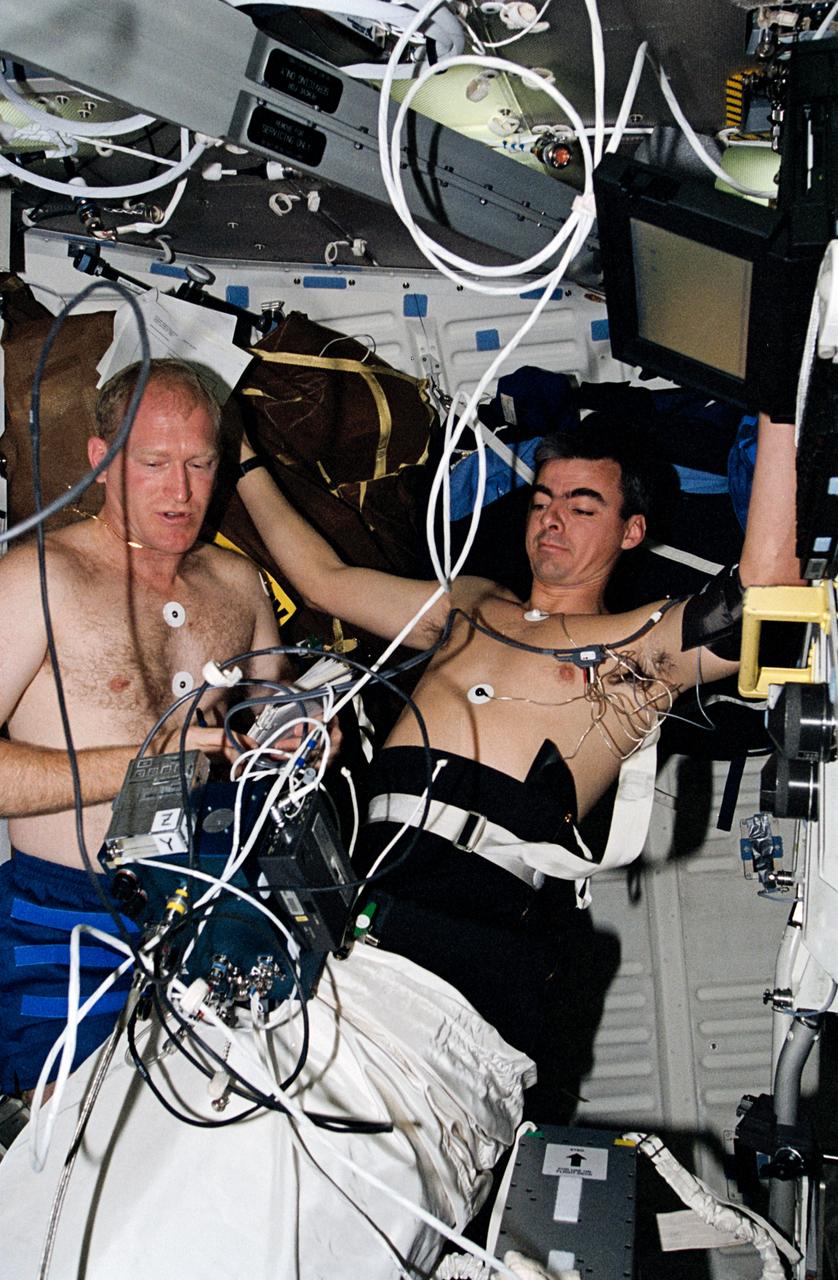
STS062-07-010 (4-18 March 1994) --- Astronaut Andrew M. Allen, pilot, participates in biomedical testing as he does a "soak" in the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) apparatus on the Columbia's middeck. Astronaut Charles D. (Sam) Gemar, mission specialist, monitors readouts from the test.
STS062-01-032 (4-14 March 1994) --- Astronaut Charles D. (Sam) Gemar, mission specialist, talks to ground controllers while assisting astronaut Andrew M. Allen with a "soak" in the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) apparatus on Columbia's middeck. The pair was joined by three other veteran NASA astronauts for 14-days of scientific research aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia in earth orbit.
S73-27707 (9 June 1973) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., Skylab 2 commander, serves as test subject for the Lower Body Negative Pressure (MO92) Experiment, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the Skylab 1/2 space station cluster in Earth orbit. Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, assists Conrad into the LBNP device. Kerwin served as monitor for the experiment. The purpose of the MO92 experiment is to provide information concerning the time course of cardiovascular adaptation during flight, and to provide inflight data for predicting the degree of orthostatic intolerance and impairment of physical capacity to be expected upon return to Earth environment. The data collected in support of MO92 blood pressure, heart rate, body temperature, vectorcardiogram, LBNPD pressure, leg volume changes, and body weight. Photo credit: NASA
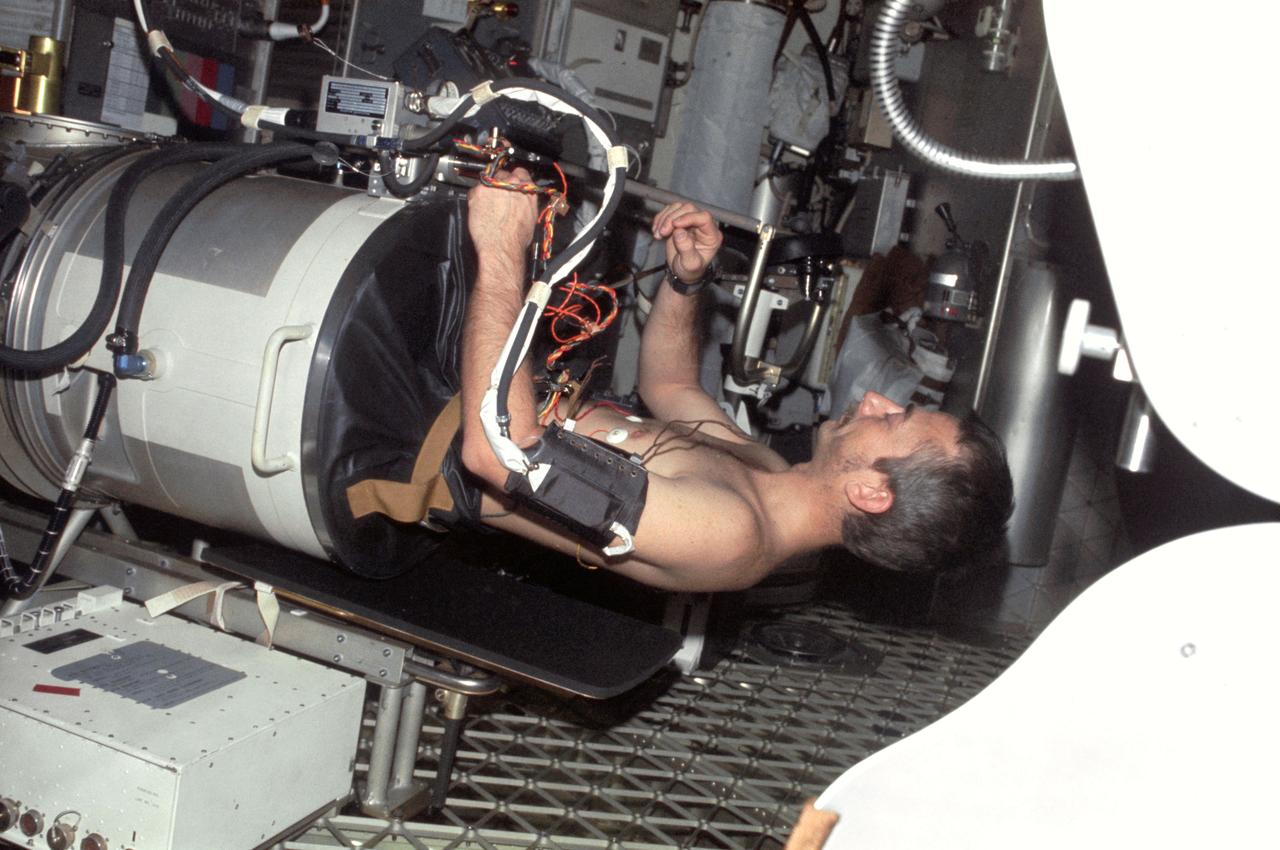

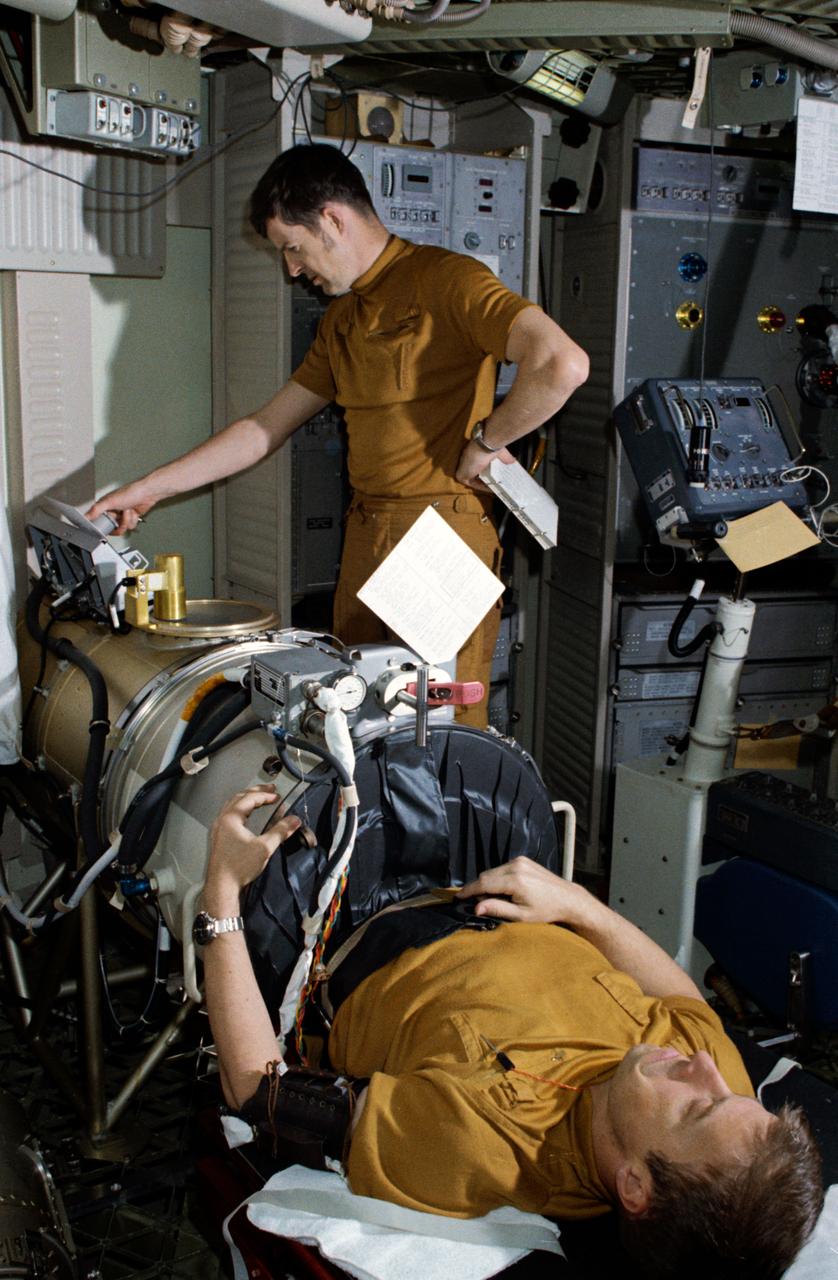
SL3-108-1278 (July-September 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, science pilot of the Skylab 3 mission, lies in the Lower Body Negative Pressure Device in the work and experiments area of the Orbital Workshop (OWS) crew quarters of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit. This picture was taken with a hand-held 35mm Nikon camera. Astronauts Garriott, Alan L. Bean and Jack R. Lousma remained with the Skylab space station in orbit for 59 days conducting numerous medical, scientific and technological experiments. The LBNPD (MO92) Experiment is to provide information concerning the time course of cardiovascular adaptation during flight, and to provide in-flight data for predicting the degree of orthostatic intolerance and impairment of physical capacity to be expected upon return to Earth environment. The bicycle ergometer is in the right foreground. Photo credit: NASA
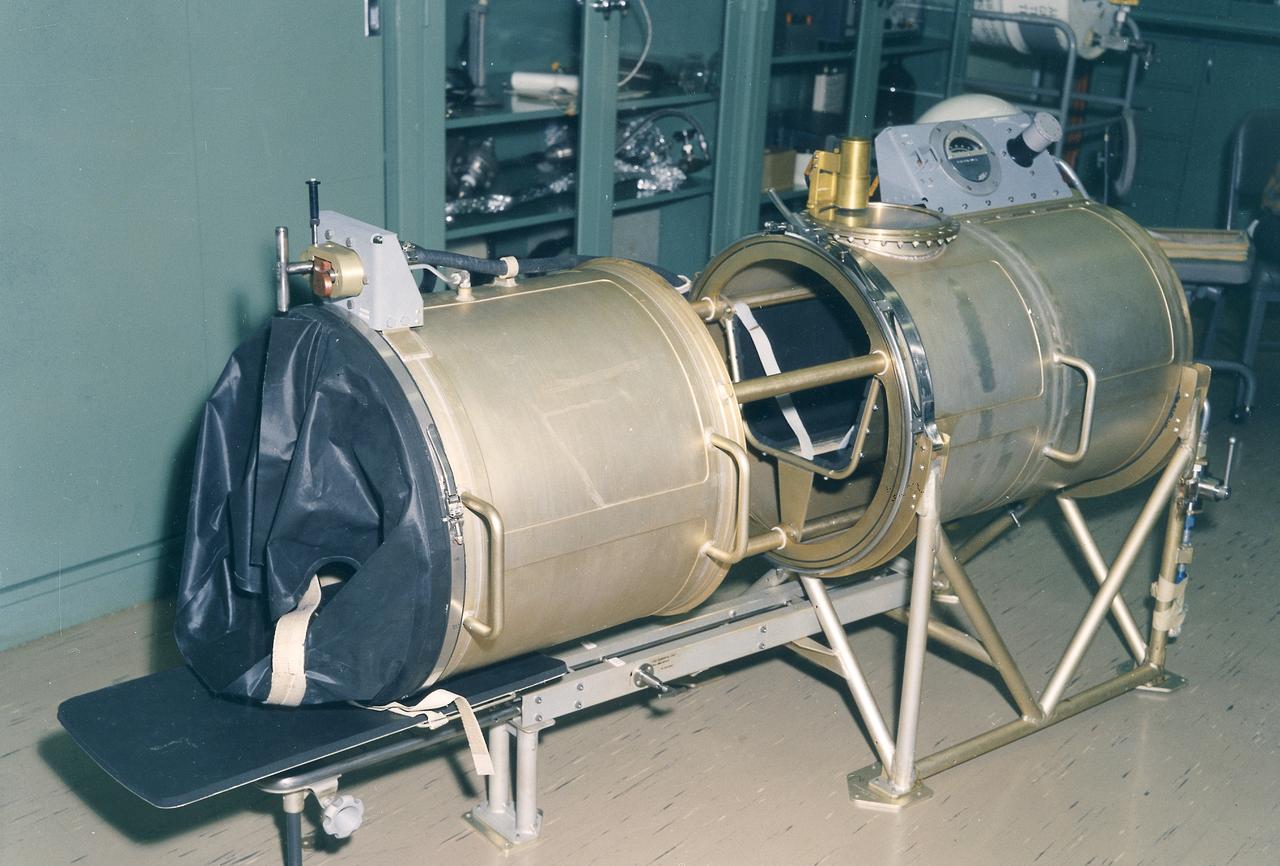
This 1970 photograph shows Skylab's In-Flight Lower Body Negative Pressure experiment facility, a medical evaluation designed to monitor changes in astronauts' cardiovascular systems during long-duration space missions. This experiment collected in-flight data for predicting the impairment of physical capacity and the degree of orthostatic intolerance to be expected upon return to Earth. Data to be collected were blood pressure, heart rate, body temperature, vectorcardiogram, lower body negative pressure, leg volume changes, and body mass. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
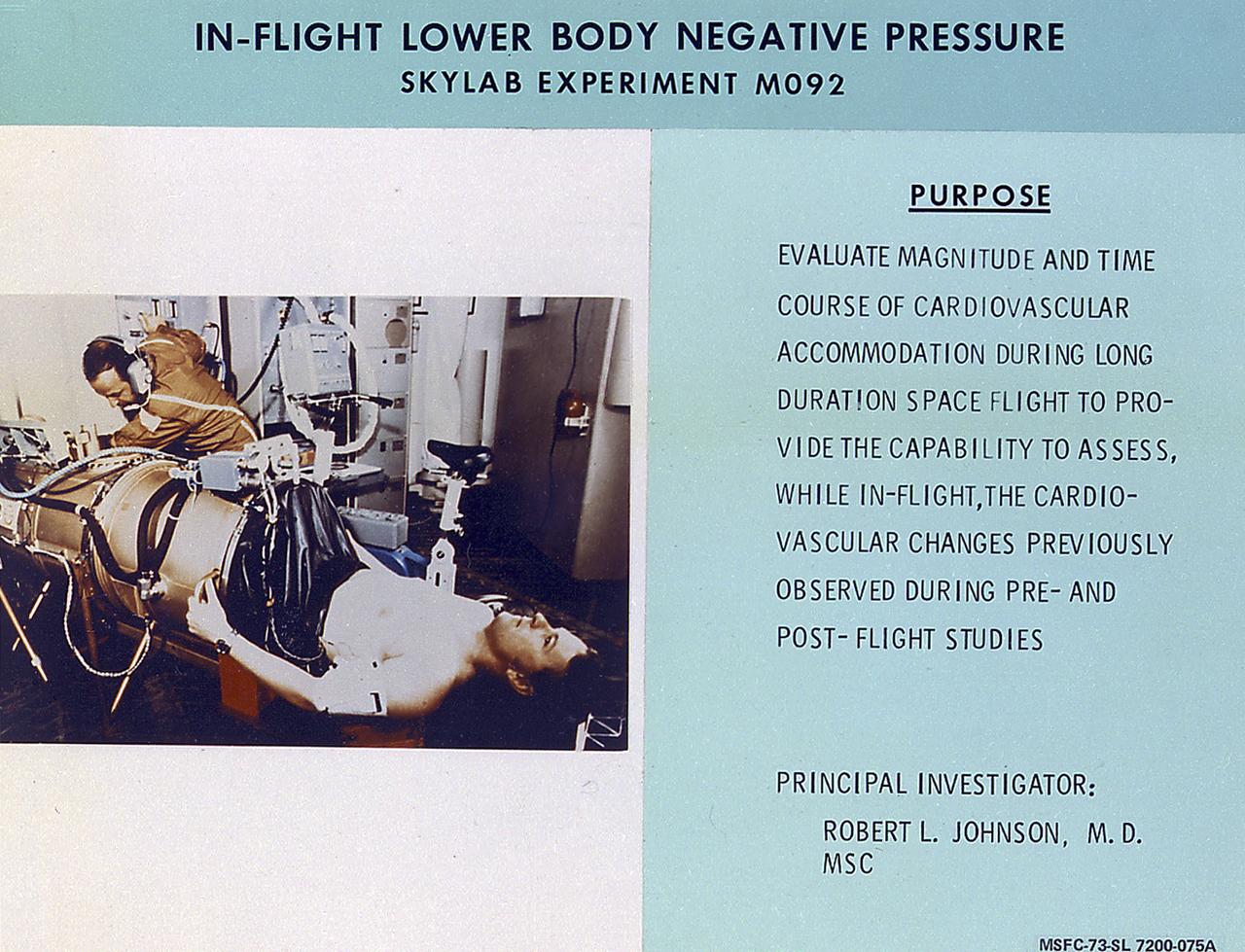
This chart details Skylab's In-Flight Lower Body Negative Pressure experiment facility, a medical evaluation designed to monitor changes in astronauts' cardiovascular systems during long-duration space missions. This experiment collected in-flight data for predicting the impairment of physical capacity and the degree of orthostatic intolerance to be expected upon return to Earth. Data to be collected were blood pressure, heart rate, body temperature, vectorcardiogram, lower body negative pressure, leg volume changes, and body mass. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
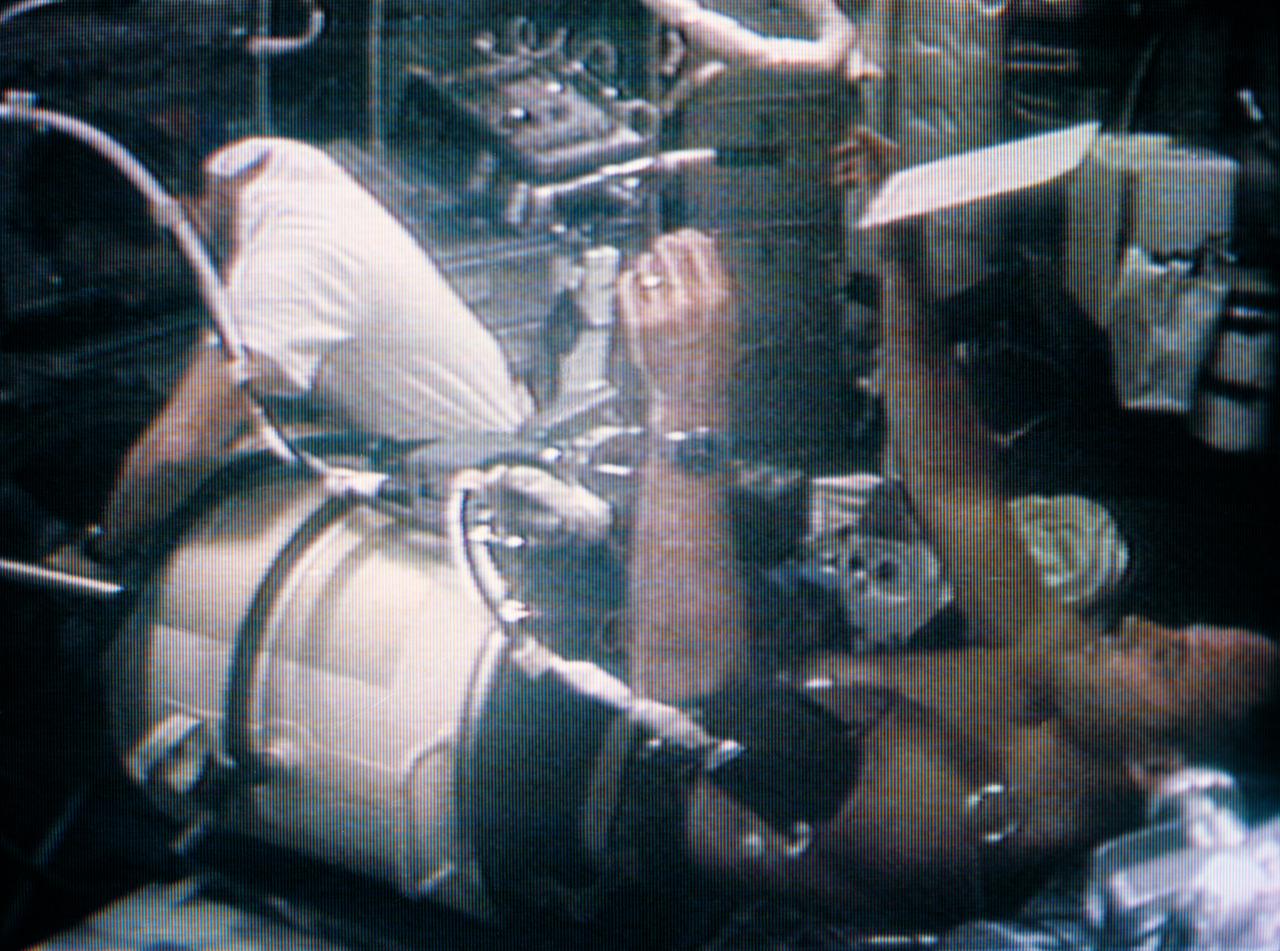

S73-34180 (7 Aug. 1973) --- A medium close-up view of astronaut Jack R. Lousma, Skylab 3 pilot, in the Lower Body Negative Pressure Device (LBNPD), as astronaut Alan L. Bean, commander, works around the leg band area. This portion of the LBNPD MO-92 experiment was televised on Aug. 7, 1973. The LBNPD experiment is to provide information concerning the time course of cardiovascular adaptation during flight, and to provide in-flight data for predicting the degree of orthostatic intolerence and impairment of physical capacity to be expected upon returning to Earth environment. The bicycle ergometer is in the background, partially visible behind Bean. Photo credit: NASA
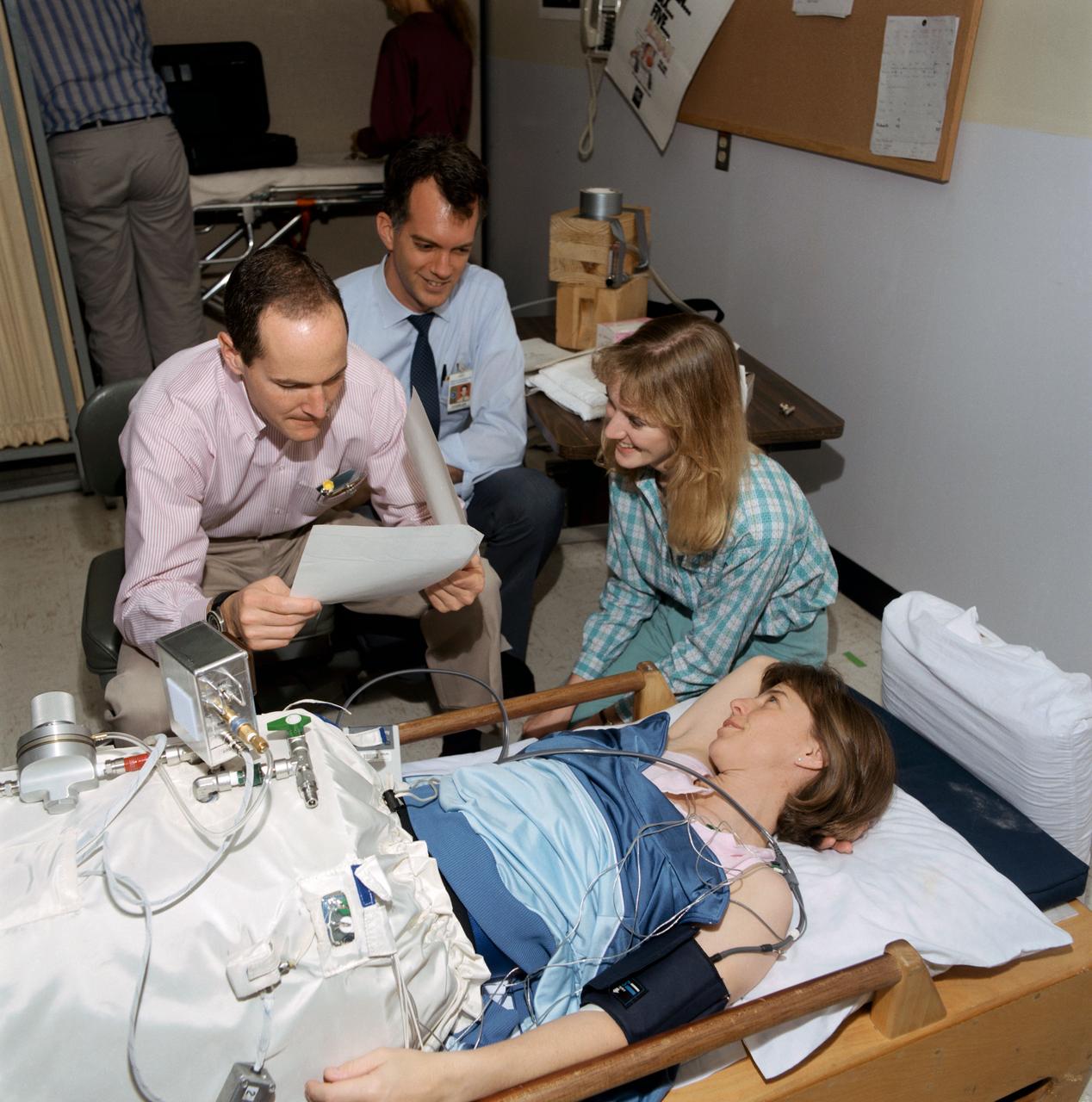
STS-32 crewmembers test the inflight lower body negative pressure (LBNP) device. Mission Specialist (MS) Bonnie J. Dunbar (lying down) inside the cylindrical LBNP device prepares for testing as principal investigator Dr. John Charles, a cardiovascular scientist in JSC's Space Biomedical Research Institute, and Michele Jones, a KRUG International biomedical engineer, review procedures with MS G. David Low. The inflight LBNP will be part of detailed supplementary objective (DSO) 0478. Photo taken by JSC photographer Jack Jacob.
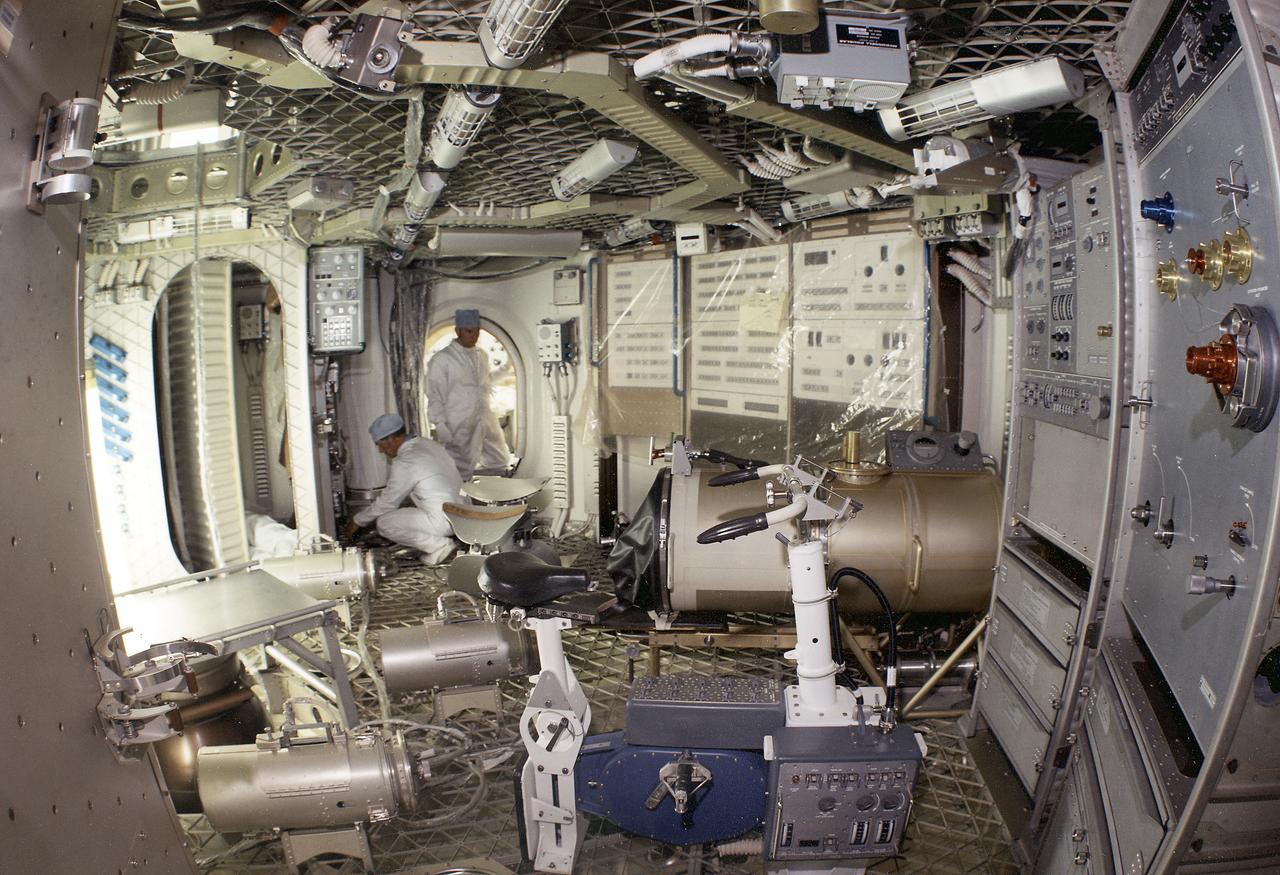
This is a wide-angle view of the Orbital Workshop lower level experiment area. In center foreground is the ergometer bicycle. In center background is a litter chair for the Human Vestibular Function experiment (Skylab Experiment M131) and in right background is the Lower Body Negative Pressure System experiment (Skylab Experiment M092). The ergometer bicycle was used for metabolic activity experiments and exercise. The purpose of the Human Vestibular (irner ear) Function experiment was to examine the effect of weightlessness on man's sensitivity and susceptibility to motion rotation, and his perception of orientation. The Lower Body Negative Pressure experiment investigated the relationship between the zero gravity environment and cardiovascular deconditioning. A characteristic of cardiovascular deconditoning is the partial failure of the blood vessels resulting in the excessive pooling of the blood in the legs when a person assumes an erect posture in a gravity field. The Marshall Space Flight Center had the program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
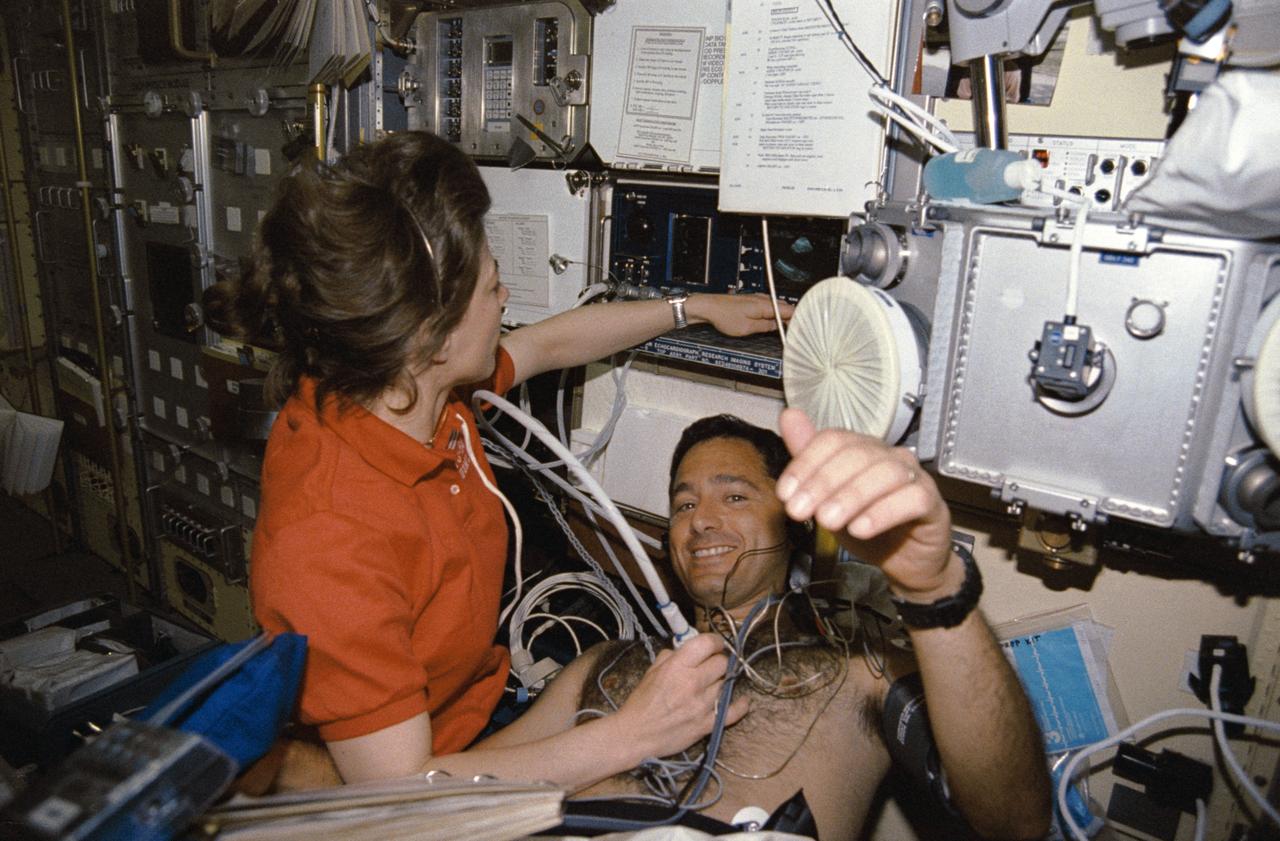
STS050-291-027 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Astronaut Bonnie J. Dunbar uses a Doppler to collect medical data from Lawrence J. DeLucas, payload specialist, during his diagnostic "run" in the Lower Body Negative Pressure device (LBNP). The Doppler is used to pick up high-frequency sound waves from the surface of the heart, thus producing pictures on the monitor of the American Flight Echocardiograph (AFE). The result of the LBNP procedure is expected to be an increased tolerance of orthostatis - or standing upright - upon return to Earth's gravity. LBNP has been used a number of times in the United States space program, as early as the Skylab missions. STS-50 is the fourth flight of the current collapsible unit. Researchers are refining the LBNP protocol which will be used operationally on future 13 through 16 day missions.
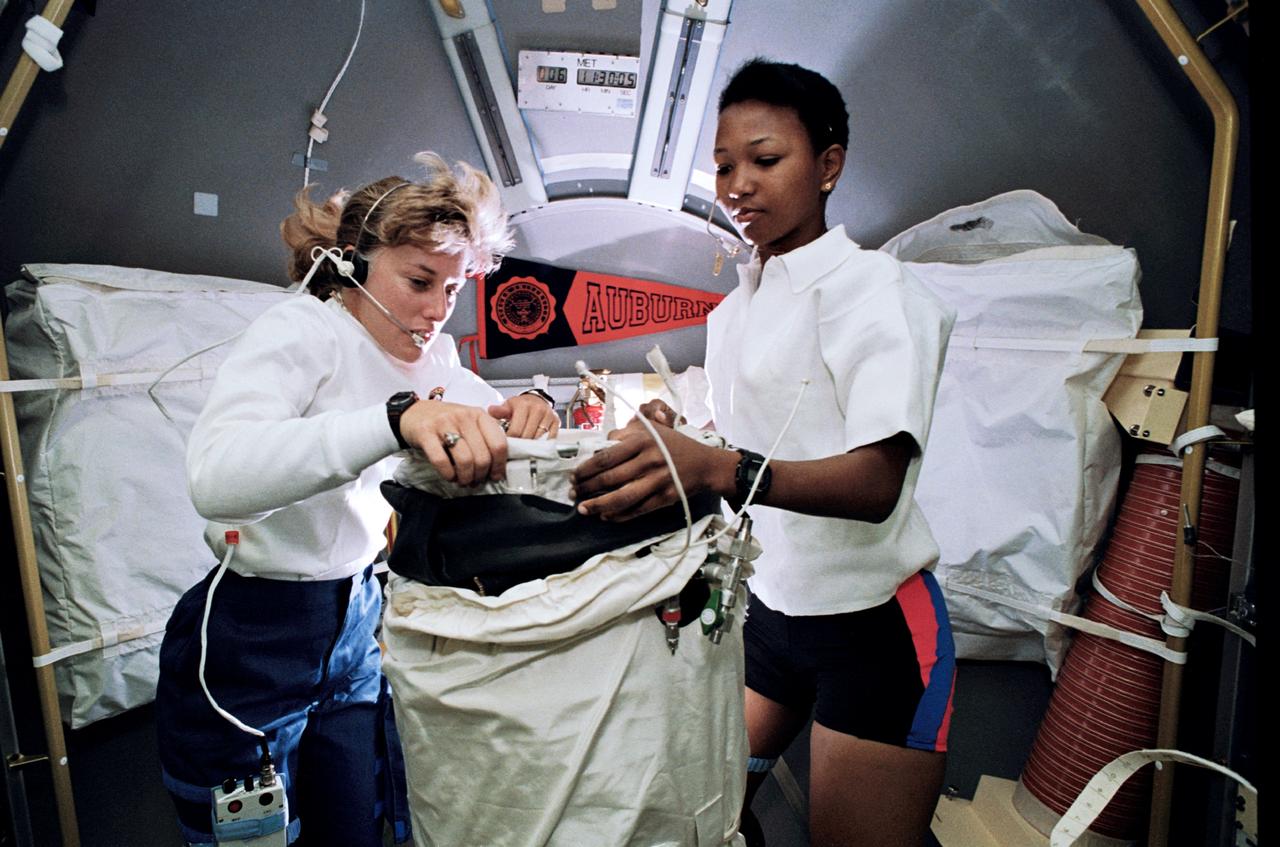
STS047-46-027 (12-20 Sept. 1992) --- Astronauts N. Jan Davis (left) and Mae C. Jemison, STS-47 mission specialists, prepare to deploy the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) apparatus in this 35mm frame photographed in the Science Module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. Making their first flight in space, the two were joined by four other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist for eight days of research. The Spacelab-J mission is a joint effort between Japan and the United States of America.
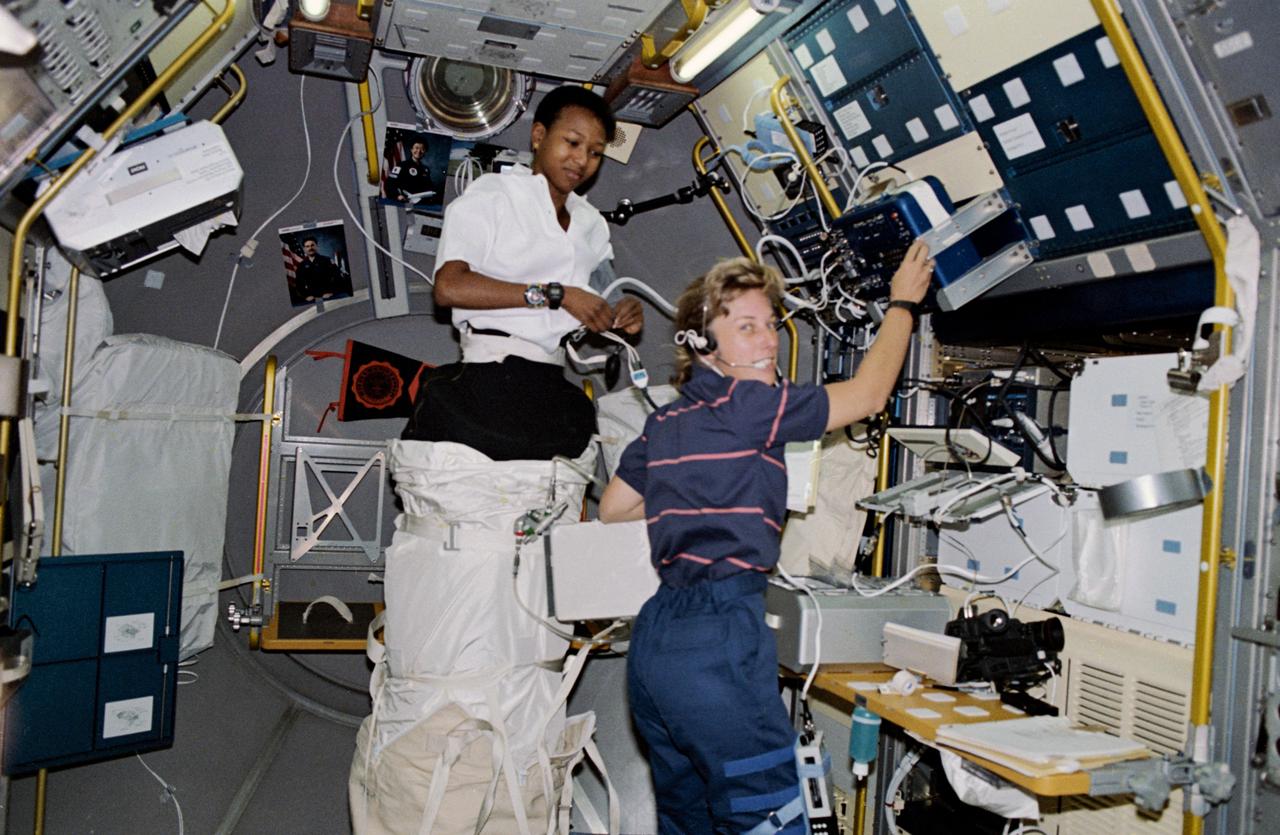

STS047-230-030 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Astronauts Mae C. Jemison (left) and N. Jan Davis, mission specialists, are pictured in the Spacelab-J science module preparing to conduct a session with the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) experiment. The two joined four other NASA astronauts and a payload specialist representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA) aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour for eight days of Spacelab-J research.
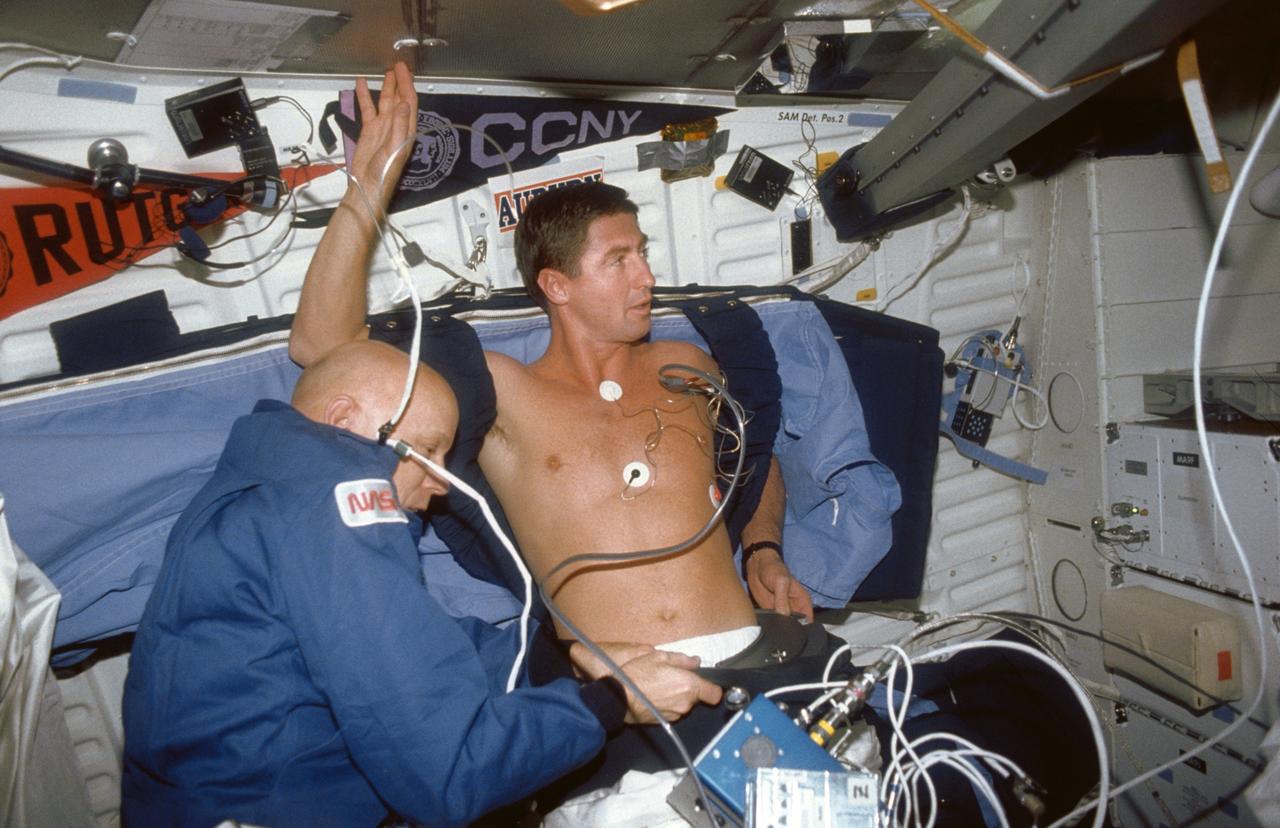

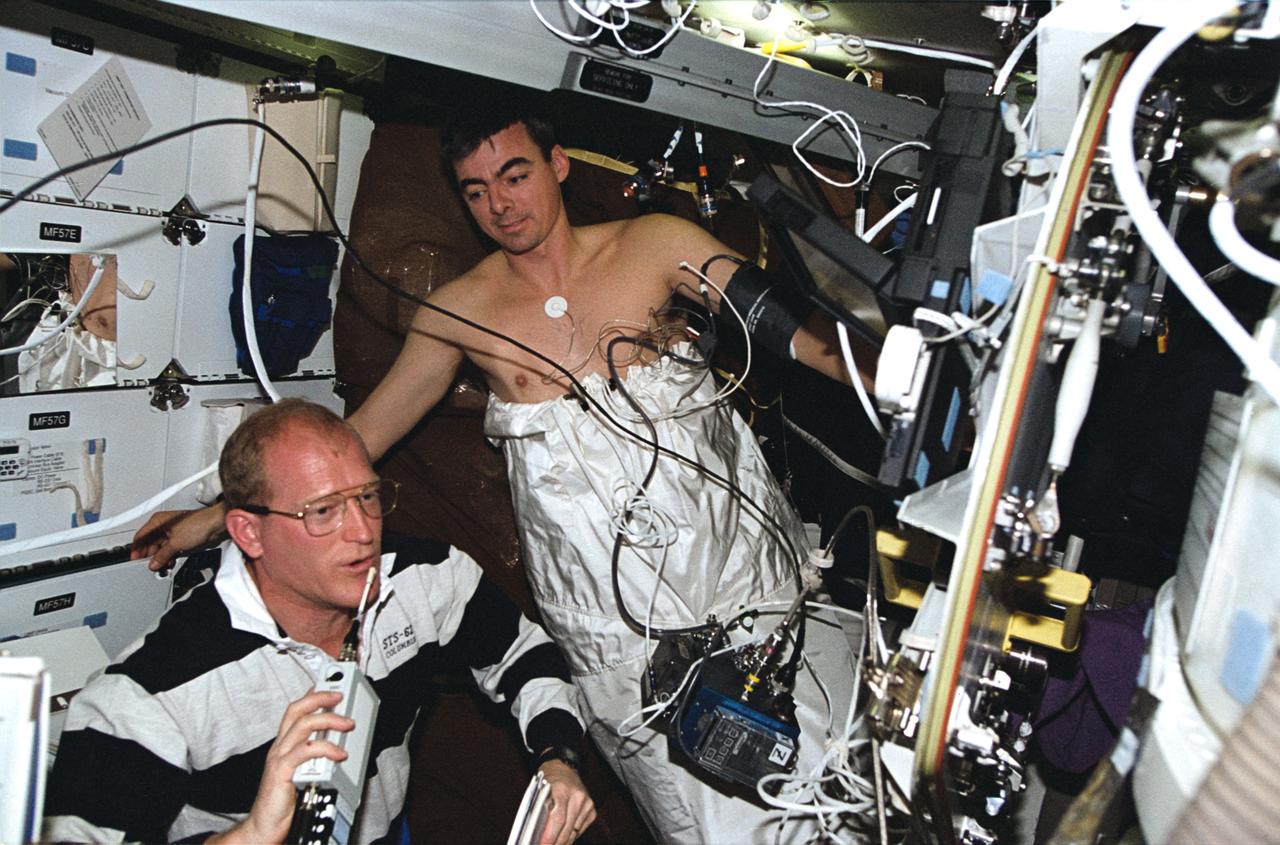
STS044-05-023 (24 Nov-1 Dec 1991) --- Astronaut F. Story Musgrave (left), Mission Specialist, assists Astronaut Terence T. (Tom) Henricks, Mission Specialist, with a Detailed Supplementary Objective (DSO) involving Lower Body Negative Pressure.
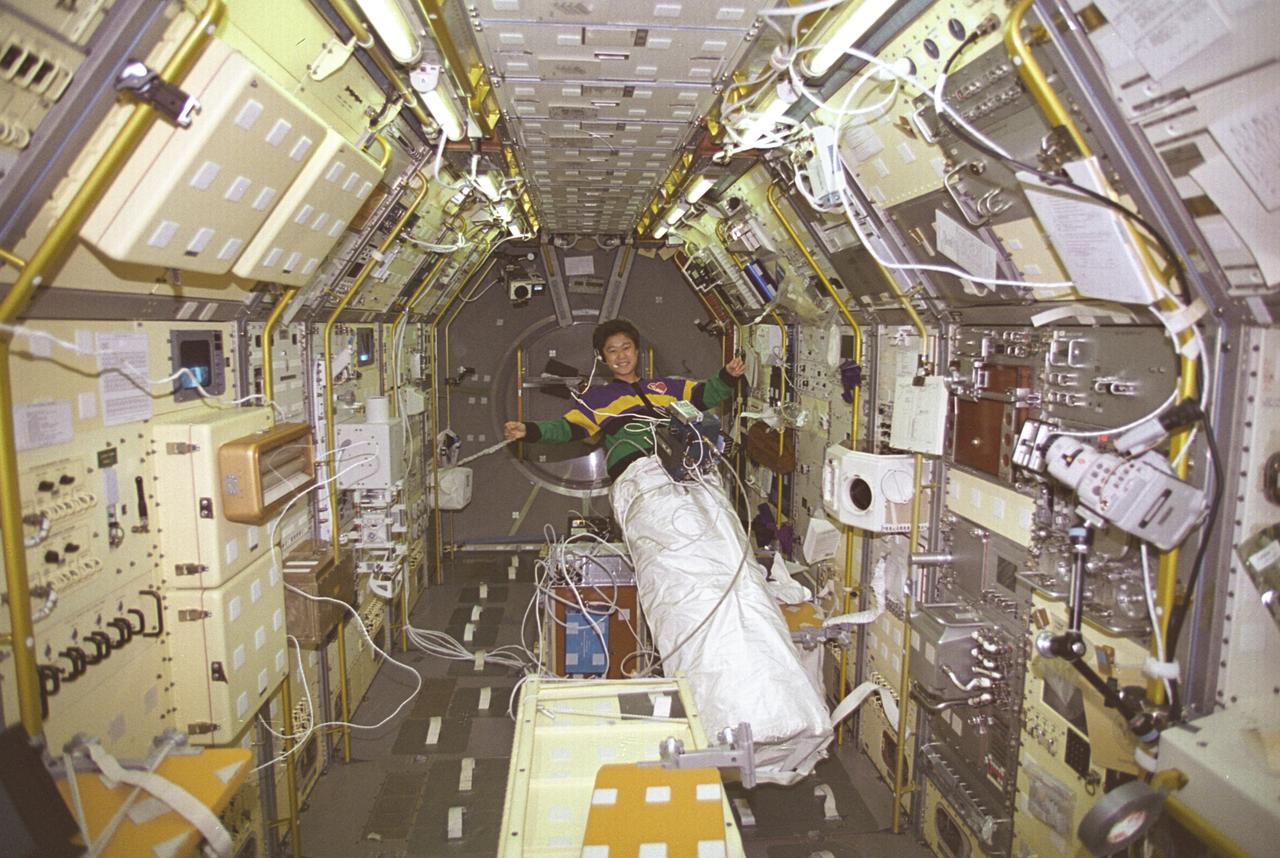

Astronaut Chiaki Mukai conducts the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) experiment inside the International Microgravity Laboratory-2 (IML-2) mission science module. Dr. Chiaki Mukai is one of the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) astronauts chosen by NASA as a payload specialist (PS). She was the second NASDA PS who flew aboard the Space Shuttle, and was the first female astronaut in Asia. When humans go into space, the lack of gravity causes many changes in the body. One change is that fluids normally kept in the lower body by gravity shift upward to the head and chest. This is why astronauts' faces appear chubby or puffy. The change in fluid volume also affects the heart. The reduced fluid volume means that there is less blood to circulate through the body. Crewmembers may experience reduced blood flow to the brain when returning to Earth. This leads to fainting or near-fainting episodes. With the use of the LBNP to simulate the pull of gravity in conjunction with fluids, salt tablets can recondition the cardiovascular system. This treatment, called "soak," is effective up to 24 hours. The LBNP uses a three-layer collapsible cylinder that seals around the crewmember's waist which simulates the effects of gravity and helps pull fluids into the lower body. The data collected will be analyzed to determine physiological changes in the crewmembers and effectiveness of the treatment. The IML-2 was the second in a series of Spacelab flights designed by the international science community to conduct research in a microgravity environment Managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, the IML-2 was launched on July 8, 1994 aboard the STS-65 Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia mission.
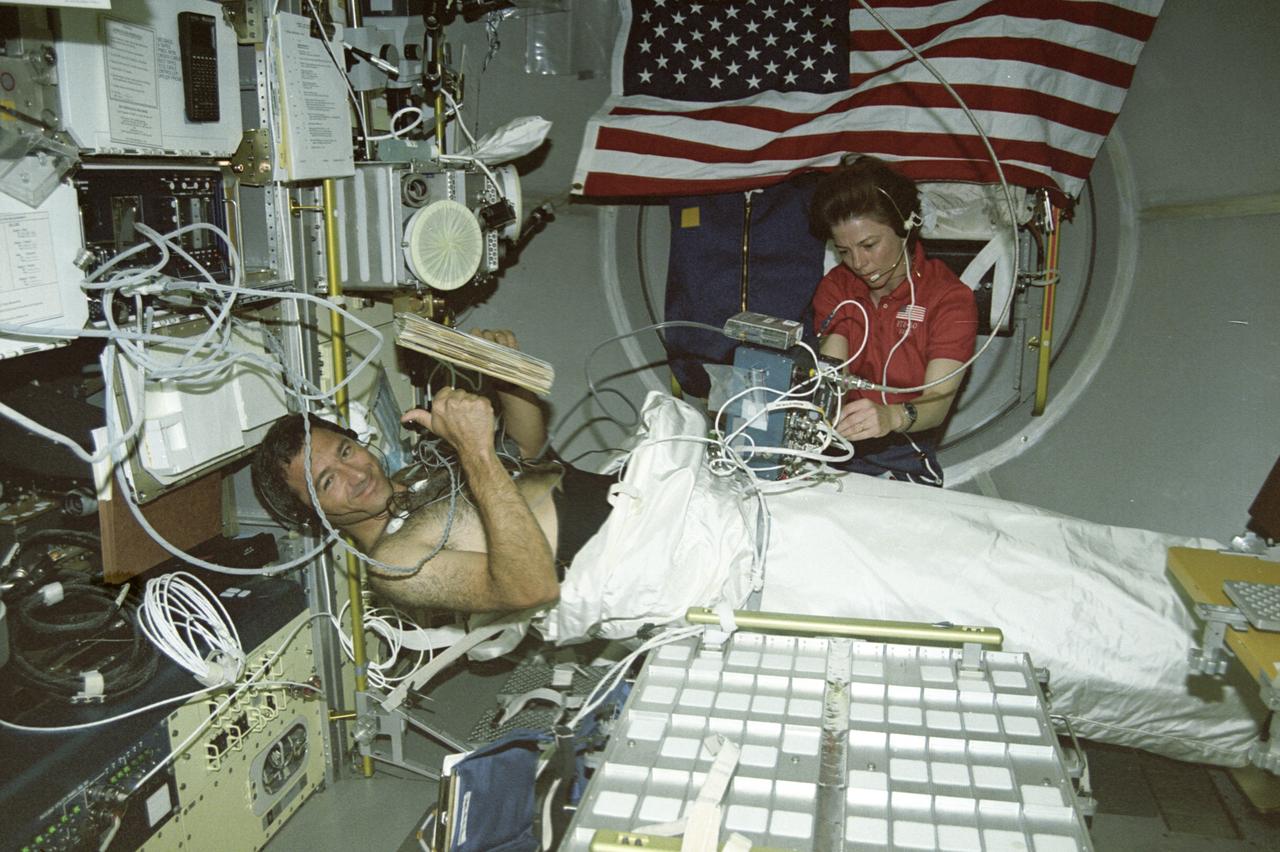

The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) flew in orbit inside the Spacelab science module for extended periods, providing scientists and researchers greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. In this photograph, Astronaut Bornie Dunbar and Astronaut Larry DeLucas are conducting the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) experiment, which is to protect the health and safety of the crew and to shorten the time required to readapt to gravity when they return to Earth. When humans go into space, the lack of gravity causes many changes in the body. One change is that fluids normally kept in the lower body by gravity, shift upward to the head and chest. This is why astronauts' faces appear chubby or puffy. The change in fluid volume also affects the heart. The reduced fluid volume means that there is less blood to circulate through the body. Crewmembers may experience reduced blood flow to the brain when returning to Earth. This leads to fainting or near-fainting episodes. With the use of LBNP to simulate the pull of gravity in conjunction with fluids, salt tablets can recondition the cardiovascular system. This treatment, called "soak," is effective up to 24 hours. The LBNP uses a three-layer collapsible cylinder that seals around the crewmember's waist which simulates the effects of gravity and helps pull fluids into the lower body. The data collected will be analyzed to determine physiological changes in the crewmembers and effectiveness of the treatment. The USML-1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-50) on June 25, 1992.
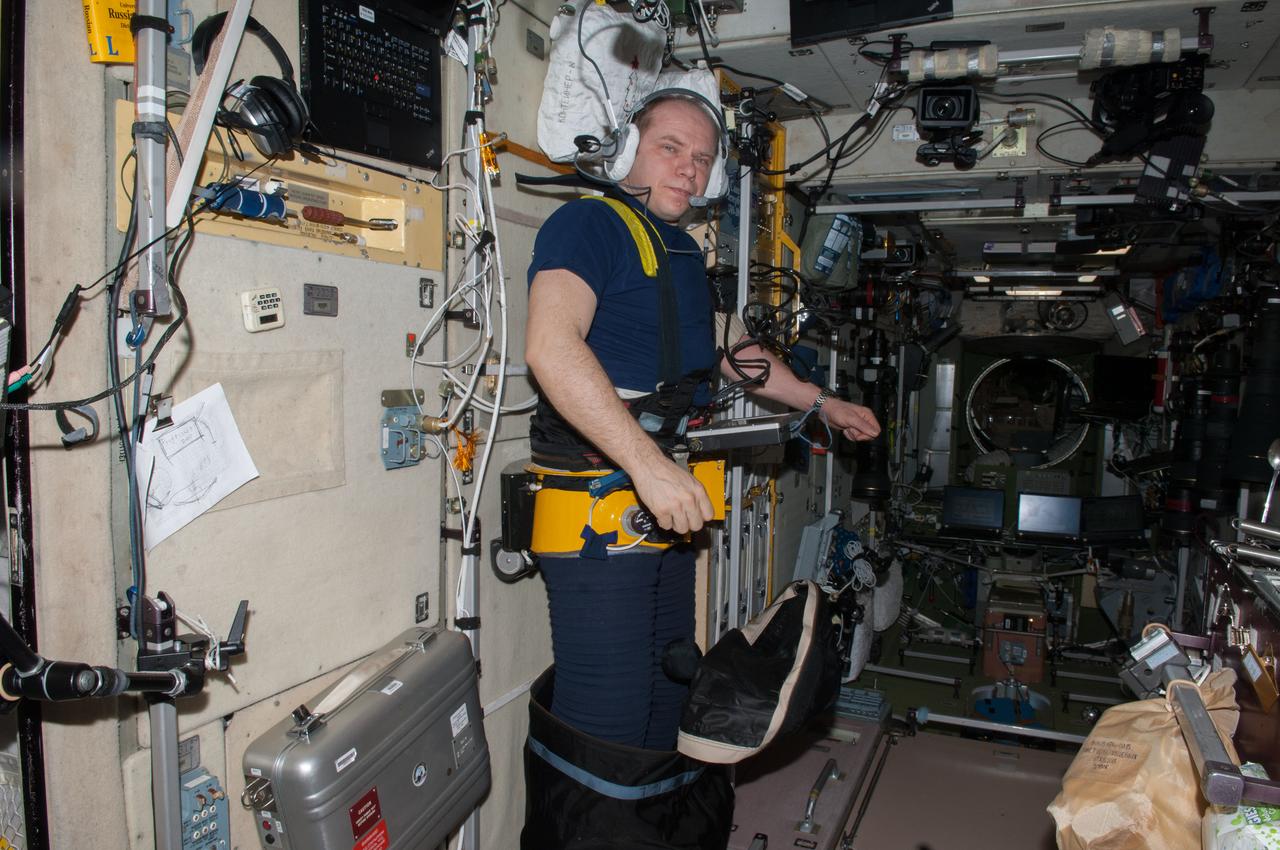

iss038e055233 (2/24/2014) --- Cosmonaut Oleg Kotov, Expedition 38 Commander, is seen during a Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) exercise. This activity was performed for the DAN investigation where researchers revealed that crew members inadvertently hold their breath longer in microgravity than on the ground, especially if the crewmember is lying face up. A better understanding of the supply of oxygen to the body in microgravity allows researchers to provide the environment necessary for adequate intracellular functions and basic human health in space.
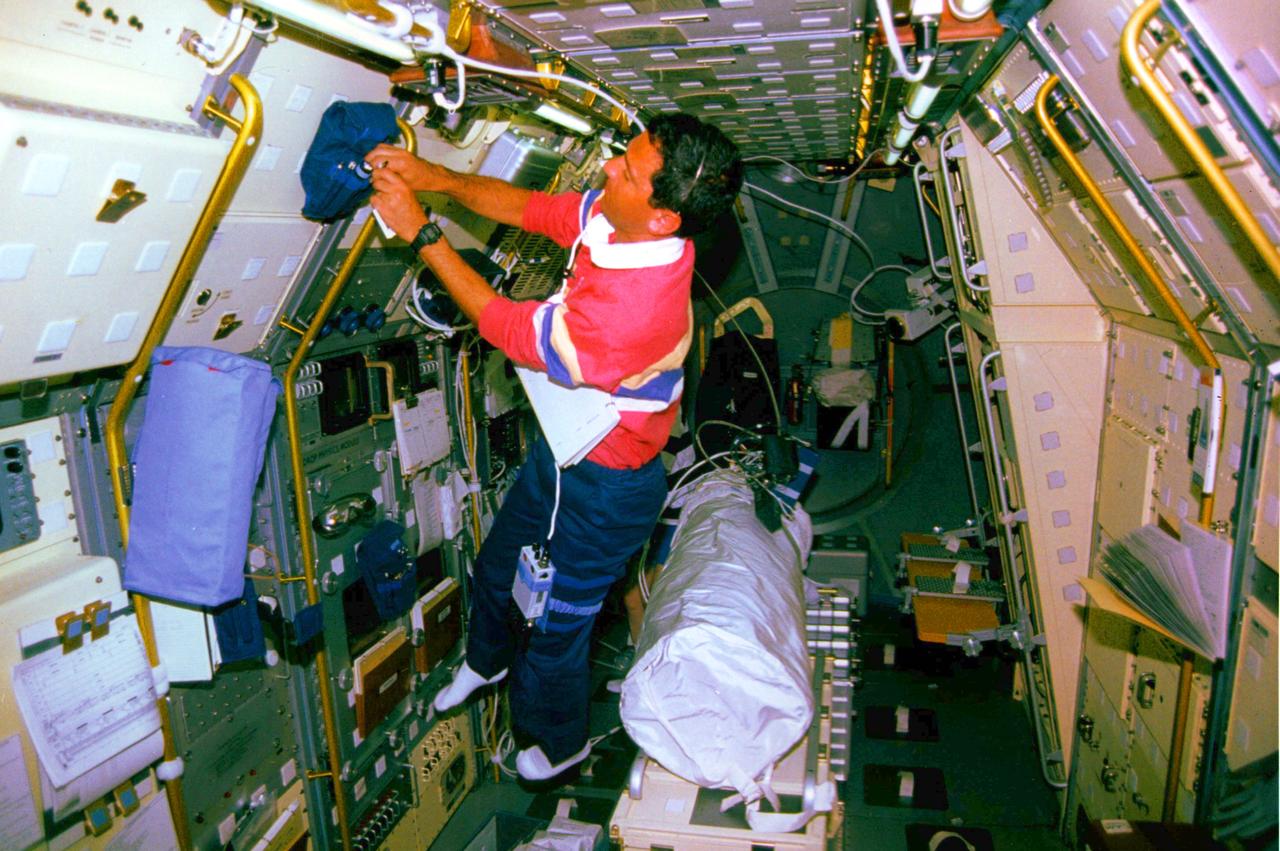

Larry DeLucas with the (LBNP) Lower Body Negative Pressure Experiment onboard STS-50.
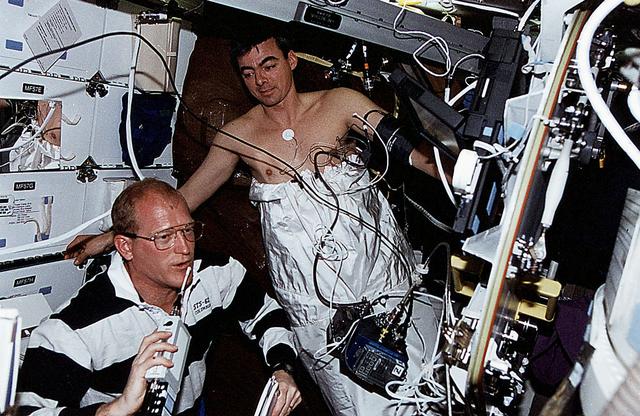
Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-62) onboard photo of Astronaut Charles (Sam) Gemar talking to ground controllers while assisting astronaut Andrew M. Allen with a soak in the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) apparatus on the middeck.
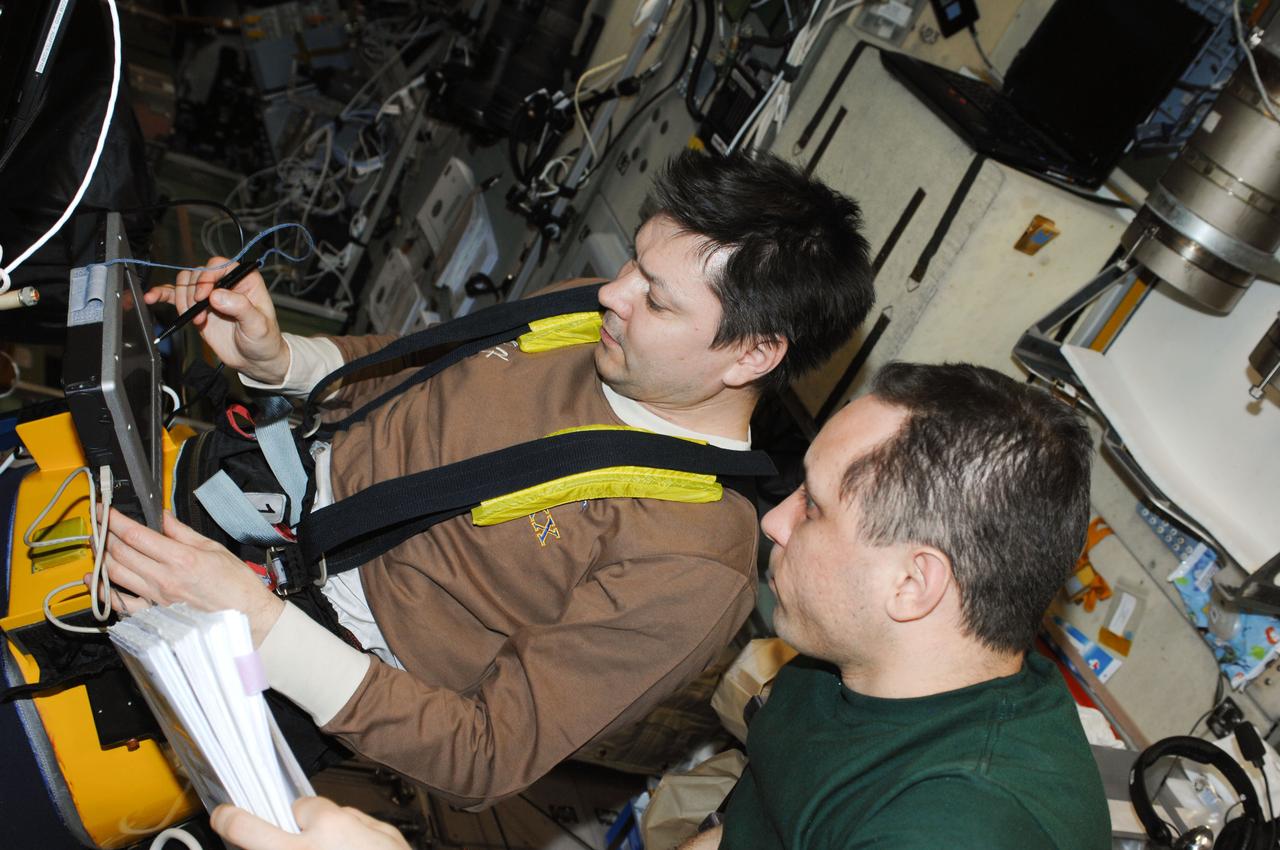

ISS030-E-104844 (28 Feb. 2012) --- In the International Space Station?s Zvezda Service Module, Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko (left) and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, work with Russian Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) or Chibis suits (PVK-1, PVK-2), converting them to the advanced version Chibis-M.
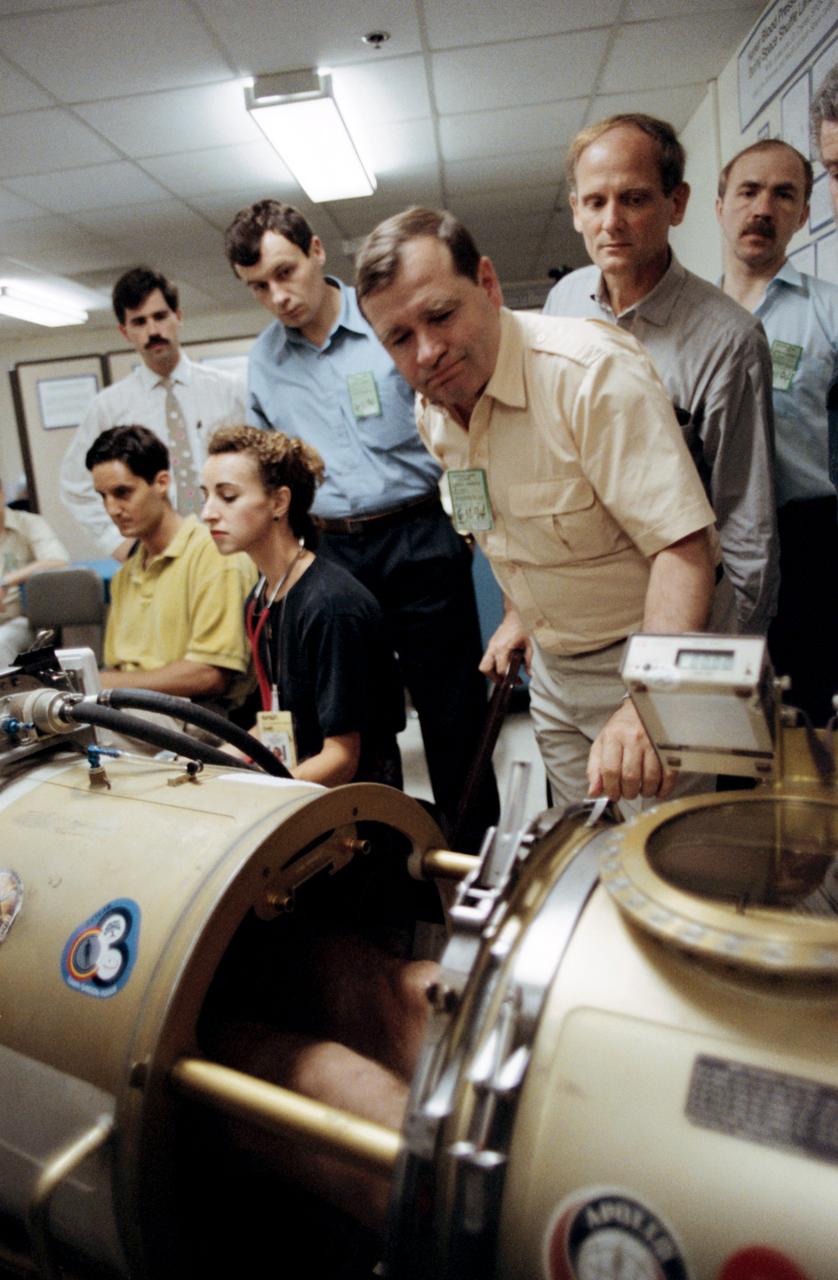

Astronaut Norman E. Thagard (right center), a guest researcher on Russia's Mir 18 mission, monitors a test of a subject (out of frame) in the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) device. Others pictured, left to right, are Todd Schlegel (seated) of the Medical Sciences Division at JSC, unidentified trainer, Linda Barrows of Krug; cosmonaut Vladimir N. Dezhurov, mission commander; cosmonaut Gennadiy M. Strekalov, Thagard and cosmonaut Alexsandr F. Poleshchuk, Mir 18 reserve flight engineer.
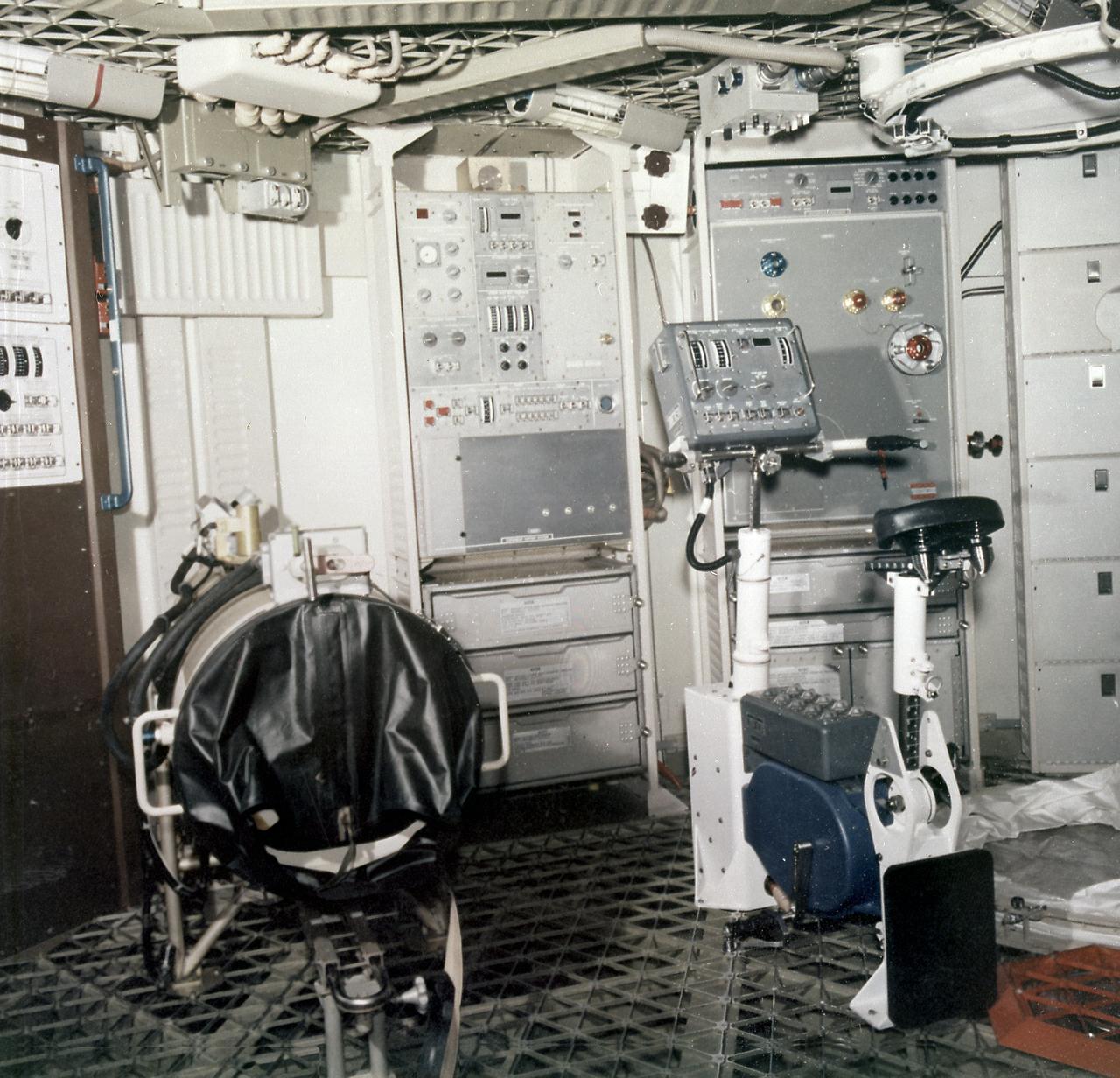

The Orbital Workshop internal arrangement shown here is the medical experimental equipment. In this view, looking from the wardroom area, are the lower-body Negative Pressure (Experiment M092) unit, left, and the ergometer for the vectorcardiograph (Experiment - M093). Both are used in several ways to keep check on the astronauts' condition and tolerance in extended weightlessness. The 1-G trainer permits the astronauts to get experience with all of the equipment and operations except the absence of gravity.

The wardroom deck of the Orbital Workshop, showing the living quarters arrangement, is seen here in good detail. From left to right is the dining area, waste management, and sleeping quarters. Portable restraints are on the wall beside the sleeping quarters. The ergometer for the vectorcardiograph (Experiment - M093) and lower-body Negative Pressure (Experiment M092) unit, used in some of the medical experiments, are in the foreground. The round brown object in the center of the room is the trash disposal airlock.

S73-20276 (1 March 1973) --- Astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot of the first manned Skylab mission, lies in the lower body negative pressure device during Skylab training at Johnson Space Center. Operating the controls in the background is scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot of the mission. They are in the work and experiments area of the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer at JSC. Photo credit: NASA

ISS008-E-21904 (April 2004) --- Astronaut C. Michael Foale, Expedition 8 commander and NASA ISS science officer, holds a portable microphone/keypad for the ARISS ham radio in one hand, and a note card with his call sign of NA1SS in the other in the Zvezda Service Module on the International Space Station (ISS). Cosmonaut Alexander Y. Kaleri, flight engineer representing Russia’s Federal Space Agency, donned in the Russian Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) or Chibis suit in preparation for a return to gravity following his stay onboard the ISS, is visible in the background.
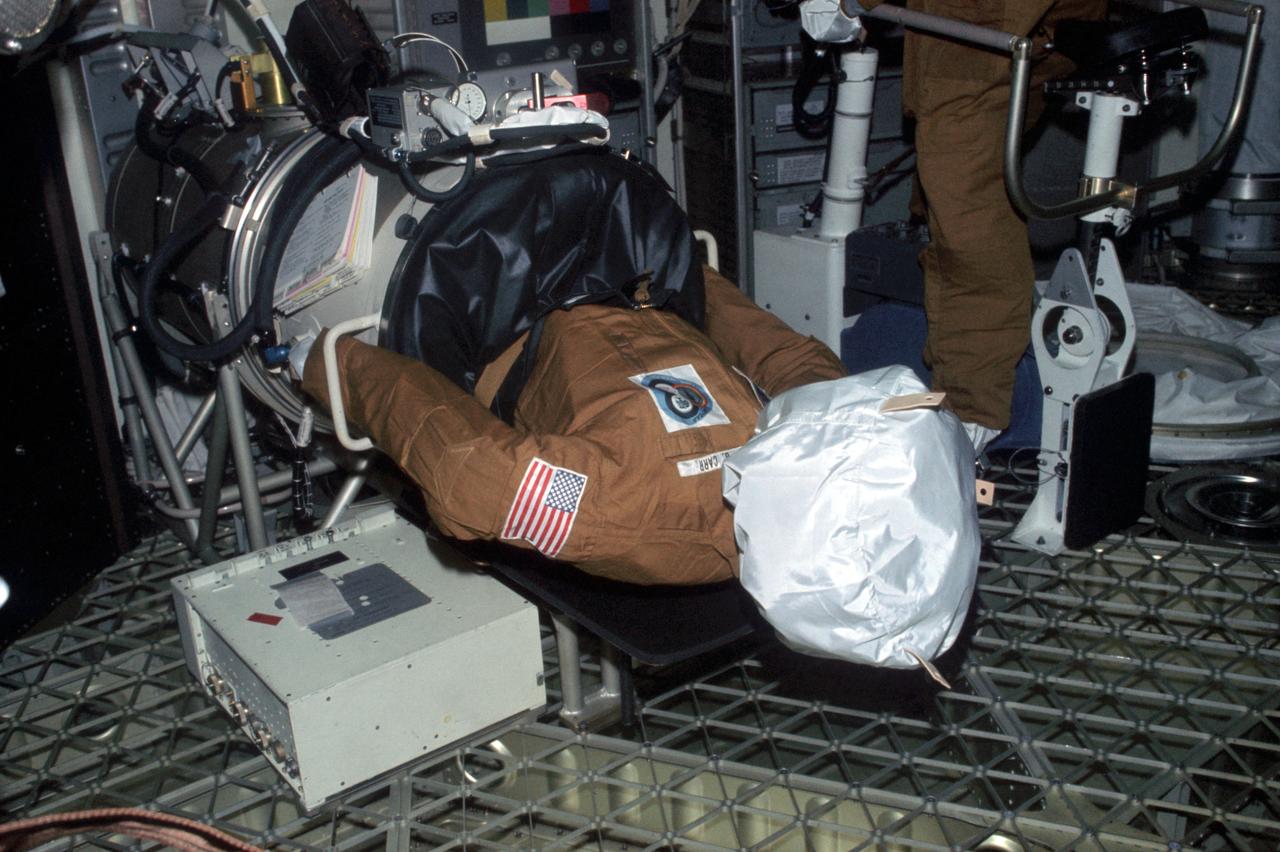

SL3-113-1586 (July-September 1973) --- This photograph is an illustration of the humorous side of the Skylab 3 crew. This dummy was left behind in the Skylab space station by the Skylab 3 crew to be found by the Skylab 4 crew. The dummy is dressed in a flight suit and placed in the Lower Body Negative Pressure Device. The name tag indicates that it represents Gerald P. Carr, Skylab 4 commander, in the background is a partial view of the dummy for William R. Pogue, Skylab 4 pilot, propped upon the bicycle ergometer. The dummy representing Edward G. Gibson, Skylab science pilot, was left in the waste compartment. Astronauts Alan L. Bean, Owen K. Garriott and Jack R. Lousma were the Skylab 3 crewmen. Photo credit: NASA

SL3-113-1587 (July-September 1973) --- This photograph is an illustration of the humorous side of the Skylab 3 crew. This dummy was left behind in the Skylab space station by the Skylab 3 crew to be found by the Skylab 4 crew. The dummy is dressed in a flight suit and propped upon the bicycle ergometer. The name tag indicated that it represents William R. Pogue, Skylab pilot. The dummy for Gerald P. Carr, Skylab 4 commander, was placed in the Lower Body Negative Pressure Device. The dummy representing Edward G. Gibson was left in the waste compartment. Astronauts Alan L. Bean, Owen K. Garriott and Jack R. Lousma were the Skylab 3 crewmen. Gibson is the Skylab 4 science pilot. Photo credit: NASA

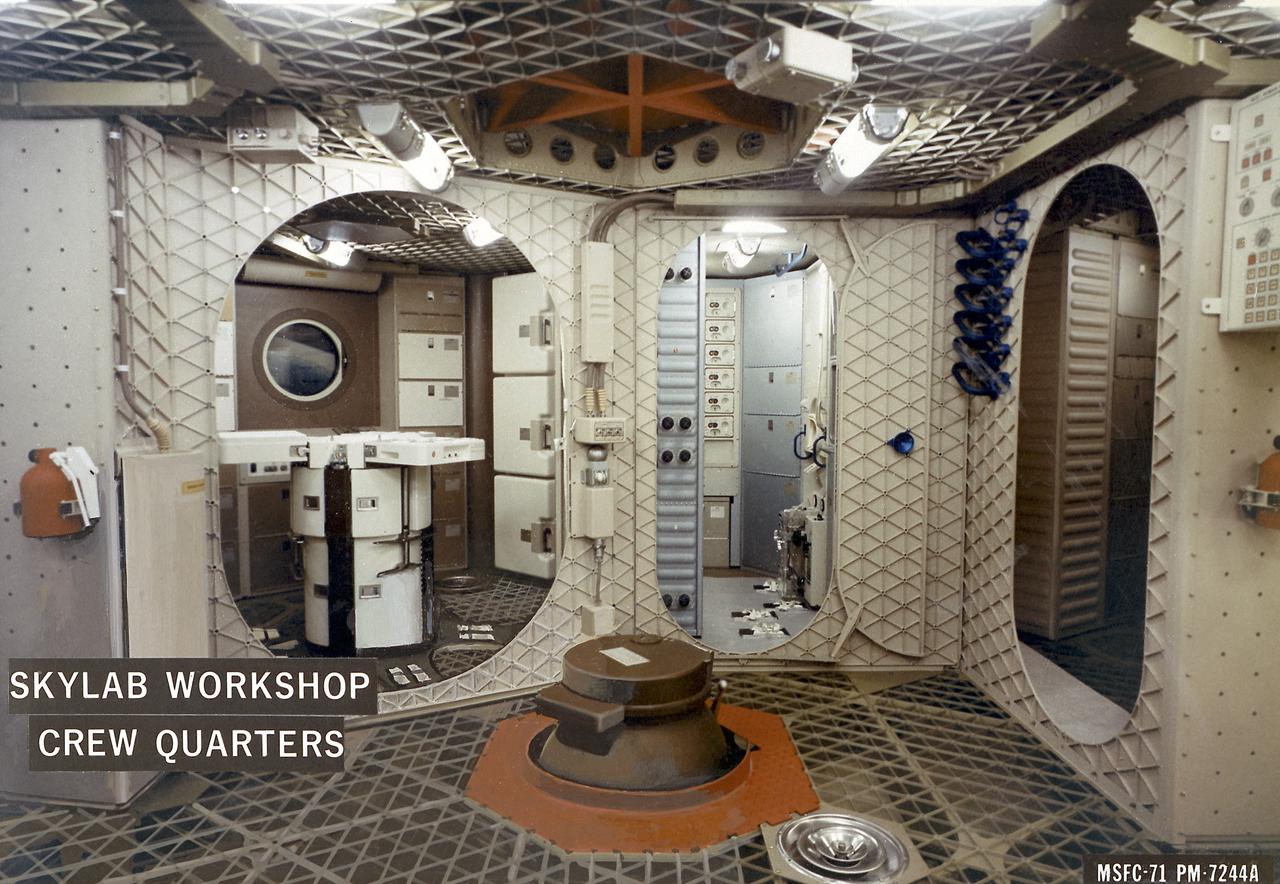
This image depicts a layout of the Skylab workshop 1-G trainer crew quarters. At left, in the sleep compartment, astronauts slept strapped to the walls of cubicles and showered at the center. Next right was the waste management area where wastes were processed and disposed. Upper right was the wardroom where astronauts prepared their meals and foods were stored. In the experiment operation area, upper left, against the far wall, was the lower-body negative-pressure device (Skylab Experiment M092) and the Ergometer for the vectorcardiogram experiment (Skylab Experiment M063). The trainers and mockups were useful in the developmental phase, while engineers and astronauts were still working out optimum designs. They provided much data applicable to the manufacture of the flight articles.