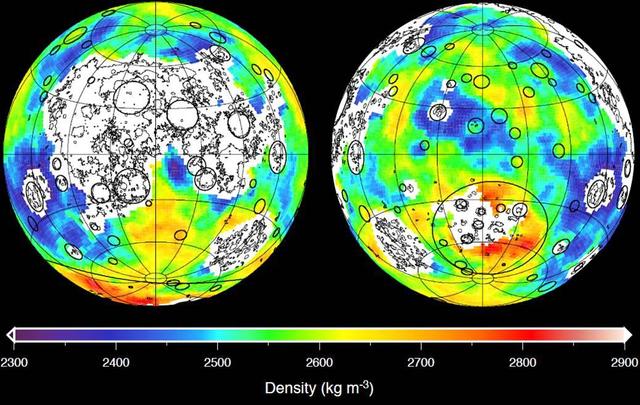
This graphic depicting the bulk density of the lunar highlands on the near and far sides of the moon was generated using gravity data from NASA GRAIL mission and topography data from NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
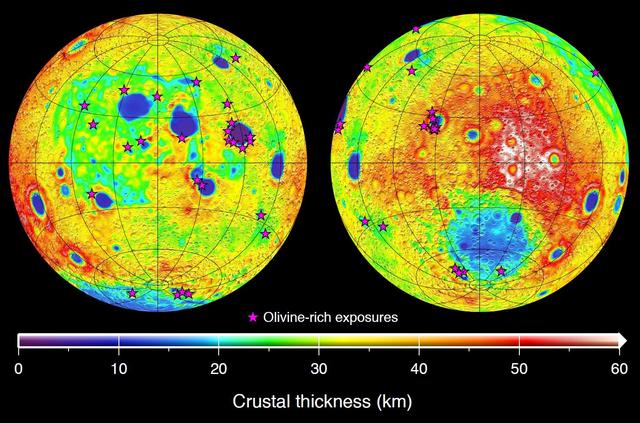
This graphic depicting the bulk density of the lunar highlands on the near and far sides of the moon was generated using gravity data from NASA GRAIL mission and topography data from NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
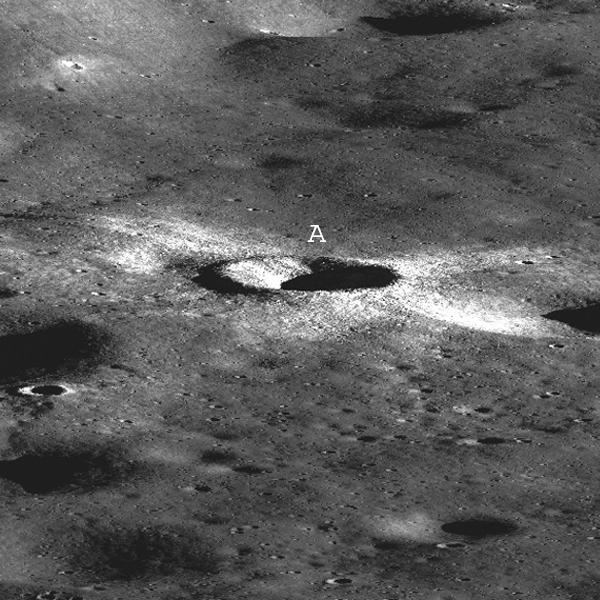

This is a synthetic perspective view looking south from the Apollo 16 landing area, topography is rendered naturally as seen by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
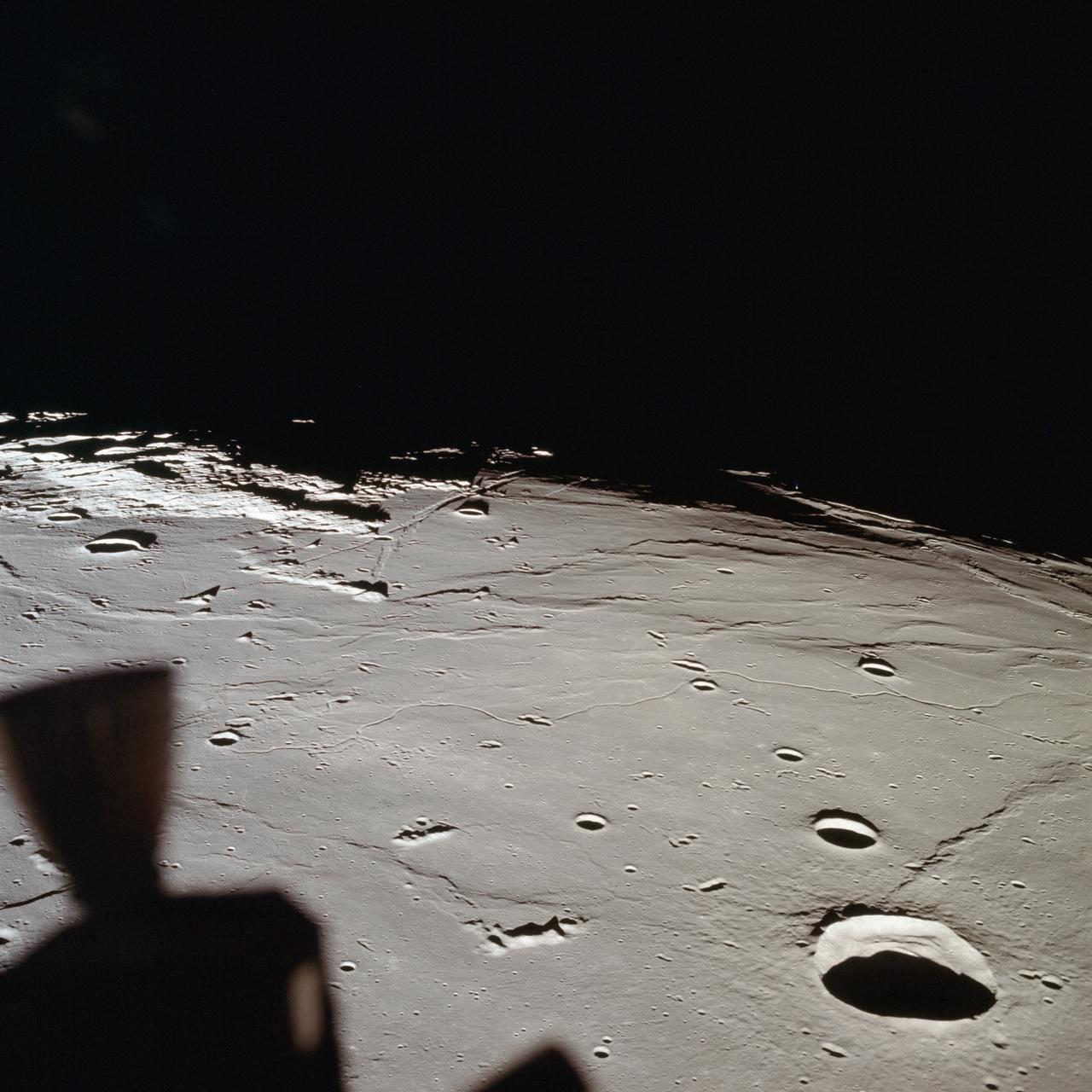

AS11-37-5437 (20 July 1969) --- The approach to Apollo Landing Site 2 in southwestern Sea of Tranquility is seen in this photograph taken from the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) in lunar orbit. When this picture was made, the LM was still docked to the Command and Service Modules (CSM). Site 2 is located just right of center at the edge of the darkness. The crater Maskelyne is the large one at the lower right. Hypatia Rille (U.S. 1) is at upper left, with the crater Moltke just to the right (north) of it. Sidewinder Rille and Diamondback Rille extend from left to right across the center of the picture. This view looks generally west.
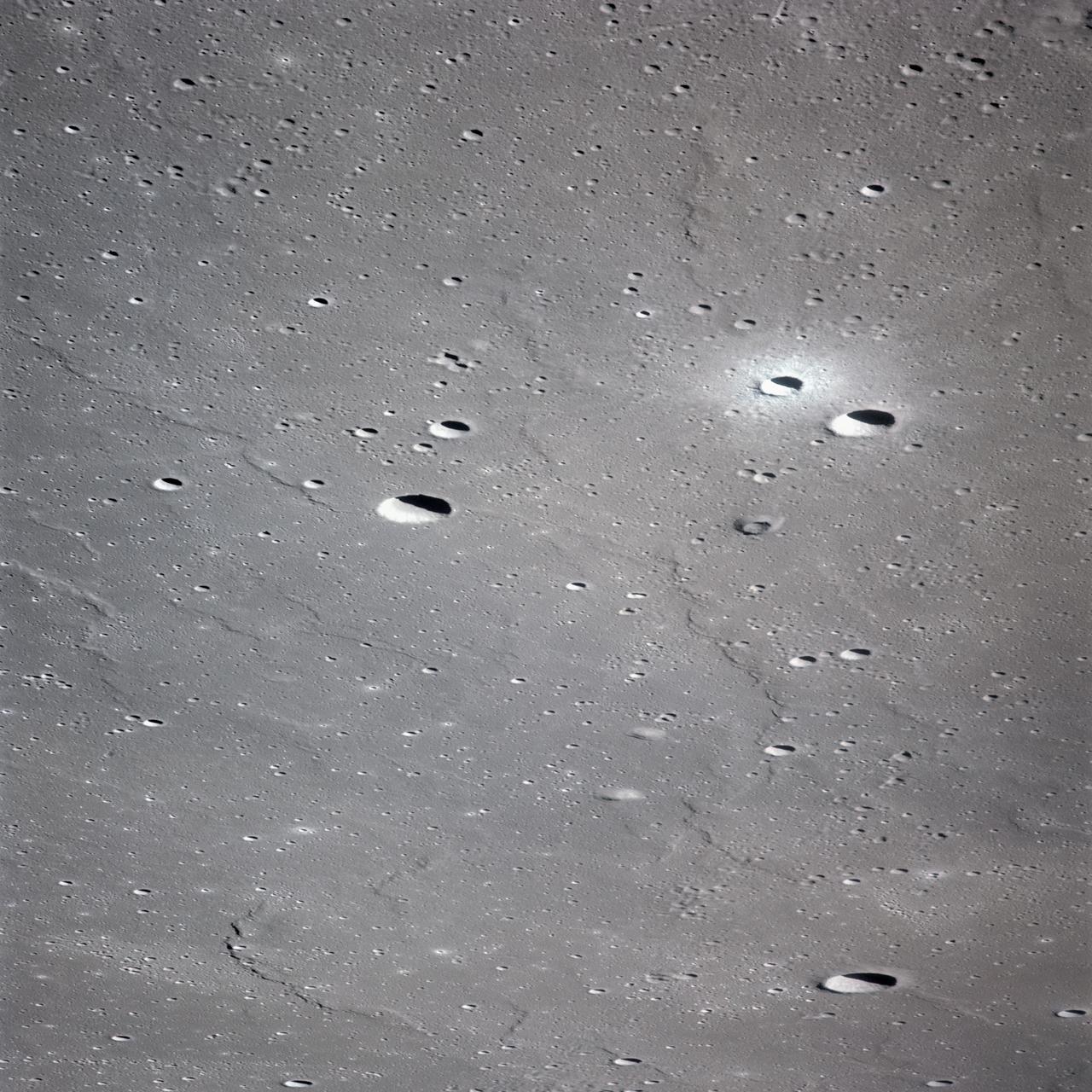

AS16-120-19237 (April 1972) --- An oblique view of a portion of the lunar nearside as photographed from the Apollo 16 spacecraft in lunar orbit. The small, bright crater is Lassell D at the northeastern edge of Mare Nubium (Sea of Clouds). The area seen in this picture is immediately west of Lassell C Crater, southwest of Guoricke Crater, and southwest of Davy Crater.
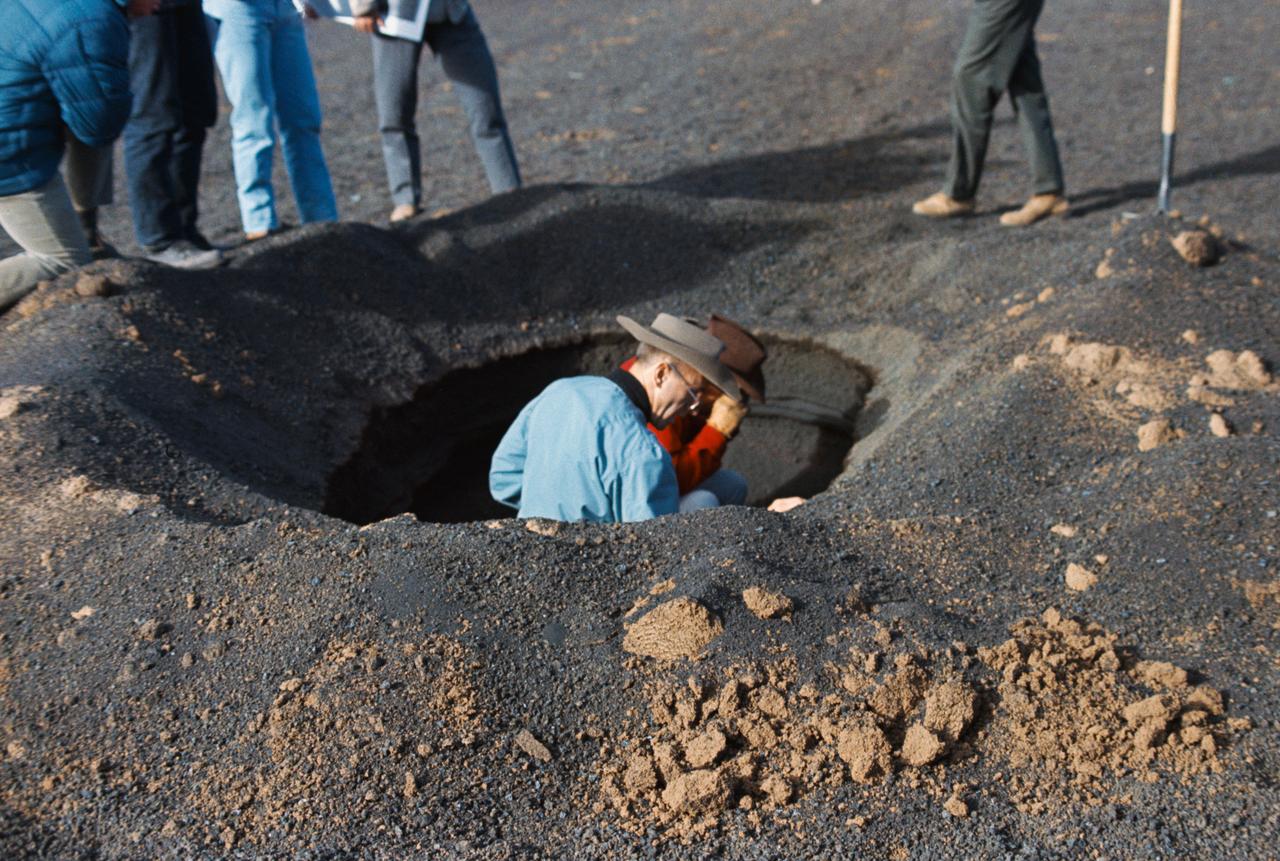

S69-55662 (10 Oct. 1969) --- Astronauts Alan L. Bean (left) and Charles Conrad Jr., the two crewmen of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission who are scheduled to participate in two lengthy periods of extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface, are pictured during a geological field trip and training at a simulated lunar surface area near Flagstaff, Arizona. Here Conrad, the Apollo 12 commander, gets a close look through hand lens at the stratigraphy (study of strata or layers beneath the surface) of a man-dug hole, while Bean, the Apollo 12 mission's lunar module pilot, looks on. The topography in this area, with several man-made modifications, resembles very closely much of the topography found on the lunar surface. While Conrad and Bean explore the lunar surface (plans call for Apollo 12 spacecraft to land in the Sea of Storms), astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot for the Apollo 12 mission, will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. The Apollo 12 mission is scheduled to lift off from Cape Kennedy on Nov. 14, 1969.
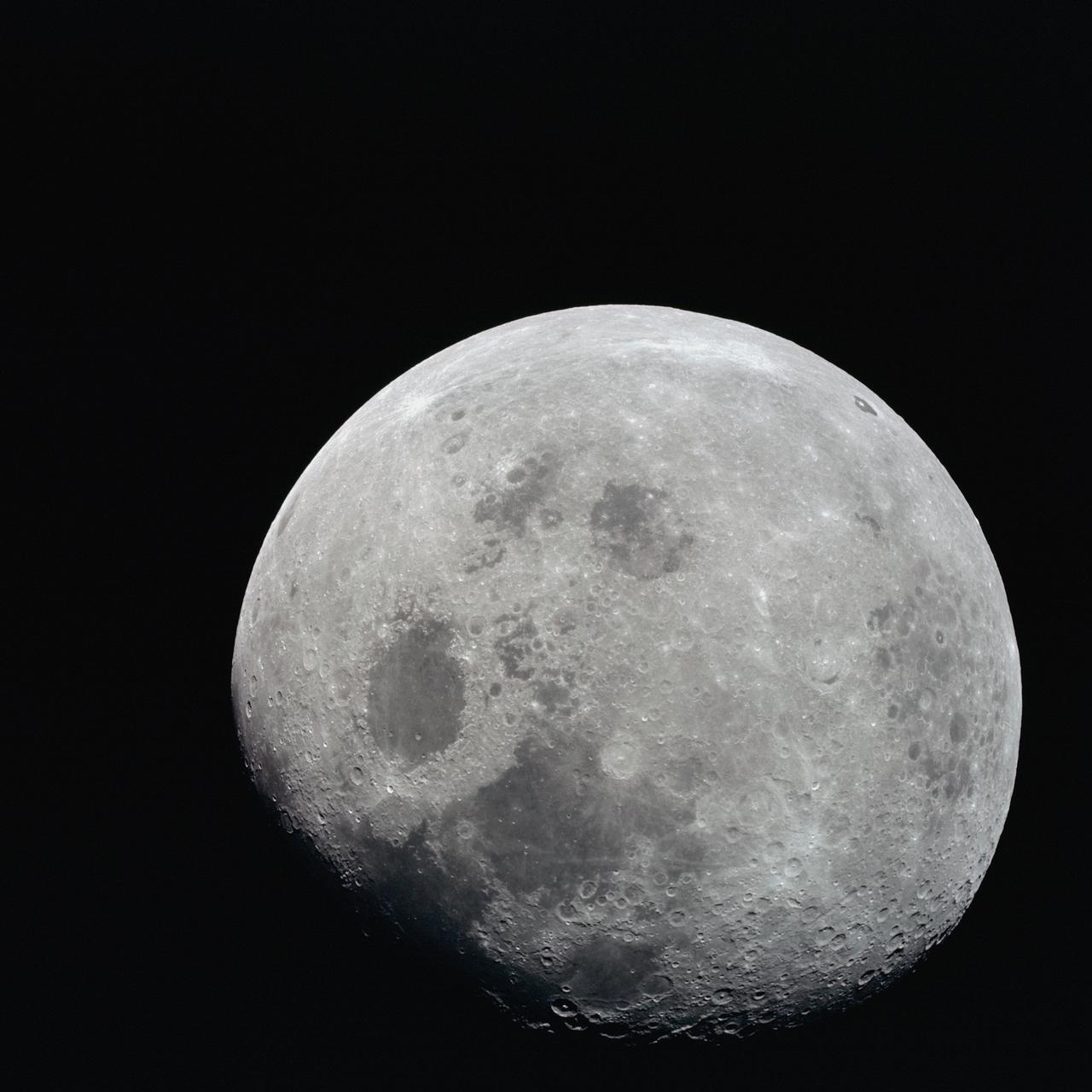

AS08-14-2506 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- This photograph of a nearly full moon was taken from the Apollo 8 spacecraft at a point above 70 degrees east longitude. (Hold picture with moon's dark portion at left). Mare Crisium, the circular, dark-colored area near the center, is near the eastern edge of the moon as viewed from Earth. Mare Nectaris is the circular mare near the terminator. The large, irregular maira are Tranquillitatis and Fecunditatis. The terminator at left side of picture crosses Mare Tranquillitatis and highlands to the south. Lunar farside features occupy most of the right half of the picture. The large, dark-colored crater Tsiolkovsky is near the limb at the lower right. Conspicuous bright rays radiate from two large craters, one to the north of Tsiolkovsky, the other near the limb in the upper half of the picture. These rayed craters were not conspicuous in Lunar Orbiter photography due to the low sun elevations when the Lunar Orbiter photography was made. The crater Langrenus is near the center of the picture at the eastern edge of Mare Fecunditatis. The lunar surface probably has less pronounced color that indicated by this print.
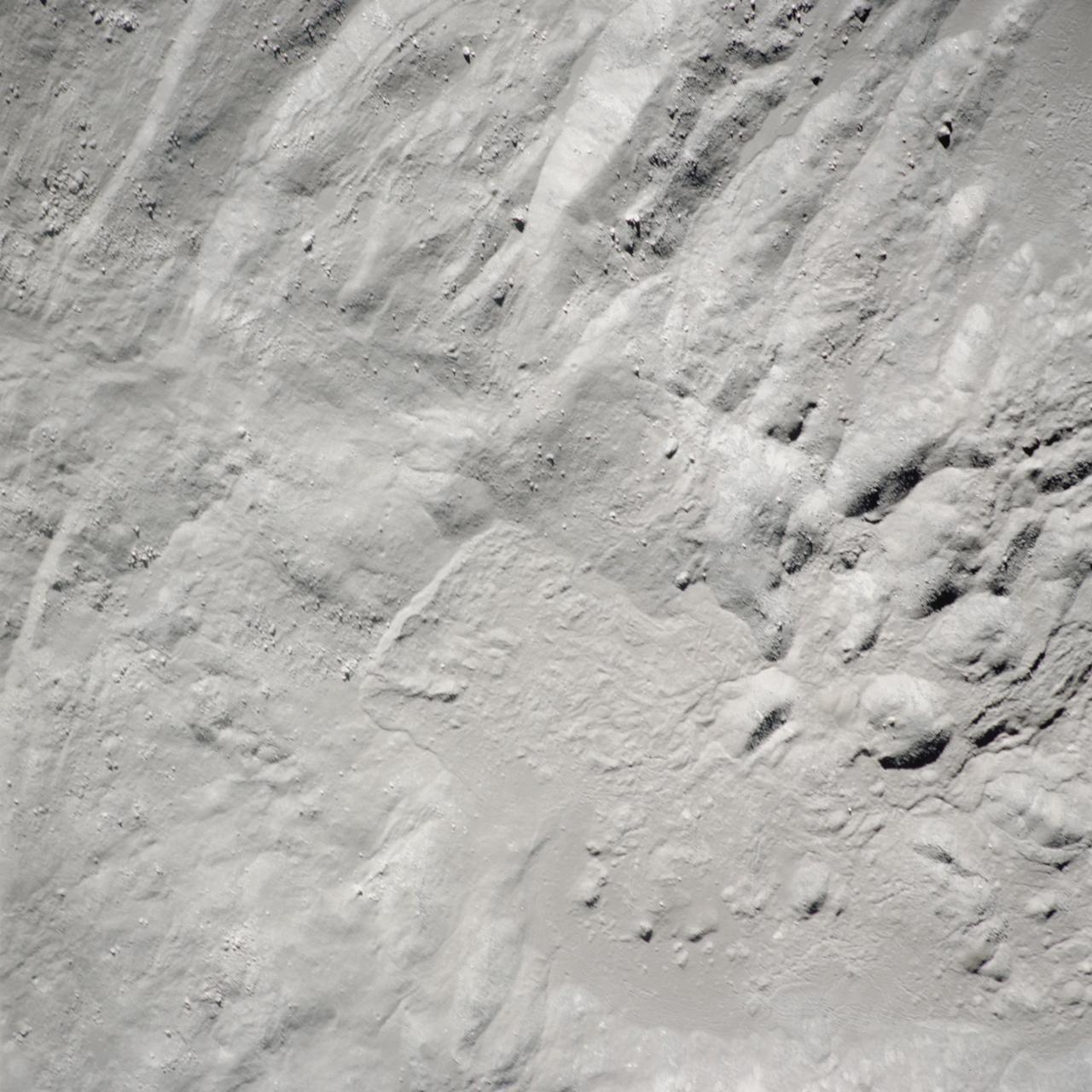

AS14-72-9975 (February 1971) --- A near vertical view of the inner wall of King Crater located on the lunar farside, as photographed from the Apollo 14 spacecraft in lunar orbit. The coordinates of the center of King Crater are 120.7 degrees east longitude and 14.3 degrees north latitude.
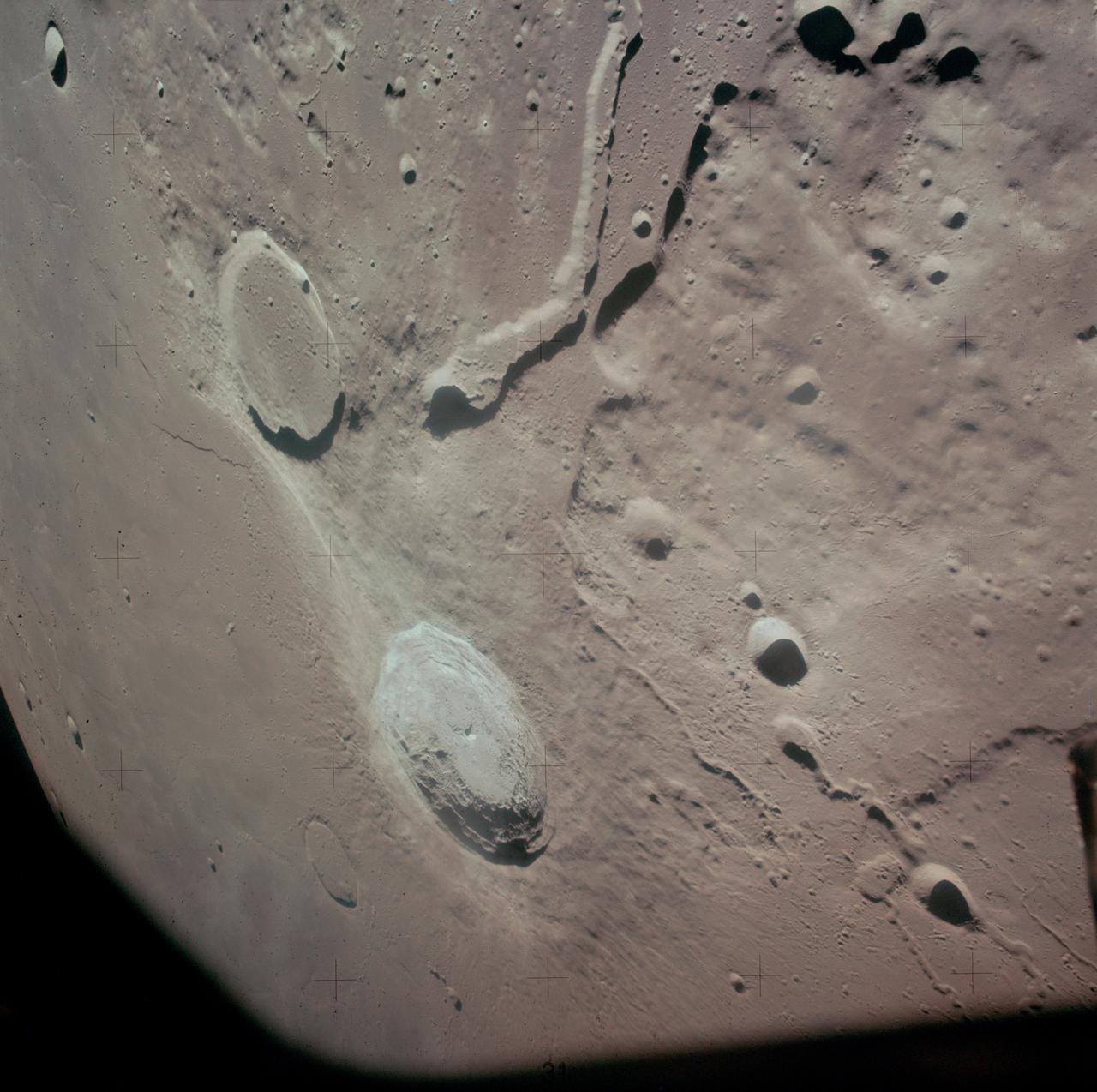

AS15-88-12002 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- An oblique view of a portion of the lunar nearside located near the northeast edge of the Ocean of Storms (Oceanus Procellarum), photographed by astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, from the Apollo 15 spacecraft in lunar orbit, showing the bright-appearing crater Aristarchus on the left, the crater Herodotus on the right, and Schroter's Valley at lower right. This view is looking southward. Aristarchus the head of Schroter's Valley, a sinuous rille in the Aristarchus Plateau, is called Cobra Head. The coordinates of the center of Aristarchus crater are 47.5 degrees west longitude and 23.6 degrees north latitude. While Worden remained in the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit, astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon.
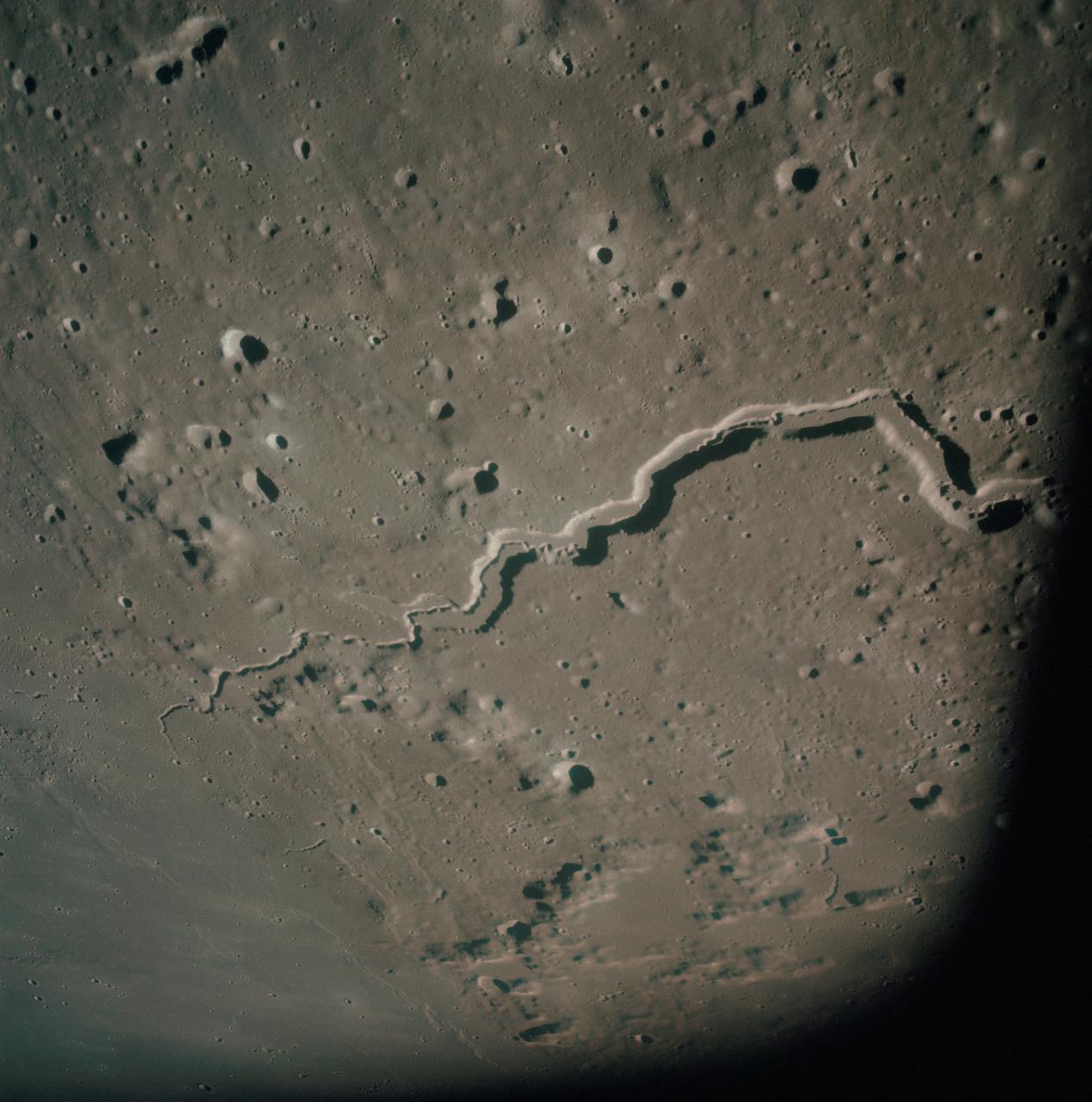

AS15-93-12628 (31 July 1971) --- The snake-like rille feature in this 70mm frame, photographed from the lunar-orbiting Apollo 15 Command and Service Modules (CSM) by astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, is Schroter's Valley. The long feature is located not far from the crater Aristarcus (out of frame) on the western side of the moon. Center coordinates of the area pictured are located at 25 degrees north latitude and 52.5 degrees west longitude. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Worden remained with the CSM in lunar orbit.
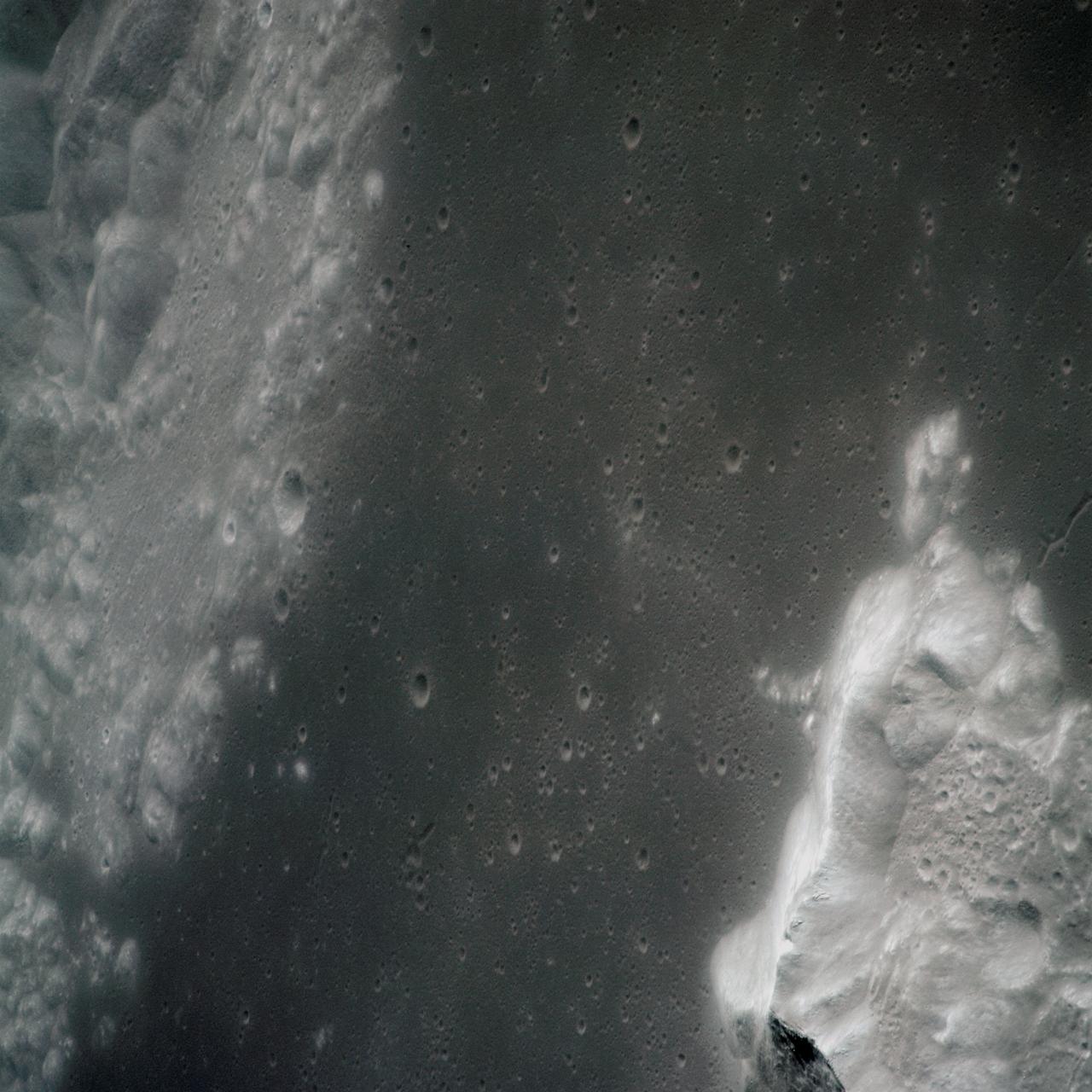

AS15-97-13160 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- A view of a portion of the crater Tsiolkovsky located in the highlands on the farside of the moon, as photographed from the Apollo 15 Command and Service Modules (CSM) by astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot. Note the dark, flat crater floor surrounding the very prominent central mountains. The mountains are in the northeastern corner of the photograph. The other upland area comprises part of the southwestern edge of the crater. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Worden remained with the CSM in lunar orbit.
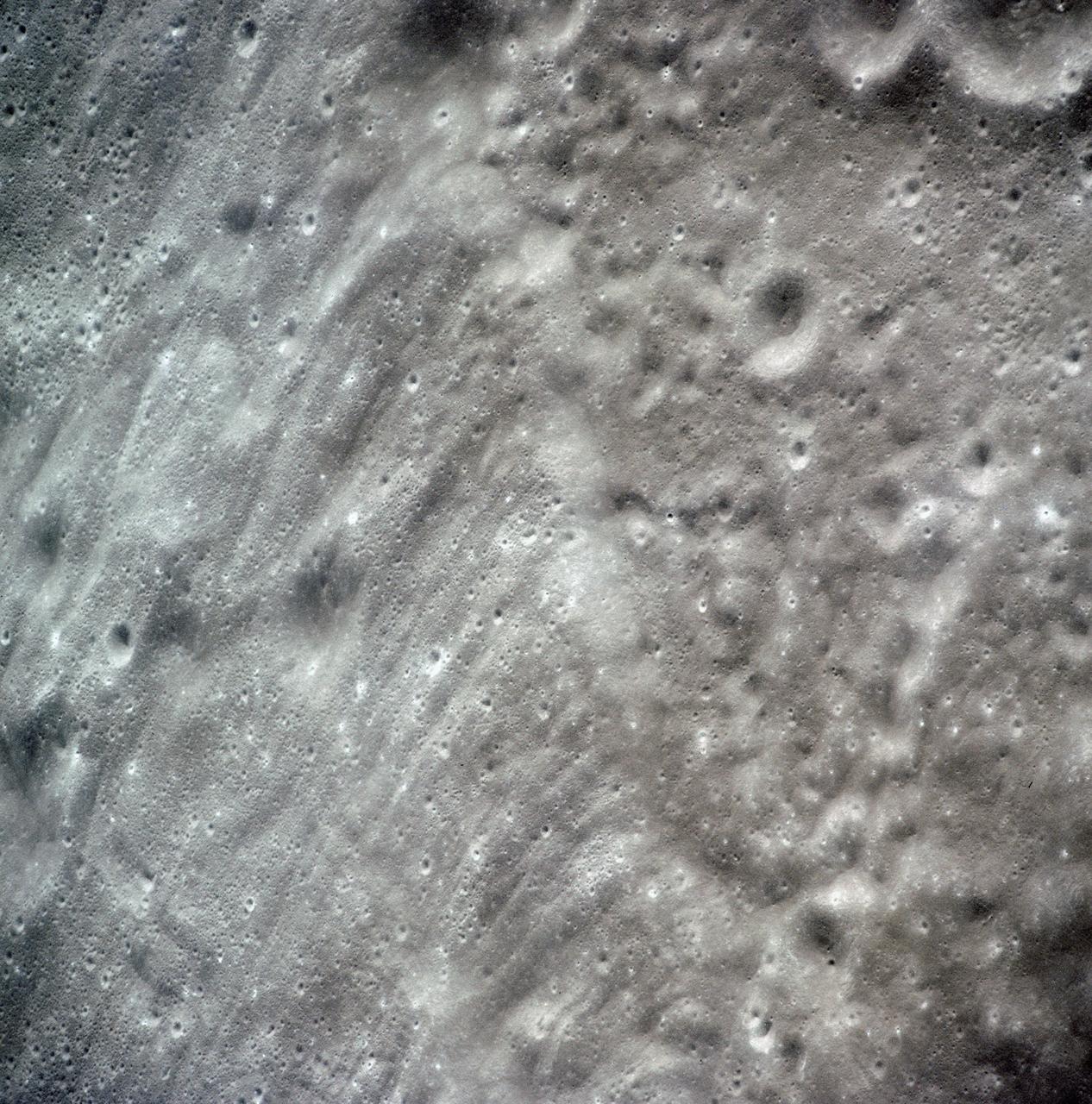

AS15-97-13168 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- A view of the flow structure on the rim and edge of the crater Tsiolkovsky in the highlands of the lunar farside, as photographed from lunar orbit by astronaut Alfred M. Worden in the Apollo 15 Command and Service Module (CSM). Note the scarp at the edge of the flow and elongated grooves on the flow surface. While astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon's Hadley-Apennine landing site, Worden remained with the CSM in lunar orbit.
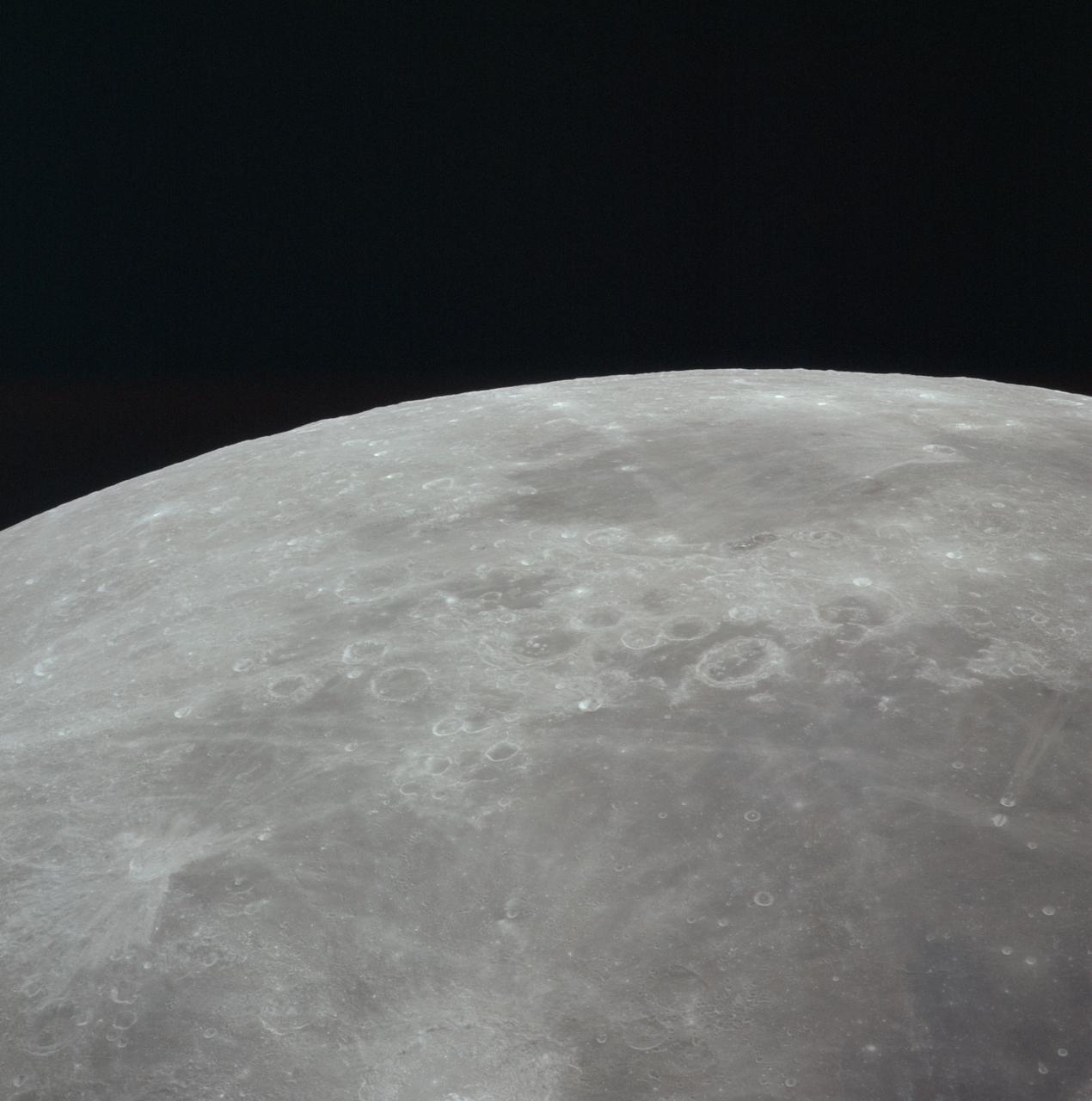

AS16-121-19449 (16-27 April 1972) --- This 70mm handheld camera's view of the moon, photographed during the Apollo 16 mission's trans-Earth coast, features Mare Fecunditatis (Sea of Fertility) in the foreground with the twin craters Messier at the lower right. Nearer the horizon is Mare Nectaris (Sea of Nectar) with craters Goclenius and Gutenberg in between. Goclenius is located at approximately 10 degrees south latitude and 45 degrees east longitude.
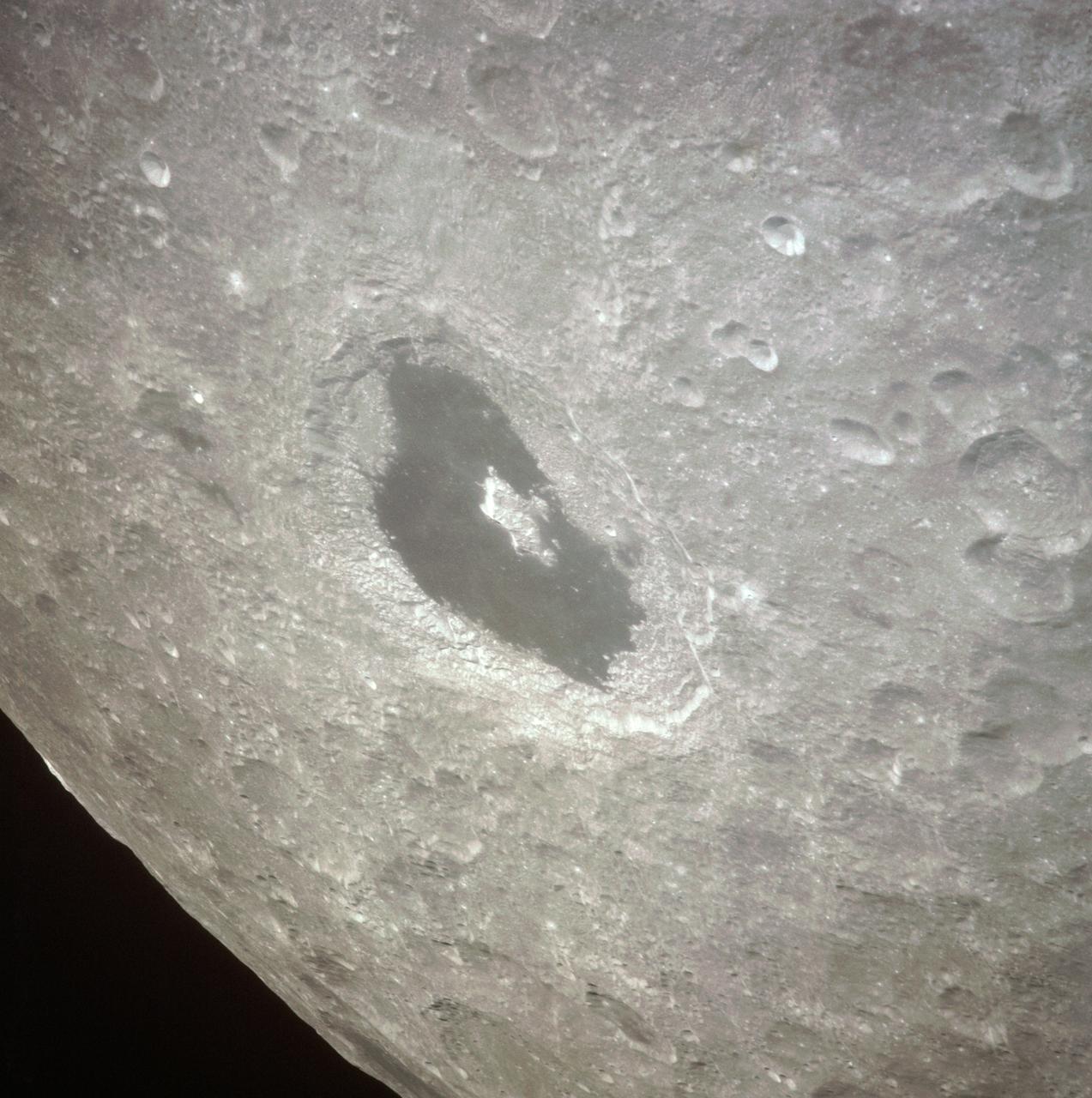

AS13-60-8659 (14 April 1970) --- Excellent view of the lunar farside showing the crater Tsiolkovsky, as photographed by the crew of the Apollo 13 mission during their lunar pass. The view is looking southeast toward the lunar horizon. The approximate coordinates of Tsiolkovsky are 128.5 degrees east longitude and 20.5 degrees south latitude. The Apollo 13 crew members were forced to cancel their scheduled lunar landing because of an apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two in the Service Module (SM).
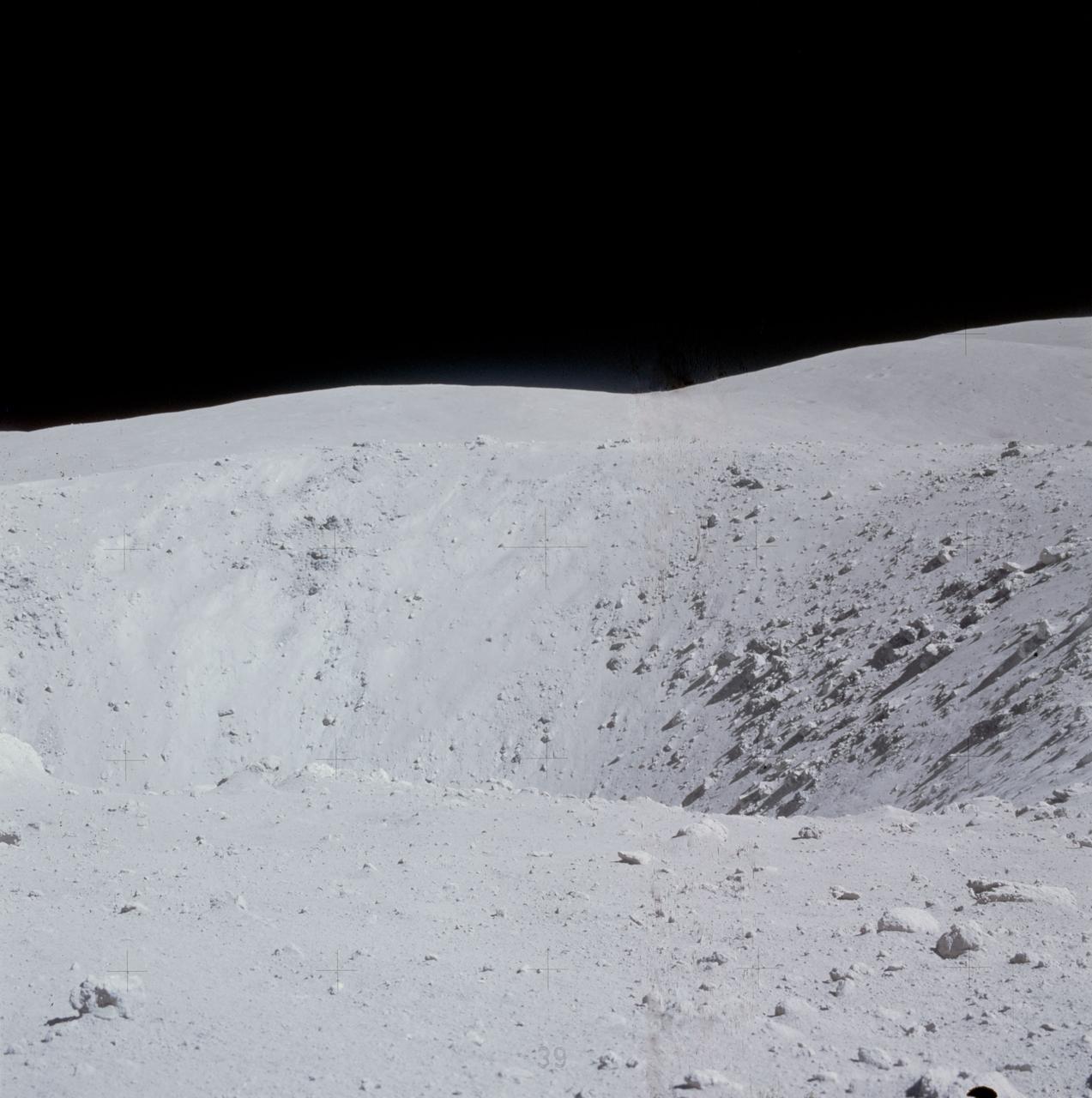

AS16-116-18599 (21 April 1972) --- A close-up view of Buster Crater, which was visited by the two moon-exploring crew men of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, during the first extravehicular activity (EVA), April 21, 1972. Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr. said the crater appeared to be larger than 50 meters, and he called it a very spectacular crater. This was the second stop for astronauts John W. Young and Duke on the mission's first EVA. Young exposed this view with his 70mm Hasselblad camera. While astronauts Young, commander; and Duke, lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
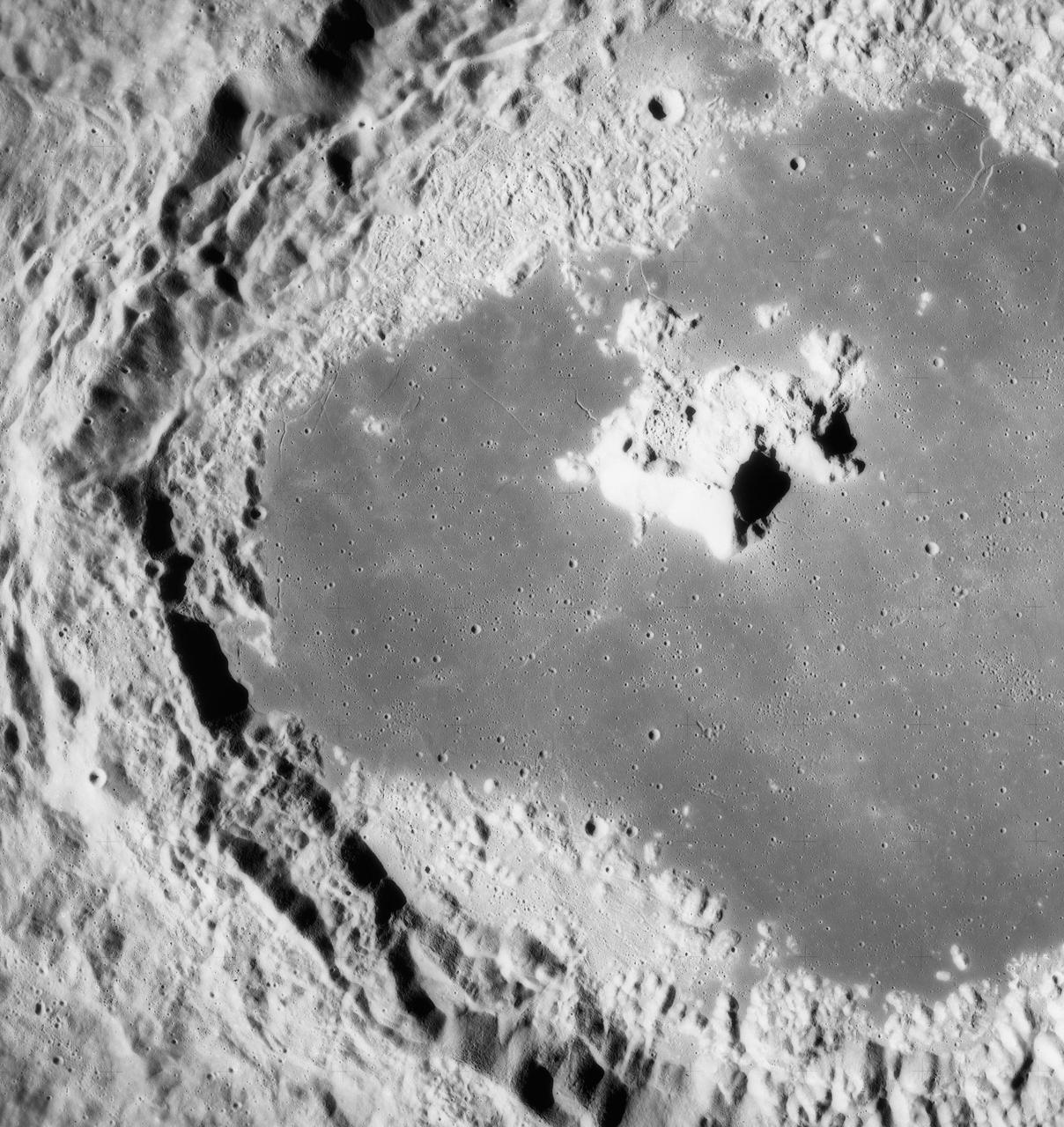

S71-44670 (31 July 1971) --- A near vertical view of the crater Tsiolkovsky on the lunar farside, as photographed by the Fairchild metric camera in the Scientific Instrument Module (SIM) bay of the Apollo 15 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. This view is looking northerly. The coordinates of the crater's central peaks are 128 degrees east longitude and 20 degrees south latitude. The mare area measured from east to west is approximately 145 kilometers (90 statute miles) across. The three-inch mapping camera was one of eight lunar orbital science experiments mounted in the SIM bay.
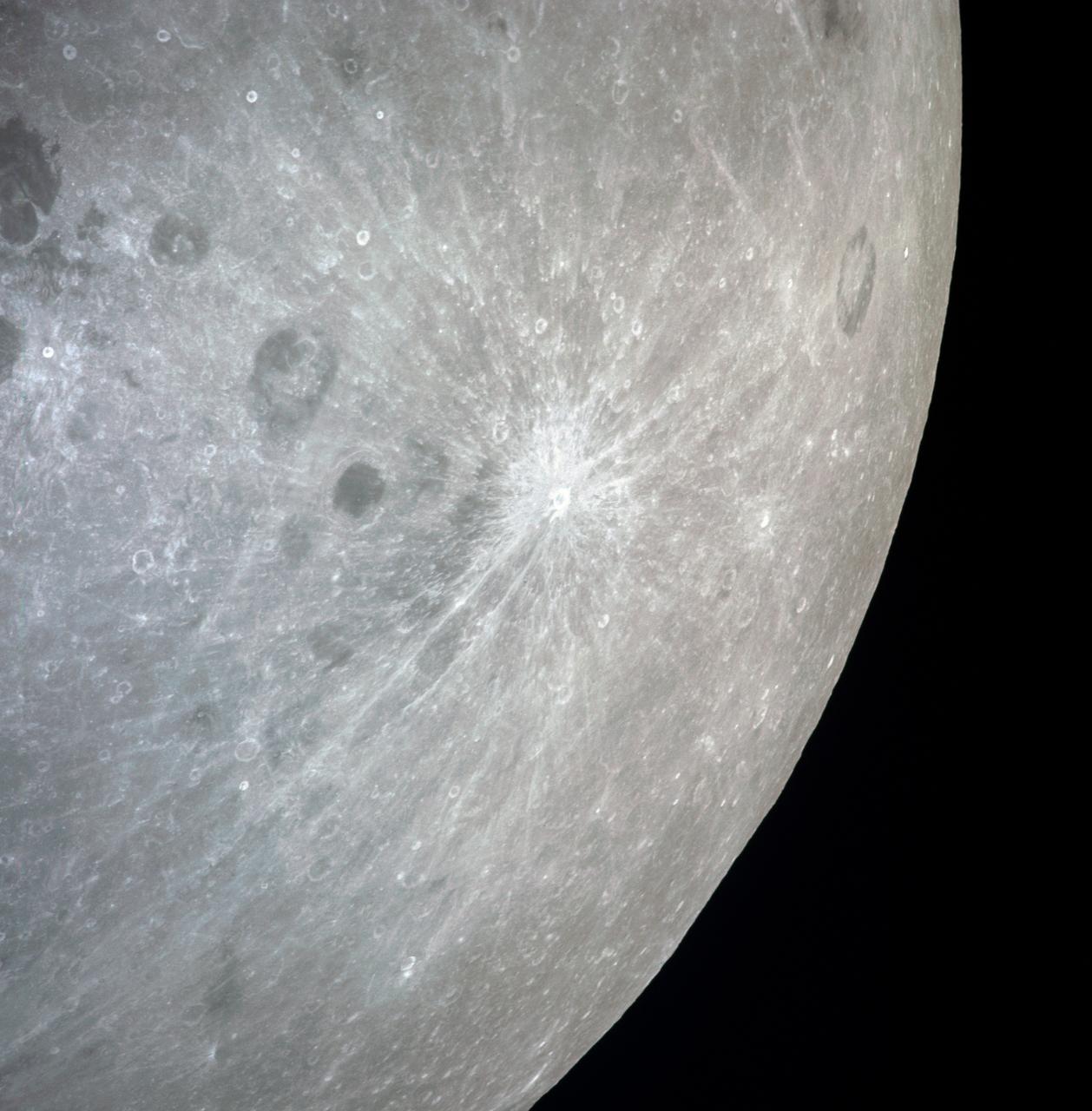

AS13-60-8675 (April 1970) --- This bright-rayed crater on the lunar farside was photographed from the Apollo 13 spacecraft during its pass around the moon. This area is northeast of Mare Marginus. The bright-rayed crater is located at about 105 degrees east longitude and 45 degrees north latitude. The crater Joliot-Curie is located between Mare Marginus and the rayed crater. This view is looking generally toward the northeast.
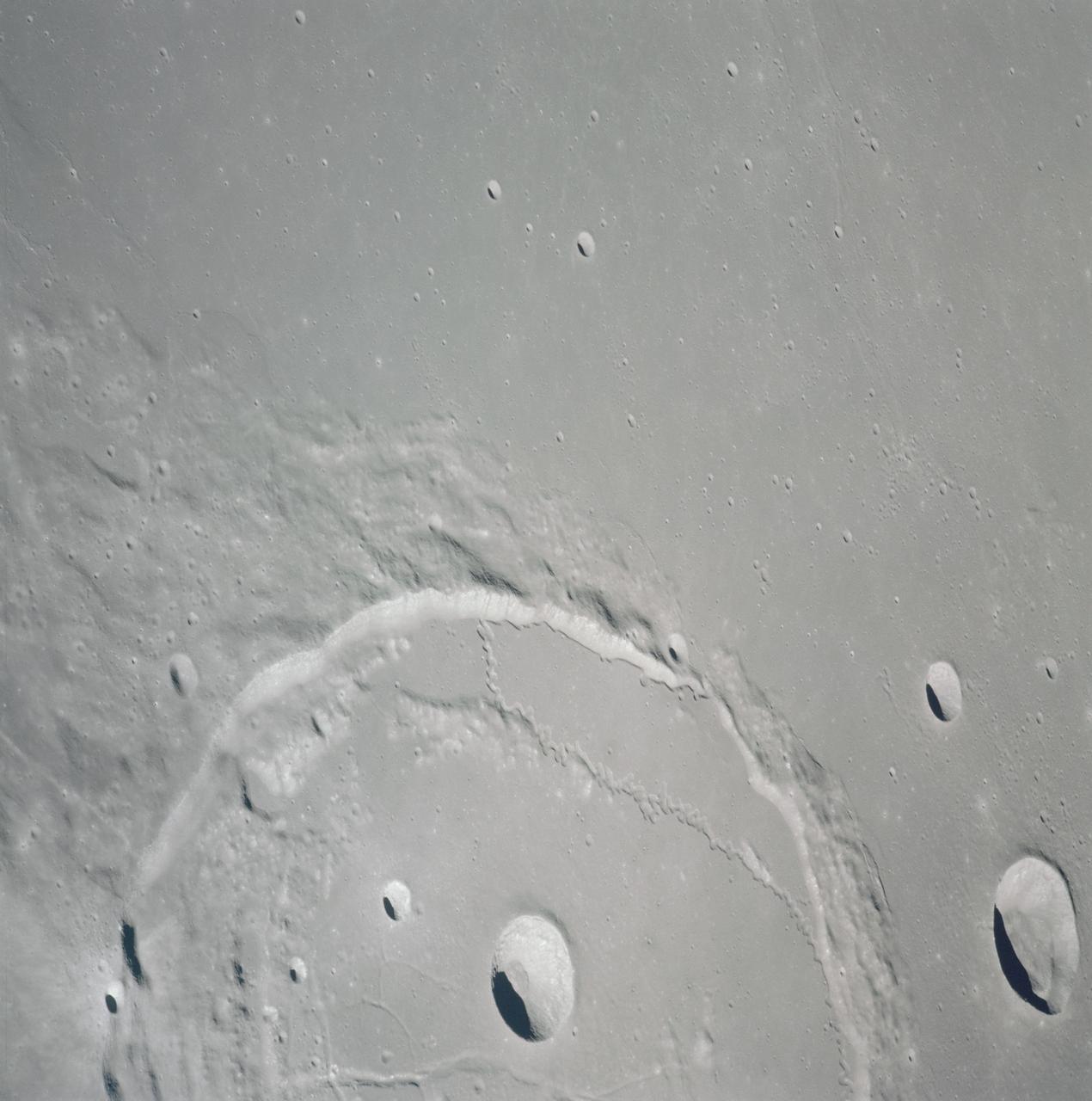

AS15-91-12366 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- The crater Posidonius at the northeastern edge of the Sea of Serenity, was photographed with a 70mm handheld Hasselblad from the Command and Service Module (CSM) by astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, in lunar orbit. While Worden remained with the CSM in lunar orbit, astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the lunar surface.
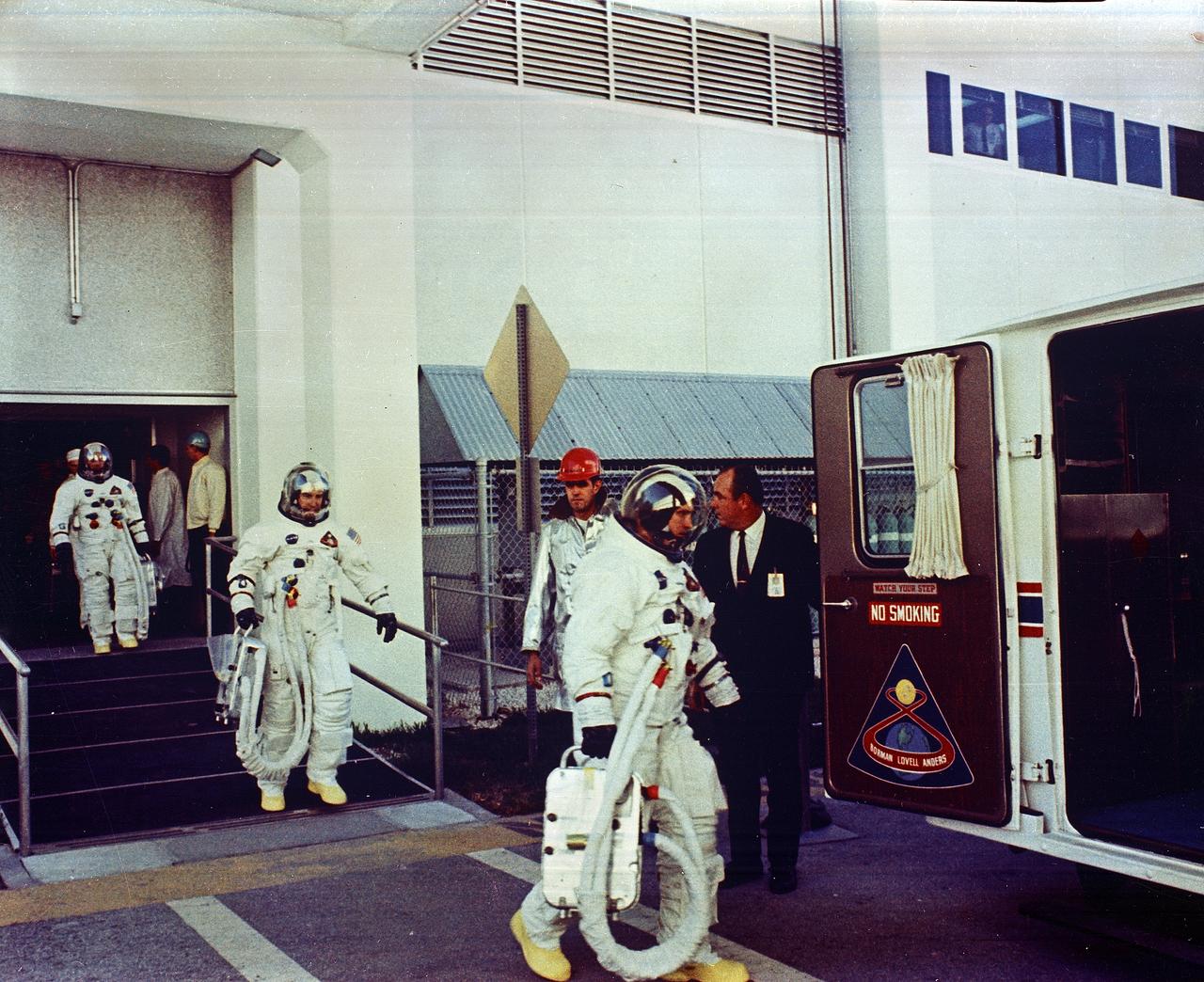

Apollo 8 Astronauts William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) Pilot; James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Frank Borman, commander, transfer to the astronaut van for the trip to the launch pad. The first manned Apollo mission launched aboard the Saturn V and first manned Apollo craft to enter lunar orbit, the SA-503, Apollo 8 mission liftoff occurred on December 21, 1968 and returned safely to Earth on December 27, 1968. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
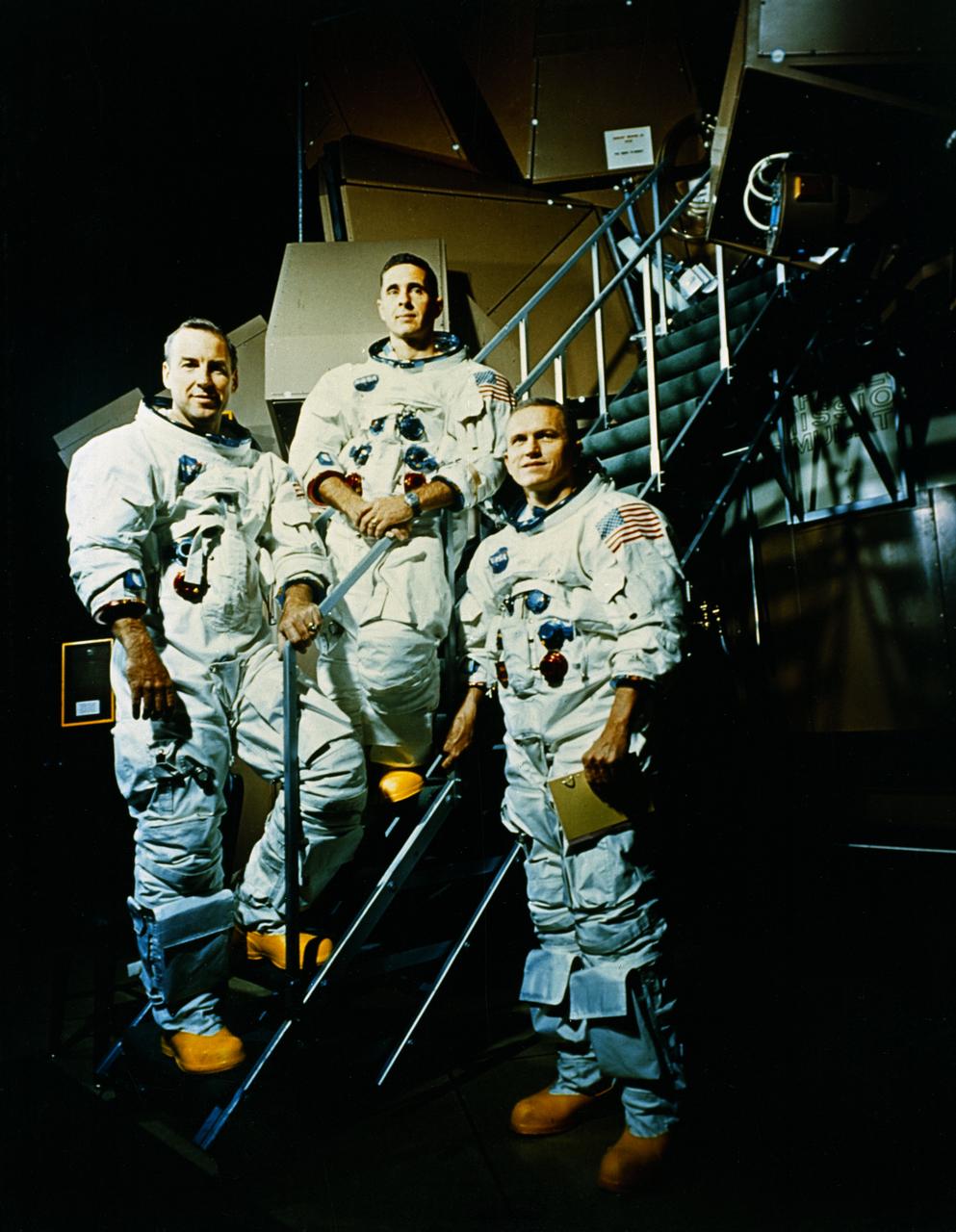

The Apollo 8 Crew included (L to R) James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot; William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) Pilot; and Frank Borman, Commander. The first manned Apollo mission launched aboard the Saturn V and first manned Apollo craft to enter lunar orbit, the SA-503, Apollo 8 mission liftoff occurred on December 21, 1968 and returned safely to Earth on December 27, 1968. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
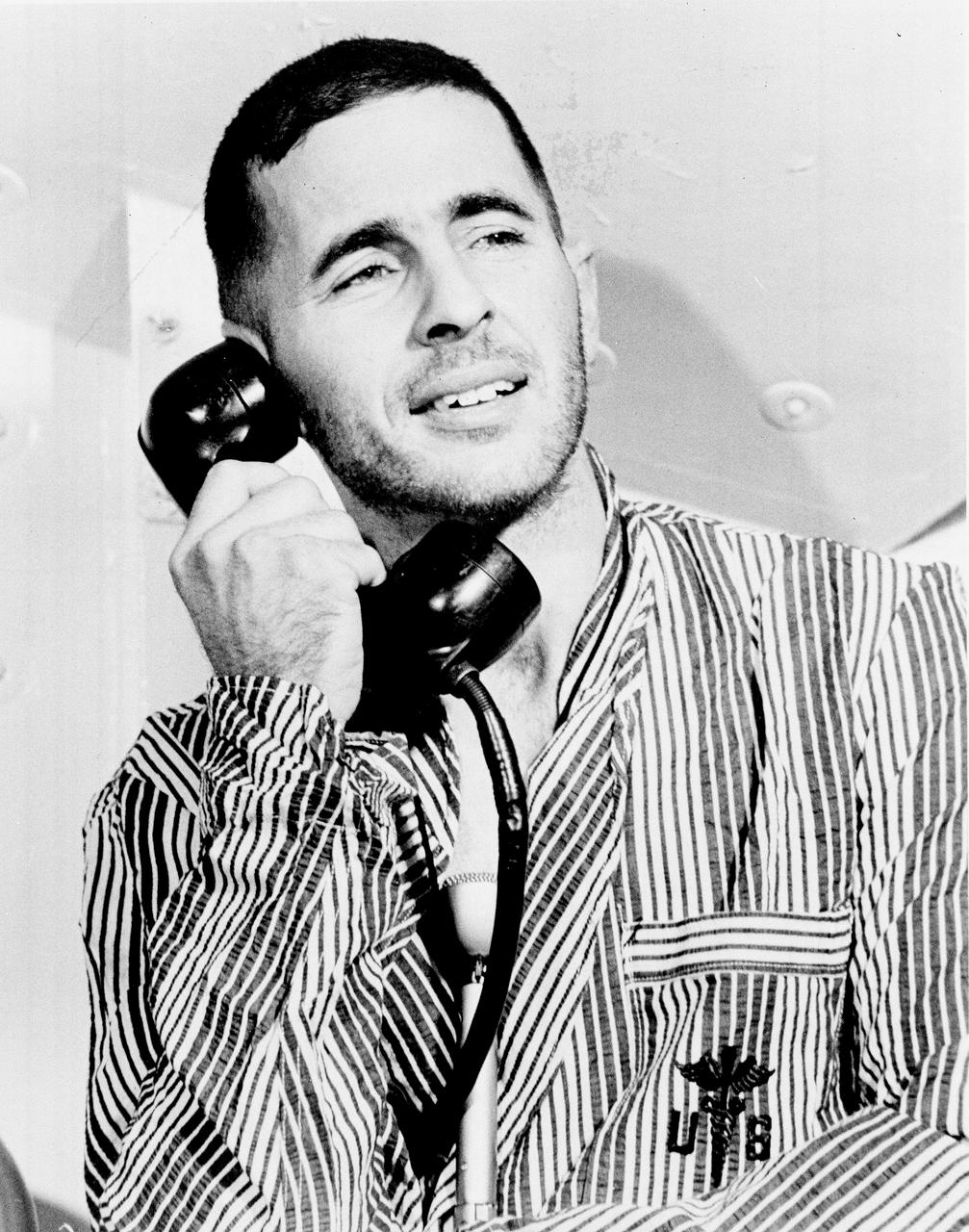

Apollo 8 Astronaut William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) pilot of the first manned Saturn V space flight into Lunar orbit, accepted a phone call from the U.S. President Lyndon B. Johnson prior to launch. Anders, along with astronauts James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot, and Frank Borman, commander, launched aboard the Apollo 8 mission on December 21, 1968 and returned safely to Earth on December 27, 1968. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.

Apollo 8 Astronaut Frank Borman, commander of the first manned Saturn V space flight into Lunar orbit, accepted a phone call from the U.S. President Lyndon B. Johnson prior to launch. Borman, along with astronauts William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) pilot, and James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot, launched aboard the Apollo 8 mission on December 21, 1968 and returned safely to Earth on December 27, 1968. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
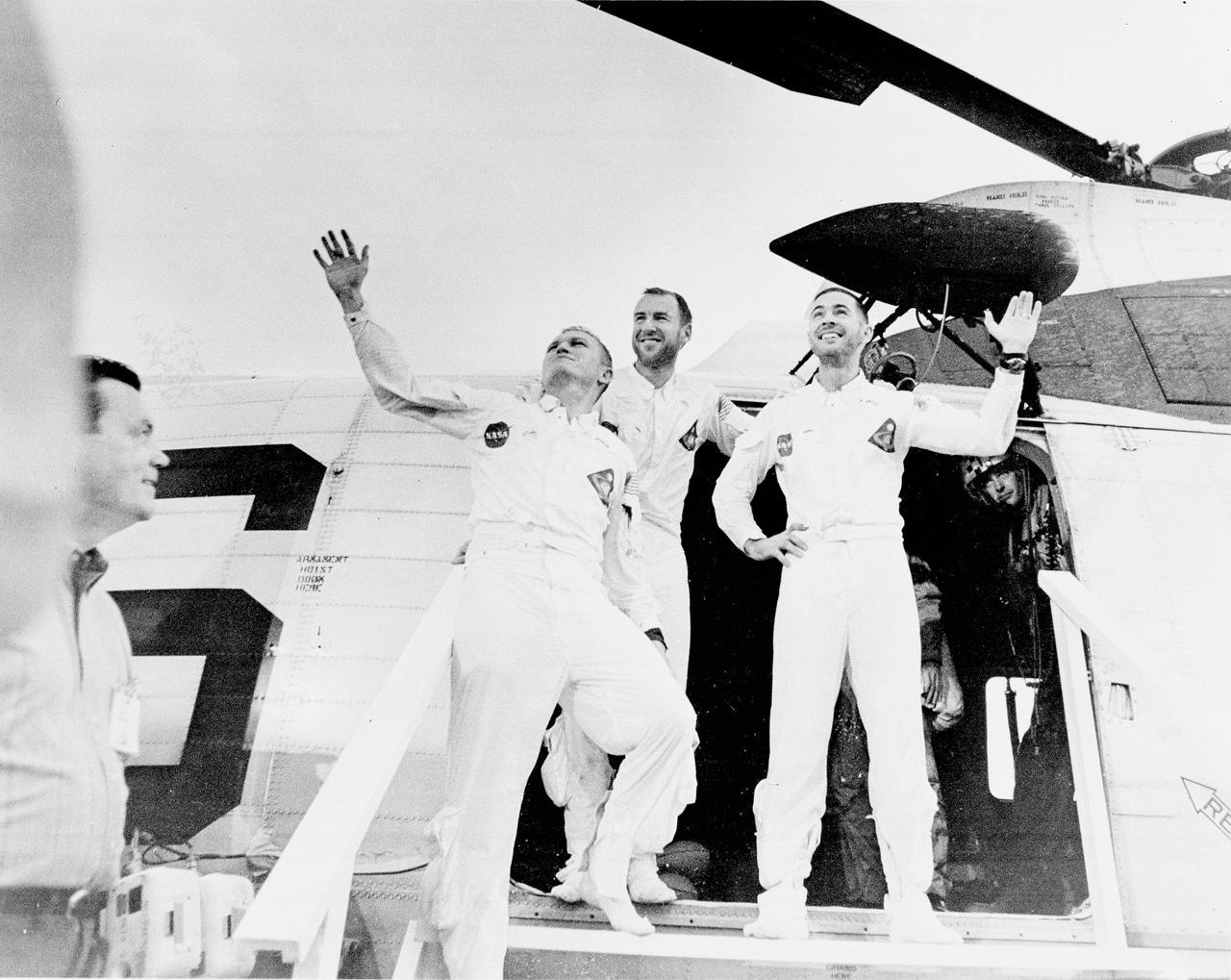

Apollo 8 served as the first manned lunar orbit mission. Liftoff occurred on December 21, 1968, carrying a three man crew consisting of astronauts Frank Borman, commander; William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) Pilot; and James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot. The three safely returned to Earth on December 27, 1968. In this photograph, the crew members are waving as they leave the recovery helicopter. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
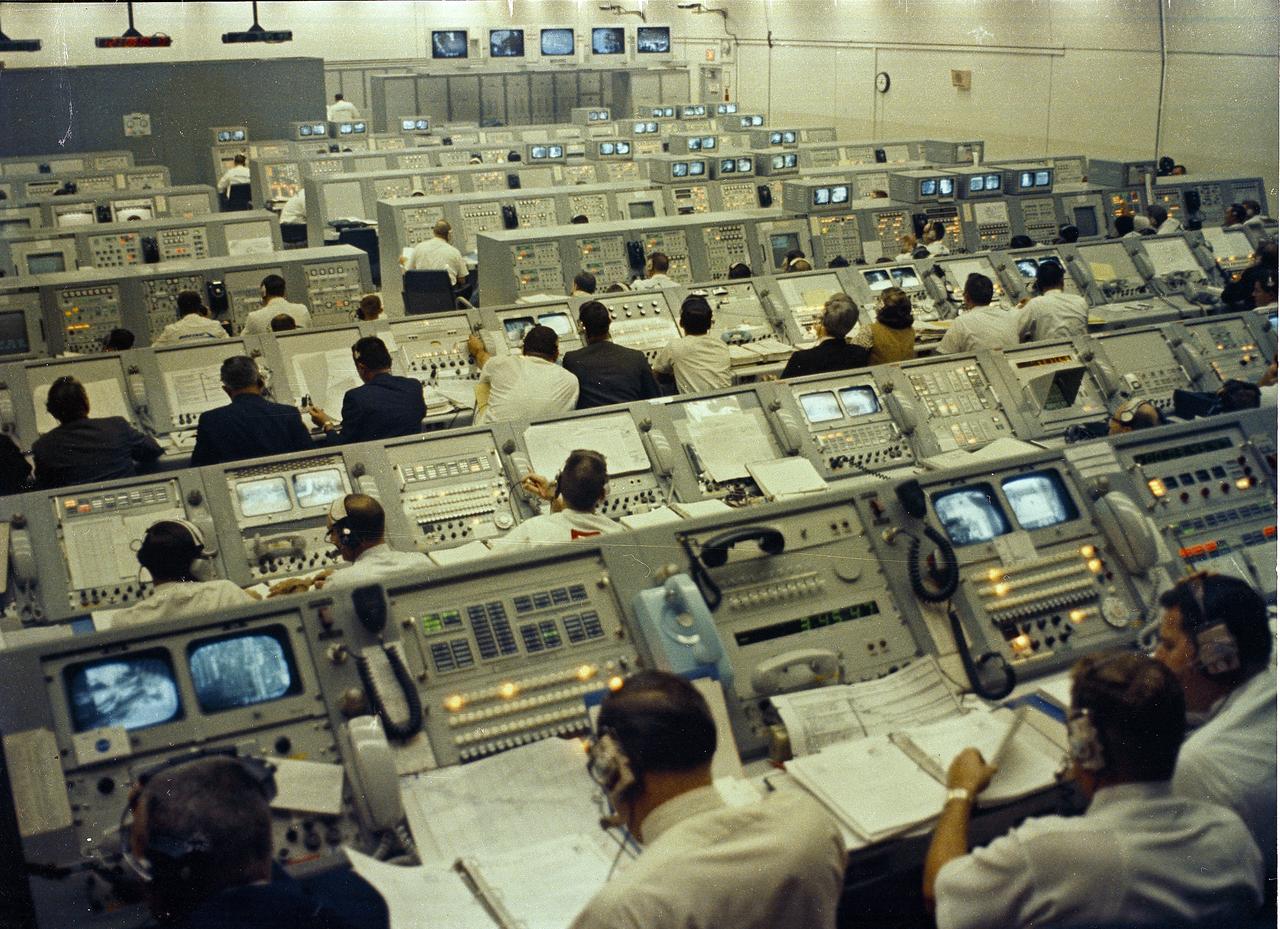

This photograph depicts a busy Launch Control Center at Kennedy Space Center during the Apollo 8 mission launch activities. Apollo 8 served as the first manned lunar orbit mission. Liftoff occurred on December 21, 1968 with a three man crew consiting of astronauts Frank Borman, commander; William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) Pilot; and James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot. The three safely returned to Earth on December 27, 1968. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
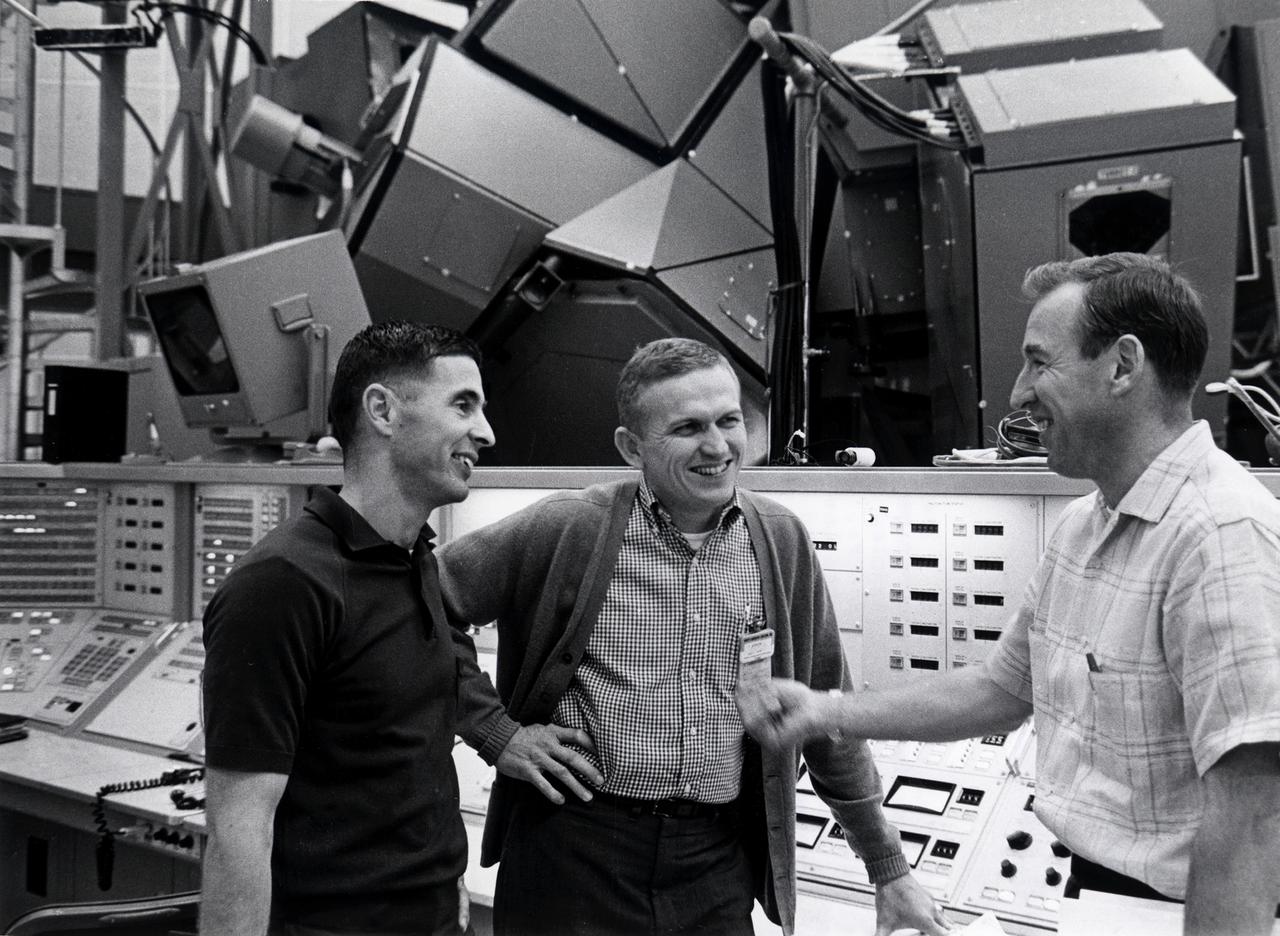

Apollo 8 crew members paused before the mission simulator during training for the first manned lunar orbital mission. Frank Borman, commander; James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot; and William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) pilot , were also the first humans to launch aboard the massive Saturn V space vehicle. Lift off occurred on December 21, 1968 and returned safely to Earth on December 27, 1968. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
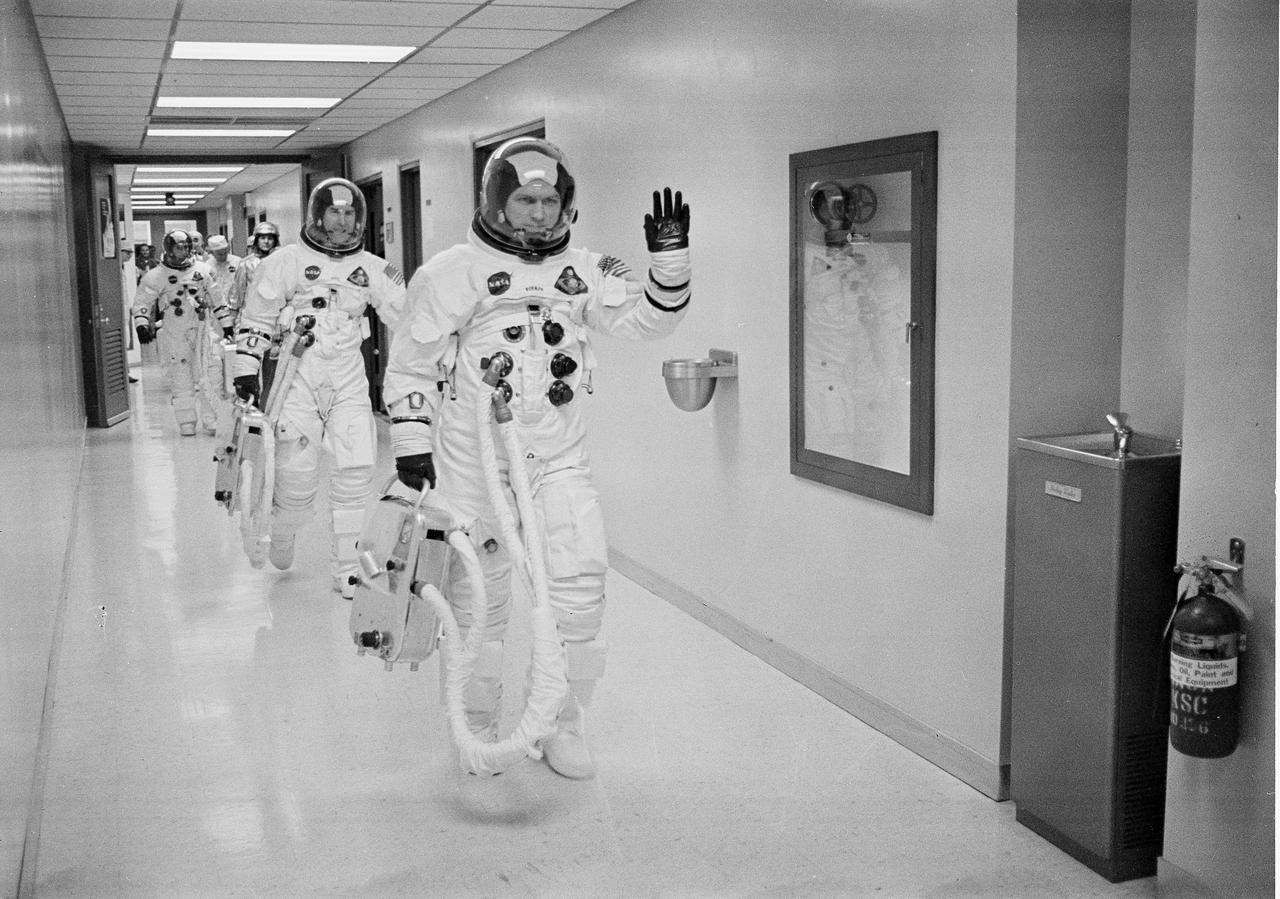

Apollo 8 Astronaut and commander Frank Borman leads the way as he and James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot; and William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) Pilot head out to the launch pad for the historical first manned Apollo mission to travel to the lunar vicinity, and first manned mission launched via the Saturn V vehicle. Liftoff occurred on December 21, 1968 and returned safely to Earth on December 27, 1968. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
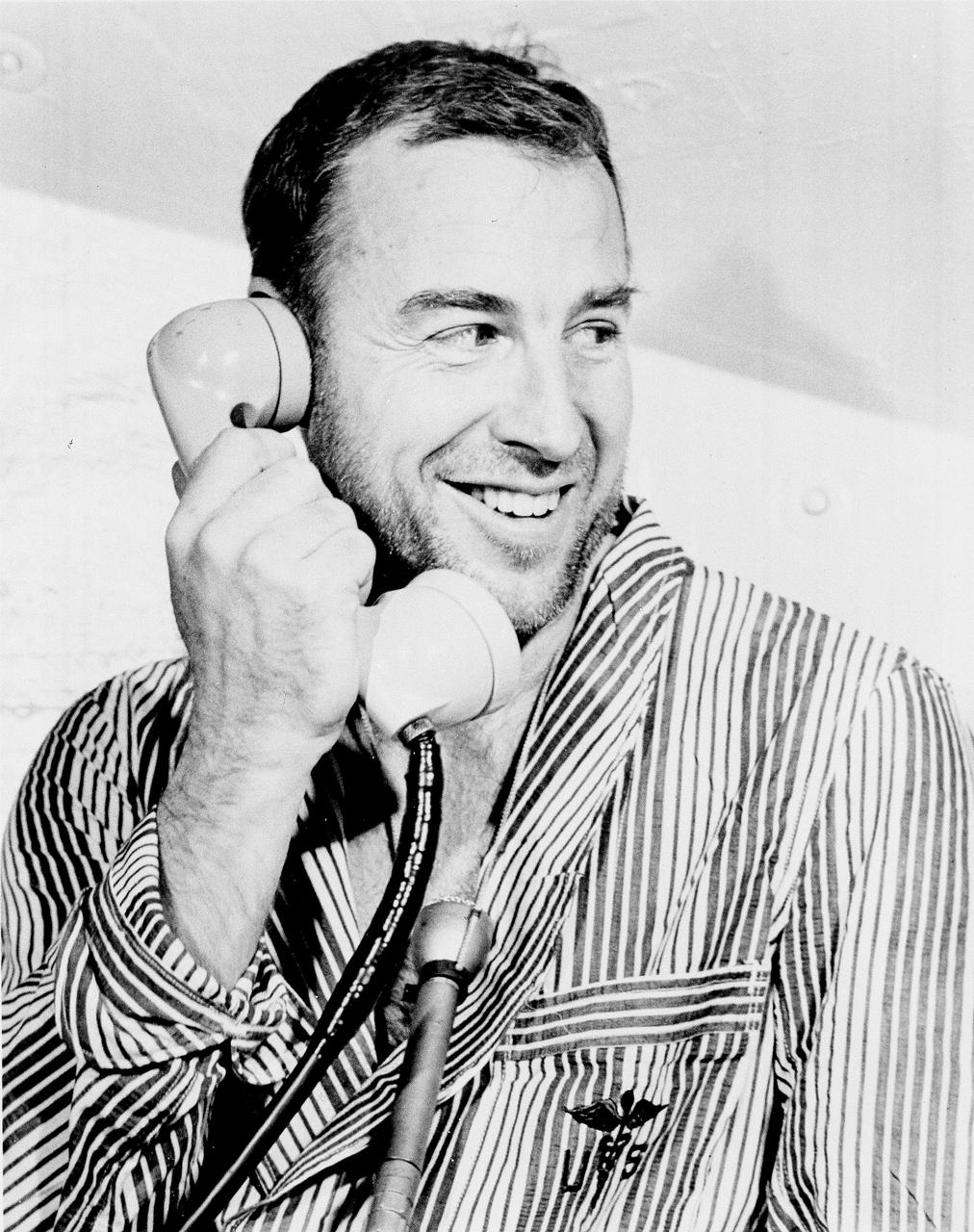

Apollo 8 Astronaut James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot of the first manned Saturn V space flight into Lunar orbit, accepted a phone call from the U.S. President Lyndon B. Johnson prior to launch. Lovell, along with astronauts William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) pilot, and Frank Borman, commander, launched aboard the Apollo 8 mission on December 21, 1968 and returned safely to Earth on December 27, 1968. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
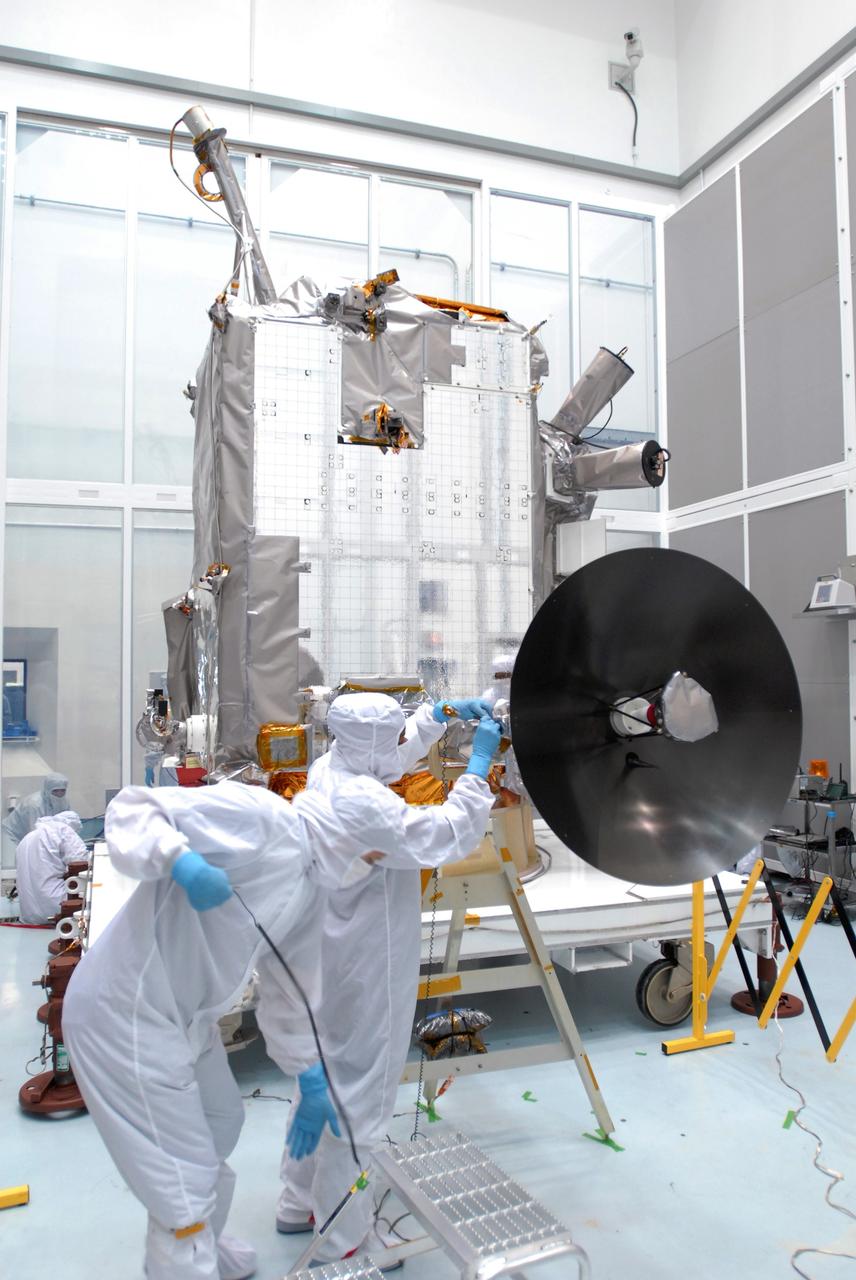

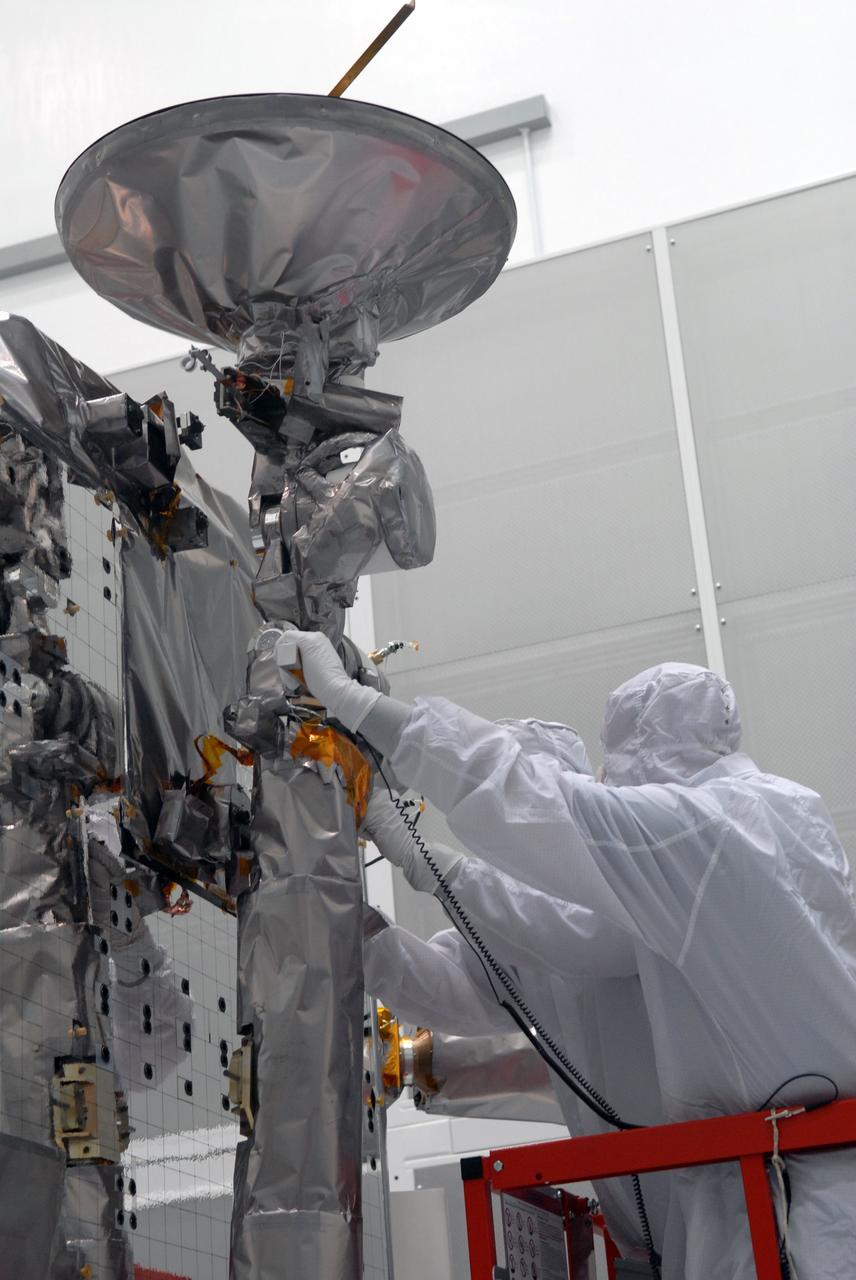
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians are testing the range of motion on the high-gain antenna for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians secure NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter's high-gain antenna into place for stowage. The antenna completed a range of motion test. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
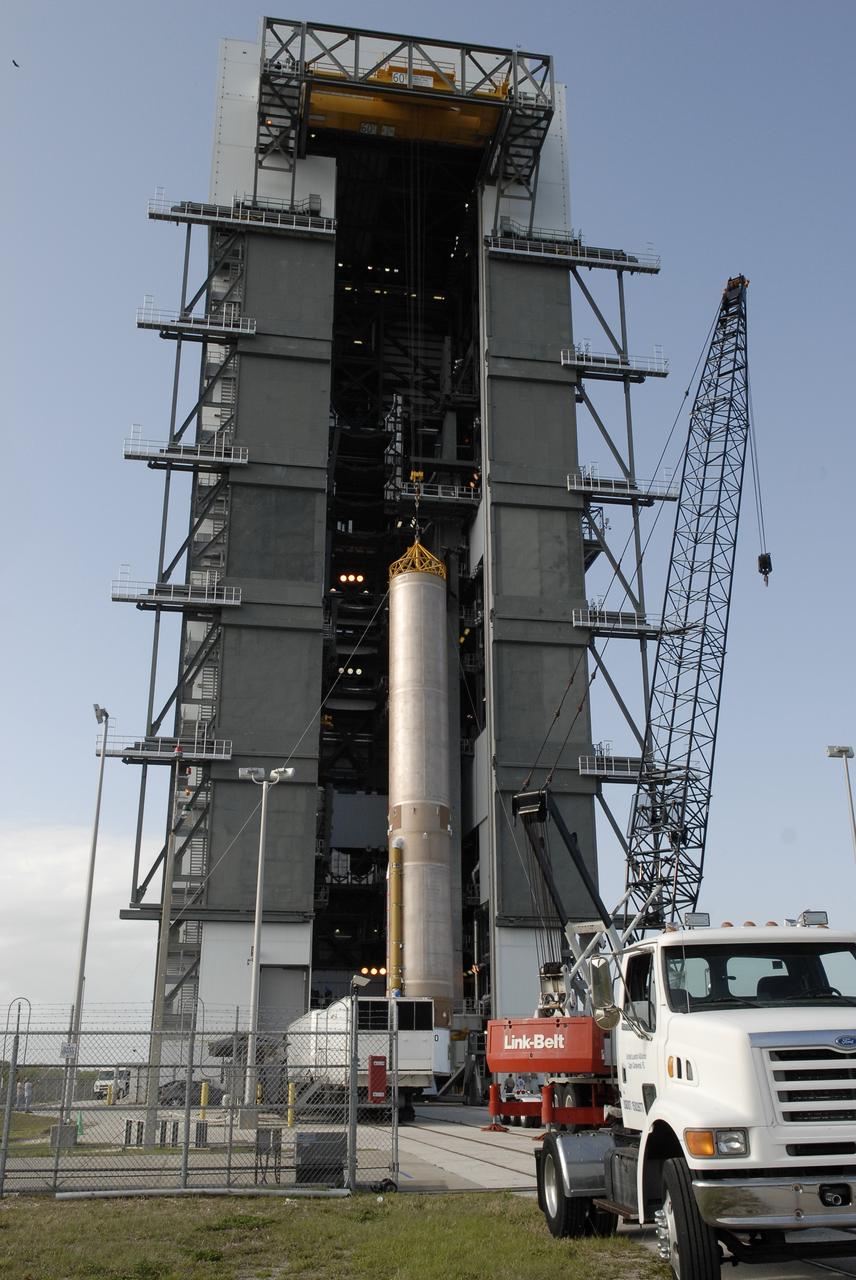

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Atlas V first stage is being moved into the Vertical Integration Facility. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
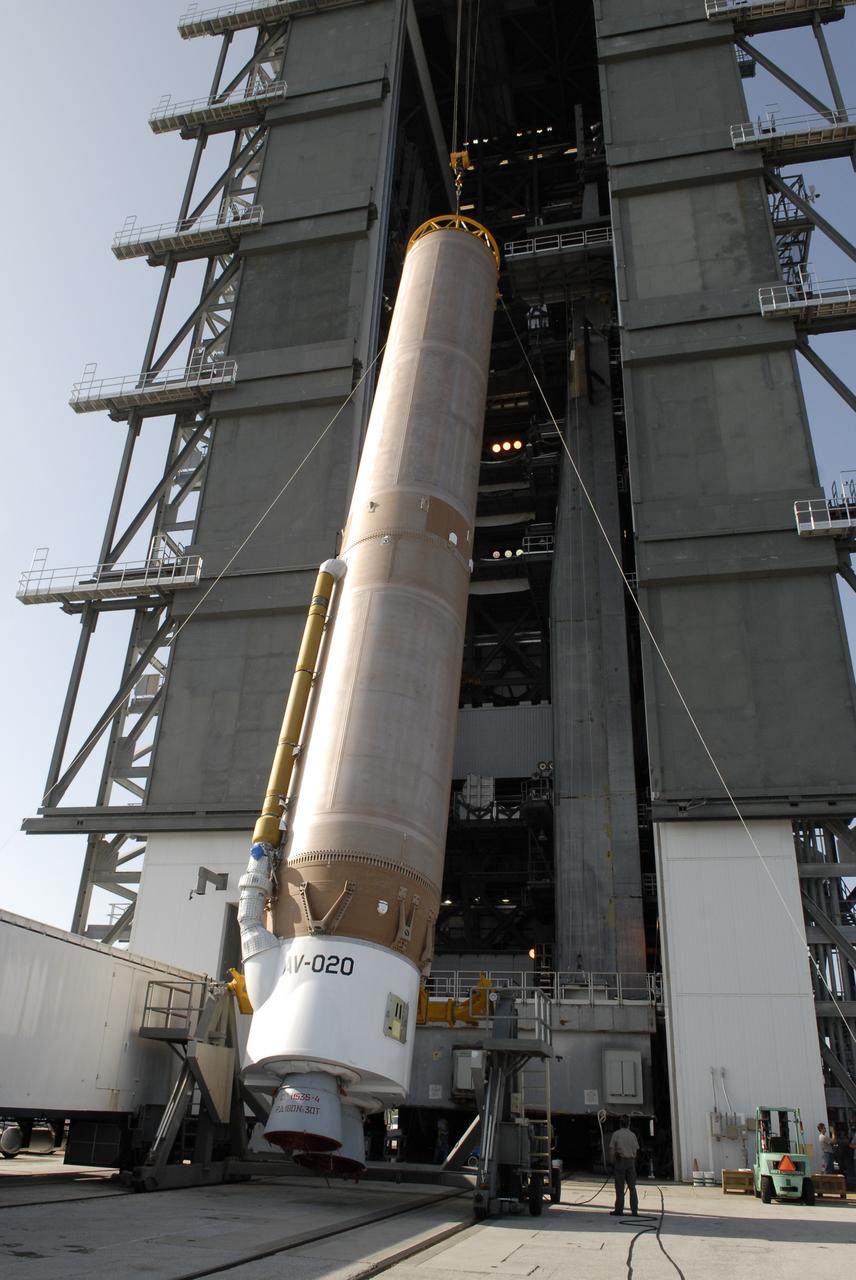

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– When the Atlas V first stage is raised to vertical, it will be lifted into the Vertical Integration Facility on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
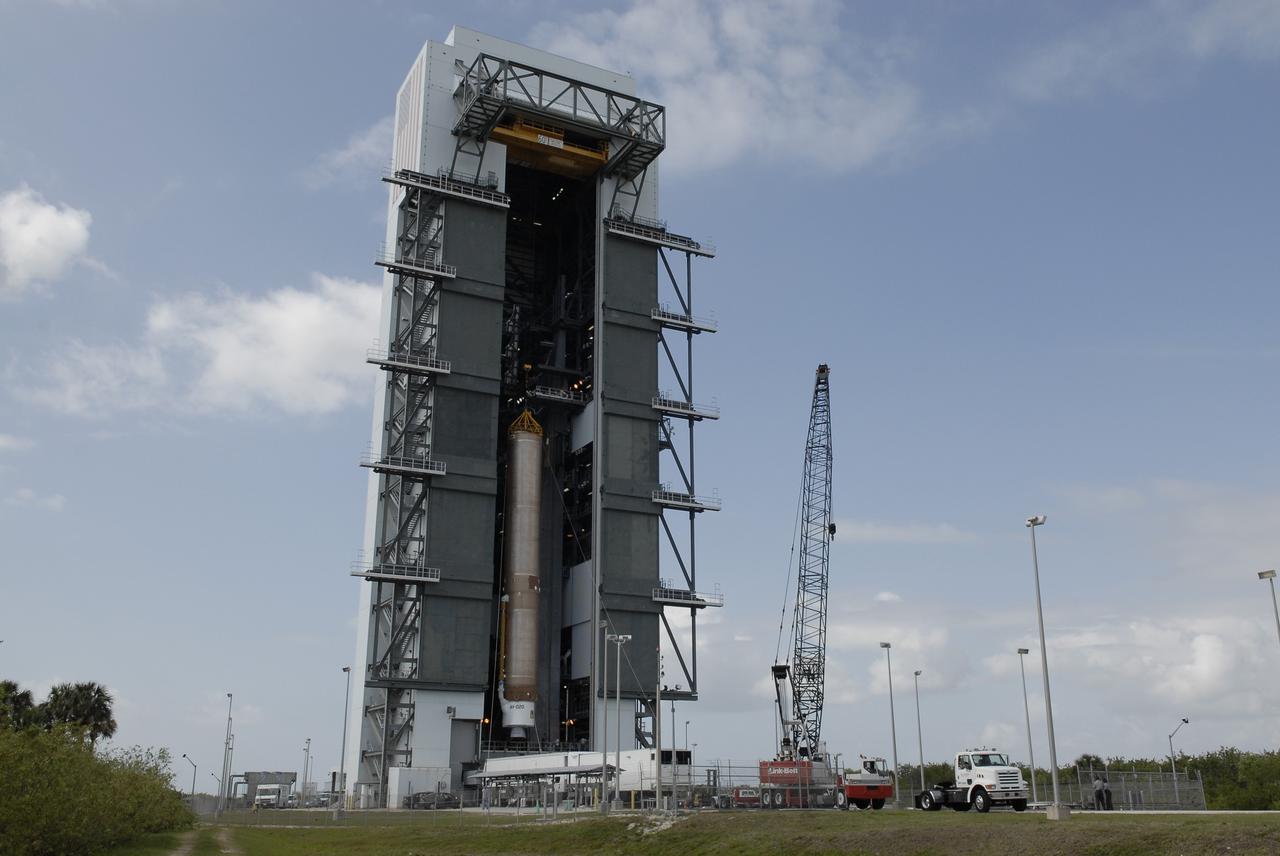

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Atlas V first stage is being moved into the Vertical Integration Facility. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
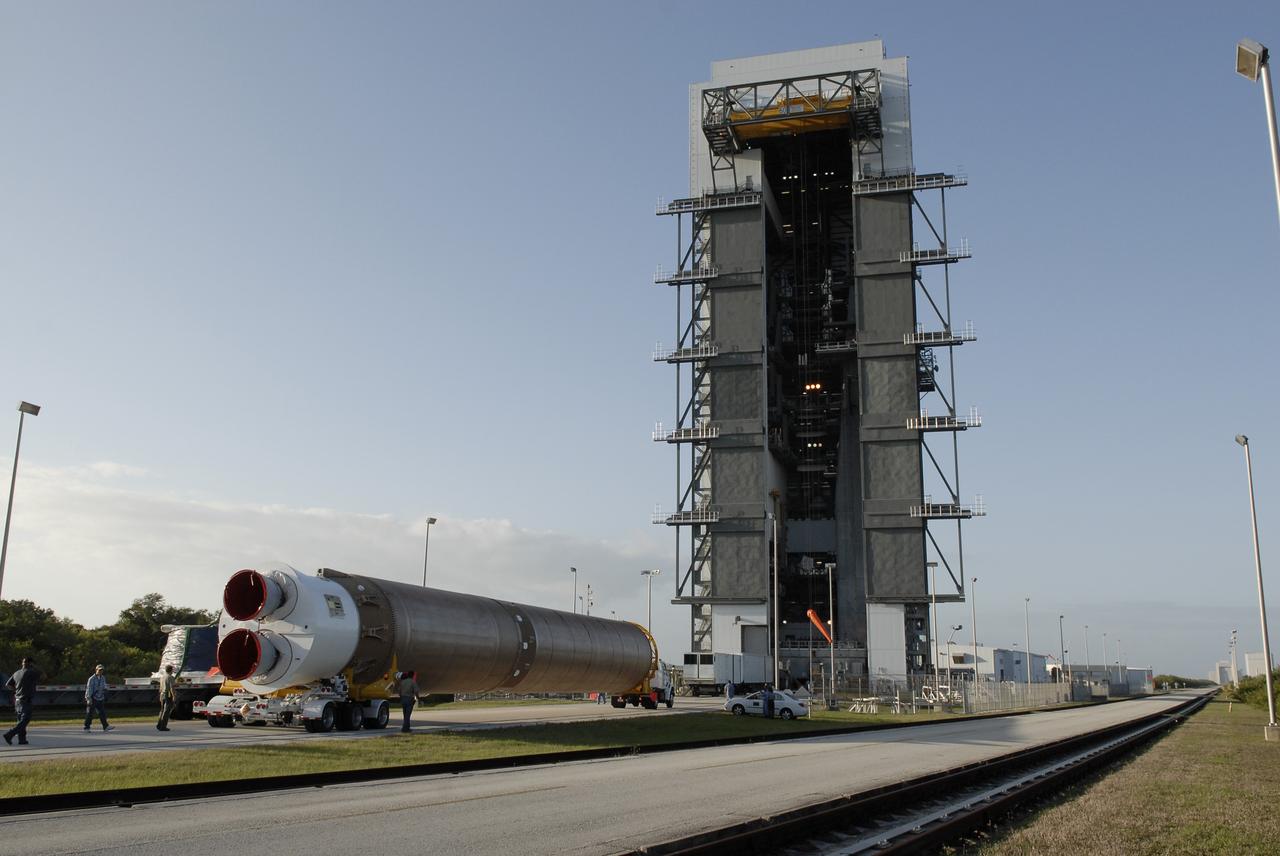

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– The Atlas V first stage arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
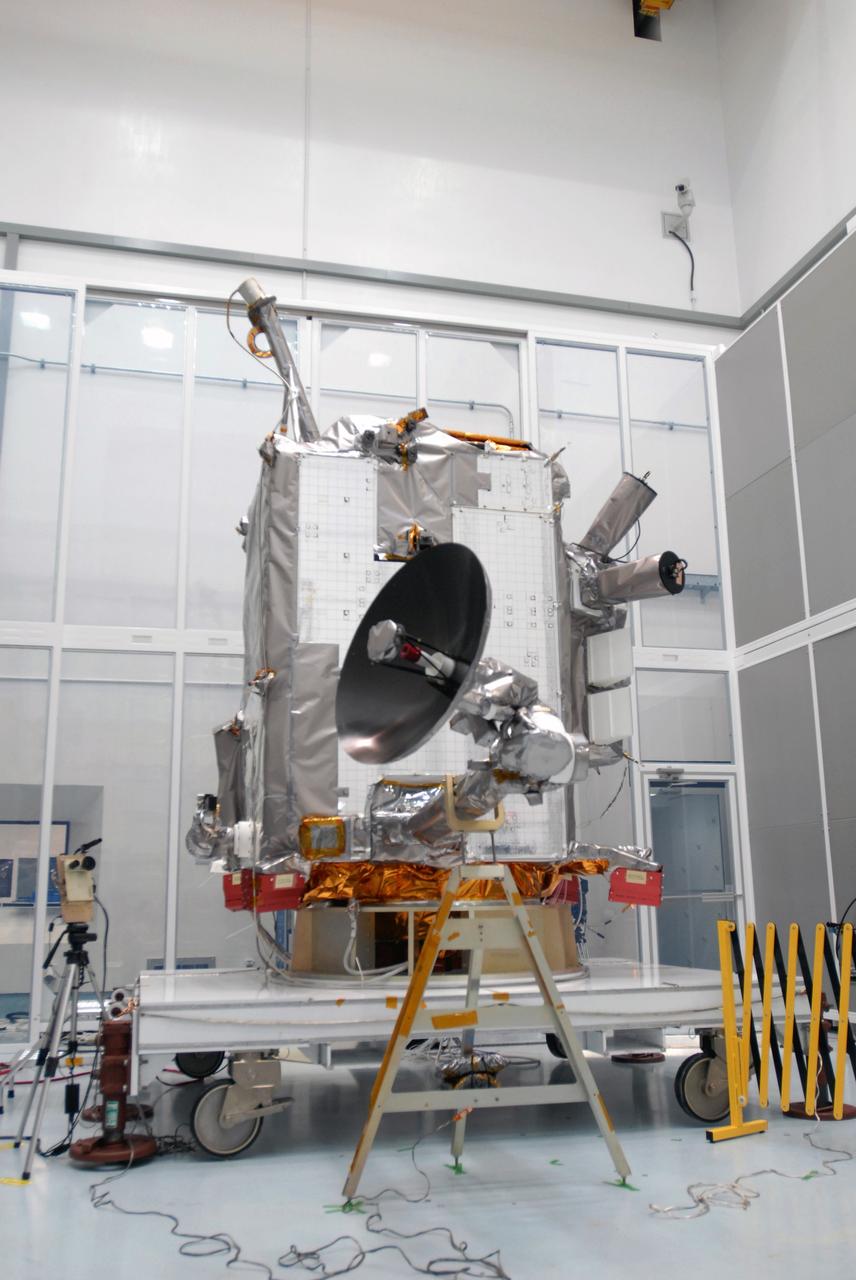

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., the range of motion is tested on the high-gain antenna for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
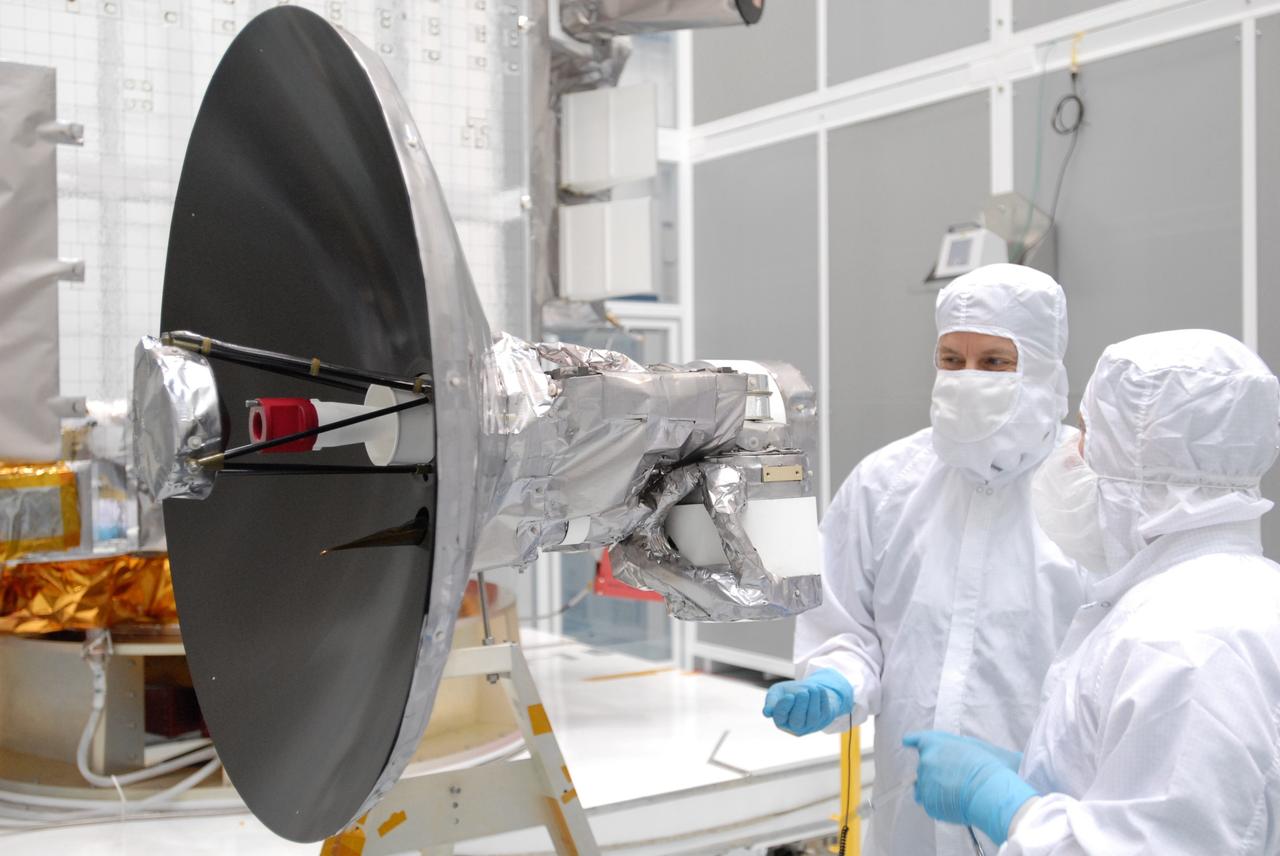

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians are testing the range of motion on the high-gain antenna for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
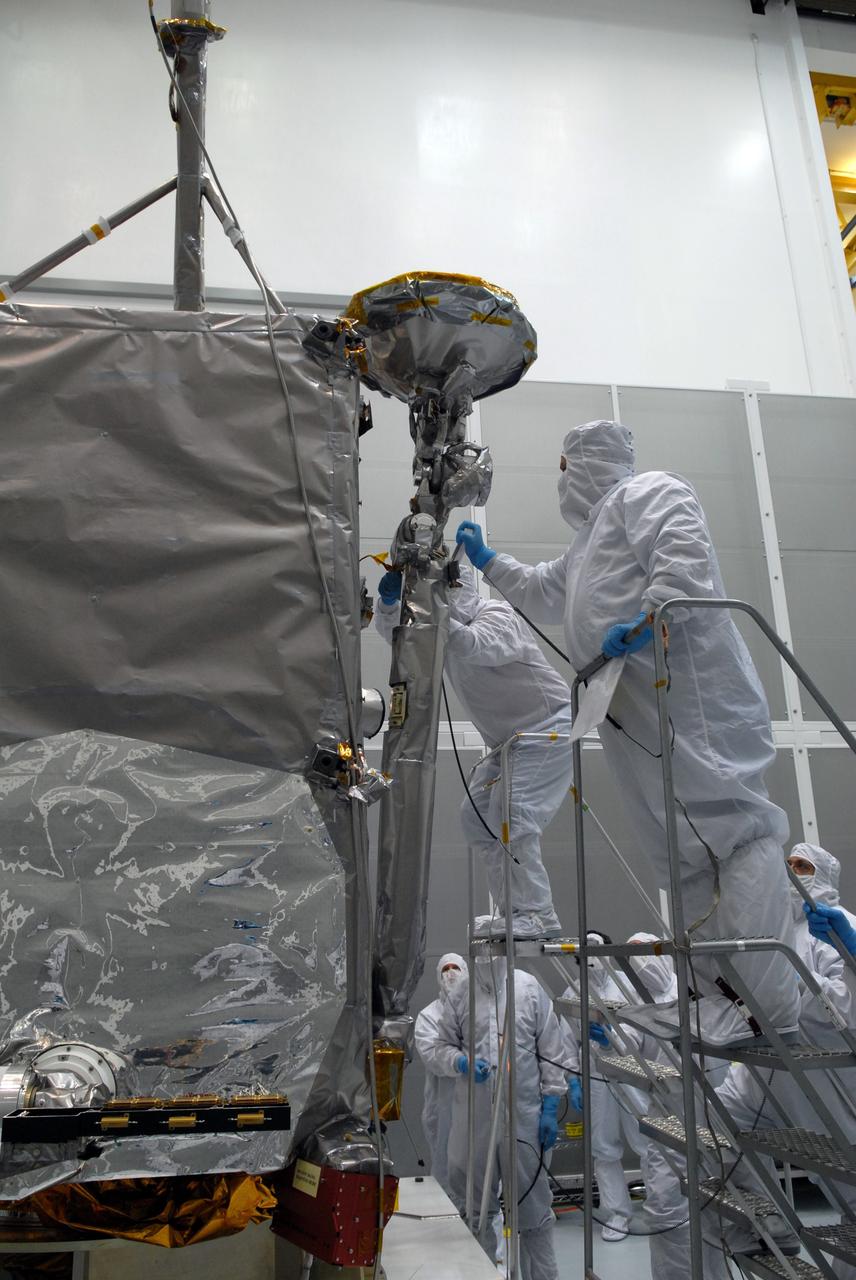

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians maneuver NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter's high-gain antenna into place for stowage. The antenna completed a range of motion test. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians maneuver NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter's high-gain antenna into place for stowage. The antenna completed a range of motion test. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
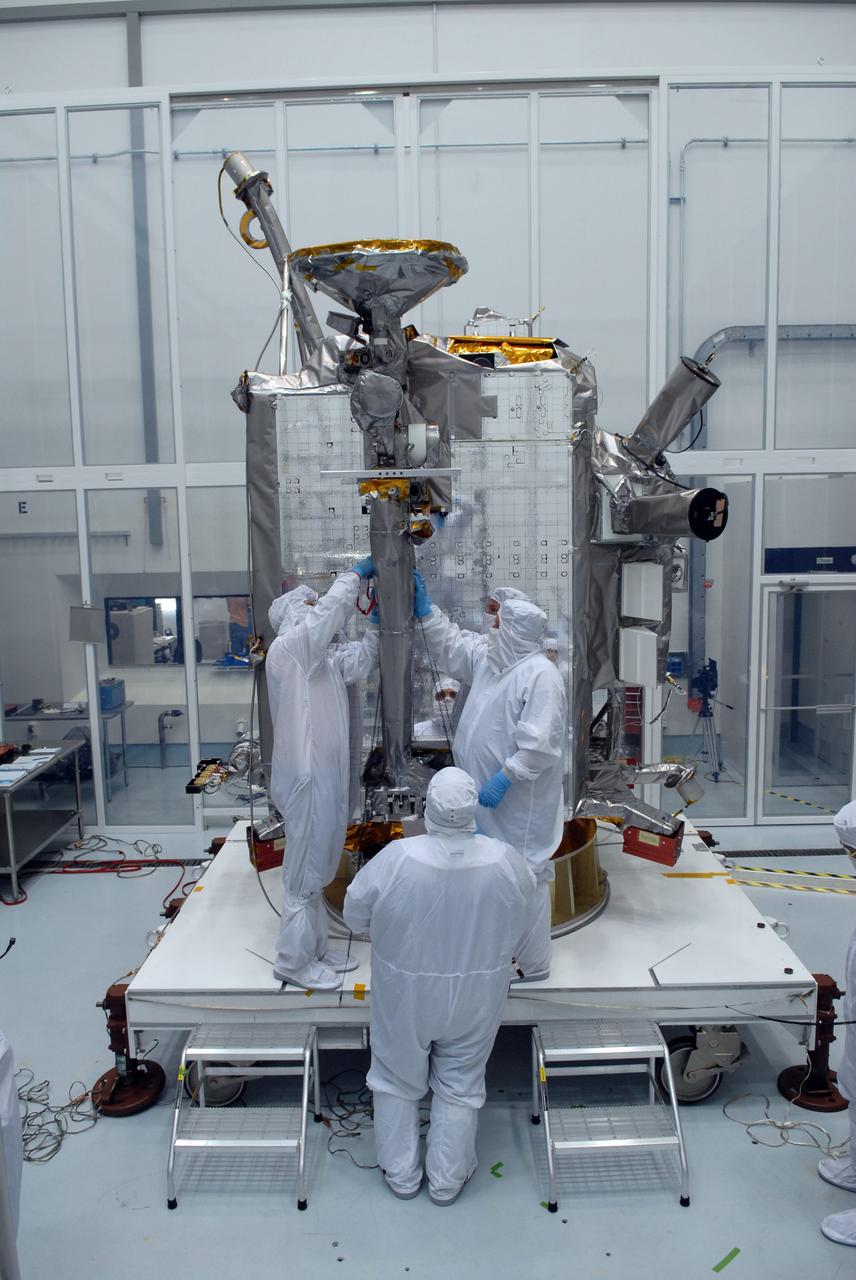

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians secure NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter's high-gain antenna into place for stowage. The antenna completed a range of motion test. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
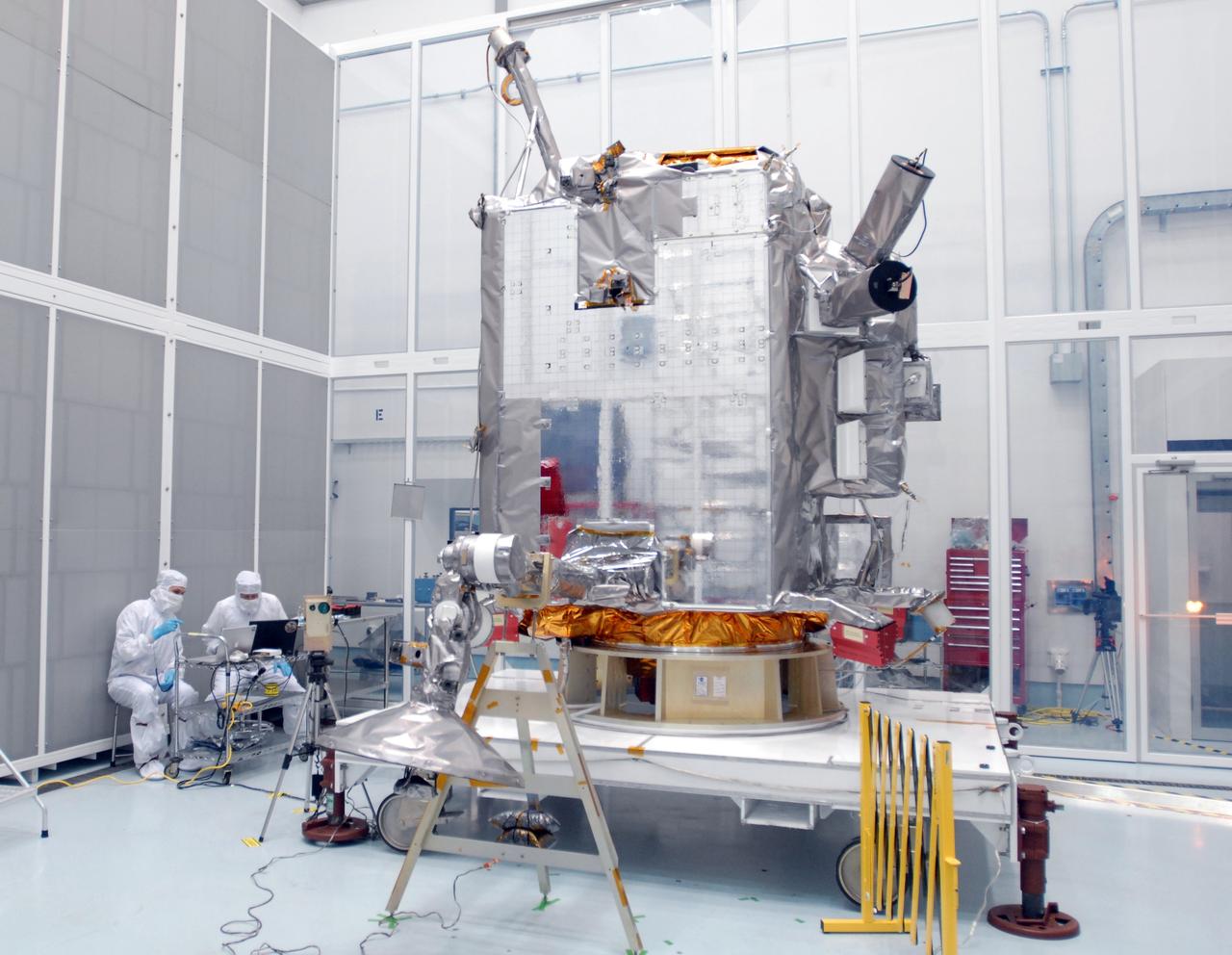

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians check data (left) as the range of motion is tested on the high-gain antenna (foreground) for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
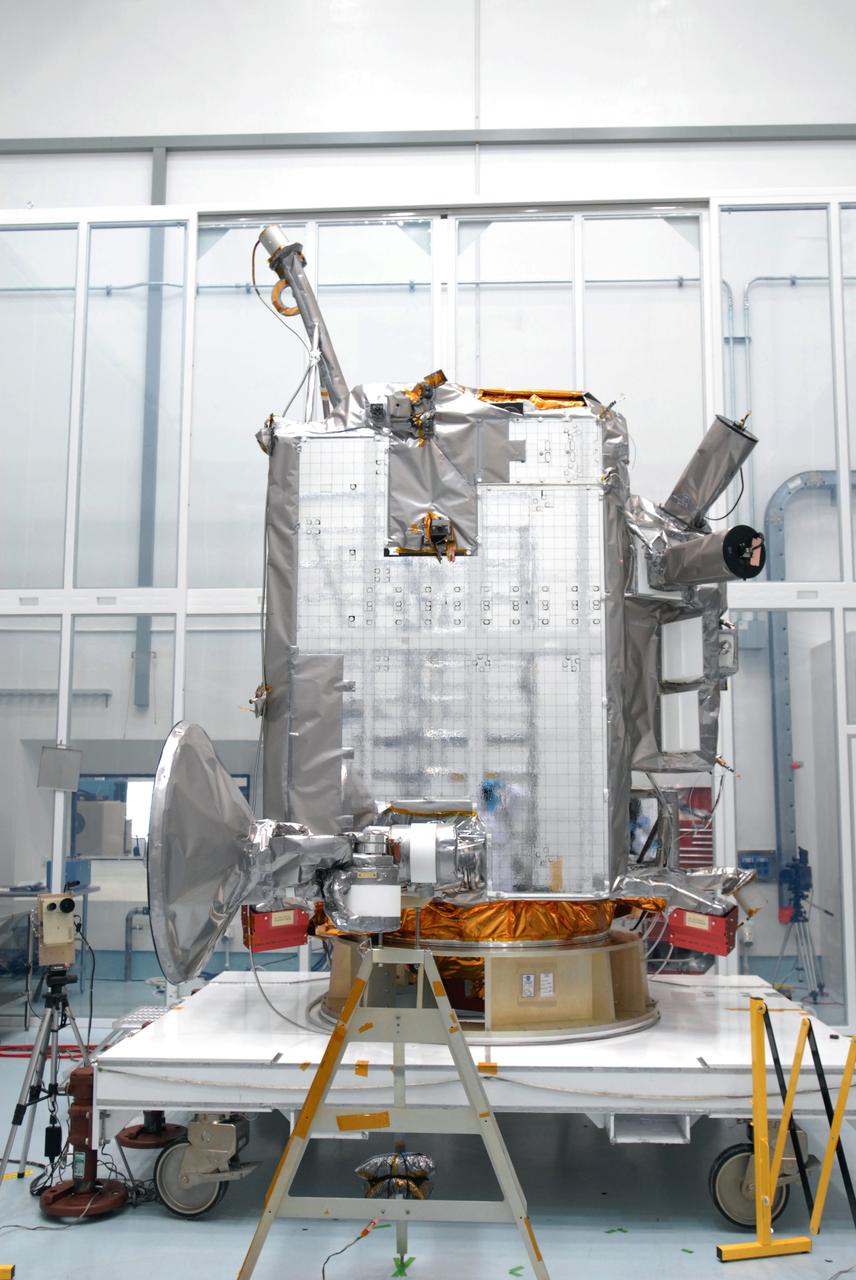

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., the range of motion is being tested on the high-gain antenna for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians begin stowing NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter's high-gain antenna. The antenna completed a range of motion test. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
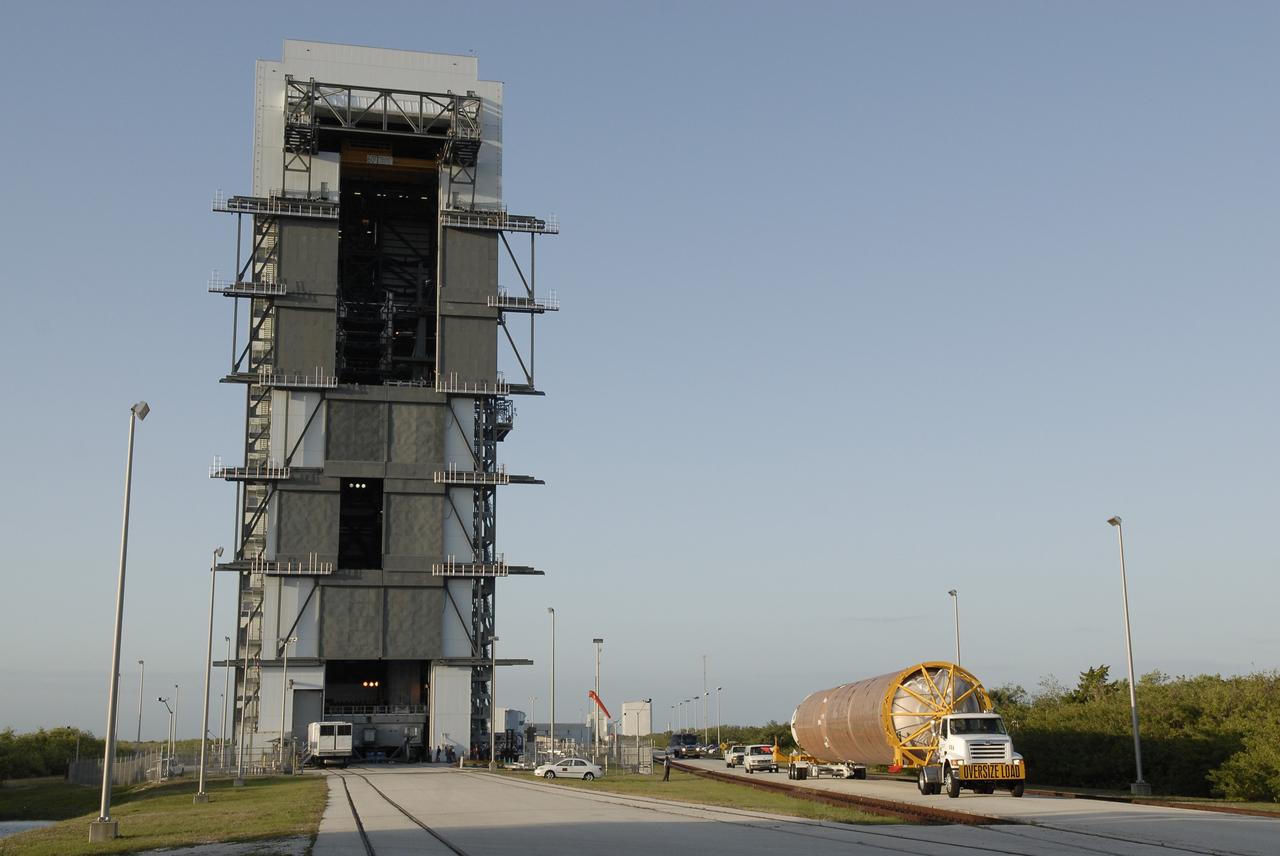

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– The Atlas V first stage arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
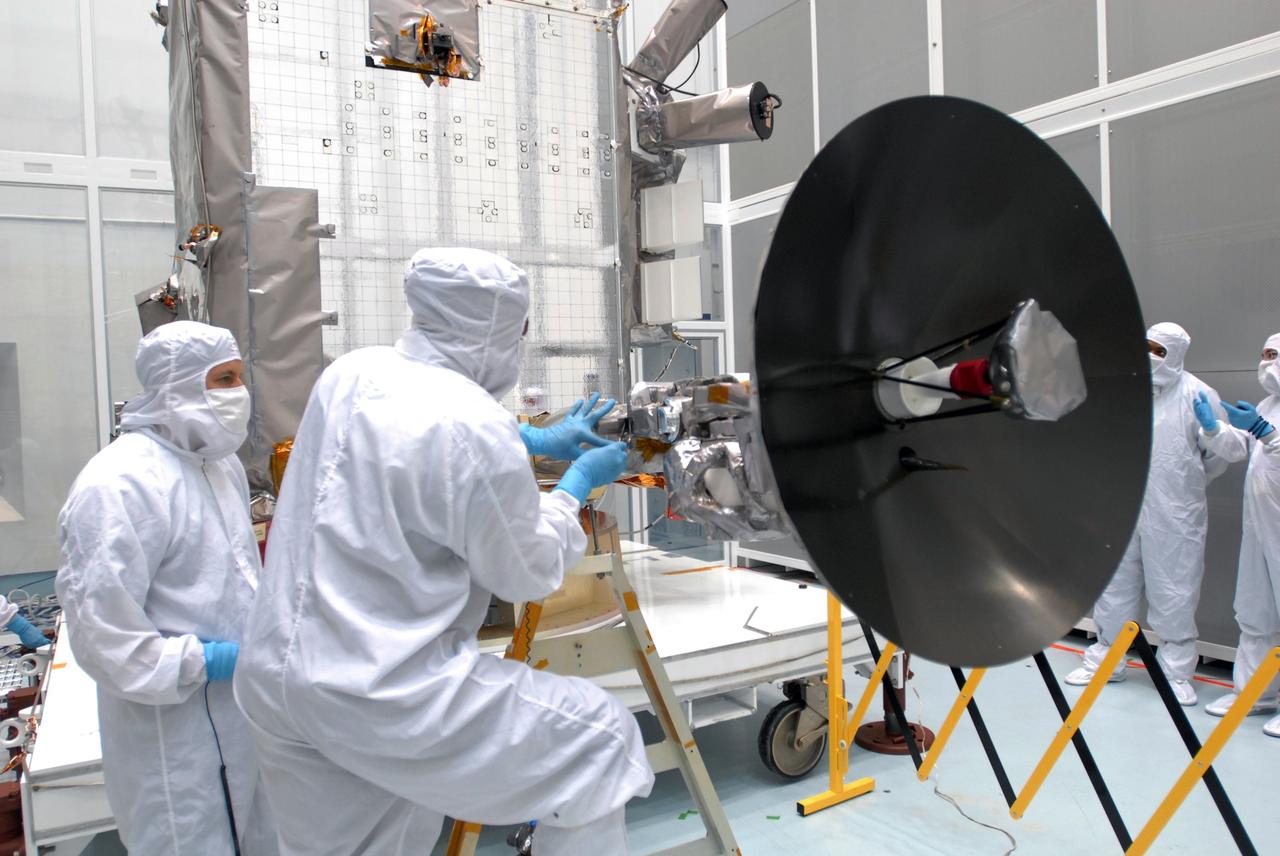

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians are testing the range of motion on the high-gain antenna for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
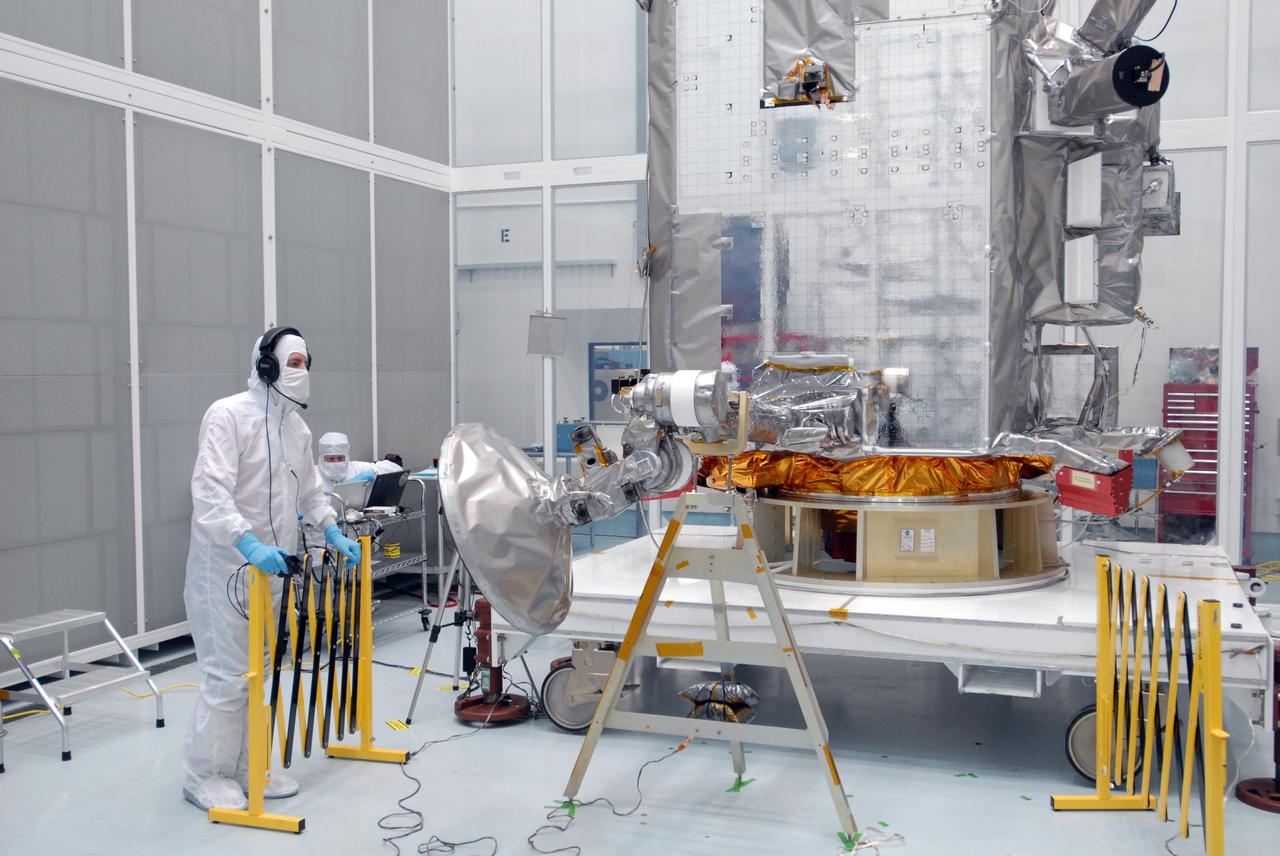

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians are testing the range of motion on the high-gain antenna for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
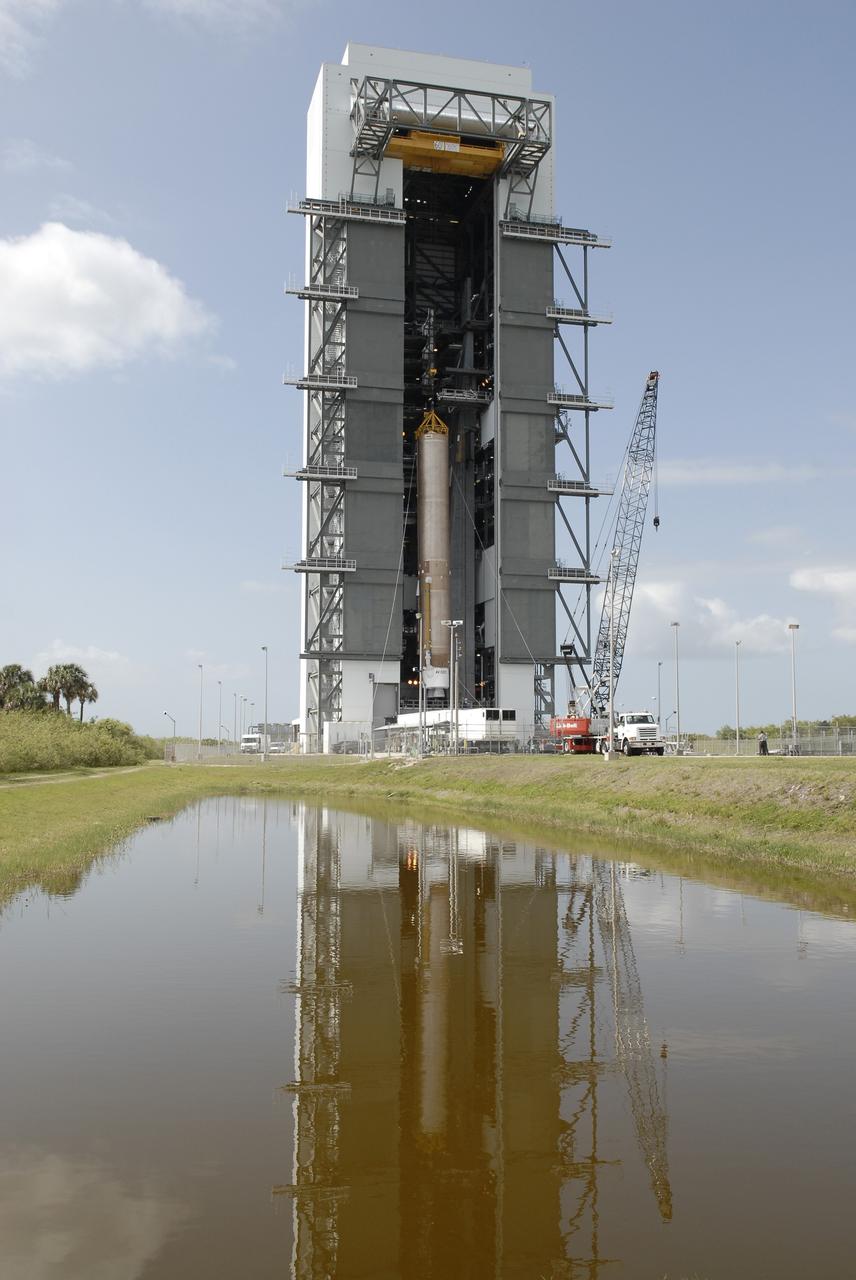

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Atlas V first stage is being moved into the Vertical Integration Facility. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
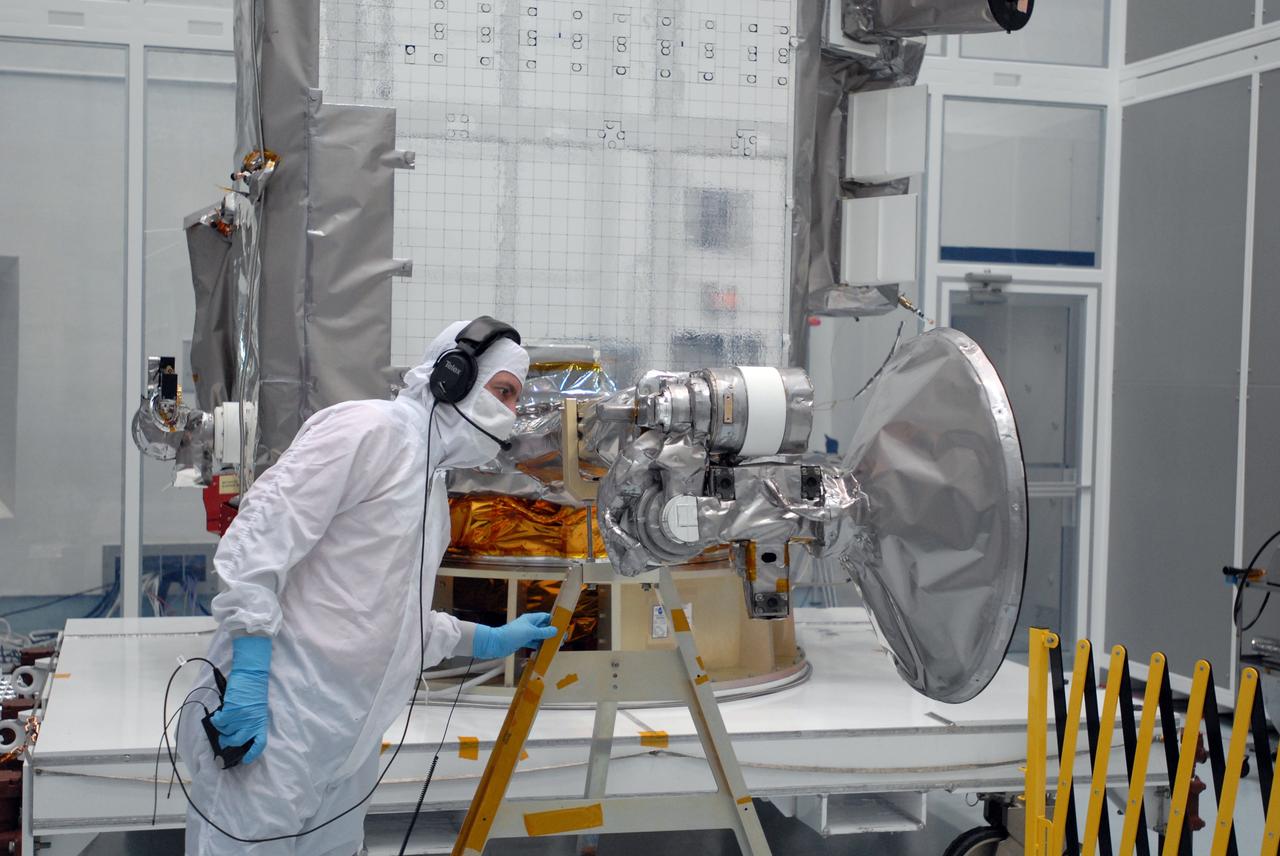

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians check data (left) as the range of motion is tested on the high-gain antenna (foreground) for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
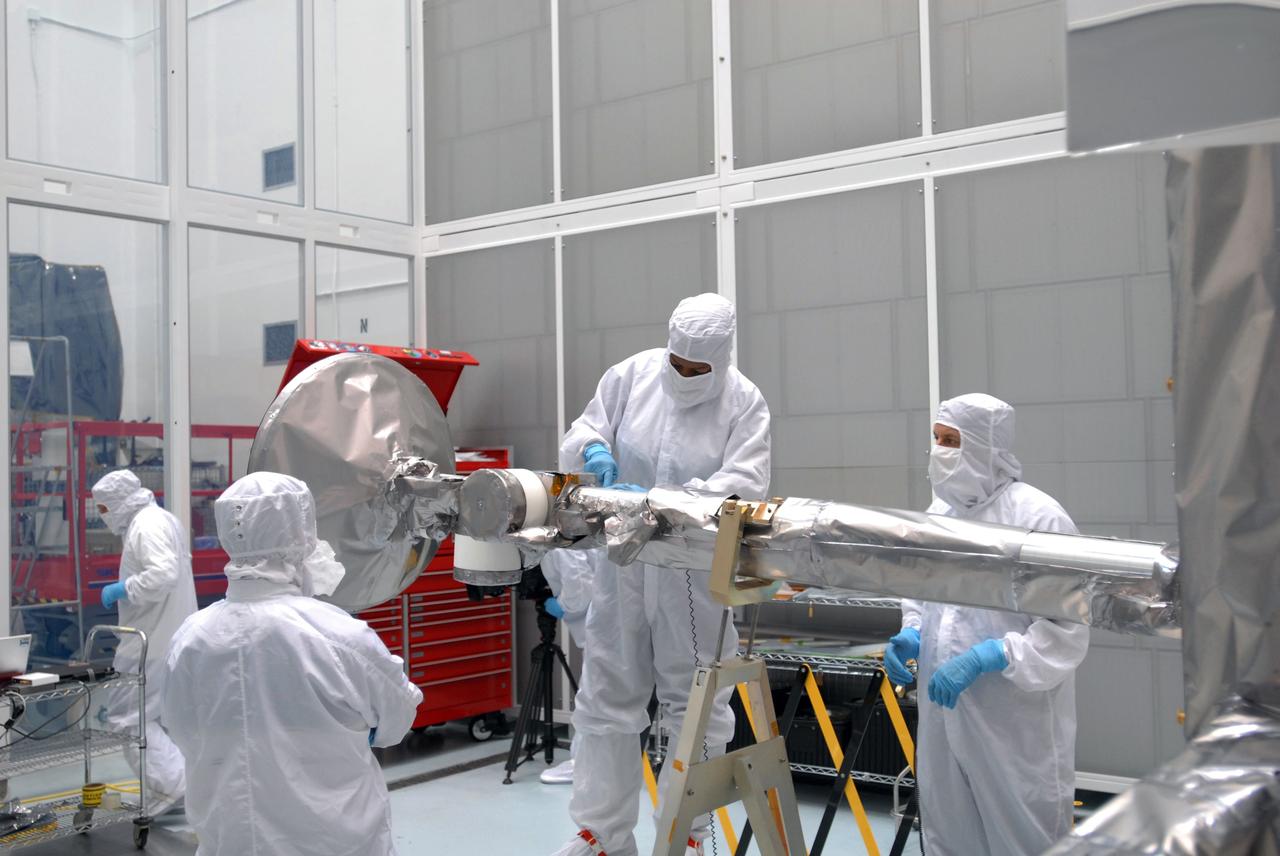

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians are testing the range of motion on the high-gain antenna for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
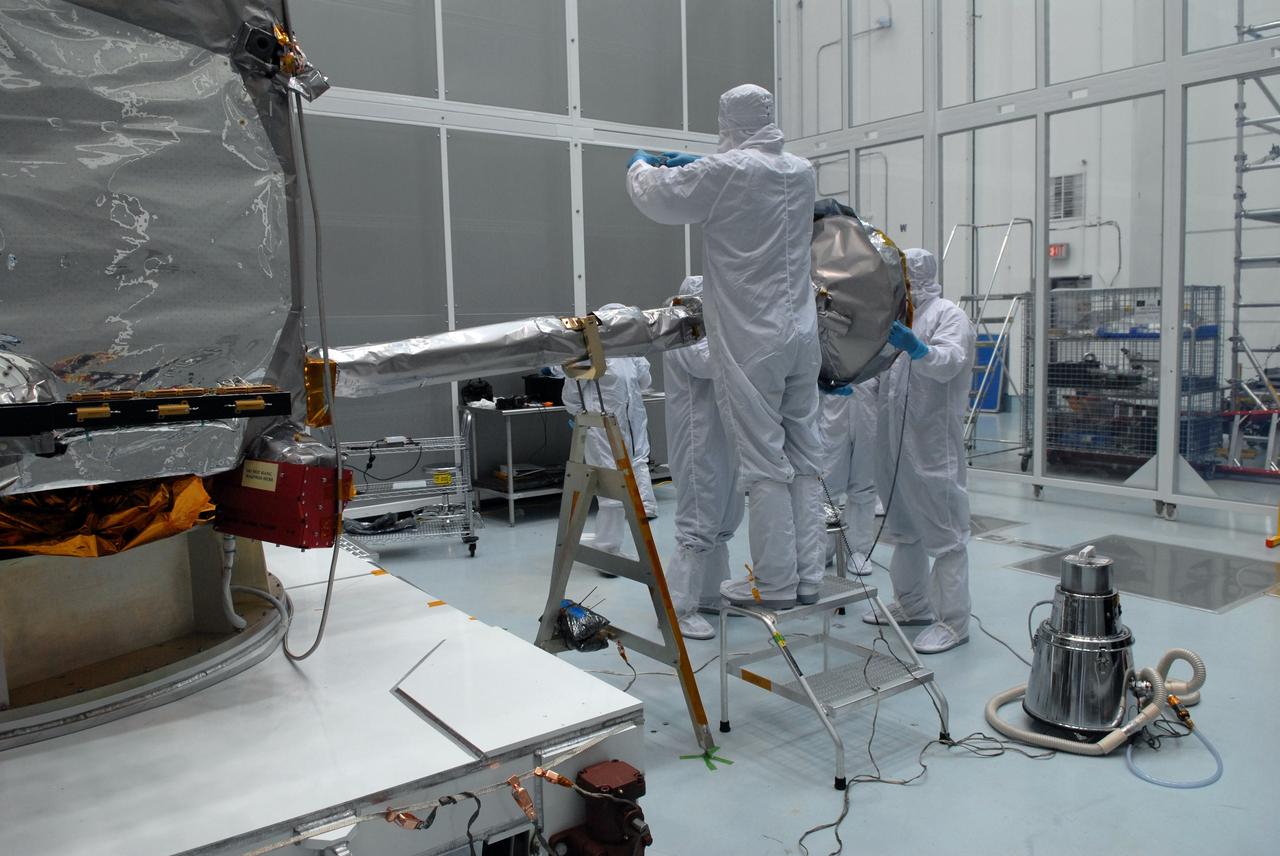

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians prepare NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter's high-gain antenna for stowage. The antenna completed a range of motion test. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
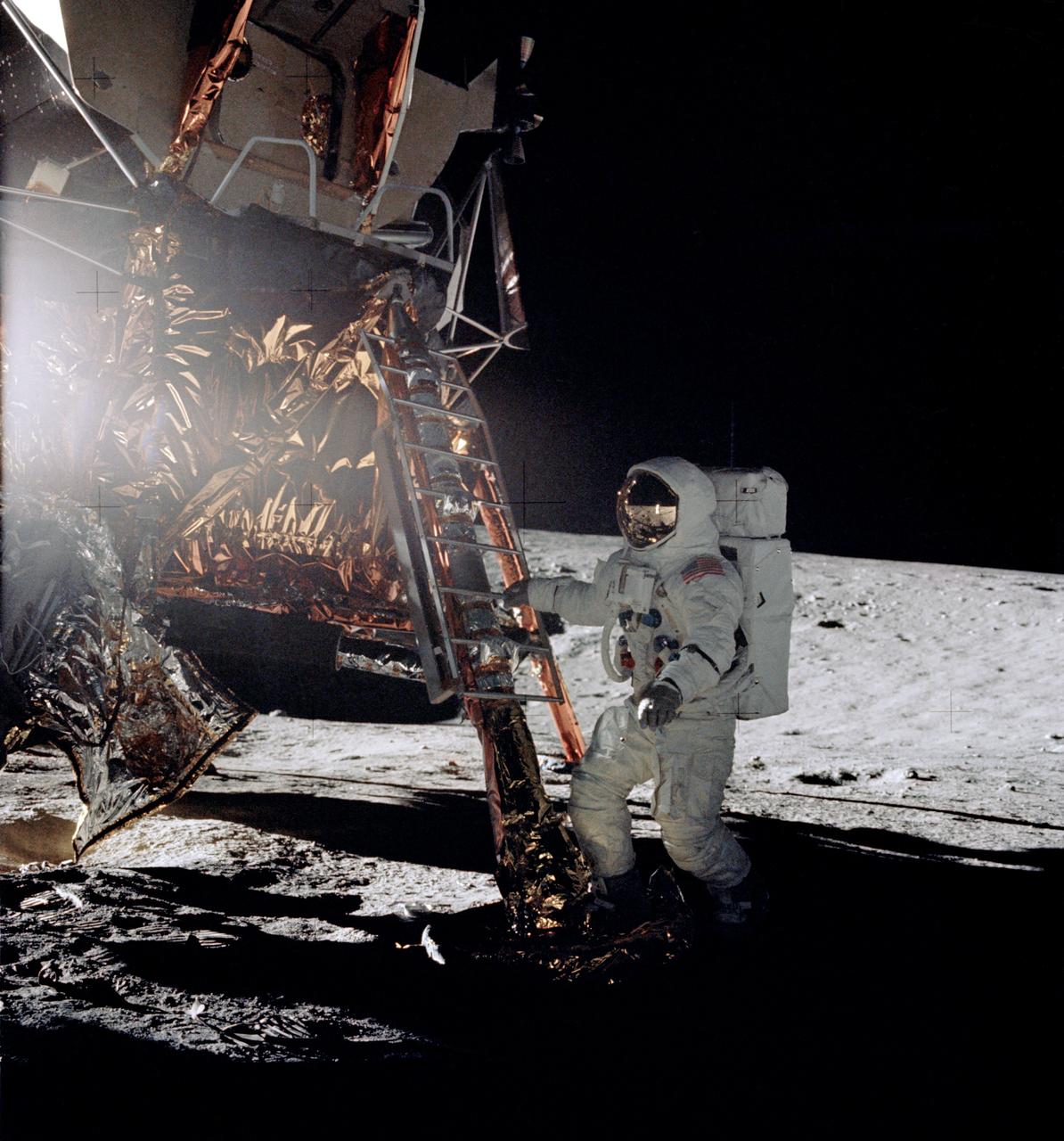

AS12-46-6729 (19 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot for the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, steps from the ladder of the Lunar Module to join astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, in extravehicular activity on Nov. 19, 1969. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.
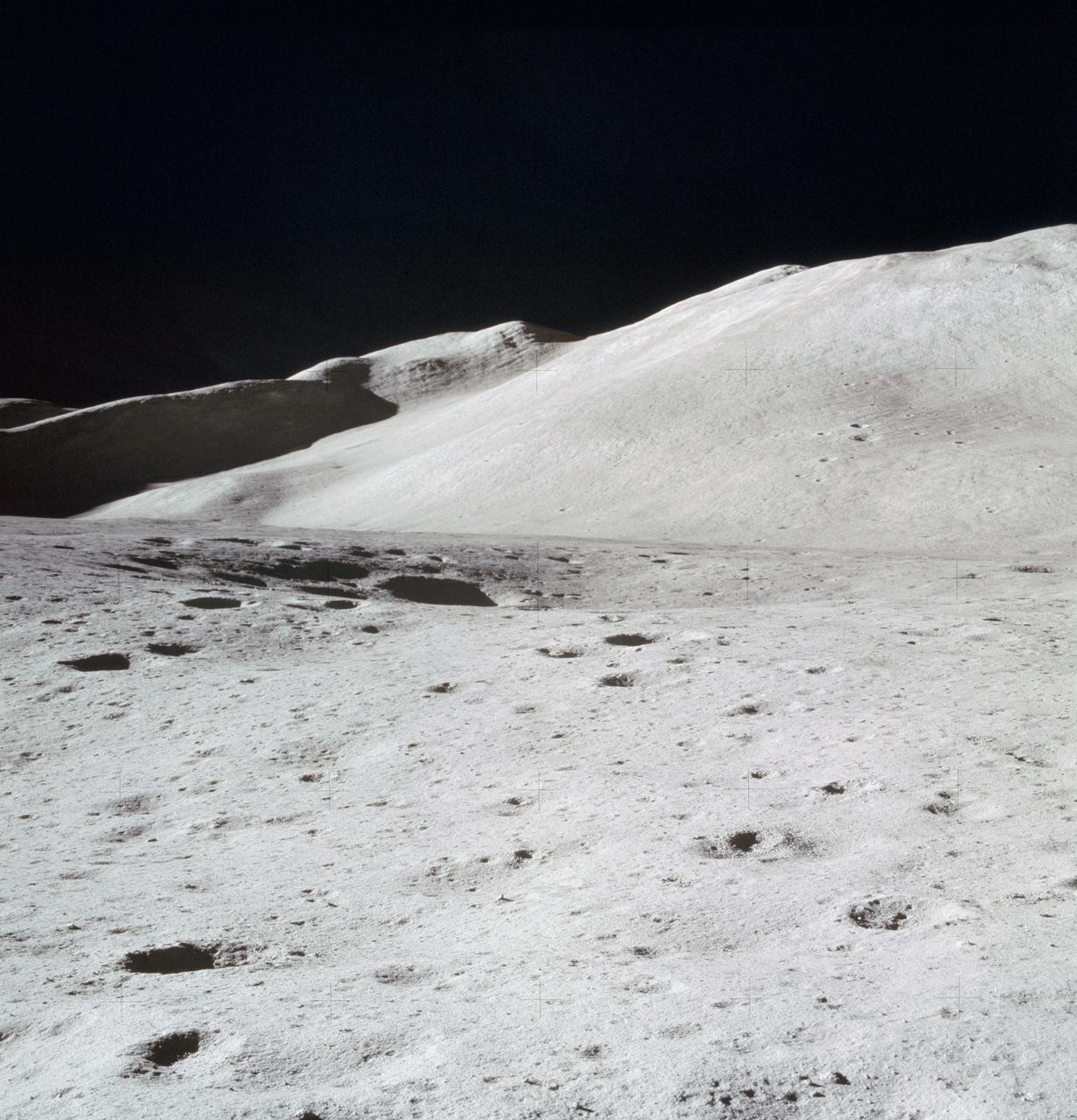

AS15-87-11748 (31 July 1971) --- A view of Hadley Delta, looking southeasterly, as photographed from the top hatch of the Apollo 15 Lunar Module (LM) by astronaut David R. Scott, commander, during his stand-up extravehicular activity (EVA) just after the LM "Falcon" touched down at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The prominent feature on the horizon in the center of the picture was called Silver Spur by the Apollo 15 crew men. Hadley Delta Mountain rises approximately 4,000 meters (about 13,124 feet) above the plain. While astronauts Scott and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Module's (CSM) in lunar orbit.
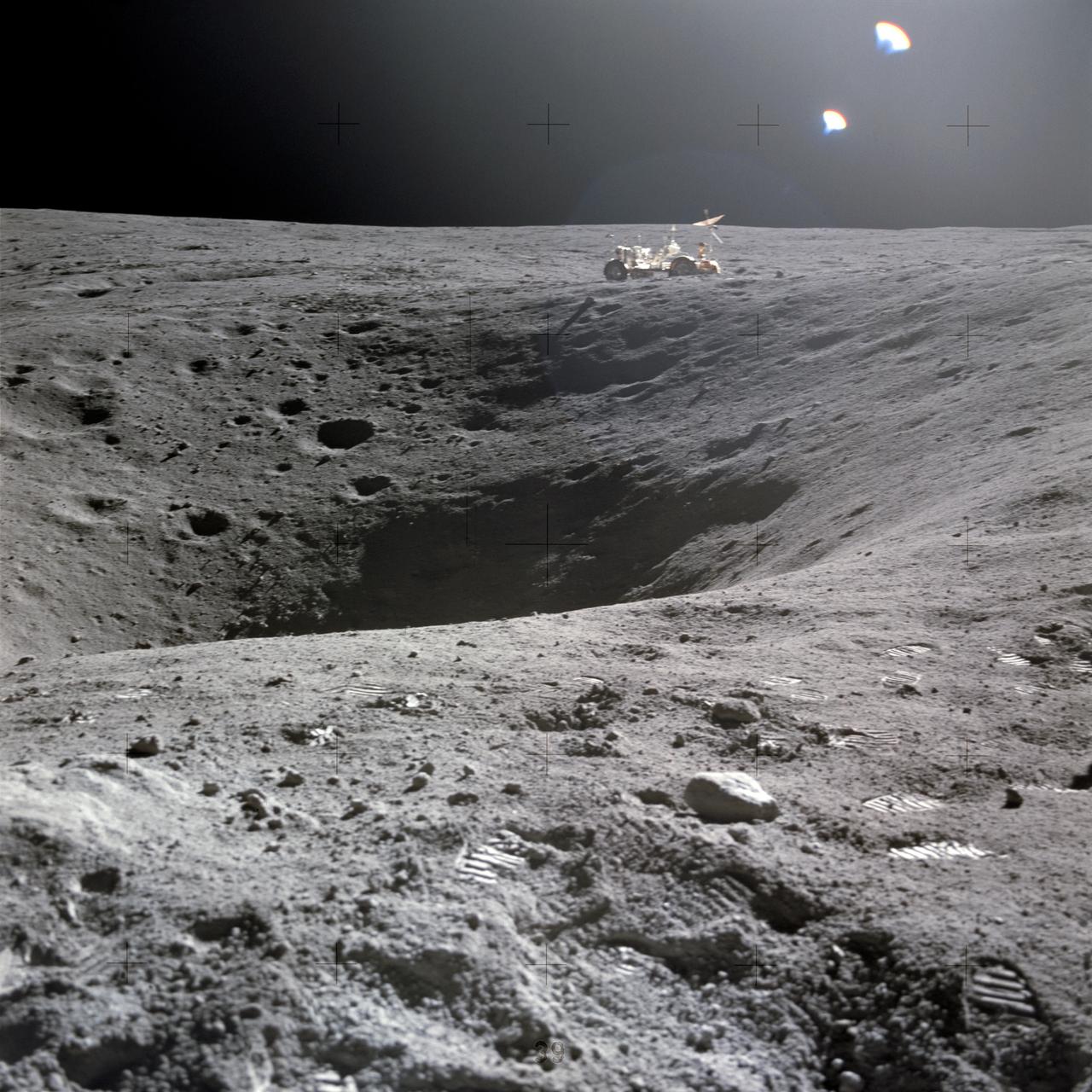

AS16-114-18422 (21 April 1972) --- A view of Plum Crater, which was visited by the two moon-exploring crewmen of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, on their first extravehicular activity (EVA) traverse, April 21, 1972. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is parked on the far side of the crater, which measures approximately 40 meters in diameter. While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
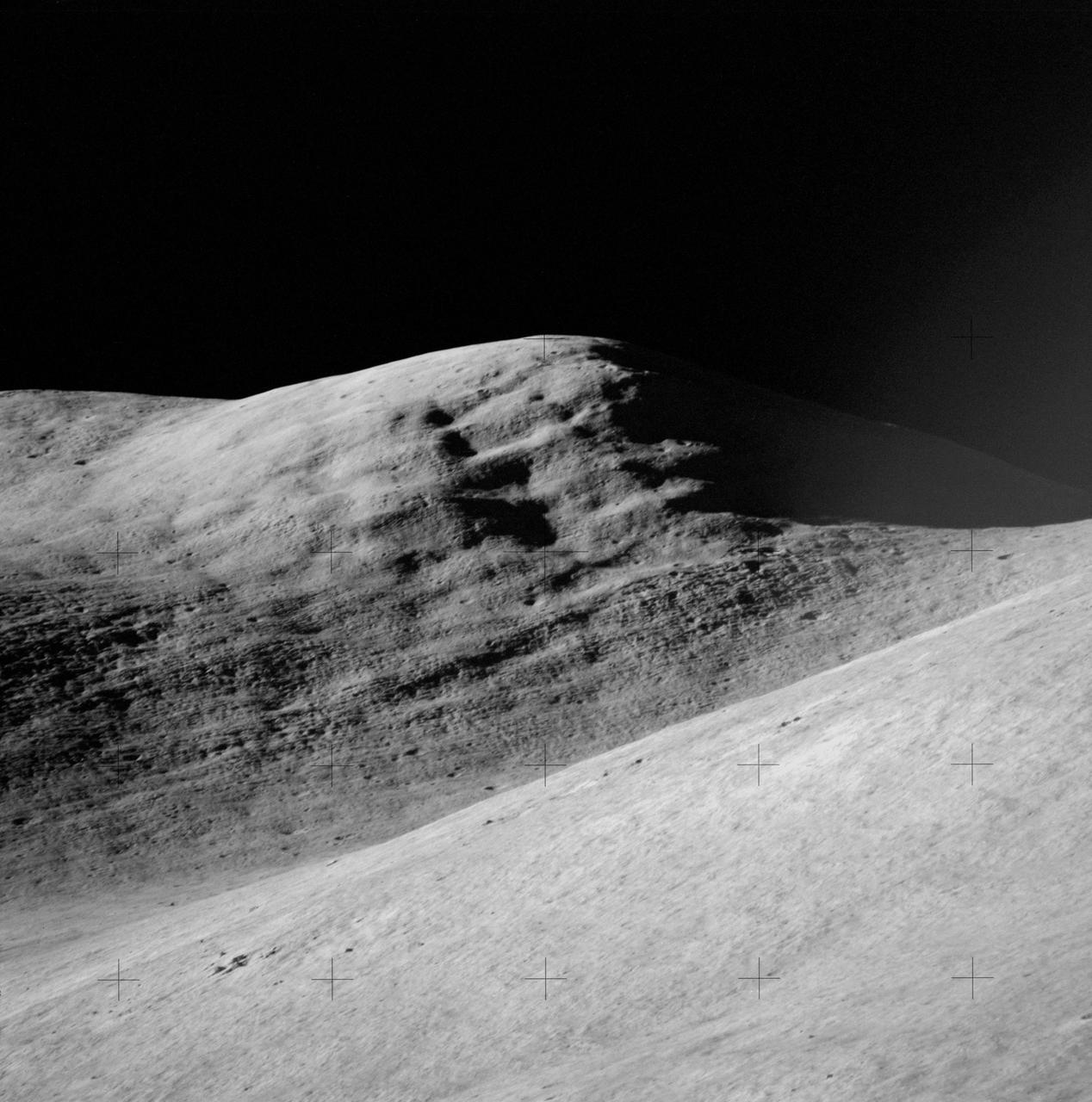

AS15-84-11250 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- A telephoto lens view of the prominent feature called Silver Spur in the Hadley Delta region, photographed during the Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The distance from the camera to the spur is about 10 miles. The field of view across the bottom is about one mile. Structural formations in the mountain are clearly visible. There are two major units. The upper unit is characterized by massive subunits, each one of which is approximately 200 feet deep. The lower major unit is characterized by thinner bedding and cross bedding.
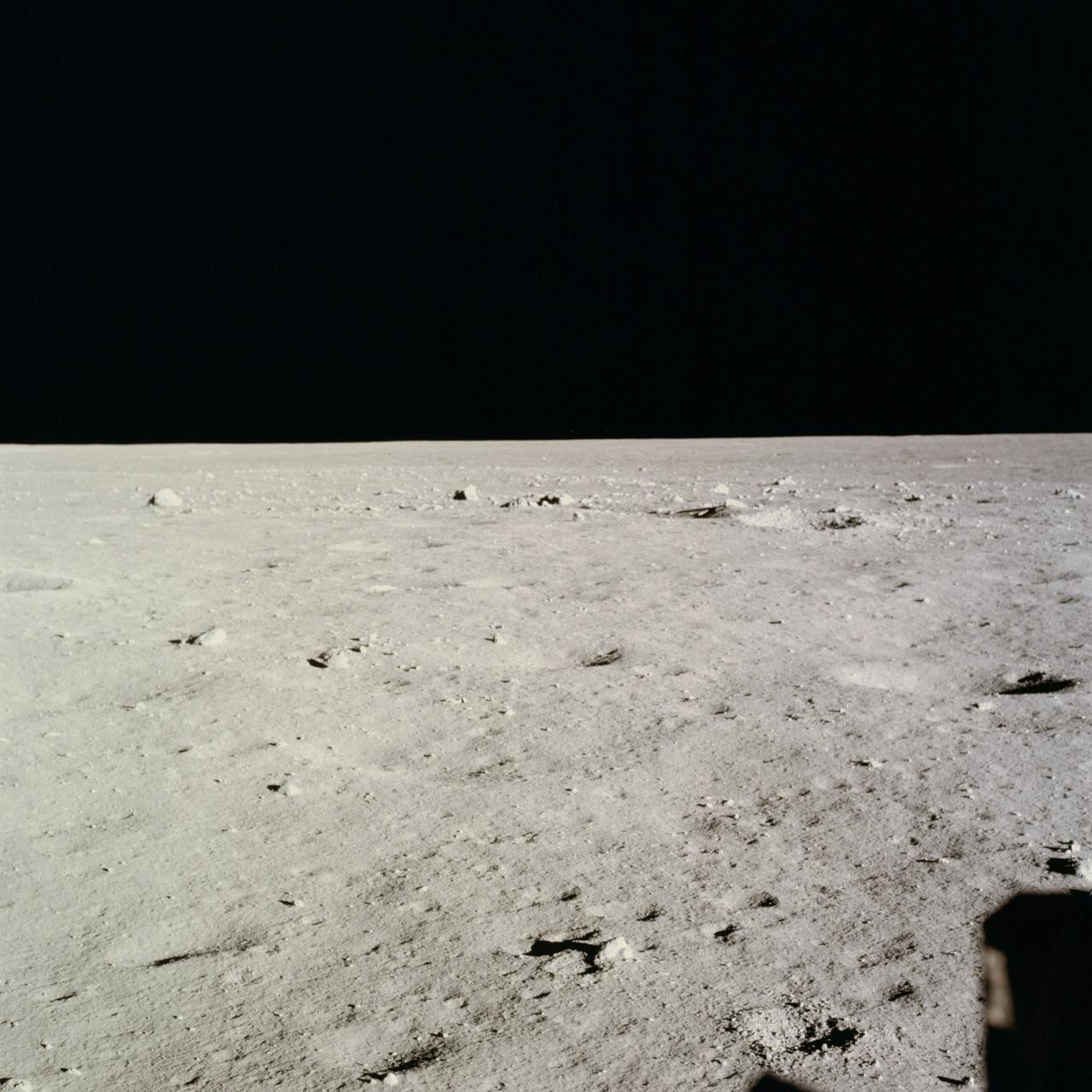

AS11-37-5458 (20 July 1969) --- This excellent view from the right-hand window of the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) shows the surface of the moon in the vicinity of where the LM touched down. Numerous small rocks and craters can be seen between the LM and the lunar horizon. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to the lunar surface.
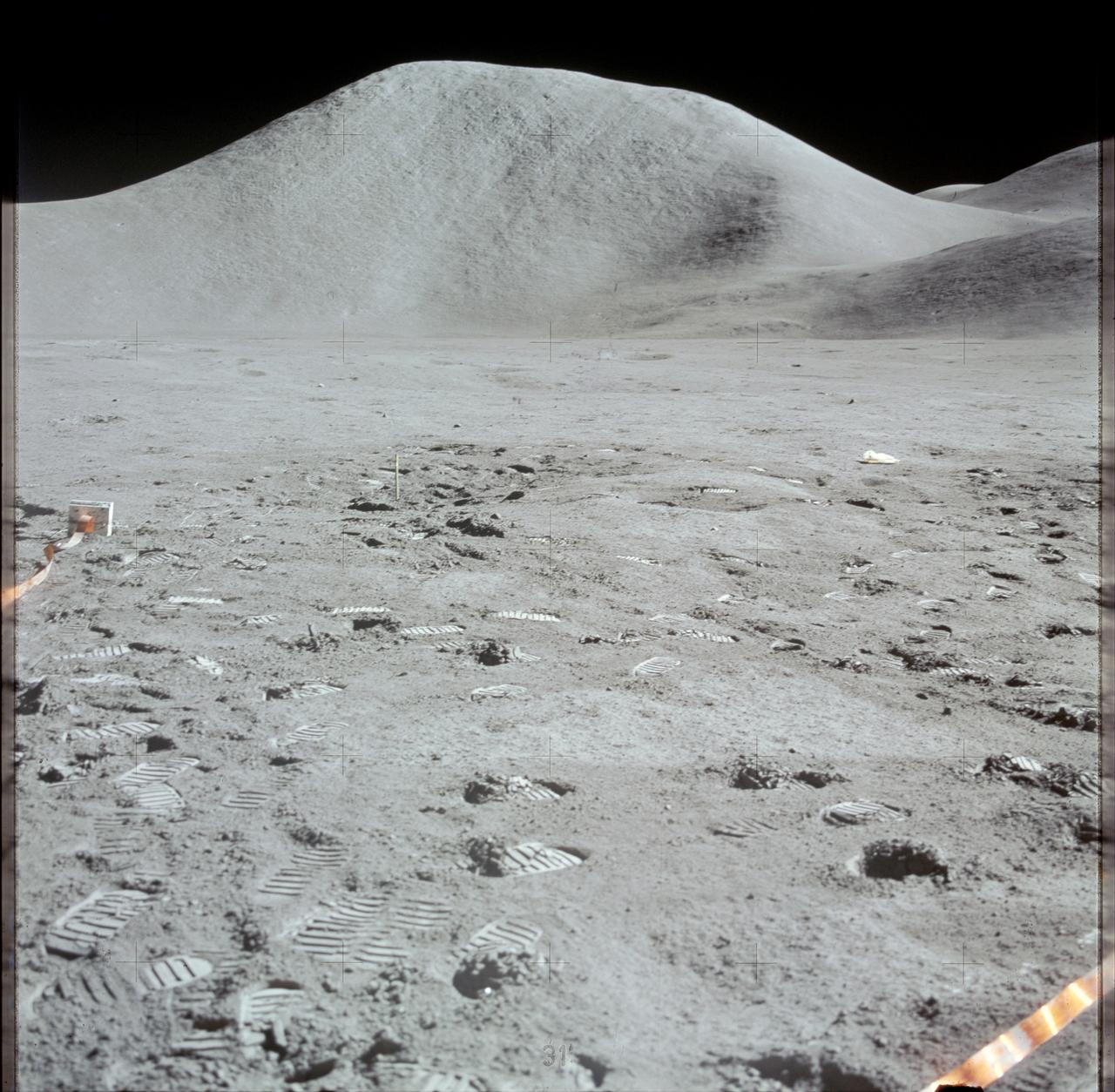

AS15-87-11849 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- An excellent view of Mount Hadley, fully lighted, showing abundant linear features, as photographed during the Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). This view is looking north from the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) site. Mount Hadley rises about 4,500 meters (approximately 14,765 feet) above the plain. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Apollo 15 Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
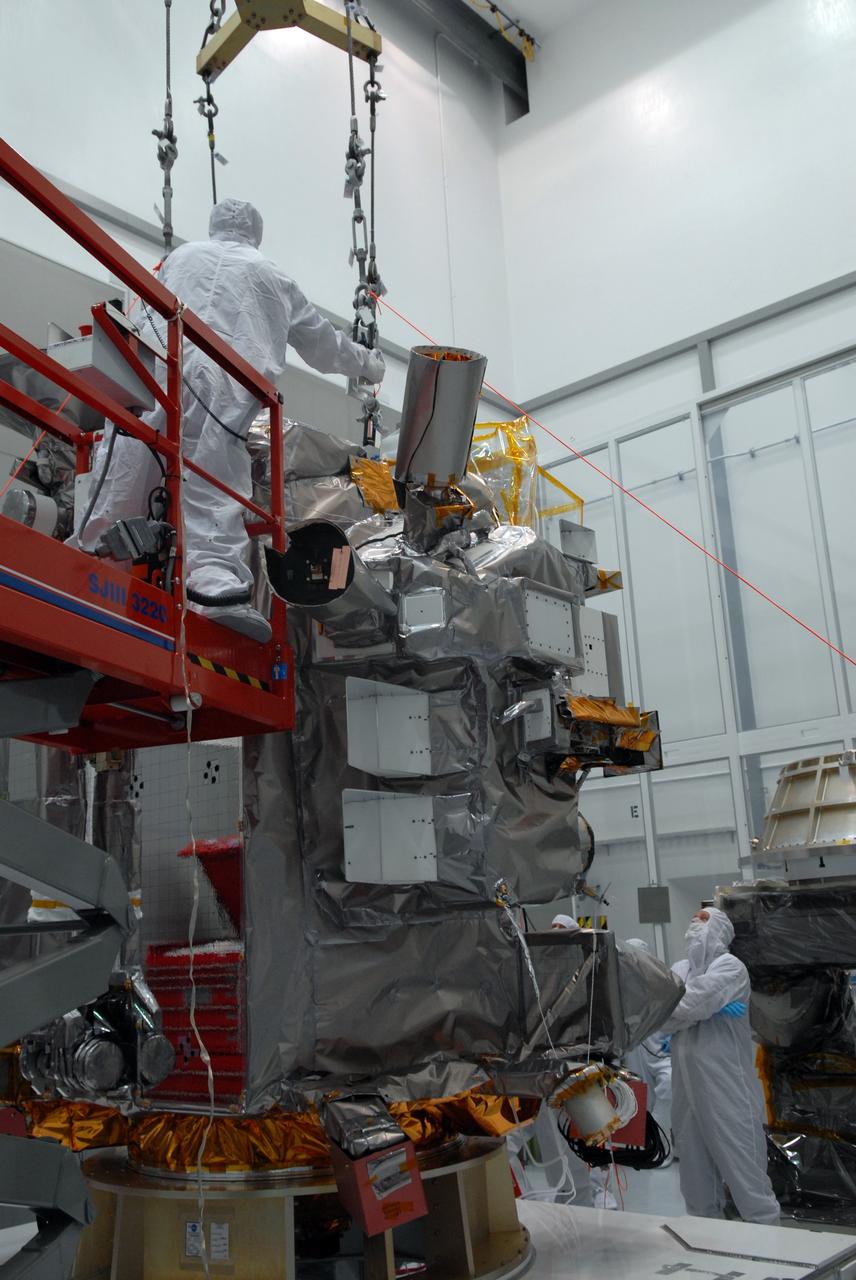

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., technicians get ready to lift NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. It will be moved to an Aronson table for rotation to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
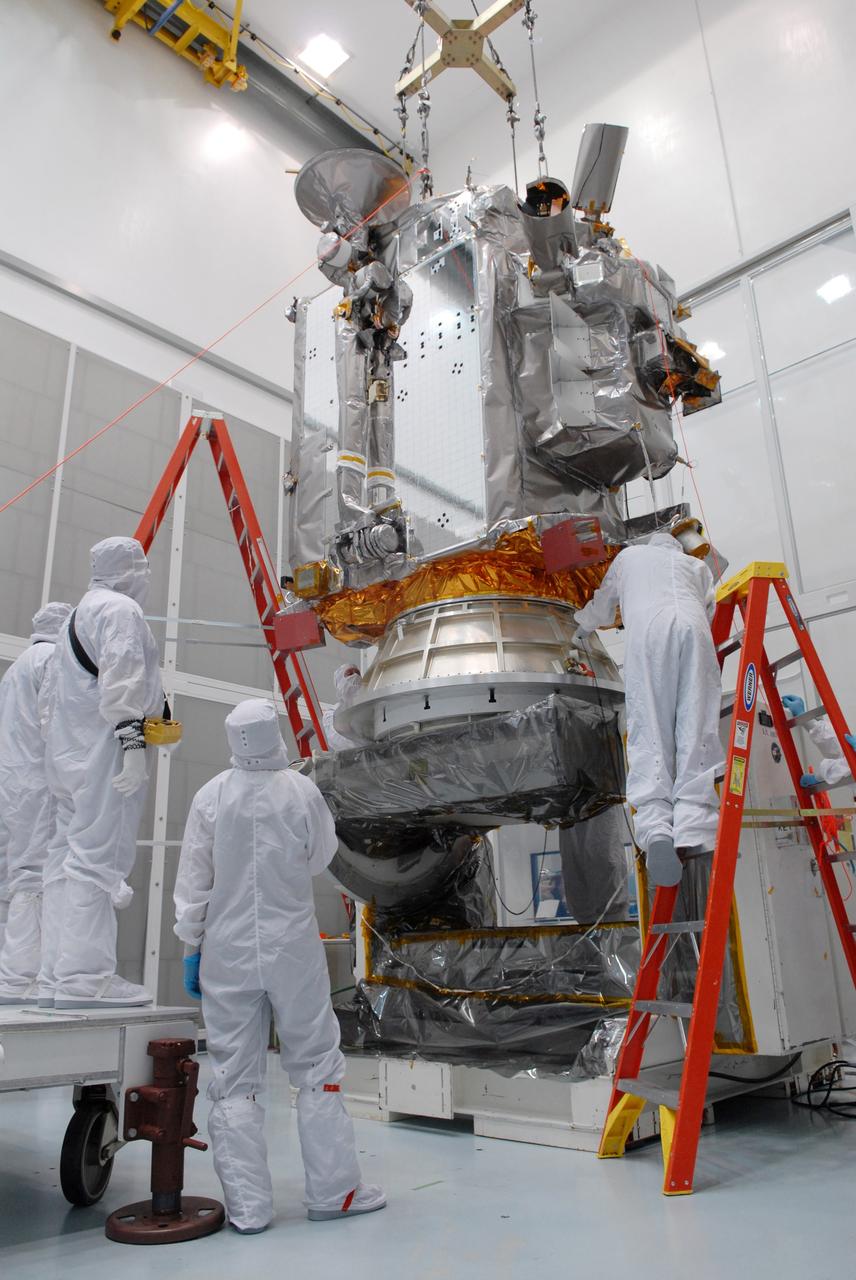

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., an overhead crane lowers NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, onto the Aronson table. The orbiter will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
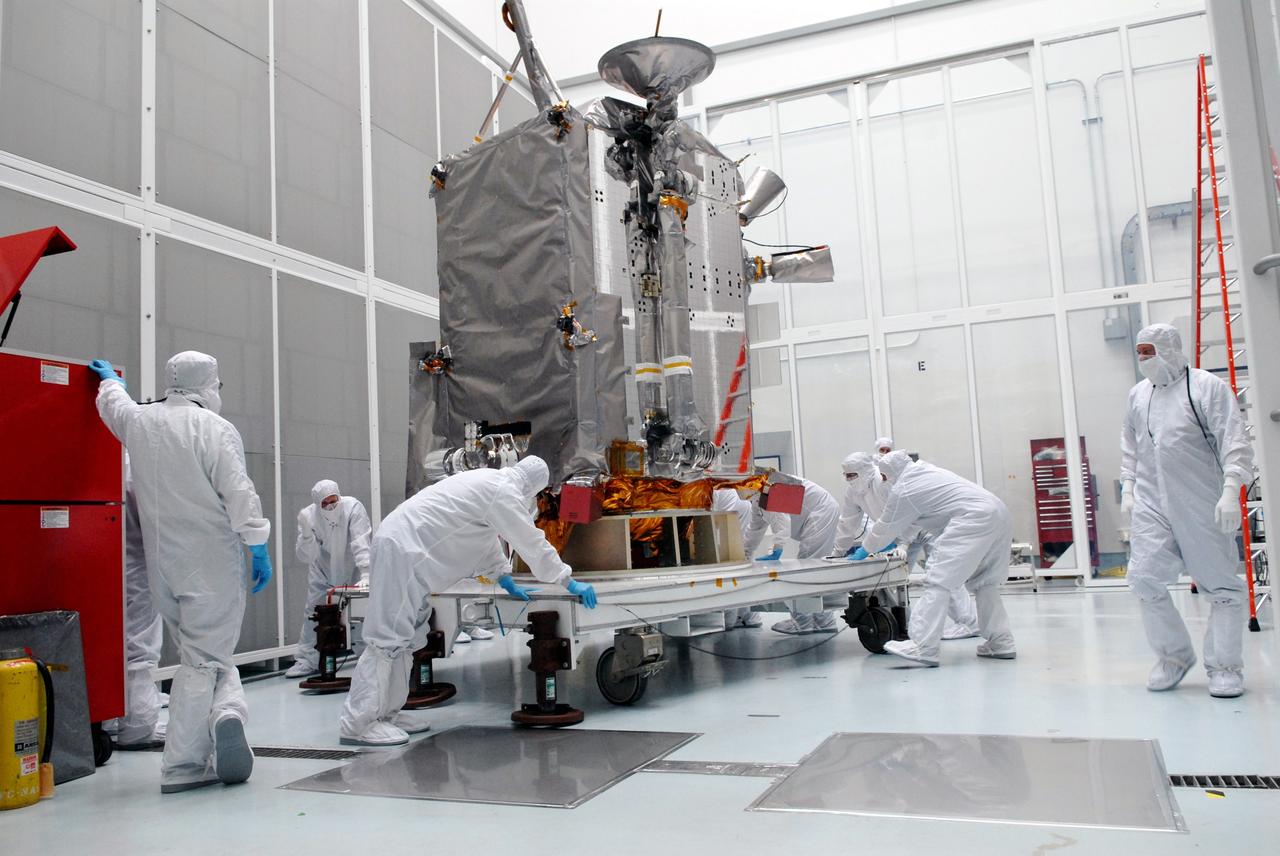

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., technicians moved the stand with NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
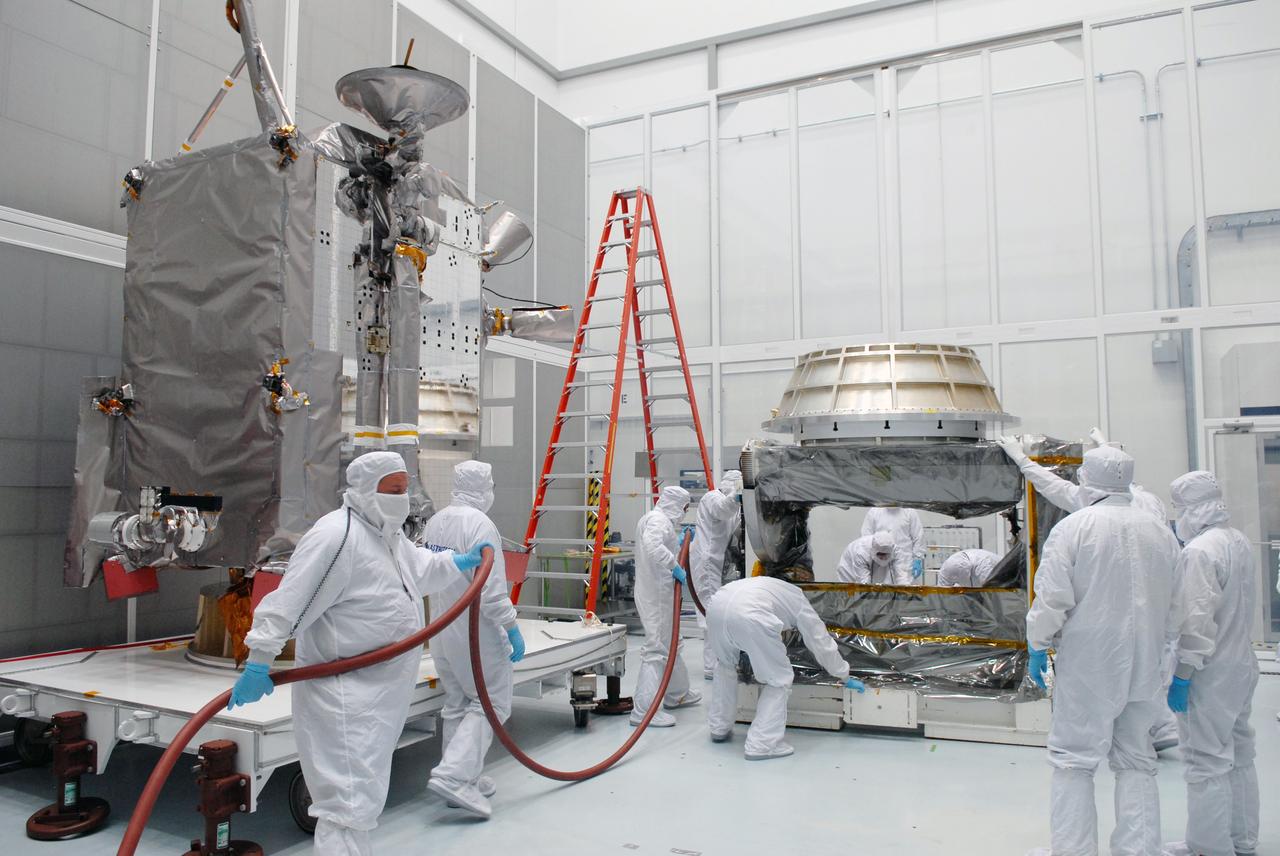

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., technicians prepare an Aronson table to receive NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, at left. The orbiter will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
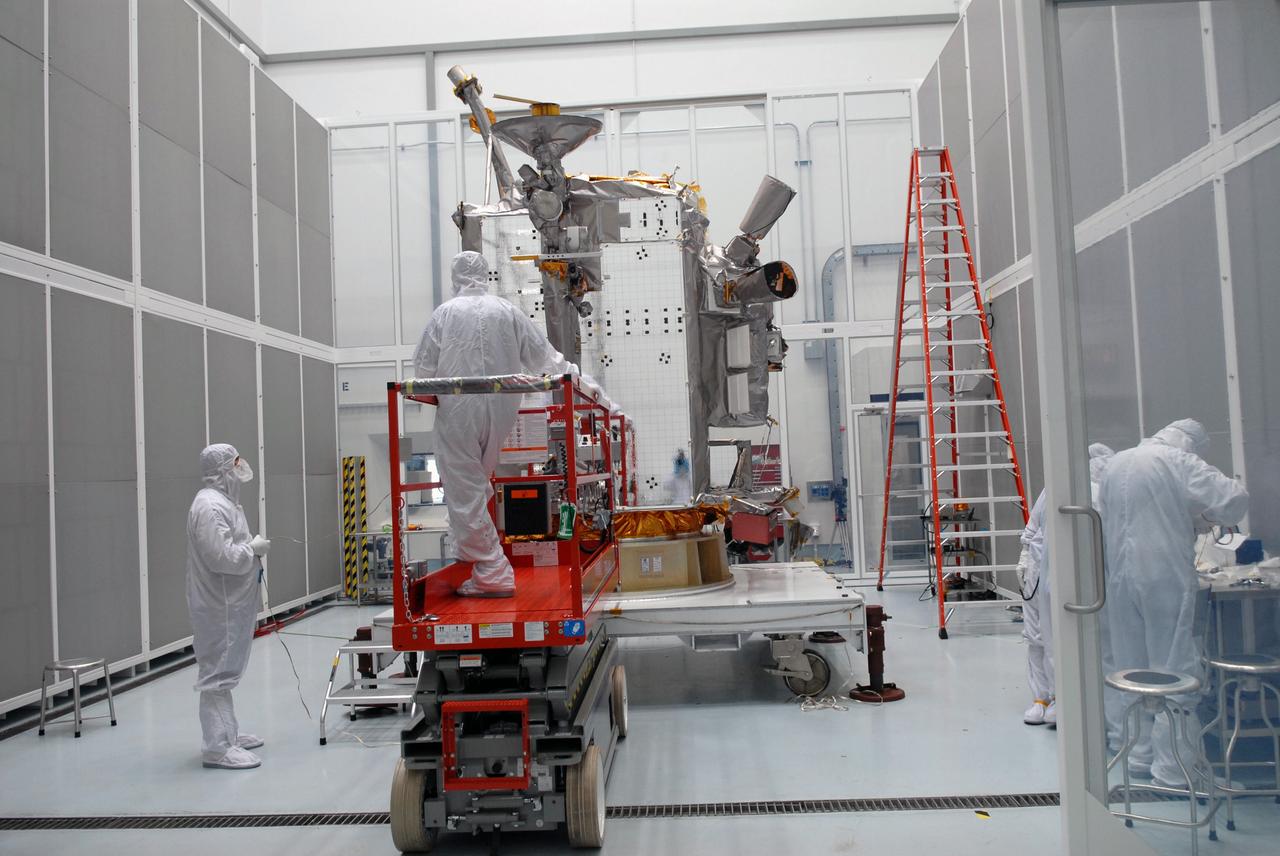

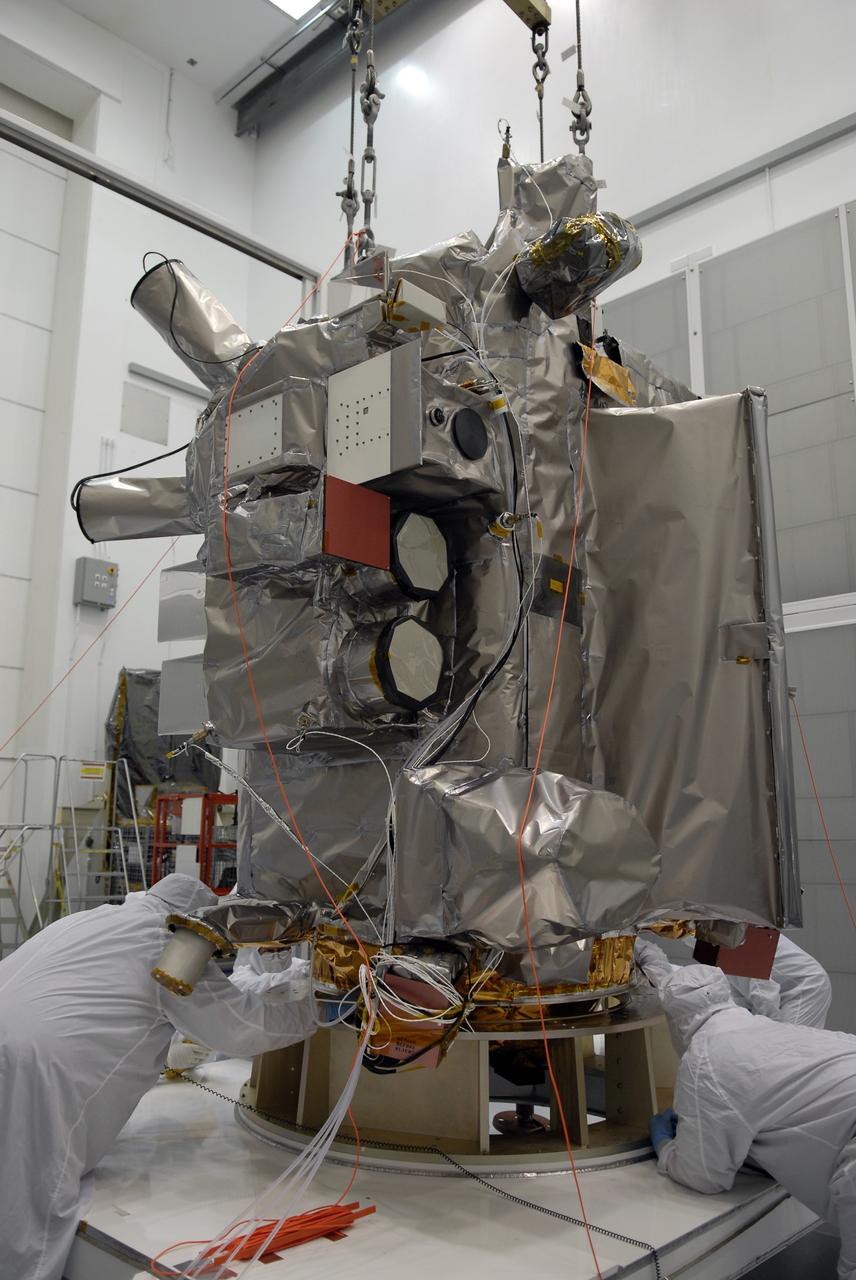
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, spacecraft is being prepared for lifting to an Aronson table. The LRO will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
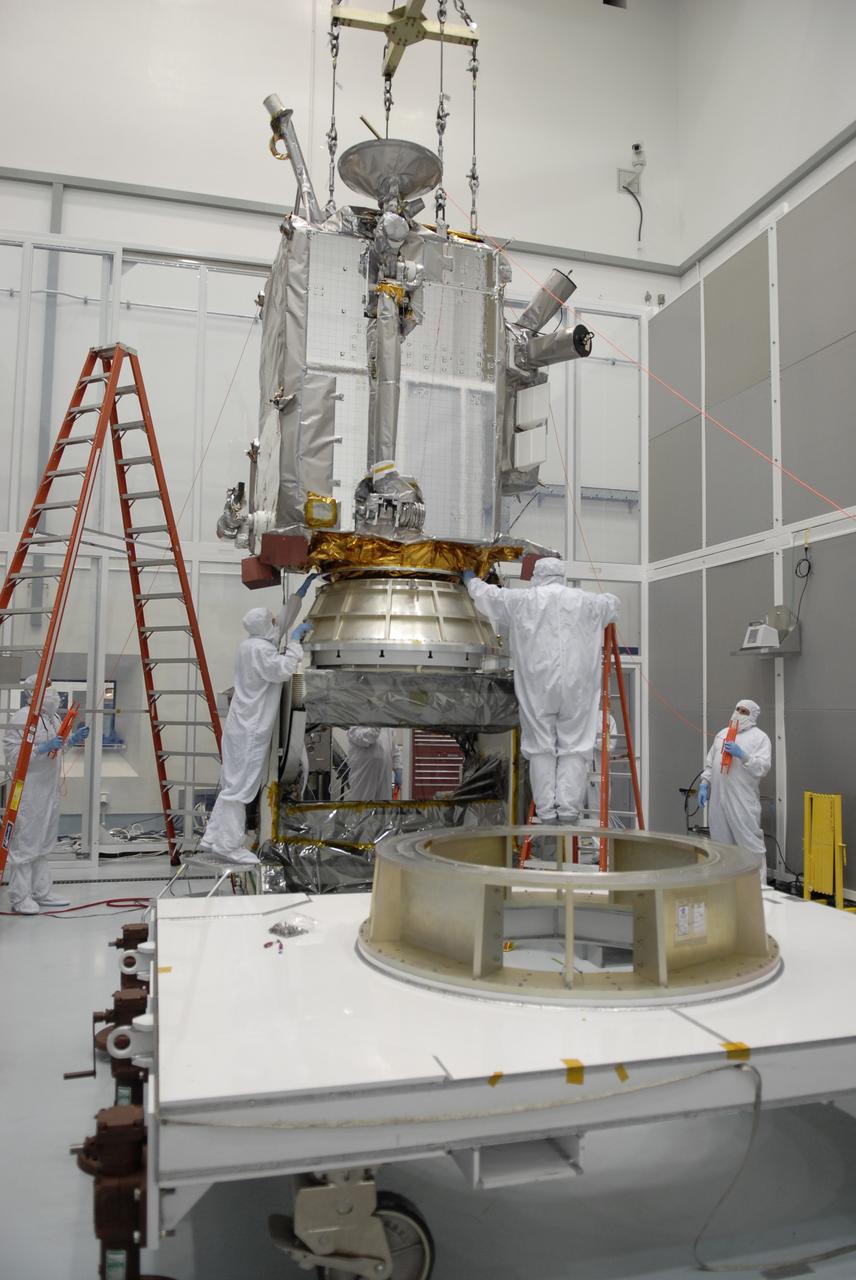

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech facility in Titusville, Fla., a crane is attached to NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The crane will move LRO to another stand. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
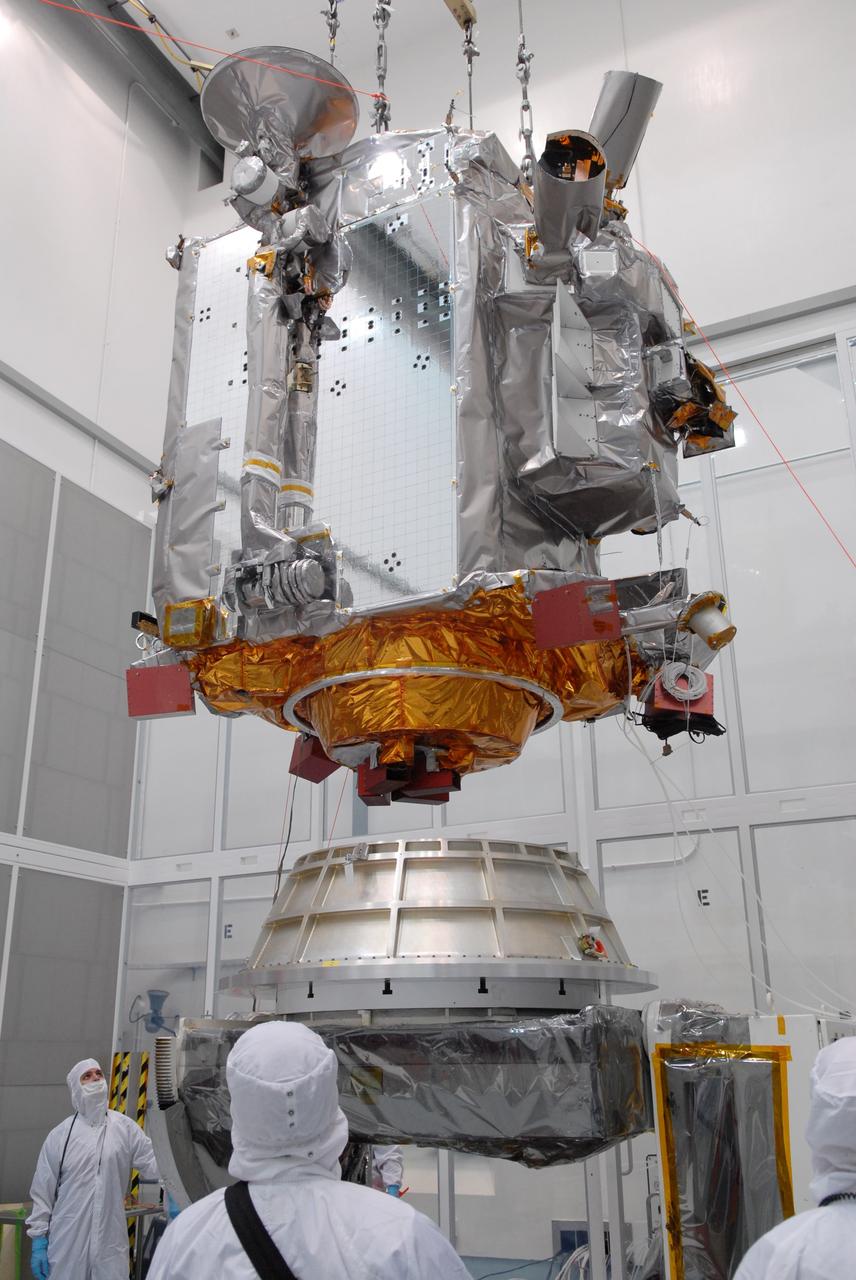

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., an overhead crane lowers NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, toward the Aronson table. The orbiter will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
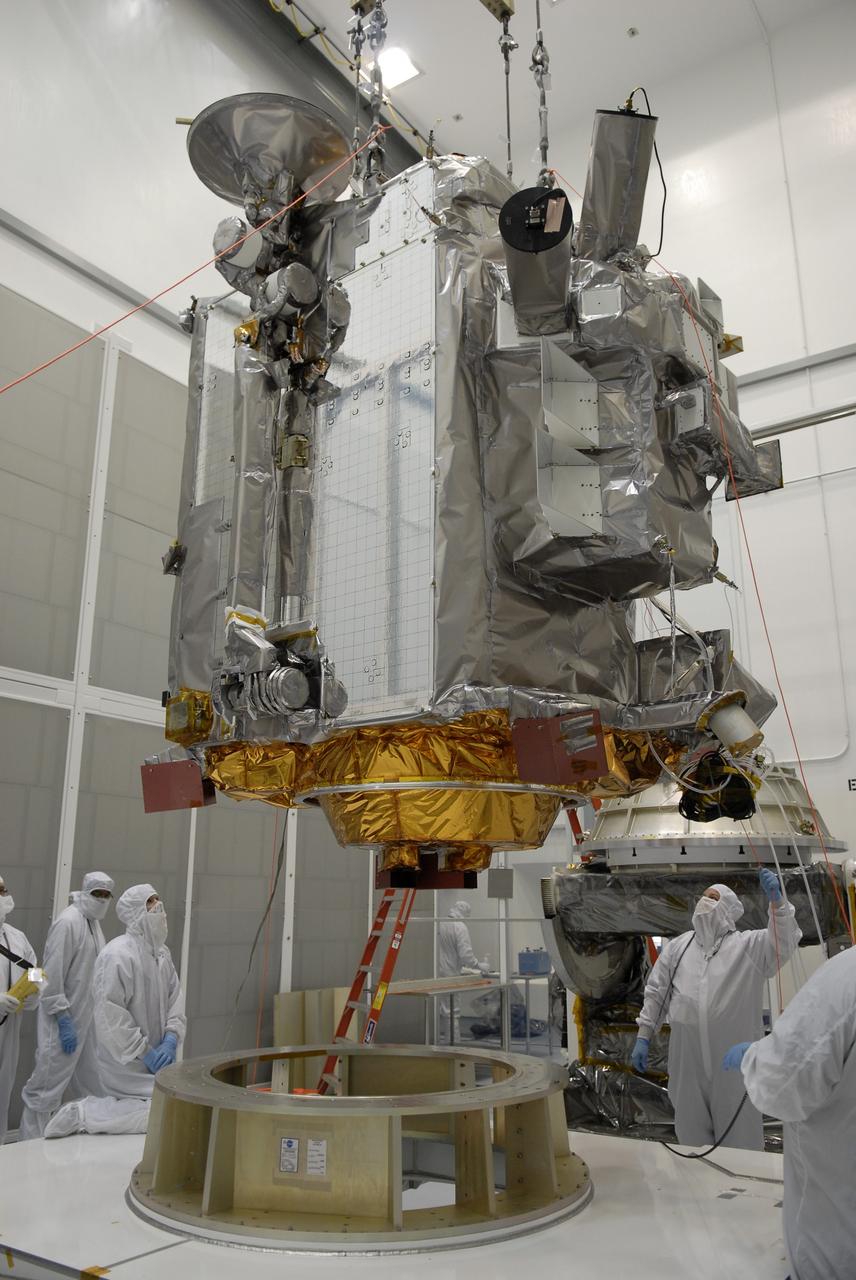

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech facility in Titusville, Fla., a crane moves NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, toward a stand in the foreground. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., technicians prepare an Aronson table to receive NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, at left. The orbiter will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech facility in Titusville, Fla., technicians secure NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, onto a stand. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
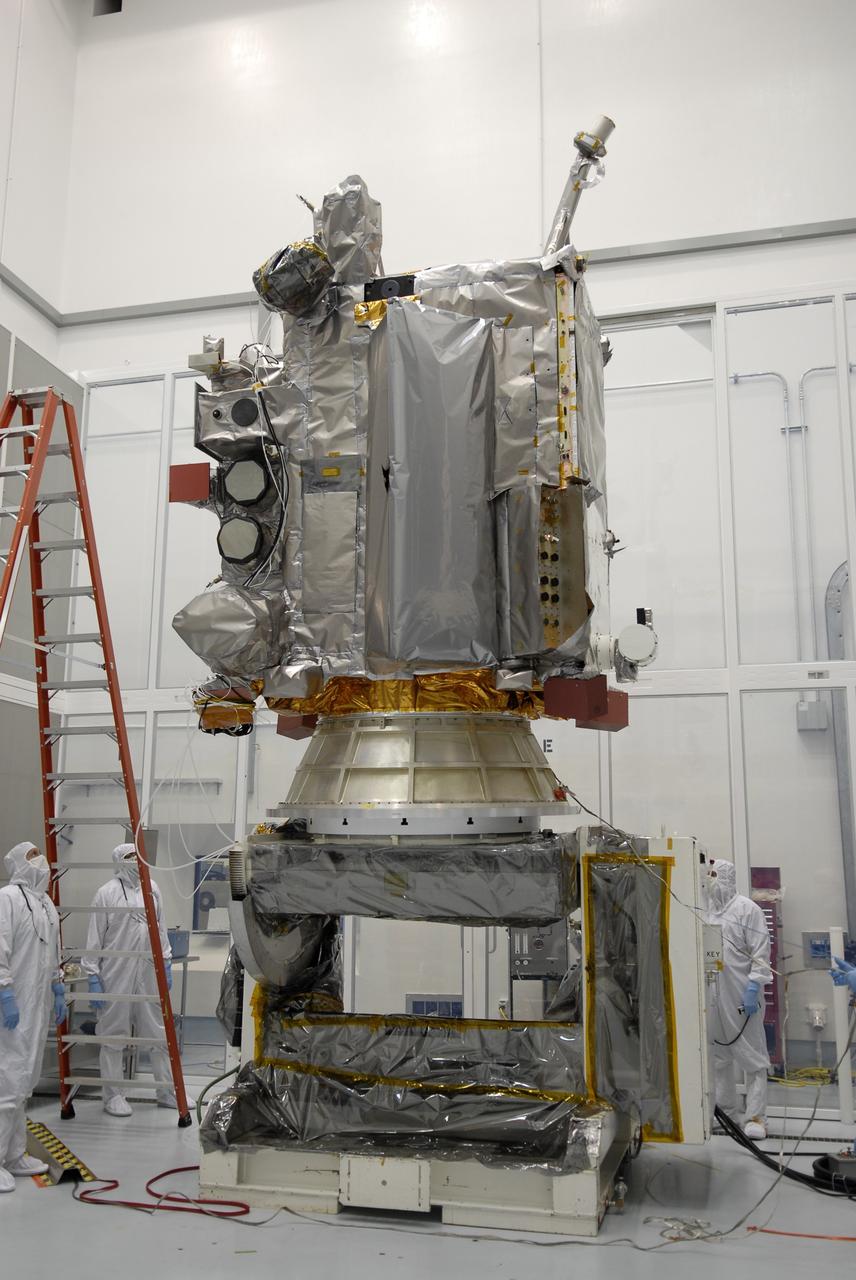

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, has been rotated to vertical on the Aronson stand. A crane will be attached to move it to another stand. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., a technician attaches cables to NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
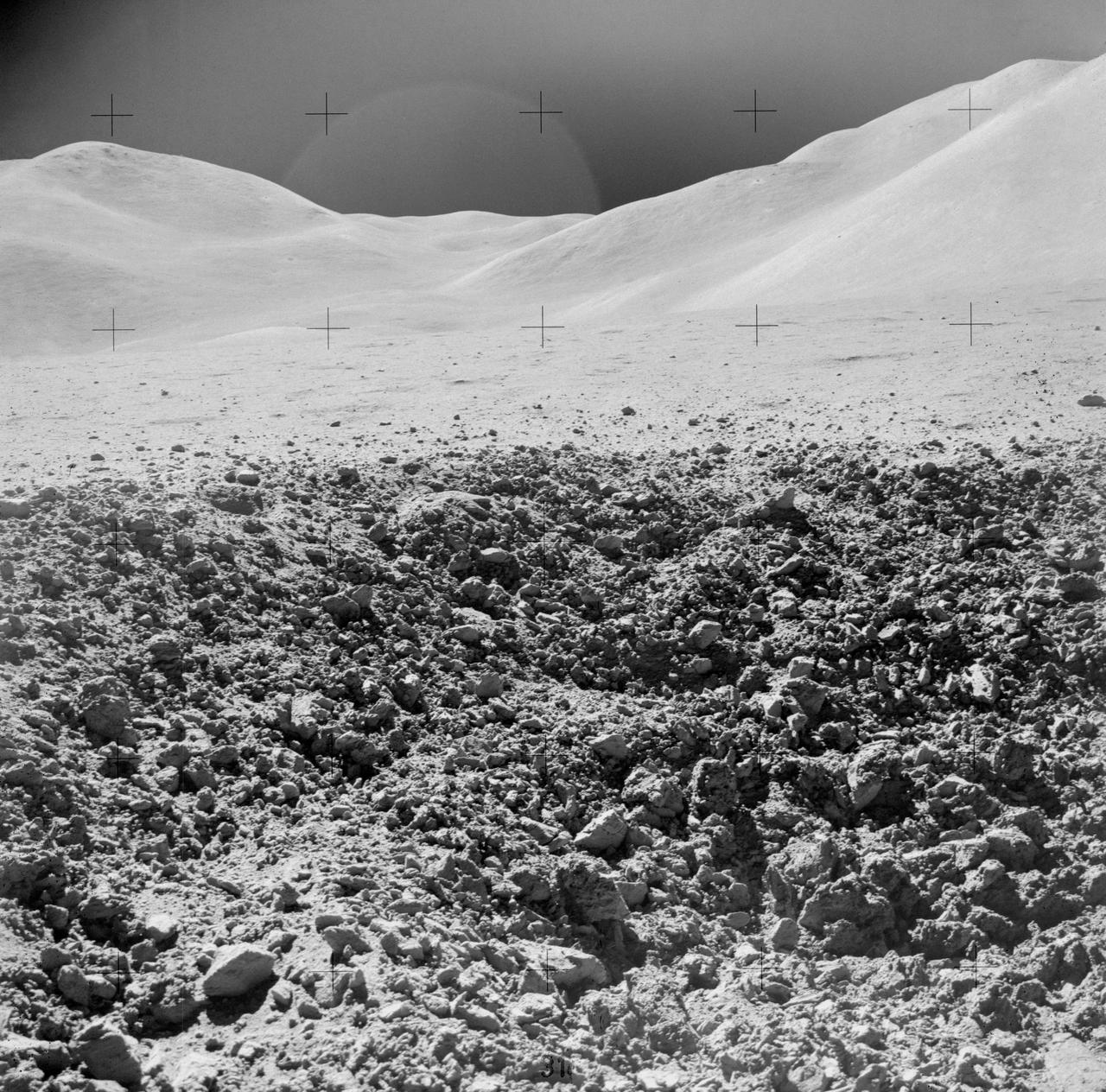

AS15-82-11082 (2 Aug. 1971) --- A close-up view of a portion of a "relatively fresh" crater, looking southeast, as photographed during the third Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA), on Aug. 2, 1971, at EVA Station No. 9, near Scarp Crater. The crater pictured is unnamed. The Apennine Front is in the background, and Hadley Delta Mountain is in the right background. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
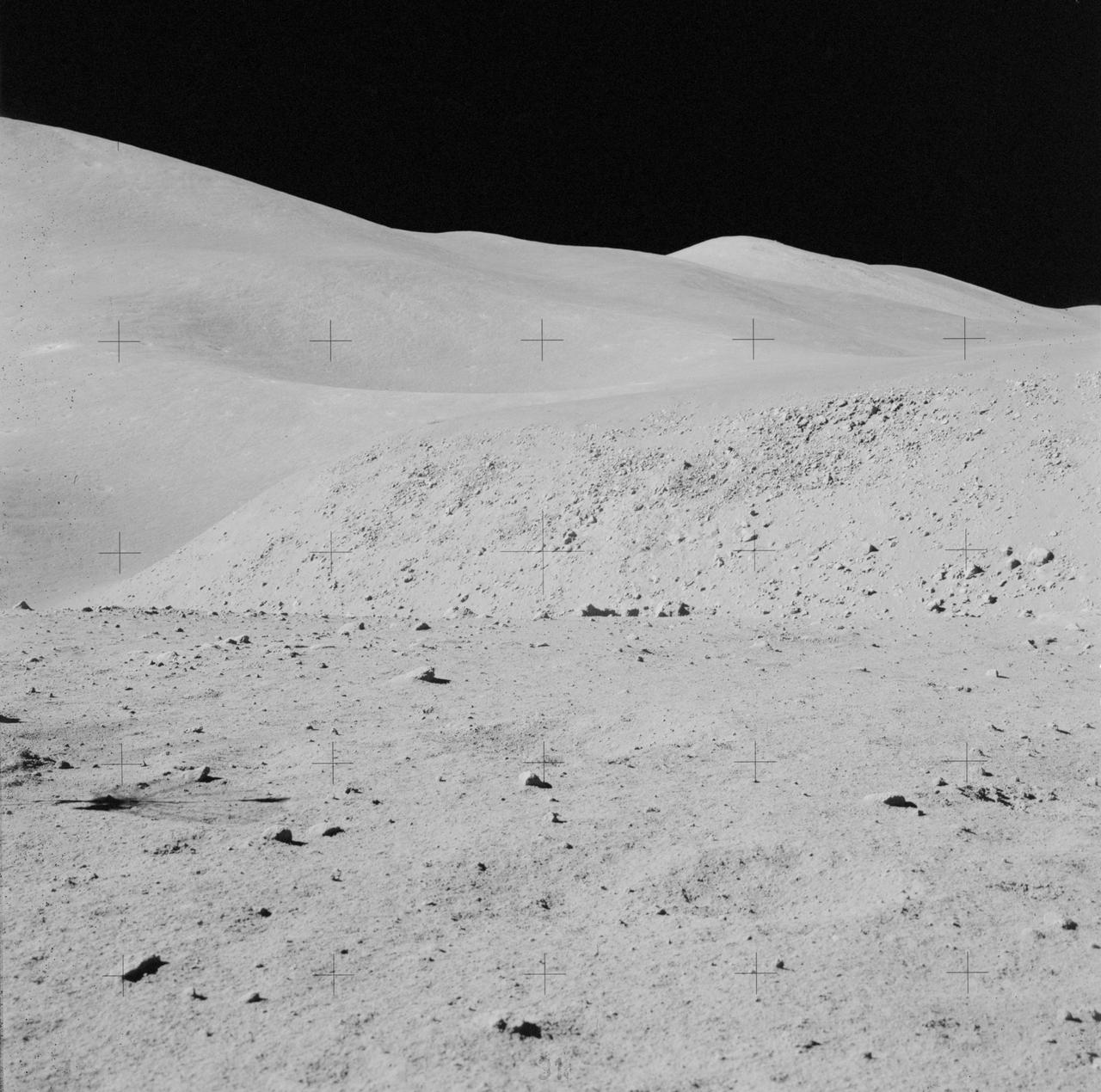

AS15-82-11123 (2 Aug. 1971) --- A view of the "strewn rock" scene encountered by Apollo 15 astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, during their third extravehicular activity (EVA) of the mission. Irwin took this photograph with a handheld 70mm camera. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
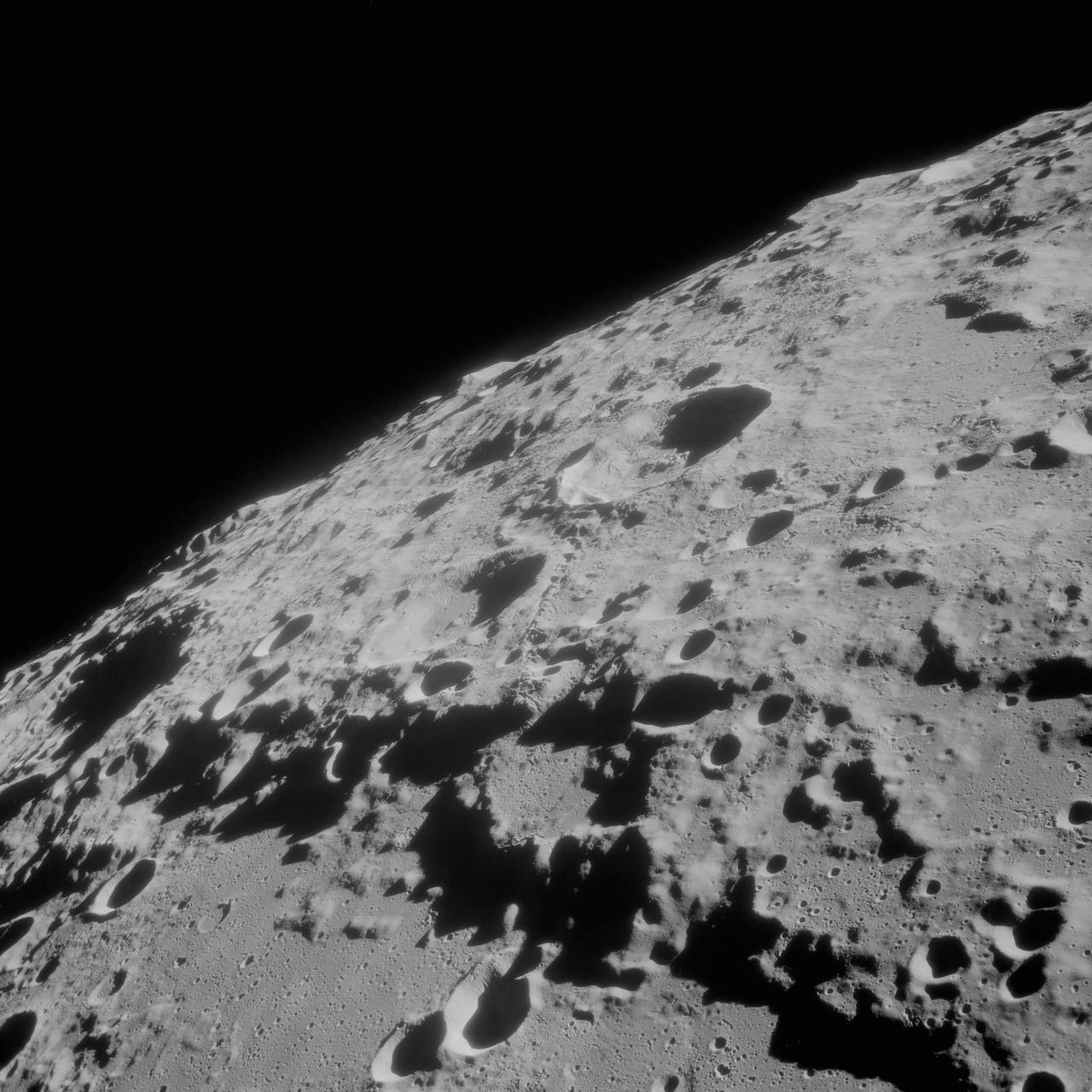

AS11-42-6248 (July 1969) --- An Apollo 11 oblique view of the lunar farside in the area of International Astronomical Union crater No. 312, which is about 30 statute miles in diameter. The center of the photograph is located at 164 degrees west longitude and 8 degrees south latitude. The sharp shadows indicate that the picture was taken at a low sun angle.
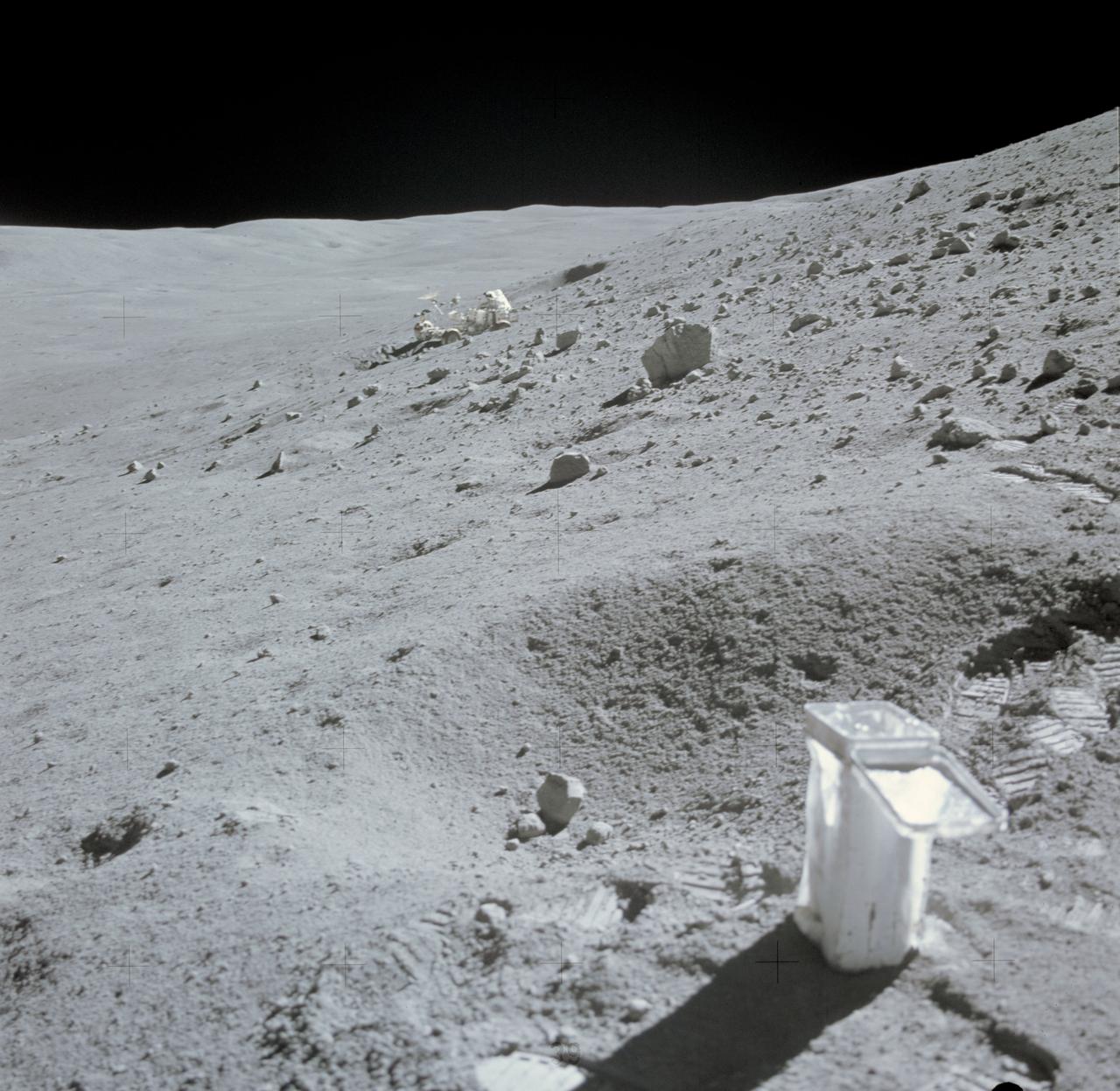

AS16-107-17473 (22 April 1972) --- The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) appears to be parked in a deep lunar depression, on the slope of Stone Mountain. This photograph of the lunar scene at Station No. 4 was taken during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. A sample collection bag is in the right foreground. Note field of small boulders at upper right. While astronauts John W. Young, commander, and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
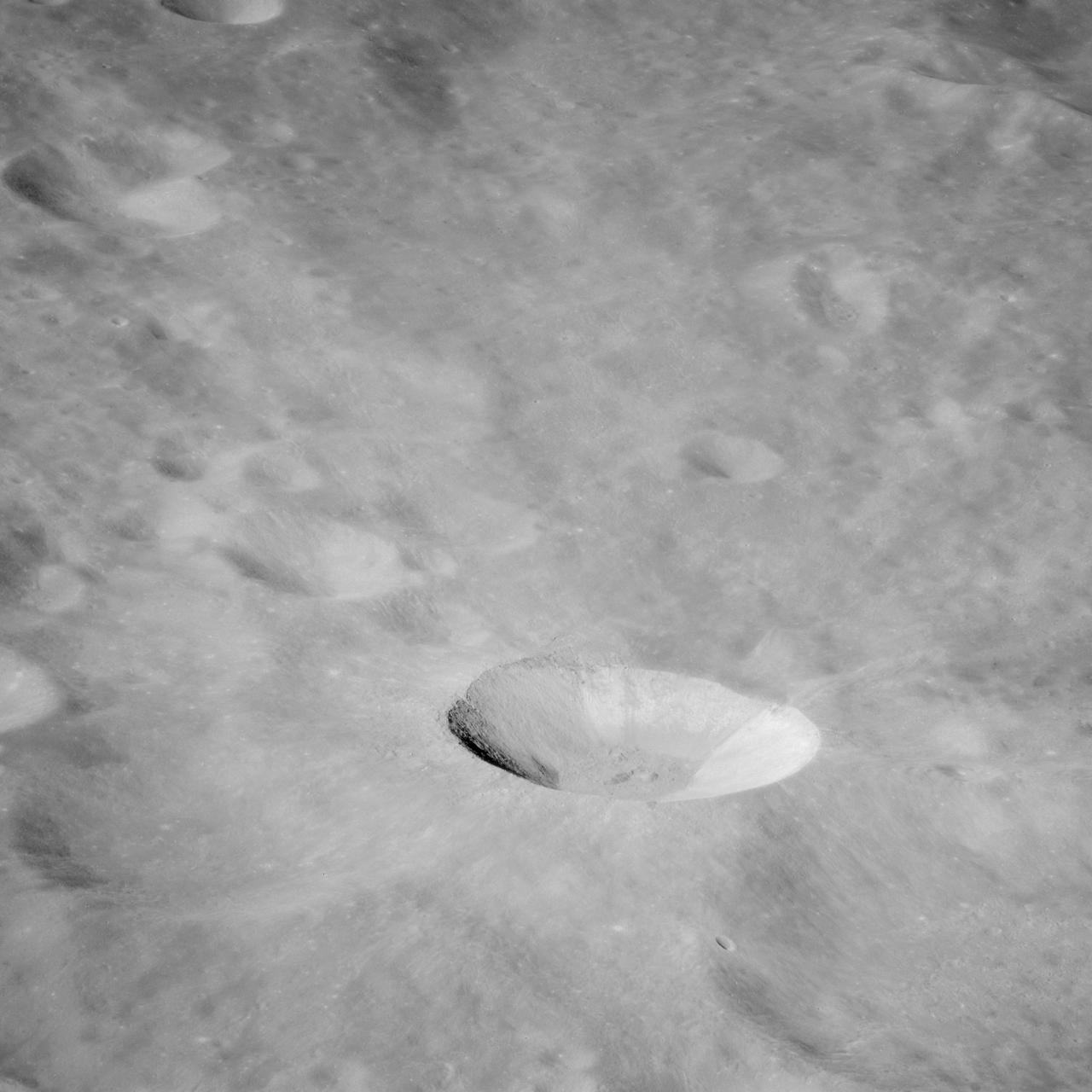

AS11-43-6412 (July 1969) --- This is a northeasterly, low-oblique view of an unmanned crater and highland area on the lunar farside, as photographed from Apollo 11. The center of the picture is located at the 167 degrees east longitude and 6 degrees north latitude. This area of the moon lies just east of International Astronomical Union crater No. 220.
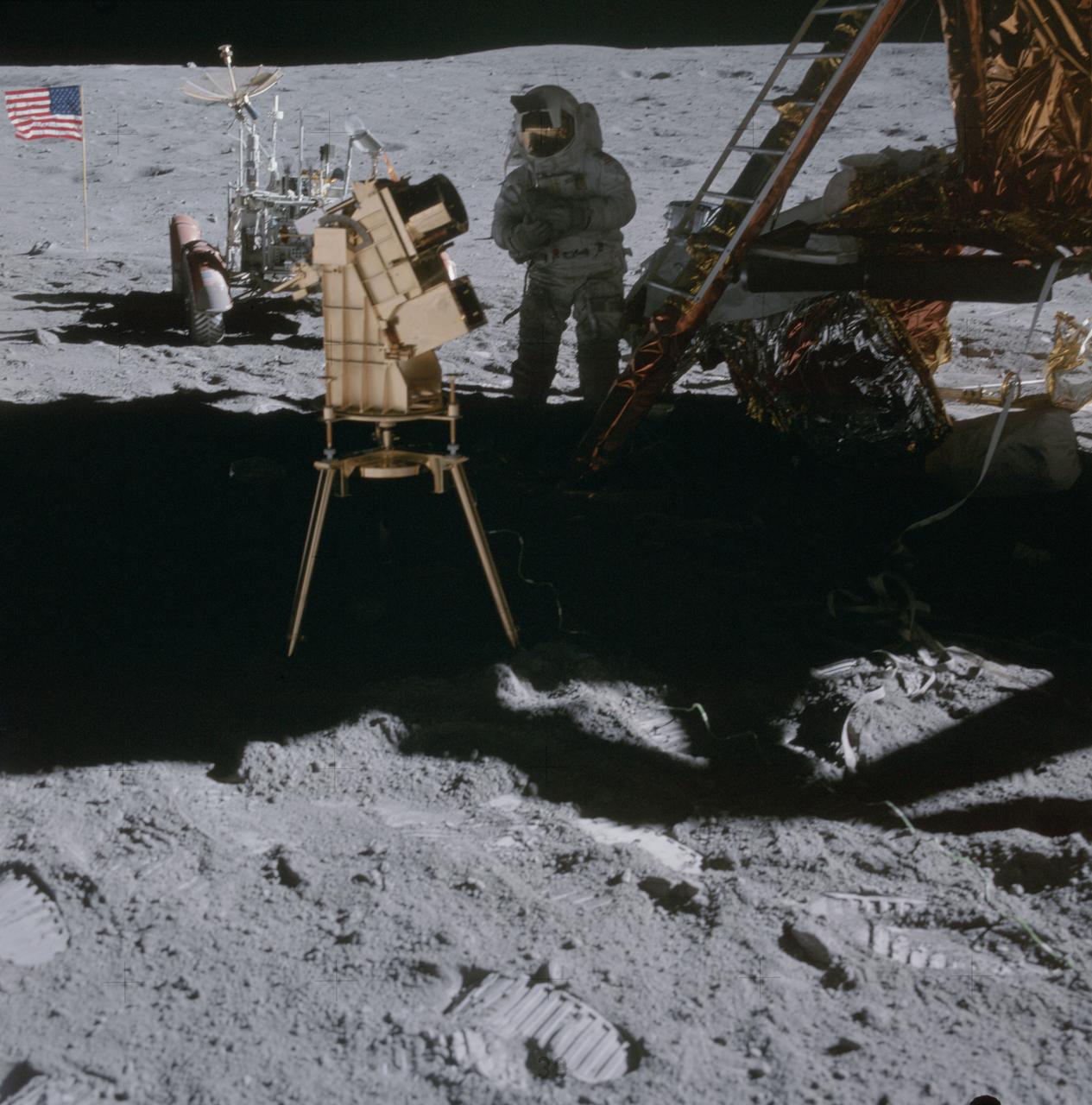

AS16-114-18439 (22 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, stands in the shadow of the Lunar Module (LM) behind the ultraviolet (UV) camera which is in operation. This photograph was taken by astronaut John W. Young, commander, during the mission's second extravehicular activity (EVA). The UV camera's gold surface is designed to maintain the correct temperature. The astronauts set the prescribed angles of azimuth and elevation (here 14 degrees for photography of the large Magellanic Cloud) and pointed the camera. Over 180 photographs and spectra in far-ultraviolet light were obtained showing clouds of hydrogen and other gases and several thousand stars. The United States flag and Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) are in the left background. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
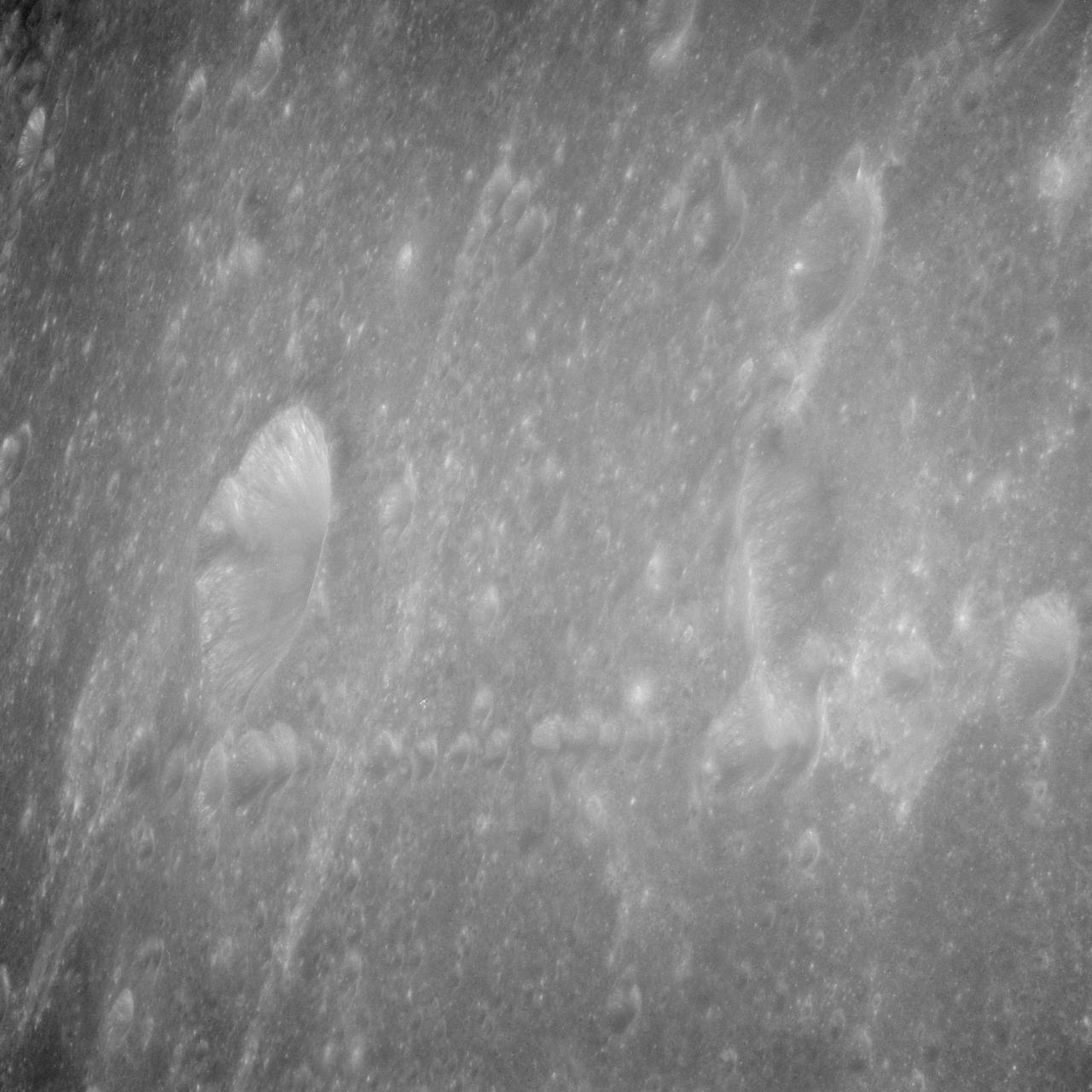
AS11-43-6439 (July 1969) --- An Apollo 11 oblique view of the lunar farside. The linear group of small craters is located within the large International Astronomical Union crater No. IX, and is centered at 139.5 degrees east longitude and 7 degrees north latitude. The absence of shadows is due to the high sun angle. The crater chain is approximately 34 statute miles in length, and the large crater adjacent to the crater is 10.5 statute miles in diameter.
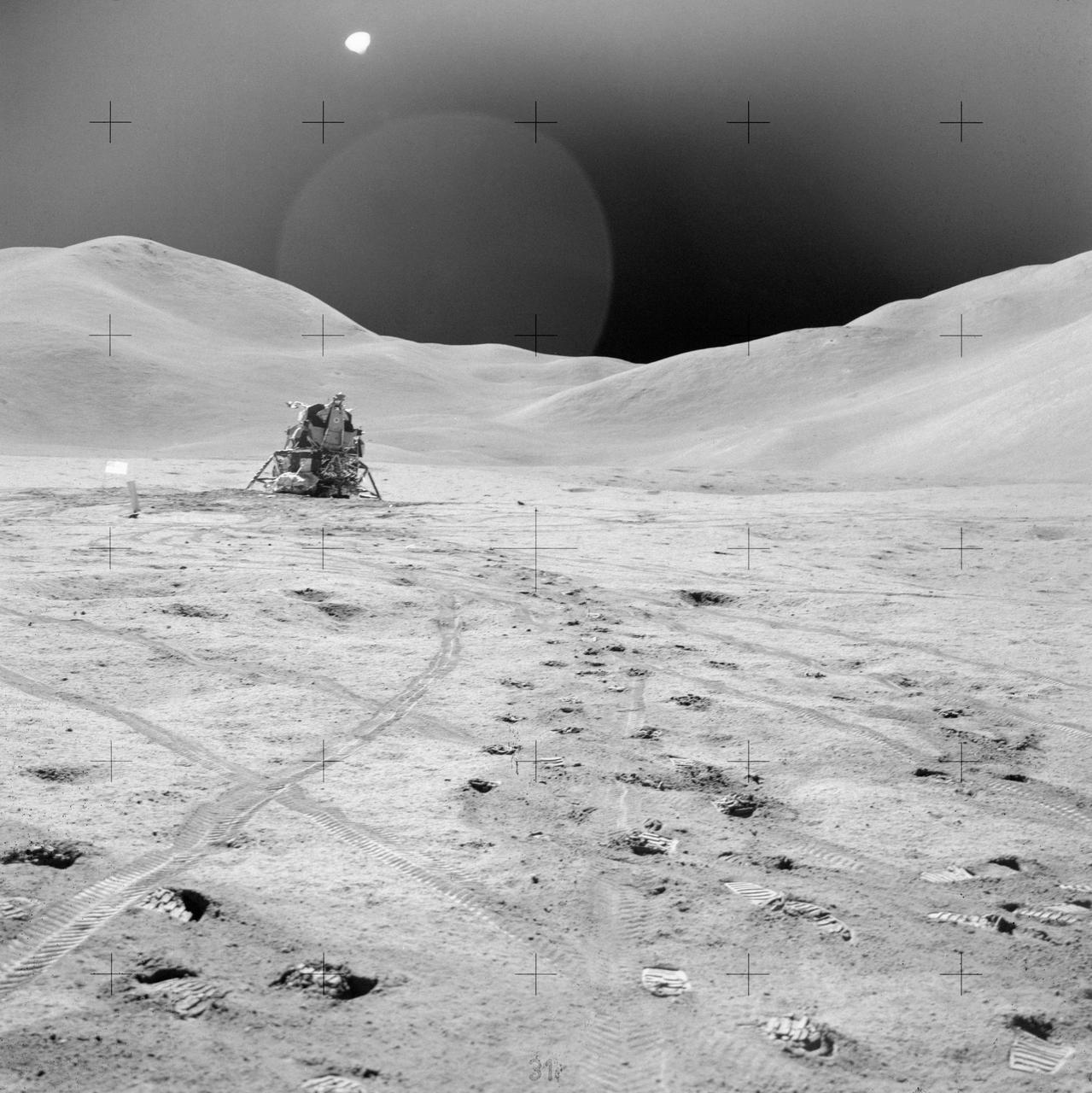

AS15-82-11057 (2 Aug. 1971) --- The Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" is photographed against the barren lunarscape during the third Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site on the lunar nearside. This view is looking southeast. The Apennine Front is in the left background; and Hadley Delta Mountain is in the right background. The object next to the United States flag is the Solar Wind Composition (SWC) experiment. Last Crater is to the right of the LM. Note bootprints and tracks of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The light spherical object at the top is a reflection in the lens of the camera. While astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
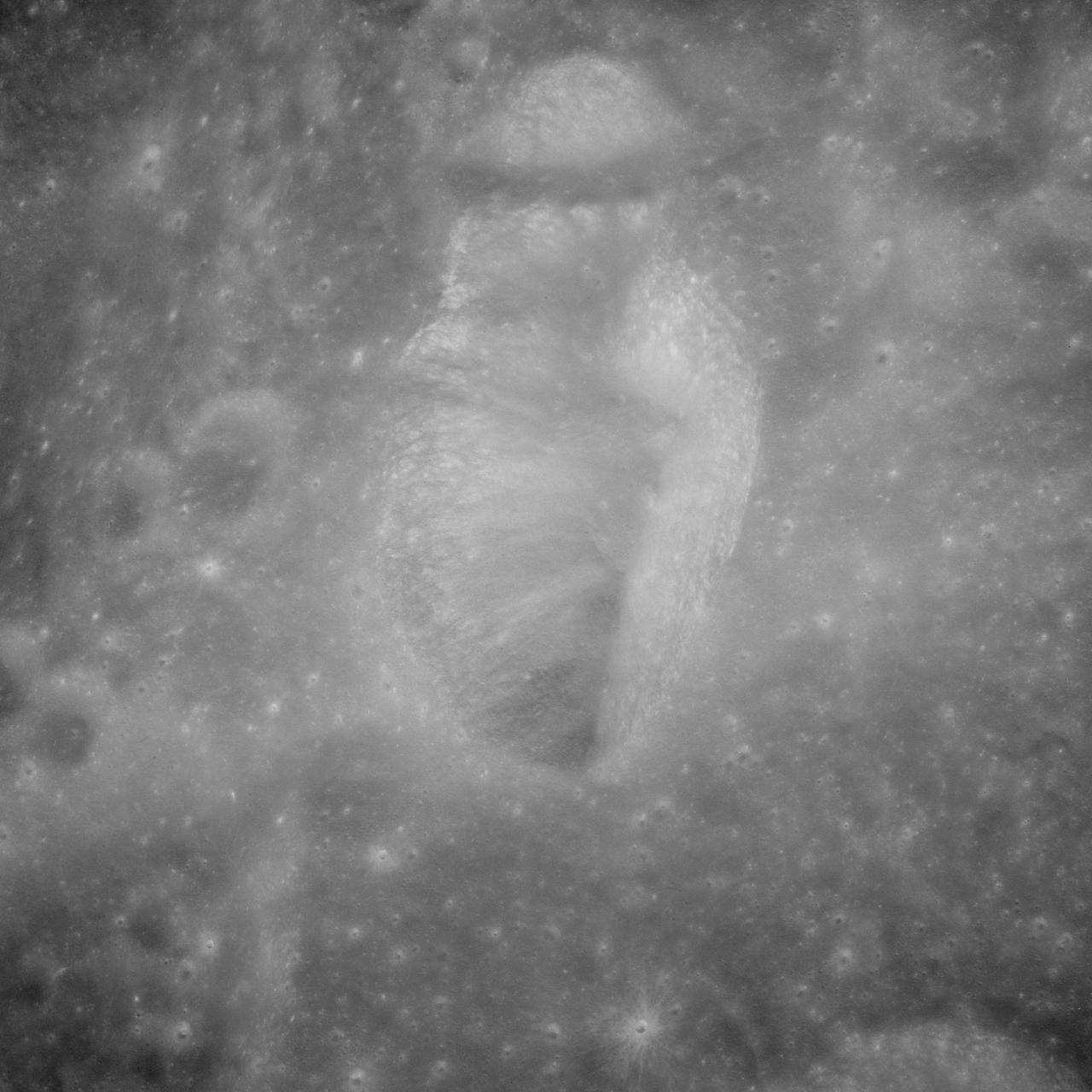
AS11-43-6422 (July 1969) --- An Apollo 11 oblique view of the lunar farside. These two odd-shaped craters are located midway between International Astronomical Union craters 218 and 220, and are centered at 155 degrees east longitude and 3 degrees north latitude. The craters total approximately 13.5 statute miles in length and 7.5 statute miles in width at their widest point.
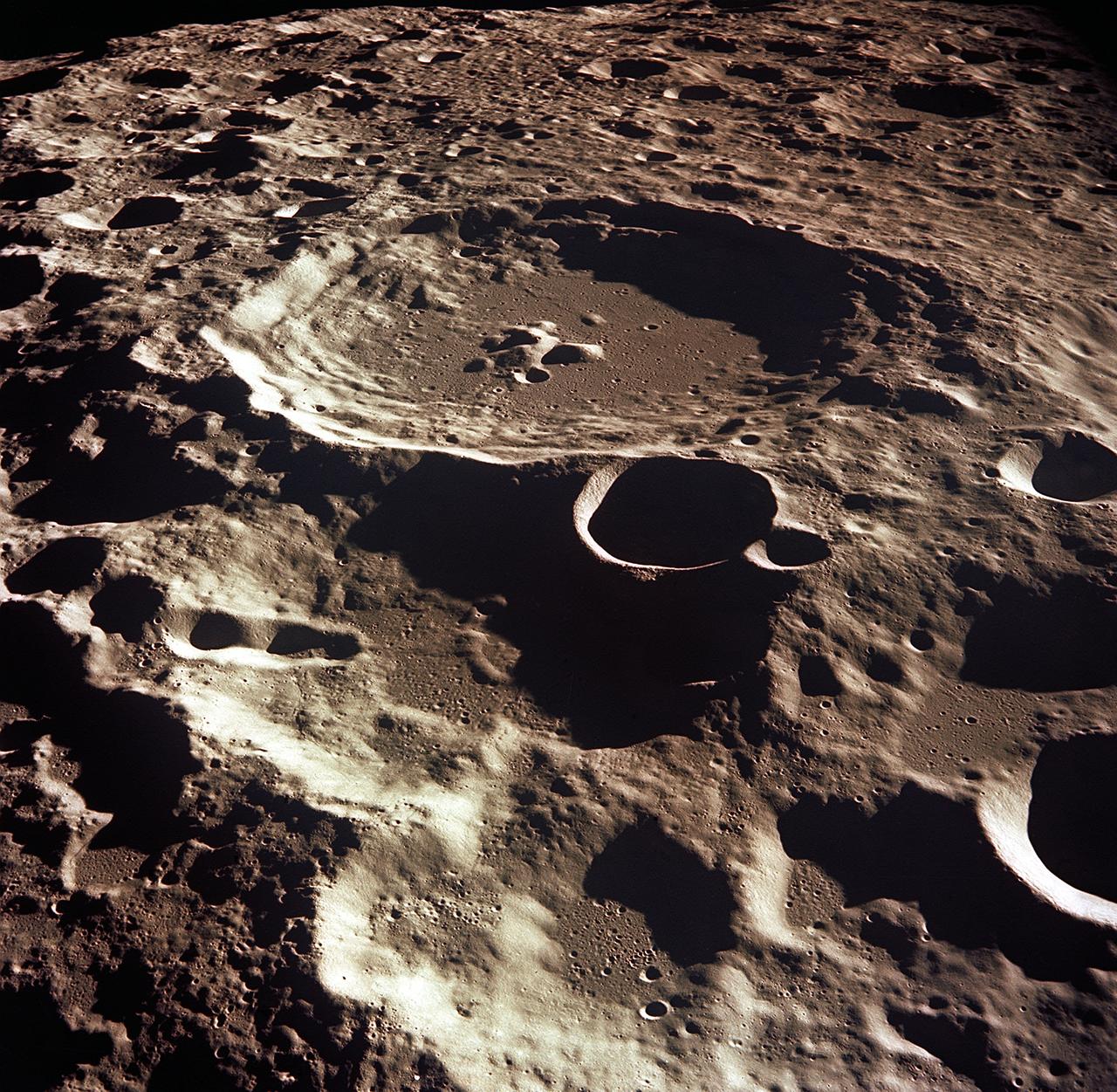

AS11-44-6609 (16-24 July 1969) --- An oblique of the Crater Daedalus on the lunar farside as seen from the Apollo 11 spacecraft in lunar orbit. The view looks southwest. Daedalus (formerly referred to as I.A.U. Crater No. 308) is located at 179 degrees east longitude and 5.5 degrees south latitude. Daedalus has a diameter of about 50 statute miles. This is a typical scene showing the rugged terrain on the farside of the moon. While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
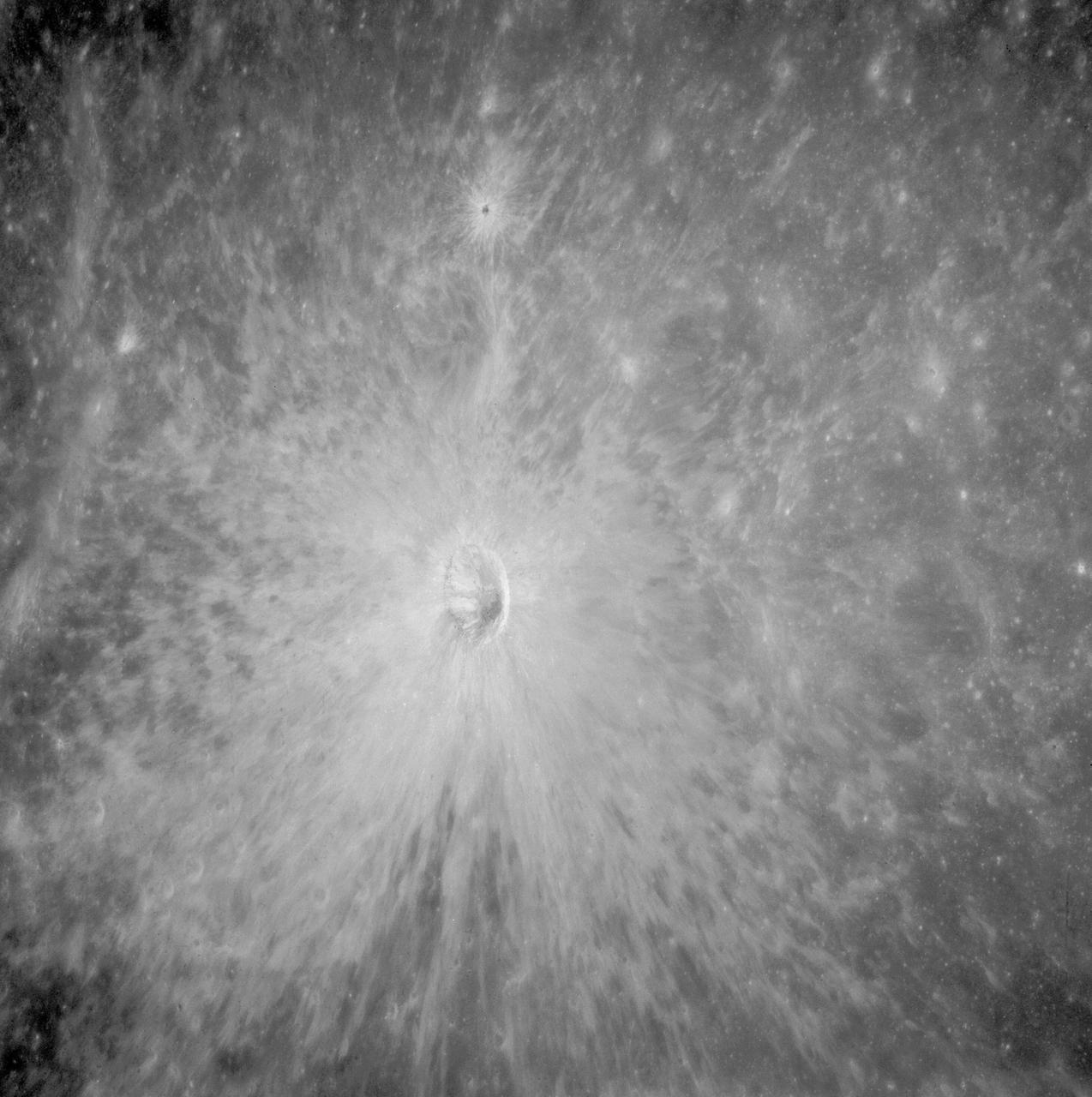

AS11-42-6285 (July 1969) --- An Apollo 11 view of a bright rayed crater on the lunar farside. The crater is unnamed. The center of this photograph is located at 100 degrees southeast longitude and 4 degrees 30 minutes north latitude. This area is just east of Smyth's Sea.
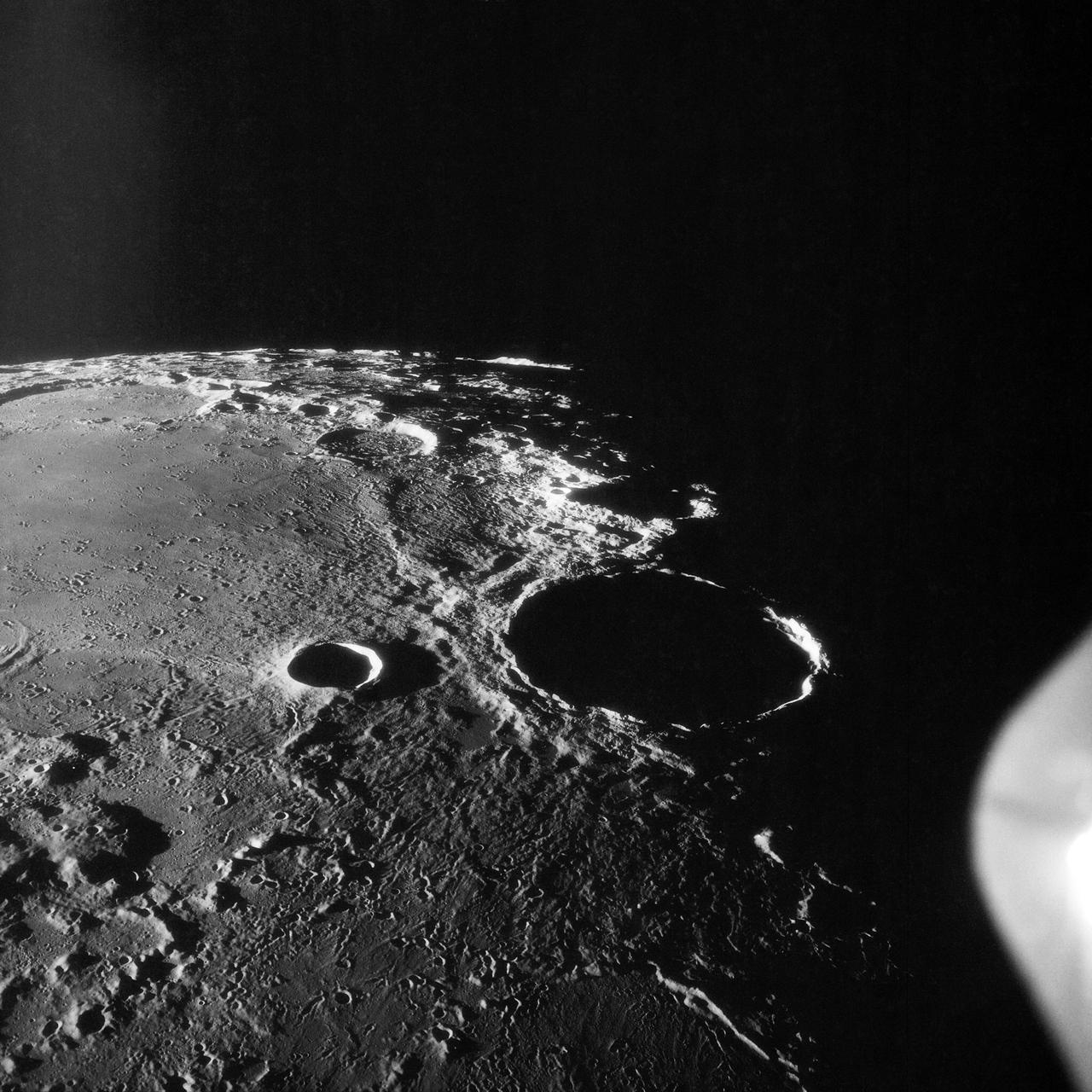

AS11-42-6237 (20 July 1969) --- An Apollo 11 oblique view of the large crater Theophilus located at the northwest edge of the Sea of Nectar on the lunar nearside. Theophilus is about 60 statute miles in diameter. The smooth area is Mare Nectaris. The smaller crater Madler, about 14 statute miles in diameter, is located to the east of Theophilus. Visible in the background are the large crater Fracastorius and the smaller crater Beaumont. The coordinates of the center of this photograph are 29 degrees east longitude and 11 degrees south latitude.
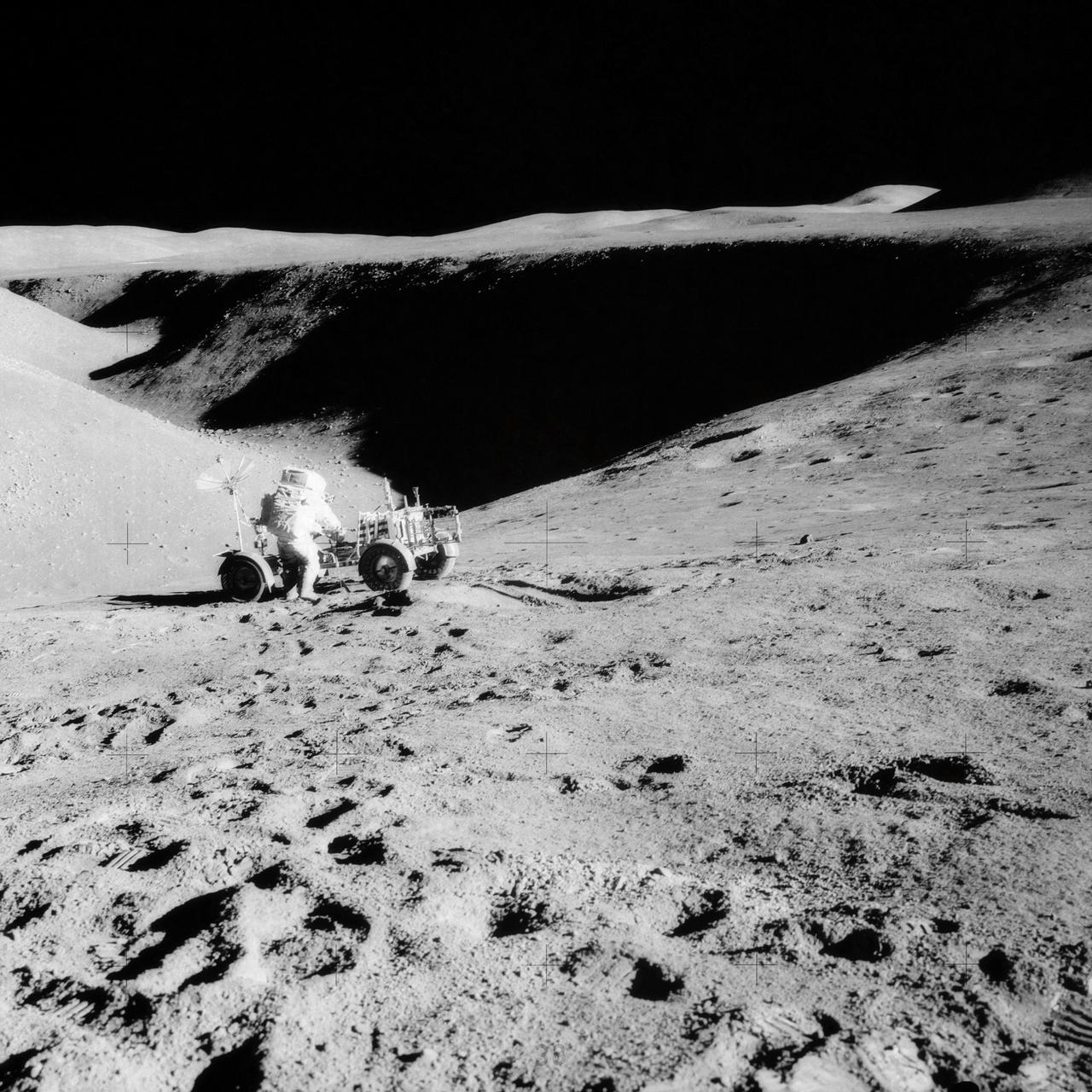

AS15-85-11451 (31 July 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, mission commander, performs a task at the Lunar Roving Vehicle parked on the edge of Hadley Rille during the first Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). This photograph was taken by astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, from the flank of St. George Crater. The view is looking north along the rille.
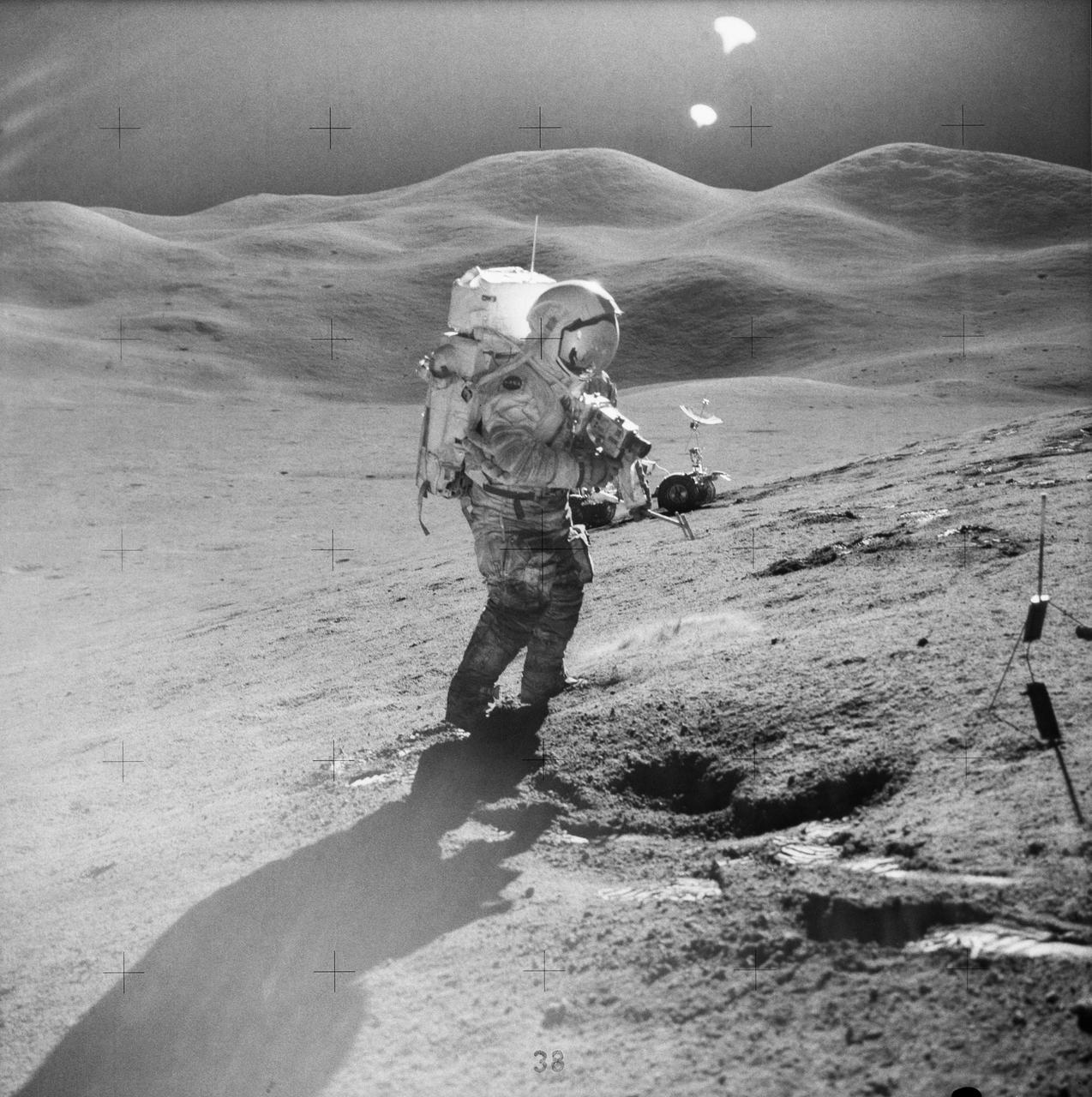

AS15-85-11514 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, commander, standing on the slope of Hadley Delta, uses a 70mm camera during Apollo 15 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. He is 10.5 miles (or 17.5 kilometers) from the base of the Apennine Mountains seen in the background. Scott carries tongs in his left hand. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is in the background. This view is looking east. While astronauts Scott and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS15-85-11437 (31 July 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, commander, with tongs and gnomon in hand, studies a boulder on the slope of Hadley Delta during the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission's first extravehicular activity (EVA). The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), "Rover", is in the right foreground. The view is looking slightly south of west. "Bennett Hill" is at extreme right. Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, took this photograph. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended together in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
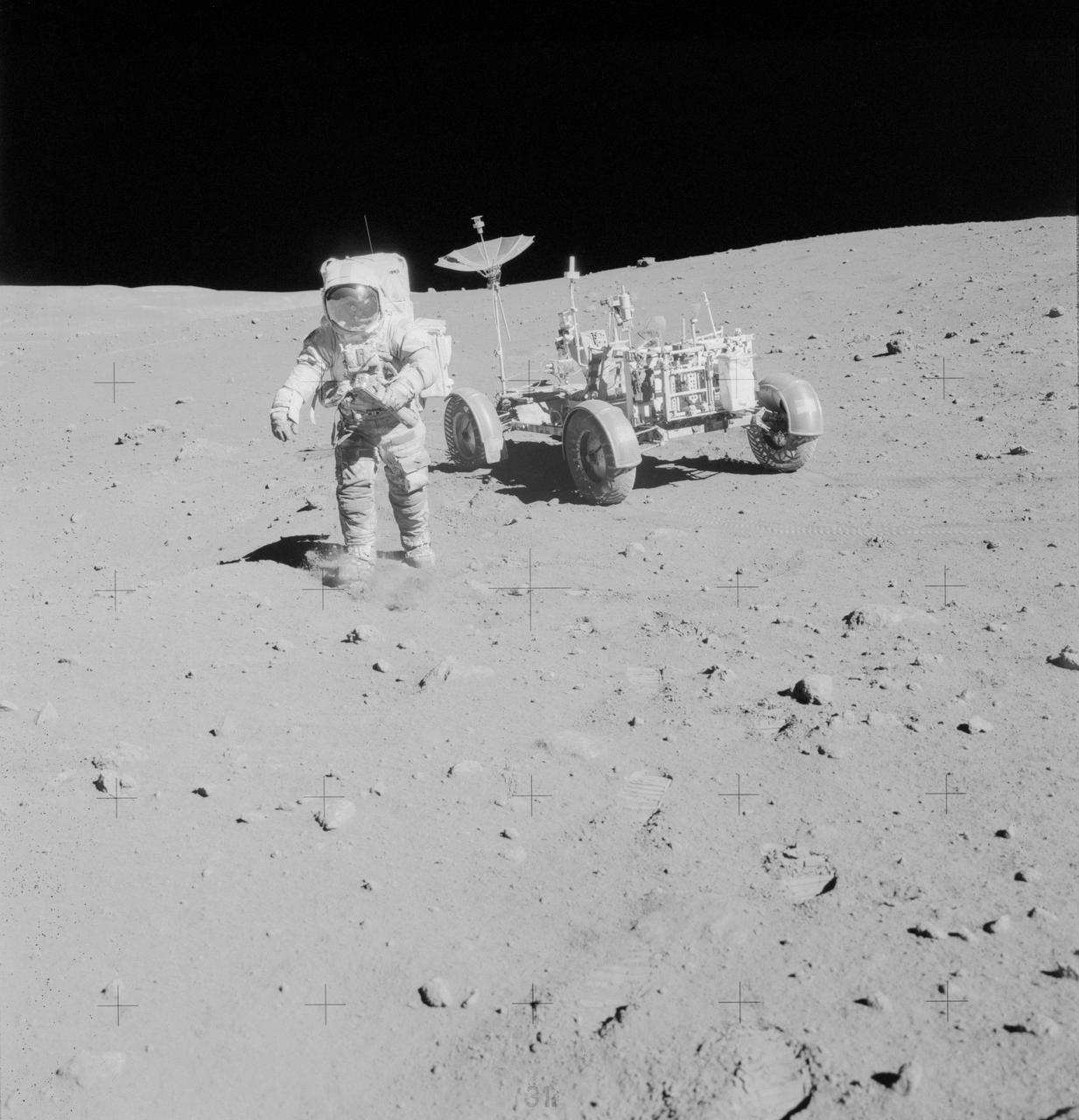

AS15-82-11168 (2 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, walks away from the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during the third Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The LRV is parked a short distance from the rim of Hadley Rille. The far wall of the rille is in the distance at extreme upper left. Irwin is holding the 500mm Hasselblad camera in his left hand. This photograph was taken by astronaut David R. Scott, commander. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

During the total solar eclipse, the Sun’s corona, only visible during the total eclipse, is shown as a crown of white flares from the surface. The red spots called Bailey's beads occurs where the moon grazes by the Sun and the rugged lunar limb topography allows beads of sunlight to shine through in some areas as photographed from NASA Armstrong’s Gulfstream III. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Thomas)

During the total solar eclipse, the Sun’s corona, only visible during the total eclipse, is shown as a crown of white flares from the surface. The red spots called Bailey's beads occurs where the moon grazes by the Sun and the rugged lunar limb topography allows beads of sunlight to shine through in some areas as photographed from NASA Armstrong’s Gulfstream III. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Thomas)
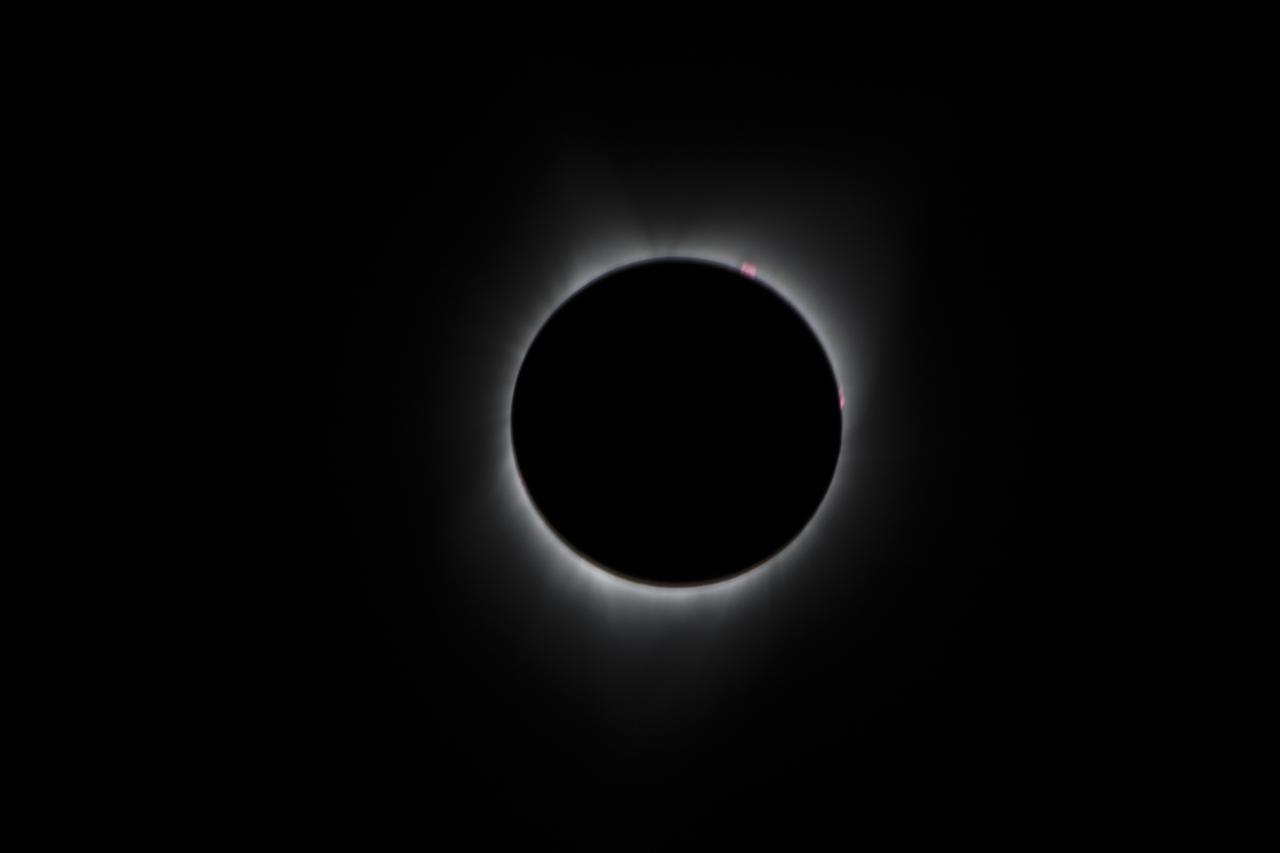

During the total solar eclipse, the Sun’s corona, only visible during the total eclipse, is shown as a crown of white flares from the surface. The red spots called Bailey's beads occurs where the moon grazes by the Sun and the rugged lunar limb topography allows beads of sunlight to shine through in some areas as photographed from NASA Armstrong’s Gulfstream III. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Thomas)
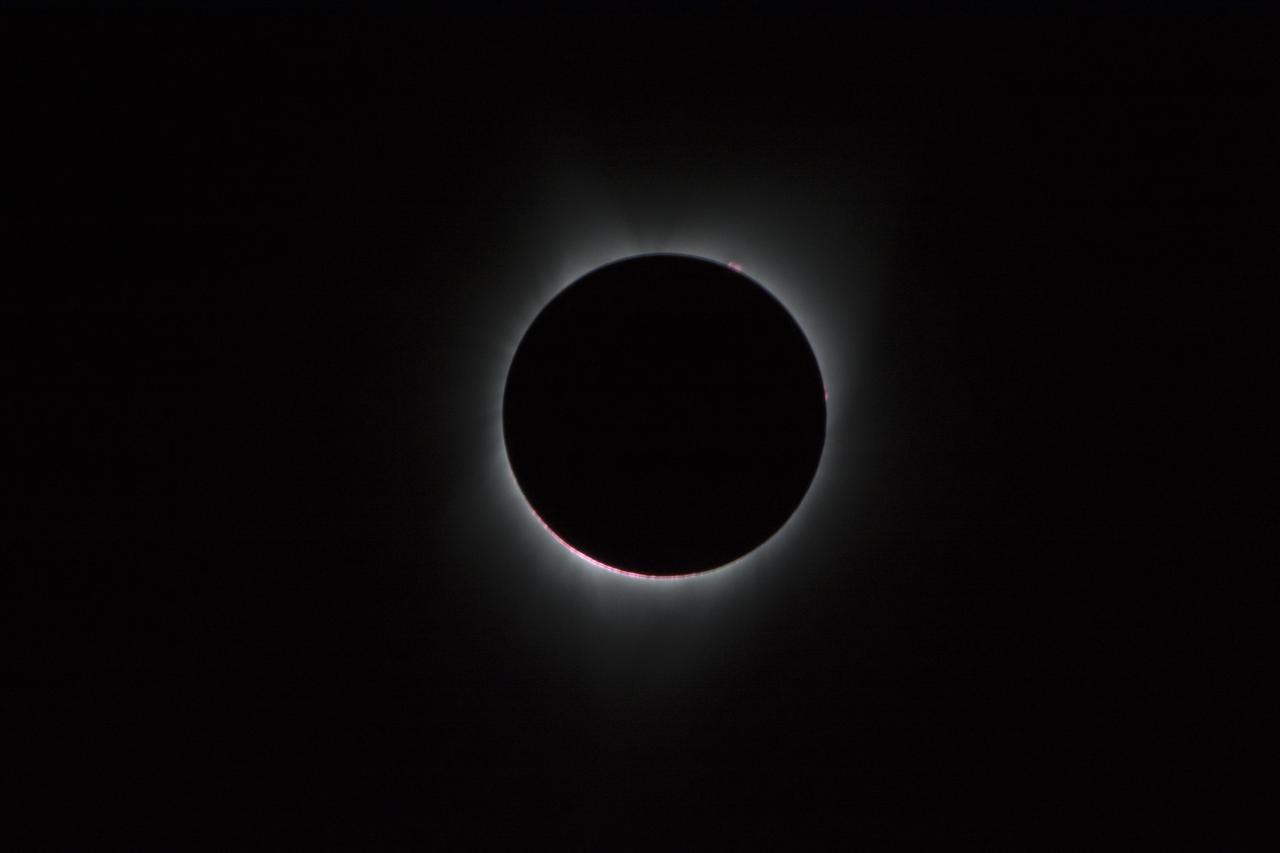

During the total solar eclipse, the Sun’s corona, only visible during the total eclipse, is shown as a crown of white flares from the surface. The red spots called Bailey's beads occurs where the moon grazes by the Sun and the rugged lunar limb topography allows beads of sunlight to shine through in some areas as photographed from NASA Armstrong’s Gulfstream III. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Thomas)
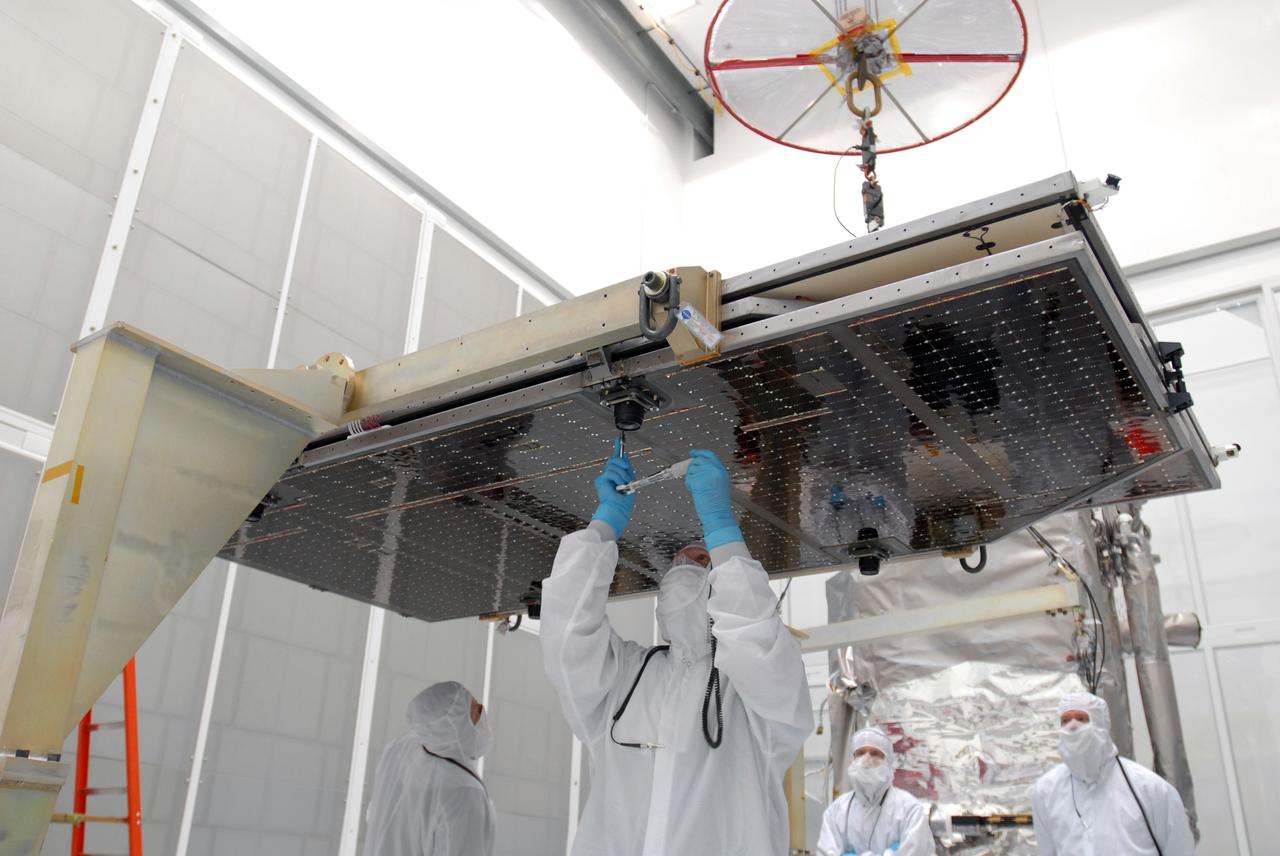

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians prepare the solar array panel for installation on the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Launch of LRO is targeted for June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
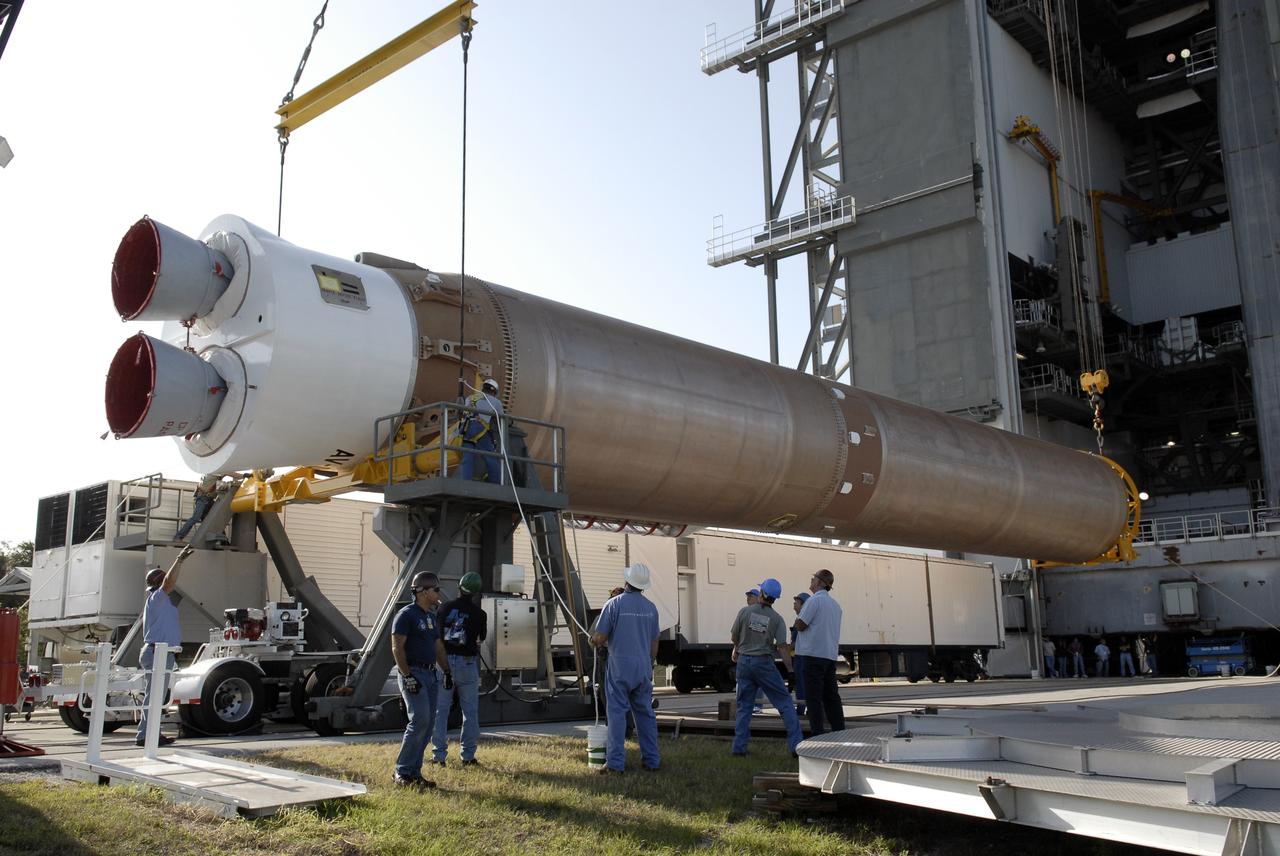

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– At the Vertical Integration Facility on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, cranes are attached to the Atlas V first stage to raise it to vertical. The Atlas will be lifted into the VIF. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
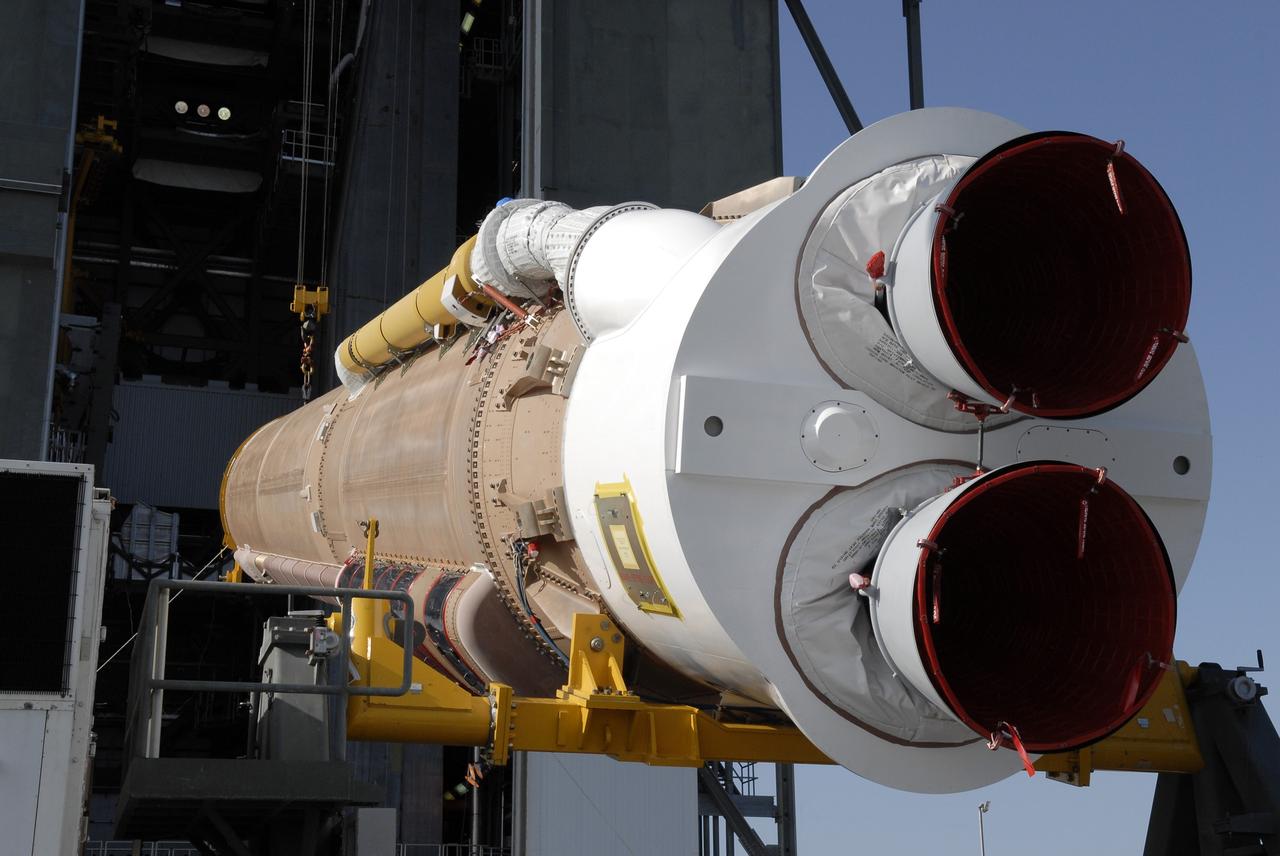

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– At the Vertical Integration Facility on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Atlas V first stage is being raised to a vertical position. The Atlas will be lifted into the VIF. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
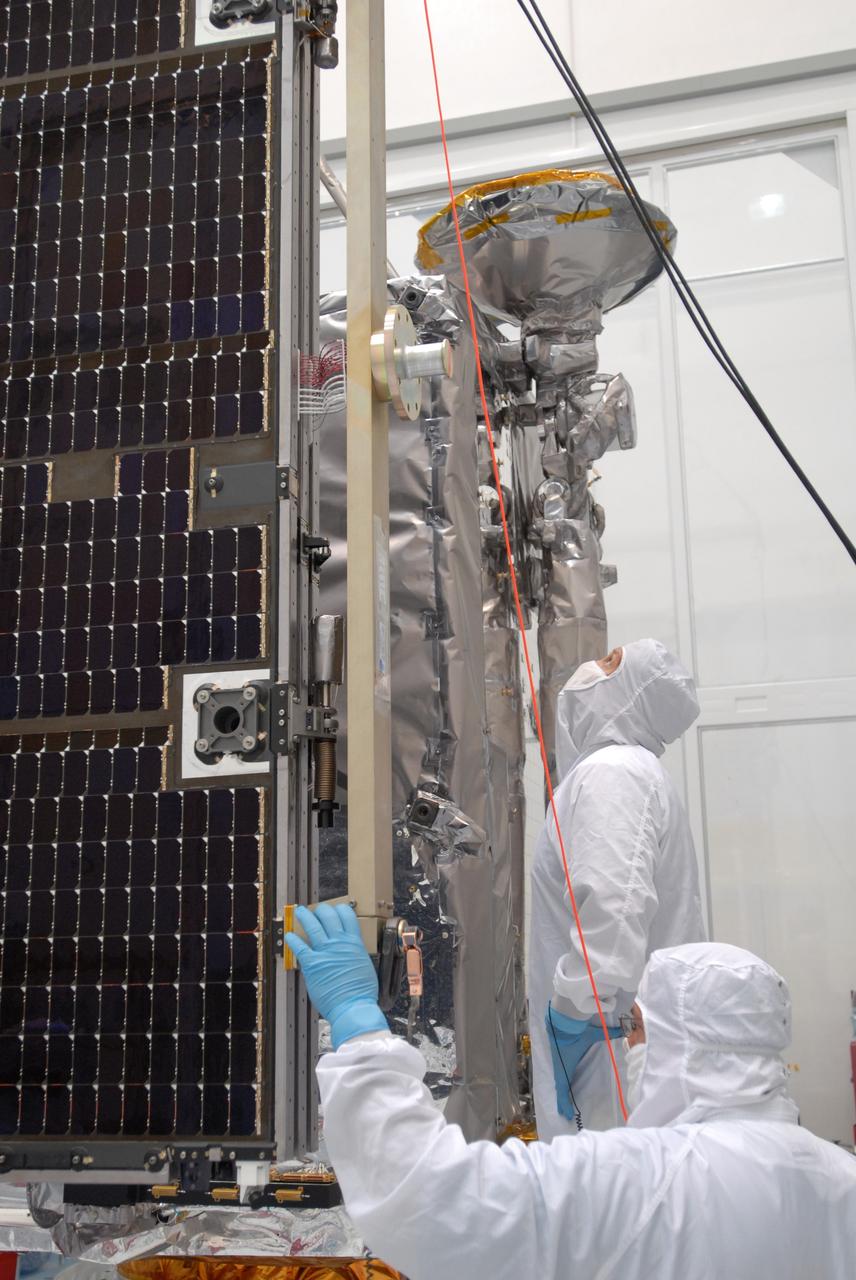

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians prepare to install the solar array panel to the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Launch of LRO is targeted for June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
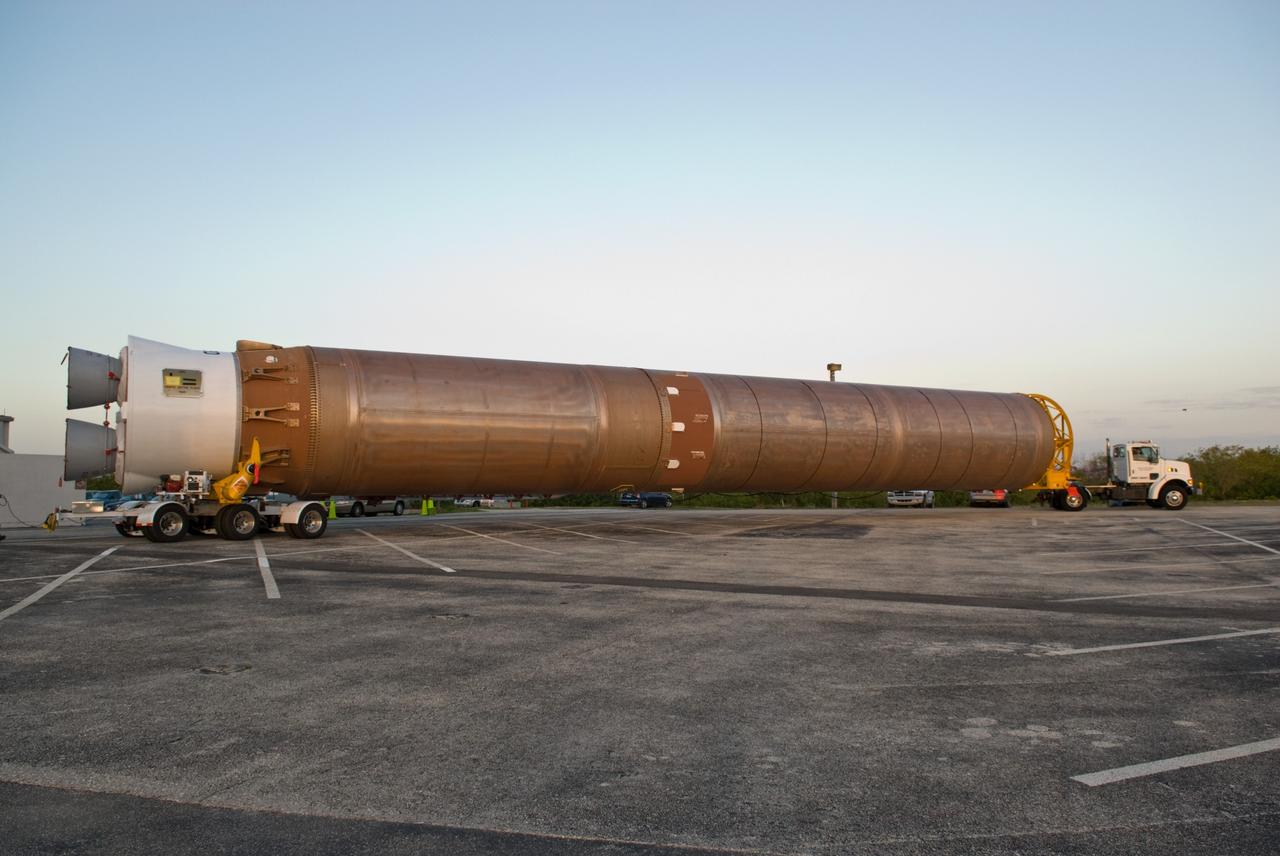

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– The Atlas V first stage is being transferred from the hangar at the Atlas Space Operations Facility to the Vertical Integration Facility near Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
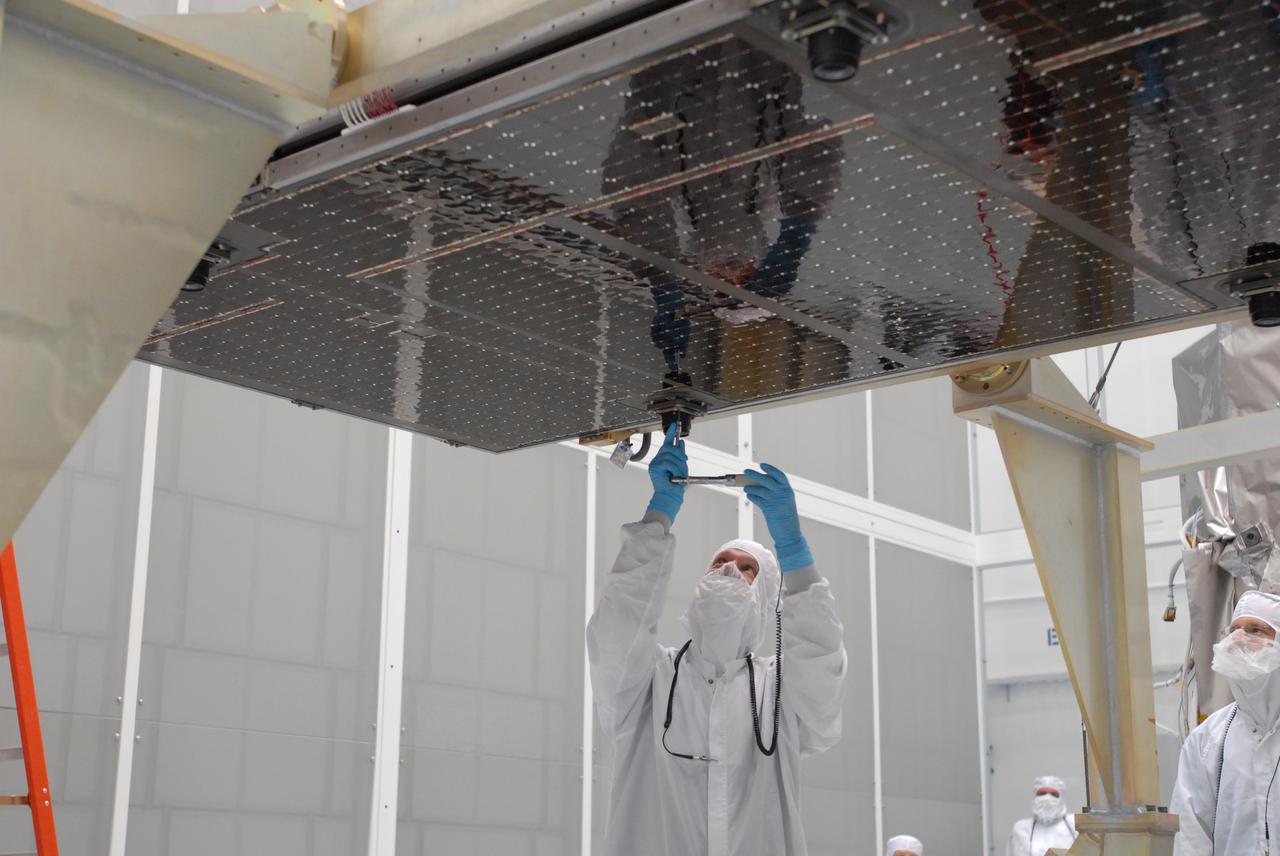

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians prepare the solar array panel for installation on the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Launch of LRO is targeted for June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
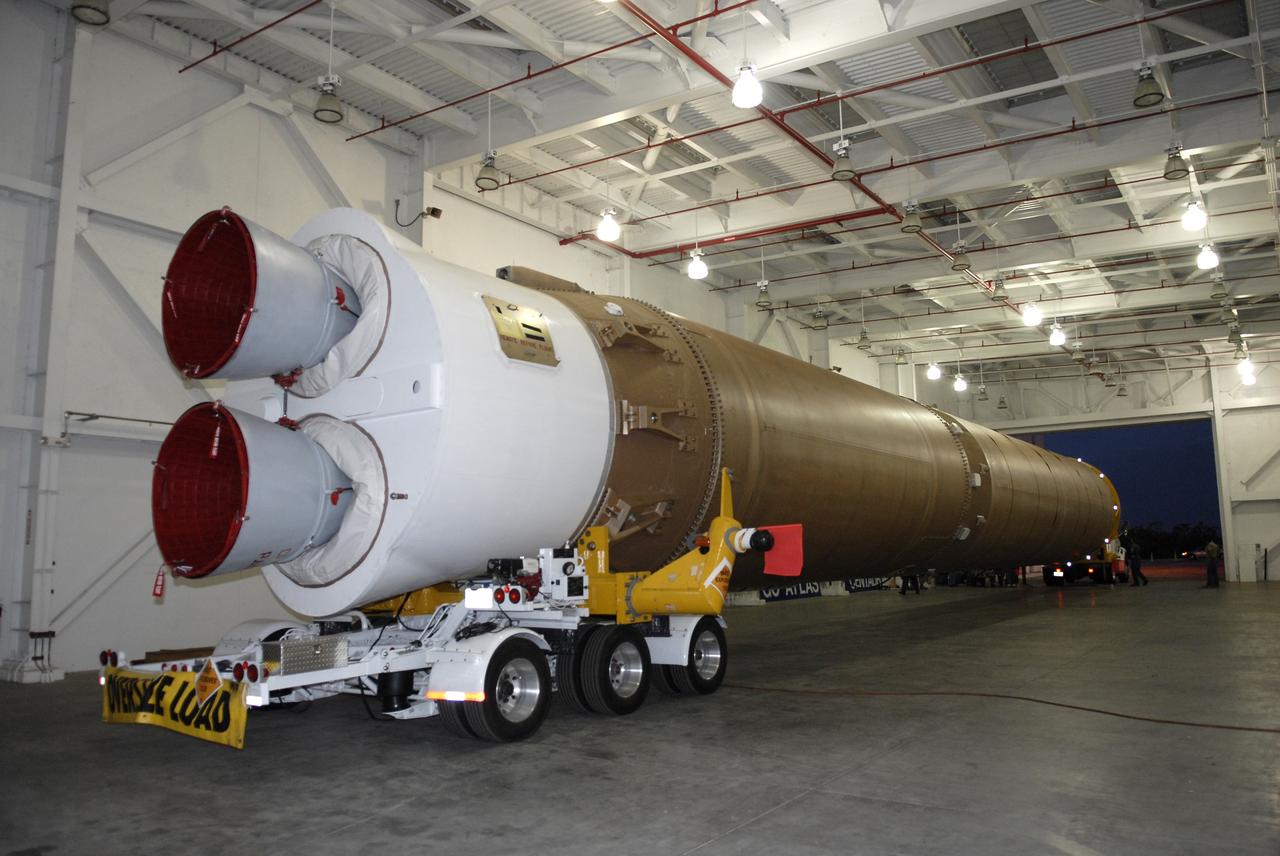

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– The Atlas V first stage is moved from the hangar at the Atlas Space Operations Facility. It is going to the Vertical Integration Facility near Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
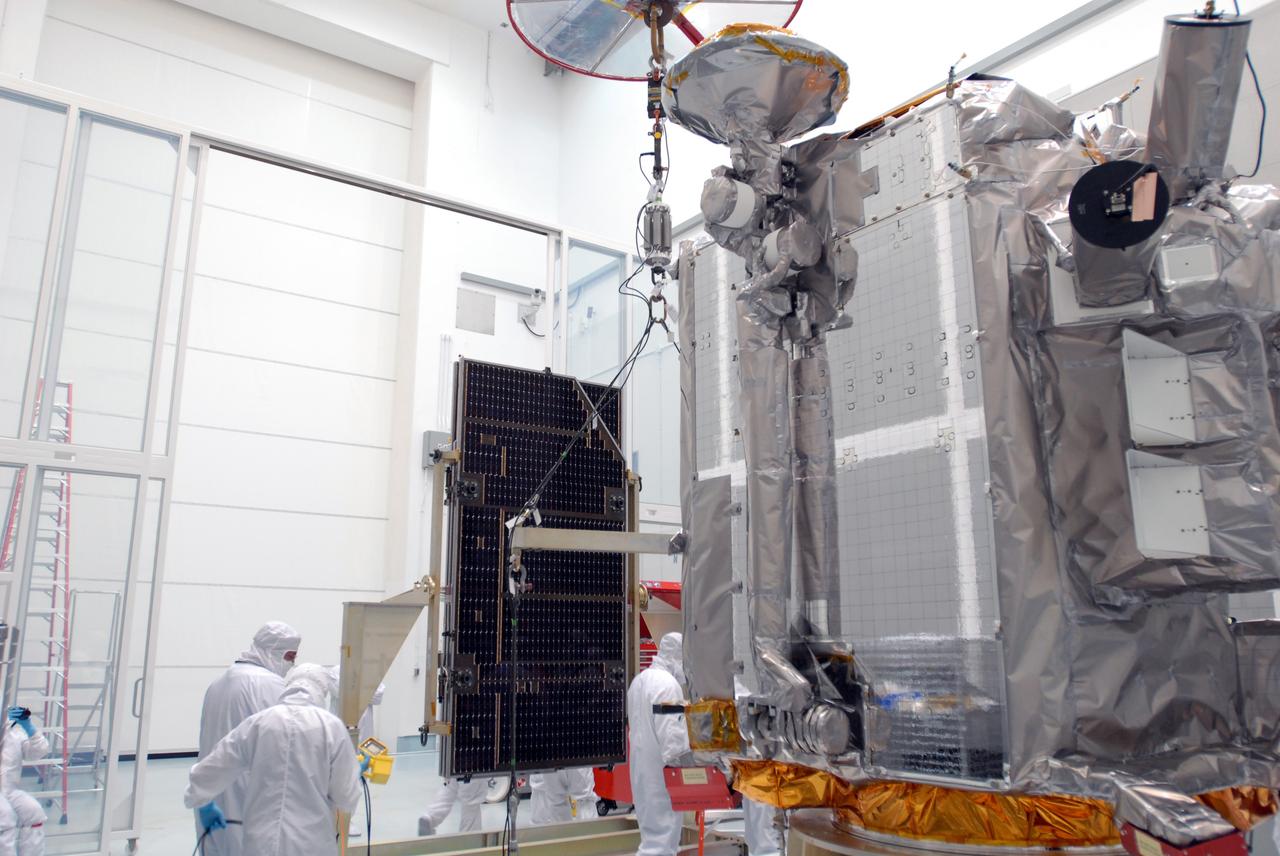

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians prepare the solar array panel for installation on the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Launch of LRO is targeted for June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
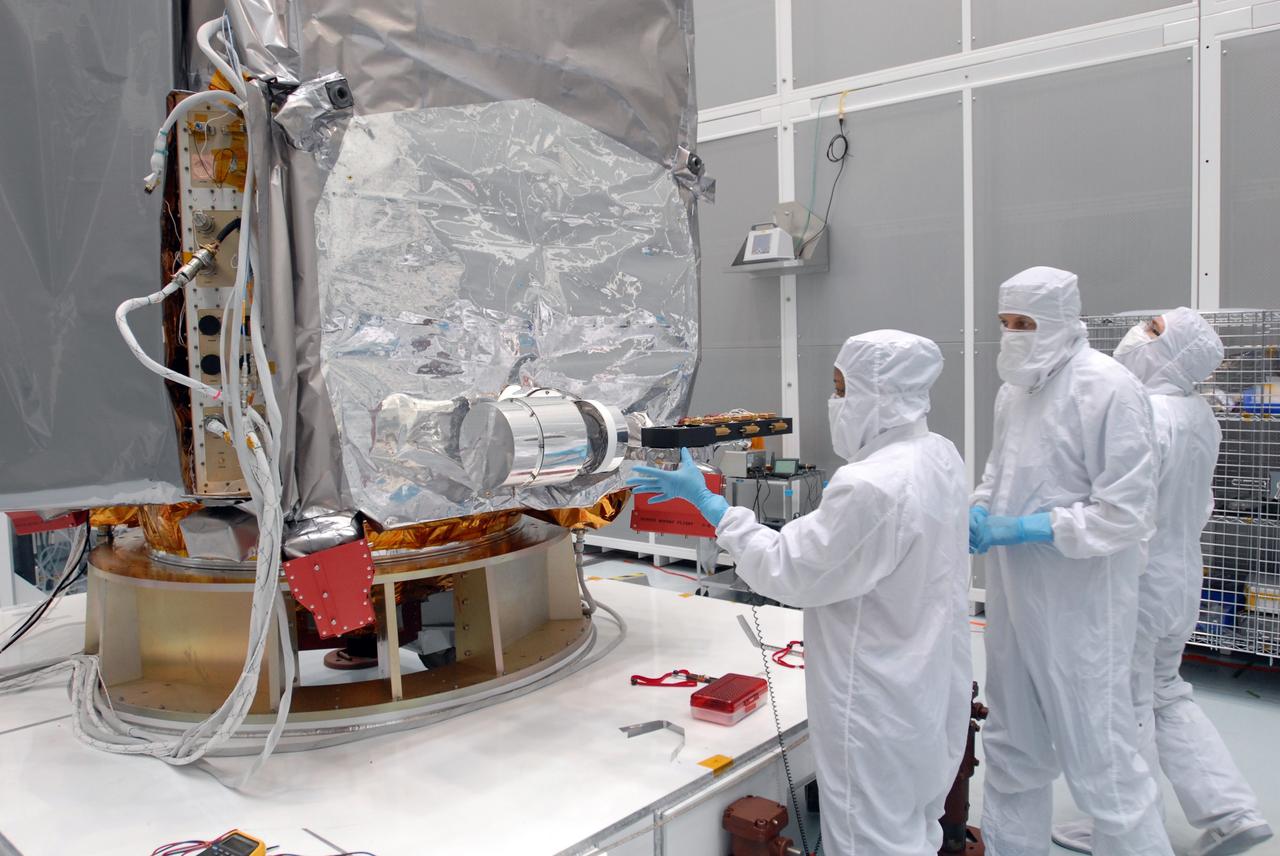

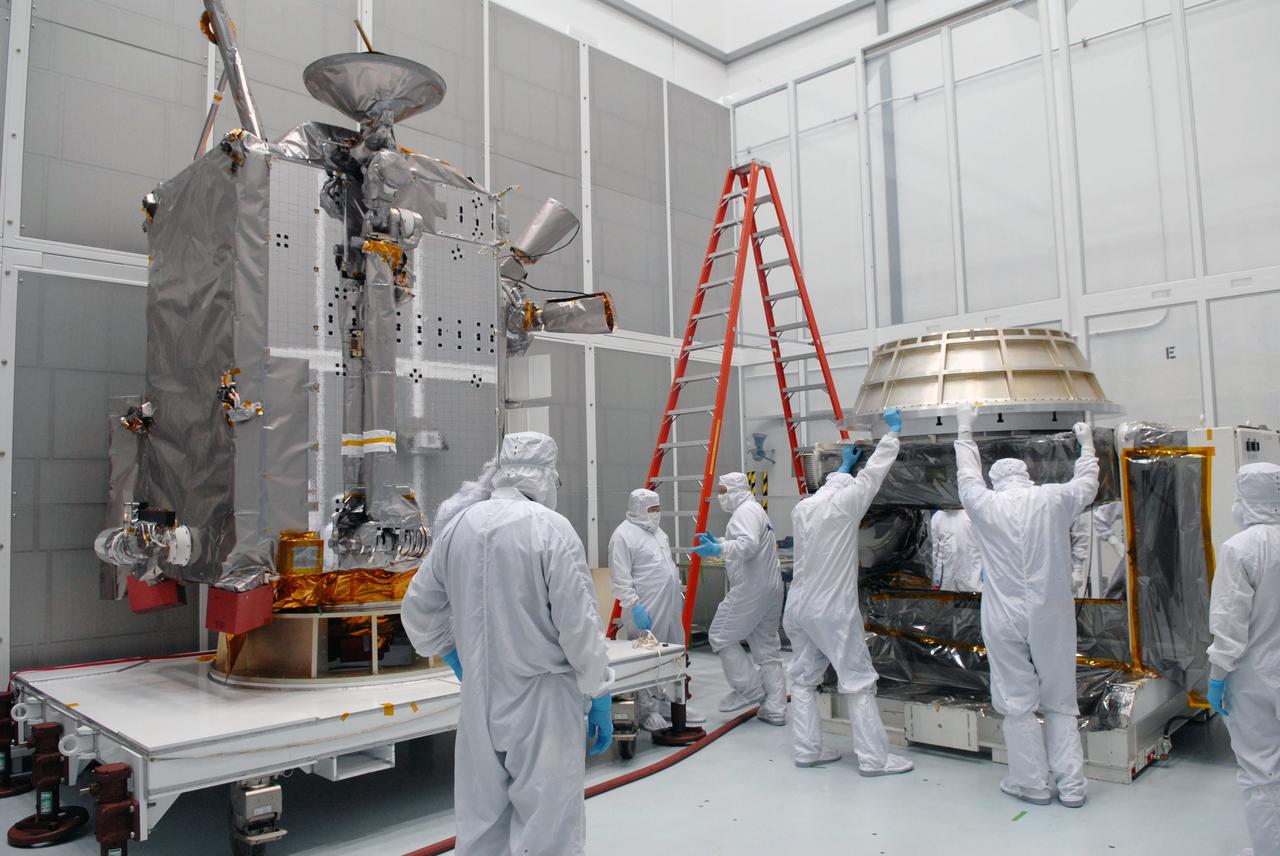
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians prepare the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, for installation of the solar array panels. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Launch of LRO is targeted for June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
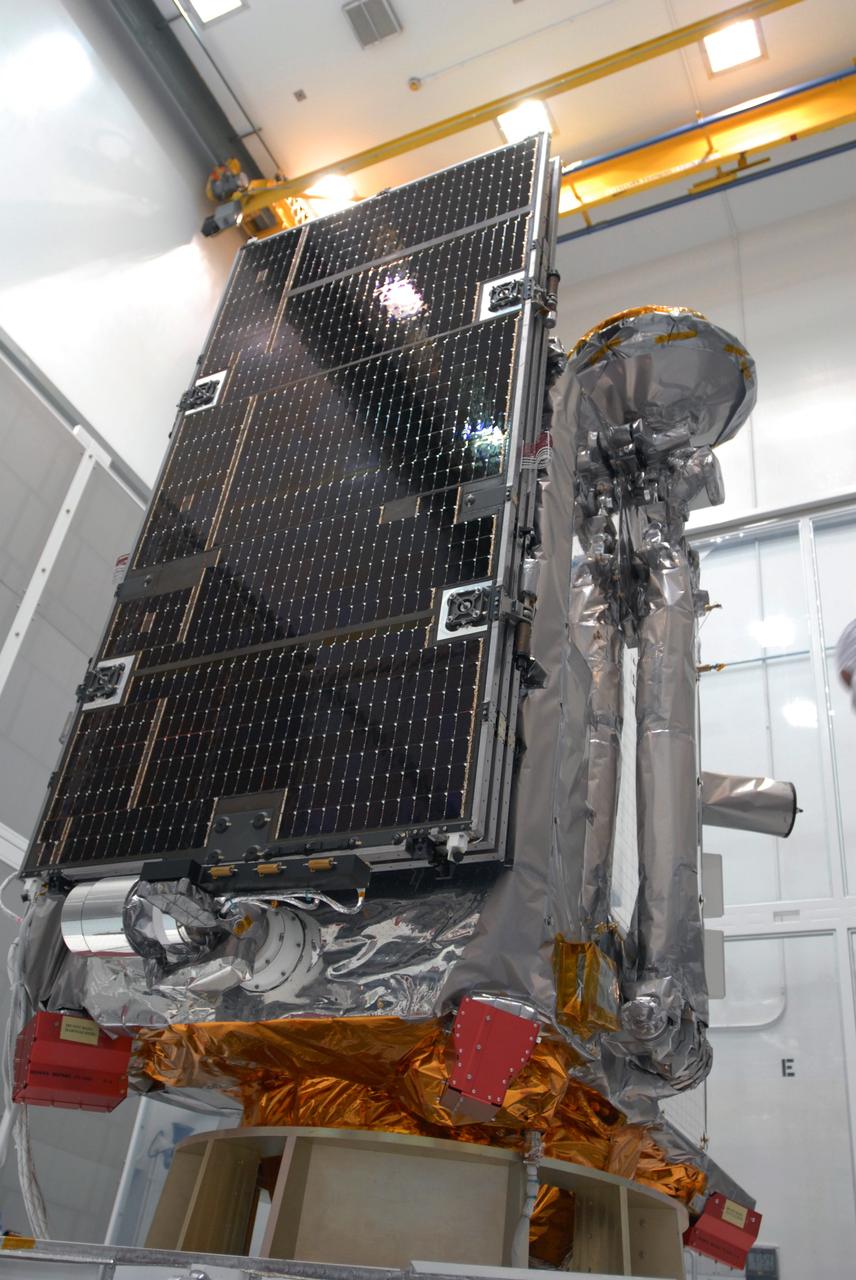

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, with a solar array panel installed. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Launch of LRO is targeted for June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
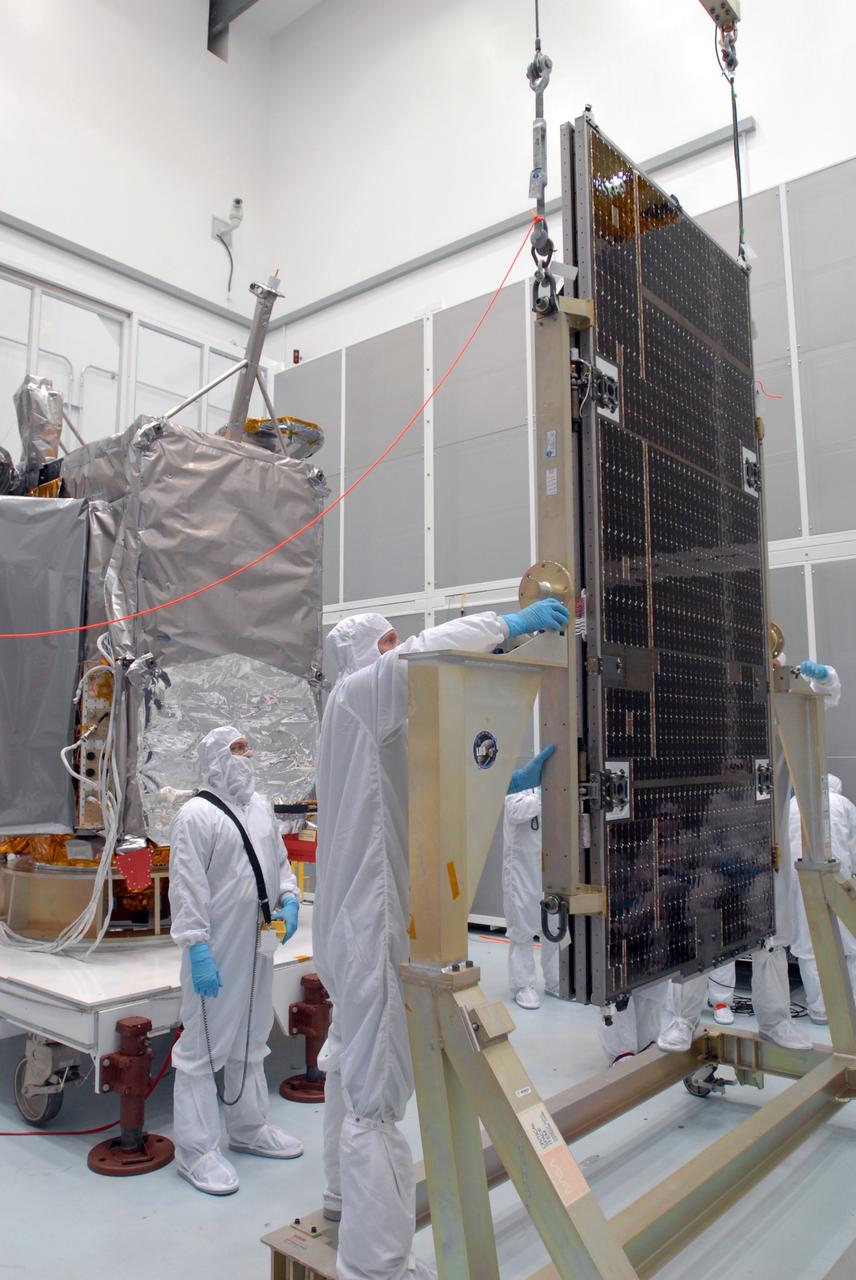

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians prepare the solar array panel for installation on the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, at left. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Launch of LRO is targeted for June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
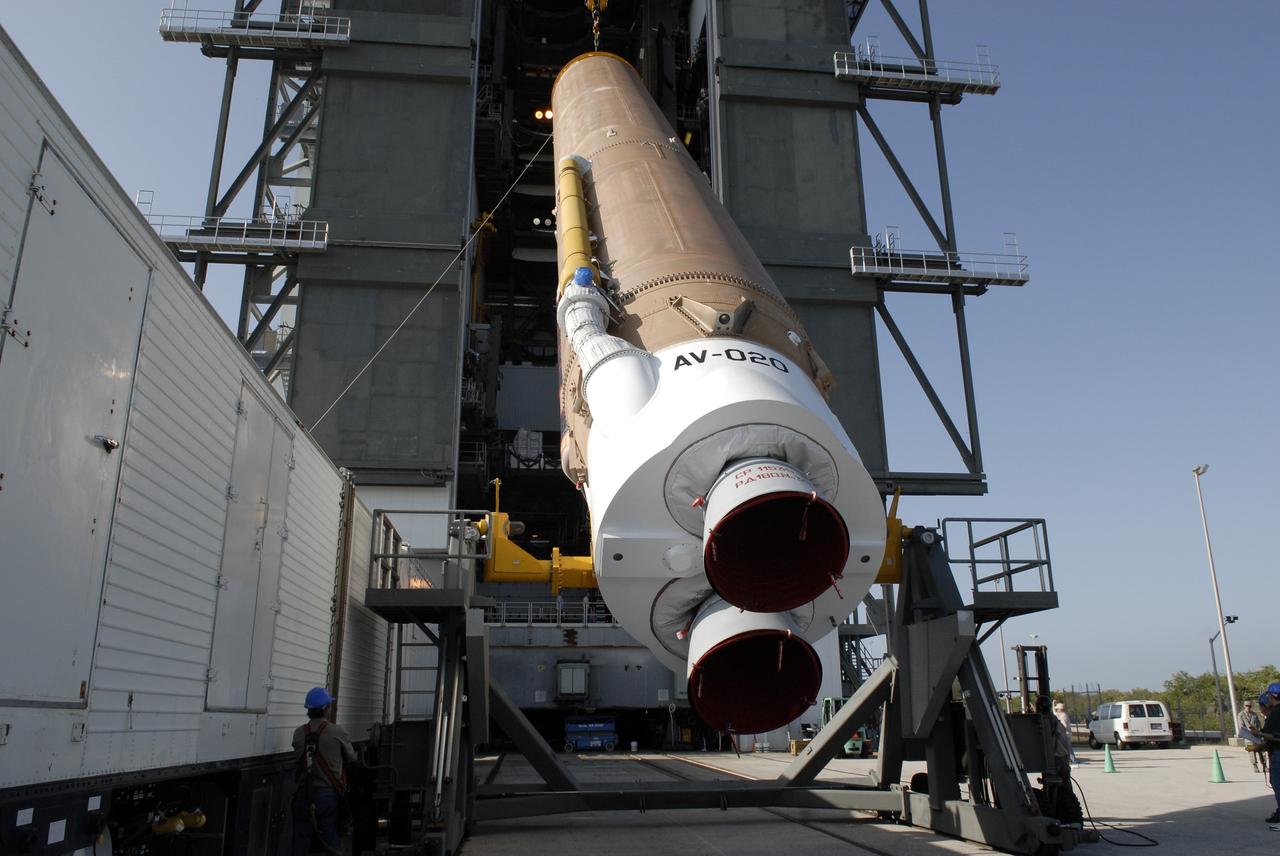

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– At the Vertical Integration Facility on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Atlas V first stage is being raised to a vertical position. The Atlas will be lifted into the VIF. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. Launch of LRO is targeted no earlier than June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., a technician prepares for the installation of the solar array panel on the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. He stands in front of the fairing that will encapsulate the spacecraft at a later date. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Launch of LRO is targeted for June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians move the solar array panel closer to the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, for installation. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Launch of LRO is targeted for June 2. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann