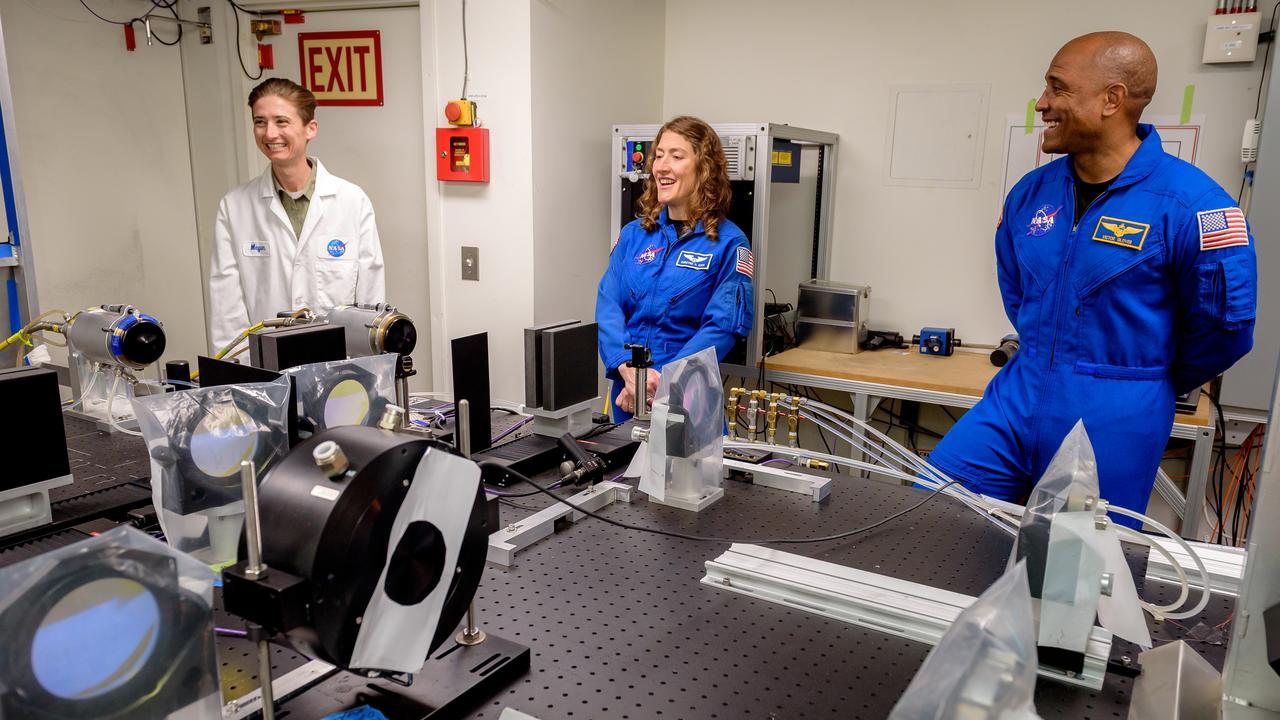

Megan MacDonald, left, leads NASA astronauts Christina Koch and Victor J. Glover, right, on a tour of the Laser Enhanced Arc Jet Facility (LEAF) laboratory, in N238. The LEAF laser augments the hypersonic shock heating experienced by a test sample during an arc jet test and provides improved test simulation quality by supplying an intense source of optical heating while the arc jet flow provides shock-driven convective heating.
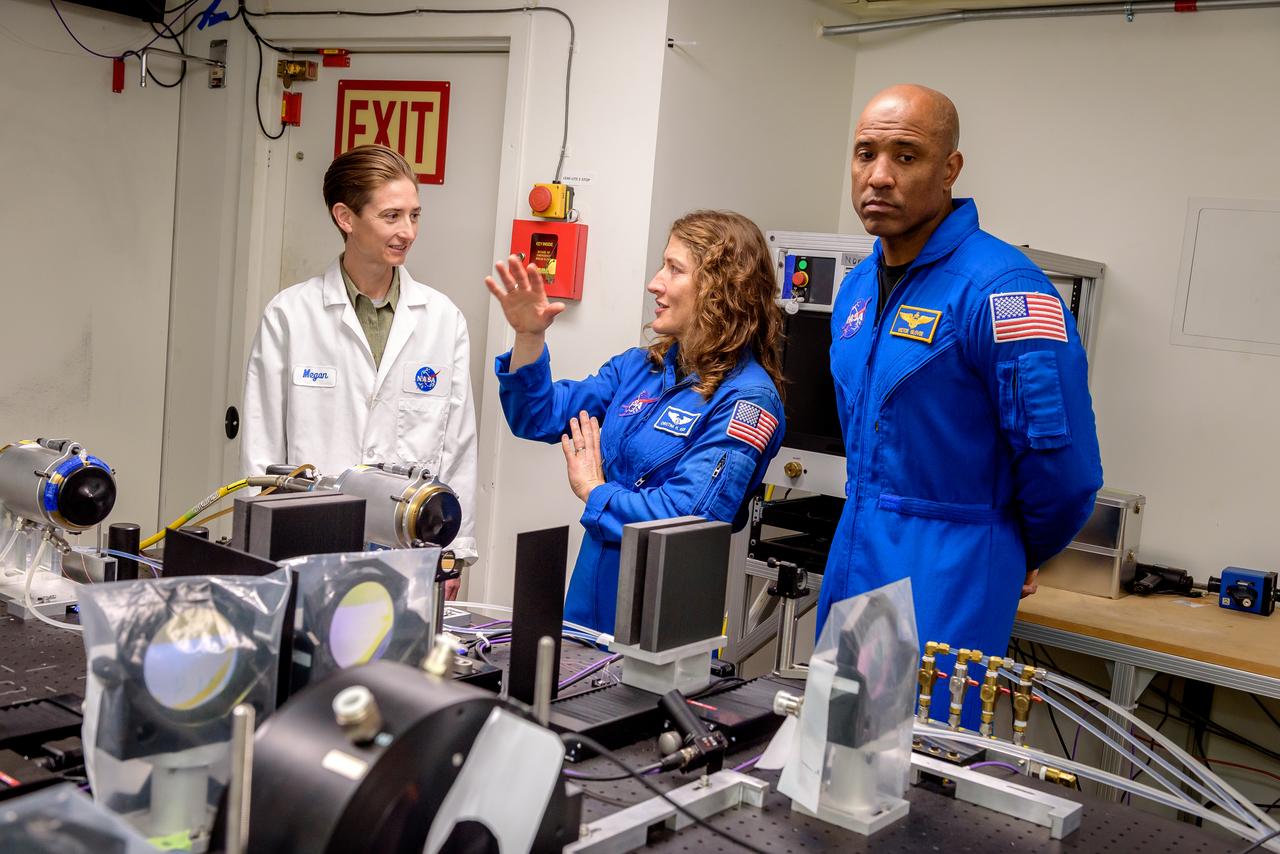

Megan MacDonald, left, leads NASA astronauts Christina Koch and Victor J. Glover, right, on a tour of the Laser Enhanced Arc Jet Facility (LEAF) laboratory, in N238. The LEAF laser augments the hypersonic shock heating experienced by a test sample during an arc jet test and provides improved test simulation quality by supplying an intense source of optical heating while the arc jet flow provides shock-driven convective heating.
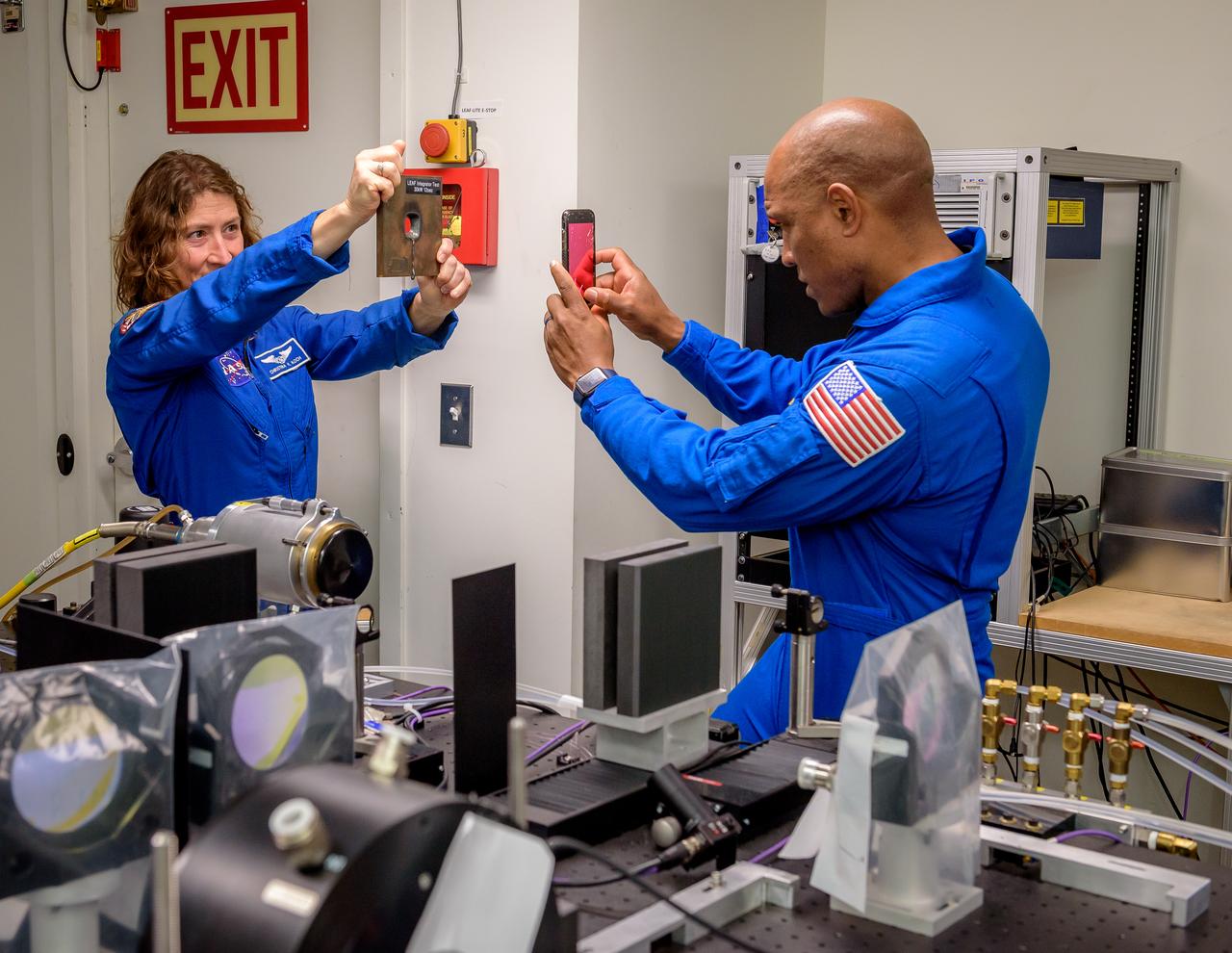

NASA Astronaut Christina Koch, left, holds a test sample for Victor J. Glover to photograph. The sample is a half-inch steel plate with a hole that was drilled by a 12-second burst from a 30kW laser in the Laser Enhanced Arc Jet Facility (LEAF) laboratory, N238.
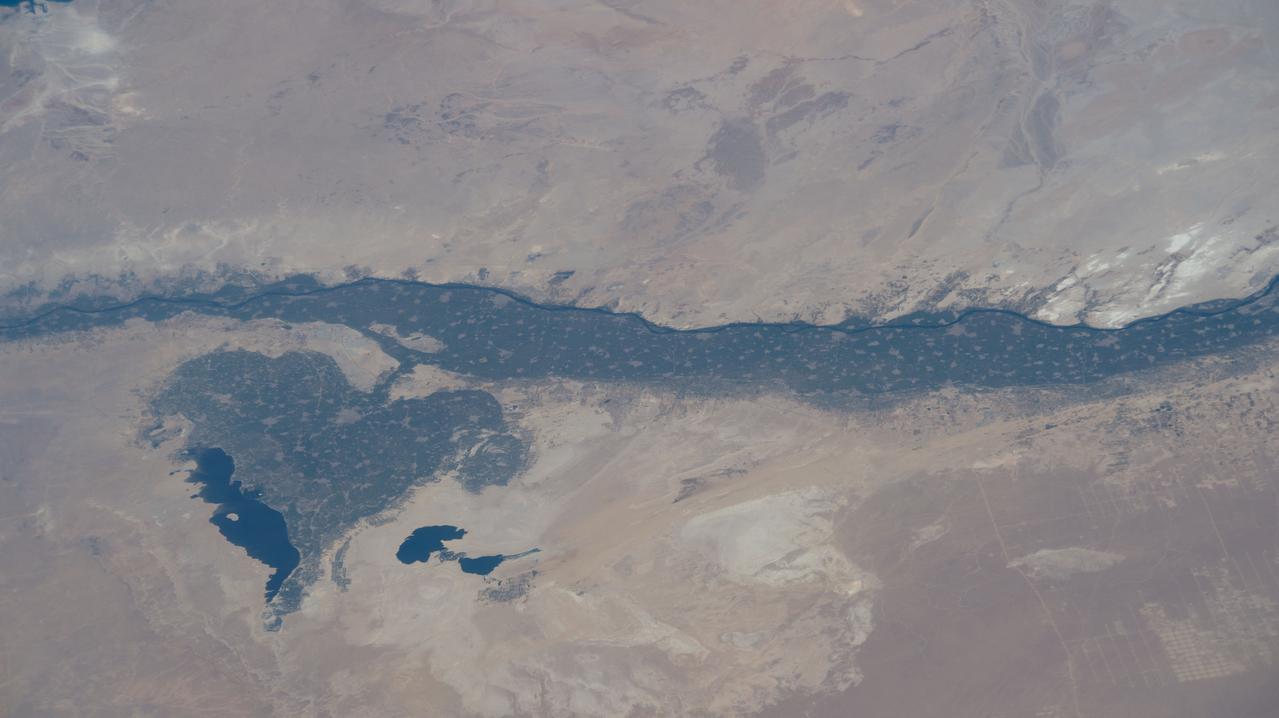

iss073e0178560 (June 14, 2025) --- The leaf-shaped Faiyum Oasis, fed by a channel of the River Nile and bordered on the west by the saltwater Qarum Lake with the Wadi El Rayan nature reserve to its southwest, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above the Libya-Egypt border.
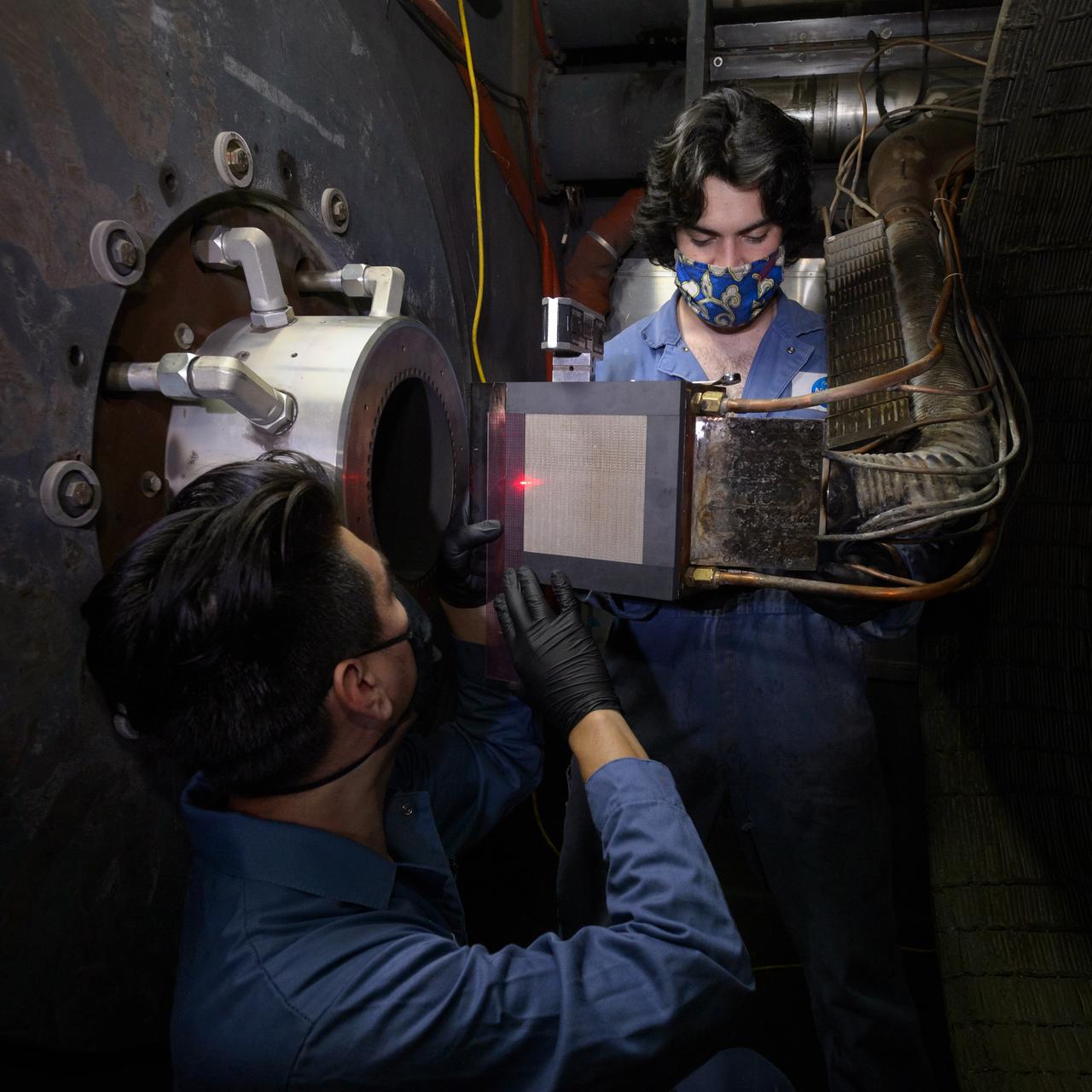

Engineering technicians Pedro Solano, left, and Aaron Poulin, right, verify alignment of an Orion heat shield test article in the Arc Jet Interaction Heating Facility, or IHF, test section. This test of Orion’s heat shield using a combination of the IHF and the Laser Enhanced Arc Jet Facility, or LEAF-Lite, capabilities will certify the heat shield for the Artemis I and Artemis II missions. This is also the first time the heat shield is tested in an environment combining the two forms of heating, radiant and convective, the spacecraft will experience on entering Earth’s atmosphere.
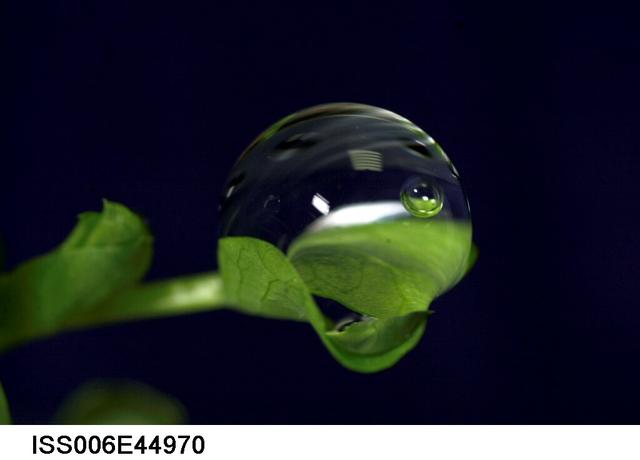

ISS006-E-44970 (9 March 2003) --- A close up view of a water droplet on a leaf on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
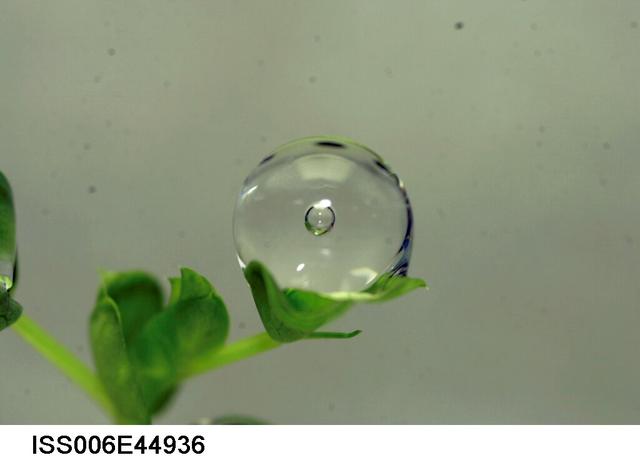

ISS006-E-44936 (9 March 2003) --- A close up view of a water droplet on a leaf on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
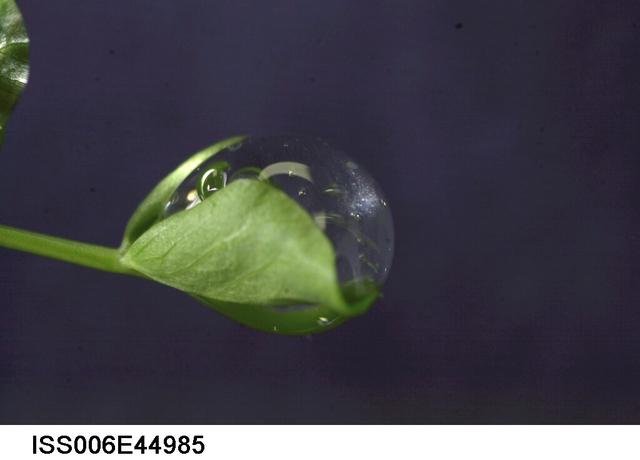

ISS006-E-44985 (10 March 2003) --- A close up view of a water droplet on a leaf on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
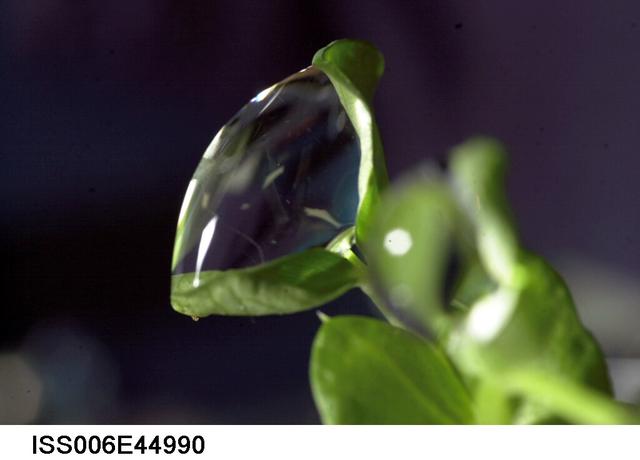

ISS006-E-44990 (10 March 2003) --- A close up view of a water droplet on a leaf on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
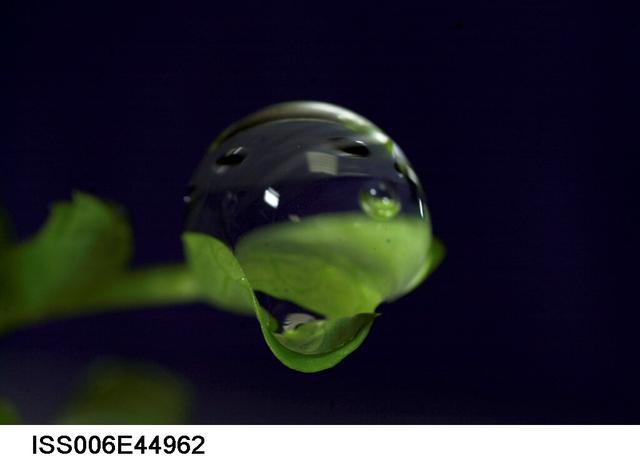

ISS006-E-44962 (9 March 2003) --- A close up view of a water droplet on a leaf on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
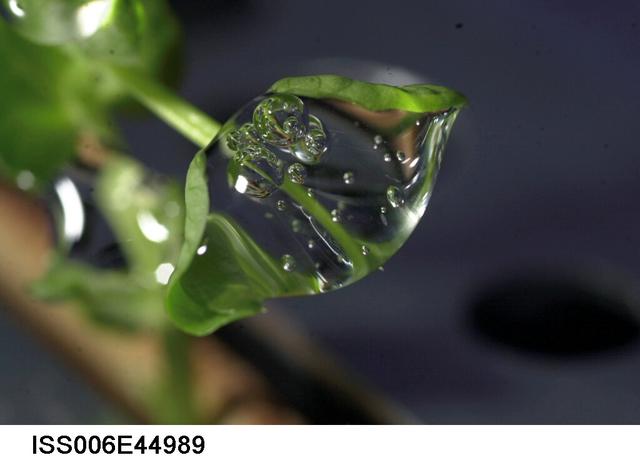

ISS006-E-44989 (10 March 2003) --- A close up view of a water droplet on a leaf on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
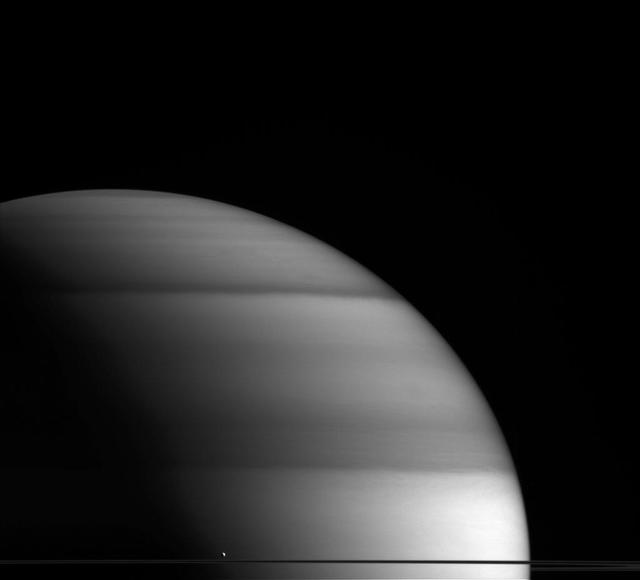

The water-world Enceladus appears here to sit atop Saturn rings like a drop of dew upon a leaf in this view from NASA Cassini spacecraft.
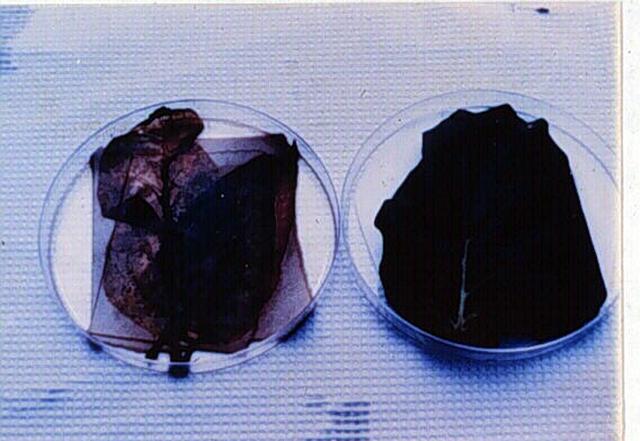
Researcher Dr. Yi Li developed a technique to manipulate certain characteristics of plant growth such as anit-senescence. For example, the tobacco leaf was clipped from a transgenic plant (right), and a wildtype plant (left). During ground-based laboratory studies, both leaves were left in a darkened area for 4 months. When retrieved, the wildtype plant leaf was dried-out and the transgenic leaf remained fresh and green. A variation of this technology that involves manipulating plant hormones has been conducted in space-based studies on tomato plants through BioServe Space Technologies. The transport and distribution of auxin, an important plant hormone has shown to be influenced by microgravity, which could lead to improving the quality of fruits and vegetables grown on Earth.
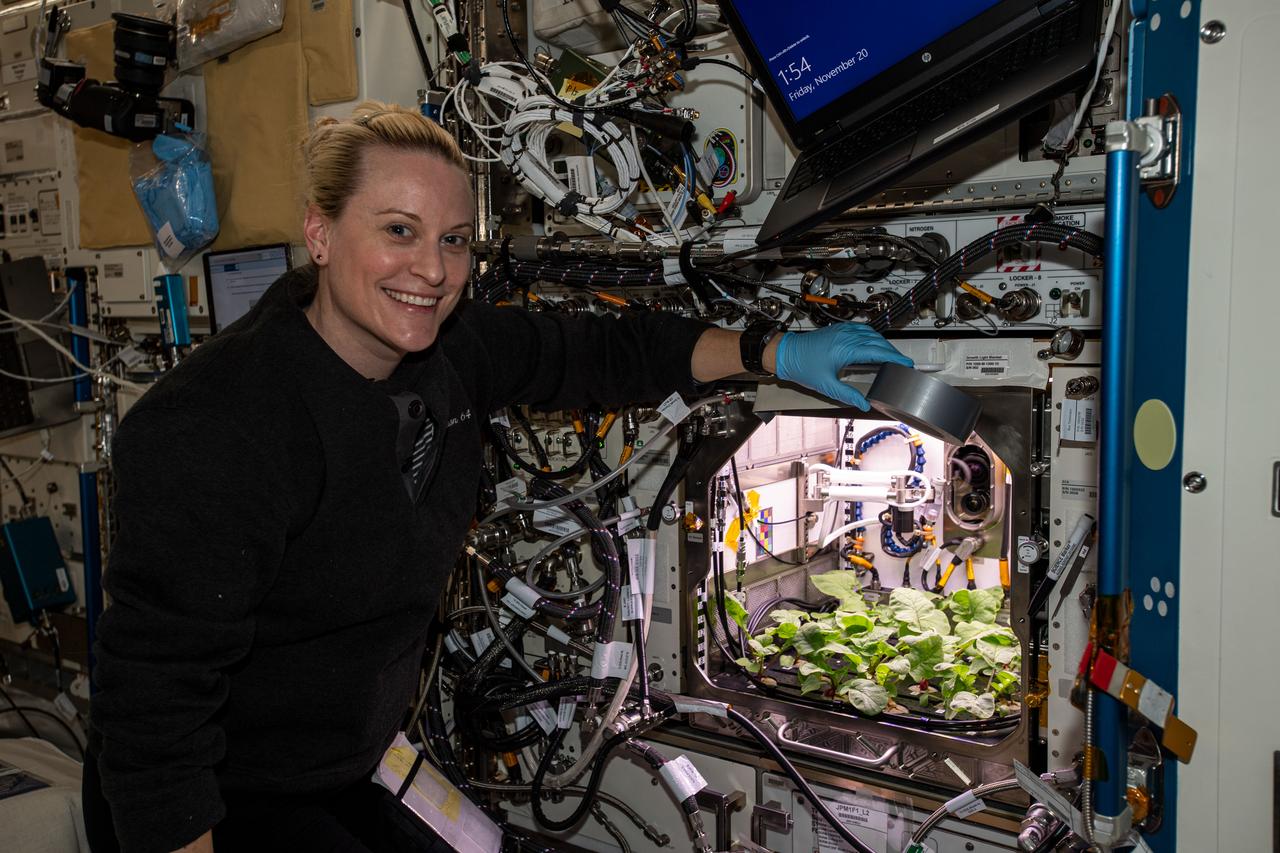

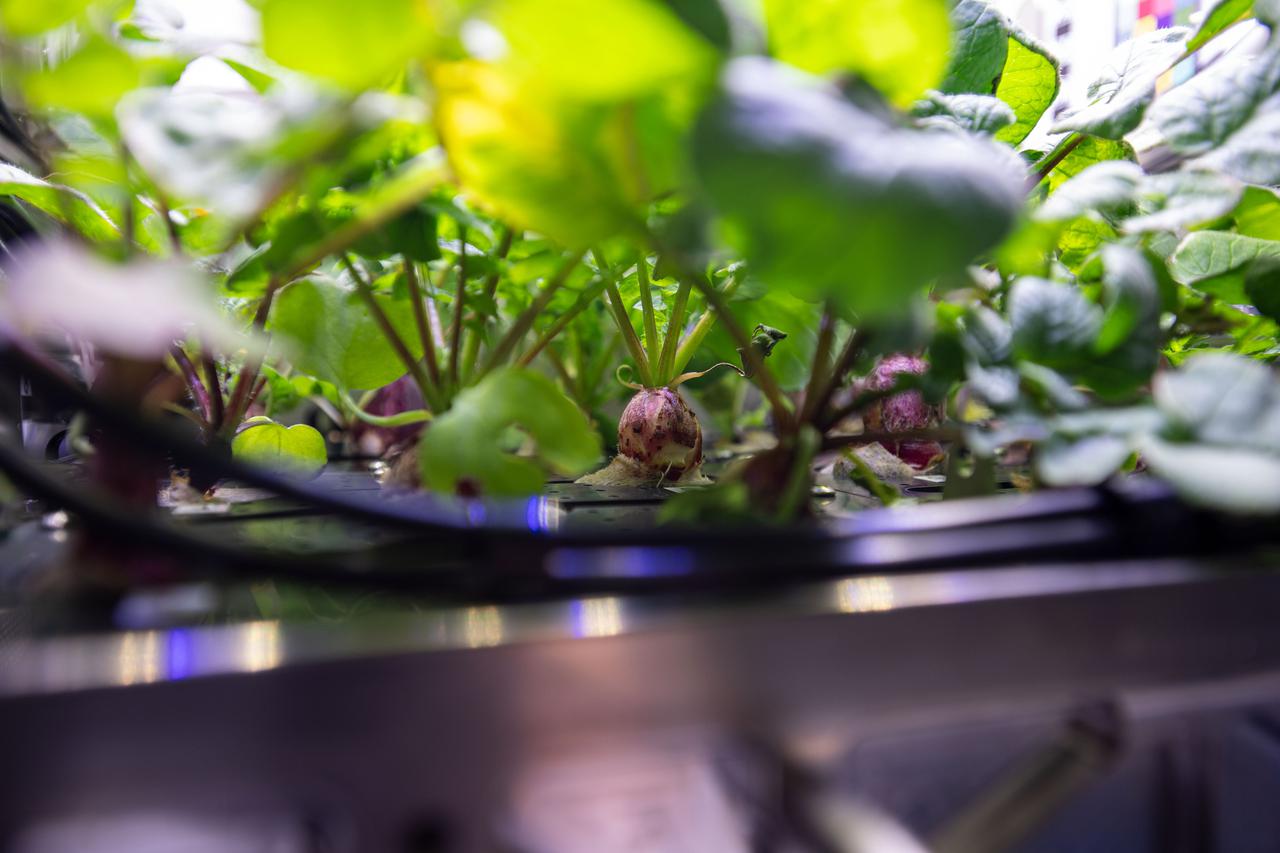
iss064e004997 (Nov. 20, 2020) --- Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Kate Rubins of NASA shows off radish plants growing inside the Columbus laboratory module's Advanced Plant Habitat before collecting leaf samples for analysis.
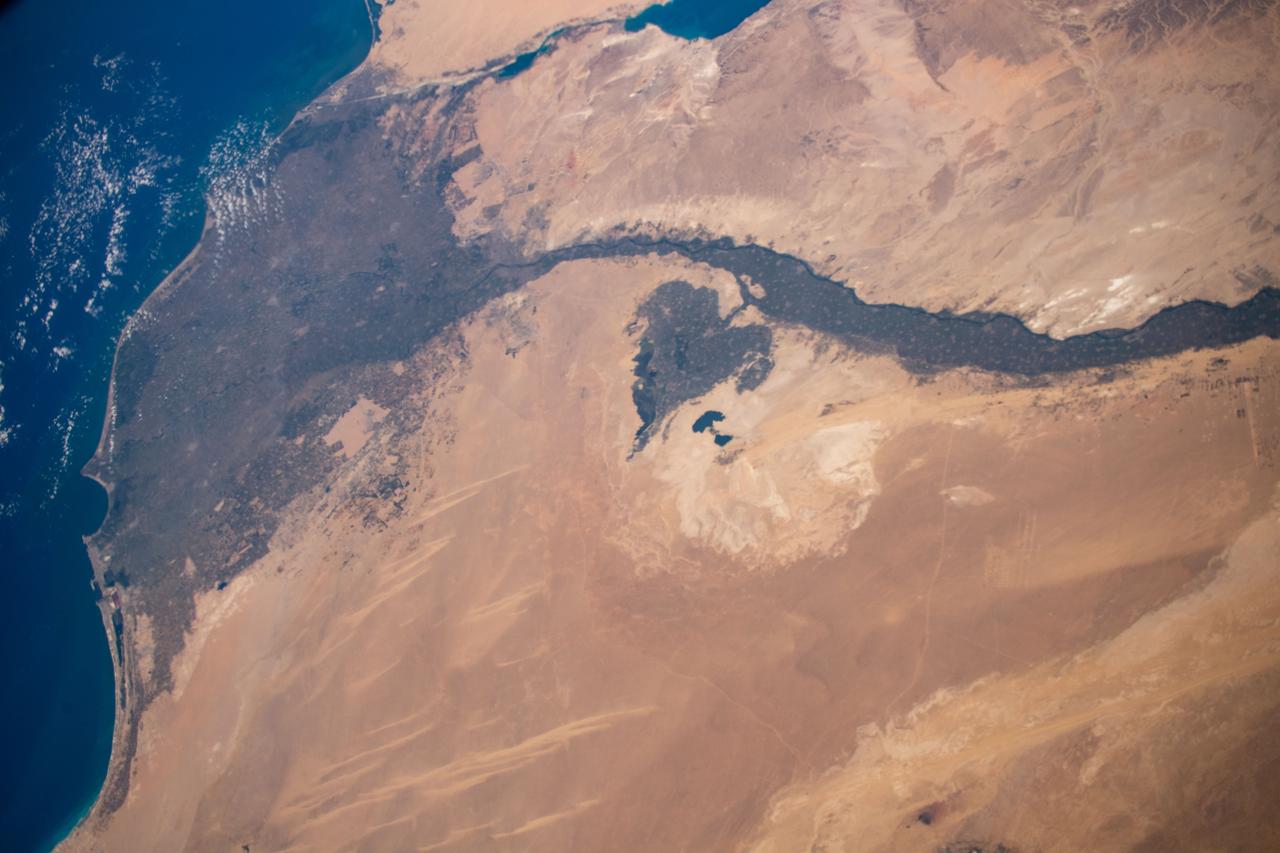

iss061e004613 (Oct. 9, 2019) --- Looking like a leaf on a vine, the Faiyum Oasis extends west of the Nile River and south of Cairo, Egypt. The fertile area at the left of the photograph is the Nile Delta opening up into the Mediterranean Sea.
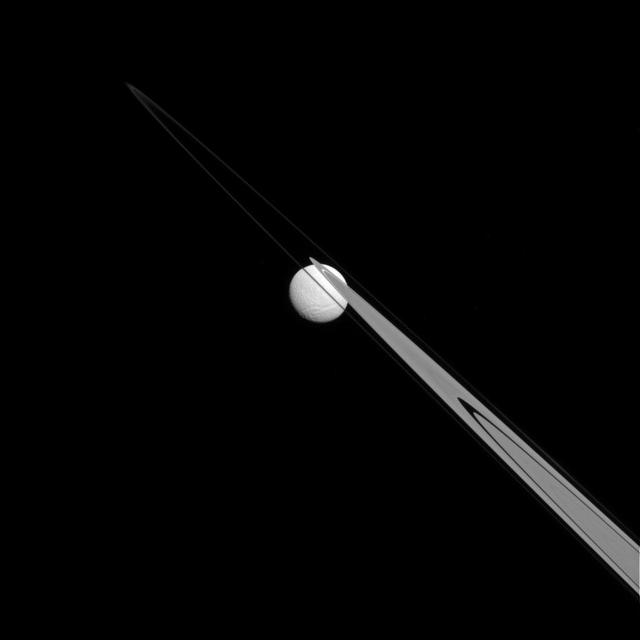

Like a drop of dew hanging on a leaf, Tethys appears to be stuck to the A and F rings from this perspective. Tethys (660 miles, or 1,062 kilometers across), like the ring particles, is composed primarily of ice. The gap in the A ring through which Tethys is visible is the Keeler gap, which is kept clear by the small moon Daphnis (not visible here). This view looks toward the Saturn-facing hemisphere of Tethys. North on Tethys is up and rotated 43 degrees to the right. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on July 14, 2014. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 1.1 million miles (1.8 million kilometers) from Tethys and at a Sun-Tethys-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 22 degrees. Image scale is 7 miles (11 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18284
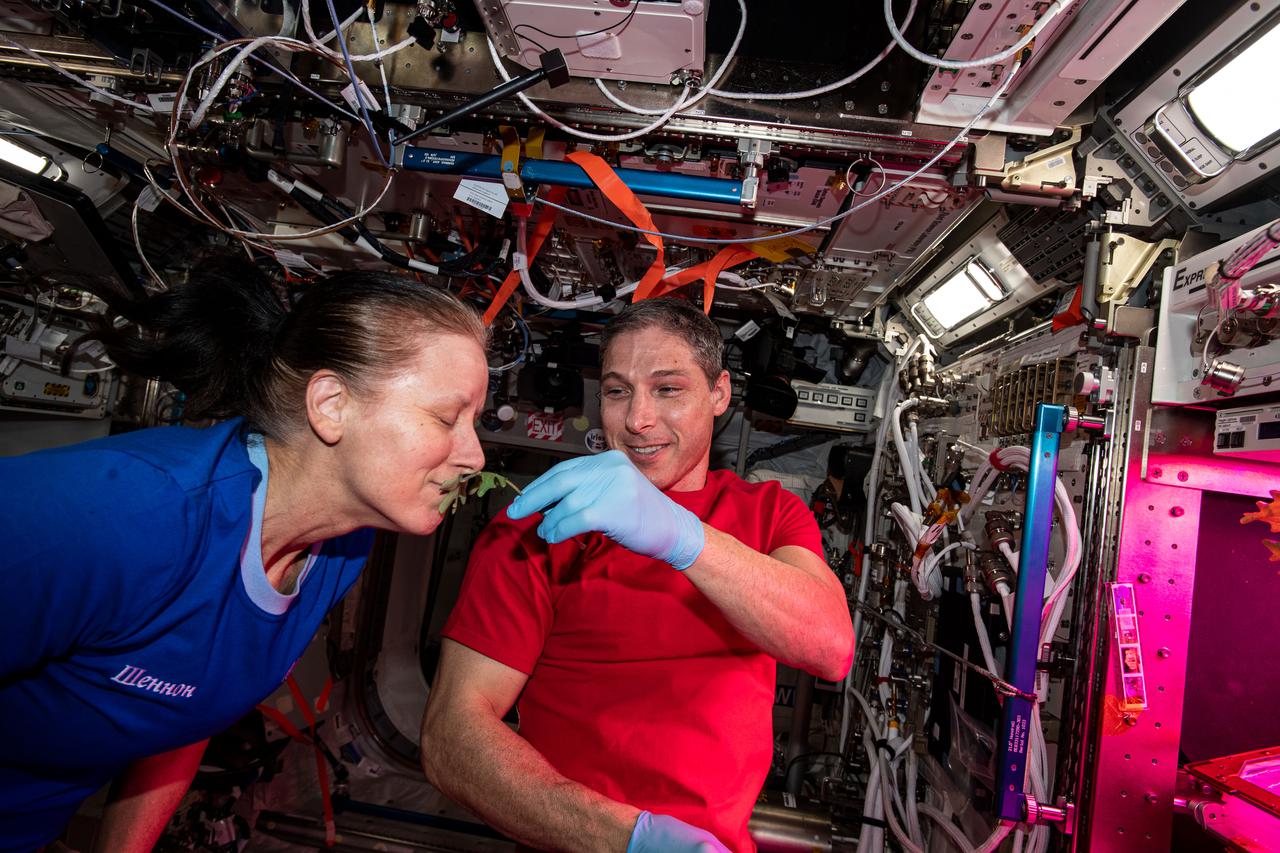

iss064e027748 (Jan. 28, 2021) --- NASA astronauts Shannon Walker and Michael Hopkins collect leaf samples from plants growing inside the European Columbus laboratory. Space agriculture is key to the success and sustainability of future human missions to the Moon, Mars and beyond.
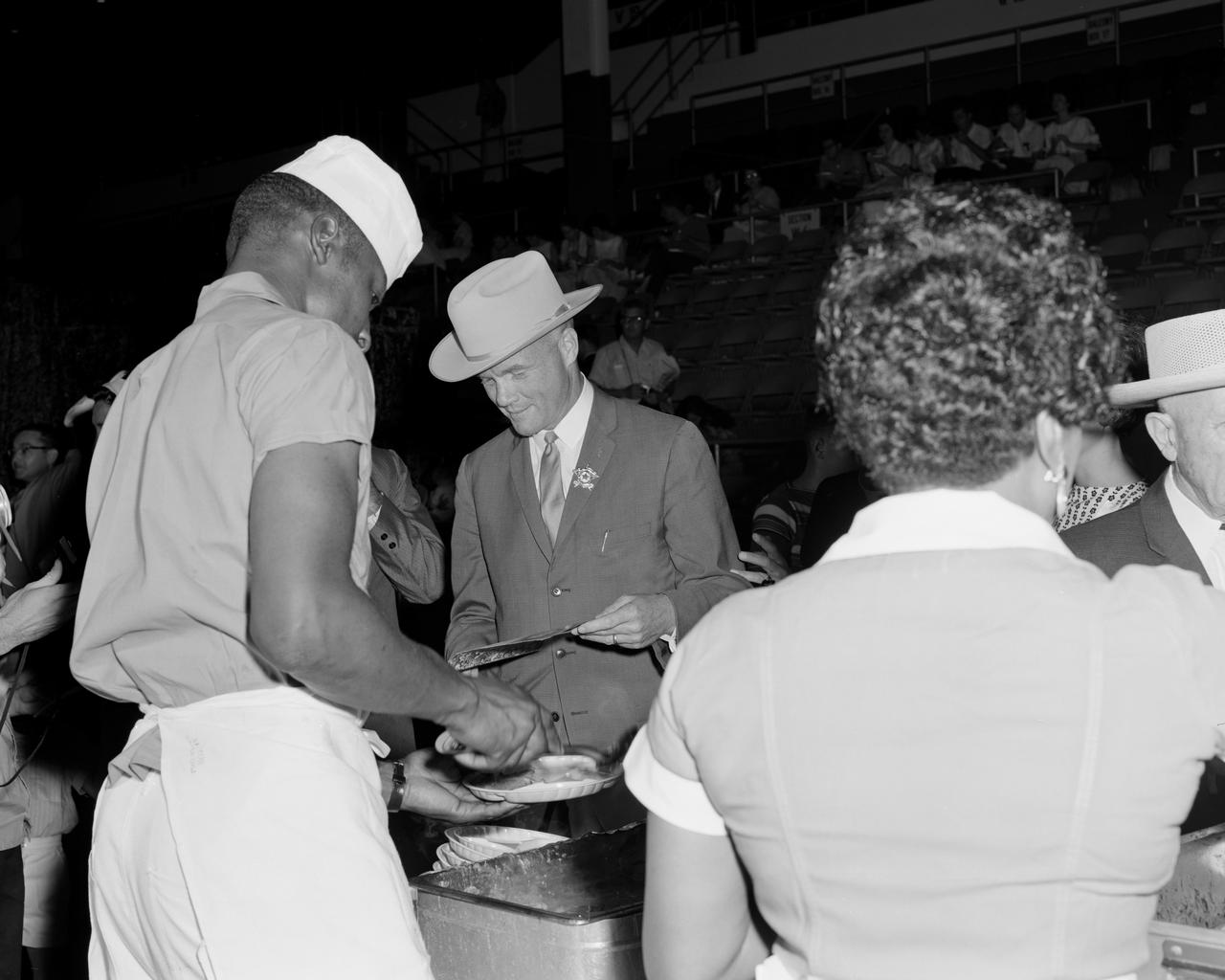

S62-03725 (4 July 1962) --- Mercury astronaut John H. Glenn Jr., wearing a new cowboy hat and a badge in the shape of a star, leafs through his program as he is served his food at the Sam Houston Coliseum. A large crowd was on hand to welcome the Mercury astronauts to Houston, Texas. Photo credit: NASA

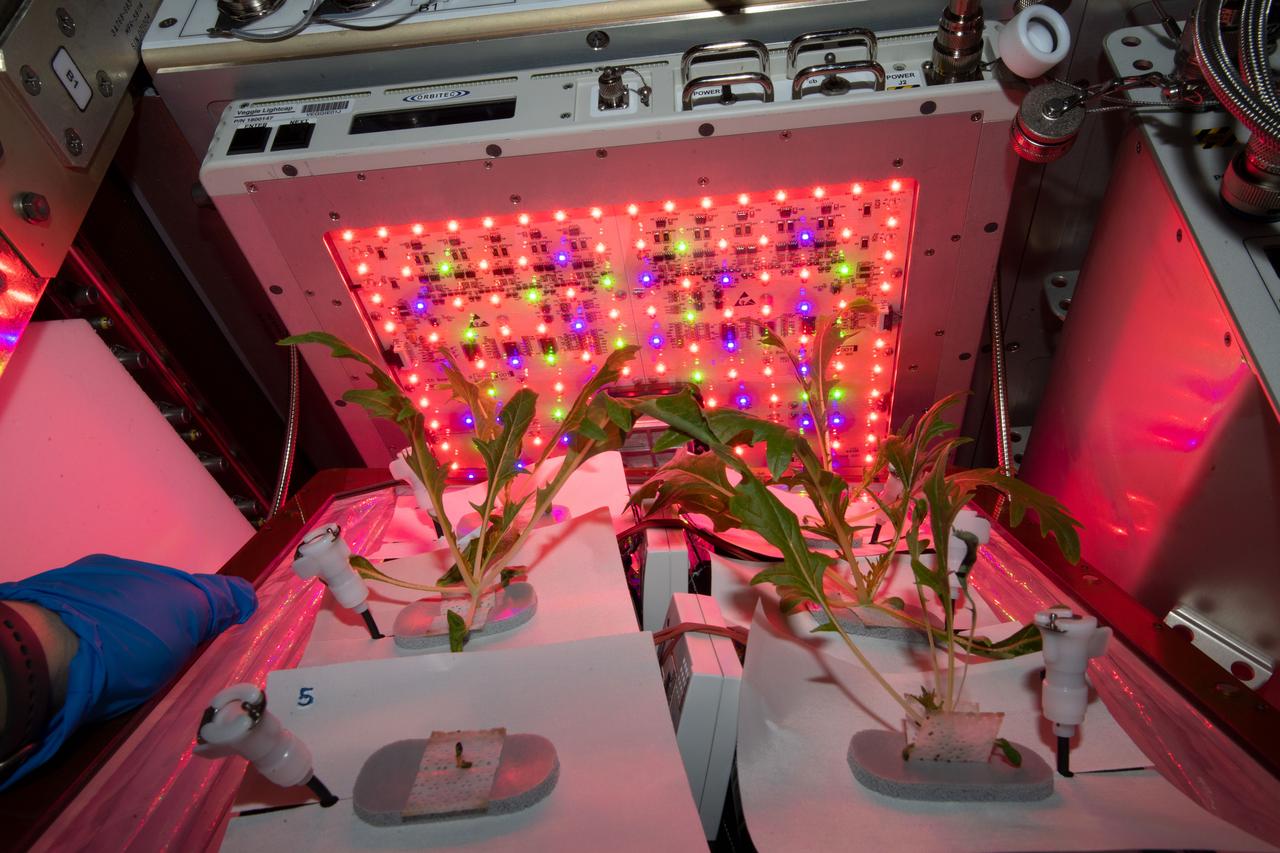
Outredgeous red leaf lettuce, Mizuna mustard and Waldmann's green lettuce are growing in the Veggie control system in the ISS environment simulator chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Growth in the chamber mimics the growth of plant experiments in the Veggie plant growth system on the International Space Station.

iss064e027787 (Jan. 28, 2021) --- NASA astronauts (from left) Shannon Walker and Kate Rubins collect leaf samples from plants growing inside the European Columbus laboratory. Space agriculture is key to the success and sustainability of future human missions to the Moon, Mars and beyond.
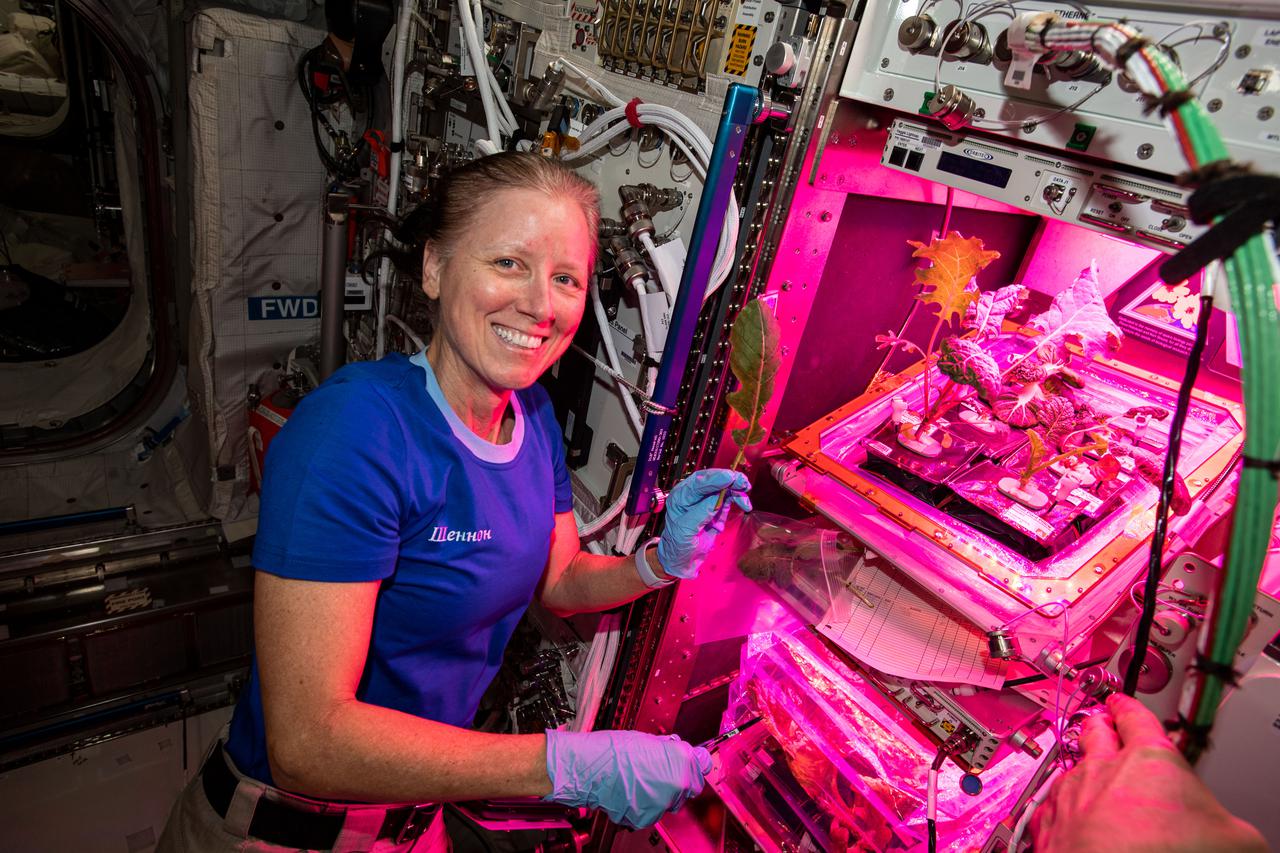

iss064e027736 (Jan. 28, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Shannon Walker collects leaf samples from plants growing inside the European Columbus laboratory. Space agriculture is key to the success and sustainability of future human missions to the Moon, Mars and beyond.
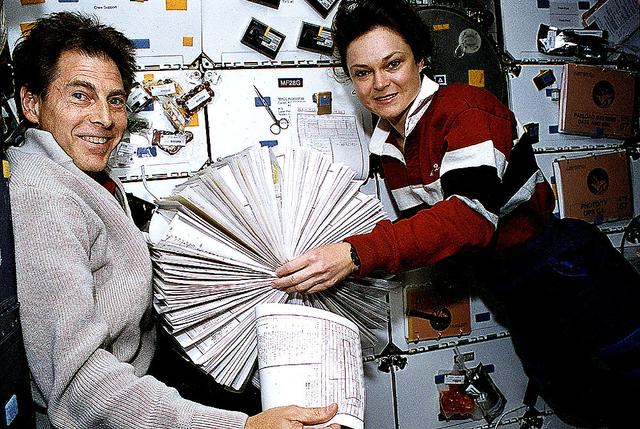

Astronaut Tamara Jernigan, STS-67 payload commander, and payload specialist Samuel T. Durrance use the absence of gravity for a perusal of Astro-2 targets in a loose-leaf, Rolodex-type collection of data. The two are in the mid-deck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour.

iss064e006479 (November 27, 2020) --- Documentation of radish plants growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat Science Carrier prior to leaf sampling operations (OPS) for the Assessment of Nutritional Value and Growth Parameters of Space-grown Plants (Plant Habitat-02) experiment. Photo was taken in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Module (JEM).
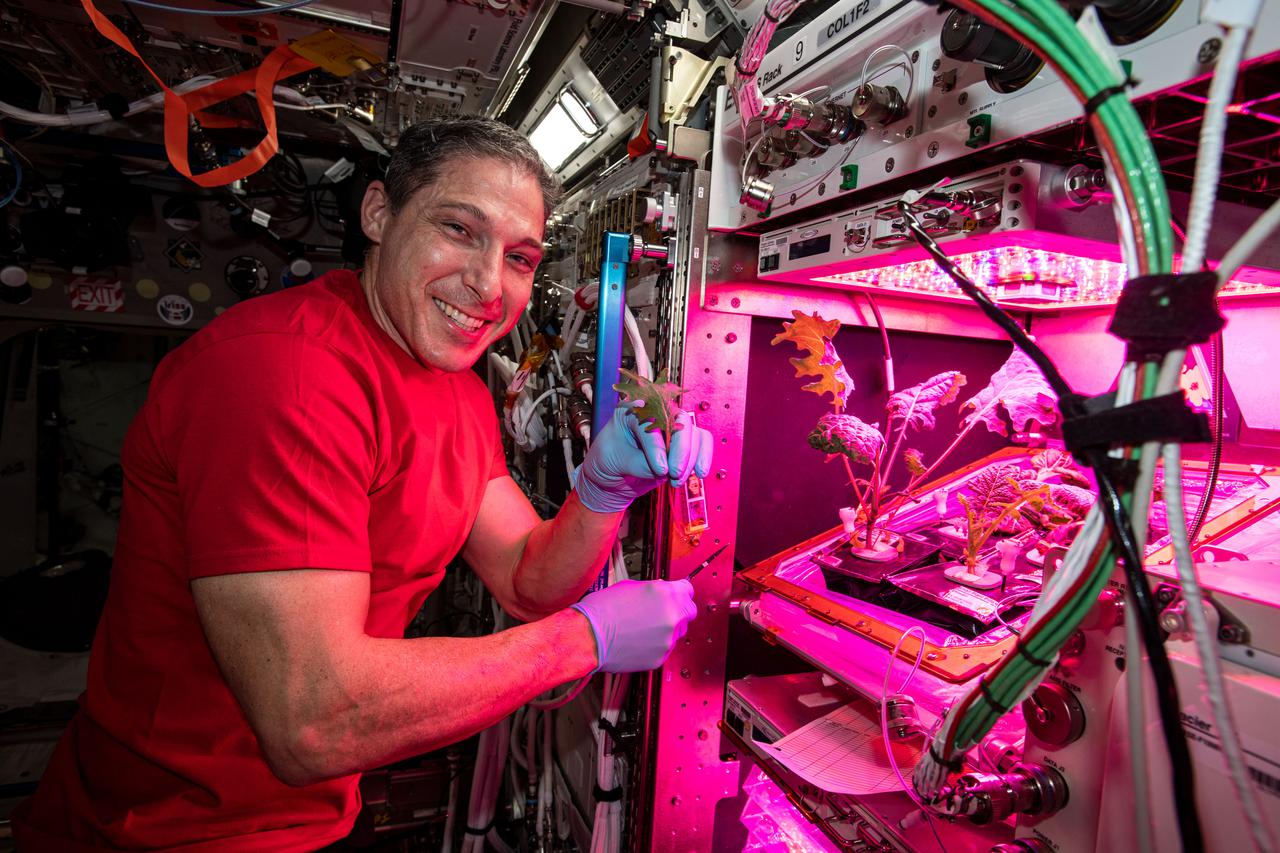

iss064e027743 (Jan. 28, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Michael Hopkins collects leaf samples from plants growing inside the European Columbus laboratory. Space agriculture is key to the success and sustainability of future human missions to the Moon, Mars and beyond.
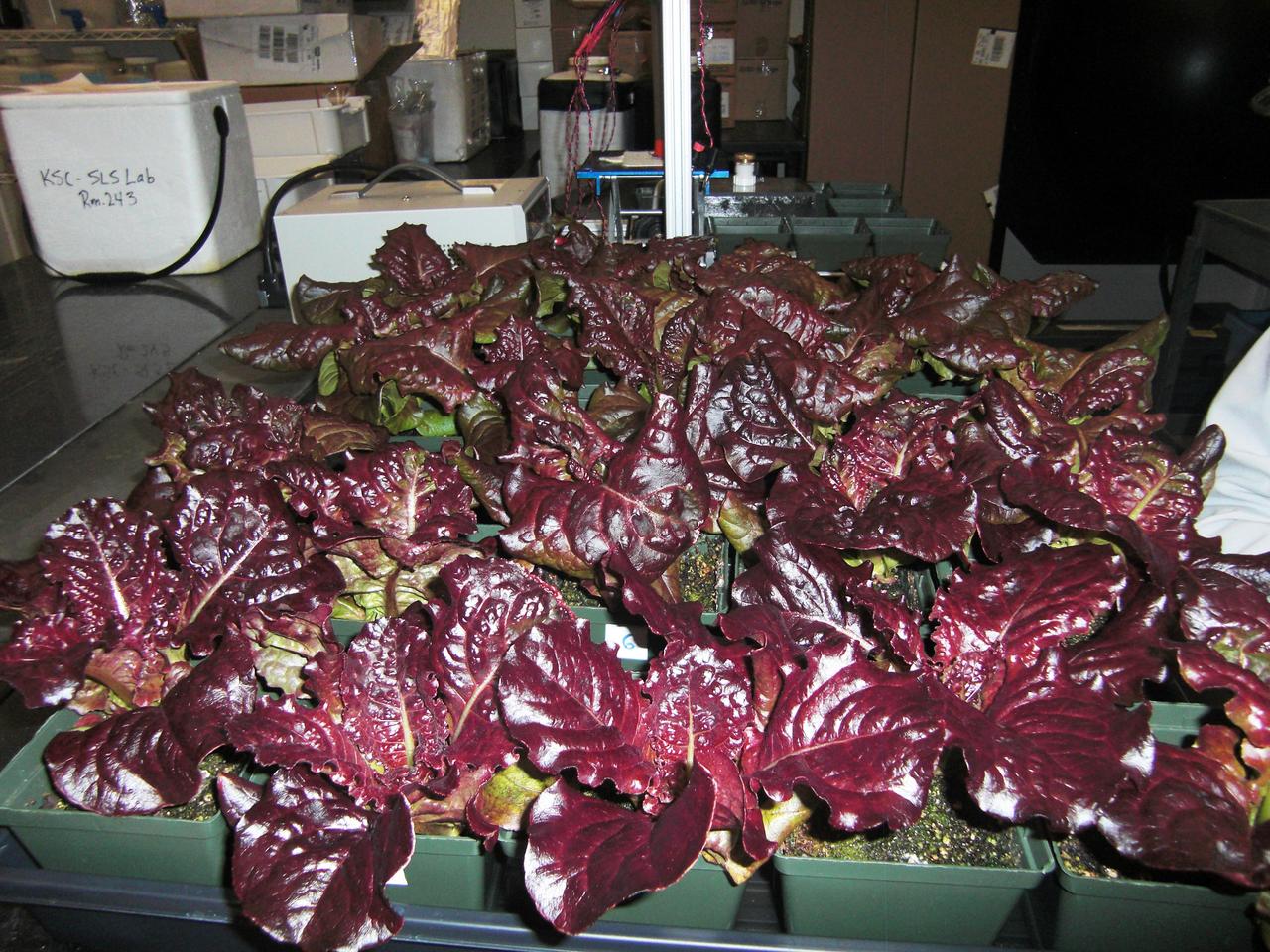

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory, or SLSL, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, red leaf lettuce plants were harvested from a plant growth chamber. The plants were grown under red and blue LED lights. The plant experiment at Kennedy is part of the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. This plant experiment studies the effects of different types of lighting on plants such as radishes and leaf lettuce. Results of these studies will help provide information on how to grow food sources for deep space exploration missions. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Ochoa-Gonzales
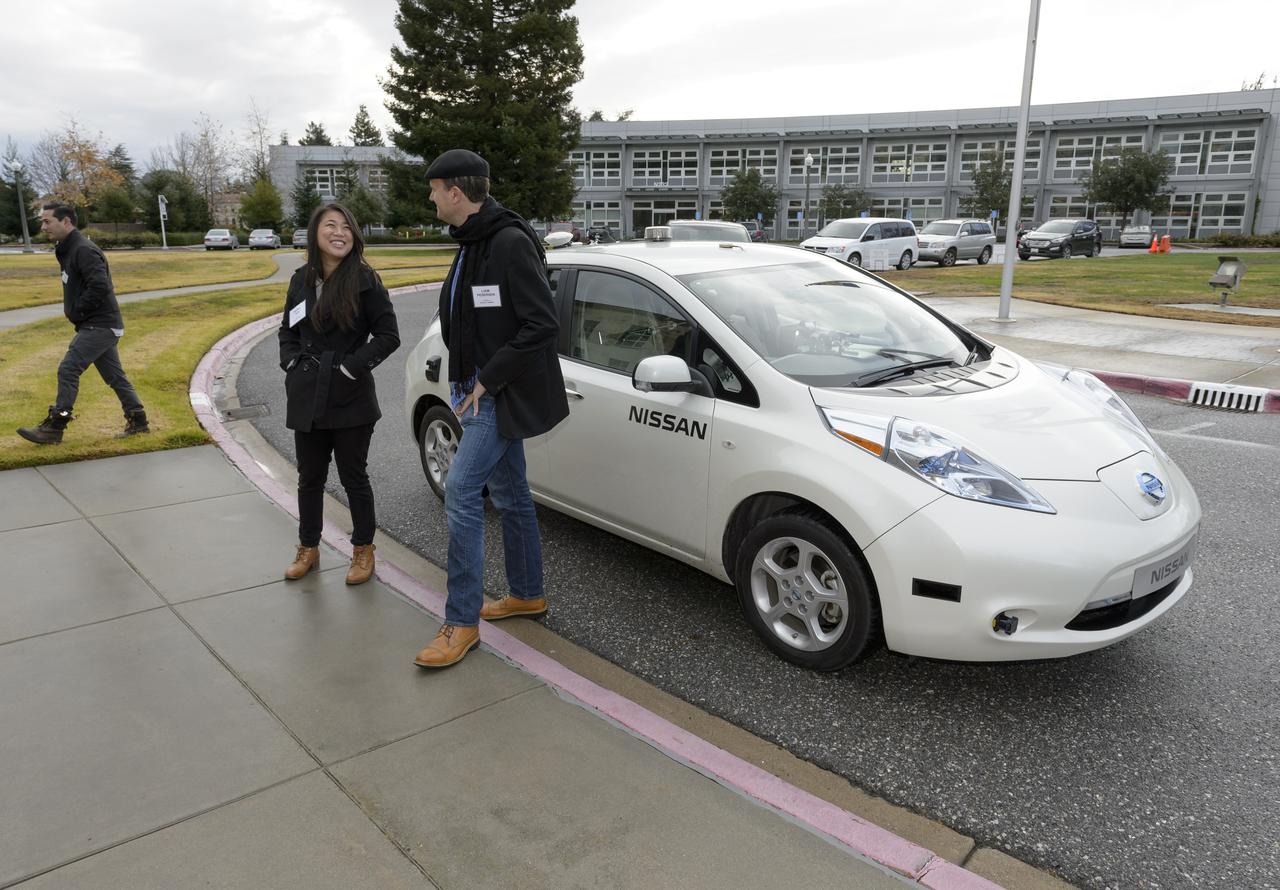

This Nissan LEAF vehicle being tested on the Ames campus is equipped with cameras, sensors and cellular data networking, and uses robotics software originally developed for Ames’ K-10 and K-REX planetary rovers to operate autonomously. Shown here are Kathy Sun and Liam Pedersen, Nissan who are awaiting the arrival of the visiting group from Renault-Nissan Alliance for a demo ride across Ames.

iss059e117376 (6/22/2019) --- Photo documentation taken during VEG-04 Water Check and Mass Measurement Device Operations aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The crew checks plants for water and waters if needed then if there are any leafs that have been broken off. The research of Veg-04A focuses on the impact of light quality and fertilizer on leafy crop growth for a 28-day grow-out.
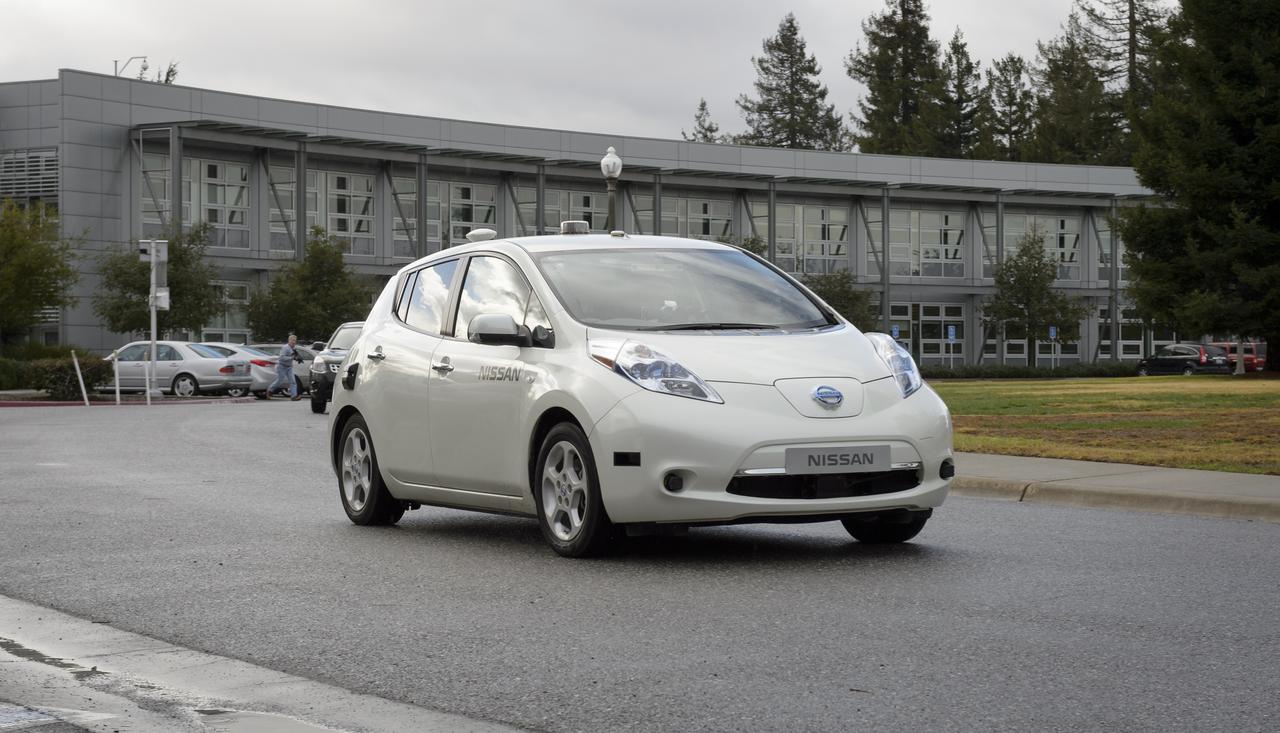

Senior executives from the Renault-Nissan Alliance, including Carlos Ghosn, chairman and CEO of Nissan, and Jose Munoz, chairman of Nissan North America, visited Ames for meetings and a showcase of the technical partnership between NASA and Nissan North America. After briefings, the group observed testing of Nissan’s all-electric LEAF as it performed safe autonomous drives across the center.

STS001-07-540 (12-14 April 1981) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander, is seated at his left side station in the flight deck of the space shuttle Columbia. He holds a loose-leaf book in which he recorded data during the flight. Soon after the launch phase of STS-1, astronauts Young and Robert L. Crippen, pilot, changed from their high altitude pressure garments into the light blue constant wear garment. Photo credit: NASA

S81-30419 (12-14 April 1981) --- Astronaut John W. Young, mans the commander?s station in the Columbia during the 36-orbit STS-1 flight. A loose leaf notebook with flight activities data floats in the weightless environment. Young is wearing a three-piece constant wear flight suit. This 35mm frame was exposed by astronaut Robert L. Crippen. Photo credit: NASA
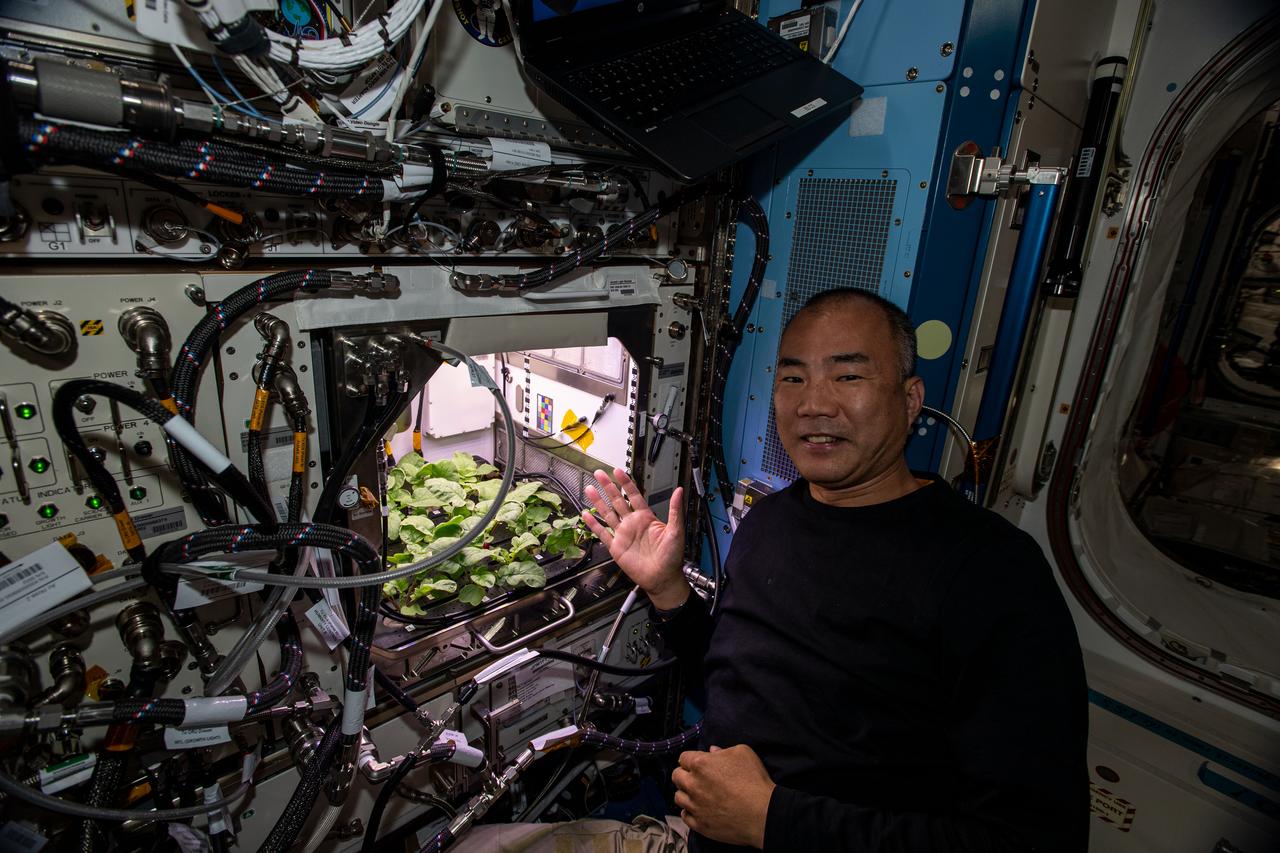

iss064e005001 (Nov. 20, 2020) --- SpaceX Crew-1 Mission Specialist and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Soichi Noguchi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) shows off radish plants growing inside the Columbus laboratory module's Advanced Plant Habitat before leaf samples were collected for analysis during his first week aboard the International Space Station.
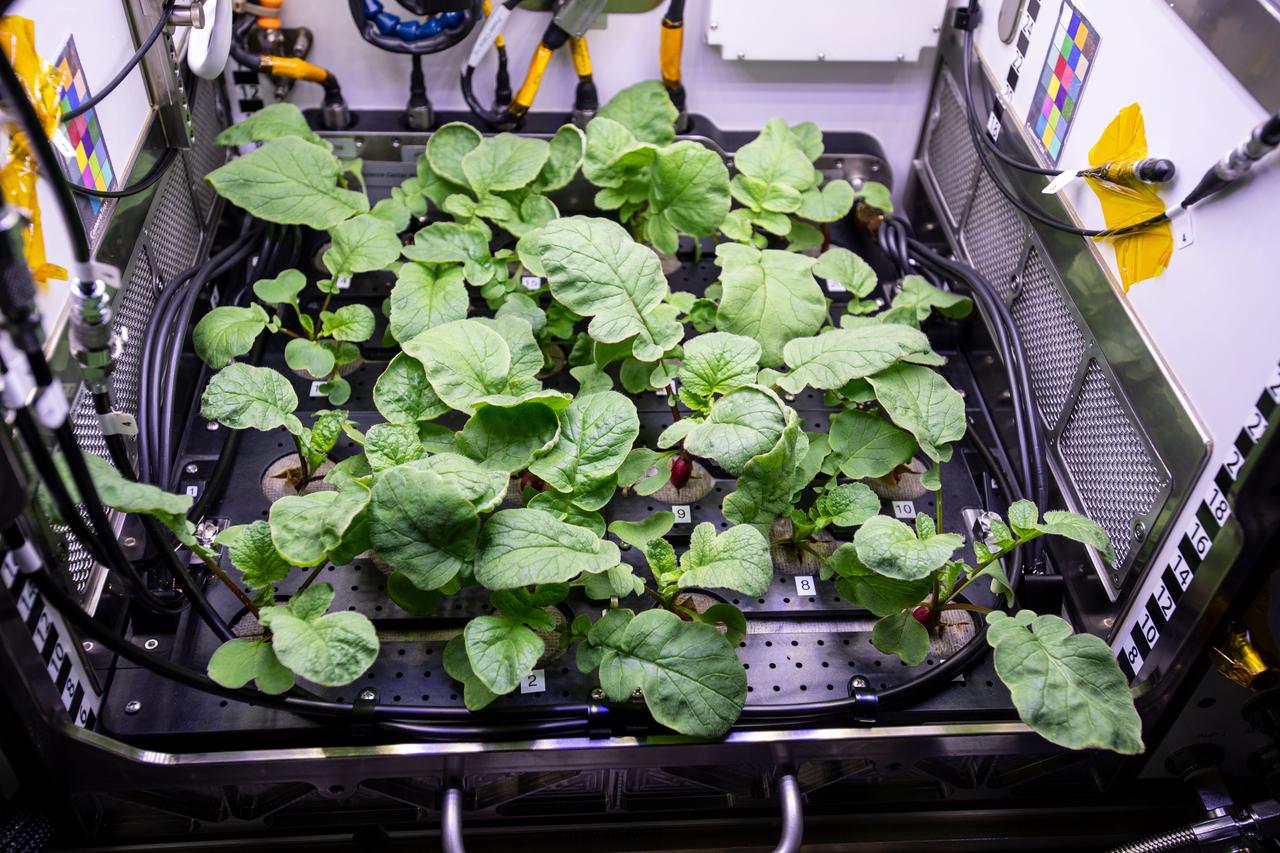

iss064e005049 (Nov. 20, 2020) --- Radish plants are pictured growing inside the Columbus laboratory module's Advanced Plant Habitat. Leaf samples were collected and stowed afterward for analysis so scientists can understand how microgravity affects the growth of plants. Space botany helps NASA and its international partners learn to sustain healthy crews on long-term missions to the Moon, Mars and beyond.
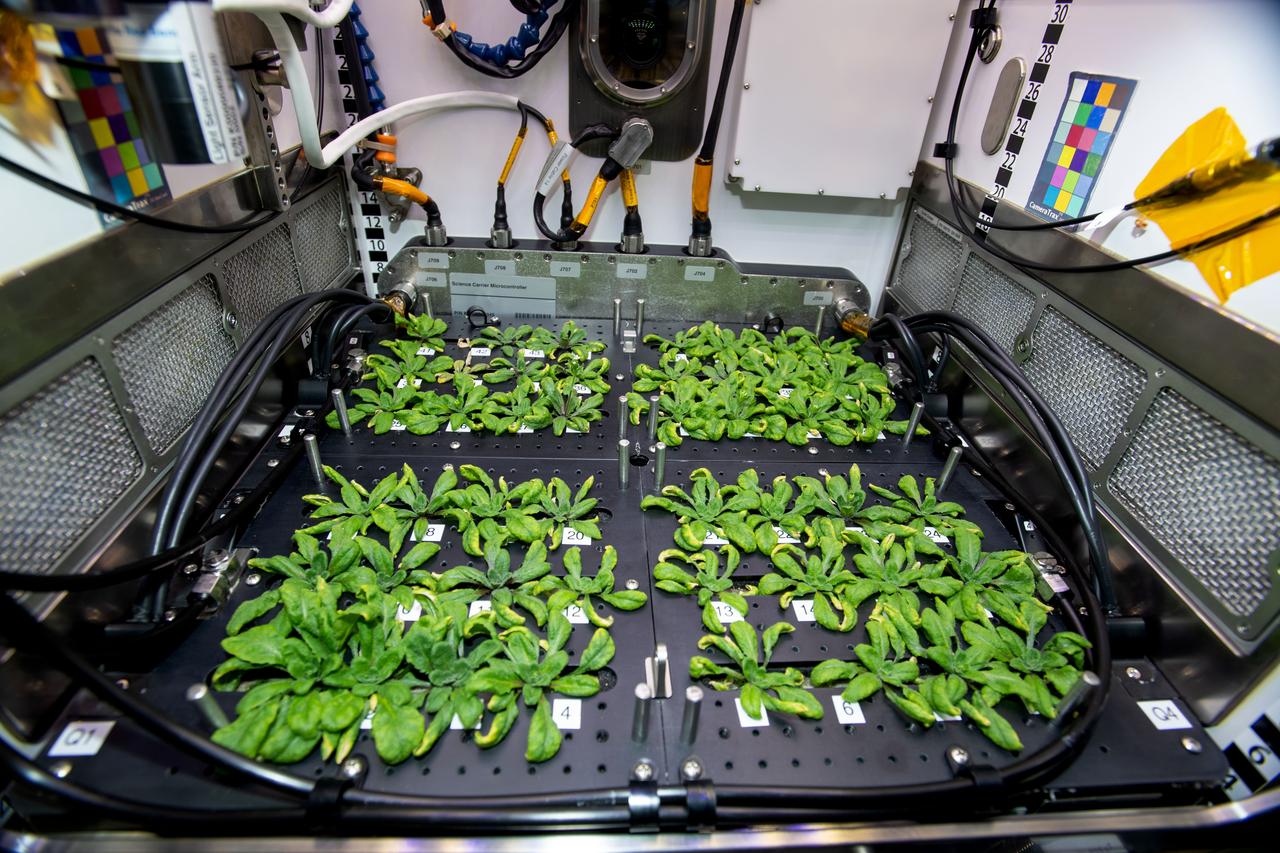

iss068e041971 (1/26/2023) --- Three-week-old Thale cress plants from the Plant Habitat-03 (PH-03) investigation are seen just before a harvest aboard the International Space Station. One leaf was harvested from each of the 48 plants and then preserved before being sent back to Earth for further analysis. The samples are critical to PH-03 as the preserved leaves allow for the transcriptome (gene expression) and methylome (epigenetic modifications) analyses. PH-03 aims to discover whether genetic changes persist through multiple plant generations, a first step in developing plants better suited for future space exploration.
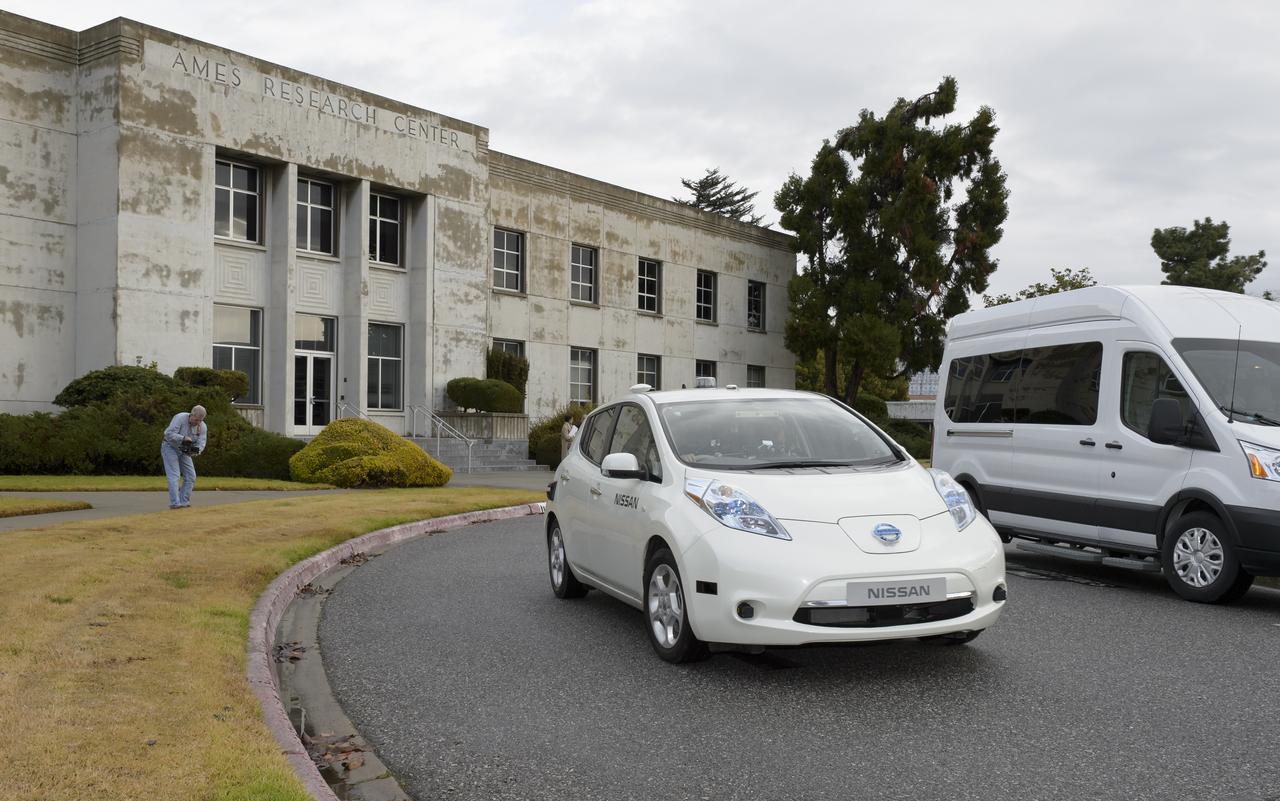

Senior executives from the Renault-Nissan Alliance, including Carlos Ghosn, chairman and CEO of Nissan, and Jose Munoz, chairman of Nissan North America, visited Ames for meetings and a showcase of the technical partnership between NASA and Nissan North America. The partnership allows researchers to develop and test autonomy algorithms, concepts, and integrated prototypes for a variety of vehicular transport applications – from rovers to self-driving cars. After briefings, a group take a ride in the autonomous vehicle to observed testing of Nissan’s all-electric LEAF as it performed safe autonomous drives across the center.

The STS-52 insignia, designed by the mission’s crew members, features a large gold star to symbolize the crew's mission on the frontiers of space. A gold star is often used to symbolize the frontier period of the American West. The red star in the shape of the Greek letter lambda represents both the laser measurements taken from the Laser Geodynamic Satellite (LAGEOS II) and the Lambda Point Experiment, which was part of the United States Microgravity Payload (USMP-l). The remote manipulator and maple leaf are emblematic of the Canadian payload specialist who conducted a series of Canadian flight experiments (CANEX-2), including the Space Vision System test.
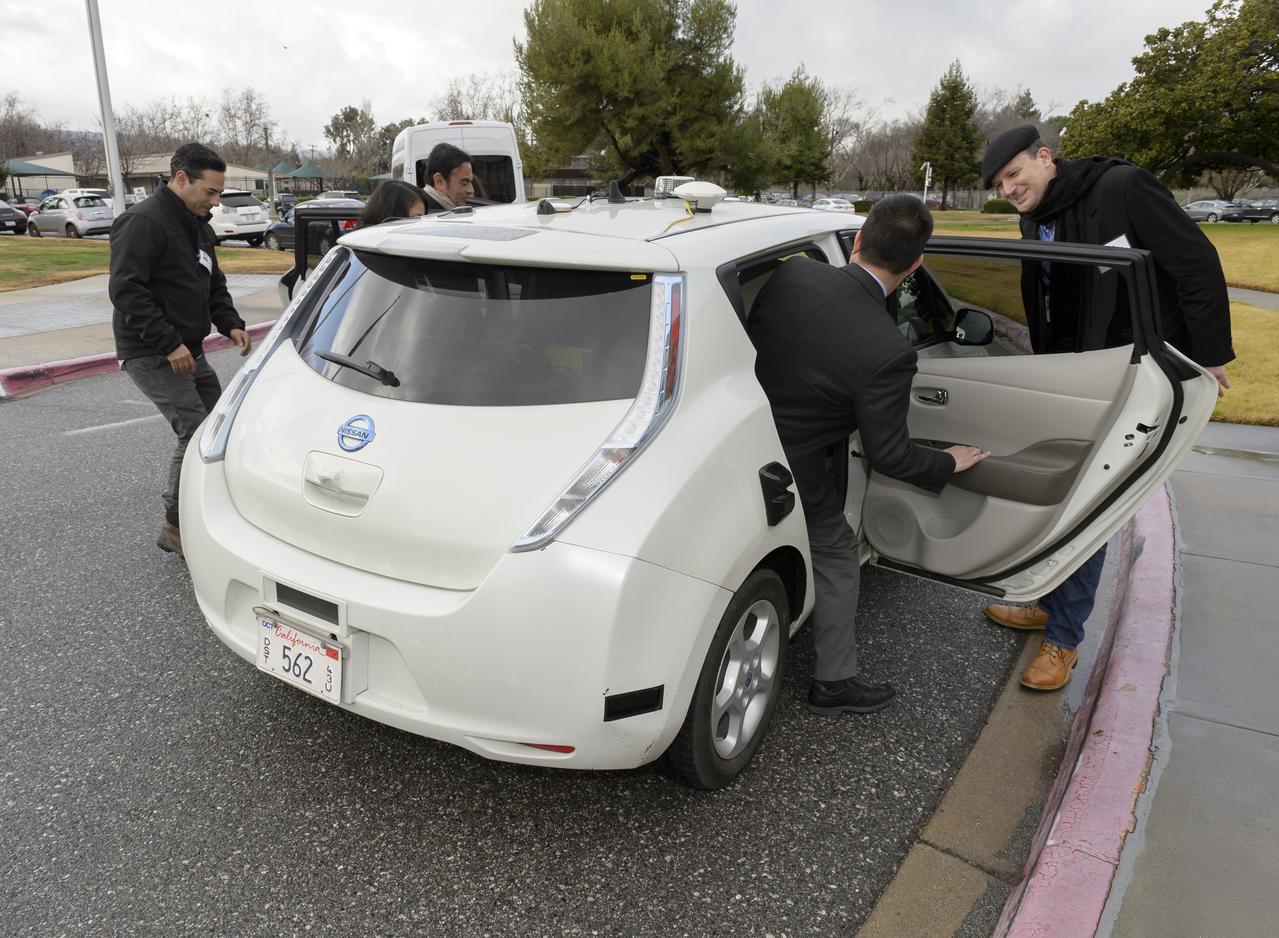

Senior executives from the Renault-Nissan Alliance, including Carlos Ghosn, chairman and CEO of Nissan, and Jose Munoz, chairman of Nissan North America, visited Ames for meetings and a showcase of the technical partnership between NASA and Nissan North America. The partnership allows researchers to develop and test autonomy algorithms, concepts, and integrated prototypes for a variety of vehicular transport applications – from rovers to self-driving cars. After briefings, a company of including Eugene Tu, Ames Center Director andLiam Pedersen, Nissan on right Carlos Ghosn, CE, Nissan on left climb into in the autonomous vehicle to observed testing of Nissan’s all-electric LEAF as it performed safe autonomous drives across the center.
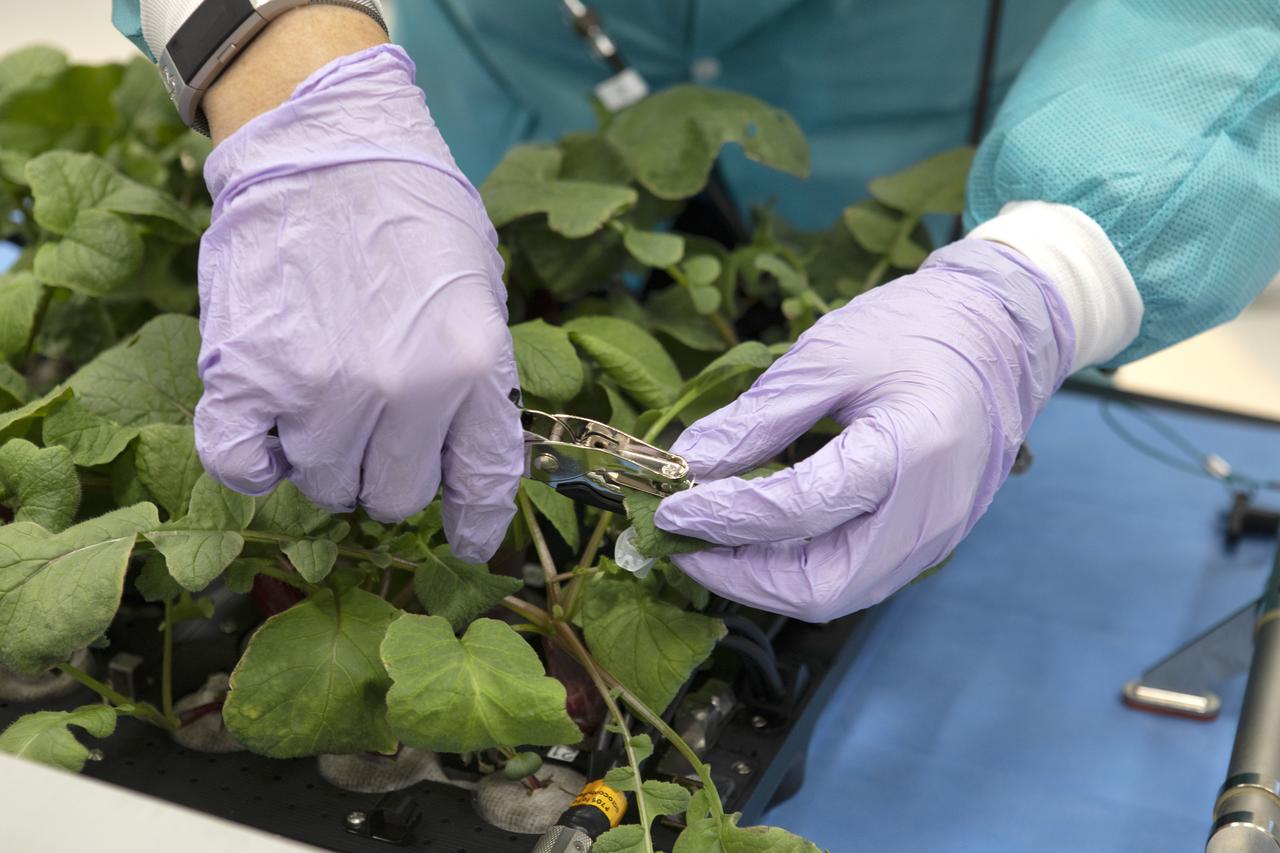

A sample of a leaf from one of the radish plant growing in the base of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit is taken inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 13, 2019. The radishes are being harvested as part of a science verification test. The APH is currently the largest plant chamber built for the agency in use on the International Space Station. It is an autonomous plant growth facility that is being used to conduct bioscience research on the space station with the goal of enabling astronauts to be sustainable on long duration missions to the Moon, Mars and beyond.
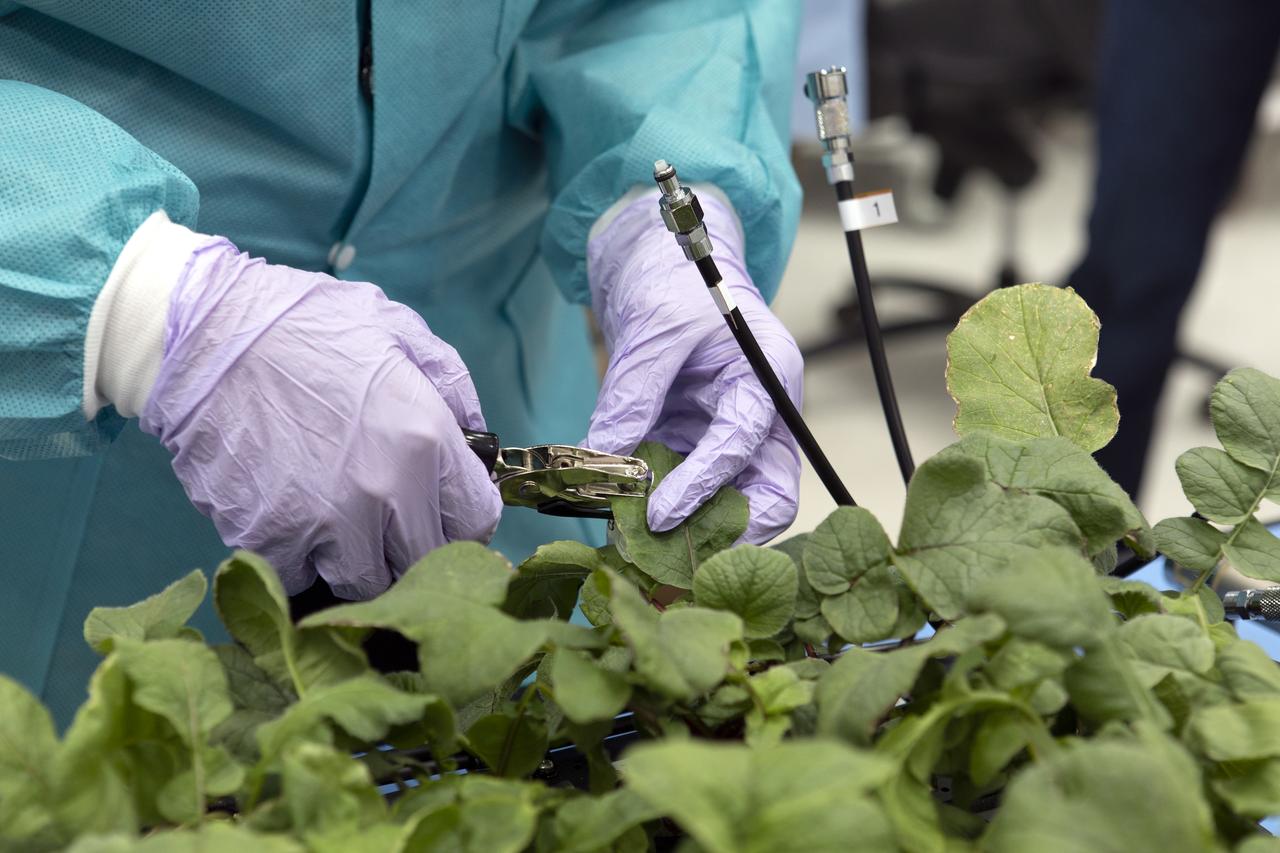

Clayton Grosse, a mechanical engineer with Techshot, uses a punch to take a sample of the leaf of a radish plant growing in the base of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit, inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 13, 2019. The radishes are being harvested as part of a science verification test. The APH is currently the largest plant chamber built for the agency in use on the International Space Station. It is an autonomous plant growth facility that is being used to conduct bioscience research on the space station with the goal of enabling astronauts to be sustainable on long duration missions to the Moon, Mars and beyond.

ISS012-E-15387 (24 Jan. 2006) --- A view of pea plants growing in the Lada greenhouse as a part of the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment located in the Zvezda Service Module photographed by an Expedition 12 crewmember on the International Space Station.
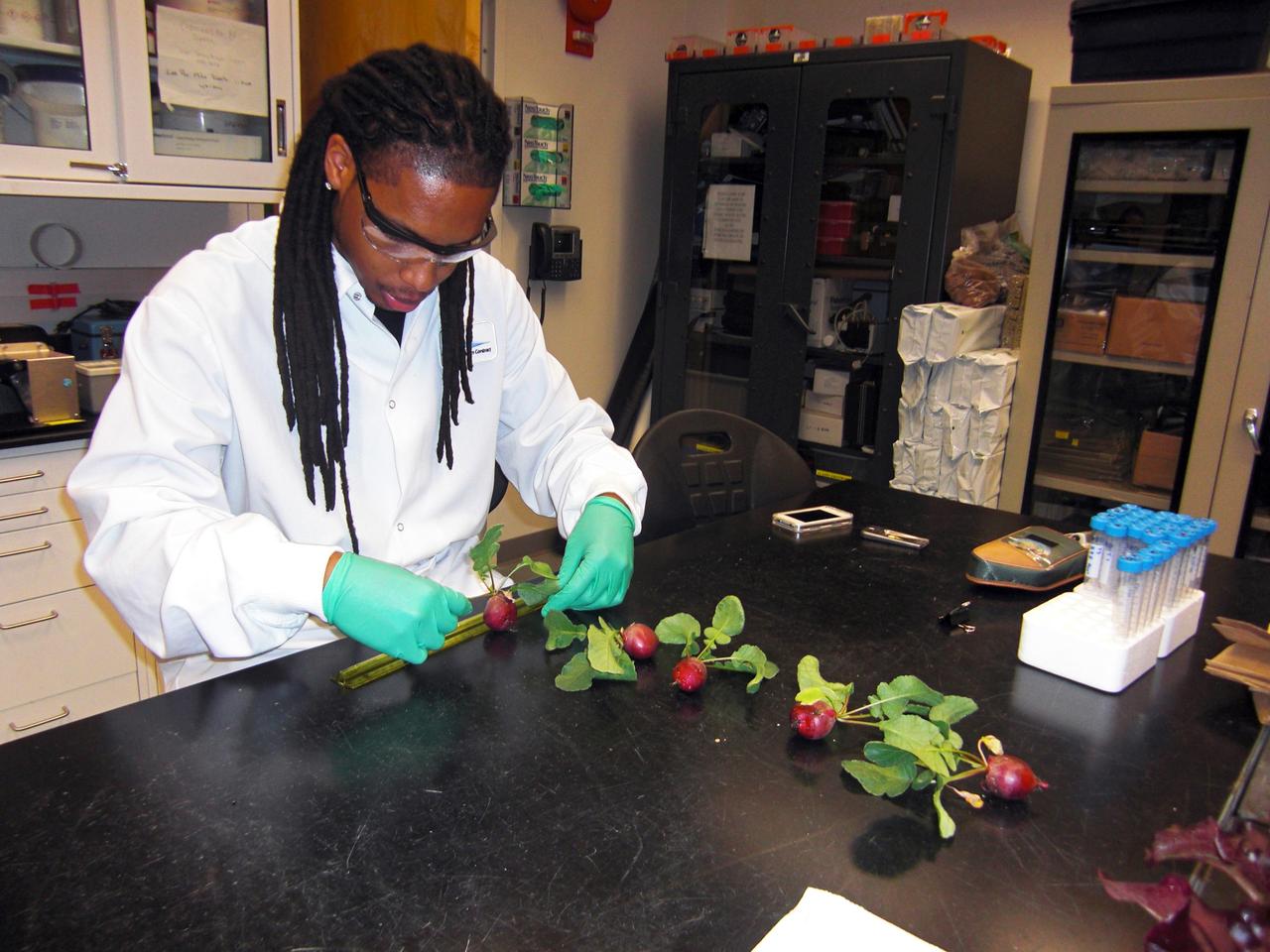

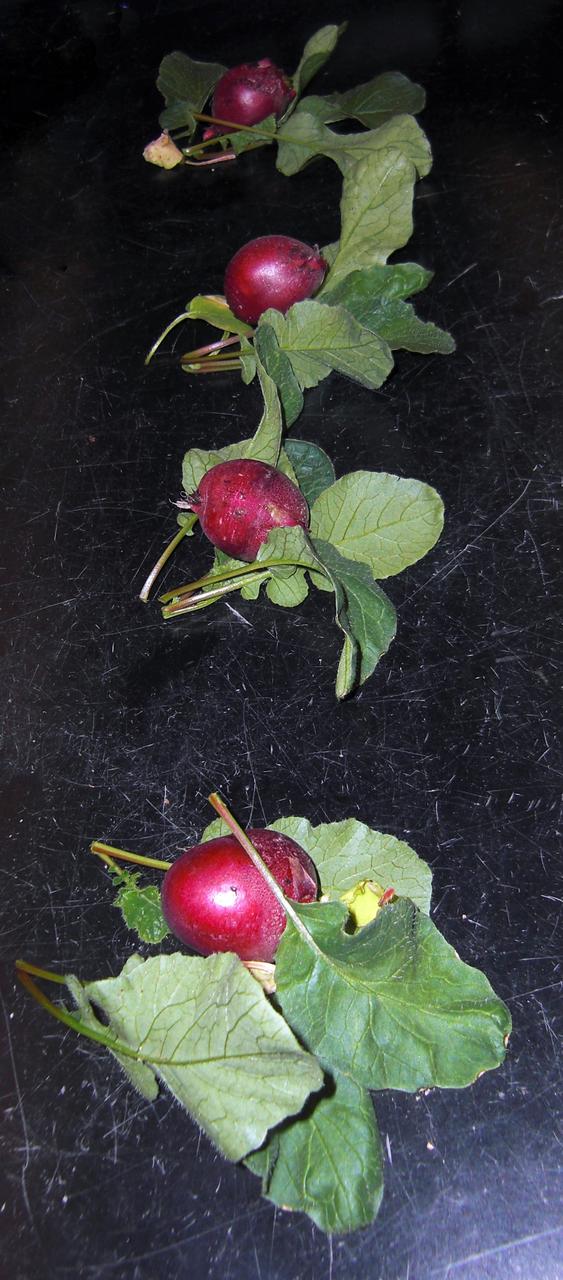
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory, or SLSL, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Dr. Matthew Mickens, a plant biologist from North Carolina Agriculture and Technical State University in North Carolina, measures radish plants that were just harvested from a plant growth chamber. The plants were grown under red and blue LED lights. The plant experiment at Kennedy is part of the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. This plant experiment studies the effects of different types of lighting on plants such as radishes and leaf lettuce. Results of these studies will help provide information on how to grow food sources for deep space exploration missions. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Ochoa-Gonzales

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory, or SLSL, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, radish plants were harvested from a plant growth chamber. The plants were grown under red and blue LED lights. The plant experiment at Kennedy is part of the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. This plant experiment studies the effects of different types of lighting on plants such as radishes and leaf lettuce. Results of these studies will help provide information on how to grow food sources for deep space exploration missions. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Ochoa-Gonzales

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, Houston -- STS118-S-001 -- The STS-118 patch represents Space Shuttle Endeavour on its mission to help complete the assembly of the International Space Station and symbolizes the pursuit of knowledge through space exploration. The flight will accomplish its ISS 13A.1 assembly tasks through a series of spacewalks, robotic operations, logistics transfers and the exchange of one of the three long-duration expedition crew members. On the patch, the top of the gold astronaut symbol overlays the starboard S-5 truss segment, highlighting its installation during the mission. The flame of knowledge represents the importance of education, and honors teachers and students everywhere. The seven white stars and the red maple leaf signify the American and Canadian crew members flying aboard Endeavour.
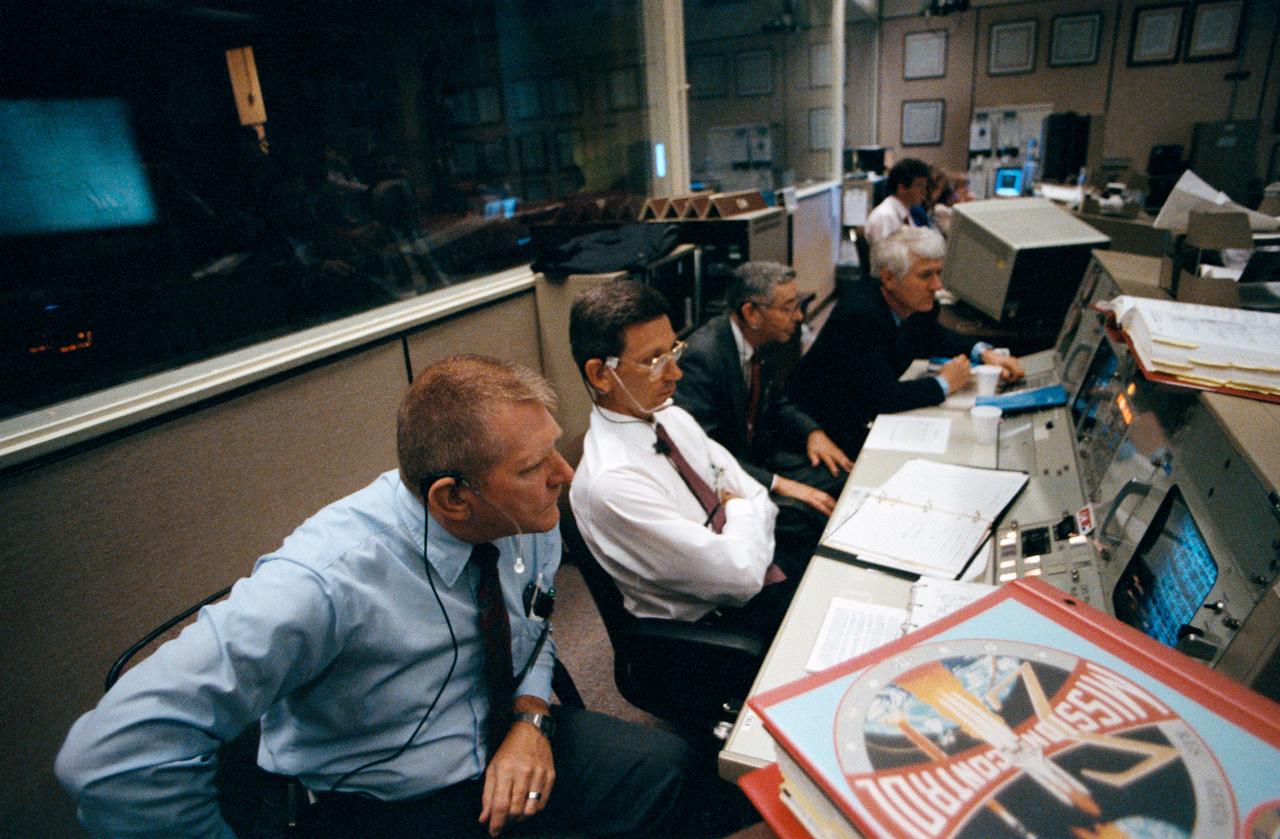

STS030-S-004 (8 May 1989) --- JSC Officials monitor early moments of NASA's STS-30 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, flight in the Flight Control Room (FCR) of JSC's Mission Control Center (MCC) Bldg 30. At the Mission Operations Directorate (MOD) console, MOD Director Eugene F. Kranz (foreground), studiously reviews data on a nearby monitor. Others in the photo are (left to right) Flight Directors Office Deputy Chief Lawrence S. Bourgeois, JSC Director Aaron Cohen, and Flight Crew Operations Deputy Director Henry W. Hartsfield, Jr. Kranz'z replete loose-leaf notebook, bearing the insignia of the flight control team members (MOD insignia), is in the foreground.

The STS-118 crew patch represents the Space Shuttle Endeavour on its mission to help complete the assembly of the International Space Station (ISS), and symbolizes the pursuit of knowledge through space exploration. The flight accomplished its ISS 13A.1 assembly tasks through a series of space walks, robotic operations, logistics transfers, and the exchange of one of the three long-duration expedition crew members. On the patch, the top of the gold astronaut symbol overlays the starboard S5 truss segment, highlighting its installation during the mission. The flame of knowledge represents the importance of education, and honors teachers and students everywhere. The seven white stars and the red maple leaf signify the American and Canadian crew members, respectively, flying aboard Endeavour.
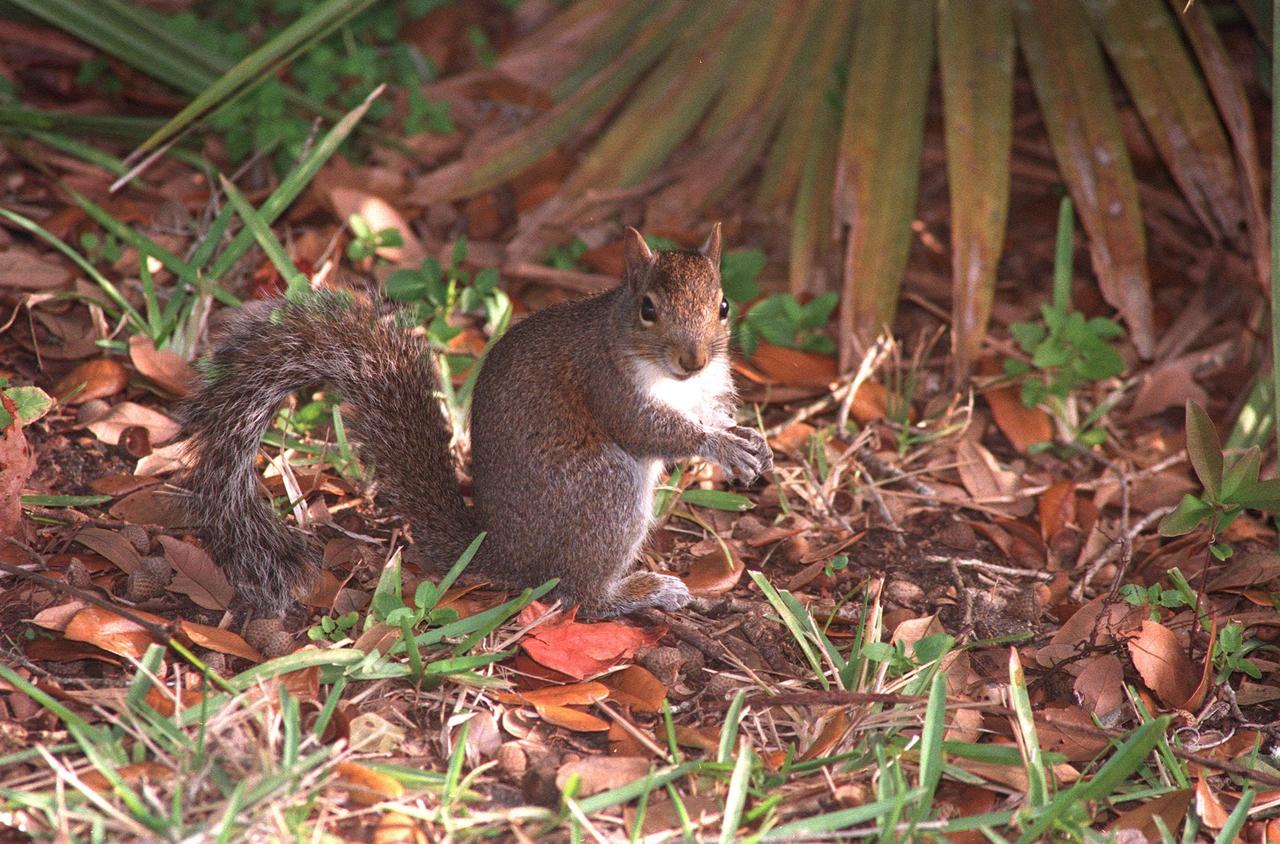

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An Eastern gray squirrel pauses in its daily search for food in the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which shares a boundary with Kennedy Space Center. The Eastern gray squirrel is found in wooded, suburban, and urban areas statewide. It nests in tree hollows or leaf nests in treetops. It forages during the day, mainly early morning and late afternoon, both on the ground and in trees, living on a diet of acorns, nuts, fruits, berries, insects, and bird eggs. Food plants include cypress, buckeyes, elms, grapes, tulip trees, mulberries, and tupelo. It breeds in late winter or early spring and again in late spring or summer, bearing two to six young. The eastern gray squirrel chatters when disturbed. The 92,000-acre wildlife refuge is a habitat for more than 310 species of birds, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles
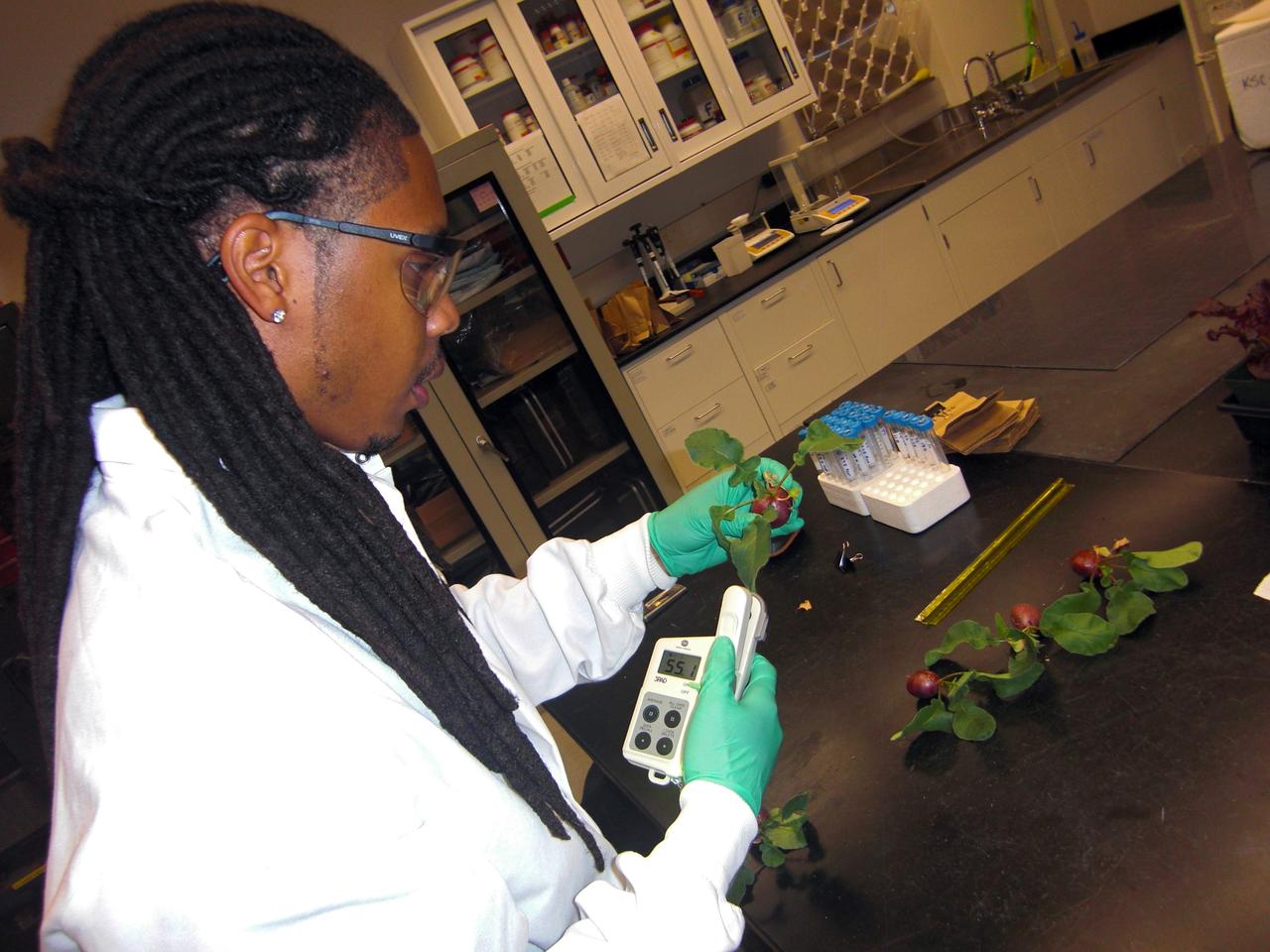

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory, or SLSL, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Dr. Matthew Mickens, a plant biologist from North Carolina Agriculture and Technical State University in North Carolina, measures radish plants that were just harvested from a plant growth chamber. The plants were grown under red and blue LED lights. The plant experiment at Kennedy is part of the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. This plant experiment studies the effects of different types of lighting on plants such as radishes and leaf lettuce. Results of these studies will help provide information on how to grow food sources for deep space exploration missions. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Ochoa-Gonzales
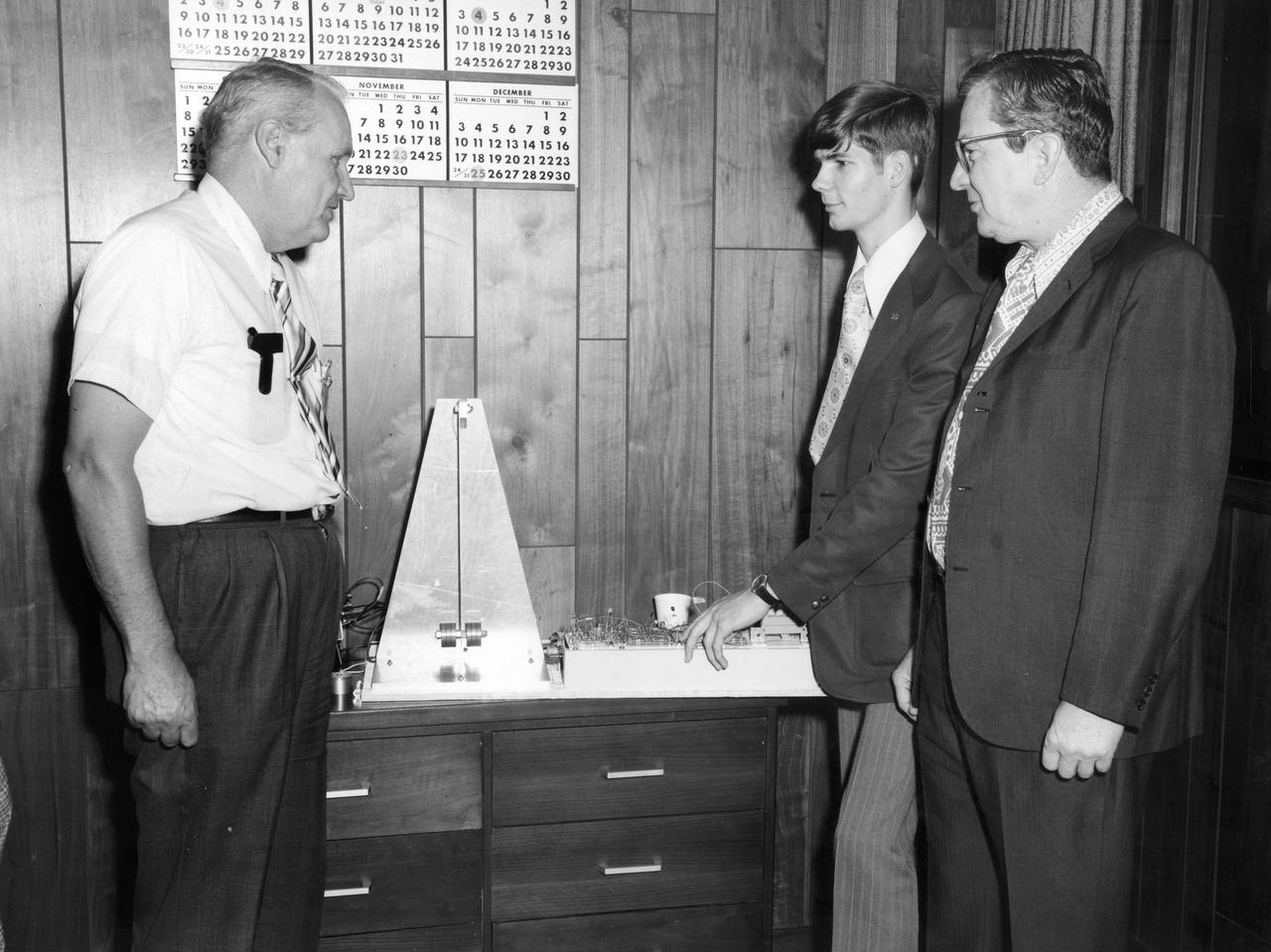

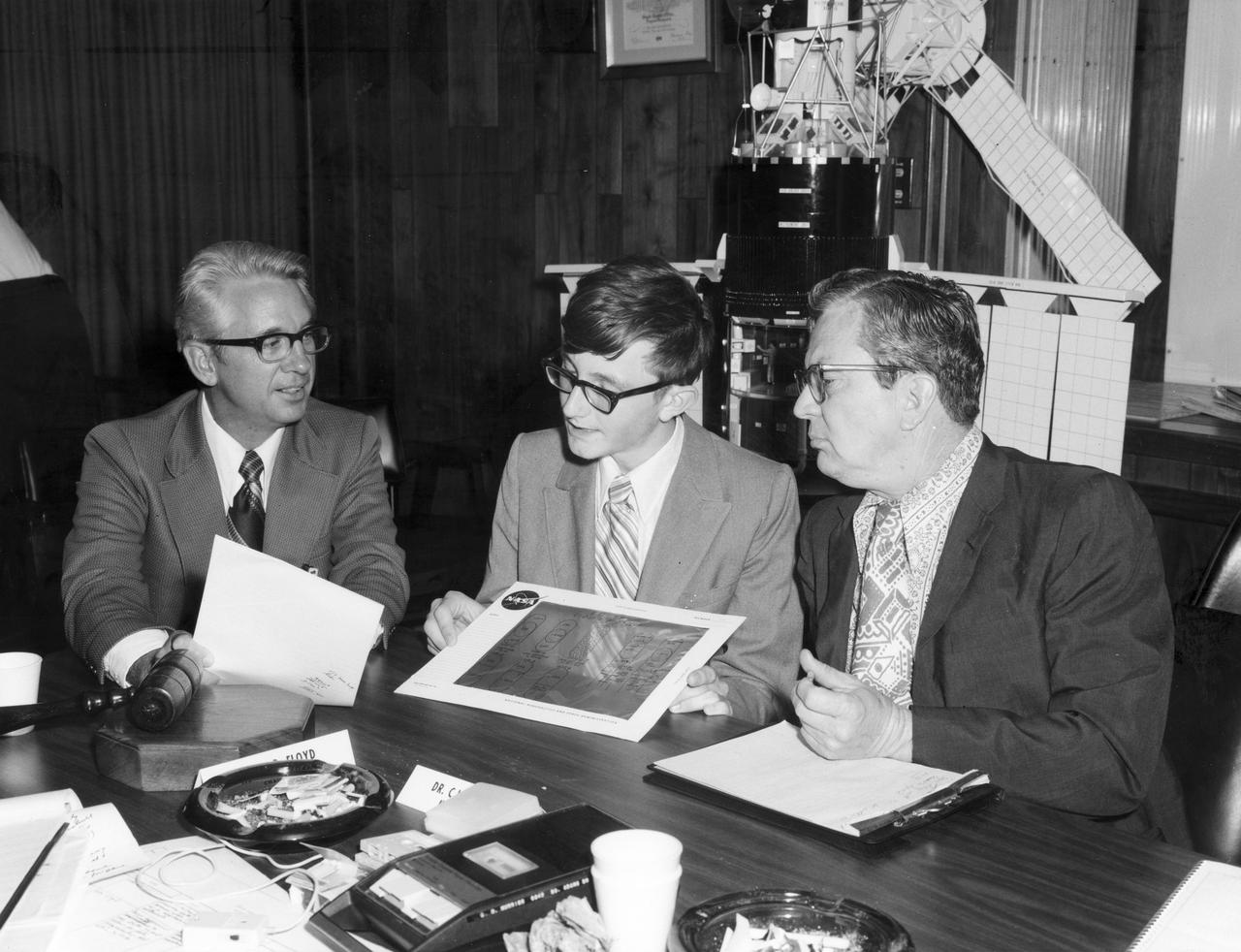
Rockford, Illinois high school student, Vincent Converse, discussed his proposed Skylab experiment with Dr. Robert Head (right) and Gene Greshman of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). His experiment, “Zero Gravity Mass Measurement” used a simple leaf spring with the mass to be weighed attached to the end. The electronic package oscillated the spring at a specific rate and the results were recorded electronically. Converse was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of equipment, such as that of Converse’s experiment.
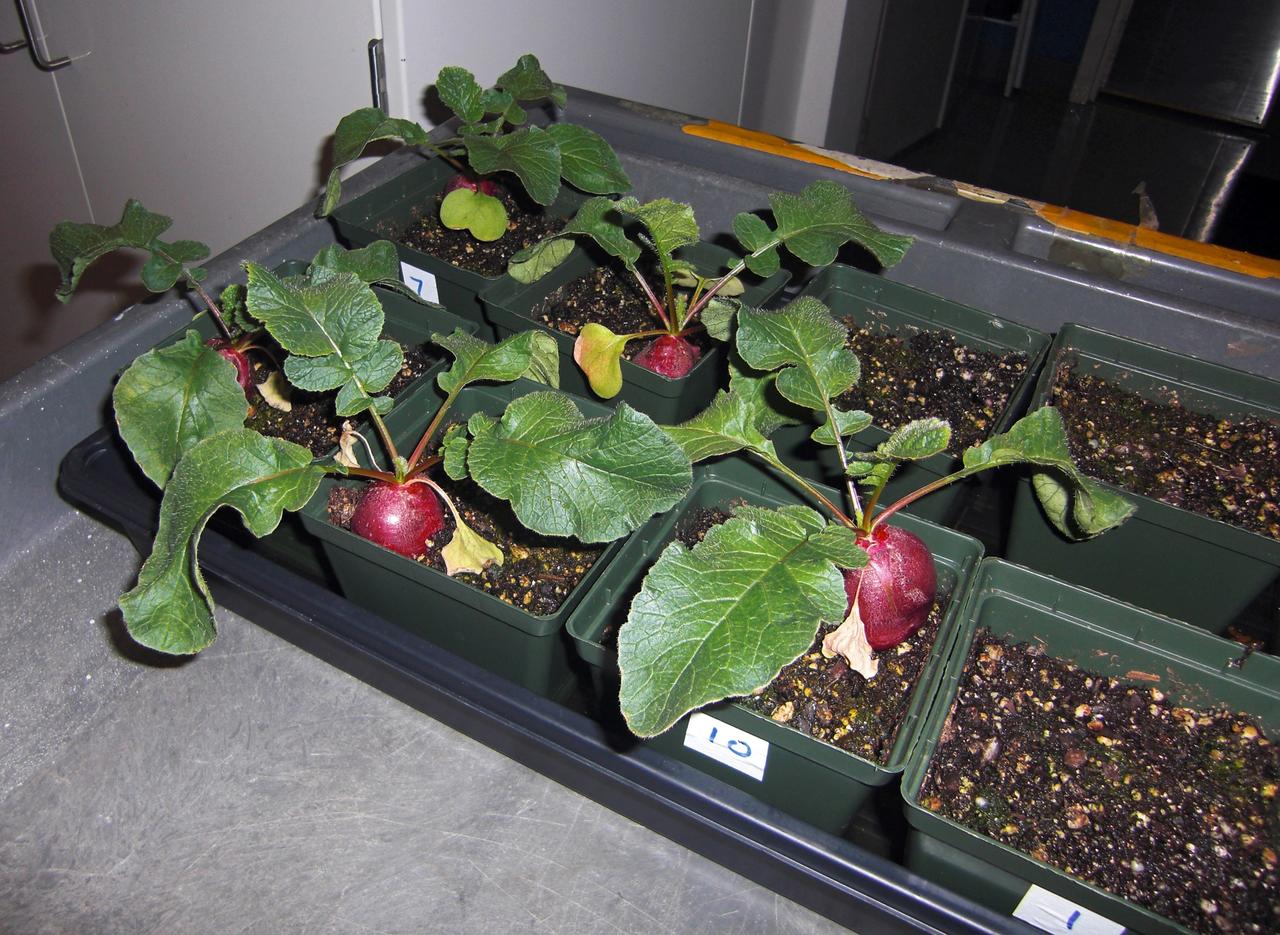

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory, or SLSL, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, radish plants are being harvested in a plant growth chamber. The plants were grown under red and blue LED lights. The plant experiment at Kennedy is part of the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, program in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. This plant experiment studies the effects of different types of lighting on plants such as radishes and leaf lettuce. Results of these studies will help provide information on how to grow food sources for deep space exploration missions. AES projects pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Frank Ochoa-Gonzales

Senior executives from the Renault-Nissan Alliance, including Carlos Ghosn, chairman and CEO of Nissan, and Jose Munoz, chairman of Nissan North America, visited Ames for meetings and a showcase of the technical partnership between NASA and Nissan North America. The partnership allows researchers to develop and test autonomy algorithms, concepts, and integrated prototypes for a variety of vehicular transport applications – from rovers to self-driving cars. After briefings, the group on left from left to right Kathy Sun and Liam Pedersen, Nissan and on right from front to back Carlos Ghosn, CE, Nissan chatted before taking a ride in the autonomous vehicle to observed testing of Nissan’s all-electric LEAF as it performed safe autonomous drives across the center.
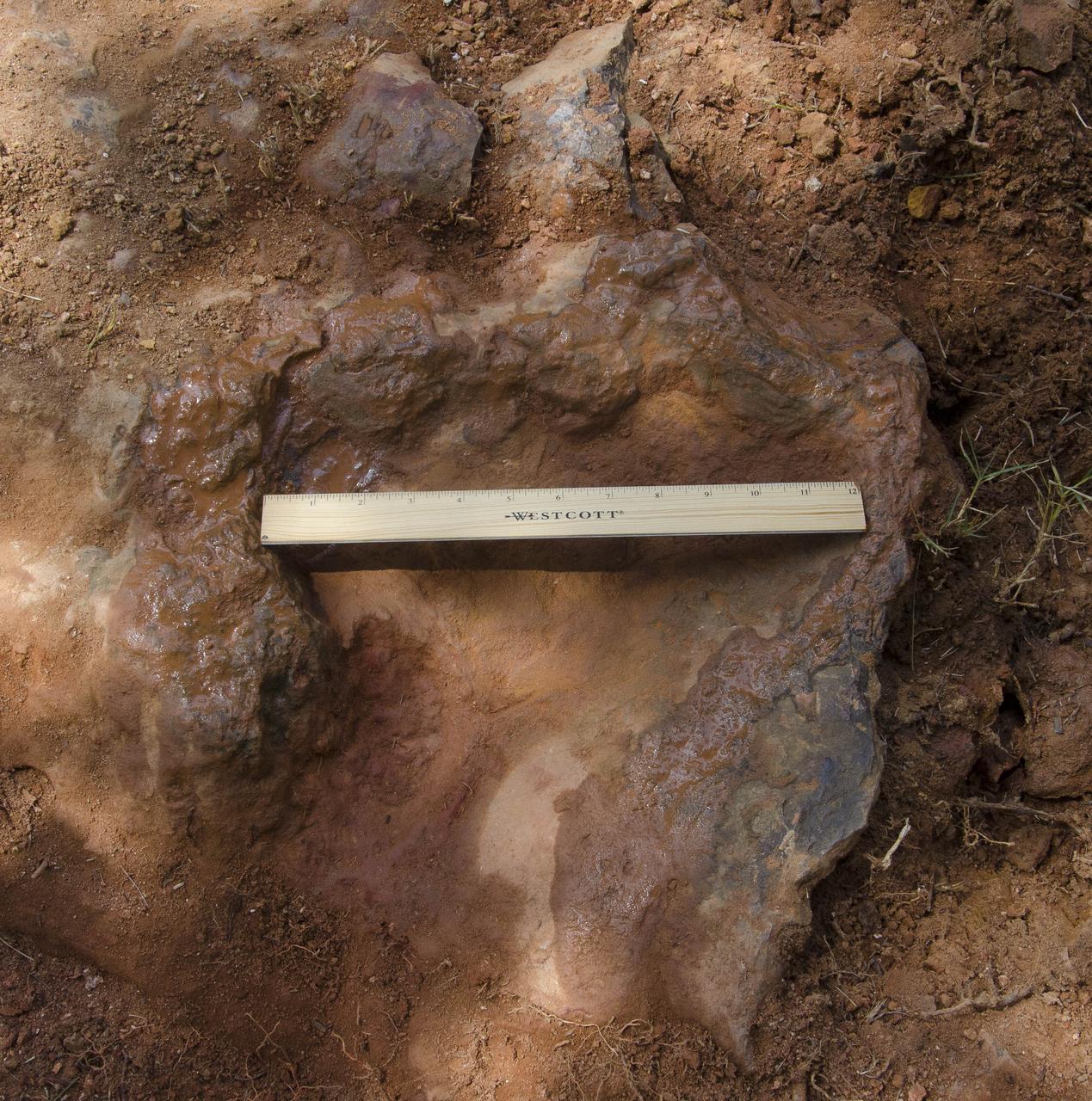

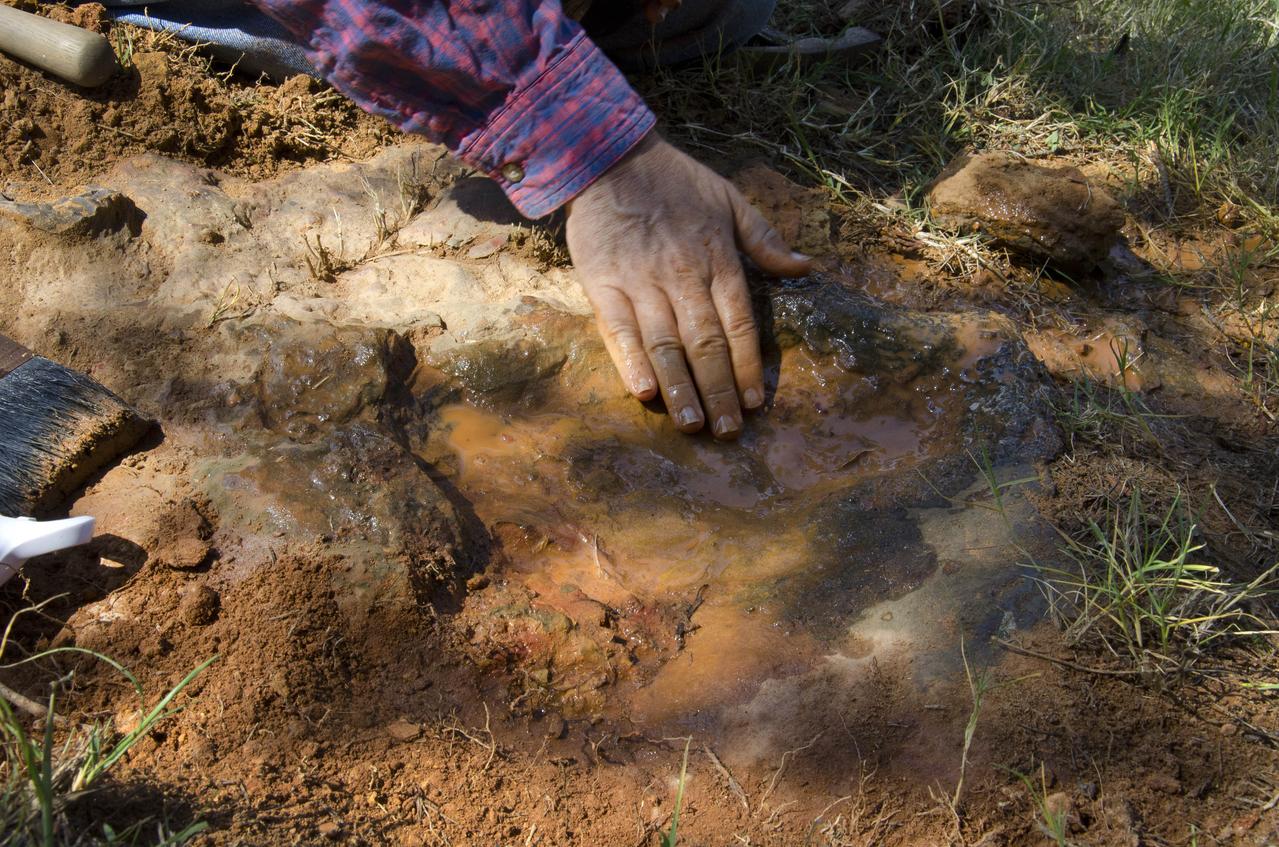
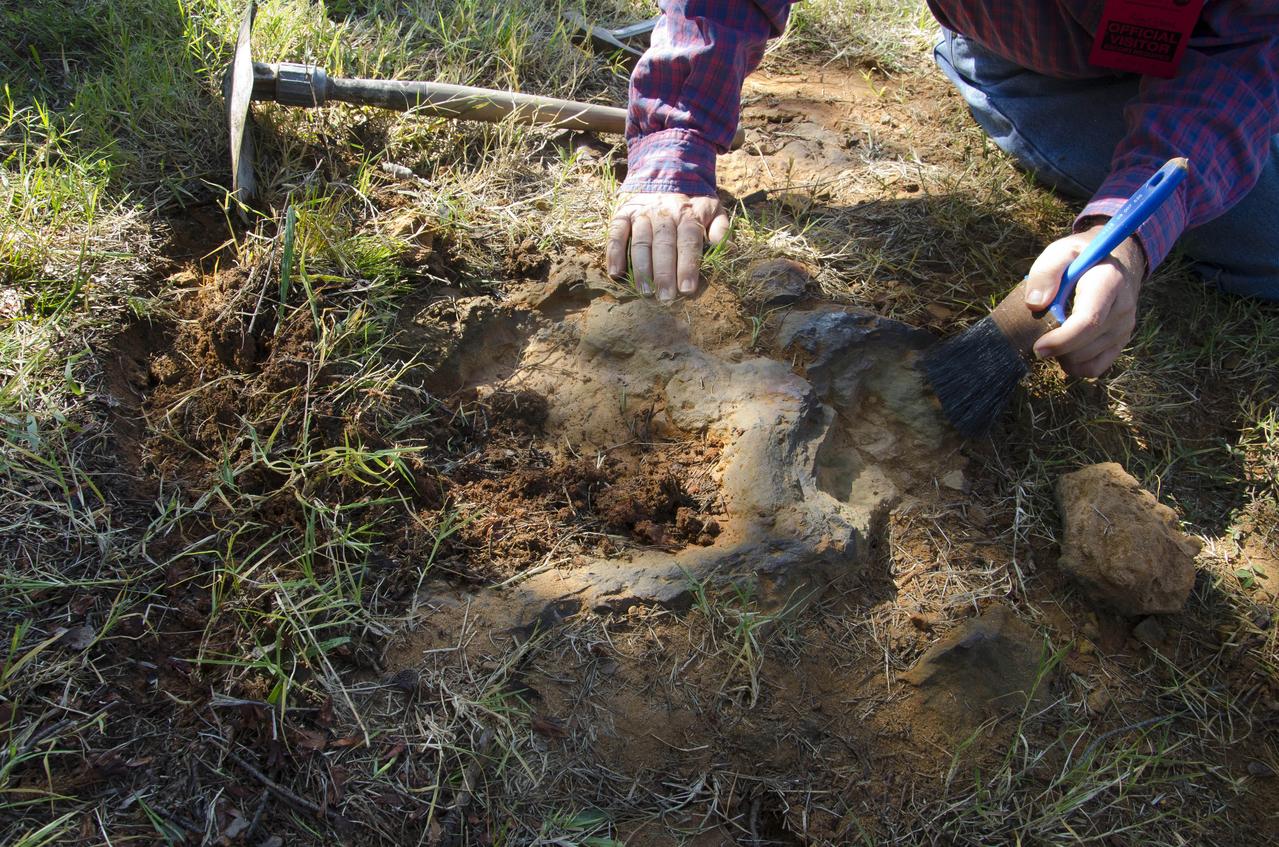
This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
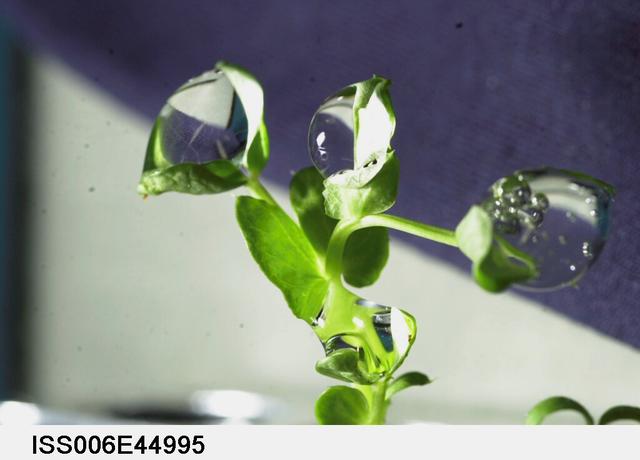

ISS006-E-44995 (10 March 2003) --- A close up view of water droplets on leaves on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
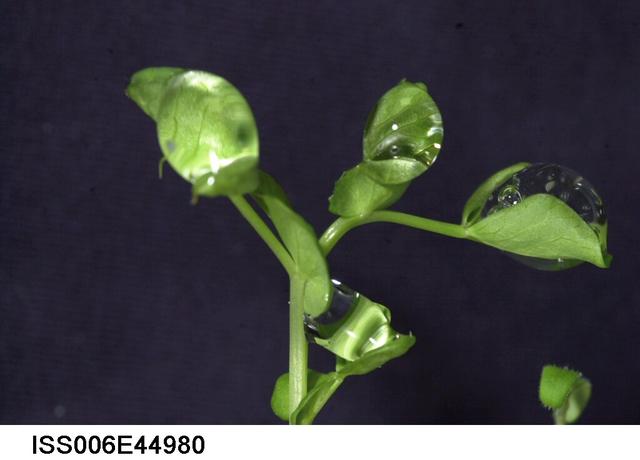

ISS006-E-44980 (10 March 2003) --- A close up view of water droplets on leaves on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).

ISS006-E-44929 (9 March 2003) --- A close up view of water droplets on leaves on the Russian BIO-5 Rasteniya-2/Lada-2 (Plants-2) plant growth experiment, which is located in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
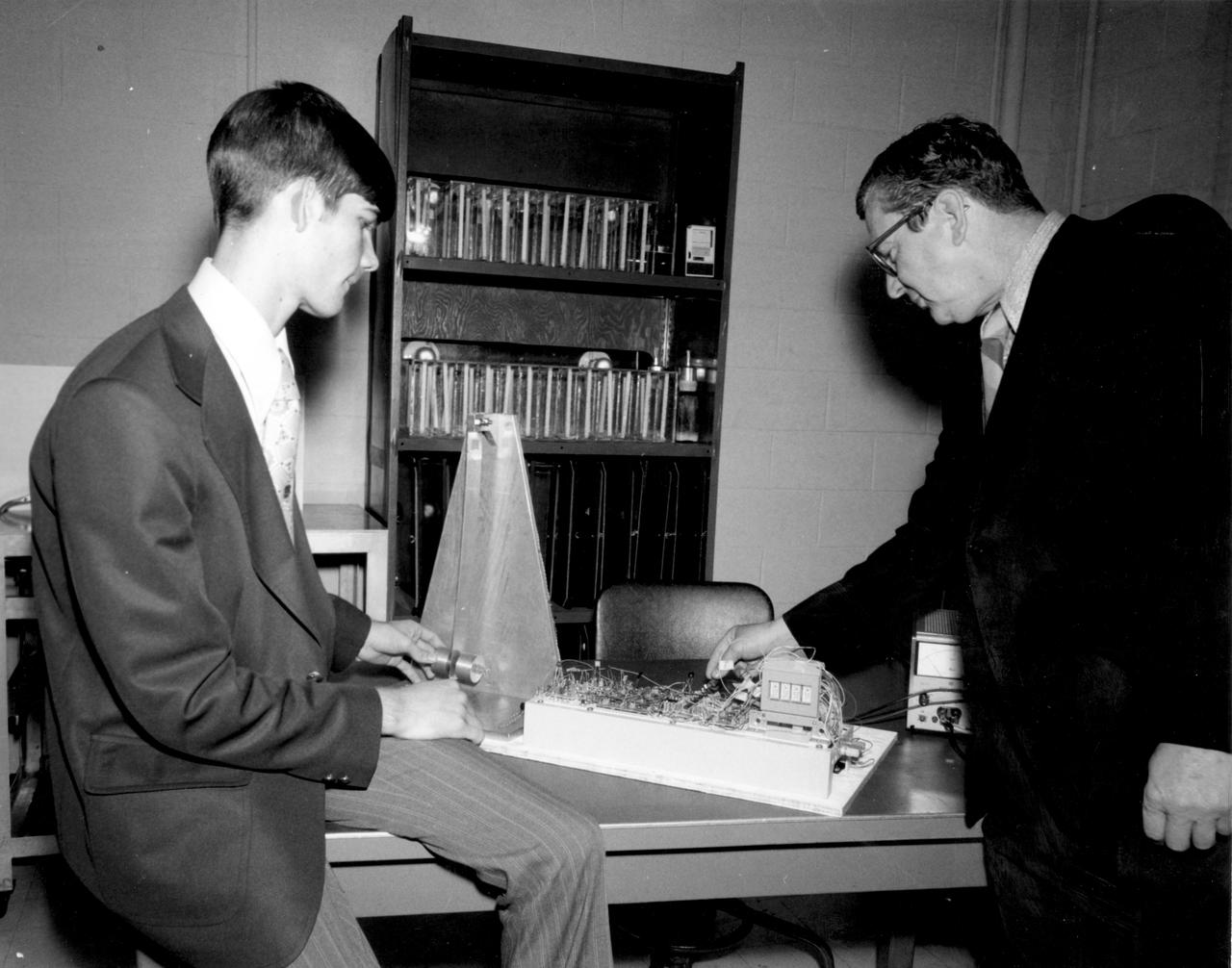

Rockford, Illinois high school student, Vincent Converse (left), and Robert Head of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), check out the equipment to be used in conducting the student’s experiment aboard the Skylab the following year. His experiment, “Zero Gravity Mass Measurement” used a simple leaf spring with the mass to be weighed attached to the end. An electronic package oscillated the spring at a specific rate and the results were recorded electronically. Converse was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC two months earlier where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
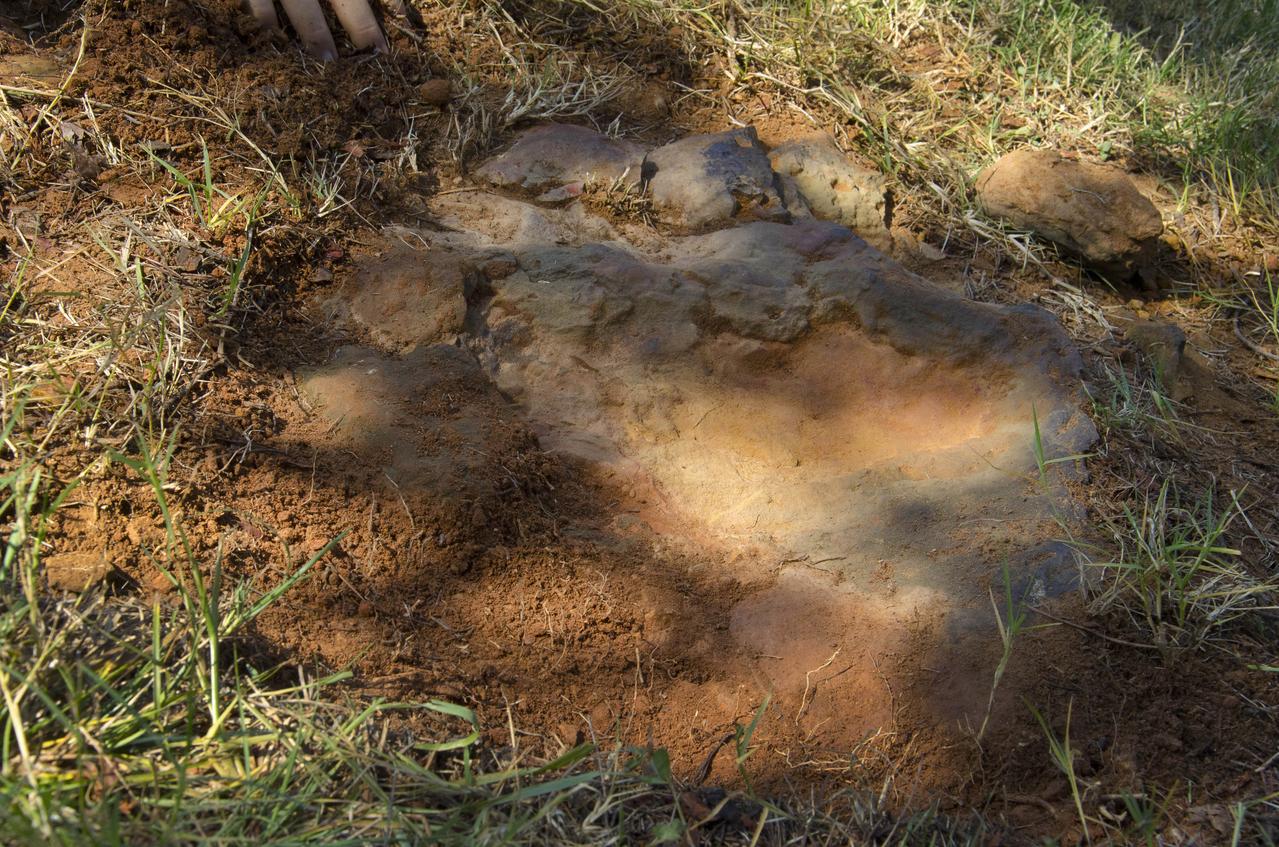

This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

ISS021-S-001 (February 2009) --- The central element of the patch is inspired by a fractal of six, symbolizing the teamwork of the six-person crew. From the basic element of one person, together six people form a much more complex and multifaceted entity, toward the infinity of the universe. The patch shows children, on Earth in the bright Sun, as our future and the reason we explore. The Soyuz and Shuttle are the vehicles that enable human space exploration today, while the International Space Station is leading to our next goals, the moon and Mars. The patch shape has six tips, geometrically sound yet reminiscent of a leaf, representing symmetry and ecological harmony, while the six stars in deep space represent the current crew and future exploration crews. The insignia design for ISS flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and cosmonauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator and NASA's international partners may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which we do not anticipate, it will be publicly announced
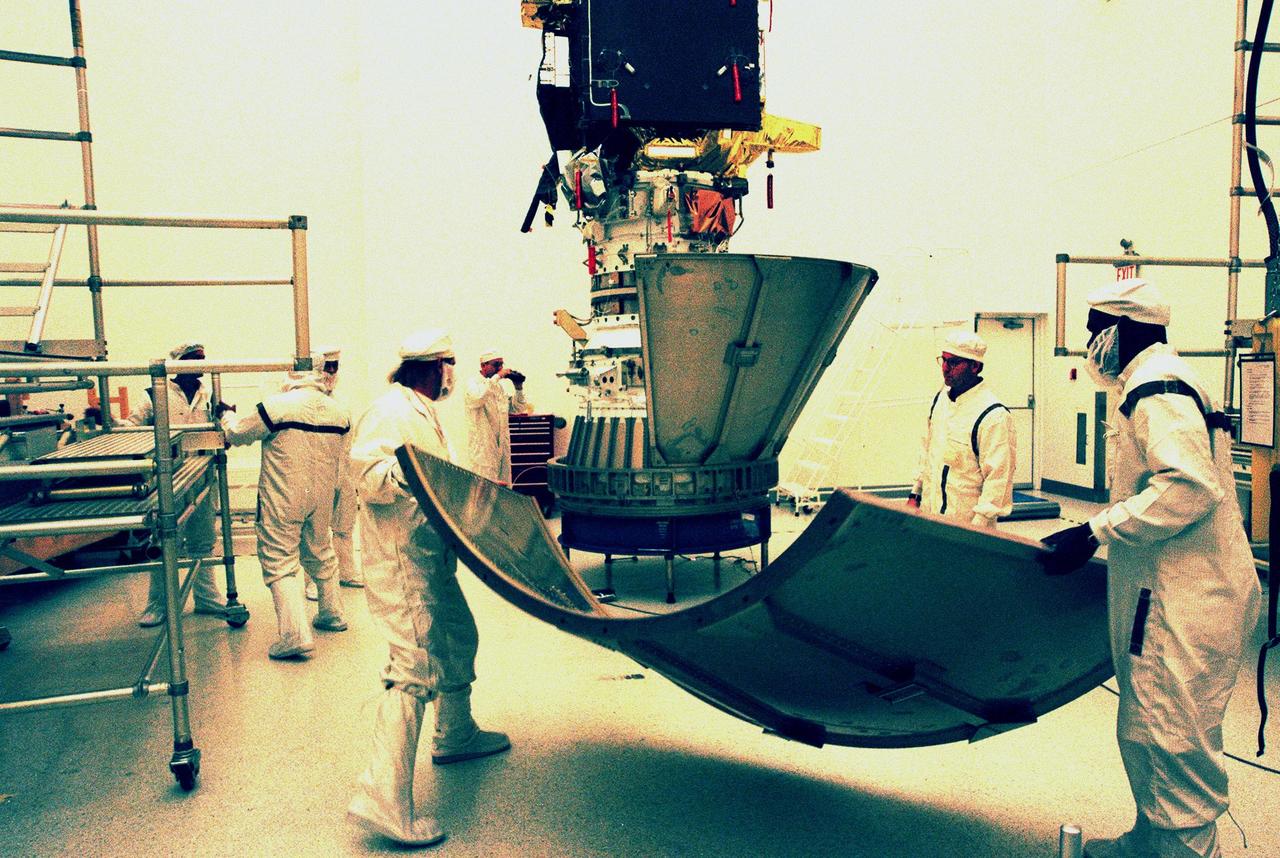
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Defense Satellite Communication Systems Processing Facility (DPF), Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), move to the workstand the second conical section leaf of the payload transportation container for Deep Space 1. The first flight in NASA's New Millennium Program, Deep Space 1 is designed to validate 12 new technologies for scientific space missions of the next century, including the engine. Propelled by the gas xenon, the engine is being flight-tested for future deep space and Earth-orbiting missions. Deceptively powerful, the ion drive emits only an eerie blue glow as ionized atoms of xenon are pushed out of the engine. While slow to pick up speed, over the long haul it can deliver 10 times as much thrust per pound of fuel as liquid or solid fuel rockets. Other onboard experiments include software that tracks celestial bodies so the spacecraft can make its own navigation decisions without the intervention of ground controllers. Deep Space 1 will complete most of its mission objectives within the first two months, but will also do a flyby of a near-Earth asteroid, 1992 KD, in July 1999. Deep Space 1 will be launched aboard a Boeing Delta 7326 rocket from Launch Pad 17A, CCAS

STS052-S-001 (July 1992) --- The insignia, designed by the STS-52 crew members, features a large gold star to symbolize the crew's mission on the frontiers of space. A gold star is often used to symbolize the frontier period of the American West. The red star in the shape of the Greek letter lambda represents both the laser measurements to be taken from the Laser Geodynamic Satellite (LAGEOS II) and the Lambda Point Experiment, which is part of the United States Microgravity Payload (USMP-1). The LAGEOS II is a joint Italian\United States satellite project intended to further our understanding of global plate tectonics. The USMP-1 is a microgravity facility which has French and United States experiments designed to test the theory of cooperative phase transitions and to study the solid\liquid interface of a metallic alloy in the low gravity environment. The Remote Manipulator System (RMS) and maple leaf are emblematic of the Canadian payload specialist who will conduct a series of Canadian flight experiments (CANEX-2), including the Space Vision System test. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which we do not anticipate, it will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA

STS118-S-001 (May 2007) --- The STS-118 patch represents space shuttle Endeavour on its mission to help complete the assembly of the International Space Station (ISS), and symbolizes the pursuit of knowledge through space exploration. The flight will accomplish its ISS 13A.1 assembly tasks through a series of spacewalks, robotic operations, logistics transfers, and the exchange of one of the three long-duration expedition crew members. On the patch, the top of the gold astronaut symbol overlays the starboard S-5 truss segment, highlighting its installation during the mission. The flame of knowledge represents the importance of education, and honors teachers and students everywhere. The seven white stars and the red maple leaf signify the American and Canadian crew members, respectively, flying aboard Endeavour. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
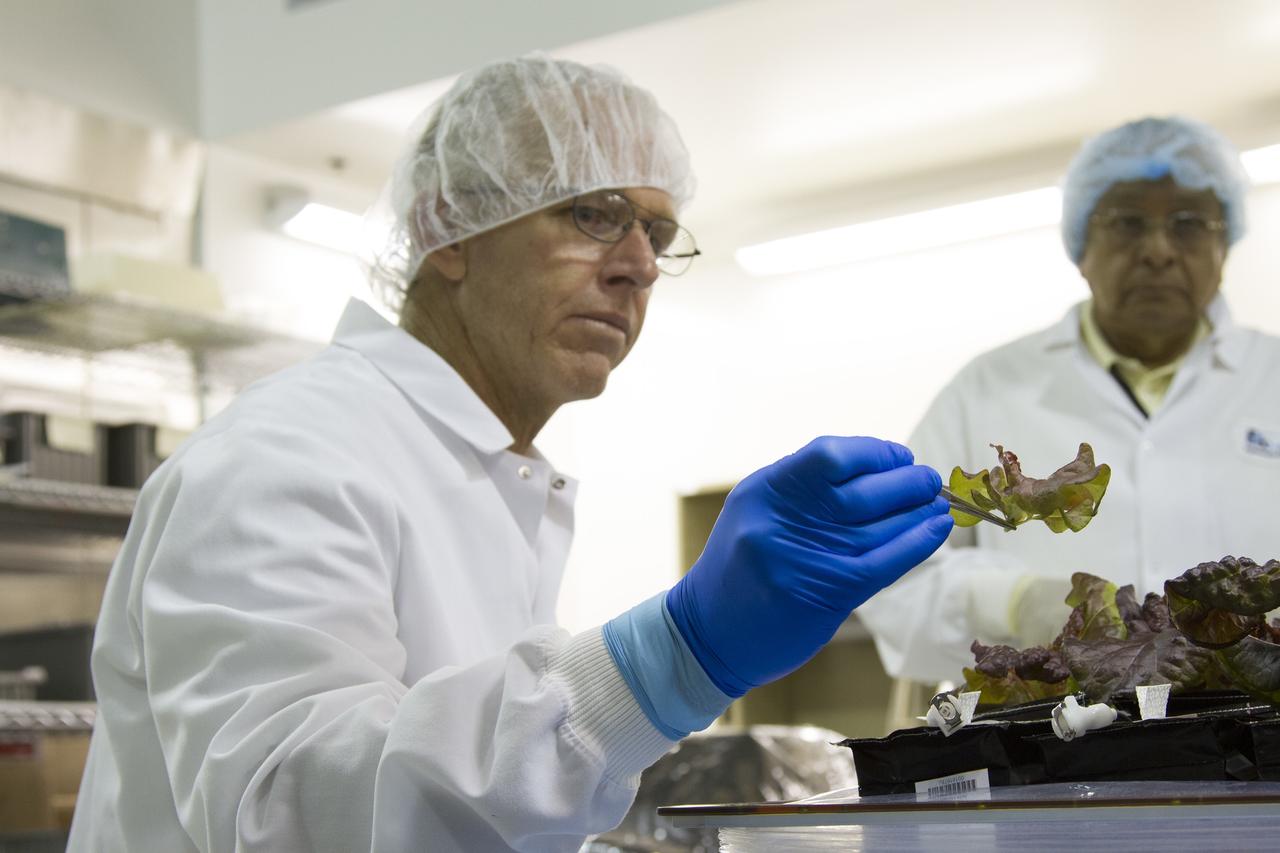

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Jim Smodell, a technician with SGT, removes an outredgeous red lettuce leaf from a plant pillow inside the Payload Development Laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility, or SSPF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the background is George Guerra, a quality control engineer with QinetiQ North America. The plant pillows were removed from the Veggie plant growth system inside a control chamber at the SSPF. The growth chamber was used as a control unit for Veggie and procedures were followed identical to those being performed on Veggie and the Veg-01 experiment on the International Space Station. The chamber mimicked the temperature, relative humidity and carbon dioxide concentration of those in the Veggie unit on the space station. Veggie and Veg-01 were delivered to the space station aboard the SpaceX-3 mission. Veggie is the first fresh food production system delivered to the station. Six plant pillows, each containing outredgeous red romaine lettuce seeds and a root mat were inserted into Veggie. The plant chamber's red, blue and green LED lights were activated. The plant growth was monitored for 33 days. On June 10, at the end of the cycle, the plants were carefully harvested, frozen and stored for return to Earth by Expedition 39 flight engineer and NASA astronaut Steve Swanson. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

Youngstown, Ohio high school student, W. Brian Dunlap (center), discusses with Dr. Robert Head (right), and Henry Floyd, both of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), his experiment to be performed aboard the Skylab the following year. His experiment, “Wave Motion Trough A Liquid in Zero Gravity” used a container attached to the end of a leaf spring which was oscillated at specific rates using two thickness differentiated types of liquids. Dunlap was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment. The equipment for the experiments was manufactured at MSFC.
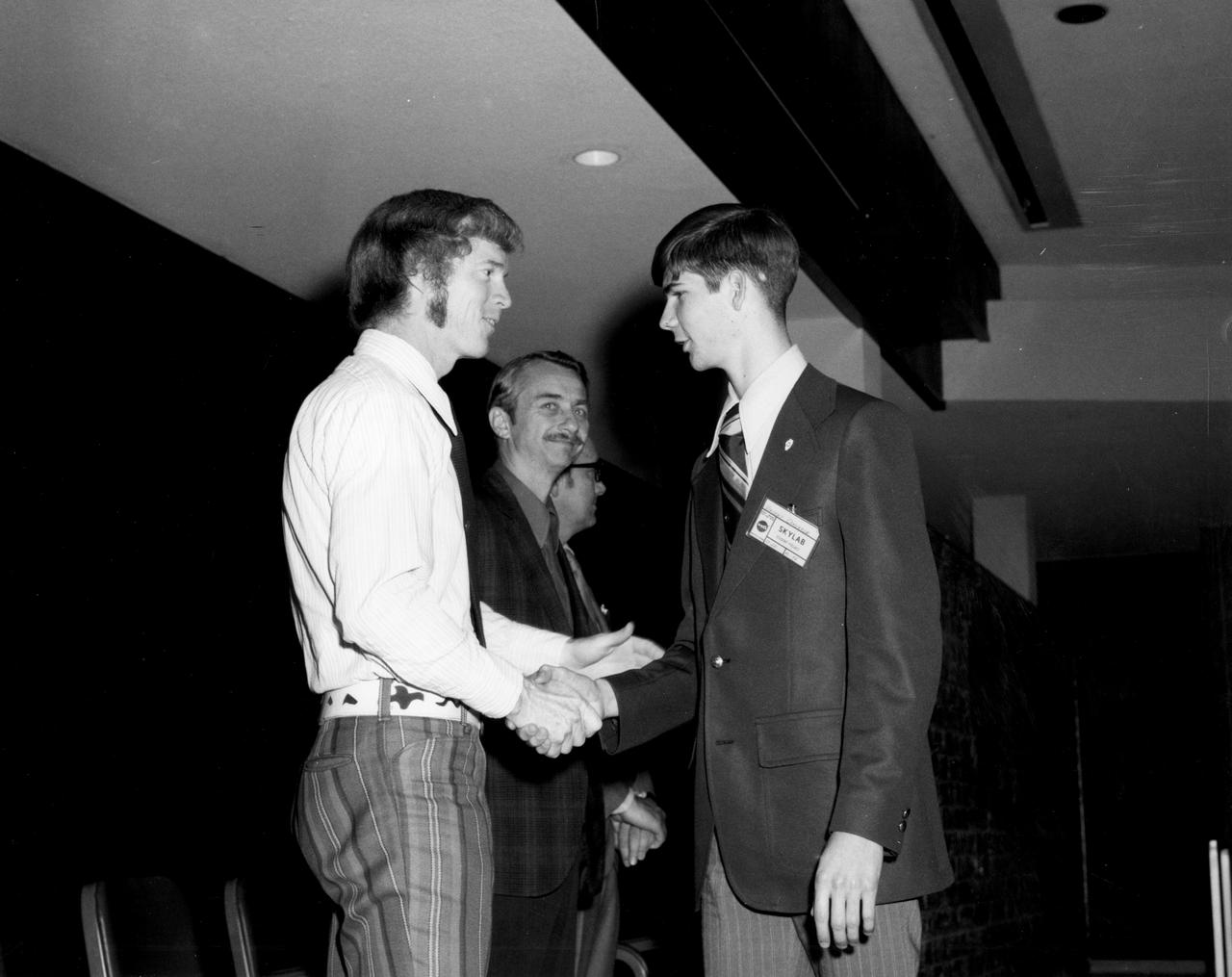

Rockford, Illinois high school student, Vincent Converse (right), is greeted by astronauts Russell L. Schweickart and Owen K. Garriott during a tour of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Converse was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. His experiment, “Zero Gravity Mass Measurement” used a simple leaf spring with the mass to be weighed attached to the end. An electronic package oscillated the spring at a specific rate and the results were recorded electronically. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipme

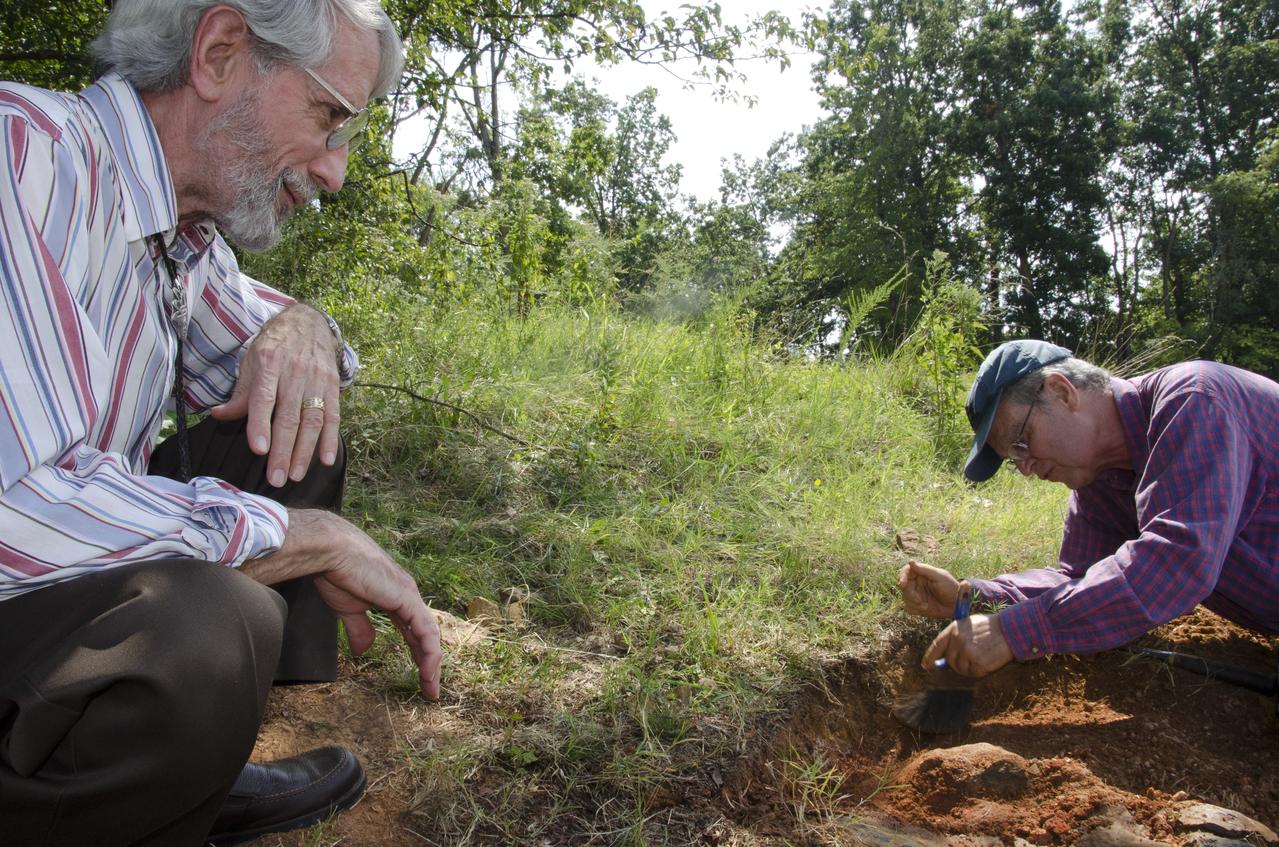
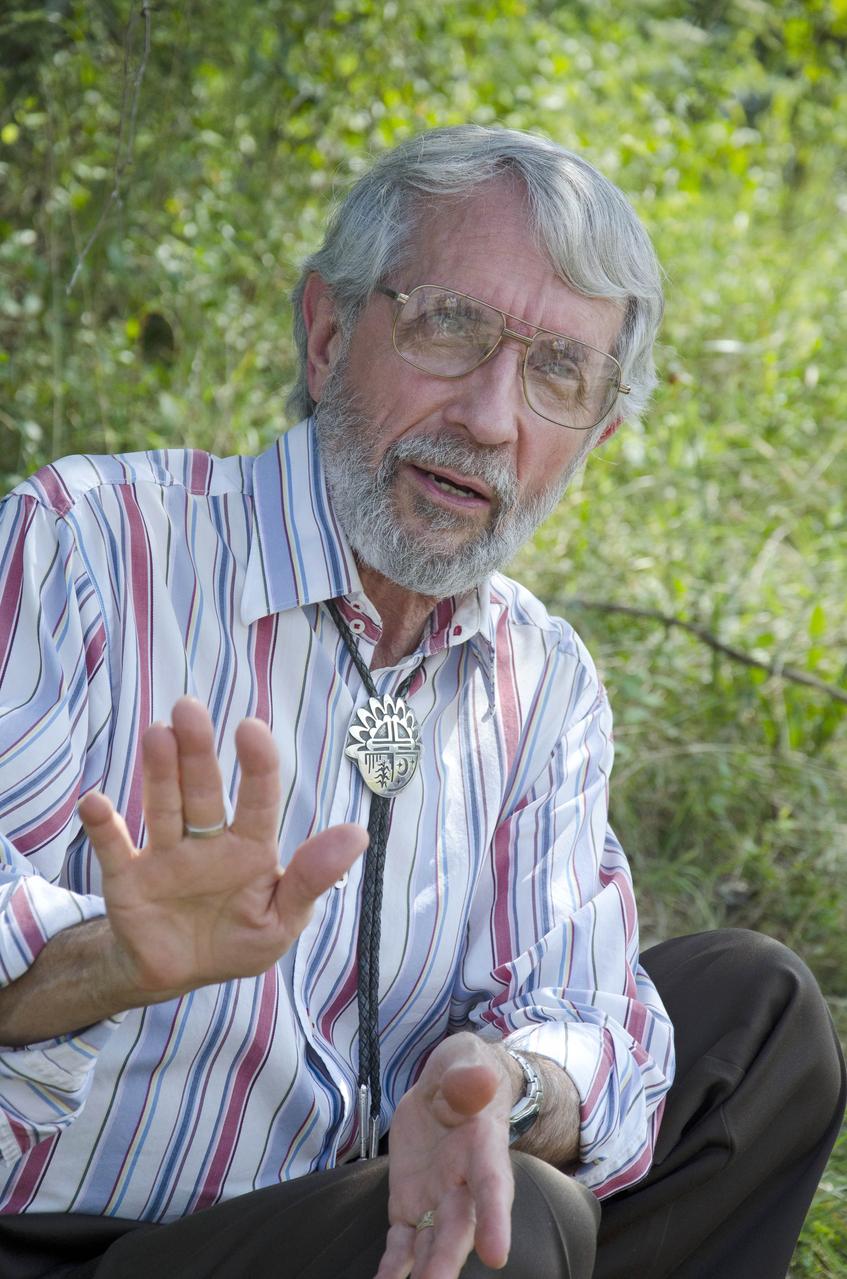
Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
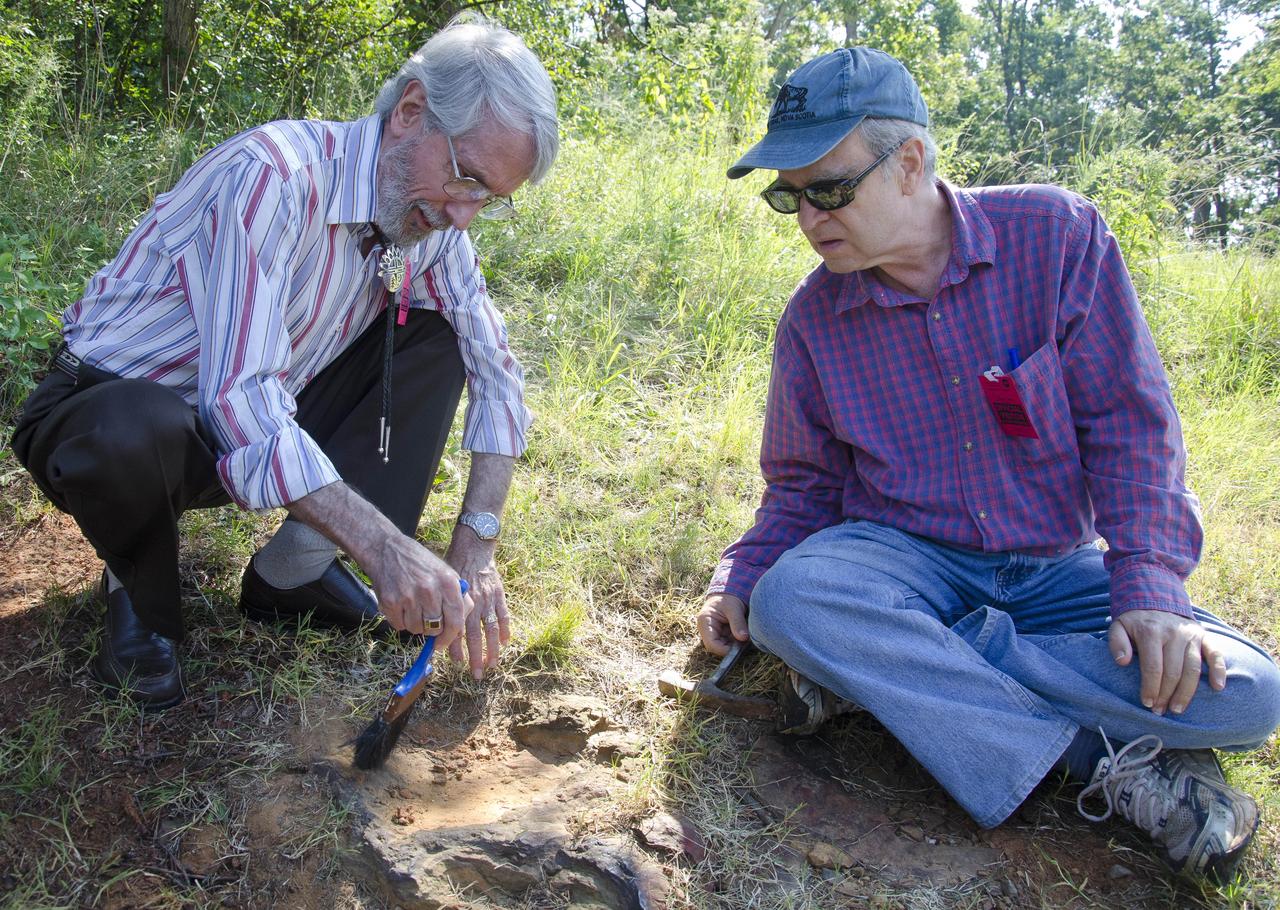

Dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford describes the cretaceous-era nodosaur track he found on the Goddard Space Flight Center campus with Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS who verified his discovery. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
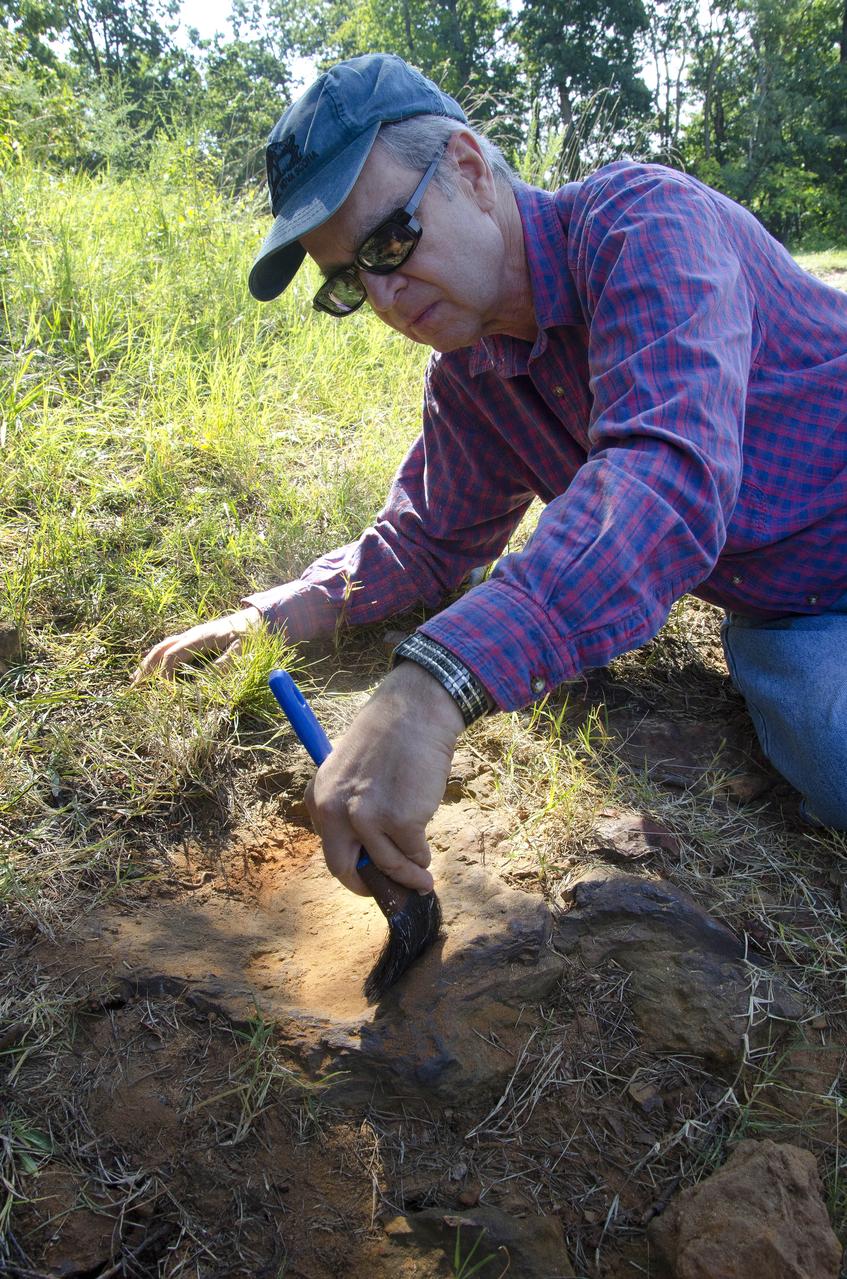

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
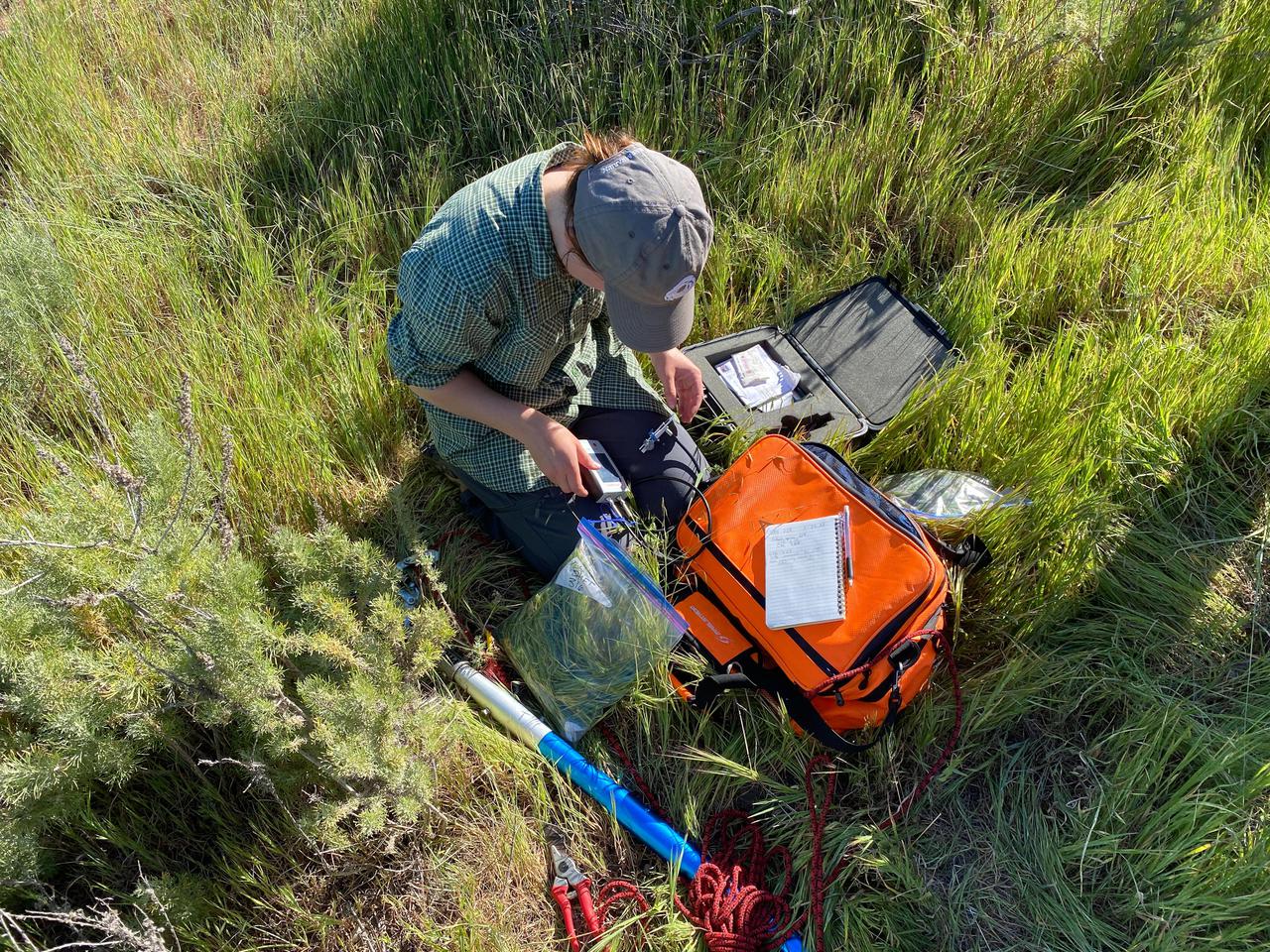

University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB) student Piper Lovegreen calibrates a sensor to measure leaf chlorophyl content of vegetation at the Jack and Laura Dangermond Preserve in Santa Barbara County on March 23, 2022. Lovegreen is among the researchers working on the Surface Biology and Geology High-Frequency Time Series (SHIFT) campaign, which is jointly led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, UCSB, and The Nature Conservancy. Operating between late February and late May 2022, SHIFT combines the ability of airborne science instruments to gather data over widespread areas with the more concentrated observations scientists conduct in the field to study the functional characteristics, health, and resilience of plant communities. The sampling and analysis done by researchers on the ground and in the ocean is intended to validate data taken by AVIRIS-NG (Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer-Next Generation). The instrument, designed at JPL, is collecting spectral data of vegetation it observes during weekly flights in an aircraft over a 640-square-mile (1,656-square-kilometer) study area in Santa Barbara County and coastal Pacific waters. The campaign is a pathfinder for NASA's proposed Surface Biology and Geology (SBG) mission. SHIFT will help scientists design data collection and processing algorithms for that mission, which would launch no earlier than 2028. The SHIFT data is also intended to support the research and conservation objectives of The Nature Conservancy, which owns the Dangermond Preserve, and UCSB, which operates the Sedgwick Reserve, another nature preserve within the study area. More than 60 scientists from institutions around the U.S. have indicated they intend to use the SHIFT data in their research. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25142

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

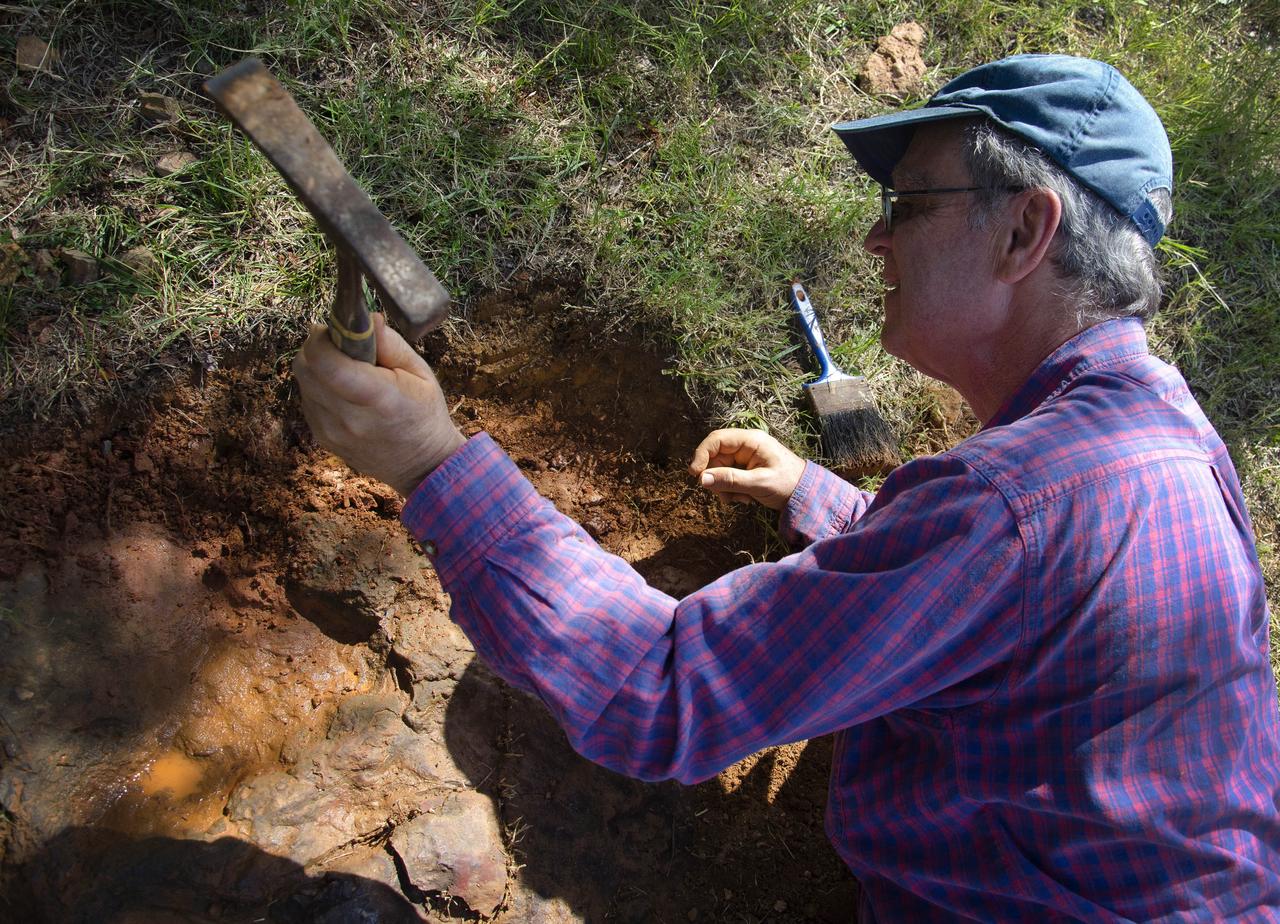
Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

On July 3, 1936, President Franklin Delano Roosevelt stood amidst the crowd in Big Meadows and officially dedicated Shenandoah National Park in Virginia. The Thematic Mapper on the Landsat satellite captured this view of the heart of Shenandoah National Park on October 10, 2010, at the height of the fall “leaf-peeping” season. The orange and brown swath across the image highlights the hilly backbone of the park, where leaves had turned to their fall colors. The 169-kilometer (105-mile) Skyline Drive that meanders across the crest of the ridge is often jammed with tourists in autumn. The park includes more than 518 miles of hiking trails, including more than 100 miles of the Appalachian Trail. The highest peak is Hawksbill Mountain at 4,051 feet (1,235 m), but the most popular with hikers is Old Rag Mountain. A circuitous eight-mile (13 kilometer) trail leads to an exposed, rocky summit 3,291 feet (1,003 meters) above sea level. The 2,200 foot elevation change from base to summit, combined with several rock scrambles, make Old Rag not only the most popular but also the most dangerous hike. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2bRnFxH" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2bRnFxH</a> Credit: NASA/Landsat5 <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford describes the cretaceous-era nodosaur track he found on the Goddard Space Flight Center campus with Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS who verified his discovery. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

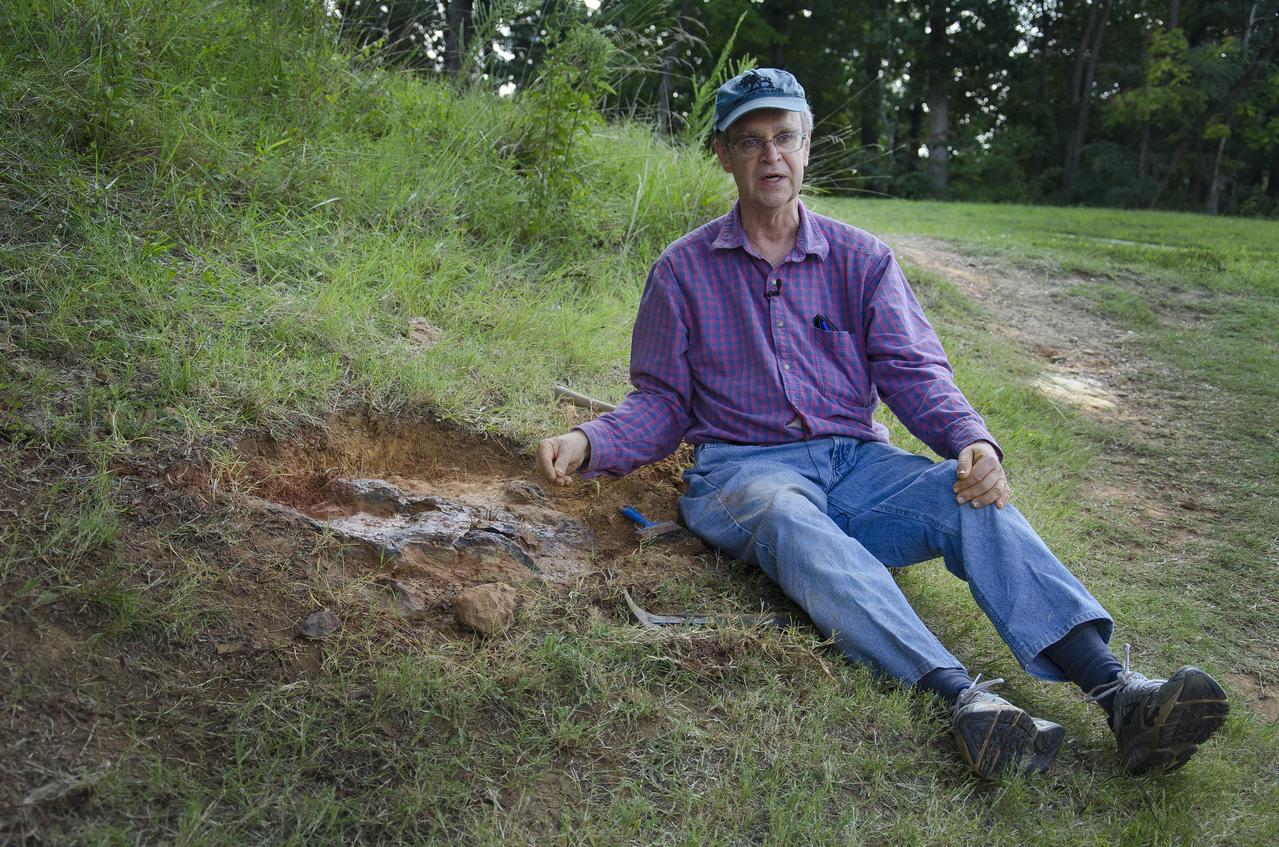
Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

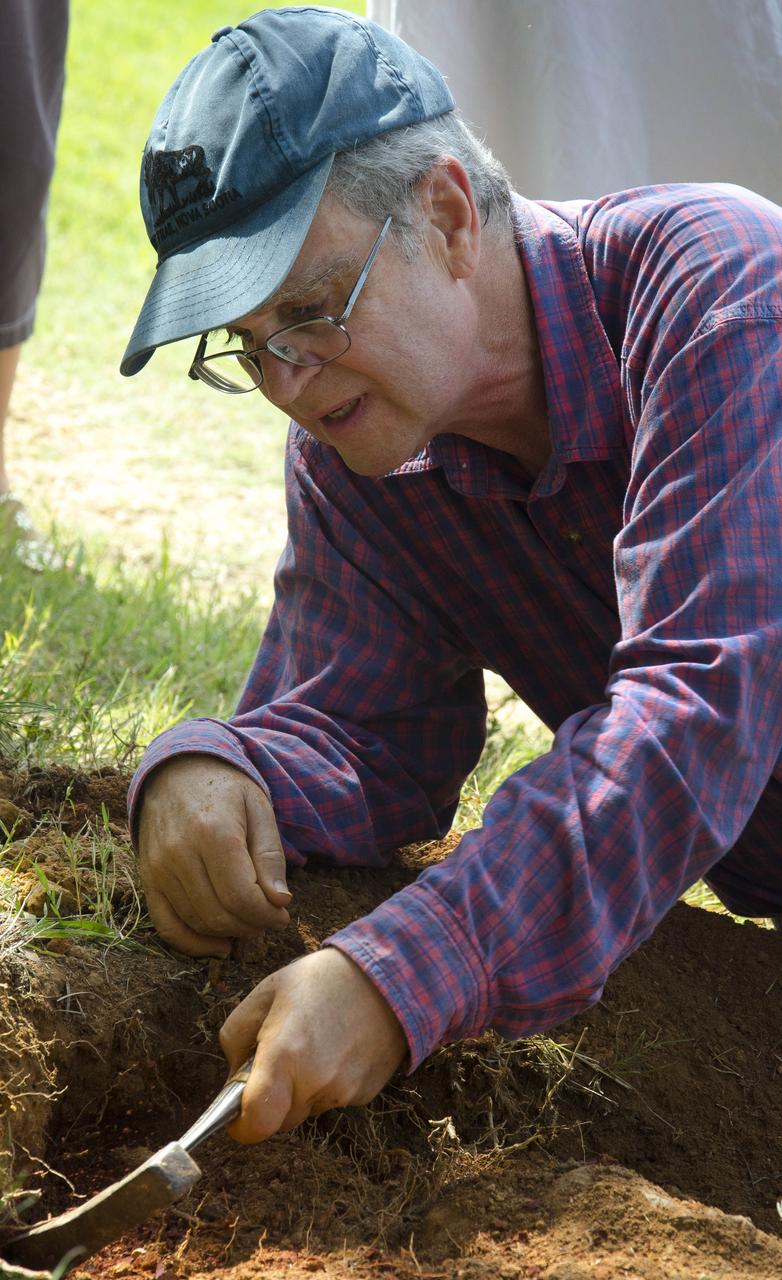
Dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford describes the cretaceous-era nodosaur track he found on the Goddard Space Flight Center campus this year. The imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

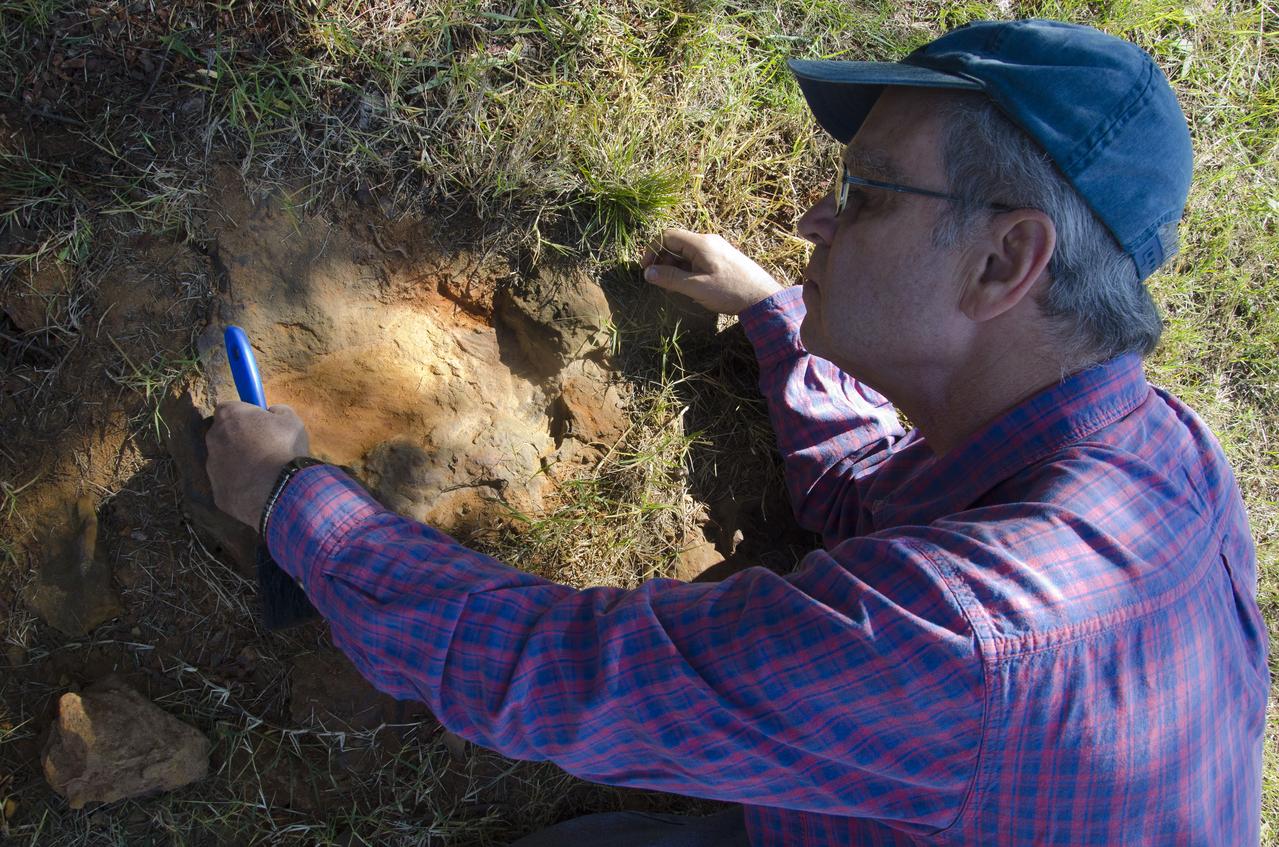
Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS verifies the recently discovered dinosaur track found on the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center campus. This imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. To read more about this discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
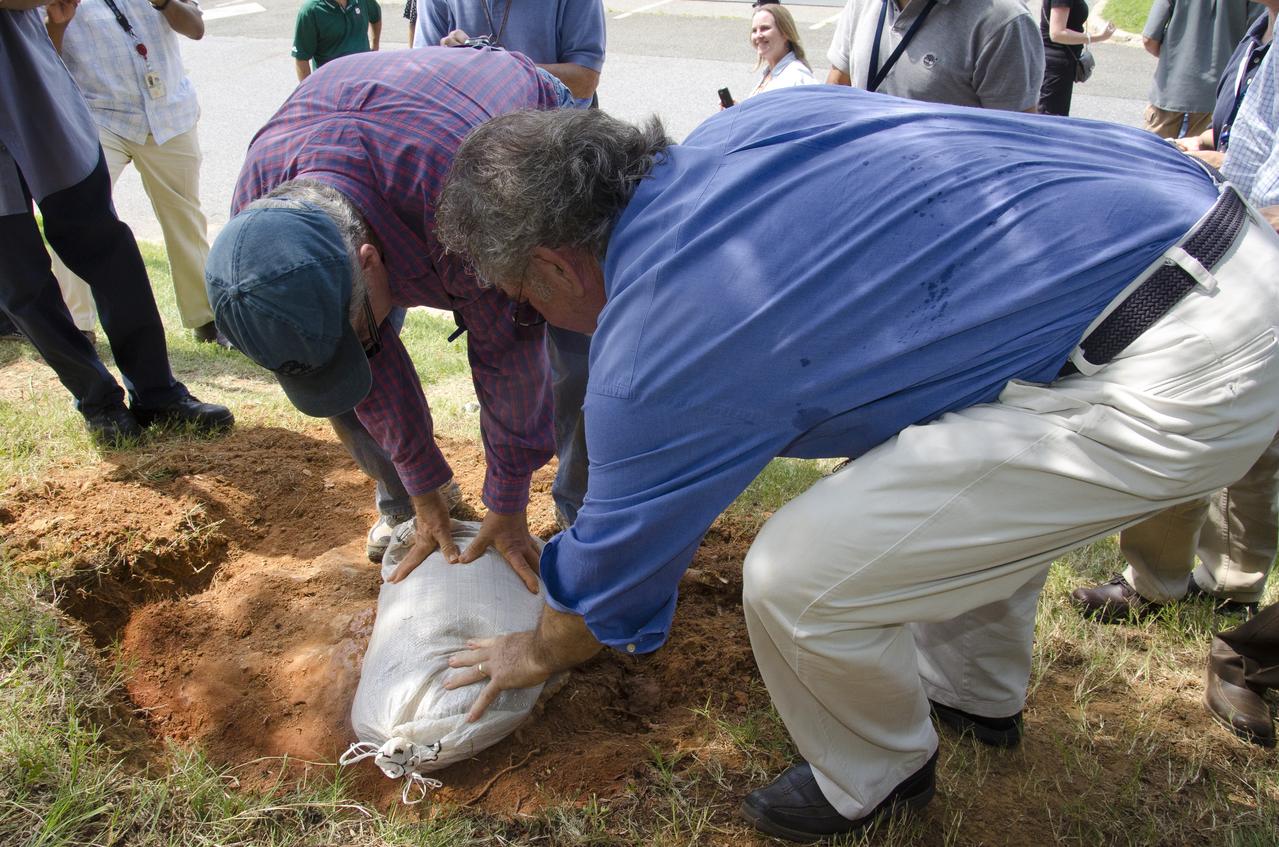

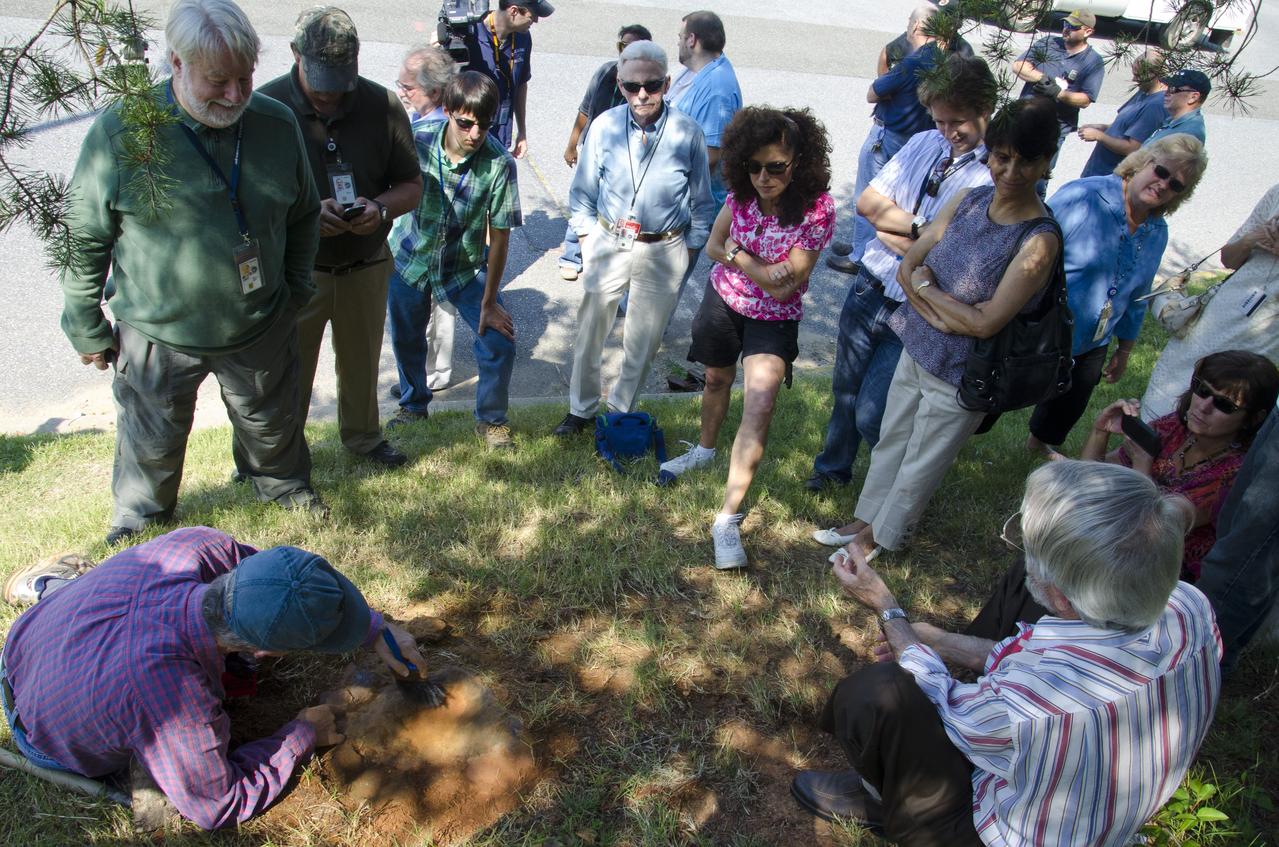
On Friday, Aug. 17, 2012, noted dinosaur hunter Ray Stanford shared the location of that footprint with Goddard’s facility management. The imprint shows the right rear foot of a nodosaur - a low-slung, spiny leaf-eater - apparently moving in haste as the heel did not fully settle in the cretaceous mud, according to dinosaur tracker Ray Stanford. It was found recently on NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center campus and is being preserved for study. Picuted here are Dr. Robert Weems, emeritus paleontologist for the USGS and Goddard Facilities Planner Alan Binstock, covering the newly discover nodosaur imprint with a sandbag to help preserve the imprecision. To read more go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/P9NYg7" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/P9NYg7</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Rebecca Roth <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
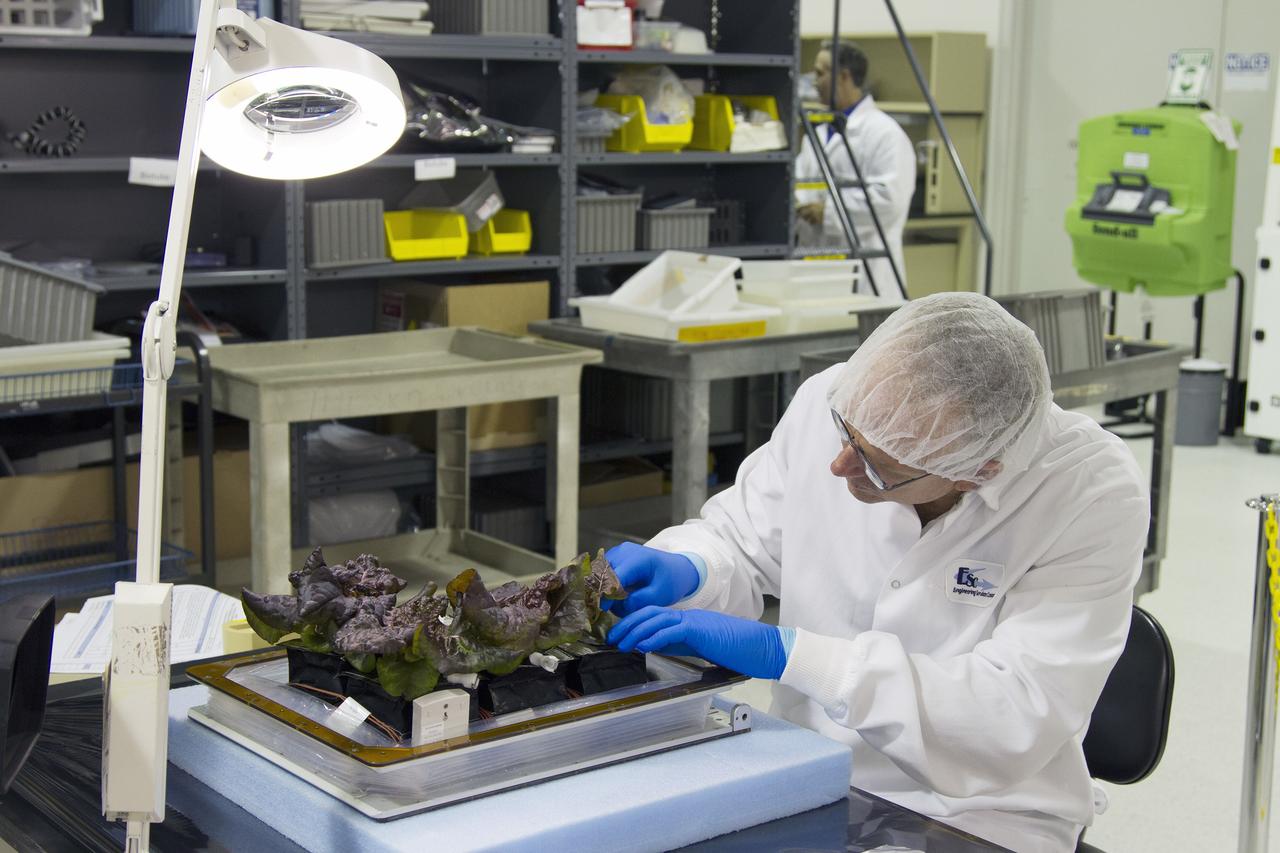

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Jim Smodell, a technician with SGT, removes an outredgeous red lettuce leaf from a plant pillow inside the Payload Development Laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility, or SSPF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The plant pillows were removed from the Veggie plant growth system inside a control chamber at the SSPF. The growth chamber was used as a control unit for Veggie and procedures were followed identical to those being performed on Veggie and the Veg-01 experiment on the International Space Station. The lettuce leaves will be wrapped and placed in a minus eighty-degree freezer, along with the plant pillows and samples swabbed from the plants, plant pillows and Veggie bellows. The chamber mimicked the temperature, relative humidity and carbon dioxide concentration of those in the Veggie unit on the space station. Veggie and Veg-01 were delivered to the space station aboard the SpaceX-3 mission. Veggie is the first fresh food production system delivered to the station. Six plant pillows, each containing outredgeous red romaine lettuce seeds and a root mat were inserted into Veggie. The plant chamber's red, blue and green LED lights were activated. The plant growth was monitored for 33 days. On June 10, at the end of the cycle, the plants were carefully harvested, frozen and stored for return to Earth by Expedition 39 flight engineer and NASA astronaut Steve Swanson. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
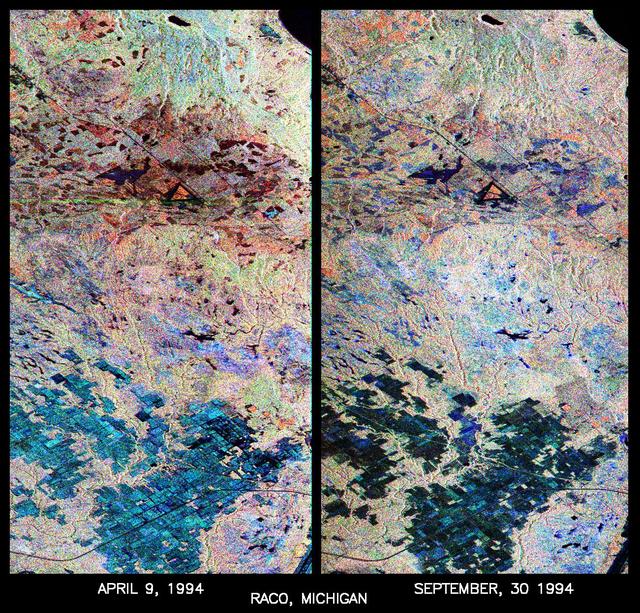
These are two false-color composites of Raco, Michigan, located at the eastern end of Michigan upper peninsula, west of Sault Ste. Marie and south of Whitefish Bay on Lake Superior. The two images (centered at 46.39 degrees north latitude, 84.88 degrees west longitude) show significant seasonal changes in the mid-latitude region of mixed deciduous and coniferous forests. The images were acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the shuttle Endeavour on the sixth orbit of each mission. In these images, red is L-band (23 cm) with horizontal/vertical polarization; green is C-band (6 cm) with horizontal/vertical polarization; blue is C-band with horizontal/horizontal polarization. The region shown is largely forested and includes a large portion of Hiawatha National Forest, as well as an agricultural region near the bottom of each image. In early April, the area was snow-covered with up to 50 centimeters (19.5 inches) of snow in forest clearings and agricultural fields. Buds had not yet broken on deciduous trees, but the trees were not frozen and sap was generally flowing. Lake Superior, in the upper right, and the small inland lakes were frozen and snow-covered on April 9, 1994. By the end of September, deciduous trees were just beginning to change color after a relatively wet period. Leaf loss was estimated at about 30 percent, depending on the species, and the soil was moist to wet after a heavy rainfall on September 28, 1994. Most agricultural fields were covered with grasses of up to 60 centimeters (23 inches) in height. In the two images the colors are related to the types of land cover (i.e. vegetation type) and the brightness is related to the amount of plant material and its relative moisture content. Significant seasonal changes between early spring and early fall are illustrated by this pair of images. For the agricultural region near the bottom of the images, the change from snow-cover to moist soil with short vegetation cover is shown by the color change from blue to green and blue. The green color corresponds to significant increases in vegetation cover and field-to-field differences in blue are the result of differences in surface roughness and soil moisture. In the forested areas, many of the conifer forests appear similar in both images (red pine forests appear red in both images). However, there is more blue and green in the September 30, 1994 image as a consequence of greater foliage and more moisture in the forest crowns. Lowland conifer forests (spruce and northern white cedars) appear as bright green in both images. Deciduous forests produce very strong radar returns at these frequencies and polarization combinations, resulting in a nearly white appearance on the images (the specific color mix is related to the local species mix). In the September 30, 1994 image, the areas of deciduous forest appear darker than in the April image because of the weaker radar signal from the foliage in the crown layer. The clear-cut areas (shown in April by the irregularly shaped dark areas in the center) change dramatically in appearance due to loss of snow cover and increases in soil moisture and vegetation cover by the end of September. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01730
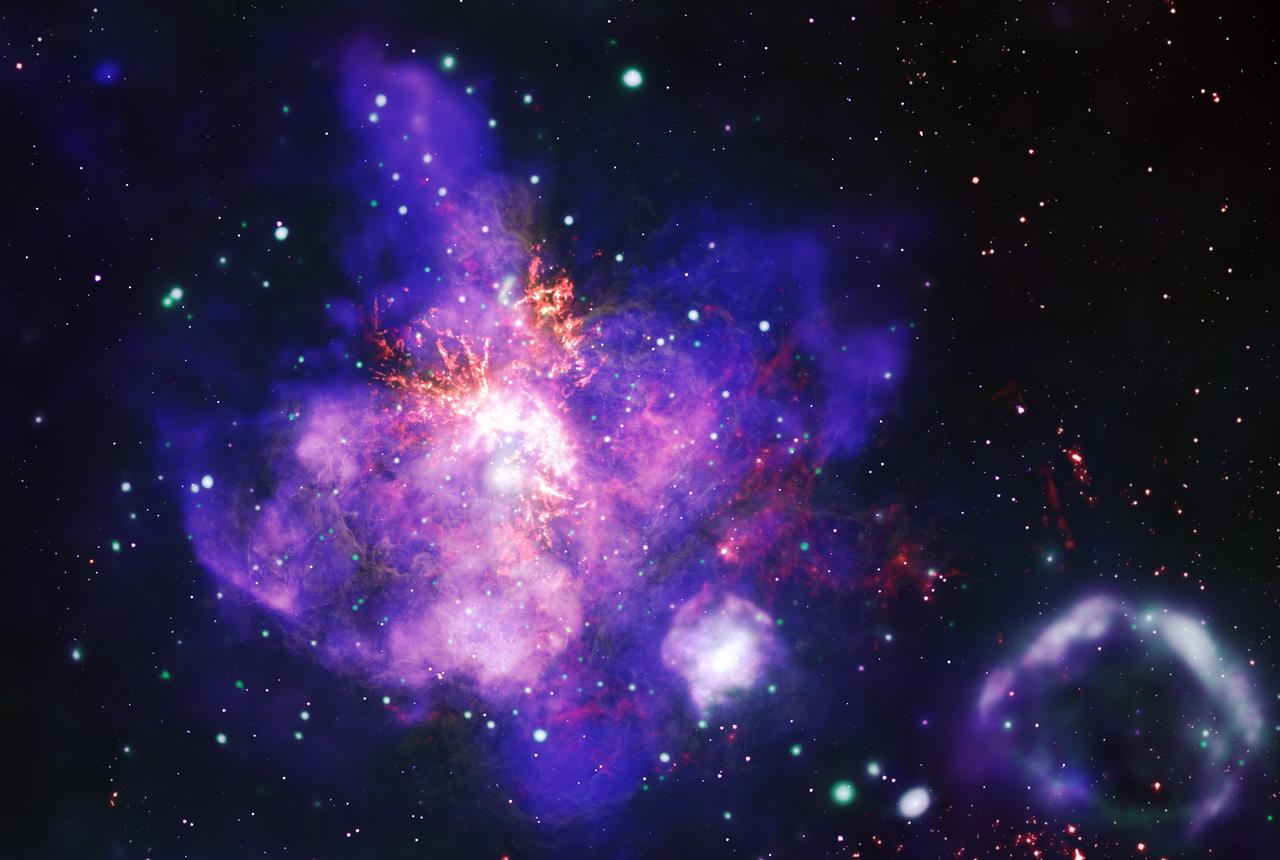

This composite image contains the deepest X-ray image ever made of the spectacular star forming region called 30 Doradus. By combining X-ray data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory (blue and green) with optical data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope (yellow) and radio data from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (orange), this stellar arrangement comes alive.