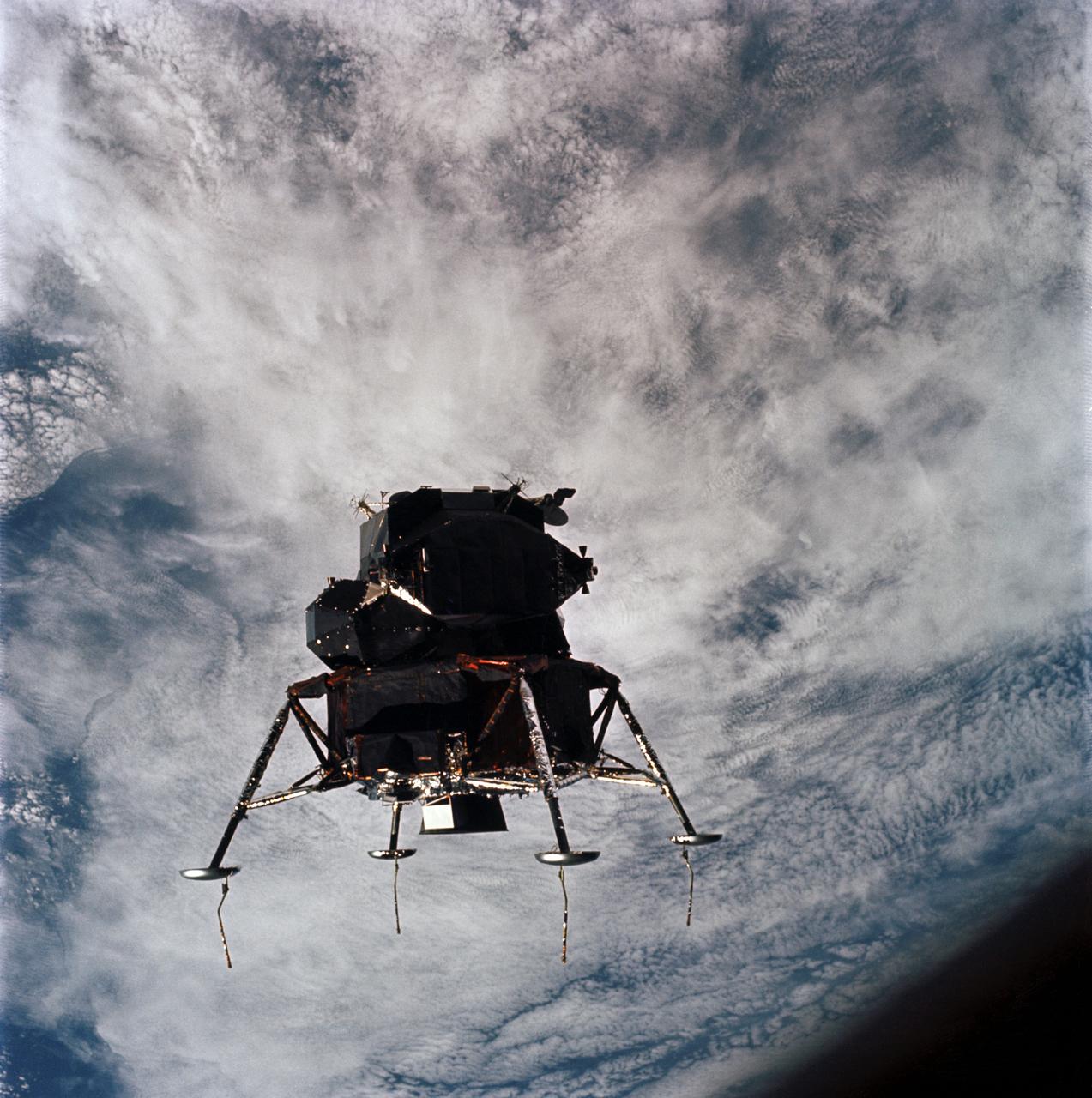

AS09-21-3199 (7 March 1969) --- Excellent view of the Apollo 9 Lunar Module, "Spider," in a lunar landing configuration, as photographed from the Command and Service Modules on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The landing gear on the "Spider" has been deployed. Lunar surface probes (sensors) extend out from the landing gear foot pads. Inside the "Spider" were astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module, "Gumdrop," while the other two astronauts checked out the Lunar Module.
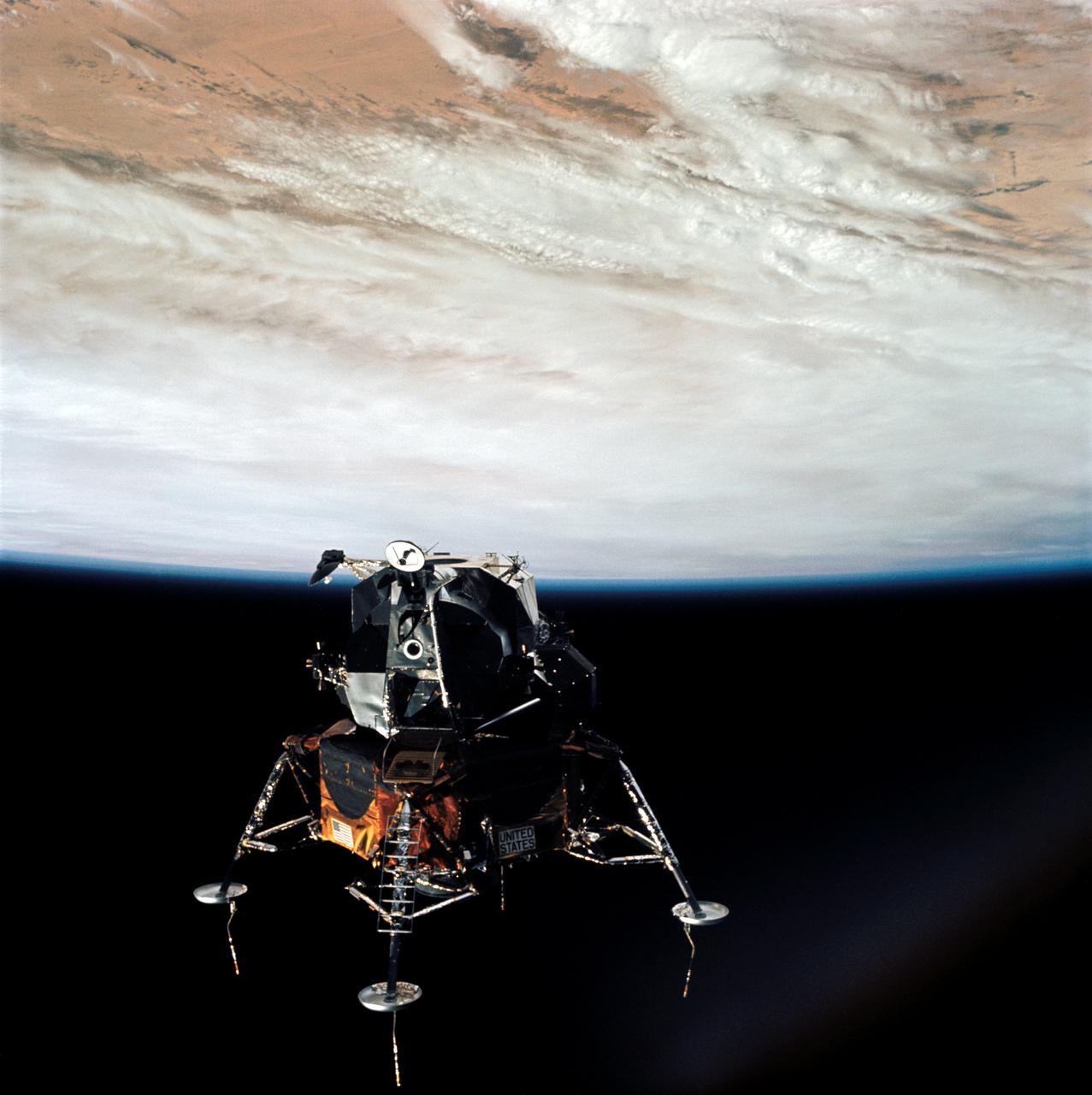

AS09-21-3212 (7 March 1969) --- A view of the Apollo 9 Lunar Module (LM), "Spider", in a lunar landing configuration, as photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The landing gear on the "Spider" has been deployed. Lunar surface probes (sensors) extend out from landing gear foot pads. Inside the "Spider" were astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander, and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module (CM), "Gumdrop", while the other two astronauts checked out the Lunar Module.
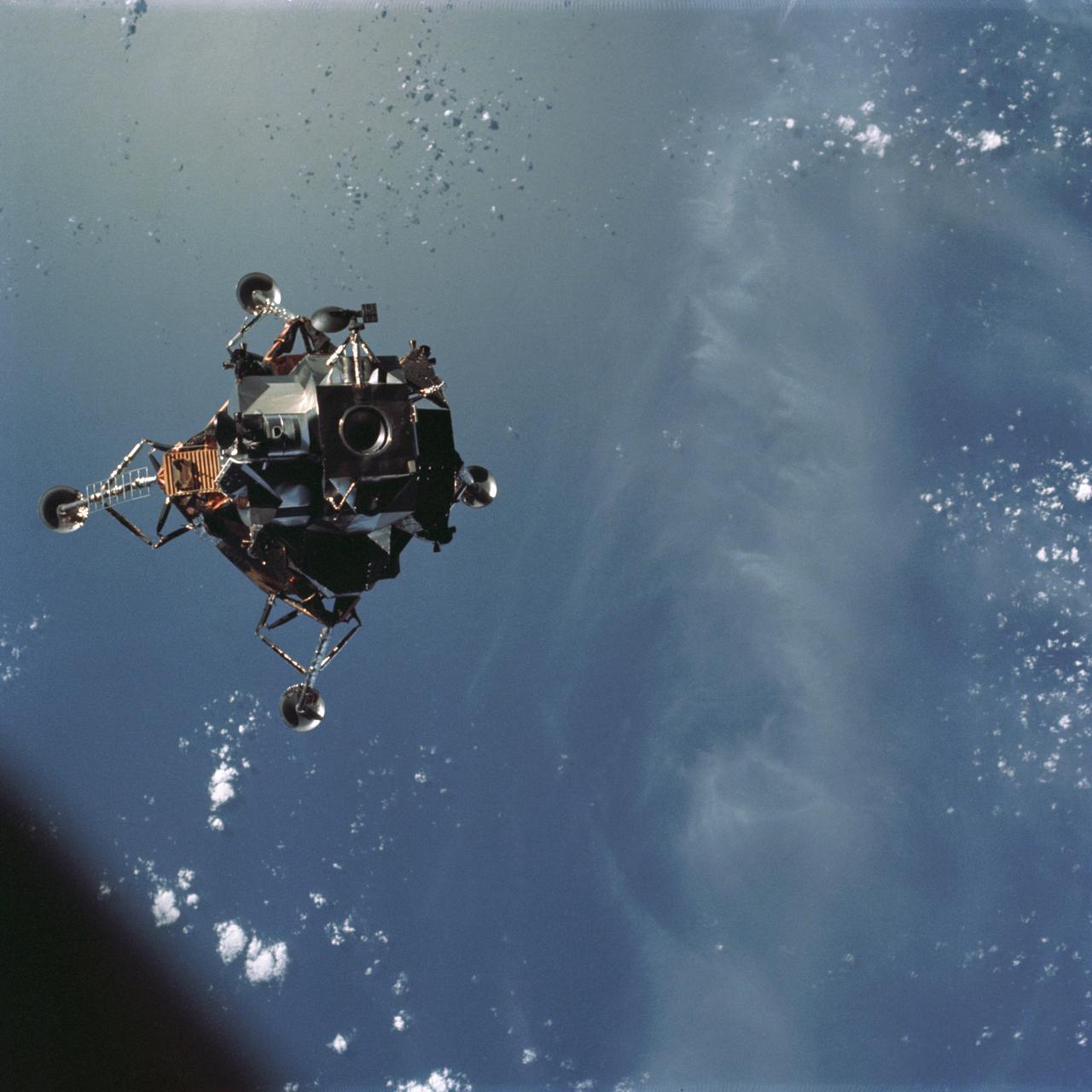

AS09-21-3181 (7 March 1969) --- A View of the Apollo 9 Lunar Module (LM), "Spider," in a lunar lading configuration, as photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The landing gear on the "Spider" has been deployed. Inside the "Spider" were astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module (CM), "Gumdrop," while the other two astronauts checked out the LM.
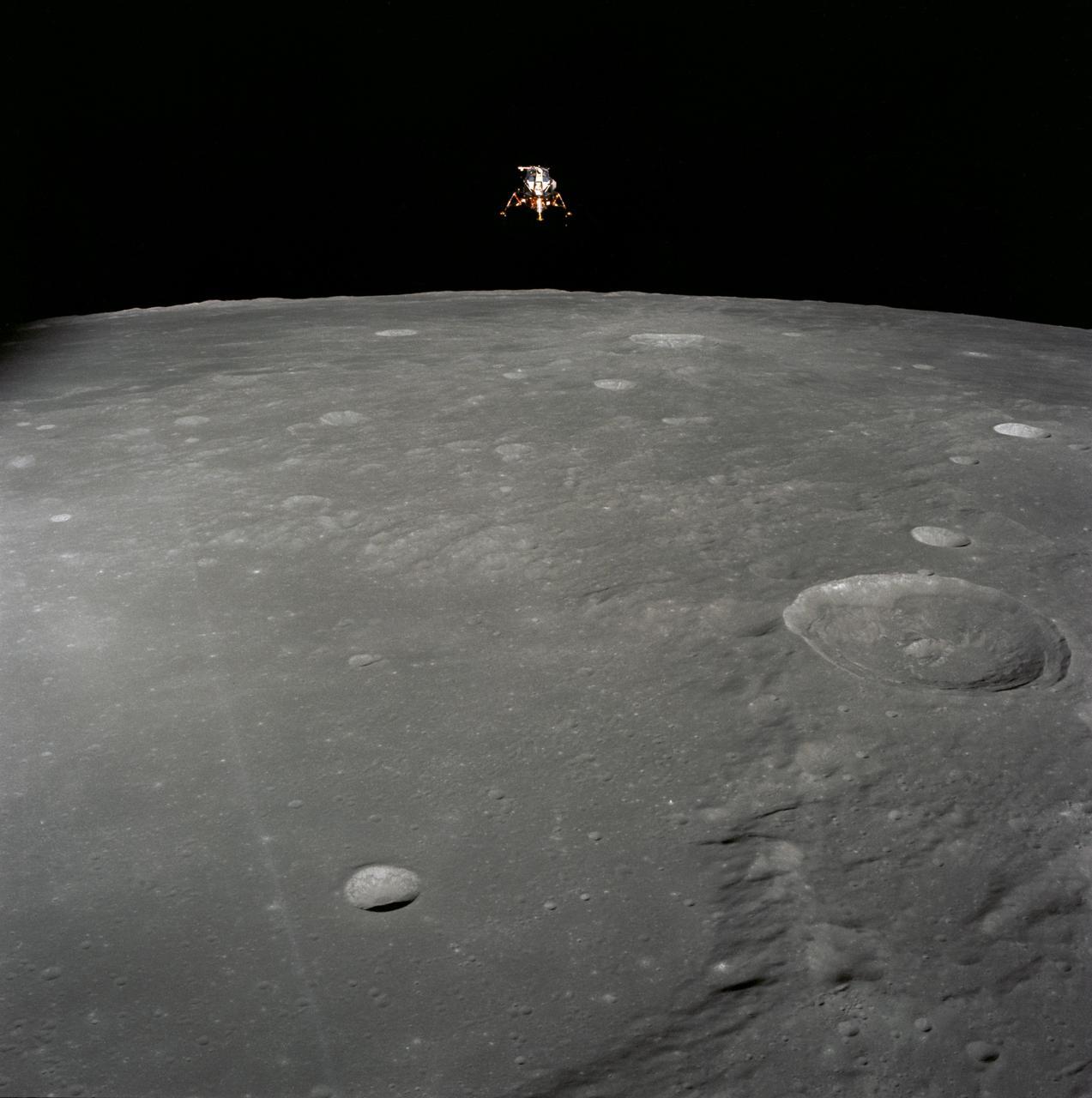

AS12-51-7507 (19 Nov. 1969) --- The Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM), in a lunar landing configuration, is photographed in lunar orbit from the Command and Service Modules (CSM). The coordinates of the center of the lunar surface shown in picture are 4.5 degrees west longitude and 7 degrees south latitude. The largest crater in the foreground is Ptolemaeus; and the second largest is Herschel. Aboard the LM were astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander; and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot. Astronaut Richard R. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Conrad and Bean descended in the LM to explore the surface of the moon. Photo credit: NASA

This 70mm frame, showintg the Apollo 17 Command/Service Modules (CSM) backdropped against the Taurus-Littrow landing site, was exposed from the lunar module (LM) prior to the LM's touchdown on the lunar surface.
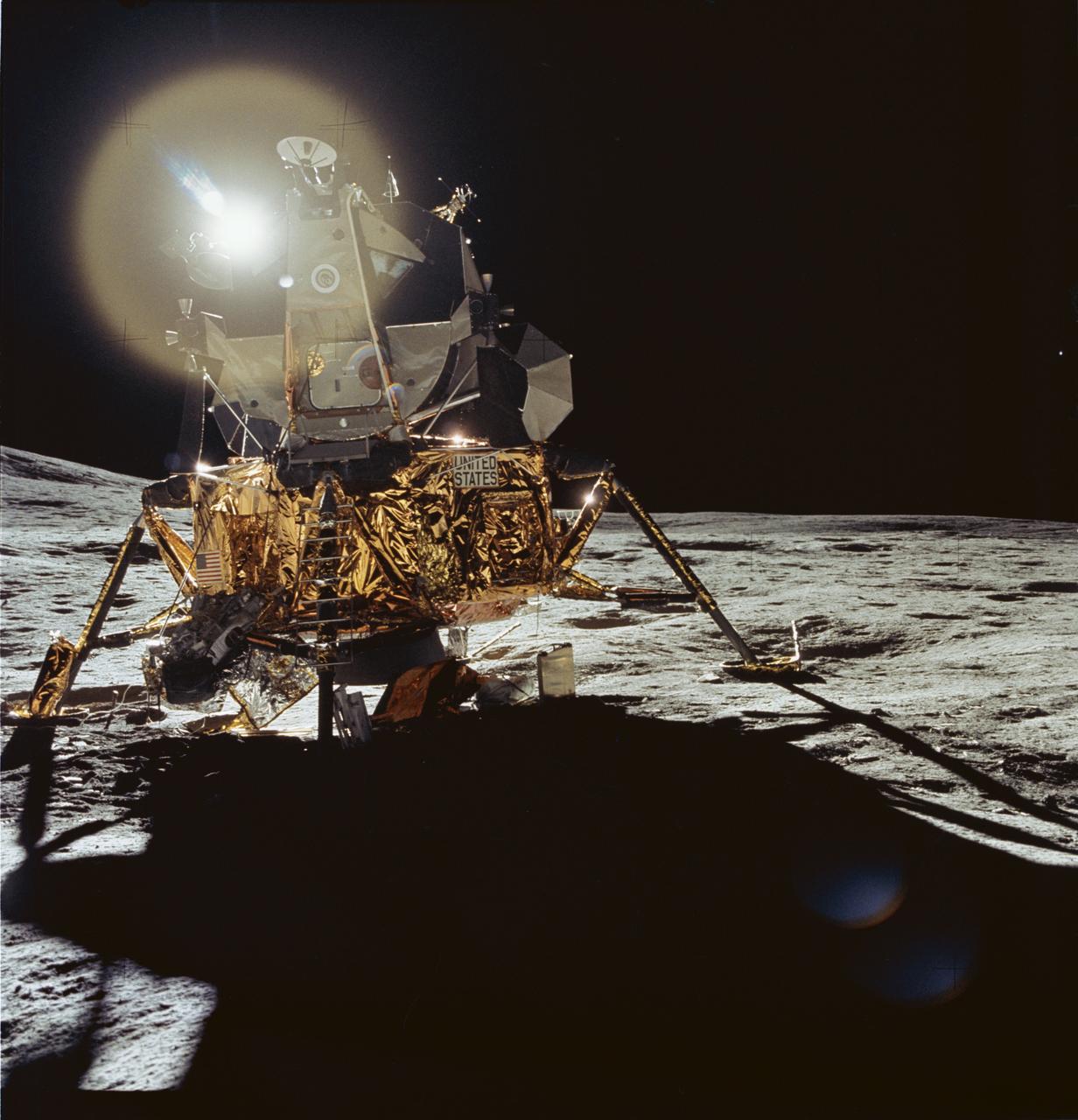

AS14-66-9306 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A front view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM), which reflects a circular flare caused by the brilliant sun, as seen by the two moon-exploring crew men of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission during their first extravehicular activity (EVA). The unusual ball of light was said by the astronauts to have a jewel-like appearance. At the extreme left the lower slope of Cone Crater can be seen. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; descended in the LM, while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
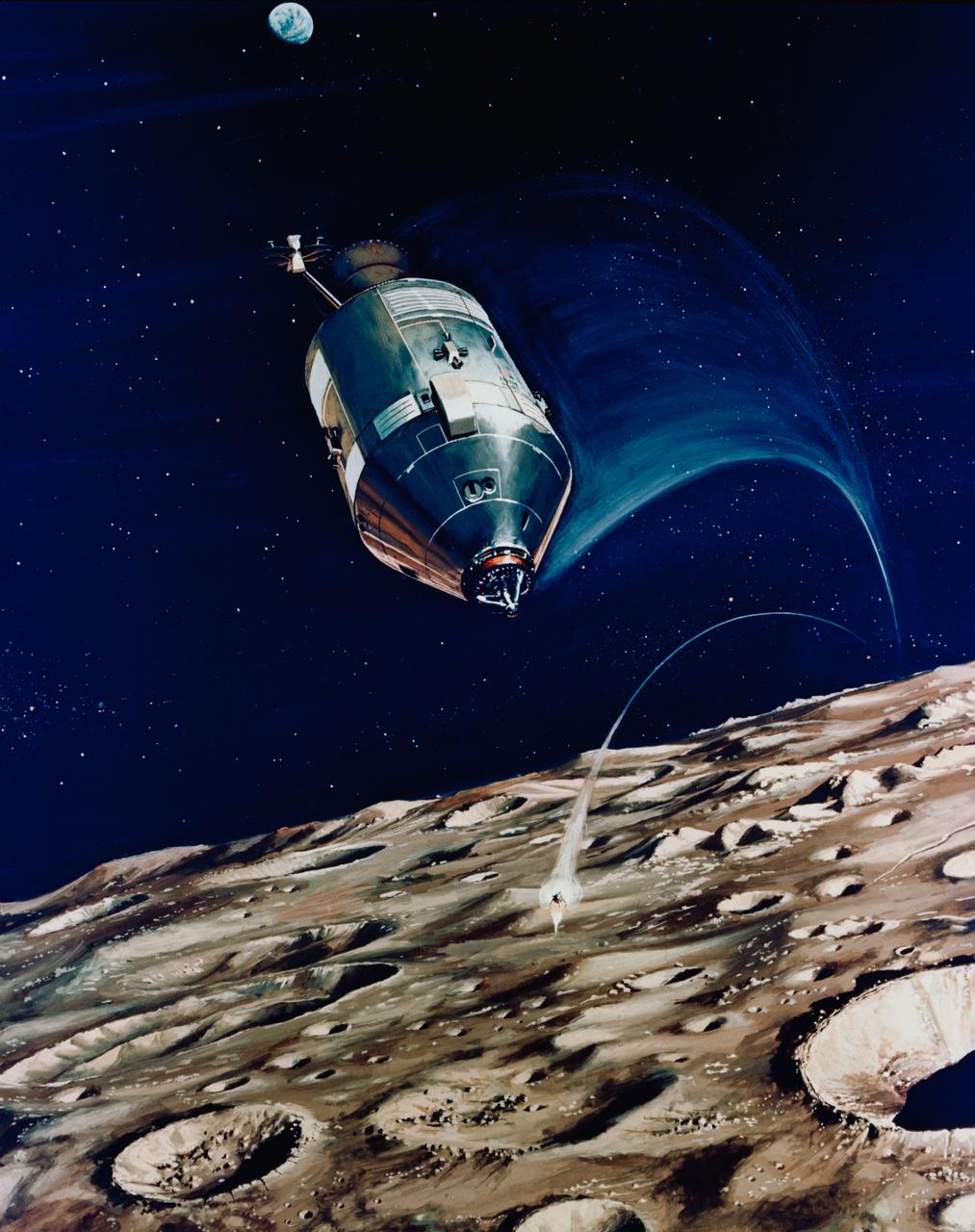

S71-16574 (11 Jan. 1971) --- An artist's concept depicting the Apollo 14 Command and Service Modules (CSM) circling the moon as the Lunar Module (LM) heads toward a lunar landing. While astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remains with the CSM in lunar orbit, astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, will descend in the LM to explore an area in the rugged Fra Mauro highlands.
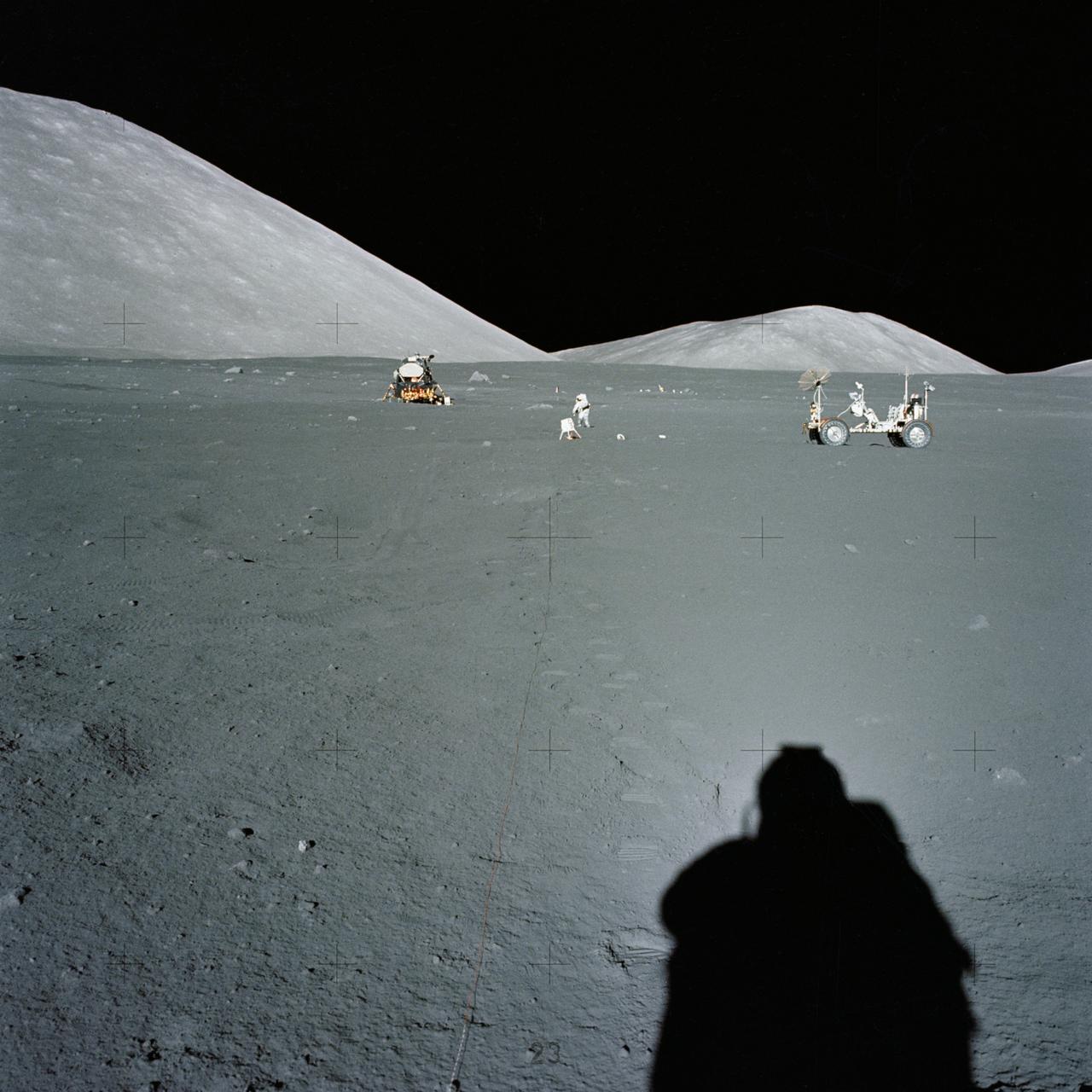

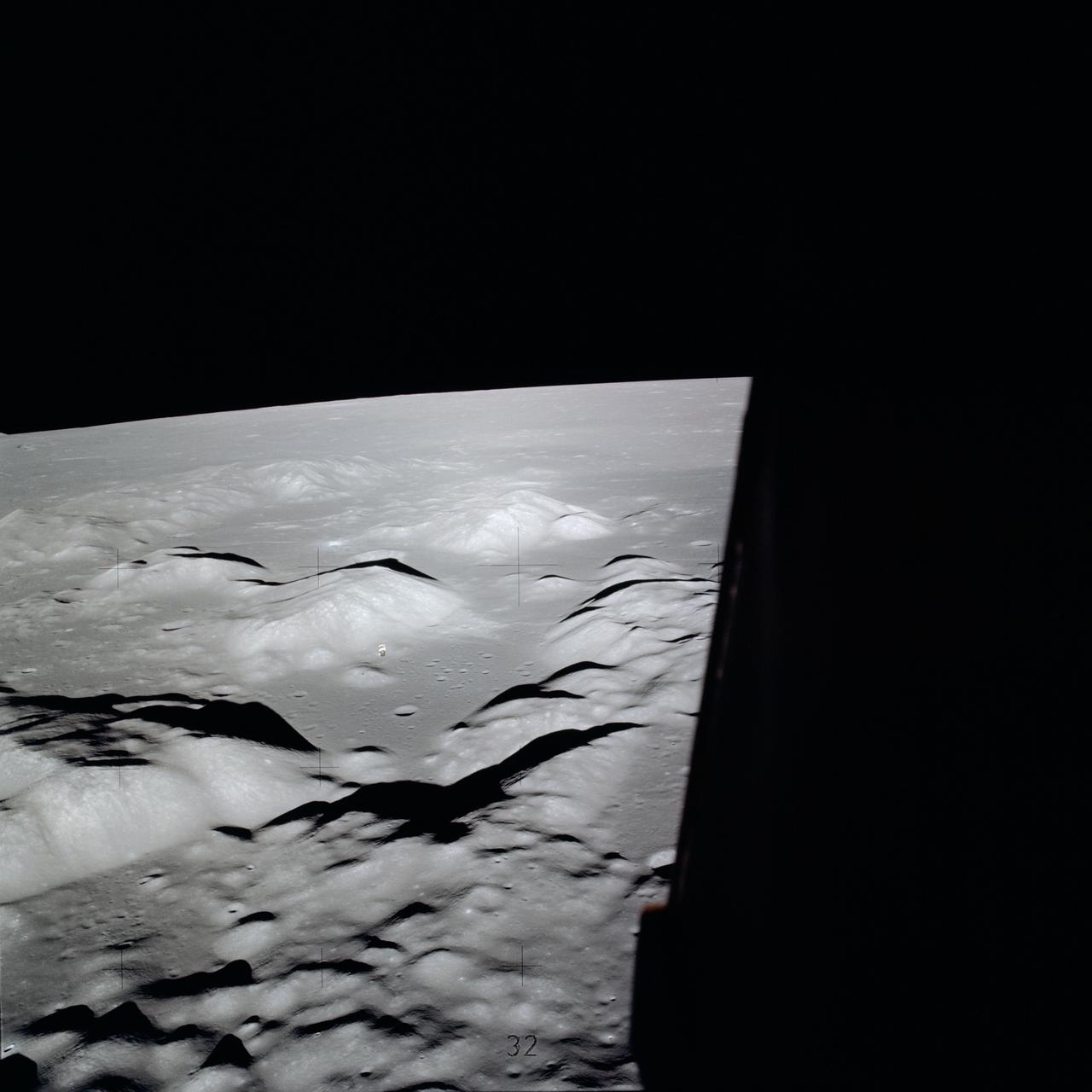
AS17-134-20435 (10 Dec. 1972) --- Wide-angle view of the Apollo 17 Taurus-Littrow lunar landing site. To the left in the background is the Lunar Module. To the right in the background is the Lunar Roving vehicle. An Apollo 17 crewmember is photographed between the two points. The shadow of the astronaut taking the photograph can be seen in the right foreground.

AS16-113-18339 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, leaps from the lunar surface as he salutes the United States flag at the Descartes landing site during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, took this picture. The Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" is on the left. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is parked beside the LM. The object behind Young (in the shade of the LM) is the Far Ultraviolet Camera/Spectrograph (FUC/S). Stone Mountain dominates the background in this lunar scene. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the LM to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.

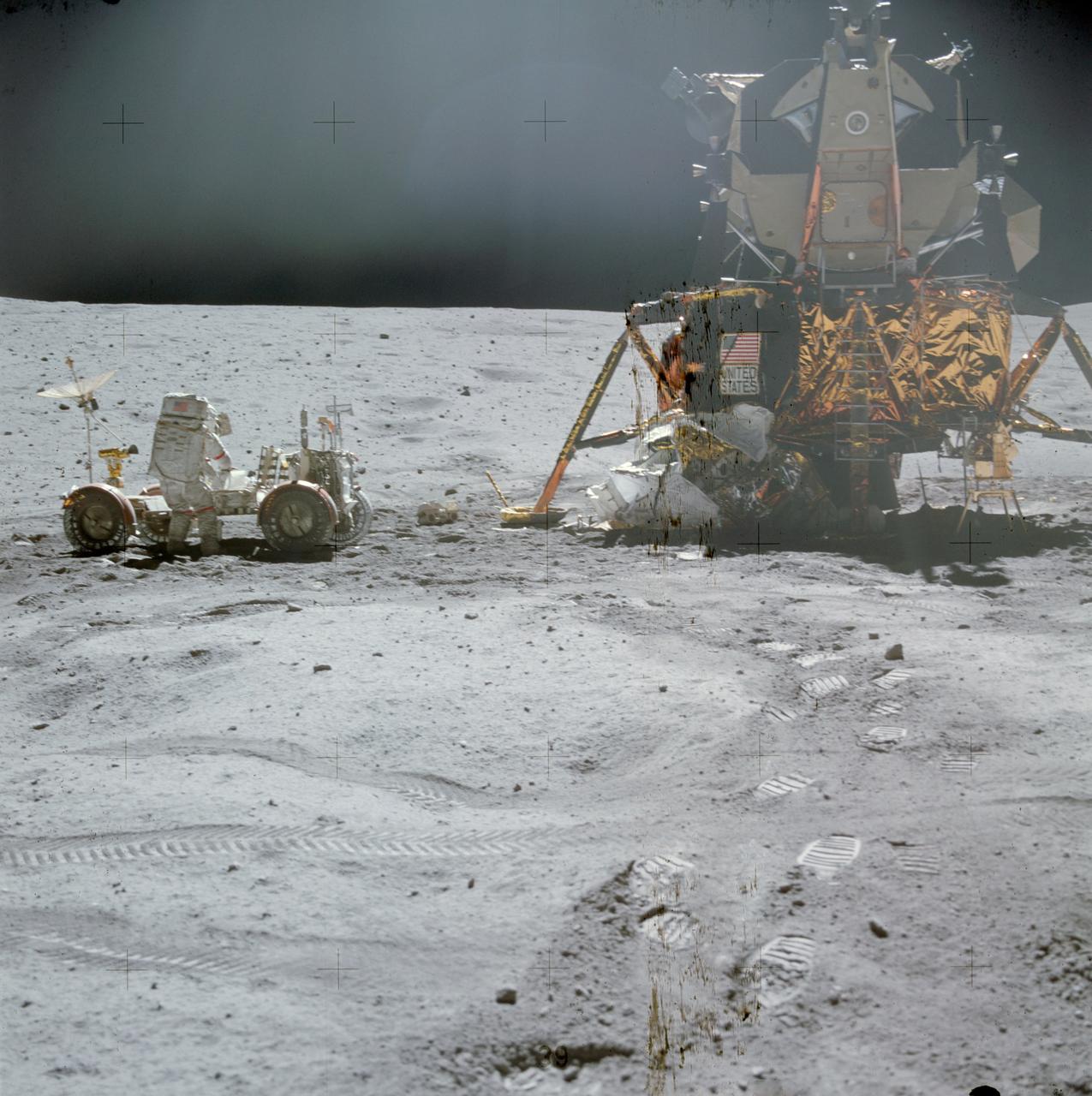
AS16-107-17436 (21 April 1972) --- An excellent view of the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" and Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), as photographed by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. Astronaut John W. Young, commander, can be seen directly behind the LRV. The lunar surface feature in the left background is Stone Mountain. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the LM to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
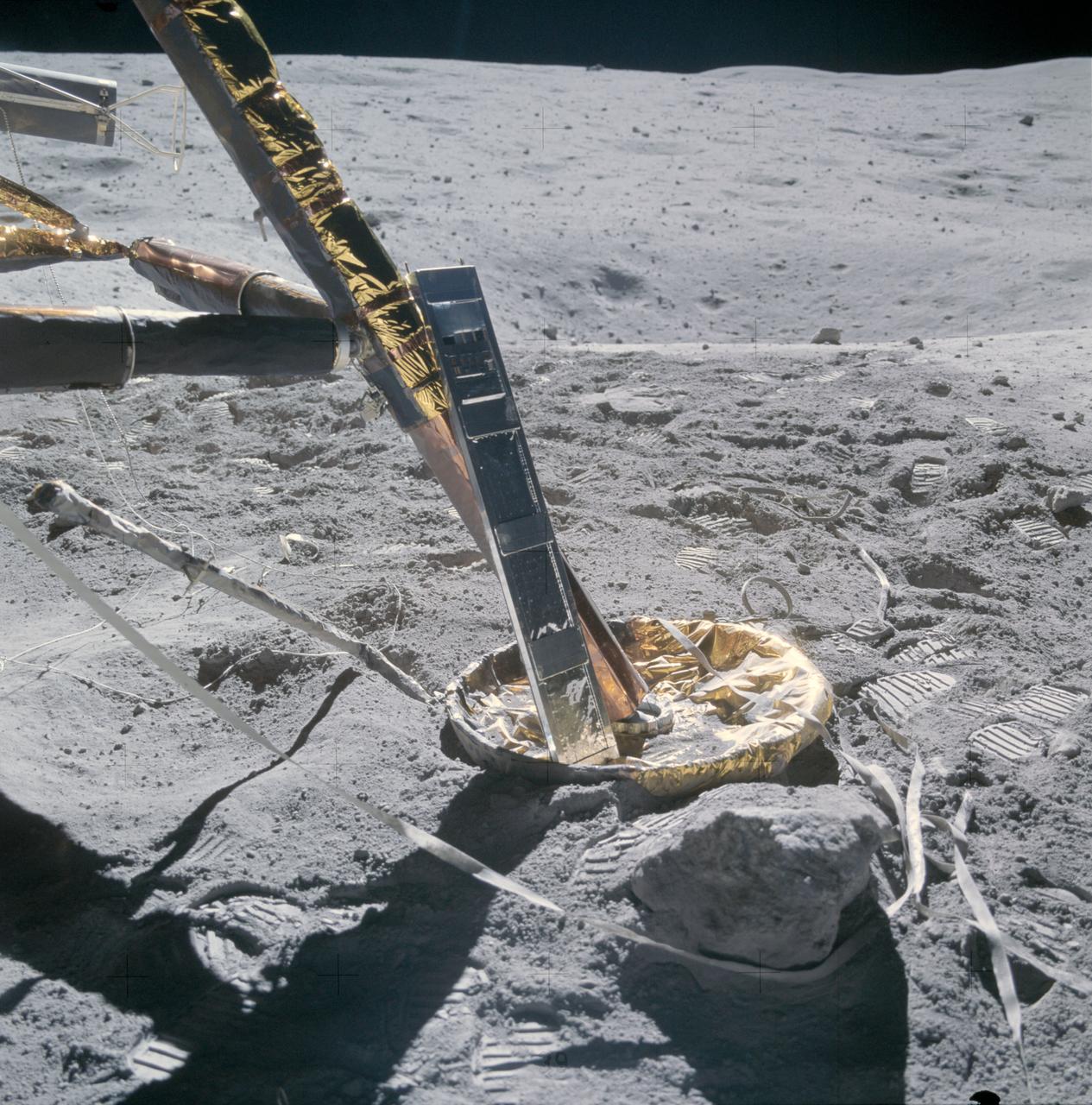

AS16-107-17442 (22 April 1972) --- A close-up view of the Apollo 16 Cosmic Ray Detector (CRD) experiment deployed at the +Y strut of the Lunar Module (LM). The crewmembers moved it to this position from near the deployment site of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) because, in the words of astronaut John W. Young, commander, "The panels were getting a little warm." Note that the LM did not skid upon landing, as evidenced by the landing contact probe's folded back (neatly) position and the lack of skid marks. While astronauts Young, and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
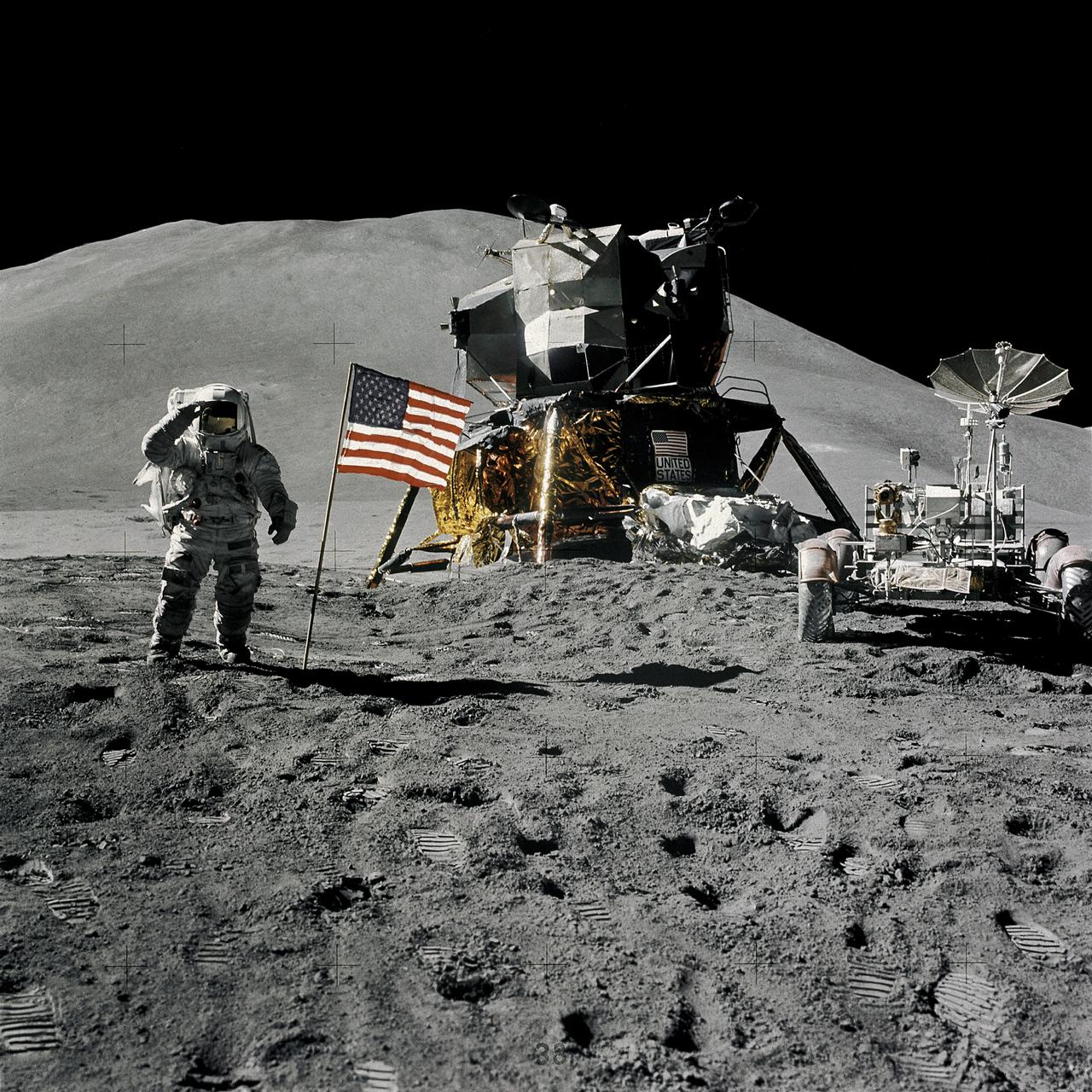

AS15-88-11866 (1 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, gives a military salute while standing beside the deployed United States flag during the Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The flag was deployed toward the end of EVA-2. The Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" is in the center. On the right is the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). This view is looking almost due south. Hadley Delta in the background rises approximately 4,000 meters (about 13,124 feet) above the plain. The base of the mountain is approximately 5 kilometers (about 3 statute miles) away. This photograph was taken by astronaut David R. Scott, Apollo 15 commander. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
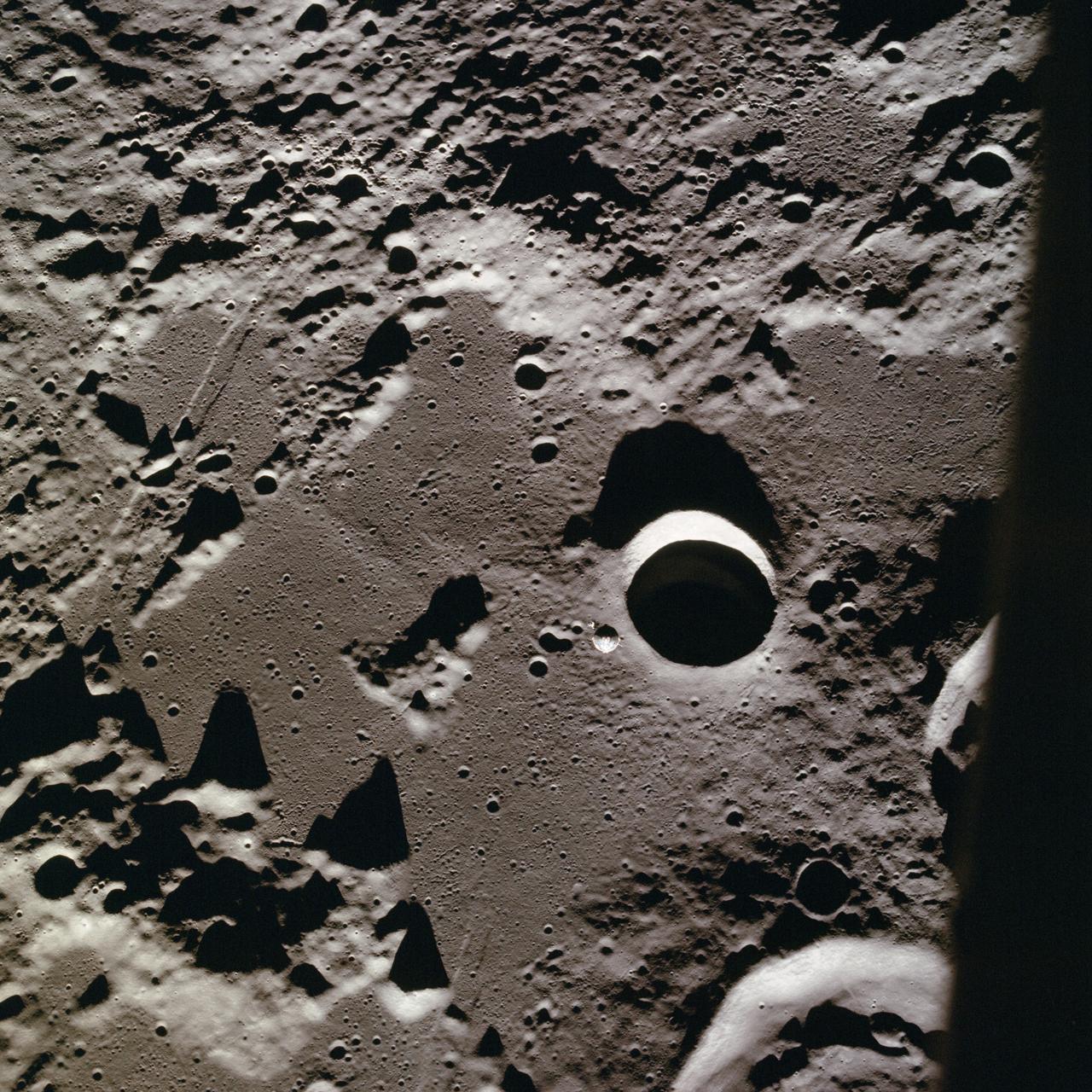

AS11-37-5448 (July 1969) --- The Apollo 11 Command and Service Modules (CSM) (tiny dot near quarter sized crater, center), with astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, aboard. The view overlooking the western Sea of Tranquility was photographed from the Lunar Module (LM). Astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, manned the LM and made their historic lunar landing on July 20, 1969. Coordinates of the center of the terrain in the photograph are 18.5 degrees longitude and .5 degrees north latitude.
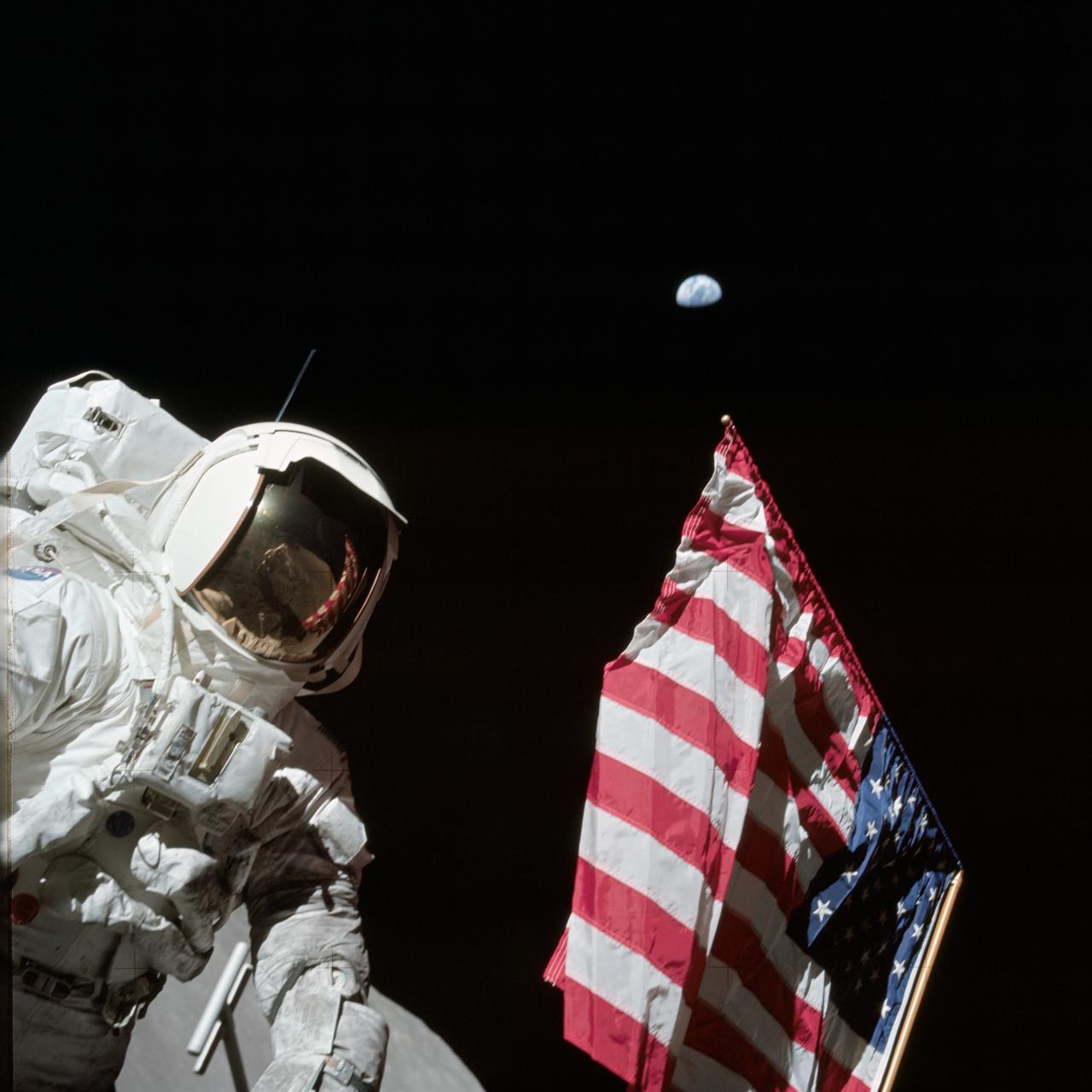

AS17-134-20384 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, is photographed next to the deployed United States flag during lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The highest part of the flag appears to point toward our planet Earth in the distant background. This picture was taken by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS11-40-5875 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the first lunar landing mission, poses for a photograph beside the deployed United States flag during an Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The Lunar Module (LM) is on the left, and the footprints of the astronauts are clearly visible in the soil of the moon. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm Hasselblad lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM, the "Eagle", to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit. Photo credit: NASA
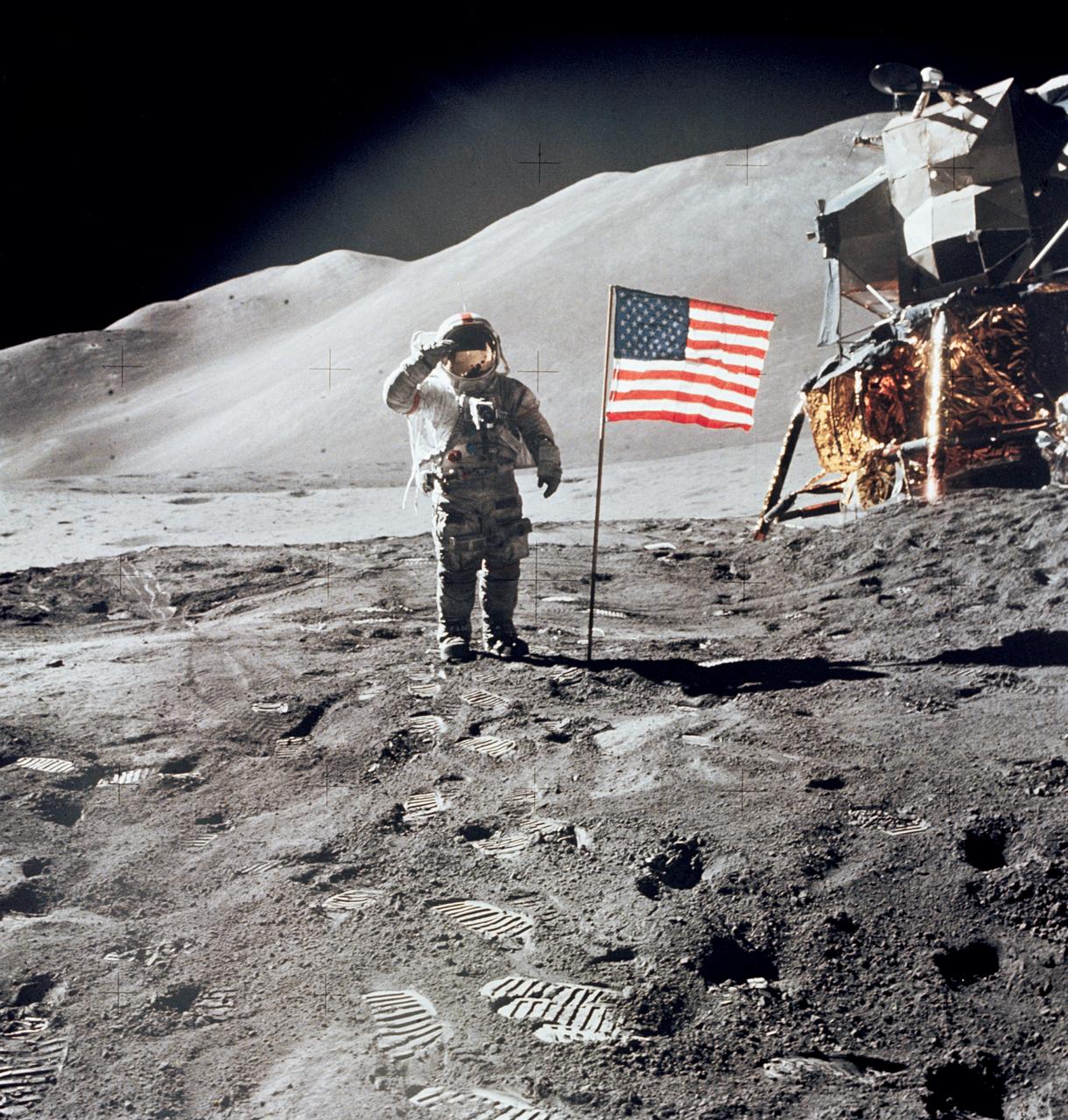

AS15-88-11863 (1 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, commander, gives a military salute while standing beside the deployed United States flag during the Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The flag was deployed toward the end of EVA-2. The Lunar Module (LM), "Falcon," is partially visible on the right. Hadley Delta in the background rises approximately 4,000 meters (about 13,124 feet) above the plain. The base of the mountain is approximately 5 kilometers (about three statue miles) away. This photograph was taken by astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained in lunar orbit in the Command and Service Modules (CSM).
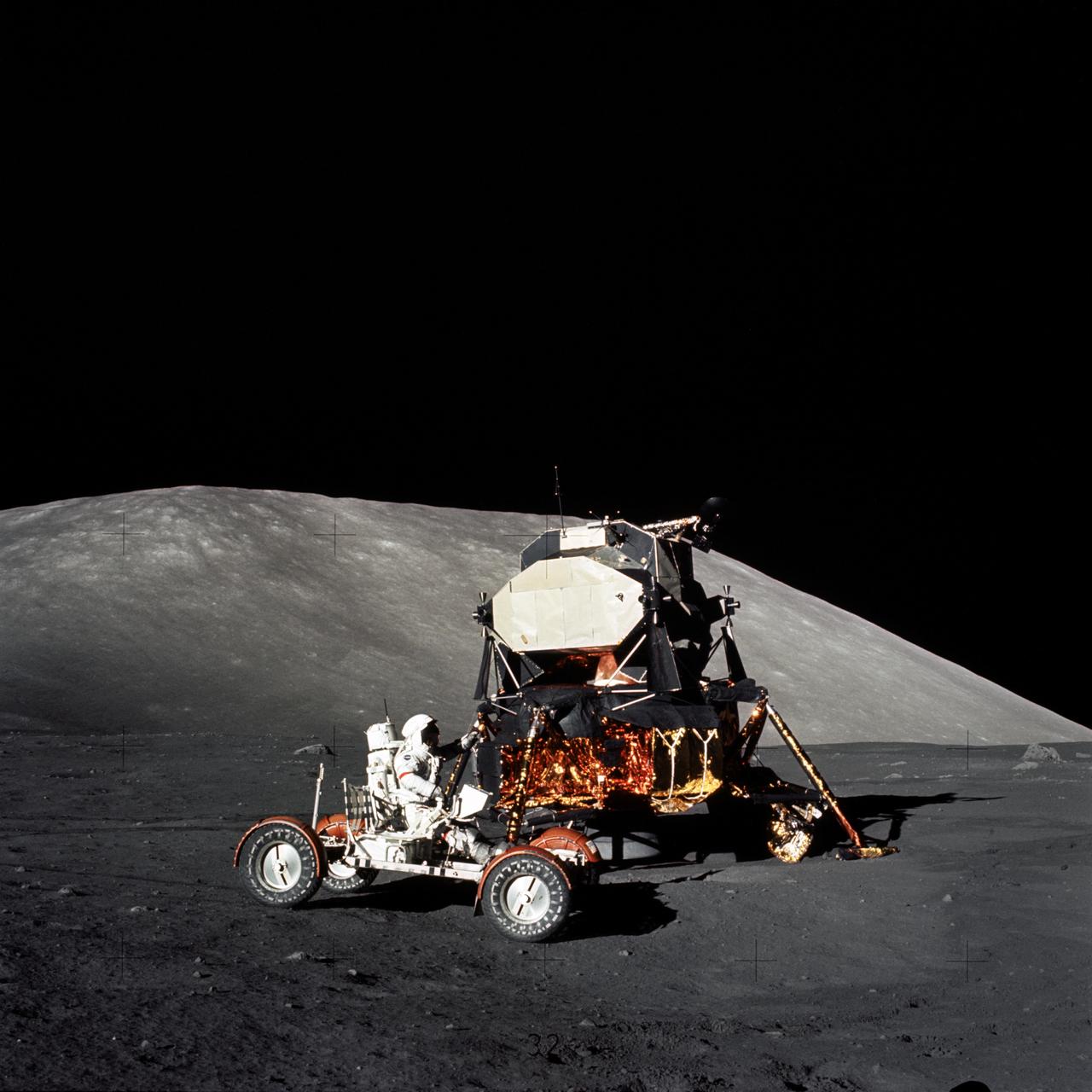

AS17-147-22527 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 mission commander, makes a short checkout of the Lunar Roving Vehicle during the early part of the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The Lunar Module is in the background. This photograph was taken by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot.
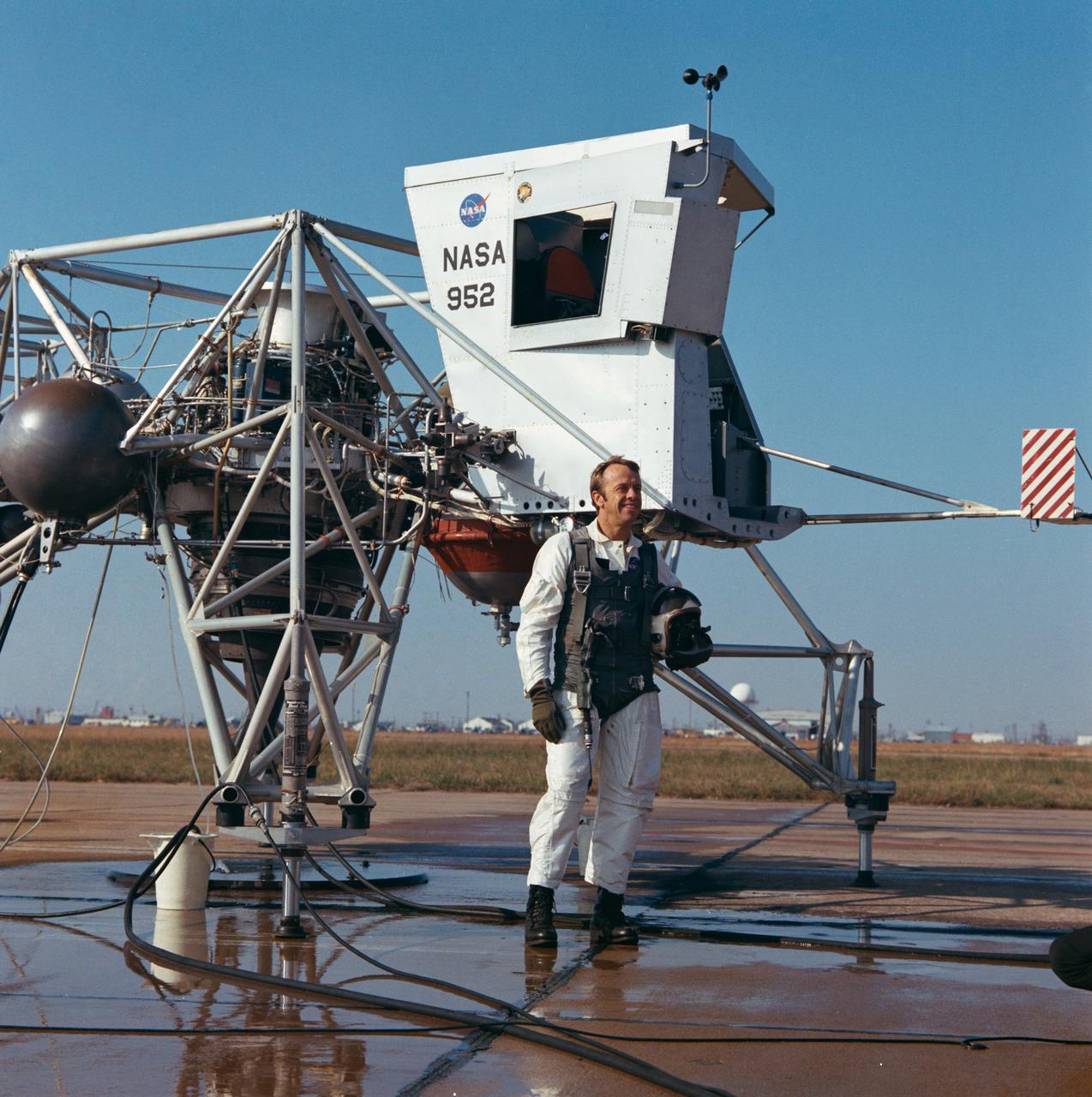

S70-56287 (14 Dec. 1970) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, stands near a Lunar Landing Training Vehicle (LLTV) prior to a test flight at Ellington Air Force Base, Houston, on Dec. 14, 1970. Shepard will be at the controls of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) when it lands on the moon in the highlands near Fra Mauro. Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Shepard and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descend in the LM to explore the moon.
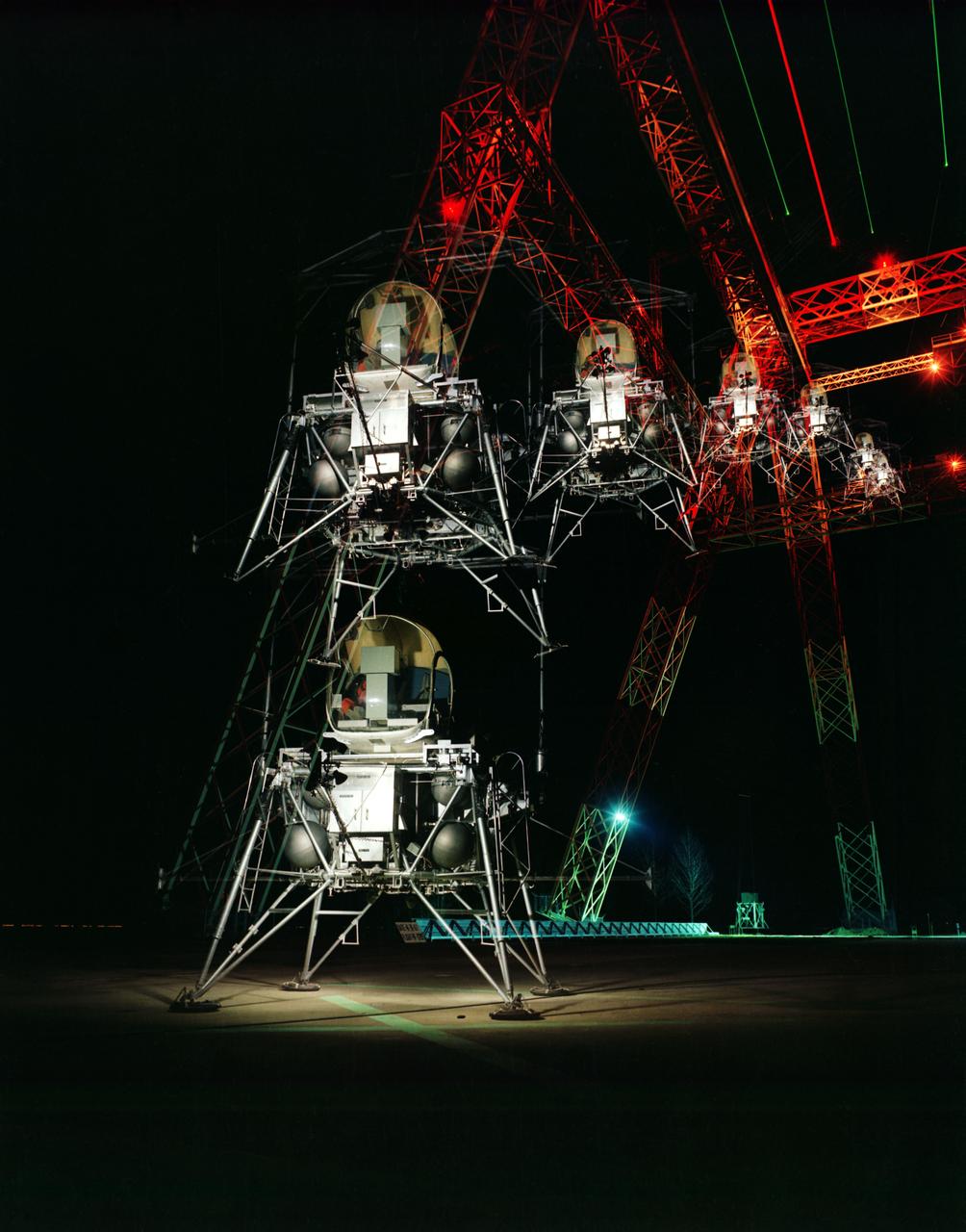

During a nighttime training session, a multiple exposure captures the movement of the Lunar Excursion Module Simulator (LEMS). The LEMS was a manned vehicle used to familiarize the Apollo astronauts with the handling characteristics of lunar-landing type vehicle. The Apollo Program is best known for the astronaut Neal Armstrong s first step on the Moon July 20, 1969. In its earliest test period, the LEMS featured a helicopter crew cabin atop the lunar landing module. Later, the helicopter crew cabin was replaced with a stand-up rectangular cabin which was more efficient for controlling maneuvers and for better viewing by the pilot. The vehicle was designed at Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA. This multiple exposure shows a simulated Moon landing of the (LEMS) trainer at Langley s Lunar Landing Research Facility. -- Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication (page 70), by James Shultz. Also published in " A Century at Langley" by Joseph Chambers, pg. 93.

During a nighttime training session, a multiple exposure captures the movement of the Lunar Excursion Module Simulator (LEMS). The LEMS was a manned vehicle used to familiarize the Apollo astronauts with the handling characteristics of lunar-landing type vehicle. The Apollo Program is best known for the astronaut Neal Armstrong s first step on the Moon July 20, 1969. In its earliest test period, the LEMS featured a helicopter crew cabin atop the lunar landing module. Later, the helicopter crew cabin was replaced with a stand-up rectangular cabin which was more efficient for controlling maneuvers and for better viewing by the pilot. The vehicle was designed at Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA. This multiple exposure shows a simulated Moon landing of the (LEMS) trainer at Langley s Lunar Landing Research Facility. -- Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication (page 70), by James Shultz. Also published in " A Century at Langley" by Joseph Chambers, pg. 93.
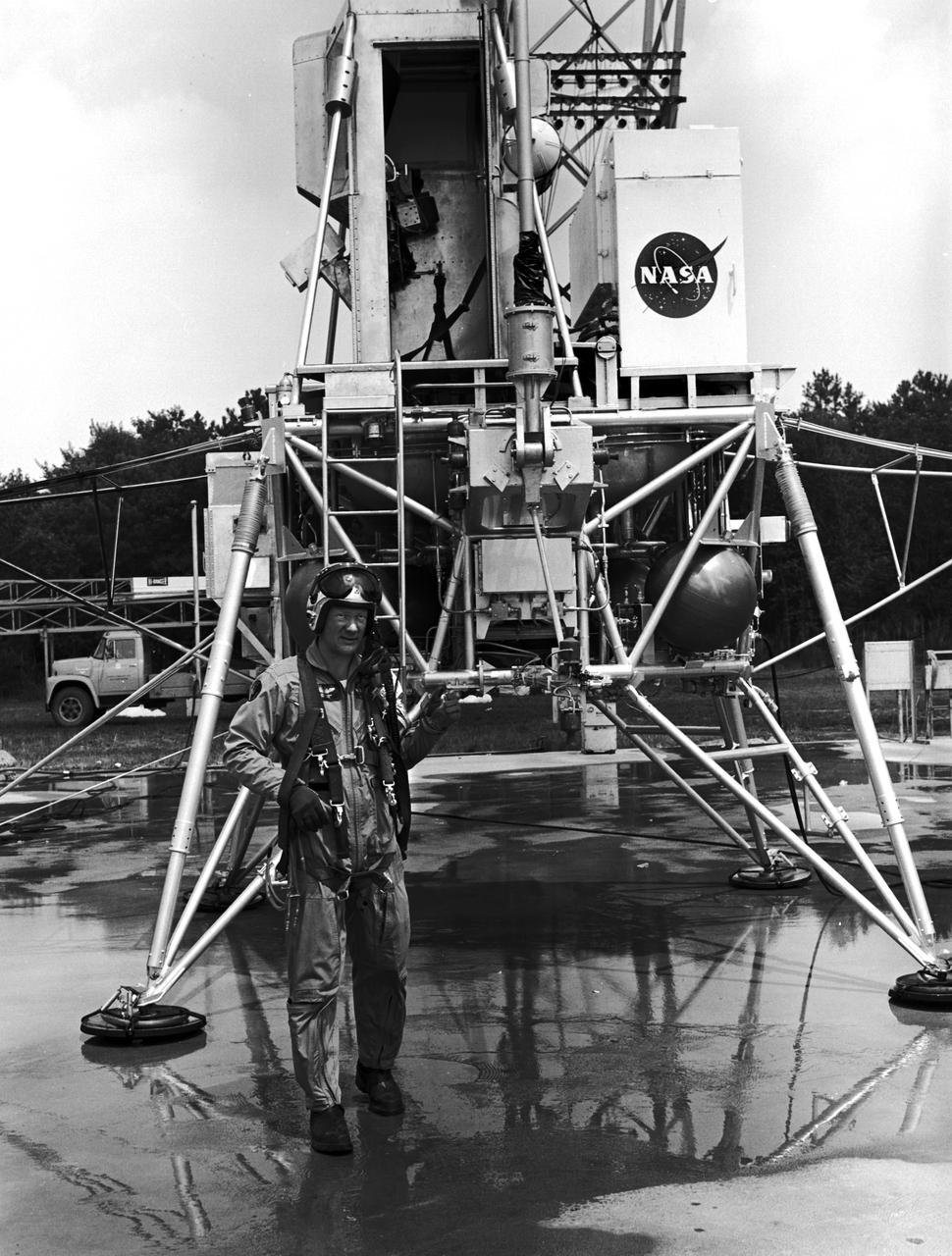

Astronaut Edwin Buzz Aldrin Lunar Module Pilot at the (LLRF) Lunar Landing Research Facility. Aldrin was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. On November 11, 1966, he and command pilot James Lovell were launched into space in the Gemini 12 spacecraft on a 4-day flight, which brought the Gemini program to a successful close. Aldrin established a new record for extravehicular activity (EVA), spending 5-1/2 hours outside the spacecraft. He served as lunar module pilot for Apollo 11, July 16-24, 1969, the first manned lunar landing mission. Aldrin followed Neil Armstrong onto the lunar surface on July 20, 1969, completing a 2-hour and 15 minute lunar EVA. In July 1971, Aldrin resigned from NASA. Aldrin has logged 289 hours and 53 minutes in space, of which, 7 hours and 52 minutes were spent in EVA. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former

Astronaut Edwin Buzz Aldrin Lunar Module Pilot at the (LLRF) Lunar Landing Research Facility. Aldrin was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. On November 11, 1966, he and command pilot James Lovell were launched into space in the Gemini 12 spacecraft on a 4-day flight, which brought the Gemini program to a successful close. Aldrin established a new record for extravehicular activity (EVA), spending 5-1/2 hours outside the spacecraft. He served as lunar module pilot for Apollo 11, July 16-24, 1969, the first manned lunar landing mission. Aldrin followed Neil Armstrong onto the lunar surface on July 20, 1969, completing a 2-hour and 15 minute lunar EVA. In July 1971, Aldrin resigned from NASA. Aldrin has logged 289 hours and 53 minutes in space, of which, 7 hours and 52 minutes were spent in EVA. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former
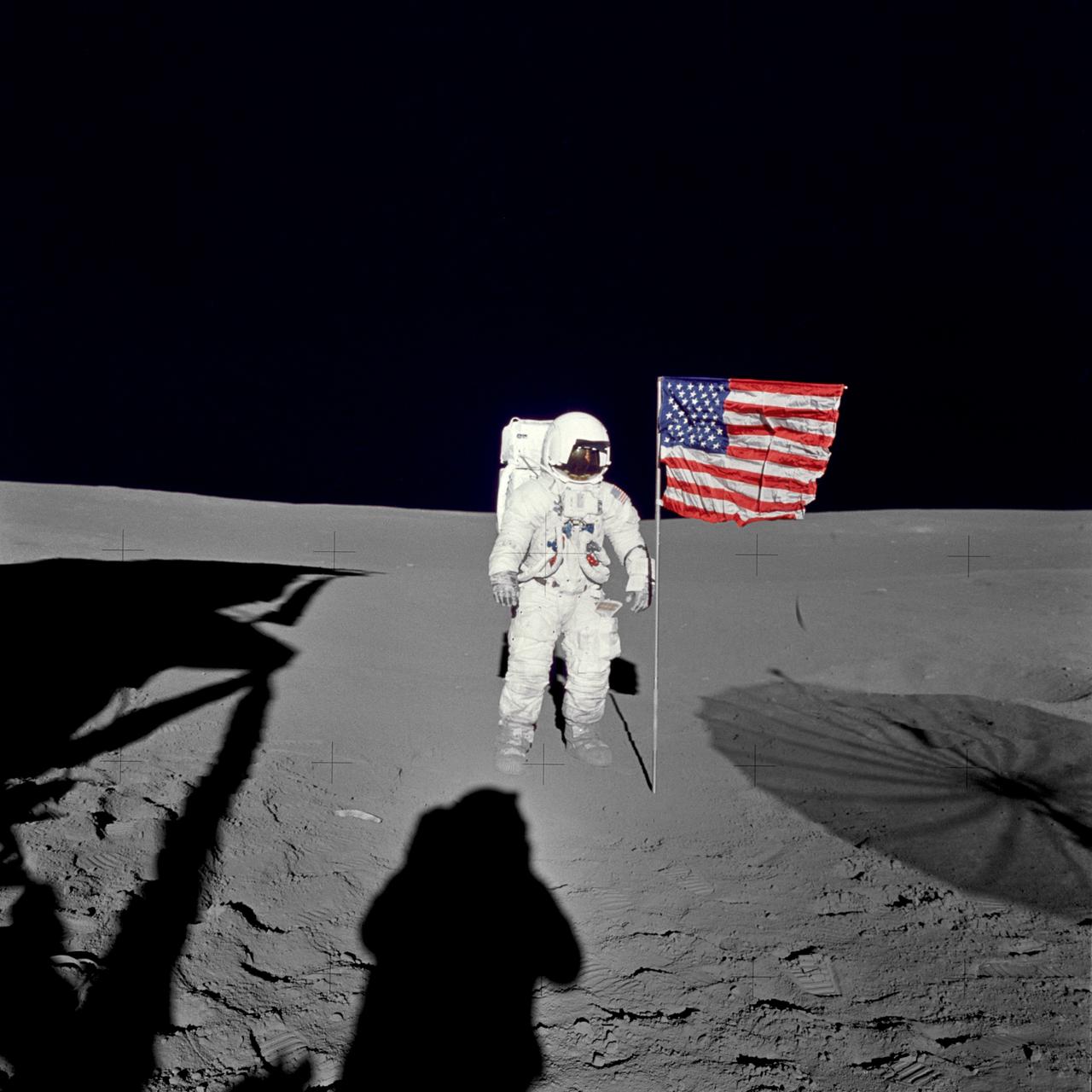

AS14-66-9233 (5 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot for the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, stands by the deployed U.S. flag on the lunar surface during the early moments of the first extravehicular activity (EVA) of the mission. He was photographed by astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., mission commander, using a 70mm modified lunar surface Hasselblad camera. While astronauts Shepard and Mitchell descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Antares" to explore the Fra Mauro region of the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Kitty Hawk" in lunar orbit.
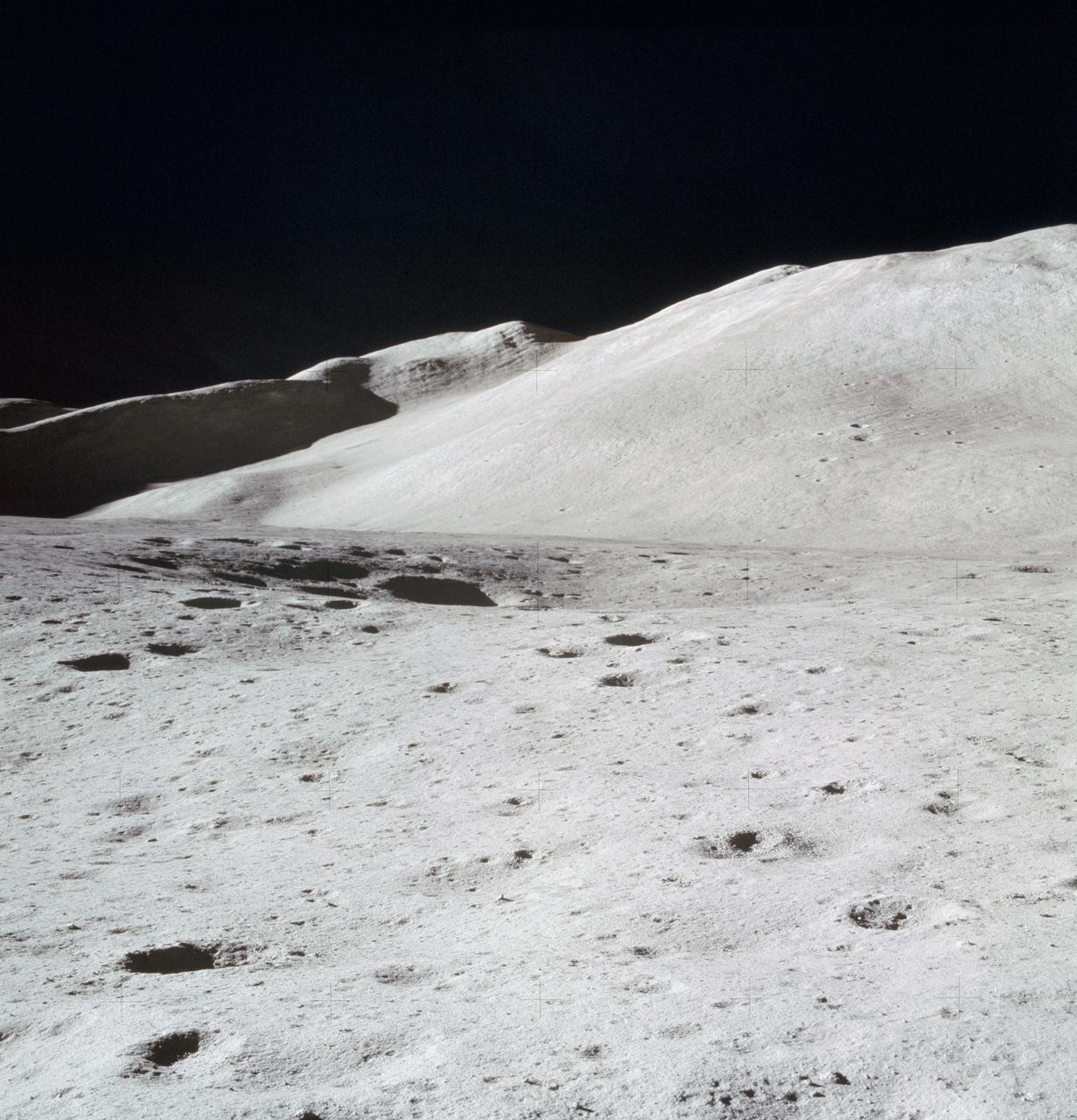

AS15-87-11748 (31 July 1971) --- A view of Hadley Delta, looking southeasterly, as photographed from the top hatch of the Apollo 15 Lunar Module (LM) by astronaut David R. Scott, commander, during his stand-up extravehicular activity (EVA) just after the LM "Falcon" touched down at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The prominent feature on the horizon in the center of the picture was called Silver Spur by the Apollo 15 crew men. Hadley Delta Mountain rises approximately 4,000 meters (about 13,124 feet) above the plain. While astronauts Scott and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Module's (CSM) in lunar orbit.
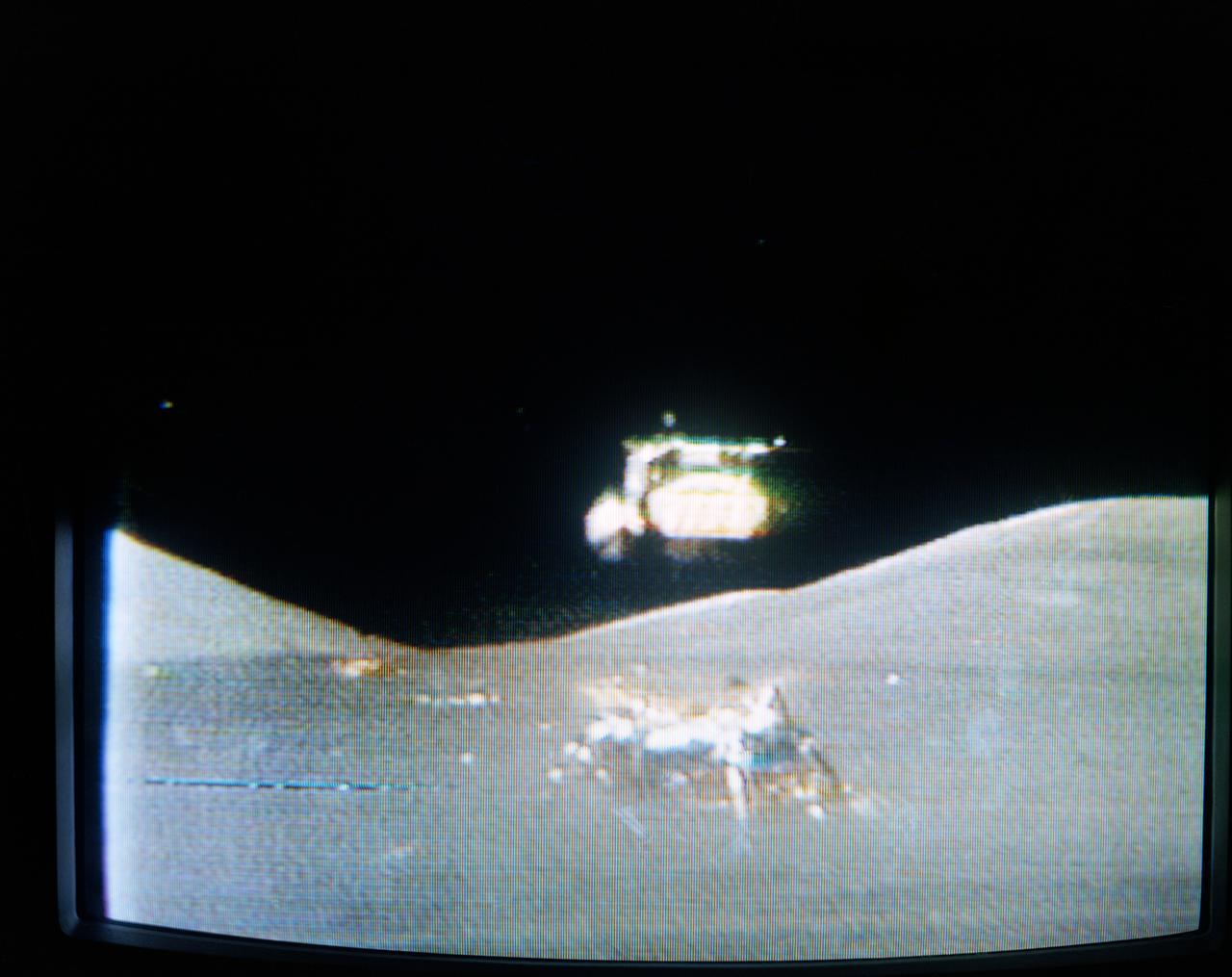

S72-55421 (14 Dec. 1972) --- The Apollo 17 Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" ascent stage leaves the Taurus-Littrow landing site as it makes its spectacular liftoff from the lunar surface, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV-mounted TV camera, remotely controlled from the Mission Control Center (MCC) in Houston, made it possible for people on Earth to watch the fantastic event. The LM liftoff was at 188:01:36 ground elapsed time, 4:54:36 p.m. (CST), Thursday, Dec. 14, 1972. The LM ascent stage, with astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt aboard, returned from the lunar surface to rejoin the Command and Service Modules (CSM) orbiting the moon. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Cernan and Schmitt explored the moon. The LM descent stage is used as a launching platform and remains behind on the moon. Here, the two stages have completely separated and the ascent stage is headed skyward.
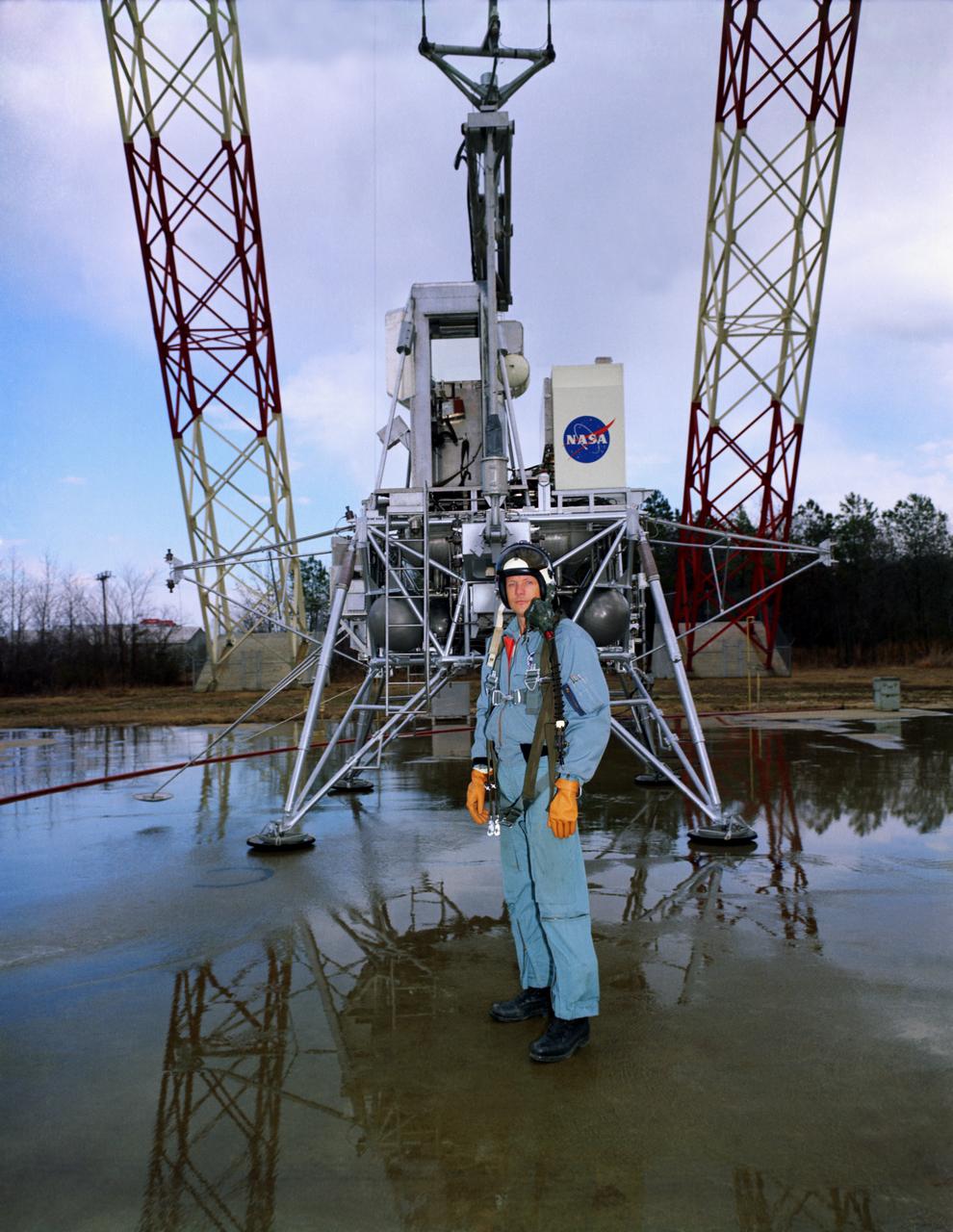

Neil Armstrong with the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM). Caption: "Not long after this photo was taken in front of the Lunar Landing Research Facility, astronaut Neil Armstrong became the first human to step upon the surface of the Moon." Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, by James Schultz, page 91. Also published in " A Century at Langley" by Joseph Chambers, pg. 95
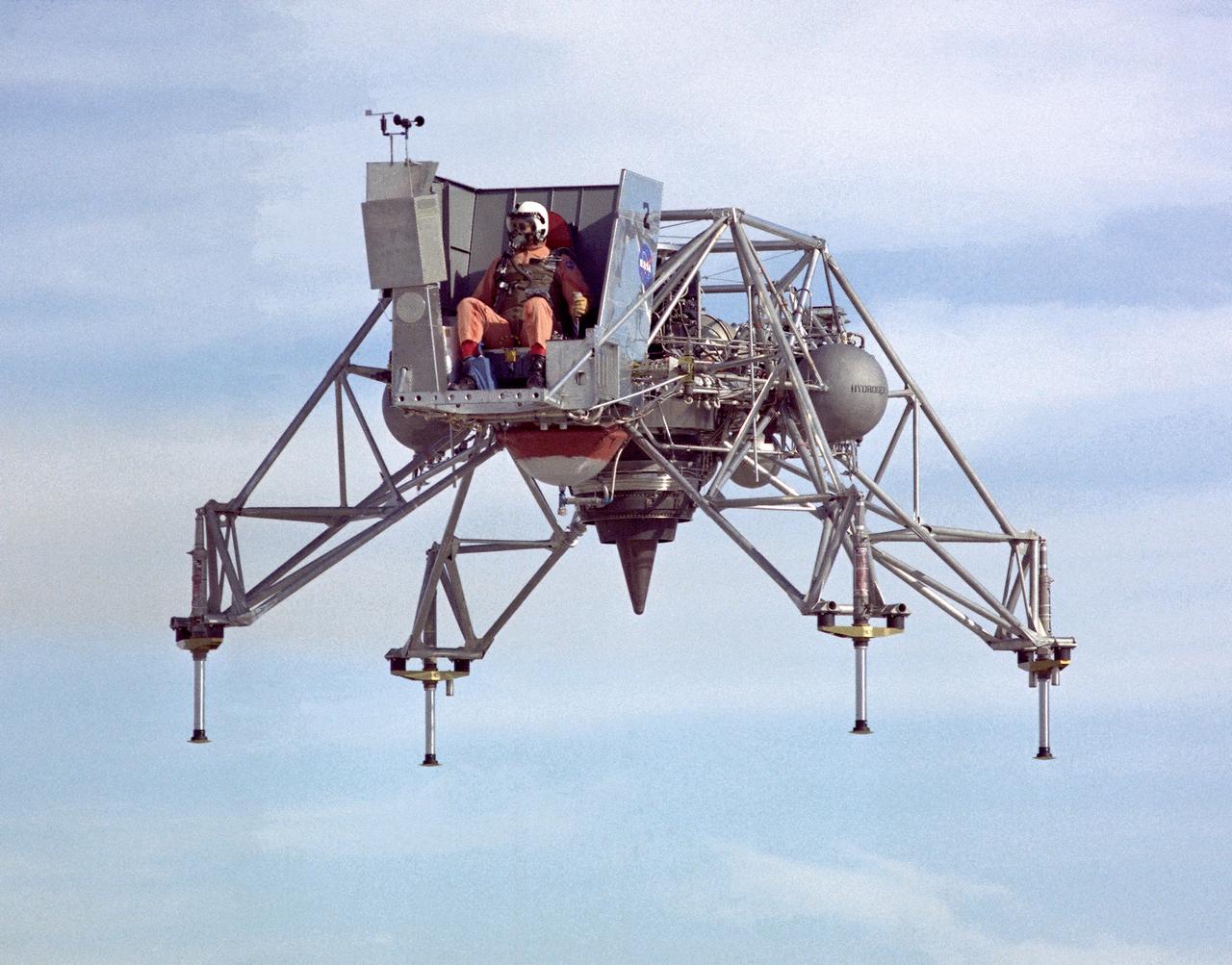
In this 1967 NASA Flight Reserch Center photograph the Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) is viewed from the front. This photograph provideds a good view of the pilot’s platform with the restrictive cockpit view like that of he real Lunar Module (LM) When Apollo planning was underway in 1960, NASA was looking for a simulator to profile the descent to the Moon's surface. Three concepts surfaced: an electronic simulator, a tethered device, and the ambitious Dryden contribution, a free-flying vehicle. All three became serious projects, but eventually the NASA Flight Research Center’s (FRC) Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) became the most significant one. After conceptual planning and meetings with engineers from Bell Aerosystems Company, Buffalo, N.Y., NASA FRC issued a $3.6 million production contract awarded in 1963, for delivery of the first of two vehicles for flight studies. Built of tubular aluminum alloy like a giant four-legged bedstead, the vehicle was to simulate a lunar landing profile from around 1500 feet to the Moon’s surface. The LLRV had a turbofan engine mounted vertically in a gimbal, with 4200 pounds of thrust. The engine, lifted the vehicle up to the test altitude and was then throttled back to support five-sixths of the vehicle's weight, thus simulating the reduced gravity of the Moon. Two lift rockets with thrust that could be varied from 100 to 500 pounds handled the LLRV's rate of descent and horizontal translations. Sixteen smaller rockets, mounted in pairs, gave the pilot control in pitch, yaw, and roll.. The pilot’s platform extended forward between two legs while an electronics platform, similarly located, extended rearward. The pilot had a zero-zero ejection seat that would then lift him away to safety. The two LLRVs were shipped from Bell to the FRC in April 1964, with program emphasis on vehicle No. 1. The first flight, Oct. 30, 1964, NASA research pilot Joe Walker flew it three times for a total of just under 60 seconds
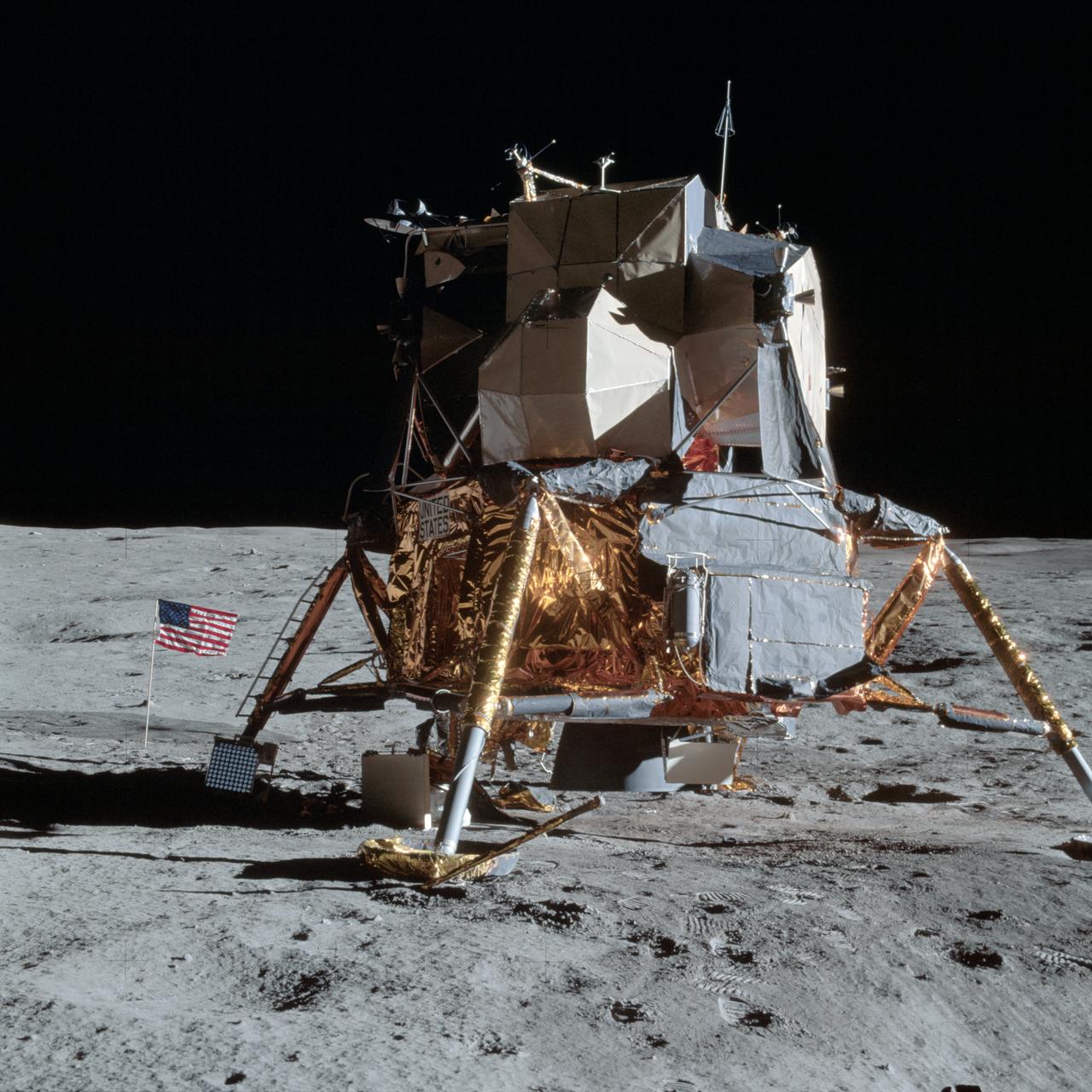
AS14-66-9277 (5 Feb. 1971) --- An excellent view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) on the moon, as photographed during the first Apollo 14 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The astronauts have already deployed the U.S. flag. Note the laser ranging retro reflector (LR-3) at the foot of the LM ladder. The LR-3 was deployed later. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
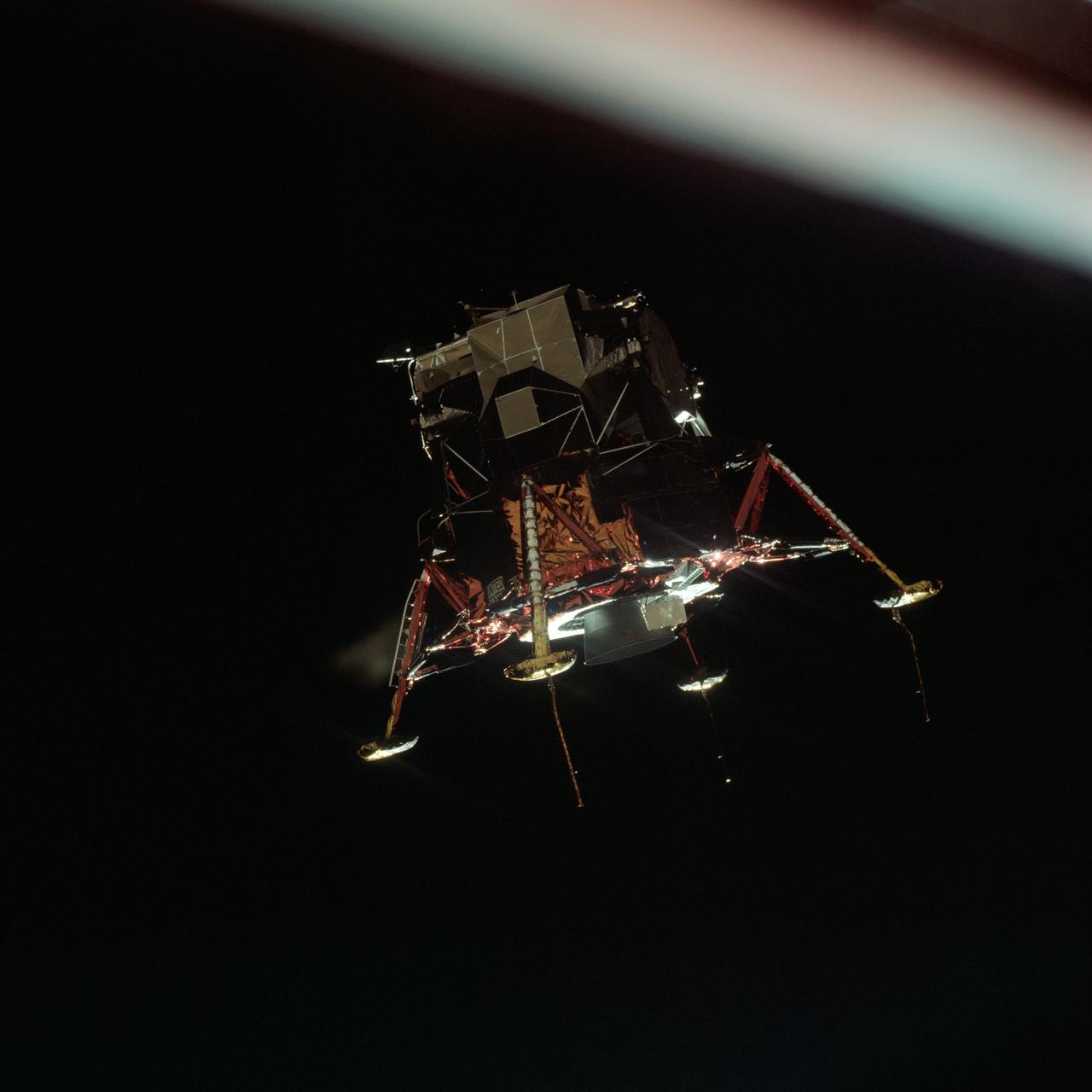

AS11-44-6581 (20 July 1969) --- The Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM), in a lunar landing configuration, is photographed in lunar orbit from the Command and Service Modules (CSM). Inside the LM were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM to explore the lunar surface. The protrusions connected to the landing pods are sensors to aid in the touchdown or landing process.
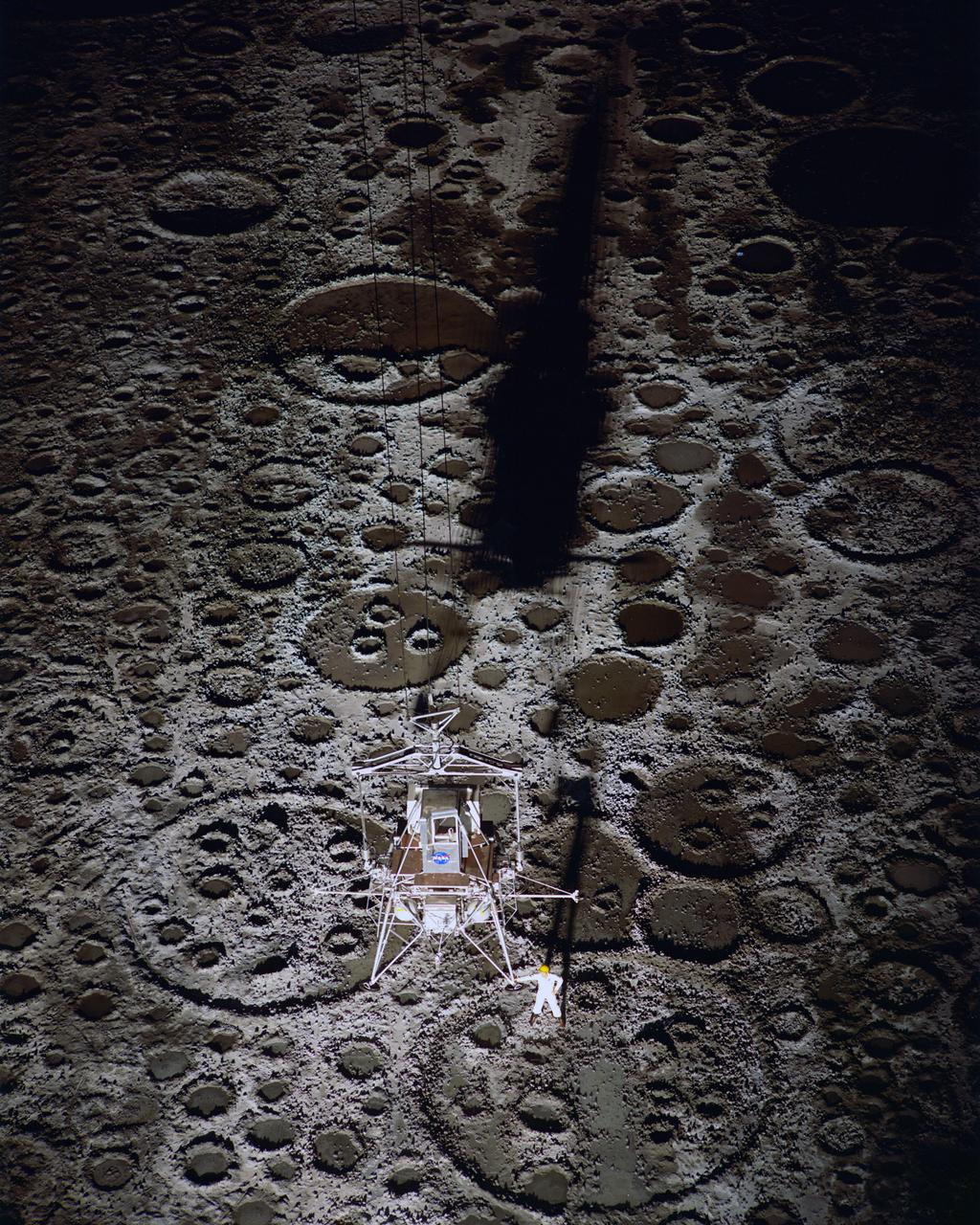

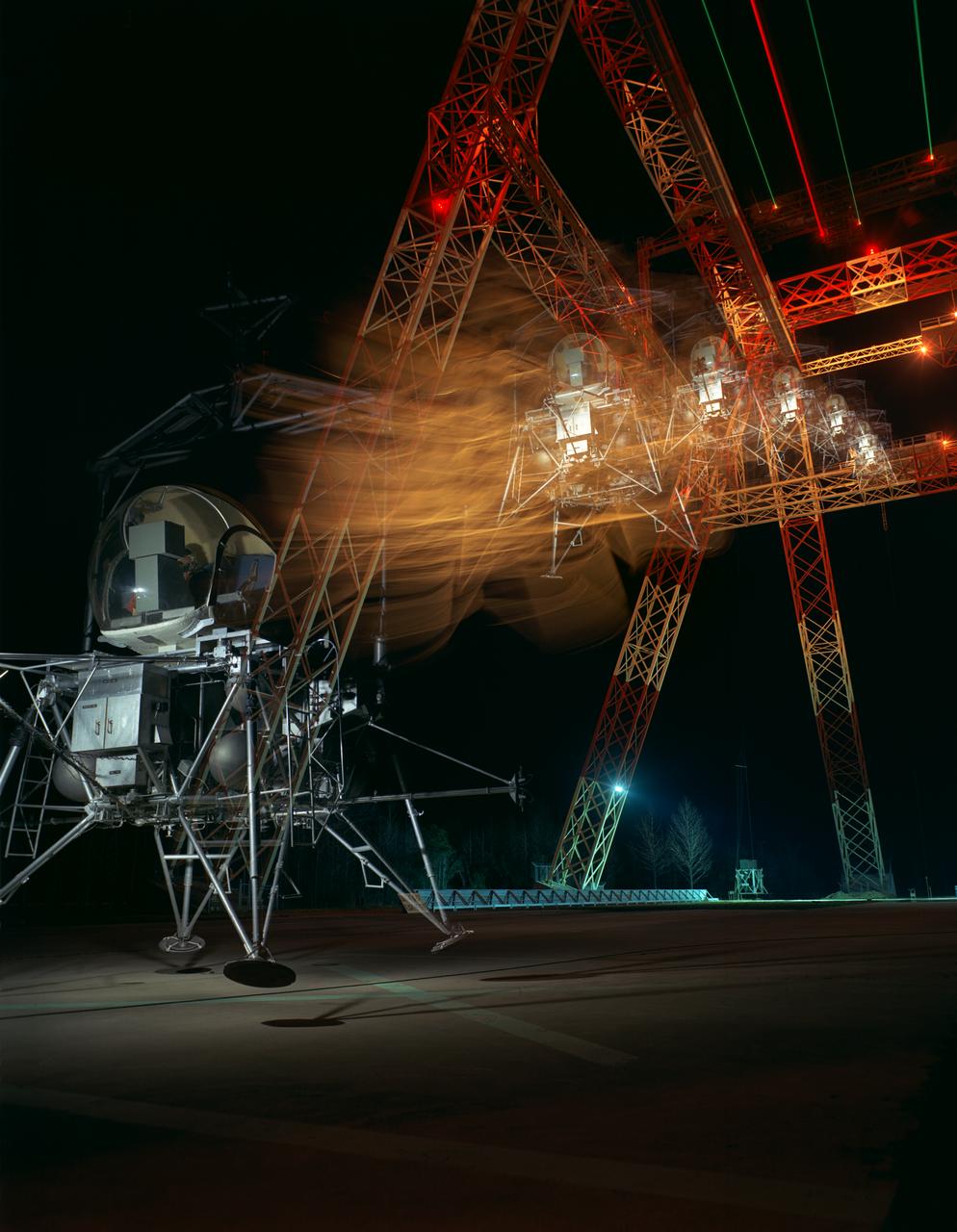
Lunar Landing Module photographed at night at the Lunar Landing Research Facility. Gantry facility 1297.
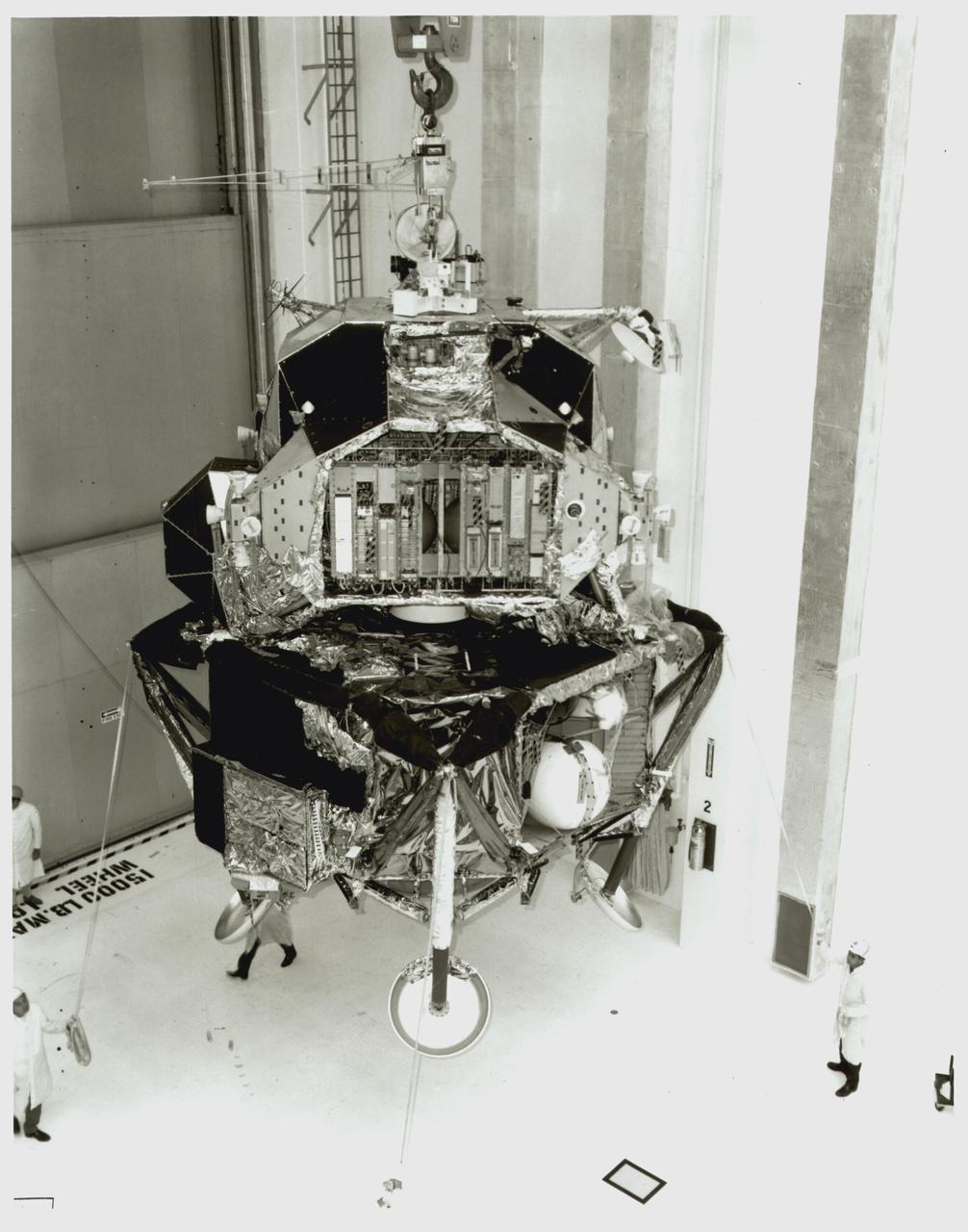
The Lunar Module for Apollo 11 moves from the landing gear fixture and mate to the spacecraft-lunar module adapter.

jsc2004e20304 - Panorama view of Apollo 17 lunar surface photos for Station 5 at the Taurus-Littrow landing site taken during the second moonwalk of the mission by Apollo 17 commander Eugene Cernan and lunar module pilot Harrison (Jack) Schmitt. The panoramas were built by combining Apollo 17 images starting with frame AS17-145-22159 through end frame AS17-145-22181. The panoramic images received minimal retouching by NASA imagery specialists, including the removal of lens flares that were problematic in stitching together the individual frames and blacking out the sky to the lunar horizon. These adjustments were made based on observations of the Moon walkers who reported that there are no stars visible in the sky due to the bright lunar surface reflection of the Sun.
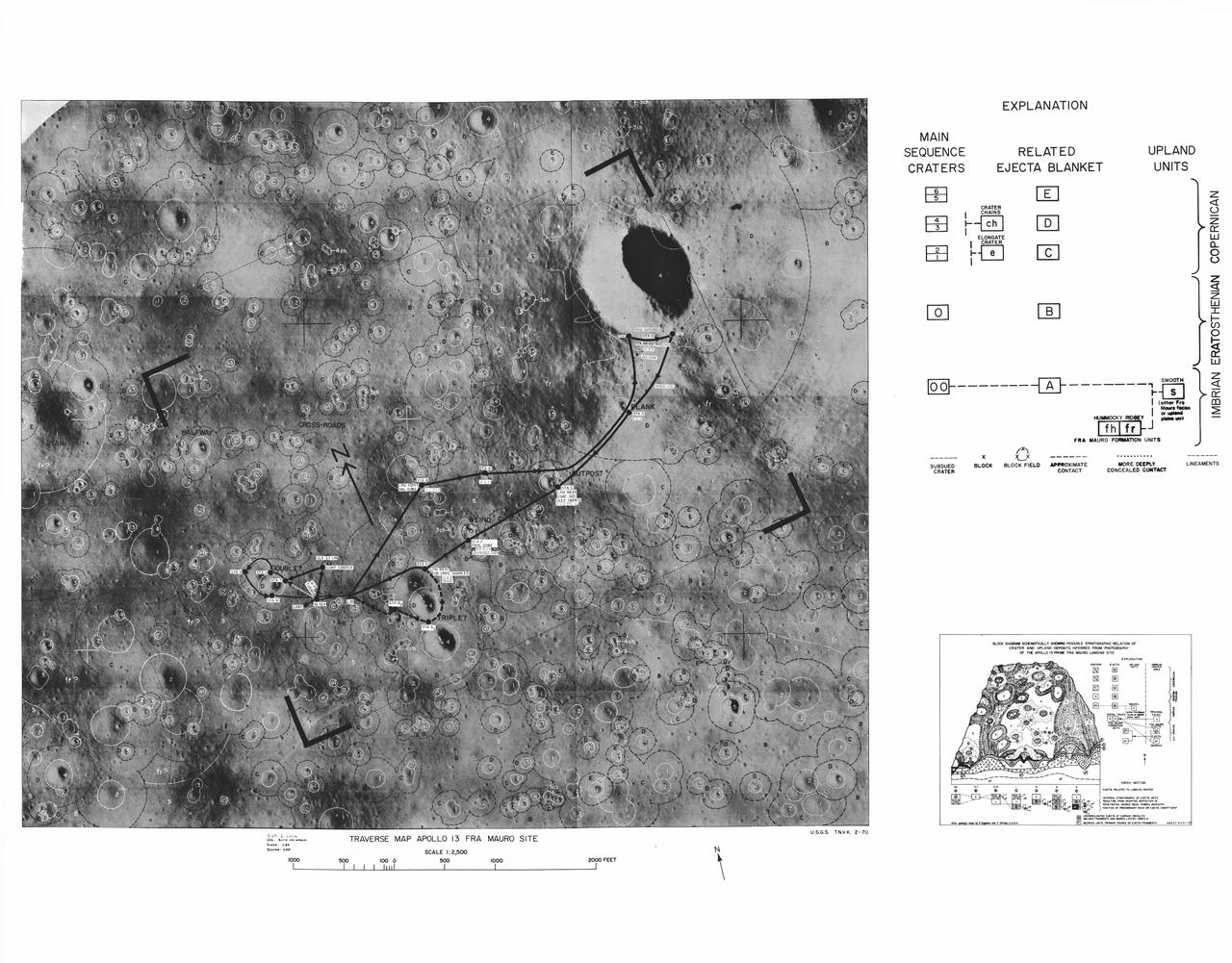
This lunar map shows the traverse plans for the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. Areas marked include Lunar module landing site, areas for the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiment Package (ALSEP) and areas for gathering of core samples.

S70-30534 (9 March 1970) --- A Lunar Landing Training Vehicle (LLTV), piloted by astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., sets down on the runway at the conclusion of a test flight at Ellington Air Force Base. Lovell is the commander of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. Lovell used the LLTV to practice lunar landing techniques in preparation for his scheduled mission. Lovell will be at the controls of the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM) when it lands on the moon in the highlands just north of Fra Mauro. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, will remain with the Apollo 13 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Lovell and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, descend in the LM to explore the moon. A hovering helicopter watches the LLTV landing.
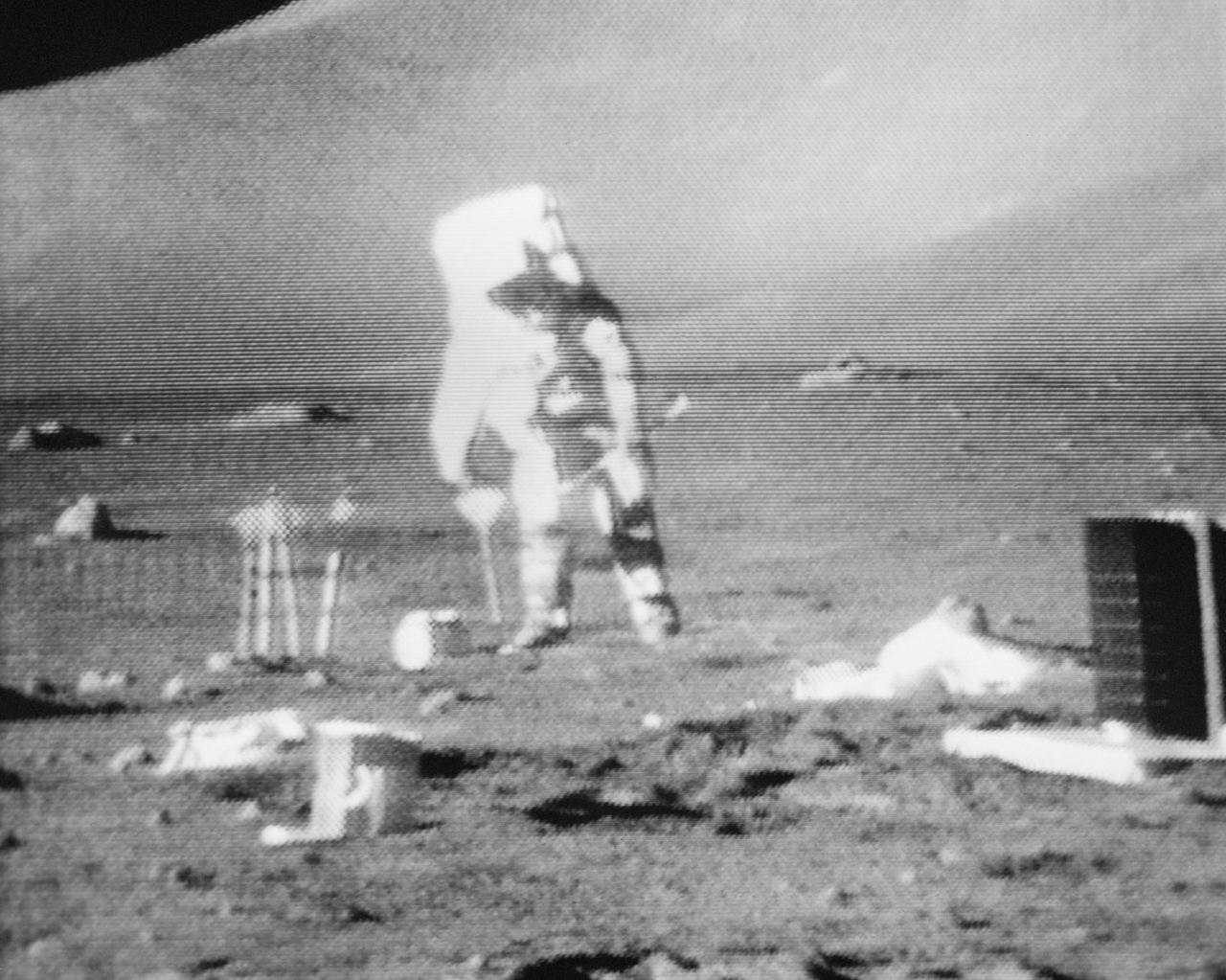

S72-55065 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt is seen anchoring the geophone module with a flag during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, in the black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Schmitt is the lunar module mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Schmitt is the lunar module pilot of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while astronauts Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan, commander, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the moon. The geophone module is part of the Lunar Seismic Profiling Experiment (S-203), a component of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP). Other ALSEP components are visible in the picture.
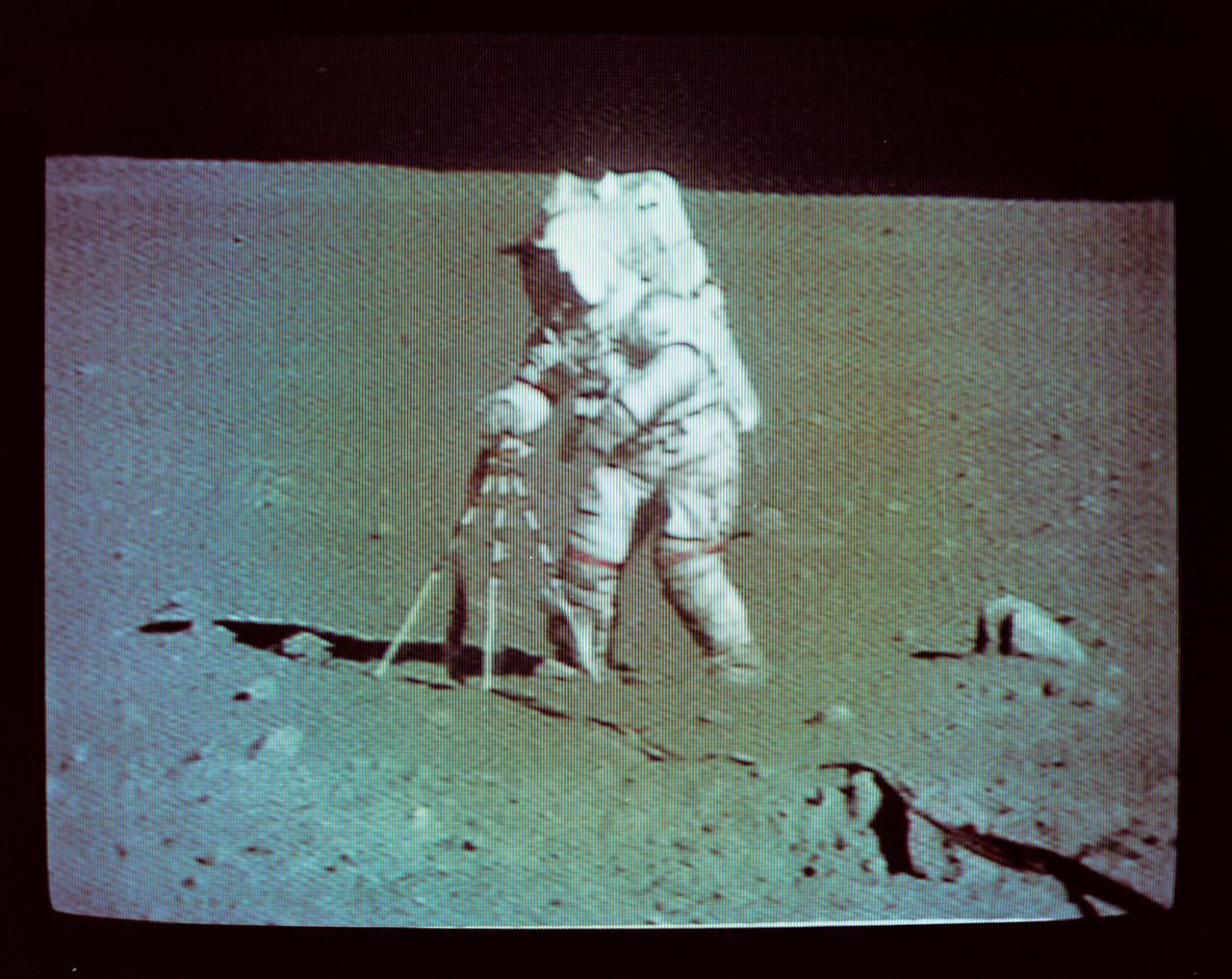

S72-35610 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, deploys the lunar Portable Magnetometer during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color television camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). While astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit, astronauts Young and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the Descartes landing site.
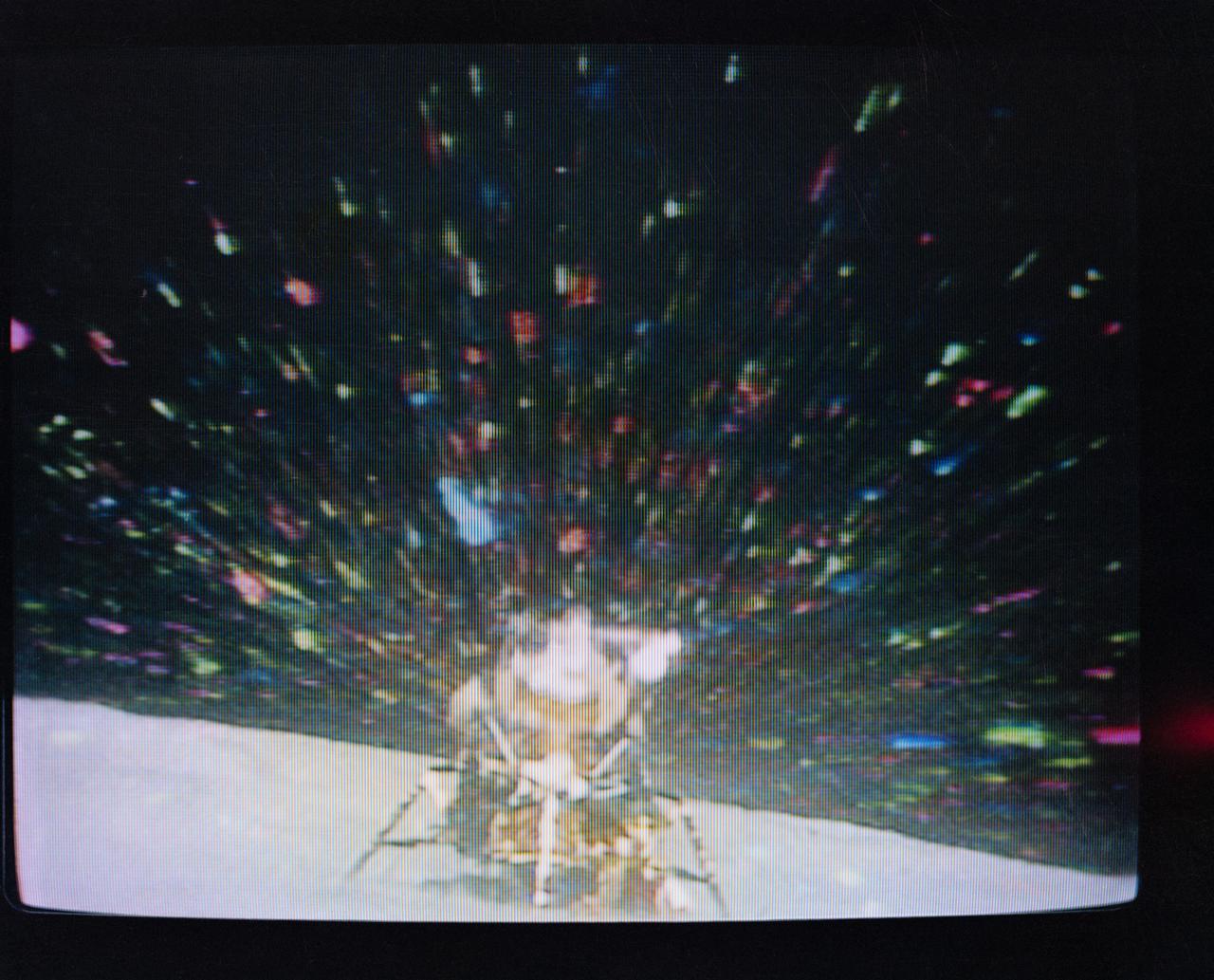

S72-35613 (22 April 1972) --- The Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" in early lunar liftoff phase is featured in this lunar scene at the Descartes landing site. The still picture is a reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 LM to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
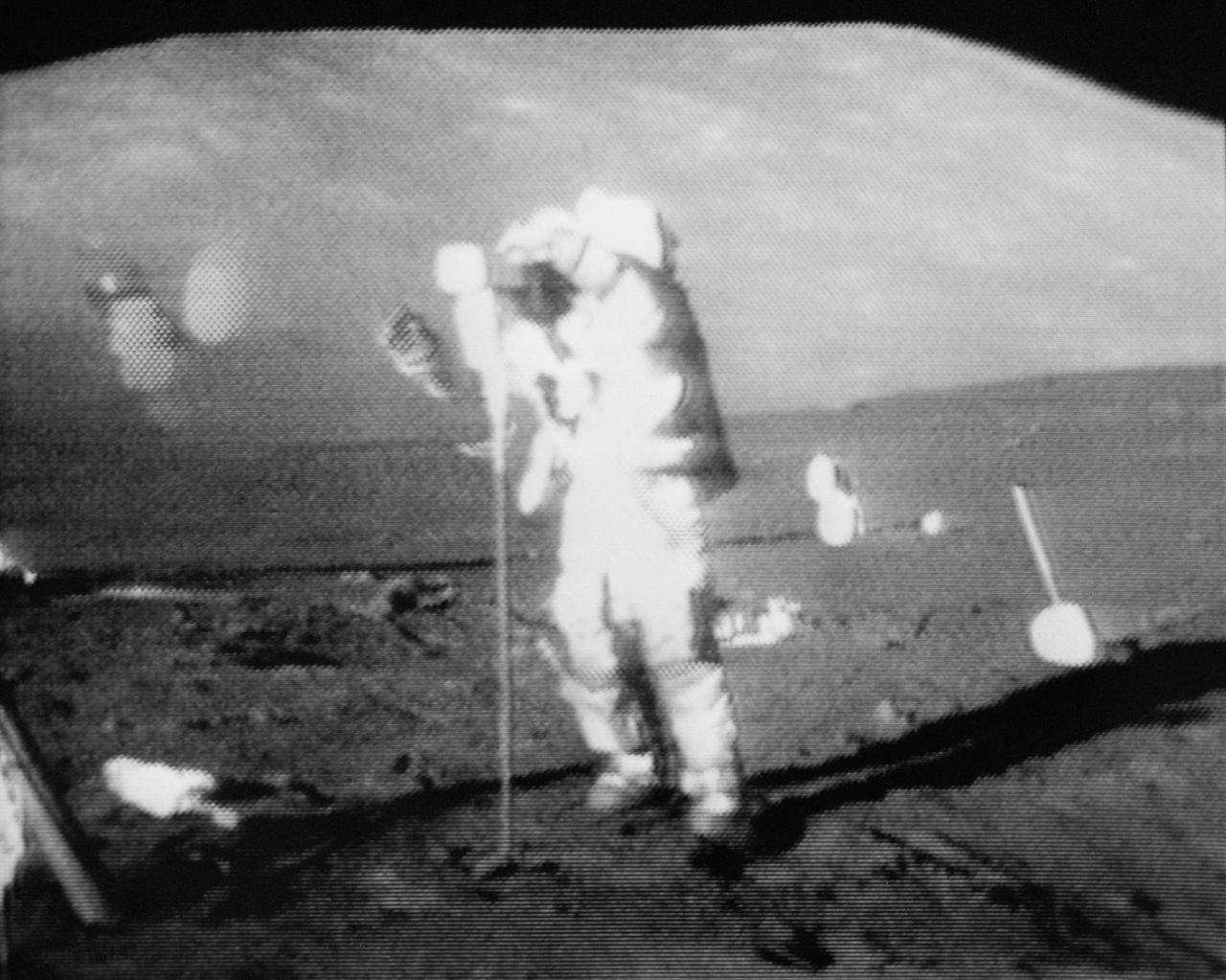

S72-55064 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan operates the Apollo Lunar Surface Drill during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, in this black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the RCA color TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Cernan is the commander of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while astronaut Cernan and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the moon.
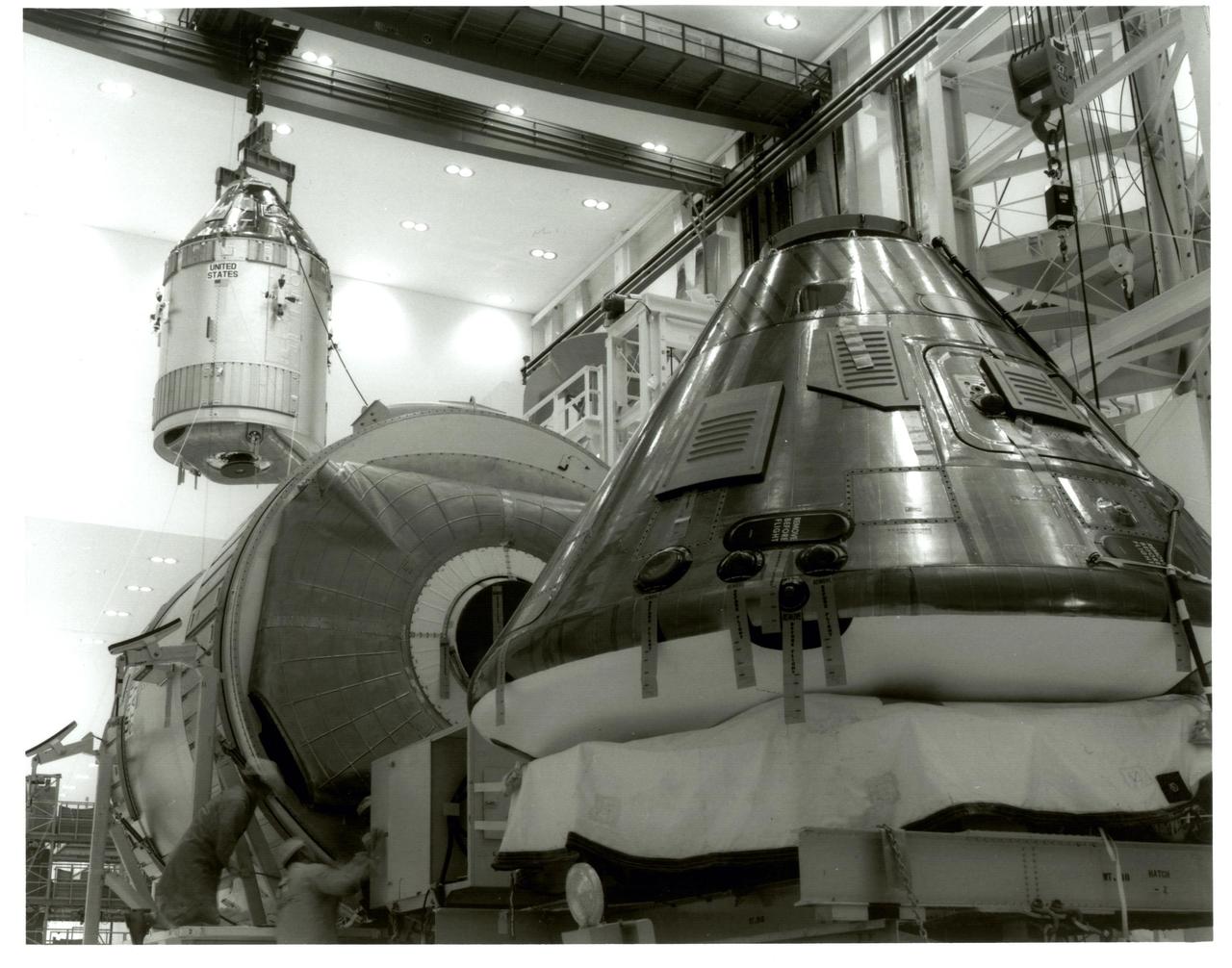

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Command Module 107 and Service Module, which are going to be used for the Apollo 11 mission, are moved from Chamber "L" to the work stand in preparation for the first manned lunar landing. Also shown in the background is the Command Module 108, which is going to be used for the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission.
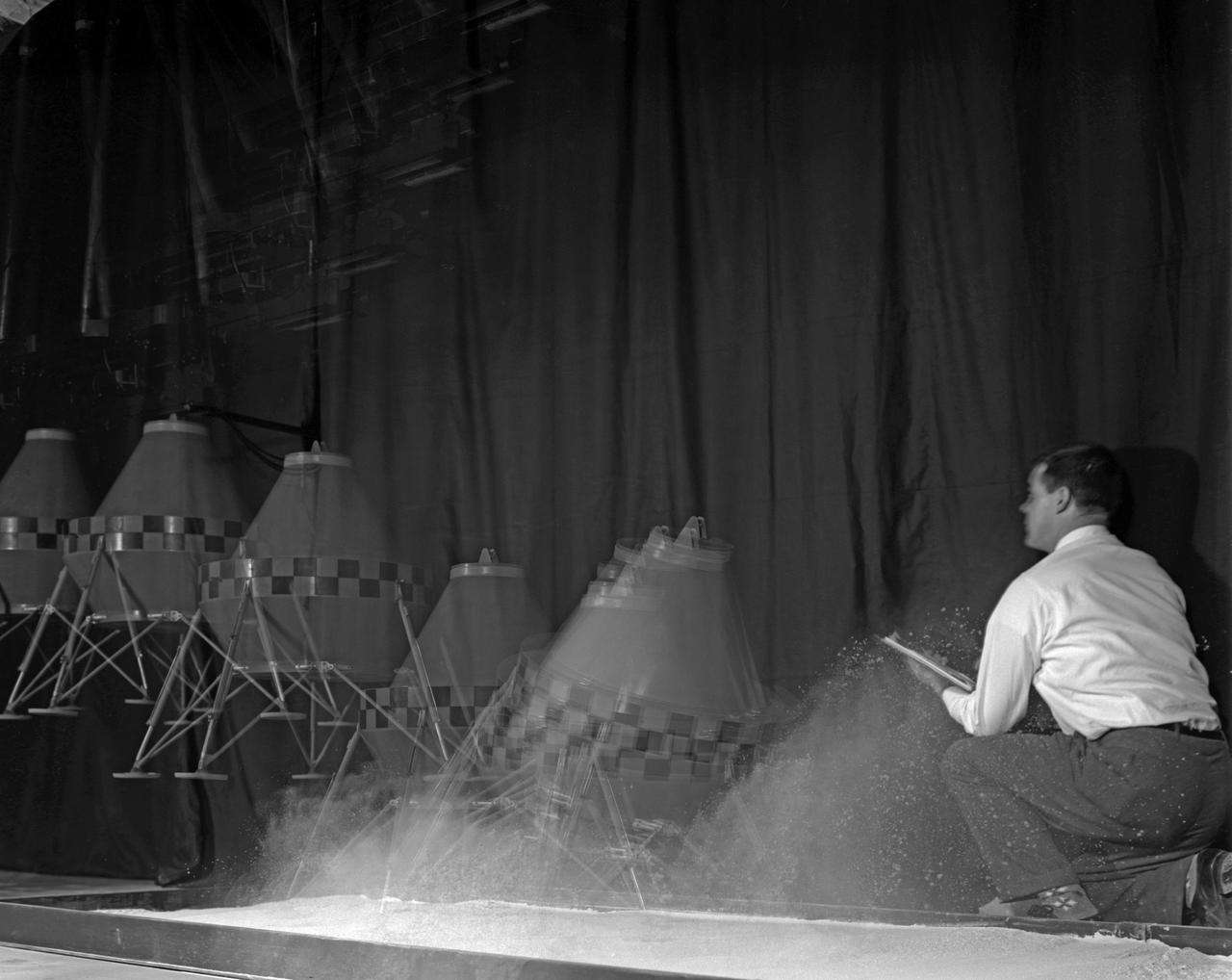

Multiple exposure of a test with a prototype Lunar Excursion Module. This test was one of many conducted at Langley of the structural dynamics of lunar landing.

S69-30520 (April 1969) --- A North American Rockwell Corporation artist's concept depicting the Apollo 10 Lunar Module descending to 50,000 feet for a close look at a lunar landing site. The Command and Service Modules remain in lunar orbit. The landing area is Site 2 on the east central part of the moon in southwestern Sea of Tranquility (Mare Tranquillitatis). The site is about 62 miles east of the rim of the crater Sabine and 118 miles west-southwest of the crater Maskelyne. Apollo 11 is scheduled to be the first lunar landing mission.
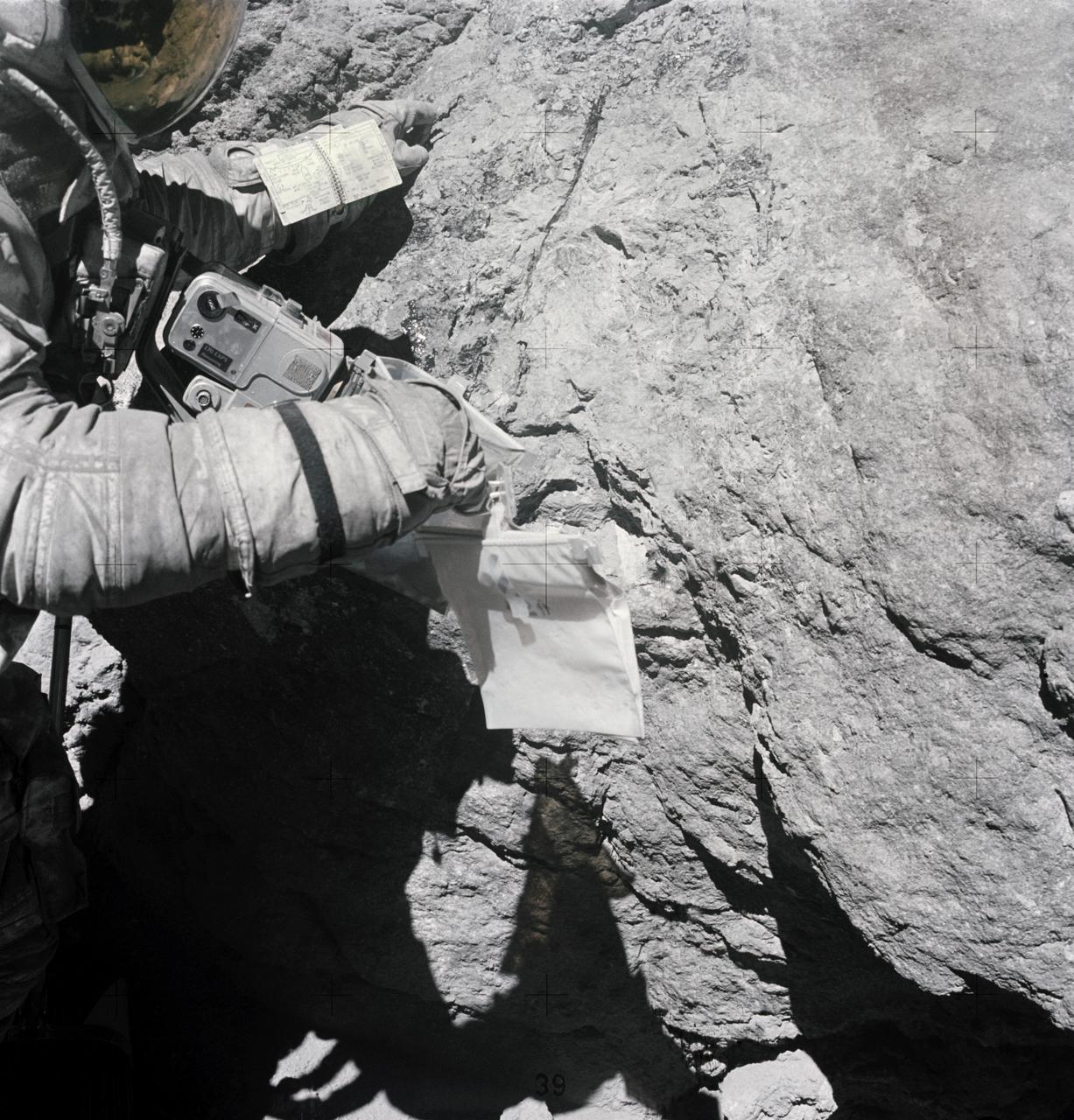

AS16-116-18649 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, examines closely the surface of a large boulder at North Ray Crater during the third Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. This picture was taken by astronaut John W. Young, commander. Note the chest-mounted 70mm Hasselblad camera. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.

S71-16637 (January 1971) --- A close-up view of the plaque which the Apollo 14 astronauts will leave behind on the moon during their lunar landing mission. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, will descend to the lunar surface in the Lunar Module (LM) "Antares". Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The seven by nine inch stainless steel plaque will be attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the LM's descent stage. Commemorative plaques were also left on the moon by the Apollo 11 and Apollo 12 astronauts.

S71-39357 (July 1971) --- A photographic replica of the plaque which the Apollo 15 astronauts will leave behind on the moon during their lunar landing mission. Astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot; will descend to the lunar surface in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon". Astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The seven by nine inch stainless steel plaque will be attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the LM's descent stage. Commemorative plaques were also left on the moon by the Apollo 11, Apollo 12 and Apollo 14 astronauts.
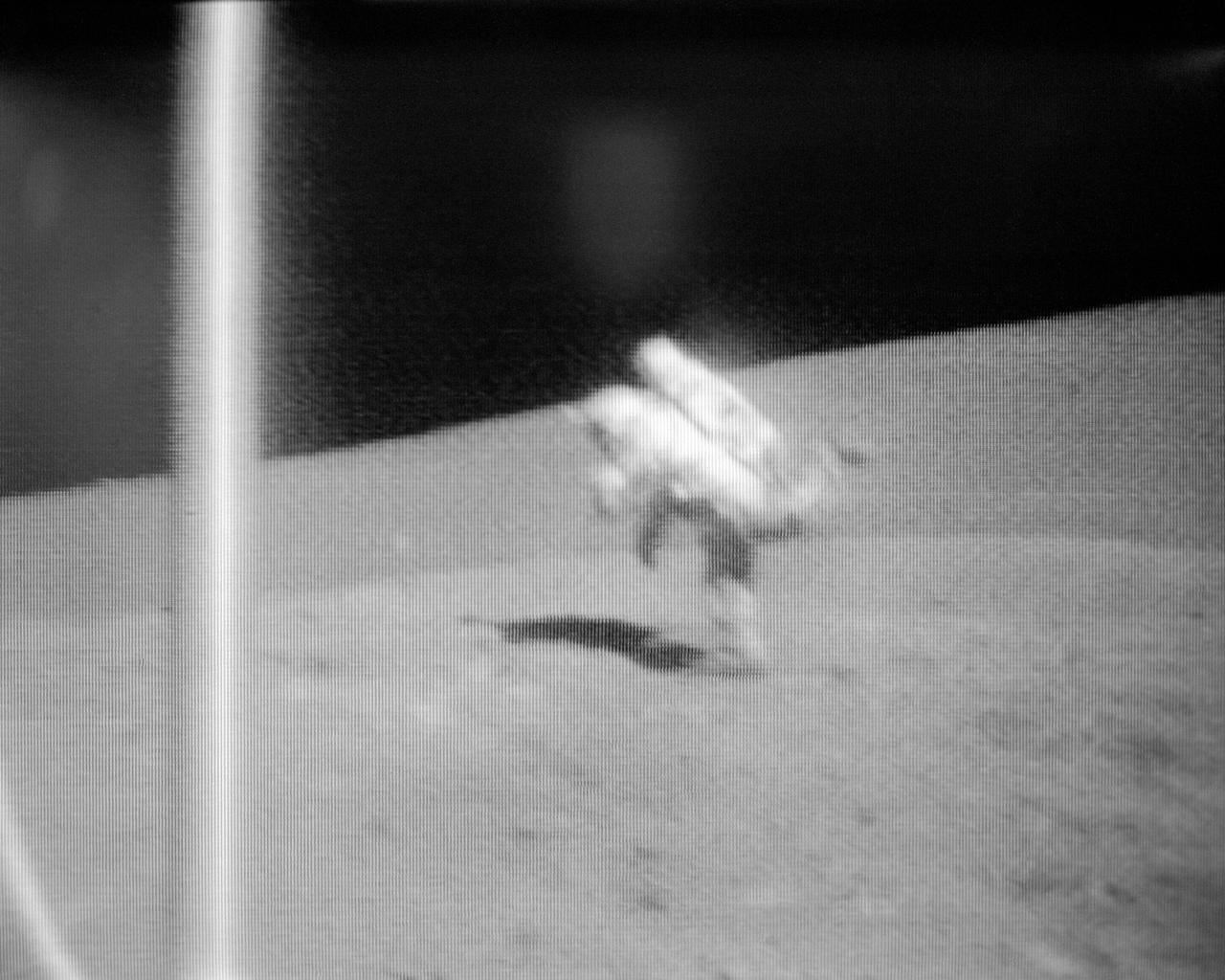

S72-55166 (12 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt loses his balance and heads for a fall during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, as seen in this black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Schmitt is lunar module pilot of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while astronauts Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan, commander, descended in the Lunar Module "Challenger" to explore the moon.

S70-34685 (April 1970) --- A photographic replica of the plaque which the Apollo 13 astronauts will leave behind on the moon during their lunar landing mission. Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, will descend to the lunar surface in the Lunar Module (LM) "Aquarius". Astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The plaque will be attached to the ladder of the landing gear strut on the LM?s descent stage. Commemorative plaques were also left on the moon by the Apollo 11 and Apollo 12 astronauts.

S72-55066 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt chips samples from a large boulder during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, in this black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Schmitt is the lunar module pilot of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while astronauts Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan, commander, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the moon.
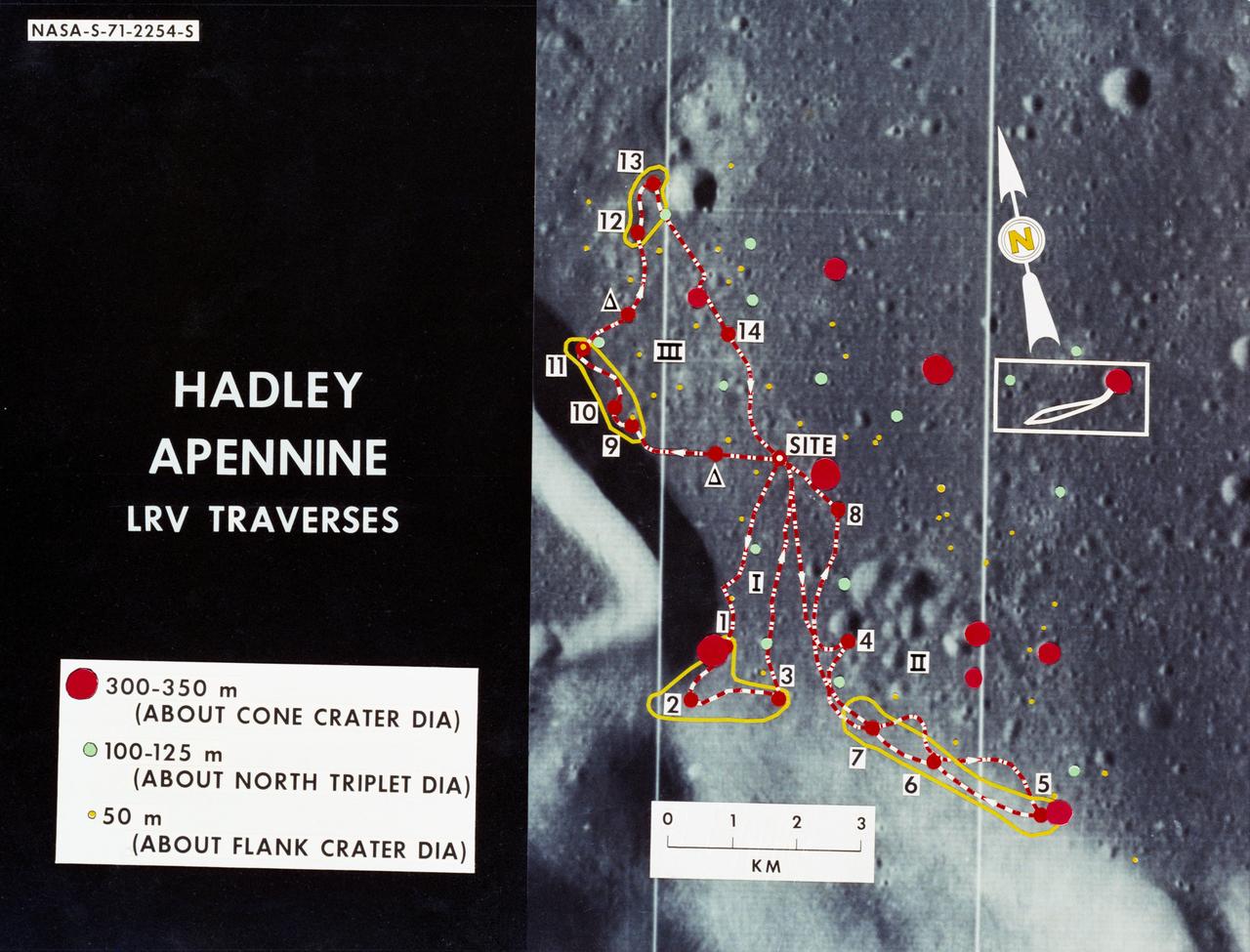
S71-02254 (June 1971) --- An enlarged Lunar Orbiter photograph showing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) traverse routes overlaid on the Hadley-Apennine landing site. Apollo 15 is to land at the point labeled "site," and a comparison of Apollo 14 crater sizes with those of Apollo 15 is included, also. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descend in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
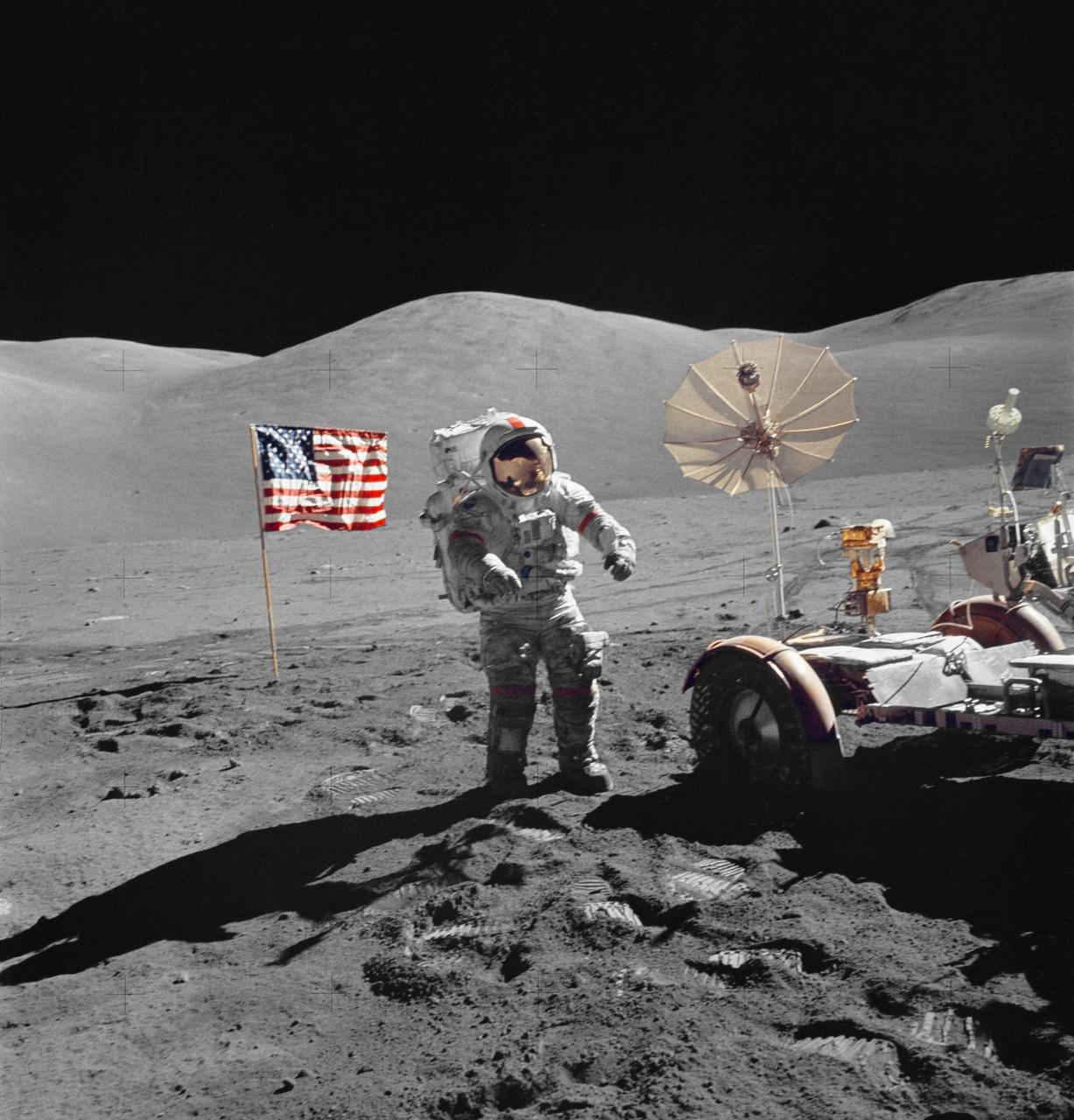

AS17-140-21388 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, mission commander, walks toward the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site of NASA's sixth and final Apollo lunar landing mission. The photograph was taken by astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
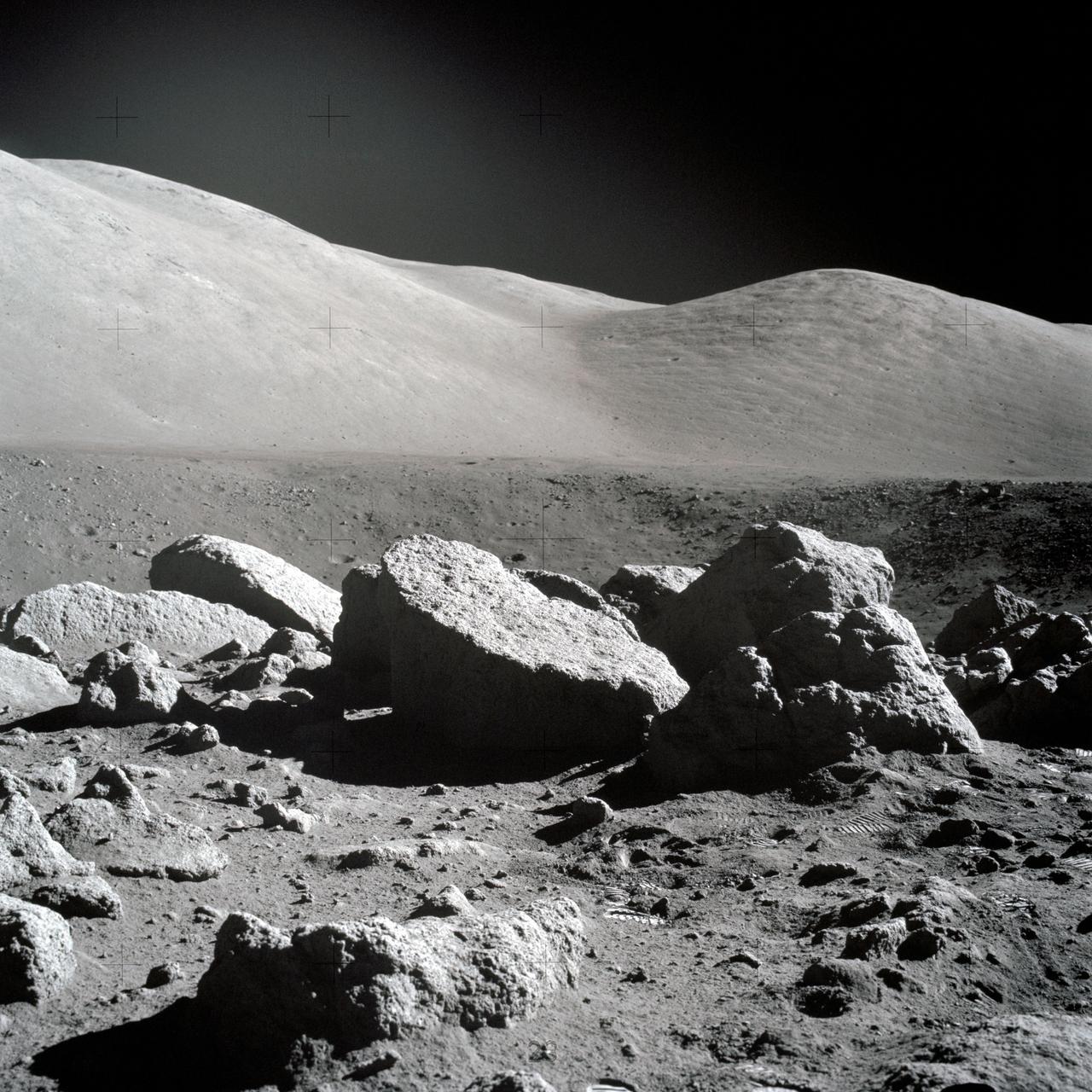

AS17-145-22183 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- One of the Apollo 17 crew took this picture of a large boulder field during lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. This view is looking northeast. Apollo 17 was the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo Program. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
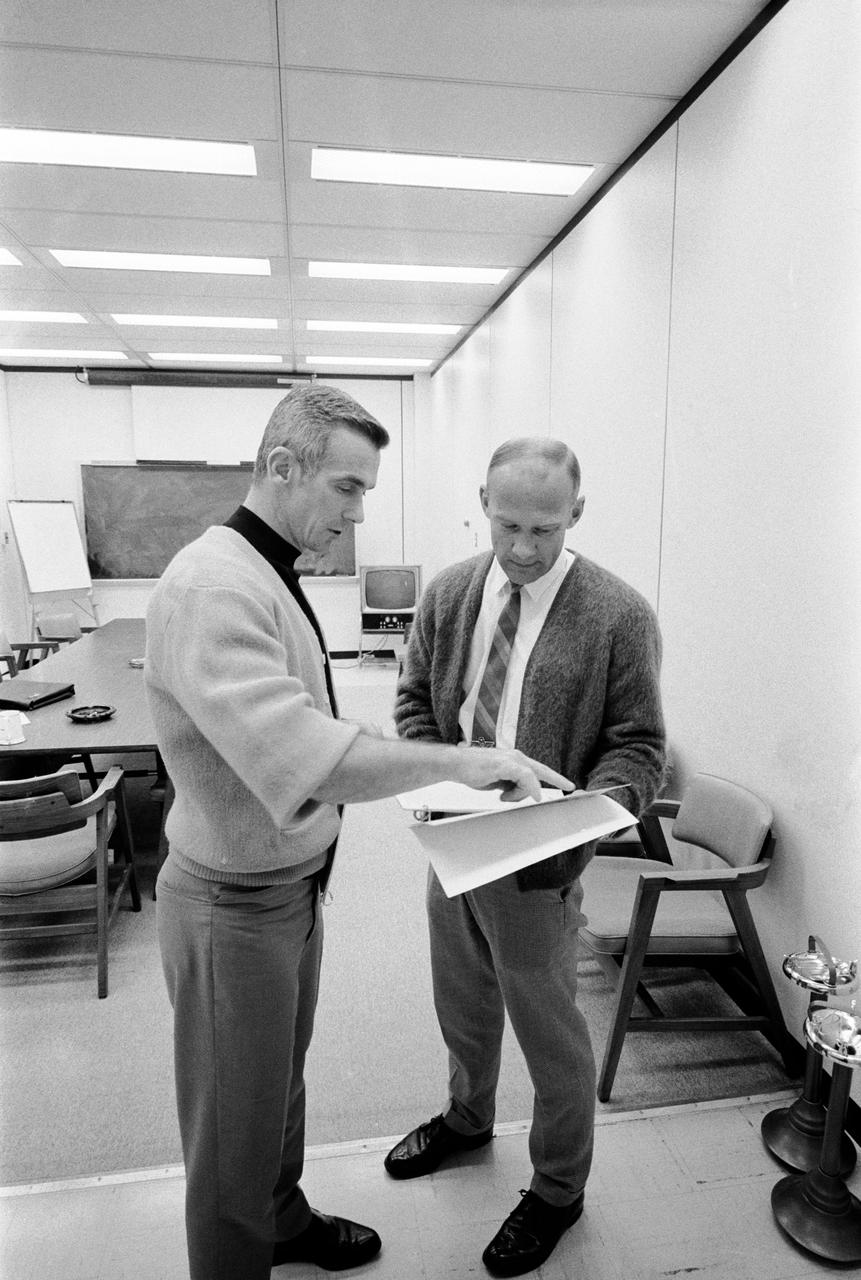

S69-35502 (June 1969) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan (left), lunar module pilot of the Apollo 10 lunar orbit mission, confers with astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during an Apollo 10 postflight de-briefing session. Aldrin is the lunar module pilot of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission.
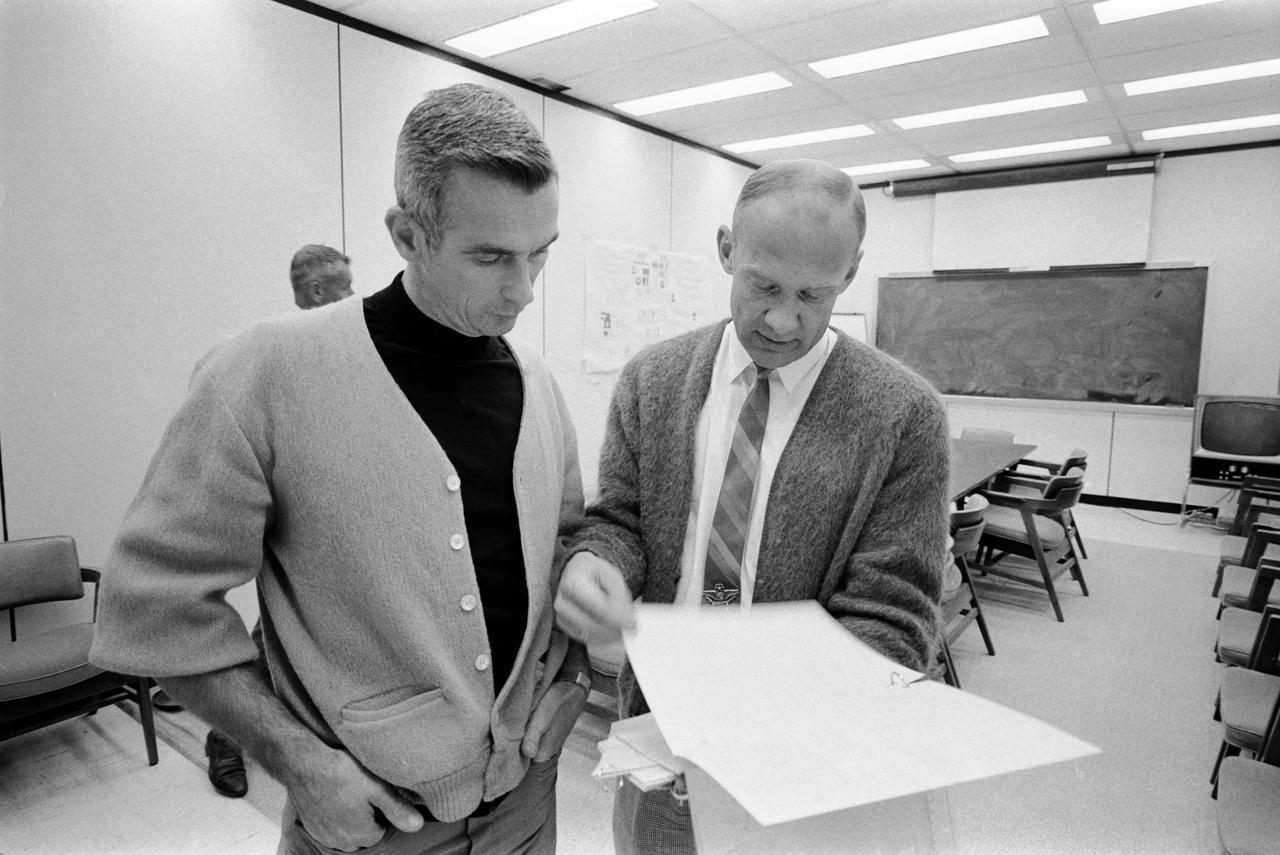

S69-35503 (June 1969) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan (left), lunar module pilot of the Apollo 10 lunar orbit mission, confers with astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during an Apollo 10 postflight de-briefing session. Aldrin is the lunar module pilot of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission.

Intrepid crater on Mars carries the name of the lunar module of NASA Apollo 12 mission, which landed on Earth moon Nov. 19, 1969. NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity recorded this stereo view on Nov. 11, 2010. 3D glasses are necessary.
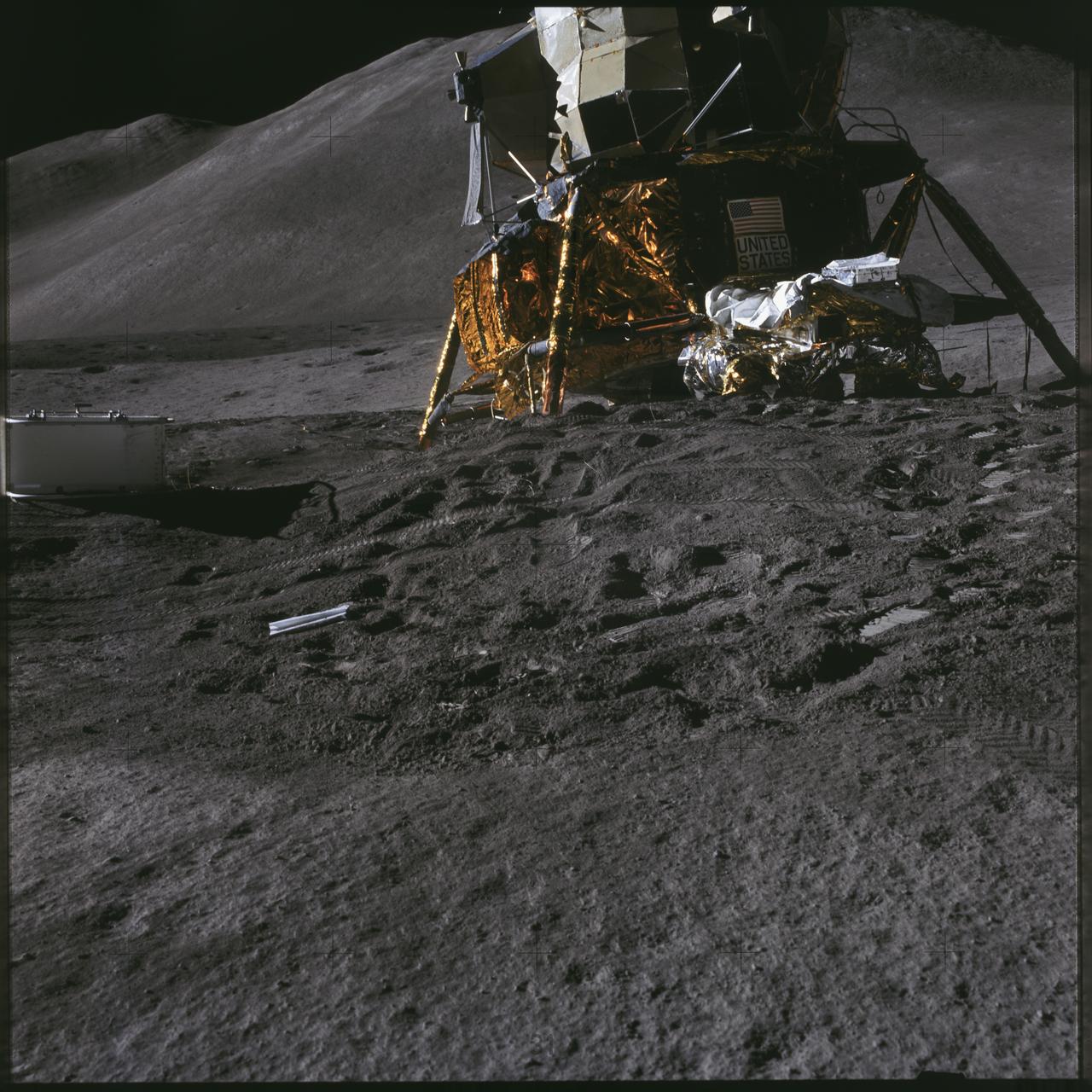

AS15-86-11600 (31 July 1971) --- A view of the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" taken early in the first Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site prior to deployment of lunar surface equipment. Hadley Delta Mountain is in the background. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
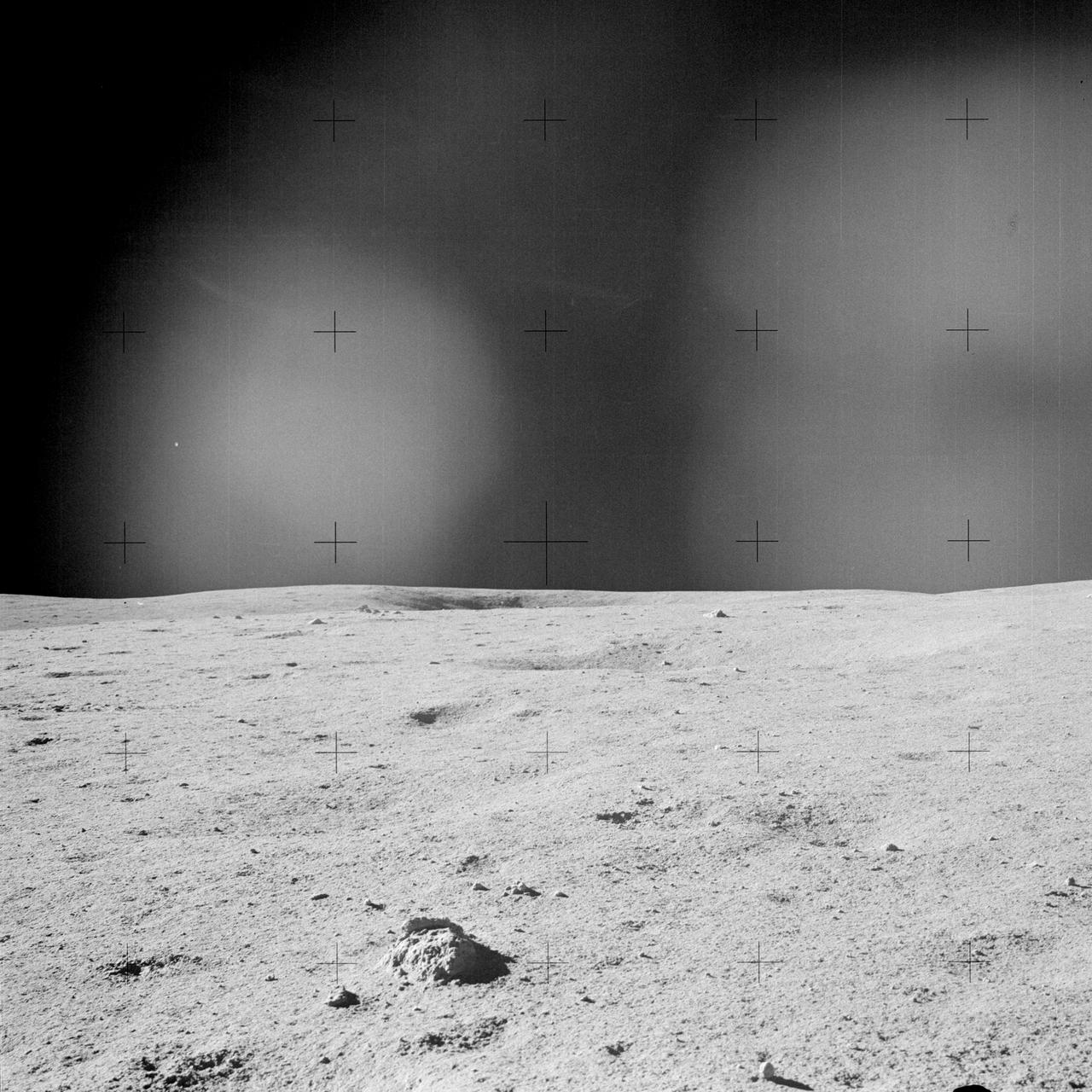

AS14-64-9181 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- A view of the lunar terrain at the Apollo 14 Fra Mauro landing site as photographed through the left window of the Lunar Module (LM). Note the clump of lunar soil in the foreground, and a crater in the center on the horizon. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
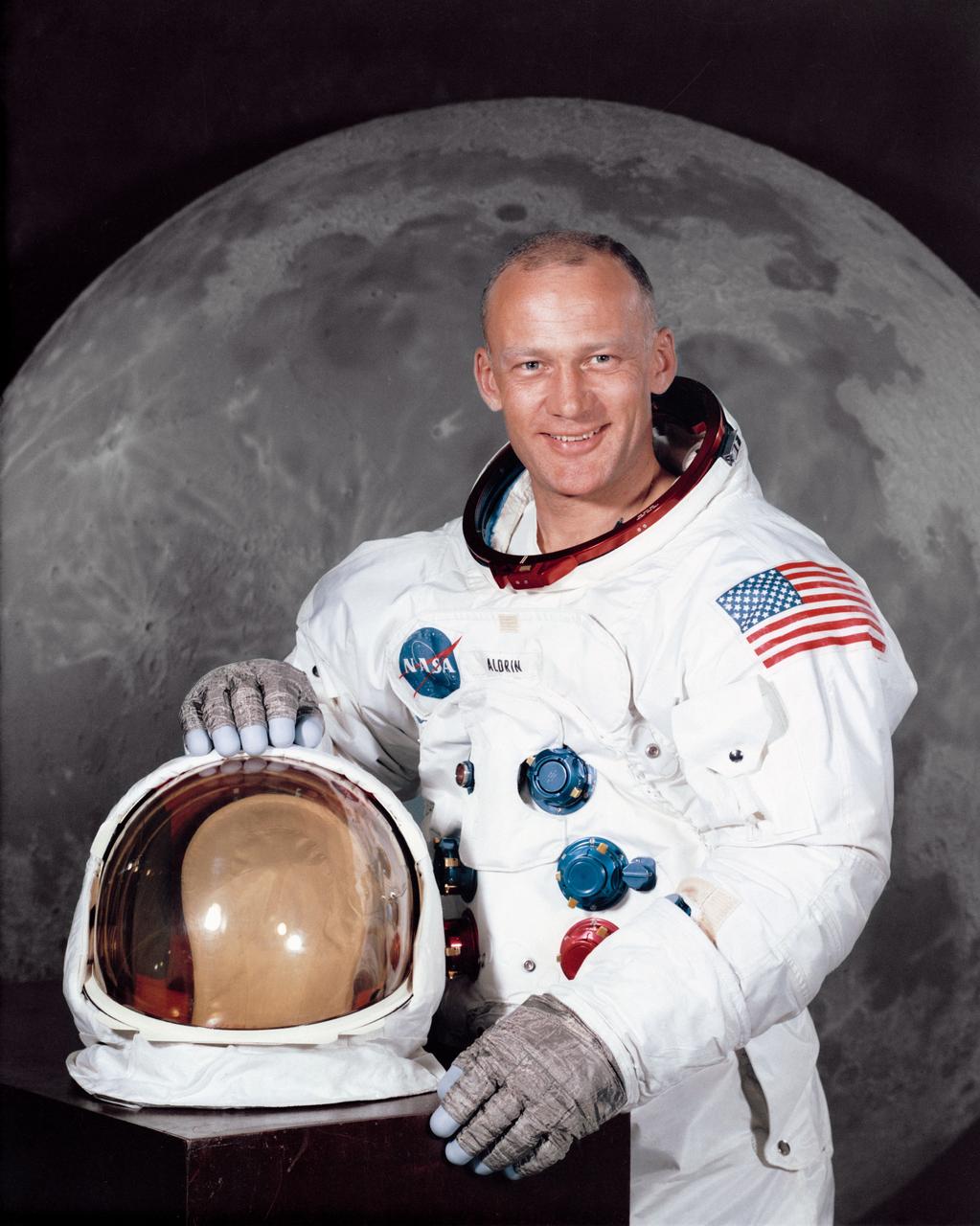

S69-31743 (July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. EDITOR'S NOTE: Aldrin was lunar module pilot of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission.
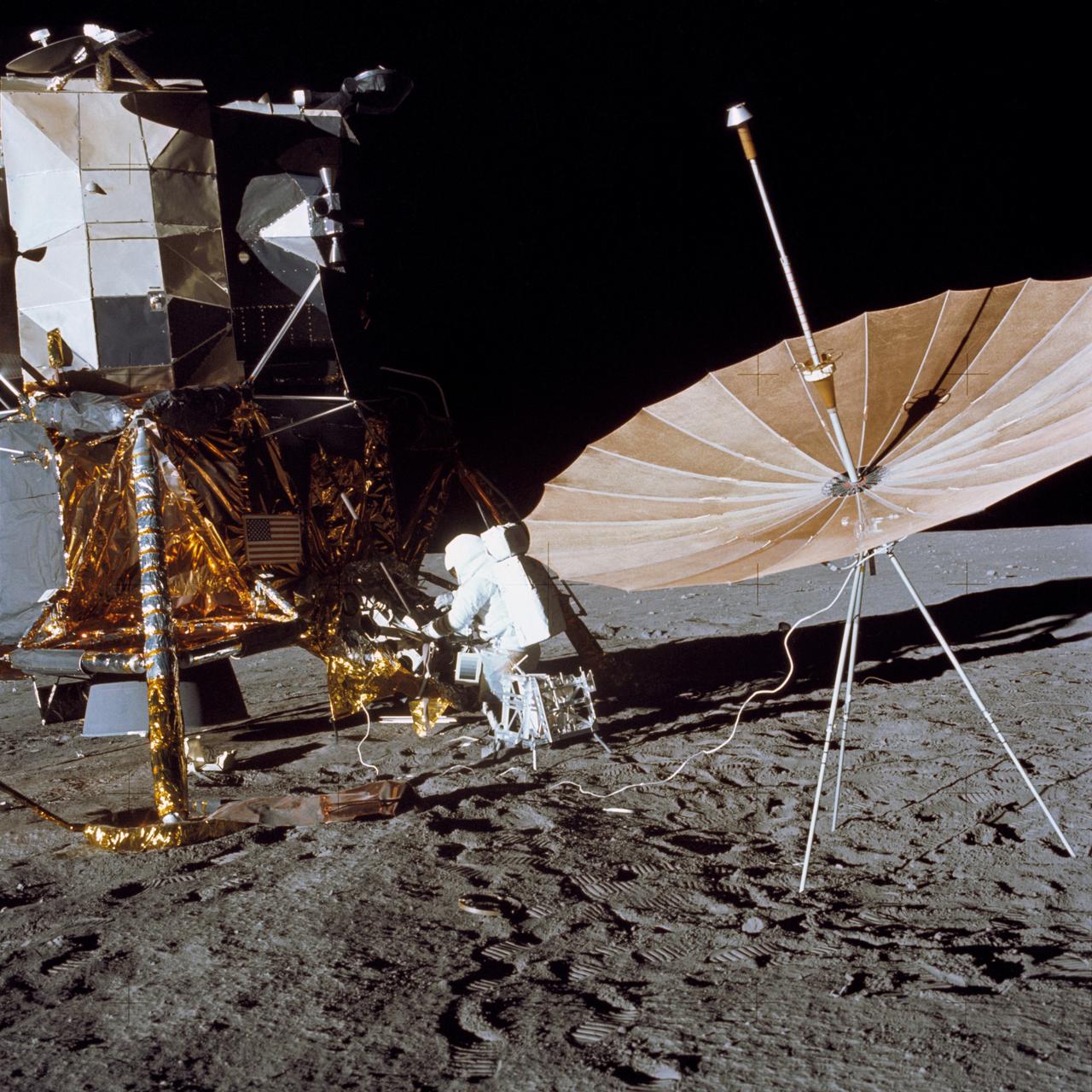

AS12-47-6988 (19 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, stands at the Module Equipment Stowage Assembly (MESA) on the Lunar Module (LM) following the first Apollo 12 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The erectable S-band antenna is already deployed at right. The carrier for the Apollo Lunar Hand Tools (ALHT) is near Conrad. While astronauts Conrad and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
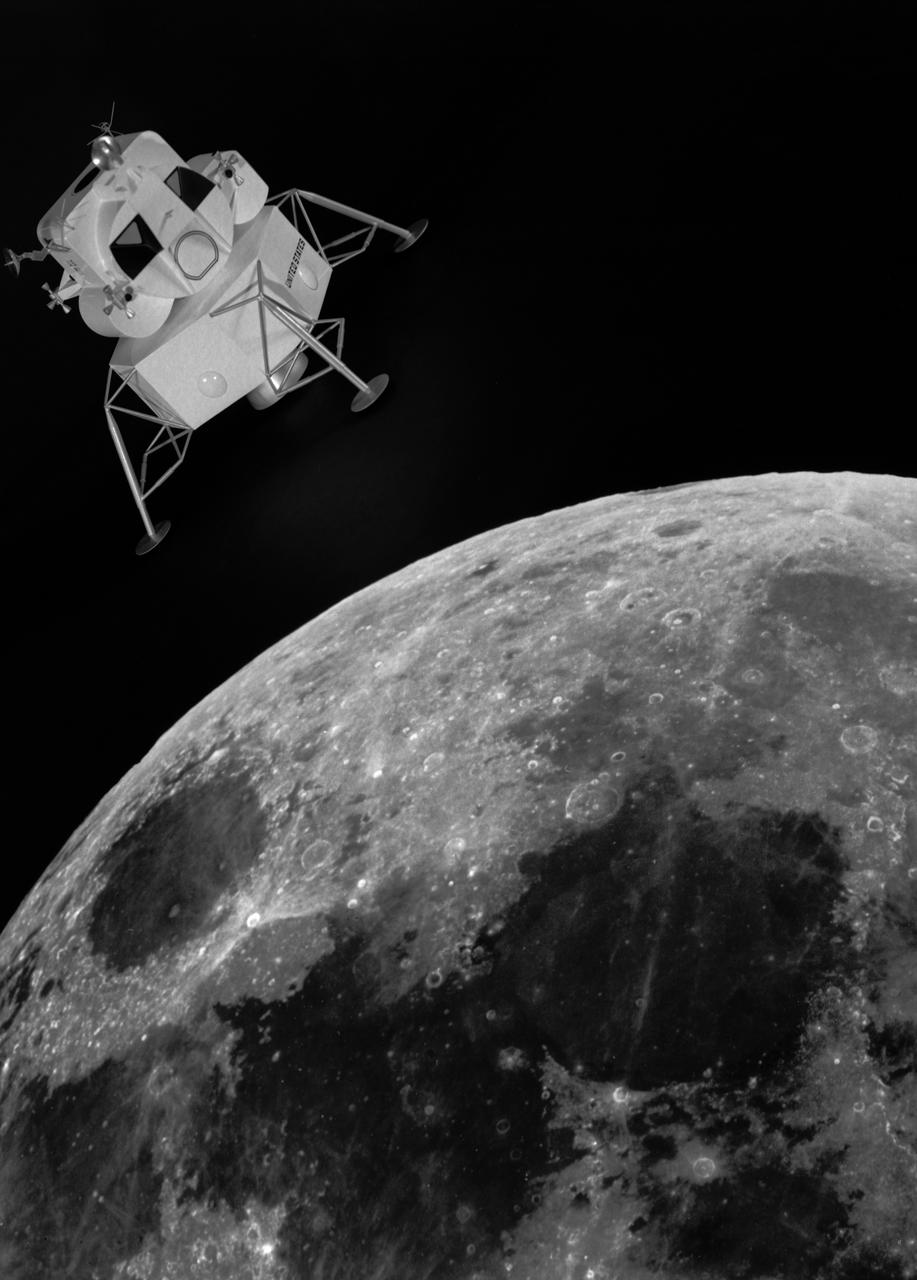

Artist rendering of the lunar excursion module approaching the moon. The lunar module design underwent gradual evolution from the first configuration proposed by Grumman in 1962. This model is a 1964 rendering. Langley had the task of building a simulator for the astronauts to practice lunar landings. The configuration of the initial vehicle used with the Lunar Landing Research Facility (LLRF) was changed in 1967 to more accurately reflect the standing position of the astronauts, cockpit arrangement, instrumentation, controls and field of view.
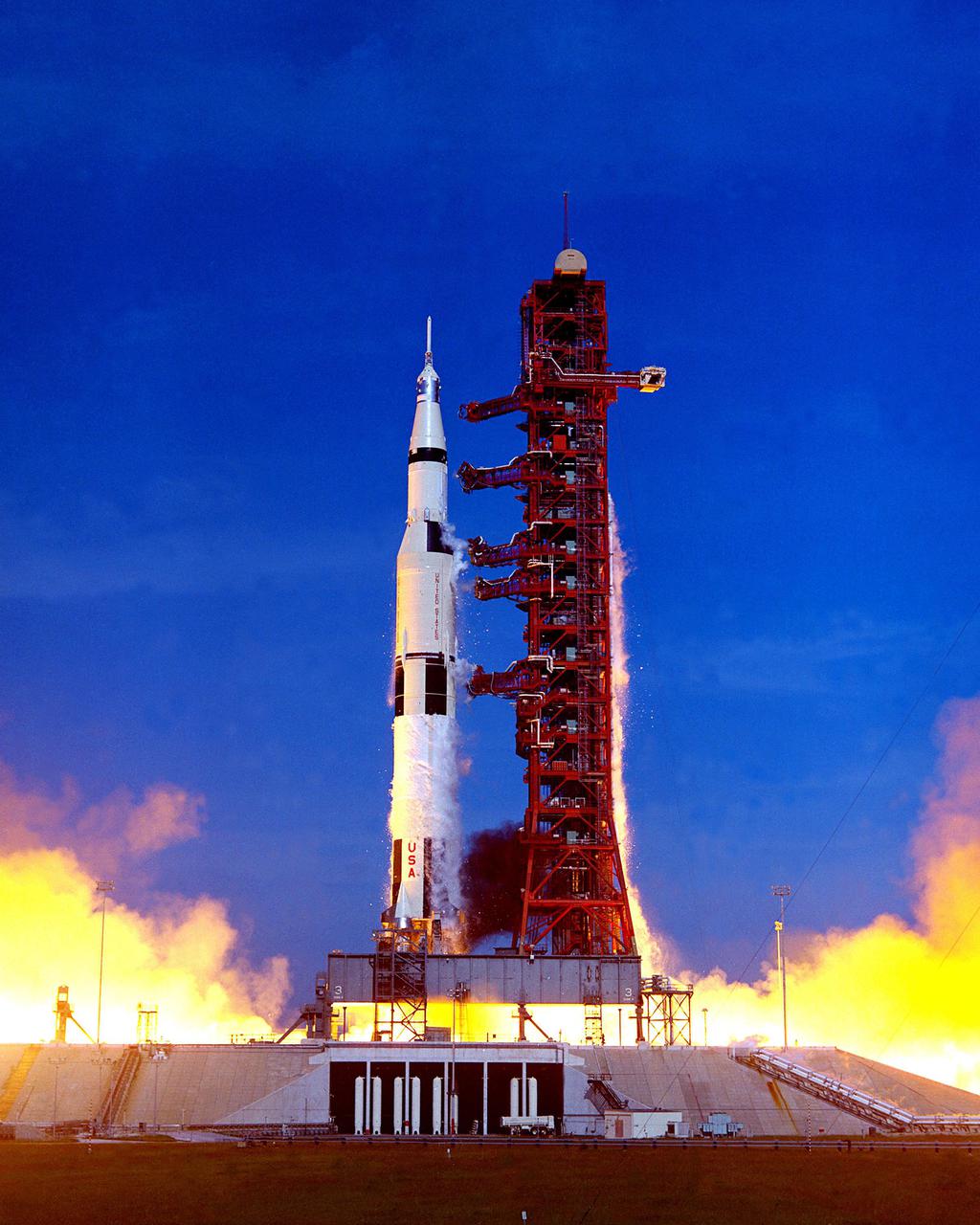

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Apollo 15 Saturn V Space Vehicle soars into the skies after liftoff at Launch Pad 39A marking the beginning of NASA's fourth Manned Lunar Landing Mission. The astronauts aboard are David R. Scott, commander; James B. Irwin, Lunar Module pilot; and Alfred M. Worden Jr., Command Module pilot. The landing site for the Lunar Module is the Hadley-Apennine area of the Moon, about 465 miles north of the Lunar Equator. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) will be used for the first time.
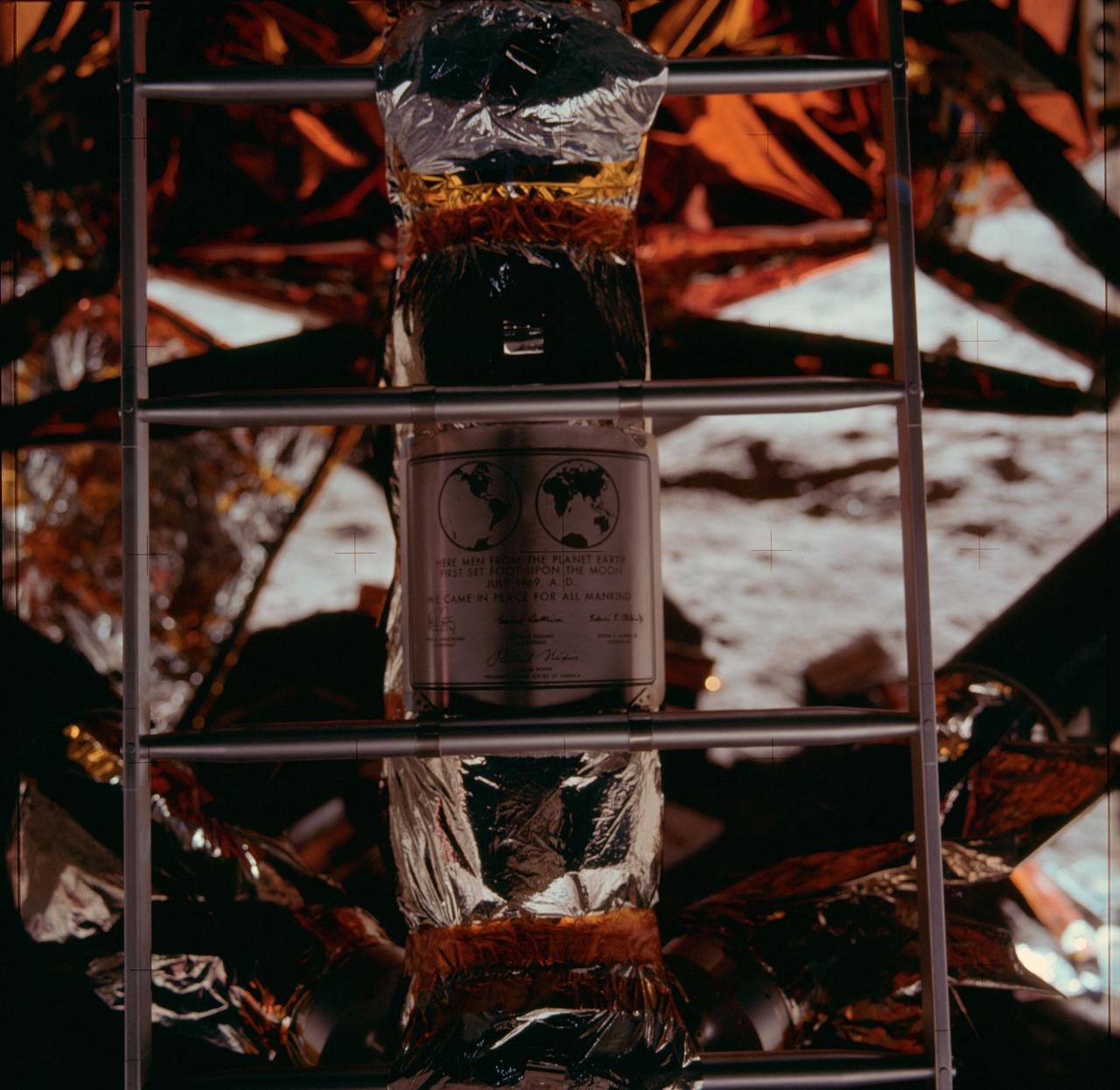

AS11-40-5899 (20 July 1969) --- Close-up view of the plaque which the Apollo 11 astronauts left on the moon in commemoration of the historic lunar landing mission. The plaque was attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the descent stage of the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM). The plaque was covered with a thin sheet of stainless steel during flight. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, explored the moon.
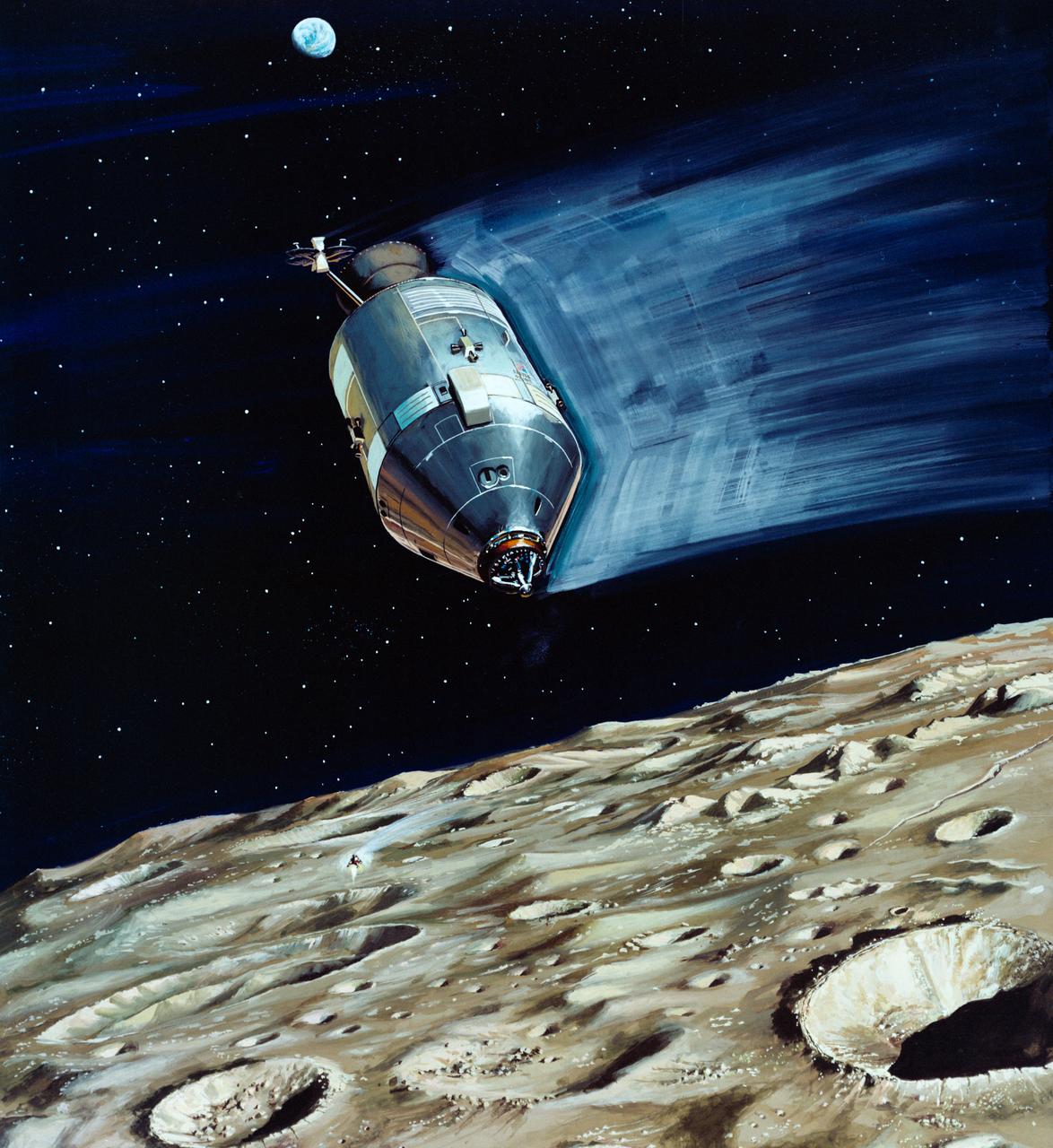

S70-31898 (March 1970) --- A North American Rockwell artist?s concept depicting the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM) descending to the Fra Mauro landing site as the Command and Service Module (CSM) remains in lunar orbit. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, will photograph the LM?s descent from the CSM. Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander, and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, will descend in the LM to explore the moon. Apollo 13 will be NASA?s third lunar landing mission.
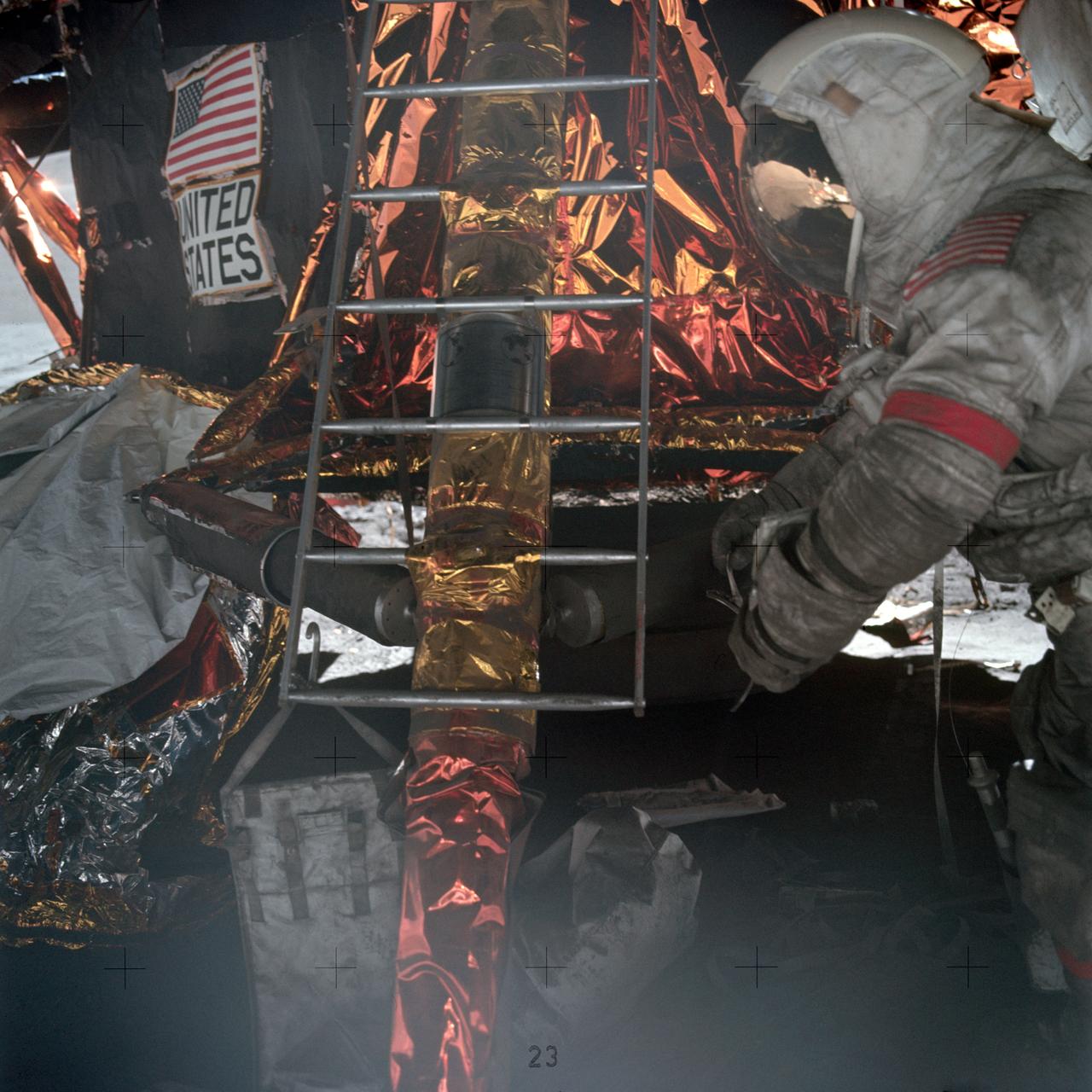

Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander, prepares to mount ladder to lunar module ascent stage. Note the plaque attached to the ladder which will be left with the descent stage when the mission lifts off from the lunar surface.
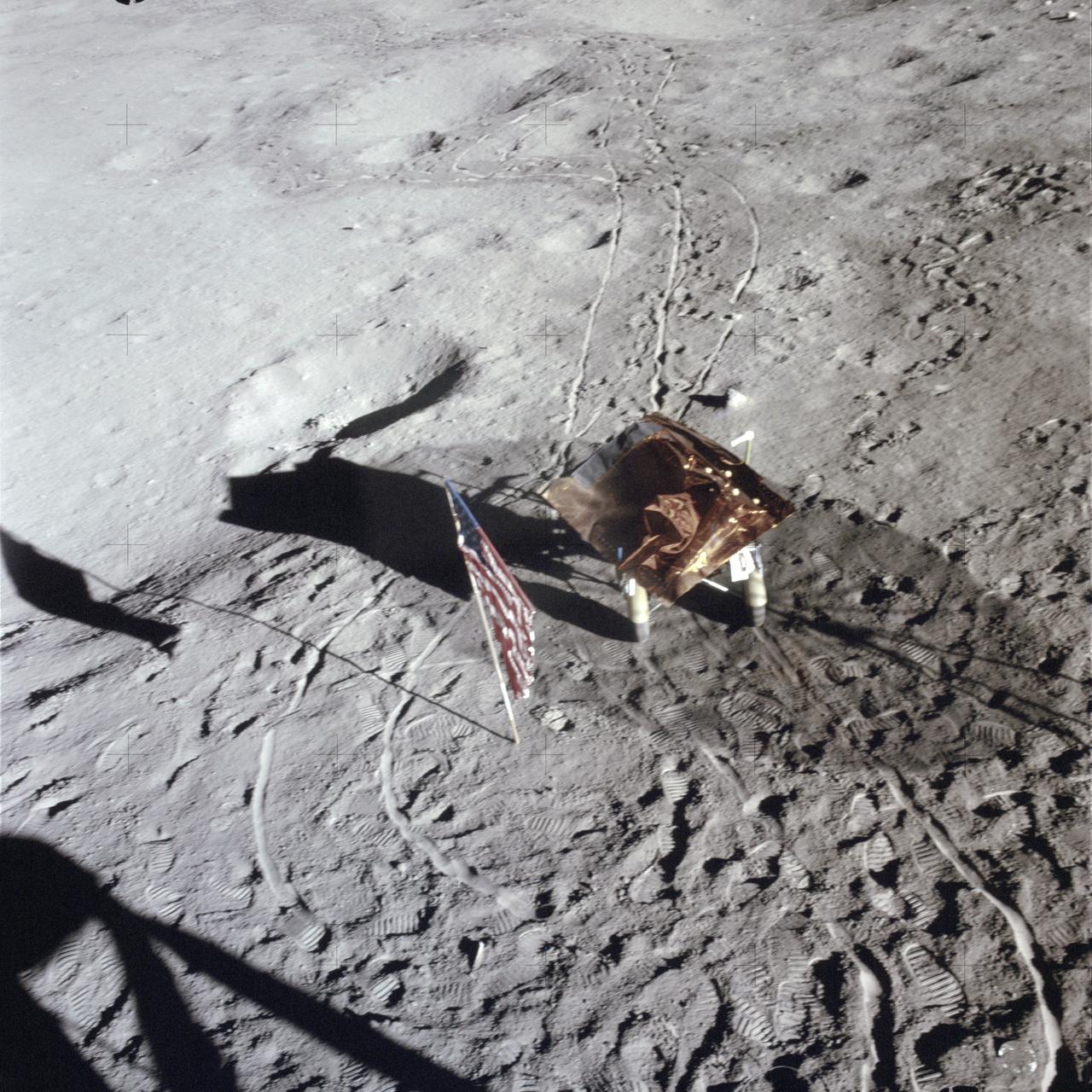

AS14-66-9325 (5 Feb. 1971) --- The third United States flag to be deployed on the lunar surface, footprints, wheel tracks and the "Rickshaw"-type portable workbench, as seen by the two moon-exploring astronauts from inside the Lunar Module (LM), give evidence of a busy first extravehicular activity (EVA) period. The two-wheeled cart is the Apollo modularized equipment transporter (MET), covered with a sheet of foil material to protect the cameras and rock box between EVAs. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
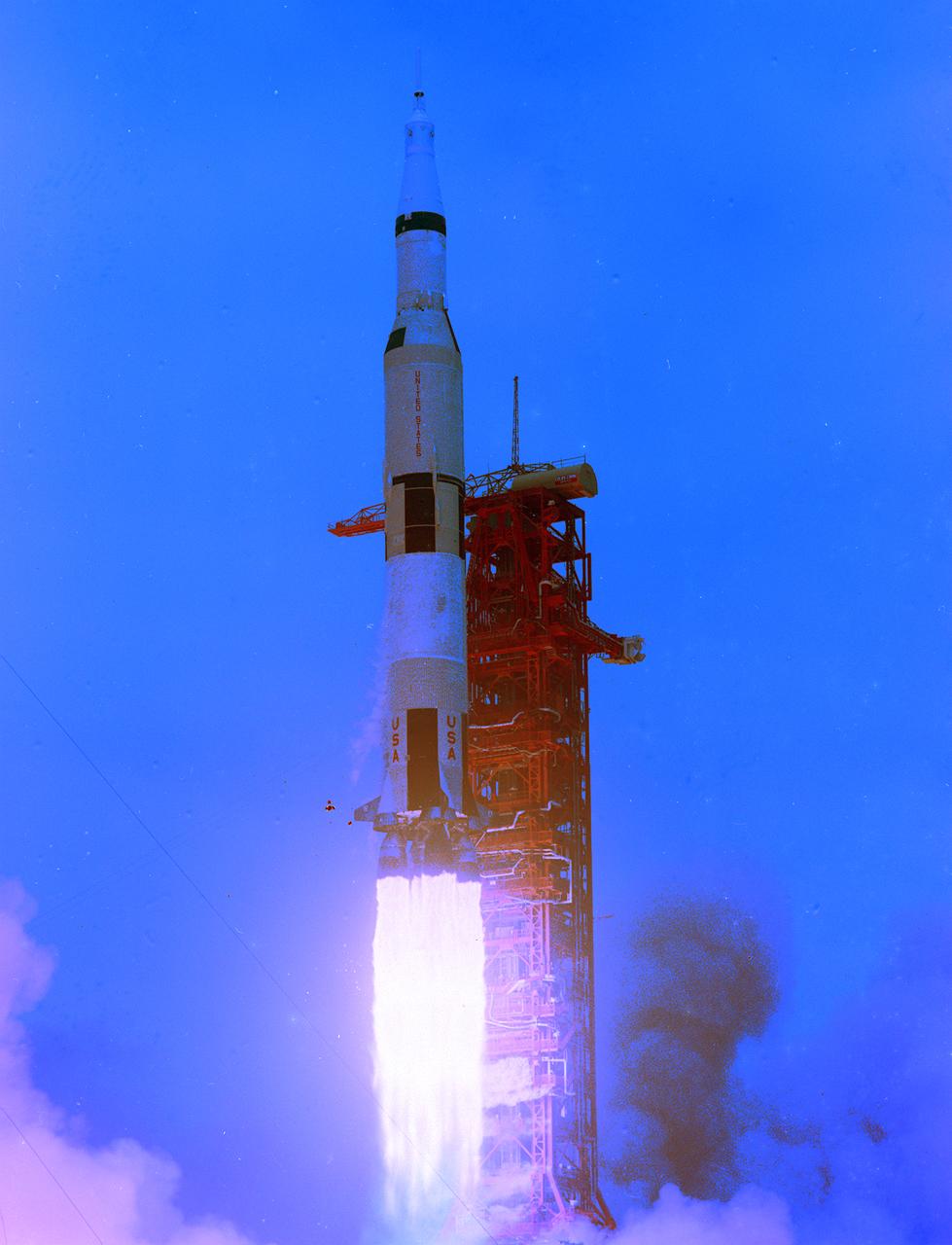

The fifth launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle (SA-505), the Apollo 10 mission with astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, John W. Young, and Eugene A. Cernan, occurred on May 18, 1969. The crew performed the first lunar orbit rendezvous, and the lunar landing mission profile was performed except for powered descent, landing, and ascent of the Lunar Module. The mission objectives were to rehearse all the steps and reproduce all the events of the Apollo 11, the first lunar landing mission, with the exception of the lunar touchdown, stay, and liftoff.
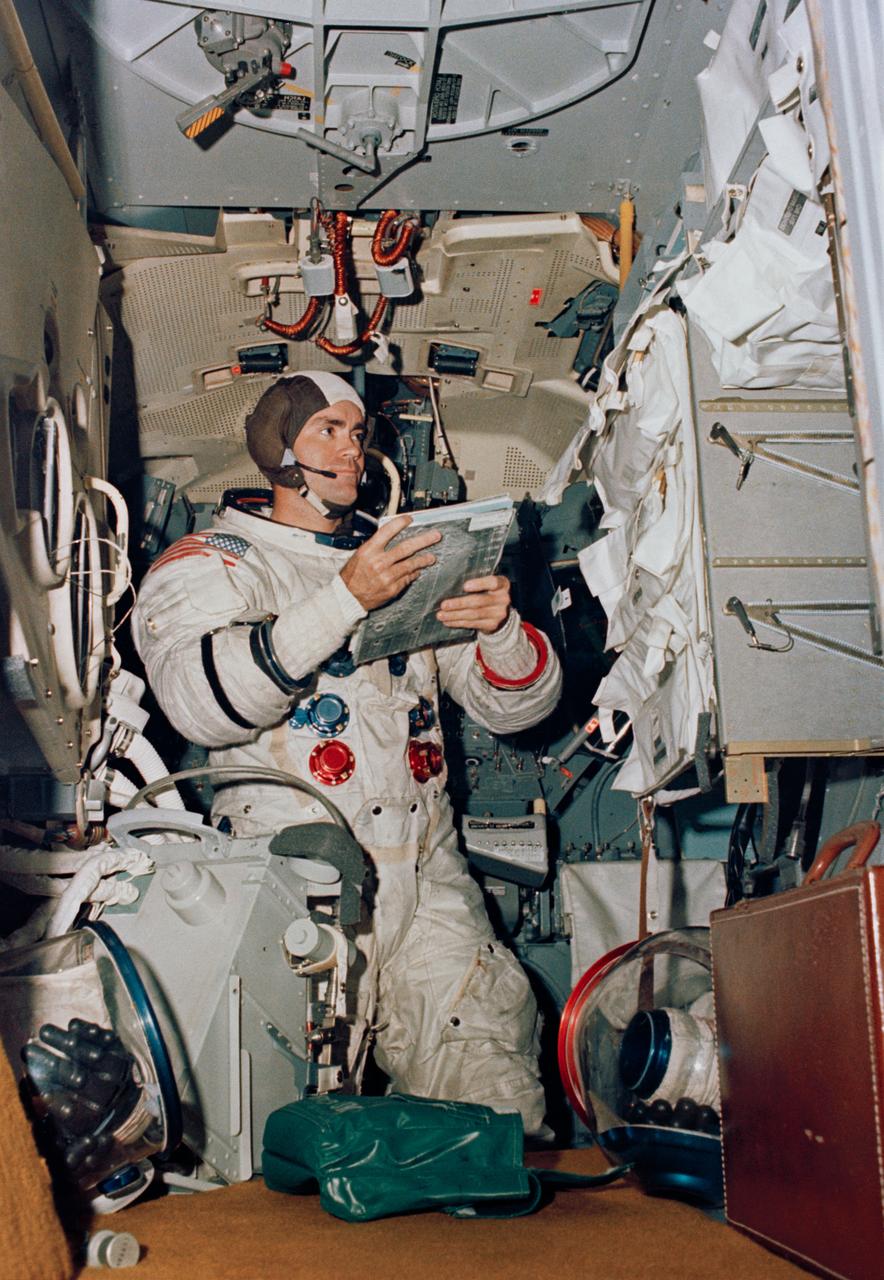

S70-34412 (4 April 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., Apollo 13 lunar module pilot, participates in simulation training in preparation for the scheduled lunar landing mission. He is in the Apollo Lunar Module Mission Simulator in the Kennedy Space Center's Flight Crew Training building.
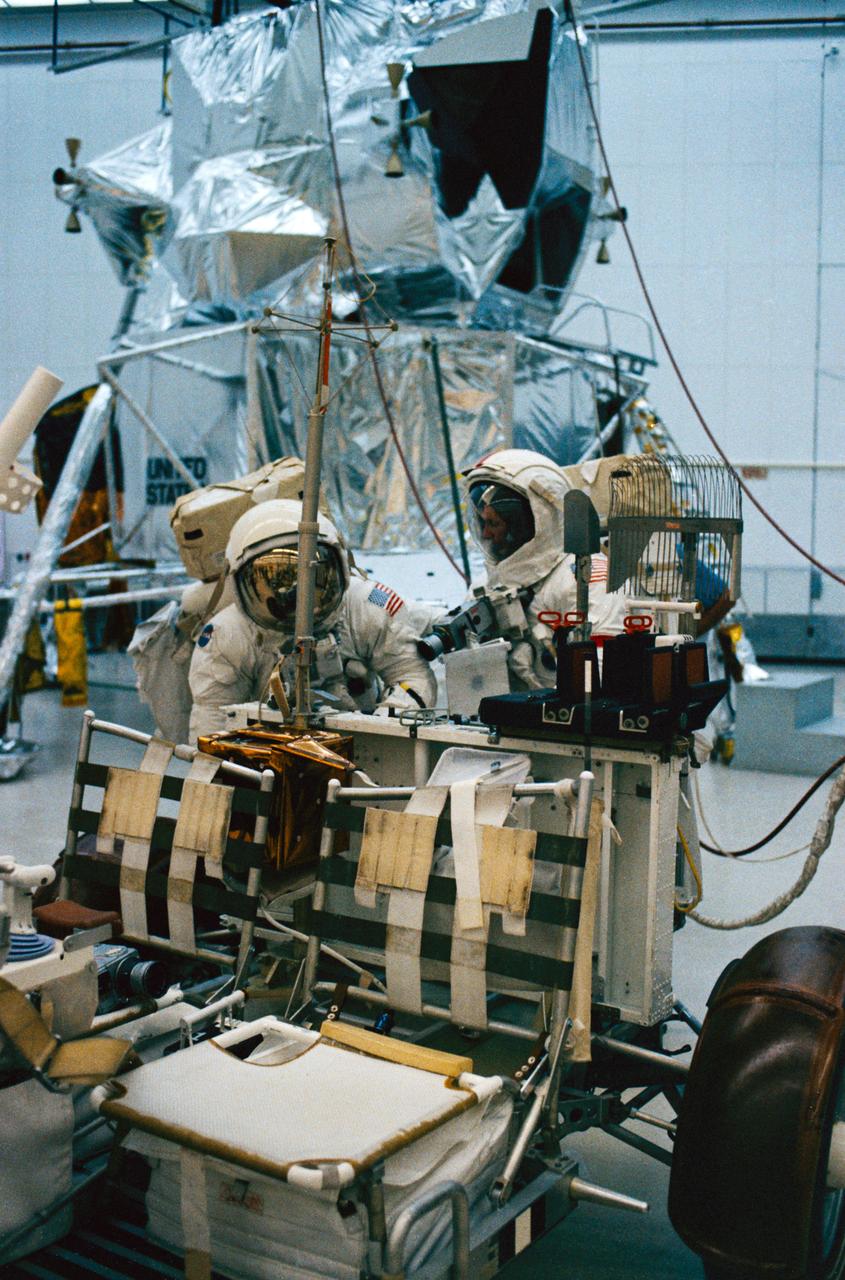
S72-48887 (September 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan (right), commander, and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, work at the aft end of a Lunar Roving Vehicle trainer during lunar surface extravehicular activity simulation training at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida. Astronauts Cernan, Schmitt, and Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, are the prime crewmen of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. A Lunar Module mock-up can be seen in the background.
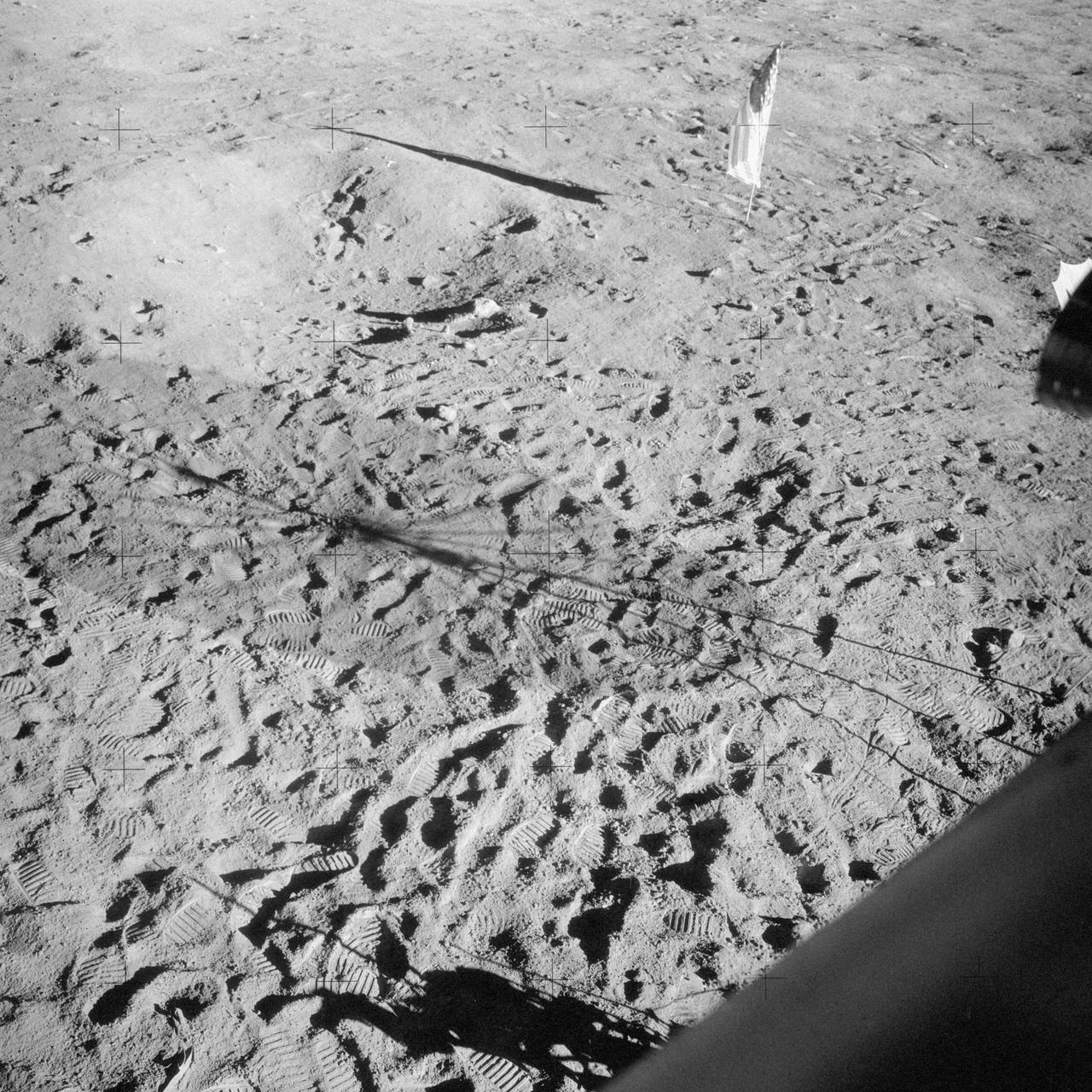

AS12-48-7160 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- This view of the lunar surface was taken by one of the two astronauts on the Apollo 12 mission during their extravehicular activity. Seen in this view are the U.S. flag, several astronaut footprints, and a small crater near their Lunar Module landing site. Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the lunar surface. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.
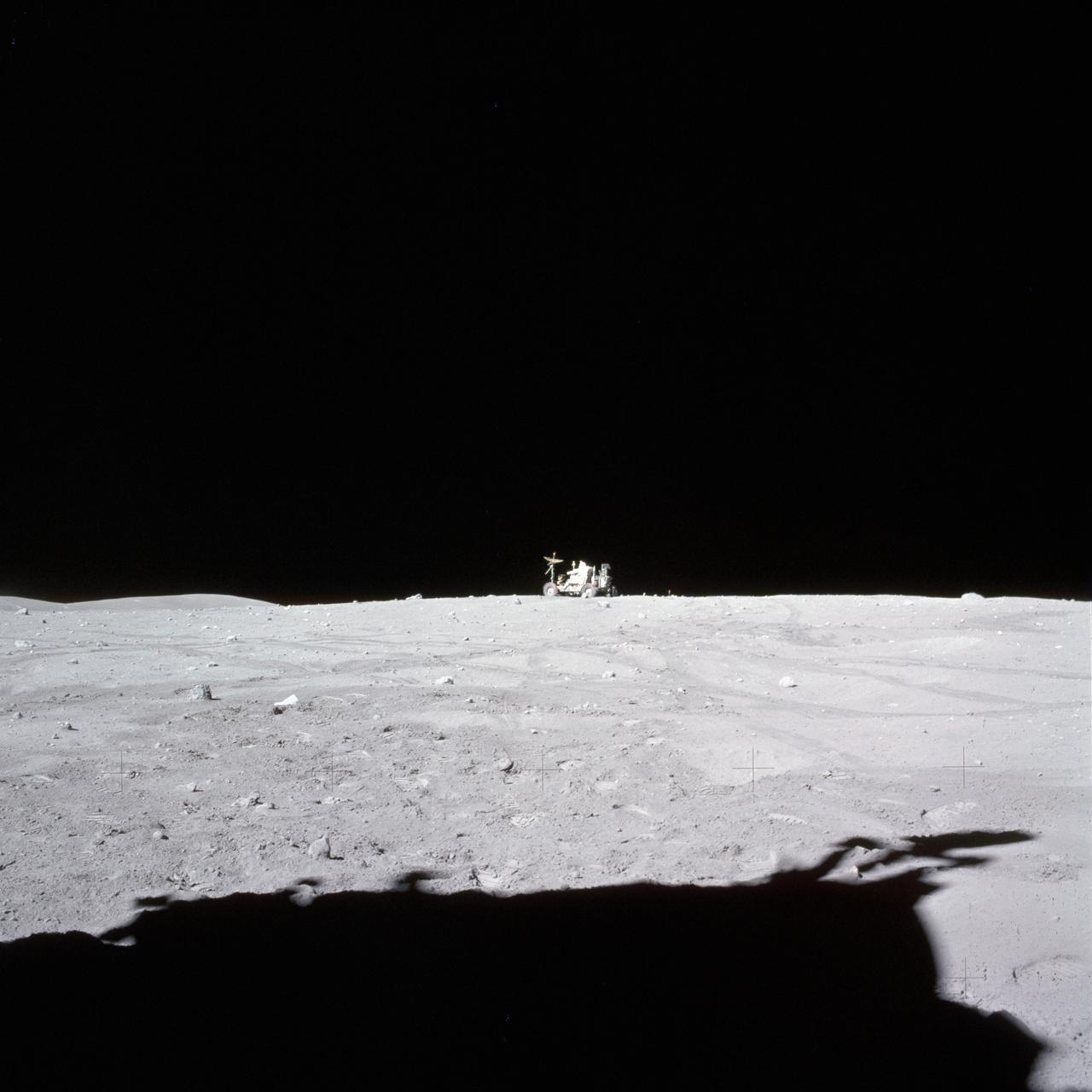

AS16-115-18559 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, drives the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) to its final parking place near the end of the third Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, took this photograph looking southward. The flank of Stone Mountain can be seen on the horizon at left. The shadow of the Lunar Module (LM) occupies much of the picture. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 LM "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
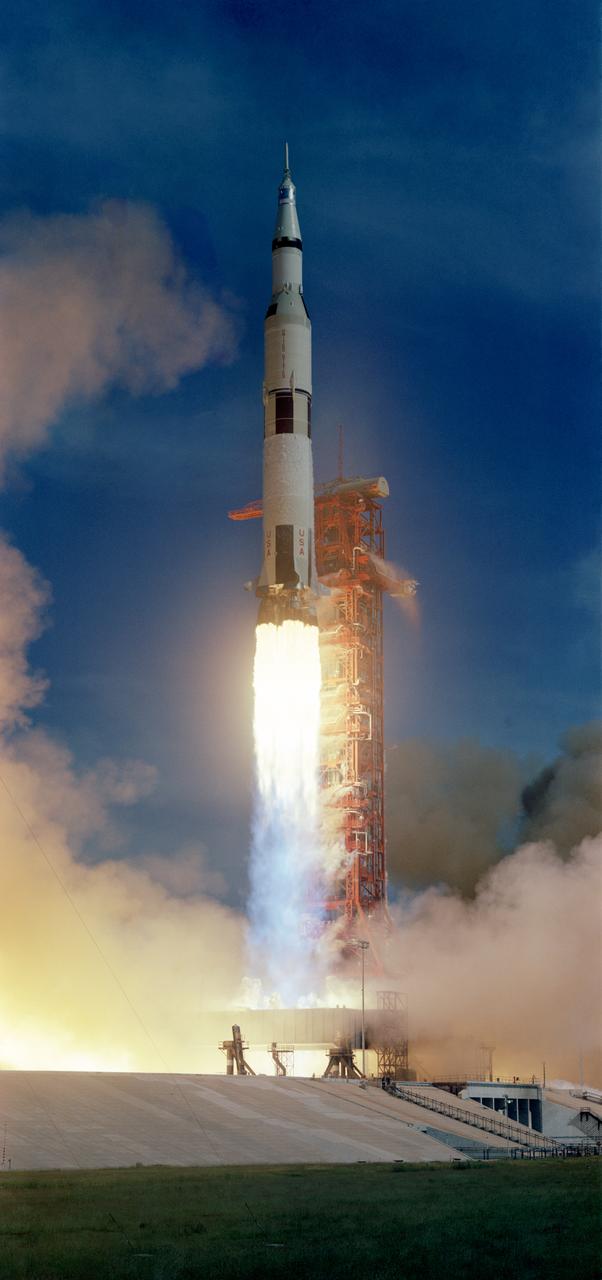

S71-41356 (26 July 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 15 (Spacecraft 112/Lunar Module 10/Saturn 510) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida, at 9:34:00:79 a.m. (EDT), July 26, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. Aboard the Apollo 15 spacecraft were astronauts David R. Scott, commander; Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. Apollo 15 is the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) fourth manned lunar landing mission. While astronauts Scott and Irwin will descend in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Worden will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
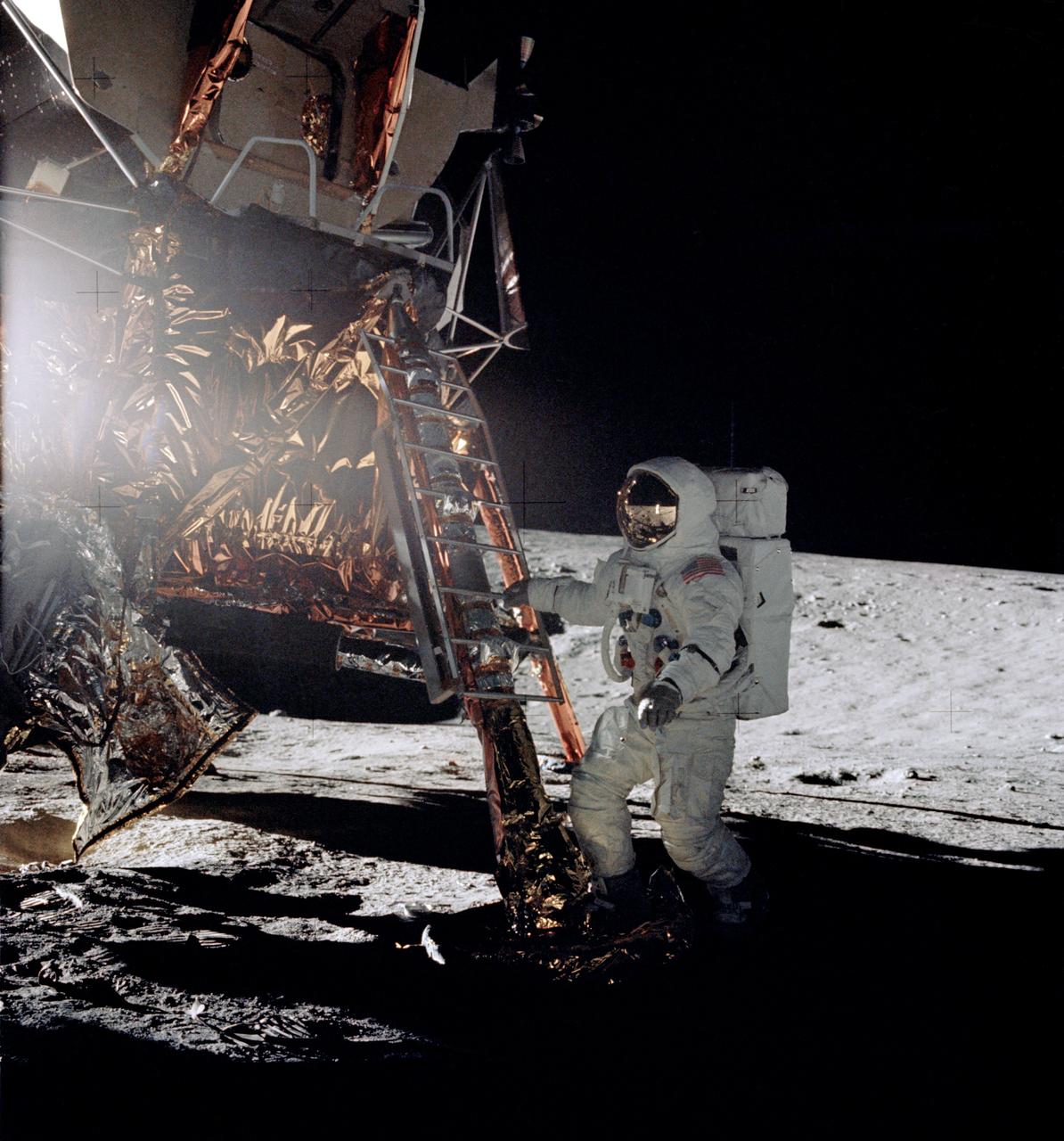

AS12-46-6729 (19 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot for the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, steps from the ladder of the Lunar Module to join astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, in extravehicular activity on Nov. 19, 1969. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.

S72-16660 (January 1972) --- These three astronauts have been selected by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as the prime crew men of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission. They are, left to right, Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot; John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot. While astronauts Young and Duke descend in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Mattingly will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
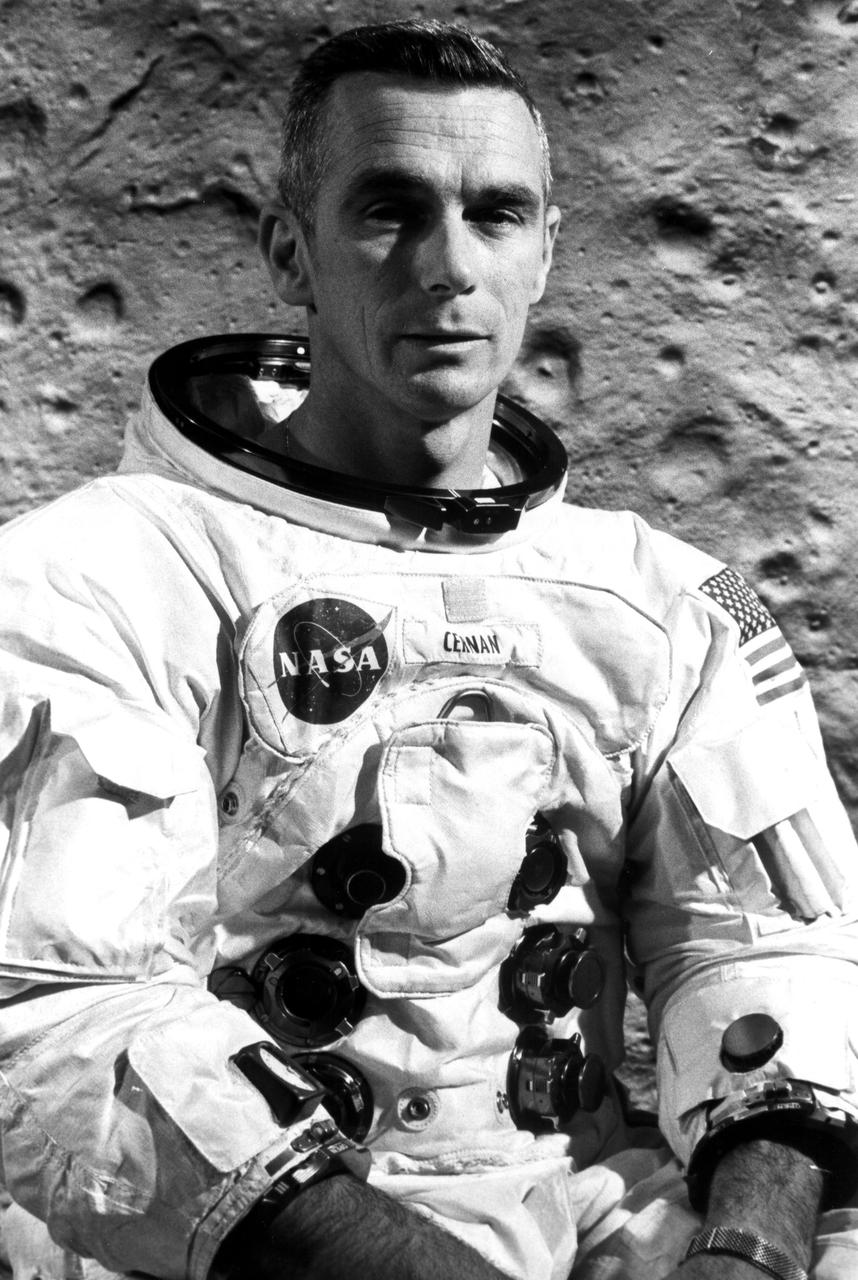

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan is lunar module pilot for Apollo 10, scheduled for launch from the nation's spaceport on May 18. Cernan and Apollo 10 Commander Thomas P. Stafford are to detach the lunar module after the spacecraft enters lunar orbit and drop down to within 10 miles of the Moon's pockmarked surface before rejoining John W. Young, command module pilot, orbiting the Moon in the command_service module. The Apollo 10 mission is a dress rehearsal for a manned lunar landing later this year.
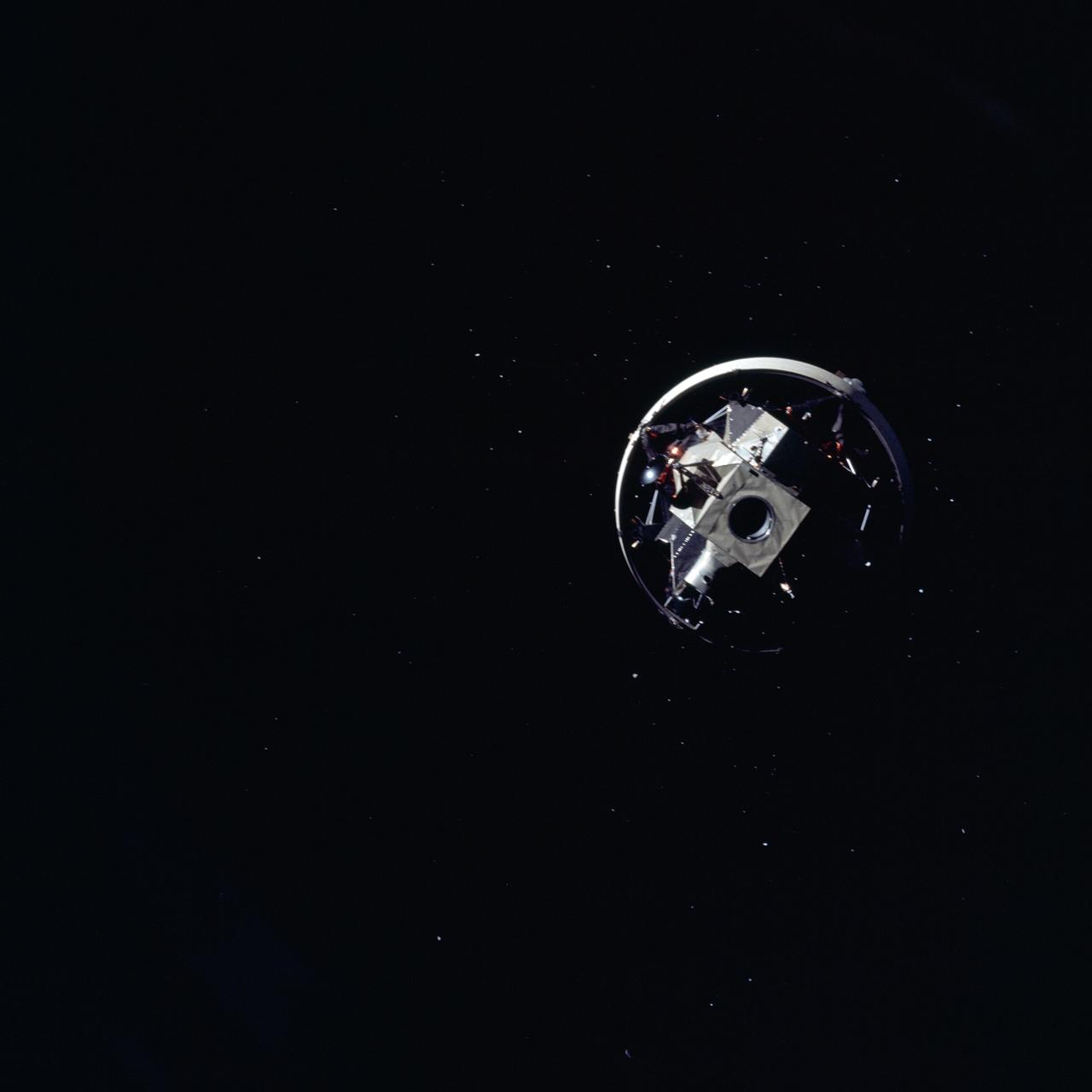

AS12-50-7328 (14 Nov. 1969) --- Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM), still attached to the Saturn V third (S-IVB) stage, is pictured as seen from Apollo 12 Command and Service Modules (CSM) on the first day of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission. This photograph was taken following CSM separation from LM/S-IVB and prior to Lunar Module extraction from the S-IVB stage. The Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter (SLA) panels have already been jettisoned.
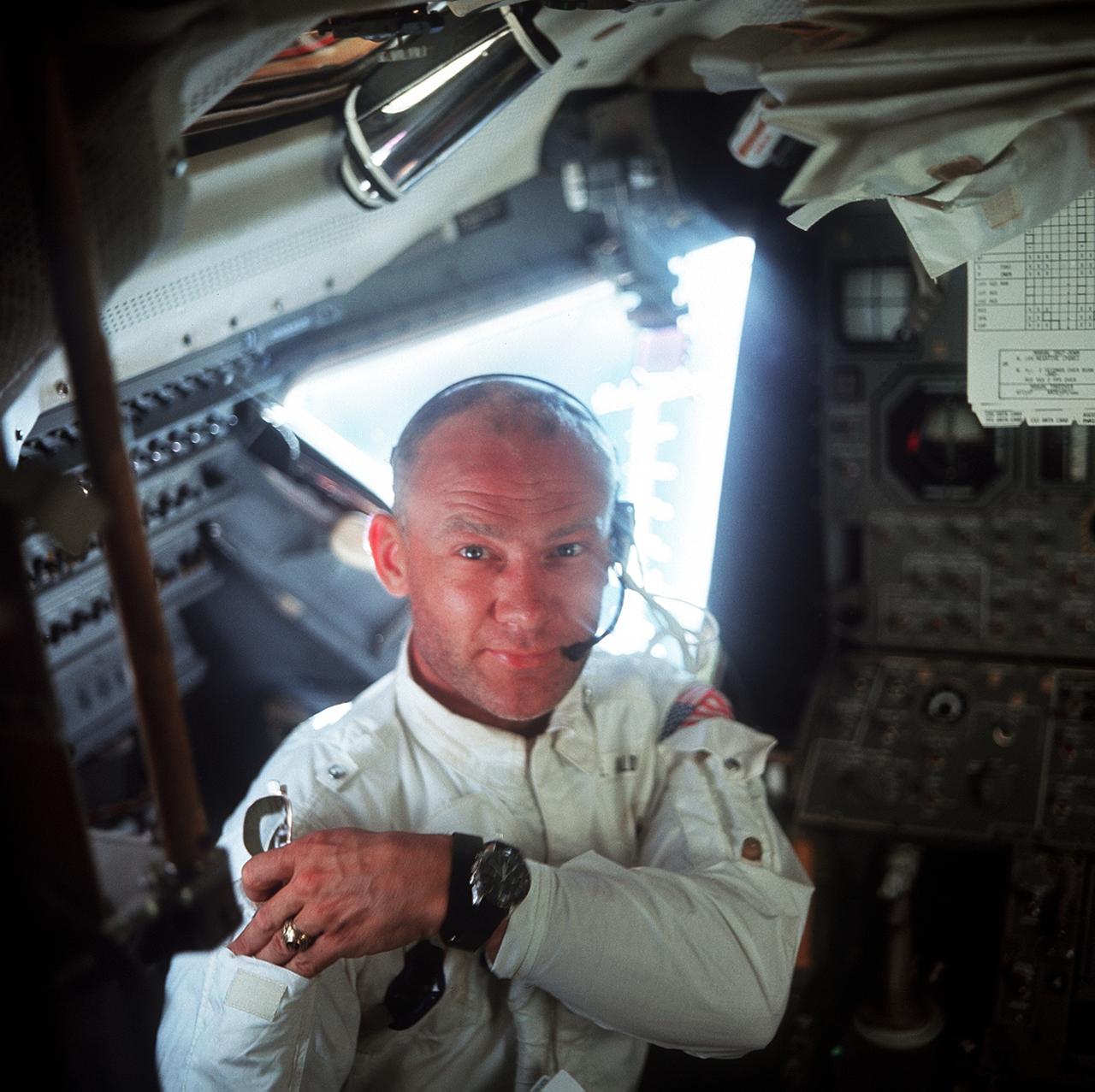

AS11-36-5390 (20 July 1969) --- This interior view of the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) shows astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, during the lunar landing mission. This picture was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
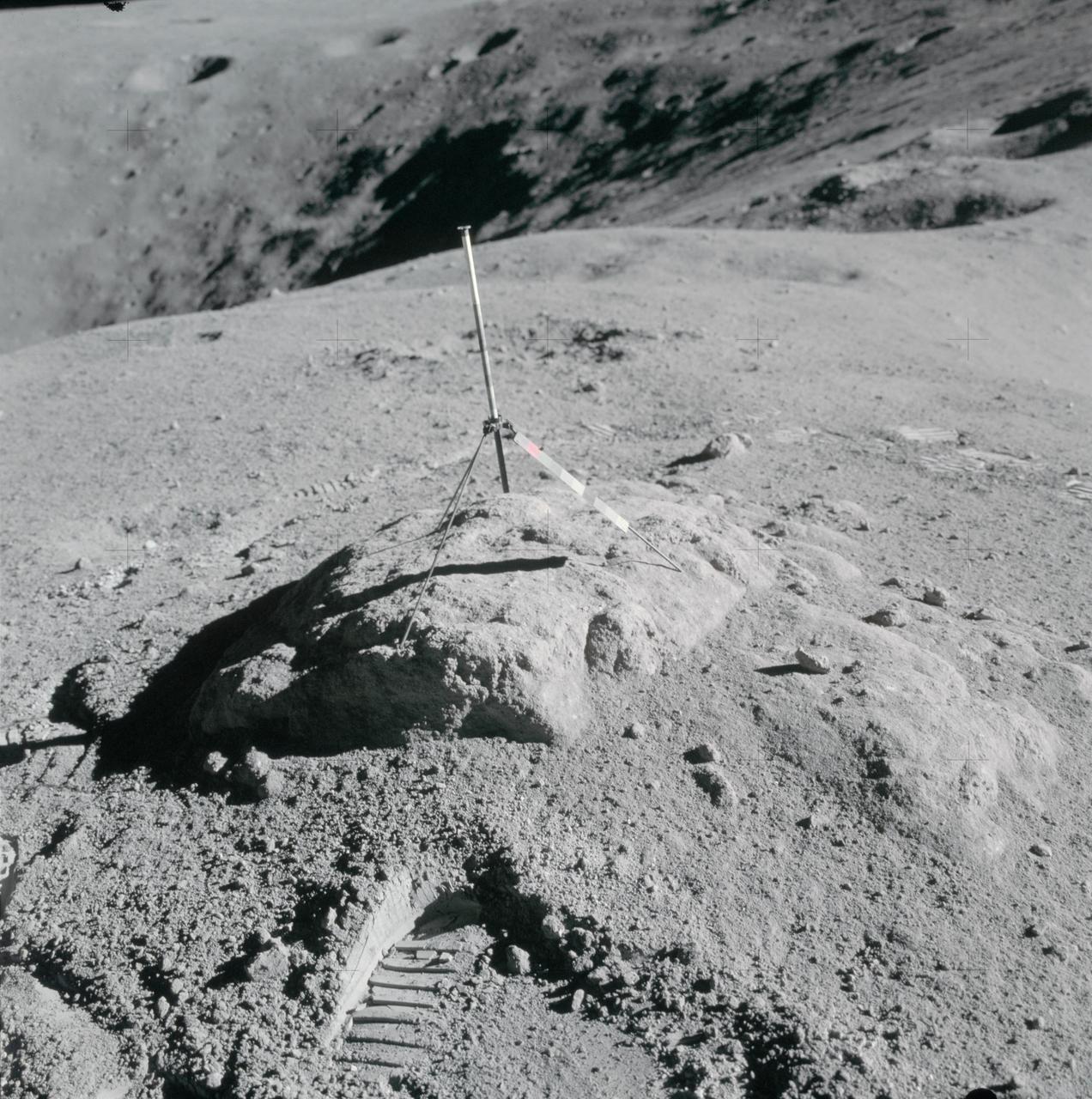

AS16-114-18412 (16-27 April 1972) --- The gnomon and color patch, one of the Apollo Lunar Hand Tools (ALHT), is deployed atop a lunar rock, in this photograph taken by one of the Apollo 16 astronauts during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. The gnomon is used as a photographic reference to establish local vertical sun angle, scale, and lunar color. The color patch, mounted on one of the legs of the tripod, provides a larger target for accurately determining colors in color photography. A portion of Flag Crater can be seen in the background. While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
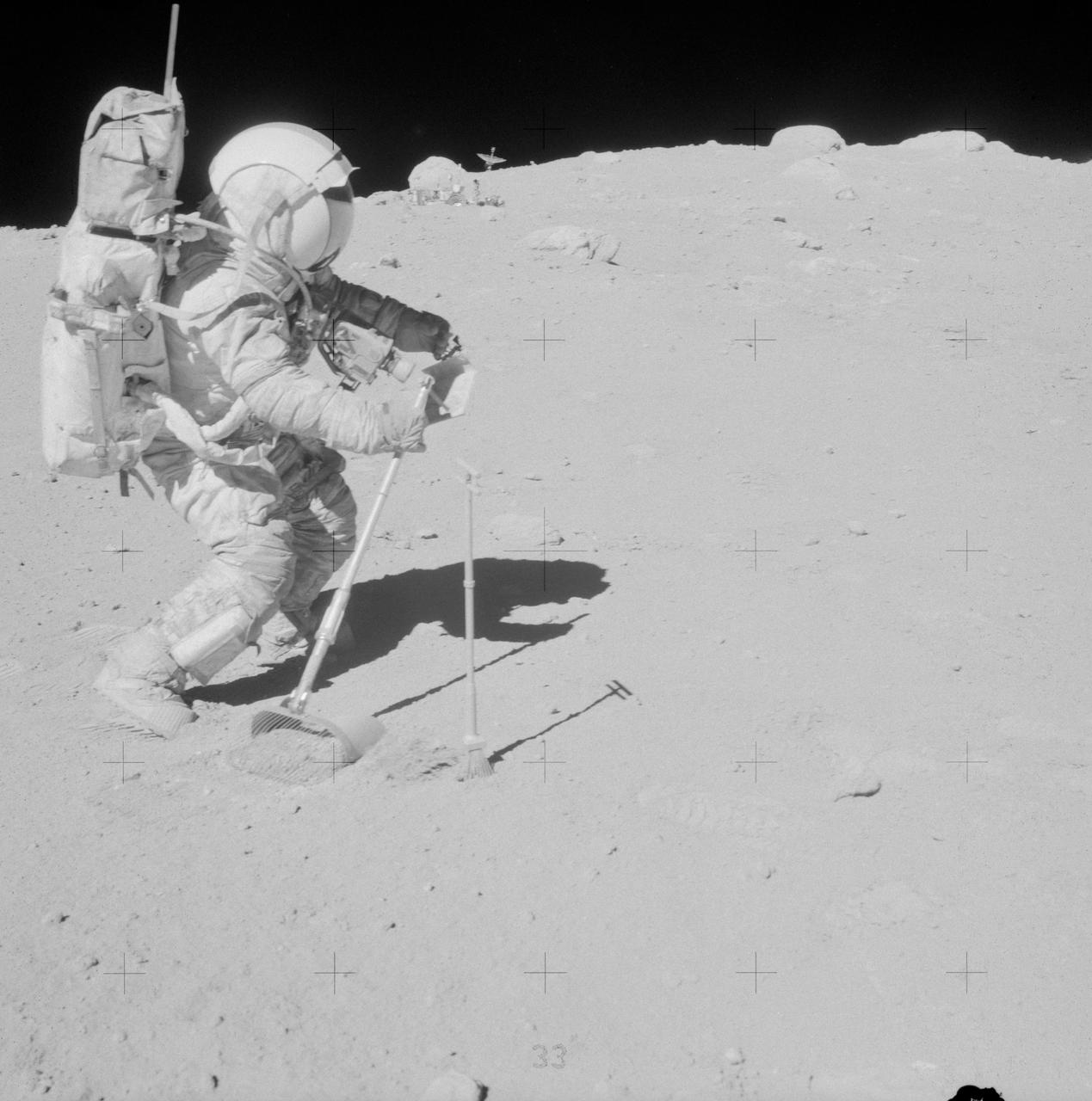

AS16-106-17340 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, is photographed collecting lunar samples near North Ray Crater during the third Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. This picture was taken by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot. Young is using the lunar surface rake and a set of tongs. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is parked in the field of large boulders in the background. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
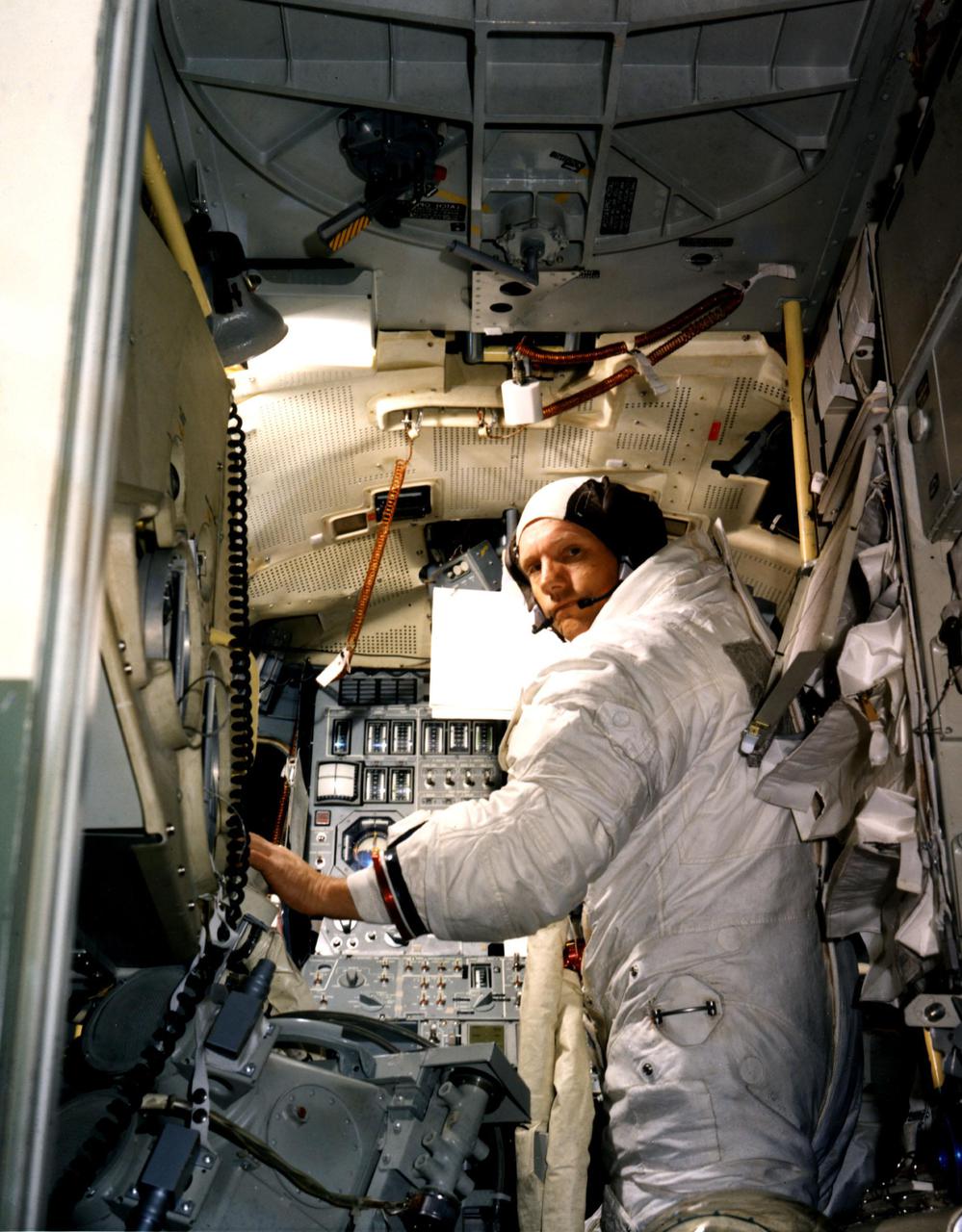

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Neil A. Armstrong, commander for the Apollo 11 Moon-landing mission, practices for the historic event in a Lunar Module simulator in the Flight Crew Training Building at KSC. Accompanying Armstrong on the Moon flight will be Command Module Pilot Michael Collins and Lunar Module Pilot Edwin E. Aldrin Jr.
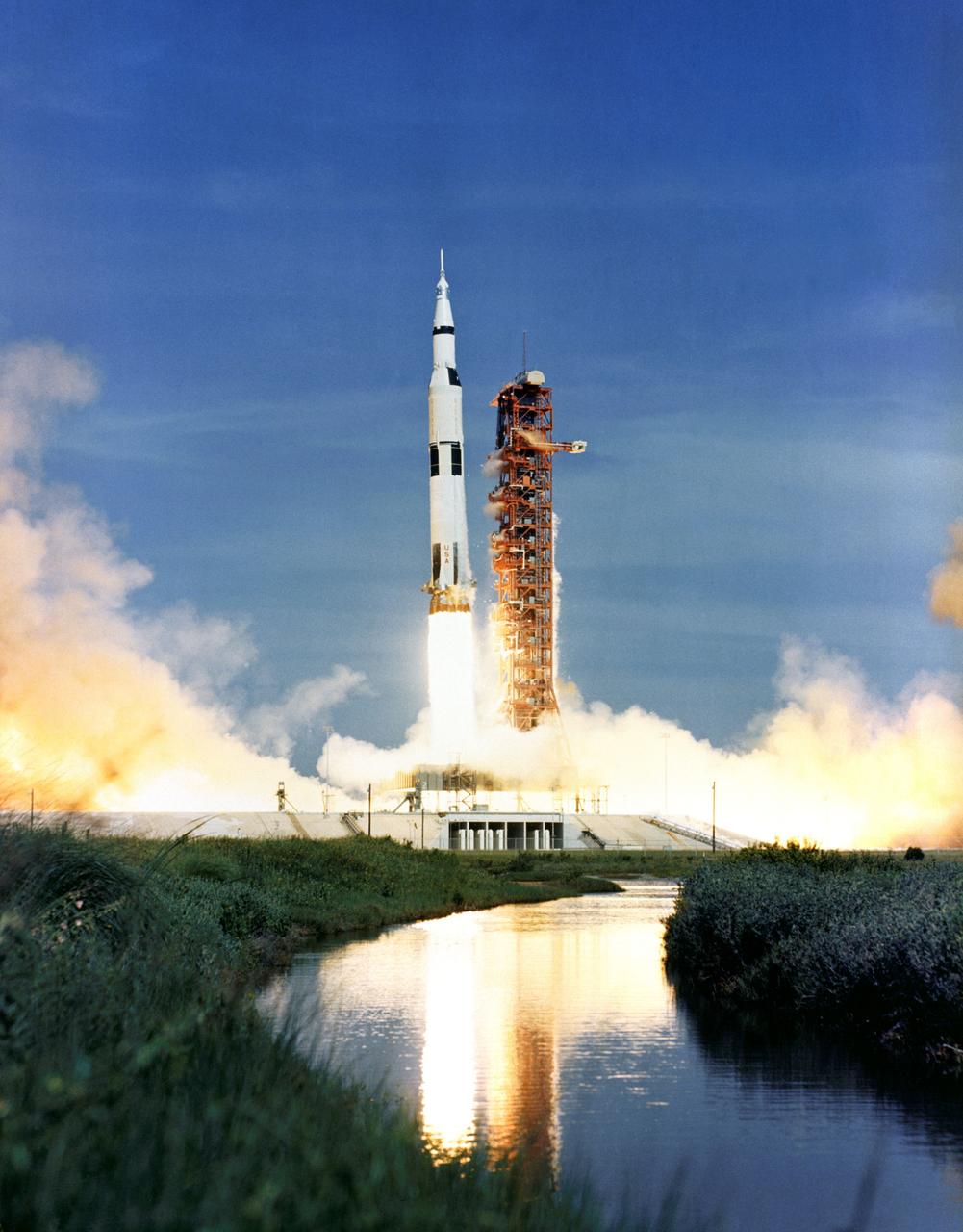

S71-41810 (26 July 1971) --- The 363-feet tall Apollo 15 (Spacecraft 112/Lunar Module 10/Saturn 510) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 9:34:00.79 a.m., July 26, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. Aboard the Apollo 15 spacecraft were astronauts David R. Scott, commander; Alfred M. Worden, commander module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. Apollo 15 is the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) fourth manned lunar landing mission.
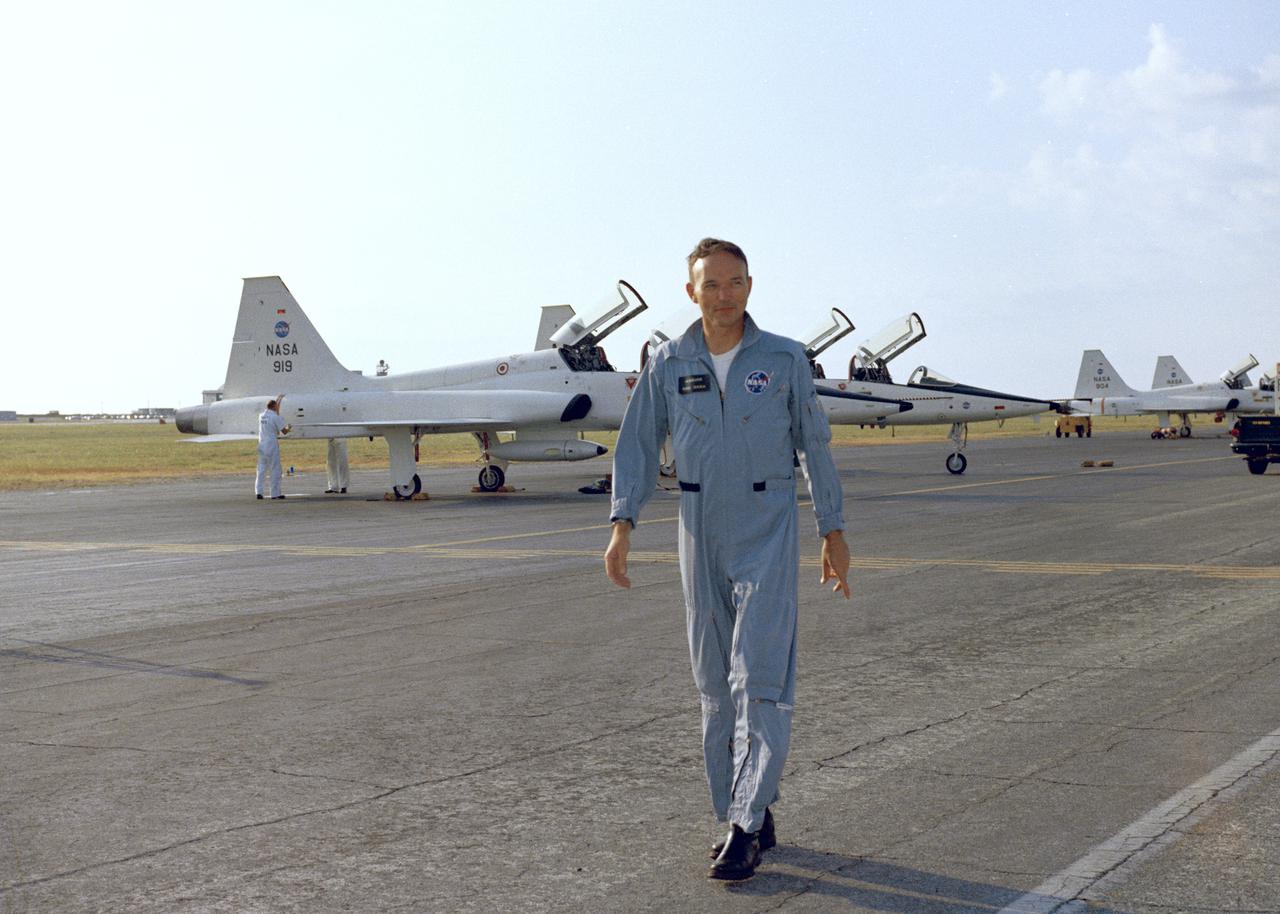

PATRICK AFB, Fla. – Apollo 11 command module pilot Michael Collins, just arrived at Patrick Air Force Base in a T-38 jet in preparation of the nation’s first lunar landing mission. Lift off atop a Saturn V launch vehicle is scheduled for July 16, 1969. During Apollo 11, the command module, Columbia, will remain in orbit around the moon while the lunar module, Eagle, carrying Armstrong and Aldrin, lands on the lunar surface. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew plans to collect lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. For more: http:__www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov_history_apollo_apollo-11_apollo-11.htm Photo credit: NASA
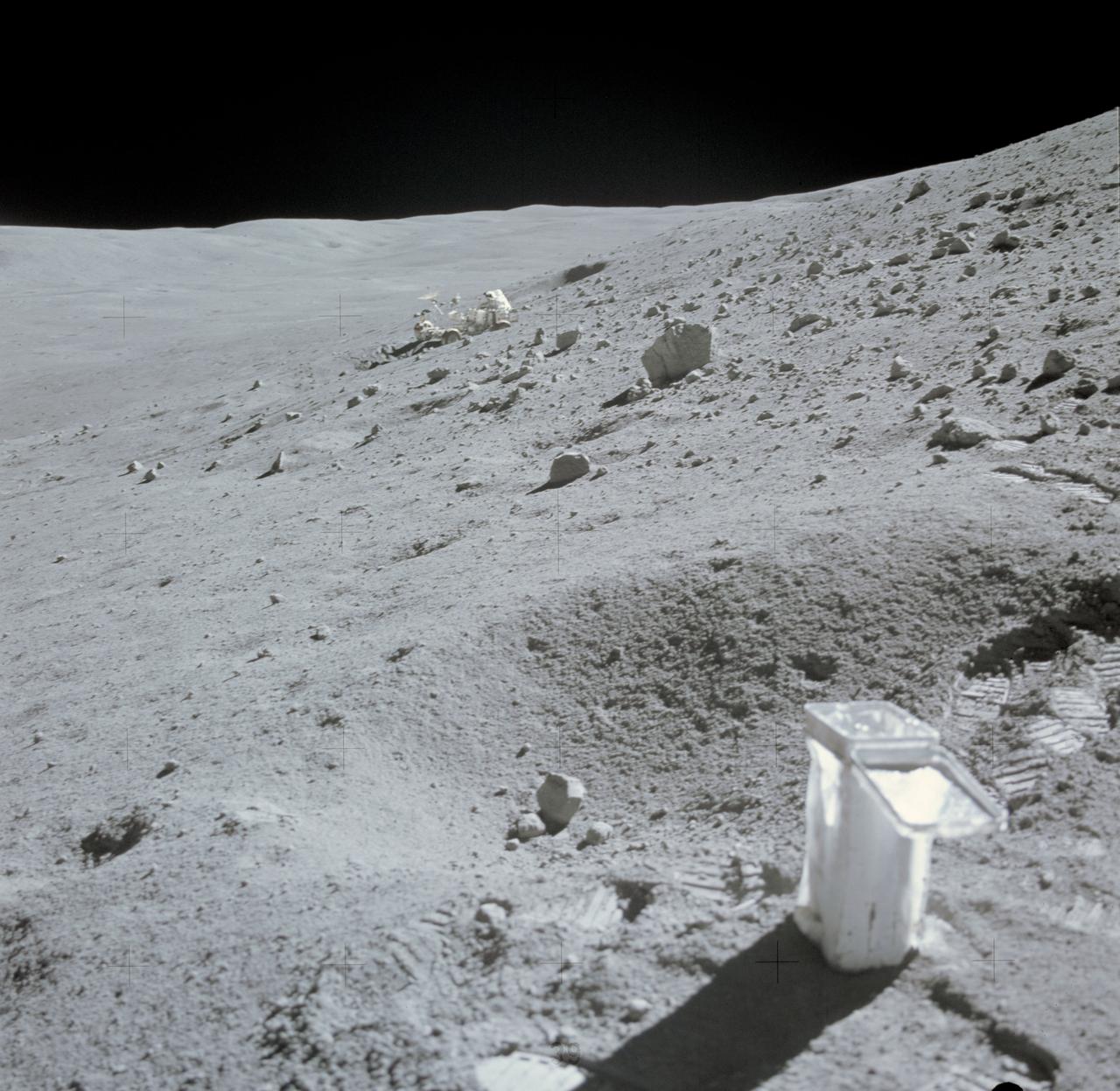

AS16-107-17473 (22 April 1972) --- The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) appears to be parked in a deep lunar depression, on the slope of Stone Mountain. This photograph of the lunar scene at Station No. 4 was taken during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. A sample collection bag is in the right foreground. Note field of small boulders at upper right. While astronauts John W. Young, commander, and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
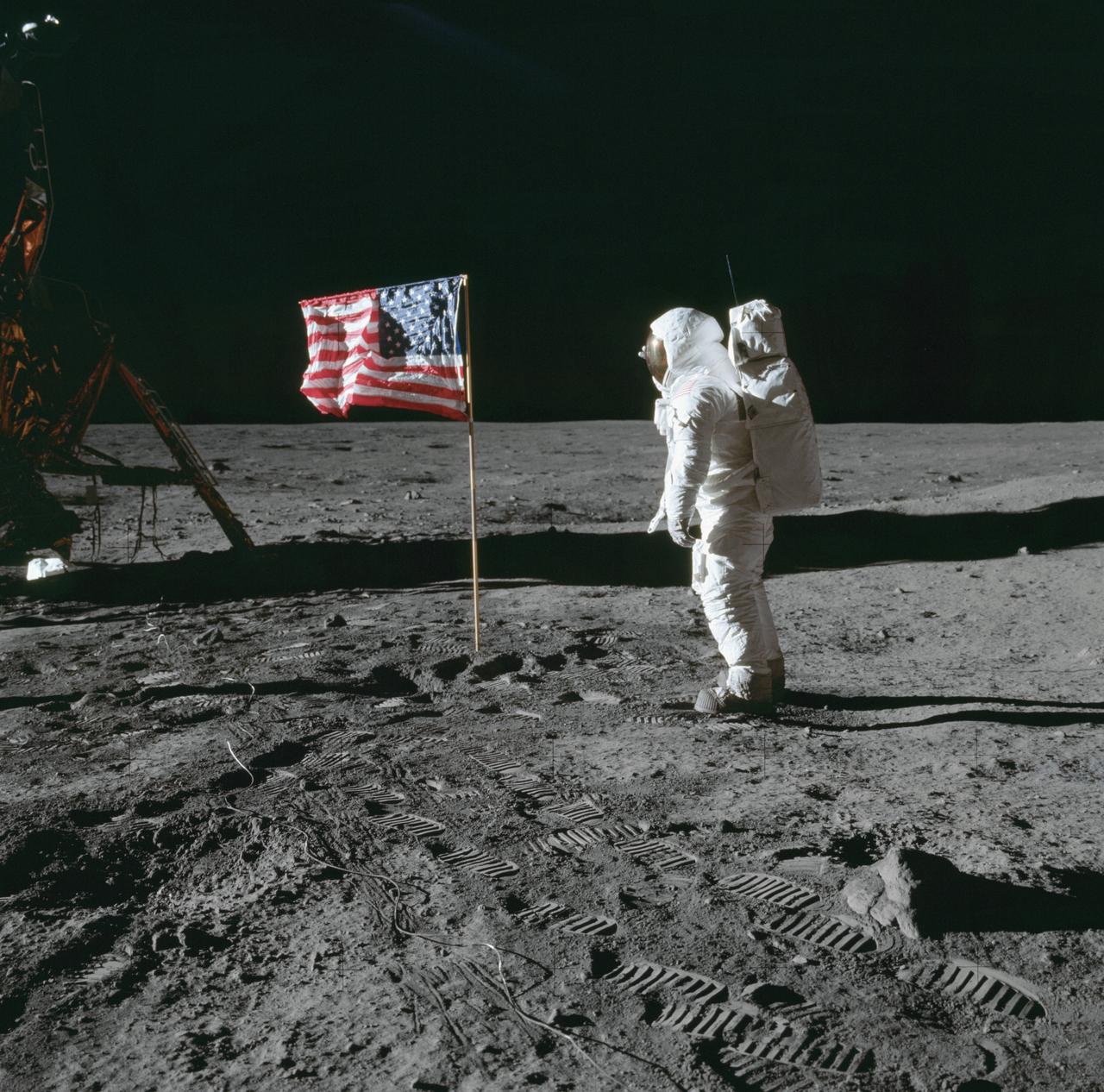

AS11-40-5874 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the first lunar landing mission, poses for a photograph beside the deployed United States flag during Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The Lunar Module (LM) is on the left, and the footprints of the astronauts are clearly visible in the soil of the moon. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm Hasselblad lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM the "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
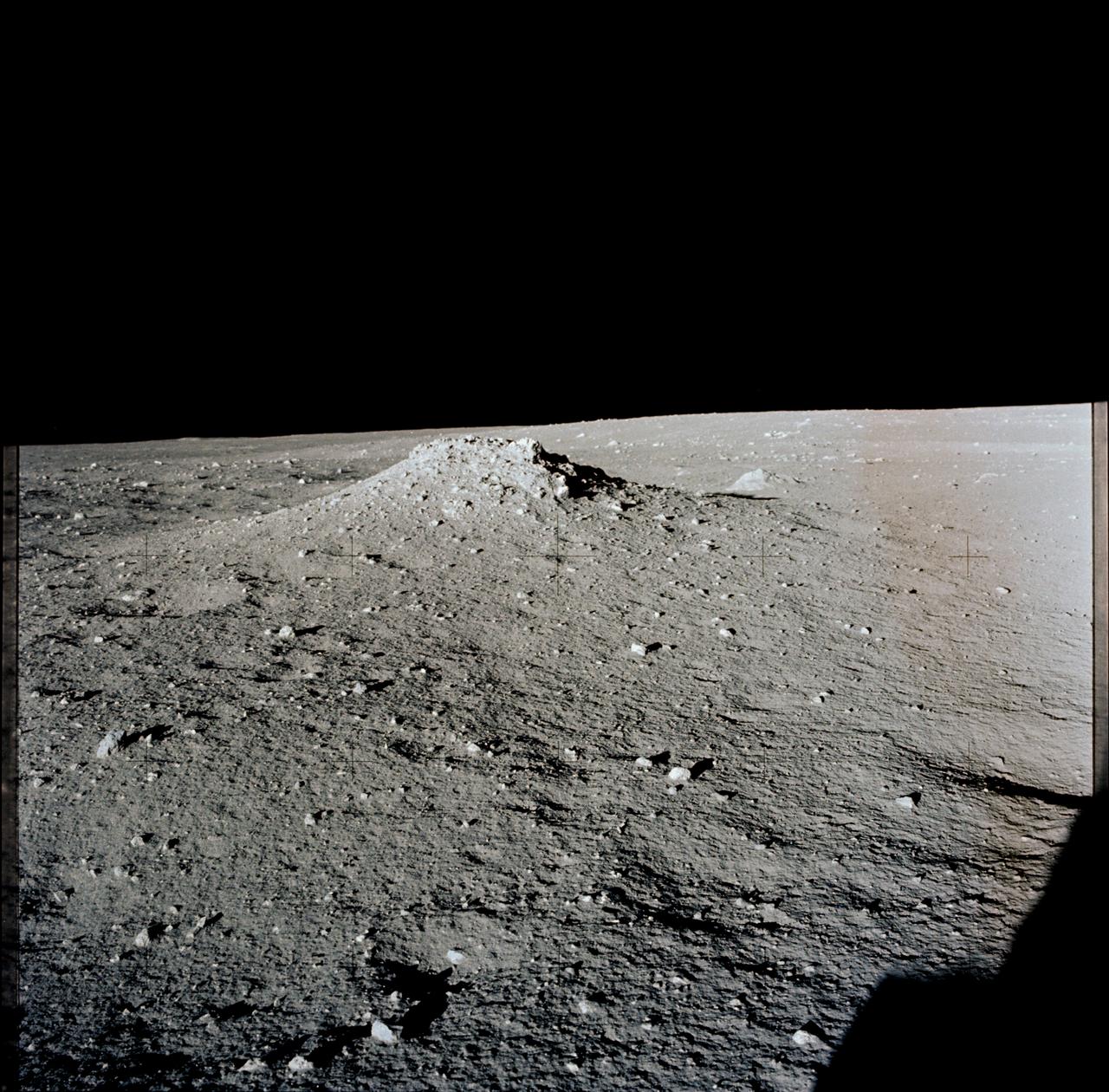

AS12-46-6795 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- A view of the lunar surface in the vicinity of the Apollo 12 lunar landing site, photographed during the extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot. Conrad and Bean encountered the odd, anthill-shaped mound during their lunar traverse. The two descended in the Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, while astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
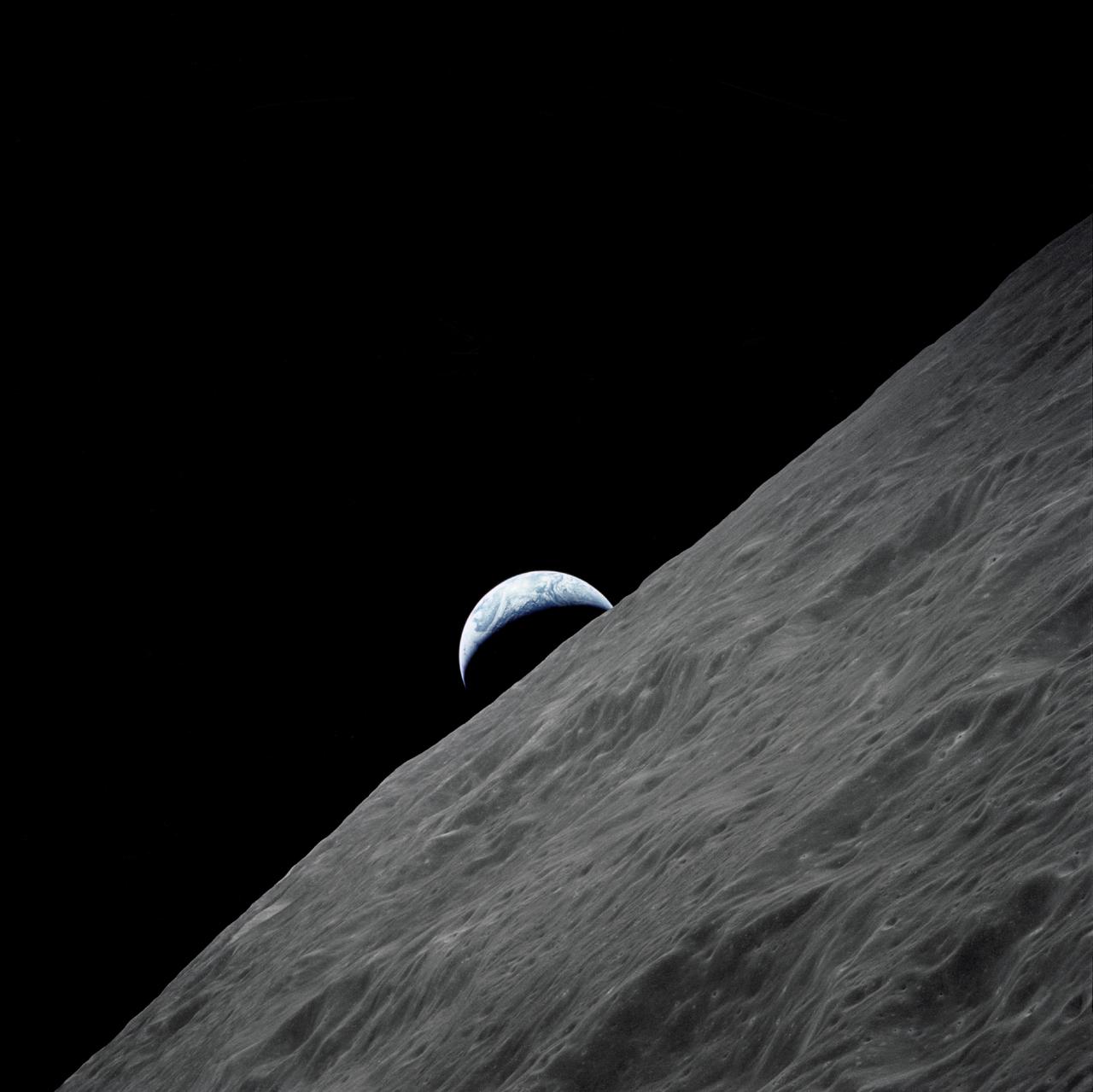

AS17-152-23274 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- The crescent Earth rises above the lunar horizon in this spectacular photograph taken from the Apollo 17 spacecraft in lunar orbit during National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) final lunar landing mission in the Apollo program. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
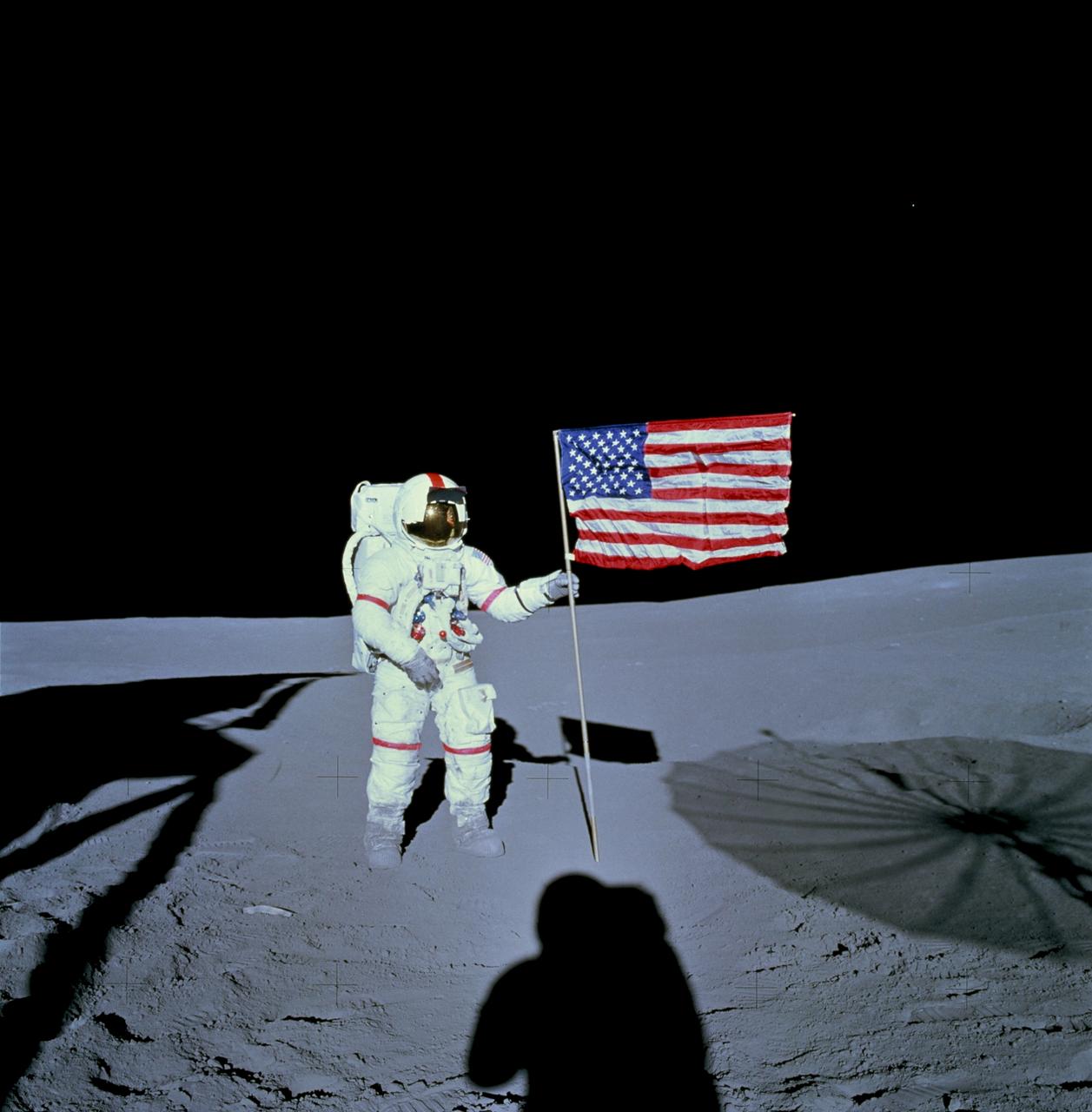

AS14-66-9232 (5 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, stands by the deployed United States flag on the lunar surface during the early moments of the first extravehicular activity (EVA) of the mission. Shadows of the Lunar Module (LM), astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, and the erectable S-Band Antenna surround the scene of the third flag implanting to be performed on the lunar surface. While astronauts Shepard and Mitchell descended in the LM ?Antares? to explore the Fra Mauro region of the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) ?Kitty Hawk? in lunar orbit.
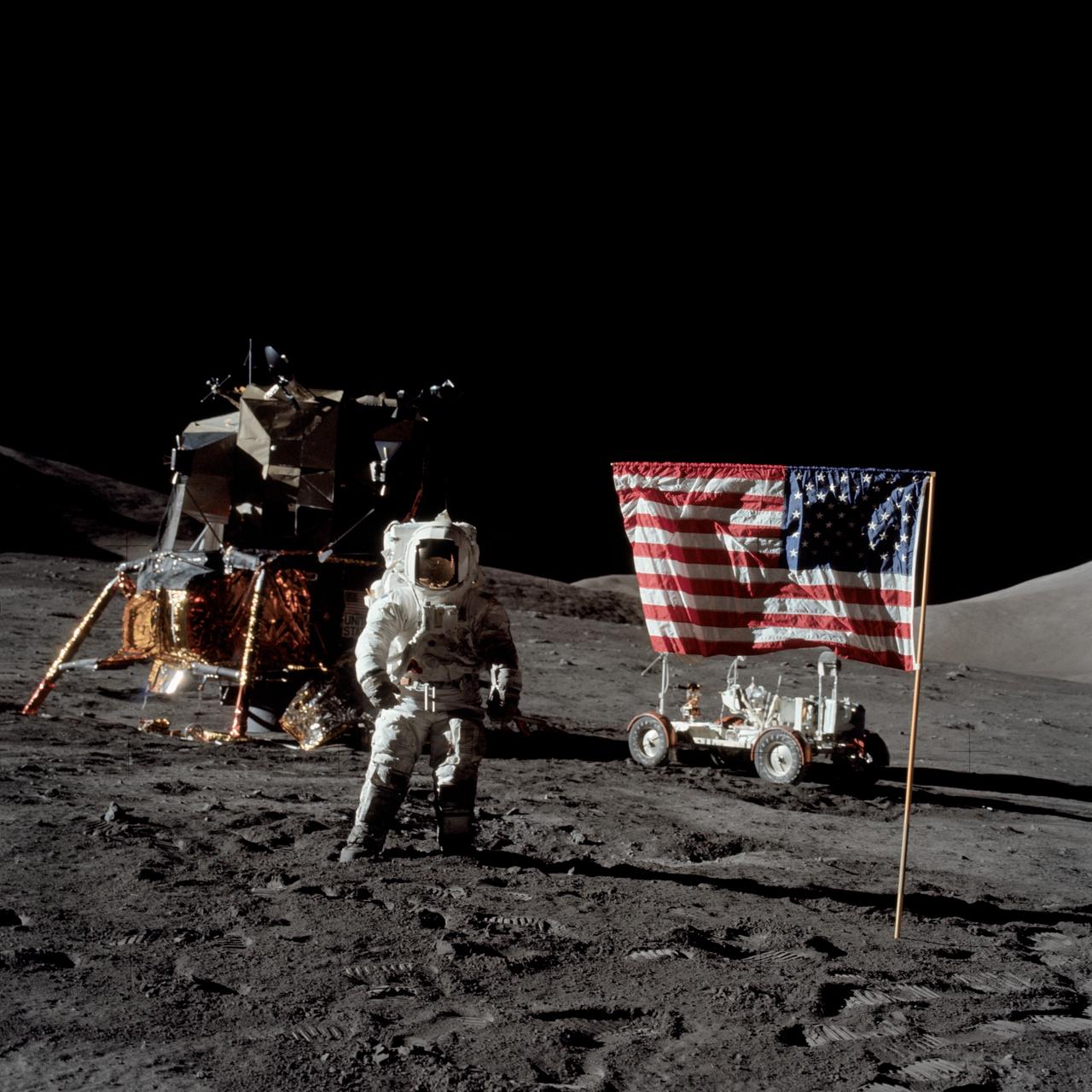

AS17-134-20382 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 lunar module pilot, stands near the deployed United States flag on the lunar surface during extravehicular activity (EVA) of NASA's final lunar landing mission in the Apollo series. The Lunar Module (LM) is at left background and the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at right background (partially obscured). The photo was made by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the LM "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
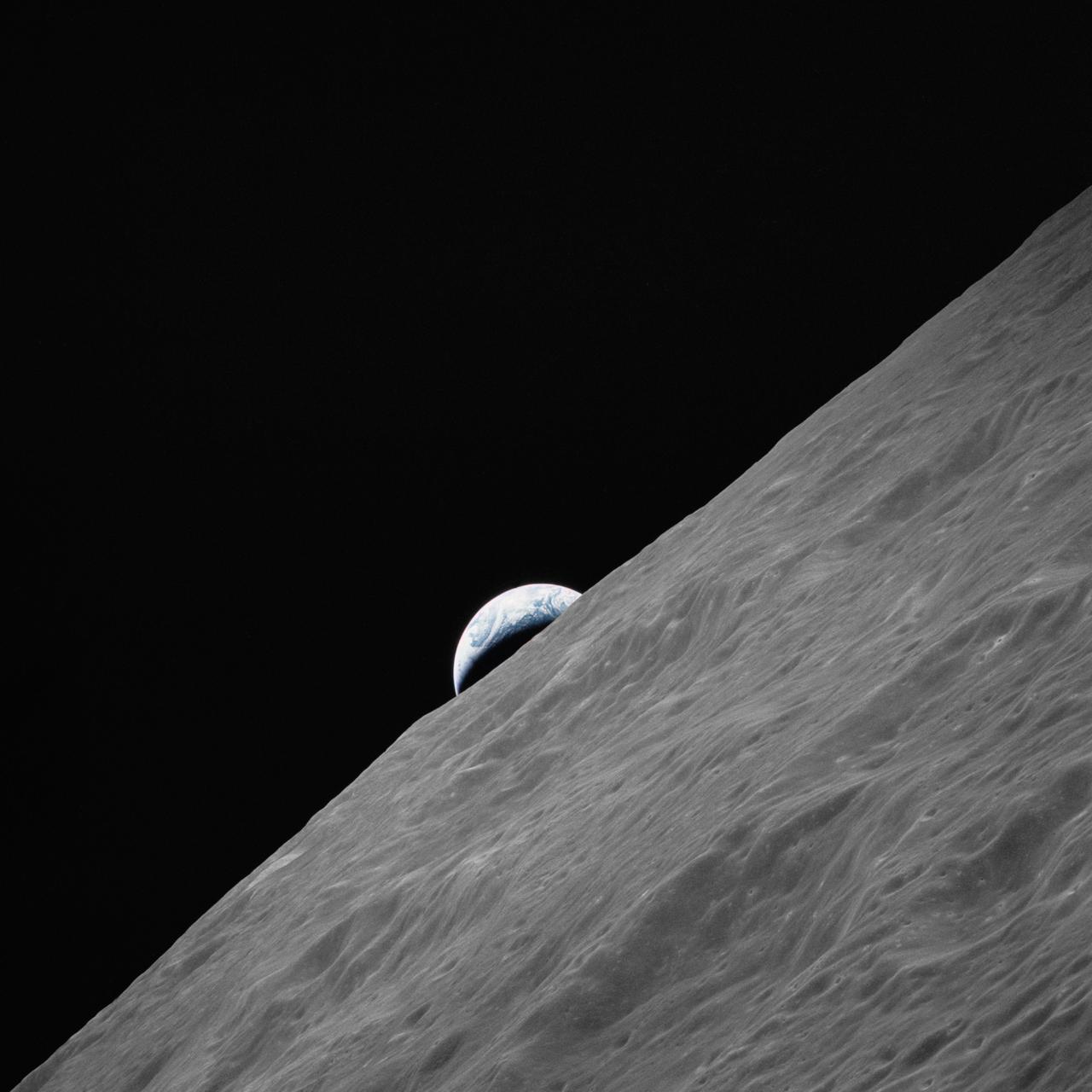

AS17-152-23272 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- The crescent Earth rises above the lunar horizon in this photograph taken from the Apollo 17 spacecraft in lunar orbit during National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) final lunar landing mission in the Apollo program. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
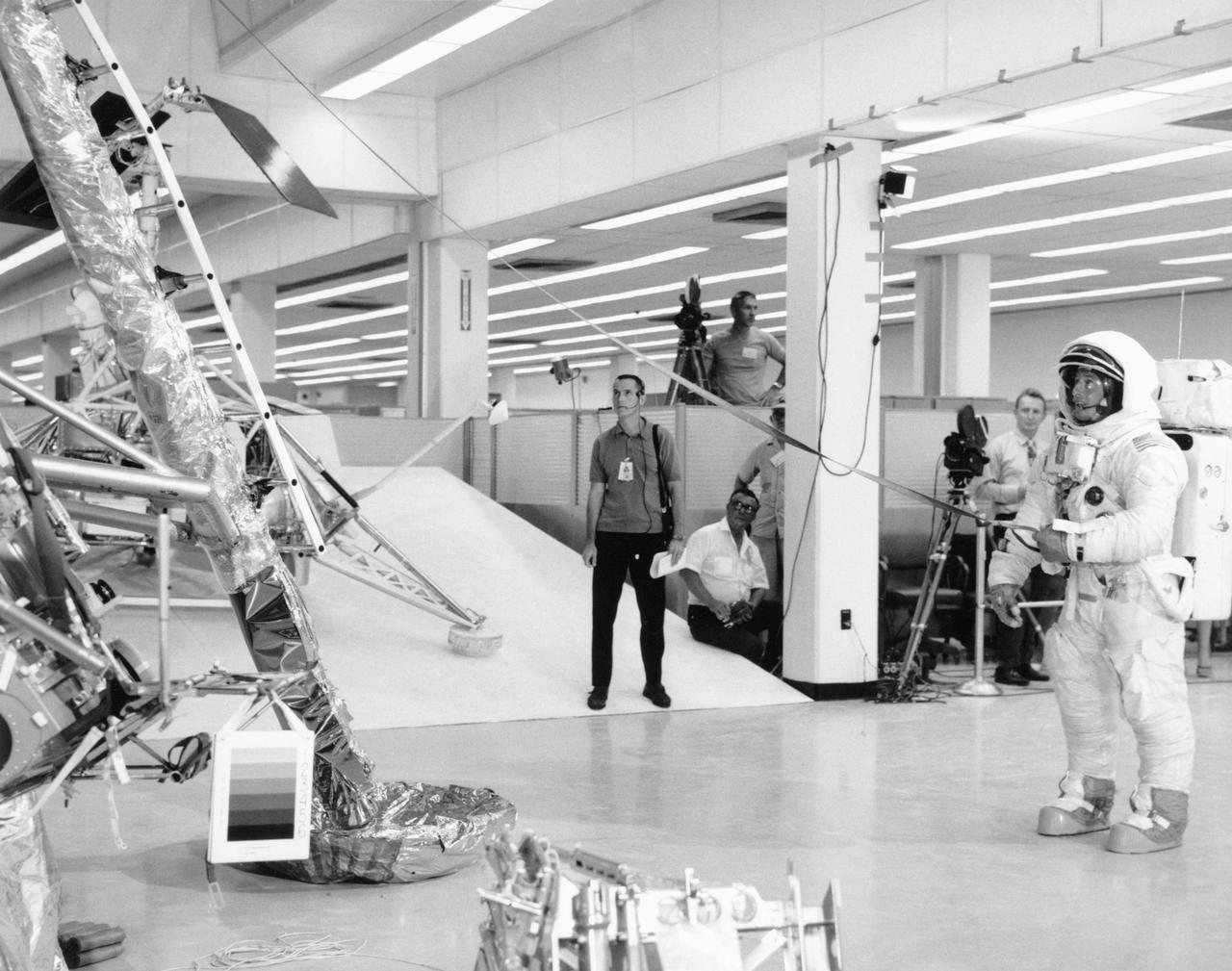

S69-54147 (October 1969) --- Two members of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission participates in lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) simulations in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Flight Crew Training Building. Here, astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, is holding the bottom end of the lunar equipment conveyor. Inside the Lunar Module (LM) and out of view is astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot. The simulations were part of a run-through of the Apollo 12 lunar surface "timeline".

AS16-116-18578 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, works at the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) just prior to deployment of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) during the first extravehicular activity (EVA) on April 21, 1972. Note the Ultraviolet (UV) Camera/Spectrometer to the right of the Lunar Module (LM) ladder. Also, note the pile of protective/thermal foil under the U.S. flag on the LM which the astronauts pulled away to get to the Modular Equipment Storage Assembly (MESA) bay. While astronauts Young and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 LM "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.

AS16-120-19332 (April 1972) --- This picture of the lunar surface was photographed from lunar orbit during the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission. Mersenius C Crater, dozens of smaller craters and several small rille features can be seen in the frame. Center point coordinates are located at 19.5 degrees south latitude and 45 degrees west longitude. While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
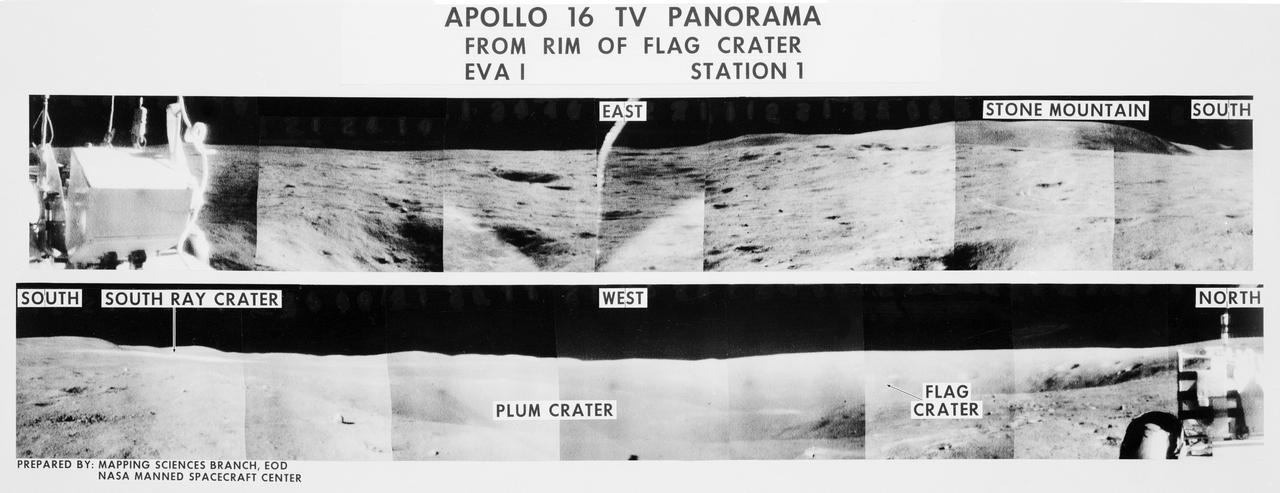
S72-35970 (21 April 1972) --- A 360-degree field of view of the Apollo 16 Descartes landing site area composed of individual scenes taken from color transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). This panorama was made while the LRV was parked at the rim of Flag Crater (Station 1) during the first Apollo 16 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) by astronauts John W. Young and Charles M. Duke Jr. The overlay identifies the directions and the key lunar terrain features. The camera panned across the rear portion of the LRV in its 360-degree sweep. Astronauts Young, commander; and Duke, lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
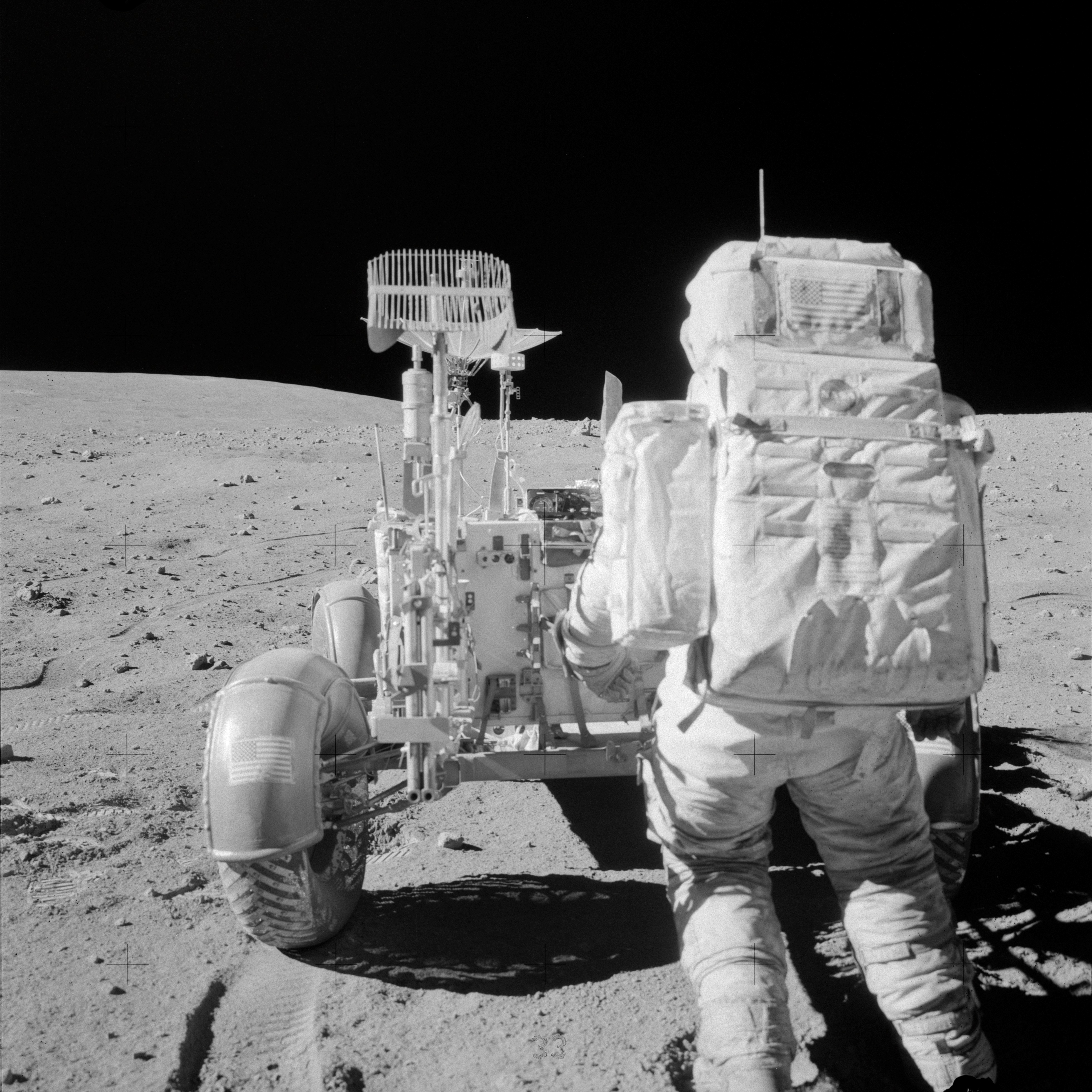

AS16-108-17622 (22 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, reaches for tools in the Apollo Lunar Hand Tool Carrier at the aft end of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. This photograph was taken by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot. This view is looking south from the base of Stone Mountain. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands region of the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
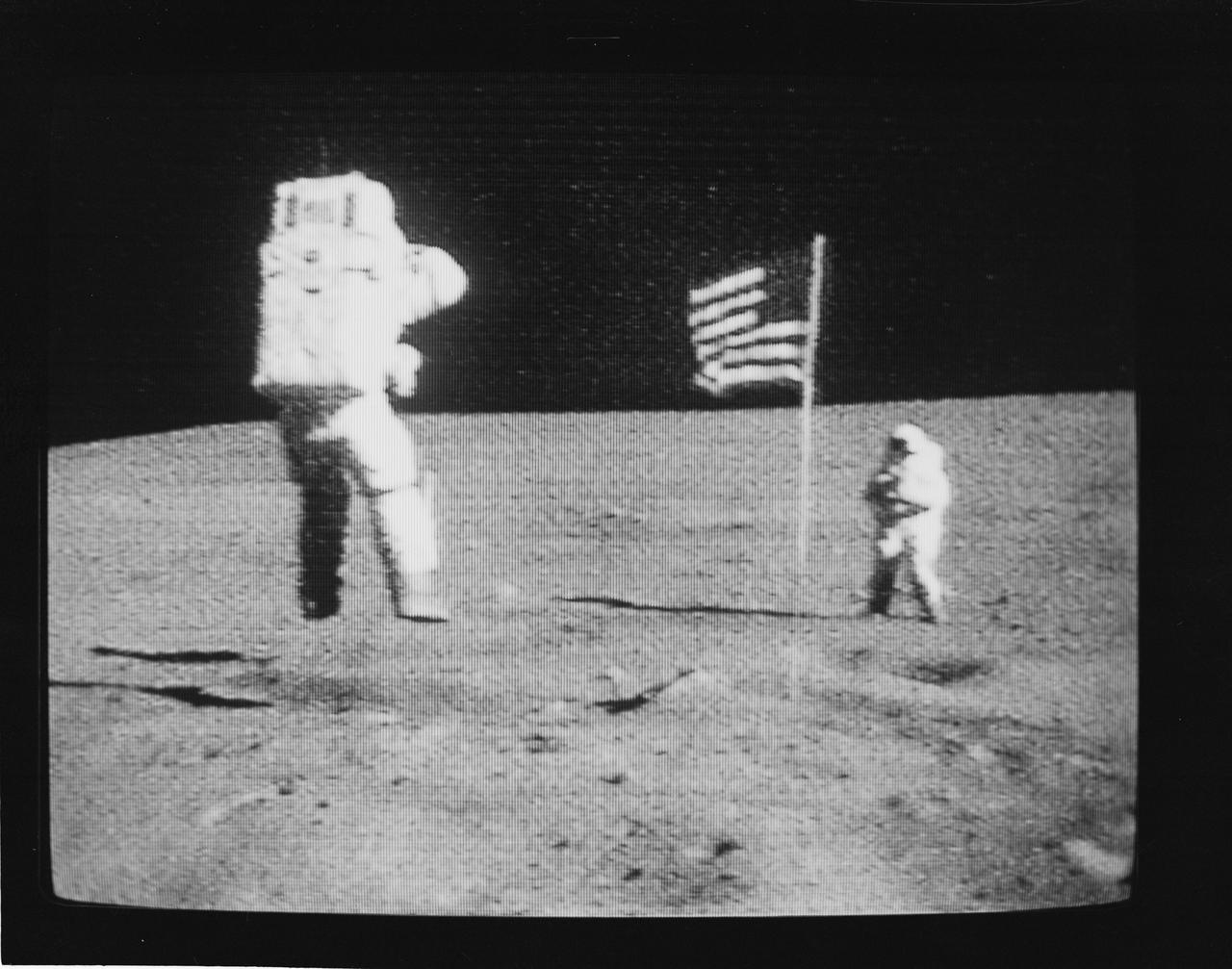

S72-35594 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, leaps from the lunar surface as he salutes the United States flag during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon, as seen in this black & white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, stands beside the flag. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
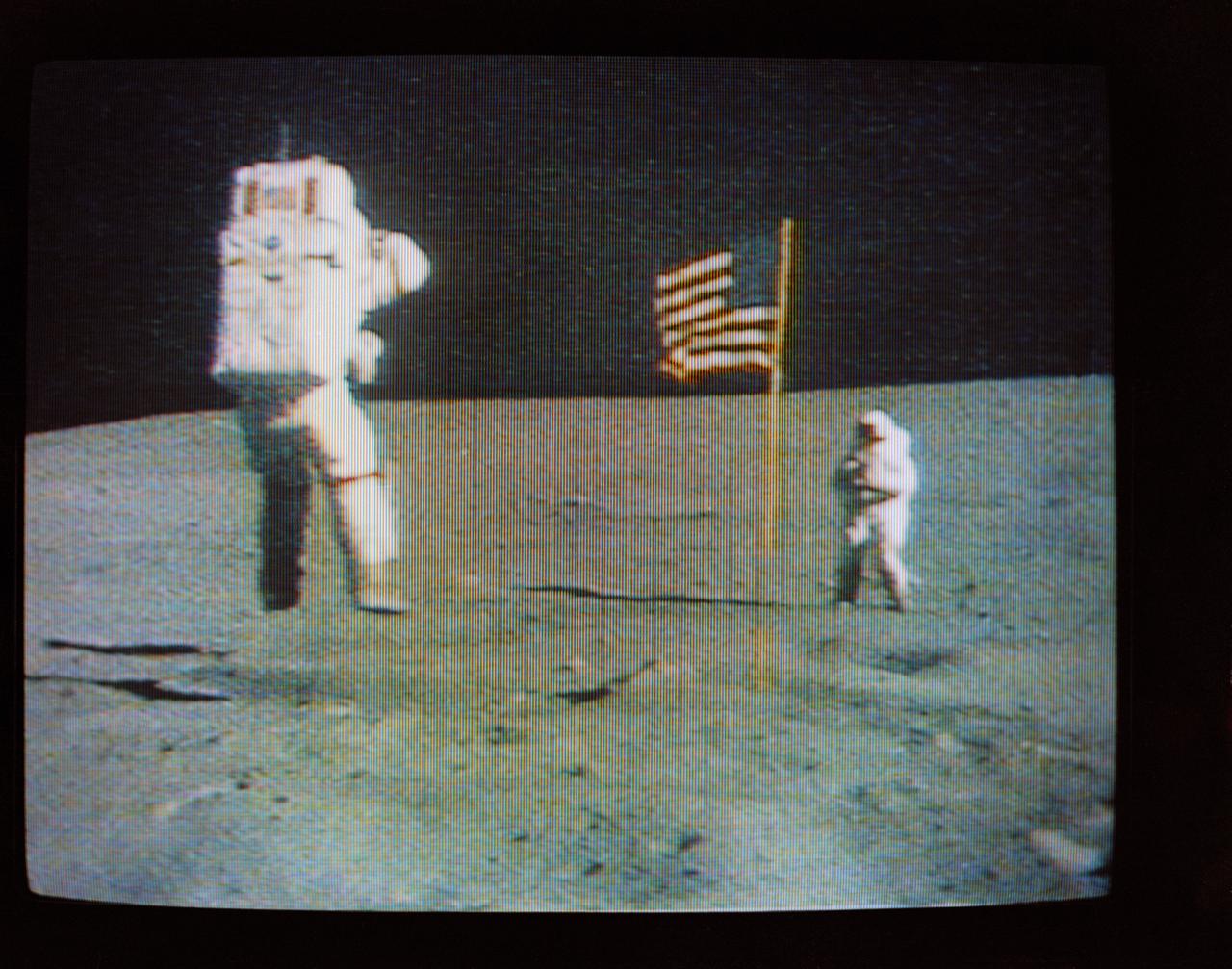

S72-35611 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, leaps from the lunar surface as he salutes the U.S. flag, during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color television camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, is standing in the background. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
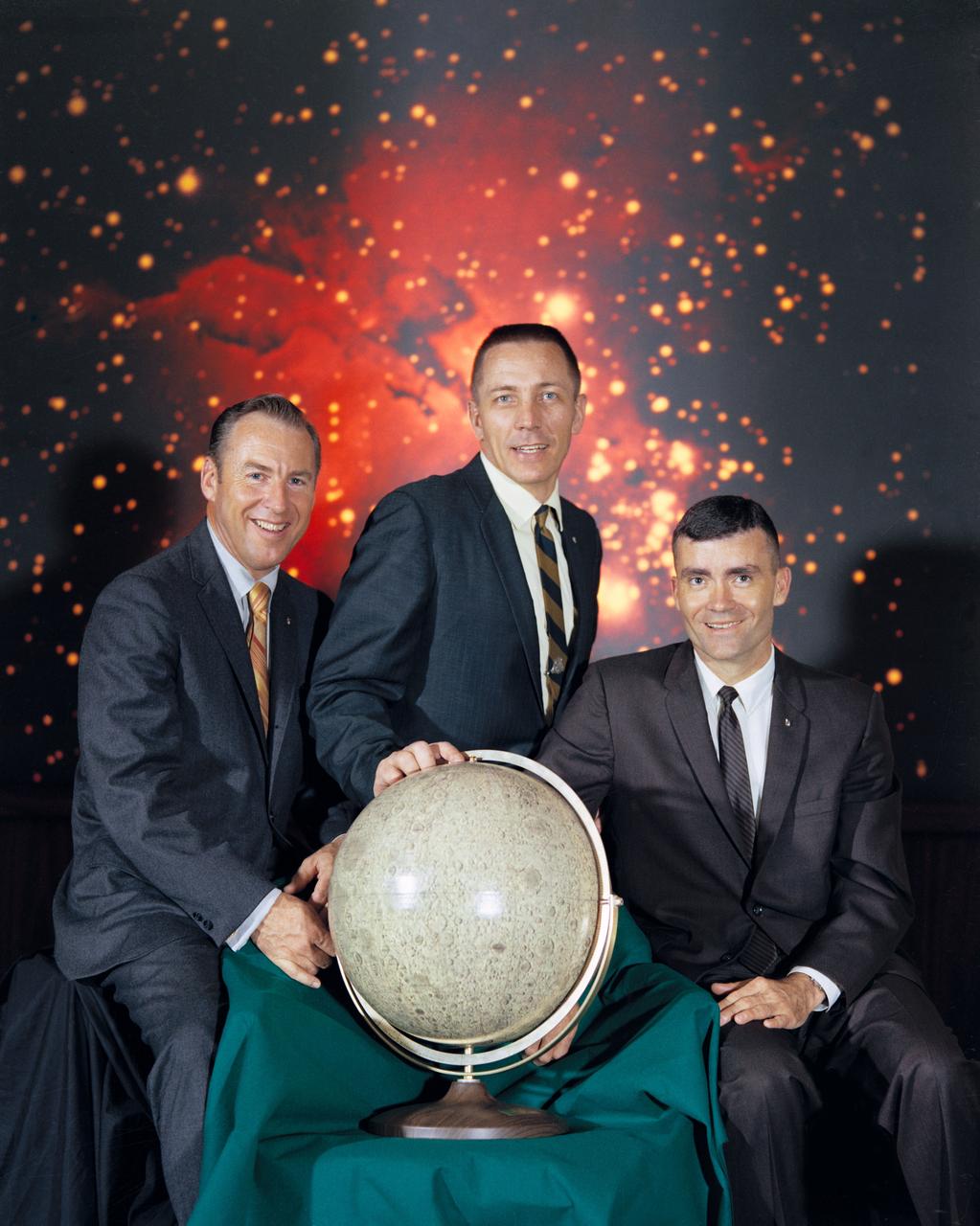

S70-36485 (April 1970) --- These three astronauts are the prime crew of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. Left to right, are James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. Apollo 13 will be the United States' third lunar landing mission.
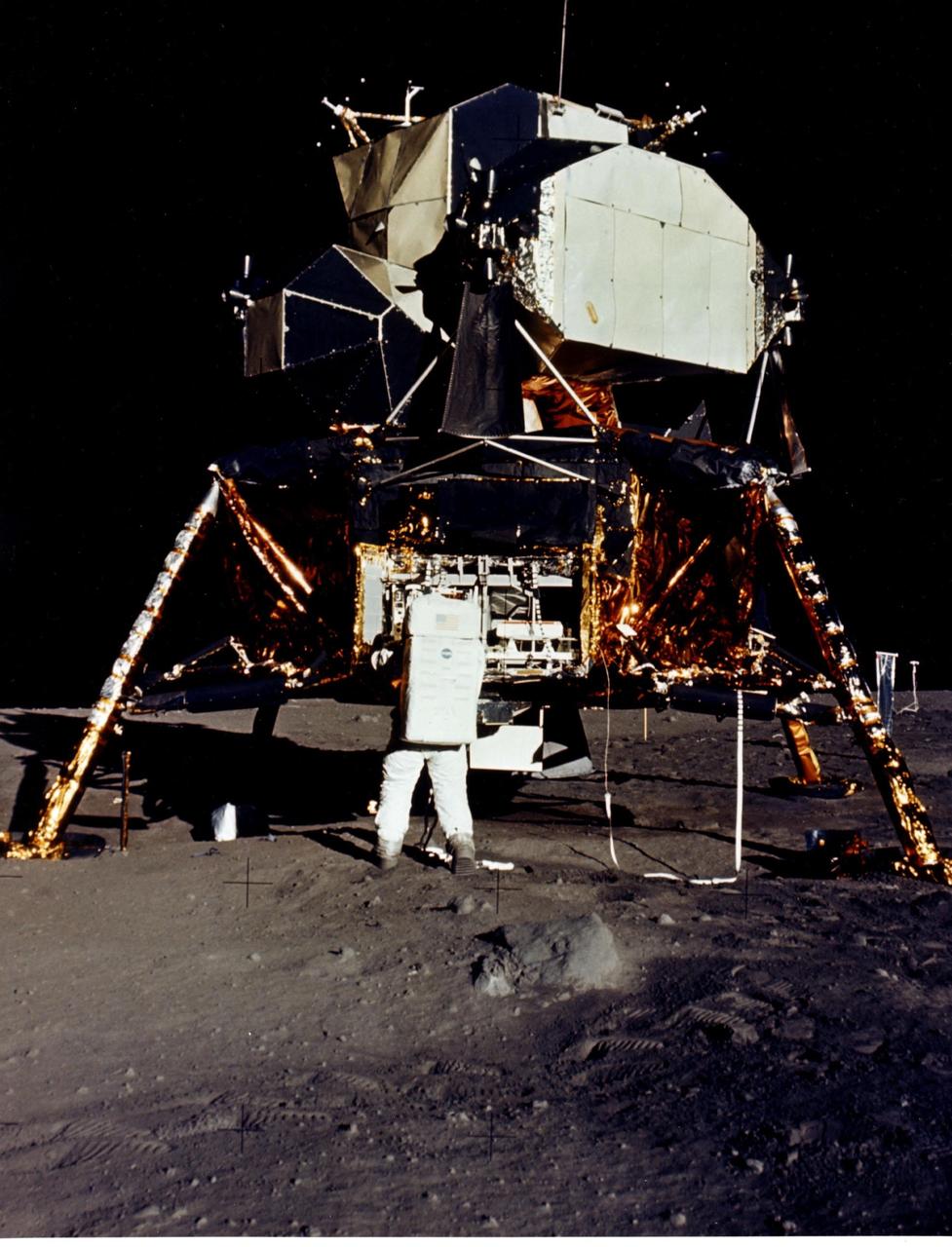

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - Man's first landing on the Moon was accomplished at 4:17 p.m. today as Lunar Module "Eagle" touched down gently on the Sea of Tranquility on the east side of the Moon. Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module Pilot, removes scientific experiment packages from a stowage area in the Lunar Module's descent stage. Left behind on the lunar surface by Aldrin and Neil A. Armstrong, Apollo 11 commander, were a Passive Seismic Experiments Package and a Laser-Ranging Retro-Reflector.
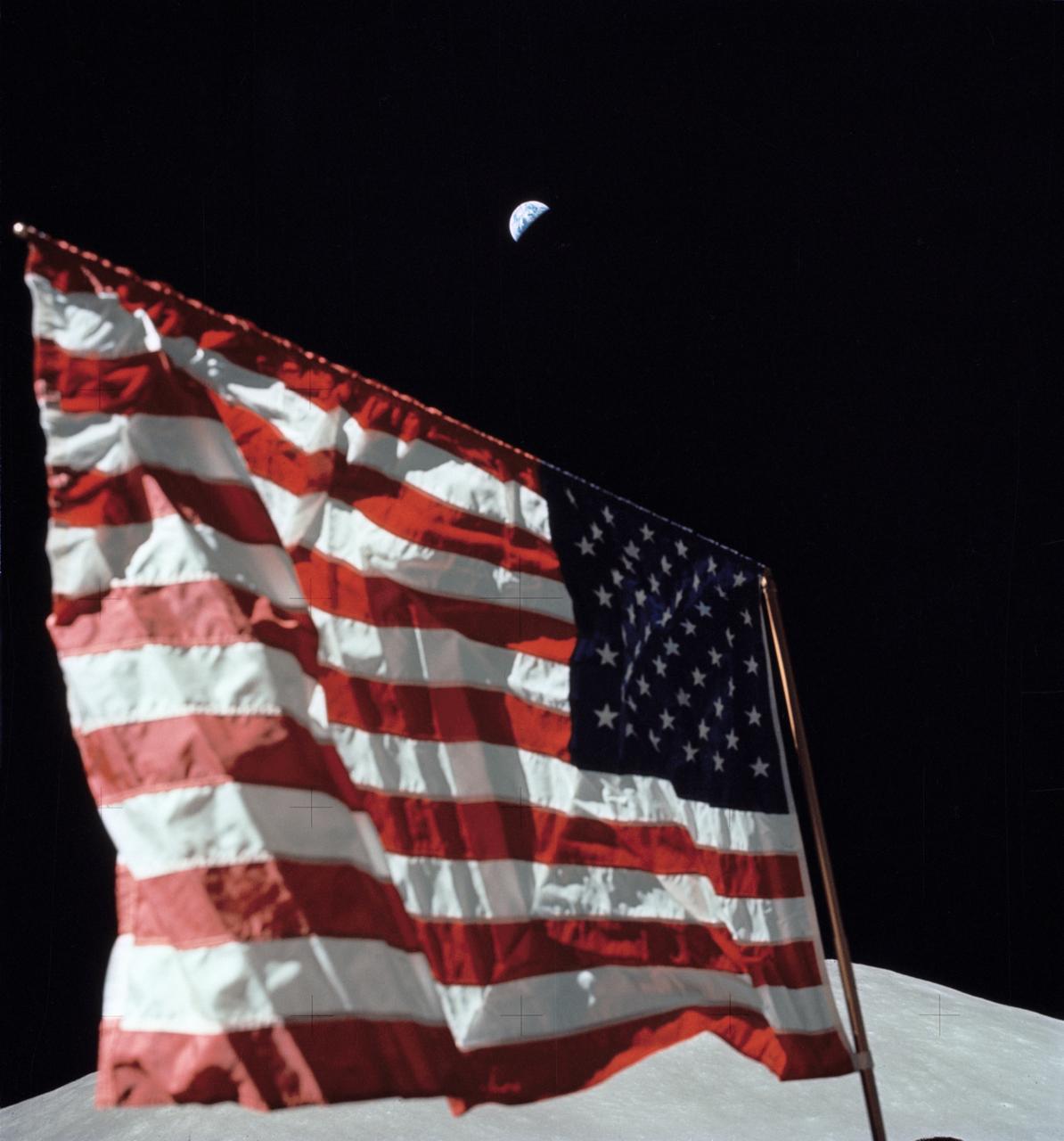

AS17-134-20466 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- A close-up view of the U.S. flag deployed on the moon at the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the crewmen of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. The crescent Earth can be seen in the far distant background above the flag. The lunar feature in the near background is South Massif. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module "Challenger" to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.
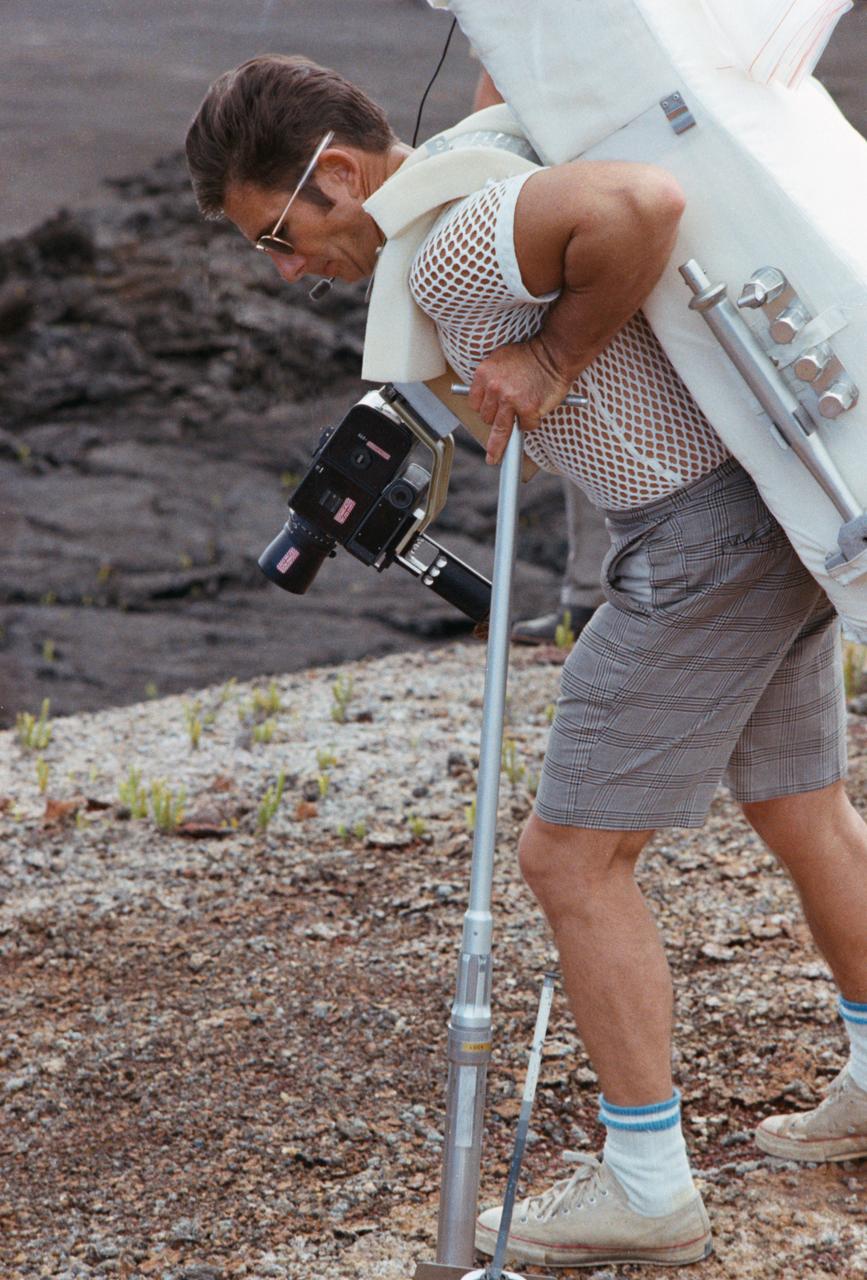

S70-56433 (December 1970) --- Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission, participates in lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) training during a visit to Hawaii. He is simulating using lunar surface geological tools to collect a core sample.

Portrait of Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, Apollo 14 lunar landing mission Command Module pilot in civilian clothes.
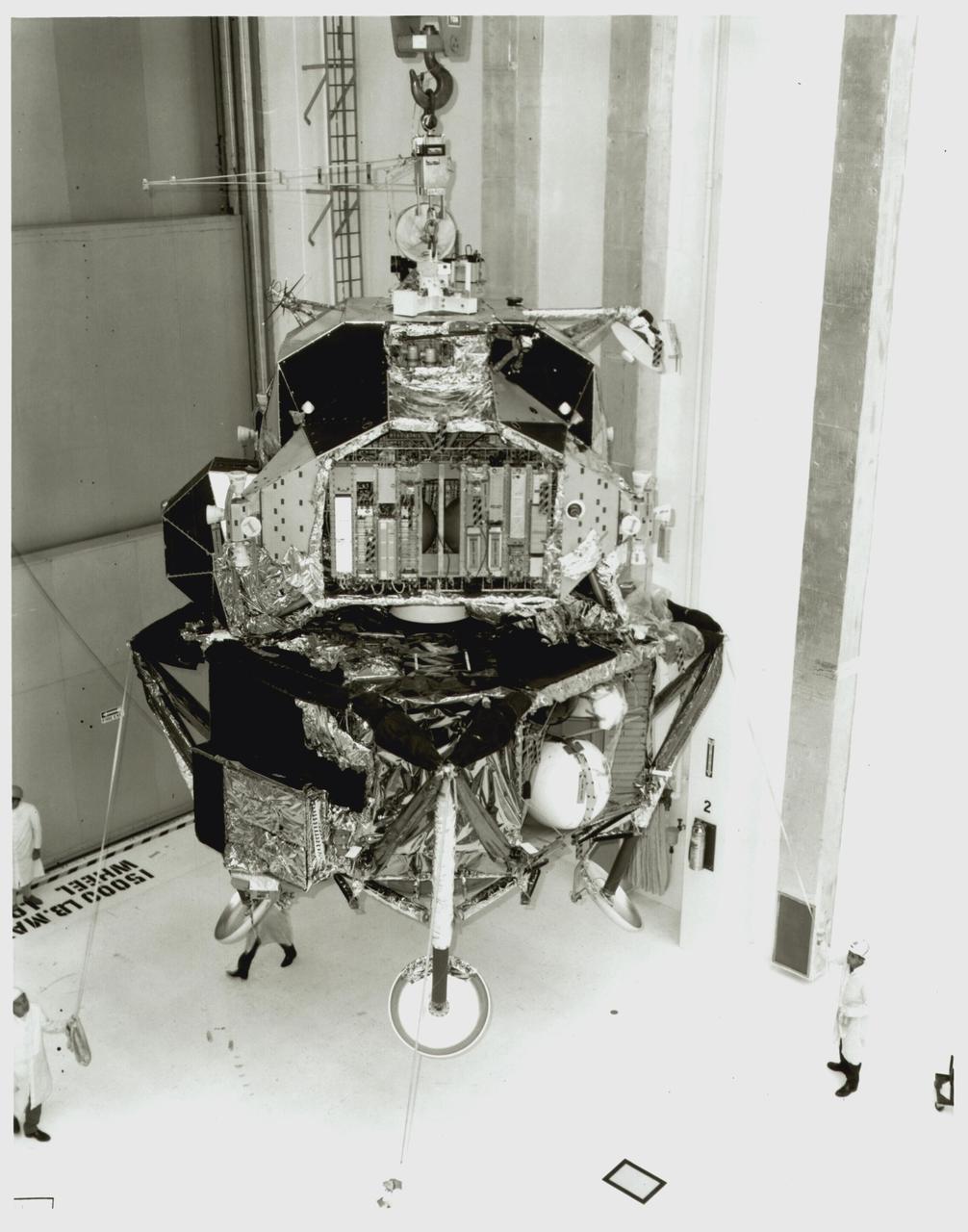
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Lunar Module 5 move from landing gear fixture and mate to SLA.
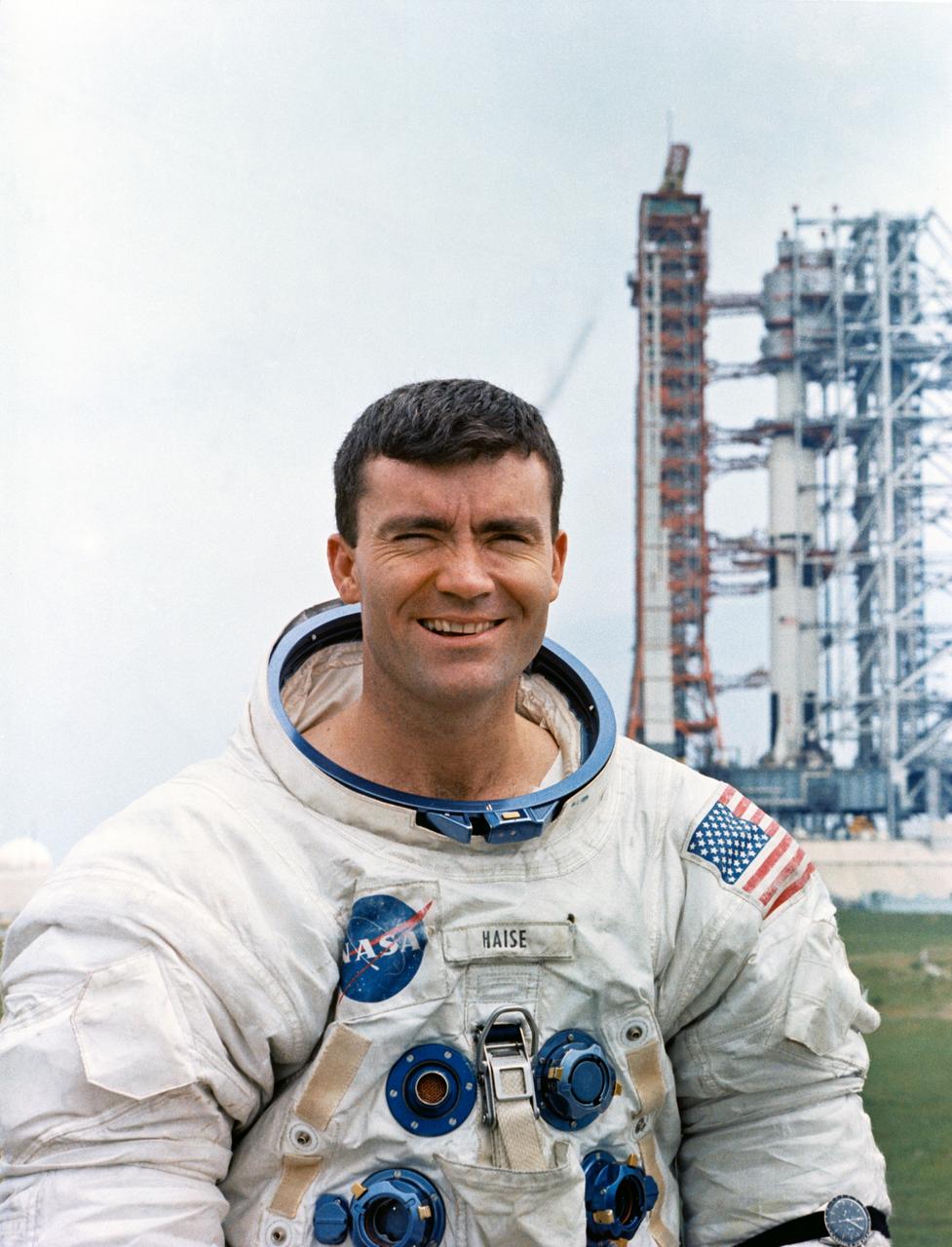

S70-34267 (April 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. Photo credit: NASA (Note, this is not the official Apollo portrait for Fred Haise)