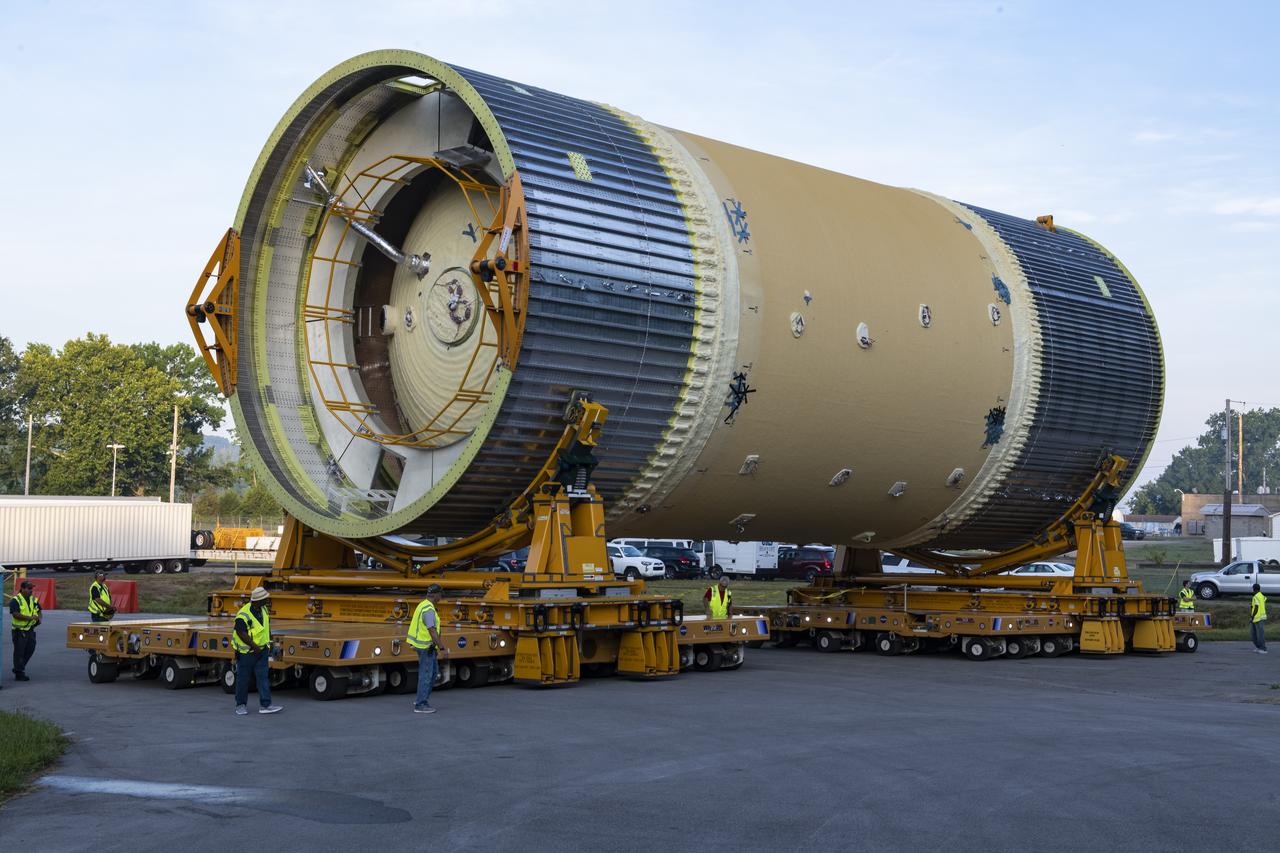

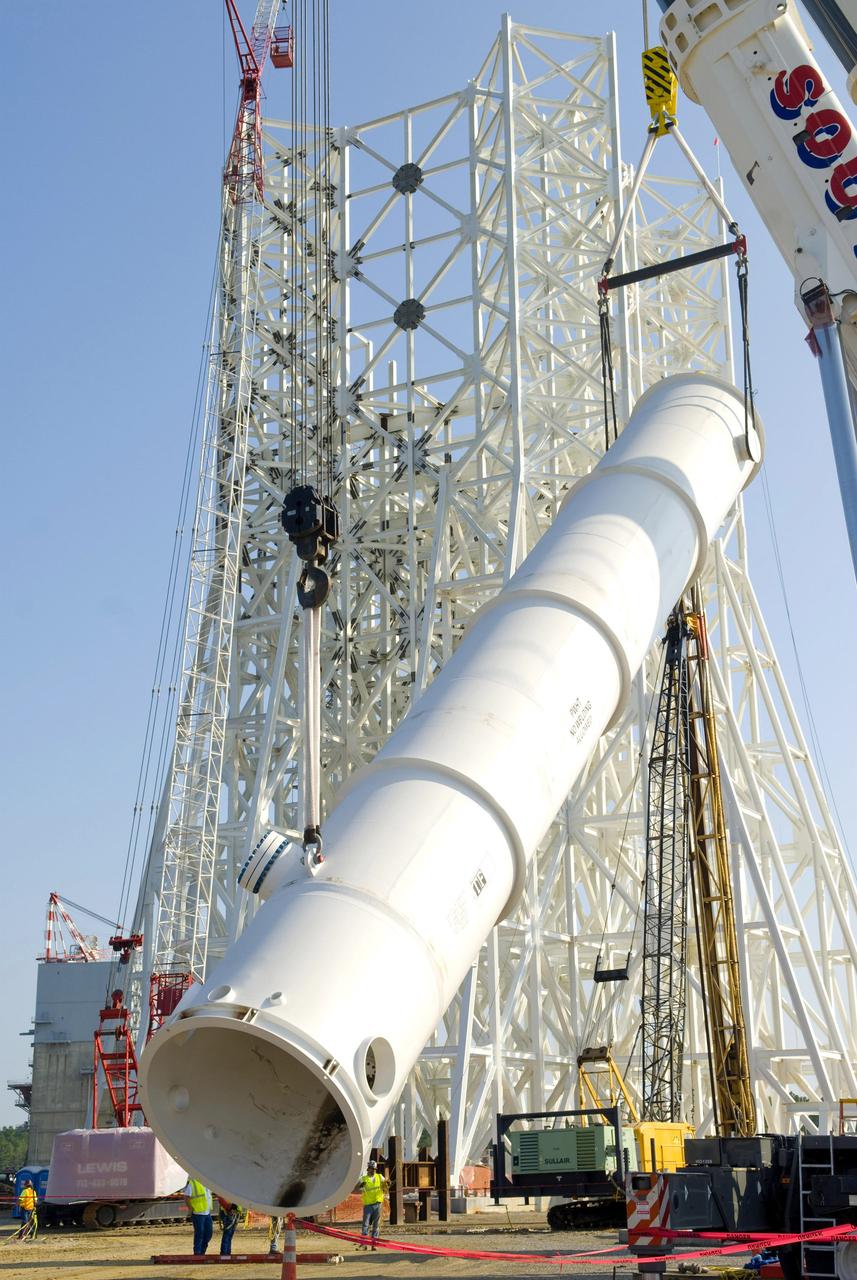
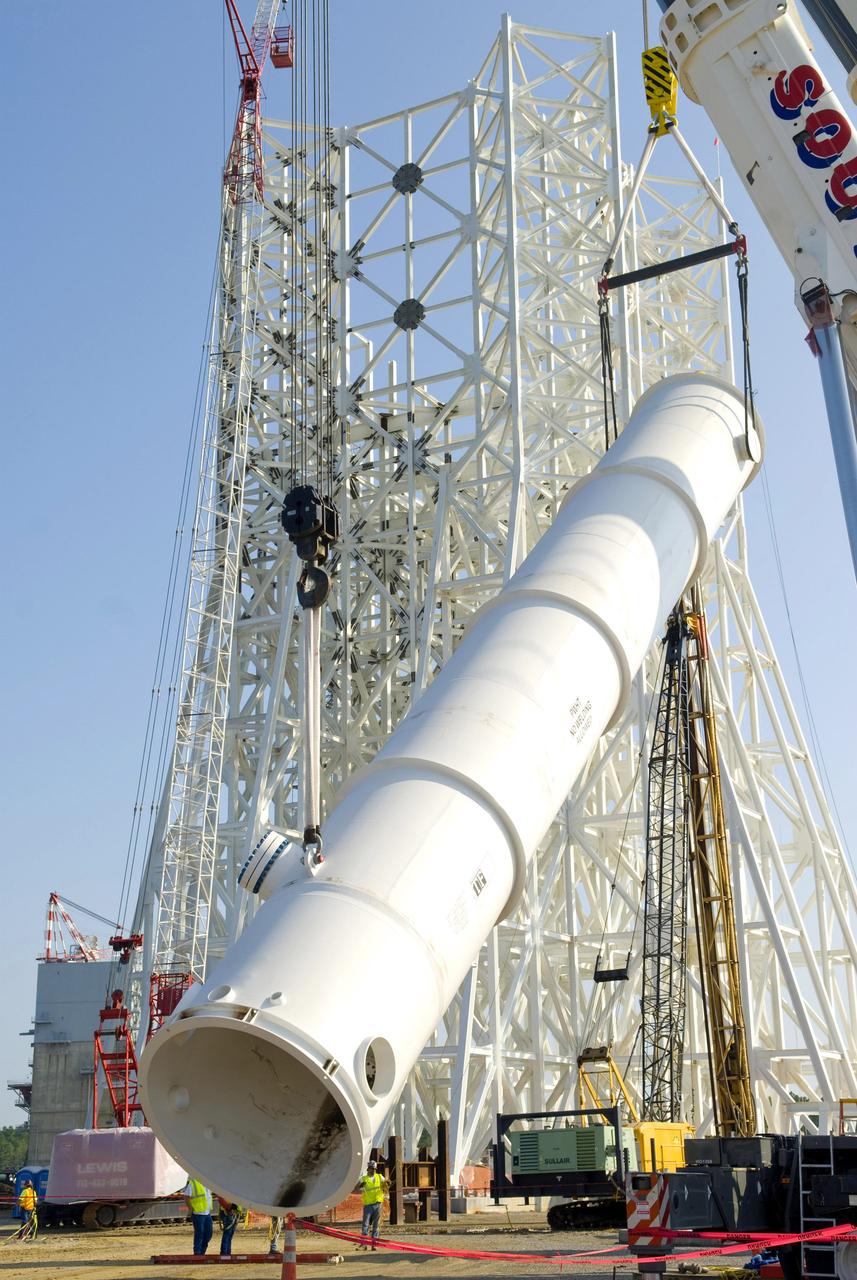
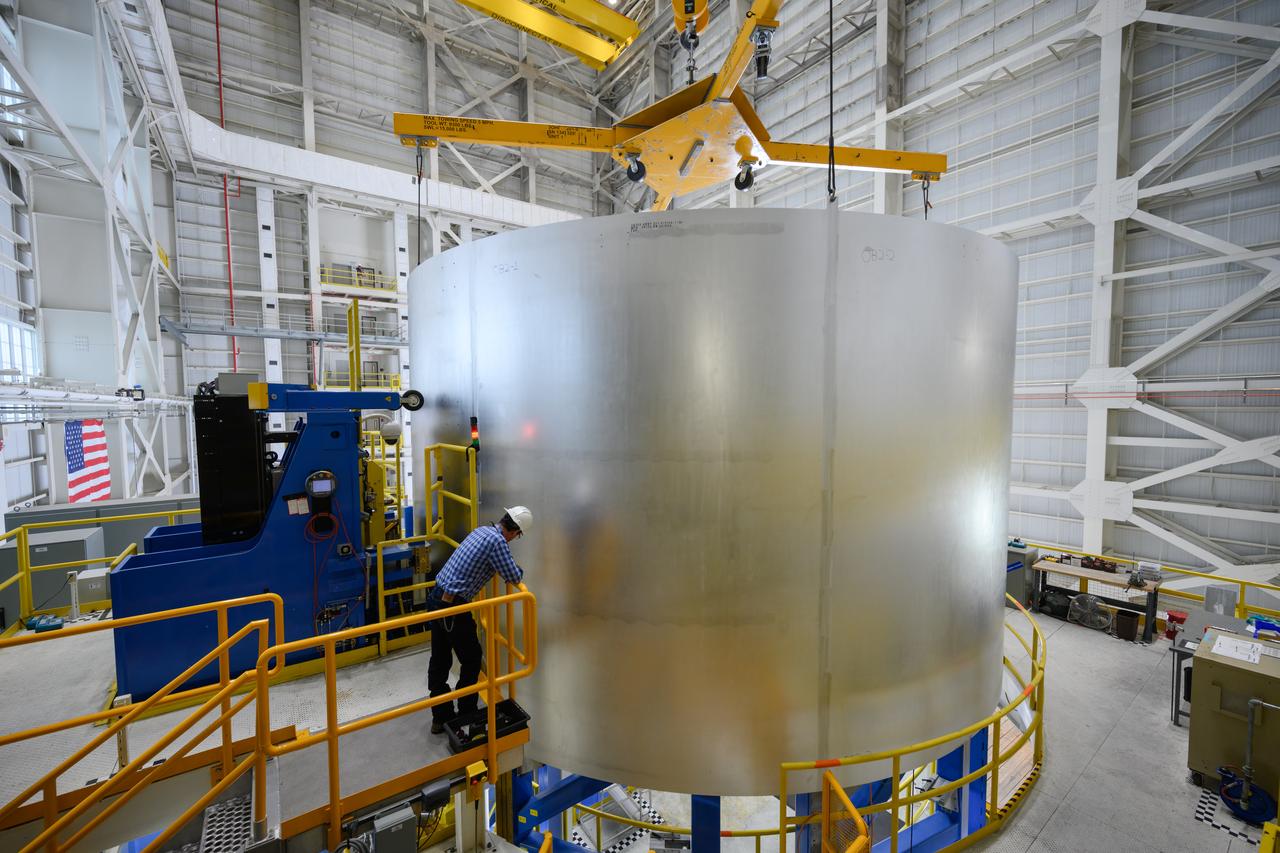
The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand.

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand.

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand.

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand.

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand.

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand.

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand.

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand.

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand.
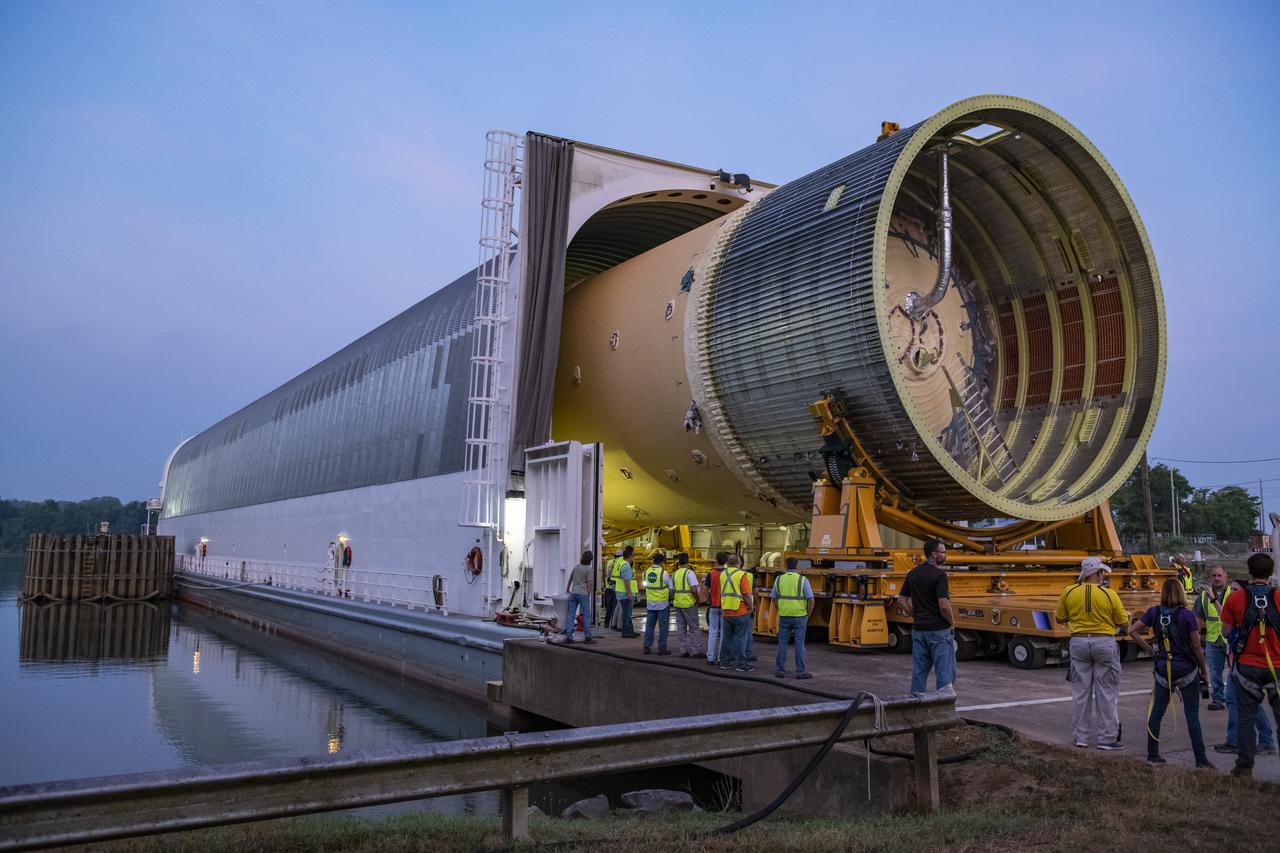

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand.

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand.
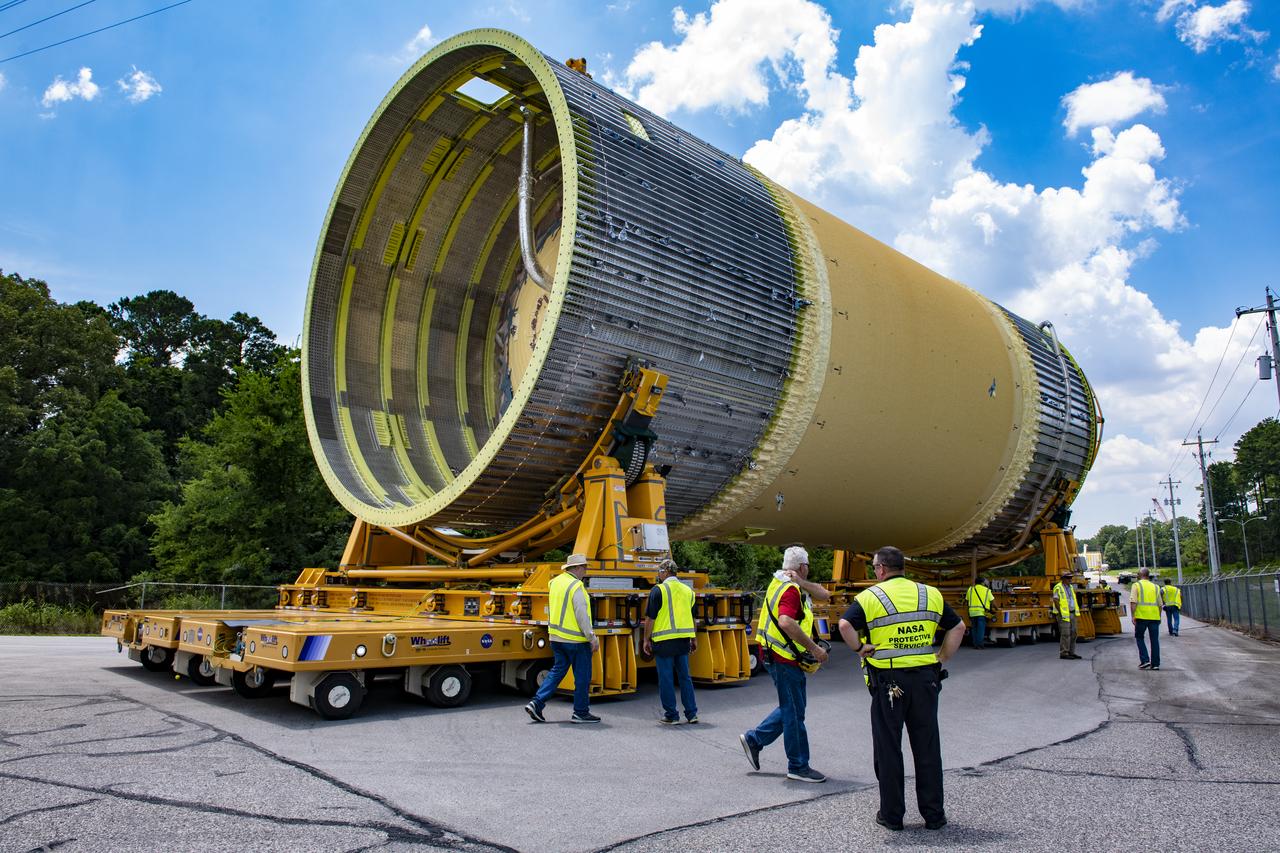

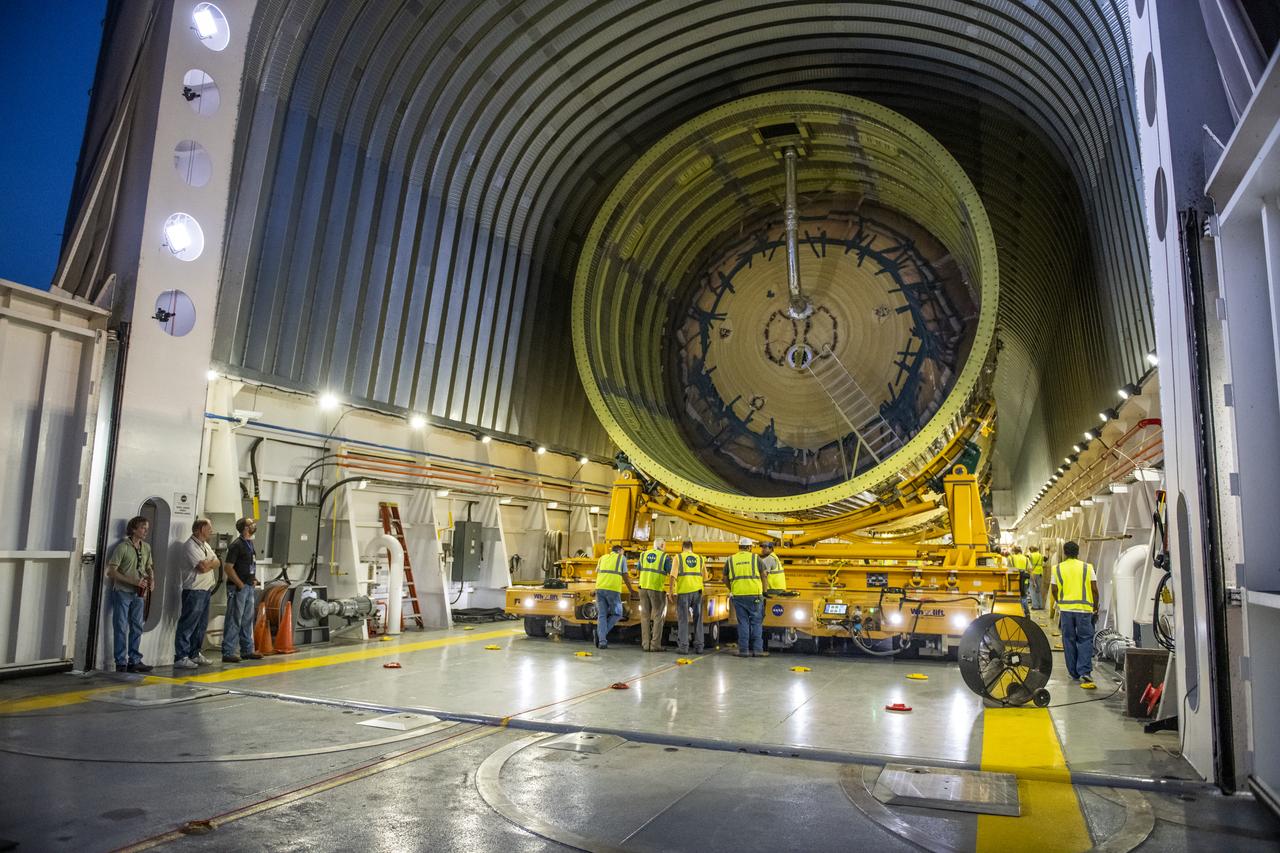
The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand 4697.
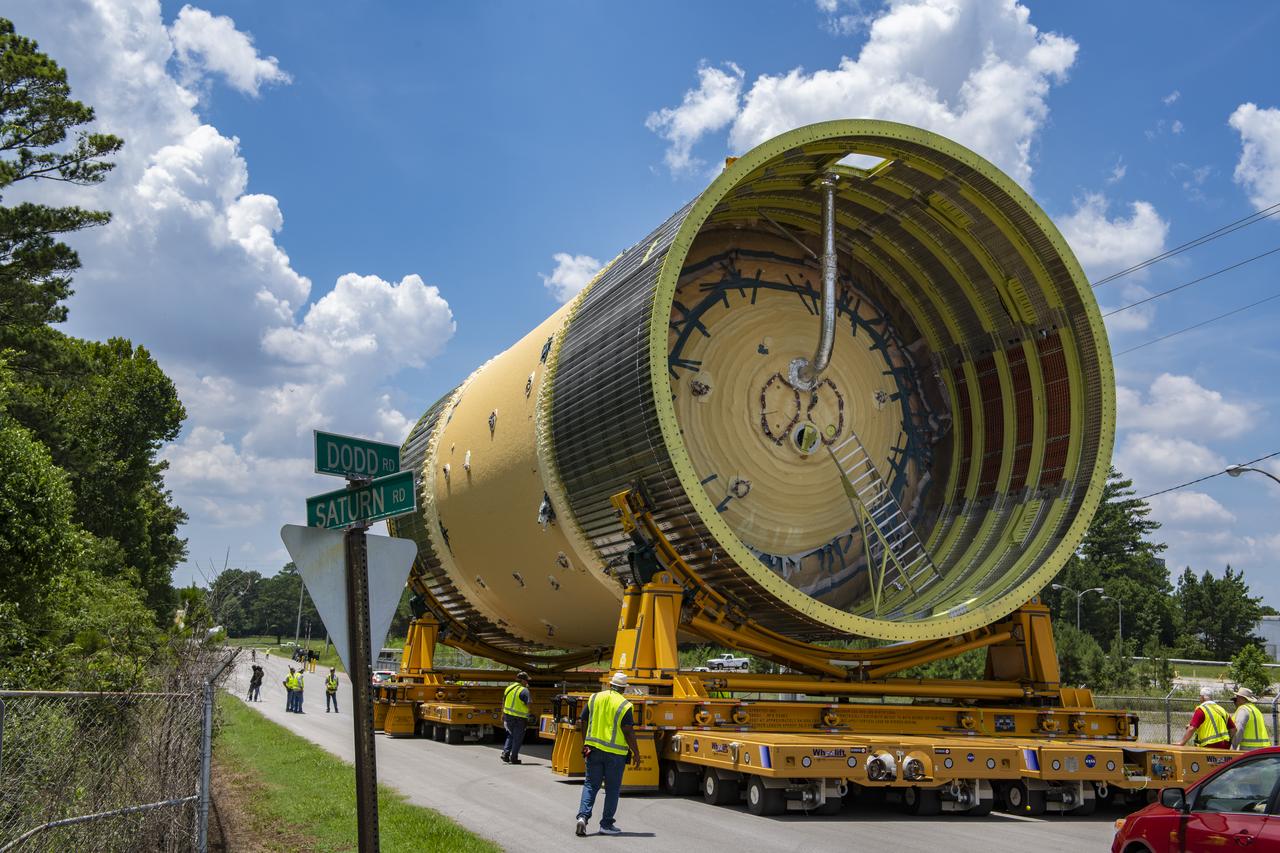

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand 4697.
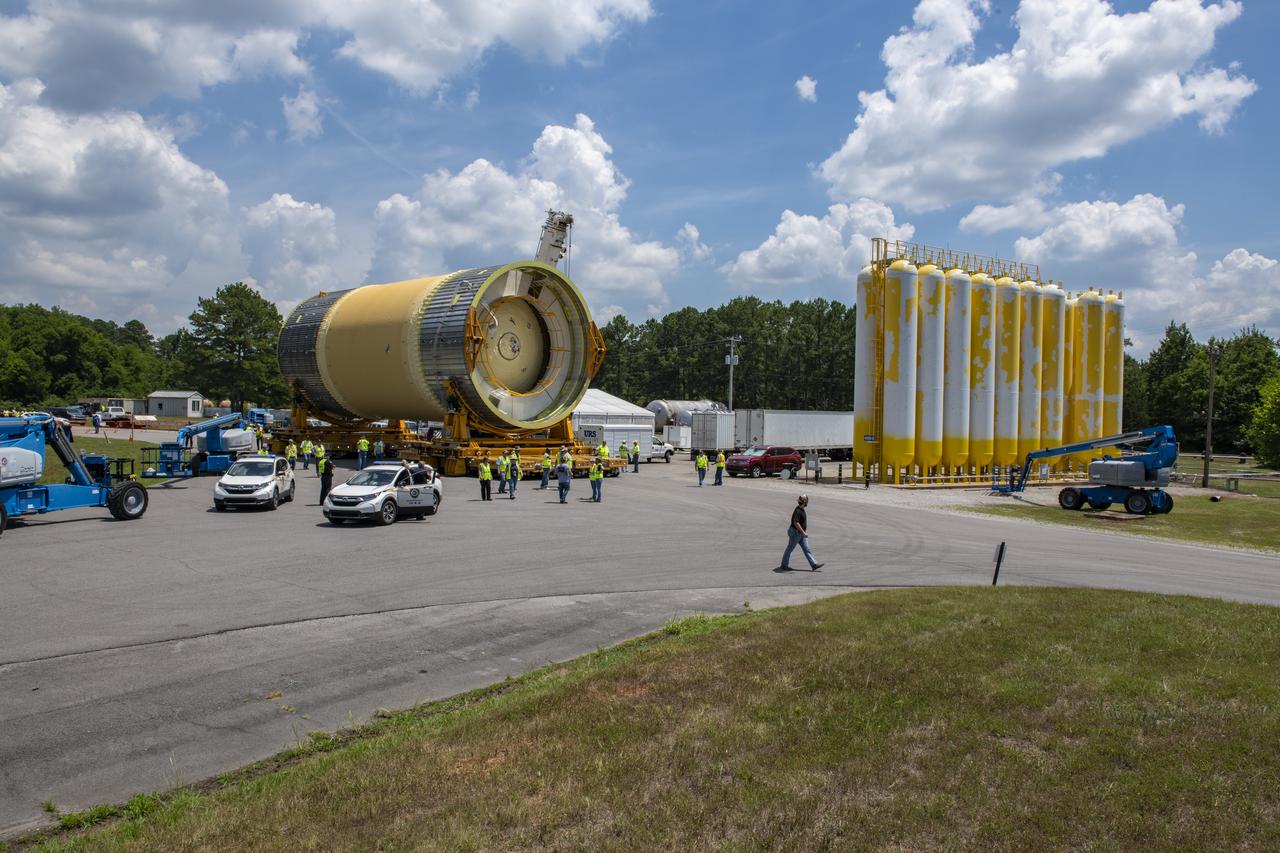

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand 4697.

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand 4697.
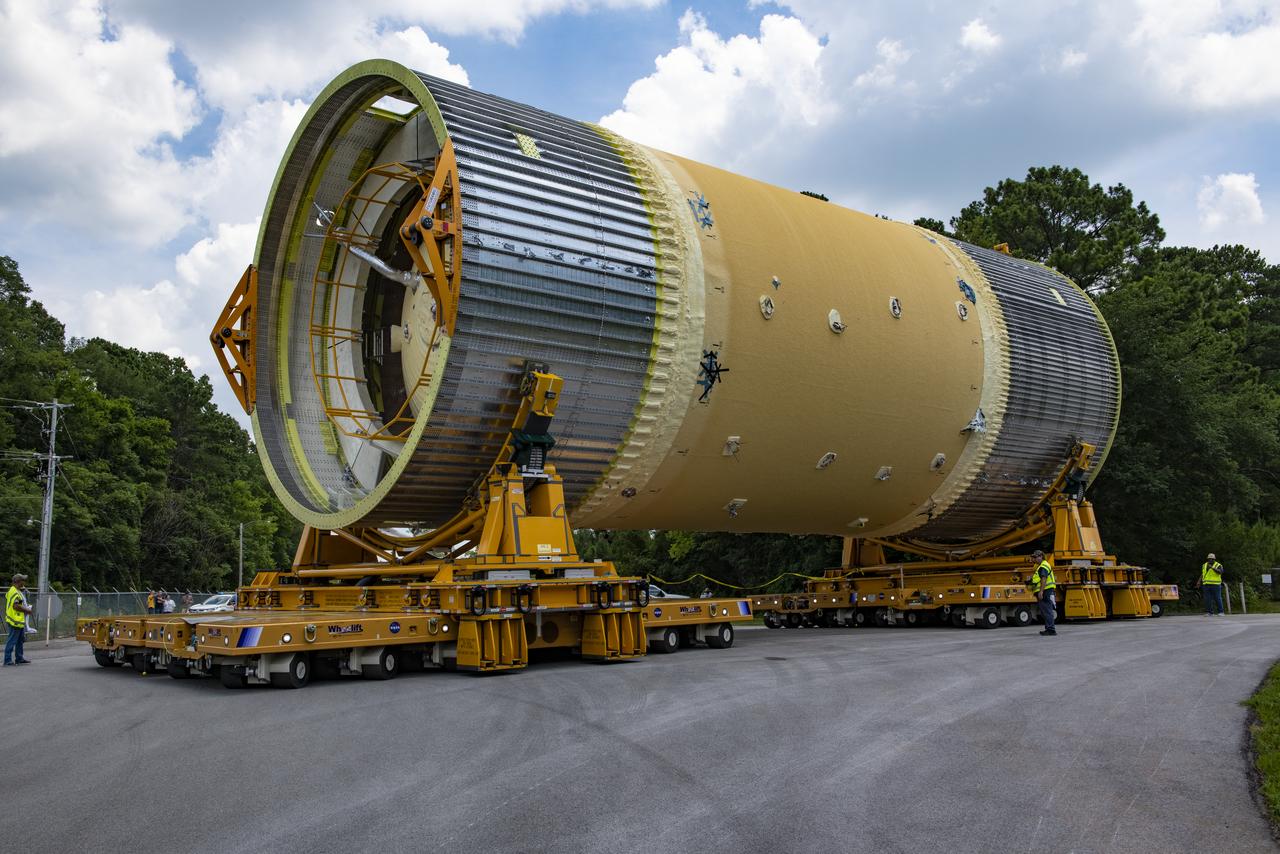

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand 4697.
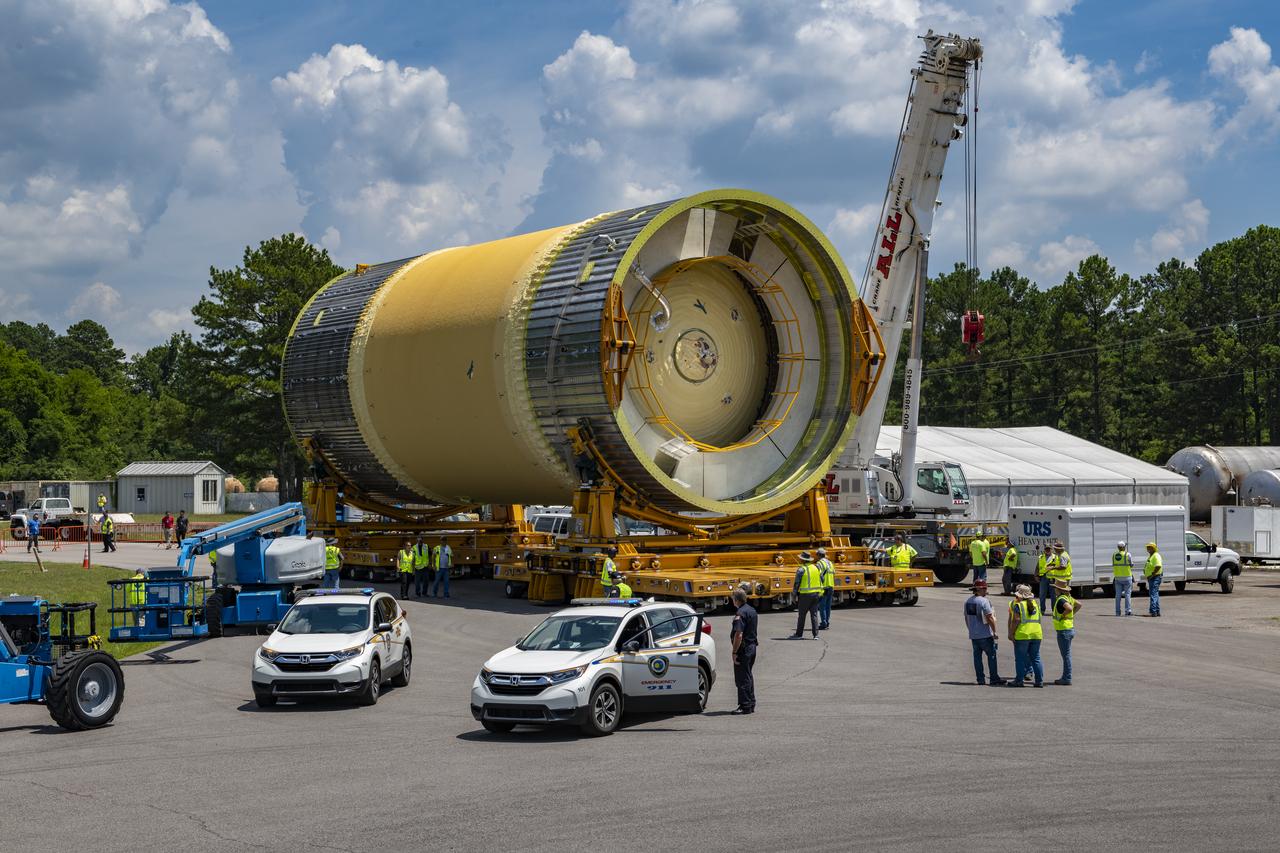

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand 4697.
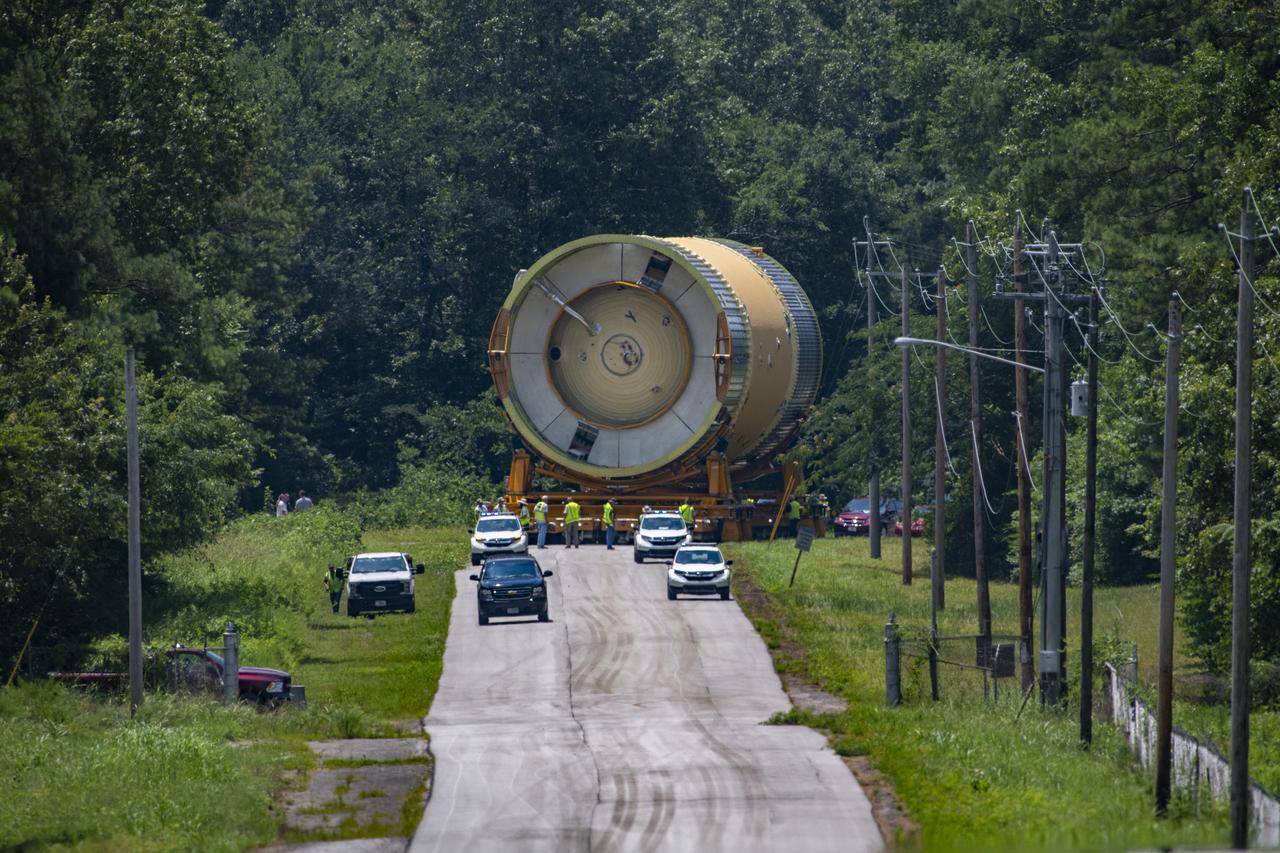

The Liquid Oxygen (LOX) tank was moved from the Pegasus barge to the west test area for placement in test stand 4697.
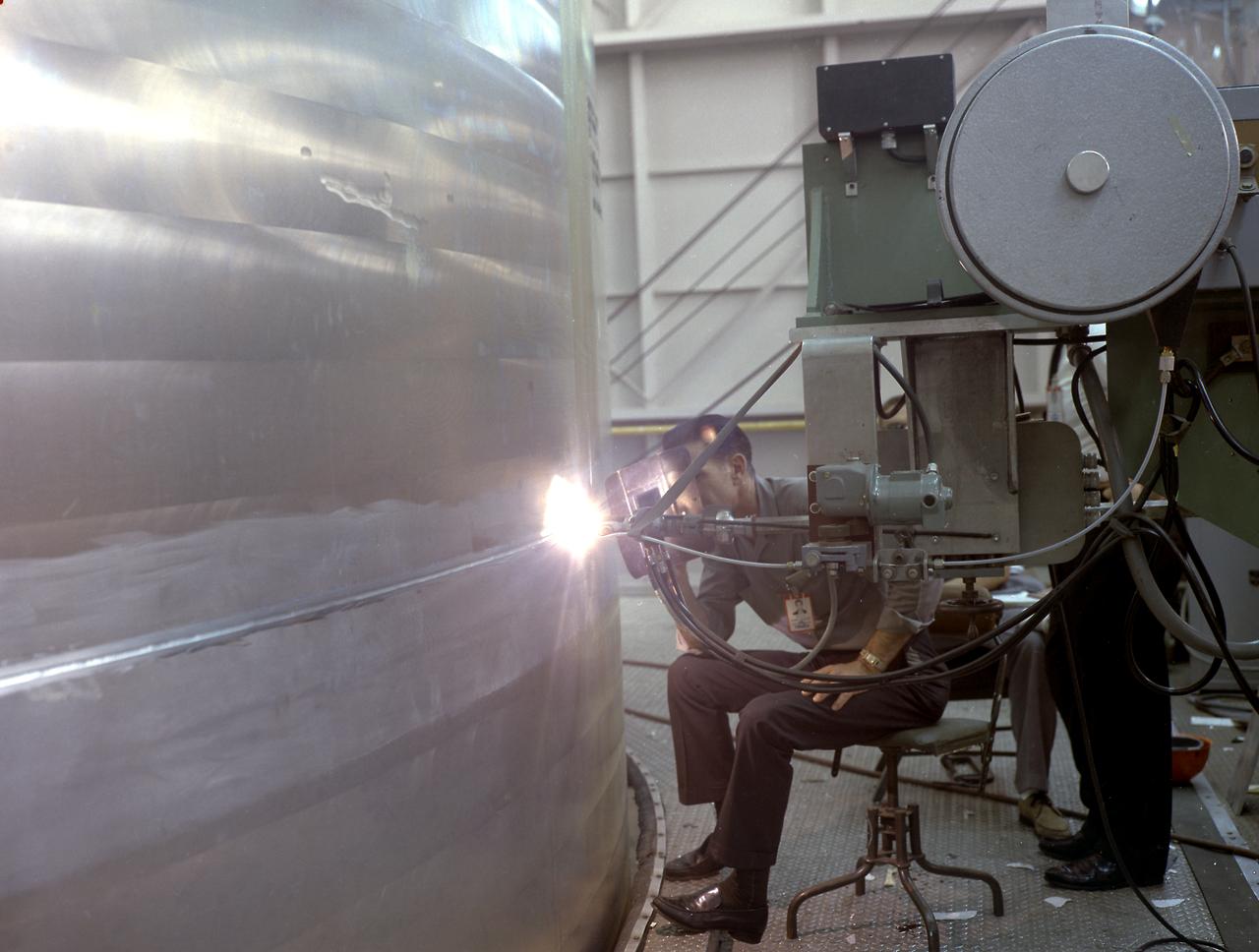

This photo shows the closeout welding operation of the liquid oxygen (LOX) tank for the Saturn V SA-501 vehicle for the Apollo 4 mission.

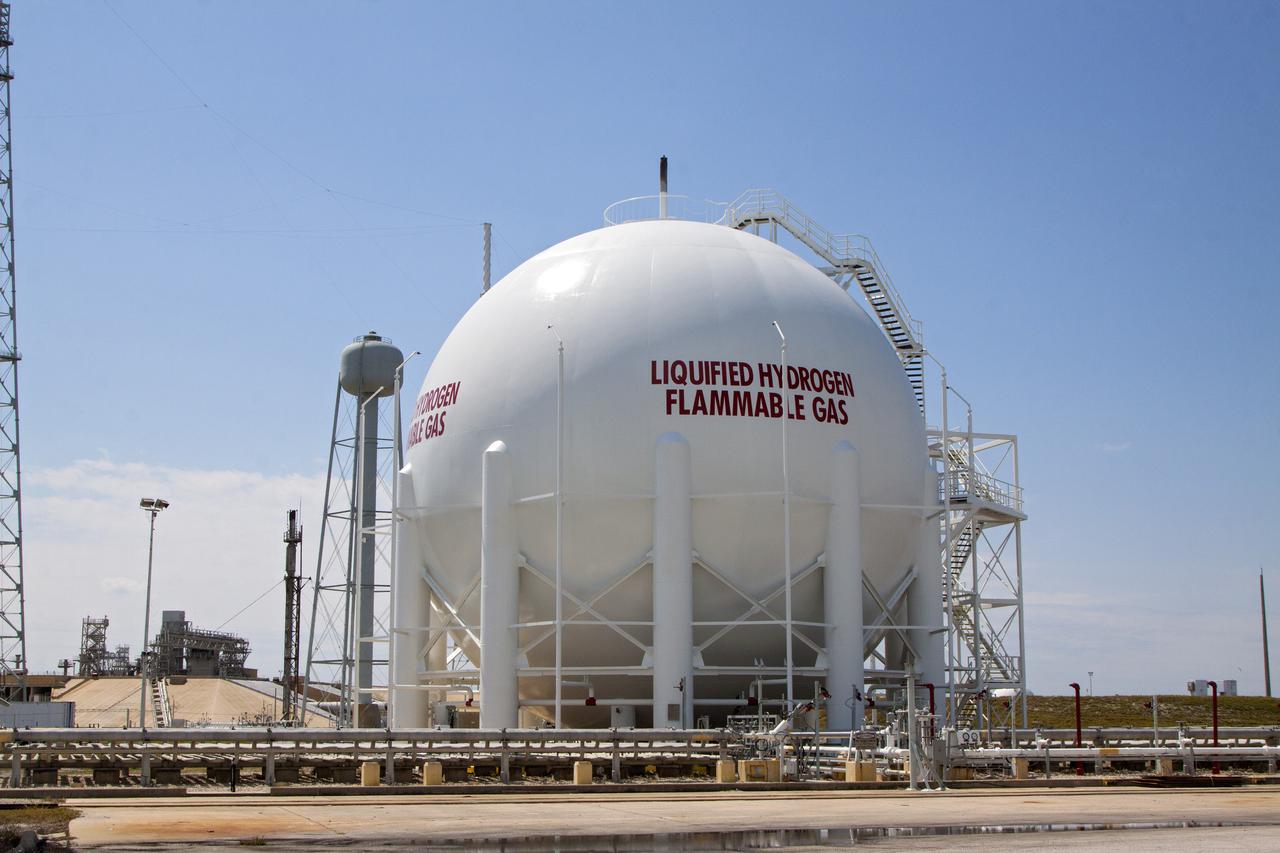
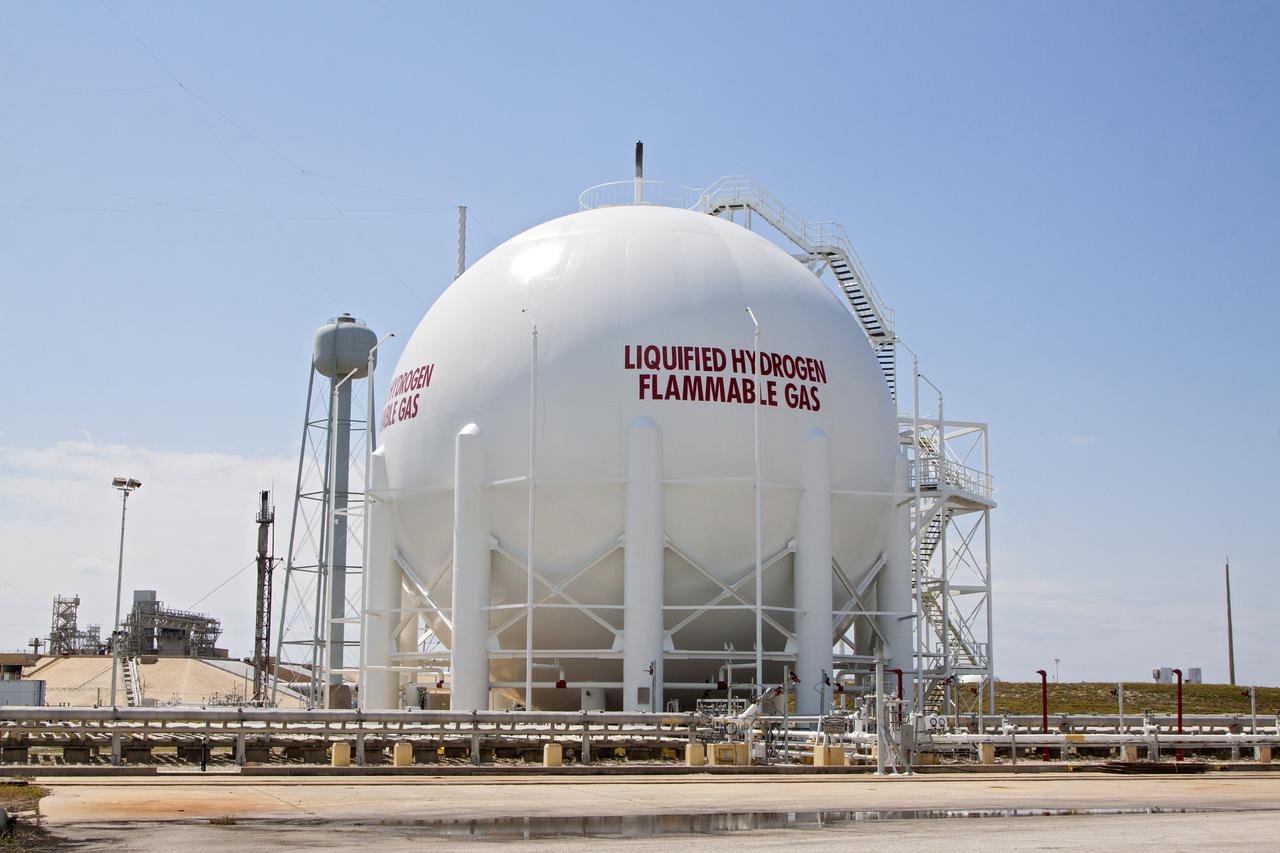
Construction of the A-3 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center continued June 8 with installation of a 35,000-gallon liquid oxygen tank atop the steel structure. The stand is being built to test next-generation rocket engines that will carry humans into deep space once more. The LOX tank and a liquid hydrogen tank to be installed atop the stand later will provide propellants for testing the engines. The A-3 Test Stand is scheduled for completion and activation in 2013.
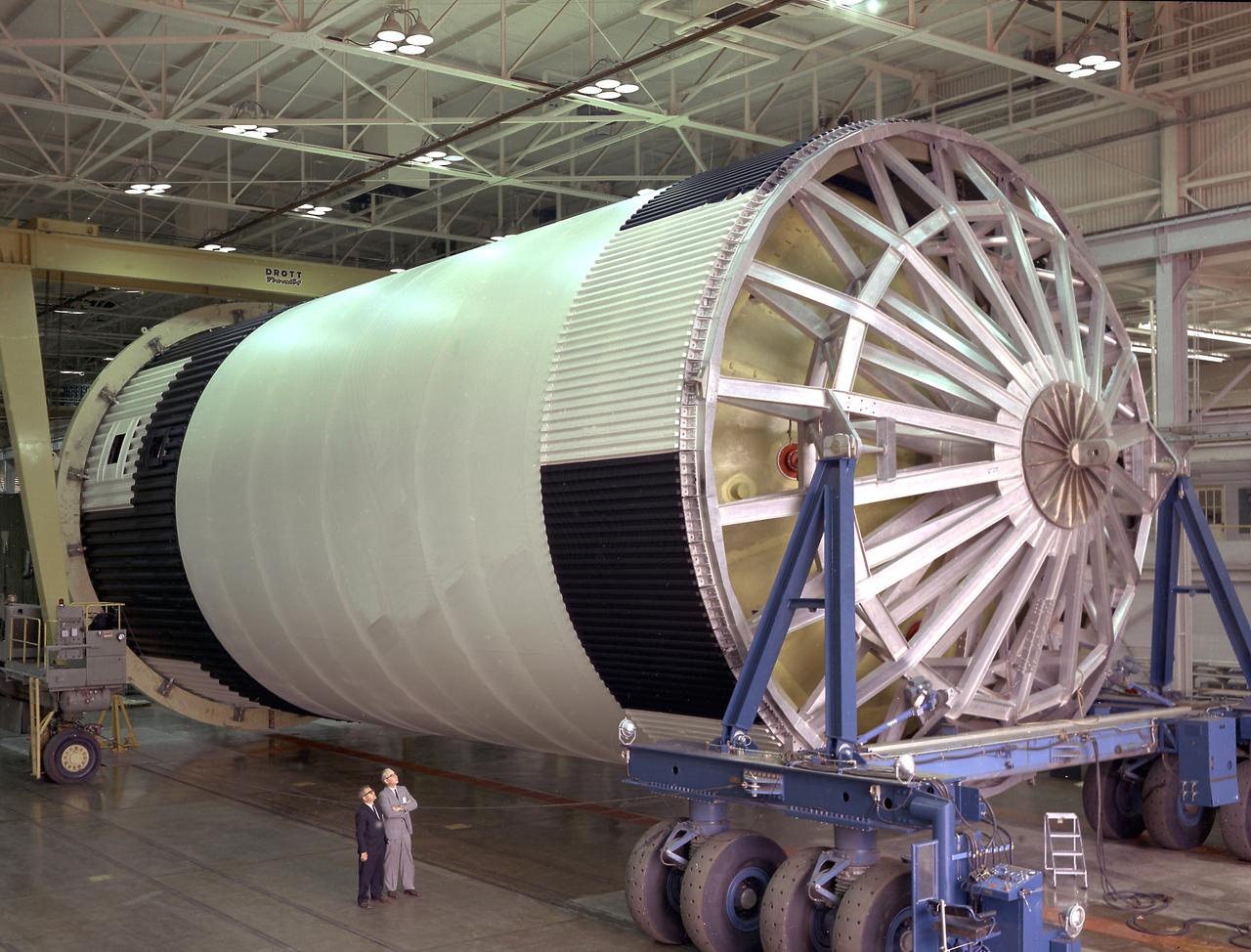

This is a picture of the assembled liquid oxygen (LOX) tank for the Saturn V S-IC (first) stage, with A-frame, that arrived to be mated to the fuel tank at a later date at the Marshall Space Flight Center, building 4705.
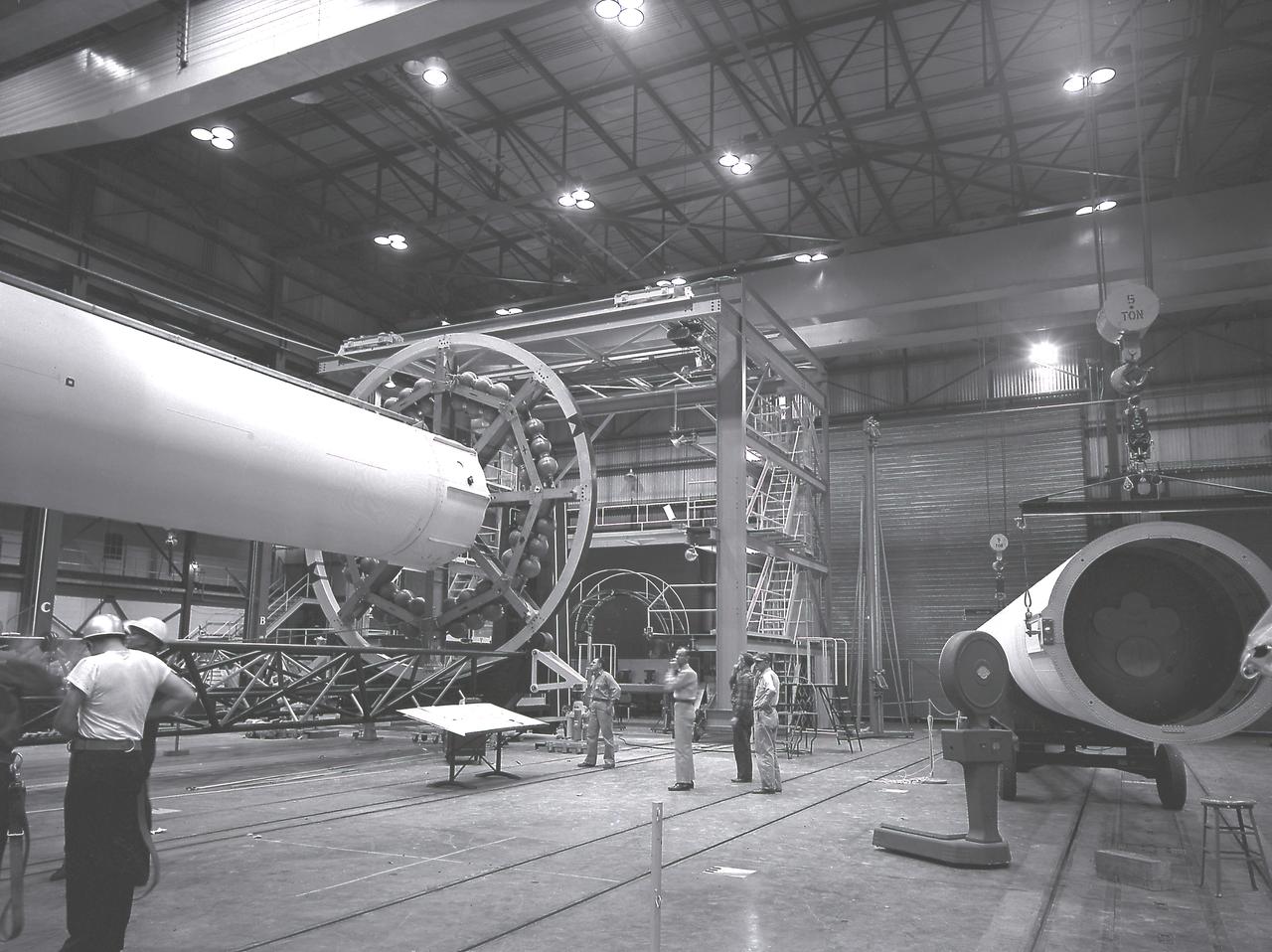

The Saturn I liquid-oxygen (LOX) tank for the Saturn I S-I stage being aligned with the end spider beam in the fabrication and engineering laboratory, building 4705, at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
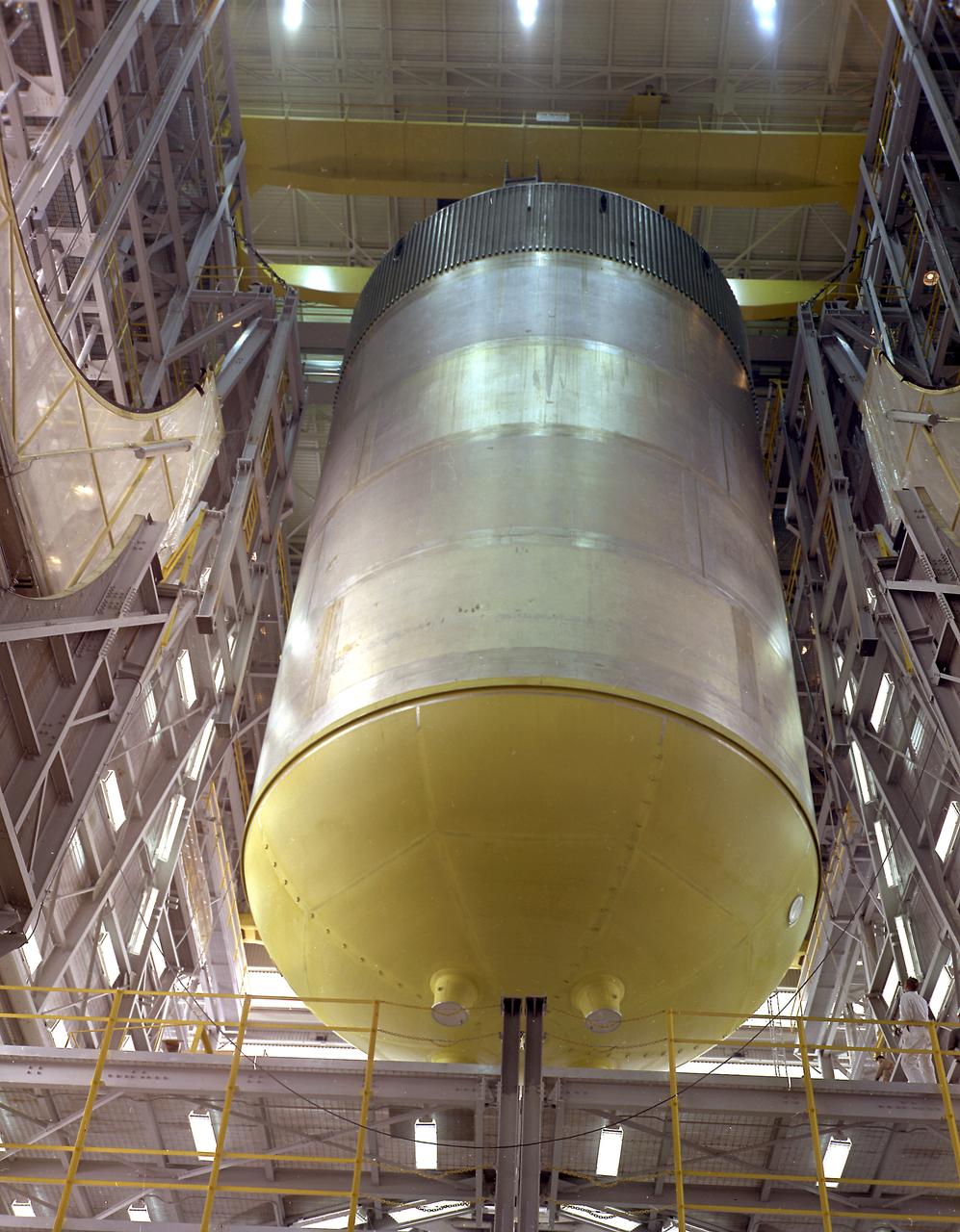

This photograph shows the Saturn V S-IC-S stage (S-IC stage for structural test) liquid oxygen (LOX) tank being lifted in the vehicle assembly building at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
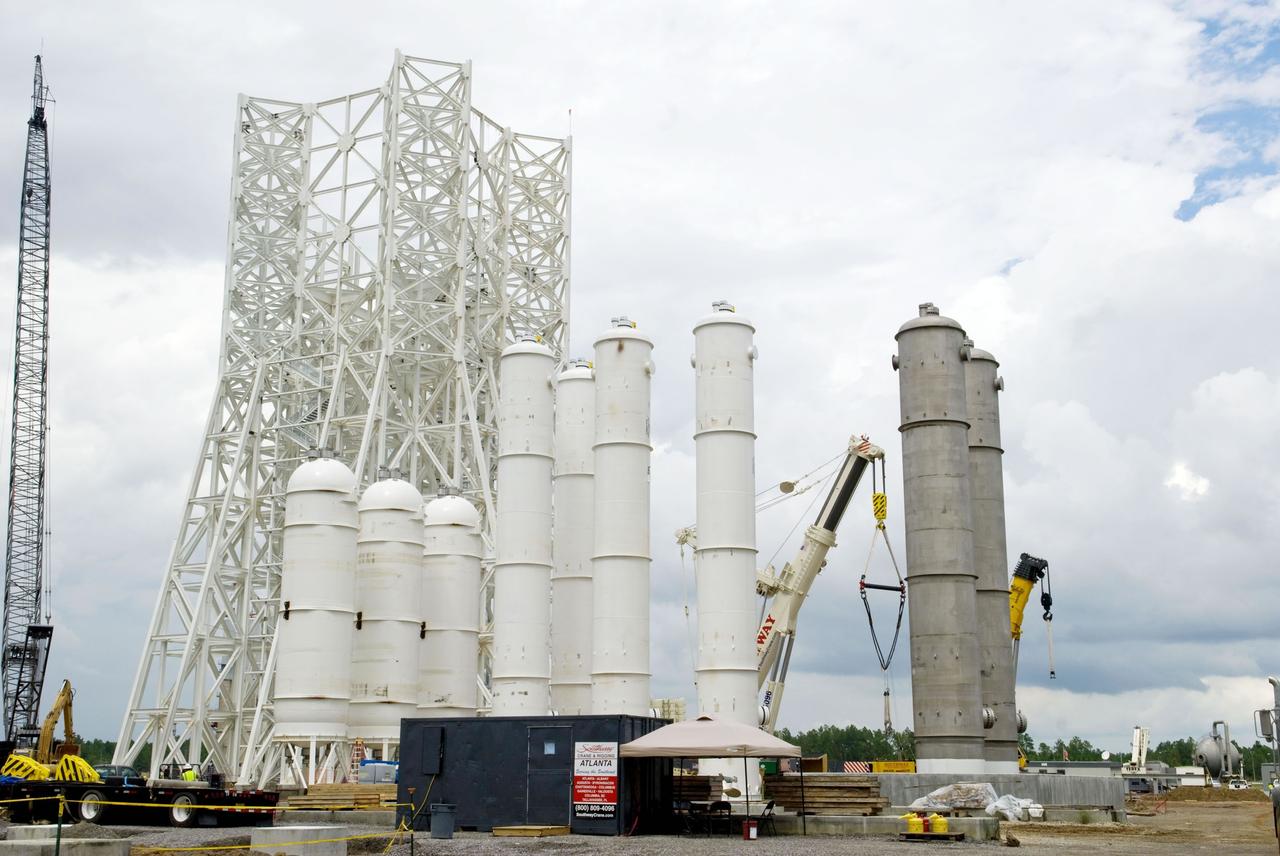

Construction of the A-3 Test Stand approaches another milestone with delivery and installation of water, isopropyl alcohol (IPA) and liquid oxygen (LOX) tanks. The three LOX tanks shown on the left and the two IPA tanks shown on the right are all 35,000 gallons each. The four water tanks in the center are 39,000 gallons each.
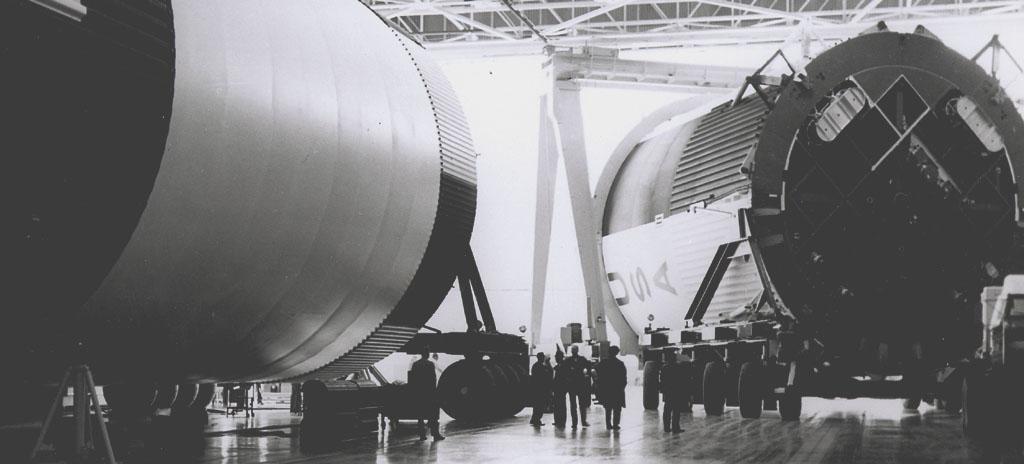

This photograph shows the Saturn V assembled LOX (Liquid Oxygen) and fuel tanks ready for transport from the Manufacturing Engineering Laboratory at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The tanks were then shipped to the launch site at Kennedy Space Center for a flight. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
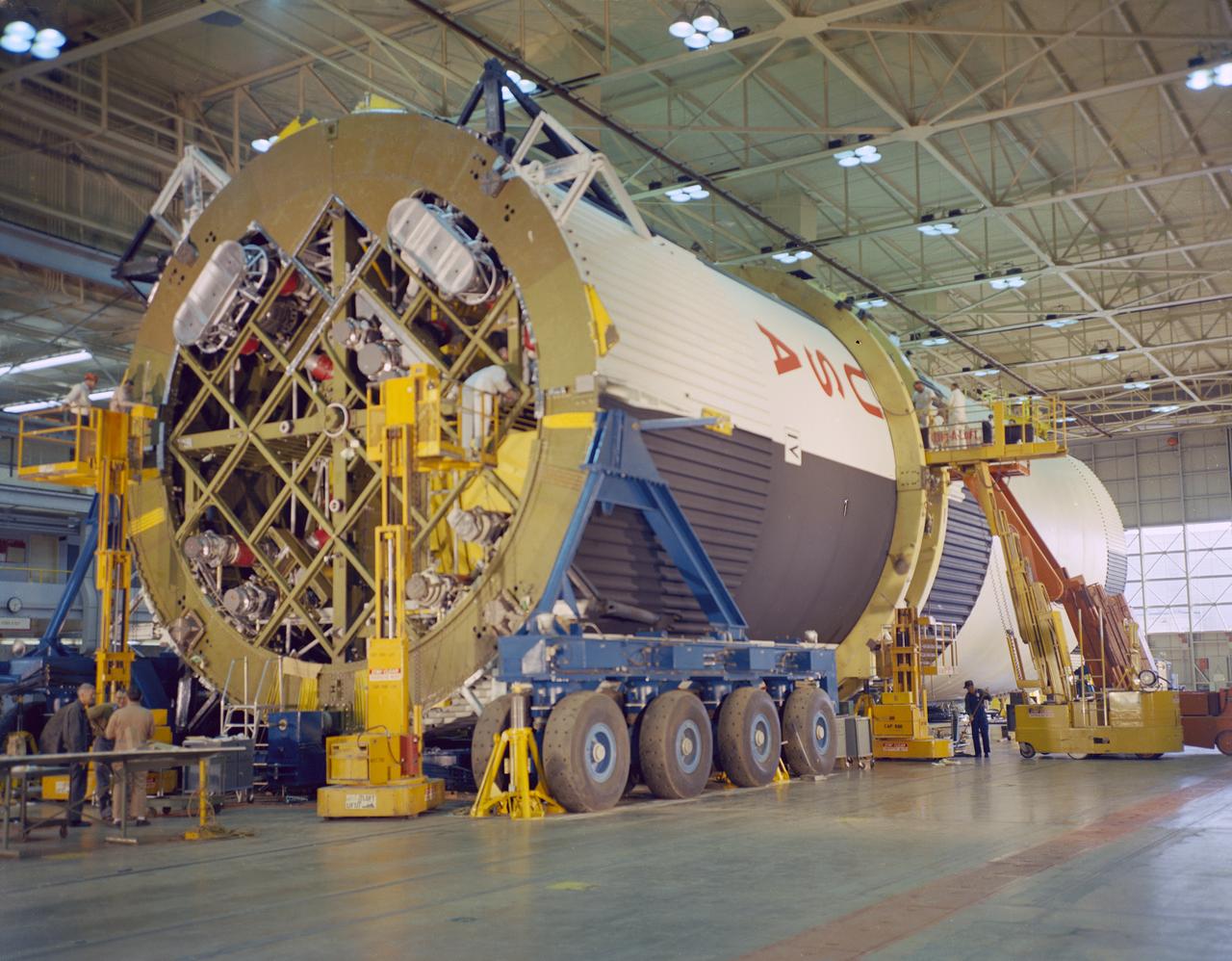

At the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the fuel tank assembly for the Saturn V S-IC-T (static test stage) fuel tank assembly is mated to the liquid oxygen (LOX) tank in building 4705. This stage underwent numerous static firings at the newly-built S-IC Static Test Stand at the MSFC west test area. The S-IC (first) stage used five F-1 engines that produced a total thrust of 7,500,000 pounds as each engine produced 1,500,000 pounds of thrust. The S-IC stage lifted the Saturn V vehicle and Apollo spacecraft from the launch pad.
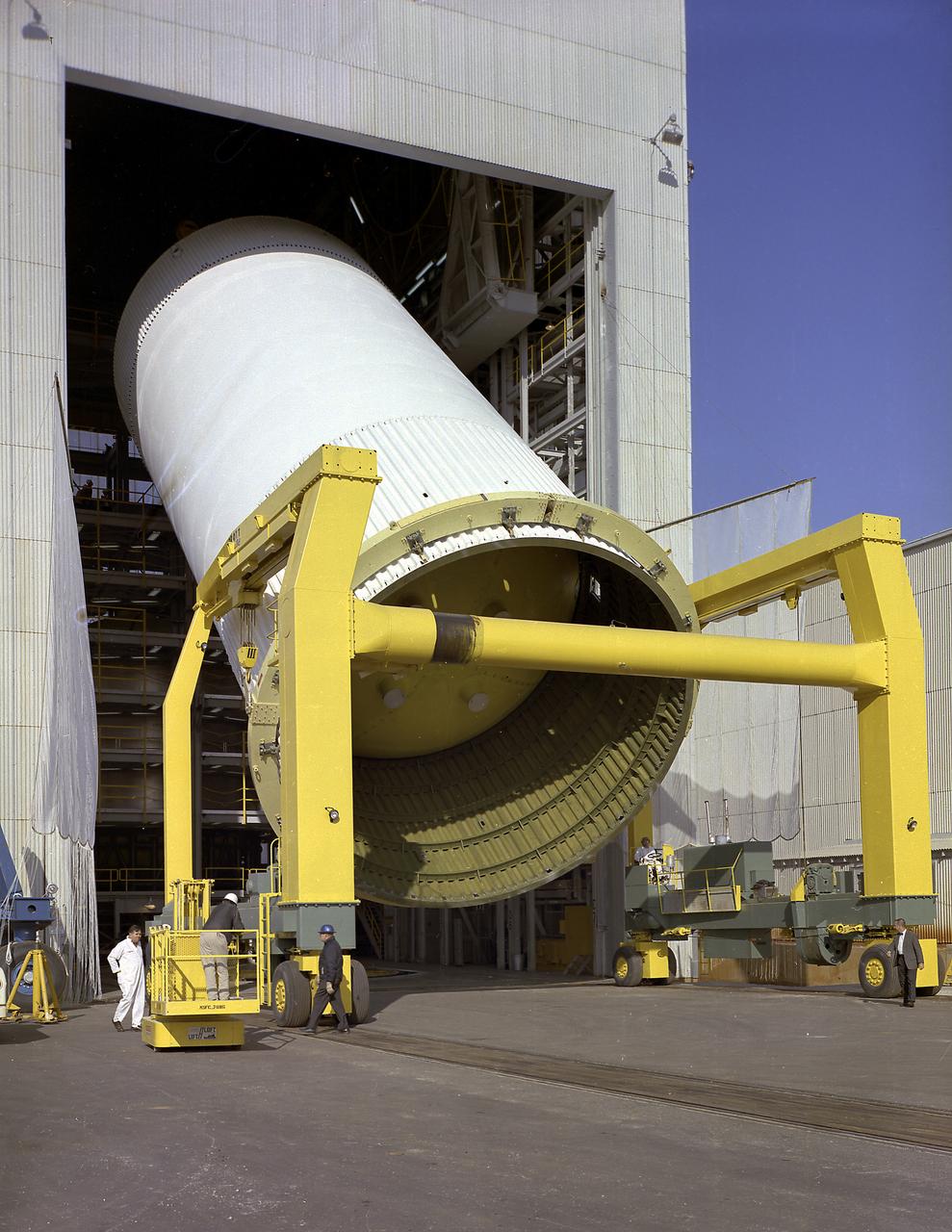

This photograph depicts engineers and technicians moving the Saturn V S-IC (First) stage liquid oxygen (LOX) tank from the Manufacturing Engineering Laboratory for load testing under simulated firing loads at the Propulsion and Vehicle Engineering Laboratory at the Marshall Space Flight Center.

On Thursday, February 10, 2022, move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the core stage 3 liquid oxygen tank (LOX) aft barrel out of the vertical friction stir weld tool to be moved for its next phase of production. Eventually, the aft barrel will be mated with the forward barrel and forward and aft domes to create the LOX tank, which will be used for the Space Launch System’s Artemis III mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

On Thursday, February 10, 2022, move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the core stage 3 liquid oxygen tank (LOX) aft barrel out of the vertical friction stir weld tool to be moved for its next phase of production. Eventually, the aft barrel will be mated with the forward barrel and forward and aft domes to create the LOX tank, which will be used for the Space Launch System’s Artemis III mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

On Thursday, February 10, 2022, move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the core stage 3 liquid oxygen tank (LOX) aft barrel out of the vertical friction stir weld tool to be moved for its next phase of production. Eventually, the aft barrel will be mated with the forward barrel and forward and aft domes to create the LOX tank, which will be used for the Space Launch System’s Artemis III mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

On Thursday, February 10, 2022, move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the core stage 3 liquid oxygen tank (LOX) aft barrel out of the vertical friction stir weld tool to be moved for its next phase of production. Eventually, the aft barrel will be mated with the forward barrel and forward and aft domes to create the LOX tank, which will be used for the Space Launch System’s Artemis III mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

On Thursday, February 10, 2022, move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the core stage 3 liquid oxygen tank (LOX) aft barrel out of the vertical friction stir weld tool to be moved for its next phase of production. Eventually, the aft barrel will be mated with the forward barrel and forward and aft domes to create the LOX tank, which will be used for the Space Launch System’s Artemis III mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

On Thursday, February 10, 2022, move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the core stage 3 liquid oxygen tank (LOX) aft barrel out of the vertical friction stir weld tool to be moved for its next phase of production. Eventually, the aft barrel will be mated with the forward barrel and forward and aft domes to create the LOX tank, which will be used for the Space Launch System’s Artemis III mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

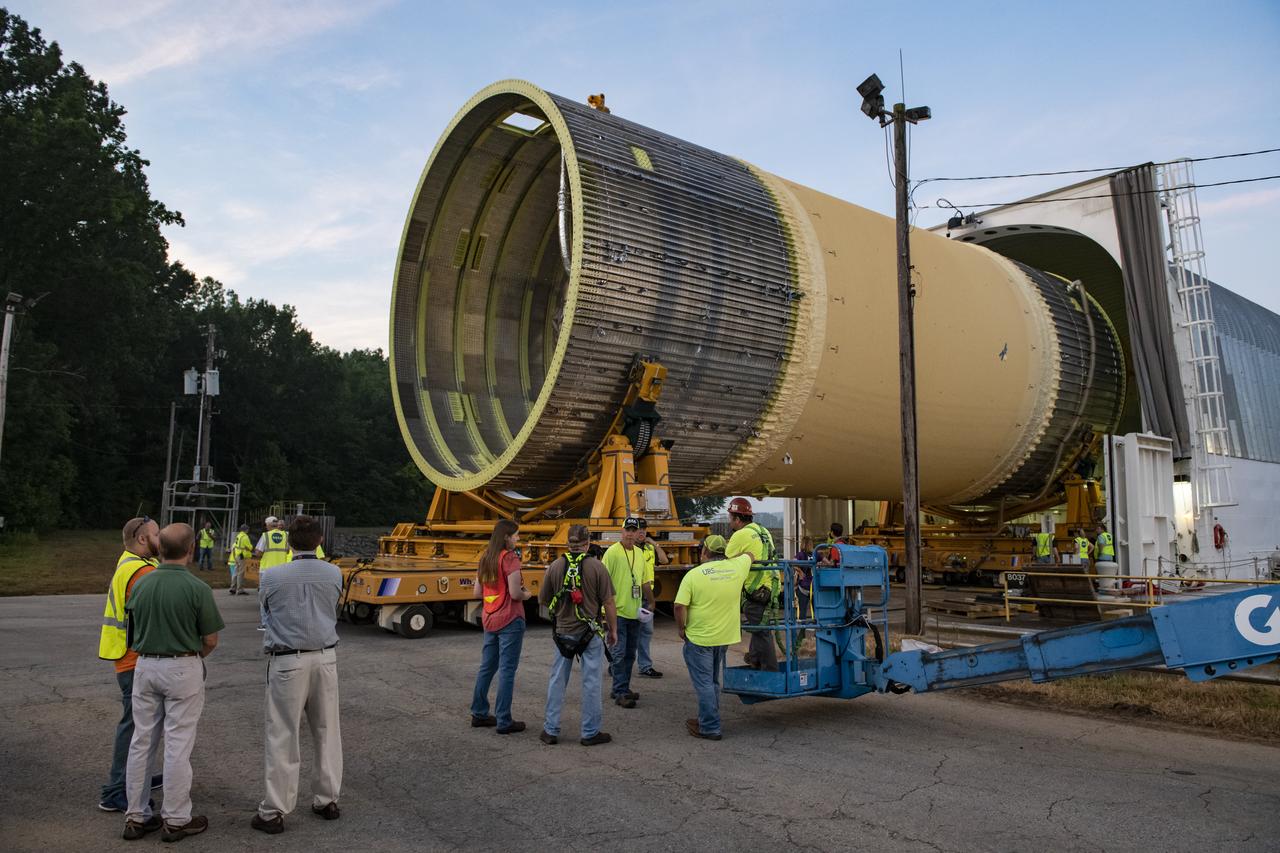
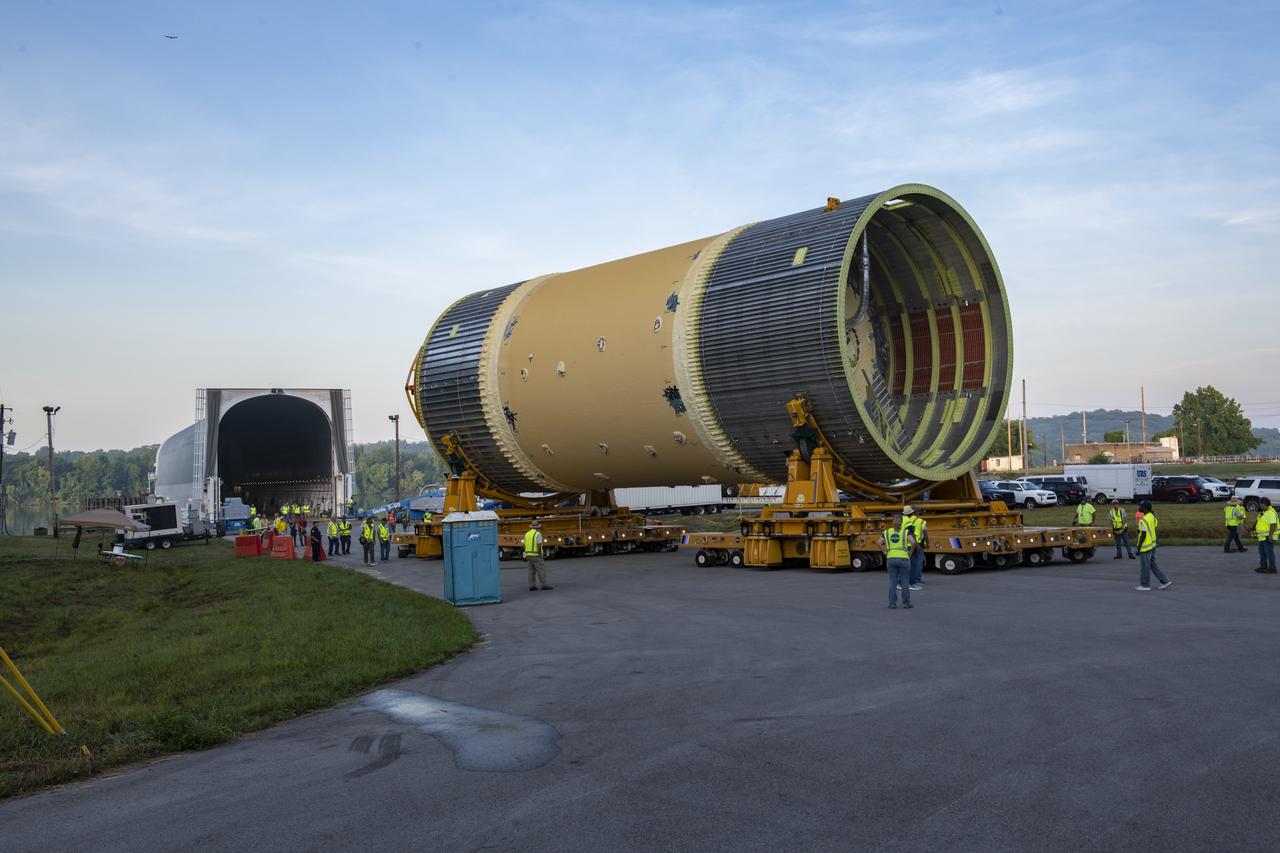
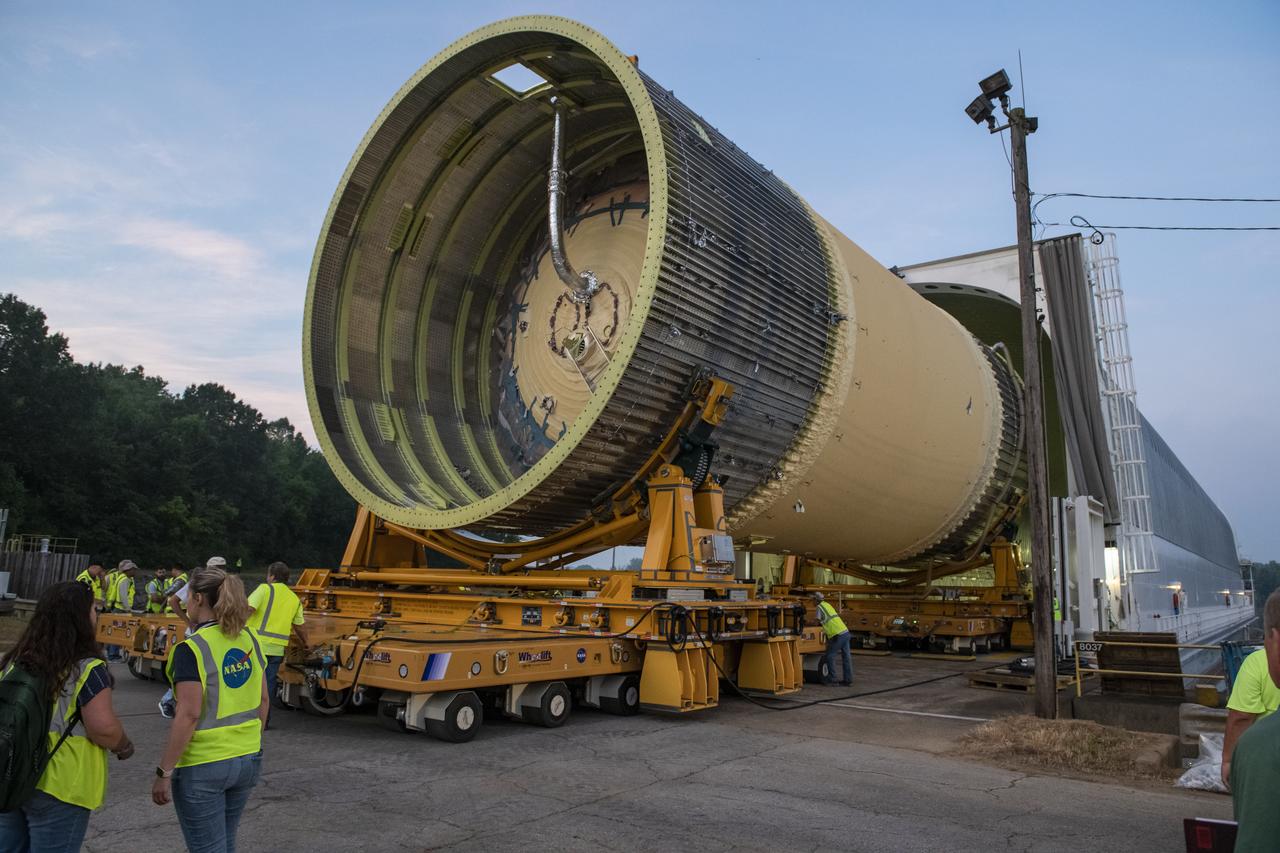
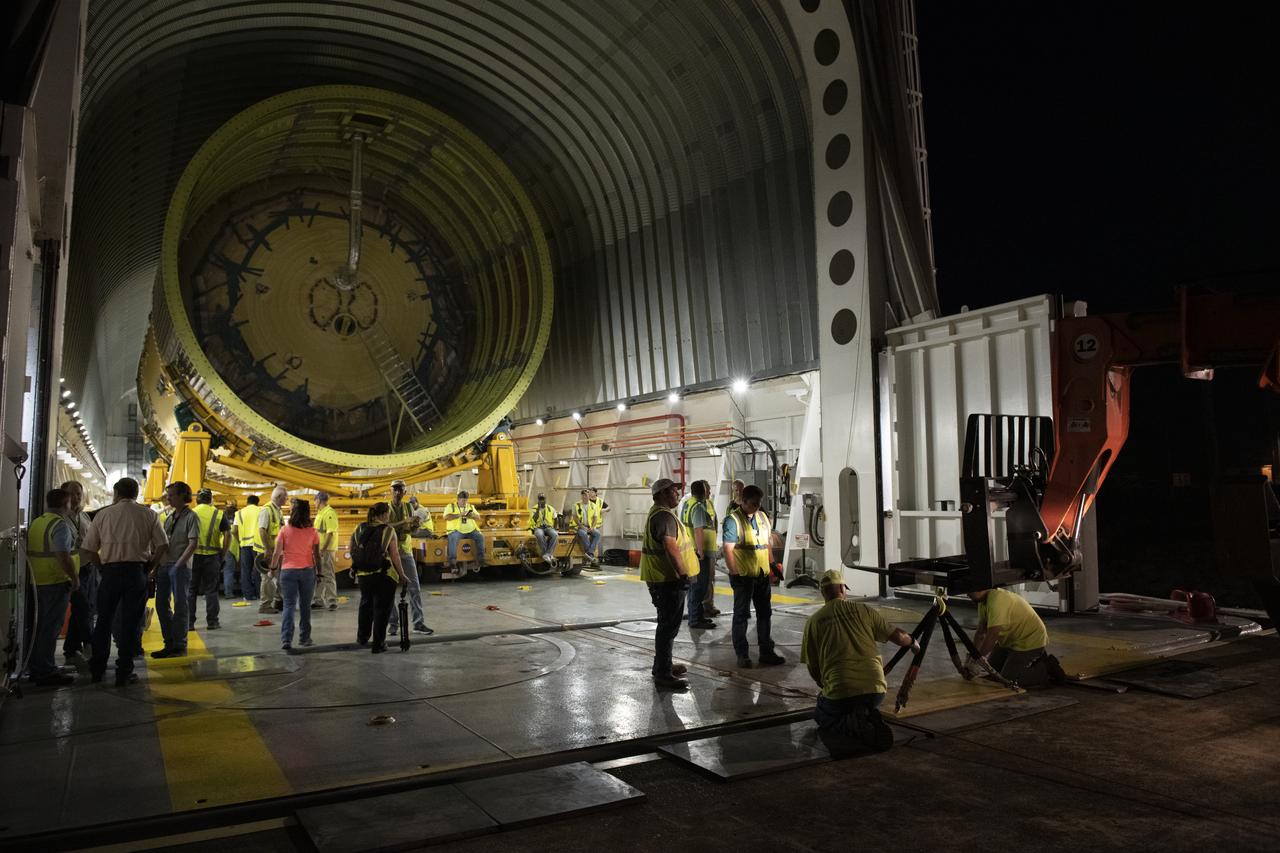
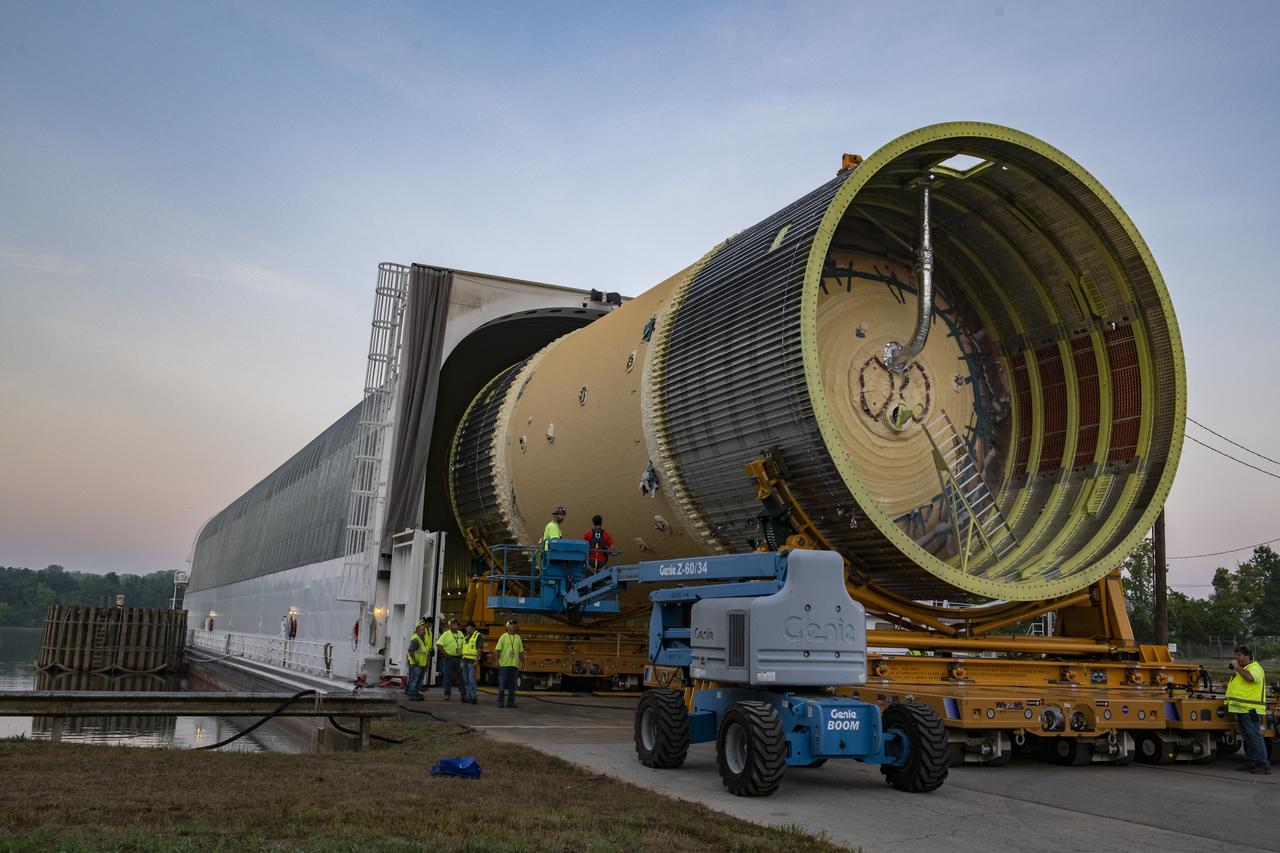
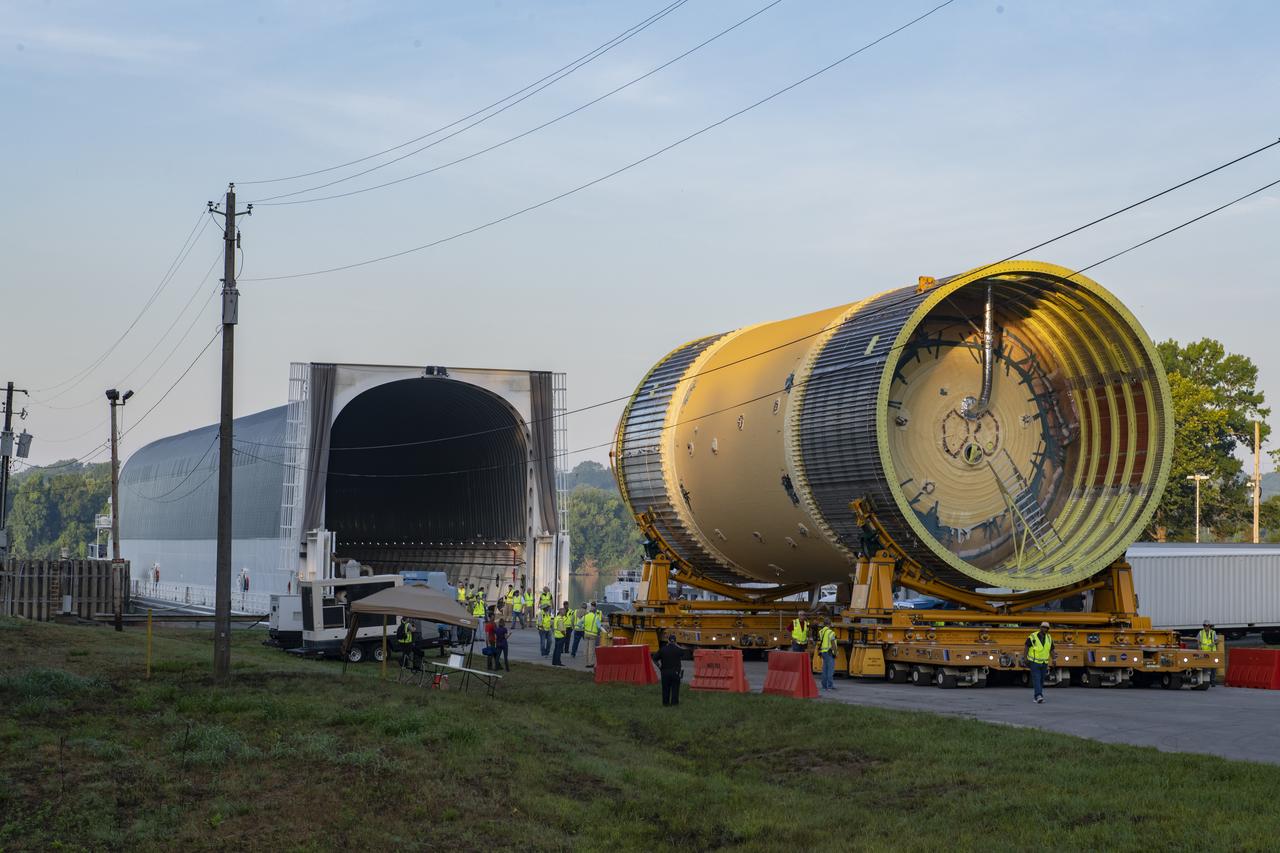
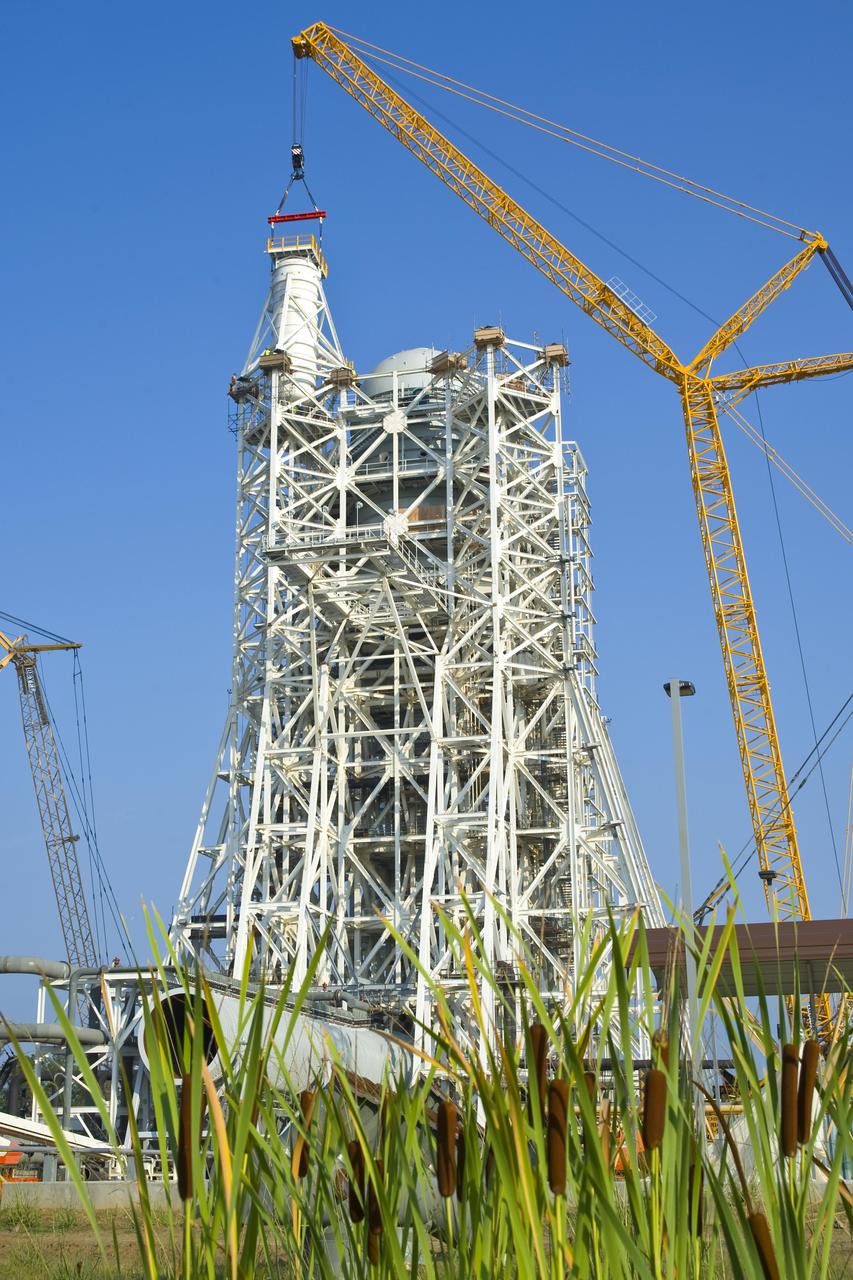
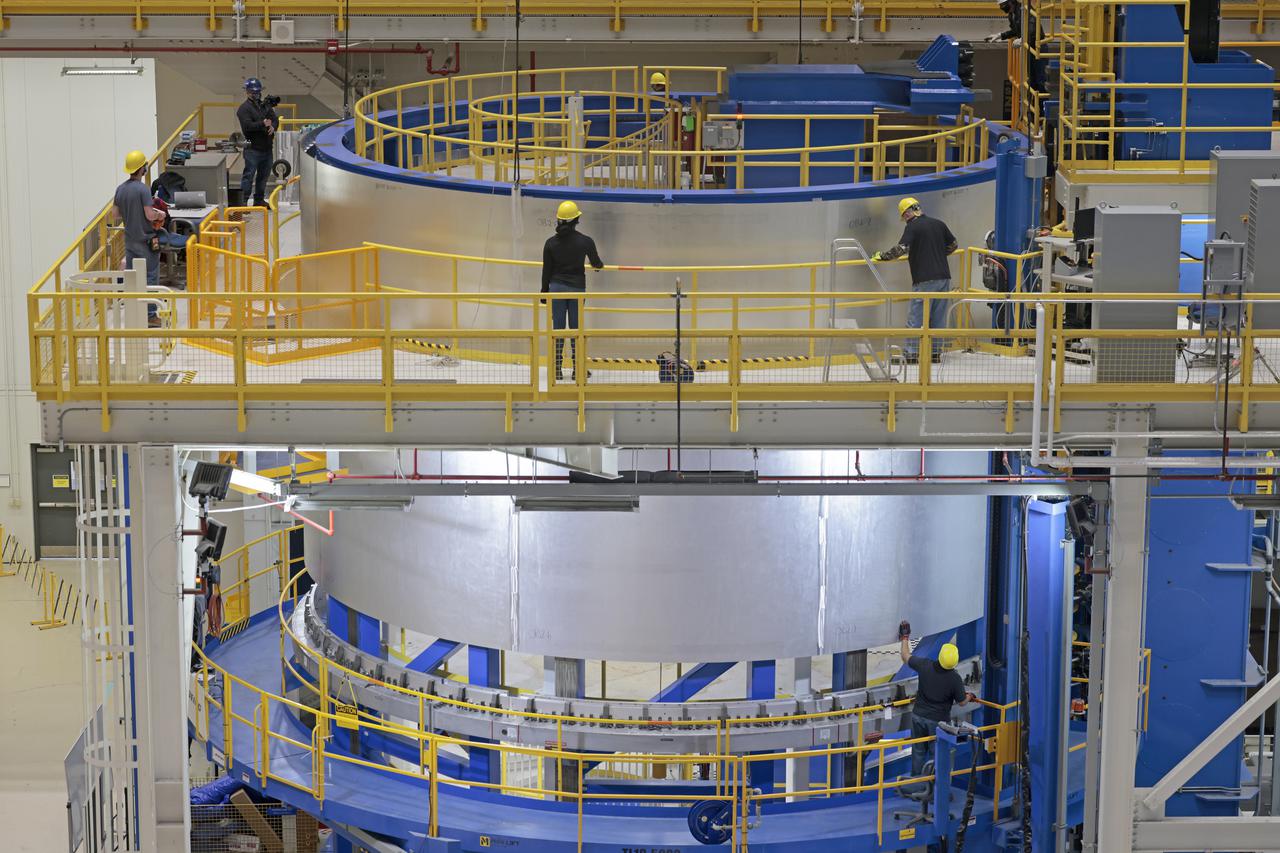
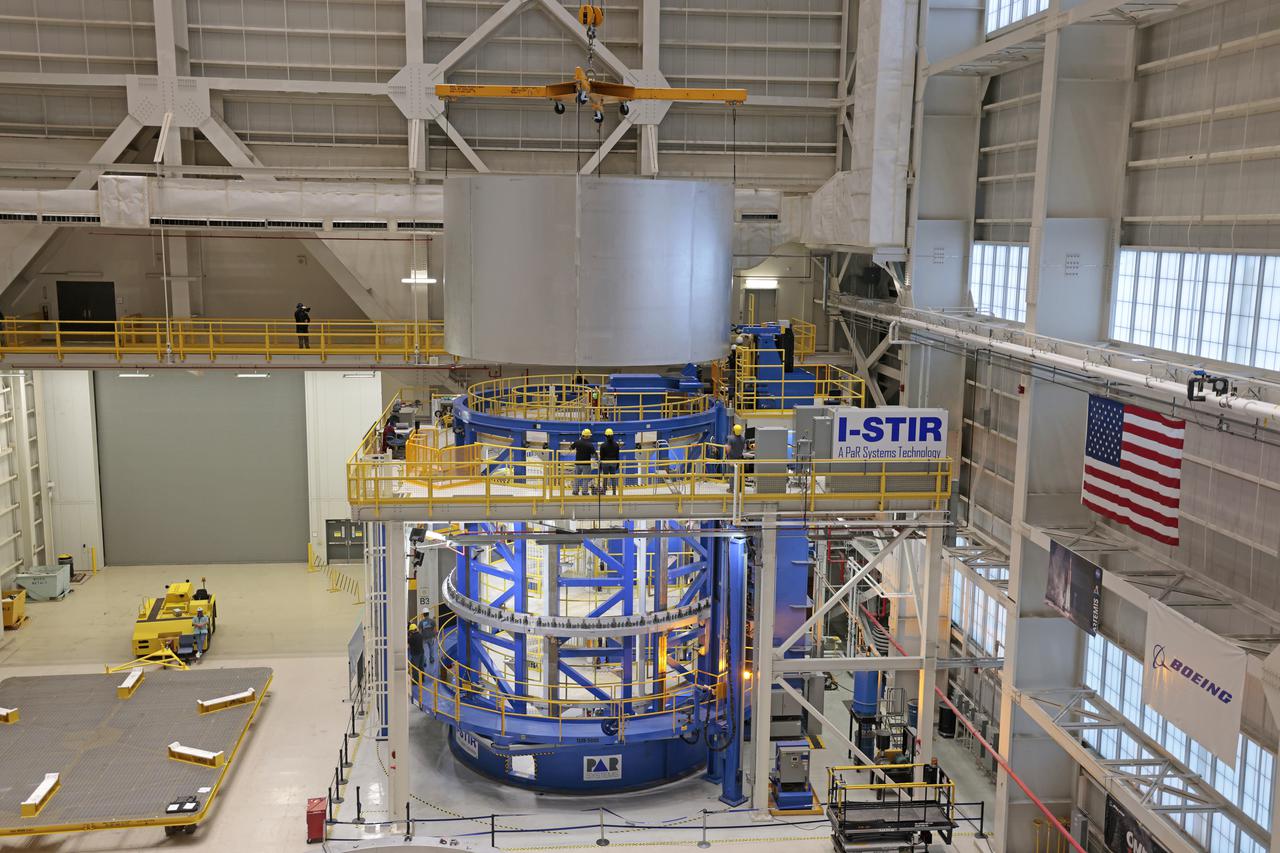
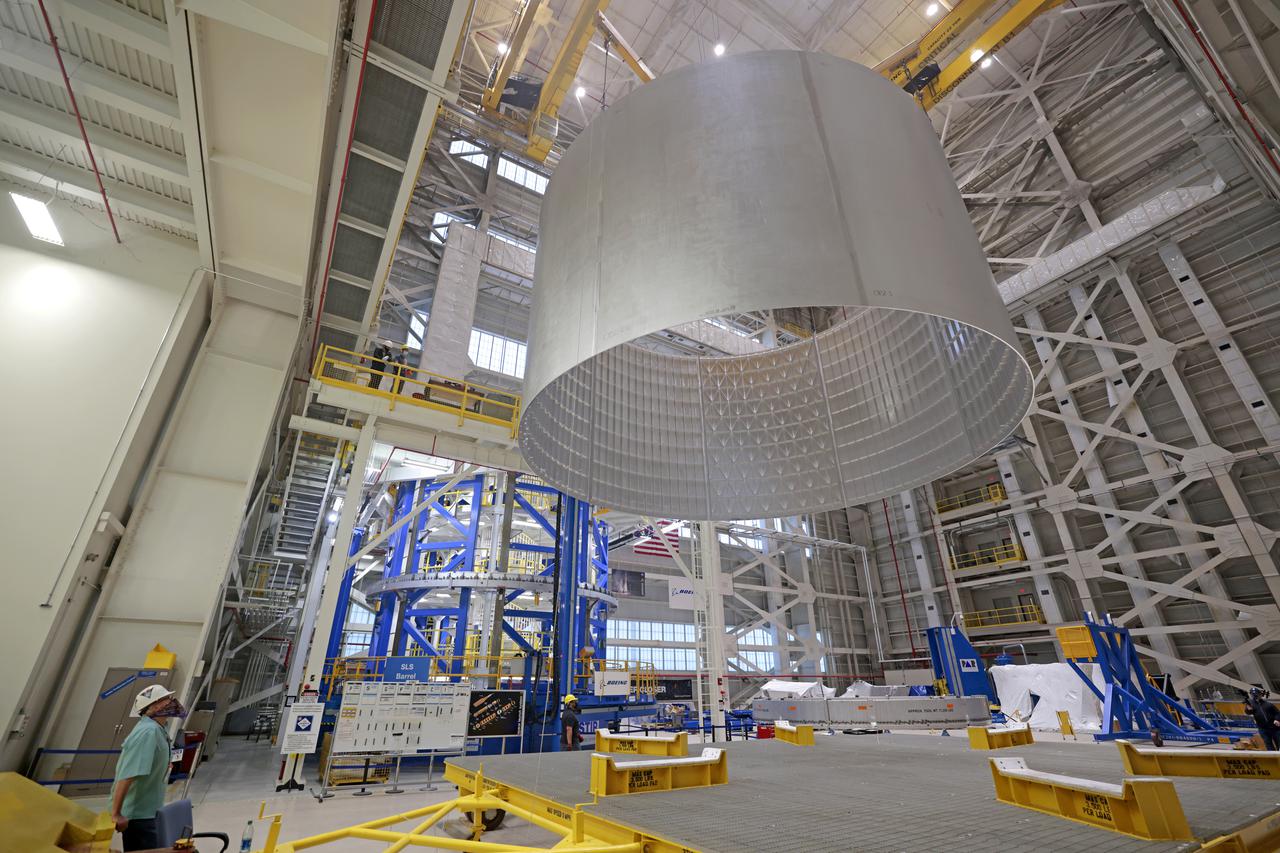
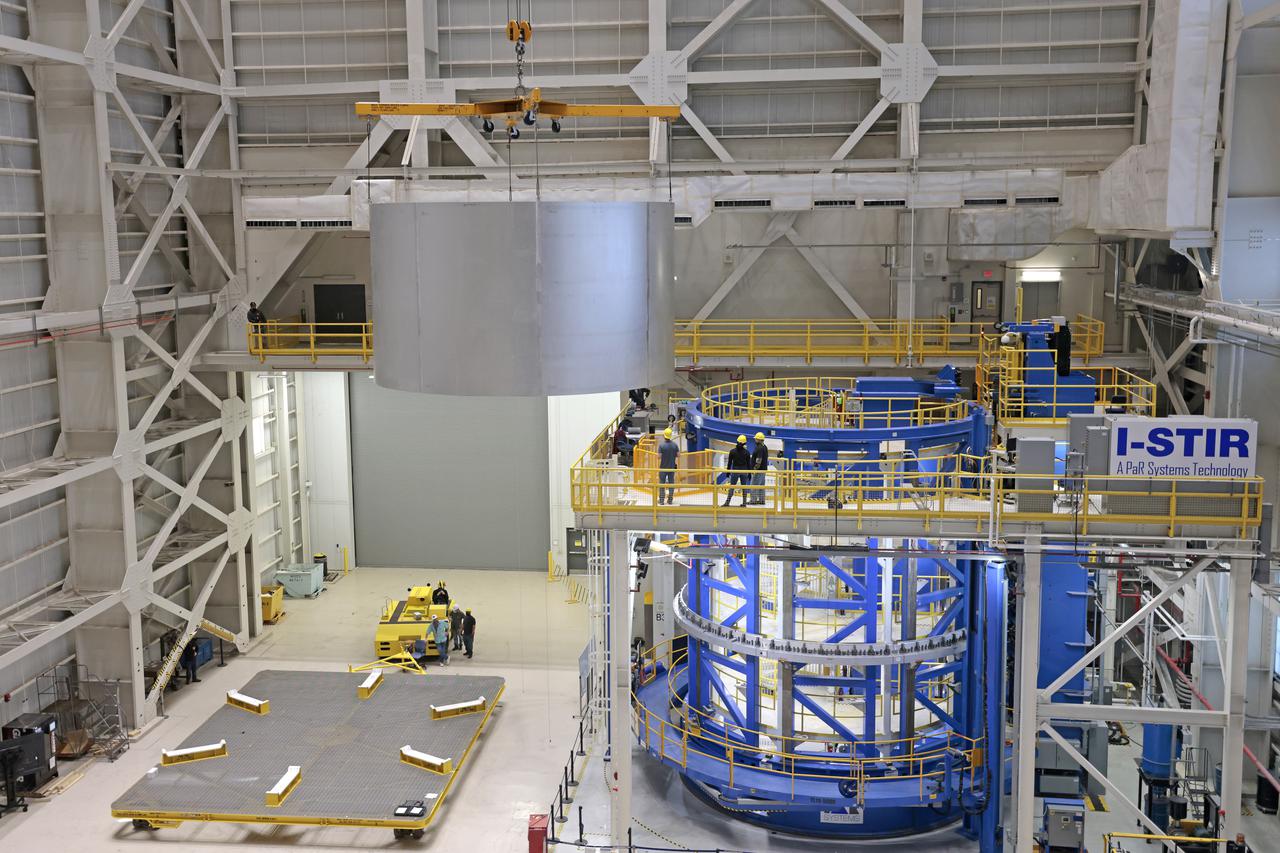
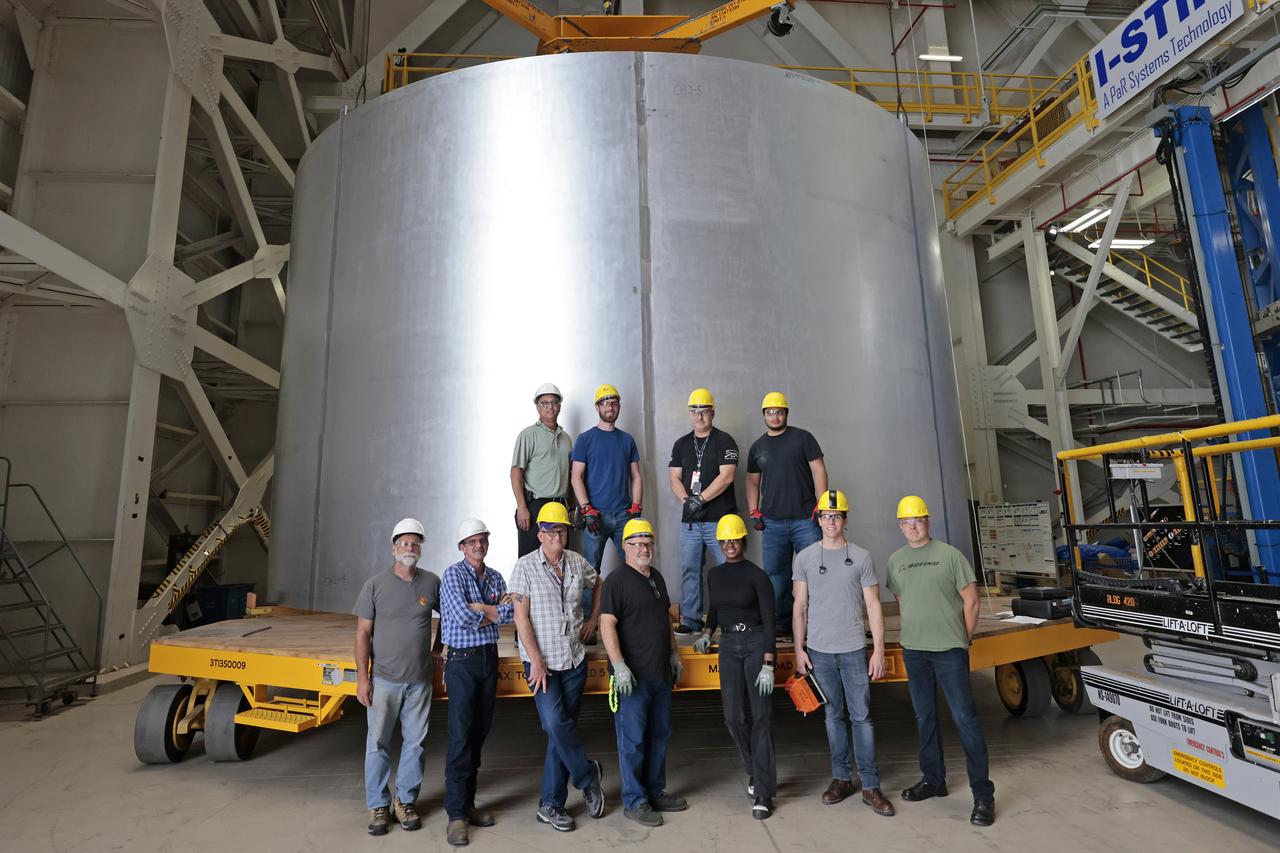
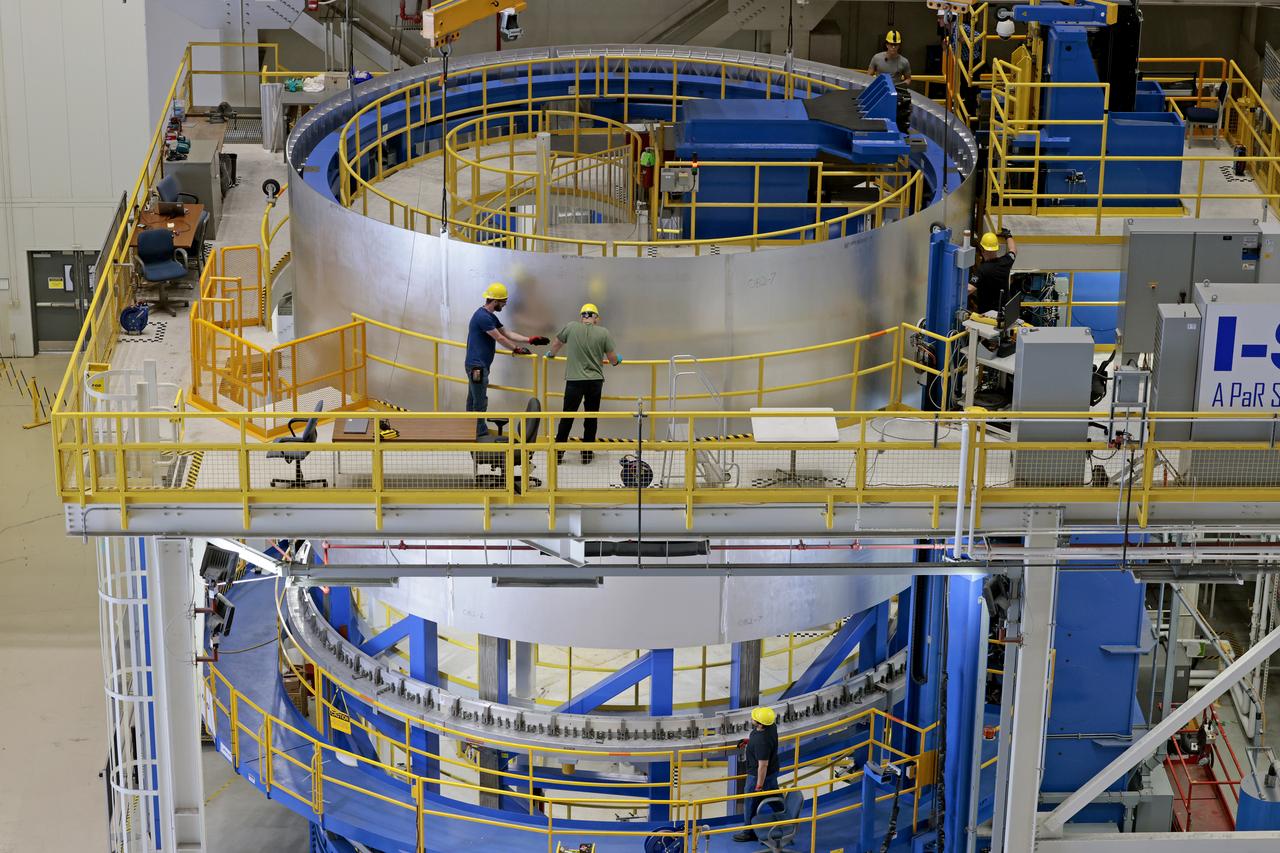
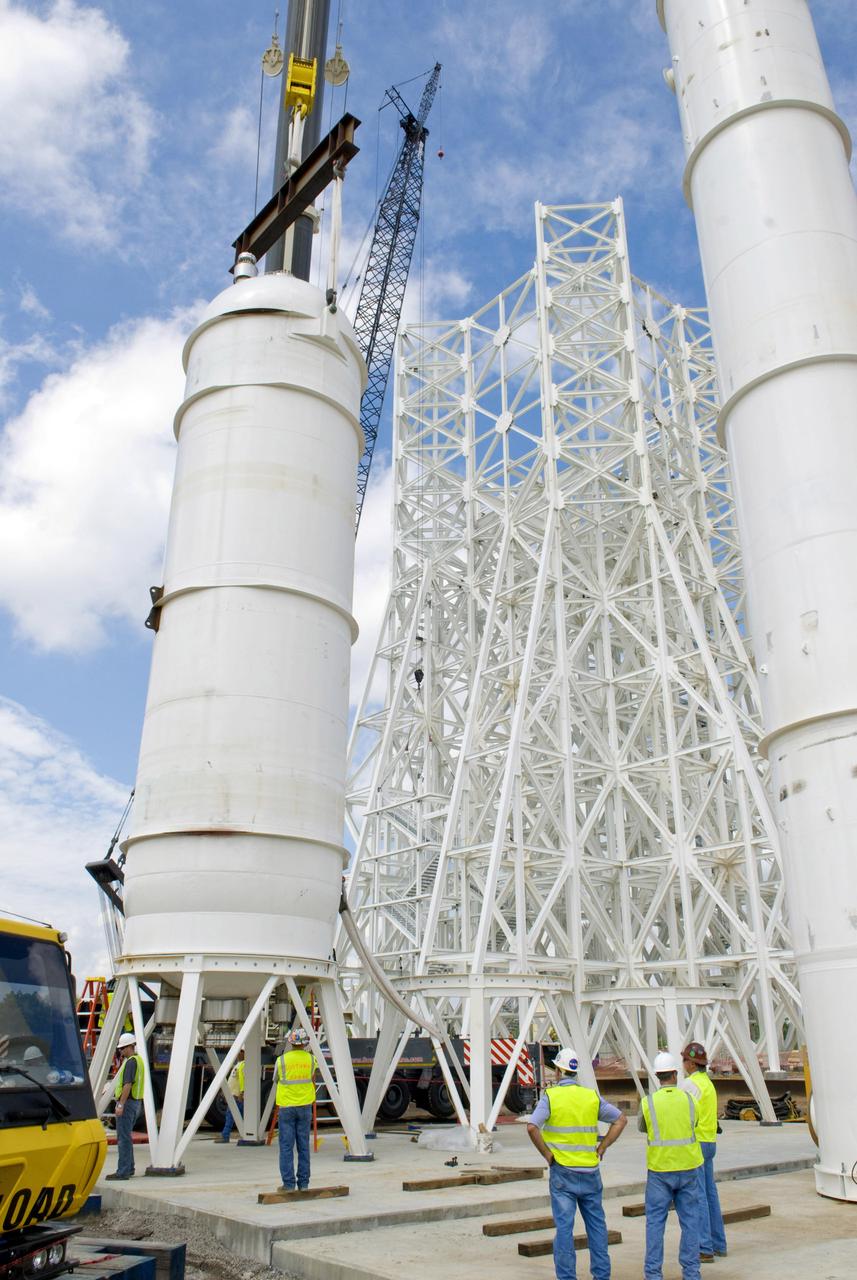
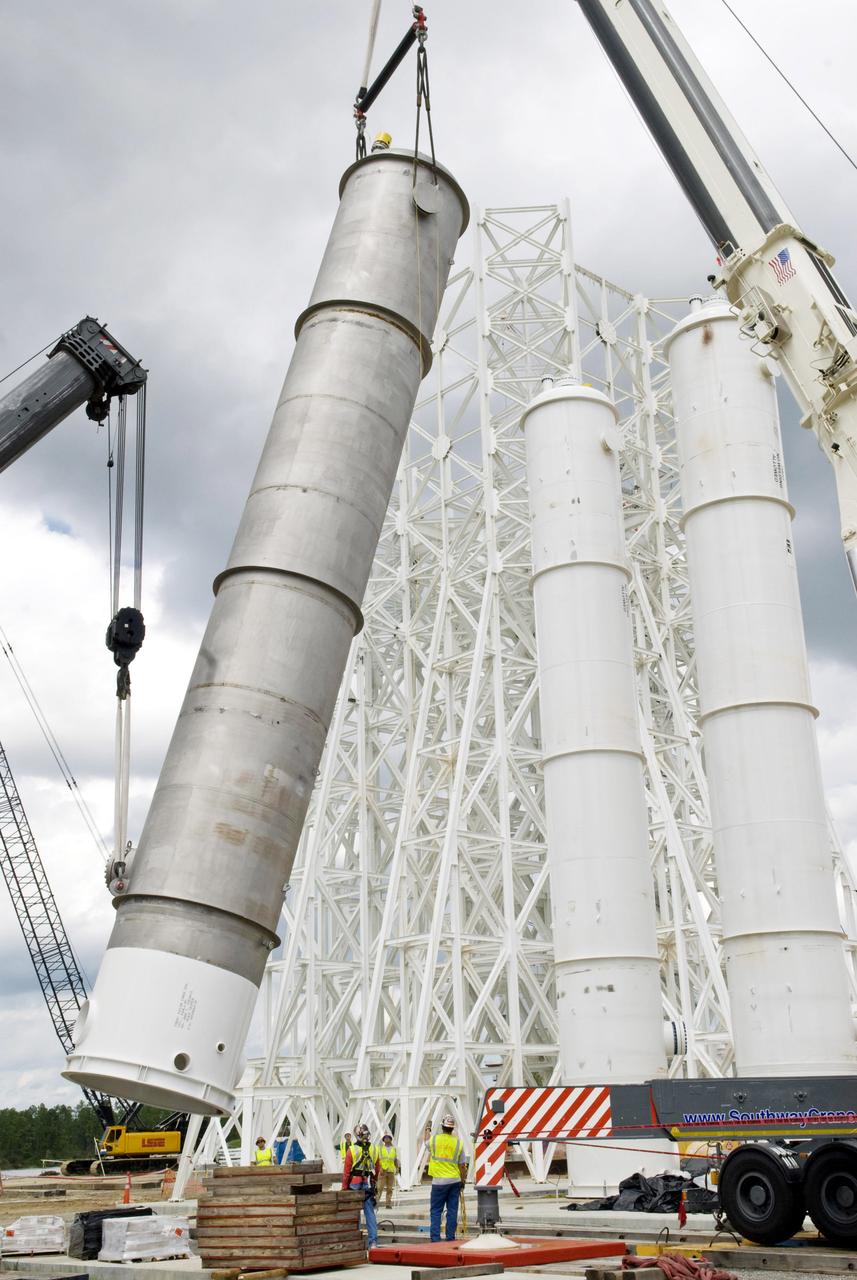
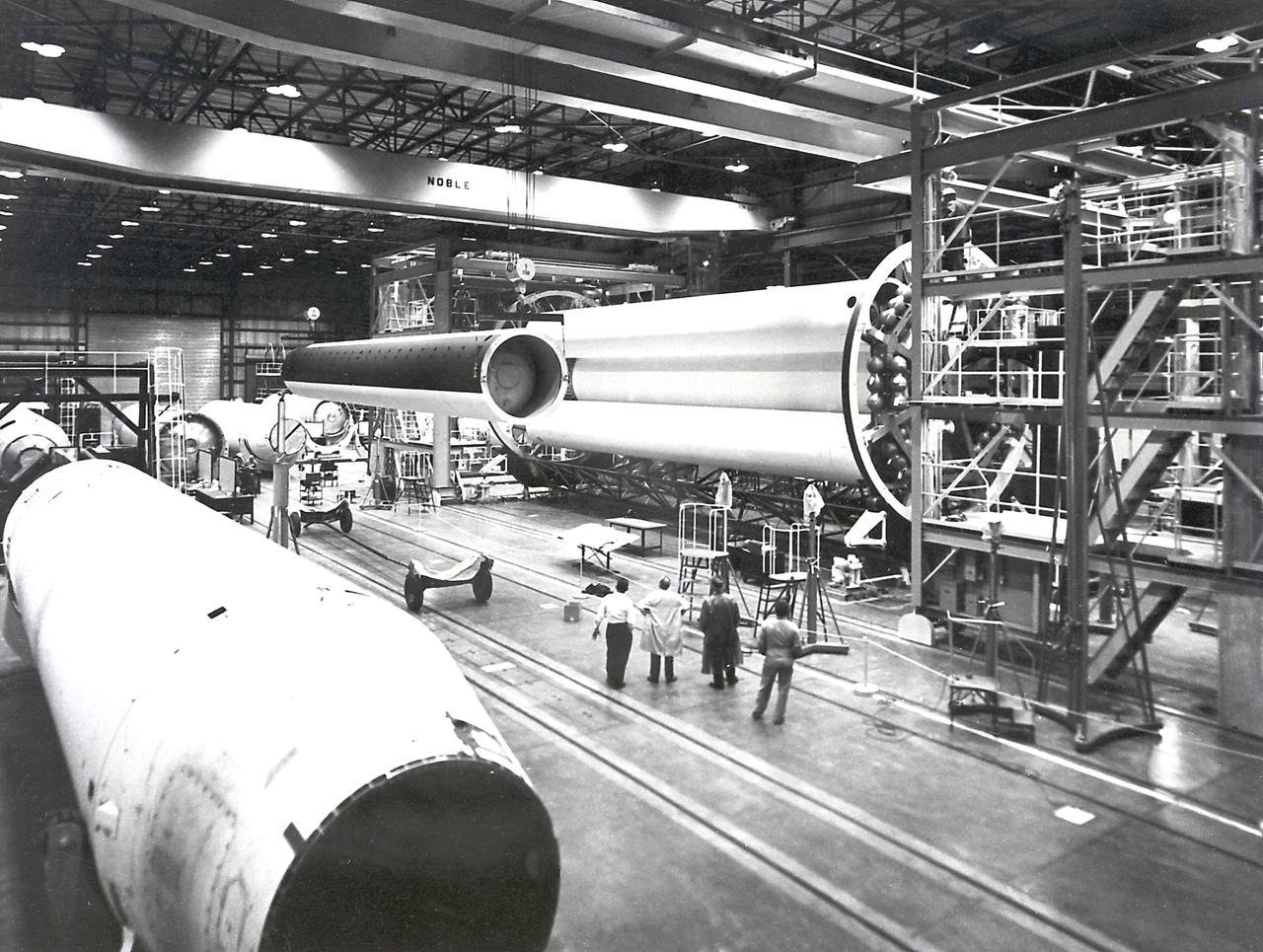
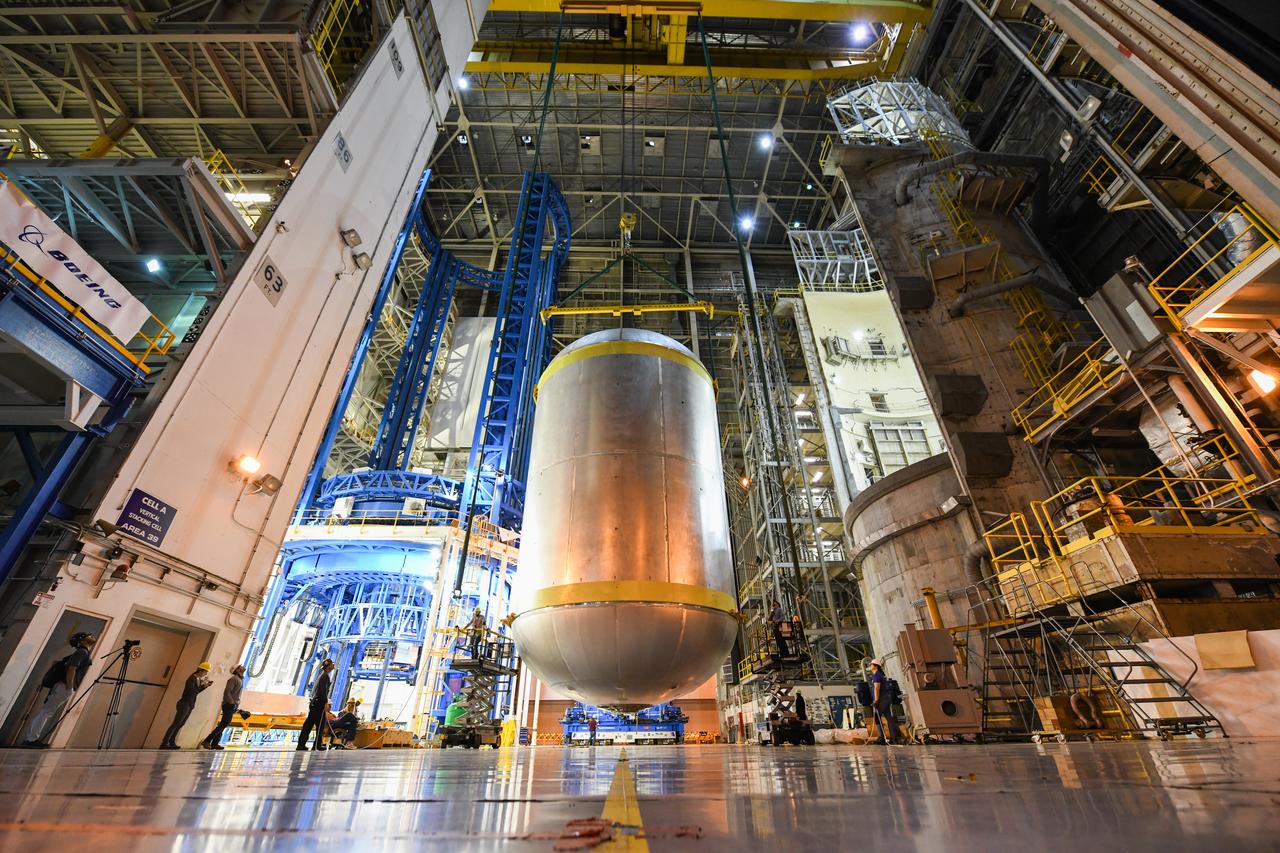
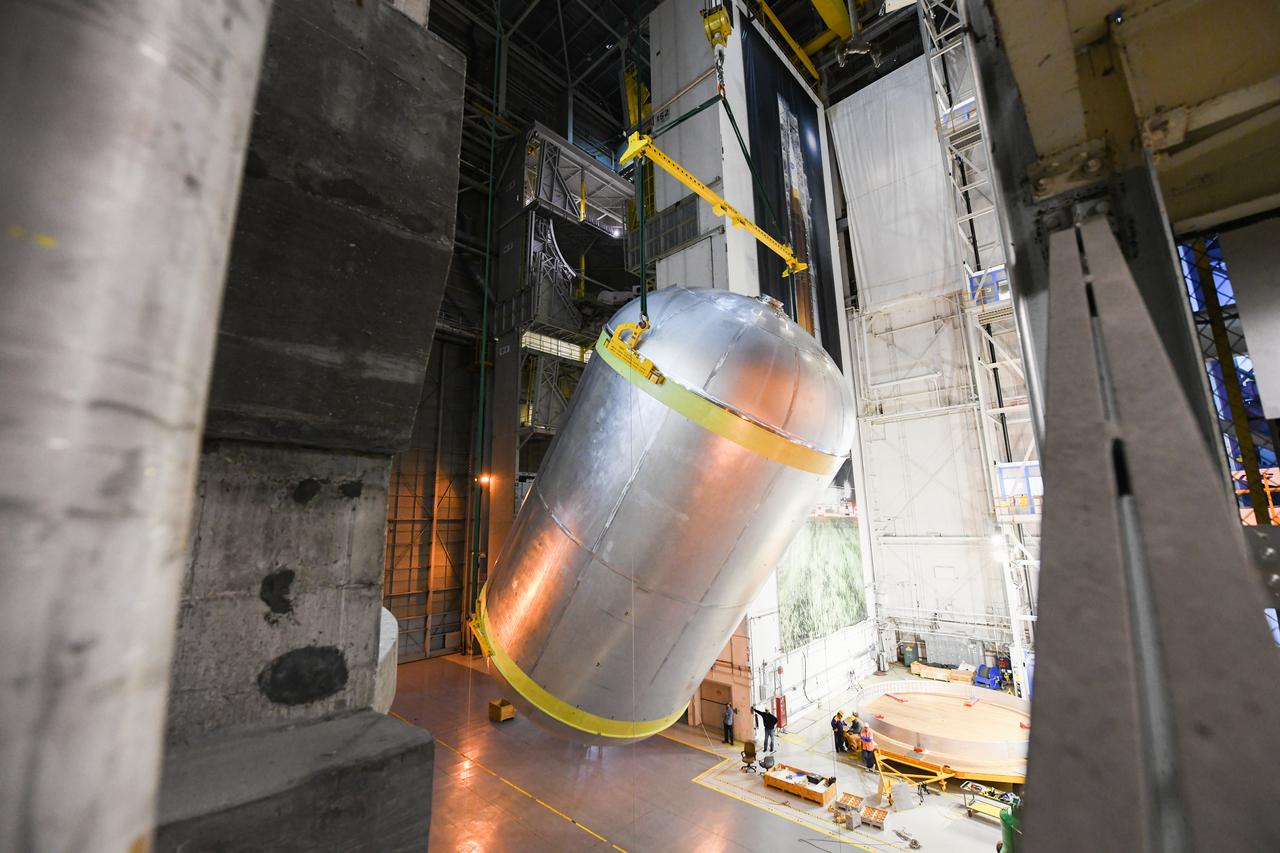
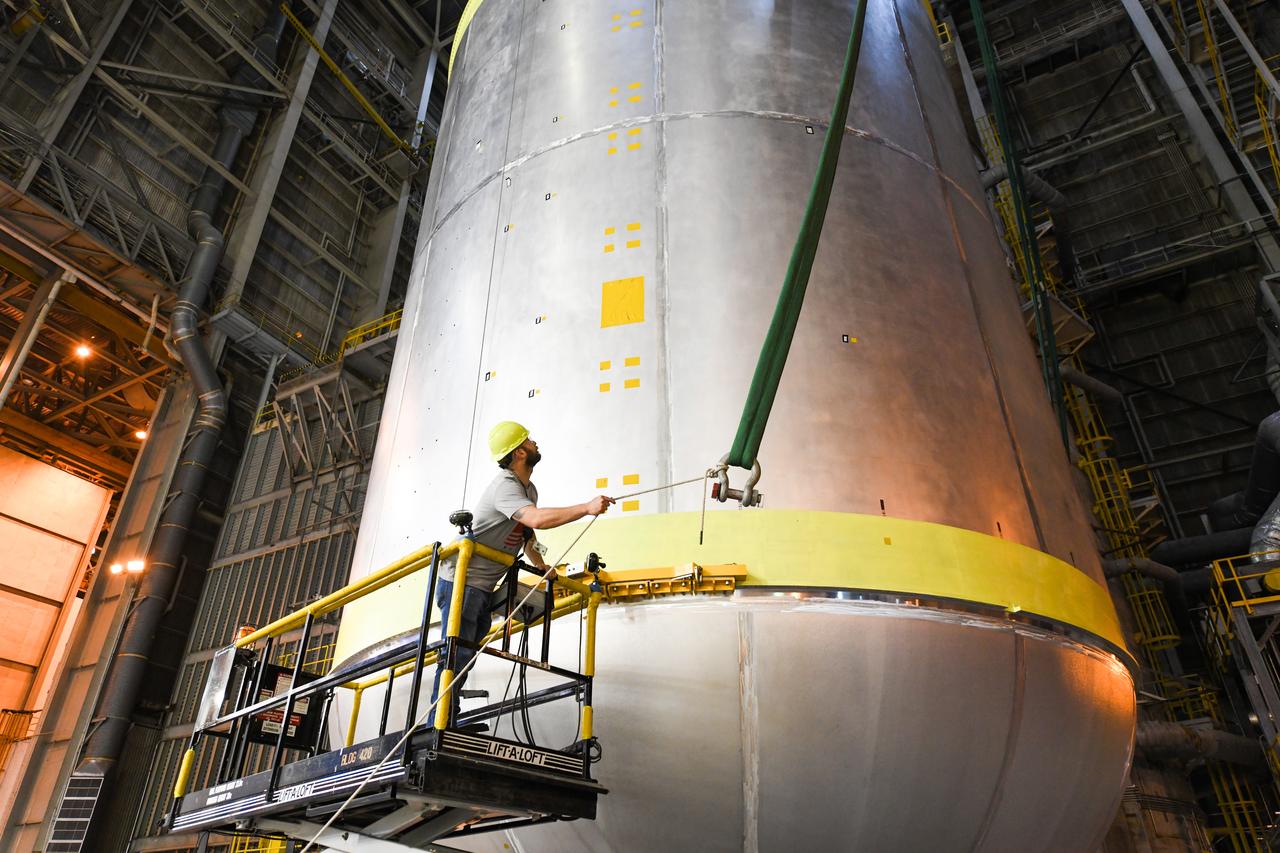
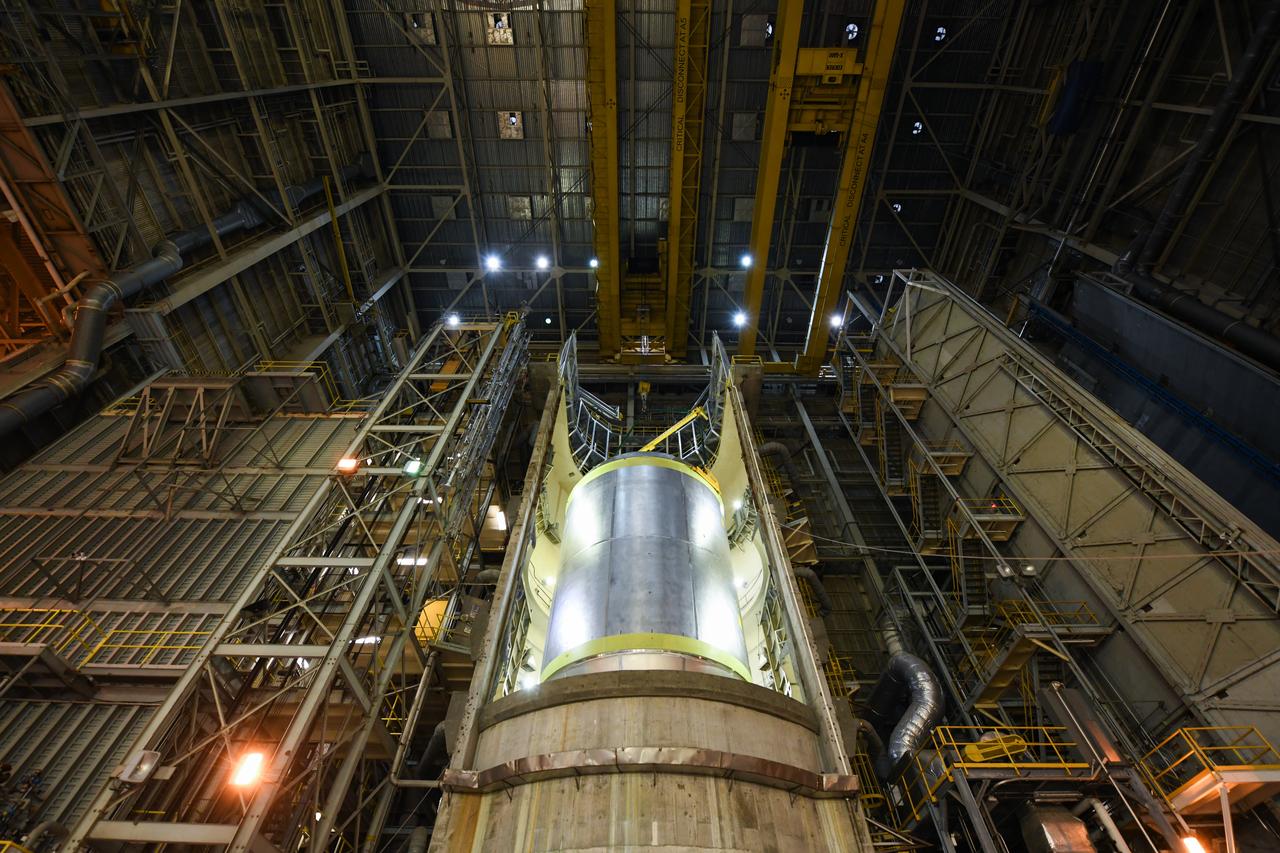
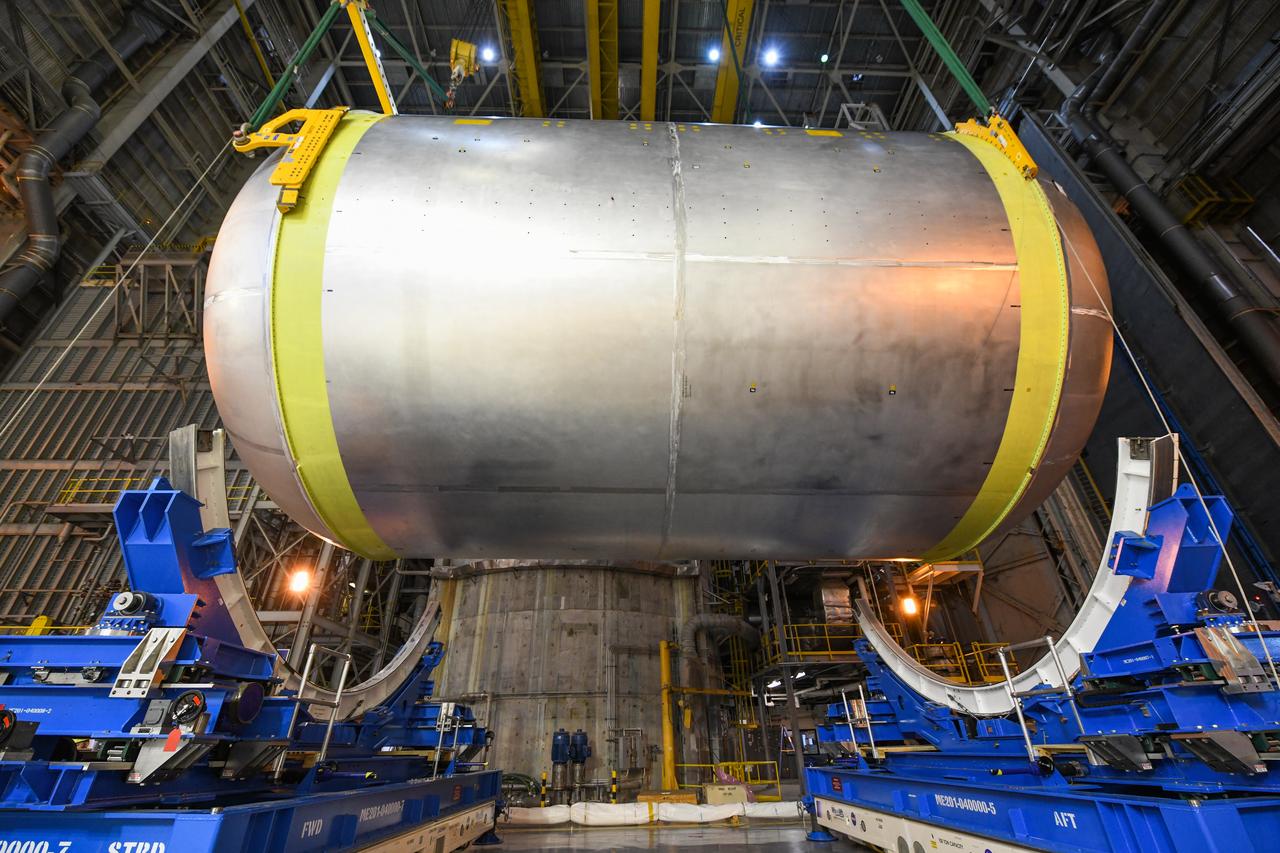
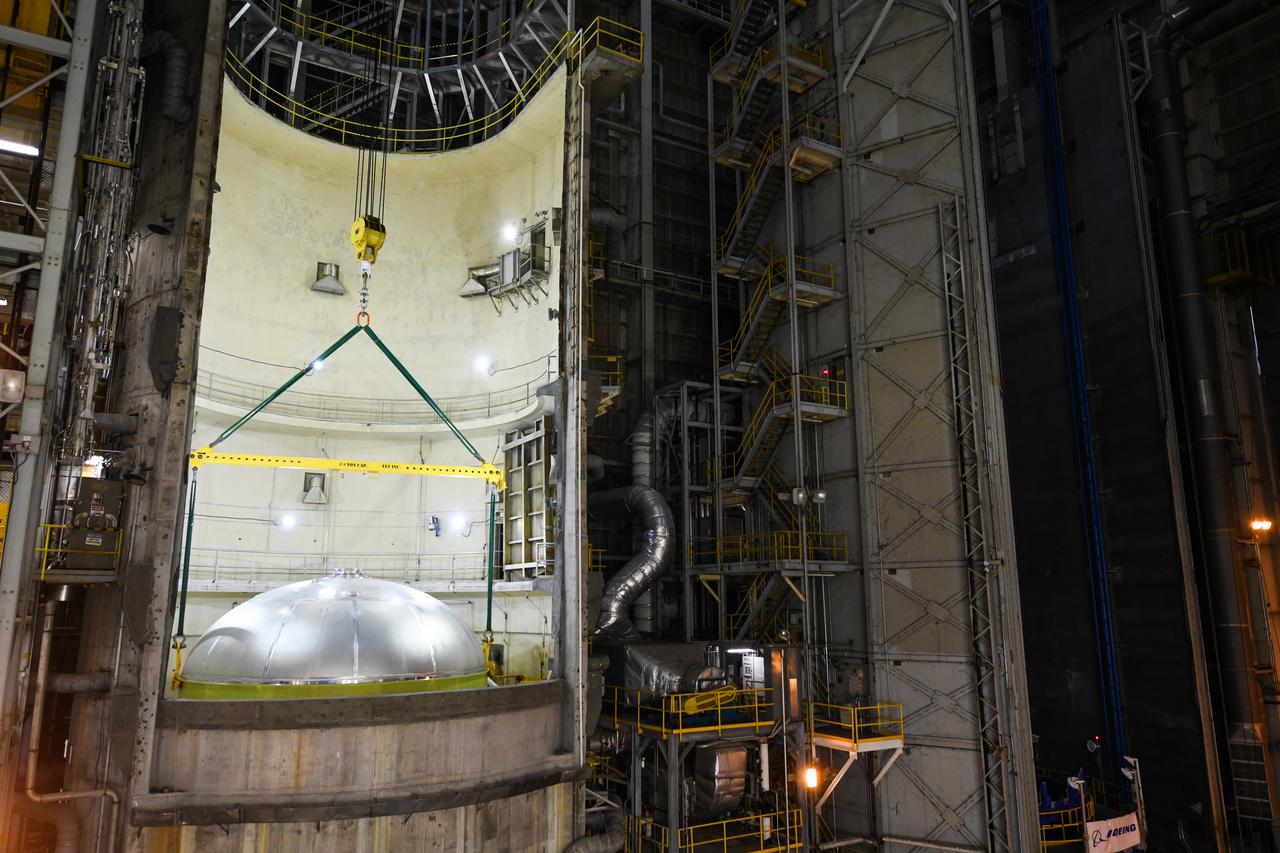
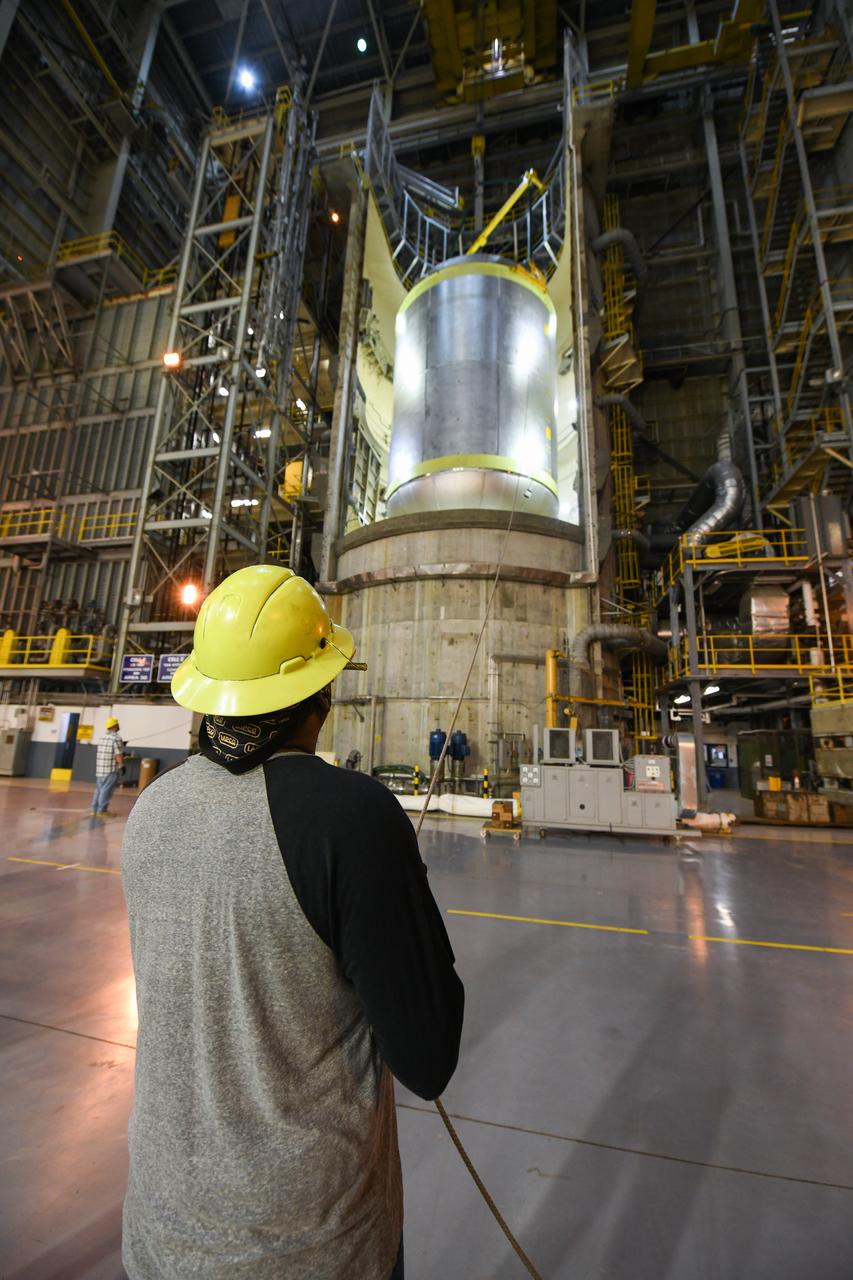
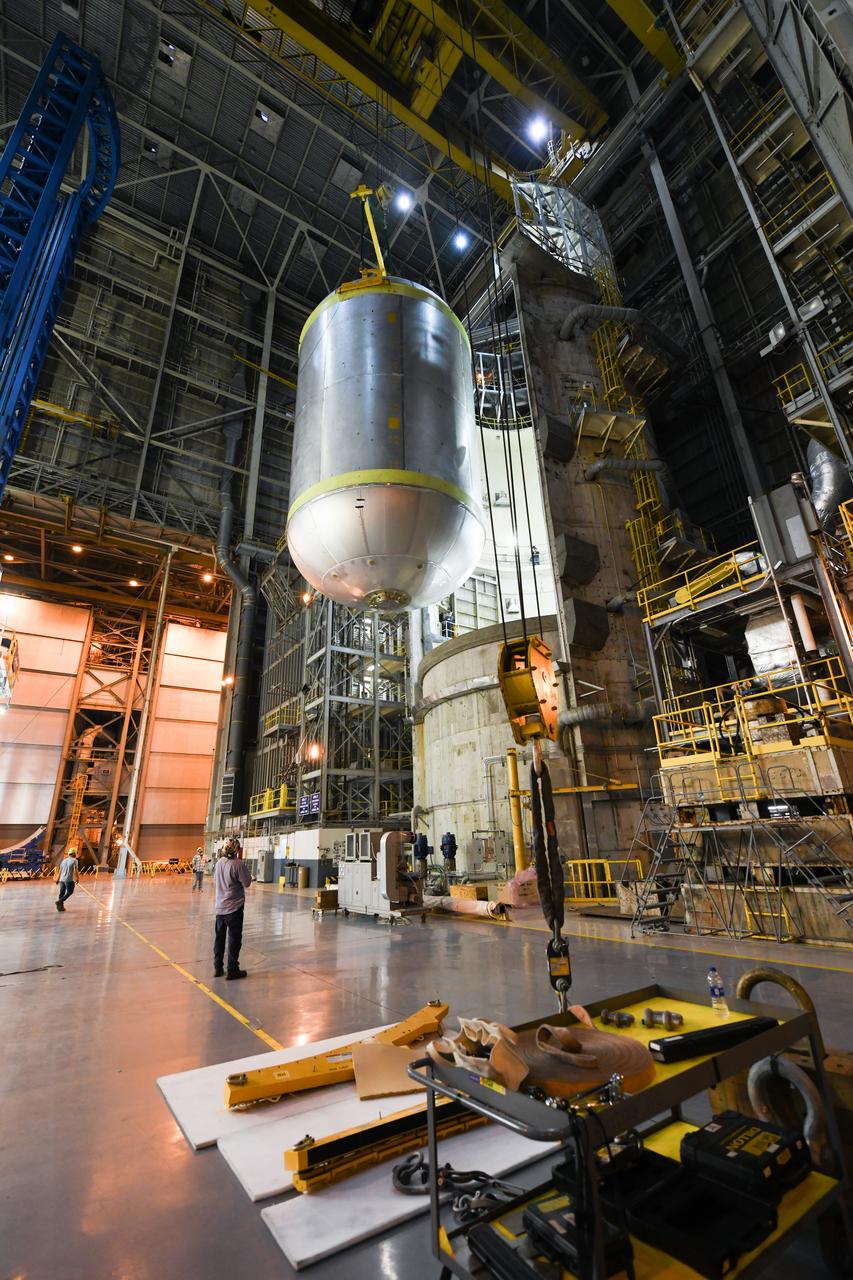
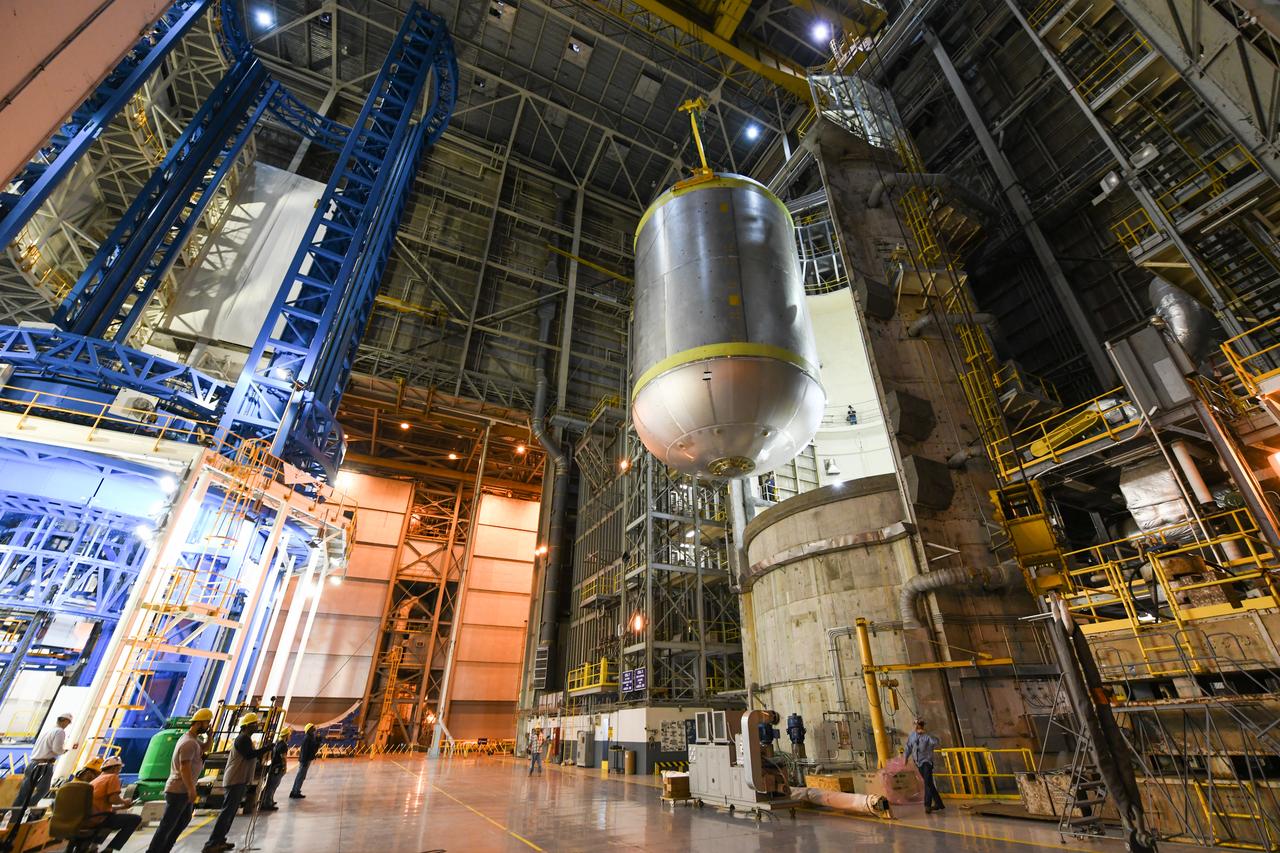
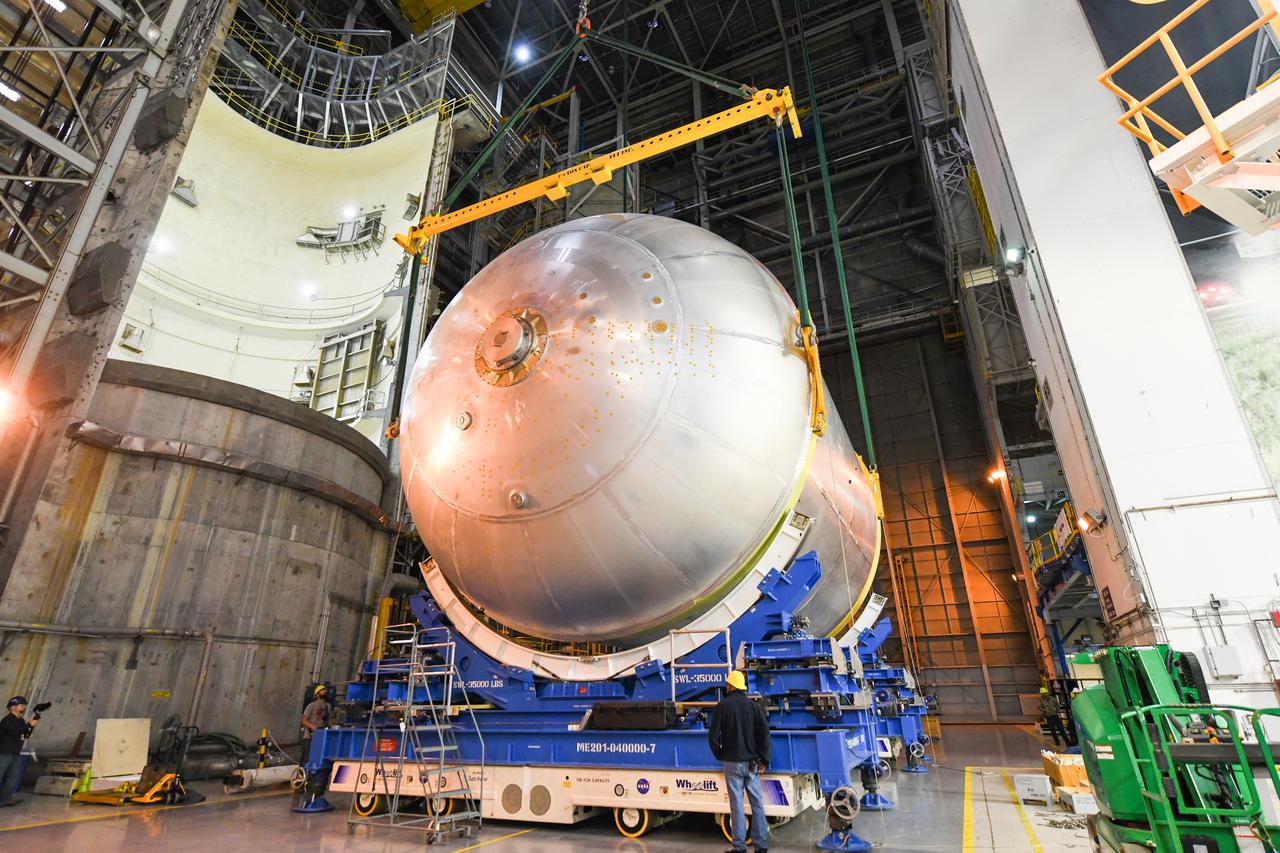
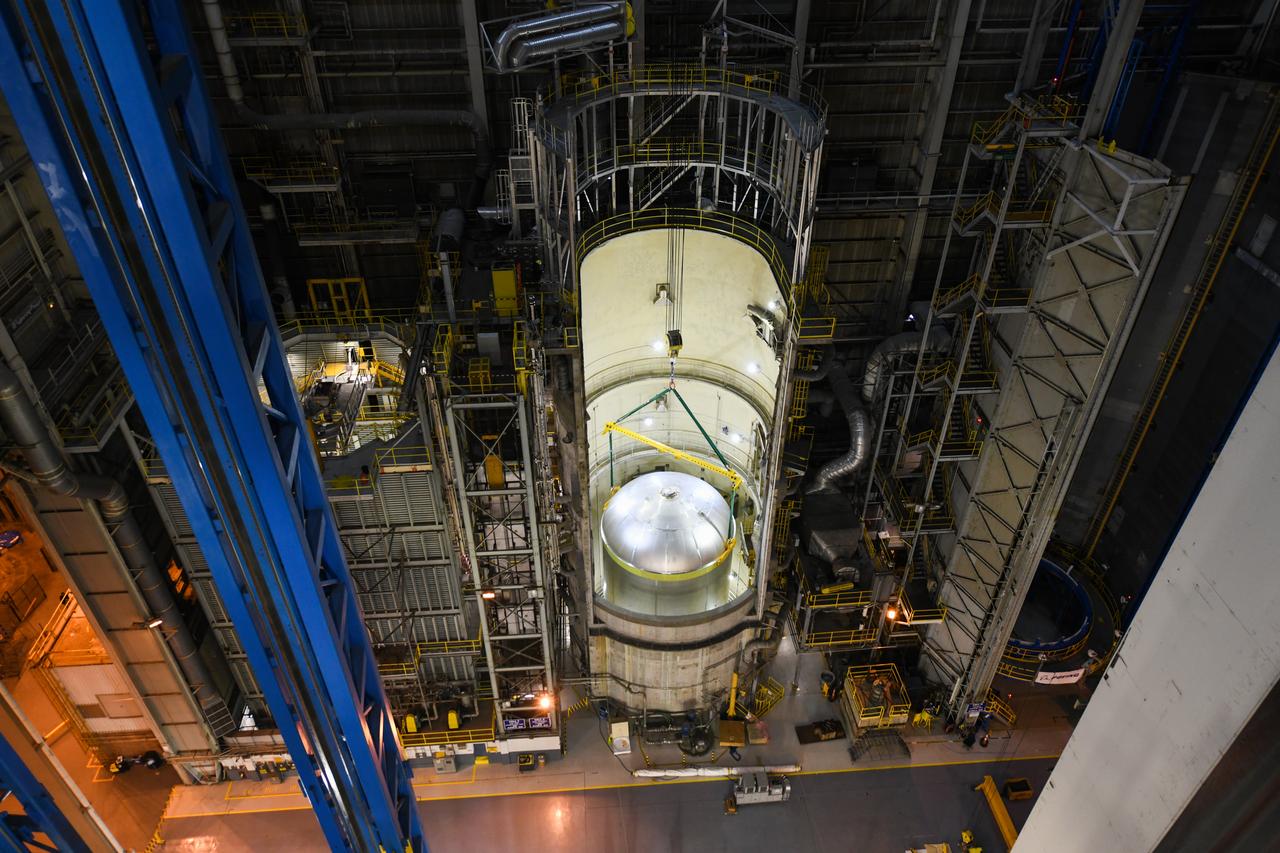
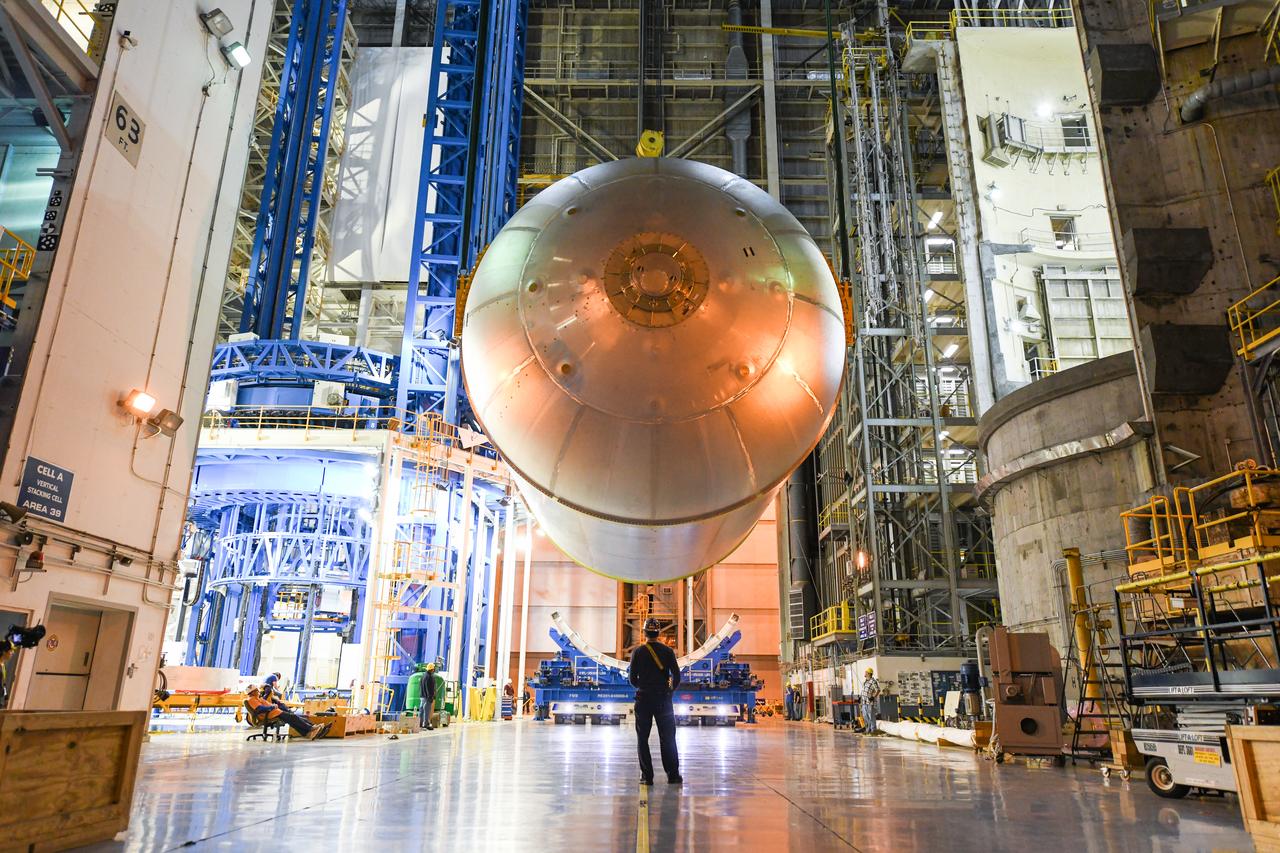
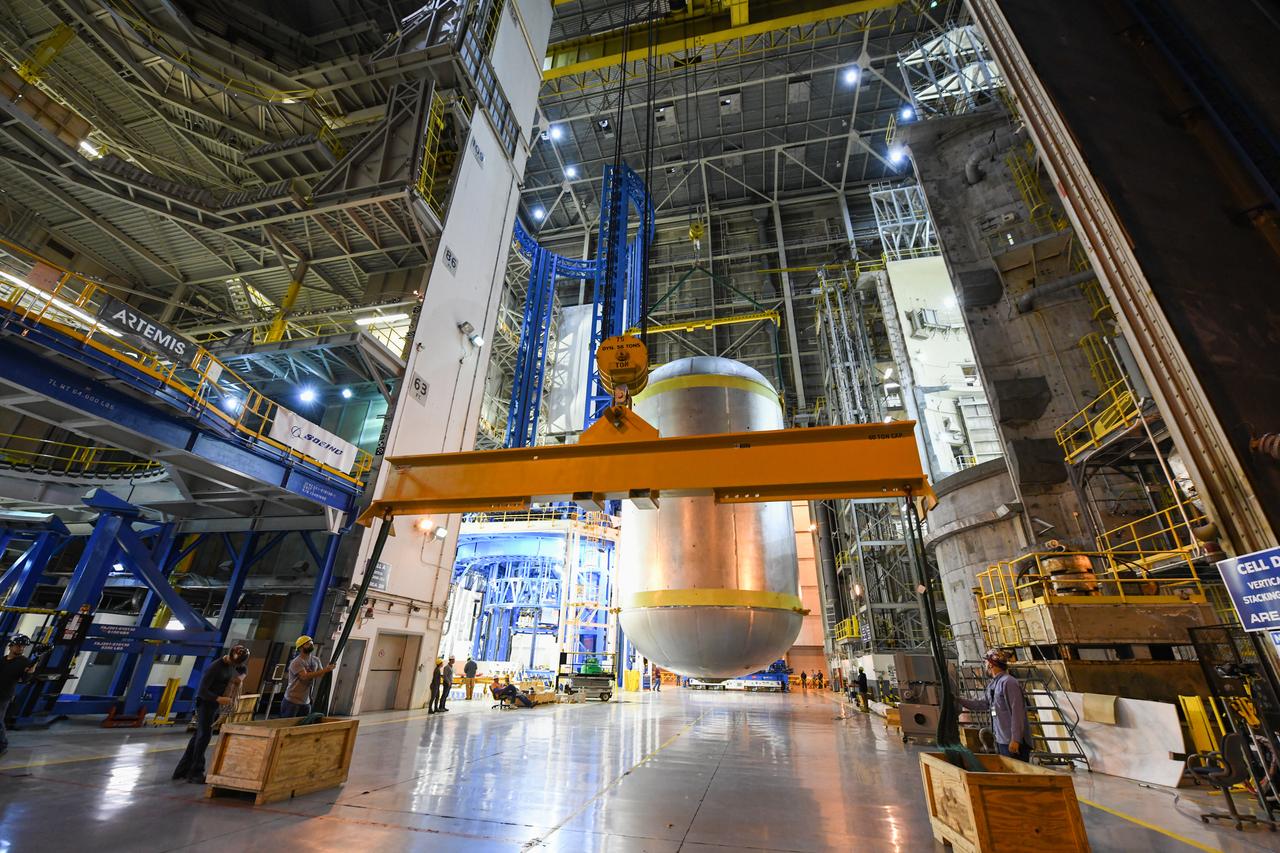
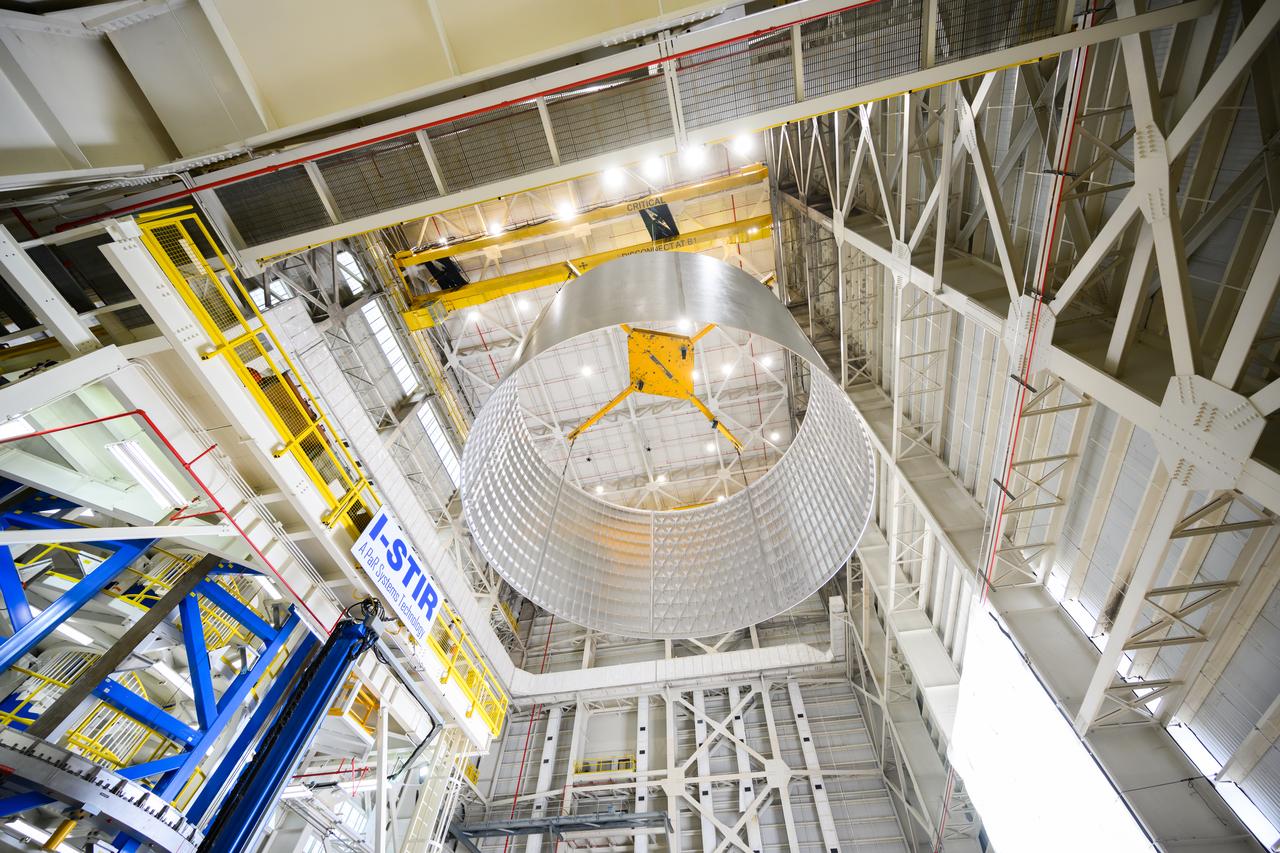
This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.

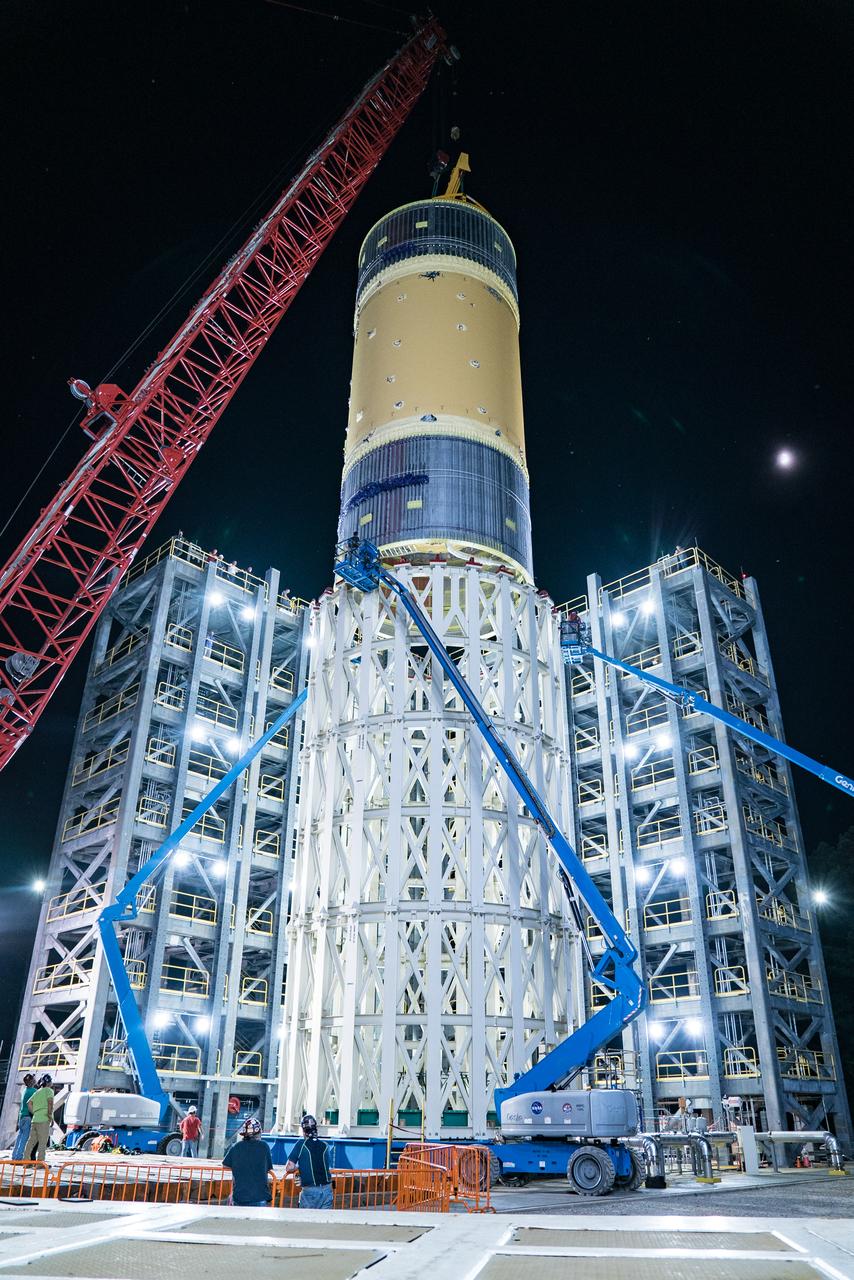
This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.

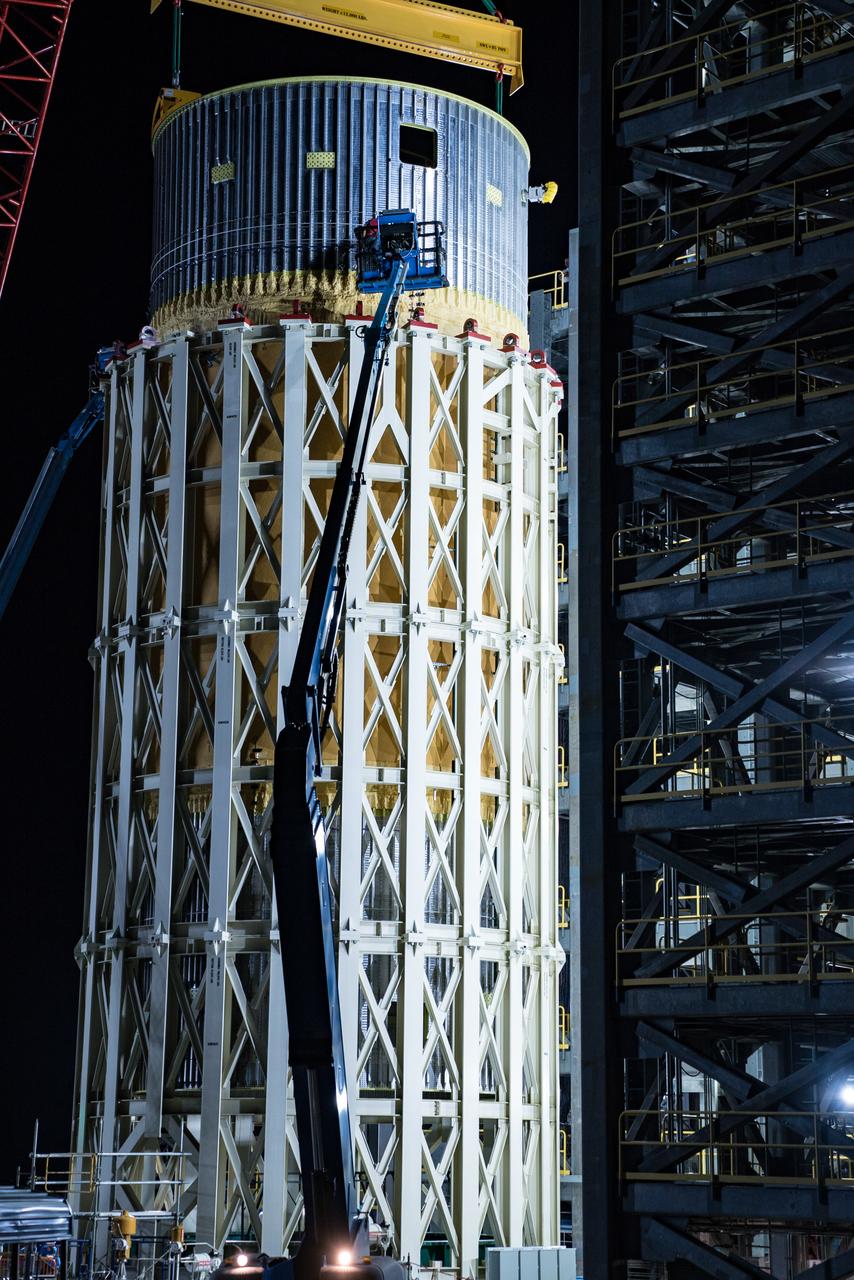
This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
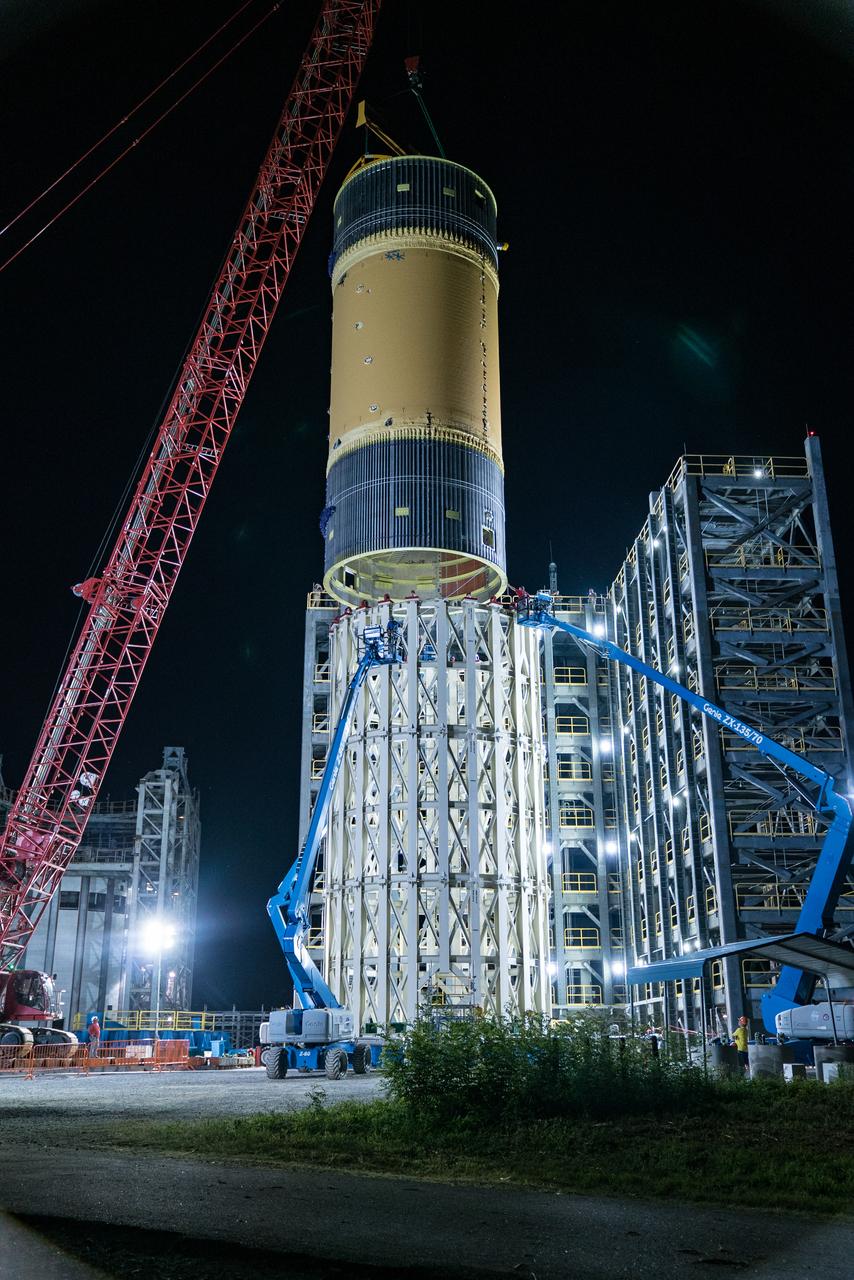

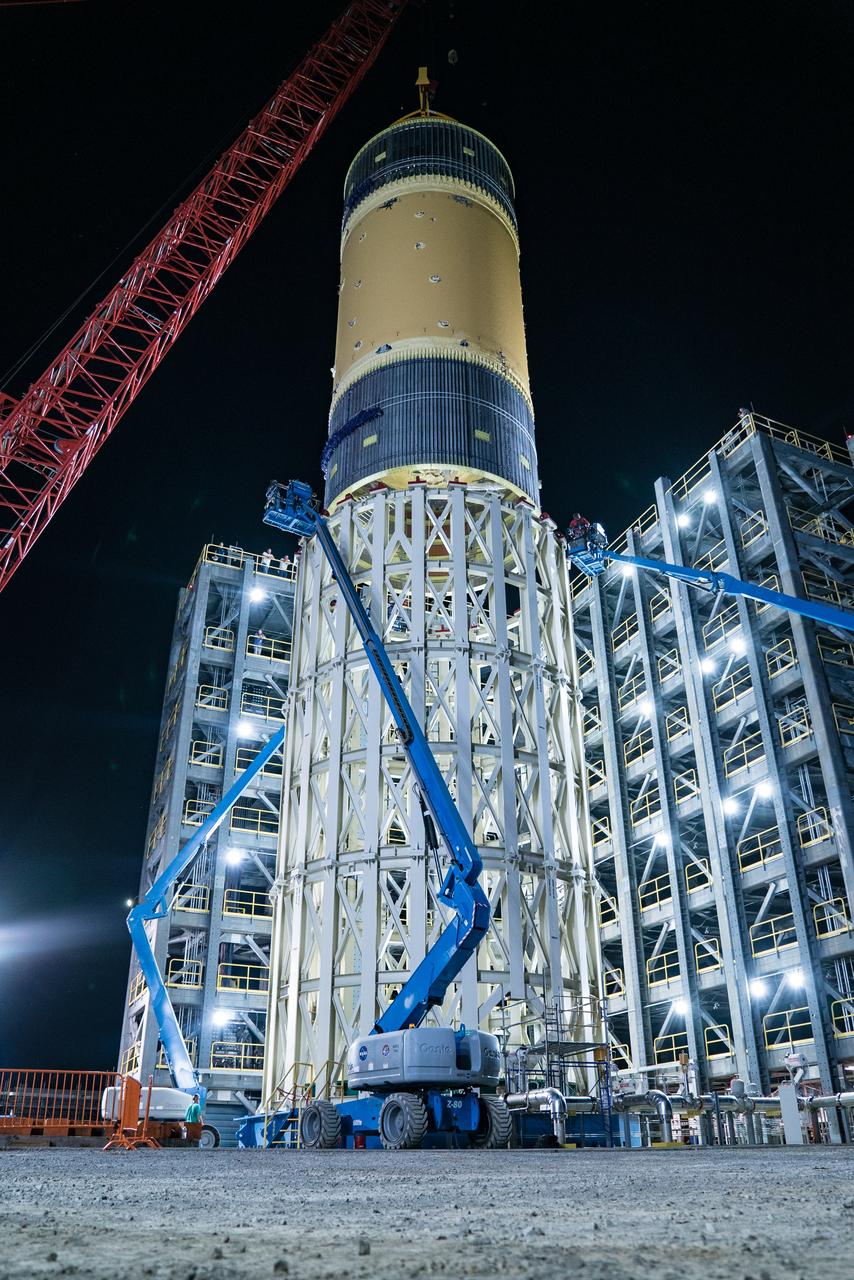
This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
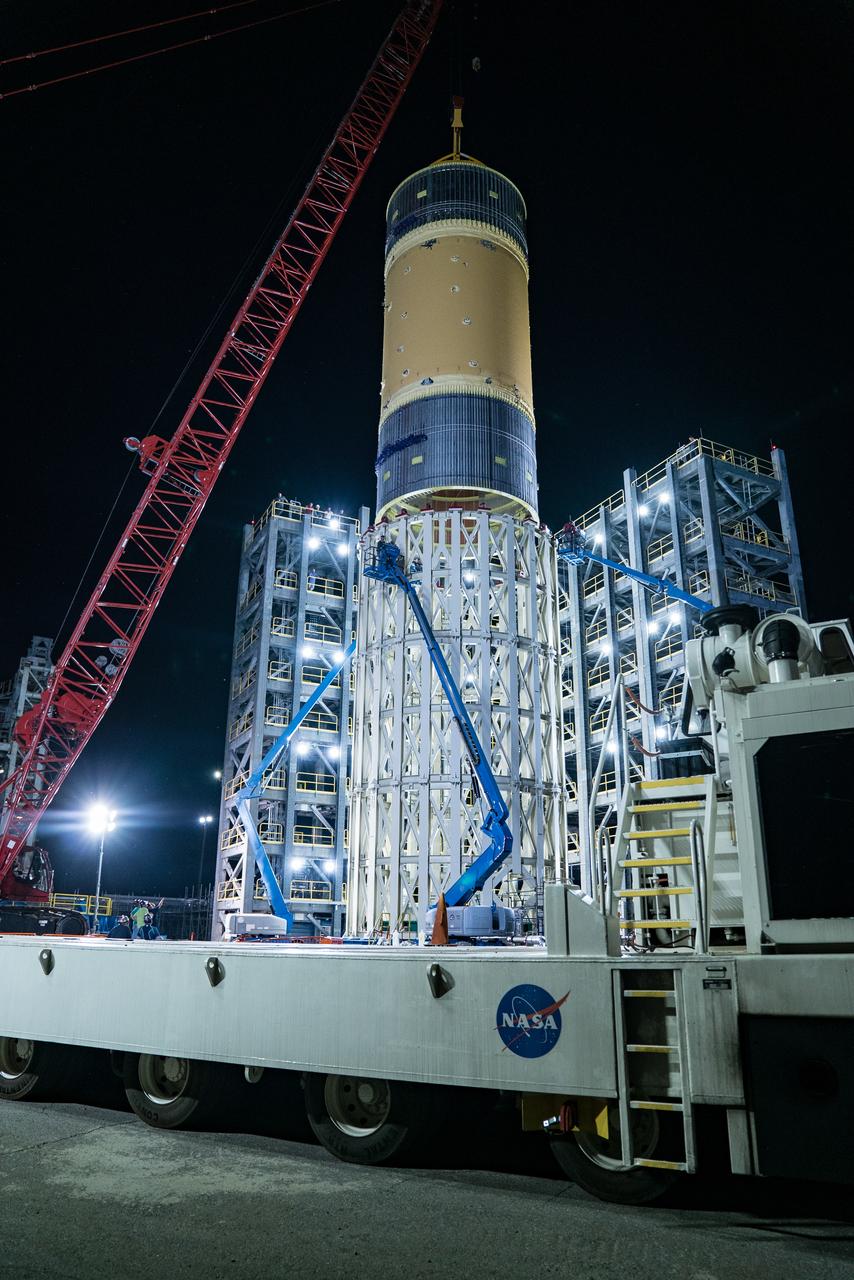

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
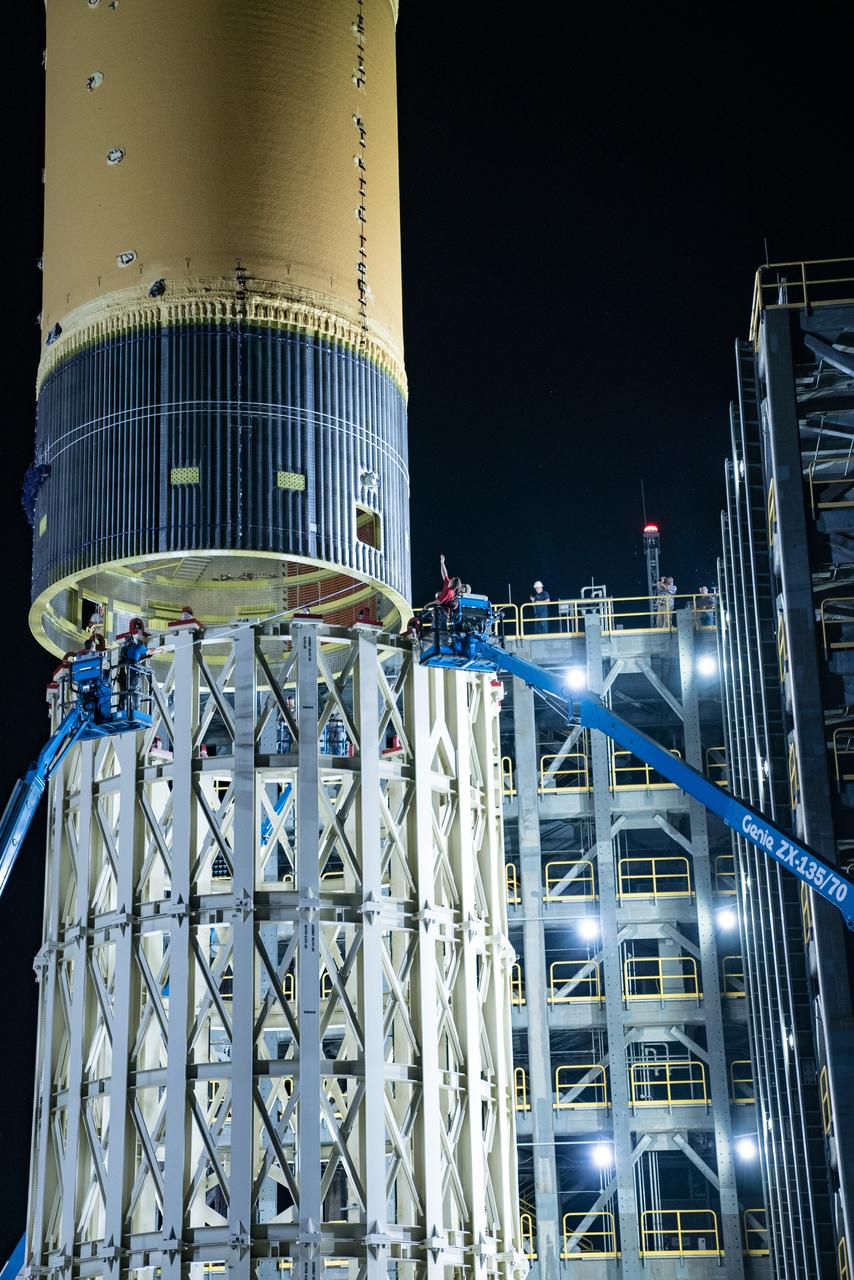

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
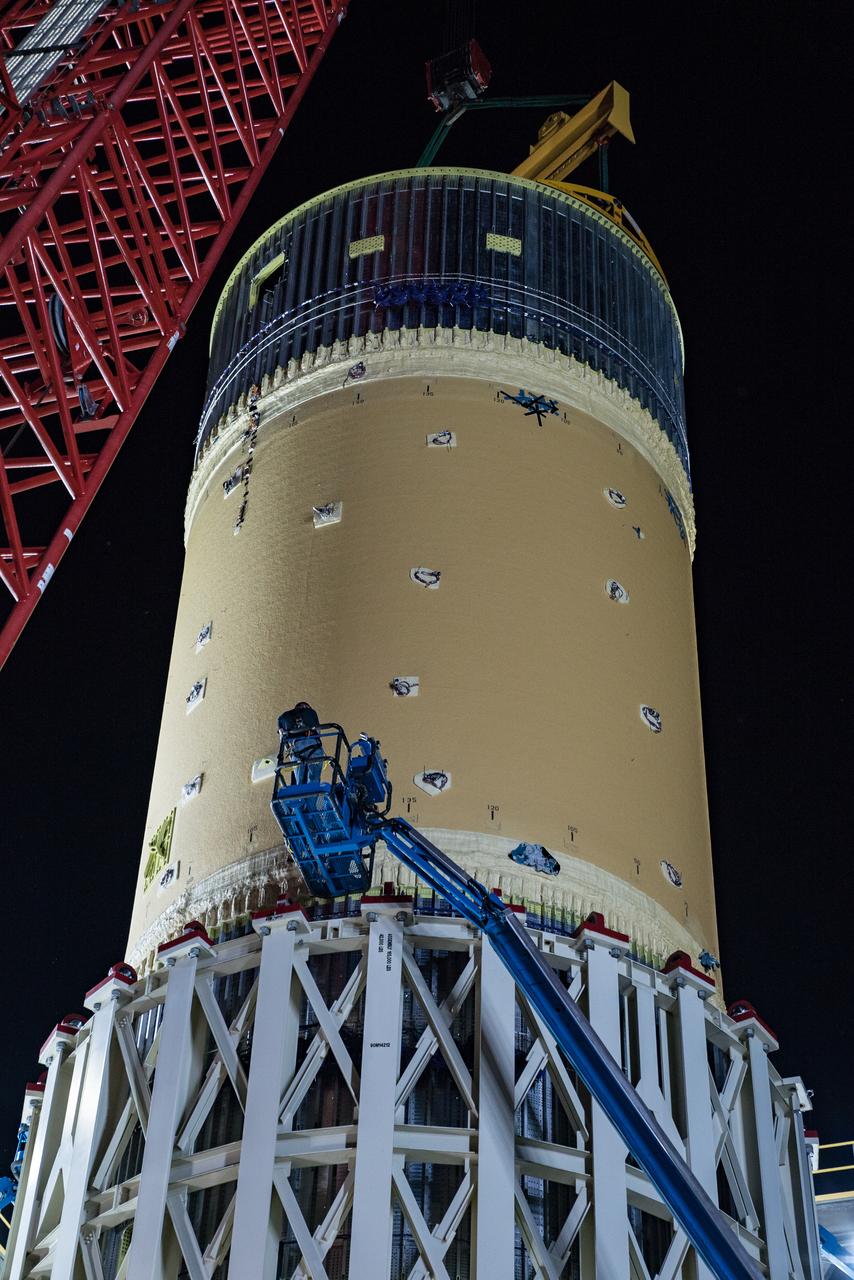

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
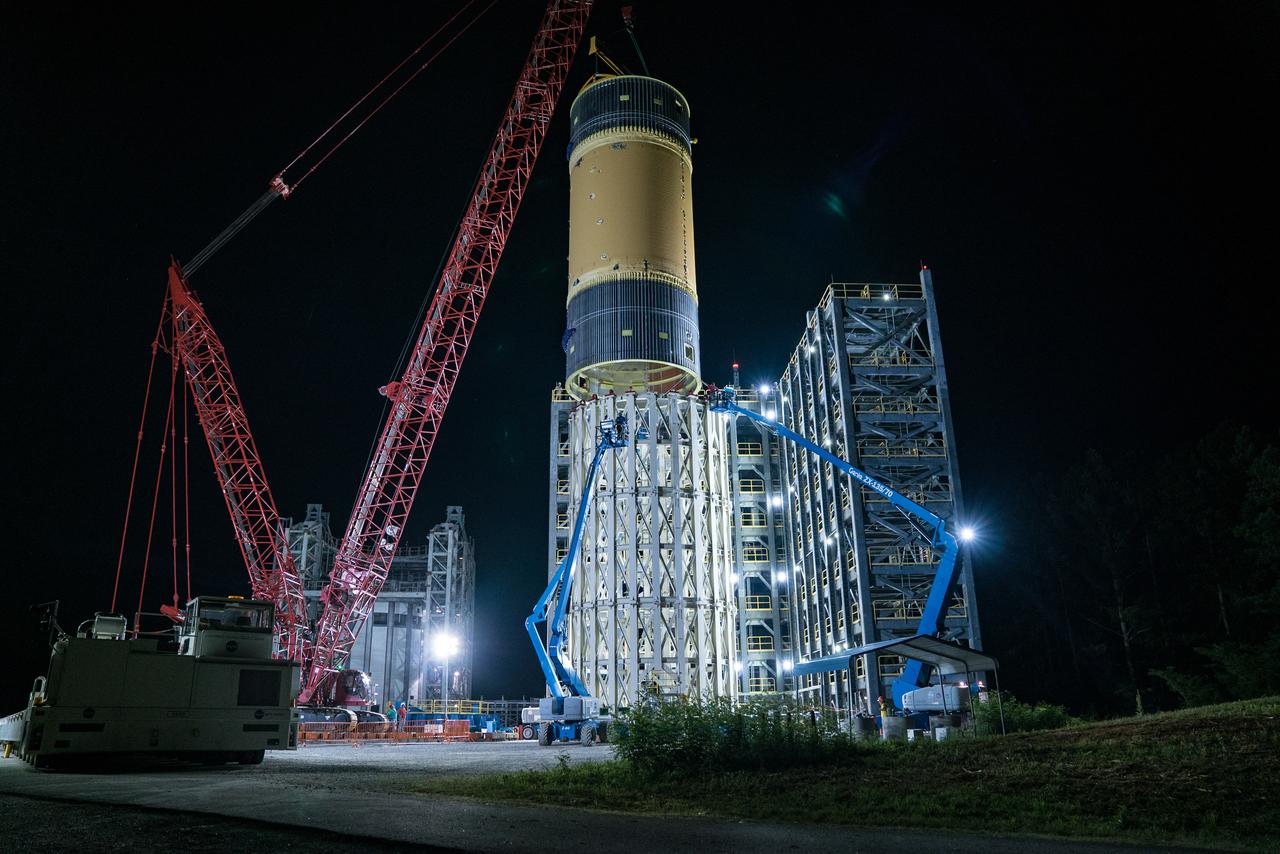

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
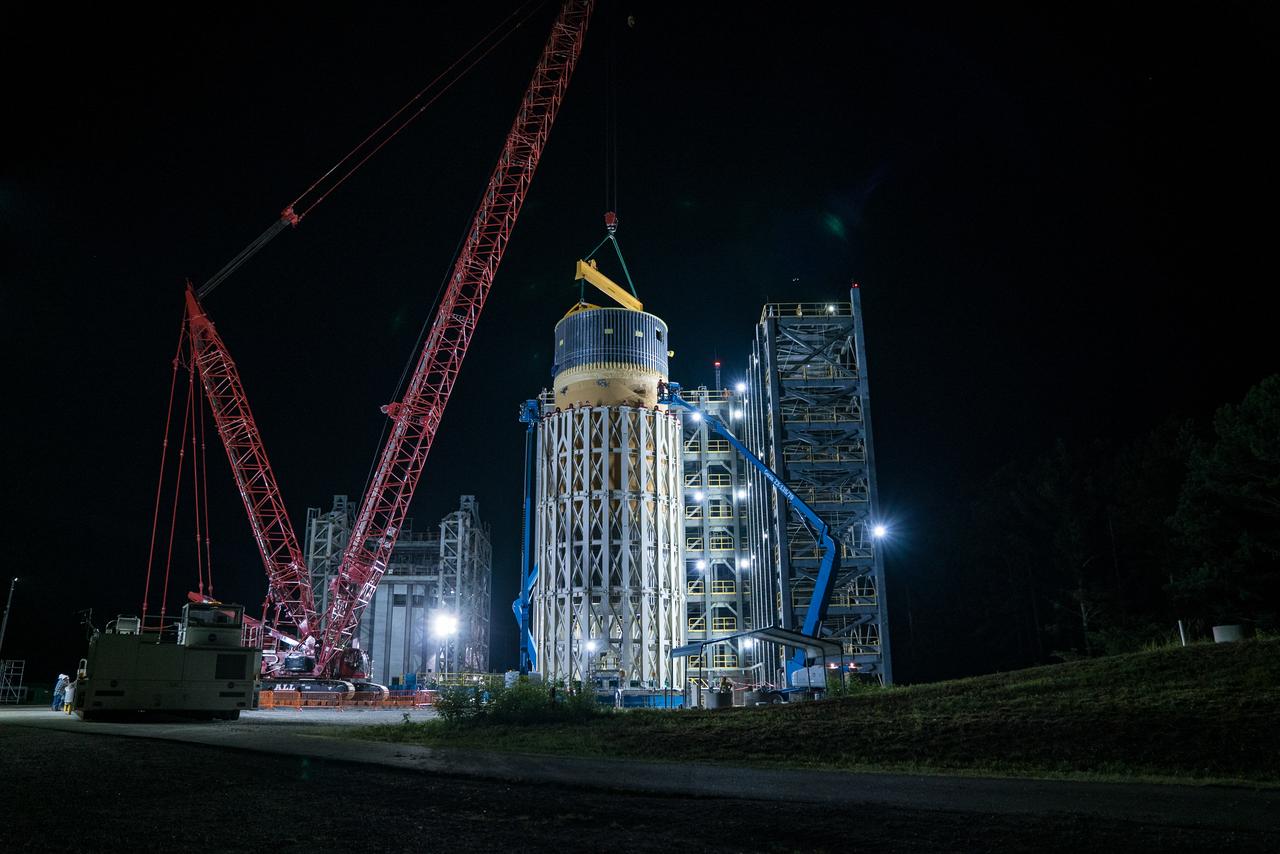

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
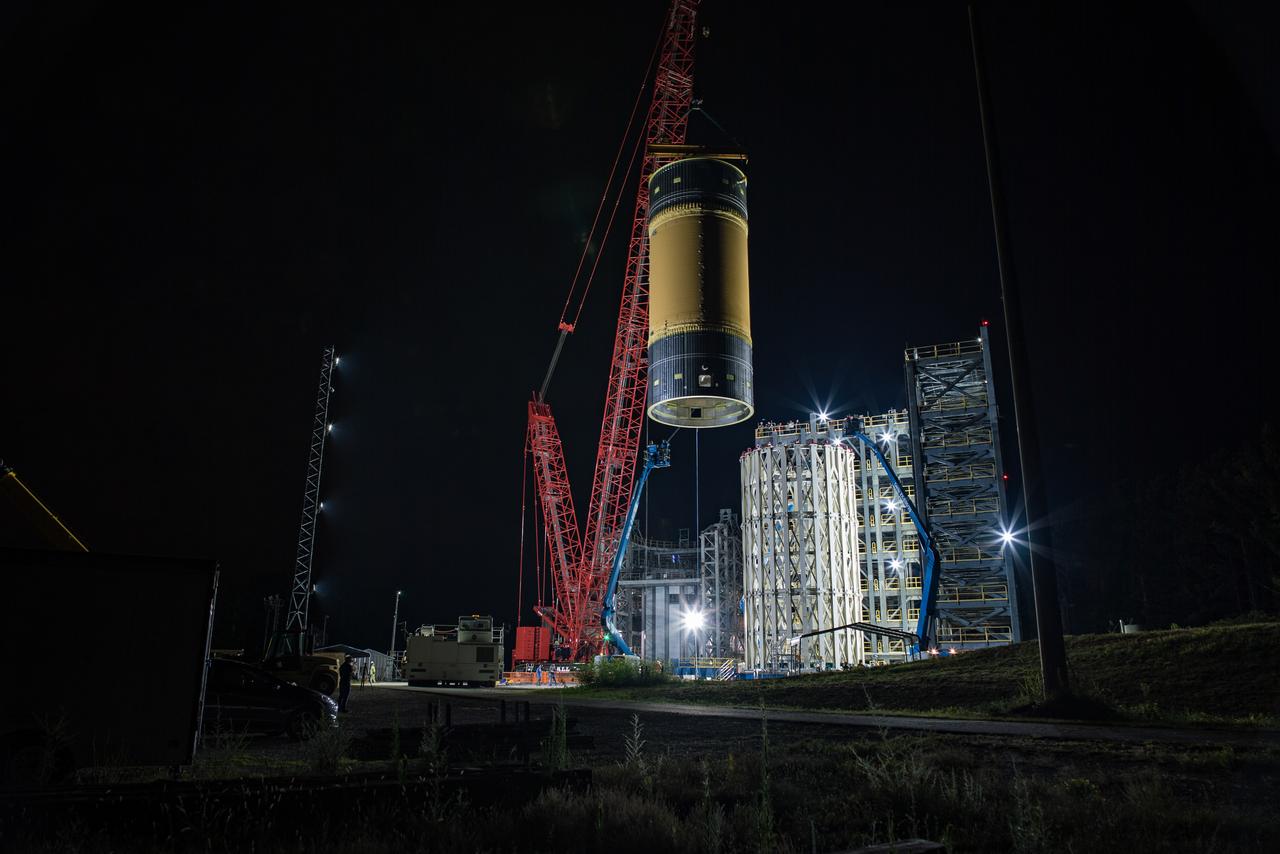

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.
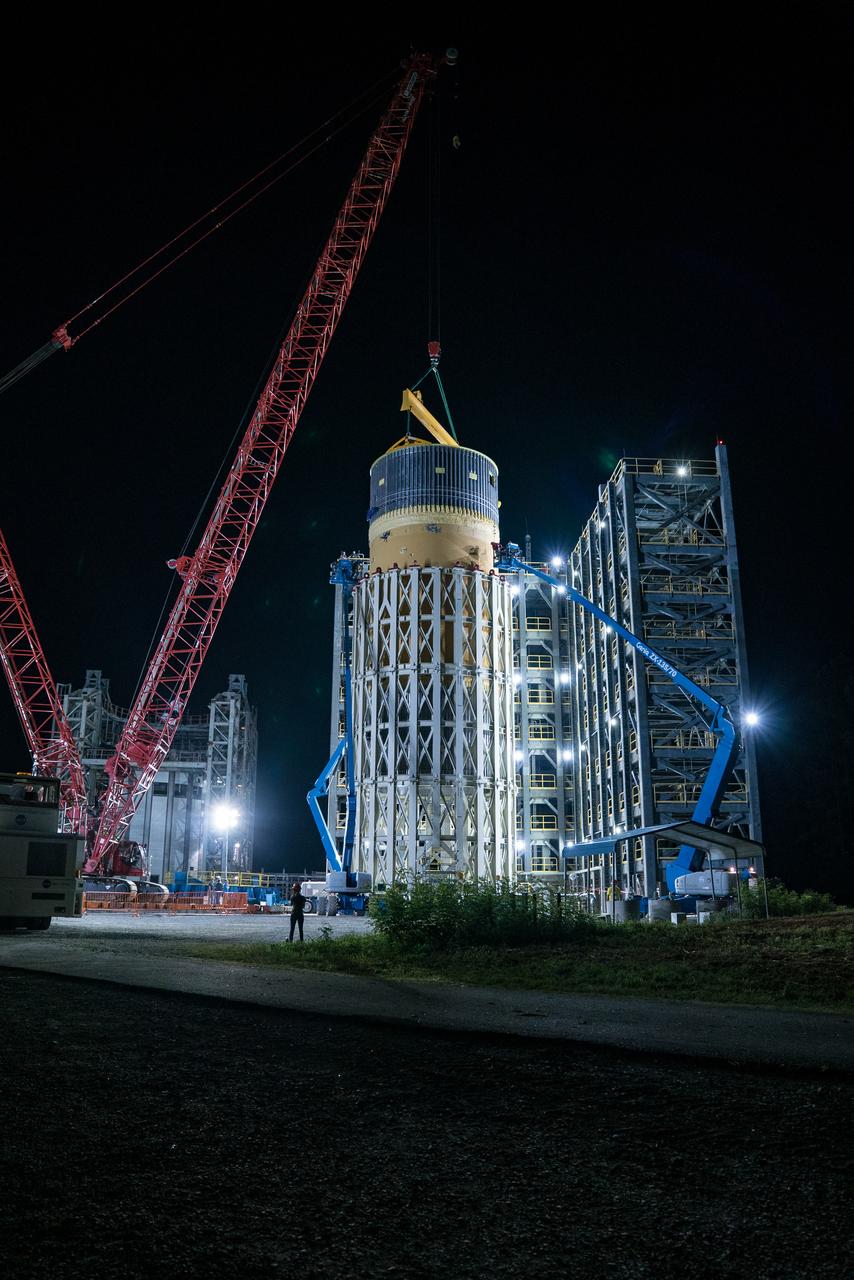

This collection of photos shows the steps NASA engineers took to lift the final structural test article for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage into Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, July 10, 2019. The liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is one of two propellant tanks in the rocket’s massive core stage that will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch Artemis 1, the first flight of NASA’s Orion spacecraft and SLS, to the Moon. The nearly 70-foot-long liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans and delivered by NASA’s barge Pegasus to Marshall. Once bolted into the test stand, dozens of hydraulic cylinders will push and pull the tank, subjecting it to the same stresses and forces it will endure during liftoff and flight, to verify it is fit for flight.

Photo shows how the Space Launch Sysetm (SLS) rocket liquid oxygen tank failed during a structural qualification test at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The photos show both the water flowing from the tank as it ruptured and the resultant tear left in the tank when it buckled during the test. Engineers pushed the liquid oxygen structural test article to the limits on purpose. The tank is a test article that is identical to tanks that are part of the SLS core stage that will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket on the Artemis missions to the Moon. During the test, hydraulic cylinders were then calibrated and positioned along the tank to apply millions of pounds of crippling force from all sides while engineers measured and recorded the effects of the launch and flight forces. For the test, water used to simulate the liquid oxygen flows out of the tank after it ruptures. The structural test campaign was conducted on the rocket to ensure the SLS rocket’s structure can endure the rigors of launch and safely send astronauts to the Moon on the Artemis missions. For more information: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/nasa-completes-artemis-sls-structural-testing-campaign.html

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the aft liquid oxygen tank (LOX) barrel out of the Vertical Weld Center (VWC) for its next phase of production. The aft barrel will eventually be mated with the forward barrel and the forward and aft domes to form the LOX tank, which will be used in the Space Launch System’s (SLS) Artemis IV mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Tuesday, May 10, 2022. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the aft liquid oxygen tank (LOX) barrel out of the Vertical Weld Center (VWC) for its next phase of production. The aft barrel will eventually be mated with the forward barrel and the forward and aft domes to form the LOX tank, which will be used in the Space Launch System’s (SLS) Artemis IV mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Tuesday, May 10, 2022. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the aft liquid oxygen tank (LOX) barrel out of the Vertical Weld Center (VWC) for its next phase of production. The aft barrel will eventually be mated with the forward barrel and the forward and aft domes to form the LOX tank, which will be used in the Space Launch System’s (SLS) Artemis IV mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Tuesday, May 10, 2022. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the aft liquid oxygen tank (LOX) barrel out of the Vertical Weld Center (VWC) for its next phase of production. The aft barrel will eventually be mated with the forward barrel and the forward and aft domes to form the LOX tank, which will be used in the Space Launch System’s (SLS) Artemis IV mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Tuesday, May 10, 2022. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
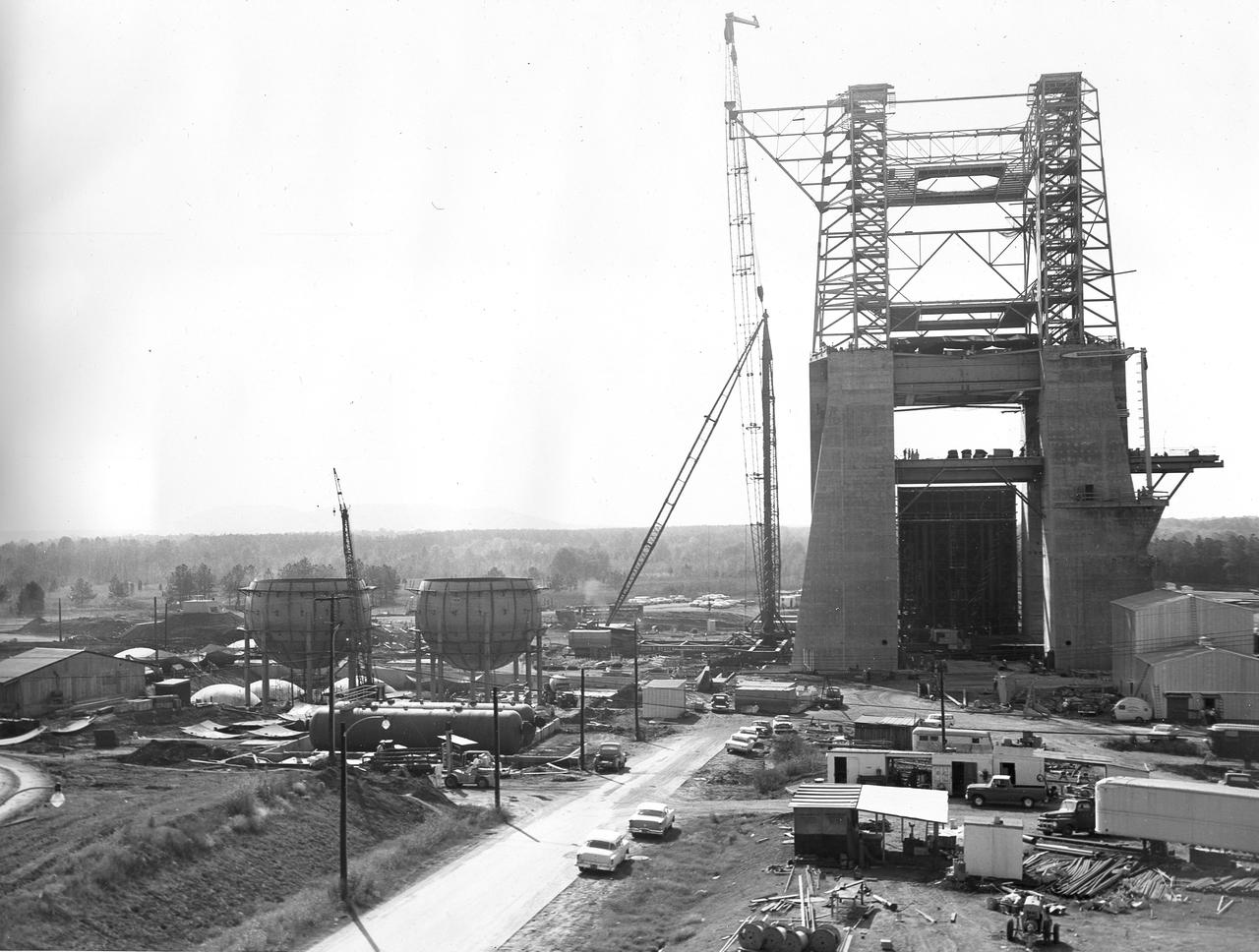

At its founding, the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) inherited the Army’s Jupiter and Redstone test stands, but much larger facilities were needed for the giant stages of the Saturn V. From 1960 to 1964, the existing stands were remodeled and a sizable new test area was developed. The new comprehensive test complex for propulsion and structural dynamics was unique within the nation and the free world, and they remain so today because they were constructed with foresight to meet the future as well as on going needs. Construction of the S-IC Static test stand complex began in 1961 in the west test area of MSFC, and was completed in 1964. The S-IC static test stand was designed to develop and test the 138-ft long and 33-ft diameter Saturn V S-IC first stage, or booster stage, weighing in at 280,000 pounds. Required to hold down the brute force of a 7,500,000-pound thrust produced by 5 F-1 engines, the S-IC static test stand was designed and constructed with the strength of hundreds of tons of steel and 12,000,000 pounds of cement, planted down to bedrock 40 feet below ground level. The foundation walls, constructed with concrete and steel, are 4 feet thick. The base structure consists of four towers with 40-foot-thick walls extending upward 144 feet above ground level. The structure was topped by a crane with a 135-foot boom. With the boom in the upright position, the stand was given an overall height of 405 feet, placing it among the highest structures in Alabama at the time. This photo shows the progress of the S-IC test stand as of October 22, 1963. Spherical liquid hydrogen tanks can be seen to the left. Just to the lower front of those are the cylindrical liquid oxygen (LOX) tanks.
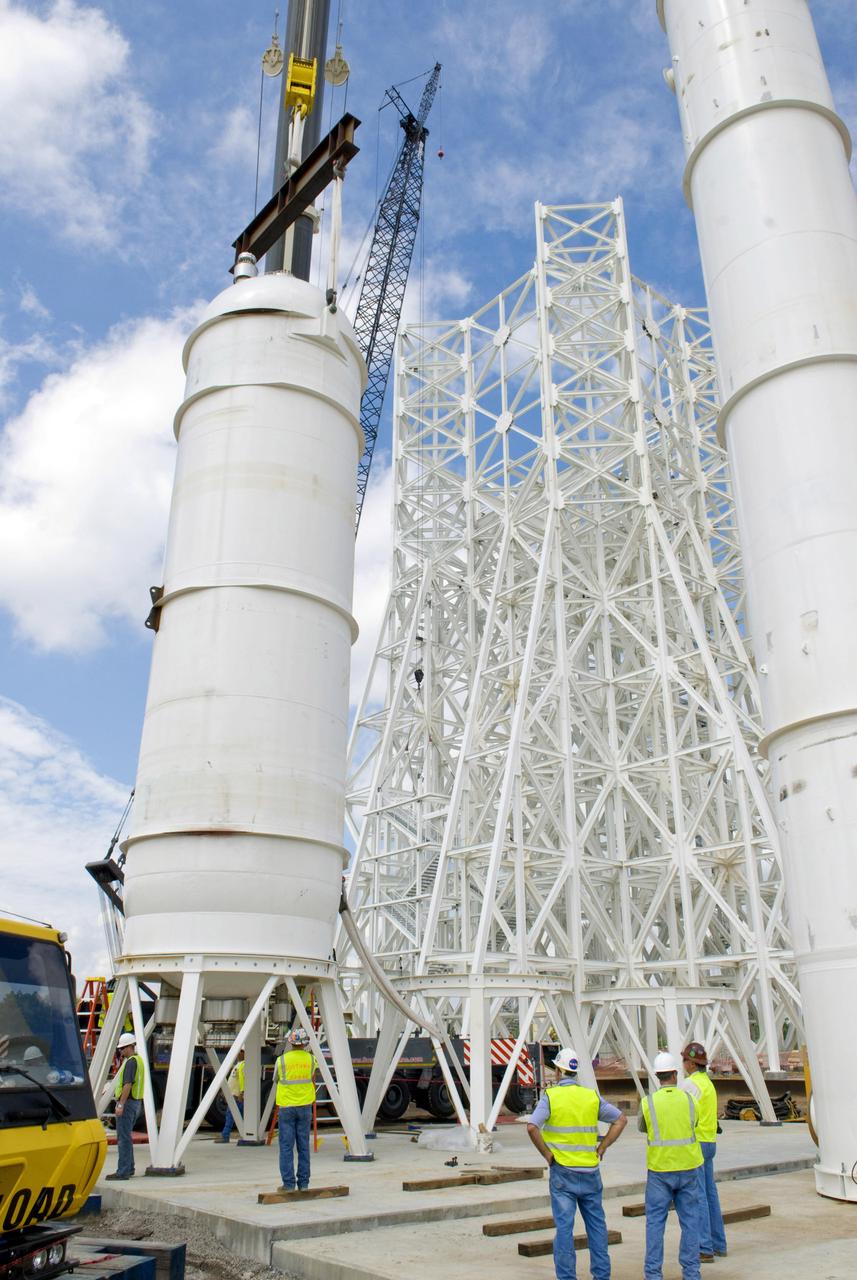

A liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is lifted into place at the A-3 Test Stand being built at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center. Fourteen LOX, isopropyl alcohol (IPA) and water tanks are being installed to support the chemical steam generators to be used on the A-3 Test Stand. The IPA and LOX tanks will provide fuel for the generators. The water will allow the generators to produce steam that will be used to reduce pressure inside the stand's test cell diffuser, enabling operators to simulate altitudes up to 100,000 feet. In that way, operators can perform the tests needed on rocket engines being built to carry humans back to the moon and possibly beyond. The A-3 Test Stand is set for completion and activation in 2011.

A liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is lifted into place at the A-3 Test Stand being built at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center. Fourteen LOX, isopropyl alcohol (IPA) and water tanks are being installed to support the chemical steam generators to be used on the A-3 Test Stand. The IPA and LOX tanks will provide fuel for the generators. The water will allow the generators to produce steam that will be used to reduce pressure inside the stand's test cell diffuser, enabling operators to simulate altitudes up to 100,000 feet. In that way, operators can perform the tests needed on rocket engines being built to carry humans back to the moon and possibly beyond. The A-3 Test Stand is set for completion and activation in 2011.

An isopropyl alcohol (IPA) tank is lifted into place at the A-3 Test Stand being built at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center. Fourteen IPA, water and liquid oxygen (LOX) tanks are being installed to support the chemical steam generators to be used on the A-3 Test Stand. The IPA and LOX tanks will provide fuel for the generators. The water will allow the generators to produce steam that will be used to reduce pressure inside the stand's test cell diffuser, enabling operators to simulate altitudes up to 100,000 feet. In that way, operators can perform the tests needed on rocket engines being built to carry humans back to the moon and possibly beyond. The A-3 Test Stand is set for completion and activation in 2011.

A water tank is lifted into place at the A-3 Test Stand being built at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center. Fourteen water, liquid oxygen (LOX) and isopropyl alcohol (IPA) tanks are being installed to support the chemical steam generators to be used on the A-3 Test Stand. The IPA and LOX tanks will provide fuel for the generators. The water will allow the generators to produce steam that will be used to reduce pressure inside the stand's test cell diffuser, enabling operators to simulate altitudes up to 100,000 feet. In that way, operators can perform the tests needed on rocket engines being built to carry humans back to the moon and possibly beyond. The A-3 Test Stand is set for completion and activation in 2011.

A water tank is lifted into place at the A-3 Test Stand being built at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center. Fourteen water, liquid oxygen (LOX) and isopropyl alcohol (IPA) tanks are being installed to support the chemical steam generators to be used on the A-3 Test Stand. The IPA and LOX tanks will provide fuel for the generators. The water will allow the generators to produce steam that will be used to reduce pressure inside the stand's test cell diffuser, enabling operators to simulate altitudes up to 100,000 feet. In that way, operators can perform the tests needed on rocket engines being built to carry humans back to the moon and possibly beyond. The A-3 Test Stand is set for completion and activation in 2011.
The Saturn I S-I stage is being assembled in the fabrication and engineering laboratory at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The two end spider beams are cornected to the central 267-centimeter diameter liquid-oxygen (LOX) tank. The 178-centimeter outer tank, used alternately for liquid oxygen and kerosene, is being lifted into position.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the liquid oxygen, or LOX, and liquid hydrogen, or LH2, tanks that supported space shuttle launches for 30 years have been sandblasted, repaired and repainted. The two tanks, designed to store super-cooled LOX and LH2, were refurbished to prepare them to support the launch of NASA’s Space Launch System and other launch vehicles. The Ground Systems Development and Operations, or GSDO, Program office at Kennedy is leading the center’s transformation to safely handle a variety of rockets and spacecraft. For more information about GSDO, visit: http:__go.nasa.gov_groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the liquid oxygen, or LOX, and liquid hydrogen, or LH2, tanks that supported space shuttle launches for 30 years have been sandblasted, repaired and repainted. The two tanks, designed to store super-cooled LOX and LH2, were refurbished to prepare them to support the launch of NASA’s Space Launch System and other launch vehicles. The Ground Systems Development and Operations, or GSDO, Program office at Kennedy is leading the center’s transformation to safely handle a variety of rockets and spacecraft. For more information about GSDO, visit: http:__go.nasa.gov_groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett
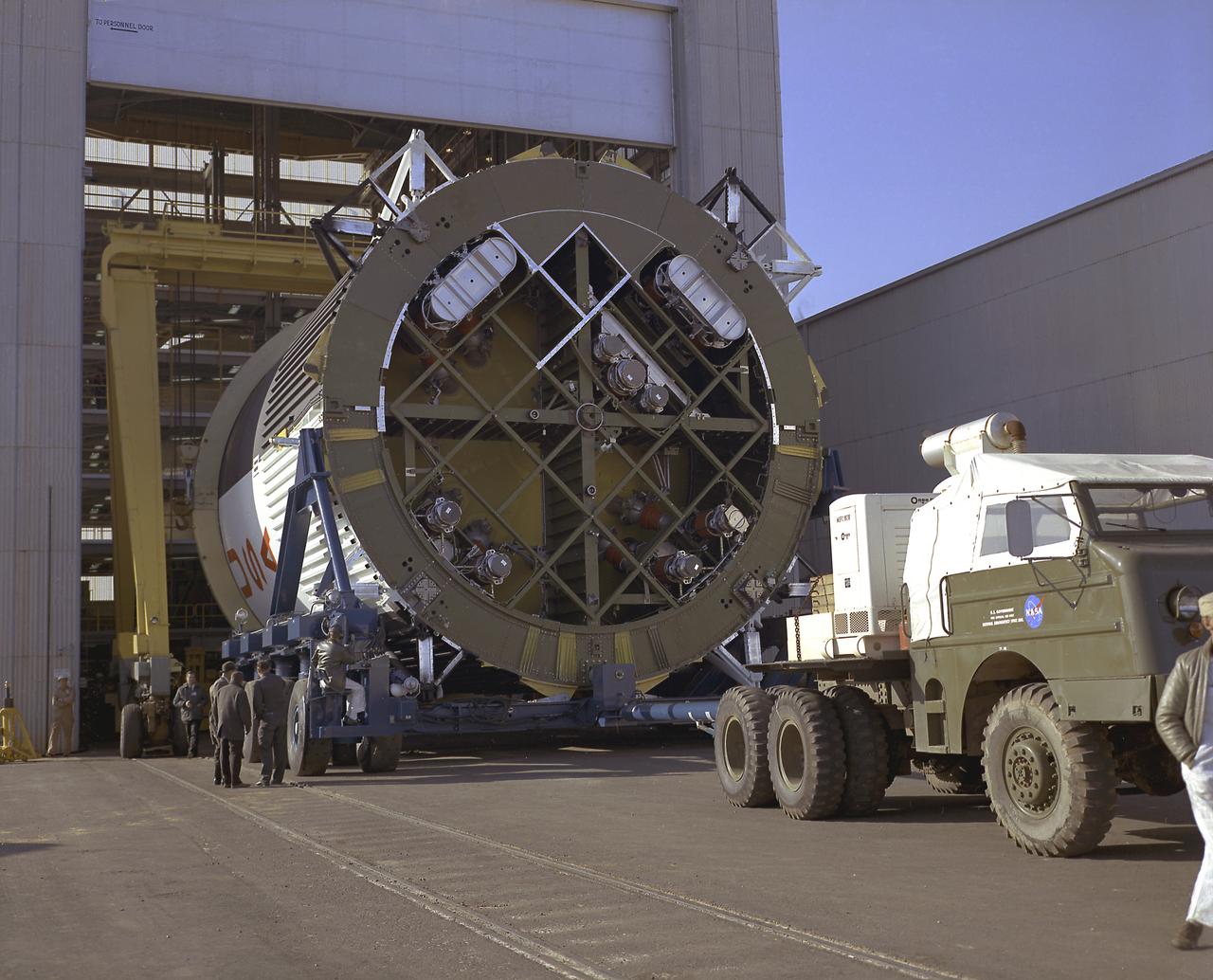

This photograph shows the fuel tank assembly for the Saturn V S-IC (first) stage being transported to the Marshall Space Flight Center, building 4705 for mating to the liquid oxygen (LOX) tank. The fuel tank carried kerosene (RP-1) as its fuel. The S-IC stage used five F-1 engines, that used kerosene and liquid oxygen as propellant and each engine provided 1,500,000 pounds of thrust. This stage lifted the entire vehicle and Apollo spacecraft from the launch pad.
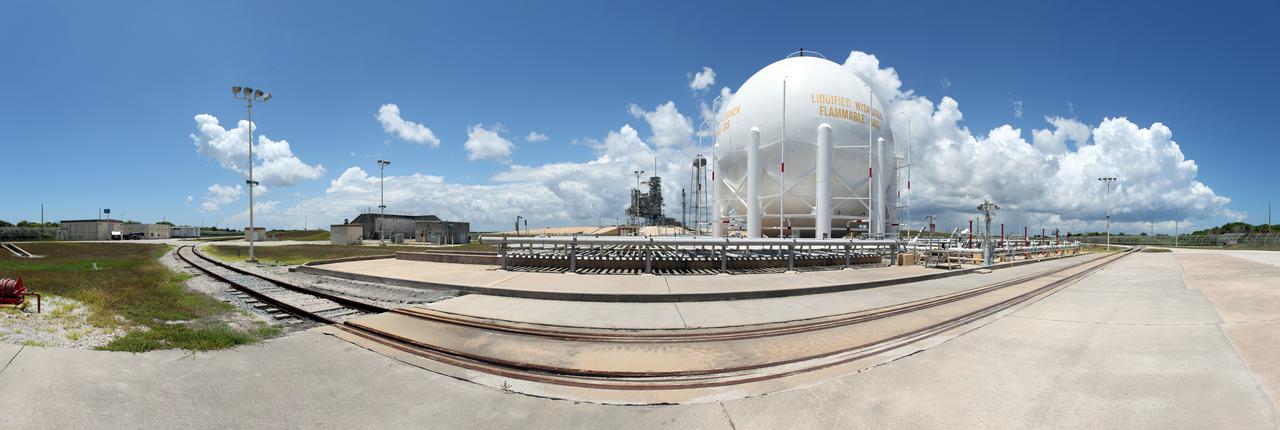

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is a liquid hydrogen, or LH2, storage tank. This large ball-shaped, vacuum-jacketed tank is used to store cryogenic propellants for the space shuttle's orange external fuel tank. The LH2 tank is located at the northeast corner of Launch Pad 39A and stores 850,000 gallons of LH2 at a temperature of minus 423 degrees F. The shuttle's external tank is loaded with about 500,000 gallons of LH2 and liquid oxygen, or LOX, about six hours prior to launch in a process known as 'tanking.' Photo credit: NASA_Frankie Martin
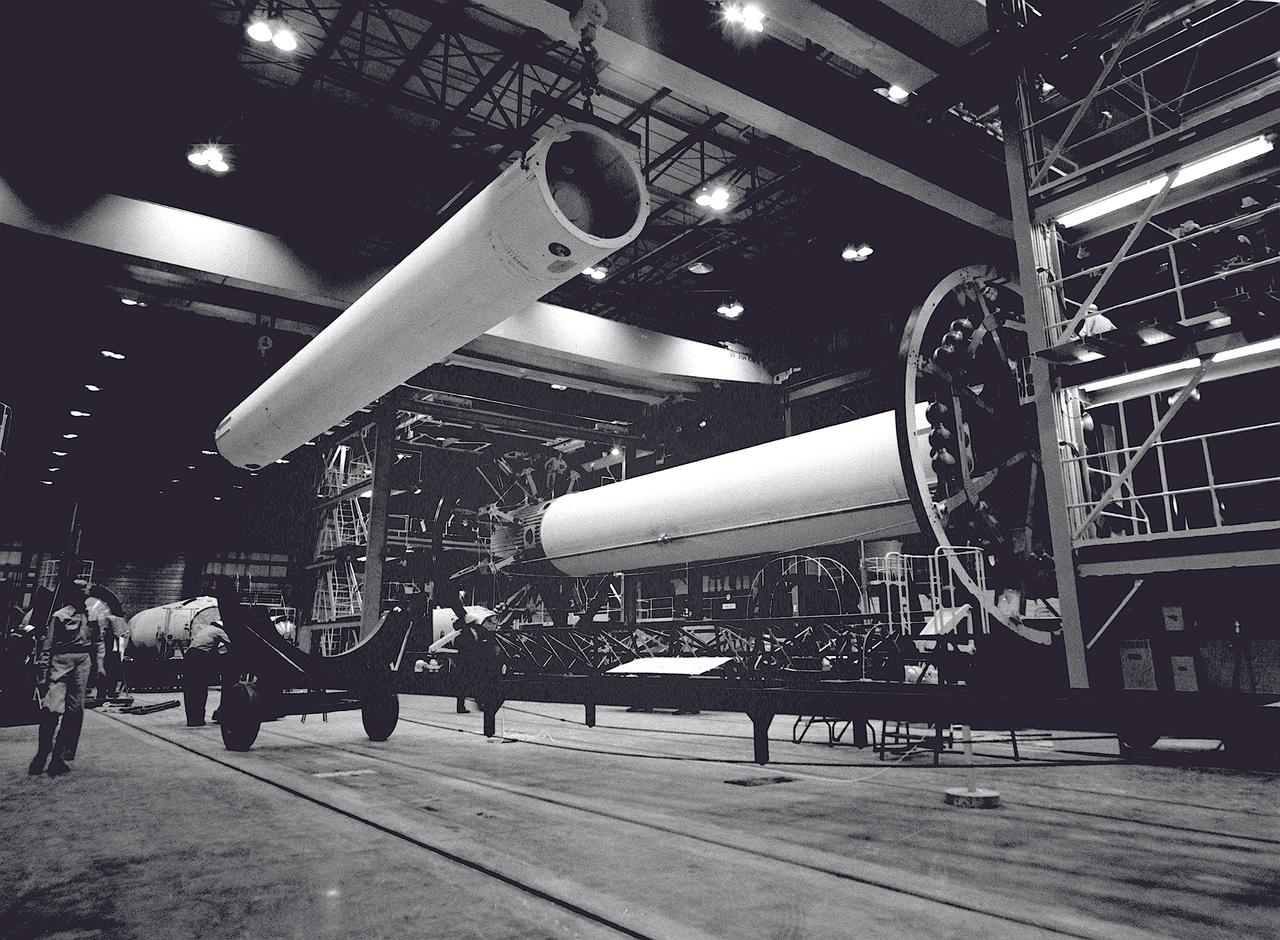

The Saturn I S-I stage is being assembled in the fabrication and engineering laboratory at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The two end spider beams are cornected to the central 267-centimeter diameter liquid-oxygen (LOX) tank. The first of the eight 178-centimeter outer tanks, used alternately for liquid oxygen and kerosene, is being lifted into position.
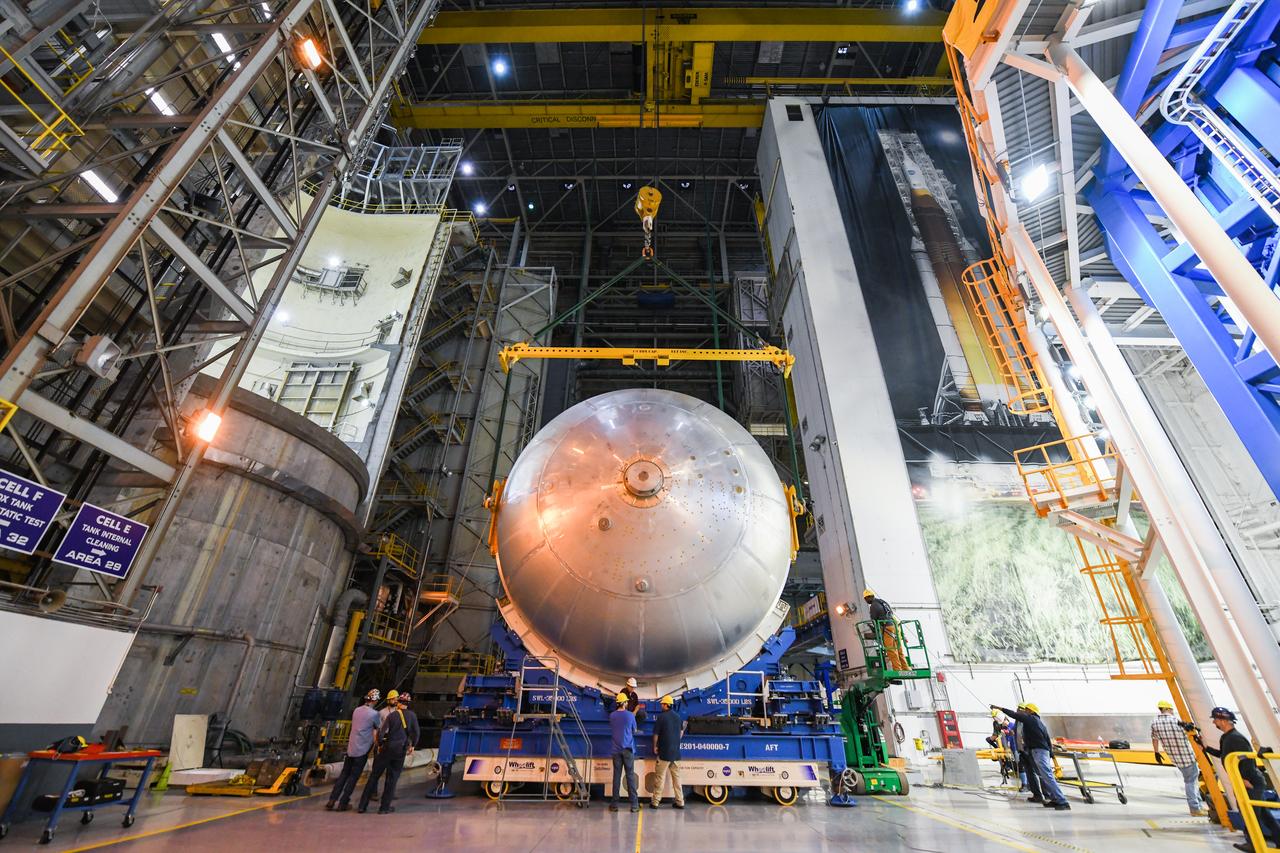

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows the latest progress NASA has made in manufacturing the liquid oxygen tank for the second core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The liquid oxygen tank will be used for the first crewed mission, Artemis II, of the agency’s Artemis program. Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans recently completed internal cleaning of the liquid oxygen, or LOX, tank at the facility. Following the cleaning, crews prepared the propellant tank for the next phase of phase of assembly in a different area of the factory by moving, or breaking over, the tank from a vertical to horizontal position. The LOX tank is one of five major elements that make up the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage. The propellant tank holds 196,000 gallons of supercooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines, and the internal cleaning ensures no contaminants make their way into the complex propulsion and engine systems of the deep space rocket. The stage, which includes a cluster of four RS-25, will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the SLS rocket and astronauts aboard NASA’s Orion spacecraft around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024. The agency’s SLS rocket offers more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through deep space and enable NASA’s Artemis lunar program. SLS, along with Orion, the human landing system, and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
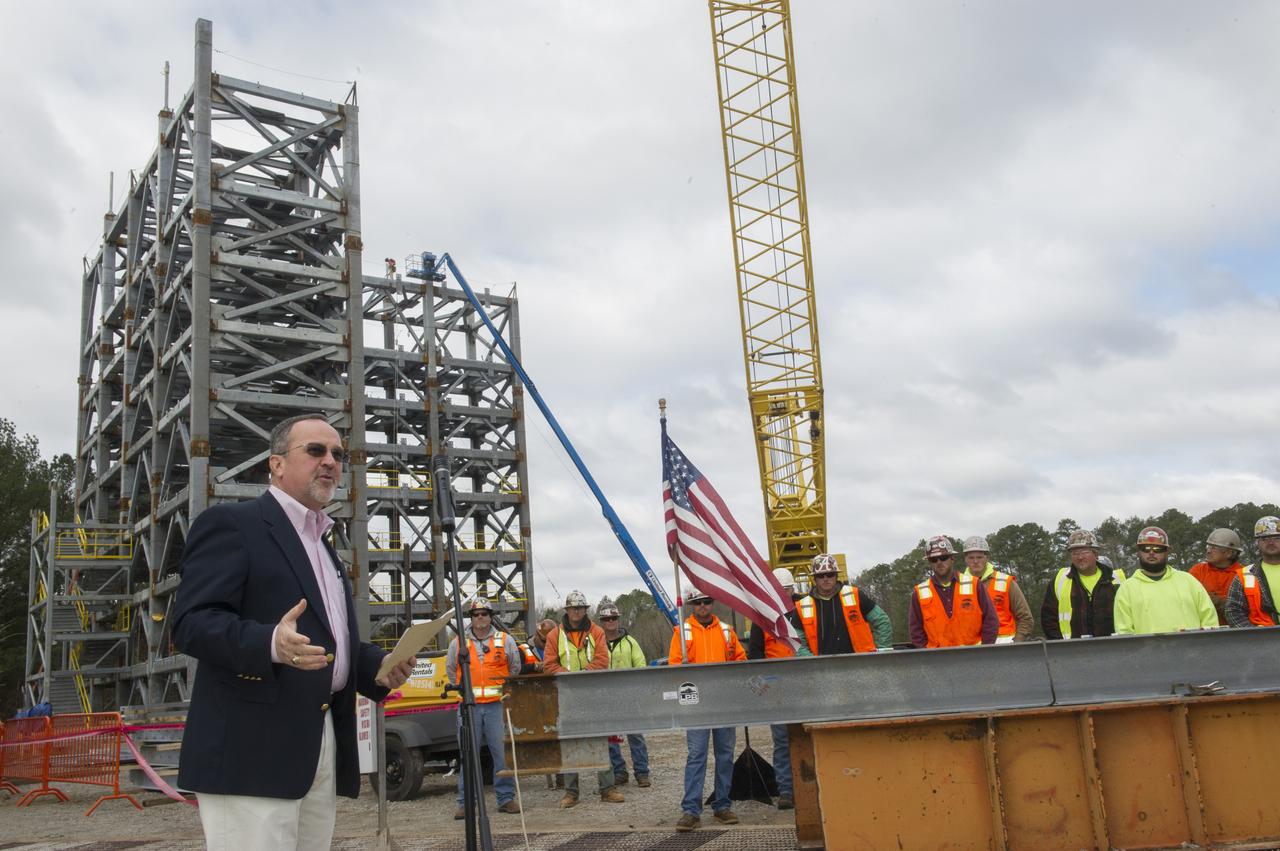

"YOUR WORK IS CRITICAL TO THE JOURNEY TO MARS," SAID SLS DEPUTY PROGRAM MANAGER JERRY COOK TO THE CONSTRUCTION CREW AT THE "TOP OUT" CEREMONY FOR TEST STAND 4697 AT MARSHALL.
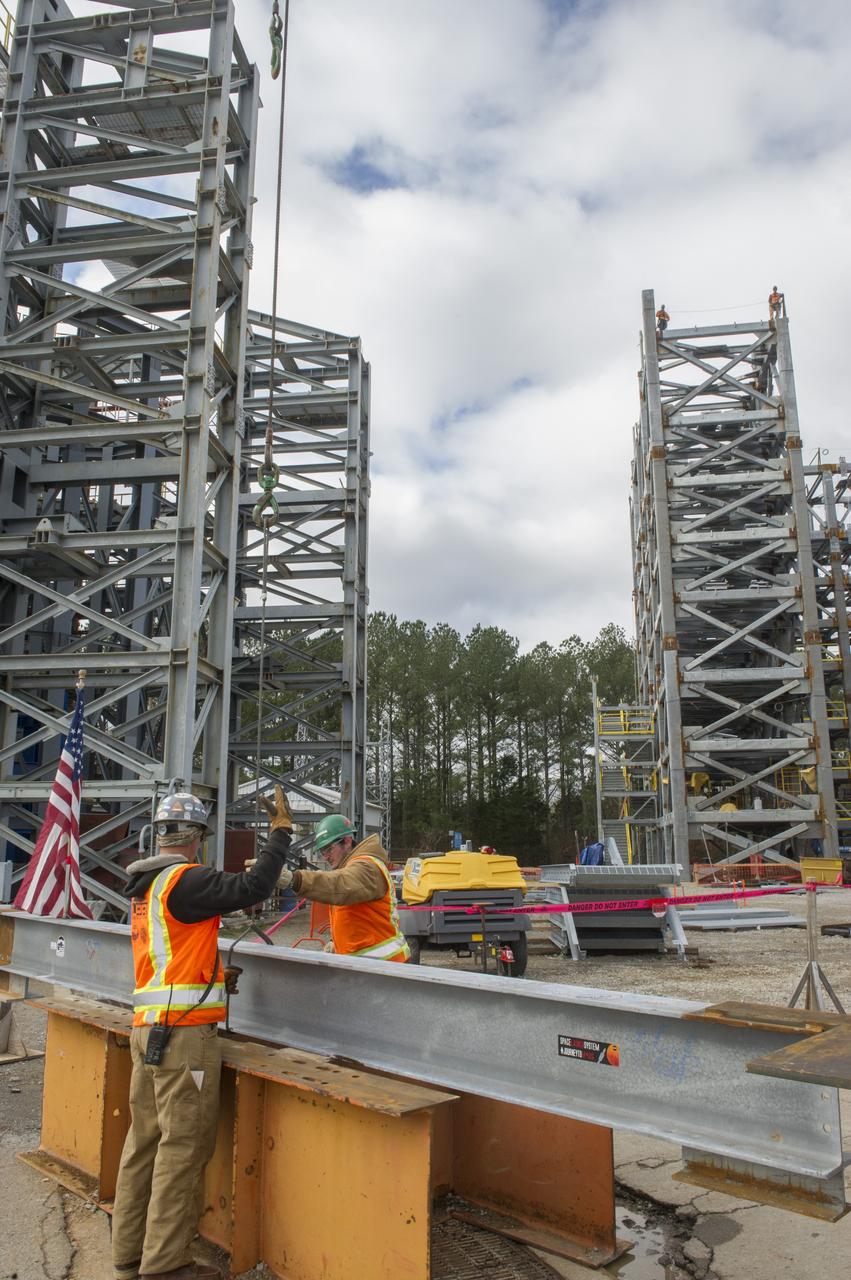

ON MARCH 4, CREW MEMBERS READIED A 900-POUND STEEL BEAM TO "TOP OUT" TEST STAND 4697, WHICH IS UNDER CONSTRUCTION TO TEST THE SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM LIQUID OXYGEN TANK AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER.

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
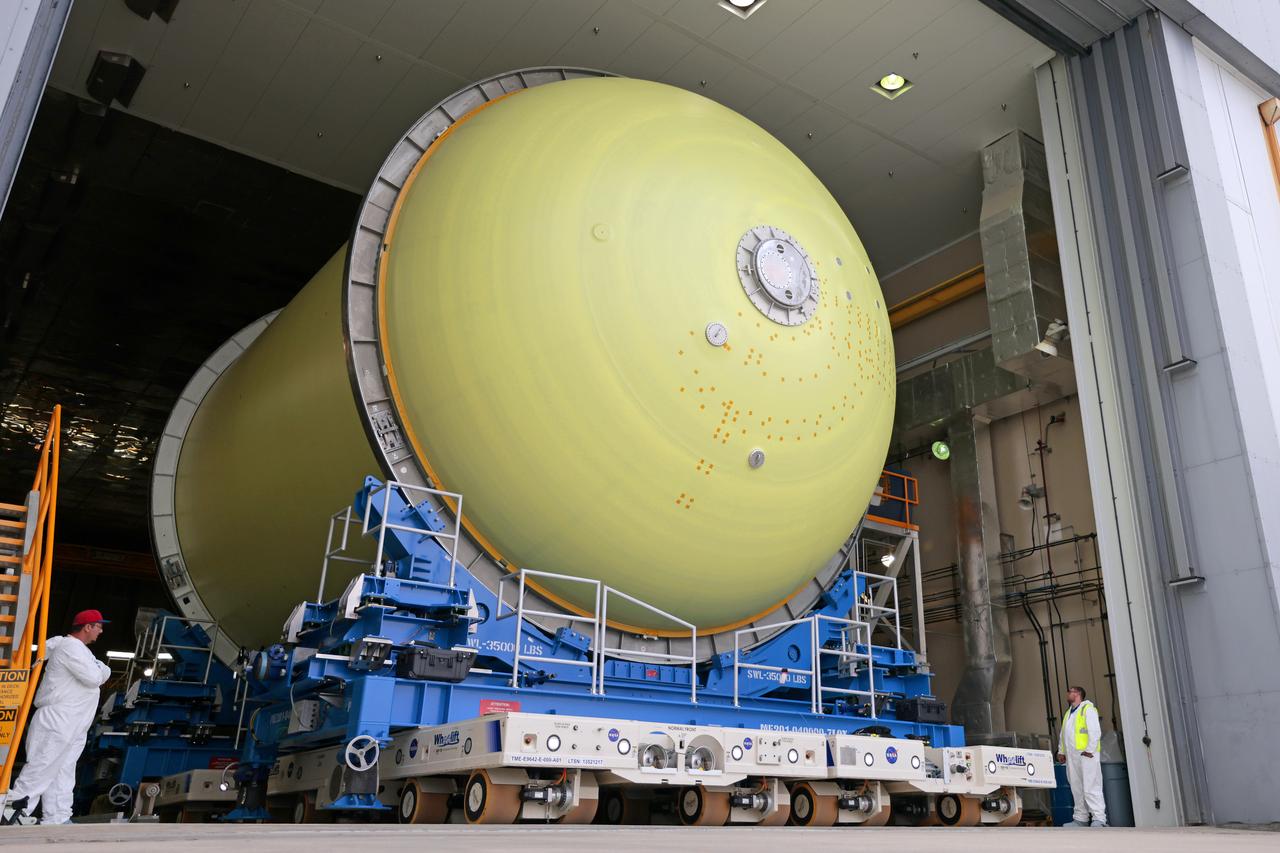

Move Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans transport a liquid oxygen tank from a detached production building to the main 43-acre rocket factory on Mar. 26. Teams recently completed primer application on the tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission. The tank will now undergo electrical installations before moving on to the next phase of production. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
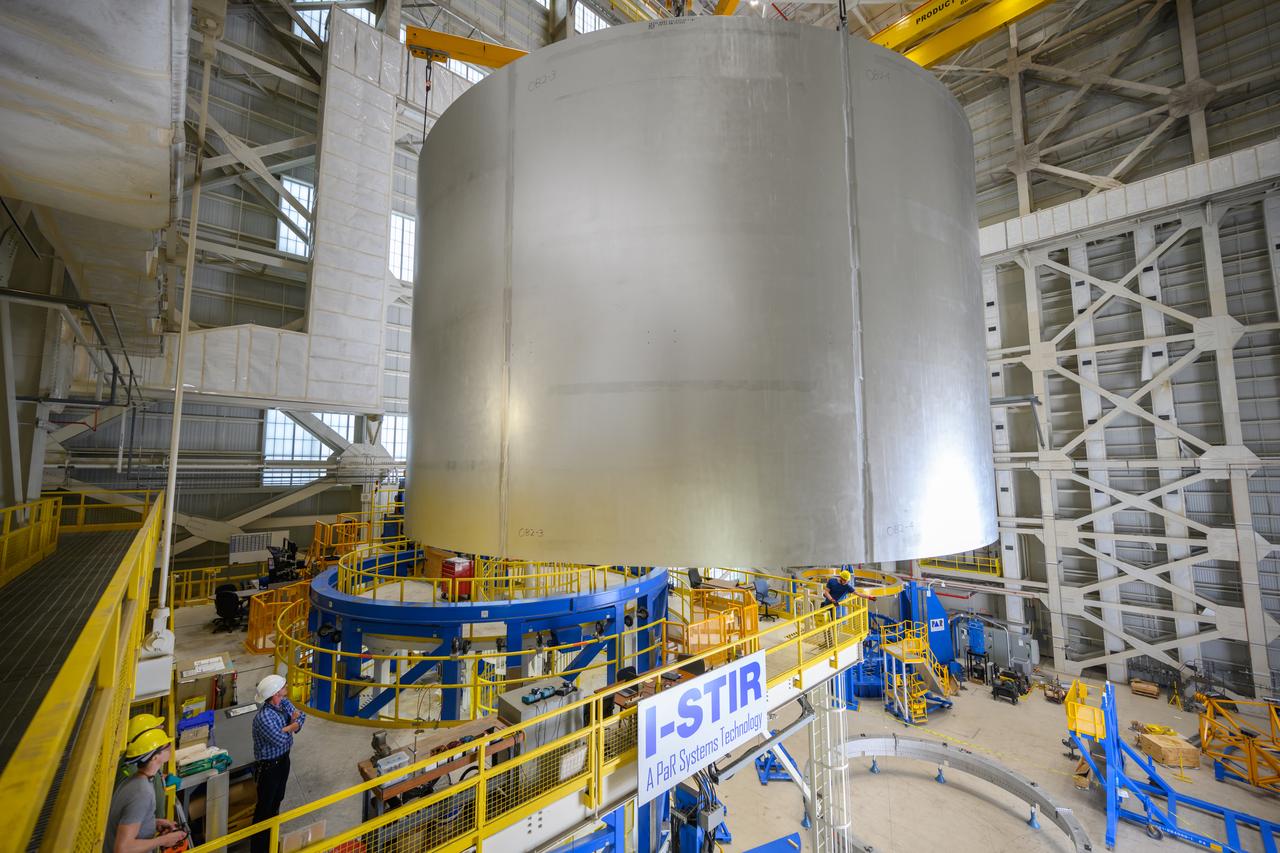

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the aft liquid oxygen tank (LOX) barrel out of the Vertical Weld Center (VWC) for its next phase of production. The aft barrel will eventually be mated with the forward barrel and the forward and aft domes to form the LOX tank, which will be used in the Space Launch System’s (SLS) Artemis IV mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Tuesday, May 10, 2022

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the aft liquid oxygen tank (LOX) barrel out of the Vertical Weld Center (VWC) for its next phase of production. The aft barrel will eventually be mated with the forward barrel and the forward and aft domes to form the LOX tank, which will be used in the Space Launch System’s (SLS) Artemis IV mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Tuesday, May 10, 2022

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the aft liquid oxygen tank (LOX) barrel out of the Vertical Weld Center (VWC) for its next phase of production. The aft barrel will eventually be mated with the forward barrel and the forward and aft domes to form the LOX tank, which will be used in the Space Launch System’s (SLS) Artemis IV mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Tuesday, May 10, 2022

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the aft liquid oxygen tank (LOX) barrel out of the Vertical Weld Center (VWC) for its next phase of production. The aft barrel will eventually be mated with the forward barrel and the forward and aft domes to form the LOX tank, which will be used in the Space Launch System’s (SLS) Artemis IV mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Tuesday, May 10, 2022

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lift the aft liquid oxygen tank (LOX) barrel out of the Vertical Weld Center (VWC) for its next phase of production. The aft barrel will eventually be mated with the forward barrel and the forward and aft domes to form the LOX tank, which will be used in the Space Launch System’s (SLS) Artemis IV mission. The LOX tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid oxygen to help fuel four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen hardware, along with the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Photographed on Tuesday, May 10, 2022
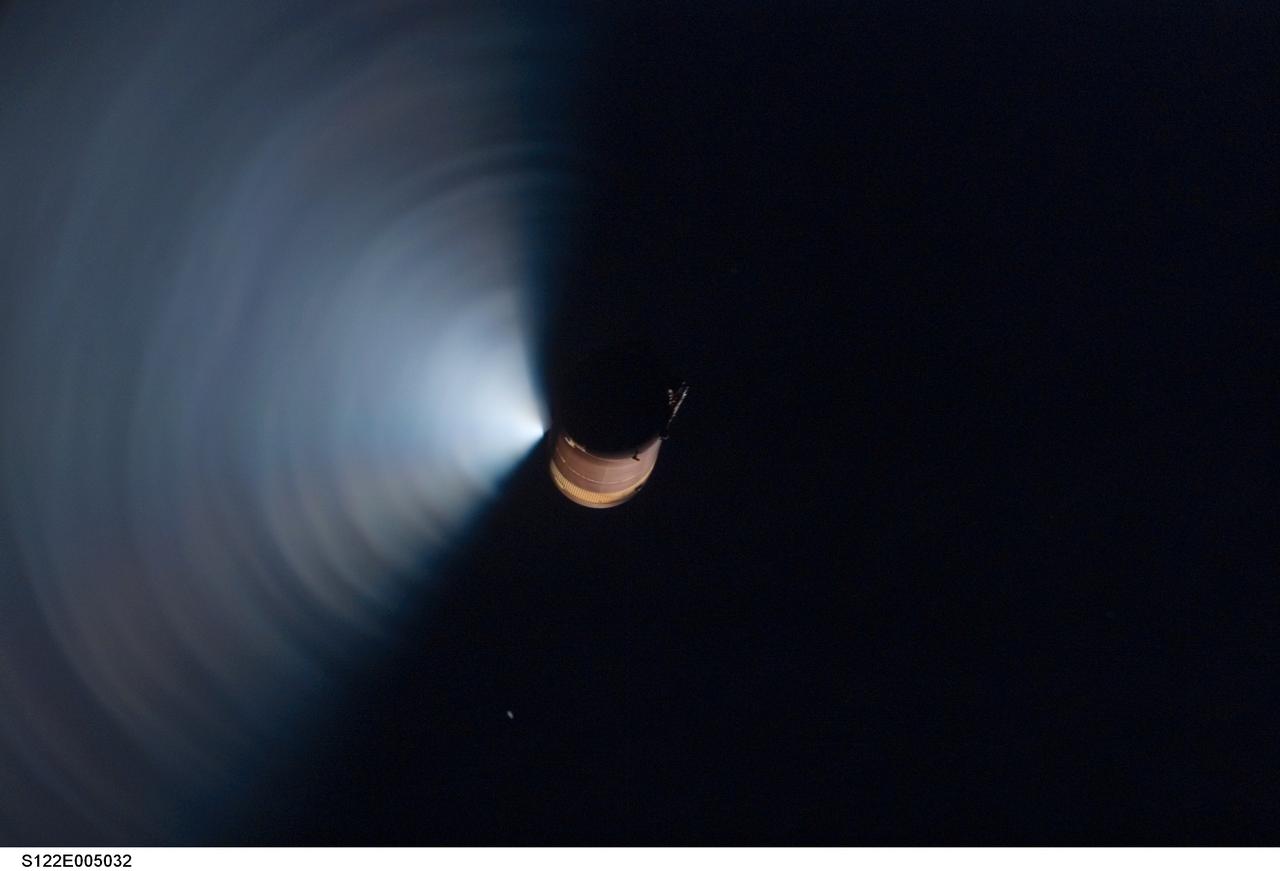

S122-E-005032 (7 Feb. 2008) --- Backdropped against the blackness of space, the STS-122 external fuel tank (ET) begins its relative separation from the Space Shuttle Atlantis. An STS-122 crewmember recorded the scene with a digital still camera. The fan-shaped bright area is the result of ET venting after orbiter separation. What happens in this nominal occurence is that the residual cryogenics in the tank heat up to some extent and the pressure increases, popping the relief valve. The residual LOX and LH2 spray out of the tank and are quite noticeable with the light reflection.
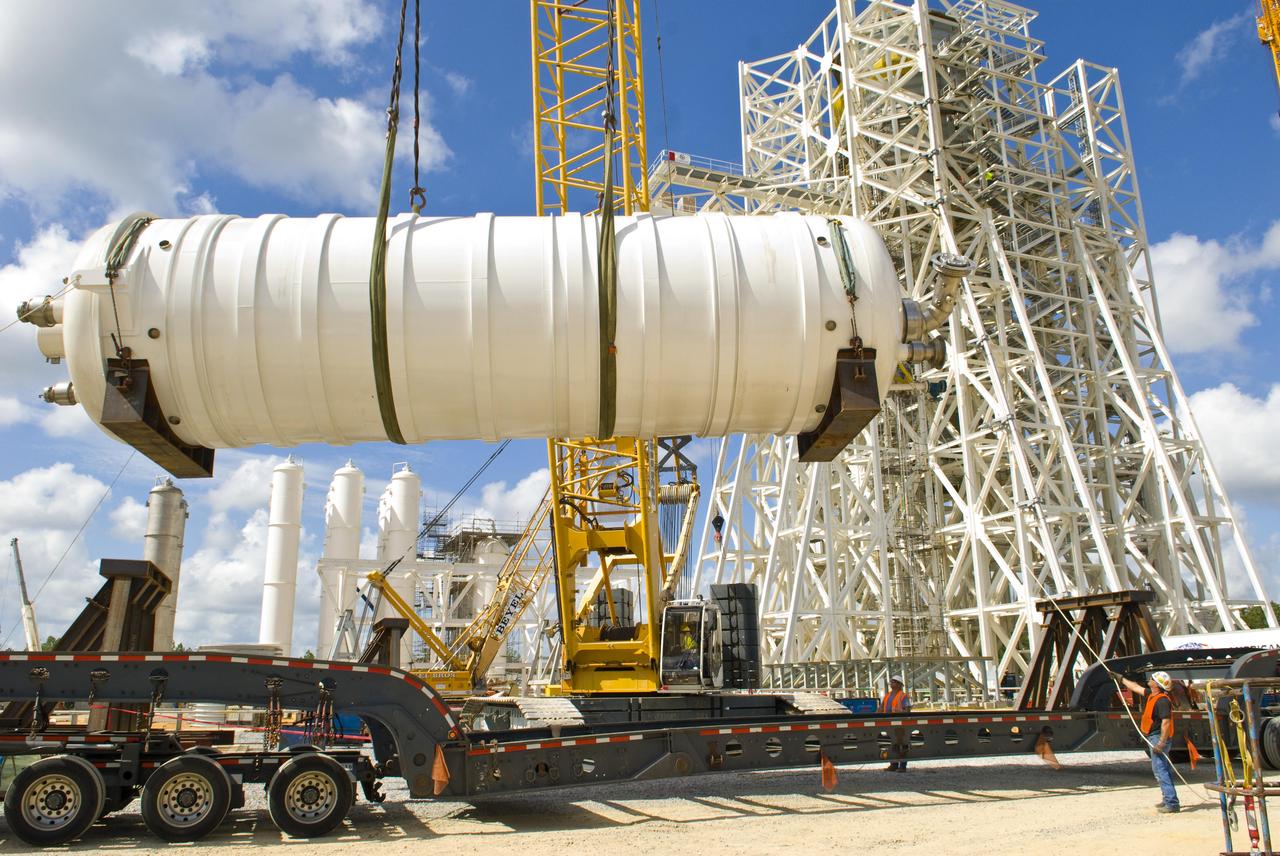

A 35,000-gallon liquid oxygen tank is placed at the A-3 Test Stand construction site on Sept. 24, 2010. The tank will provide propellant for tests of next-generation rocket engines at the stand. It will be placed upright on top of the stand, helping to increase the overall height to 300 feet. Once completed, the A-3 Test Stand will enable operators to test rocket engines at simulated altitudes of up to 100,000 feet. The A-3 stand is the first large rocket engine test structure to be built at Stennis Space Center since the 1960s.

This image shows technicians and engineers move and connect the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) to the intertank as they continue the process of the forward join on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The forward join connects the forward skirt, the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) and the intertank structures to form the top part of the SLS rocket’s core stage. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows technicians and engineers move and connect the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) to the intertank as they continue the process of the forward join on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The forward join connects the forward skirt, the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) and the intertank structures to form the top part of the SLS rocket’s core stage. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows technicians and engineers move and connect the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) to the intertank as they continue the process of the forward join on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The forward join connects the forward skirt, the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) and the intertank structures to form the top part of the SLS rocket’s core stage. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows technicians and engineers move and connect the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) to the intertank as they continue the process of the forward join on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The forward join connects the forward skirt, the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) and the intertank structures to form the top part of the SLS rocket’s core stage. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
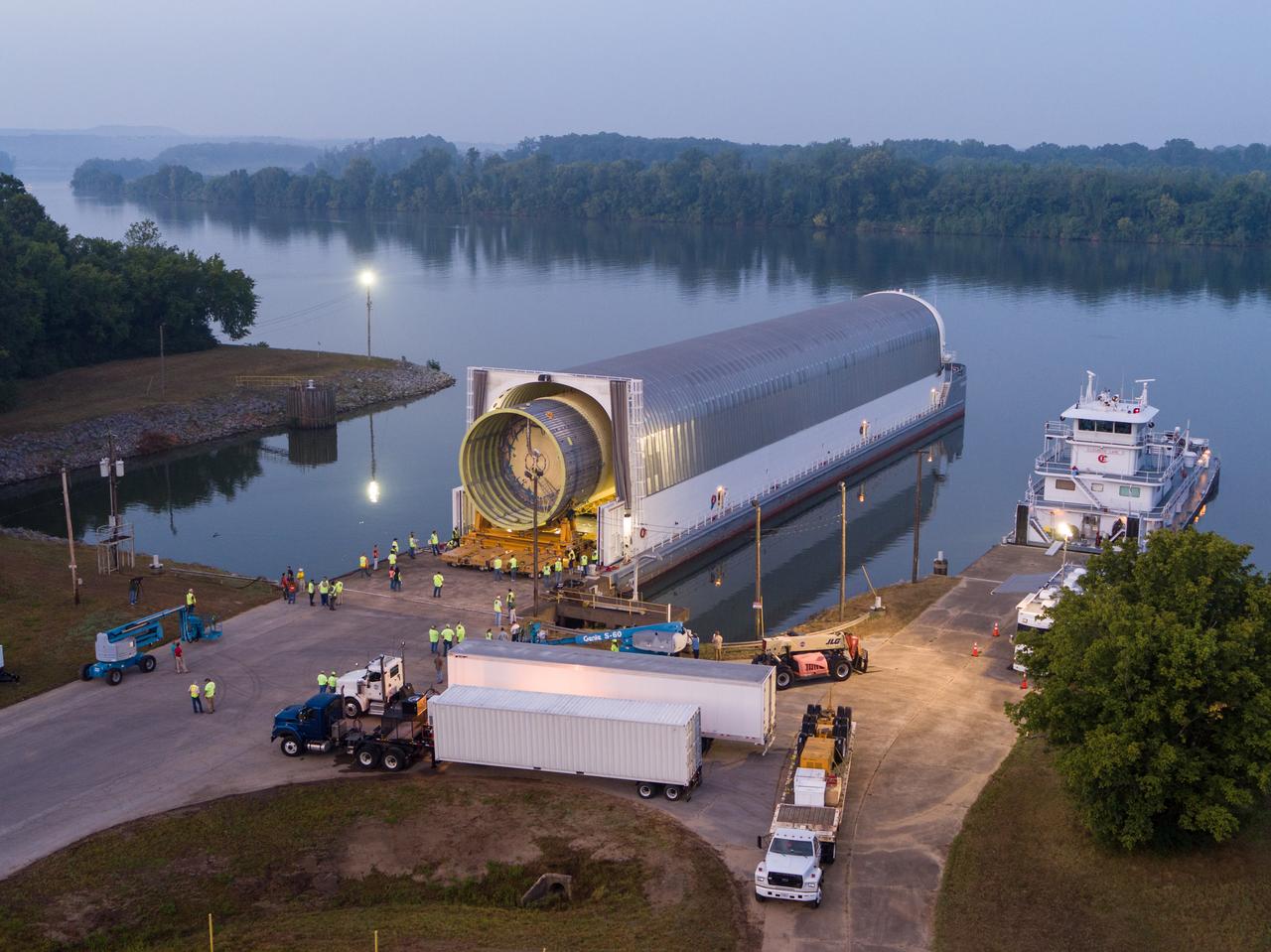

LOX STA unload from Pegasus at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center
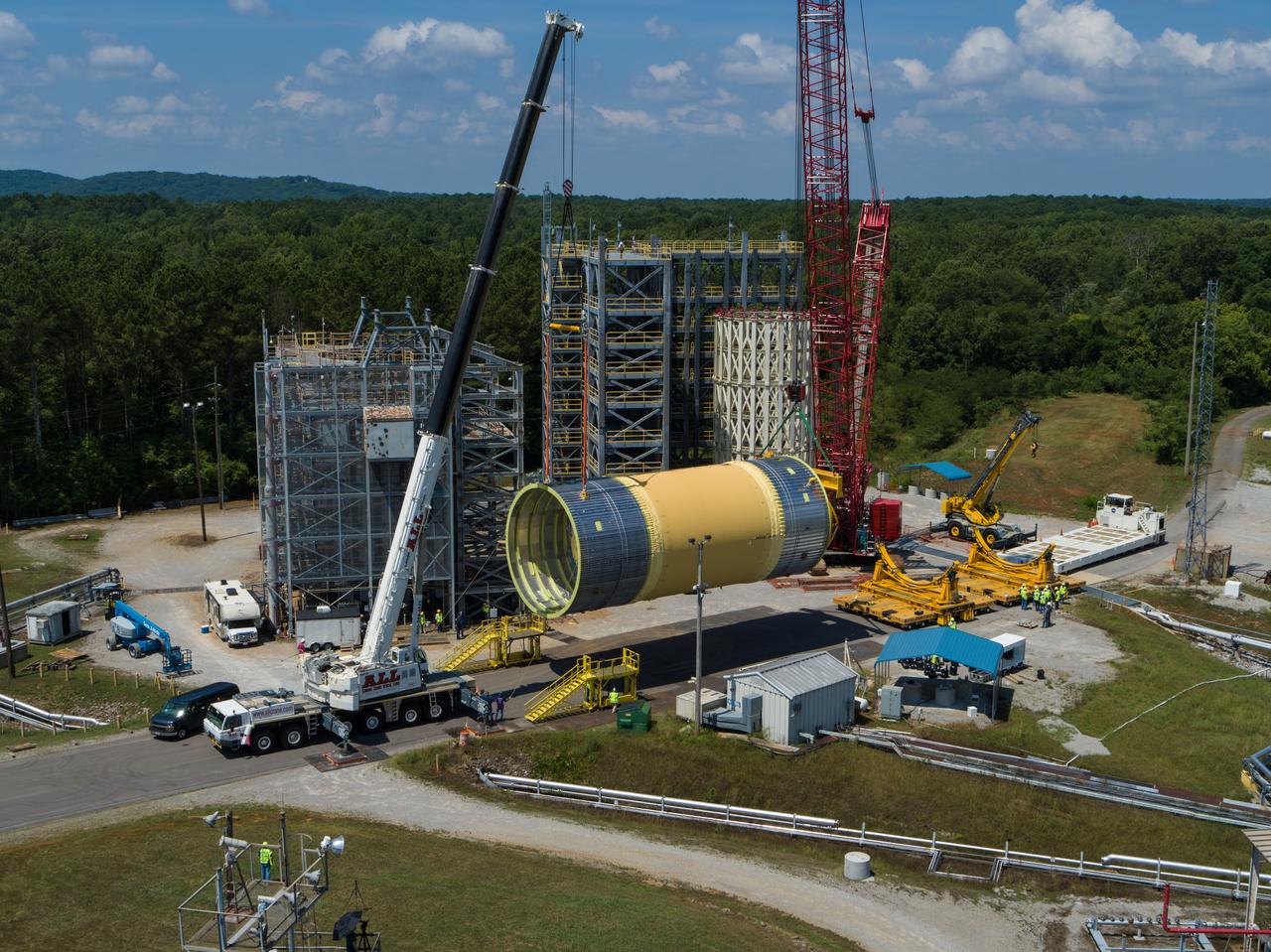

LOX STA breakover at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center
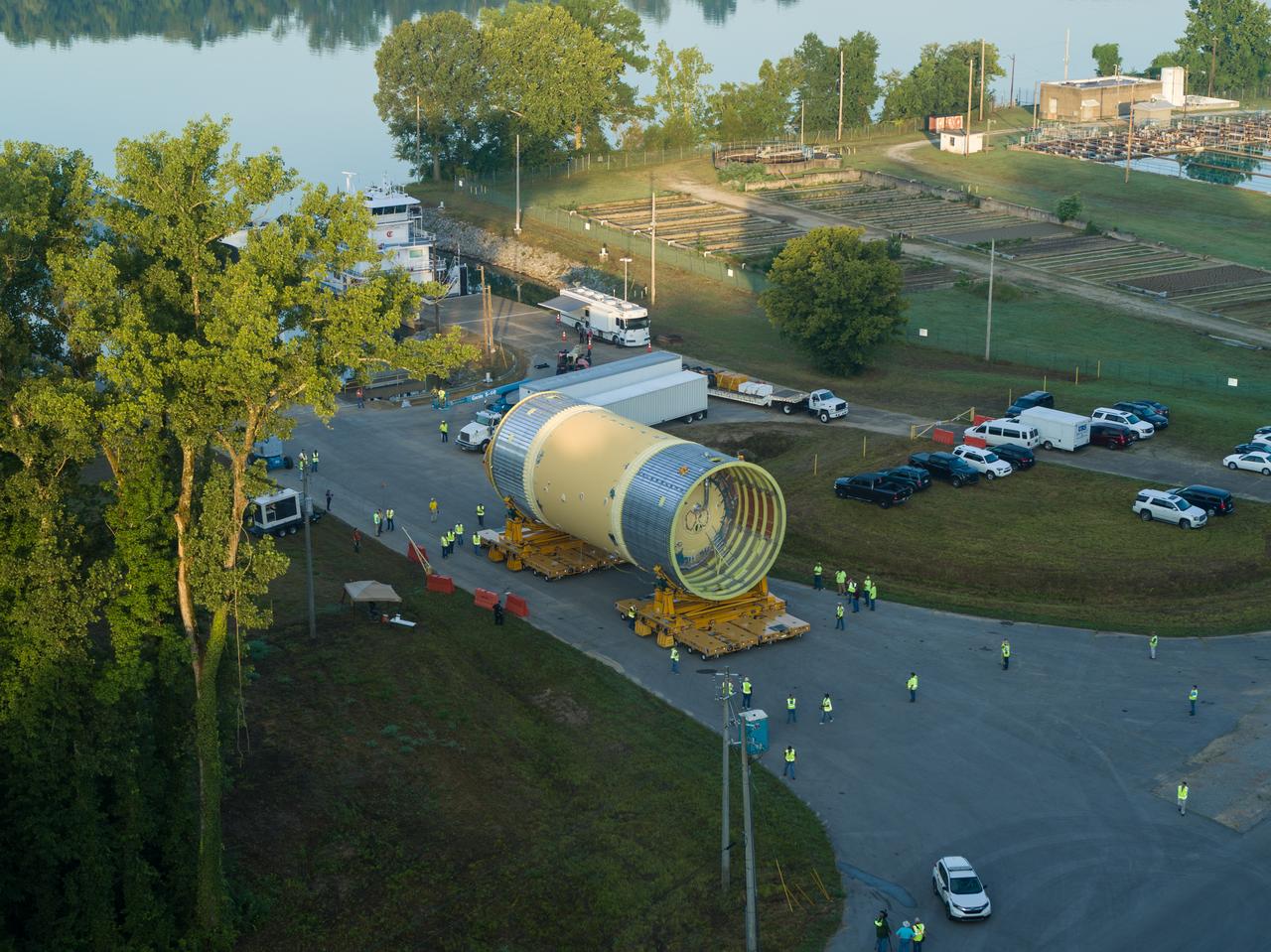

LOX STA unload from Pegasus at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center
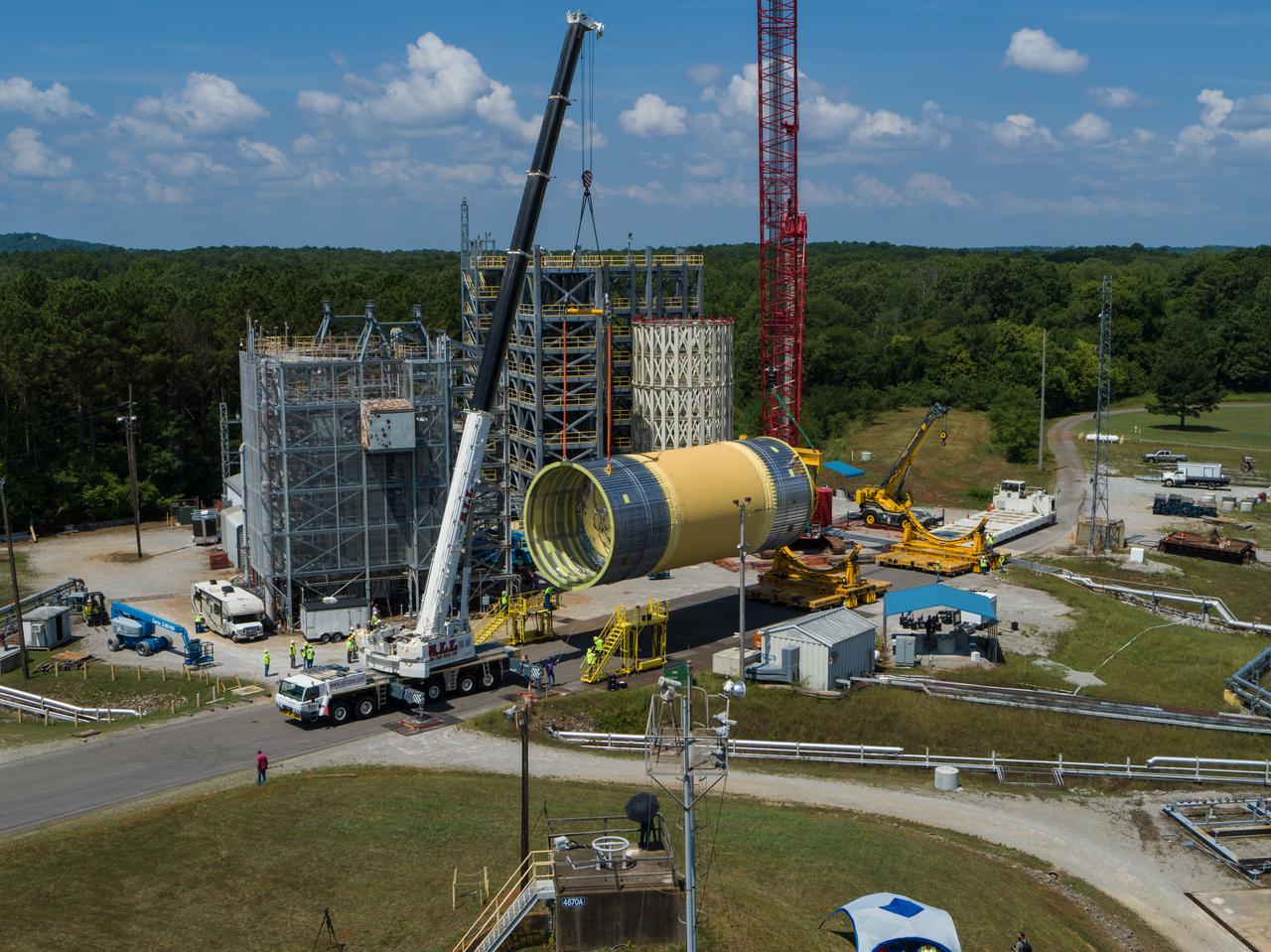

LOX STA breakover at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center

LOX STA unload from Pegasus at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center

LOX STA breakover at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center
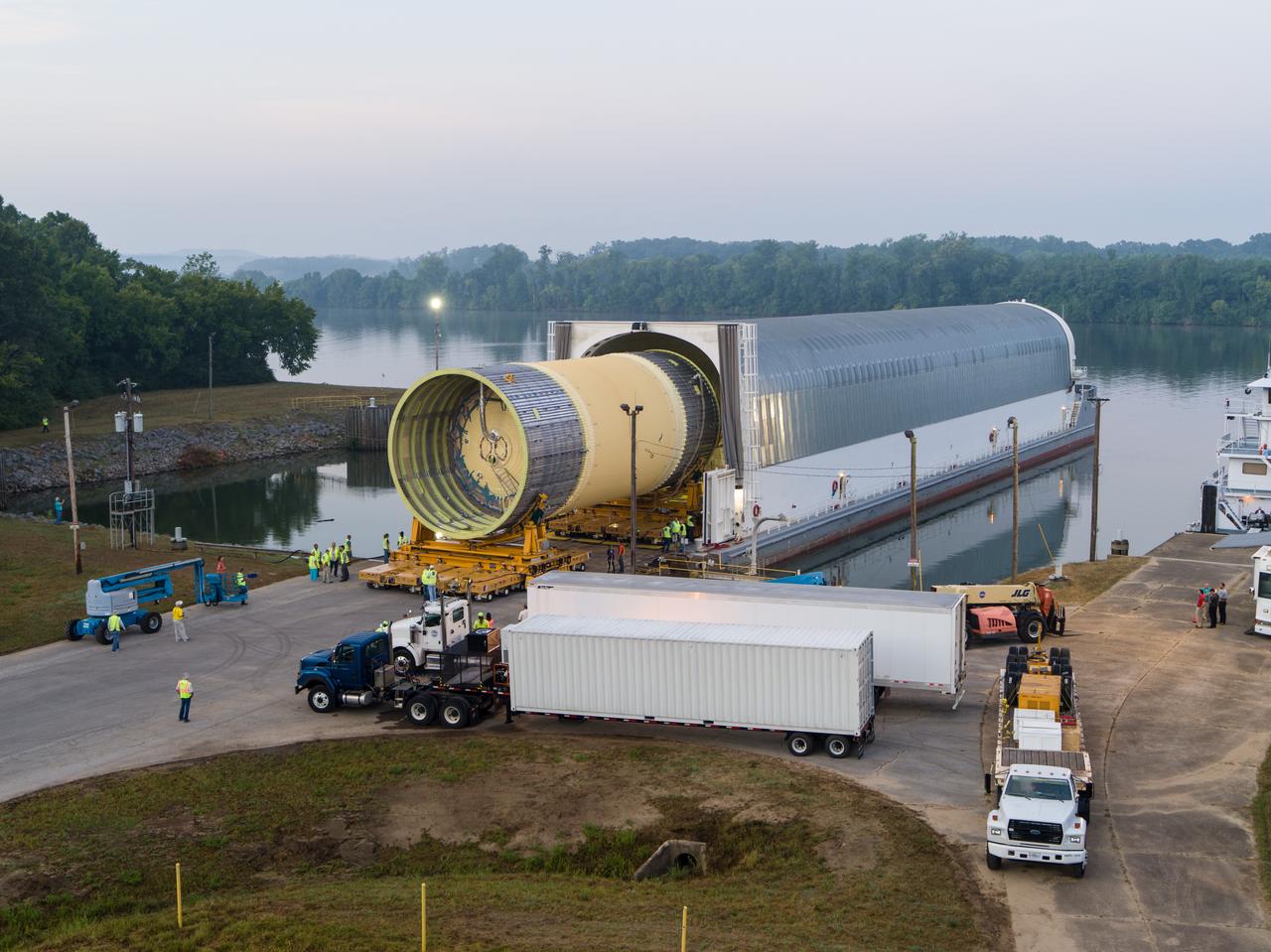

LOX STA unload from Pegasus at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center
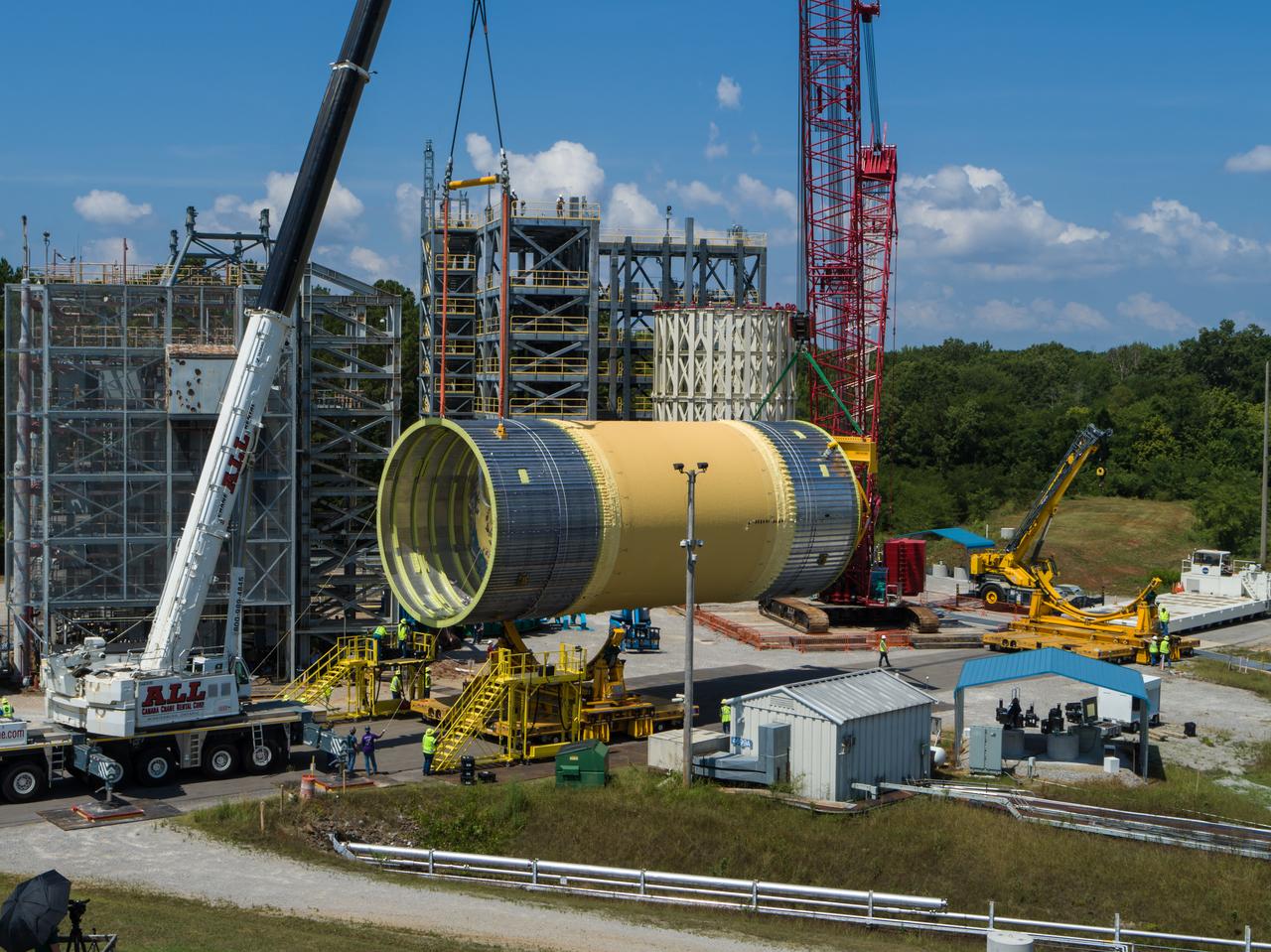

LOX STA breakover at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center
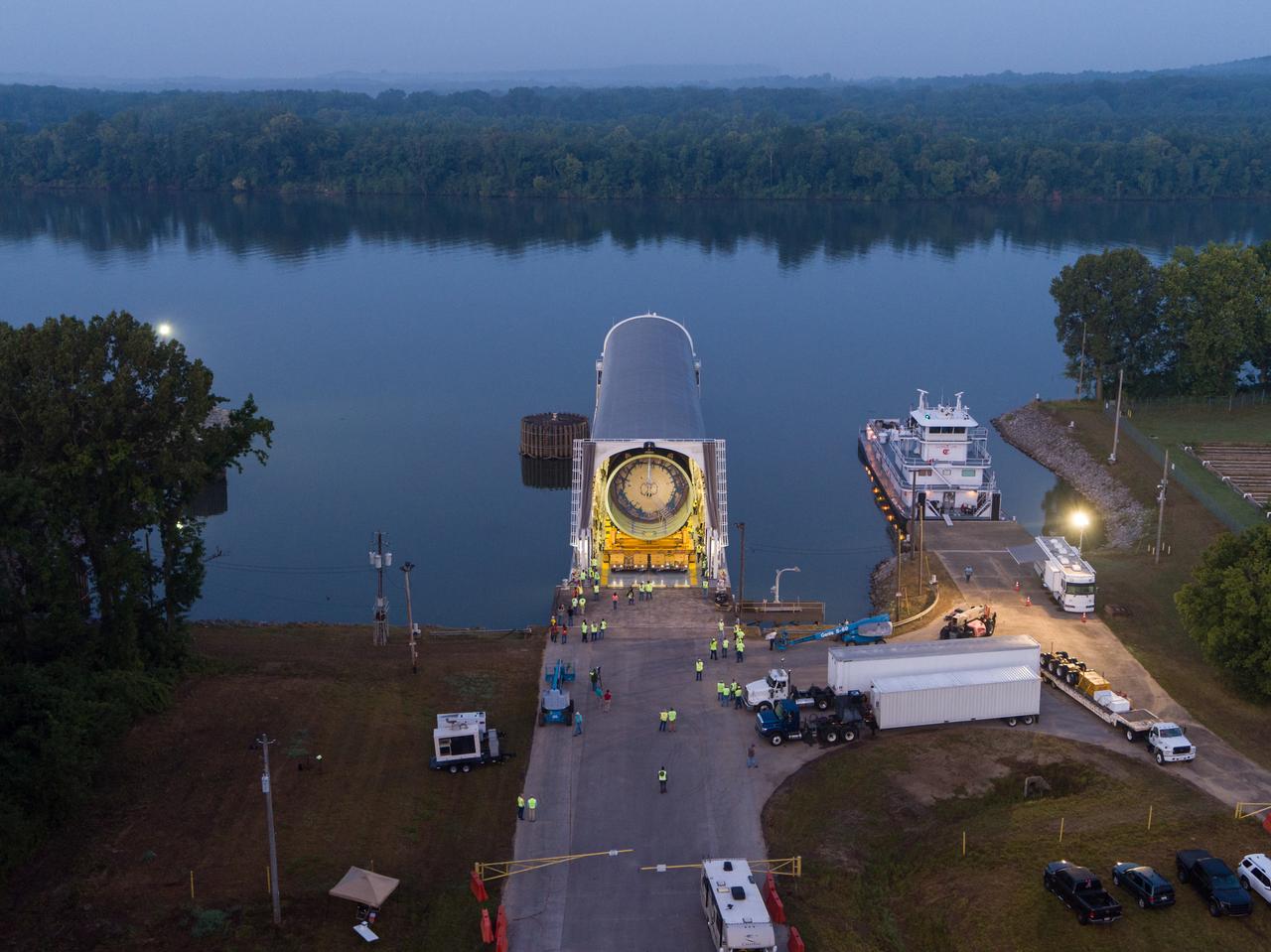

LOX STA unload from Pegasus at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center
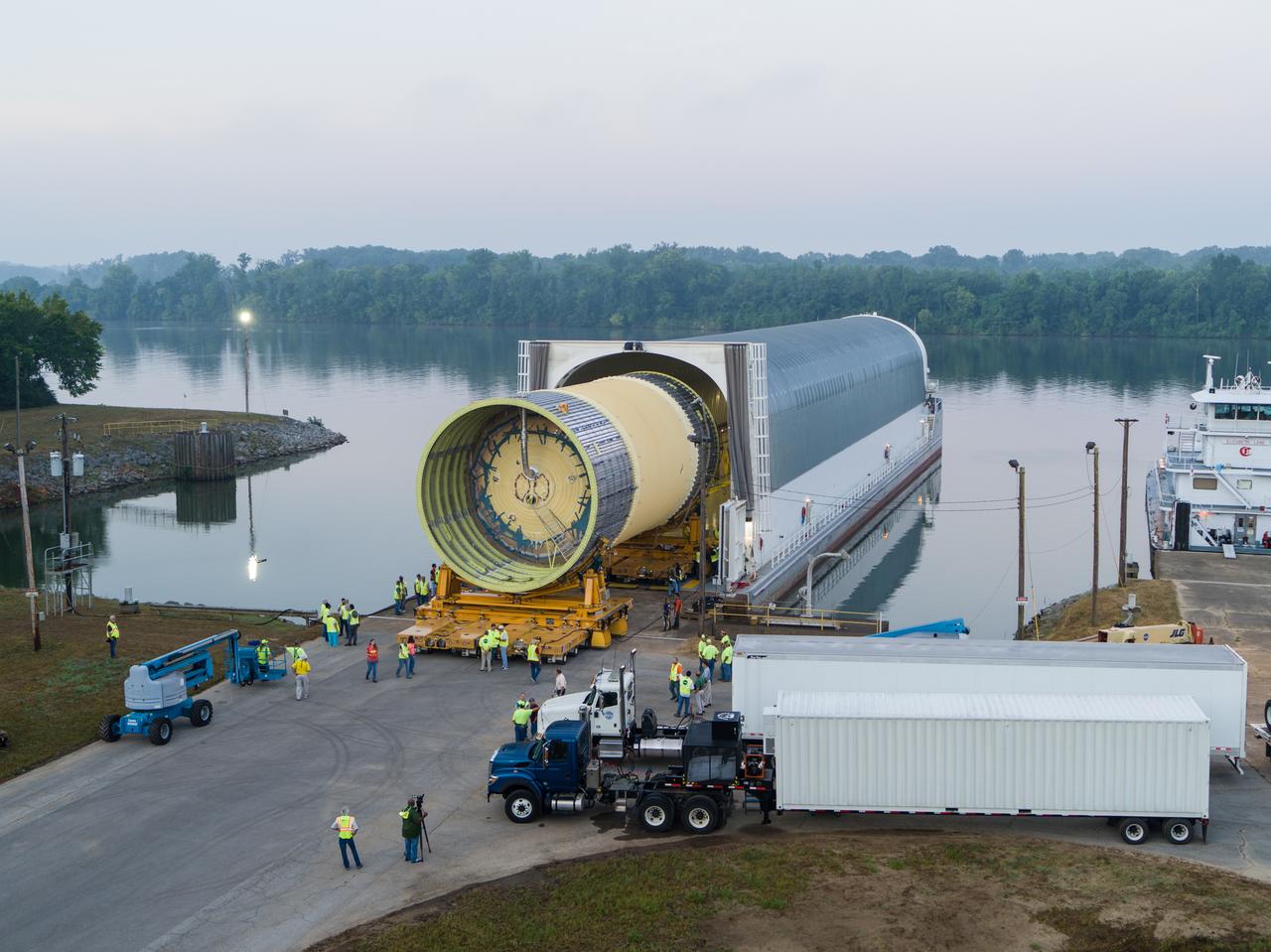

LOX STA unload from Pegasus at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center