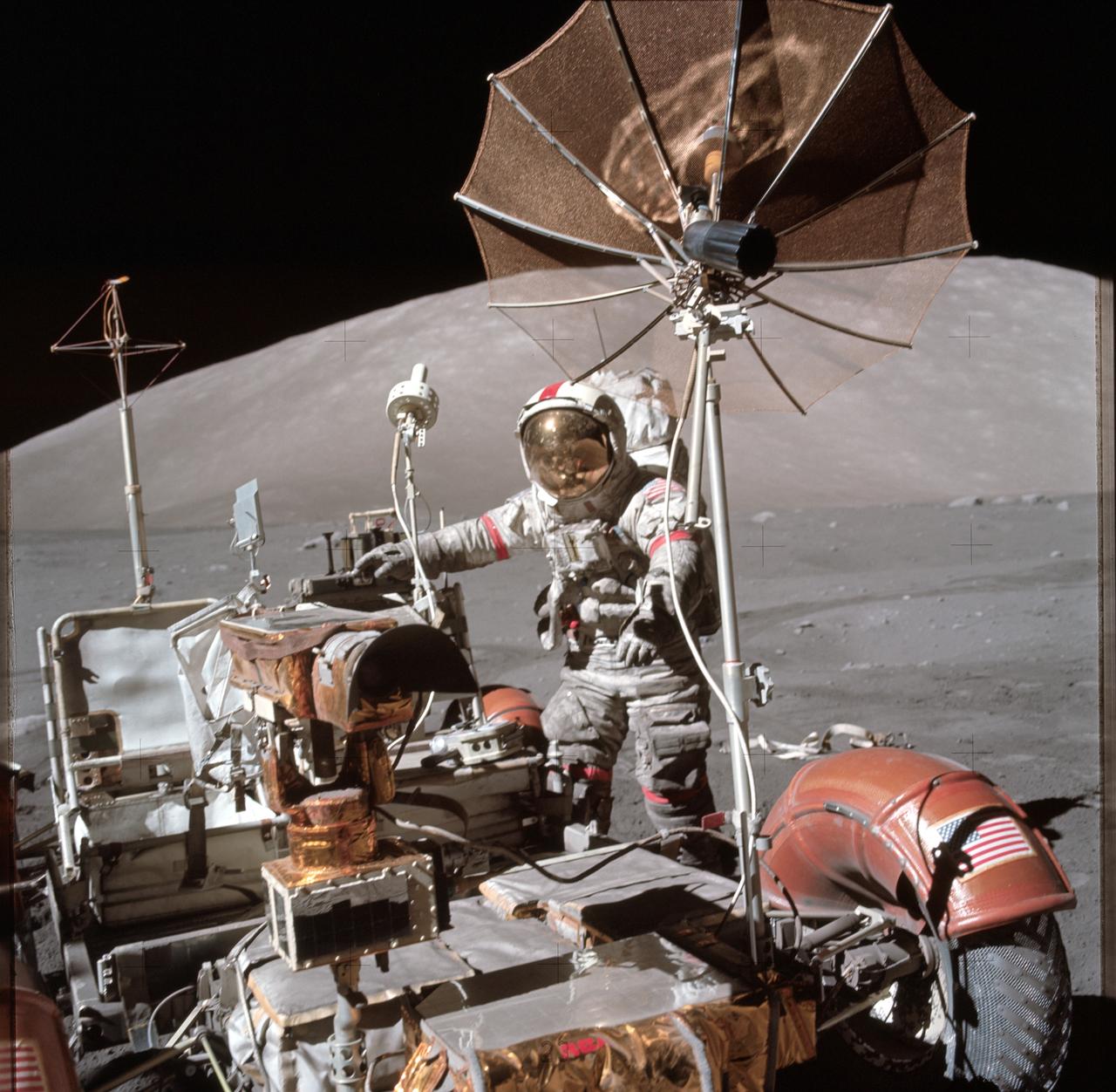

AS17-134-20476 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander, approaches the parked Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the lunar surface during the flight's third period of extravehicular activity (EVA). South Massif can be seen in the background. The photograph was taken with a hand-held Hasselblad camera by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. While the two explored the surface of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
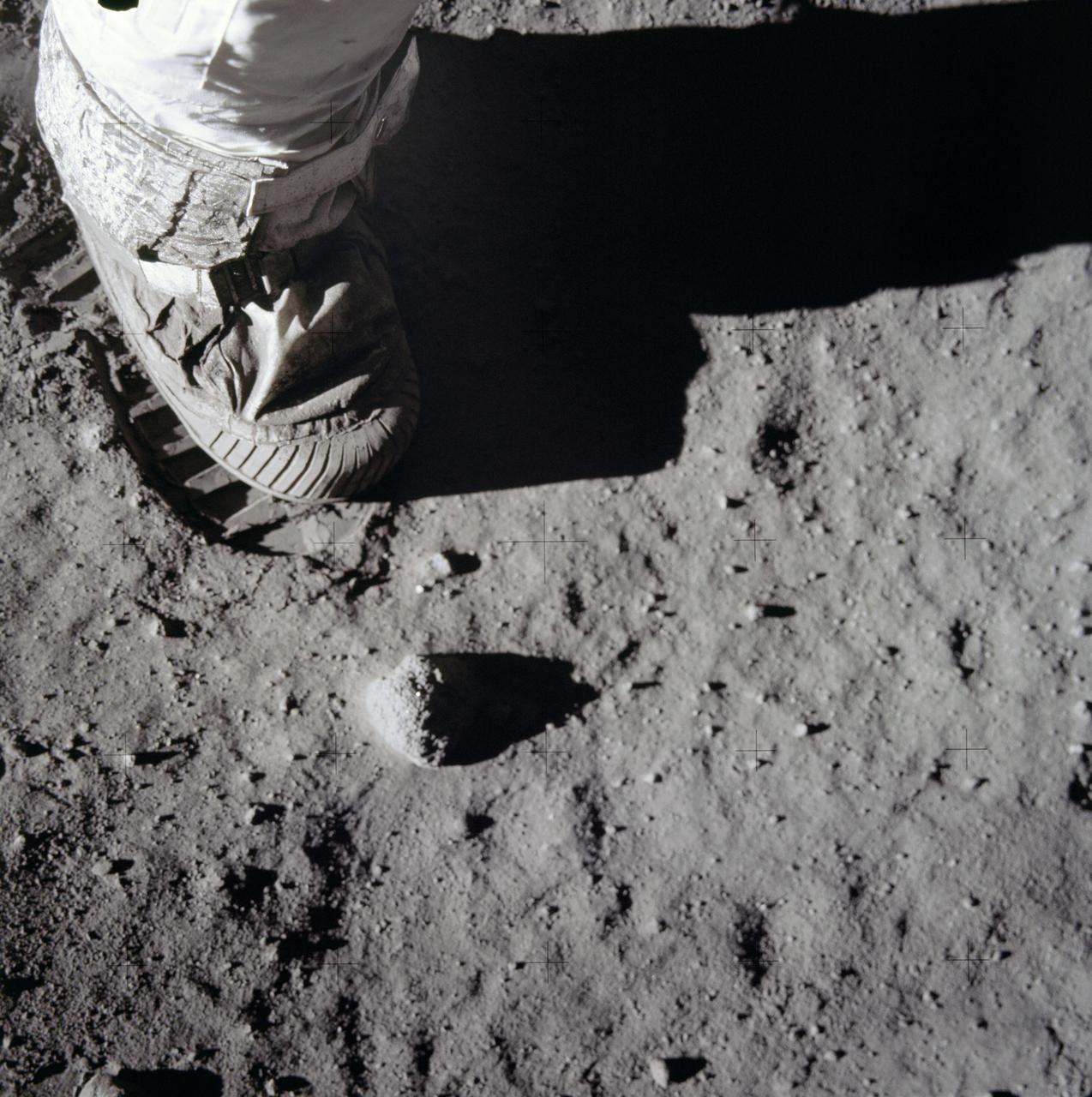

AS11-40-5880 (20 July 1969) --- A close-up view of an astronaut's boot and bootprint in the lunar soil, photographed with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin A. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM)" Columbia" in lunar orbit.
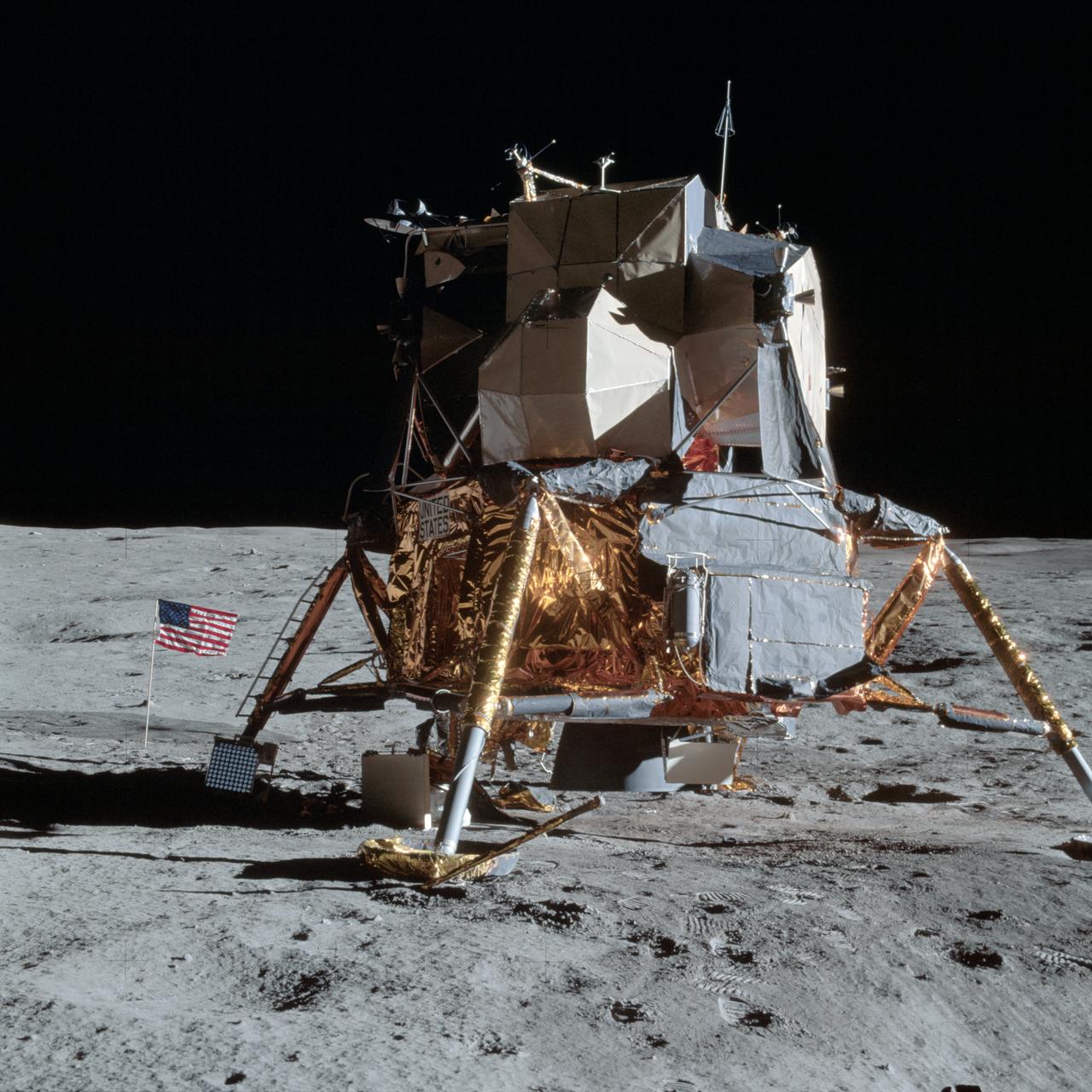
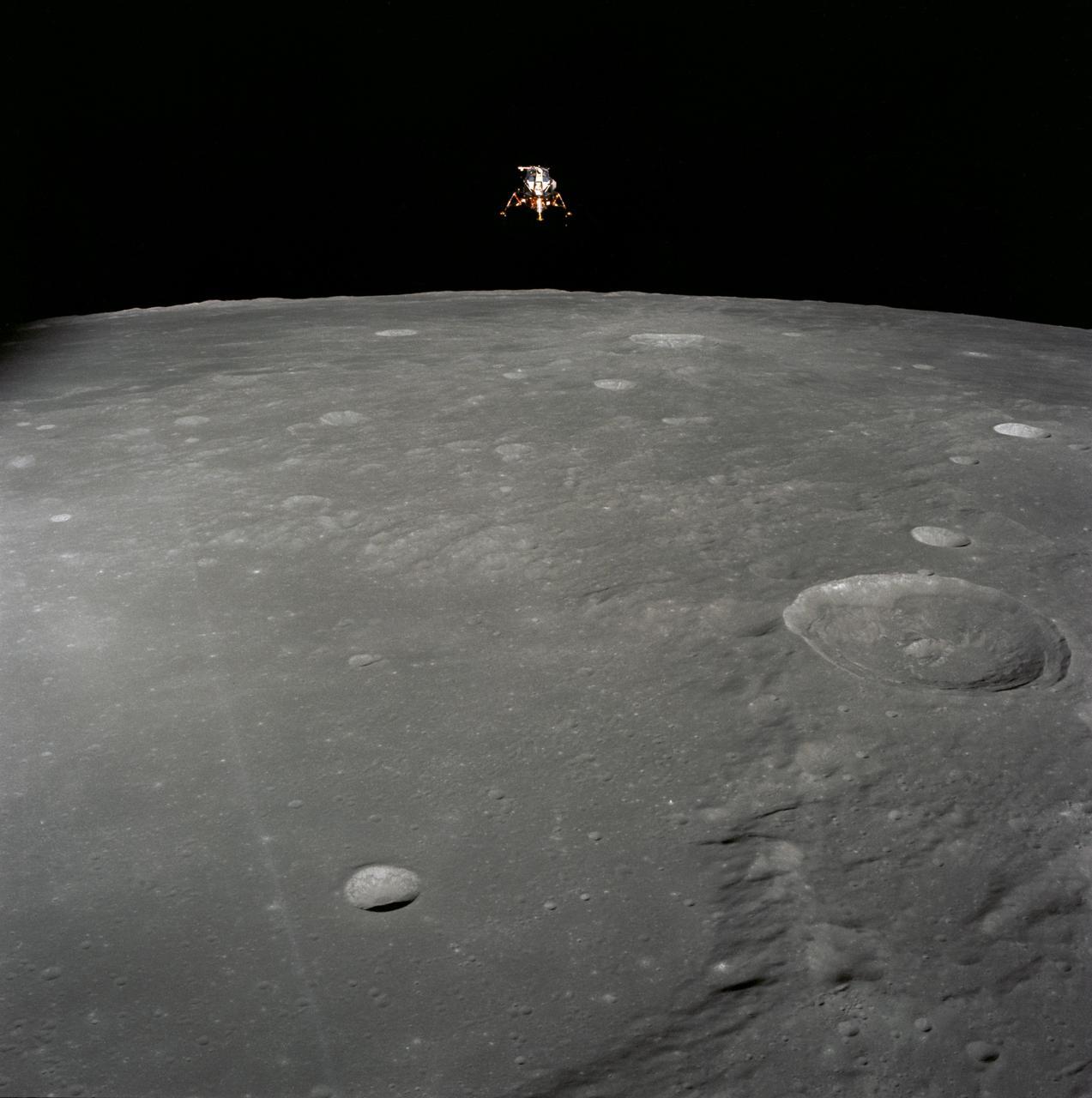
AS14-66-9277 (5 Feb. 1971) --- An excellent view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) on the moon, as photographed during the first Apollo 14 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The astronauts have already deployed the U.S. flag. Note the laser ranging retro reflector (LR-3) at the foot of the LM ladder. The LR-3 was deployed later. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
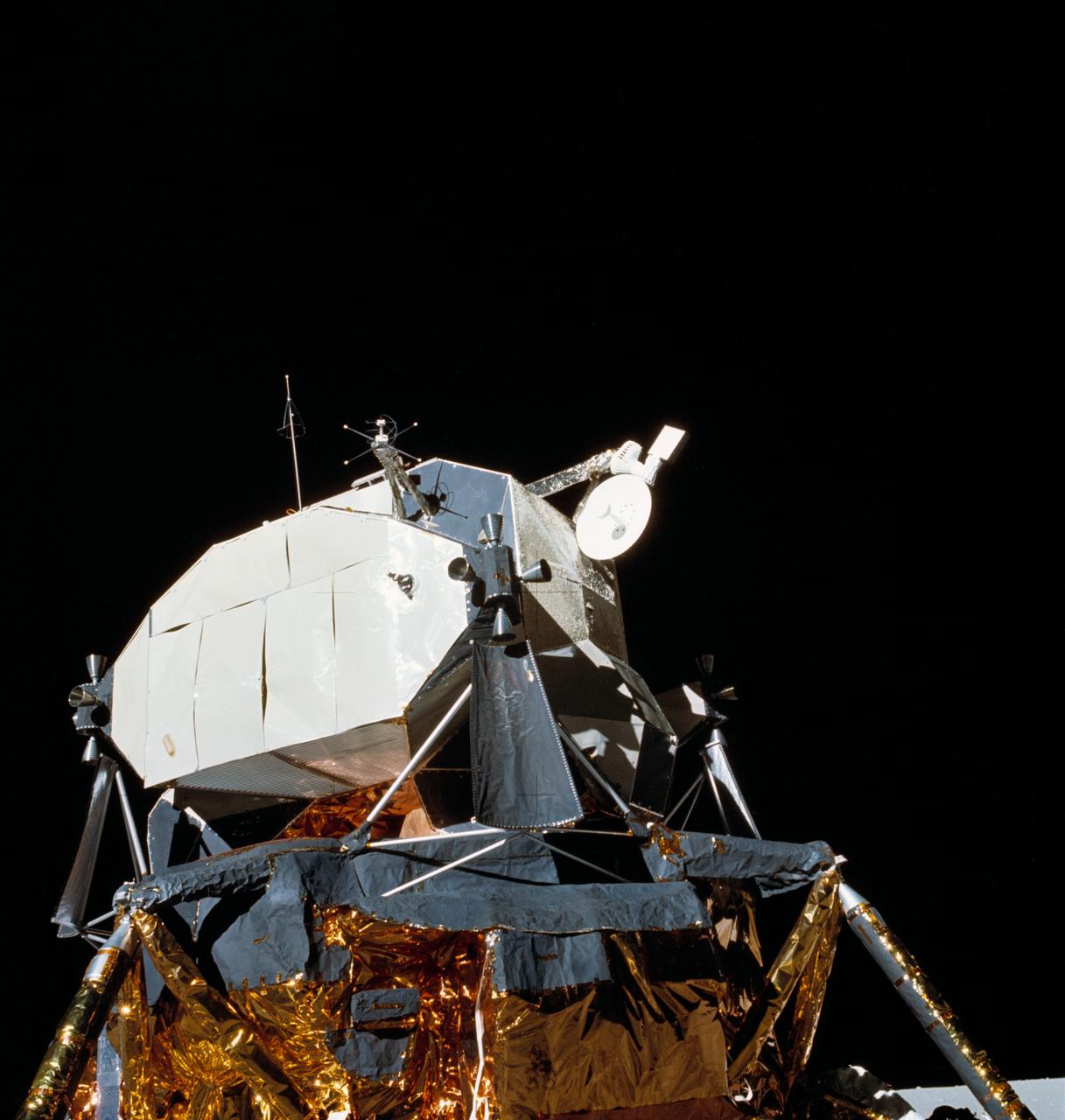

AS16-113-18334 (21 April 1972) --- View of the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" parked on the lunar surface. During their post mission press conference, the Apollo 16 crewmembers called attention to the steerable S-band antenna, which was "frozen" in a yaw axis during much of the flight. This view of the LM was photographed by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., the lunar module pilot, during the mission's first extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronauts John W. Young, commander, and Duke had earlier descended in the LM to explore the Descartes region of the moon, while astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.

AS11-40-5875 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the first lunar landing mission, poses for a photograph beside the deployed United States flag during an Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The Lunar Module (LM) is on the left, and the footprints of the astronauts are clearly visible in the soil of the moon. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm Hasselblad lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM, the "Eagle", to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit. Photo credit: NASA

AS11-40-5878 (20 July 1969) --- A close-up view of an astronaut's bootprint in the lunar soil, photographed with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
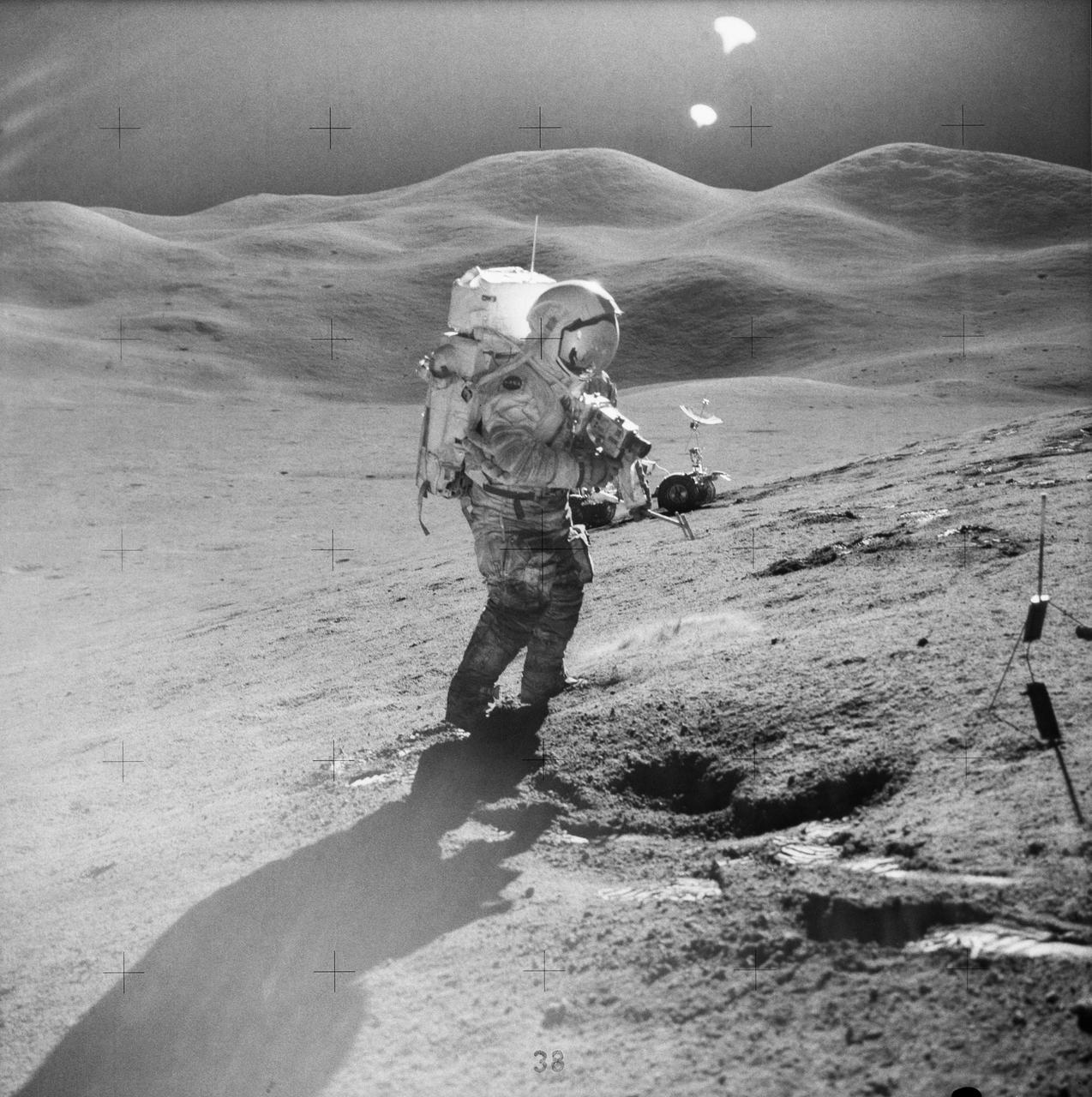

AS15-85-11514 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, commander, standing on the slope of Hadley Delta, uses a 70mm camera during Apollo 15 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. He is 10.5 miles (or 17.5 kilometers) from the base of the Apennine Mountains seen in the background. Scott carries tongs in his left hand. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is in the background. This view is looking east. While astronauts Scott and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
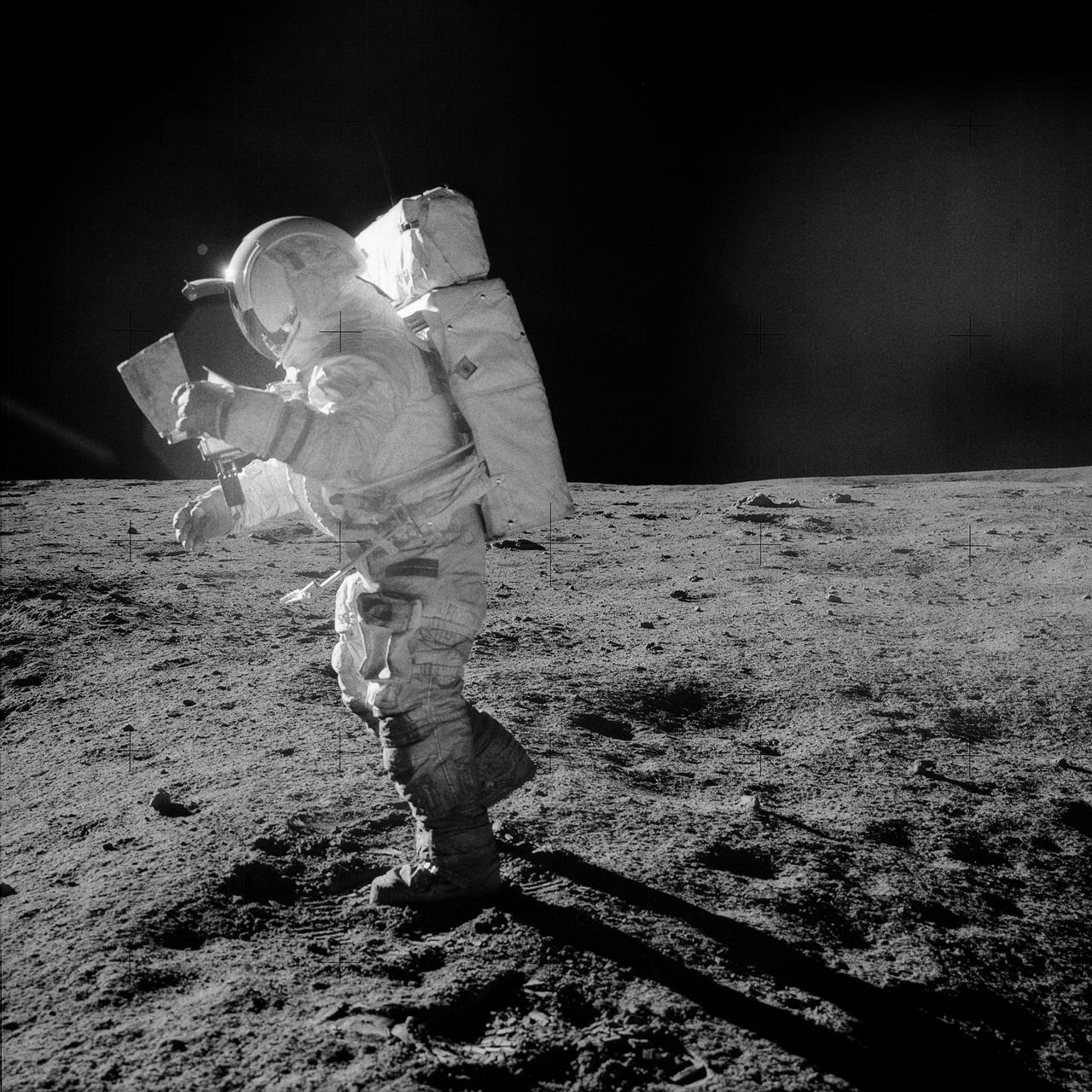

AS14-64-9089 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, moves across the lunar surface as he looks over a traverse map during an extravehicular activity (EVA). Lunar dust can be seen clinging to the boots and legs of the space suit. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Mitchell explored the lunar surface while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, orbited the moon in the Command and Service Modules (CSM).
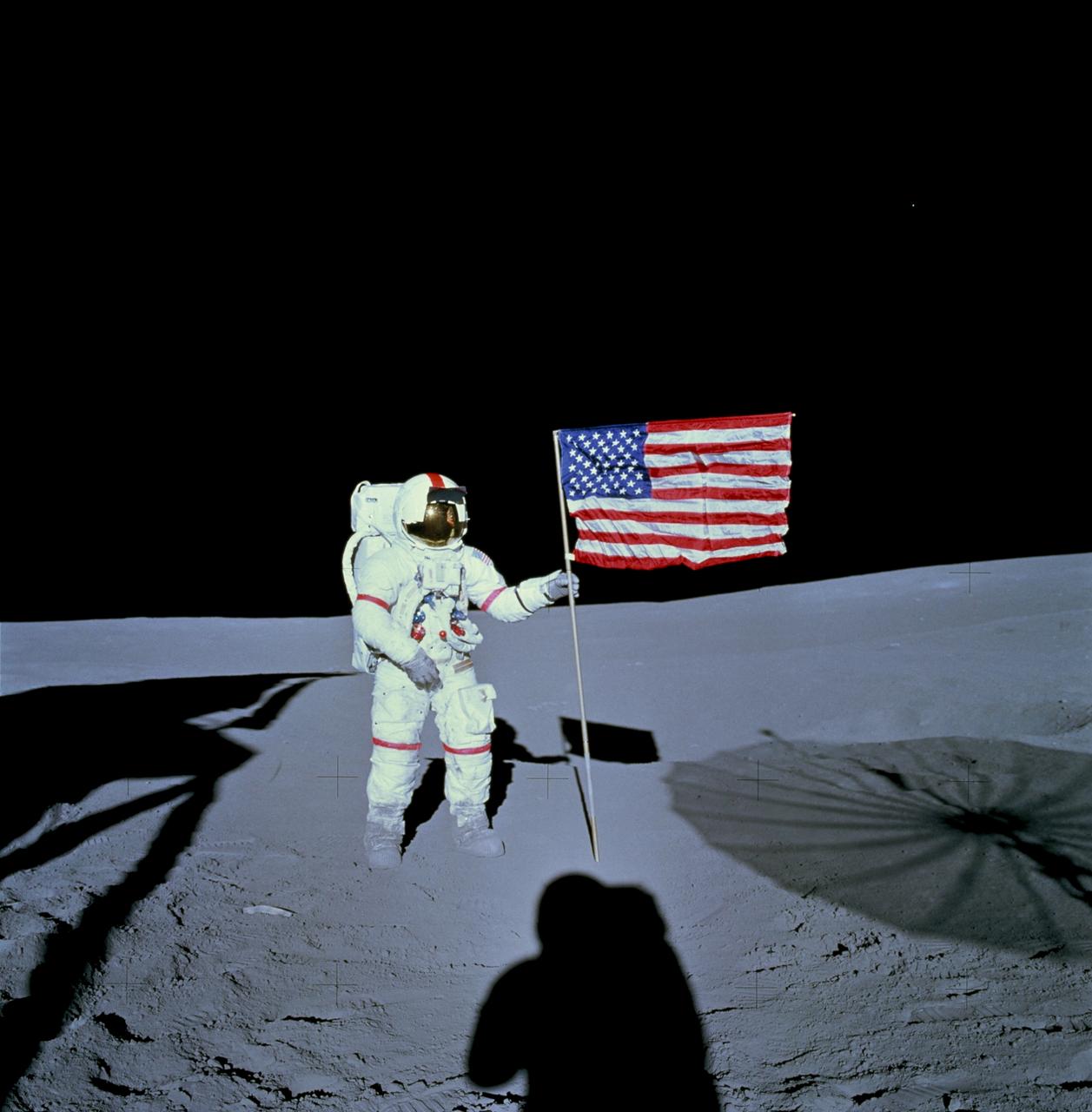

AS14-66-9232 (5 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, stands by the deployed United States flag on the lunar surface during the early moments of the first extravehicular activity (EVA) of the mission. Shadows of the Lunar Module (LM), astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, and the erectable S-Band Antenna surround the scene of the third flag implanting to be performed on the lunar surface. While astronauts Shepard and Mitchell descended in the LM ?Antares? to explore the Fra Mauro region of the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) ?Kitty Hawk? in lunar orbit.
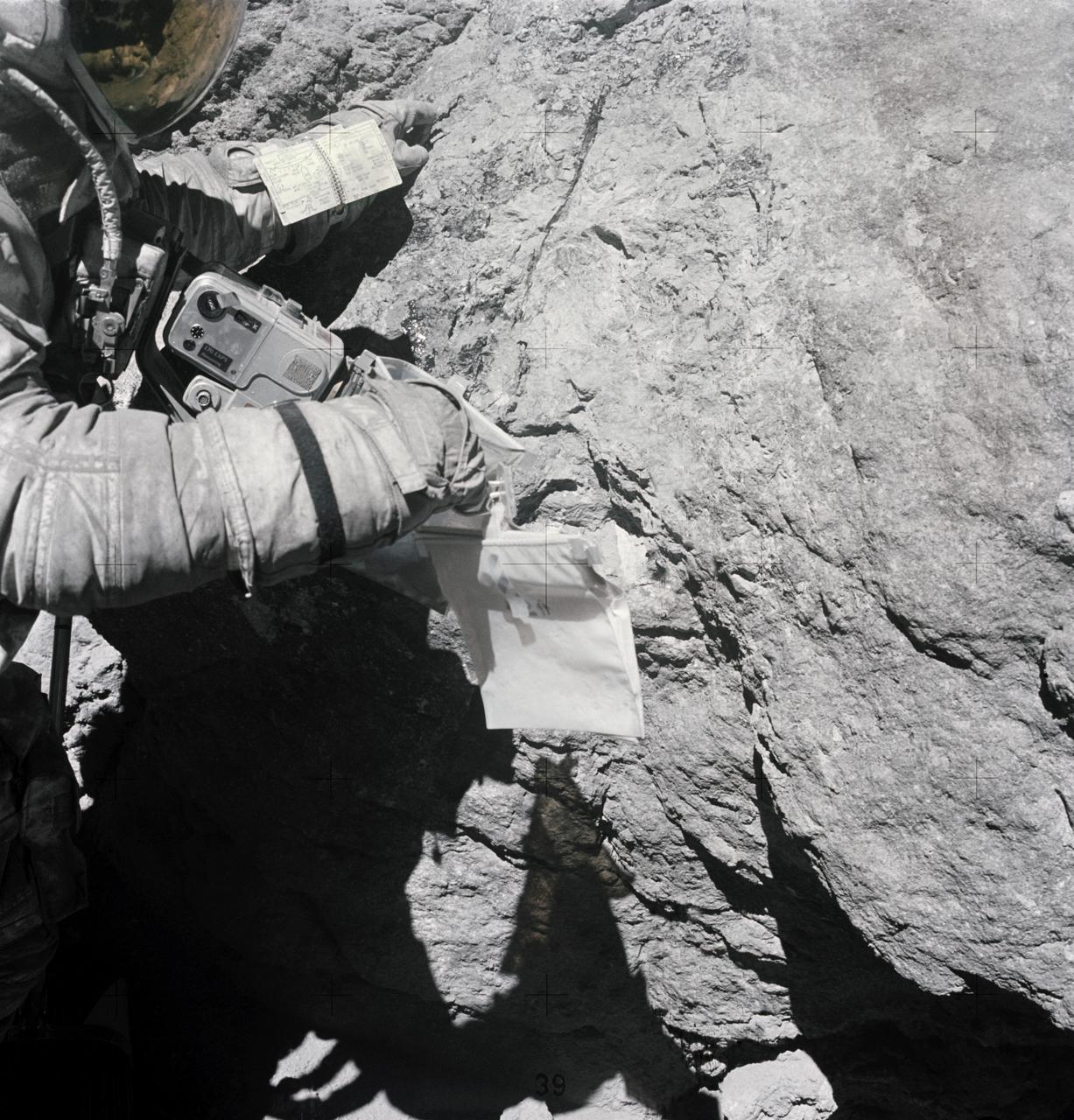

AS16-116-18649 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, examines closely the surface of a large boulder at North Ray Crater during the third Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. This picture was taken by astronaut John W. Young, commander. Note the chest-mounted 70mm Hasselblad camera. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
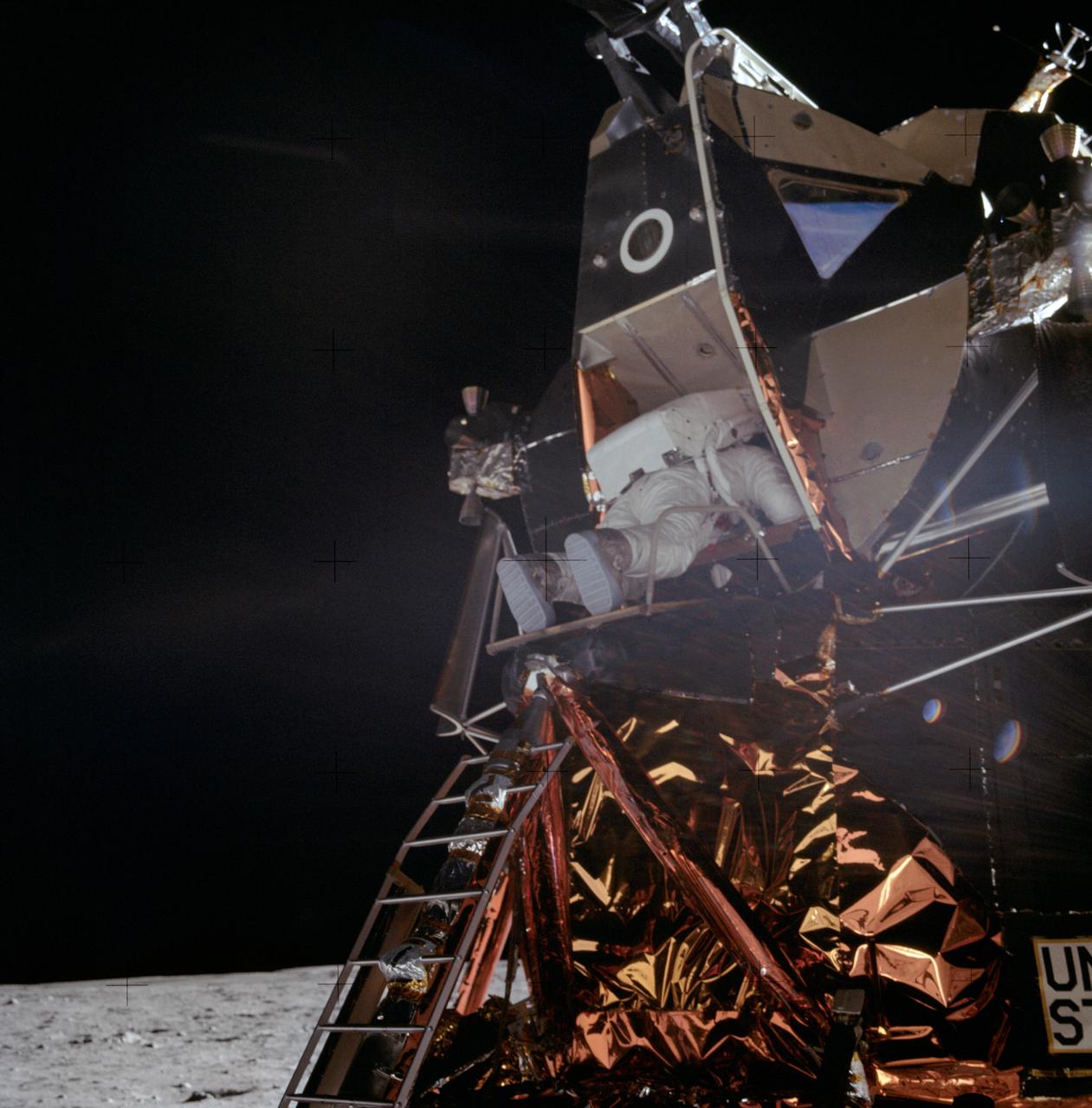

AS11-40-5863 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, is photographed egressing the Lunar Module (LM) during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. This photograph was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, with a 70mm lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

AS16-113-18339 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, leaps from the lunar surface as he salutes the United States flag at the Descartes landing site during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, took this picture. The Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" is on the left. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is parked beside the LM. The object behind Young (in the shade of the LM) is the Far Ultraviolet Camera/Spectrograph (FUC/S). Stone Mountain dominates the background in this lunar scene. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the LM to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
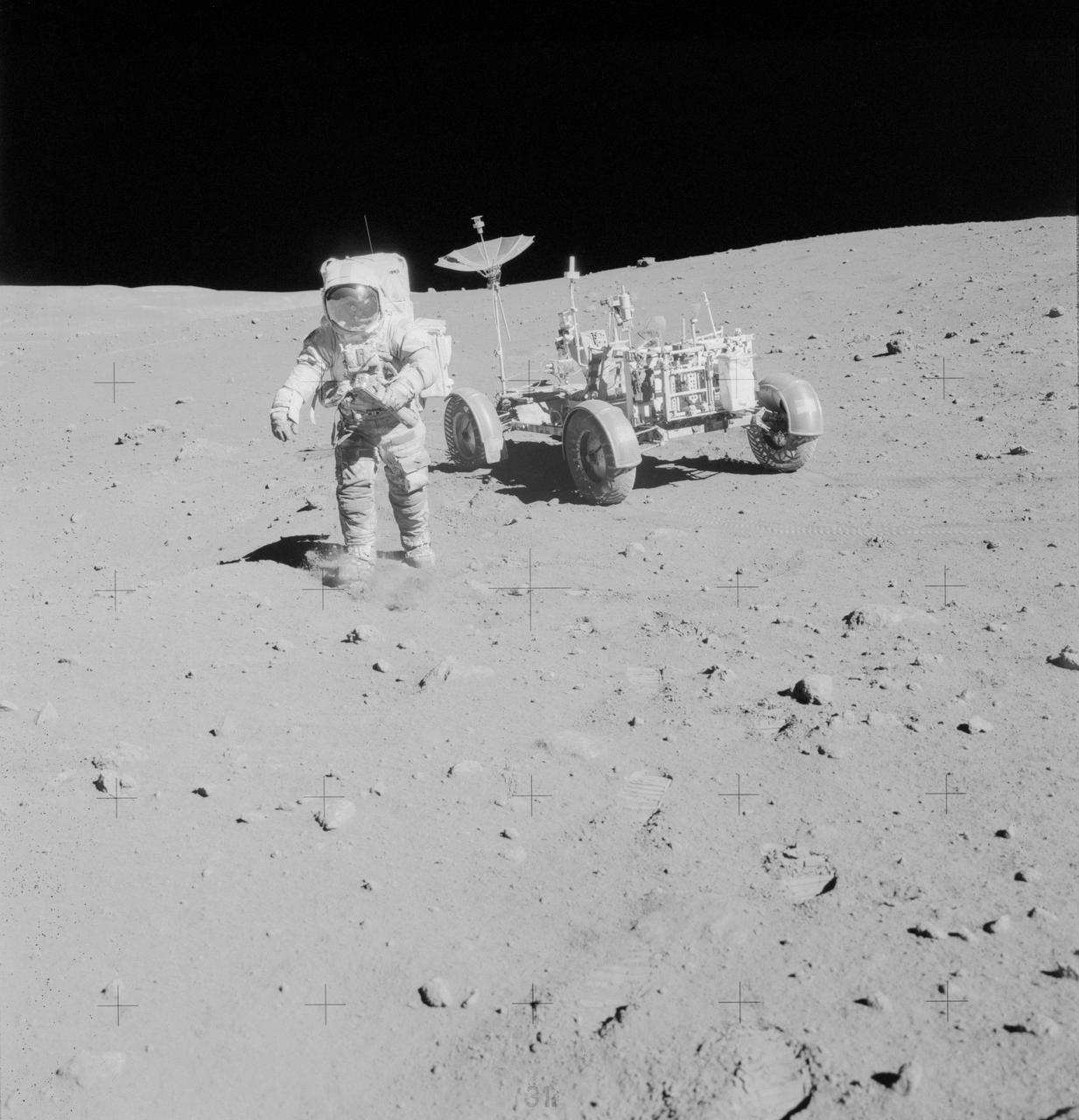

AS15-82-11168 (2 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, walks away from the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during the third Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The LRV is parked a short distance from the rim of Hadley Rille. The far wall of the rille is in the distance at extreme upper left. Irwin is holding the 500mm Hasselblad camera in his left hand. This photograph was taken by astronaut David R. Scott, commander. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
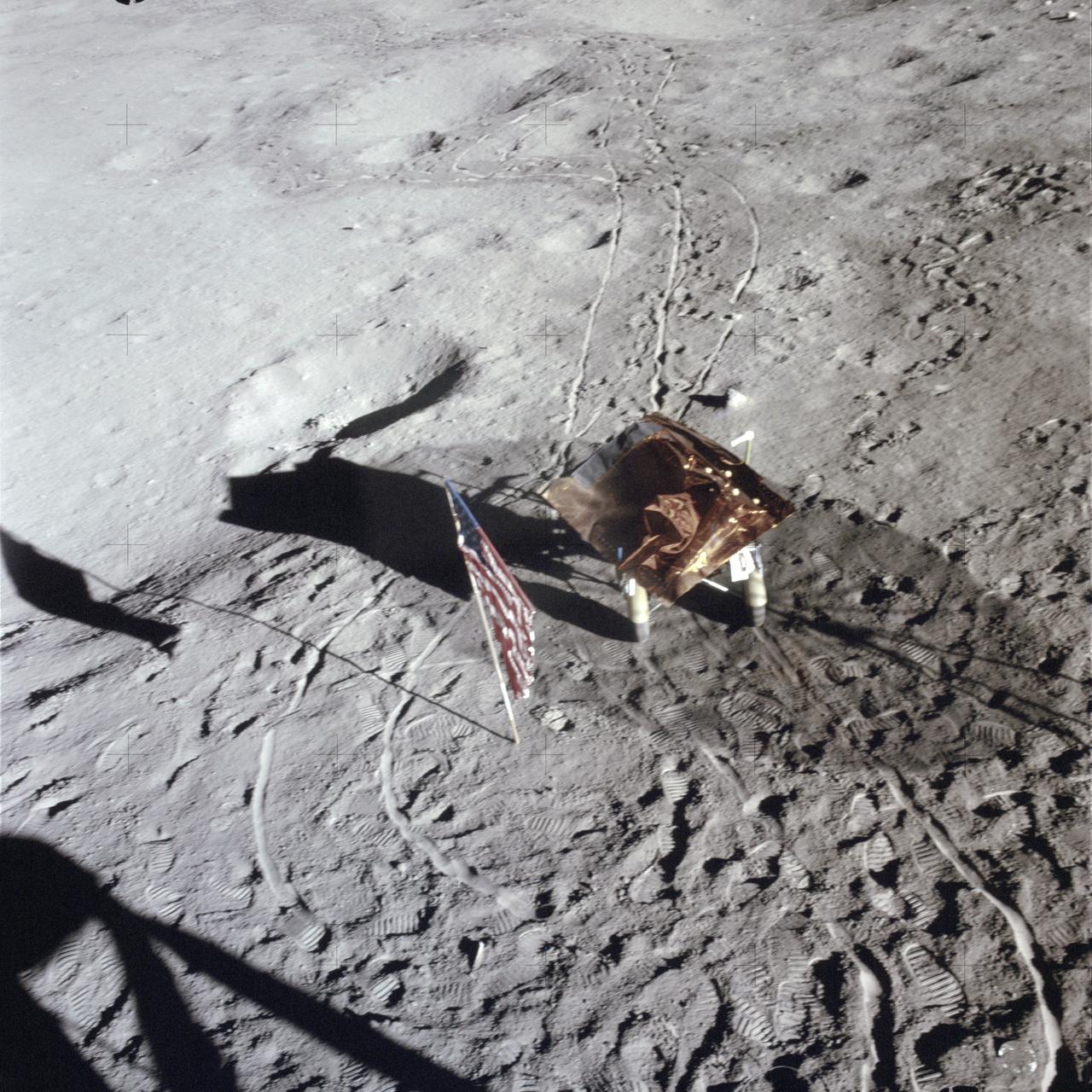

AS14-66-9325 (5 Feb. 1971) --- The third United States flag to be deployed on the lunar surface, footprints, wheel tracks and the "Rickshaw"-type portable workbench, as seen by the two moon-exploring astronauts from inside the Lunar Module (LM), give evidence of a busy first extravehicular activity (EVA) period. The two-wheeled cart is the Apollo modularized equipment transporter (MET), covered with a sheet of foil material to protect the cameras and rock box between EVAs. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

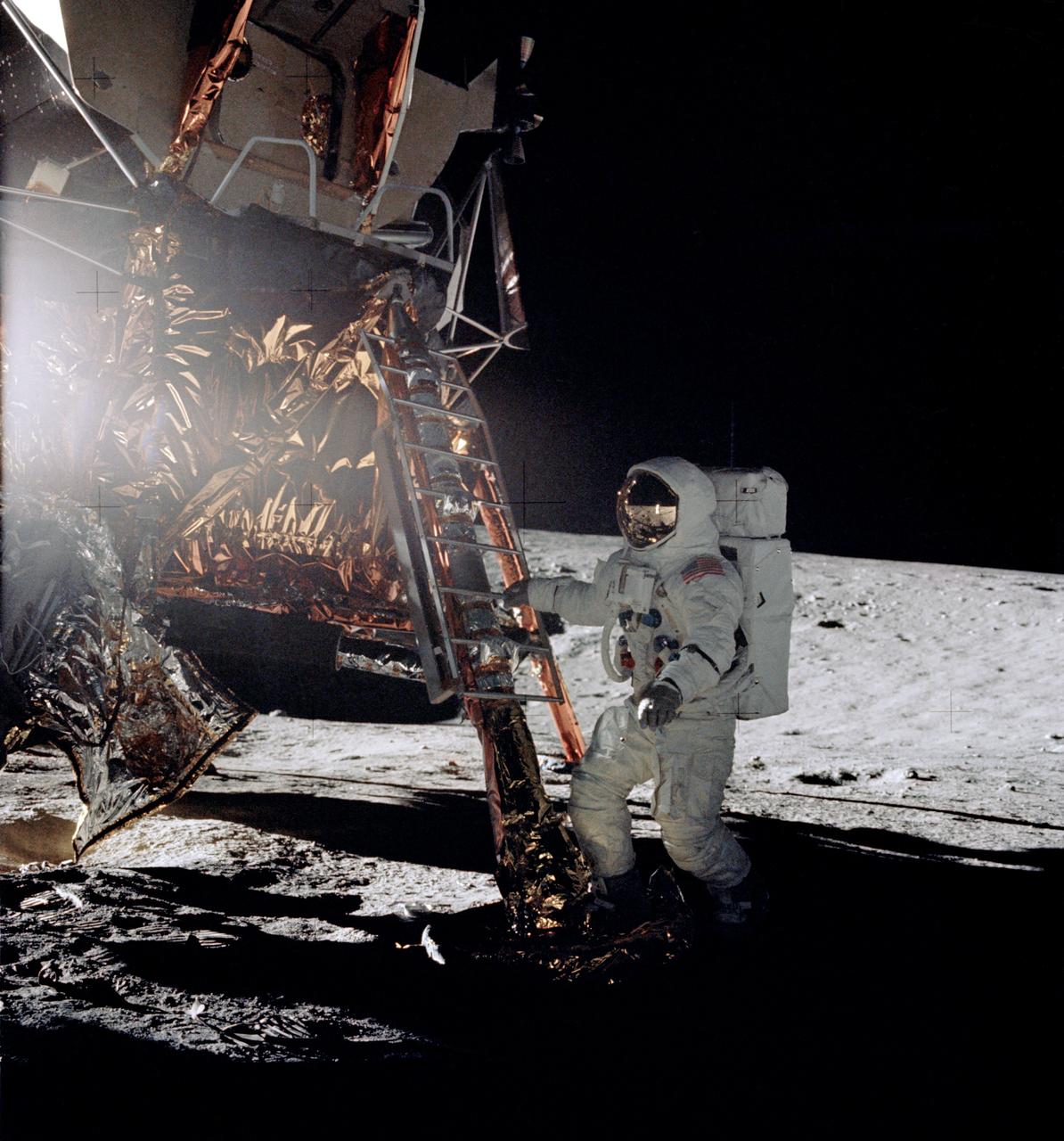
AS11-40-5868 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descends the steps of the Lunar Module (LM) ladder as he prepares to walk on the moon. He had just egressed the LM. This photograph was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). While Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM "Eagle" to explore the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
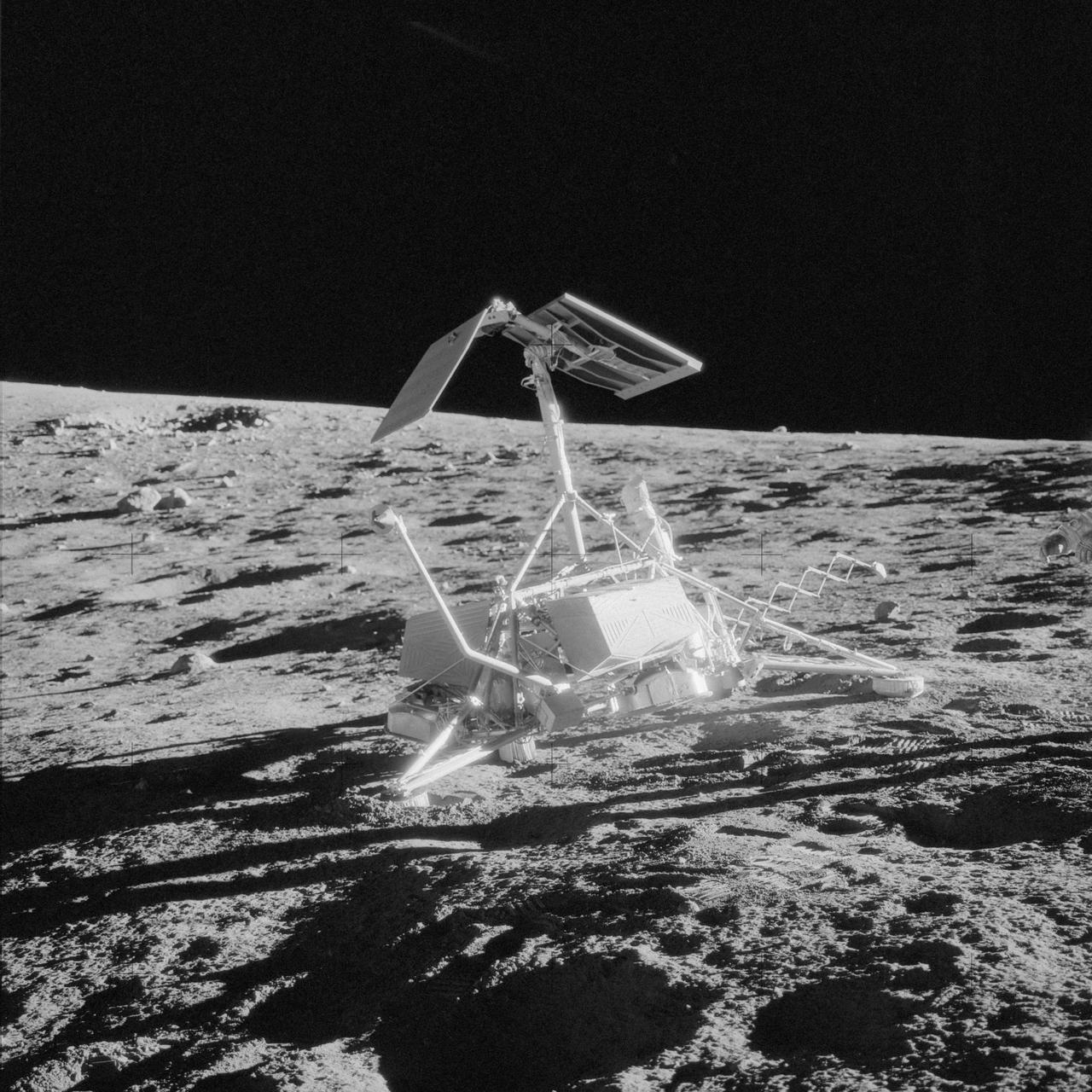

AS12-48-7121 (20 Nov. 1969) --- An excellent view of the unmanned Surveyor 3 spacecraft which was photographed during the Apollo 12 second extravehicular activity (EVA) on the surface of the moon. The Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM), with astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, aboard landed within 600 feet of Surveyor 3 in the Ocean of Storms. The television camera and several other pieces were taken from Surveyor 3 and brought back to Earth for scientific examination. Surveyor 3 landed on the side of this small crater in the Ocean of Storms on April 19, 1967. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 12 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while Conrad and Bean descended to explore the moon.
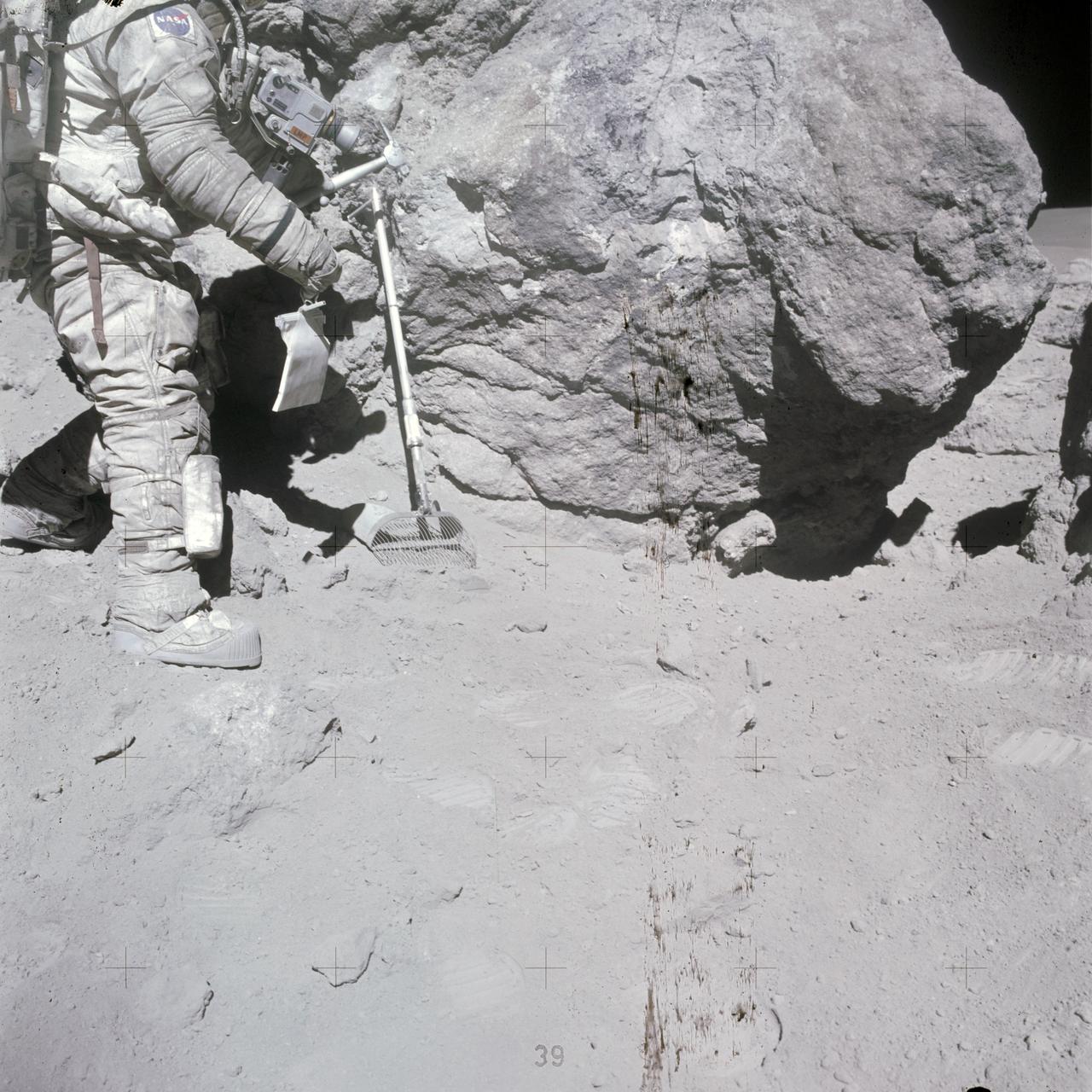

AS16-116-18653 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., Apollo 16 lunar module pilot, stands at a big rock adjacent (south) to the huge "House Rock" (barely out of view at right edge). Note shadow at extreme right center where the two moon-exploring crew members of the mission sampled what they referred to as the "east-by-west split of House Rock" or the open space between this rock and "House Rock". At their post-mission press conference, the crewmen expressed the opinion that this rock was once a part of "House Rock" which had broken away. The two sampled the big boulder seen here also. Duke has a sample bag in his hand, and a lunar surface rake leans against the large boulder. Astronaut John W. Young, commander, exposed this view with a color magazine in his 70mm Hasselblad camera. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
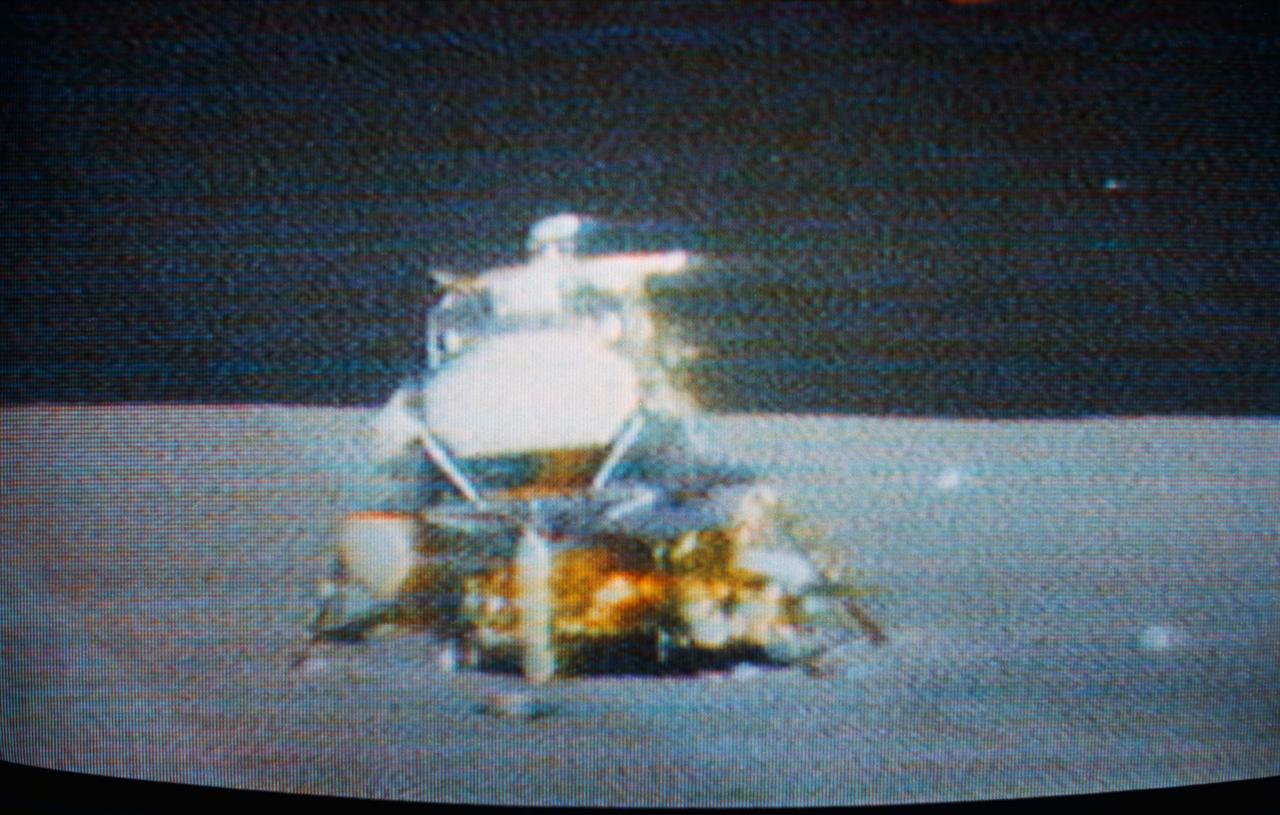

S71-41511 (2 Aug. 1971) --- The Apollo 15 Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" is seen only seconds before ascent stage liftoff in this color reproduction taken from a transmission made by the RCA color television camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was parked about 300 feet east of the LM. The LRV-mounted TV camera, remotely controlled from the Mission Control Center (MCC), made it possible for people on Earth to watch the LM's launch from the moon. The LM liftoff was at 171:37 ground elapsed time. The "Falcon" ascent stage, with astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, aboard, returned from the lunar surface to rejoin the Command and Service Modules (CSM) orbiting the moon. Astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Scott and Irwin explored the moon. The LM descent stage is used as a launching platform and remains behind on the moon. This is part one of a four-part sequence.
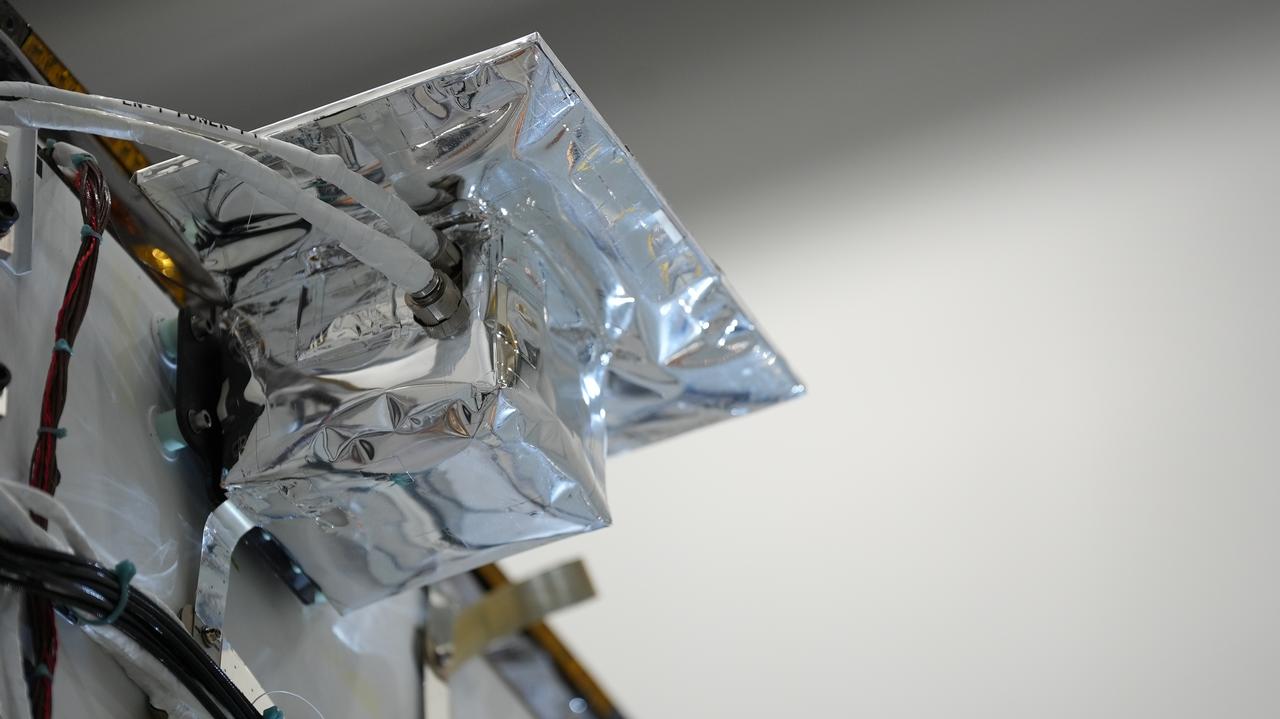

Lunar Node-1, an autonomous navigation payload that will change how human explorers safely traverse the Moon’s surface and live and work in lunar orbit, awaits liftoff as part of Intuitive Machines’ IM-1 mission, its first under NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative. LN-1 was developed, built, and tested at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.
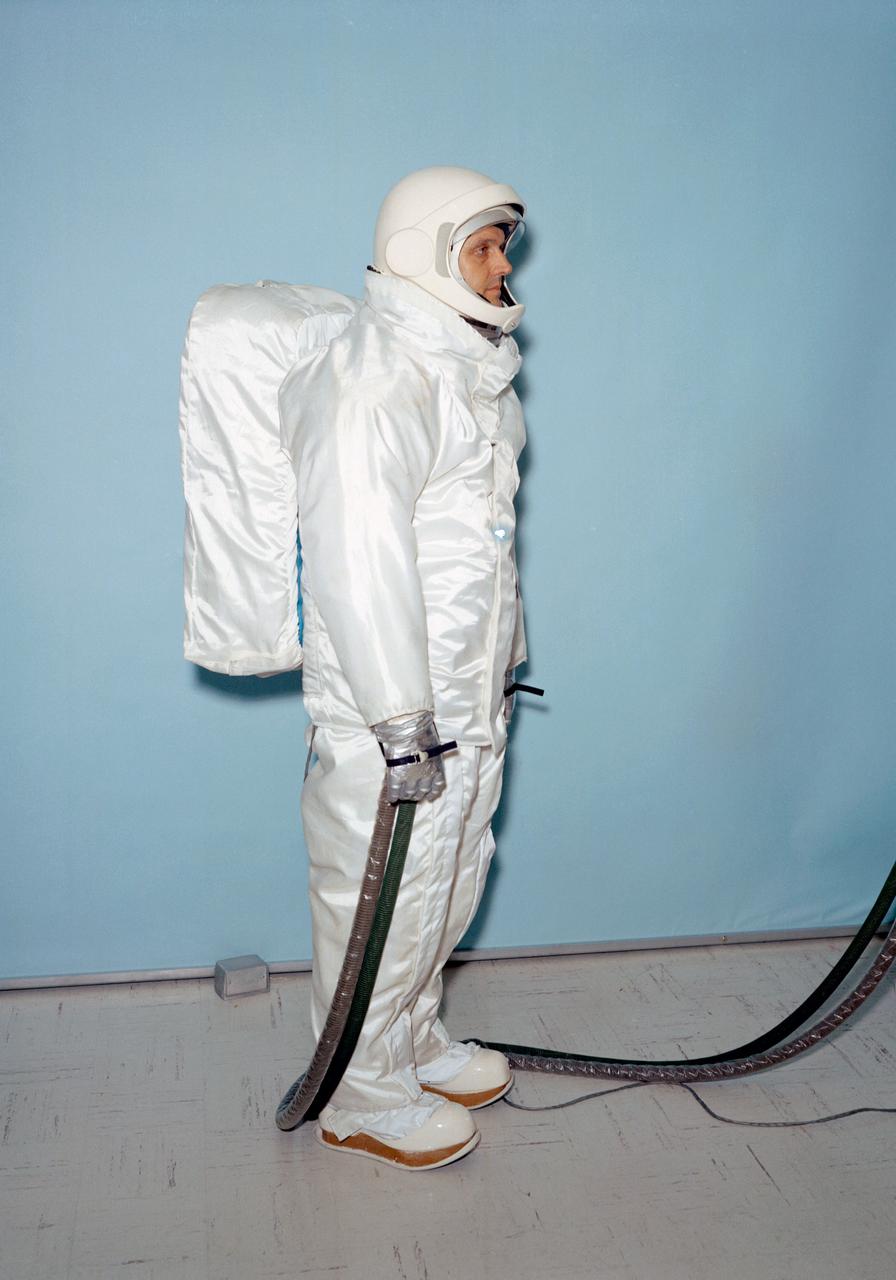

Test subject wears Apollo overgarment designed specially for use by astronauts on lunar surface missions. The overgarment is worn over the Apollo space suit.
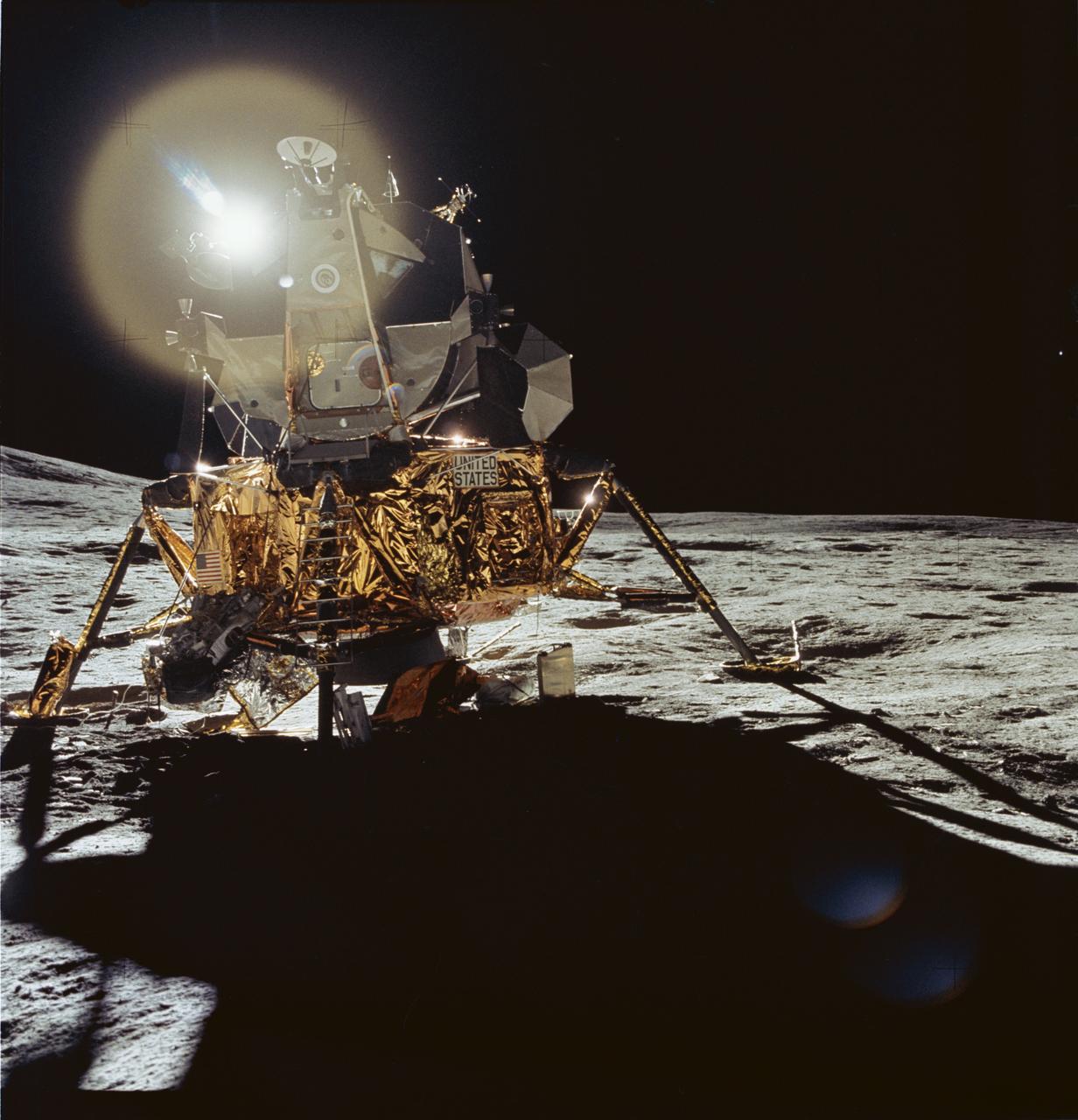

AS14-66-9306 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A front view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM), which reflects a circular flare caused by the brilliant sun, as seen by the two moon-exploring crew men of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission during their first extravehicular activity (EVA). The unusual ball of light was said by the astronauts to have a jewel-like appearance. At the extreme left the lower slope of Cone Crater can be seen. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; descended in the LM, while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
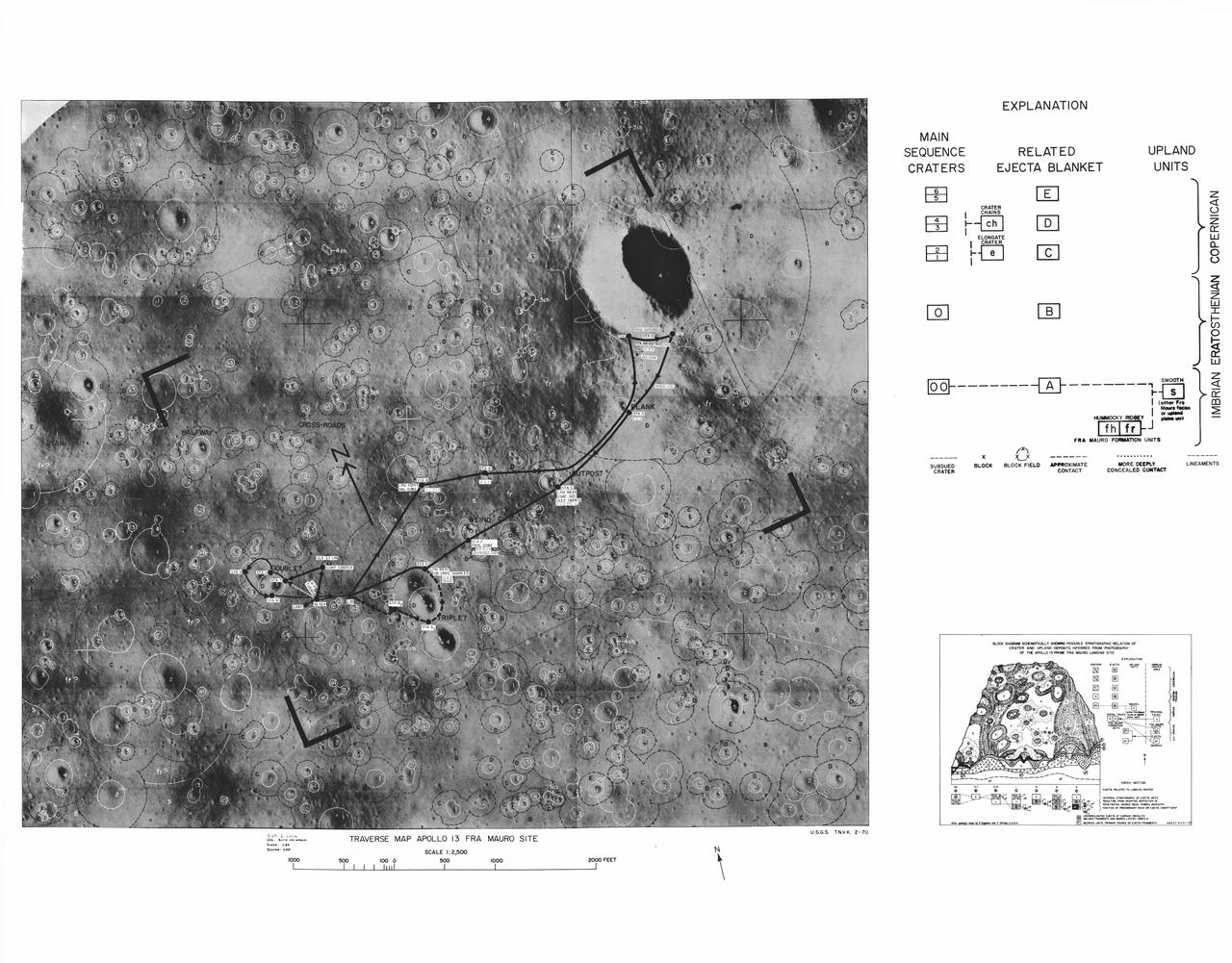
This lunar map shows the traverse plans for the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. Areas marked include Lunar module landing site, areas for the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiment Package (ALSEP) and areas for gathering of core samples.
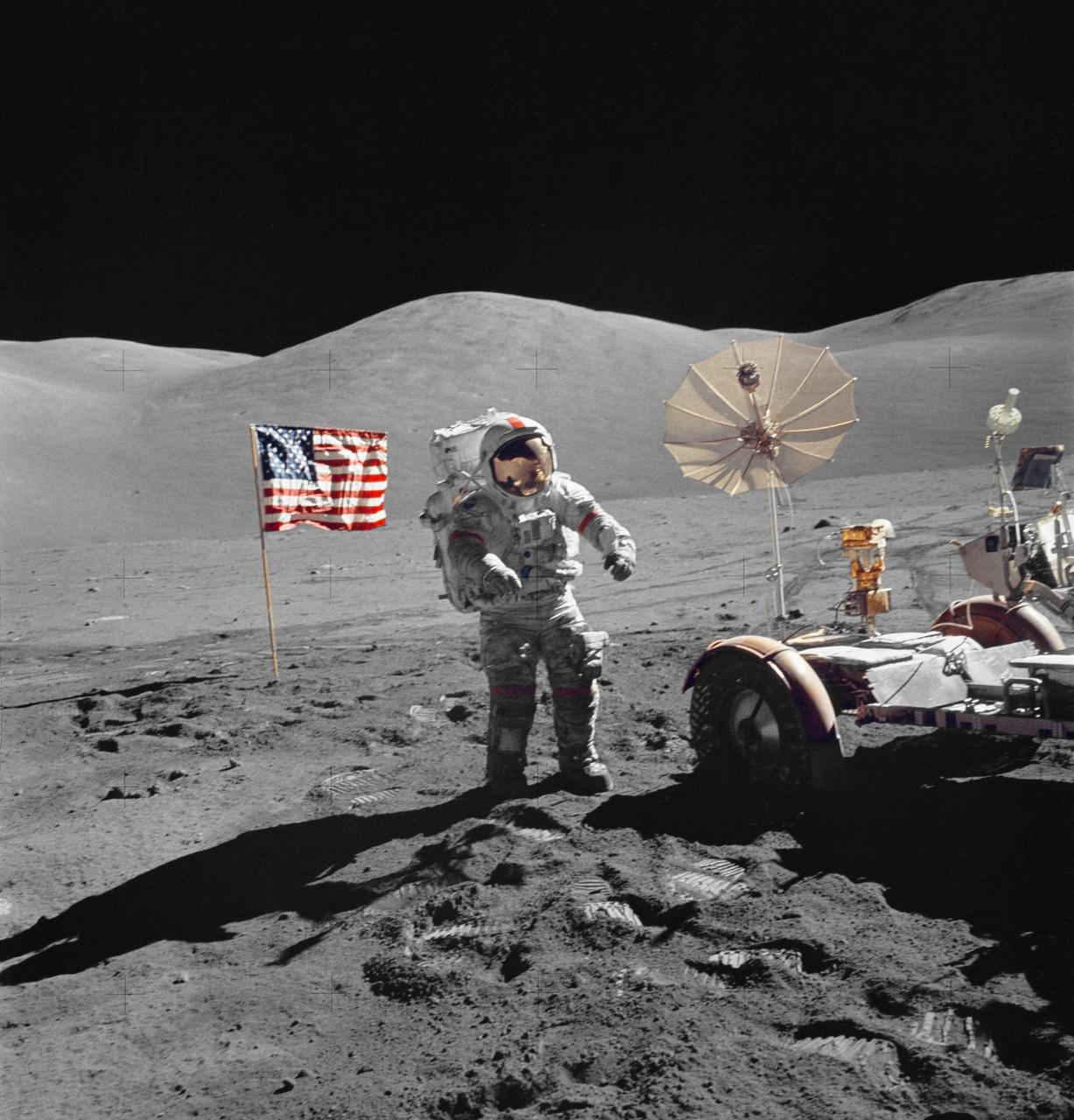

AS17-140-21388 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, mission commander, walks toward the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site of NASA's sixth and final Apollo lunar landing mission. The photograph was taken by astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
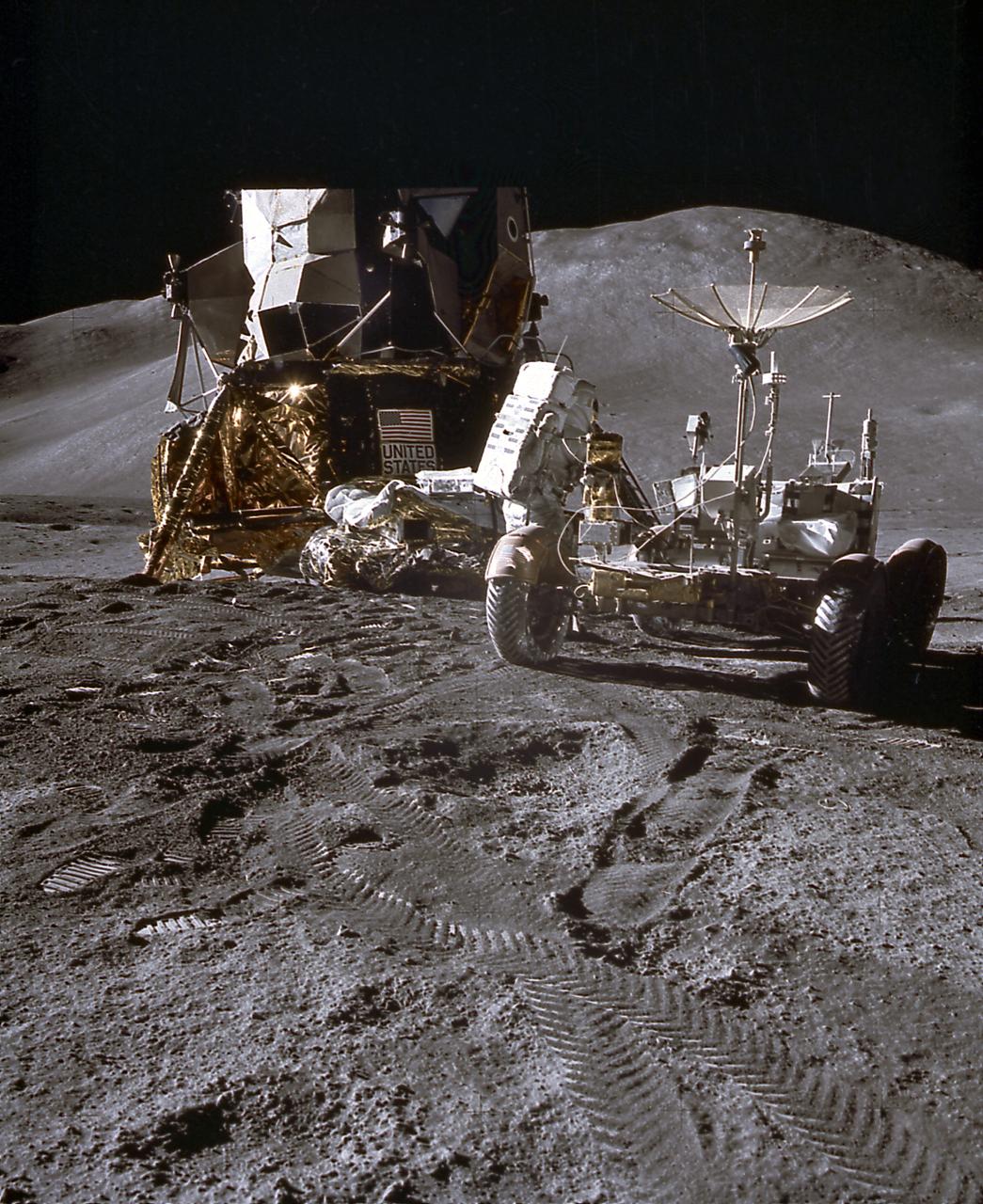

This photograph of an astronaut getting the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) ready for exploration of the lunar surface was taken during activities of the Apollo 15 mission. Designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company, the LRV was first used on the Apollo 15 mission and increased the range of astronauts' mobility and productivity on the lunar surface.
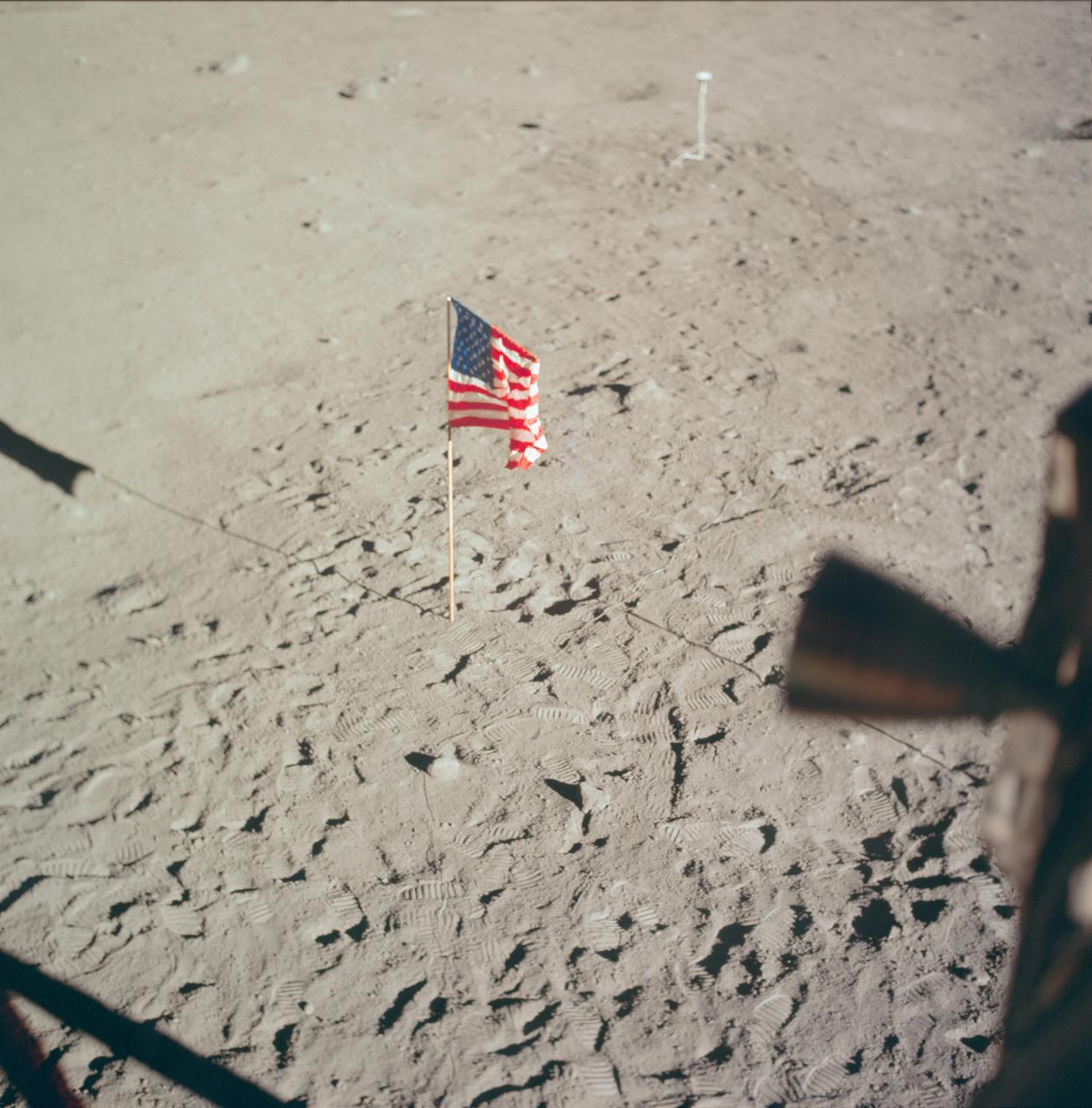
AS11-37-5545 (20 July 1969) --- The flag of the United States, deployed on the surface of the moon, dominates this photograph taken from inside the Lunar Module (LM). The footprints of astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. stand out very clearly. In the far background is the deployed black and white lunar surface television camera which televised the Apollo 11 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Armstrong, commander, and Aldrin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
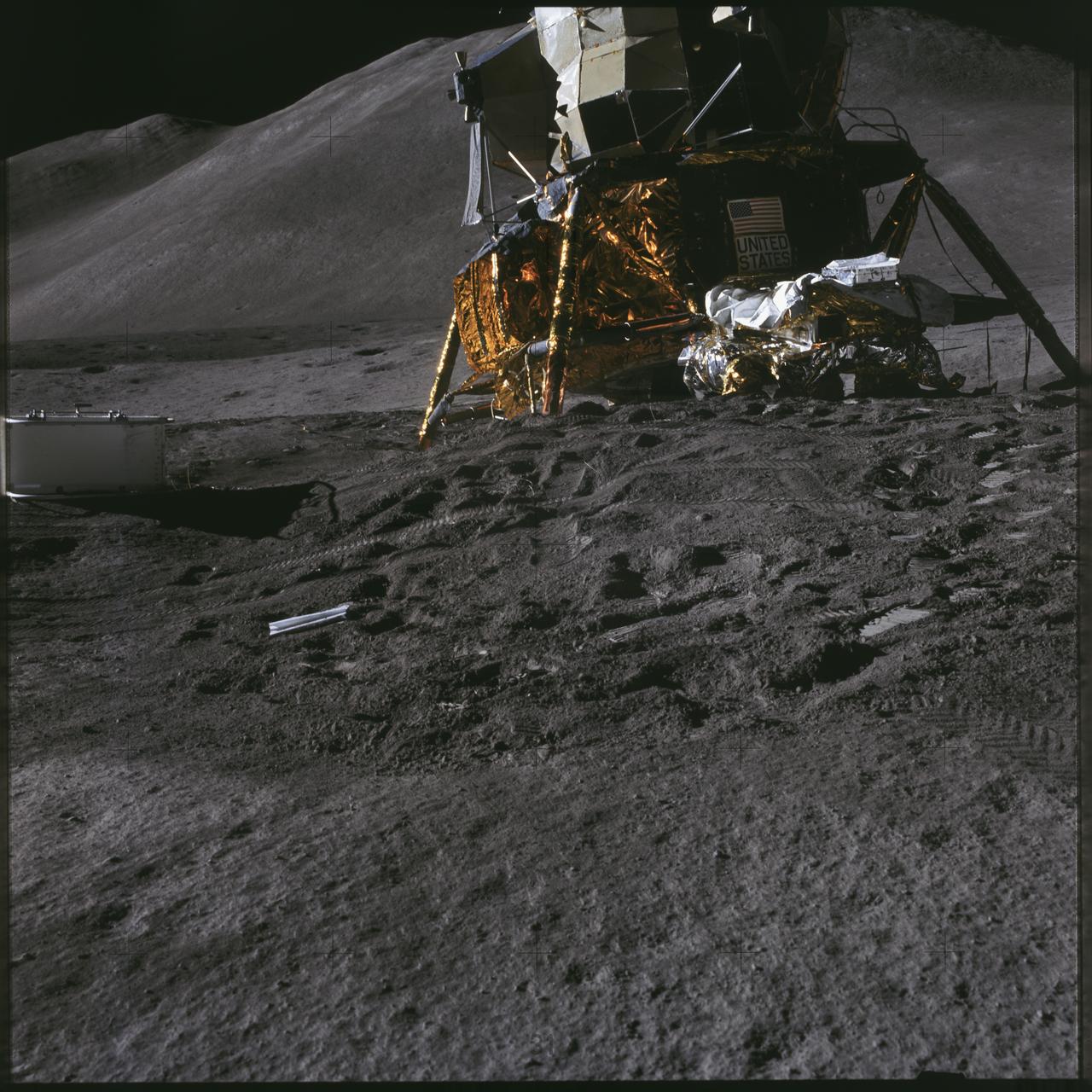

AS15-86-11600 (31 July 1971) --- A view of the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" taken early in the first Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site prior to deployment of lunar surface equipment. Hadley Delta Mountain is in the background. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
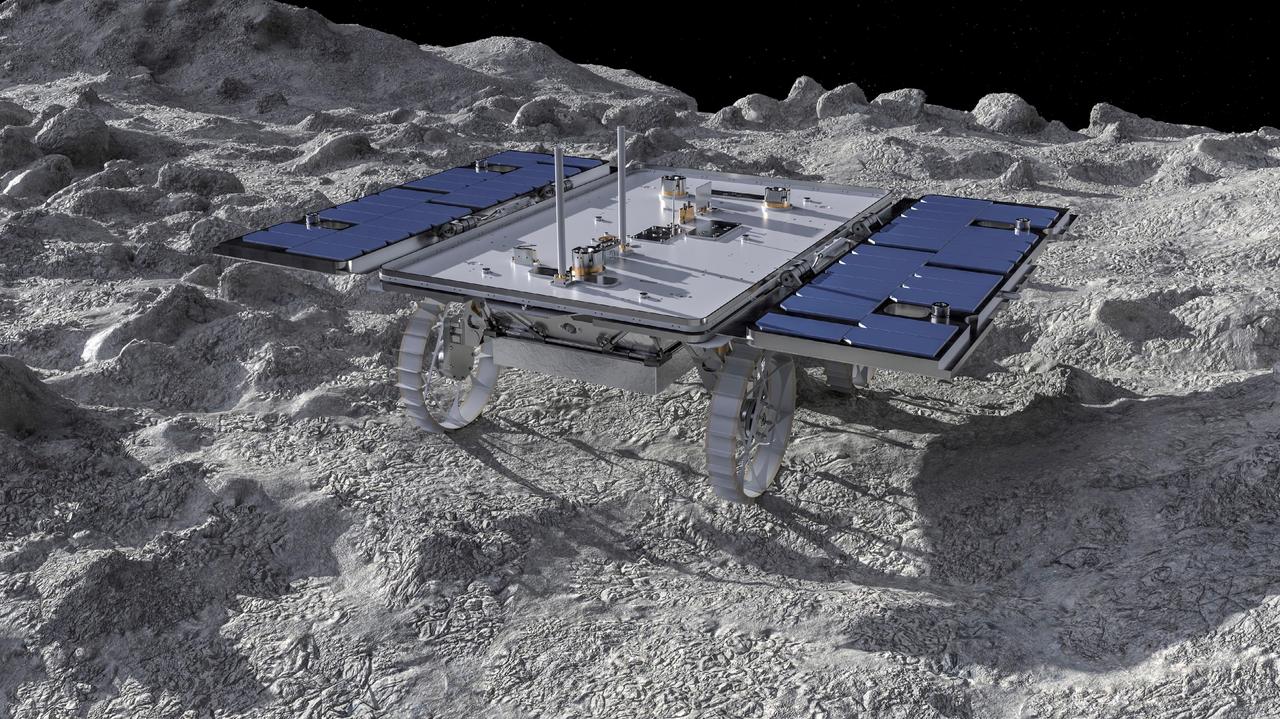

This artist's concept depicts a small rover – part of NASA's CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) technology demonstration headed for the Moon – on the lunar surface. Motiv Space Systems in Pasadena, California, created the rendering and is collaborating with NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on critical rover and mobility functions. Slated to arrive aboard a lunar lander in 2024 under NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, CADRE is designed to demonstrate that multiple robots can cooperate and explore together autonomously – without direct input from human mission controllers. A trio of the miniature solar-powered rovers, each about the size of a carry-on suitcase, will explore the Moon as a team, communicating via radio with each other and a base station aboard a lunar lander. By taking simultaneous measurements from multiple locations, CADRE will also demonstrate how multirobot missions can record data impossible for a single robot to achieve – a tantalizing prospect for future missions. Motiv contributed subsystems and hardware elements for three of four CADRE systems, including designing and building the mobility system and rover chassis, the base station, the rover deployers, and the motor controller boards. The company also procured and tested the actuators with the flight motor controller boards. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26161
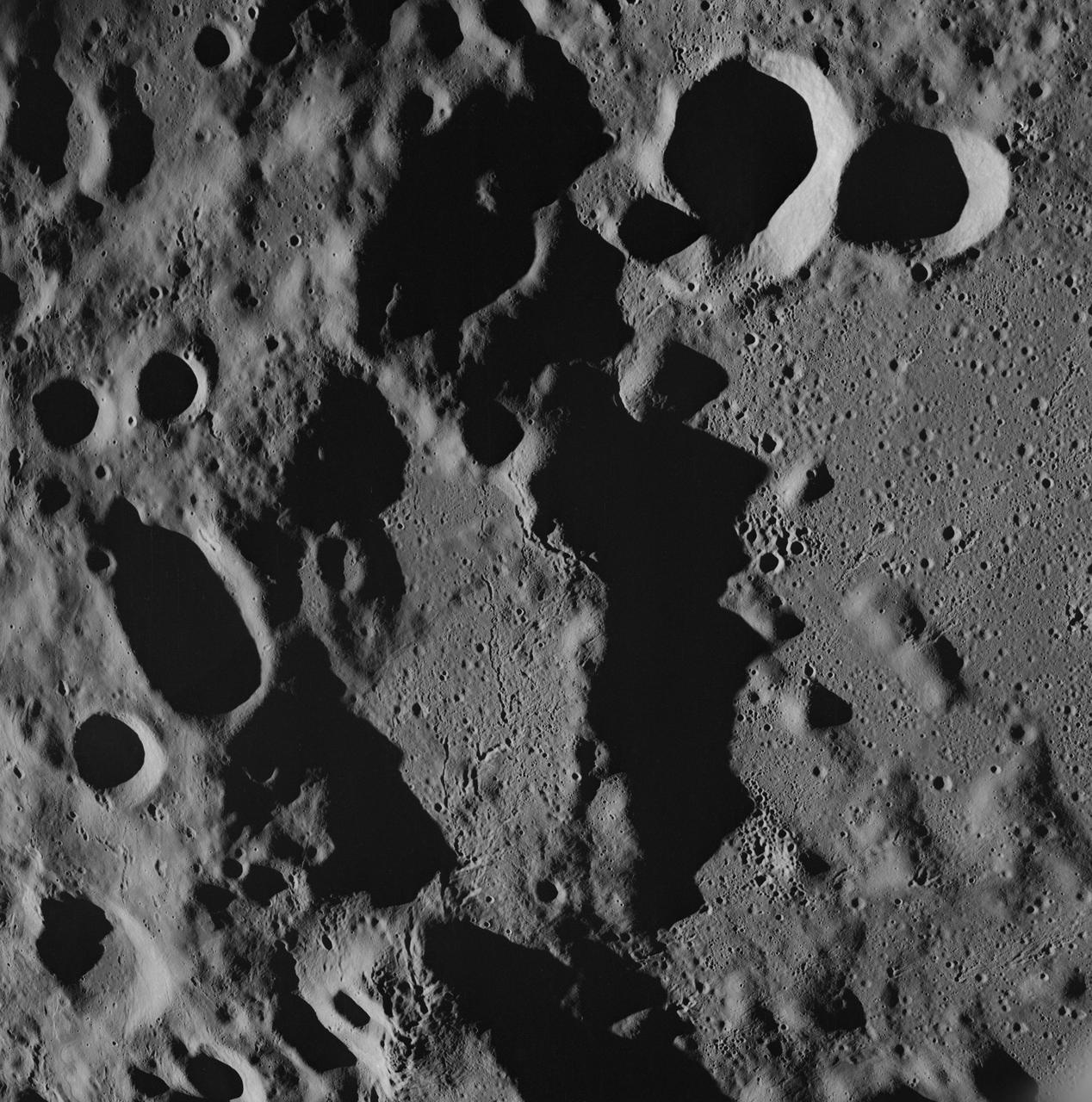

AS08-17-2670 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- Near vertical view of the lunar farside as photographed from the Apollo 8 spacecraft. The center of the picture is located approximately at 162 degrees west longitude and 6 degrees south latitude.
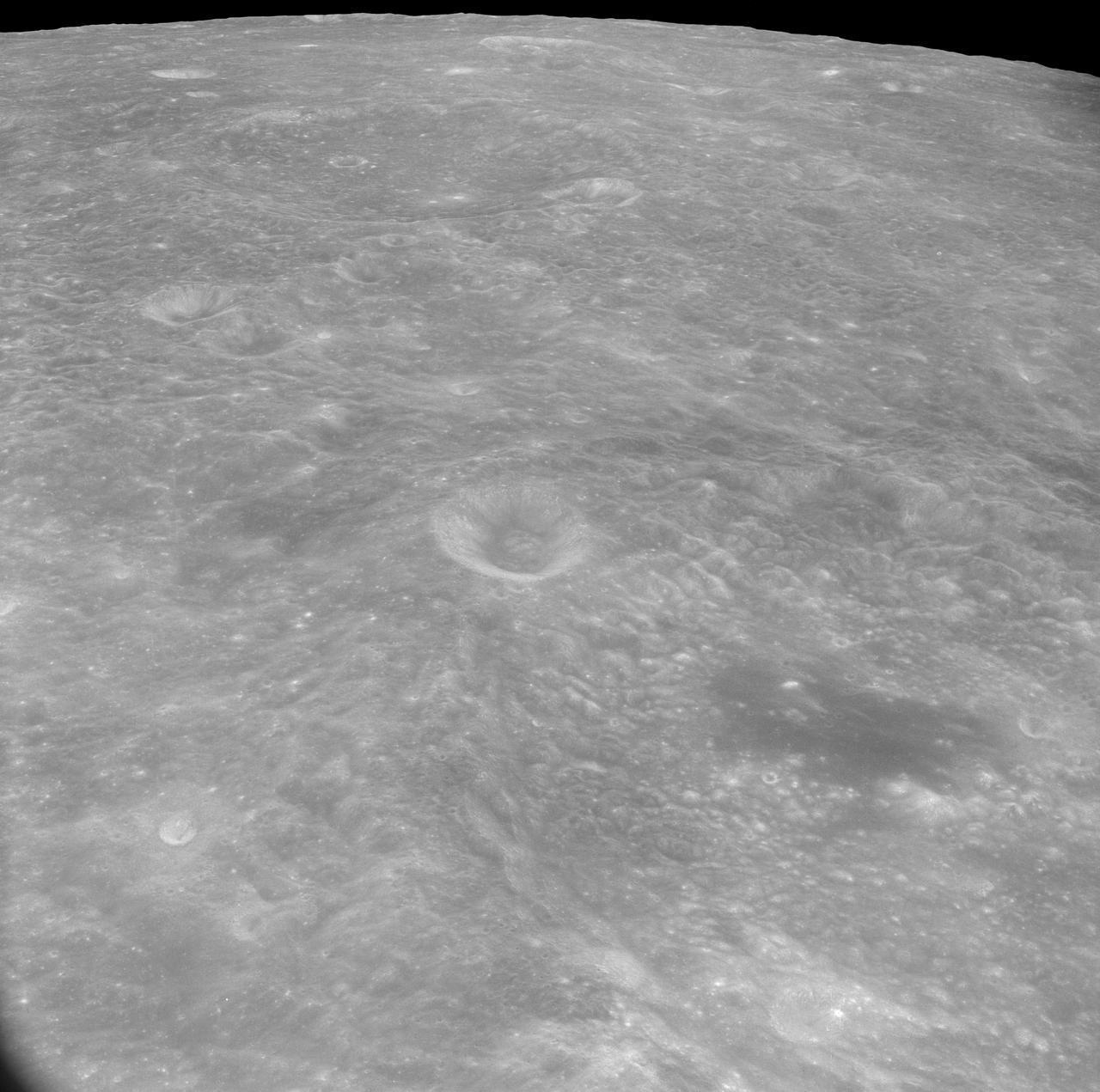

AS8-17-2744 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- Oblique view of the lunar surface taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking westward showing typical lunar farside terrain. (HOLD PICTURE SO THAT DARK IRREGULAR AREA SURROUNDED BY LIGHT SPOTS IS IN THE LOWER RIGHT QUARTER). The sharp crater near the center of then scene is near 117 degrees east longitude and 5 degrees south latitude; and it is 25 kilometers (15 statute miles) in diameter. That crater is on the rim of a large crater that occupies the lower right quarter of the photograph.
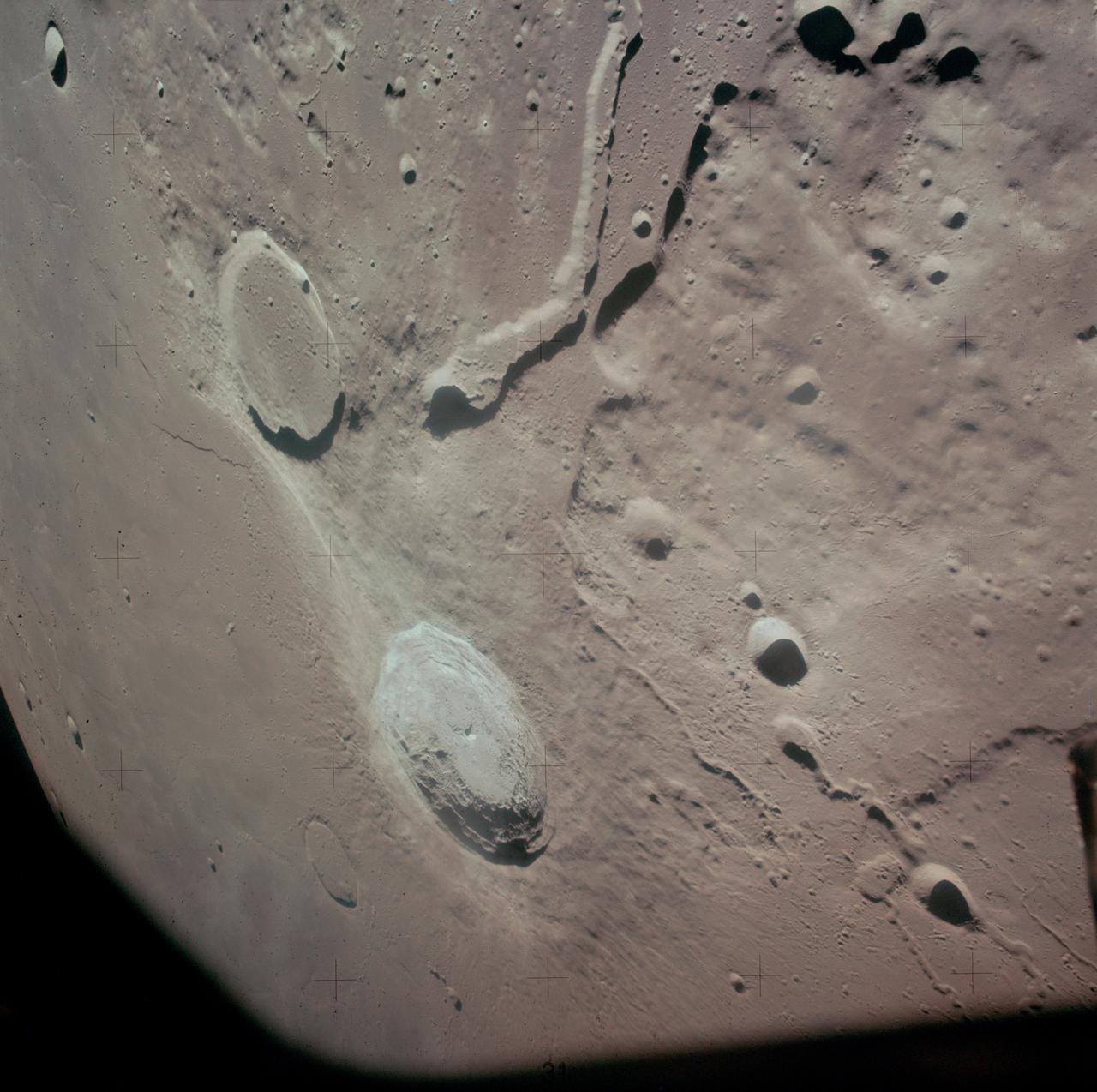

AS15-88-12002 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- An oblique view of a portion of the lunar nearside located near the northeast edge of the Ocean of Storms (Oceanus Procellarum), photographed by astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, from the Apollo 15 spacecraft in lunar orbit, showing the bright-appearing crater Aristarchus on the left, the crater Herodotus on the right, and Schroter's Valley at lower right. This view is looking southward. Aristarchus the head of Schroter's Valley, a sinuous rille in the Aristarchus Plateau, is called Cobra Head. The coordinates of the center of Aristarchus crater are 47.5 degrees west longitude and 23.6 degrees north latitude. While Worden remained in the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit, astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon.
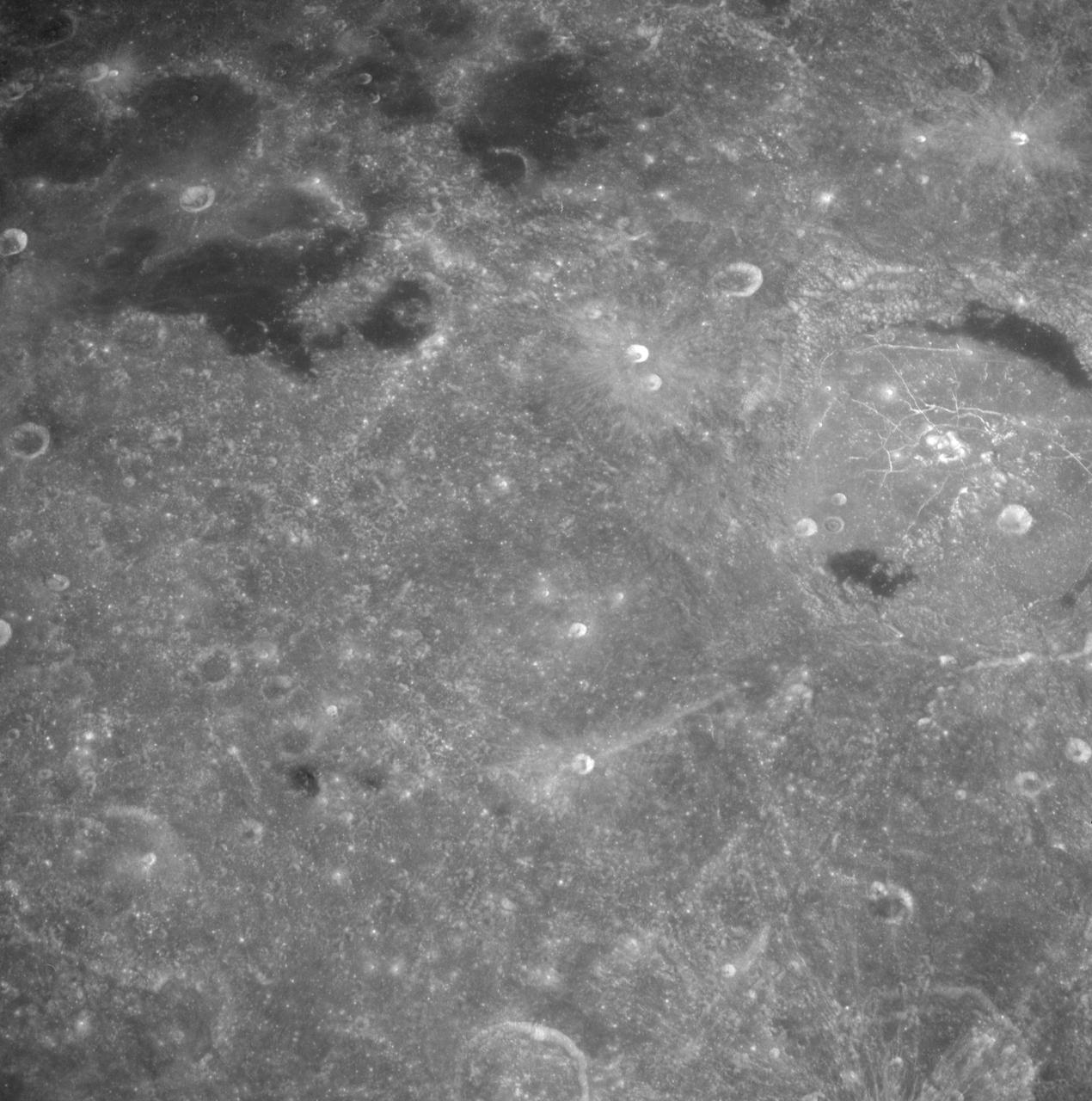

AS08-12-2193 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- View of the lunar surface taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking southward from high altitude across the Southern Sea. (Hold picture with AS8 number in upper right corner). The bright-rayed crater near the horizon is located near 130 degrees east longitude and 70 degrees south latitude. The dark-floored crater near the middle of the right side of the photograph is about 70 kilometers (45 statute miles) in diameter. Both features are beyond the eastern limb of the moon as viewed from Earth; neither has a name.
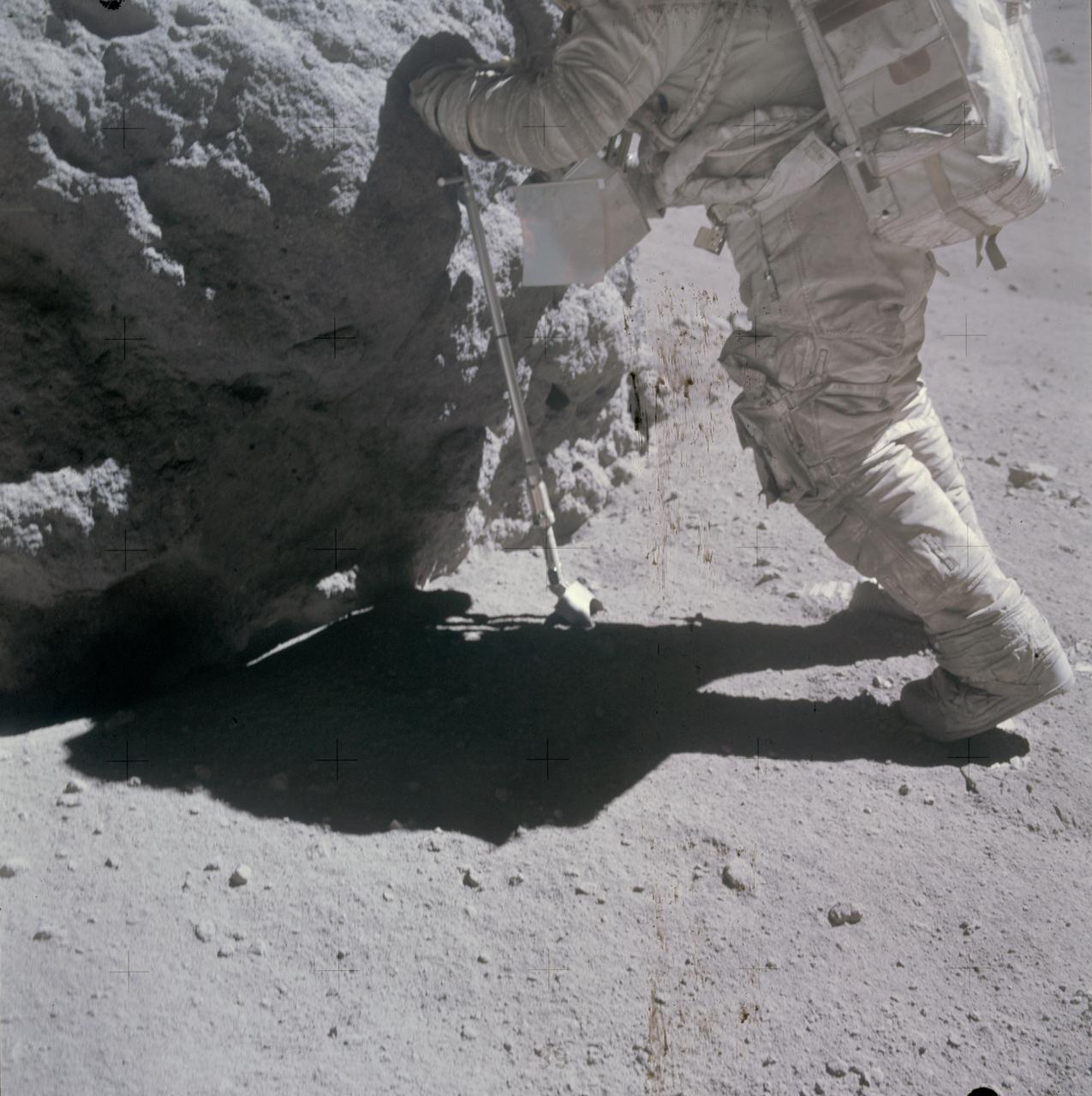

AS16-116-18671 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, works at the "Shadow Rock", discovered during the missions third extravehicular activity (EVA) in the area of North Ray Crater (Station 13), April 23, 1972. The scoop, a geological hand tool, leans against the rock. This view was exposed by astronaut John W. Young, commander. The two moon-exploring crew men sampled this rock, which got its name because of a permanently shadowed area it protected. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
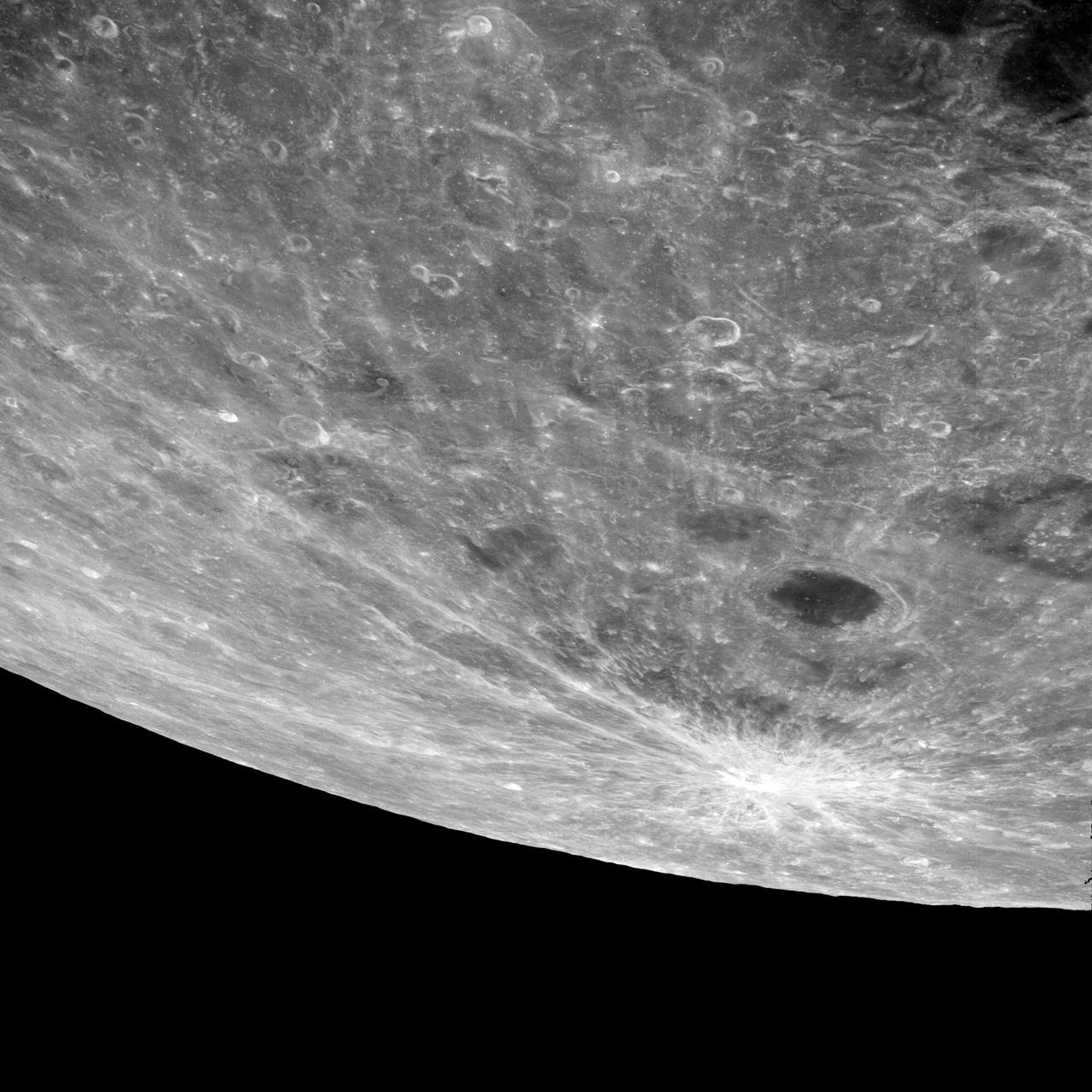
AS08-12-2209 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- High altitude oblique view of the lunar surface, looking northeastward, as seen from the Apollo 8 spacecraft. The crater Joliot-Curie, about 175 kilometers in diameter and centered near 94 degrees east longitude and 27 degrees north latitude, is near the center of the left side of this photograph. The bright rayed crater near the horizon is probably located near 105 degrees east longitude and 45 degrees north latitude. Long, narrow rays that have been reported in the polar region of Earth facing hemisphere may radiate from this crater.
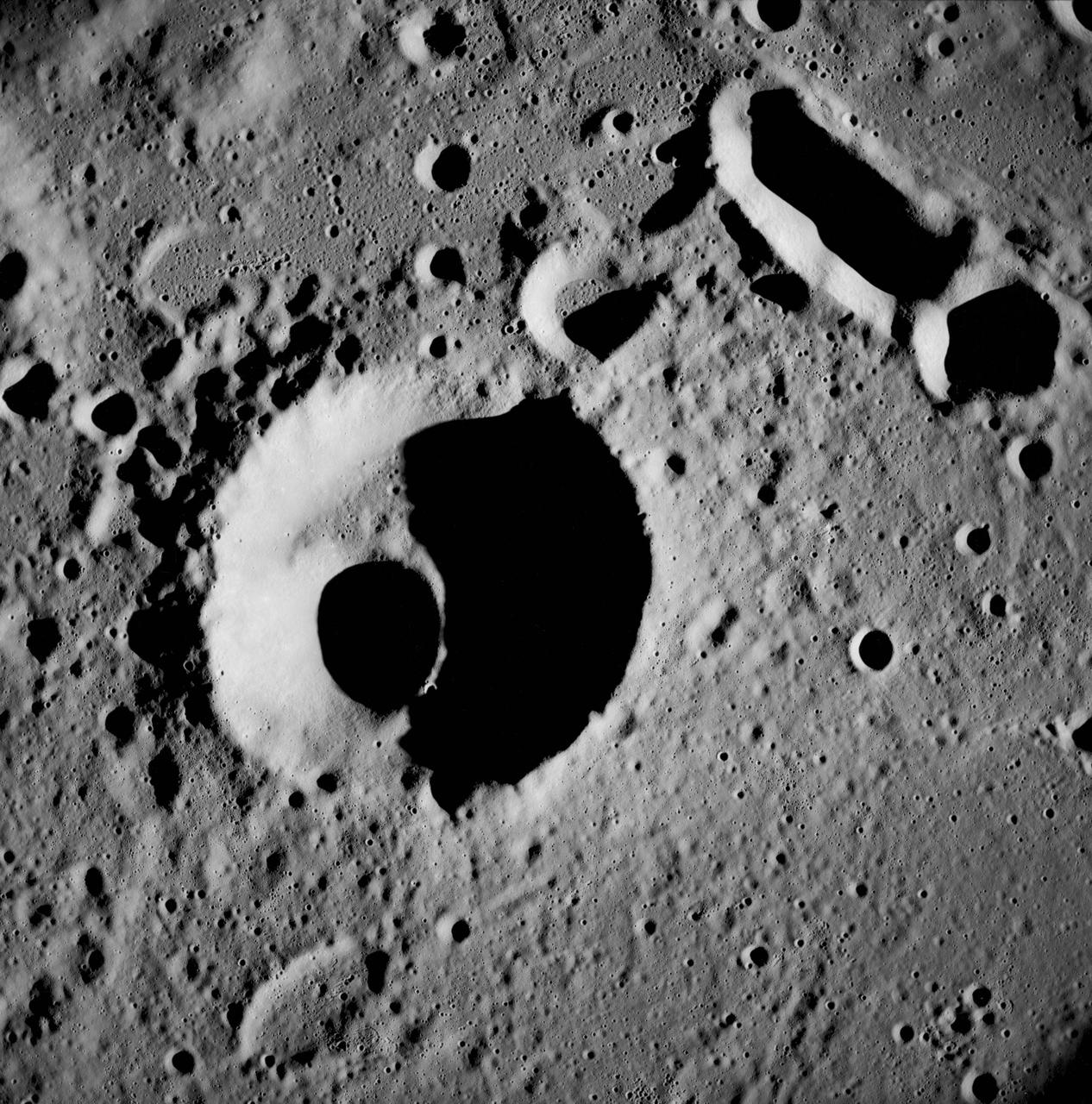

AS08-12-2052 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- This near-vertical photograph from the Apollo 8 spacecraft covers an area of approximately 50 x 50 statute miles within a 250-statute-miles-in-diameter crater on the lunar farside. The center of this large crater is located at about 157 degrees west longitude and 4 degrees south latitude. The large crater in the center of the picture is about 20 statute miles in diameter.
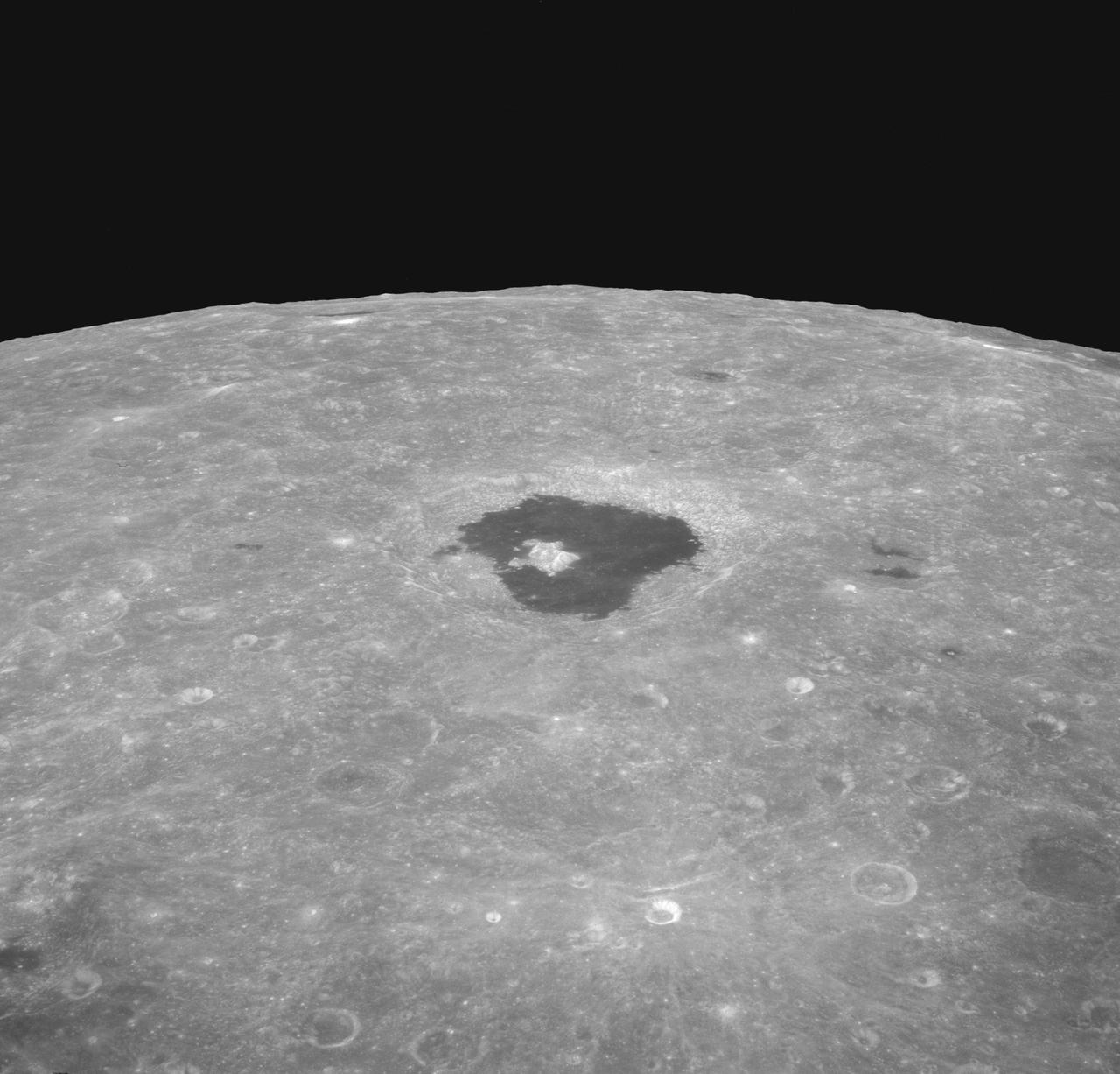

AS08-12-2196 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- An oblique view from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking eastward across the lunar surface from about 115 degrees east longitude to the horizon near 180 degrees east longitude. The crater Tsiolkovsky in the center of the picture is 150 kilometers wide and is located at 129 degrees east longitude and 21 degrees south latitude. While in lunar orbit, Apollo 8 moved toward the camera position over the terrain along the left (north) side of this photograph.
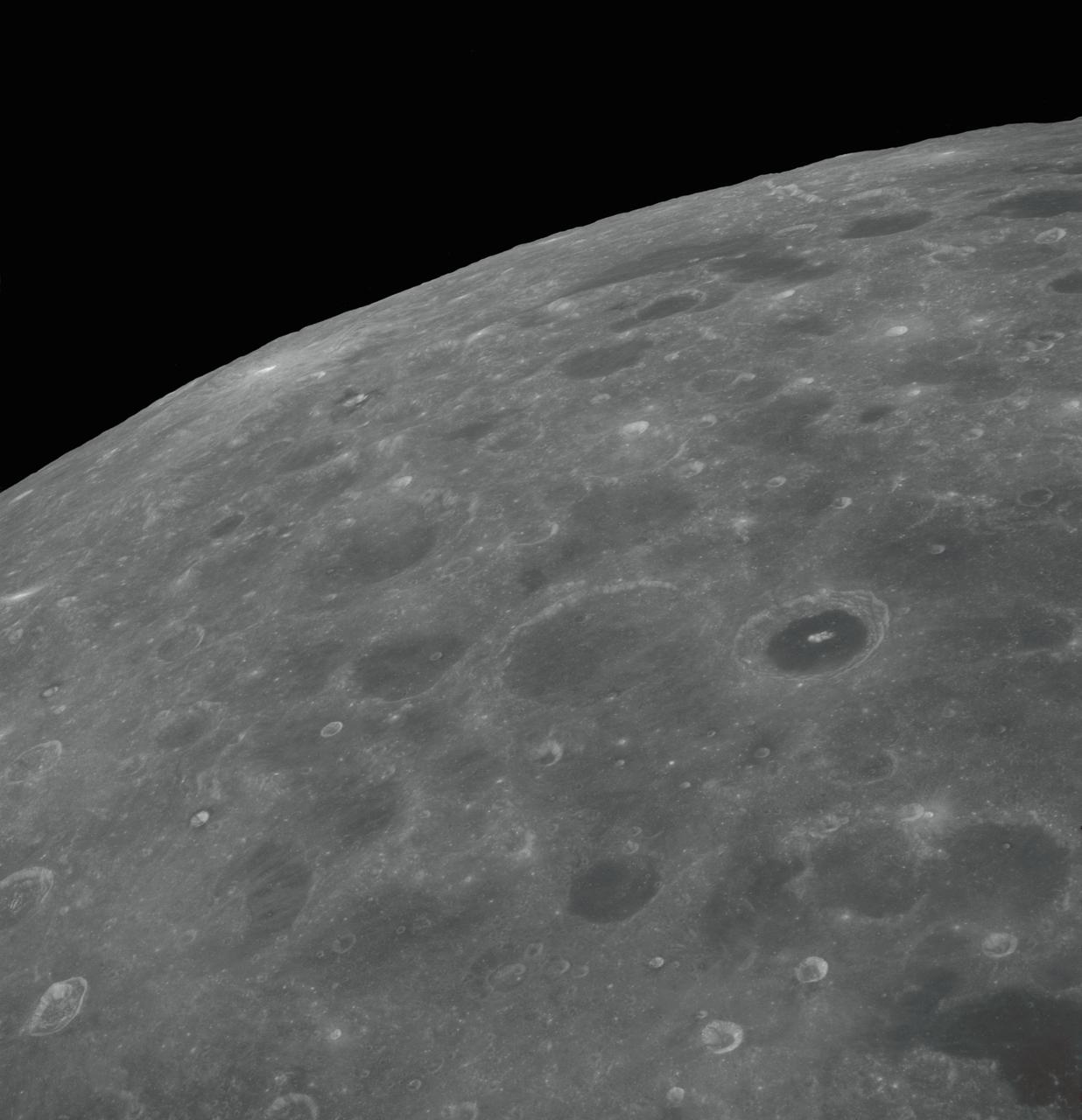

AS08-12-2192 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- View of the lunar surface taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking southward from high altitude across the Southern Sea. (Hold picture with AS8 number in upper right corner). The bright-rayed crater near the horizon is located near 130 degrees east longitude and 70 degrees south latitude. The dark-floored crater near the middle of the right side of the photograph is about 70 kilometers (45 statute miles) in diameter. Both features are beyond the eastern limb of the moon as viewed from Earth; neither has a name.
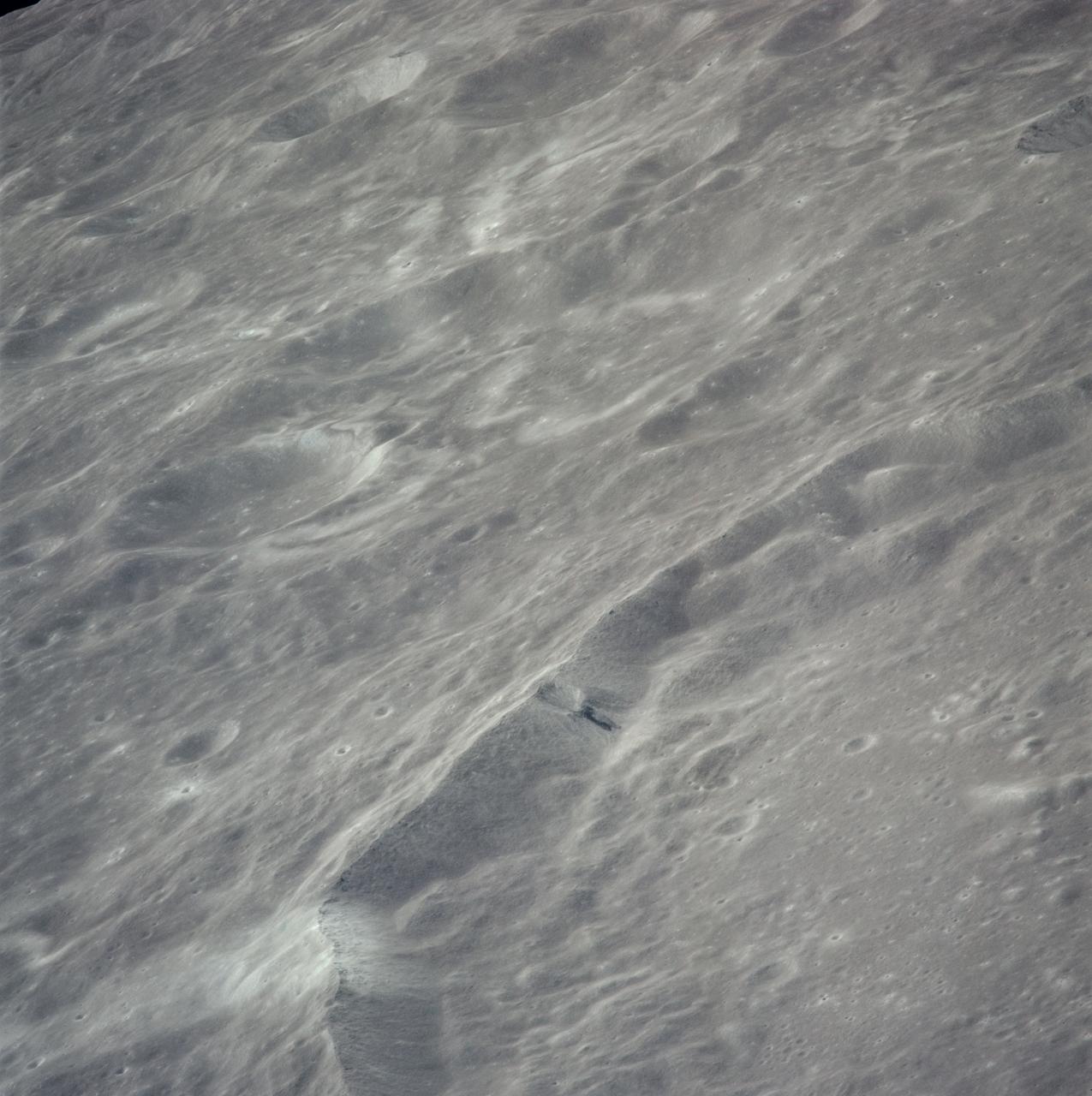

AS16-121-19407 (April 1972) --- An oblique view of a rim of Guyot Crater on the lunar farside, as photographed from the Apollo 16 spacecraft in lunar orbit. The coordinates of the center of Guyot Crater are 116.5 degrees east longitude and 10.5 degrees north latitude. Note the black coloration which appears to be lava flow down the side of the crater rim. While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
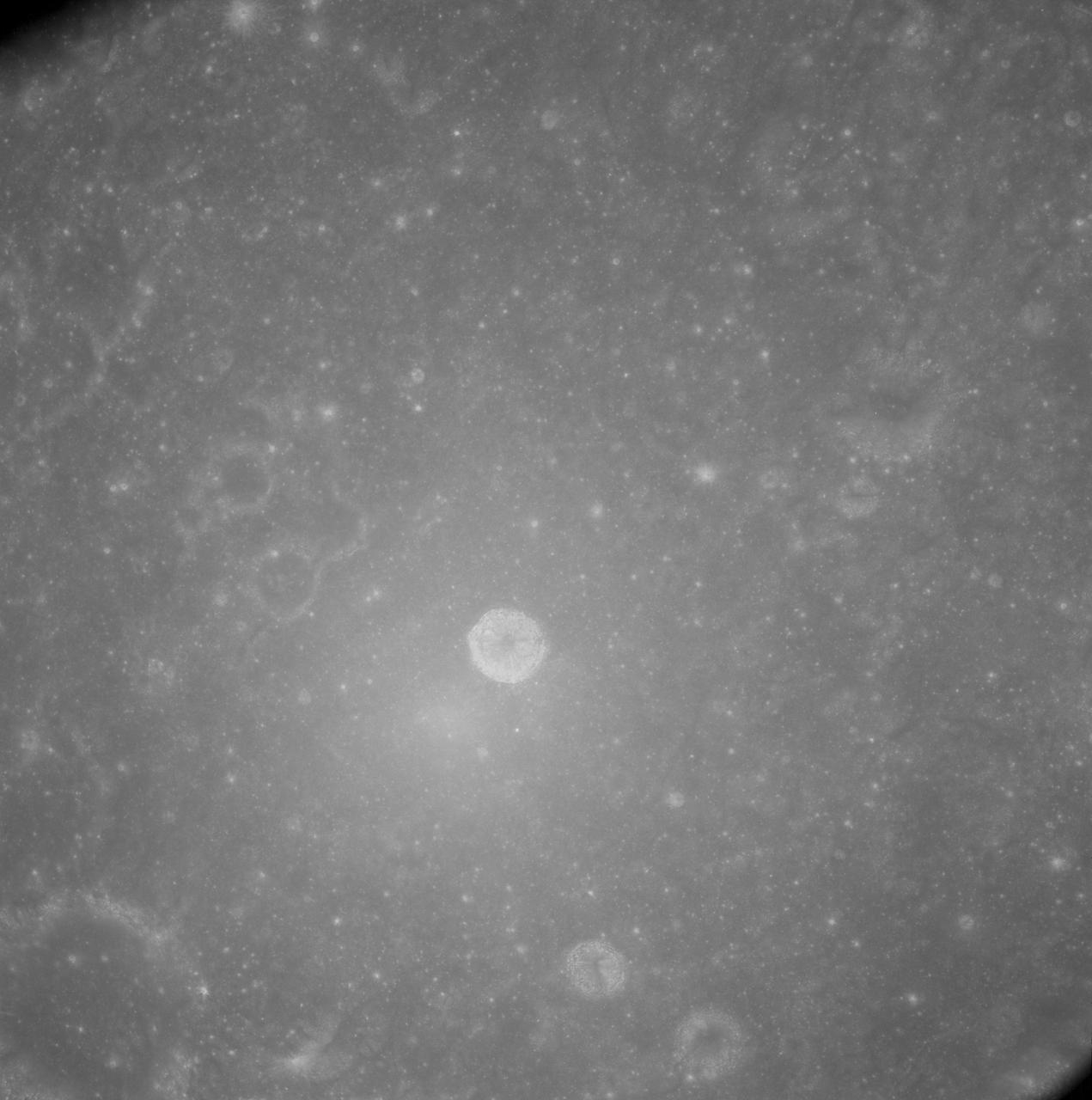

AS08-12-2148 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- View of the lunar surface as photographed from the Apollo 8 spacecraft. Zero-phase bright spot. With near-vertical sun illumination, topographical detail is washed out and differences in surface brightness are accentuated. The numerous small bright-halo craters become conspicuous. A few larger craters have extremely bright inner walls that are commonly streaked by darker material. The bright glow near the conspicuous bright-walled crater is a halo that surrounds the position of the spacecraft shadow.
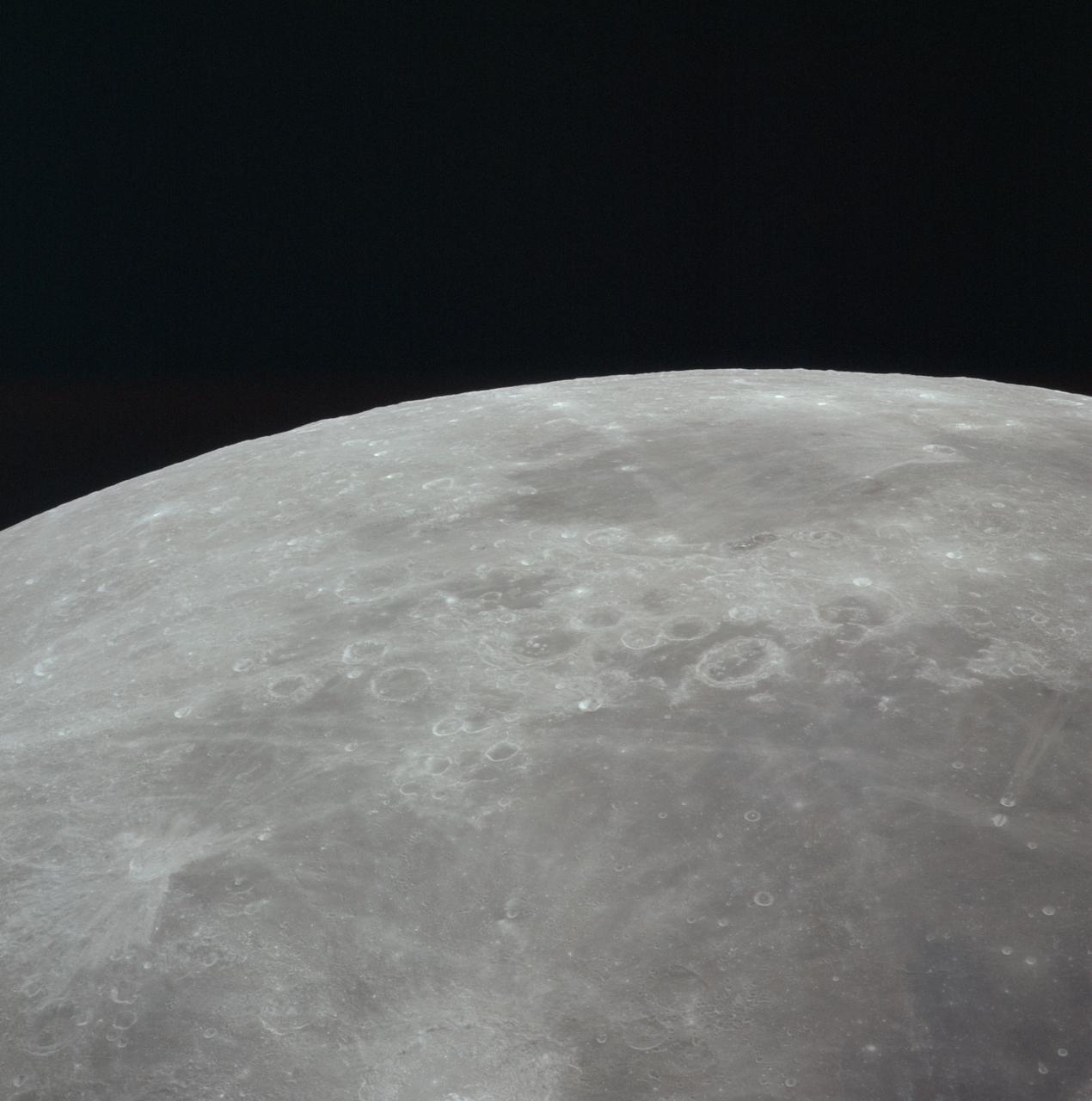

AS16-121-19449 (16-27 April 1972) --- This 70mm handheld camera's view of the moon, photographed during the Apollo 16 mission's trans-Earth coast, features Mare Fecunditatis (Sea of Fertility) in the foreground with the twin craters Messier at the lower right. Nearer the horizon is Mare Nectaris (Sea of Nectar) with craters Goclenius and Gutenberg in between. Goclenius is located at approximately 10 degrees south latitude and 45 degrees east longitude.
AS8-17-2704 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- Near vertical view of the lunar farside as photographed from the Apollo 8 spacecraft. This crater, which is about 22 statute miles in diameter, is located at 167 degrees east longitude and 11 degrees south latitude. This crater is located on the eastern edge of a much larger unnamed crater which is about 90 statute miles in diameter.

AS11-44-6642 (21 July 1969) --- The Apollo 11 Lunar Module ascent stage, with astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. aboard, is photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) during rendezvous in lunar orbit. The Lunar Module (LM) was making its docking approach to the CSM. Astronaut Michael Collins remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while the other two crewmen explored the lunar surface. The large, dark-colored area in the background is Smyth's Sea, centered at 85 degrees east longitude and 2 degrees south latitude on the lunar surface (nearside). This view looks west. The Earth rises above the lunar horizon.
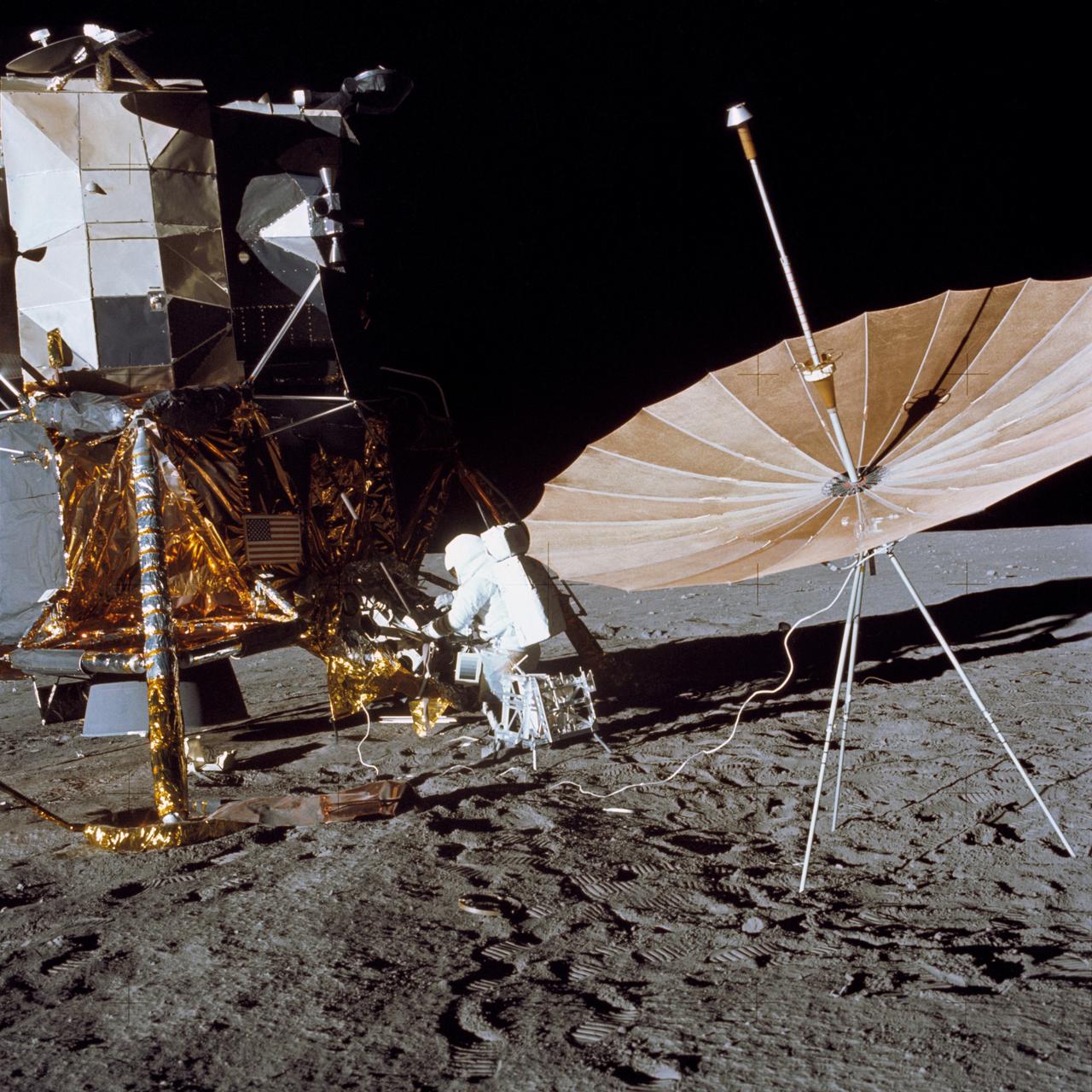

AS12-47-6988 (19 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, stands at the Module Equipment Stowage Assembly (MESA) on the Lunar Module (LM) following the first Apollo 12 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The erectable S-band antenna is already deployed at right. The carrier for the Apollo Lunar Hand Tools (ALHT) is near Conrad. While astronauts Conrad and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
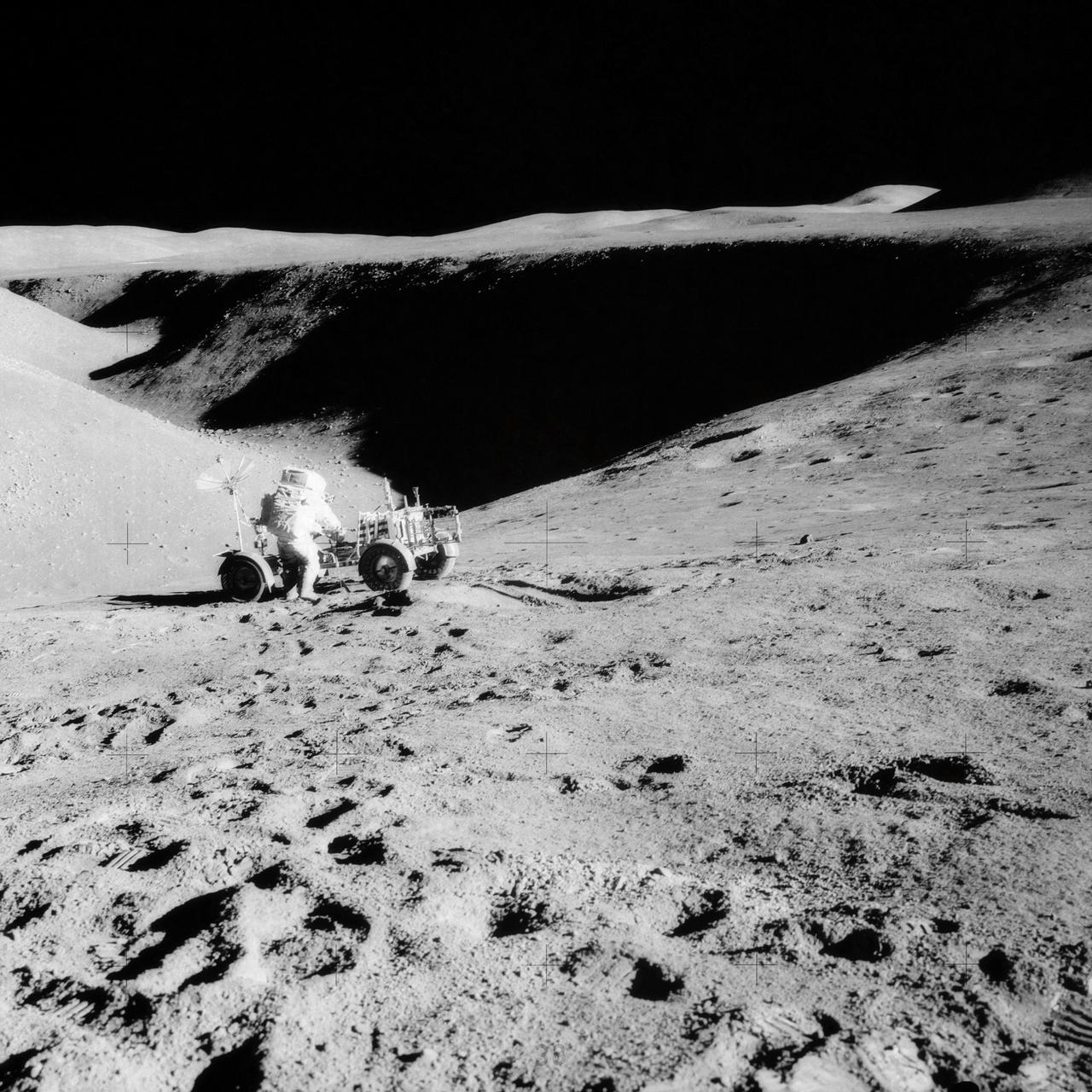

AS15-85-11451 (31 July 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, mission commander, performs a task at the Lunar Roving Vehicle parked on the edge of Hadley Rille during the first Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). This photograph was taken by astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, from the flank of St. George Crater. The view is looking north along the rille.

AS15-85-11437 (31 July 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, commander, with tongs and gnomon in hand, studies a boulder on the slope of Hadley Delta during the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission's first extravehicular activity (EVA). The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), "Rover", is in the right foreground. The view is looking slightly south of west. "Bennett Hill" is at extreme right. Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, took this photograph. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended together in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
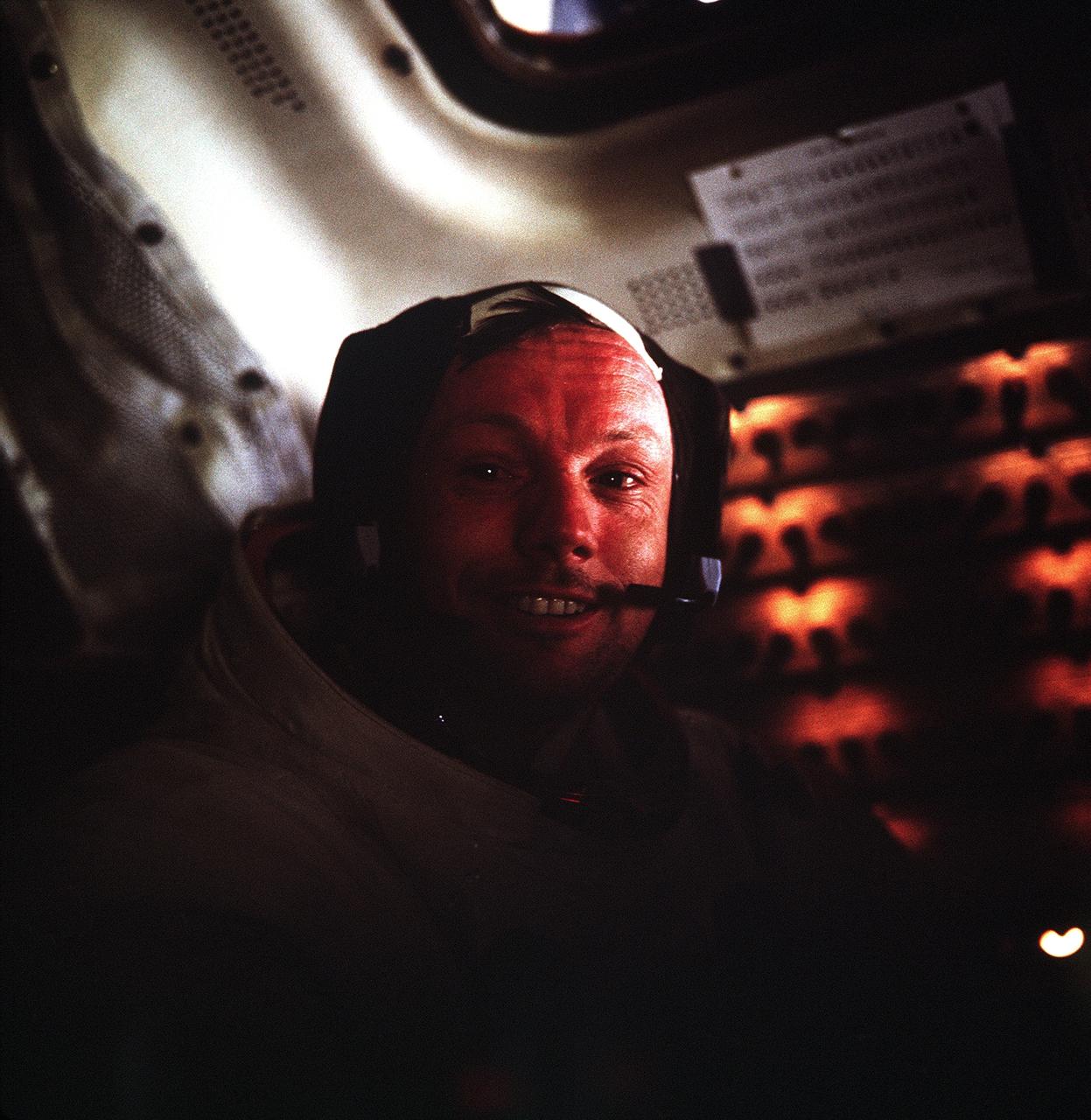

AS11-37-5528 (20 July 1969) --- This photograph of astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, Apollo 11 commander, was taken inside the Lunar Module (LM) while the LM rested on the lunar surface. Astronauts Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, had already completed their historic extravehicular activity (EVA) when this picture was made. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while Armstrong and Aldrin explored the moon's surface.
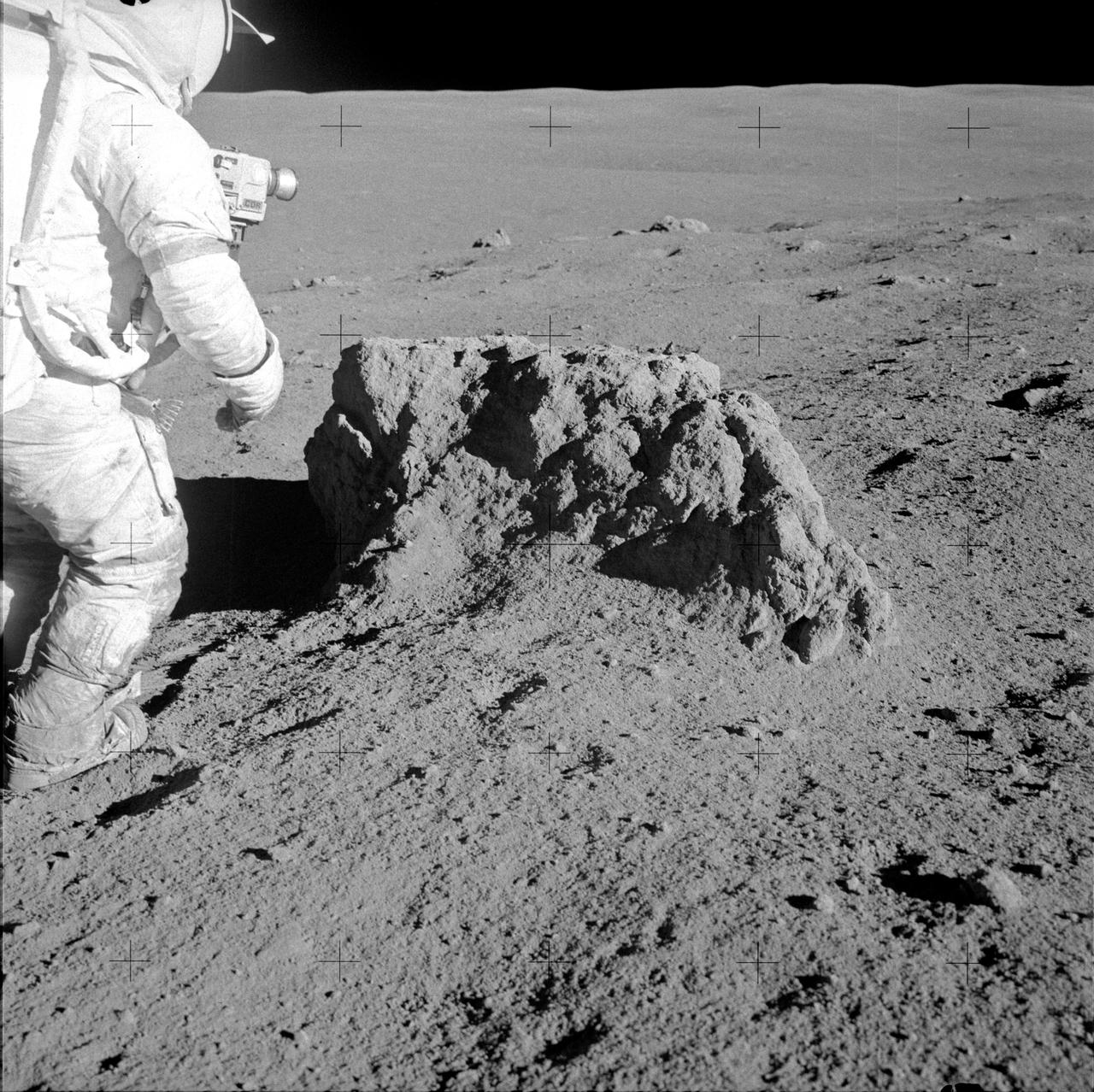

AS14-68-9414 (6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., Apollo 14 commander, stands beside a large boulder on the lunar surface during the mission's second extravehicular activity (EVA), on Feb. 6, 1971. Note the lunar dust clinging to Shepard's space suit. Astronauts Shepard and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, explored the lunar surface while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, orbited the moon in the Command and Service Modules (CSM).
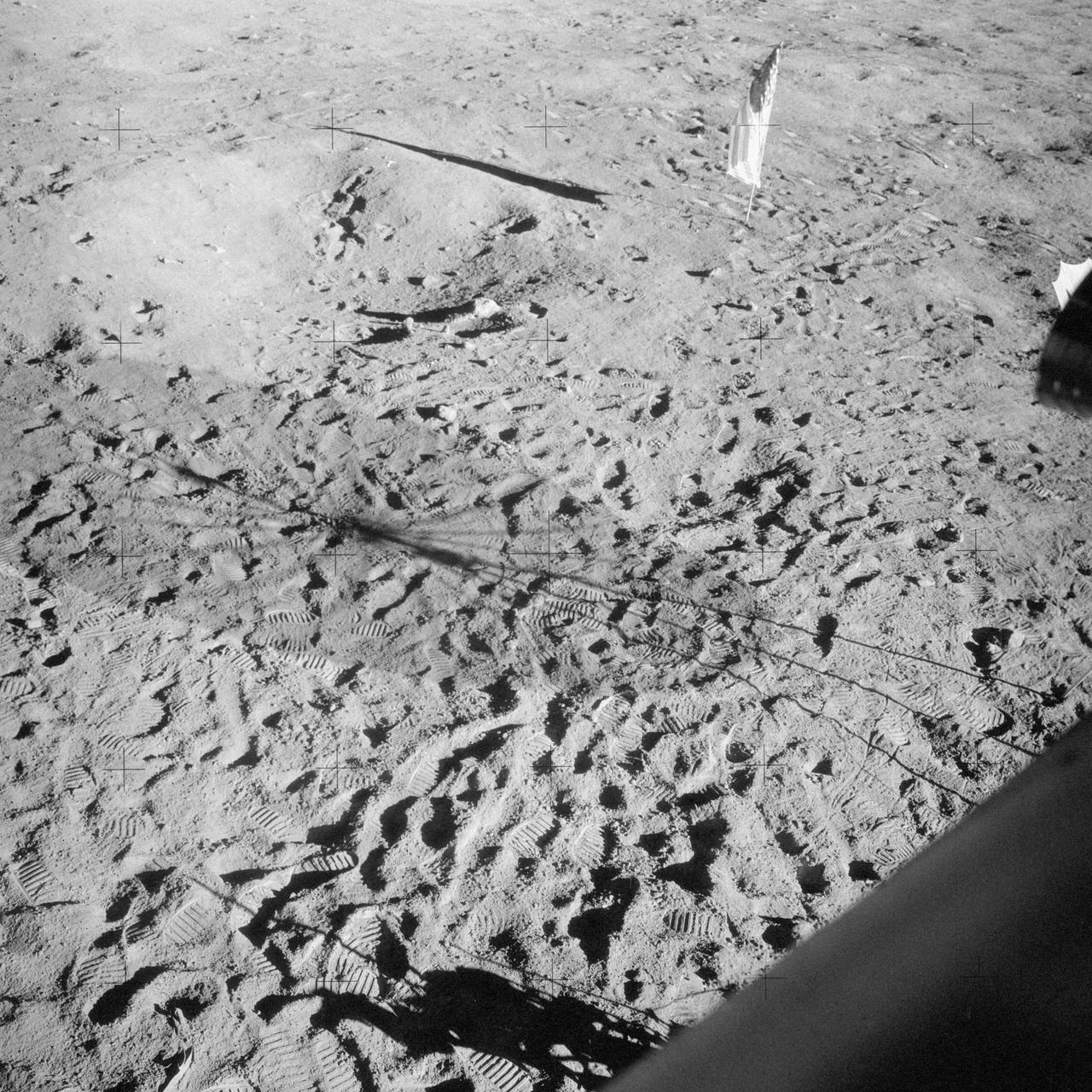

AS12-48-7160 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- This view of the lunar surface was taken by one of the two astronauts on the Apollo 12 mission during their extravehicular activity. Seen in this view are the U.S. flag, several astronaut footprints, and a small crater near their Lunar Module landing site. Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the lunar surface. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.
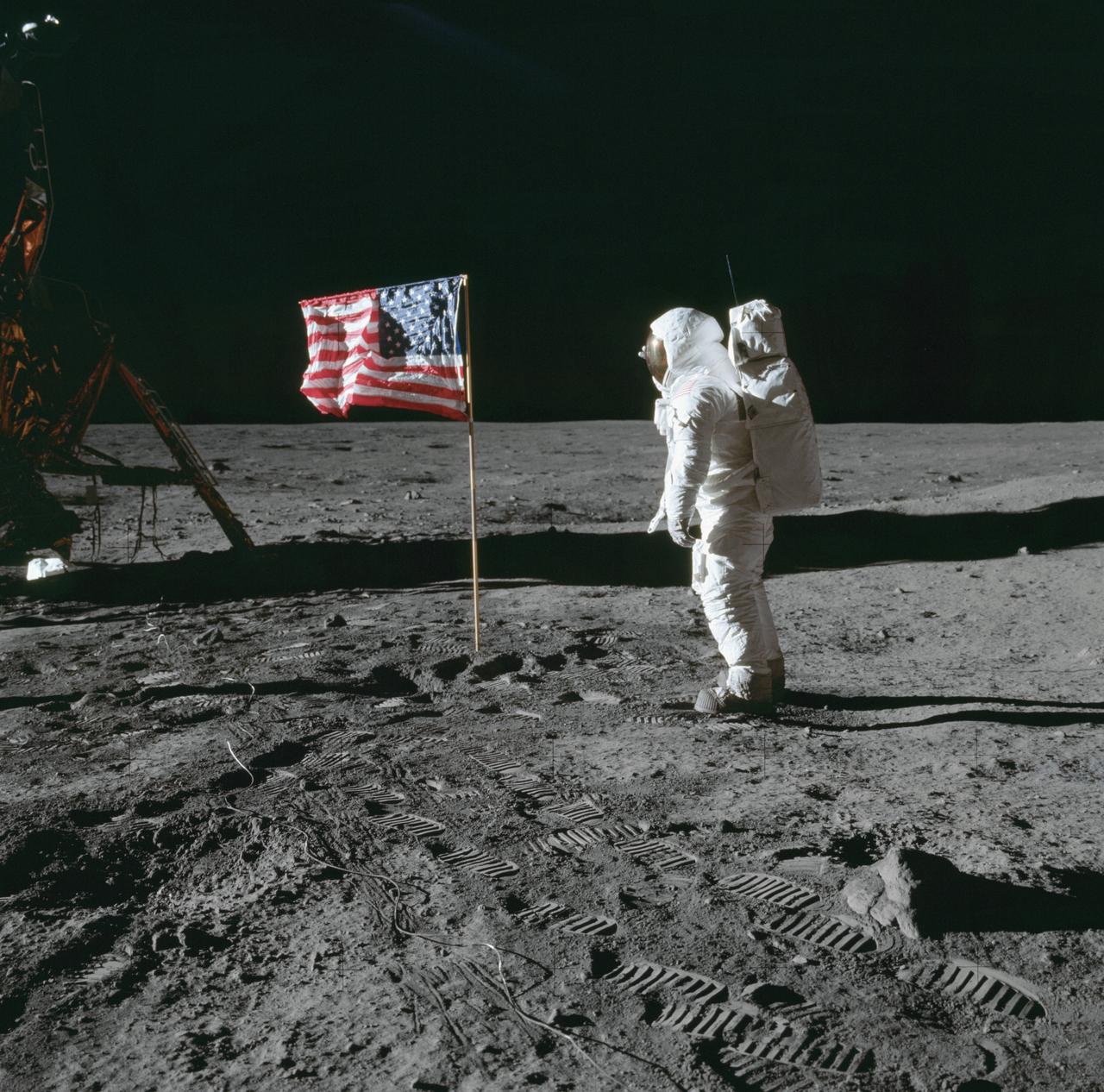

AS11-40-5874 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the first lunar landing mission, poses for a photograph beside the deployed United States flag during Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The Lunar Module (LM) is on the left, and the footprints of the astronauts are clearly visible in the soil of the moon. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm Hasselblad lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM the "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

AS12-51-7507 (19 Nov. 1969) --- The Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM), in a lunar landing configuration, is photographed in lunar orbit from the Command and Service Modules (CSM). The coordinates of the center of the lunar surface shown in picture are 4.5 degrees west longitude and 7 degrees south latitude. The largest crater in the foreground is Ptolemaeus; and the second largest is Herschel. Aboard the LM were astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander; and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot. Astronaut Richard R. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Conrad and Bean descended in the LM to explore the surface of the moon. Photo credit: NASA
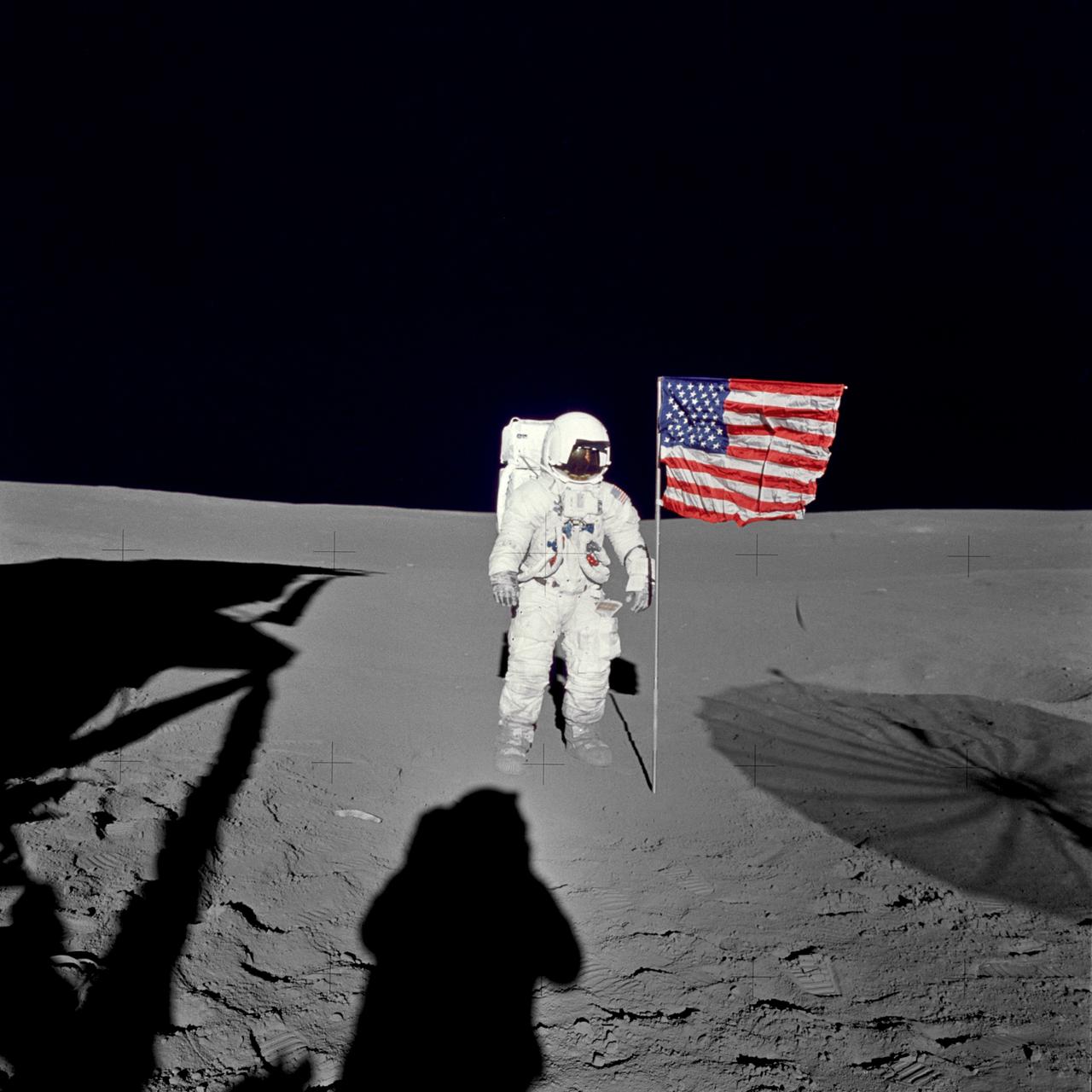

AS14-66-9233 (5 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot for the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, stands by the deployed U.S. flag on the lunar surface during the early moments of the first extravehicular activity (EVA) of the mission. He was photographed by astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., mission commander, using a 70mm modified lunar surface Hasselblad camera. While astronauts Shepard and Mitchell descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Antares" to explore the Fra Mauro region of the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Kitty Hawk" in lunar orbit.
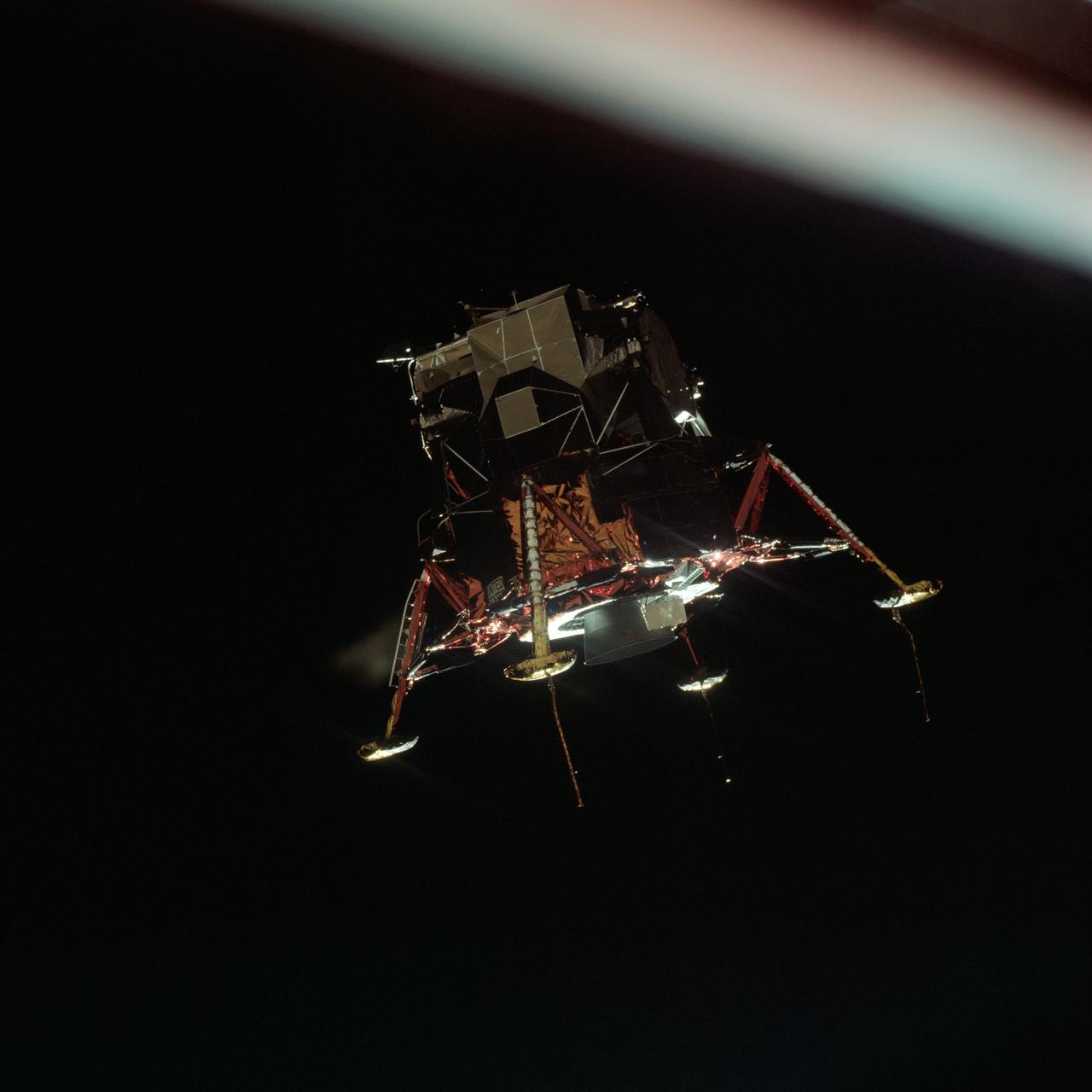

AS11-44-6581 (20 July 1969) --- The Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM), in a lunar landing configuration, is photographed in lunar orbit from the Command and Service Modules (CSM). Inside the LM were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM to explore the lunar surface. The protrusions connected to the landing pods are sensors to aid in the touchdown or landing process.
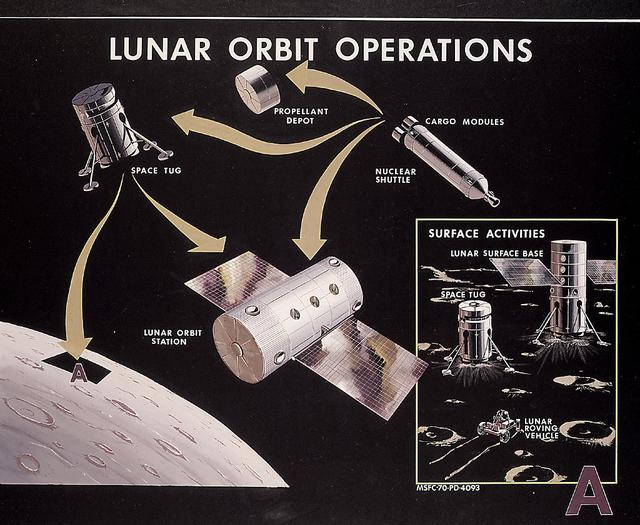
This 1970 artist's concept shows the Nuclear Shuttle and Space Tug operating in conjunction with other spacecraft to support lunar exploration. Marshall Space Flight Center plans during the late 1960s for lunar orbital and surface bases required extensive logistics operations in lunar orbit.
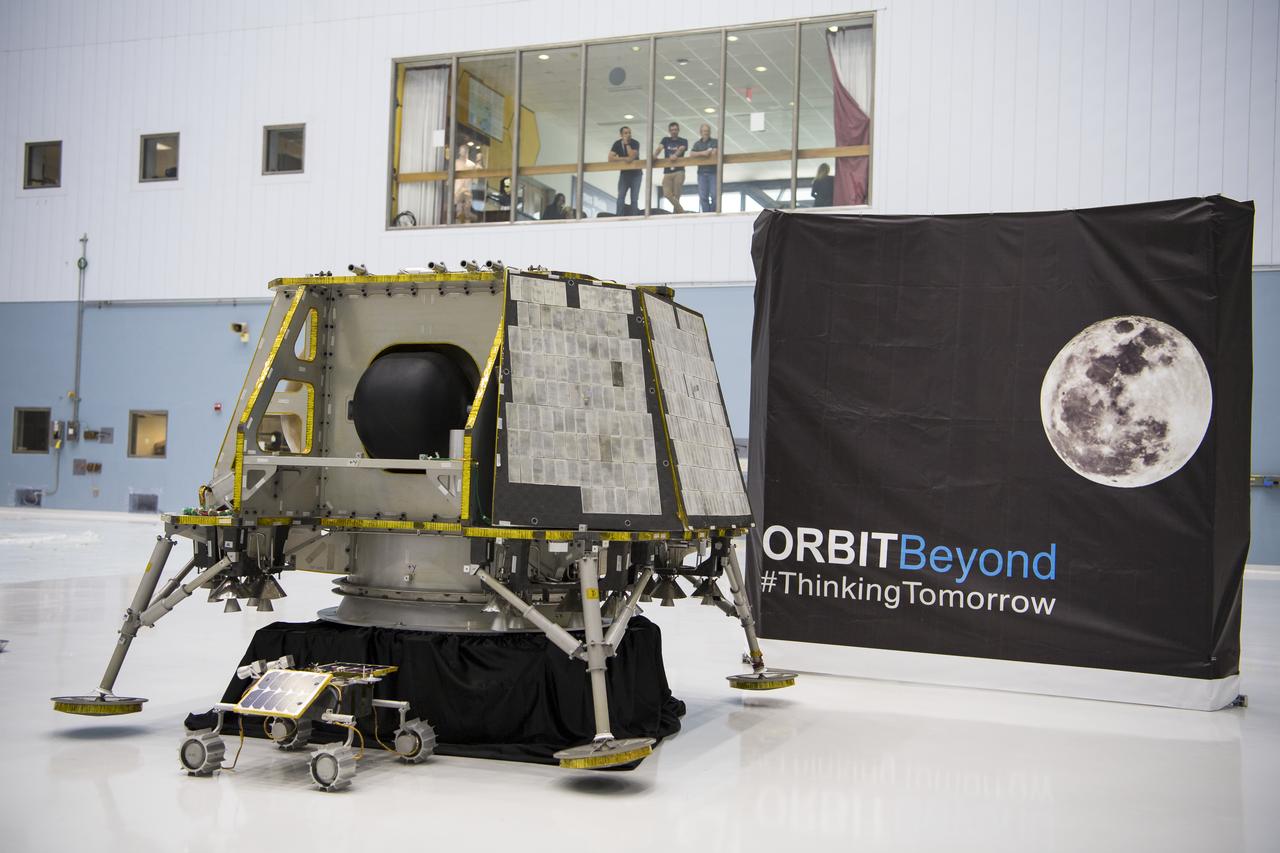

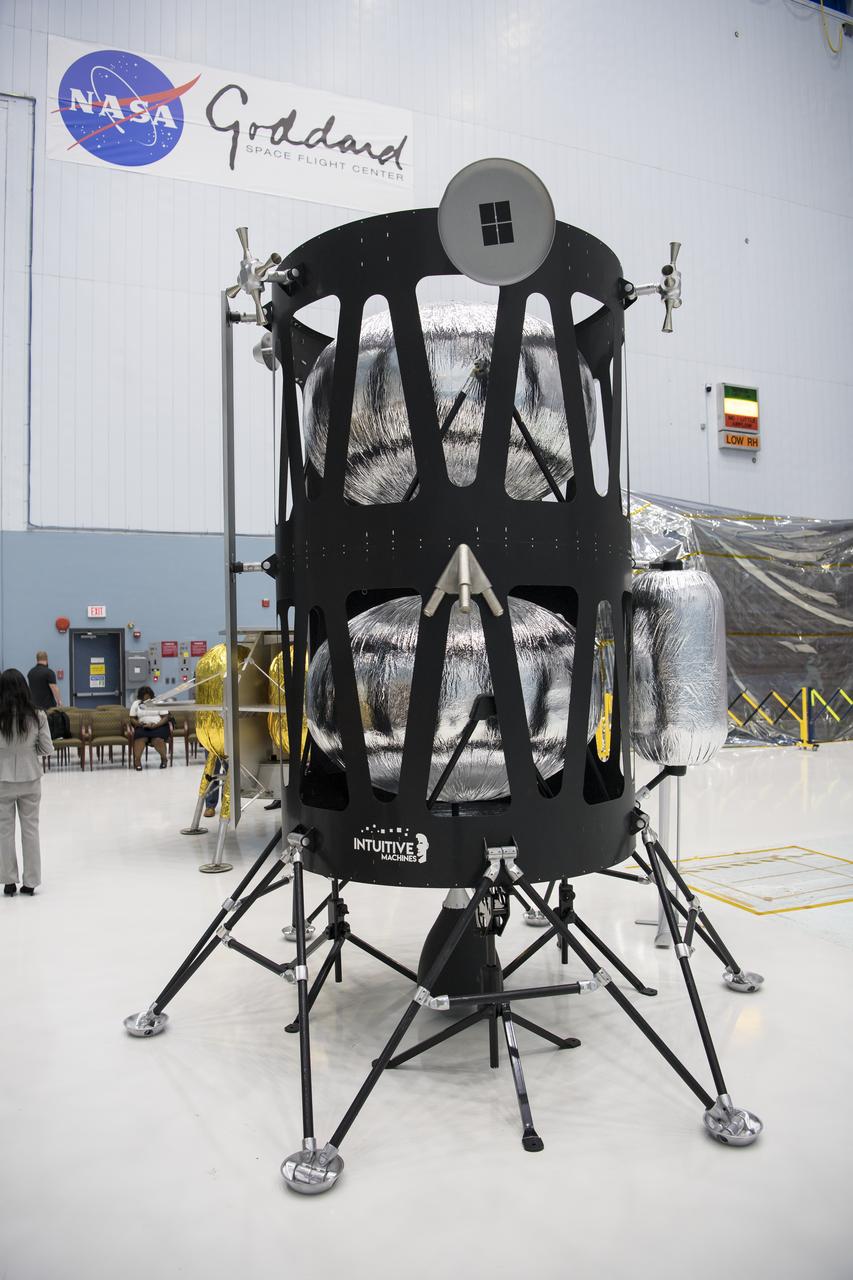
The OrbitBeyond lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
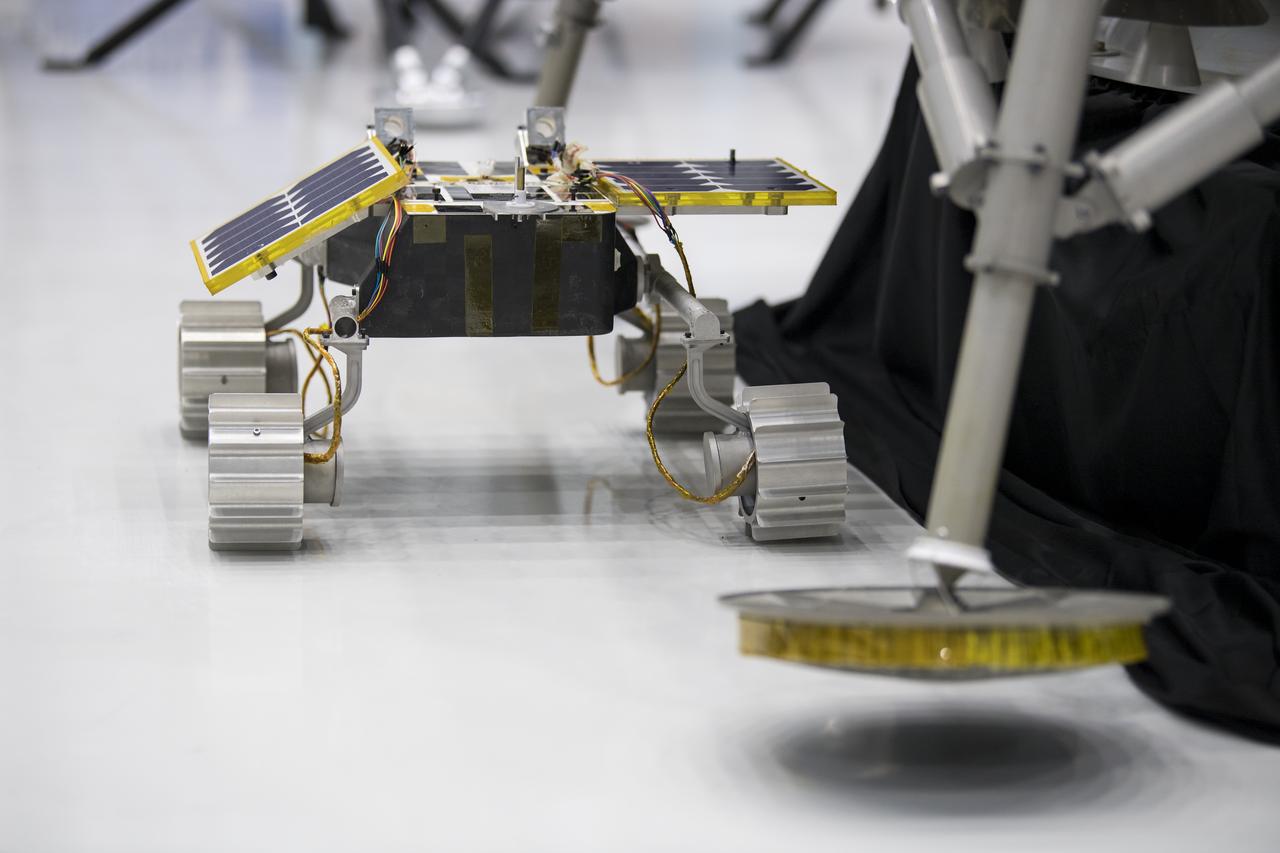

The OrbitBeyond lunar rover is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Artist’s concept of a dual mode Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Lunar surface. This represents the Grumman version in an unmanned configuration. The LRV was developed under the direction of MSFC to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.

Artist’s concept of a Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) Mobility Test Article (MTA) on the Lunar surface. The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
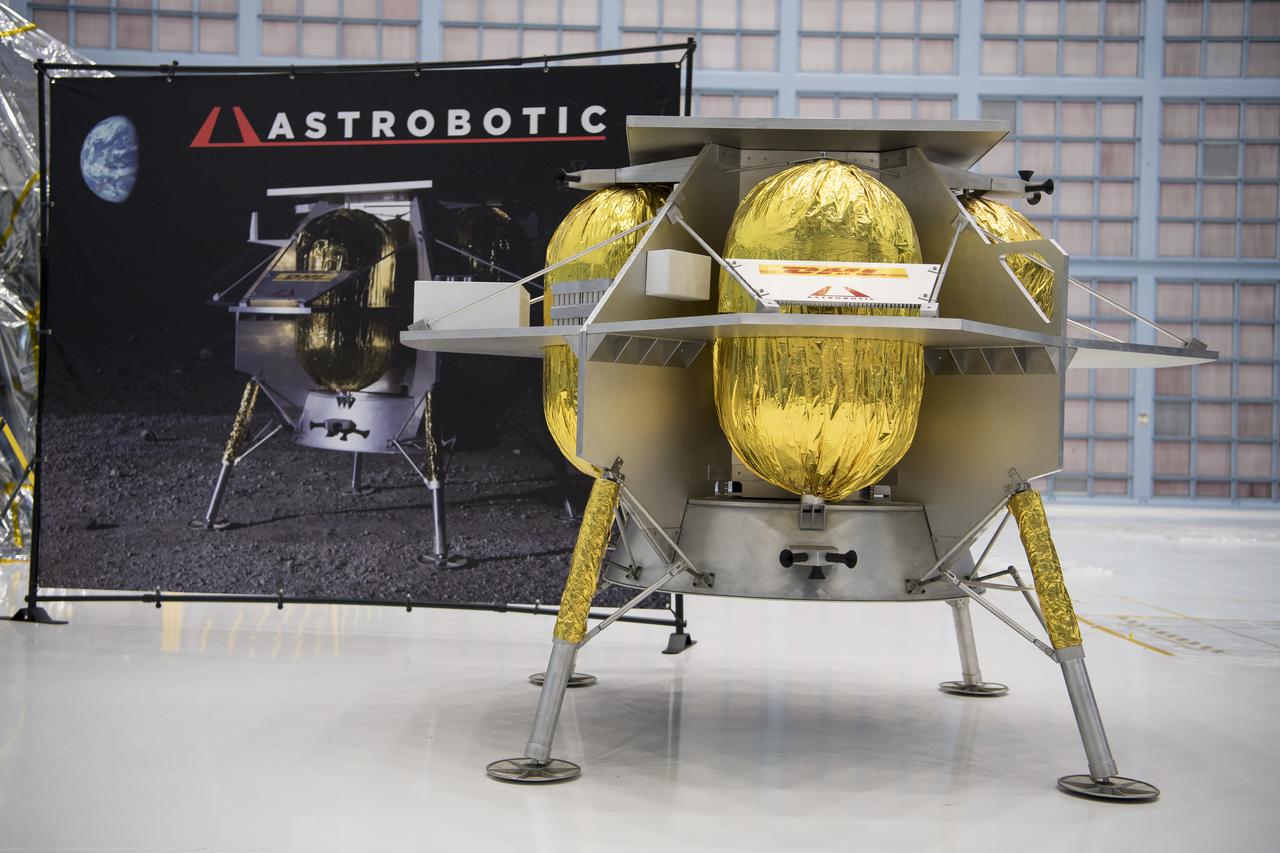

The Astrobotic lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
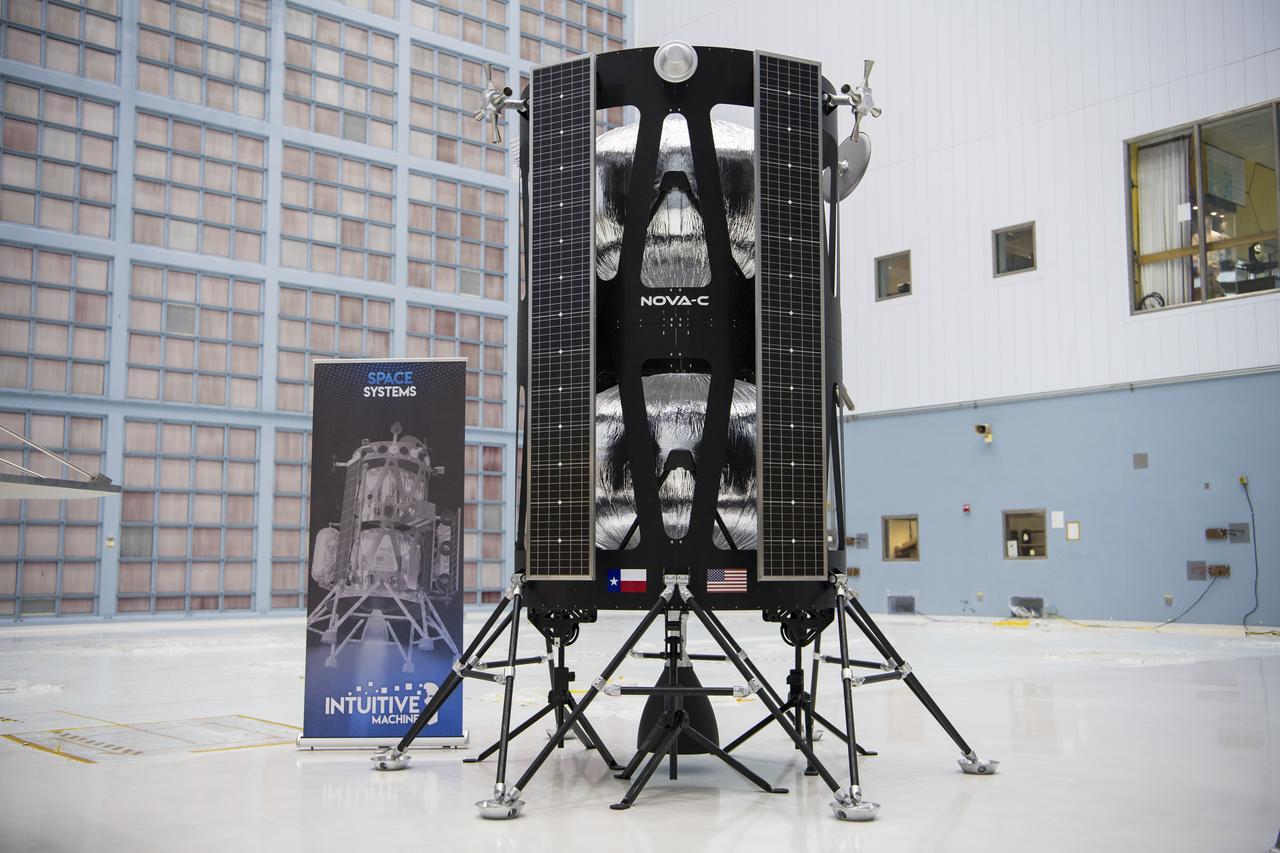

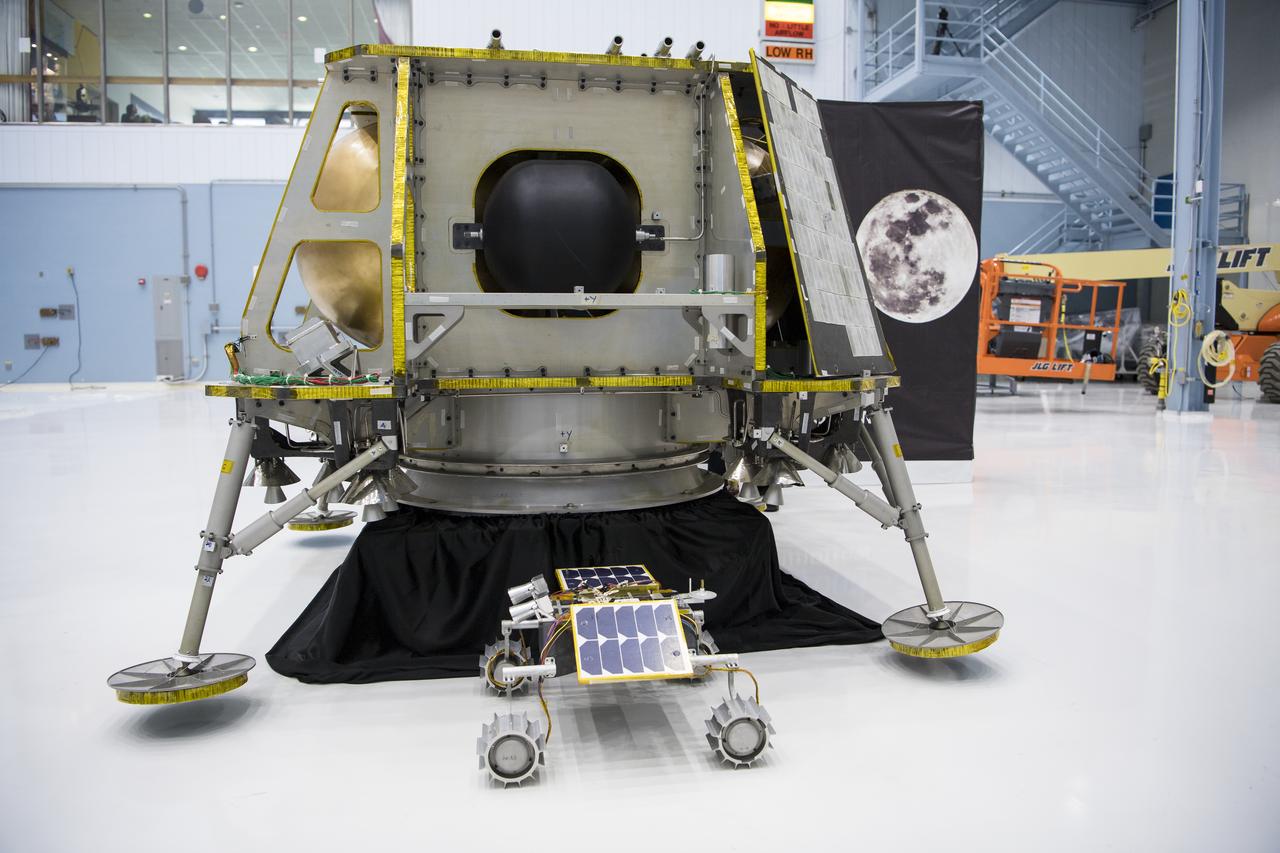
The Intuitive Machines lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

The OrbitBeyond lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
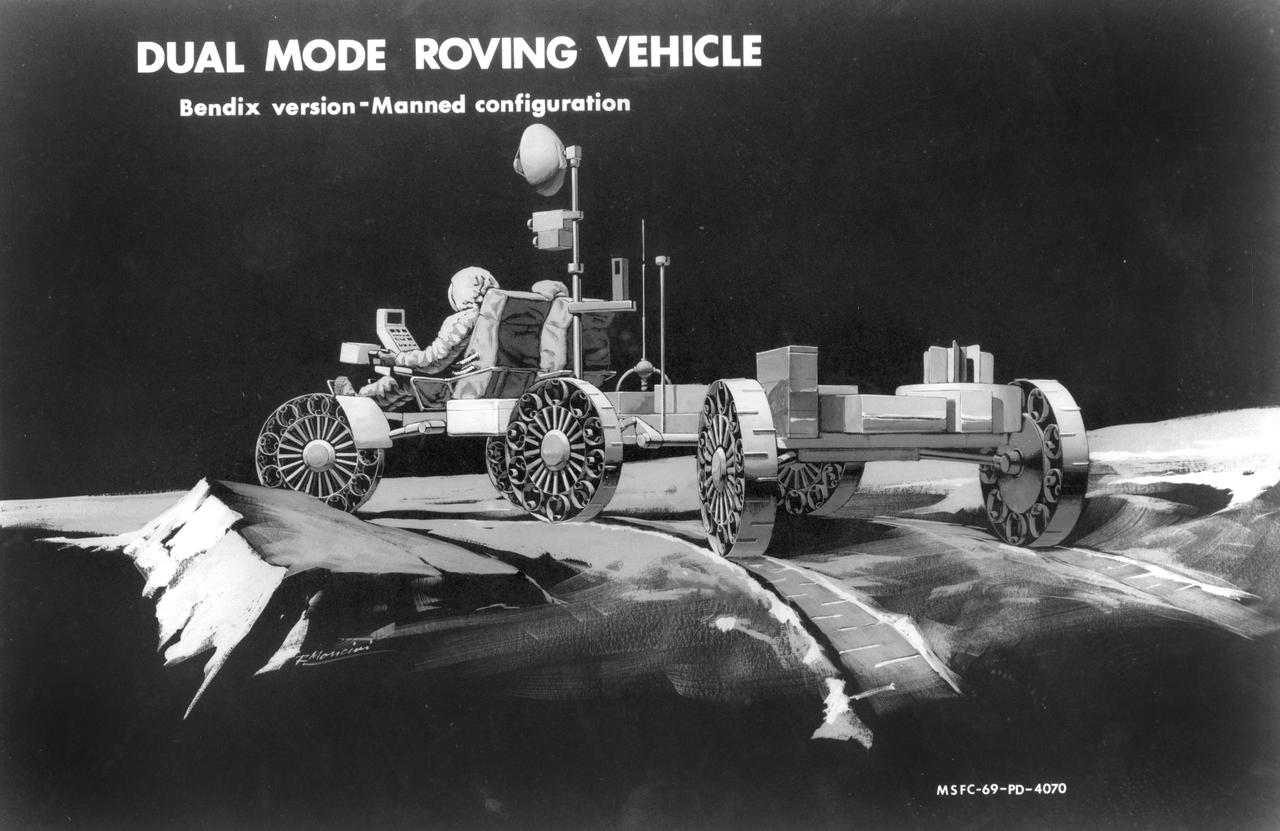
Artist’s concept of a dual mode Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Lunar surface. This represents the Bendix version in an unmanned configuration. The LRV was developed under the direction of MSFC to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
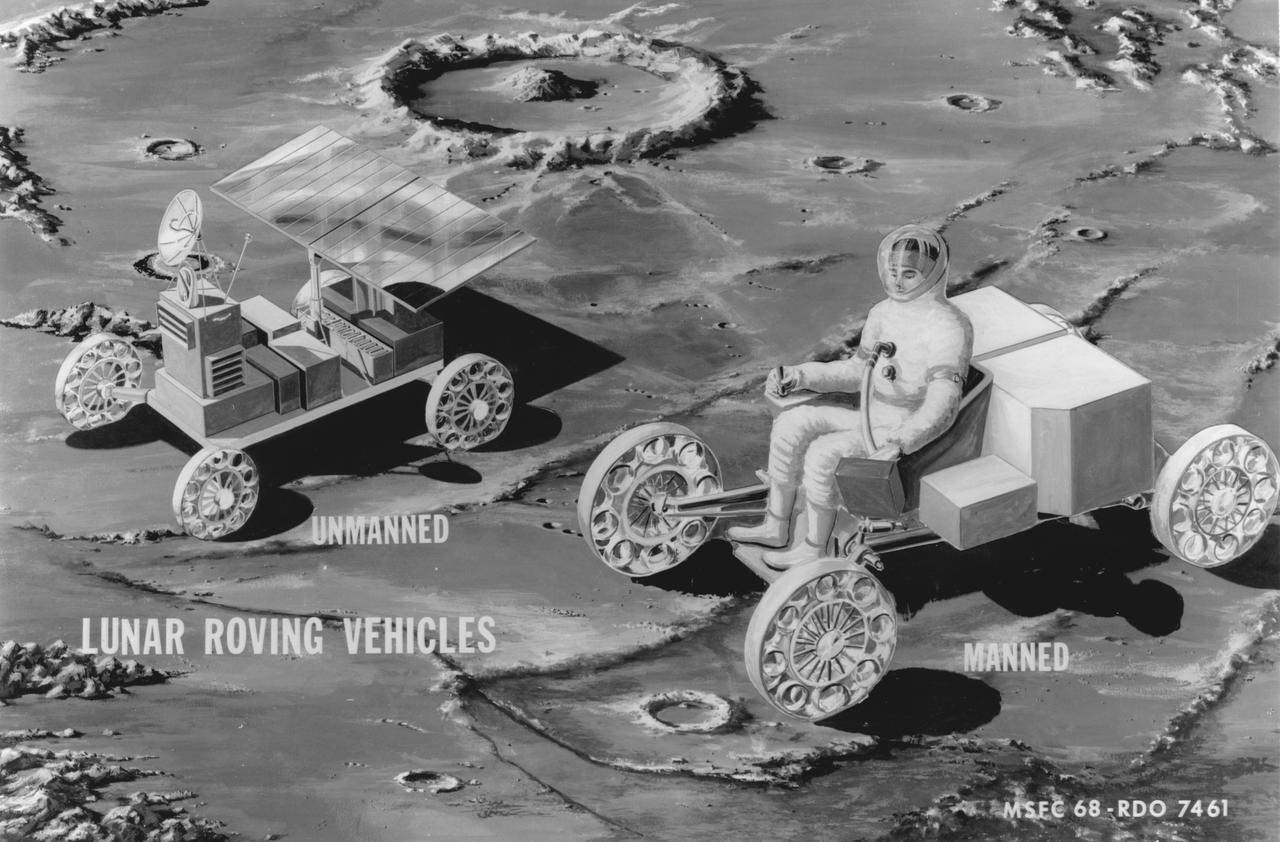
Artist’s manned and unmanned concepts of a Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) Mobility Test Article (MTA) on the Lunar surface. The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.

The Intuitive Machines lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
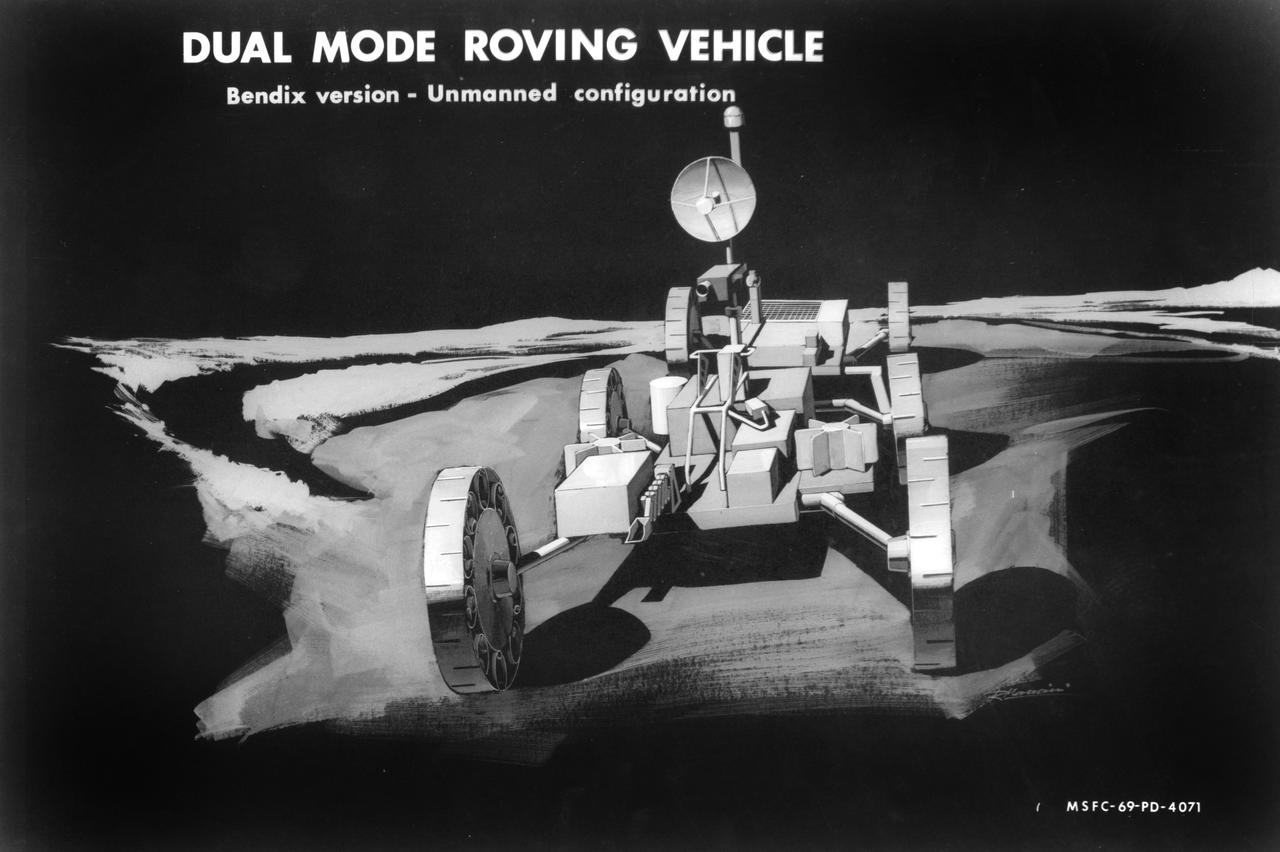
Artist’s concept of a dual mode Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Lunar surface. This represents the Bendix version in an unmanned configuration. The LRV was developed under the direction of MSFC to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.

AS12-46-6729 (19 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot for the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, steps from the ladder of the Lunar Module to join astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, in extravehicular activity on Nov. 19, 1969. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.

AS08-17-2821 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- This oblique view of the lunar surface taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking westward across the Sea of Tranquility shows Apollo Landing Site East 2 illuminated by a sun that is six to eight degrees above the eastern horizon. The landing site is on the dark gray, smooth surface of the Sea of Tranquility and north (to the right) of the bright highland terrain at the lower left corner of the photograph. The landing site is about four tenths of the distance from the left to right margin of the photograph.
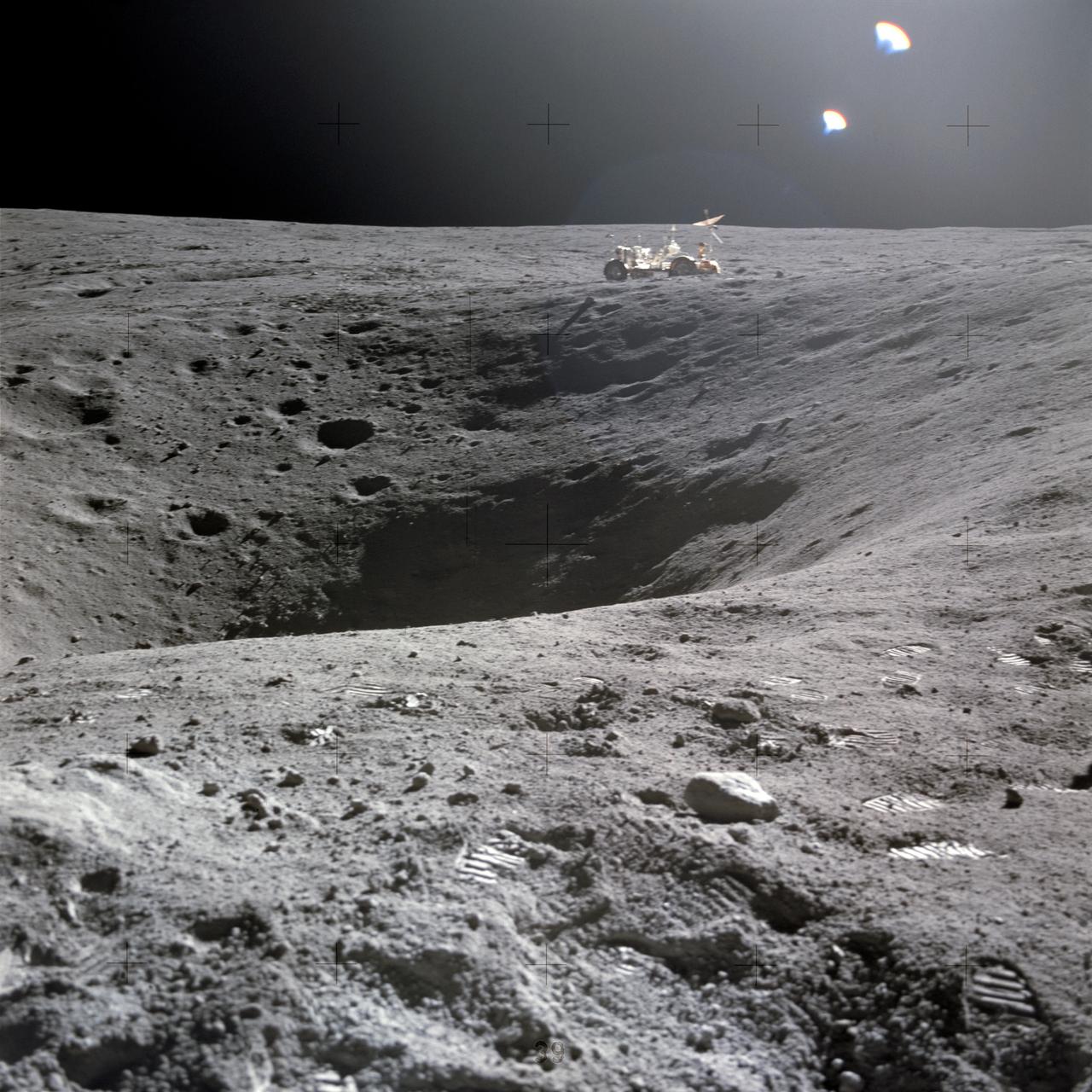

AS16-114-18422 (21 April 1972) --- A view of Plum Crater, which was visited by the two moon-exploring crewmen of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, on their first extravehicular activity (EVA) traverse, April 21, 1972. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is parked on the far side of the crater, which measures approximately 40 meters in diameter. While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
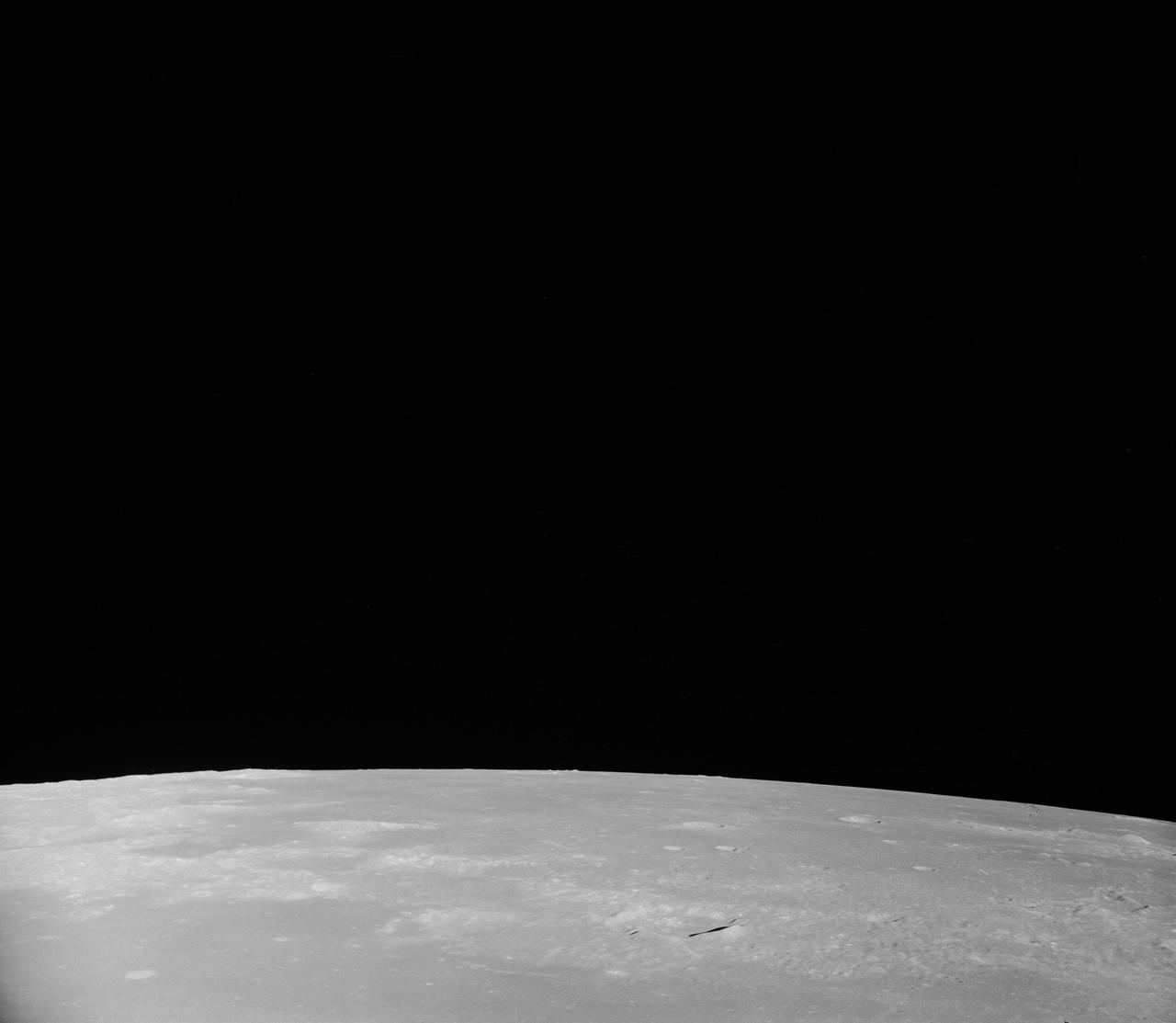

AS08-17-2814 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- This oblique view of the lunar surface taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking westward across the Sea of Fertility into the Sea of Tranquility shows the terrain the astronauts will see as the approach Apollo Landing Site East 2. The landing site is at the horizon about one-third of the distance from the left to the right photograph margin. The prominent crater in the highlands near the center of the picture is Secchi, about 25 kilometers (15 statute miles) in diameter.
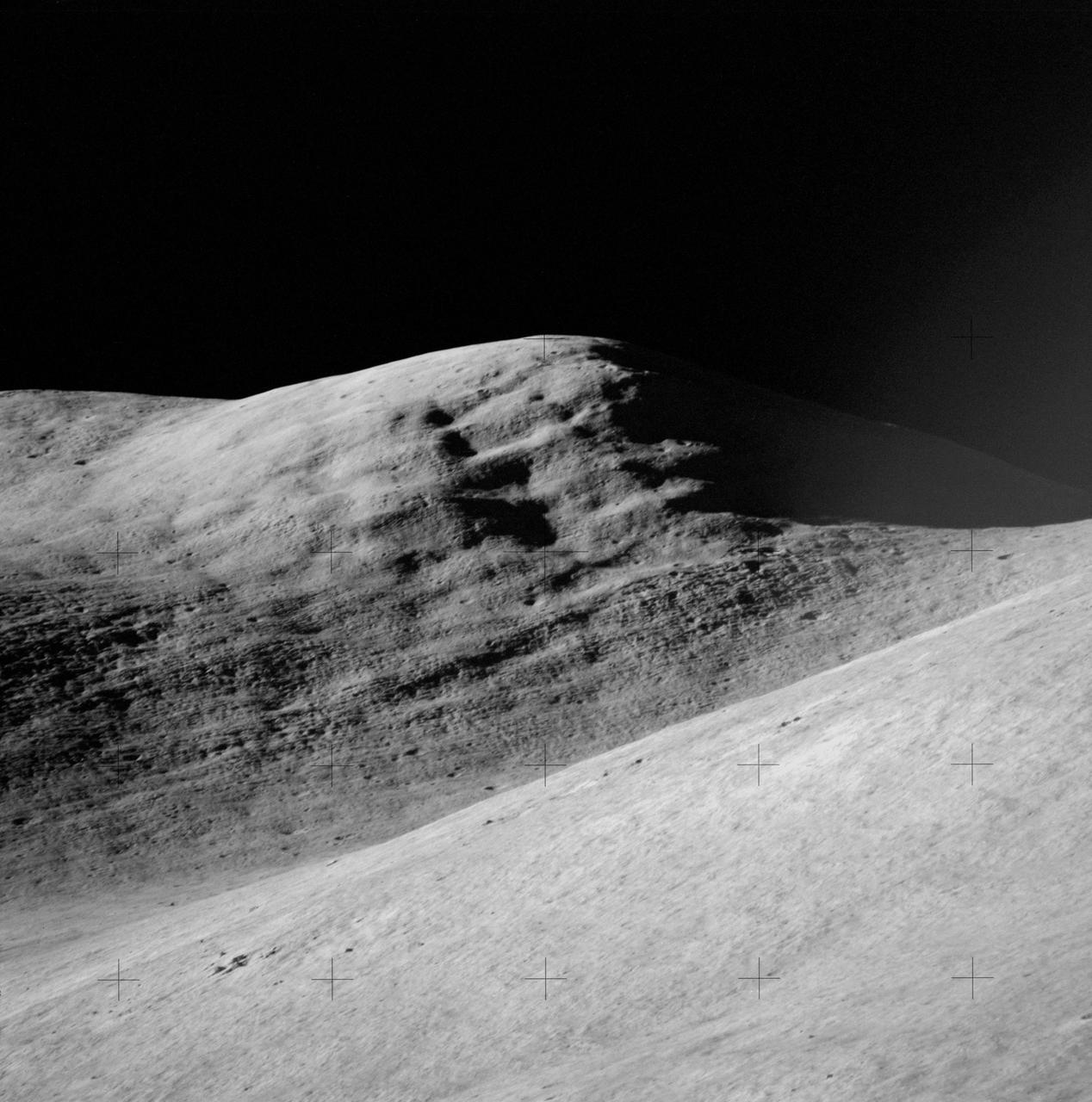

AS15-84-11250 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- A telephoto lens view of the prominent feature called Silver Spur in the Hadley Delta region, photographed during the Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The distance from the camera to the spur is about 10 miles. The field of view across the bottom is about one mile. Structural formations in the mountain are clearly visible. There are two major units. The upper unit is characterized by massive subunits, each one of which is approximately 200 feet deep. The lower major unit is characterized by thinner bedding and cross bedding.
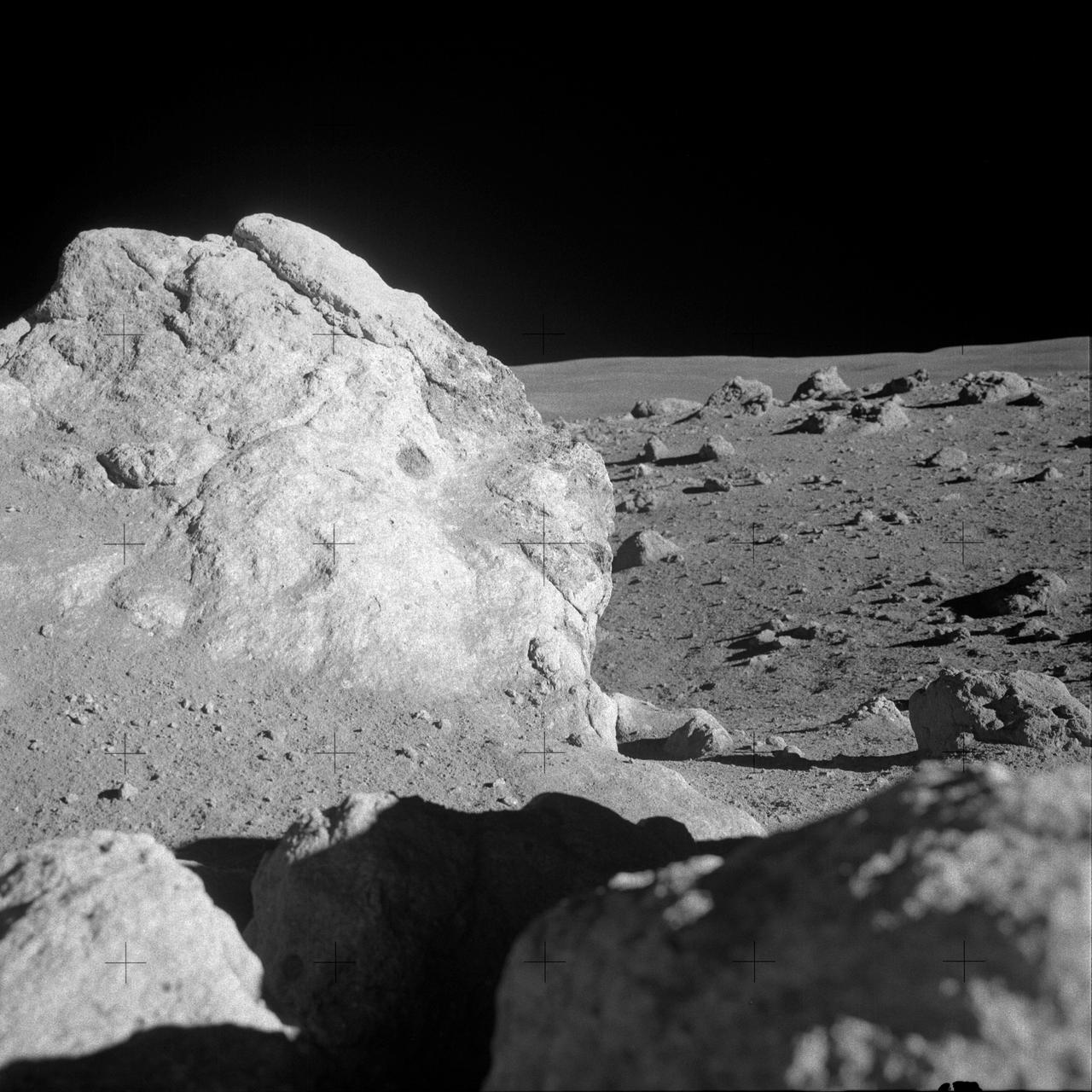

AS14-68-9451 (6 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of a large boulder in a field of boulders near the rim of Cone Crater, which was photographed by the Apollo 14 moon-explorers during the mission's second extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) to explore the lunar surface while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS11-40-5902 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, walks on the surface of the moon near a leg of the Lunar Module during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, Apollo 11 commander, took this photograph with a 70mm lunar surface camera. The astronauts' bootprints are clearly visible in the foreground. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

AS11-40-5903 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, walks on the surface of the moon near the leg of the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this photograph with a 70mm lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

AS11-37-5505 (20 July 1969) --- This photograph shows in fine detail the impressions in the lunar soil made by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Armstrong, commander, and Aldrin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

AS12-46-6832 (19 Nov. 1969) --- A close-up view of a lunar mound as photographed during the Apollo 12 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 12 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon.

S71-39867 (June 1971) --- Astronauts David R. Scott (right), commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, are shown on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida, during Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) simulations. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descend in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS14-66-9244 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- An excellent view of the lunar terrain looking through the right window of the Lunar Module (LM), photographed by one of the Apollo 14 astronauts during their stay on the lunar surface. Pothole-sized craters can be seen in the foreground. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
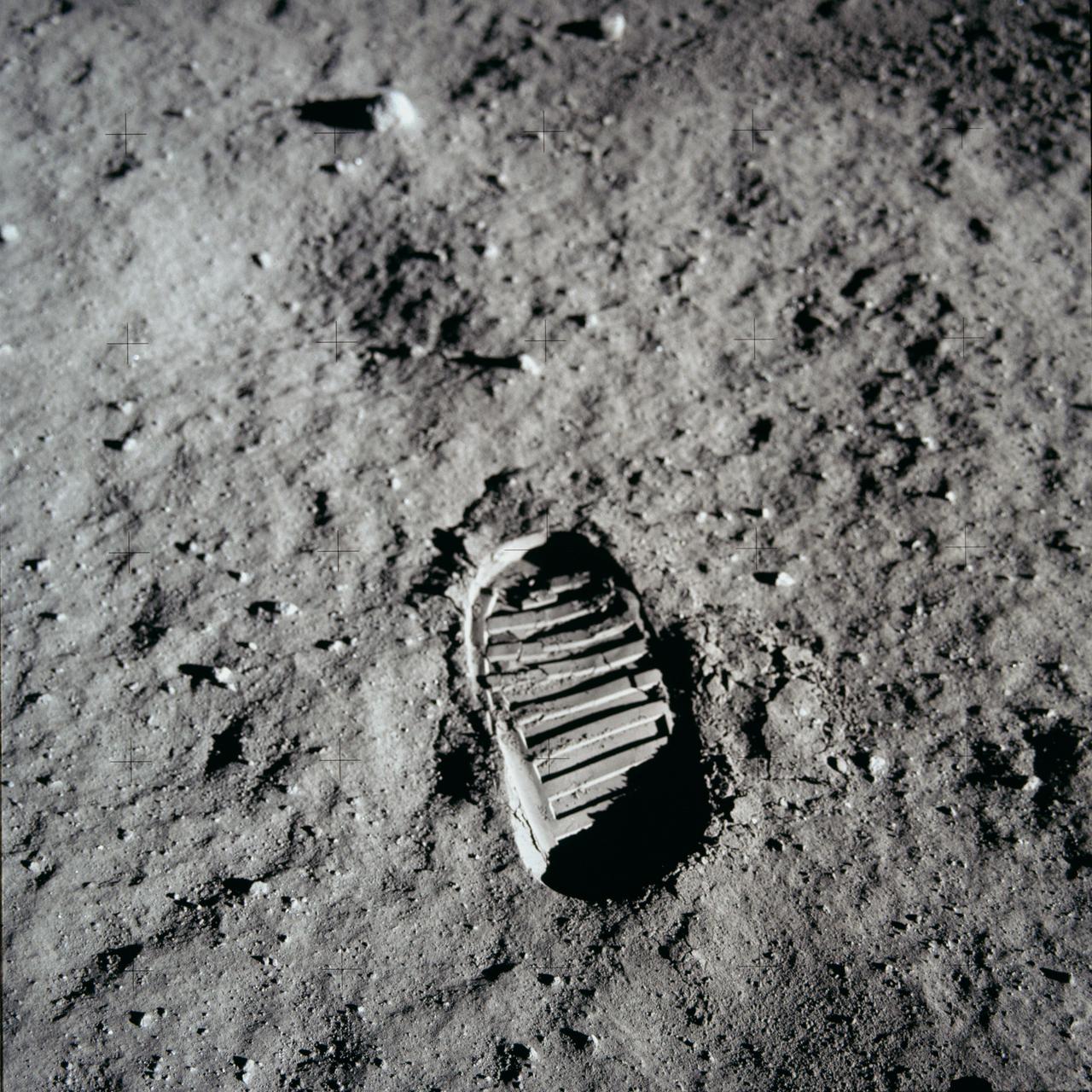

AS11-40-5877 (20 July 1969) --- A close-up view of an astronaut's bootprint in the lunar soil, photographed with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
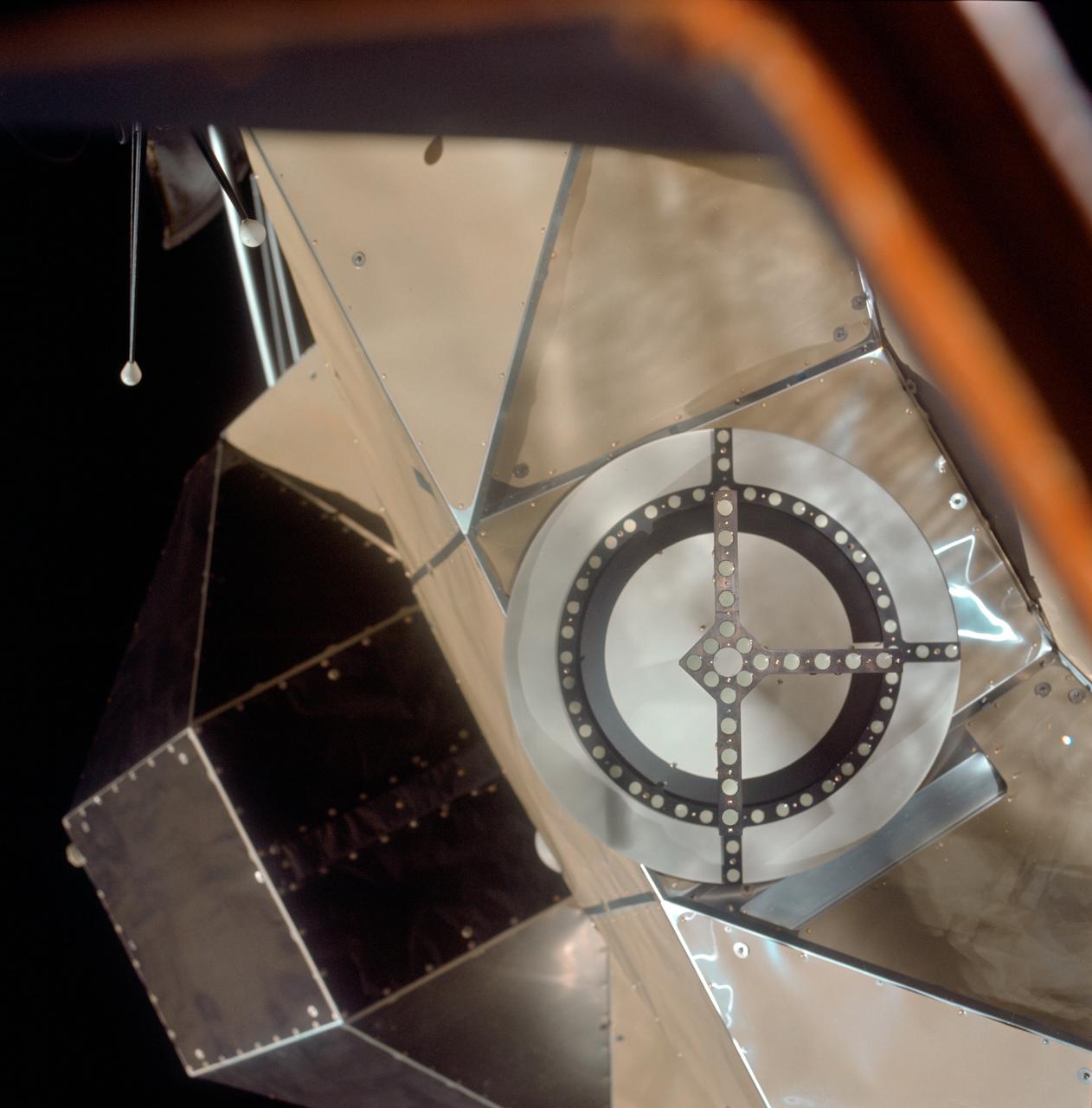

AS11-36-5365 (21 July 1969) --- A close-up view of the docking target on the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) photographed from the Command Module during the LM/CSM docking in lunar orbit. Astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, in the LM, were returning from the lunar surface. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while Armstrong and Aldrin explored the moon.
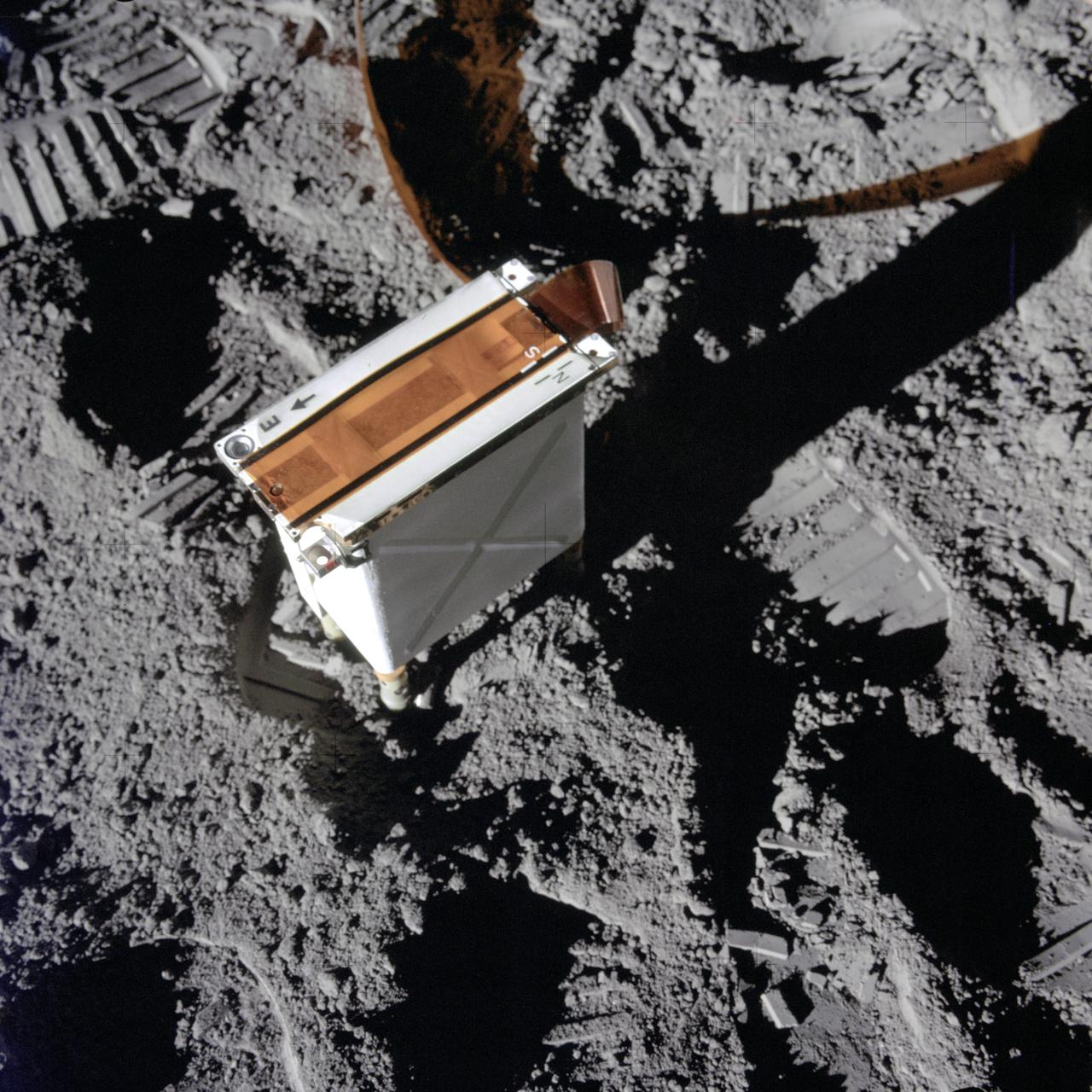

AS14-67-9364 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of the charged particle lunar environment experiment (CPLEE), a component of the Apollo lunar surface experiments package (ALSEP) which was deployed on the moon by the Apollo 14 astronauts. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
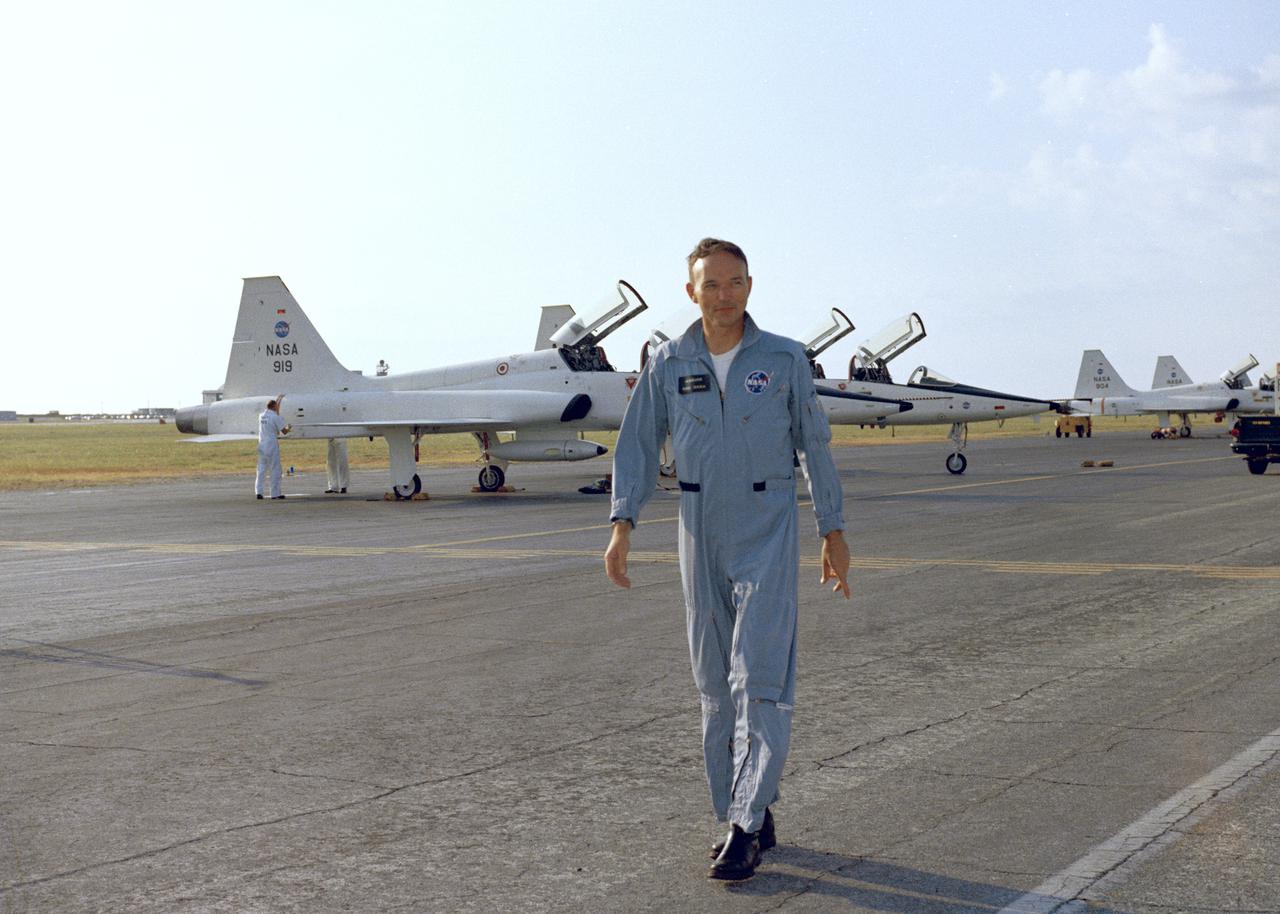

PATRICK AFB, Fla. – Apollo 11 command module pilot Michael Collins, just arrived at Patrick Air Force Base in a T-38 jet in preparation of the nation’s first lunar landing mission. Lift off atop a Saturn V launch vehicle is scheduled for July 16, 1969. During Apollo 11, the command module, Columbia, will remain in orbit around the moon while the lunar module, Eagle, carrying Armstrong and Aldrin, lands on the lunar surface. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew plans to collect lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. For more: http:__www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov_history_apollo_apollo-11_apollo-11.htm Photo credit: NASA
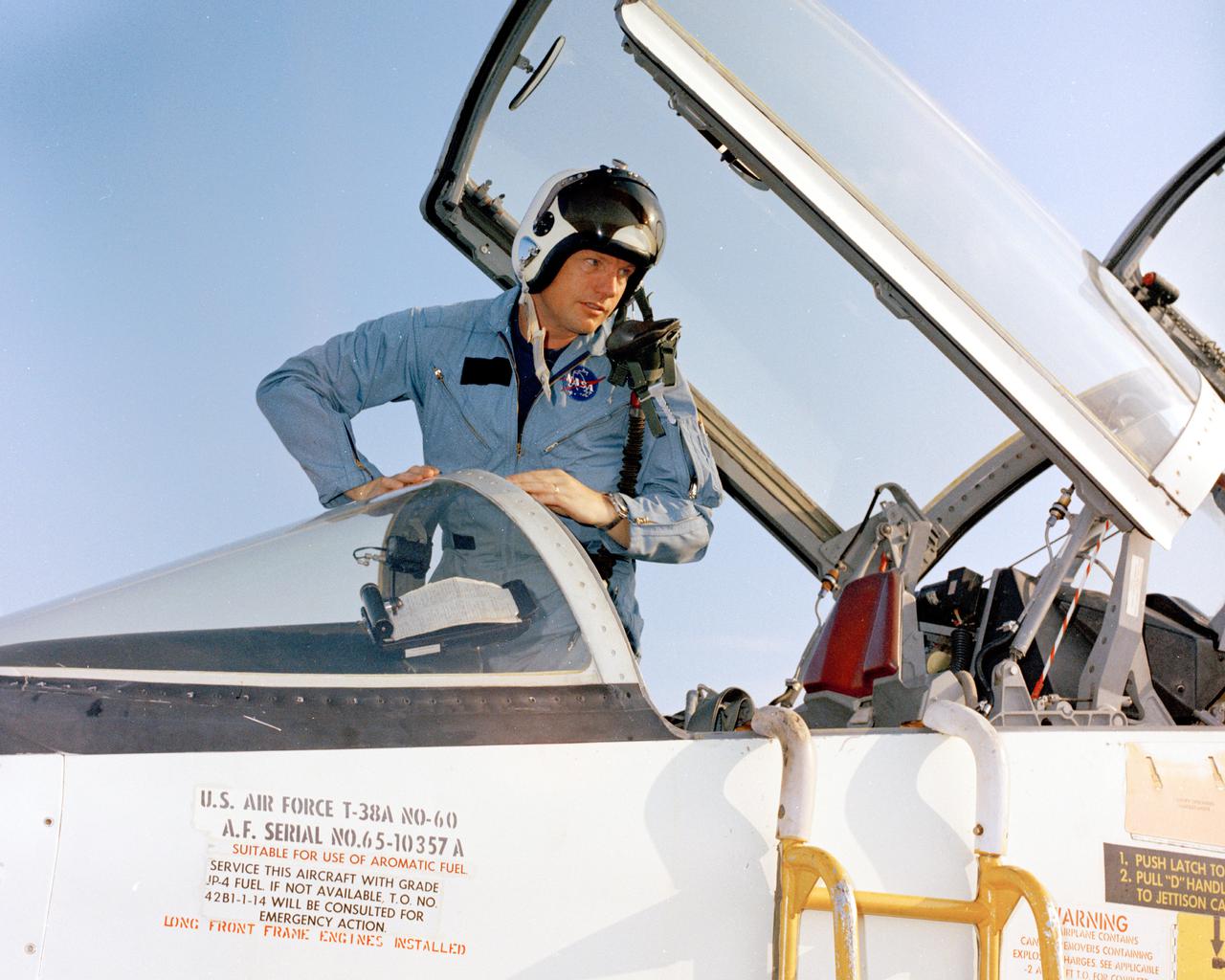

PATRICK AFB, Fla. – In preparation of the nation’s first lunar landing mission, Apollo 11 crew members arrive at Patrick Air Force Base, Florida. Mission commander Neil Armstrong climbs out of a T-38 jet. Lift off atop a Saturn V launch vehicle is scheduled for July 16, 1969. During Apollo 11 the command module, Columbia, will remain in orbit around the moon while the lunar module, Eagle, carrying Armstrong and Aldrin, lands on the lunar surface. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew plans to collect lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. For more: http:__www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov_history_apollo_apollo-11_apollo-11.htm Photo credit: NASA

This is a photo of the Apollo 15 Lunar Module, Falcon, on the lunar surface. Apollo 15 launched from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) on July 26, 1971 via a Saturn V launch vehicle. Aboard was a crew of three astronauts including David R. Scott, Mission Commander; James B. Irwin, Lunar Module Pilot; and Alfred M. Worden, Command Module Pilot. The first mission designed to explore the Moon over longer periods, greater ranges and with more instruments for the collection of scientific data than on previous missions, the mission included the introduction of a $40,000,000 lunar roving vehicle (LRV) that reached a top speed of 16 kph (10 mph) across the Moon's surface. The successful Apollo 15 lunar landing mission was the first in a series of three advanced missions planned for the Apollo program. The primary scientific objectives were to observe the lunar surface, survey and sample material and surface features in a preselected area of the Hadley-Apennine region, setup and activation of surface experiments and conduct in-flight experiments and photographic tasks from lunar orbit. Apollo 15 televised the first lunar liftoff and recorded a walk in deep space by Alfred Worden. Both the Saturn V rocket and the LRV were developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
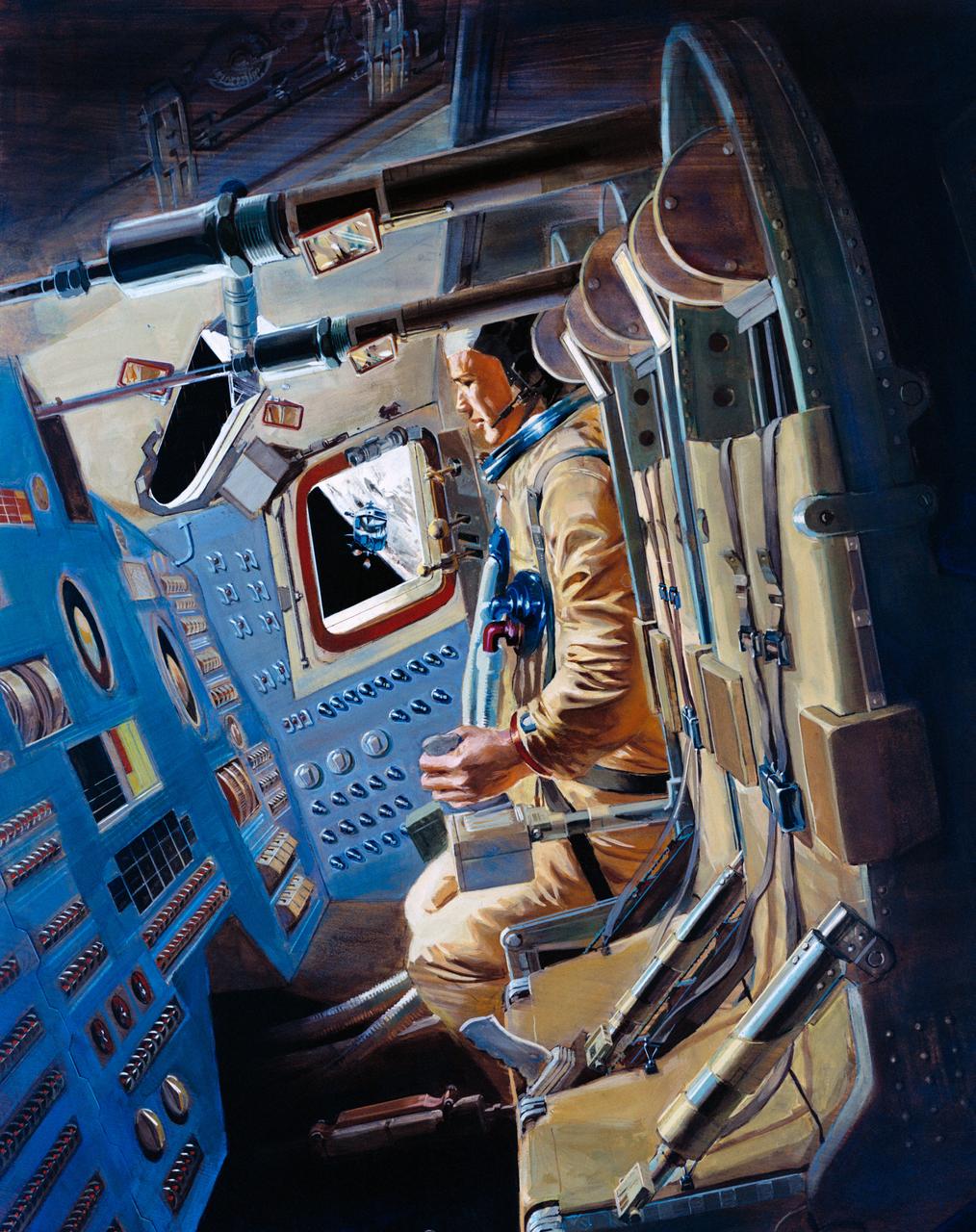

S69-58005 (10 Nov. 1969) --- An artist's concept of the Apollo 12 Command Module's (CM) interior, with the command module pilot at the controls. The Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM) and a portion of the lunar surface are seen out of the window. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr. will maneuver the Apollo 12 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, explore the moon.
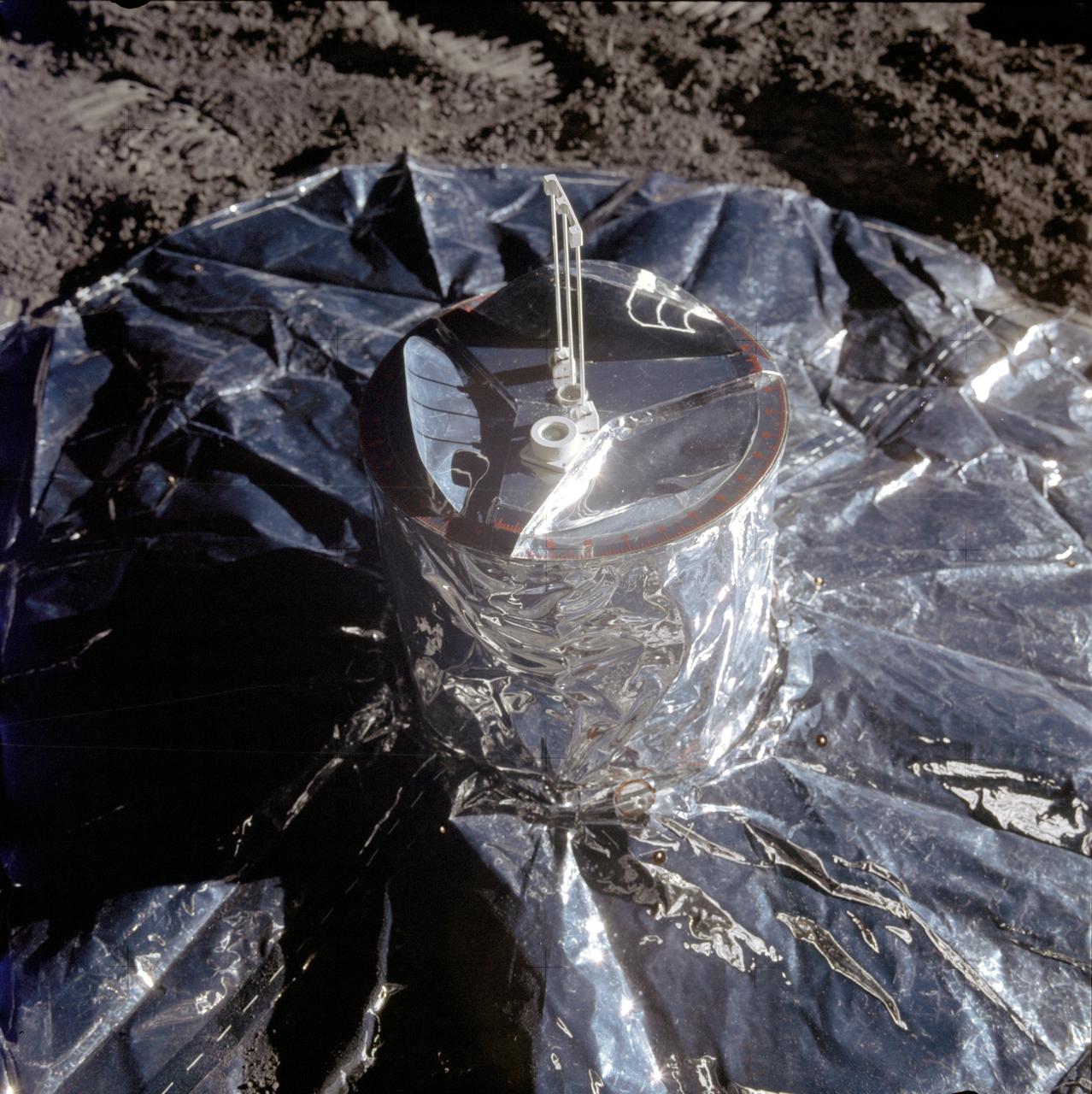

AS14-67-9362 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of the passive seismic experiment (PSE), a component of the Apollo lunar surface experiments package (ALSEP), which was deployed on the moon by the Apollo 14 astronauts during their first extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
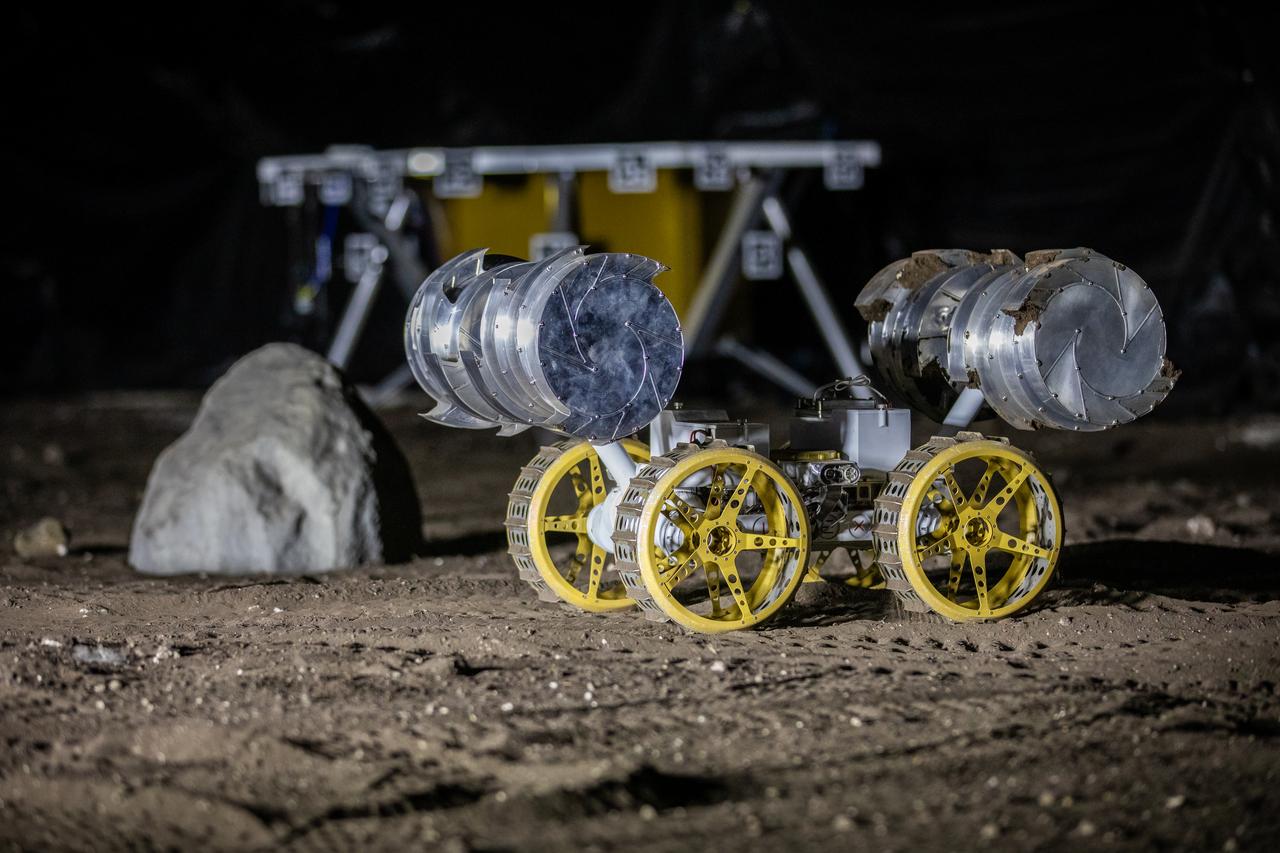

NASA’s ISRU Pilot Excavator (IPEx) performs a simulated lunar mission in a testbed at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center on Friday, Aug. 30, 2024. IPEx functions as both an excavator and a dump truck to mine and transport lunar regolith, the loose rocky material on the Moon’s surface, which is crucial for future lunar missions and In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) processes. This dual capability makes IPEx an indispensable tool for sustainable lunar exploration.
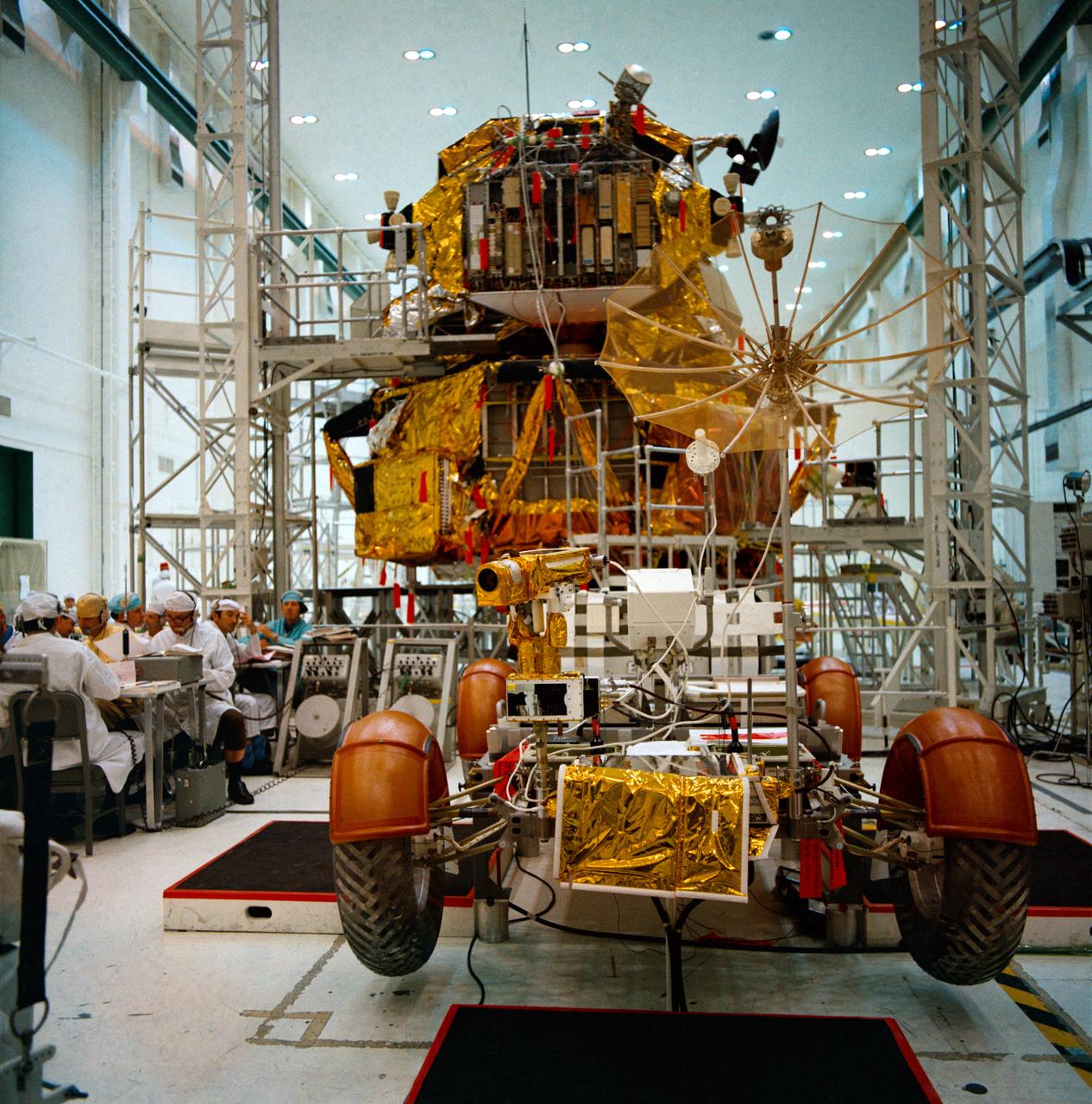

S71-30542 (21 April 1971) --- An overall view of the Apollo 15 Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) and the Lunar Module (LM) during simulations at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, will man the LRV on the lunar surface during their August 1971 traverses. Rover 1 will permit the astronauts to cover a larger area of the moon for exploration and sample collecting than on previous missions.
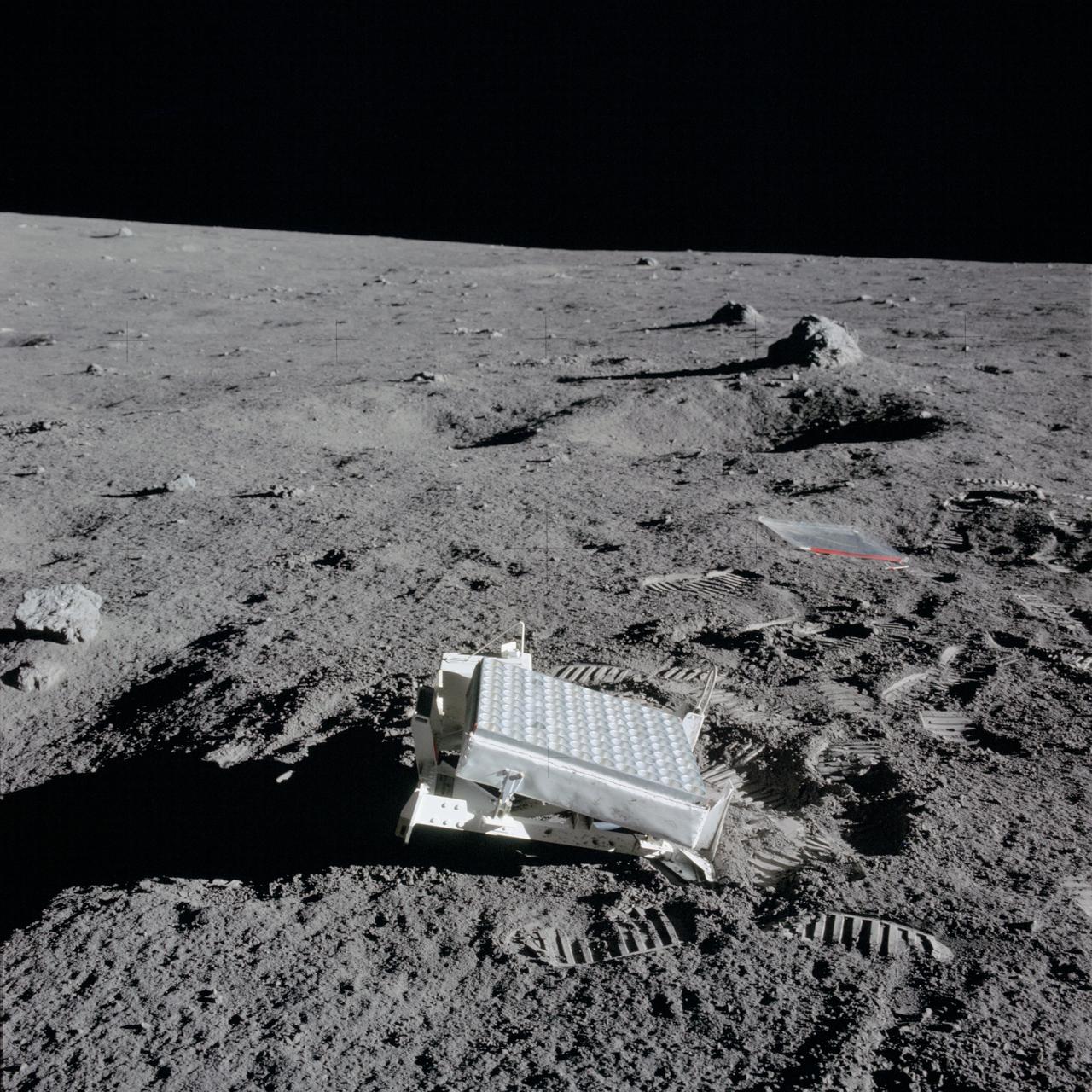
AS14-67-9386 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of the laser ranging retro reflector (LR3) which the Apollo 14 astronauts deployed on the moon during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS14-66-9241 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, makes a pan with the lunar surface television camera during an extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. This photograph was taken by fellow astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander. While Shepard and Mitchell descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
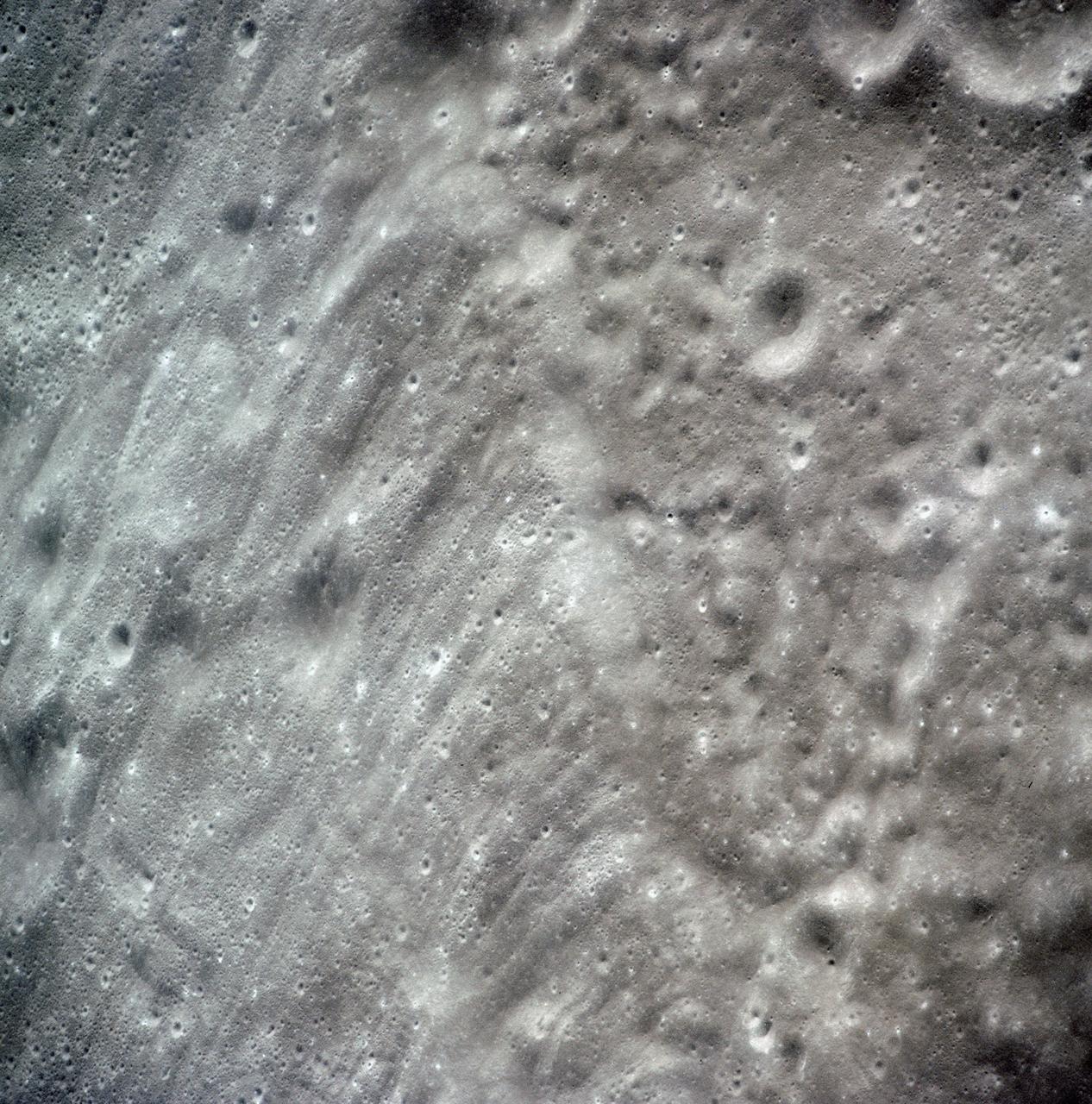

AS15-97-13168 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- A view of the flow structure on the rim and edge of the crater Tsiolkovsky in the highlands of the lunar farside, as photographed from lunar orbit by astronaut Alfred M. Worden in the Apollo 15 Command and Service Module (CSM). Note the scarp at the edge of the flow and elongated grooves on the flow surface. While astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon's Hadley-Apennine landing site, Worden remained with the CSM in lunar orbit.

AS14-66-9278 (5 Feb. 1971) --- An excellent view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) on the moon, as photographed during the first Apollo 14 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
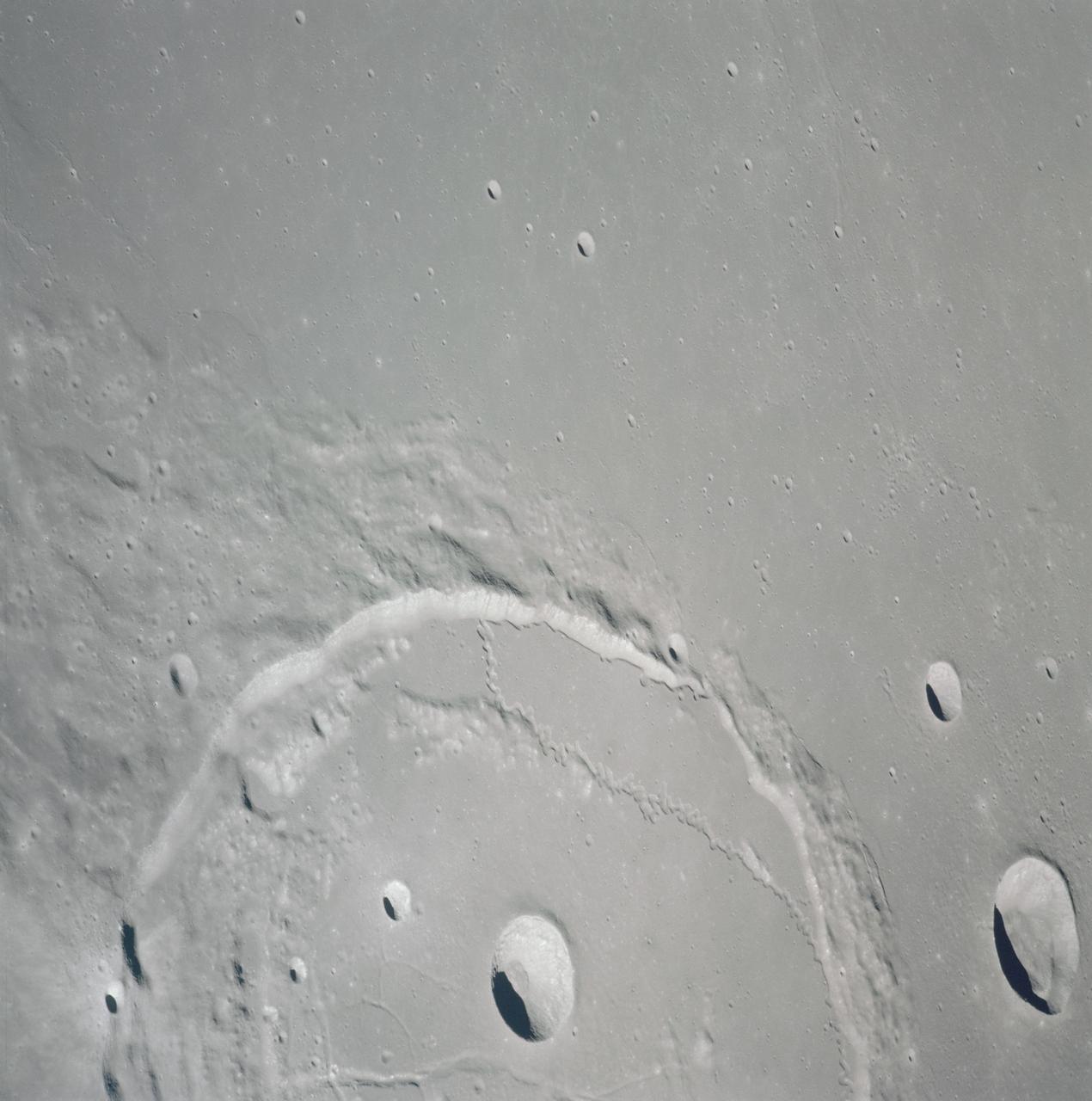

AS15-91-12366 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- The crater Posidonius at the northeastern edge of the Sea of Serenity, was photographed with a 70mm handheld Hasselblad from the Command and Service Module (CSM) by astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, in lunar orbit. While Worden remained with the CSM in lunar orbit, astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the lunar surface.
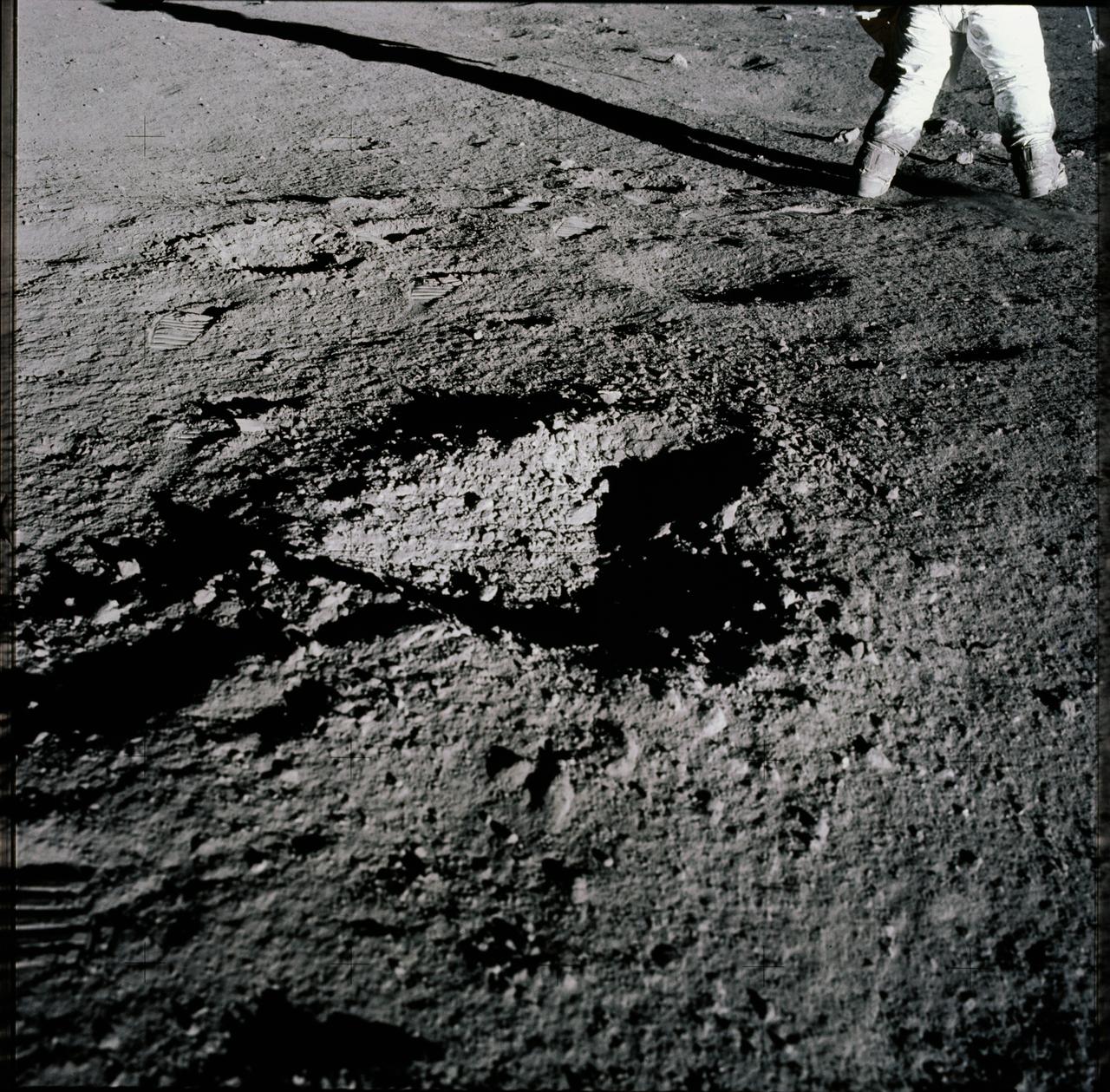

AS12-47-6938 (19 Nov. 1969) --- A close-up view of a heart-shaped depression (crater) in the lunar surface, as photographed during the Apollo 12 extravehicular activity (EVA). The legs of astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, can be seen in the background. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Conrad and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon.
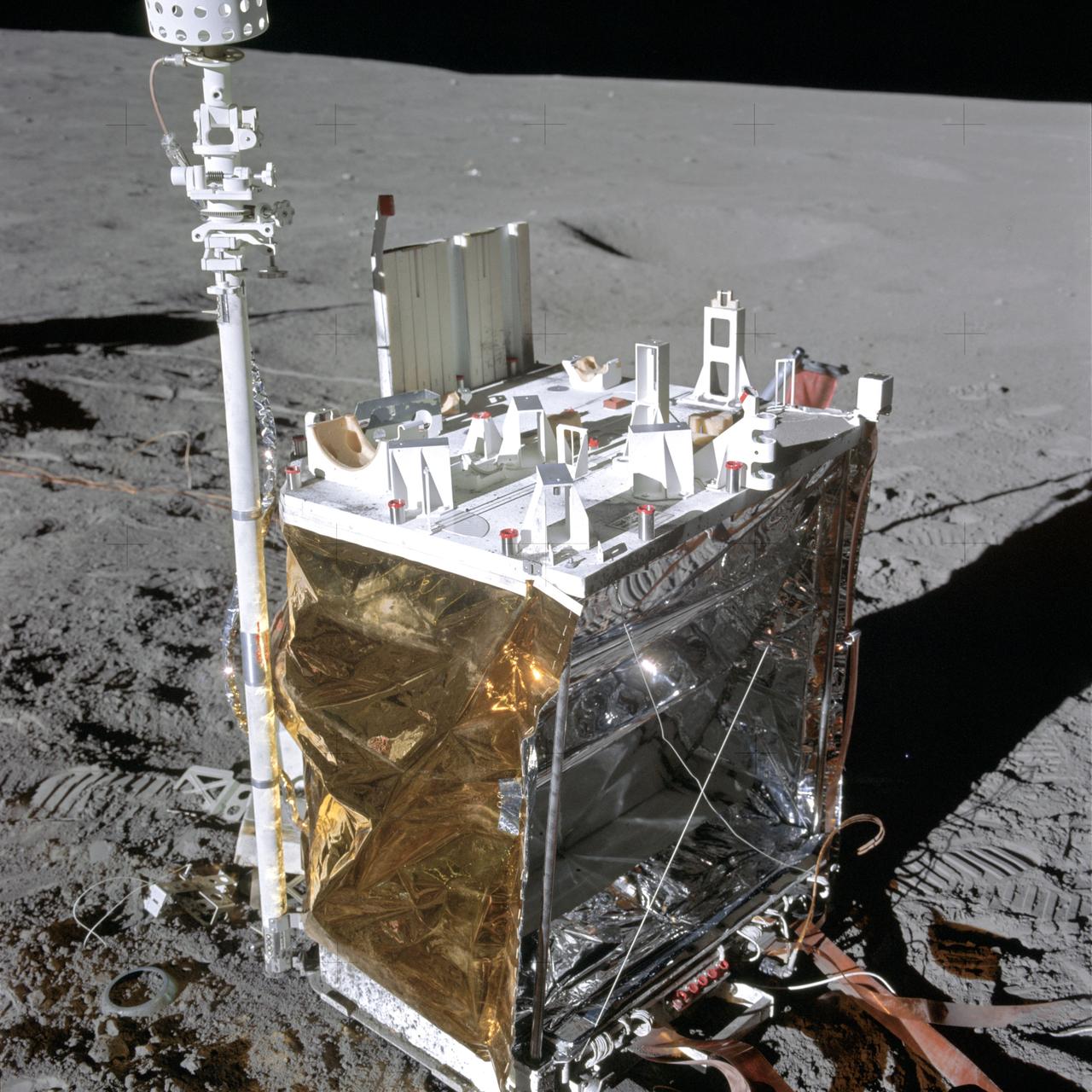
AS14-67-9379 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A close-up view of the central station (CS) of the Apollo lunar surface experiments package (ALSEP), which was deployed on the moon by the Apollo 14 astronauts during their first extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
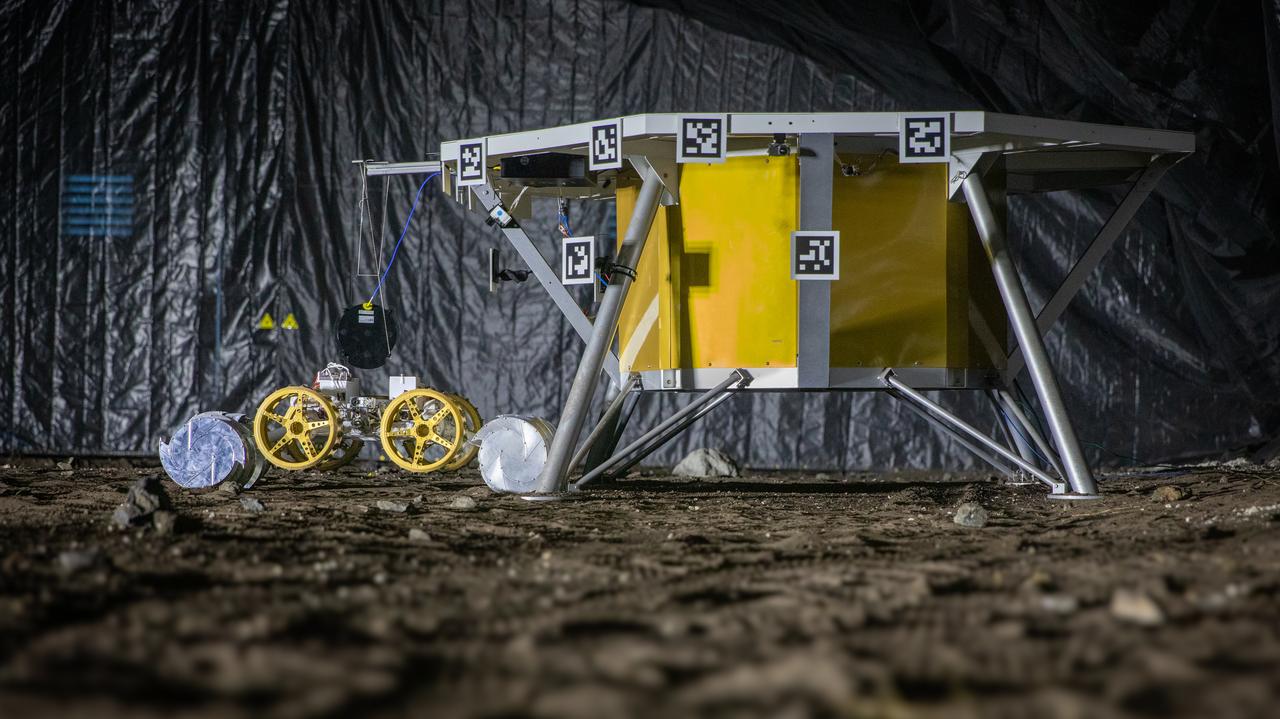

NASA’s ISRU Pilot Excavator (IPEx) performs a simulated lunar mission in a testbed at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center on Friday, Aug. 30, 2024. IPEx functions as both an excavator and a dump truck to mine and transport lunar regolith, the loose rocky material on the Moon’s surface, which is crucial for future lunar missions and In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) processes. This dual capability makes IPEx an indispensable tool for sustainable lunar exploration.
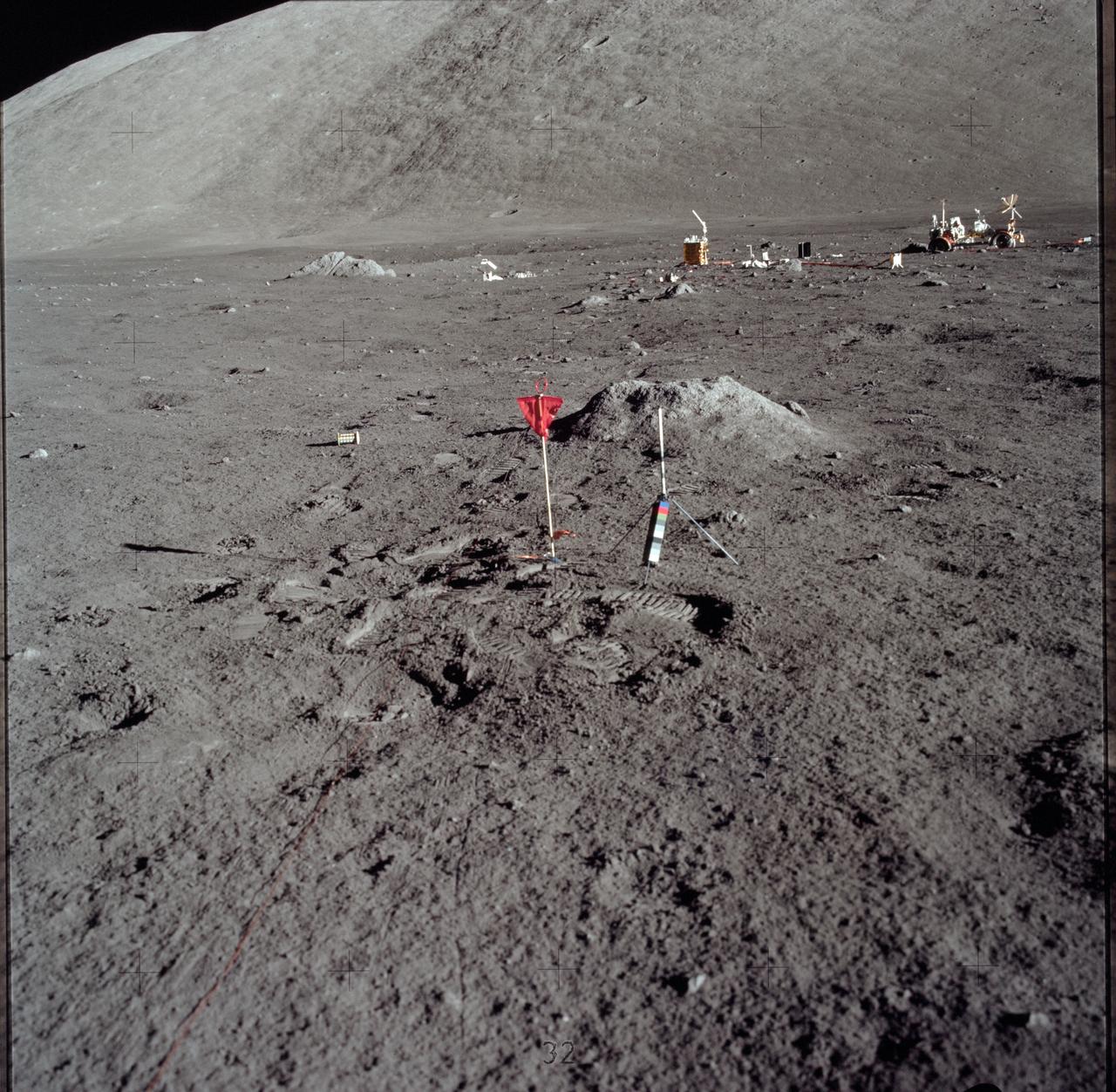

AS17-147-22548 (11 Dec. 1972) --- This is a photograph of the LSP geosphere flag on the lunar surface. The gnomon is in the foreground, while Apollo Lunar Scientific Experiments Package (ALSEP) and north Massif is in the background. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is also seen in the right background. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
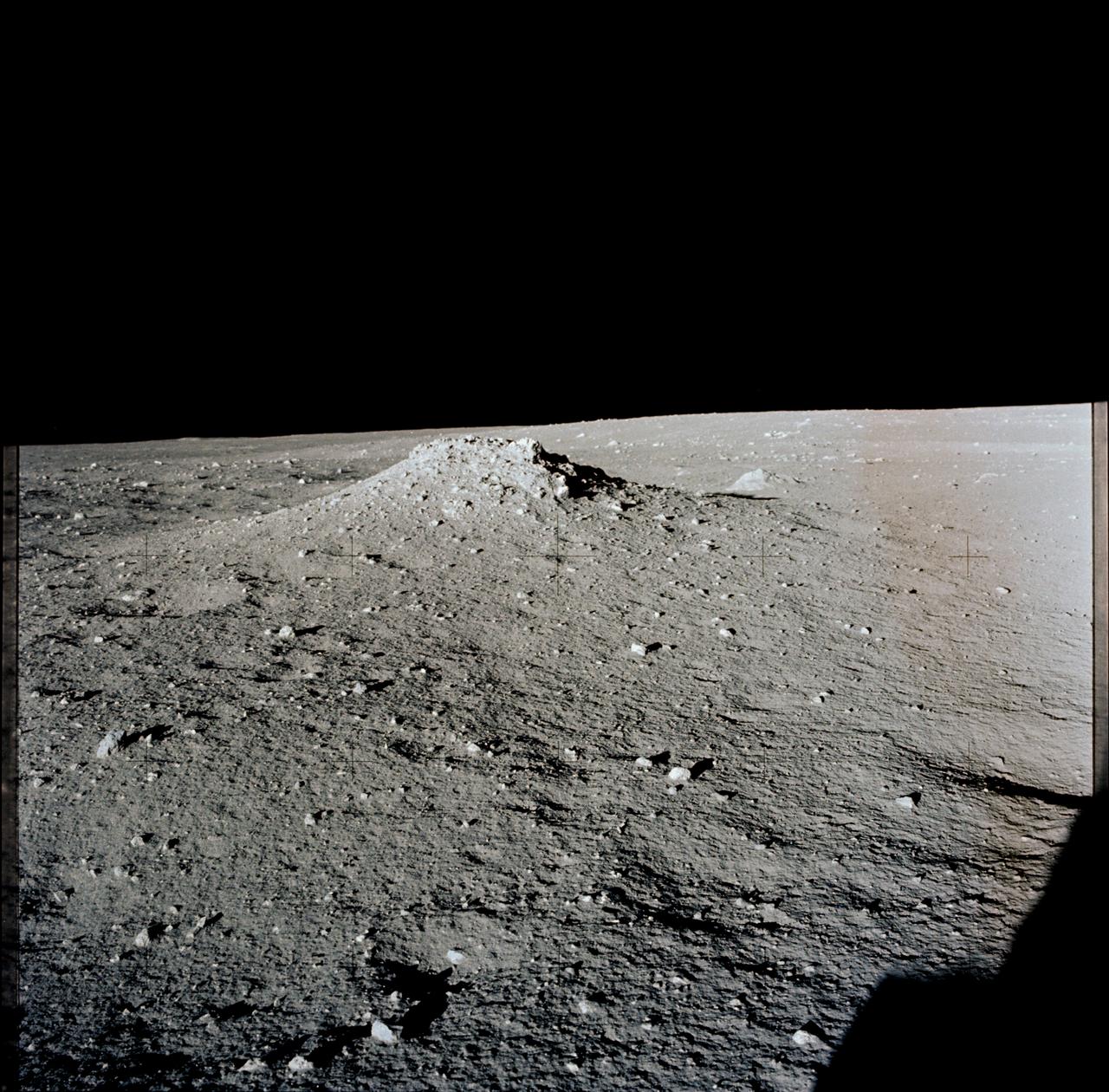

AS12-46-6795 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- A view of the lunar surface in the vicinity of the Apollo 12 lunar landing site, photographed during the extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot. Conrad and Bean encountered the odd, anthill-shaped mound during their lunar traverse. The two descended in the Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, while astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
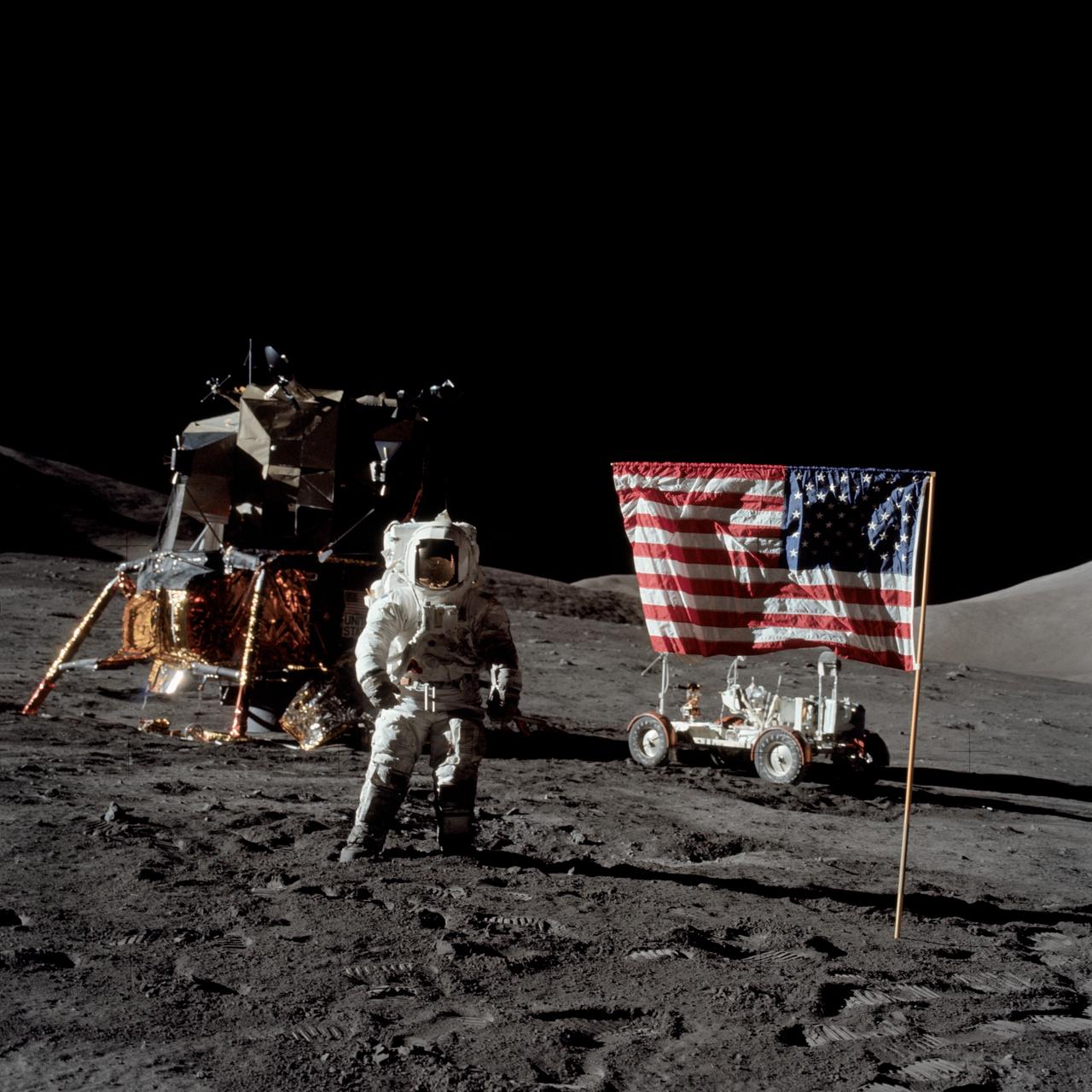

AS17-134-20382 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 lunar module pilot, stands near the deployed United States flag on the lunar surface during extravehicular activity (EVA) of NASA's final lunar landing mission in the Apollo series. The Lunar Module (LM) is at left background and the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at right background (partially obscured). The photo was made by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the LM "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
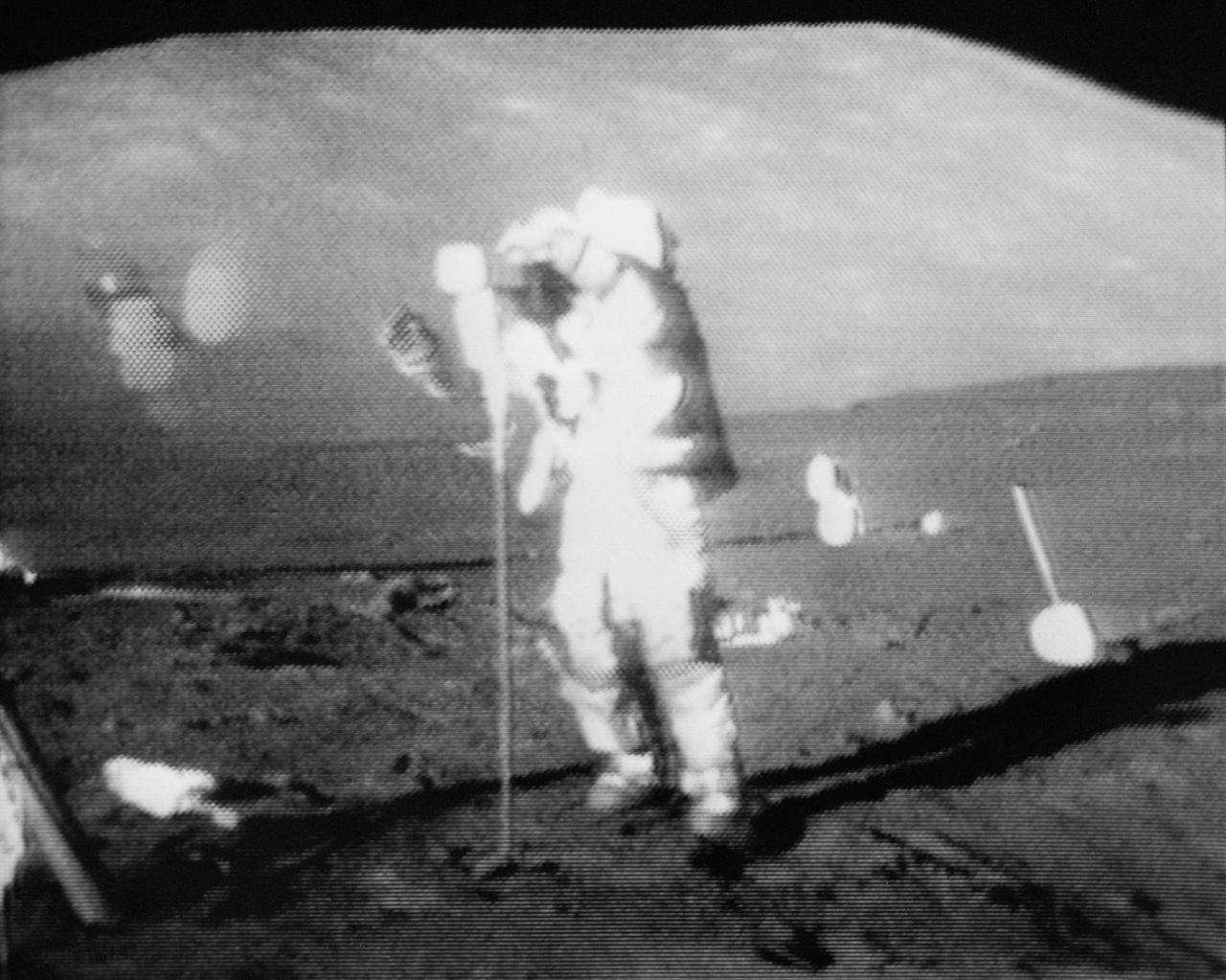

S72-55064 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan operates the Apollo Lunar Surface Drill during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, in this black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the RCA color TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Cernan is the commander of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while astronaut Cernan and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the moon.
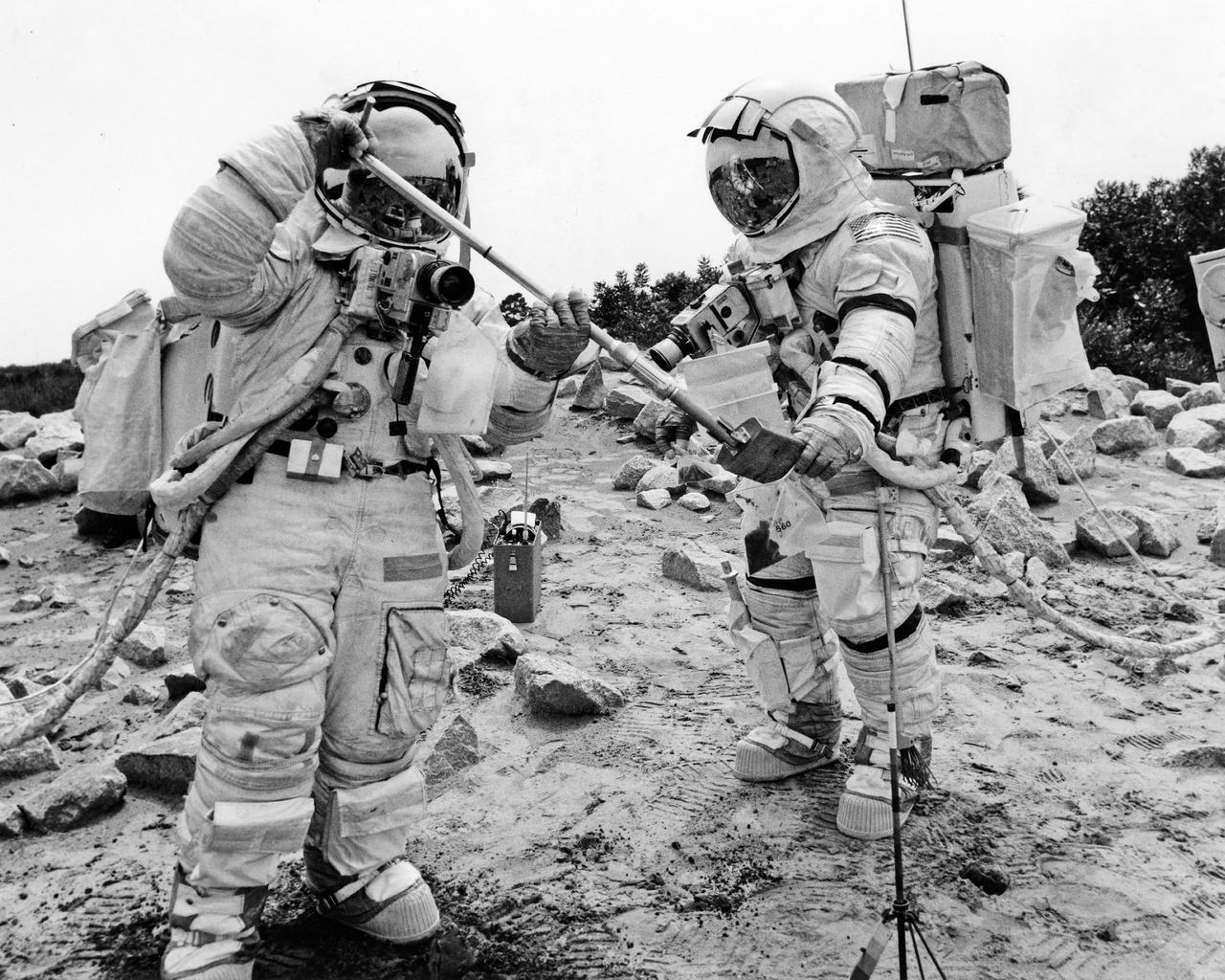

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Apollo 17 Lunar Module Pilot Harrison H. Schmitt, left, scoops soil samples into a specimen bag held by Mission Commander Eugene A. Cernan during a mock lunar surface training exercise conducted at the Kennedy Space Center. Schmitt and Cernan are scheduled to remain on the lunar surface 75 hours, leaving their lunar module spacecraft three times to explore the Moon’s Taurus-Littrow region. Launch of the Apollo Saturn V spacecraft vehicle, also with Astronaut Command Module Pilot Ronald E. Evans onboard, is scheduled no earlier than December 6, 1972. Photo credit: NASA
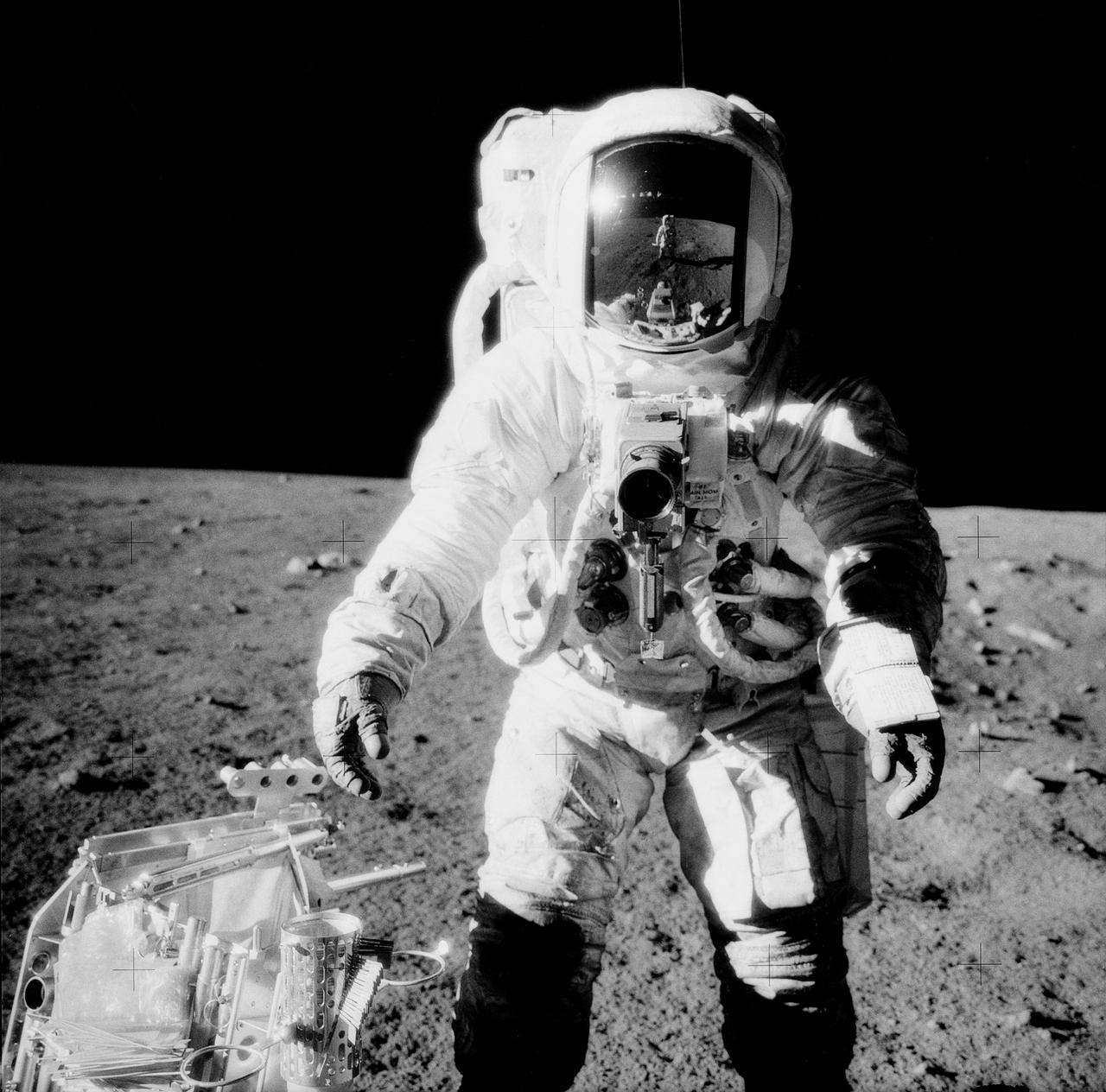

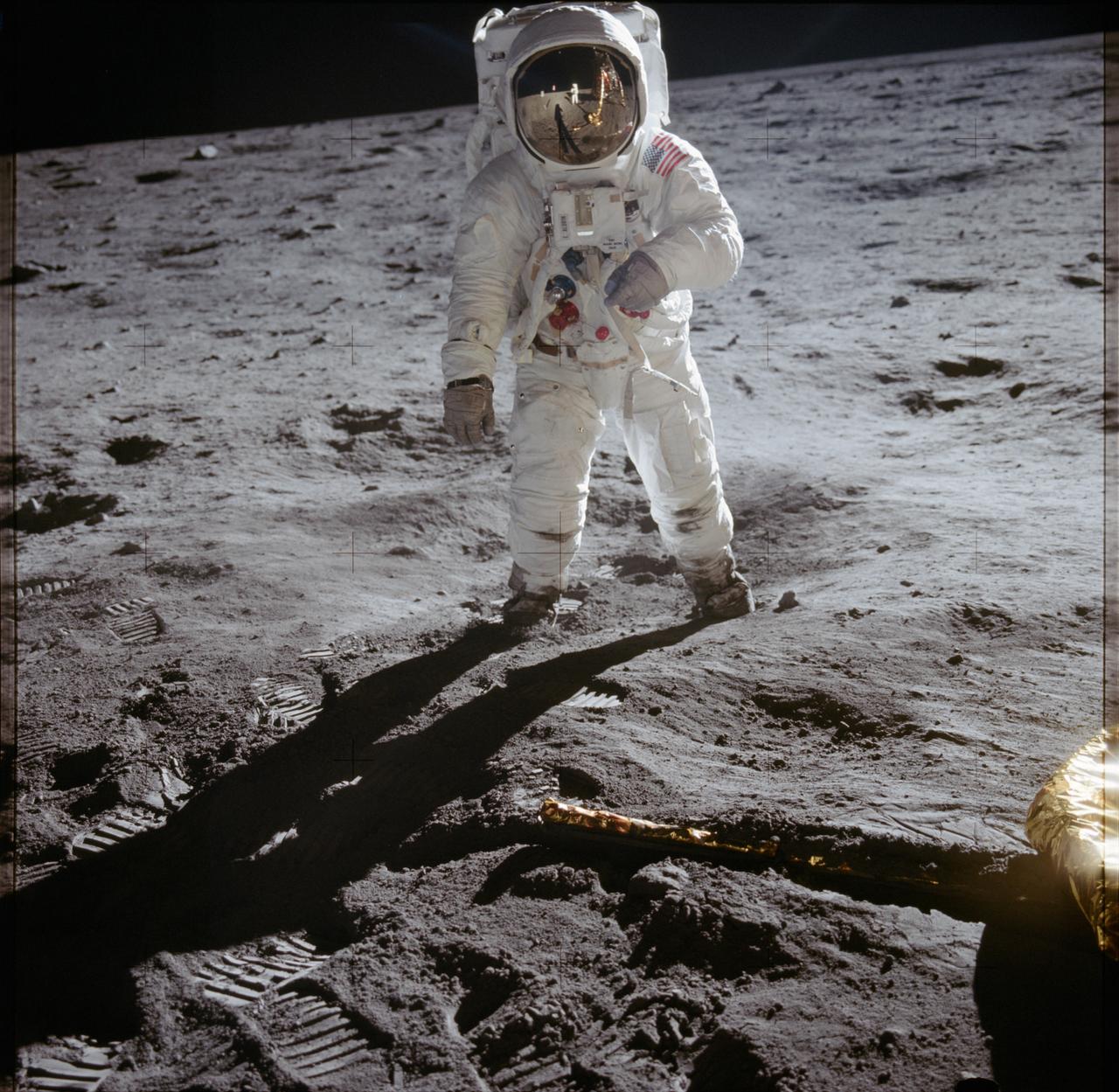
AS12-49-7281 (19-20 Nov 1969) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, pauses near a tool carrier during extravehicular activity (EVA) on the Moon's surface. Astronaut Charles Conrad, Jr., commander, who took the black and white photo, is reflected in Bean's helmet visor. Conrad and Bean had descended in the Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM) "Intrepid" to explore the lunar surface while Astronaut Richard F. Gordon, Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Yankee Clipper" in lunar orbit. Photo credit: NASA
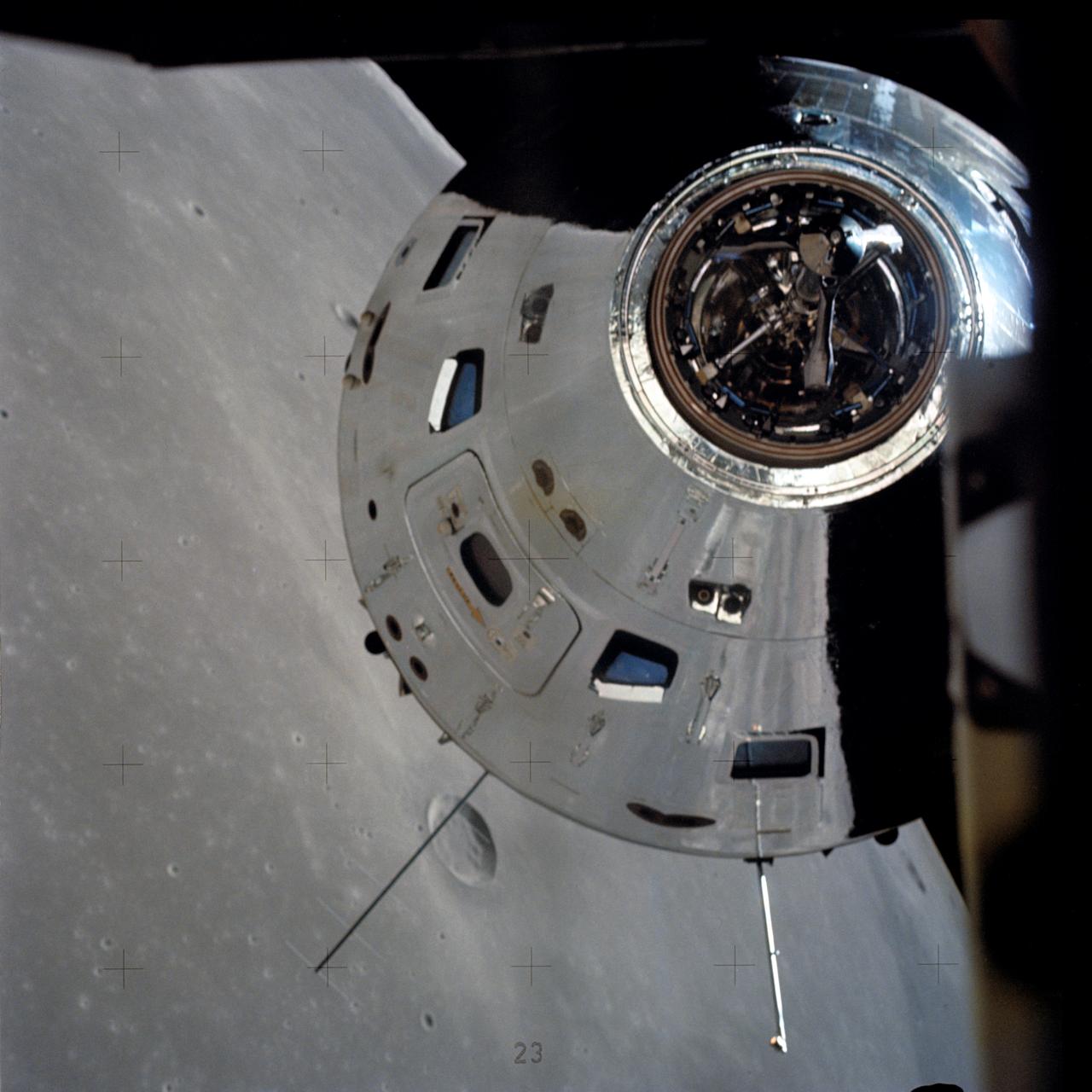

AS17-145-22273 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- In this view, taken from the Lunar Module (LM), the Command and Service Module (CSM) are seen preparing to rendezvous with the LM. Note the reflection of the lunar surface on the CSM. The CSM, is piloted by Ronald E. Evans; while astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander; and Harrison W. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, are onboard the LM, following their extravehicular activities (EVA) on the moon's surface. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the LM "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Evans remained with the CSM "America" in lunar orbit.