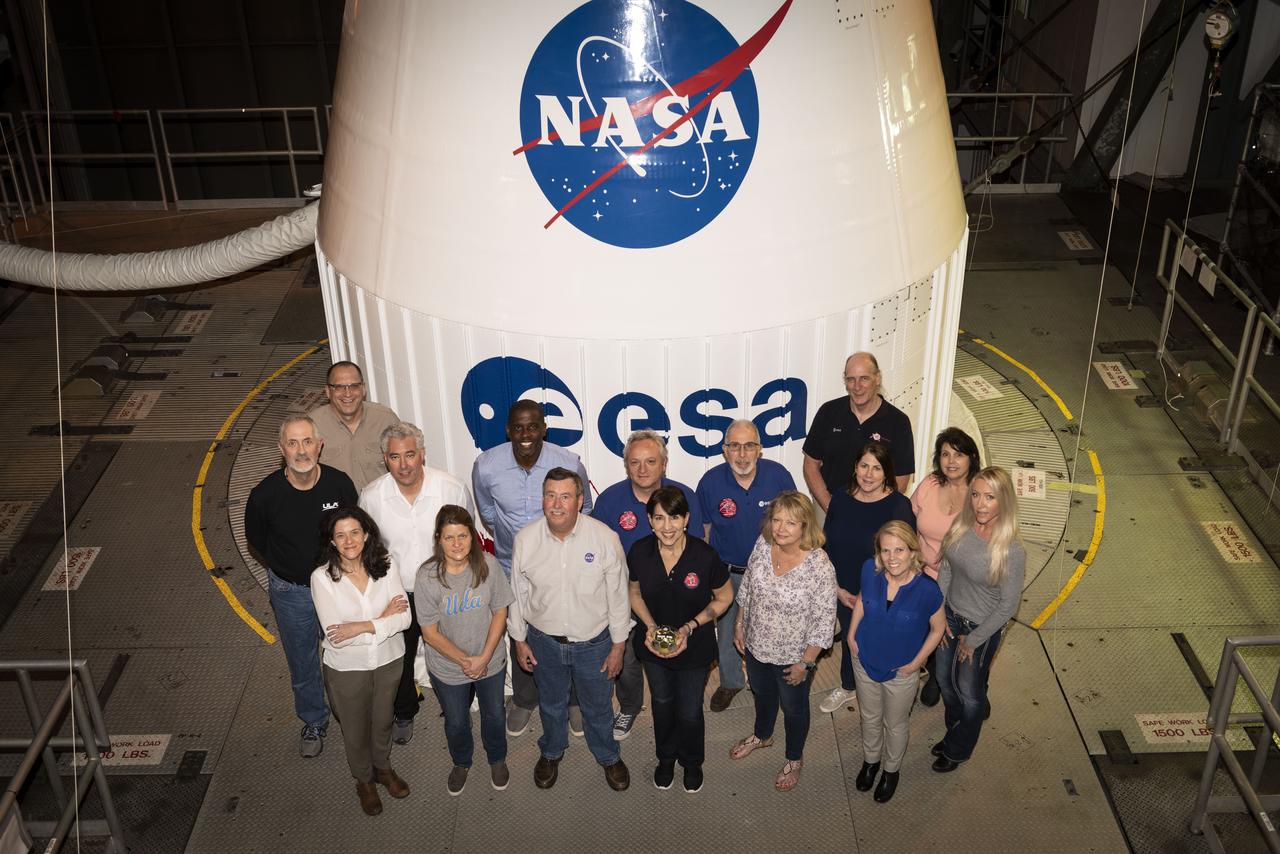

Members of the Goddard Space Flight Center Solar Orbiter Collaboration Project Office, along with Launch Services Program’s (LSP) Jim Behling (back left), launch site integration manager, pose in front of the Solar Orbiter spacecraft inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 in Florida. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s LSP, based at Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The Laminar Soot Processes (LSP) experiment under way during the Microgravity Sciences Lab-1 mission in 1997. LSP-2 will fly in the STS-107 Research 1 mission in 2001. The principal investigator is Dr. Gerard Faeth of the University of Michigan. LSP uses a small jet burner, similar to a classroom butane lighter, that produces flames up to 60 mm (2.3 in) long. Measurements include color TV cameras and a temperature sensor, and laser images whose darkness indicates the quantity of soot produced in the flame. Glenn Research in Cleveland, OH, manages the project.
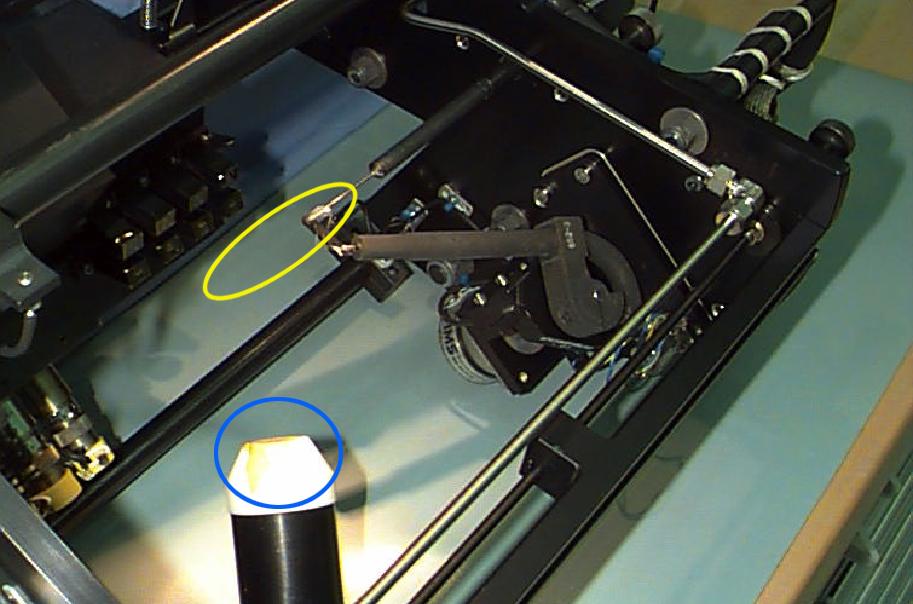
Interior of the Equipment Module for the Laminar Soot Processes (LSP-2) experiment that fly in the STS-107 Research 1 mission in 2002 (LSP-1 flew on Microgravity Sciences Lab-1 mission in 1997). The principal investigator is Dr. Gerard Faeth of the University of Michigan. LSP uses a small jet burner (yellow ellipse), similar to a classroom butane lighter, that produces flames up to 60 mm (2.3 in) long. Measurements include color TV cameras and a radiometer or heat sensor (blue circle), and laser images whose darkness indicates the quantity of soot produced in the flame. Glenn Research in Cleveland, OH, manages the project.
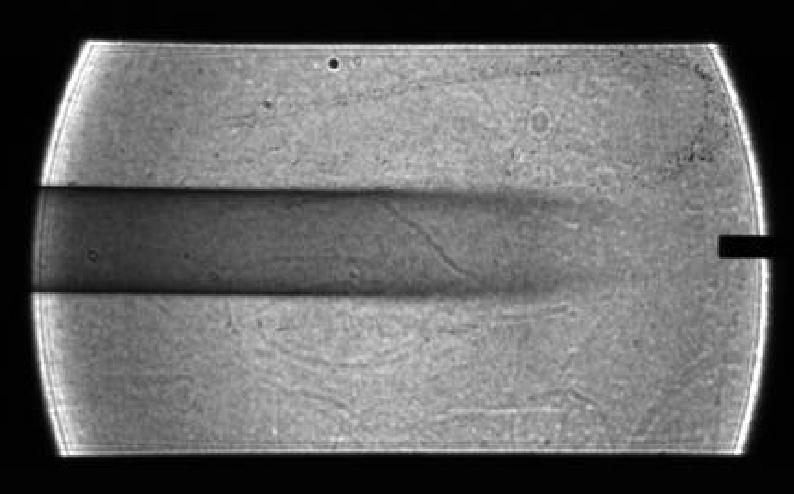
Image of soot (smoke) plume made for the Laminar Soot Processes (LSP) experiment during the Microgravity Sciences Lab-1 mission in 1997. LSP-2 will fly in the STS-107 Research 1 mission in 2002. The principal investigator is Dr. Gerard Faeth of the University of Michigan. LSP uses a small jet burner, similar to a classroom butane lighter, that produces flames up to 60 mm (2.3 in) long. Measurements include color TV cameras and a temperature sensor, and laser images whose darkness indicates the quantity of soot produced in the flame. Glenn Research in Cleveland, OH, manages the project.
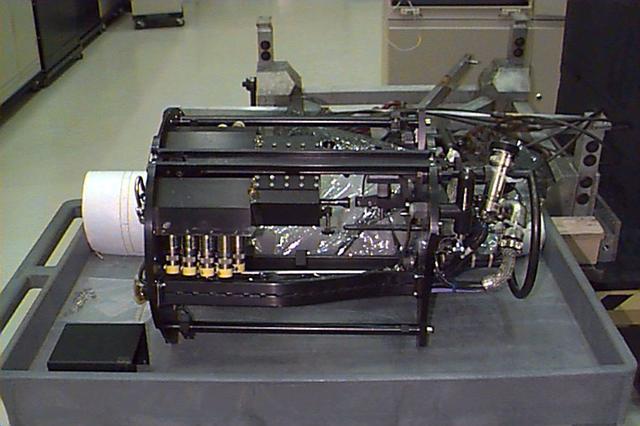
The Laminar Soot Processes (LSP) Experiment Mounting Structure (EMS) was used to conduct the LSP experiment on Combustion Module-1. The EMS was inserted into the nozzle on the EMS and ignited by a hot wire igniter. The flame and its soot emitting properties were studied.
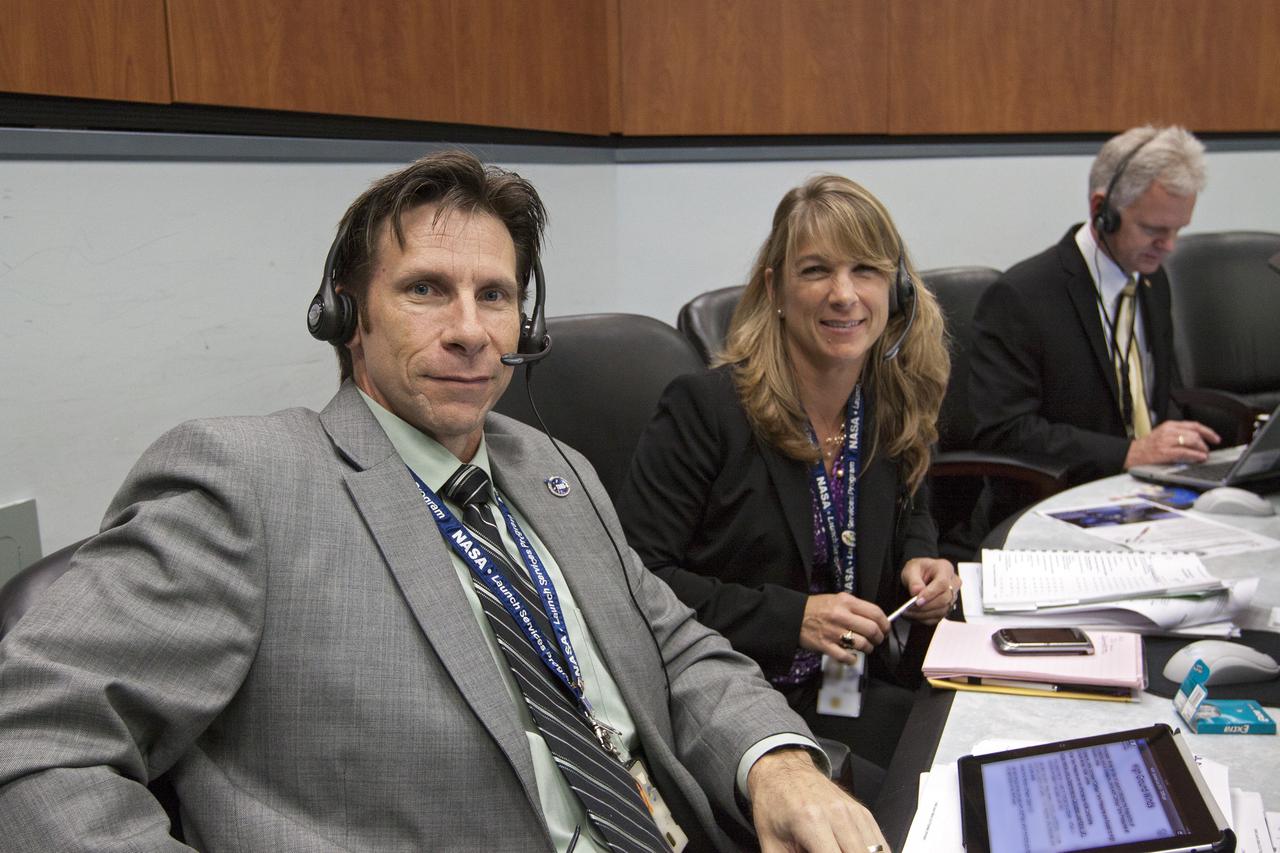

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Amanda Mitskevich, program manager of NASA's Launch Services Program, or LSP, center, and Chuck Dovale, deputy program manager of LSP, monitors the countdown for the launch of the TDRS-K spacecraft on an Atlas V rocket. The launch teams for NASA and the United Launch Alliance work inside the Atlas Space Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., known as the ASOC. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett
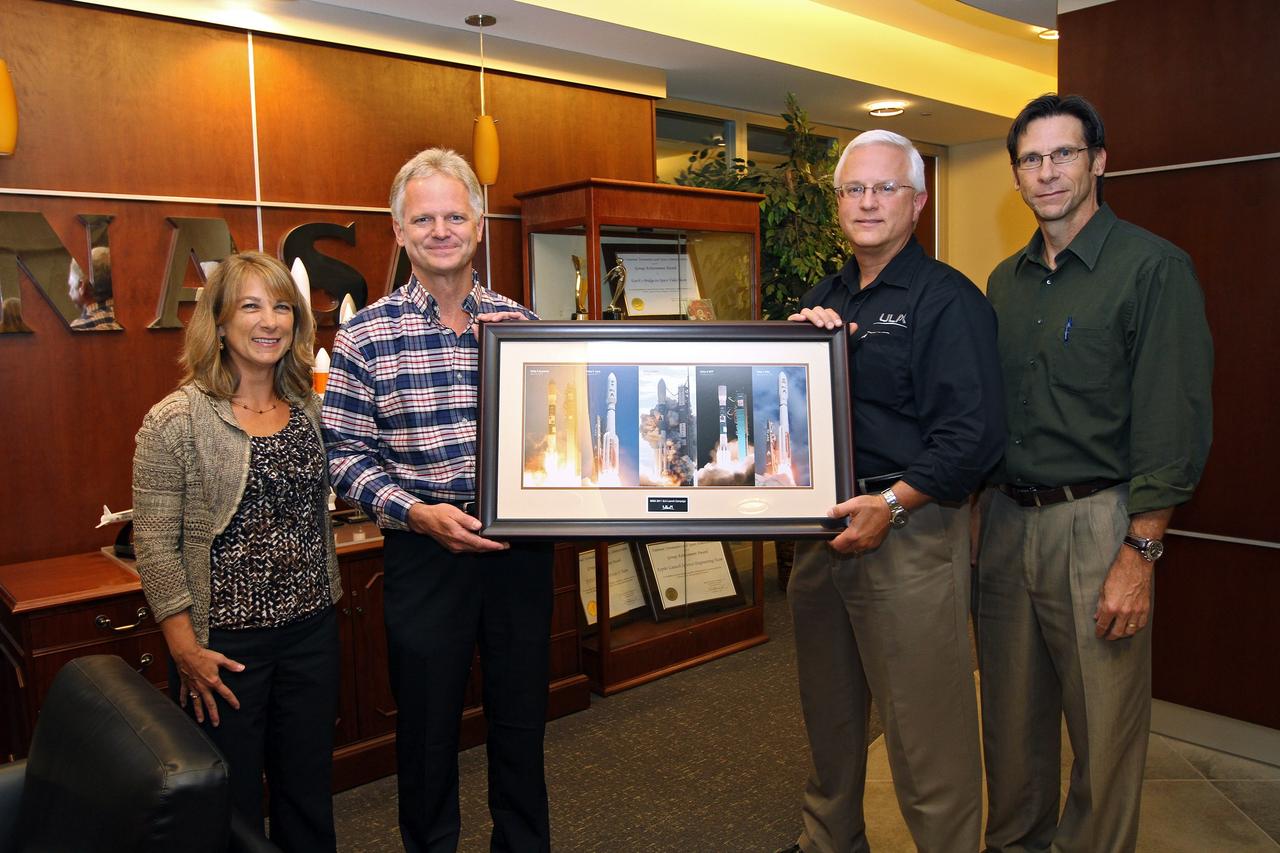

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Launch Services Program, or LSP, Program Manager Amanda Mitskevich, at far left, was presented with a framed commemorative collage of five United Launch Alliance, or ULA, mission photos in 2011 from Jim Sponnick, second from left, vice president of Mission Operations at ULA. Also at the presentation, were ULA Program Manager for NASA Missions Vern Thorp and LSP Deputy Program Manager Chuck Dovale. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
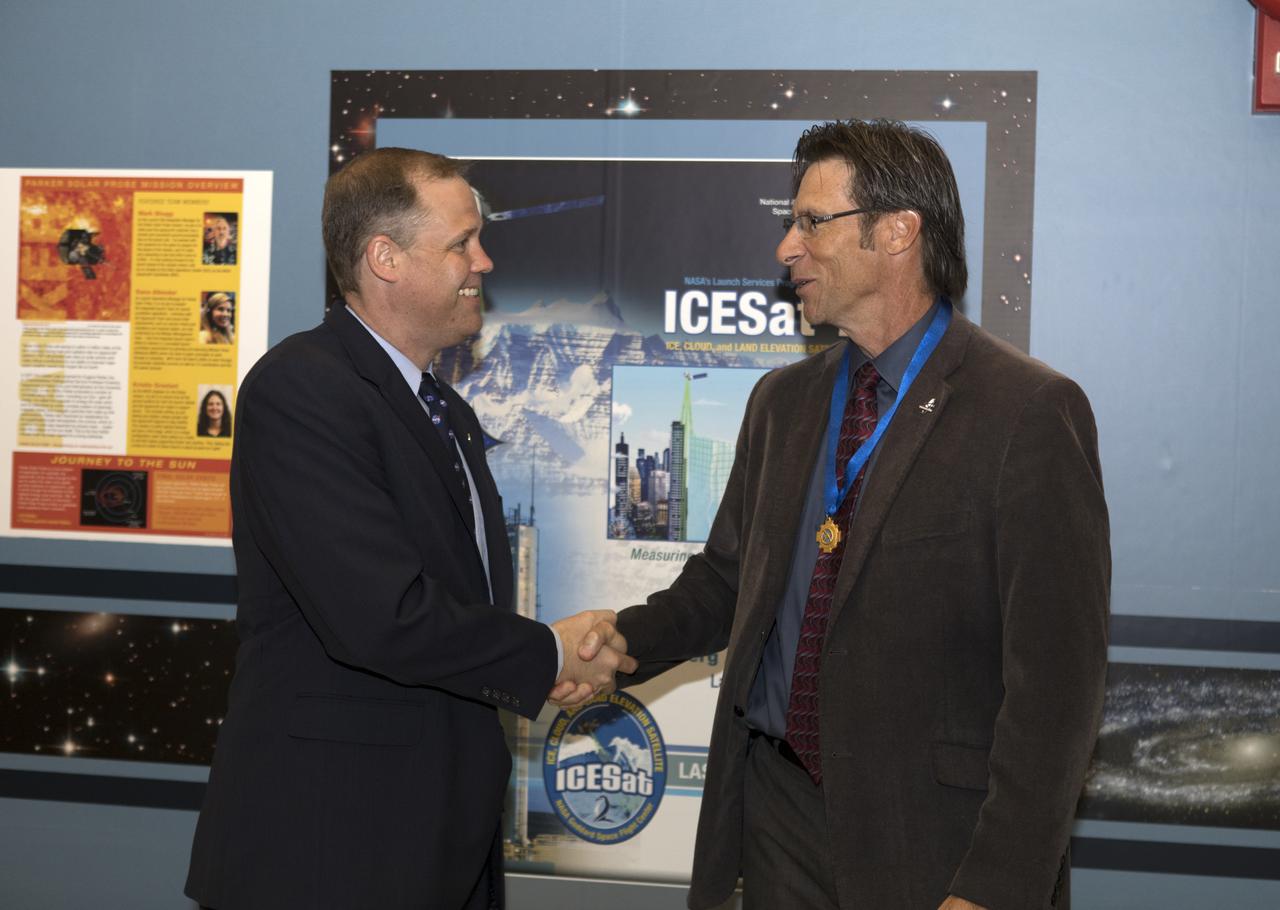

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, congratulates Chuck Dovale, deputy program manager for the Launch Services Program (LSP), on Aug. 7, 2018, during a visit to the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Bridenstine presented a NASA Distinguished Service Medal to Dovale. During his tour of Hangar AE and LSP's Mission Director's Center, Bridenstine received updates on LSP missions and accomplishments.
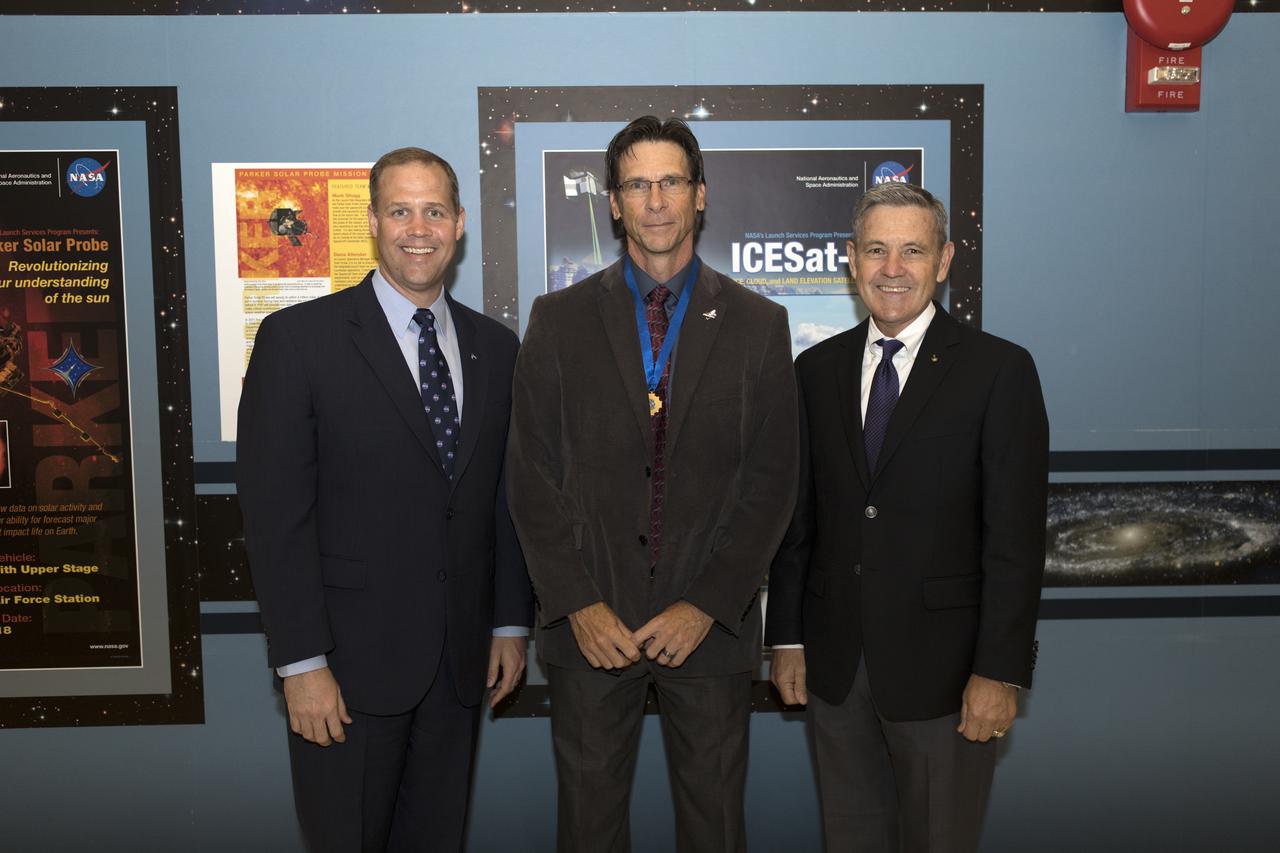

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, tours Kennedy Space Center facilities and awards Chuck Dovale, center, deputy program manager for the Launch Services Program (LSP), a NASA Distinguished Service Medal on Aug. 7, 2018. At right is Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana. During his tour of Hangar AE and LSP's Mission Director's Center, Bridenstine received updates on LSP missions and accomplishments.
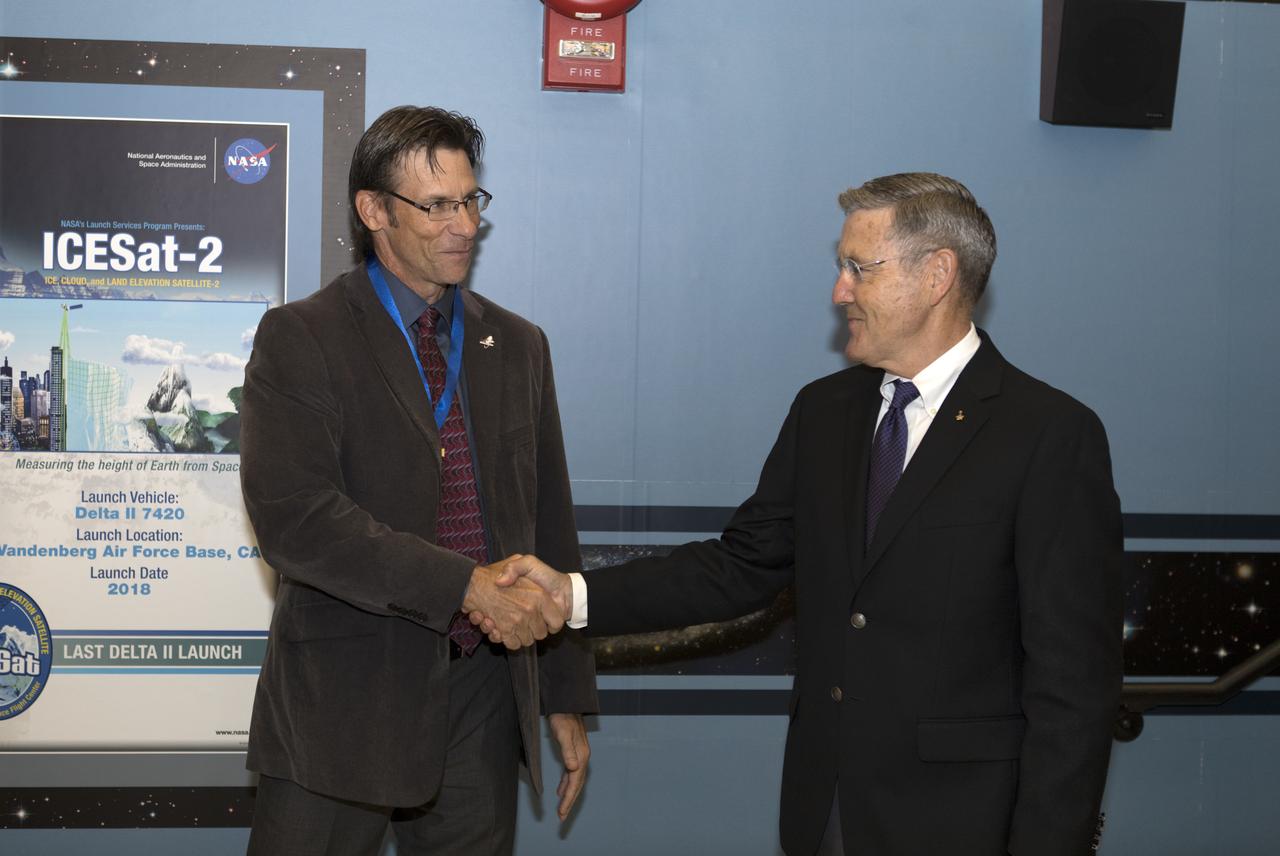

NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, at right, congratulates Chuck Dovale, deputy program manager for the Launch Services Program (LSP), on Aug. 7, 2018. During a visit to the center, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine presents a NASA Distinguished Service Medal to Dovale. During his tour of Hangar AE and LSP's Mission Director's Center, Bridenstine received updates on LSP missions and accomplishments.
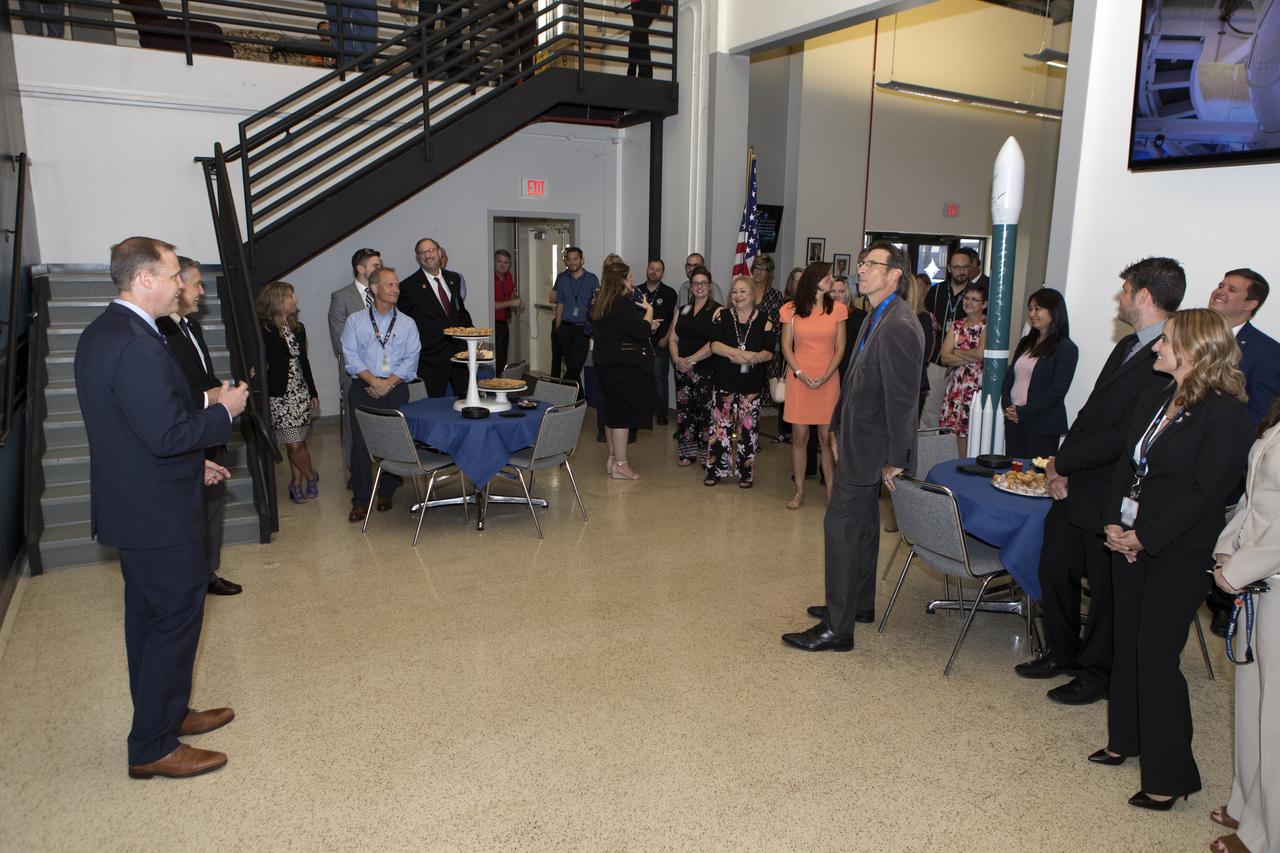

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, tours Hangar AE and the Launch Services Program's (LSP) Mission Director's Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Aug. 7, 2018. Bridenstine spoke to workers and received updates on LSP missions and accomplishments. At right, standing near a chair, is Chuck Dovale, deputy program manager for LSP. Bridenstine presented a NASA Distinguished Service Medal to Dovale.
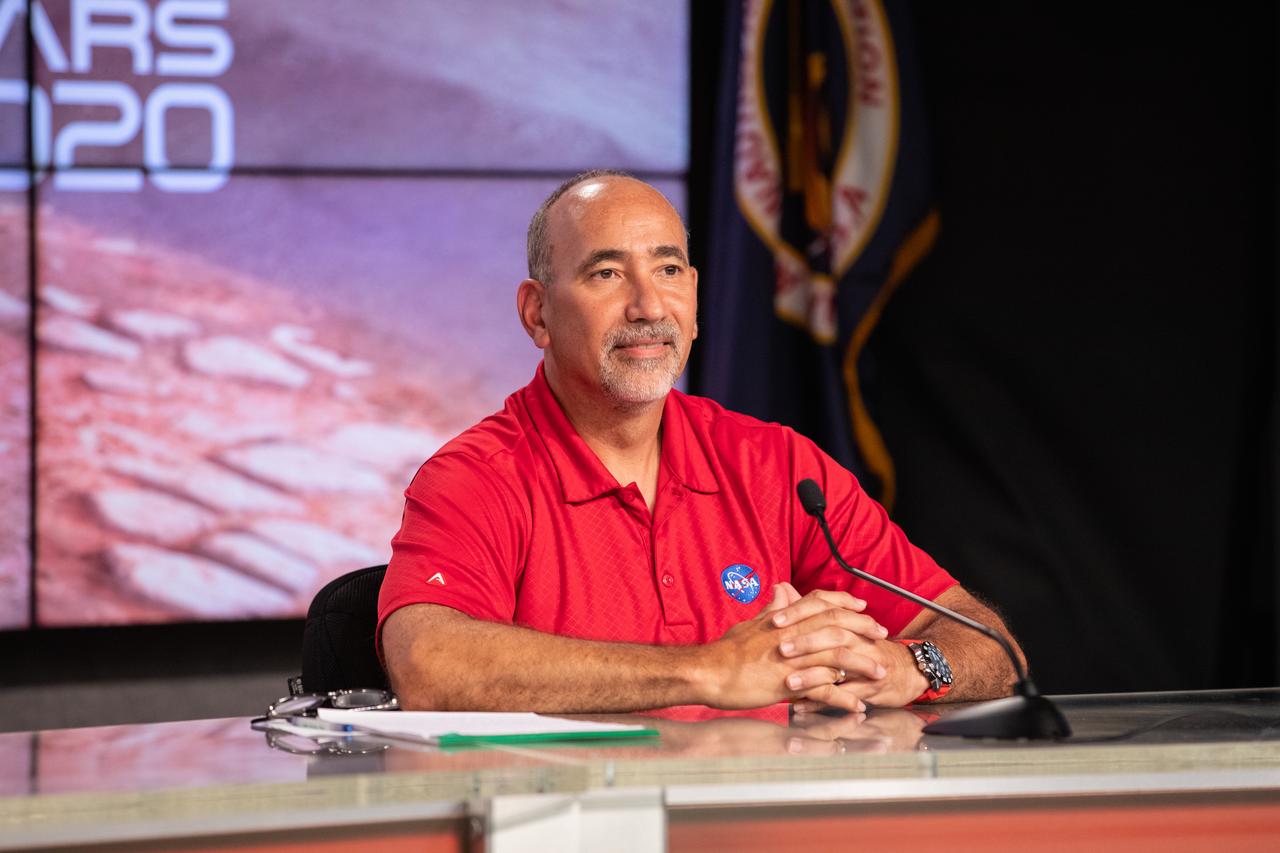

NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Chief of Flight Projects Office Albert Sierra participates in a “Mars 2020 Social Media Q&A: En Español” program on Wednesday, July 22, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The event featured representatives from LSP and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Thursday, July 30. The two-hour window opens at 7:50 a.m. EDT. LSP, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
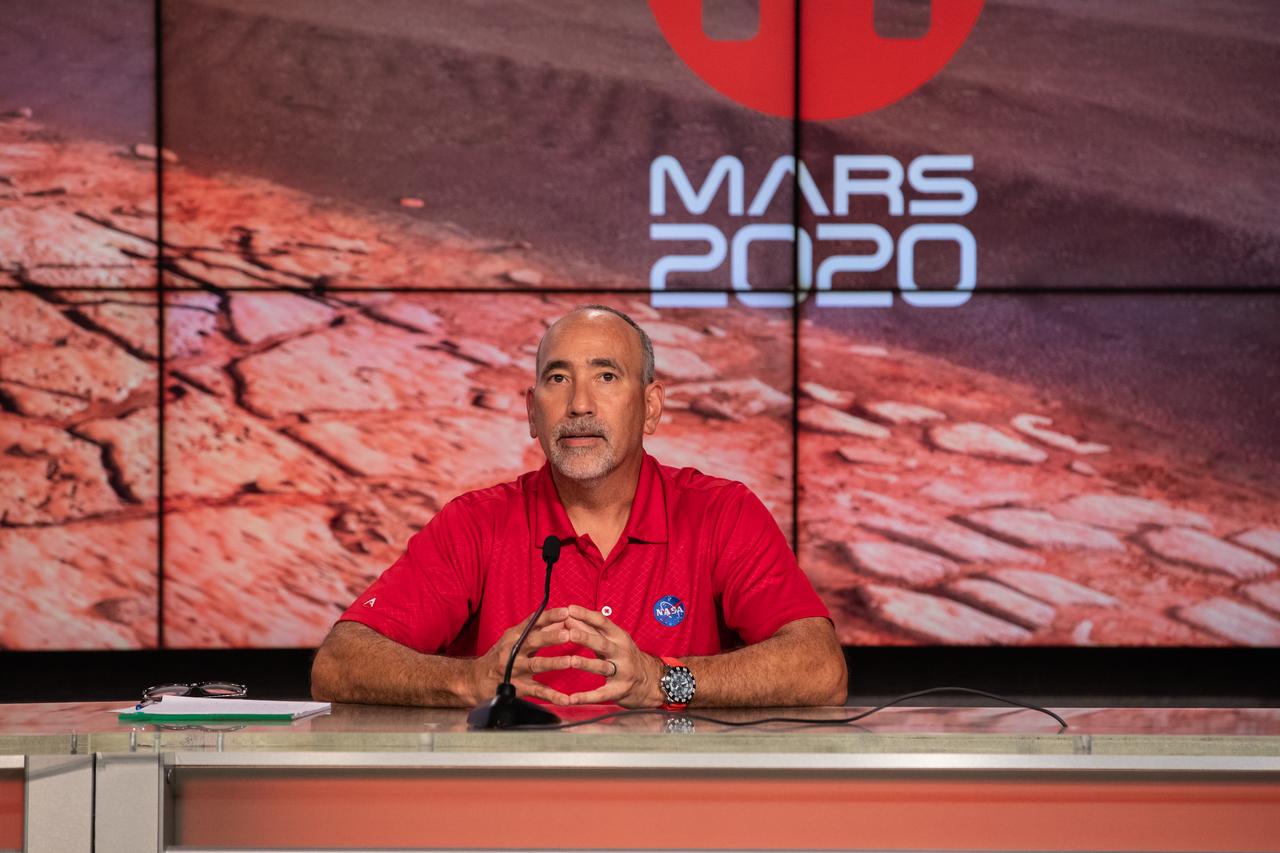

NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Chief of Flight Projects Office Albert Sierra participates in a “Mars 2020 Social Media Q&A: En Español” program on Wednesday, July 22, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The event featured representatives from LSP and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Thursday, July 30. The two-hour window opens at 7:50 a.m. EDT. LSP, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
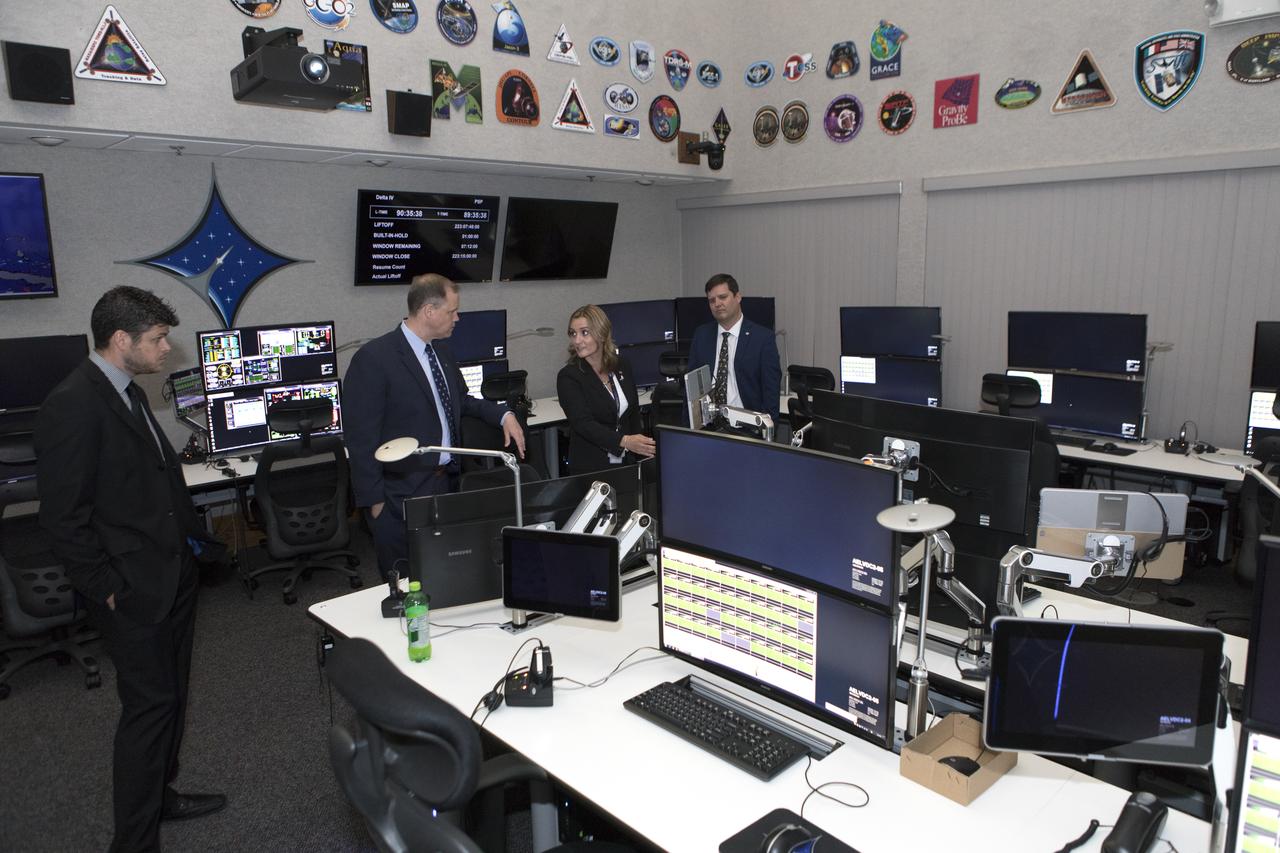

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, second from left, tours the Launch Services Program's Mission Director's Center in Hangar AE, on Aug. 7, 2018, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Bridenstine talked with workers and received updates on LSP missions and accomplishments.

NASA Public Affairs Specialist Kristi Irastorza, left, and NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Chief of Flight Projects Office Albert Sierra, participate in a “Mars 2020 Social Media Q&A: En Español” program on Wednesday, July 22, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The event featured representatives from LSP and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Thursday, July 30. The two-hour window opens at 7:50 a.m. EDT. LSP, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
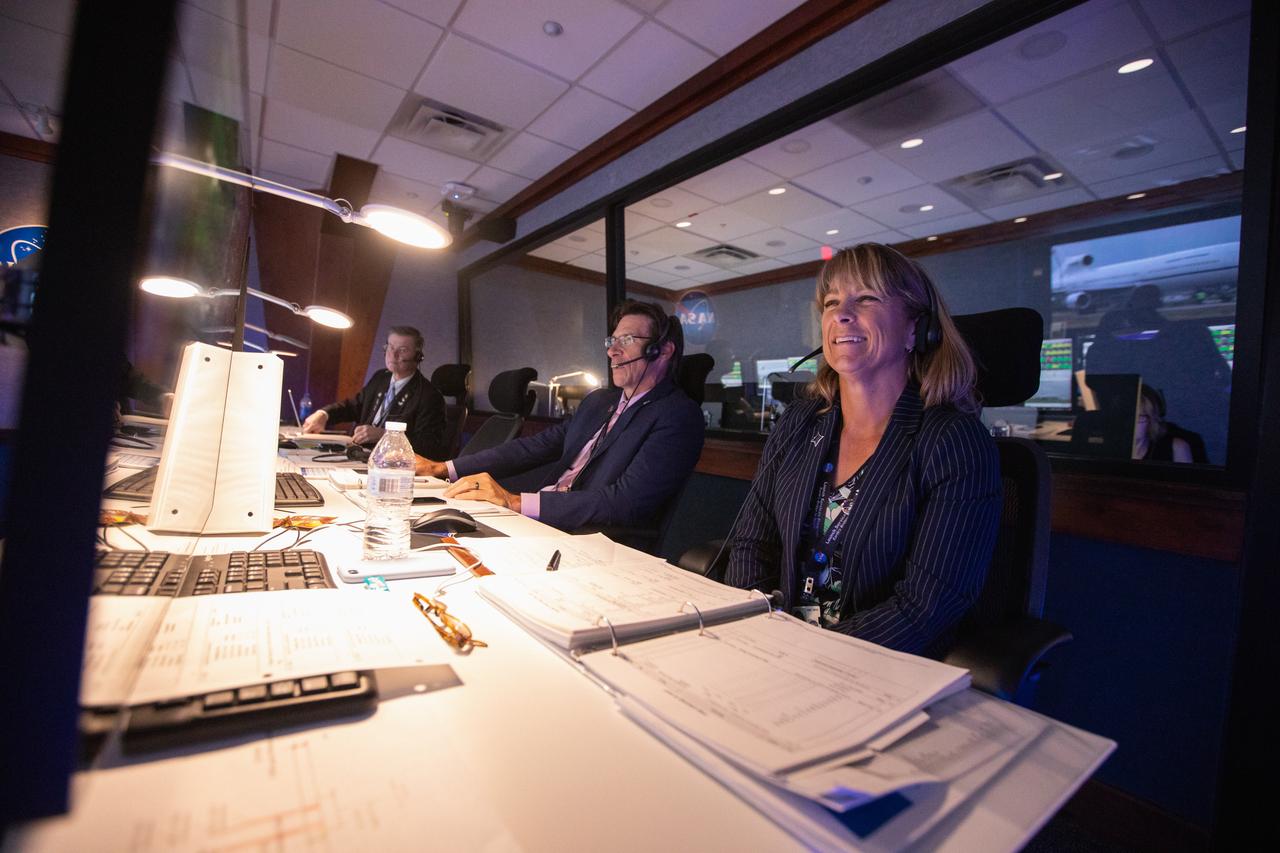

Inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), Amanda Mitskevich, right, program manager in NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), and Chuck Dovale, second from right, LSP deputy program manager, monitor the launch of the agency’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON). The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The ICON launch was managed by LSP.
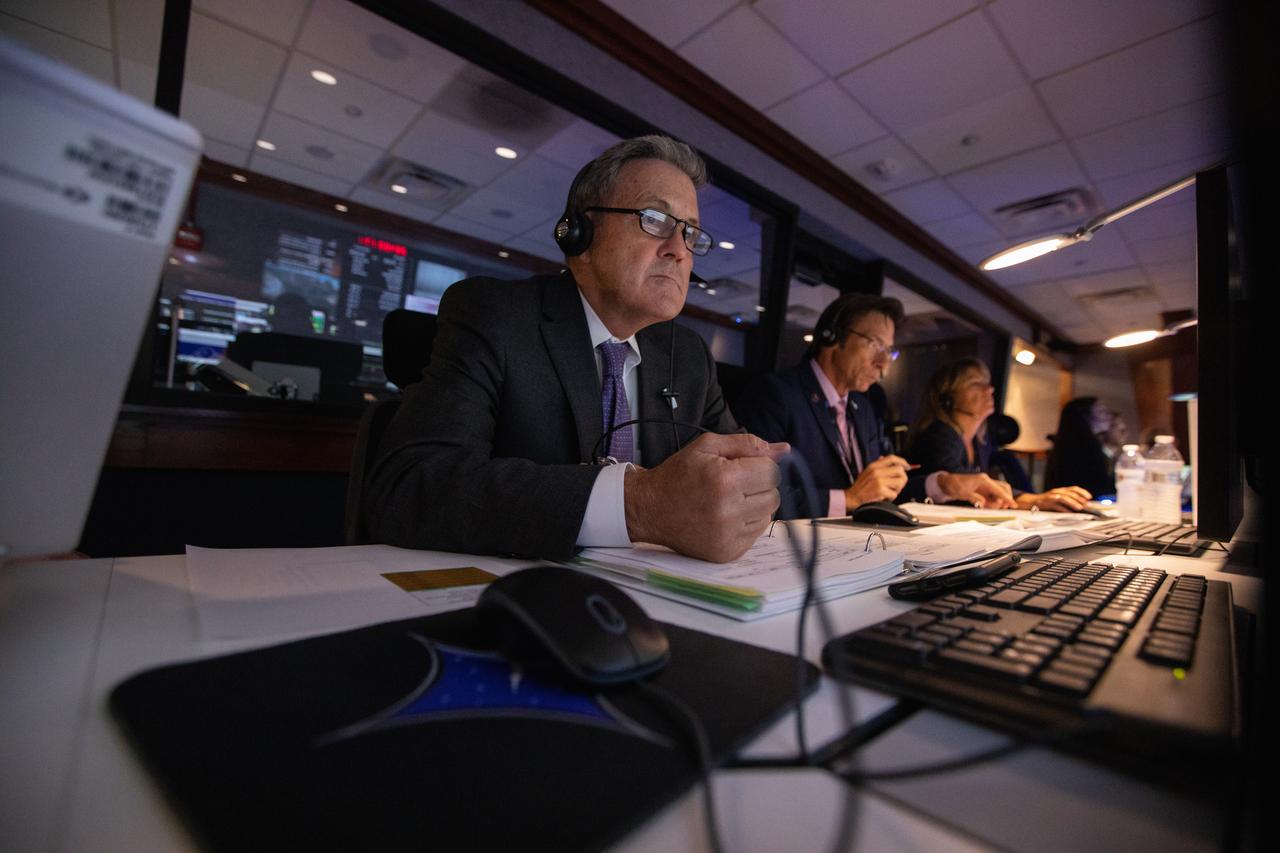

From left, Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Deputy Program Manager Chuck Dovale and LSP Program Manager Amanda Mitskevich monitor the launch of the agency’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The ICON launch was managed by LSP.
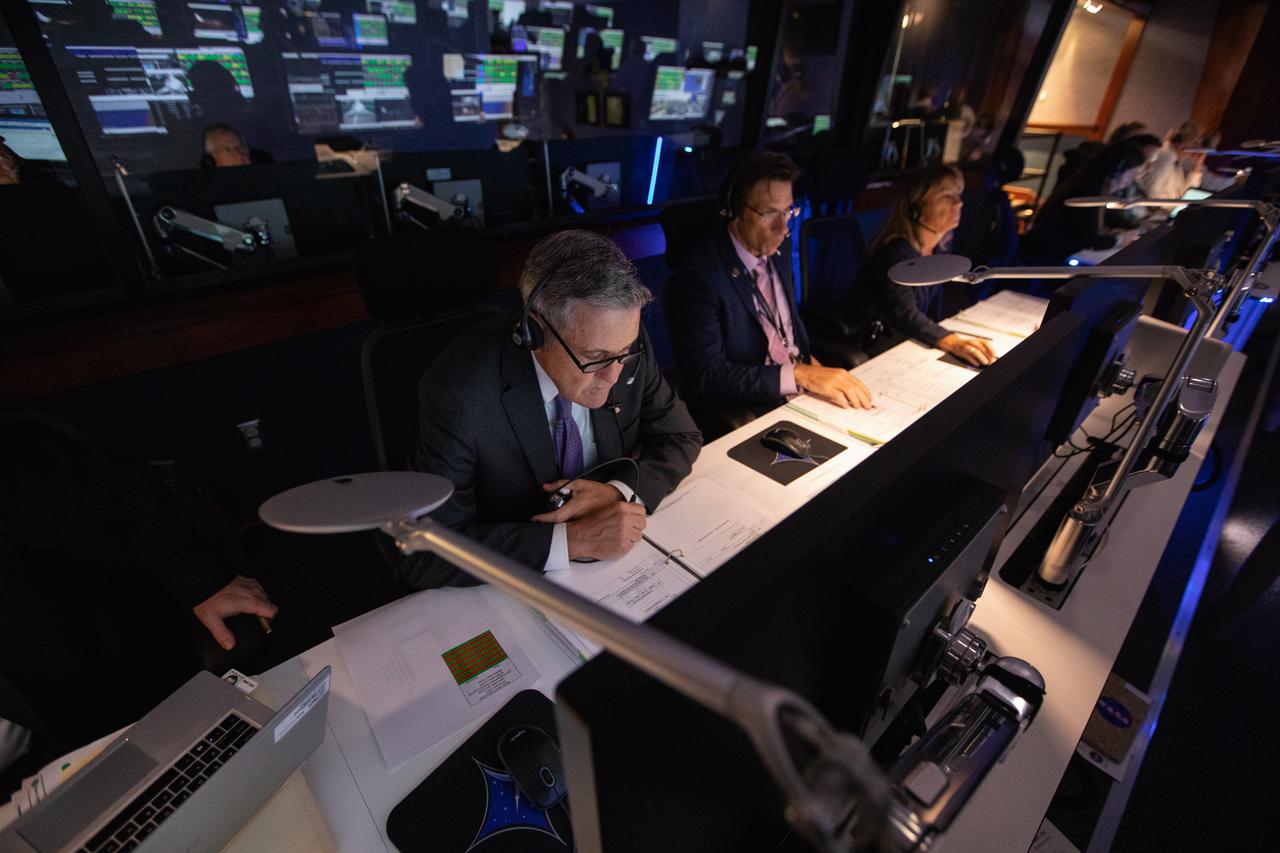

From left, Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Deputy Program Manager Chuck Dovale and LSP Program Manager Amanda Mitskevich monitor the launch of the agency’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The ICON launch was managed by LSP.
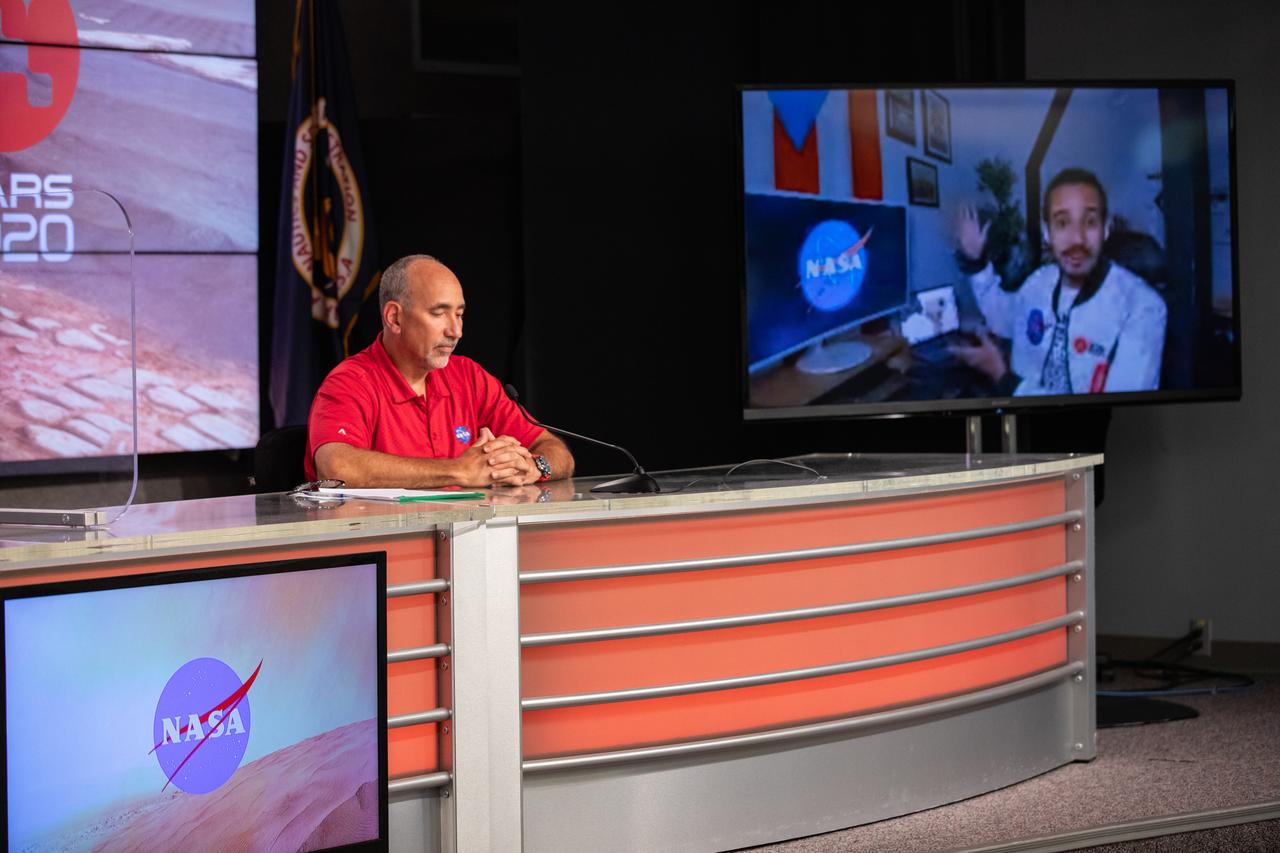

Elio Morillo, a Mars 2020 system testbed engineer from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, speaks remotely while Albert Sierra, NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) chief of Flight Projects Office, listens during a “Mars 2020 Social Media Q&A: En Español” program on Wednesday, July 22, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The event featured representatives from LSP and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Thursday, July 30. The two-hour window opens at 7:50 a.m. EDT. LSP, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.

NASA Public Affairs Specialist Kristi Irastorza, left, and NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Chief of Flight Projects Office Albert Sierra, participate in a “Mars 2020 Social Media Q&A: En Español” program on Wednesday, July 22, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The event featured representatives from LSP and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Thursday, July 30. The two-hour window opens at 7:50 a.m. EDT. LSP, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
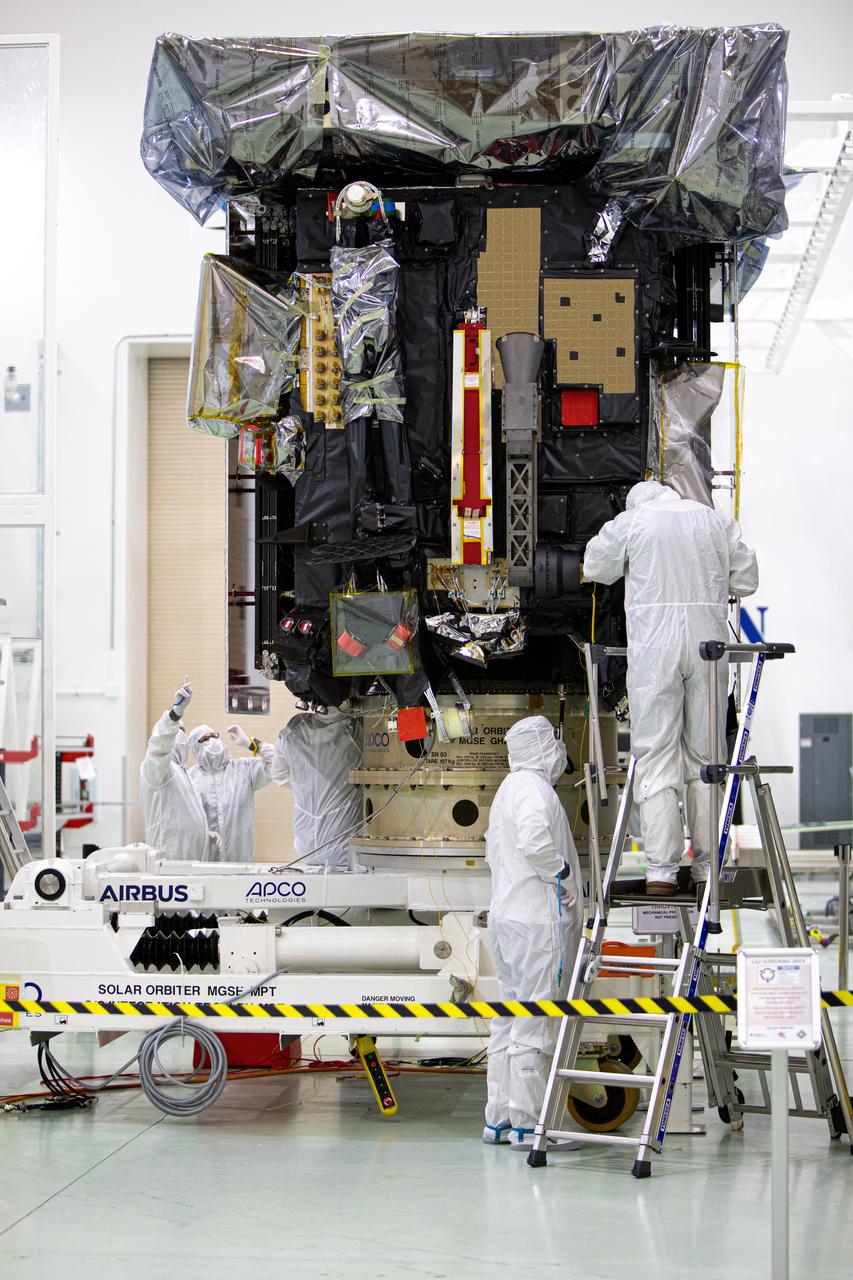

Members of the media were given the opportunity to view and photograph the Solar Orbiter spacecraft up close inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, on Dec. 16, 2019. Representatives from NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), the European Space Agency (ESA), United Launch Alliance (ULA), Airbus Defence and Space, and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center provided an overview of the mission, spacecraft and launch vehicle. Solar Orbiter is a space mission of international collaboration between ESA and NASA, and the spacecraft has been developed by Airbus. The mission will study the Sun and how it can affect the space environment throughout the solar system, and it also will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. Solar Orbiter is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 aboard a ULA Atlas V rocket at 11:27 p.m. EST on Feb. 5, 2020. LSP will manage the launch.
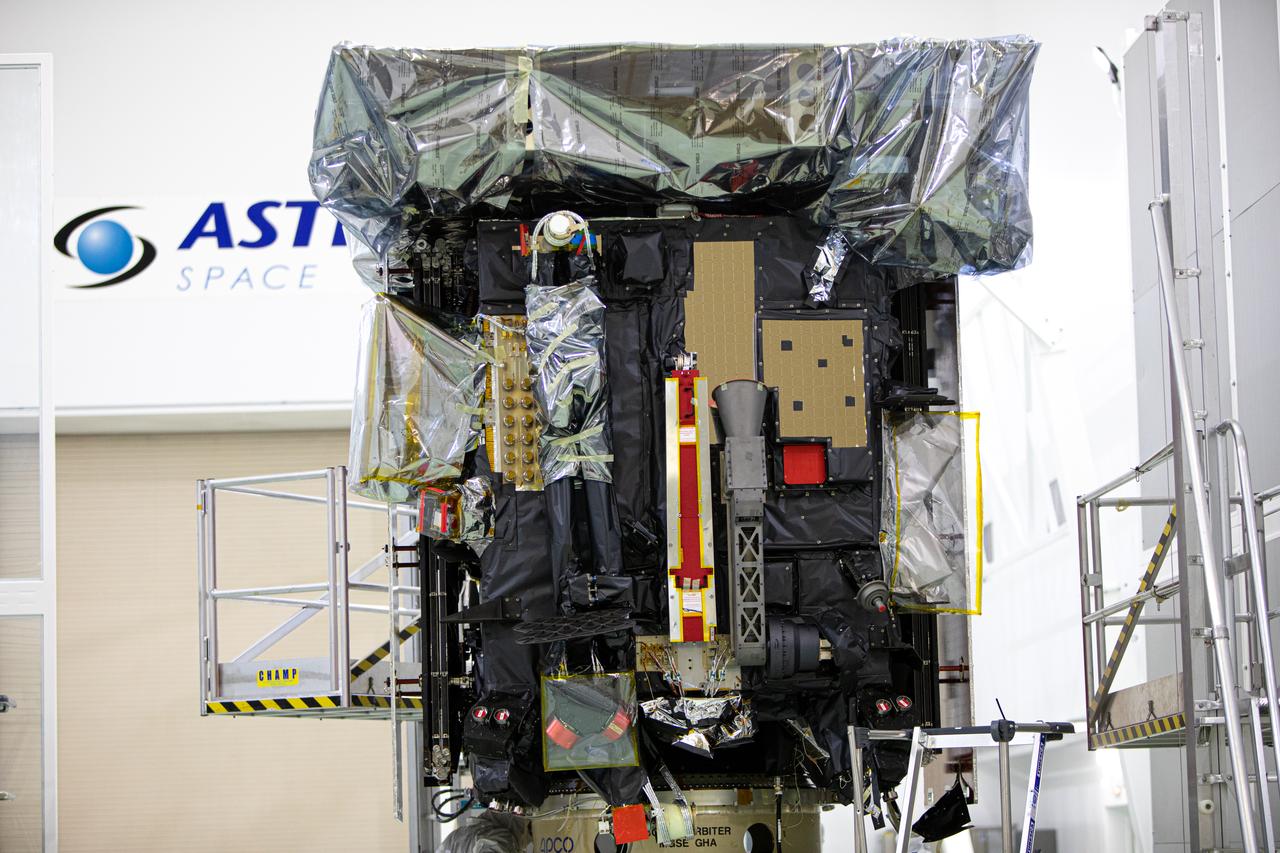

Members of the media were given the opportunity to view and photograph the Solar Orbiter spacecraft up close inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, on Dec. 16, 2019. Representatives from NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), the European Space Agency (ESA), United Launch Alliance (ULA), Airbus Defence and Space, and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center provided an overview of the mission, spacecraft and launch vehicle. Solar Orbiter is a space mission of international collaboration between ESA and NASA, and the spacecraft has been developed by Airbus. The mission will study the Sun and how it can affect the space environment throughout the solar system, and it also will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. Solar Orbiter is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 aboard a ULA Atlas V rocket at 11:27 p.m. EST on Feb. 5, 2020. LSP will manage the launch.
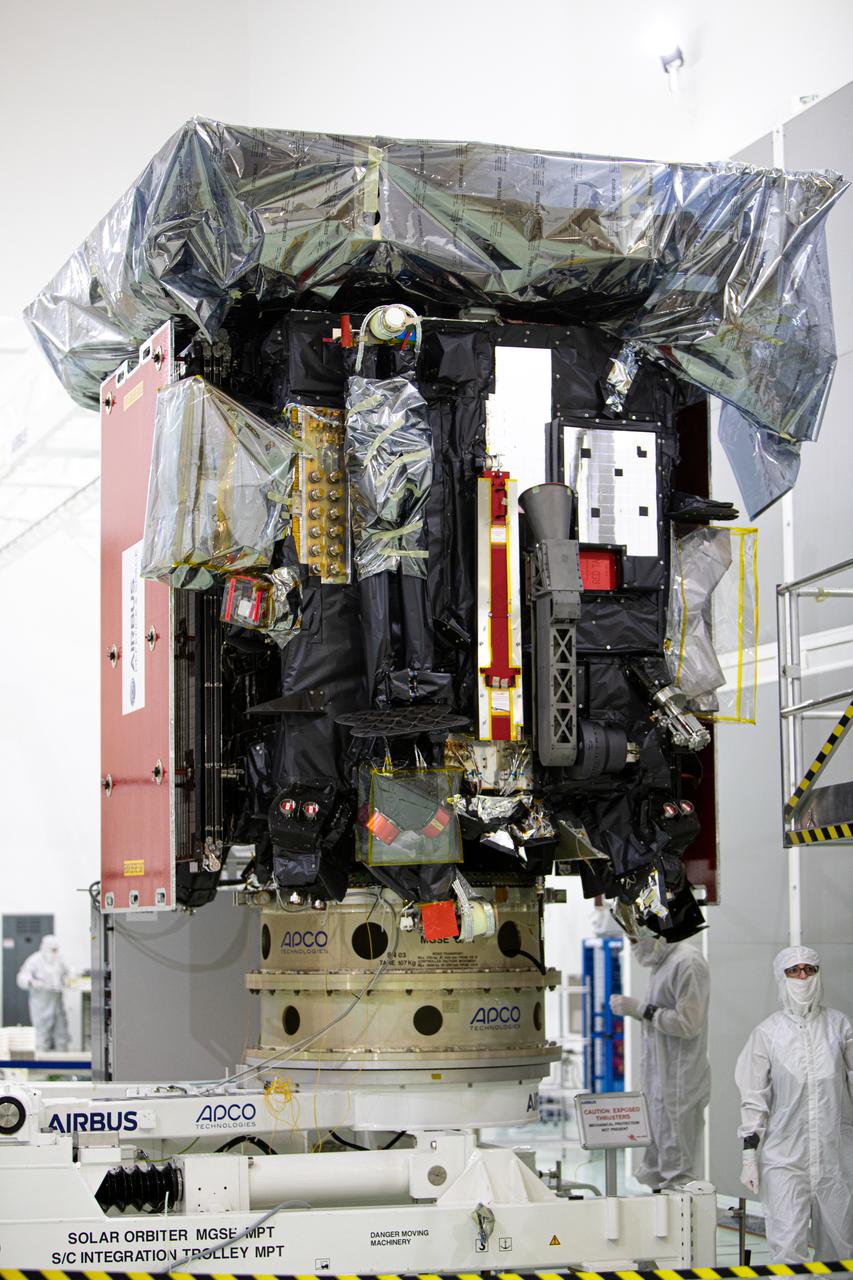

Members of the media were given the opportunity to view and photograph the Solar Orbiter spacecraft up close inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, on Dec. 16, 2019. Representatives from NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), the European Space Agency (ESA), United Launch Alliance (ULA), Airbus Defence and Space, and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center provided an overview of the mission, spacecraft and launch vehicle. Solar Orbiter is a space mission of international collaboration between ESA and NASA, and the spacecraft has been developed by Airbus. The mission will study the Sun and how it can affect the space environment throughout the solar system, and it also will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. Solar Orbiter is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 aboard a ULA Atlas V rocket at 11:27 p.m. EST on Feb. 5, 2020. LSP will manage the launch.

Members of the media were given the opportunity to view and photograph the Solar Orbiter spacecraft up close inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, on Dec. 16, 2019. Representatives from NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), the European Space Agency (ESA), United Launch Alliance (ULA), Airbus Defence and Space, and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center provided an overview of the mission, spacecraft and launch vehicle. Solar Orbiter is a space mission of international collaboration between ESA and NASA, and the spacecraft has been developed by Airbus. The mission will study the Sun and how it can affect the space environment throughout the solar system, and it also will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. Solar Orbiter is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 aboard a ULA Atlas V rocket at 11:27 p.m. EST on Feb. 5, 2020. LSP will manage the launch.
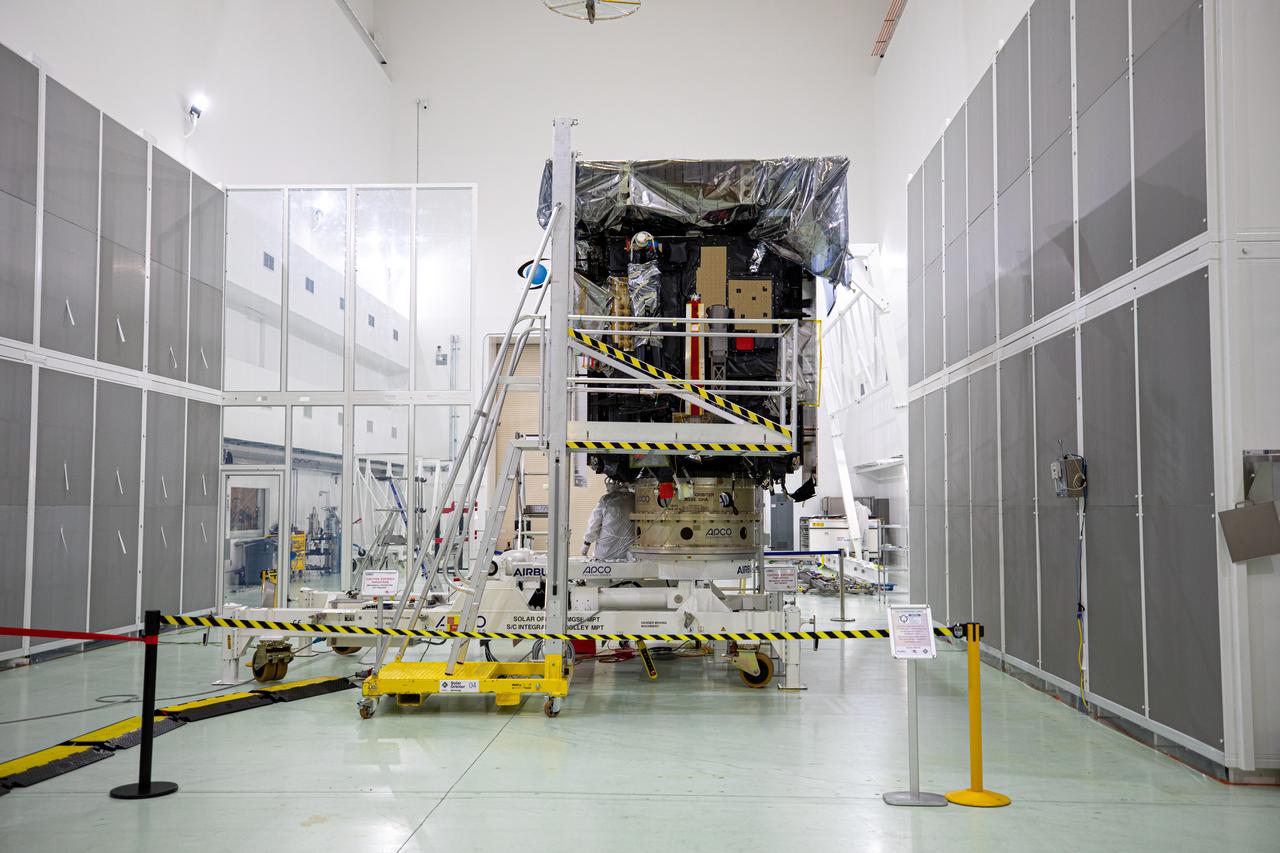

Members of the media were given the opportunity to view and photograph the Solar Orbiter spacecraft up close inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, on Dec. 16, 2019. Representatives from NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), the European Space Agency (ESA), United Launch Alliance (ULA), Airbus Defence and Space, and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center provided an overview of the mission, spacecraft and launch vehicle. Solar Orbiter is a space mission of international collaboration between ESA and NASA, and the spacecraft has been developed by Airbus. The mission will study the Sun and how it can affect the space environment throughout the solar system, and it also will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. Solar Orbiter is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 aboard a ULA Atlas V rocket at 11:27 p.m. EST on Feb. 5, 2020. LSP will manage the launch.

Members of the media were given the opportunity to view and photograph the Solar Orbiter spacecraft up close inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, on Dec. 16, 2019. Representatives from NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), the European Space Agency (ESA), United Launch Alliance (ULA), Airbus Defence and Space, and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center provided an overview of the mission, spacecraft and launch vehicle. Solar Orbiter is a space mission of international collaboration between ESA and NASA, and the spacecraft has been developed by Airbus. The mission will study the Sun and how it can affect the space environment throughout the solar system, and it also will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. Solar Orbiter is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 aboard a ULA Atlas V rocket at 11:27 p.m. EST on Feb. 5, 2020. LSP will manage the launch.
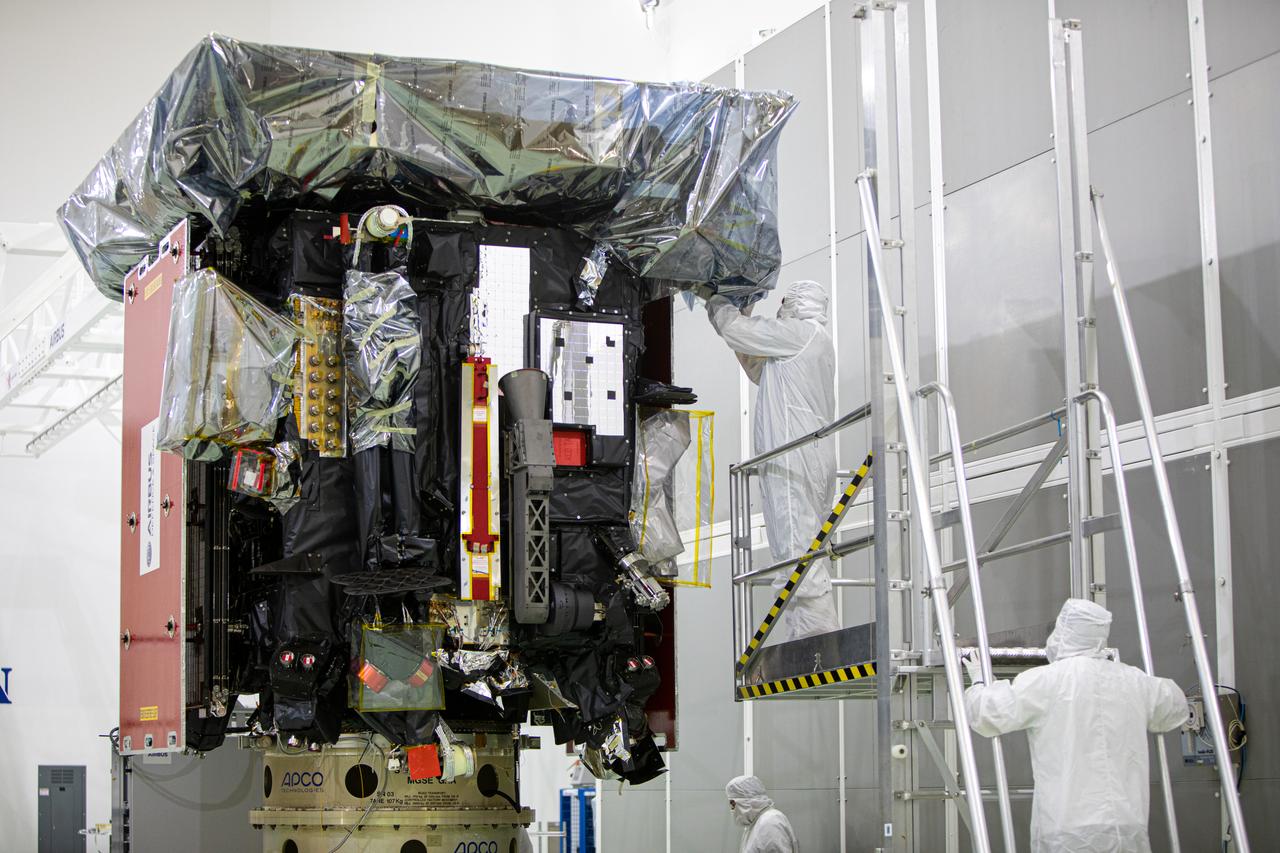

Members of the media were given the opportunity to view and photograph the Solar Orbiter spacecraft up close inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, on Dec. 16, 2019. Representatives from NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), the European Space Agency (ESA), United Launch Alliance (ULA), Airbus Defence and Space, and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center provided an overview of the mission, spacecraft and launch vehicle. Solar Orbiter is a space mission of international collaboration between ESA and NASA, and the spacecraft has been developed by Airbus. The mission will study the Sun and how it can affect the space environment throughout the solar system, and it also will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. Solar Orbiter is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 aboard a ULA Atlas V rocket at 11:27 p.m. EST on Feb. 5, 2020. LSP will manage the launch.
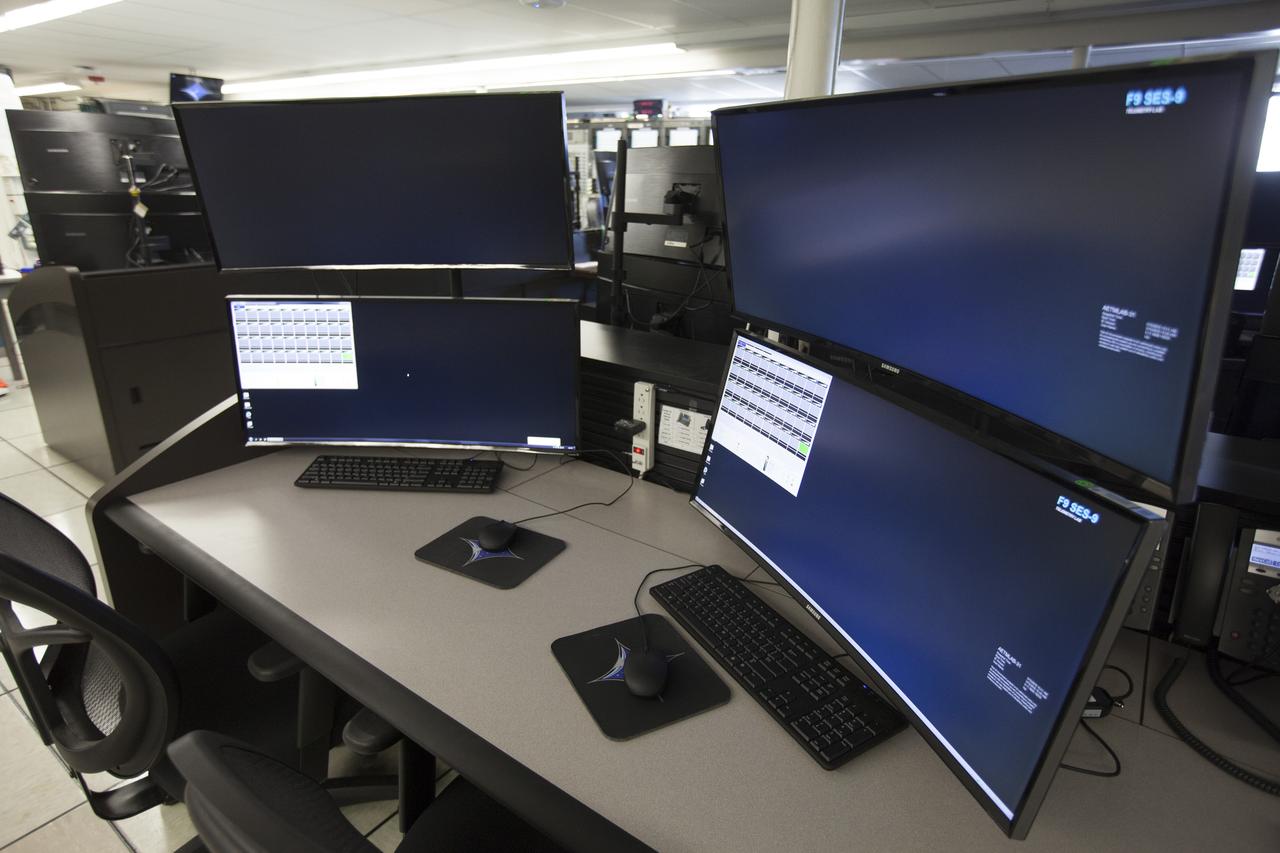

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Telemetry Room - showing the engineering consule upgrades.
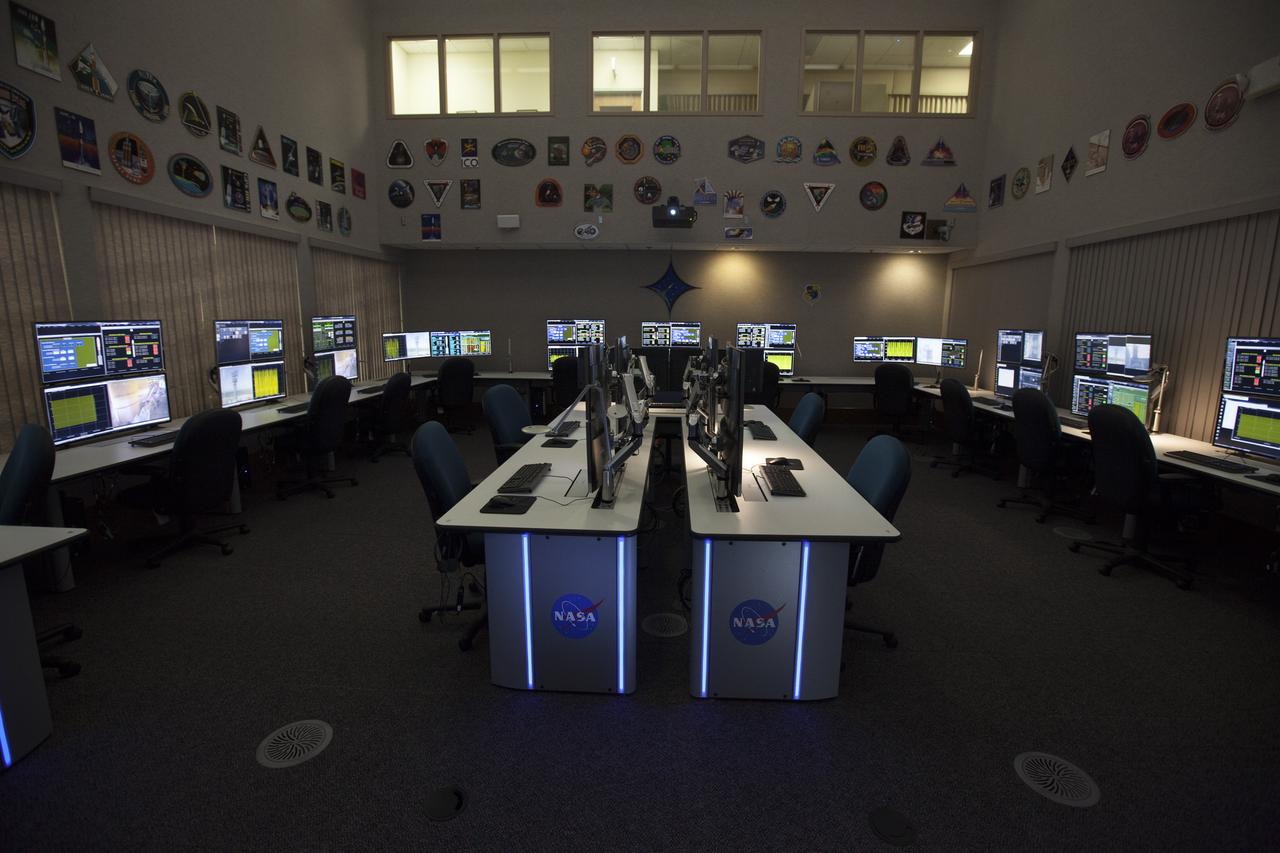

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #2 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #1 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.
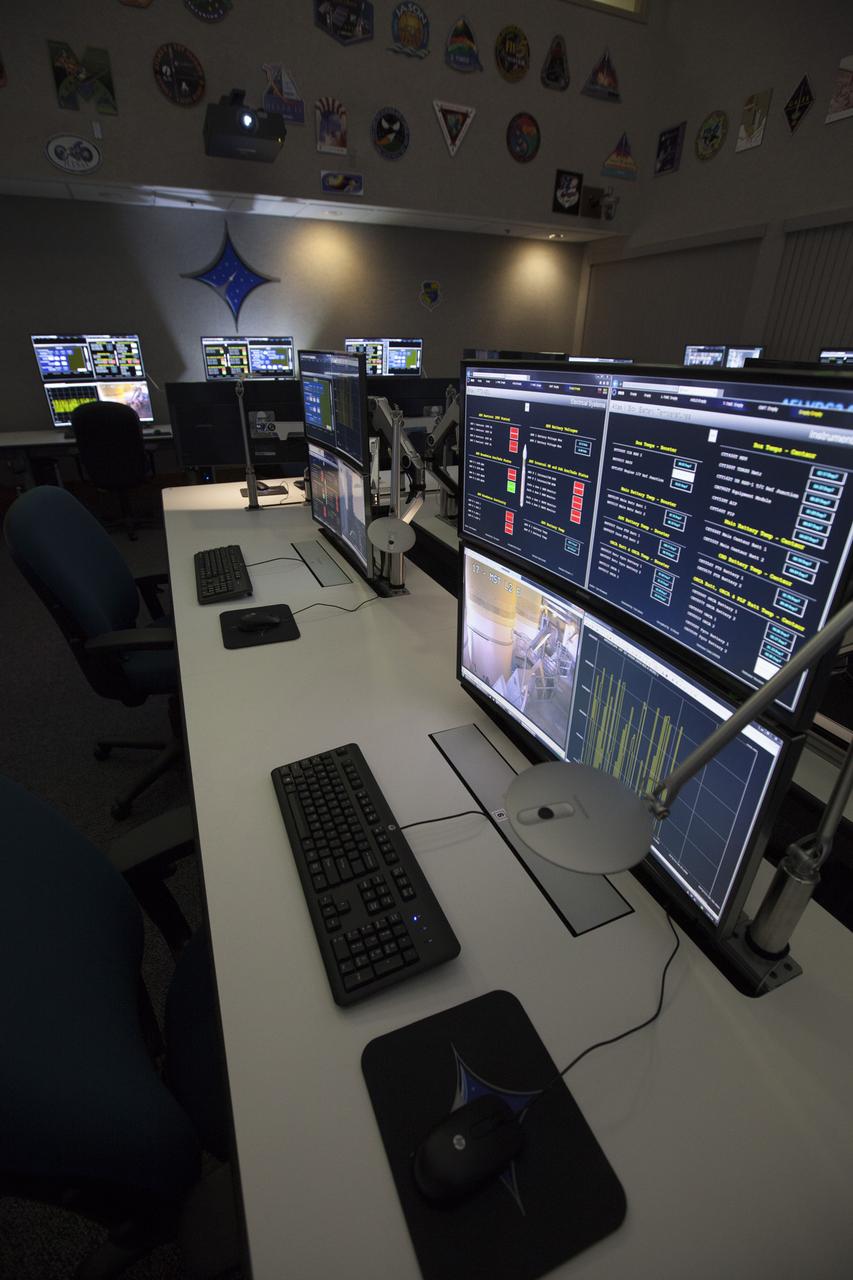

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #2 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #1 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #2 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #2 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #1 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #2 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #1 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #2 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #1 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #2 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #2 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #1 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #2 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #2 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Telemetry Room - showing the engineering consule upgrades.

Photos of the Launch Vehicle Data Center (LVDC) in Hangar AE - Room #2 of LVDC - showing the engineering consule upgrades.
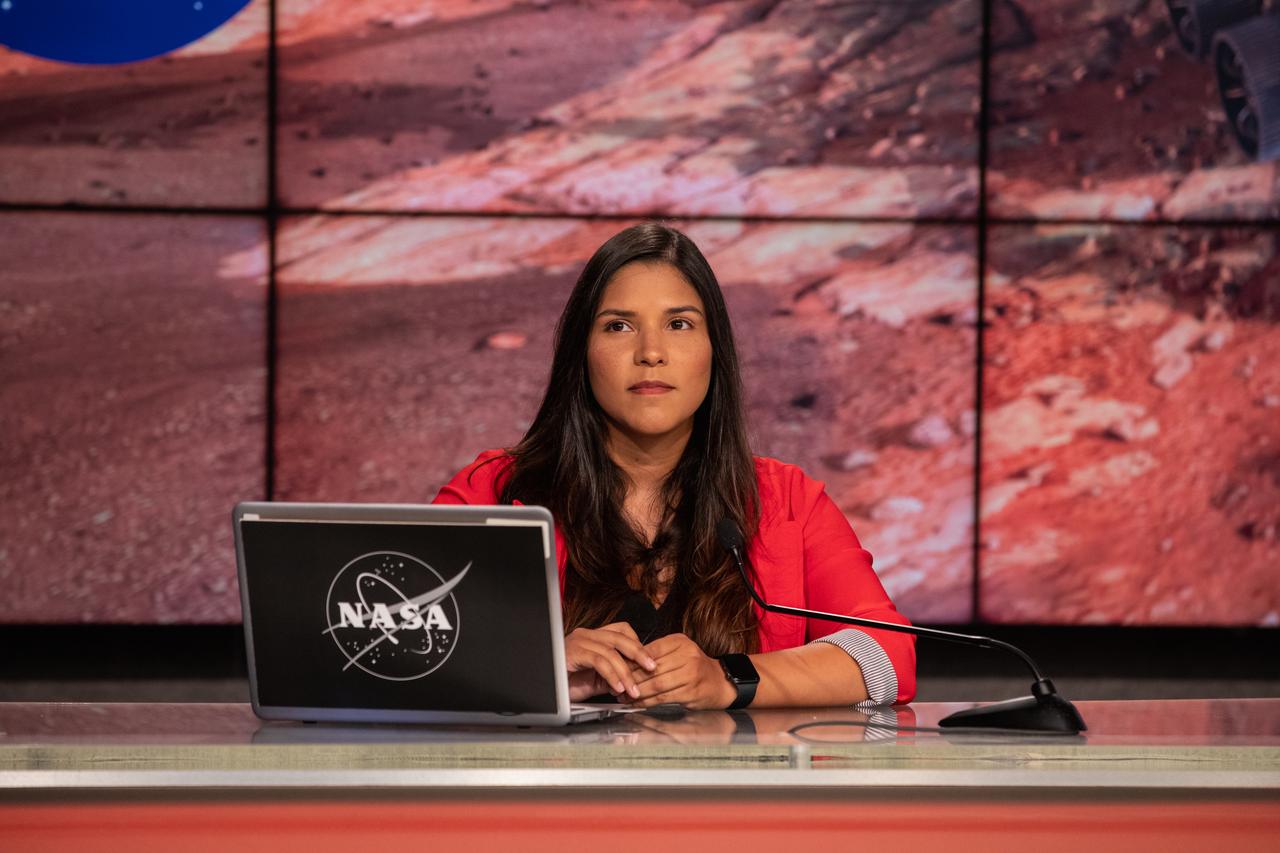

NASA Public Affairs Specialist Kristi Irastorza hosts a “Mars 2020 Social Media Q&A: En Español” program on Wednesday, July 22, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The event featured representatives from NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Thursday, July 30. The two-hour window opens at 7:50 a.m. EDT. LSP, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
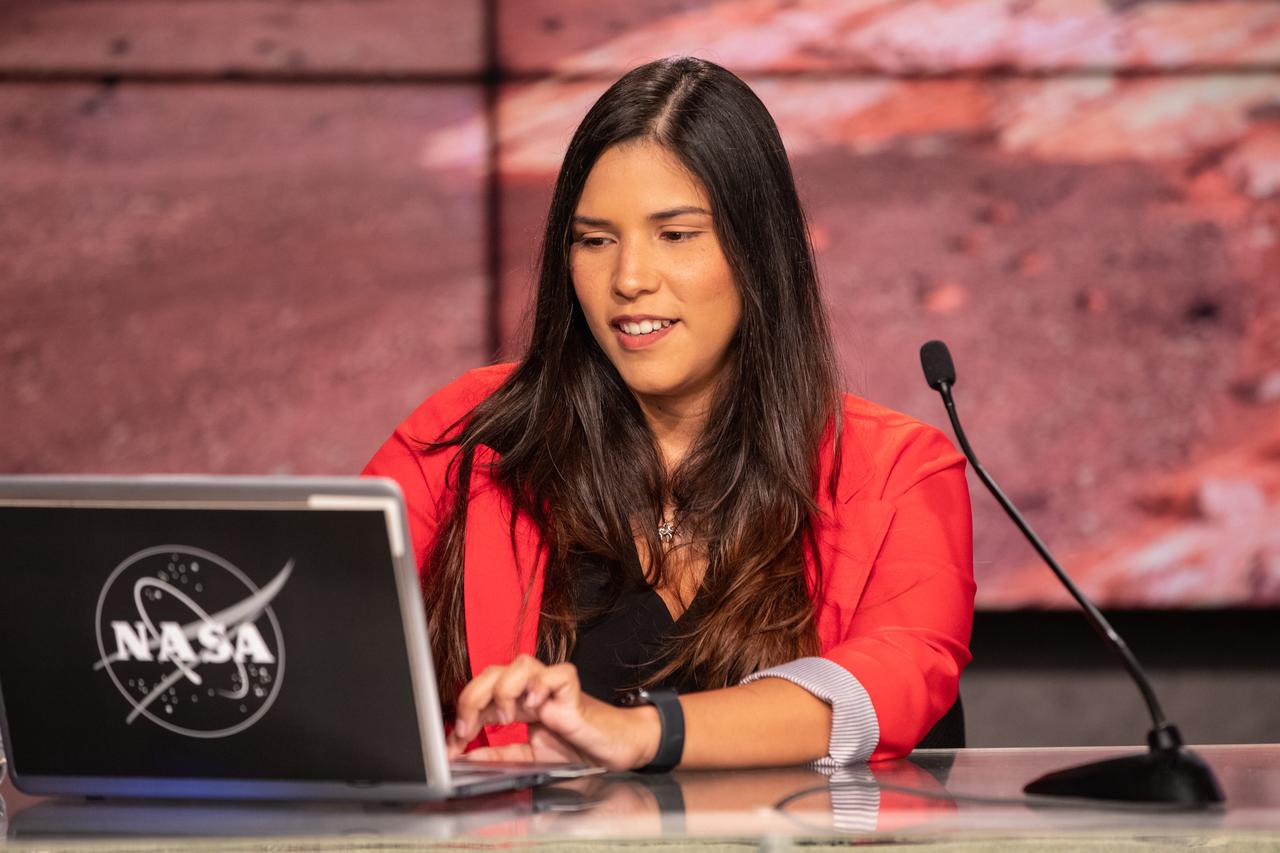

NASA Public Affairs Specialist Kristi Irastorza hosts a “Mars 2020 Social Media Q&A: En Español” program on Wednesday, July 22, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The event featured representatives from NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Thursday, July 30. The two-hour window opens at 7:50 a.m. EDT. LSP, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
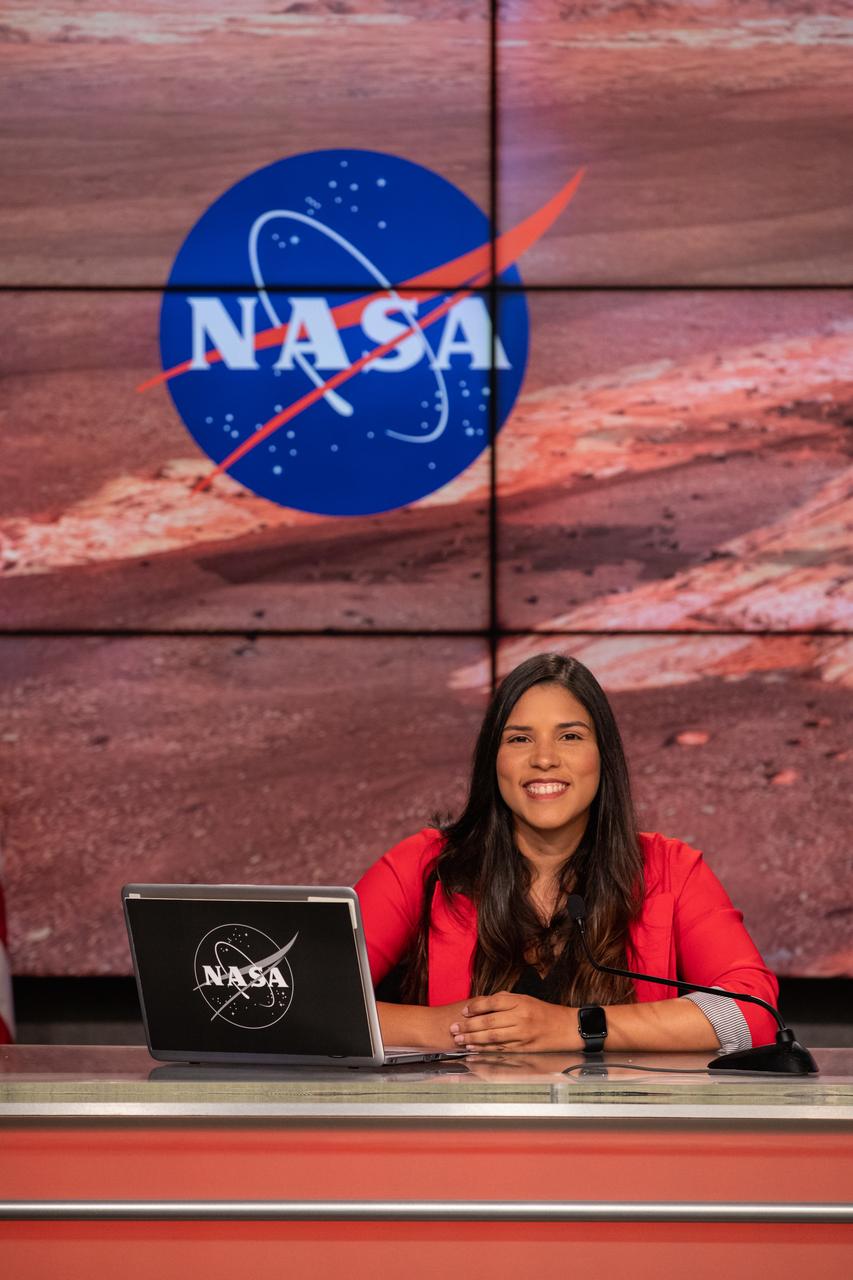

NASA Public Affairs Specialist Kristi Irastorza hosts a “Mars 2020 Social Media Q&A: En Español” program on Wednesday, July 22, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The event featured representatives from NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to lift off aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Thursday, July 30. The two-hour window opens at 7:50 a.m. EDT. LSP, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
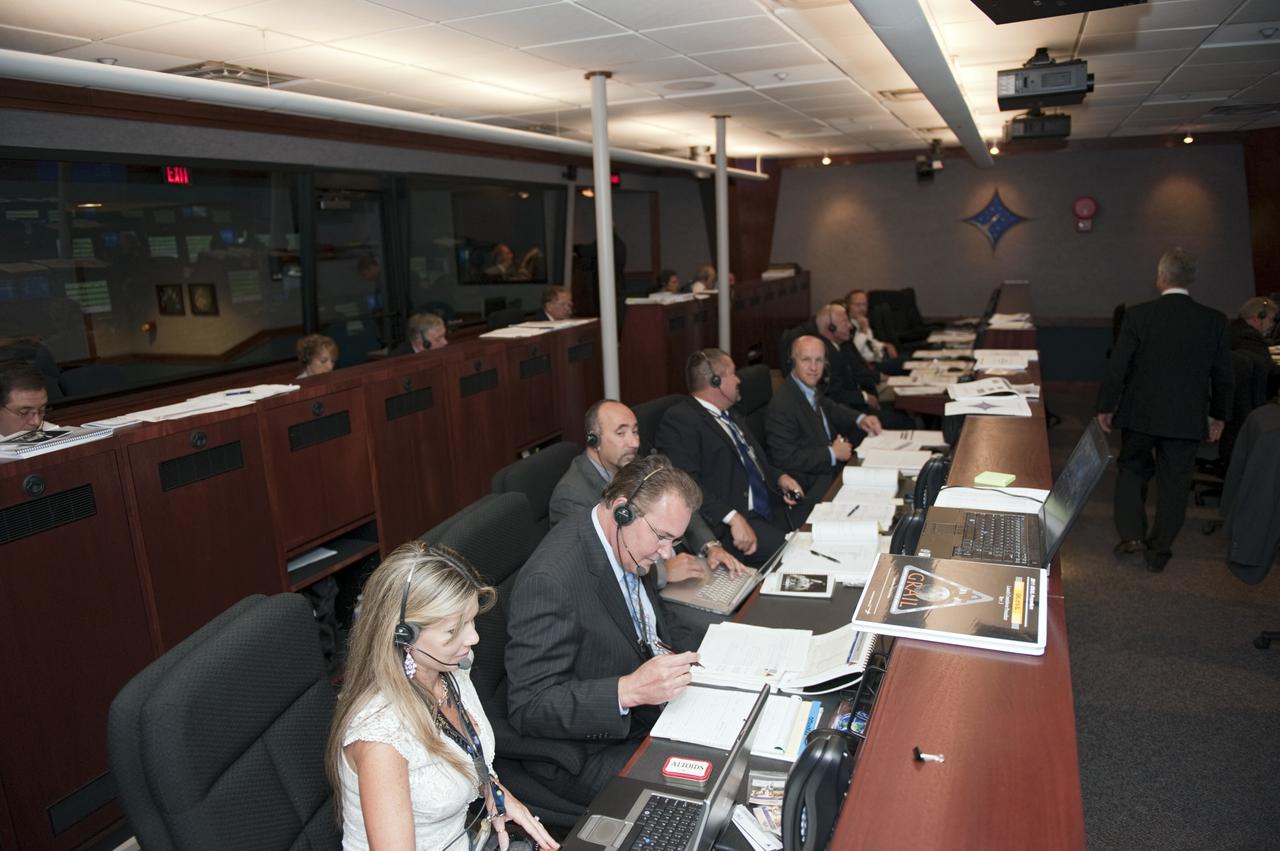

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, members of NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) launch team monitor GRAIL's launch countdown from the Mission Directors Center in Hangar AE. From left are Dana Grieco, launch operations manager, Analex, NASA's Launch Services Program (LSP); Bruce Reid, GRAIL mission manager, LSP; Al Sierra, manager of the Flight Project Office, LSP; Omar Baez, GRAIL assistant launch director, LSP; and Tim Dunn, GRAIL launch director, LSP; David Lehman, spacecraft mission director and GRAIL project manager, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL); and John Henk, GRAIL program manager, Lockheed Martin Space Systems. Launch is scheduled for 8:37:06 a.m. EDT Sept. 8 from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem around the moon to precisely measure and map variations in the moon's gravitational field. The mission will provide the most accurate global gravity field to date for any planet, including Earth. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
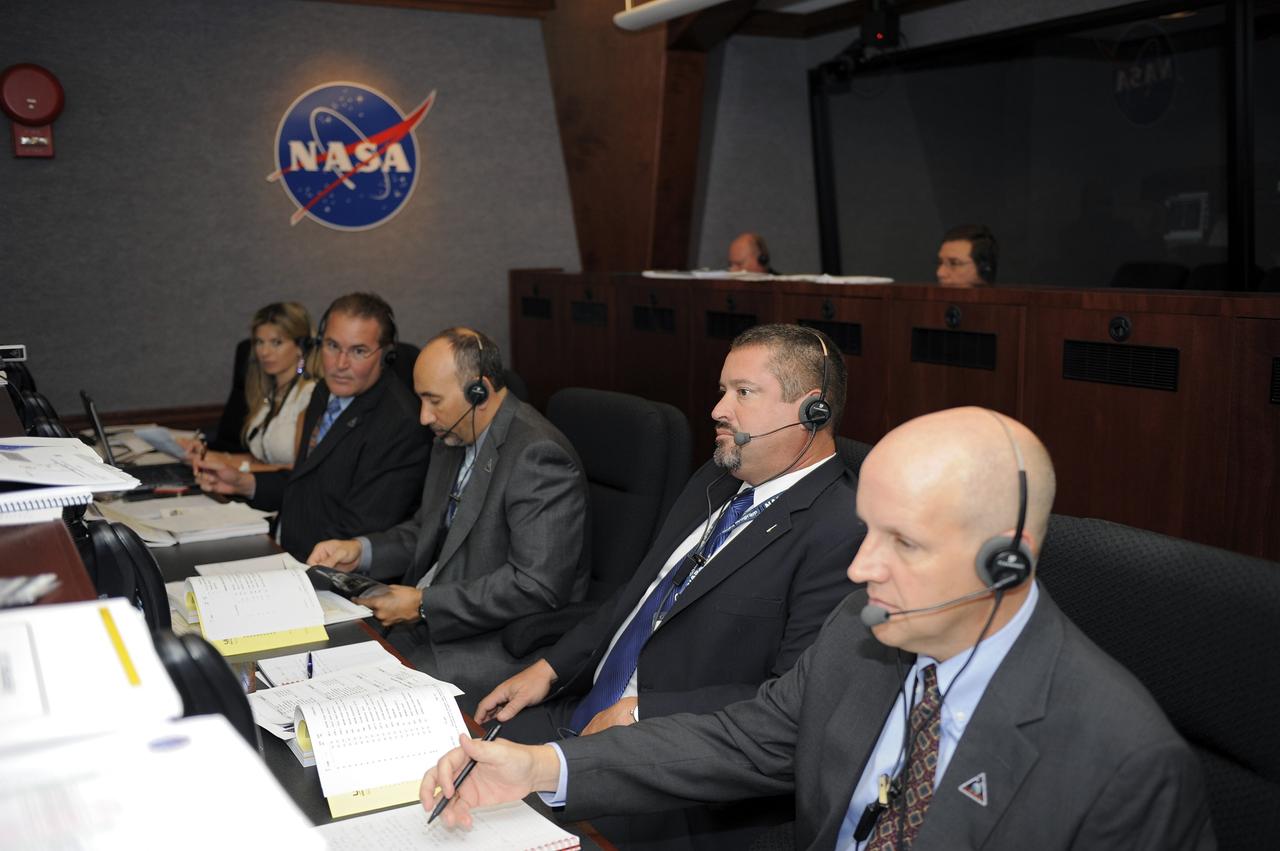

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, members of NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) launch team monitor GRAIL's launch countdown from the Mission Directors Center in Hangar AE. From left are Dana Grieco, launch operations manager, Analex, NASA's Launch Services Program (LSP); Bruce Reid, GRAIL mission manager, LSP; Al Sierra, manager of the Flight Project Office, LSP; Omar Baez, GRAIL assistant launch director, LSP; and Tim Dunn, GRAIL launch director, LSP. Launch is scheduled for 8:37:06 a.m. EDT Sept. 8 from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem around the moon to precisely measure and map variations in the moon's gravitational field. The mission will provide the most accurate global gravity field to date for any planet, including Earth. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
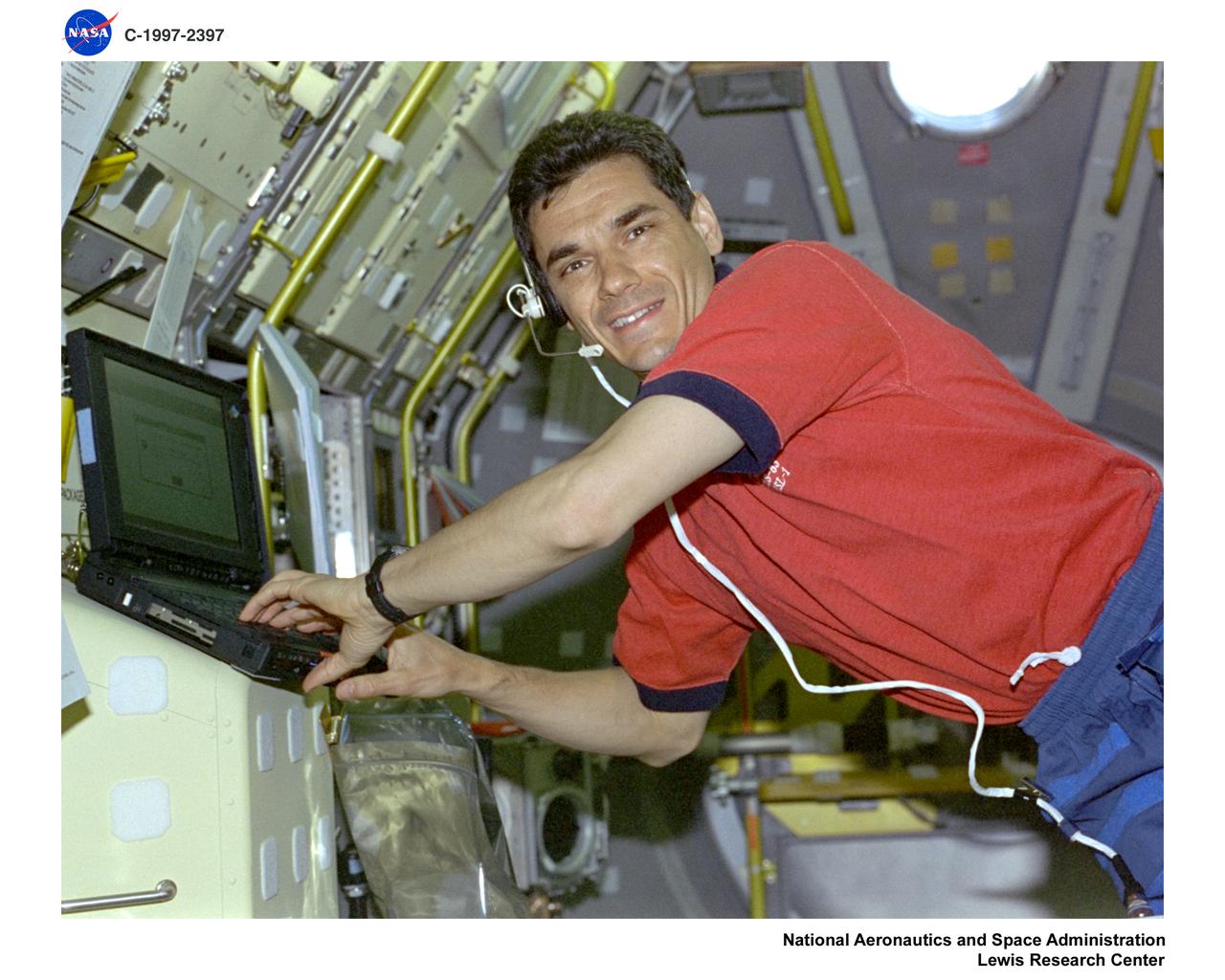

STS-83 SOFBALL AND LSP STRUCTURES OF FLAMEBALLS AT LOW LEWIS NUMBER AND LAMINATOR SOOT PROCESSING
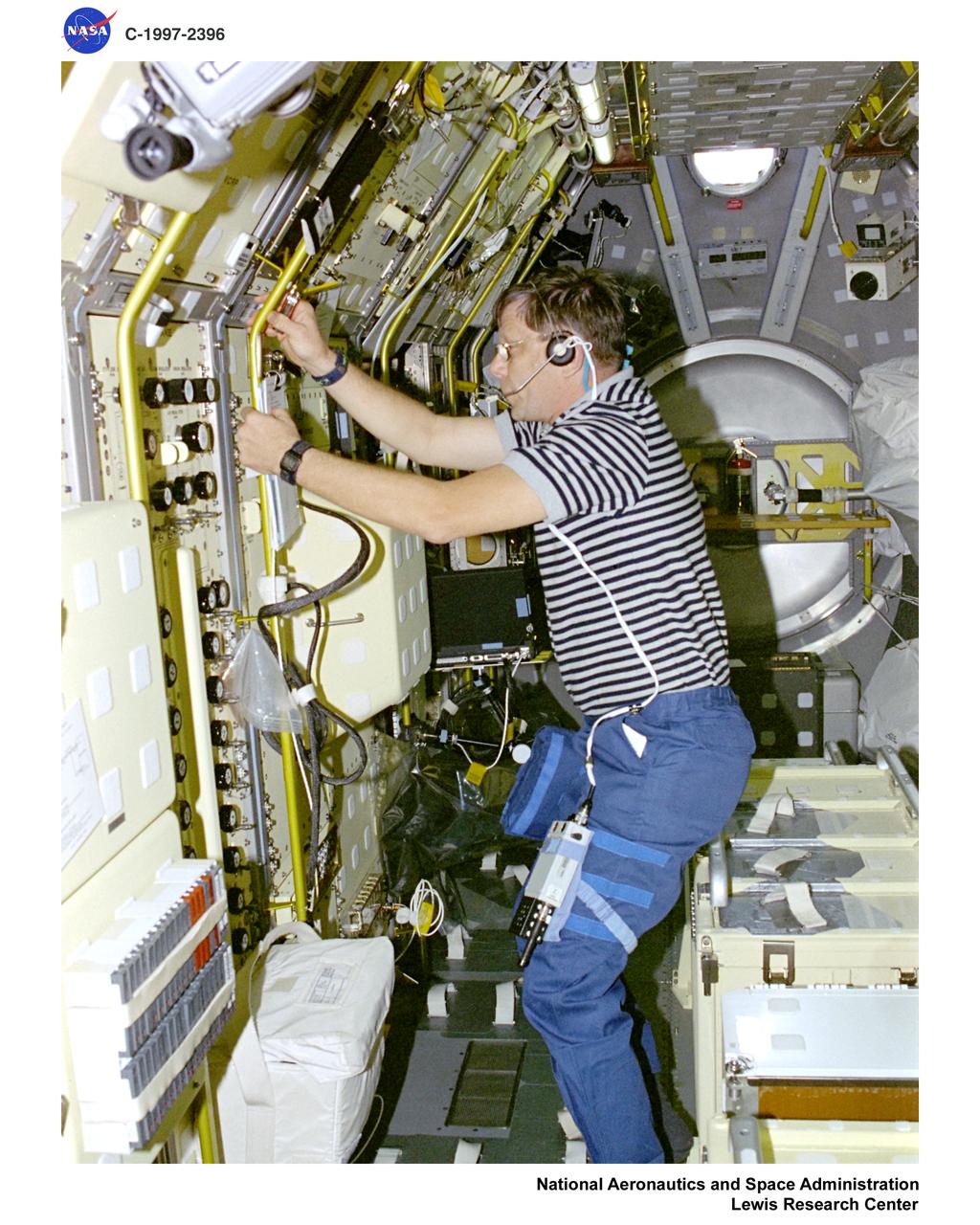

STS-83 SOFBALL AND LSP STRUCTURES OF FLAMEBALLS AT LOW LEWIS NUMBER AND LAMINATOR SOOT PROCESSING
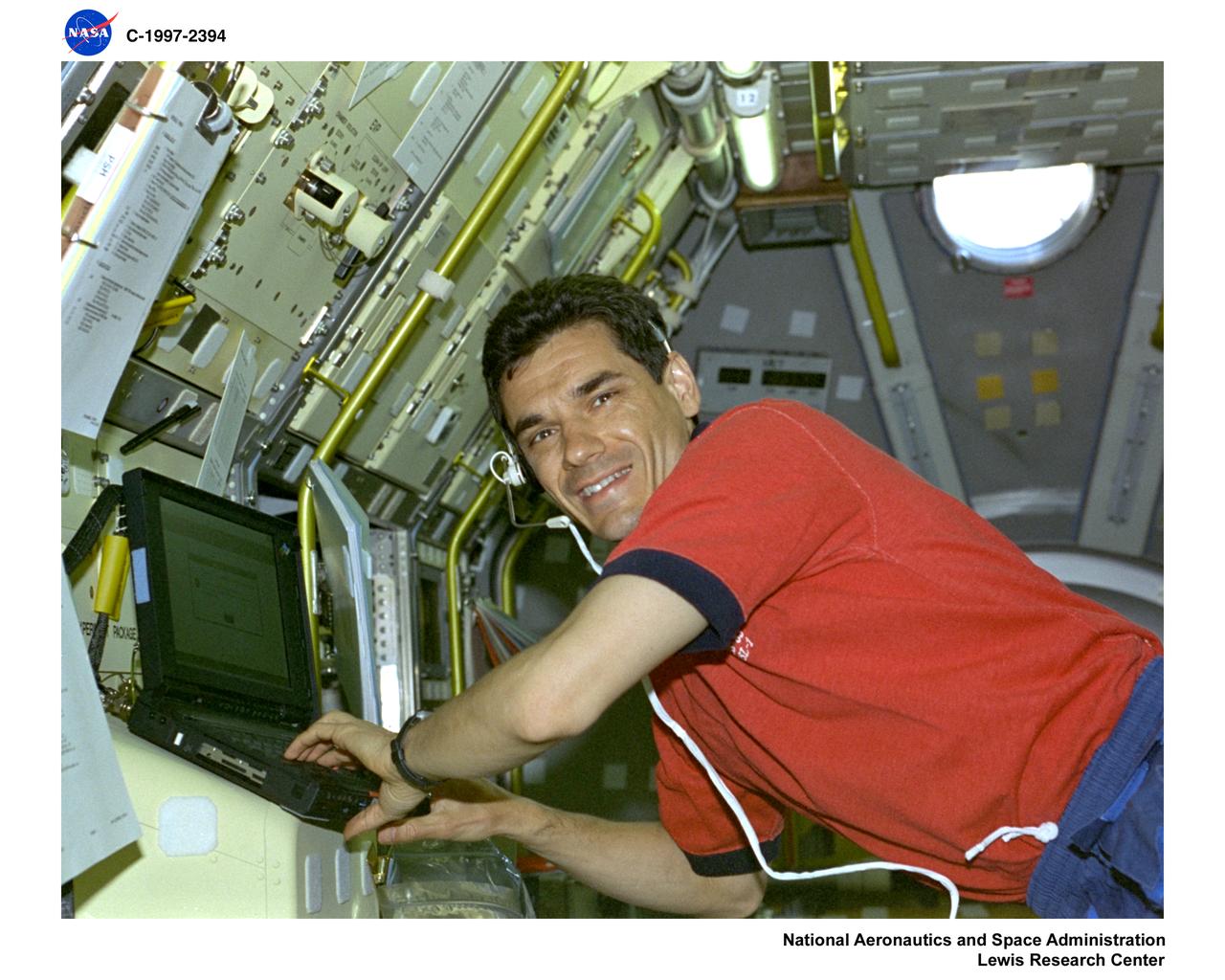

STS-83 SOFBALL AND LSP STRUCTURES OF FLAMEBALLS AT LOW LEWIS NUMBER AND LAMINATOR SOOT PROCESSING
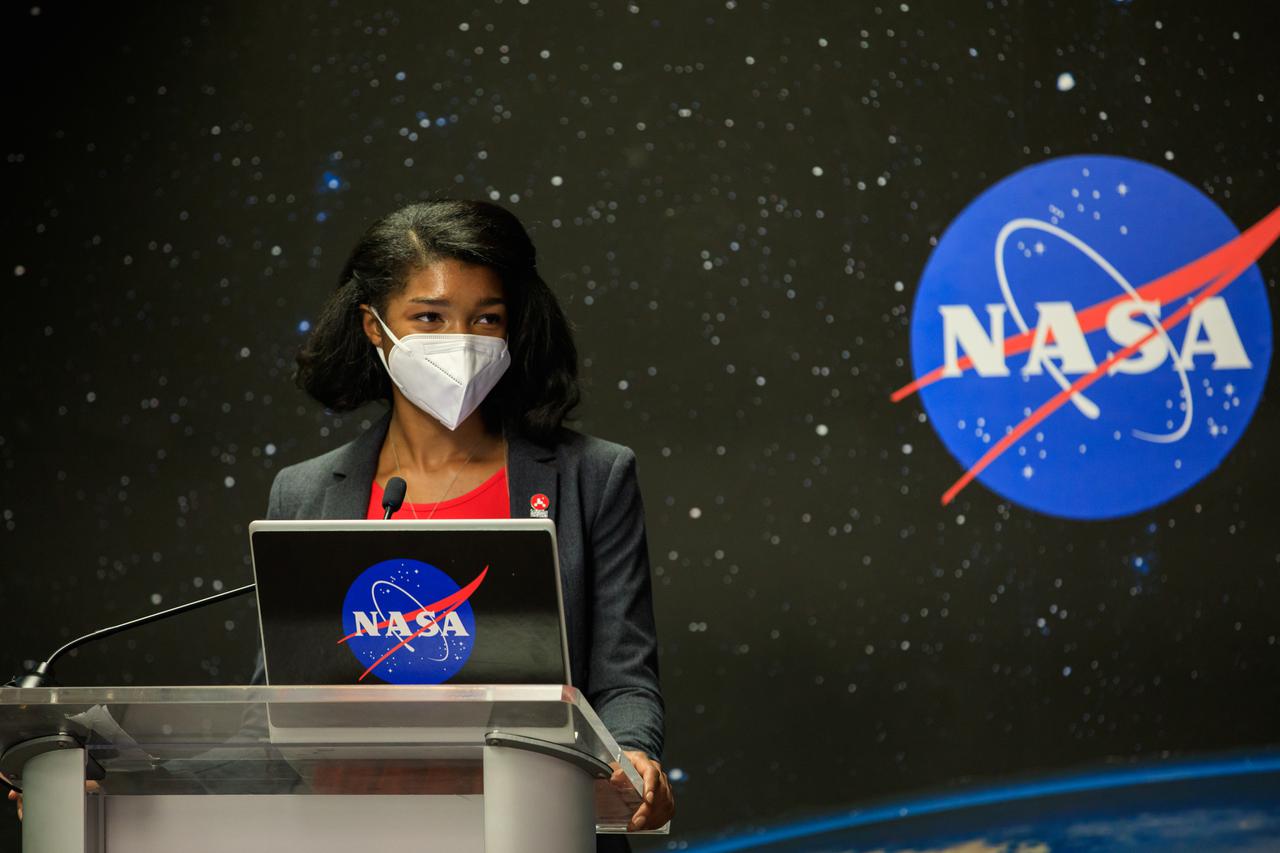

NASA Communications’ Jasmine Hopkins moderates a Mars 2020 Facebook live event inside the Press Site auditorium at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 12, 2021. Participants included United Launch Alliance (ULA) Launch Conductor Dillon Rice and NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Launch Director Tim Dunn. During the event, Rice and Dunn discussed the partnership between ULA and LSP, as well as major milestones that led to the Mars 2020 launch, and how launches to Mars have changed over time. NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover lifted off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on July 30, 2020, and is slated to touch down on the Red Planet Feb. 18, 2021.

United Launch Alliance (ULA) Launch Conductor Dillon Rice, left, and NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Launch Director Tim Dunn participate in a Mars 2020 Facebook live event inside the Press Site auditorium at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 12, 2021. During the event, Rice and Dunn discussed the partnership between ULA and LSP, as well as major milestones that led to the Mars 2020 launch, and how launches to Mars have changed over time. NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover lifted off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on July 30, 2020, and is slated to touch down on the Red Planet Feb. 18, 2021.
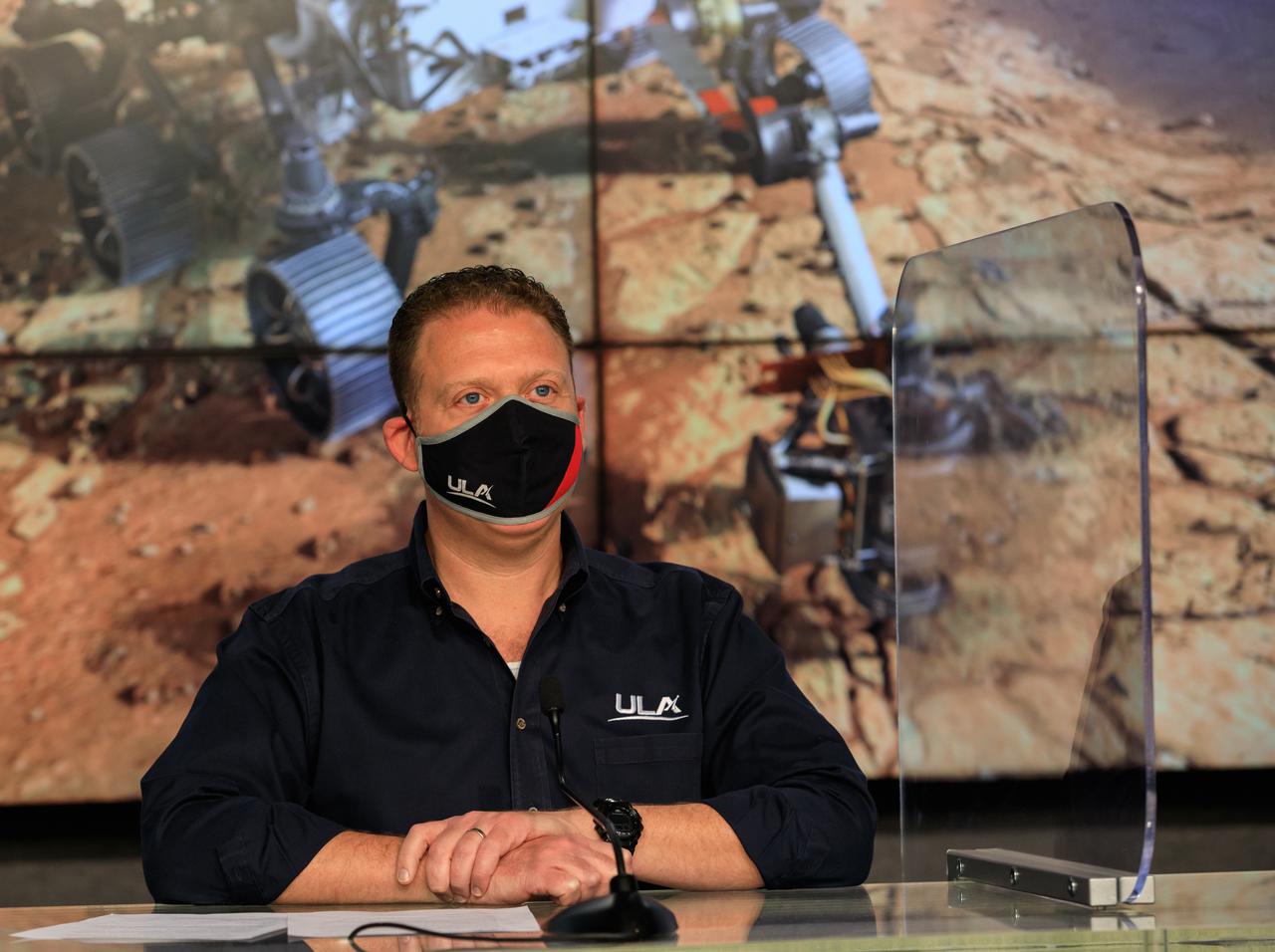

United Launch Alliance (ULA) Launch Conductor Dillon Rice participates in a Mars 2020 Facebook live event inside the Press Site auditorium at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 12, 2021. During the event, Rice and Tim Dunn, launch director for NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), discussed the partnership between ULA and LSP, as well as major milestones that led to the Mars 2020 launch, and how launches to Mars have changed over time. NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover lifted off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on July 30, 2020, and is slated to touch down on the Red Planet Feb. 18, 2021.
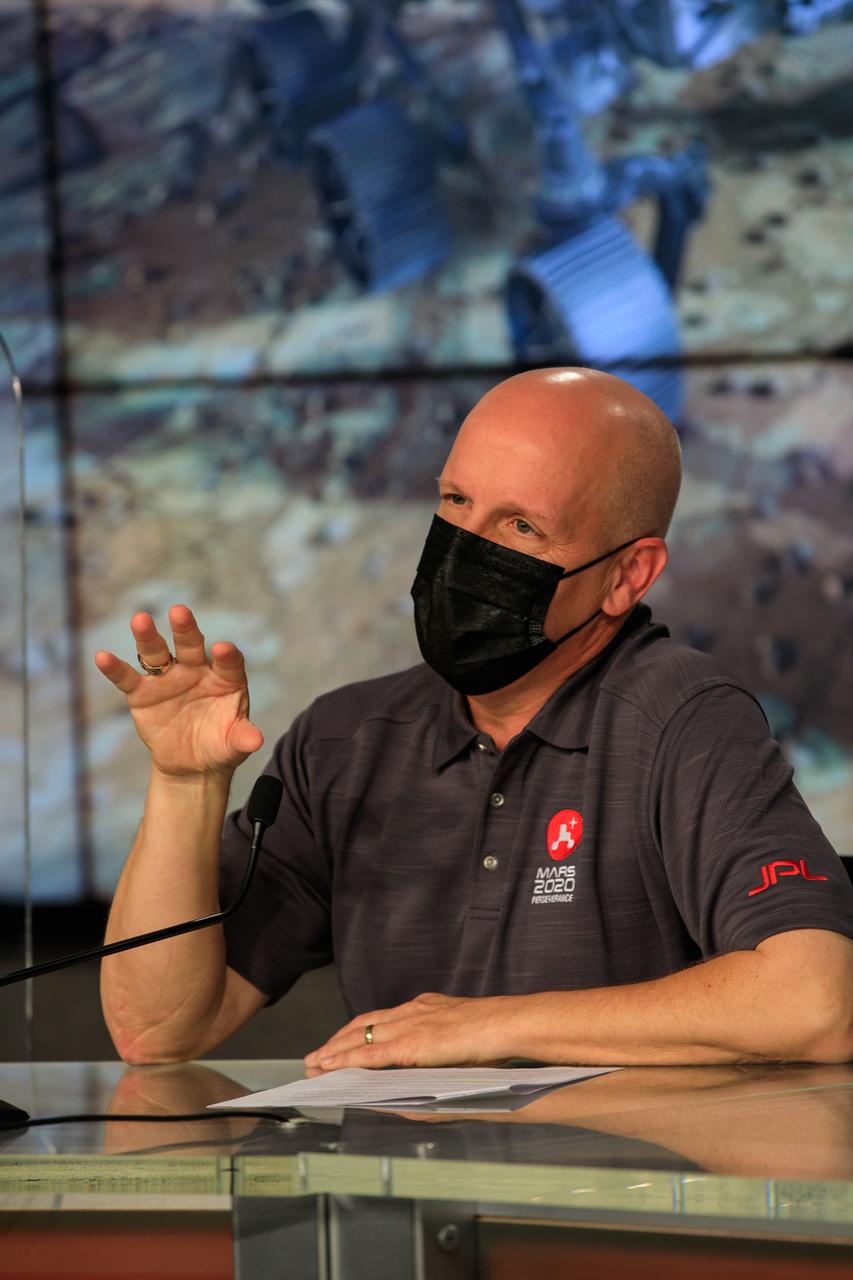

NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Launch Director Tim Dunn participates in a Mars 2020 Facebook live event inside the Press Site auditorium at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 12, 2021. During the event, Dunn and Dillon Rice, launch conductor for United Launch Alliance (ULA), discussed the partnership between ULA and LSP, as well as major milestones that led to the Mars 2020 launch, and how launches to Mars have changed over time. NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover lifted off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on July 30, 2020, and is slated to touch down on the Red Planet Feb. 18, 2021.
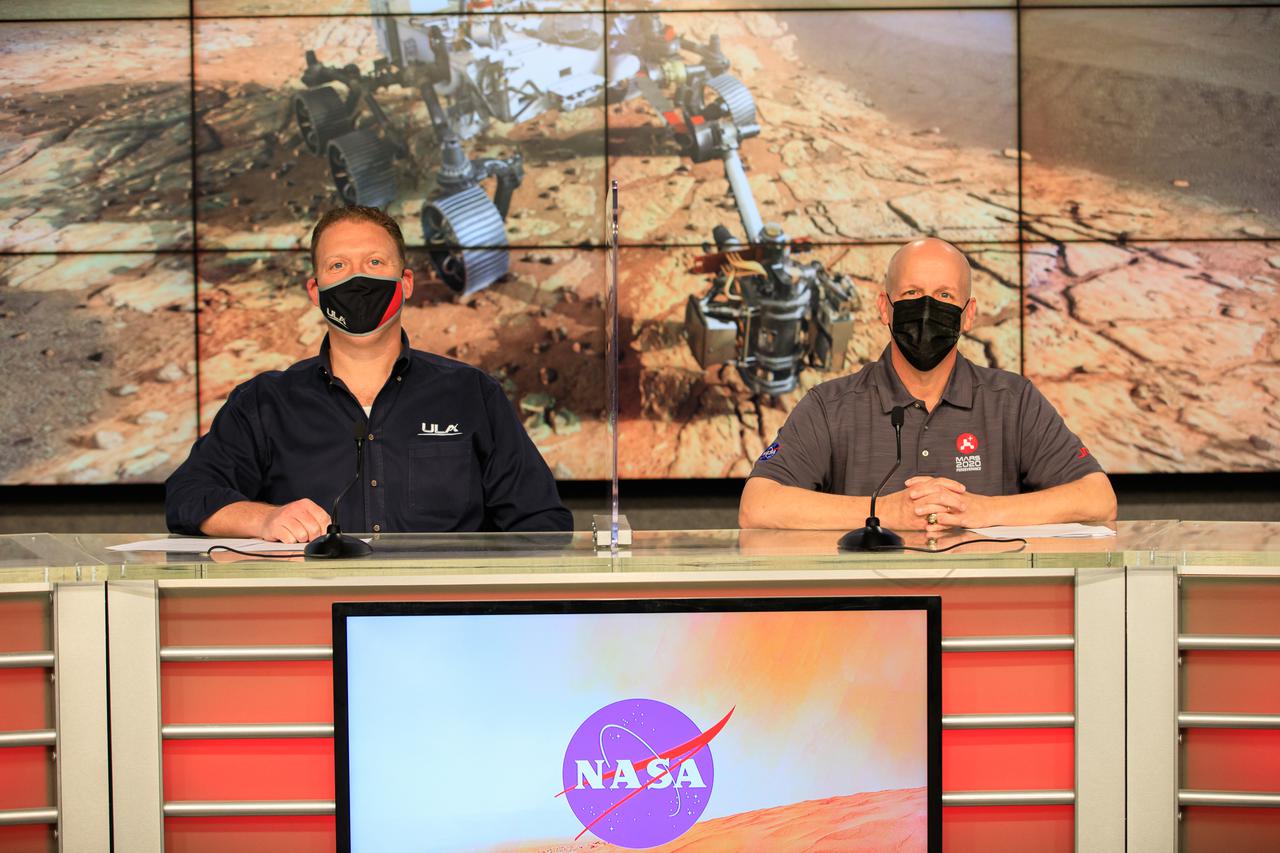

United Launch Alliance (ULA) Launch Conductor Dillon Rice, left, and NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) Launch Director Tim Dunn participate in a Mars 2020 Facebook live event inside the Press Site auditorium at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 12, 2021. During the event, Rice and Dunn discussed the partnership between ULA and LSP, as well as major milestones that led to the Mars 2020 launch, and how launches to Mars have changed over time. NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover lifted off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on July 30, 2020, and is slated to touch down on the Red Planet Feb. 18, 2021.
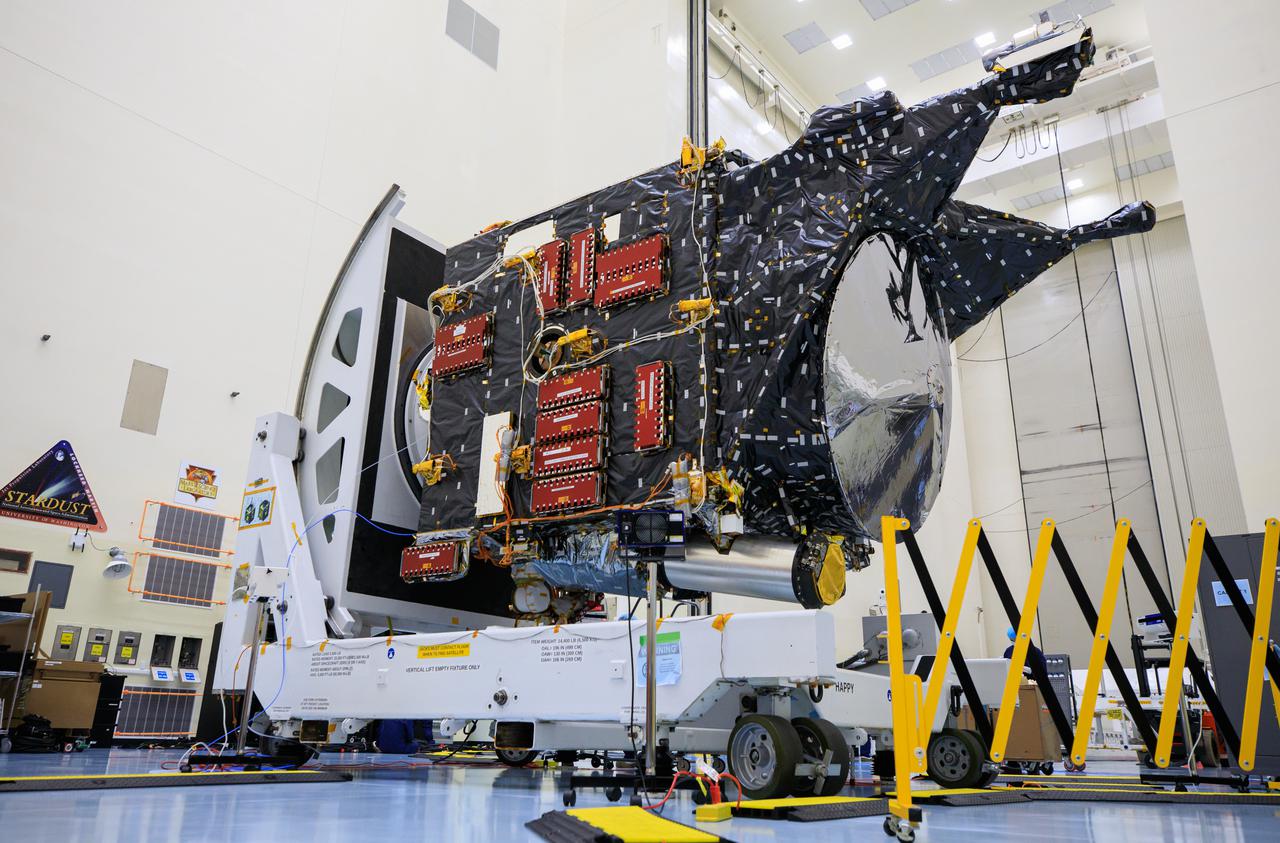

NASA’s Psyche spacecraft undergoes processing and servicing ahead of launch atop a work stand inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 3, 2022. Psyche is targeting to lift off aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.

NASA’s Psyche spacecraft undergoes processing and servicing ahead of launch atop a work stand inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 3, 2022. Psyche is targeting to lift off aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
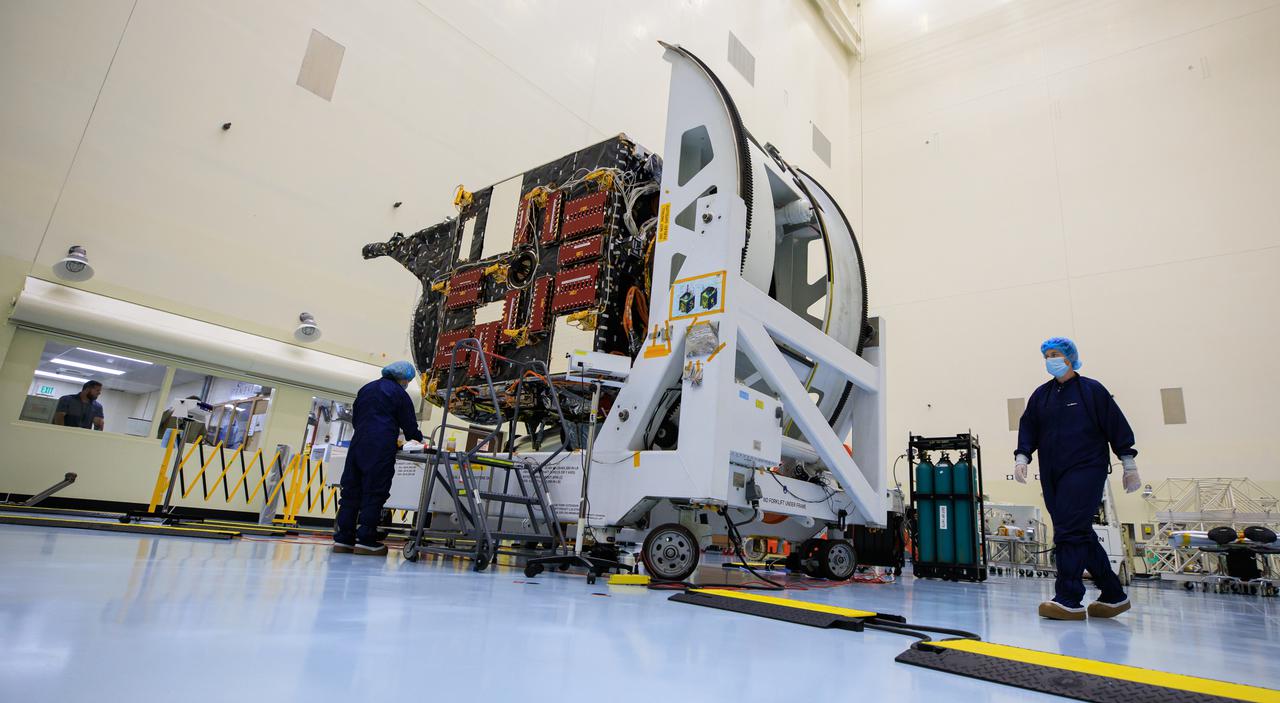

NASA’s Psyche spacecraft undergoes processing and servicing ahead of launch atop a work stand inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 3, 2022. Psyche is targeting to lift off aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
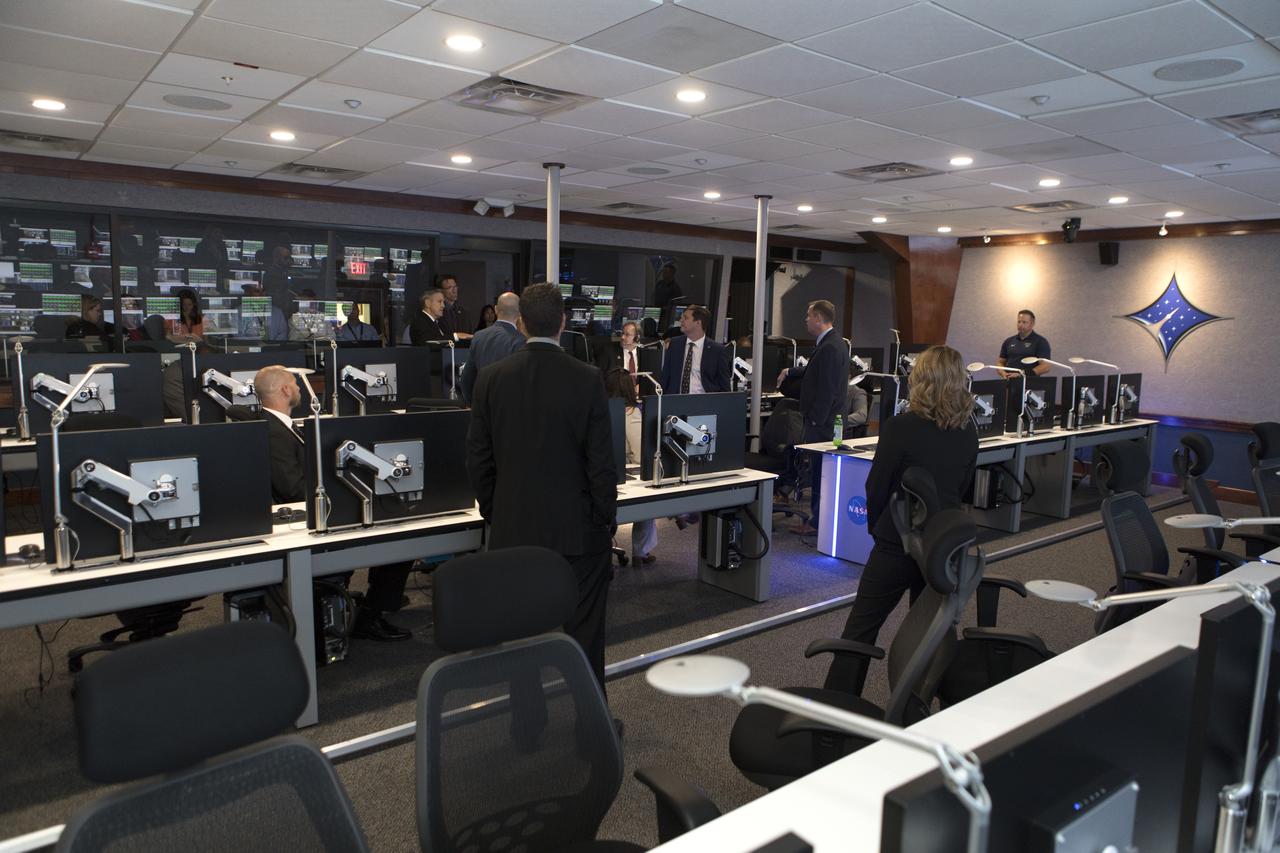

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, third row from front, second from right, tours the Launch Services Program's Mission Director's Center in Hangar AE, on Aug. 7, 2018, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, first row up front, center, updates the administrator on LSP missions and accomplishments.
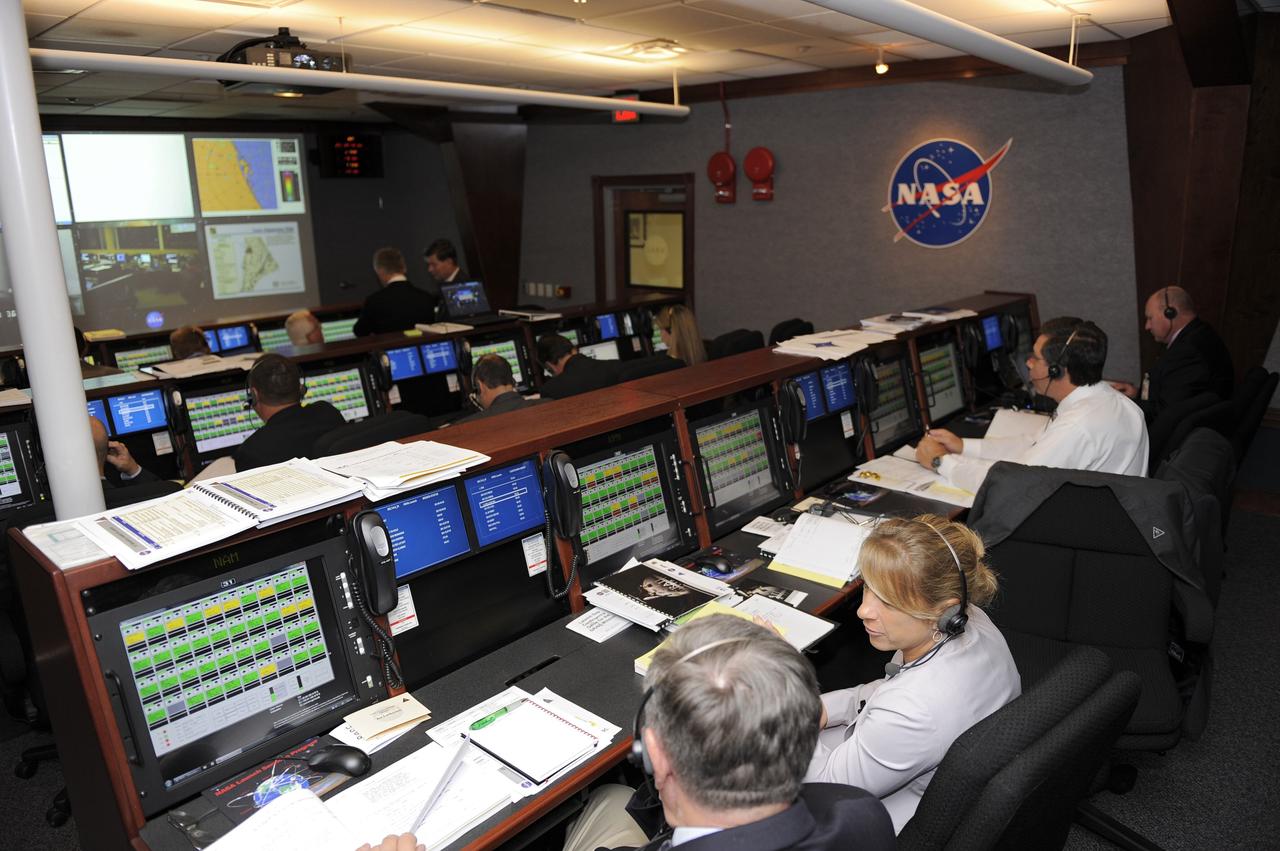

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, members of NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) launch team monitor GRAIL's launch countdown from the Mission Directors Center in Hangar AE. From left are Joe Lackovich, NASA advisory manager, NASA's Launch Services Program (LSP); Amanda Mitskevich, manager, LSP; and Oscar Toledo, NASA Headquarters senior advisor, LSP. Launch is scheduled for 8:37:06 a.m. EDT Sept. 8 from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem around the moon to precisely measure and map variations in the moon's gravitational field. The mission will provide the most accurate global gravity field to date for any planet, including Earth. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
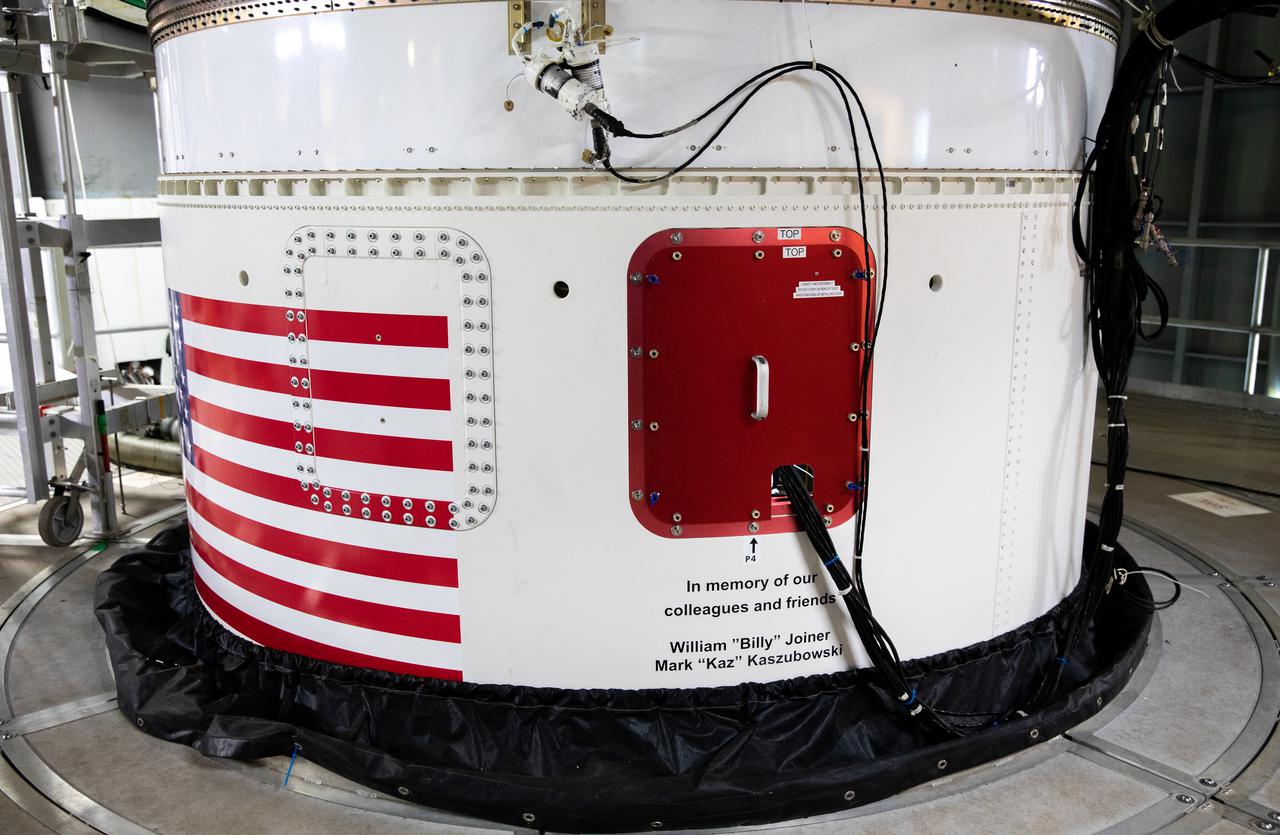
The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.
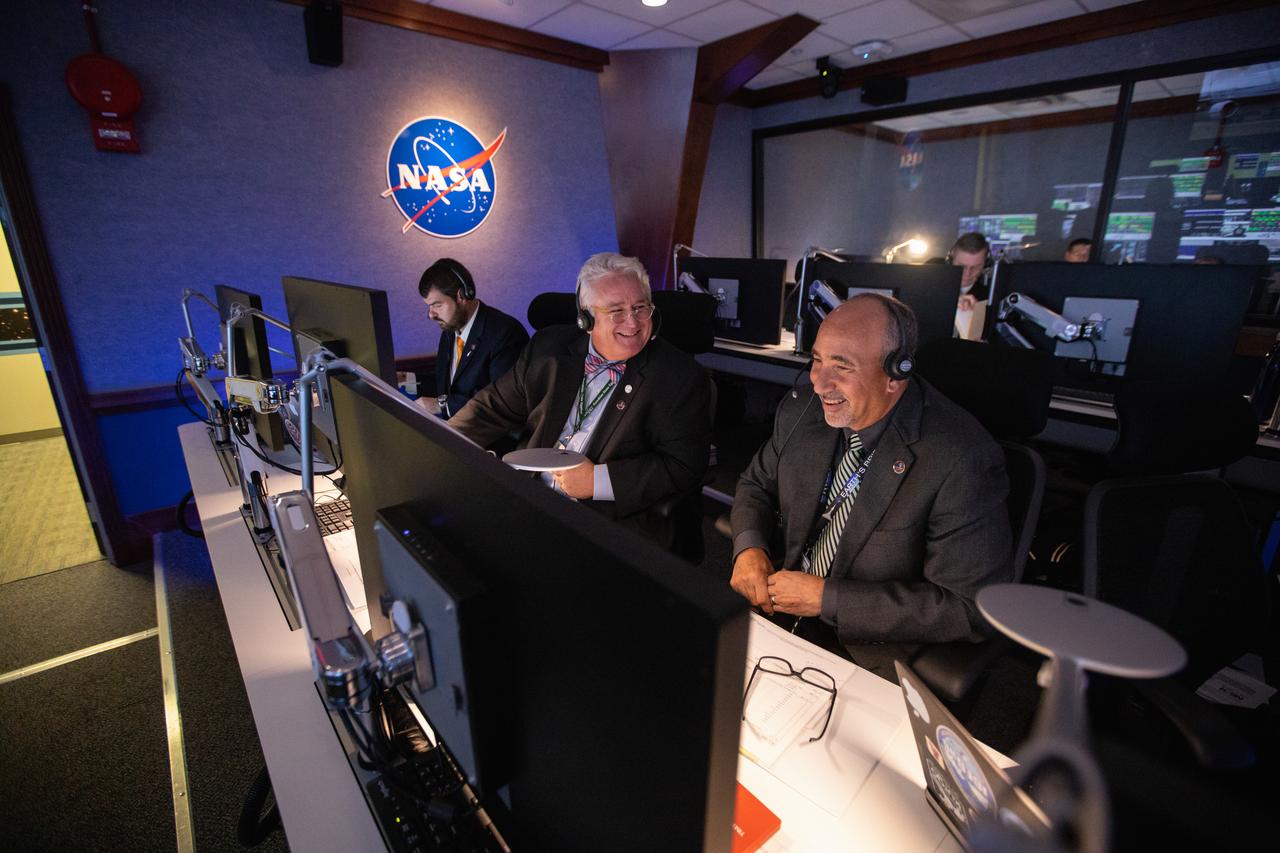

Albert Sierra (right), chief of NASA’s Launch Services Program’s (LSP) Flight Projects Office, and Garrett Lee Skrobot (second from right), senior mission manager, monitor the launch of the agency’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The ICON launch was managed by LSP.

Omar Baez, right, launch director in NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), monitors the launch of the agency’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The ICON launch was managed by LSP.
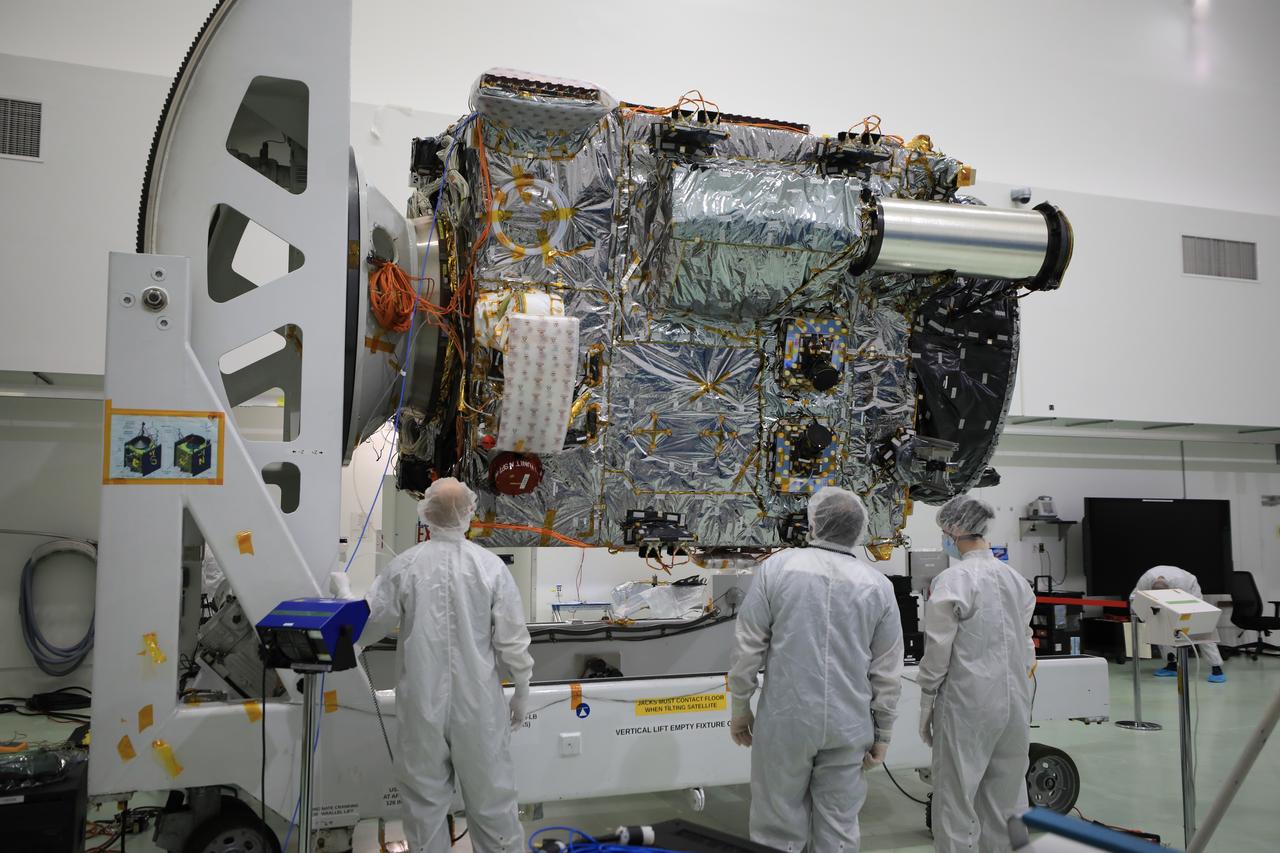

A team prepares NASA’s Psyche spacecraft for launch inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 8, 2022. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for no earlier than Oct. 10, 2023. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
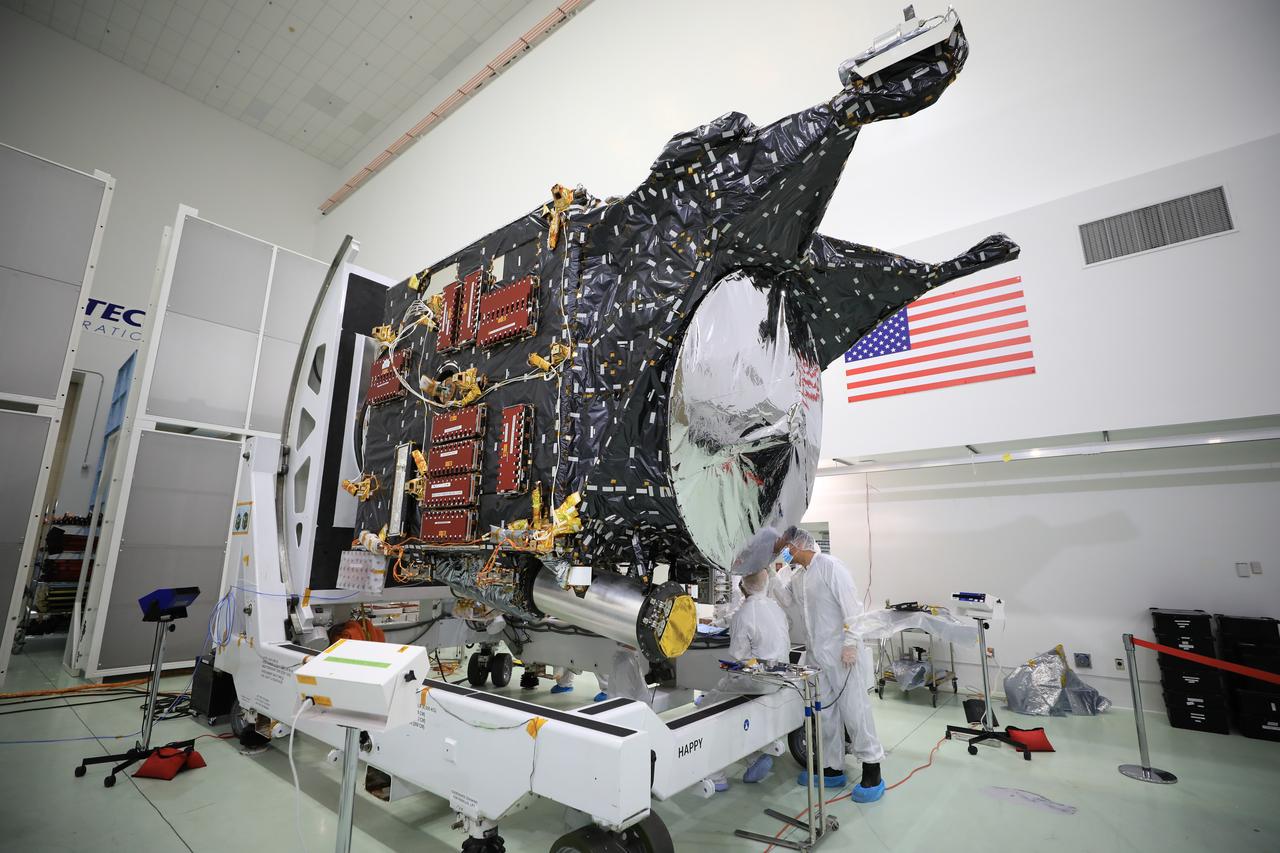

A team prepares NASA’s Psyche spacecraft for launch inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 8, 2022. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for no earlier than Oct. 10, 2023. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
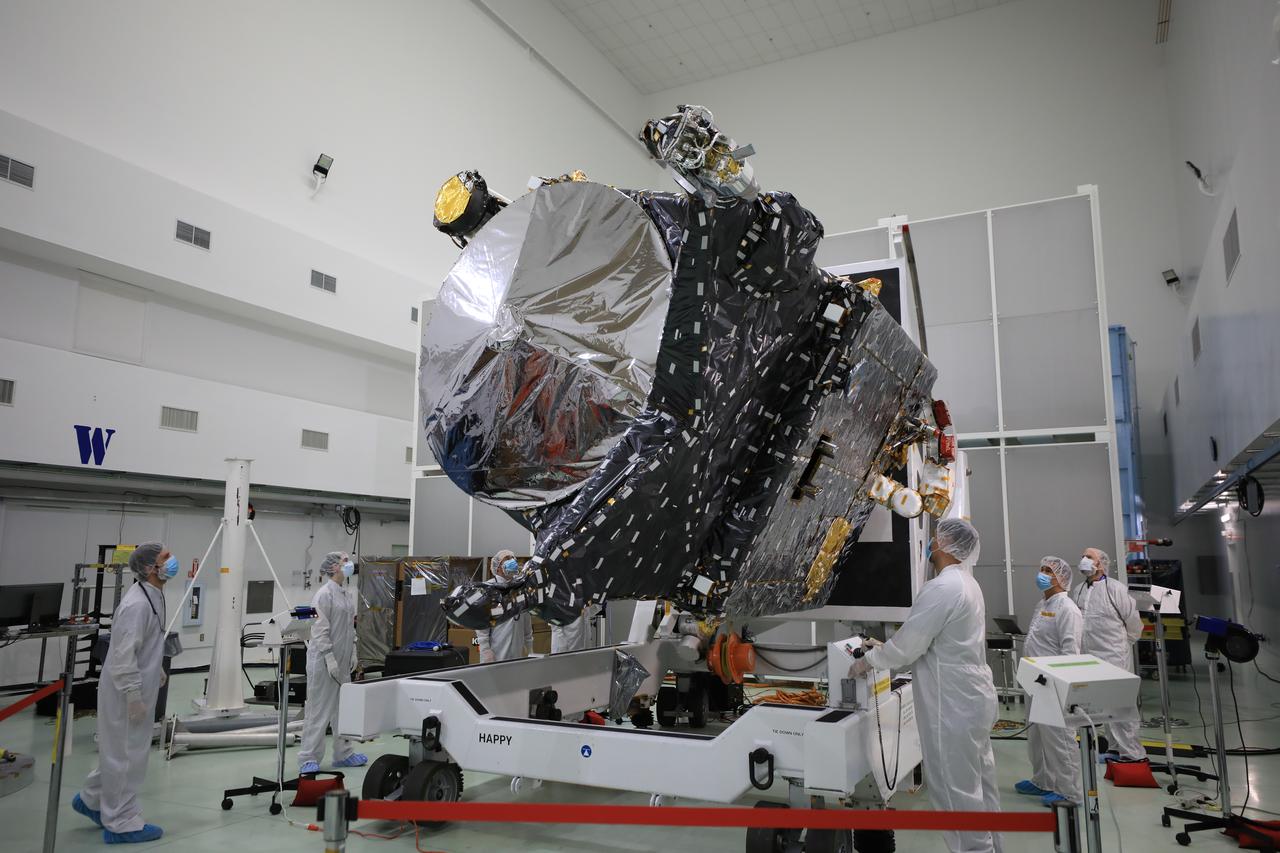

Technicians rotate NASA’s Psyche spacecraft during prelaunch processing inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 8, 2022. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for no earlier than Oct. 10, 2023. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
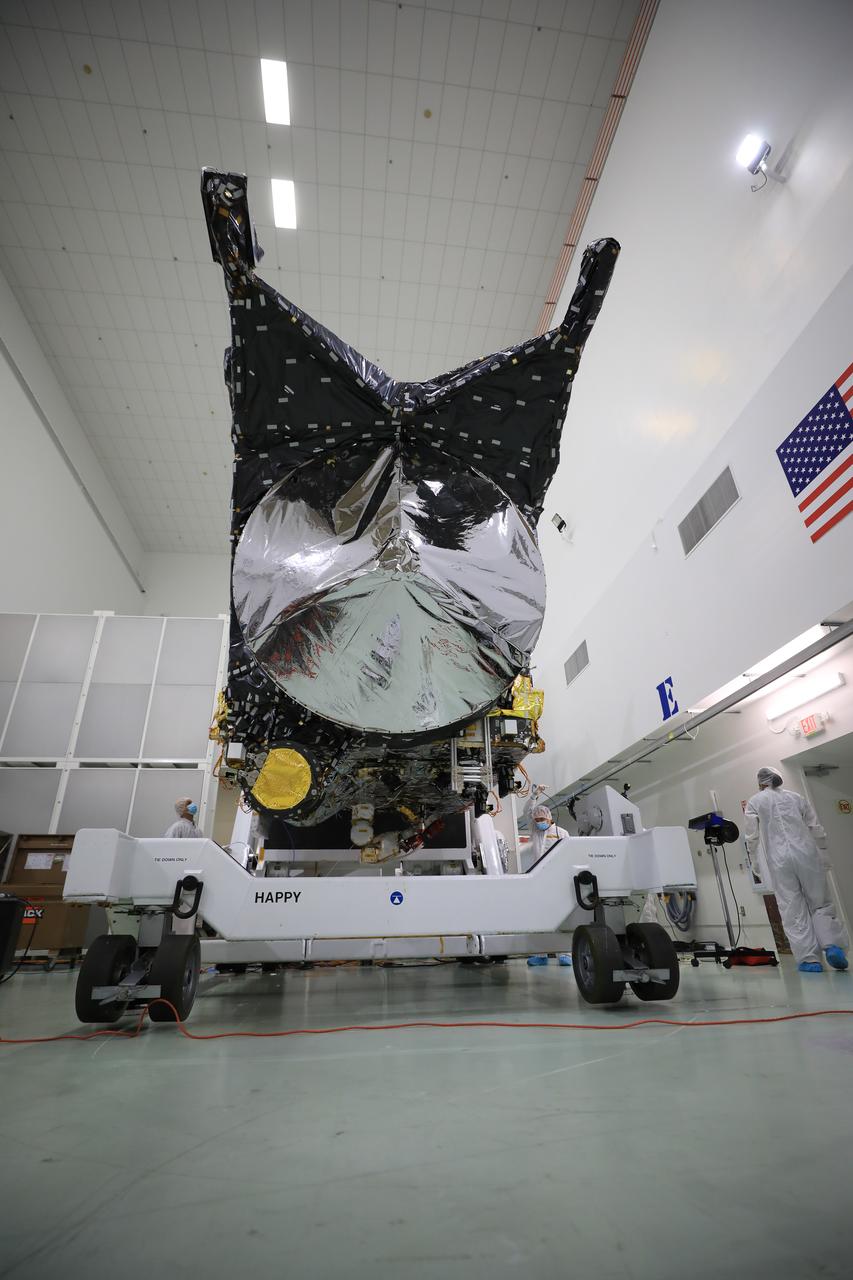

A team prepares NASA’s Psyche spacecraft for launch inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 8, 2022. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for no earlier than Oct. 10, 2023. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
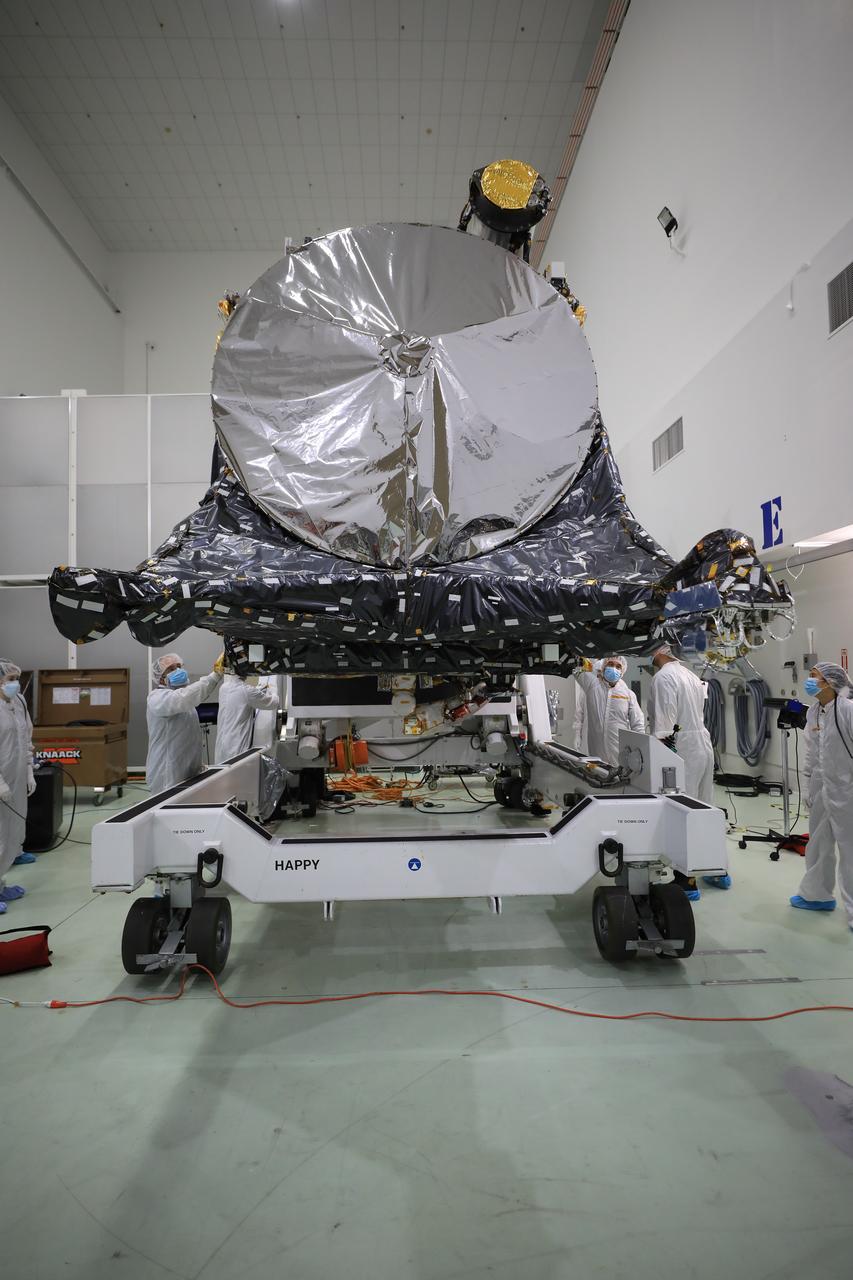

A team prepares NASA’s Psyche spacecraft for launch inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 8, 2022. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for no earlier than Oct. 10, 2023. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
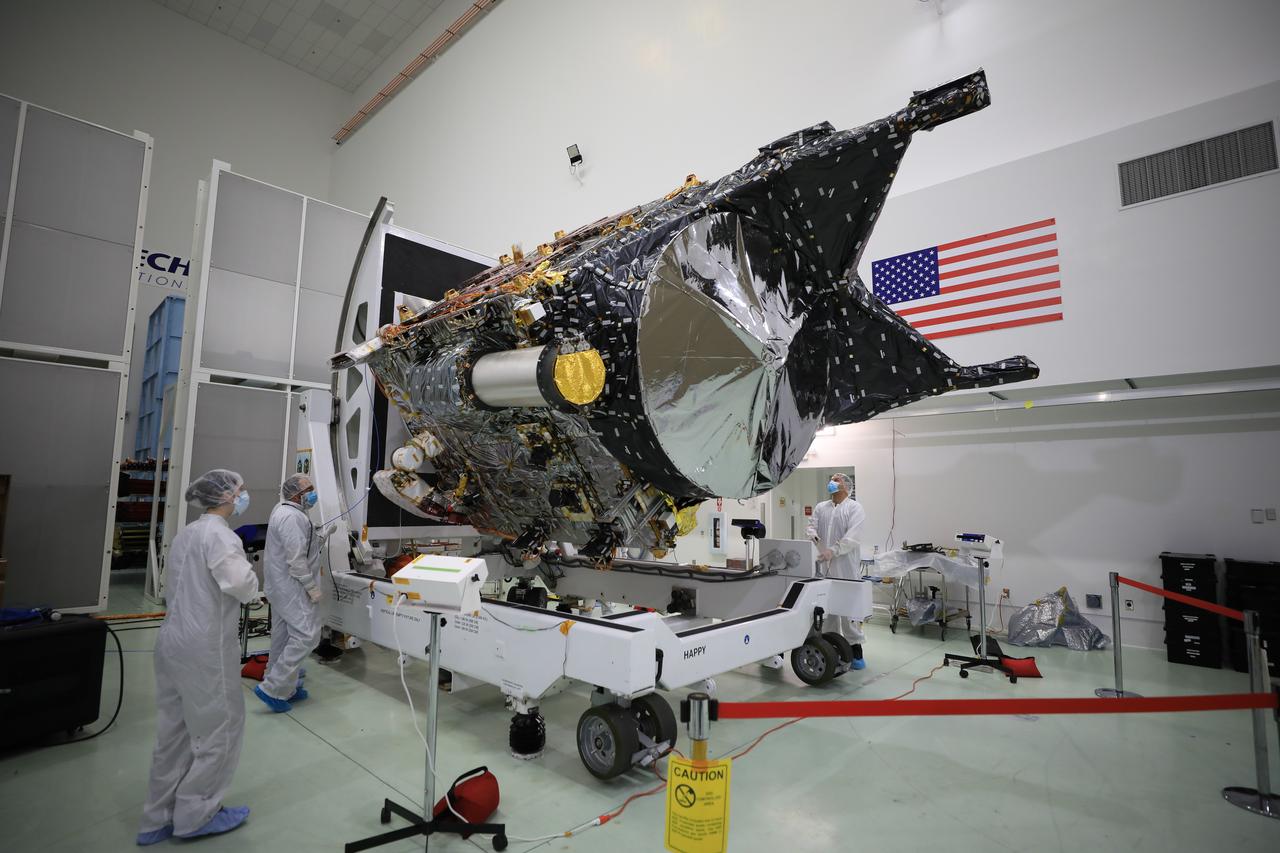

A team prepares NASA’s Psyche spacecraft for launch inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 8, 2022. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for no earlier than Oct. 10, 2023. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
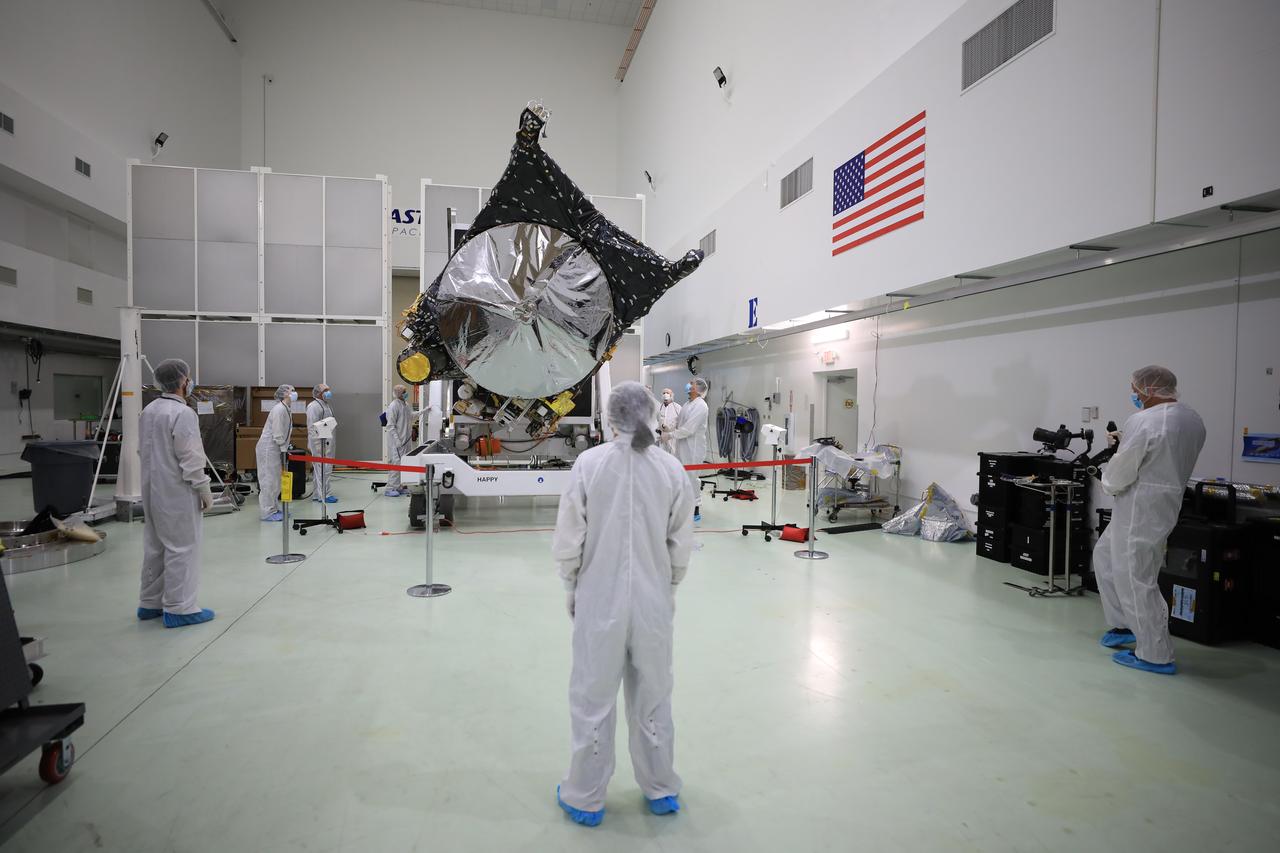

Prelaunch processing of NASA’s Psyche spacecraft is underway inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 8, 2022. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for no earlier than Oct. 10, 2023. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Portrait of Omar Baez Jr., NASA launch director for the Launch Services Program (LSP) at NASA's John F. Kennedy Space Center. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
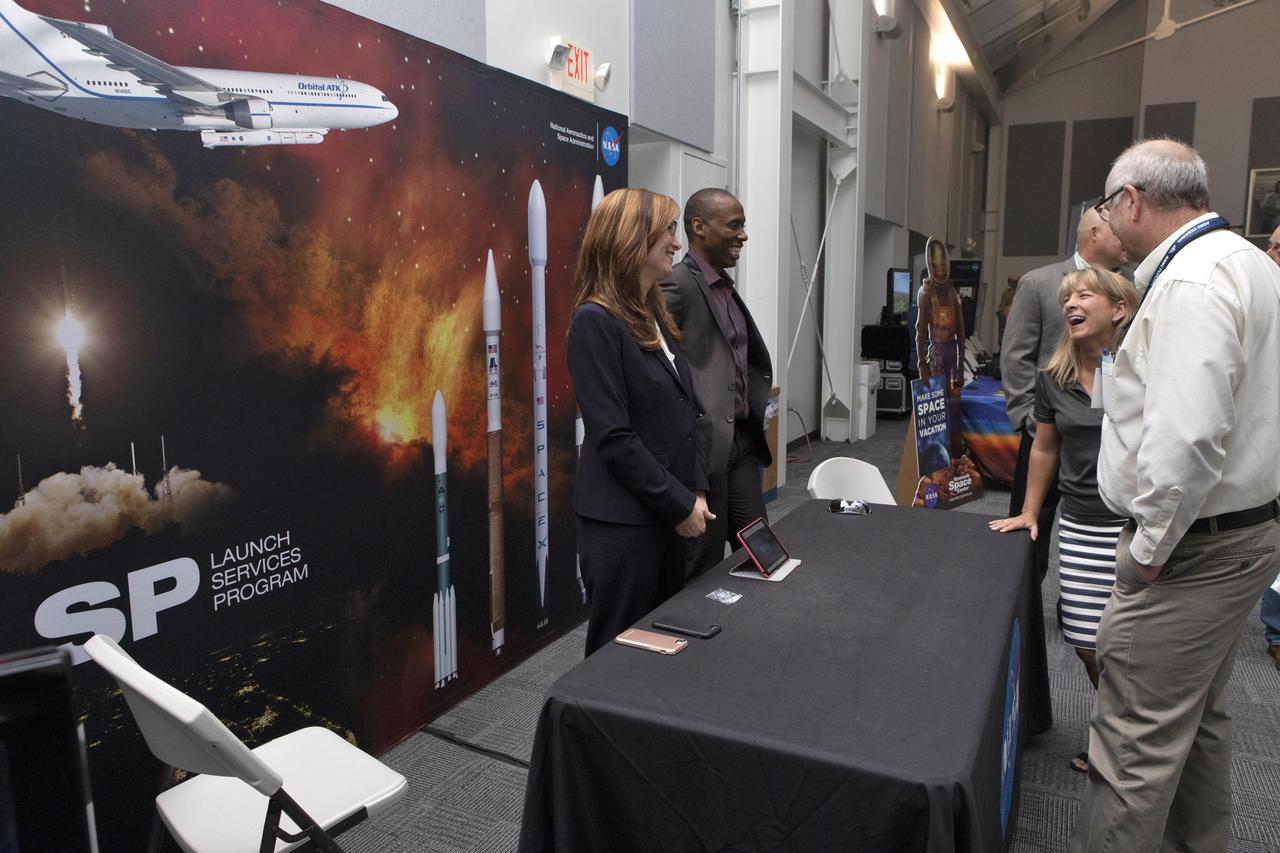

Guests visit with representatives from the Launch Services Program (LSP) during NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana’s update to community leaders, business executives, partners, educators and government leaders March 29, 2019, at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Cabana’s presentation covered recent accomplishments and future plans for Kennedy-led programs, including the Commercial Crew Program, Exploration Ground Systems, LSP, Exploration Research and Technology, and Center Planning and Development. After the presentation, guests had the opportunity to ask questions and visit displays from the programs and some of the commercial partners.
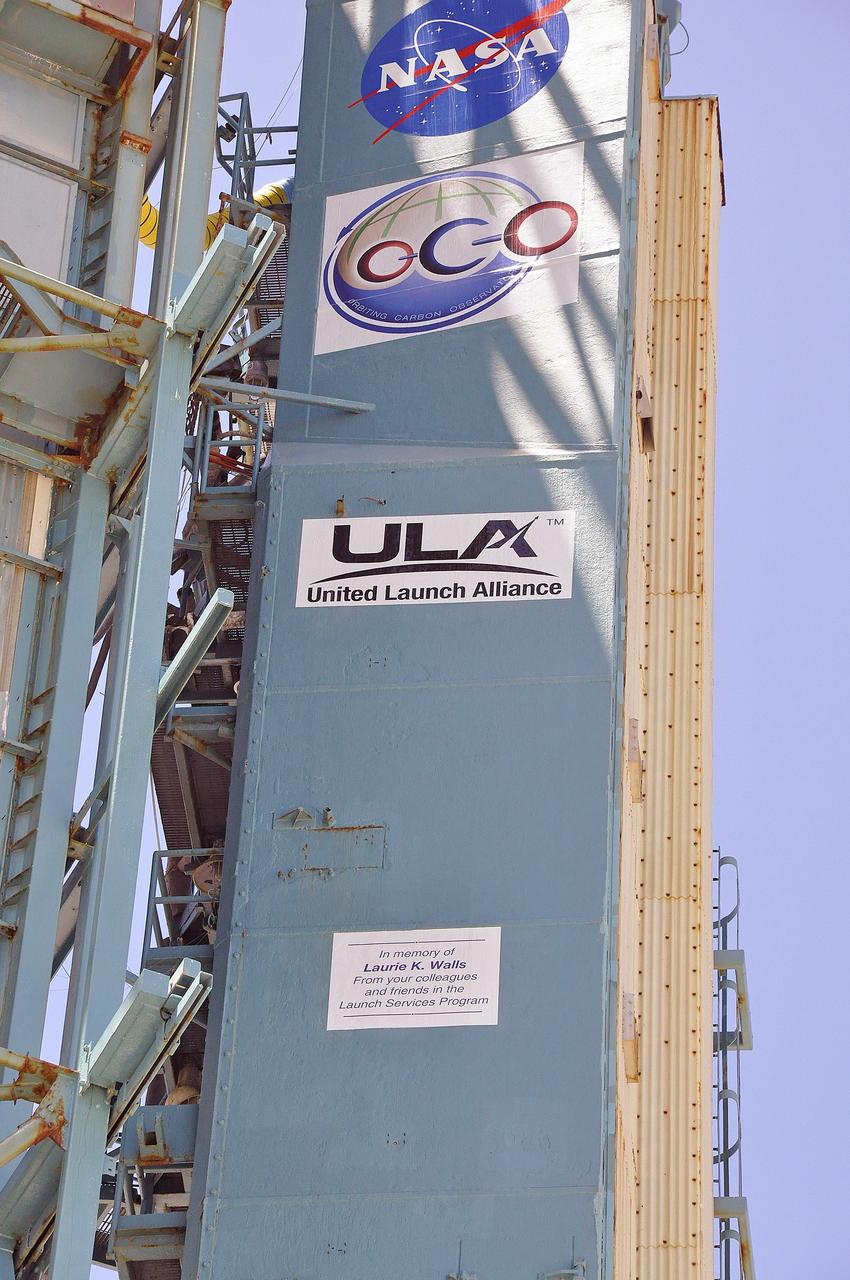

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A memorial plaque honoring Laurie K. Walls is affixed to the umbilical tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California for the launch of NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2. Walls, a thermal analysis engineer with the Launch Services Program, or LSP, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, died June 4. This dedication to Walls from the members of the launch team was read during the OCO-2 countdown commentary: "The OCO-2 mission has special meaning to NASA's Launch Services Program as we have dedicated it to one of our LSP Teammates, Laurie Walls. Laurie began her career over 30 years ago as a thermal engineer for McDonnell Douglas in Huntsville, Alabama, supporting NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. She moved to Florida in 1985. Shortly after coming to Florida, Laurie became a civil servant working on the Shuttle program return to flight effort post-Challenger. In 1998, Laurie joined the newly formed Launch Services Program as one of the founding members of the flight analysis group. She served in LSP as the thermal discipline expert until her untimely death earlier this month. Laurie worked thermal issues for numerous NASA Delta II and Atlas V missions. Additionally, she provided key thermal support for both Delta II Heavy development and Atlas V Certification. Laurie was an integral member of LSP's family and she was truly dedicated to NASA and the LSP team. She will be greatly missed. We honor Laurie with a special memorial placed on the SLC-2 umbilical tower, and we thank ULA for helping to make this happen." Launch of OCO-2 is scheduled for 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. To learn more about NASA's Launch Services Program, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy/launchingrockets/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
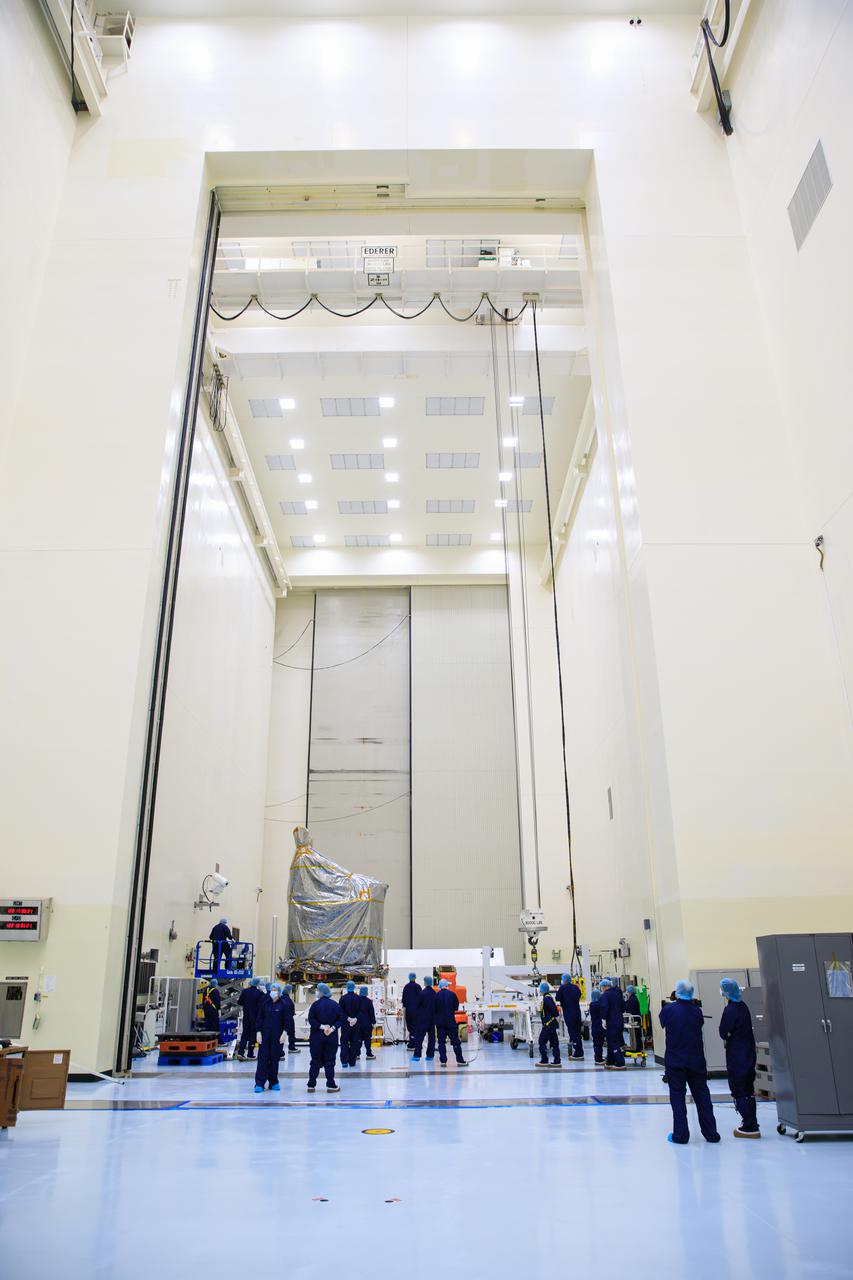

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians prepare to move the agency’s Psyche spacecraft – recently removed from its shipping container and inside a protective covering – to a work stand on May 2, 2022. Psyche is scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
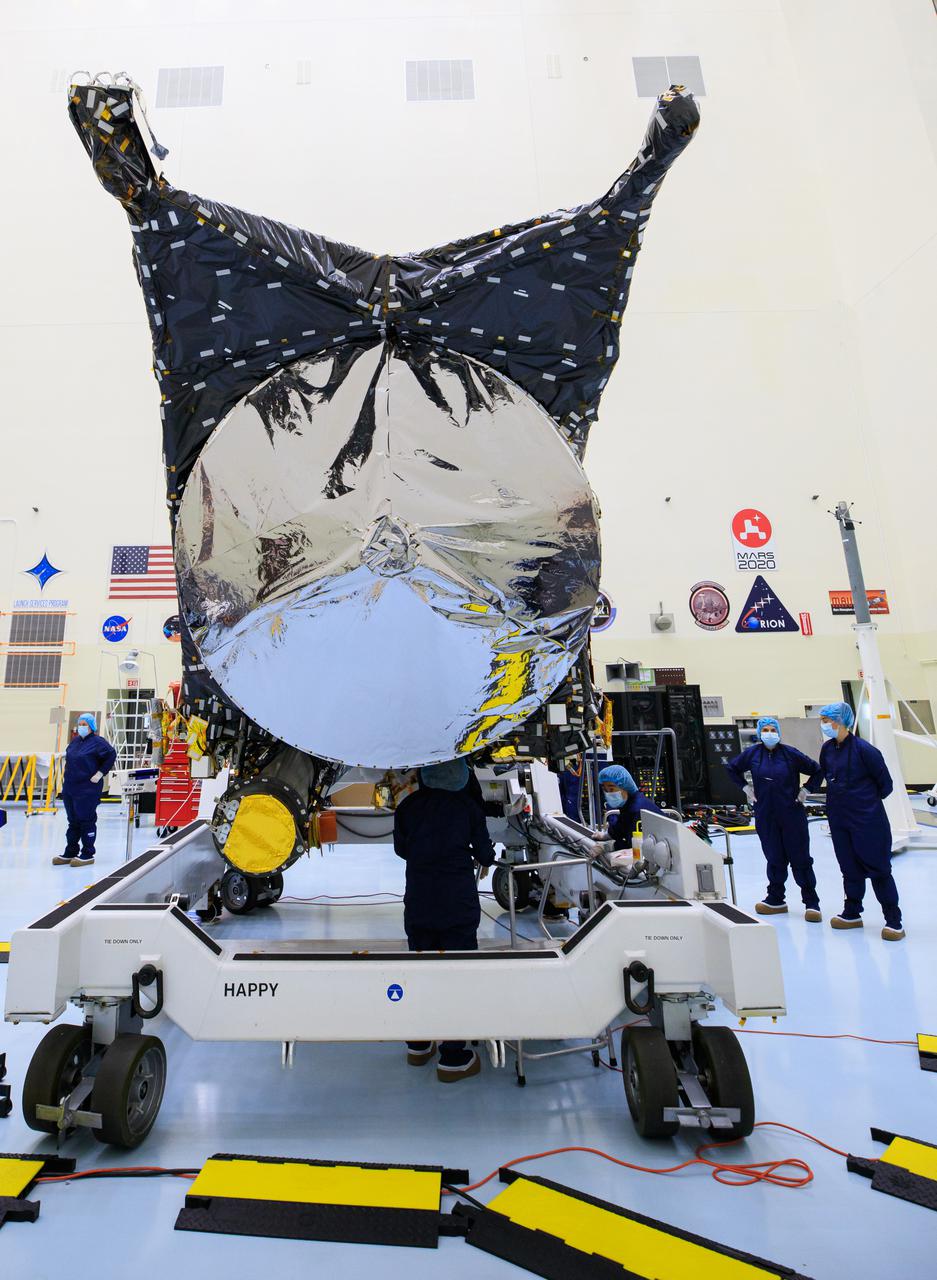

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida perform work on the agency’s Psyche spacecraft inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) on May 3, 2022. While inside the PHSF, the spacecraft will undergo routine processing and servicing ahead of launch. Psyche is targeting to lift off aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
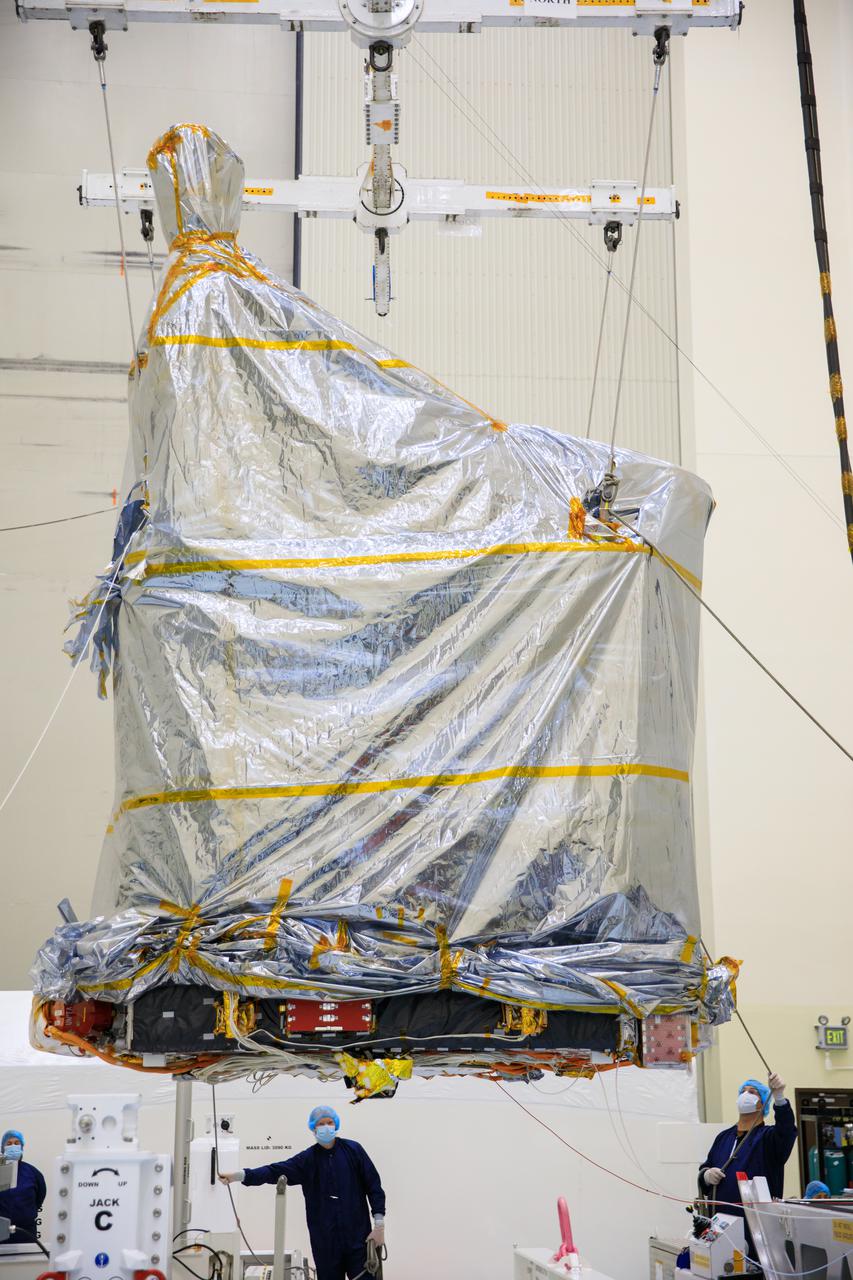

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the agency’s Psyche spacecraft – recently removed from its shipping container and inside a protective covering – is moved by crane to a work stand on Monday, May 2, 2022. Psyche is scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
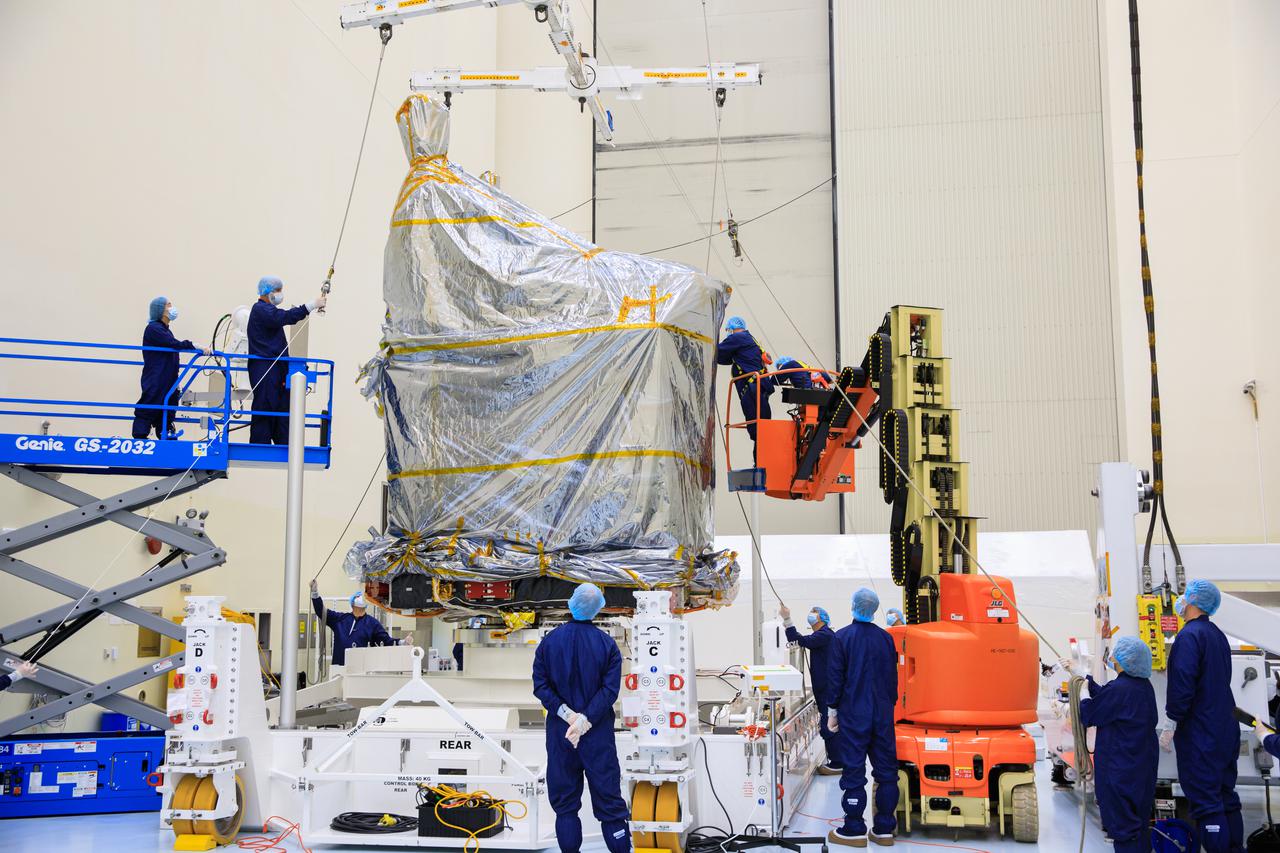

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the agency’s Psyche spacecraft – recently removed from its shipping container and inside a protective covering – is moved by crane to a work stand on Monday, May 2, 2022. Psyche is scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida perform work on the agency’s Psyche spacecraft inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) on May 3, 2022. While inside the PHSF, the spacecraft will undergo routine processing and servicing ahead of launch. Psyche is targeting to lift off aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
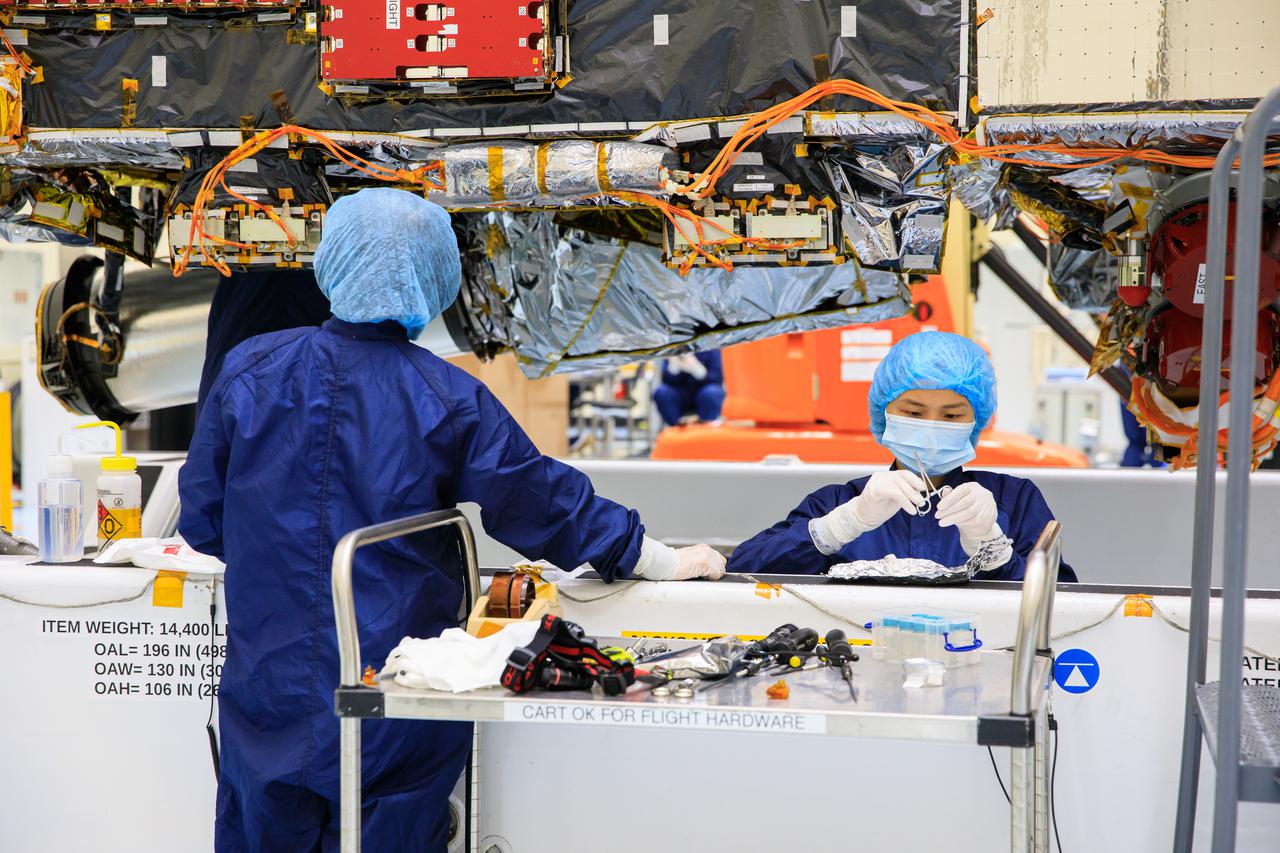

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida perform work on the agency’s Psyche spacecraft inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) on May 3, 2022. While inside the PHSF, the spacecraft will undergo routine processing and servicing ahead of launch. Psyche is targeting to lift off aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
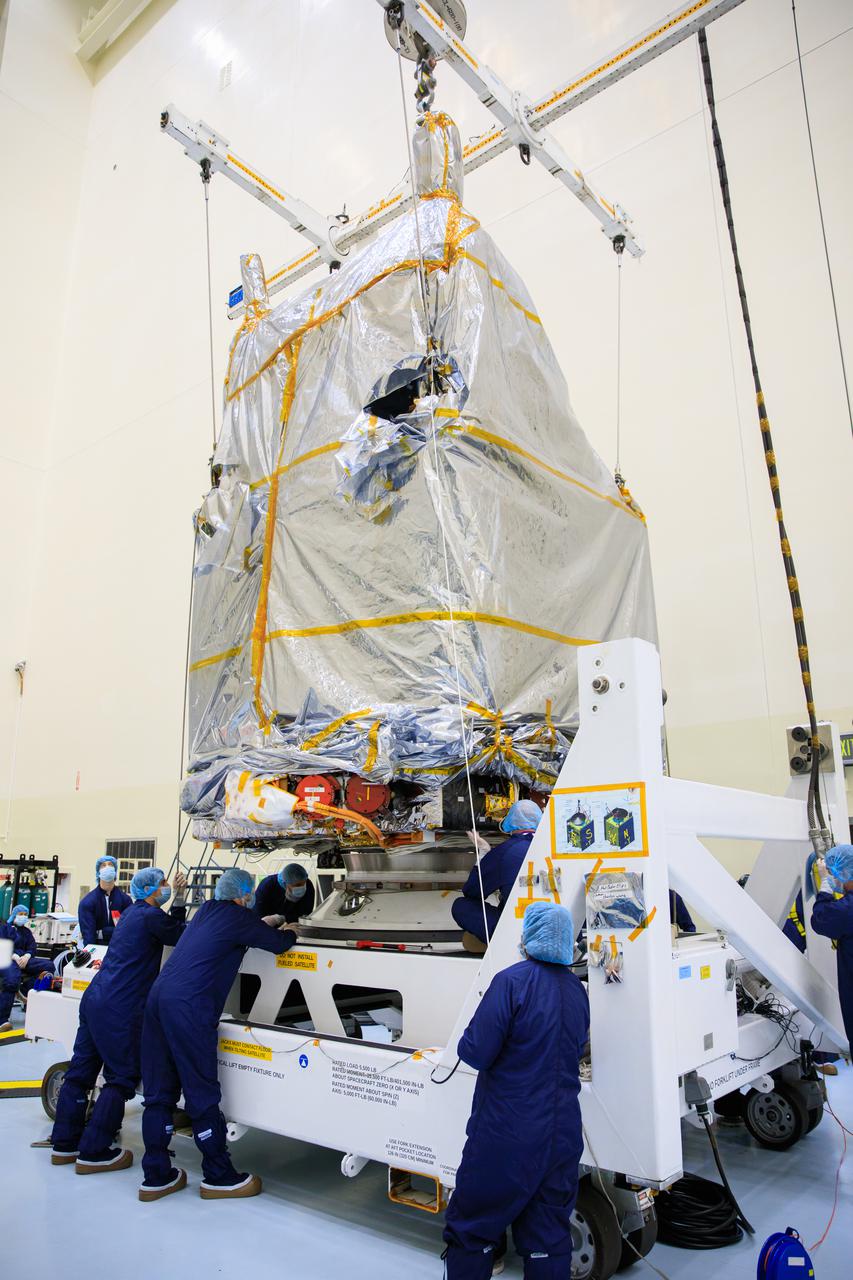

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the agency’s Psyche spacecraft – recently removed from its shipping container and inside a protective covering – is moved by crane to a work stand on Monday, May 2, 2022. Psyche is scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
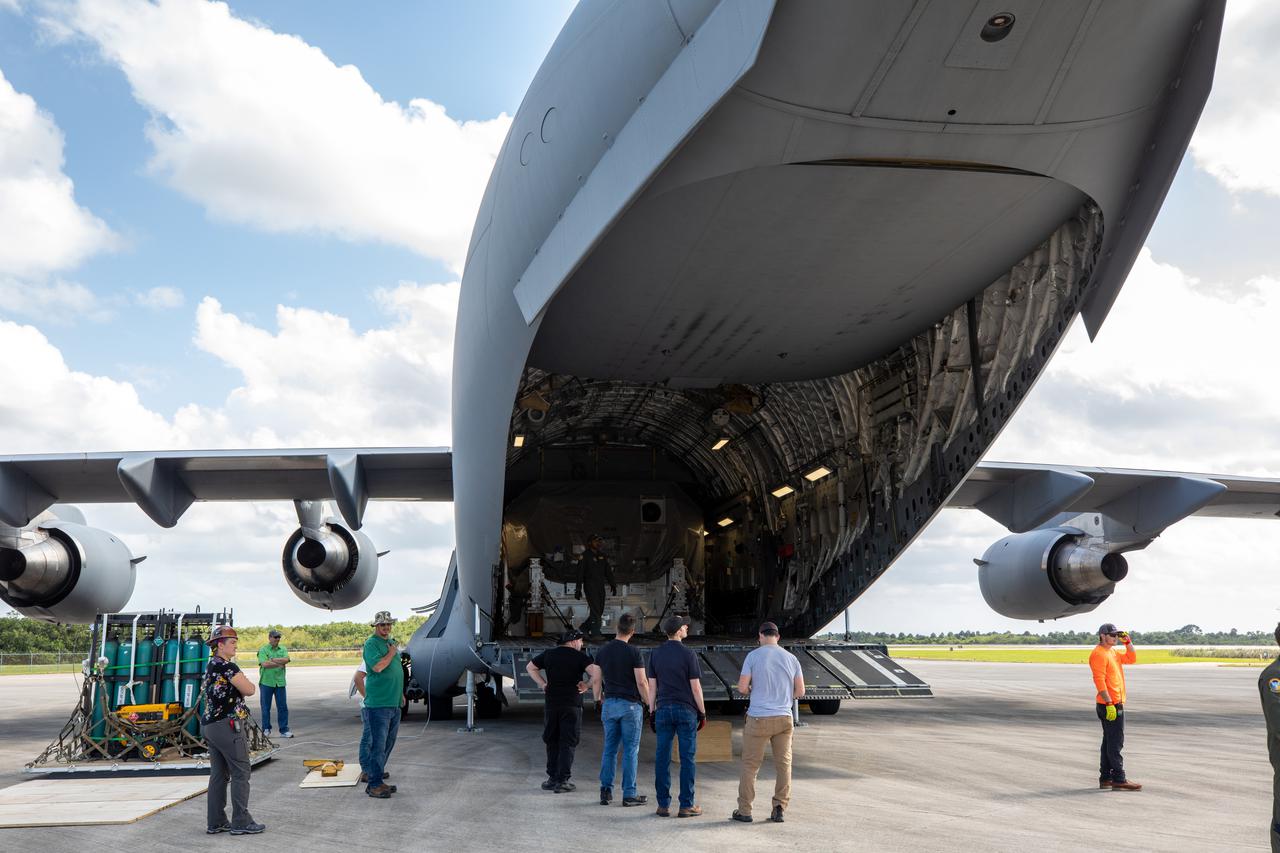

Preparations are underway to offload NASA’s Psyche spacecraft from the C-17 aircraft it arrived aboard at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility in Florida on April 29, 2022. Psyche arrived from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California. Psyche is scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use its solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
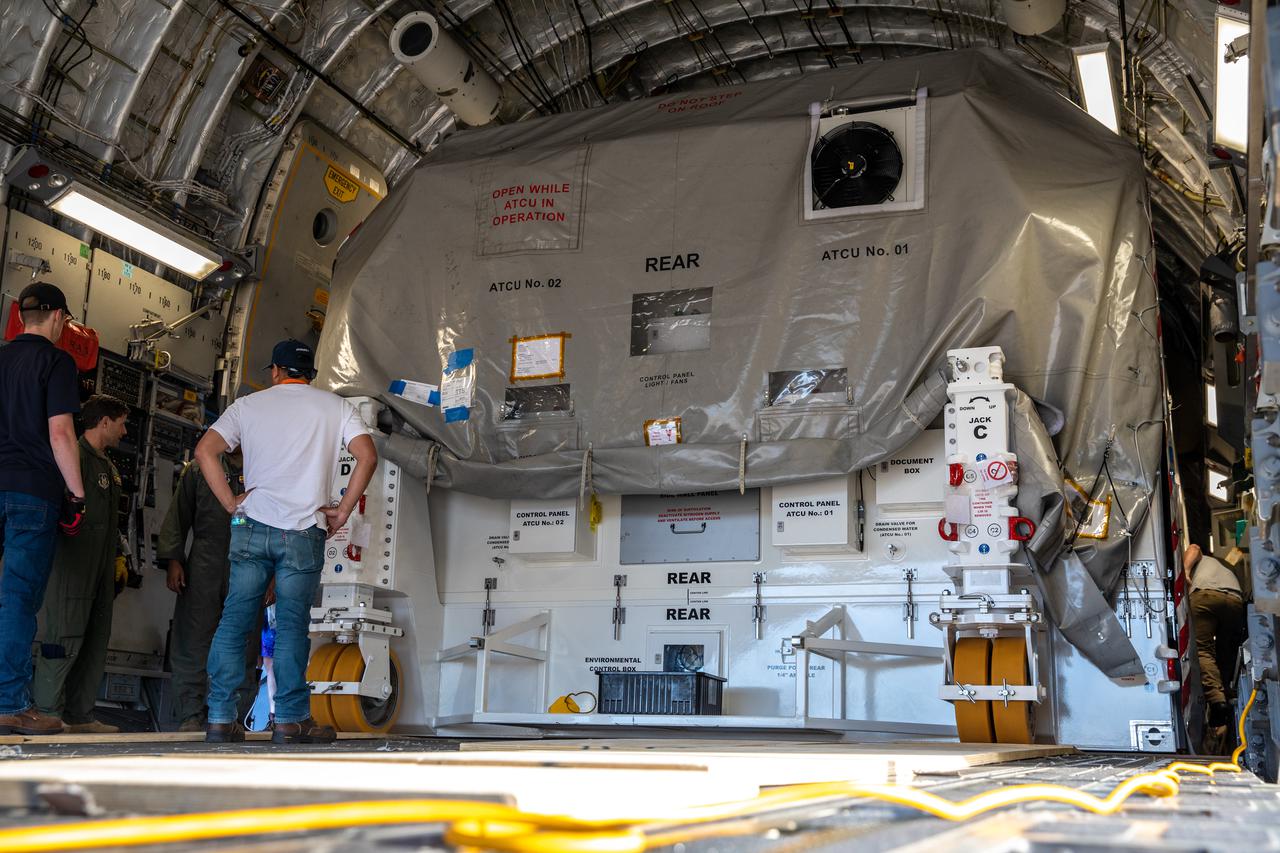

Preparations are underway to offload NASA’s Psyche spacecraft from the C-17 aircraft it arrived aboard at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility in Florida on April 29, 2022. Psyche arrived from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California. Psyche is scheduled to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on Aug. 1, 2022. The spacecraft will use its solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Psyche will be the 14th mission in the agency's Discovery program and LSP’s 100th primary mission.
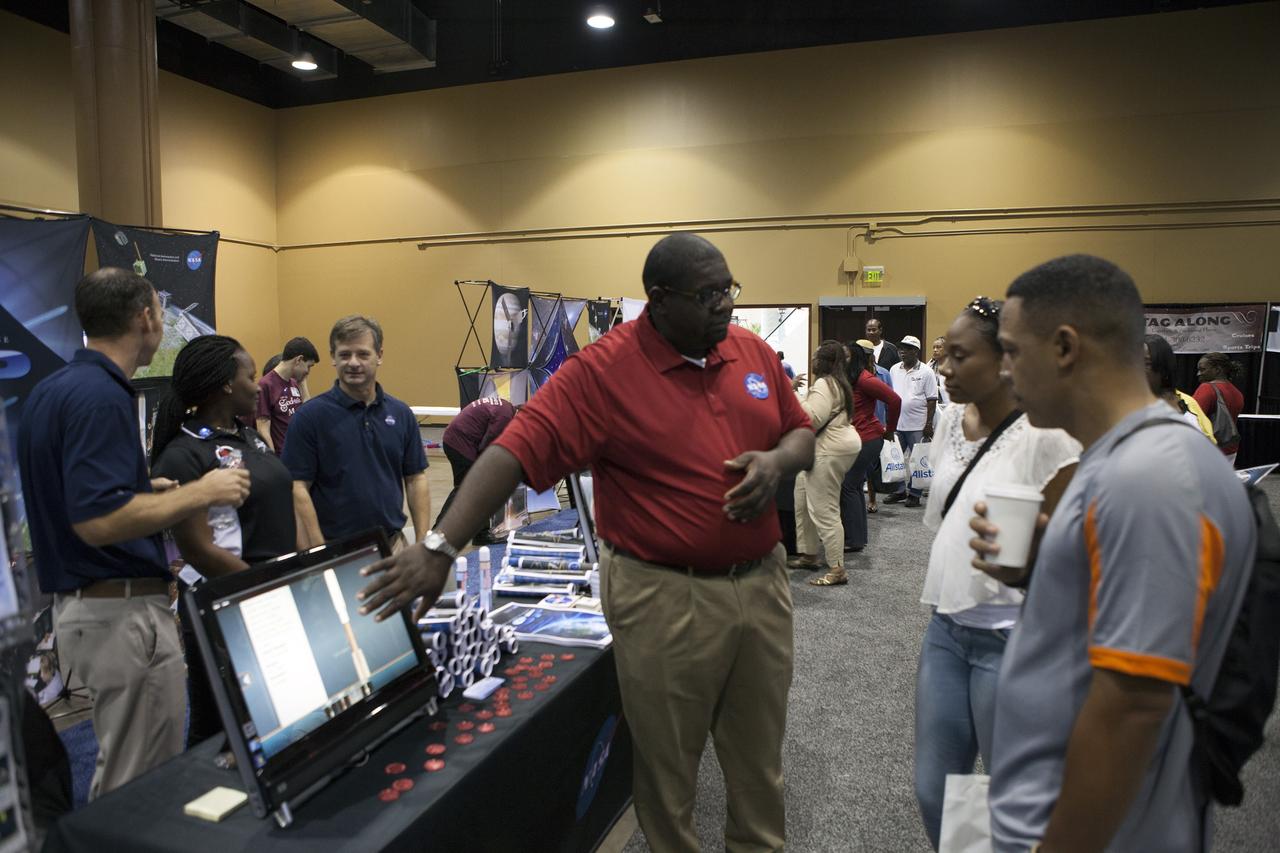

KISSIMMEE, Fla. – Guests at the Tom Joyner Family Reunion listen as Malcom Boston of the Fleet System Integration Branch of the Launch Services Program LSP explains a computer demonstration on rockets. Behind the table, from the left, are Brian Norton, Emily Fields and Randy Mizelle, all from the Program Planning Office in LSP. The Tom Joyner Family Reunion is designed to present uplifting programs, entertainment and information about growing, diverse communities. An annual event of the nationally-syndicated Tom Joyner Morning Show, the many exhibits included NASA's participation focusing on encouraging young people to consider studies and careers in STEM -- science, technology, engineering and math. NASA's Education Division promoted the benefits of math and scientific learning along with career opportunities offered by the space agency. The activities took place at the Gaylord Palms Resort in Kissimmee, Florida, during the Labor Day weekend. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

From left, Alan Zide, Solar Orbiter Program executive, NASA Headquarters; Tim Dunn, launch director, NASA Launch Services Program (LSP); and Scott Messer, NASA LSP Program Manager, United Launch Alliance, participate in a prelaunch news conference for the Solar Orbiter mission at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 7, 2020. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. The spacecraft was developed by Airbus Defence and Space. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Solar Orbiter will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Feb. 9, 2020, from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
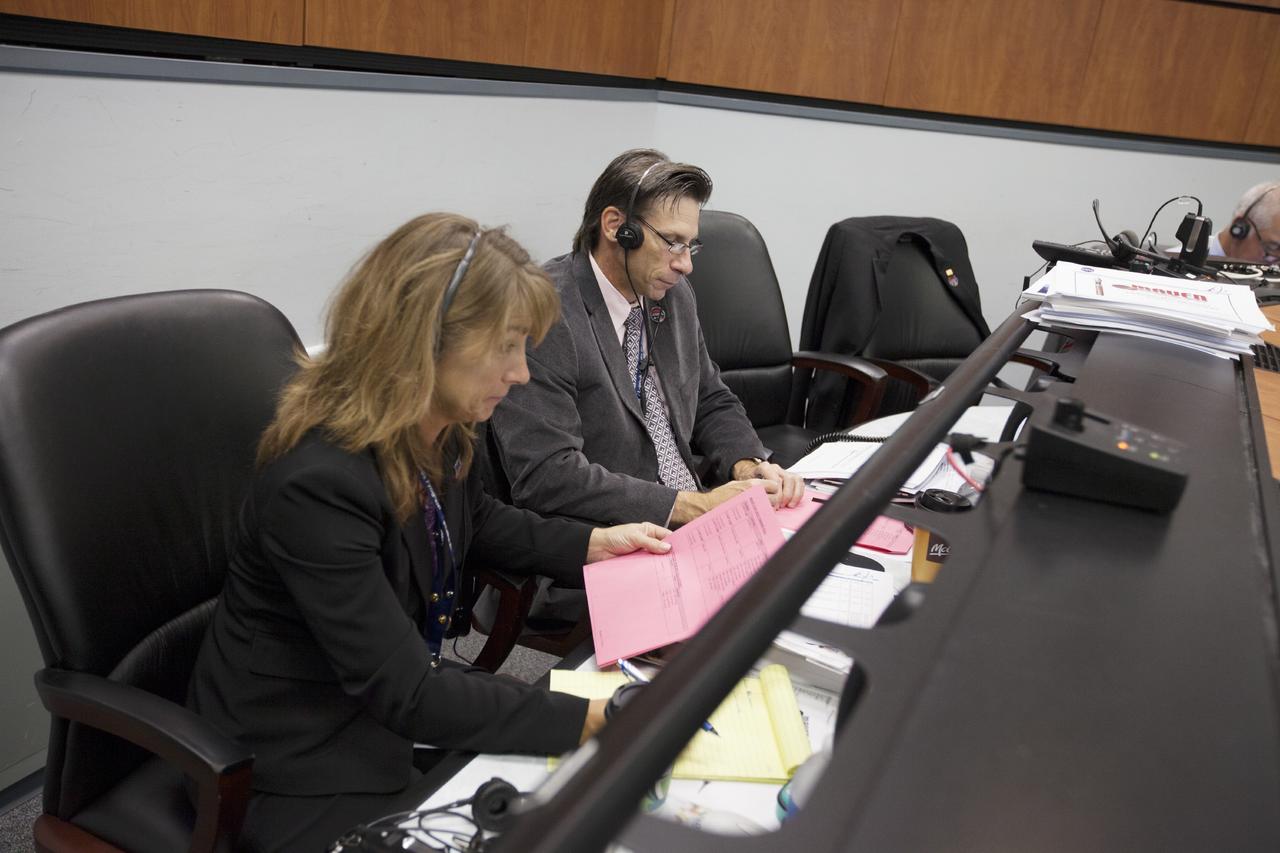

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center NASA managers monitor progress of the countdown for the launch the agency's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft. From the left are Amanda Mitskevich, program manager of NASA's Launch Services Program, or LSP, and Chuck Dovale, deputy program manager of LSP. MAVEN was launched on Nov. 18, 2013 from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
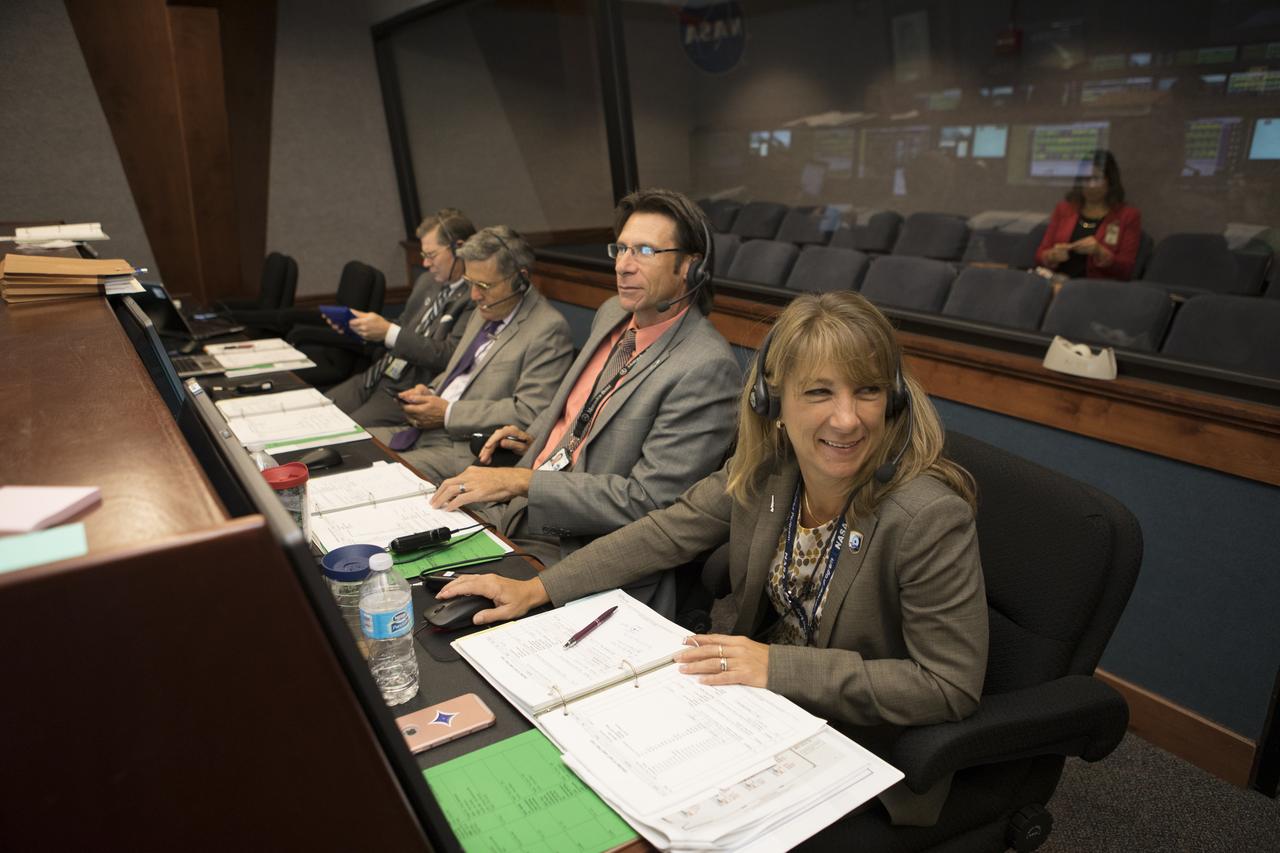

In the Mission Director's Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Amanda Mitskevich, facing the camera, is program manager for NASA's Launch Services Program (LSP) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Seated next to her is Chuck Dovale, deputy LSP program manager. They are monitoring the progress of preparations to launch eight Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System, or CYGNSS, spacecraft. The CYGNSS satellites will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a crucial role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
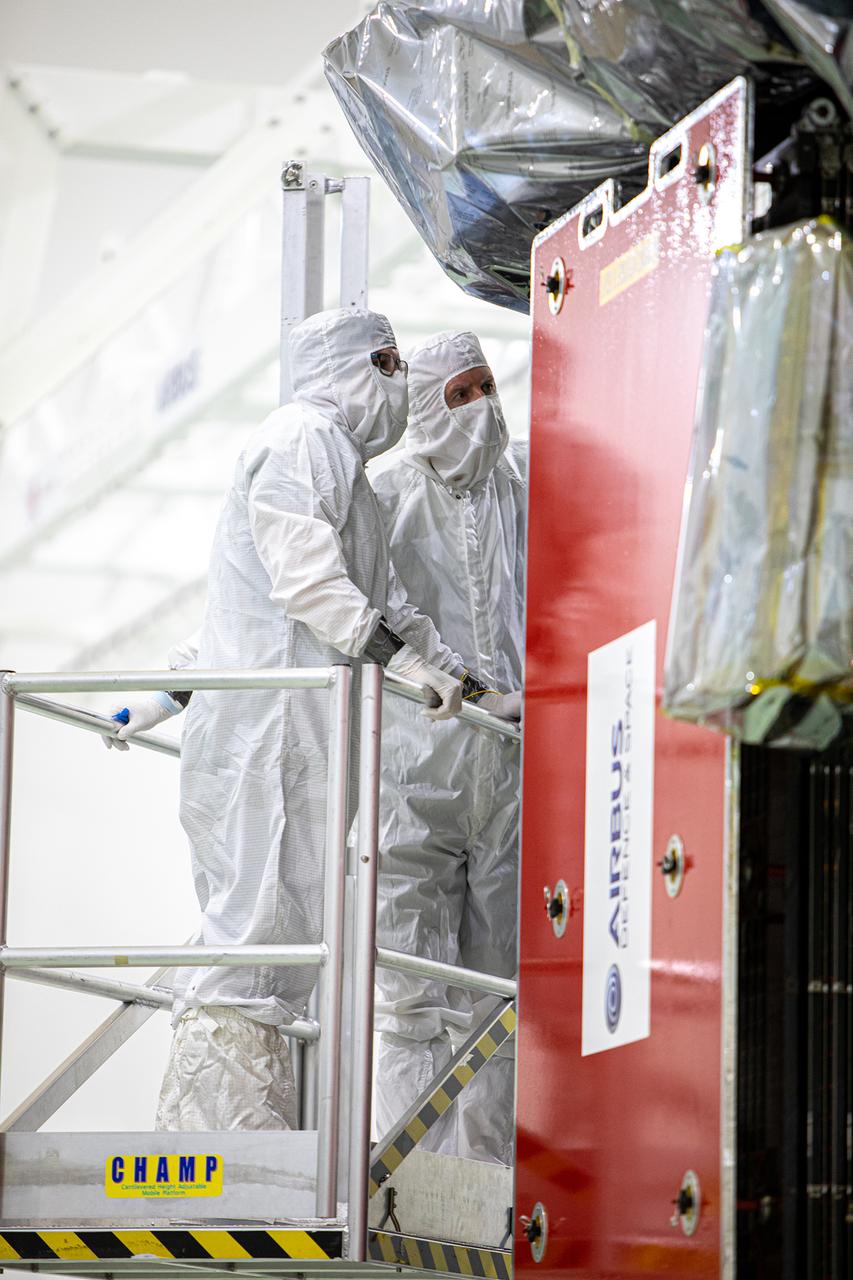

Members of the European Space Agency (ESA)/Airbus Defence and Space Solar Orbiter team inspect the Solar Orbiter spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, on Dec. 16, 2019. On this day, media personnel were given the opportunity to view and photograph the spacecraft up close. Representatives from NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), ESA, United Launch Alliance (ULA), Airbus, and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center provided an overview of the mission, spacecraft and launch vehicle. Solar Orbiter is a space mission of international collaboration between ESA and NASA, and the spacecraft has been developed by Airbus. The mission will study the Sun and how it can affect the space environment throughout the solar system, and it also will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles.
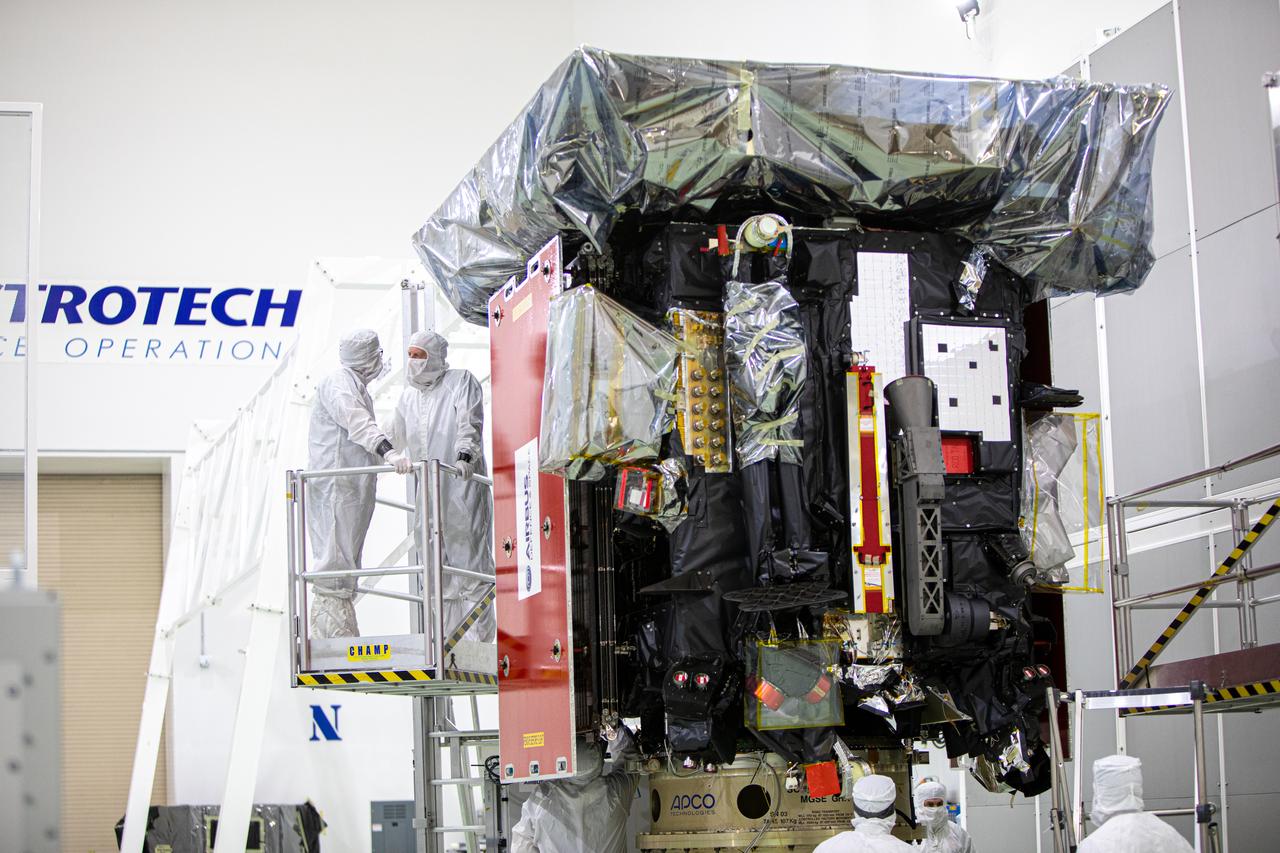

Members of the European Space Agency (ESA)/Airbus Defence and Space Solar Orbiter team inspect the Solar Orbiter spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, on Dec. 16, 2019. On this day, media personnel were given the opportunity to view and photograph the spacecraft up close. Representatives from NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), ESA, United Launch Alliance (ULA), Airbus, and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center provided an overview of the mission, spacecraft and launch vehicle. Solar Orbiter is a space mission of international collaboration between ESA and NASA, and the spacecraft has been developed by Airbus. The mission will study the Sun and how it can affect the space environment throughout the solar system, and it also will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles.
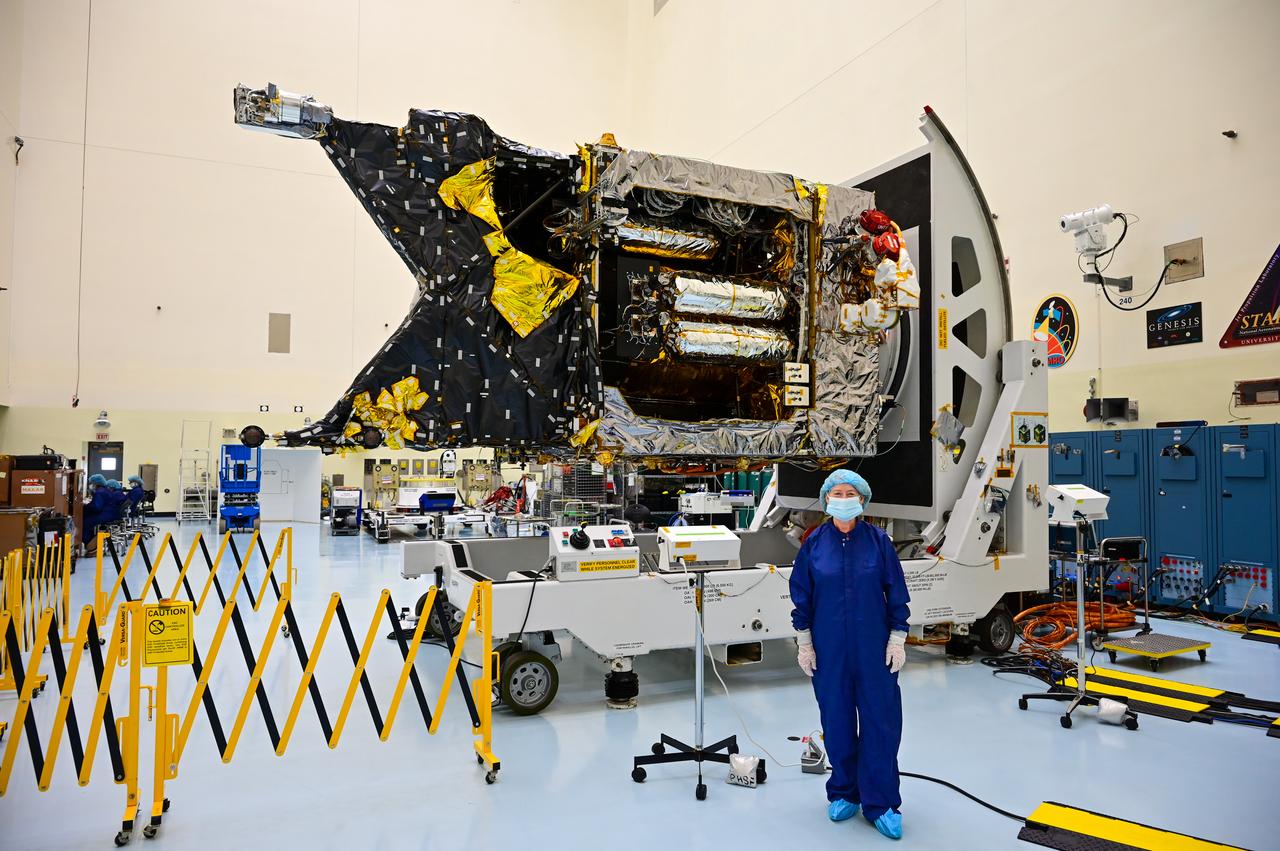

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy visits Kennedy Space Center in Florida and views the agency’s Psyche spacecraft inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on May 19, 2022. The mission is targeting an Aug. 1 launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
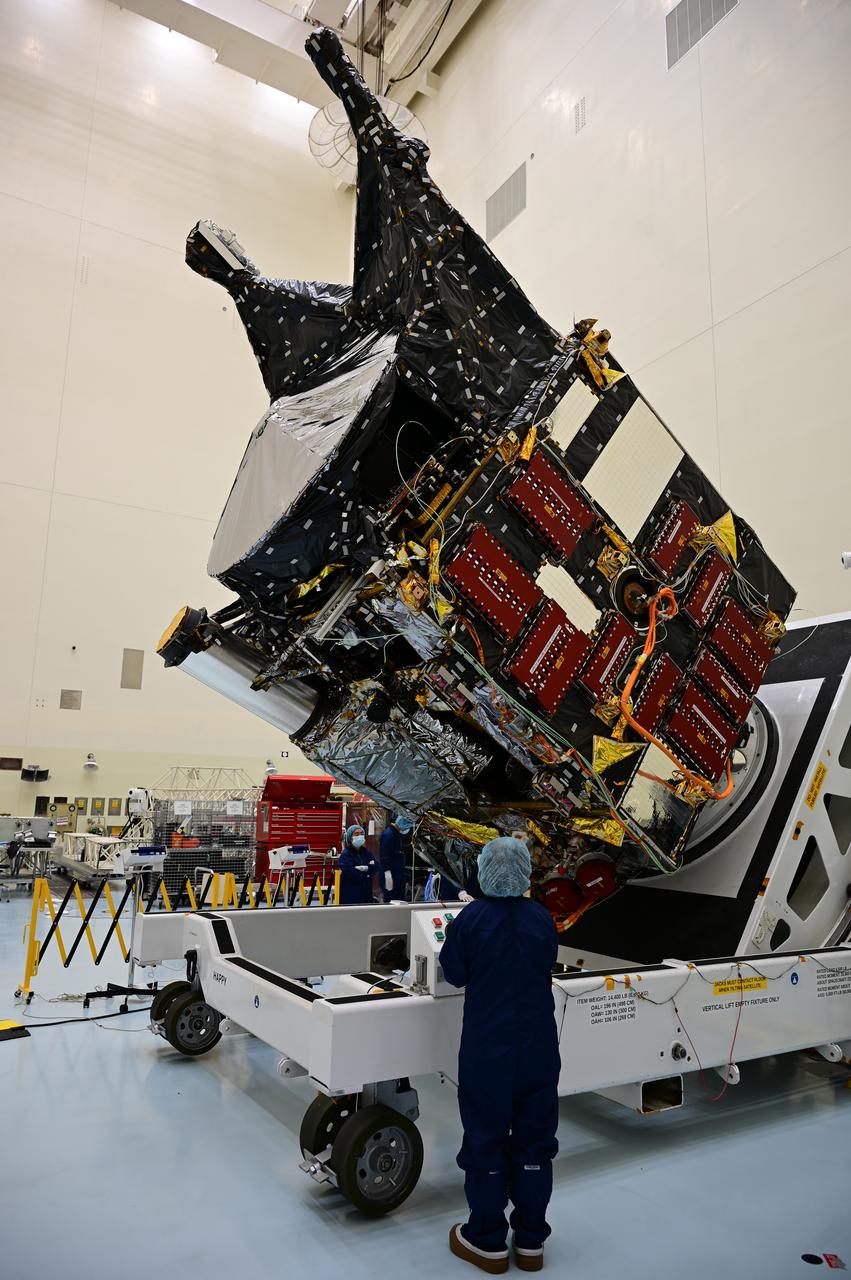

A team working on NASA’s Psyche spacecraft transitioned it from a vertical to a horizontal test configuration during prelaunch processing inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 9, 2022. The mission is targeting an Aug. 1 launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
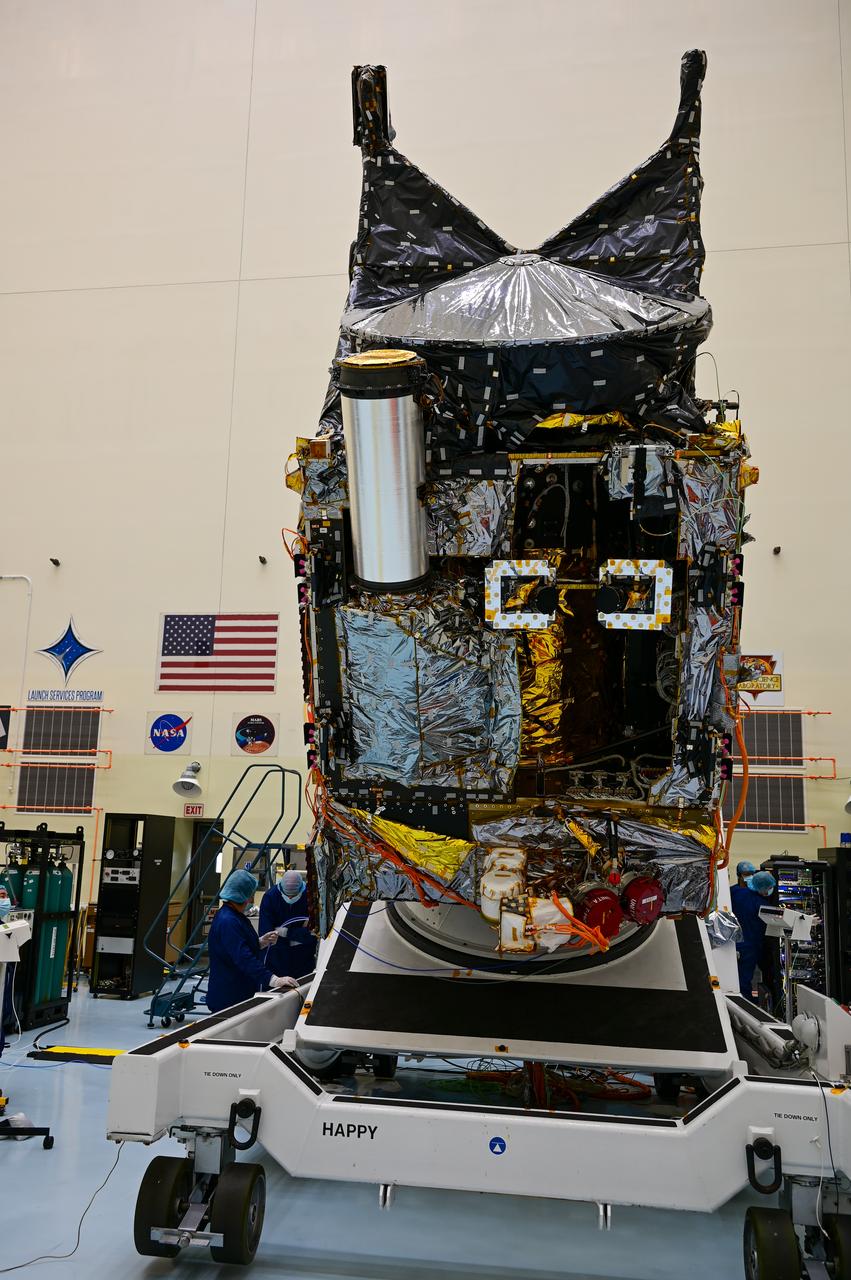

A team working on NASA’s Psyche spacecraft transitioning it from a vertical to horizontal test configuration during prelaunch processing inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 9, 2022. The mission is targeting an Aug. 1 launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.
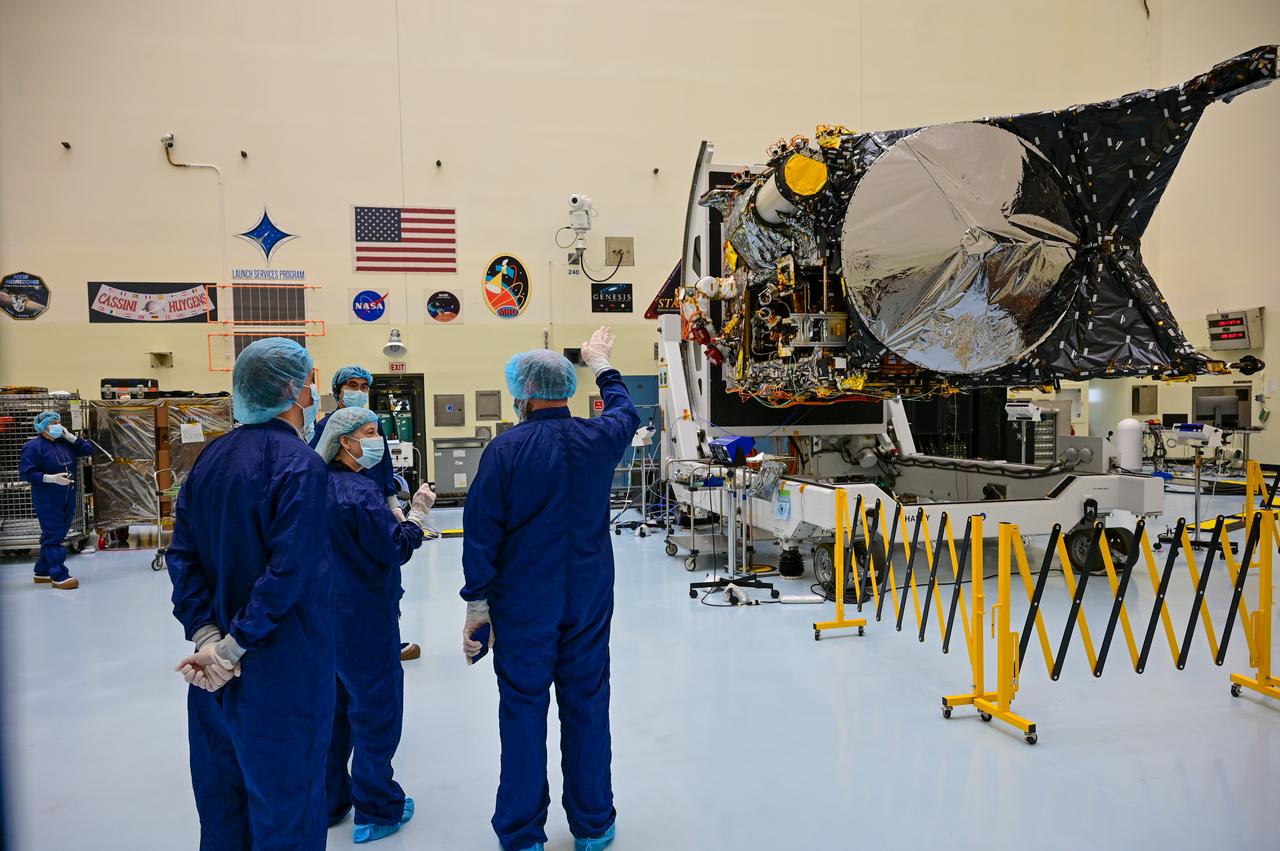

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy visits Kennedy Space Center in Florida and receives a briefing by team members from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory on the agency’s Psyche spacecraft inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility on May 19, 2022. Melroy is in view second from right. The mission is targeting an Aug. 1 launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. The spacecraft will use solar-electric propulsion to travel approximately 1.5 billion miles to rendezvous with its namesake asteroid in 2026. The Psyche mission is led by Arizona State University. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for the mission’s overall management, system engineering, integration and testing, and mission operations. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, provided the high-power solar electric propulsion spacecraft chassis. NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP), based at Kennedy, is managing the launch.