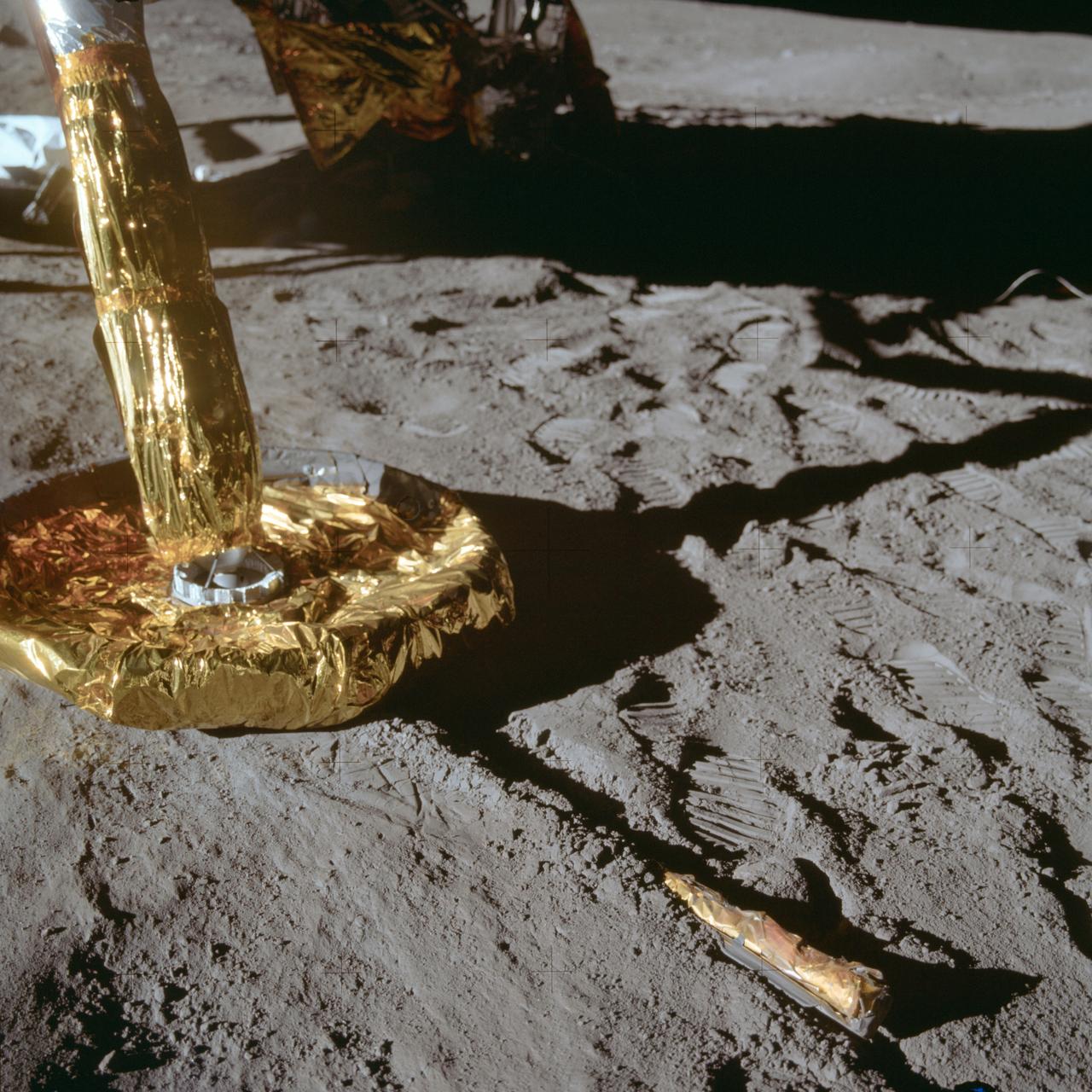

A close-up view of a footpad of the Apollo 11 Lunar Module as it rested on the surface of the Moon. The stick-like protruding object is a lunar surface sensing probe. This photograph was take with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the extravehicular activity of Astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin on July 20, 1969.
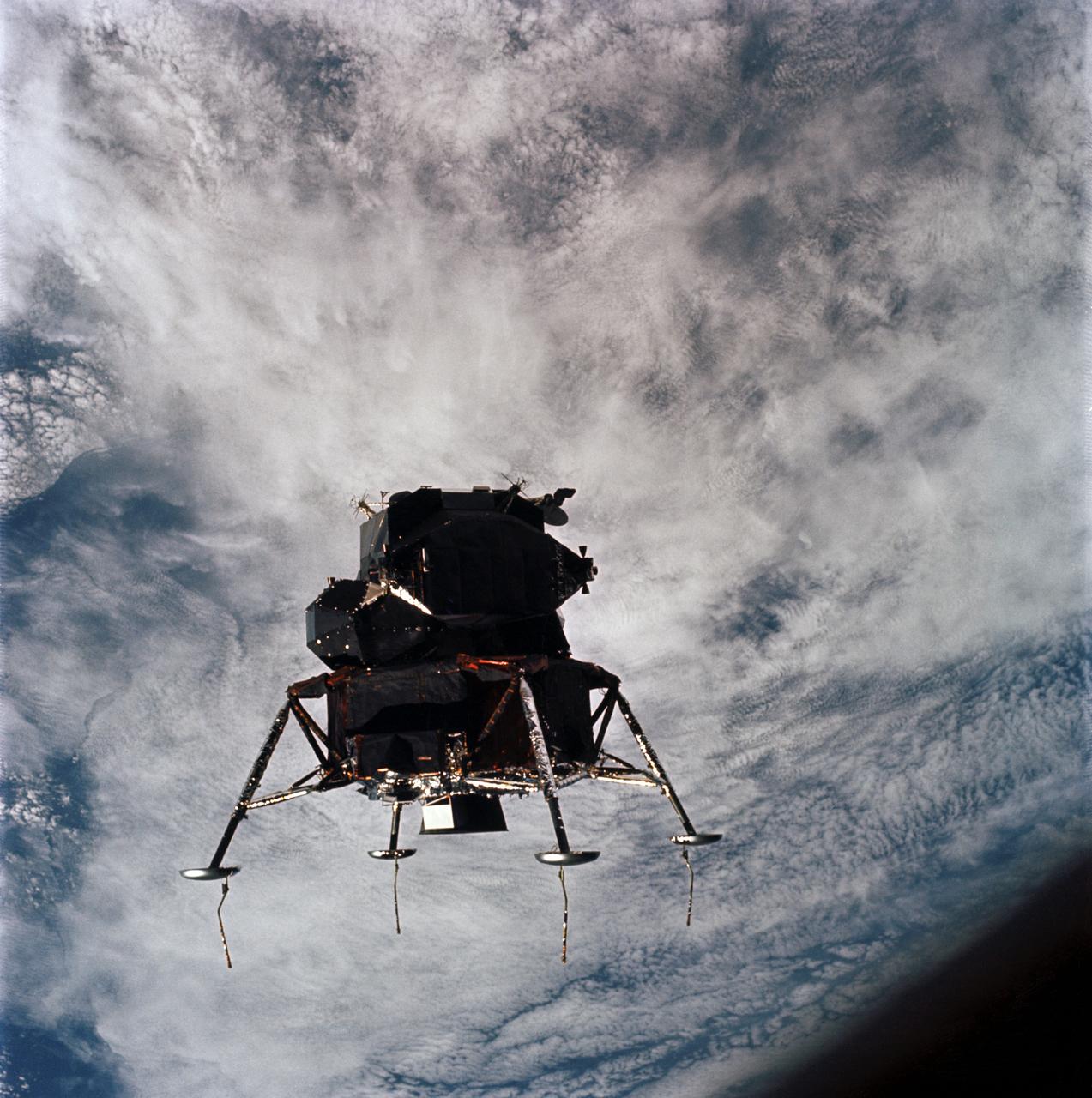

AS09-21-3199 (7 March 1969) --- Excellent view of the Apollo 9 Lunar Module, "Spider," in a lunar landing configuration, as photographed from the Command and Service Modules on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The landing gear on the "Spider" has been deployed. Lunar surface probes (sensors) extend out from the landing gear foot pads. Inside the "Spider" were astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module, "Gumdrop," while the other two astronauts checked out the Lunar Module.
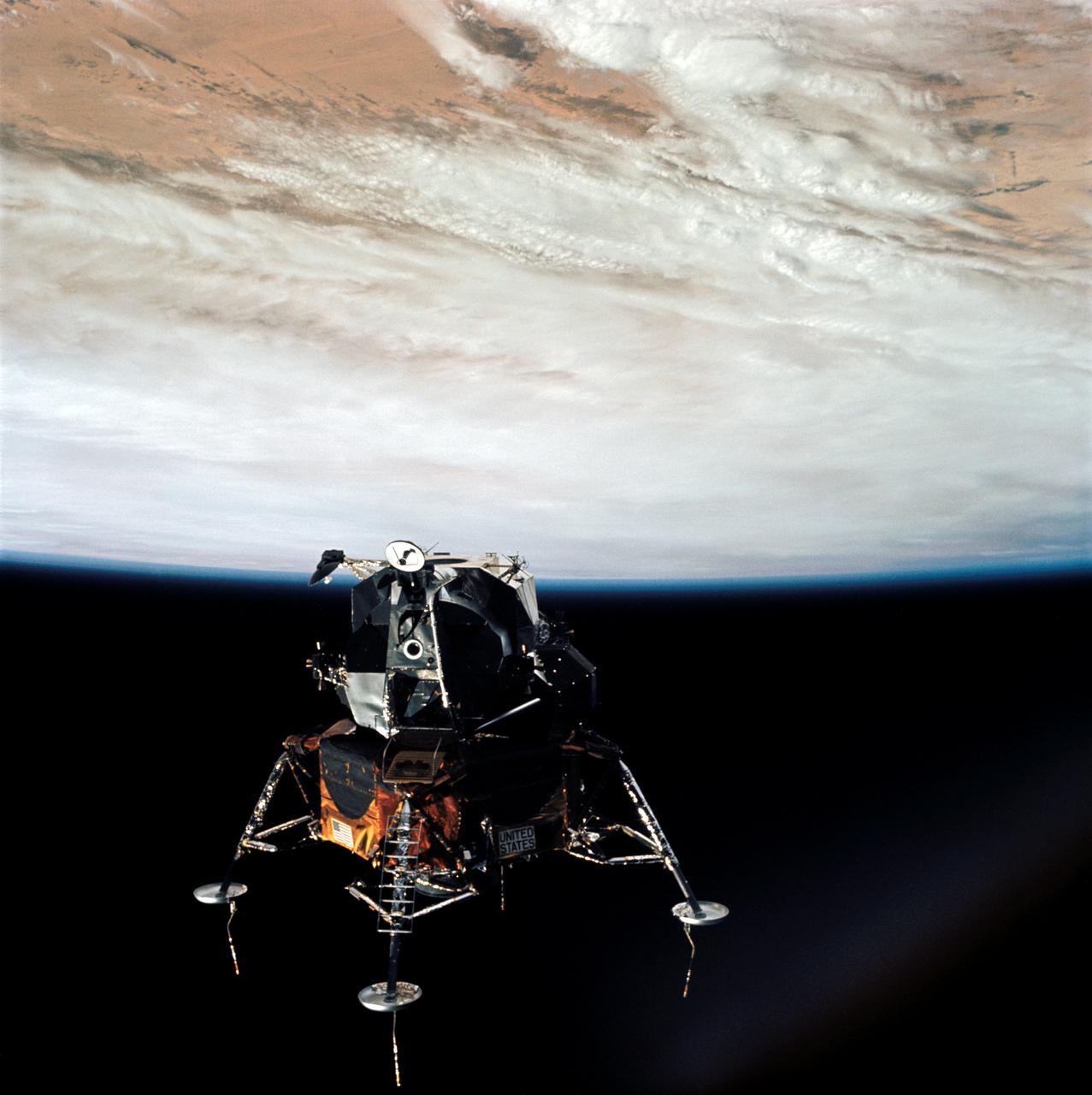

AS09-21-3212 (7 March 1969) --- A view of the Apollo 9 Lunar Module (LM), "Spider", in a lunar landing configuration, as photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The landing gear on the "Spider" has been deployed. Lunar surface probes (sensors) extend out from landing gear foot pads. Inside the "Spider" were astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander, and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module (CM), "Gumdrop", while the other two astronauts checked out the Lunar Module.
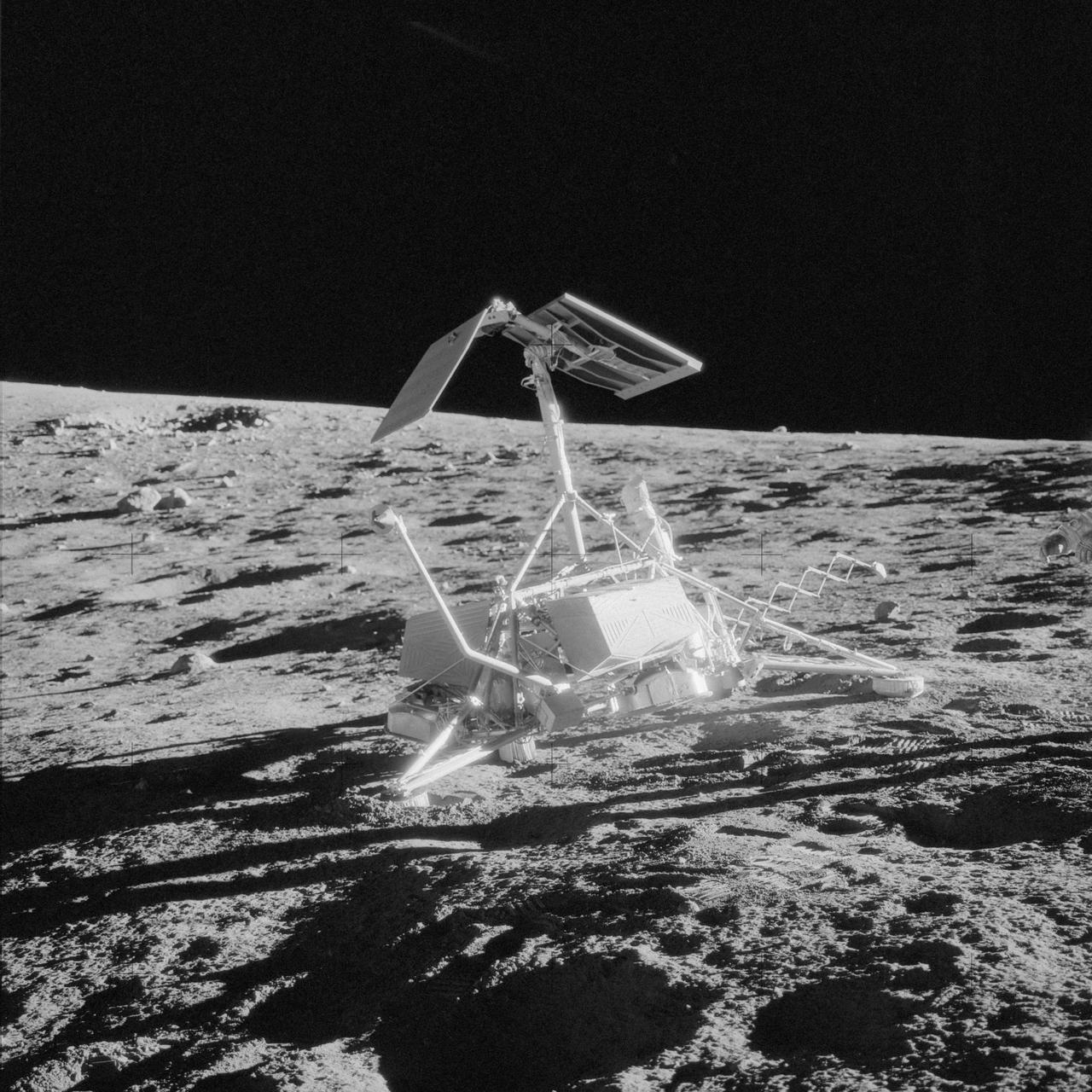

AS12-48-7121 (20 Nov. 1969) --- An excellent view of the unmanned Surveyor 3 spacecraft which was photographed during the Apollo 12 second extravehicular activity (EVA) on the surface of the moon. The Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM), with astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, aboard landed within 600 feet of Surveyor 3 in the Ocean of Storms. The television camera and several other pieces were taken from Surveyor 3 and brought back to Earth for scientific examination. Surveyor 3 landed on the side of this small crater in the Ocean of Storms on April 19, 1967. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 12 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while Conrad and Bean descended to explore the moon.
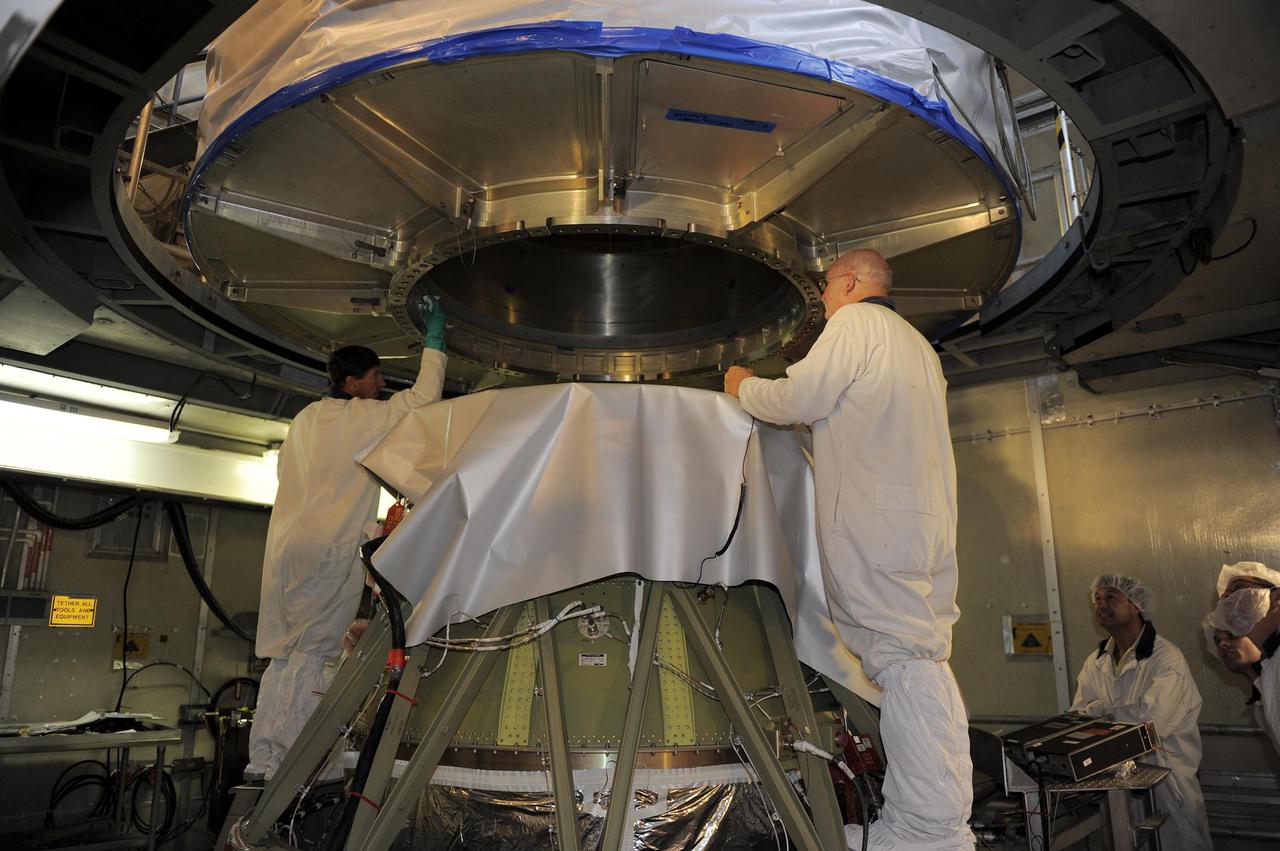

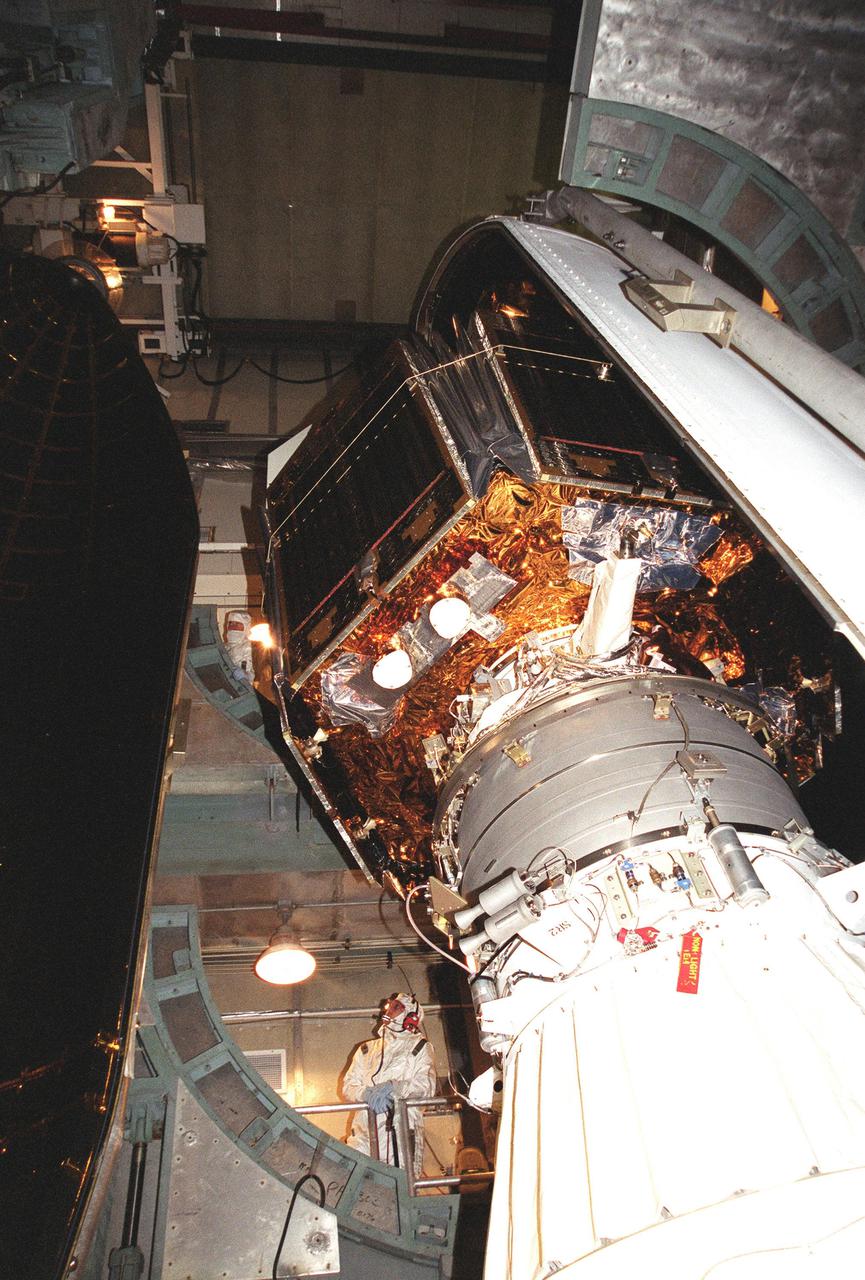
NASA twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory GRAIL spacecraft are lowered onto the second stage of their Delta II launch vehicle. At top is the spacecraft adapter ring which holds the two lunar probes in their side-by-side launch configuration.
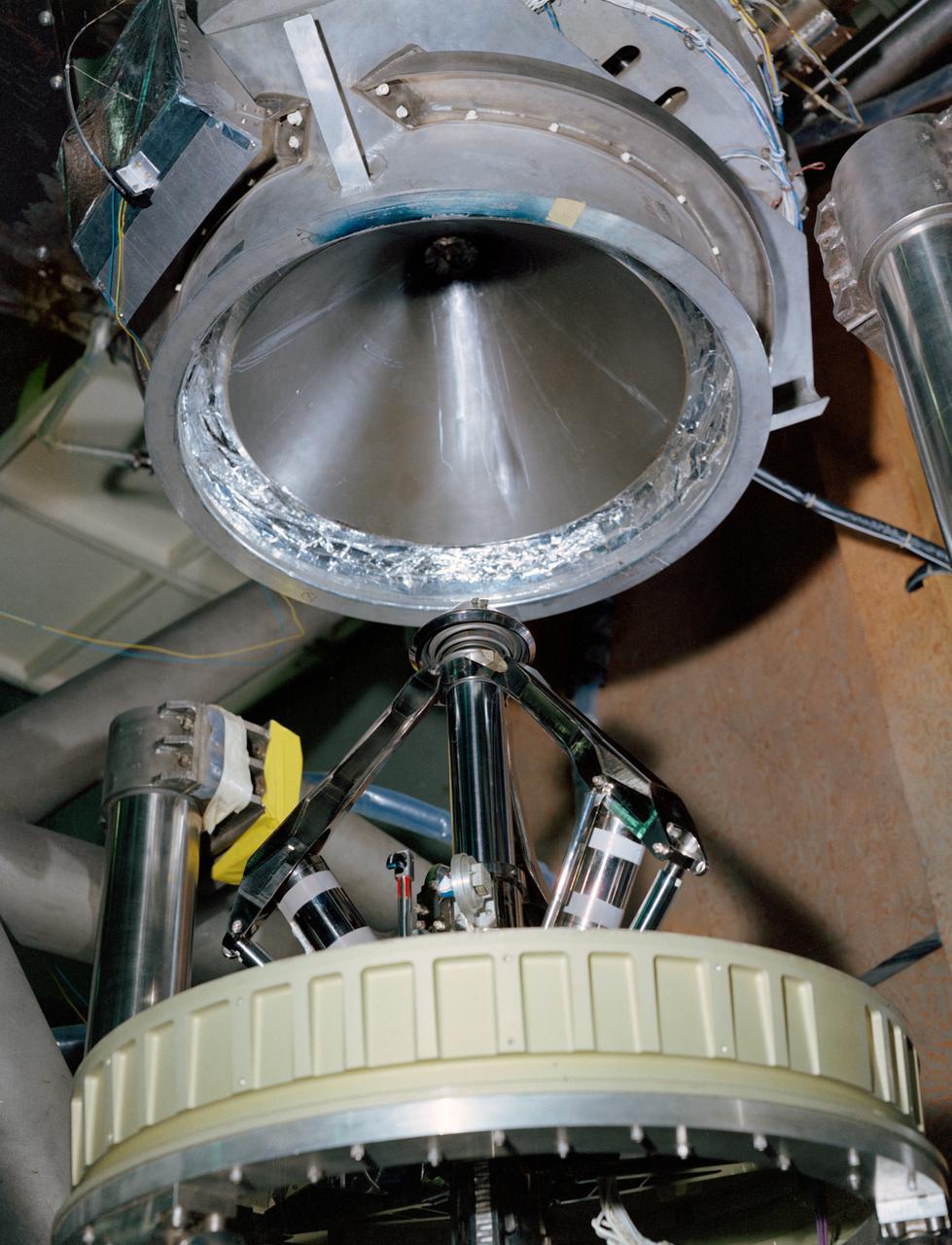
S68-50869 (1968) --- An engineering set up illustrating the docking system of the Apollo spacecraft. During docking maneuvers the docking probe on the Command Module engages the cone-shaped drogue of the Lunar Module. The primary docking structure is the tunnel through which the astronauts transfer from one module to the other. This tunnel is partly in the nose of the Command Module and partly in the top of the Lunar Module. Following CSM/LM docking the drogue and probe are removed to open the passageway between the modules.
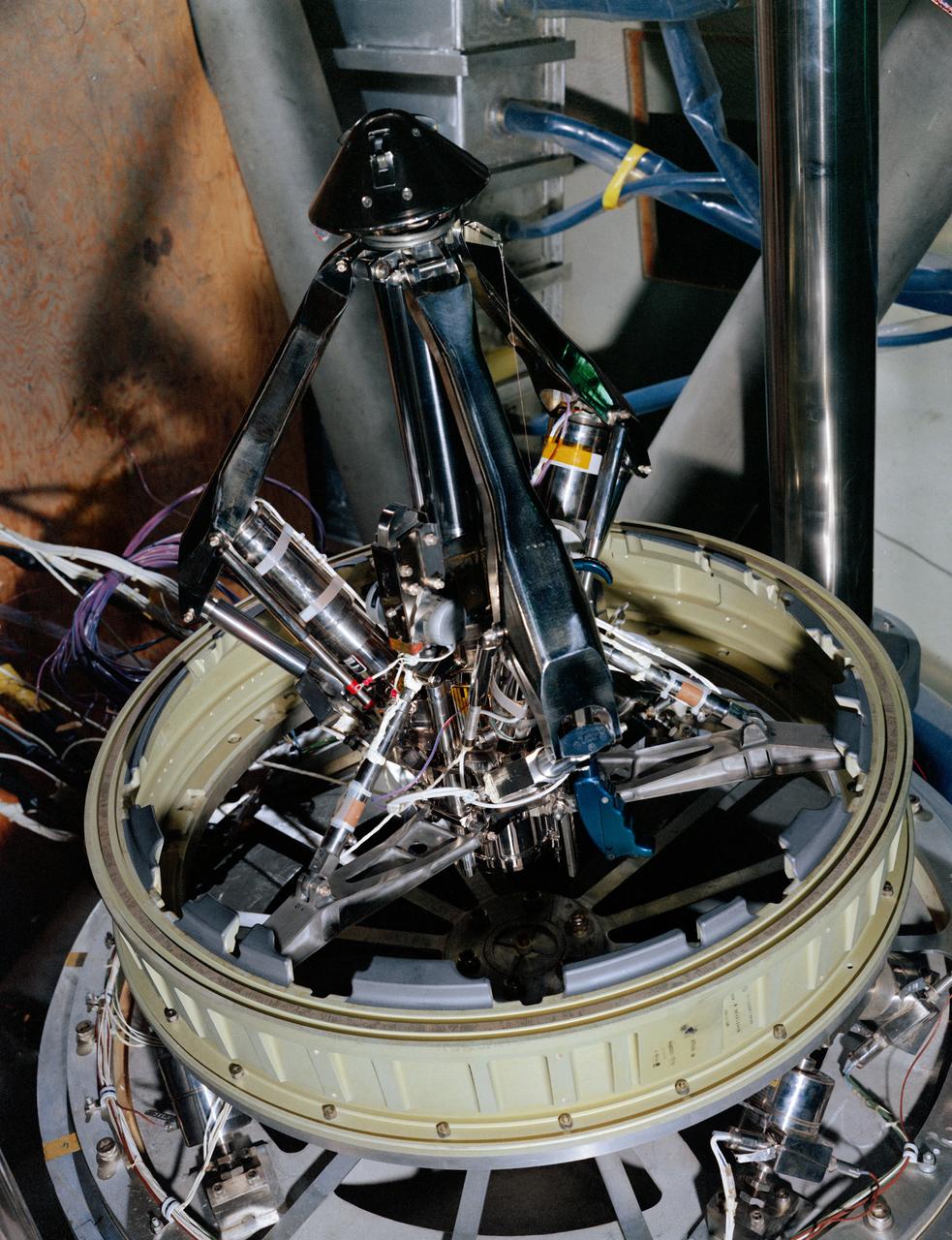

S68-50870 (1968) --- An engineering set up illustrating the probe portion of the docking system of the Apollo spacecraft. During docking maneuvers the docking probe on the Command Module (CM) engages the cone shaped drogue of the Lunar Module (LM). The primary docking structure is the tunnel through which the astronauts transfer from one module to the other. This tunnel is partly in the nose of the CM and partly in the top of the LM. Following CSM/LM docking the drogue and probe are removed to open the passageway between the modules.
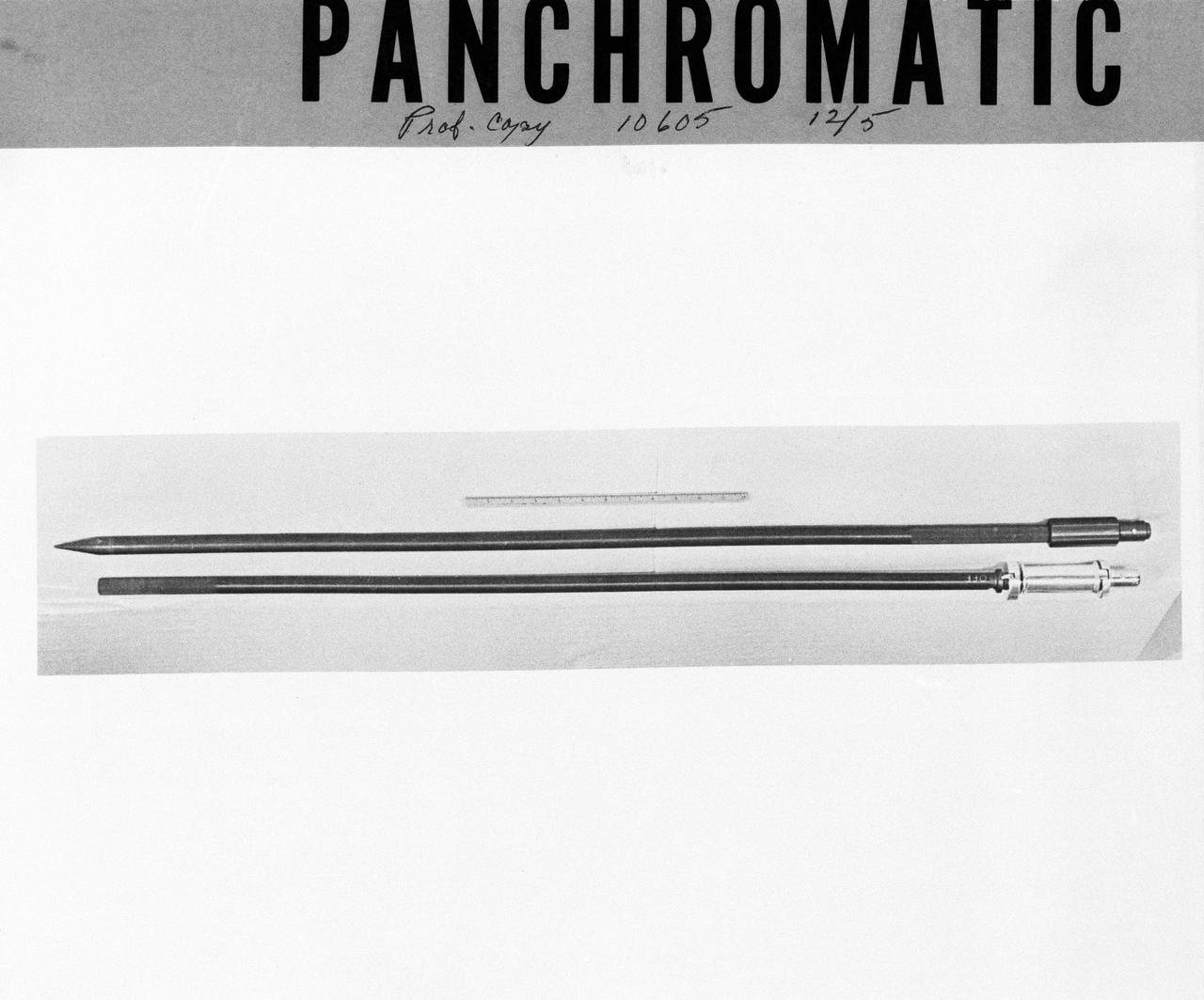
S72-53949 (November 1972) --- The upper and bottom sections of the Lunar Neutron Probe Experiment (S-229), in a stowed configuration, which will be used at the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. The purpose of this experiment is to measure neutron capture rates in the lunar regolith, measure variation of neutron capture rates as a function of depth beneath the lunar surface, and gain information on the lunar neutron energy spectrum.
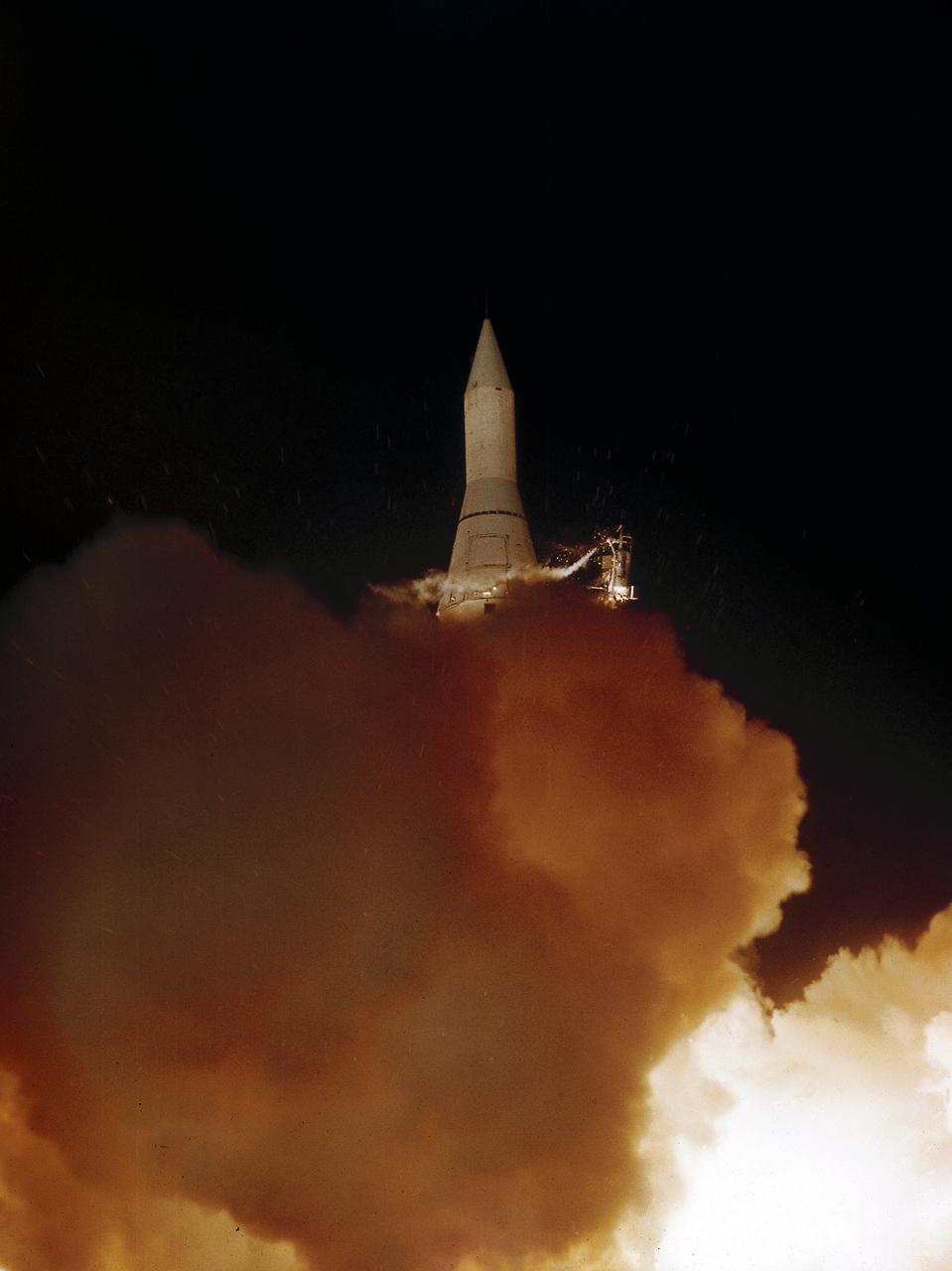

The launch of Juno II (AM-14), carrying the lunar and planetary exploration satellite in orbit, Pioneer IV, on March 3, 1959. the Pioneer IV probe was the first U.S. satellite to orbit the Sun.
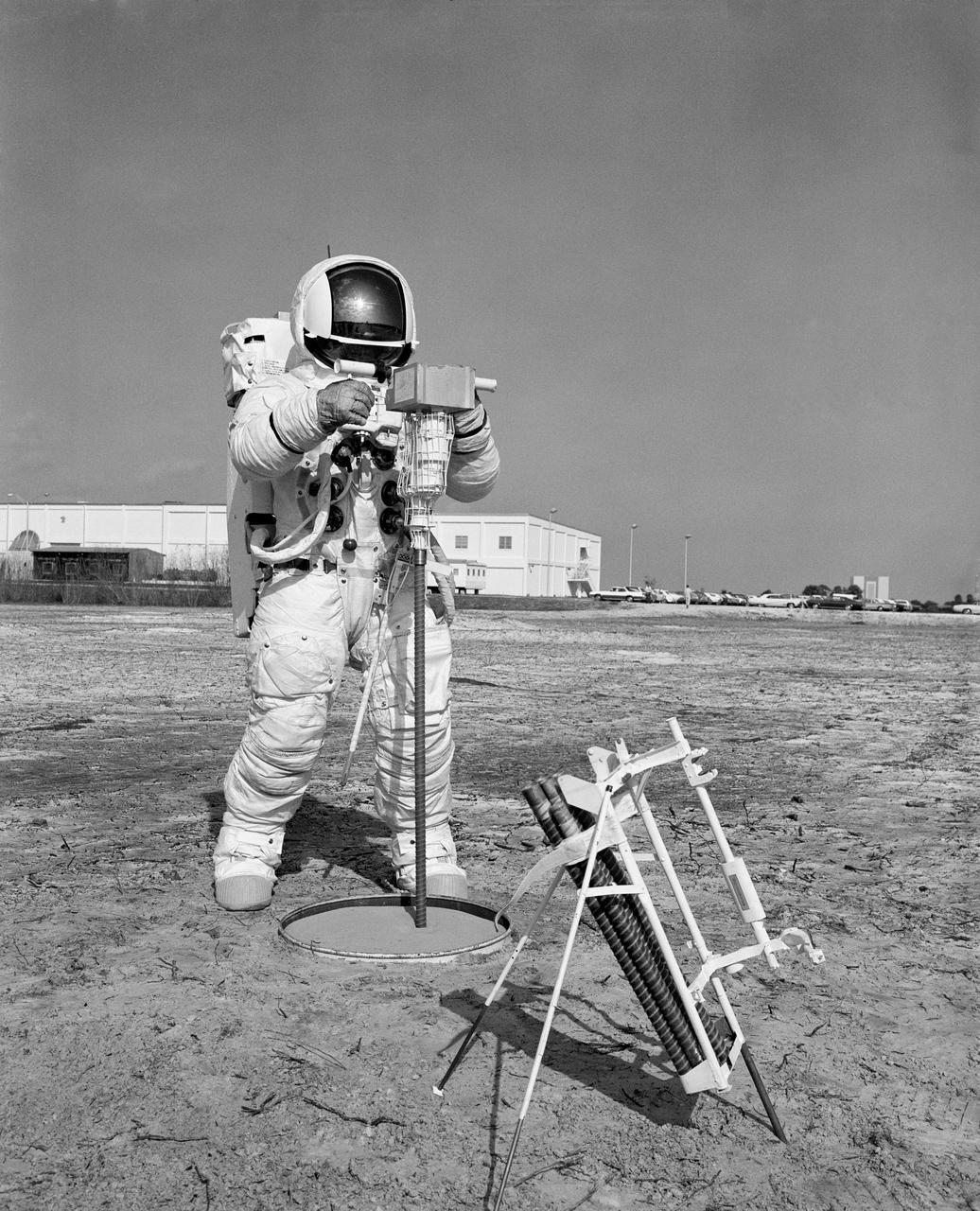

S70-29673 (28 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, participates in a walk-through of the extravehicular activity timeline at the Kennedy Space Center. Here, Haise uses an Apollo Lunar Surface Drill to dig a three-meter heat flow probe hole. The heat flow experiment on Apollo 13 will have an electronic instrument which will measure the outward flux of heat from the moon?s interior.
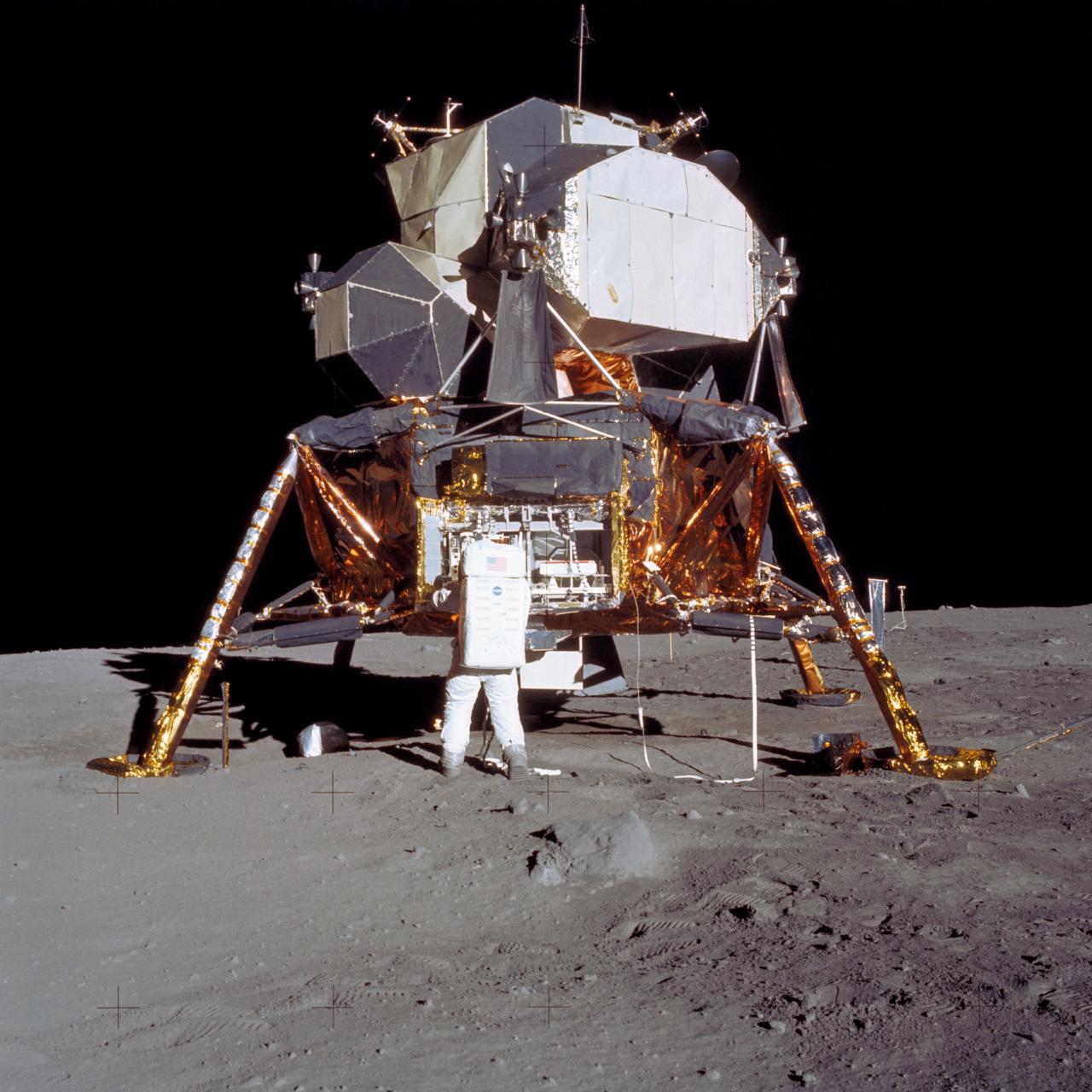

AS11-40-5927 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, prepares to deploy the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP) during the Apollo 11 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm lunar surface camera. During flight the EASEP is stowed in the Lunar Module's (LM) scientific equipment bay at the left year quadrant of the descent stage looking forward. Aldrin is removing the EASEP from its stowed position. Photo credit: NASA
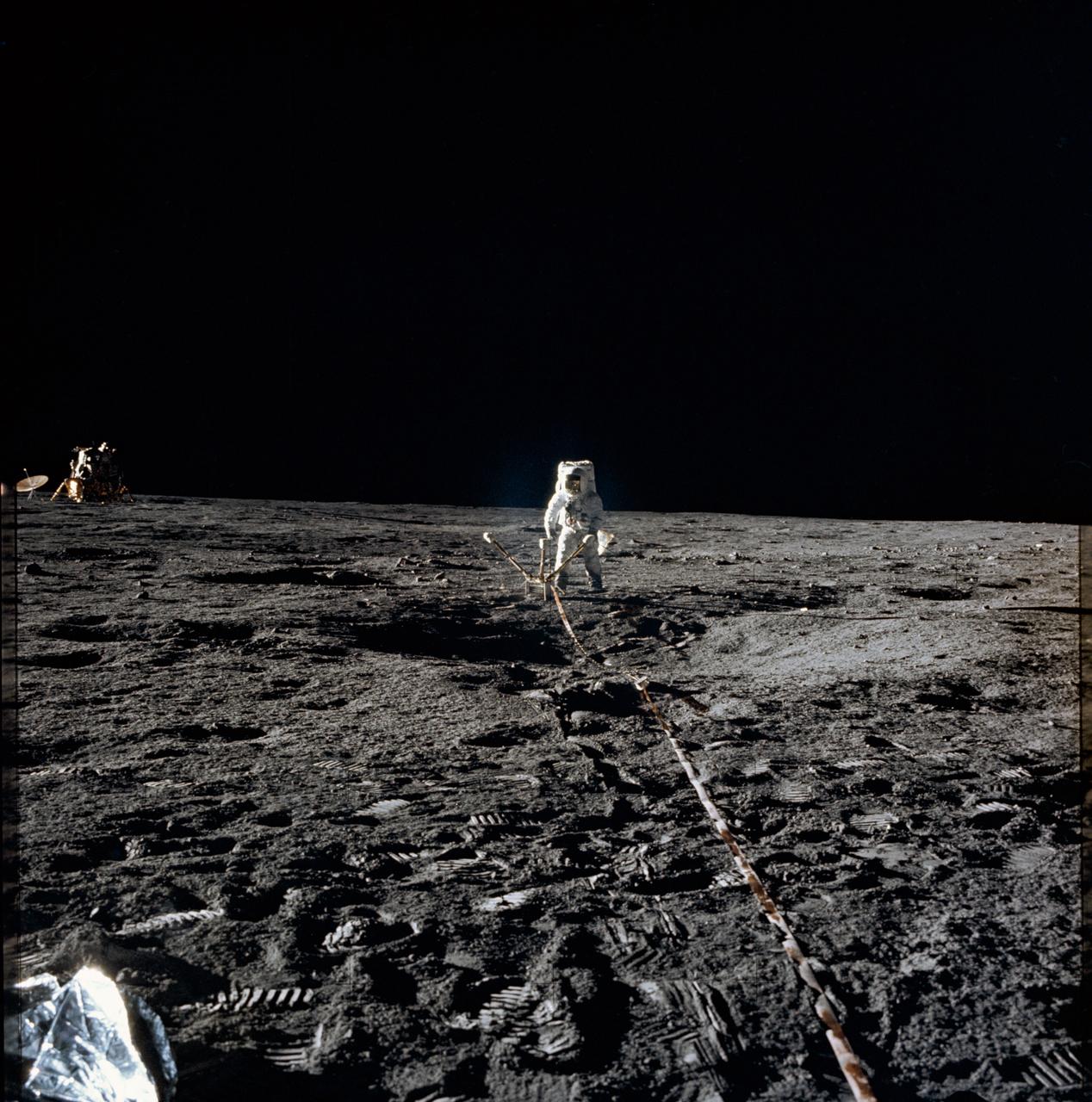

Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, deploys the Lunar Surface Magnetometer (LSM) during the first Apollo 12 extravehicular activity on the Moon. The LSM is a component of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP). The Lunar Module can be seen in the left background.
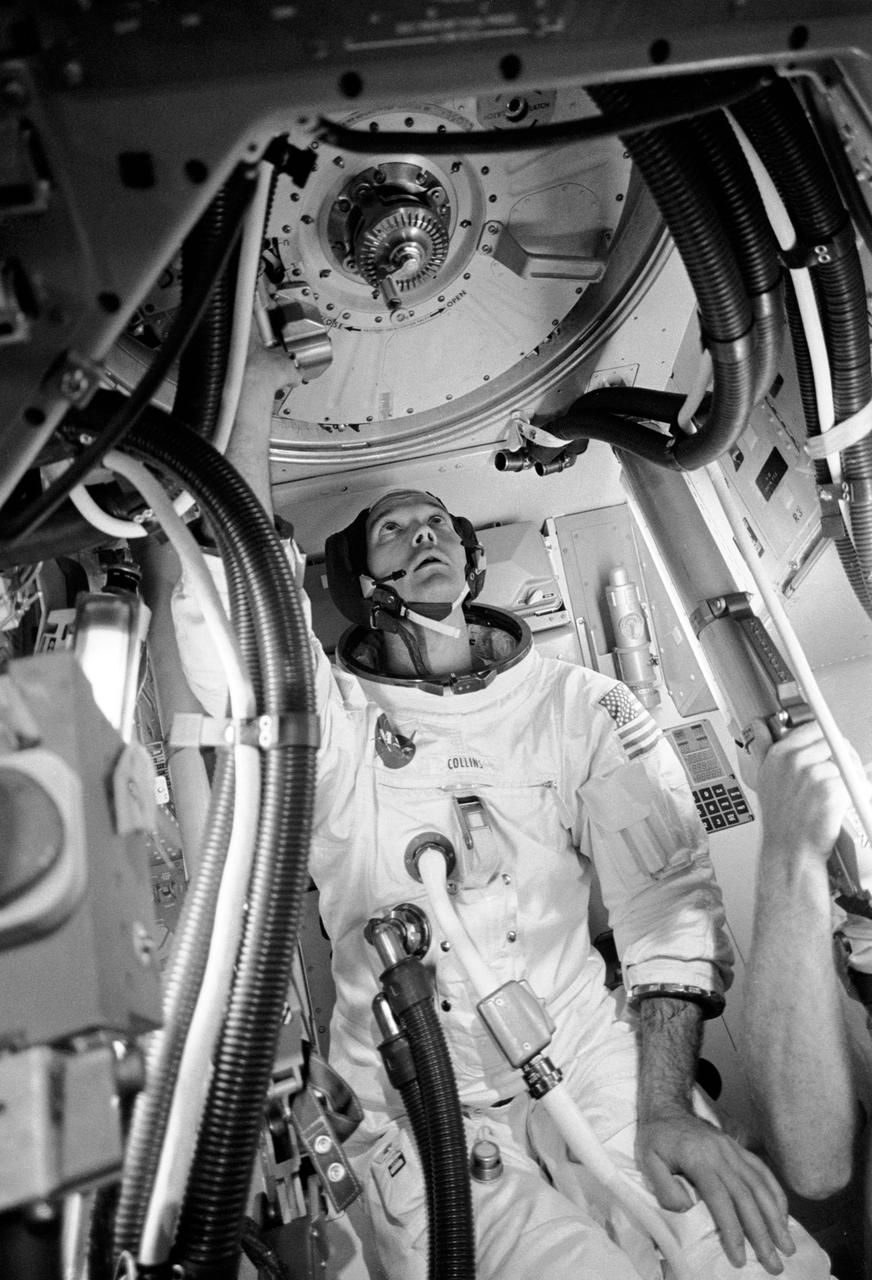

S69-38323 (28 June 1969) --- Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot of the Apollo 11 flight, is seen inside an Apollo Command Module (CM) mockup in Building 5 practicing procedures with the Apollo docking mechanism in preparation for the scheduled Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. Collins is at the CM's docking tunnel which provides passageway to and from the Lunar Module (LM) following docking, and after removal of the tunnel hatches, docking probe and drogue.
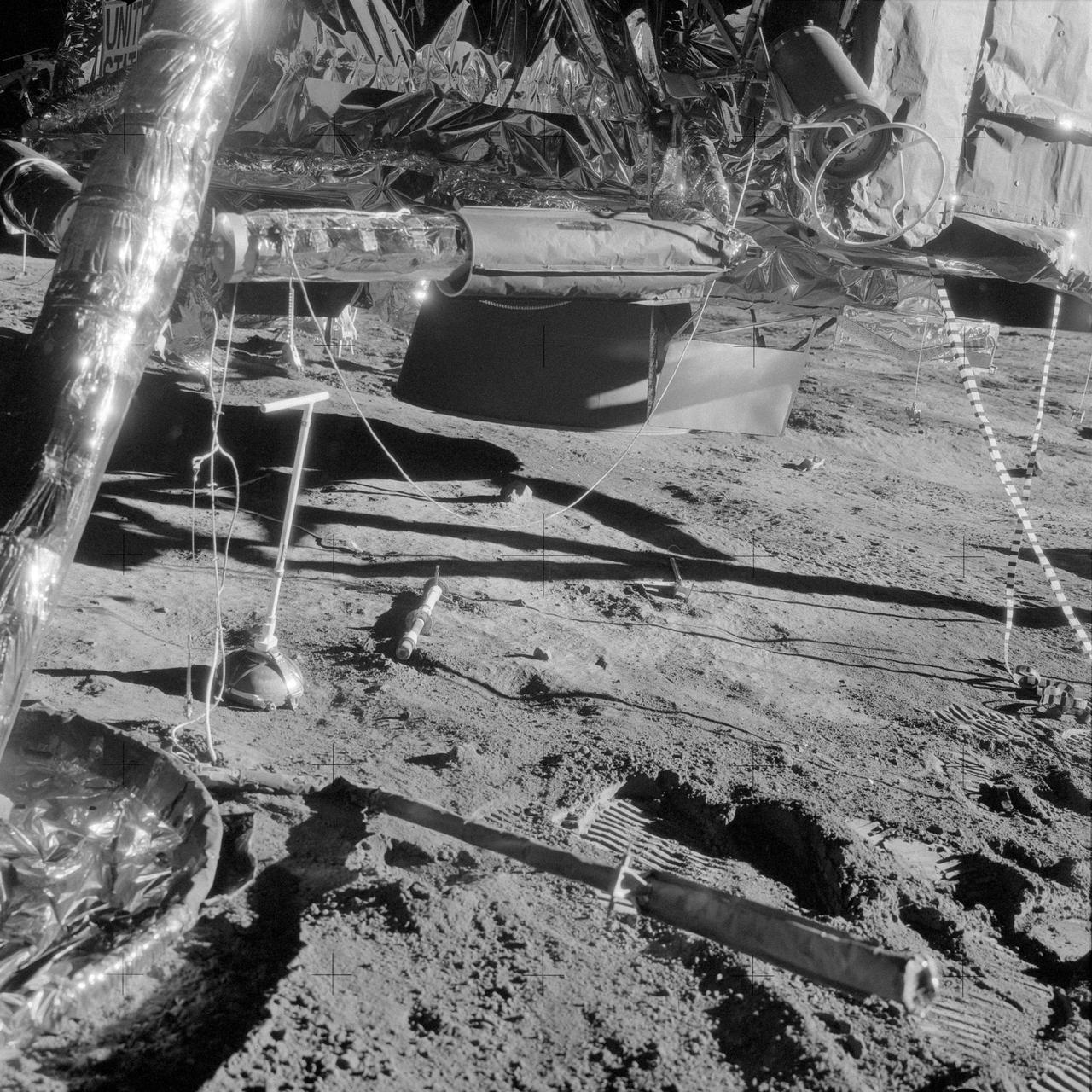

AS12-48-7034 (19 Nov. 1969) --- A close-up view of a portion of quadrant II of the descent stage of the Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM), photographed during the Apollo 12 extravehicular activity (EVA). At lower left is the LM's Y footpad. The empty Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (RTG) fuel cask is at upper right. The fuel capsule has already been removed and placed in the RTG. The RTG furnishes power for the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) which the Apollo 12 astronauts deployed on the moon. The LM's descent engine skirt is in the center background. The rod-like object protruding out from under the footpad is a lunar surface sensing probe. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander; and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon.
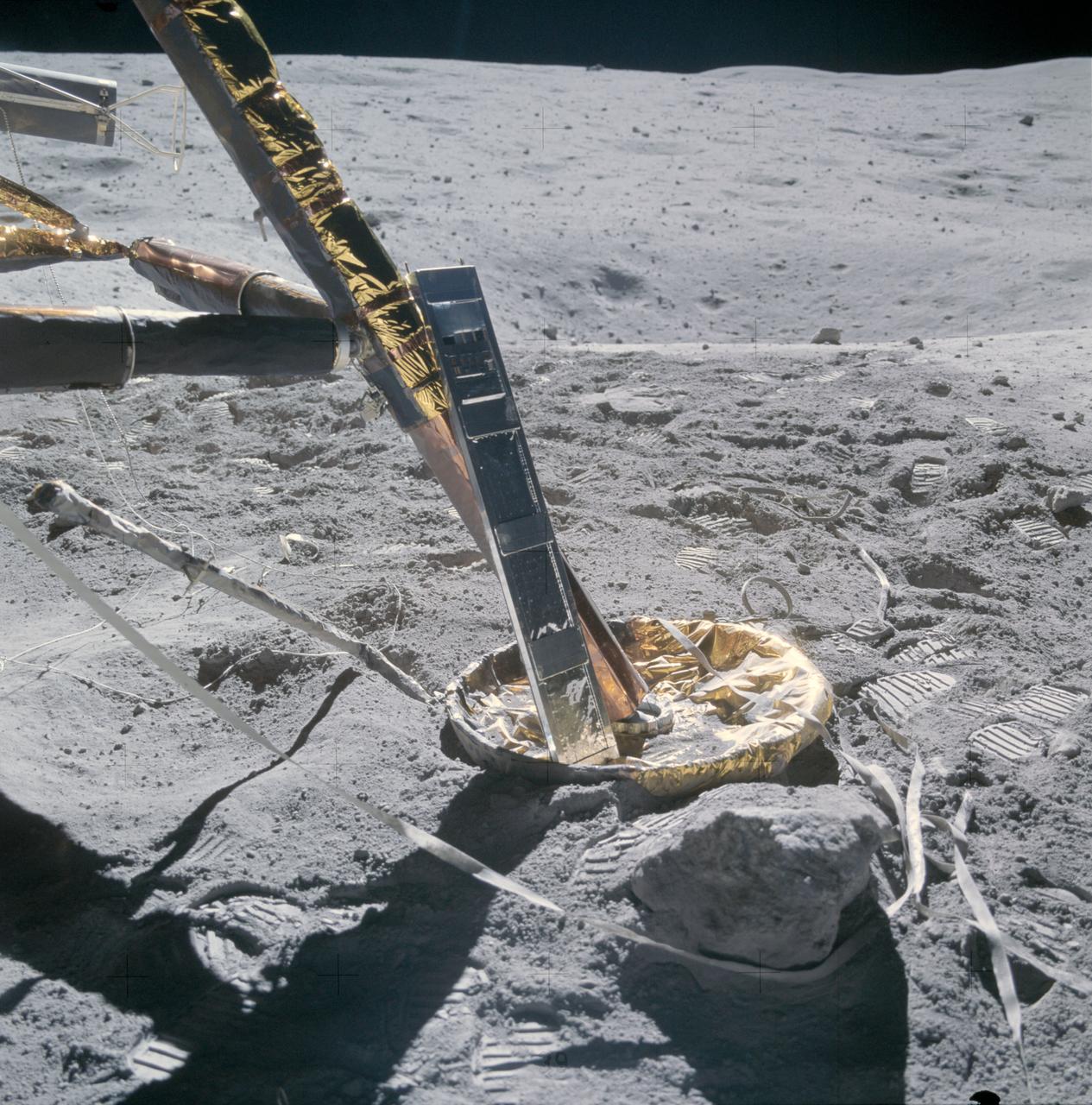

AS16-107-17442 (22 April 1972) --- A close-up view of the Apollo 16 Cosmic Ray Detector (CRD) experiment deployed at the +Y strut of the Lunar Module (LM). The crewmembers moved it to this position from near the deployment site of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) because, in the words of astronaut John W. Young, commander, "The panels were getting a little warm." Note that the LM did not skid upon landing, as evidenced by the landing contact probe's folded back (neatly) position and the lack of skid marks. While astronauts Young, and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the canister is removed from the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP). Launch of MAP via a Boeing Delta II rocket is scheduled for June 30. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Workers at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, place protective covers around the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. Launch of MAP via a Boeing Delta II rocket is scheduled for June 30. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures
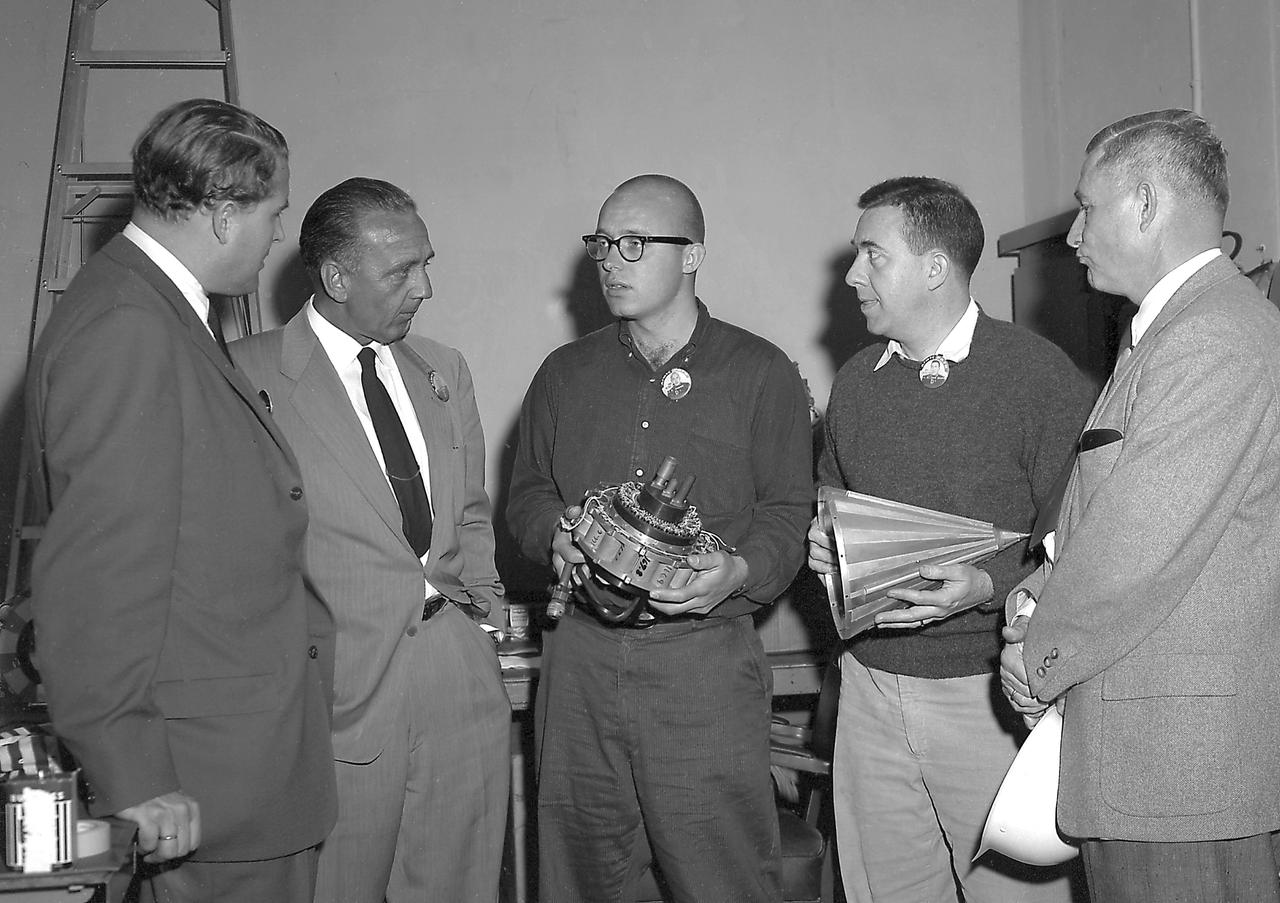

In this photo, Director of the U.S. Army Ballistic Missile Agency's (ABMA) Development Operations Division, Dr. Wernher von Braun, and Director of Missile Firing Division, Dr. Kurt Debus, are shown with unidentified individuals, discussing two components that would make up the Pioneer IV Lunar Probe. The mercury batteries (left) were used to power the radio transmitter, cosmic radiation counter and other instruments in Pioneer IV. The conical shroud placed over the instruments of Pioneer IV was plated with gold to improve conductivity. The metal surface also served as the anterna for the probe's instruments signaling back to the Earth receiving stations.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers place a cover over the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. Launch of MAP via a Boeing Delta II rocket is scheduled for June 30. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Workers at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, place protective covers around the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. Launch of MAP via a Boeing Delta II rocket is scheduled for June 30. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Engineers in Hangar A&E, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, wait to track the launch of the Boeing Delta II rocket carrying the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. The screens above the console show the rocket on the launch pad. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University. Launch is scheduled for 3:46 p.m. EDT
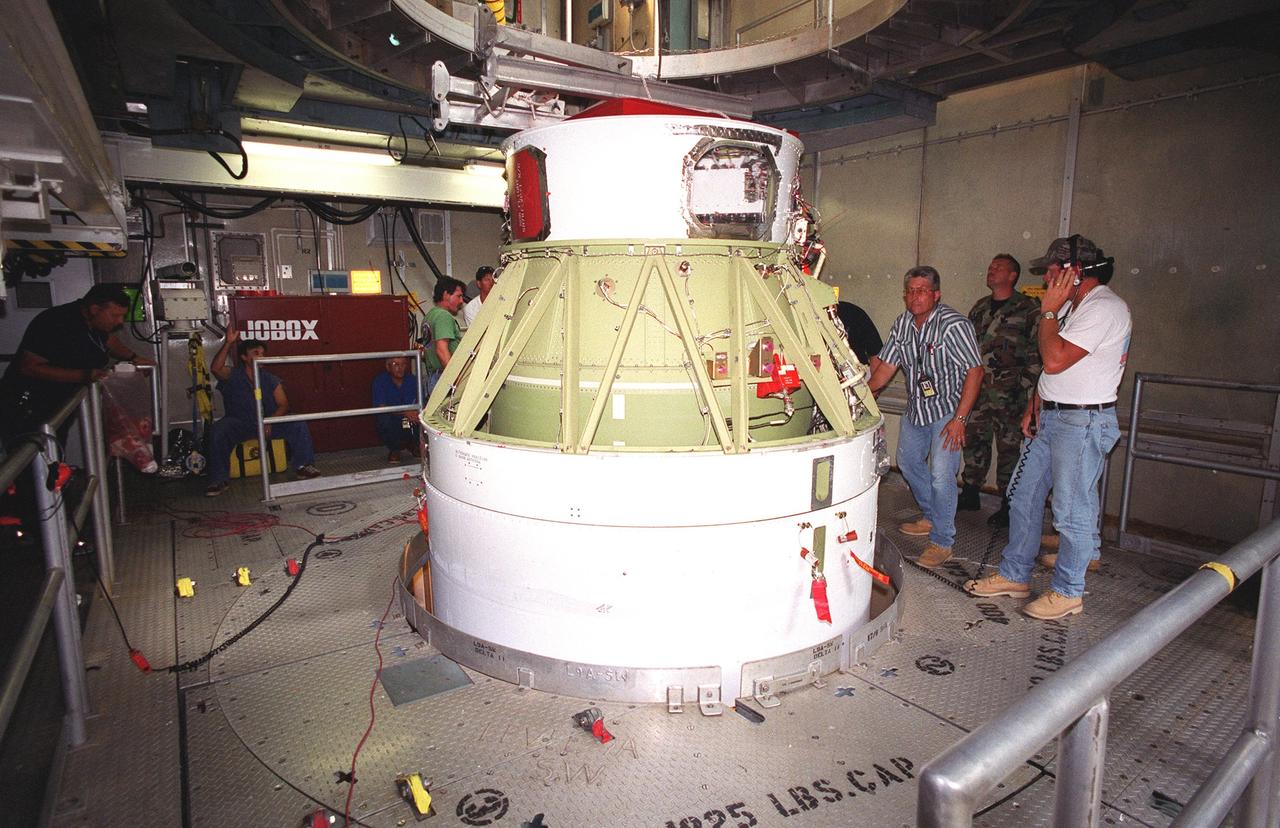

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the second stage of a Boeing Delta 7425-10 rocket is lifted into position as preparations to launch NASA's Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) on June 30 continue. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission.; The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University
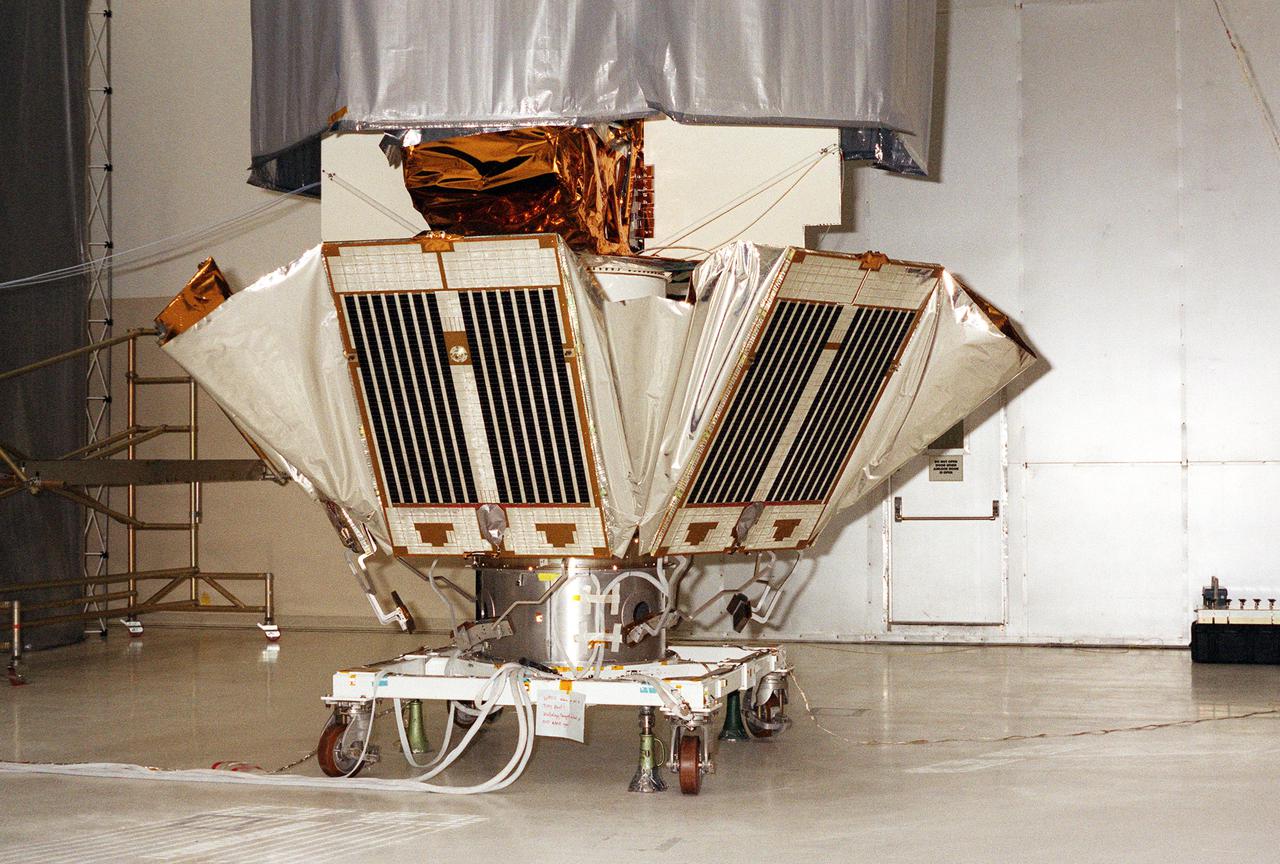

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Solar panels on the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft begin deployment in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2. MAP is scheduled for launch on June 30 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University
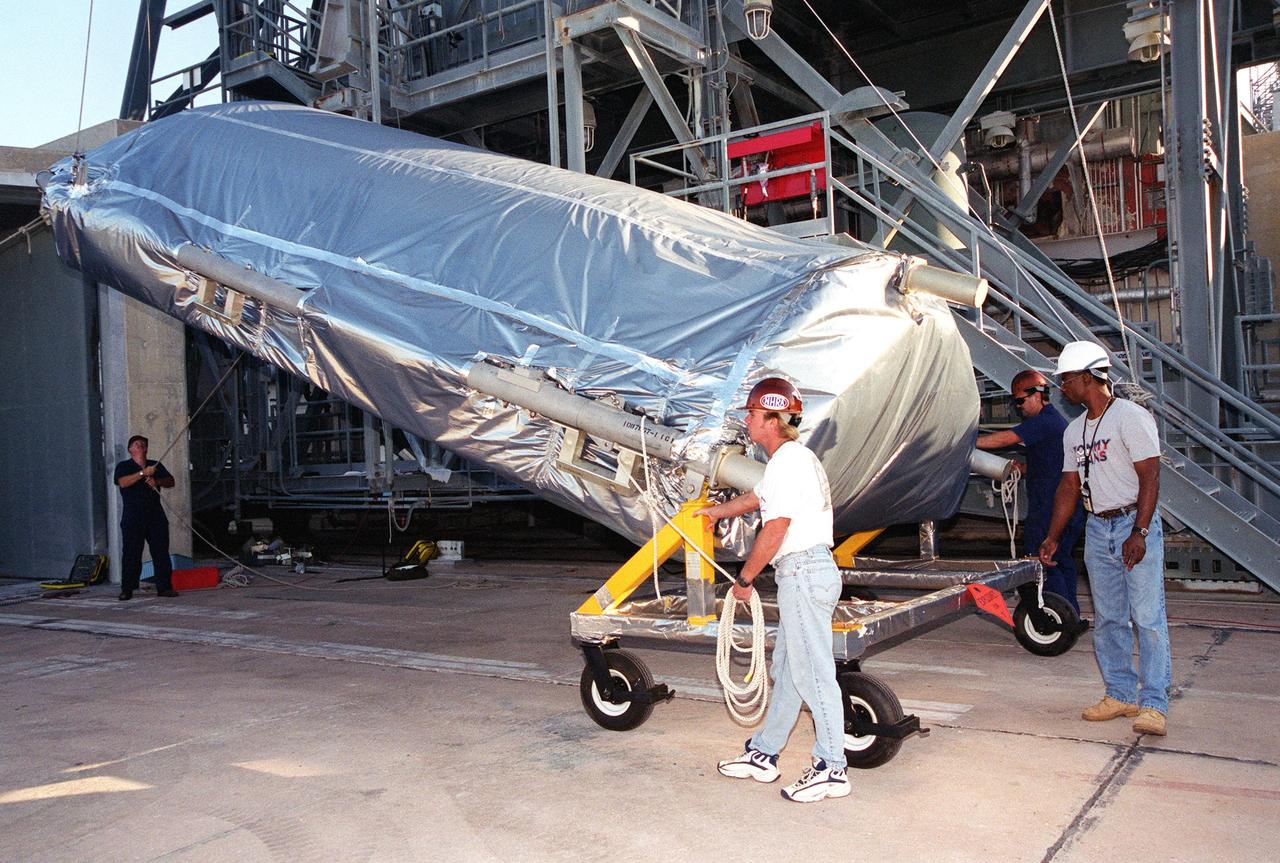

At the gantry on Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the fairing for the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft is raised for its lift to the White Room. There it will wait for the arrival of the spacecraft. MAP is scheduled for launch on June 30 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University
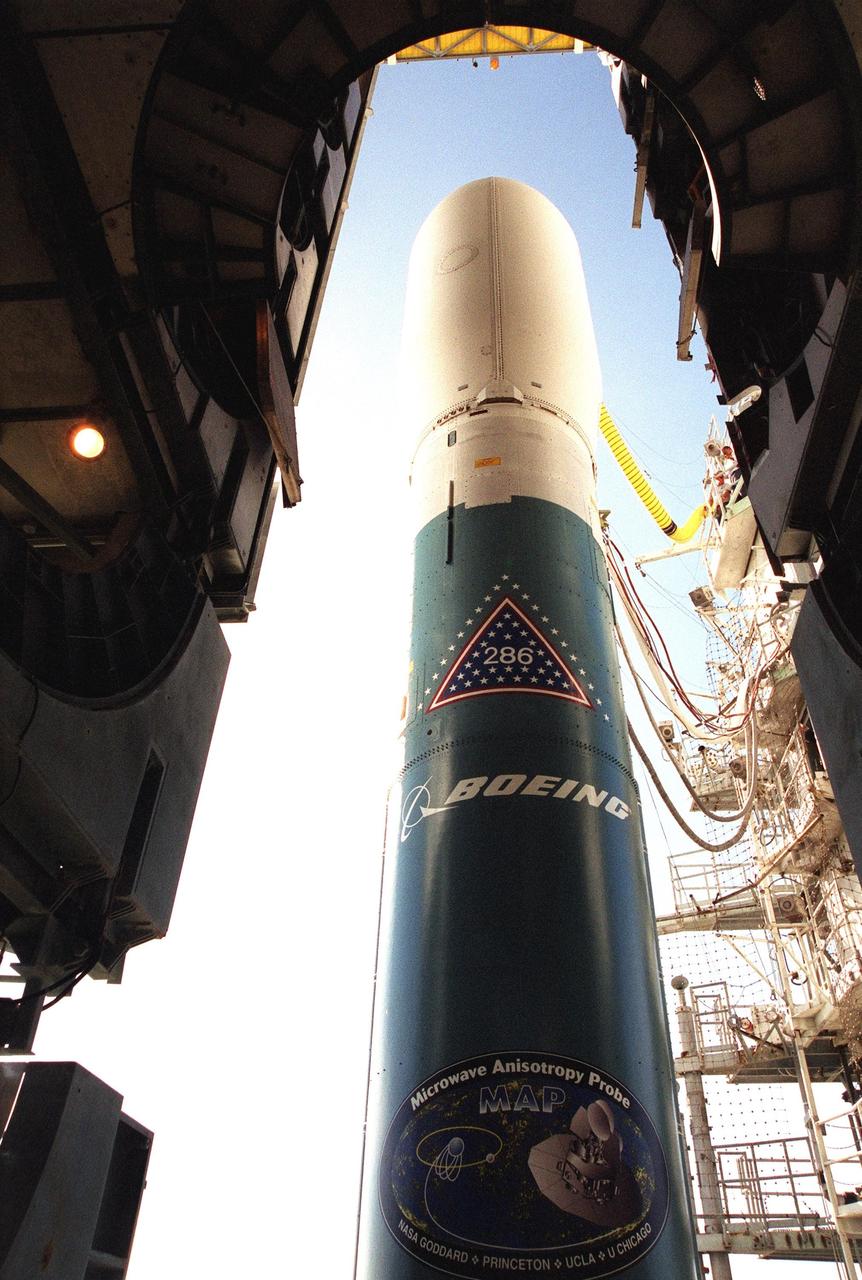

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Boeing Delta II rocket is poised for flight on Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, after rollback of the Mobile Service Tower. Topping the rocket is the payload, the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. Launch is scheduled at 3:46 p.m. EDT June 30. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University
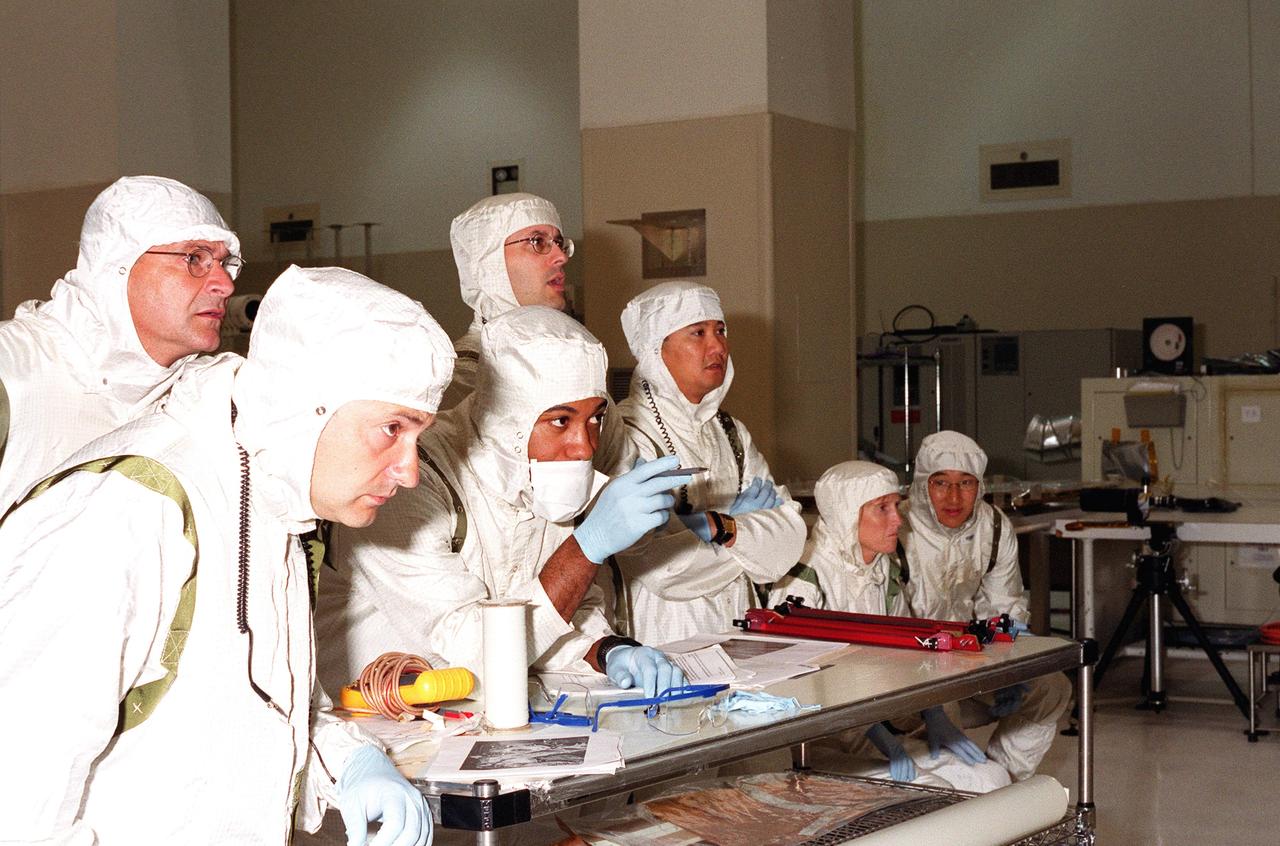

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Scientists and other workers watch as the solar panels on the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft are deployed in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2. MAP is scheduled for launch on June 30 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Delta II rocket, carrying the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft, arcs through the cloud-washed blue sky while photographers try to capture the spectacle from the ground. The successful launch from Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, occurred at 3:46:46 p.m. EDT. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University
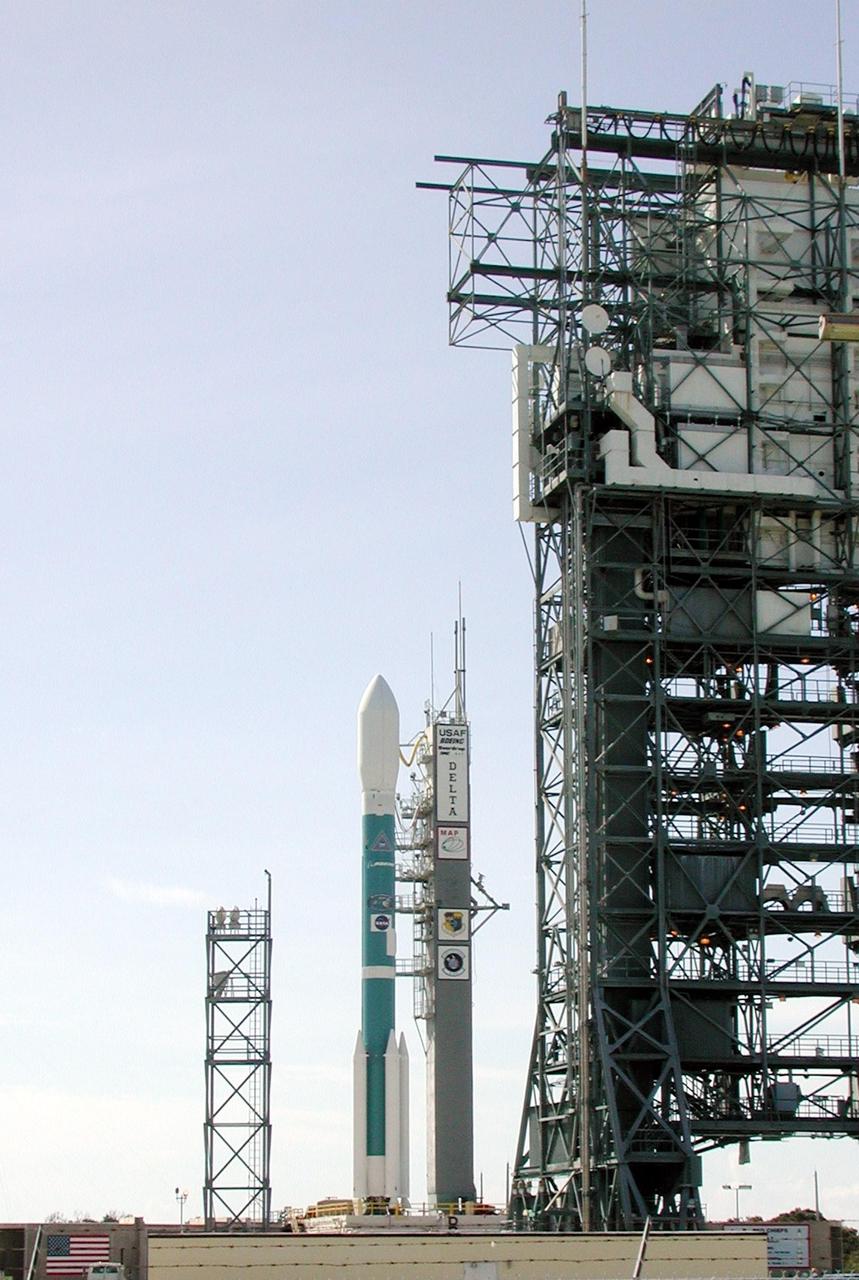

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Boeing Delta II rocket is poised for flight on Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, after rollback of the Mobile Service Tower (right). Topping the rocket is the payload, the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. Launch is scheduled at 3:46 p.m. EDT June 30. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Boeing Delta II rocket is poised for flight on Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, after rollback of the Mobile Service Tower (right). Topping the rocket is the payload, the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. Launch is scheduled at 3:46 p.m. EDT June 30. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University
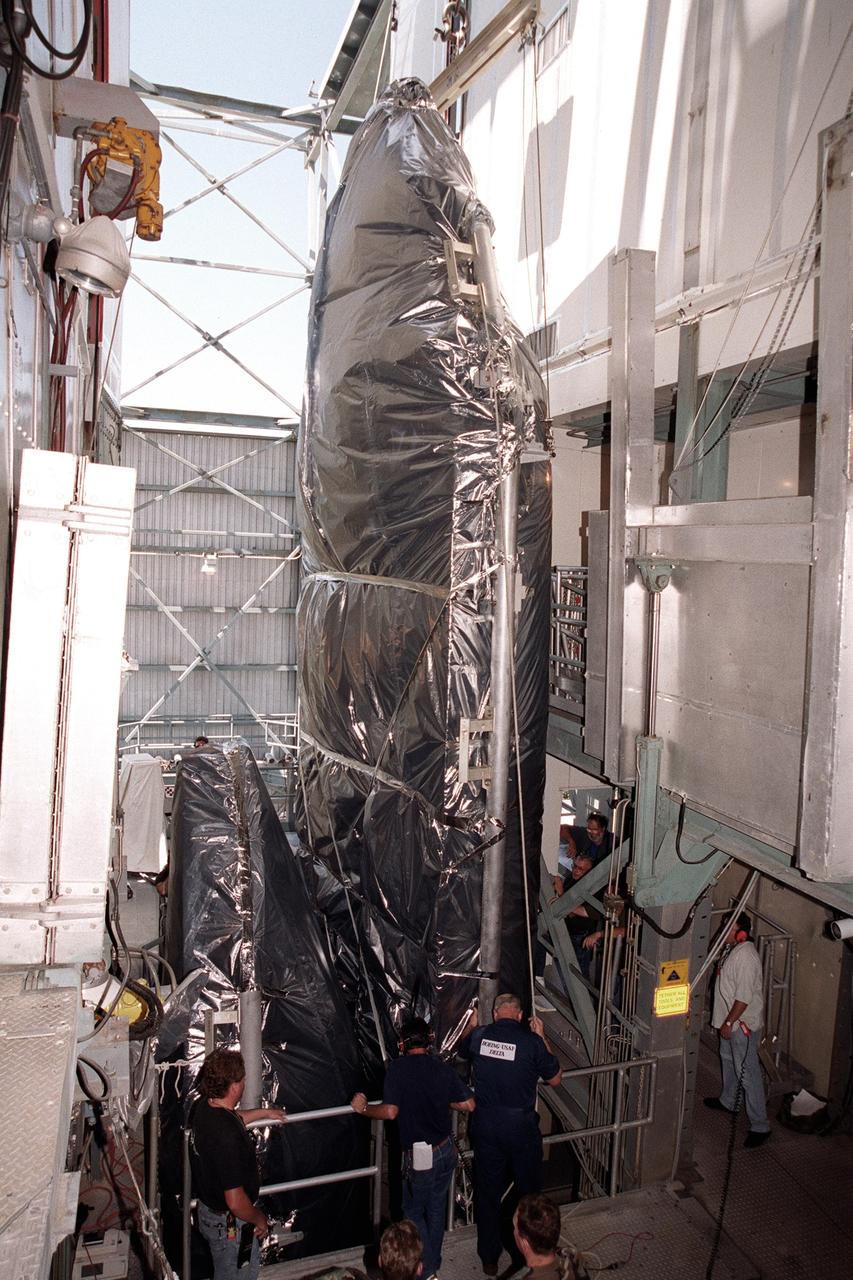

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At the gantry on Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the fairing for the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft arrives in the White Room. There it will wait for the arrival of the spacecraft. MAP is scheduled for launch on June 30 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University
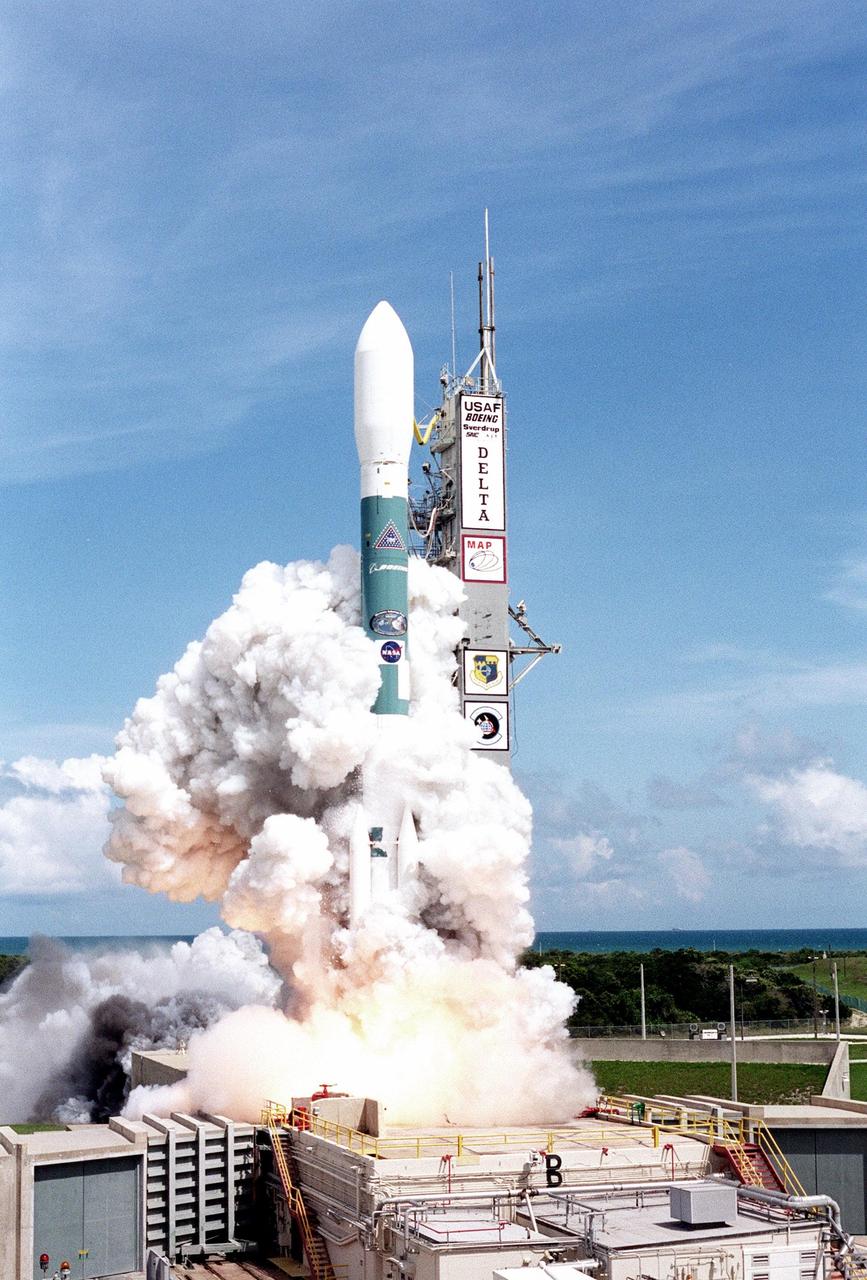
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Wrapped in billows of smoke and steam, the Boeing Delta II rocket lifts off Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. The successful launch occurred at 3:46:46 p.m. EDT. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University
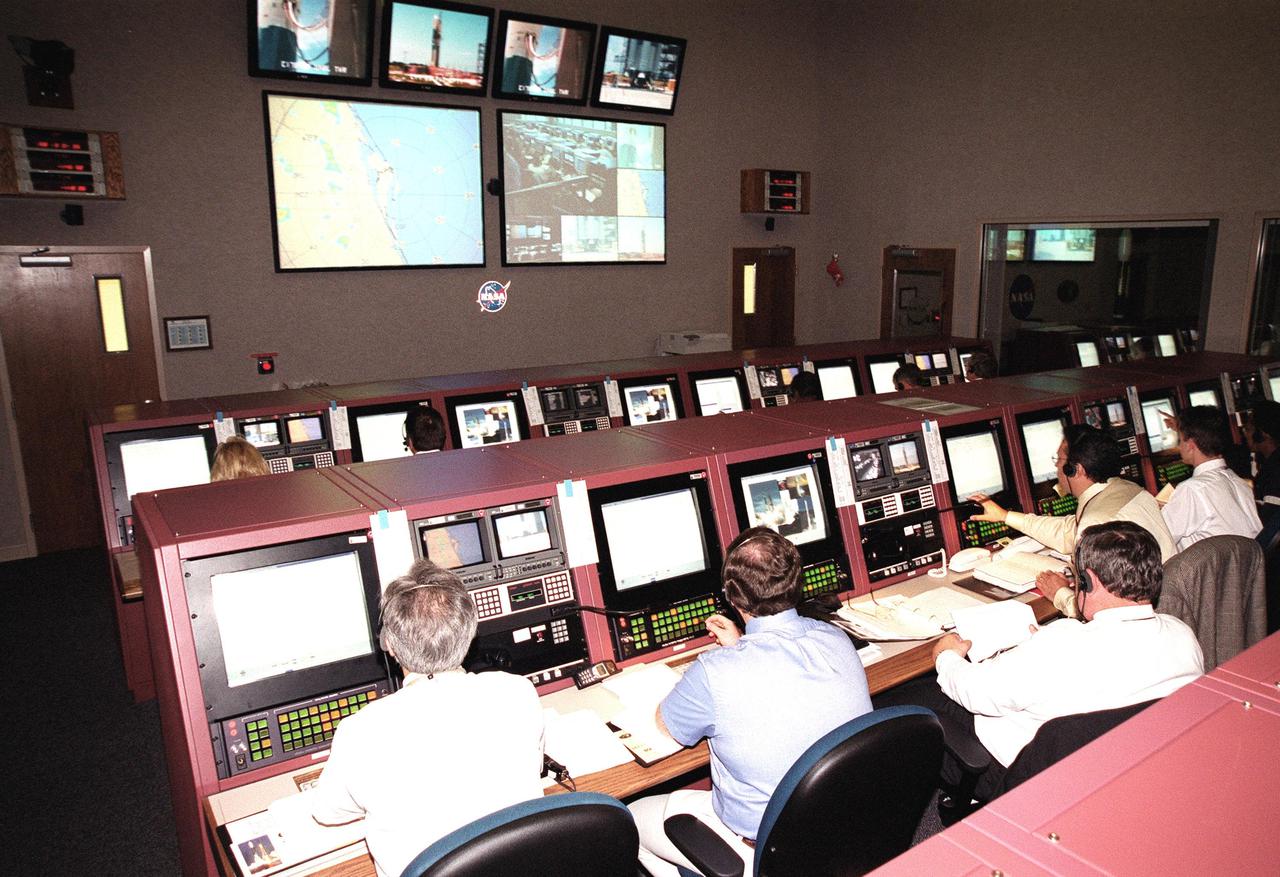

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The launch of the Boeing Delta II rocket carrying the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft is tracked inside Hangar AandE, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The successful launch from Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, occurred at 3:46:46 p.m. EDT. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University
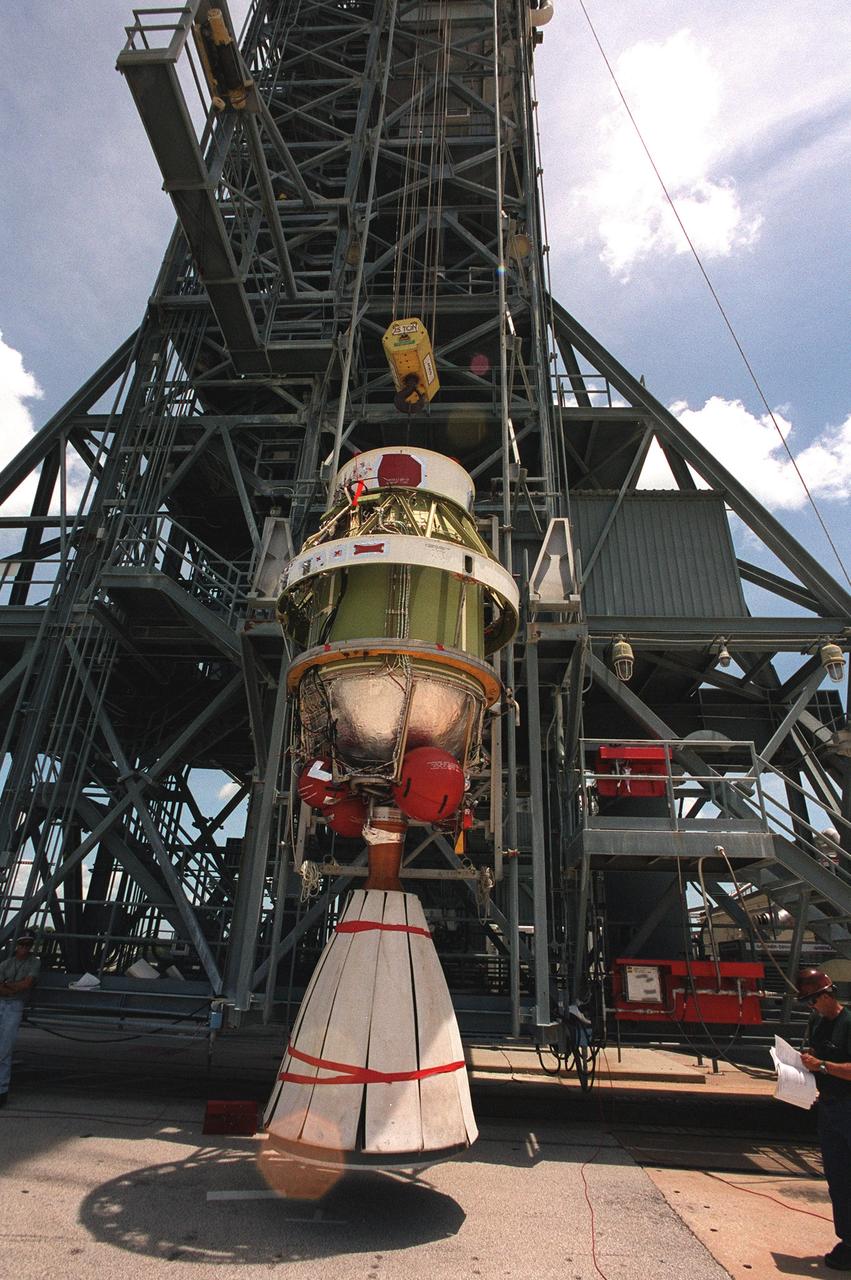

On Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the second stage of a Boeing Delta 7425-10 rocket is lifted into position as preparations to launch NASA's Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) on June 30 continue. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission.; The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University
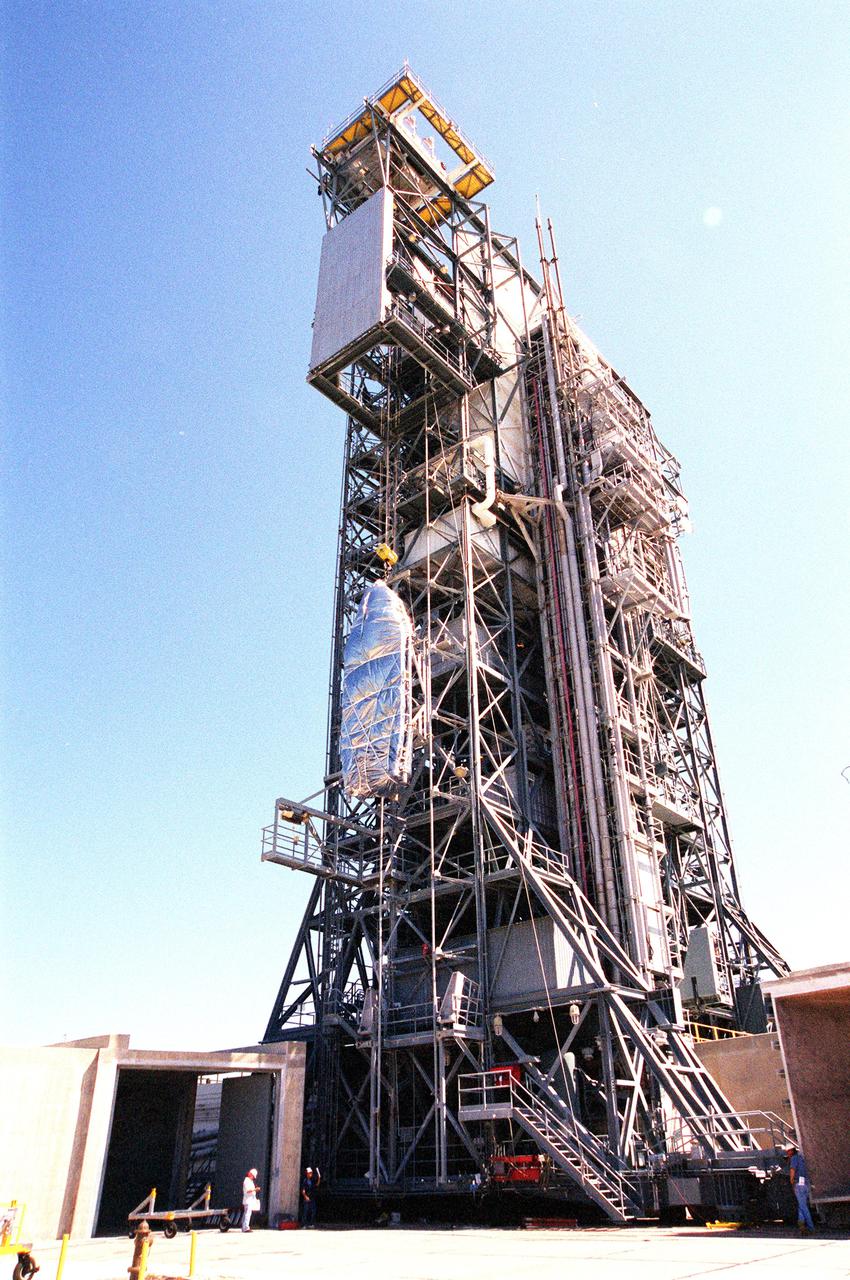

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the fairing for the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft is lifted up the gantry to the White Room. There it will wait for the arrival of the spacecraft. MAP is scheduled for launch on June 30 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University
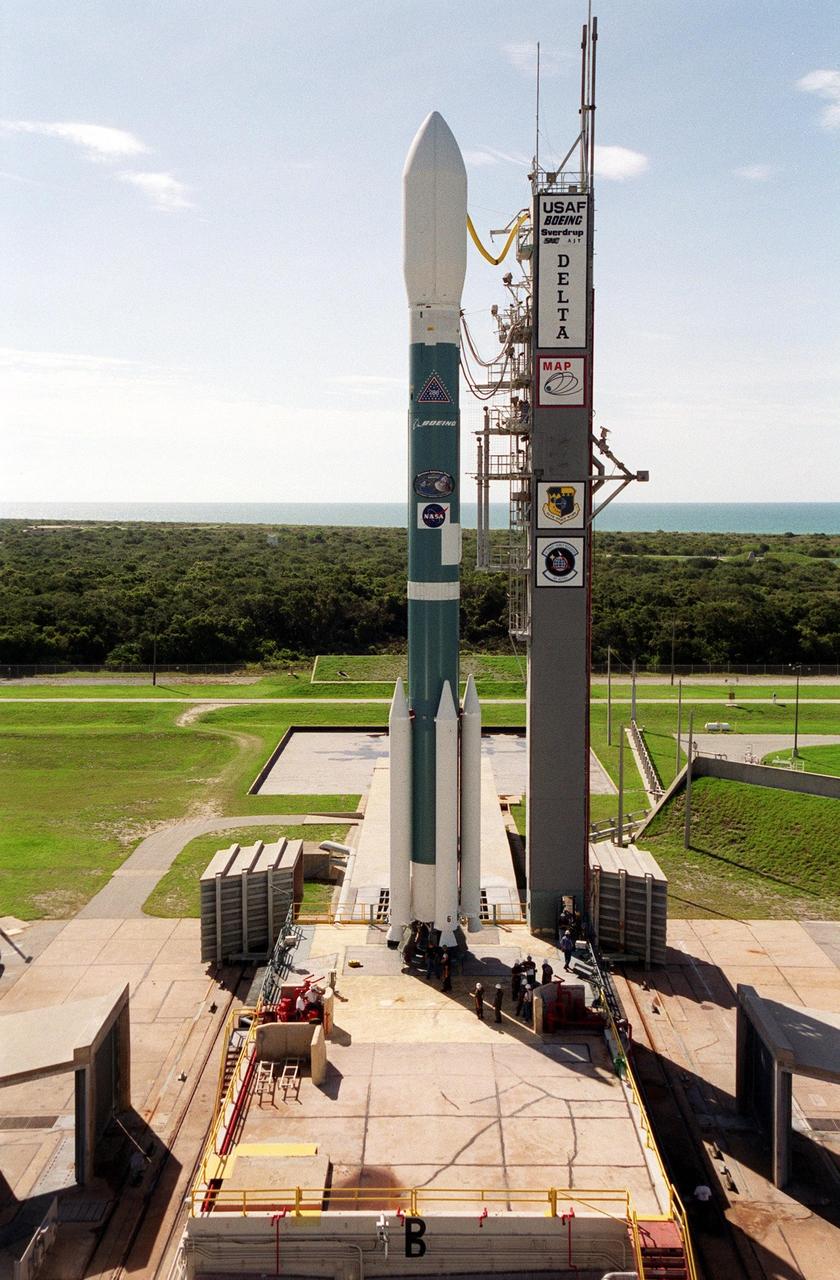

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The morning sky is nearly clear over Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and the waiting Boeing/Delta II rocket. The Atlantic Ocean can be seen on the horizon. Topping the rocket is the payload, the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. Launch is scheduled at 3:46 p.m. EDT June 30. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University
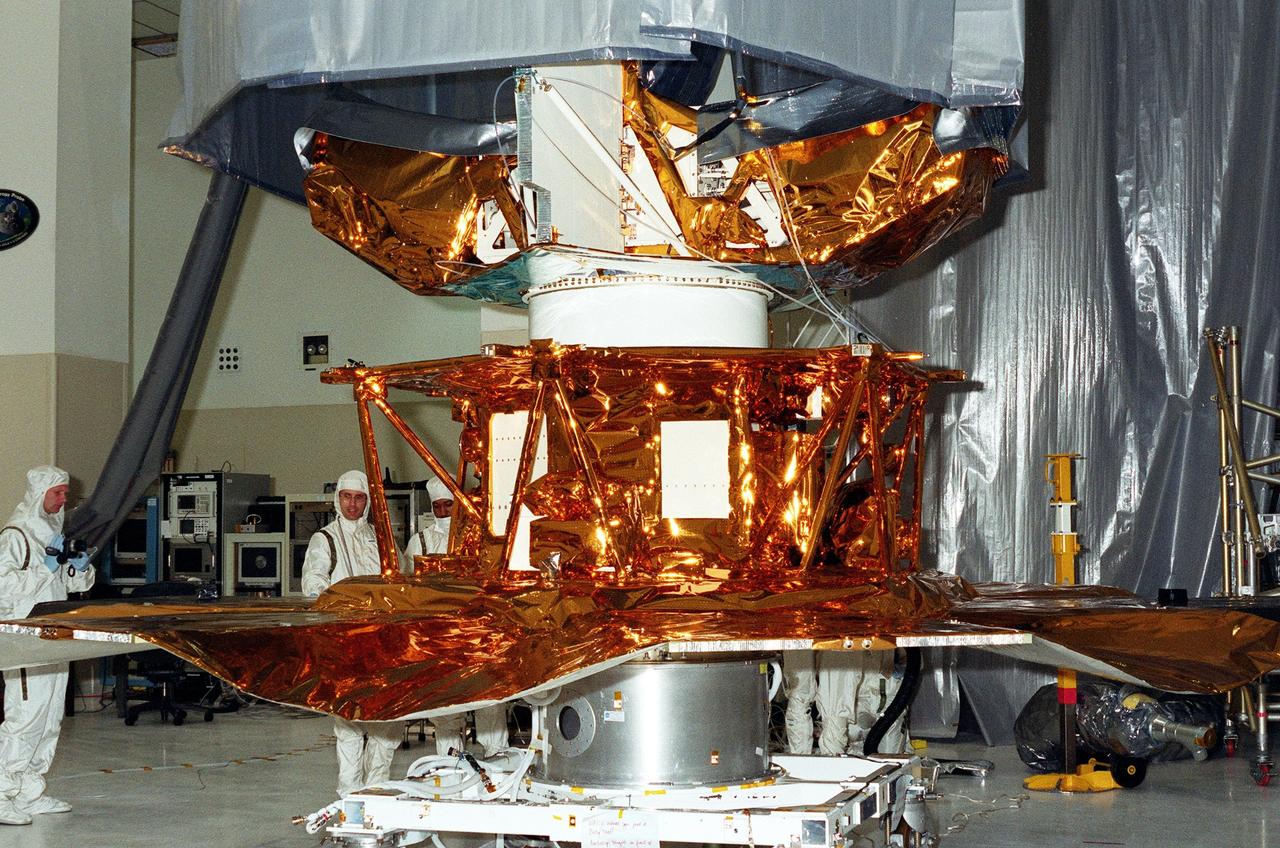
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Scientists and other workers watch as the solar panels on the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft are deployed in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility 2. MAP is scheduled for launch on June 30 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University
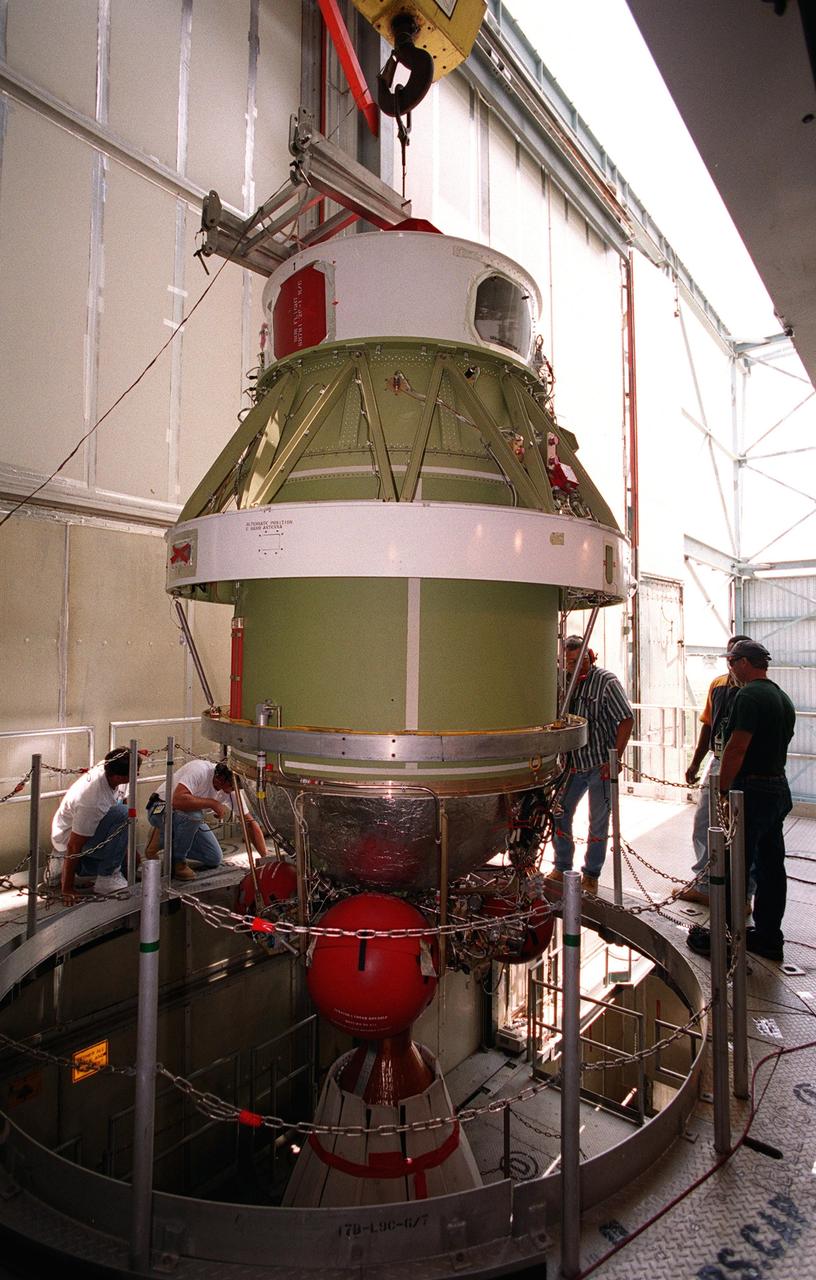

On Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the second stage of a Boeing Delta 7425-10 rocket is lifted into position as preparations to launch NASA's Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) on June 30 continue. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission.; The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Boeing Delta II rocket is poised for flight on Launch Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, after rollback of the Mobile Service Tower. Topping the rocket is the payload, the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. Launch is scheduled at 3:46 p.m. EDT June 30. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft. The probe is a product of Goddard Space Flight Center in partnership with Princeton University

Managed by Marshall Space Flight Center, the Space Tug concept was intended to be a reusable multipurpose space vehicle designed to transport payloads to different orbital inclinations. Utilizing mission-specific combinations of its three primary modules (crew, propulsion, and cargo) and a variety of supplementary kits, the Space Tug was capable of numerous space applications. This 1970 artist's concept illustrates several examples of how the Tug's propulsion module could be implemented to support missions such as landing large payloads on a lunar surface, returning crew and cargo to lunar orbit, launching planetary probes from Earth orbit, and space station support.The Space Tug program was cancelled and did not become a reality.
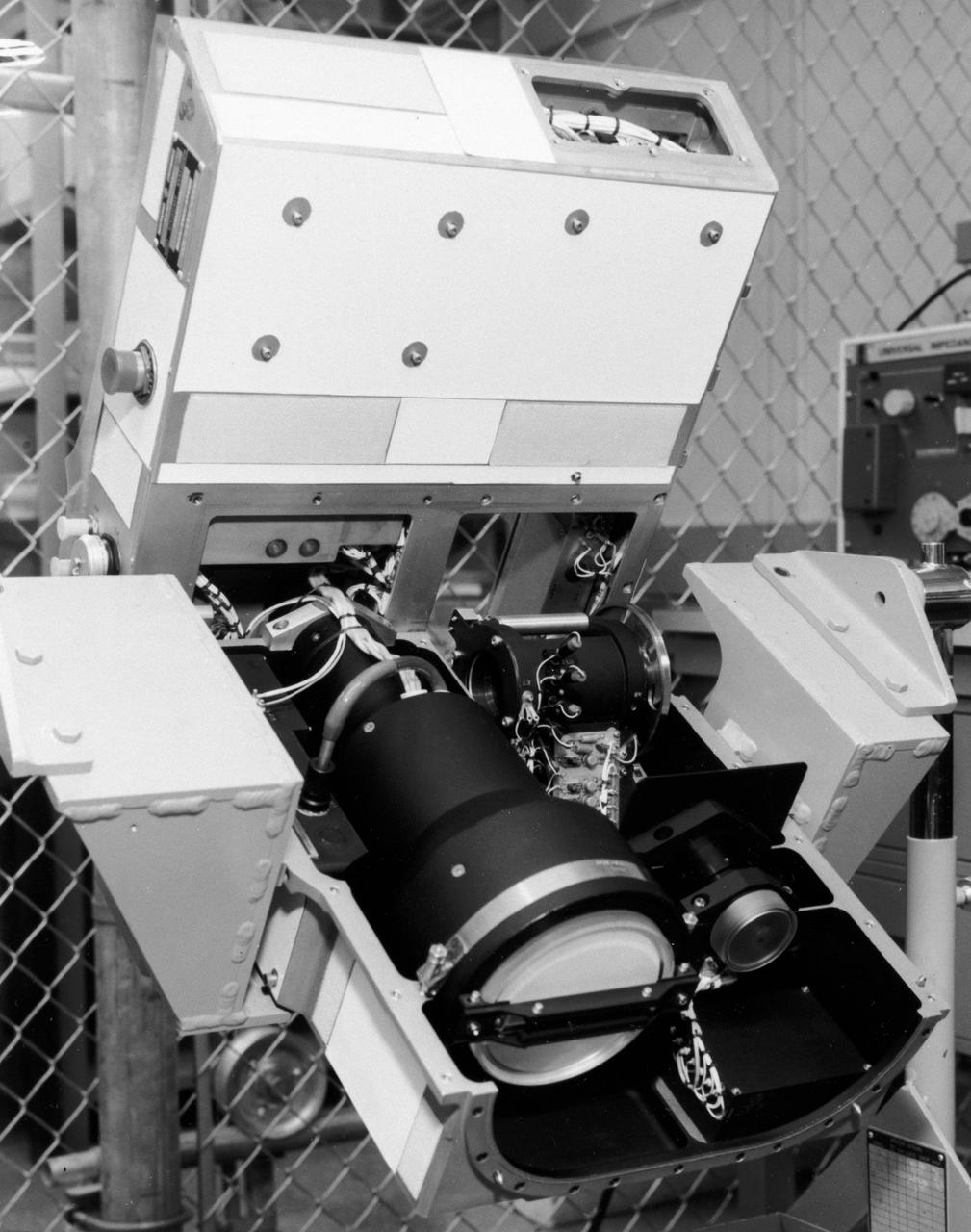

S72-49482 (November 1972) --- The Optical Recorder of the Lunar Sounder Experiment (S-209) which will be mounted in the SIM bay of the Apollo 17 Service Module. The three functional parts of the Lunar Sounder are the optical recorder, the coherent synthetic aperture radar, and the antennas, a retractable dipole for HF and a yagi for VHF. The Lunar Sounder will probe three-quarters of a mile below the moon's surface from the orbiting Apollo 17 spacecraft. Electronic data recorded on film will be retrieved by the crew during trans-Earth EVA. Geologic information on the lunar interior obtained by the sounder will permit scientific investigation of underground rock layers, lava flow patterns, rille (canyon) structures, mascon properties, and any areas containing water. A prototype lunar sounder has been flight tested in aircraft over selected Earth sites to confirm the equipment design and develop scientific analysis techniques. The Lunar Sounder Experiment was developed by North American Rockwell's (NR) Space Division for NASA's Manned Spacecraft Center to provide data for a scientific investigation team with representatives from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, University of Utah, University of Michigan, U.S. Geological Survey, and NASA Ames Research Center.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft are attached to the spacecraft adapter ring in their launch configuration in Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. Preparations are under way to transport the lunar probes to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This 3-D image shows NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory lunar spacecraft attached to the spacecraft adapter ring in their launch configuration in Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. To view this image, use green and magenta 3-D glasses. Preparations are under way to transport the lunar probes to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
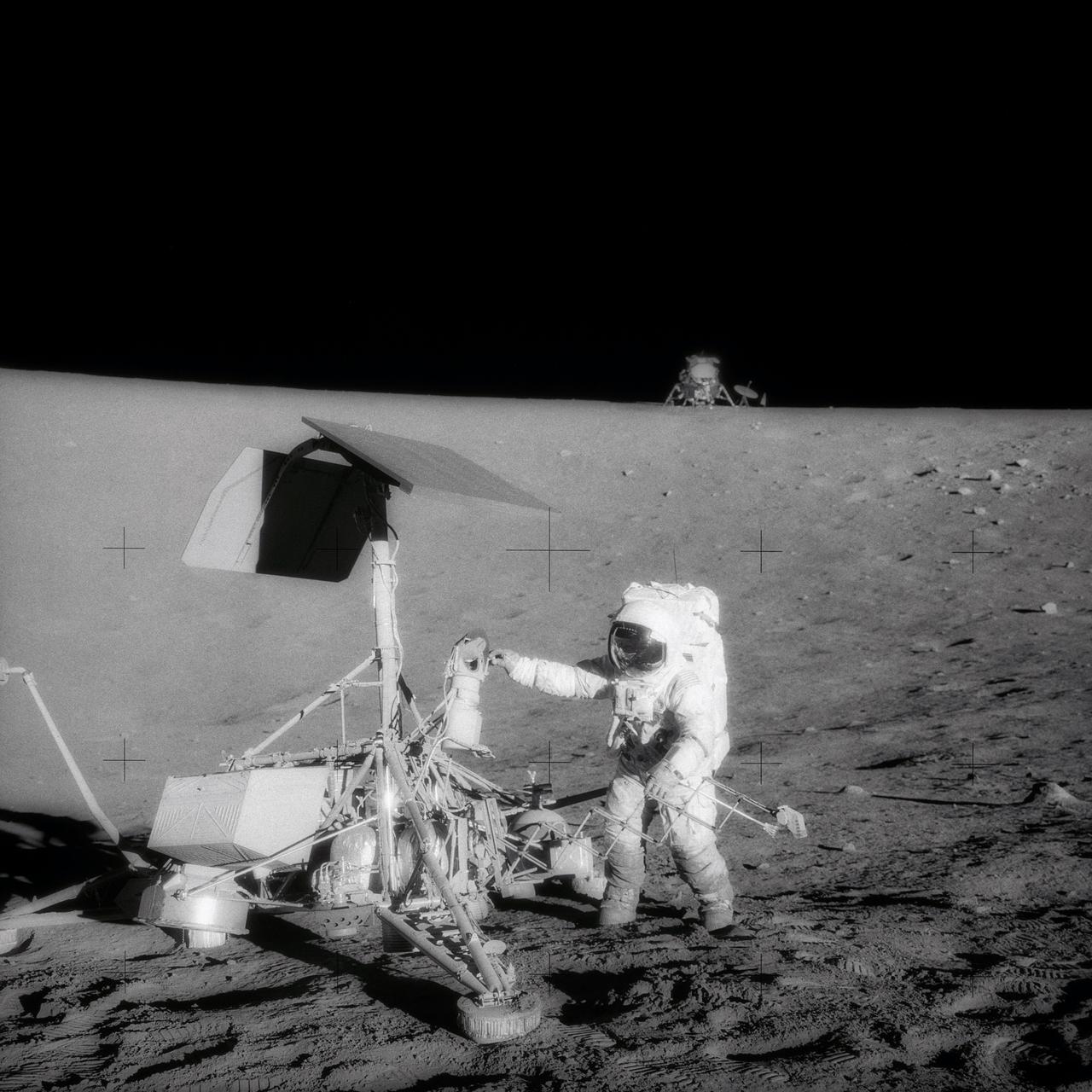
AS12-48-7133 (20 Nov. 1969) --- This unusual photograph, taken during the second Apollo 12 extravehicular activity (EVA), shows two U.S. spacecraft on the surface of the moon. The Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM) is in the background. The unmanned Surveyor 3 spacecraft is in the foreground. The Apollo 12 LM, with astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. and Alan L. Bean aboard, landed about 600 feet from Surveyor 3 in the Ocean of Storms. The television camera and several other pieces were taken from Surveyor 3 and brought back to Earth for scientific examination. Here, Conrad examines the Surveyor's TV camera prior to detaching it. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr. remained with the Apollo 12 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while Conrad and Bean descended in the LM to explore the moon. Surveyor 3 soft-landed on the moon on April 19, 1967.

Managed by Marshall Space Flight Center, the Space Tug was a reusable multipurpose space vehicle designed to transport payloads to different orbital inclinations. Utilizing mission-specific combinations of its three primary modules (crew, propulsion, and cargo) and a variety of supplementary kits, the Space Tug was capable of numerous space applications. This 1970 artist's concept depicts the Tug's propulsion module launching a space probe into lunar orbit.
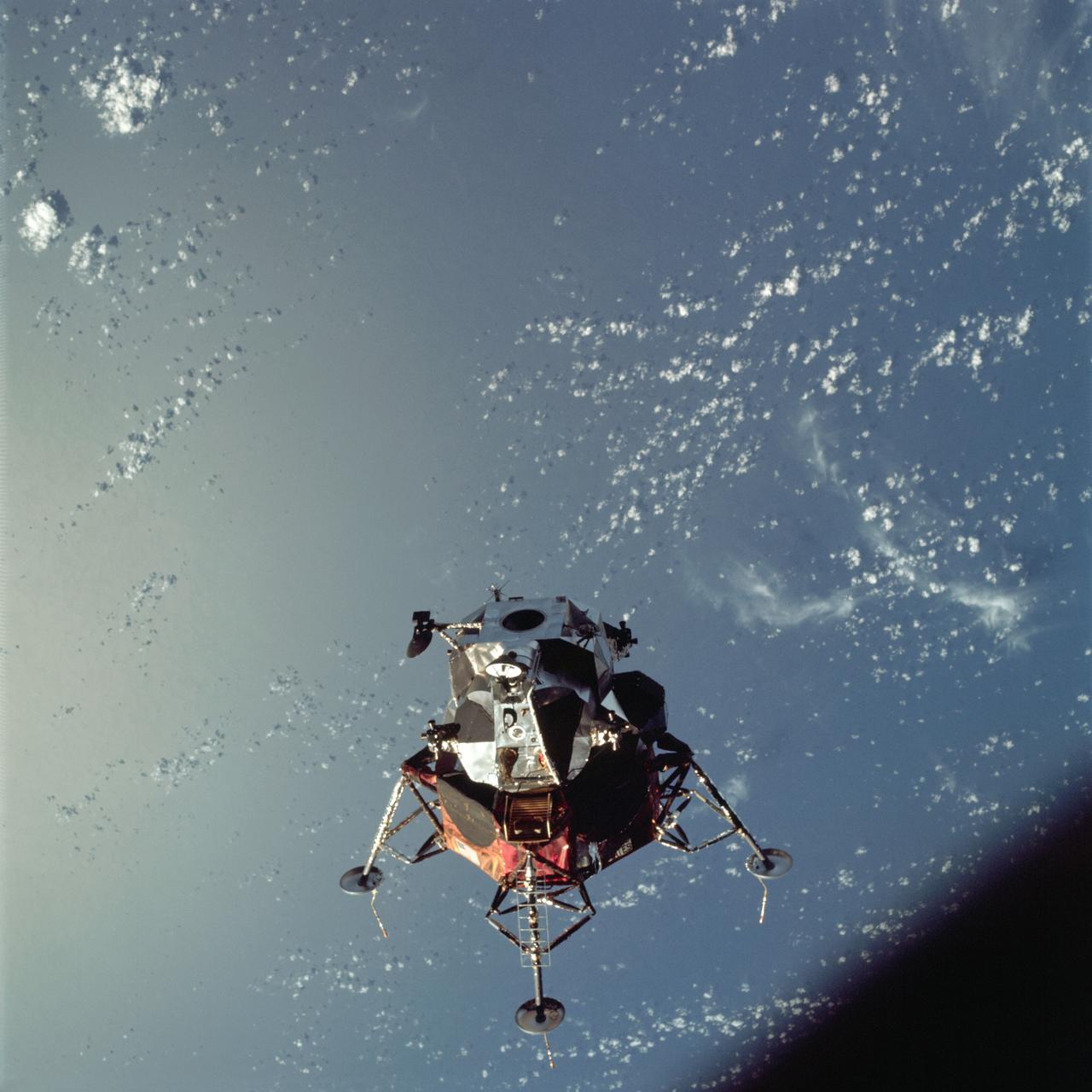

AS09-21-3183 (7 March 1969) --- A view of the Apollo 9 Lunar Module (LM) "Spider" in a lunar landing configuration, as photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The landing gear on the "Spider" has been deployed. Lunar surface probes (sensors) extend out from the landing gear foot pads. Inside the "Spider" were astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module (CM), "Gumdrop," while the other two astronauts checked out the LM. Schweickart, lunar module pilot, is photographed from the CM "Gumdrop" during his extravehicular activity (EVA) on the fourth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The CSM is docked with the LM. Astronaut James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander, was inside the LM "Spider." Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the CM.
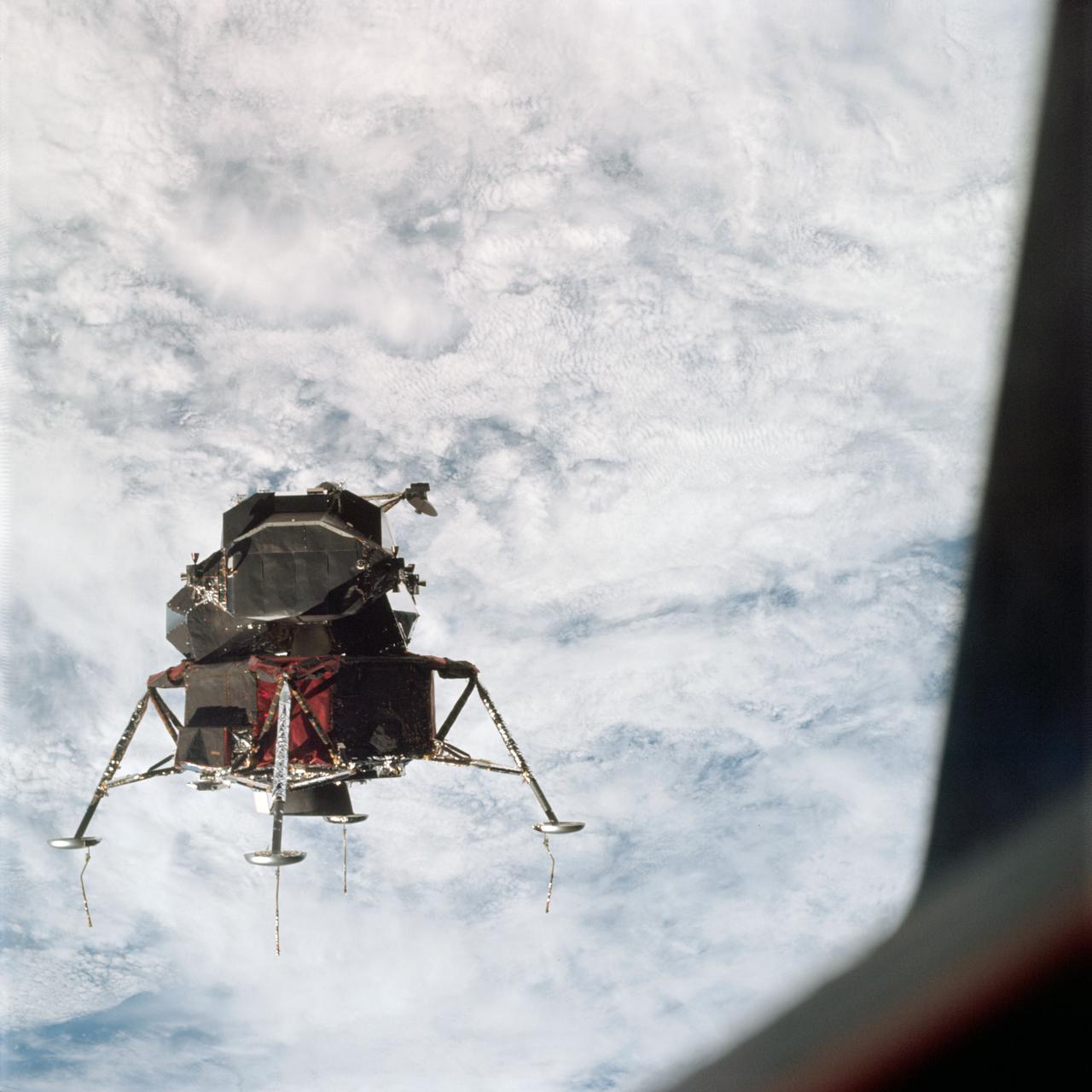

AS09-21-3197 (7 March 1969) --- A view of the Apollo 9 Lunar Module (LM) "Spider" in a lunar landing configuration, as photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The landing gear on the "Spider" has been deployed. Lunar surface probes (sensors) extend out from the landing gear foot pads. Inside the "Spider" were astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module (CM), "Gumdrop," while the other two astronauts checked out the LM. Schweickart, lunar module pilot, is photographed from the CM "Gumdrop" during his extravehicular activity (EVA) on the fourth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The CSM is docked with the LM. Astronaut James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander, was inside the LM "Spider." Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the CM.
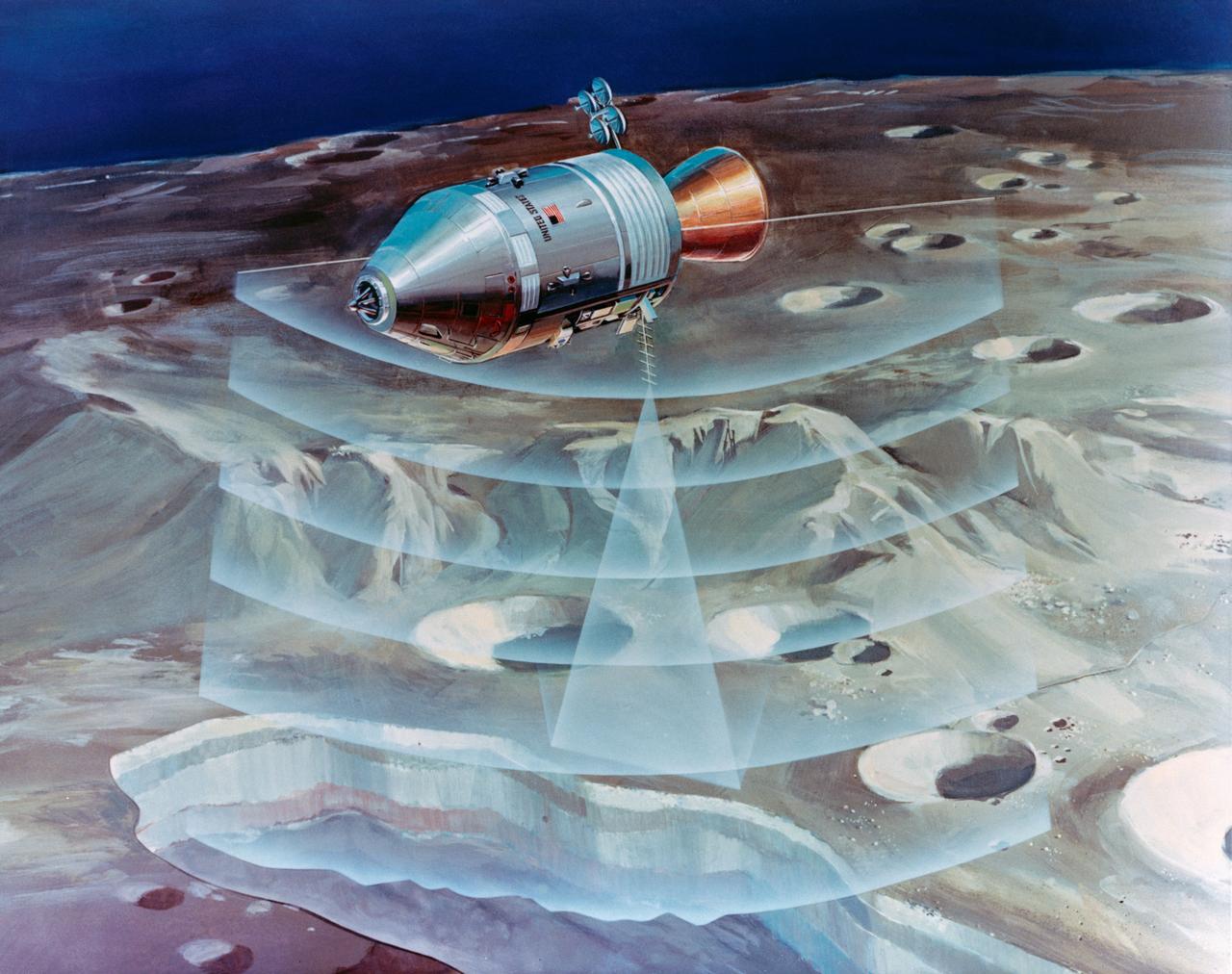

S72-53472 (November 1972) --- An artist's concept illustrating how radar beams of the Apollo 17 lunar sounder experiment will probe three-quarters of a mile below the moon's surface from the orbiting spacecraft. The Lunar Sounder will be mounted in the SIM bay of the Apollo 17 Service Module. Electronic data recorded on film will be retrieved by the crew during trans-Earth EVA. Geologic information on the lunar interior obtained by the sounder will permit scientific investigation of underground rock layers, lava flow patterns, rille (canyon) structures, mascon properties, and any areas containing water. A prototype lunar sounder has been flight tested in aircraft over selected Earth sites to confirm the equipment design and develop scientific analysis techniques. The Lunar Sounder Experiment (S-209) was developed by North American Rockwell's (NR) Space Division for NASA's Manned Spacecraft Center to provide data for a scientific investigation team with representatives from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, University of Utah, University of Michigan, U.S. Geological Survey, and NASA Ames Research Center.
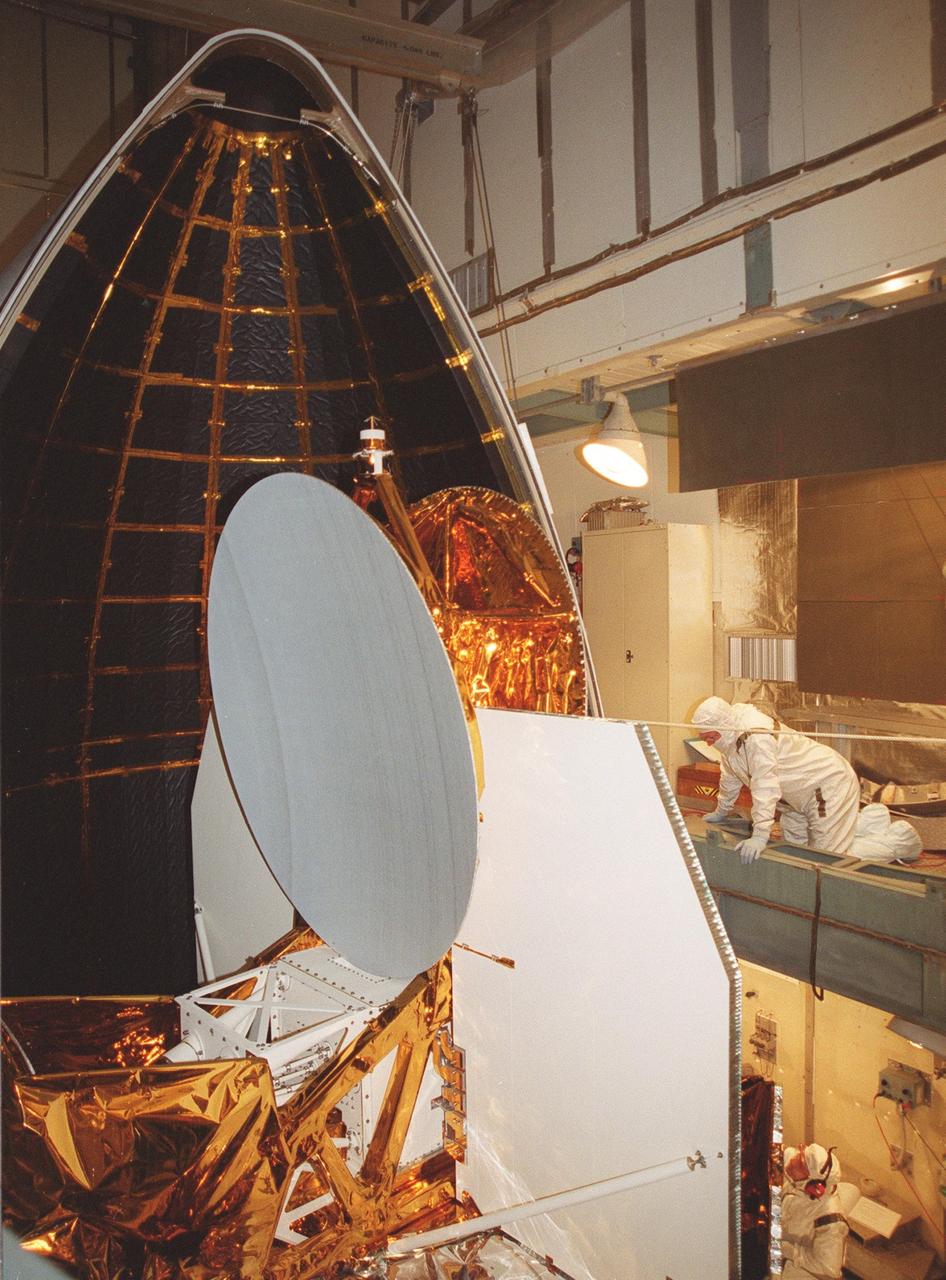
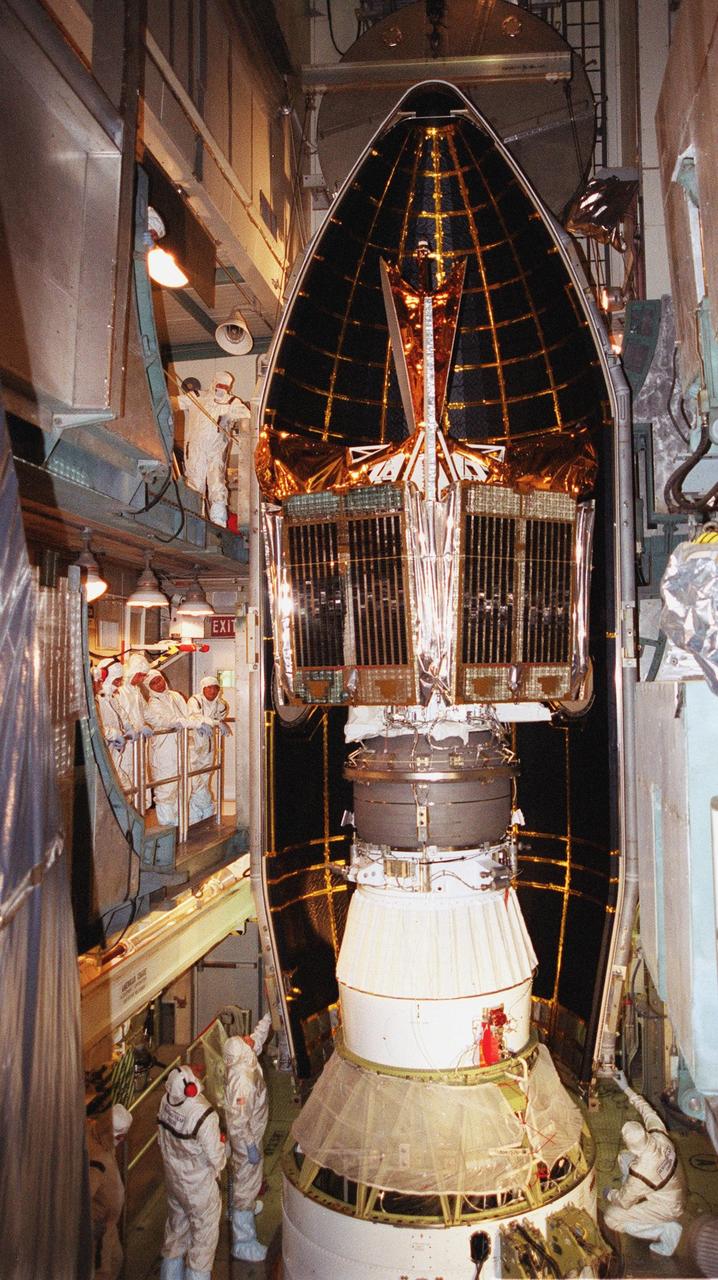
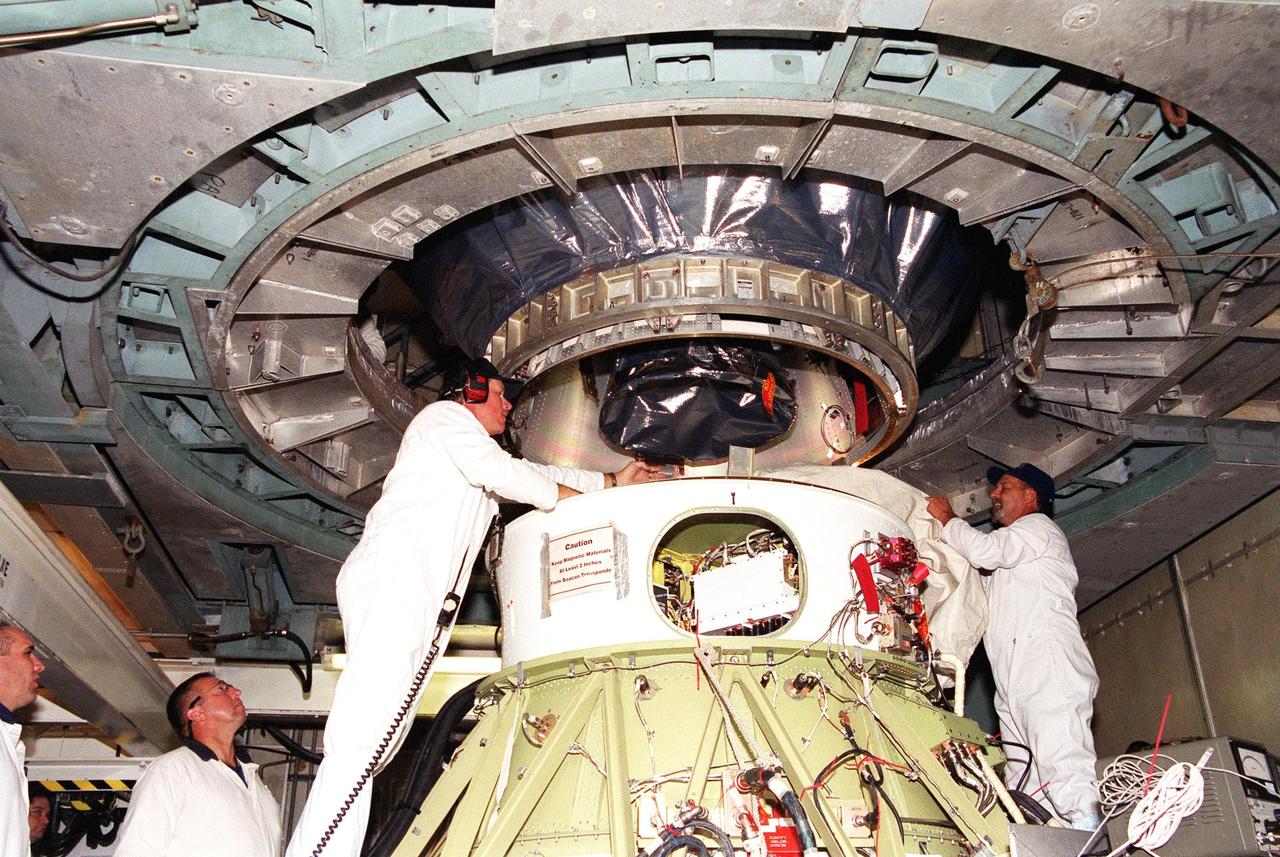
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft is encapsulated with the fairing. With one half already in place (right), the second half (left) moves into position. MAP is scheduled for launch on June 30 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft
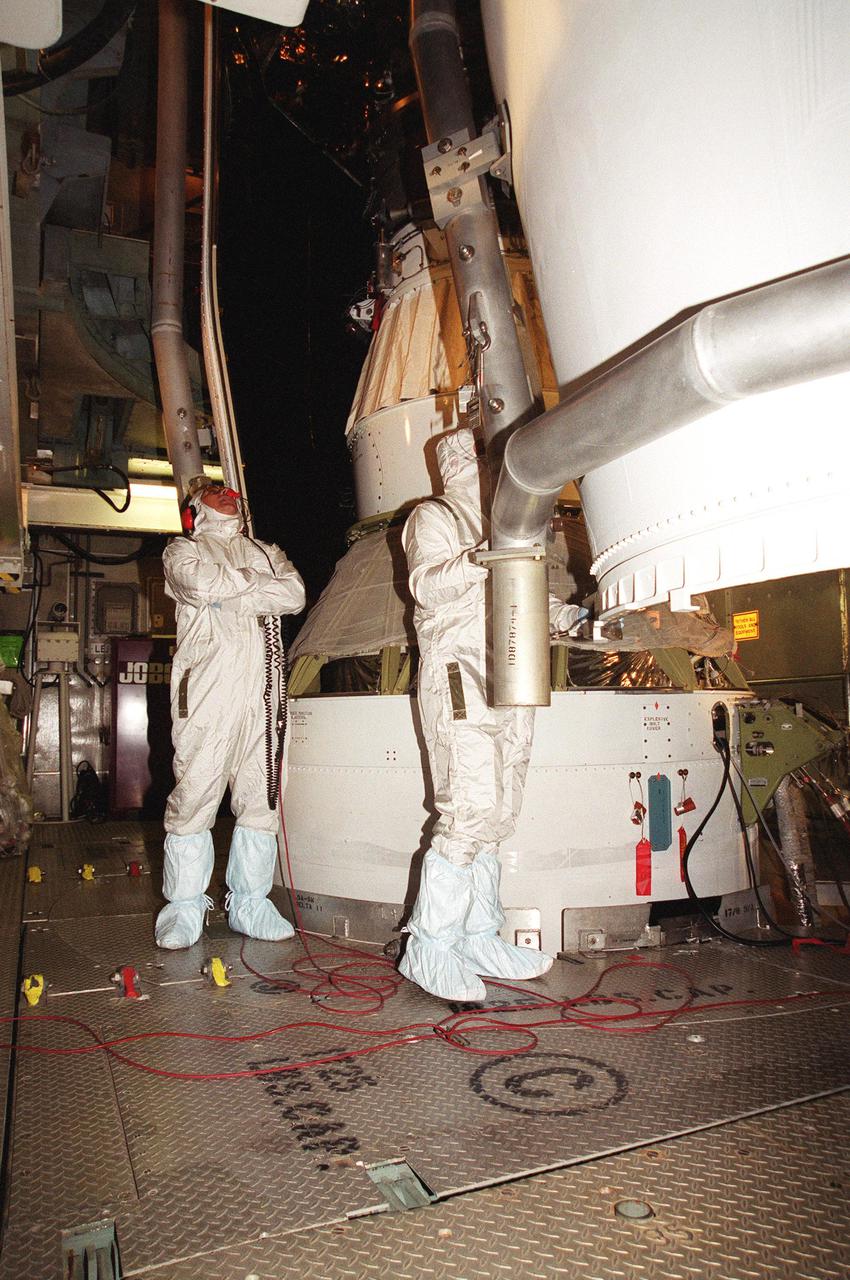

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Workers at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, oversee the fairing installation on the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. MAP is scheduled for launch on June 30 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft
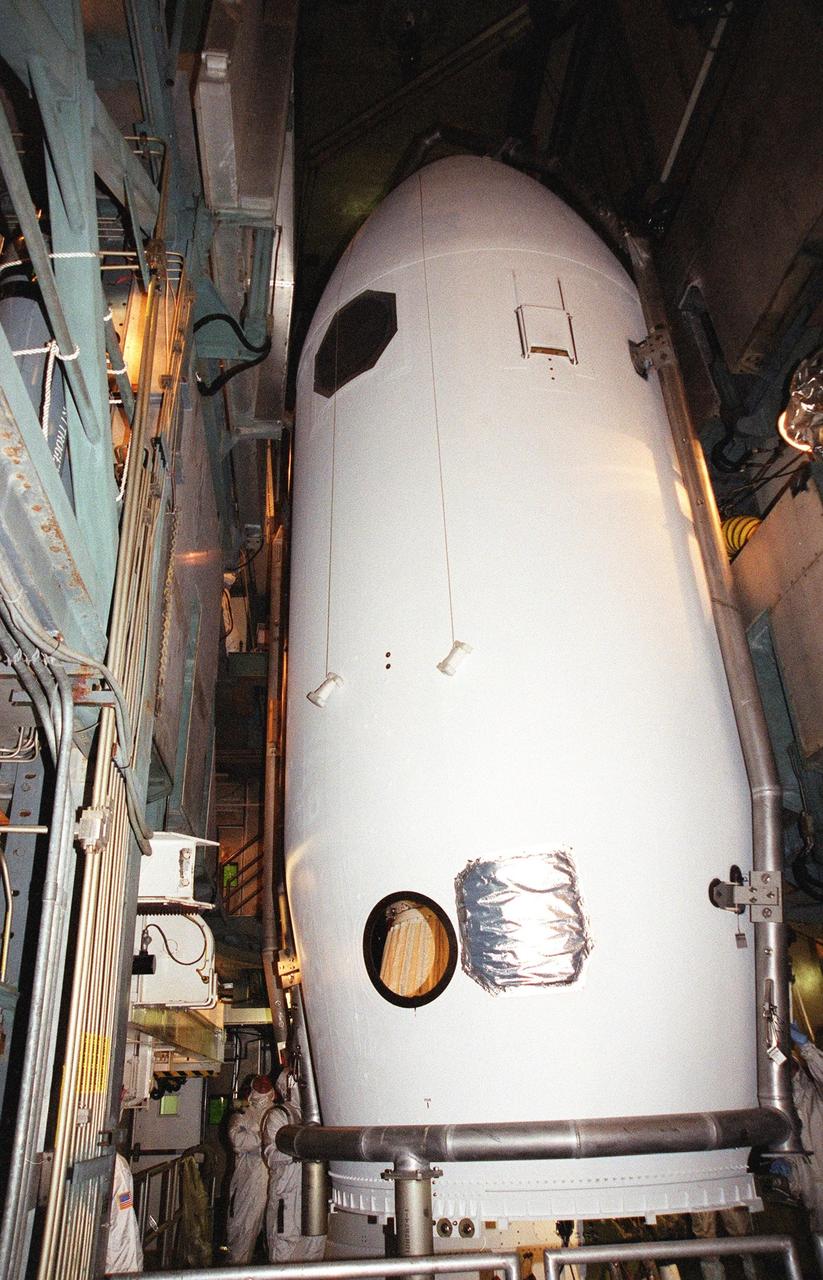
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The fairing closes around the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MAP is scheduled for launch on June 30 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the fairing is moved into position around the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. MAP is scheduled for launch on June 30 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft
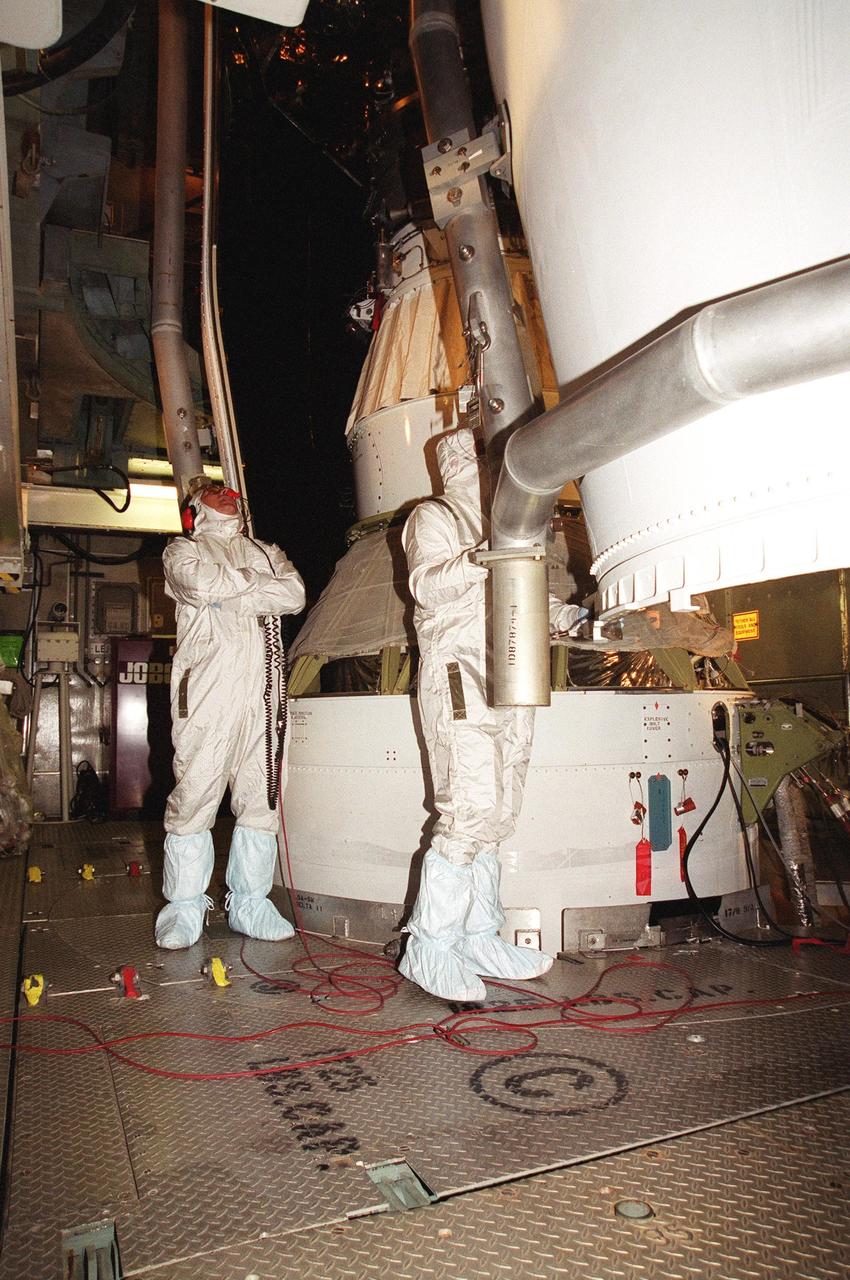

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Workers at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, oversee the fairing installation on the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. MAP is scheduled for launch on June 30 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Workers at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, watch as fairing moves into position around the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft. MAP is scheduled for launch on June 30 aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures. The MAP instrument will be continuously shaded from the Sun, Earth, and Moon by the spacecraft
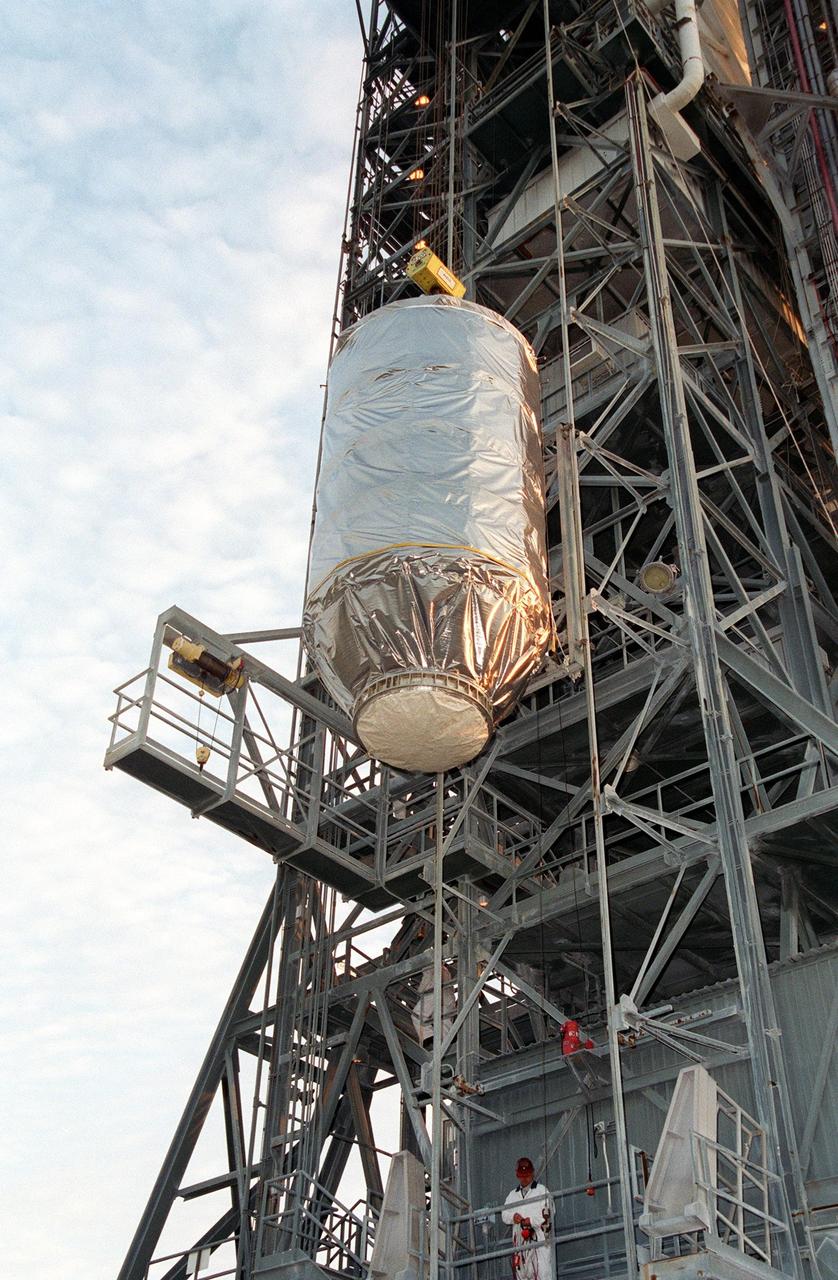

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft is lifted up the gantry on Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, where it will undergo final testing and installation of the payload fairing. Launch of MAP via a Boeing Delta II rocket is scheduled for June 30. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) spacecraft arrives at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. MAP will be lifted up the gantry for final testing and installation of the payload fairing. Launch of MAP via a Boeing Delta II rocket is scheduled for June 30. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures

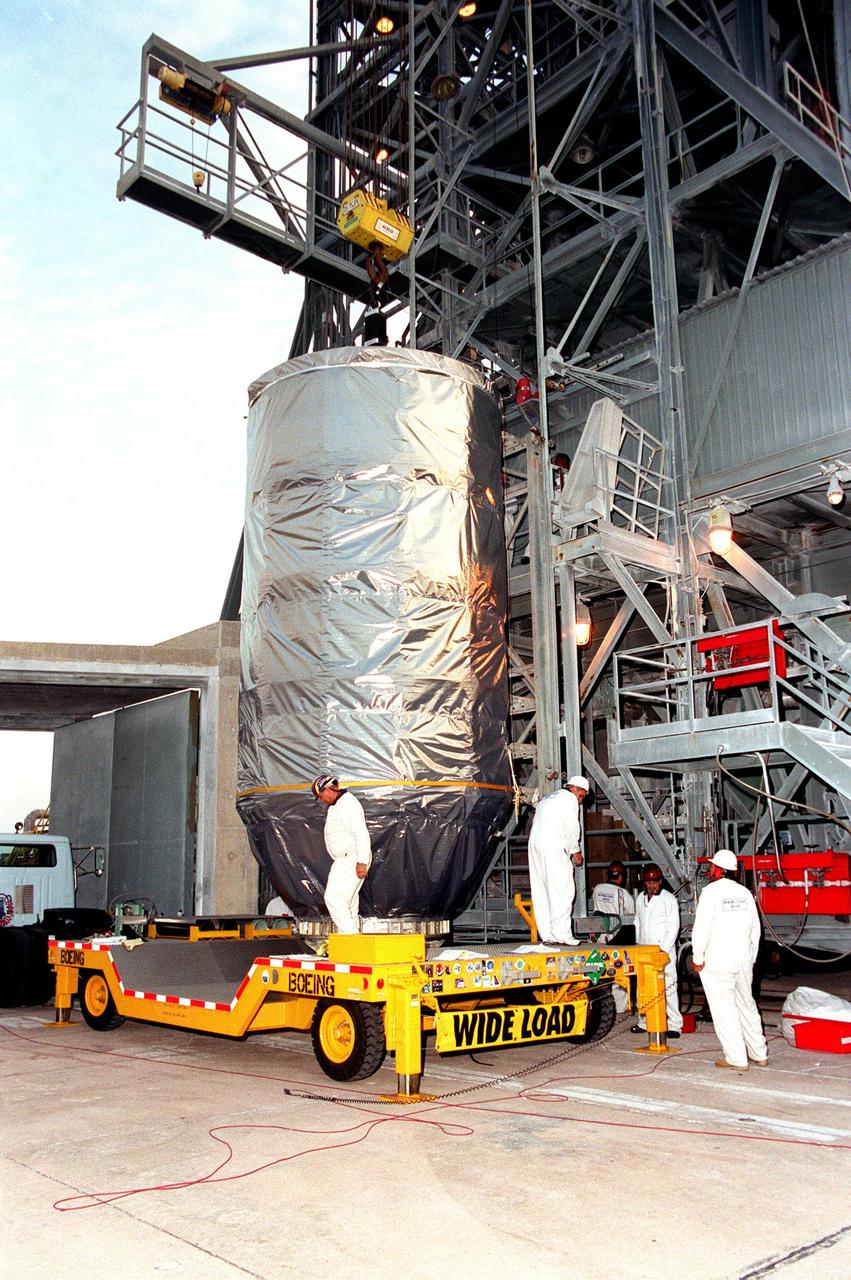
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers keep watch while the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP) is lowered into position on the Delta II rocket below. Launch of MAP via a Boeing Delta II rocket is scheduled for June 30. The launch will place MAP into a lunar-assisted trajectory to the Sun-Earth for a 27-month mission. The probe will measure small fluctuations in the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation to an accuracy of one millionth of a degree. These measurements should reveal the size, matter content, age, geometry and fate of the universe. They will also reveal the primordial structure that grew to form galaxies and will test ideas about the origins of these primordial structures
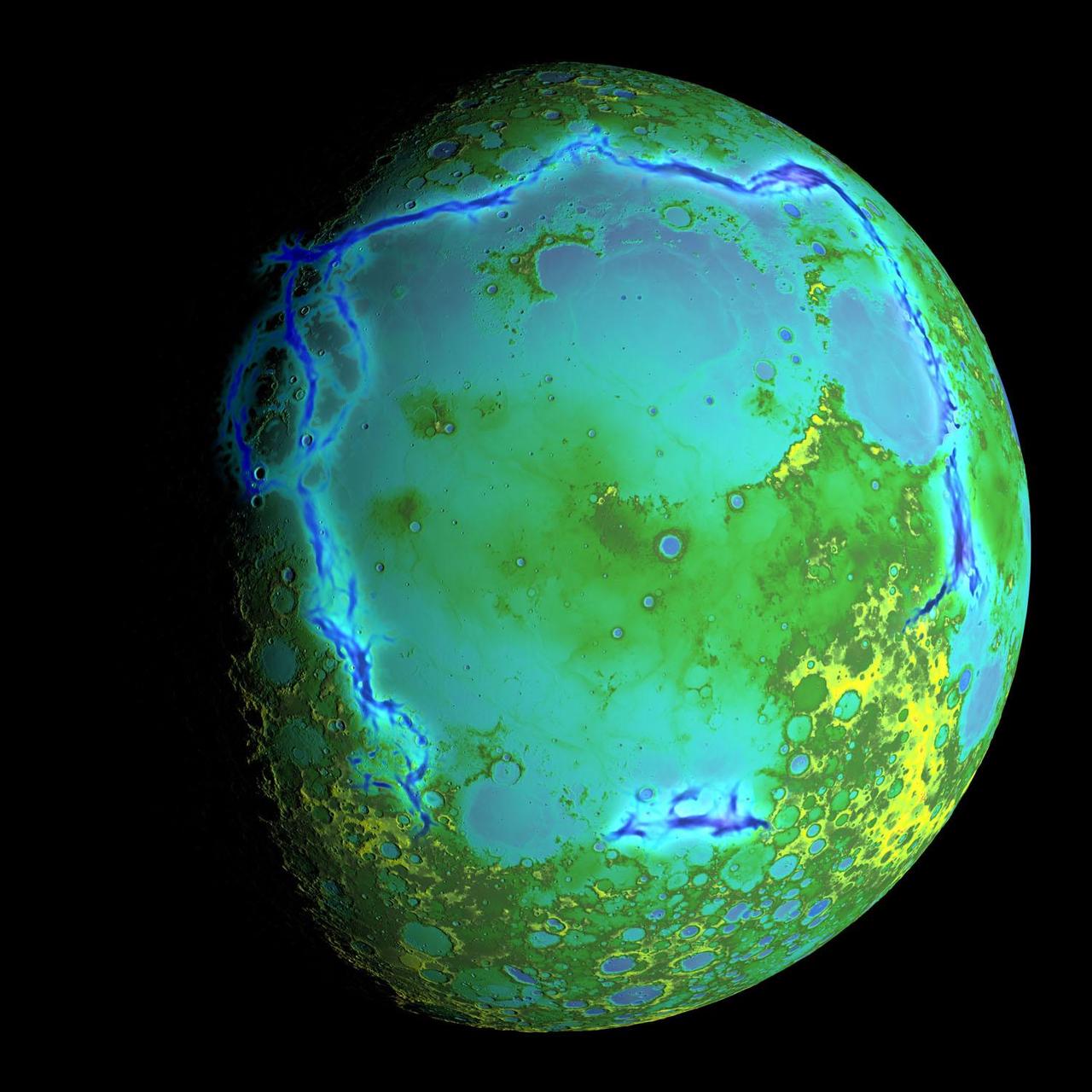
Topography of Earth's moon generated from data collected by the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter, aboard NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, with the gravity anomalies bordering the Procellarum region superimposed in blue. The border structures are shown using gravity gradients calculated with data from NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission. These gravity anomalies are interpreted as ancient lava-flooded rift zones buried beneath the volcanic plains (or maria) on the nearside of the Moon. Launched as GRAIL A and GRAIL B in September 2011, the probes, renamed Ebb and Flow, operated in a nearly circular orbit near the poles of the moon at an altitude of about 34 miles (55 kilometers) until their mission ended in December 2012. The distance between the twin probes changed slightly as they flew over areas of greater and lesser gravity caused by visible features, such as mountains and craters, and by masses hidden beneath the lunar surface. The twin spacecraft flew in a nearly circular orbit until the end of the mission on Dec. 17, 2012, when the probes intentionally were sent into the moon's surface. NASA later named the impact site in honor of late astronaut Sally K. Ride, who was America's first woman in space and a member of the GRAIL mission team. GRAIL's prime and extended science missions generated the highest-resolution gravity field map of any celestial body. The map will provide a better understanding of how Earth and other rocky planets in the solar system formed and evolved. The GRAIL mission was managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The mission was part of the Discovery Program managed at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. GRAIL was built by Lockheed Martin Space Systems in Denver. For more information about GRAIL, please visit <a href="http://grail.nasa.gov" rel="nofollow">grail.nasa.gov</a>. Credit: NASA/Colorado School of Mines/MIT/GSFC/Scientific Visualization Studio
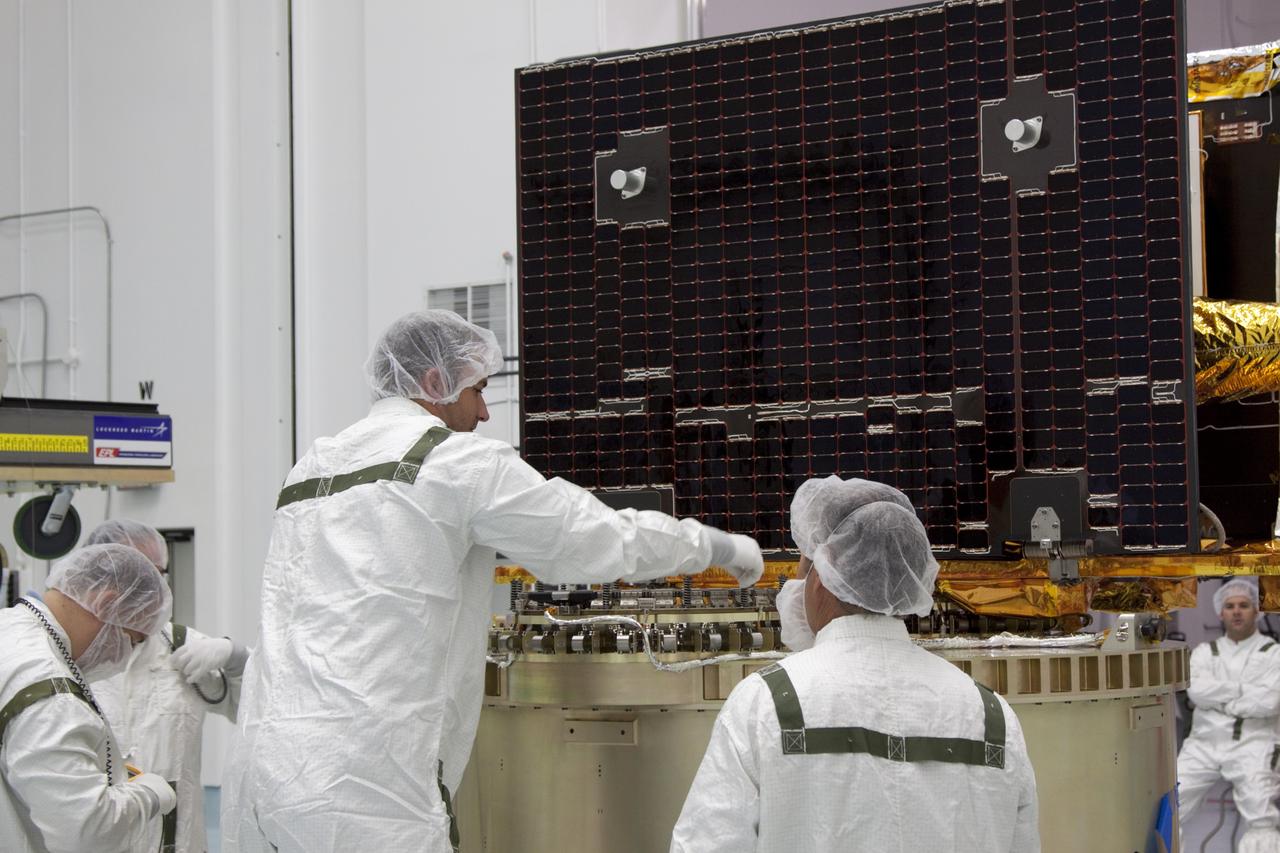

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Lockheed Martin technician secures NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
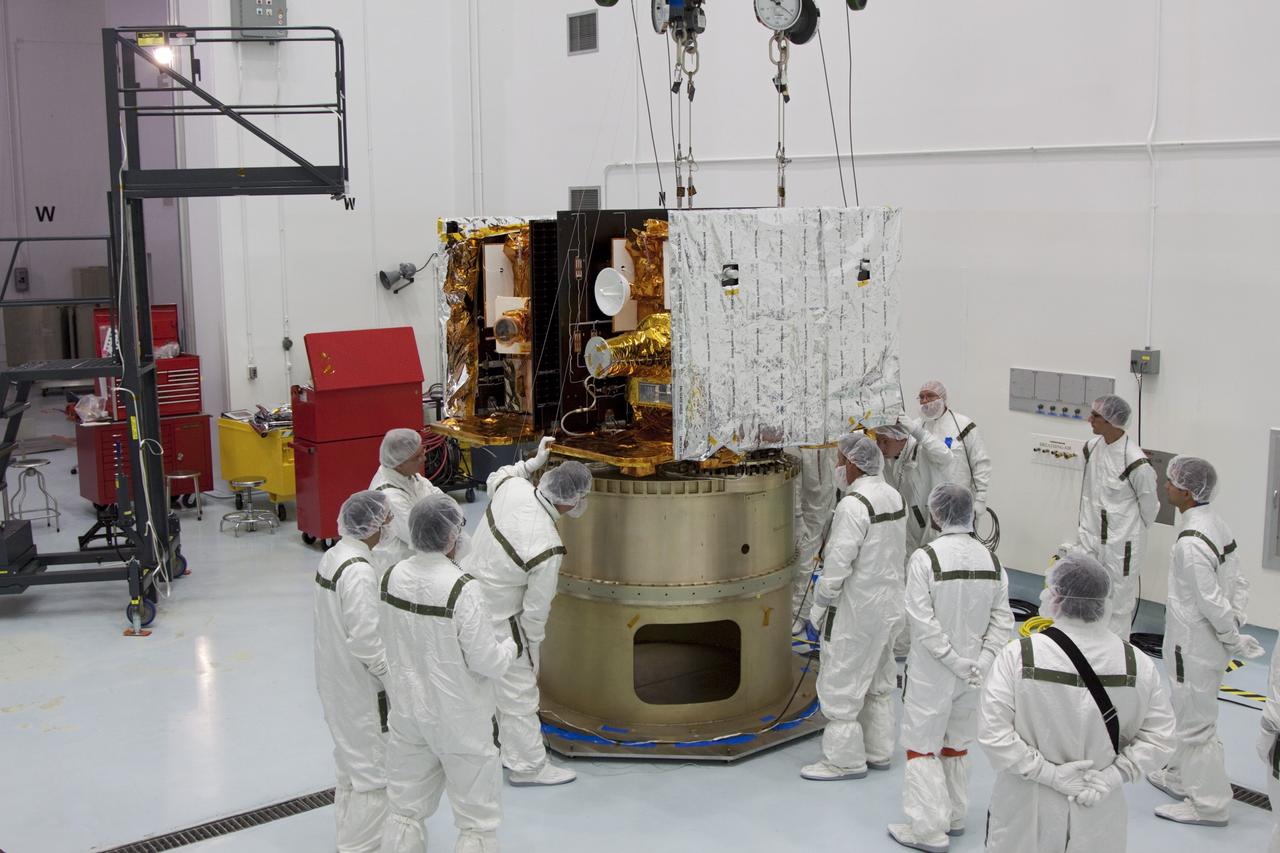

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the placement of NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe on the spacecraft adapter ring. GRAIL-B is already secured to the ring, at left. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
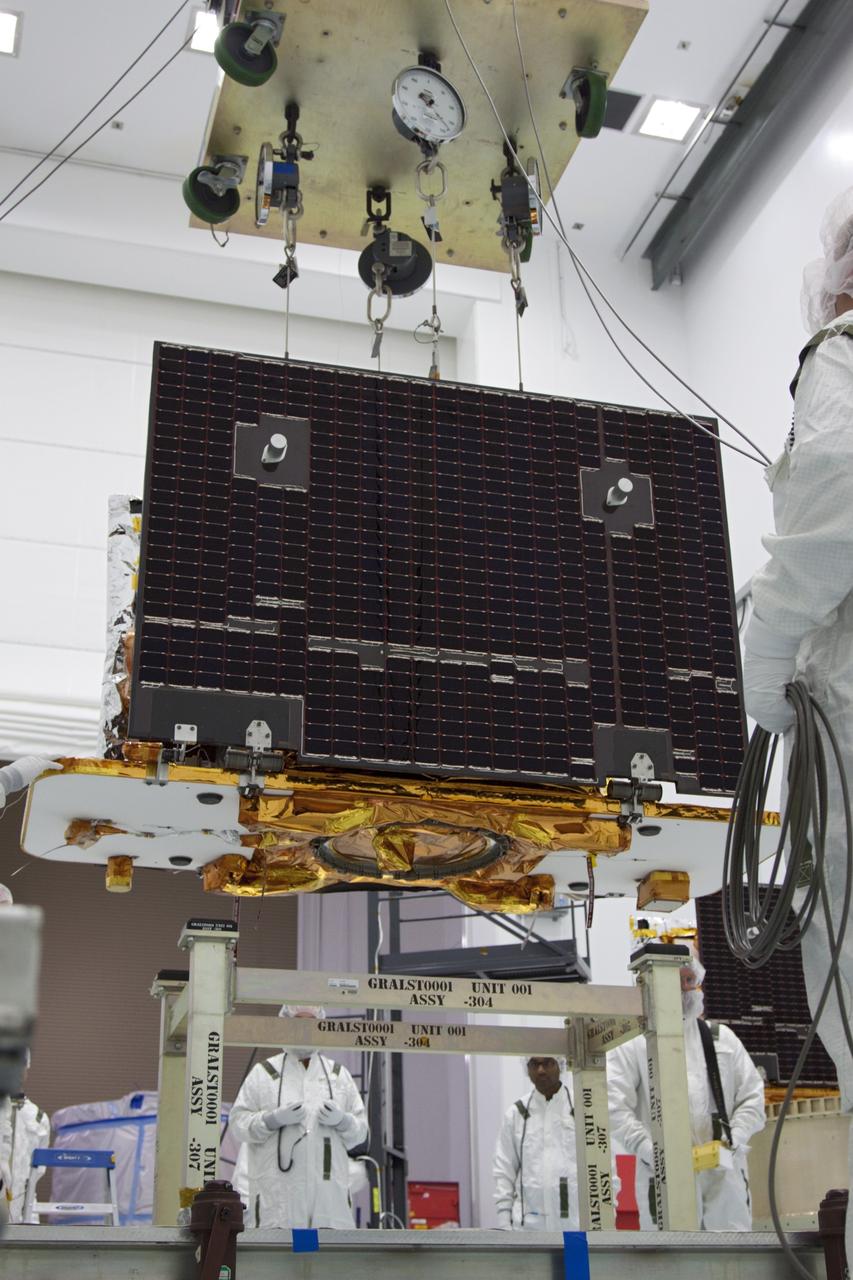

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe is lifted from its workstand. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
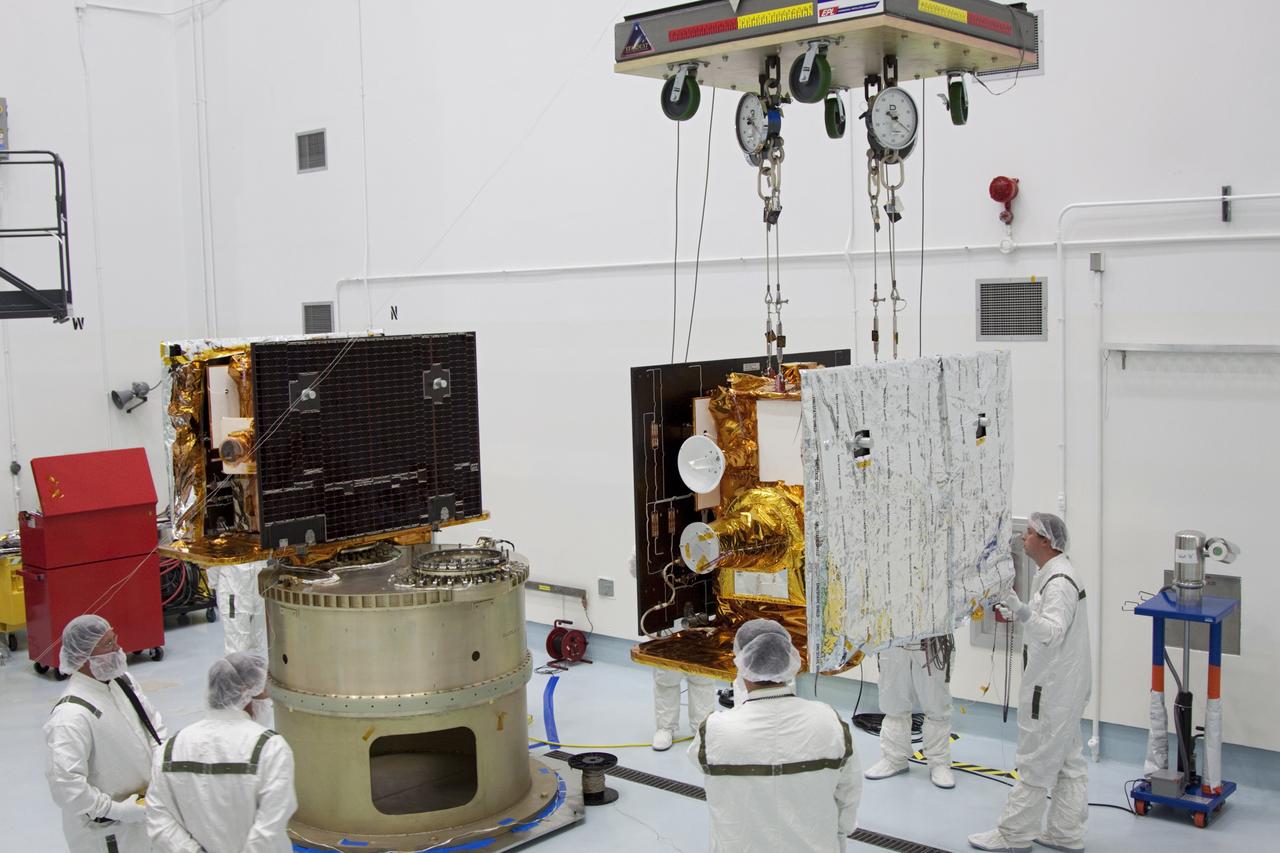

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe slowly approaches the spacecraft adapter ring, at left, where GRAIL-B is already secured. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
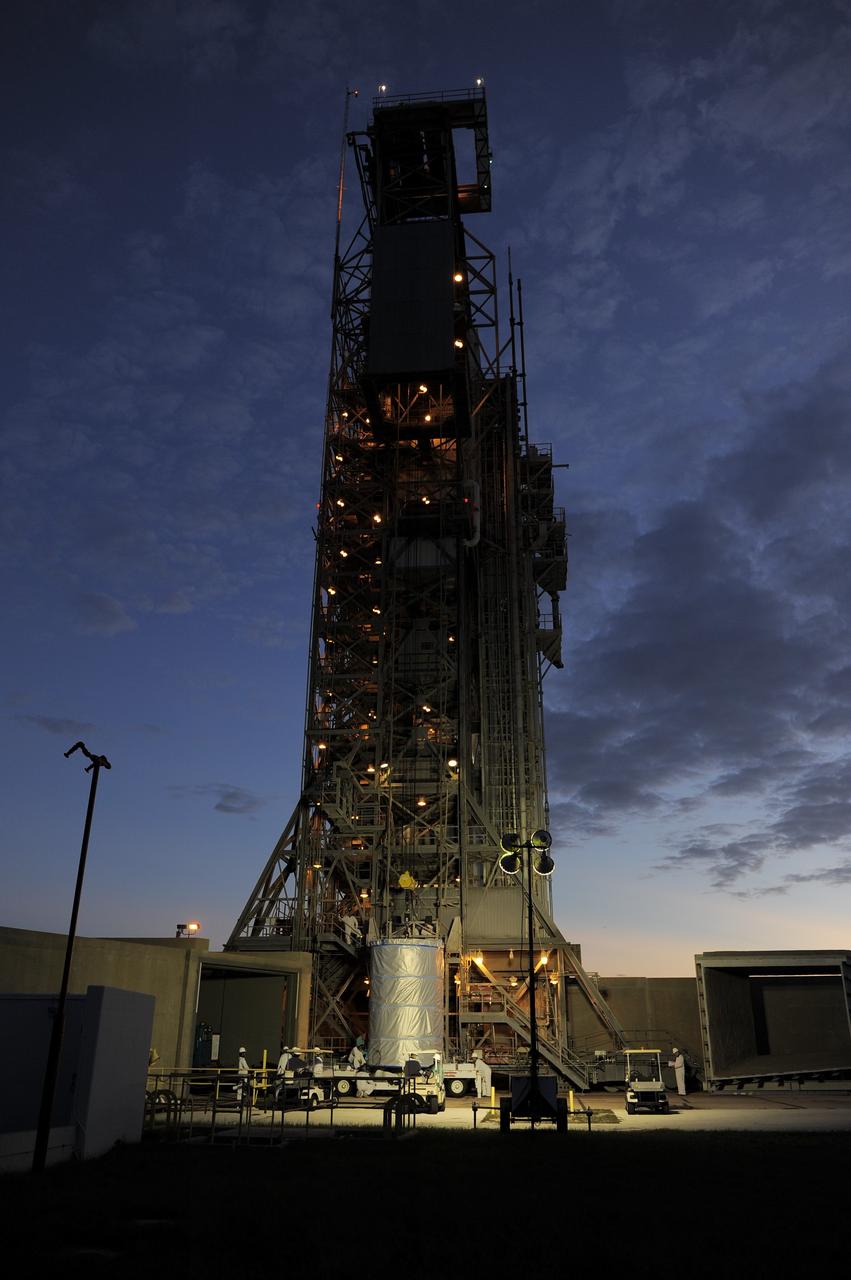

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft are lifted to the top of their launch pad at Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room in the Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
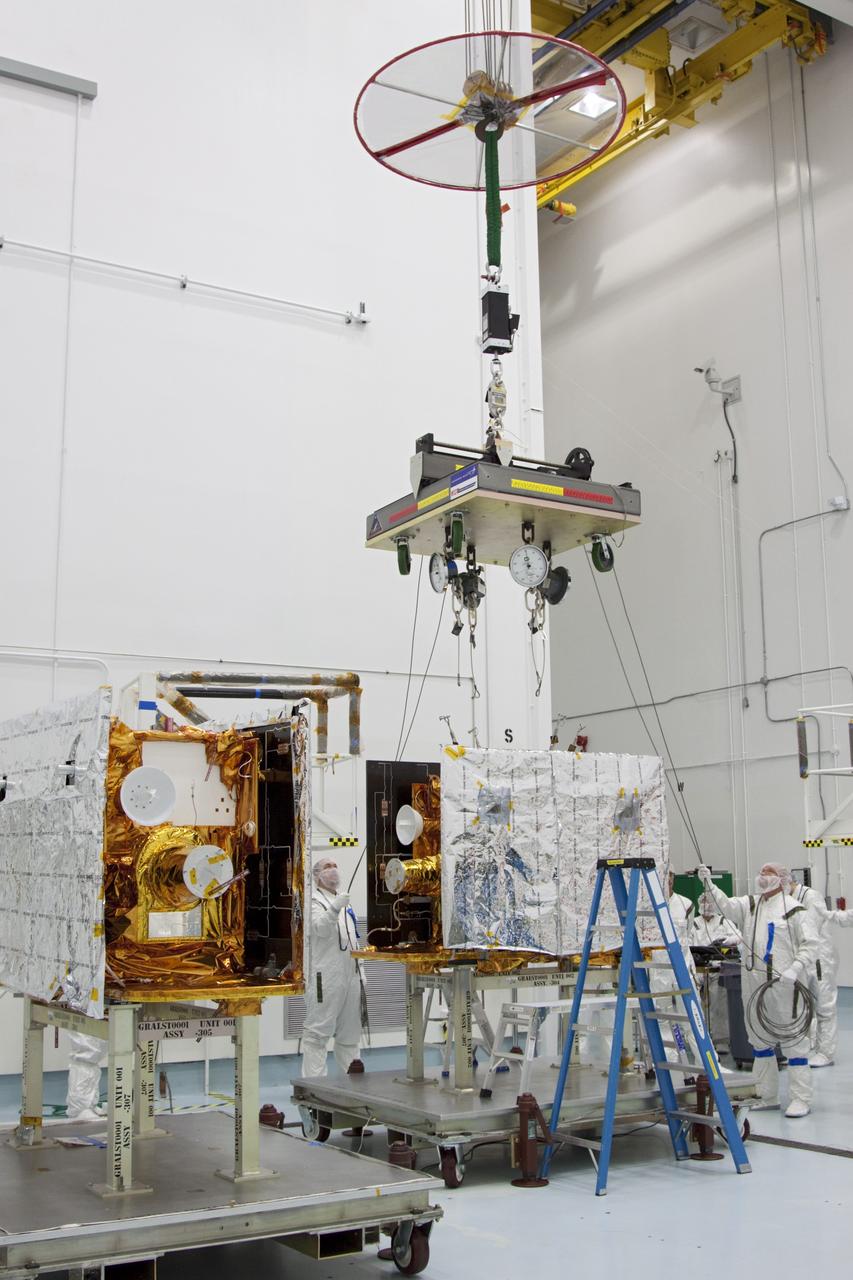

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a lifting device moves into position over NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe. At left is GRAIL-A. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

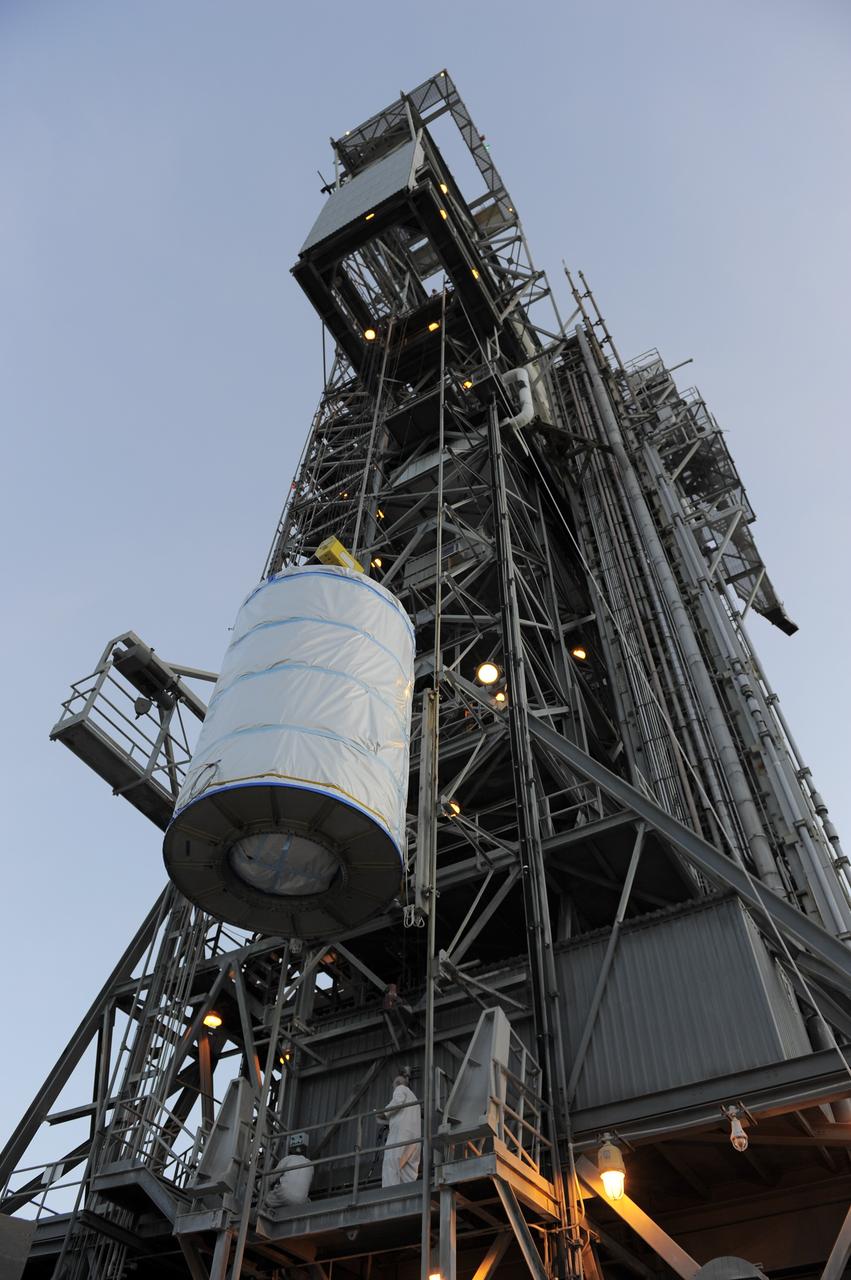
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians lower NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft into place atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket on Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft are lifted to the top of their launch pad at Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room in the Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
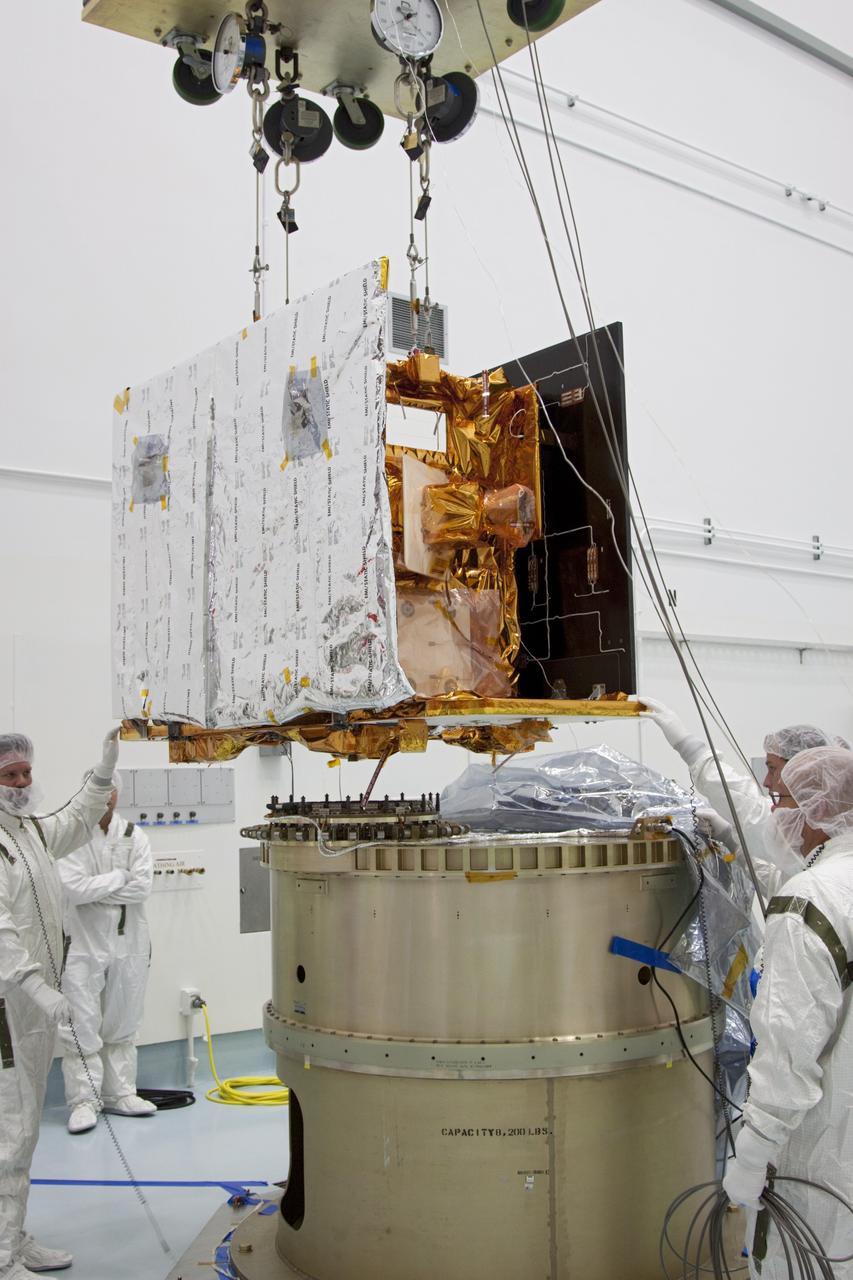

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe is lowered toward the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
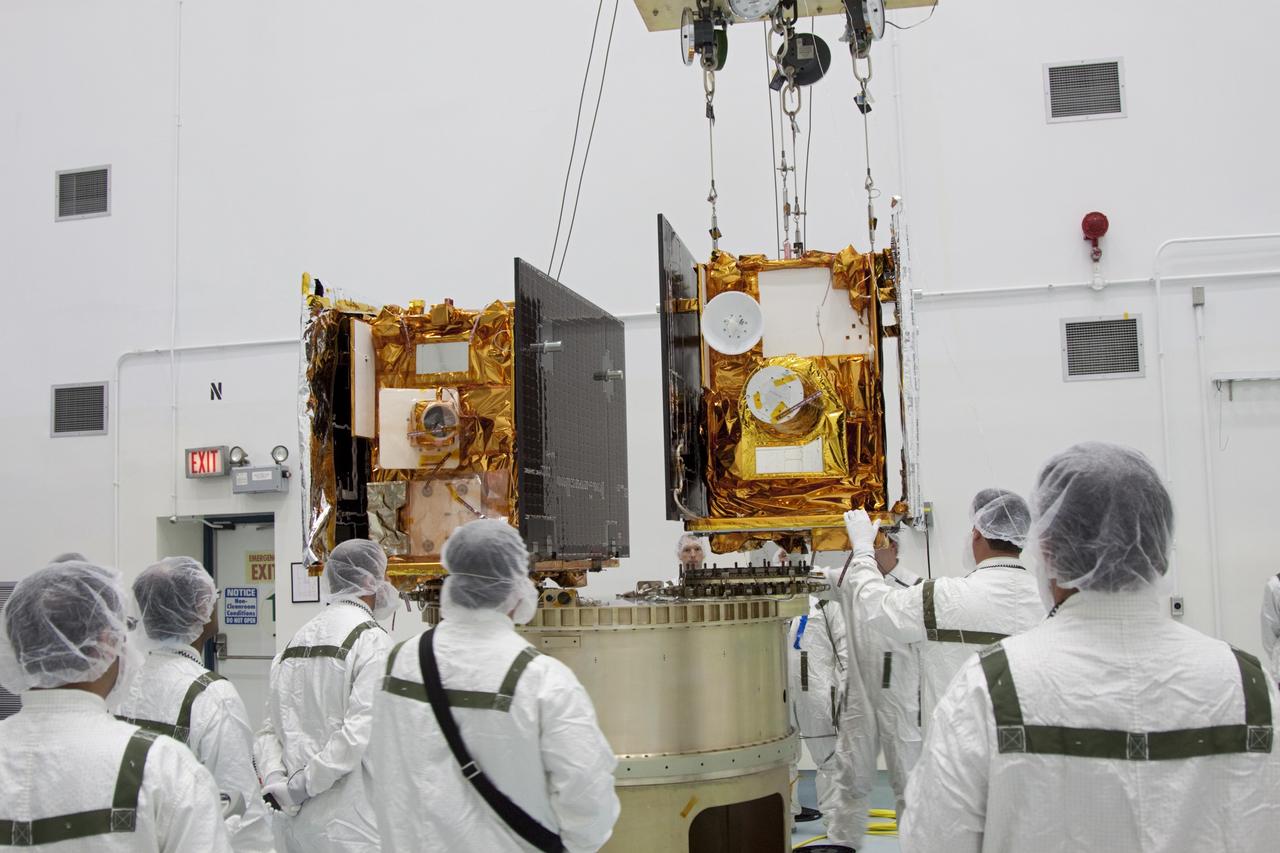

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe us lowered toward the spacecraft adapter ring. GRAIL-B is already secured to the ring, at left. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
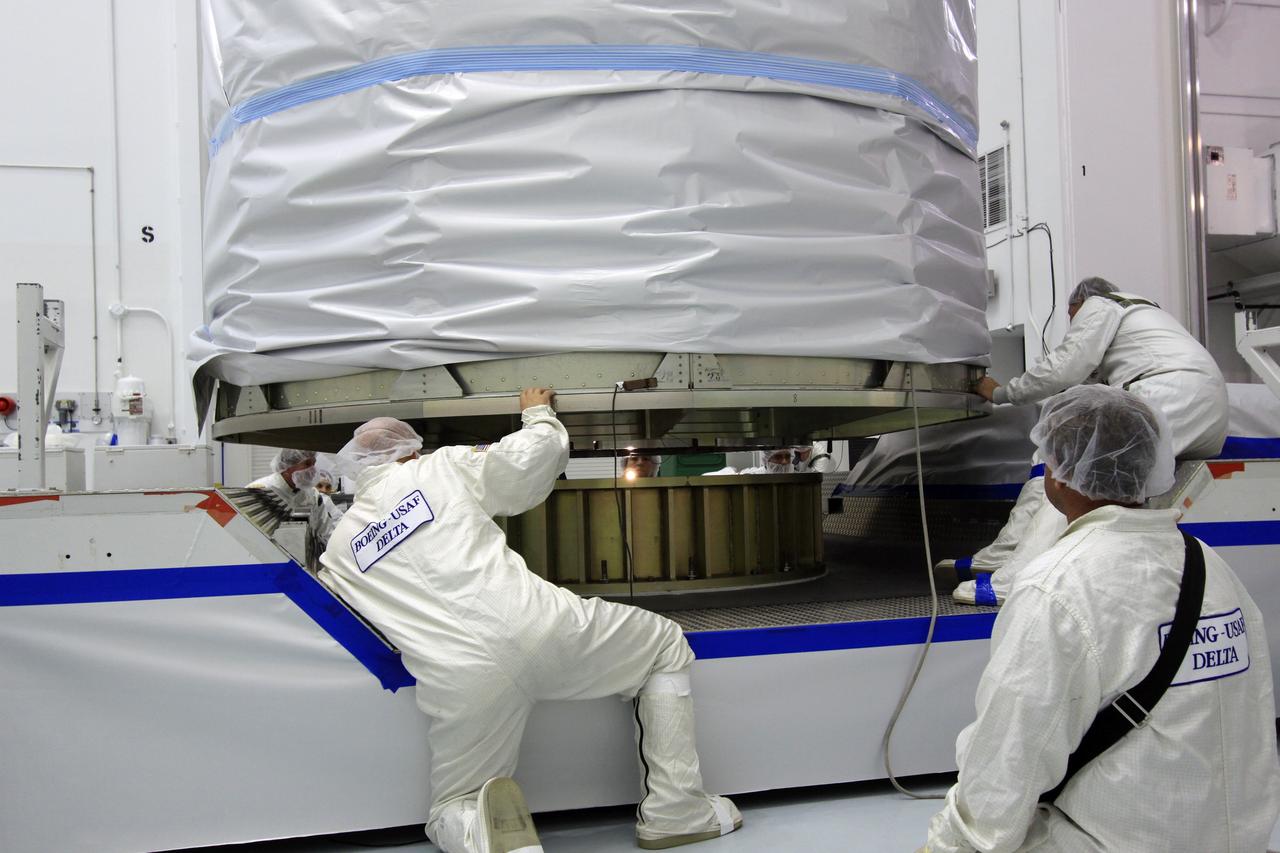

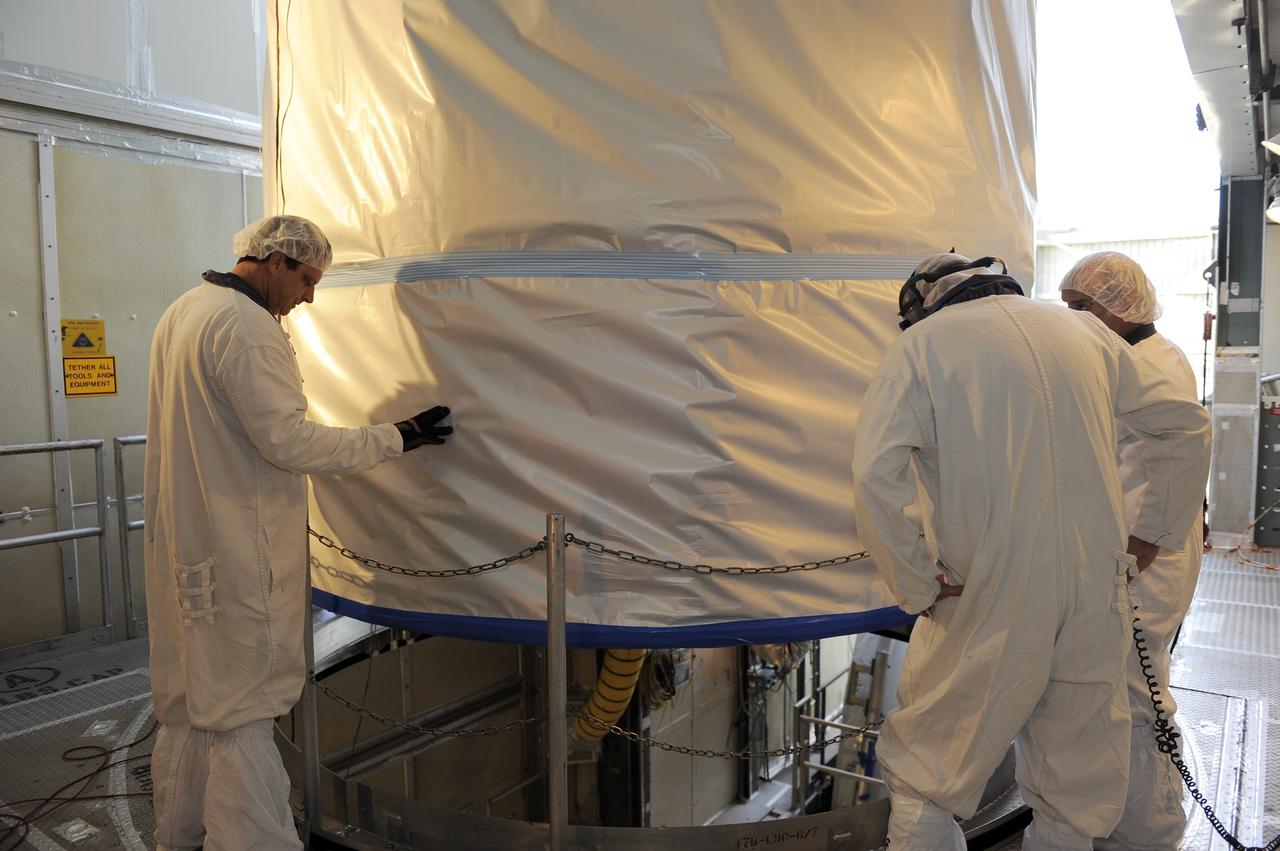
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians guide the protective canister enclosing NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory spacecraft into place on a transportation pallet. Preparations are under way to move the lunar probes, attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, to the launch pad. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
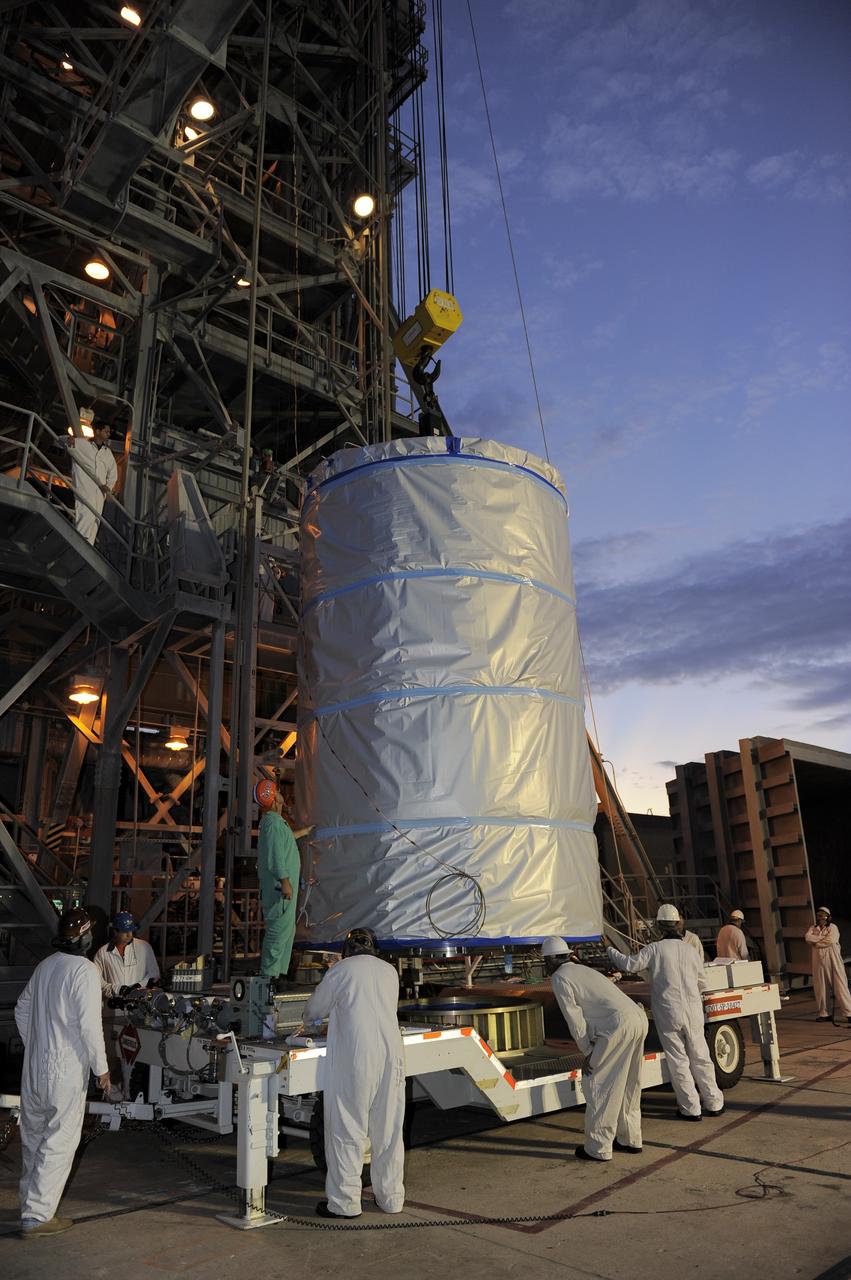

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft are lifted to the top of their launch pad at Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room in the Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
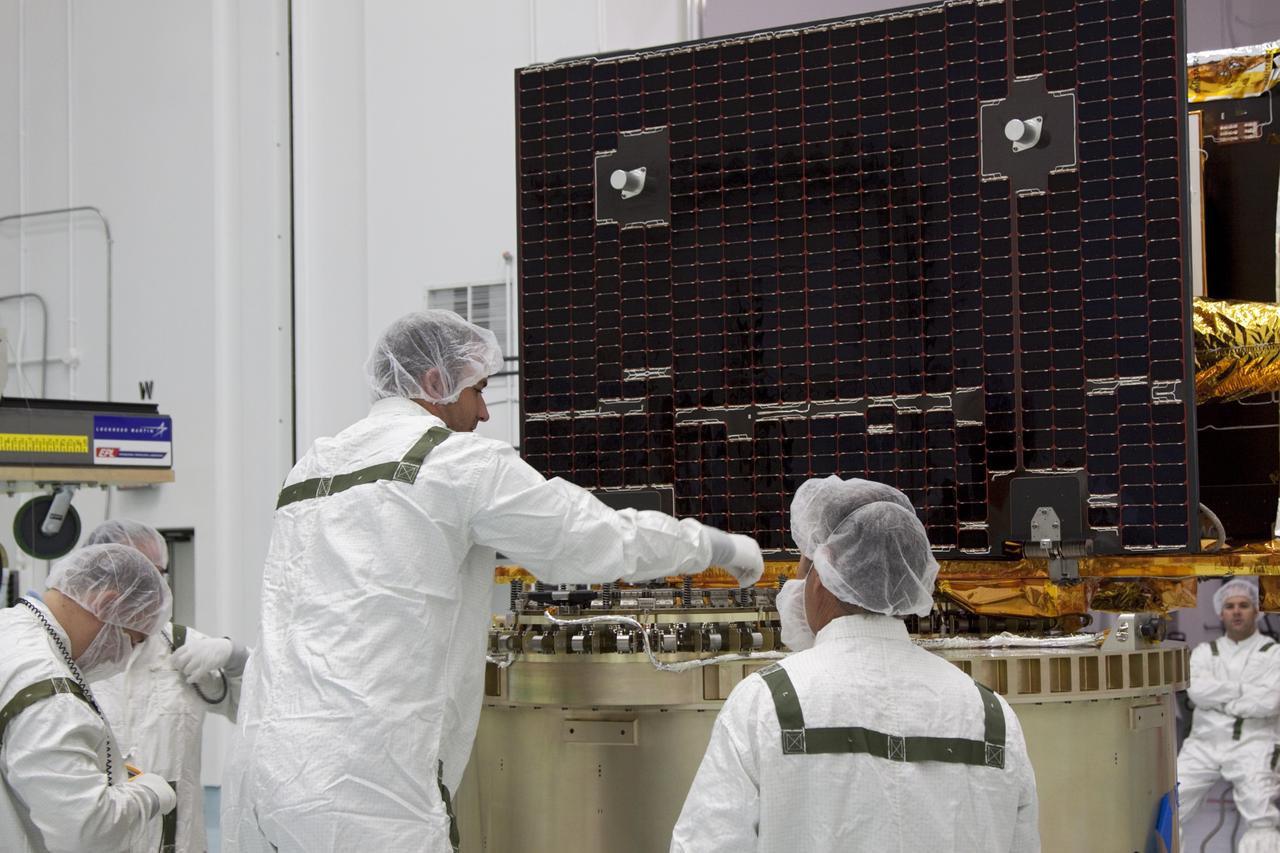

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe is secured on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
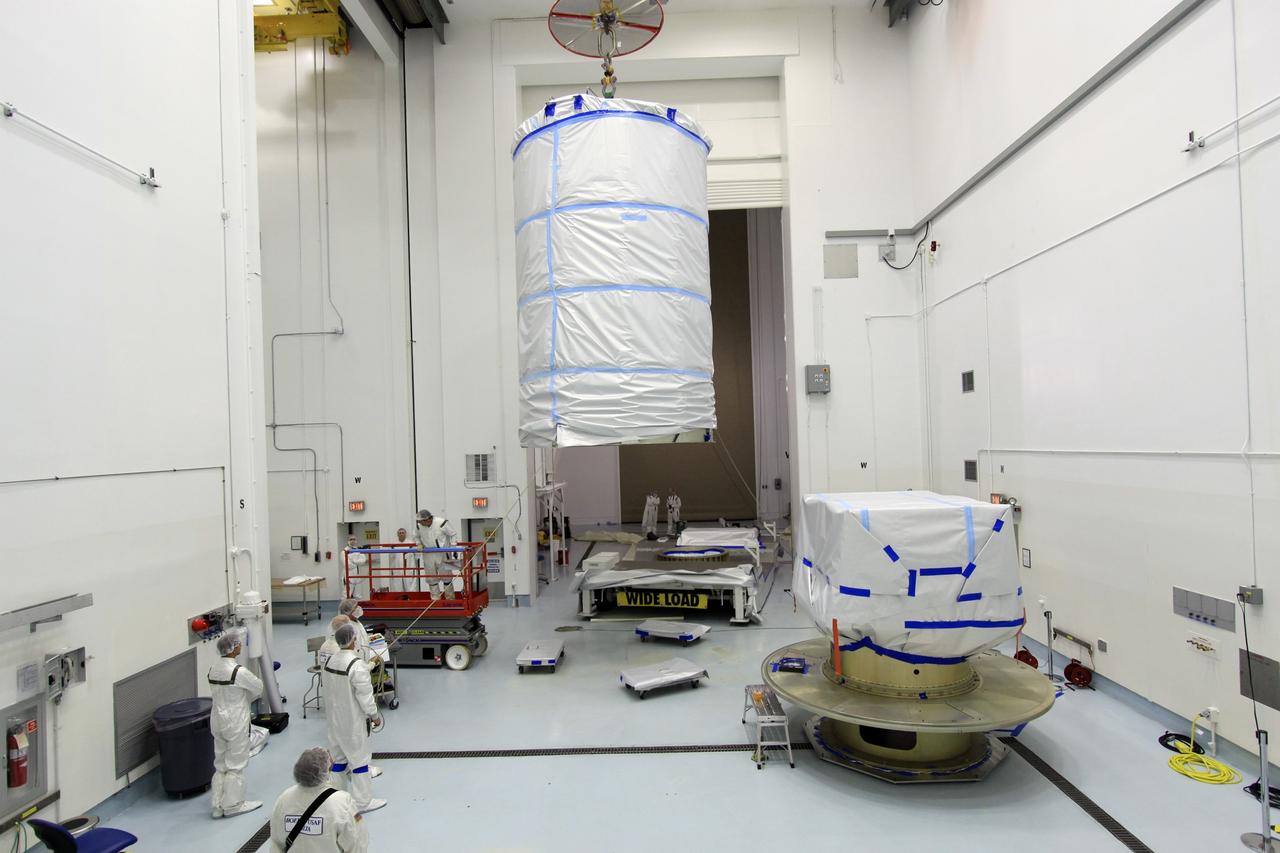

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a crane lifts the protective canister that will enclose NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory spacecraft, at right, during transport to the launch pad. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
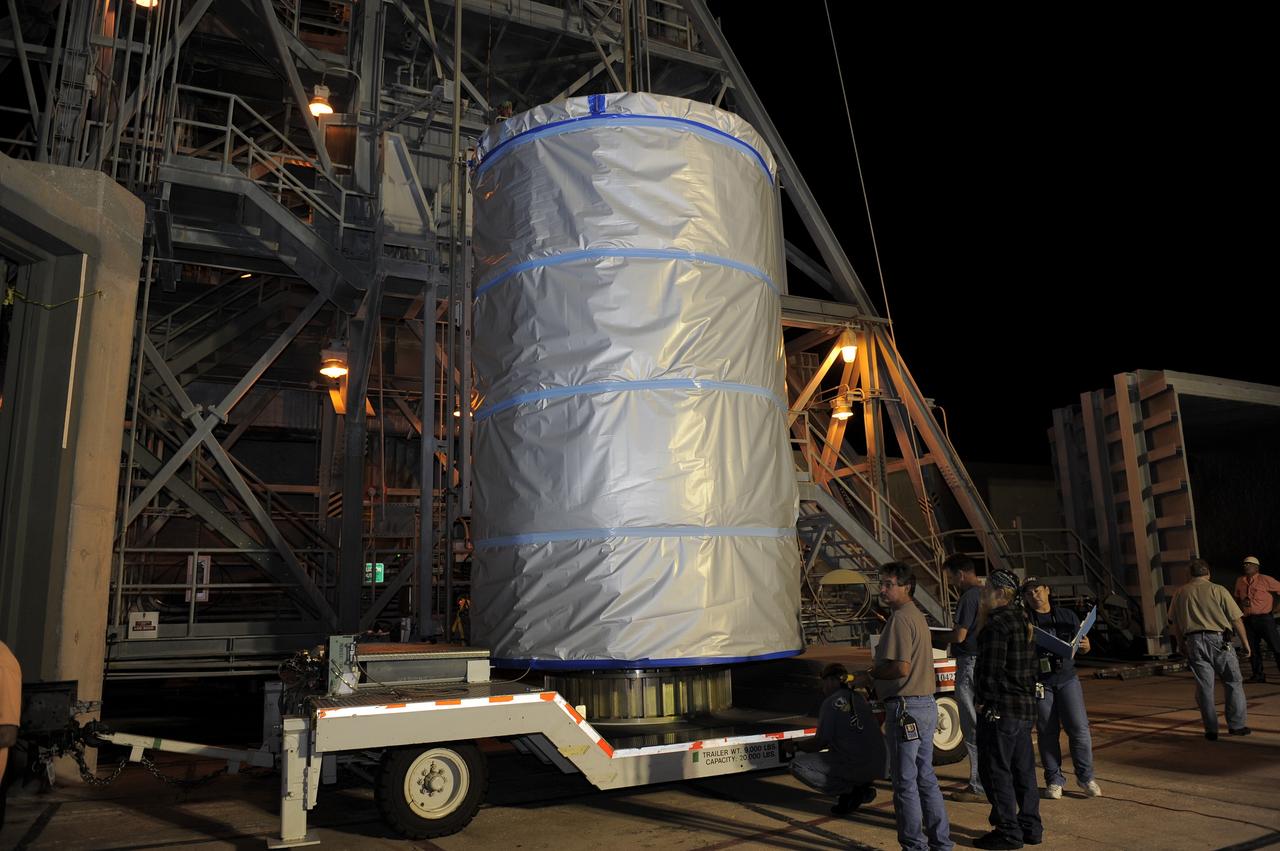

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft will be lifted to the top of their launch pad at Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room in the Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
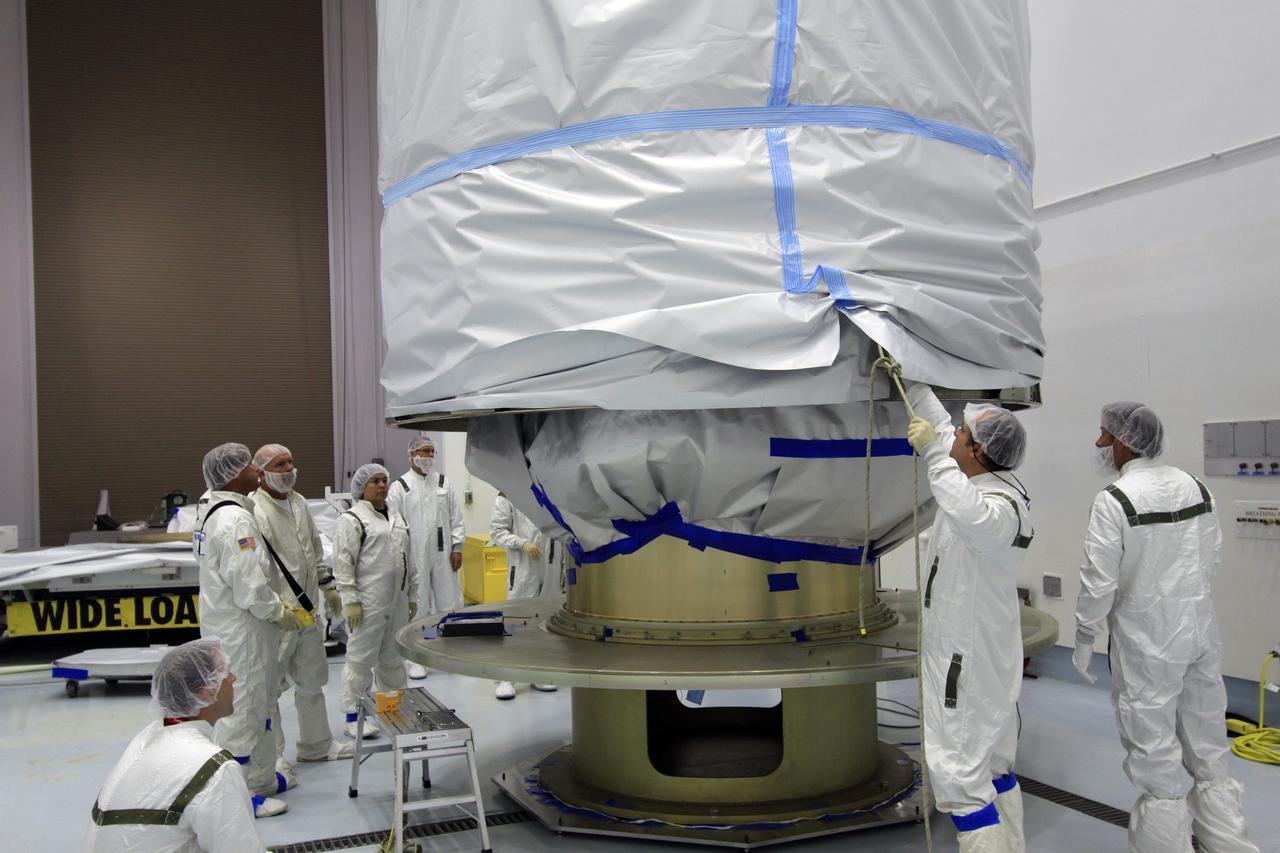

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a protective canister is lowered around NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory spacecraft during preparations to transport them to the launch pad. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
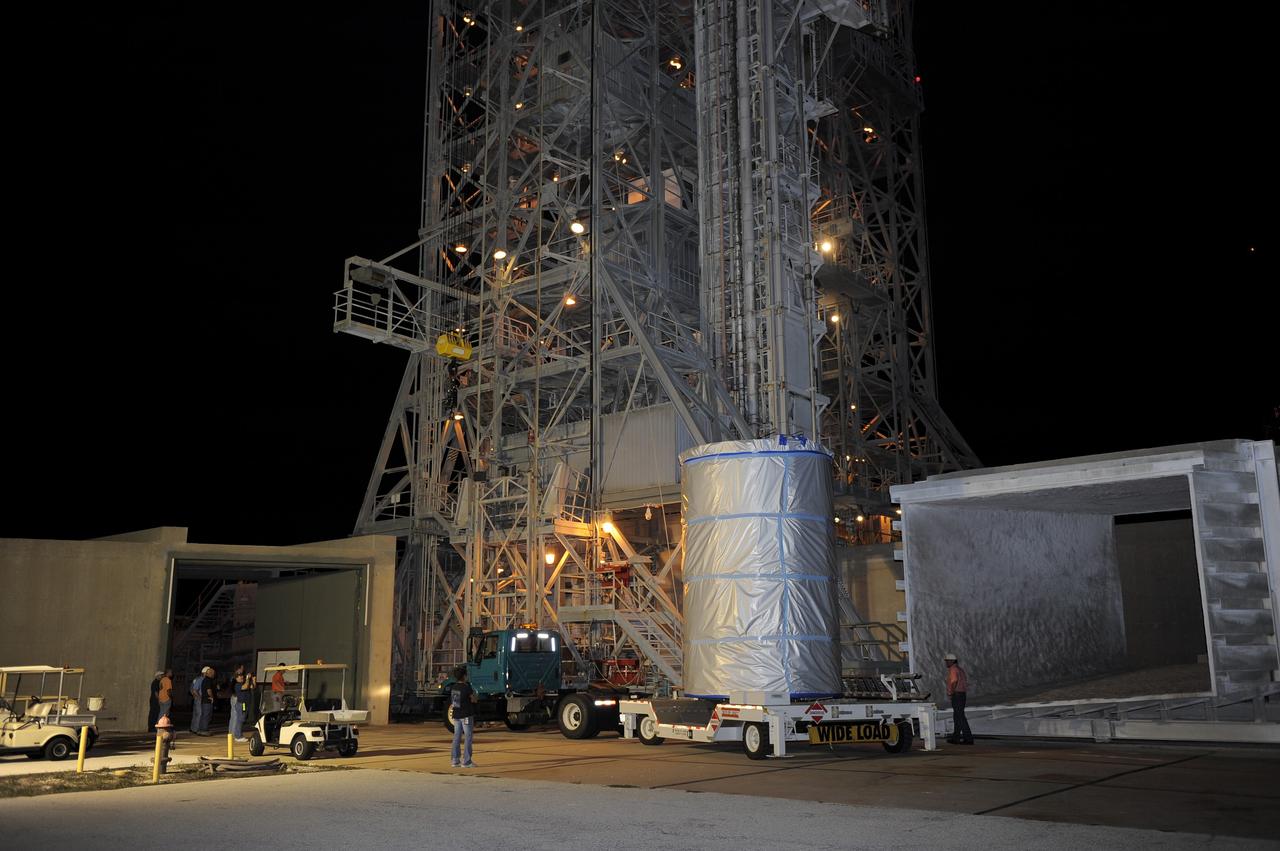

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft arrives at their launch pad at Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room in the Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
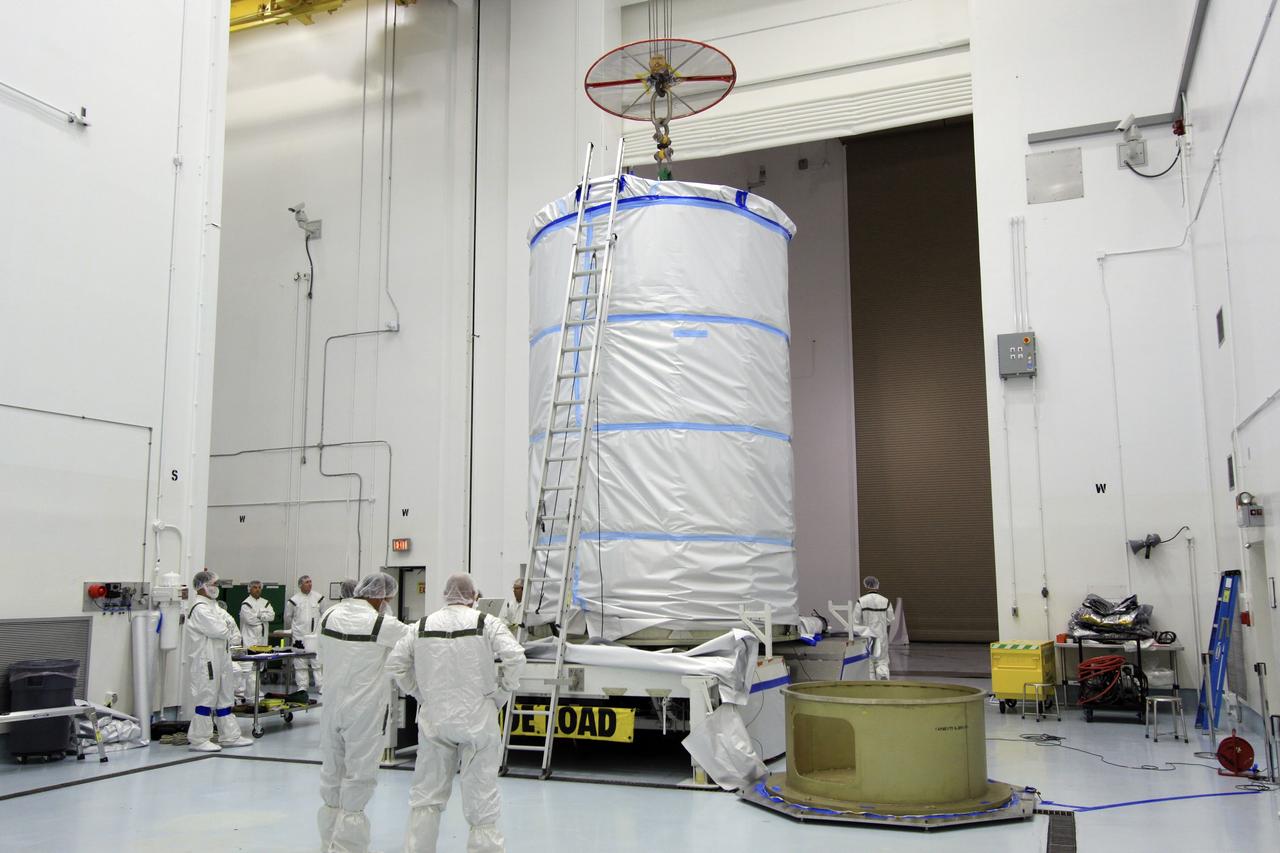

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the protective canister enclosing NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory spacecraft is secured on a transportation pallet. Preparations are under way to move the lunar probes, attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, to the launch pad. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
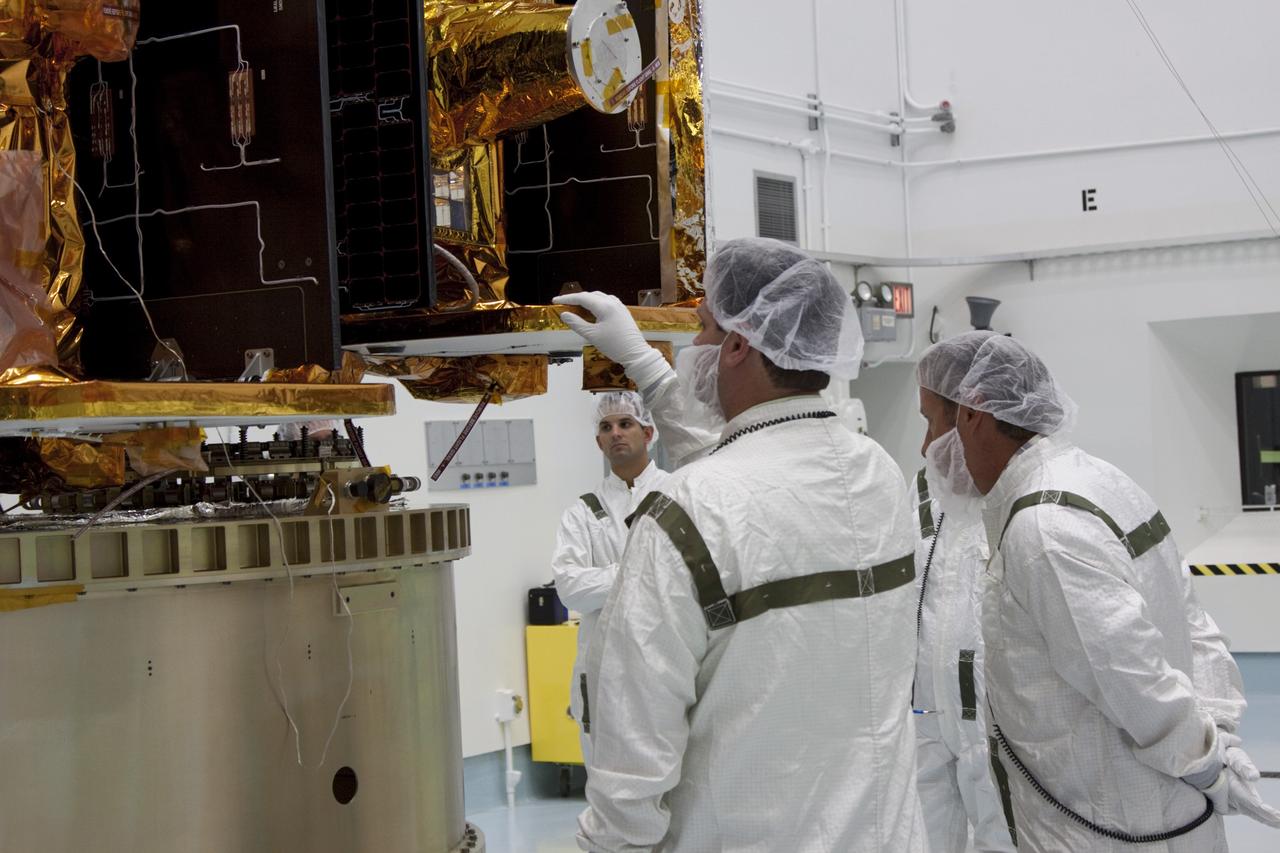

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians verify that NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe is positioned correctly on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
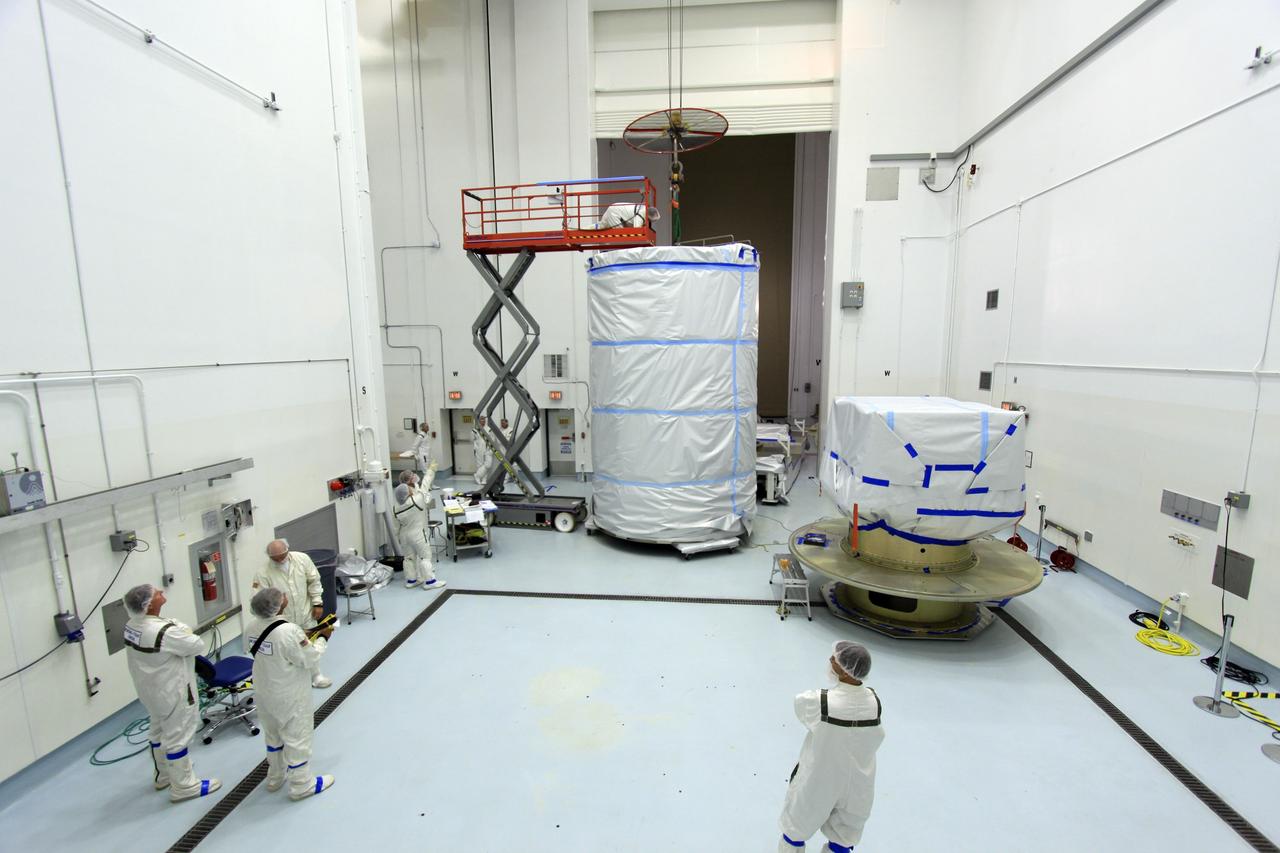

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., preparations are under way to enclose NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory spacecraft, at right, in a protective canister for transport to the launch pad. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
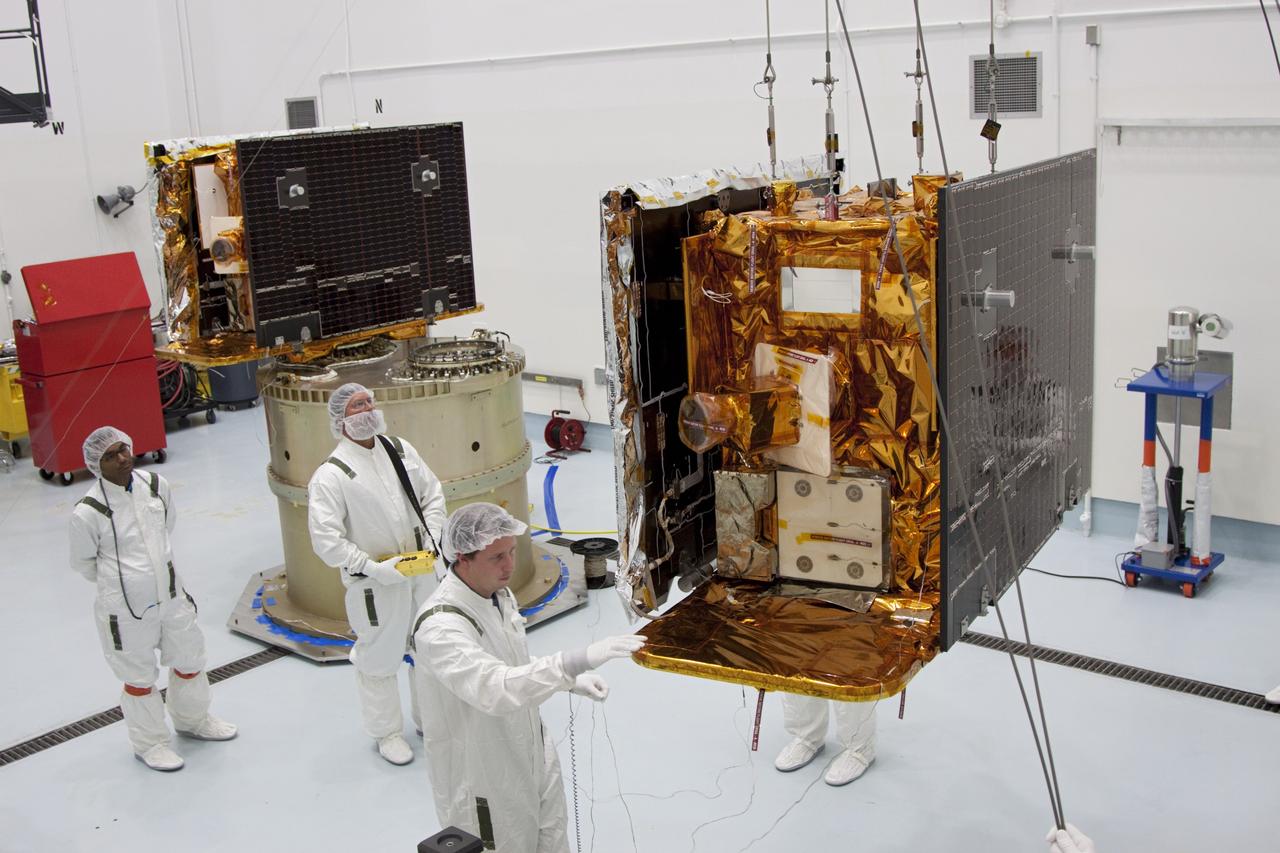

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe is lifted from its workstand and across the clean room toward the spacecraft adapter ring, at left, where GRAIL-B is already secured. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
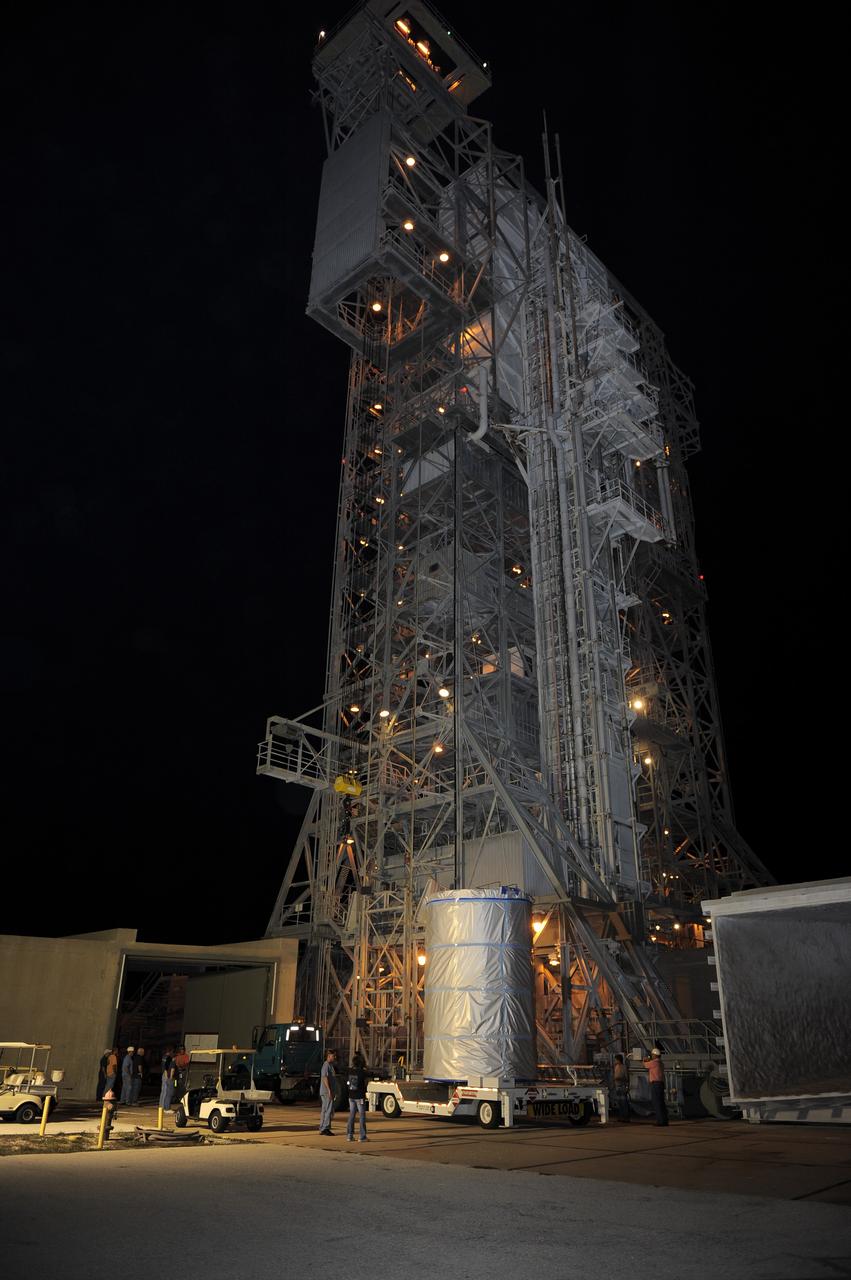

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft arrives at their launch pad at Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room in the Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe is lifted from its workstand. The spacecraft will be transferred to the spacecraft adapter ring, at left, where GRAIL-B is already secured. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians adjust the position of NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe on the spacecraft adapter ring. GRAIL-B is already secured to the ring, at left. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
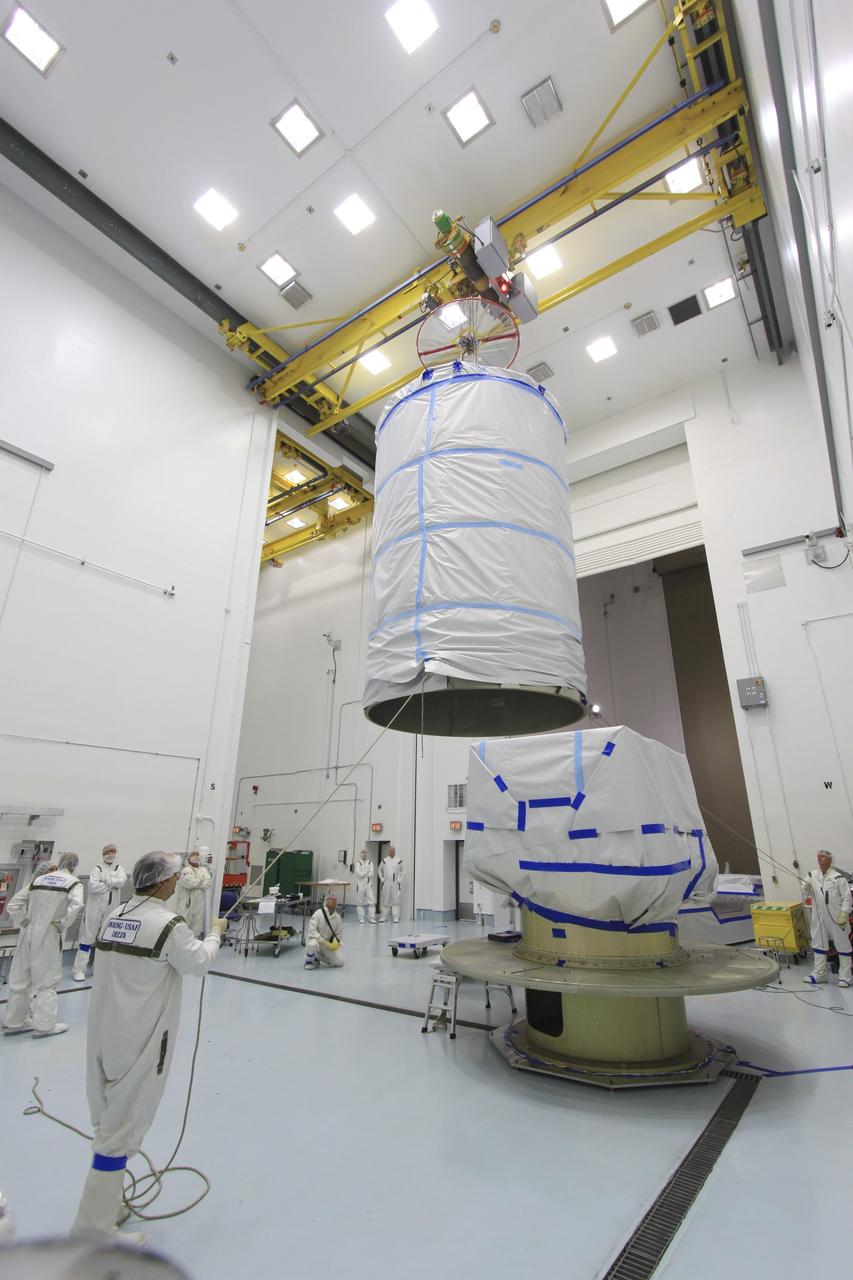

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a crane lowers a protective canister toward NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory spacecraft during preparations to transport them to the launch pad. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
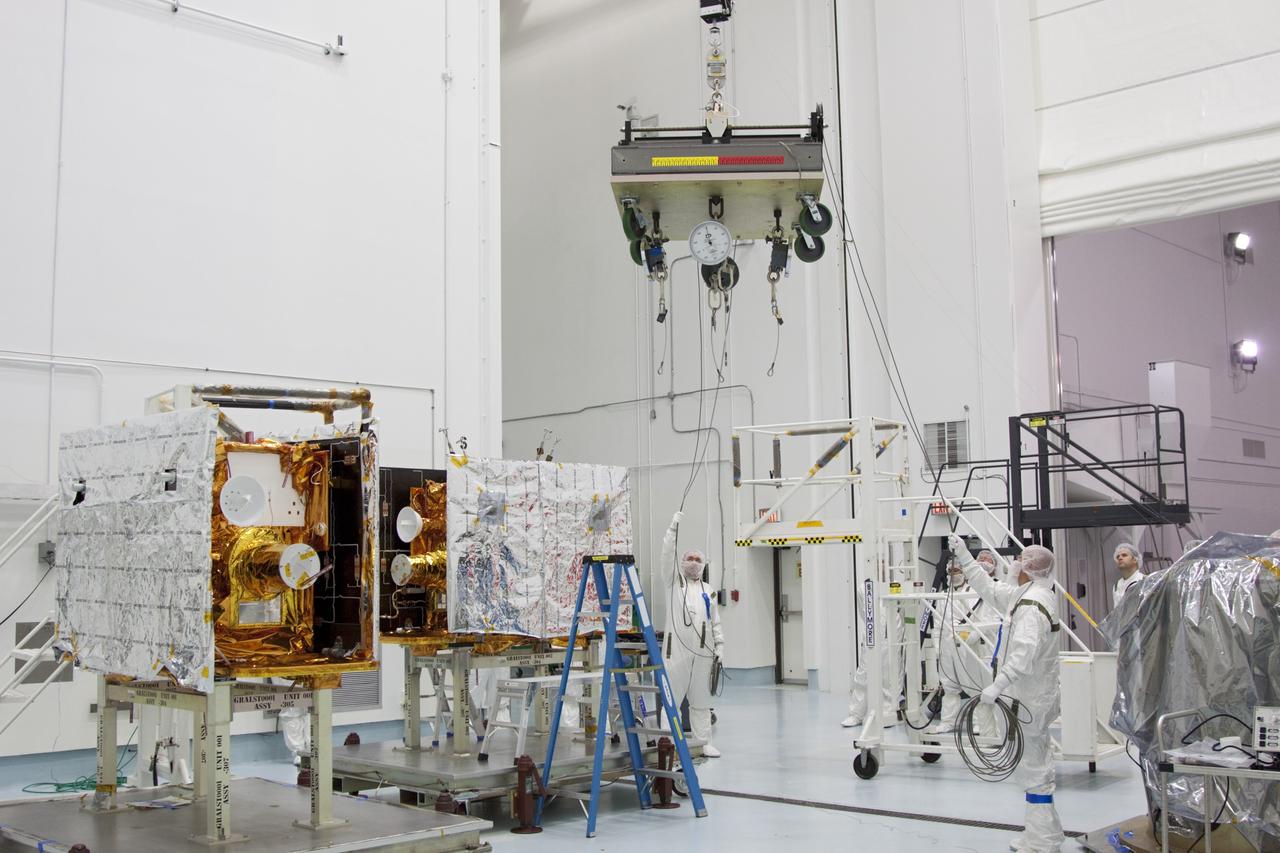

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians move a lifting device toward NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe. At left is GRAIL-A. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
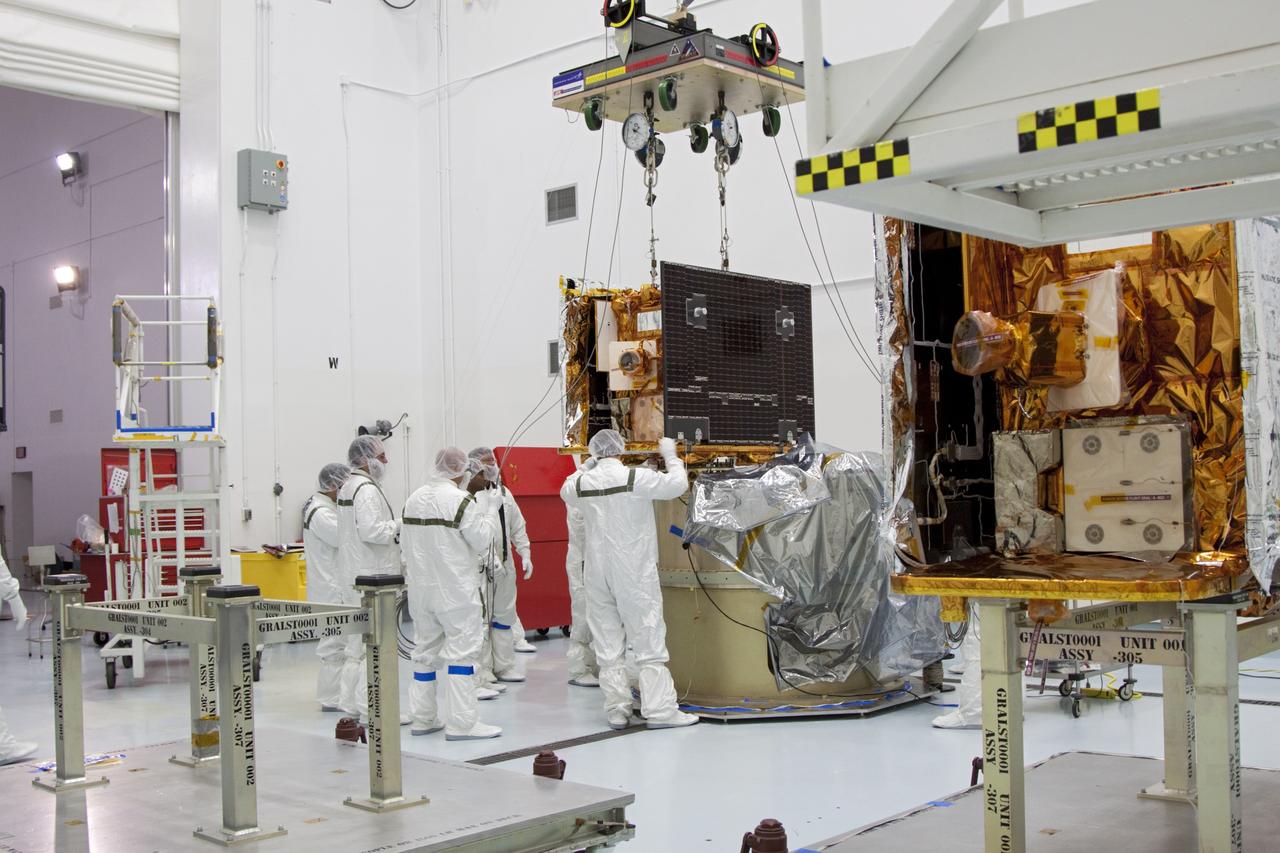

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe comes to rest on the spacecraft adapter ring. At right is GRAIL-A. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
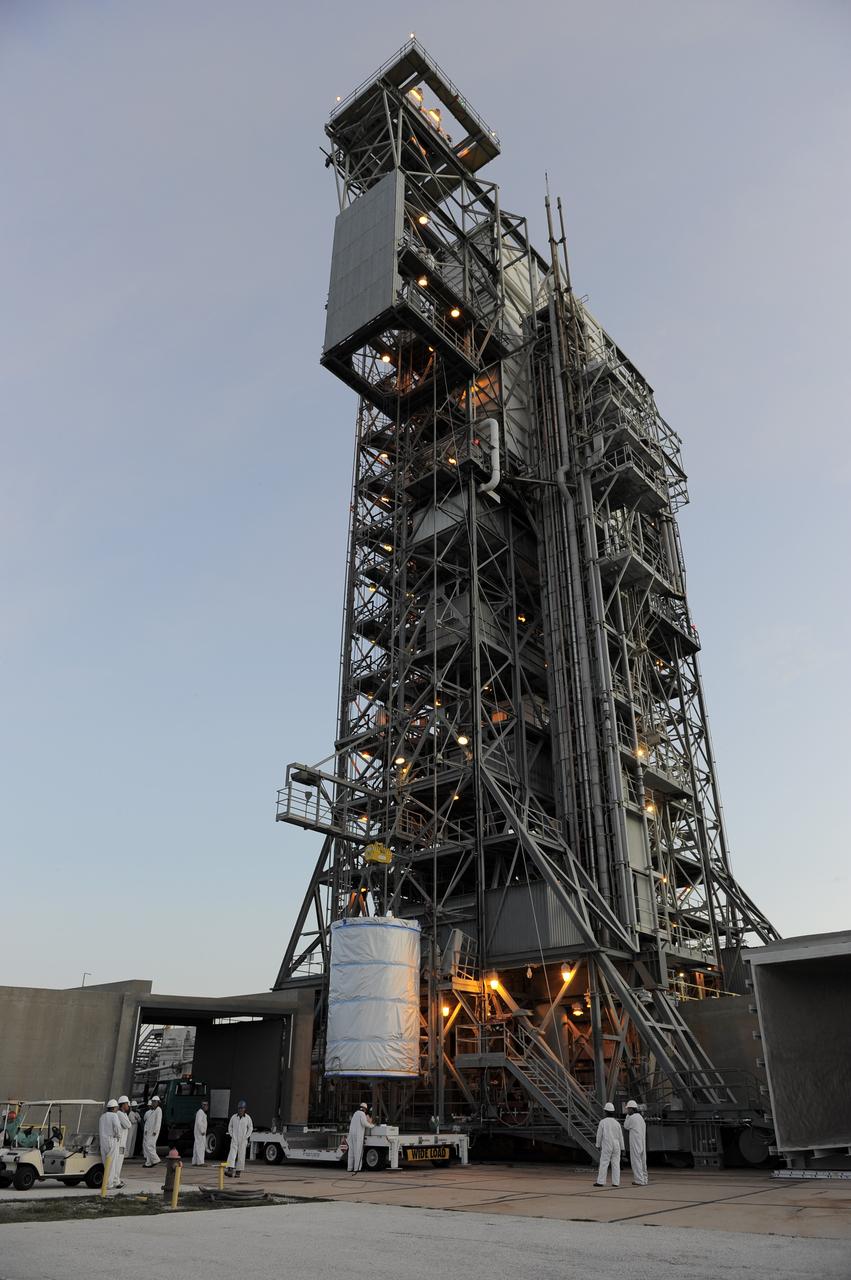

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft are lifted to the top of their launch pad at Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room in the Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians verify that NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe is lifted carefully from its workstand. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
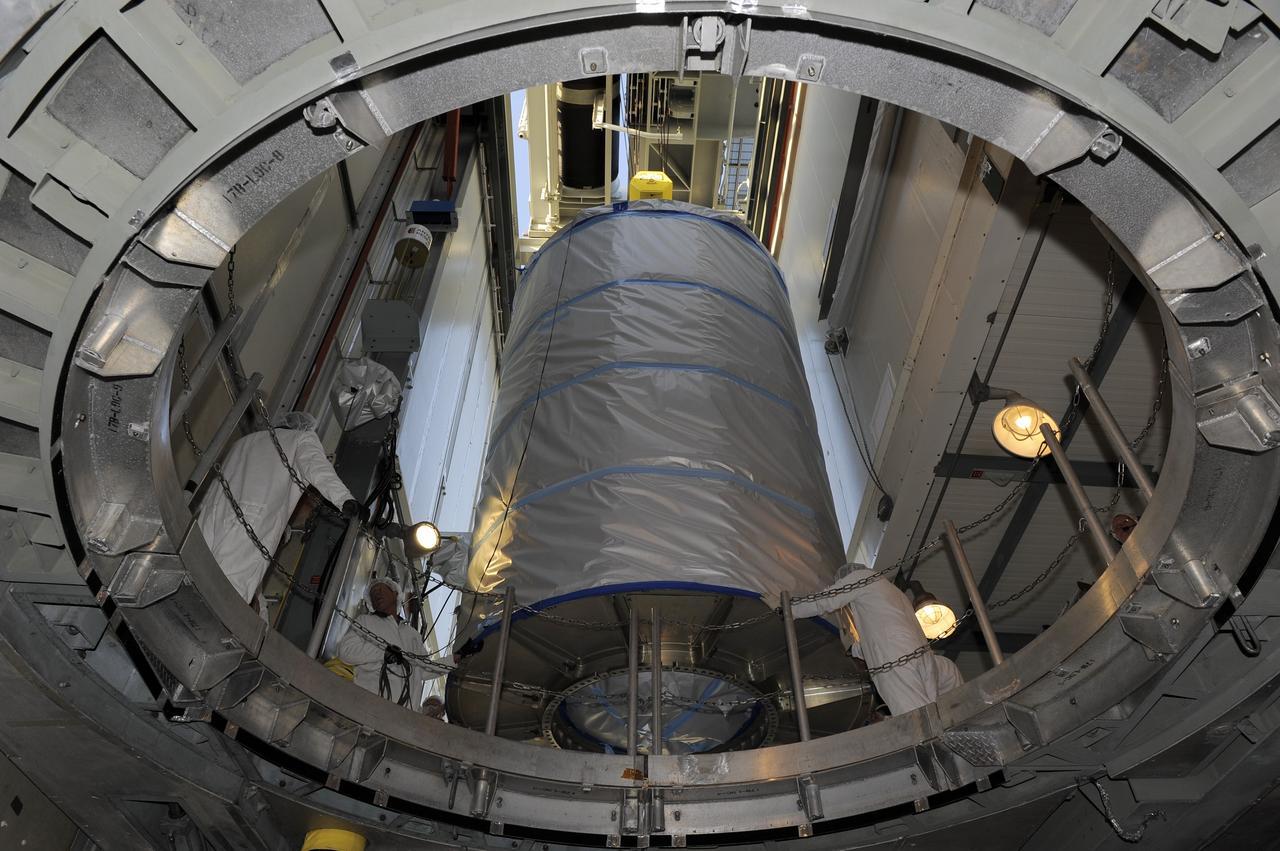

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians lower NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft into place atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket on Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
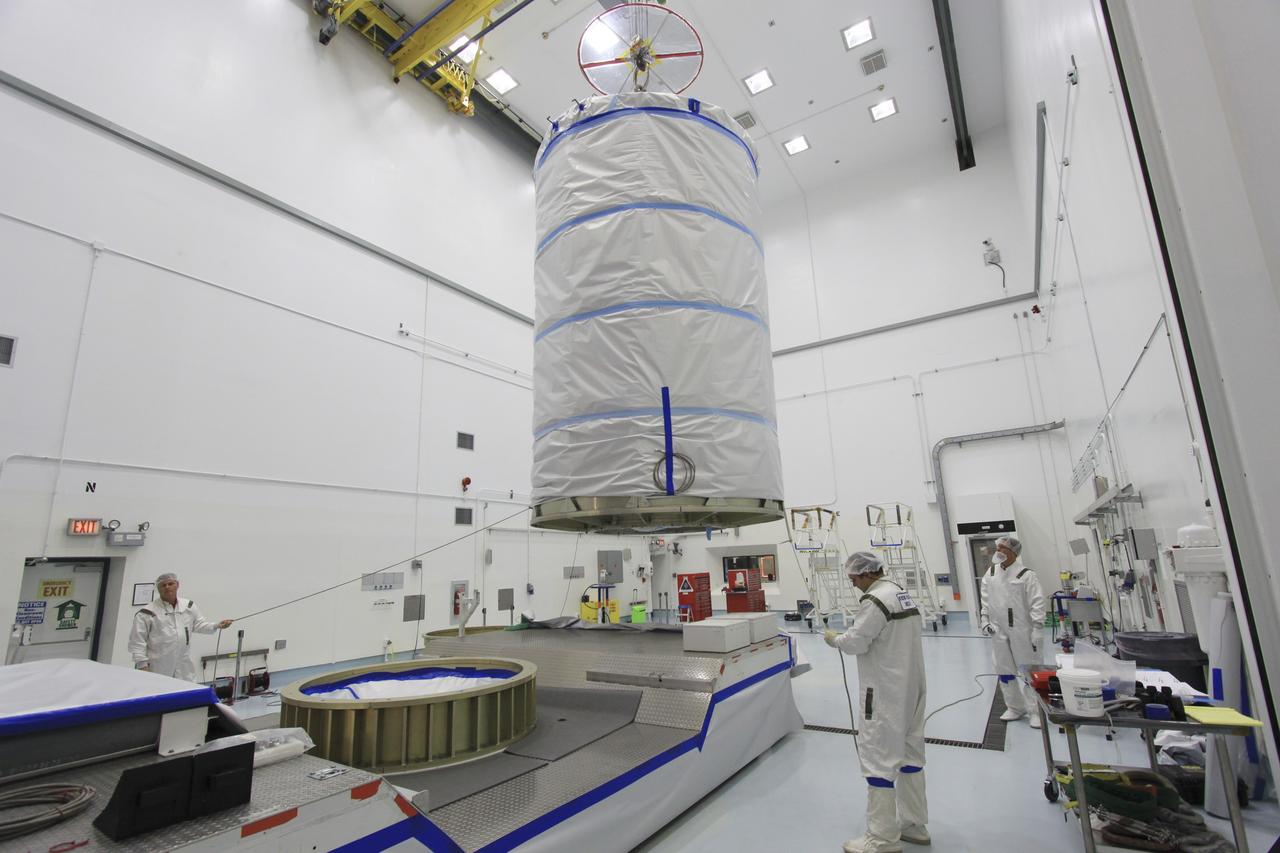

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a protective canister enclosing NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory spacecraft is lifted toward a transportation pallet. Preparations are under way to move the lunar probes, attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, to the launch pad. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
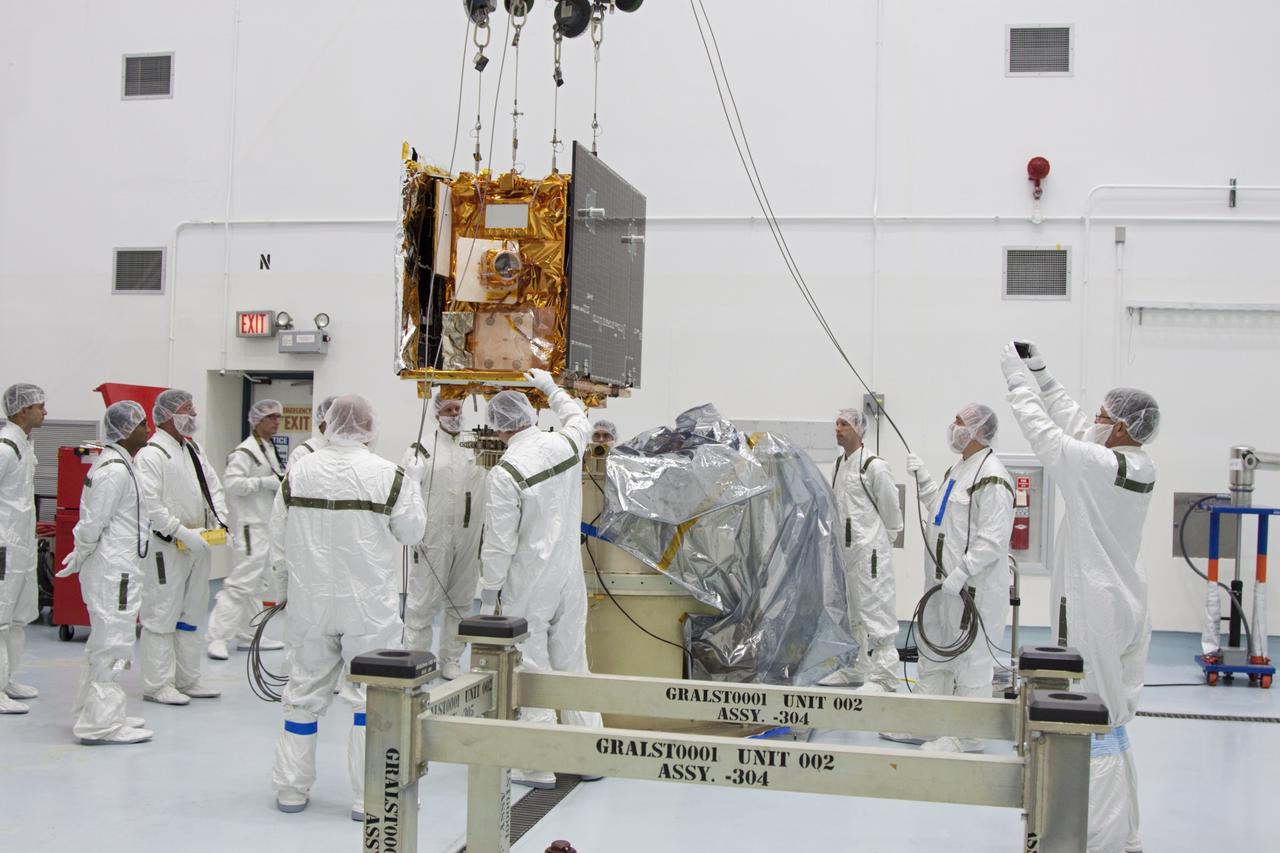

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians lower NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe into position on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
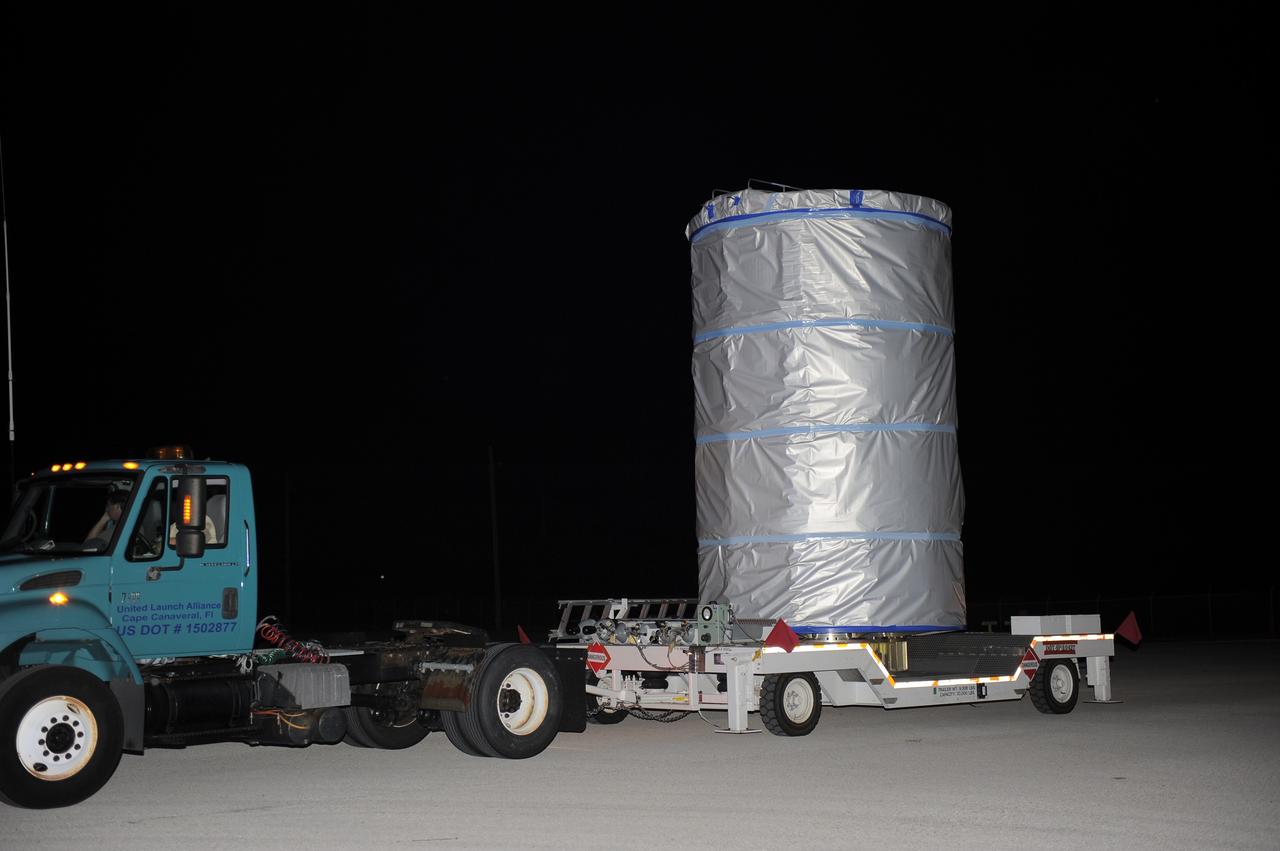

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft are transported from the Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., to their launch pad at Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians verify that NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe is in the correct position on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians position NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe on the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
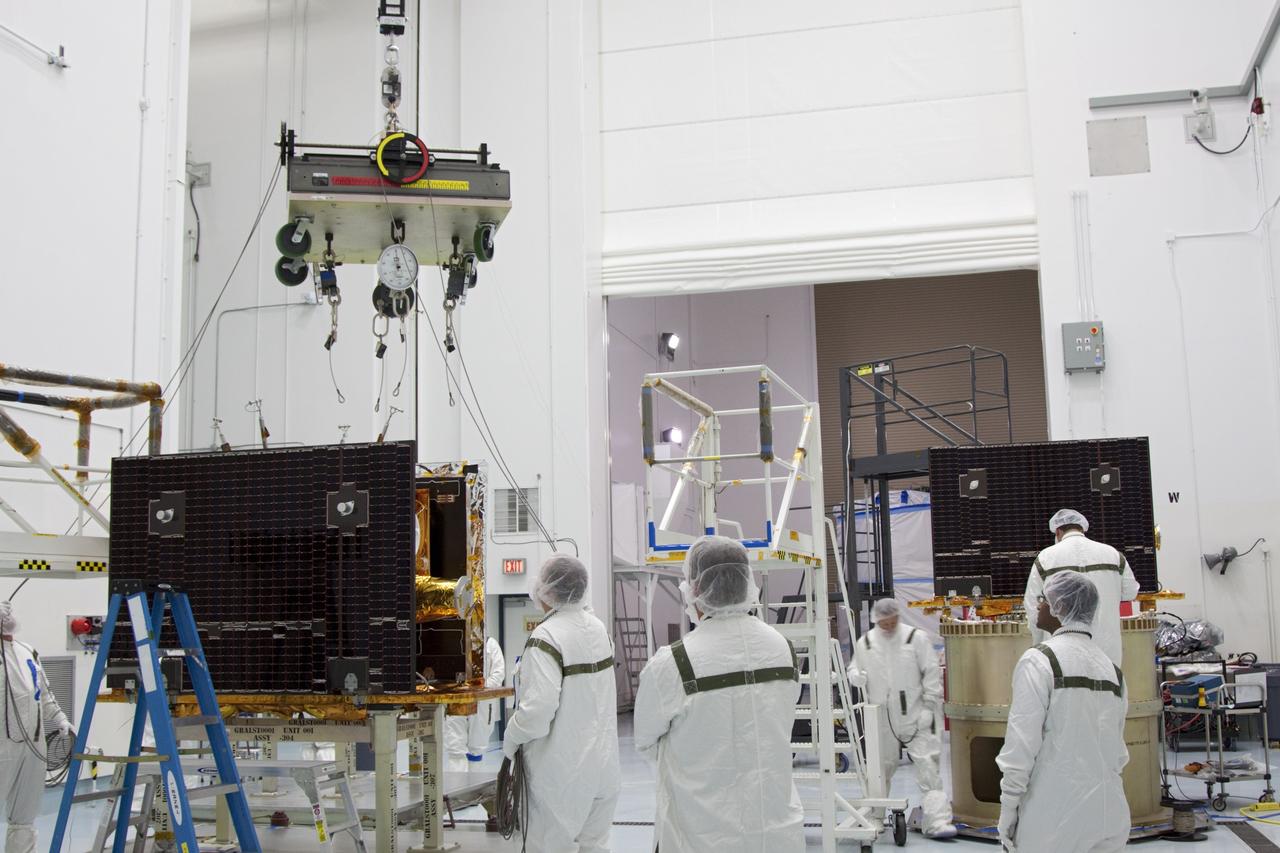

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the lifting device moves toward NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe. The spacecraft will be transferred to the spacecraft adapter ring, at right, where GRAIL-B is being secured. After the twin spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
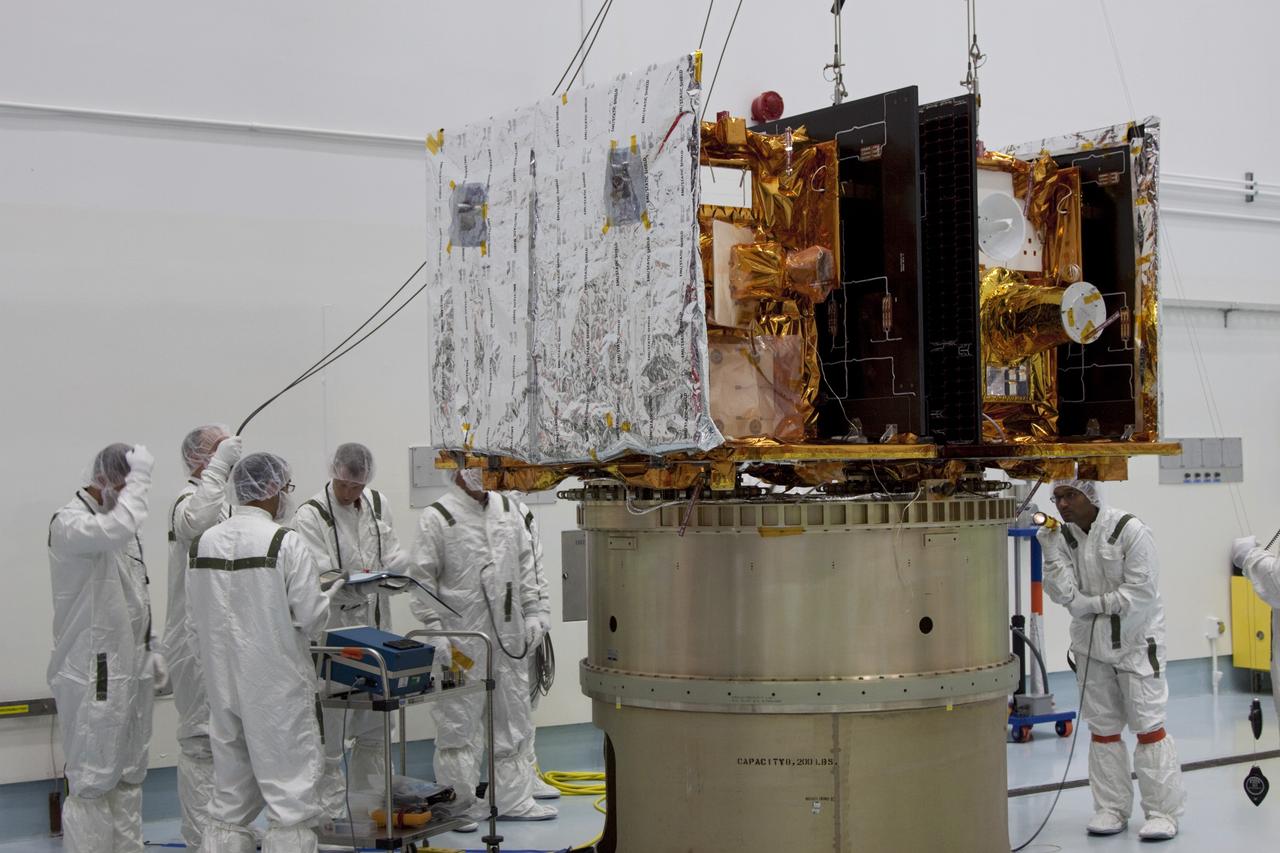

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians verify that NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe is in position and ready to be secured to the spacecraft adapter ring. GRAIL-B is secured to the ring, at left. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
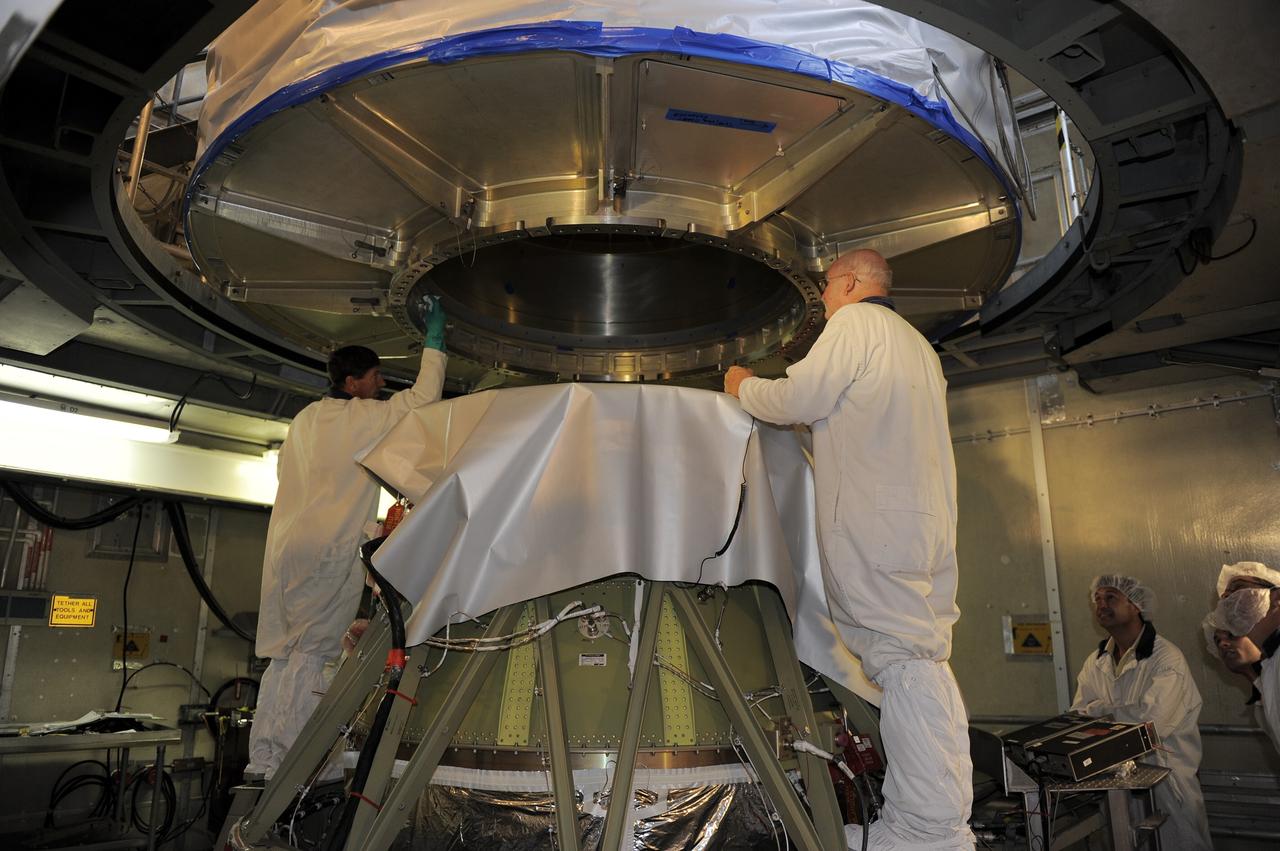

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians lower NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft into place atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket on Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
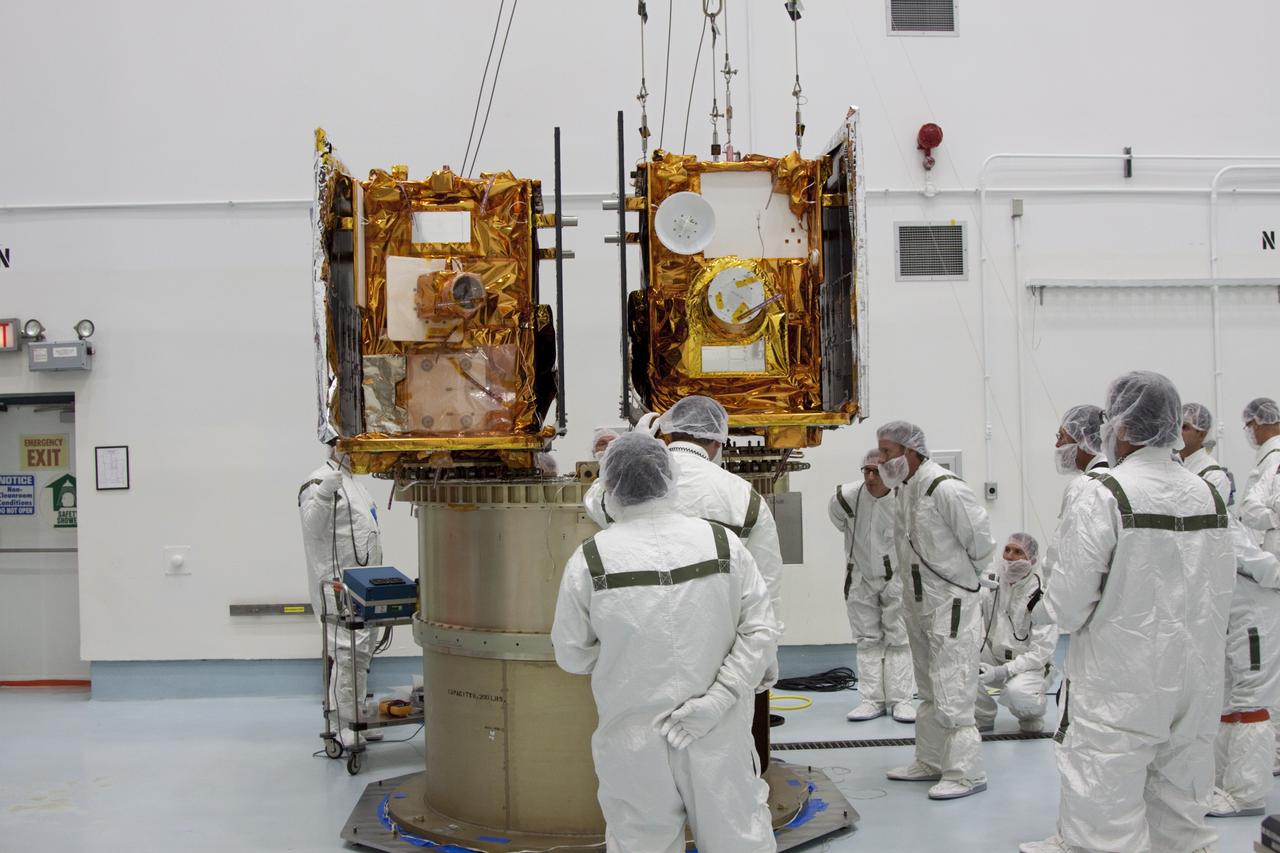

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the placement of NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe on the spacecraft adapter ring. GRAIL-B is already secured to the ring, at left. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
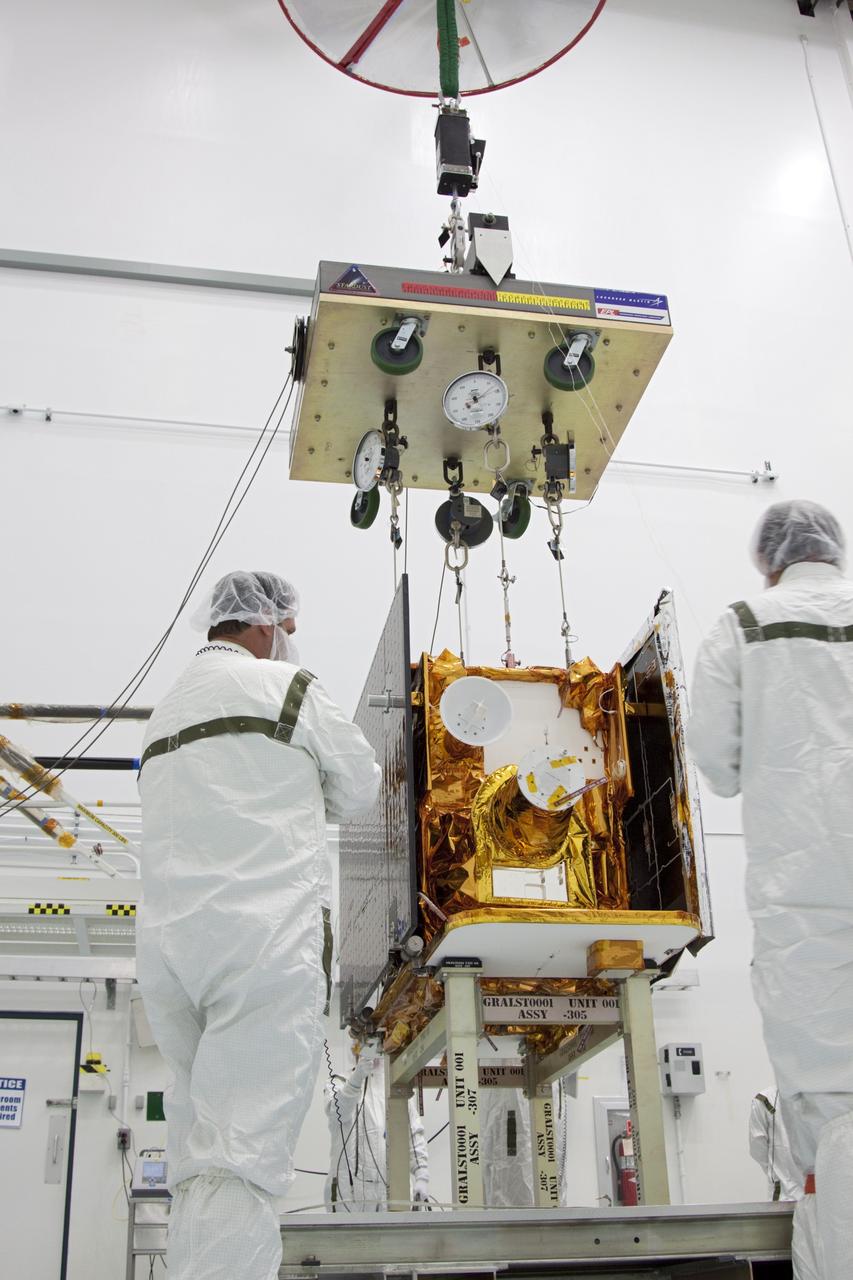

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a lifting device is attached to NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-A (GRAIL-A) lunar probe to move it from its workstand. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
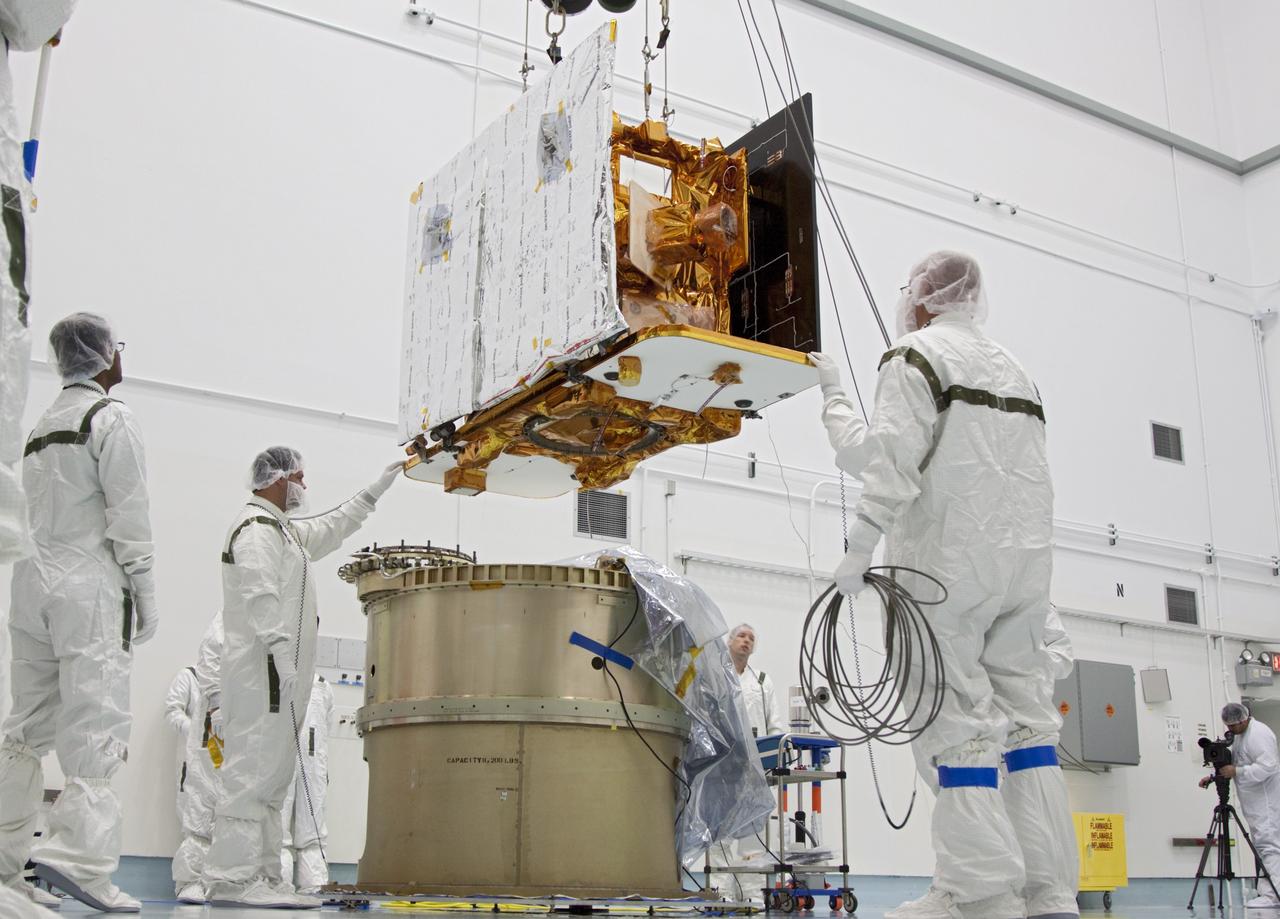

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., Lockheed Martin technicians lower NASA's Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory-B (GRAIL-B) lunar probe toward the spacecraft adapter ring. After the twin GRAIL spacecraft are attached to the adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, they will be transported to the launch pad. GRAIL will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
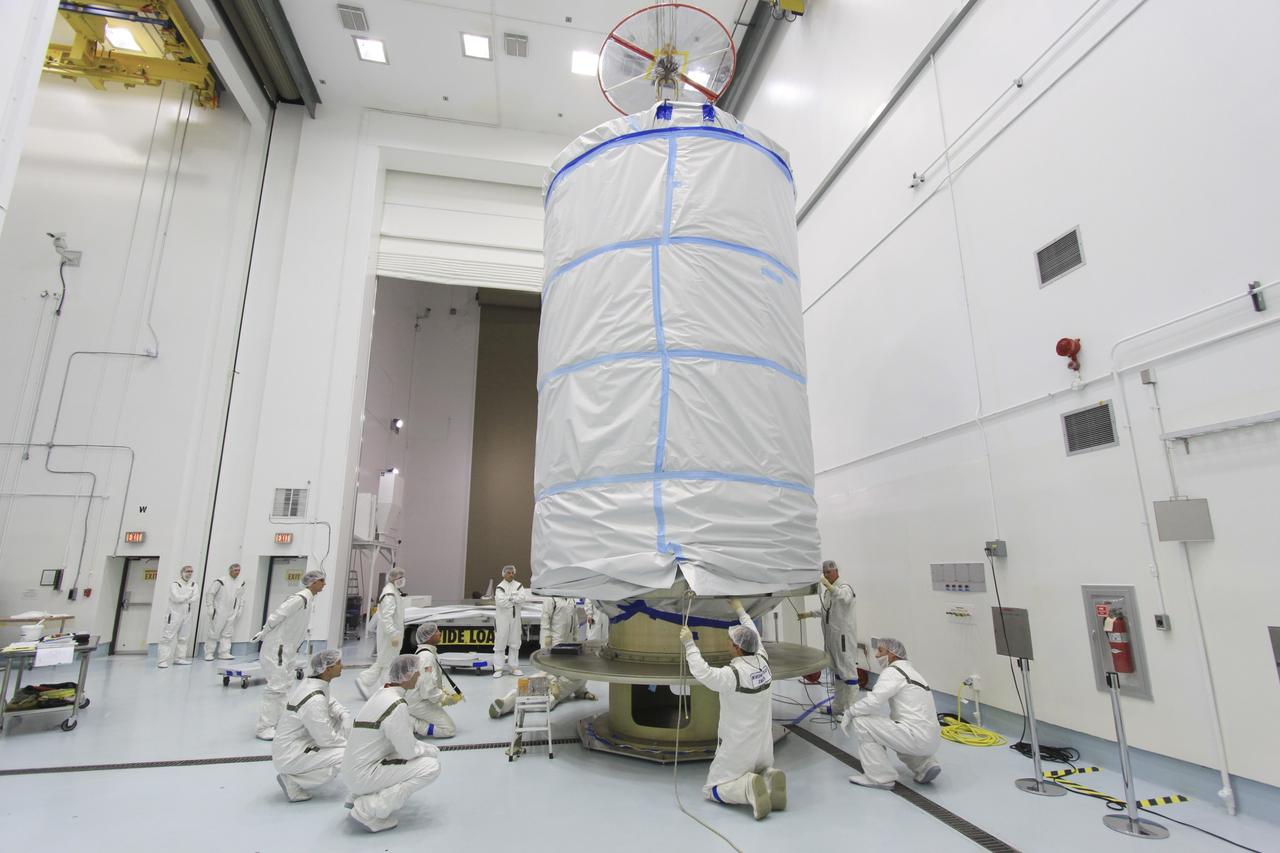

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Astrotech Space Operation's payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a protective canister encases NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory spacecraft. Preparations are under way to transport the lunar probes, attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration, to the launch pad. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 17B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's twin Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) spacecraft are in place atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket on Space Launch Complex 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The lunar probes are attached to a spacecraft adapter ring in their side-by-side launch configuration and wrapped in plastic to prevent contamination outside the clean room. The spacecraft will fly in tandem orbits around the moon for several months to measure its gravity field. GRAIL's primary science objectives are to determine the structure of the lunar interior, from crust to core, and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon. Launch is scheduled for Sept. 8. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett