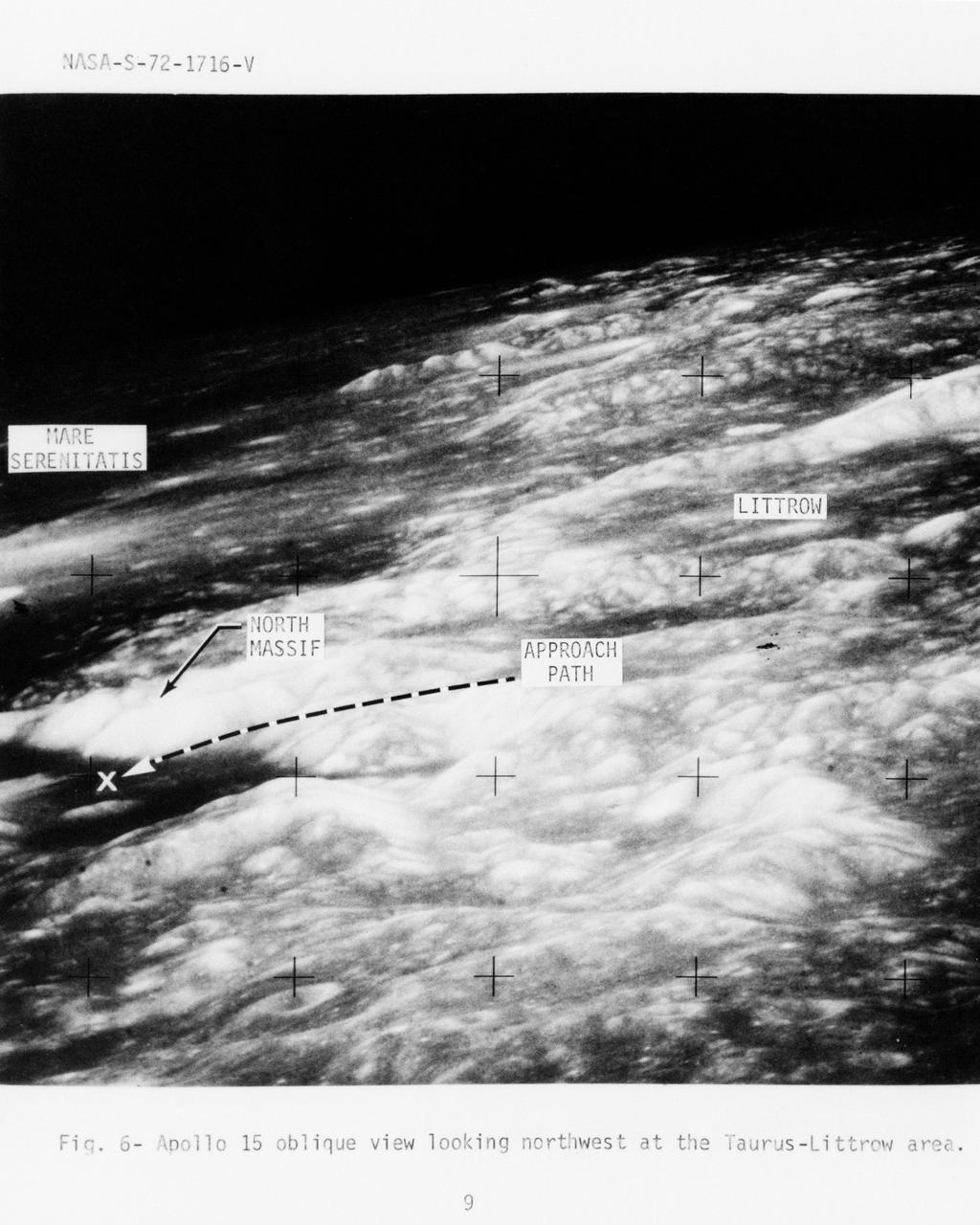
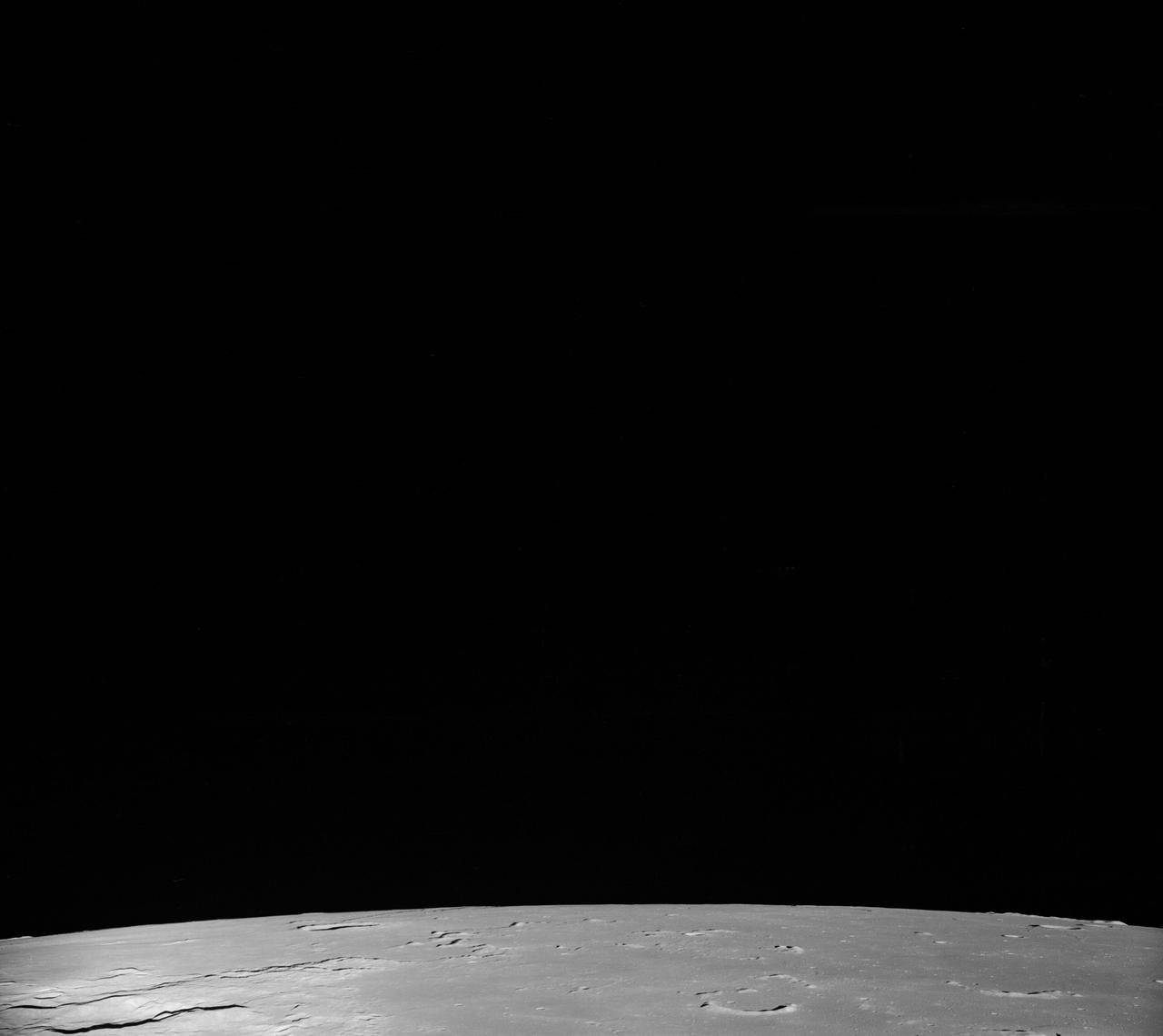
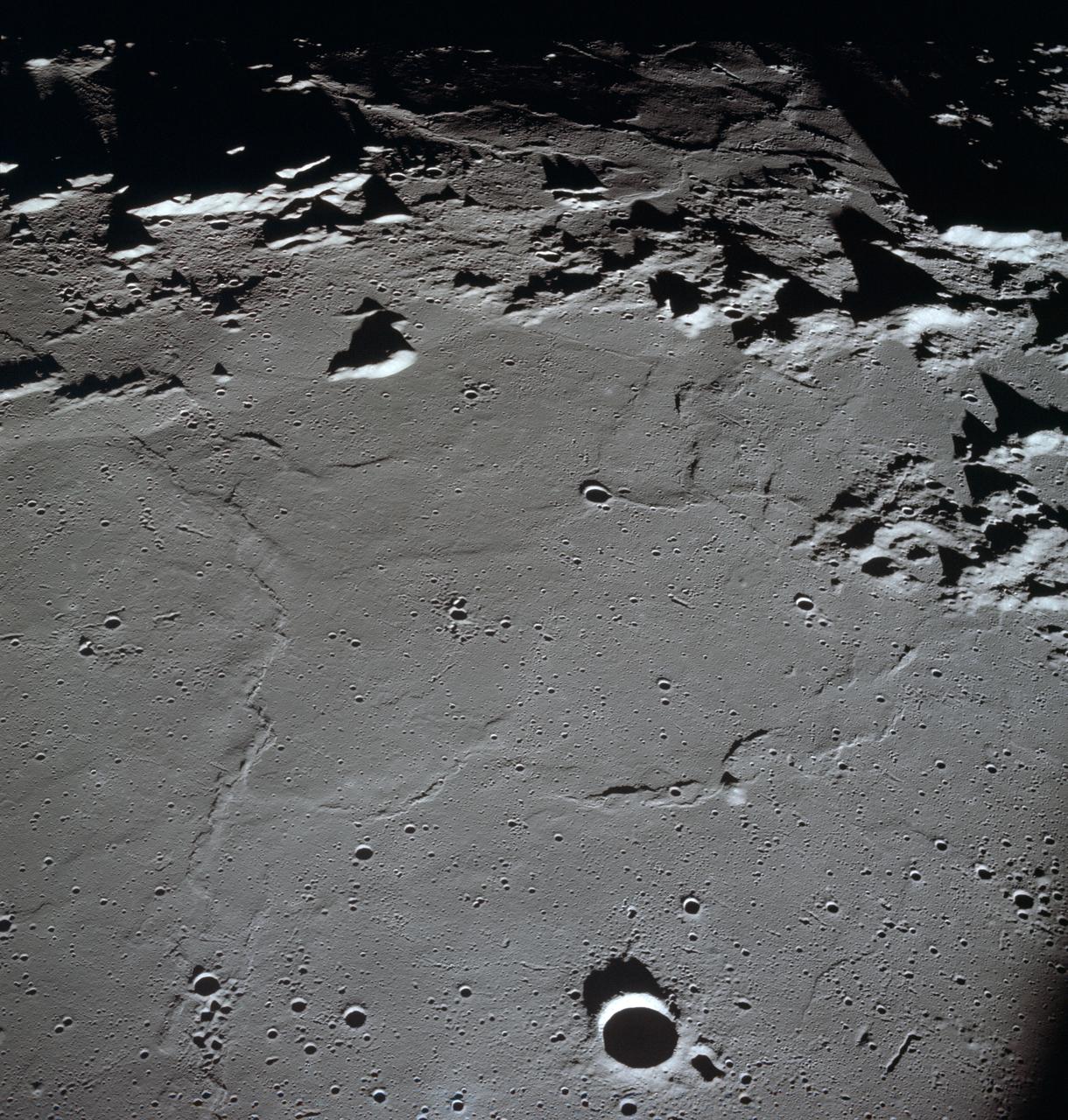
S72-01716 (July 1972) --- An oblique view of the Taurus-Littrow area on the lunar nearside, as photographed from the Apollo 15 spacecraft in lunar orbit. This is an enlarged view. The "X" marks the landing site of the scheduled Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. The overlay points out several features in the photograph. The coordinates of the Apollo 17 touchdown point are 30 degrees 44 minutes 58 seconds east longitude and 20 degrees 9 minutes 50 seconds north latitude.
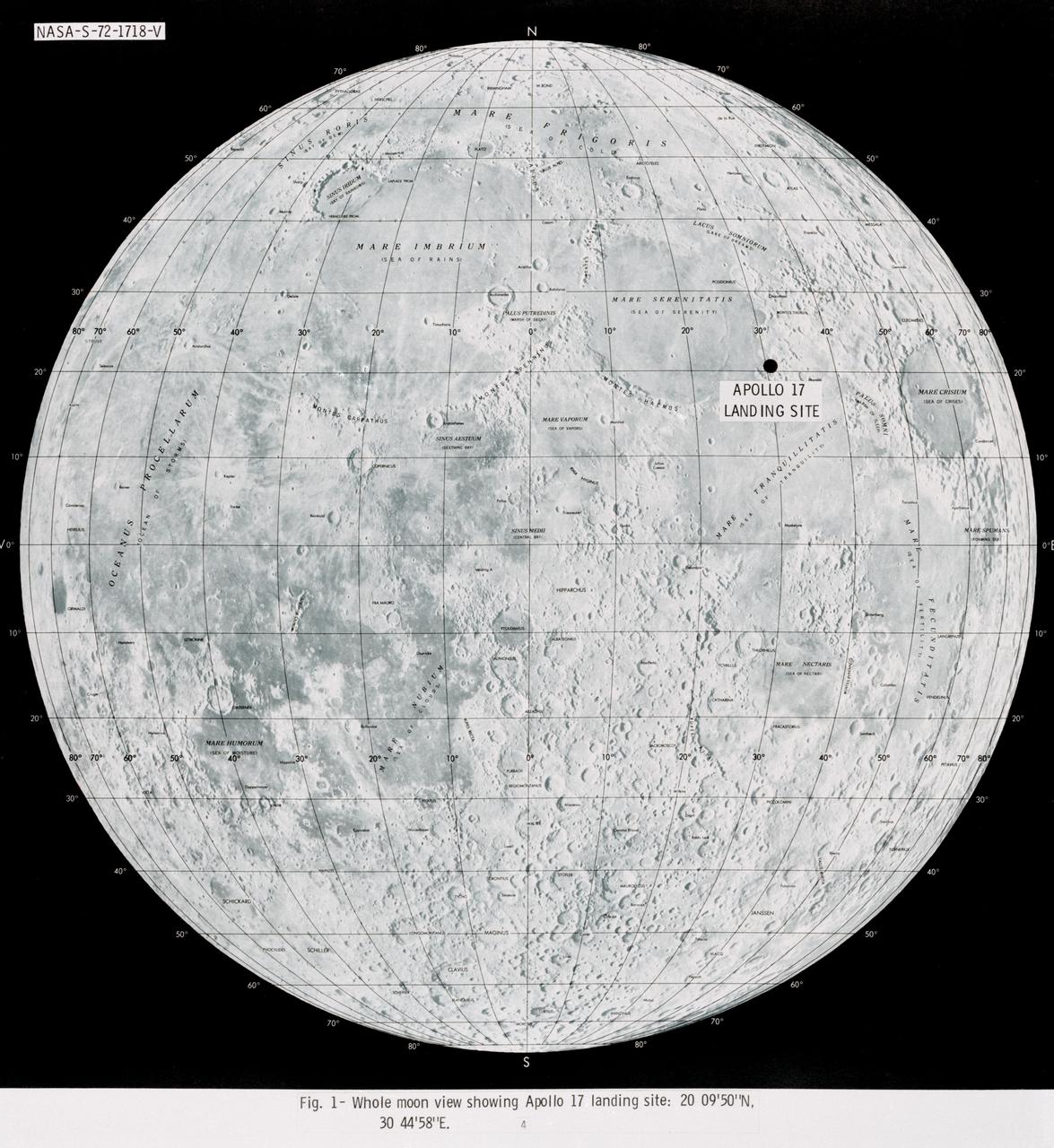

S72-01718 (July 1972) --- A photographic illustration of a full moon showing the location of the Apollo 17 landing site on the lunar nearside. The black dot pinpointing the landing site is in the Taurus-Littrow area at the southeastern edge of the Sea of Serenity. The coordinates of the landing point are 30 degrees 44 minutes 58 seconds east longitude and 20 degrees 9 minutes 50 seconds north latitude.
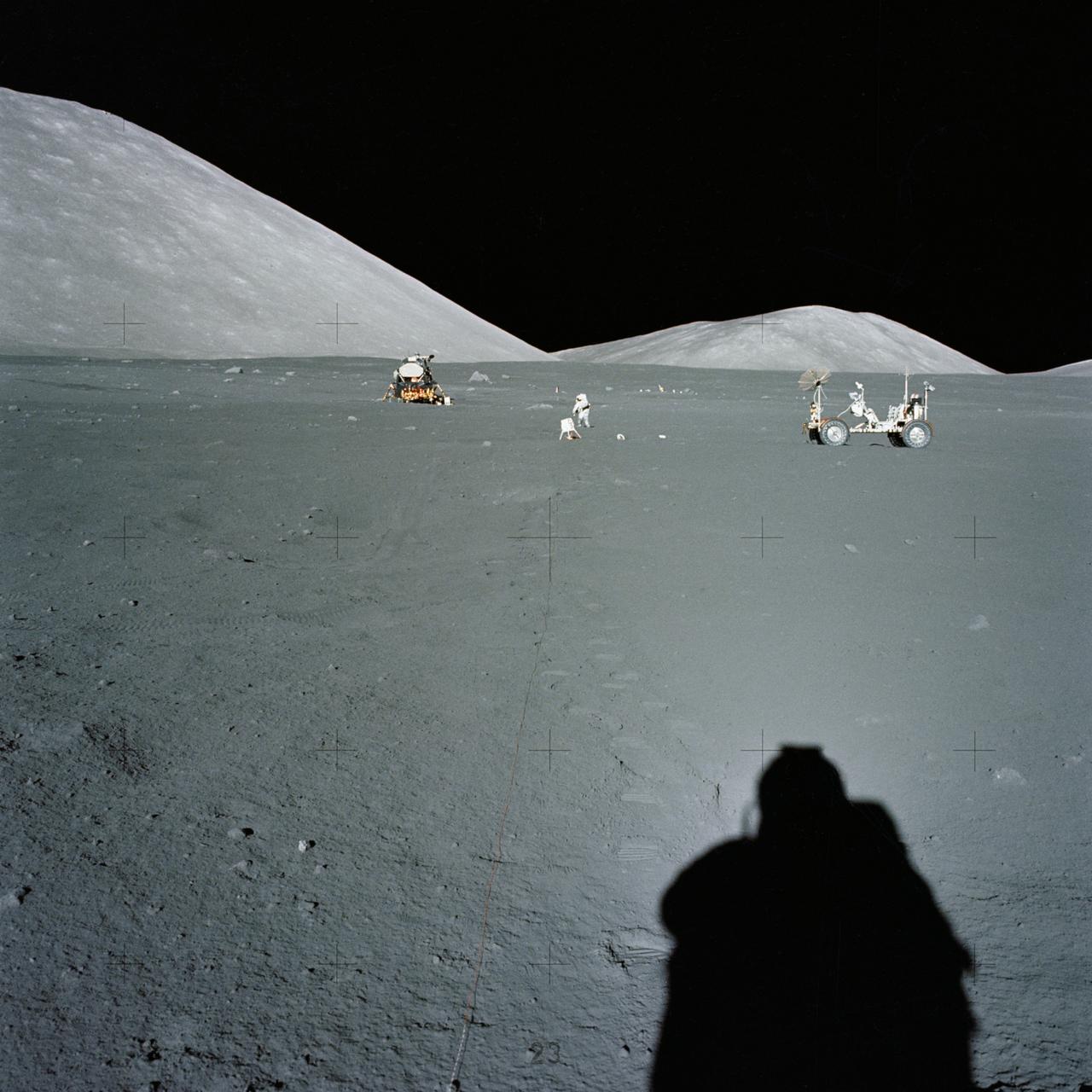

AS17-134-20435 (10 Dec. 1972) --- Wide-angle view of the Apollo 17 Taurus-Littrow lunar landing site. To the left in the background is the Lunar Module. To the right in the background is the Lunar Roving vehicle. An Apollo 17 crewmember is photographed between the two points. The shadow of the astronaut taking the photograph can be seen in the right foreground.

This 70mm frame, showintg the Apollo 17 Command/Service Modules (CSM) backdropped against the Taurus-Littrow landing site, was exposed from the lunar module (LM) prior to the LM's touchdown on the lunar surface.

S71-44150 (February 1971) --- A vertical view of the Apollo 16 landing site located in the Descartes area on the lunar nearside. The overlay indicates the location of the proposed touchdown point for the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM). Descartes is located west of the Sea of Nectar and southwest of the Sea of Tranquility. This photograph was taken with a 500mm lens camera from lunar orbit by the Apollo 16 crew. Astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 LM "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
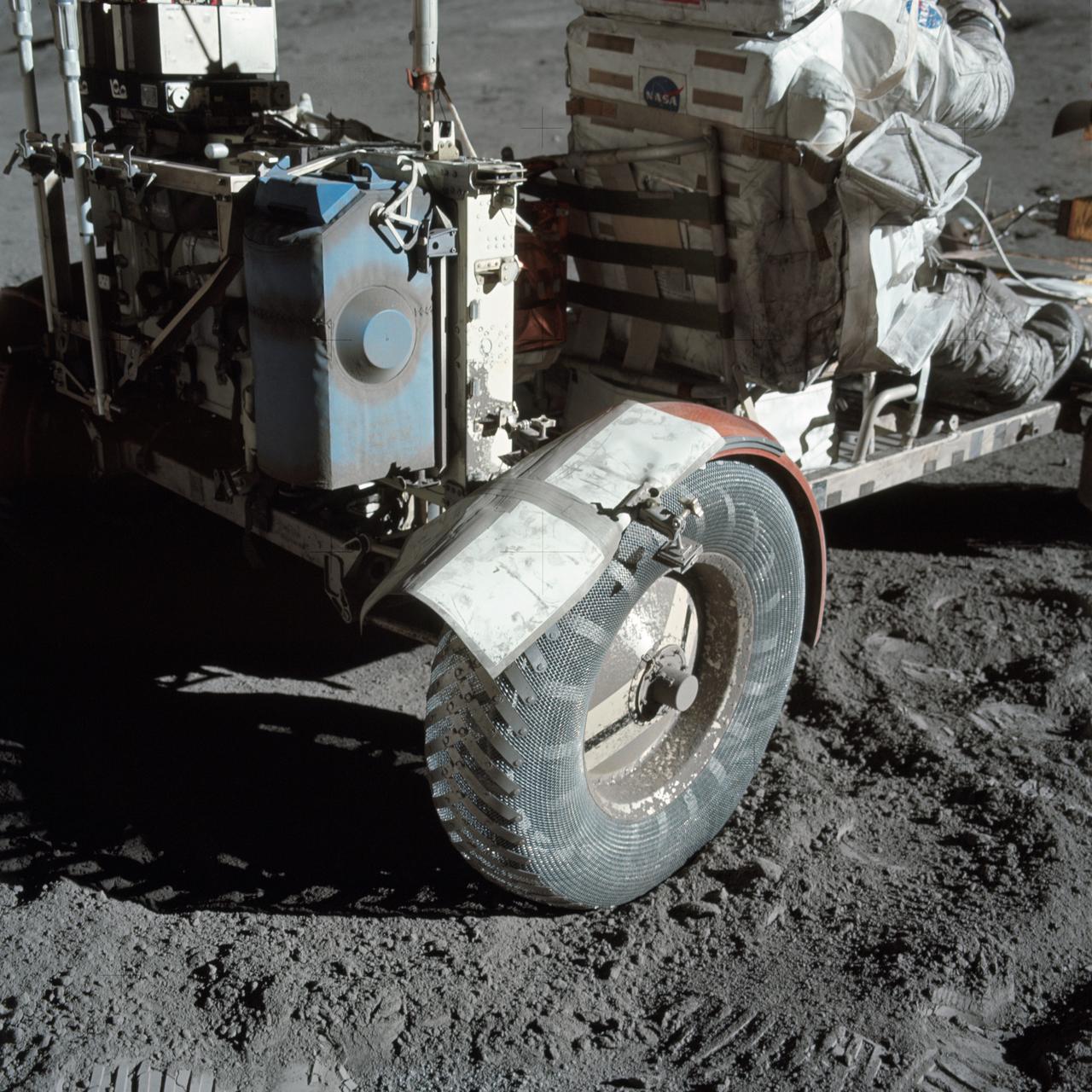

AS17-137-20979 (12 Dec. 1972) --- A close-up view of the lunar roving vehicle (LRV) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site photographed during Apollo 17 lunar surface extravehicular activity. Note the makeshift repair arrangement on the right rear fender of the LRV. During EVA-1 a hammer got underneath the fender and a part of it was knocked off. Astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt were reporting a problem with lunar dust because of the damage fender. Following a suggestion from astronaut John W. Young in the Mission Control Center at Houston the crewmen repaired the fender early in EVA-2 using lunar maps and clamps from the optical alignment telescope lamp. Schmitt is seated in the rover. Cernan took this picture.
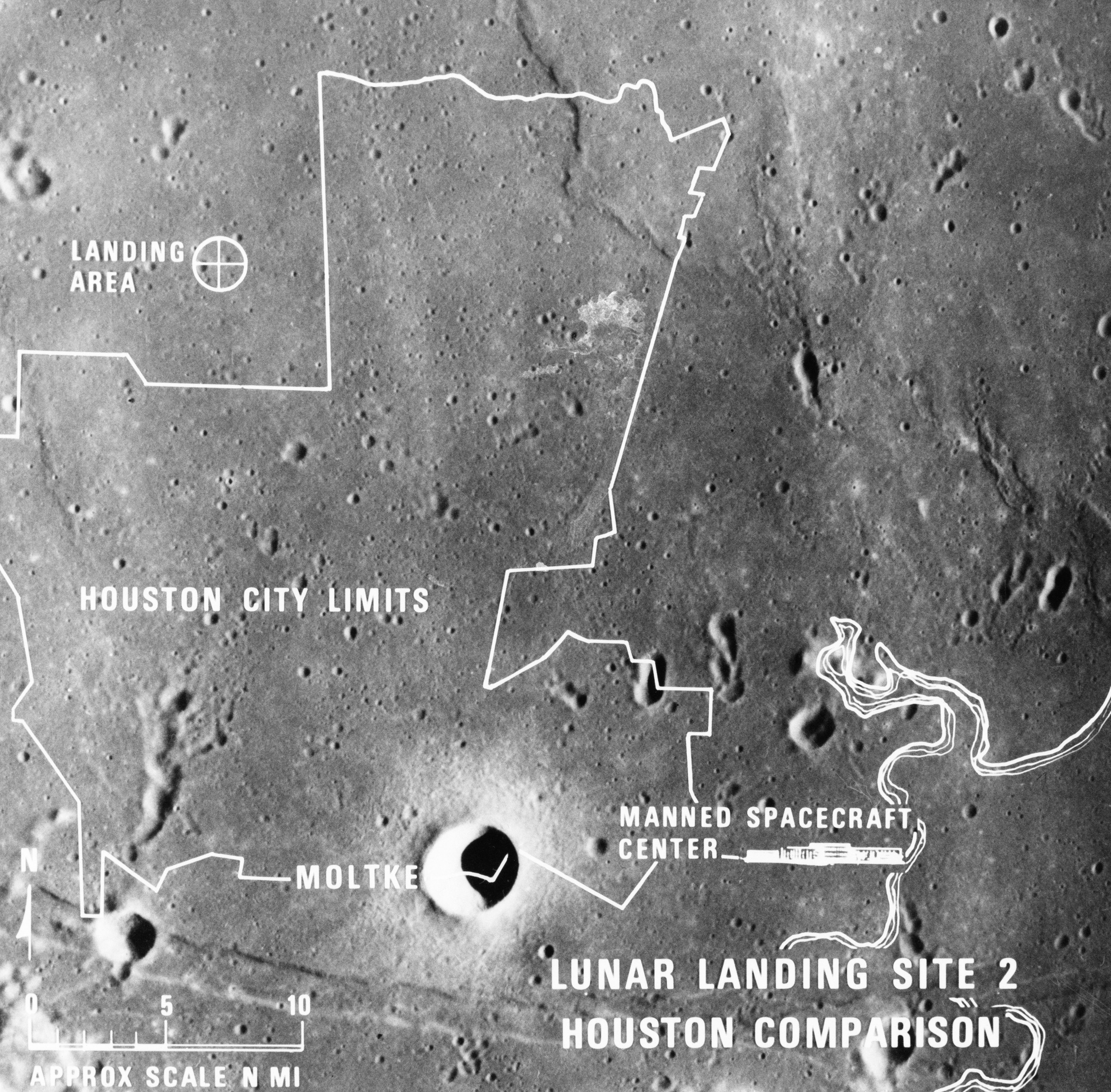
S69-38671 (July 1969) --- A photographic illustration comparing the size of Apollo Landing Site 2 with that of the metropolitan Houston, Texas area. Site 2 is one of three Apollo 11 lunar landing sites. This will be the landing site if Apollo 11 is launched on July 16, 1969, as scheduled. Site 2 is located at 23 degrees 42 minutes 28 seconds east longitude and 0 degrees 42 minutes 50 seconds north latitude in southwestern Mare Tranquillitatis (Sea of Tranquility). (The white overlay is printed over a lunar surface photograph taken from Apollo 10 during its lunar orbit mission and is numbered AS10-31-4537.)
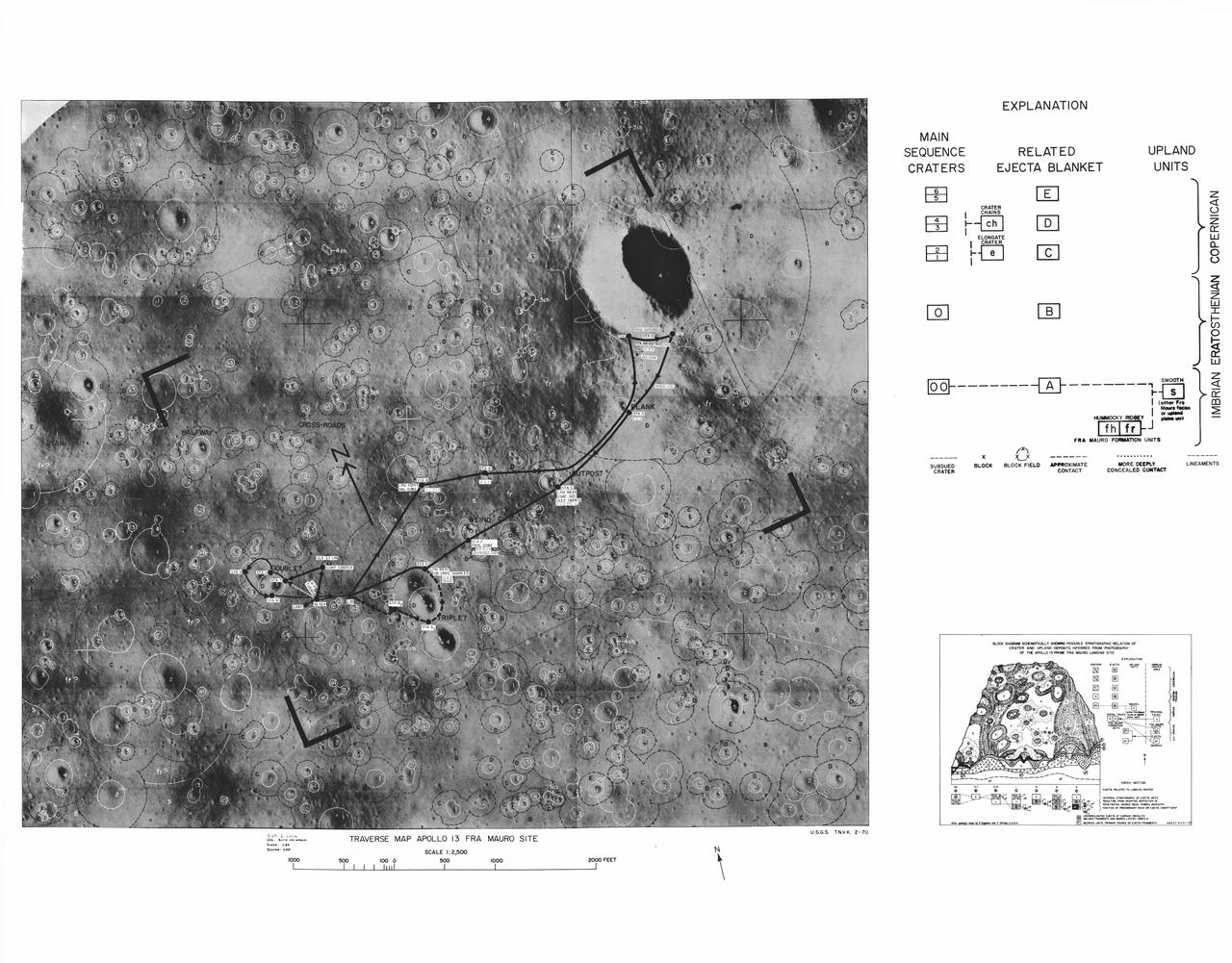
This lunar map shows the traverse plans for the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. Areas marked include Lunar module landing site, areas for the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiment Package (ALSEP) and areas for gathering of core samples.
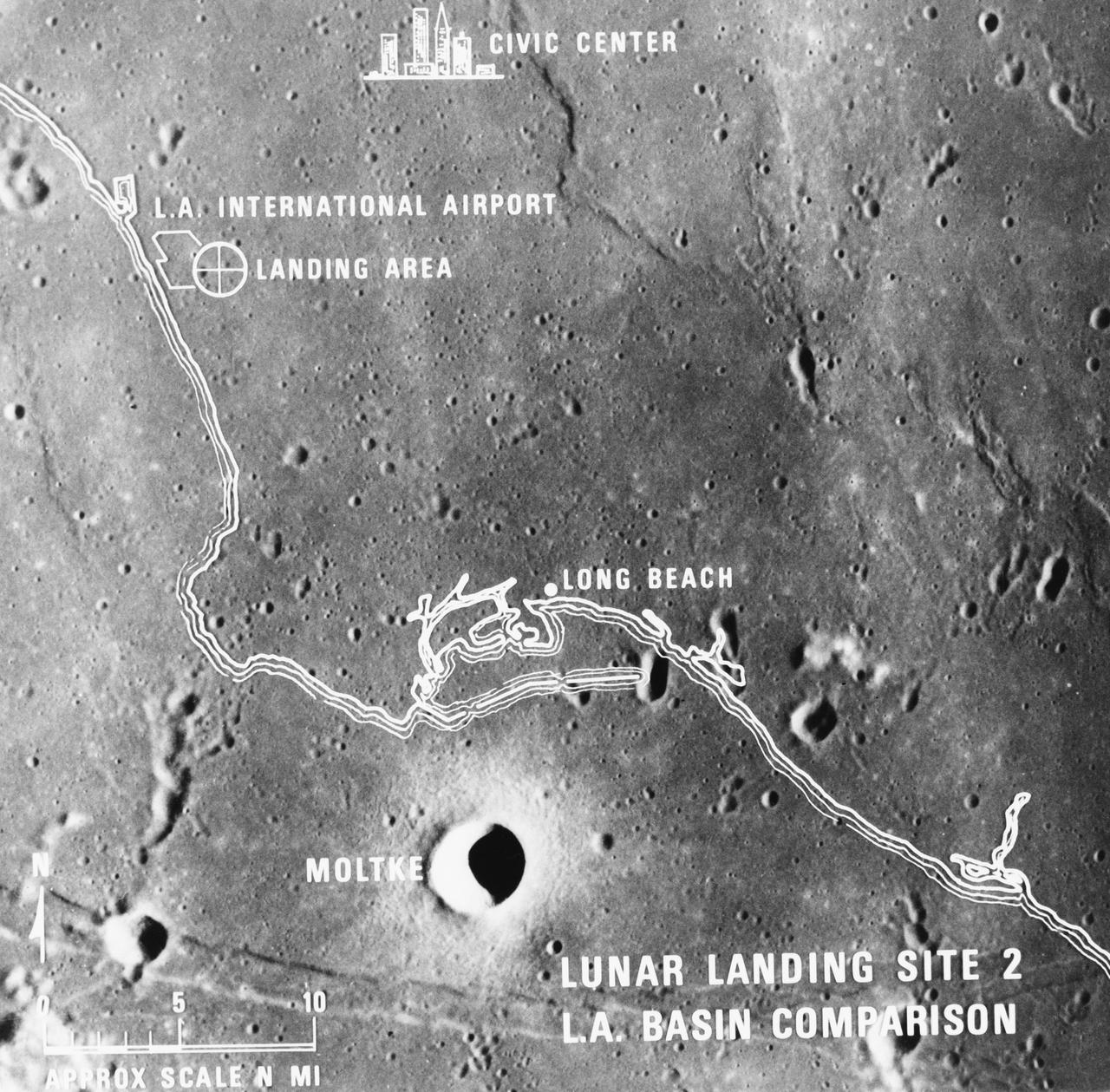

S69-38670 (July 1969) --- A photographic illustration comparing the size of Apollo Landing Site 2 with that of the metropolitan Los Angeles, California area. Site 2 is one of three Apollo 11 lunar landing sites. This will be the landing site if Apollo 11 is launched on July 16, 1969, as scheduled. Site 2 is located at 23 degrees 42 minutes 28 seconds east longitude and 0 degrees 42 minutes 50 seconds north latitude in southwestern Mare Tranquillitatis (Sea of Tranquility). (The white overlay is printed over a lunar surface photograph taken from Apollo 10 during its lunar orbit mission and is numbered AS10-31-4537.)
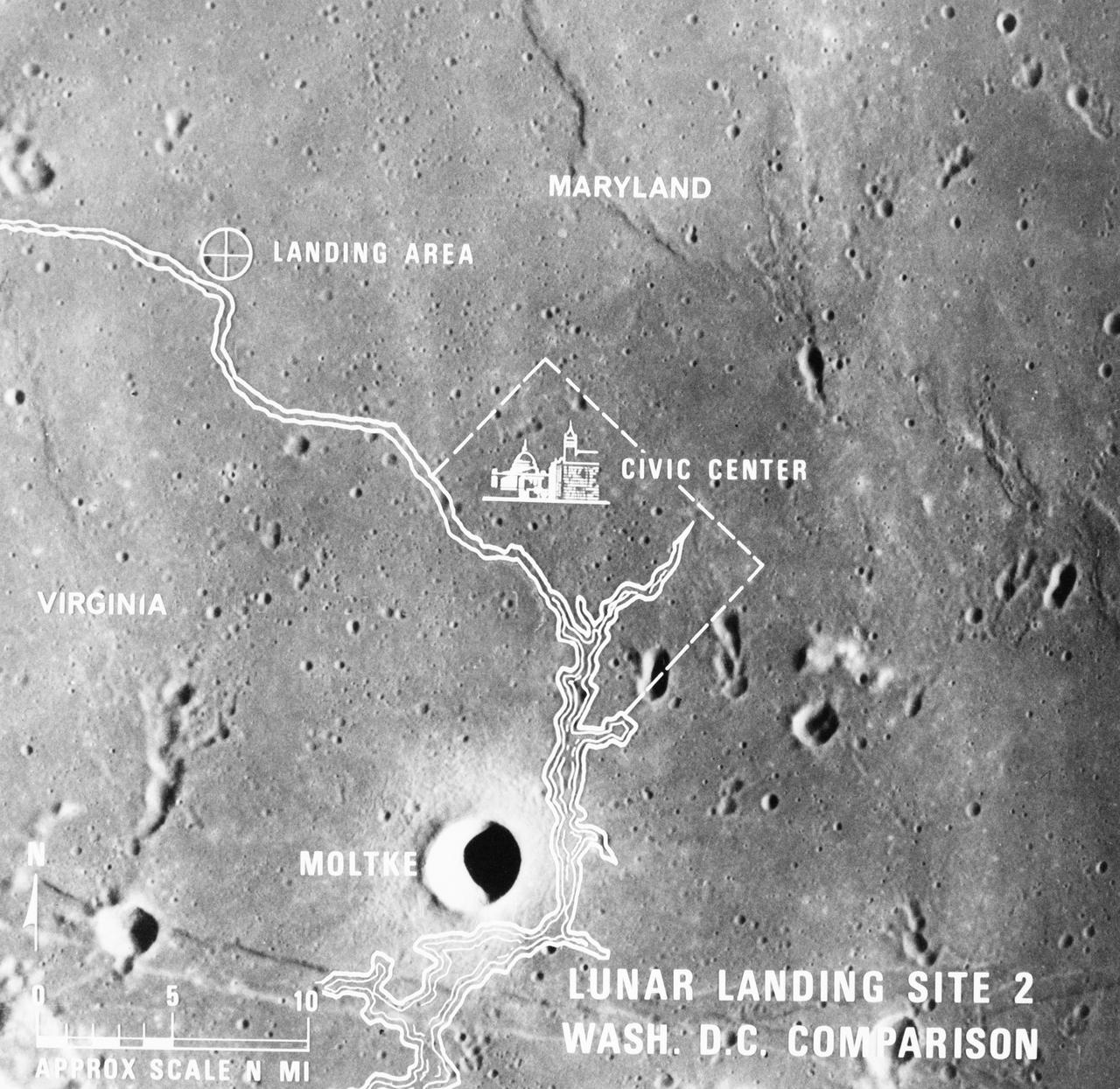

S69-38667 (July 1969) --- A photographic illustration comparing the size of Apollo Landing Site 2 with that of the metropolitan Washington, D.C. area. Site 2 is one of three Apollo 11 lunar landing sites. This will be the landing site if Apollo 11 is launched on July 16, 1969, as scheduled. Site 2 is located at 23 degrees 42 minutes 28 seconds east longitude and 0 degrees 42 minutes 50 seconds north latitude in southwestern Mare Tranquillitatis (Sea of Tranquility). (The white overlay is printed over a lunar surface photograph taken from Apollo 10 during its lunar orbit mission and is numbered AS10-31-4537.)
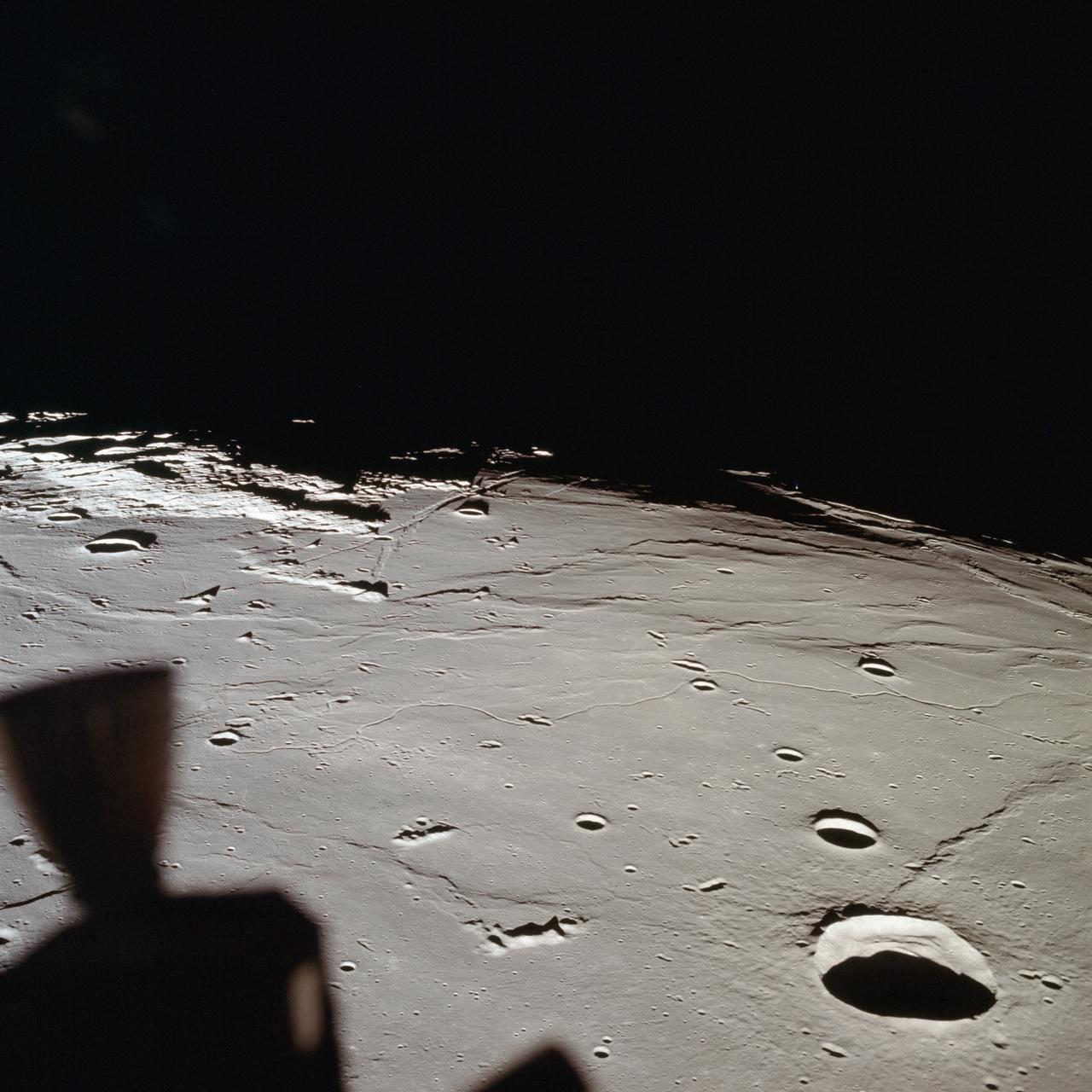

AS11-37-5437 (20 July 1969) --- The approach to Apollo Landing Site 2 in southwestern Sea of Tranquility is seen in this photograph taken from the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) in lunar orbit. When this picture was made, the LM was still docked to the Command and Service Modules (CSM). Site 2 is located just right of center at the edge of the darkness. The crater Maskelyne is the large one at the lower right. Hypatia Rille (U.S. 1) is at upper left, with the crater Moltke just to the right (north) of it. Sidewinder Rille and Diamondback Rille extend from left to right across the center of the picture. This view looks generally west.

AS08-17-2821 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- This oblique view of the lunar surface taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking westward across the Sea of Tranquility shows Apollo Landing Site East 2 illuminated by a sun that is six to eight degrees above the eastern horizon. The landing site is on the dark gray, smooth surface of the Sea of Tranquility and north (to the right) of the bright highland terrain at the lower left corner of the photograph. The landing site is about four tenths of the distance from the left to right margin of the photograph.

AS16-107-17436 (21 April 1972) --- An excellent view of the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" and Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), as photographed by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. Astronaut John W. Young, commander, can be seen directly behind the LRV. The lunar surface feature in the left background is Stone Mountain. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the LM to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.

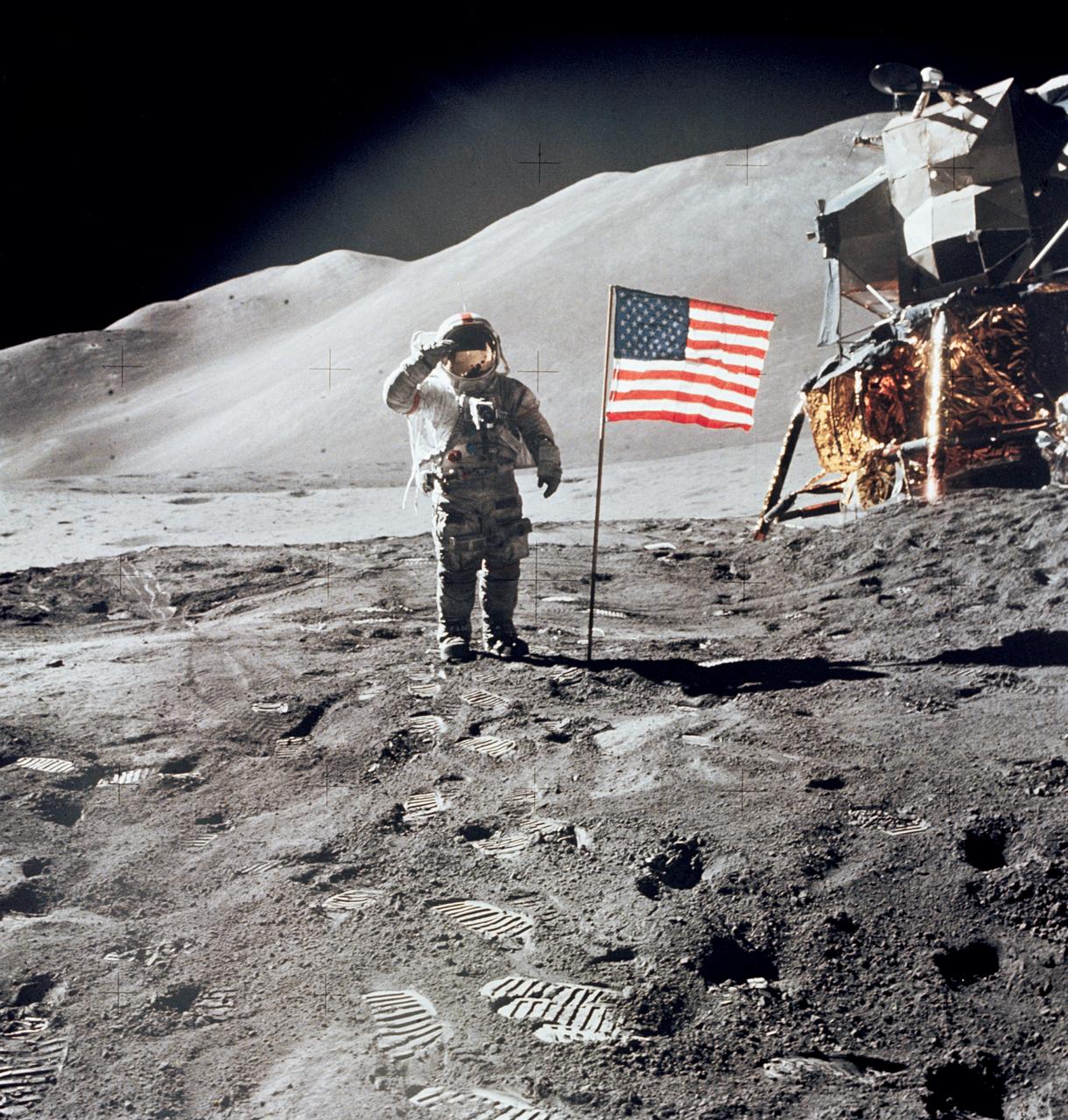
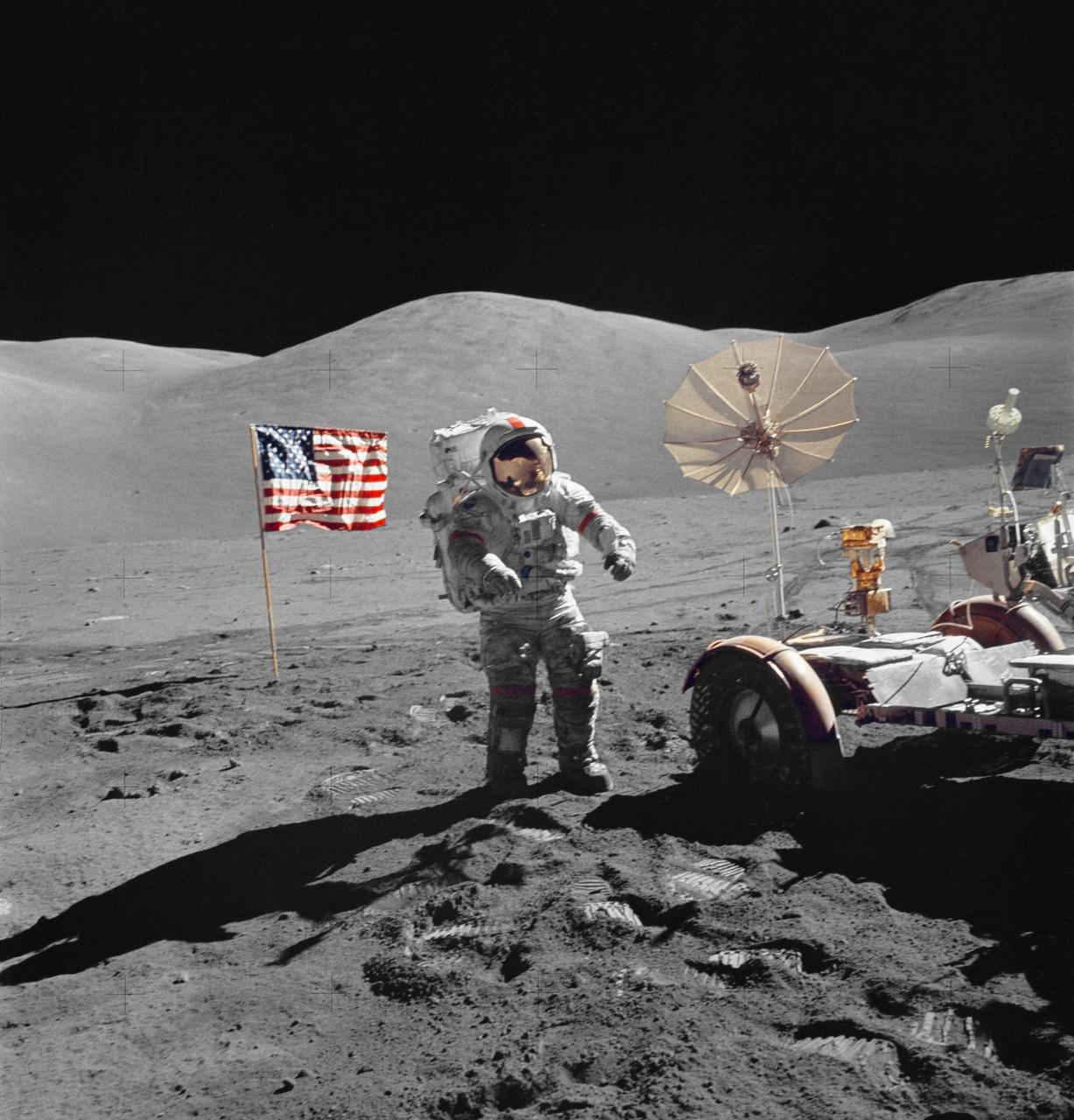
AS16-113-18339 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, leaps from the lunar surface as he salutes the United States flag at the Descartes landing site during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, took this picture. The Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" is on the left. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is parked beside the LM. The object behind Young (in the shade of the LM) is the Far Ultraviolet Camera/Spectrograph (FUC/S). Stone Mountain dominates the background in this lunar scene. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the LM to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
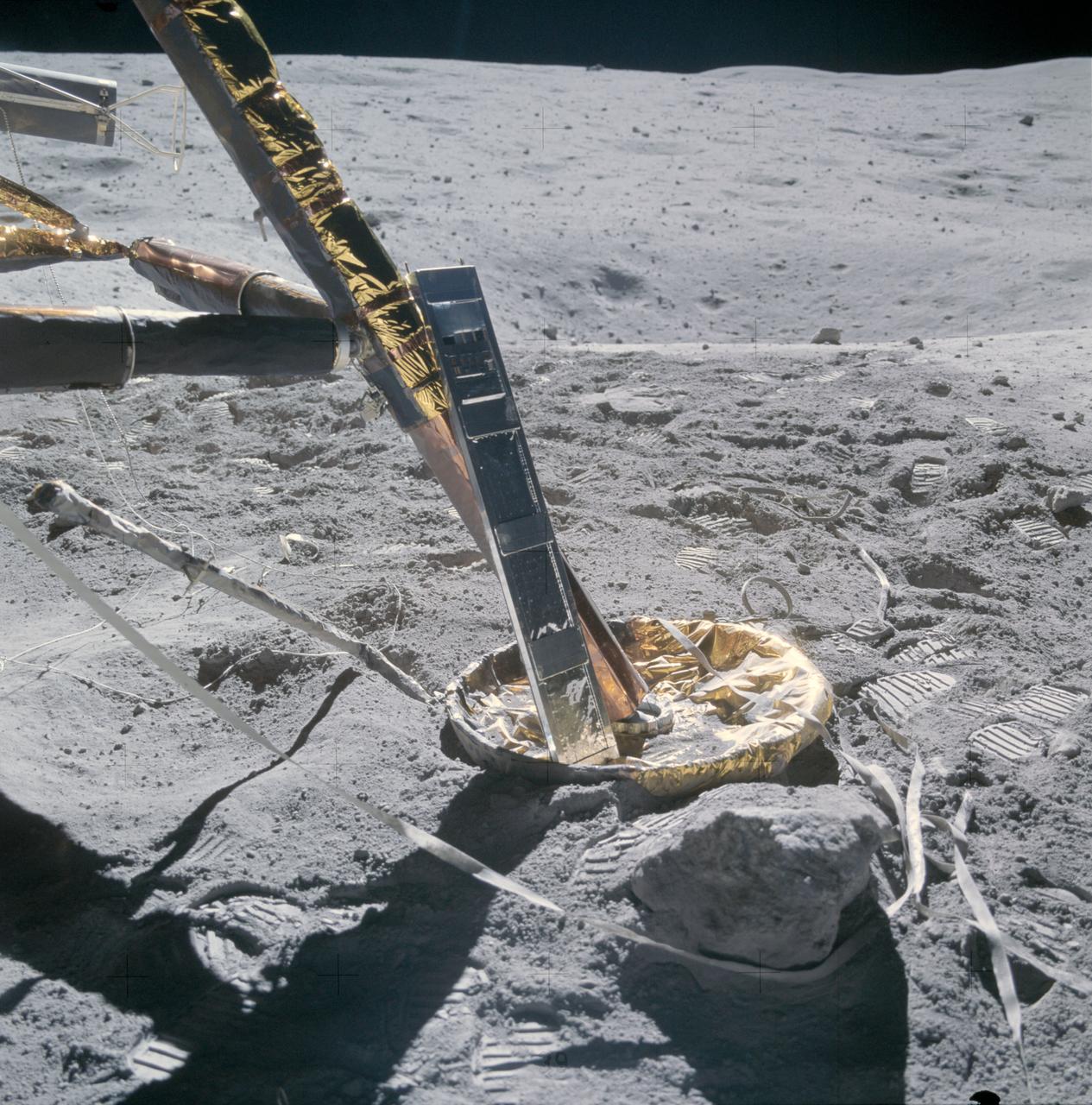

AS16-107-17442 (22 April 1972) --- A close-up view of the Apollo 16 Cosmic Ray Detector (CRD) experiment deployed at the +Y strut of the Lunar Module (LM). The crewmembers moved it to this position from near the deployment site of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) because, in the words of astronaut John W. Young, commander, "The panels were getting a little warm." Note that the LM did not skid upon landing, as evidenced by the landing contact probe's folded back (neatly) position and the lack of skid marks. While astronauts Young, and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
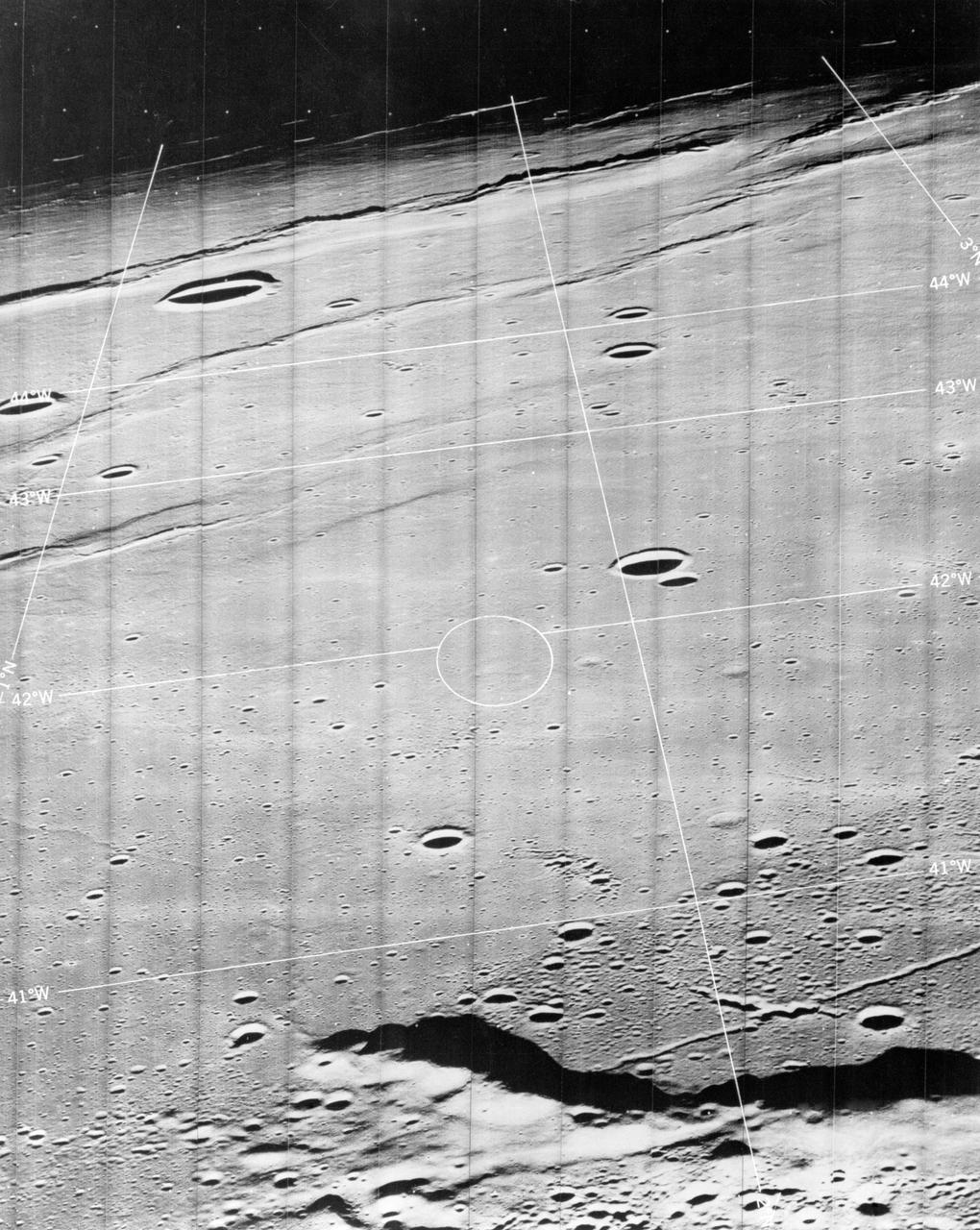

S69-54553 (October 1969) --- If the Apollo 12 launch is postponed until Nov. 16, 1969, the lunar landing will be made in this area in the Sea of Storms. (The prime launch window is Nov. 14, 1969, at 11:22 a.m. (EST), landing at Site 7.) This site (Site 5) is located at 41 degrees 40 minutes west longitude and 1 degree 40 minutes north latitude. This photograph was taken by Lunar Orbiter 3 on Feb. 21, 1967, at an altitude of 32 miles (51.8 kilometers) above the moon. This view is looking west with the sun almost directly behind the spacecraft. These approximates show the landing site as it will look to Apollo astronauts as they approach the site. The actual target site is represented by the ellipse which measures three by five miles. The lines indicate coordinates on the moon near the target site.
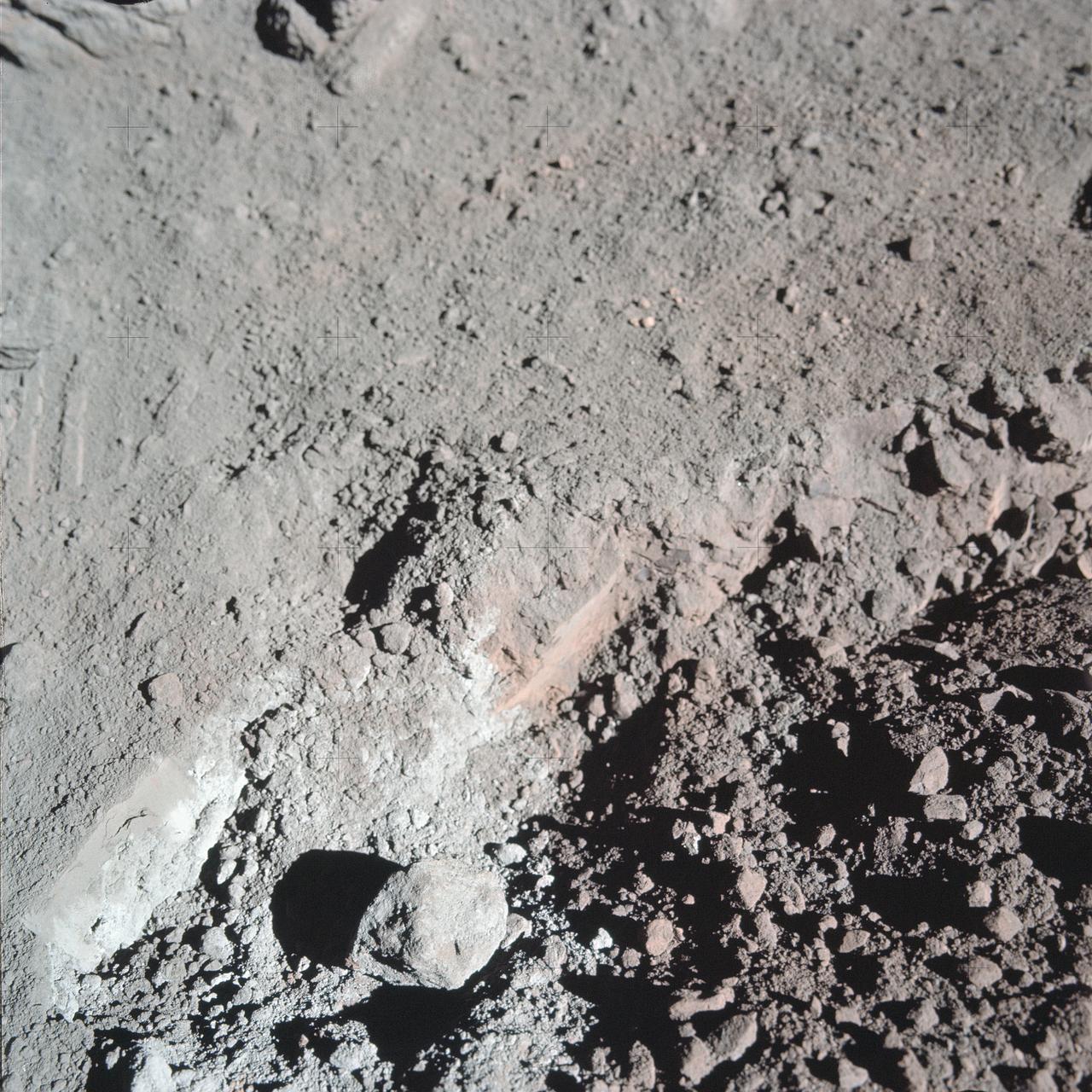

AS17-137-20989 (12 Dec. 1972) --- A close-up view of the much-publicized orange soil which the Apollo 17 crewmen found at Station 4 (Shorty Crater) during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The orange soil was first spotted by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt. While astronauts Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The orange soil was never seen by the crewmen of the other lunar landing missions - Apollo 11 (Sea of Tranquility); Apollo 12 (Ocean of Storms); Apollo 14 (Fra Mauro); Apollo 15 (Hadley-Apennines); and Apollo 16 (Descartes).
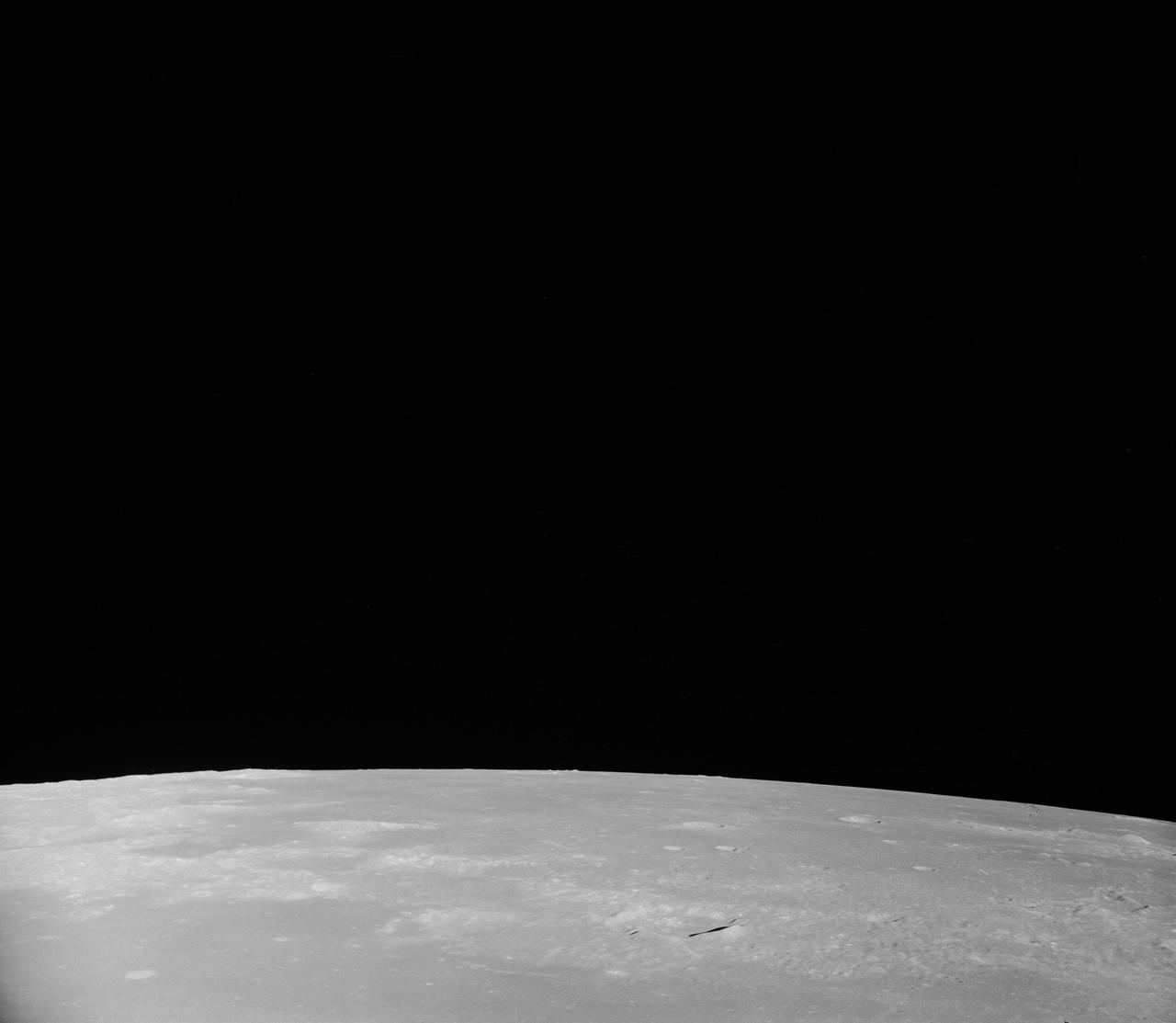

AS08-17-2814 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- This oblique view of the lunar surface taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft looking westward across the Sea of Fertility into the Sea of Tranquility shows the terrain the astronauts will see as the approach Apollo Landing Site East 2. The landing site is at the horizon about one-third of the distance from the left to the right photograph margin. The prominent crater in the highlands near the center of the picture is Secchi, about 25 kilometers (15 statute miles) in diameter.
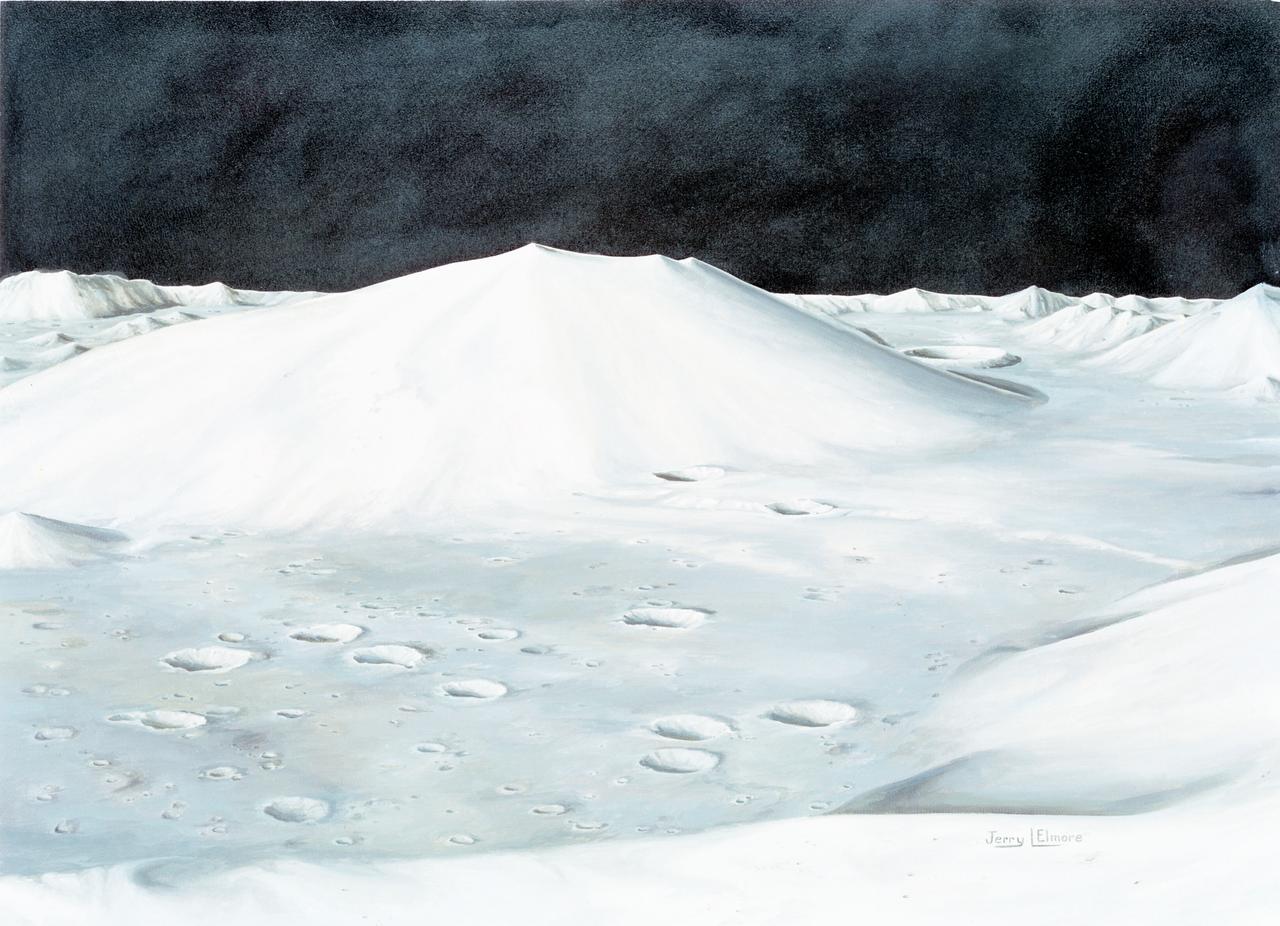

S72-49761 (October 1972) --- An artist's concept illustrating the topographical layout of the Taurus-Littrow landing site of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. The Lunar Module touchdown point is in the center of the smooth area in the middle of the picture. The imposing mountain in the center is South Massif. A portion of North Massif is in the lower right corner of the photograph. Note the ridge-like feature extending from South Massif to North Massif. The southern portion of the ridge is called Lee Scarp and the northerly portion Lincoln Scarp. (This concept is by JSC artist Jerry Elmore).

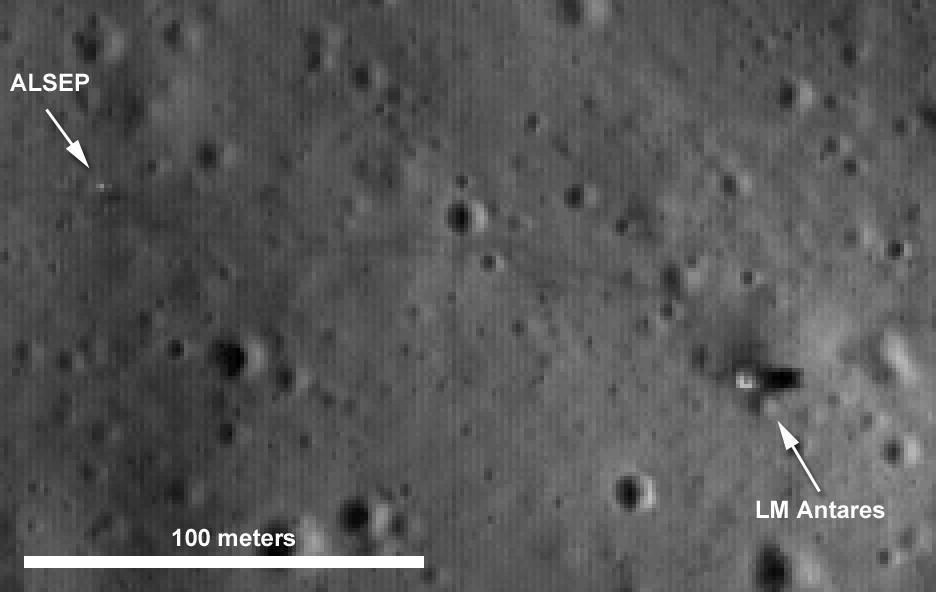
S69-57076 (November 1969) --- This photograph taken by Lunar Orbiter 3 shows the prime Apollo 12 lunar landing site, which is located 1,000 feet east and 500 feet north of Surveyor 3. The landing ellipse is 7.2 nautical miles by 2.6 nautical miles. The coordinates of the ellipse center are 2 degrees 56 minutes 33 seconds (2.943 degrees) south latitude and 23 degrees 26 minutes 36 seconds (23.443 degrees) west longitude, and the elevation is 1,735,900 meters. The coordinates of Surveyor 3 are 2 degrees 57 minutes 10 seconds (2.953 degrees) south latitude, and 23 degrees 27 minutes 10 seconds (23.453 degrees) west longitude.
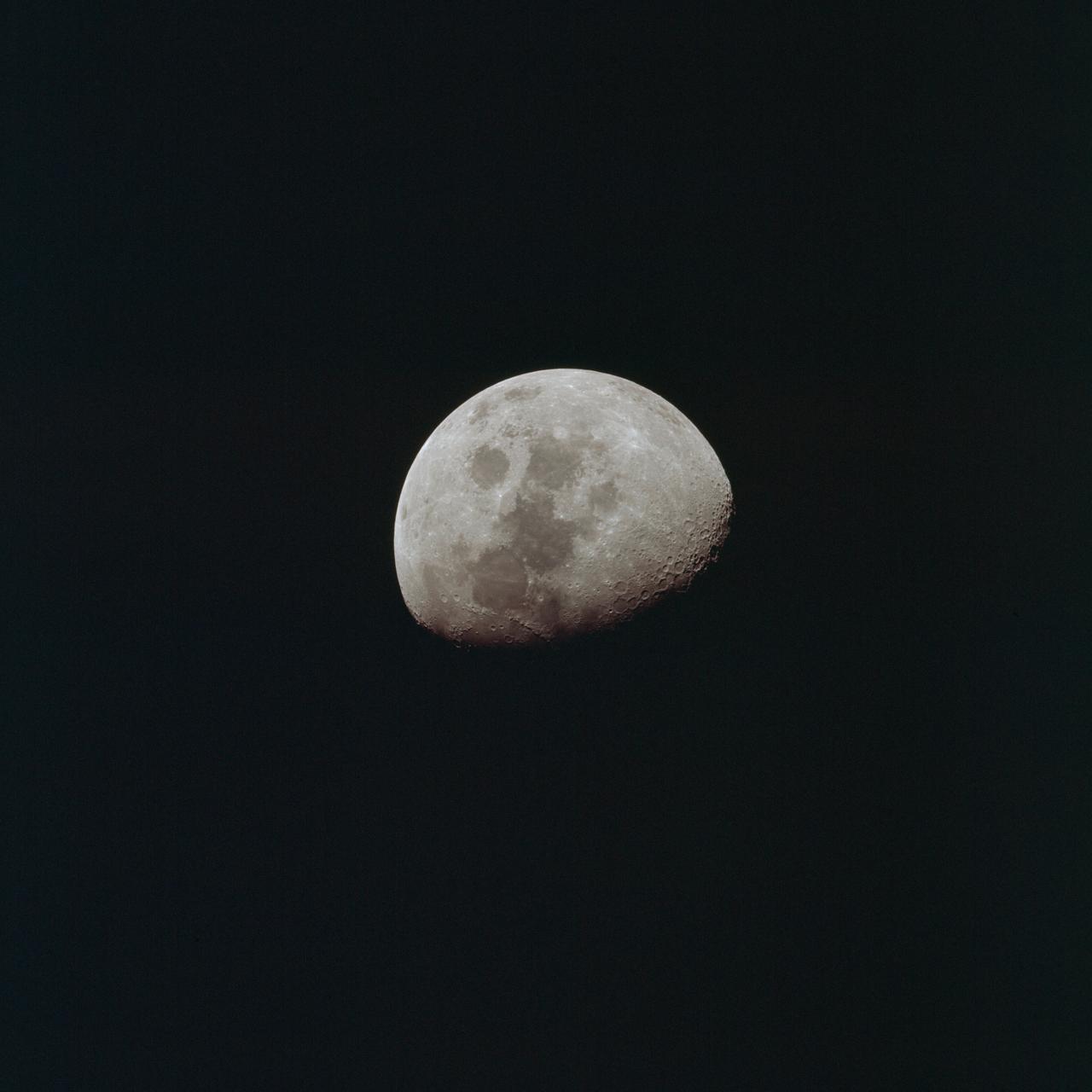

AS10-27-3956 (24 May 1969) --- This photograph of the moon was taken after trans-Earth insertion when the Apollo 10 spacecraft was high above the lunar equator near 27 degrees east longitude. North is about 20 degrees left of the top of the photograph. Apollo Landing Site 3 is on the lighted side of the terminator in a dark area just north of the equator. Apollo Landing Site 2 is near the lower left margin of the Sea of Tranquility (Mare Tranquillitatis), which is the large, dark area near the center of the photograph.
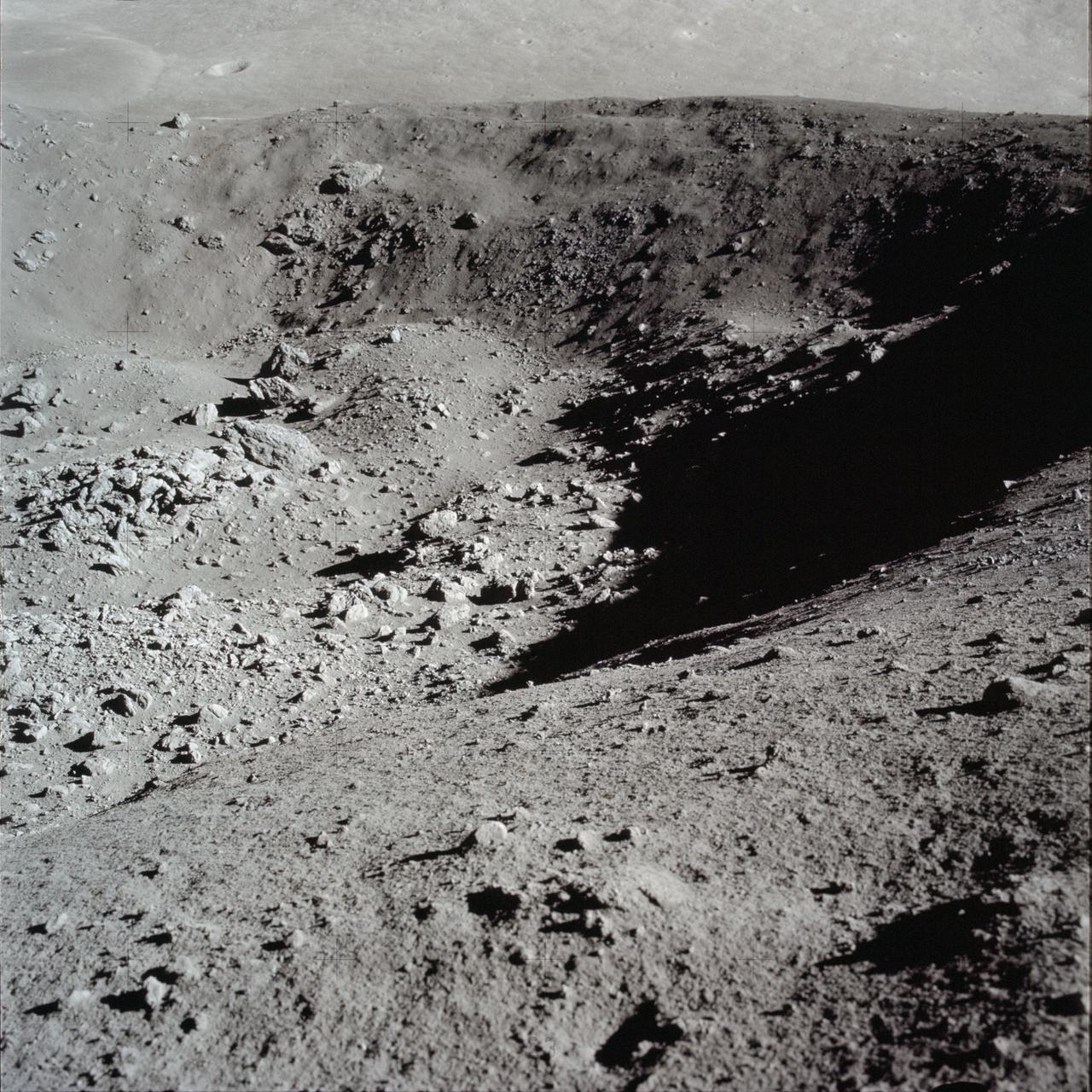

AS17-137-20992 (12 Dec. 1972) --- A view looking into Shorty Crater, taken at Station 4, showing the orange soil. Astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt found the orange soil on the moon during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.

AS16-114-18423 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, is photographed collecting lunar samples at Station No. 1, during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA), at the Descartes landing site. This picture, looking eastward, was taken by astronaut John W. Young, commander. Duke is standing at the rim of Plum Crater. The parked Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) can be seen in the left background. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands region of the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
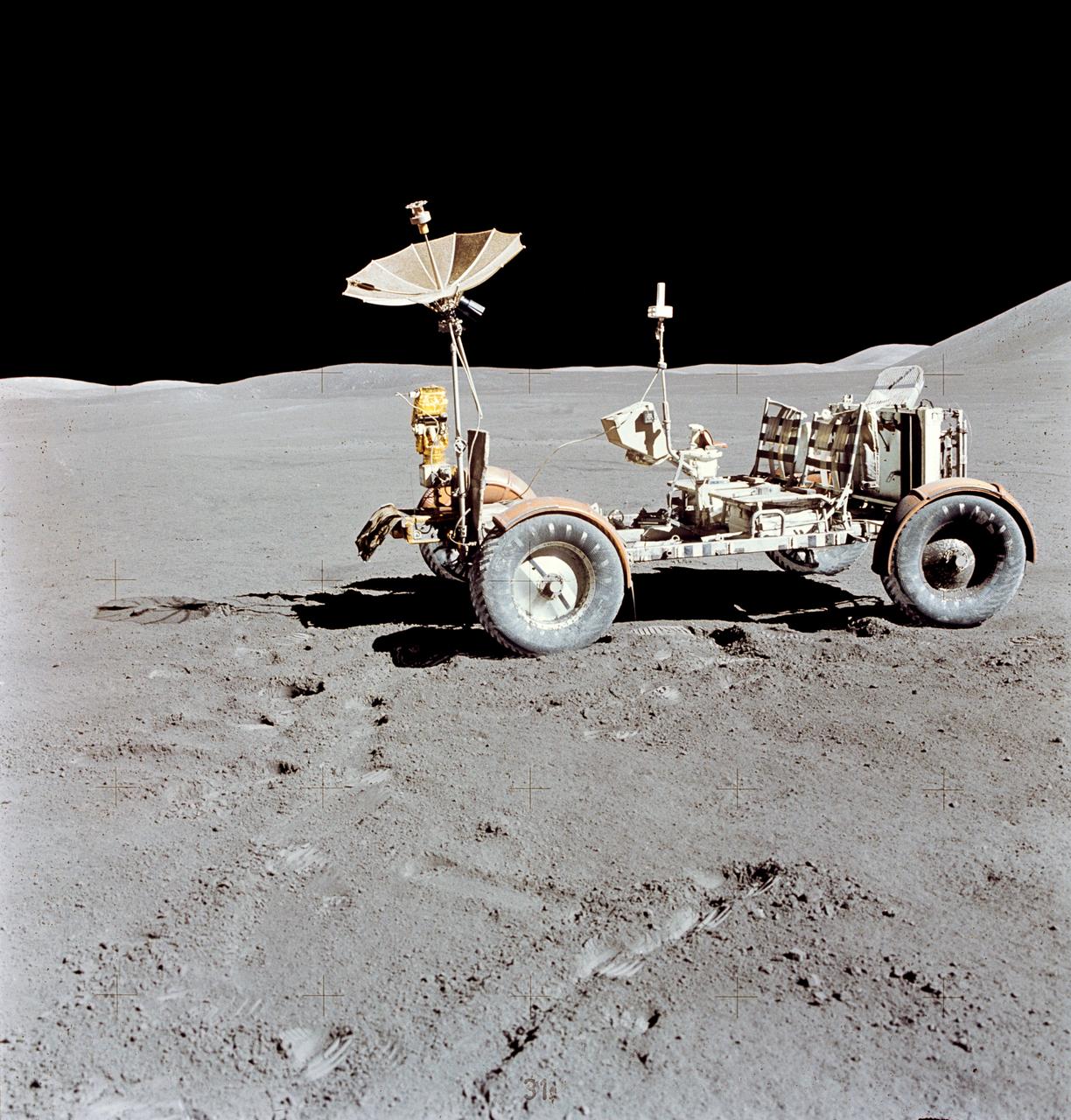

AS15-88-11901 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is photographed alone against the desolate lunar background during the third Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. This view is looking north. The west edge of Mount Hadley is at the upper right edge of the picture. Mount Hadley rises approximately 4,500 meters (about 4,765 feet) above the plain. The most distant lunar feature visible is approximately 25 kilometers (about 15.5 statute miles) away. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
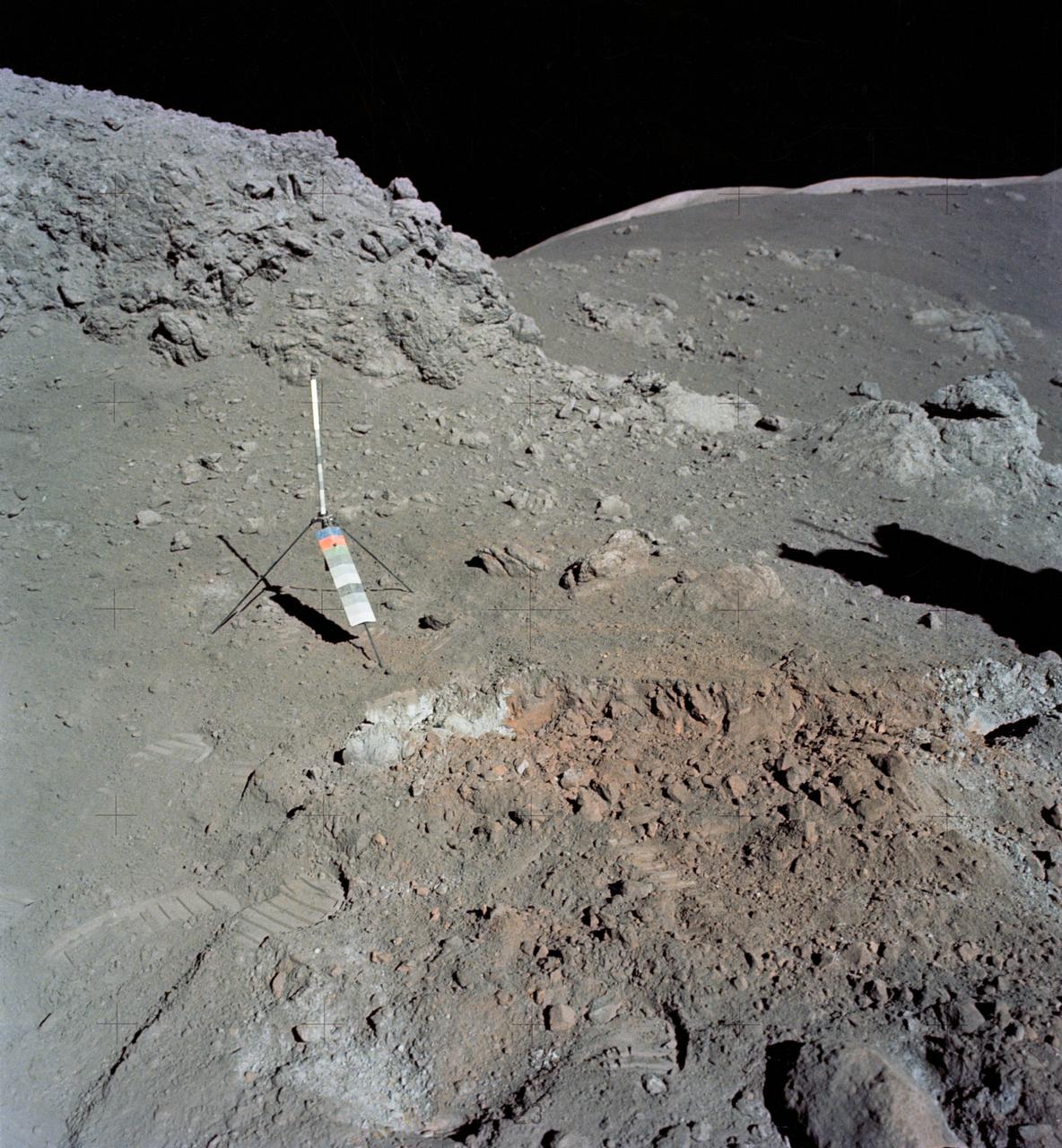

AS17-137-20990 (12 Dec. 1972) --- A view of the area at Station 4 (Shorty Crater) showing the now highly-publicized orange soil which the Apollo 17 crew members found on the moon during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The tripod-like object is the gnomon and photometric chart assembly which is used as a photographic reference to establish local vertical sun angle, scale and lunar color. The gnomon is one of the Apollo lunar geology hand tools. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit. Schmitt was the crew man who first spotted the orange soil.
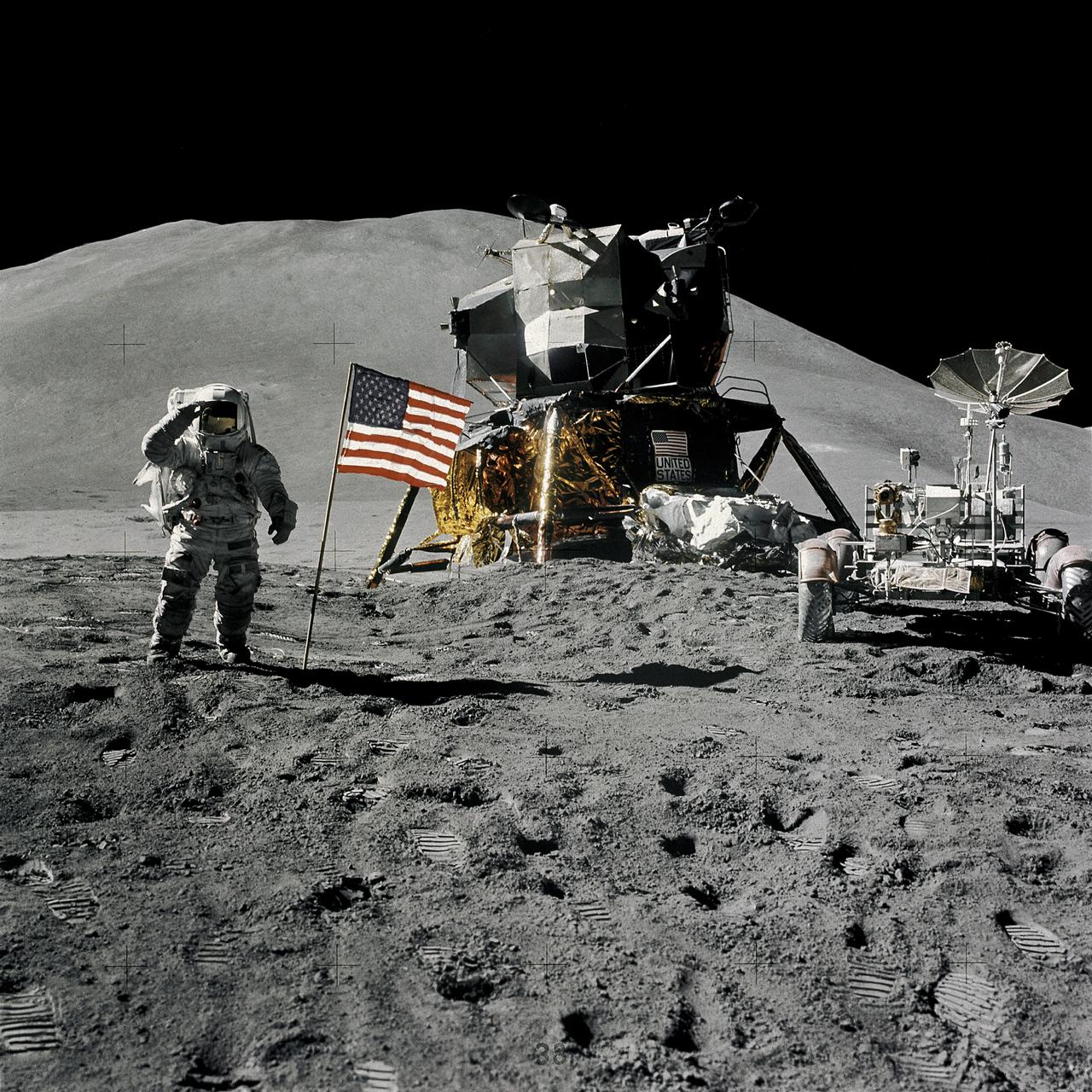

AS15-88-11866 (1 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, gives a military salute while standing beside the deployed United States flag during the Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The flag was deployed toward the end of EVA-2. The Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" is in the center. On the right is the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). This view is looking almost due south. Hadley Delta in the background rises approximately 4,000 meters (about 13,124 feet) above the plain. The base of the mountain is approximately 5 kilometers (about 3 statute miles) away. This photograph was taken by astronaut David R. Scott, Apollo 15 commander. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
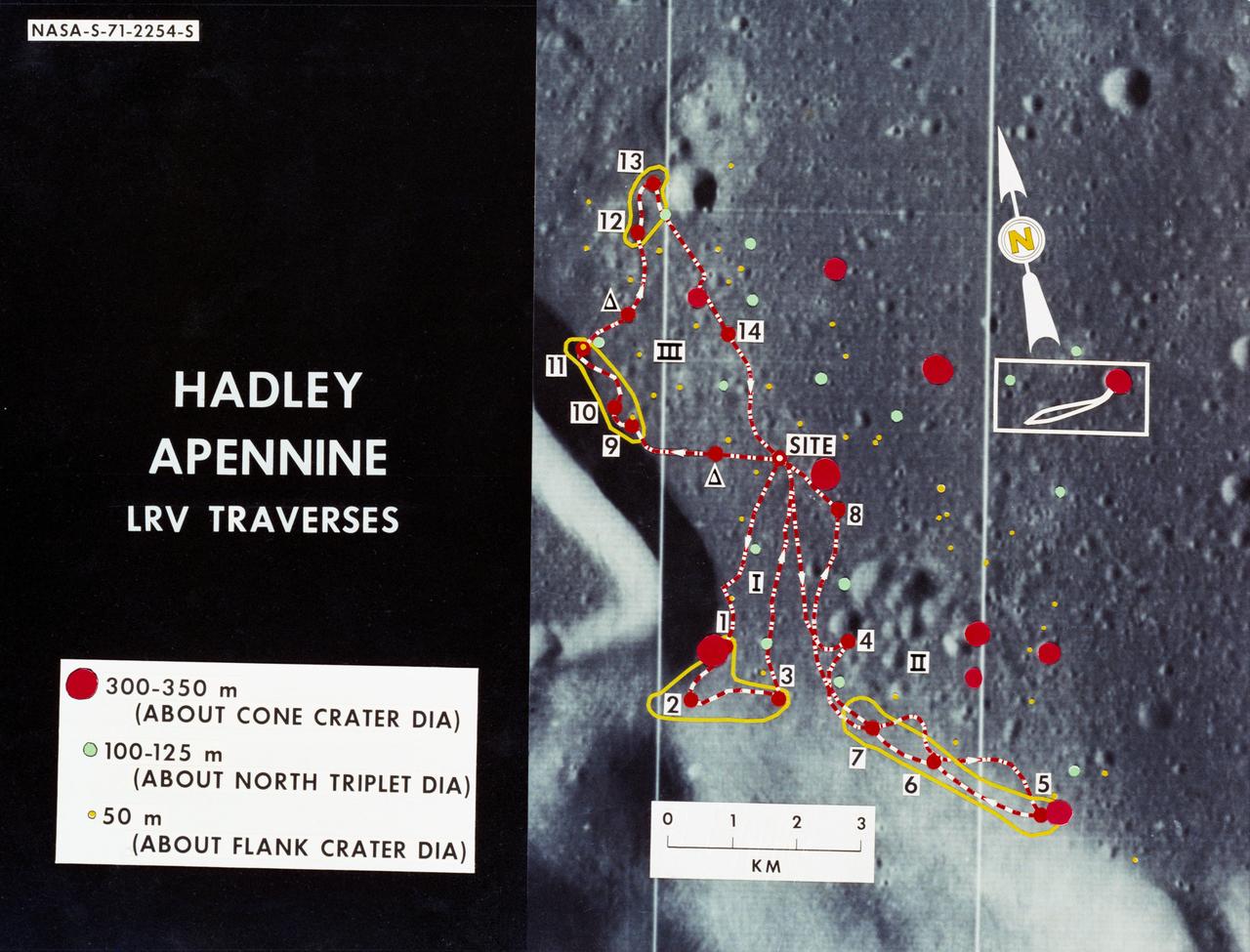
S71-02254 (June 1971) --- An enlarged Lunar Orbiter photograph showing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) traverse routes overlaid on the Hadley-Apennine landing site. Apollo 15 is to land at the point labeled "site," and a comparison of Apollo 14 crater sizes with those of Apollo 15 is included, also. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descend in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
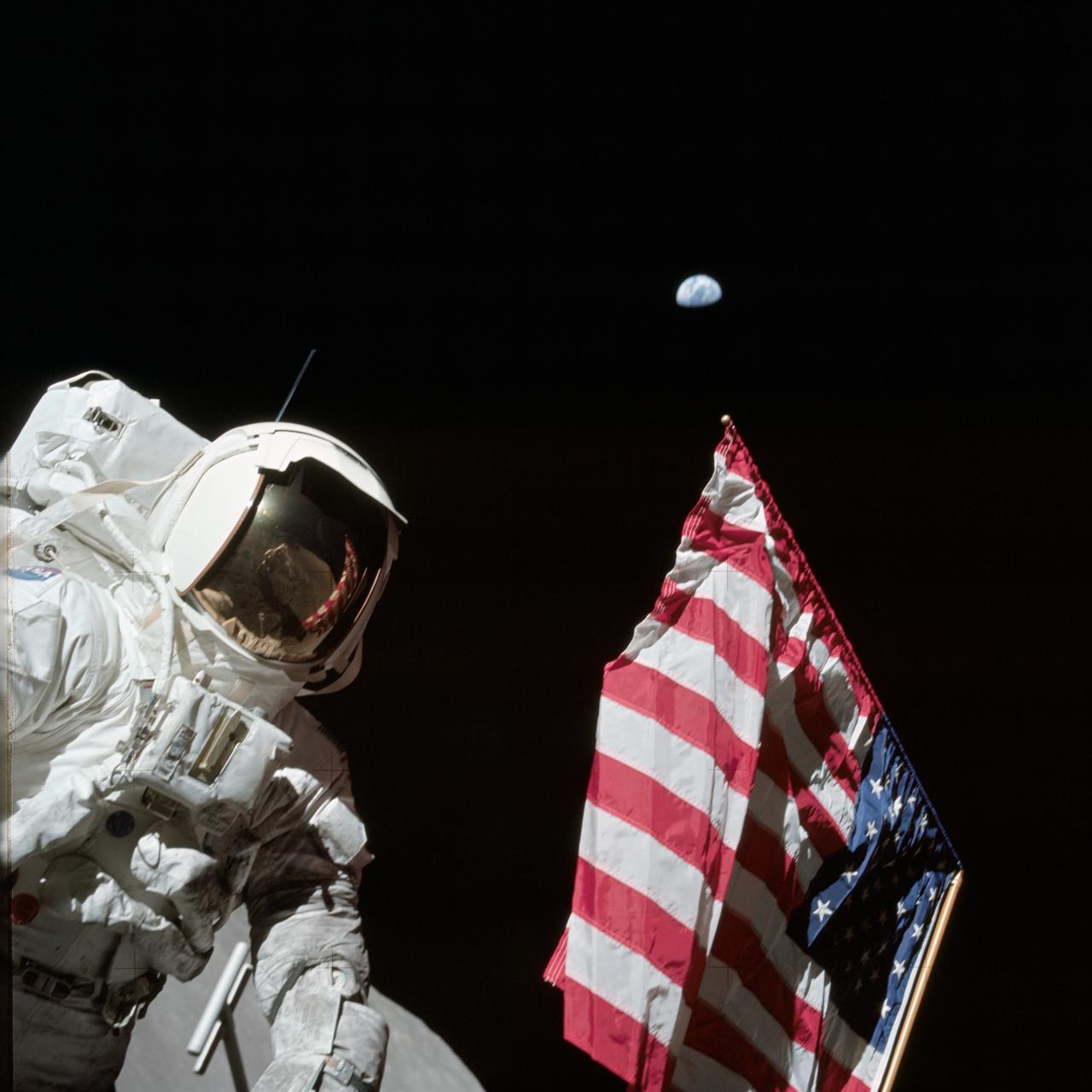

AS17-134-20384 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, is photographed next to the deployed United States flag during lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The highest part of the flag appears to point toward our planet Earth in the distant background. This picture was taken by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS10-31-4537 (18-26 May 1969) --- This near vertical photograph taken from the Apollo 10 Command and Service Modules shows features typical of the Sea of Tranquility near Apollo Landing Site 2. HOLD PICTURE WITH PRONOUNCED LINEAR FEATURE PARALLEL TO LEFT MARGIN. The proposed landing area for Apollo 11 (Lunar Landing Site 2) is a relatively smooth maria area in the upper right quadrant of the photographed area. Apollo 10 traveled from the bottom to the top of the picture. The prominent linear feature at left is Hypatia Rille (called "U.S. 1" by the Apollo 10 crew). The prominent crater centered in Hypatia Rille at top left is Moltke AC (code name "Chuck Hole"). Moltke, the prominent crater to the right of Hypatia Rille, is centered near 24.2 degrees east longitude, and 0.6 degrees south latitude.

AS15-88-11863 (1 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, commander, gives a military salute while standing beside the deployed United States flag during the Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The flag was deployed toward the end of EVA-2. The Lunar Module (LM), "Falcon," is partially visible on the right. Hadley Delta in the background rises approximately 4,000 meters (about 13,124 feet) above the plain. The base of the mountain is approximately 5 kilometers (about three statue miles) away. This photograph was taken by astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained in lunar orbit in the Command and Service Modules (CSM).

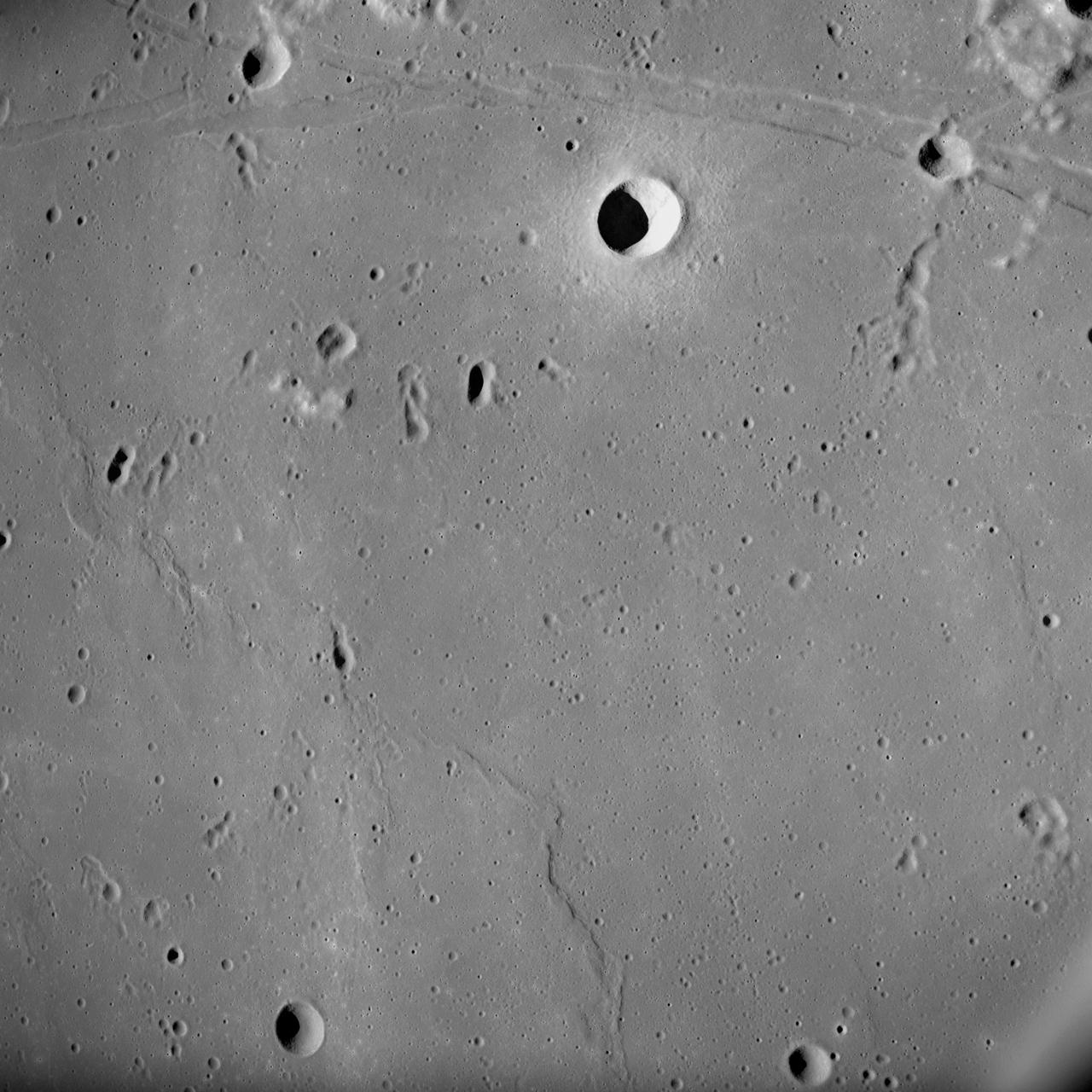
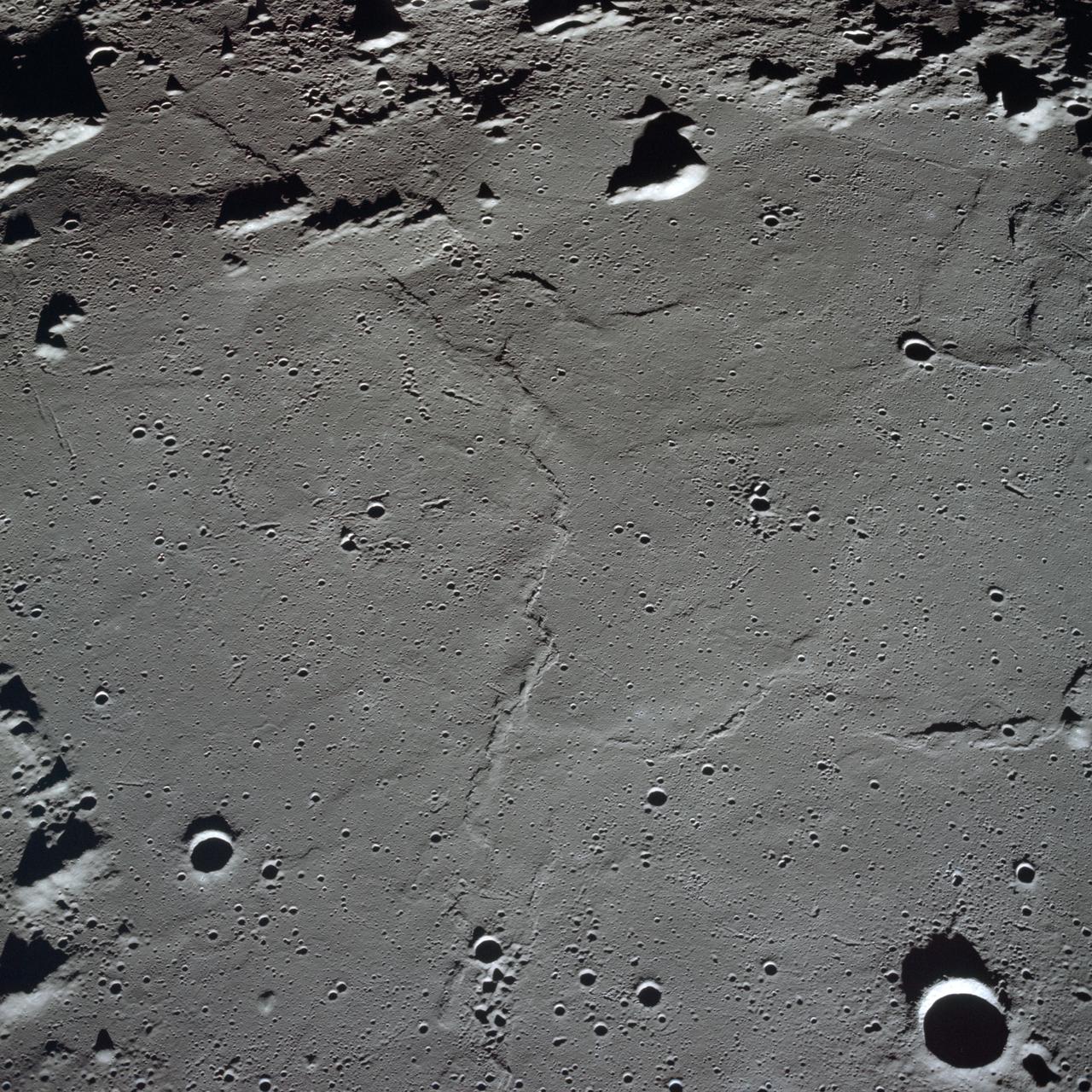
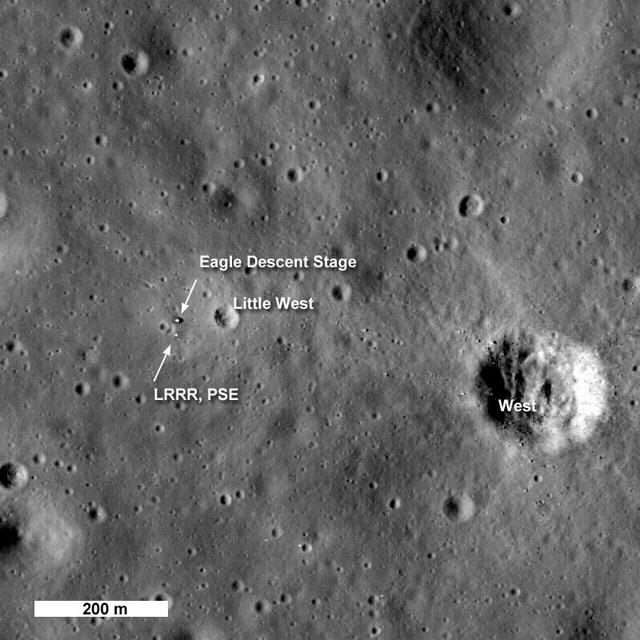
NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter first look at the Apollo landing sites.

AS10-27-3908 (18-26 May 1969) --- An Apollo 10 photograph of the lunar nearside looking westward across Apollo Landing Site 3 in Central Bay. Bruce, the prominent crater in the lower right corner, is about 3.7 statute miles in diameter. Topographic features on the surface of Central Bay are accentuated by the low sun angle.
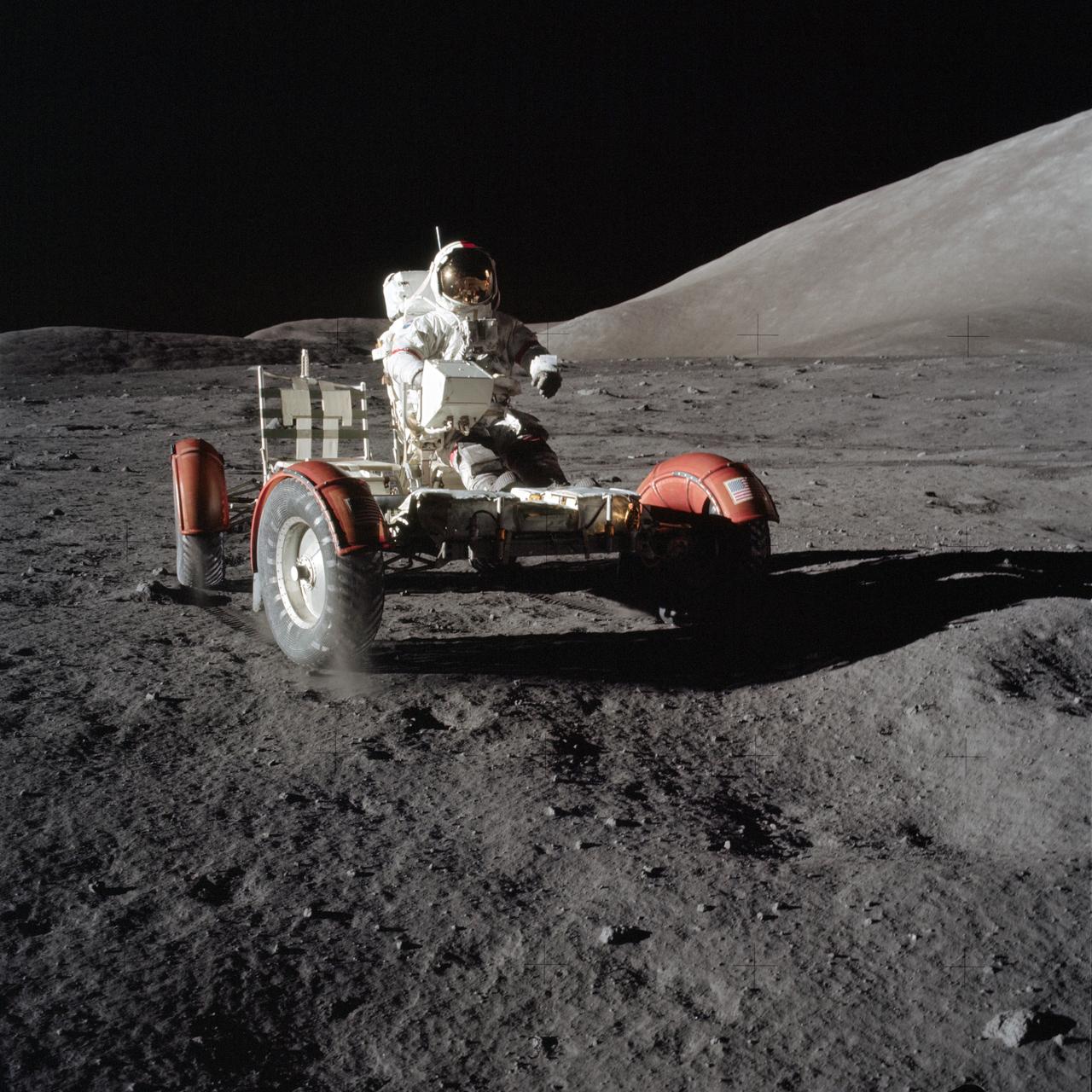

AS17-147-22526 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander, makes a short checkout of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during the early part of the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. This view of the "stripped down" LRV is prior to loading up. Equipment later loaded onto the LRV included the ground-controlled television assembly, the lunar communications relay unit, hi-gain antenna, low-gain antenna, aft tool pallet, lunar tools and scientific gear. This photograph was taken by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. The mountain in the right background is the east end of South Massif. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
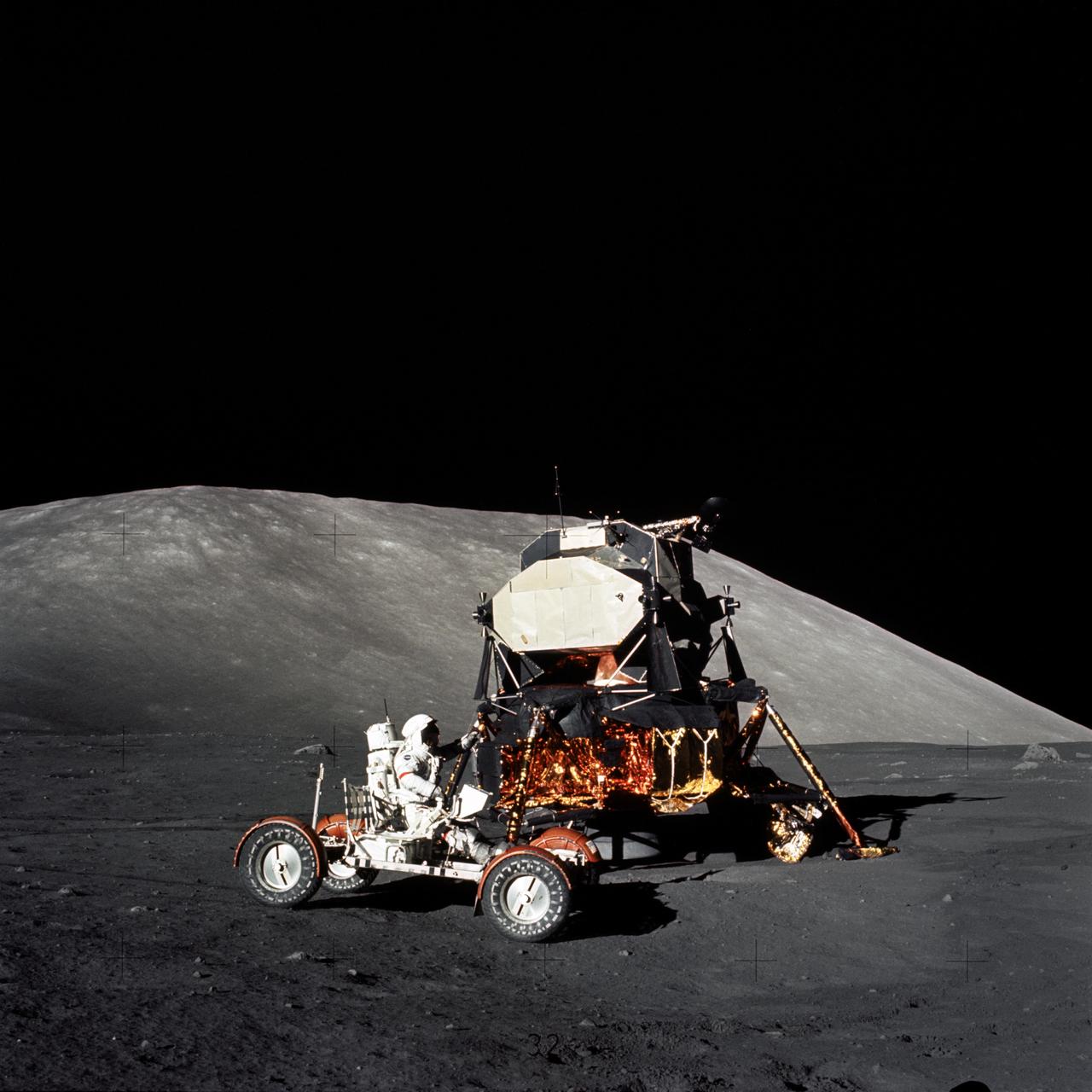

AS17-147-22527 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 mission commander, makes a short checkout of the Lunar Roving Vehicle during the early part of the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The Lunar Module is in the background. This photograph was taken by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot.
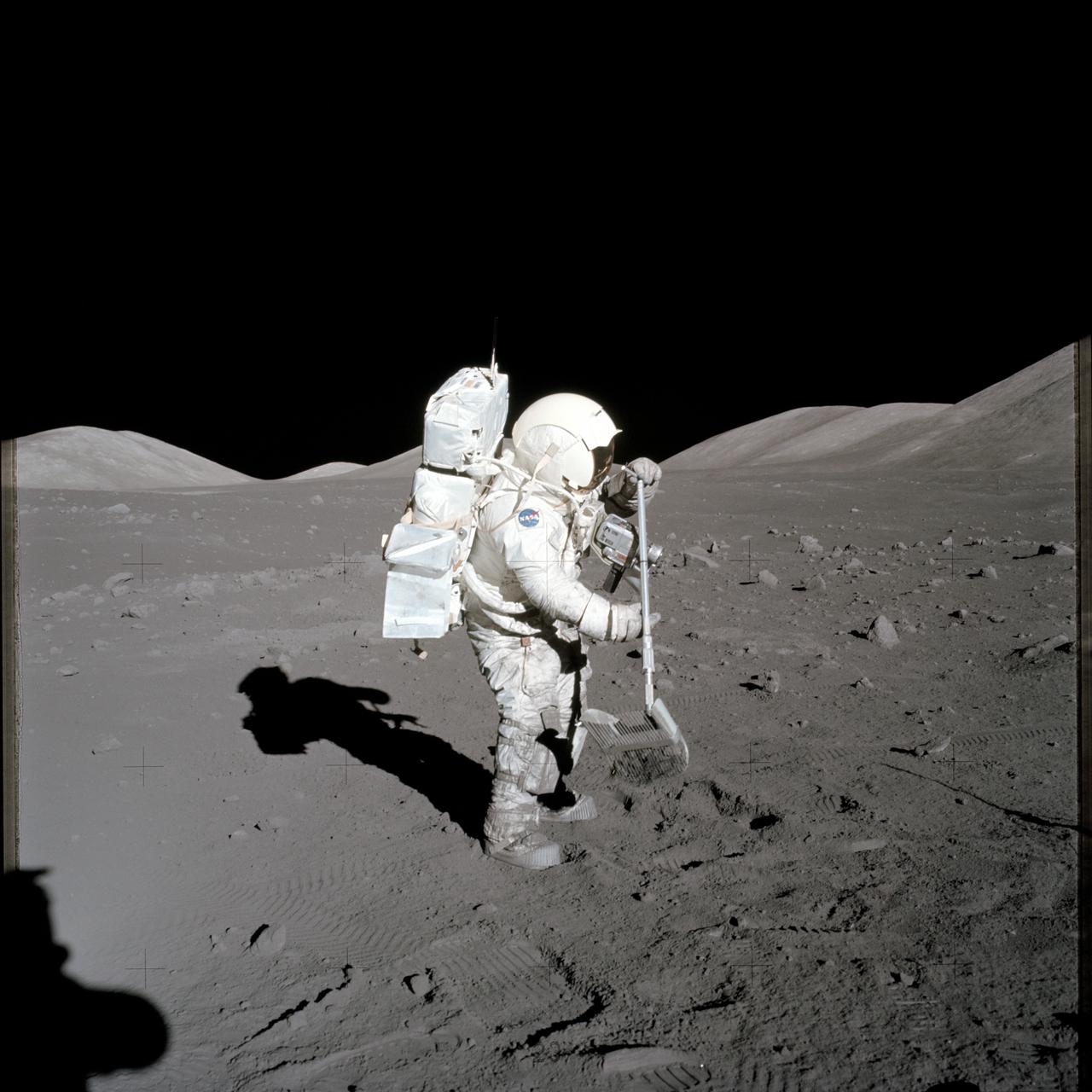

AS17-134-20425 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, collects lunar rake samples at Station 1 during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. This picture was taken by astronaut Eugene Cernan, commander. The lunar rake, an Apollo lunar geology hand tool, is used to collect discrete samples of rocks and rock chips ranging in size from one-half inch (1.3 centimeter) to one inch (2.5 centimeter).
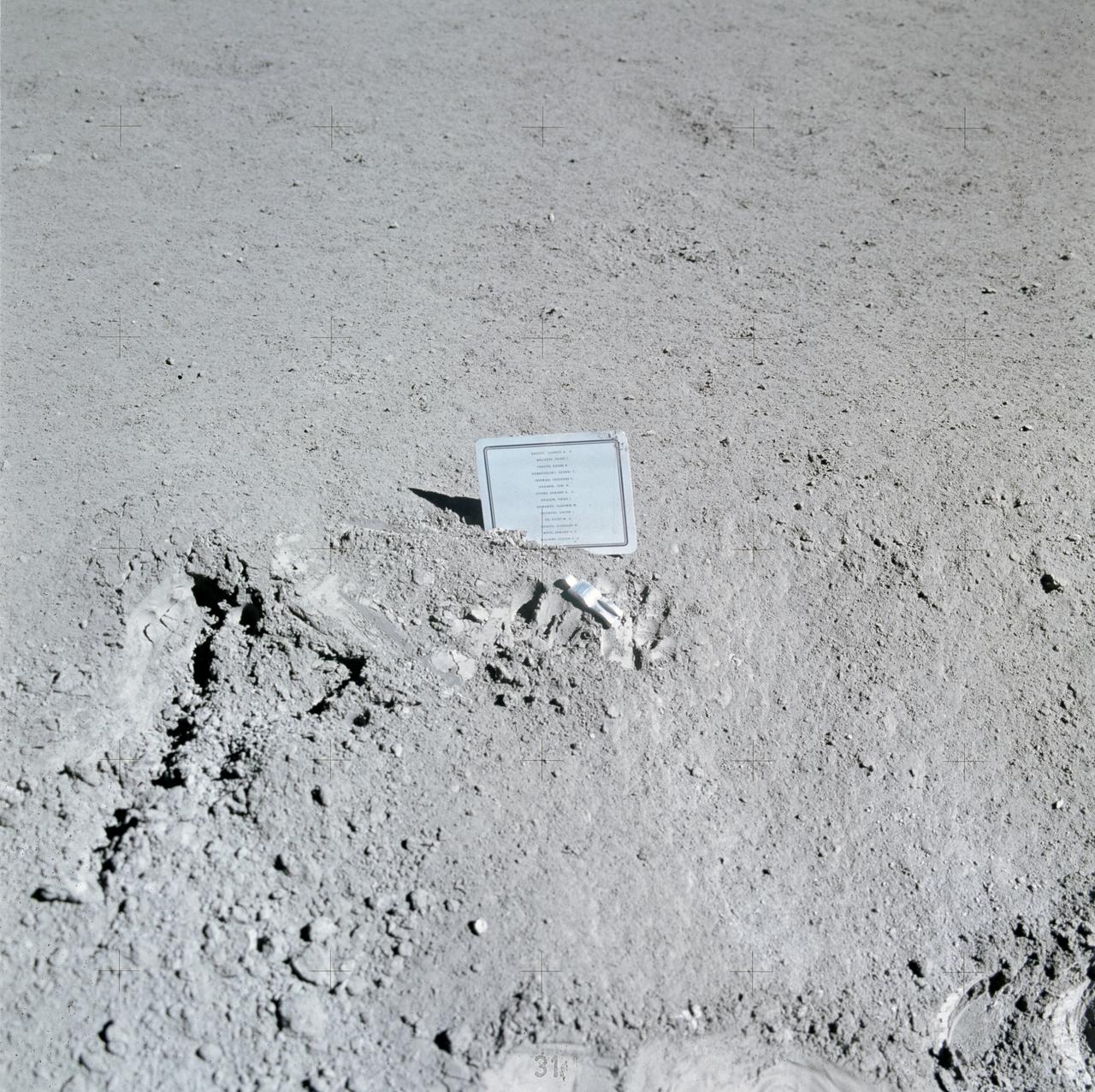

AS15-88-11894 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- A close-up view of a commemorative plaque left on the moon at the Hadley-Apennine landing site in memory of 14 NASA astronauts and USSR cosmonauts, now deceased. Their names are inscribed in alphabetical order on the plaque. The plaque was stuck in the lunar soil by astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, during their Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). The names on the plaque are Charles A. Bassett II, Pavel I. Belyayev, Roger B. Chaffee, Georgi Dobrovolsky, Theodore C. Freeman, Yuri A. Gagarin, Edward G. Givens Jr., Virgil I. Grissom, Vladimir Komarov, Viktor Patsayev, Elliot M. See Jr., Vladislav Volkov, Edward H. White II, and Clifton C. Williams Jr. The tiny, man-like object represents the figure of a fallen astronaut/cosmonaut. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
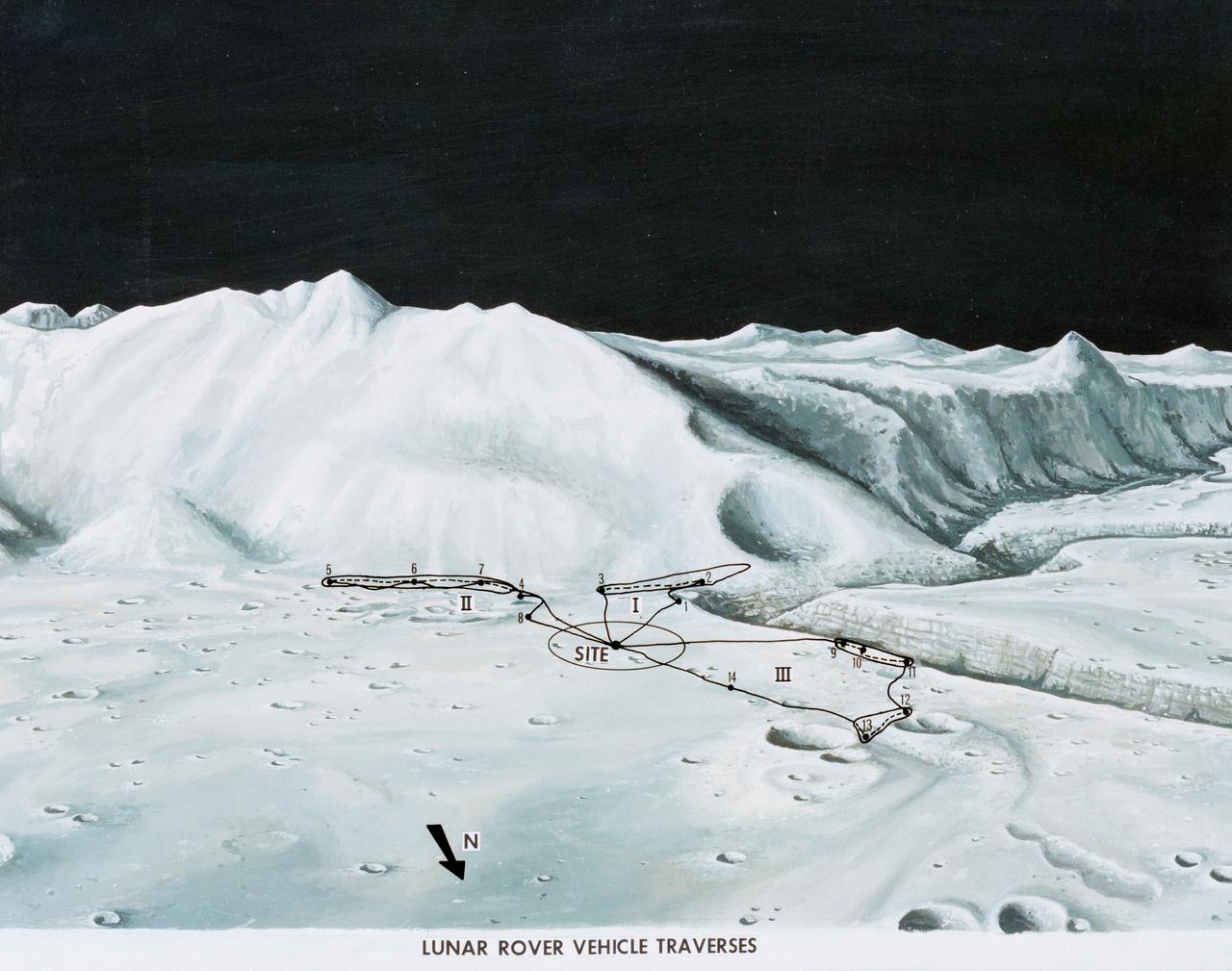

S71-33433 (1 July 1971) --- An artist's concept of the Hadley-Apennine landing site, depicting the traverses planned on the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission using the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The Roman numerals indicate the three periods of extravehicular activity (EVA). The Arabic numbers represent the station stops. This artist's concept was excerpted from "On the Moon with Apollo 15: A Guidebook to Hadley Rille and the Apennine Mountains," by Gene Simmons. The station stops indicated here are keyed to information given in the publication. Artwork by Jerry Elmore.
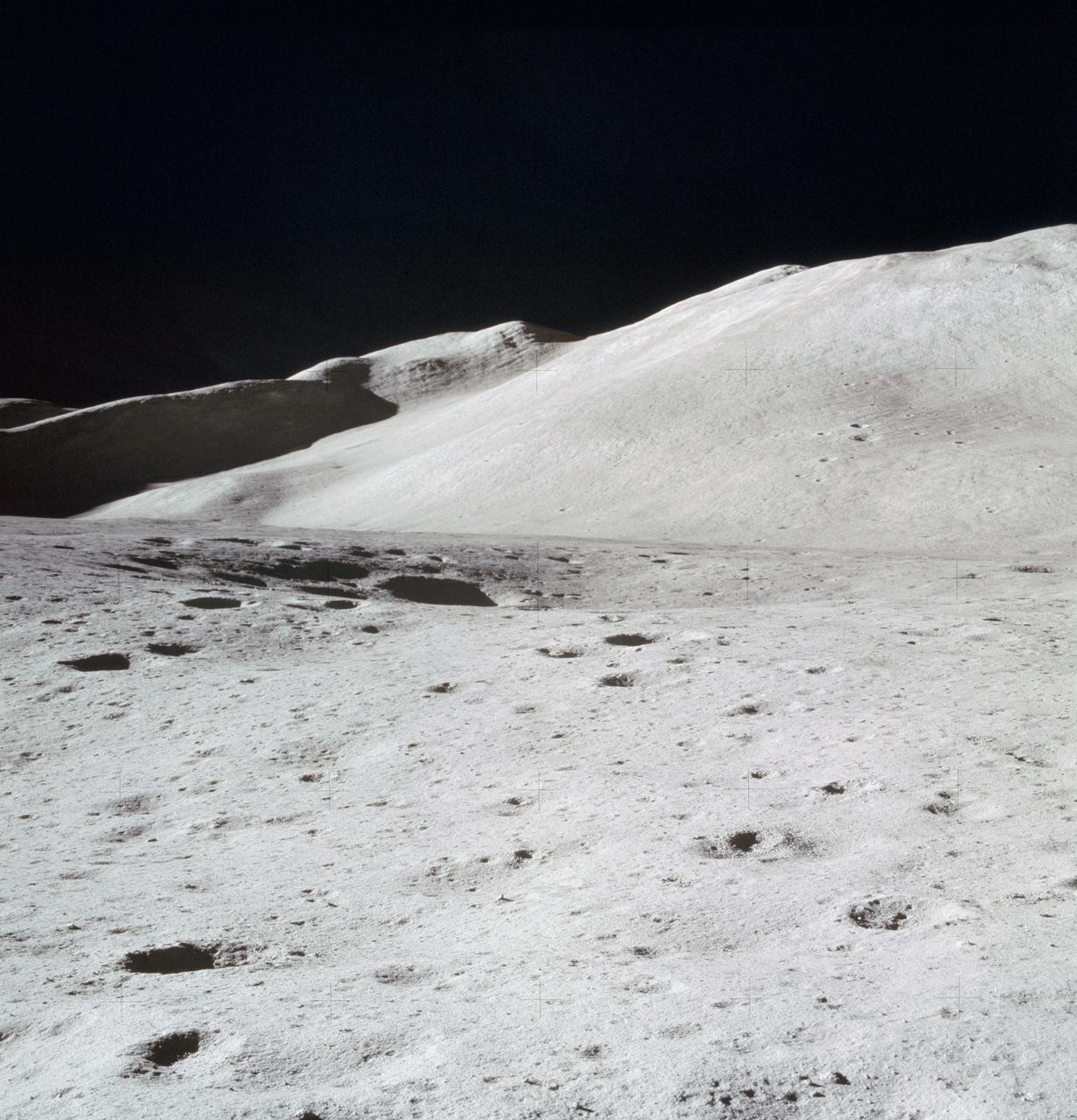

AS15-87-11748 (31 July 1971) --- A view of Hadley Delta, looking southeasterly, as photographed from the top hatch of the Apollo 15 Lunar Module (LM) by astronaut David R. Scott, commander, during his stand-up extravehicular activity (EVA) just after the LM "Falcon" touched down at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The prominent feature on the horizon in the center of the picture was called Silver Spur by the Apollo 15 crew men. Hadley Delta Mountain rises approximately 4,000 meters (about 13,124 feet) above the plain. While astronauts Scott and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Module's (CSM) in lunar orbit.
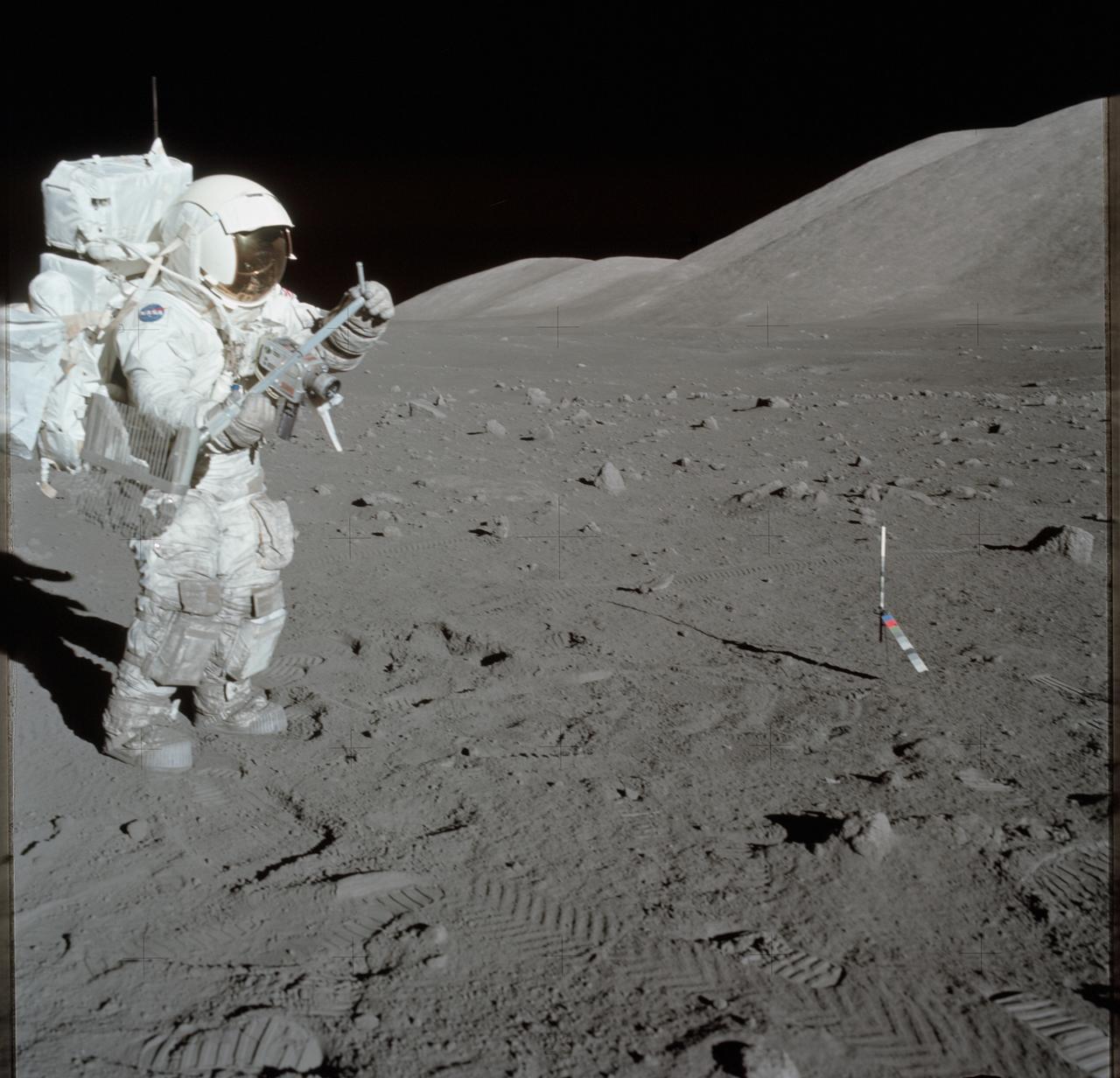

AS17-134-20426 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt collects lunar rake samples at Station 1 during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. This picture was taken by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander. Schmitt is the lunar module pilot. The Lunar Rake, an Apollo Lunar Geology Hand Tool, is used to collect discrete samples of rocks and rock chips ranging in size from one-half inch (1.3 cm) to one inch (2.5 cm).
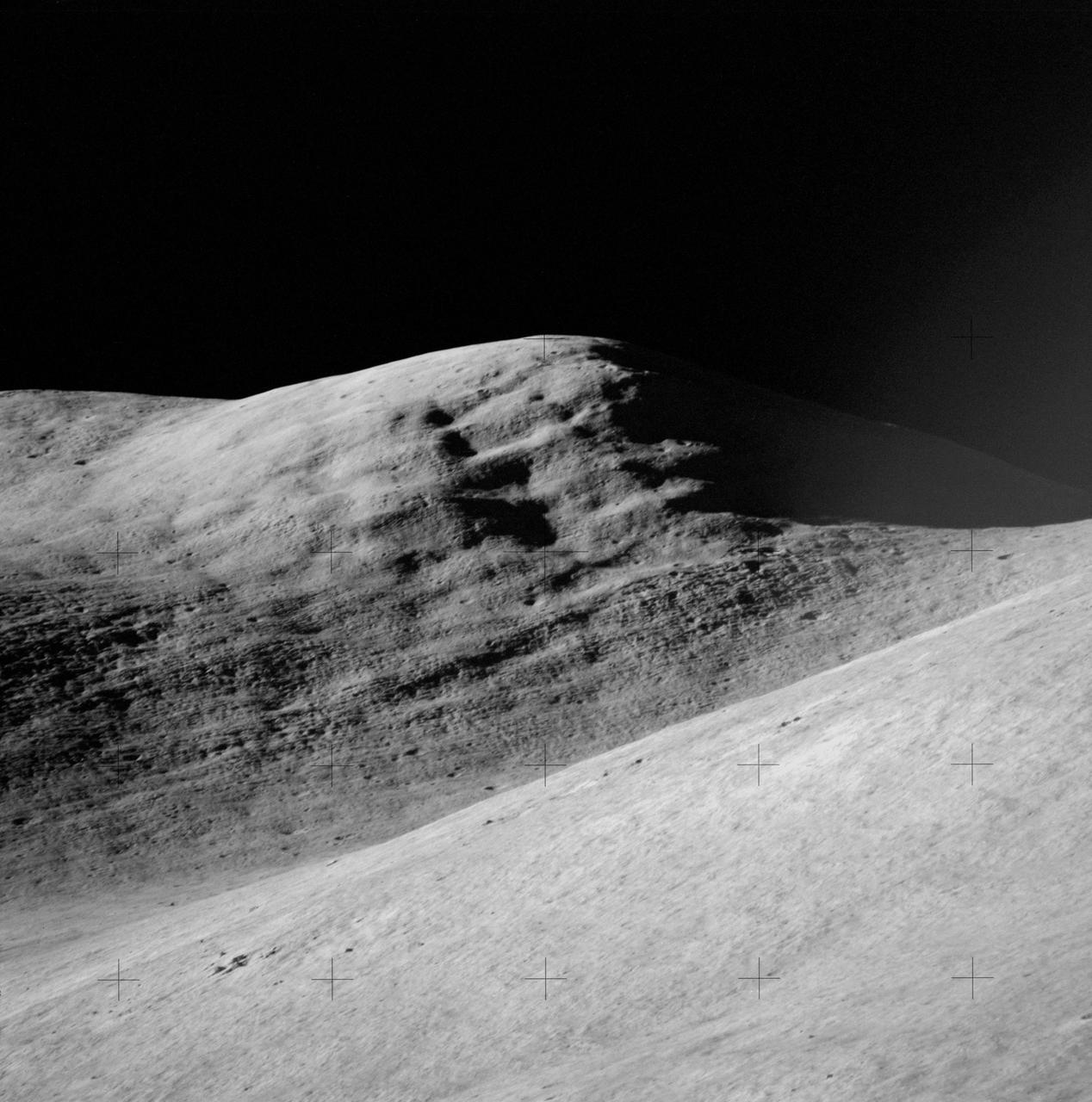

AS15-84-11250 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- A telephoto lens view of the prominent feature called Silver Spur in the Hadley Delta region, photographed during the Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The distance from the camera to the spur is about 10 miles. The field of view across the bottom is about one mile. Structural formations in the mountain are clearly visible. There are two major units. The upper unit is characterized by massive subunits, each one of which is approximately 200 feet deep. The lower major unit is characterized by thinner bedding and cross bedding.

One month after its first image of the Apollo 11 landing site was acquired, NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter passed over the site again providing a new view of the historic site.

New view of the Apollo 12 landing site in Oceanus Procellarum imaged from NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter mapping orbit.

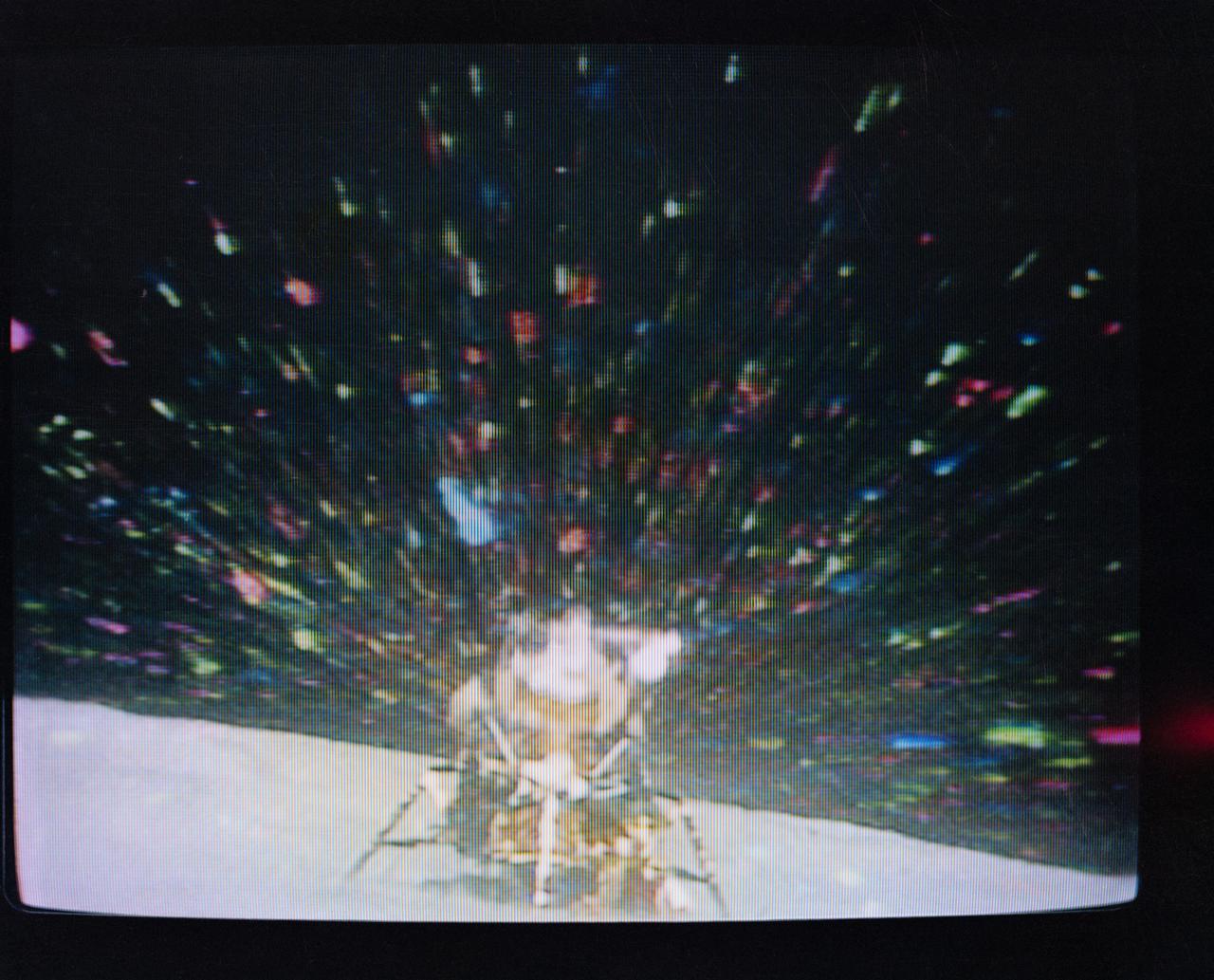
S72-55421 (14 Dec. 1972) --- The Apollo 17 Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" ascent stage leaves the Taurus-Littrow landing site as it makes its spectacular liftoff from the lunar surface, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV-mounted TV camera, remotely controlled from the Mission Control Center (MCC) in Houston, made it possible for people on Earth to watch the fantastic event. The LM liftoff was at 188:01:36 ground elapsed time, 4:54:36 p.m. (CST), Thursday, Dec. 14, 1972. The LM ascent stage, with astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt aboard, returned from the lunar surface to rejoin the Command and Service Modules (CSM) orbiting the moon. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Cernan and Schmitt explored the moon. The LM descent stage is used as a launching platform and remains behind on the moon. Here, the two stages have completely separated and the ascent stage is headed skyward.

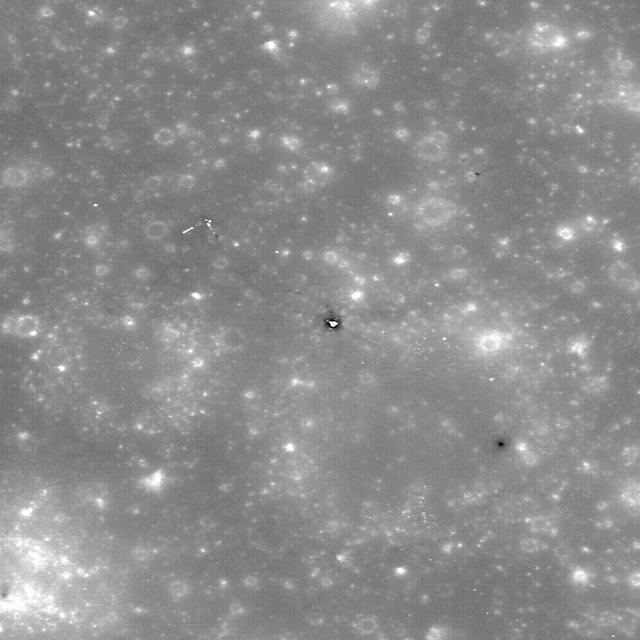
This uncalibrated image from NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter shows the Apollo 14 landing site and nearby Cone crater. The trail followed by the astronauts can clearly be discerned.

S69-30520 (April 1969) --- A North American Rockwell Corporation artist's concept depicting the Apollo 10 Lunar Module descending to 50,000 feet for a close look at a lunar landing site. The Command and Service Modules remain in lunar orbit. The landing area is Site 2 on the east central part of the moon in southwestern Sea of Tranquility (Mare Tranquillitatis). The site is about 62 miles east of the rim of the crater Sabine and 118 miles west-southwest of the crater Maskelyne. Apollo 11 is scheduled to be the first lunar landing mission.

jsc2004e20304 - Panorama view of Apollo 17 lunar surface photos for Station 5 at the Taurus-Littrow landing site taken during the second moonwalk of the mission by Apollo 17 commander Eugene Cernan and lunar module pilot Harrison (Jack) Schmitt. The panoramas were built by combining Apollo 17 images starting with frame AS17-145-22159 through end frame AS17-145-22181. The panoramic images received minimal retouching by NASA imagery specialists, including the removal of lens flares that were problematic in stitching together the individual frames and blacking out the sky to the lunar horizon. These adjustments were made based on observations of the Moon walkers who reported that there are no stars visible in the sky due to the bright lunar surface reflection of the Sun.

S72-03145 (October 1972) --- A vertical view of the Apollo 17 Taurus-Littrow site with an overlay to illustrate the three planned Apollo 17 traverses using the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The EVA-1 traverse has a single station (1); the EVA-2 traverse has four stations (2,3,4,5); and the EVA-3 traverse has five stations (6,7,8,9,10). Stations 10-A and 10-B are alternate locations for Station 10. In addition to the major stations mentioned above, brief stops are planned for sampling between stations using the LRV sampler tool (note diamond-shaped figures), and for deploying explosive charges associated with the Lunar Seismic Profiling Experiment (LSPE - note black x-marks).
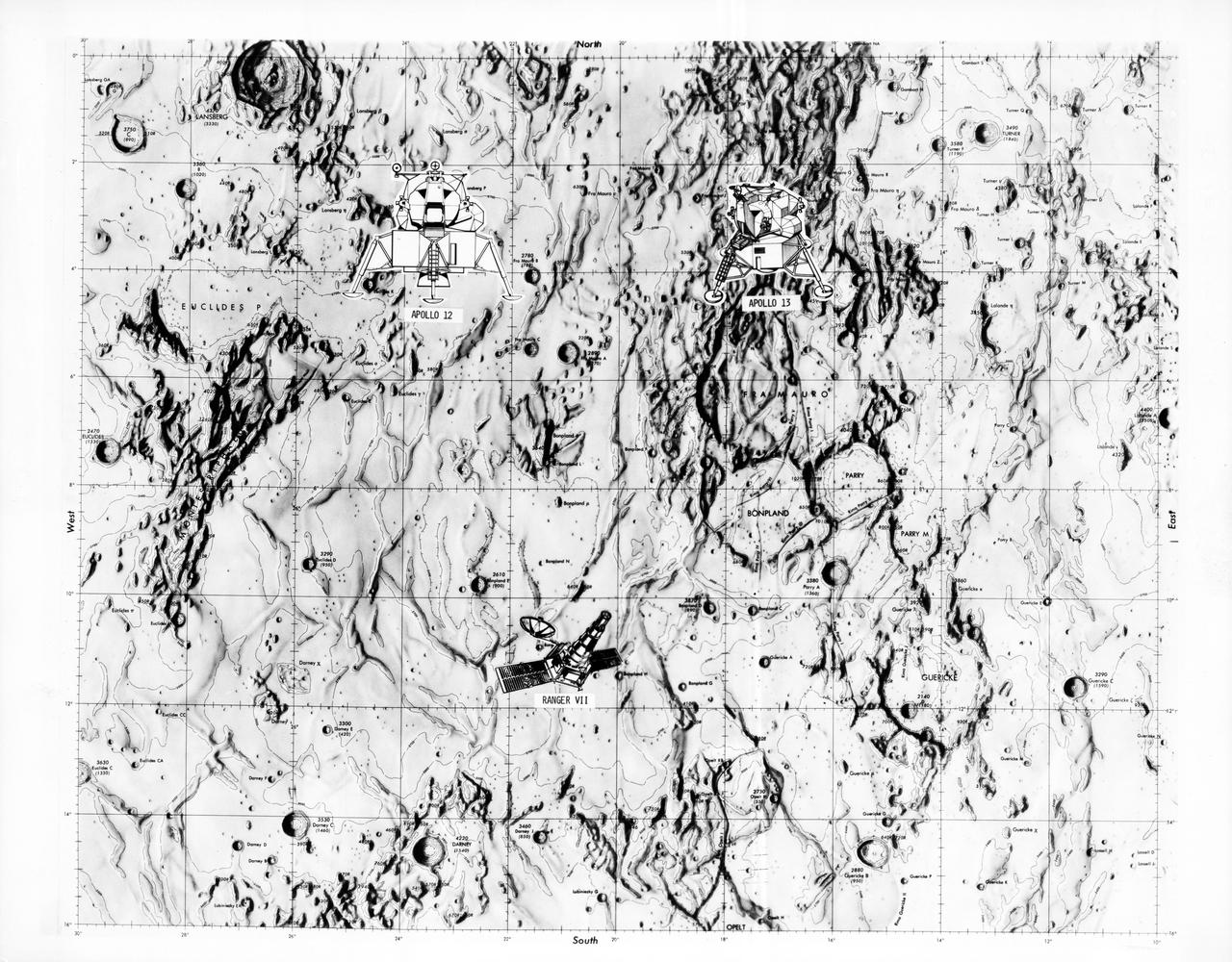
S70-28115 (January 1970) --- This overlay map of terrain on the lunar nearside shows the area of the landing site of the upcoming Apollo 13 mission, in relation to two previous NASA landings. The proposed Apollo 13 landing site is located in the highlands north of Fra Mauro. The coordinates of the planned site are 17.550 degrees west longitude and 3.617 degrees south latitude. The landing site of the Apollo 12 mission, which was highlighted by a lunar landing on Nov. 19, 1969, is located approximately 105 nautical miles west of the Apollo 13 site. The landing site of the unmanned Ranger 7 space vehicle, which impacted on the moon on July 31, 1964, at 10.74 degrees south latitude and 20.7 degrees west longitude, is approximately 130 nautical miles south-southwest of the Apollo 13 site, and approximately 140 nautical miles south-southeast of the Apollo 12 site.

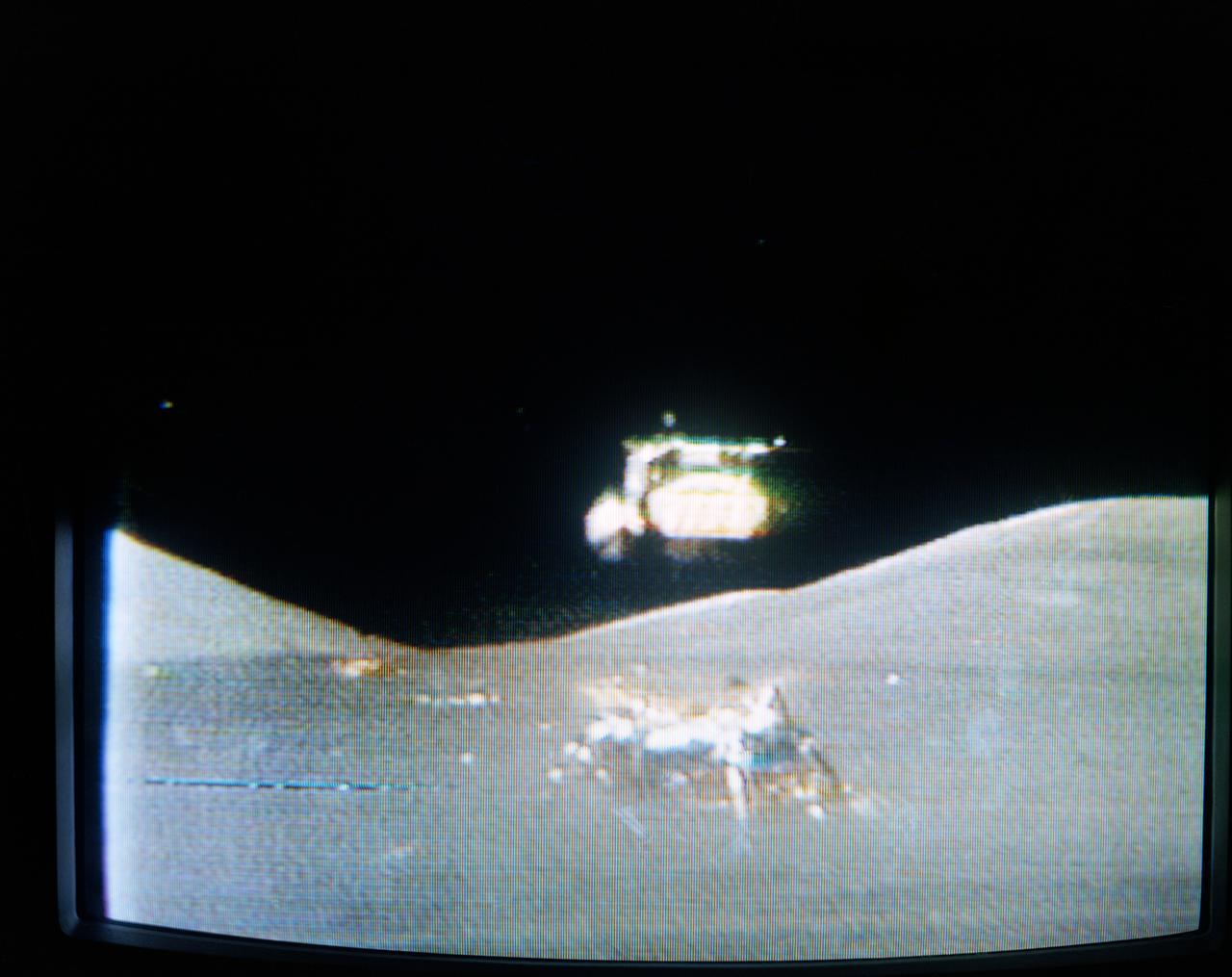
S72-35613 (22 April 1972) --- The Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" in early lunar liftoff phase is featured in this lunar scene at the Descartes landing site. The still picture is a reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 LM to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
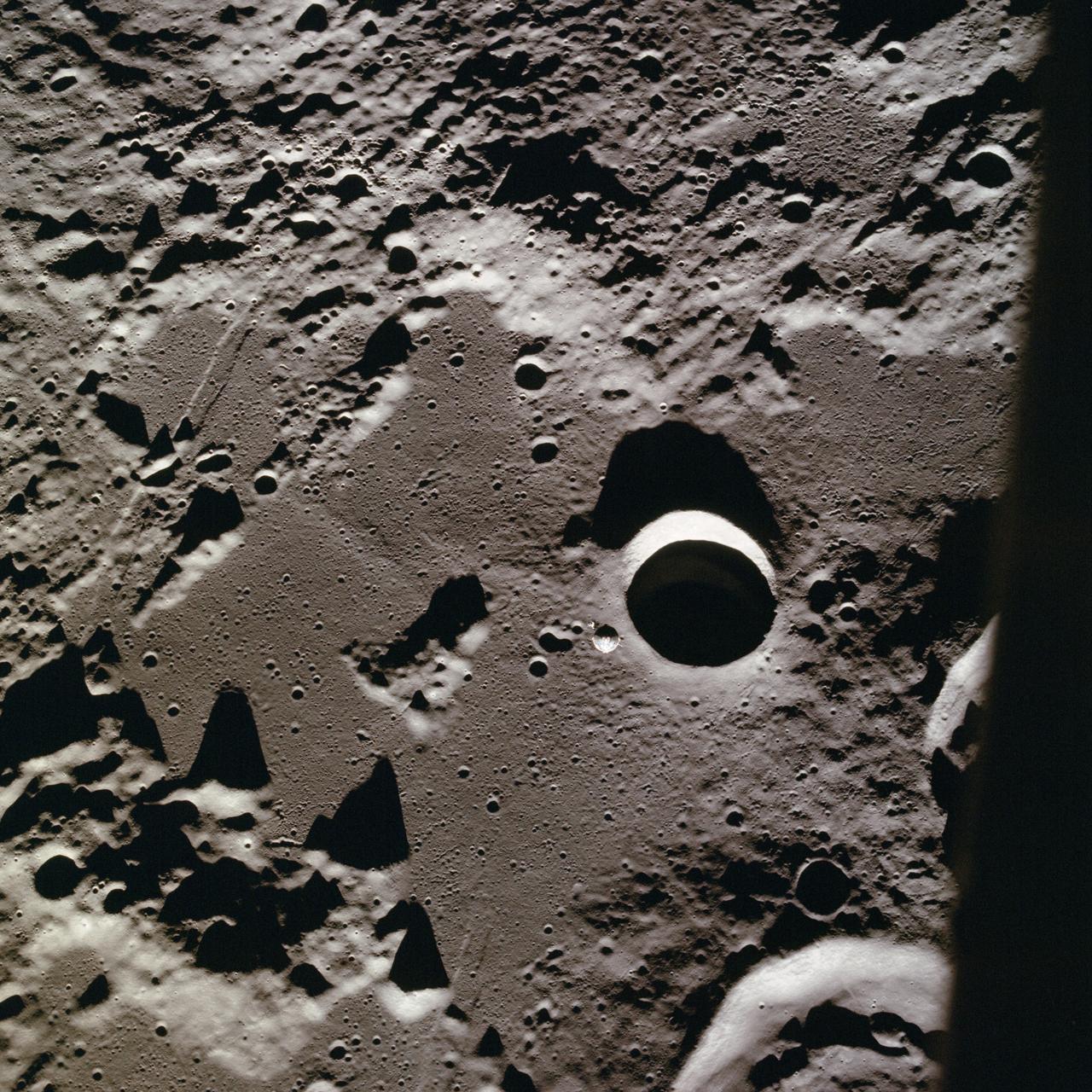

AS11-37-5448 (July 1969) --- The Apollo 11 Command and Service Modules (CSM) (tiny dot near quarter sized crater, center), with astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, aboard. The view overlooking the western Sea of Tranquility was photographed from the Lunar Module (LM). Astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, manned the LM and made their historic lunar landing on July 20, 1969. Coordinates of the center of the terrain in the photograph are 18.5 degrees longitude and .5 degrees north latitude.
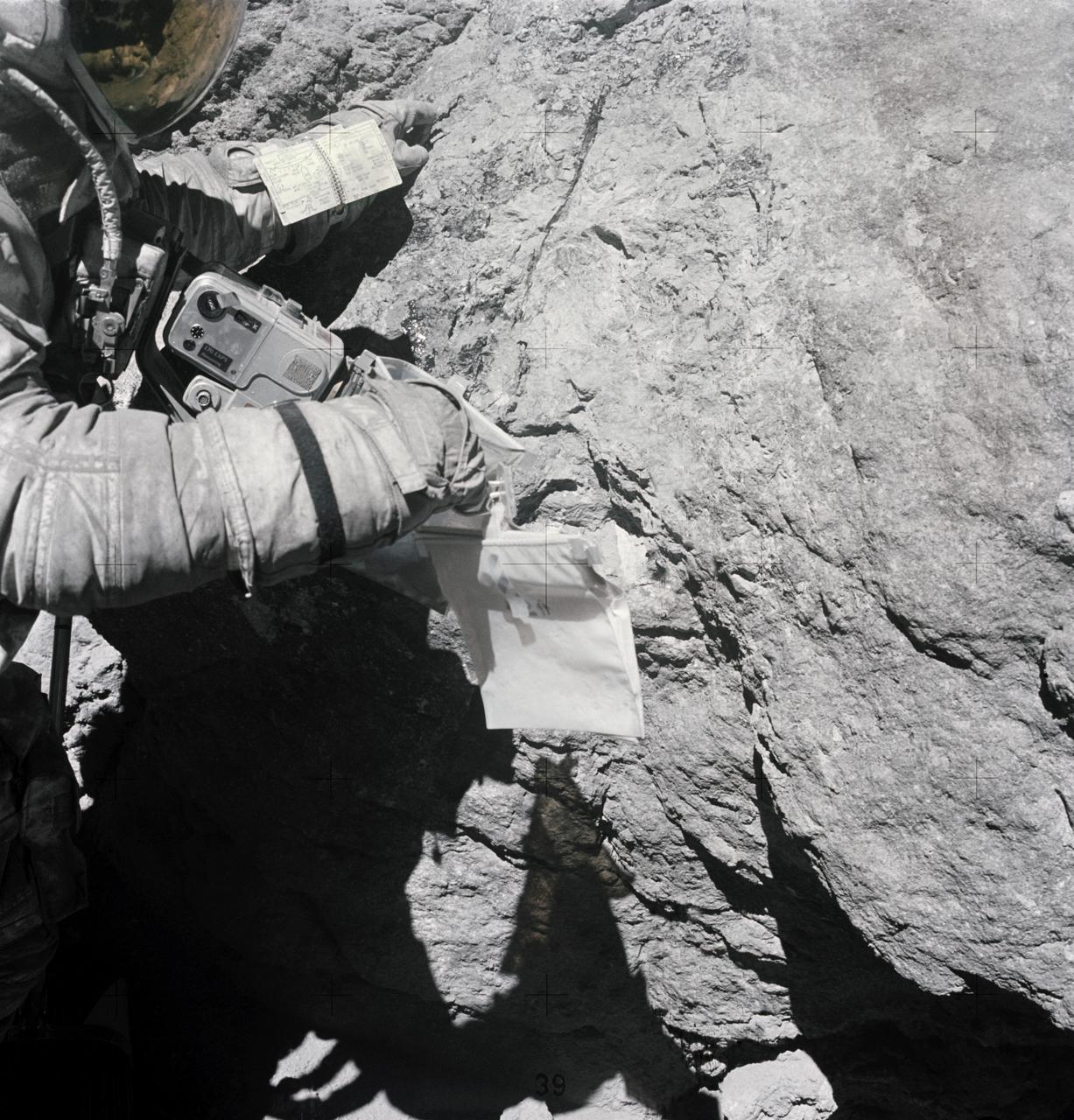

AS16-116-18649 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, examines closely the surface of a large boulder at North Ray Crater during the third Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. This picture was taken by astronaut John W. Young, commander. Note the chest-mounted 70mm Hasselblad camera. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
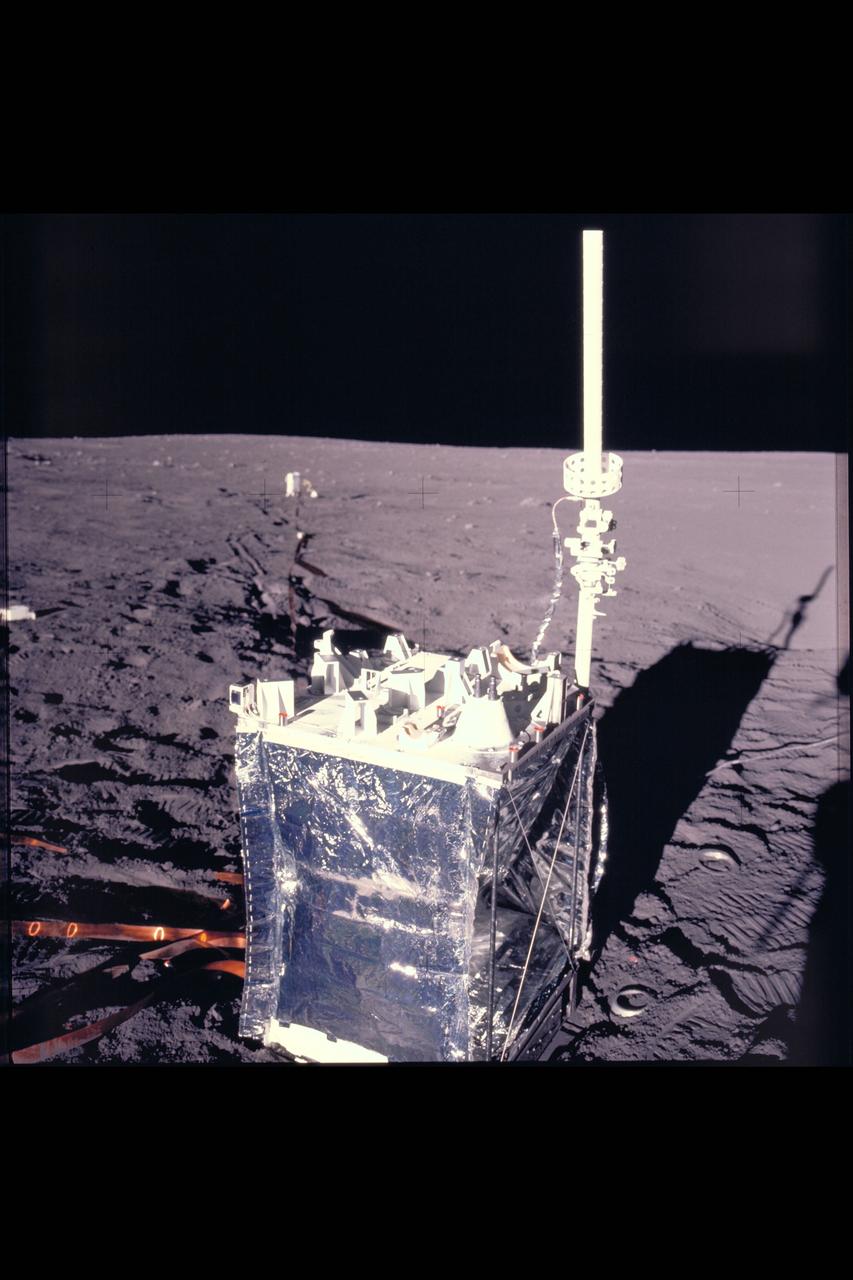
Apollo Crew landing site showing deployment of ALSEP (Apollo Lunar Surface expeiments package)
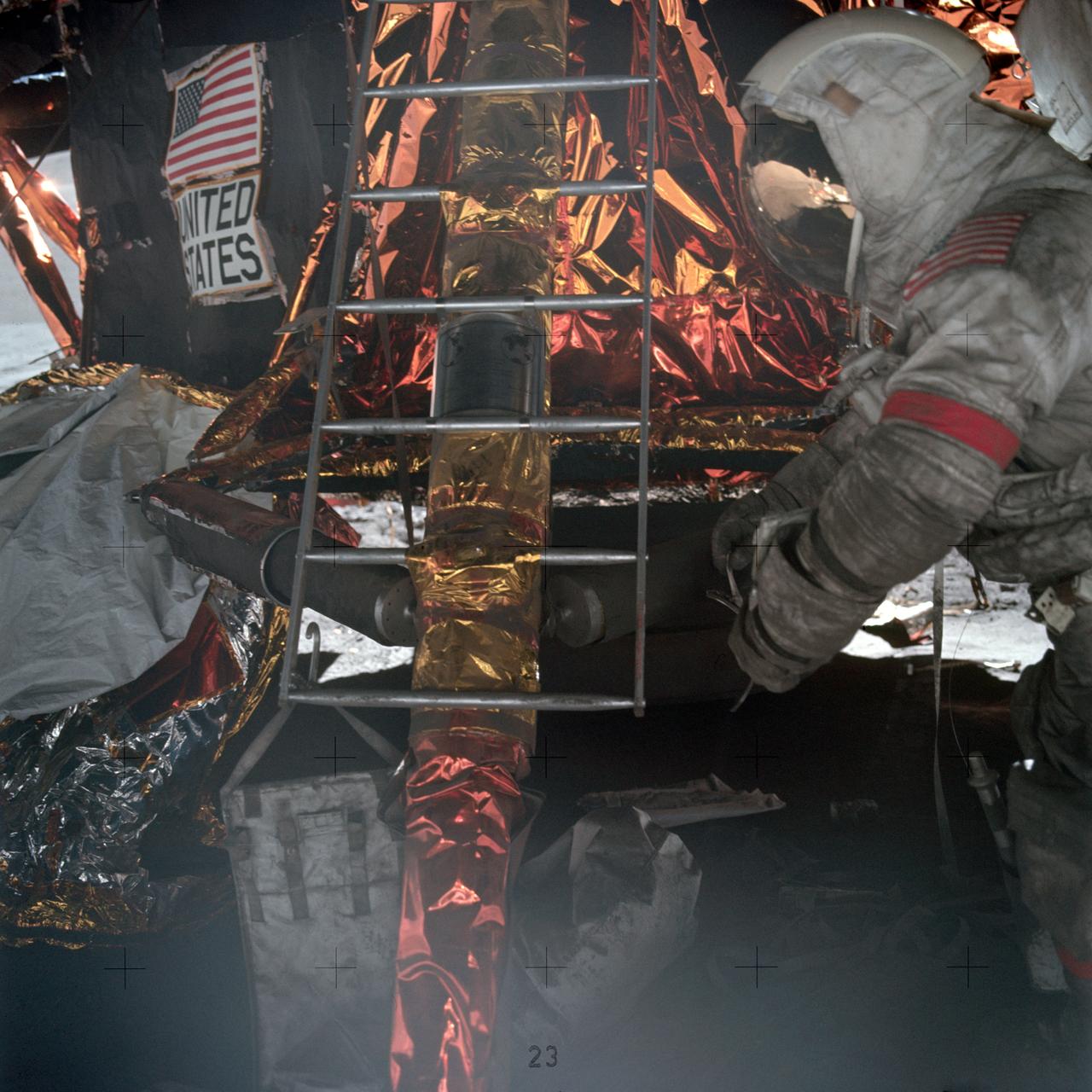

Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander, prepares to mount ladder to lunar module ascent stage. Note the plaque attached to the ladder which will be left with the descent stage when the mission lifts off from the lunar surface.

AS10-29-4321 (18-26 May 1969) --- An Apollo 10 oblique view of the western portion of the Sea of Tranquility. The area in the picture is located approximately 70 nautical miles east-southeast of Apollo Landing Site 2. The flat terrain pitted by moderate-sized craters is typical of this portion of Mare Tranquillitatis.

AS10-27-3907 (18-26 May 1969) --- Apollo 10 westward view across Apollo Landing Site 3 in the Central Bay. Apollo Landing Site 3 is in the middle distance at the left margin of the pronounced ridge in the left half of the photograph. Bruce, the prominent crater, near the bottom of the scene, is about 6 kilometers (3.7 statute miles) in diameter. Topographic features on the surface of the Central Bay are accentuated by the low sun angle. Sun angles range from near 6 degrees at the bottom of the photograph to less than one degree at the top.
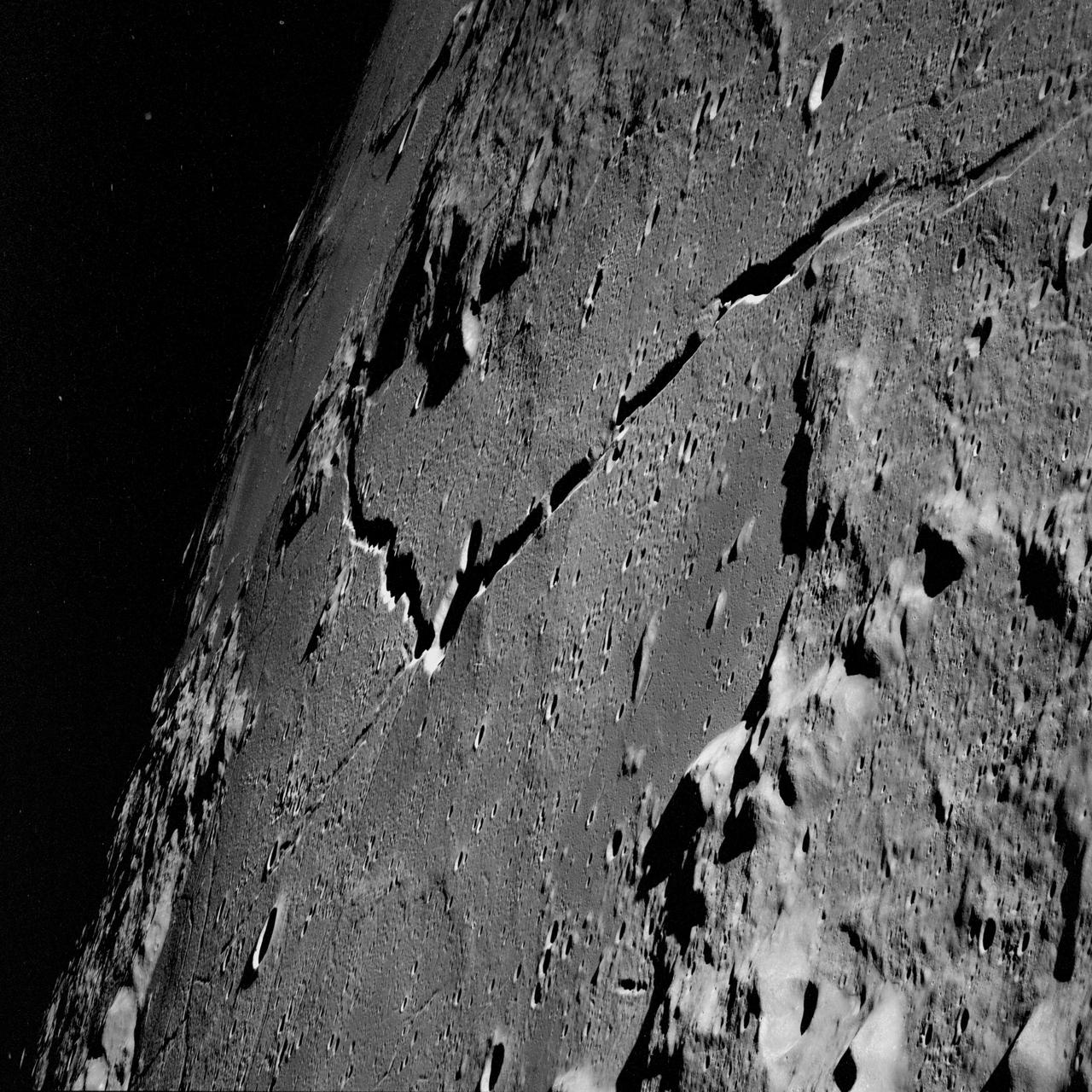
AS10-31-4650 (18-26 May 1969) --- This Apollo 10 oblique telephoto view of the lunar nearside is centered on the crater Hyginus located at 6.3 degrees north latitude, near the northeast margin of Central Bay. HOLD PICTURE WITH SKY AT TOP. The crater is about 10 kilometers (6.5 statue miles) in diameter. From the crater the prominent Hyginus Rille extends east-southeast toward the camera and northwest toward the Sea of Vapors. The rille is about 3 kilometers (2 statue miles) wide and more than 200 kilometers (130 statue miles) long. The horizon is not visible in this photograph, taken from the Command and Service Modules. The sunrise terminator is between the spacecraft and the horizon. At the time this picture was taken Apollo 10 was 325 kilometers (200 statute miles) southeast of Hyginus.
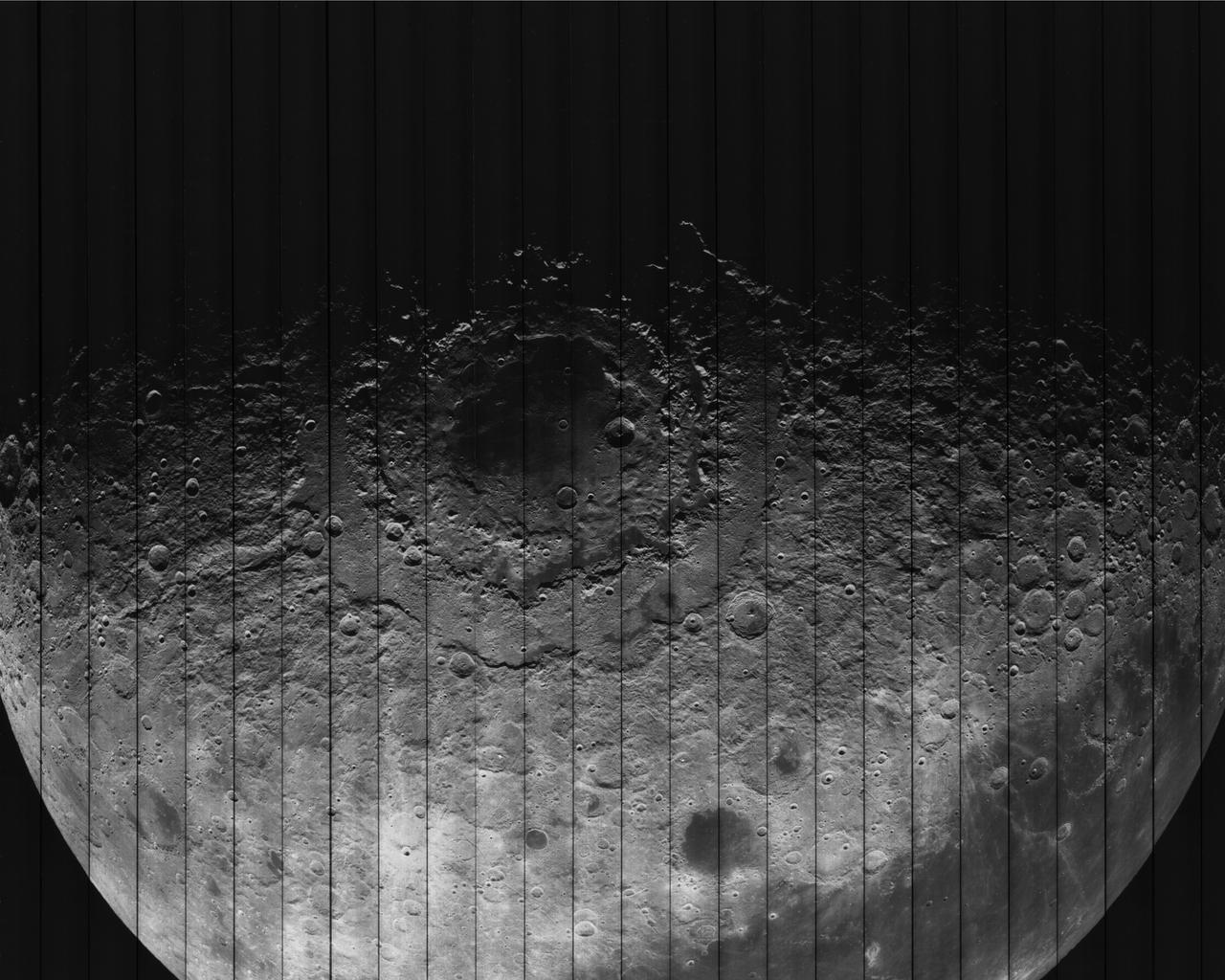
This photo was taken by Lunar Orbiter IV. In it's mission to photograph areas on the new and far side of the Moon and supplemental photography of suggested Apollo landing sites.
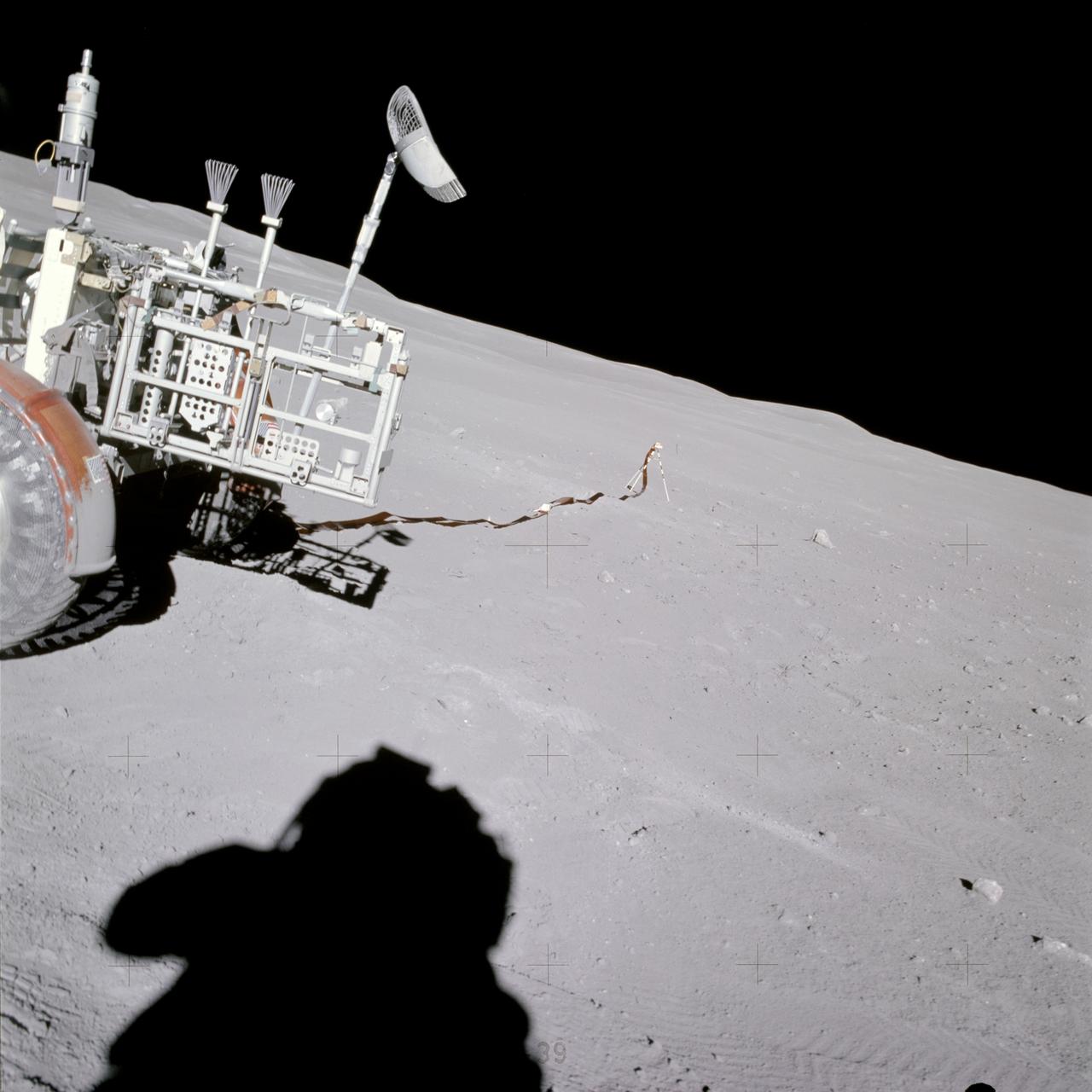

AS16-114-18433 (22 April 1972) --- View of the Lunar Portable Magnetometer mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) which was parked at Station No. 2 on the Descartes lunar landing site. The Apollo 16 crew photographed it during their second extravehicular activity (EVA). Note the shadow of the astronaut taking the photograph in the left foreground.
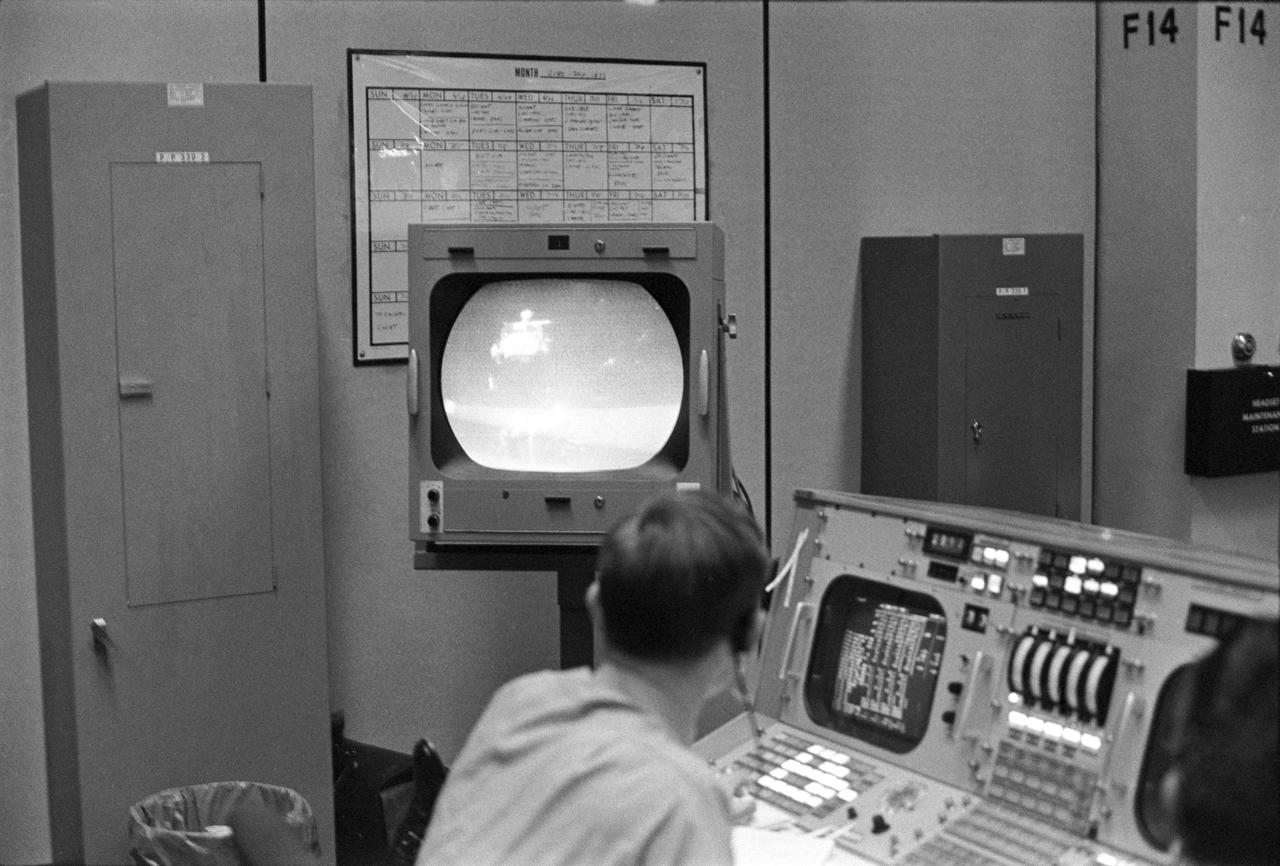

View of a photograph of the television (TV) monitor in the MCC showing a picture being transmitted from the color TV camera mounted on the parked Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) at the Hadley-Apennine Landing Site showing the liftoff of the Apollo 15 Lunar Module (LM) Ascent Stage from the Lunar surface. MSC, Houston, TX
S70-54740 (December 1970) --- A lunar orbiter photograph showing a vertical view of the Apollo 14 landing site located in the Fra Mauro highlands on the lunar nearside. The predicted landing point is 17 degrees 27 minutes 46 seconds west longitude and 3 degrees 40 minutes 19 seconds south latitude. North is toward the right side of the picture. Cone Crater, the largest lunar feature visible, is located near the northeast corner of the photograph. The landing point is between Triplet Crater and Doublet Crater in the center of the picture.

Stafford standing next to training simulator Note: 1968-L-08723 same image in black and white. General Stafford was commander of Apollo 10 in May 1969, first flight of the lunar module to the moon, he descended to nine miles above the moon performing the entire lunar landing mission except the actual landing. He performed the first rendezvous around the Moon, and designated the first lunar landing site. NASA.gov/https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former
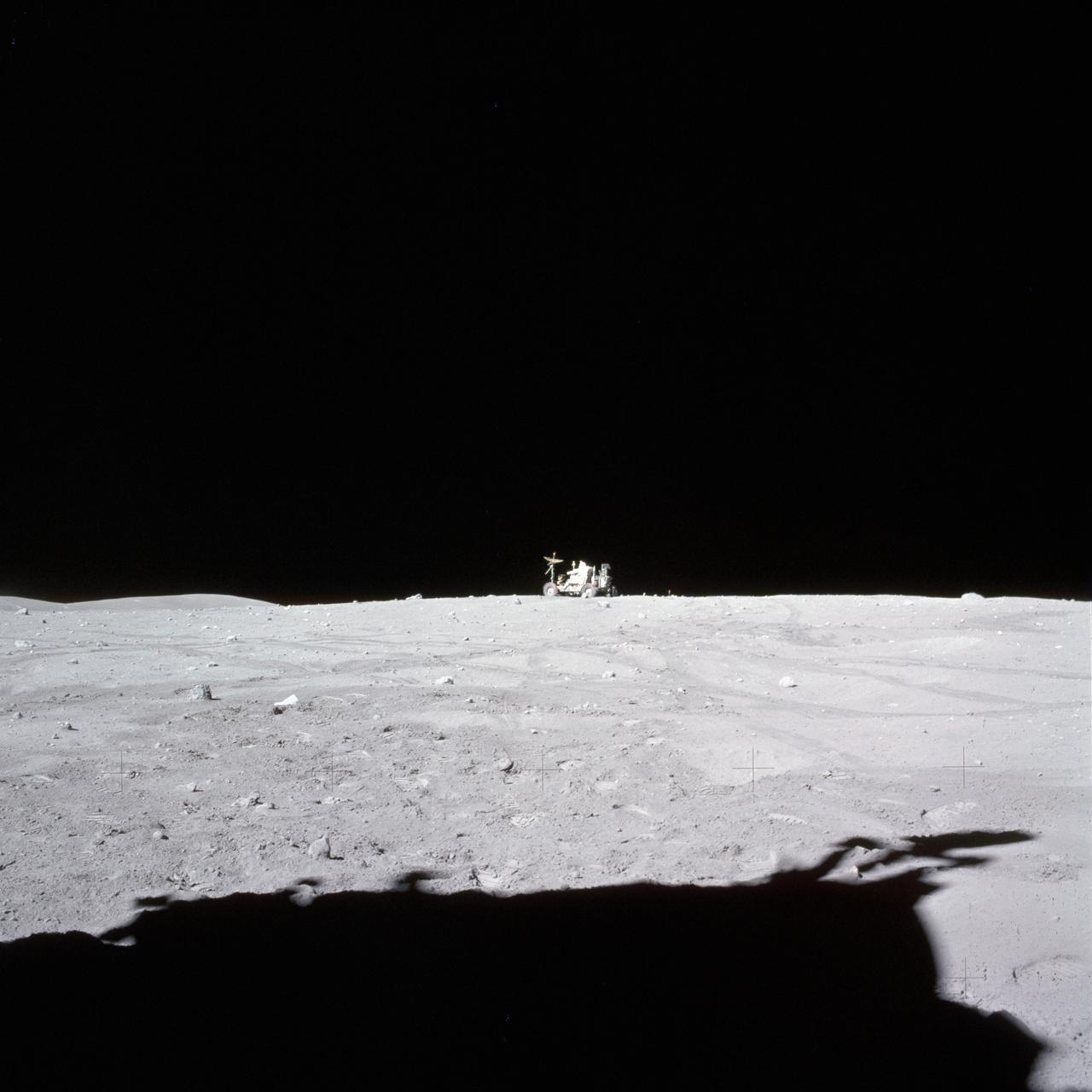

AS16-115-18559 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, drives the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) to its final parking place near the end of the third Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, took this photograph looking southward. The flank of Stone Mountain can be seen on the horizon at left. The shadow of the Lunar Module (LM) occupies much of the picture. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 LM "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
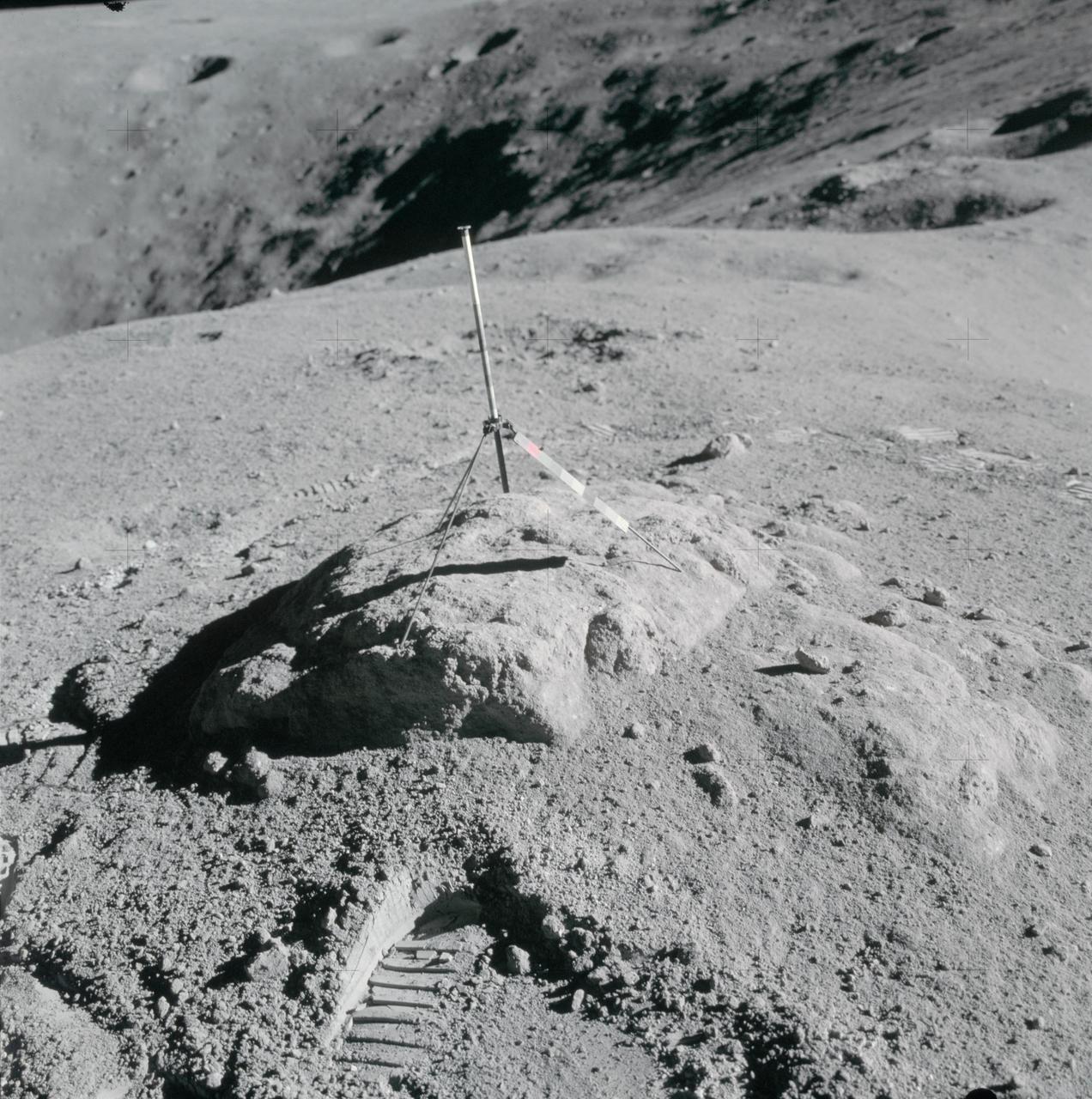

AS16-114-18412 (16-27 April 1972) --- The gnomon and color patch, one of the Apollo Lunar Hand Tools (ALHT), is deployed atop a lunar rock, in this photograph taken by one of the Apollo 16 astronauts during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. The gnomon is used as a photographic reference to establish local vertical sun angle, scale, and lunar color. The color patch, mounted on one of the legs of the tripod, provides a larger target for accurately determining colors in color photography. A portion of Flag Crater can be seen in the background. While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
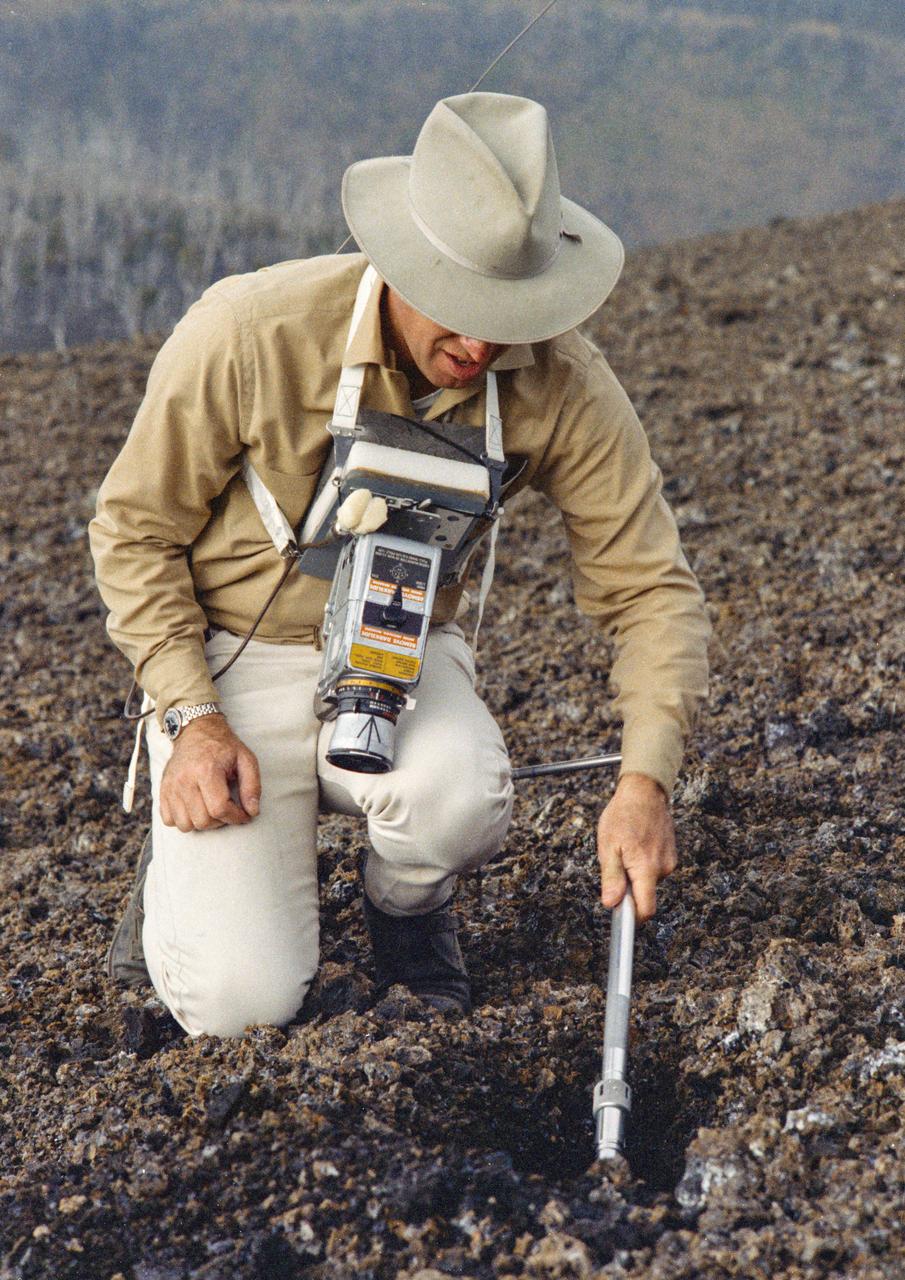

S70-20272 (December 1969) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander of the upcoming Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, uses a scoop from the Apollo Lunar Hand Tools (ALHT) during a simulated lunar surface traverse at the Kapoho, Hawaii training site. While at the Hawaii training sites, Lovell and Haise are participating in thorough rehearsals of their extravehicular activity (EVA). Photo credit: NASA
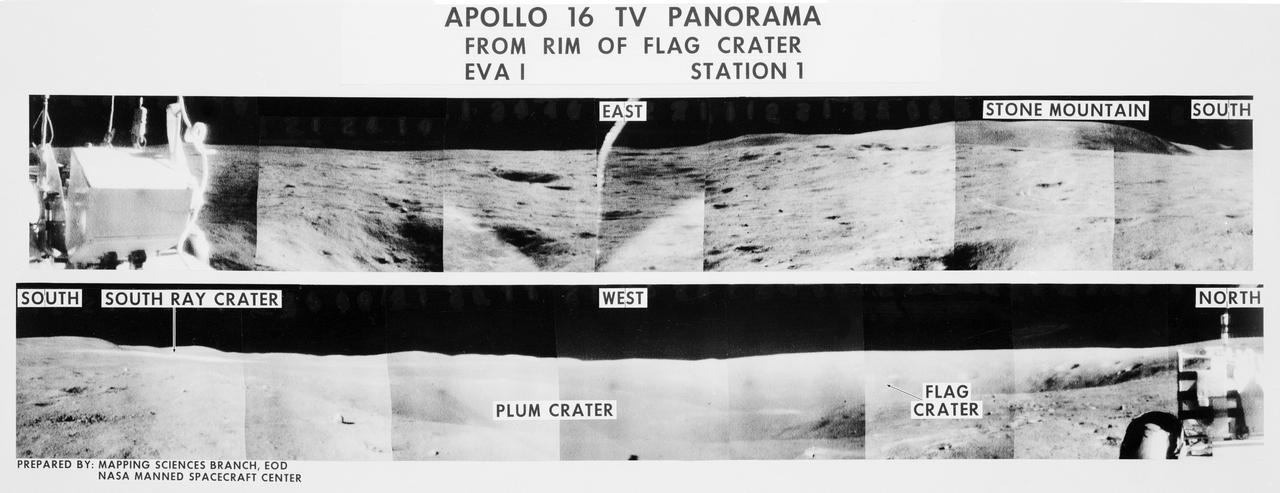
S72-35970 (21 April 1972) --- A 360-degree field of view of the Apollo 16 Descartes landing site area composed of individual scenes taken from color transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). This panorama was made while the LRV was parked at the rim of Flag Crater (Station 1) during the first Apollo 16 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) by astronauts John W. Young and Charles M. Duke Jr. The overlay identifies the directions and the key lunar terrain features. The camera panned across the rear portion of the LRV in its 360-degree sweep. Astronauts Young, commander; and Duke, lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
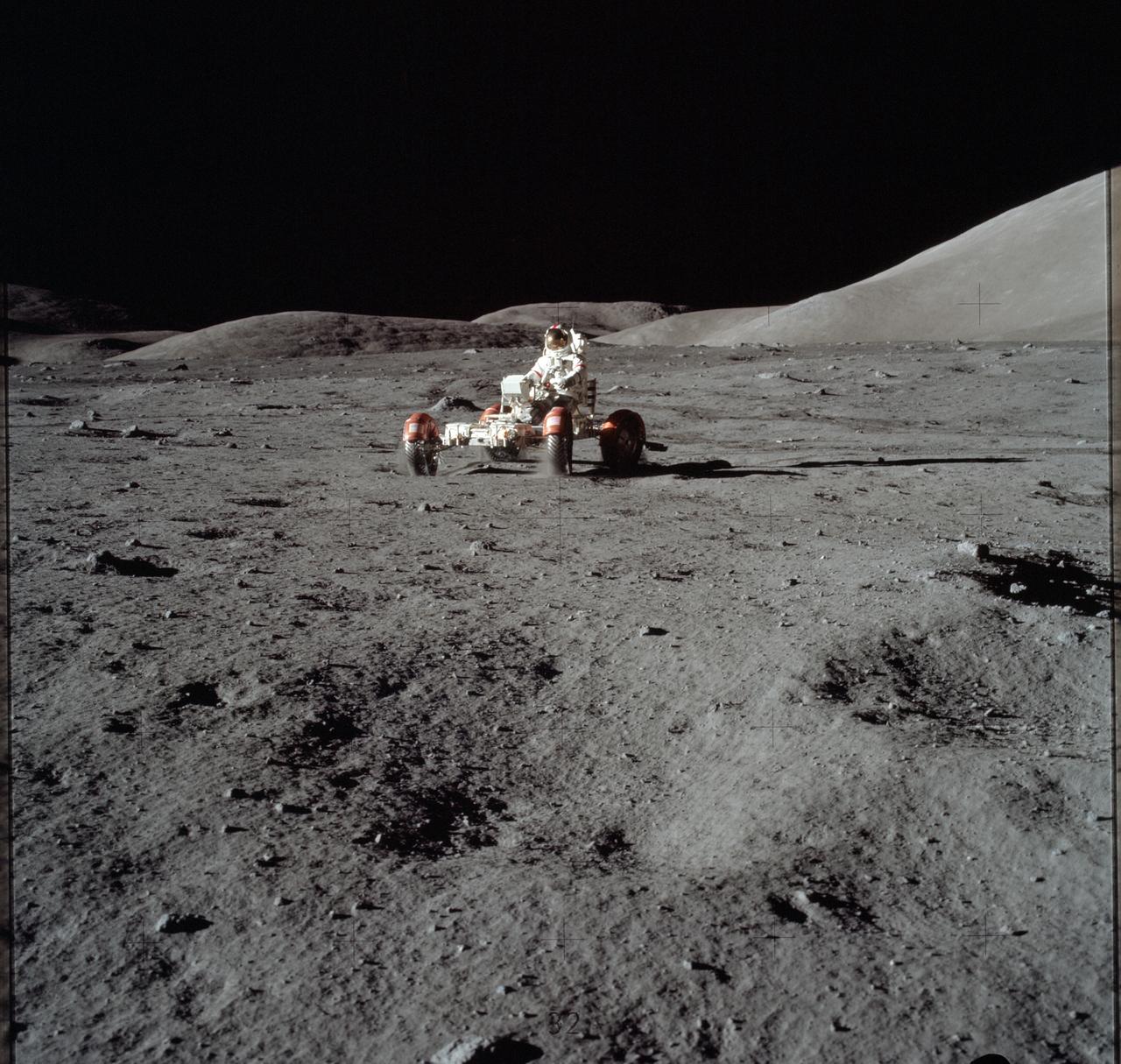

AS17-147-22523 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan is seen test driving the "stripped down" Lunar Rover Vehicle (LRV) prior to loading the LRV up. Equipment later loaded onto the LRV included the ground controlled television assembly, the lunar communications relay unit, the hi-gain antenna, the low-gain antenna, aft tool pallet, and lunar tools and scientific gear.
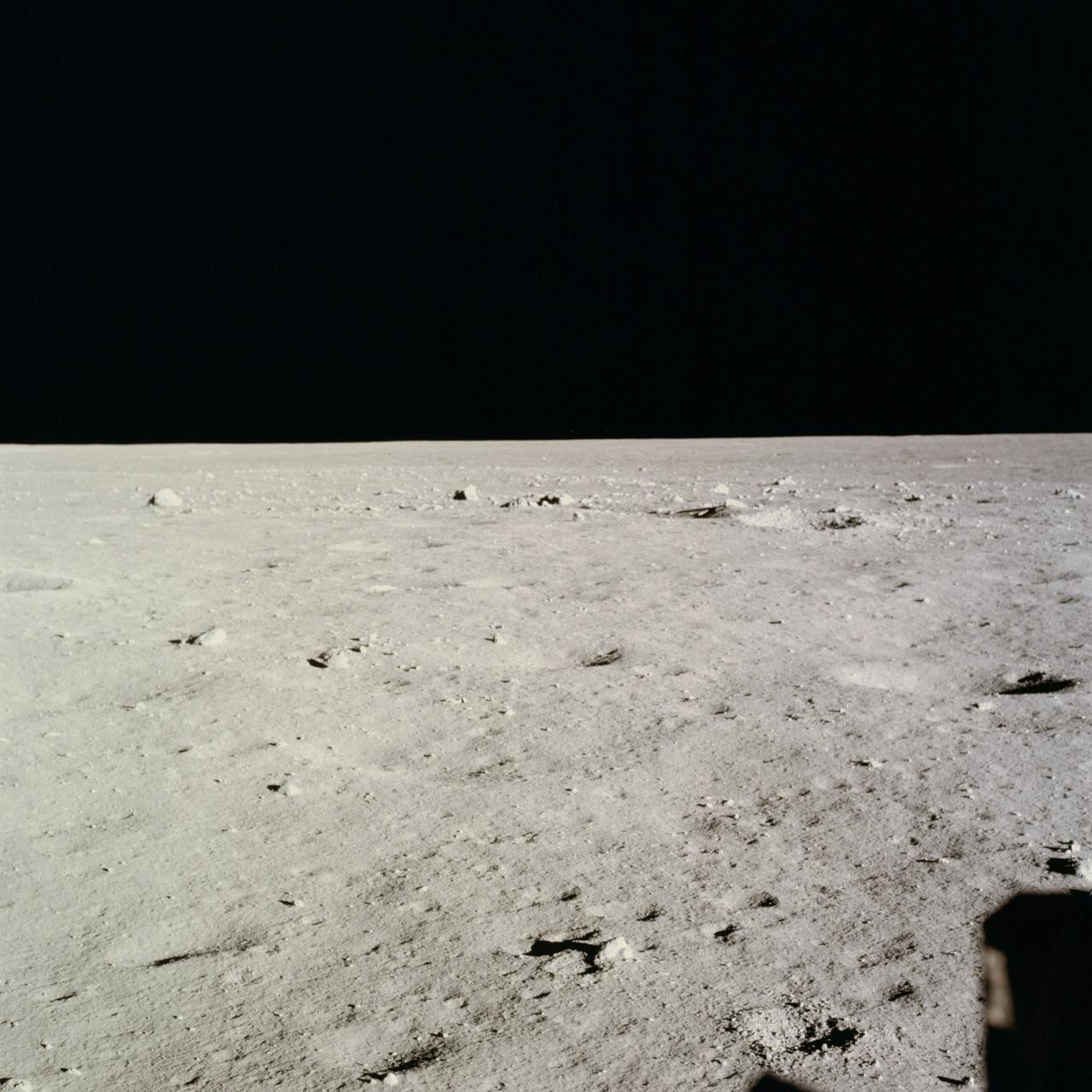

AS11-37-5458 (20 July 1969) --- This excellent view from the right-hand window of the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) shows the surface of the moon in the vicinity of where the LM touched down. Numerous small rocks and craters can be seen between the LM and the lunar horizon. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to the lunar surface.

AS15-87-11849 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- An excellent view of Mount Hadley, fully lighted, showing abundant linear features, as photographed during the Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). This view is looking north from the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) site. Mount Hadley rises about 4,500 meters (approximately 14,765 feet) above the plain. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Apollo 15 Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS14-69-9560 (February 1971) --- This 500mm vertical frame taken from the Apollo 14 spacecraft is of the Apollo 16 proposed landing site "Descartes". The actual location of the target area is near the upper left. This photograph was taken with a 56 degree sun angle. The large bright crater is approximately one kilometer in diameter and has a distinctive ray pattern which serves as an excellent landmark.
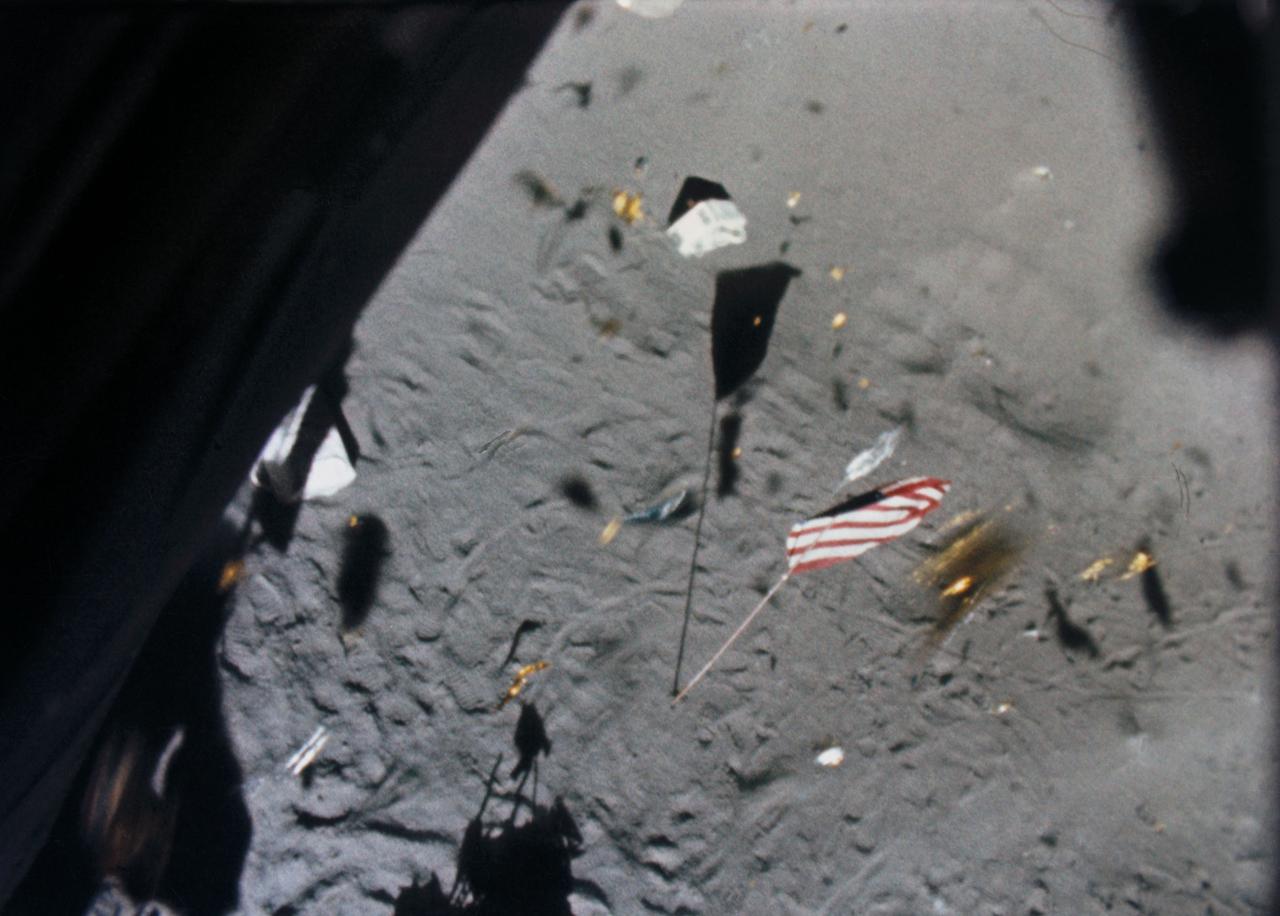

S71-19500 (6 Feb. 1971) --- The Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) ascent stage lifts off the lunar surface and the powerful LM engine causes a brief force of wind which scatters gold-colored foil, covering the LM, and disturbs the U.S. flag. This picture was taken from film exposed by the 16mm data acquisition camera - which was mounted inside the LM.
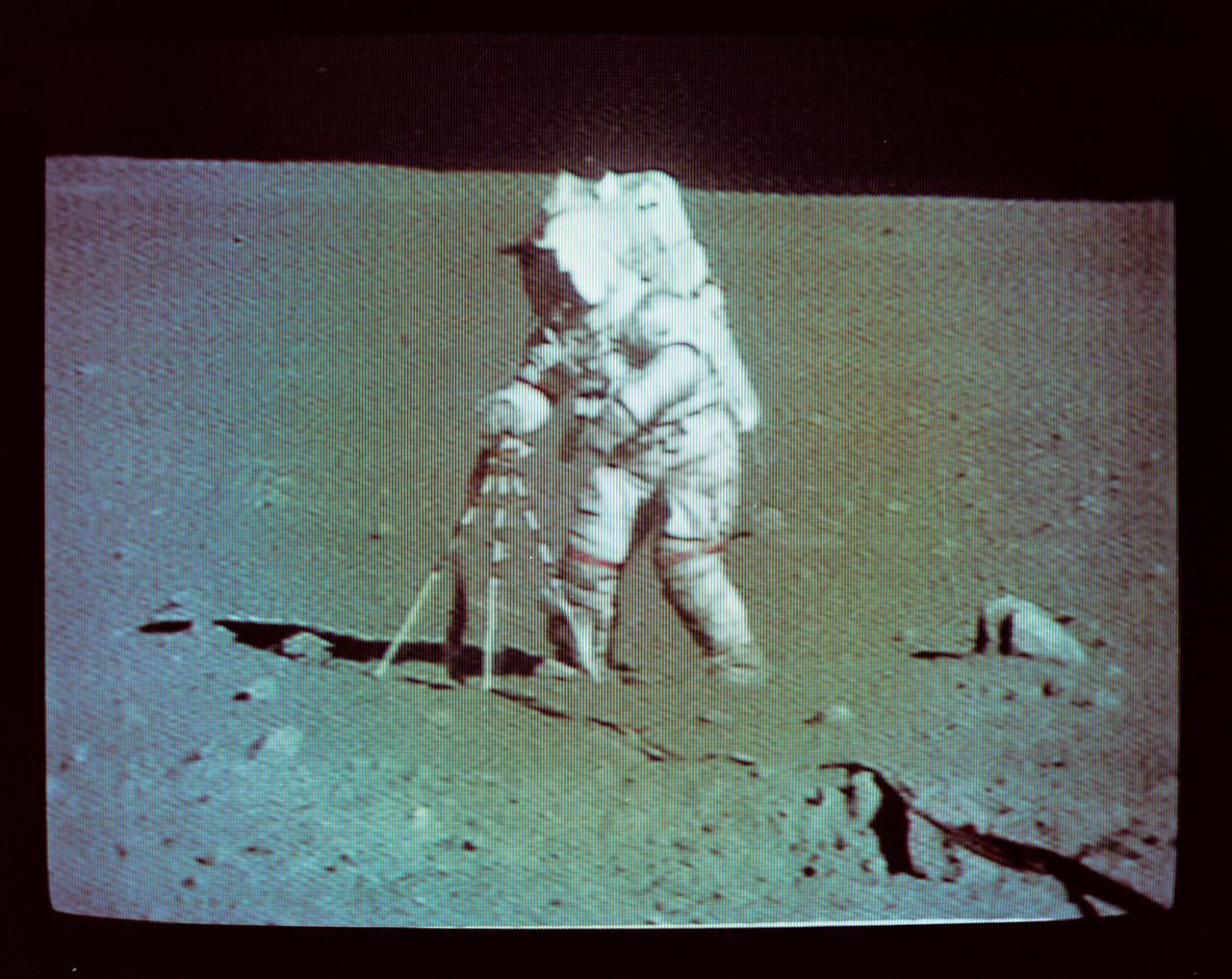

S72-35610 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, deploys the lunar Portable Magnetometer during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color television camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). While astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit, astronauts Young and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the Descartes landing site.
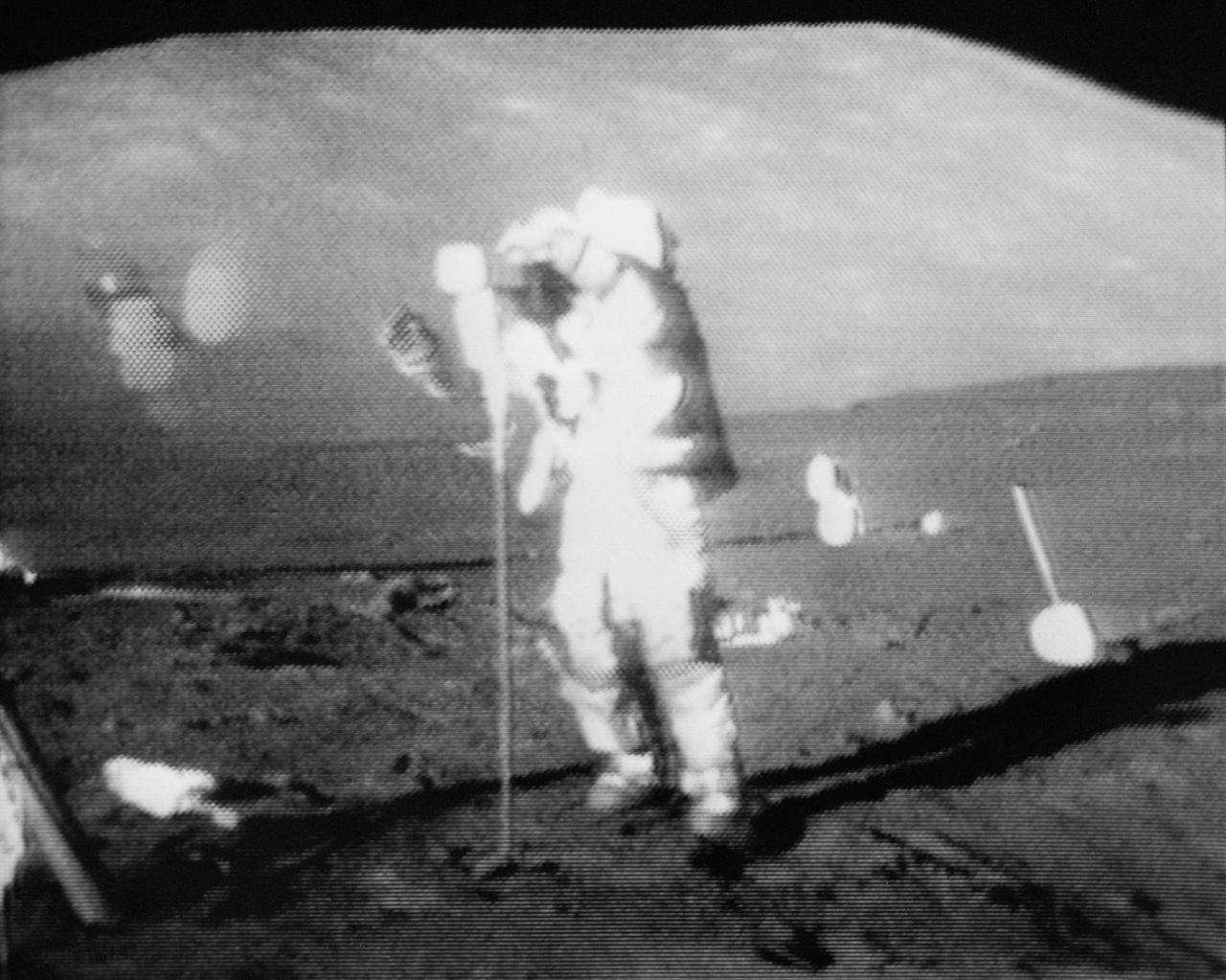

S72-55064 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan operates the Apollo Lunar Surface Drill during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, in this black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the RCA color TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Cernan is the commander of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while astronaut Cernan and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the moon.

S69-44464 (July 1969) --- Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong took this series of pictures of the landing site of Apollo 11's Lunar Module (LM) Eagle on the lunar surface. Glare in the middle of the top frames is the result of the Hasselblad being aimed toward the sun.
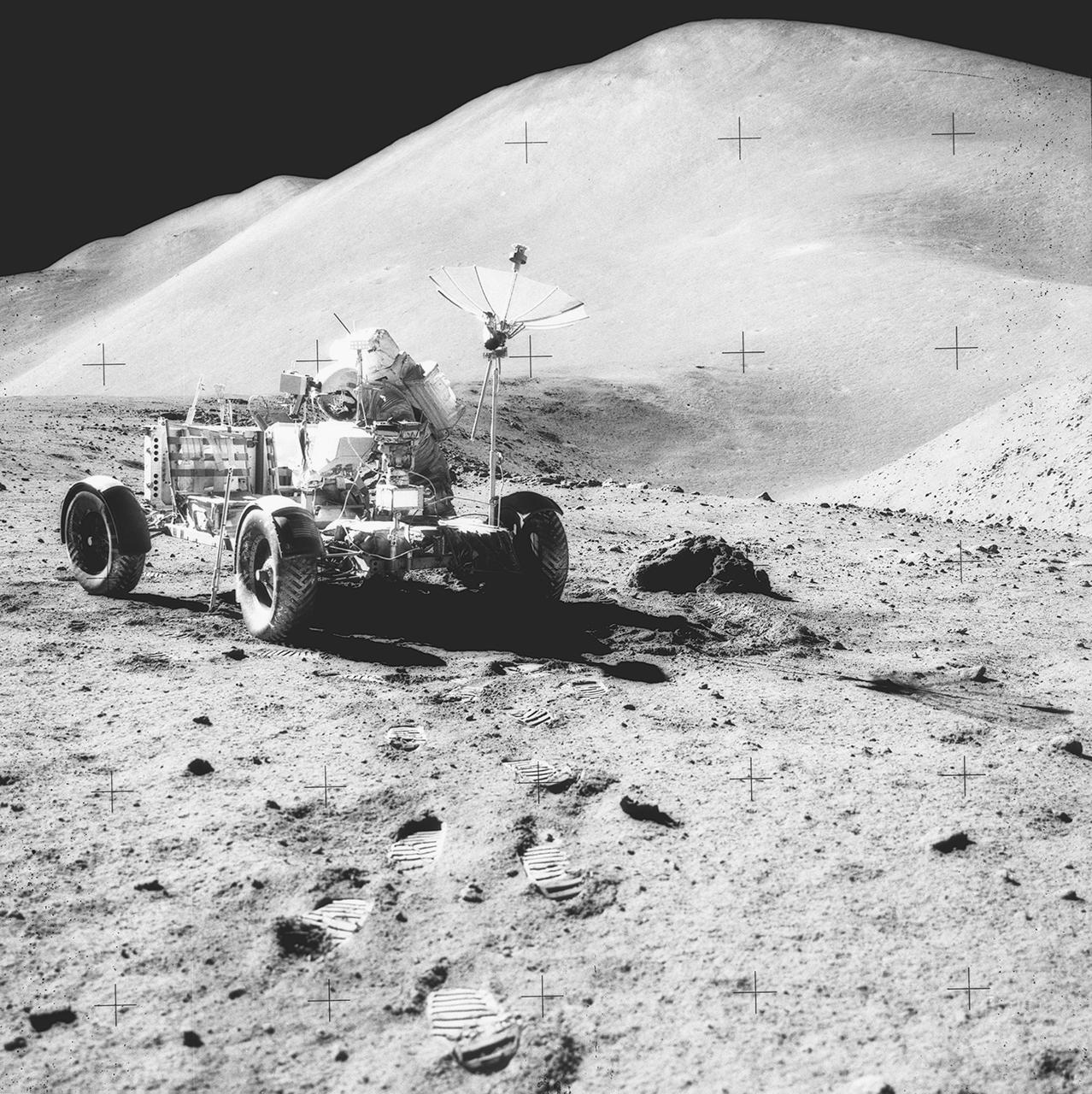

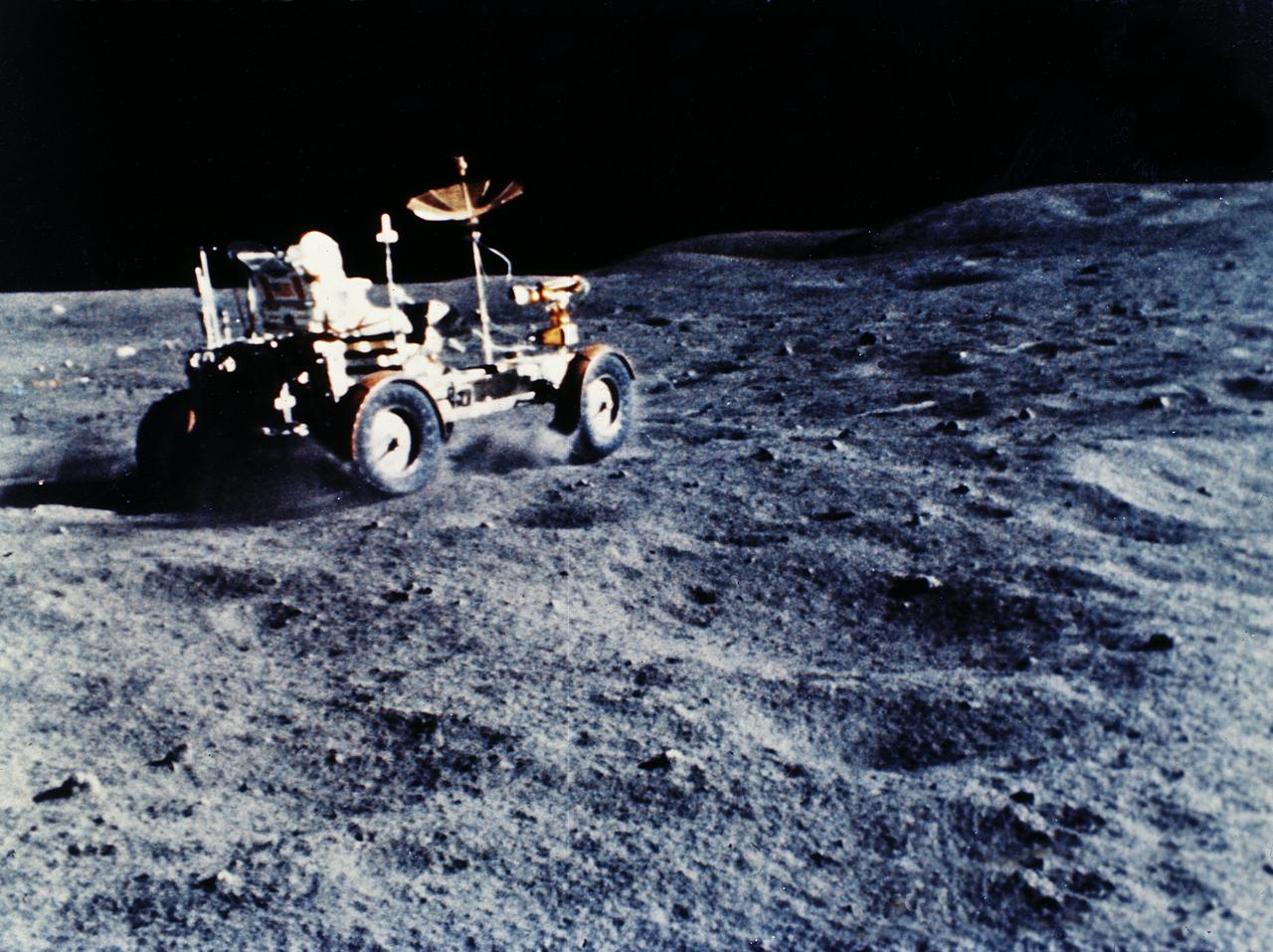
The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions, Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17, in 1971 and 1972 to permit the crew to travel several miles from the lunar landing site. This photograph was taken during the Apollo 15 mission.
The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17, in 1971 and 1972, to permit the crew to travel several miles from the lunar landing site. This photograph was taken during the Apollo 16 mission.
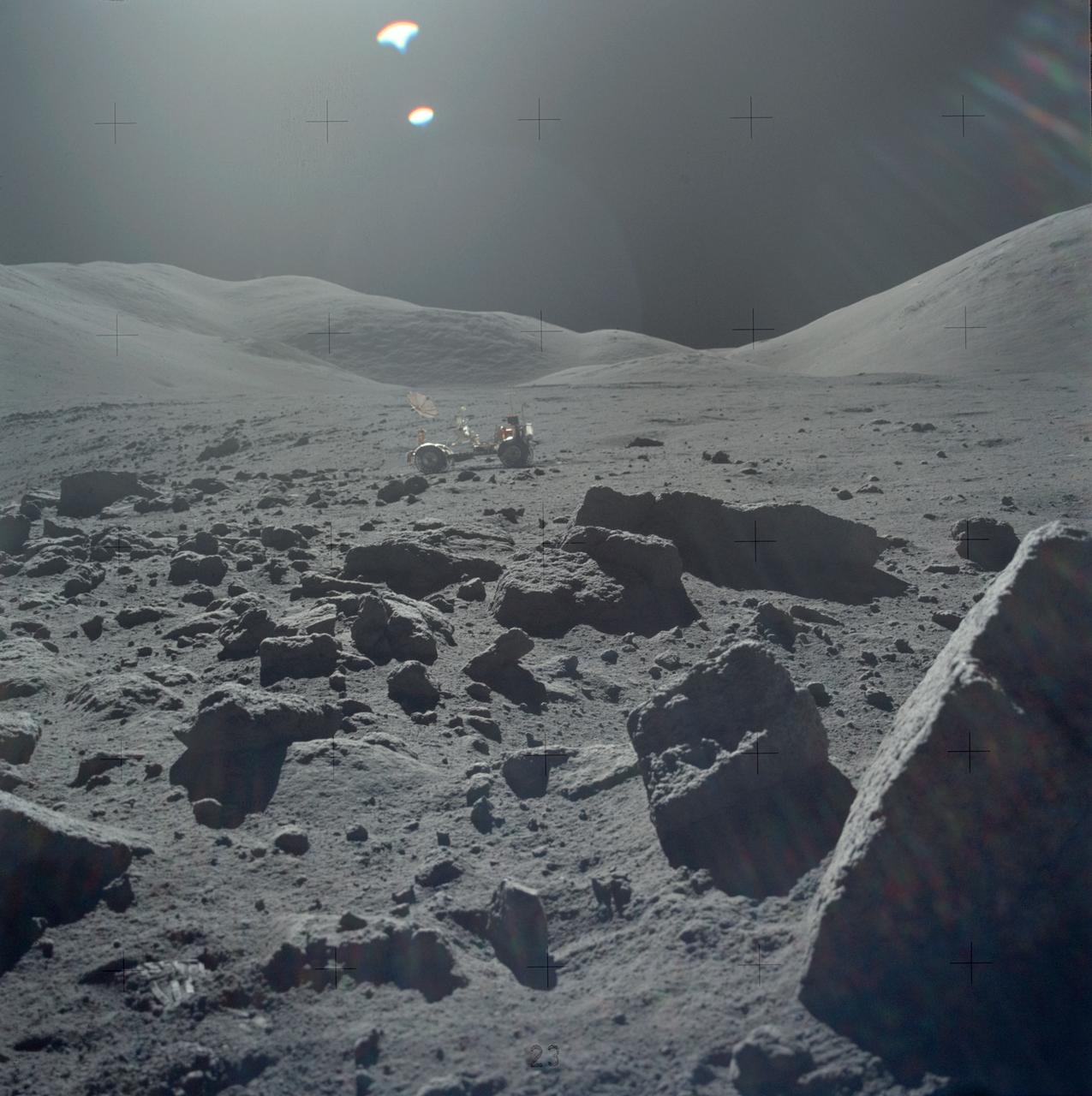

AS17-145-22162 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- One of the Apollo 17 crew photographed this view during lunar surface extravehicular activities (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The Lunar Rover Vehicle (LRV), which was used extensively by astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt, is visible in the background.
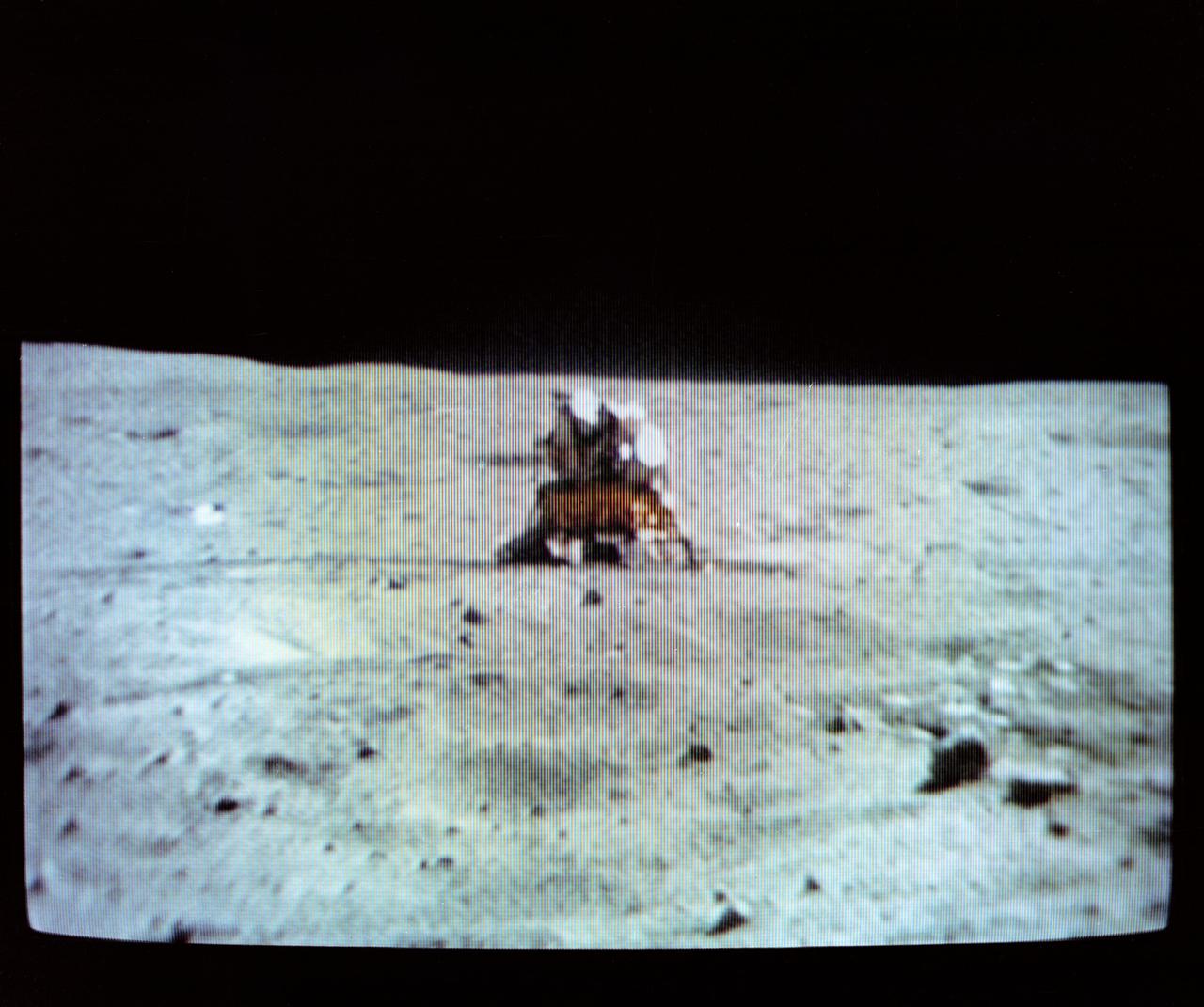

S72-35612 (22 April 1972) --- The Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" dominates the lunar scene at the Descartes landing site, as seen in the reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). Astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 LM to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit. Note U.S. flag deployed on the left. This picture was made during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA).
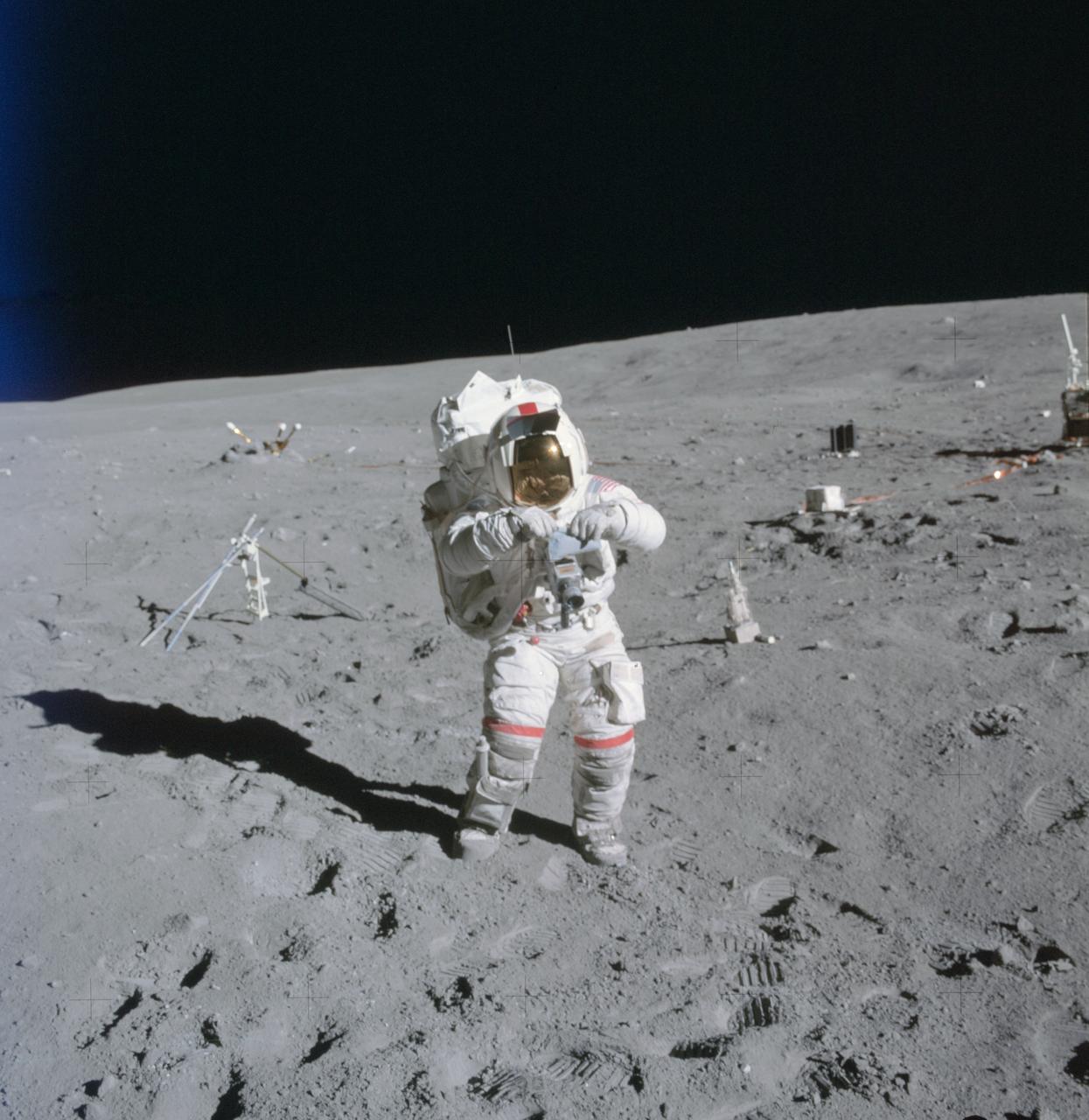

AS16-114-18388 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, stands at the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) deployment site during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. The components of the ALSEP are in the background. The lunar surface drill is just behind and to the right of astronaut Young. The drill's rack and bore stems are to the left. The three-sensor Lunar Surface Magnetometer is beyond the rack. The dark object in the right background is the Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (RTG). Between the RTG and the drill is the Heat Flow Experiment. A part of the Central Station is at the right center edge of the picture. This photograph was taken by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot.

AS16-110-17960 (22 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander, replaces tools in the Apollo Lunar Hand Tool (ALHT) carrier at the aft end of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the high side of Stone Mountain at the Descartes landing site. Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, took this photograph near the conclusion of Station 4 activities. Smoky Mountain, with the large Ravine Crater on its flank, is in the left background. This view is looking northeast. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
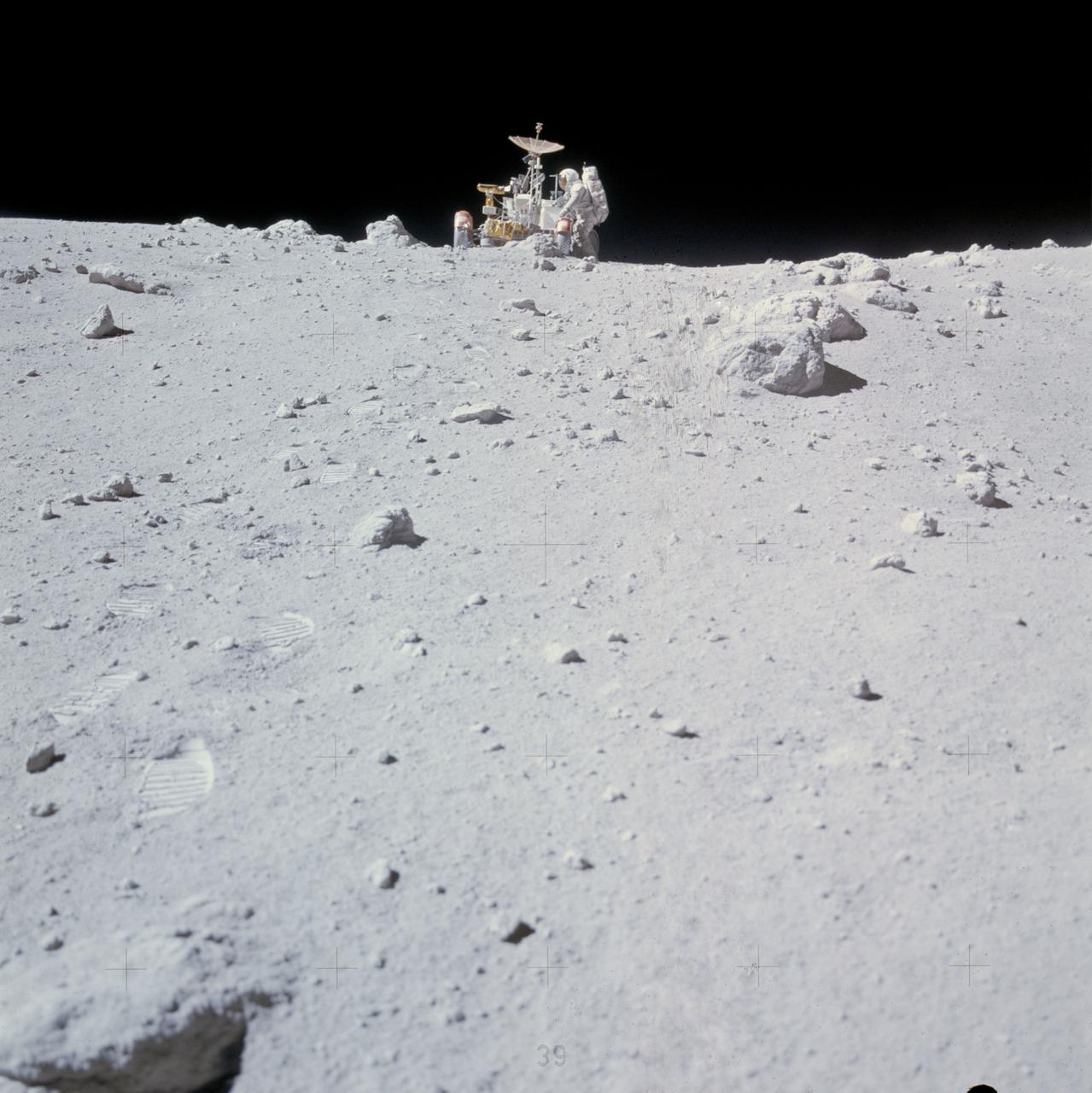

AS16-116-18607 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr. works at the front of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) parked in this rock field at a North Ray Crater geological site during the mission's third extravehicular activity (EVA) on April 23, 1972. Astronaut John W. Young took this picture with a 70mm Hasselblad camera. While astronauts Young, commander; and Duke, lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
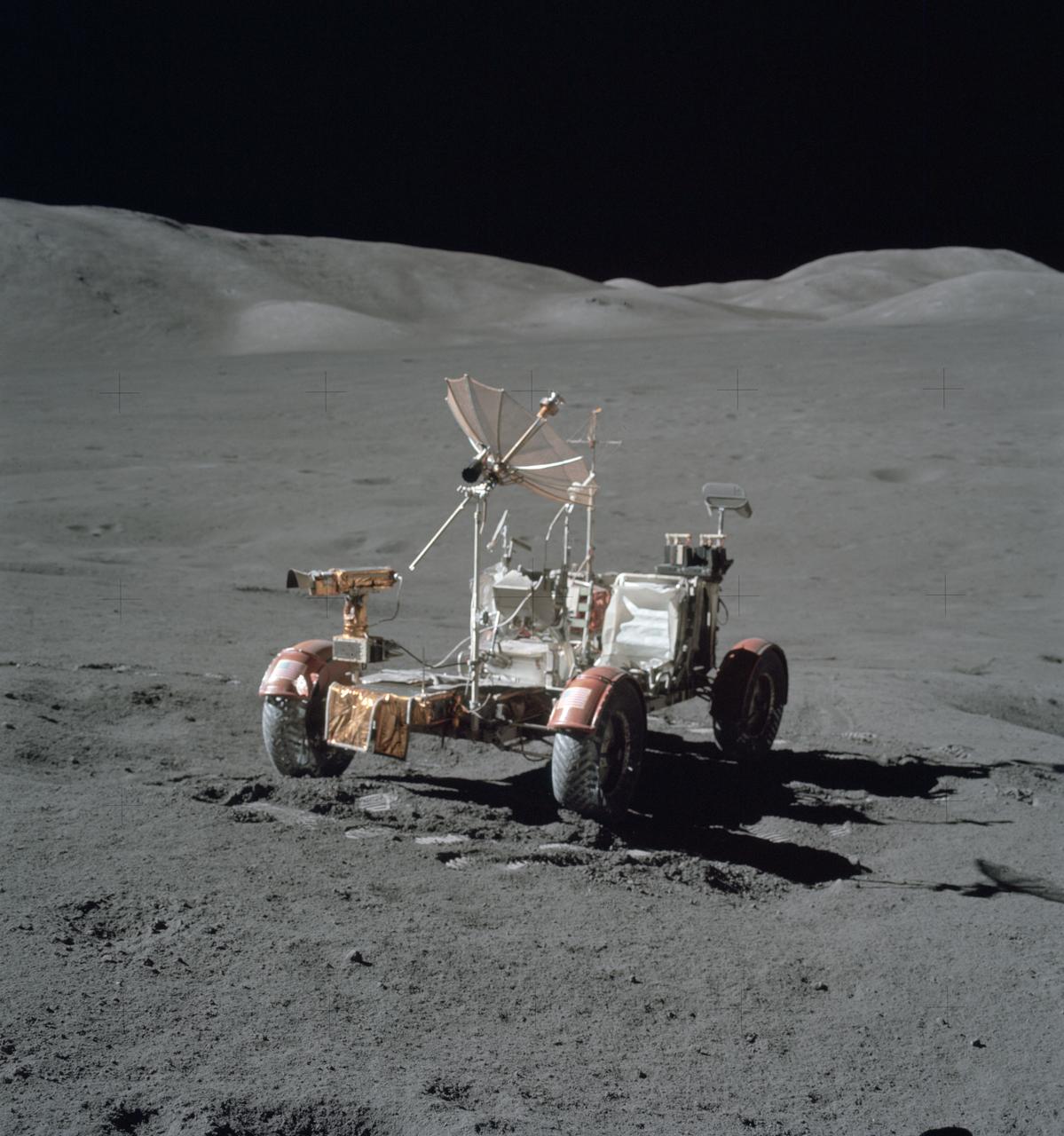

AS17-146-22367 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- This is an excellent view of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) which was used extensively by astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt at the Taurus-Littrow landing site.

This is the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission crew portrait. Pictured from left to right are: Thomas K. Mattingly II, Command Module pilot; John W. Young, Mission Commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., Lunar Module pilot. Launched from the Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 1972, Apollo 16 spent three days on Earth's Moon. The first study of the highlands area, the landing site for Apollo 16 was the Descartes Highlands. The fifth lunar landing mission out of six, Apollo 16 was famous for deploying and using an ultraviolet telescope as the first lunar observatory. The telescope photographed ultraviolet light emitted by Earth and other celestial objects. The Lunar Roving Vehicle, developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, was also used for collecting rocks and data on the mysterious lunar highlands. In this photo, astronaut John W. Young photographs Charles M. Duke, Jr. collecting rock samples at the Descartes landing site. Duke stands by Plum Crater while the Lunar Roving Vehicle waits parked in the background. High above, Thomas K. Mattingly orbits in the Command Module. The mission ended April 27, 1972 as the crew splashed down into the Pacific Ocean.

AS15-86-11600 (31 July 1971) --- A view of the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" taken early in the first Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site prior to deployment of lunar surface equipment. Hadley Delta Mountain is in the background. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS14-64-9181 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- A view of the lunar terrain at the Apollo 14 Fra Mauro landing site as photographed through the left window of the Lunar Module (LM). Note the clump of lunar soil in the foreground, and a crater in the center on the horizon. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
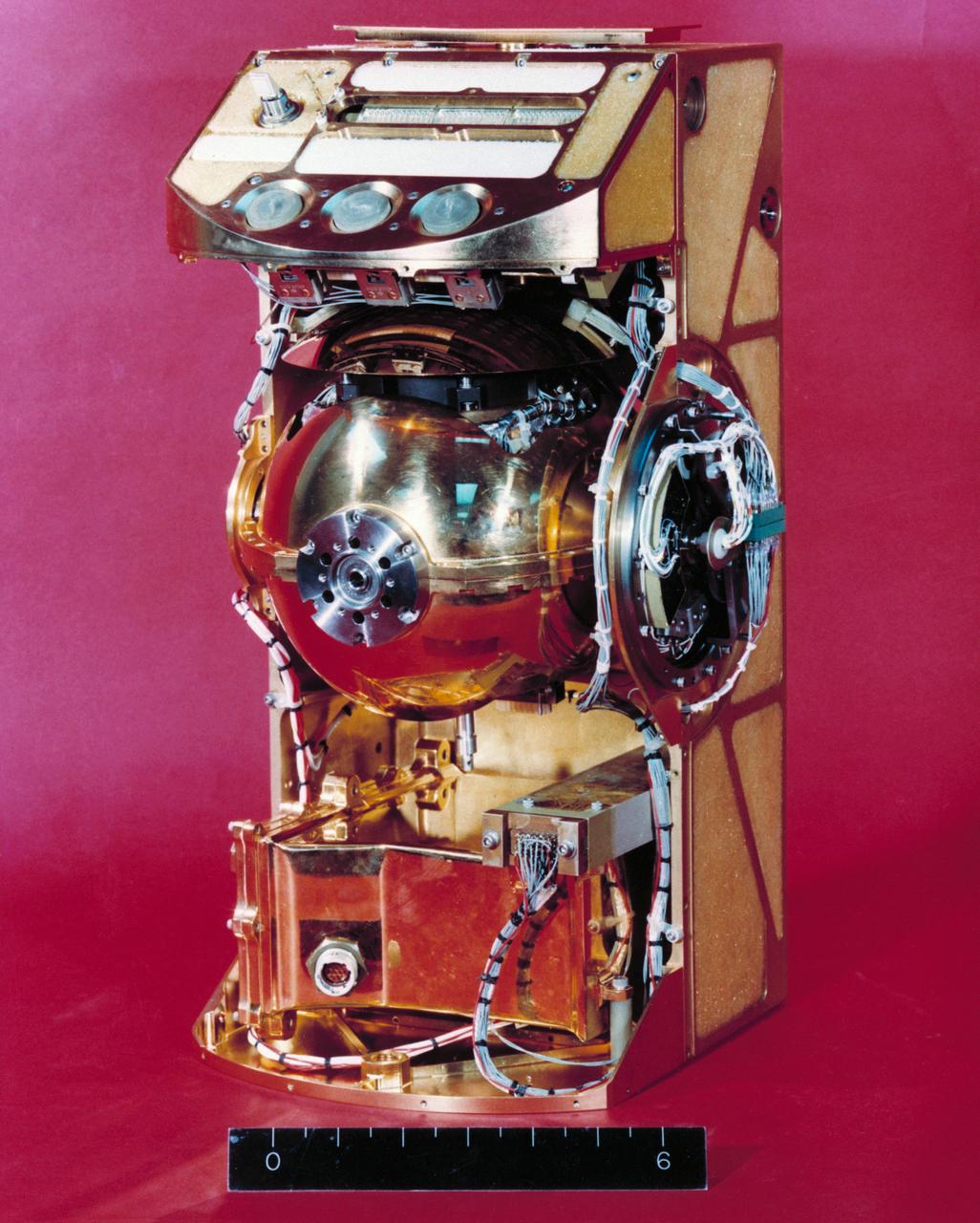
S72-53952 (November 1972) --- The Traverse Gravimeter Experiment (S-199), with cover removed, which will be used by the Apollo 17 crewmen at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The purposes of this experiment are to make a high accuracy relative survey of the lunar gravitational field in the lunar landing area and to make an Earth-moon gravity tie. Specific experiment objectives related to these purposes are to: (1) measure the value of gravity, relative to the value at a lunar base station, at selected known locations along the lunar traverse; (2) measure the value of gravity at a known point on the lunar surface (base station) relative to the value of gravity at a known point on Earth.
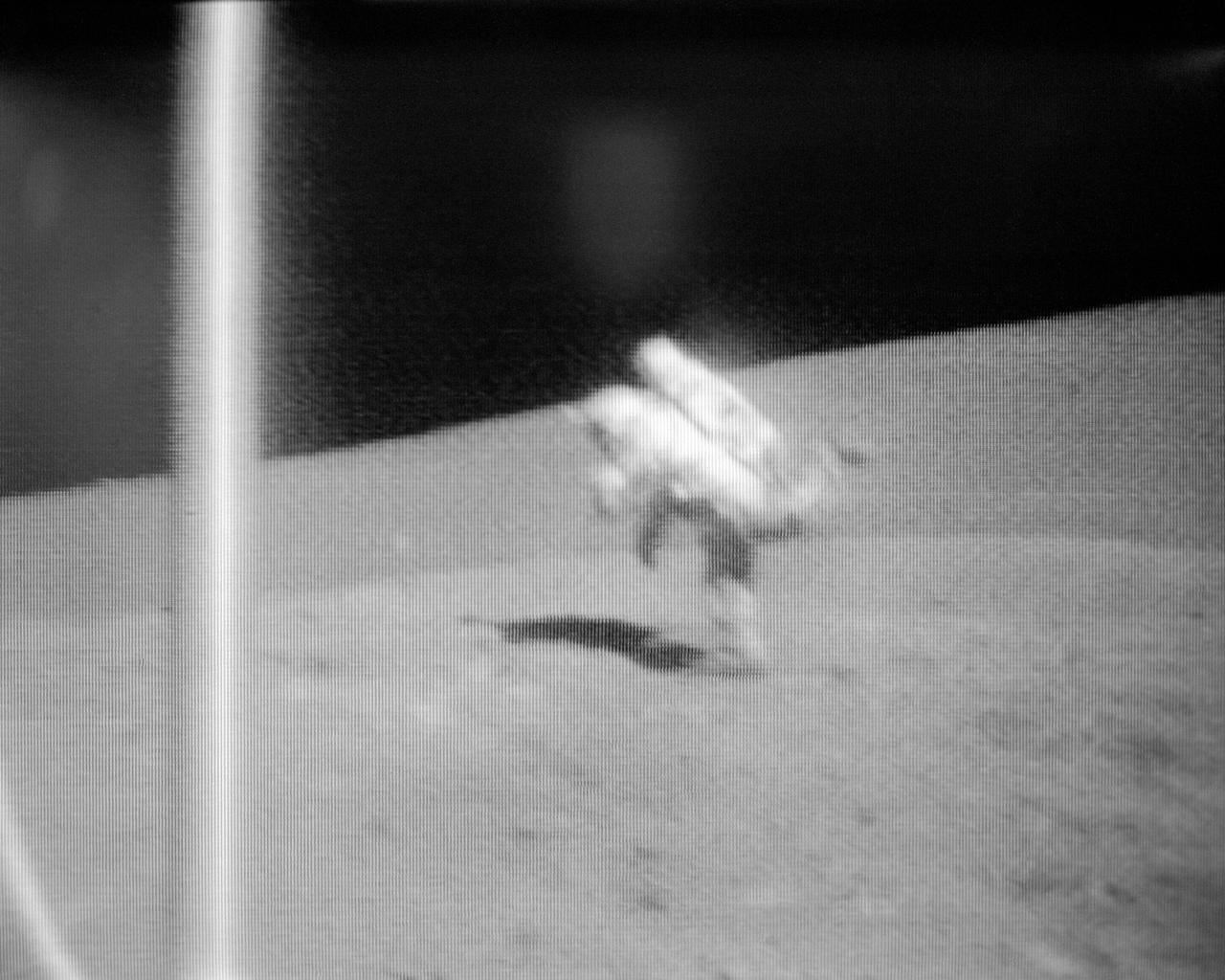

S72-55166 (12 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt loses his balance and heads for a fall during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, as seen in this black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Schmitt is lunar module pilot of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while astronauts Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan, commander, descended in the Lunar Module "Challenger" to explore the moon.

S72-55066 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt chips samples from a large boulder during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, in this black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Schmitt is the lunar module pilot of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while astronauts Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan, commander, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the moon.

AS17-140-21388 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, mission commander, walks toward the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site of NASA's sixth and final Apollo lunar landing mission. The photograph was taken by astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
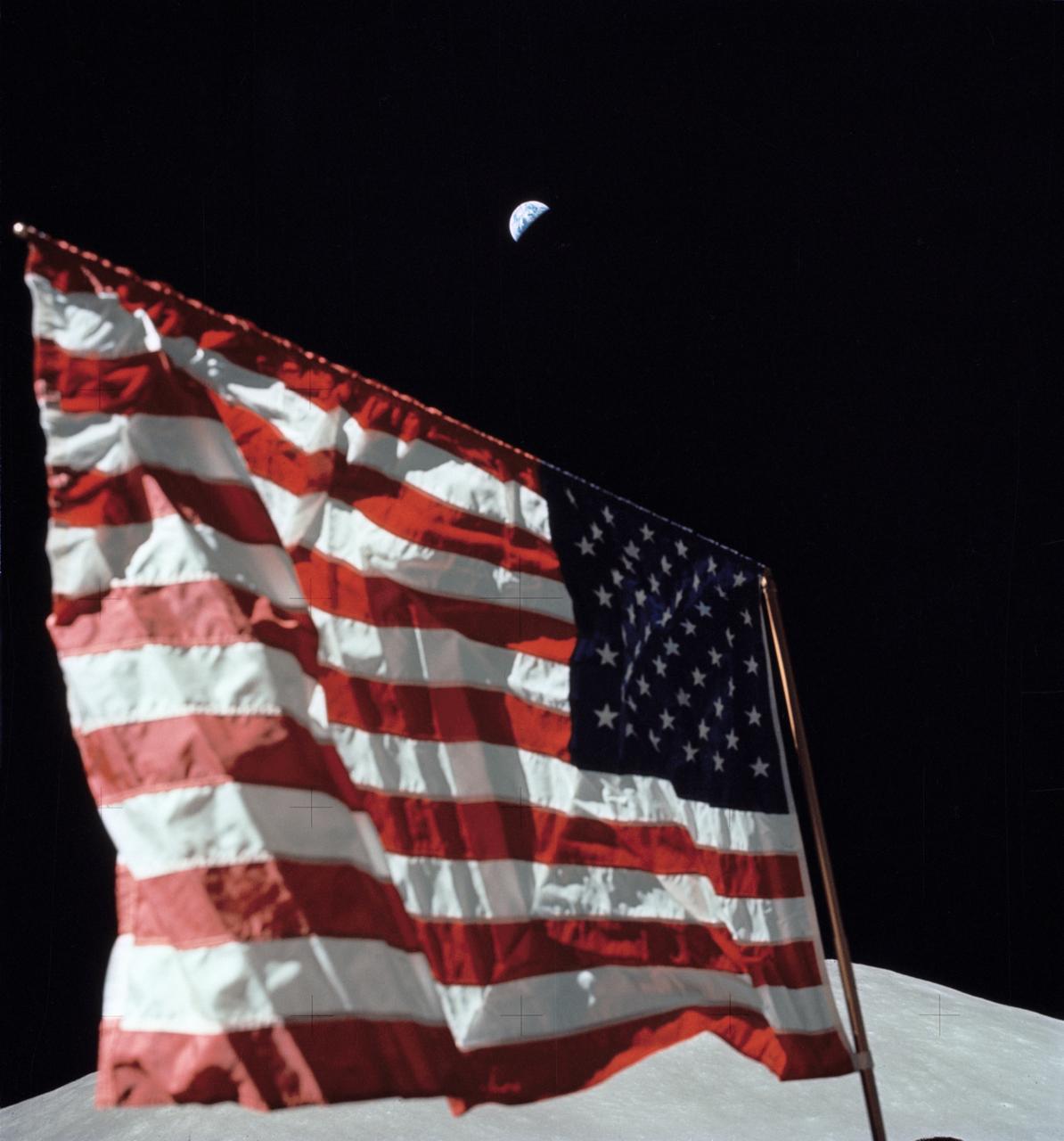

AS17-134-20466 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- A close-up view of the U.S. flag deployed on the moon at the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the crewmen of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. The crescent Earth can be seen in the far distant background above the flag. The lunar feature in the near background is South Massif. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module "Challenger" to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.
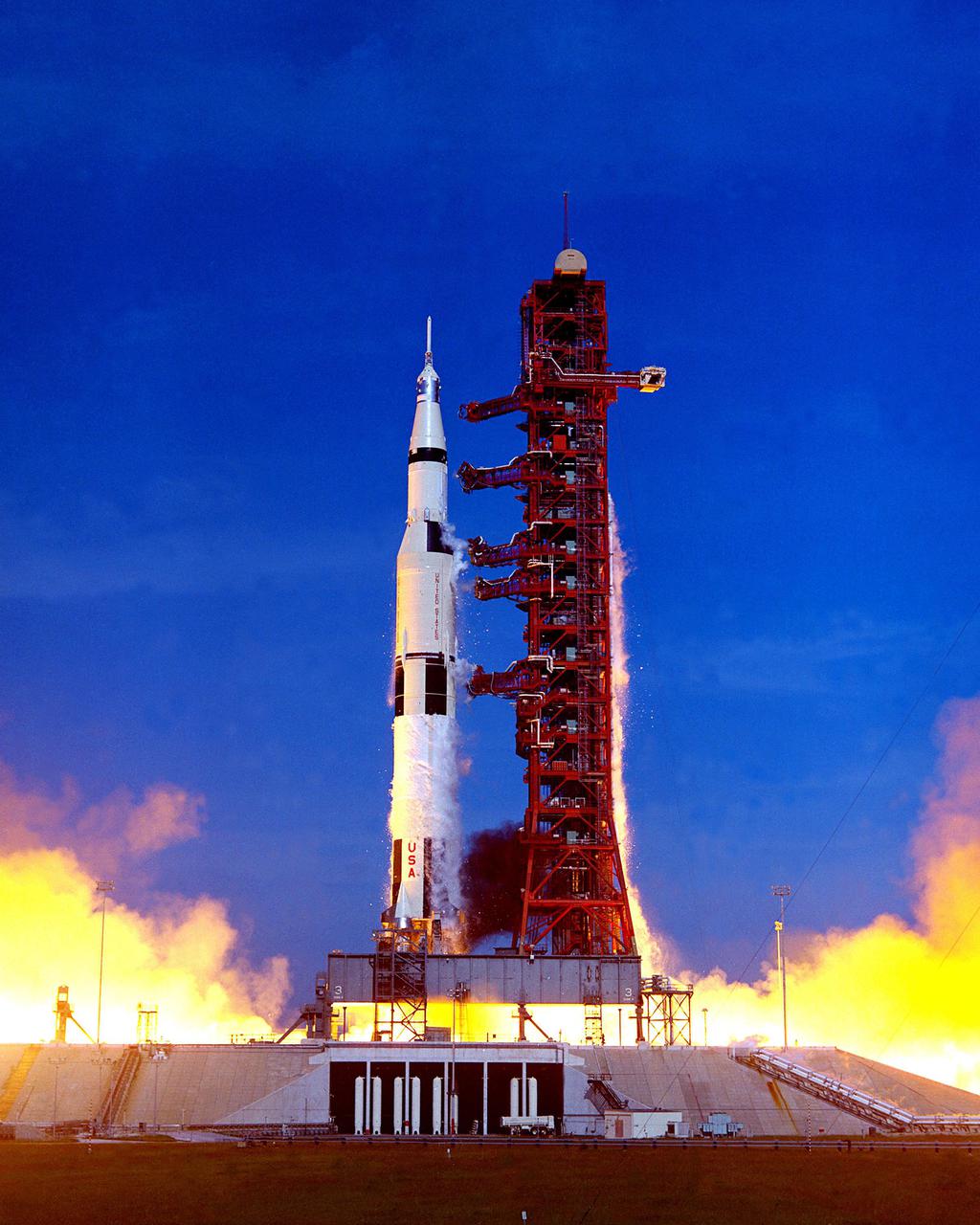

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Apollo 15 Saturn V Space Vehicle soars into the skies after liftoff at Launch Pad 39A marking the beginning of NASA's fourth Manned Lunar Landing Mission. The astronauts aboard are David R. Scott, commander; James B. Irwin, Lunar Module pilot; and Alfred M. Worden Jr., Command Module pilot. The landing site for the Lunar Module is the Hadley-Apennine area of the Moon, about 465 miles north of the Lunar Equator. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) will be used for the first time.
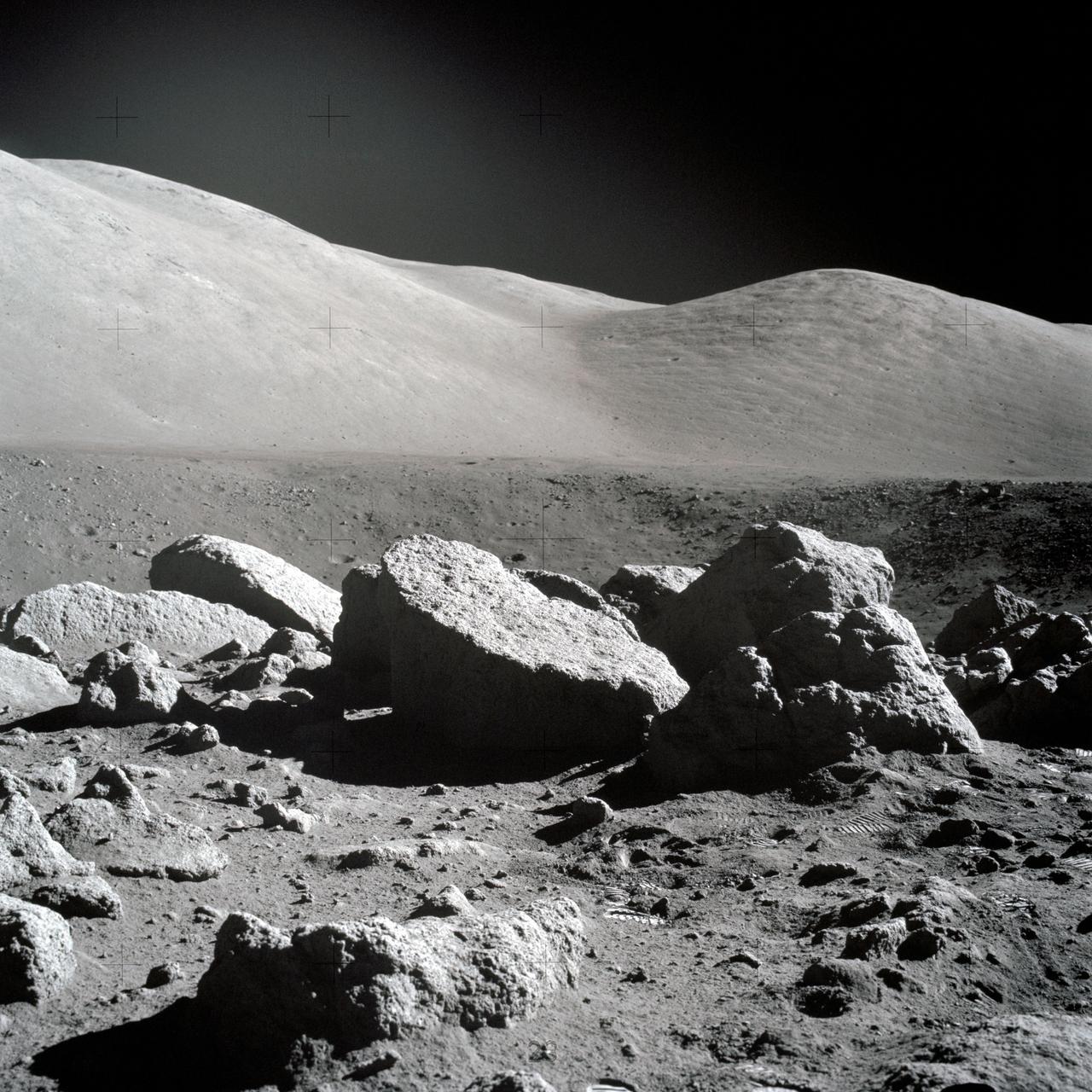

AS17-145-22183 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- One of the Apollo 17 crew took this picture of a large boulder field during lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. This view is looking northeast. Apollo 17 was the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo Program. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
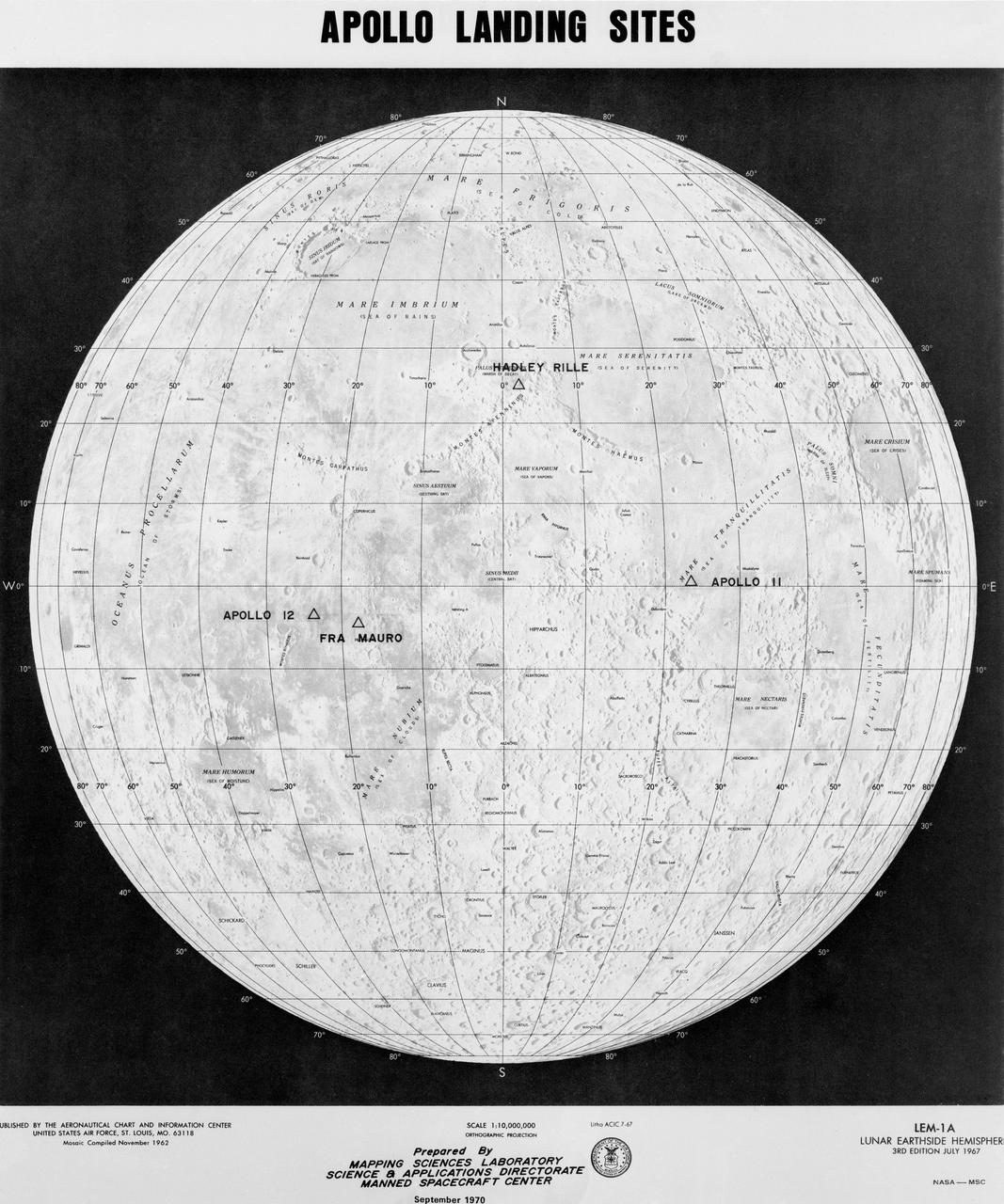
S70-50761 (September 1970) --- This map prepared by Mapping Sciences Laboratory, Science & Applications Directorate at the Manned Spacecraft Center, shows the projected Apollo landing sites. Apollo 11 completed a successful lunar landing mission in the Sea of Tranquility in July 1969. Apollo 12 completed a successful lunar landing mission in the Ocean of Storms in November 1969.

S72-55169 (14 Dec. 1972) --- A photographic replica of the plaque which the Apollo 17 astronauts left behind at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. Apollo 17 is the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. The commemorative plaque was unveiled at the close of the third extravehicular activity (EVA). The plaque is made of stainless steel measuring nine by seven and five-eighths inches, and one-sixteenth inch thick. It is attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the descent stage of Apollo 17 Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger".
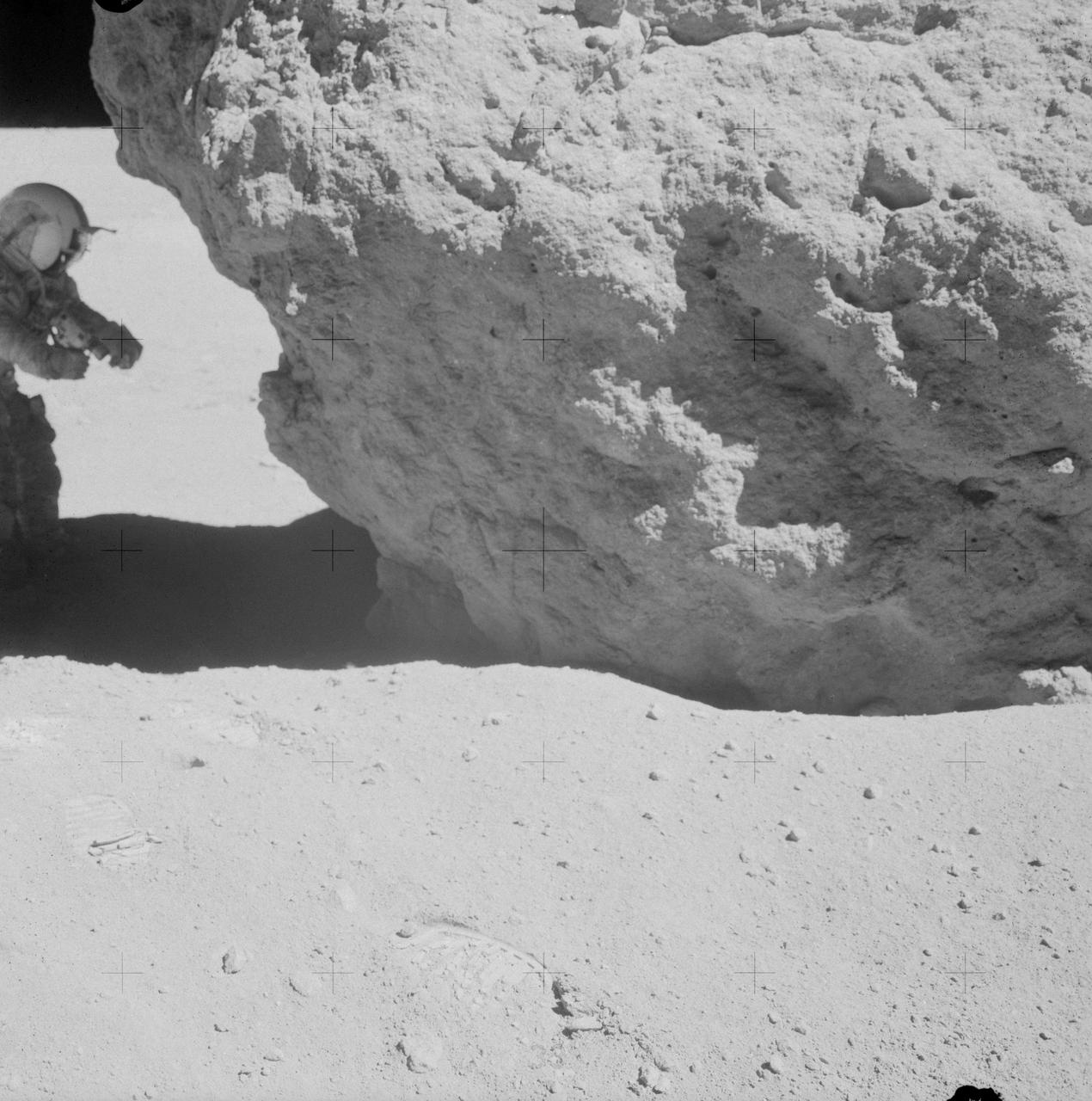

AS16-106-17413 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, looks over a large boulder at Station No.13 during the third Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. This was the site of the permanently shadowed soil sample which was taken from a hole extending under overhanging rock. Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, took this photograph. Concerning Young's reaching under the big rock, Duke remarked: "You do that in west Texas and you get a rattlesnake!"
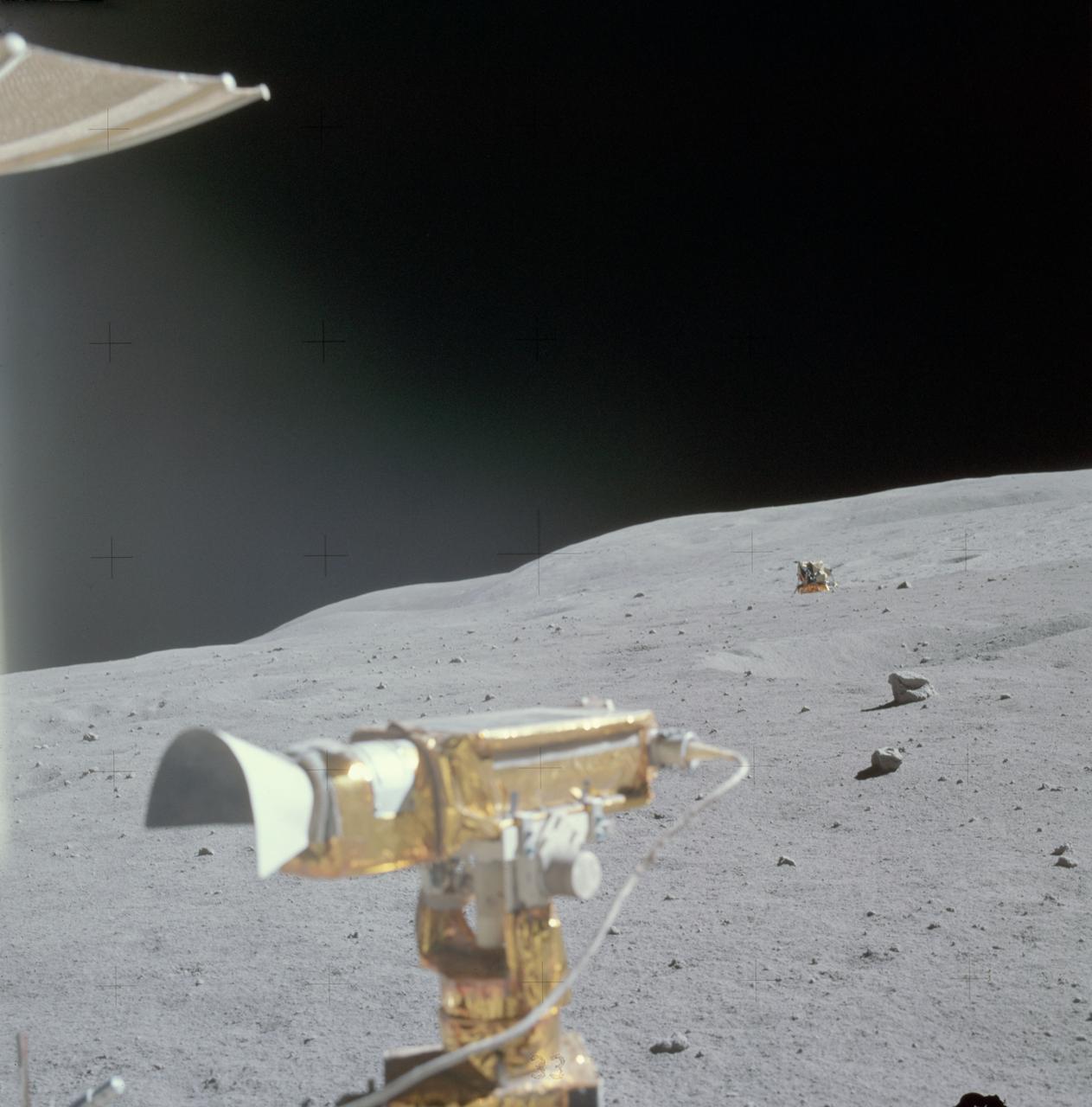
AS16-115-18549 (22 April 1972) --- The Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" is photographed from a distance by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, aboard the moving Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). Astronauts Duke and John W. Young, commander, were returning from their excursion to Stone Mountain during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA). The RCA color television camera mounted on the LRV is in the foreground. A portion of the LRV's high-gain antenna is at top left. Smoky Mountain rises behind the LM in this north-looking view at the Descartes landing site. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
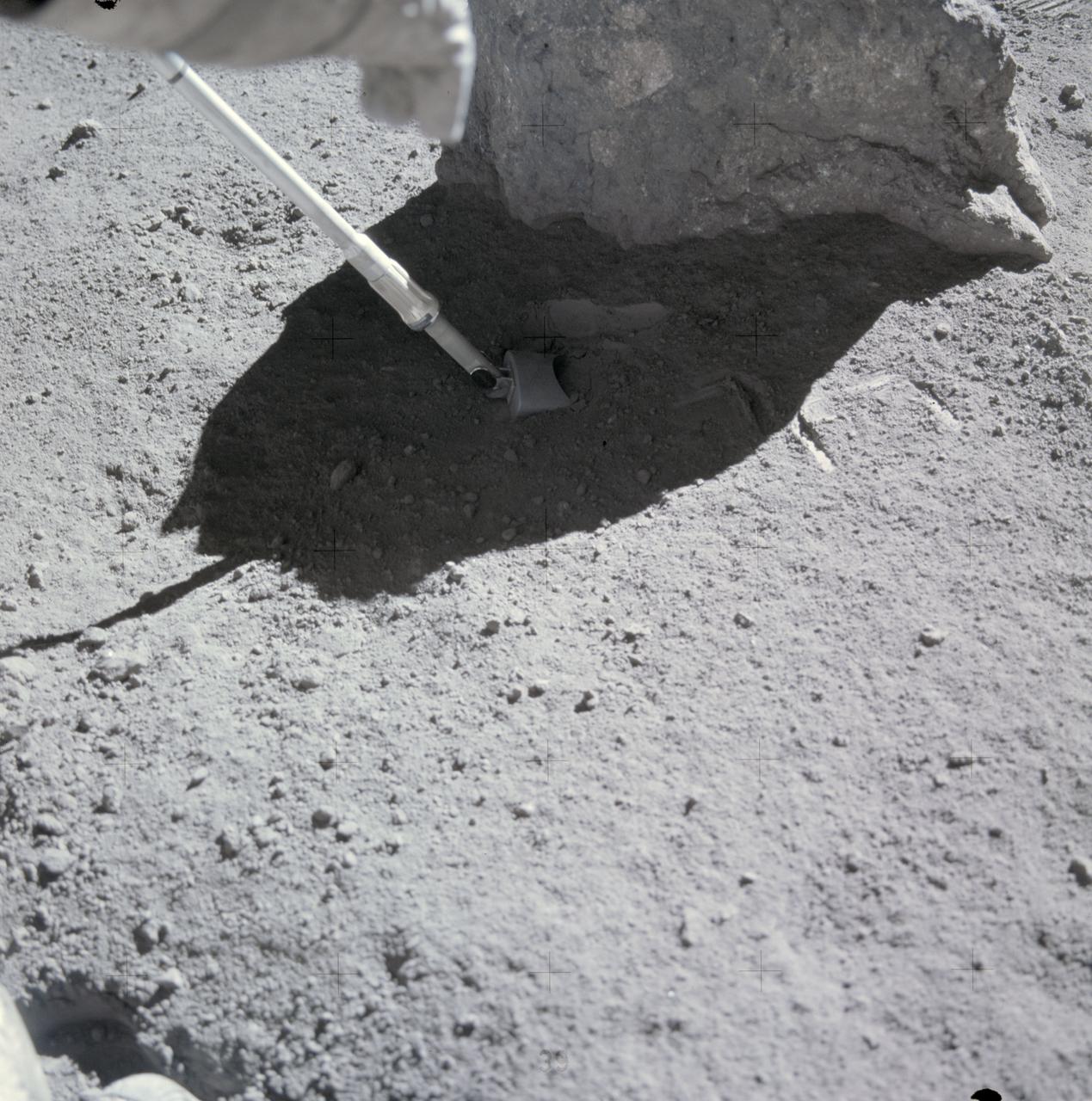

AS16-107-17561 (16-27 April 1972) --- One of the Apollo 16 astronauts scoops up lunar soil at the base of a small boulder at Station No. 9 during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. Depressions to the right of the scoop were made when a surface sample was taken. This photograph was taken just before the boulder was rolled over. While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
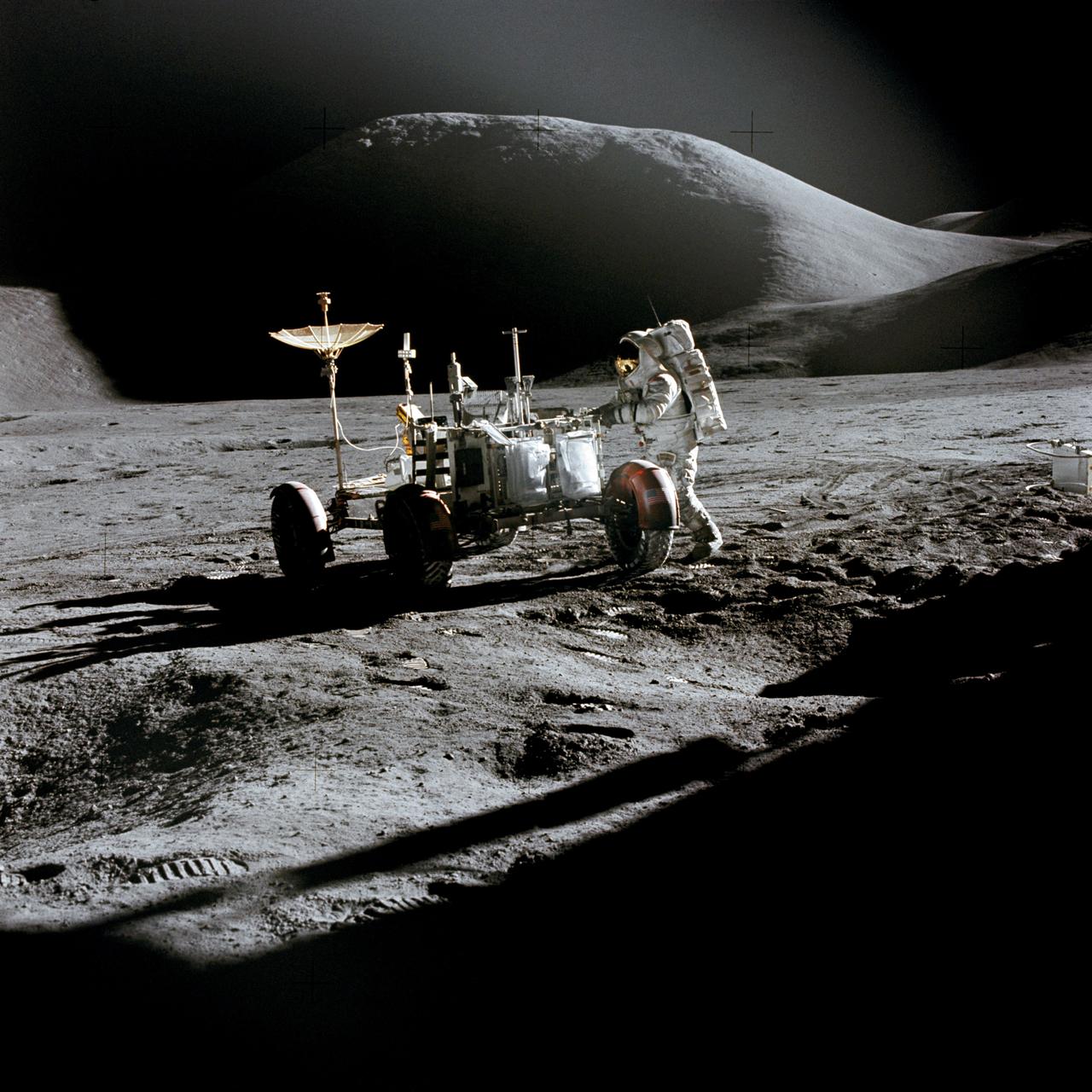

AS15-86-11603 (31 July 1971) --- Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, works at the Lunar Roving Vehicle during the first Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The shadow of the Lunar Module "Falcon" is in the foreground. This view is looking northeast, with Mount Hadley in the background. This photograph was taken by astronaut David R. Scott, commander.
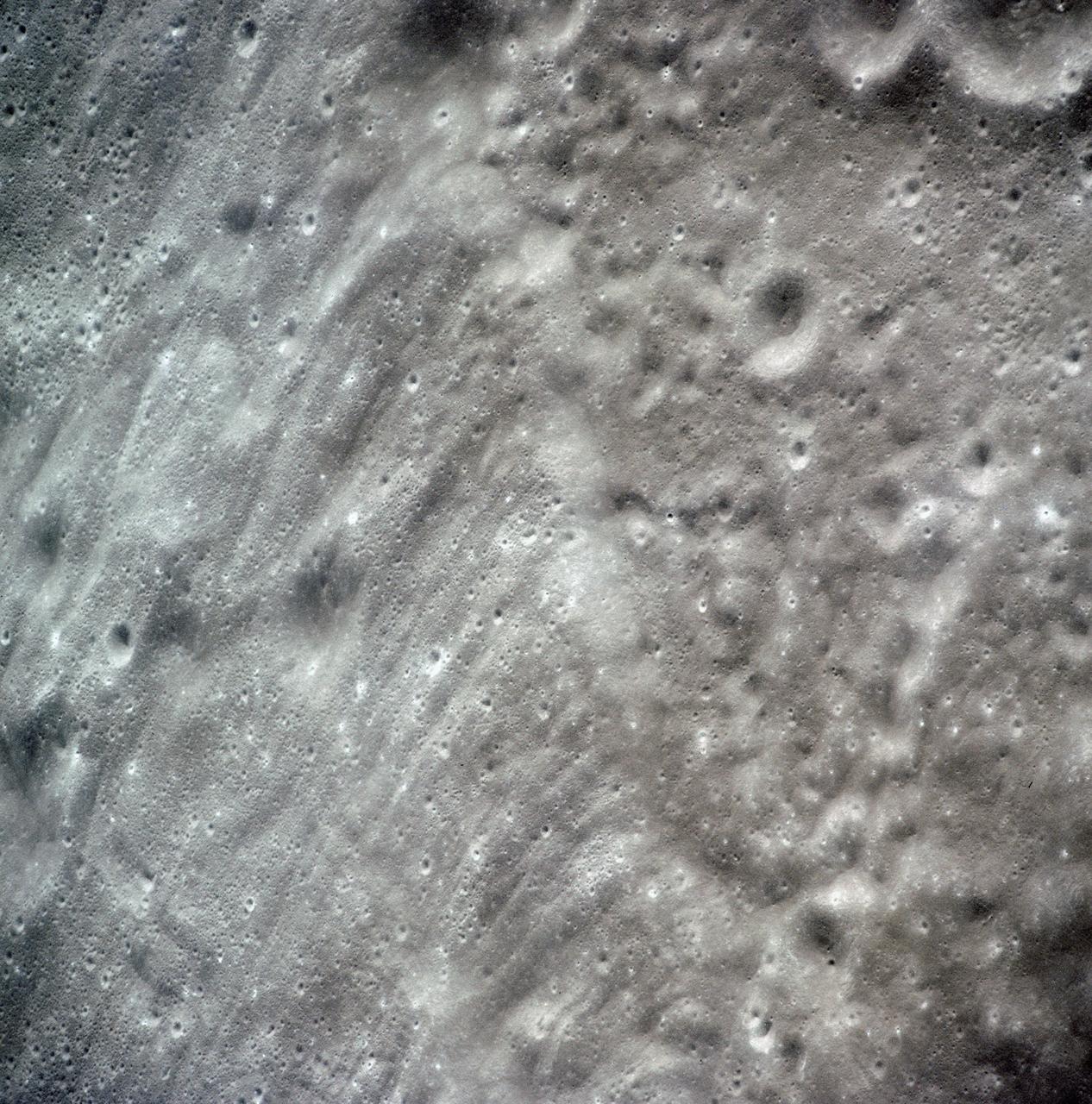

AS15-97-13168 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- A view of the flow structure on the rim and edge of the crater Tsiolkovsky in the highlands of the lunar farside, as photographed from lunar orbit by astronaut Alfred M. Worden in the Apollo 15 Command and Service Module (CSM). Note the scarp at the edge of the flow and elongated grooves on the flow surface. While astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon's Hadley-Apennine landing site, Worden remained with the CSM in lunar orbit.
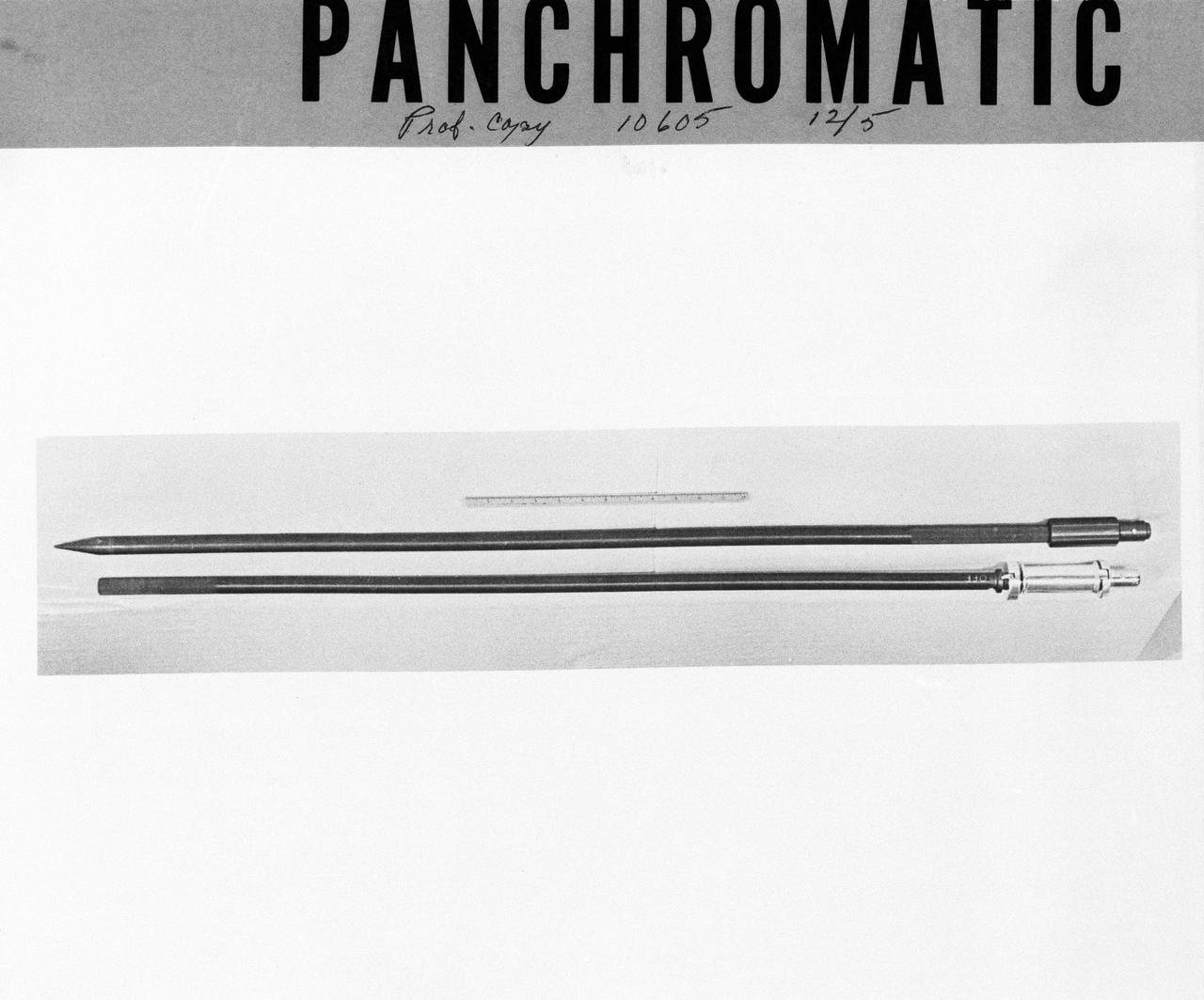
S72-53949 (November 1972) --- The upper and bottom sections of the Lunar Neutron Probe Experiment (S-229), in a stowed configuration, which will be used at the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. The purpose of this experiment is to measure neutron capture rates in the lunar regolith, measure variation of neutron capture rates as a function of depth beneath the lunar surface, and gain information on the lunar neutron energy spectrum.
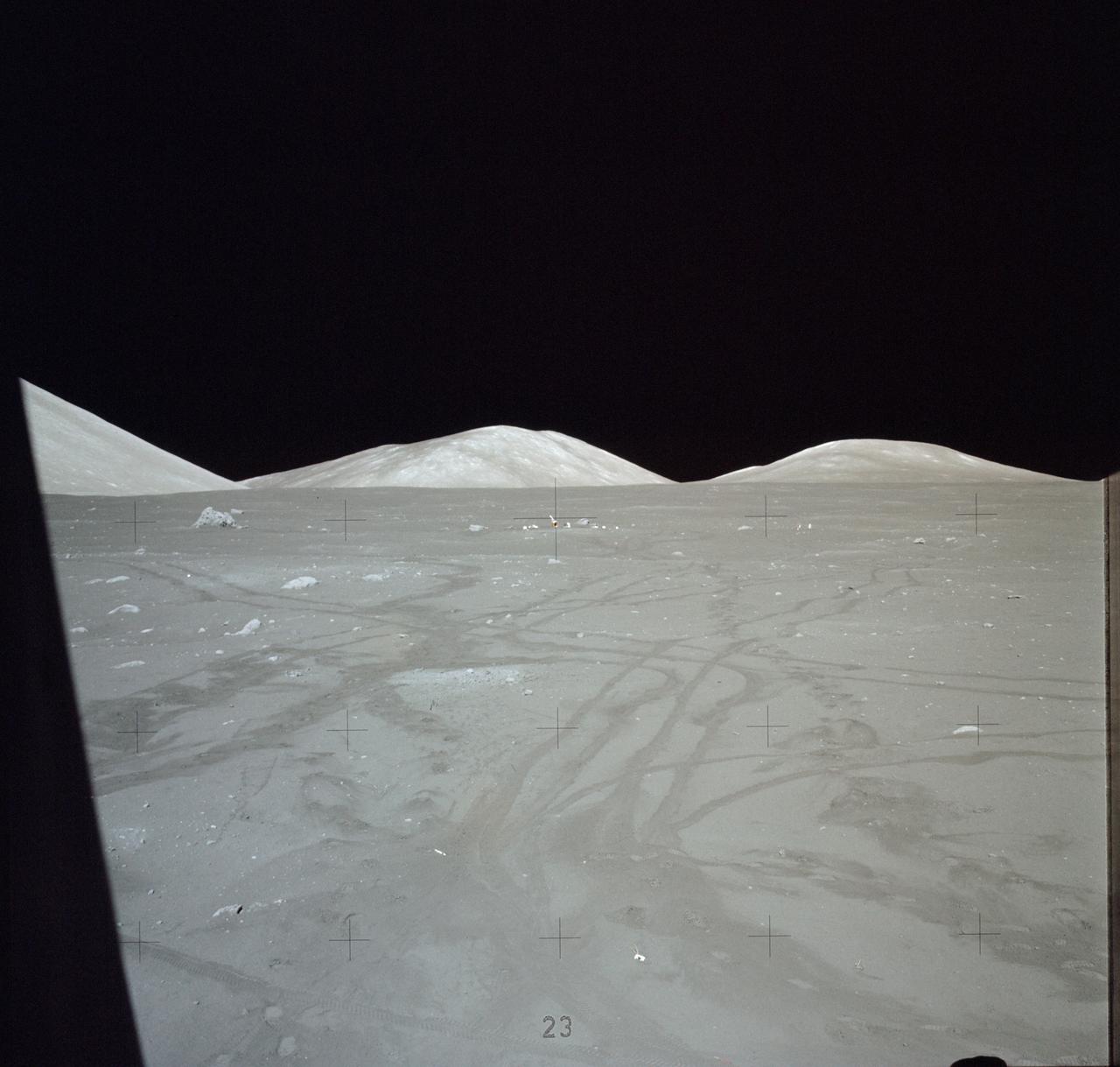

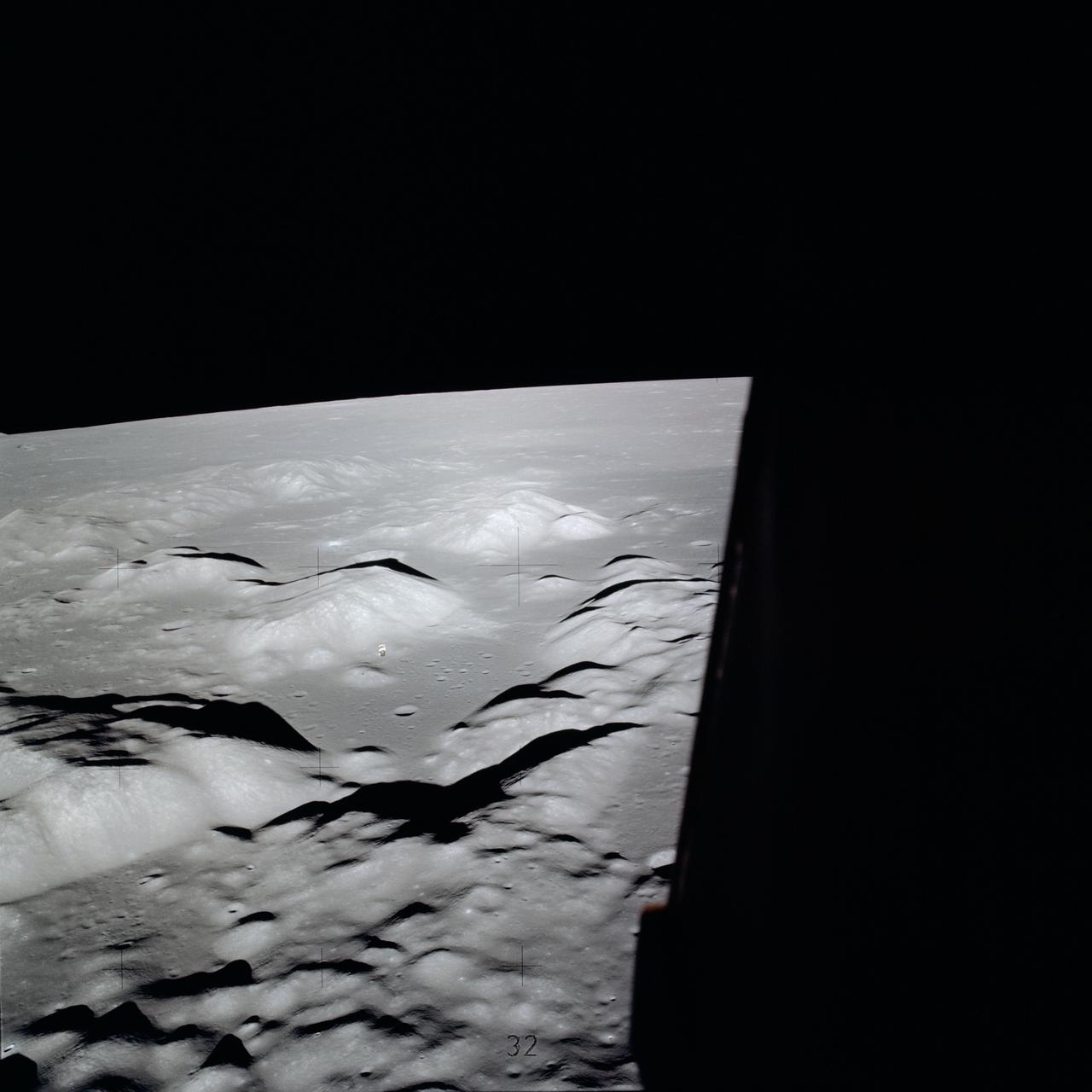
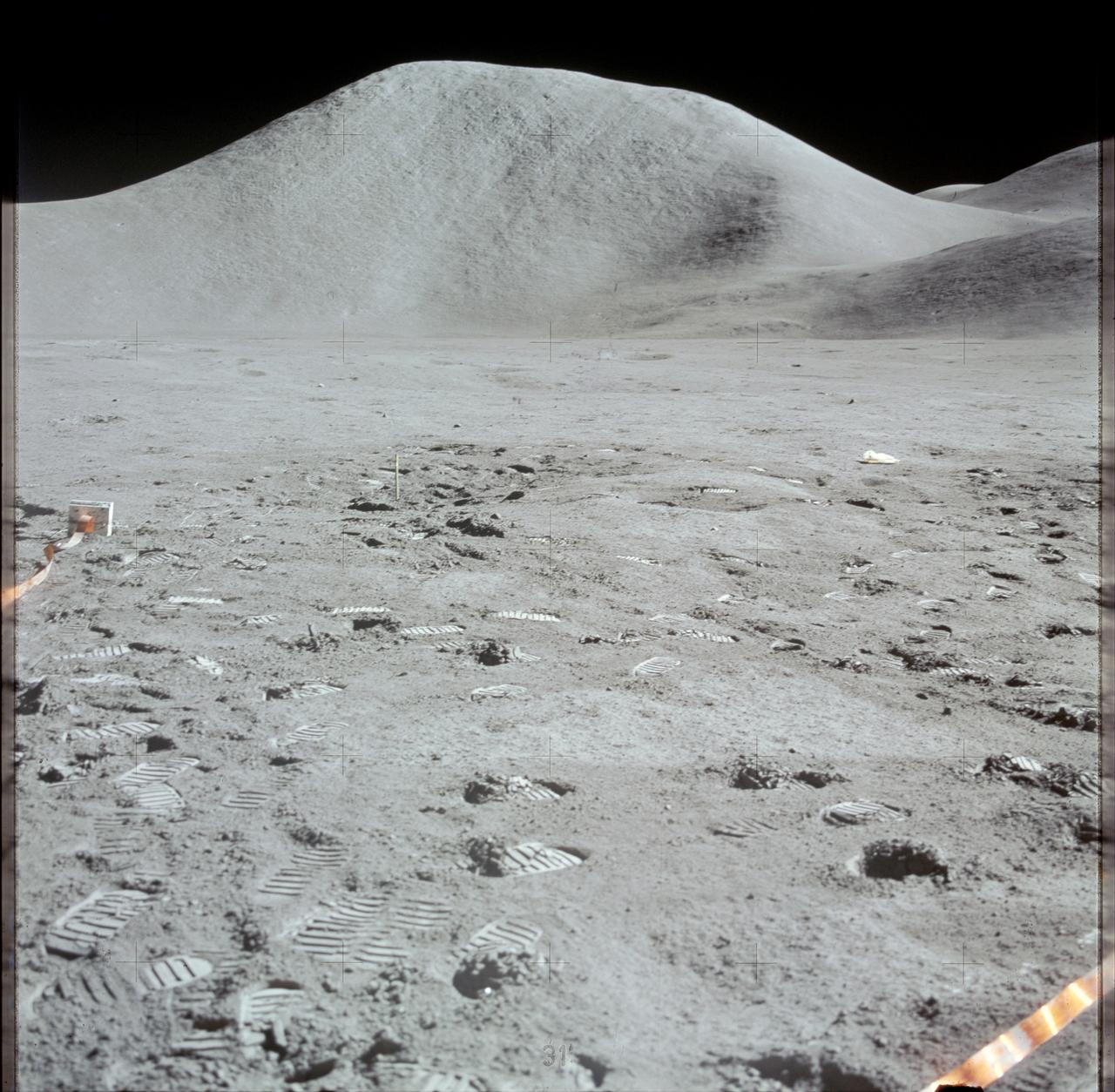
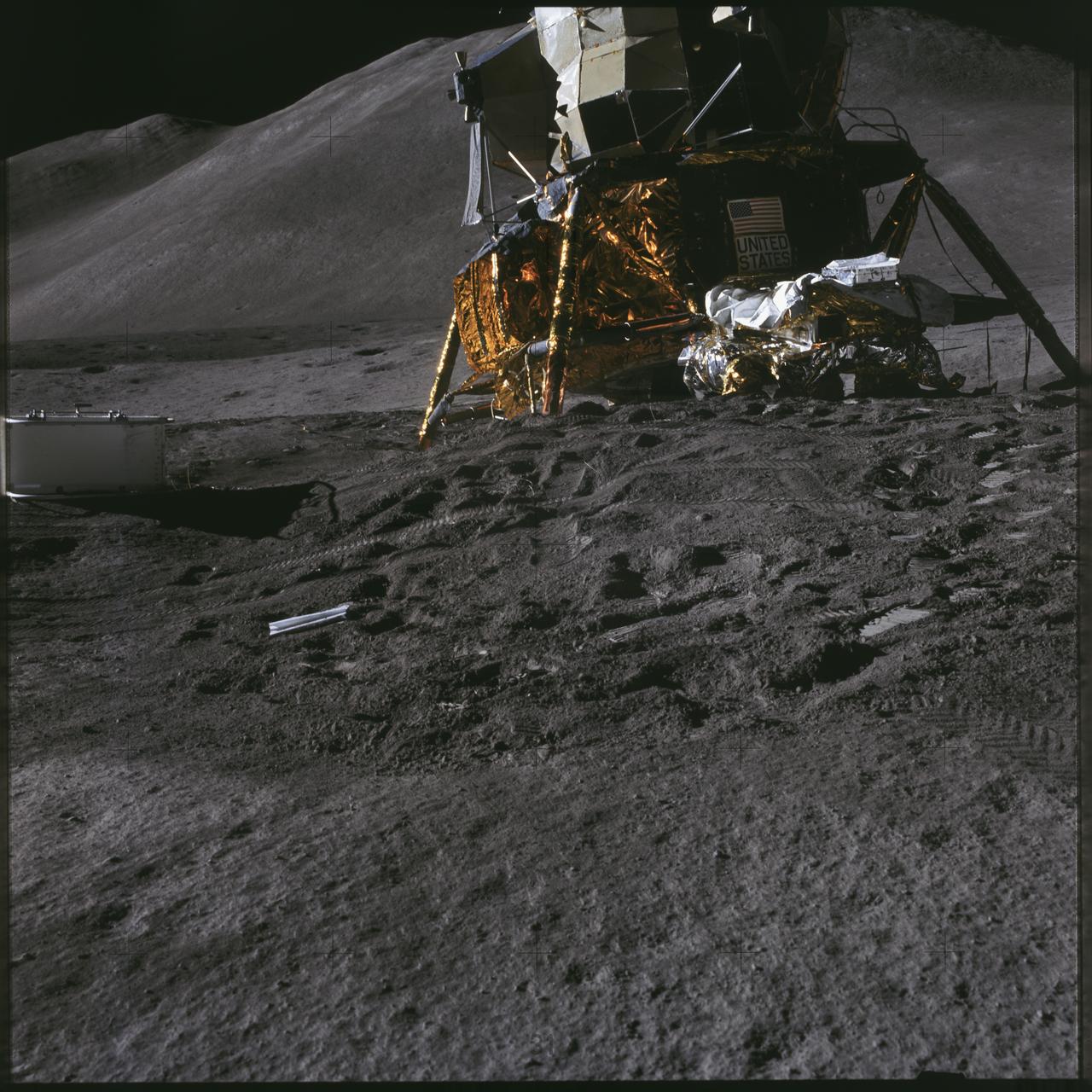
AS17-140-21355 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- This picture of the lunar surface was taken from the window of the lunar module at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. Astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt were inside the lunar module preparing for the mission's third spacewalk. Tracks made by lunar roving vehicle (LRV) and the astronauts' bootprints from earlier spacewalks are seen in the foreground.