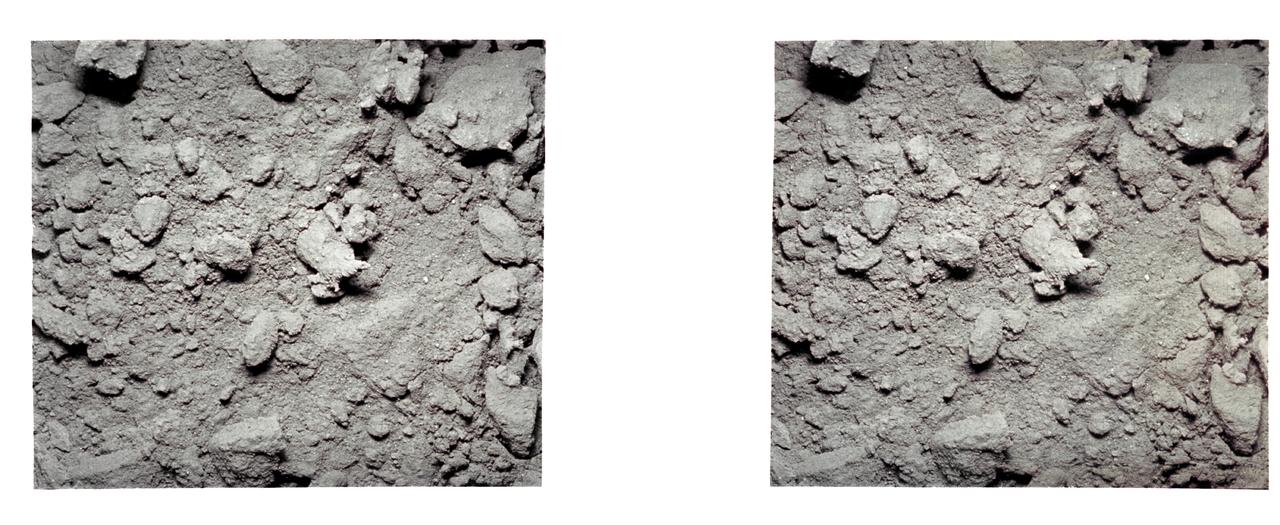

AS12-57-8455 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- An Apollo 12 stereo view showing a three-inch square of the lunar surface. The exposure was made with an Apollo 35mm stereo close-up camera during extravehicular activity of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission. The camera was developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. The three-inch square is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the Apollo 12 Lunar Module to explore the moon while astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr. remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit in the capacity of command module pilot.
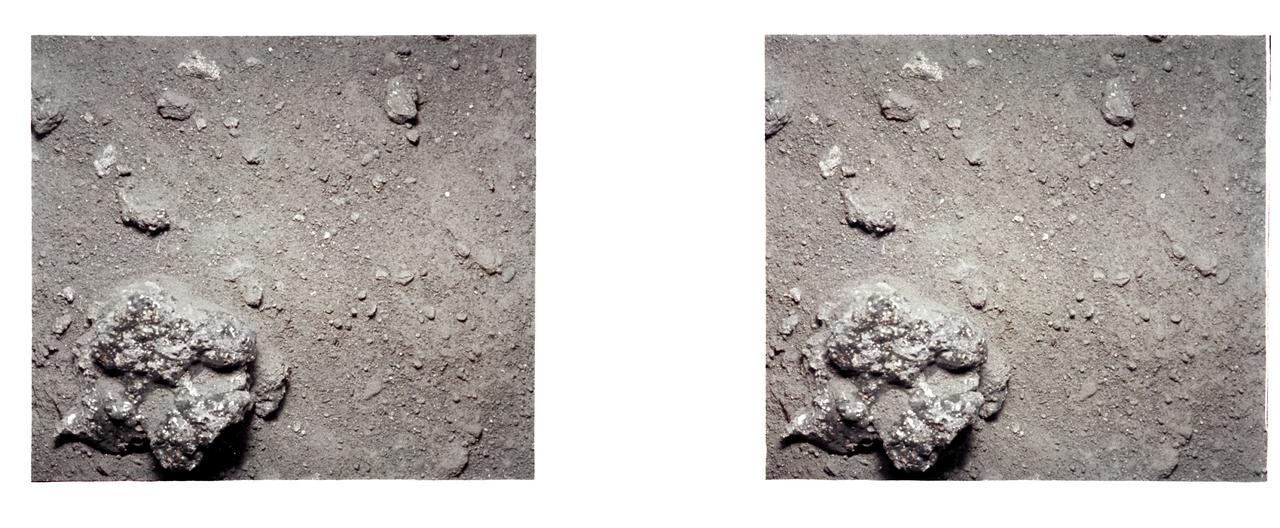

AS12-57-8452 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- An Apollo 12 stereo view showing a three-inch square of the lunar surface. The exposure was made with an Apollo 35mm stereo close-up camera during extravehicular activity of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission. The camera was developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. The three-inch square is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the Apollo 12 Lunar Module to explore the moon while astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr. remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit in the capacity of command module pilot.
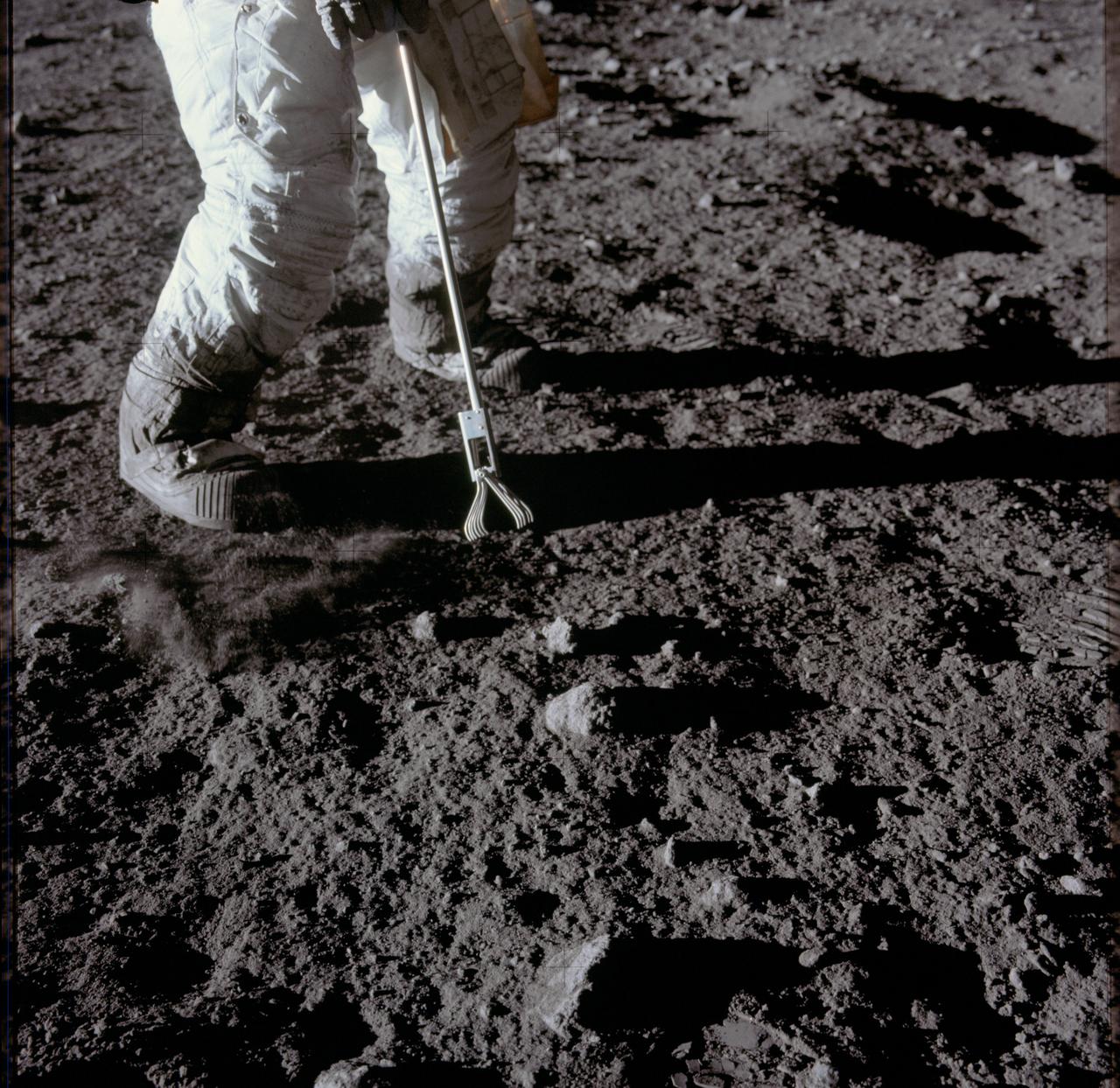

AS12-47-6932 (19 Nov. 1969) --- Close-up view of a set of tongs, an Apollo Lunar Hand Tool, being used by astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, to pick up lunar samples during the Apollo 12 extravehicular activity. This photograph shows Conrad's legs and a good view of the lunar soil.
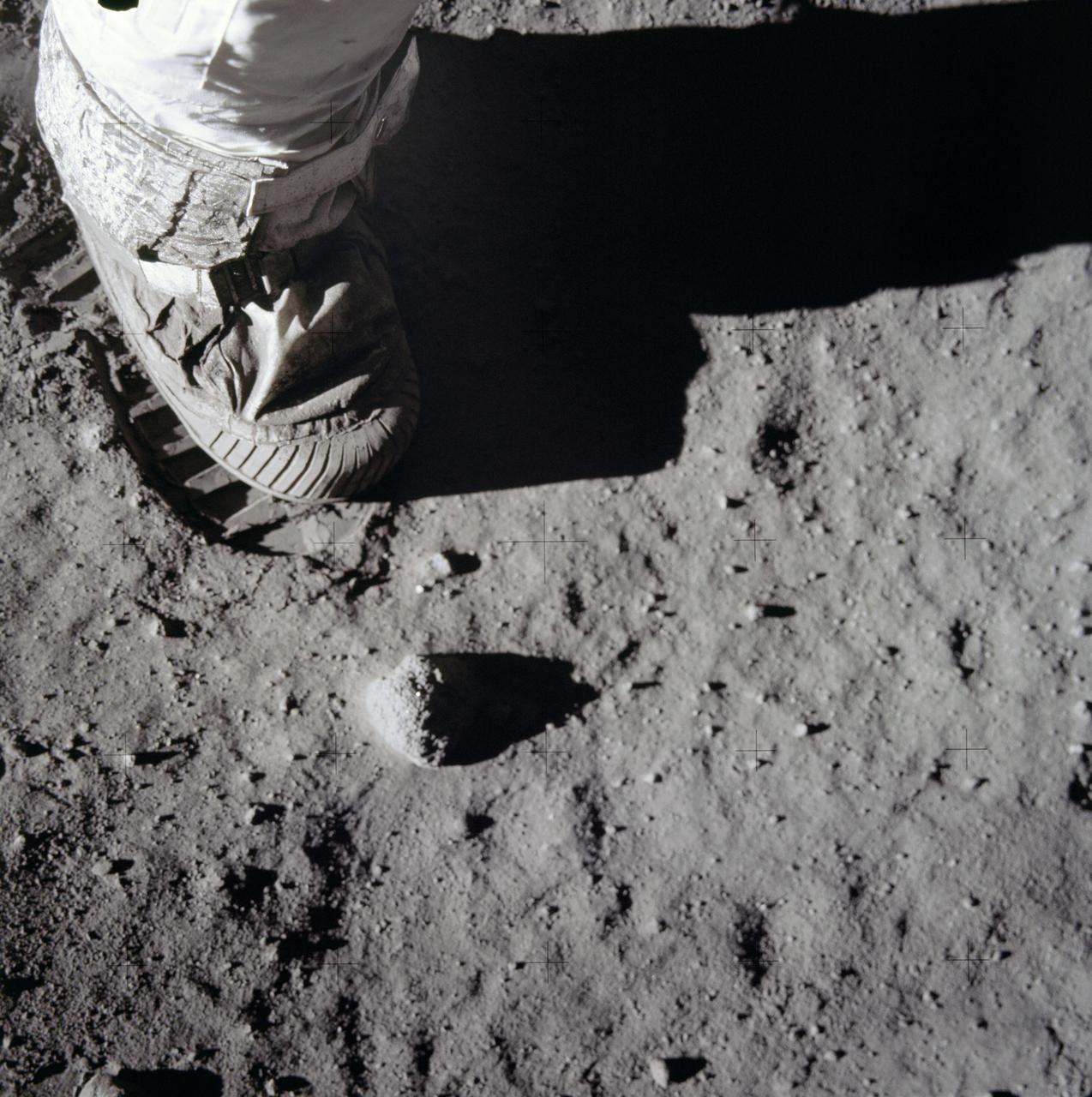

AS11-40-5880 (20 July 1969) --- A close-up view of an astronaut's boot and bootprint in the lunar soil, photographed with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin A. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM)" Columbia" in lunar orbit.

S69-53666 (30 Sept. 1969) --- A close-up view of numerous fern plants growing in a sprinkling of lunar soil brought back from the lunar surface by the crew of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. The photograph of the fern plants was taken 50 days after the plants were exposed to the lunar matter. The plants - Onoclea sensidilis, or more commonly known as Sensitive Fern - were photographed on a dish containing the minimal nutrients for germination. The cabbage-like, darker circle of plants, about 3/8-inch tall at the highest point, is germinating in contact with the lunar material, but the lighter colored, blurred plant material surrounding the cabbage-like clump is not in contact with any of the lunar soil. The strong thrive of these plants has been termed surprising and outstanding by MSC plant specialists.
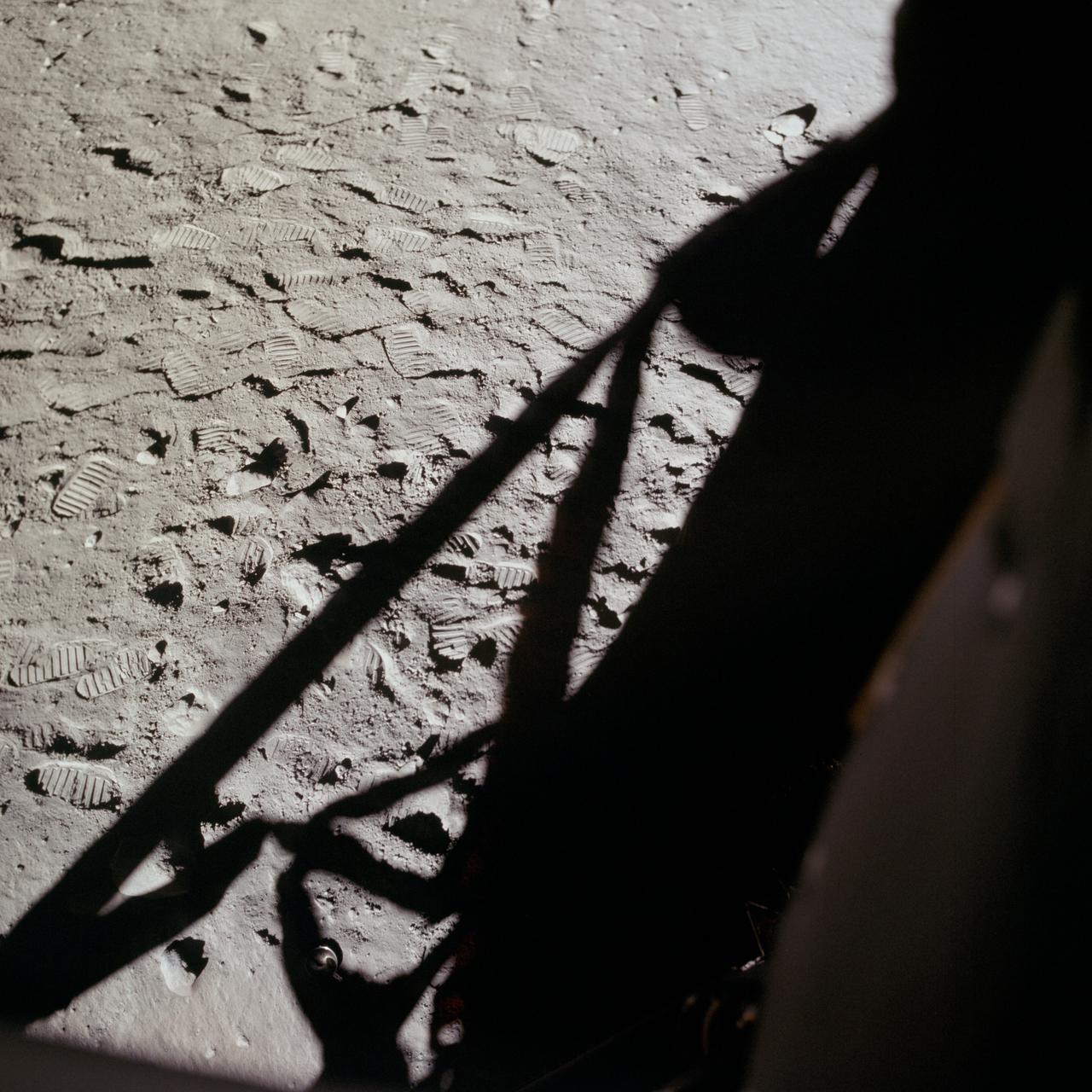

AS11-37-5505 (20 July 1969) --- This photograph shows in fine detail the impressions in the lunar soil made by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Armstrong, commander, and Aldrin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
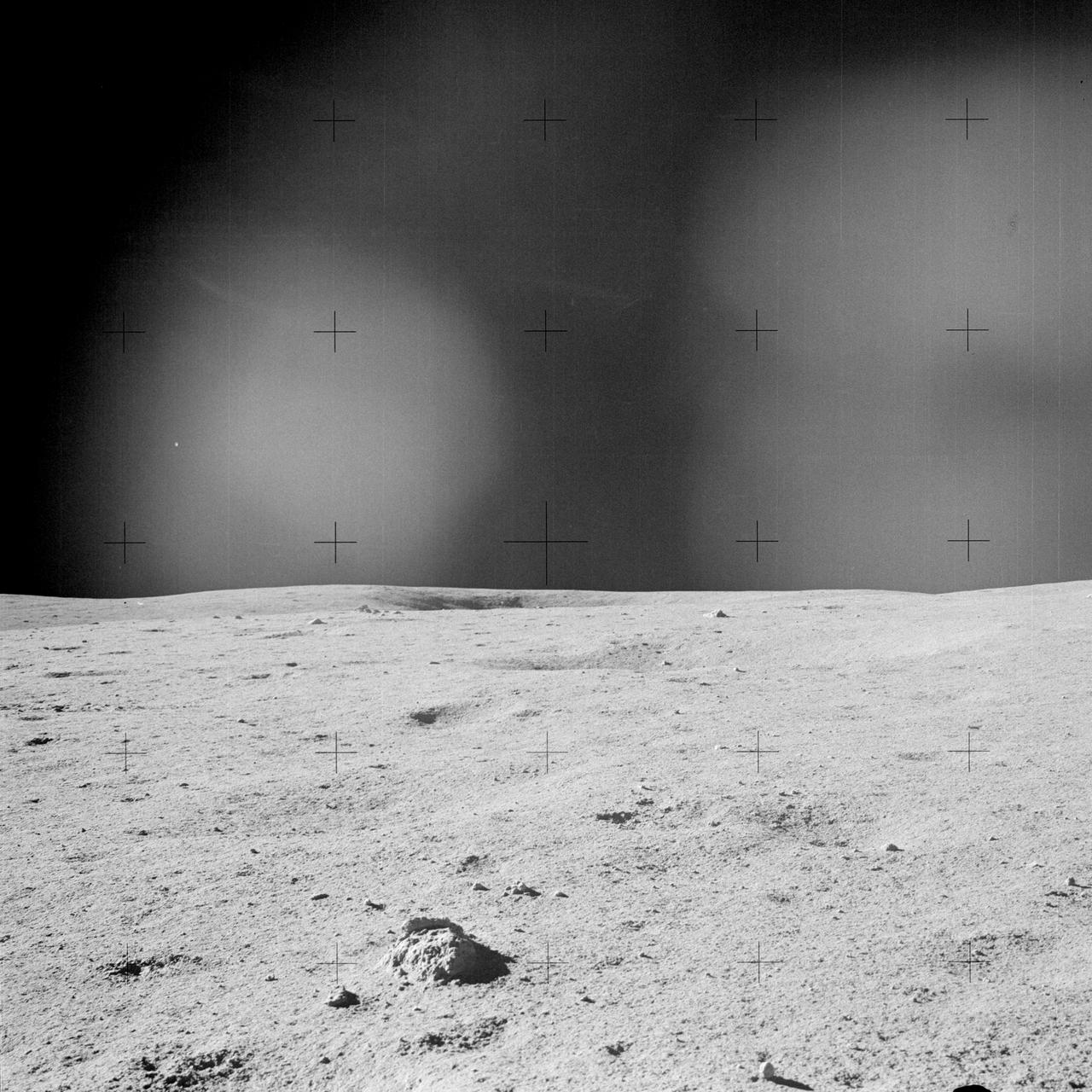

AS14-64-9181 (5-6 Feb. 1971) --- A view of the lunar terrain at the Apollo 14 Fra Mauro landing site as photographed through the left window of the Lunar Module (LM). Note the clump of lunar soil in the foreground, and a crater in the center on the horizon. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
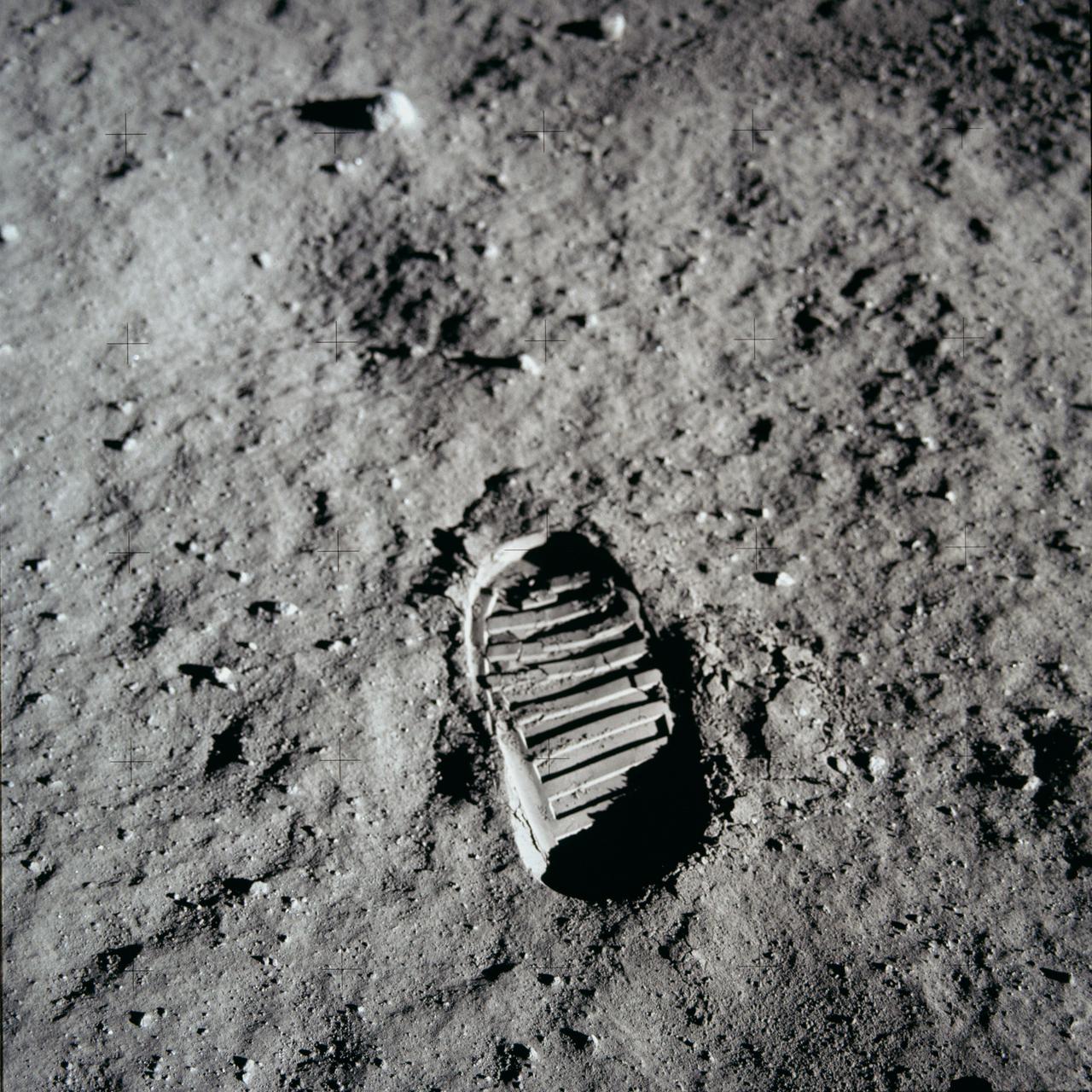

AS11-40-5877 (20 July 1969) --- A close-up view of an astronaut's bootprint in the lunar soil, photographed with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

AS11-40-5878 (20 July 1969) --- A close-up view of an astronaut's bootprint in the lunar soil, photographed with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
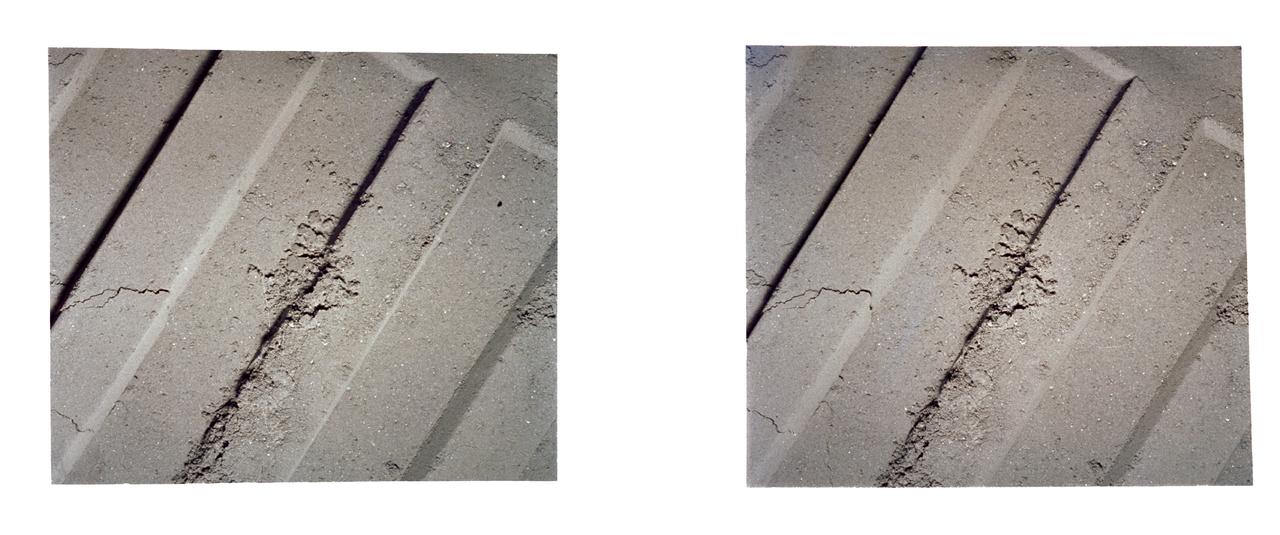

AS12-57-8448 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- An Apollo 12 stereo view showing a three-inch square of the lunar surface upon which an astronaut had stepped. Taken during extravehicular activity of astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. and Alan L. Bean, the exposure of the boot imprint was made with an Apollo 35mm stereo close-up camera. The camera was developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. The three-inch square is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. While astronauts Conrad and Bean descended in their Apollo 12 Lunar Module to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr. remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.
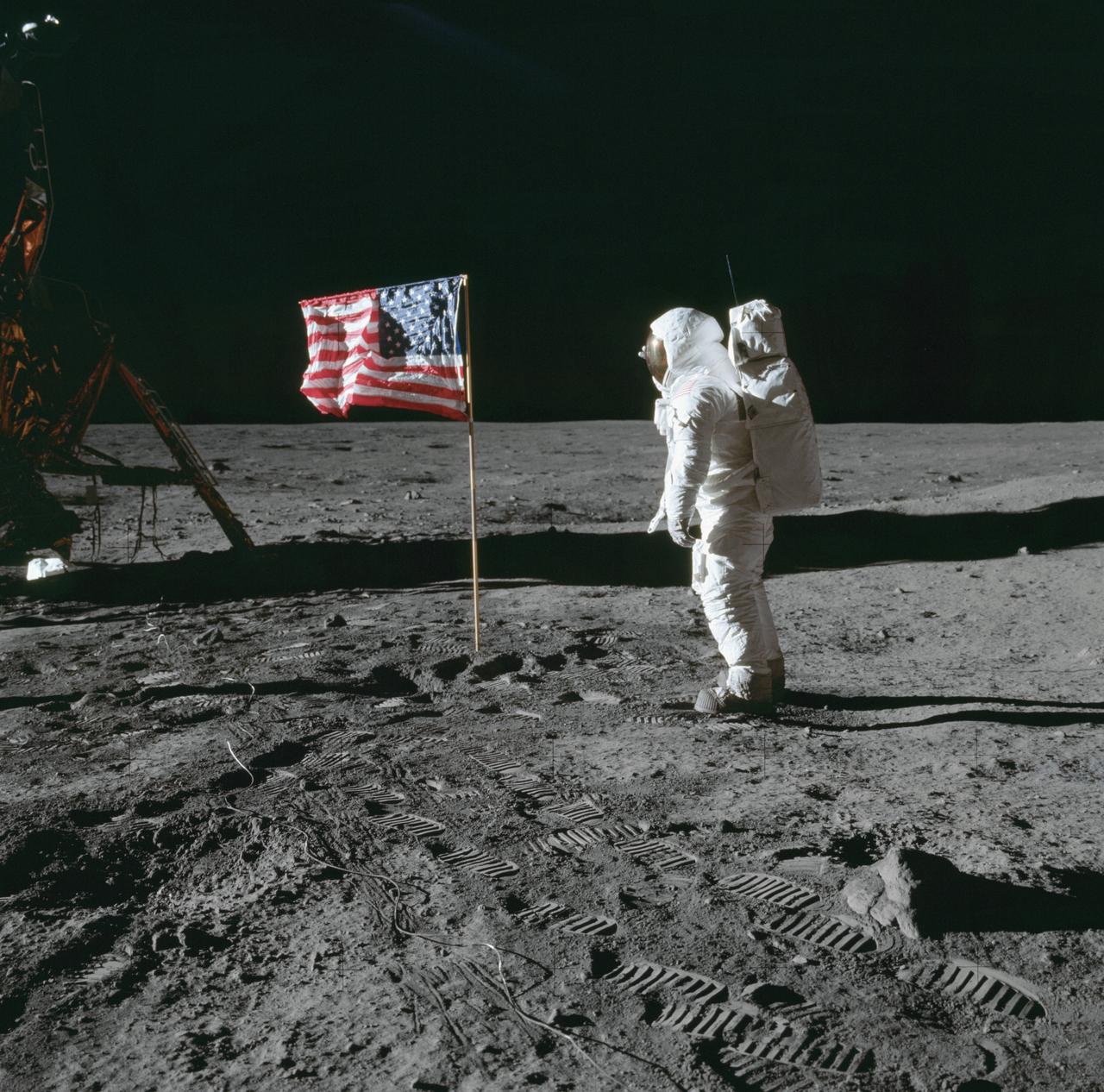

AS11-40-5874 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the first lunar landing mission, poses for a photograph beside the deployed United States flag during Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The Lunar Module (LM) is on the left, and the footprints of the astronauts are clearly visible in the soil of the moon. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm Hasselblad lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM the "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

AS11-40-5875 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot of the first lunar landing mission, poses for a photograph beside the deployed United States flag during an Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The Lunar Module (LM) is on the left, and the footprints of the astronauts are clearly visible in the soil of the moon. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm Hasselblad lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM, the "Eagle", to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit. Photo credit: NASA
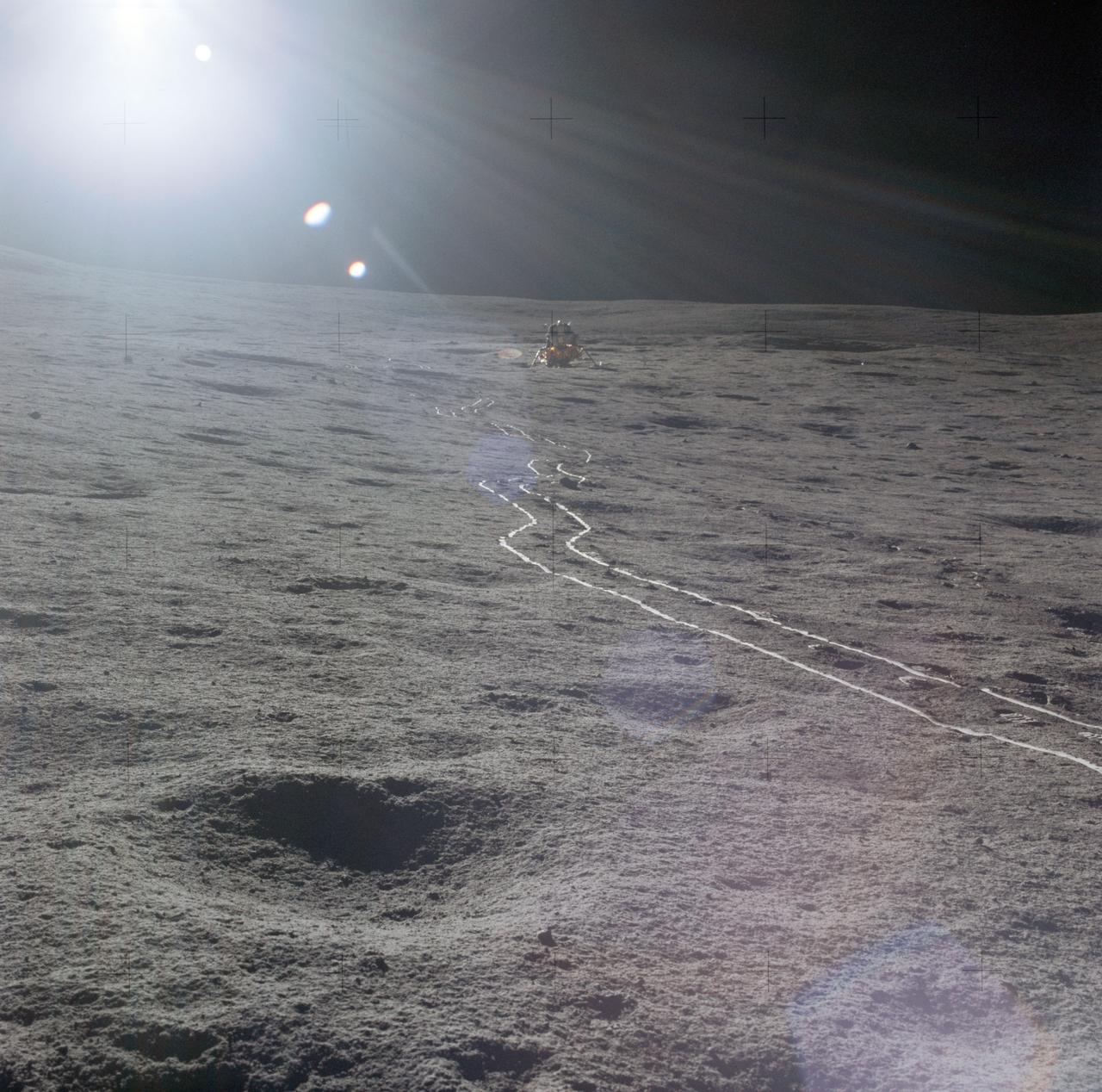

AS14-67-9367 (5 Feb. 1971) --- The Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) as seen by the two moon-exploring crewmen of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, photographed against a brilliant sun glare during the first extravehicular activity (EVA). A bright trail left in the lunar soil by the two-wheeled modularized equipment transporter (MET) leads from the LM. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, were exploring the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, was maneuvering the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
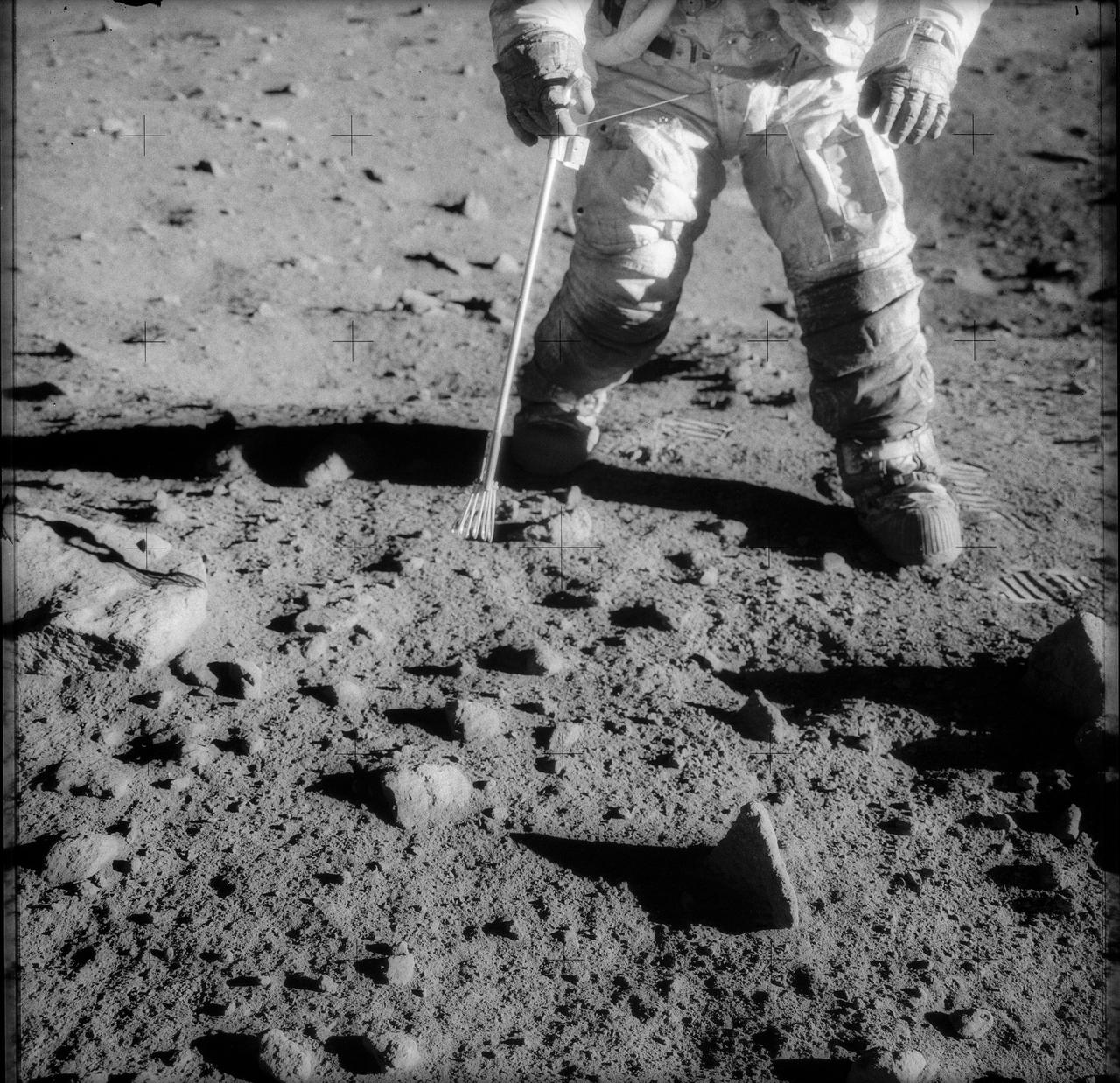

AS12-48-7149 (20 Nov. 1969) --- A close-up view of astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, photographed during the extravehicular activity (EVA) on the surface of the moon. An EVA checklist is on Conrad's left wrist. A set of tongs, an Apollo Lunar Hand Tool (ALHT), is held in his right hand. Several footprints can be seen. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Conrad and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon. Note lunar soil on the suit of Conrad, especially around the knees and below.
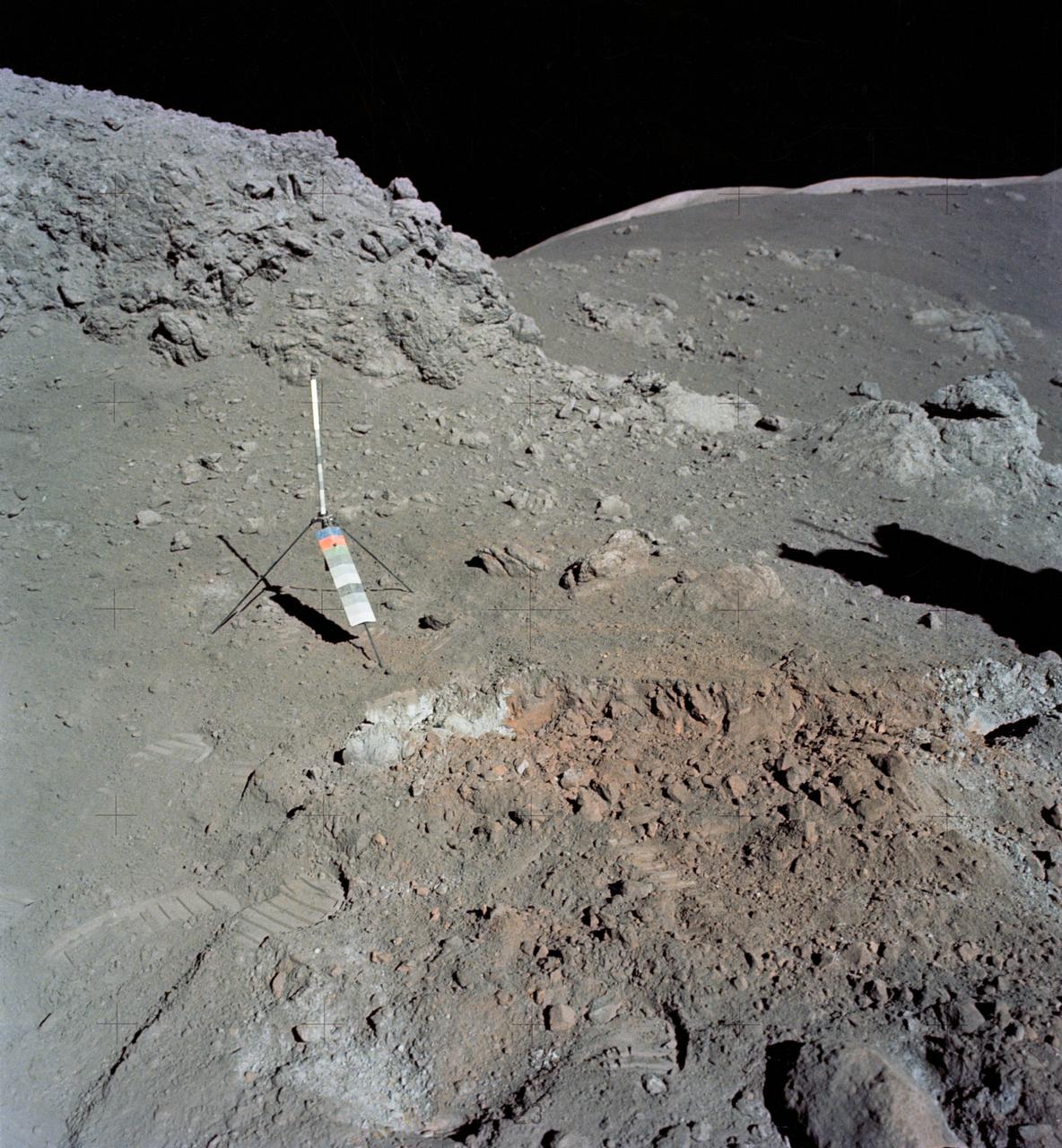

AS17-137-20990 (12 Dec. 1972) --- A view of the area at Station 4 (Shorty Crater) showing the now highly-publicized orange soil which the Apollo 17 crew members found on the moon during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The tripod-like object is the gnomon and photometric chart assembly which is used as a photographic reference to establish local vertical sun angle, scale and lunar color. The gnomon is one of the Apollo lunar geology hand tools. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit. Schmitt was the crew man who first spotted the orange soil.
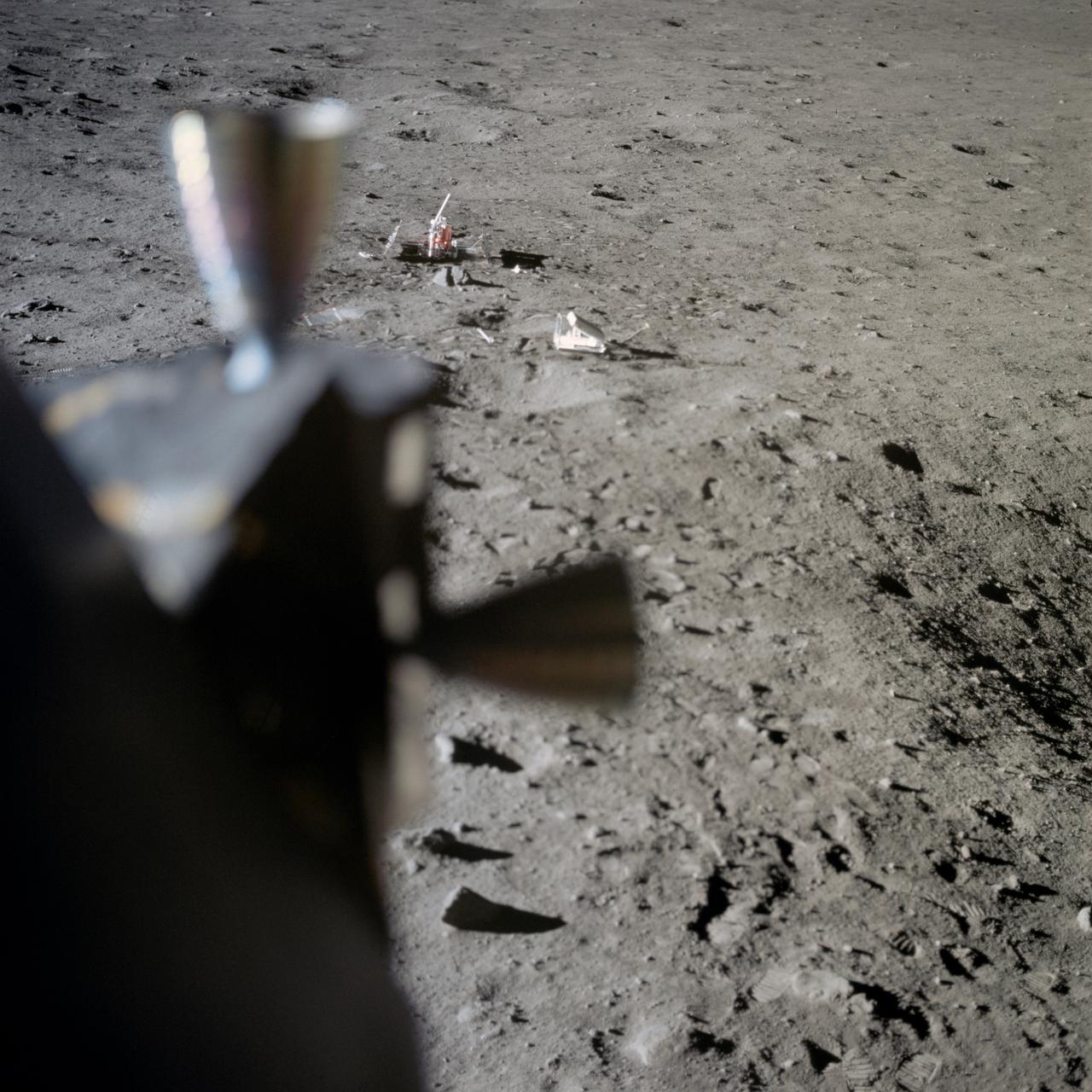

AS11-37-5551 (20 July 1969) --- Two components of the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP) are seen deployed on the lunar surface in this view photographed from inside the Lunar Module (LM). In the far background is the Passive Seismic Experiment Package (PSEP); and to the right and closer to the camera is the Laser Ranging Retro-Reflector (LR-3). The footprints of Apollo 11 astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. are very distinct in the lunar soil.
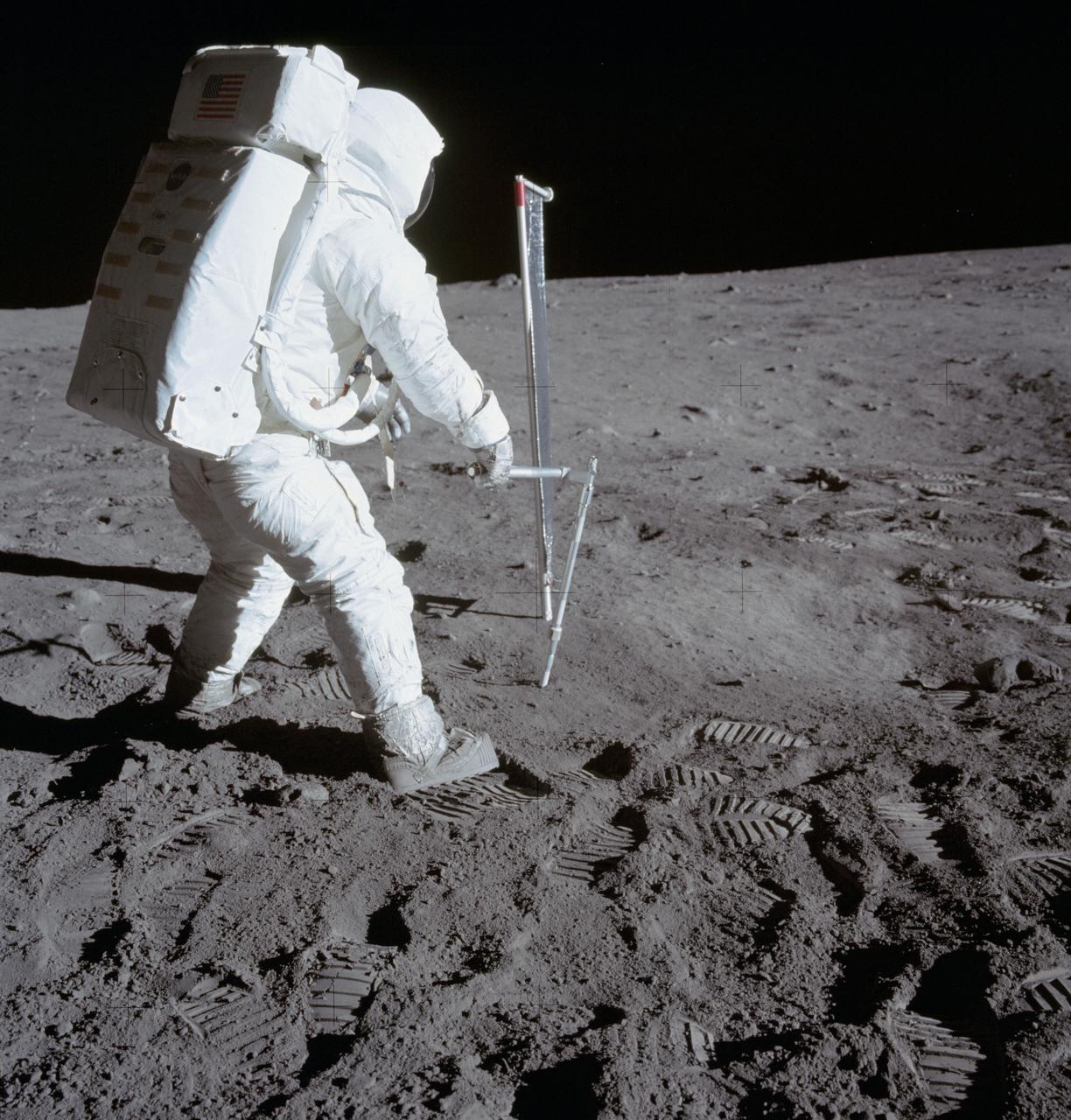

AS11-40-5964 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, is photographed during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. He is driving one of two core tubes into the lunar soil. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm lunar surface camera. Aldrin stands near the Solar Wind Composition (SWC) experiment, a component of the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP, deployed earlier). The SWC is in the center background.
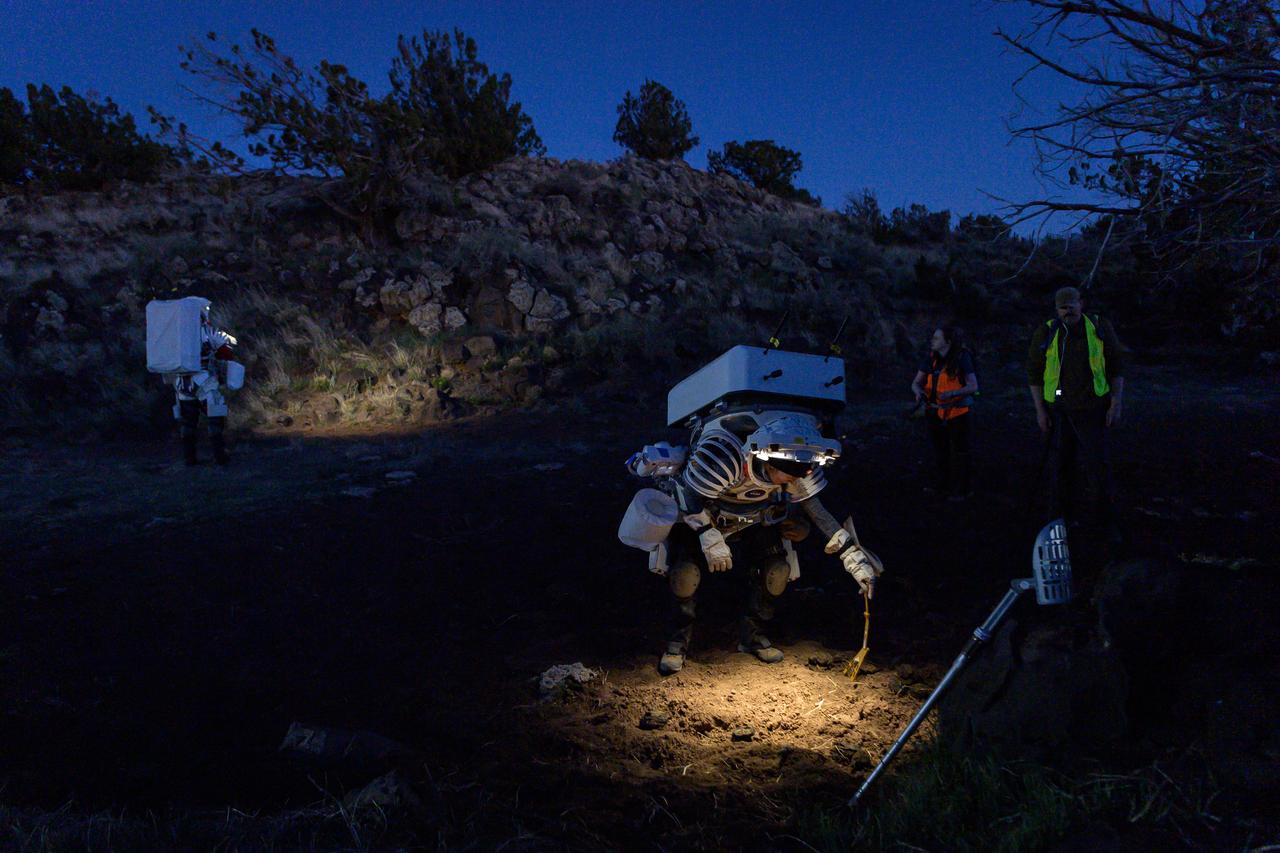

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins places a sample marker in the soil before collecting a sample during a nighttime simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 16, 2024. A sample marker provides a photographic reference point for science samples collected on the lunar surface. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

The second manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 12 launched from launch pad 39-A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on November 14, 1969 via a Saturn Five launch vehicle. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard Apollo 12 was a crew of three astronauts: Alan L. Bean, pilot of the Lunar Module (LM), Intrepid; Richard Gordon, pilot of the Command Module (CM), Yankee Clipper; and Spacecraft Commander Charles Conrad. The LM, Intrepid, landed astronauts Conrad and Bean on the lunar surface in what’s known as the Ocean of Storms while astronaut Richard Gordon piloted the CM, Yankee Clipper, in a parking orbit around the Moon. Their lunar soil activities included the deployment of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP), finding the unmanned Surveyor 3 that landed on the Moon on April 19, 1967, and collecting 75 pounds (34 kilograms) of rock samples. In this photograph, one of the astronauts on the Moon’s surface is holding a container of lunar soil. The other astronaut is seen reflected in his helmet. Apollo 12 safely returned to Earth on November 24, 1969.
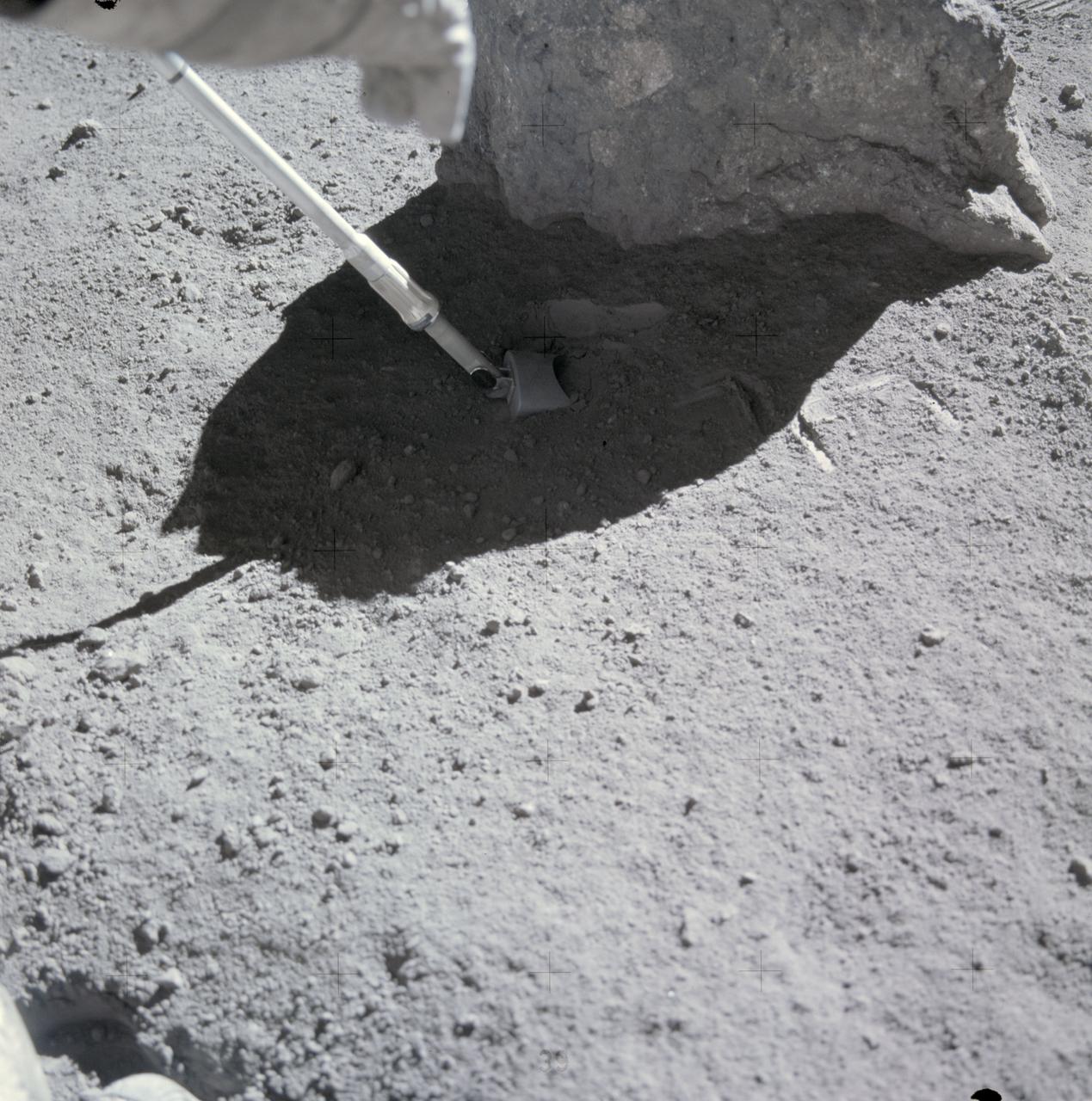

AS16-107-17561 (16-27 April 1972) --- One of the Apollo 16 astronauts scoops up lunar soil at the base of a small boulder at Station No. 9 during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. Depressions to the right of the scoop were made when a surface sample was taken. This photograph was taken just before the boulder was rolled over. While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
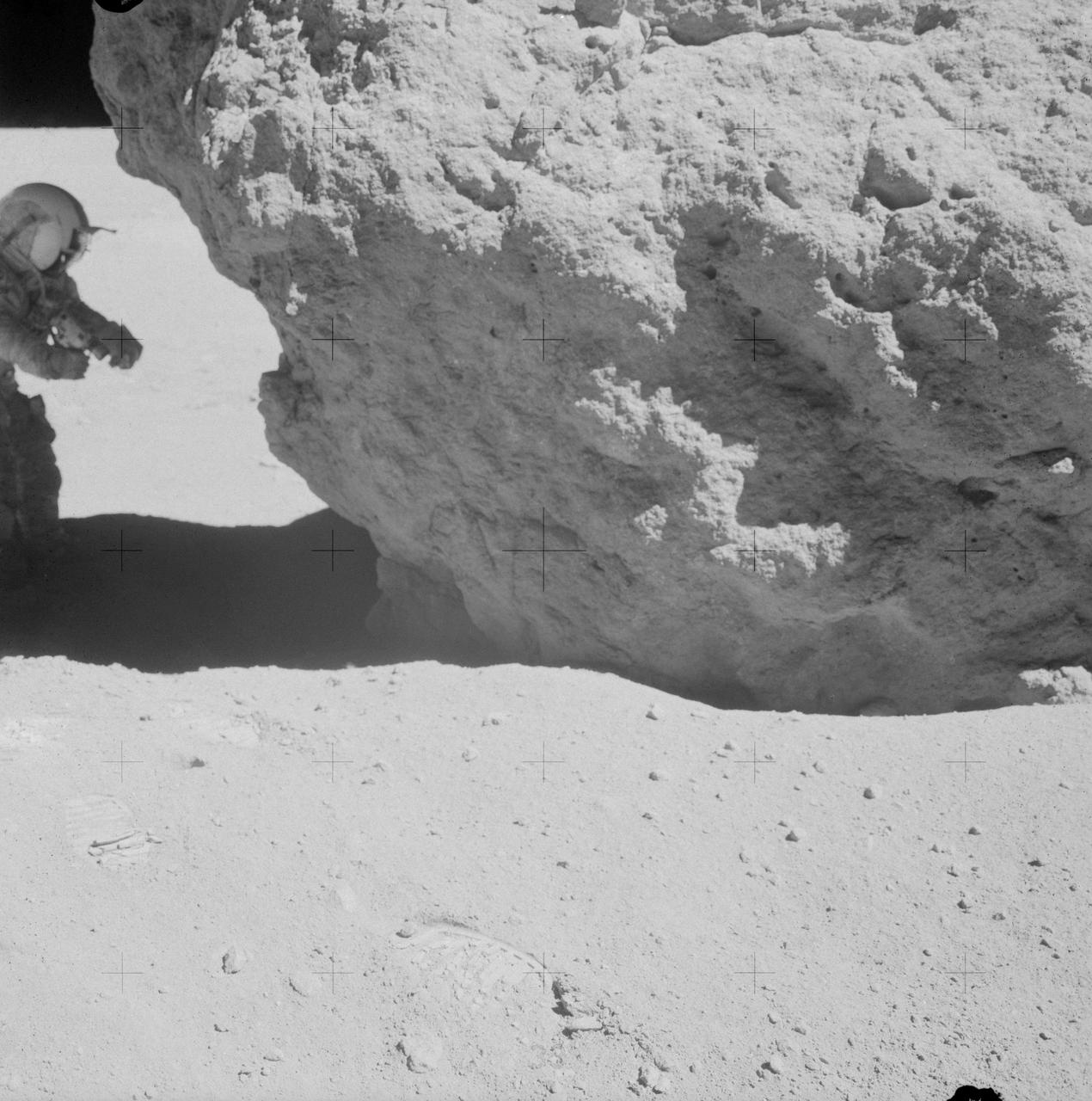

AS16-106-17413 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, looks over a large boulder at Station No.13 during the third Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. This was the site of the permanently shadowed soil sample which was taken from a hole extending under overhanging rock. Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, took this photograph. Concerning Young's reaching under the big rock, Duke remarked: "You do that in west Texas and you get a rattlesnake!"
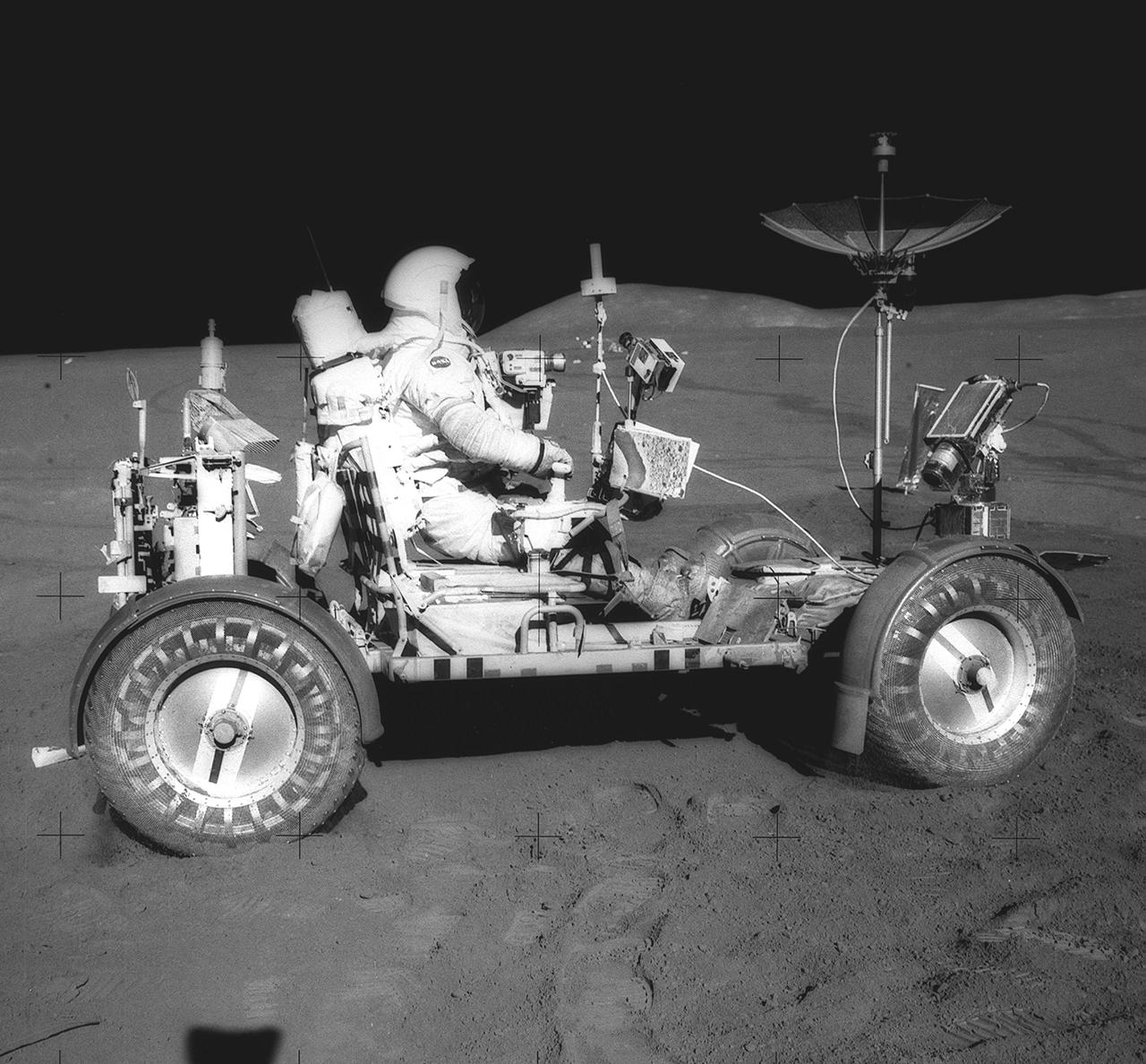

This photograph was taken during the Apollo 15 mission on the lunar surface. Astronaut David R. Scott waits in the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) for astronaut James Irwin for the return trip to the Lunar Module, Falcon, with rocks and soil collected near the Hadley-Apernine landing site. The Apollo 15 was the first mission to use the LRV. Powered by battery, the lightweight electric car greatly increased the range of mobility and productivity on the scientific traverses for astronauts. It weighed 462 pounds (77 pounds on the Moon) and could carry two suited astronauts, their gear and cameras, and several hundred pounds of bagged samples. The LRV's mobility was quite high. It could climb and descend slopes of about 25 degrees. The LRV was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
The second manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 12 launched from launch pad 39-A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on November 14, 1969 via a Saturn V launch vehicle. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard Apollo 12 was a crew of three astronauts: Alan L. Bean, pilot of the Lunar Module (LM), Intrepid; Richard Gordon, pilot of the Command Module (CM), Yankee Clipper; and Spacecraft Commander Charles Conrad. The LM, Intrepid, landed astronauts Conrad and Bean on the lunar surface in what’s known as the Ocean of Storms while astronaut Richard Gordon piloted the CM, Yankee Clipper, in a parking orbit around the Moon. Lunar soil activities included the deployment of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP), finding the unmanned Surveyor 3 that landed on the Moon on April 19, 1967, and collecting 75 pounds (34 kilograms) of rock samples, some of which can be seen in this photograph. Apollo 12 safely returned to Earth on November 24, 1969.
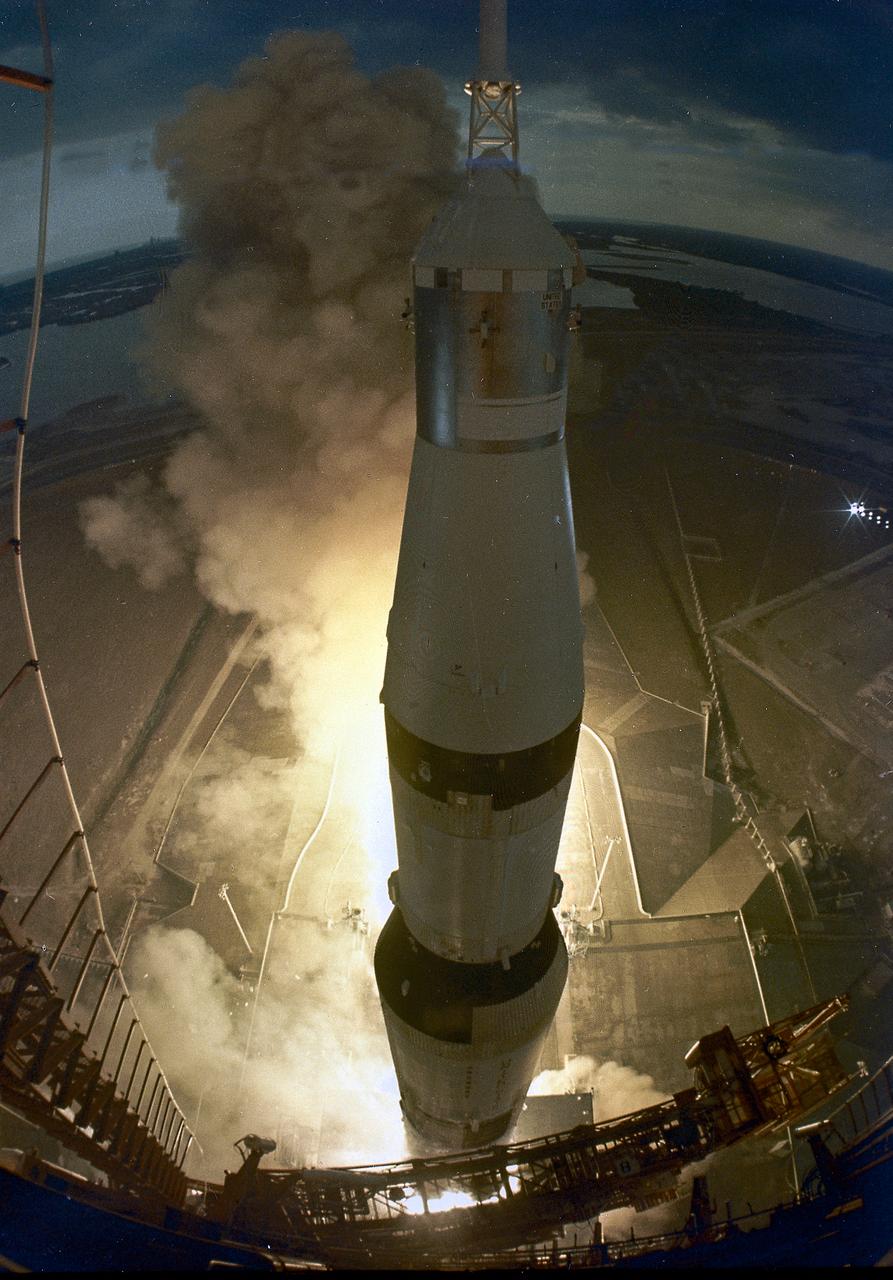

This is a view from sequential photographs of the Apollo 14 liftoff taken by a remote camera atop the 360-foot gantry level of Launch Complex 39A. The Apollo 14, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Mission commander Alan B. Shepard Jr., Command Module pilot Stuart A. Roosa, and Lunar Module pilot Edgar D. Mitchell, lifted off from launch complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center on January 31, 1971. It was the third manned lunar landing, the first manned landing in exploration of the lunar highlands, and it demonstrated pinpoint landing capability. The major goal of Apollo 14 was the scientific exploration of the Moon in the foothills of the rugged Fra Mauro region. Activities of astronauts Shepard and Mitchell, during extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface, included setting up an automated scientific laboratory called Apollo Lunar Scientific Experiments Package (ALSEP), and collecting a total of about 95 pounds (43 kilograms) of Moon rock and soil for a geological investigation back on the Earth.
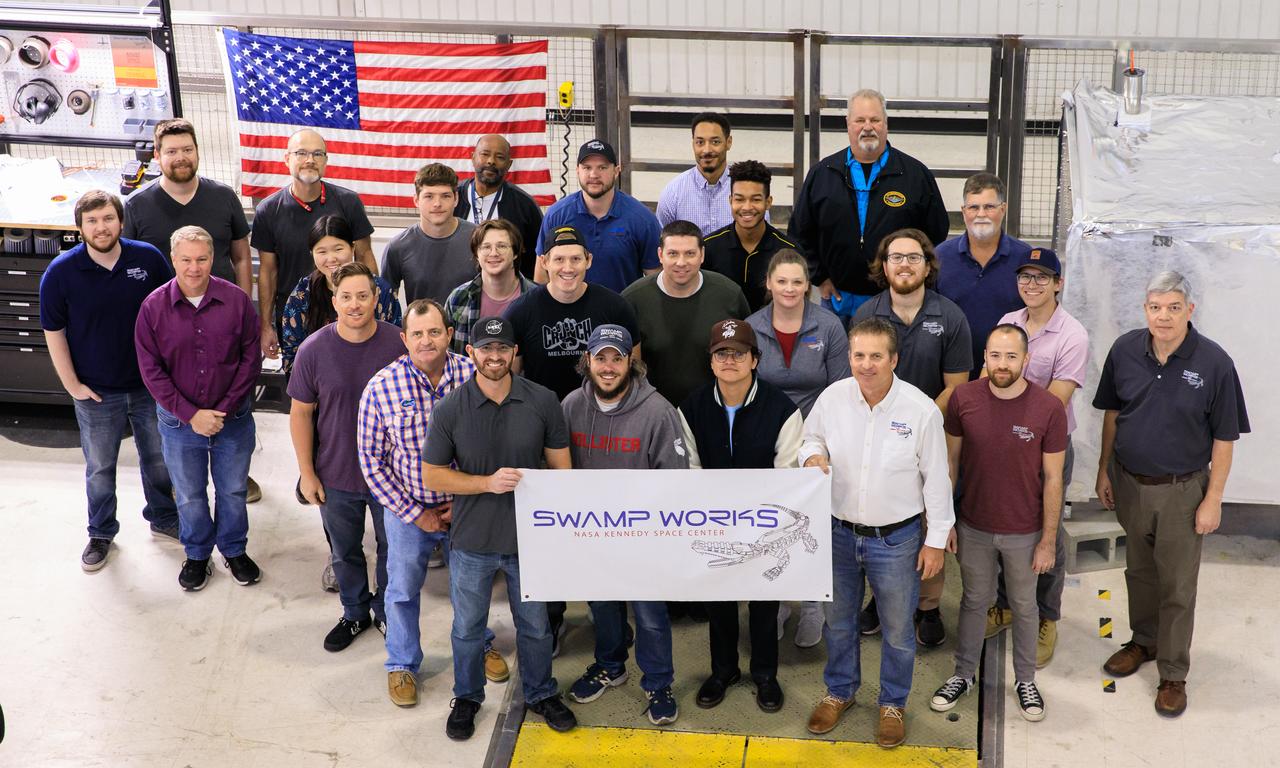

Groups from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) laboratory and the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory (ESPL) gather for a photograph to celebrate the 10th anniversary of Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 13, 2023. Studies of the mechanics of materials in a launch pad environment are performed in the GMRO lab. The team also develops technologies for handling lunar and Martian regolith, including excavator technologies, pneumatic transport of soil, and magnetic handling of soil. The ESPL group performs scientific investigations to protect flight hardware and launch equipment from the phenomenon of electrostatic discharges, commonly known as sparks.
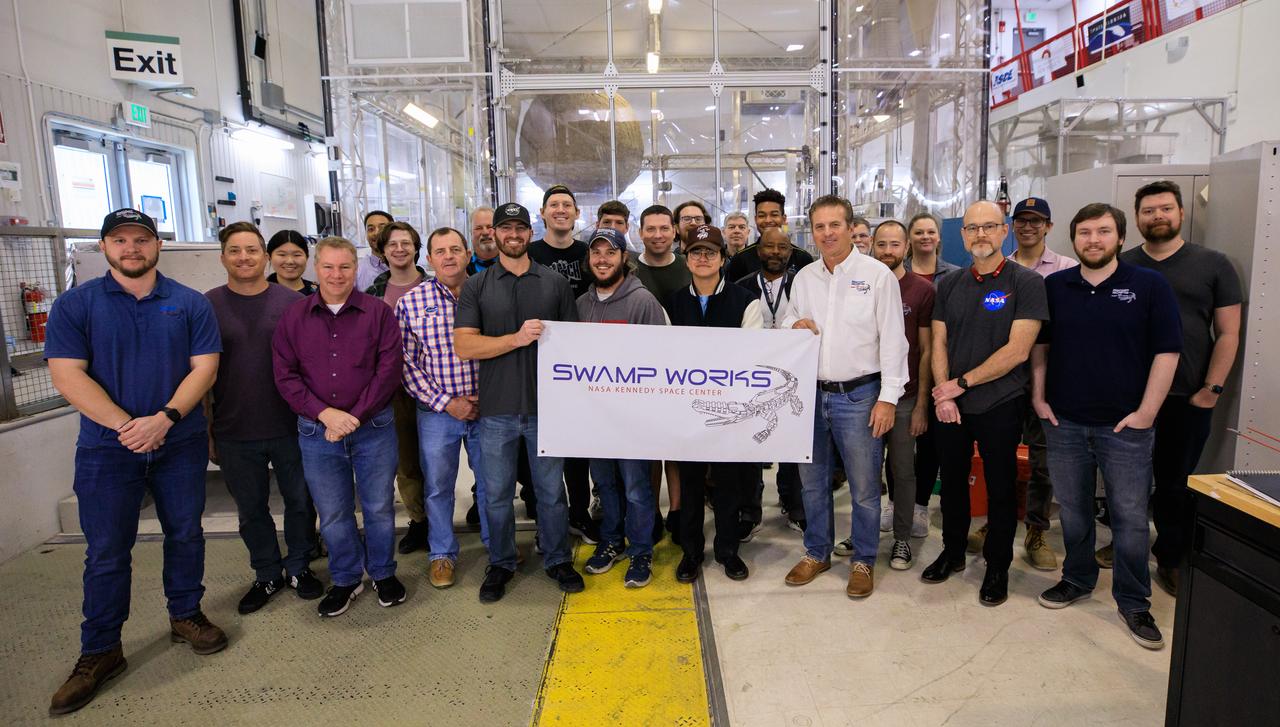

Groups from the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations (GMRO) laboratory and the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory (ESPL) gather for a photograph to celebrate the 10th anniversary of Swamp Works at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 13, 2023. Studies of the mechanics of materials in a launch pad environment are performed in the GMRO lab. The team also develops technologies for handling lunar and Martian regolith, including excavator technologies, pneumatic transport of soil, and magnetic handling of soil. The ESPL group performs scientific investigations to protect flight hardware and launch equipment from the phenomenon of electrostatic discharges, commonly known as sparks.
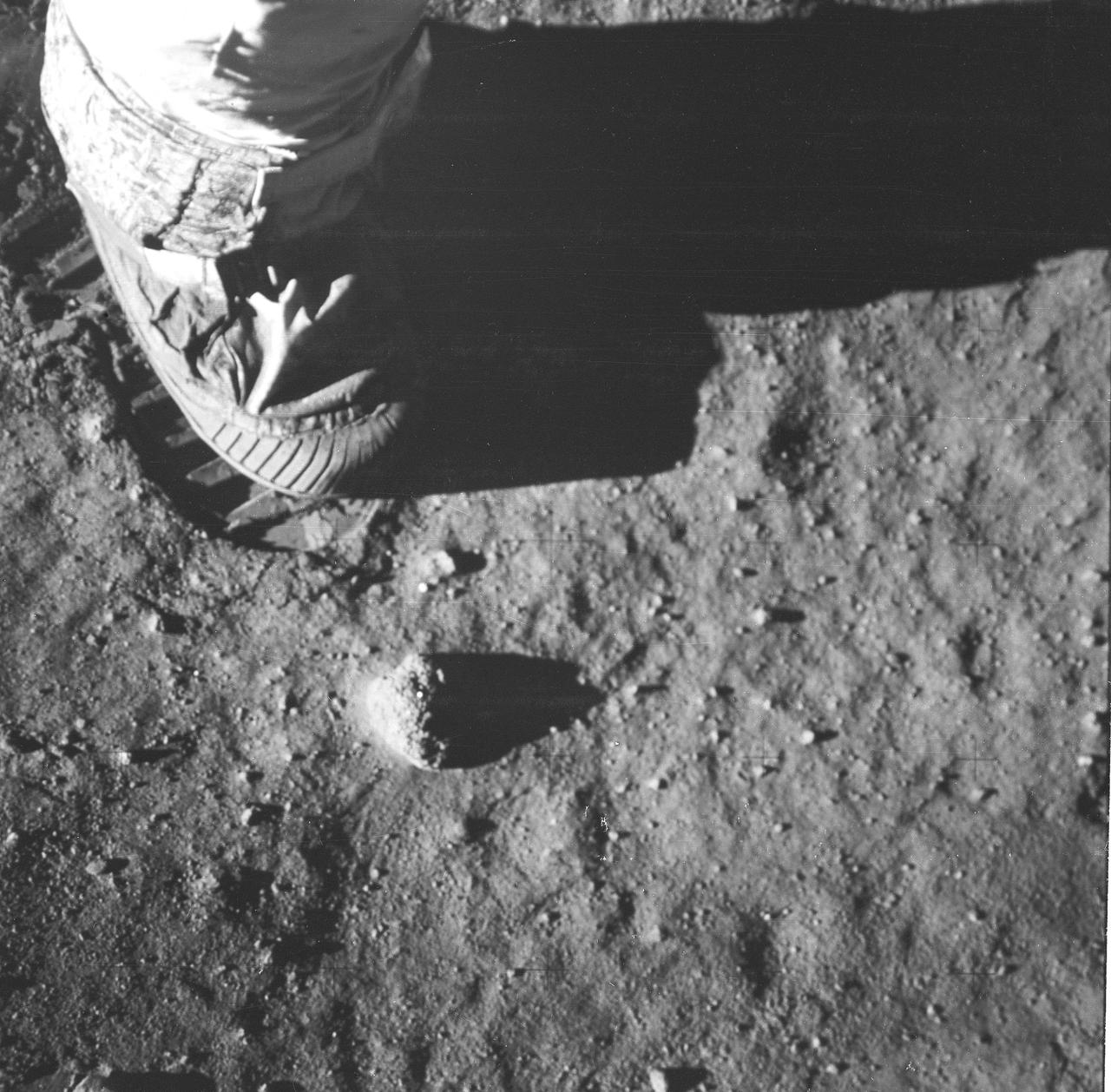

This is a close-up view of an astronaut’s foot and footprint in the lunar soil, photographed by a 70 mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). The first manned lunar mission launched via a Saturn V launch vehicle from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. The 3-man crew aboard the flight consisted of astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, mission commander; Edwin E. Aldrin, Jr., Lunar Module (LM) Pilot; and Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot. The LM landed on the moon’s surface on July 20, 1969 in the region known as Mare Tranquilitatis (the Sea of Tranquility). Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface. As he stepped off the LM, Armstrong proclaimed, “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind”. He was followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin, describing the lunar surface as magnificent desolation. Astronaut Collins piloted the CM in a parking orbit around the Moon. During a 2½ hour surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material which was returned to Earth for analysis. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.

This is a close-up view of an astronaut’s footprint in the lunar soil, photographed by a 70 mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 lunar surface extravehicular activity. The first manned lunar mission, the Apollo 11 launched aboard a Saturn V launch vehicle from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The 3-man crew aboard the flight consisted of Neil A, Armstrong, mission commander; Edwin E. Aldrin, Jr., Lunar Module Pilot; and Michael Collins, Command Module pilot. The LM landed on the moon’s surface on July 20, 1969 in the region known as Mare Tranquilitatis (the Sea of Tranquility). Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface. As he stepped off the LM, Armstrong proclaimed, “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind”. He was followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin, describing the lunar surface as Magnificent desolation. Astronaut Collins piloted the Command Module in a parking orbit around the Moon. The crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material which was returned to Earth for analysis. The surface exploration was concluded in 2½ hours. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. von Braun.
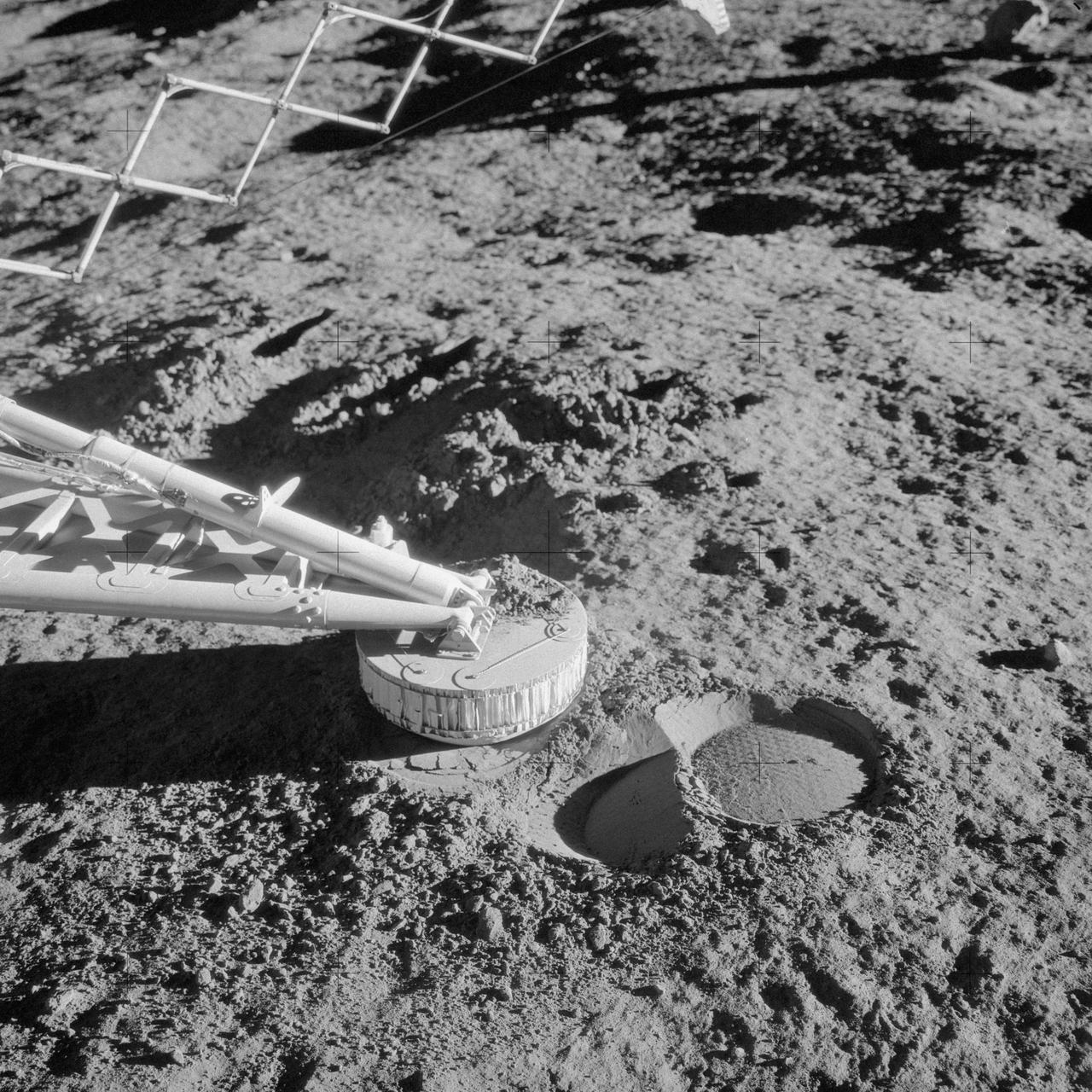

AS12-48-7110 (20 Nov. 1969) --- A close-up view of a footpad and surface sampler with scoop (arm, out of frame) on the Surveyor 3 spacecraft which was photographed by the Apollo 12 astronauts during their second extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. The Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM), with astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. and Alan L. Bean aboard, touched down in the Ocean of Storms only 600 feet from Surveyor 3. The television camera and several other pieces were taken from Surveyor 3 and brought back to Earth for scientific examination. The unmanned spacecraft soft-landed on the moon on April 19, 1967. Note the imprint in the lunar soil which was caused when the Surveyor 3 bounced upon landing.
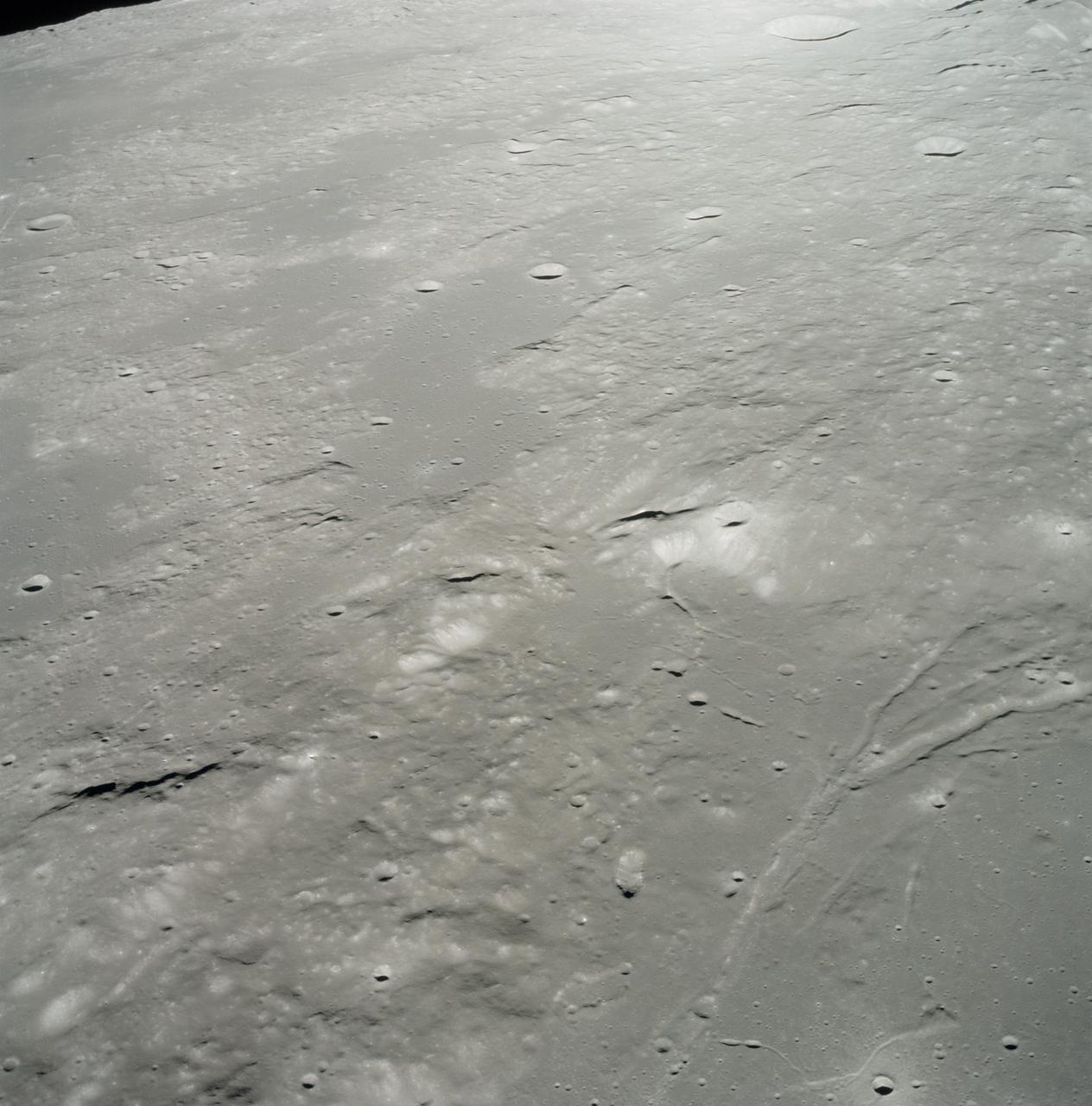

AS17-153-23572 (15 Dec. 1972) --- An oblique view of the Sulpicius Gallus region on the southwestern edge of the Sea of Serenity looking westward across the Haemus Mountains, as photographed from the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules during its 65th revolution of the moon. This photograph shows the slight orange cast which was identified by astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot. The region shown in the picture is about 600 kilometers (360 statute miles) west across Mare Serentatis from the Taurus-Littrow landing site where scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt, lunar module pilot, discovered an orange soil sample composed of fine glass particles rich in iron and titanium. North is toward the right. Rima Sulpicius Gallus is the lunar trench or valley (right foreground) that crosses the edge of the Mare and divides into three branches as it runs to the northwest. The crater Sulpicius Gallus is just off the photograph at the bottom right. Note that several small craters in the dark portion of the picture (east) show a more distinct orange cast. The coordinates of the center of this photograph are about 8.4 degrees east longitude and 19.8 degrees north latitude.
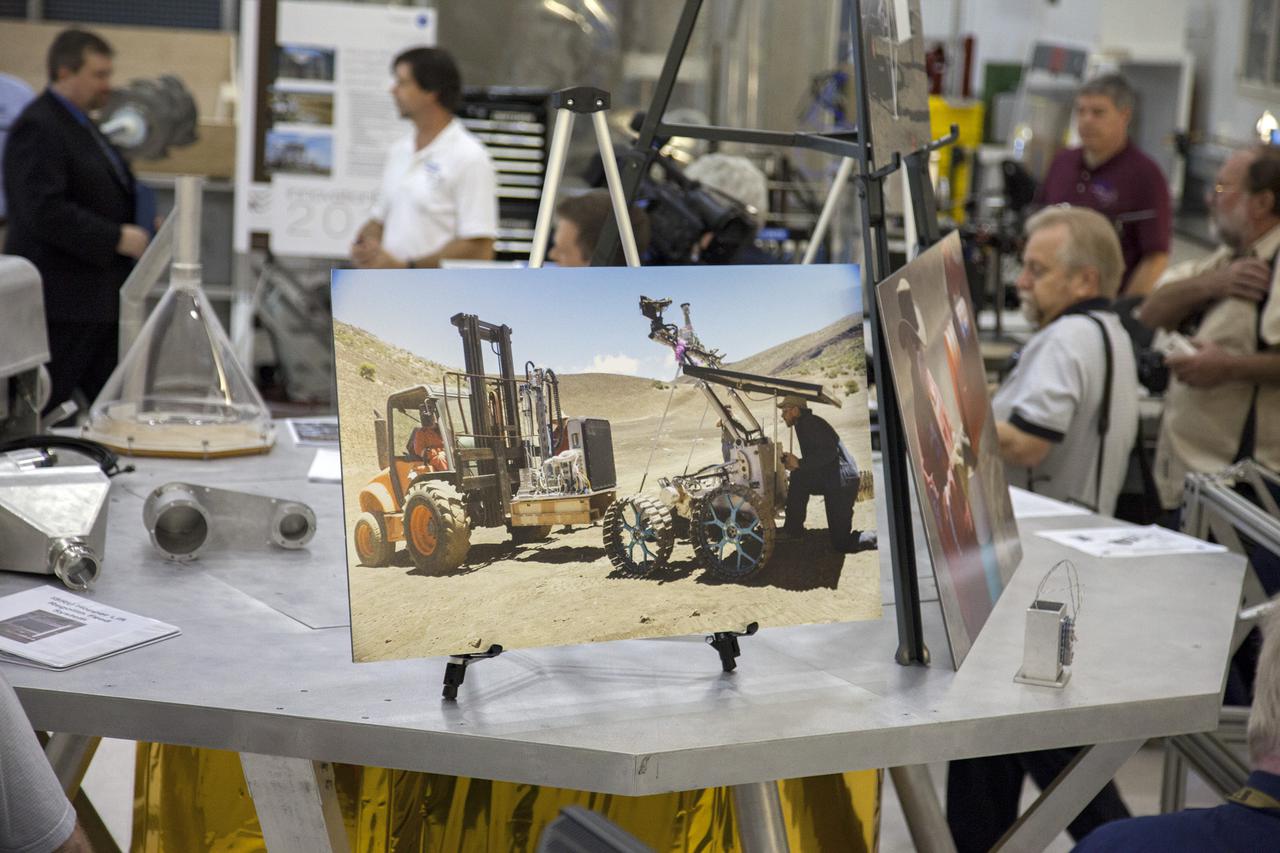

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A photograph of NASA's Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatiles Extraction, or RESOLVE, rover is on display atop a RESOLVE lander during a media tour of the Swamp Works at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload under development to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA used the lander to conduct field tests outside Hilo, Hawaii, in July 2012. Kennedy's Swamp Works provides rapid, innovative and cost-effective exploration mission solutions, leveraging partnerships across NASA, industry and academia. Kennedy's research and technology mission is to improve spaceports on Earth, as well as lay the groundwork for establishing spaceports at destinations in space. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_centers_kennedy_exploration_researchtech_index.html. Photo credit: NASA_Frankie Martin