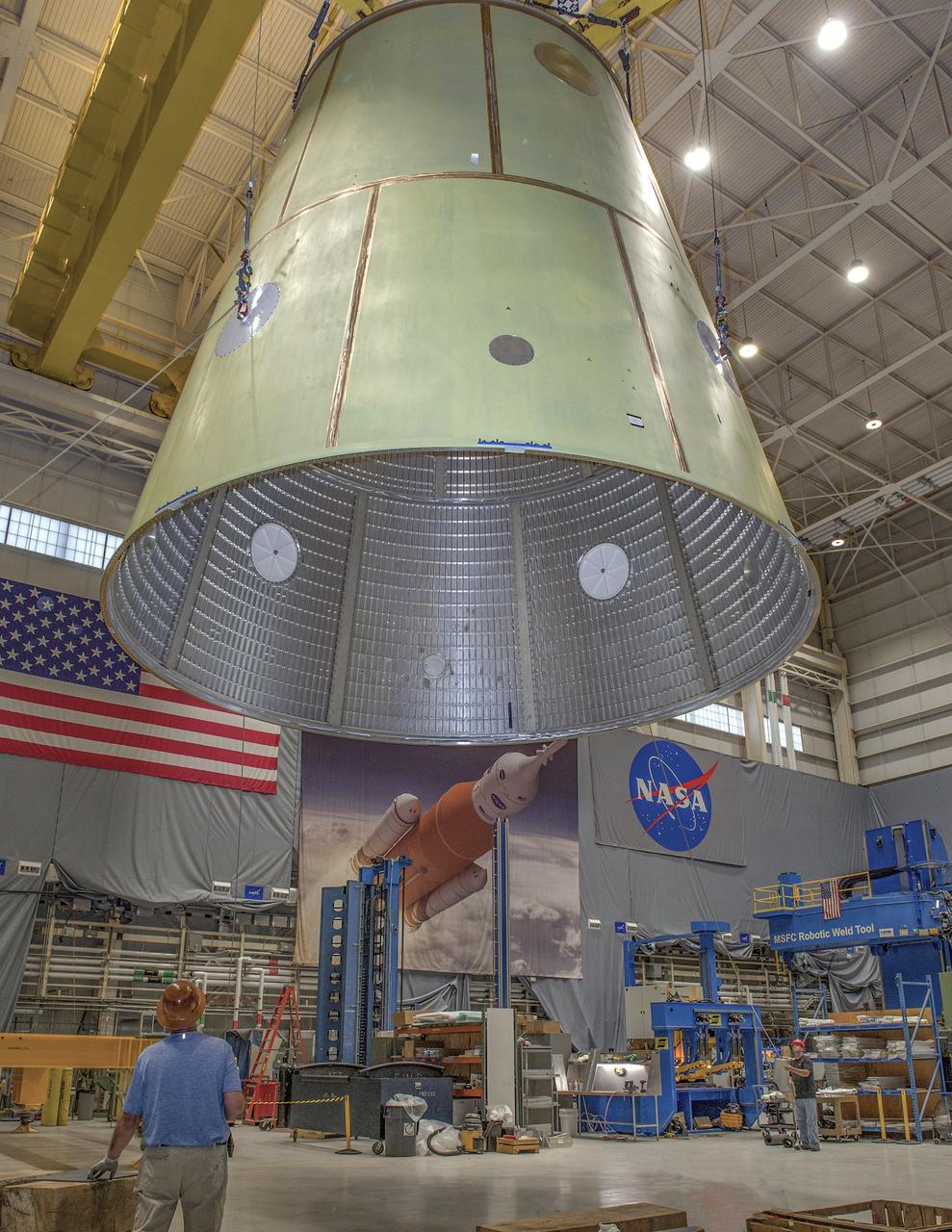

Lifting of the Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) in preparation for transport. The LVSA was fabricated in the EM32 Advanced Welding Development Facility at the NASA George C. Marshall Space Flight Center. The LVSA was welded using the conventional and self-reacting friction stir process and has approximately 375 feet of weld.
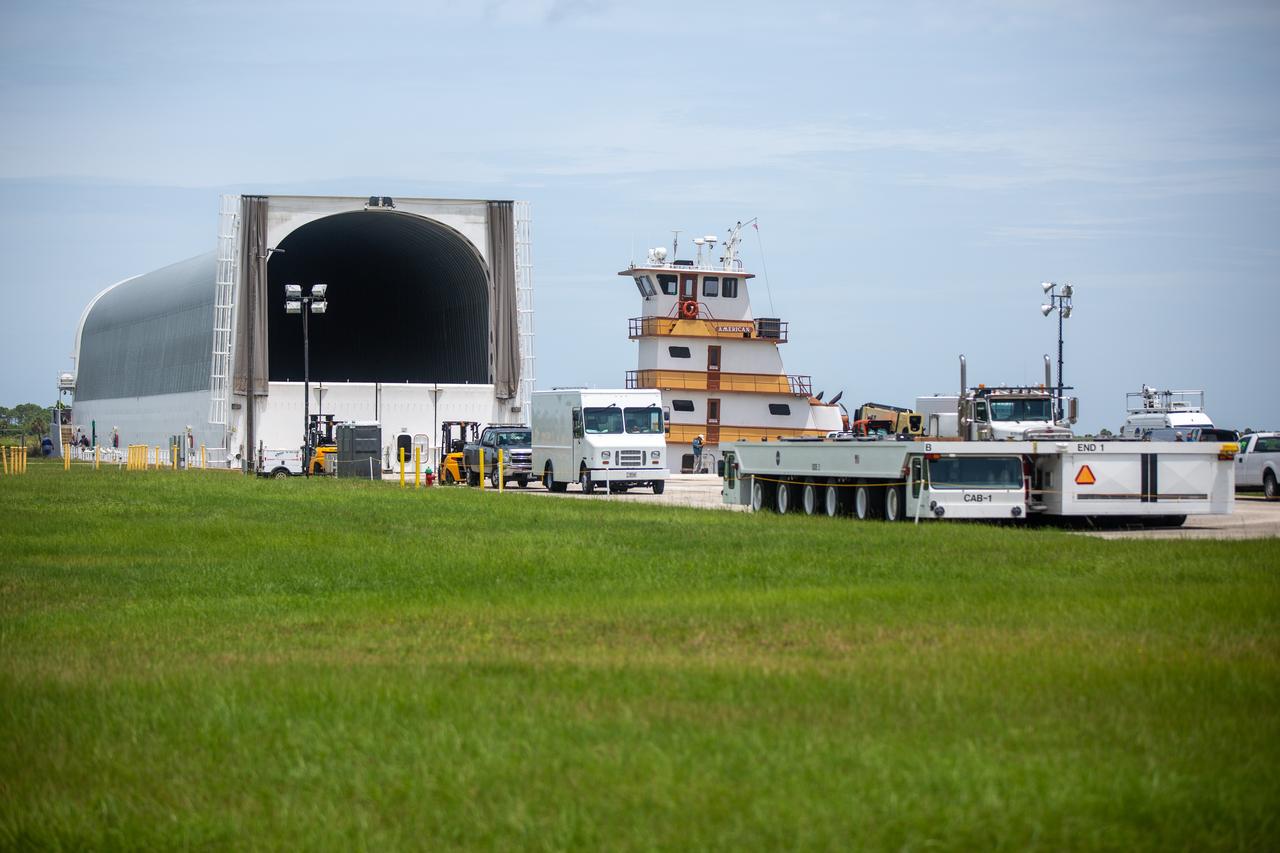

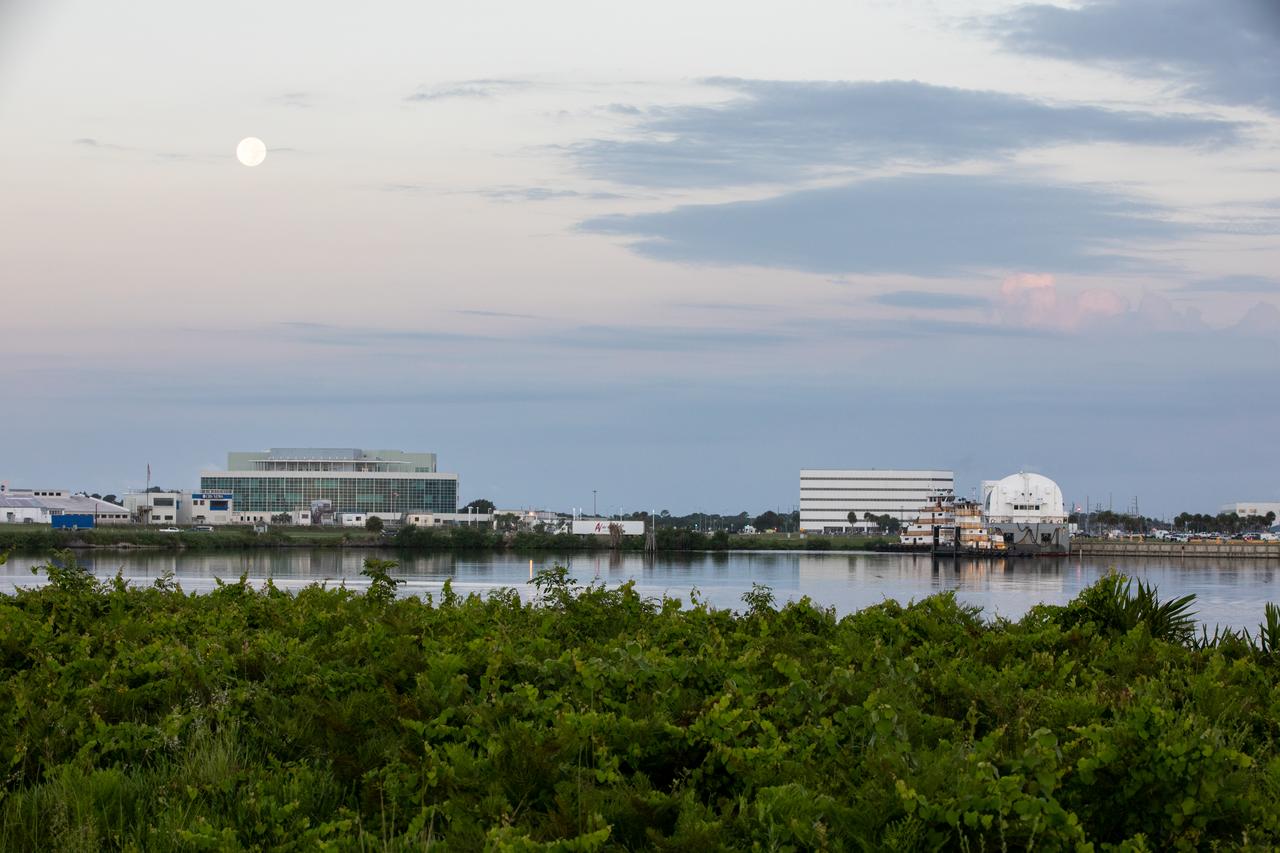
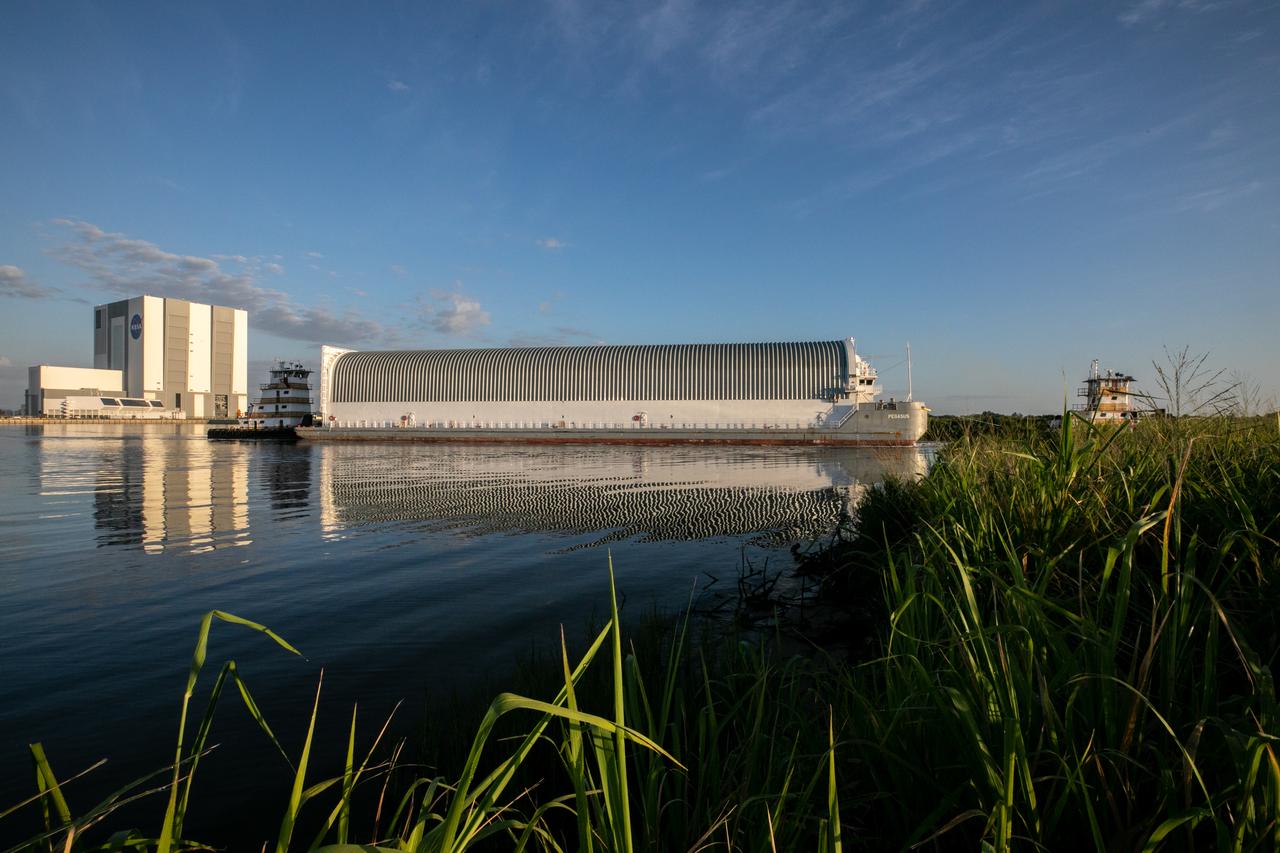
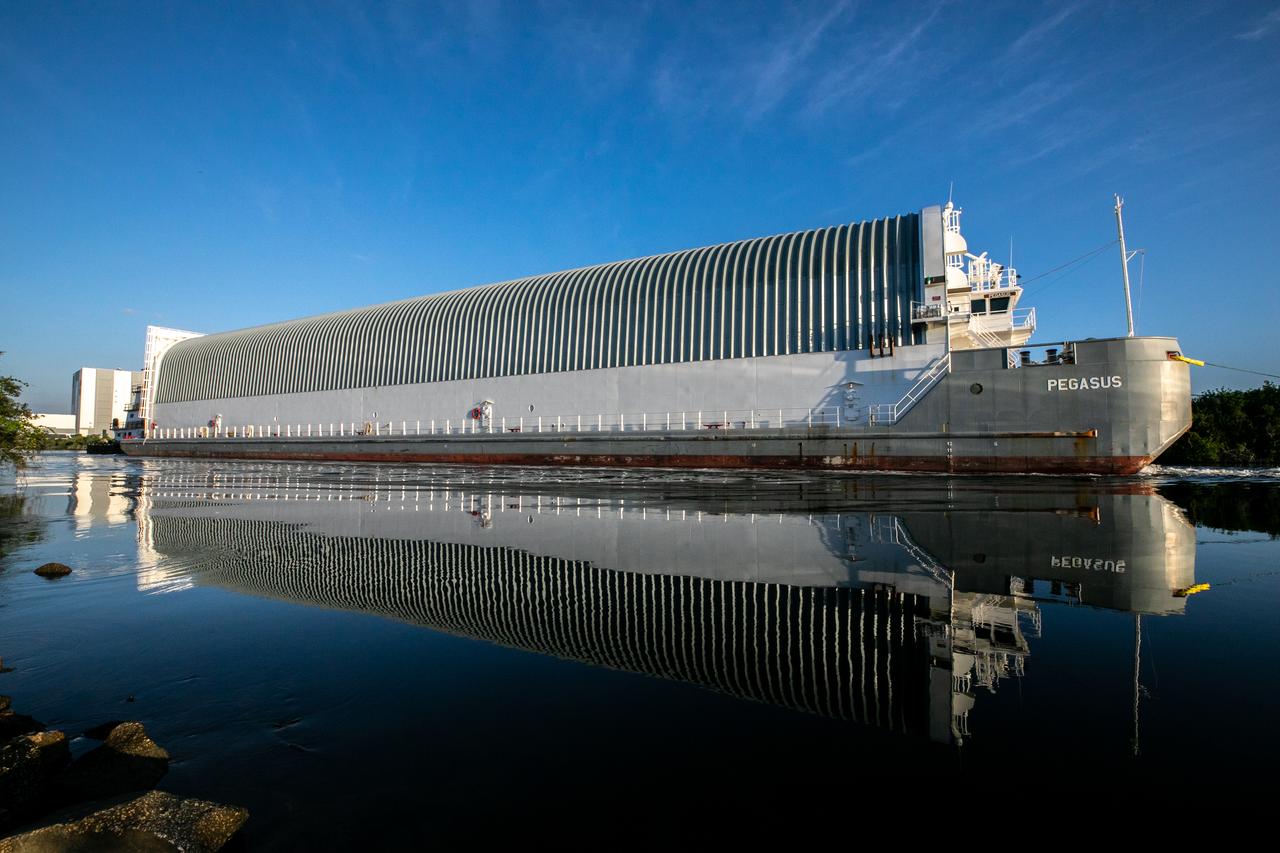
NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, arrives at the Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on July 29, 2020. Traveling to Florida from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, the LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage for the Artemis I launch. Once the LVSA is offloaded, it will be moved to High Bay 4 in the Vehicle Assembly Building for processing ahead of launch. The first launch under the agency’s Artemis program, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
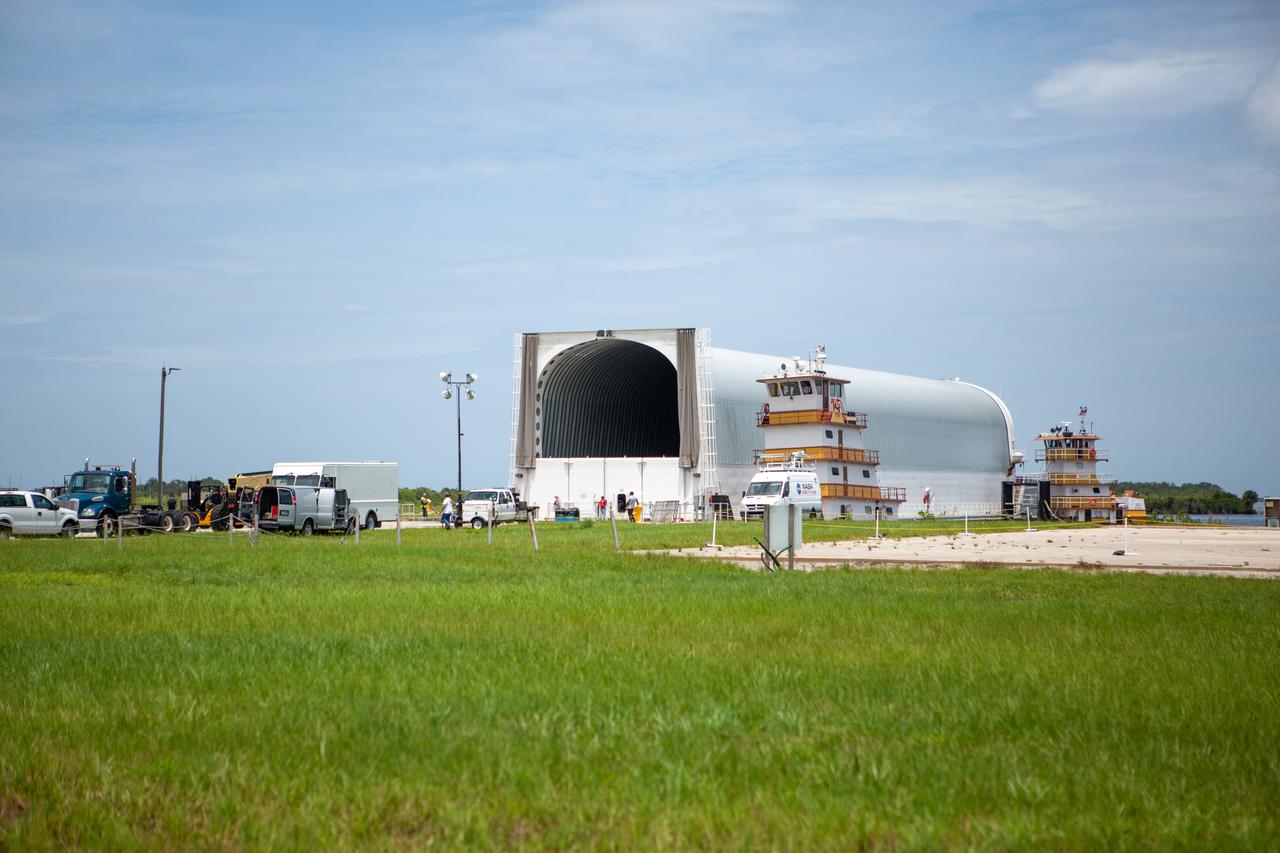

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, arrives at the Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on July 29, 2020. Traveling to Florida from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, the LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage for the Artemis I launch. Once the LVSA is offloaded, it will be moved to High Bay 4 in the Vehicle Assembly Building for processing ahead of launch. The first launch under the agency’s Artemis program, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, arrives at the Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on July 29, 2020. Traveling to Florida from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, the LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage for the Artemis I launch. Once the LVSA is offloaded, it will be moved to High Bay 4 in the Vehicle Assembly Building for processing ahead of launch. The first launch under the agency’s Artemis program, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
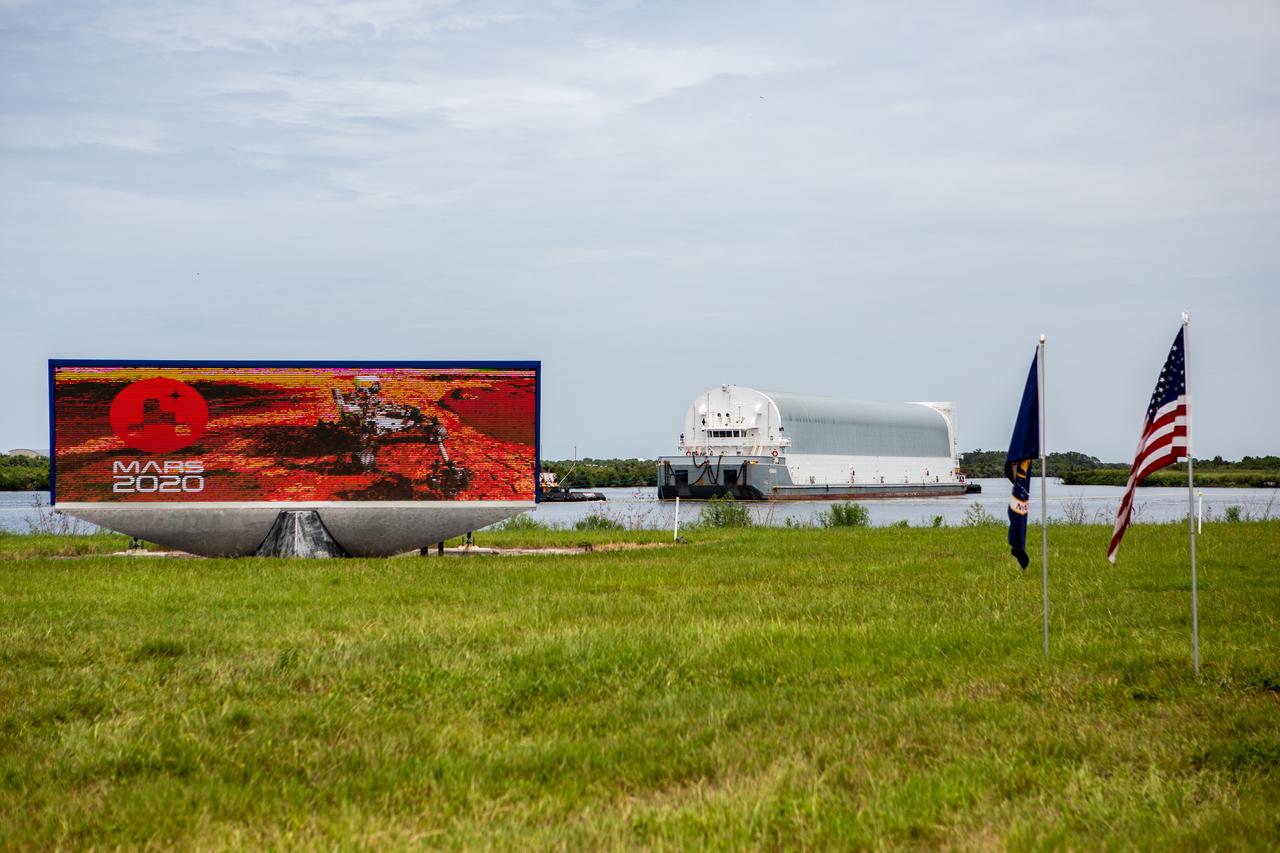

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, approaches the Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on July 29, 2020. Traveling to Florida from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, the LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage for the Artemis I launch. Once the LVSA is offloaded, it will be moved to High Bay 4 in the Vehicle Assembly Building for processing ahead of launch. The first launch under the agency’s Artemis program, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, arrives at the Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on July 29, 2020. Traveling to Florida from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, the LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage for the Artemis I launch. Once the LVSA is offloaded, it will be moved to High Bay 4 in the Vehicle Assembly Building for processing ahead of launch. The first launch under the agency’s Artemis program, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
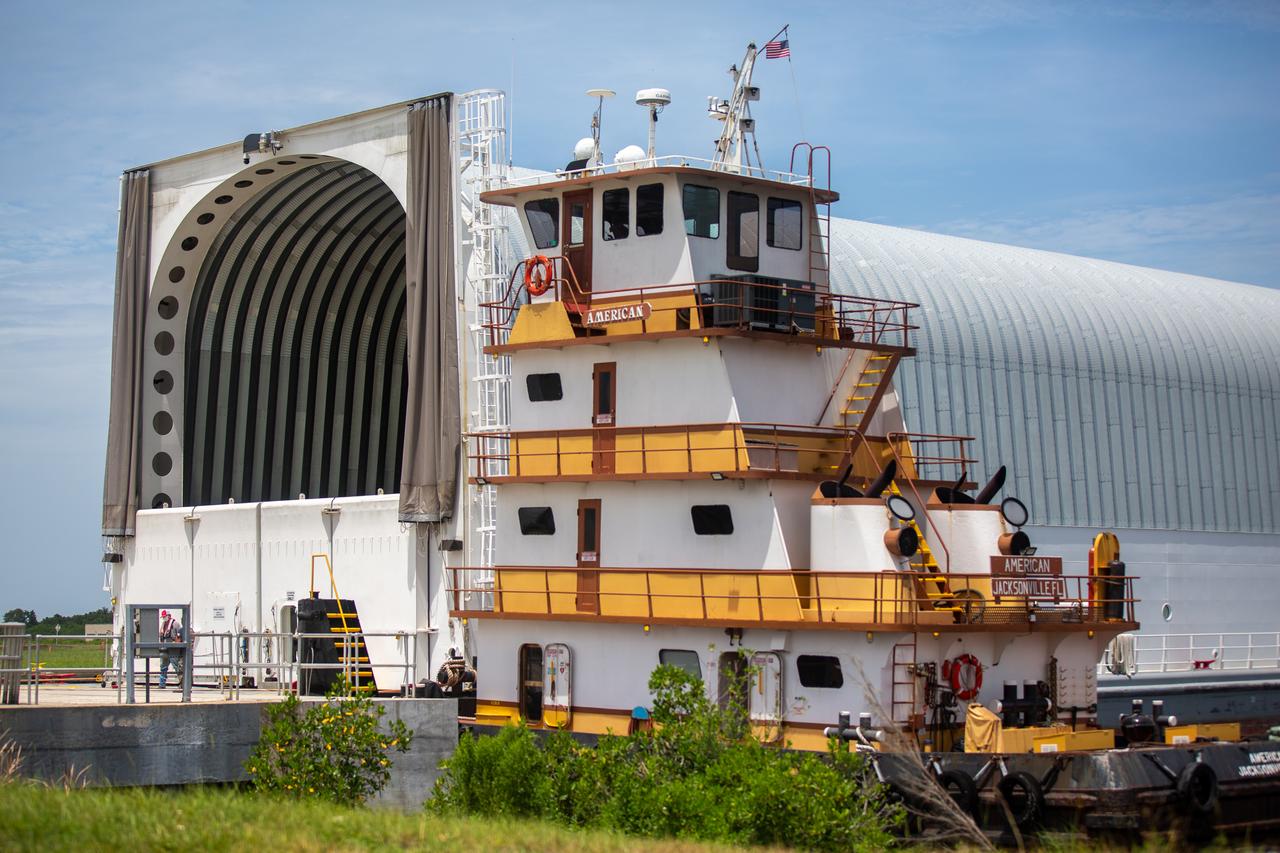

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, arrives at the Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on July 29, 2020. Traveling to Florida from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, the LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage for the Artemis I launch. Once the LVSA is offloaded, it will be moved to High Bay 4 in the Vehicle Assembly Building for processing ahead of launch. The first launch under the agency’s Artemis program, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
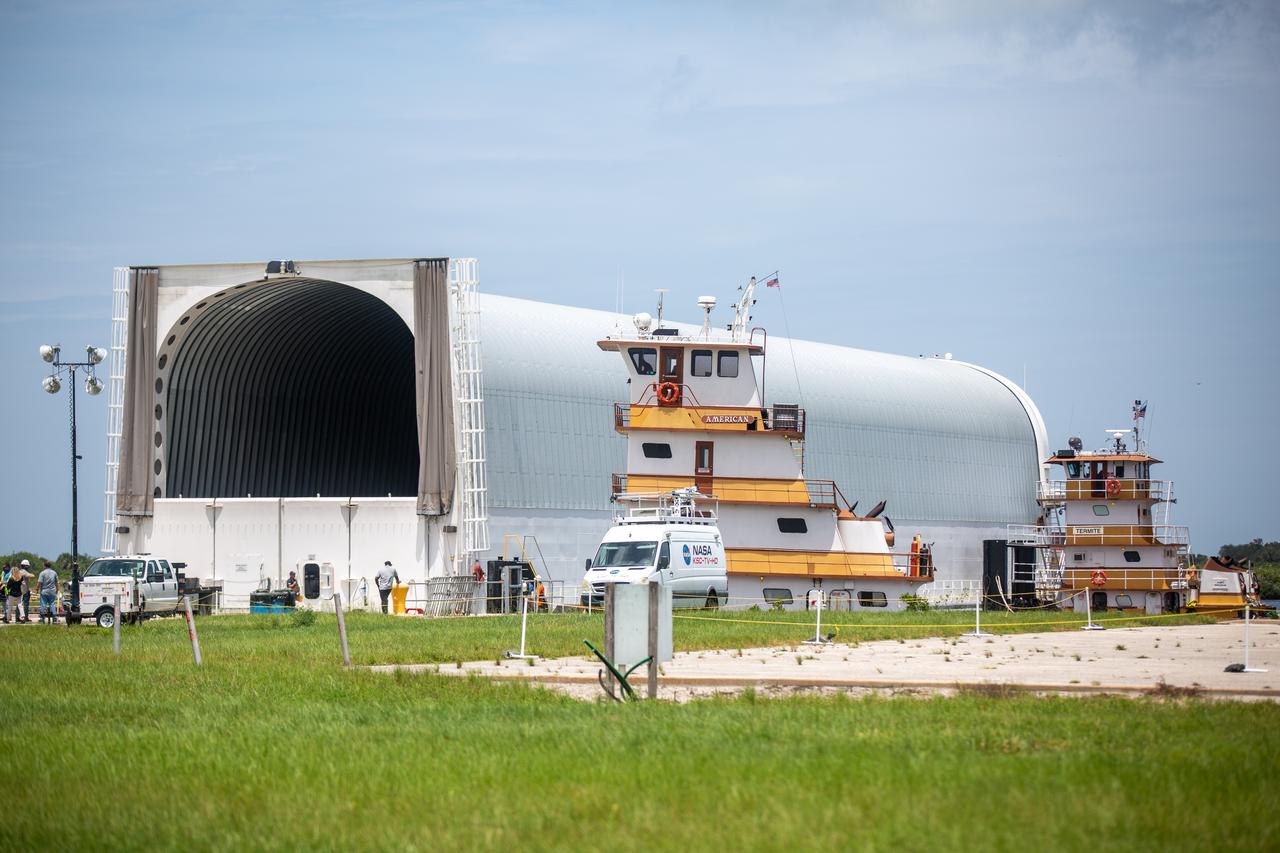

NASA’s Pegasus barge, carrying the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, arrives at the Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on July 29, 2020. Traveling to Florida from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, the LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage for the Artemis I launch. Once the LVSA is offloaded, it will be moved to High Bay 4 in the Vehicle Assembly Building for processing ahead of launch. The first launch under the agency’s Artemis program, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
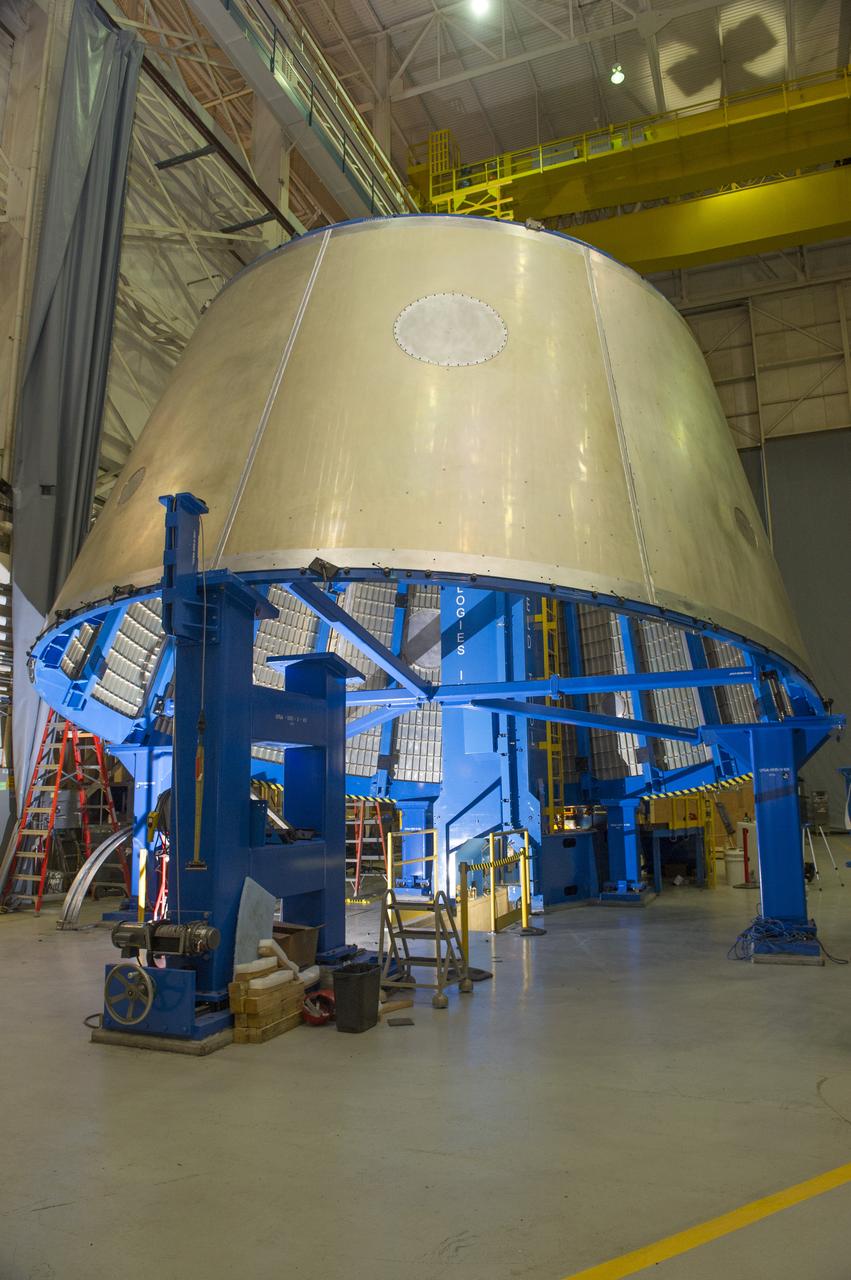

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
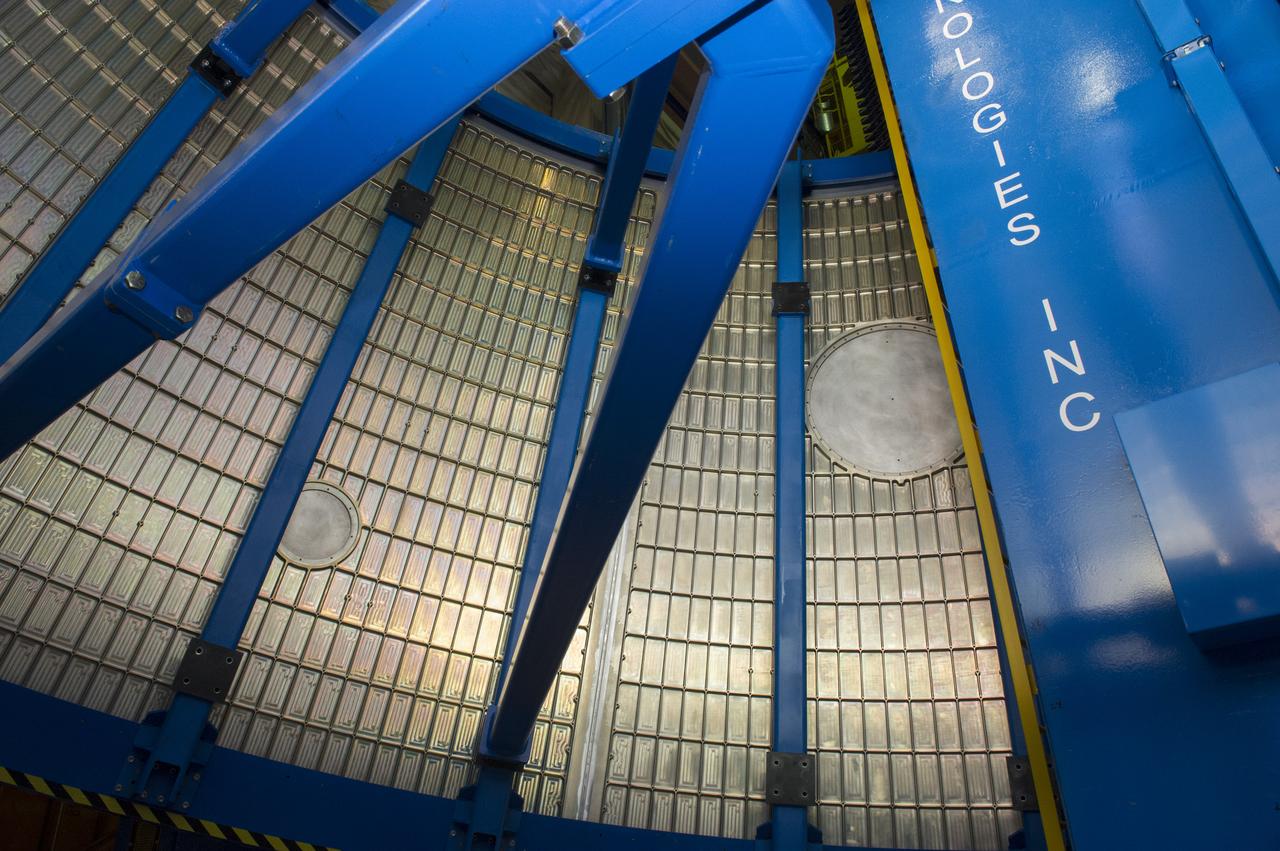

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Weld #7
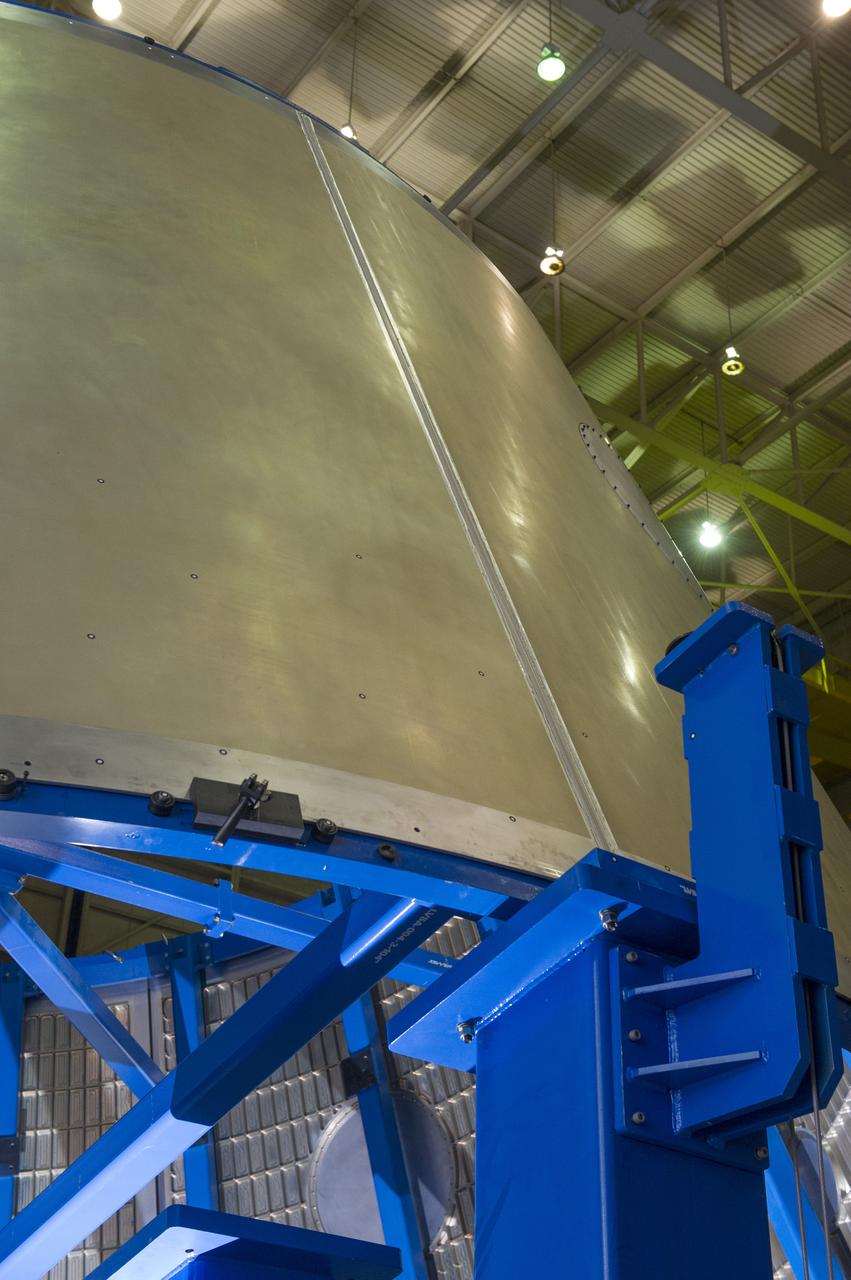

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
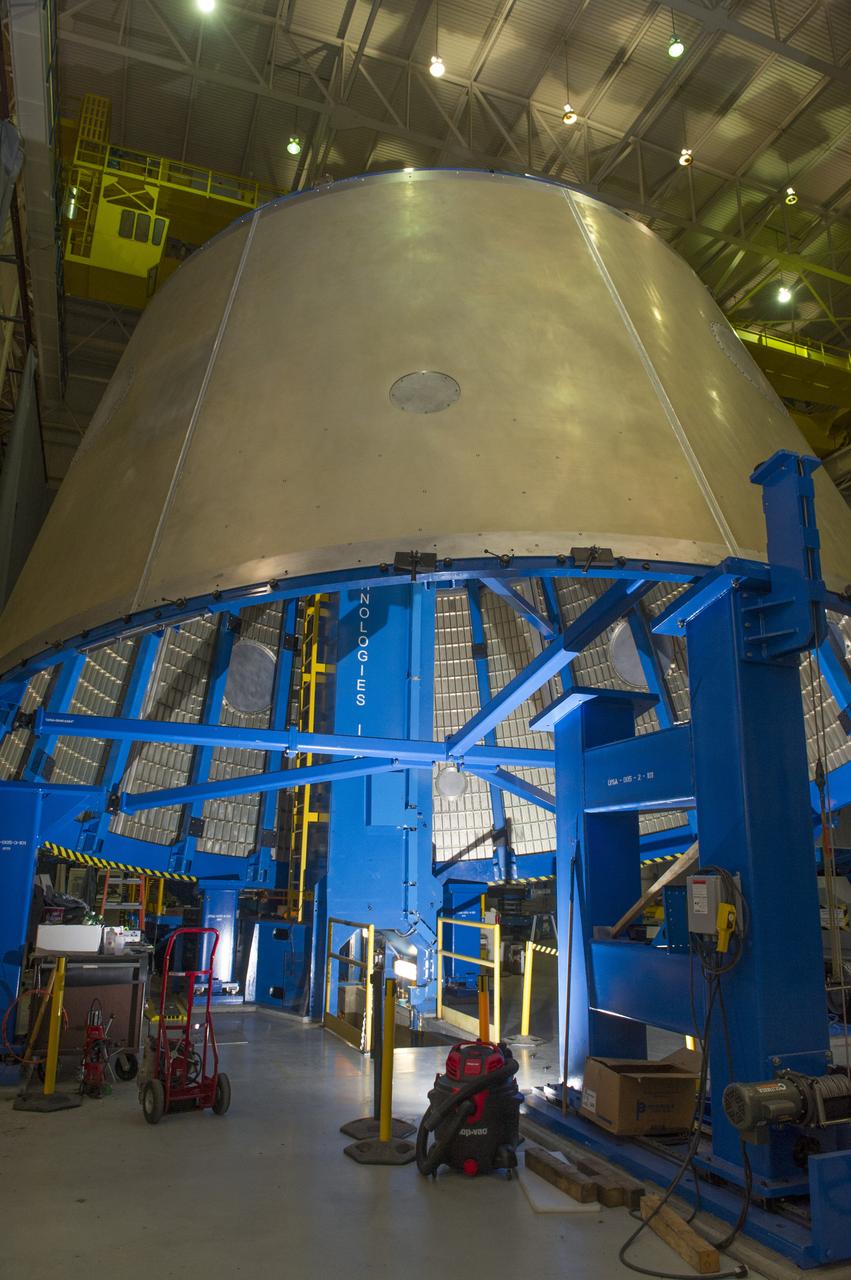

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
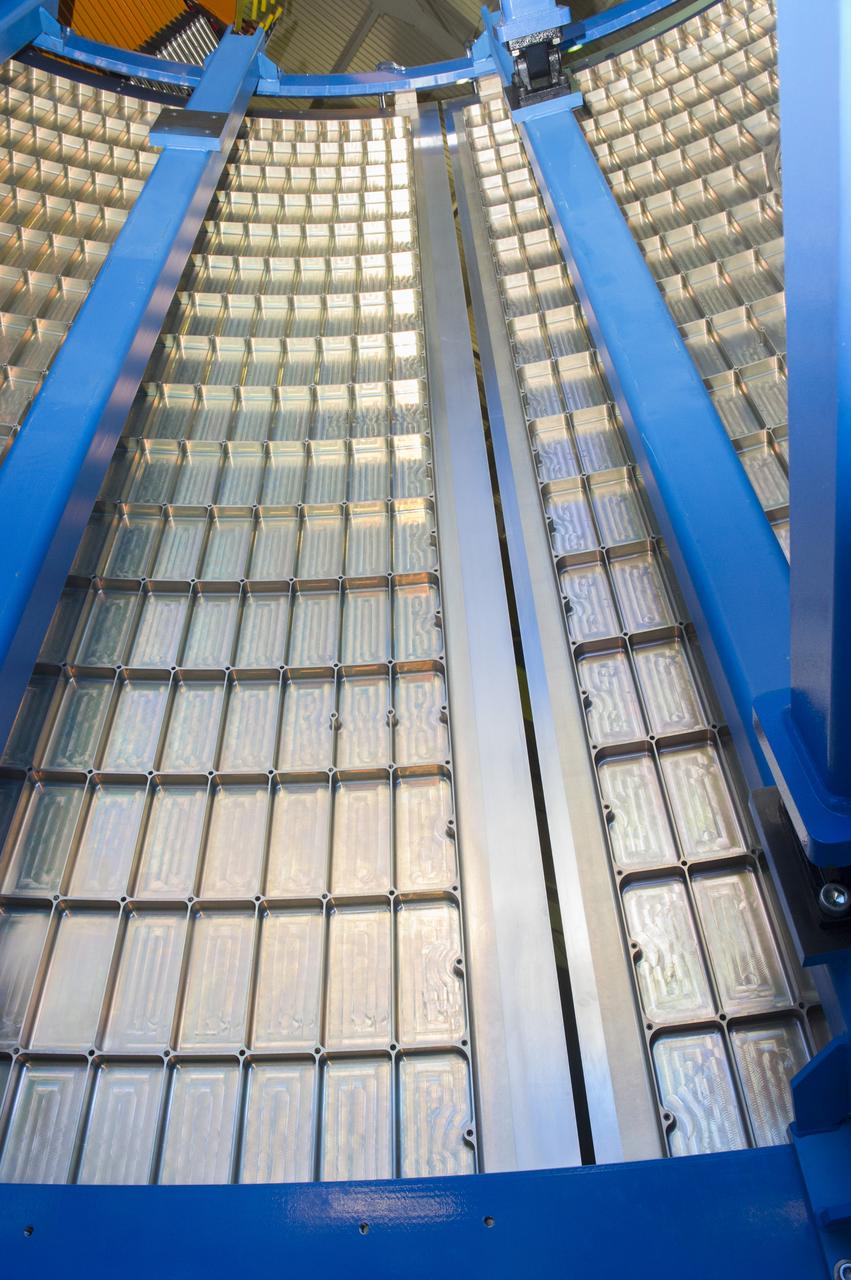

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
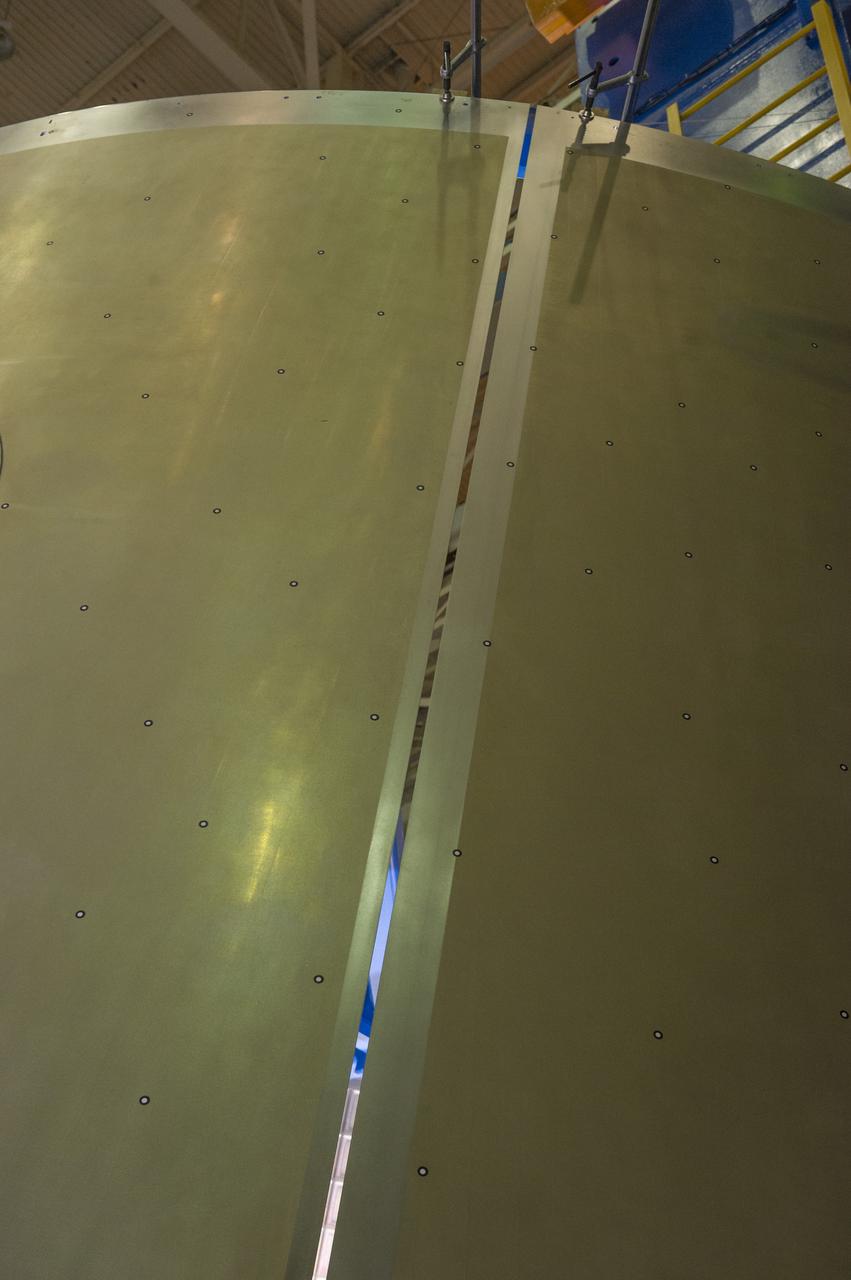

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
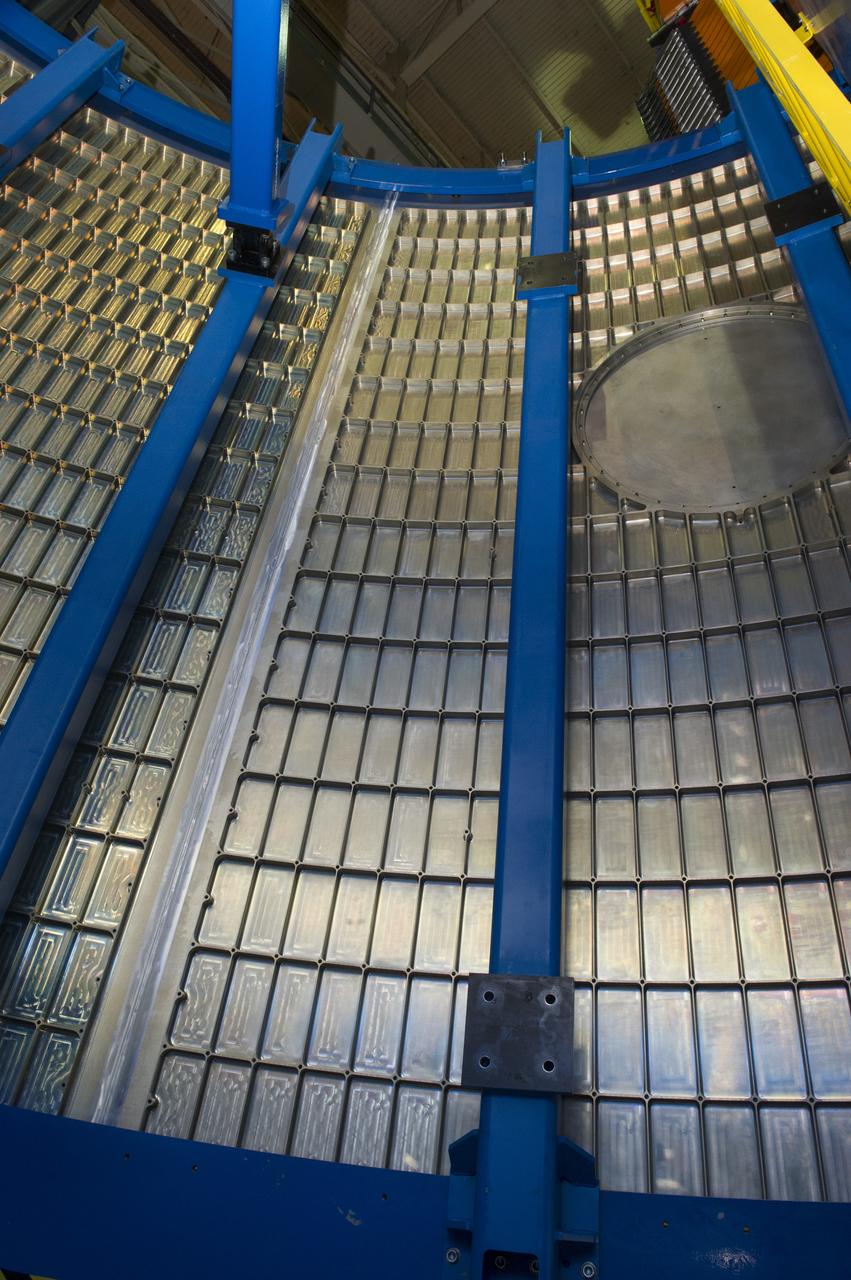

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
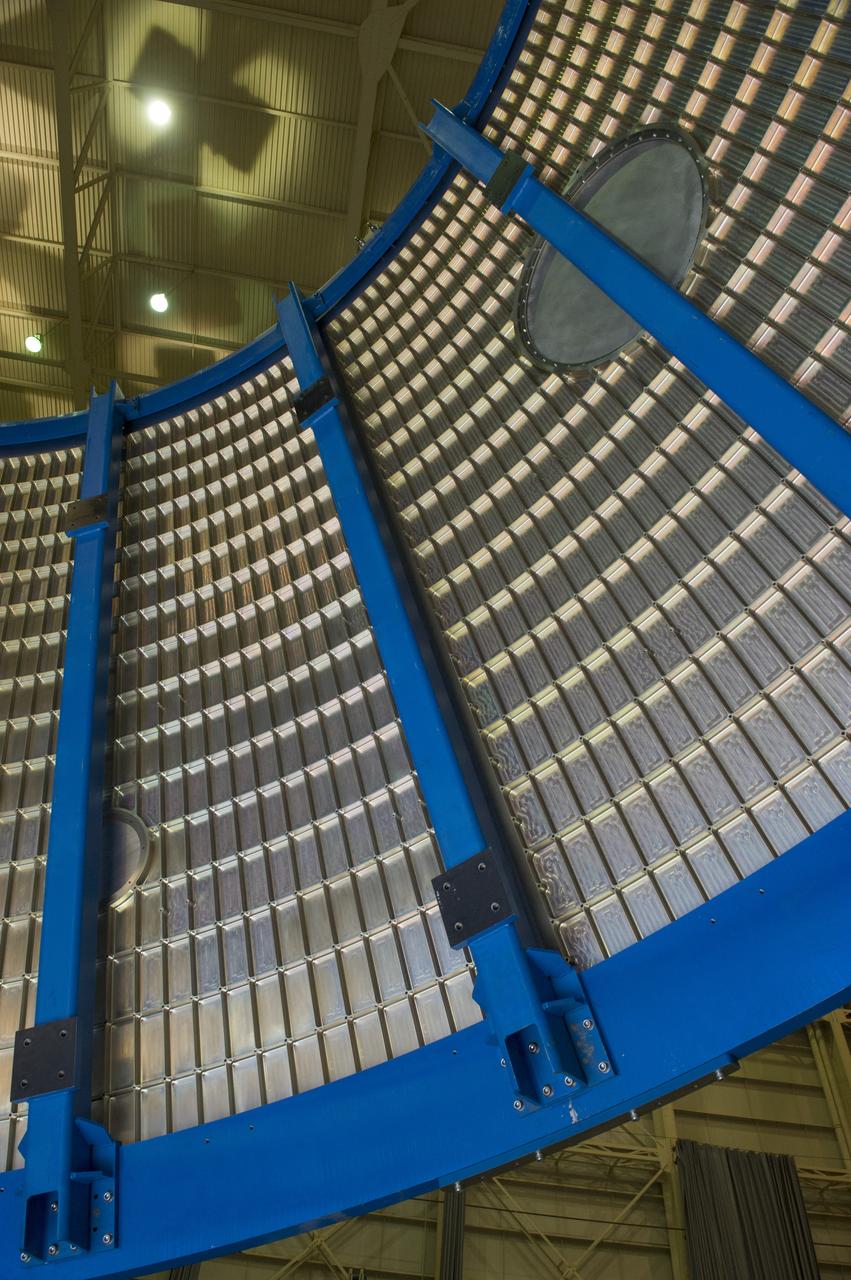

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
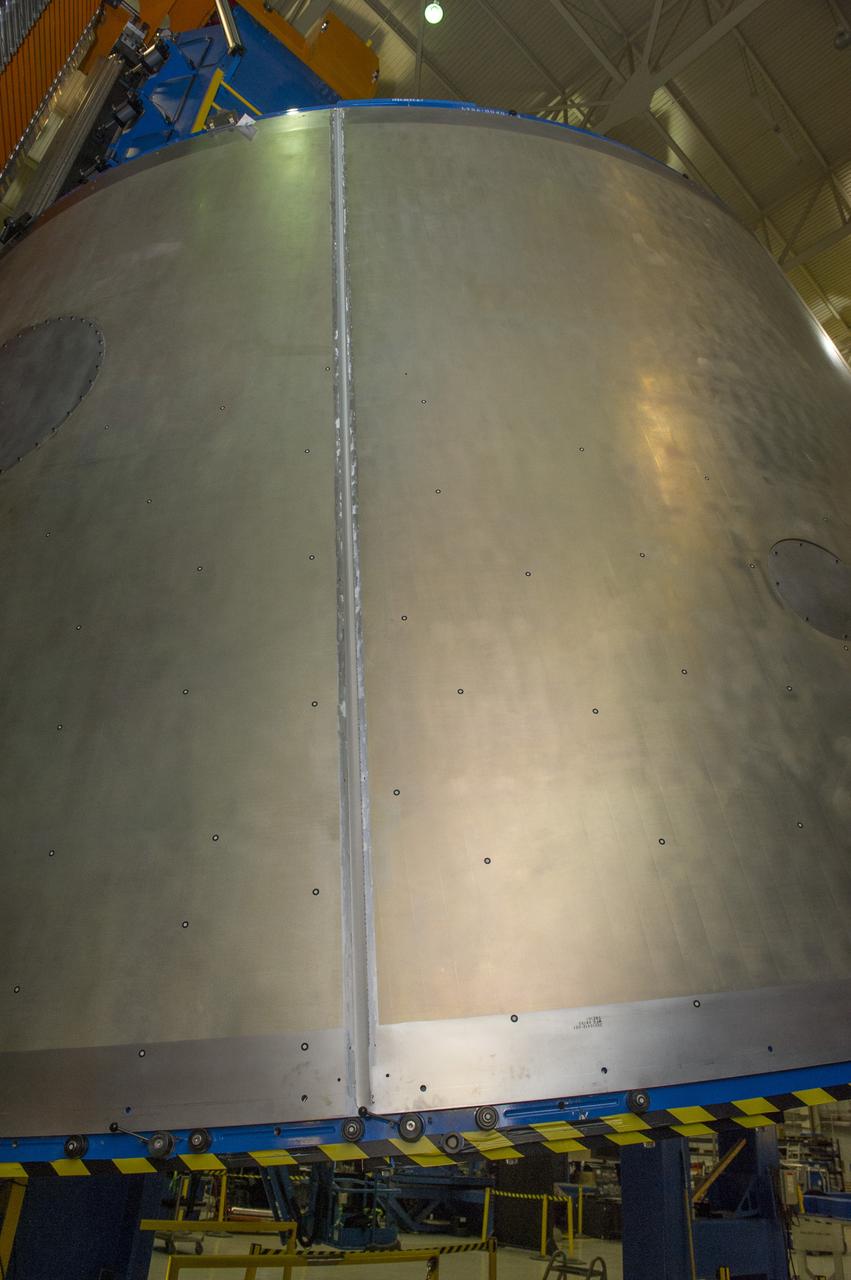

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
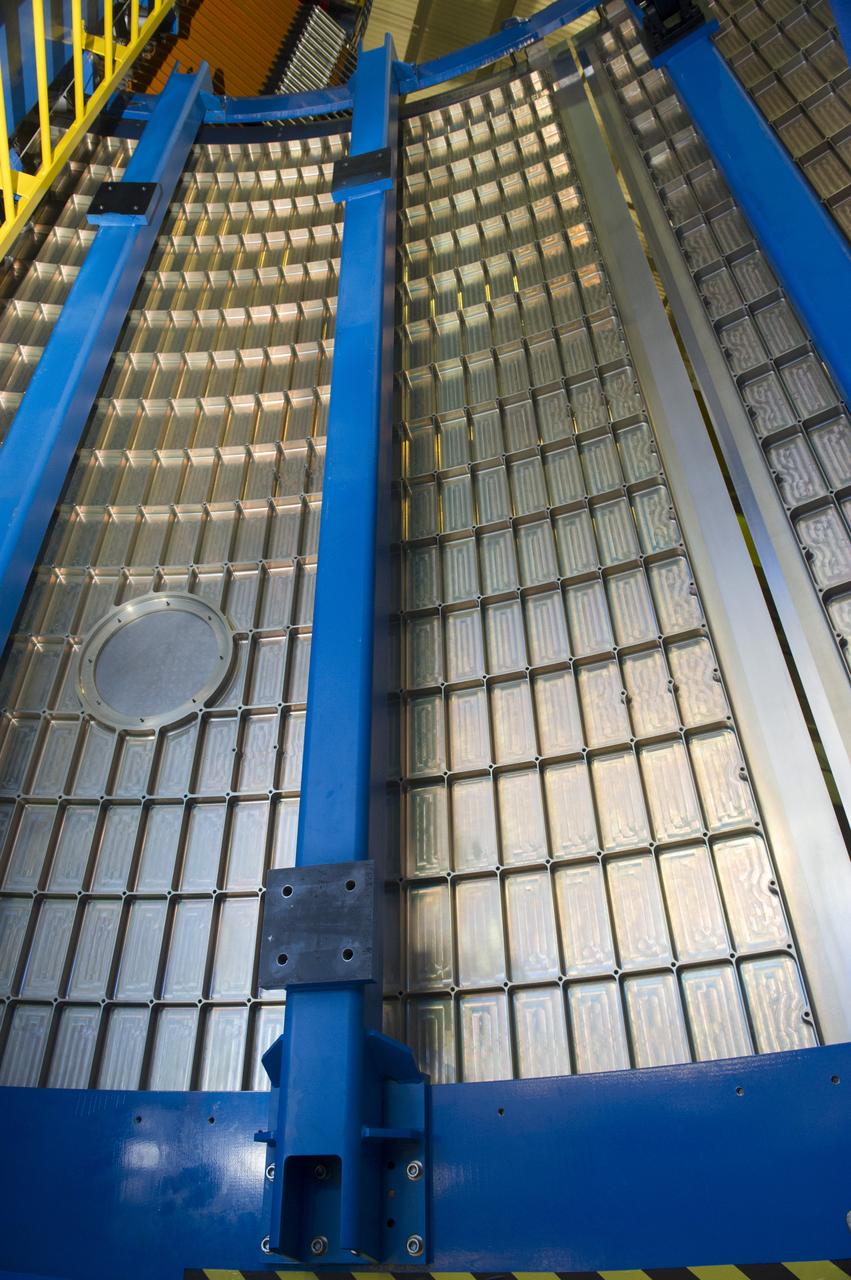

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
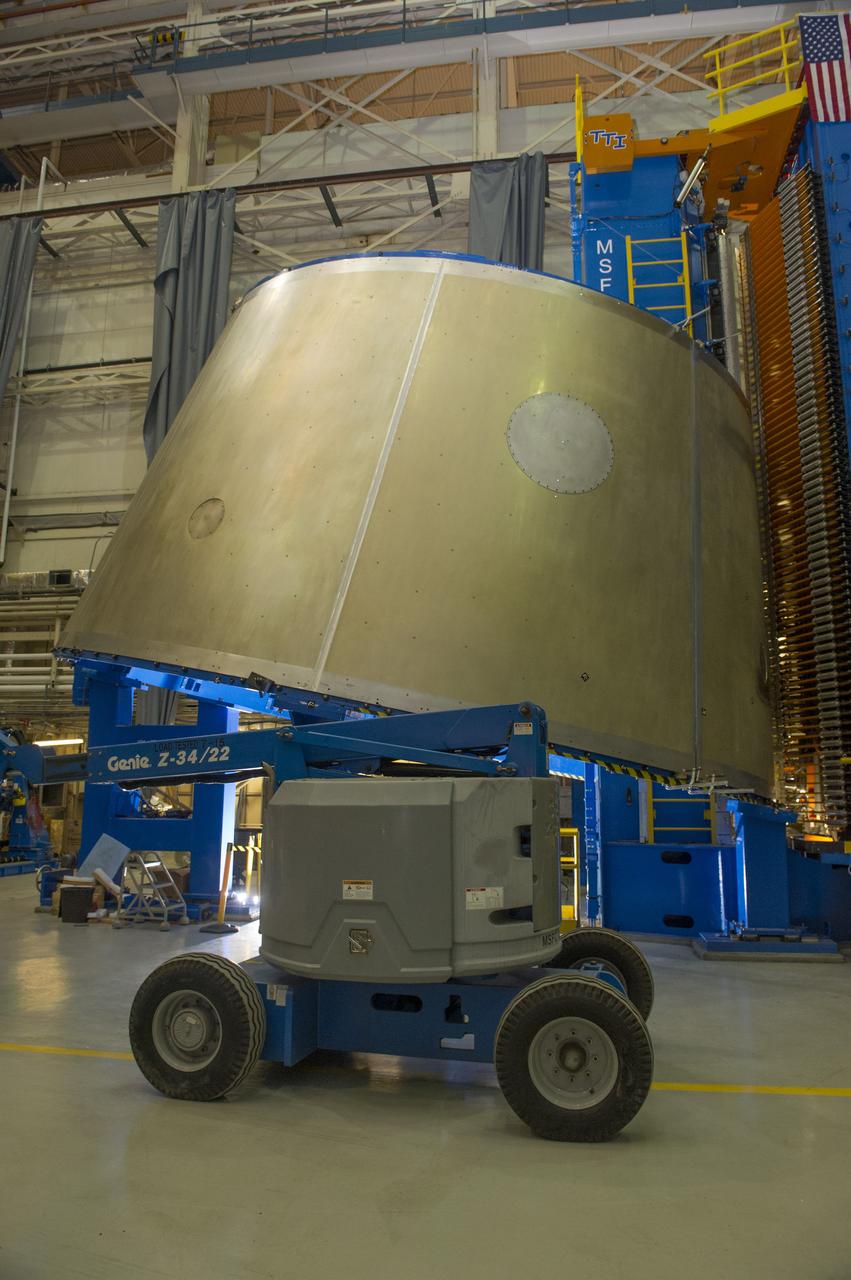

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
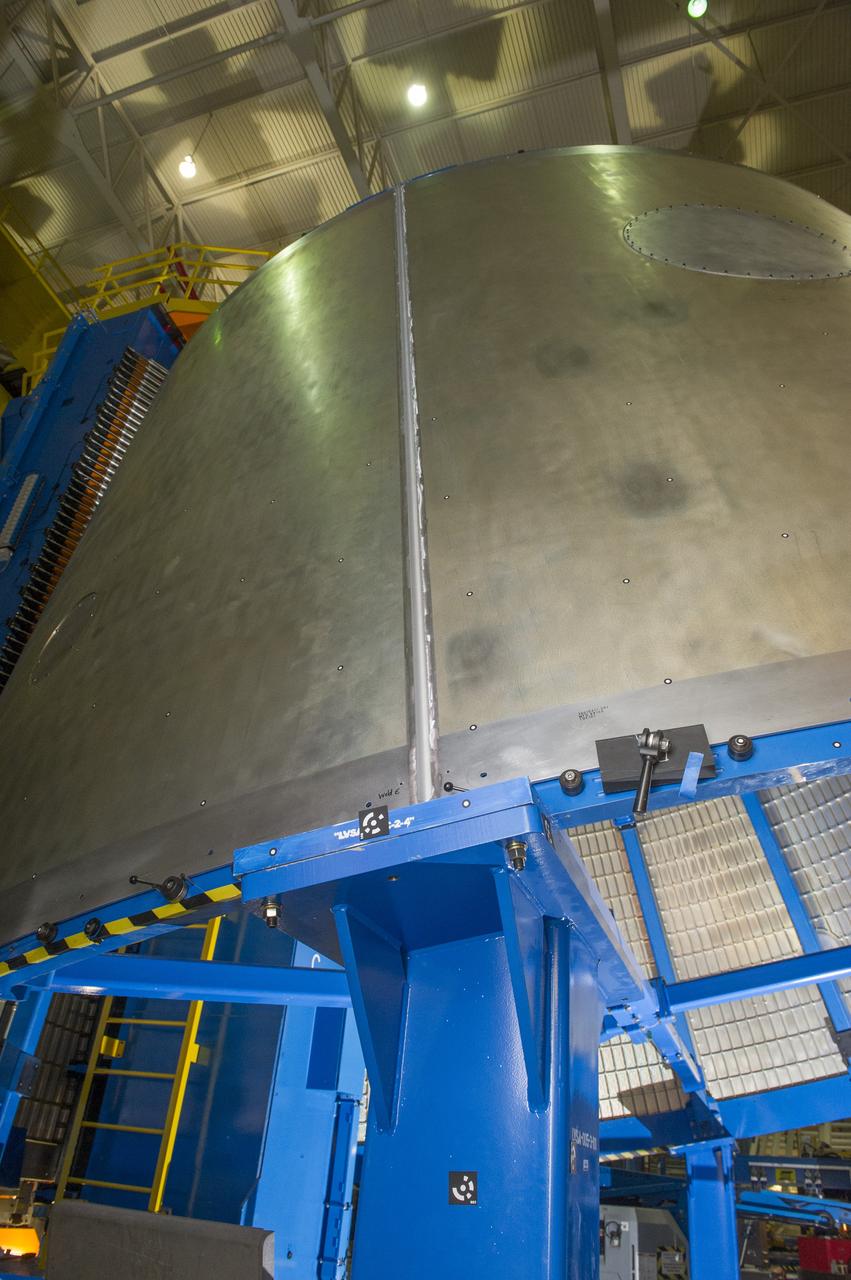

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
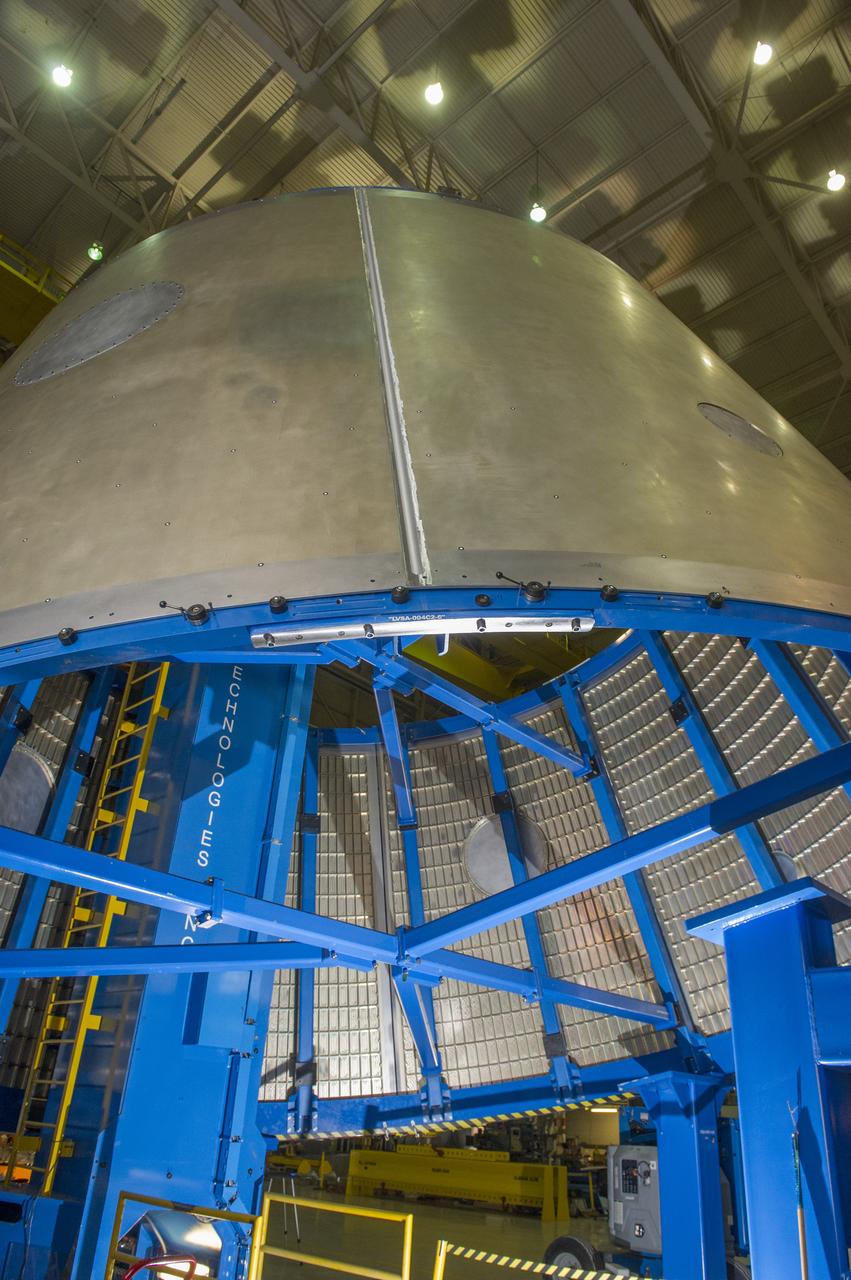

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
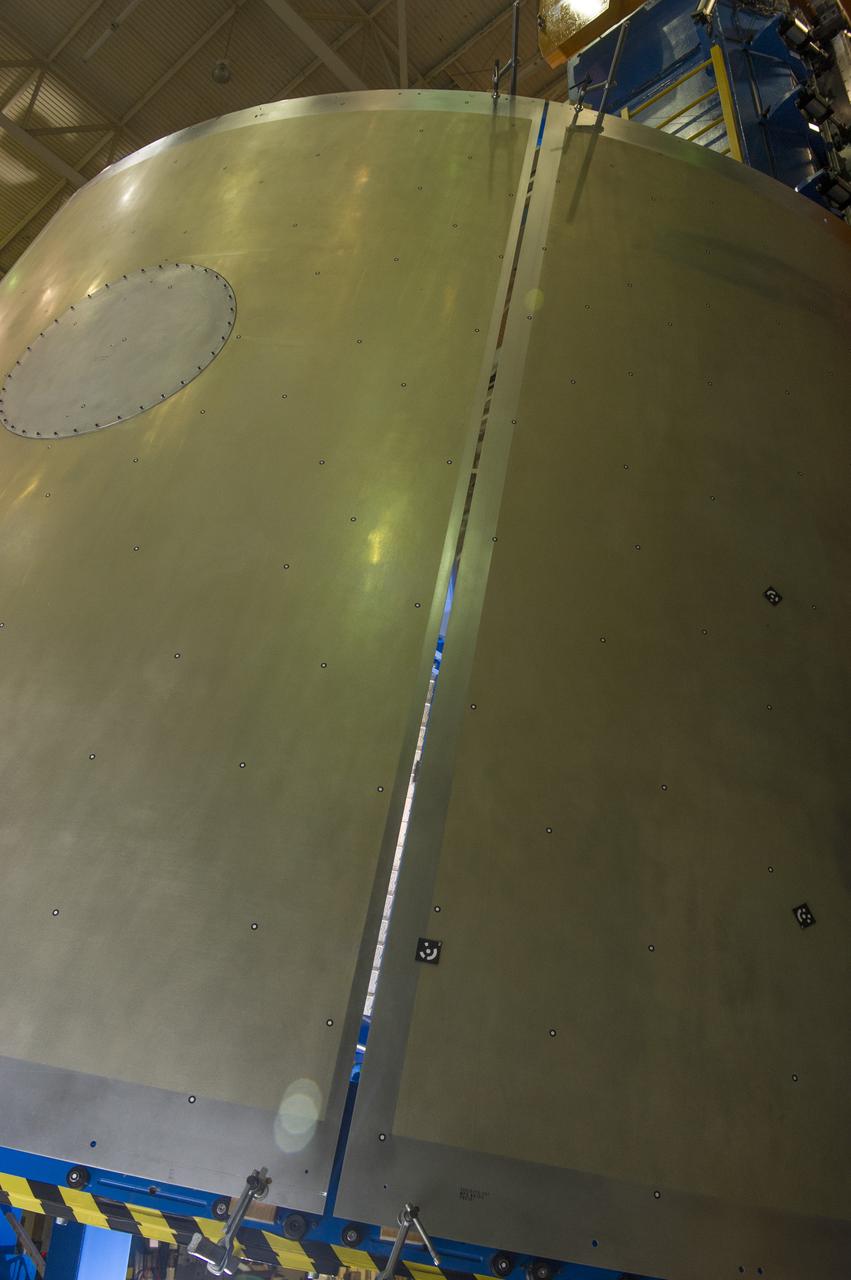

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
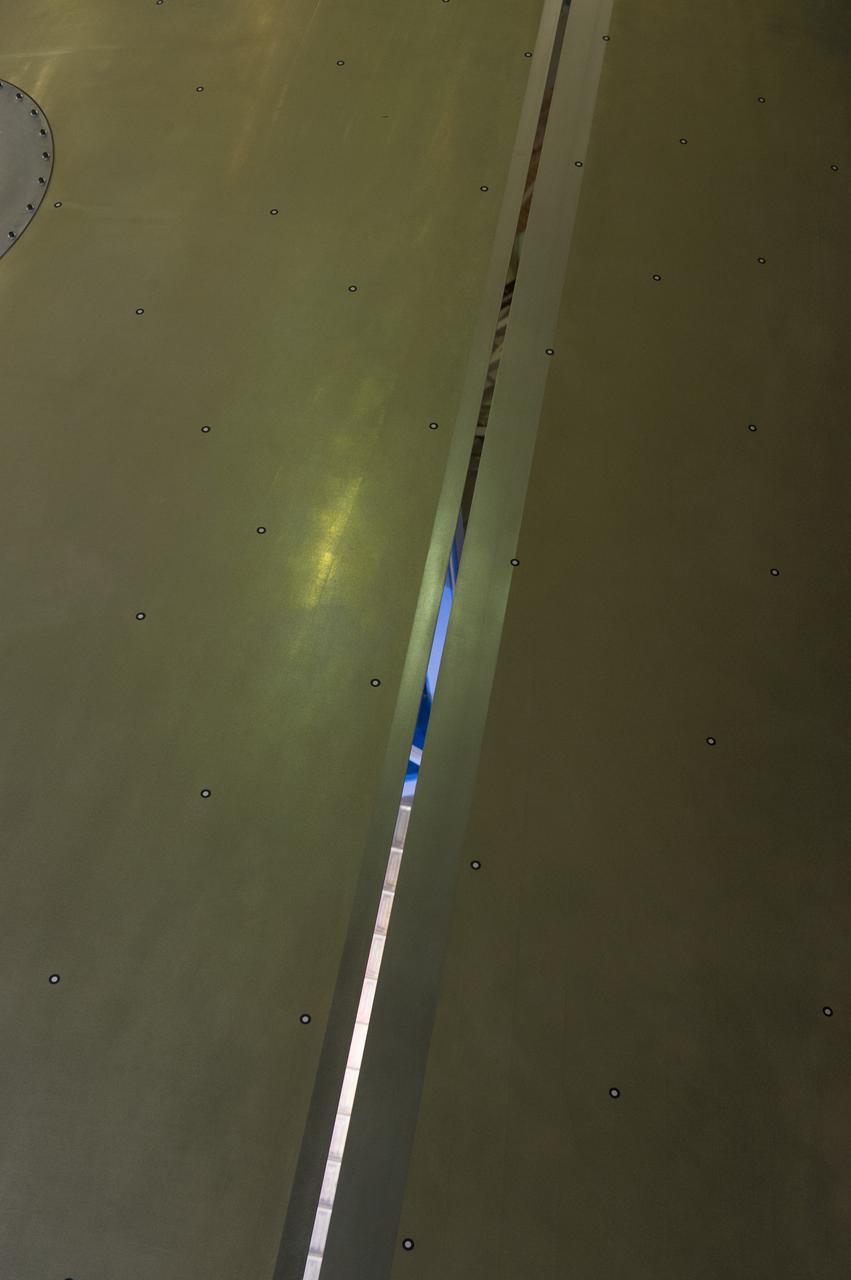

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
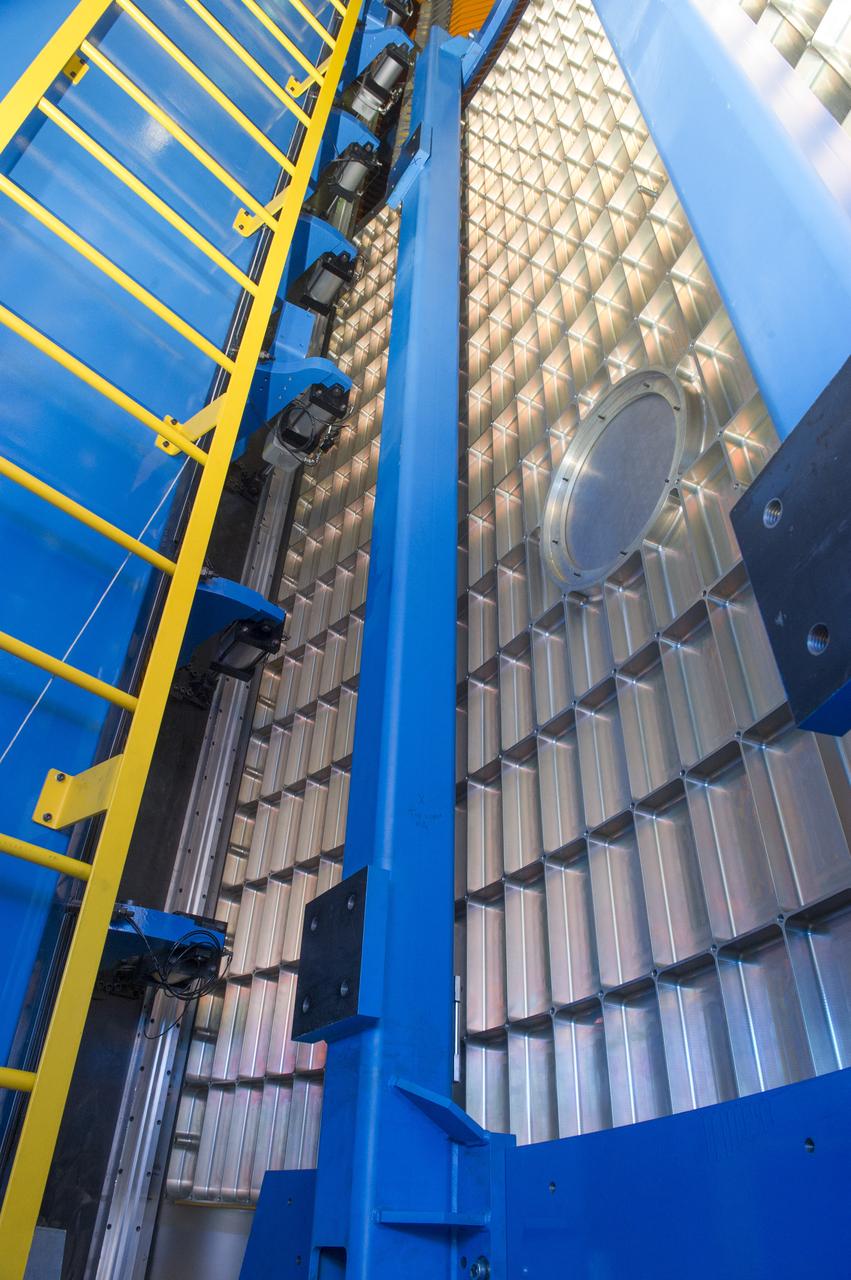

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
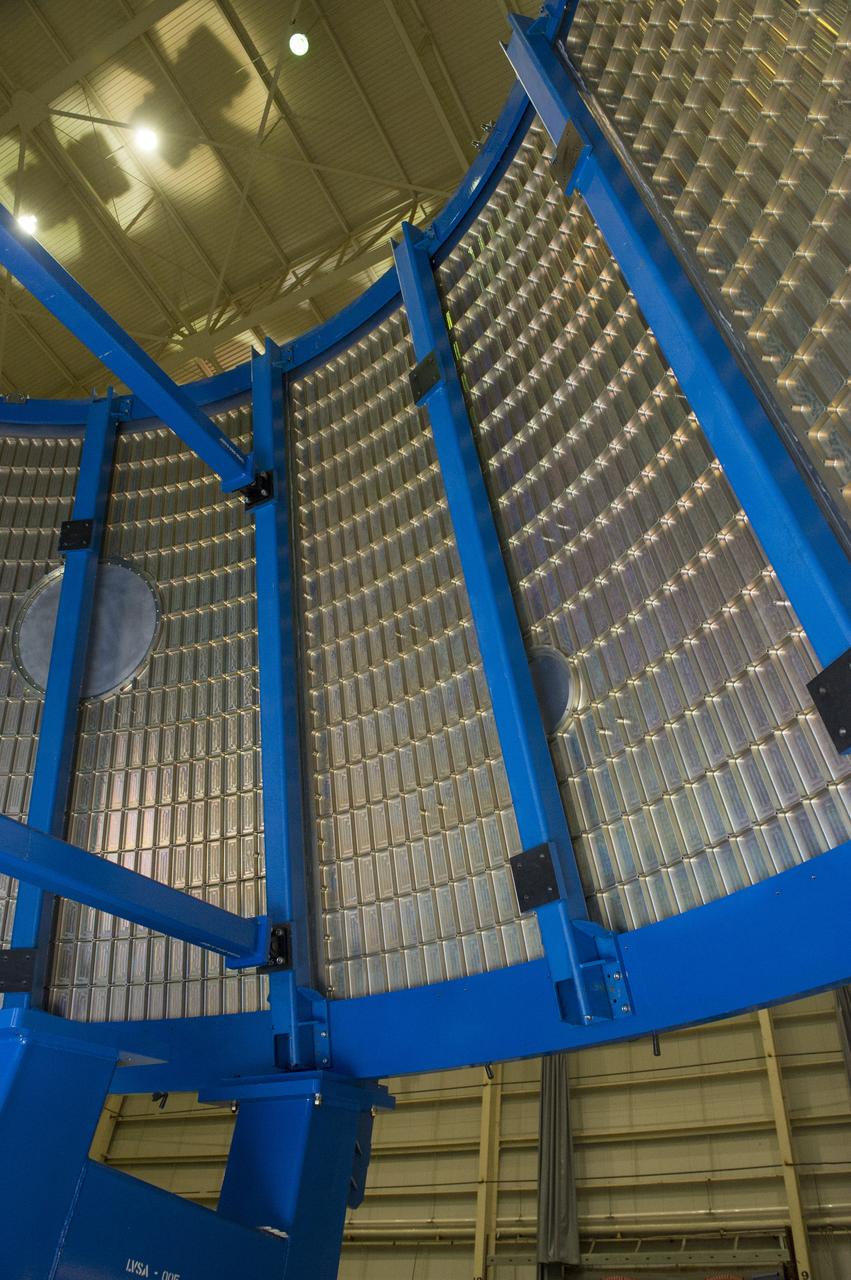
Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
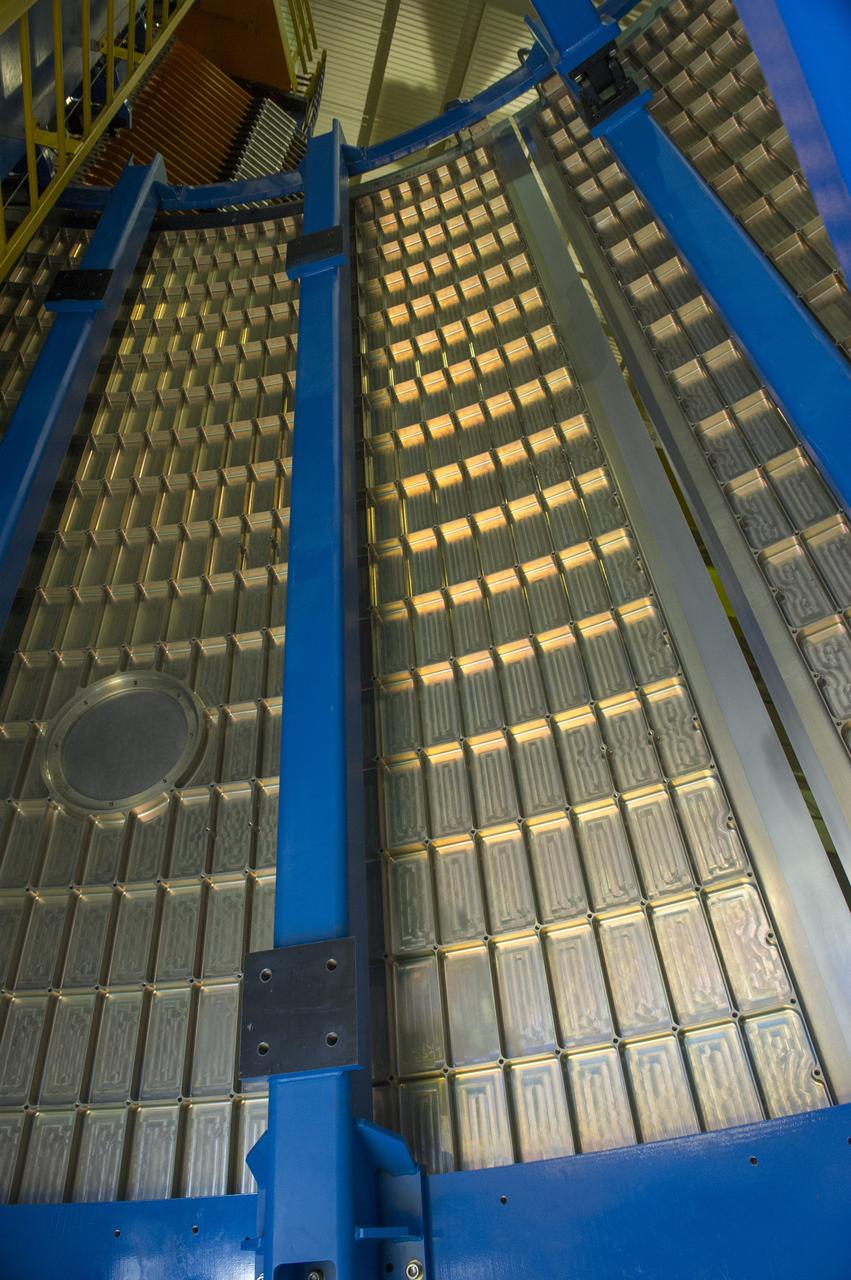

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
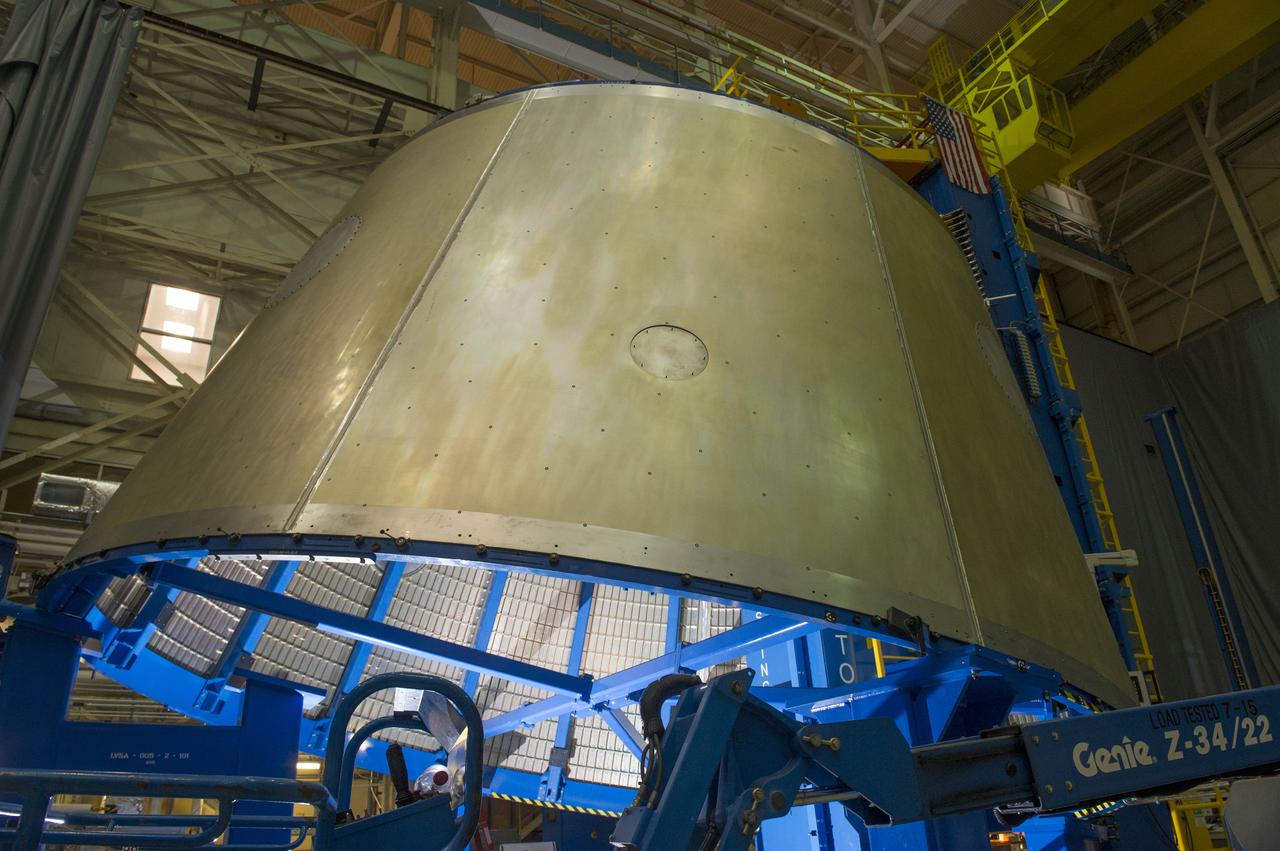

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
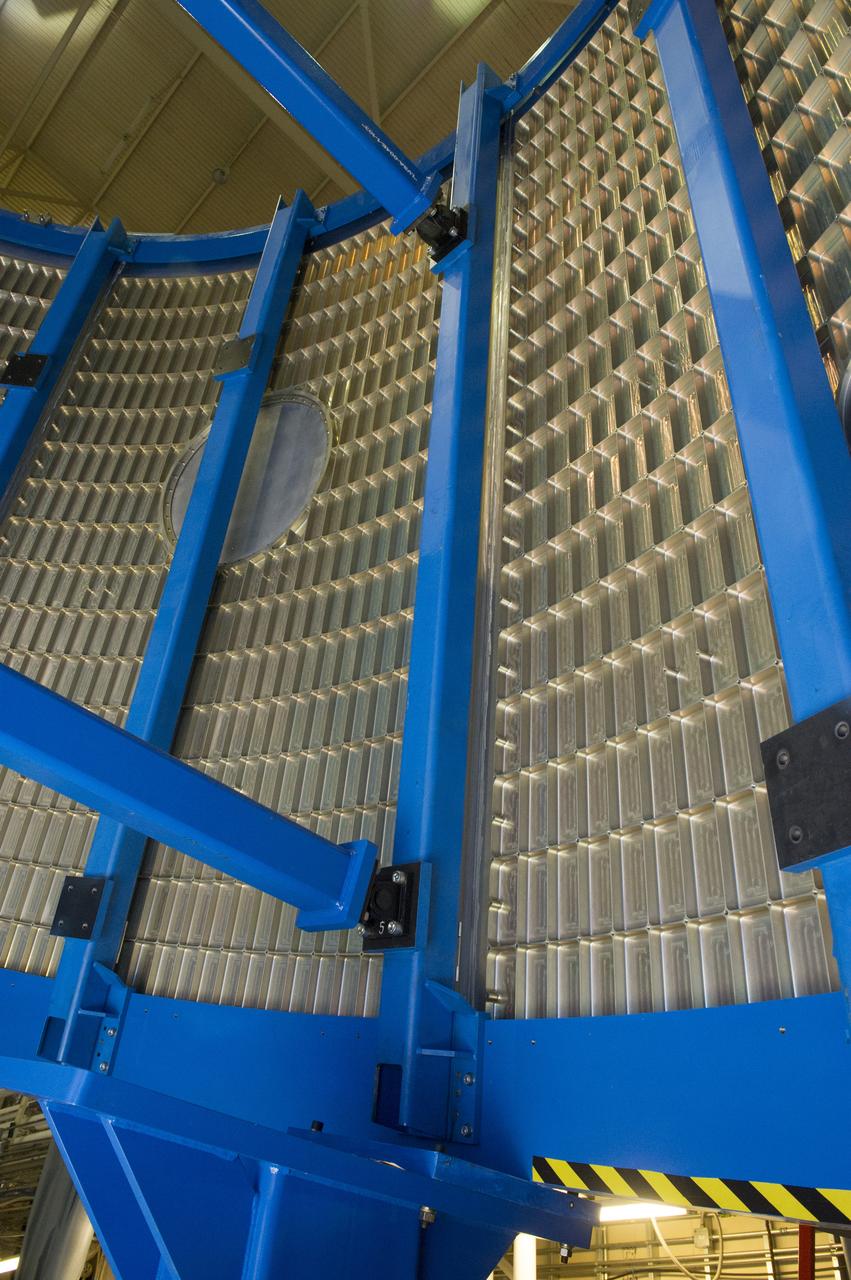

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
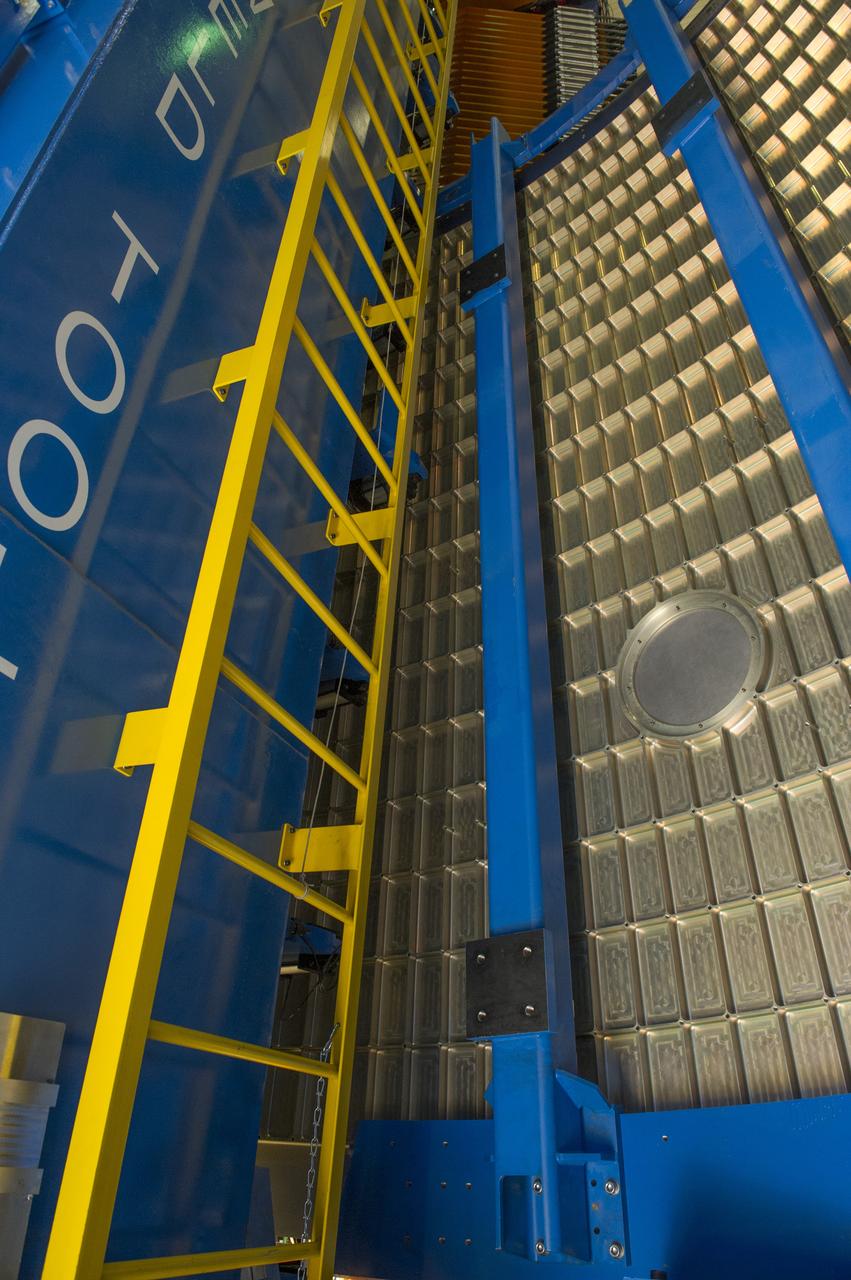
Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter (LVSA) Aft Cone Post Weld #7
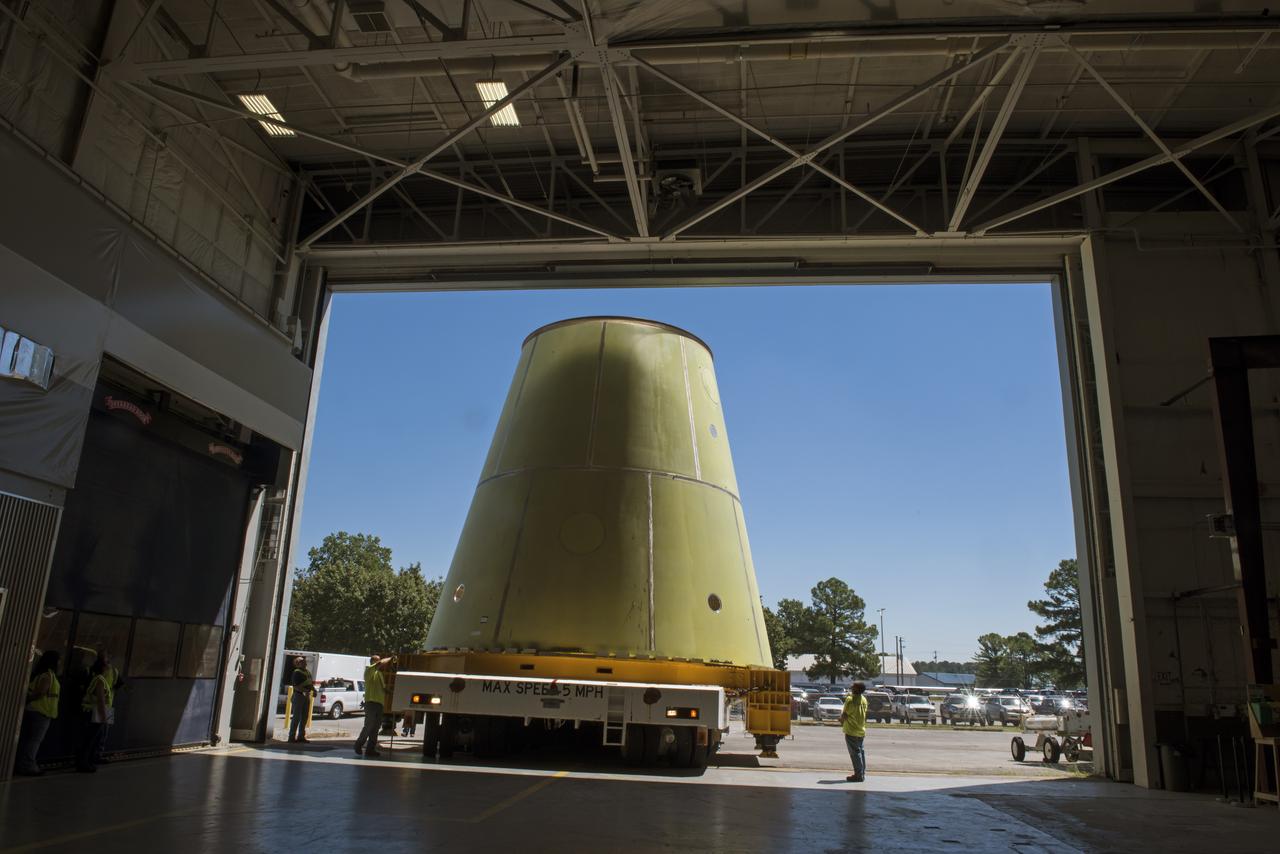

A NASA KAMAG transporter moves the Space Launch System’s launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) to an area where spray-on foam insulation will be applied. The LVSA recently completed manufacturing on a 30 foot welding tool at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Al. The LVSA will be coated with insulation that will protect it during it’s trip to space. The LVSA provides structural support and connects the core stage and the interim cryogenic propulsion stage during the first integrated flight of SLS and Orion.
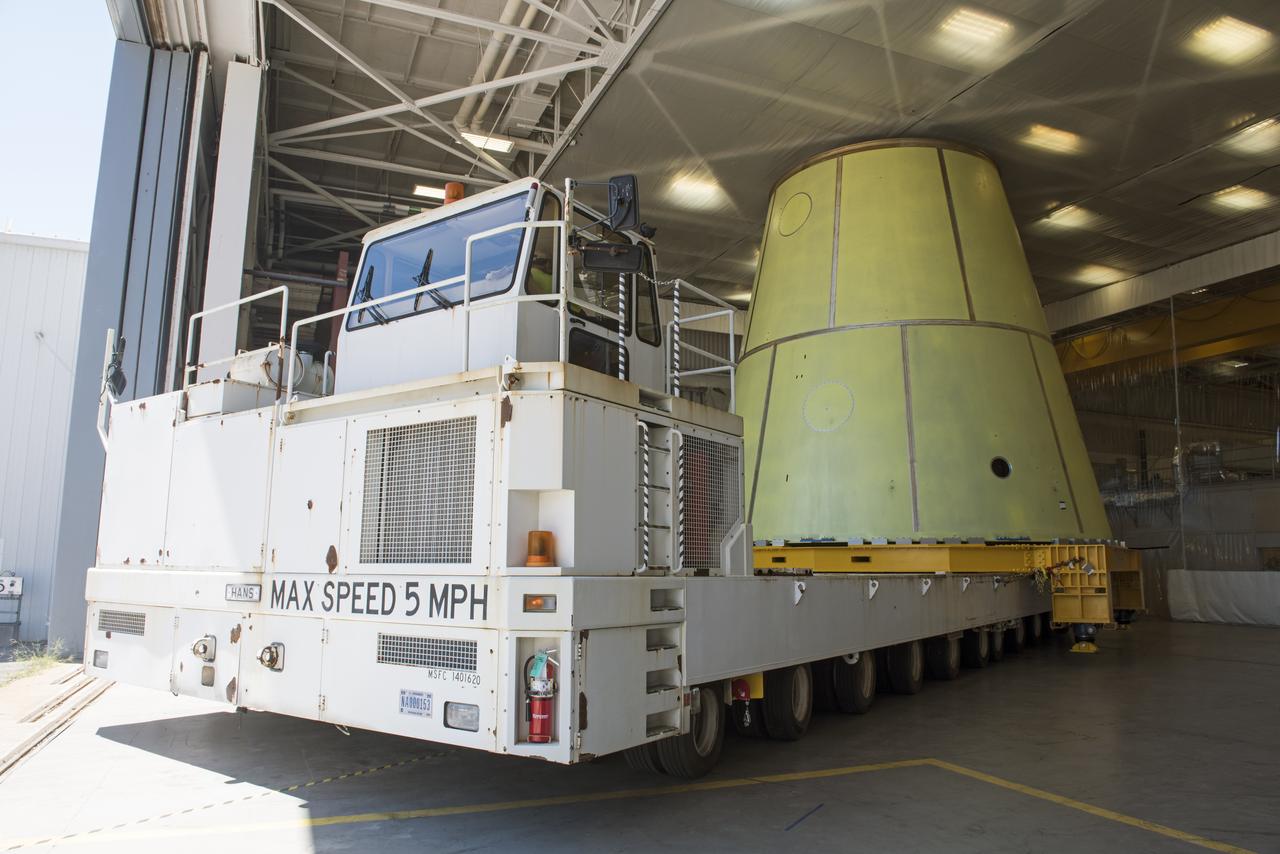

A NASA KAMAG transporter moves the Space Launch System’s launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) to an area where spray-on foam insulation will be applied. The LVSA recently completed manufacturing on a 30 foot welding tool at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Al. The LVSA will be coated with insulation that will protect it during it’s trip to space. The LVSA provides structural support and connects the core stage and the interim cryogenic propulsion stage during the first integrated flight of SLS and Orion.
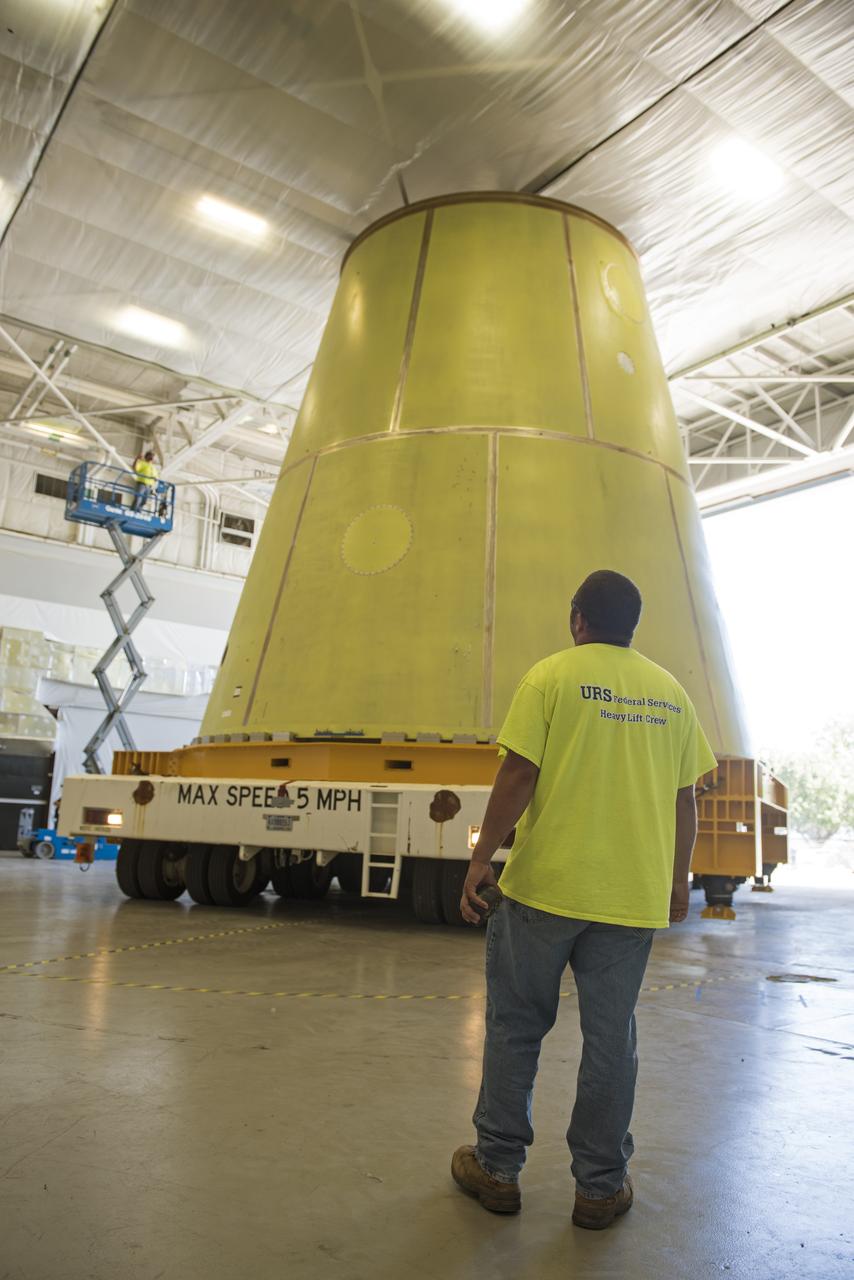

A NASA KAMAG transporter moves the Space Launch System’s launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) to an area where spray-on foam insulation will be applied. The LVSA recently completed manufacturing on a 30 foot welding tool at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Al. The LVSA will be coated with insulation that will protect it during it’s trip to space. The LVSA provides structural support and connects the core stage and the interim cryogenic propulsion stage during the first integrated flight of SLS and Orion.
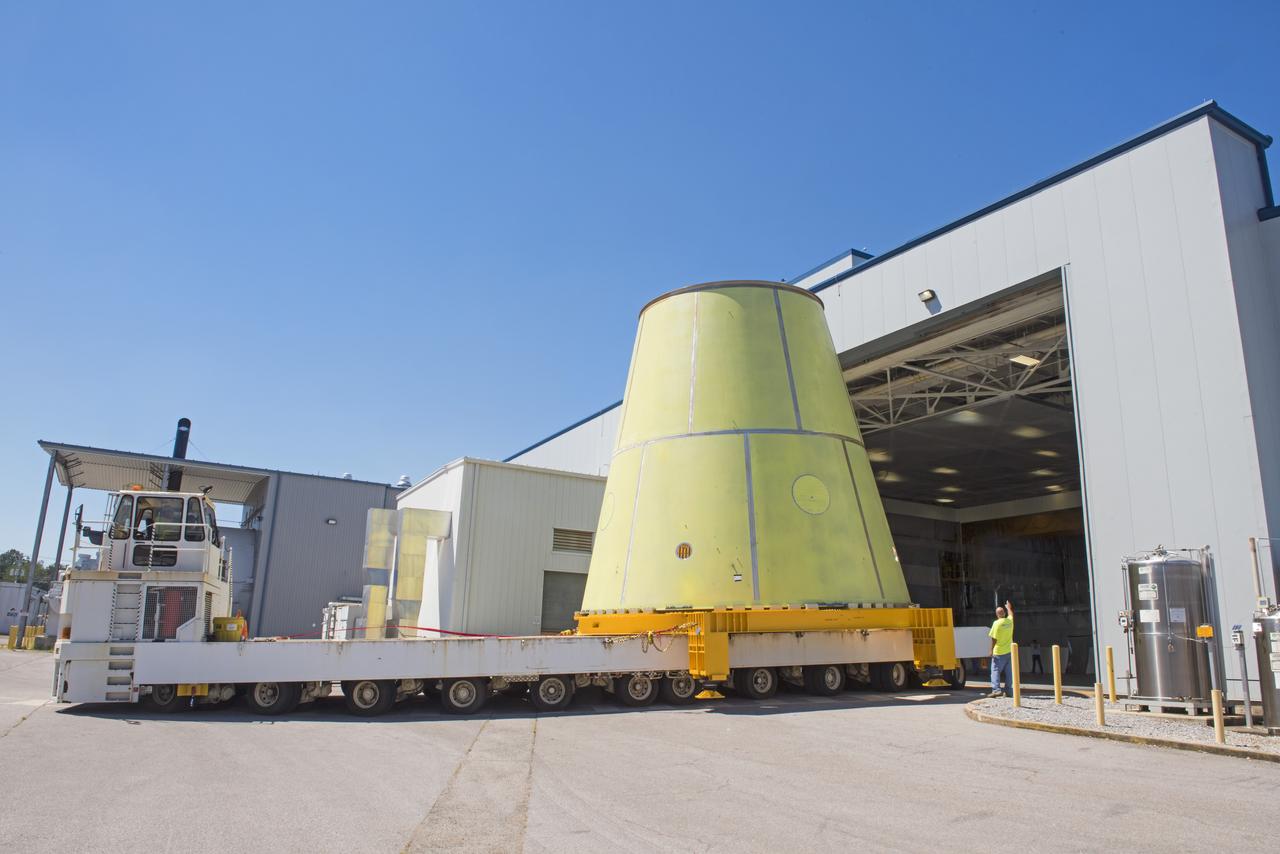

A NASA KAMAG transporter moves the Space Launch System’s launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) to an area where spray-on foam insulation will be applied. The LVSA recently completed manufacturing on a 30 foot welding tool at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Al. The LVSA will be coated with insulation that will protect it during it’s trip to space. The LVSA provides structural support and connects the core stage and the interim cryogenic propulsion stage during the first integrated flight of SLS and Orion.
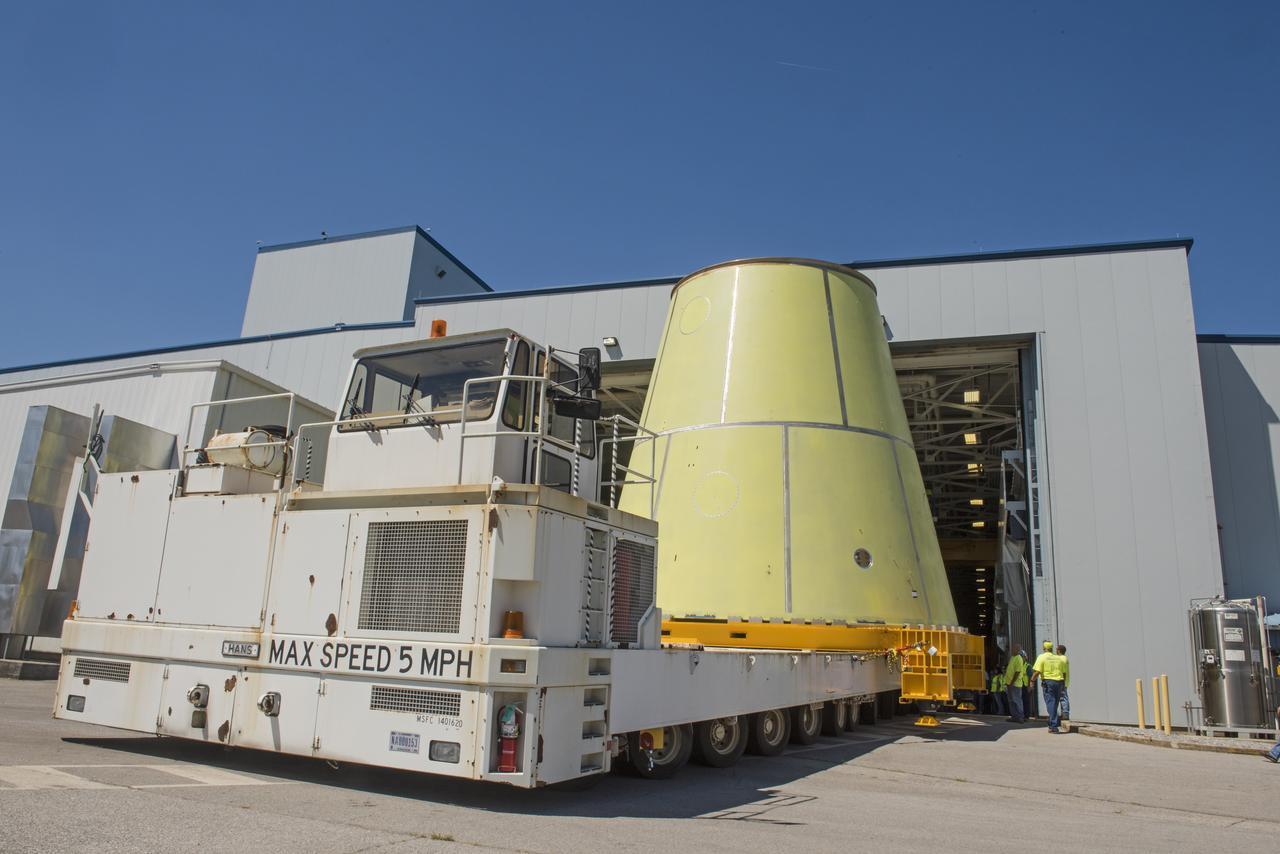

A NASA KAMAG transporter moves the Space Launch System’s launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) to an area where spray-on foam insulation will be applied. The LVSA recently completed manufacturing on a 30 foot welding tool at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Al. The LVSA will be coated with insulation that will protect it during it’s trip to space. The LVSA provides structural support and connects the core stage and the interim cryogenic propulsion stage during the first integrated flight of SLS and Orion.
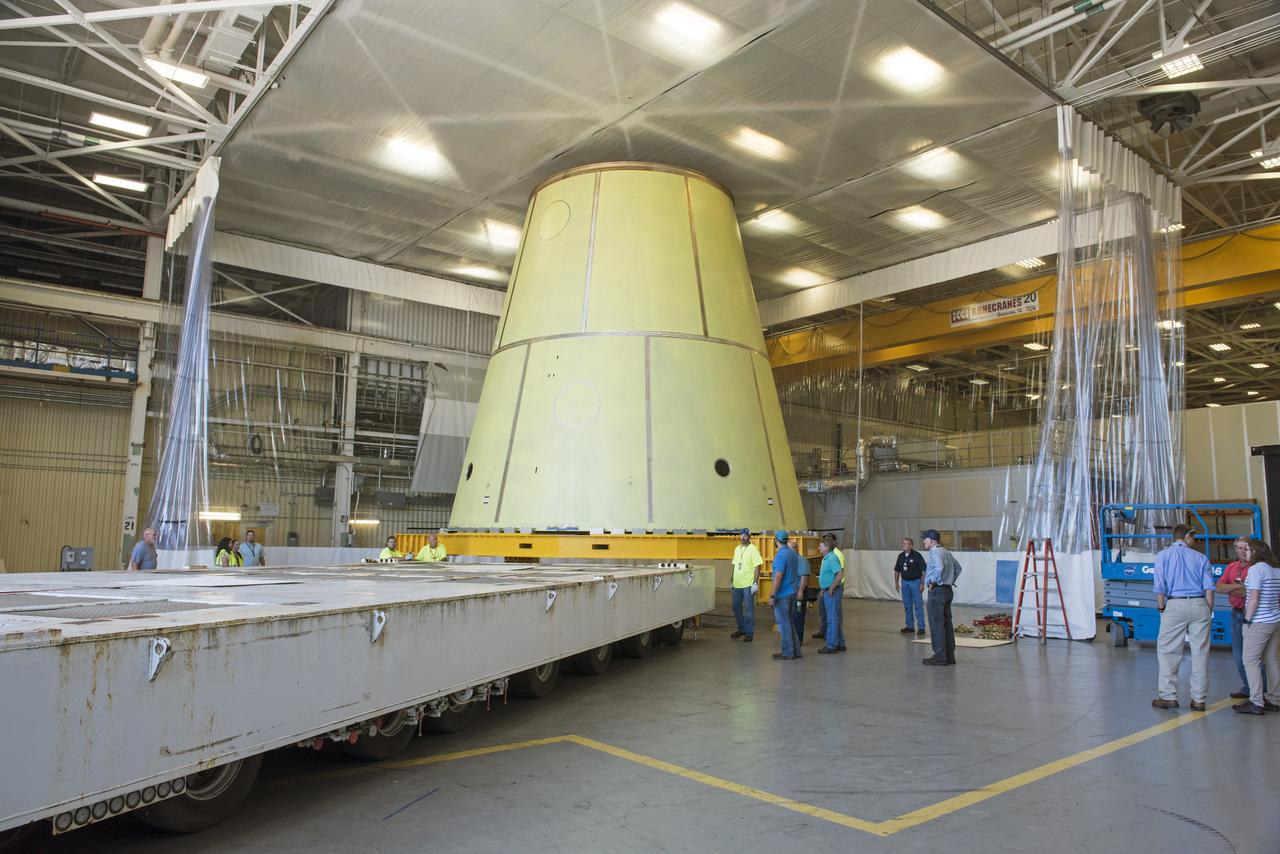

A NASA KAMAG transporter moves the Space Launch System’s launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) to an area where spray-on foam insulation will be applied. The LVSA recently completed manufacturing on a 30 foot welding tool at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Al. The LVSA will be coated with insulation that will protect it during it’s trip to space. The LVSA provides structural support and connects the core stage and the interim cryogenic propulsion stage during the first integrated flight of SLS and Orion.
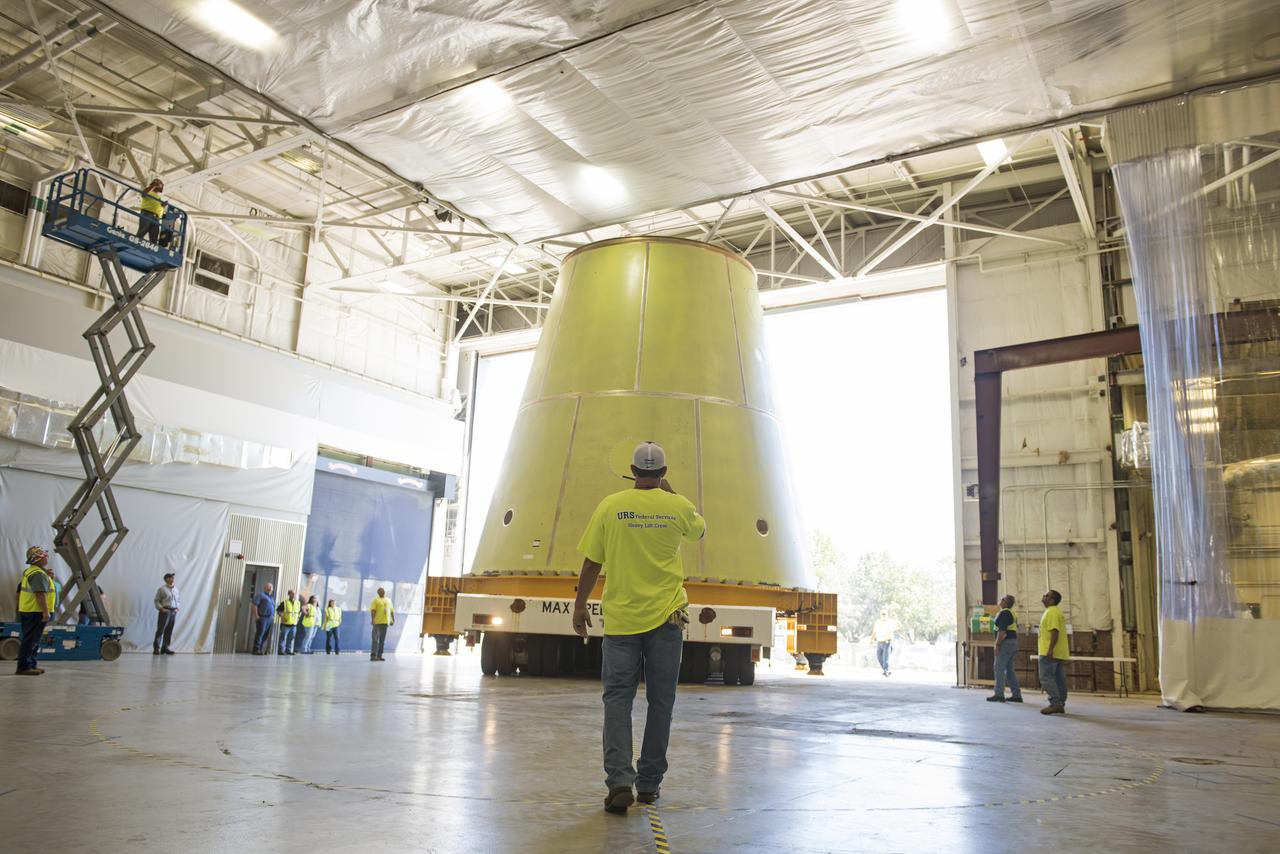

A NASA KAMAG transporter moves the Space Launch System’s launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) to an area where spray-on foam insulation will be applied. The LVSA recently completed manufacturing on a 30 foot welding tool at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Al. The LVSA will be coated with insulation that will protect it during it’s trip to space. The LVSA provides structural support and connects the core stage and the interim cryogenic propulsion stage during the first integrated flight of SLS and Orion.
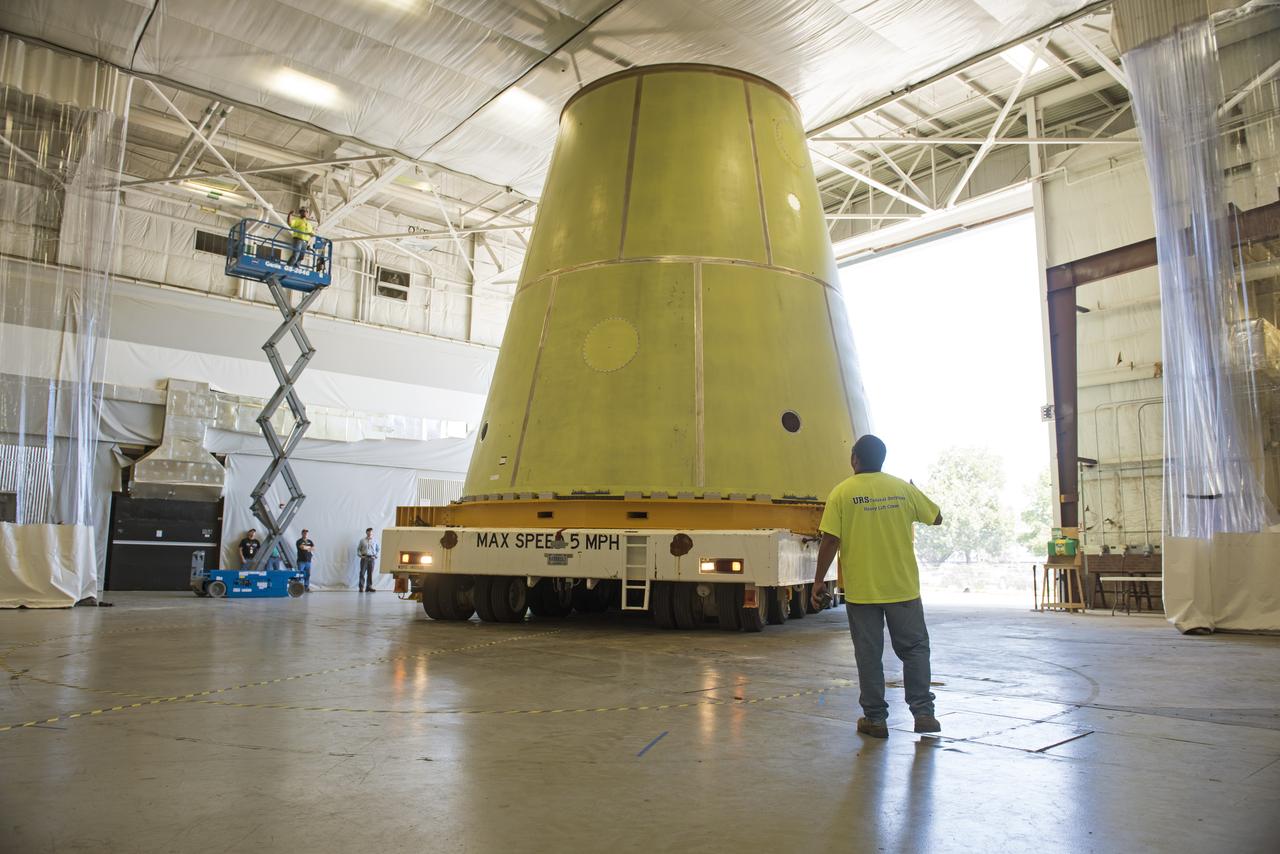

A NASA KAMAG transporter moves the Space Launch System’s launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) to an area where spray-on foam insulation will be applied. The LVSA recently completed manufacturing on a 30 foot welding tool at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Al. The LVSA will be coated with insulation that will protect it during it’s trip to space. The LVSA provides structural support and connects the core stage and the interim cryogenic propulsion stage during the first integrated flight of SLS and Orion.
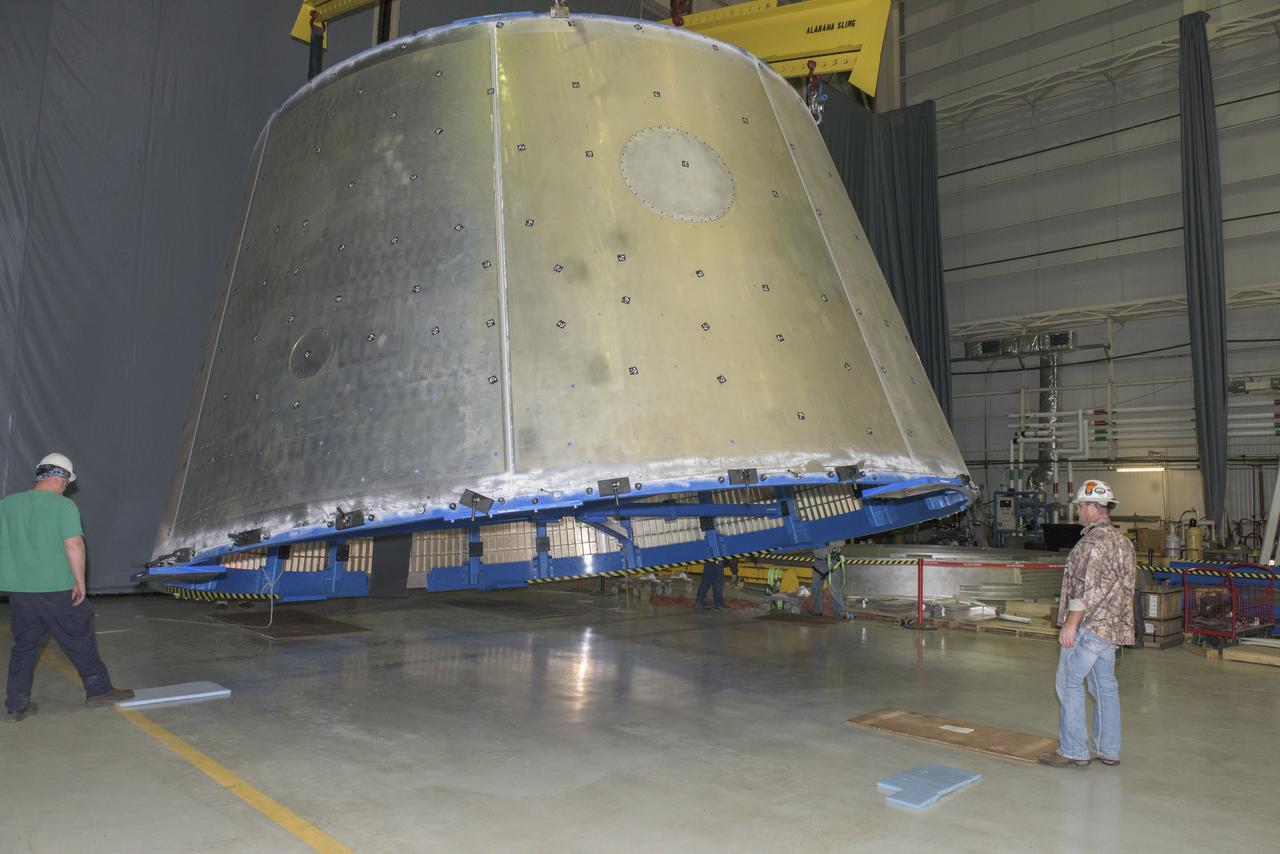

LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (LVSA) AFT CONE MOVE FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL TO THE FLOOR OF BLDG 4755
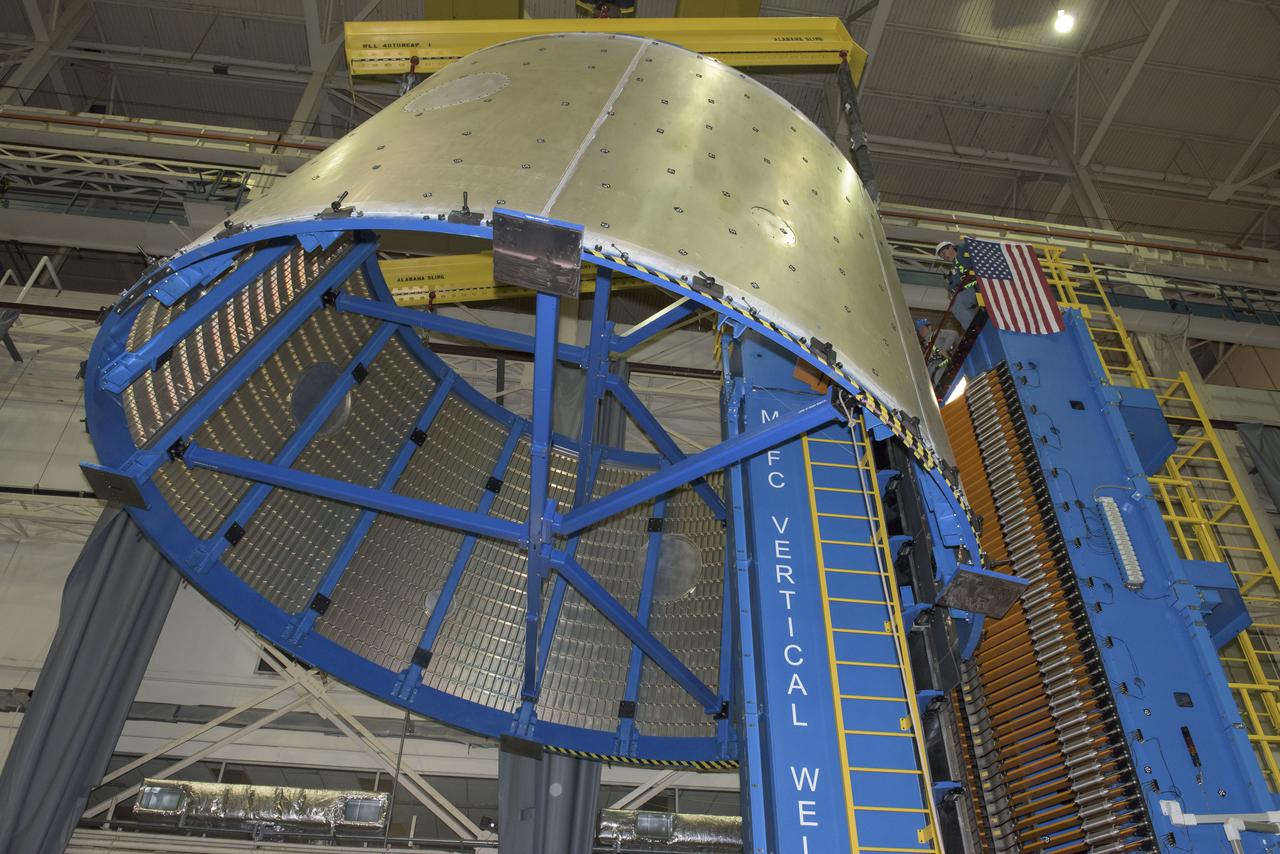

LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (LVSA) AFT CONE MOVE FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL TO THE FLOOR OF BLDG 4755
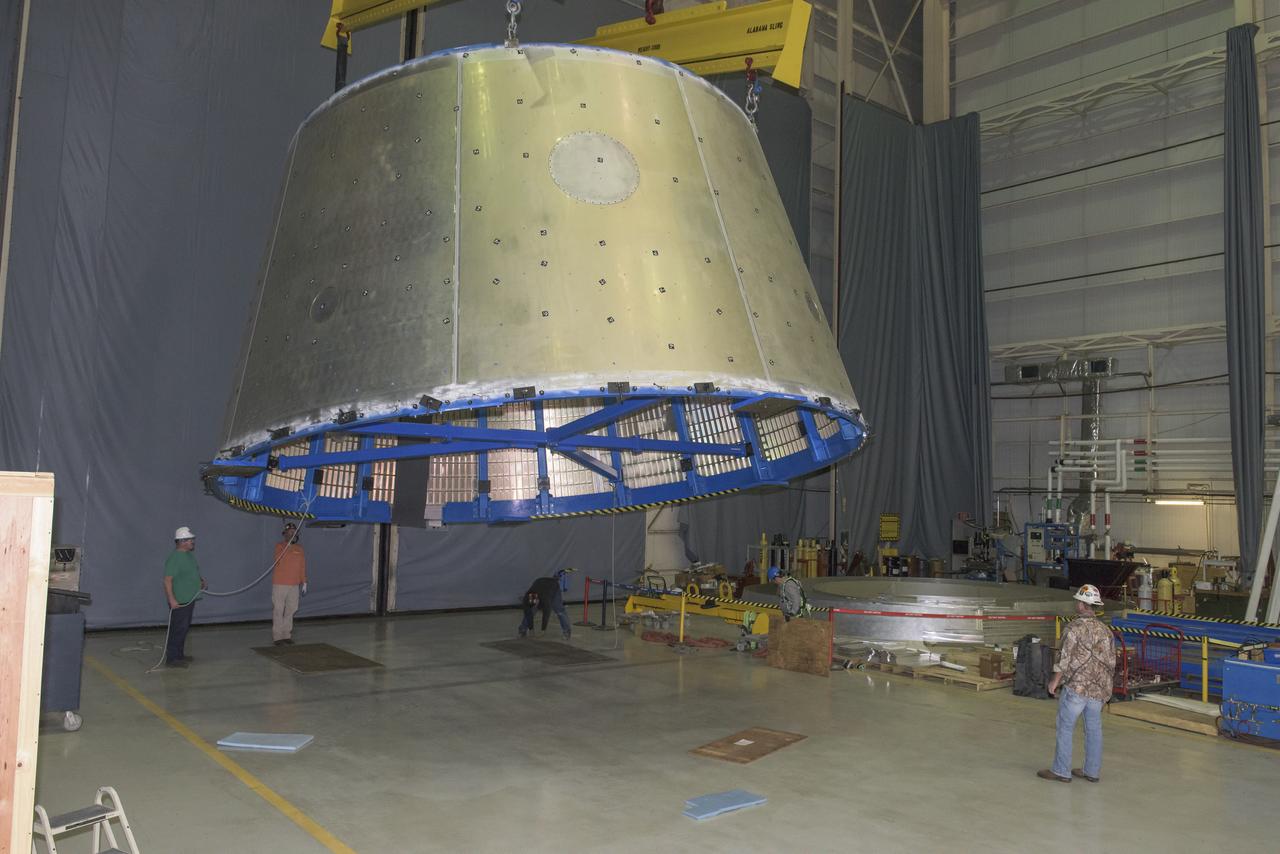

LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (LVSA) AFT CONE MOVE FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL TO THE FLOOR OF BLDG 4755

LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (LVSA) AFT CONE MOVE FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL TO THE FLOOR OF BLDG 4755
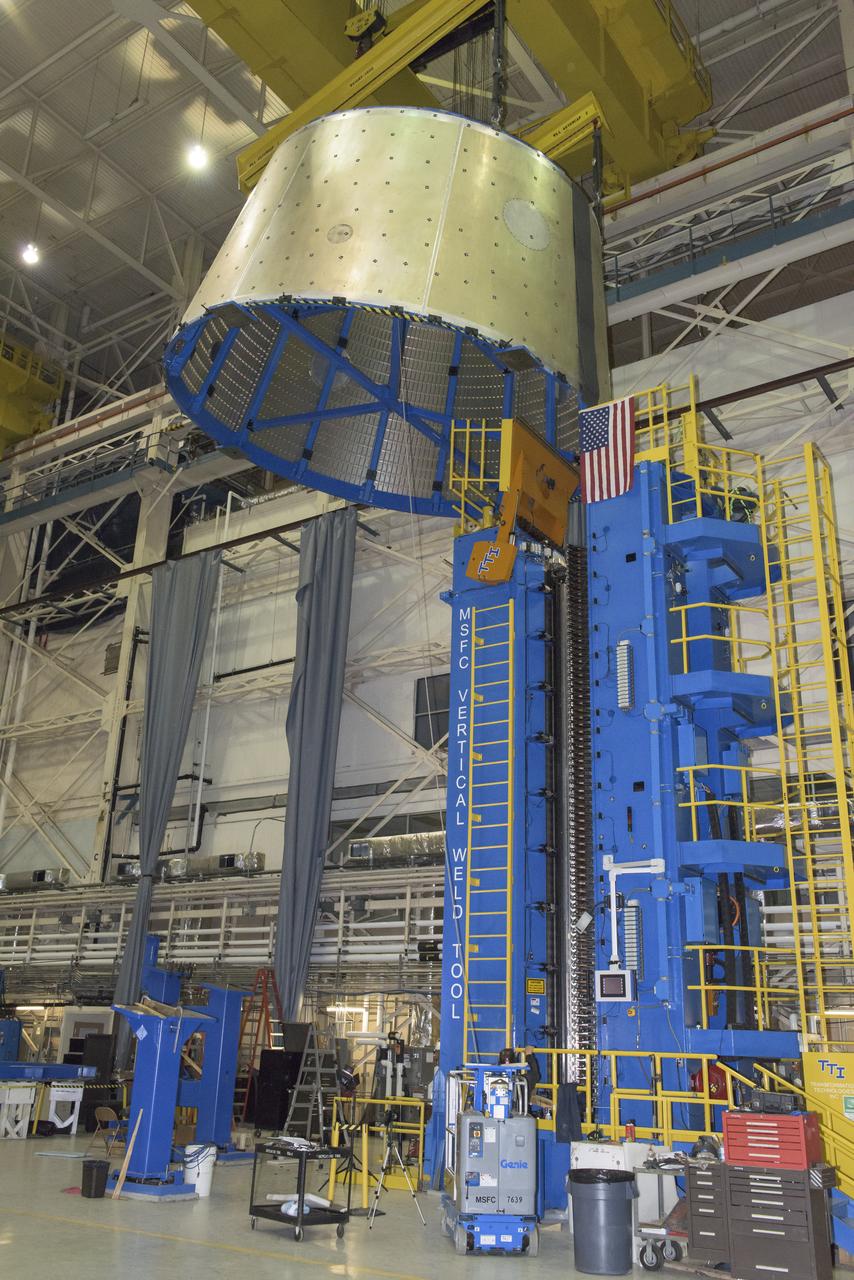

LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (LVSA) AFT CONE MOVE FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL TO THE FLOOR OF BLDG 4755
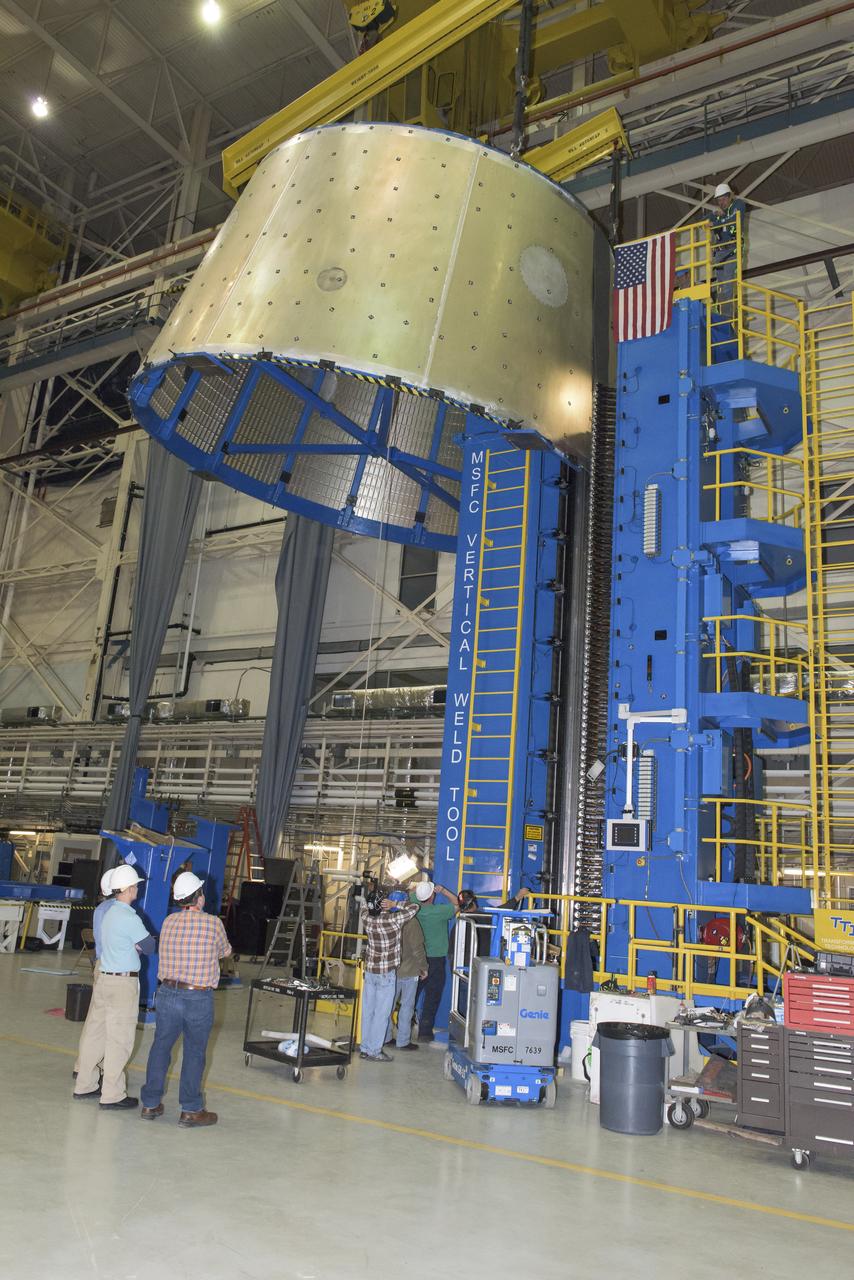

LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (LVSA) AFT CONE MOVE FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL TO THE FLOOR OF BLDG 4755
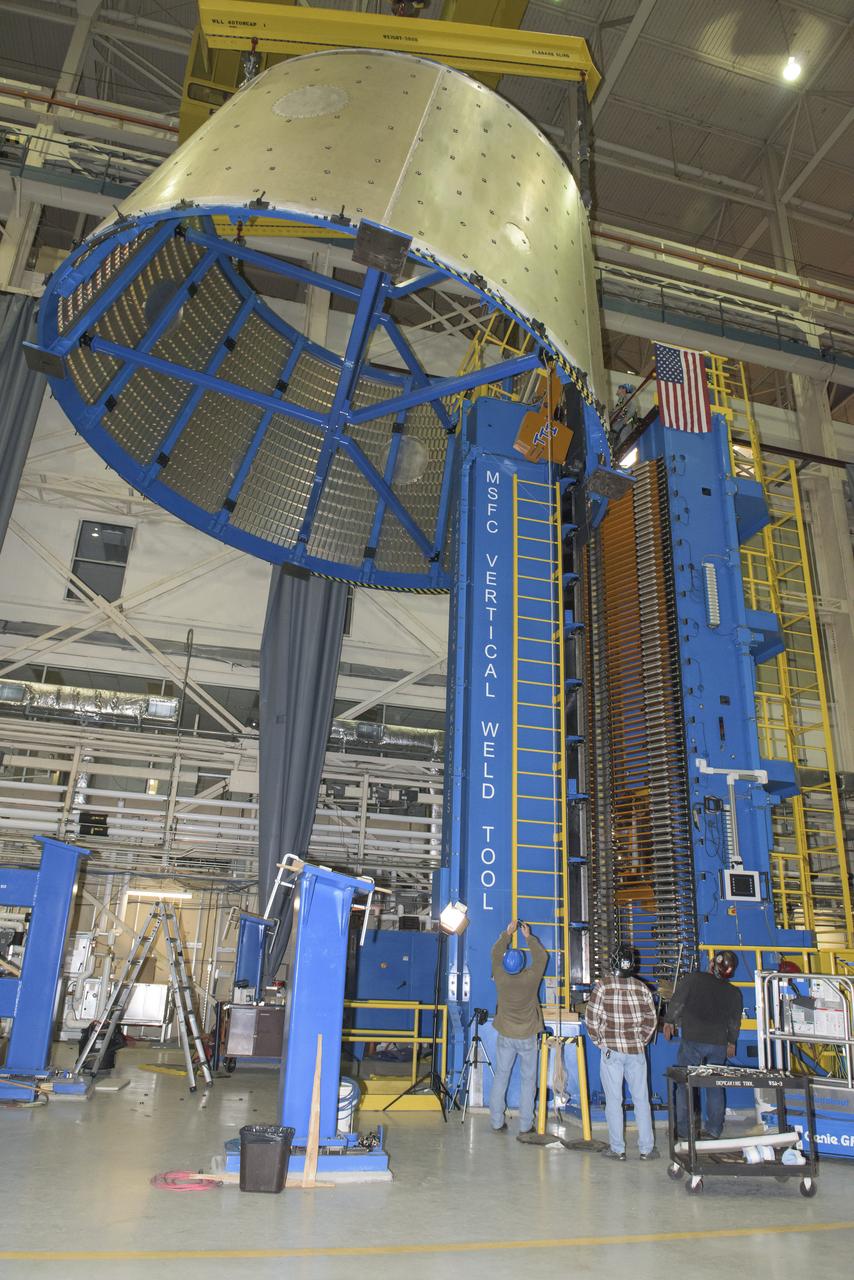

LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (LVSA) AFT CONE MOVE FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL TO THE FLOOR OF BLDG 4755
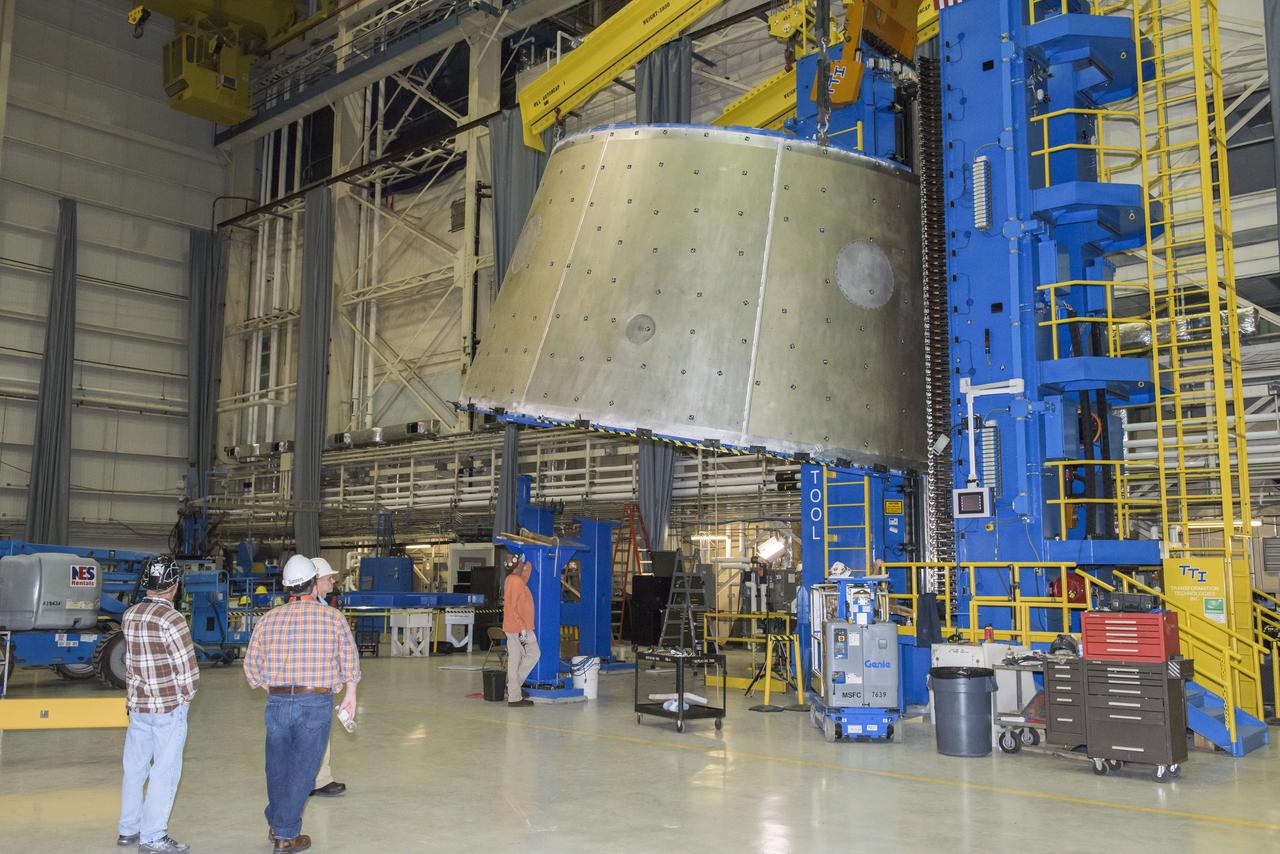

LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (LVSA) AFT CONE MOVE FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL TO THE FLOOR OF BLDG 4755
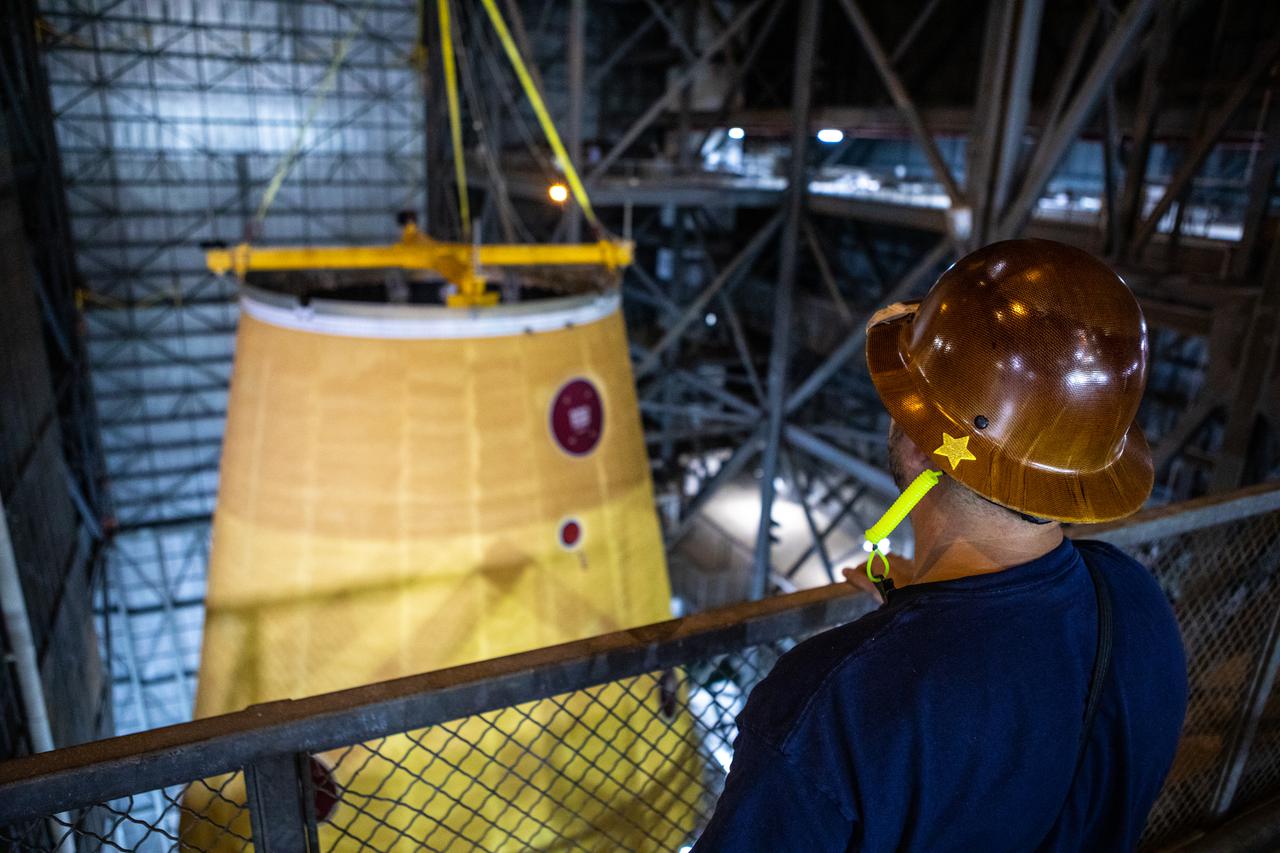

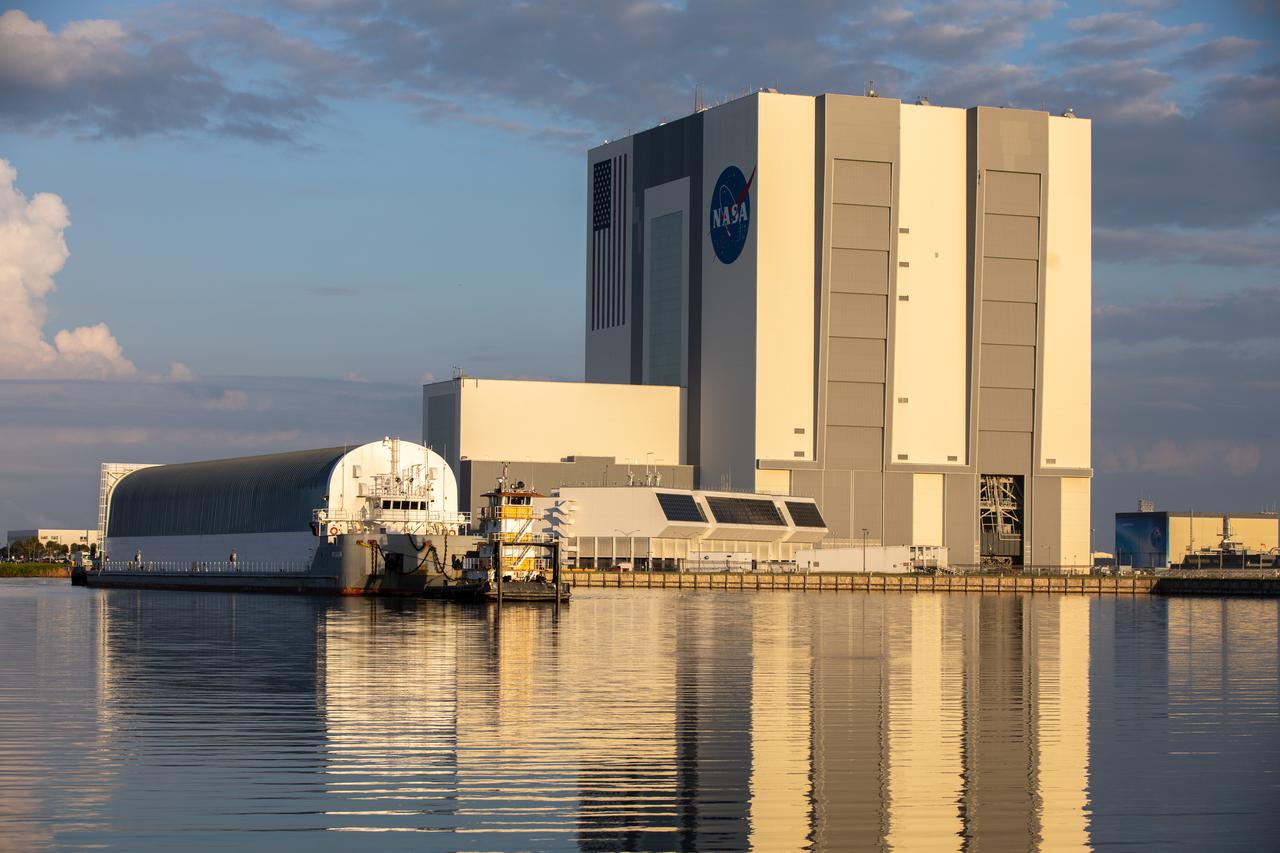
Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the massive SLS core stage on the mobile launcher in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 22, 2021. Engineers used one of five VAB cranes to lift the adapter almost 250-feet in the air and then slowly lower it on to the core stage. The LVSA arrived at Kennedy from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, in July 2020 and has remained in the VAB for processing. During integration, known as “stacking,” the LVSA is bolted to the forward skirt of the core stage, connecting the core stage and the interim cryogenic propulsion stage in preparation for the first flight of the rocket and the Orion spacecraft during Artemis I. The ICPS’s RL10 engine will fit down inside the LVSA, which protects the engine during launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights in which NASA will land the first woman and person of color on the Moon.
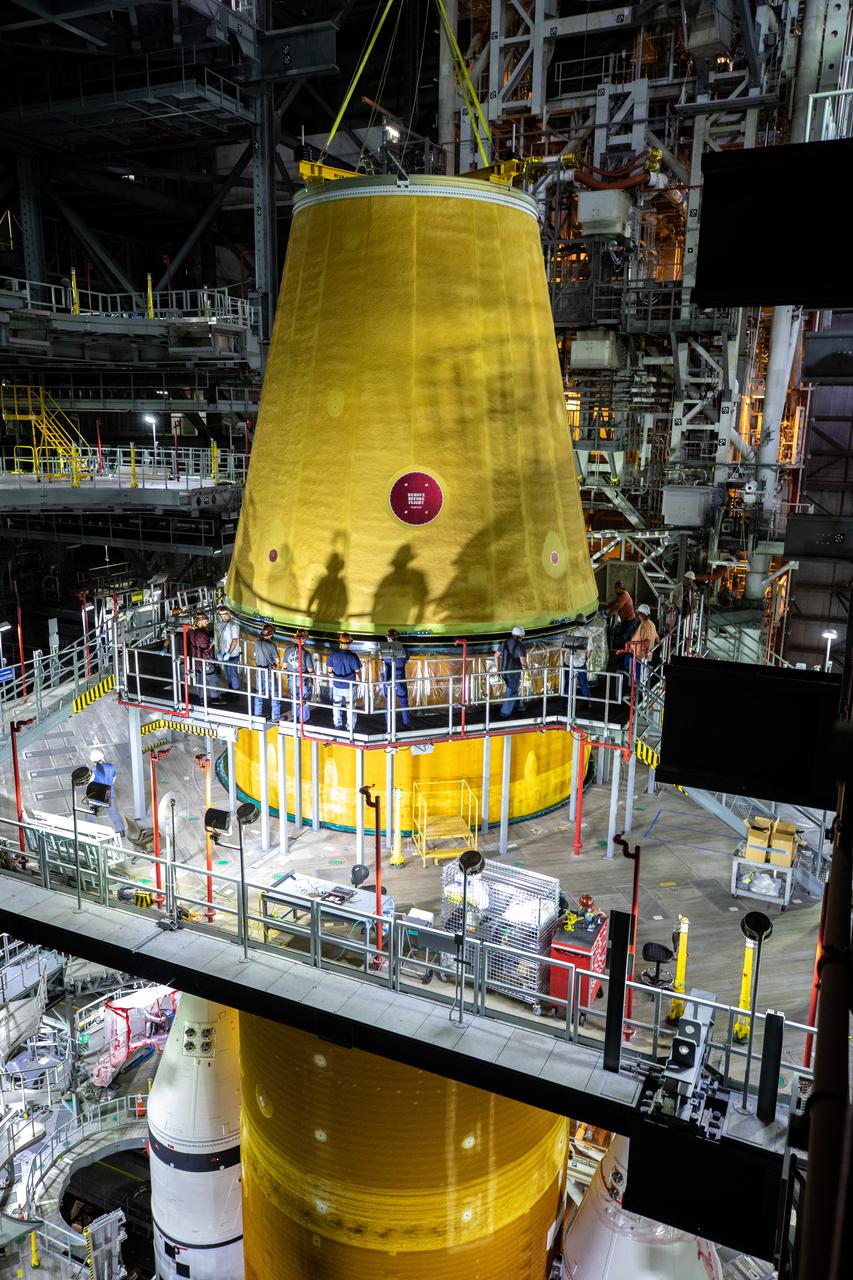

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the massive SLS core stage on the mobile launcher in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 22, 2021. Engineers used one of five VAB cranes to lift the adapter almost 250-feet in the air and then slowly lower it on to the core stage. The LVSA arrived at Kennedy from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, in July 2020 and has remained in the VAB for processing. During integration, known as “stacking,” the LVSA is bolted to the forward skirt of the core stage, connecting the core stage and the interim cryogenic propulsion stage in preparation for the first flight of the rocket and the Orion spacecraft during Artemis I. The ICPS’s RL10 engine will fit down inside the LVSA, which protects the engine during launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights in which NASA will land the first woman and person of color on the Moon.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) sits in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), while teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) with the massive SLS core stage on the mobile launcher at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 22, 2021. Engineers used one of five VAB cranes to lift the adapter almost 250-feet in the air and then slowly lower it on to the core stage. The LVSA arrived at Kennedy from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, in July 2020 and has remained in the VAB for processing. During integration, known as “stacking,” the LVSA is bolted to the forward skirt of the core stage, connecting the core stage and the ICPS in preparation for the first flight of the rocket and the Orion spacecraft during Artemis I. The ICPS will provide Orion spacecraft with the push needed for its flight around the Moon. The ICPS’s RL10 engine will fit down inside the LVSA, which protects the engine during launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights in which NASA will land the first woman and person of color on the Moon.

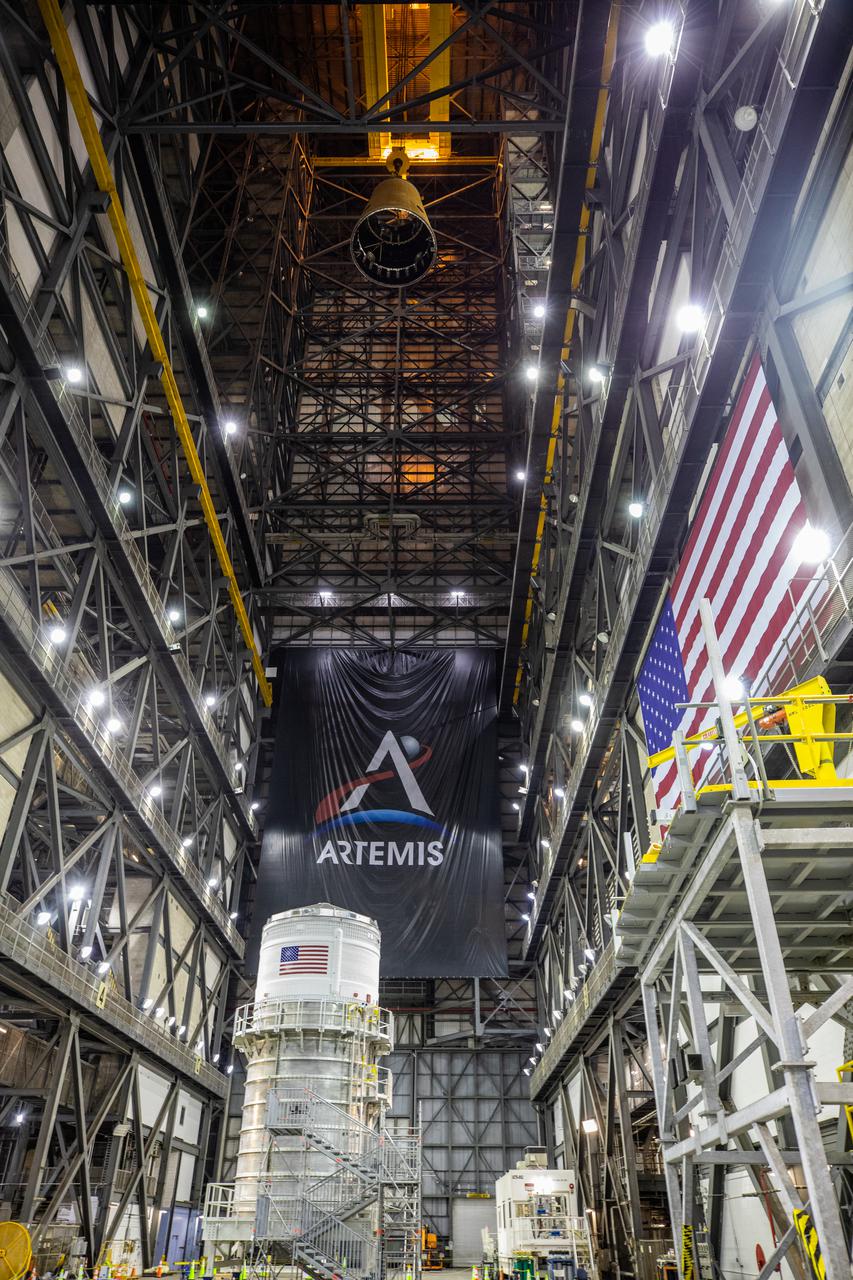
Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs prepare to integrate the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the massive SLS core stage on the mobile launcher in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 22, 2021. The LVSA arrived at Kennedy from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, in July 2020 and has remained in the VAB for processing. During integration, known as “stacking,” the LVSA will be bolted to the forward skirt of the core stage, connecting the core stage and the interim cryogenic propulsion stage in preparation for the first flight of the rocket and the Orion spacecraft during Artemis I. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights in which NASA will land the first woman and person of color on the Moon.
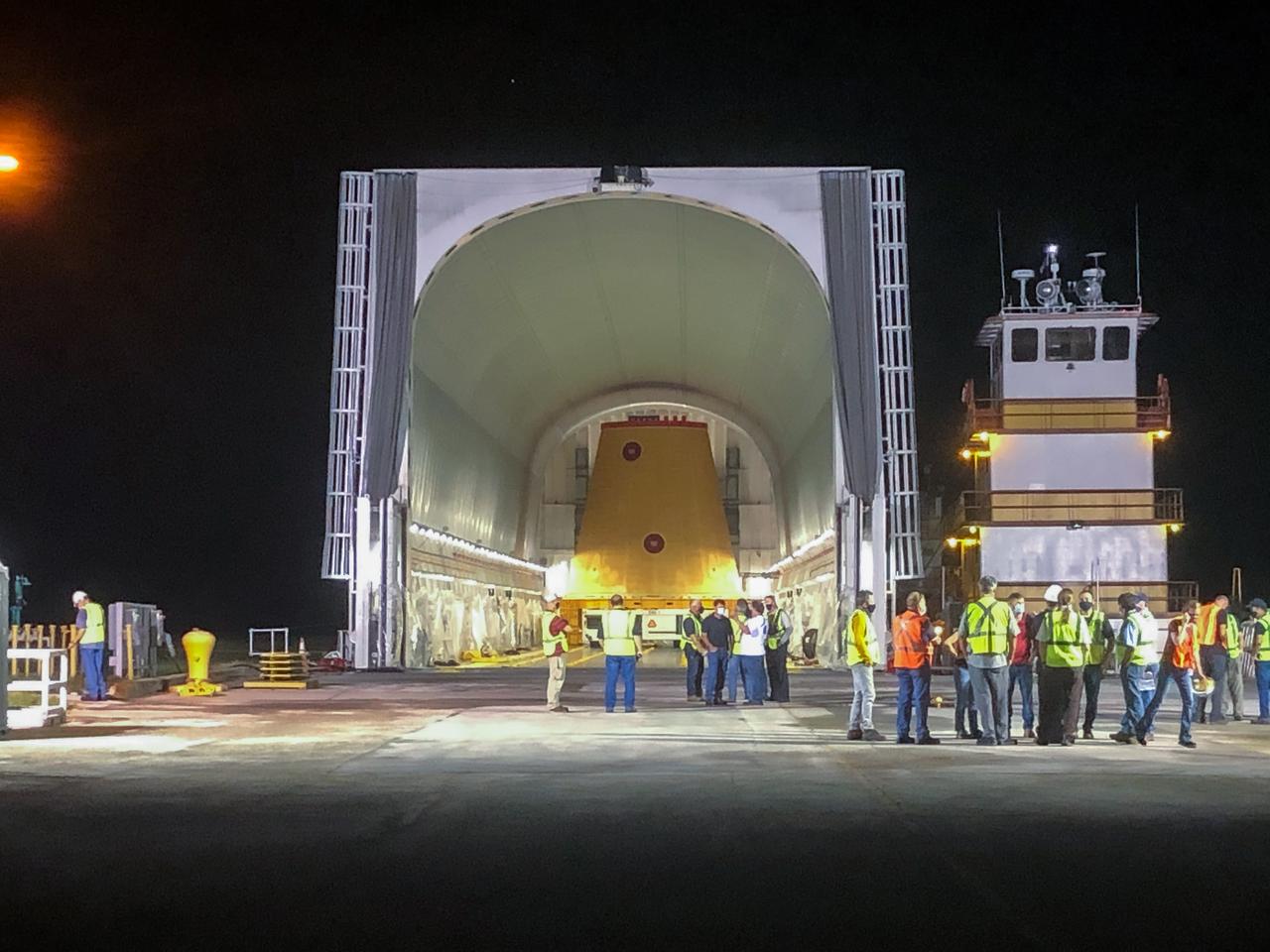

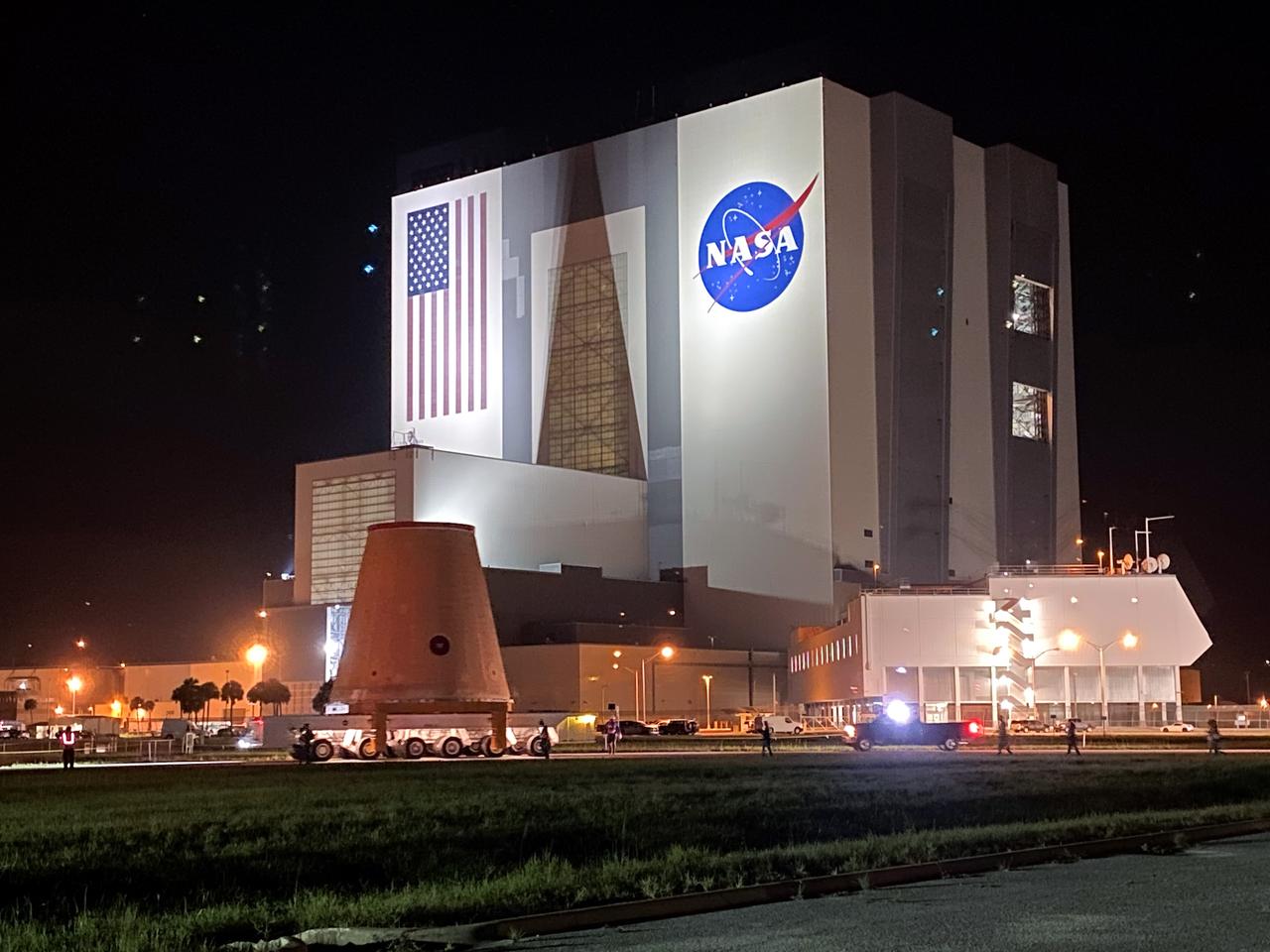
Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems prepare to offload the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and move it to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
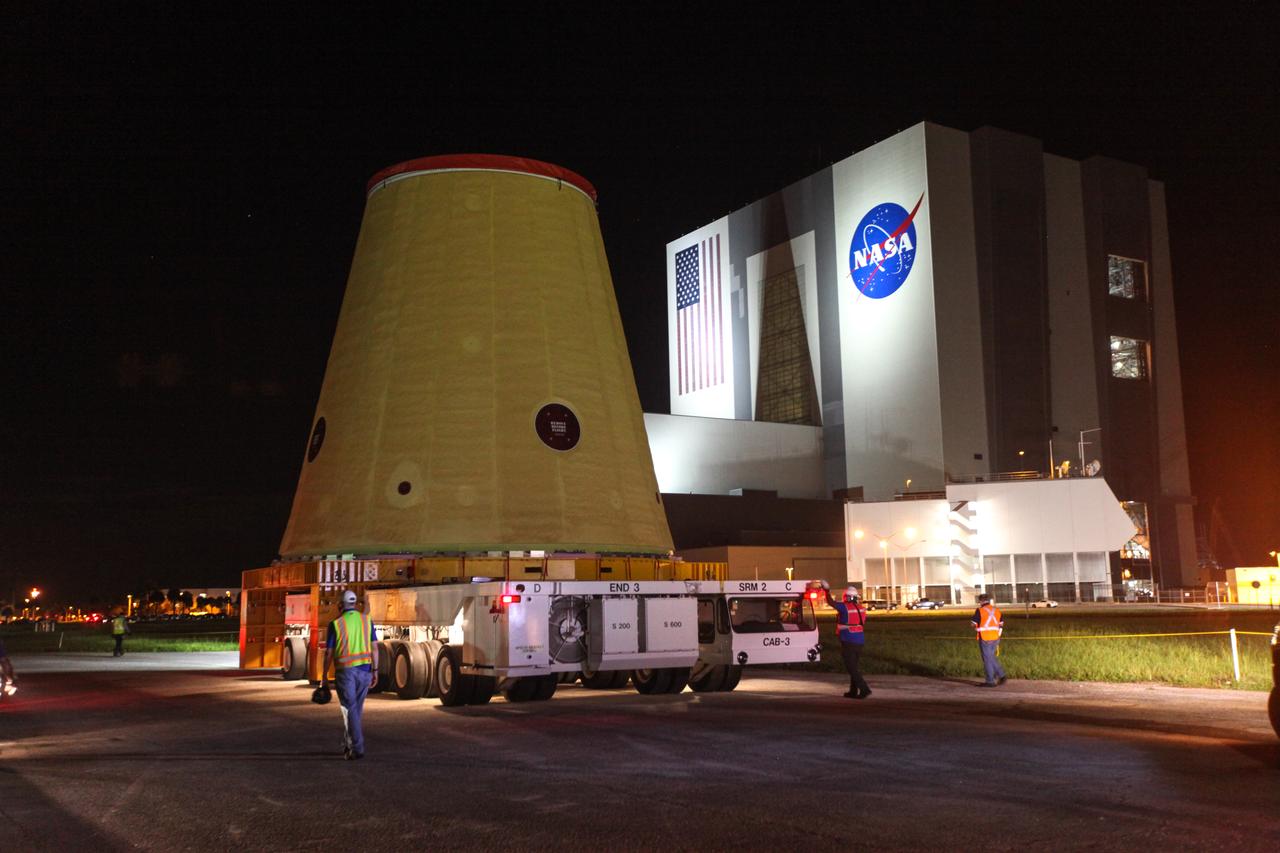

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
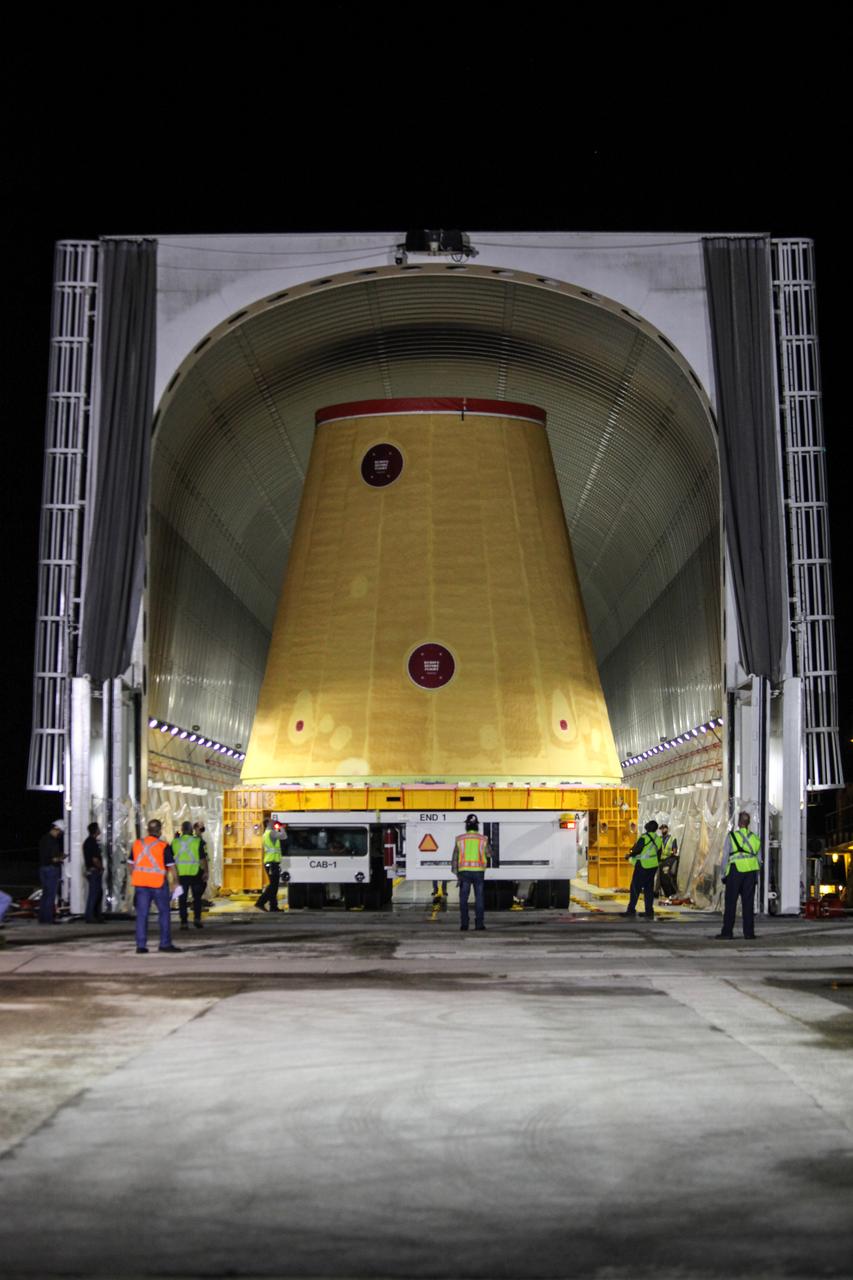

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems prepare to offload the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and move it to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
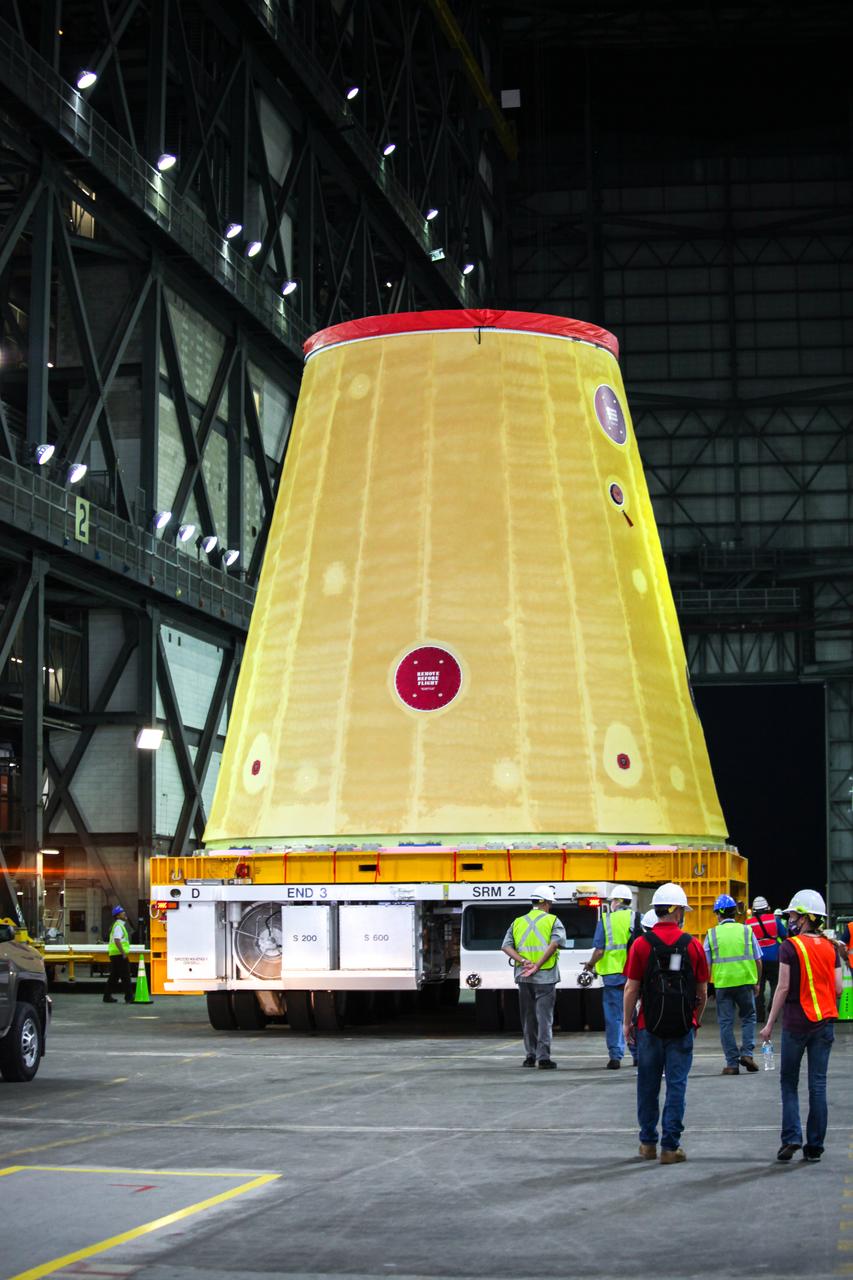

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket into the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
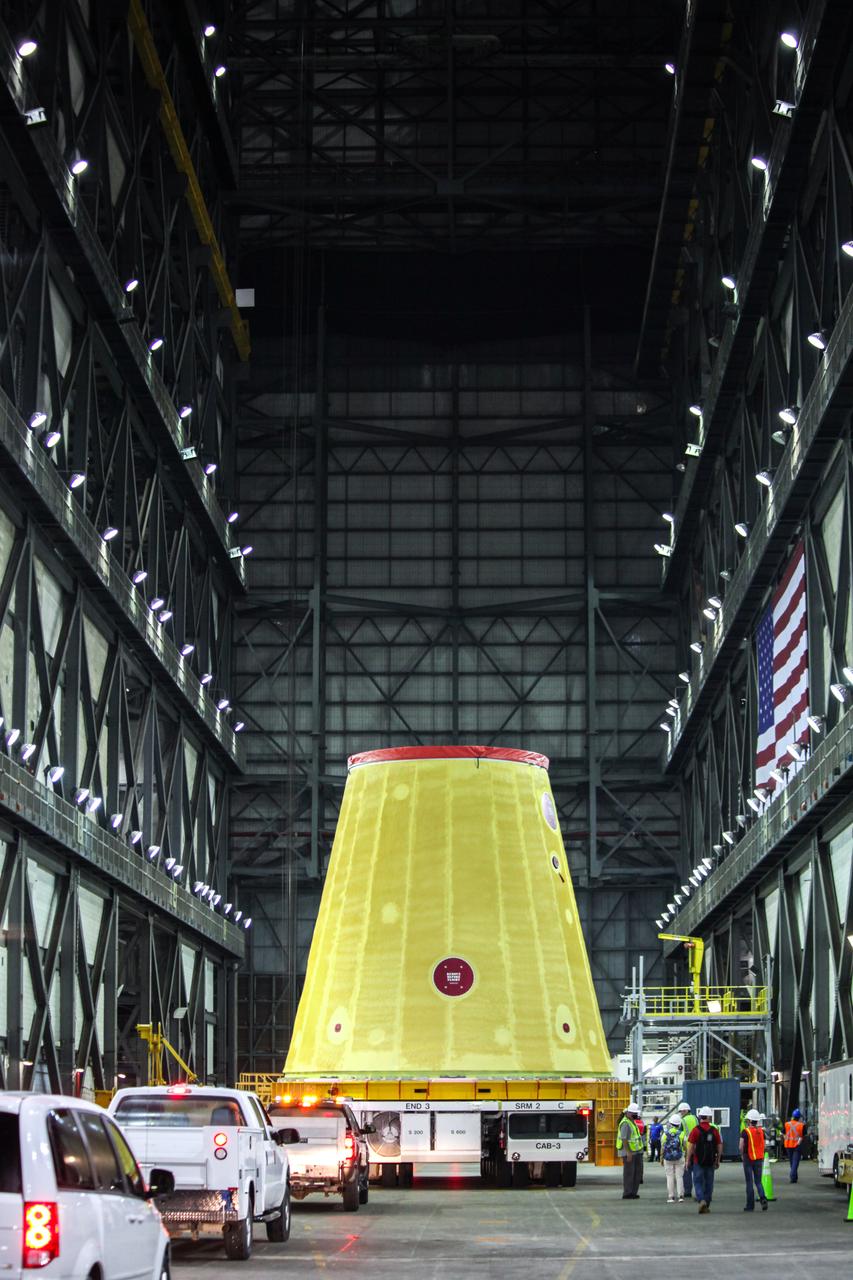

The launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
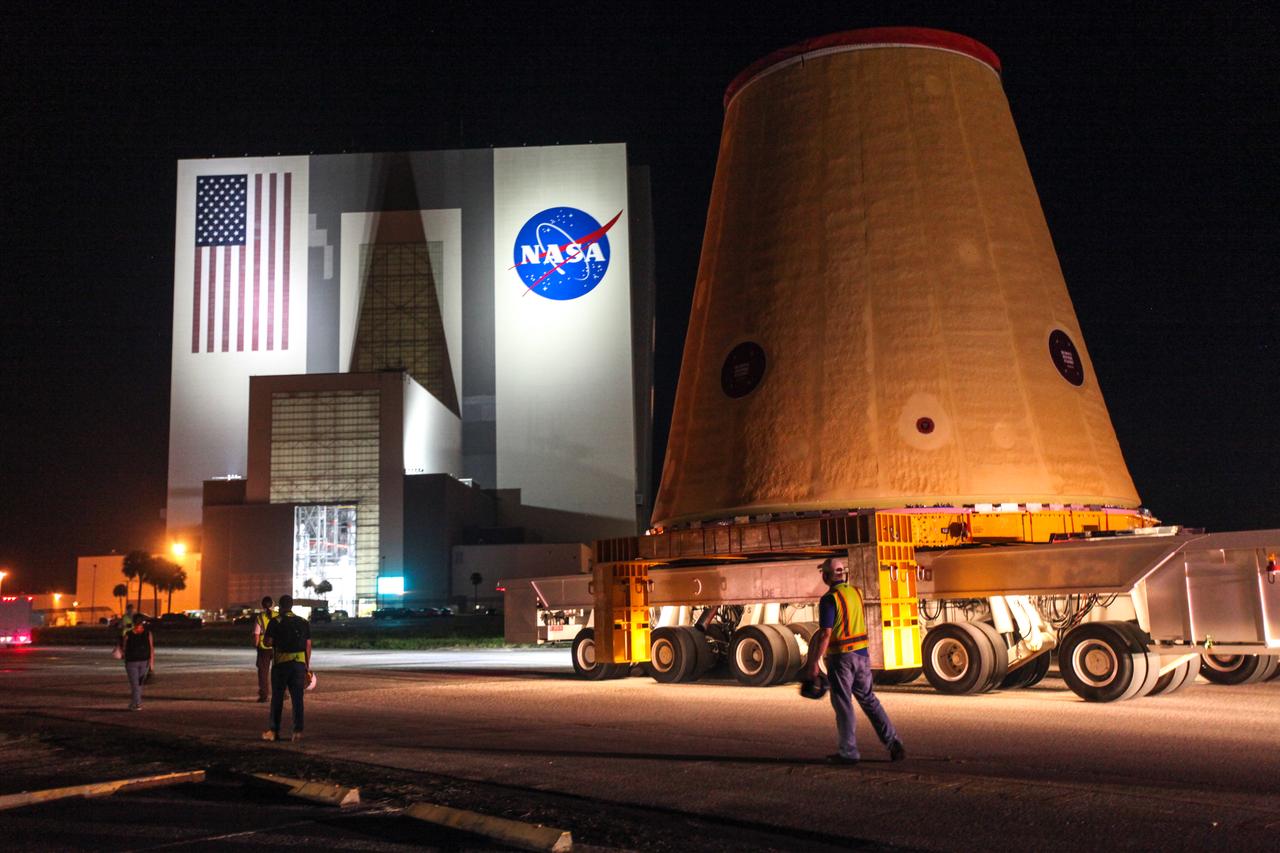

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
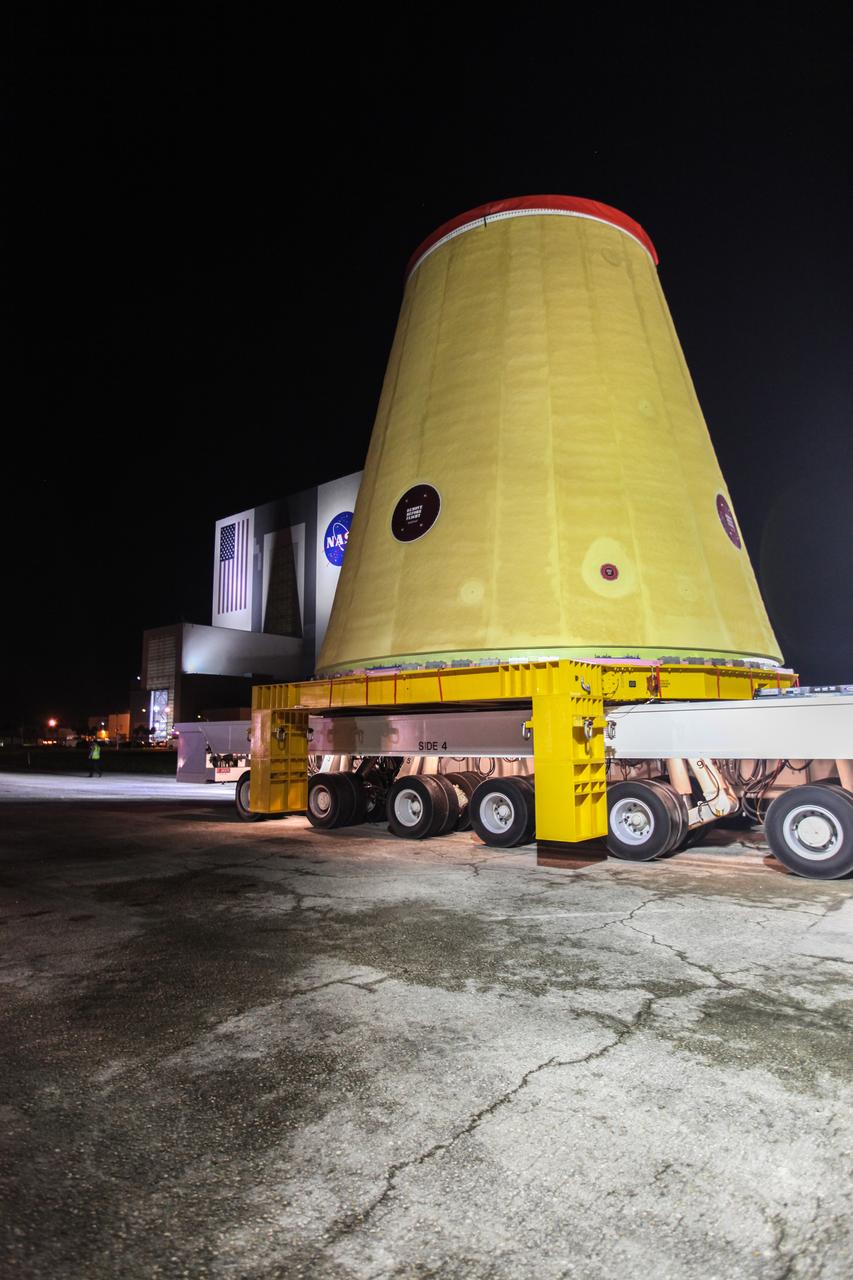

The launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) for processing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
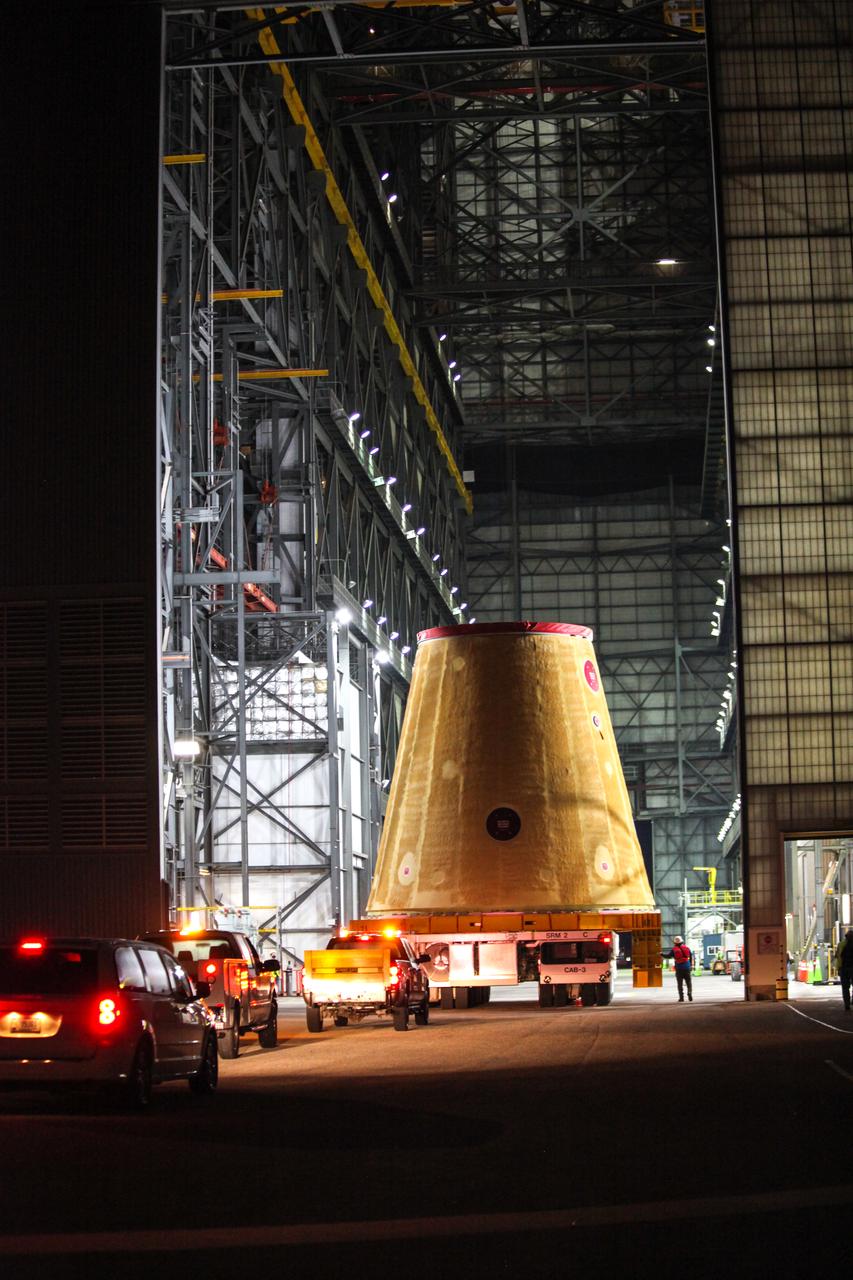

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket into the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
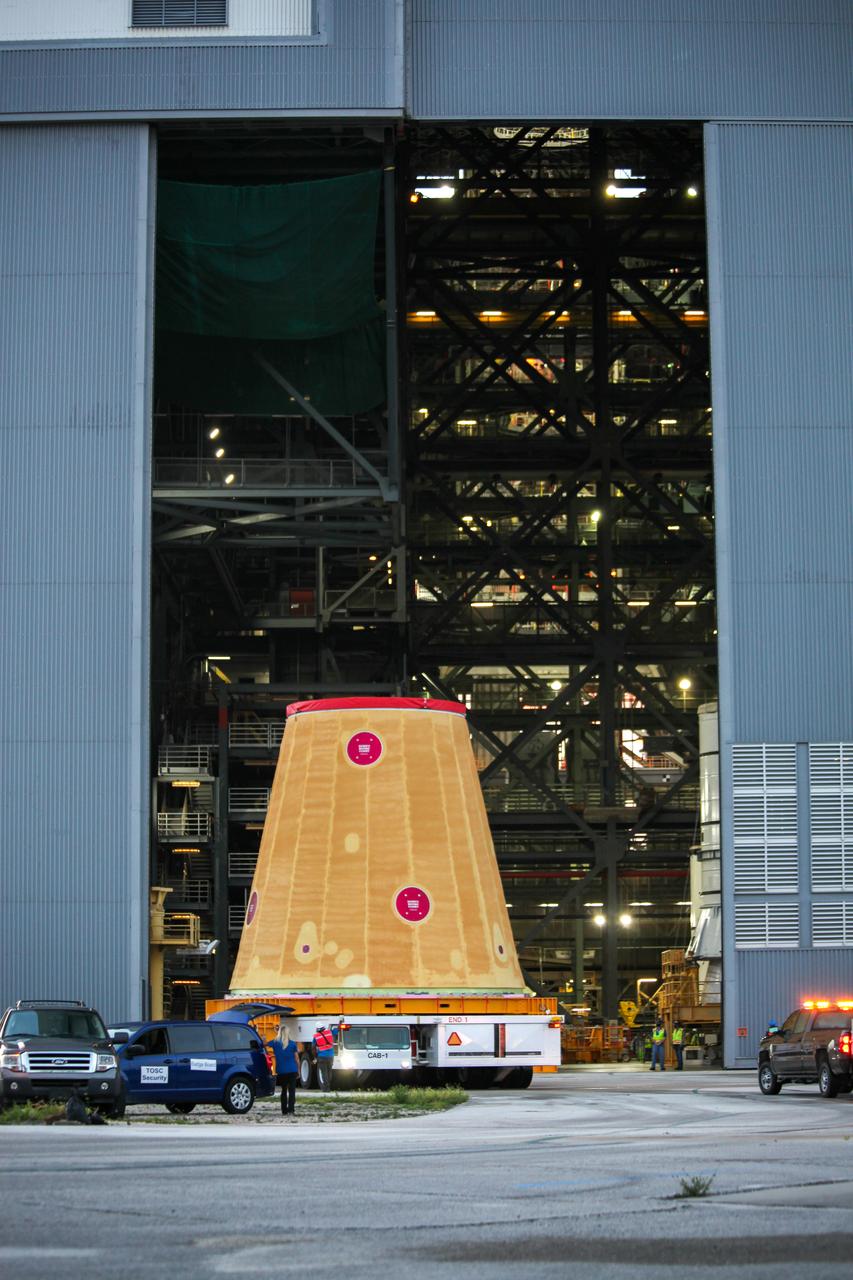

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket into the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
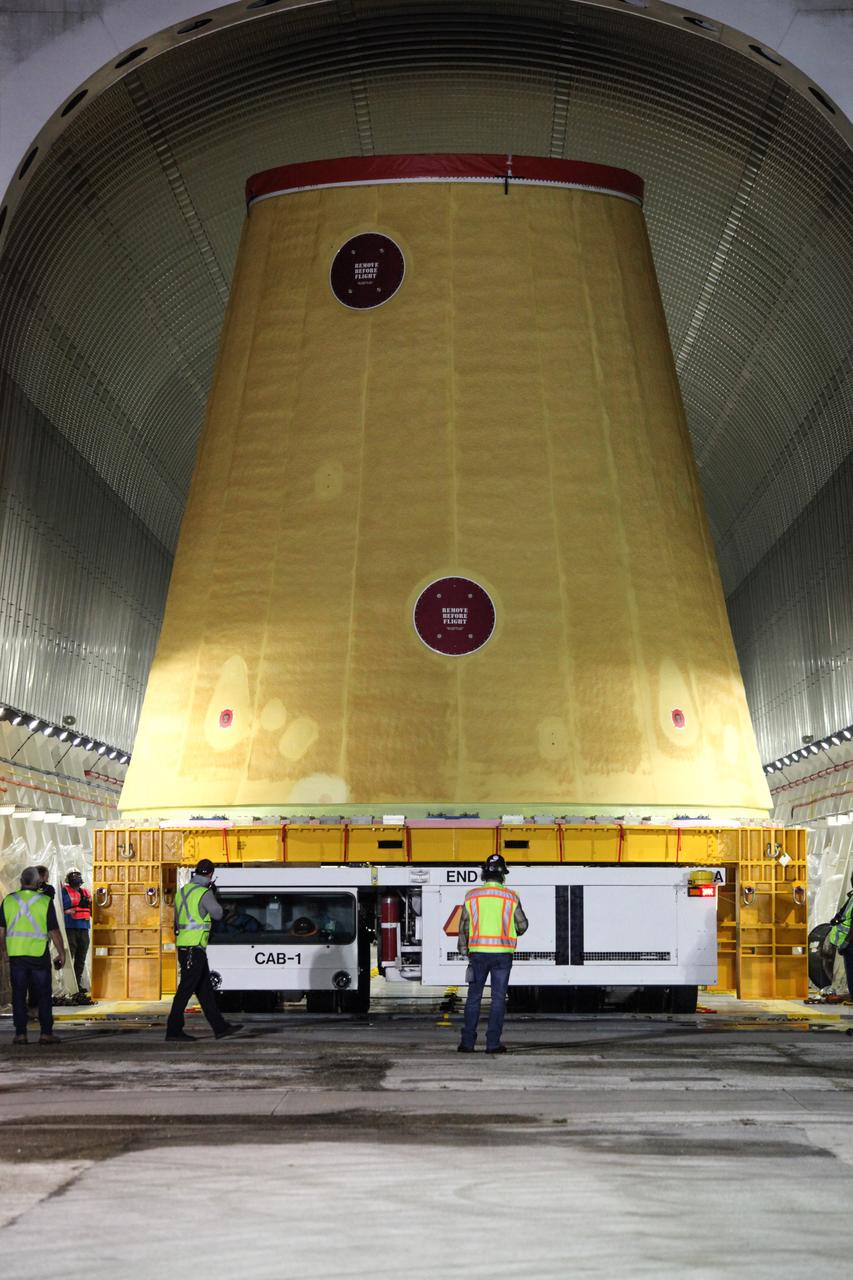

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems begin to offload the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and move it to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
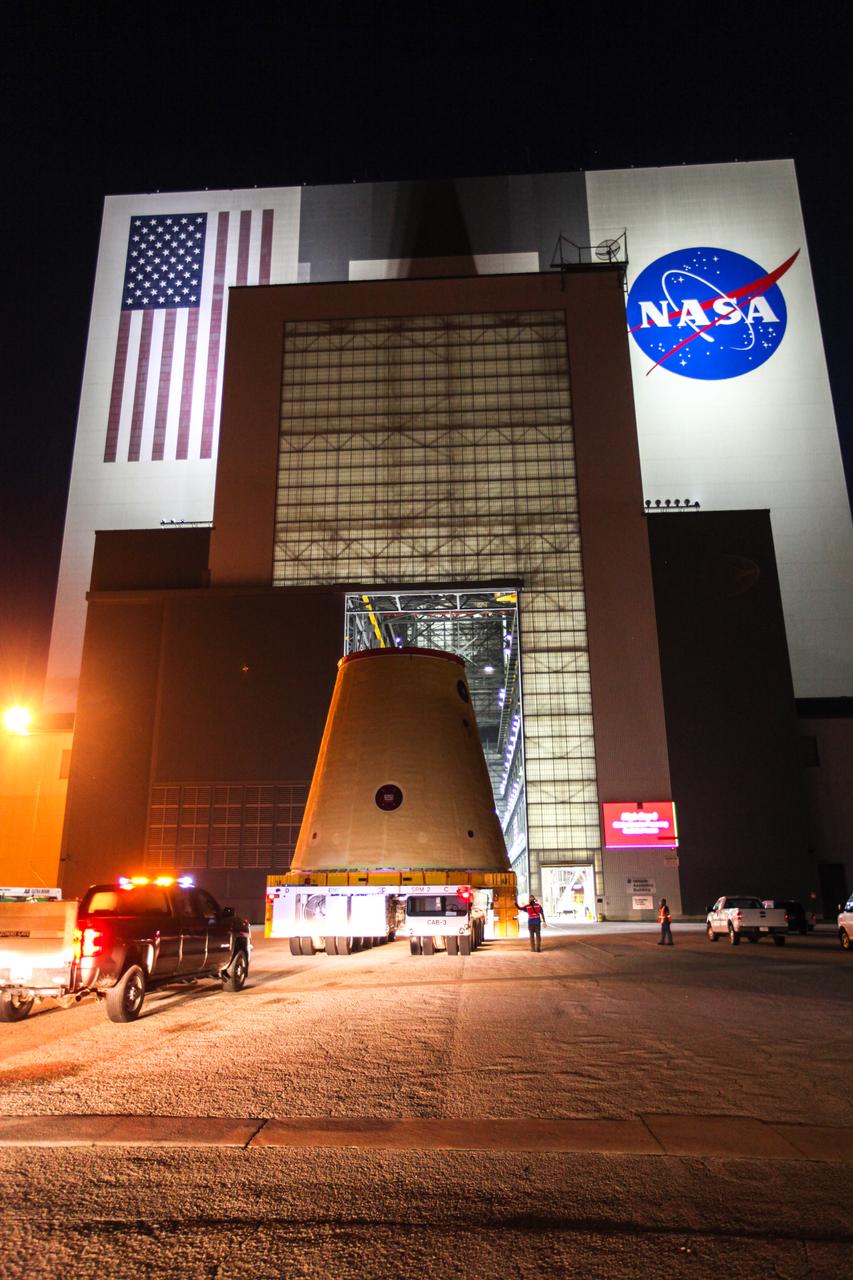

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket into the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
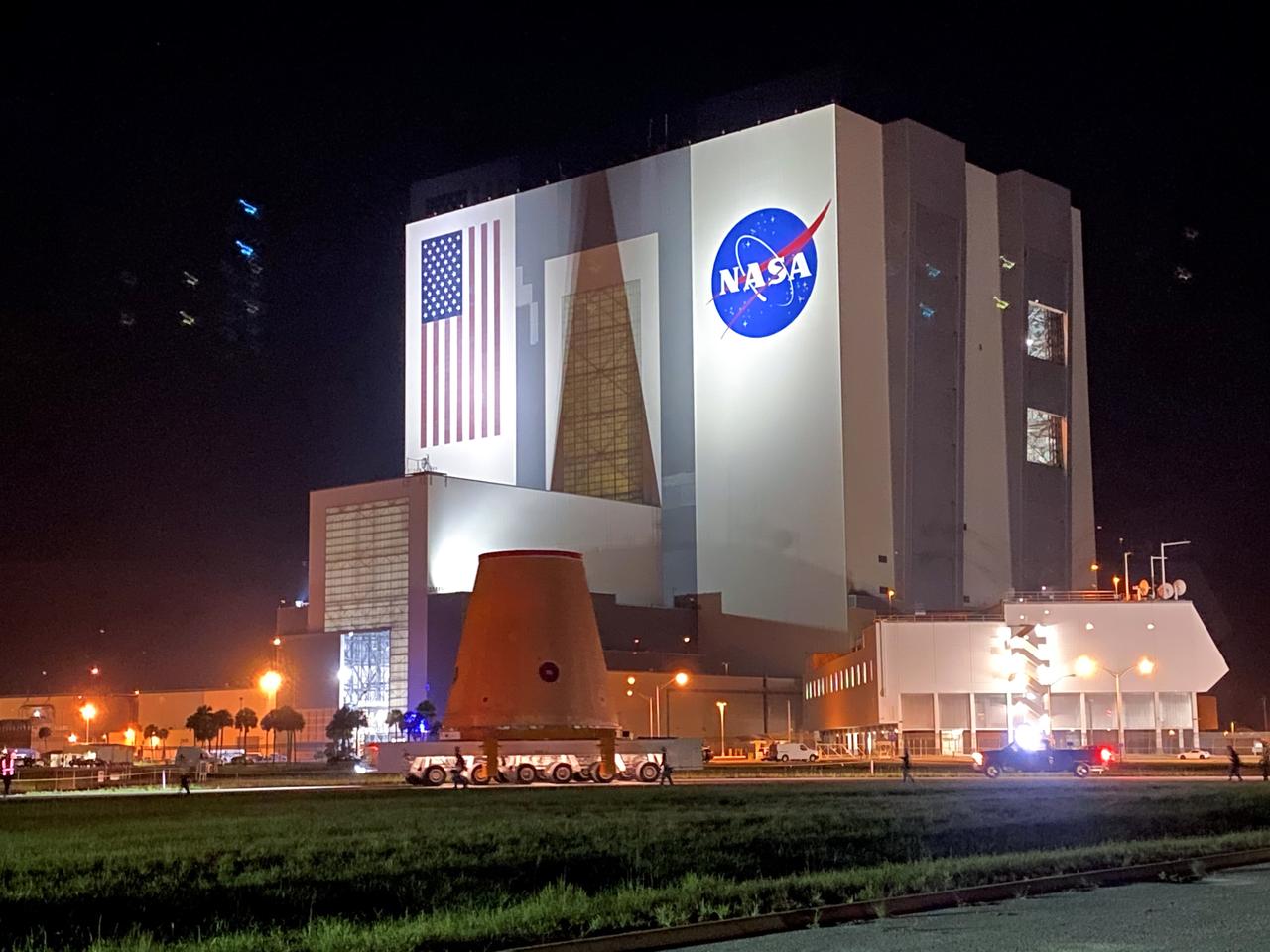

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
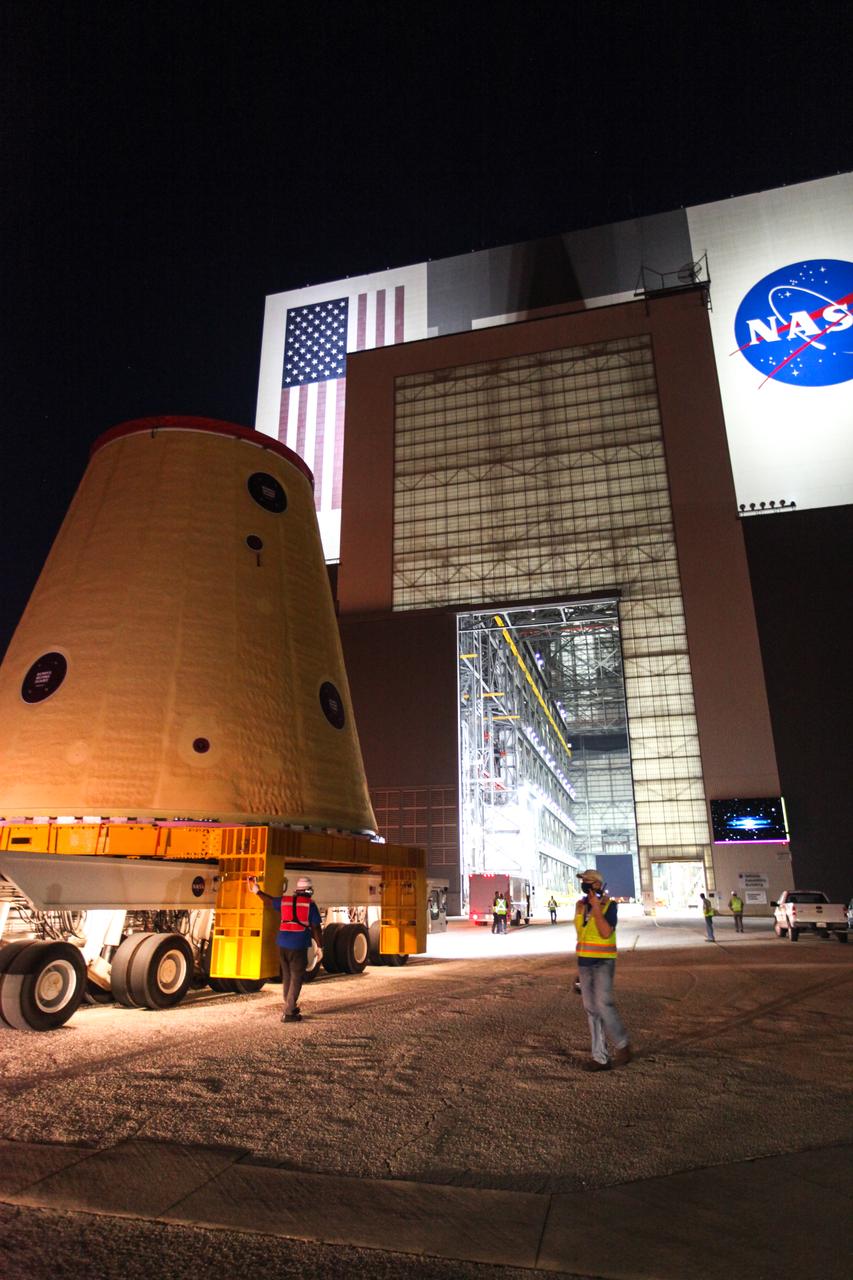

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket into the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
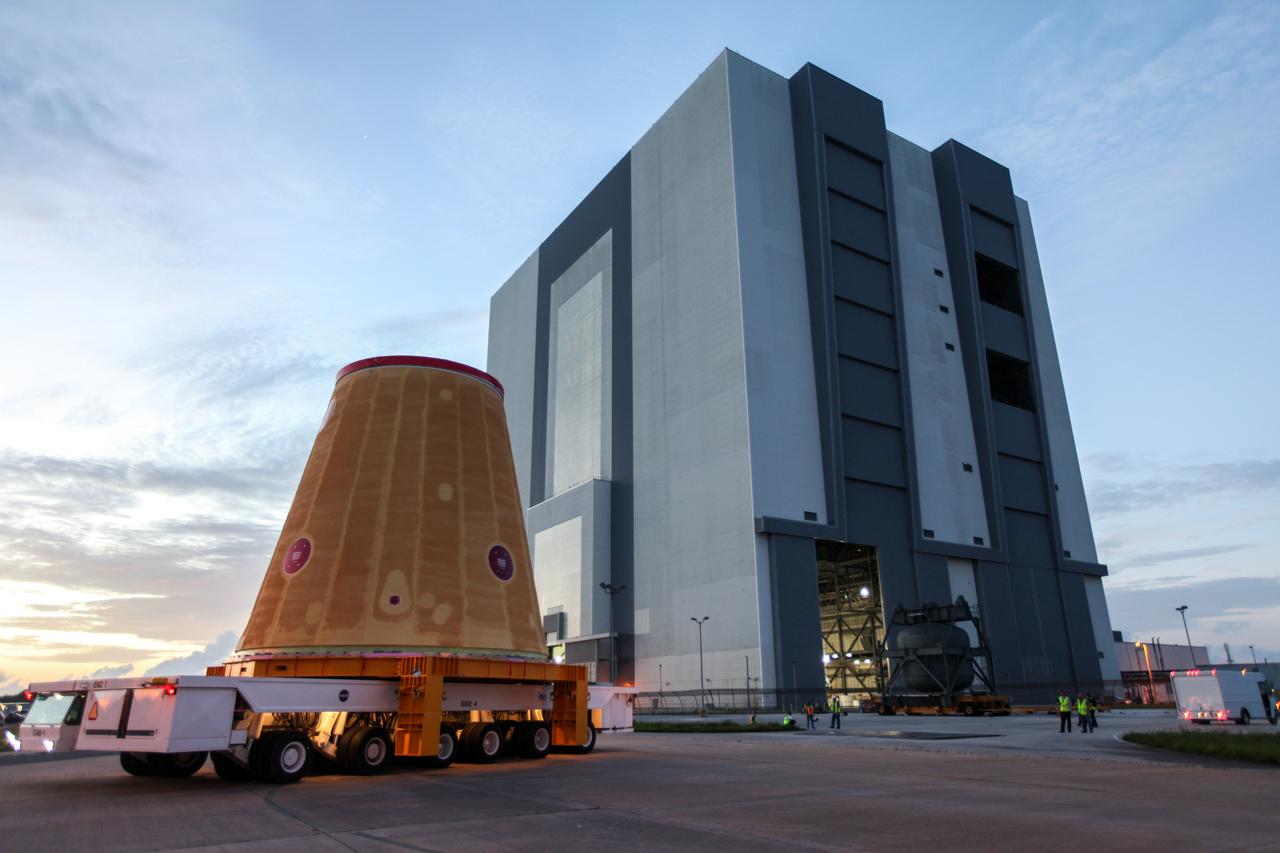

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
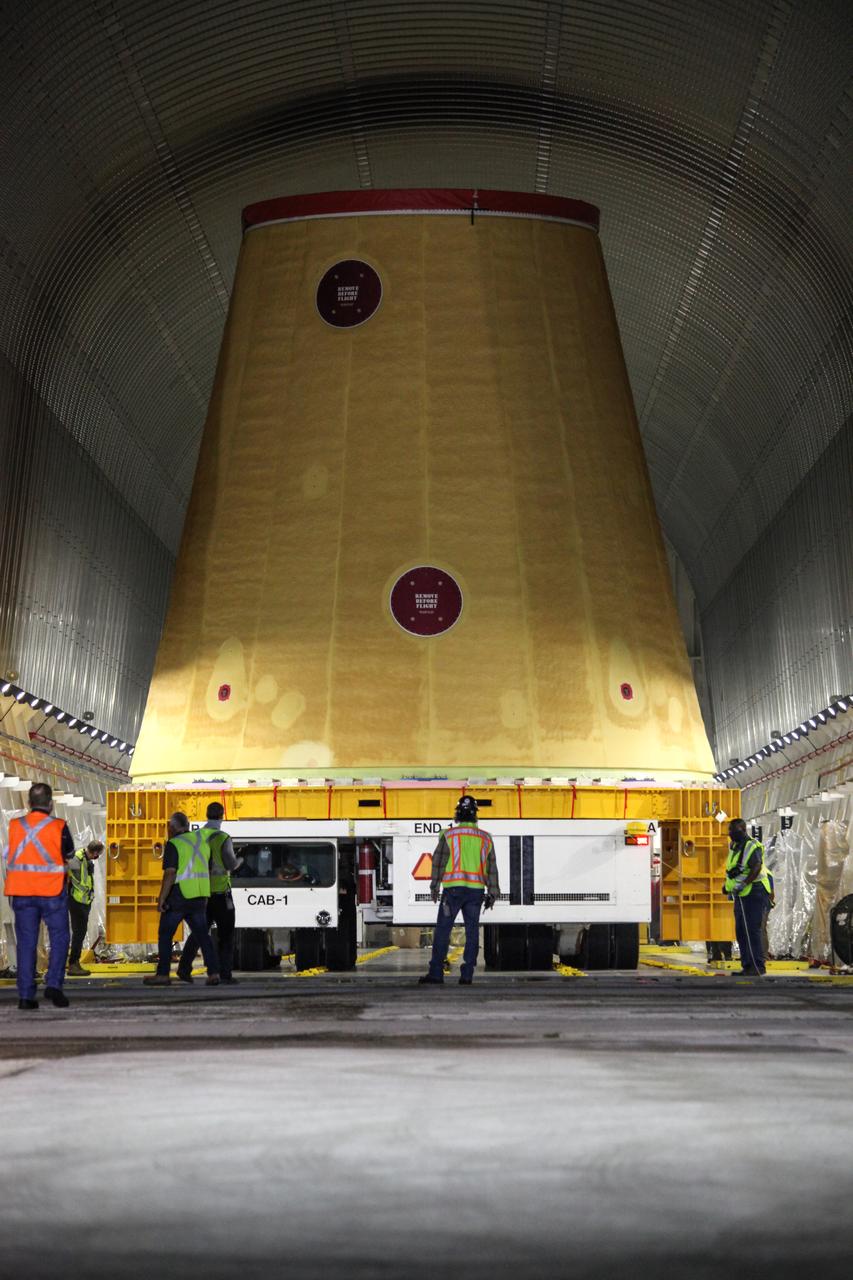

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems prepare to offload the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and move it to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
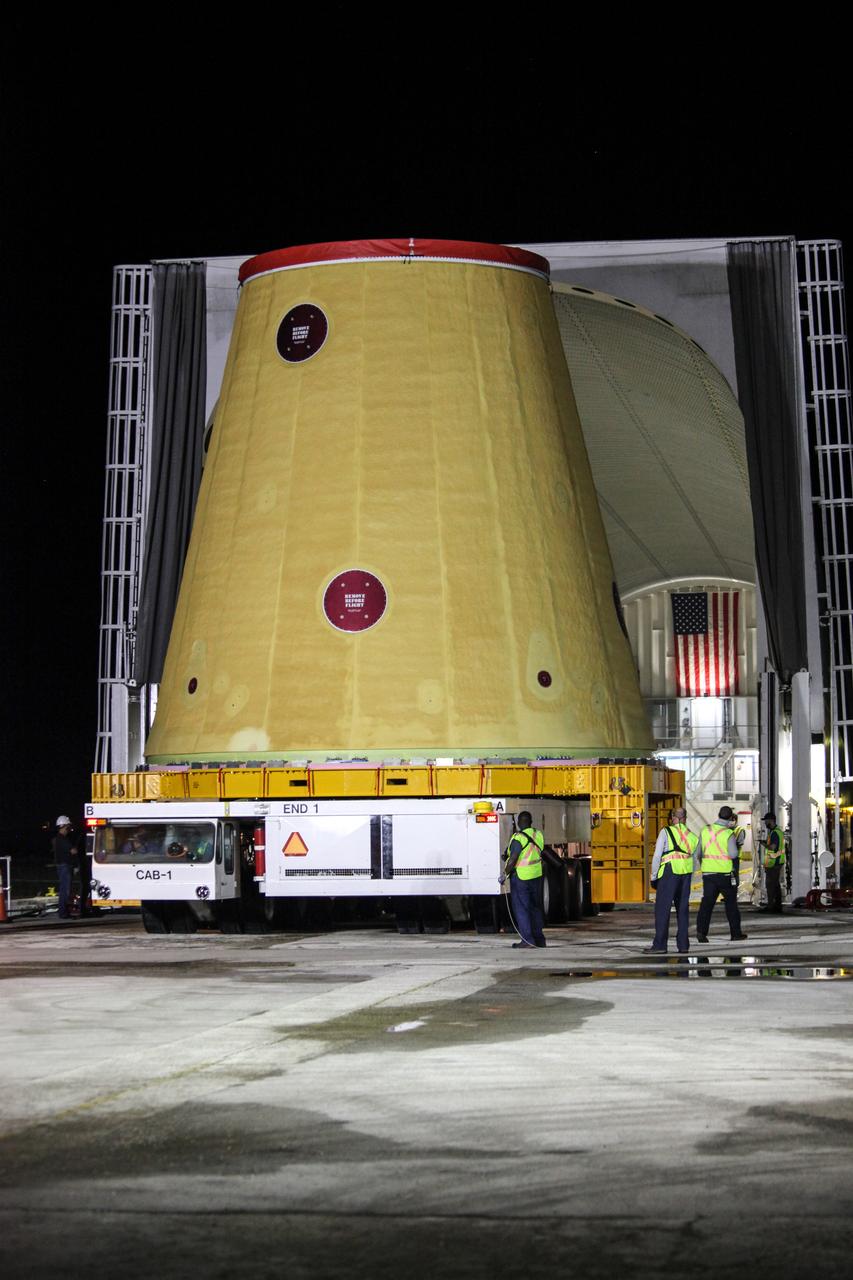

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket off of the Pegasus barge for transportation to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. The LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
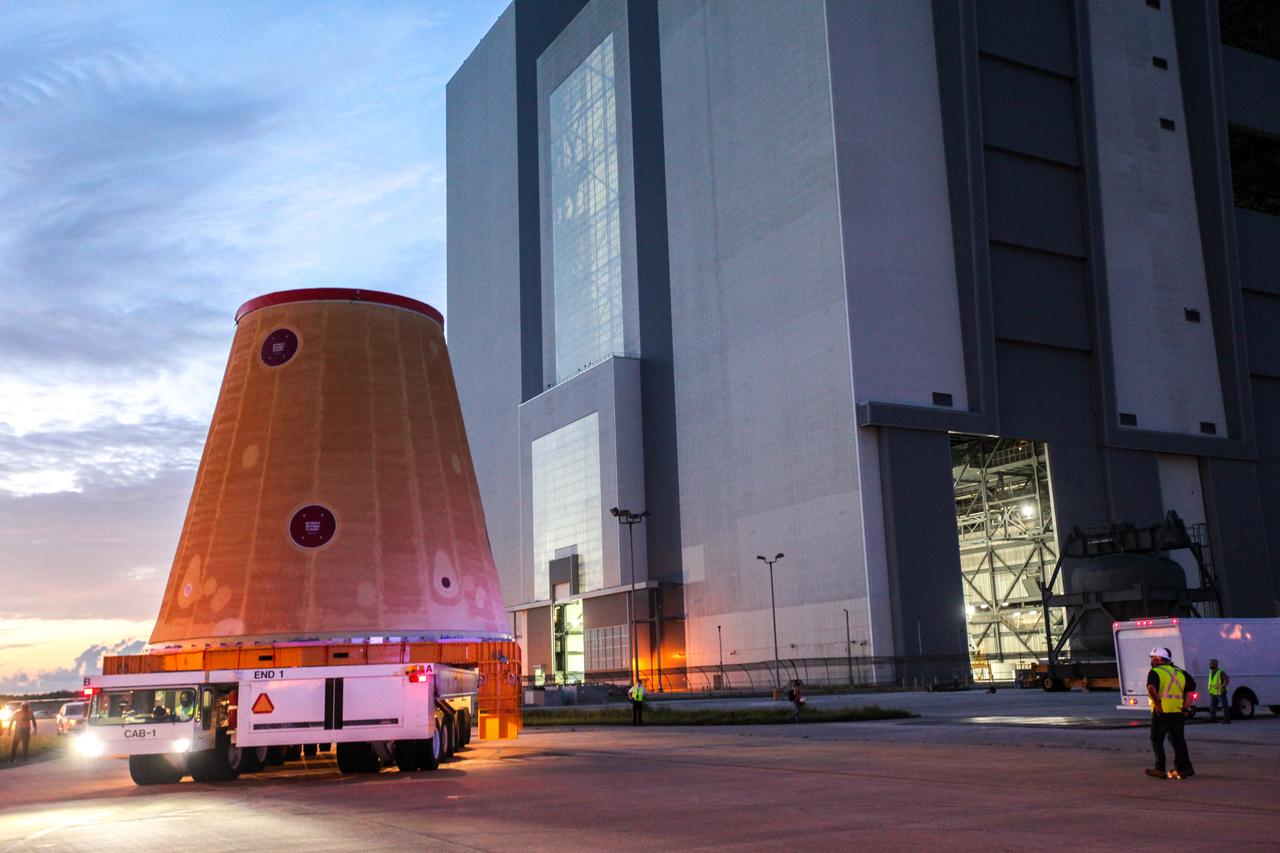

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
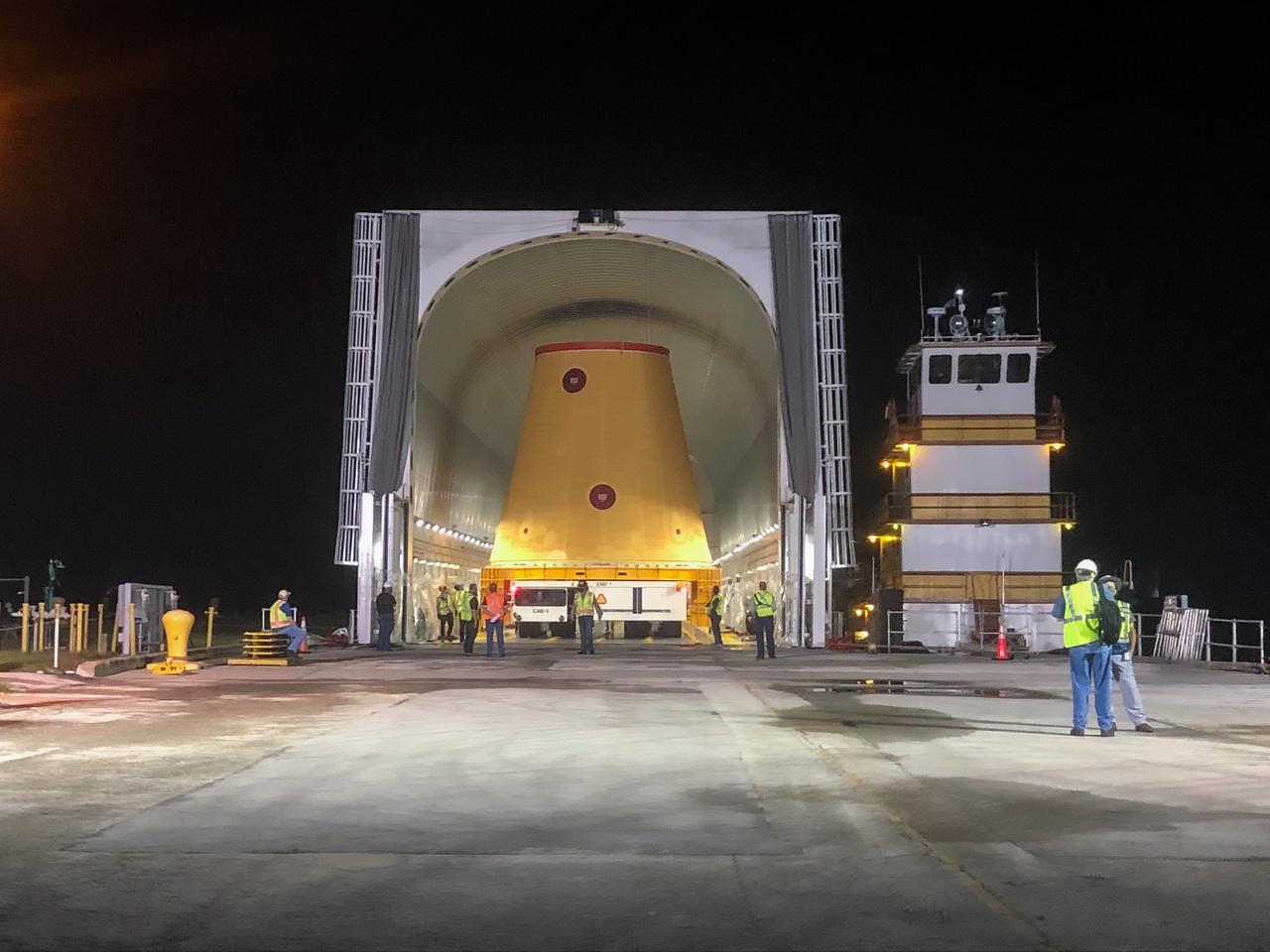

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems prepare to offload the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and move it to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
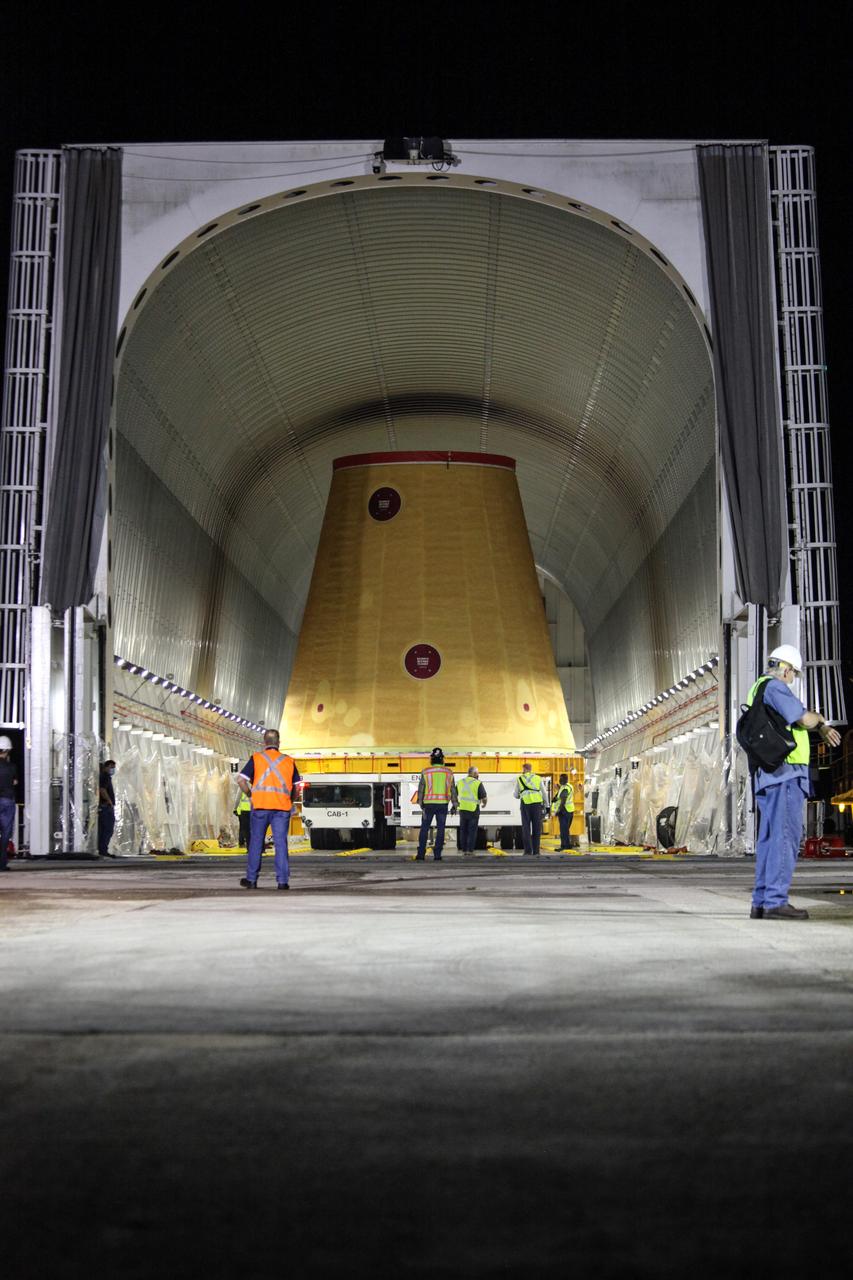

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems prepare to offload the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and move it to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
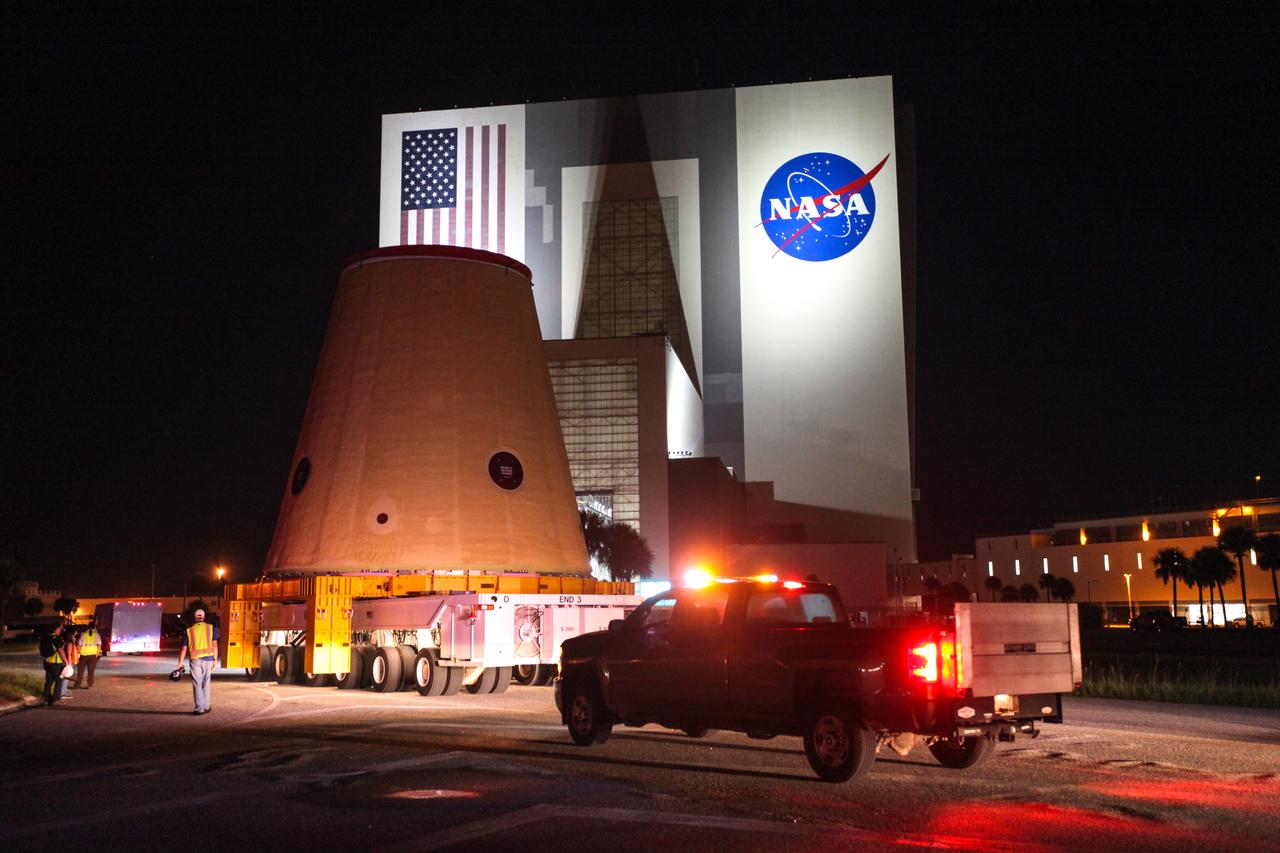

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
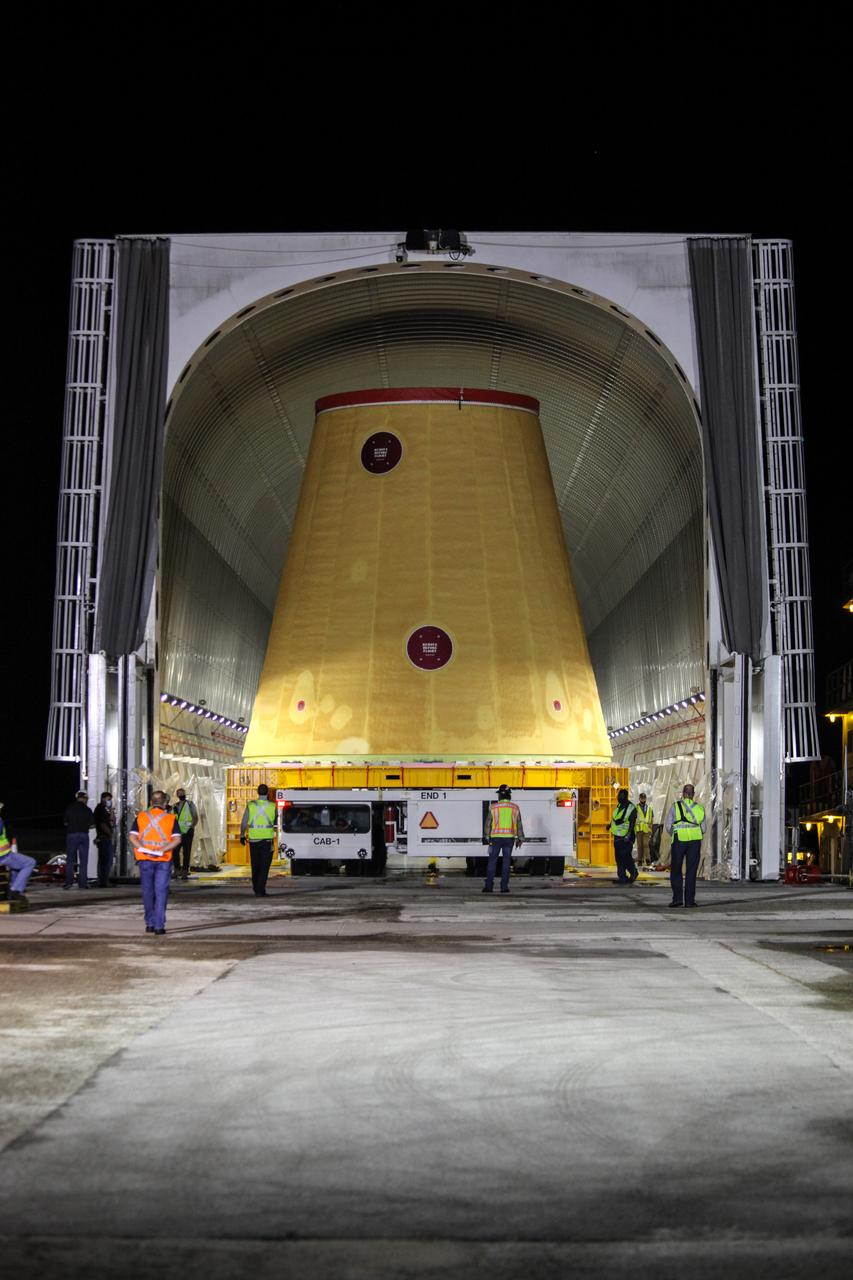

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems begin to offload the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and move it to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
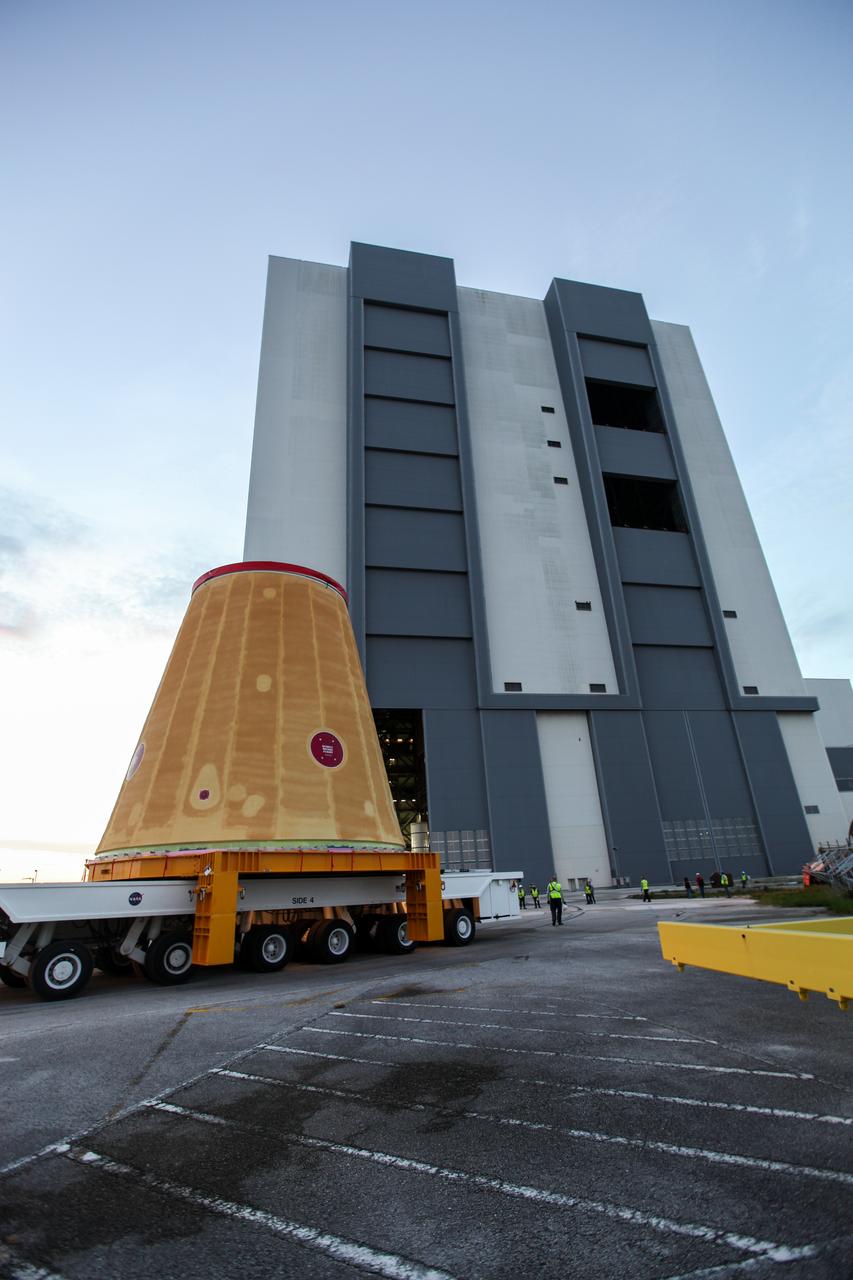

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems move the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on July 30, 2020, for processing. Carried by NASA’s Pegasus barge, the LVSA arrived at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf after departing from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The LVSA will connect the SLS core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will remain in the VAB until it’s time for stacking on the mobile launcher ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
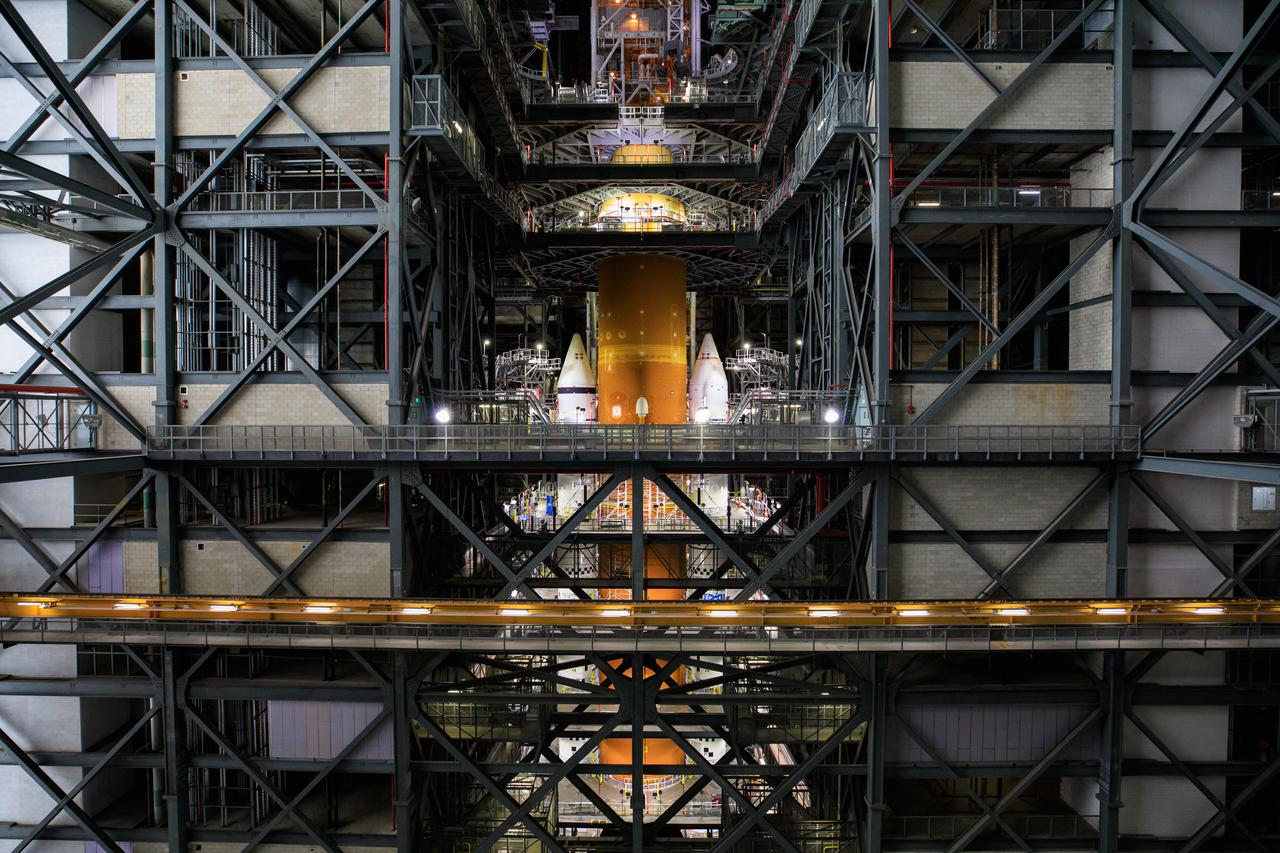

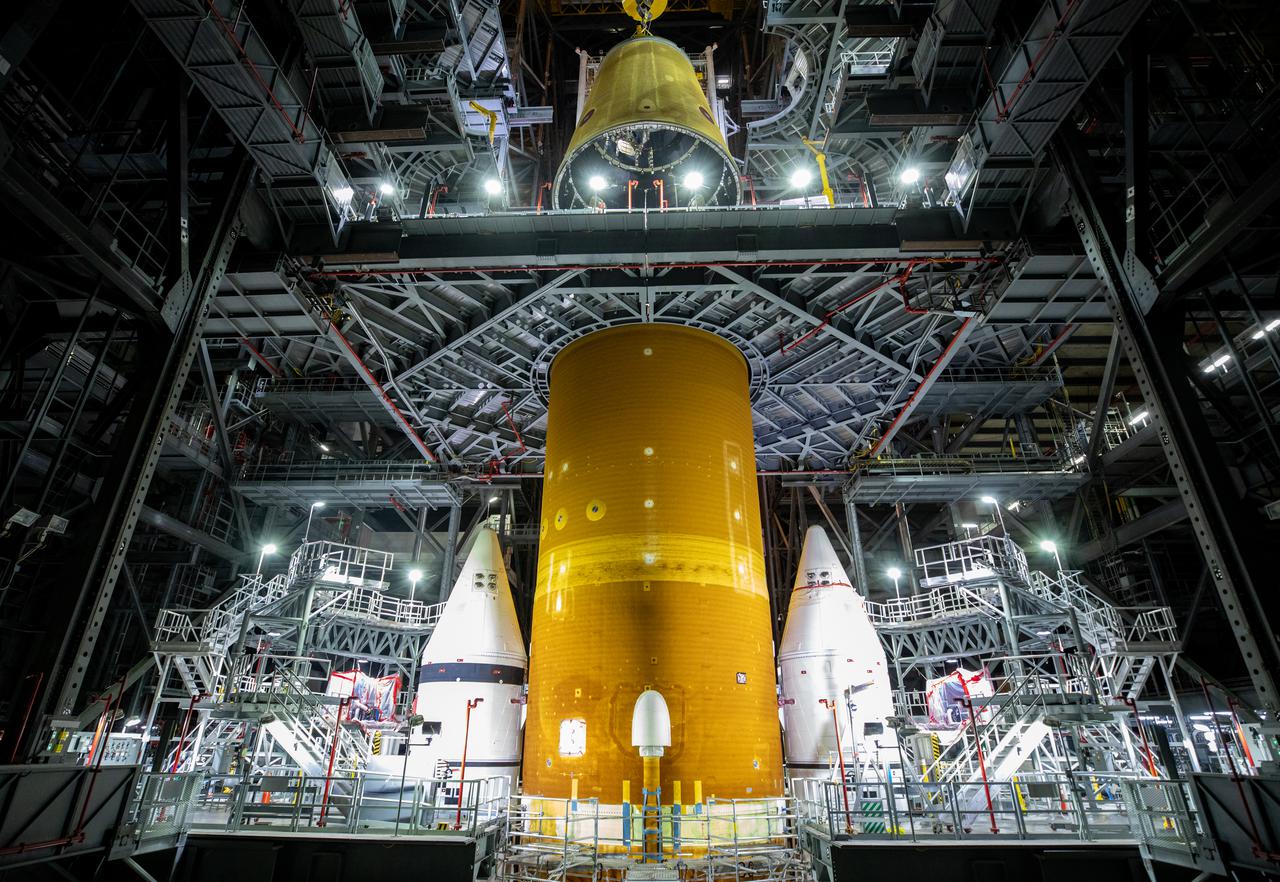
Seen here is the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket atop the massive SLS core stage on the mobile launcher in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 24, 2021. Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs used one of five VAB cranes to lift the adapter almost 250-feet in the air and then slowly lower it on to the core stage earlier this week. The LVSA arrived at Kennedy from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, in July 2020 and has remained in the VAB for processing. During integration, known as “stacking,” the LVSA is bolted to the forward skirt of the core stage, connecting the core stage and the interim cryogenic propulsion stage in preparation for the first flight of the rocket and the Orion spacecraft during Artemis I. The ICPS’s RL10 engine will fit down inside the LVSA, which protects the engine during launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights in which NASA will land the first woman and person of color on the Moon.
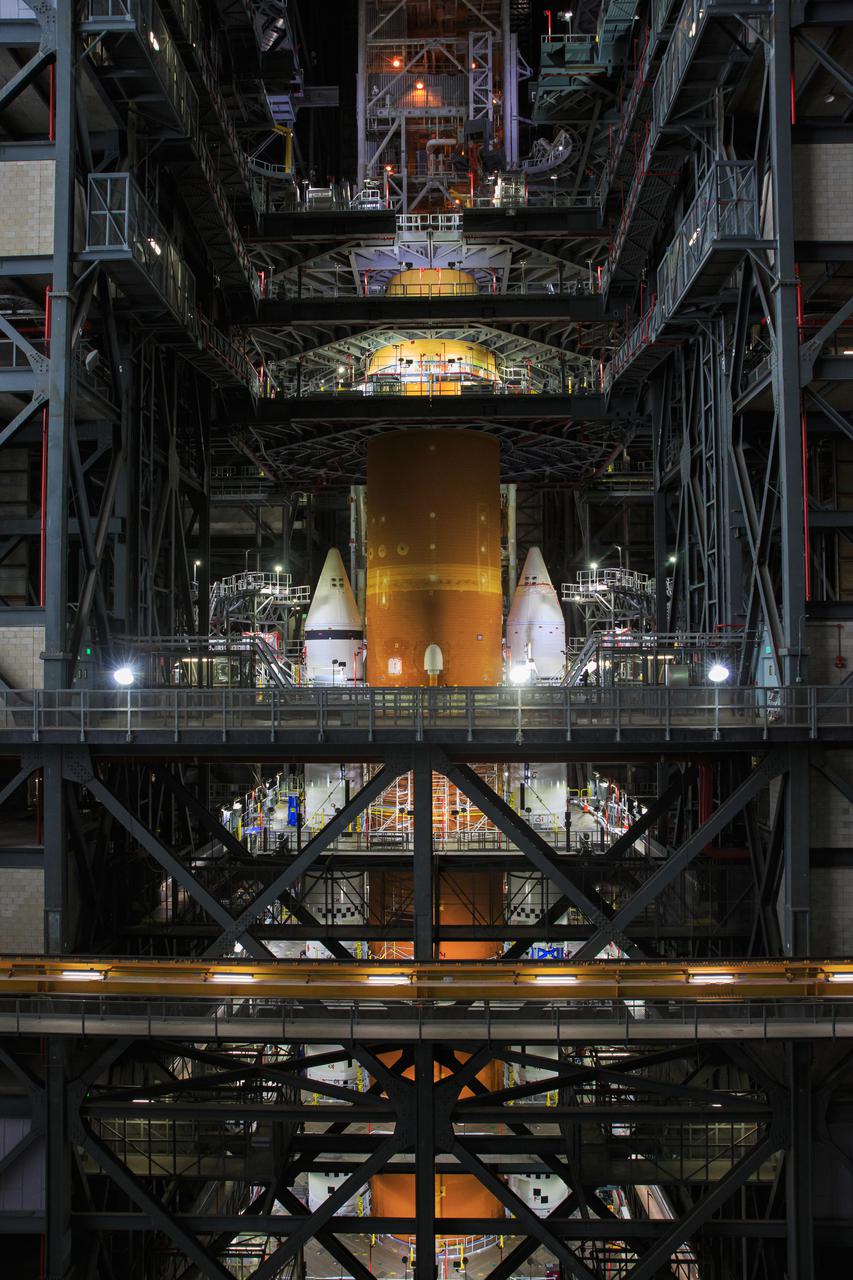

Seen here is the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket atop the massive SLS core stage on the mobile launcher in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 24, 2021. Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs used one of five VAB cranes to lift the adapter almost 250-feet in the air and then slowly lower it on to the core stage earlier this week. The LVSA arrived at Kennedy from the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, in July 2020 and has remained in the VAB for processing. During integration, known as “stacking,” the LVSA is bolted to the forward skirt of the core stage, connecting the core stage and the interim cryogenic propulsion stage in preparation for the first flight of the rocket and the Orion spacecraft during Artemis I. The ICPS’s RL10 engine will fit down inside the LVSA, which protects the engine during launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights in which NASA will land the first woman and person of color on the Moon.
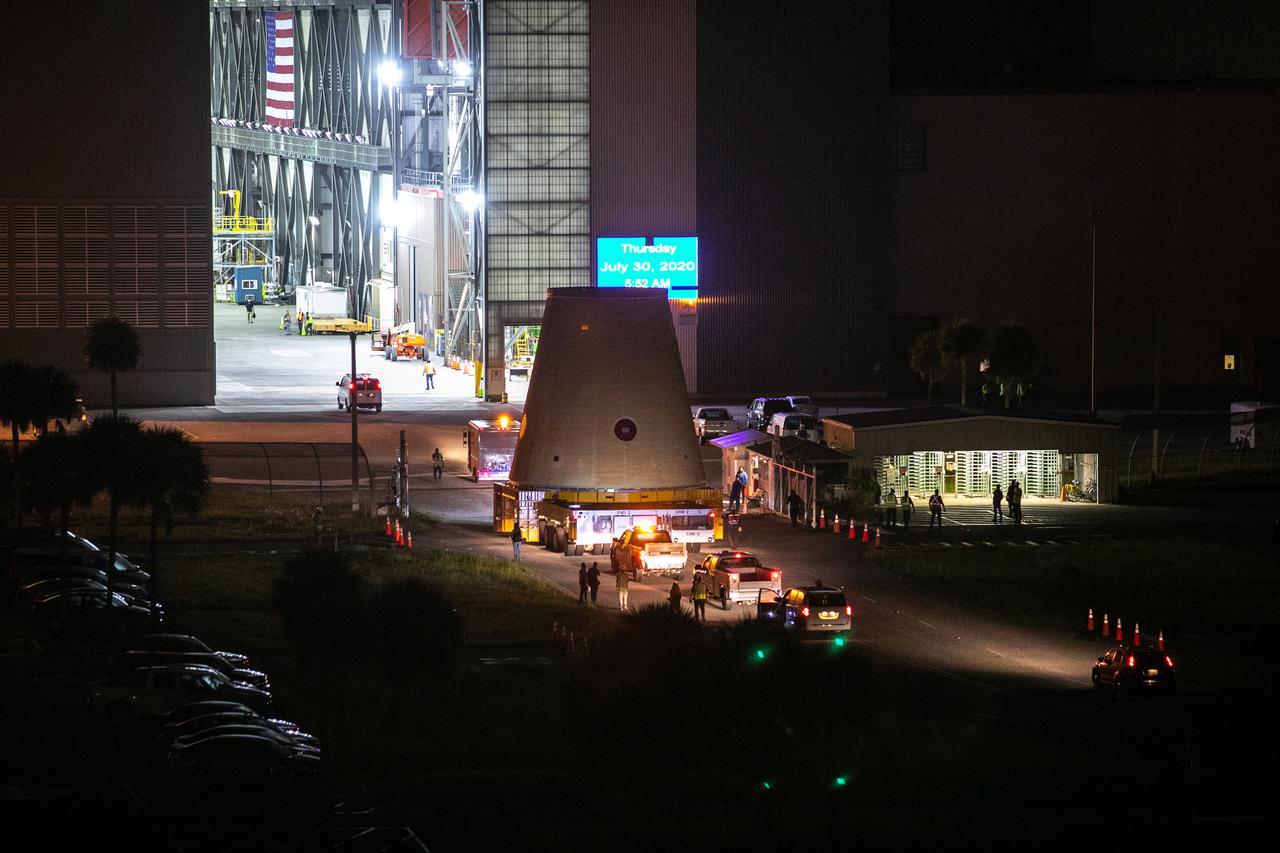

The Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter for the Space Launch System rocket arrived at the barge at Kennedy Space Center for ground processing and integration for the launch of Artemis I.
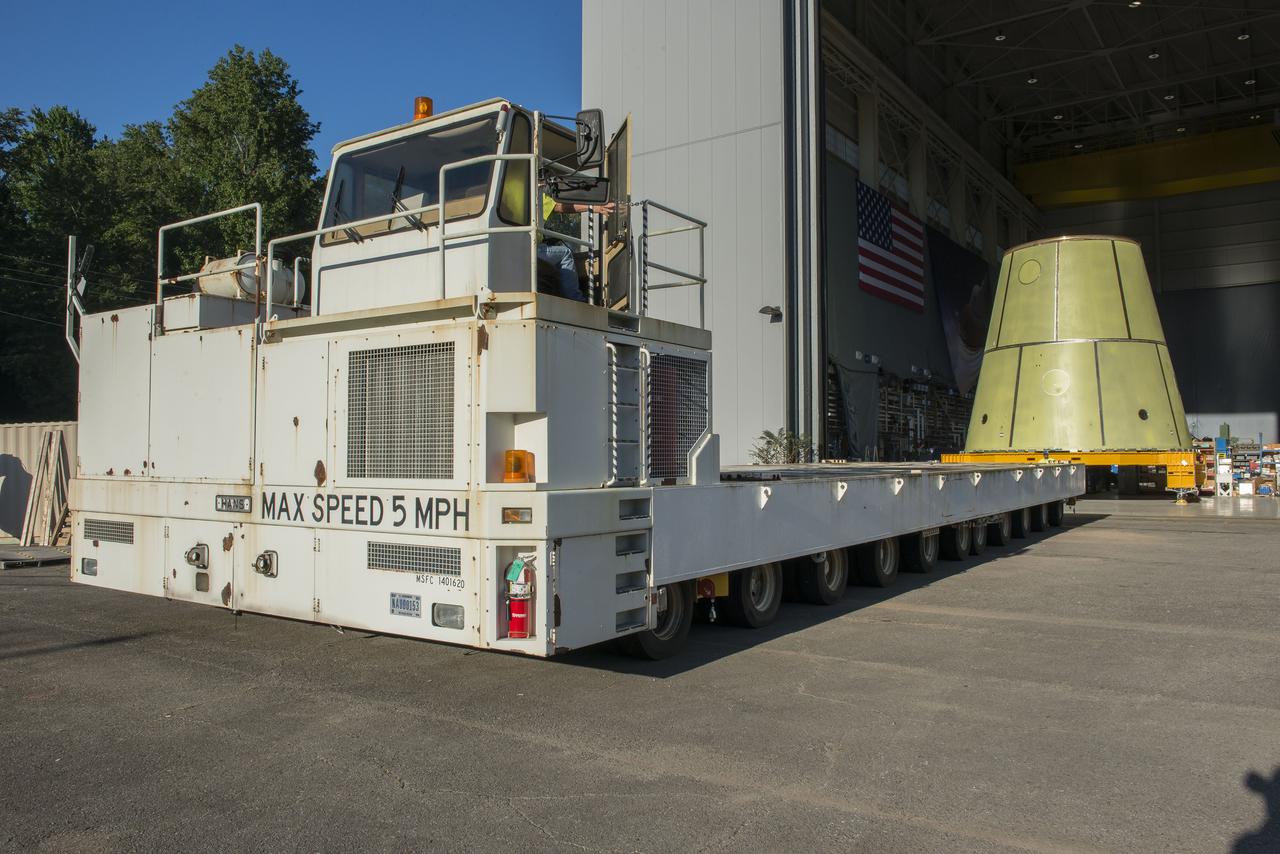

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter being loaded on the KMag for transportation to building 4707 for further testing.
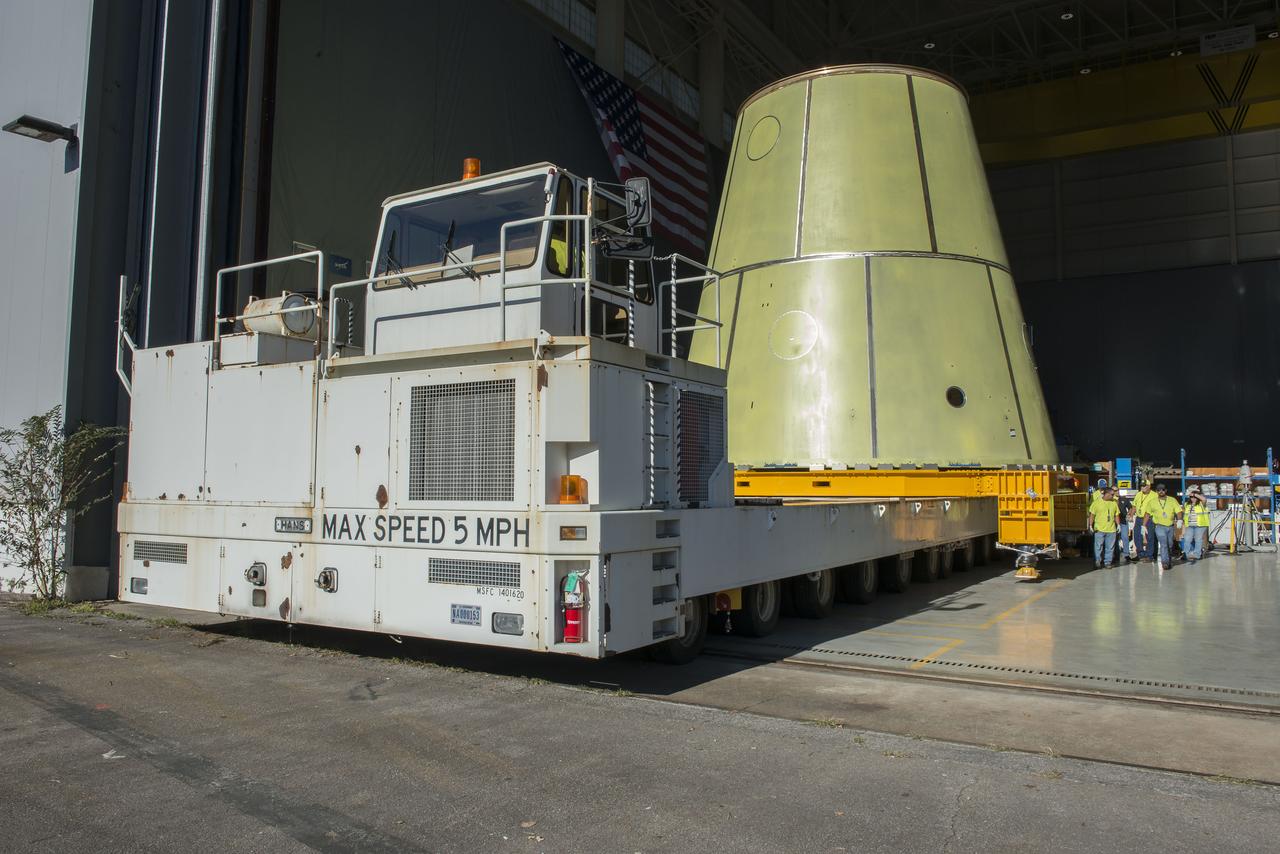

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter being loaded on the KMag for transportation to building 4707 for further testing.
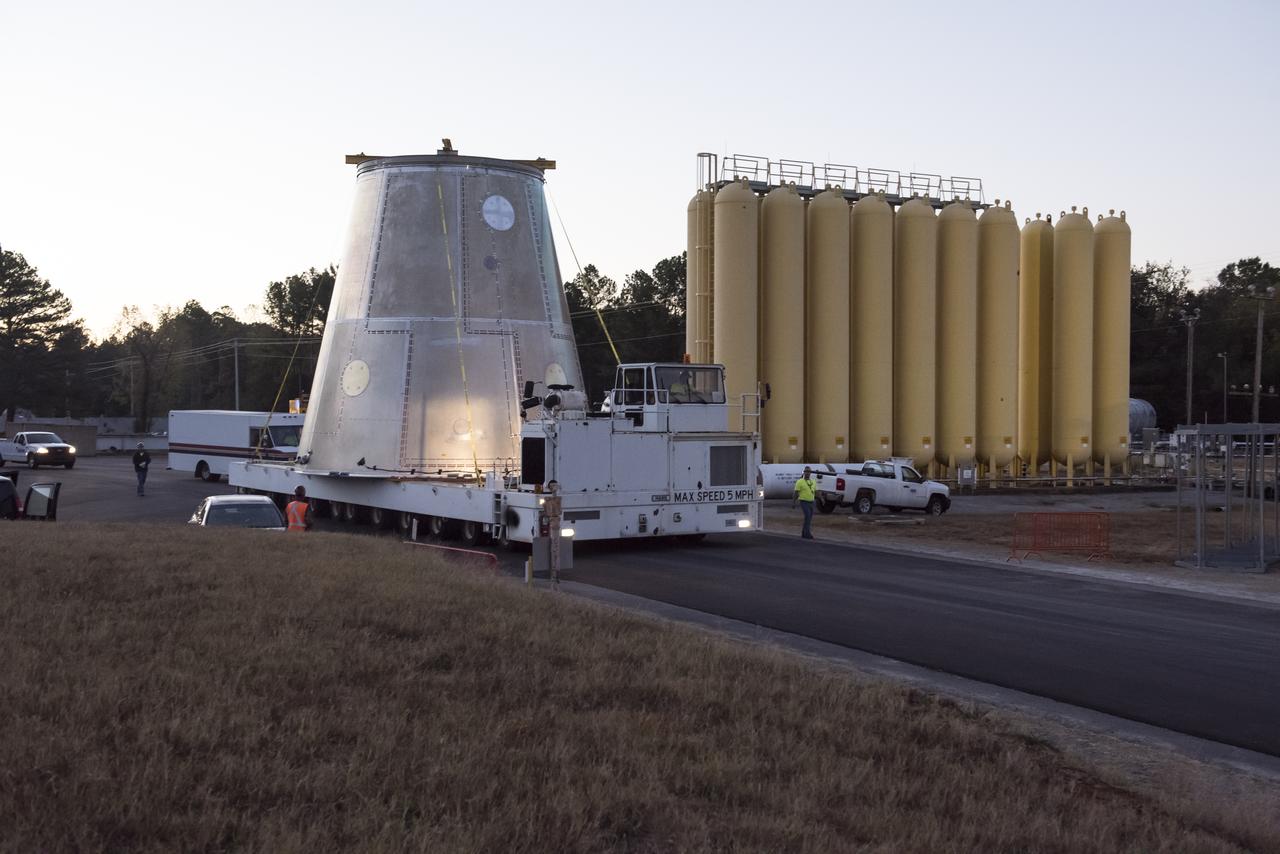

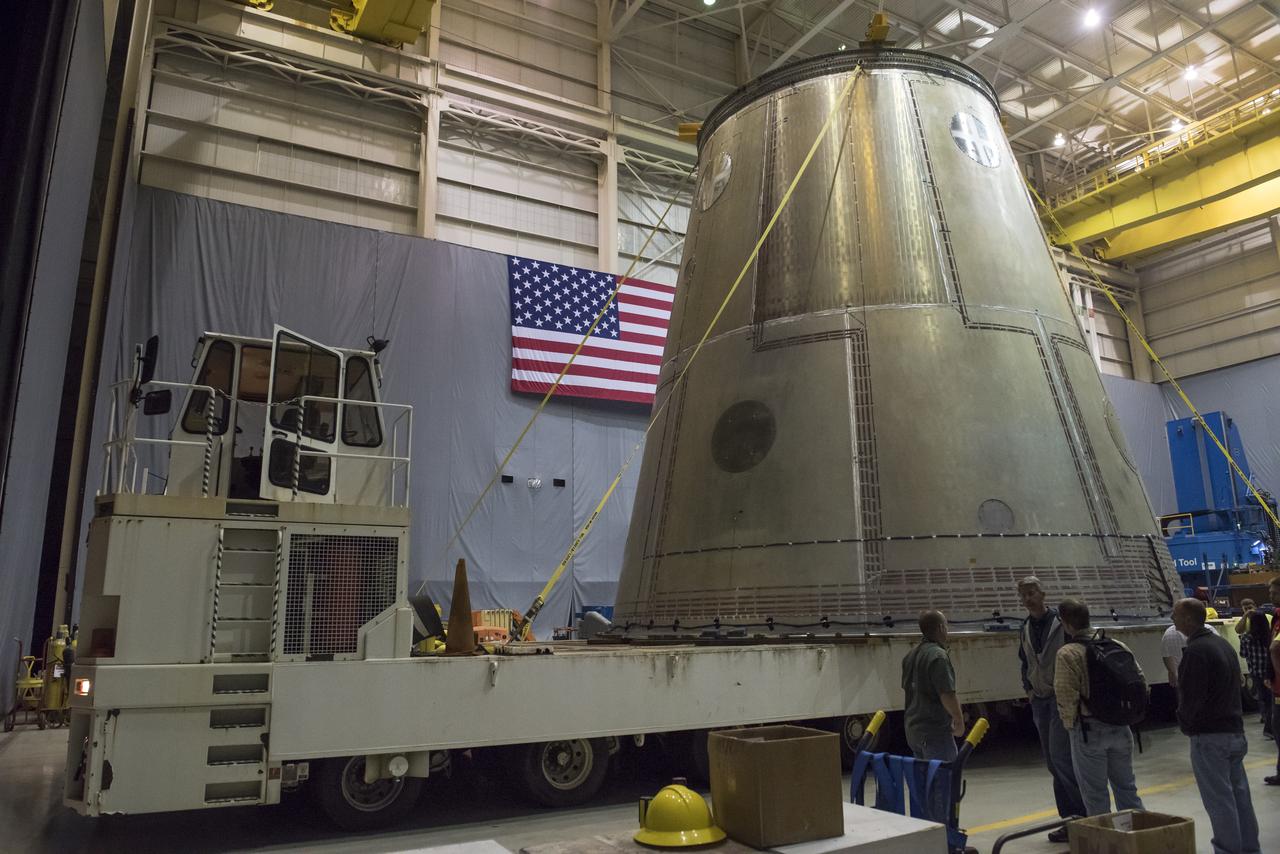
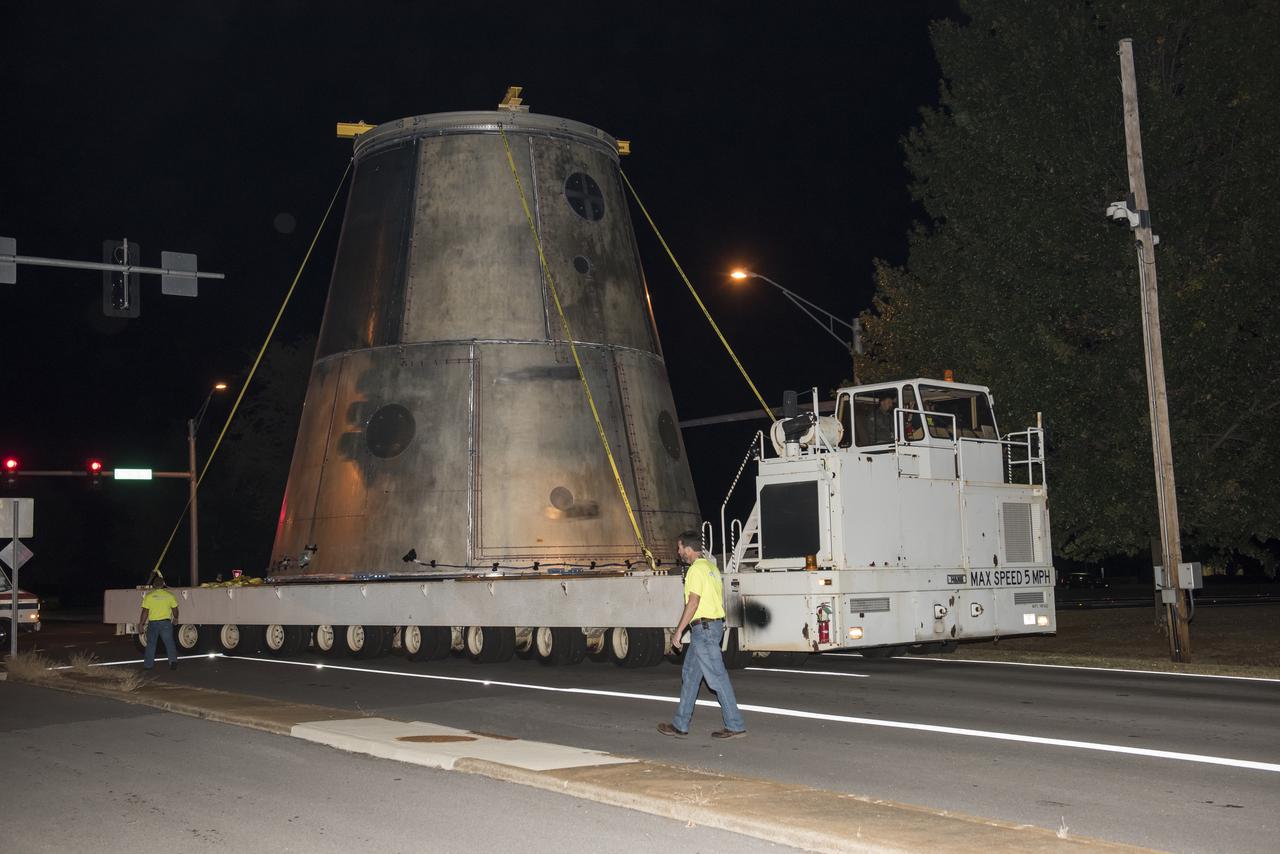
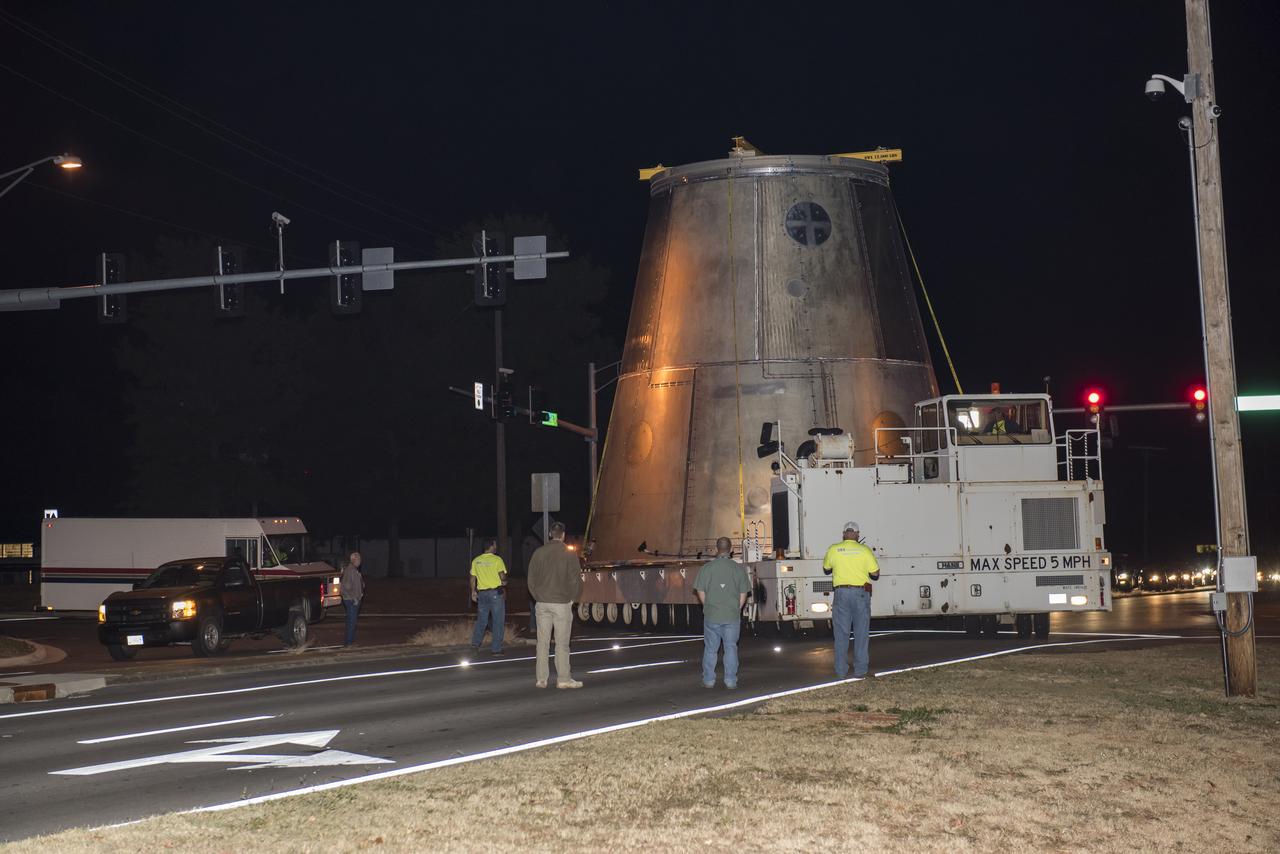
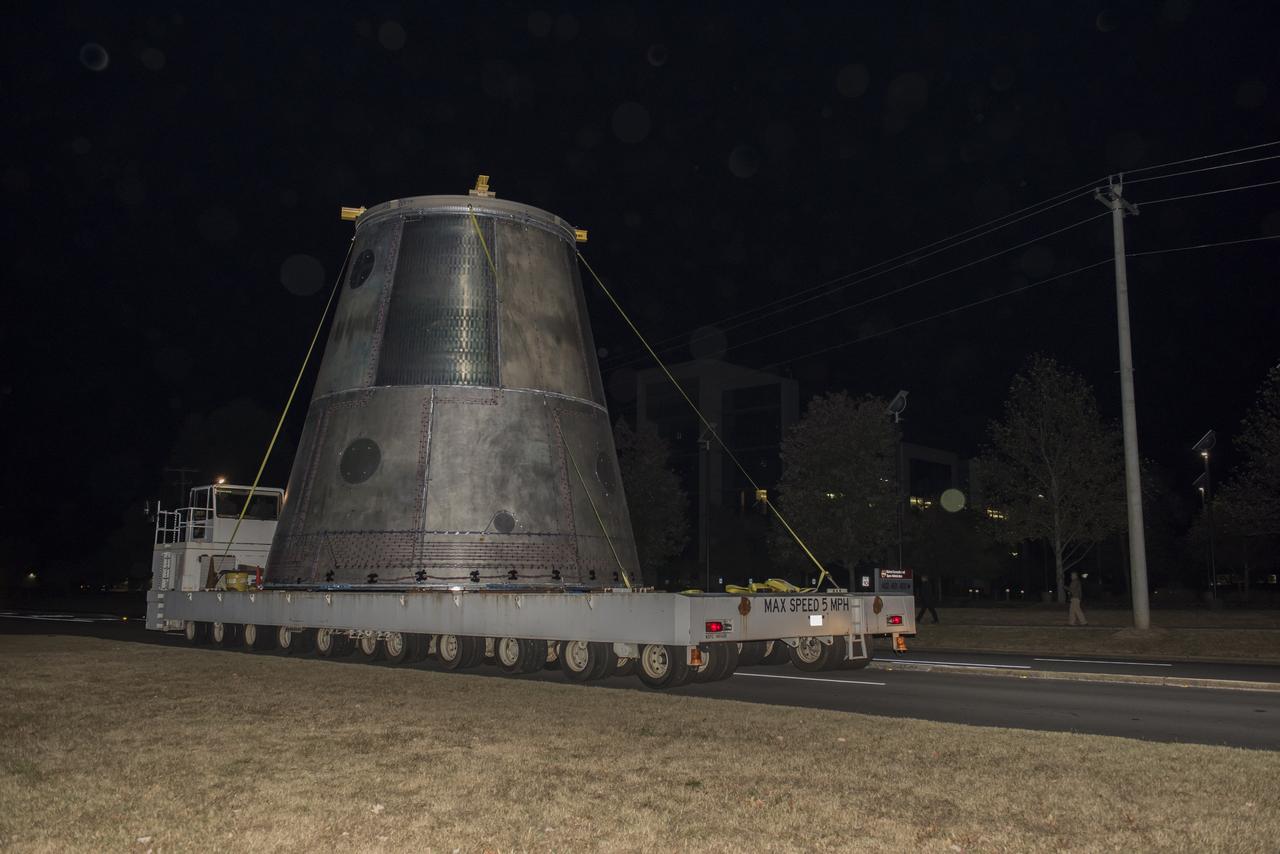
A SLS LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER IS MOVED FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL STATION IN MSFC’S BUILDING 4755 TO THE WEST TEST AREA’S TEST STAND 4699 WHERE IT WILL UNDERGO FURTHER TESTING OF ITS ABILITY TO WITHSTAND THE STRESSES RELATED TO LAUNCH AND SPACE TRAVEL.
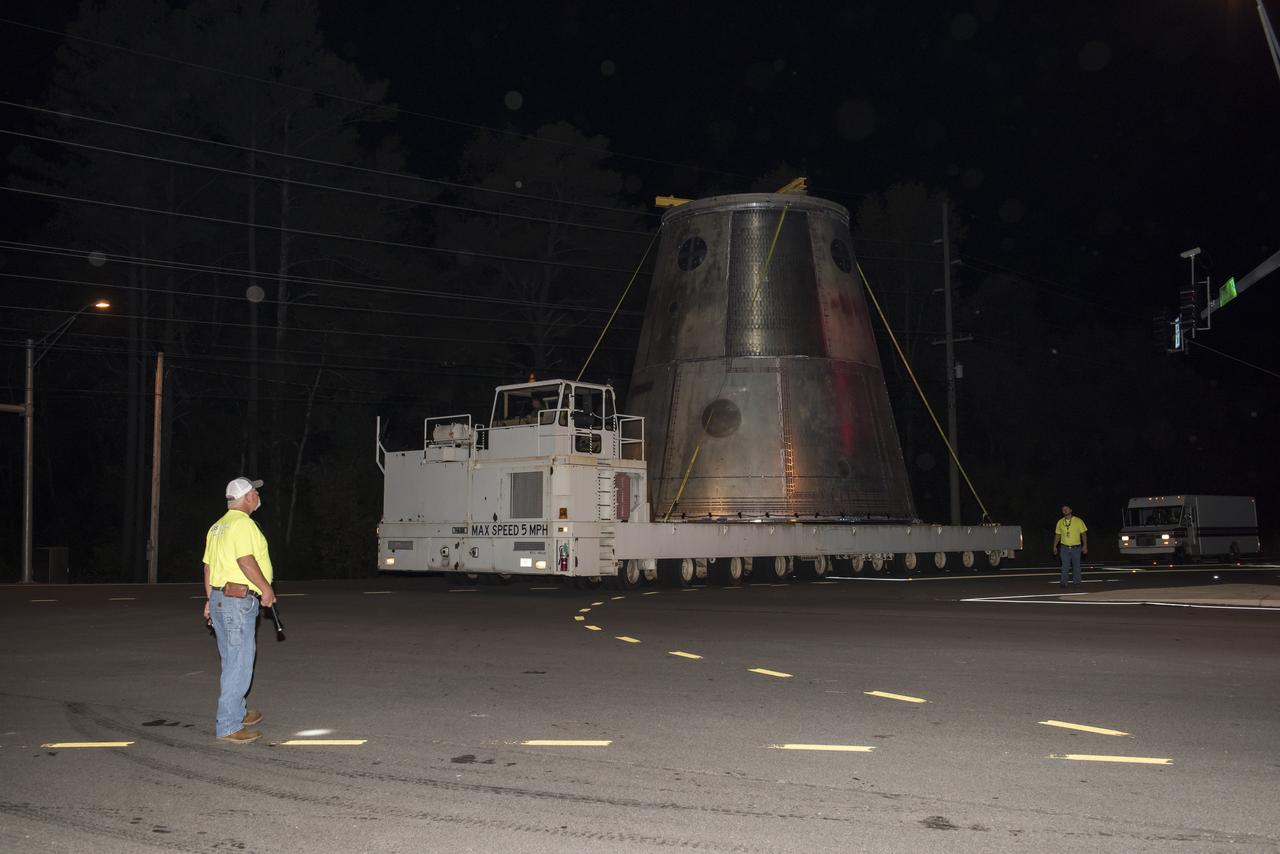

A SLS LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER IS MOVED FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL STATION IN MSFC’S BUILDING 4755 TO THE WEST TEST AREA’S TEST STAND 4699 WHERE IT WILL UNDERGO FURTHER TESTING OF ITS ABILITY TO WITHSTAND THE STRESSES RELATED TO LAUNCH AND SPACE TRAVEL.
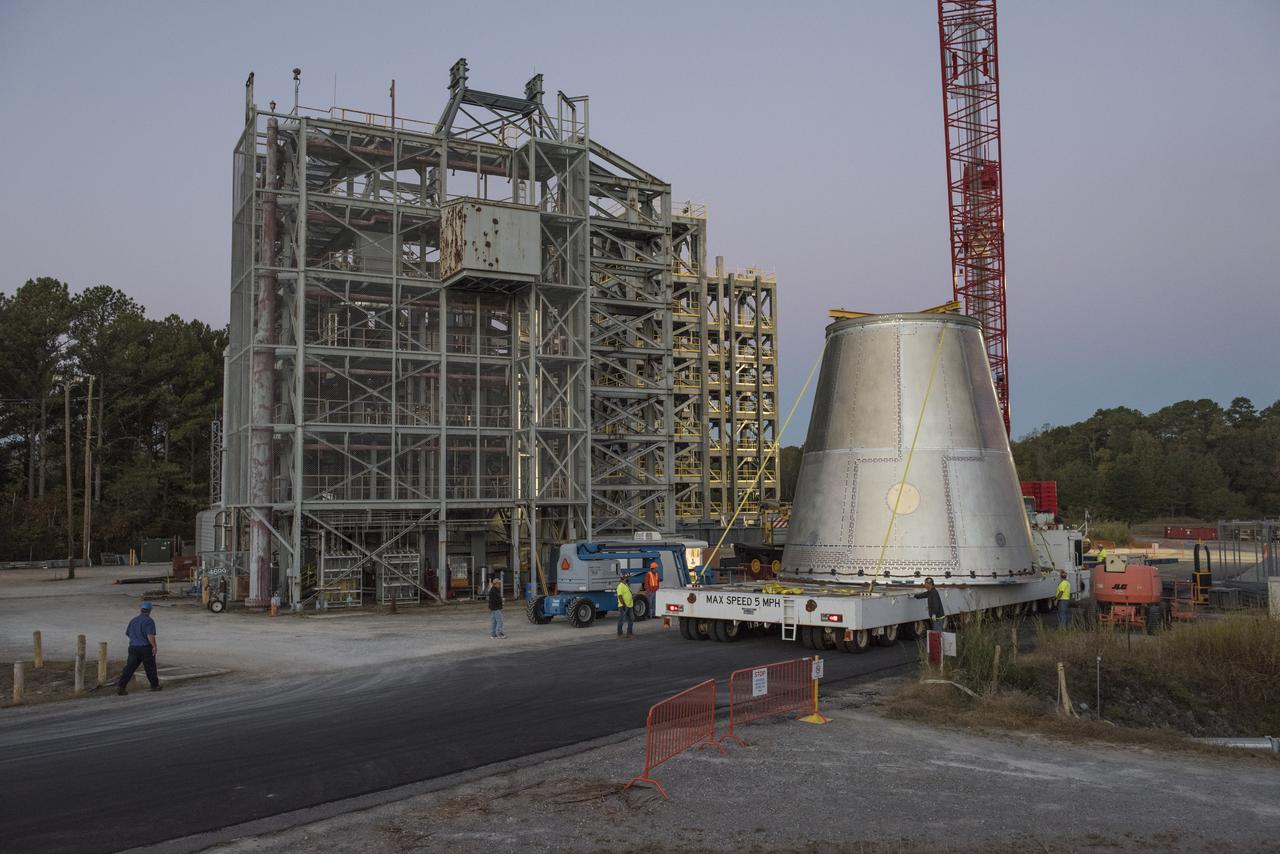

A SLS LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER IS MOVED FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL STATION IN MSFC’S BUILDING 4755 TO THE WEST TEST AREA’S TEST STAND 4699 WHERE IT WILL UNDERGO FURTHER TESTING OF ITS ABILITY TO WITHSTAND THE STRESSES RELATED TO LAUNCH AND SPACE TRAVEL.
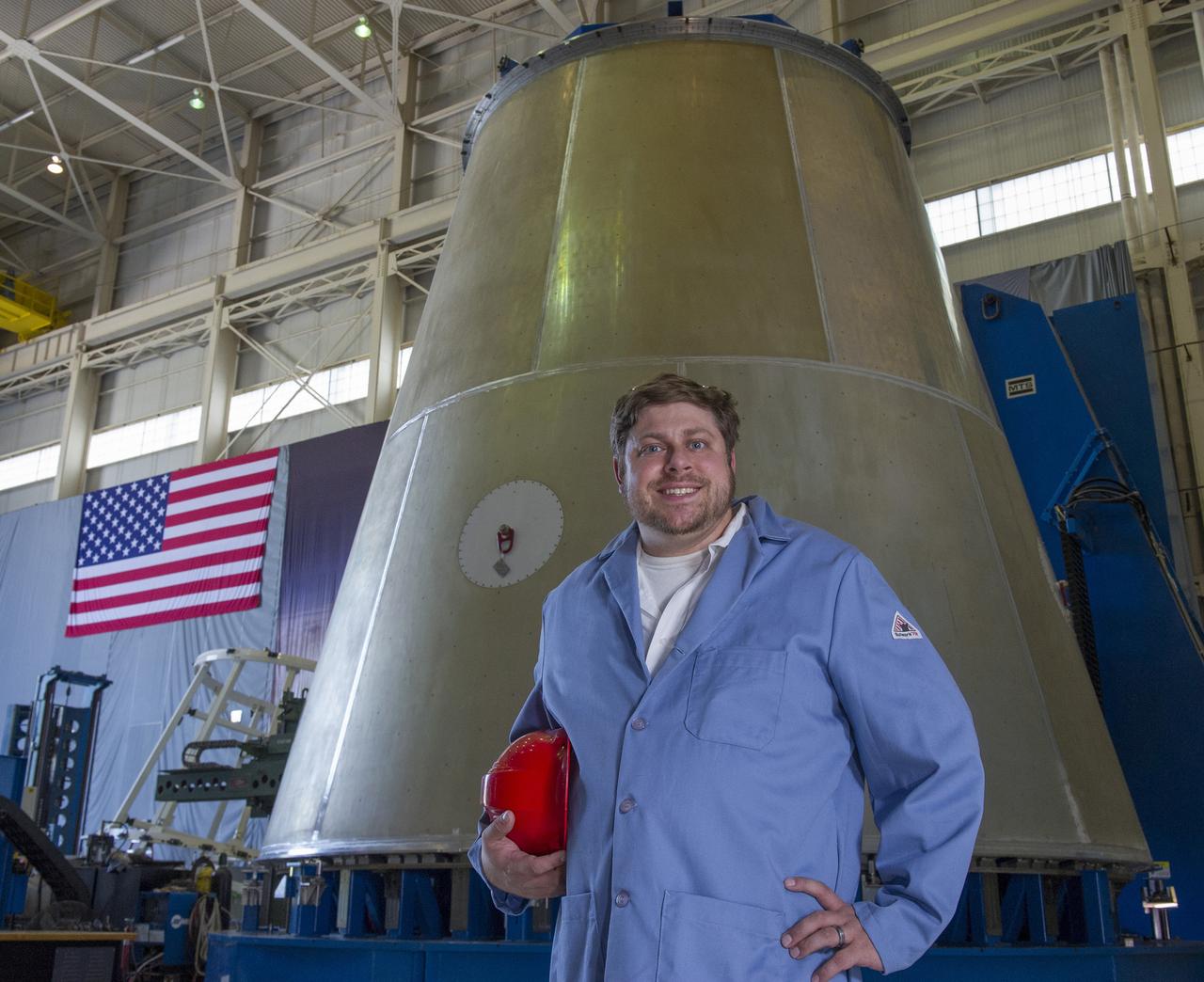

MARSHALL WELD ENGINEER JUSTIN LITTELL POSES WITH LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER
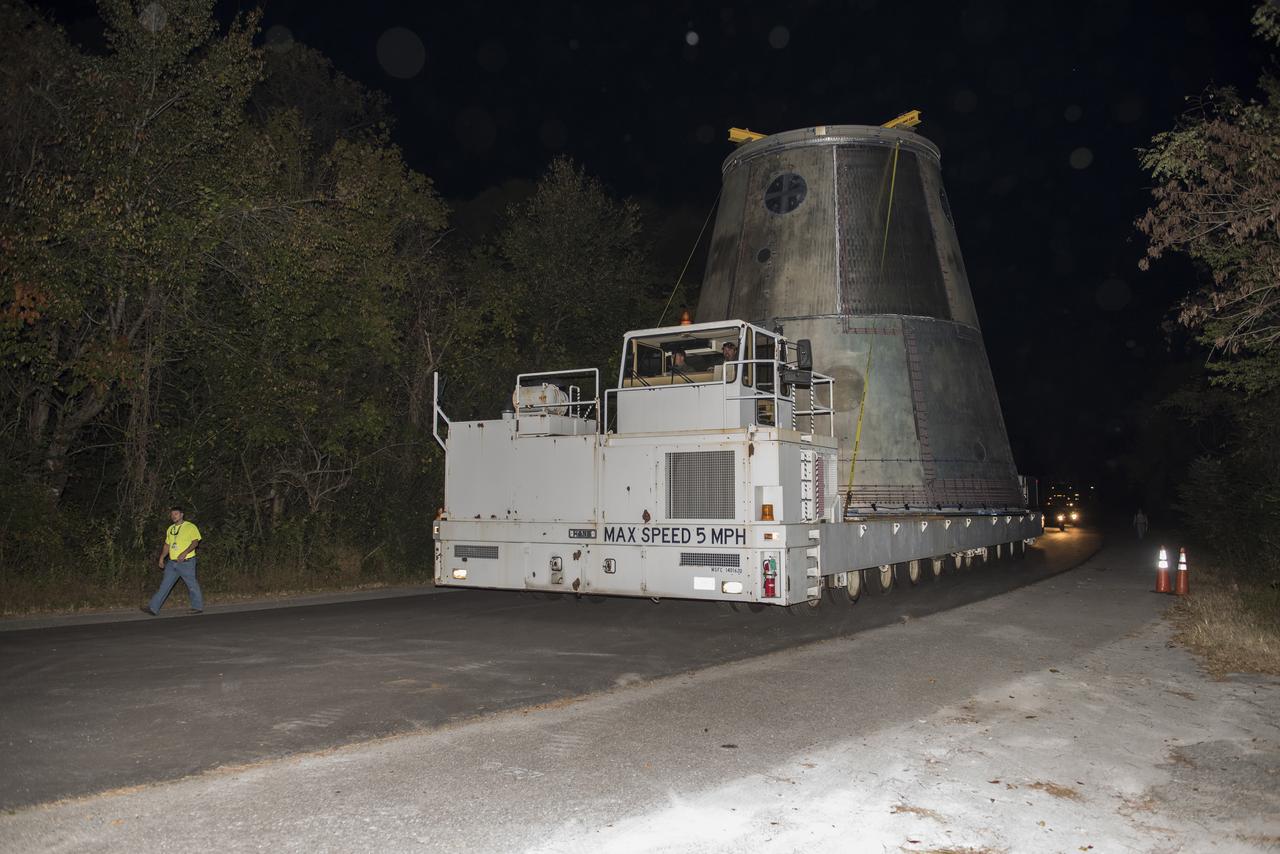

A SLS LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER IS MOVED FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL STATION IN MSFC’S BUILDING 4755 TO THE WEST TEST AREA’S TEST STAND 4699 WHERE IT WILL UNDERGO FURTHER TESTING OF ITS ABILITY TO WITHSTAND THE STRESSES RELATED TO LAUNCH AND SPACE TRAVEL.

A SLS LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER IS MOVED FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL STATION IN MSFC’S BUILDING 4755 TO THE WEST TEST AREA’S TEST STAND 4699 WHERE IT WILL UNDERGO FURTHER TESTING OF ITS ABILITY TO WITHSTAND THE STRESSES RELATED TO LAUNCH AND SPACE TRAVEL.

A SLS LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER IS MOVED FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL STATION IN MSFC’S BUILDING 4755 TO THE WEST TEST AREA’S TEST STAND 4699 WHERE IT WILL UNDERGO FURTHER TESTING OF ITS ABILITY TO WITHSTAND THE STRESSES RELATED TO LAUNCH AND SPACE TRAVEL.

A SLS LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER IS MOVED FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL STATION IN MSFC’S BUILDING 4755 TO THE WEST TEST AREA’S TEST STAND 4699 WHERE IT WILL UNDERGO FURTHER TESTING OF ITS ABILITY TO WITHSTAND THE STRESSES RELATED TO LAUNCH AND SPACE TRAVEL.

A SLS LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER IS MOVED FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL STATION IN MSFC’S BUILDING 4755 TO THE WEST TEST AREA’S TEST STAND 4699 WHERE IT WILL UNDERGO FURTHER TESTING OF ITS ABILITY TO WITHSTAND THE STRESSES RELATED TO LAUNCH AND SPACE TRAVEL.
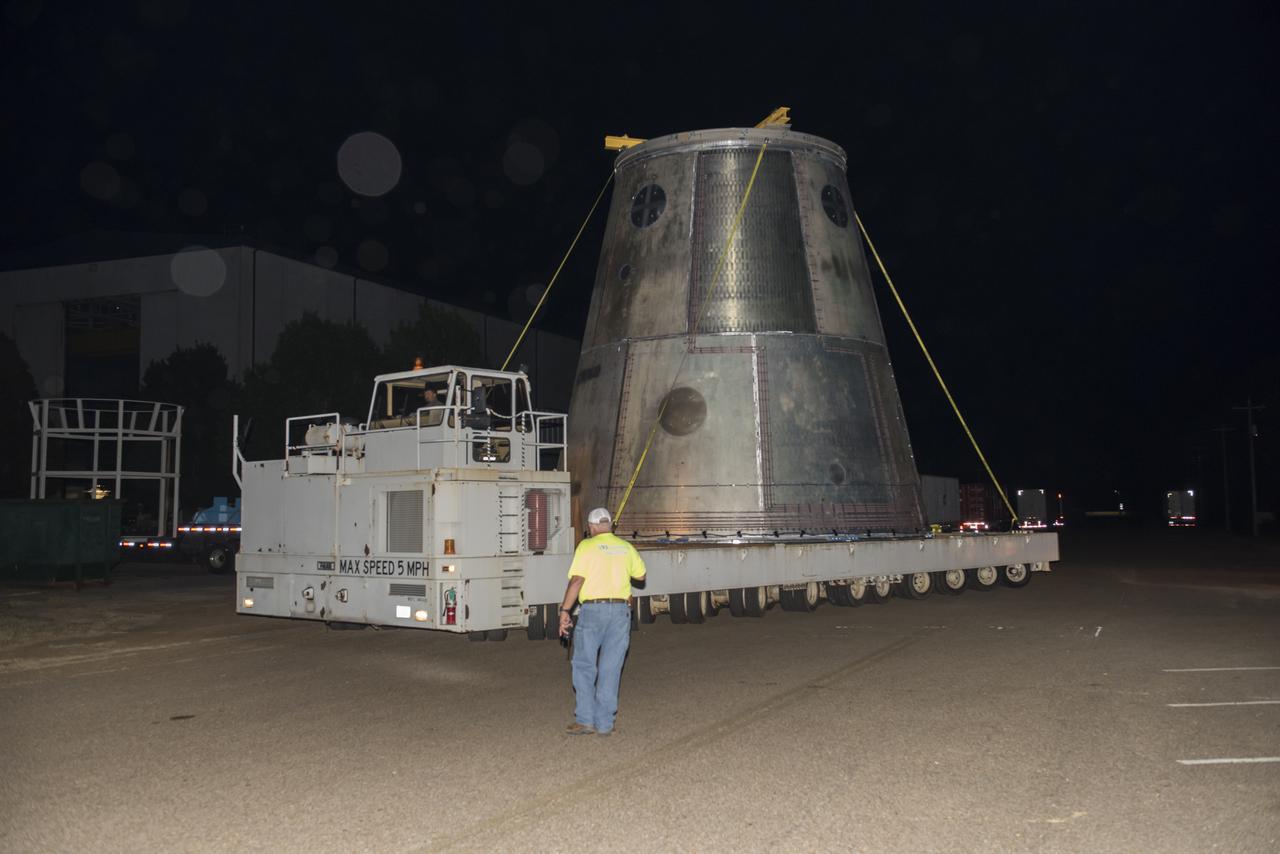

A SLS LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER IS MOVED FROM THE VERTICAL WELD TOOL STATION IN MSFC’S BUILDING 4755 TO THE WEST TEST AREA’S TEST STAND 4699 WHERE IT WILL UNDERGO FURTHER TESTING OF ITS ABILITY TO WITHSTAND THE STRESSES RELATED TO LAUNCH AND SPACE TRAVEL.
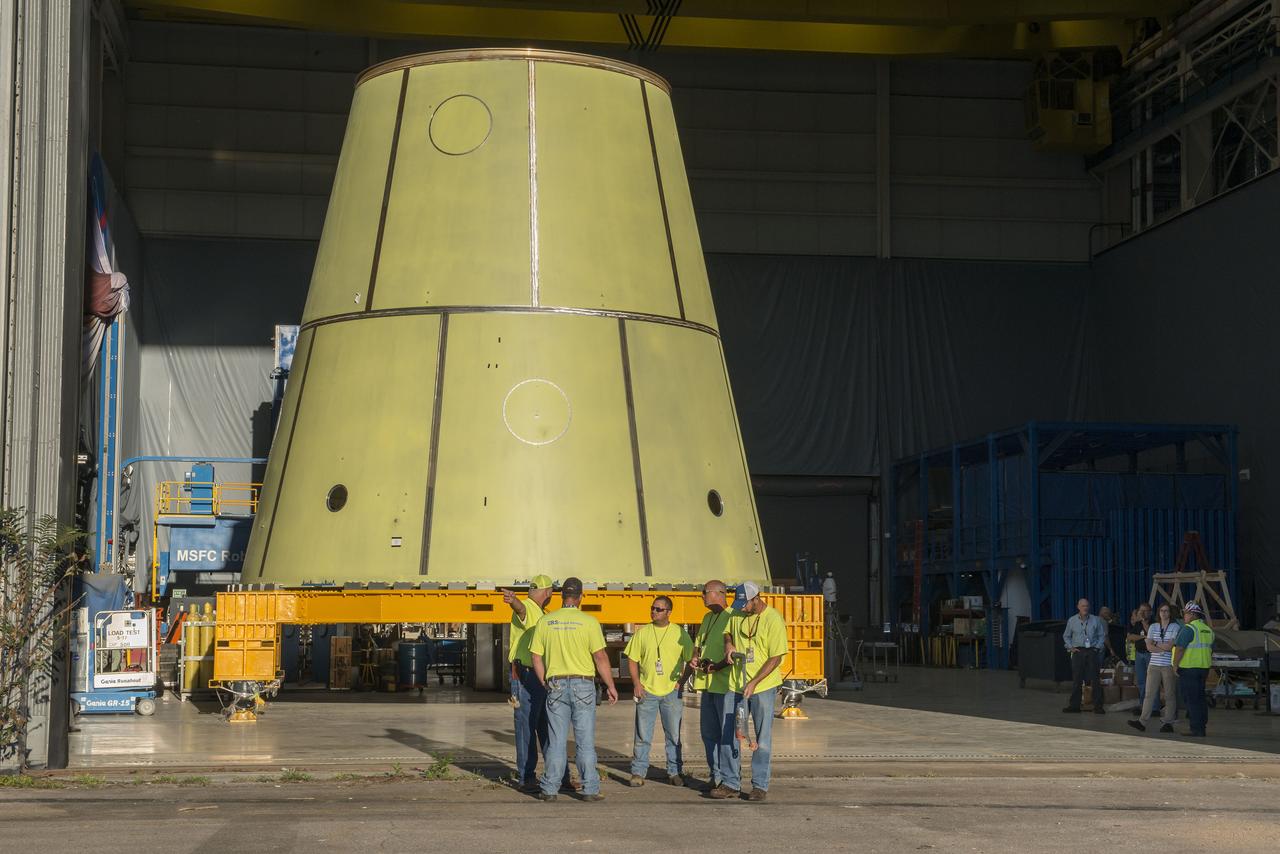

Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter being loaded on the KMag for transportation to building 4707 for further testing.

BUILDING 4205 GALLERY, EXTERIOR AND INTERIOR VIEWS

RICK BURT, RIGHT, DIRECTOR OF SAFETY AND MISSION ASSURANCE TALKS WITH ANDY SCHORR, ASSISTANT MANAGER OF THE SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM'S SPACECRAFT PAYLOAD INTEGRATION AND EVOLUTION OFFICE. BEHIND THEM IS THE LAUNCH VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTOR, WHICH WAS DESIGNED AND MANUFACTURED AT MARSHALL AND WILL CONNECT TWO MAJOR SLS UPPER SECTIONS
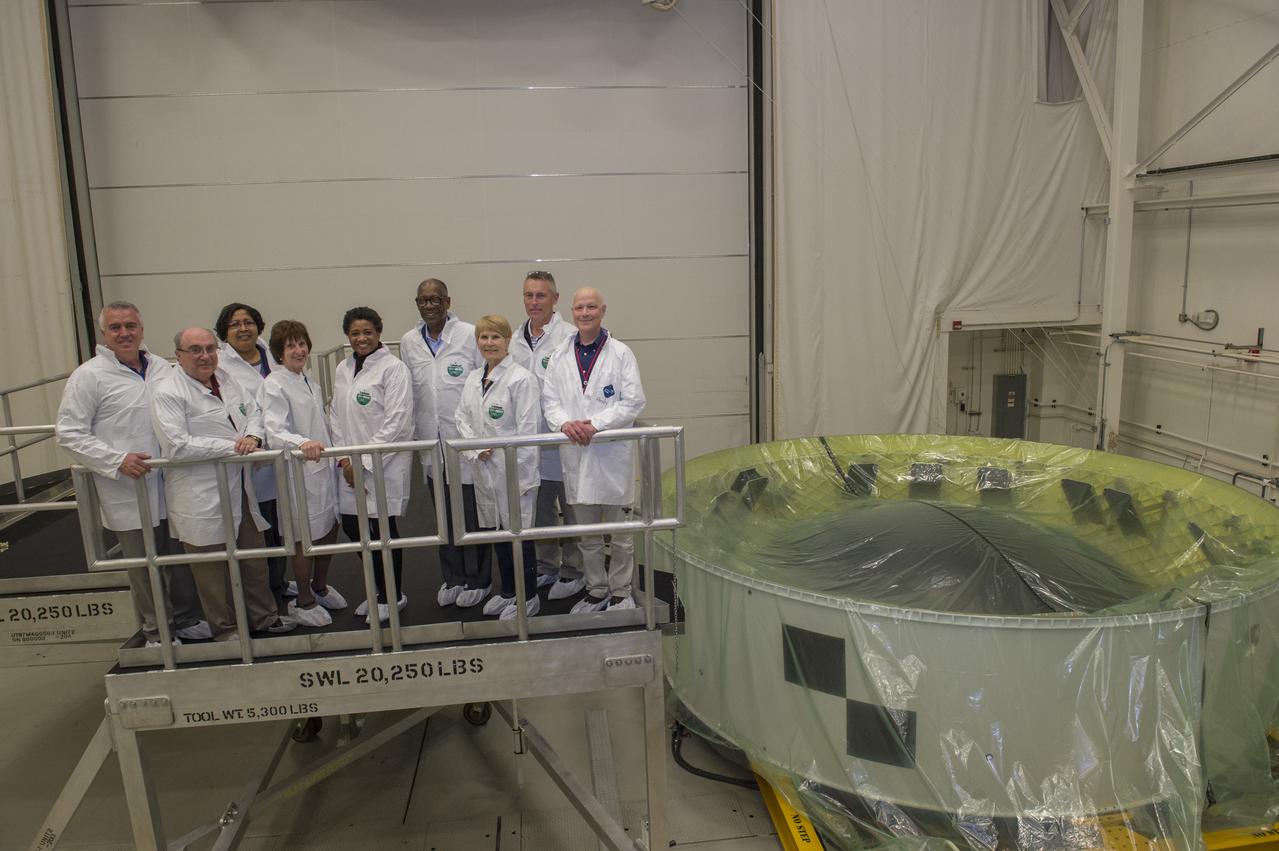

ASAP, (Aerospace Safety Advisory Panel), members, Dr. Sandra Magnus, Dr. Donald P. McErlean, Dr. George Nield, Captain Christopher Saindon, Mr. David West, Dr. Patricia Sanders, Ms. Carol Hamilton, Ms. Evette Whatley, Ms. Paula Frankel, view LVSA, (Launch Vehicle Stage Adapter), and Orion Stage Adapter. Members were escorted to buildings 4707 and 4708 by Andrew Schorr, Deputy Manager for Spacecraft/Payload Integration & Evolution Office (SPIE)

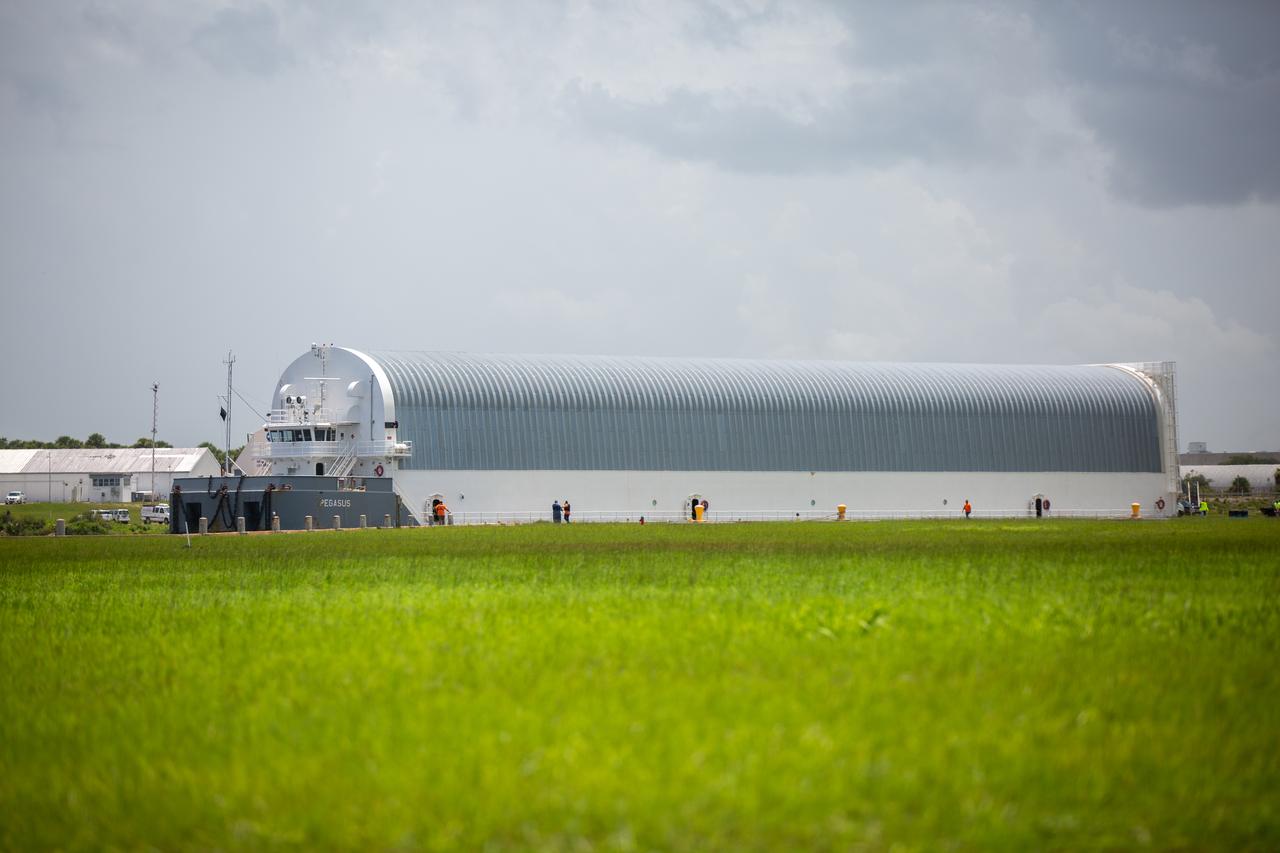
NASA’s Pegasus barge, seen off toward the right, prepares to depart from the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 4, 2020, for its trip to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana. The Pegasus barge arrived at Kennedy on July 29, delivering the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket – the most powerful rocket NASA has ever built, providing the muscle necessary to get to the Moon and eventually to Mars. The LVSA – now undergoing processing inside the Vehicle Assembly Building – will connect the core stage of the rocket to the upper stage. The next time the Pegasus barge returns to Kennedy, it will be carrying the SLS core stage – the final piece of the rocket that needs to be delivered ahead of the Artemis I launch.

NASA’s Pegasus barge departs from the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 4, 2020, for its trip to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana. The Pegasus barge arrived at Kennedy on July 29, delivering the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket – the most powerful rocket NASA has ever built, providing the muscle necessary to get to the Moon and eventually to Mars. In the background is the Vehicle Assembly Building, where the LVSA – hardware that will connect the core stage of the rocket to the upper stage – is now undergoing processing. The next time the Pegasus barge returns to Kennedy, it will be carrying the SLS core stage – the final piece of the rocket that needs to be delivered ahead of the Artemis I launch.

NASA’s Pegasus barge departs from the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 4, 2020, for its trip to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana. The Pegasus barge arrived at Kennedy on July 29, delivering the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket – the most powerful rocket NASA has ever built, providing the muscle necessary to get to the Moon and eventually to Mars. In the background is the Vehicle Assembly Building, where the LVSA – hardware that will connect the core stage of the rocket to the upper stage – is now undergoing processing. The next time the Pegasus barge returns to Kennedy, it will be carrying the SLS core stage – the final piece of the rocket that needs to be delivered ahead of the Artemis I launch.

NASA’s Pegasus barge departs from the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 4, 2020, for its trip to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana. The Pegasus barge arrived at Kennedy on July 29, delivering the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket – the most powerful rocket NASA has ever built, providing the muscle necessary to get to the Moon and eventually to Mars. In the background is the Vehicle Assembly Building, where the LVSA – hardware that will connect the core stage of the rocket to the upper stage – is now undergoing processing. The next time the Pegasus barge returns to Kennedy, it will be carrying the SLS core stage – the final piece of the rocket that needs to be delivered ahead of the Artemis I launch.

These images show NASA’s Pegasus barge at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as it transported the Artemis I launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of the agency’s Space Launch System rocket to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Leaving with the adapter from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Pegasus made a brief stop at Michoud to offload supplies and equipment before continuing its to Kennedy. The LVSA connects the deep space rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage to the rocket’s upper stage and will be used for Artemis I, the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon through NASA’s Artemis program. Once at Kennedy, the LVSA will undergo Artemis I launch preparations. Only the SLS core stage, currently in final testing at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, remains to be shipped to Kennedy on Pegasus. The core stage is produced at Michoud. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Offering more payload mass, volume capacity and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.