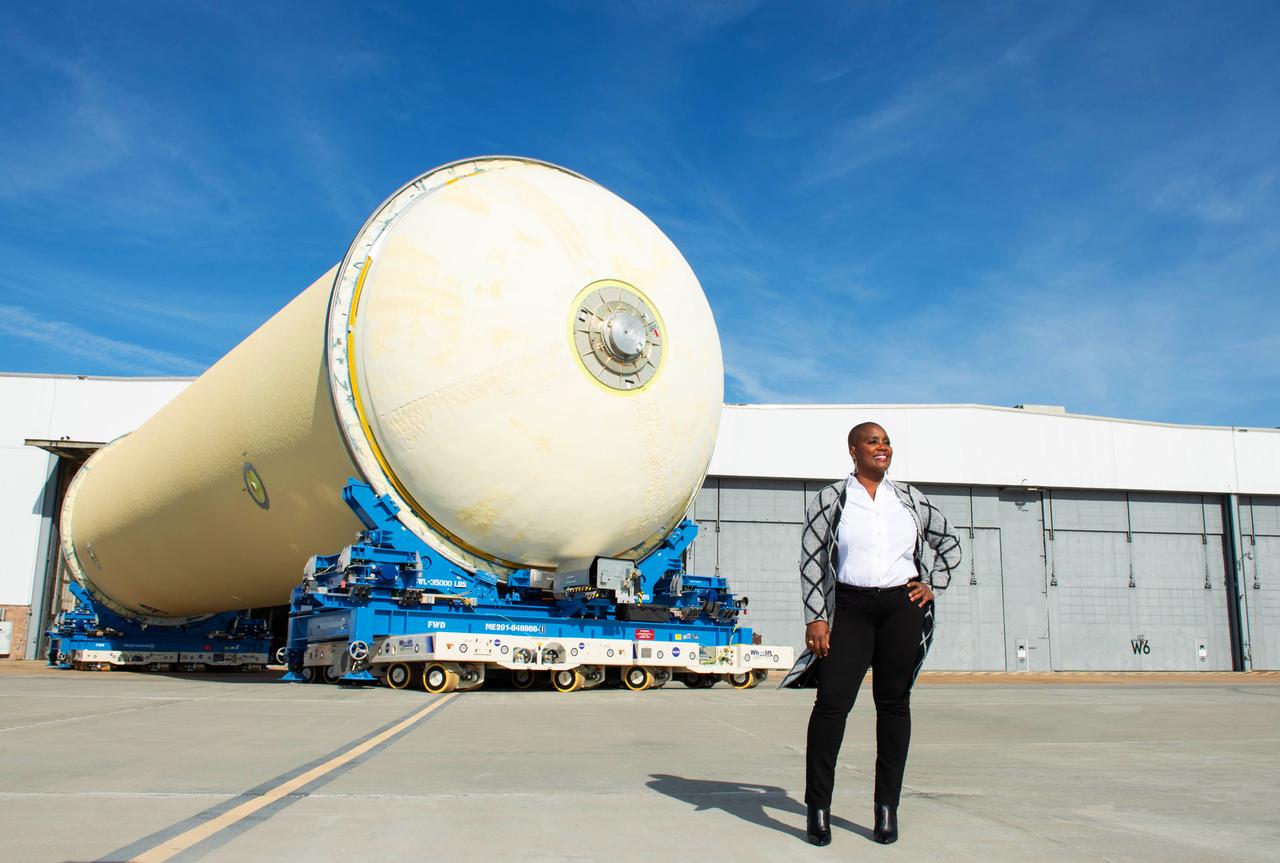

CS1 LH2 Move into Area 47
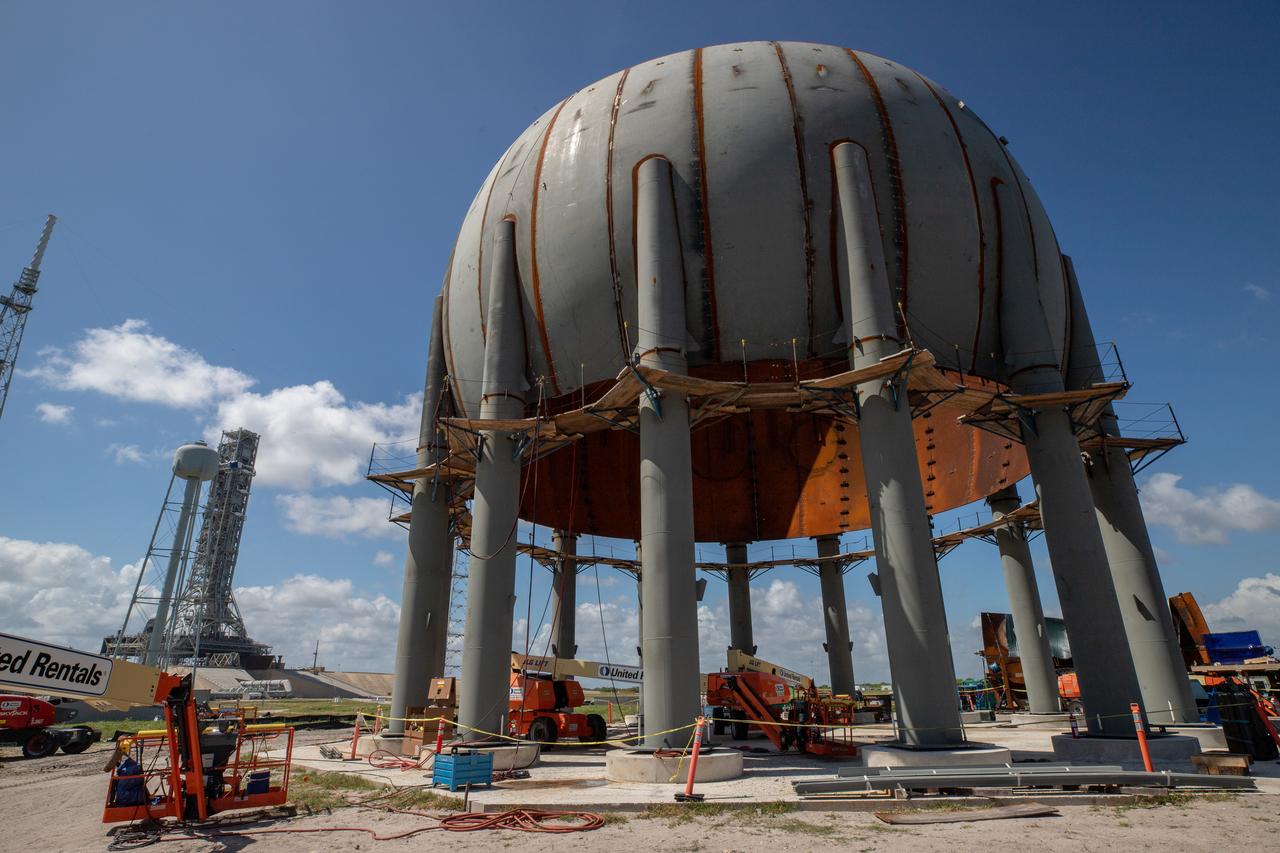

Build-up of a new liquid hydrogen (LH2) storage tank is in progress on Oct. 1, 2019, at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new tank will hold 1.25 million gallons of usable LH2 to support future launches from the pad, including Artemis missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
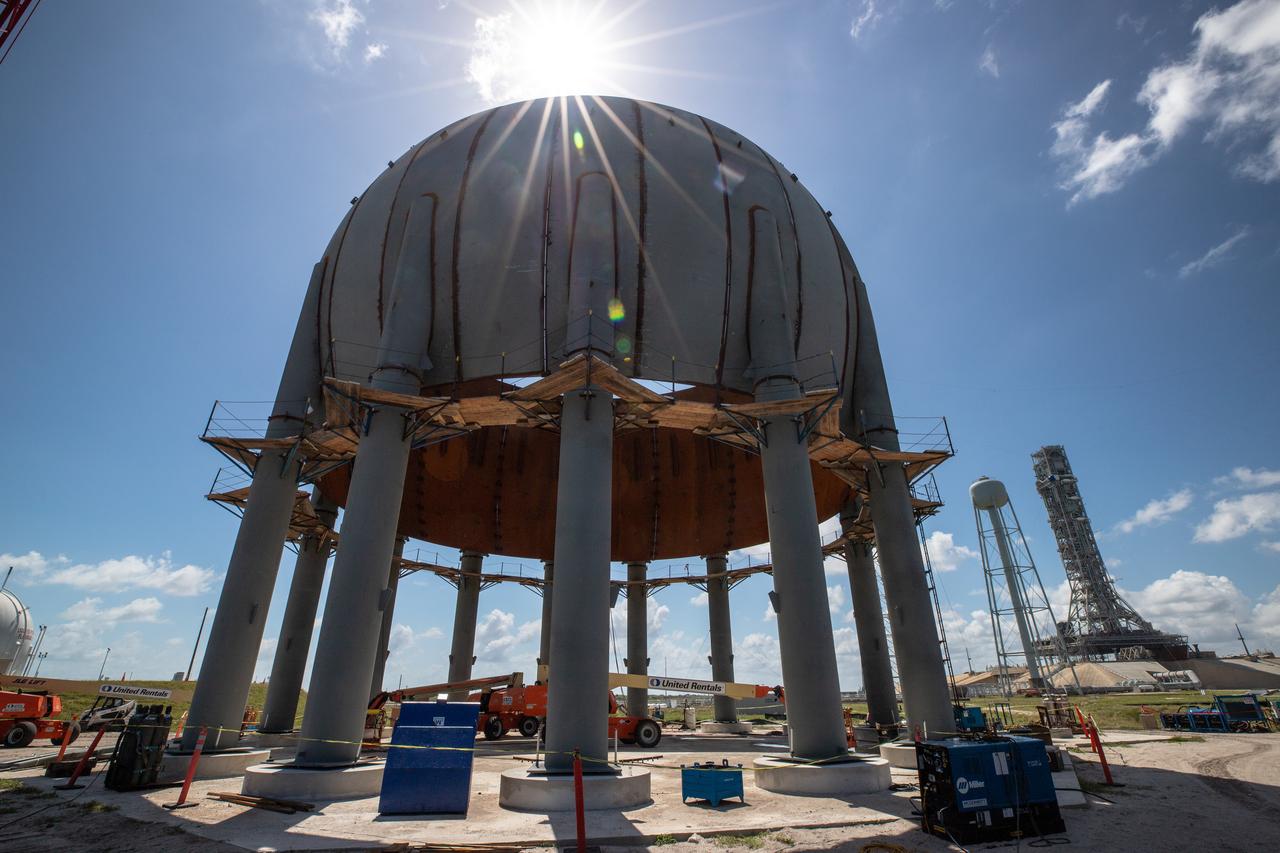

Build-up of a new liquid hydrogen (LH2) storage tank is in progress on Oct. 1, 2019, at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new tank will hold 1.25 million gallons of usable LH2 to support future launches from the pad, including Artemis missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
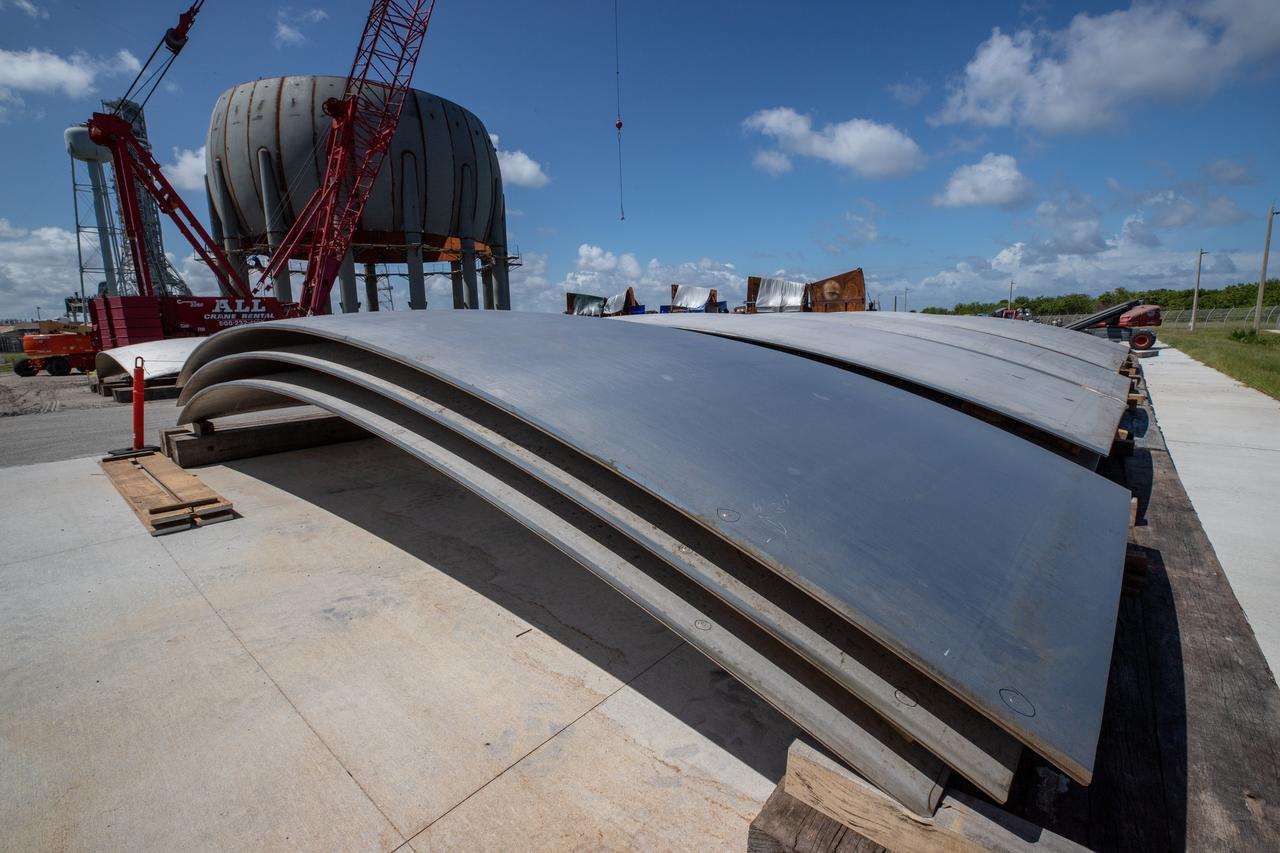

Build-up of a new liquid hydrogen (LH2) storage tank is in progress on Oct. 1, 2019, at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new tank will hold 1.25 million gallons of usable LH2 to support future launches from the pad, including Artemis missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
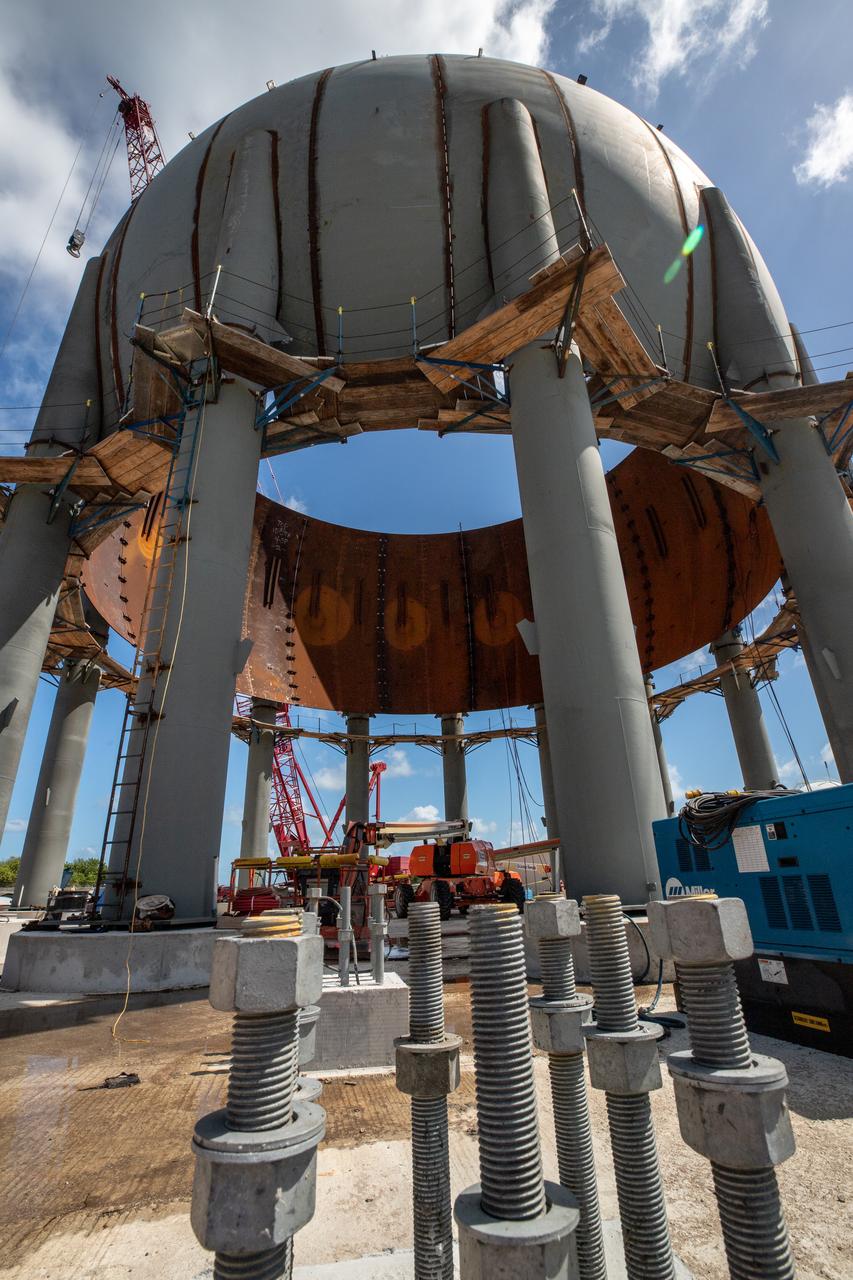

Build-up of a new liquid hydrogen (LH2) storage tank is in progress on Oct. 1, 2019, at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new tank will hold 1.25 million gallons of usable LH2 to support future launches from the pad, including Artemis missions to the Moon and on to Mars.

Build-up of a new liquid hydrogen (LH2) storage tank is in progress on Oct. 1, 2019, at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new tank will hold 1.25 million gallons of usable LH2 to support future launches from the pad, including Artemis missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
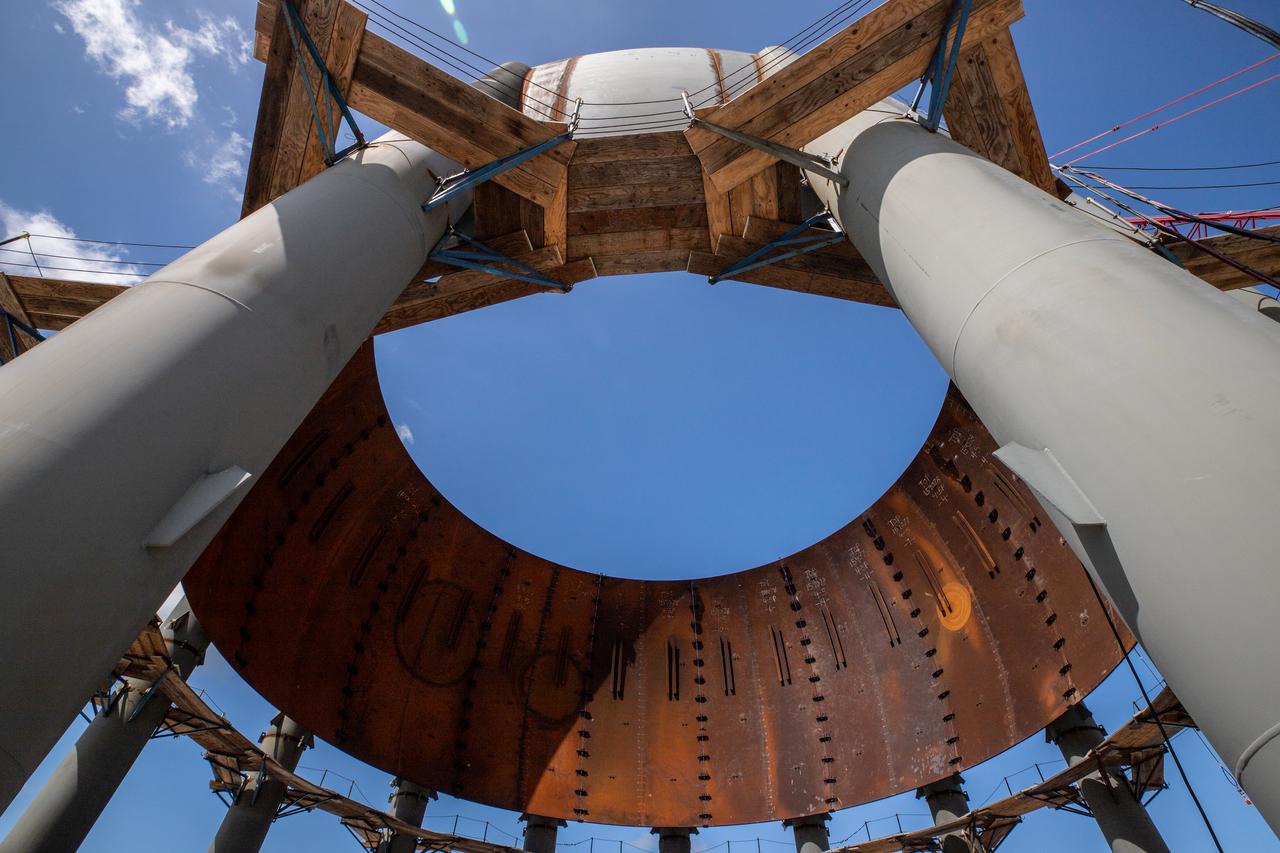

Build-up of a new liquid hydrogen (LH2) storage tank is in progress on Oct. 1, 2019, at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new tank will hold 1.25 million gallons of usable LH2 to support future launches from the pad, including Artemis missions to the Moon and on to Mars.

Build-up of a new liquid hydrogen (LH2) storage tank is in progress on Oct. 1, 2019, at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new tank will hold 1.25 million gallons of usable LH2 to support future launches from the pad, including Artemis missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
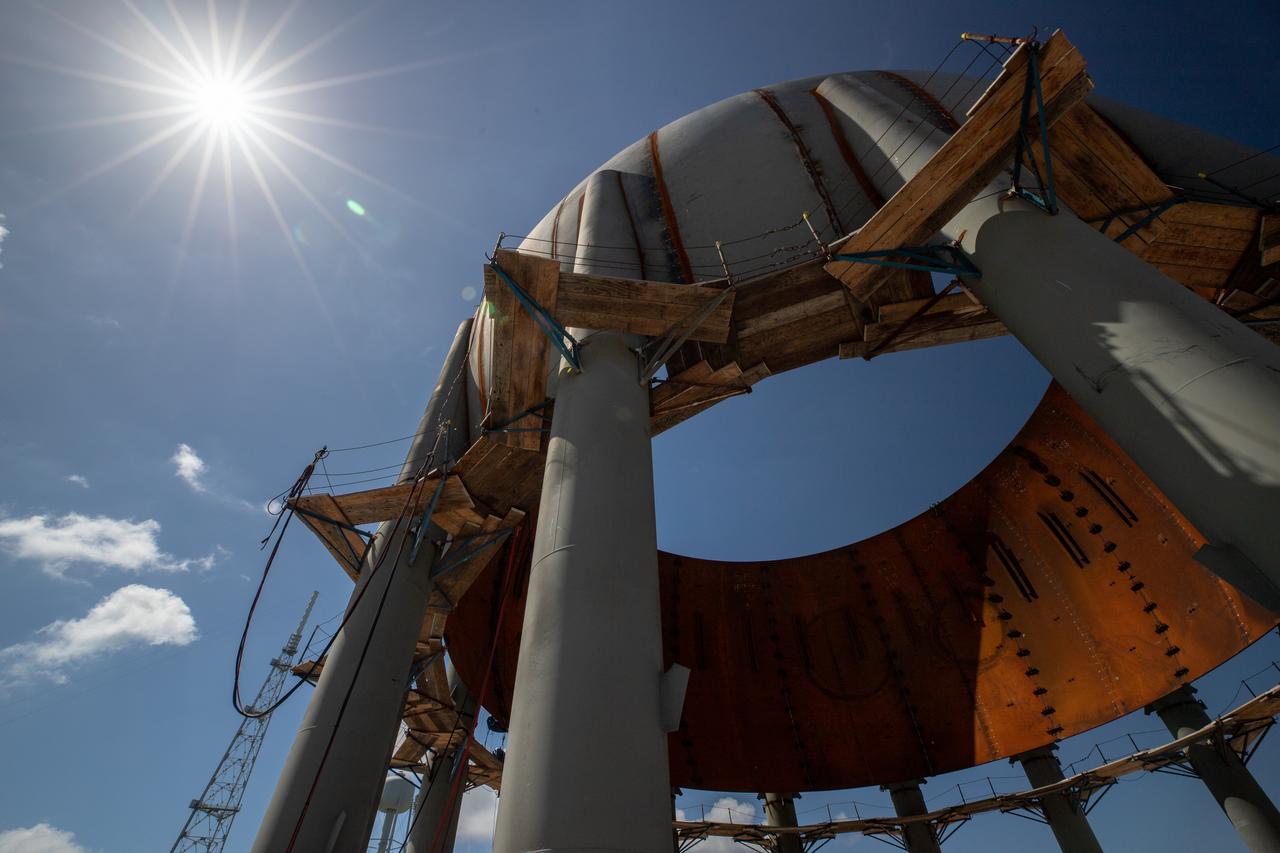

Build-up of a new liquid hydrogen (LH2) storage tank is in progress on Oct. 1, 2019, at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new tank will hold 1.25 million gallons of usable LH2 to support future launches from the pad, including Artemis missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
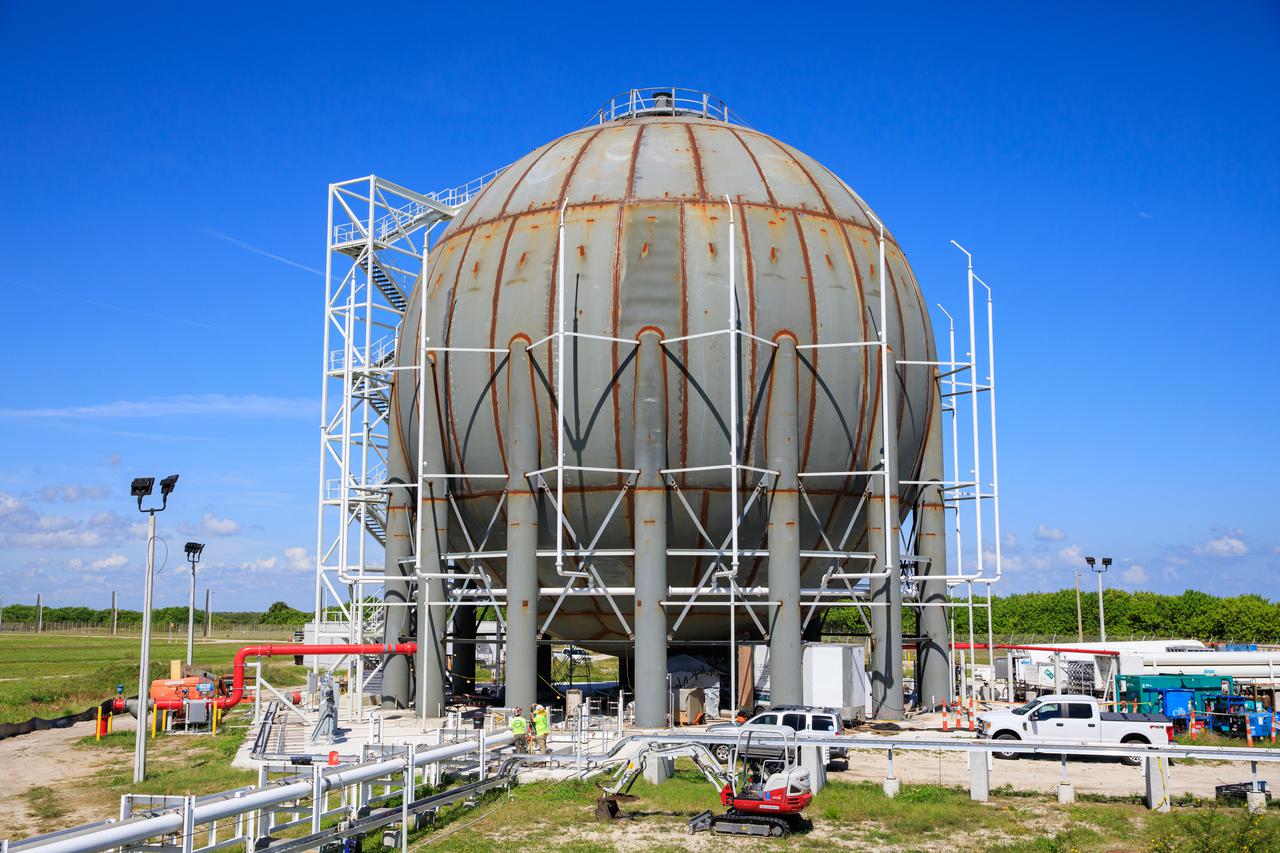

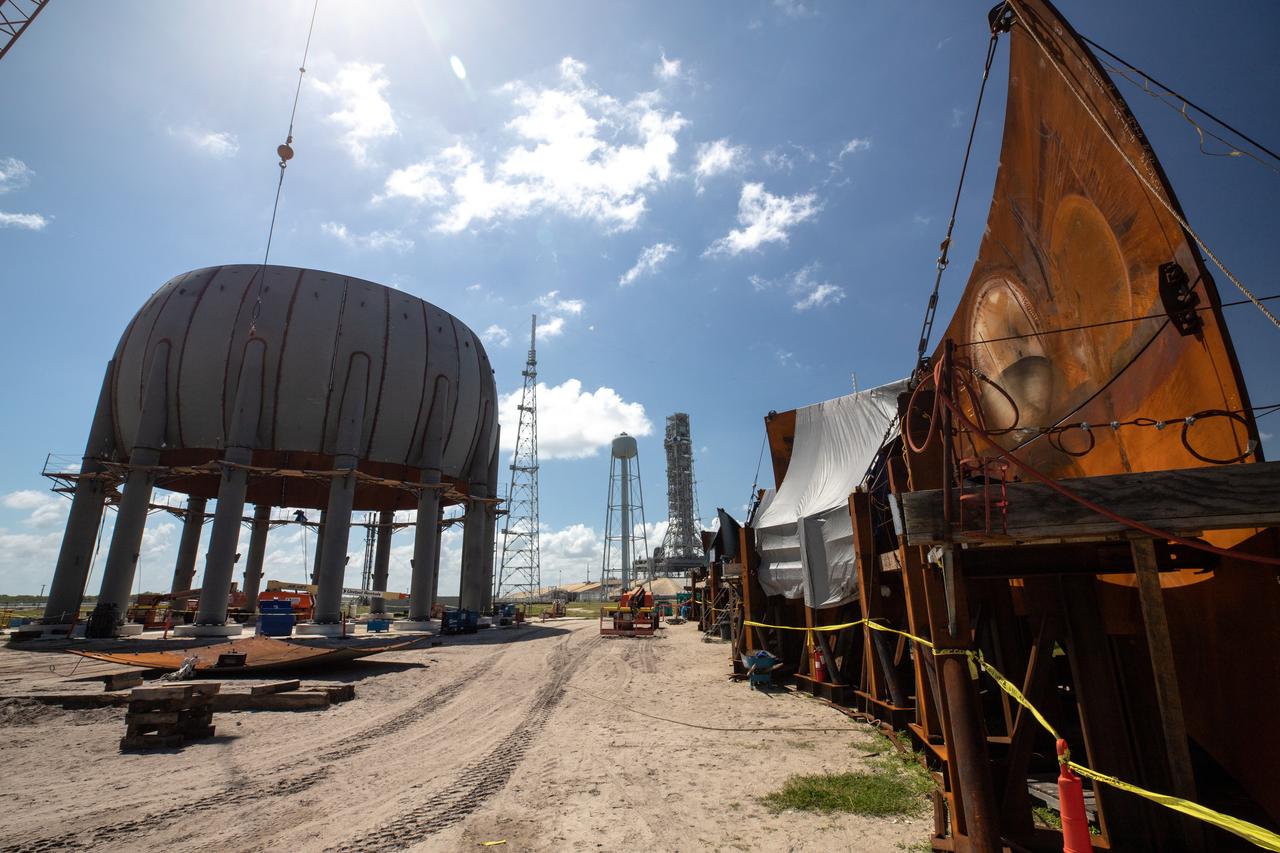
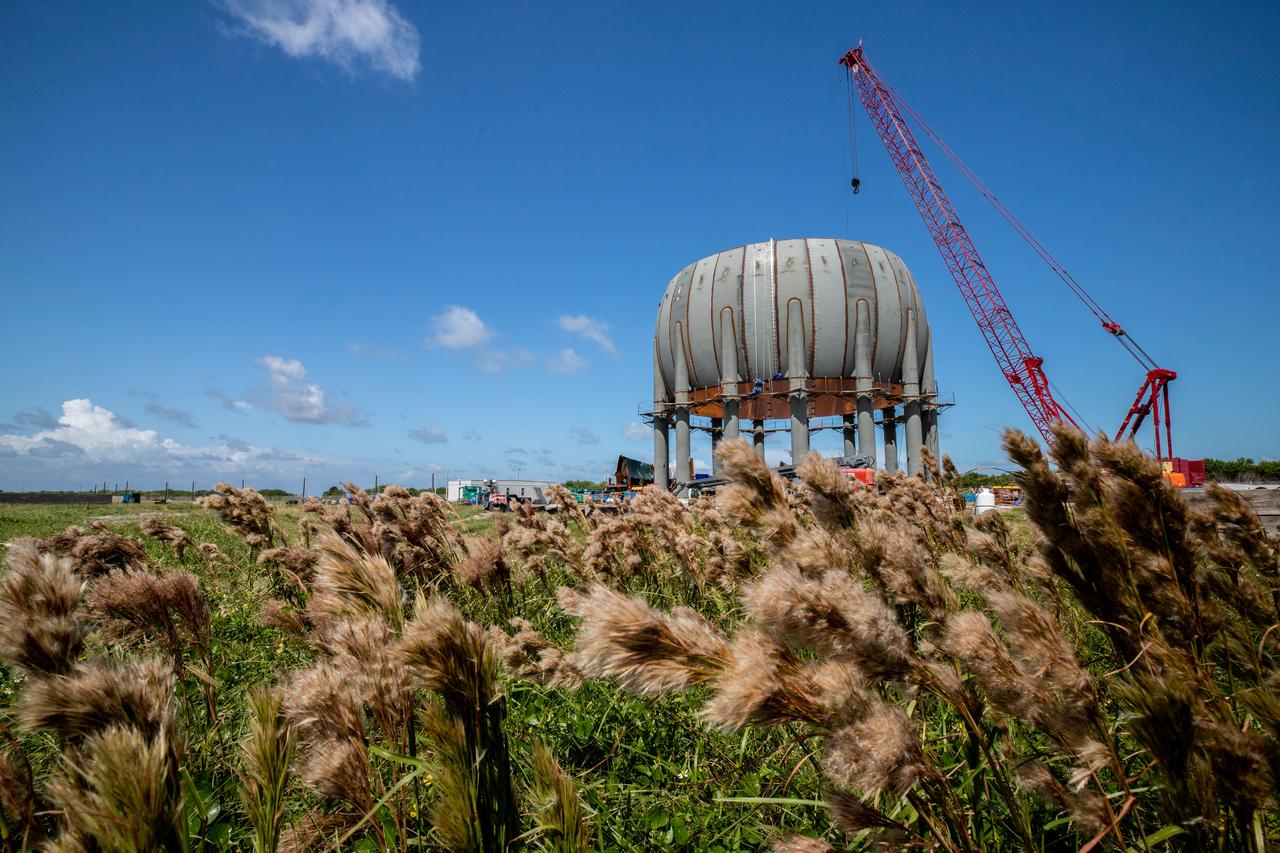
Seen here is a newly constructed liquid hydrogen (LH2) storage tank at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 1, 2021. With construction now complete, teams will focus on painting the tank next. The storage tank, capable of holding 1.25 million gallons of LH2, will be used to support future Artemis missions to the Moon and, eventually, Mars. Through Artemis, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, paving the way for a long-term presence in lunar orbit.
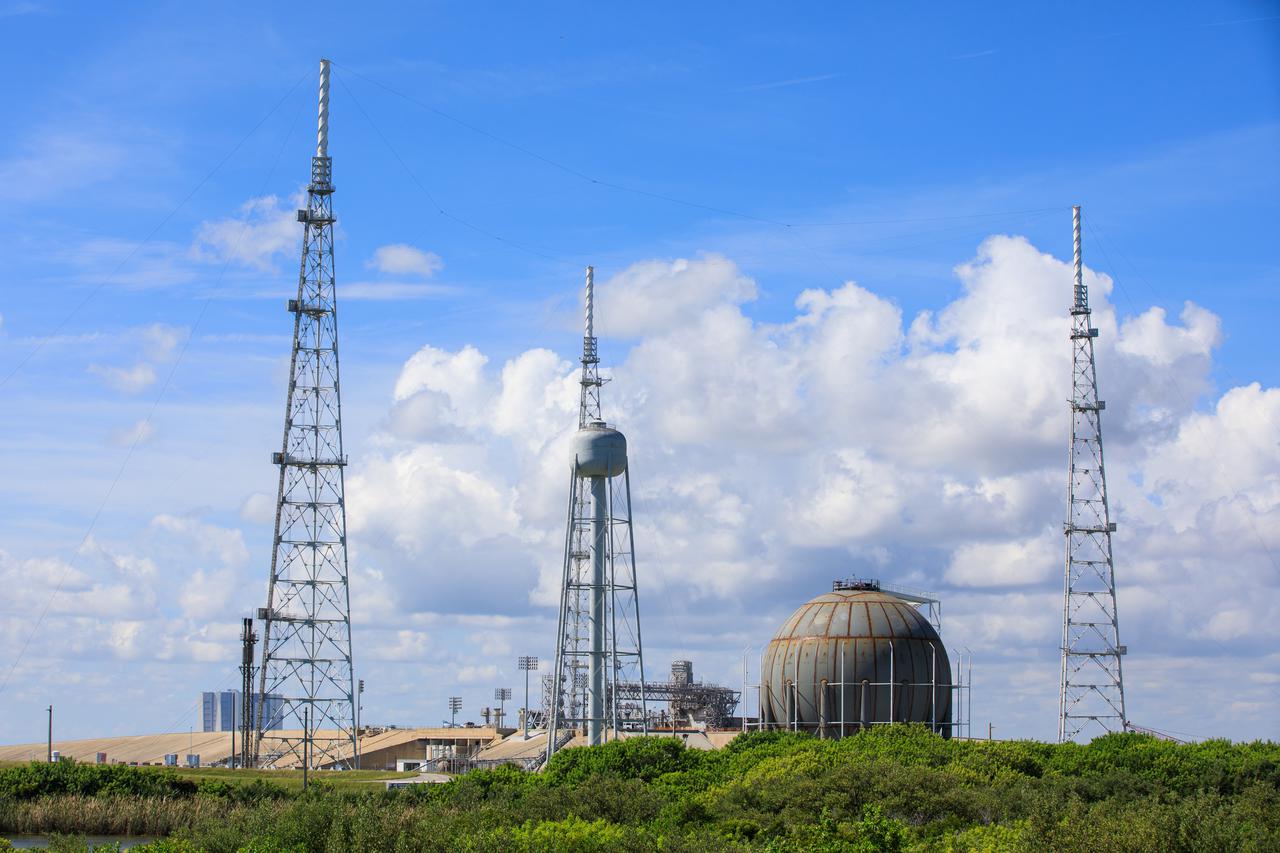

Seen here is a newly constructed liquid hydrogen (LH2) storage tank at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 1, 2021. With construction now complete, teams will focus on painting the tank next. The storage tank, capable of holding 1.25 million gallons of LH2, will be used to support future Artemis missions to the Moon and, eventually, Mars. Through Artemis, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, paving the way for a long-term presence in lunar orbit.
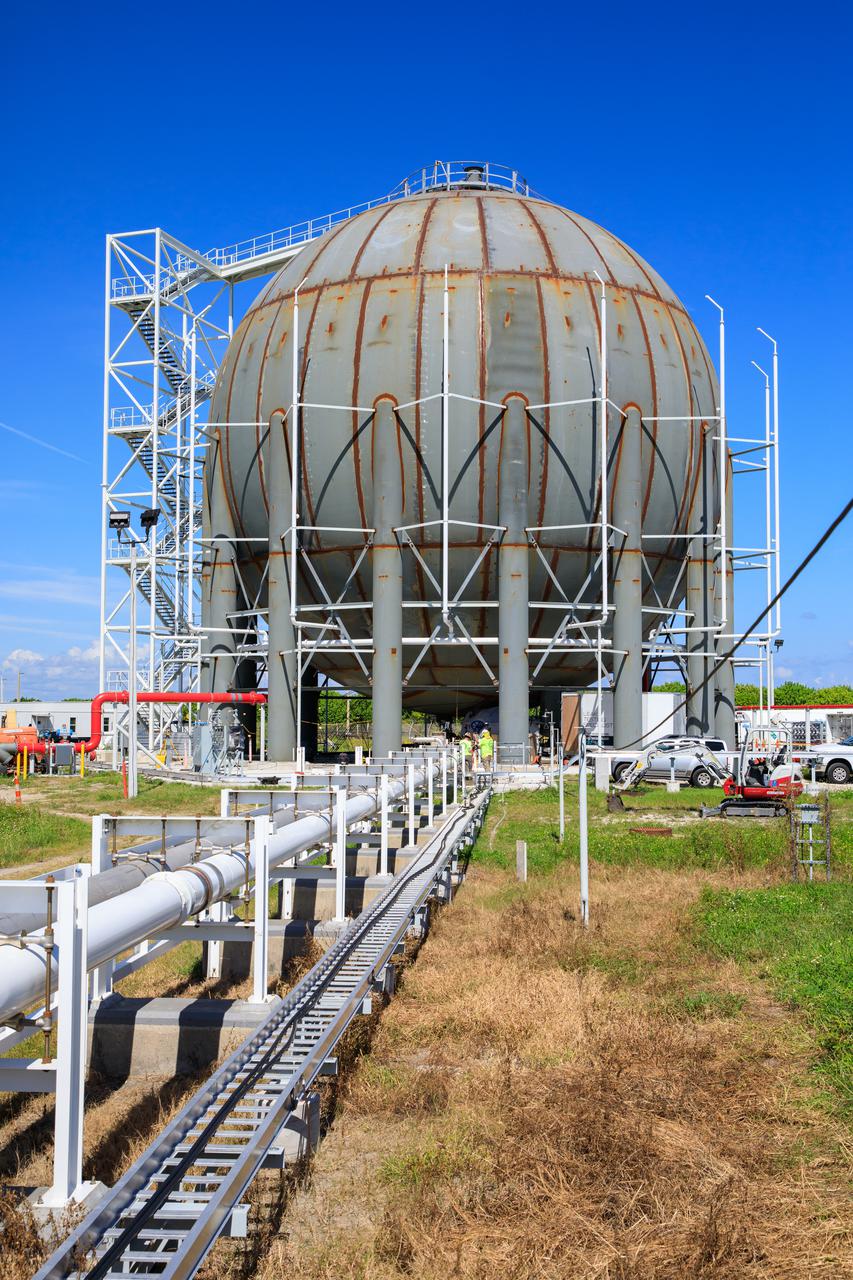

Seen here is a newly constructed liquid hydrogen (LH2) storage tank at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 1, 2021. With construction now complete, teams will focus on painting the tank next. The storage tank, capable of holding 1.25 million gallons of LH2, will be used to support future Artemis missions to the Moon and, eventually, Mars. Through Artemis, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, paving the way for a long-term presence in lunar orbit.

Seen here is a newly constructed liquid hydrogen (LH2) storage tank at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 1, 2021. With construction now complete, teams will focus on painting the tank next. The storage tank, capable of holding 1.25 million gallons of LH2, will be used to support future Artemis missions to the Moon and, eventually, Mars. Through Artemis, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, paving the way for a long-term presence in lunar orbit.
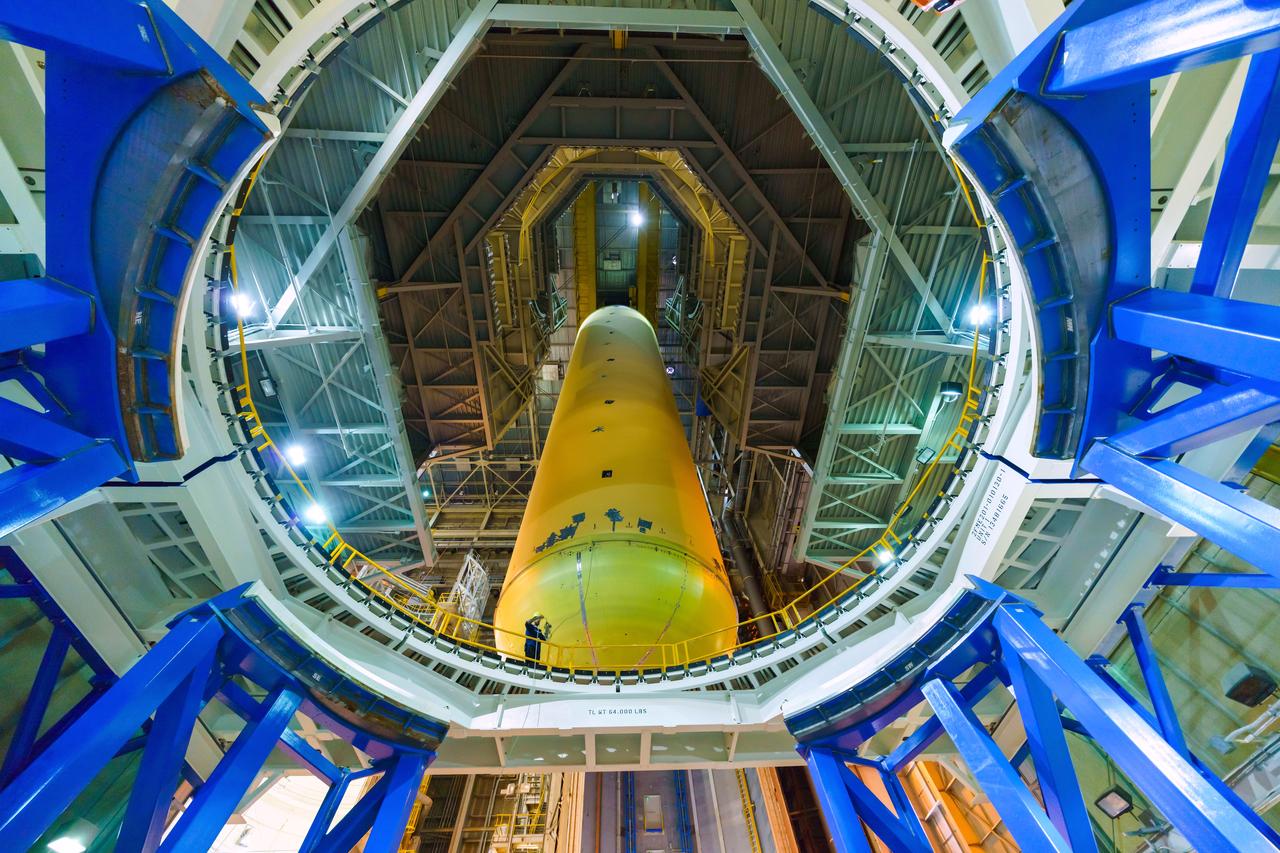

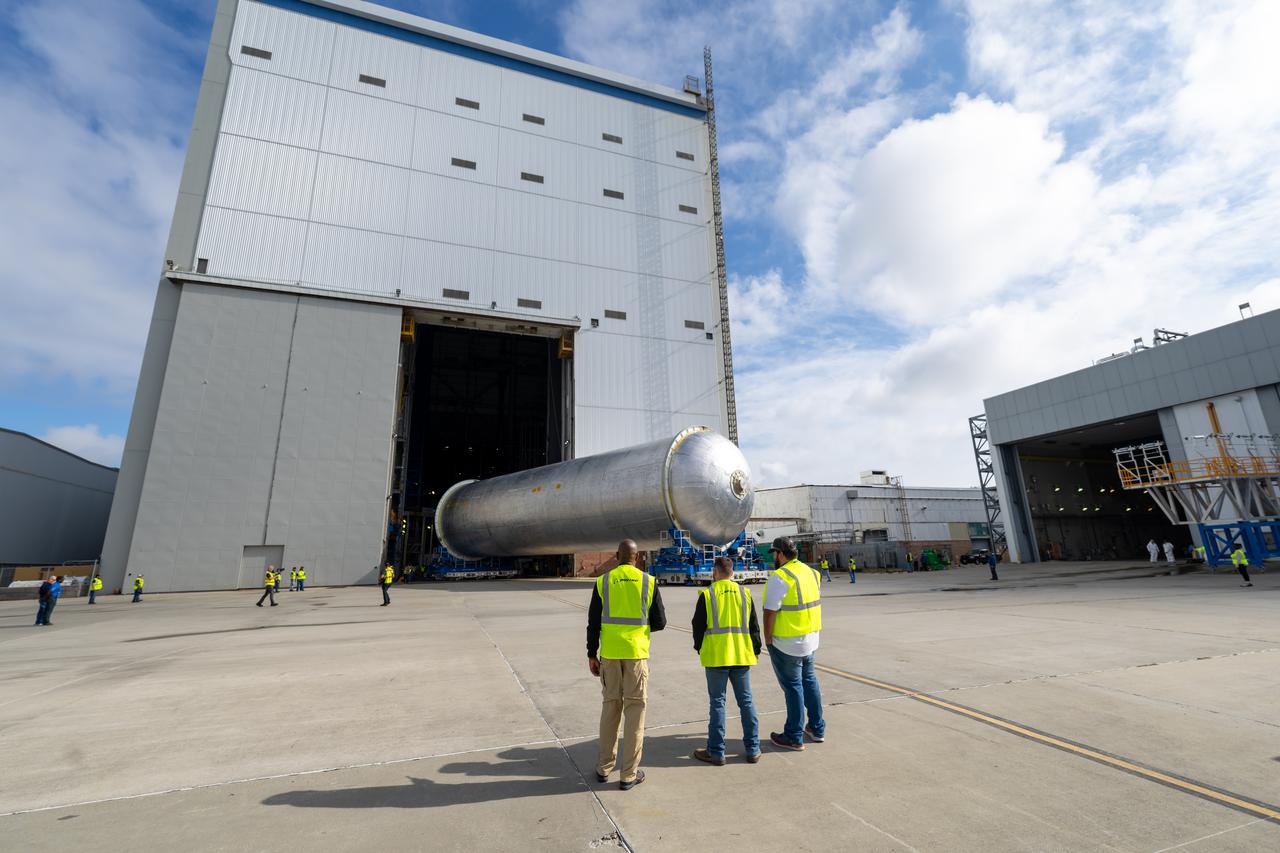
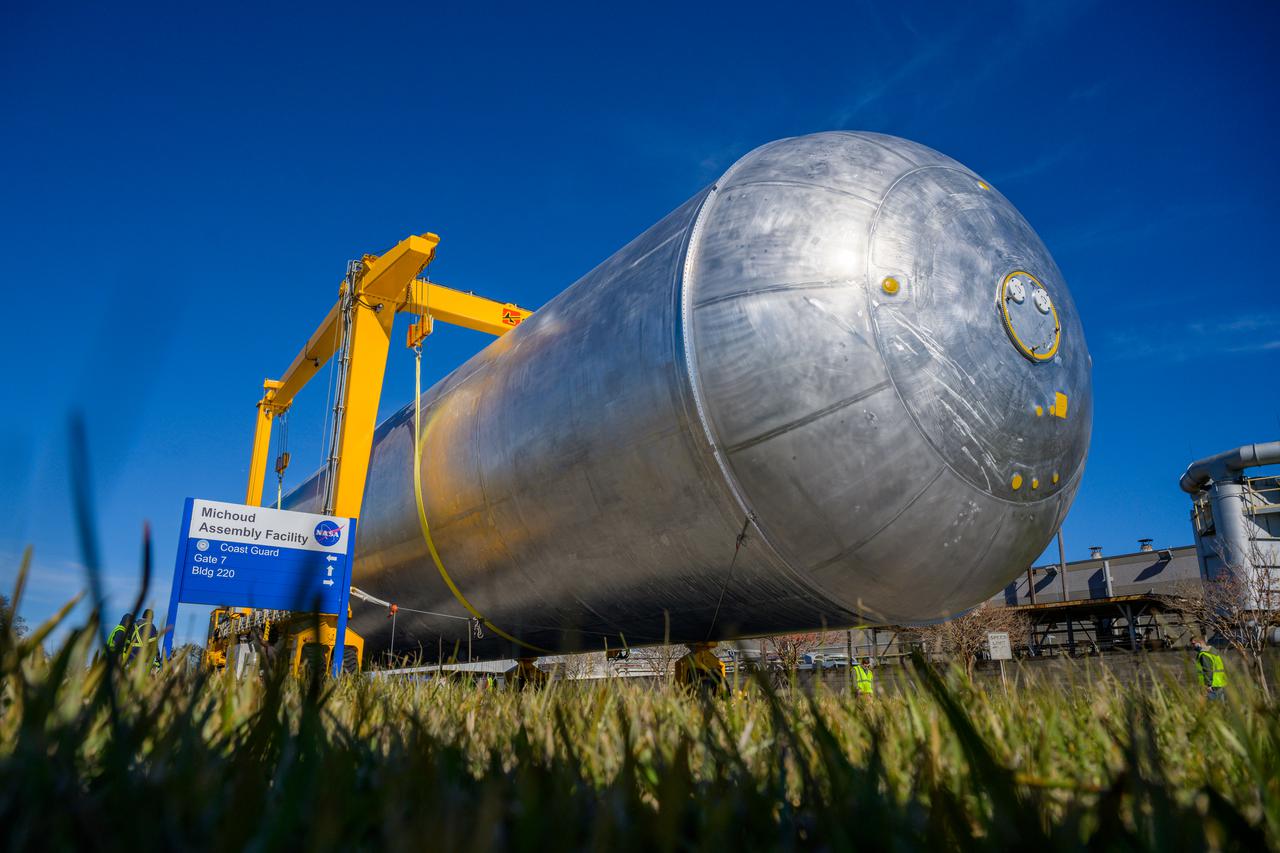
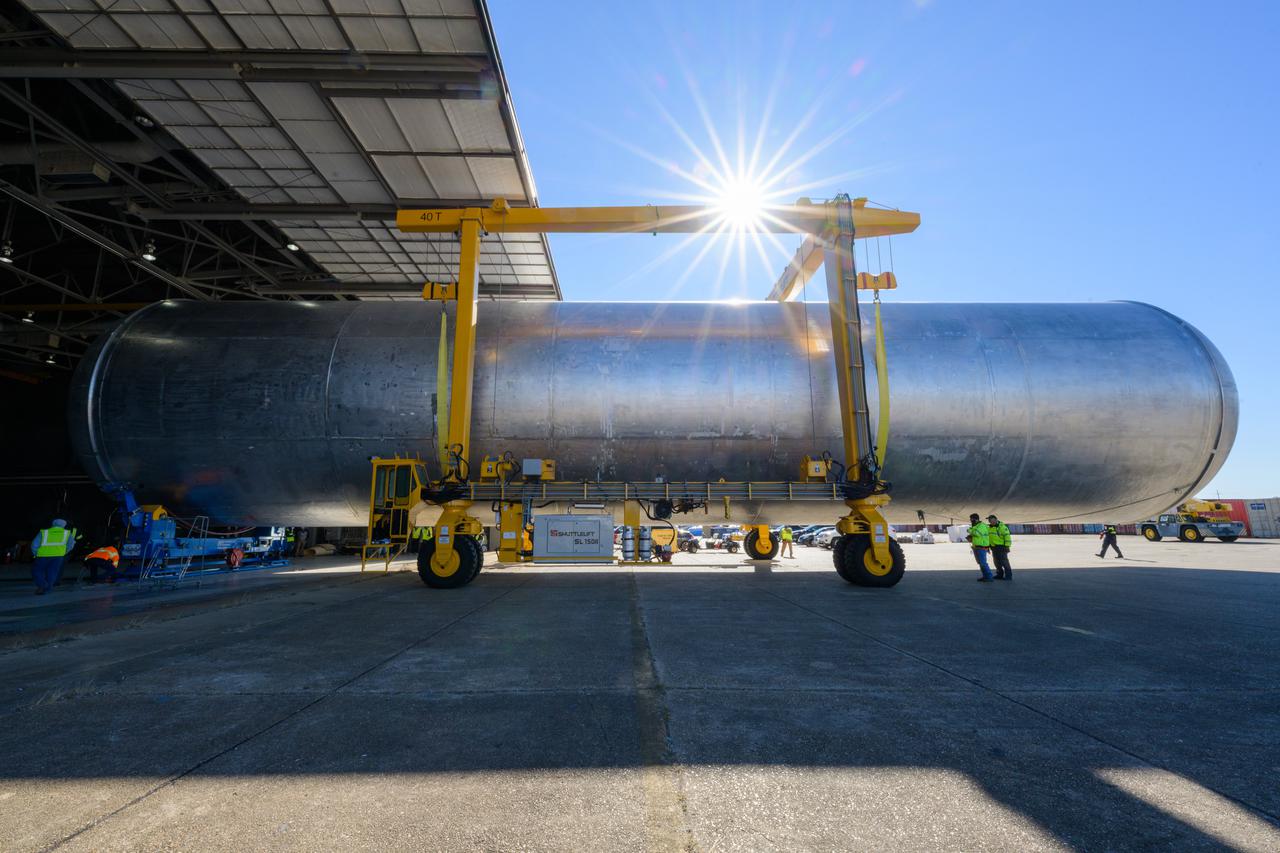
New Orleans, LA - NASA's Space Launch System Liquid Hydrogen(LH2) Stactic Test Article(STA) is lifted into Cell A at the Michoud Assembly Facillty. The tank will be brought to Marshall Space Flight Center for testing.

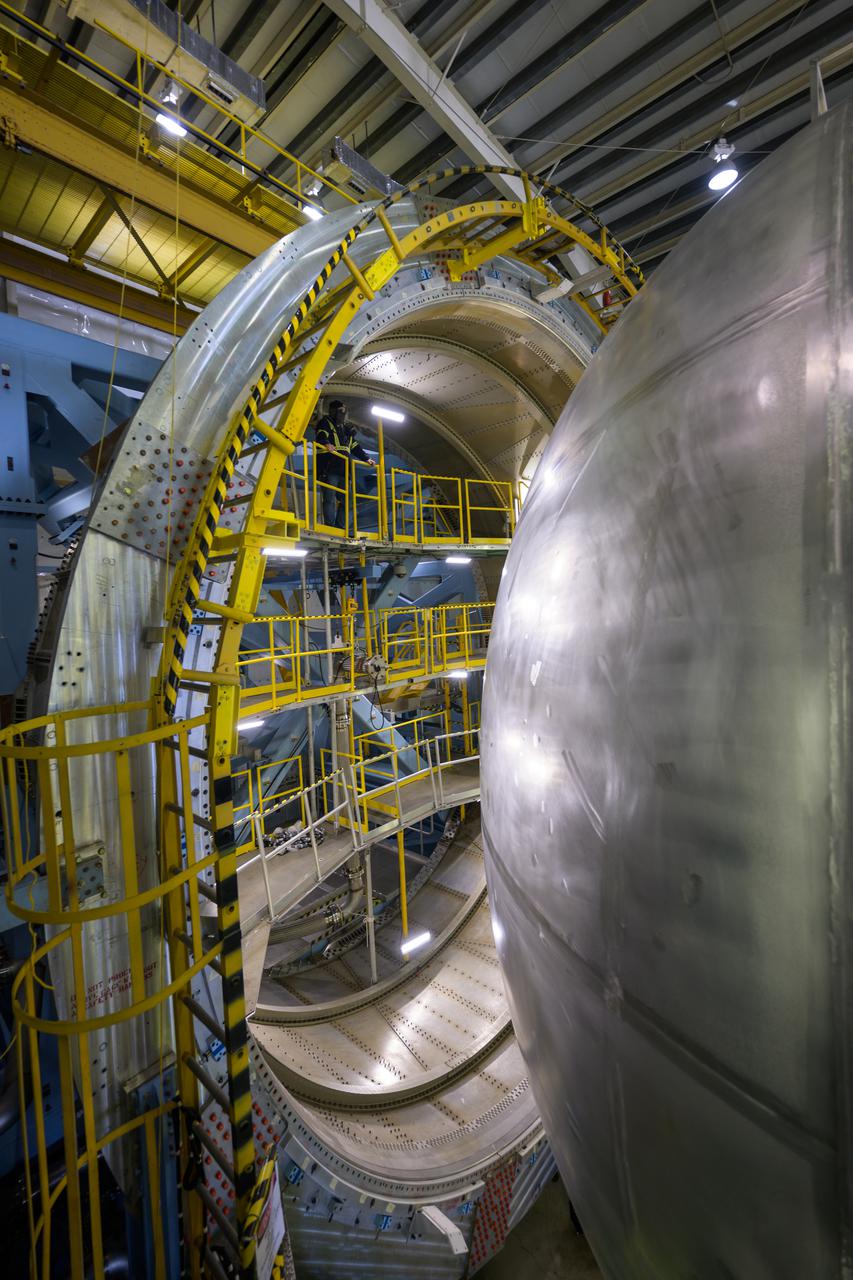
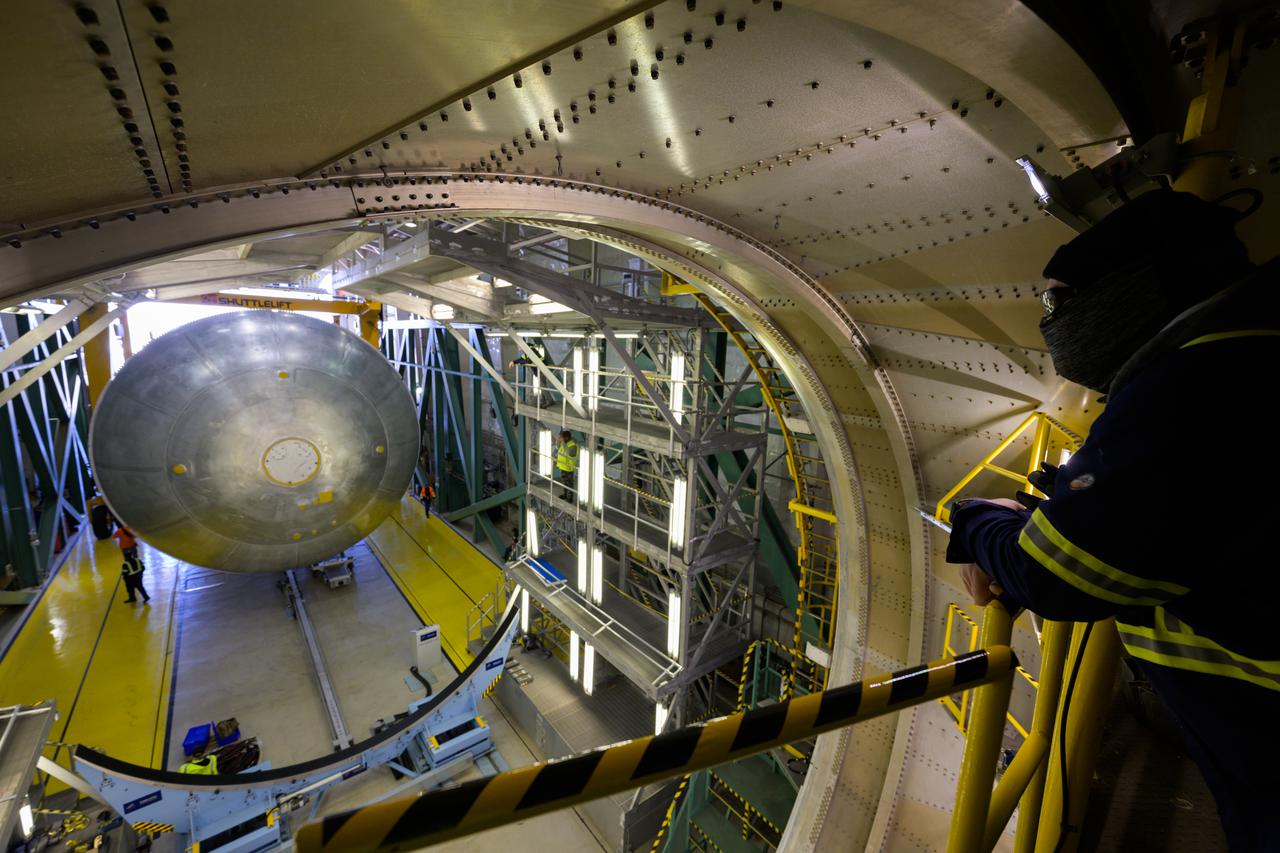
LH2 STA in NASA Marshall Space Flight Center West Test Area Test Stand.

LH2 STA in NASA Marshall Space Flight Center West Test Area Test Stand.

LH2 STA in NASA Marshall Space Flight Center West Test Area Test Stand.

LH2 STA in NASA Marshall Space Flight Center West Test Area Test Stand.

LH2 STA in NASA Marshall Space Flight Center West Test Area Test Stand.

LH2 STA in NASA Marshall Space Flight Center West Test Area Test Stand.
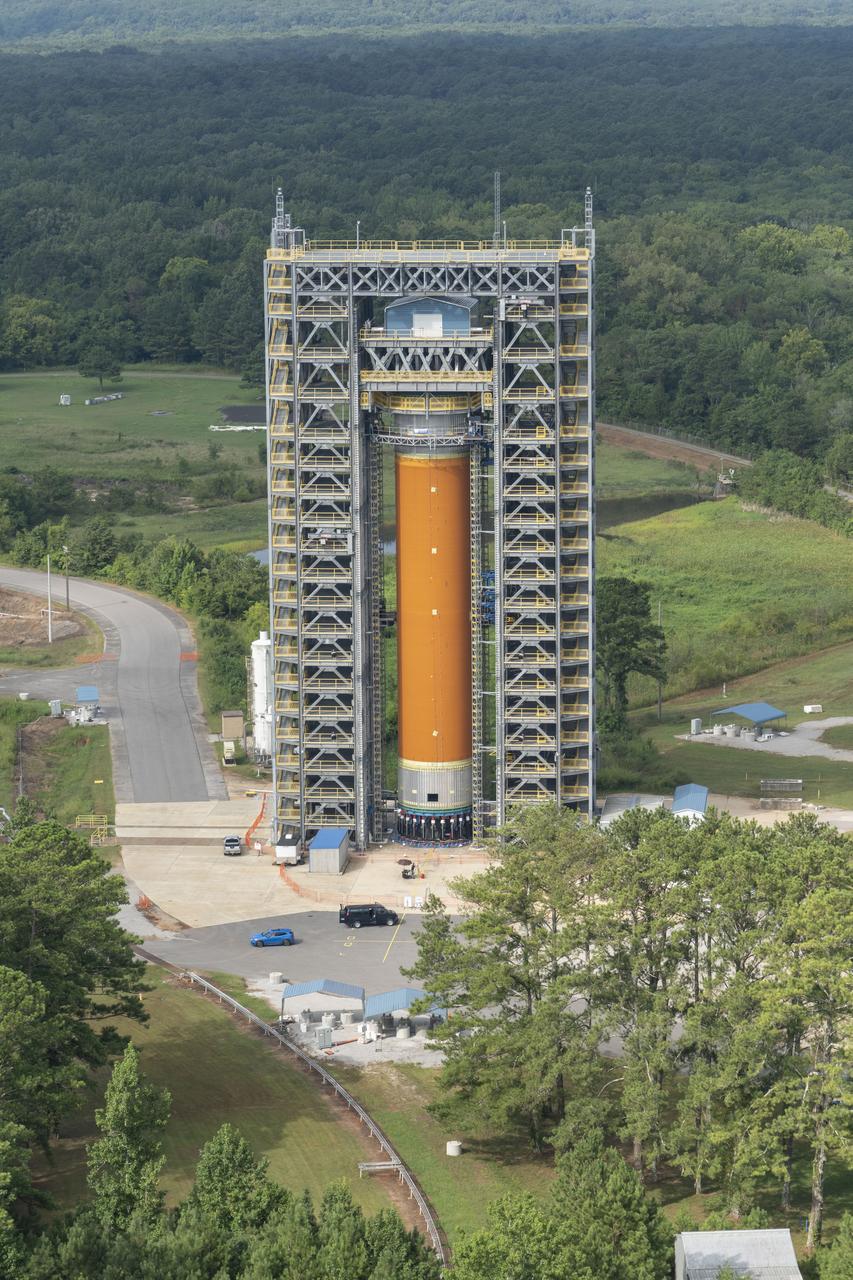

Aerial photograph of MSFC test stand 4693 with the Liquid Hydrogen test article (LH2) in the stand

Aerial photograph of MSFC test stand 4693 with the Liquid Hydrogen test article (LH2) in the stand
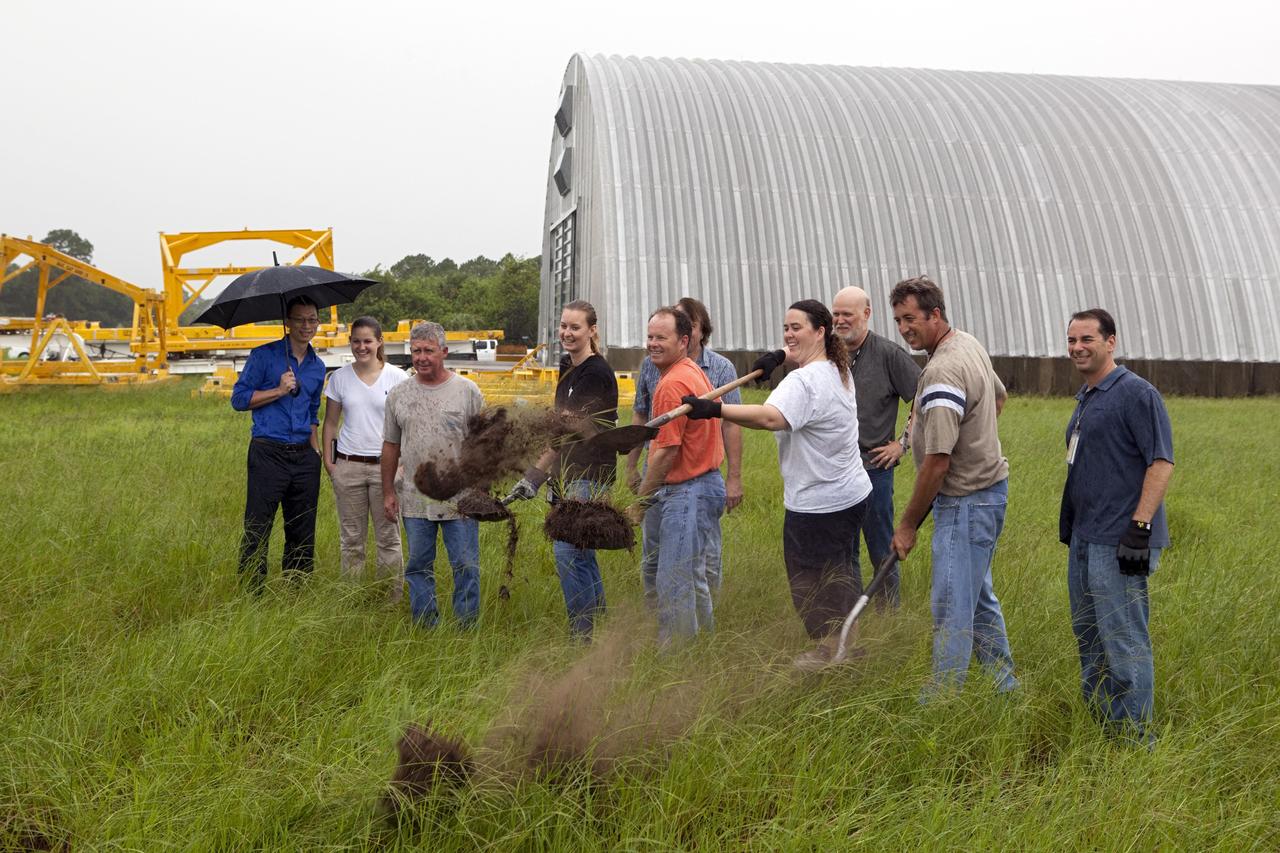

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Hypergolic Maintenance Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a groundbreaking ceremony was held to mark the location of the Ground Operations Demonstration Unit Liquid Hydrogen, or GODU LH2, test site. From left, are Johnny Nguyen, Fluids Test and Technology Development branch chief Emily Watkins, engineering intern Jeff Walls, Engineering Services Contract, or ESC, Cryogenics Test Lab engineer Kelly Currin, systems engineer Stephen Huff and Rudy Werlink partially hidden, cryogenics engineers Angela Krenn, systems engineer Doug Hammond, command and control engineer in the electrical division William Notardonato, GODU LH2 project manager and Kevin Jumper, ESC Cryogenics Test Lab manager. The GODU LH2 test site is one of the projects in NASA’s Advanced Exploration Systems Program. The site will be used to demonstrate advanced liquid hydrogen systems that are cost and energy efficient ways to store and transfer liquid hydrogen during process, loading, launch and spaceflight. The main components of the site will be a storage tank and a cryogenic refrigerator. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
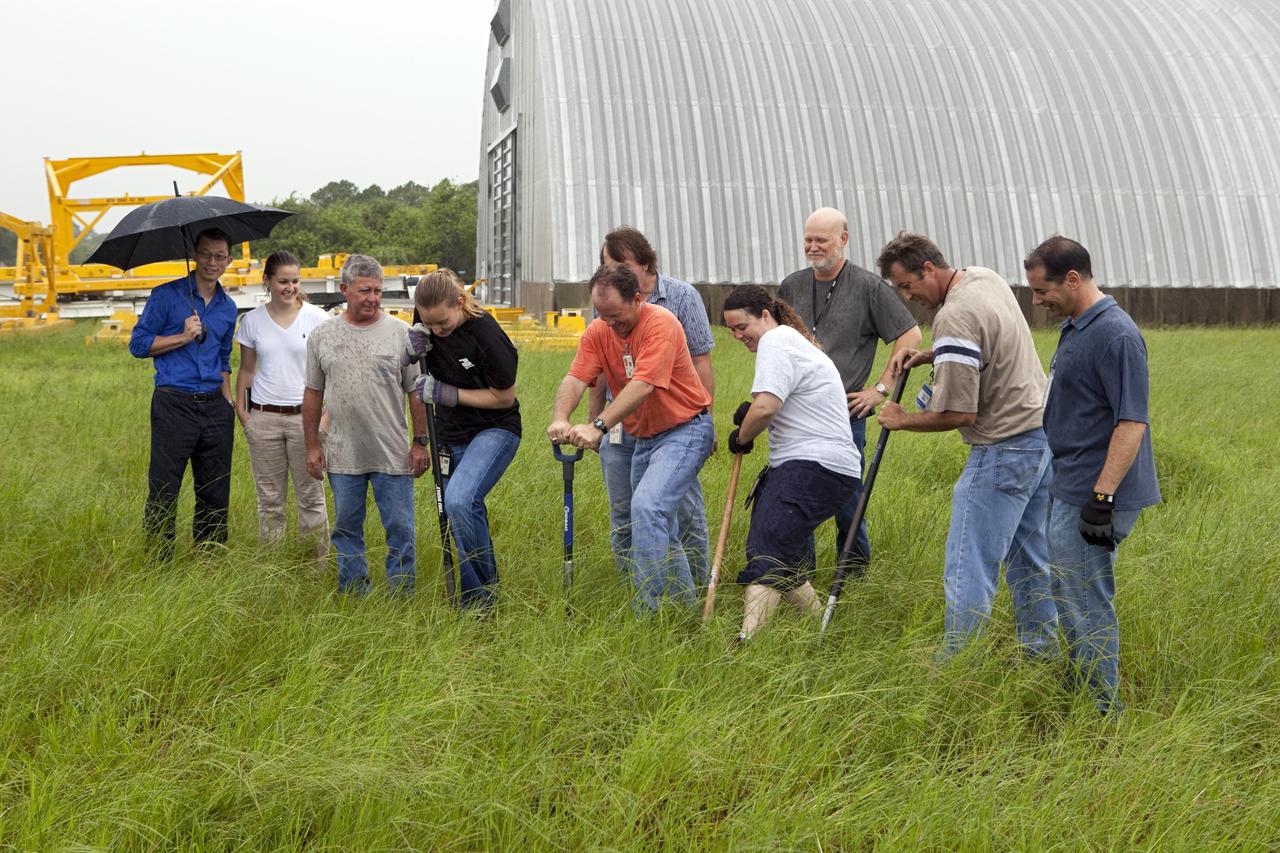

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Hypergolic Maintenance Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a groundbreaking ceremony was held to mark the location of the Ground Operations Demonstration Unit Liquid Hydrogen, or GODU LH2, test site. From left, are Johnny Nguyen, Fluids Test and Technology Development branch chief Emily Watkins, engineering intern Jeff Walls, Engineering Services Contract, or ESC, Cryogenics Test Lab engineer Kelly Currin, systems engineer Stephen Huff and Rudy Werlink partially hidden, cryogenics engineers Angela Krenn, systems engineer Doug Hammond, command and control engineer in the electrical division William Notardonato, GODU LH2 project manager and Kevin Jumper, ESC Cryogenics Test Lab manager. The GODU LH2 test site is one of the projects in NASA’s Advanced Exploration Systems Program. The site will be used to demonstrate advanced liquid hydrogen systems that are cost and energy efficient ways to store and transfer liquid hydrogen during process, loading, launch and spaceflight. The main components of the site will be a storage tank and a cryogenic refrigerator. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
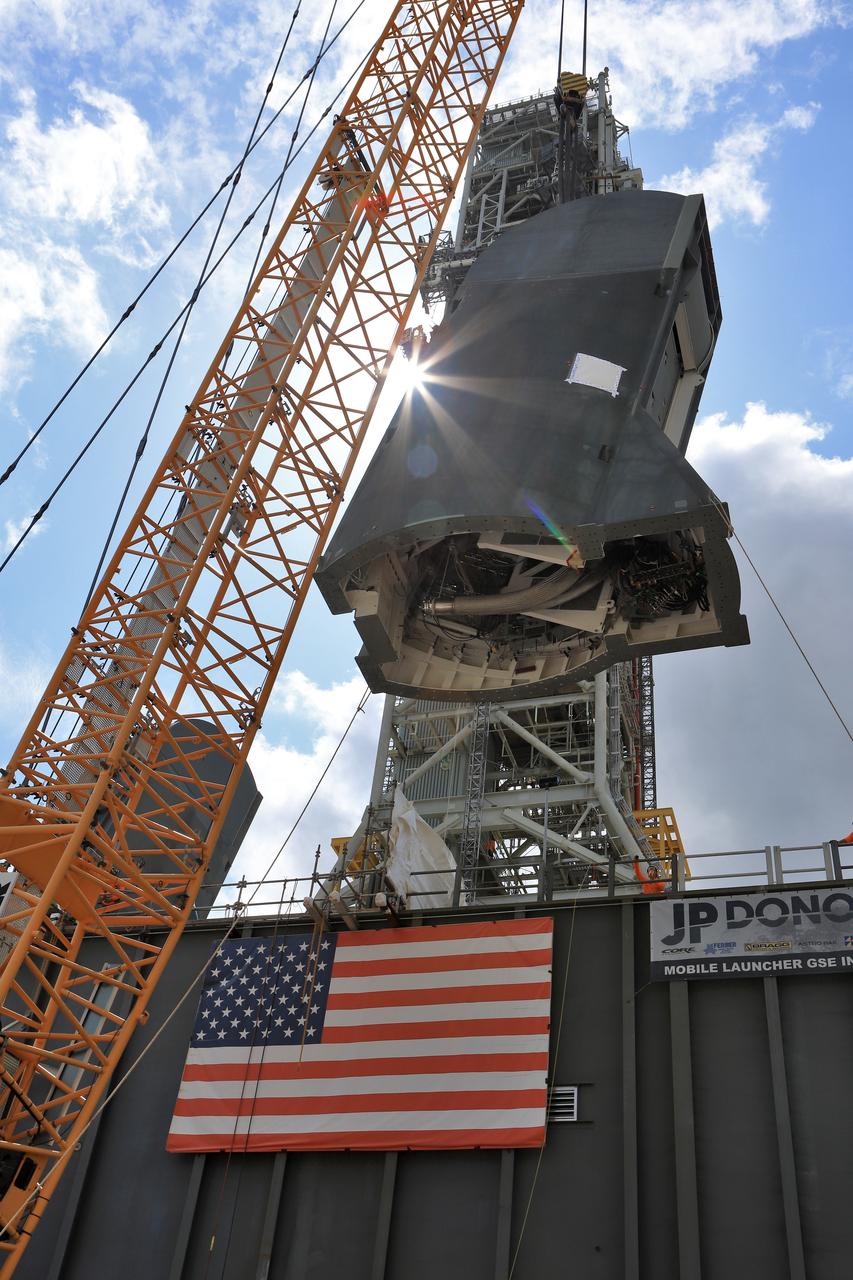

The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lifted by crane for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.

The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU), at left, is lowered for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. In view at right is the TSMU that will provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
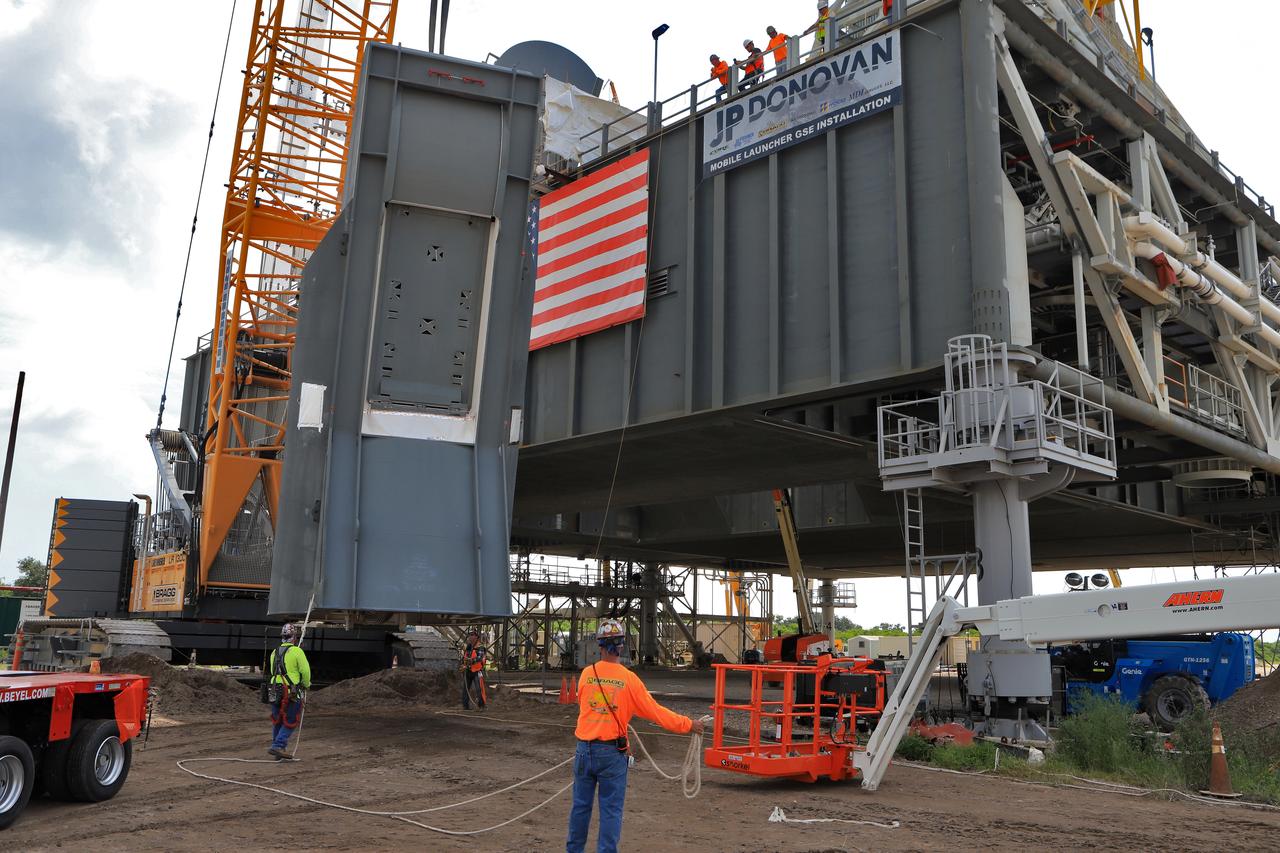

Construction workers with JP Donovan assist as a crane lifts the second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals up for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
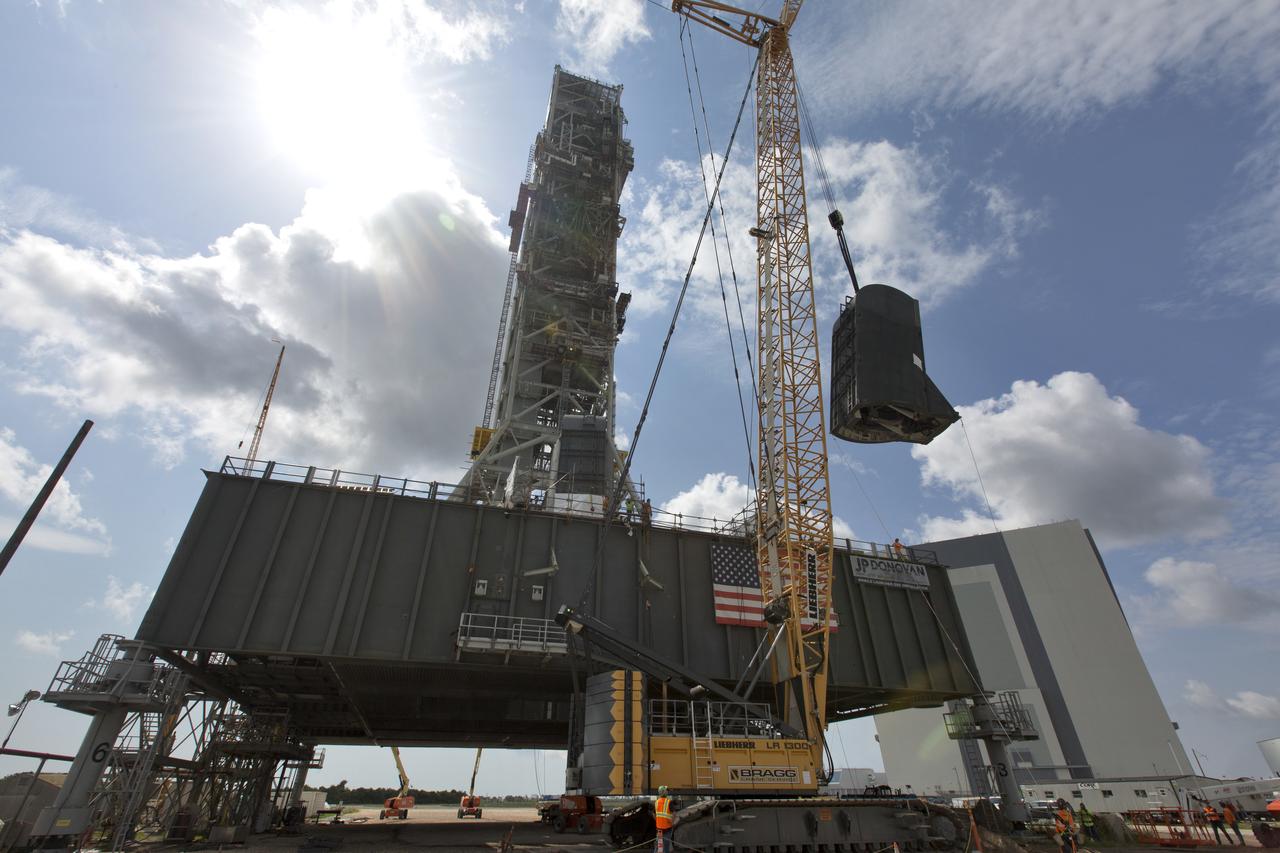

The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lifted by crane for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
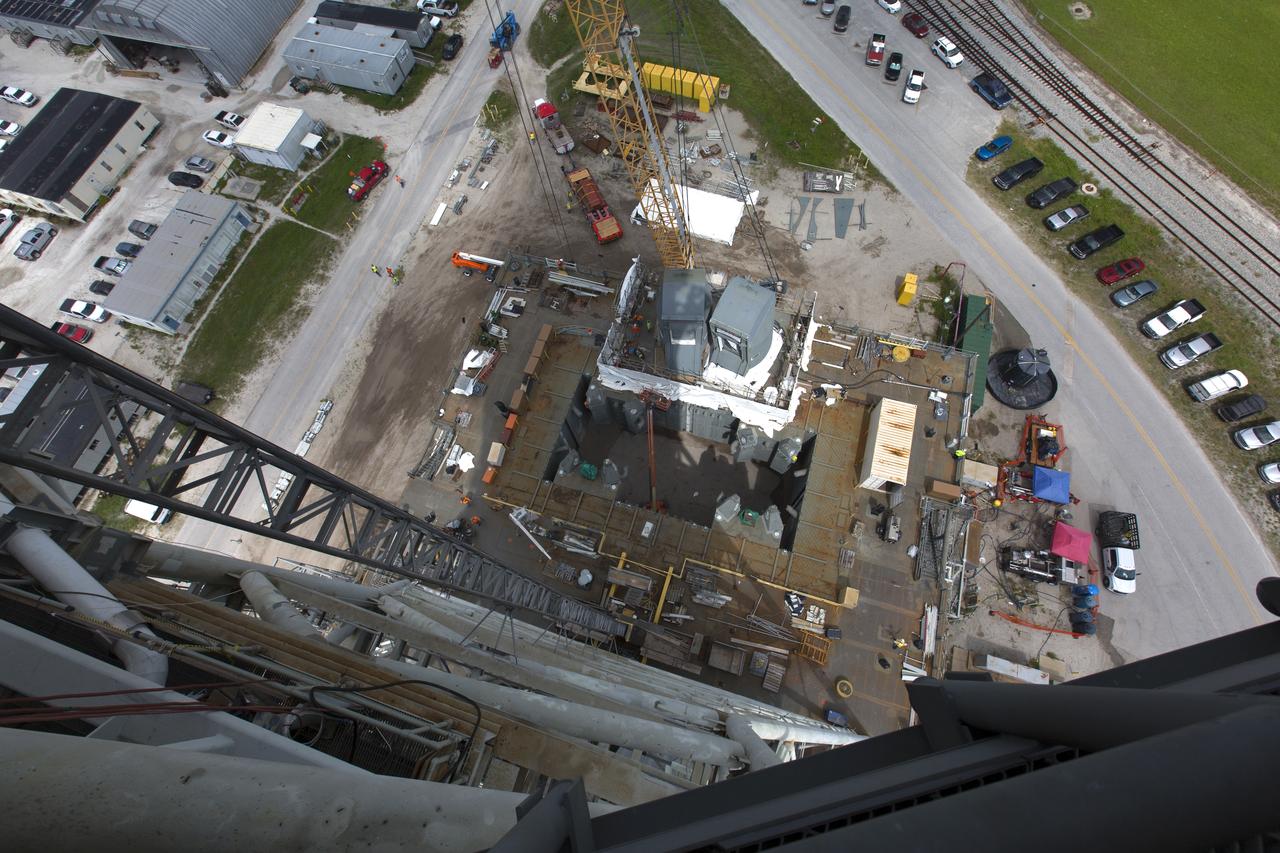

In this view from high above on the mobile launcher tower, a crane is used to lower the second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU) for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. In view at right is the TSMU that will provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
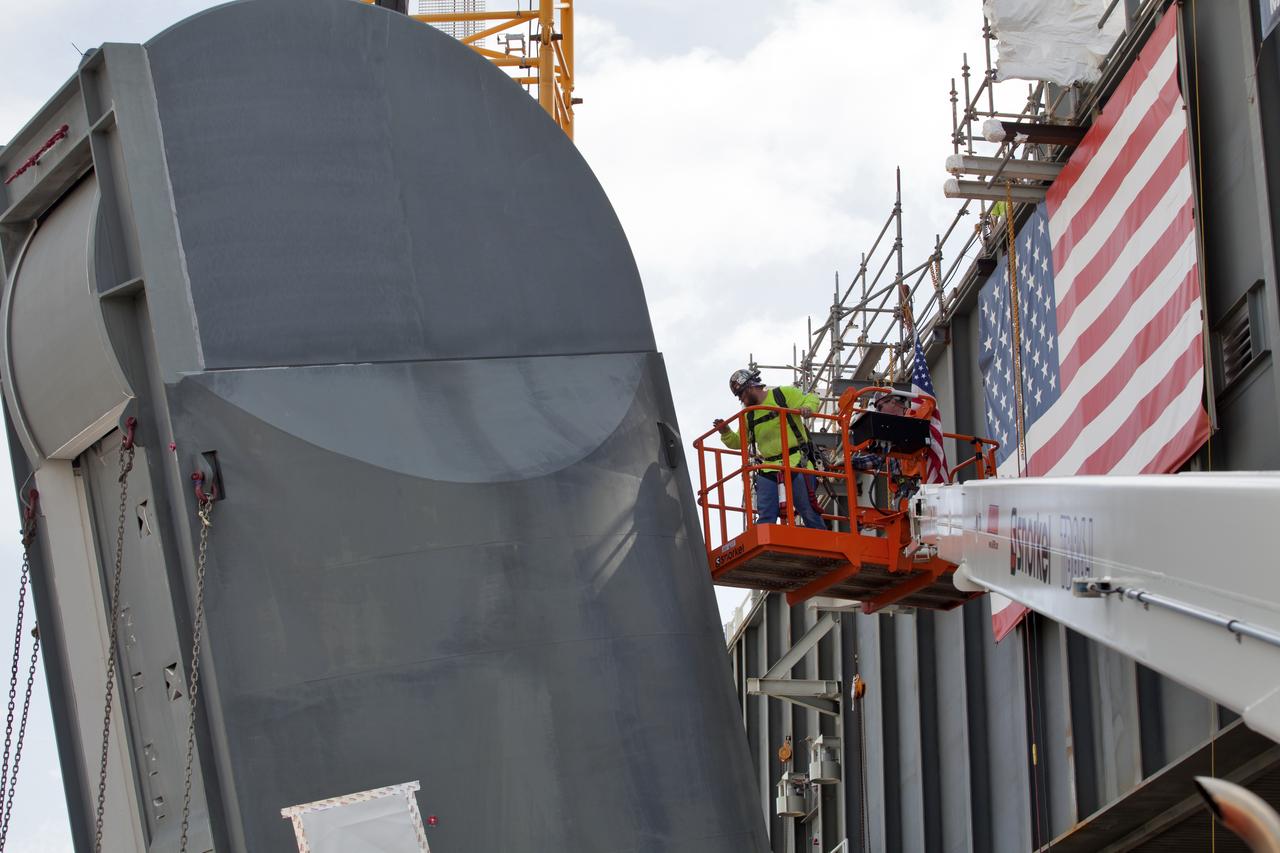

Preparations are underway to install the second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
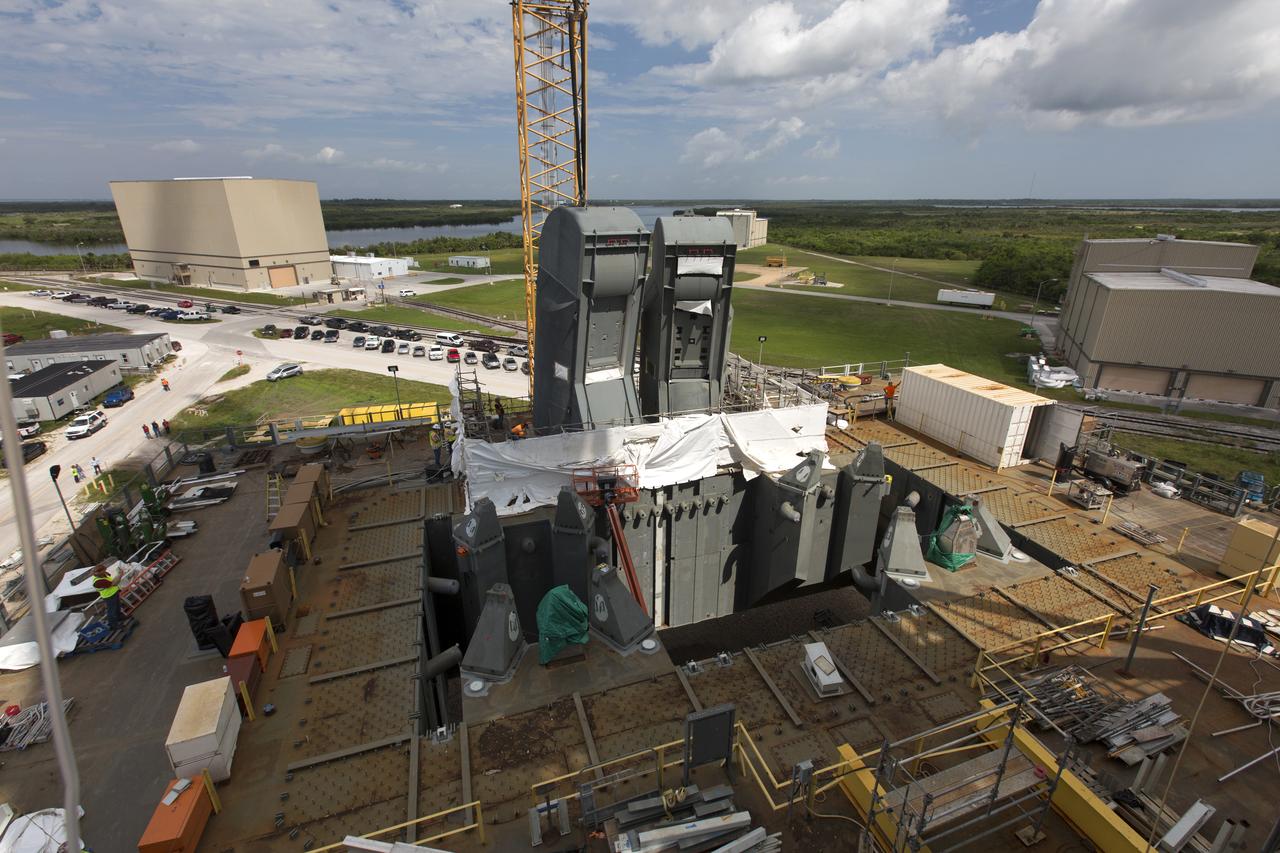

The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU), at left, is lowered for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. In view at right is the TSMU that will provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
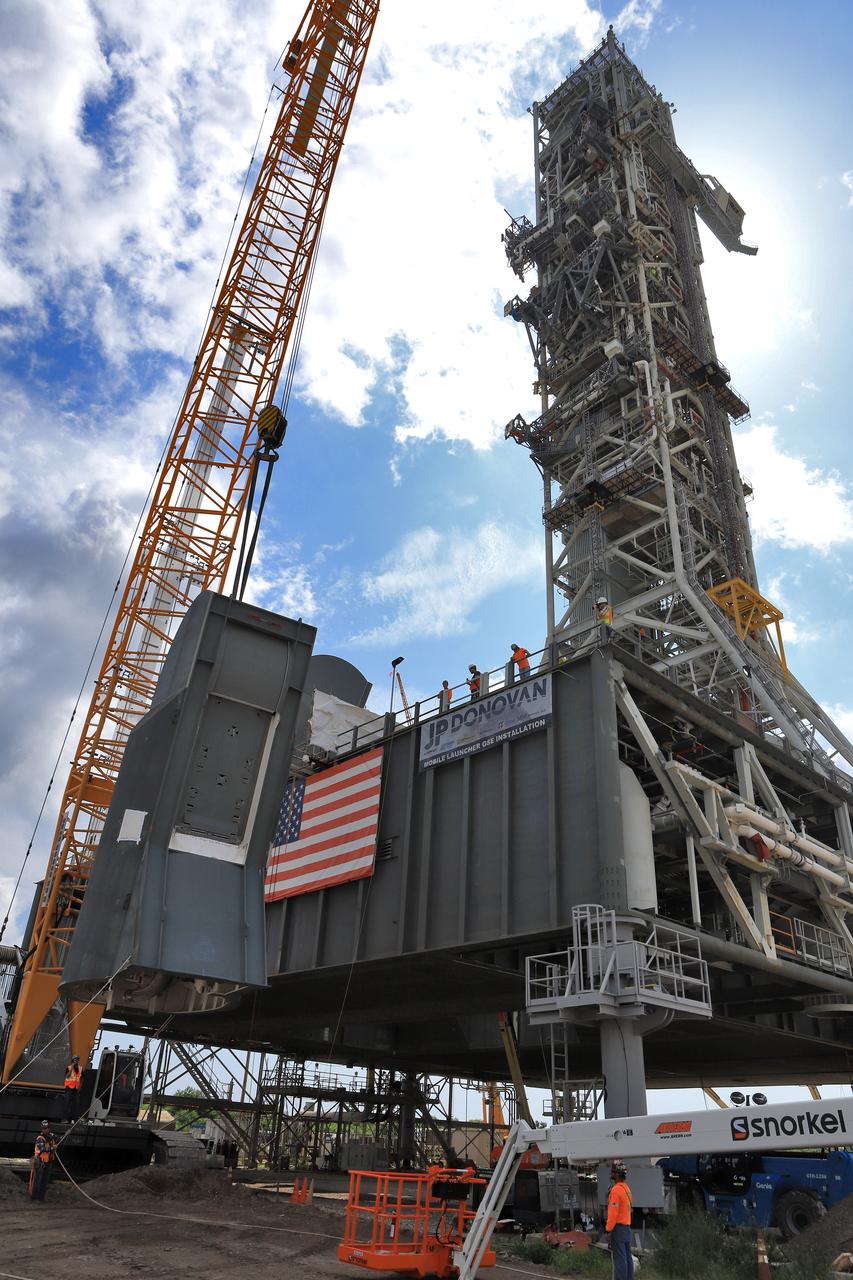

The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lifted by crane for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
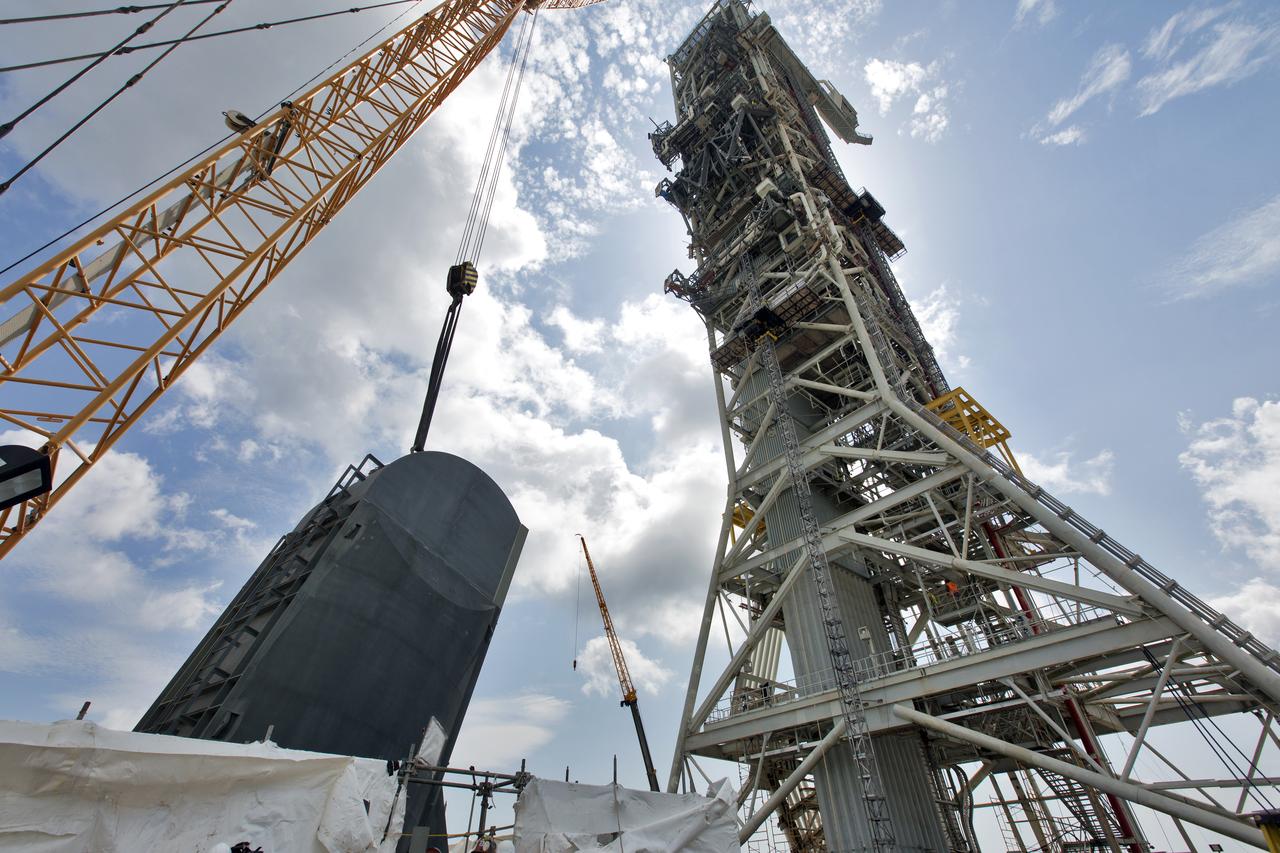

The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lowered by crane for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
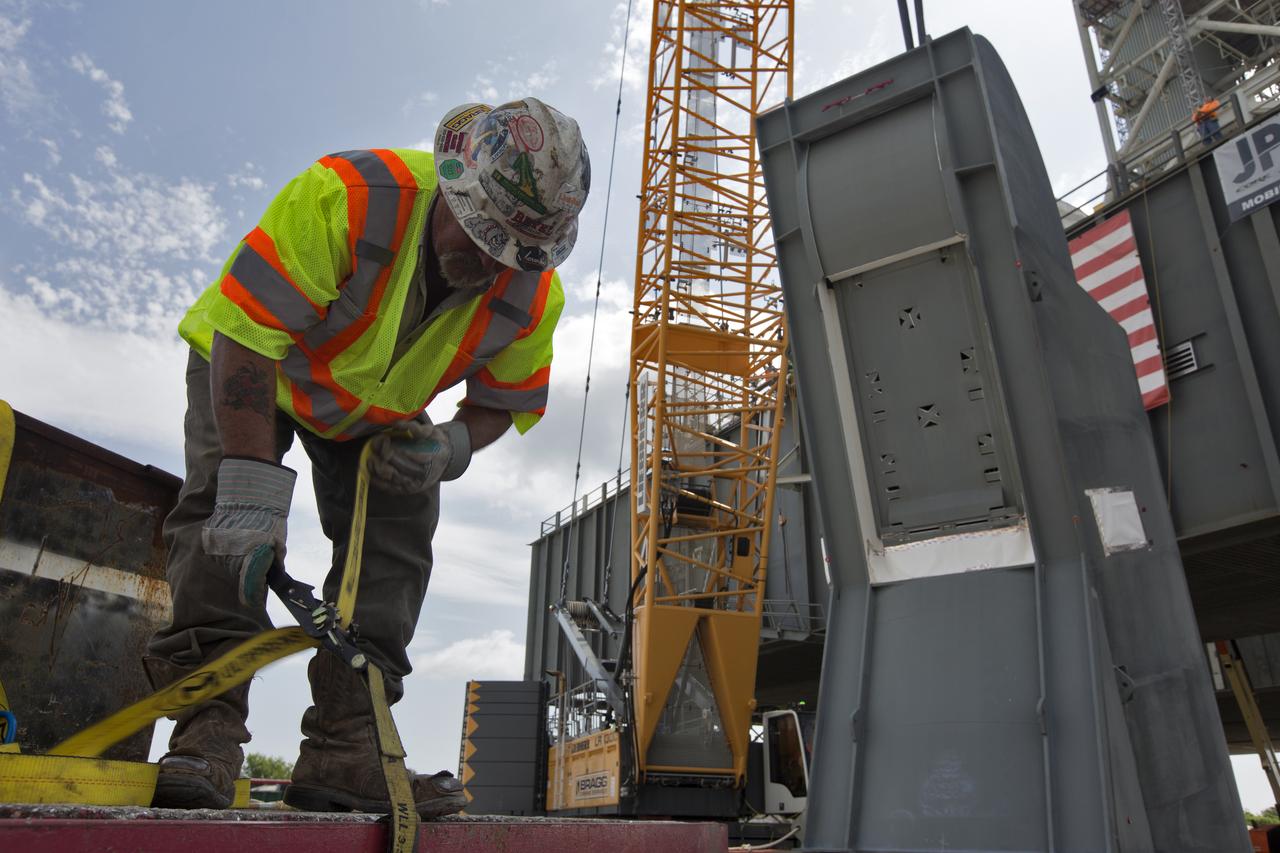

A JP Donovan construction worker makes preparations for lifting of the second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
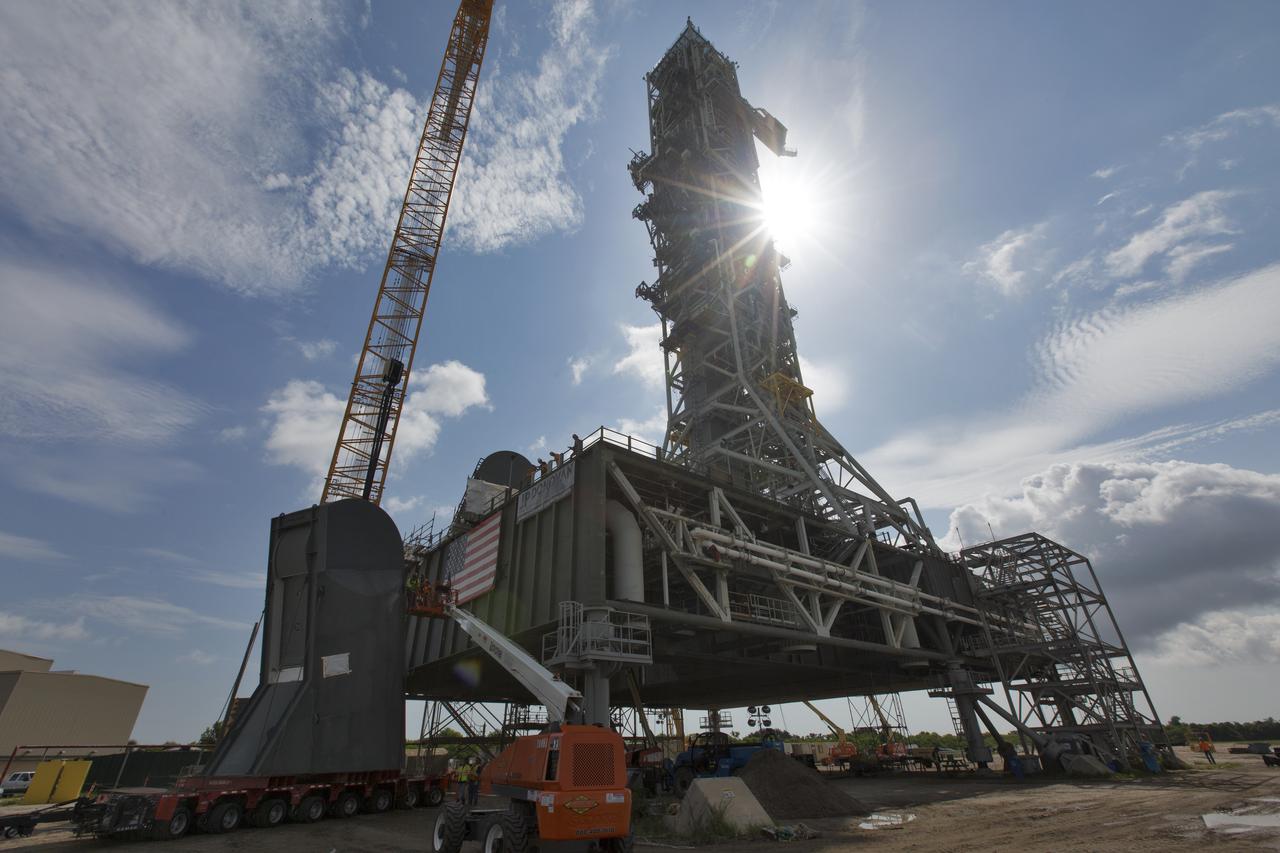

Preparations are underway to install the second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
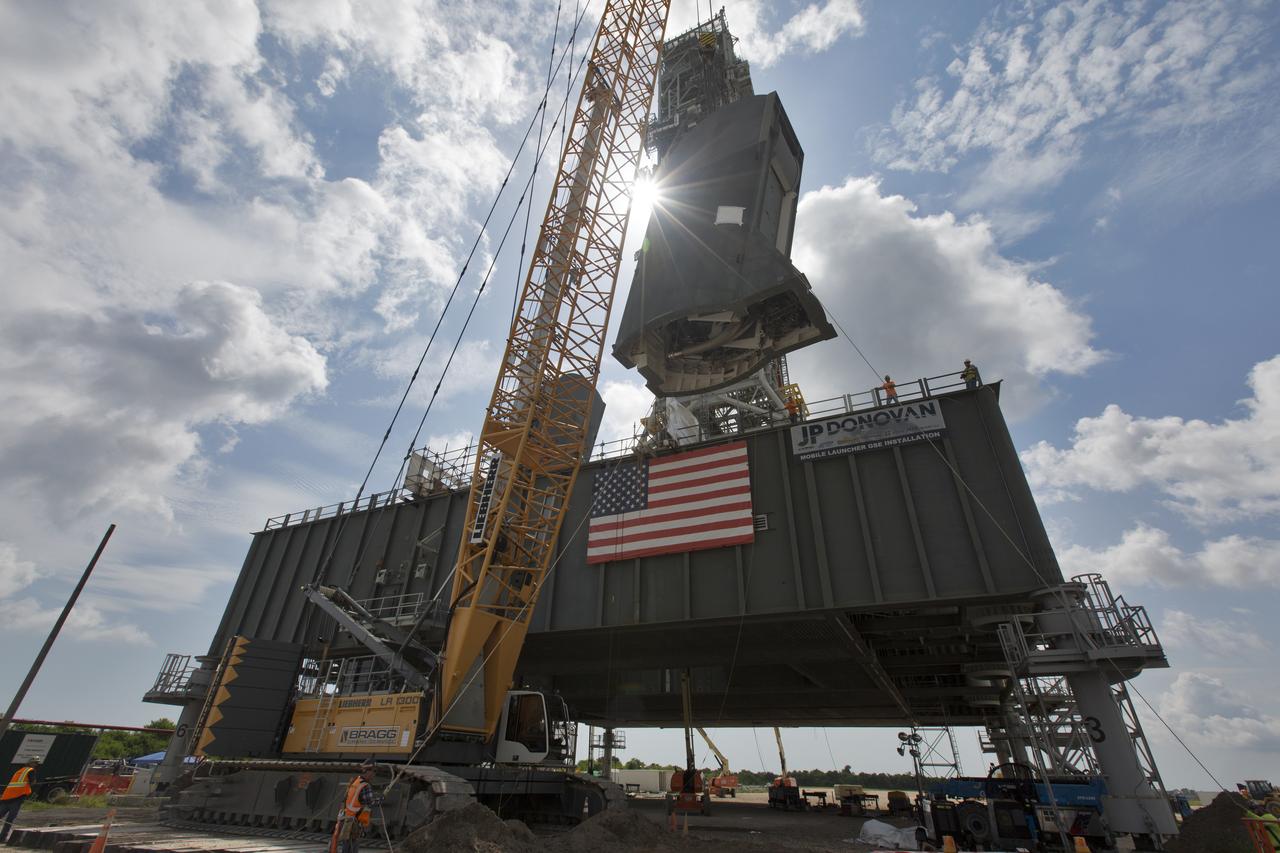

The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals is lifted by crane for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.

Shown is the disassembly, examination, refurbishment and testing of the LH2 ( liquid hydrogen) and LOX (liquid oxygen) vent and relief valves for the S-IVB-211 engine stage in support of the Constellation/Ares project. This image is extracted from high definition video and is the highest resolution available.
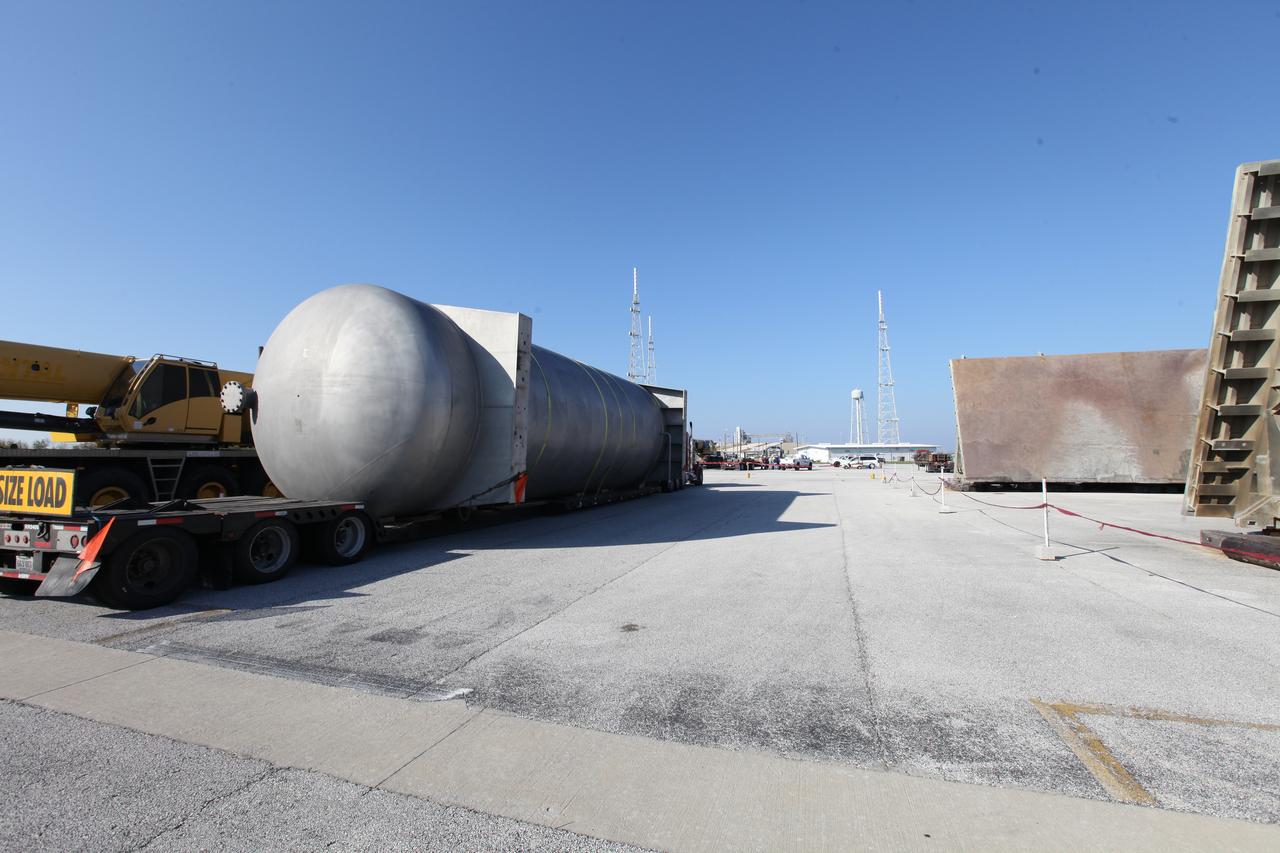

A new liquid hydrogen separator tank arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will be lifted and rotated for delivery to Launch Pad 39B. The new separator/storage tank will be added to the pad's existing hydrogen vent system to assure gaseous hydrogen is delivered downstream to the flare stack. The 60,000 gallon tank was built by INOXCVA, in Baytown, Texas, a subcontractor of Precision Mechanical Inc. in Cocoa Florida. The new tank will support all future launches from the pad.
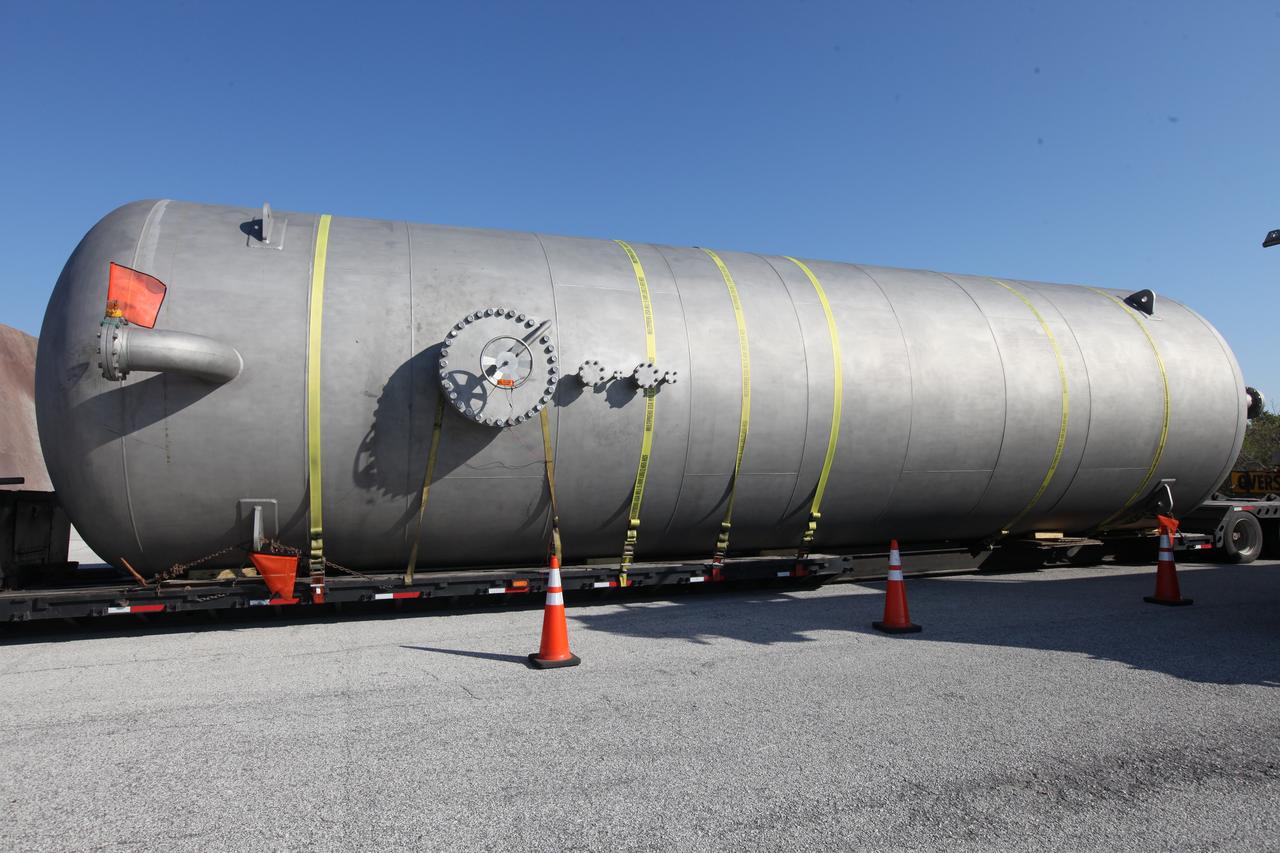

A new liquid hydrogen separator tank arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will be lifted and rotated for delivery to Launch Pad 39B. The new separator/storage tank will be added to the pad's existing hydrogen vent system to assure gaseous hydrogen is delivered downstream to the flare stack. The 60,000 gallon tank was built by INOXCVA, in Baytown, Texas, a subcontractor of Precision Mechanical Inc. in Cocoa Florida. The new tank will support all future launches from the pad.
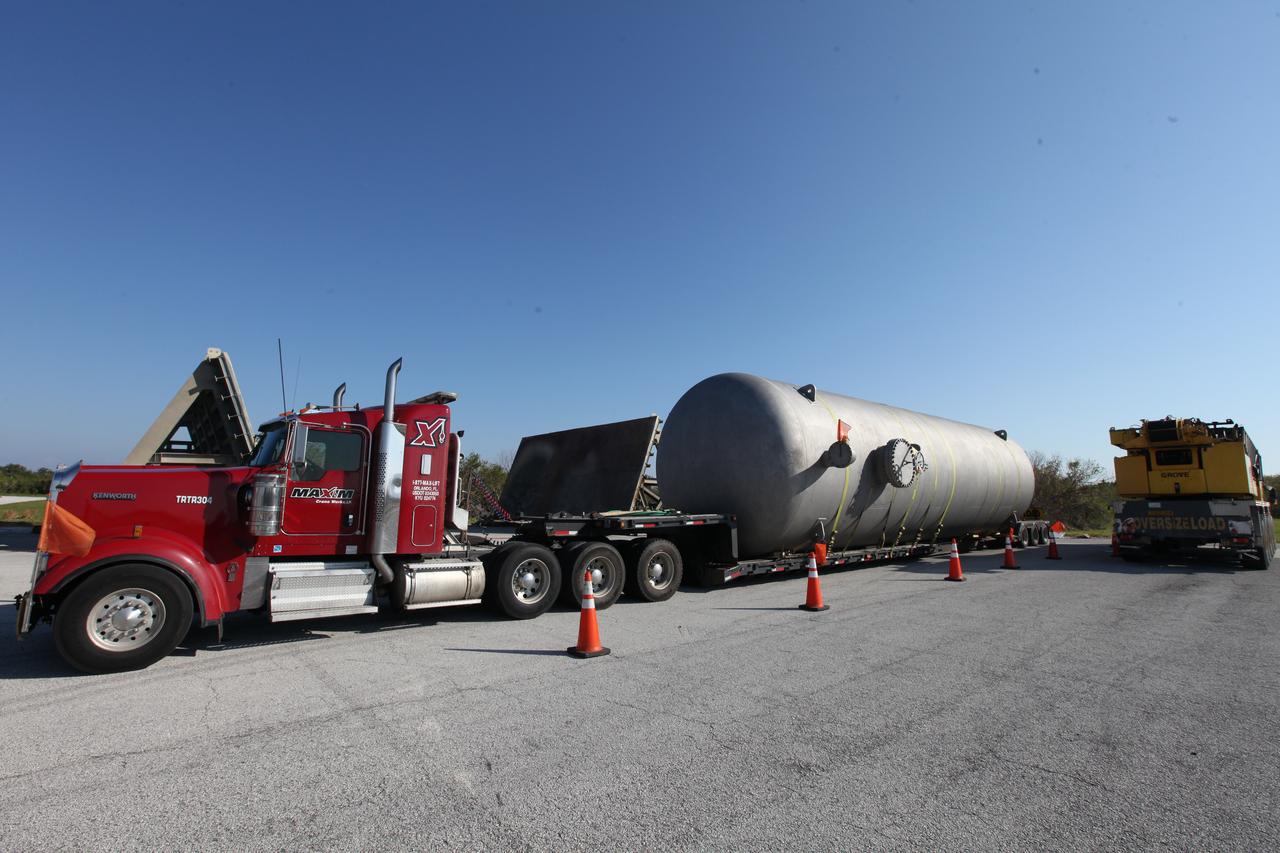

A new liquid hydrogen separator tank arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank will be lifted and rotated for delivery to Launch Pad 39B. The new separator/storage tank will be added to the pad's existing hydrogen vent system to assure gaseous hydrogen is delivered downstream to the flare stack. The 60,000 gallon tank was built by INOXCVA, in Baytown, Texas, a subcontractor of Precision Mechanical Inc. in Cocoa Florida. The new tank will support all future launches from the pad.
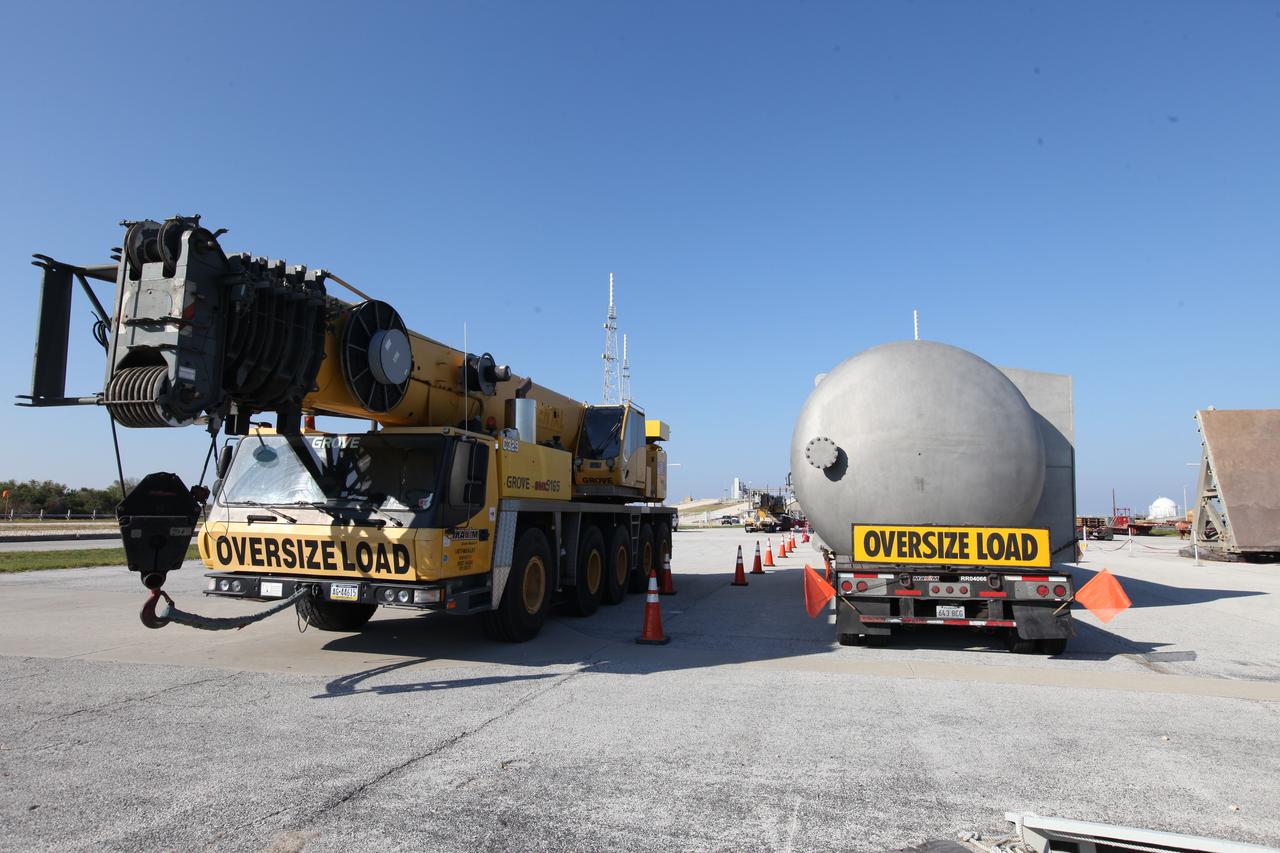

A new liquid hydrogen separator tank arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A crane will be used to lift and rotate the tank for delivery to Launch Pad 39B. The new separator/storage tank will be added to the pad's existing hydrogen vent system to assure gaseous hydrogen is delivered downstream to the flare stack. The 60,000 gallon tank was built by INOXCVA, in Baytown, Texas, a subcontractor of Precision Mechanical Inc. in Cocoa Florida. The new tank will support all future launches from the pad.
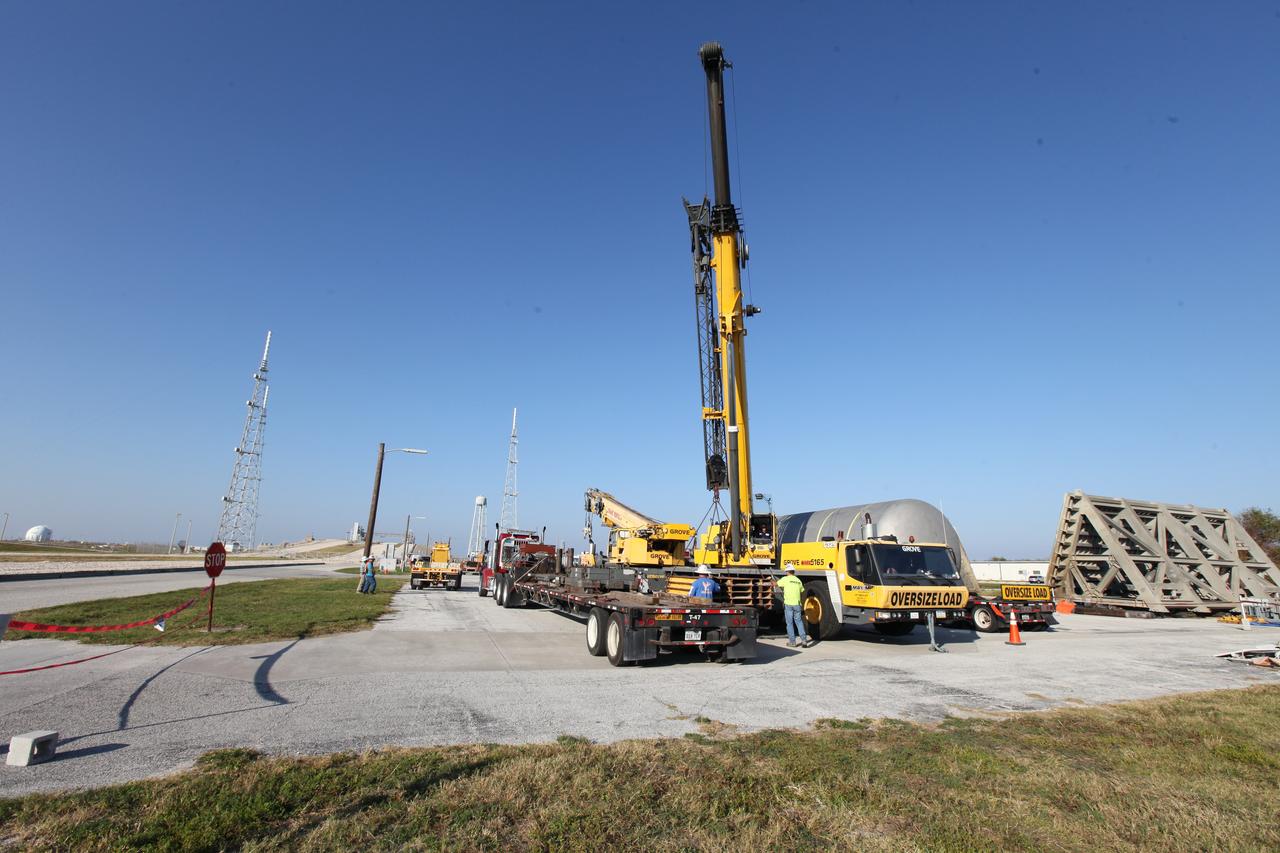

A new liquid hydrogen separator tank arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A crane will be used to lift and rotate the tank for delivery to Launch Pad 39B. The new separator/storage tank will be added to the pad's existing hydrogen vent system to assure gaseous hydrogen is delivered downstream to the flare stack. The 60,000 gallon tank was built by INOXCVA, in Baytown, Texas, a subcontractor of Precision Mechanical Inc. in Cocoa Florida. The new tank will support all future launches from the pad.
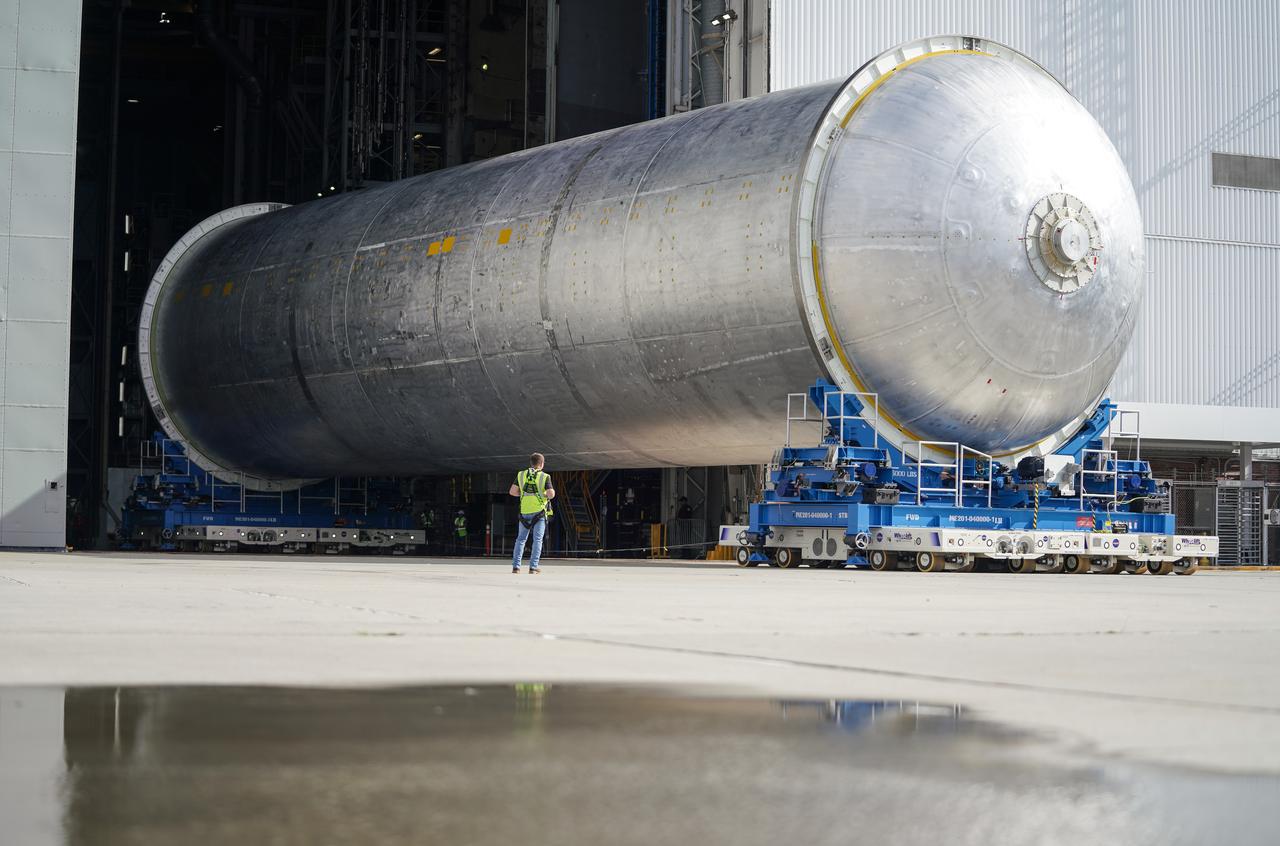

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
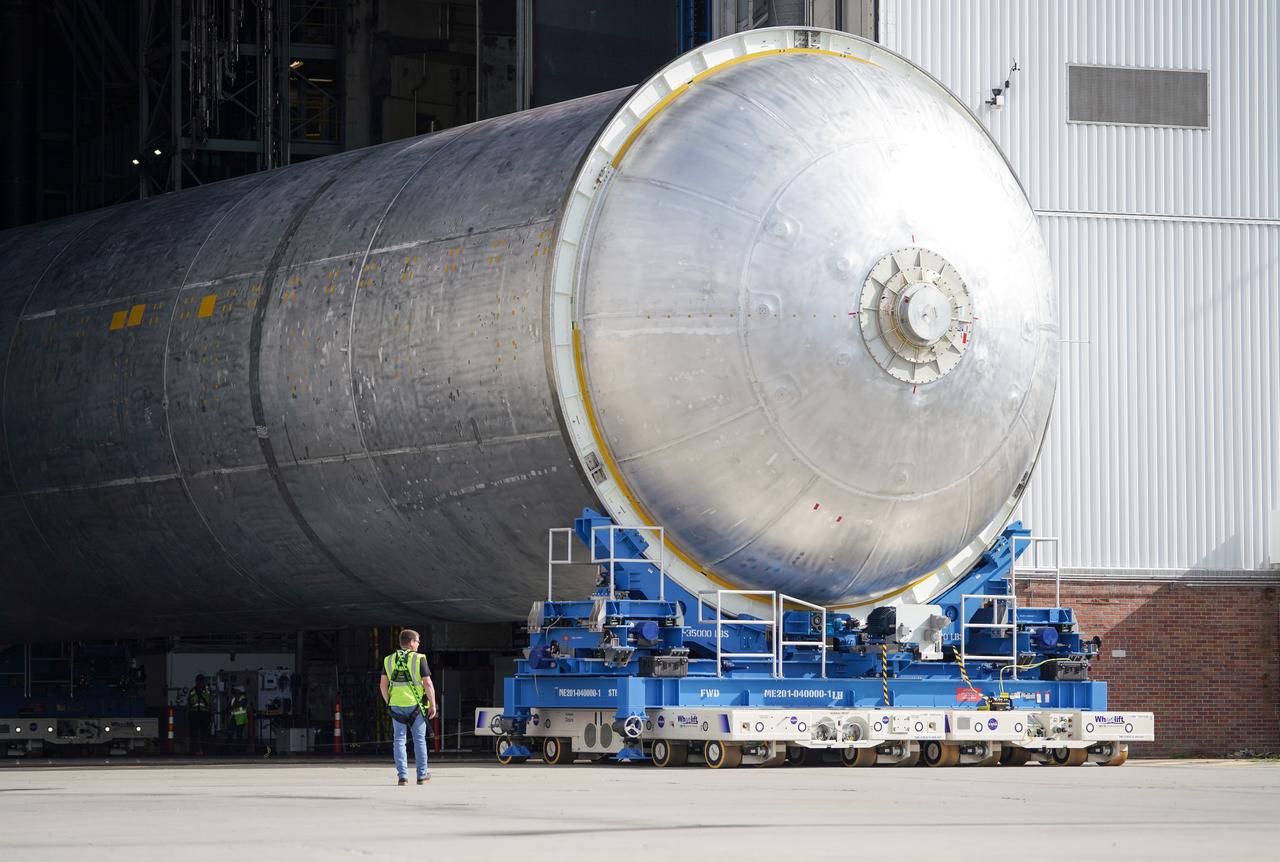

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
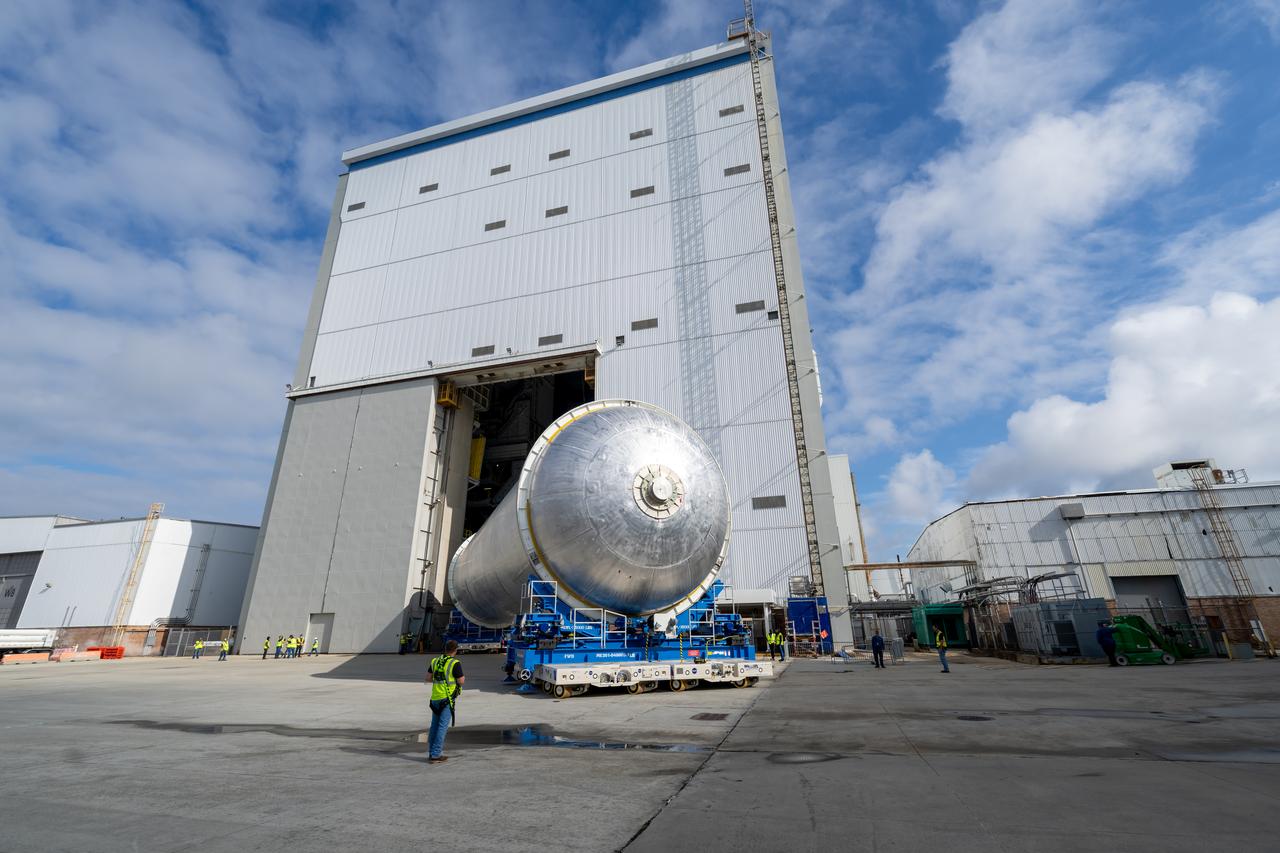

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
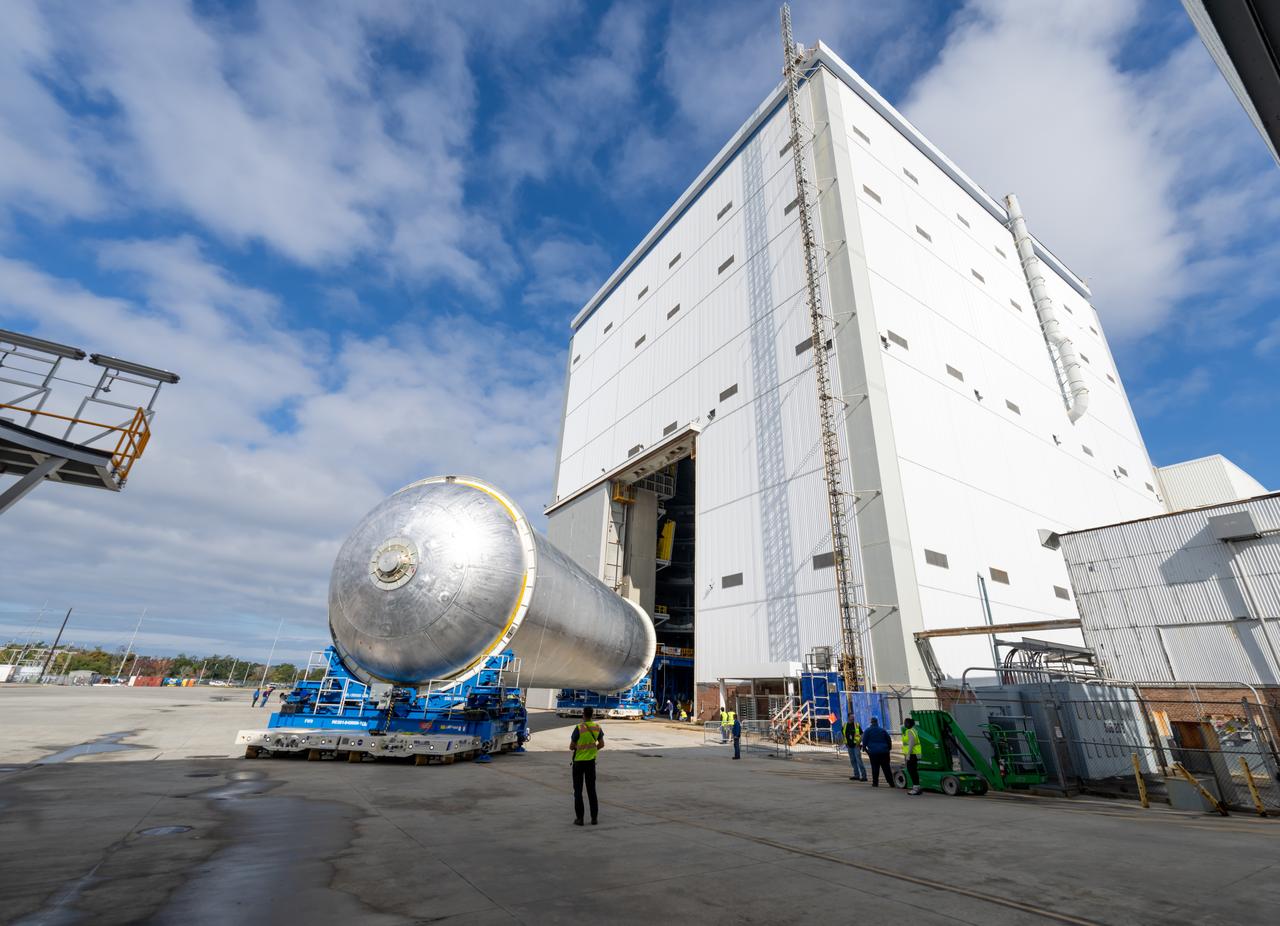

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
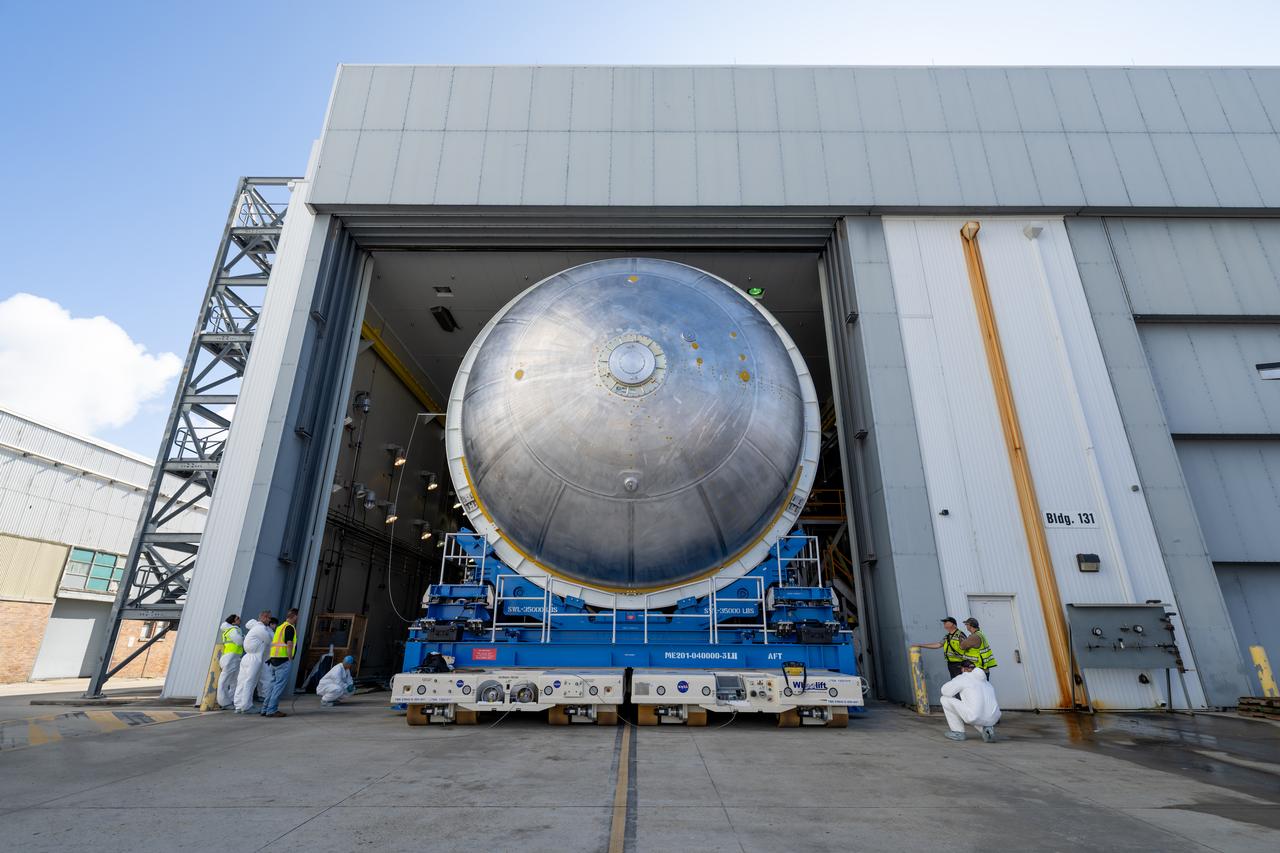

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
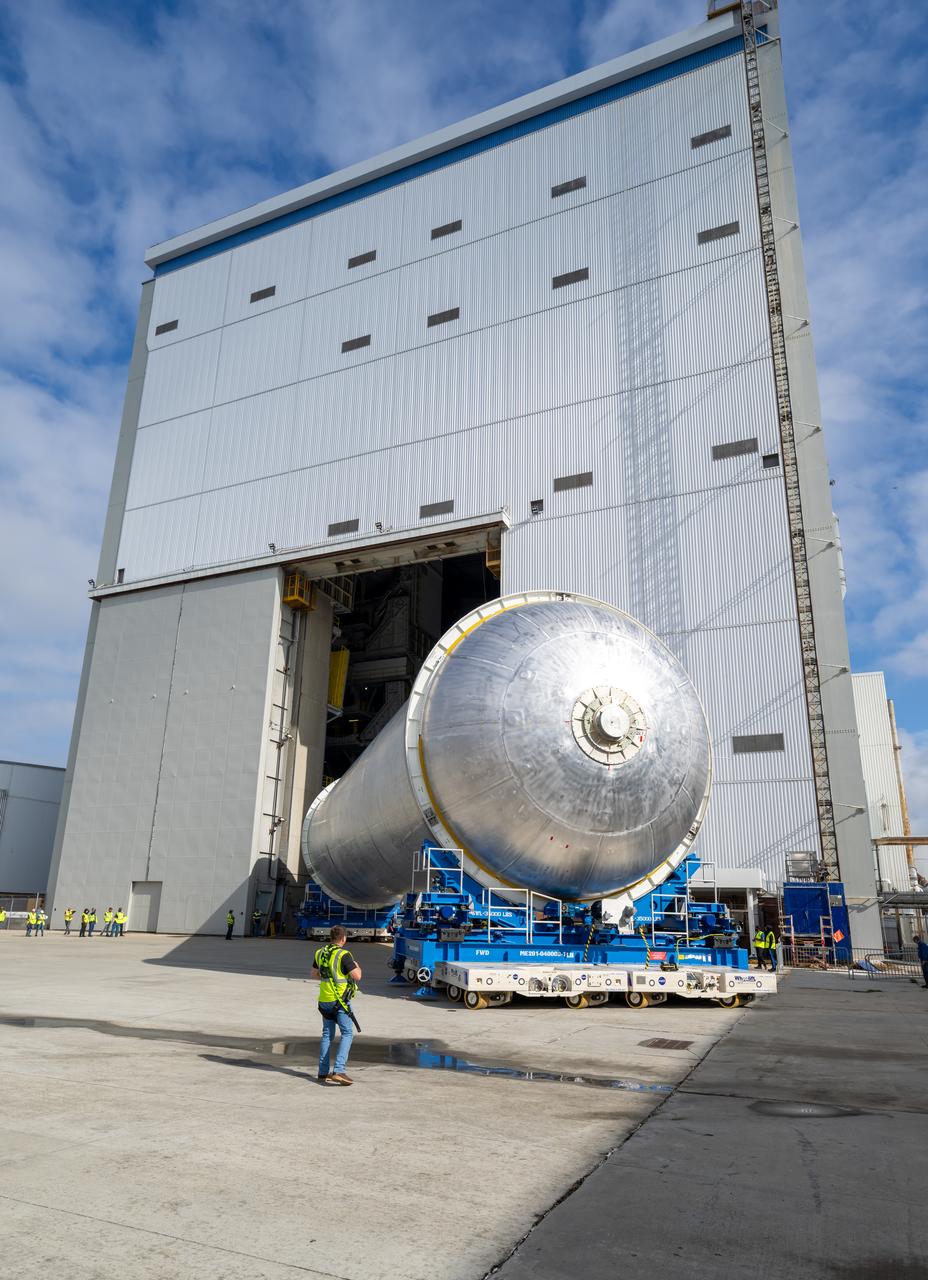

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
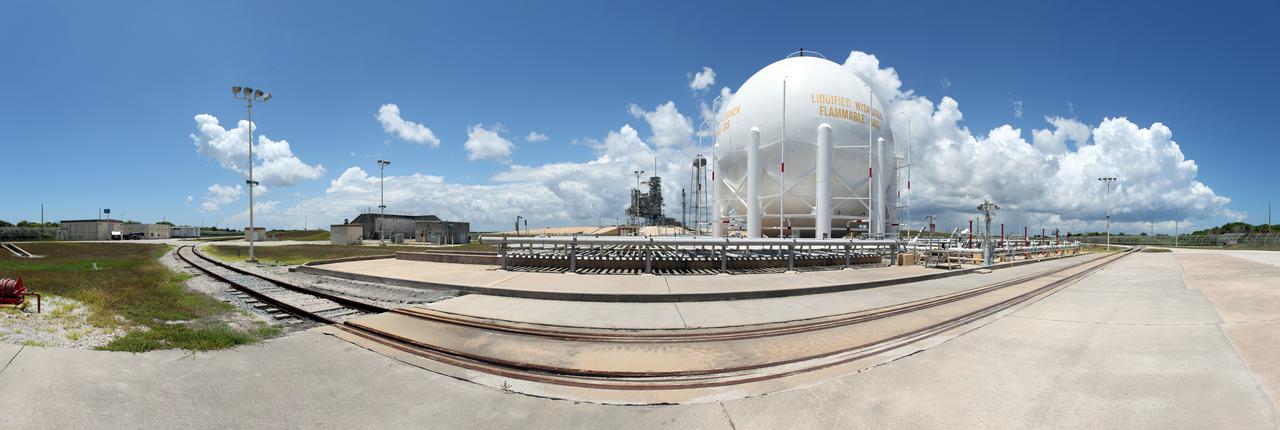

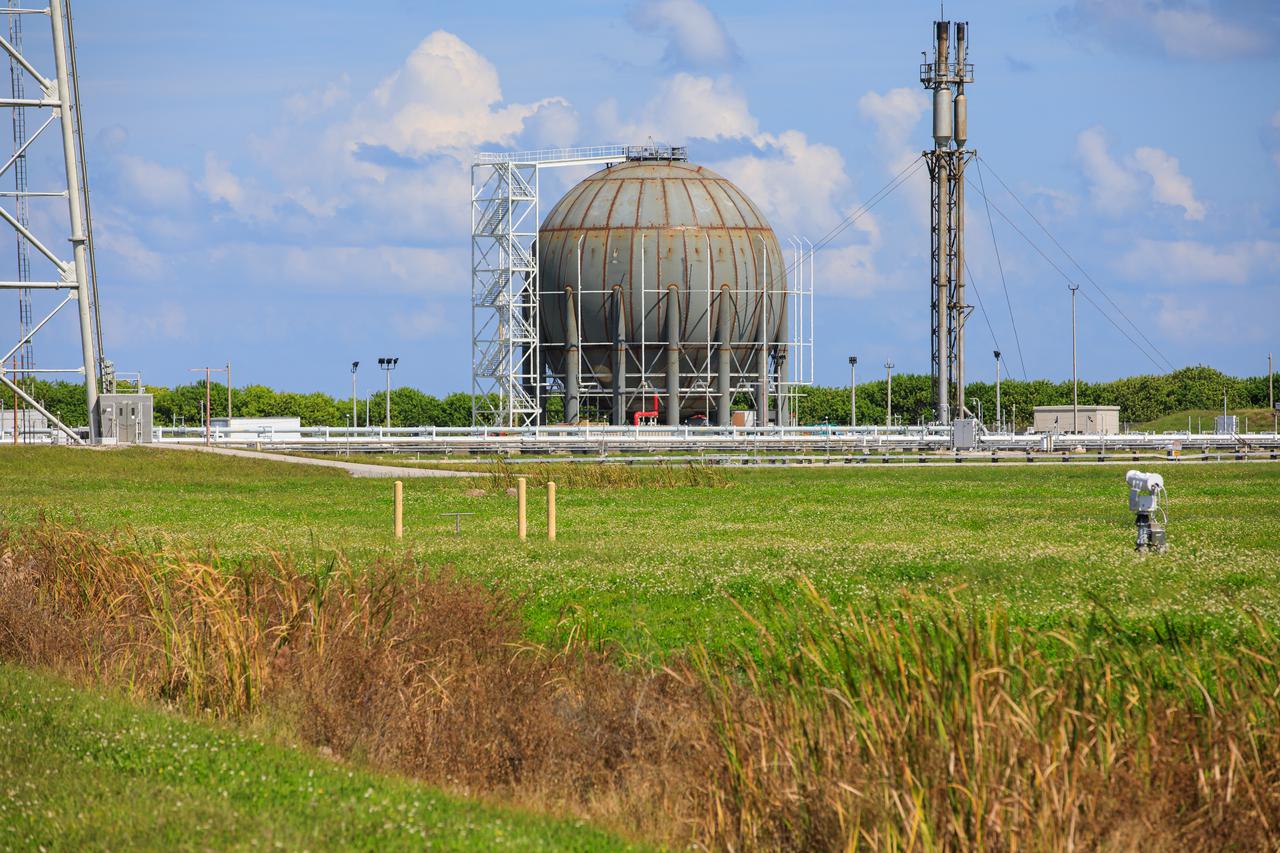
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is a liquid hydrogen, or LH2, storage tank. This large ball-shaped, vacuum-jacketed tank is used to store cryogenic propellants for the space shuttle's orange external fuel tank. The LH2 tank is located at the northeast corner of Launch Pad 39A and stores 850,000 gallons of LH2 at a temperature of minus 423 degrees F. The shuttle's external tank is loaded with about 500,000 gallons of LH2 and liquid oxygen, or LOX, about six hours prior to launch in a process known as 'tanking.' Photo credit: NASA_Frankie Martin
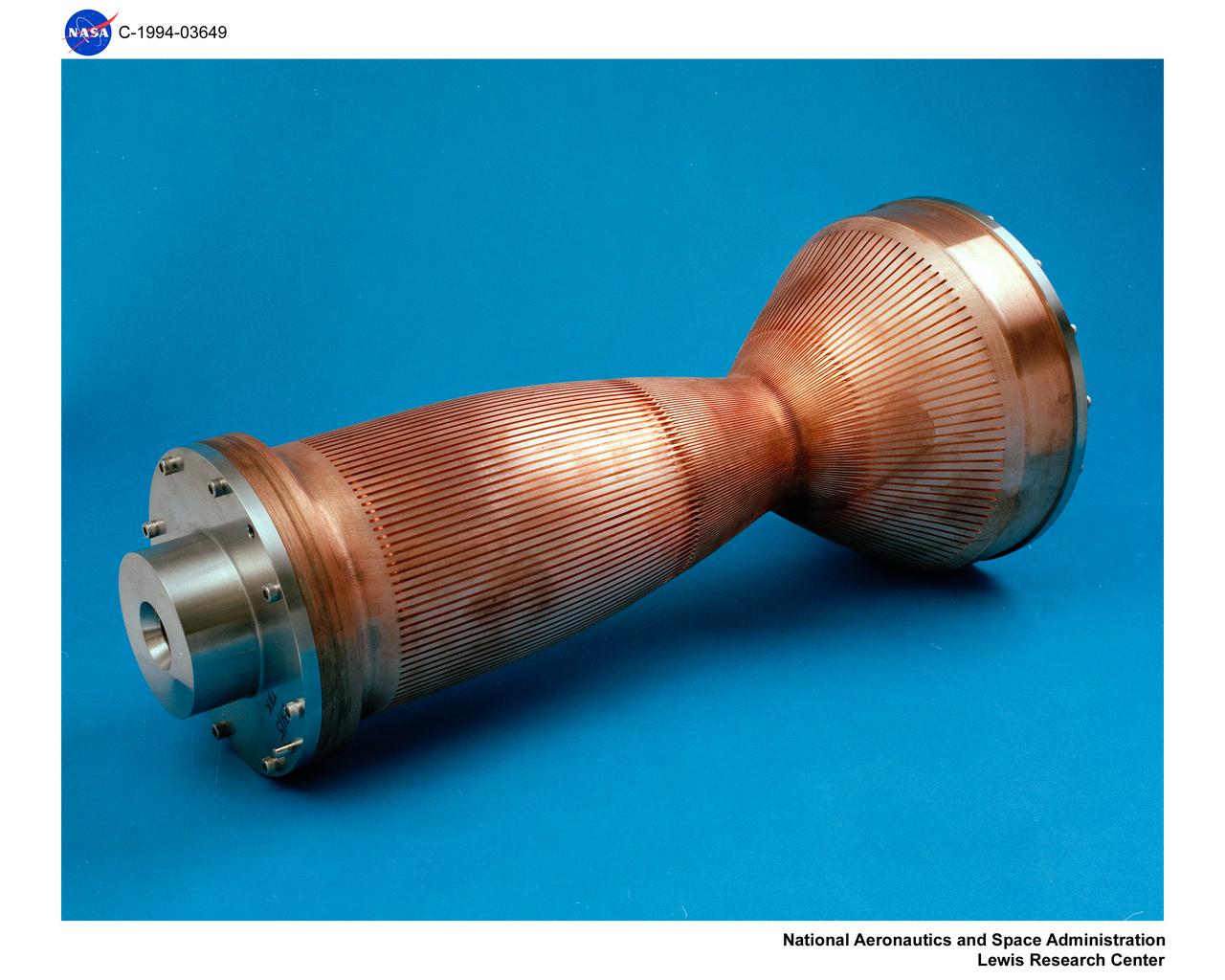

COPPER INNER LINER FOR HIGH ASPECT RATIO LH2 COOLED ENGINE
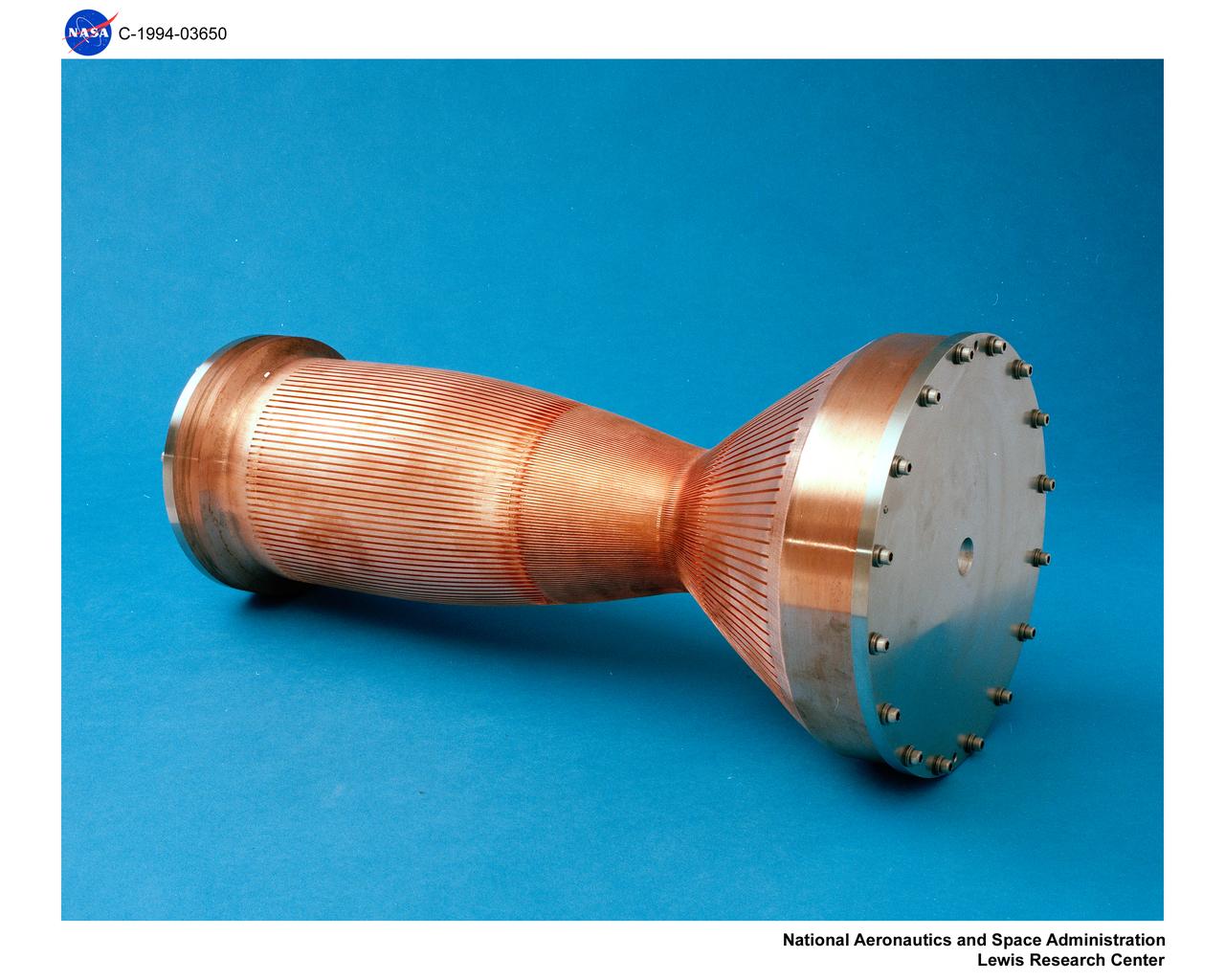

COPPER INNER LINER FOR HIGH ASPECT RATIO LH2 COOLED ENGINE

Tanker trucks deliver liquid hydrogen (LH2) to replenish the large sphere used to store the propellant at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Launch Pad 39B, to support the Artemis I mission, Wednesday, Aug. 31, 2022. Teams will conduct the next launch attempt of the Moon rocket and Orion spacecraft on Saturday, Sept. 3, 2022. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
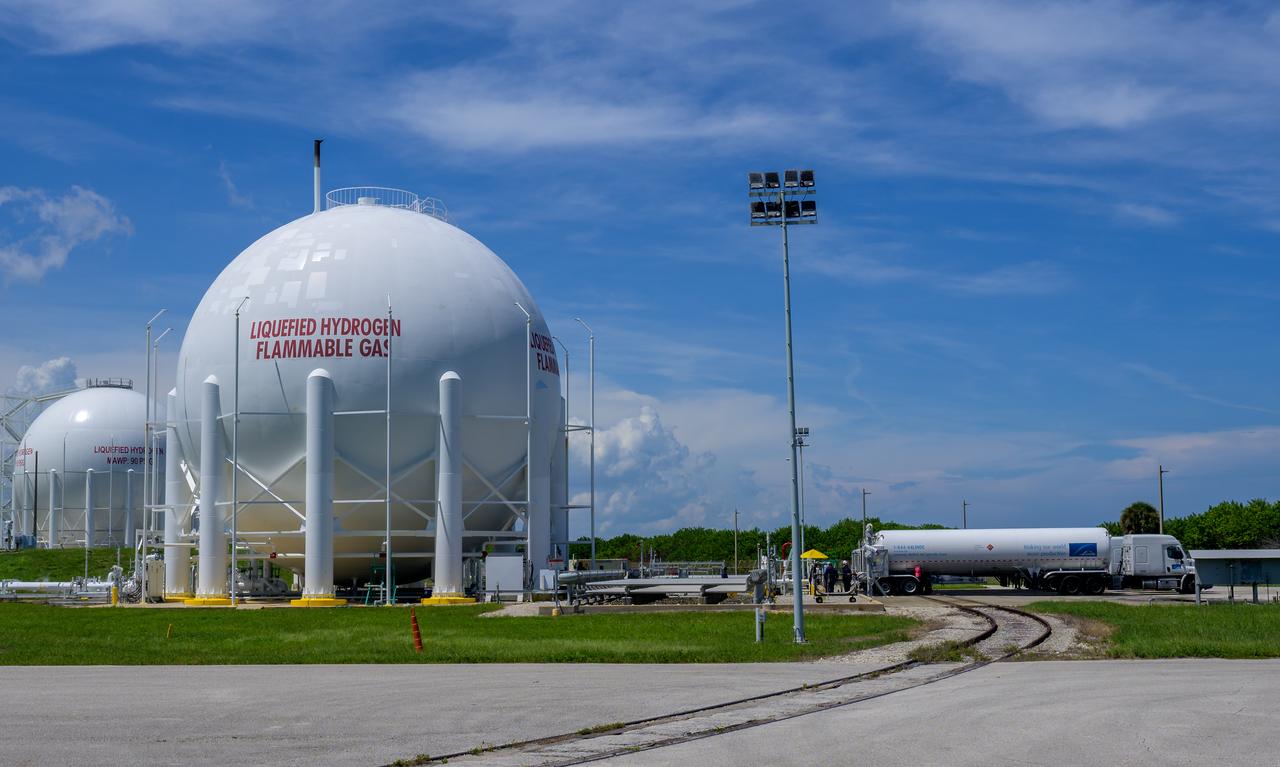

Tanker trucks deliver liquid hydrogen (LH2) to replenish the large sphere used to store the propellant at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Launch Pad 39B, to support the Artemis I mission, Wednesday, Aug. 31, 2022. Teams will conduct the next launch attempt of the Moon rocket and Orion spacecraft on Saturday, Sept. 3, 2022. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
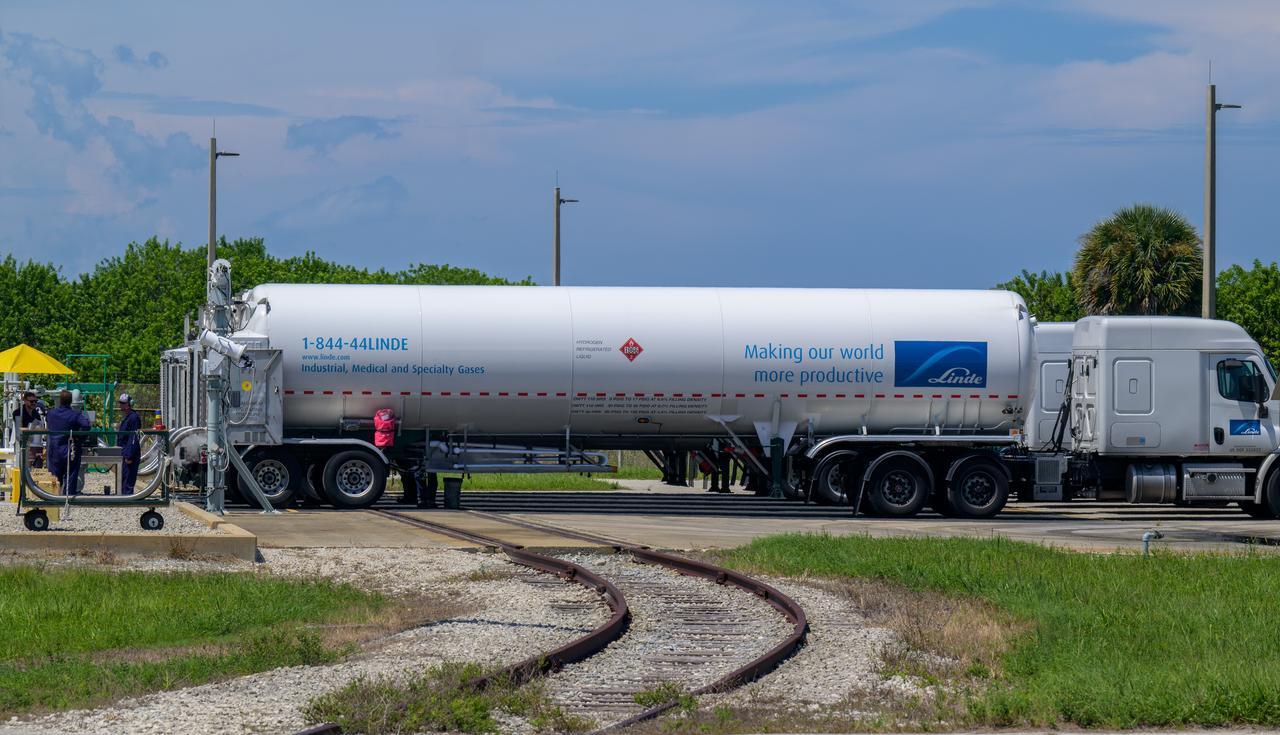

Tanker trucks deliver liquid hydrogen (LH2) to replenish the large sphere used to store the propellant at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Launch Pad 39B, to support the Artemis I mission, Wednesday, Aug. 31, 2022. Teams will conduct the next launch attempt of the Moon rocket and Orion spacecraft on Saturday, Sept. 3, 2022. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
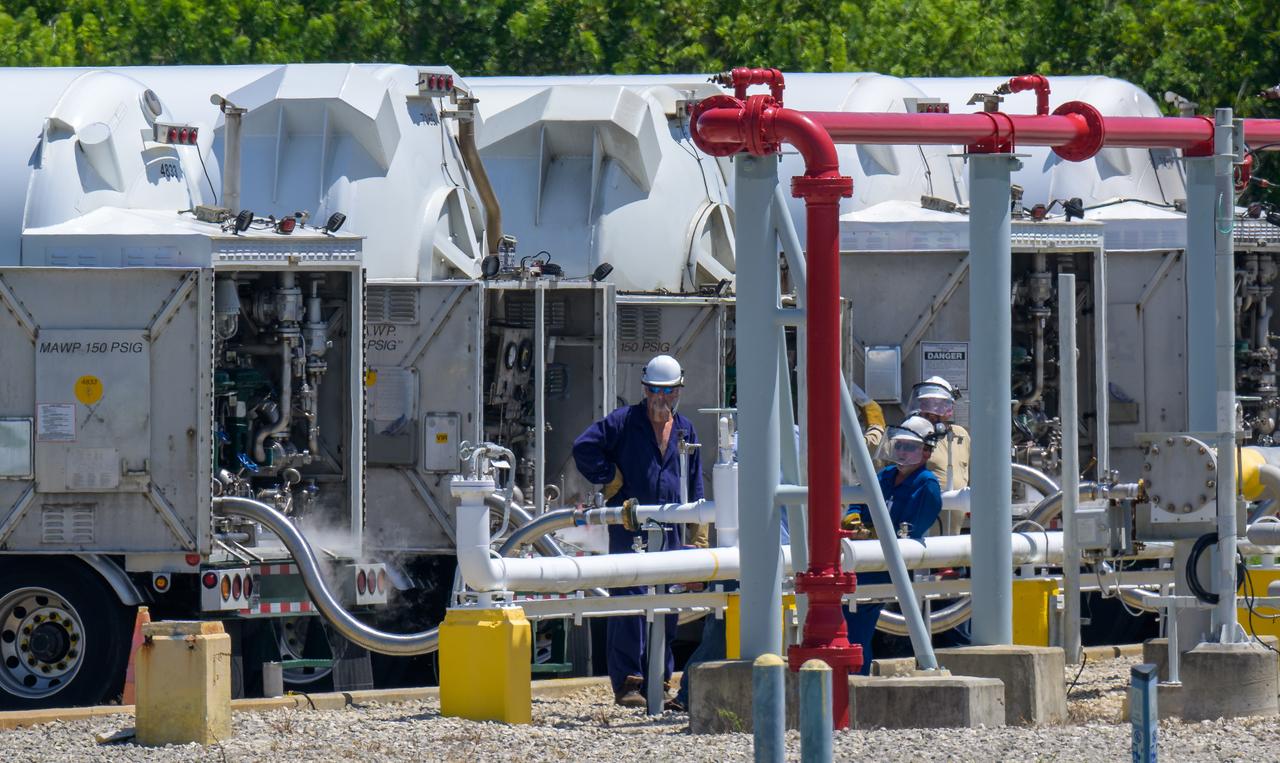

Tanker trucks deliver liquid hydrogen (LH2) to replenish the large sphere used to store the propellant at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Launch Pad 39B, to support the Artemis I mission, Wednesday, Aug. 31, 2022. Teams will conduct the next launch attempt of the Moon rocket and Orion spacecraft on Saturday, Sept. 3, 2022. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
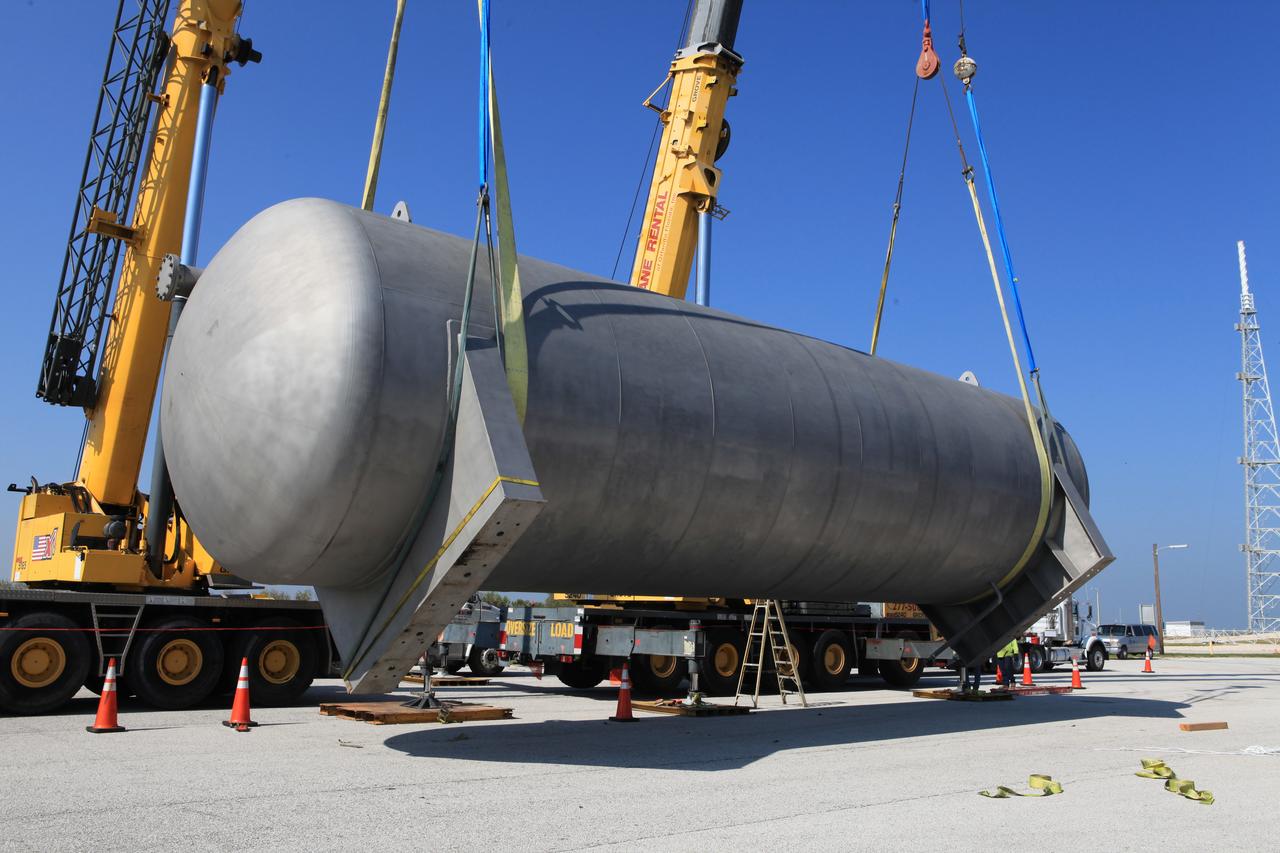

A new liquid hydrogen separator tank arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A crane is used to lift the tank and rotate it before it is delivered to Launch Pad 39B. The new separator/storage tank will be added to the pad's existing hydrogen vent system to assure gaseous hydrogen is delivered downstream to the flare stack. The 60,000 gallon tank was built by INOXCVA, in Baytown, Texas, a subcontractor of Precision Mechanical Inc. in Cocoa Florida. The new tank will support all future launches from the pad.
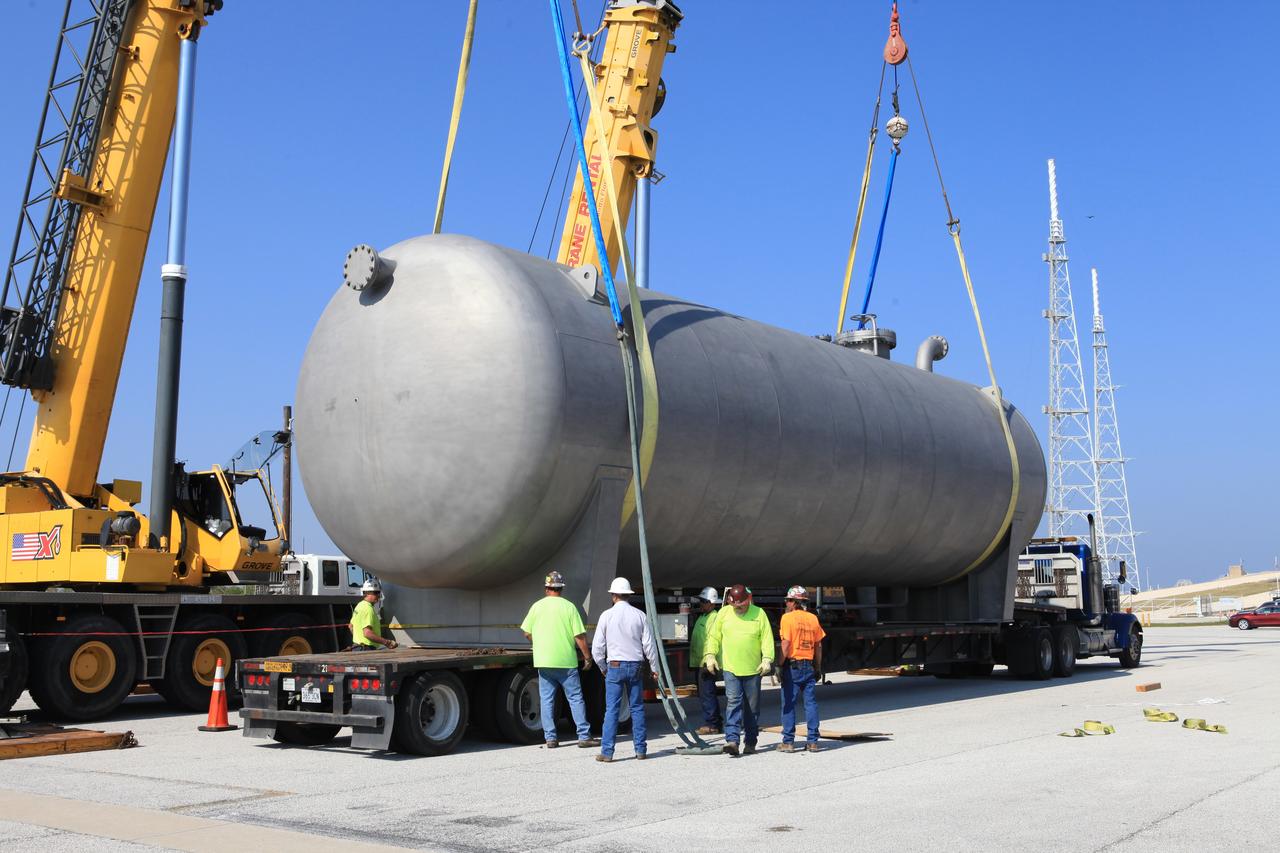

A new liquid hydrogen separator tank arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tank has been lifted and rotated by crane and lowered back onto the flatbed truck for transport to Launch Pad 39B. The new separator/storage tank will be added to the pad's existing hydrogen vent system to assure gaseous hydrogen is delivered downstream to the flare stack. The 60,000 gallon tank was built by INOXCVA, in Baytown, Texas, a subcontractor of Precision Mechanical Inc. in Cocoa Florida. The new tank will support all future launches from the pad.
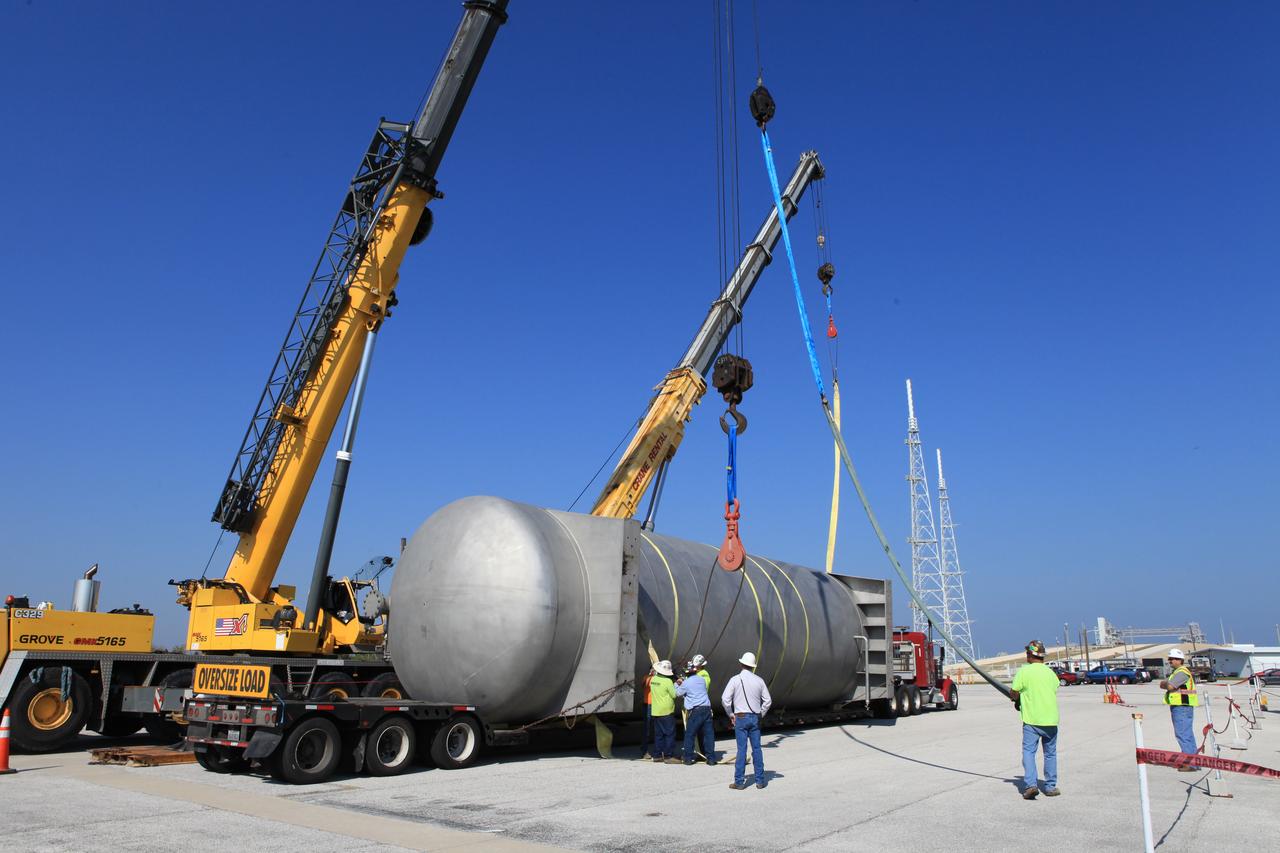

A new liquid hydrogen separator tank arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A crane is used to lift and rotate the tank before delivery to Launch Pad 39B. The new separator/storage tank will be added to the pad's existing hydrogen vent system to assure gaseous hydrogen is delivered downstream to the flare stack. The 60,000 gallon tank was built by INOXCVA, in Baytown, Texas, a subcontractor of Precision Mechanical Inc. in Cocoa Florida. The new tank will support all future launches from the pad.
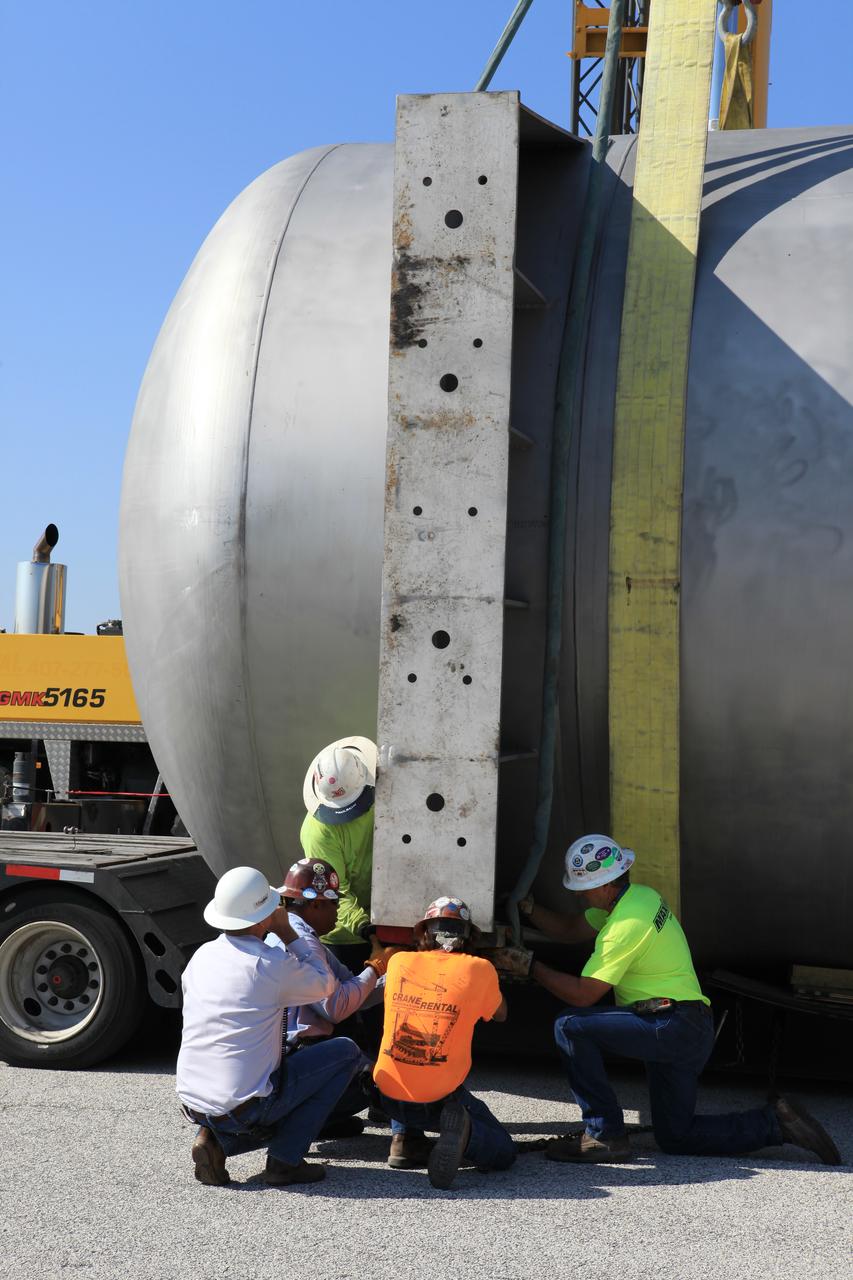

A new liquid hydrogen separator tank arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Construction workers check lines as a crane is attached to the tank to lift and rotate it before it is delivered to Launch Pad 39B. The new separator/storage tank will be added to the pad's existing hydrogen vent system to assure gaseous hydrogen is delivered downstream to the flare stack. The 60,000 gallon tank was built by INOXCVA, in Baytown, Texas, a subcontractor of Precision Mechanical Inc. in Cocoa Florida. The new tank will support all future launches from the pad.
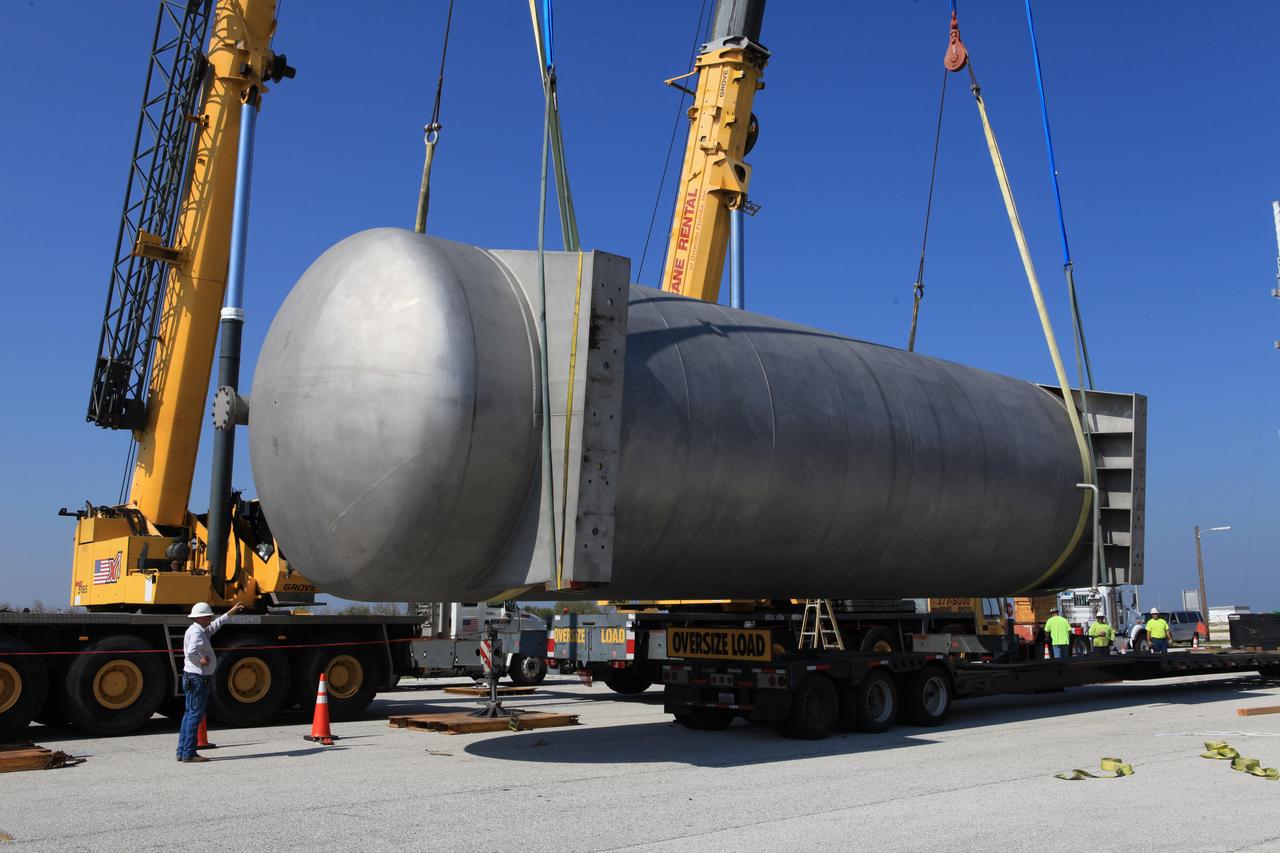

A new liquid hydrogen separator tank arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A crane has been attached to the tank to lift and rotate it before it is delivered to Launch Pad 39B. The new separator/storage tank will be added to the pad's existing hydrogen vent system to assure gaseous hydrogen is delivered downstream to the flare stack. The 60,000 gallon tank was built by INOXCVA, in Baytown, Texas, a subcontractor of Precision Mechanical Inc. in Cocoa Florida. The new tank will support all future launches from the pad.
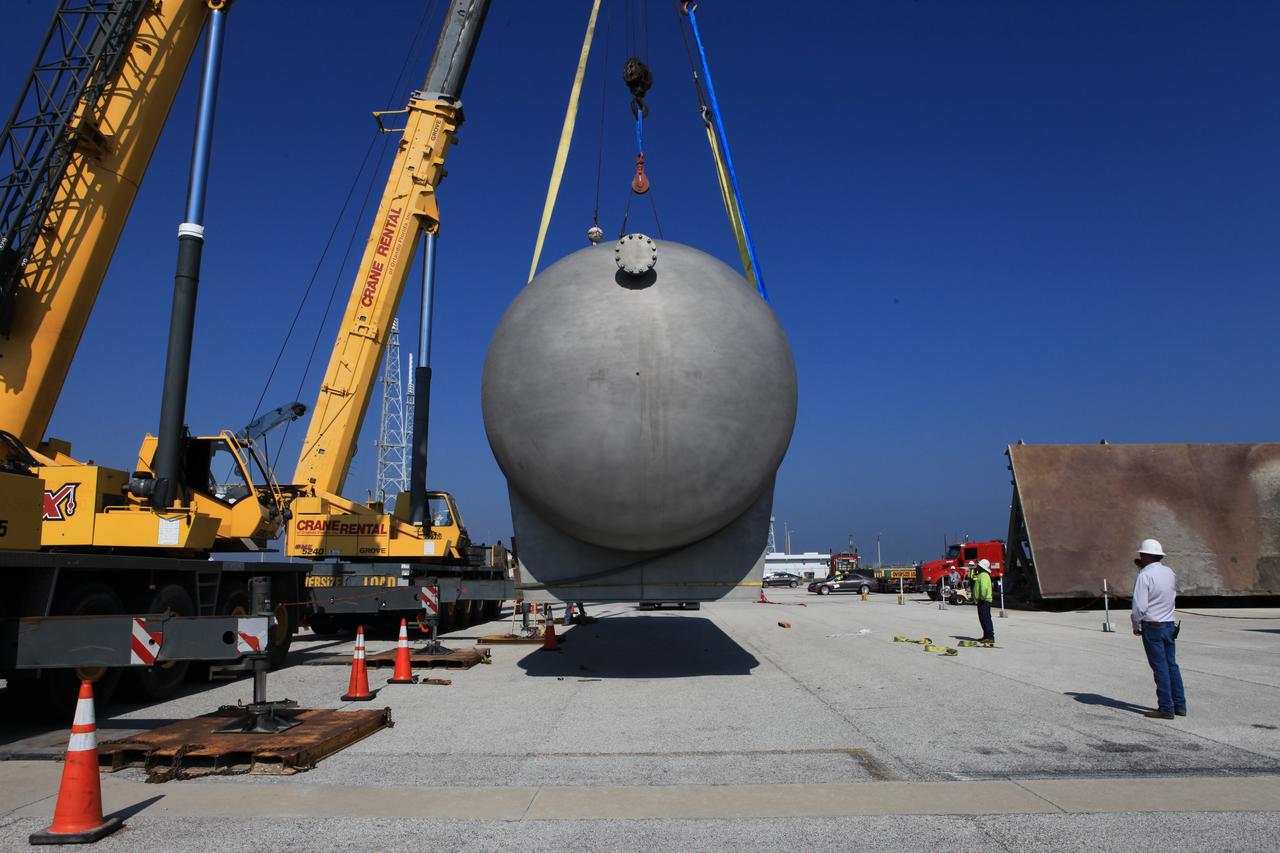

A new liquid hydrogen separator tank arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A crane is used to lift and rotate the tank before it is delivered to Launch Pad 39B. The new separator/storage tank will be added to the pad's existing hydrogen vent system to assure gaseous hydrogen is delivered downstream to the flare stack. The 60,000 gallon tank was built by INOXCVA, in Baytown, Texas, a subcontractor of Precision Mechanical Inc. in Cocoa Florida. The new tank will support all future launches from the pad.
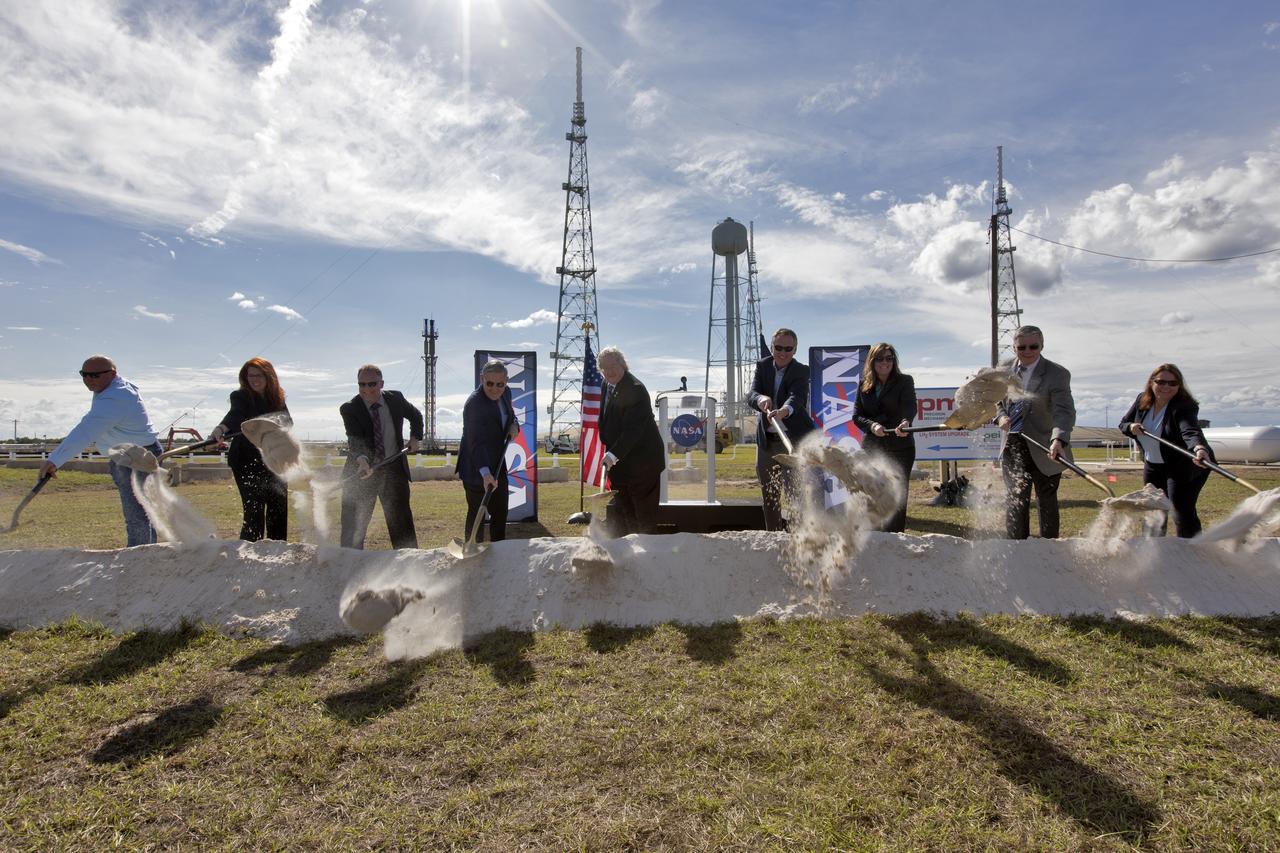

On Dec. 19, 2018, at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39B, agency and contractor managers break ground for a new liquid hydrogen tank. Participating, from the left, are Todd Gray, president of Precision Mechanical, prime contractor for the project; Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, launch director; Shawn Quinn, director of Engineering; Bob Cabana, center director; Bill Hill, deputy associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development at NASA Headquarters in Washington; Mike Bolger, program manager for Exploration Ground Systems (EGS); Jennifer Kunz, deputy program manager for EGS, Andy Allen, general manager for Jacobs, NASA's Test and Operations Support Contractor; and Regina Spellman, launch pad senior project manager in EGS. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.
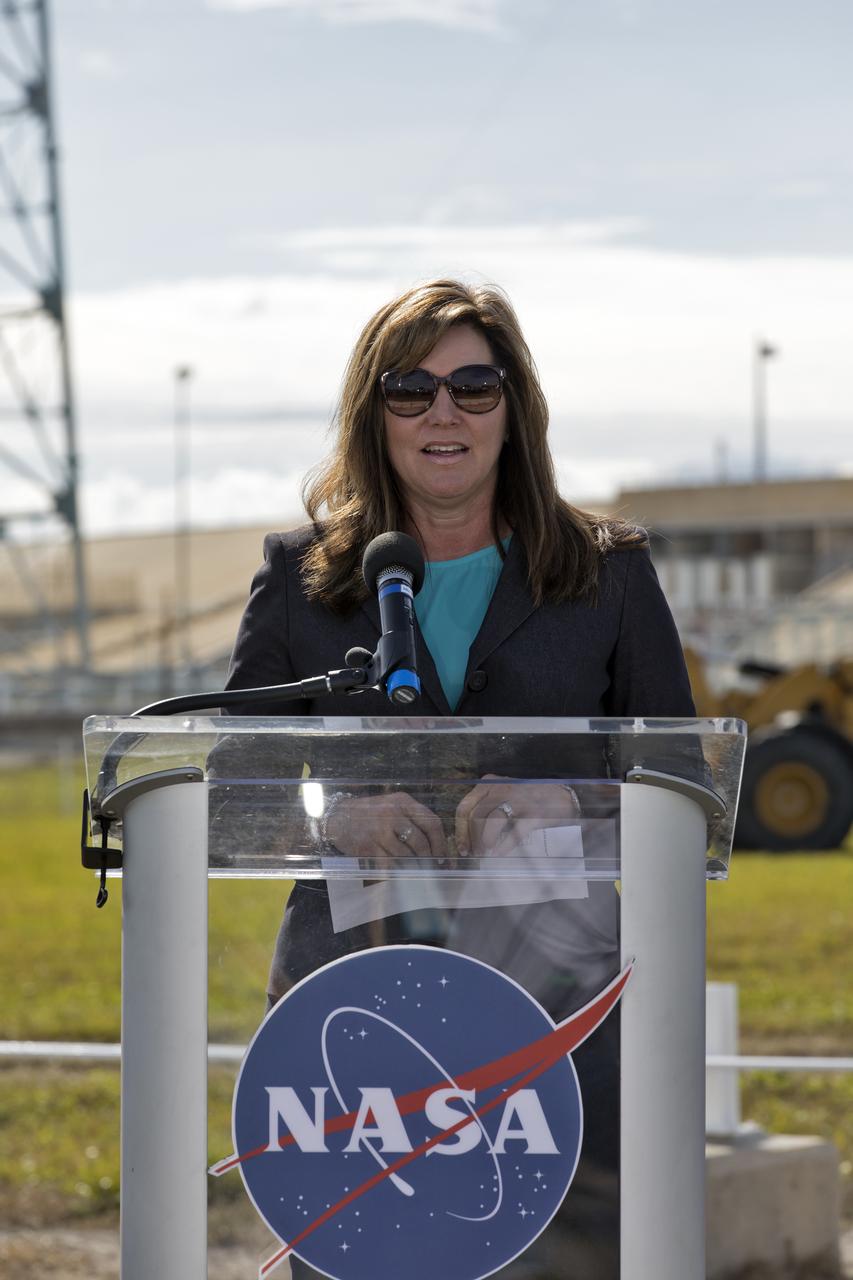

On Dec. 19, 2018, Jennifer Kunz, deputy program manager for Exploration Ground Systems, speaks during a groundbreaking ceremony for a new liquid hydrogen tank for Launch Complex 39B at the agency's Kennedy Space Center. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.
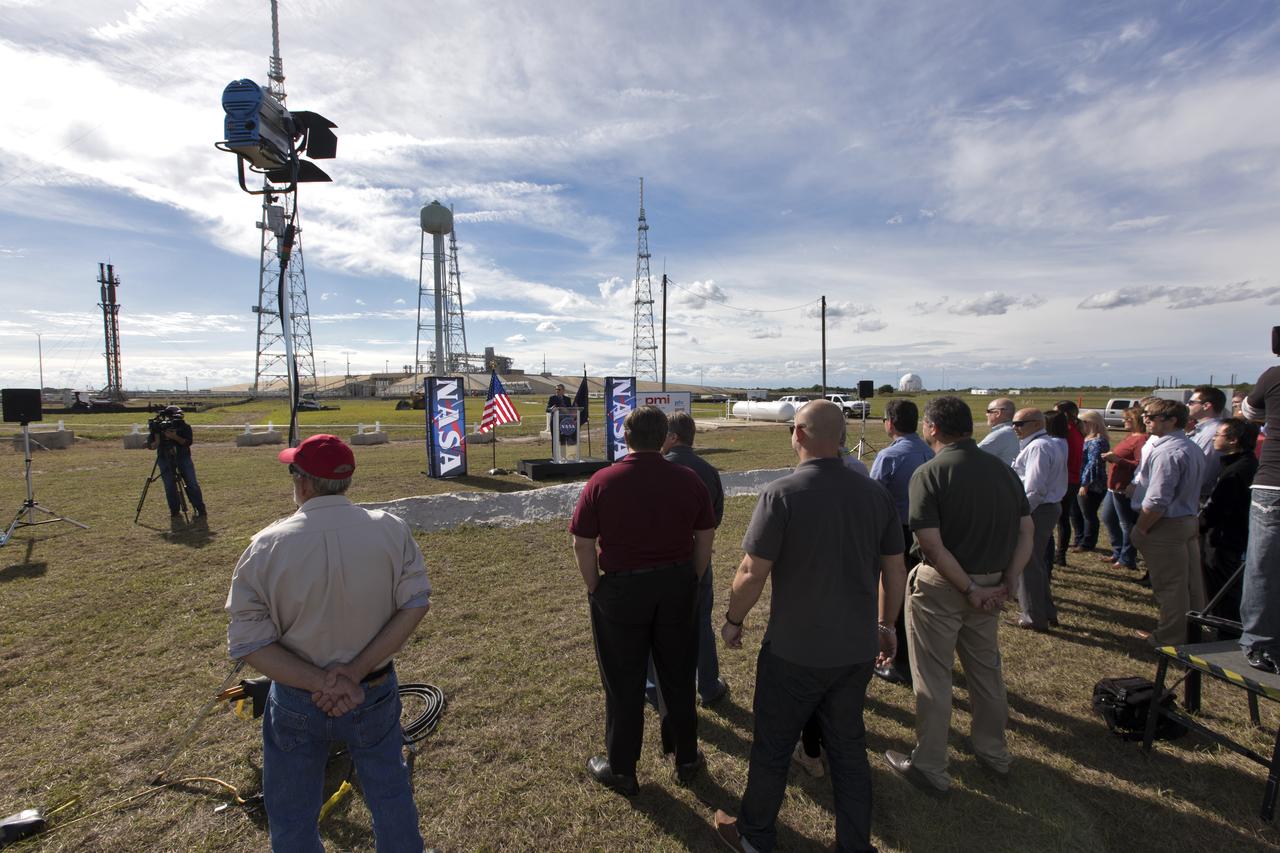

On Dec. 19, 2018, NASA and contractor managers gathered for a groundbreaking ceremony for a new liquid hydrogen tank for Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.

On Dec. 19, 2018, NASA Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson speaks during a groundbreaking ceremony for a new liquid hydrogen tank for Launch Complex 39B at the agency's Kennedy Space Center. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.
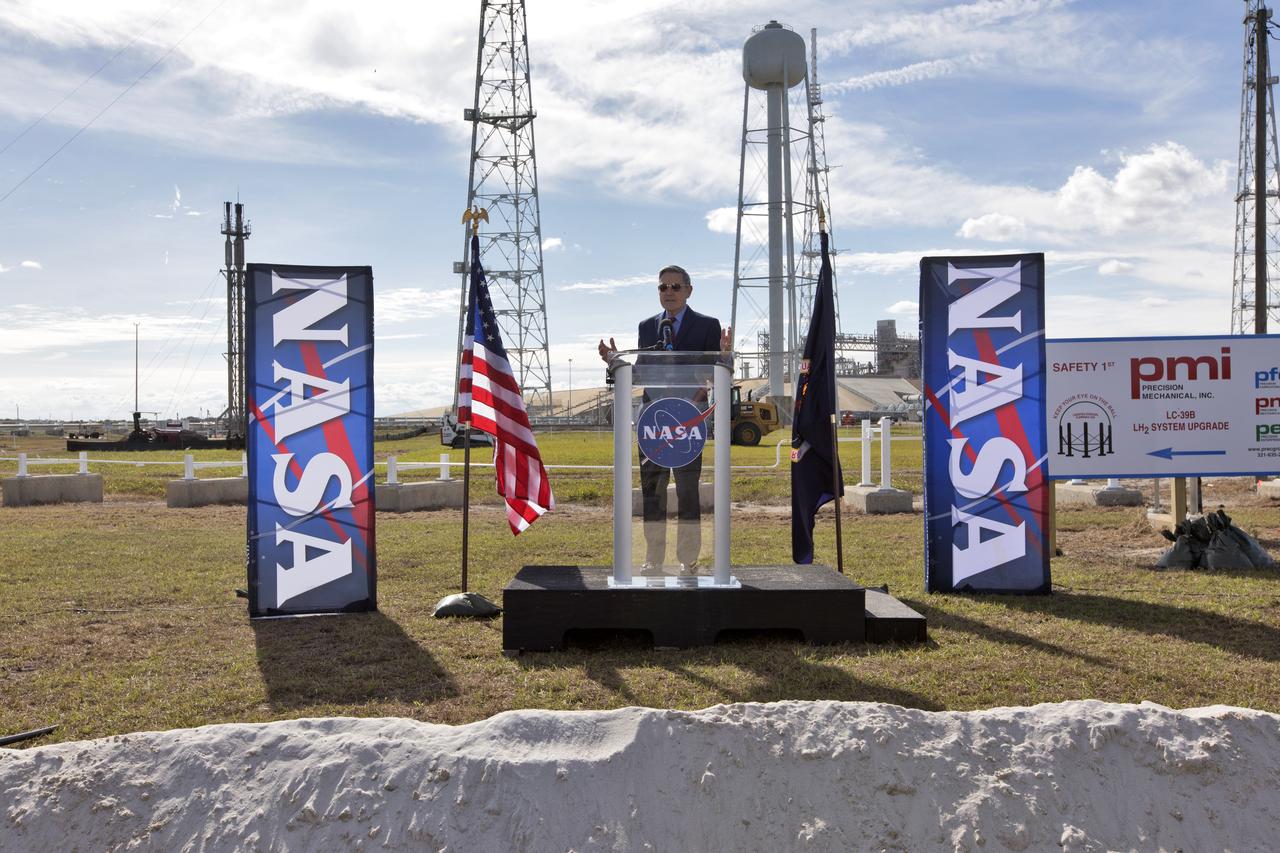

On Dec. 19, 2018, Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana speaks during a groundbreaking ceremony for a new liquid hydrogen tank for Launch Complex 39B at the space center. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.

On Dec. 19, 2018, Bill Hill, deputy associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development at NASA Headquarters in Washington, speaks during a groundbreaking ceremony for a new liquid hydrogen tank for Launch Complex 39B at the agency's Kennedy Space Center. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.
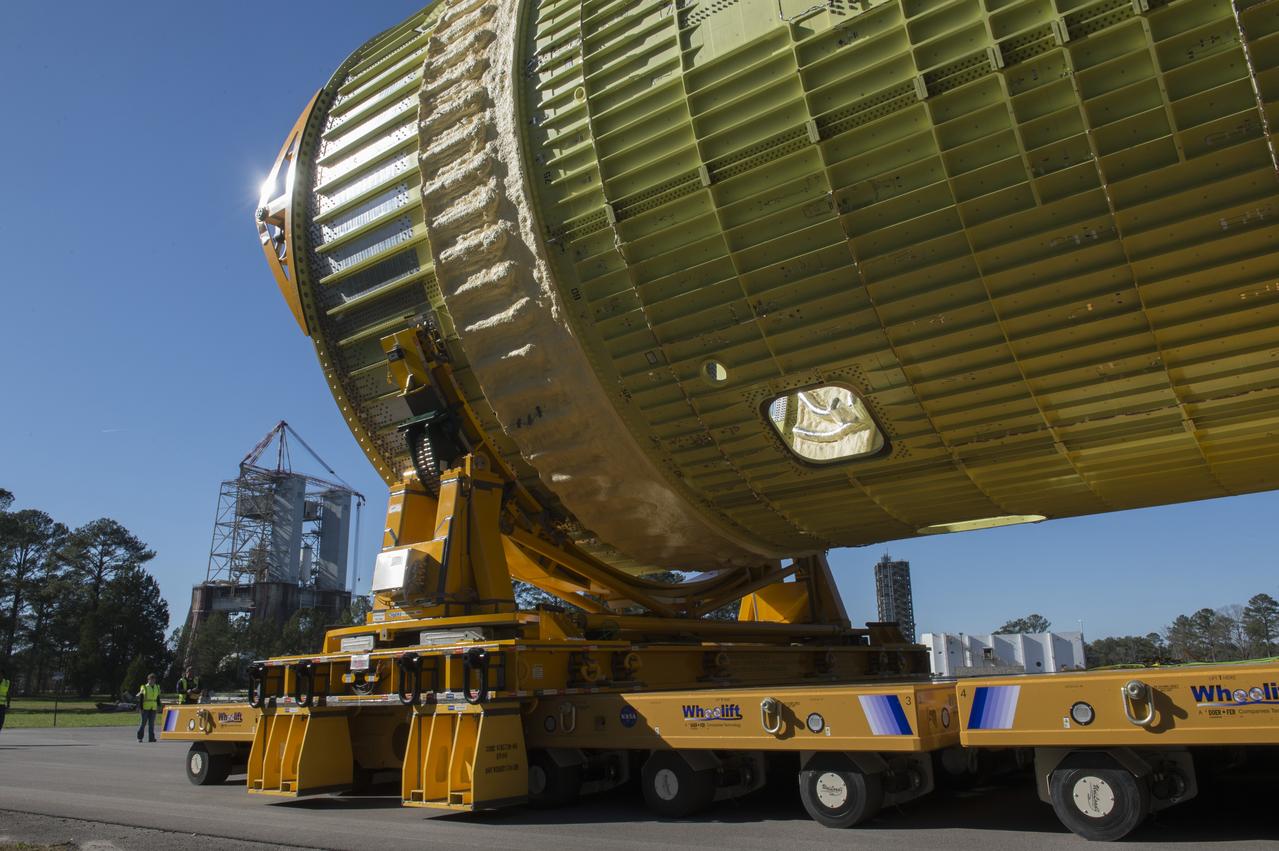

The SLS Stages Intertank Structural Test Assembly (STA) is rolling off the NASA Pegasus Barge at the MSFC Dock enroute to the MSFC 4619 Load Test Annex test facility for qualification testing via MSFC West Test Area. Historic Saturn 1-C test stand on far left, blockhouse 4670 on far right, SLS LH2 test stand, 4693, in center.
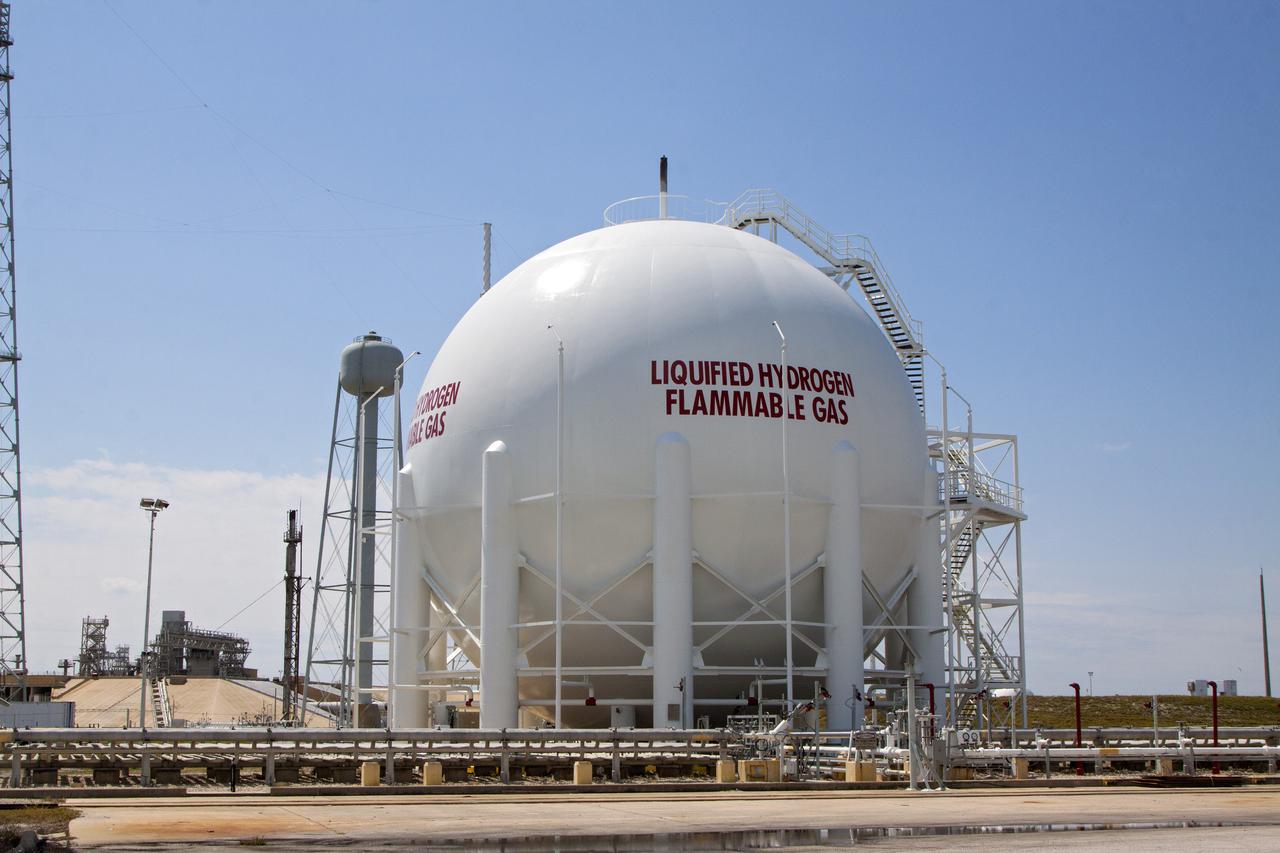

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the liquid oxygen, or LOX, and liquid hydrogen, or LH2, tanks that supported space shuttle launches for 30 years have been sandblasted, repaired and repainted. The two tanks, designed to store super-cooled LOX and LH2, were refurbished to prepare them to support the launch of NASA’s Space Launch System and other launch vehicles. The Ground Systems Development and Operations, or GSDO, Program office at Kennedy is leading the center’s transformation to safely handle a variety of rockets and spacecraft. For more information about GSDO, visit: http:__go.nasa.gov_groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett
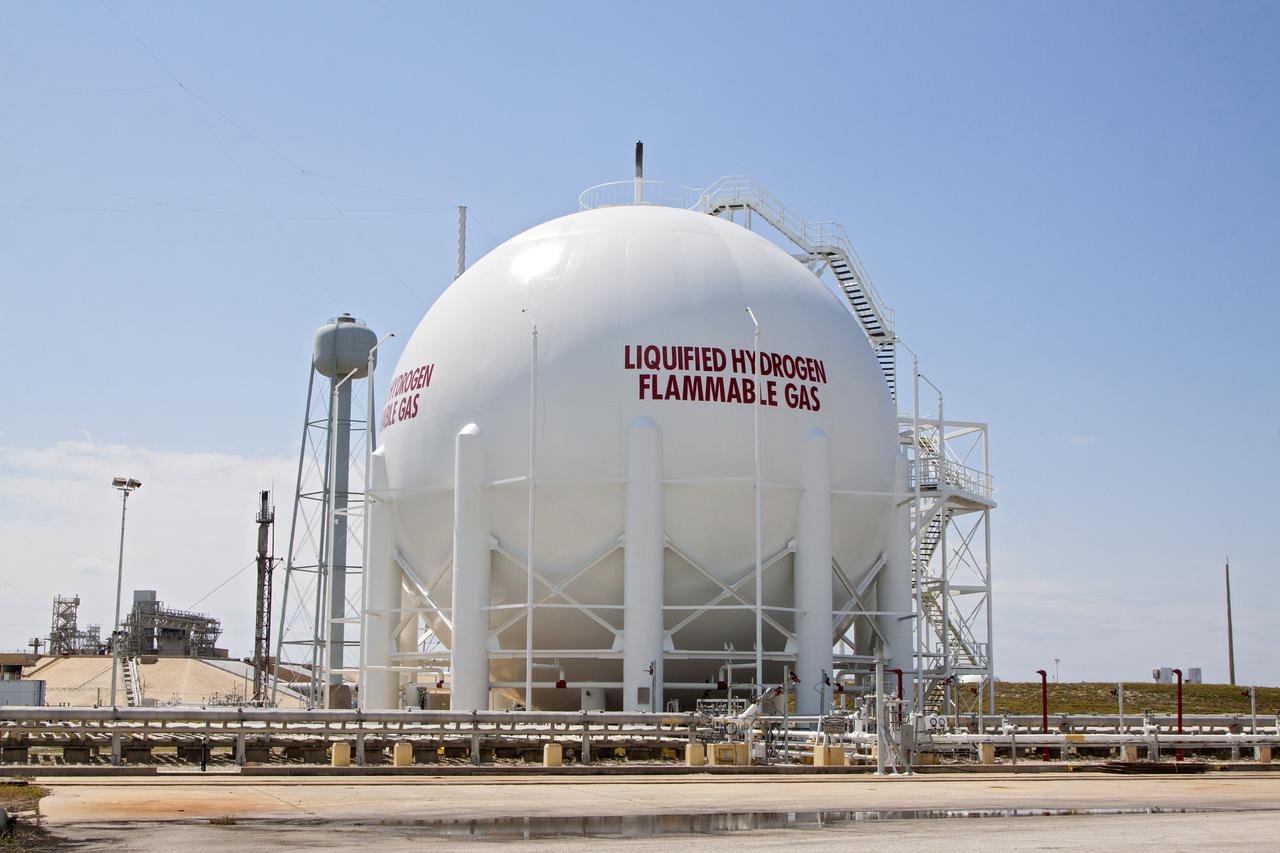

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the liquid oxygen, or LOX, and liquid hydrogen, or LH2, tanks that supported space shuttle launches for 30 years have been sandblasted, repaired and repainted. The two tanks, designed to store super-cooled LOX and LH2, were refurbished to prepare them to support the launch of NASA’s Space Launch System and other launch vehicles. The Ground Systems Development and Operations, or GSDO, Program office at Kennedy is leading the center’s transformation to safely handle a variety of rockets and spacecraft. For more information about GSDO, visit: http:__go.nasa.gov_groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett
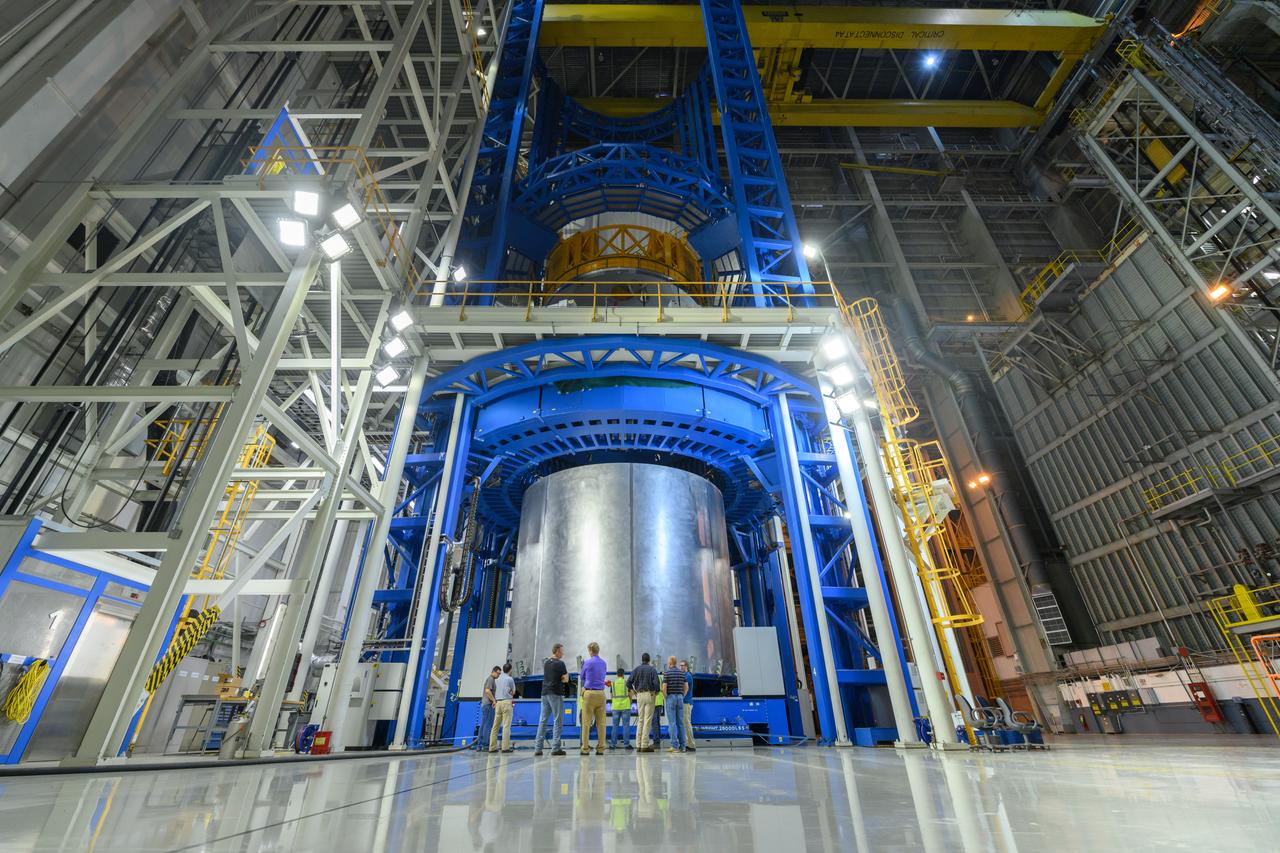

Space Launch System Corestage-2 Liquid Hydrogen(LH2) tank is under construction at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility. Here you can see 1 of 5 barrels being loaded in the Vertical Assembly Center tool where it will be welded.
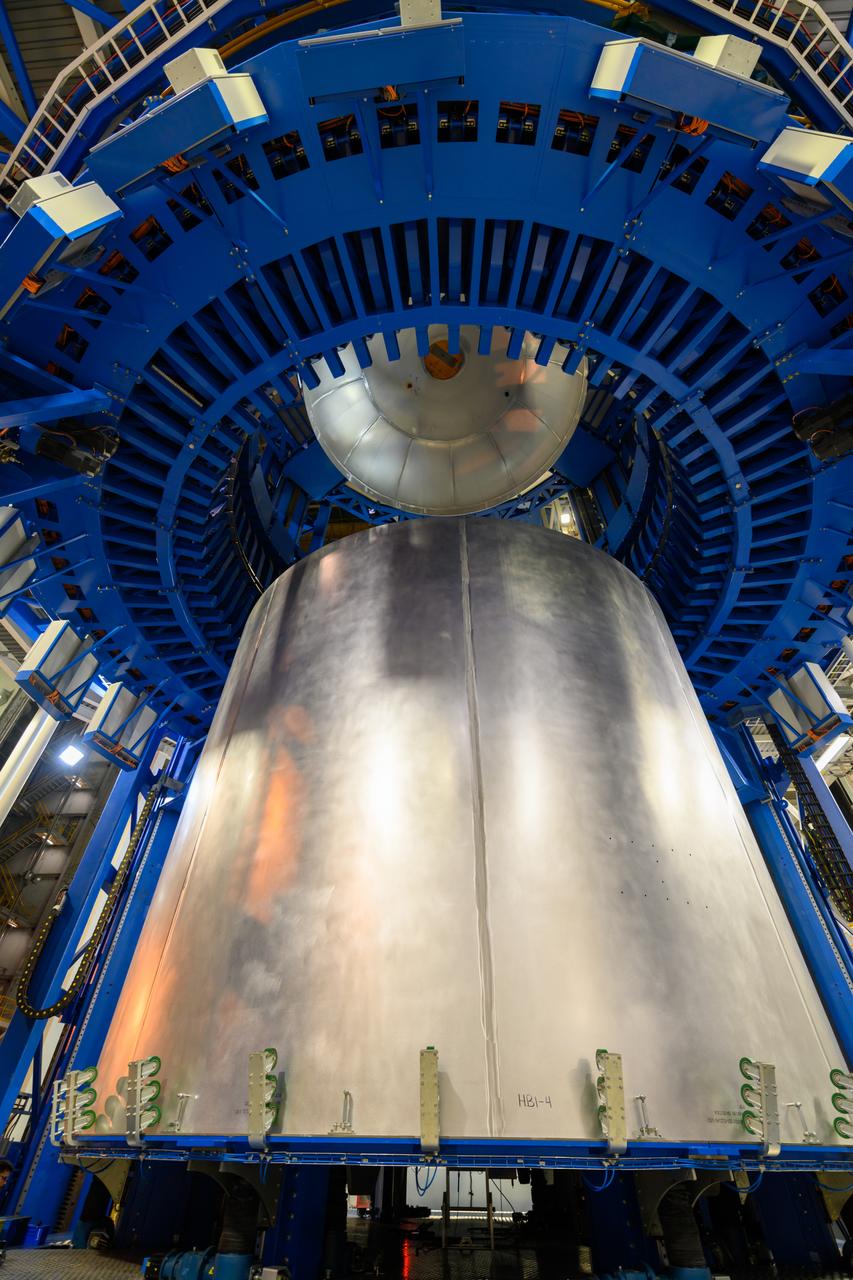

Space Launch System Corestage-2 Liquid Hydrogen(LH2) tank is under construction at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility. Here you can see 1 of 5 barrels being loaded in the Vertical Assembly Center tool where it will be welded.
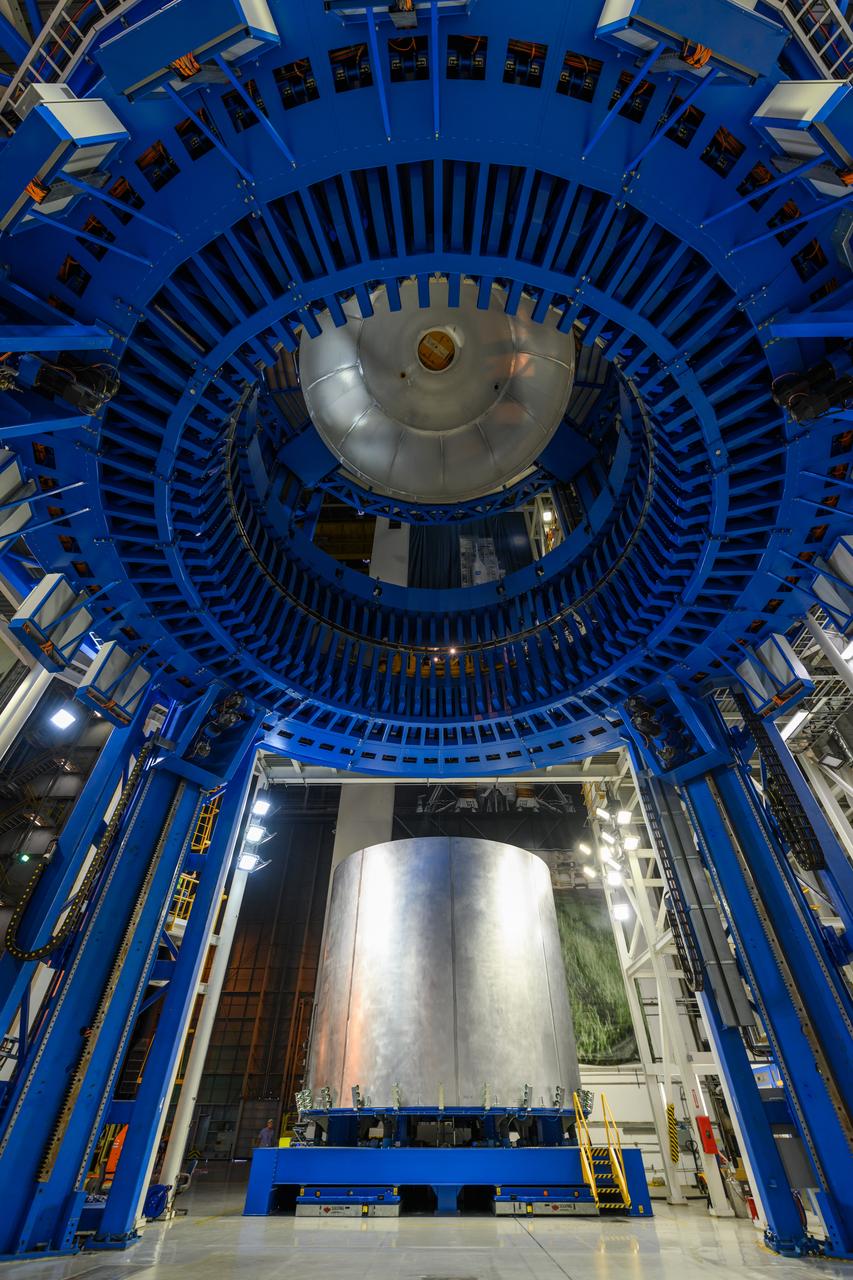
Space Launch System Corestage-2 Liquid Hydrogen(LH2) tank is under construction at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility. Here you can see 1 of 5 barrels being loaded in the Vertical Assembly Center tool where it will be welded.
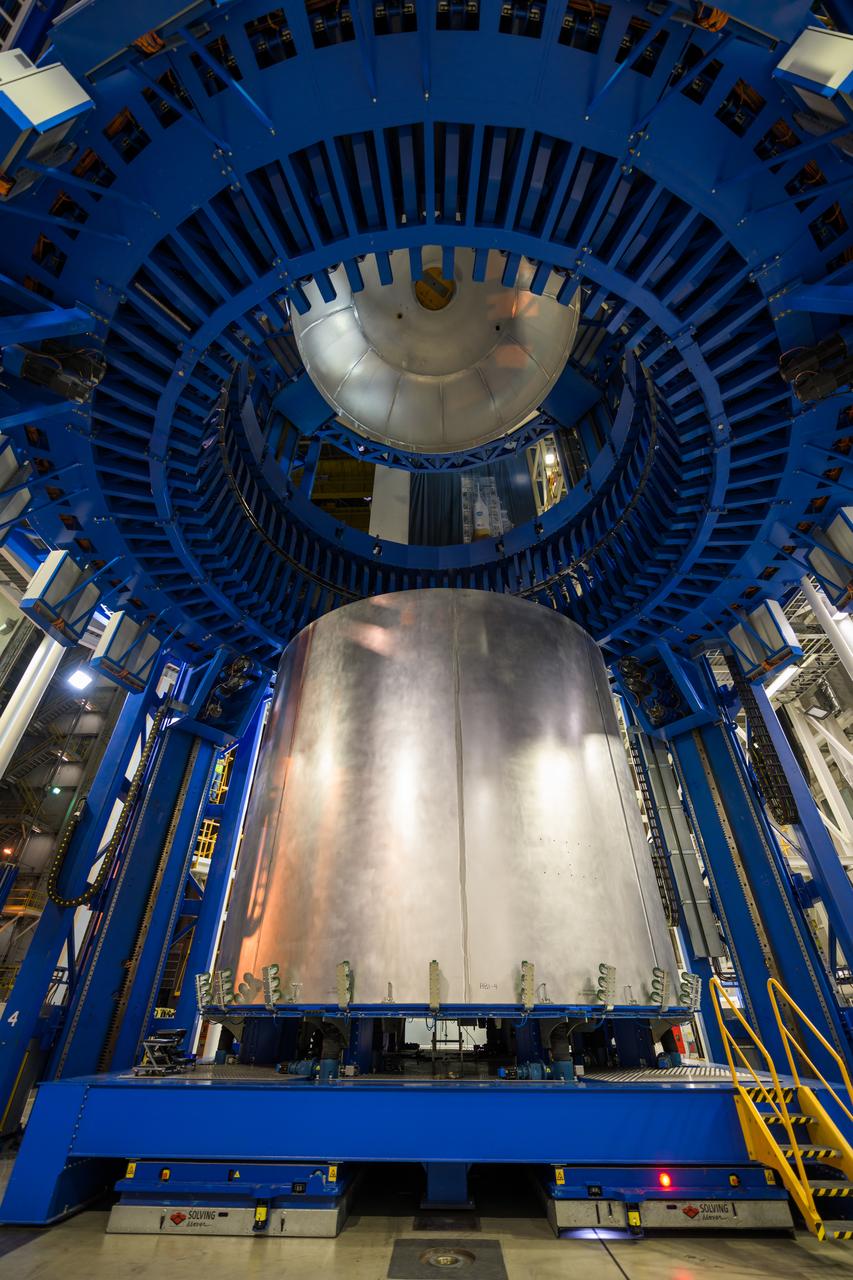

Space Launch System Corestage-2 Liquid Hydrogen(LH2) tank is under construction at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility. Here you can see 1 of 5 barrels being loaded in the Vertical Assembly Center tool where it will be welded.
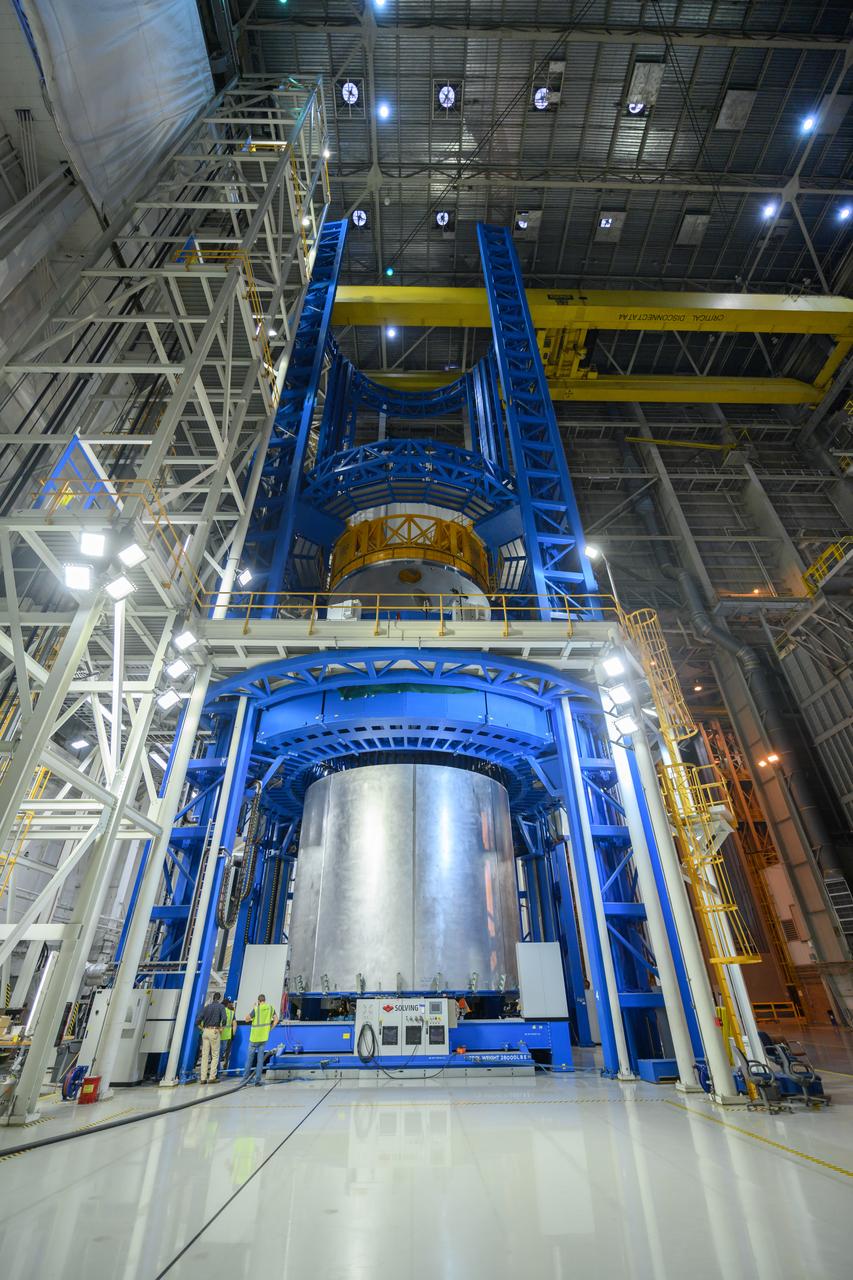

Space Launch System Corestage-2 Liquid Hydrogen(LH2) tank is under construction at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility. Here you can see 1 of 5 barrels being loaded in the Vertical Assembly Center tool where it will be welded.
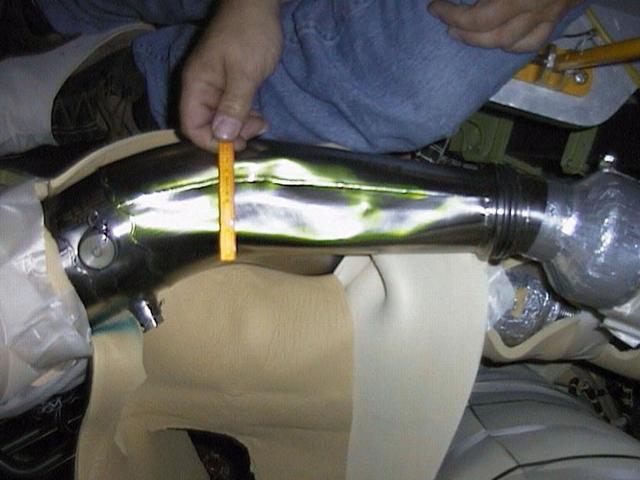

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A small ruler shows the relative size of the bent LH2 recirculation line in Space Shuttle Discovery's engine compartment. Underneath the line is material draped to protect other components. The 12-inch-long dent was discovered during routine aft compartment inspections Tuesday, Dec. 7. The LH2 line recirculates hydrogen from the Shuttle main engines back to the external tank during prelaunch engine conditioning. The line is being replaced and managers expect the replacement work to take about 3 days, followed by system retests and final aft compartment close-outs. Preliminary assessments reflect a launch date of Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-103 no earlier than Dec. 16. STS-103 is the third servicing mission for the Hubble Space Telescope
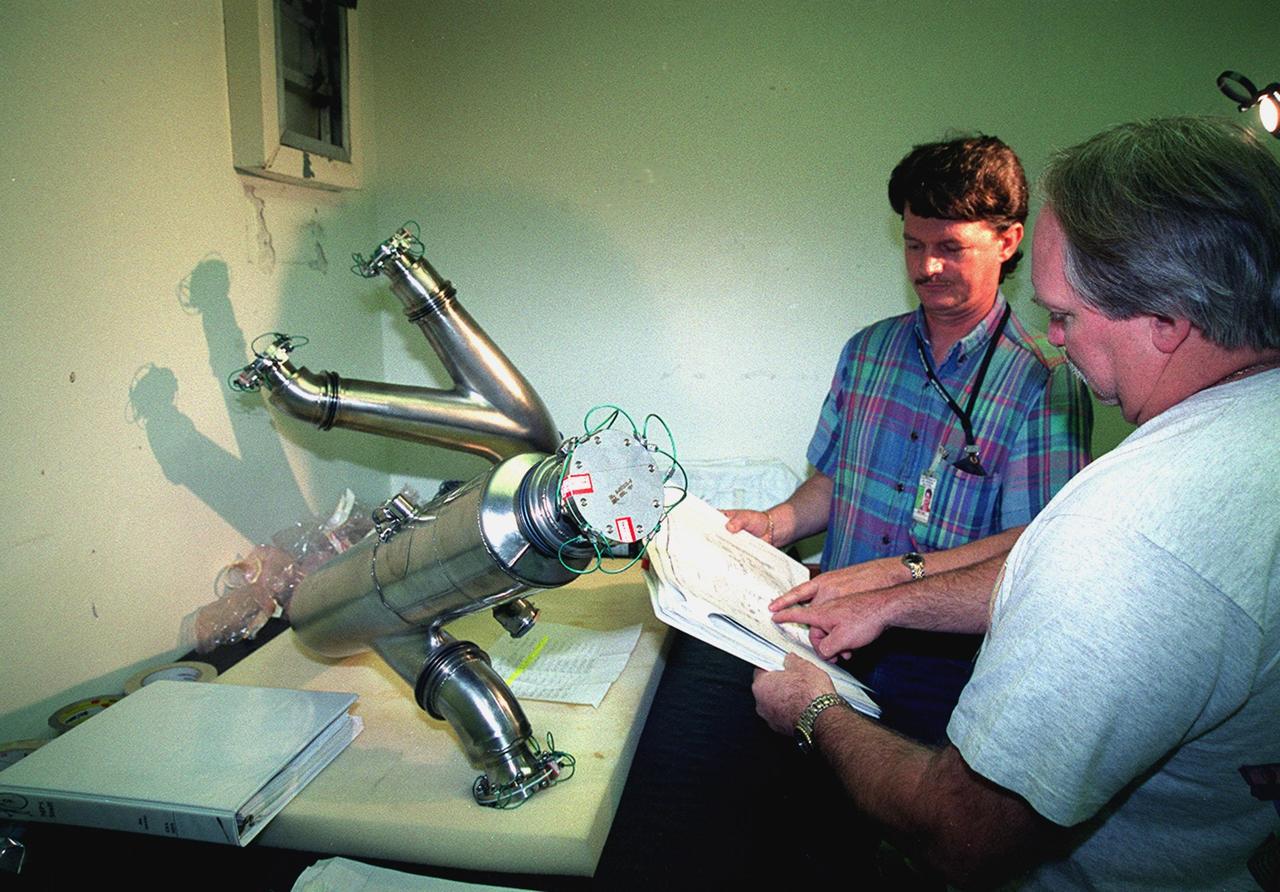
James Stickley (left) and Derry Dilby (right), who are with United Space Alliance, check over a spare four-inch diameter LH2 recirculation line that will be used to replace a damaged LH2 line in the orbiter Discovery. The line recirculates hydrogen from the Shuttle main engines back to the external tank during prelaunch engine conditioning. Workers noted a dent in the line during routine aft compartment inspections Tuesday, Dec. 7. The dent measures 12 inches long and about ½-inch deep. Managers expect the replacement work to take about 3 days, followed by system retests and final aft compartment close-outs. Preliminary assessments reflect a launch date of Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-103 no earlier than Dec. 16. STS-103 is the third servicing mission for the Hubble Space Telescope
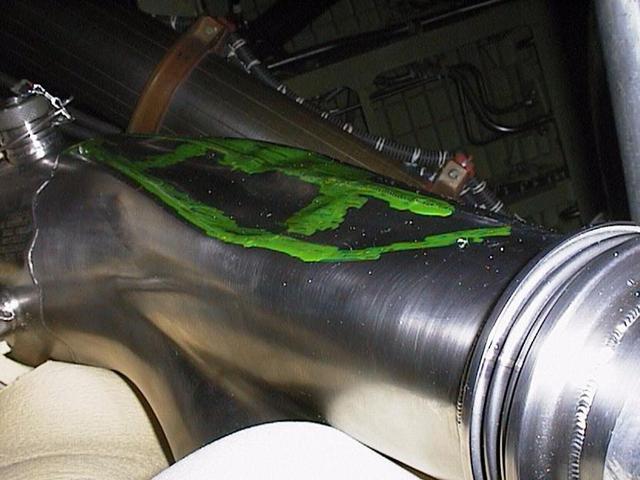

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Green dye penetrant helps pinpoint the dent discovered in this LH2 recirculation line in Space Shuttle Discovery's engine compartment. The 12-inch-long dent was discovered during routine aft compartment inspections Tuesday, Dec. 7. The LH2 line recirculates hydrogen from the Shuttle main engines back to the external tank during prelaunch engine conditioning. The line is being replaced and managers expect the replacement work to take about 3 days, followed by system retests and final aft compartment close-outs. Preliminary assessments reflect a launch date of Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-103 no earlier than Dec. 16. STS-103 is the third servicing mission for the Hubble Space Telescope
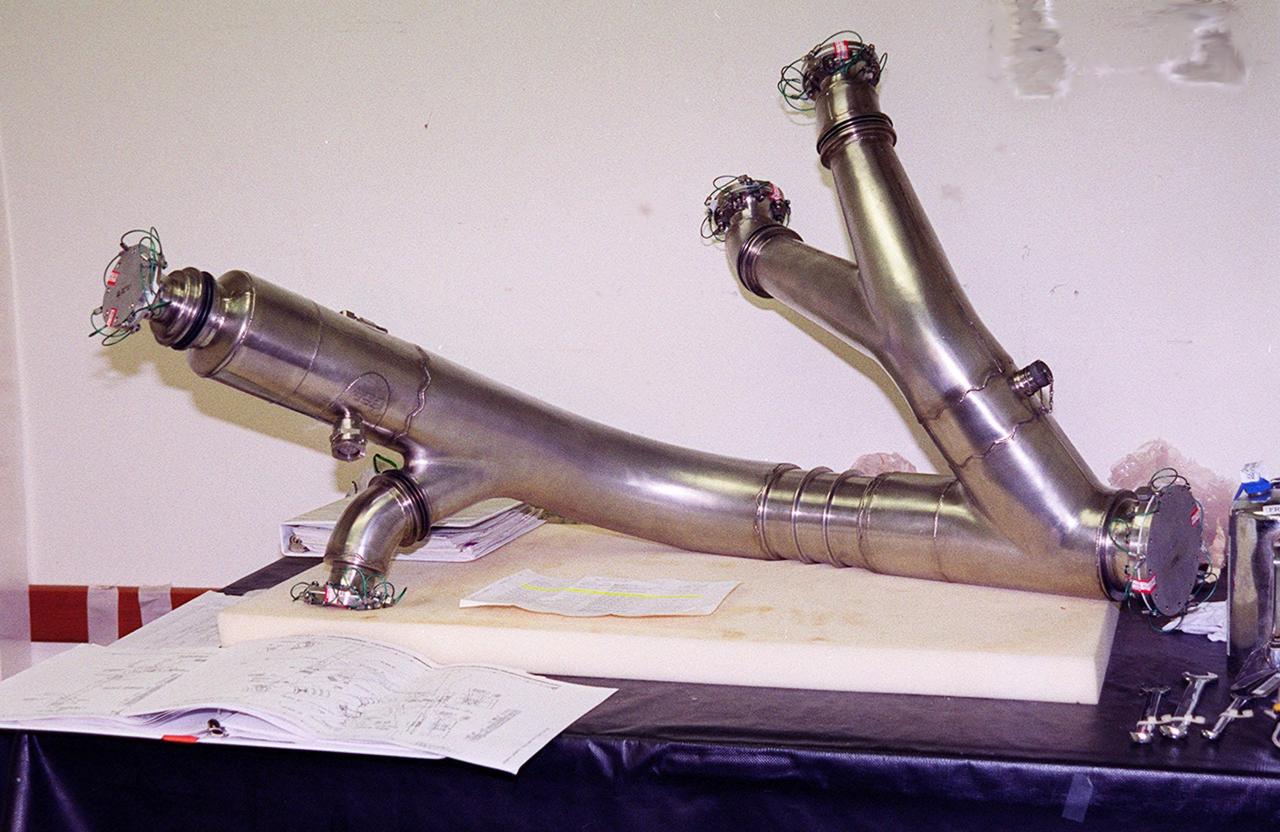
A spare four-inch diameter LH2 recirculation line (shown in photo) will be used to replace a damaged LH2 line in the orbiter Discovery. The line recirculates hydrogen from the Shuttle main engines back to the external tank during prelaunch engine conditioning. Workers noted a dent in the line during routine aft compartment inspections Tuesday, Dec. 7. The dent measures 12 inches long and about ½-inch deep. Managers expect the replacement work to take about 3 days, followed by system retests and final aft compartment close-outs. Preliminary assessments reflect a launch date of Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-103 no earlier than Dec. 16. STS-103 is the third servicing mission for the Hubble Space Telescope
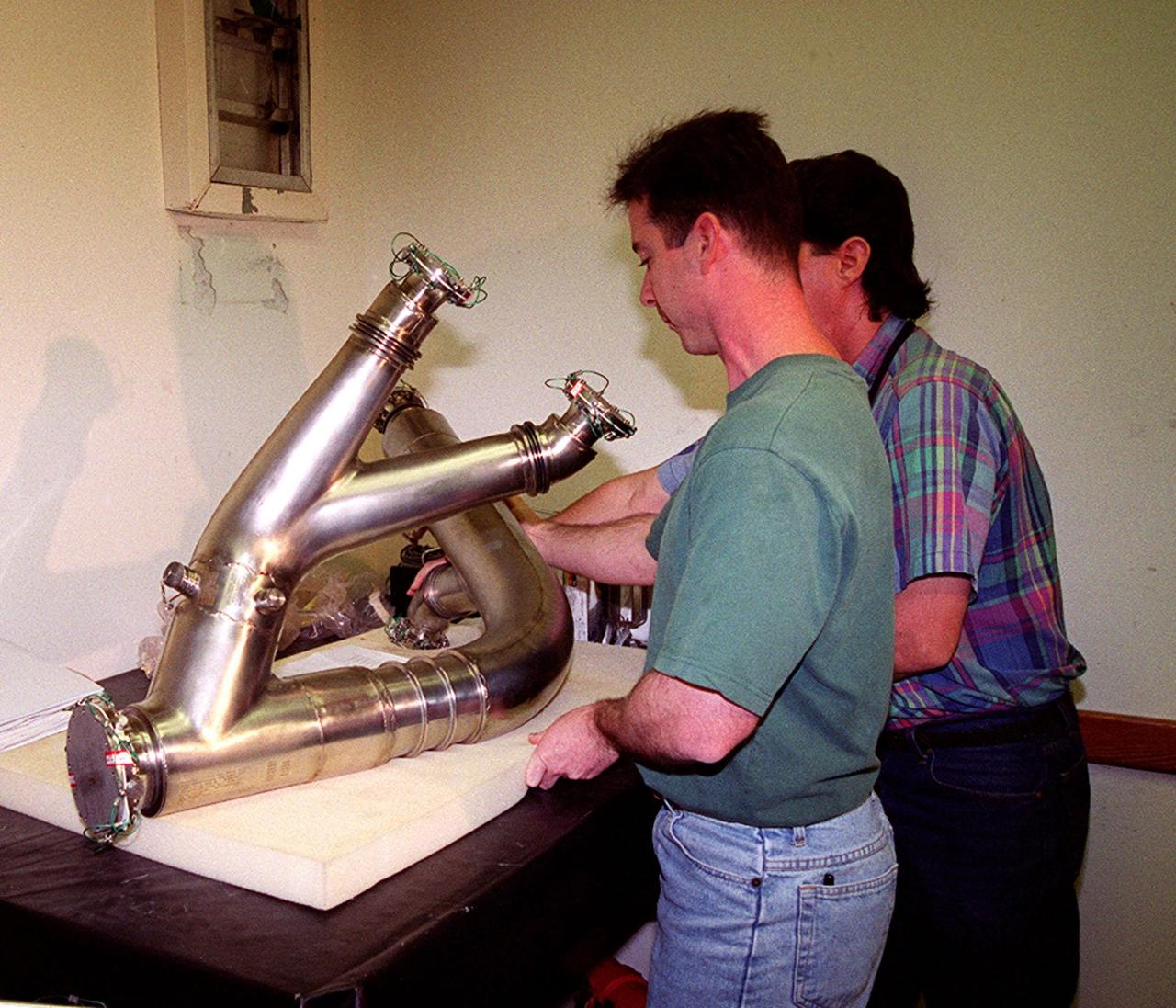

Gary Hamilton (left) and James Stickley, both with United Space Alliance, check out a spare four-inch diameter LH2 recirculation line that will be used to replace a damaged LH2 line in the orbiter Discovery. The line recirculates hydrogen from the Shuttle main engines back to the external tank during prelaunch engine conditioning. Workers noted a dent in the line during routine aft compartment inspections Tuesday, Dec. 7. The dent measures 12 inches long and about ½-inch deep. Managers expect the replacement work to take about 3 days, followed by system retests and final aft compartment close-outs. Preliminary assessments reflect a launch date of Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-103 no earlier than Dec. 16. STS-103 is the third servicing mission for the Hubble Space Telescope
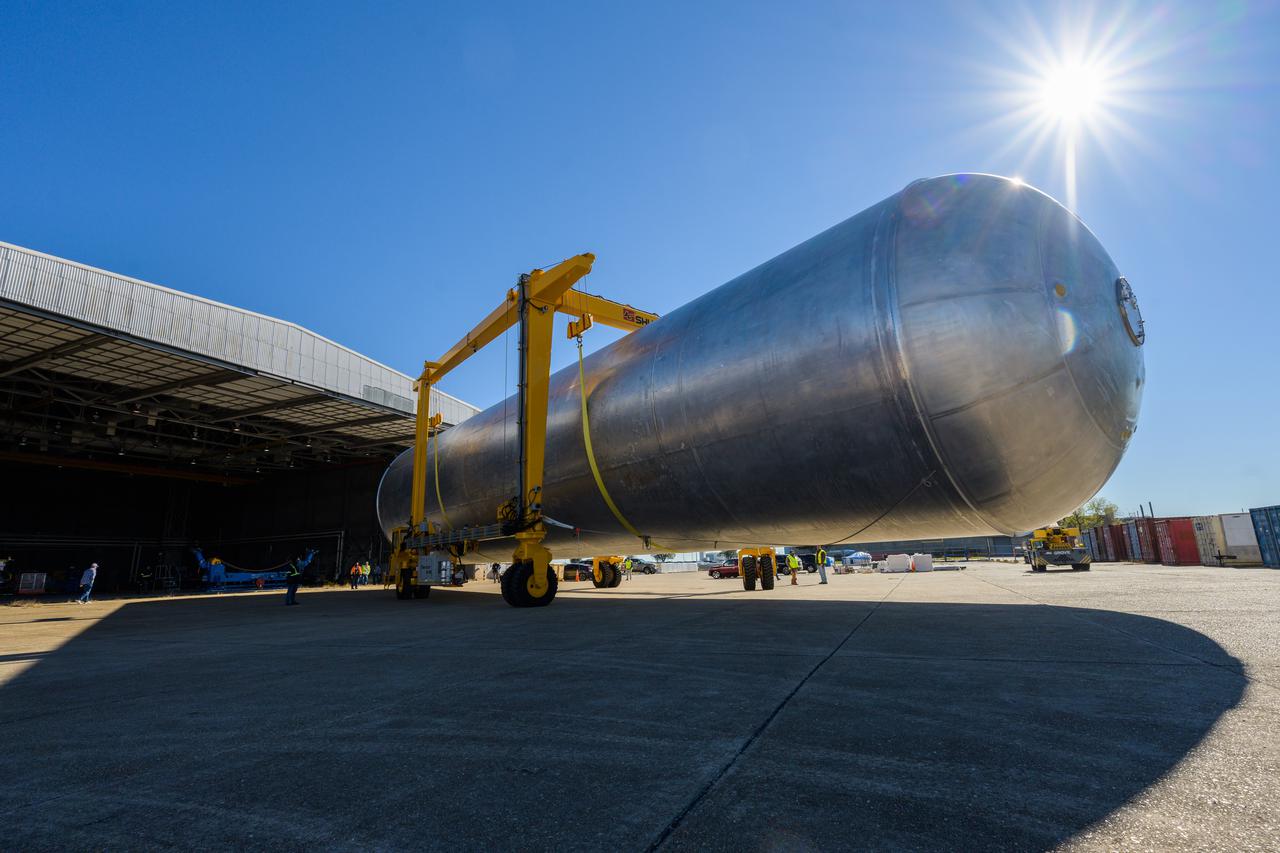

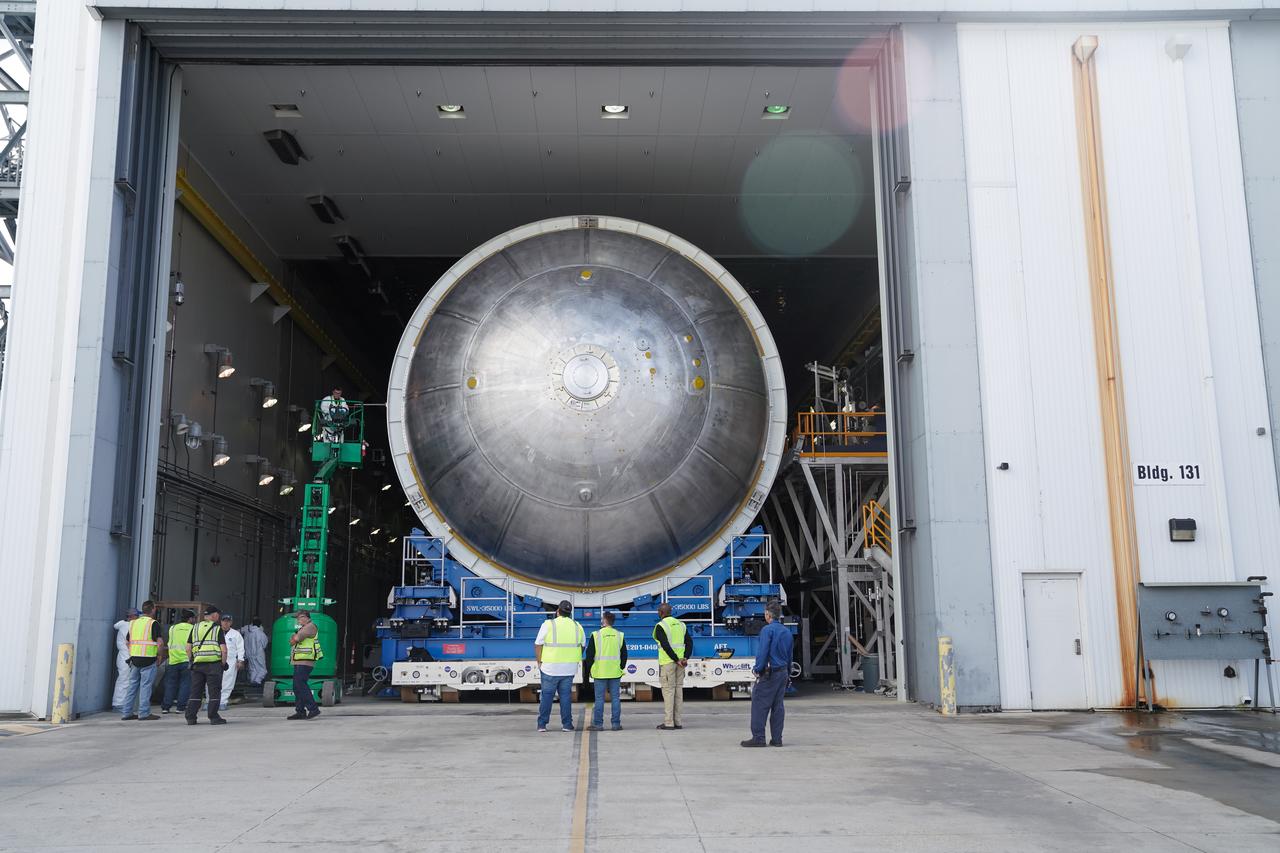
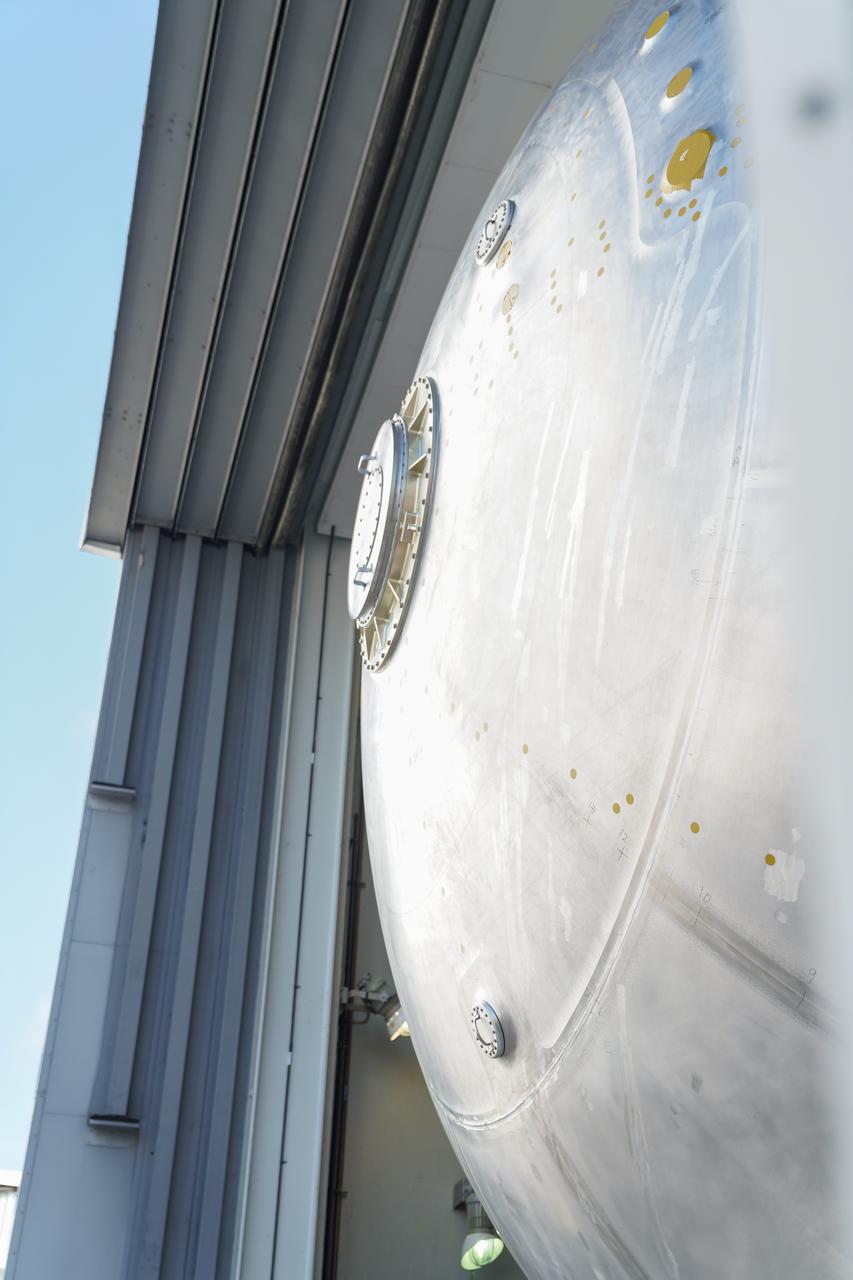
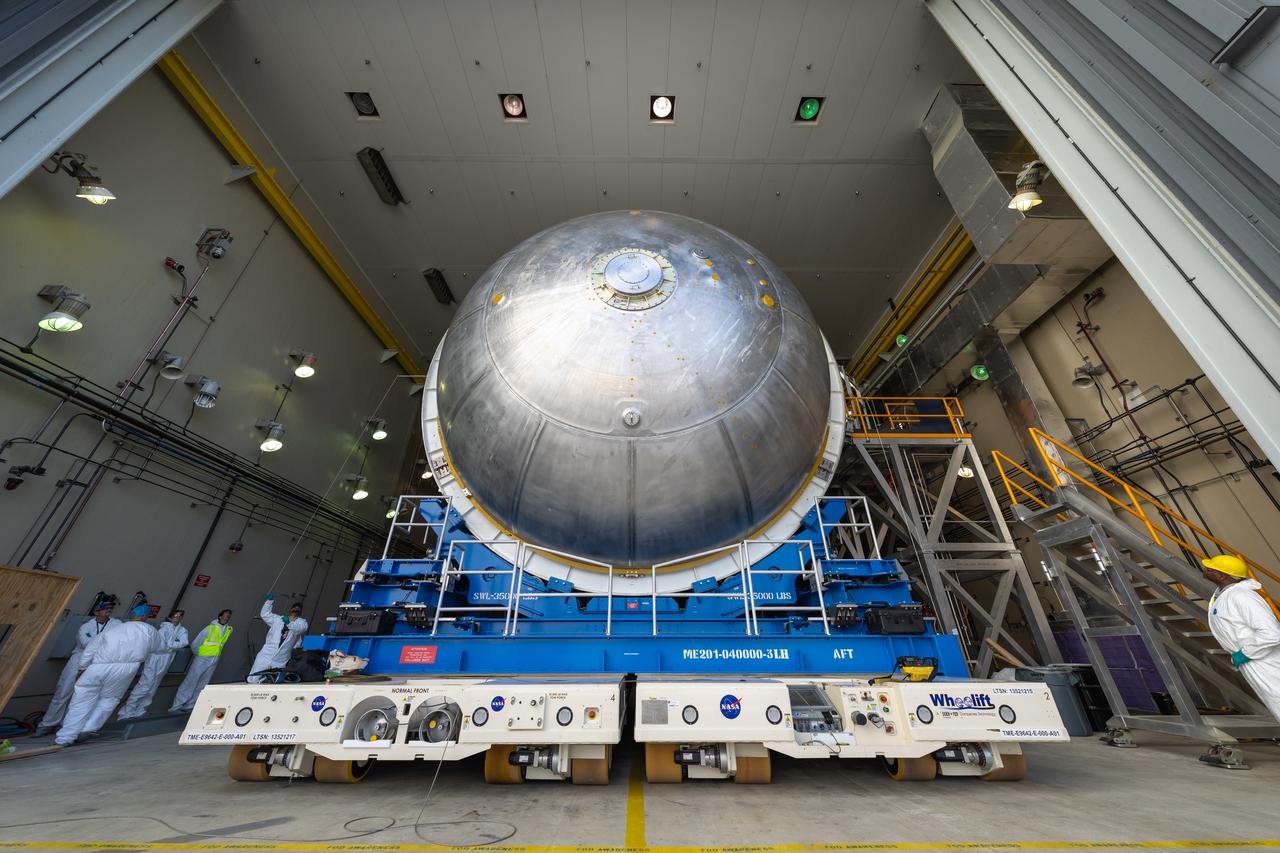
The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
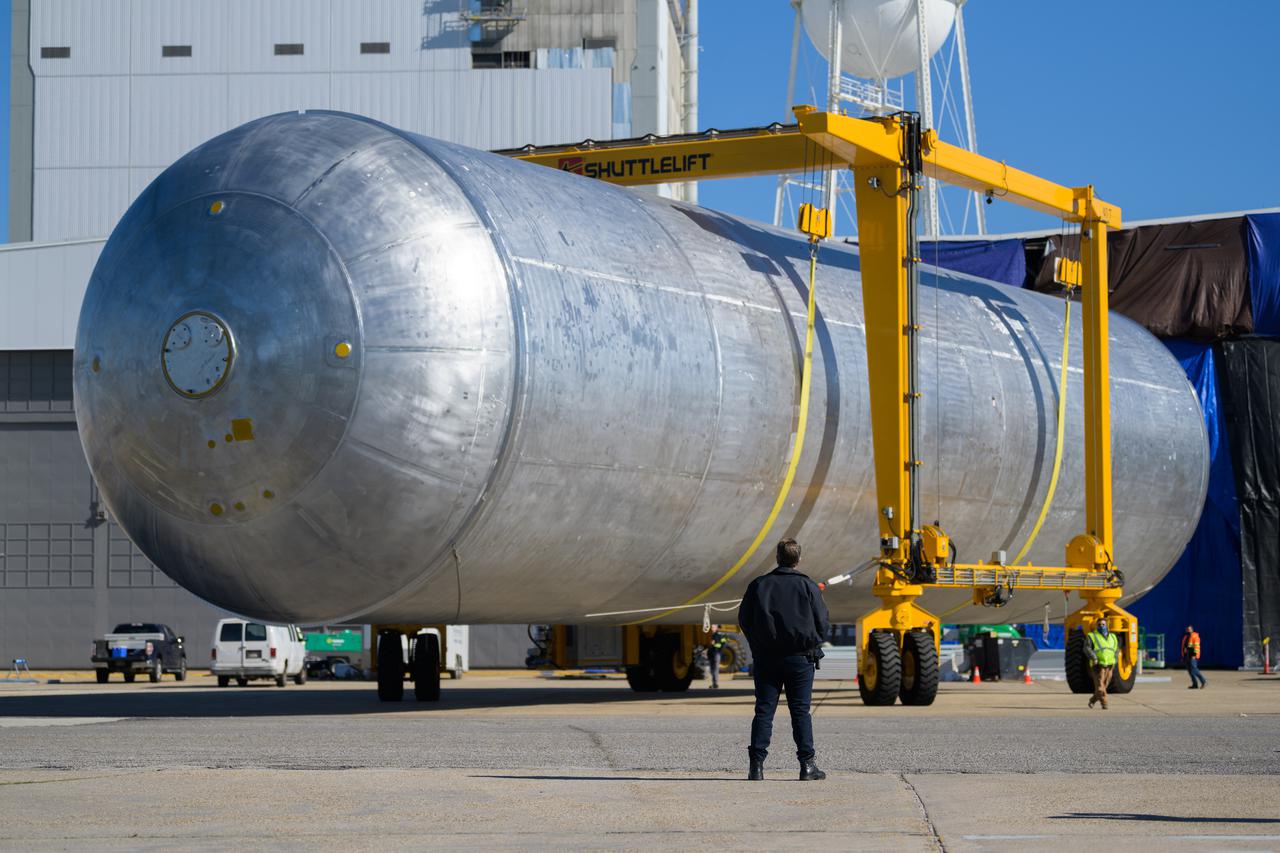

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
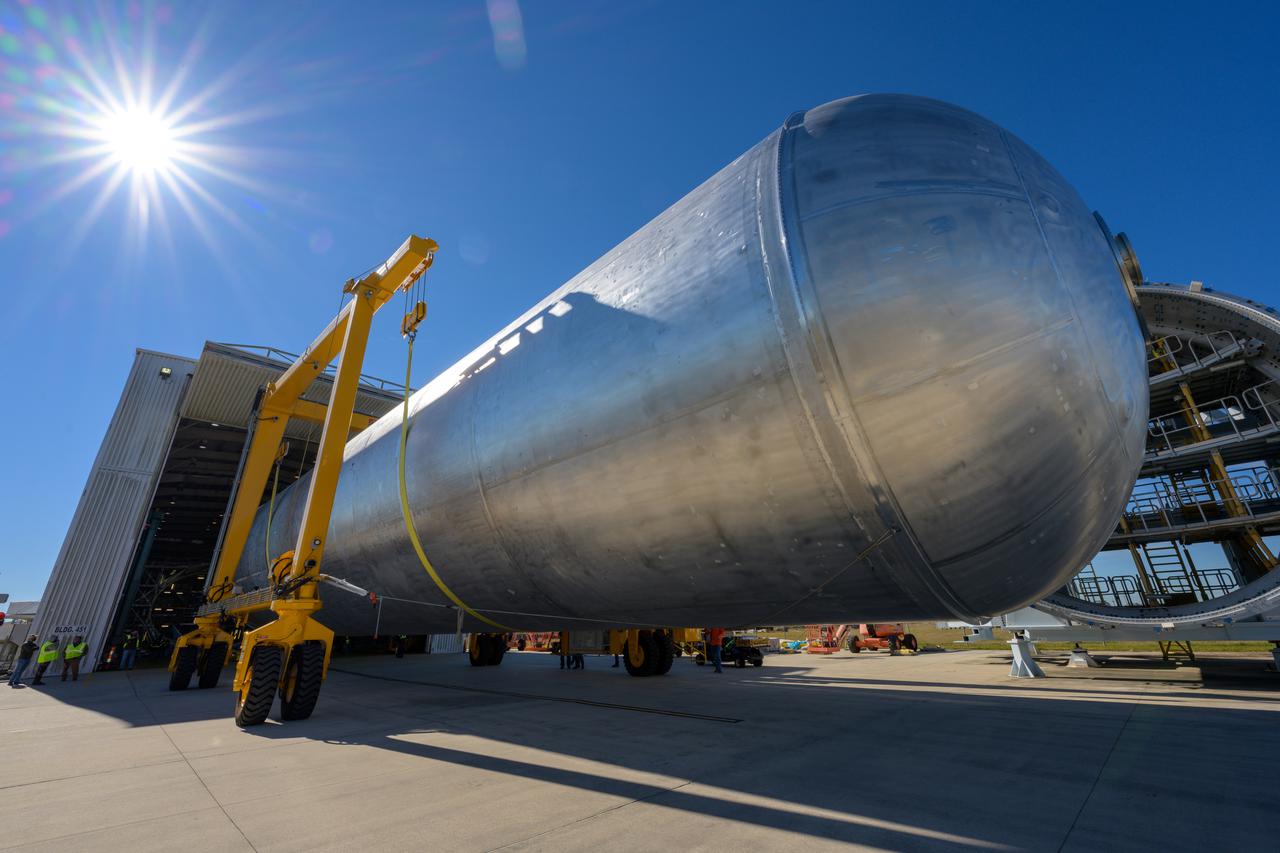

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
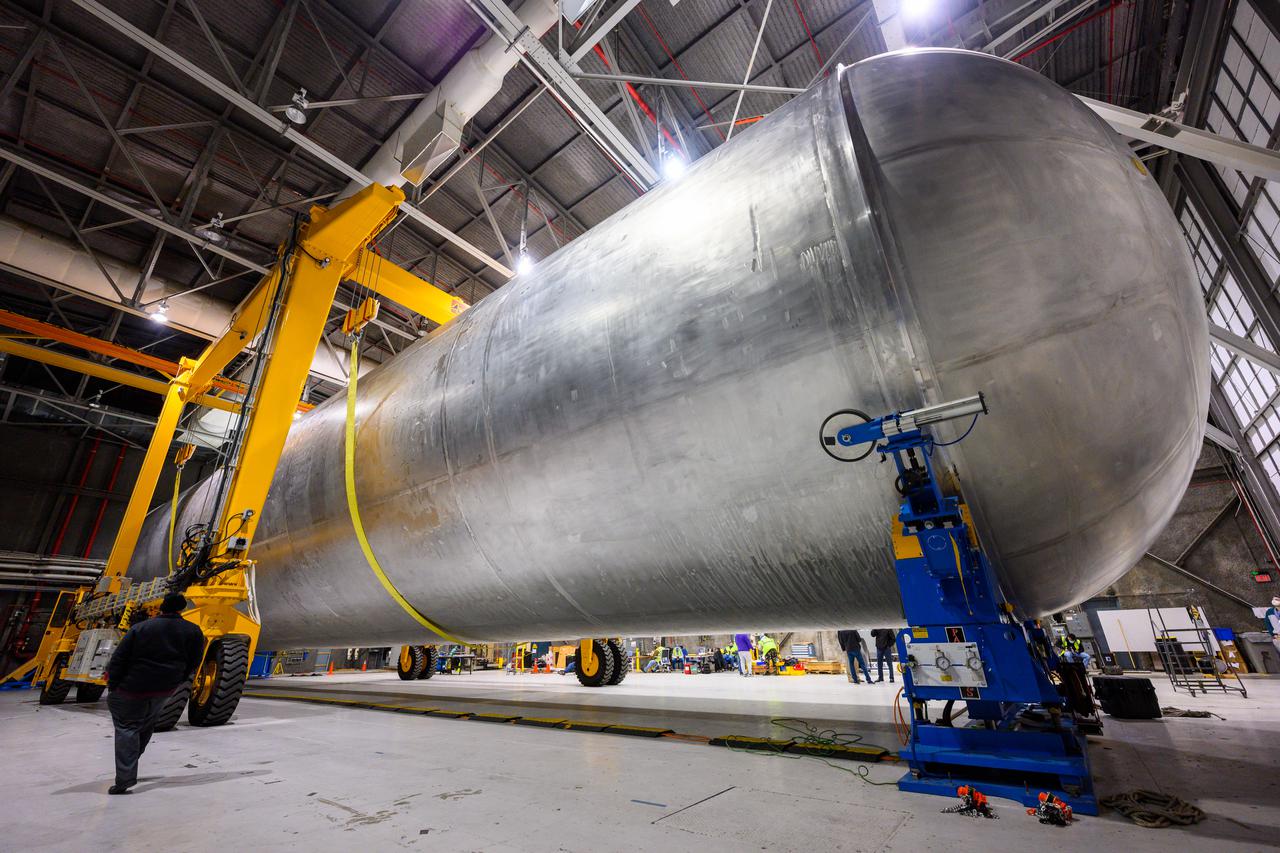

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
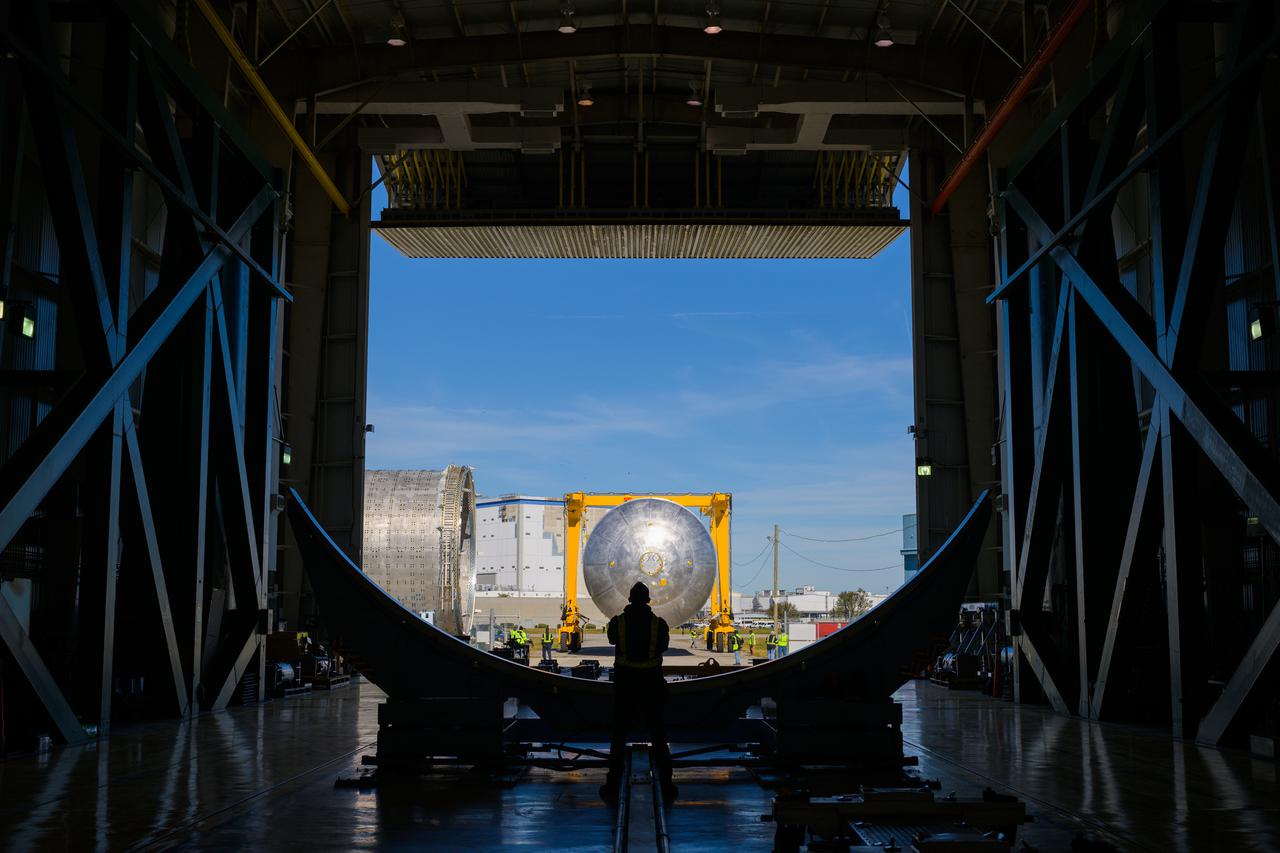

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
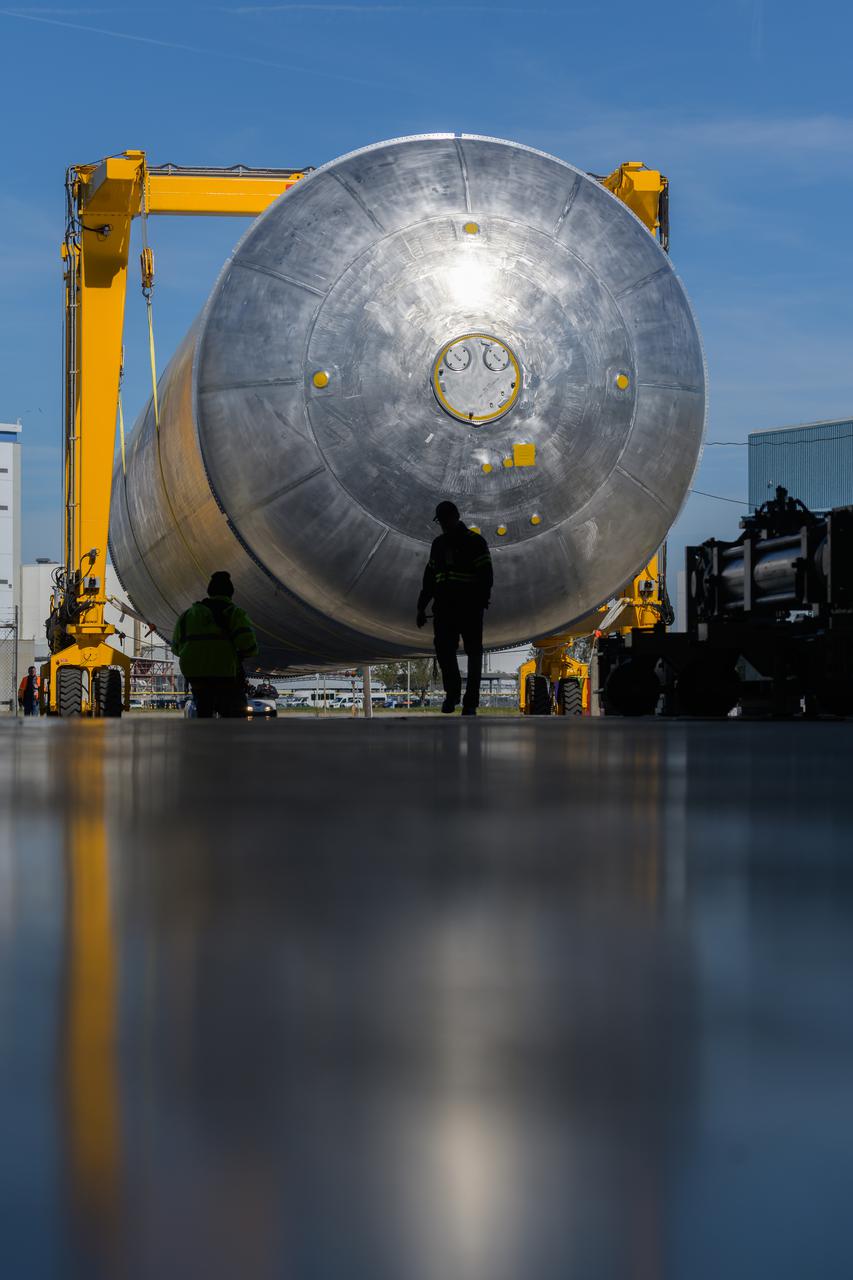

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
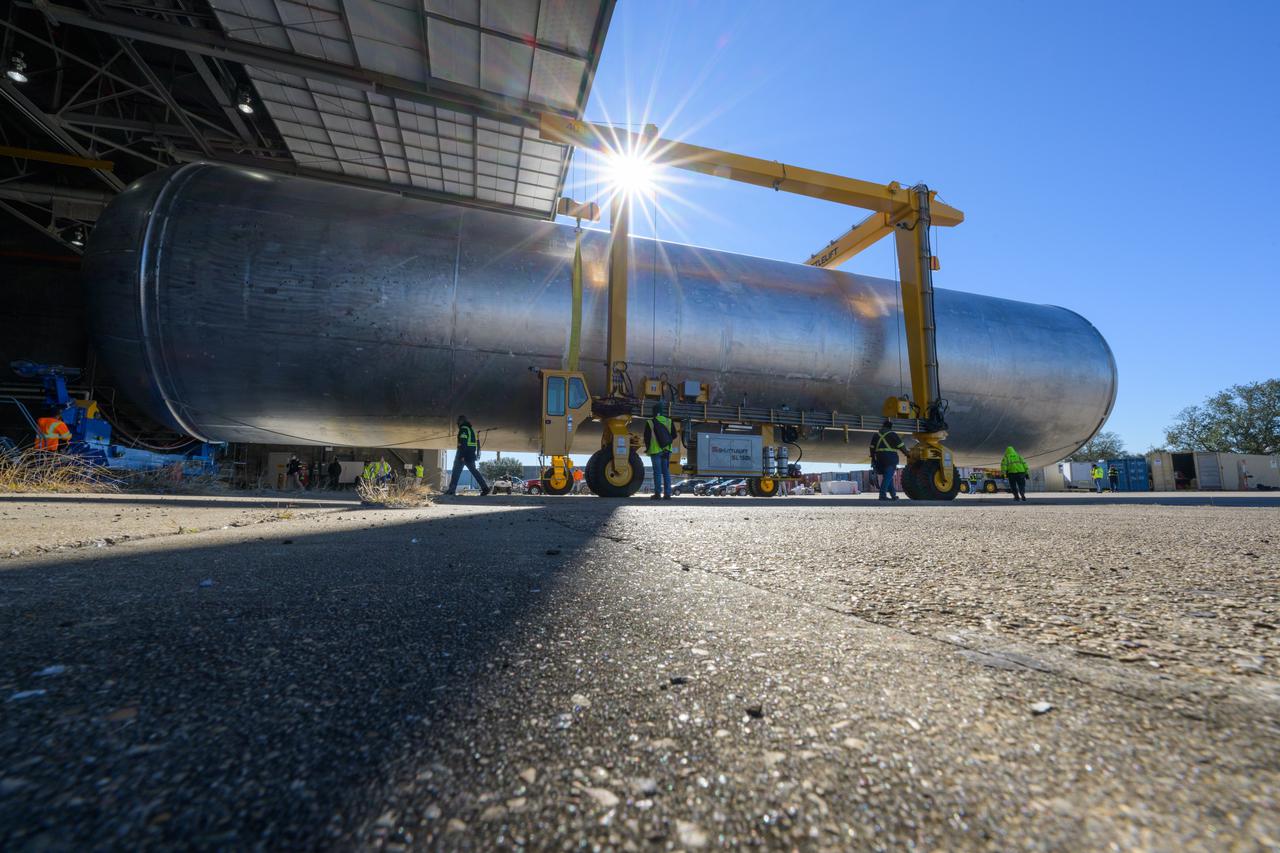

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
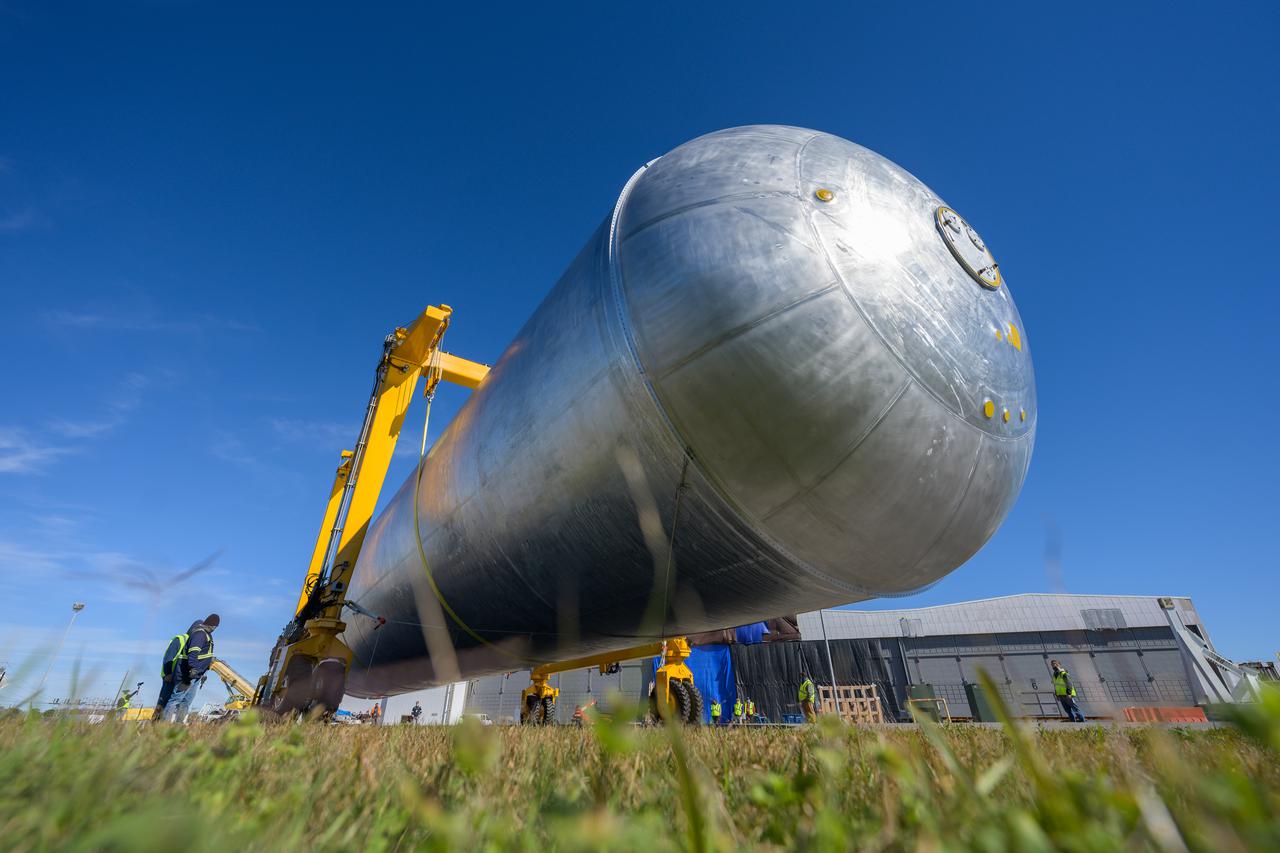

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
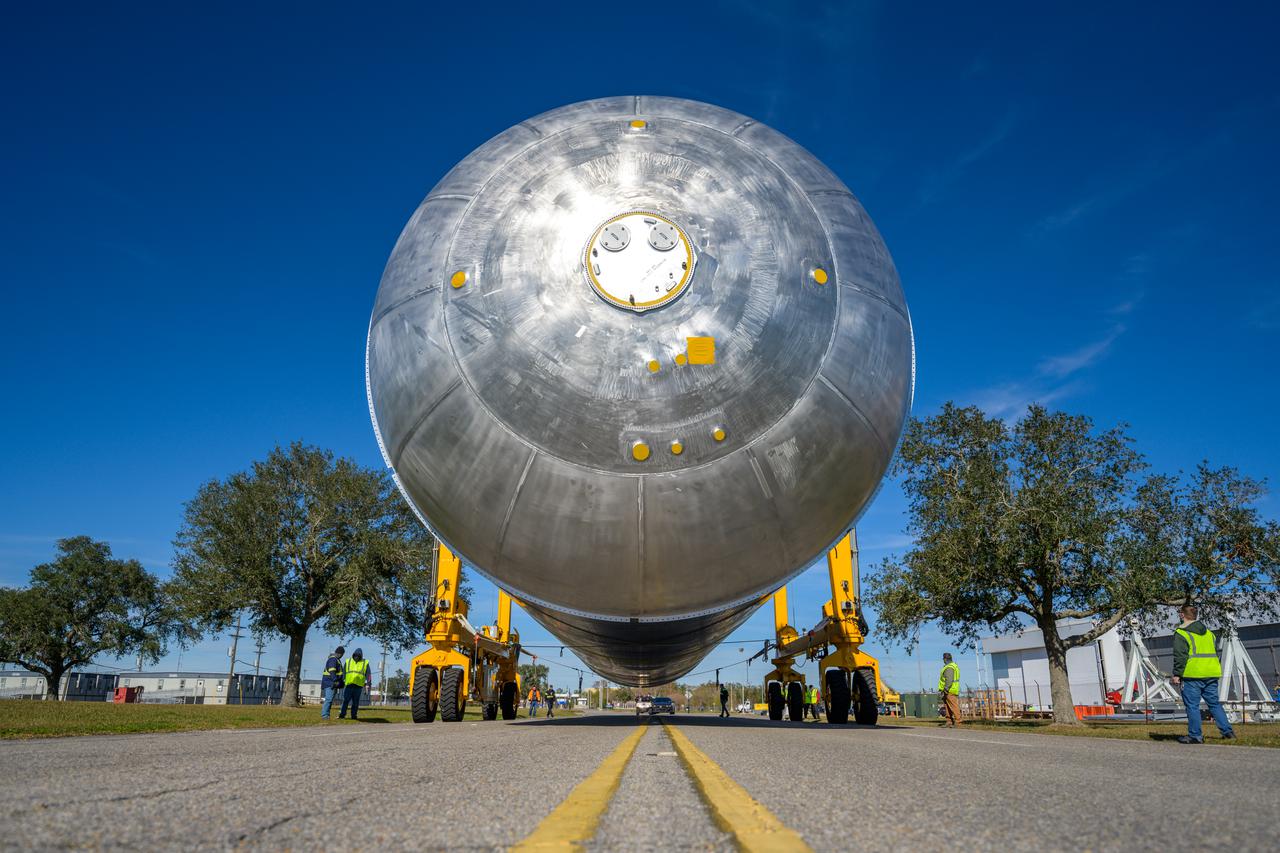

The liquid hydrogen tank that will be part of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage is being prepared for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Eventually, the tank will be connected to the engine section that will house the four RS-25 engines. Once the aft simulator is attached, the LH2 tank undergoes non-destructive evaluation, which will test weld strength and ensure the tank is structurally sound. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis III mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
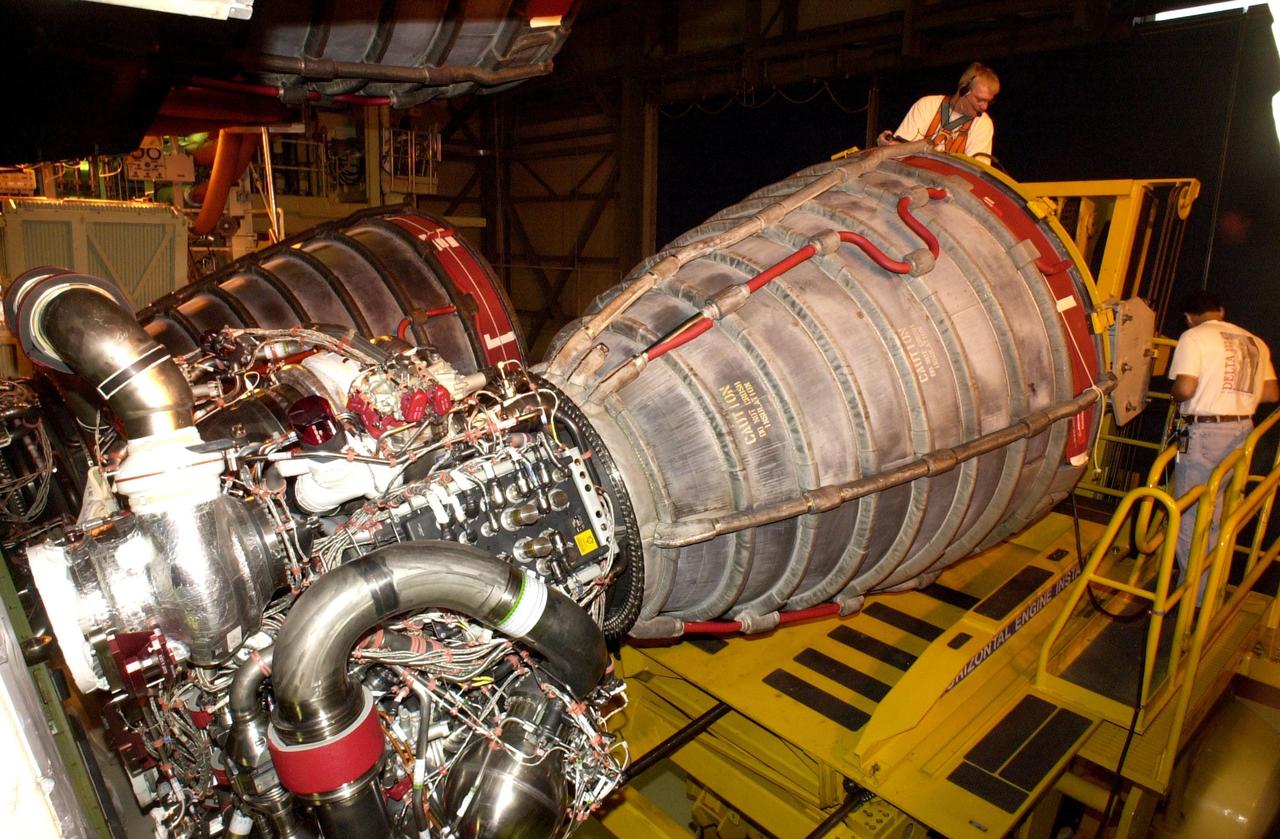

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Columbia's engine no. 2 is about to be pulled from the orbiter. After small cracks were discovered on the LH2 Main Propulsion System (MPS) flow liners in two other orbiters, program managers decided to move forward with inspections on Columbia before clearing it for flight on STS-107. The heat shields were removed, and after removing the three main engines, inspections of the flow liners will follow. The July 19 launch of Columbia on STS-107 has been delayed a few weeks
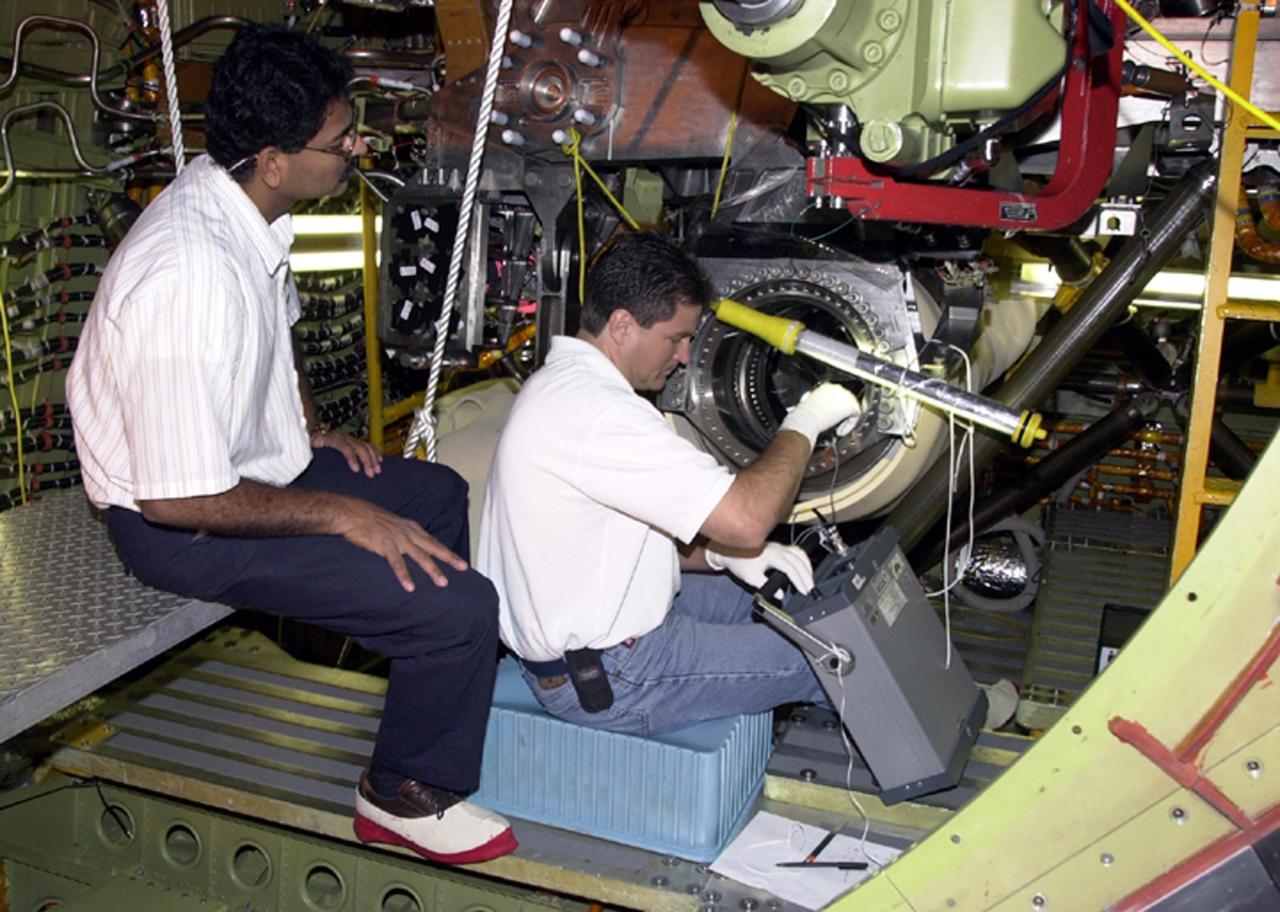

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After engine removal on Columbia, the flow line is being inspected by (left) A.J. Koshti, with The Boeing Co., and (right) Ken Tauer, with United Space Alliance. The inspection is the result of small cracks being discovered on the LH2 Main Propulsion System (MPS) flow liners in two other orbiters. Program managers decided to conduct inspections on Columbia before clearing it for flight on STS-107. The July 19 launch of Columbia on STS-107 has been delayed a few weeks
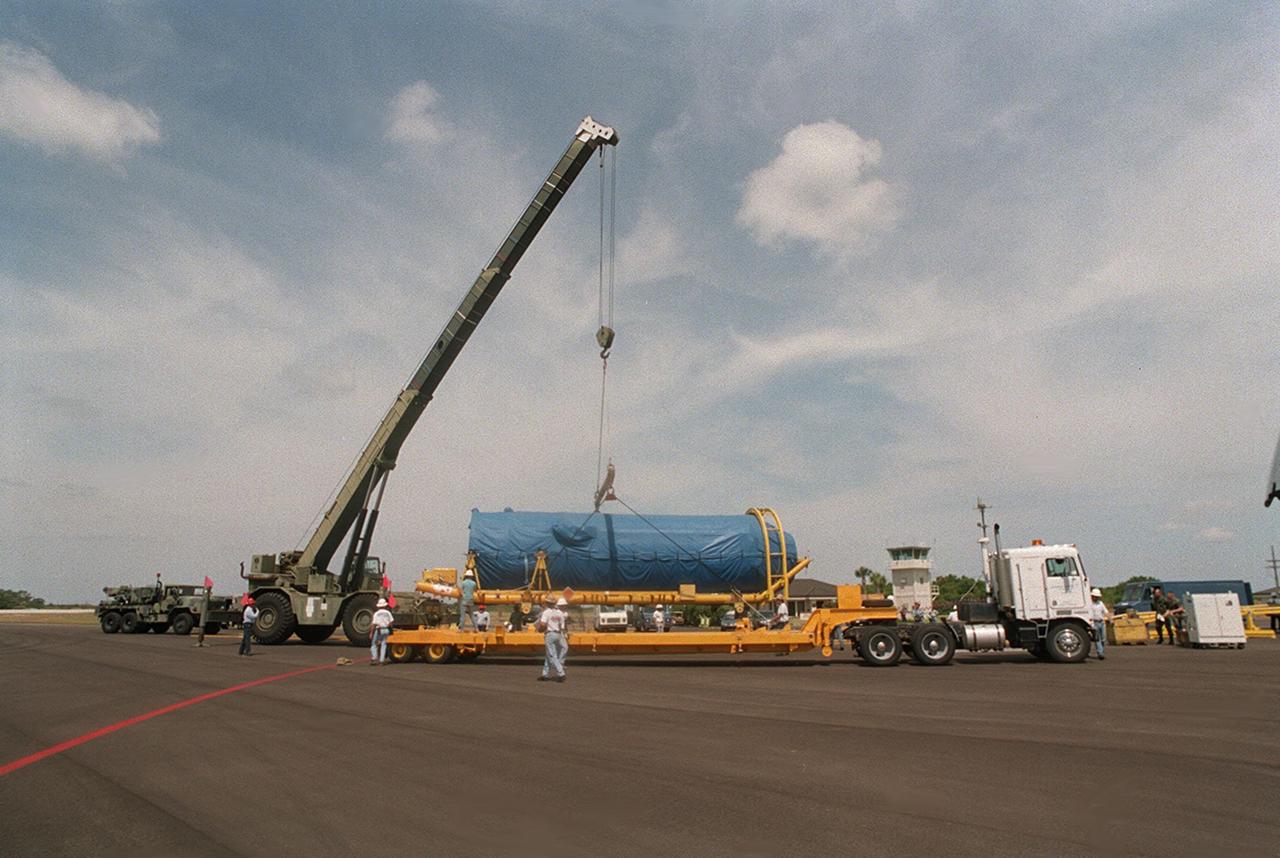

At Cape Canaveral Air Force skid strip, the Centaur upper stage is placed aboard a transporter after arriving aboard a Russian cargo plane, the Antenov 124. The Centaur will be coupled with an Atlas IIA to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Centaur, manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin, is 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter and 10.0 m (33-ft) long. It uses liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LO2) propellants