 and new engine shop (north side), OPF Modular Office Building, Thermal Protection System Facility, and a crawler-transporter (to its left). In front of the VAB are OPF 1 and OPF 2. At right is the Processing Control Center. West of OPF 3 is the Mobile Launch Platform. In the upper left corner is Launch Pad B; at the far right is the turn basin, with the Press Site located just below it to the right.
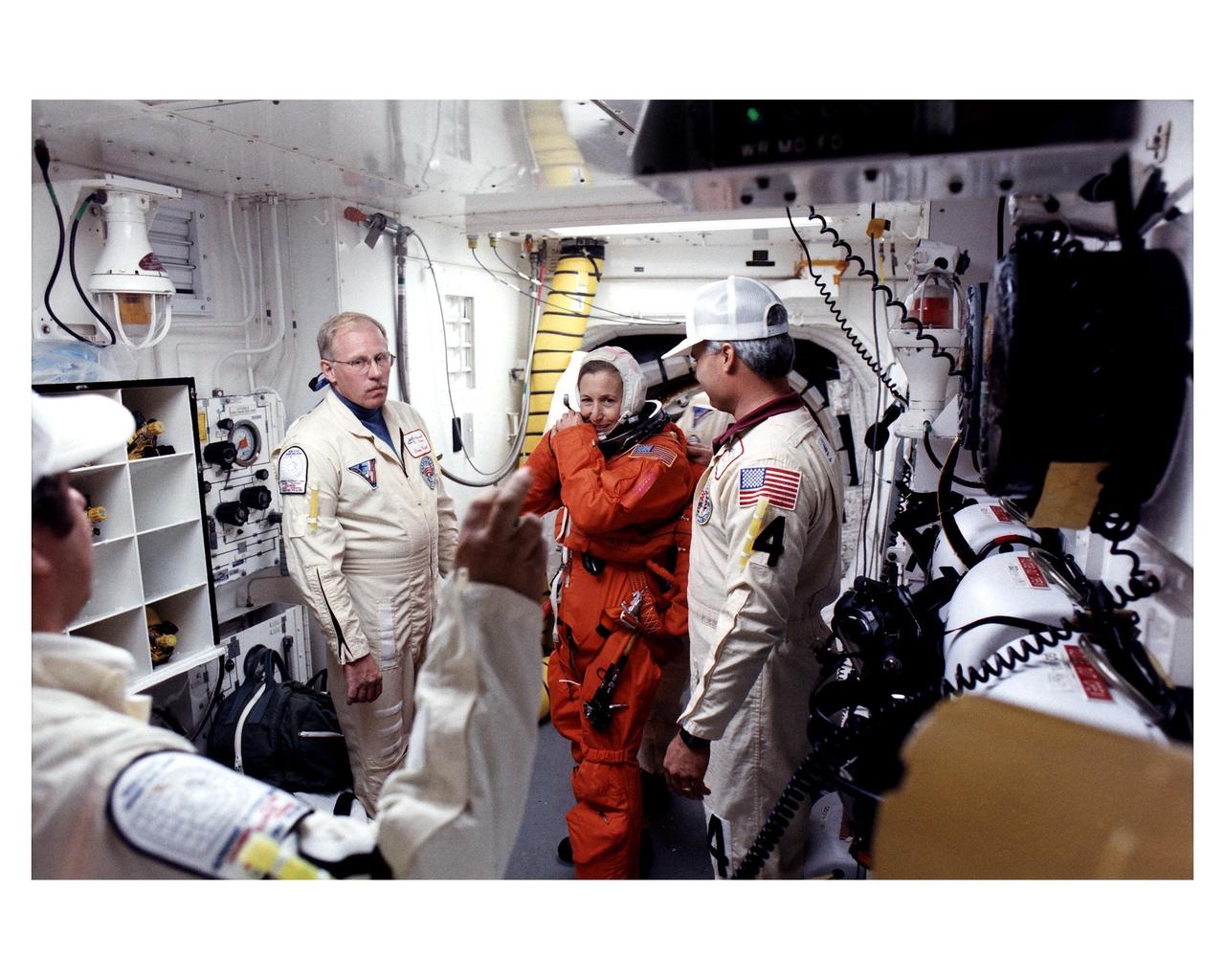

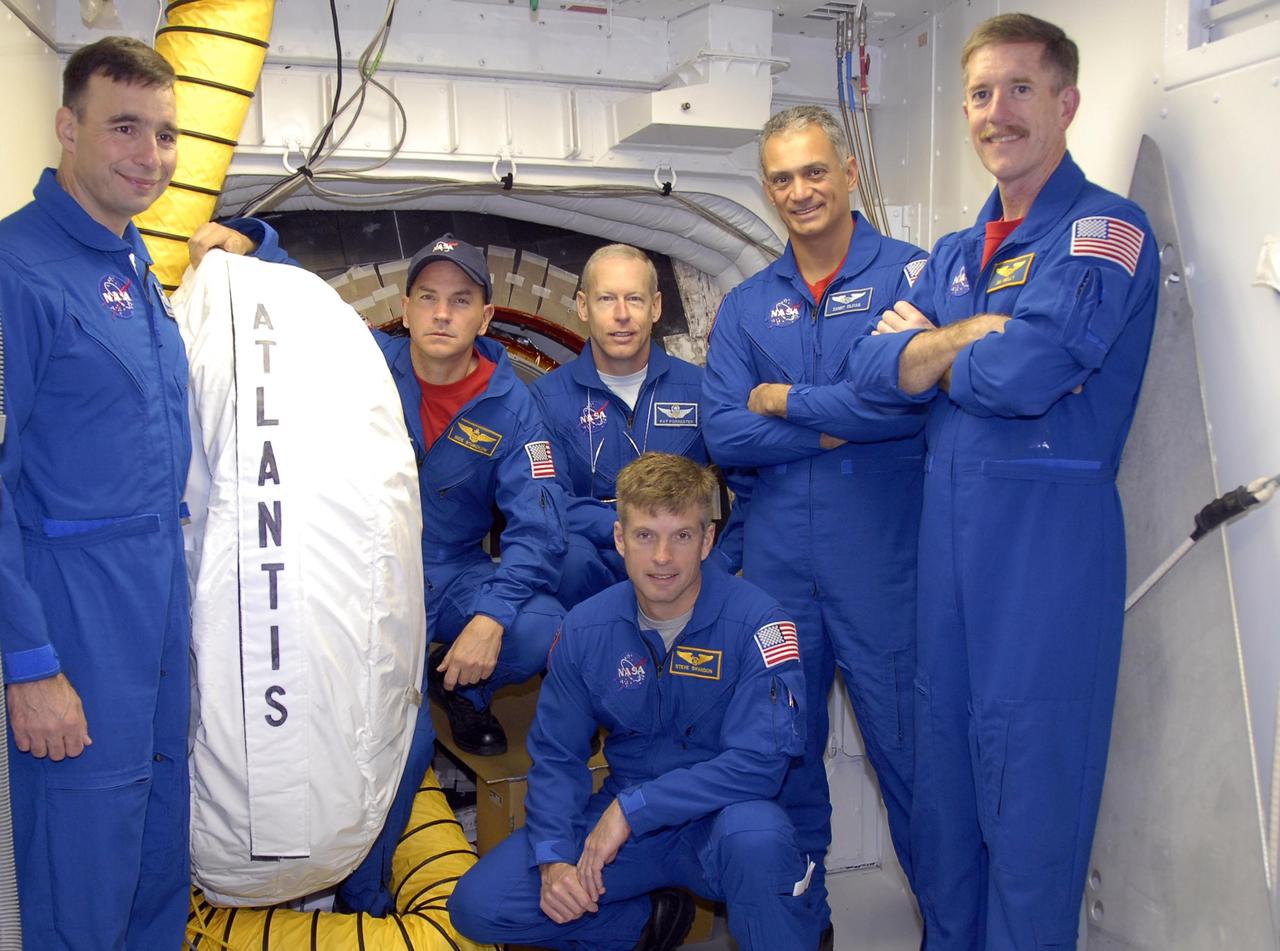
STS-81 crew in the White Room at LC 39
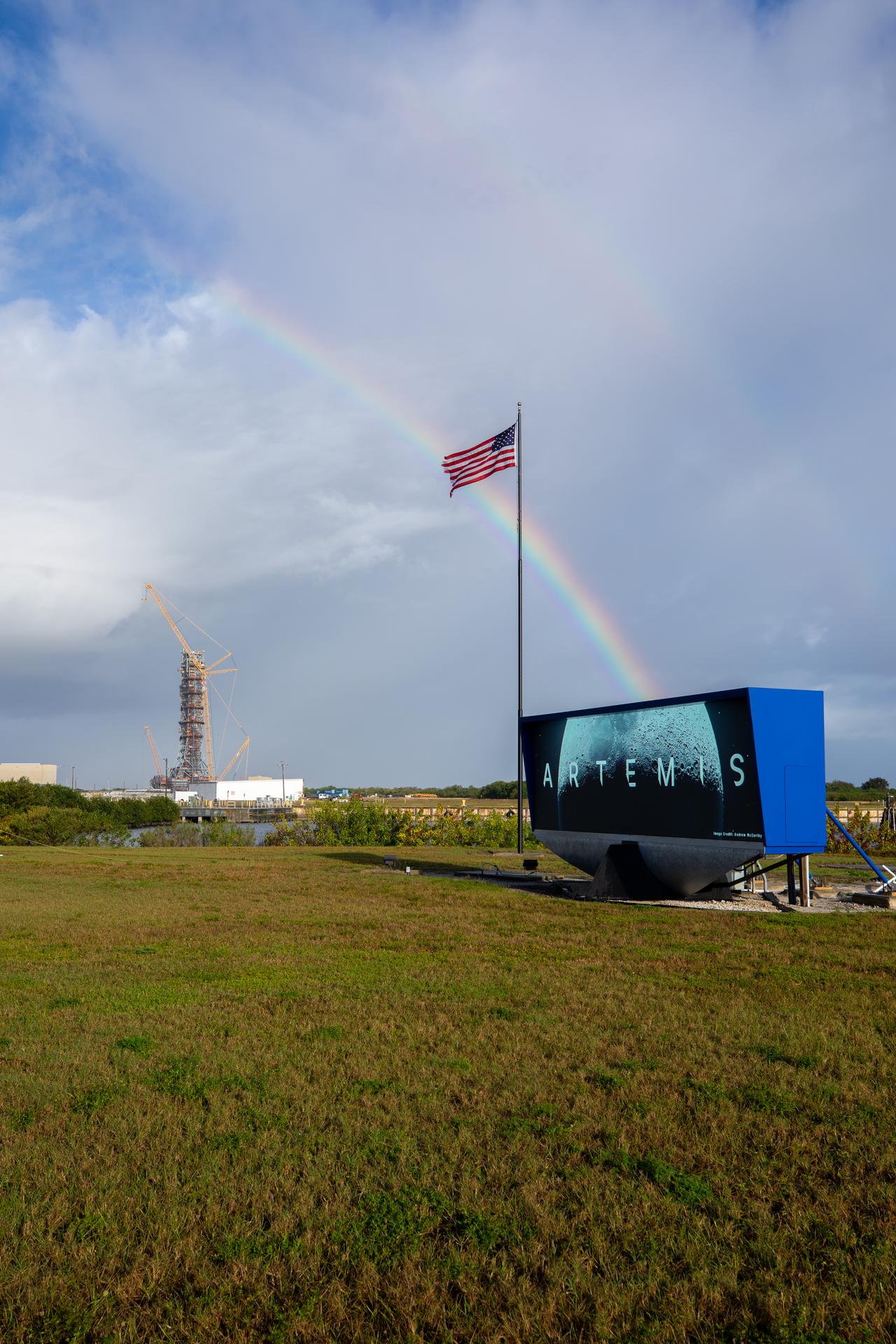

Rain showers create a rainbow near countdown clock featuring the Artemis Moon logo at the NASA News Center at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Dec. 19, 2025.
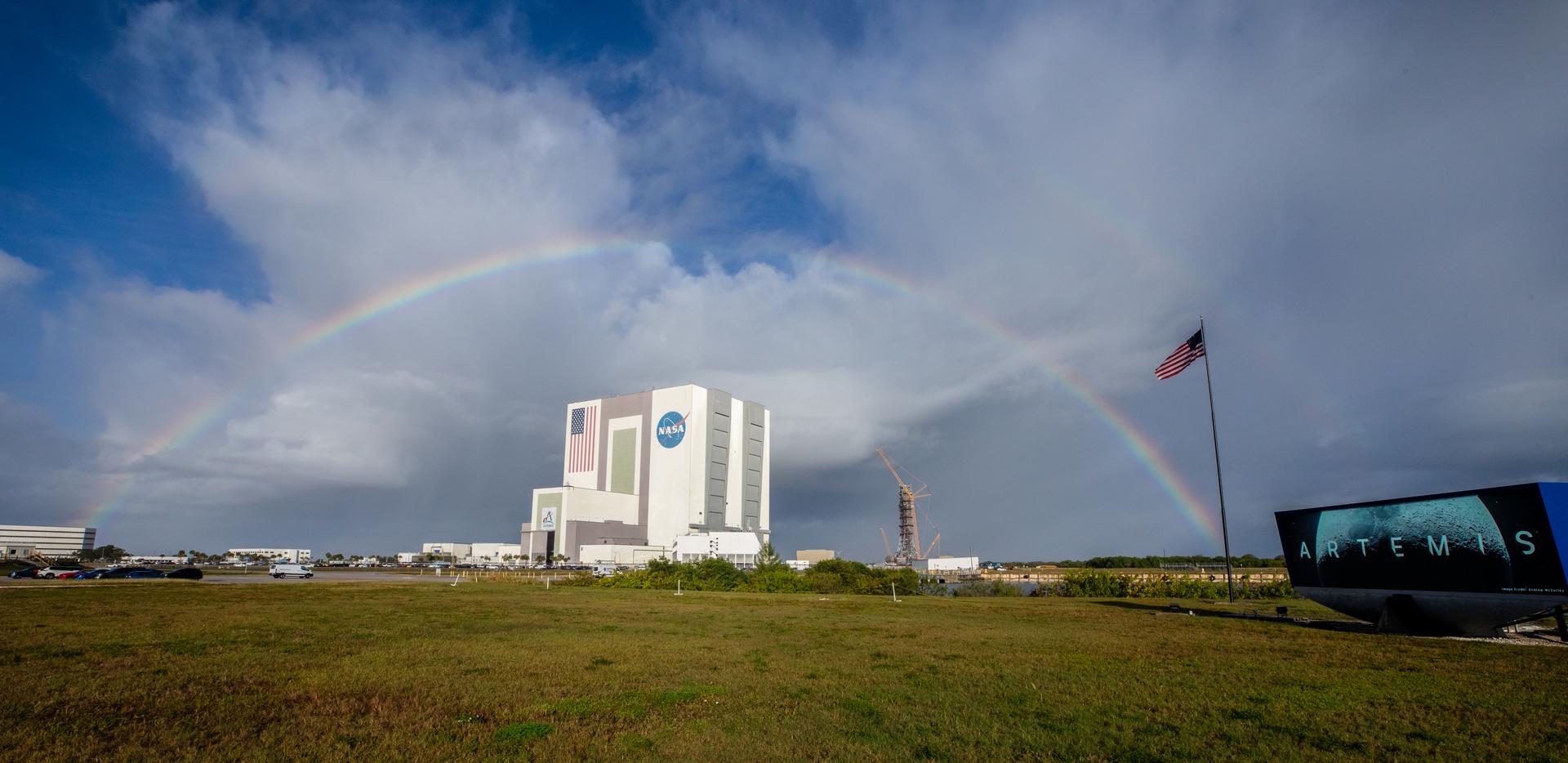

Rain showers create a rainbow over the Vehicle Assembly Building near countdown clock featuring the Artemis Moon logo at the NASA News Center at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Dec. 19, 2025.

The Artemis flag is removed from NASA News Center property at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 6, 2023, following the successful Artemis I mission. At left is former Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) Senior Technical Integration Manager Phil Weber, joined by former EGS Manager Mike Bolger. Both men served in their respective roles during Artemis I, retiring at the end of 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft lifted off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022. Orion splashed down in the Pacific Ocean on Dec. 11 and arrived back at Kennedy on Dec. 30. Artemis I sets the stage for the next mission of SLS and Orion to fly crew around the Moon on Artemis II.
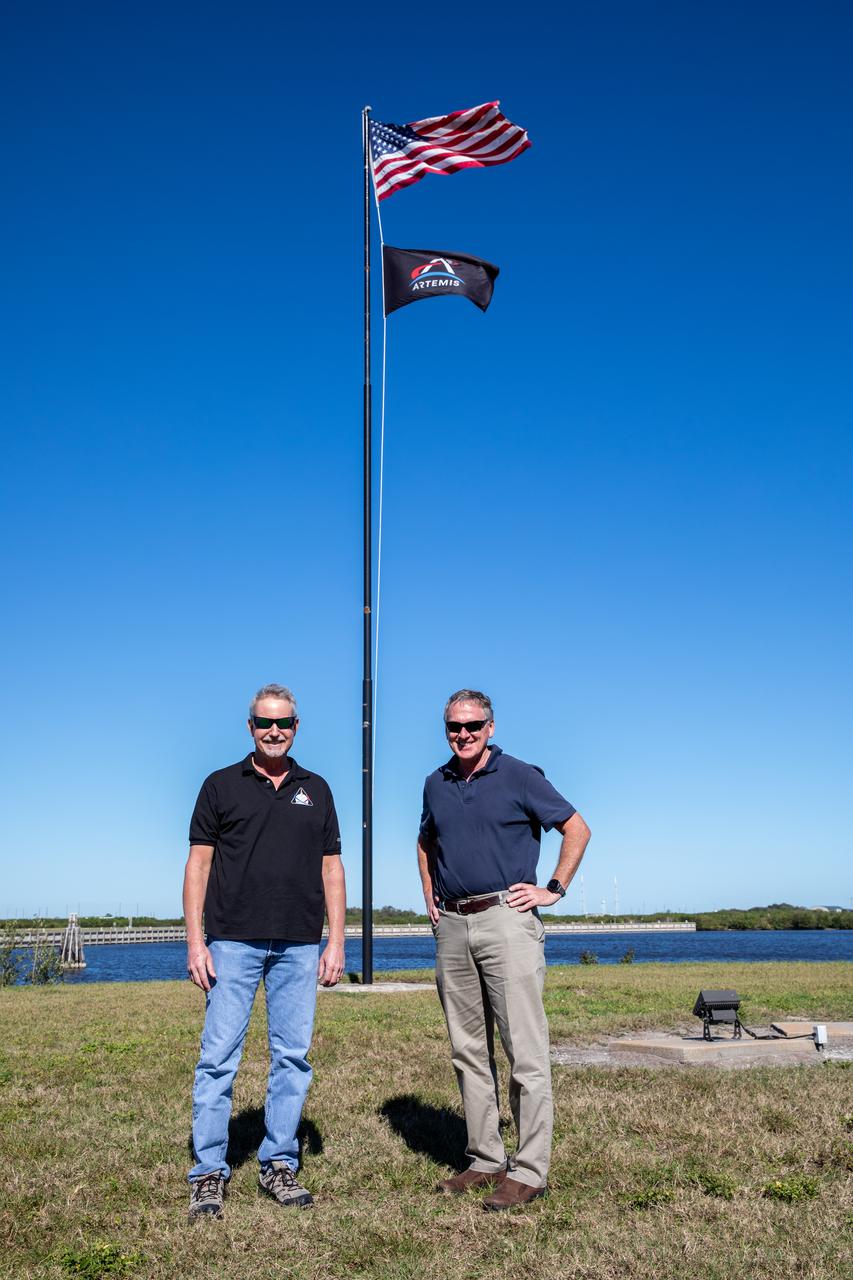

The Artemis flag is removed from NASA News Center property at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 6, 2023, following the successful Artemis I mission. At left is former Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) Senior Technical Integration Manager Phil Weber, joined by former EGS Manager Mike Bolger. Both men served in their respective roles during Artemis I, retiring at the end of 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft lifted off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022. Orion splashed down in the Pacific Ocean on Dec. 11 and arrived back at Kennedy on Dec. 30. Artemis I sets the stage for the next mission of SLS and Orion to fly crew around the Moon on Artemis II.

The Artemis flag is removed from NASA News Center property at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 6, 2023, following the successful Artemis I mission. At left is former Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) Senior Technical Integration Manager Phil Weber, joined by former EGS Manager Mike Bolger. Both men served in their respective roles during Artemis I, retiring at the end of 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft lifted off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022. Orion splashed down in the Pacific Ocean on Dec. 11 and arrived back at Kennedy on Dec. 30. Artemis I sets the stage for the next mission of SLS and Orion to fly crew around the Moon on Artemis II.
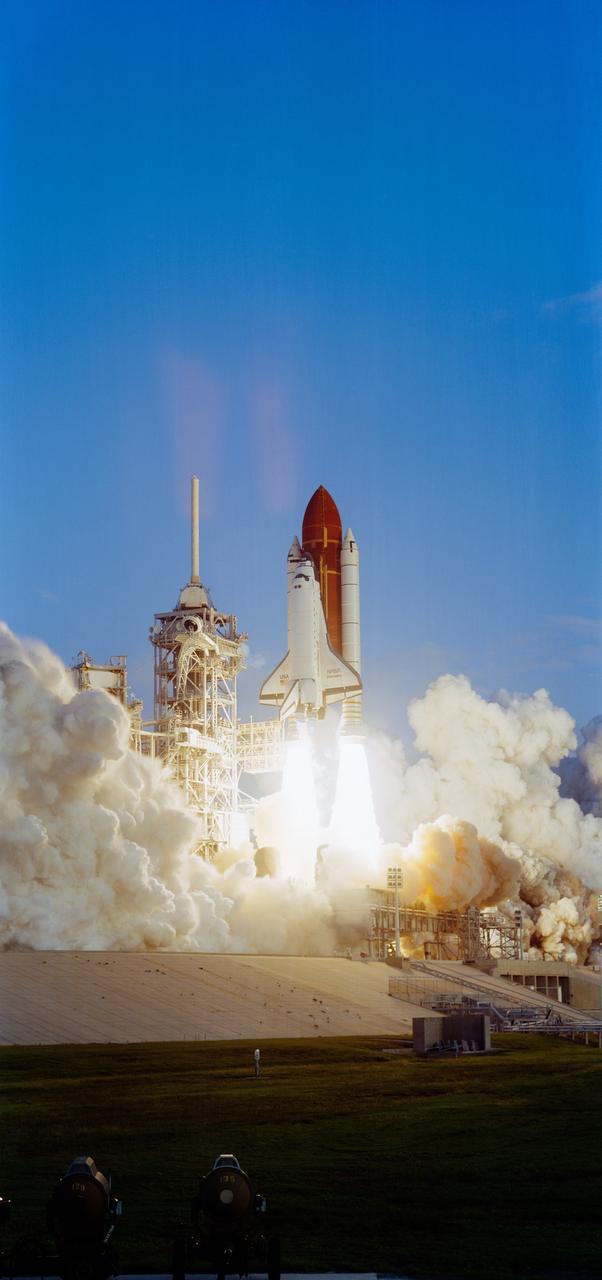

STS-41 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, lifts off from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39 mobile launcher platform at 7:47 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). OV-103 riding atop the external tank (ET) and flanked by two solid rocket boosters (SRBs), is captured just moments after liftoff. Not yet clear of the fixed service structure (FSS) tower, OV-103 is highlighted against the cloudless morning sky. Exhaust smoke billows from the SRBs and the space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) creating a cloud over the launch pad area.
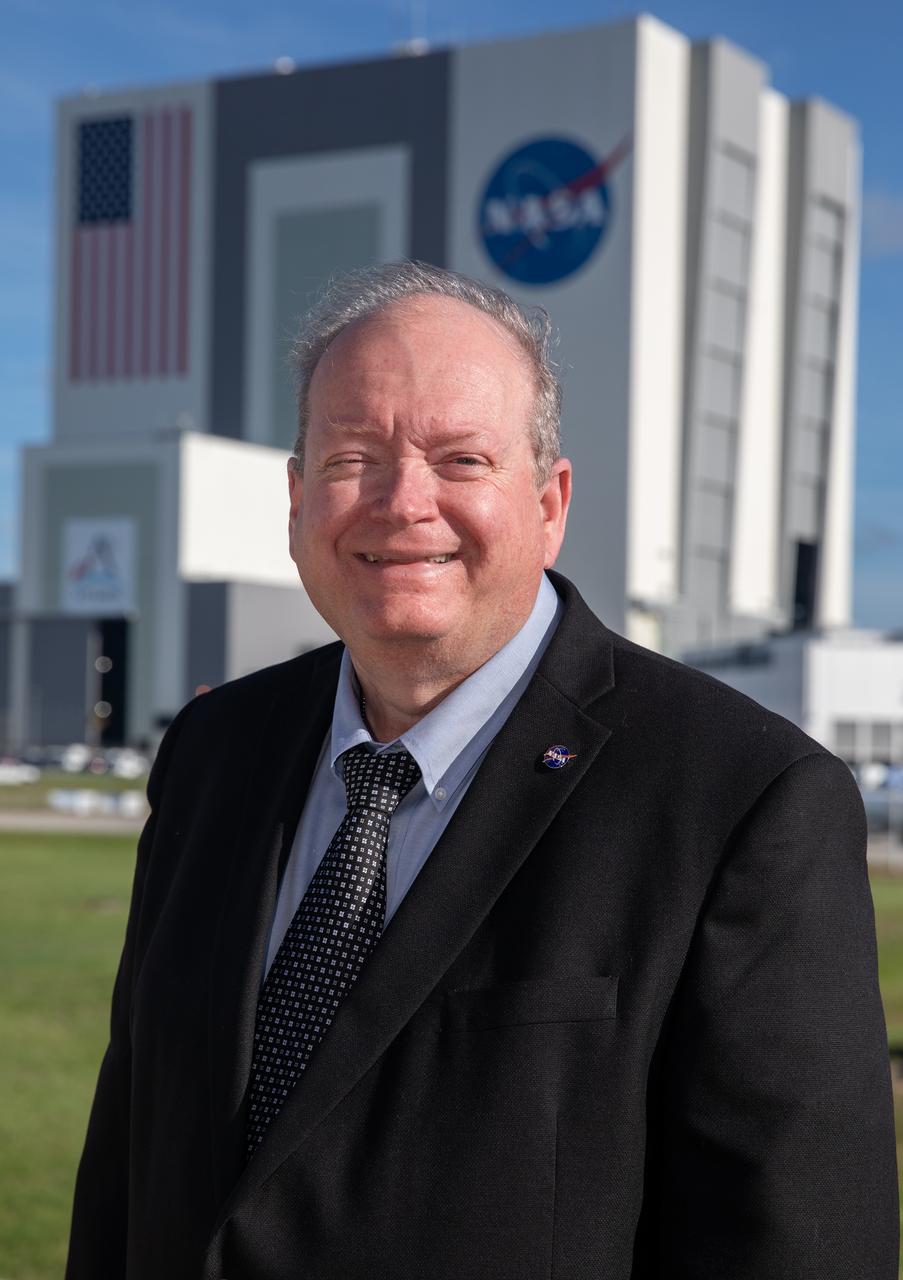
NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Associate Director of Management Burt Summerfield is shown with the Florida spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building in the background on June 29, 2022. Summerfield, who began his career at the center in 1982, is responsible for management of Kennedy’s Center Management and Operations (CMO) budget. His duties include executing the center’s strategic analysis, planning, business development, and communications capability that guide key center decisions and relationships.

Launch Complex 39 Construction: Launch Complex 39 LC-39 was originally designed and built to launch American astronauts toward the moon. The complex stretches inland from the Atlantic Ocean across four miles of what, until 1963, was a land of intermittent marshes and sandy scrub growth. In less than four years, starting with 1963 and ending with 1966, it was transformed into an operational spaceport embodying a mobile concept: rockets and spacecraft are erected in one area and transported to a separate location for launch. A total of 153 vehicles have been launched from LC-39. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
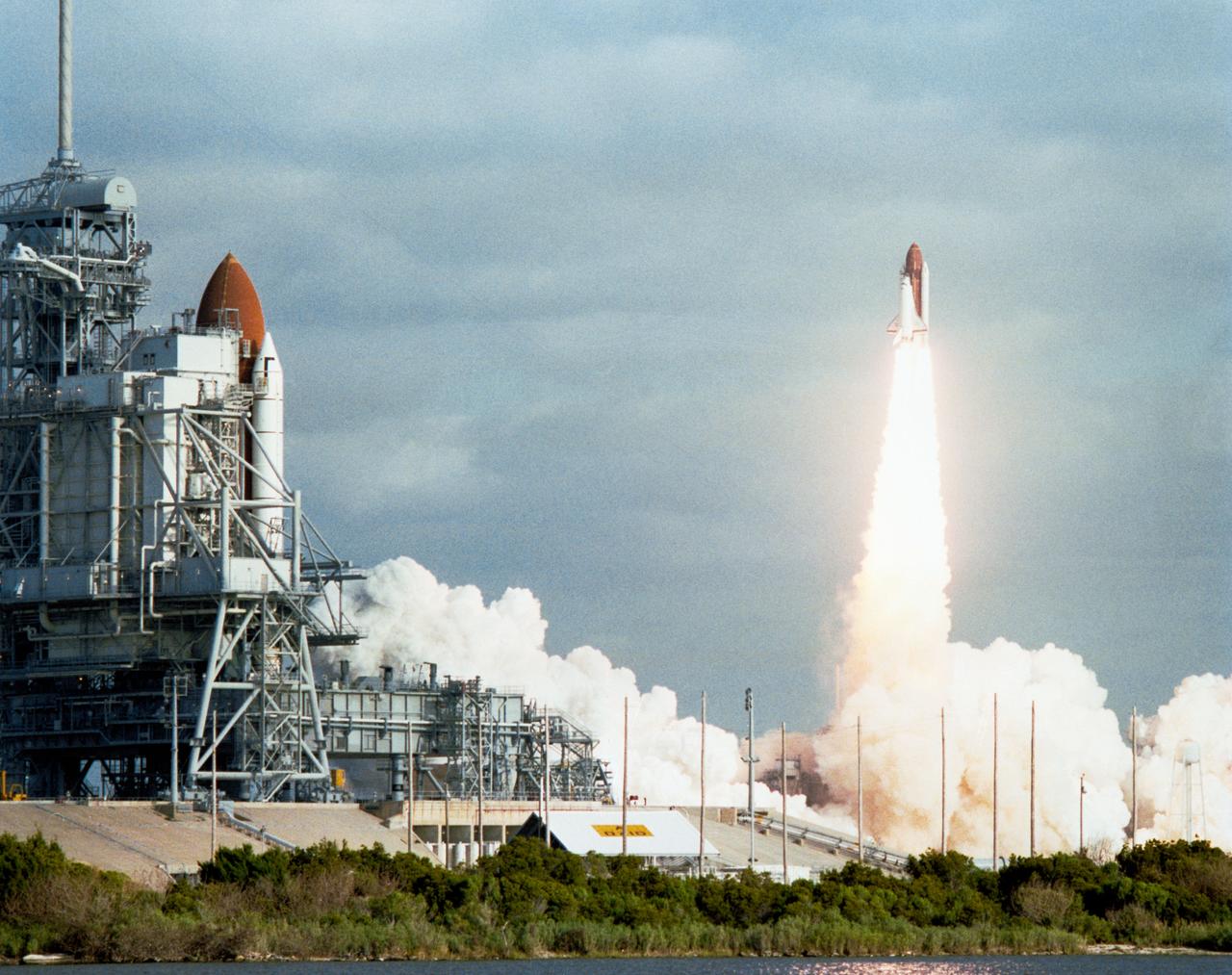

STS-31 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, lifts off from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) 39 Pad B. In the foreground STS-35 Columbia, OV-102, is visible on launch pad 39A. This event marked the first time since January 1986 that there was an orbiter on each pad. LC 39 pads are separated by 1.6 miles. View provided by KSC with alternate number KSC-90PC-610.
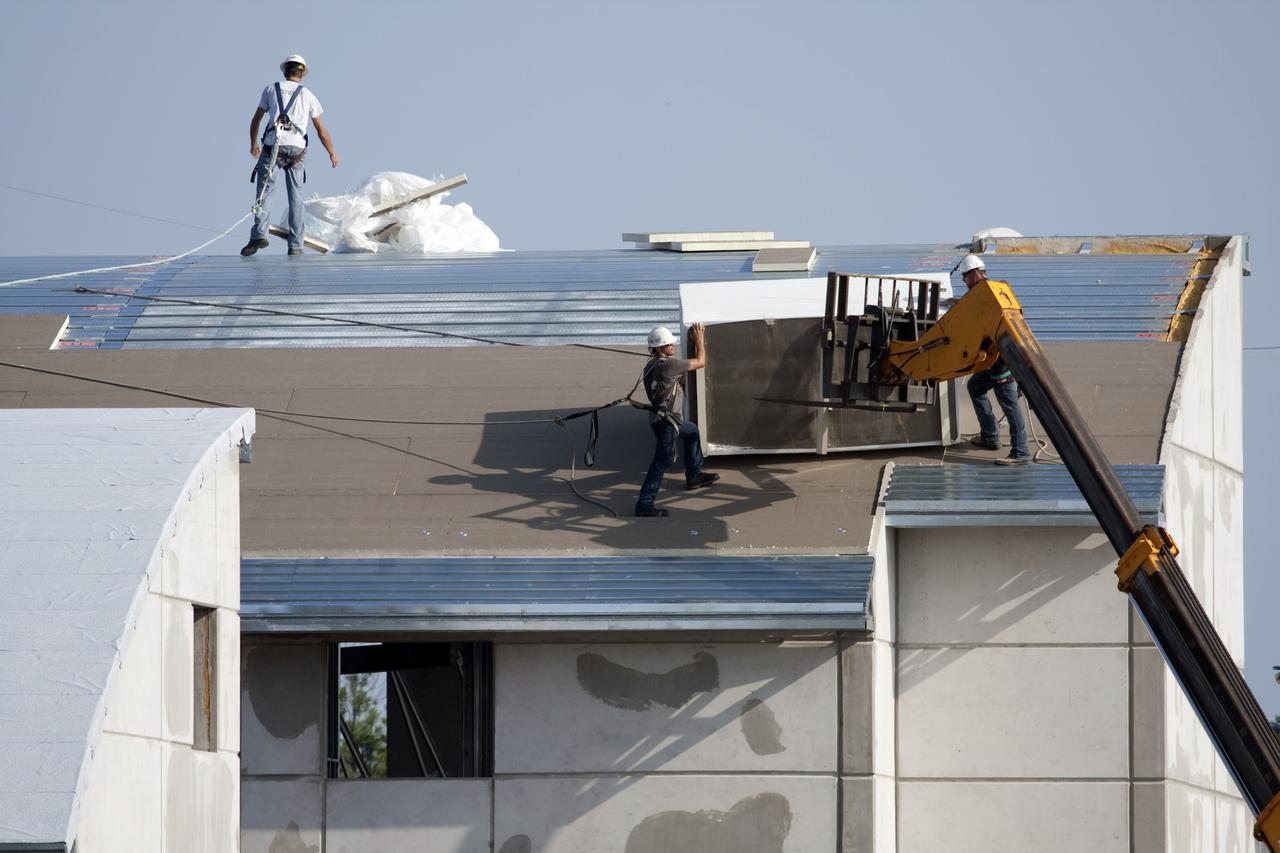

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, insulation material is delivered to roofers on one of the Propellants North Administrative and Maintenance Facility buildings by a boom lift. The insulation has an R-40 rating, compared to the insulation under the roof of an average home which has a rating of R-10 or R-15. The facility will have a two-story administrative building to house managers, mechanics and technicians who fuel spacecraft at Kennedy adjacent to an 1,800-square-foot single-story shop to store cryogenic fuel transfer equipment. The new facility will feature high-efficiency roofs and walls, “Cool Dry Quiet” air conditioning with energy recovery technology, efficient lighting, and other sustainable features. The facility is striving to qualify for the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, or LEED, Platinum certification. If successful, Propellants North will be the first Kennedy facility to achieve this highest of LEED ratings after it is completed in December 2010. The facility was designed for NASA by Jones Edmunds and Associates. H. W. Davis Construction is the construction contractor. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis
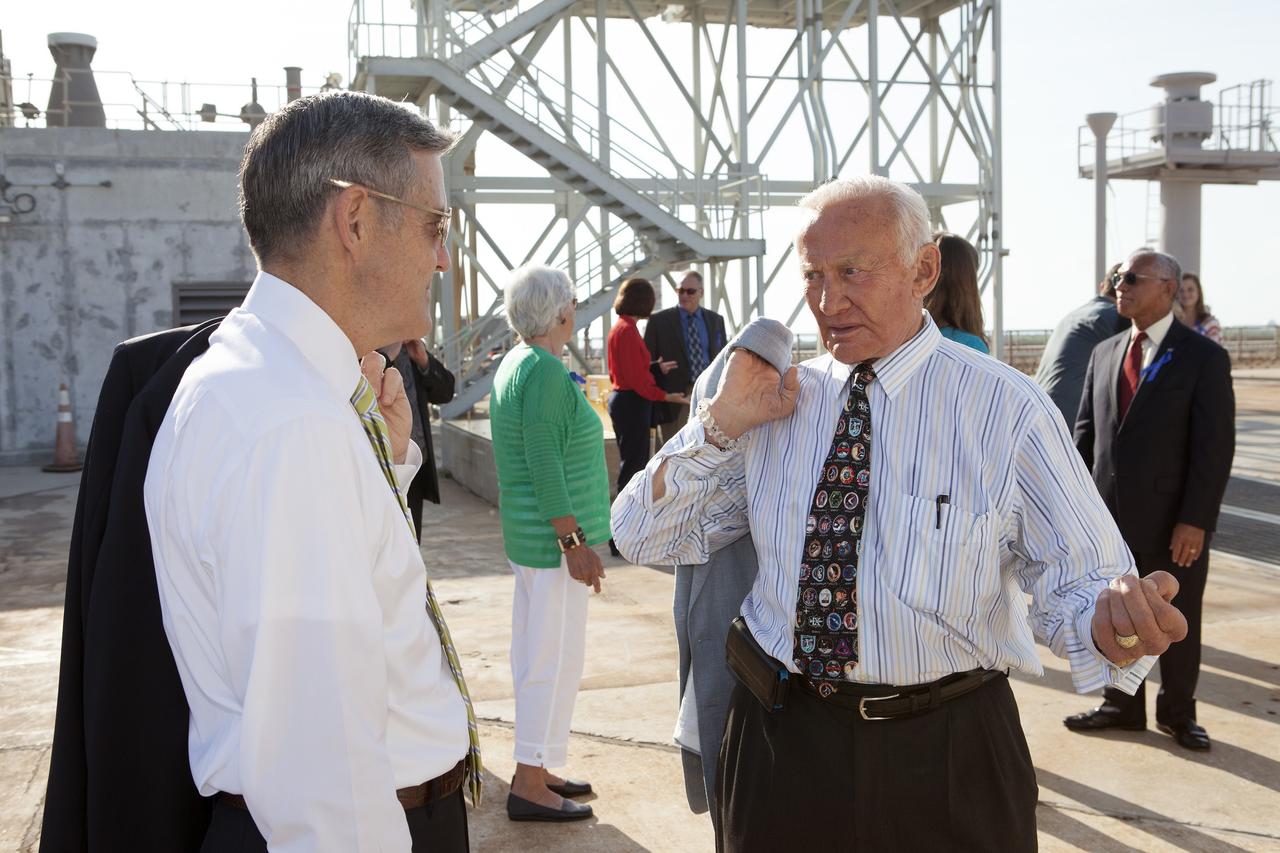

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Center Director Robert Cabana, left, briefs Apollo 11 astronaut Buzz Aldren, right, on the changes underway to Launch Pad 39B. Behind them are the visiting Apollo astronauts' families and friends.The pad is being modified to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft which will lift off atop the Space Launch System rocket. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The visit was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, the Apollo 11 astronauts landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module Eagle on July 20, 1969. For more, visit http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
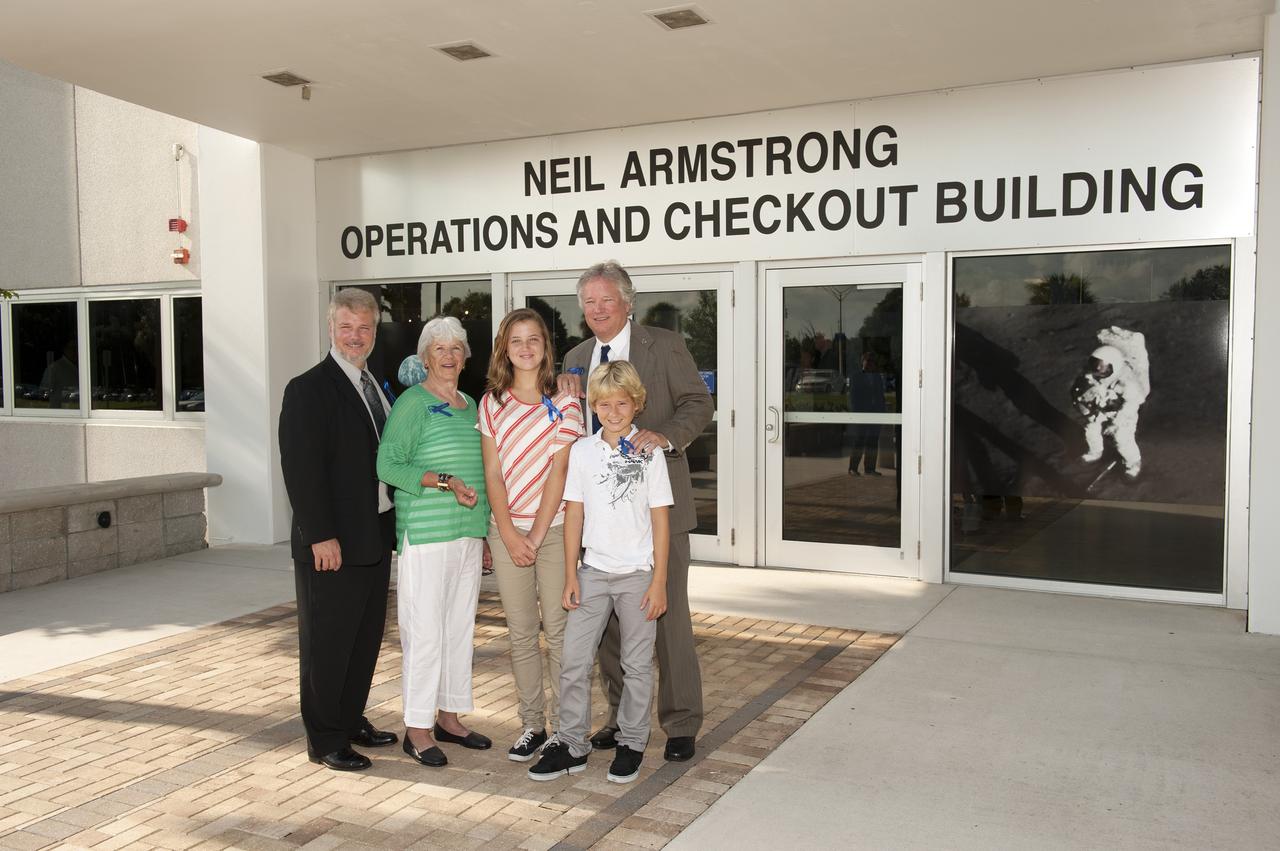

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the family of Neil Armstrong poses for a group portrait in front of the refurbished Operations and Checkout Building. From left are Armstrong's son Mark, his former wife Janet, his granddaughter Lily, his son Rick and his grandson Bryce. Armstrong, an Apollo 11 astronaut, was the first person to set foot on the moon and for whom the facility is newly named. The building's high bay is being used to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft, which will lift off atop the Space Launch System rocket. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The visit of the former astronauts was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, Neil Armstrong and Aldrin landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module Eagle on July 20, 1969. Meanwhile, crewmate Collins orbited above in the command module Columbia. For more, visit http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell
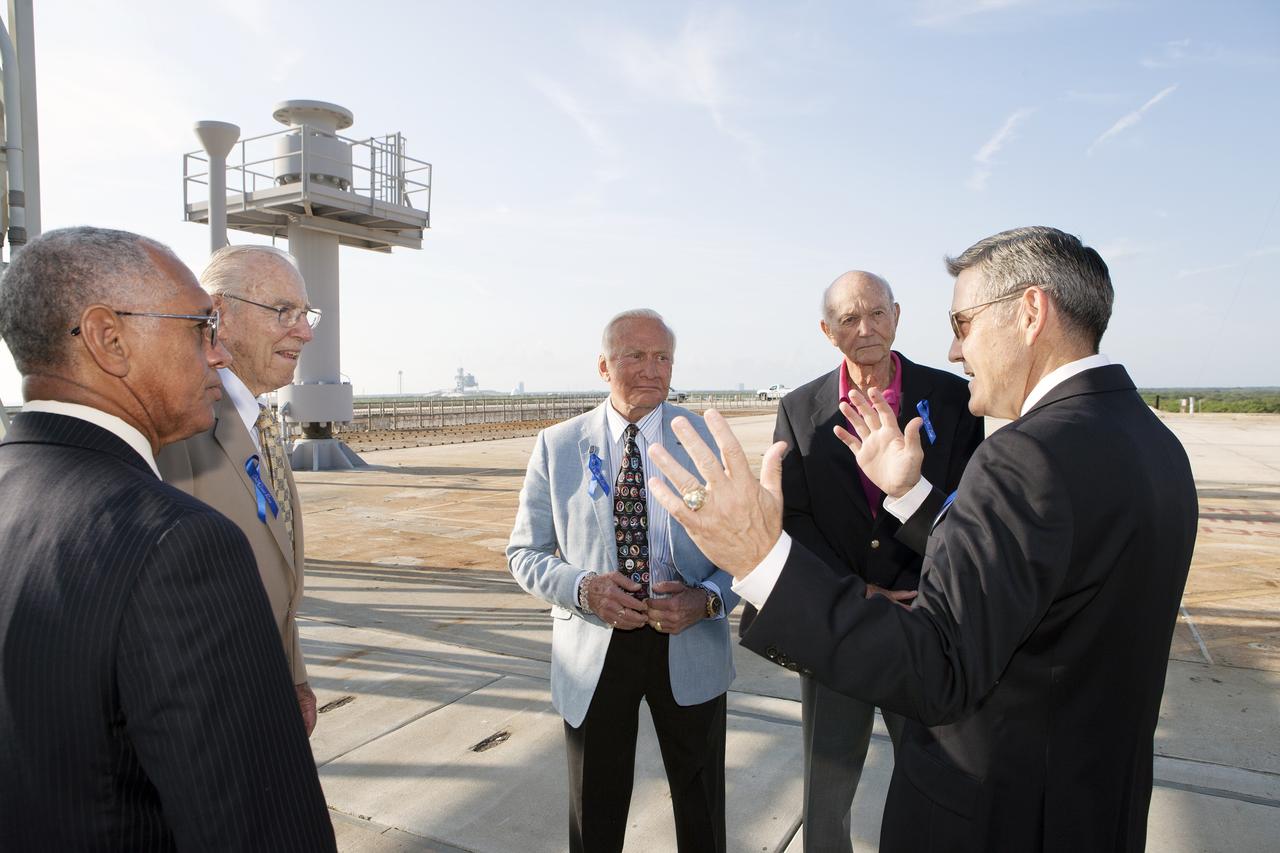

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Center Director Bob Cabana, at right, briefs Apollo astronauts on the changes underway to Launch Pad 39B. From left are NASA administrator Charles Bolden, Apollo astronauts Jim Lovell, Buzz Aldrin and Mike Collins, and Cabana. The pad is being modified to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft which will lift off atop the Space Launch System rocket. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The visit of the former astronauts was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, Neil Armstrong and Aldrin landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module Eagle on July 20, 1969. Meanwhile, crewmate Collins orbited above in the command module Columbia. For more, visit http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
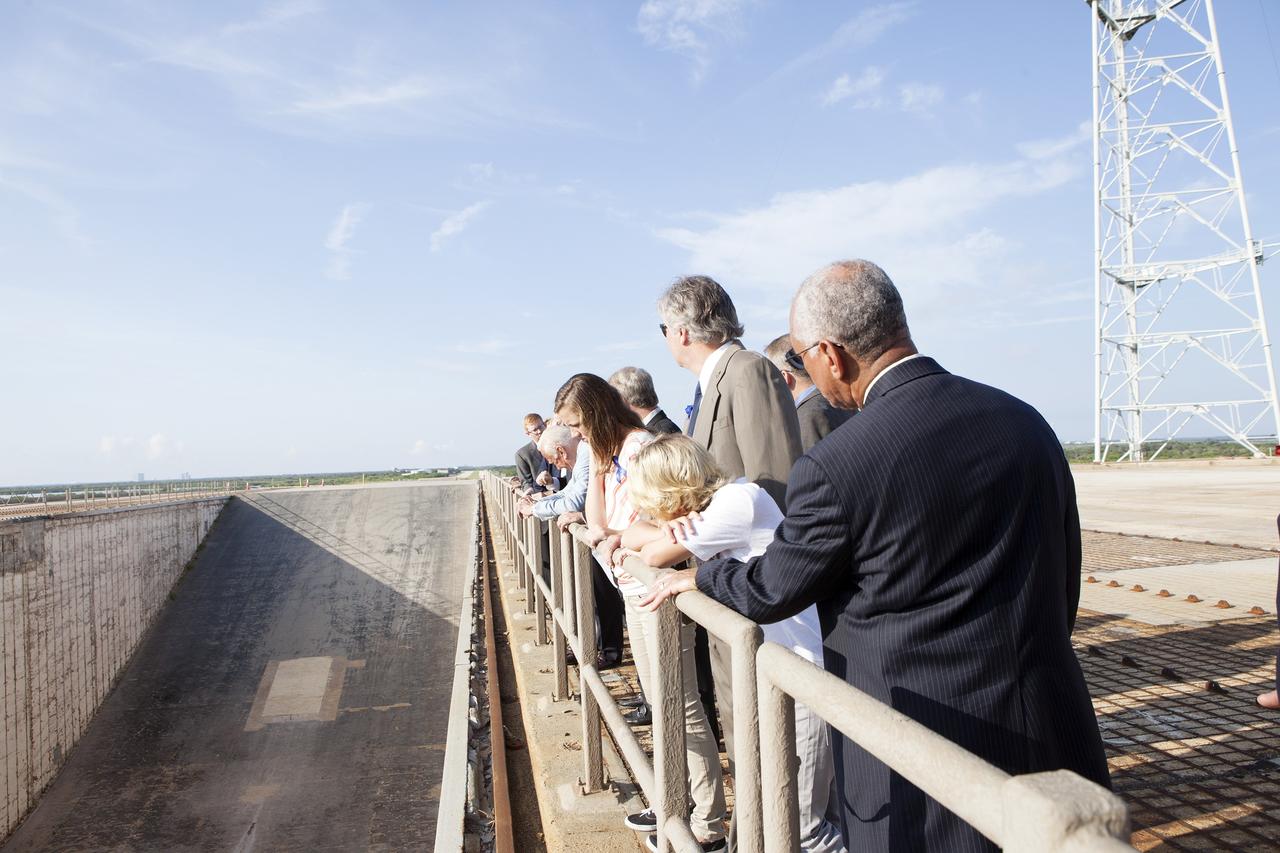

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA administrator Charles Bolden, at right, enjoys an unobstructed view of the flame trench on Launch Pad 39B with Apollo astronauts and their families and friends. The pad is being modified to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft which will lift off atop the Space Launch System rocket. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The visit of the former astronauts was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, the Apollo 11 astronauts landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module Eagle on July 20, 1969. For more, visit http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
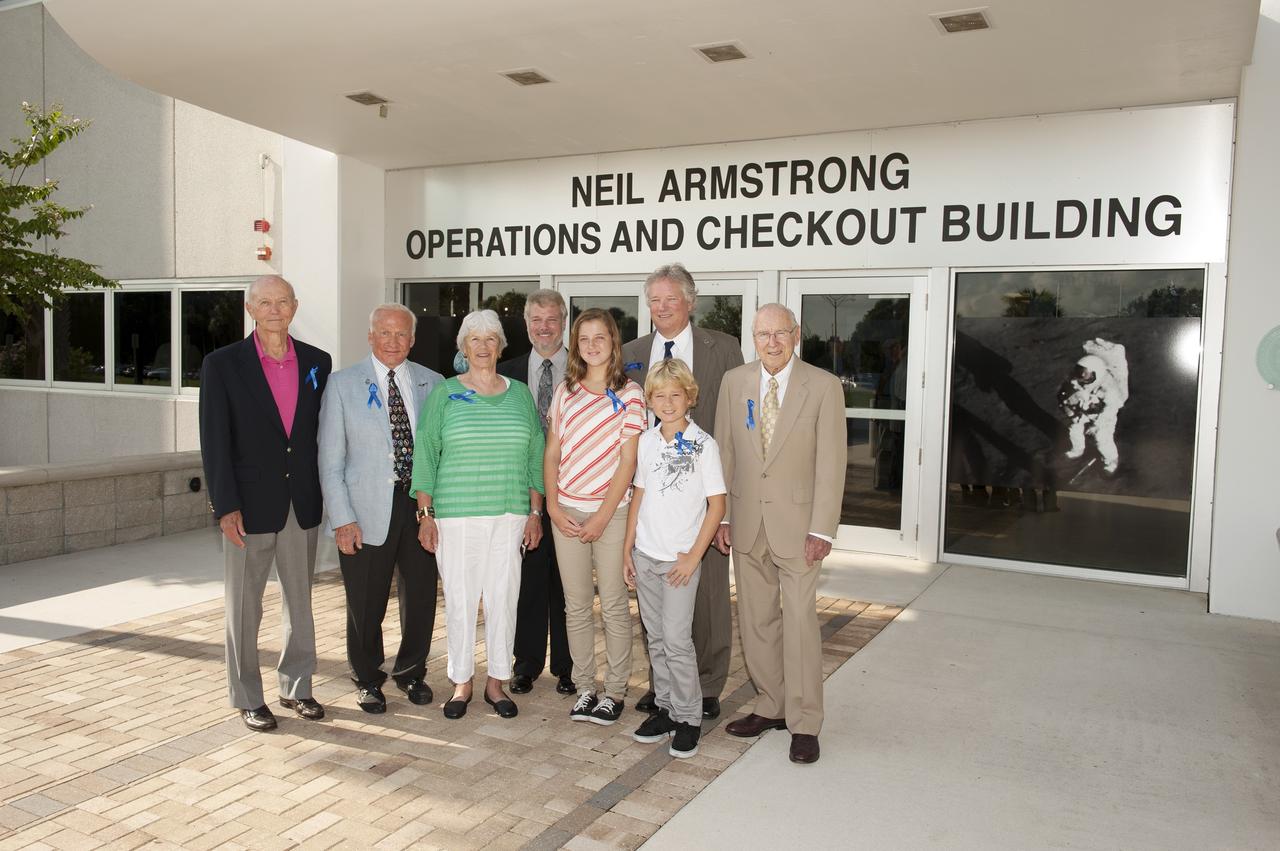

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, visiting Apollo astronauts have a group portrait taken in front of the refurbished Operations and Checkout Building, with the family of Neil Armstrong, the Apollo 11 astronaut who was the first person to set foot on the moon and for whom the facility is newly named. From left are Apollo 11 astronauts Mike Collins and Buzz Aldrin, Armstrong's former wife Janet, his son Rick, his granddaughter Lily, his son Rick, his grandson Bryce, and Apollo 8 and 13 astronaut Jim Lovell. The building's high bay is being used to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft, which will lift off atop the Space Launch System rocket. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The visit of the former astronauts was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, Neil Armstrong and Aldrin landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module Eagle on July 20, 1969. Meanwhile, crewmate Collins orbited above in the command module Columbia. For more, visit http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Apollo astronauts, from left, Jim Lovell, Buzz Aldrin and Mike Collins pause during their tour of Launch Pad 39B for a group portrait. The pad is being modified to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft which will lift off atop the Space Launch System rocket. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The visit of the former astronauts was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, Neil Armstrong and Aldrin landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module Eagle on July 20, 1969. Meanwhile, crewmate Collins orbited above in the command module Columbia. For more, visit http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
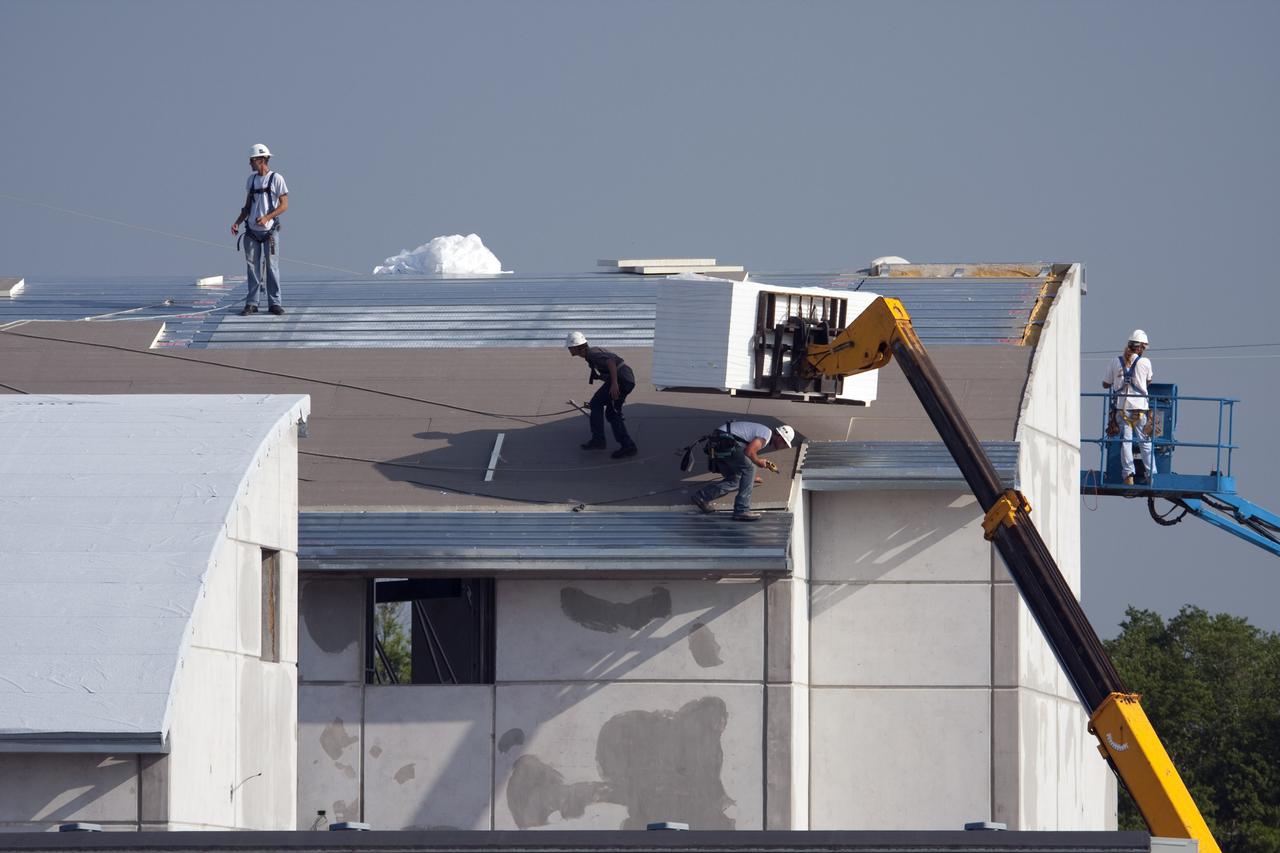

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a boom lift delivers insulation material to the workers installing it on the roof of one of the Propellants North Administrative and Maintenance Facility buildings. The insulation has an R-40 rating, compared to the insulation under the roof of an average home which has a rating of R-10 or R-15. The facility will have a two-story administrative building to house managers, mechanics and technicians who fuel spacecraft at Kennedy adjacent to an 1,800-square-foot single-story shop to store cryogenic fuel transfer equipment. The new facility will feature high-efficiency roofs and walls, “Cool Dry Quiet” air conditioning with energy recovery technology, efficient lighting, and other sustainable features. The facility is striving to qualify for the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, or LEED, Platinum certification. If successful, Propellants North will be the first Kennedy facility to achieve this highest of LEED ratings after it is completed in December 2010. The facility was designed for NASA by Jones Edmunds and Associates. H. W. Davis Construction is the construction contractor. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA officials showcase the modifications underway at Launch Pad 39 B to Apollo astronauts visiting the center. From left are NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, Apollos 8 and 13 astronaut Jim Lovell, Apollo 11 astronauts Buzz Aldrin and Mike Collins, and Center Director Bob Cabana. The pad is being modified to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft which will lift off atop the Space Launch System rocket. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The visit of the former astronauts was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, Neil Armstrong and Aldrin landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module Eagle on July 20, 1969. Meanwhile, crewmate Collins orbited above in the command module Columbia. For more, visit http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
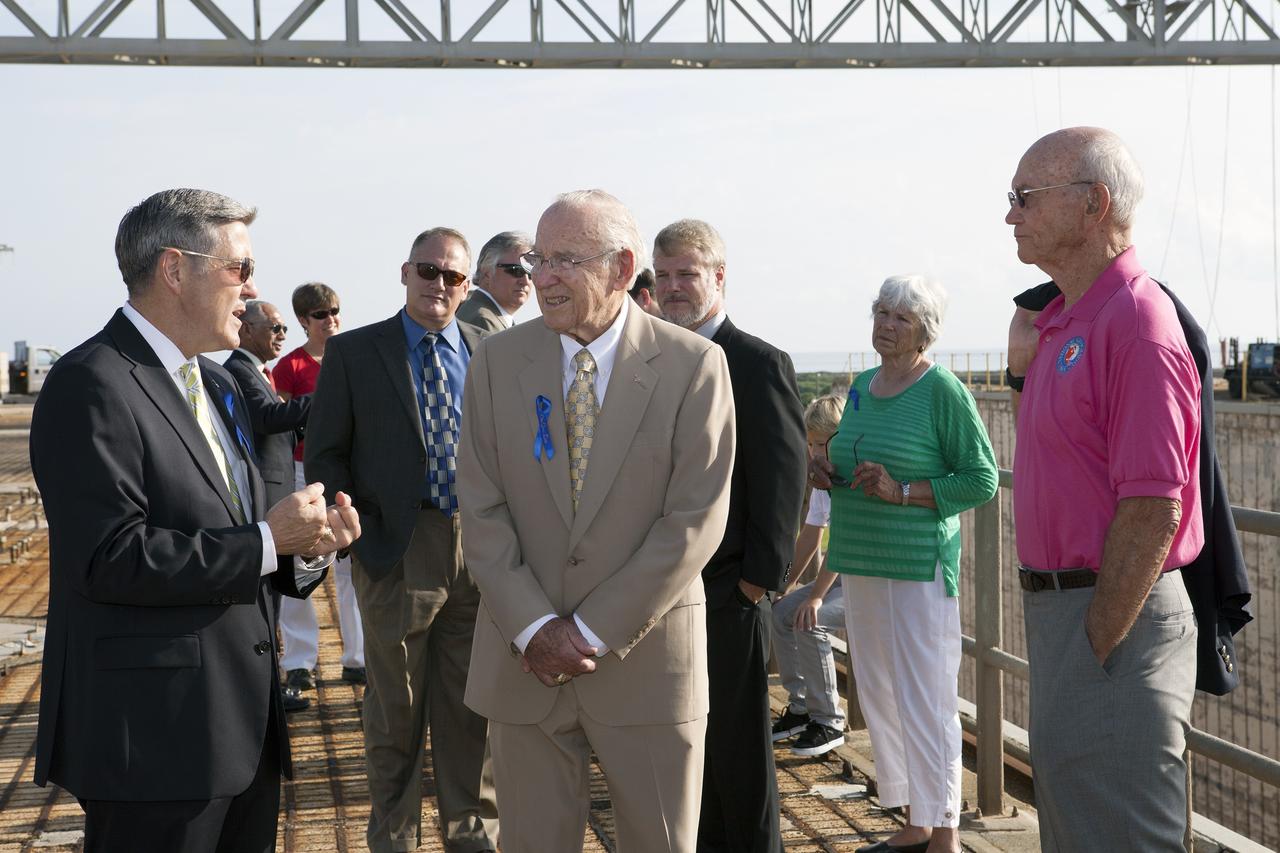

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Center Director Robert Cabana, left, briefs Apollo astronauts Jim Lovell, center, and Mike Collins, right, on the changes underway to Launch Pad 39B. Behind them are the astronauts' families and friends. The pad is being modified to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft which will lift off atop the Space Launch System rocket. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The visit of the former astronauts was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, the Apollo 11 astronauts landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module Eagle on July 20, 1969. For more, visit http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, visiting Apollo astronauts have a group portrait taken in front of the refurbished Operations and Checkout Building, newly named for Apollo 11 astronaut Neil Armstrong, the first person to set foot on the moon. From left are Mike Collins, Buzz Aldrin and Jim Lovell. The building's high bay is being used to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft, which will lift off atop the Space Launch System rocket. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The visit of the former astronauts was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, Neil Armstrong and Aldrin landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module Eagle on July 20, 1969. Meanwhile, crewmate Collins orbited above in the command module Columbia. For more, visit http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, work is underway to transform the center into a multi-user spaceport. Launch Pad 39B, in the foreground, is being modified to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft which will lift off atop the Space Launch System rocket. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. On April 14, NASA signed a property agreement with SpaceX of Hawthorne, Calif., for use and occupancy of Launch Pad 39A, in the distance, to serve as a platform to support SpaceX's future launch activities. For more, visit http://www.nasa.gov/kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA officials and Apollo astronauts have a group portrait taken in front of the refurbished Operations and Checkout Building, newly named for Apollo 11 astronaut Neil Armstrong, the first person to set foot on the moon. From left are NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, Apollo astronauts Mike Collins, Buzz Aldrin and Jim Lovell, and Center Director Robert Cabana. The building's high bay is being used to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft, which will lift off atop the Space Launch System rocket. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The visit of the former astronauts was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, Neil Armstrong and Aldrin landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module Eagle on July 20, 1969. Meanwhile, crewmate Collins orbited above in the command module Columbia. For more, visit http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission. Photo credit: NASA/Kevin O'Connell
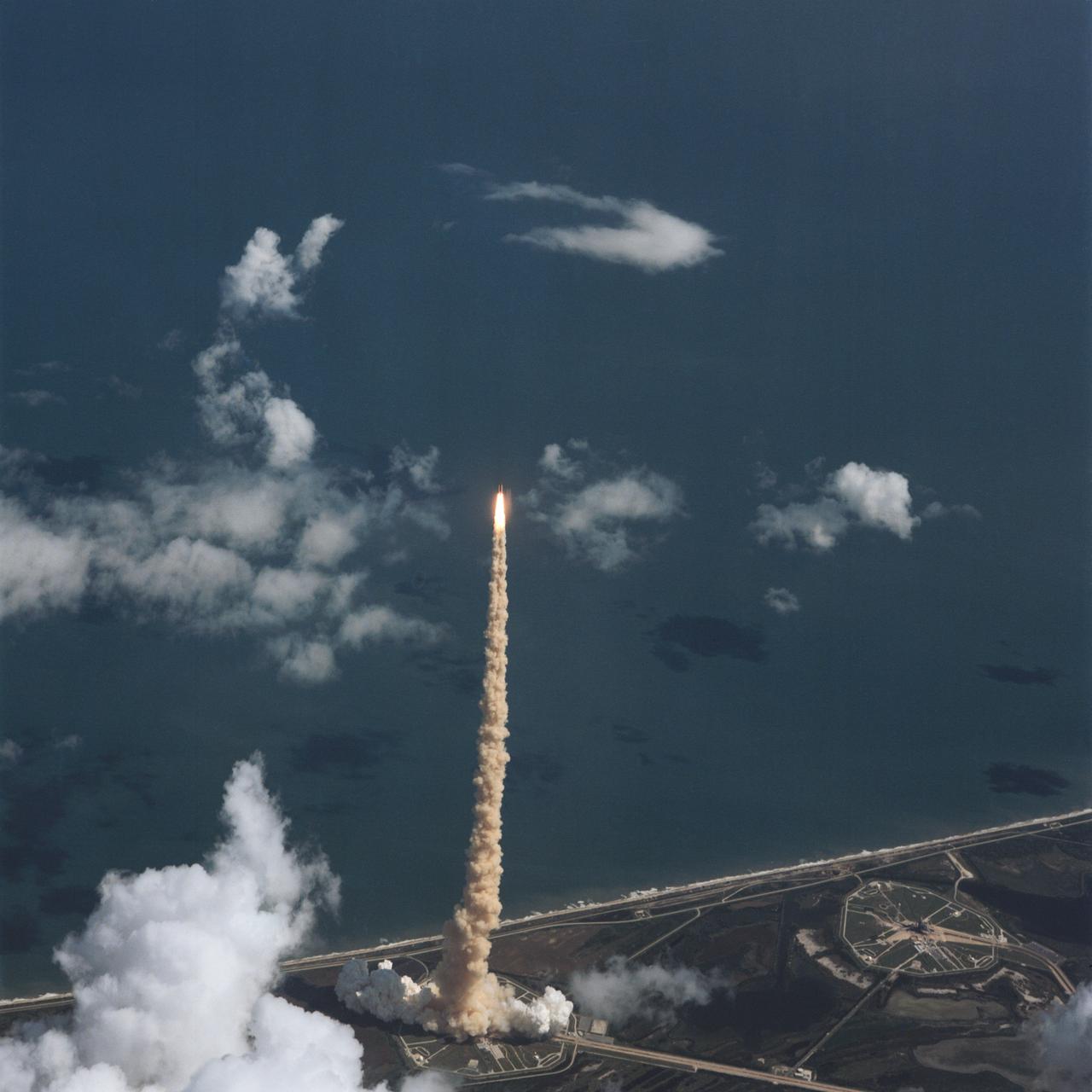

STS-34 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, lifts off from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39B at 12:53:39:983 pm Eastern Daylight Time (EDT). This aerial view shows OV-104, its external tank (ET), and two solid rocket boosters (SRBs) rising high above LC Pad 39B atop a plume of exhaust smoke. Atlantic Ocean is visible in the background. The liftoff marks the beginning of a five-day mission in space.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of a mobile launcher platform that is parked in the Launch Complex 39 Area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platform, which is a moveable base for the launch of space shuttle, is a two-story steel structure 25 feet high, 160 feet long and 135 feet wide. It is constructed of welded steel up to 6 inches thick. The platform rests on six 22-foot-tall pedestals. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

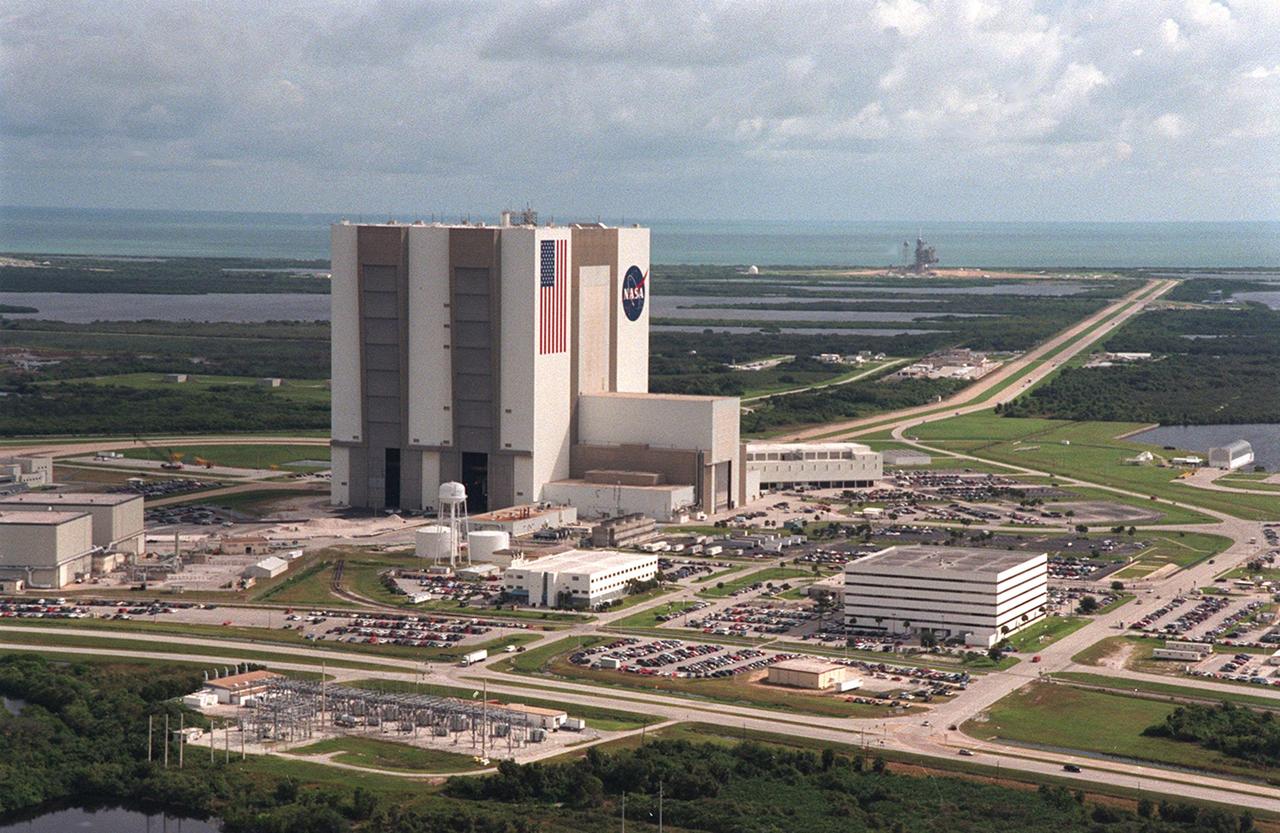
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This fisheye view shows storm clouds gathering over Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a common occurrence at this time of the year in Florida. The NASA News Center is at far left. The 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building towers above the complex, in the center, with the Launch Control Center nestled at its base to the right. The turn basin is behind the trees, at right. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Chamberland
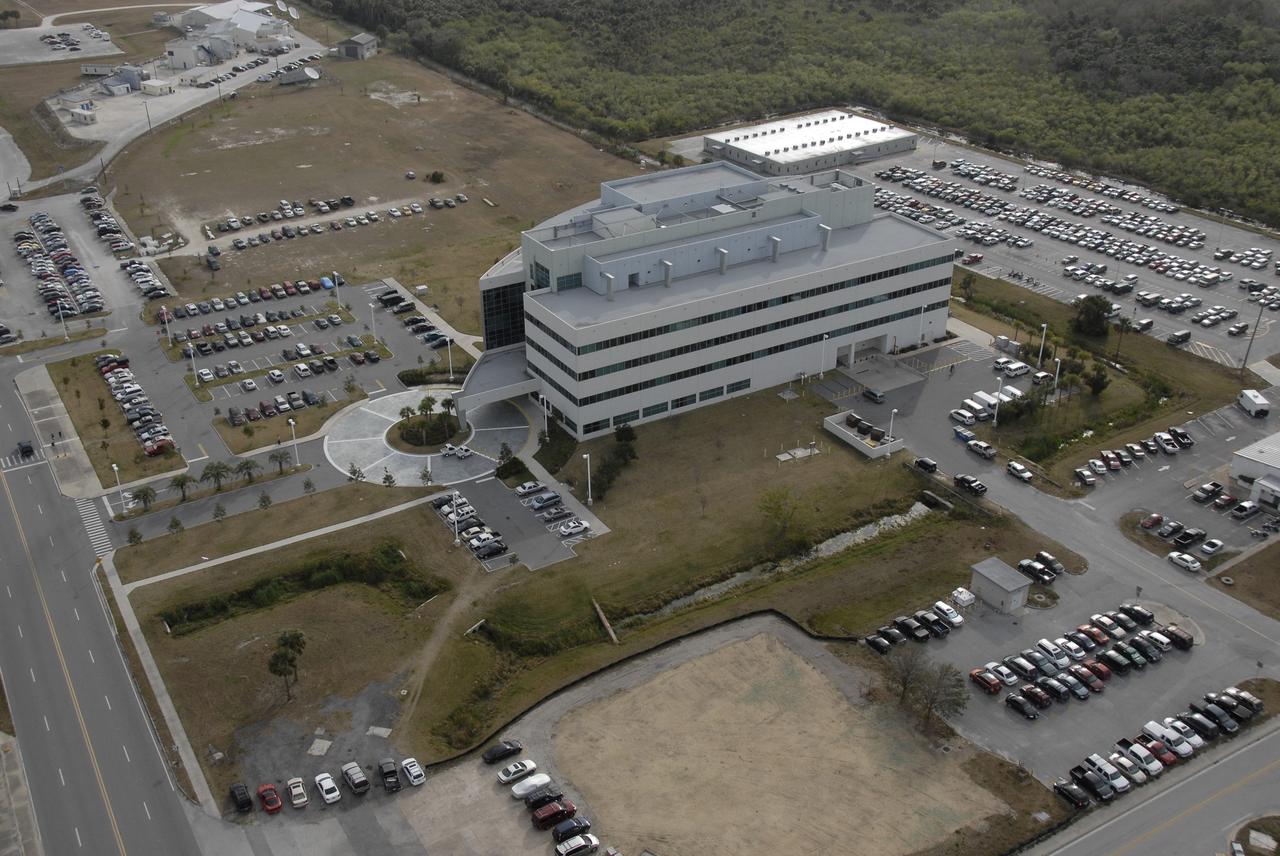

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – – An aerial view of the Operations Support Building II in the Launch Complex 39 Area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

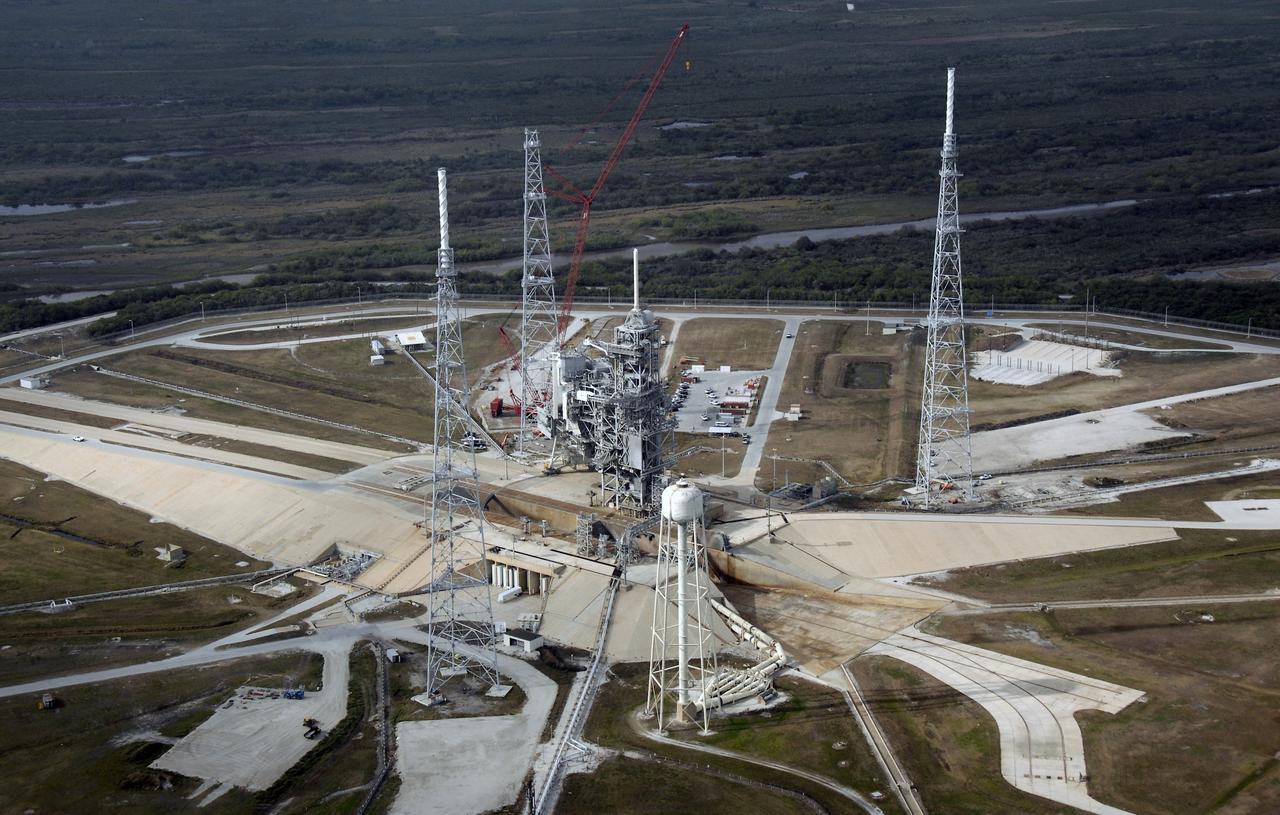
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the newly erected lightning towers on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The two towers at center and right contain the lightning mast on top; the one at left does not. At center are the fixed and rotating service structures that have served the Space Shuttle Program. In the foreground is the tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water used for sound suppression during a shuttle liftoff. The new lightning protection system is being built for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Each of the towers is 500 feet tall with an additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares rocket launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the newly erected lightning towers on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The two towers at left and right contain the lightning mast on top; the one at center does not. At center are the fixed and rotating service structures that have served the Space Shuttle Program. In the foreground is the tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water used for sound suppression during a shuttle liftoff. The new lightning protection system is being built for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Each of the towers is 500 feet tall with an additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares rocket launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
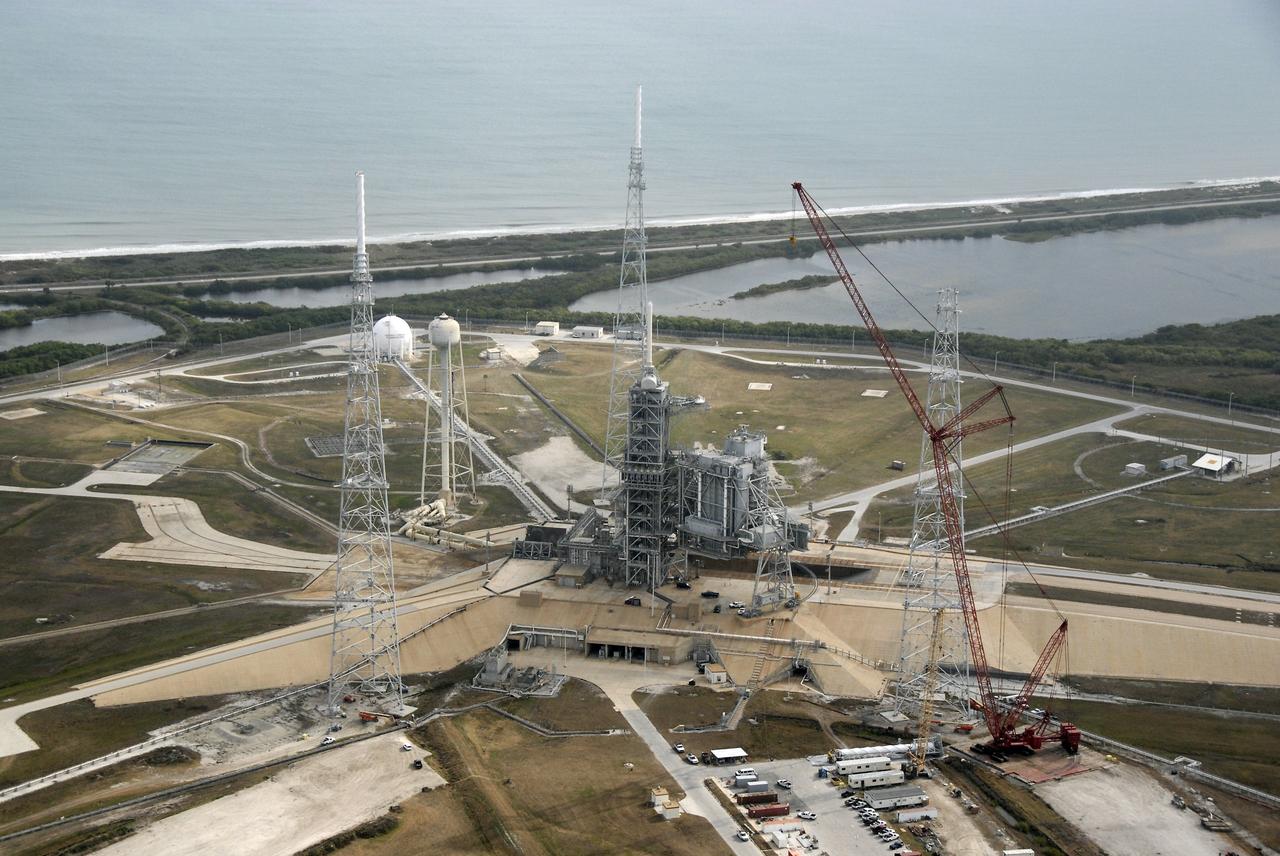

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the newly erected lightning towers on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The two towers at left and center contain the lightning mast on top; the one at right does not. At center are the fixed and rotating service structures that have served the Space Shuttle Program. Beyond the pad is the Atlantic Ocean. The new lightning protection system is being built for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Each of the towers is 500 feet tall with an additional 100-foot fiberglass mast atop supporting a wire catenary system. This improved lightning protection system allows for the taller height of the Ares I rocket compared to the space shuttle. Pad 39B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including the Ares I-X test flight that is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
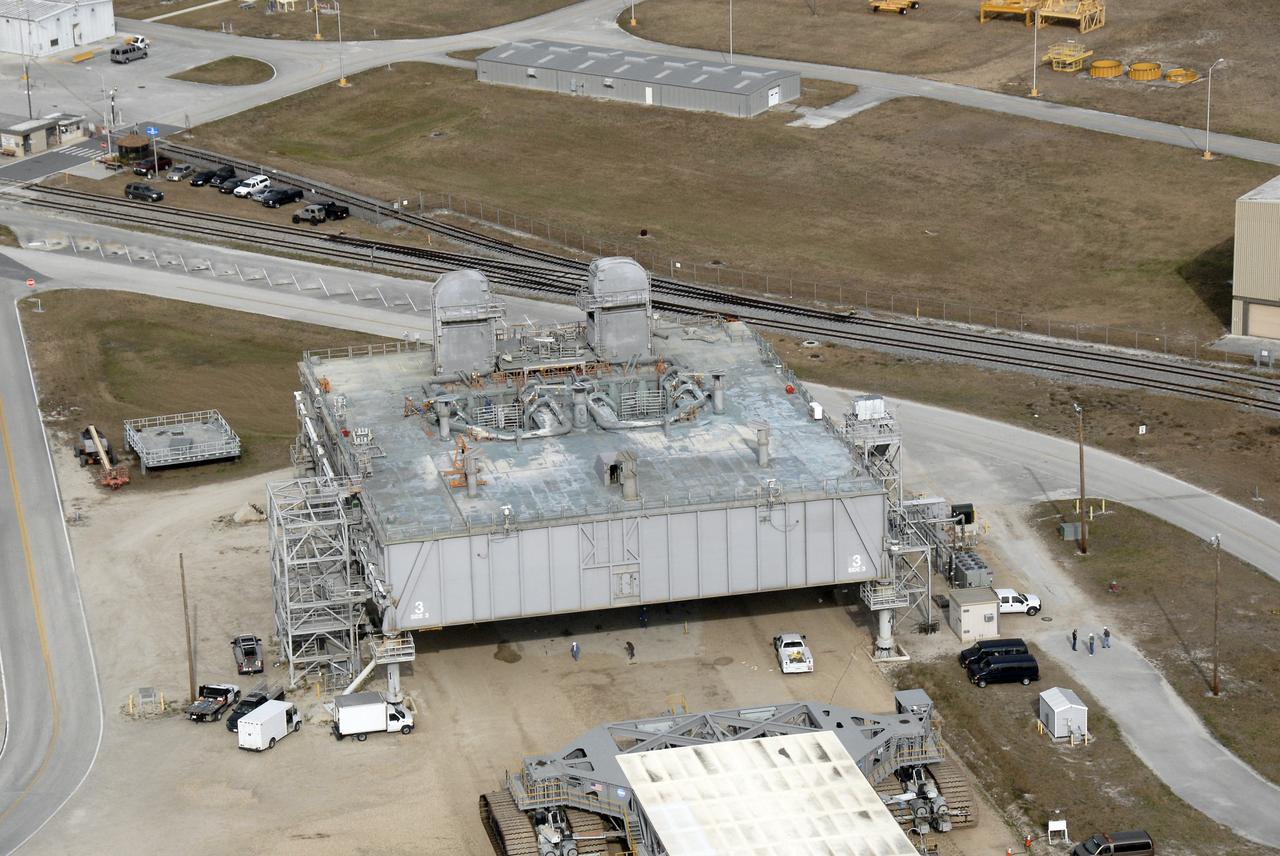

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of a mobile launcher platform that is parked in the Launch Complex 39 Area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platform, which is a moveable base for the launch of space shuttle, is a two-story steel structure 25 feet high, 160 feet long and 135 feet wide. It is constructed of welded steel up to 6 inches thick. The platform rests on six 22-foot-tall pedestals. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
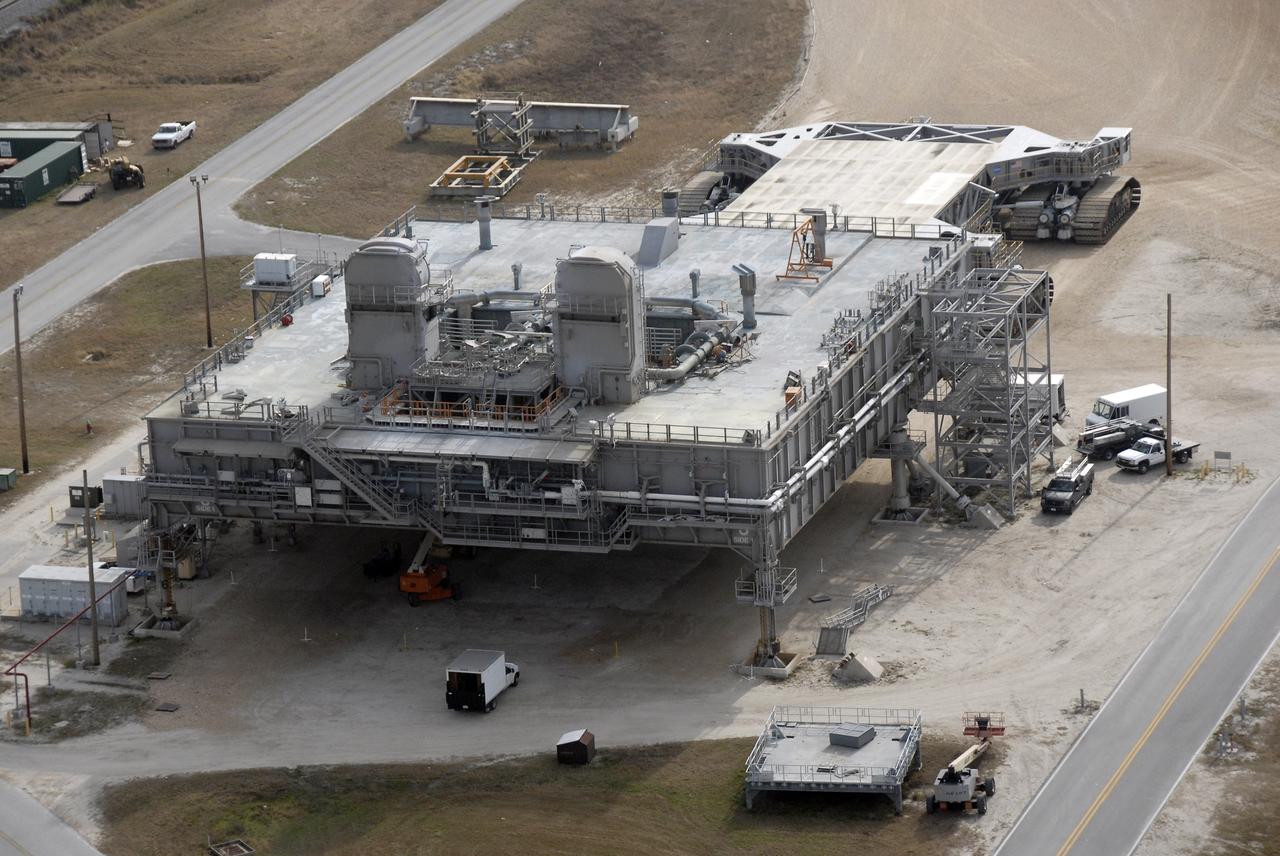

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of a mobile launcher platform that is parked in the Launch Complex 39 Area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The platform, which is a moveable base for the launch of space shuttle, is a two-story steel structure 25 feet high, 160 feet long and 135 feet wide. It is constructed of welded steel up to 6 inches thick. The platform rests on six 22-foot-tall pedestals. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
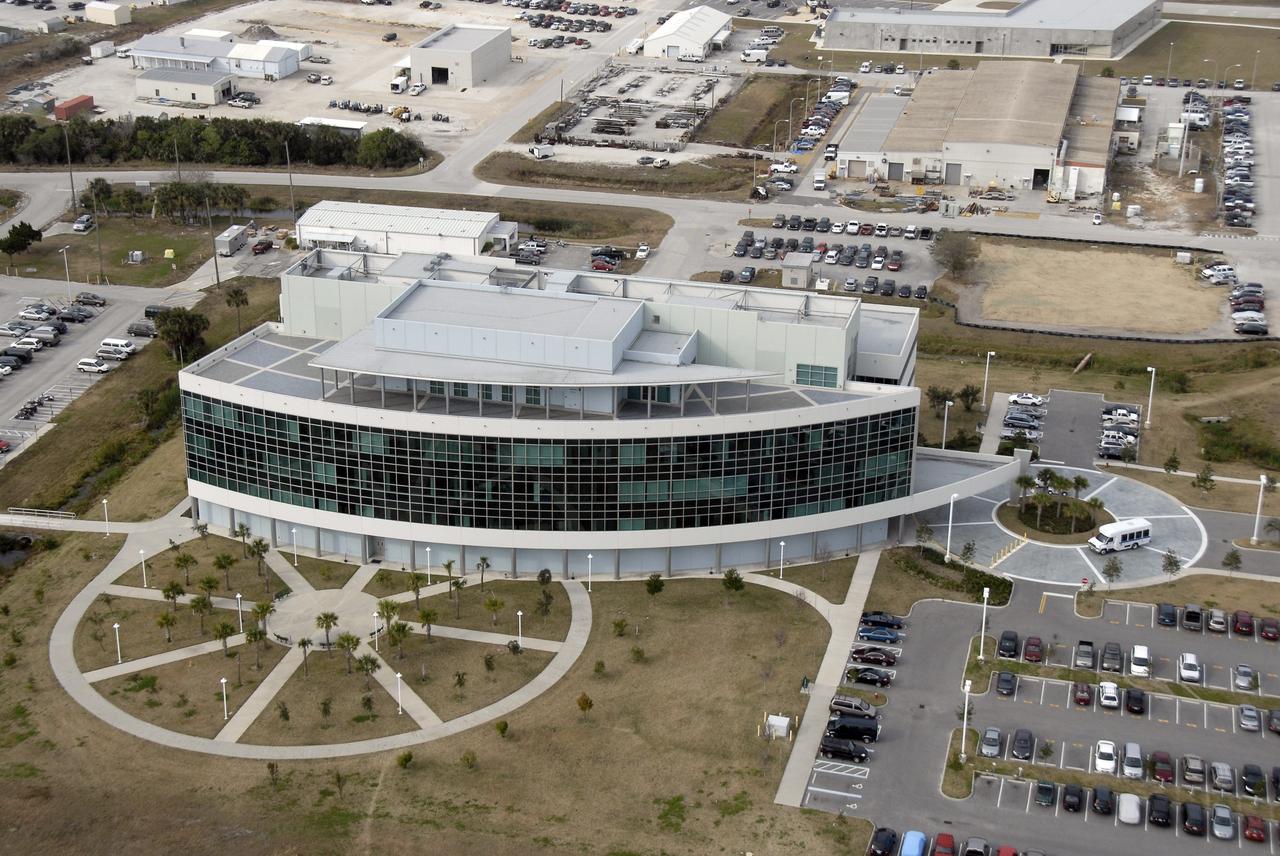

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the Operations Support Building II in the Launch Complex 39 Area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panorama of windows faces the launch pads. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

An aerial view of Launch Complex 39 area shows the Vehicle Assembly Building (center), with the Launch Control Center on its right. On the west side (lower end) are (left to right) the Orbiter Processing Facility, Process Control Center and Operations Support Building. Looking east (upper end) are Launch Pads 39-A (right) and 39-B (just above the VAB). The crawlerway stretches between the VAB and the launch pads toward the Atlantic Ocean, seen beyond them. At right is the turn basin where new external tanks are brought via ship, shown at its offloading site.

A broad aerial view west of Launch Complex 39 Area shows a multitude of facilities. Starting with the Shuttle Landing Facility, at bottom center is a circle around a windsock, a landing aid for pilots; at bottom right is a portion of the landing strip. In the center is the parking tarmac with its mate/demate device on the left corner. To the right is the remote launch vehicle hangar, still under construction. At the upper right is the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The tow-way road runs from the landing strip to the Orbiter Processing Facility, next to the VAB. The Kennedy Parkway North extends from the left side toward the VAB. The long white building next to the parkway is the Apollo/Saturn V Center. Above it, slightly visible on the horizon (left), is Launch Complex 39, Pad B.
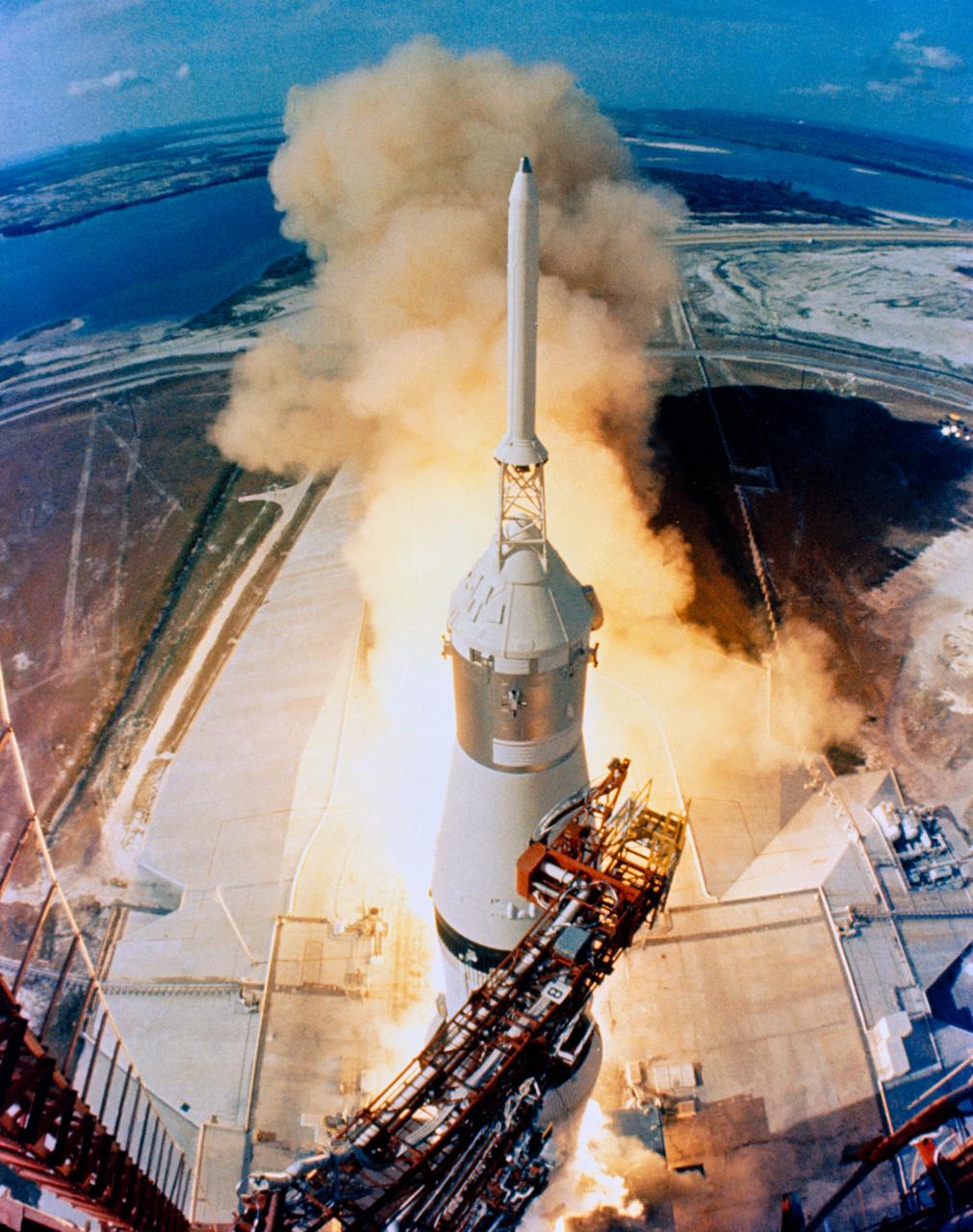

The huge, 363-foot tall Apollo XI Spacecraft 107/Lunar Module (LM)-5/Saturn 506) Space Vehicle is launched from Pad "A", Launch Complex (LC)-39, KSC, at 9:32 a.m. (EDT), 07/16/1969. This view of the liftoff was taken by a camera mounted on the Mobile Launch Tower. KSC, FL
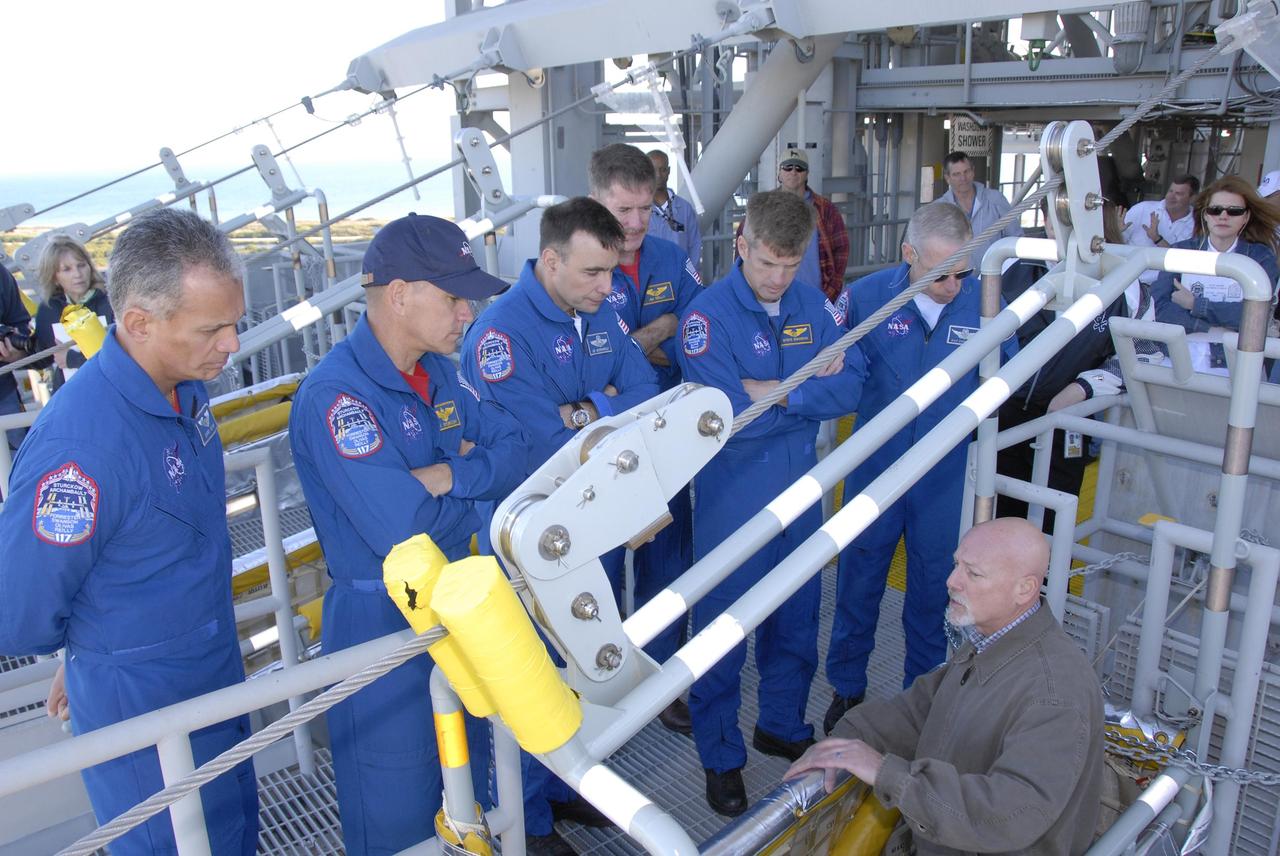

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the 195-foot level of the fixed service structure on Launch Pad 39A, STS-117 crew members receive instruction on emergency egress during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. From left are Mission Specialist Danny Olivas, Commander Rick Sturckow, Pilot Lee Archambault, and Mission Specialists James Reilly, Steven Swanson and Patrick Forrester. They are practicing the emergency egress procedure using the slidewire basket system to get off the pad. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
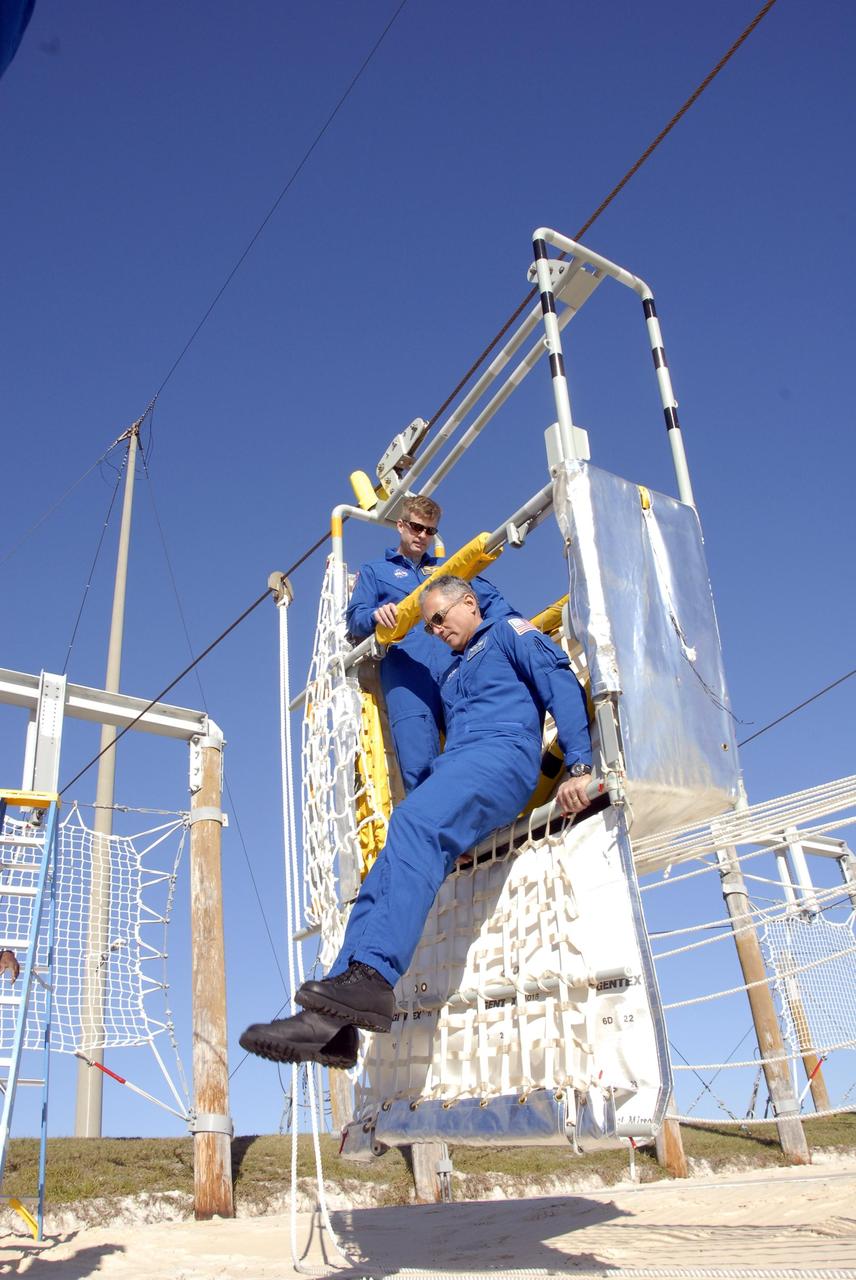

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Launch Pad 39A area, Mission STS-117 crew members receive instruction on emergency egress using the slidewire basket system during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. Here, Mission Specialists Steven Swanson (left) and Danny Olivas (right) practice exiting from the slidewire basket. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
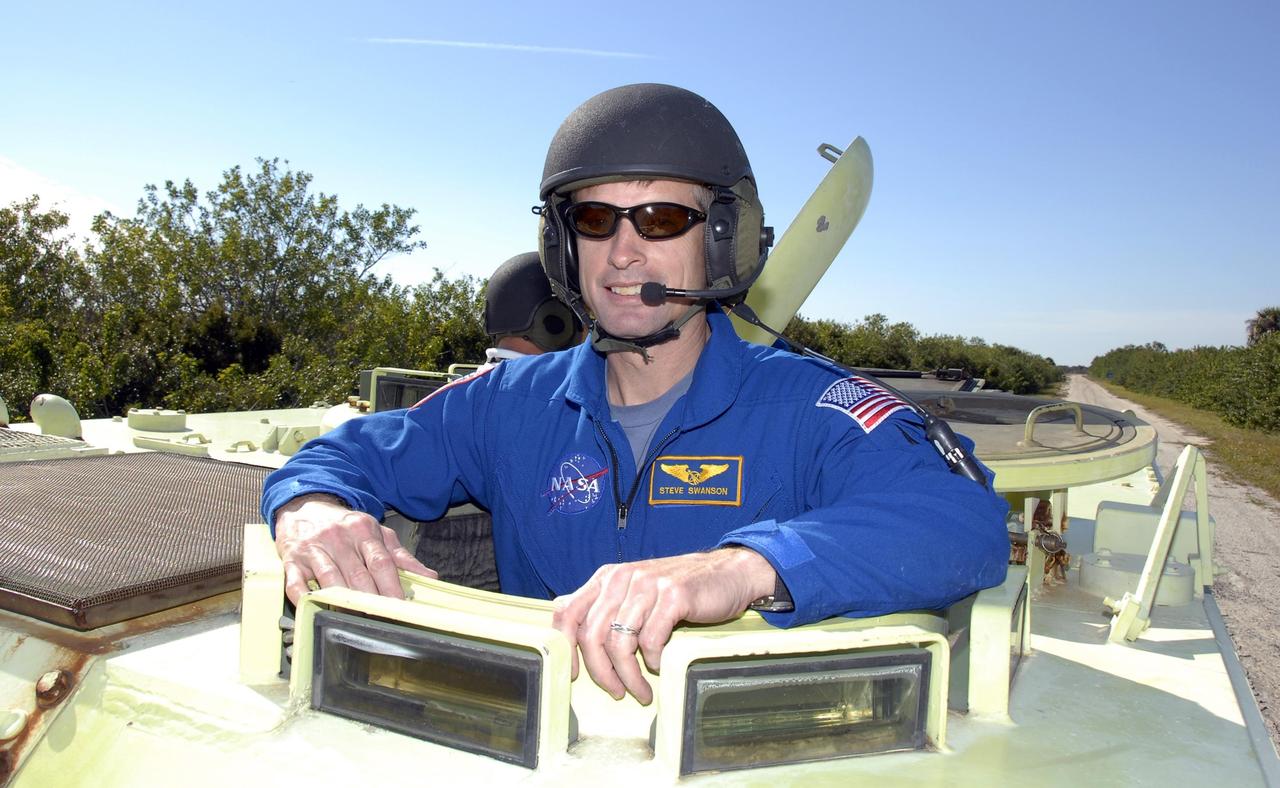

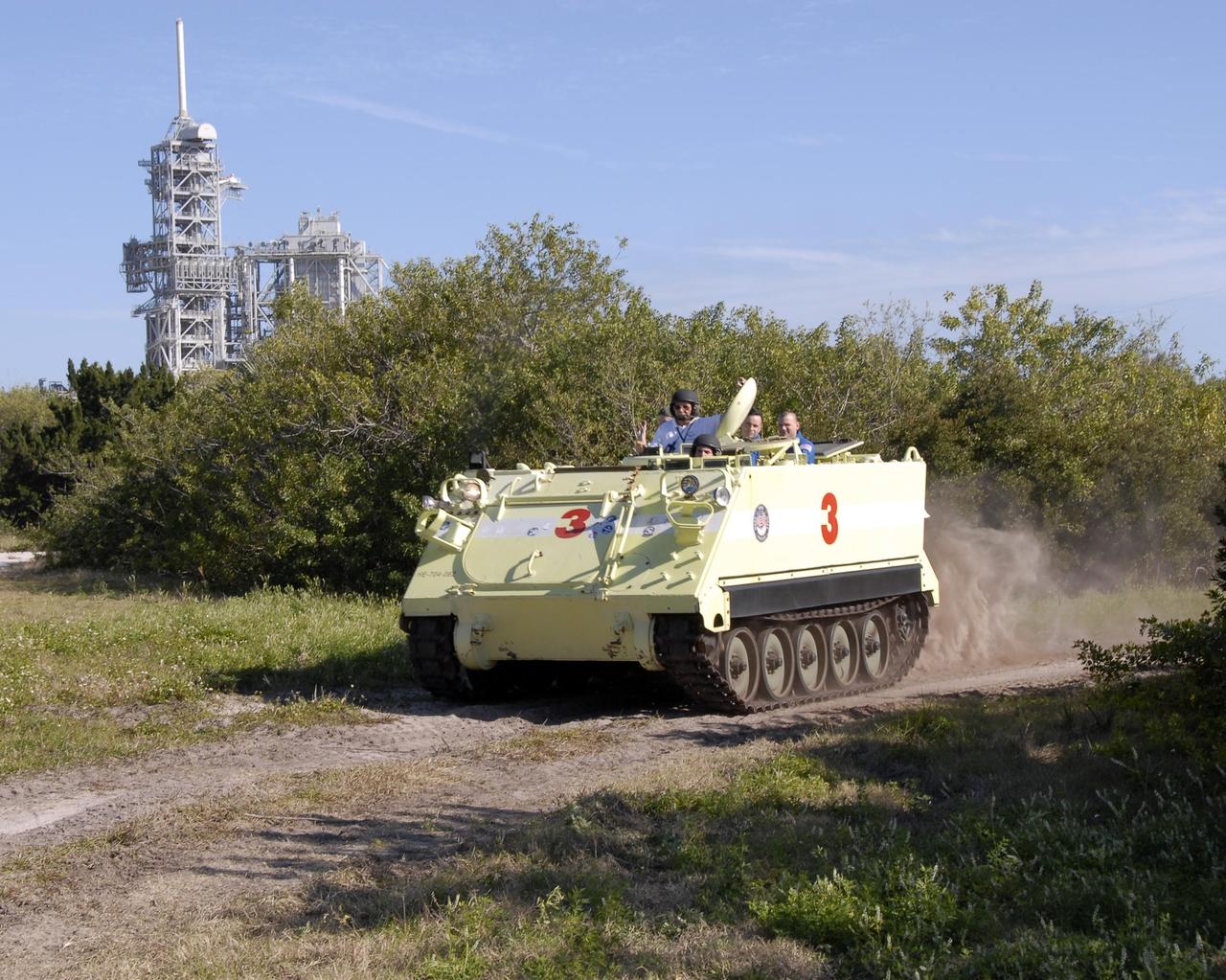
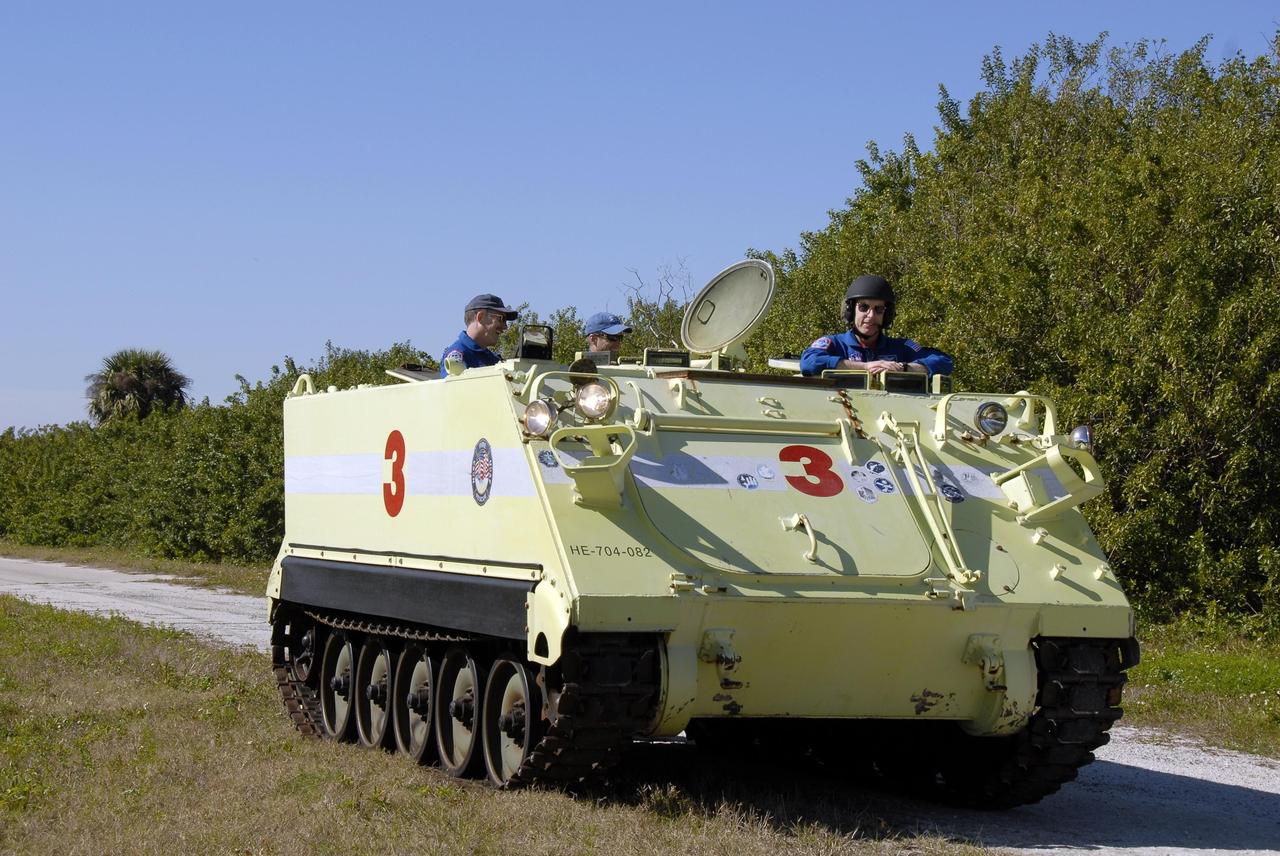
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 39, STS-117 Mission Specialist Steven Swanson is helmeted and ready to practice driving an M-113 armored personnel carrier. The astronauts on the STS-117 crew are participating in M-113 armored personnel carrier training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities, a dress rehearsal for their launch, targeted for March 15. The M-113 could be used to move the crew away from the launch pad quickly in the event of an emergency. The TCDT also includes pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, the Mission STS-117 crew members receive instruction on emergency egress during a walkdown of the 195-foot level of the fixed service structure at Launch Pad 39A. From the left are Mission Specialists Steven Swanson, Danny Olivas and Patrick Forrester, Pilot Lee Archambault, Commander Rick Sturckow and Mission Specialist James Reilly. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
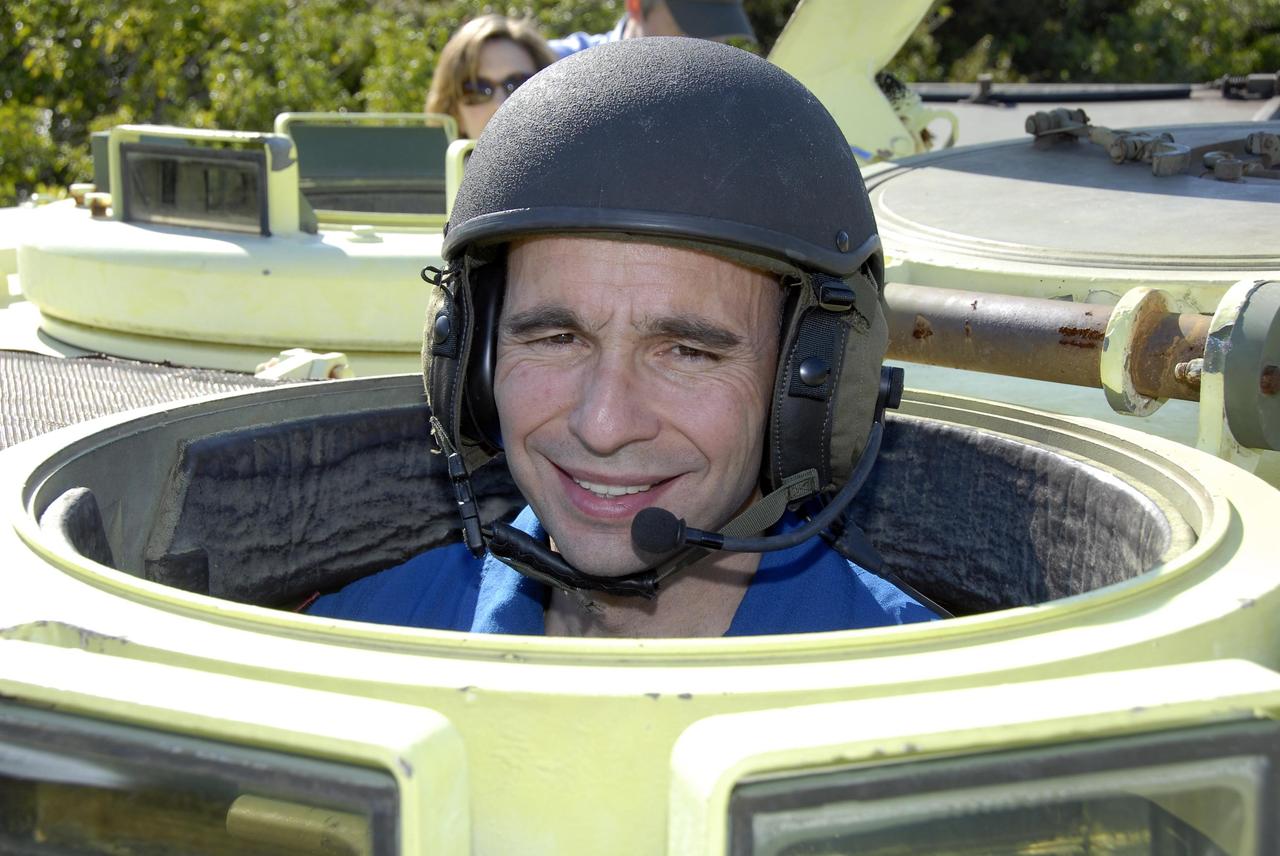

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 39, STS-117 Pilot Lee Archambault is helmeted and ready to practice driving an M-113 armored personnel carrier. The astronauts on the STS-117 crew are participating in M-113 armored personnel carrier training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities, a dress rehearsal for their launch, targeted for March 15. The M-113 could be used to move the crew away from the launch pad quickly in the event of an emergency. The TCDT also includes pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
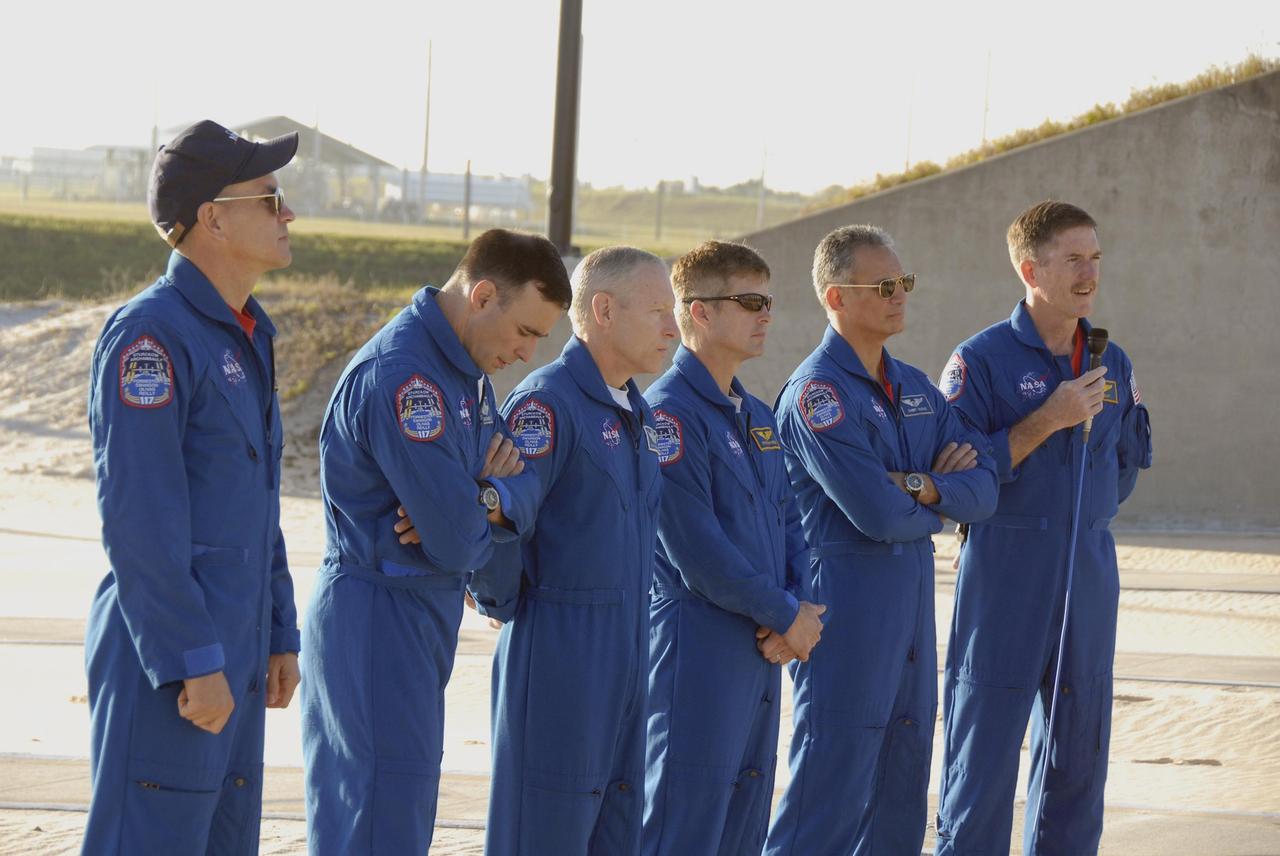

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities at Launch Pad 39A, the Mission STS-117 crew members speak to the media during a question-and-answer session. From the left are Commander Rick Sturckow, Pilot Lee Archambault, and Mission Specialists Patrick Forrester, Steven Swanson, Danny Olivas and James Reilly. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
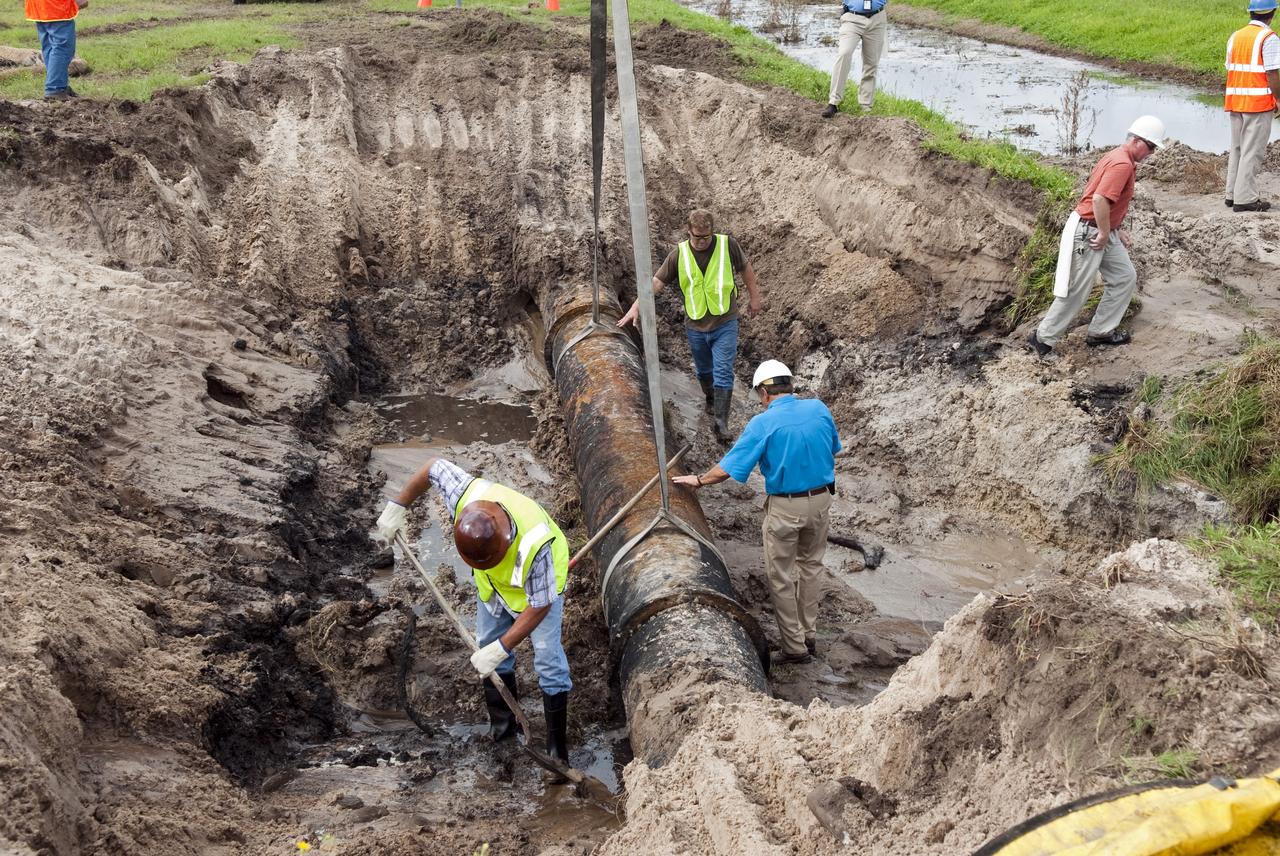

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crew begins to fix a major water main break in a 24-inch cast iron pipe in the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building and the Launch Control Center. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
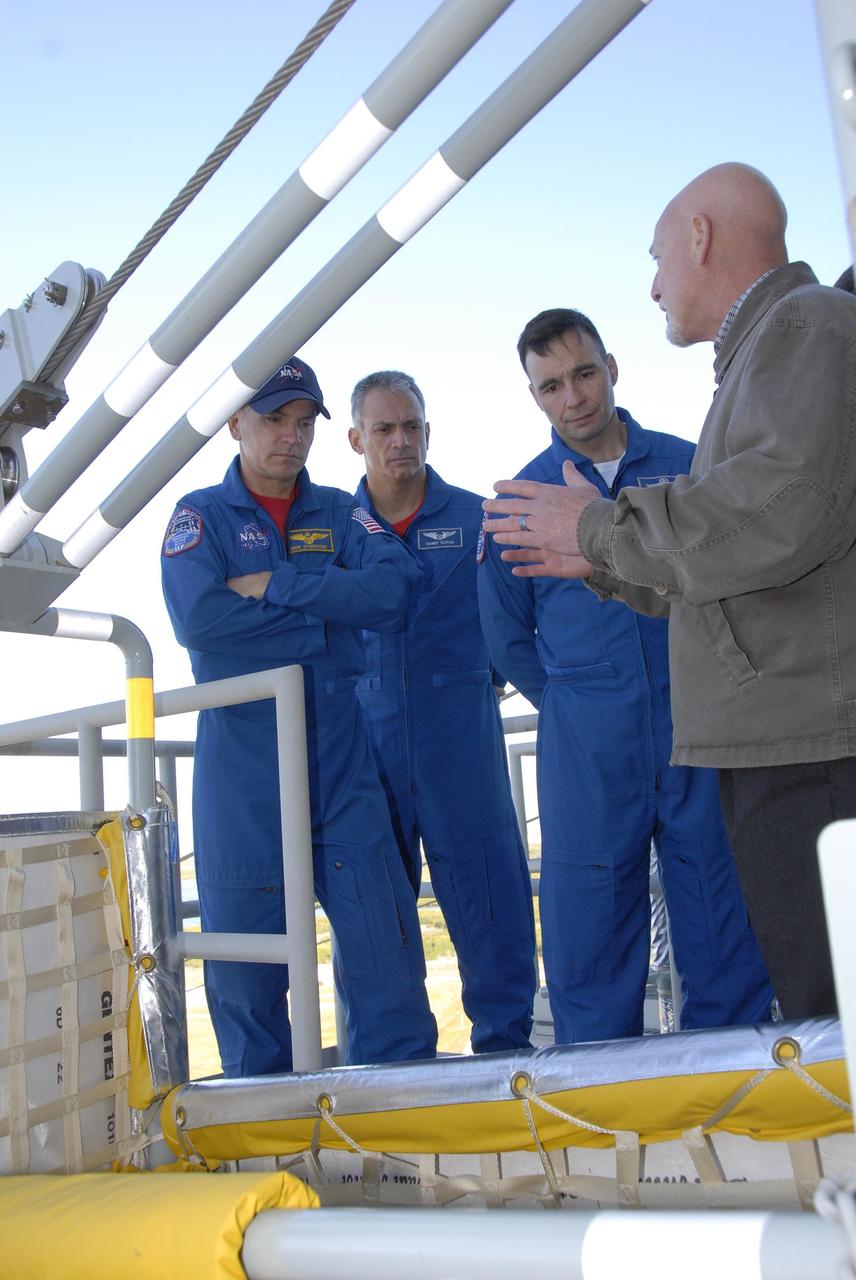

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the 195-foot level of the fixed service structure on Launch Pad 39A, STS-117 crew members receive instruction on emergency egress during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. From left are Commander Rick Sturckow, Mission Specialist Danny Olivas and Pilot Lee Archambault. They and other crew members are practicing the emergency egress procedure using the slidewire basket system to get off the pad. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
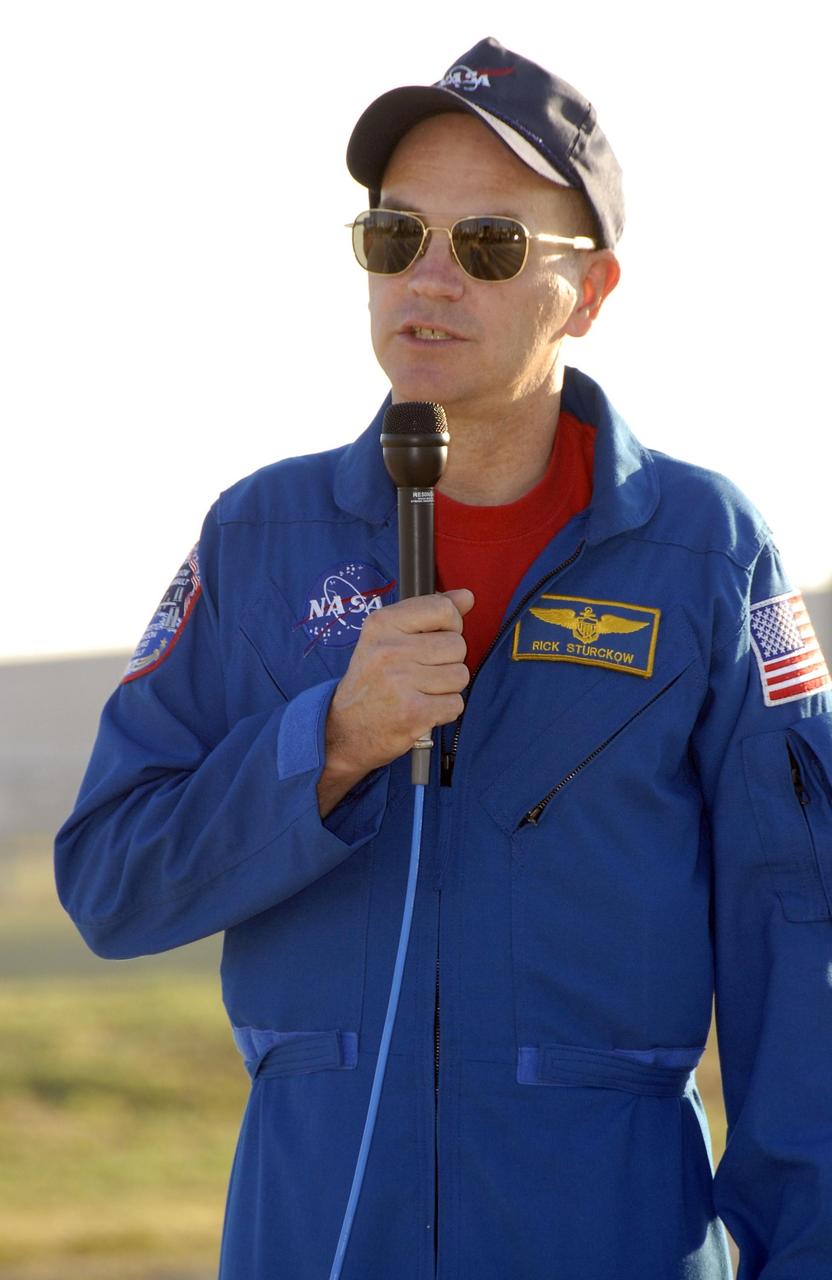

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Mission STS-117 Commander Rick Sturckow speaks to the media during a question-and-answer session at Launch Pad 39A during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 39, members of the STS-117 crew are instructed in the operation of an M-113 armored personnel carrier by astronaut rescue team leader Capt. George Hoggard (left). The astronauts on the STS-117 crew are participating in M-113 armored personnel carrier training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities, a dress rehearsal for their launch, targeted for March 15. The M-113 could be used to move the crew away from the launch pad quickly in the event of an emergency. The TCDT also includes pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
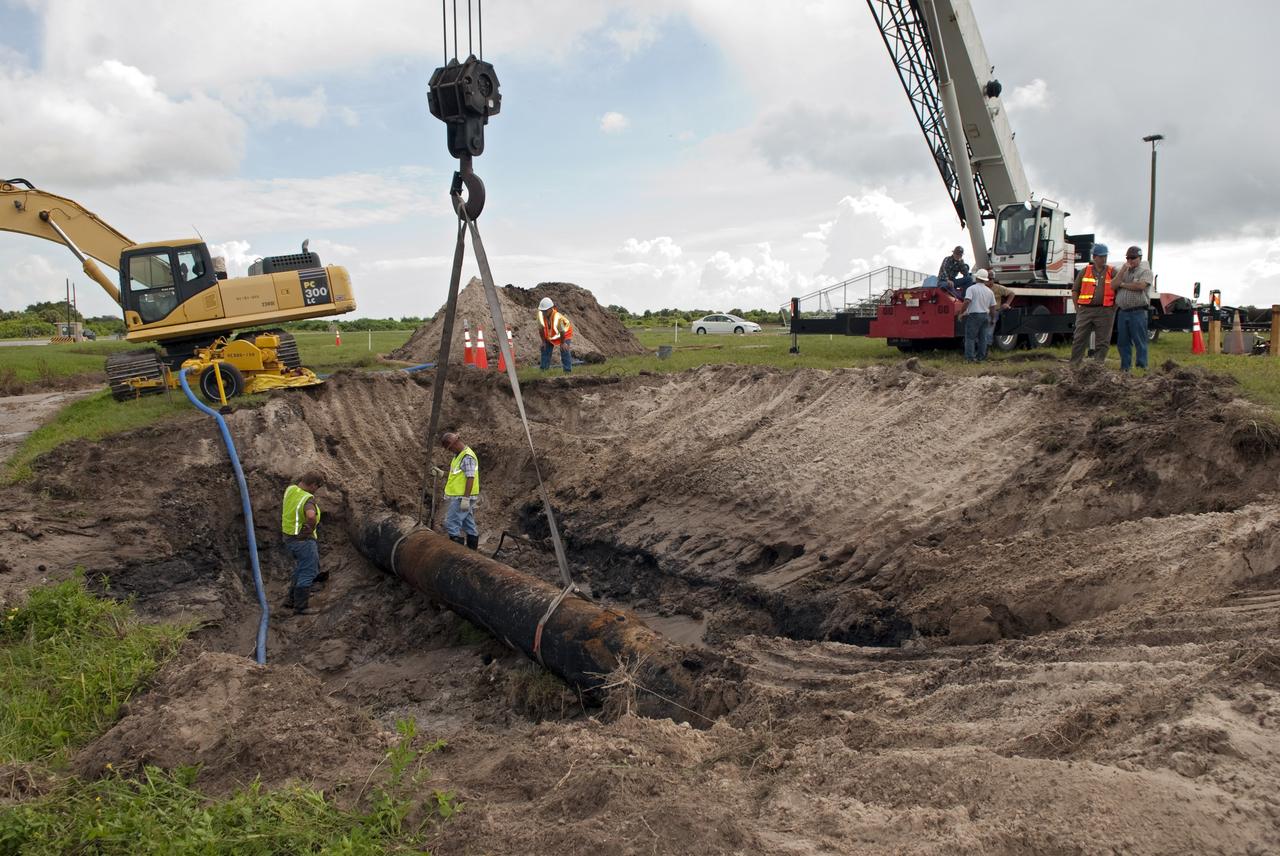

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crew begins to fix a major water main break in a 24-inch cast iron pipe in the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building and the Launch Control Center. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
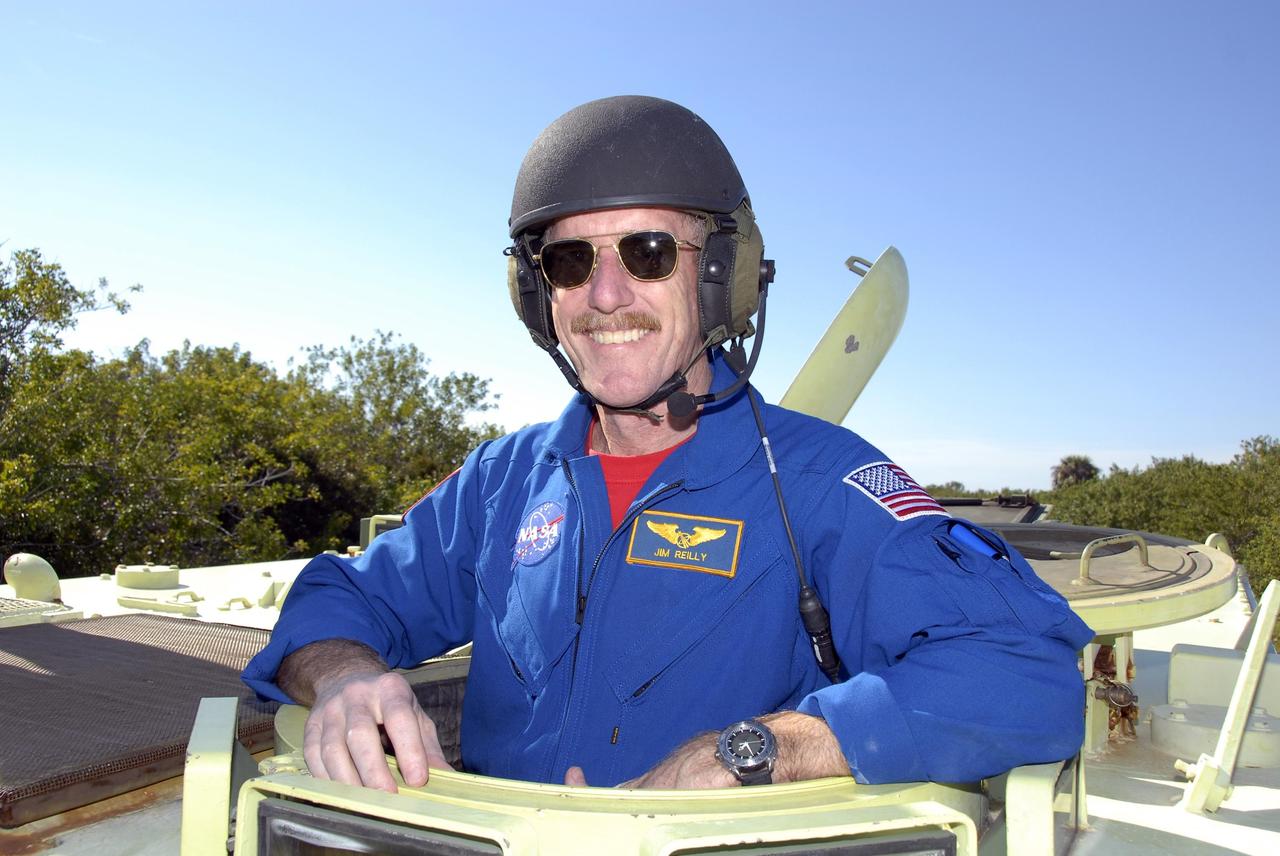

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 39, STS-117 Mission Specialist James Reilly is helmeted and ready to practice driving an M-113 armored personnel carrier. The astronauts on the STS-117 crew are participating in M-113 armored personnel carrier training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities, a dress rehearsal for their launch, targeted for March 15. The M-113 could be used to move the crew away from the launch pad quickly in the event of an emergency. The TCDT also includes pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
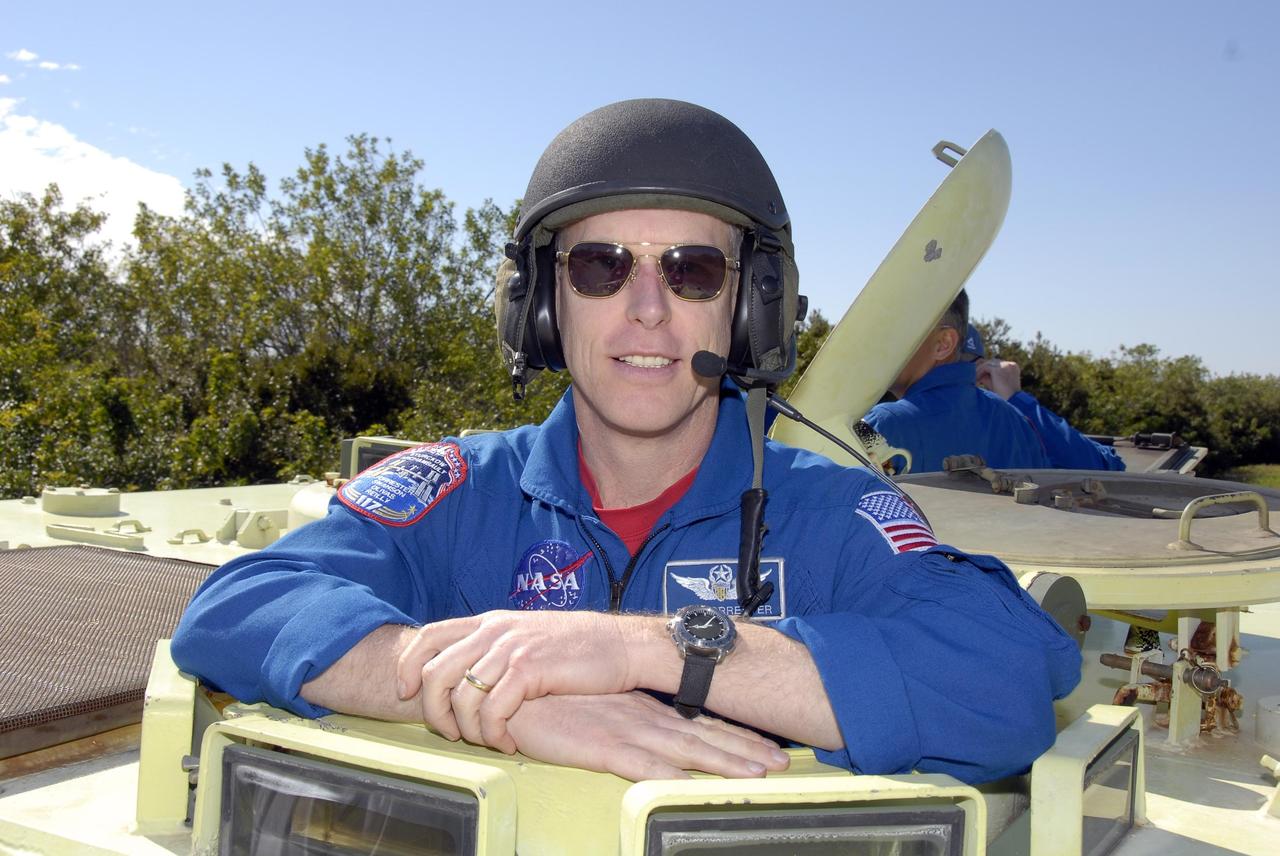

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 39, STS-117 Mission Specialist Patrick Forrester is helmeted and ready to practice driving an M-113 armored personnel carrier. The astronauts on the STS-117 crew are participating in M-113 armored personnel carrier training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities, a dress rehearsal for their launch, targeted for March 15. The M-113 could be used to move the crew away from the launch pad quickly in the event of an emergency. The TCDT also includes pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
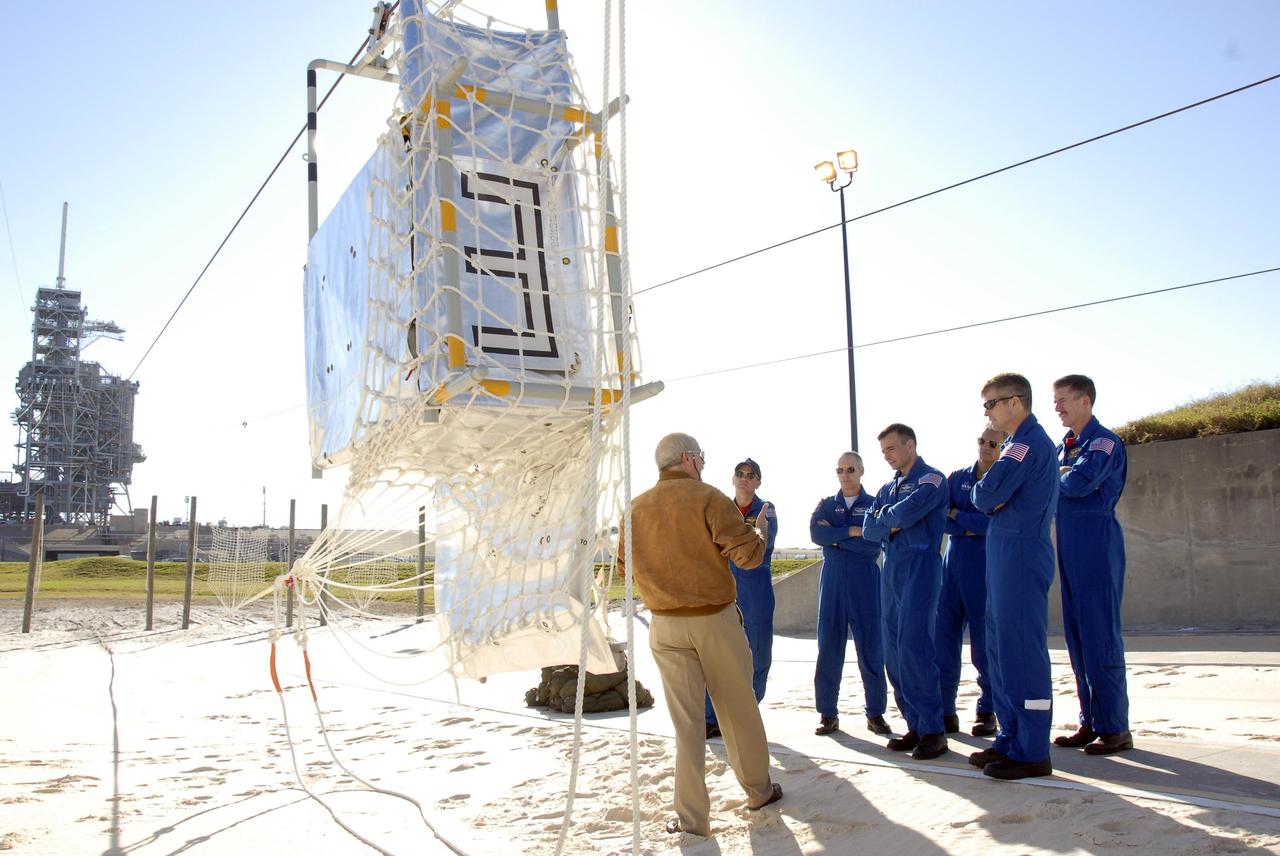

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Launch Pad 39A area, Mission STS-117 crew members receive instruction on emergency egress using the slidewire basket system during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. From left are Commander Rick Sturckow, Mission Specialist Patrick Forrester, Pilot Lee Archambault, and Mission Specialists Danny Olivas, Steven Swanson and James Reilly. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, the Mission STS-117 crew members participate in an emergency egress walkdown at Launch Pad 39A. On the 195-foot level of the fixed service structure inside the white room are Mission Specialist Steven Swanson (kneeling), and standing from left, Pilot Lee Archambault, Commander Rick Sturckow, and Mission Specialists Patrick Forrester, Danny Olivas and James Reilly. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
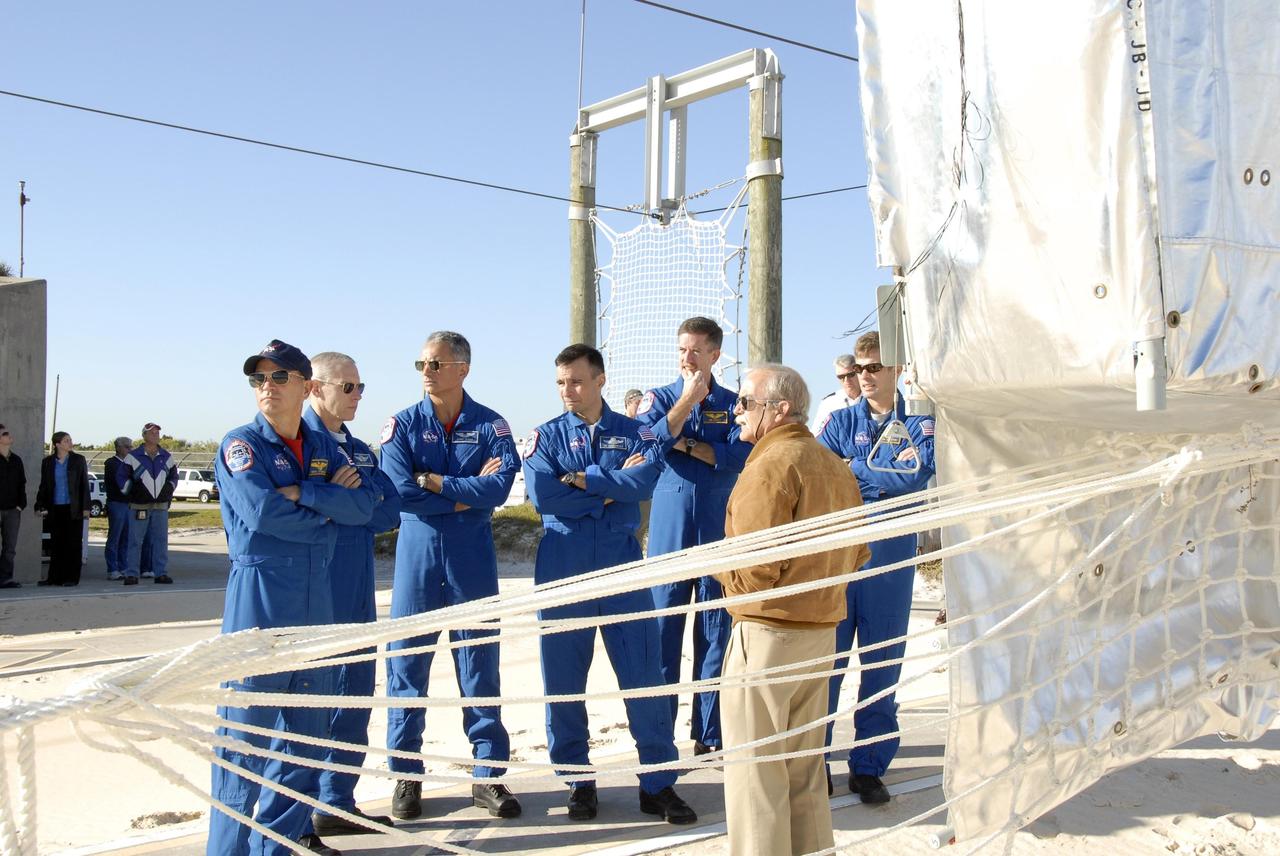

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Launch Pad 39A area, Mission STS-117 crew members receive instruction on emergency egress using the slidewire basket system during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. From left are Commander Rick Sturckow, Mission Specialists Patrick Forrester and Danny Olivas, Pilot Lee Archambault, and Mission Specialists James Reilly and Steven Swanson. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
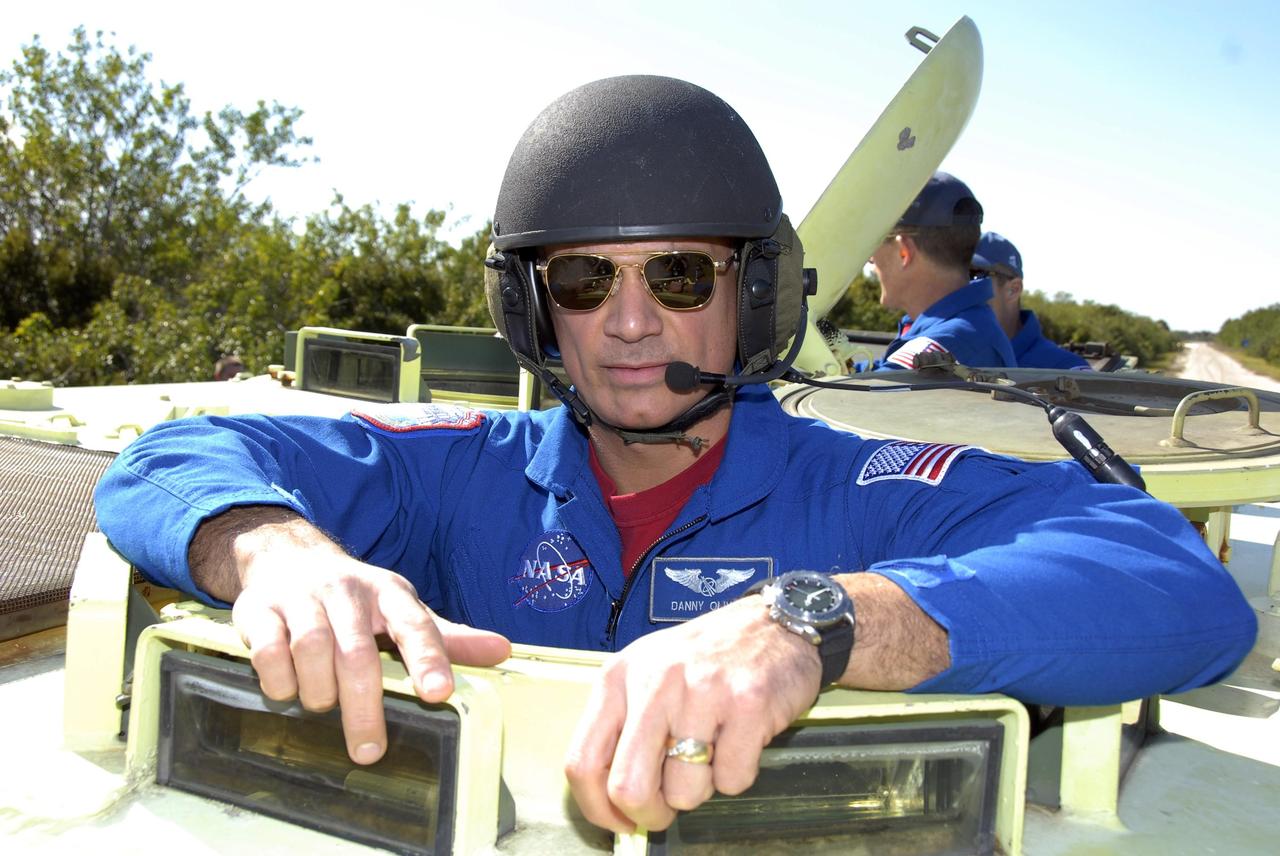

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 39, STS-117 Mission Specialist Danny Olivas is helmeted and ready to practice driving an M-113 armored personnel carrier. The astronauts on the STS-117 crew are participating in M-113 armored personnel carrier training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities, a dress rehearsal for their launch, targeted for March 15. The M-113 could be used to move the crew away from the launch pad quickly in the event of an emergency. The TCDT also includes pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
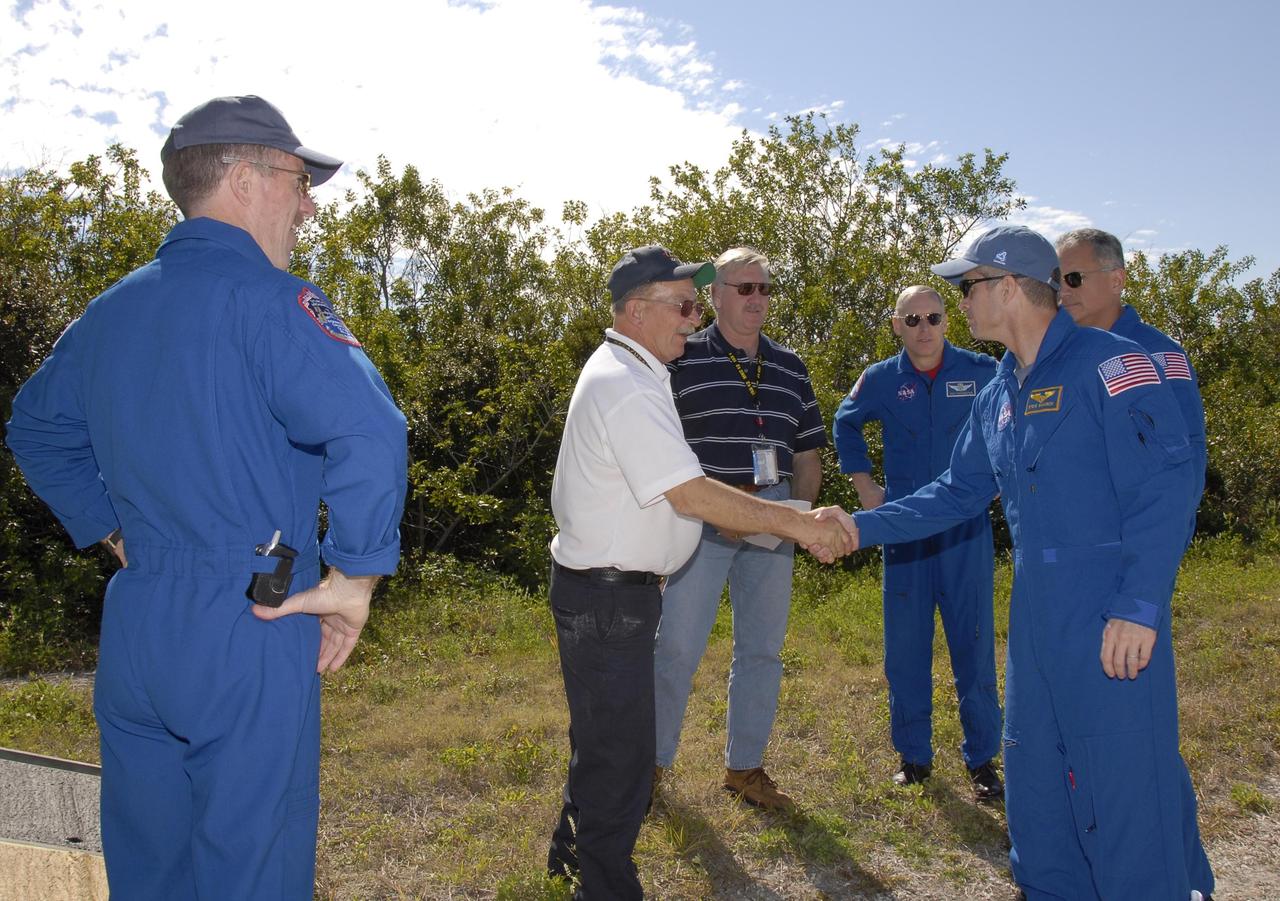

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 39, astronaut rescue team leader Capt. George Hoggard, second from left, greets STS-117 Mission Specialist Steven Swanson as fellow crew members, from left, Mission Specialists James Reilly, Patrick Forrester and Danny Olivas look on. The astronauts on the STS-117 crew are participating in M-113 armored personnel carrier training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities, a dress rehearsal for their launch, targeted for March 15. The M-113 could be used to move the crew away from the launch pad quickly in the event of an emergency. The TCDT also includes pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
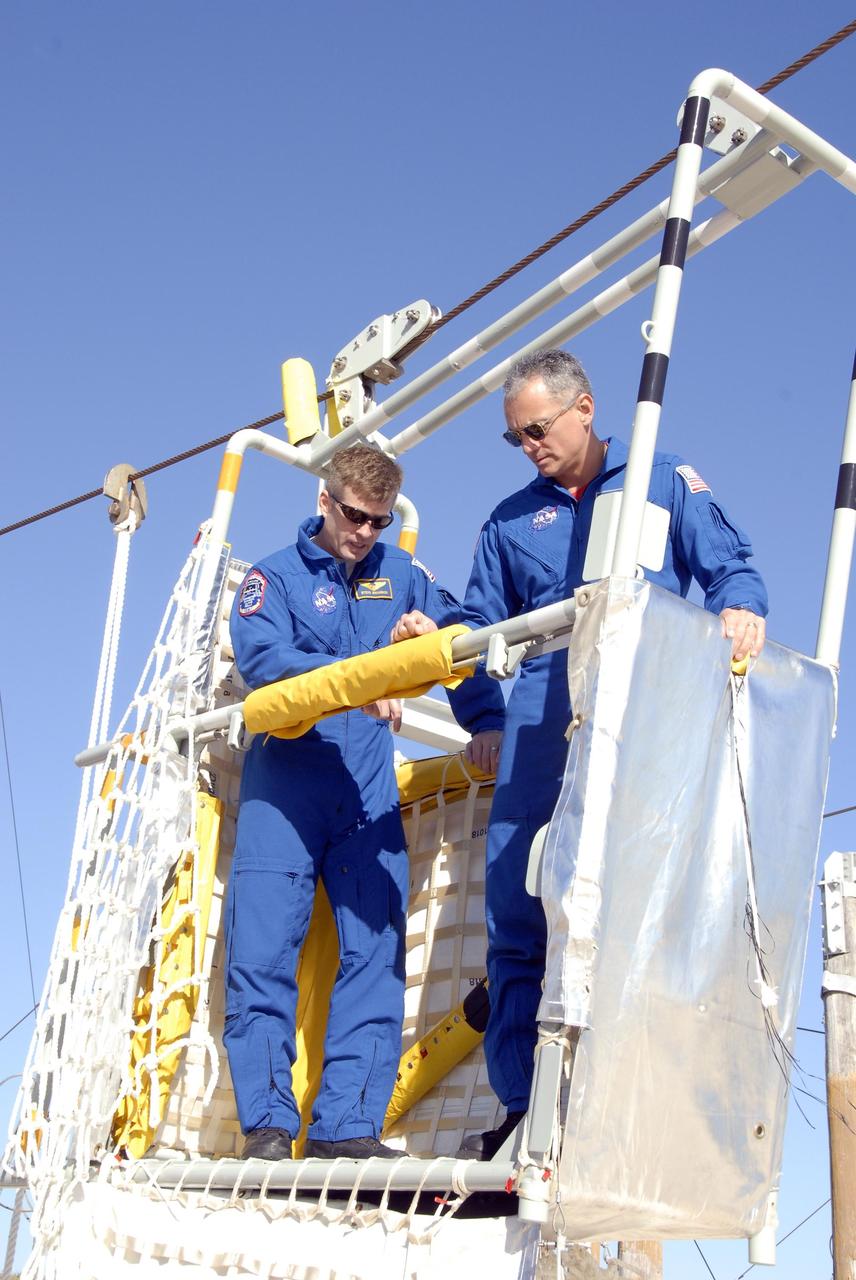

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Launch Pad 39A area, Mission STS-117 crew members receive instruction on emergency egress using the slidewire basket system during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. Here, Mission Specialists Steven Swanson (left) and Danny Olivas (right) practice exiting from the slidewire basket. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
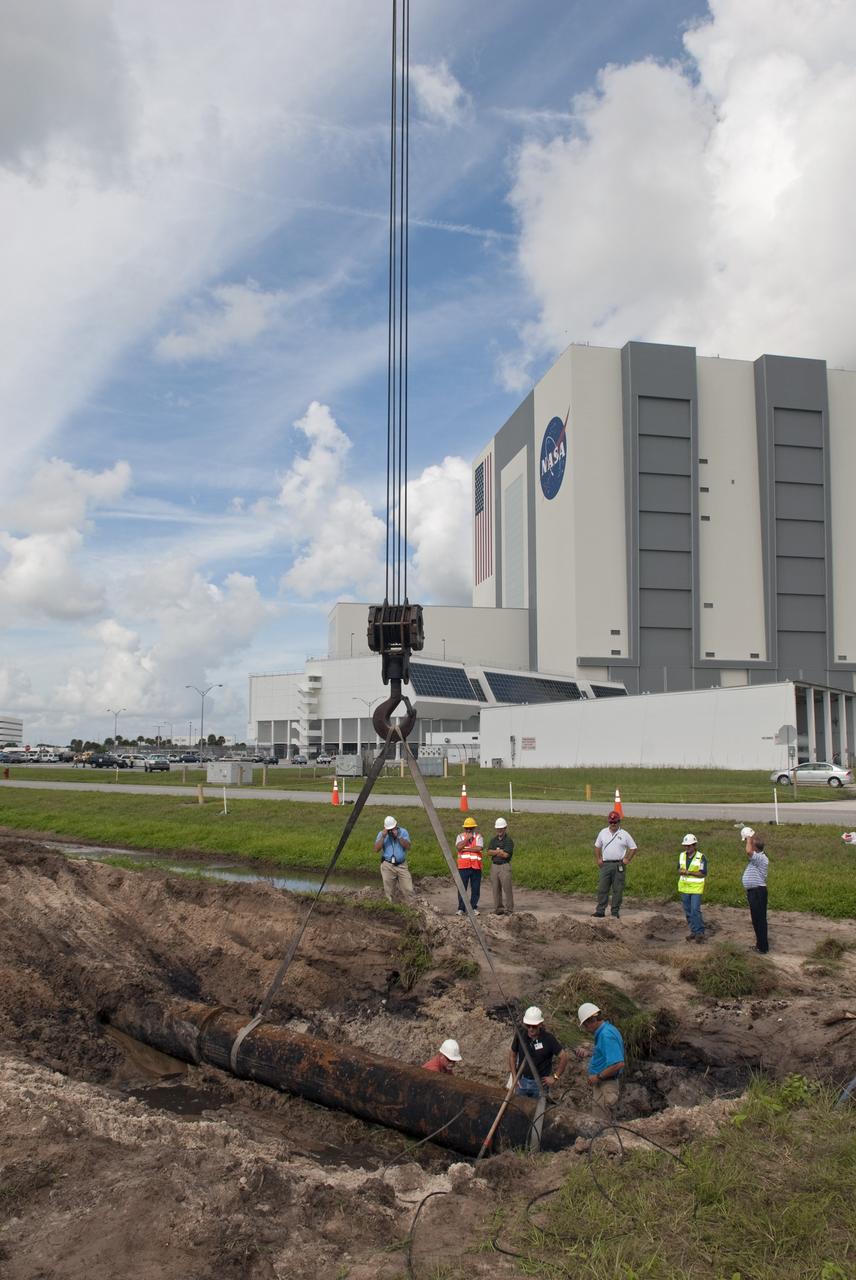

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crew begins to fix a major water main break in a 24-inch cast iron pipe in the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building and the Launch Control Center. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
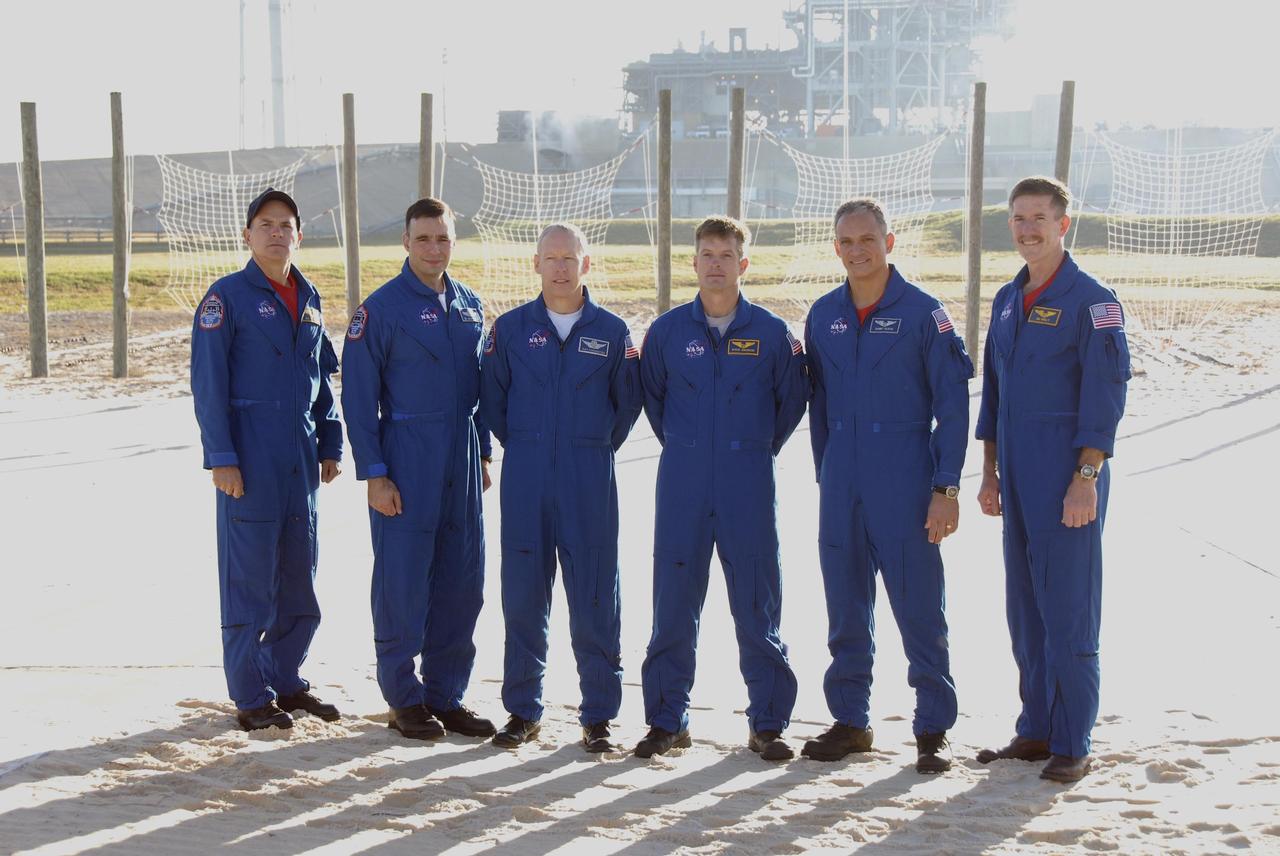

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities at Launch Pad 39A, the Mission STS-117 crew members take time to speak to the media during a question-and-answer session. From the left are Commander Rick Sturckow, Pilot Lee Archambault, and Mission Specialists Patrick Forrester, Steven Swanson, Danny Olivas and James Reilly. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
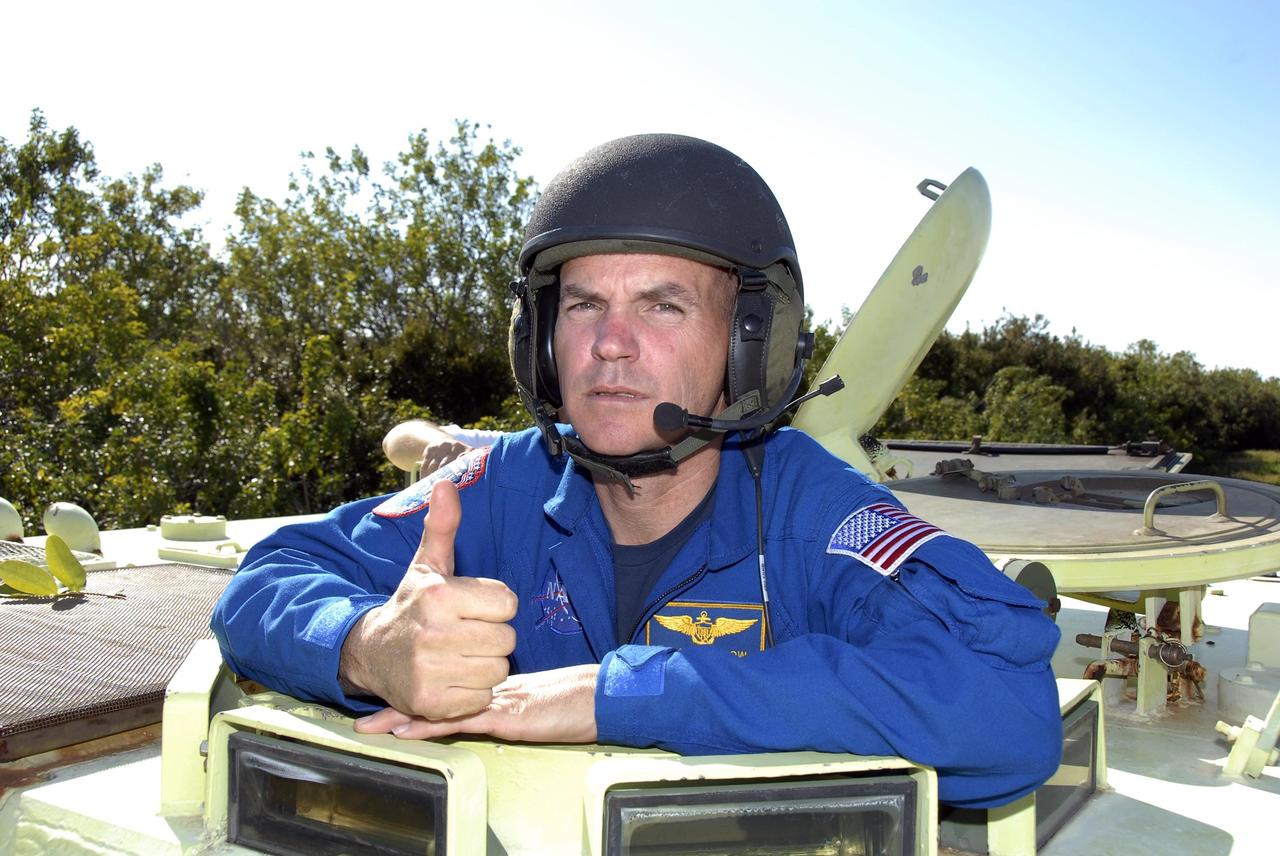

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 39, STS-117 Commander Rick Sturckow signals that he is ready to practice driving an M-113 armored personnel carrier. The astronauts on the STS-117 crew are participating in M-113 armored personnel carrier training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities, a dress rehearsal for their launch, targeted for March 15. The M-113 could be used to move the crew away from the launch pad quickly in the event of an emergency. The TCDT also includes pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
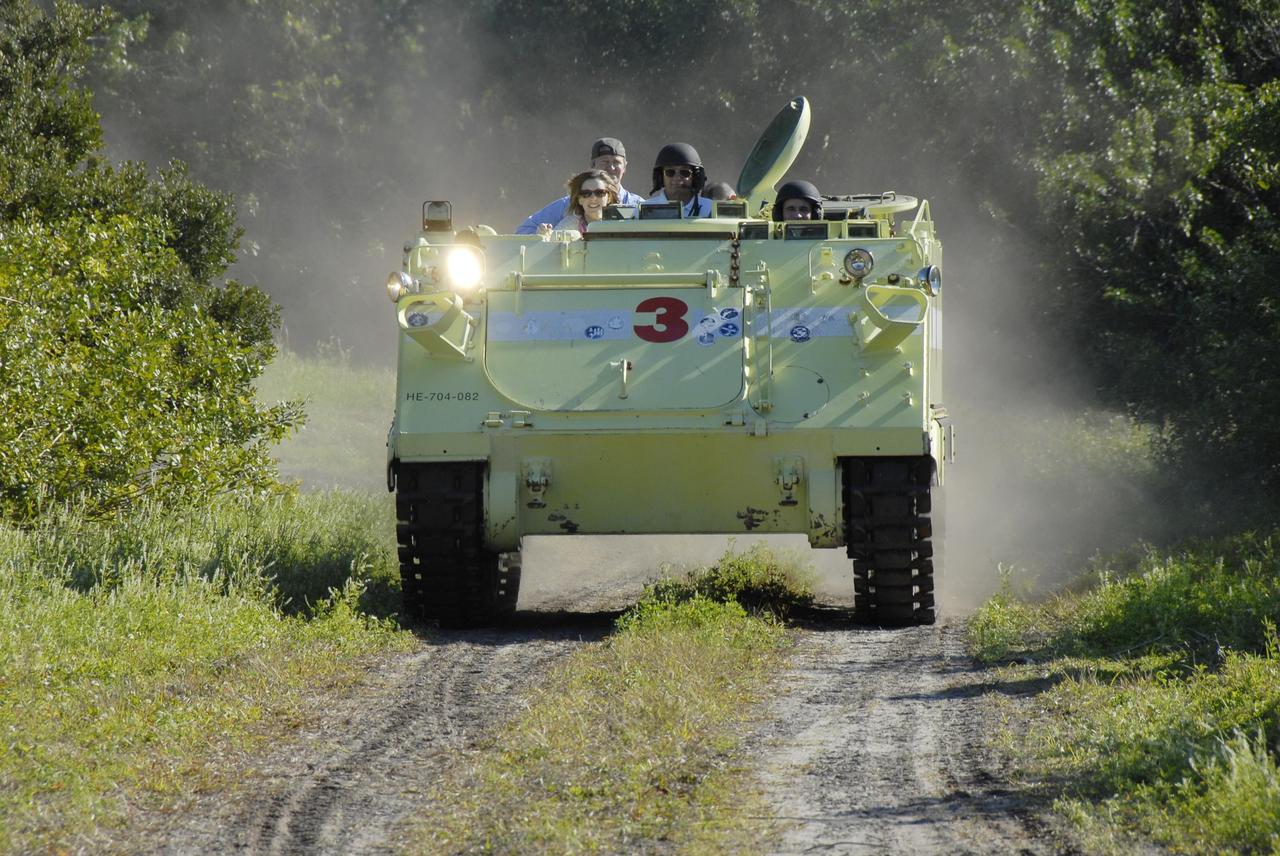

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 39, members of the STS-117 crew are instructed in the operation of an M-113 armored personnel carrier by the astronaut rescue team. The astronauts on the STS-117 crew are participating in M-113 armored personnel carrier training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities, a dress rehearsal for their launch, targeted for March 15. The M-113 could be used to move the crew away from the launch pad quickly in the event of an emergency. The TCDT also includes pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
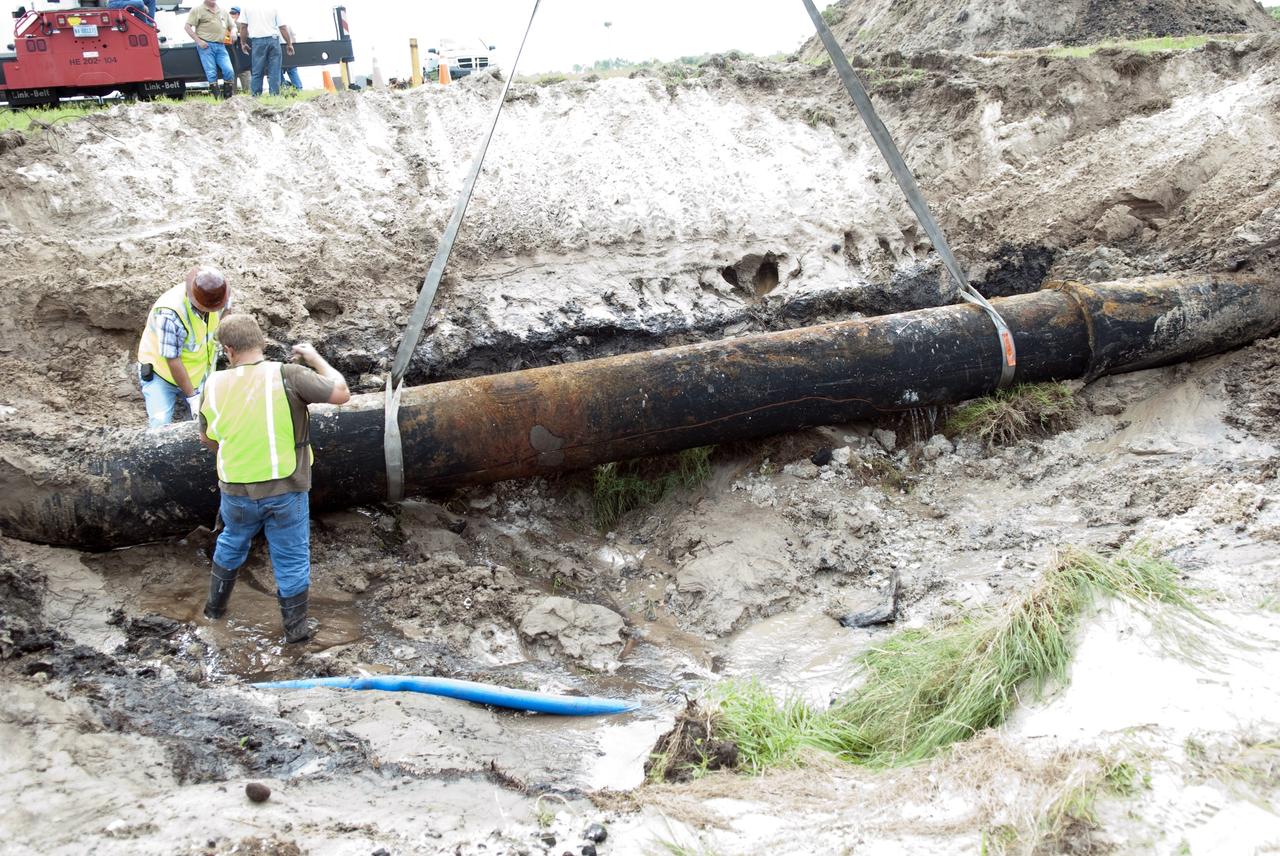

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crew begins to fix a major water main break in a 24-inch cast iron pipe in the Launch Complex-39 Turn Basin area, across from the Vehicle Assembly Building and the Launch Control Center. This photo shows the approximately 15-foot-long crack along the bottom of pipe and water draining out. Kennedy was closed to non-essential personnel the morning of Sept. 8 while crews assessed the break and restored water to the center. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
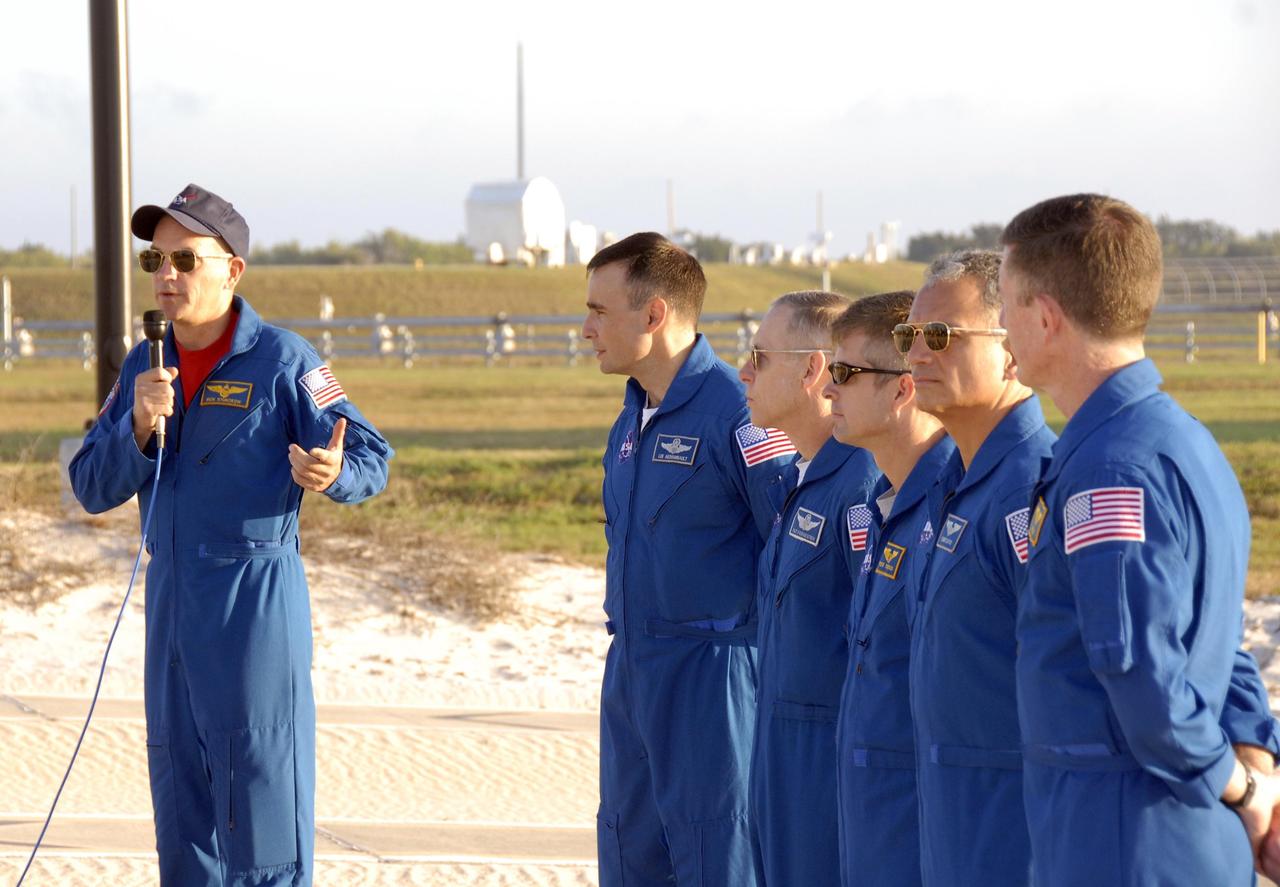

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities at Launch Pad 39A, Mission STS-117 Commander Rick Sturckow (left) speaks to the media during a question-and-answer session. To his left are Pilot Lee Archambault, and Mission Specialists Patrick Forrester, Steven Swanson, Danny Olivas and James Reilly. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
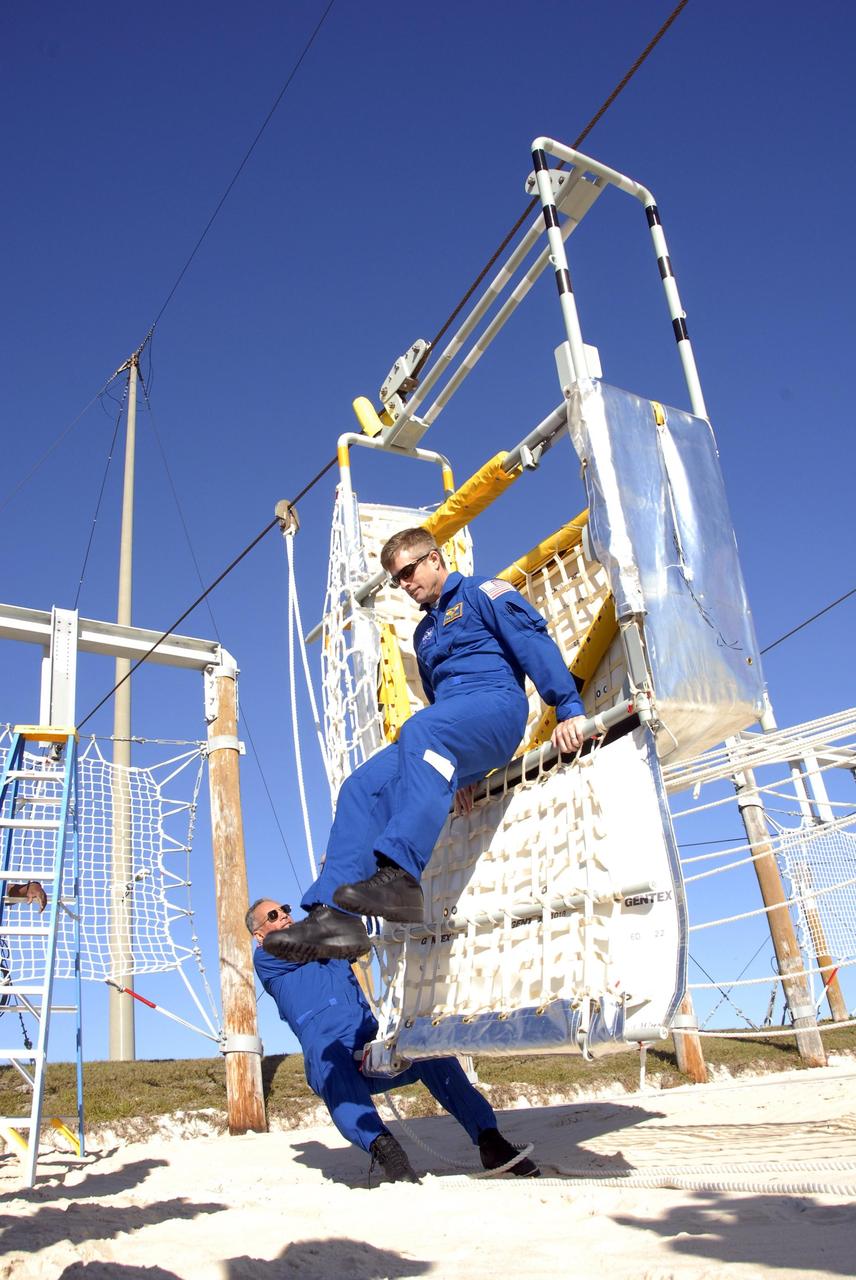

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Launch Pad 39A area, Mission STS-117 crew members receive instruction on emergency egress using the slidewire basket system during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. Here, Mission Specialist Steven Swanson (right) practices exiting from the slidewire basket. as Mission Specialist Danny Olivas assists. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
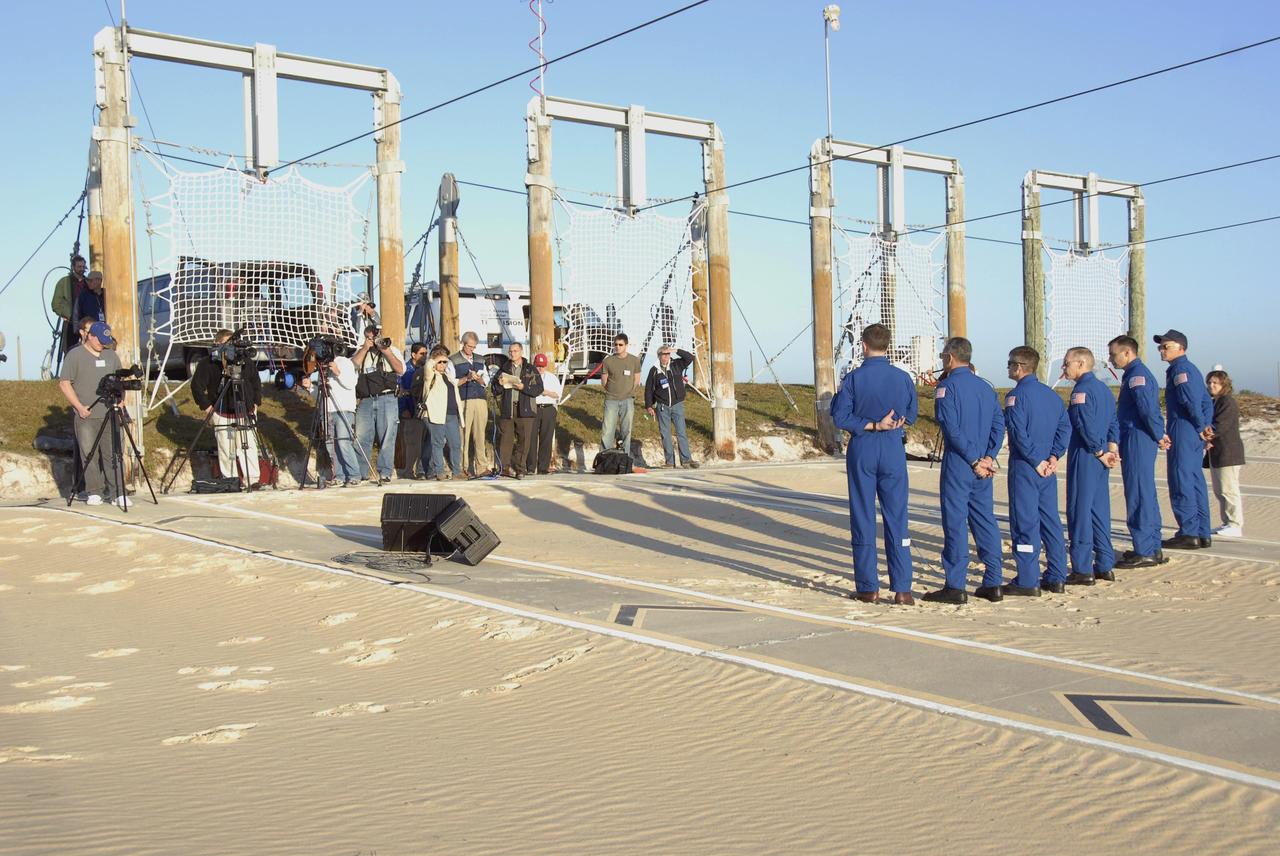

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities at Launch Pad 39A, the Mission STS-117 crew members speak to the media during a question-and-answer session. From the left are Mission Specialists James Reilly, Danny Olivas, Steven Swanson and Patrick Forrester, Pilot Lee Archambault and Commander Rick Sturckow, along with NASA Public Affairs Specialist Jessica Rye. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
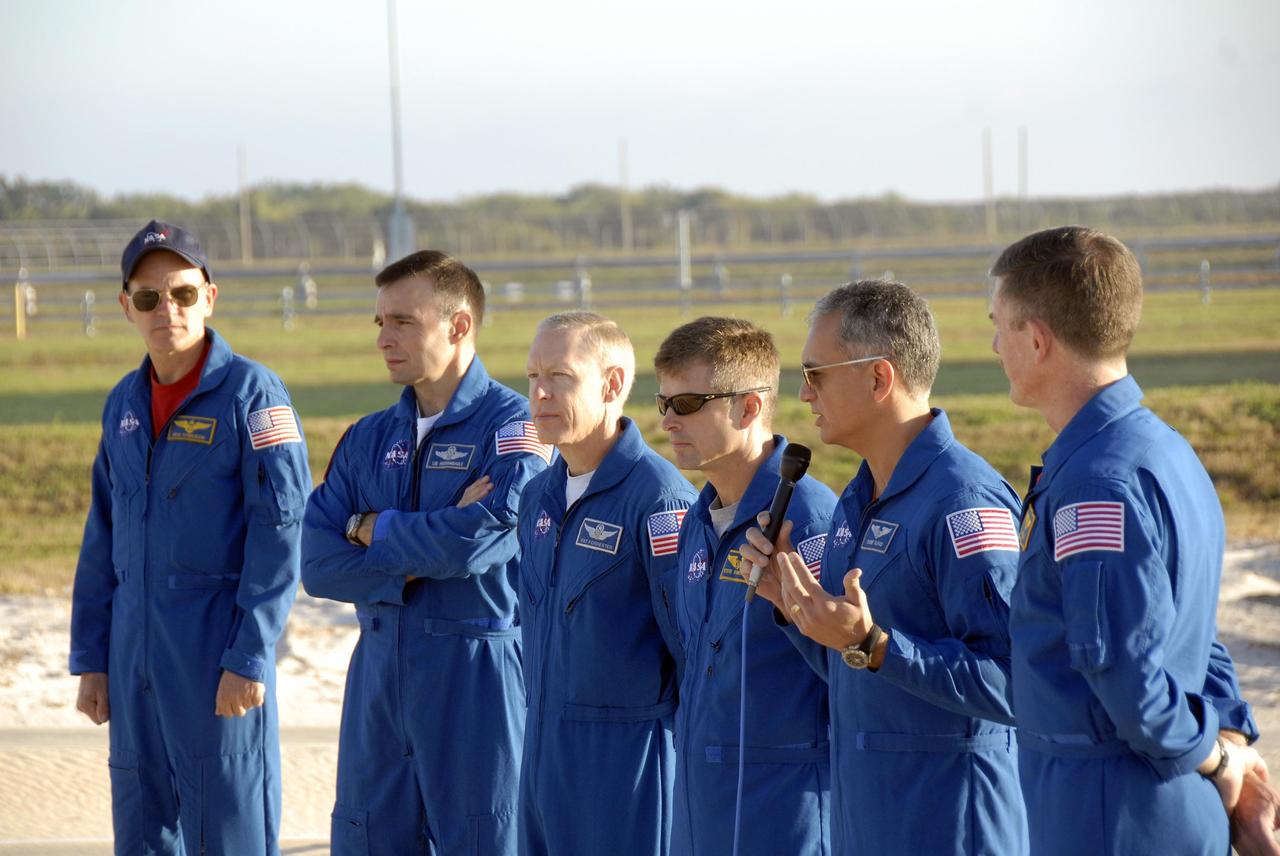

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities at Launch Pad 39A, the Mission STS-117 crew members speak to the media during a question-and-answer session. From the left are Commander Rick Sturckow, Pilot Lee Archambault, and Mission Specialists Patrick Forrester, Steven Swanson, Danny Olivas and James Reilly. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
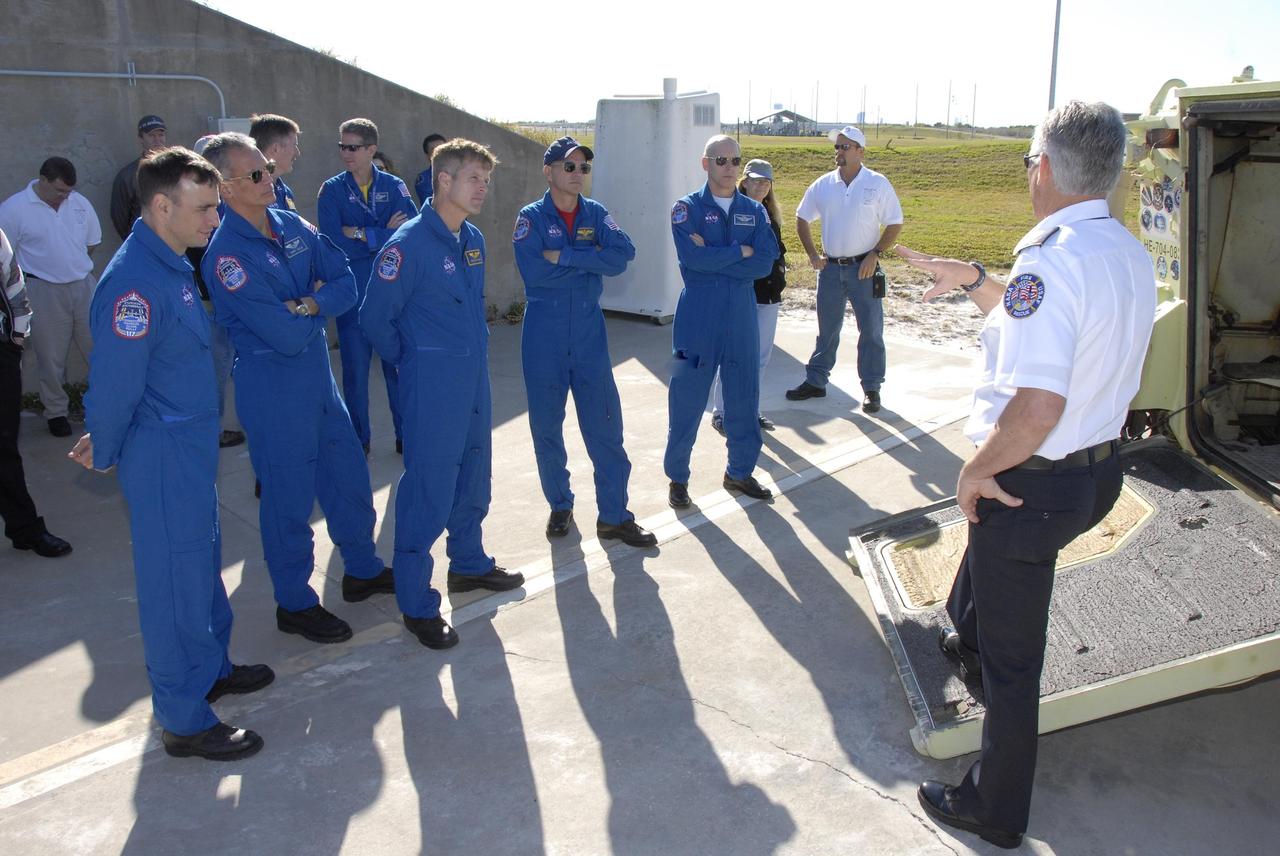

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Mission STS-117 crew members receive emergency egress instruction at Launch Pad 39A during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. From the left in front are Pilot Lee Archambault, Mission Specialists Danny Olivas and Steven Swanson, Commander Rick Sturckow and Mission Specialist Patrick Forrester. Directly behind Olivas is Mission Specialist James Reilly. At right is a partial view of the M-113 armored personnel carrier. The TCDT also includes M-113 armored personnel carrier training, and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 39, STS-117 Mission Specialist Patrick Forrester (right) waits his turn to practice driving an M-113 armored personnel carrier as fellow crew members look on. The astronauts on the STS-117 crew are participating in M-113 armored personnel carrier training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities, a dress rehearsal for their launch, targeted for March 15. The M-113 could be used to move the crew away from the launch pad quickly in the event of an emergency. The TCDT also includes pad emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The mission payload aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis is the S3/S4 integrated truss structure, along with a third set of solar arrays and batteries. The crew of six astronauts will install the truss to continue assembly of the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
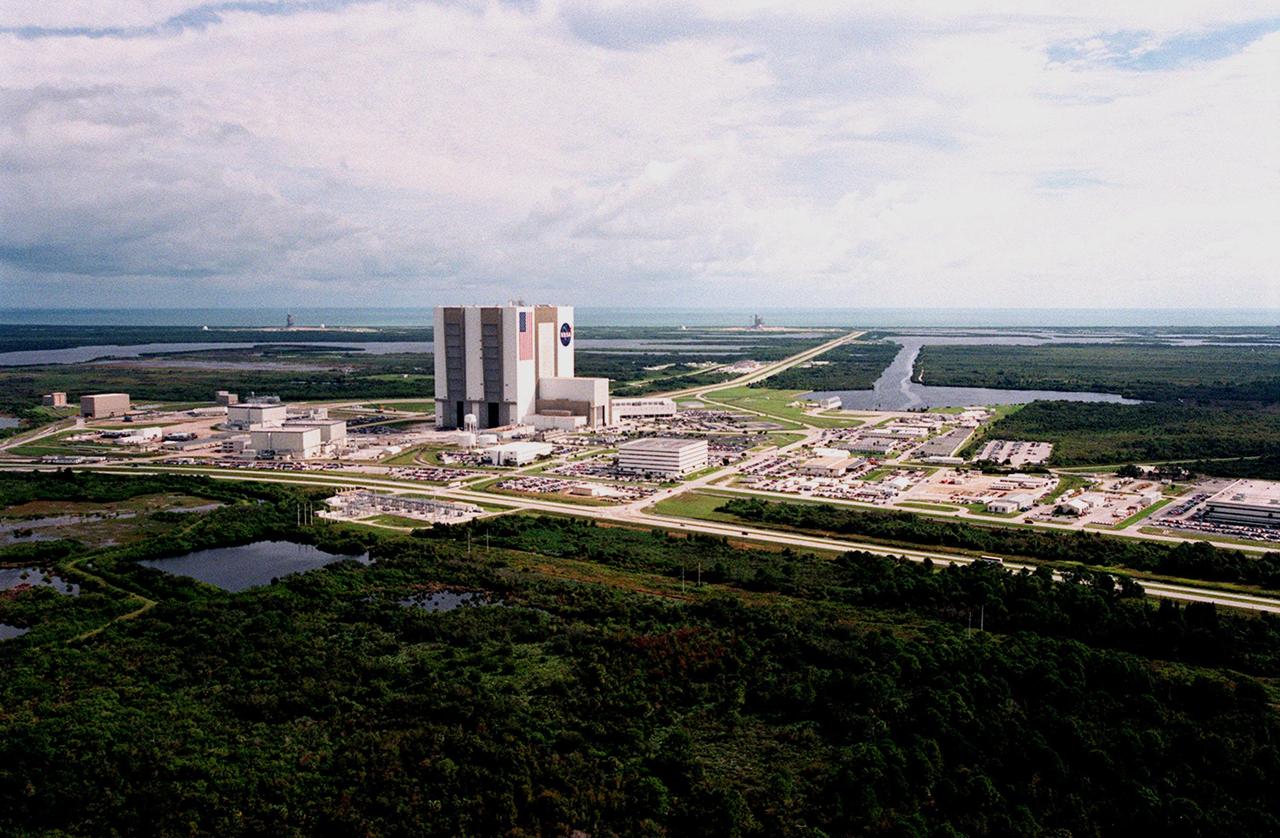

An aerial view of Launch Complex 39 Area shows the Vehicle Assembly Building (center), surrounded by (right) the Launch Control Center, (lower area, left to right) the Orbiter Processing Facility, Process Control Center and Operations Support Building. Looking toward the Atlantic Ocean (top) can be seen Launch Pads 39-A (right) and 39-B. The crawlerway stretches between the VAB and the launch pads. To the right of the crawlerway is the turn basin where new external tanks are brought from Louisiana via ship. The road bordering the buildings is Kennedy Parkway North.

A brilliant blue sky serves as the backdrop for a panoramic view of the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building, mobile launcher at left, and Launch Control Center at right, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. These facilities are being upgraded for NASA's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft for launches to deep space destinations, including the Moon, Mars and beyond.
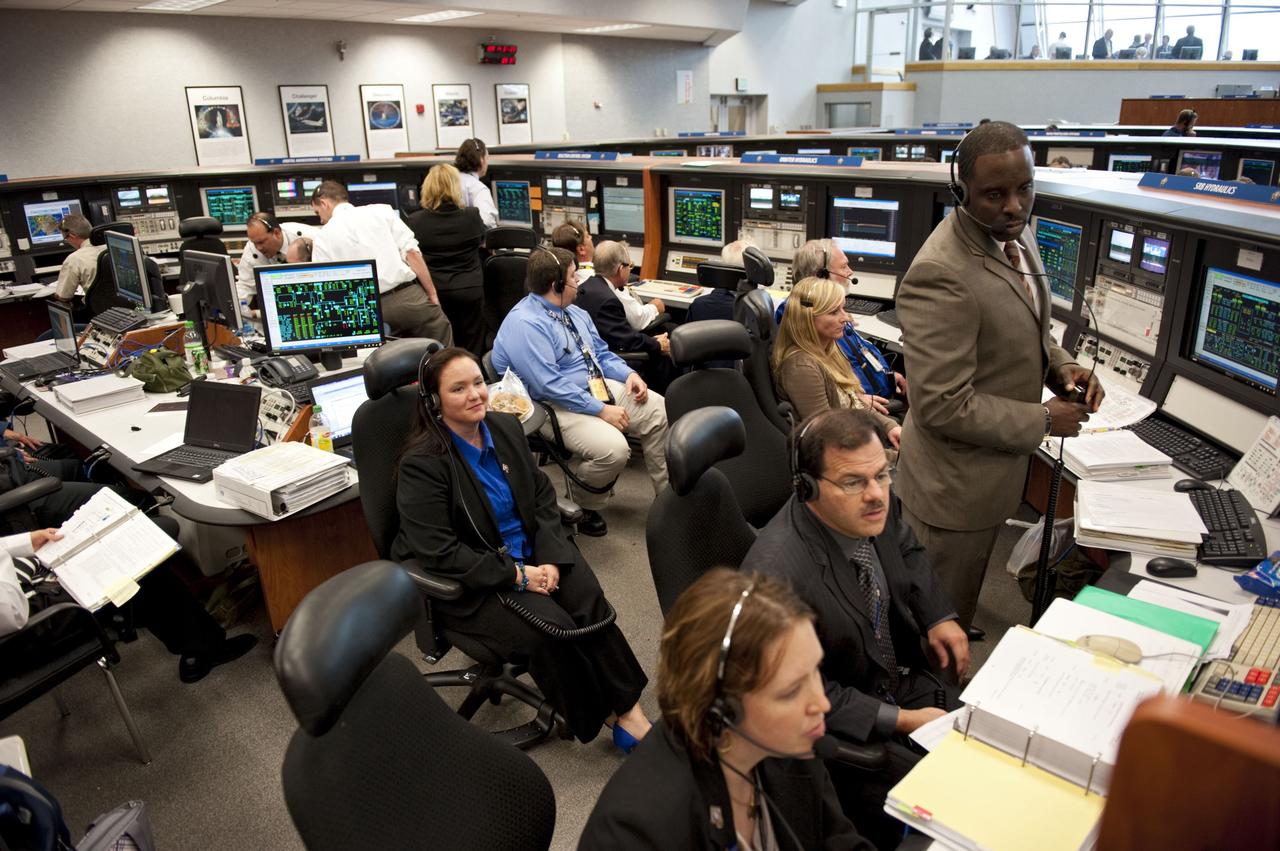

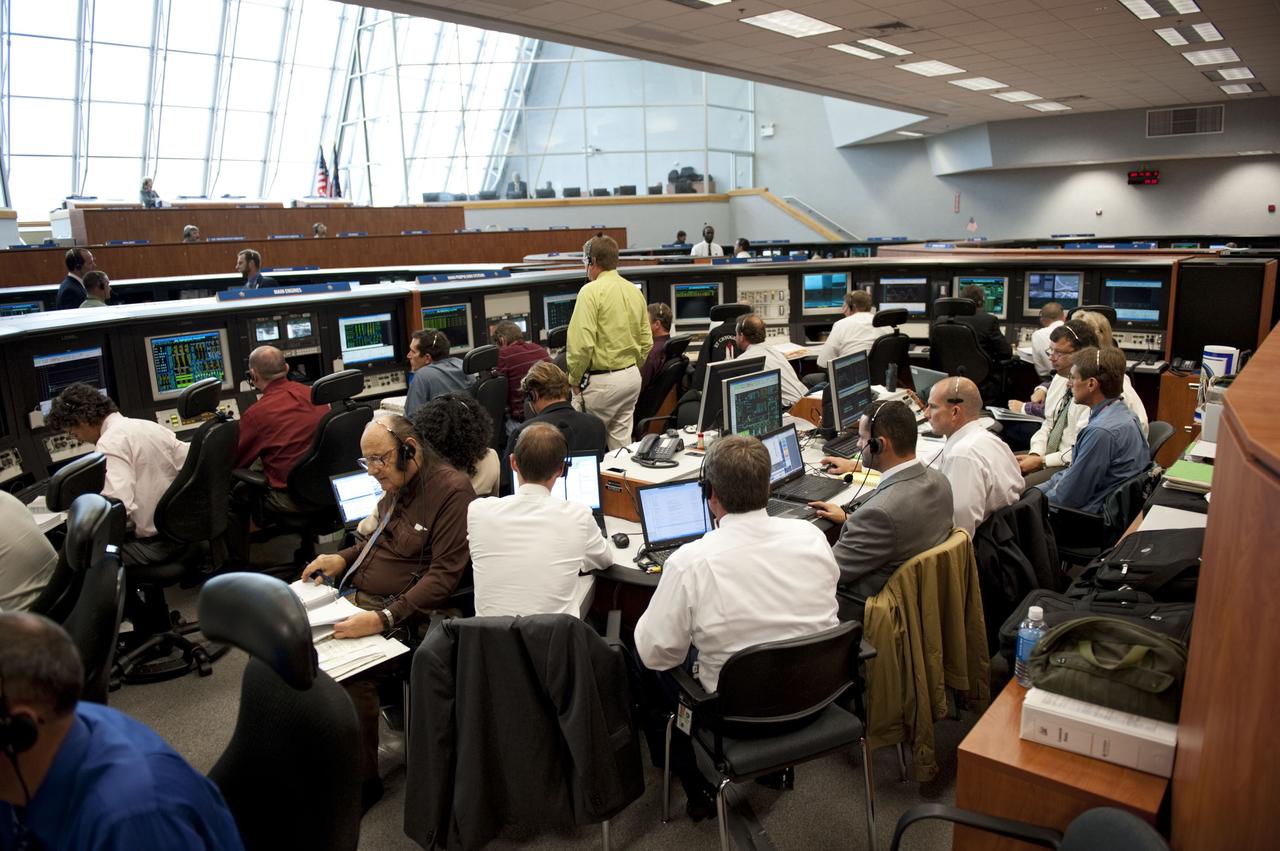
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
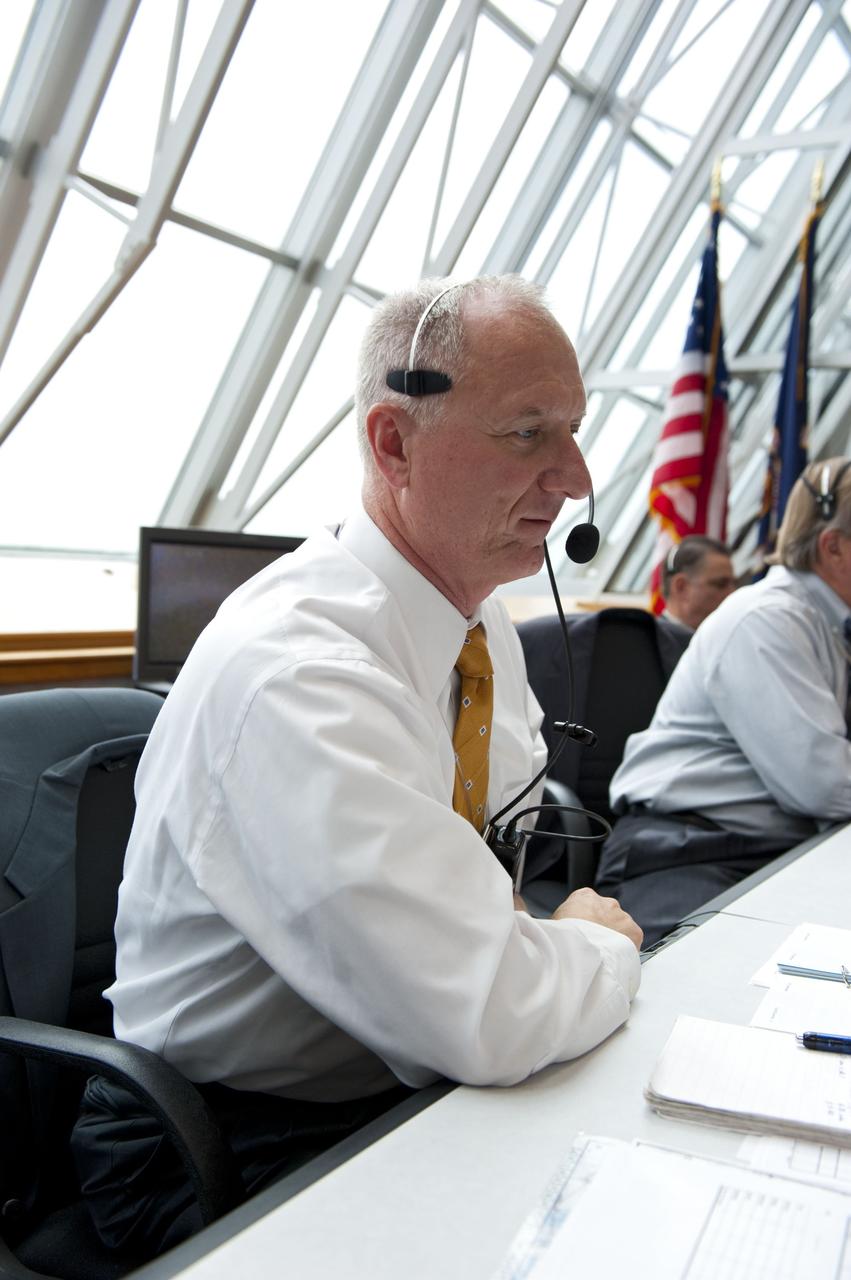

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen here is Assistant Launch Director Pete Nickolenko. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
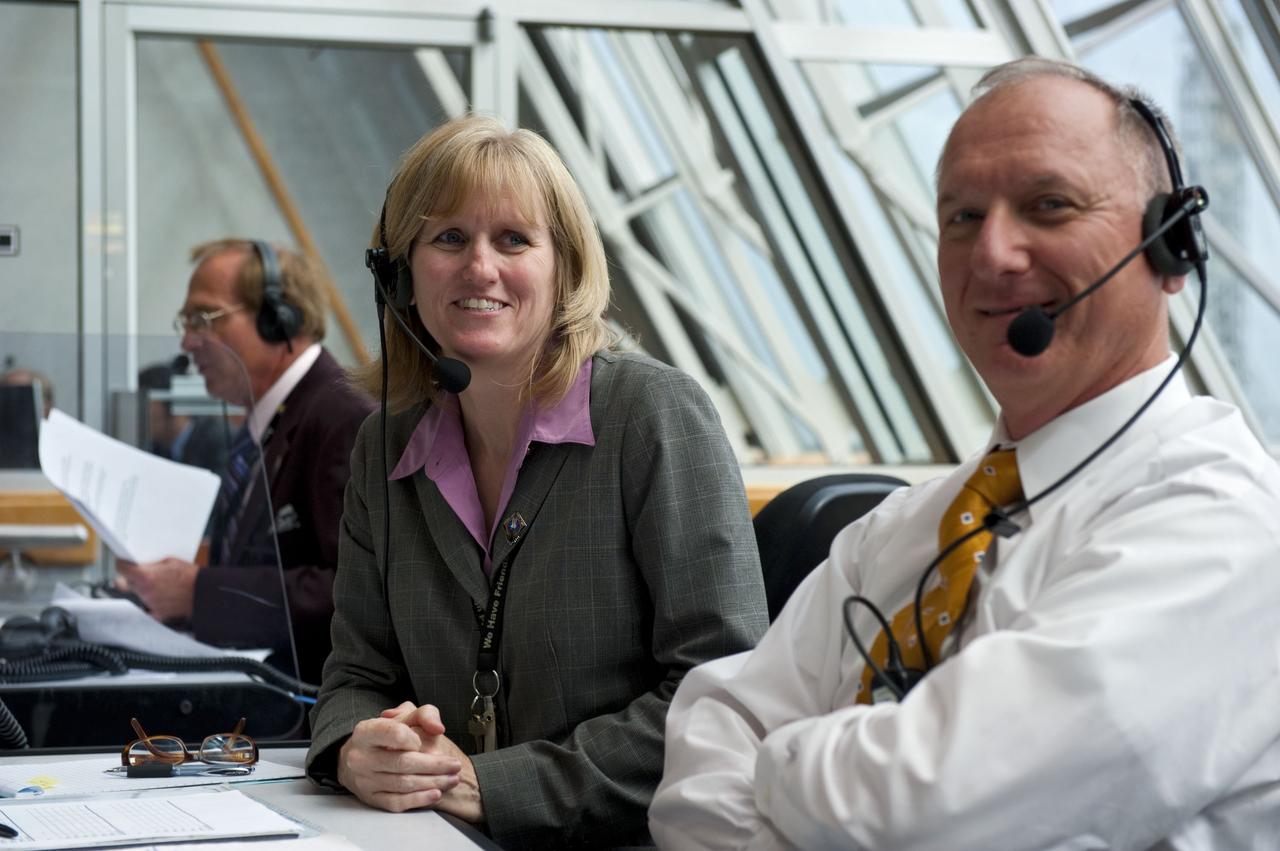

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen here are Assistant Launch Director Pete Nickolenko (right), Atlantis NASA Flow Director Angie Brewer and NASA Commentator and Public Affairs Officer George Diller. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
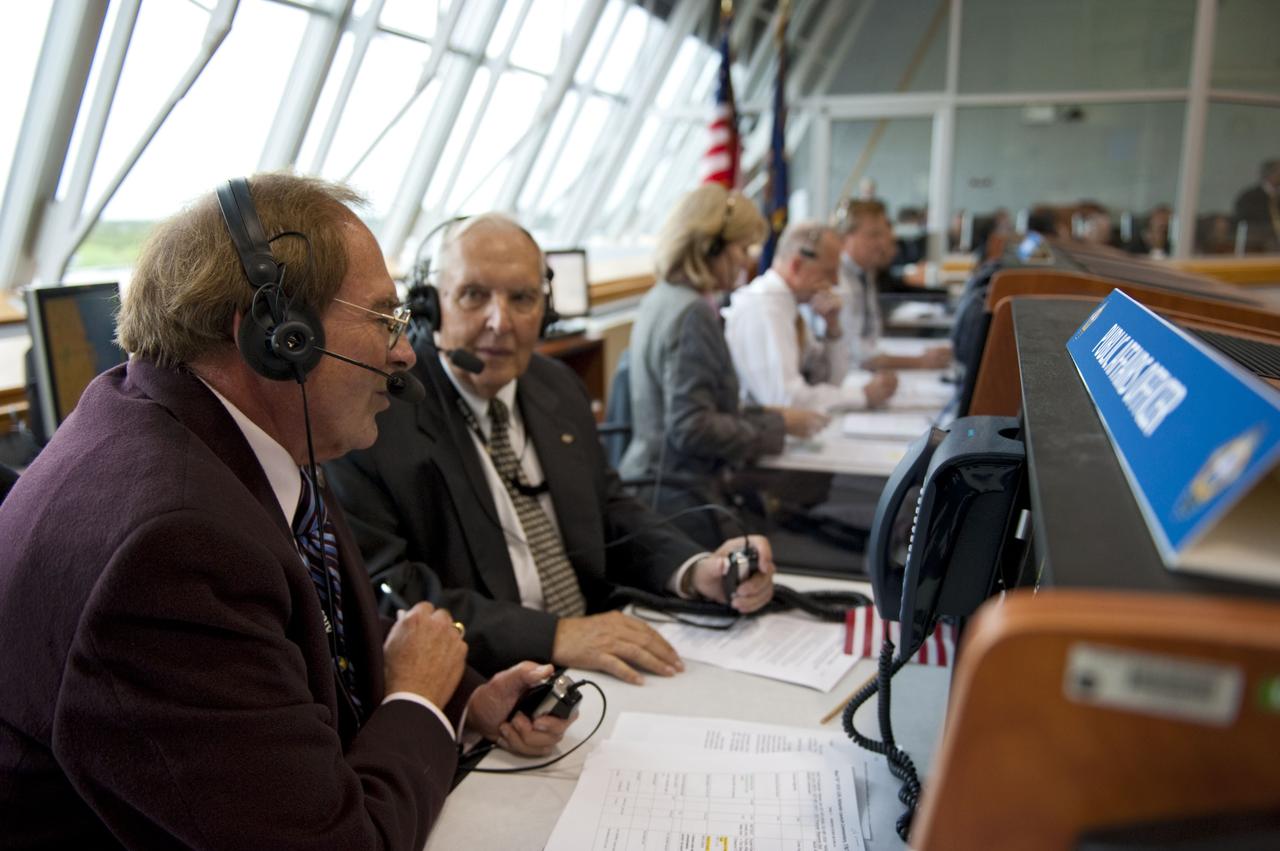

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Launch Commentator and Public Affairs Officer George Diller interviews former Kennedy Director of Public Affairs Hugh Harris during prelaunch activities before liftoff of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
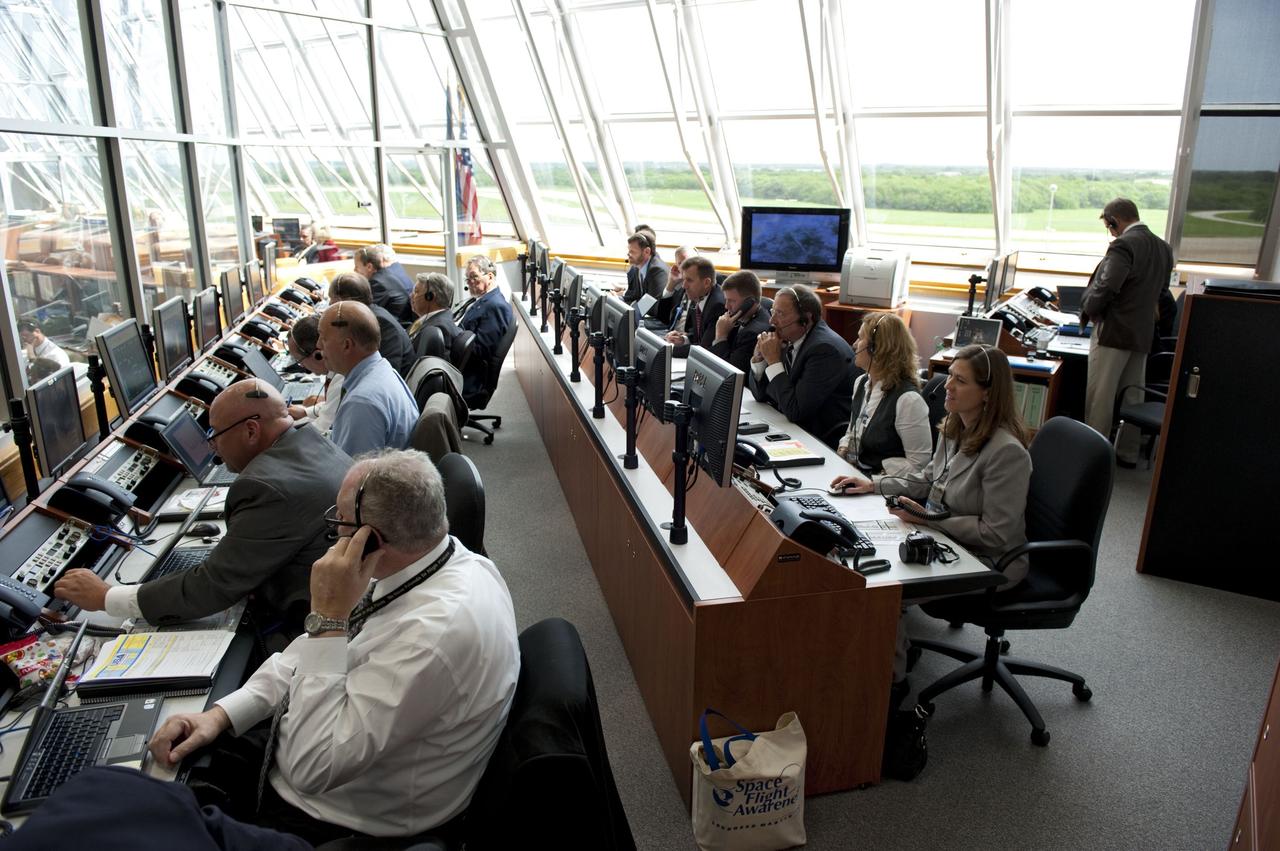

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Seen here is the “Launch America” banner for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP) on the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2021. NASA and SpaceX are preparing for Crew-3 – the third crew rotation flight to the International Space Station for CCP – and part of that includes conducting a dress rehearsal ahead of launch. On Oct. 28, NASA’s SpaceX Crew-3 astronauts and launch teams rehearsed countdown operations, concluding with the Go/No-Go poll for Falcon-9 fueling. The Crew-3 mission will carry NASA astronauts Raja Chari, Tom Marshburn, and Kayla Barron, as well as ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer to the space station for a six-month stay. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft are scheduled to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A no earlier than Nov. 6 at 11:36 p.m. EDT.
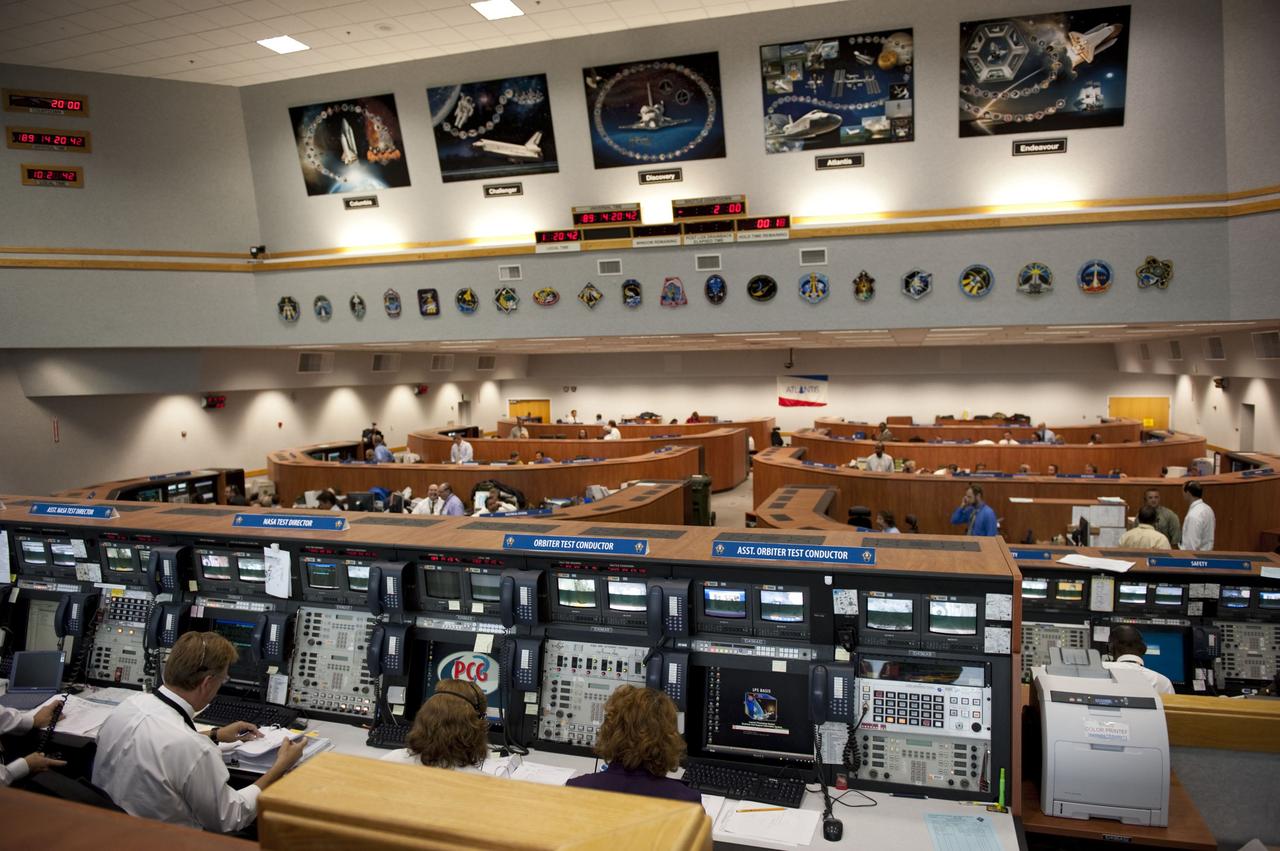

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Above the space shuttle countdown clock are five orbiter tributes on display. The tributes feature major accomplishments and significant achievements made by each shuttle, as well as mission patches and processing milestones. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
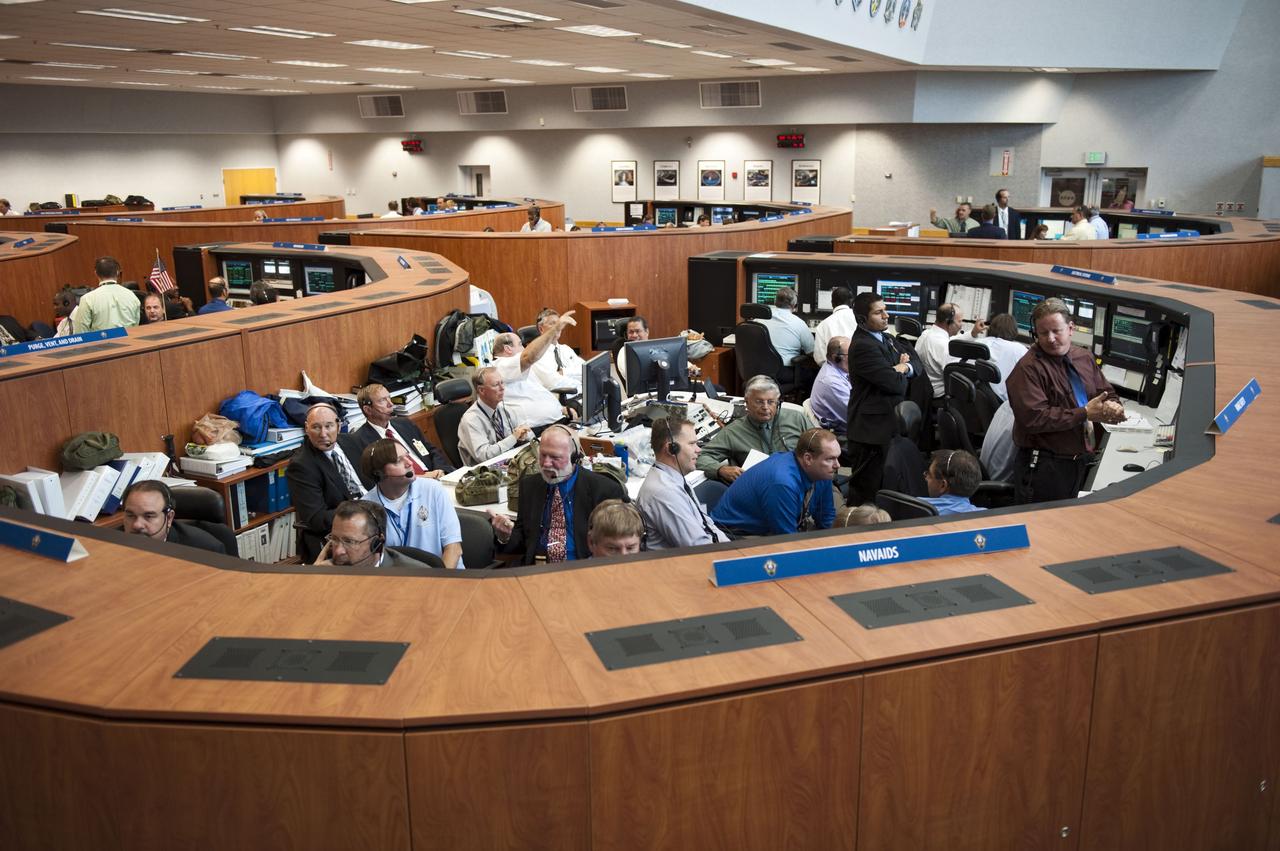

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
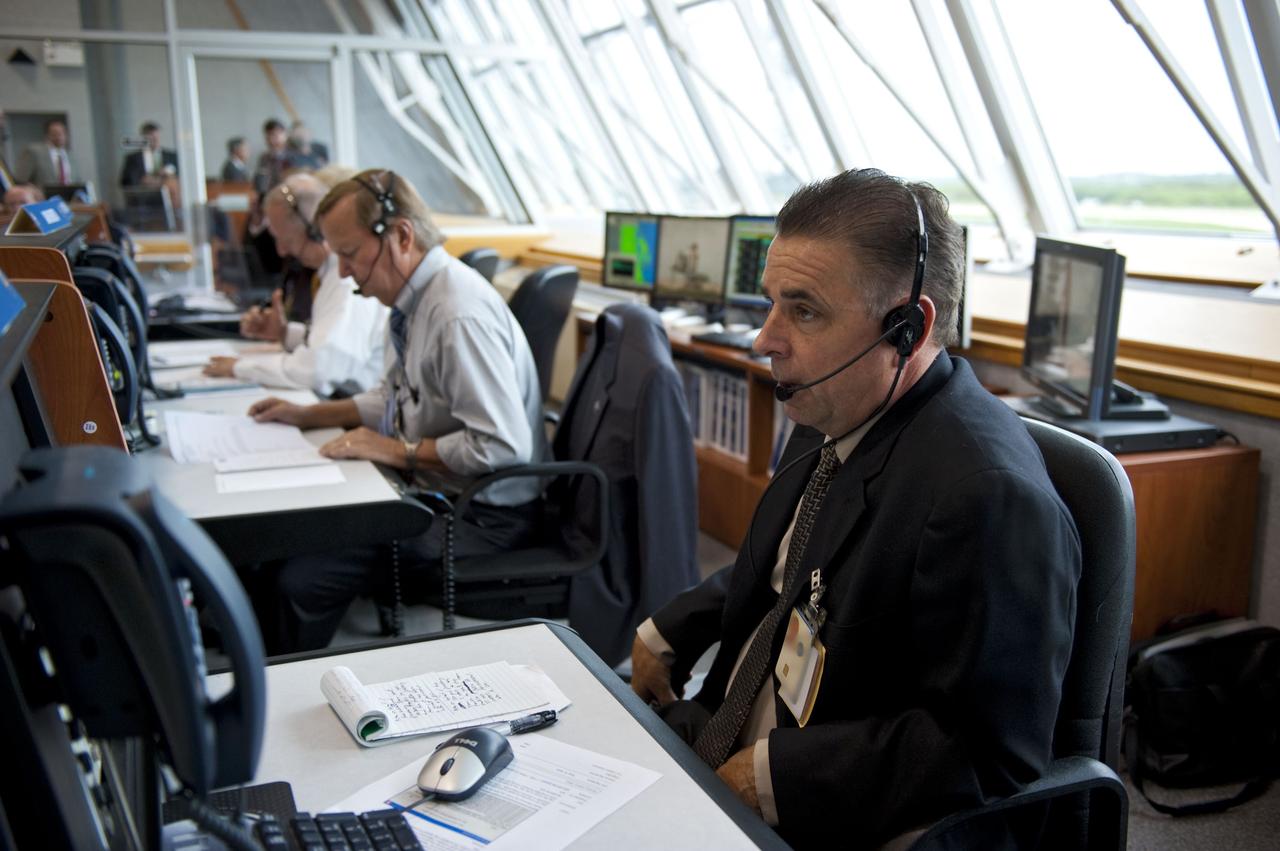

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen here are Assistant Launch Director Pete Nickolenko (background) Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach and Payloads Launch Manager and Deputy Director of ISS and Spacecraft Processing at Kennedy, Bill Dowdell. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
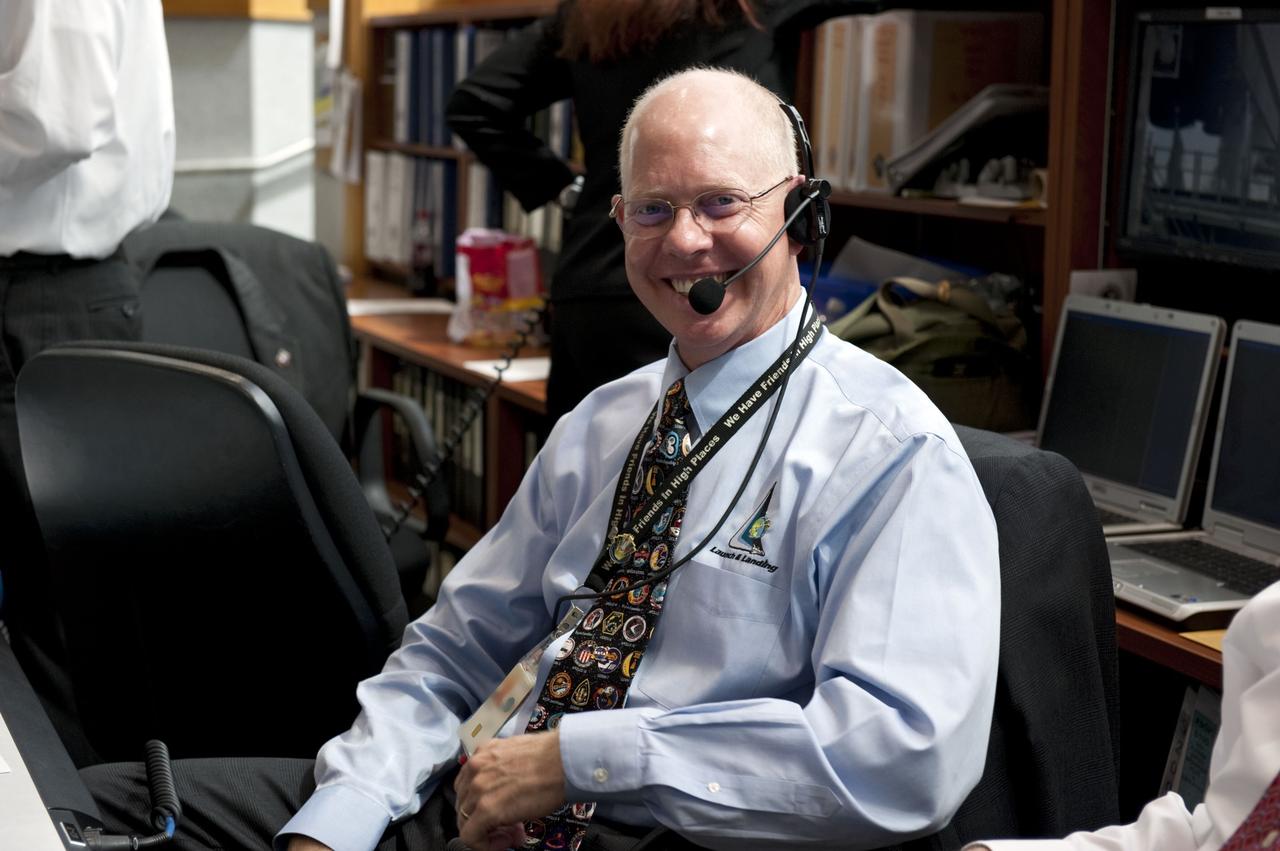

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen here is NASA Test Director Steve Payne. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
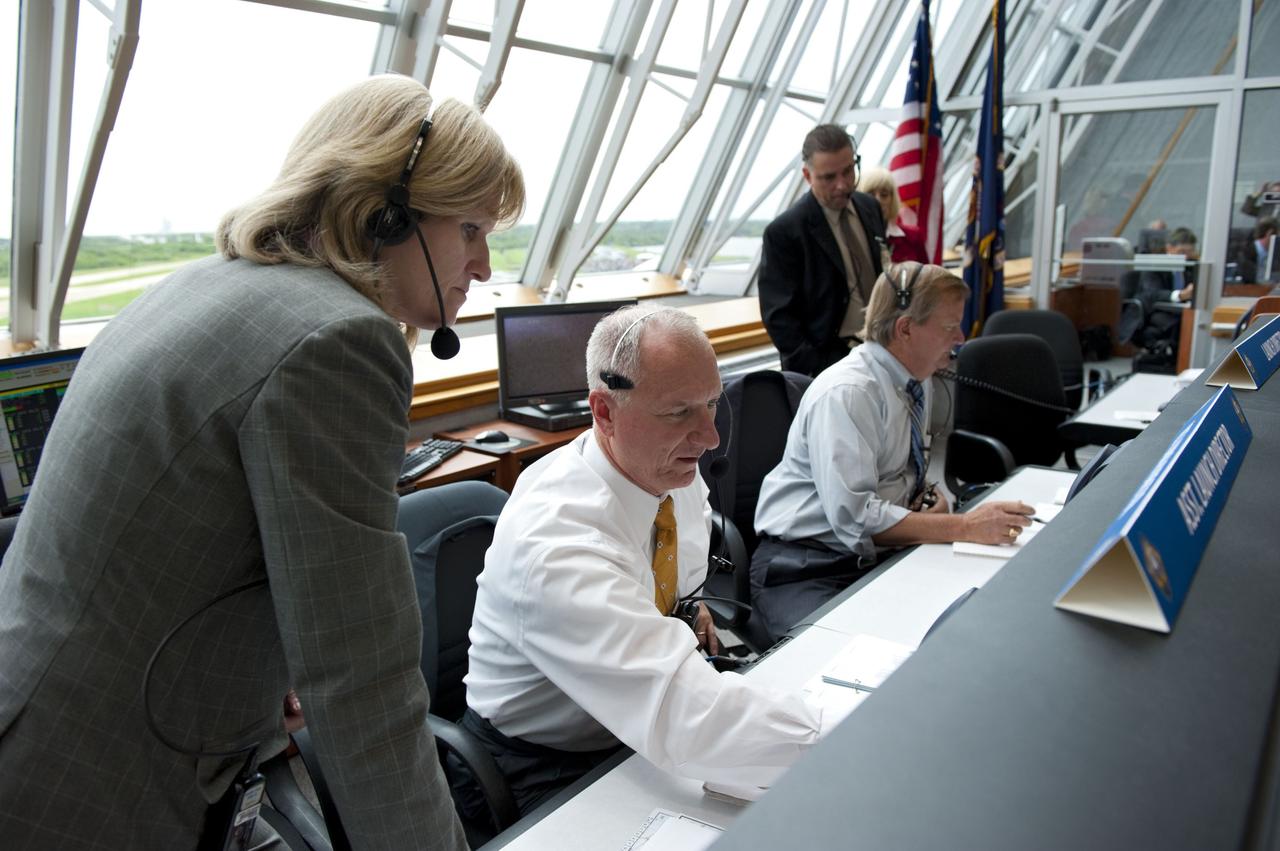

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen here are Atlantis NASA Flow Director Angie Brewer, Assistant Launch Director Pete Nickolenko, Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach and Payloads Launch Manager and Deputy Director of ISS and Spacecraft Processing at Kennedy, Bill Dowdell. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
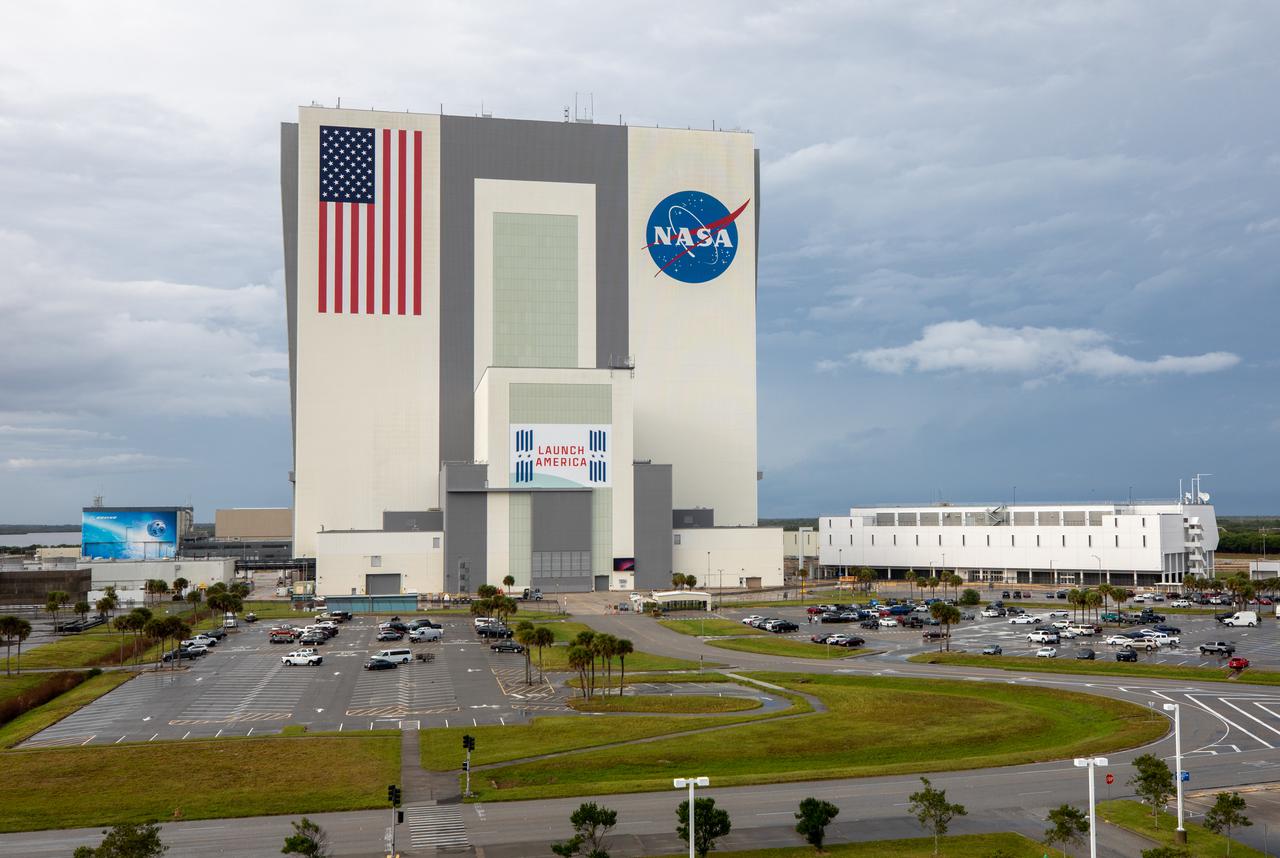

Kennedy Space Center’s iconic Vehicle Assembly Building is photographed just before NASA’s SpaceX Crew-3 astronauts and launch teams participate in a countdown dress rehearsal on Oct. 28, 2021, in preparation for the upcoming Crew-3 launch. The mission will carry NASA astronauts Raja Chari, Tom Marshburn, and Kayla Barron, as well as ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer to the International Space Station for a six-month stay. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft are scheduled to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A in Florida no earlier than Nov. 6 at 11:36 p.m. EDT. Crew-3 is the third crew rotation flight to the space station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, and the first flight of a new Crew Dragon spacecraft.
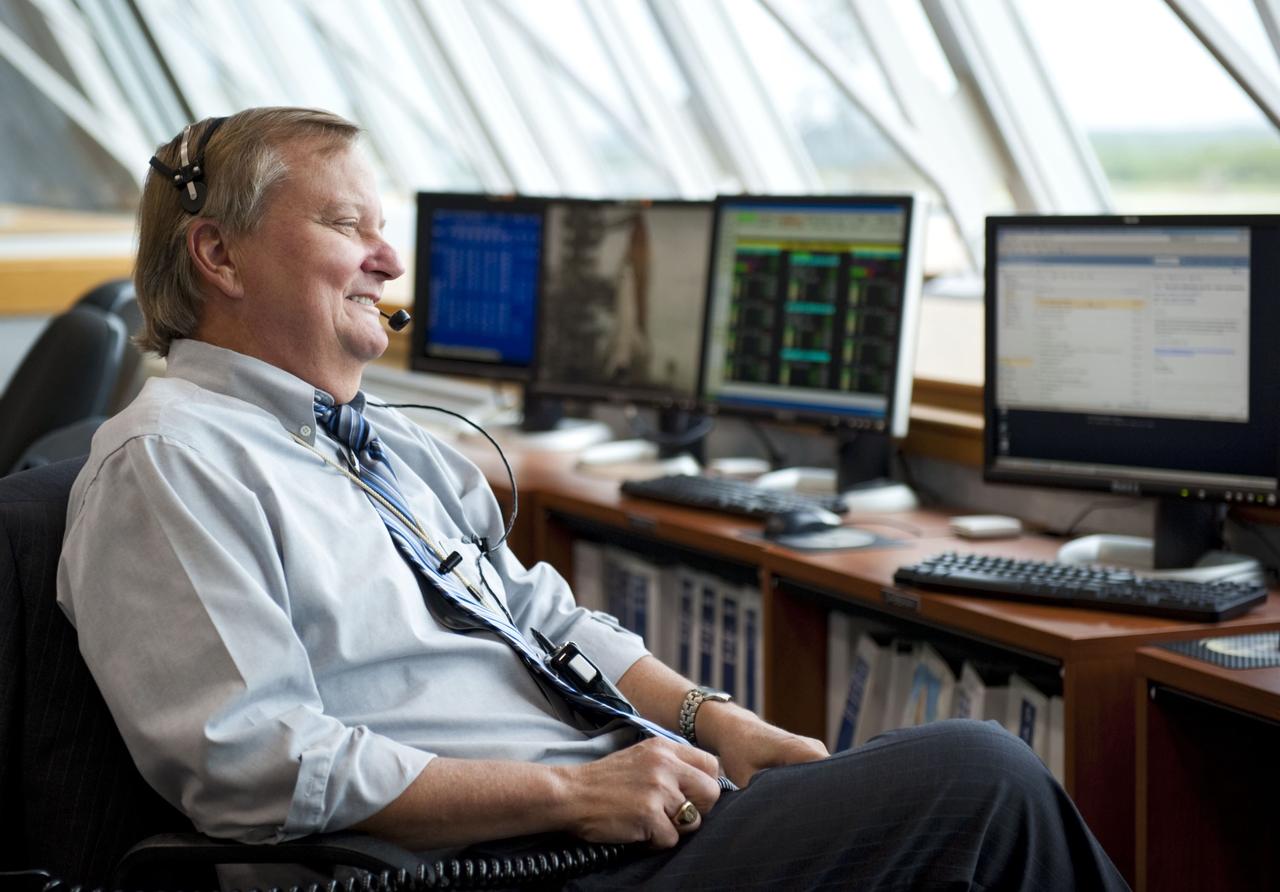

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach, enjoys a light moment during the countdown to liftoff of space shuttle Atlantis to the International Space Station in Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
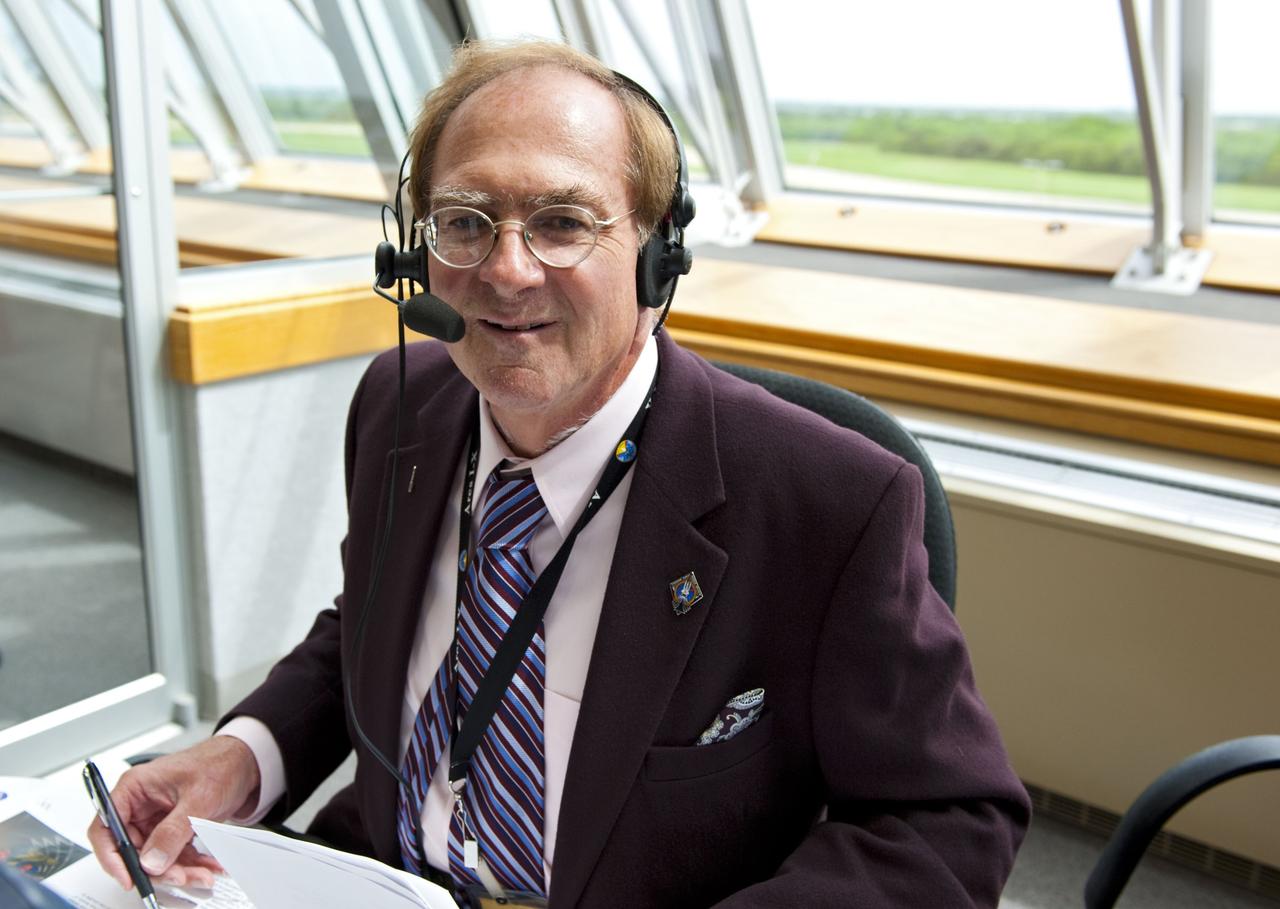

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Commentator and Public Affairs Officer George Diller provides live launch coverage of space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 mission to the International Space Station for NASA TV. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
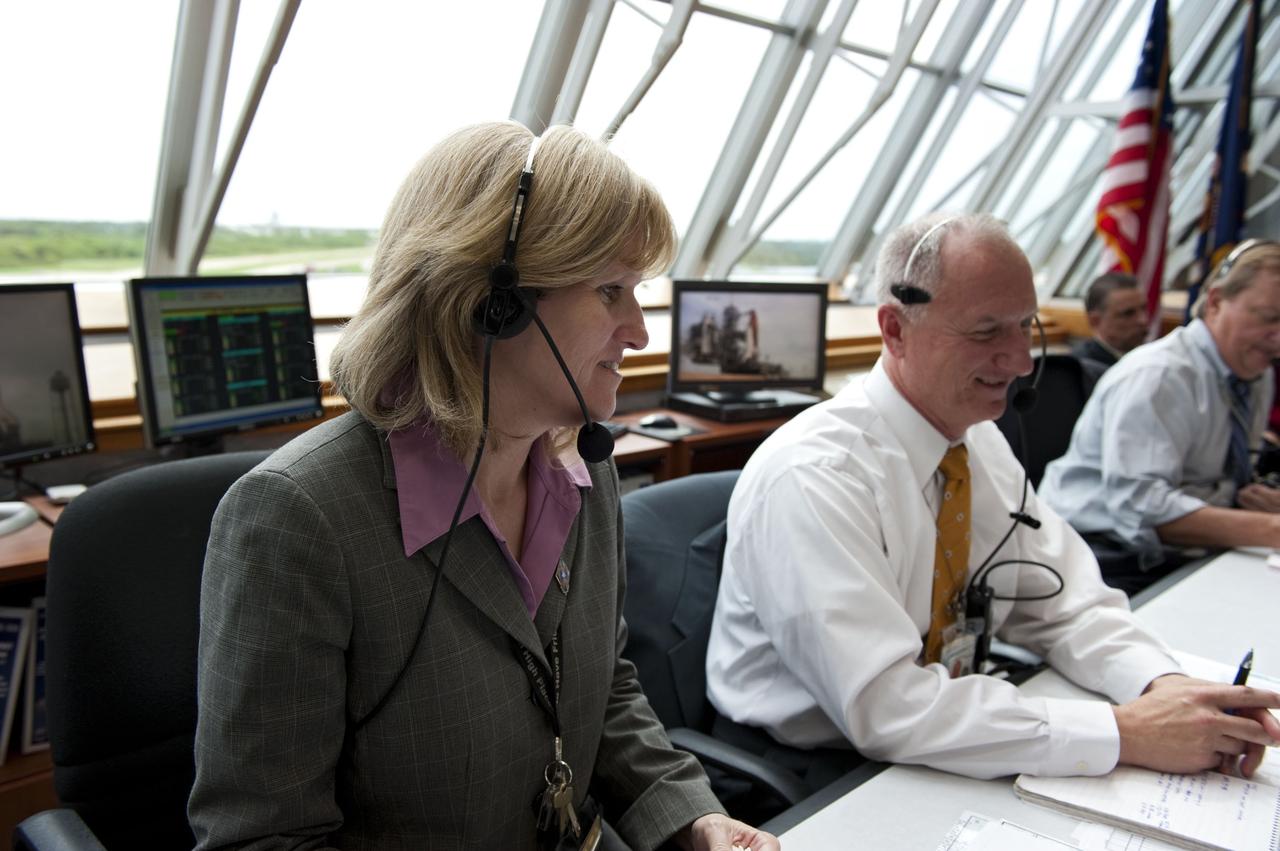

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen here are Atlantis NASA Flow Director Angie Brewer, Assistant Launch Director Pete Nickolenko and Shuttle Launch Director Mike Leinbach (far right). Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Administrator Charles Bolden (right), Associate Administrator for Space Operations Bill Gerstenmaier and Space Shuttle Program Manager John Shannon monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, launch team members monitor the countdown to the launch of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Seen here is the “Launch America” banner for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP) on the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2021. NASA and SpaceX are preparing for Crew-3 – the third crew rotation flight to the International Space Station for CCP – and part of that includes conducting a dress rehearsal ahead of launch. On Oct. 28, NASA’s SpaceX Crew-3 astronauts and launch teams rehearsed countdown operations, concluding with the Go/No-Go poll for Falcon-9 fueling. The Crew-3 mission will carry NASA astronauts Raja Chari, Tom Marshburn, and Kayla Barron, as well as ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Matthias Maurer to the space station for a six-month stay. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft are scheduled to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A no earlier than Nov. 6 at 11:36 p.m. EDT.