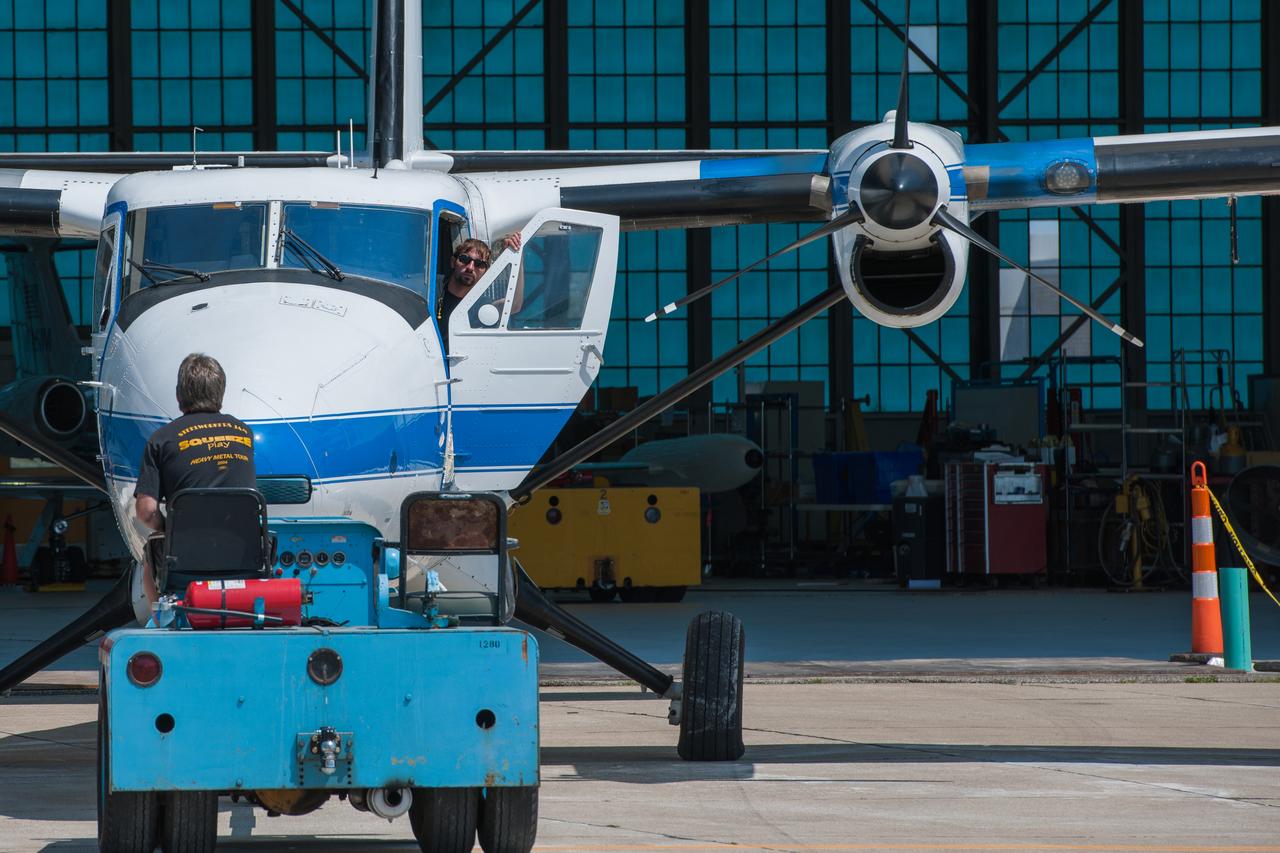

Aircraft mechanics reposition the Twin Otter after a research flight. The aircraft was used to gather data from Lake Erie for the Algae Bloom Project.
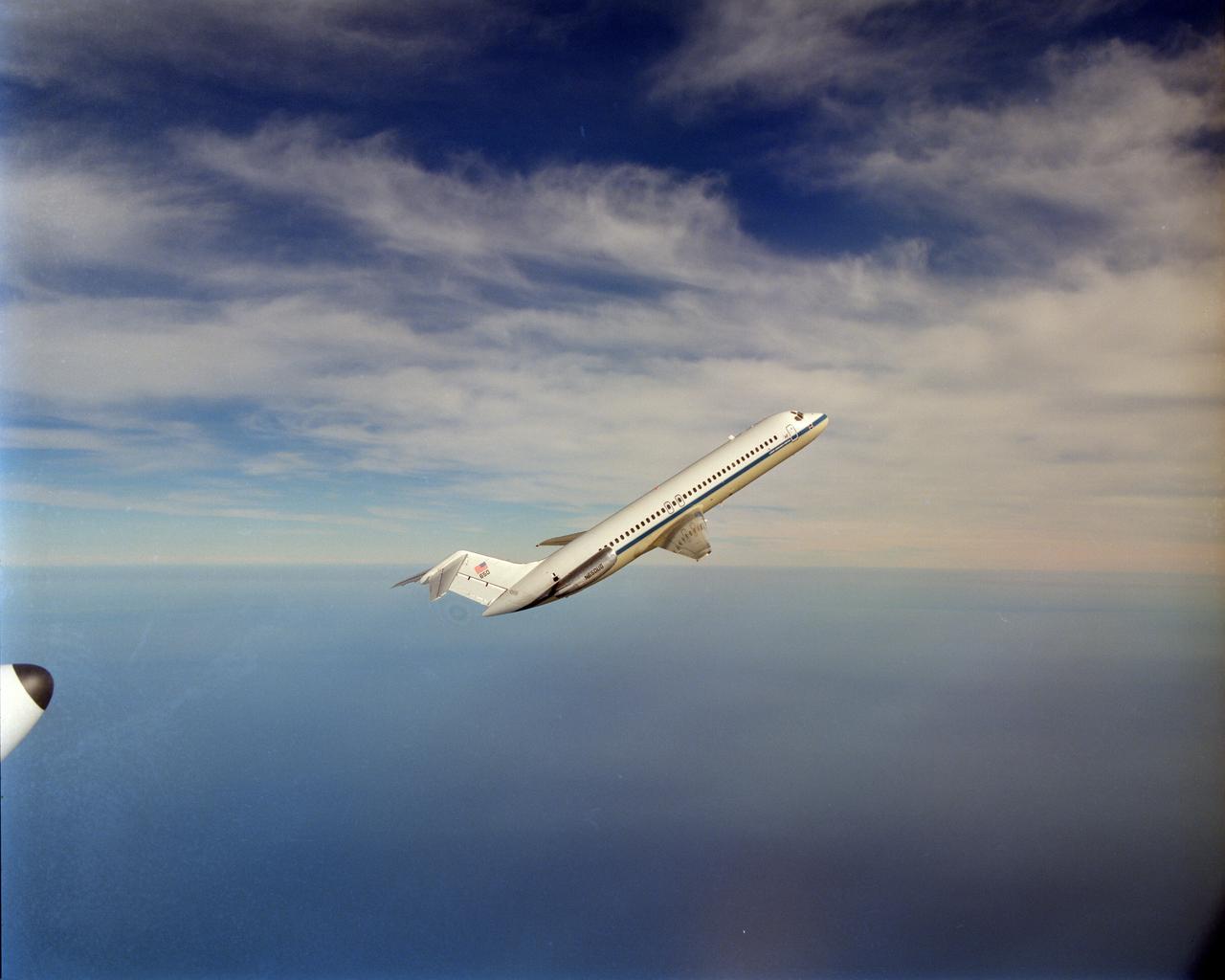

NASA aircraft DC-9 microgravity plane performs it's first test parabolas over Lake Erie. This was photographed by the NASA Glenn Lear Jet in a chase plane configuration.

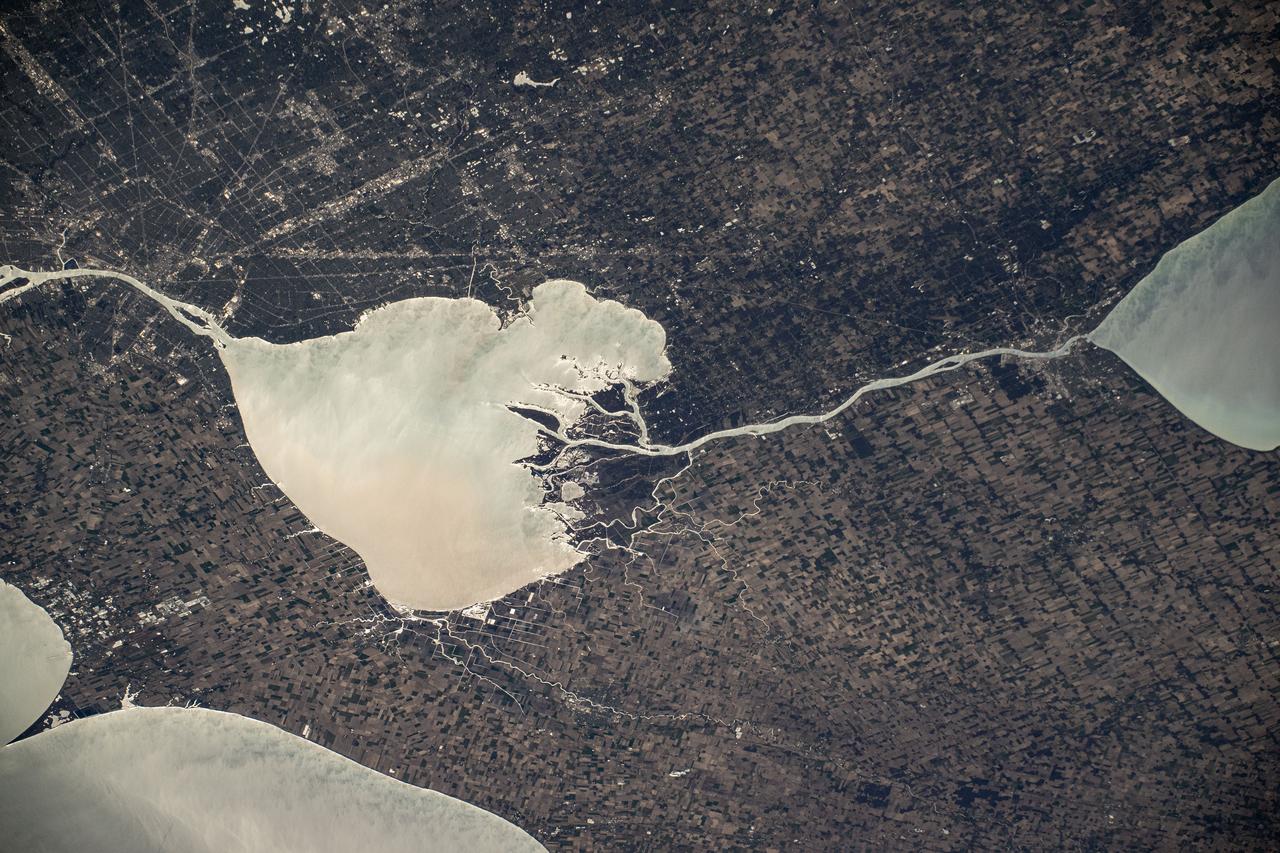
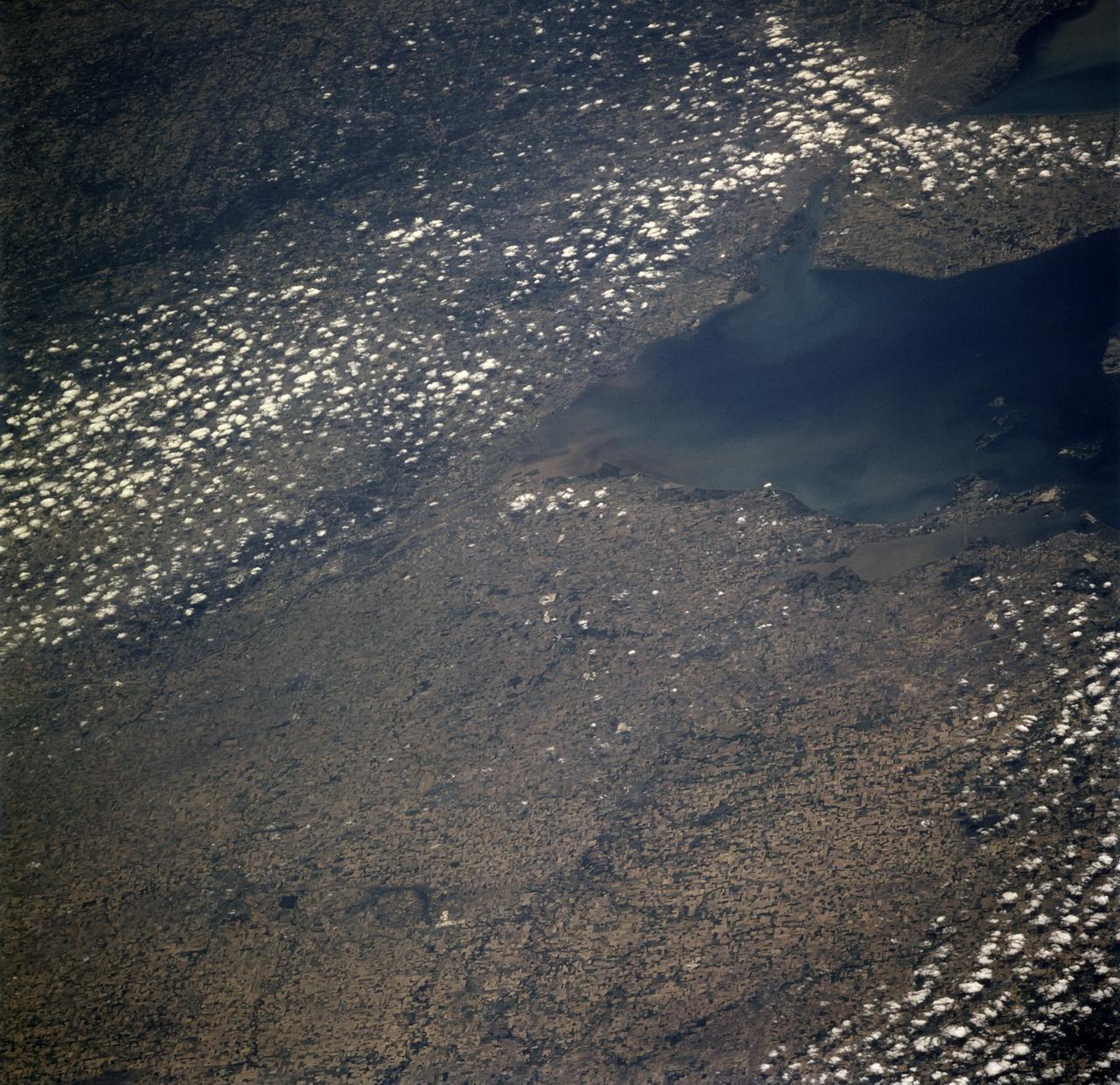
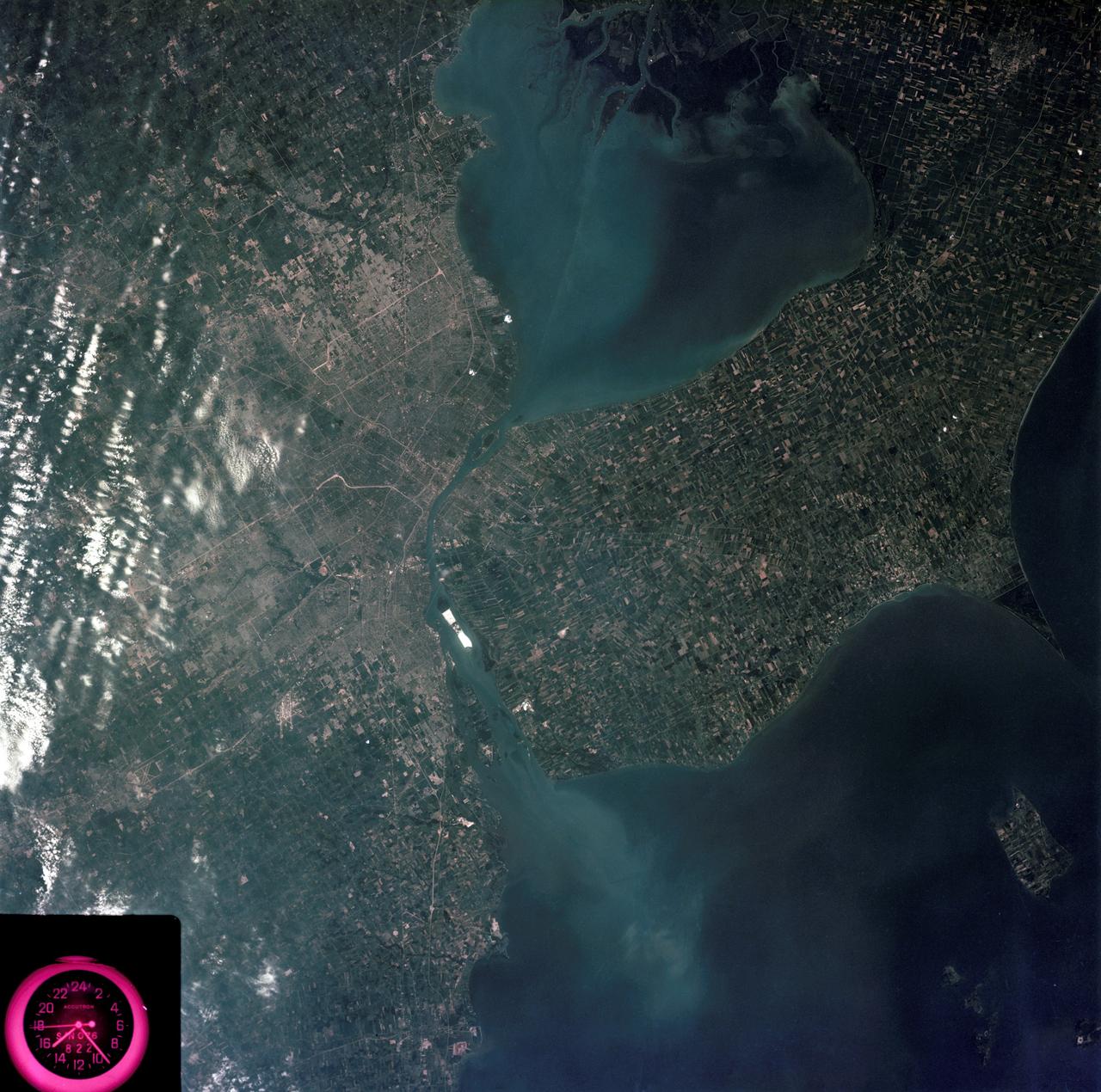
SL2-05-390 (22 June 1973) --- Greater Detroit (42.0N, 82.5W) is located at the southeastern border of Michigan on the Detroit River across from Windsor, Ontario, Canada and Lake Huron to the north. The river connecting Lake Erie is a channel left over from the Ice Age Glaciers. The land use pattern in this scene is typical of this part of the upper Midwest. The once extensive forests have been cleared for farmland and pasture, but narrow rows of trees still line farm boundaries. Photo credit: NASA
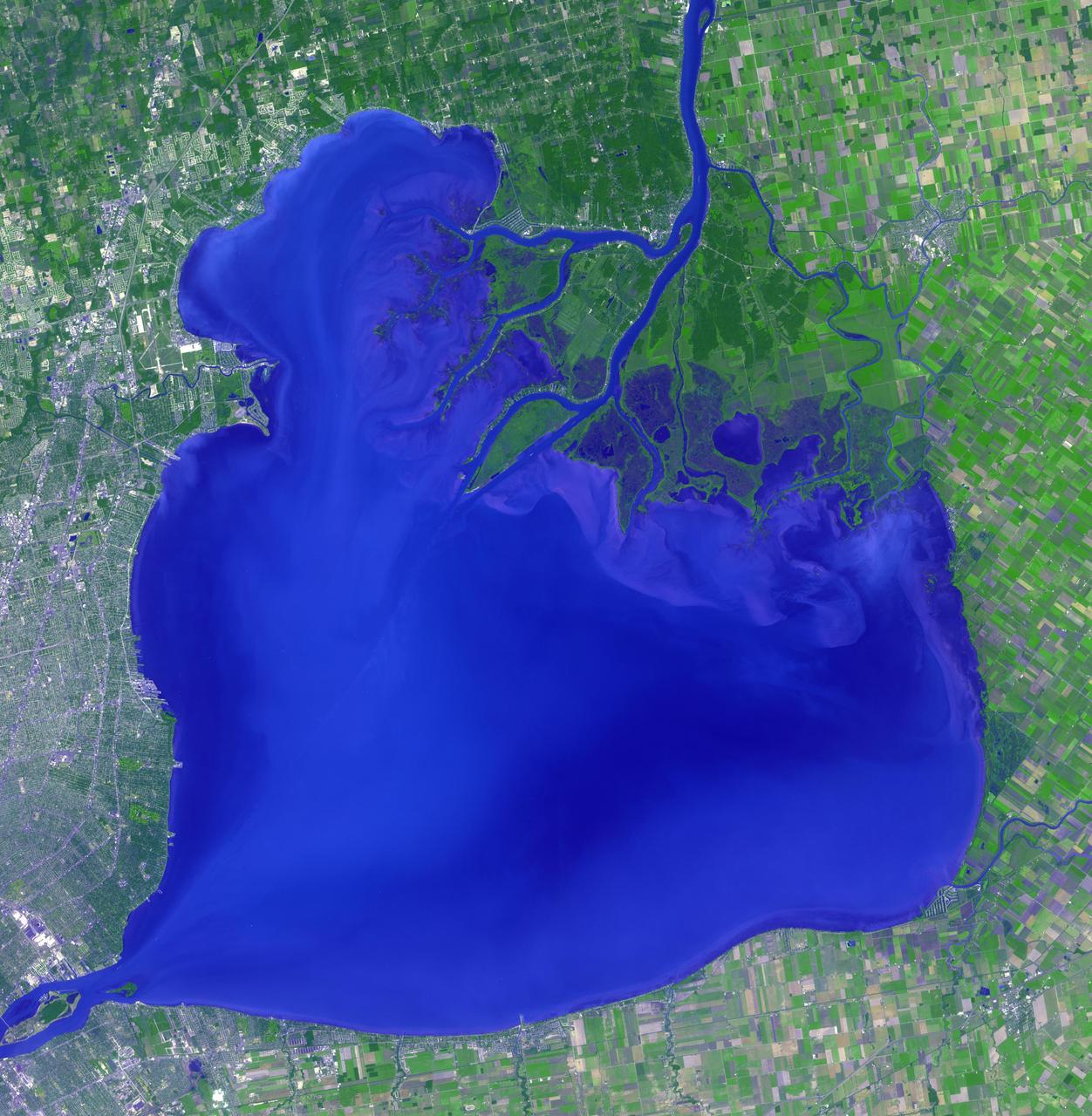

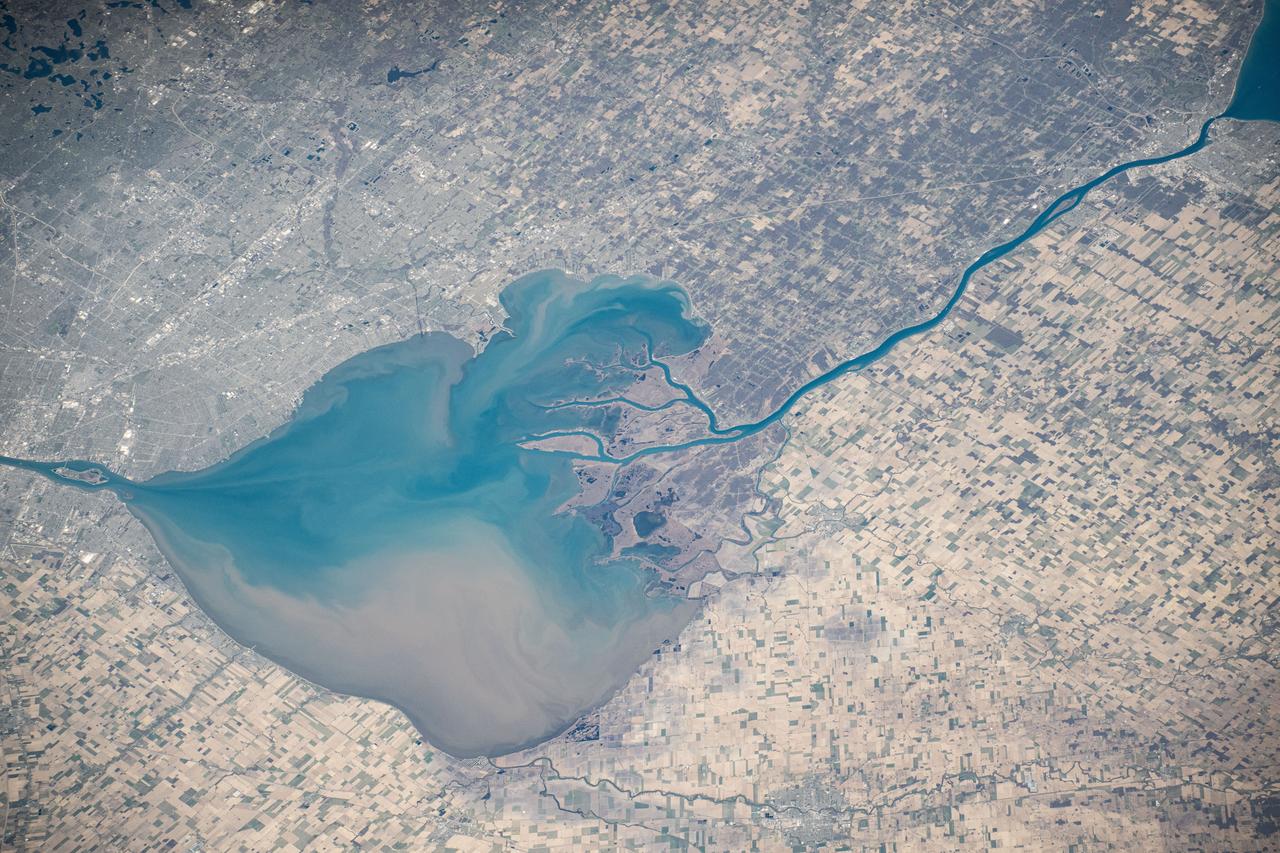
Lake St. Clair connects Lake Huron, via the St. Clair River, to Lake Erie, via the Detroit River. It is named after Claire of Assisi, on whose feast day it was first navigated by French explorers in 1679. The lake covers an area of about 1100 square kilometers, with an average depth of 3.5 meters. Both the U.S. and Canada maintain a deep shipping channel through the lake. The image was acquired September 9, 2002, covers an area of 51.4 by 52.5 kilometers, and is located at 42.5 degrees north, 82.7 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23234
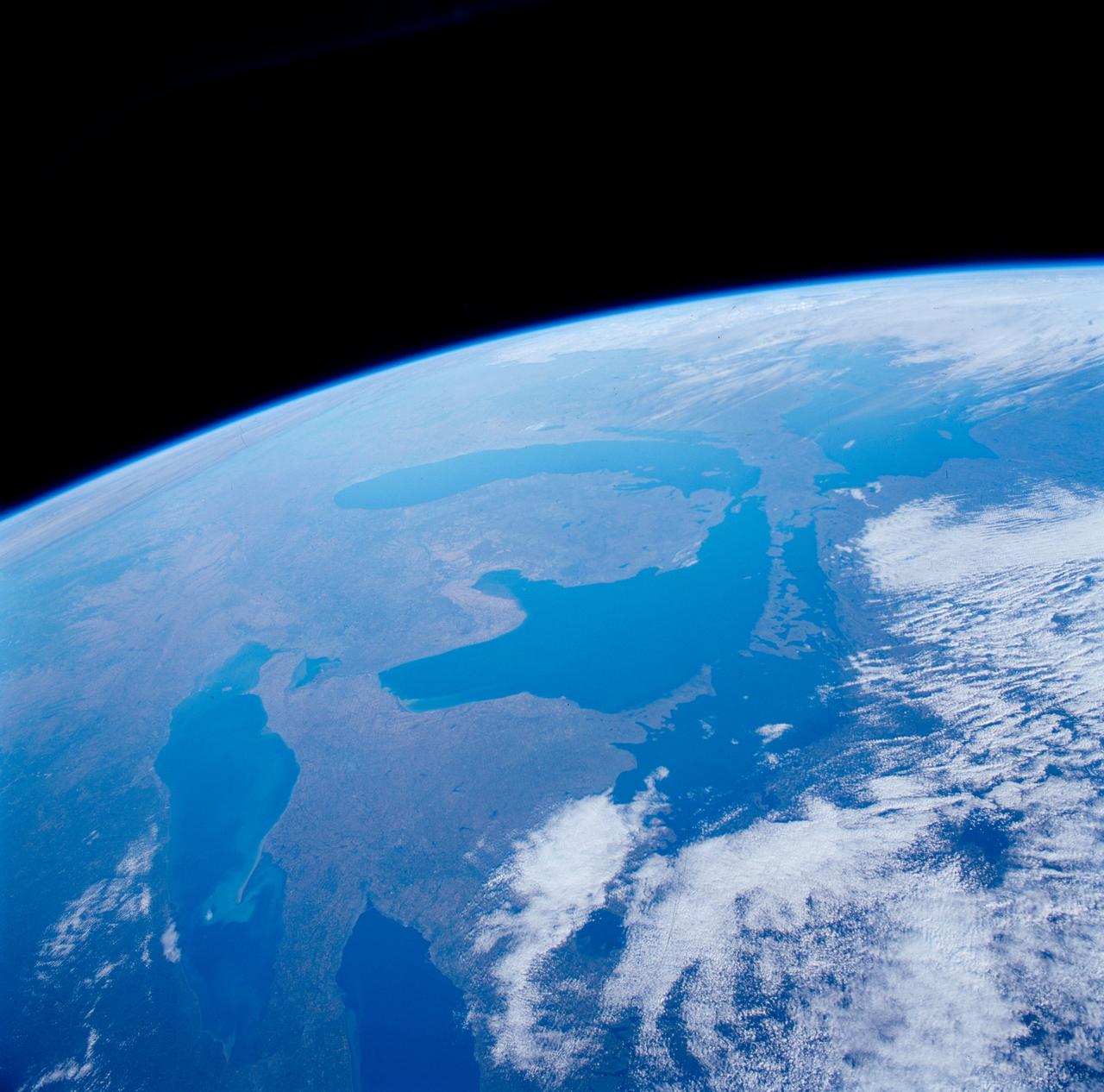

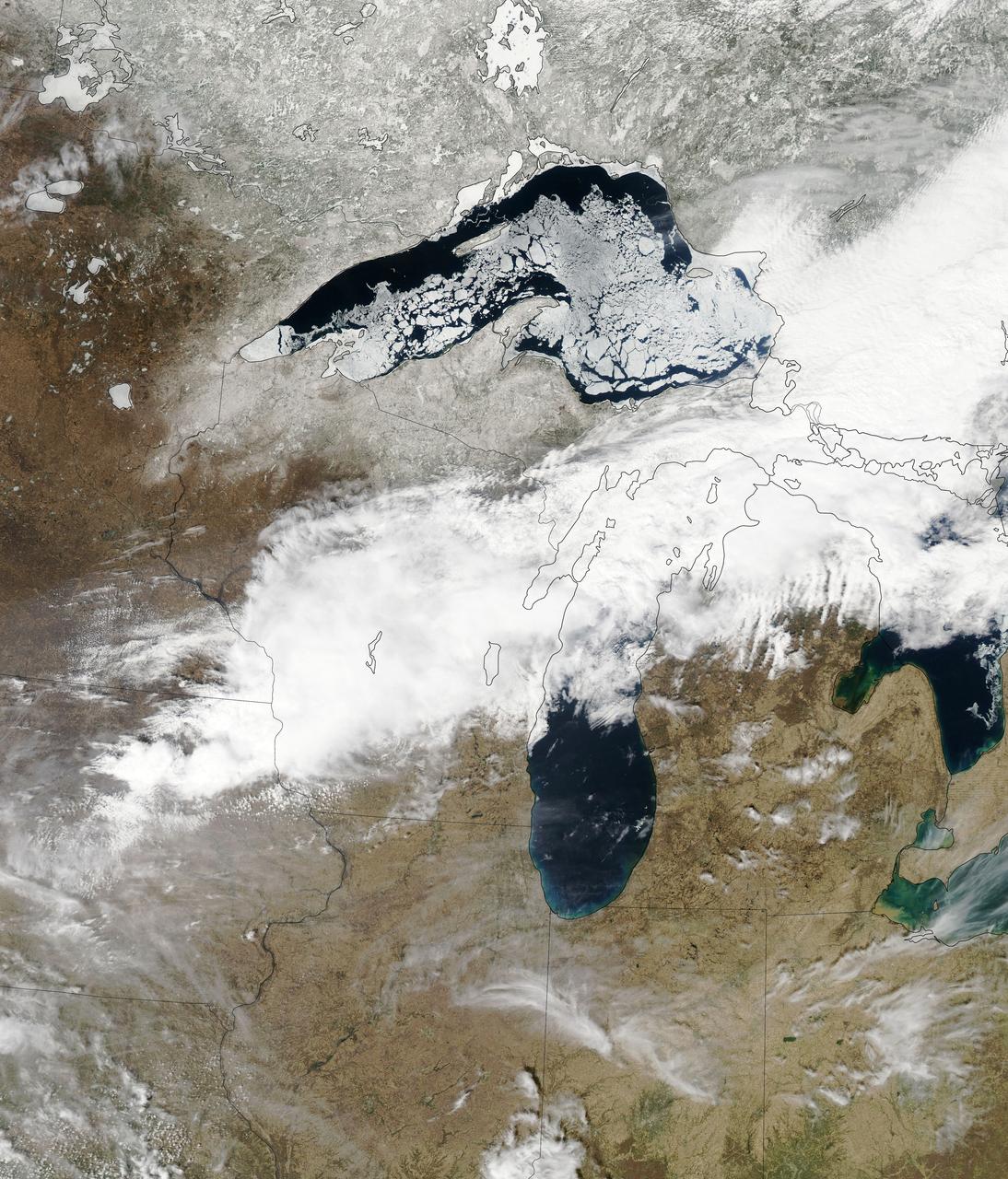
STS084-710-098 (15-24 May 1997) --- A rare view of the Great Lakes captured in one frame. The Great Lakes region is home to 8.5 million Canadians and 32.5 million Americans. At center is Lake Huron and Georgian Bay. Above Lake Huron and towards the horizon is Lake Michigan, the only Great Lake to be located entirely within the United States. To the right of Lake Michigan, and partially under clouds, is Lake Superior the second largest lake in the world after the Caspian Sea. Lake Erie is located to the left of Lake Huron. Next to Lake Erie is Lake Ontario. According to geologists, the Great Lakes were created by glacial processes that began about 1,000,000 years ago.

Magee Marsh Wildlife Area is in northwest Ohio along the shores of Lake Erie. It is internationally known for attracting significant numbers of migrating warblers in the spring. Every May, 60,000 to 80,000 avid birders converge for the annual birding festival. The image was acquired September 18, 2024, covers an area of 13.7 by 17.4 km, and is located at 41.6 degrees north, 83.2 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26622
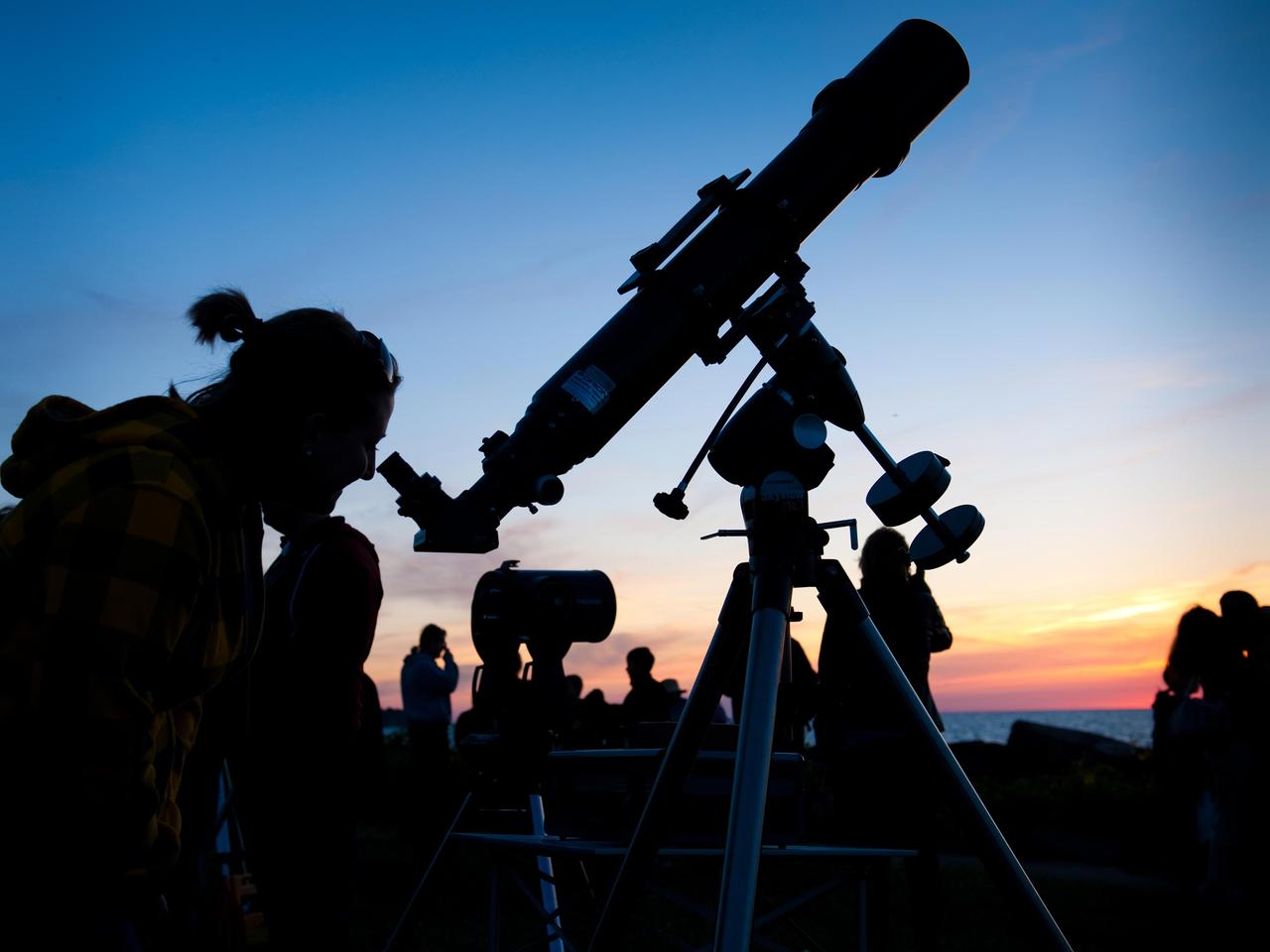

Beautiful skies prevailed on the evening of the Venus Transit when NASA Glenn brought telescopes to Edgewater Park on Lake Erie for a view of the event.
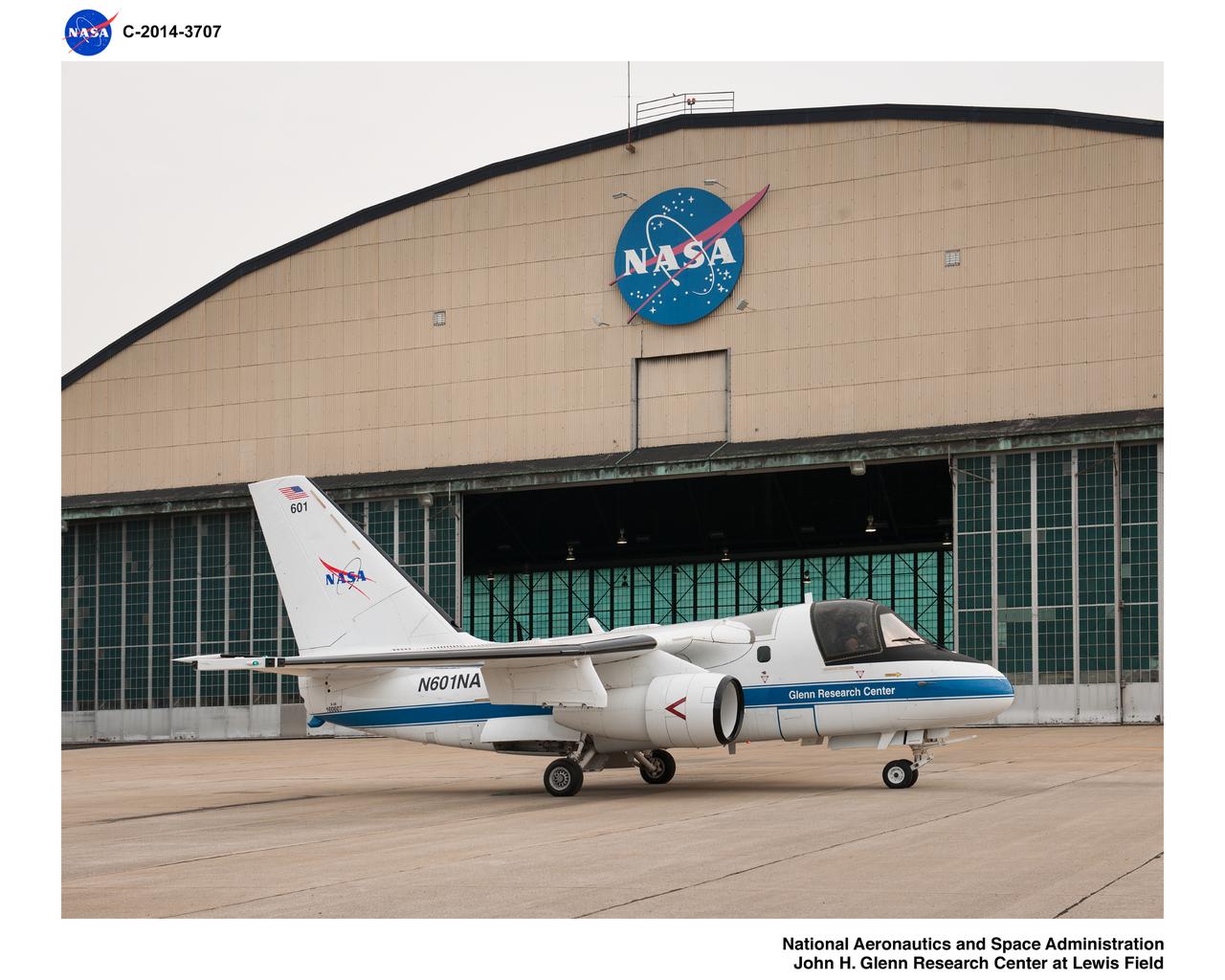

Pre-Flight Check Out of Lockheed Martin S-3B Viking Aircraft #N601NA in preparation for the Lake Erie Algal Bloom Flight Campaign
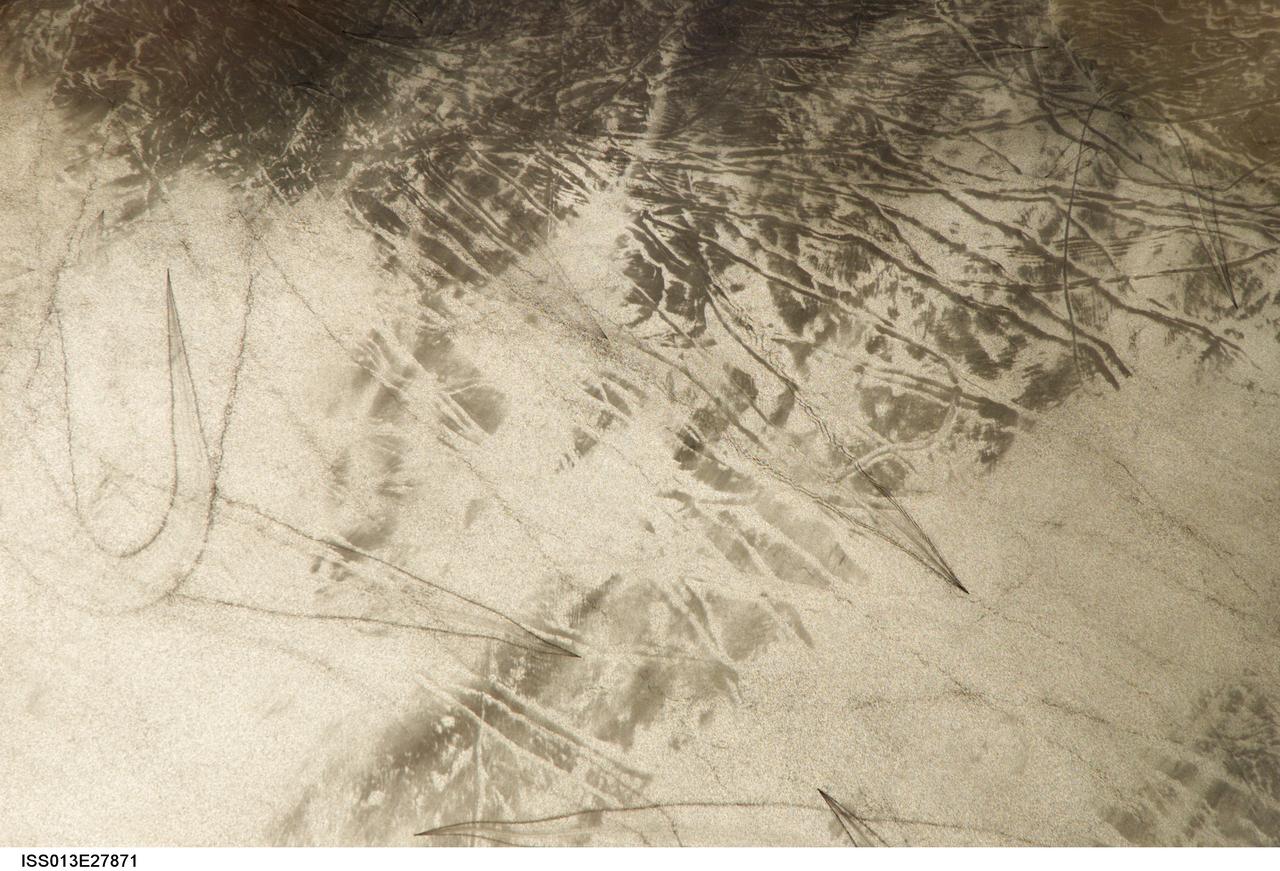
ISS013-E-27871 (28 May 2006) --- Considerable sunglint emphasizes features on Lake Erie in this image photographed by an Expedition 13 crewmember on the International Space Station. This detailed, south-looking image shows features on the surface of Lake Erie, about 30 miles west of Cleveland, Ohio. At left, a thin, V-shaped wake curves back towards the shore. This type of wake is typically created by a small, light craft such as a speedboat or sailboat under power.

iss073e0000553 (April 22, 2025) --- The freshwater Lake St. Clair rests in between Detroit, Michigan (left), and Ontario, Canada, and connects Lake Huron and Lake Erie in North America in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above.

iss073e0000460 (April 22, 2025) --- The sun's glint beams off the freshwater Lake St. Clair, sits in between Lake Huron (right) and Lake Erie (bottom left), and separates Detroit, Michigan (top left) from Ontario, Canada, in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above.

iss064e051420 (April 2, 2021) --- The Detroit River, pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 264 miles above, separates Detroit, Michigan, from Windsor in Ontario, Canada. The Detroit River also connects to Lake St. Clair (pictured at top) and Lake Erie (out of frame).
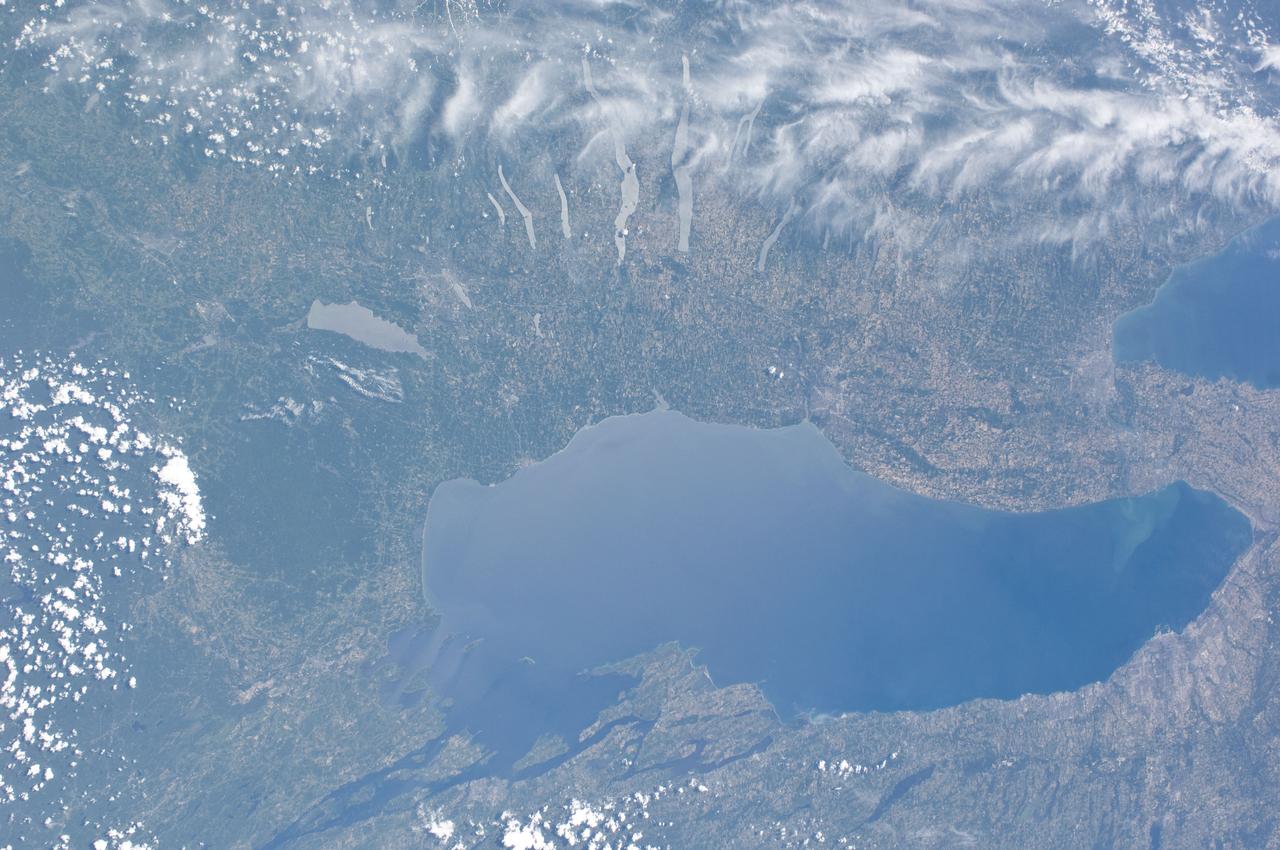

ISS028-E-013201 (4 July 2011) --- This nadir view from the International Space Station, flying at an altitude of approximately 220 miles, shows parts of two countries, including the Finger Lakes area of New York and part of two Great Lakes -- Ontario and Erie and the Niagara River, which connects them.
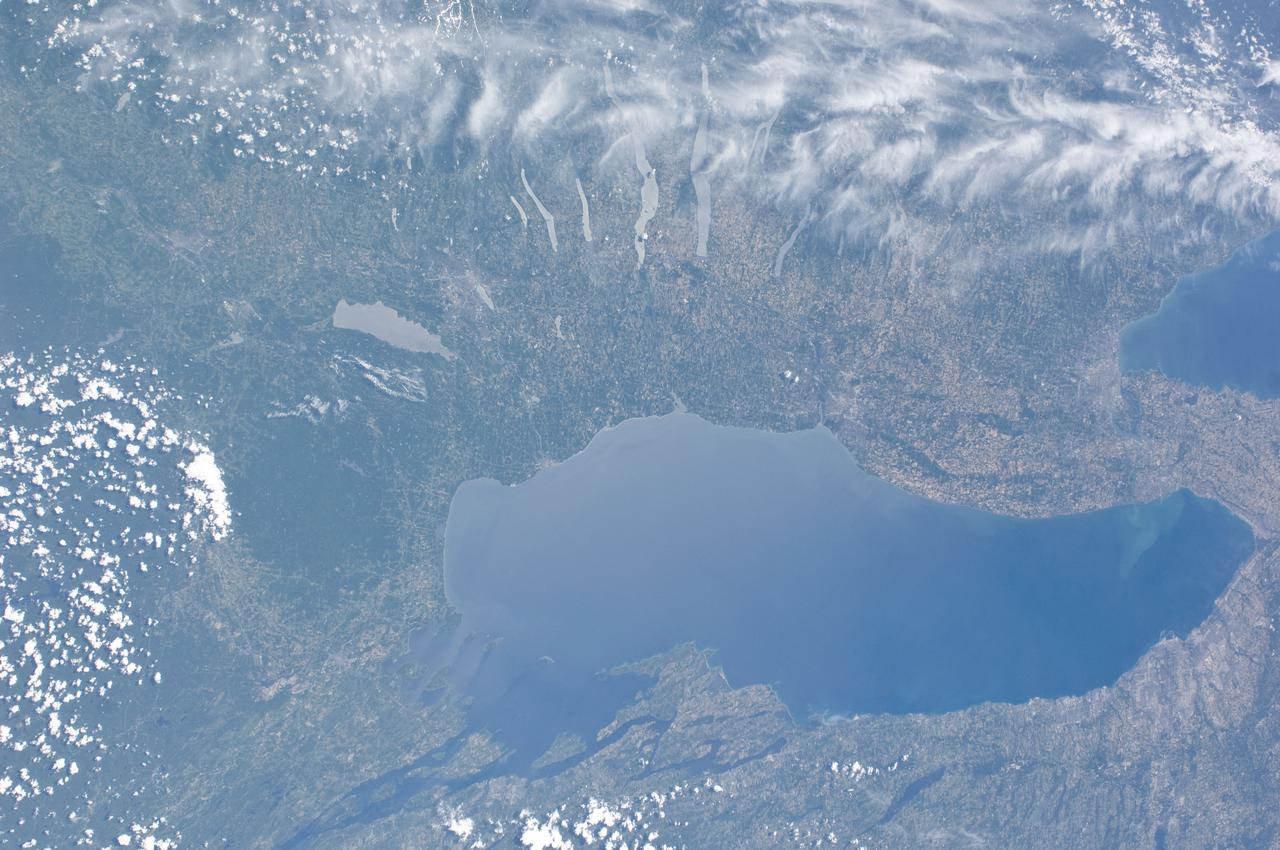

ISS028-E-013202 (4 July 2011) --- This nadir view from the International Space Station, flying at an altitude of approximately 220 miles, shows parts of two countries, including the Finger Lakes area of New York and part of two Great Lakes -- Ontario and Erie and the Niagara River, which connects them.

iss071e000004 (April 7, 2024) --- Lakes Michigan, Huron, and Erie figure prominently in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 261 miles above The Prairie State of Illinois.
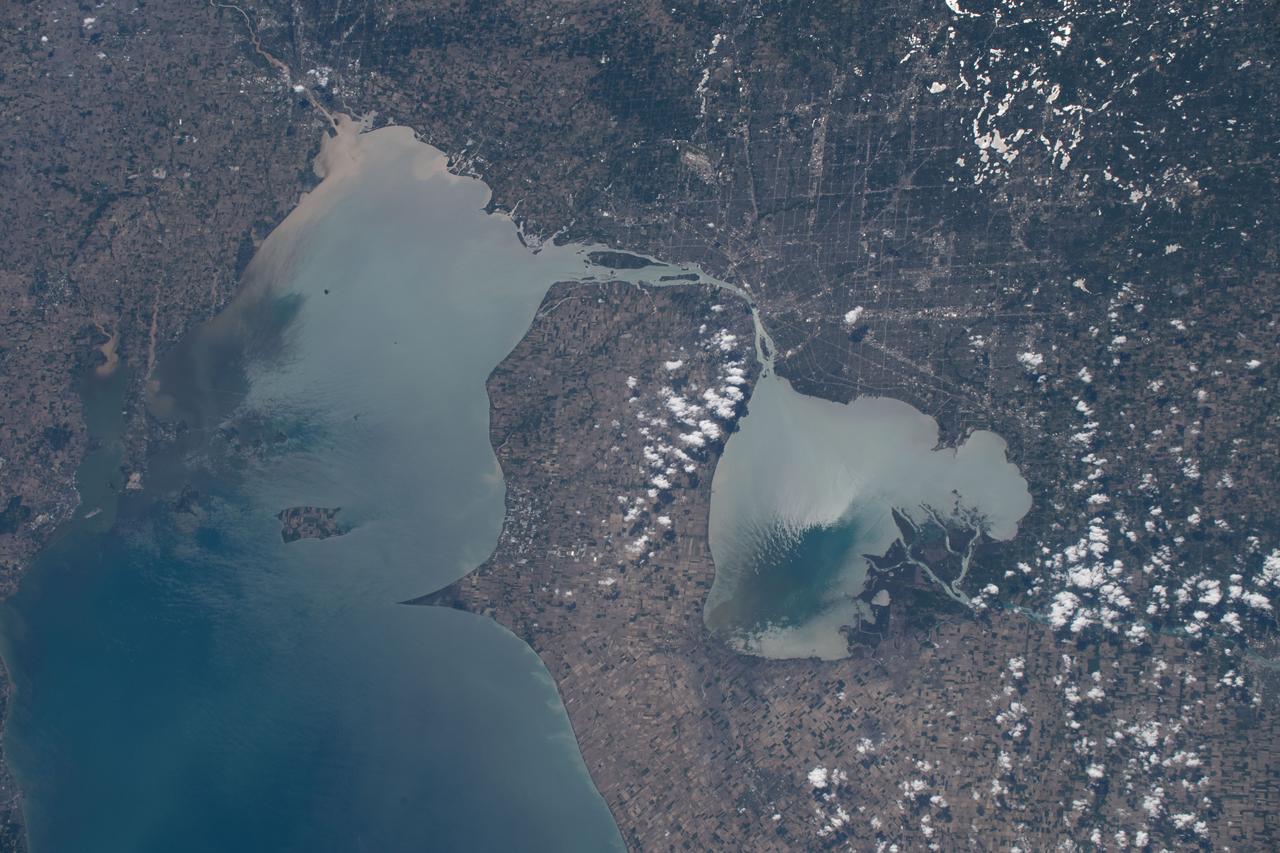

iss059e090279 (June 3, 2019) --- Lakes Erie and St. Clair and the cities of Detroit, Michigan and Toledo, Ohio are pictured as the International Space Station orbited 257 miles over North America.
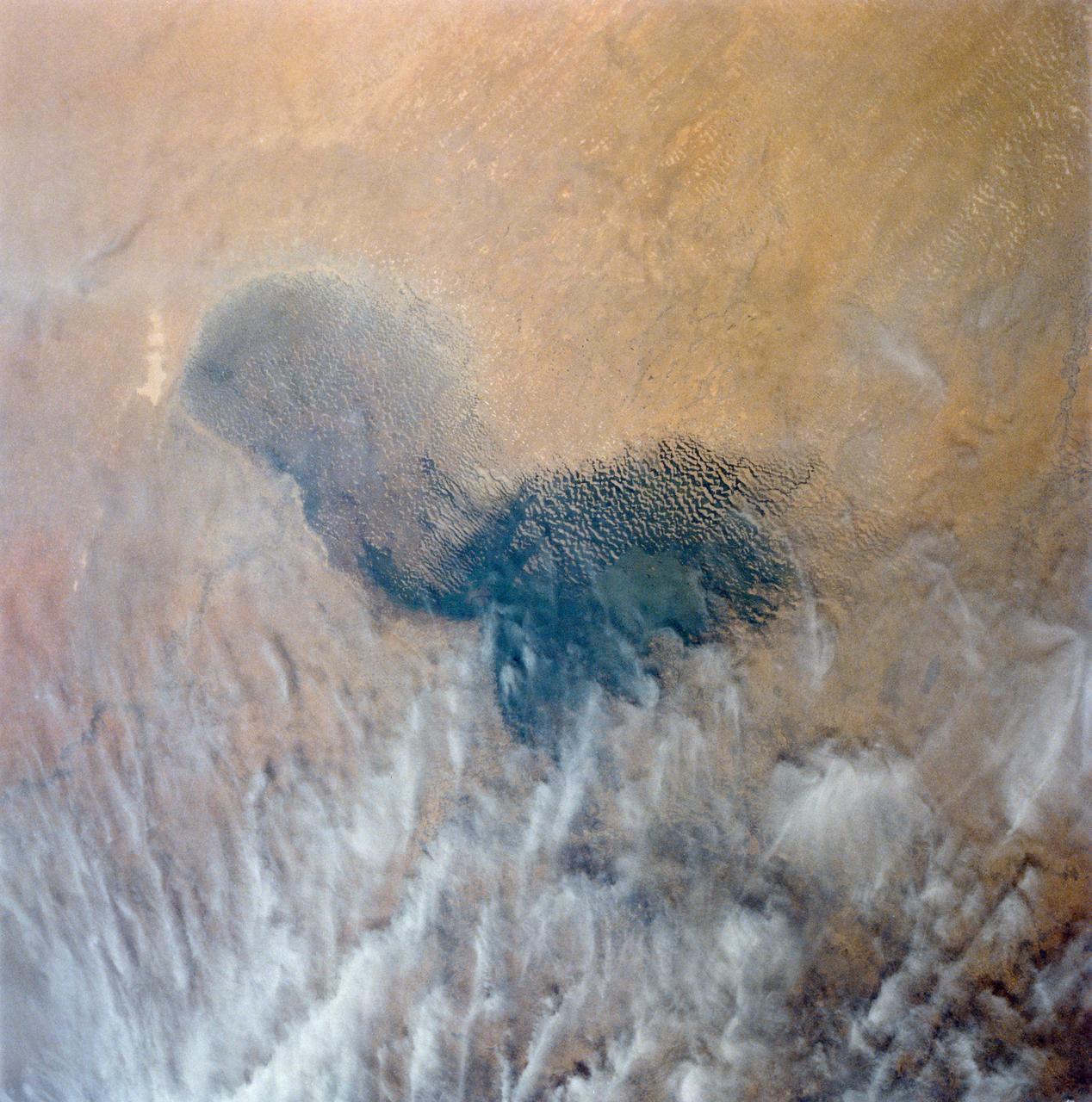

Africa's Lake Chad where the borders of Chad, Niger, Nigeria and Cameroon merge (13.0N, 14.0E) has been undergoing change for the past 25 to 30 years when it was first noticed that the lake is drying up. Since then, astronauts have been photographing it on a regular basis to record the diminishing lake bed. This lake was once the aproximate size of Lake Erie but is now only about half that size and is still receeding.
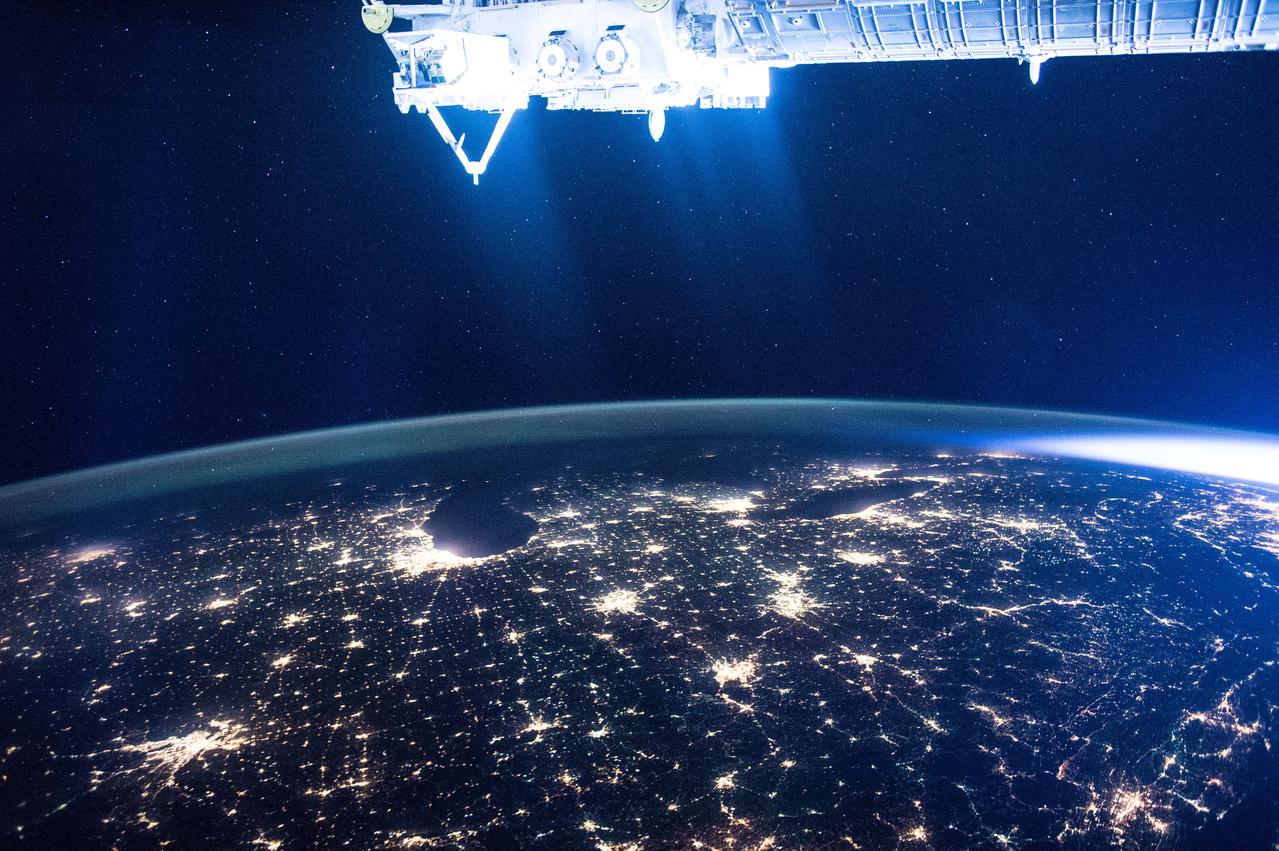

ISS046e005404 (01/05/2016) --- The glittering lights of the American Midwest illuminate the Earth in this captivating image taken by the International Space Station Expedition 46 crew on Jan. 5, 2016. The picture, which was taken while the station was flying above Alabama, shows numerous major cities, including the major city of Chicago (middle-left) situated on the Lake Michigan coastline. Also in view are three of the American Great Lakes, including Lake Michigan (left), Lake Huron (middle) and Lake Erie (right).

ISS015-E-05624 (29 April 2007) --- The Niagara River, eastern end of Lake Erie and western end of Lake Ontario are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 15 crewmember on the International Space Station. In contrast, an image photographed by an Expedition 14 crewmember just a month earlier on March 21, 2007 (ISS014-E-17999) shows Lake Erie clogged with ice that is pushed against the shore line by the prevailing weather systems from the west. These two images document the breakup of the Lake Erie ice pack, the unofficial signature of spring for residents of Buffalo and Niagara Falls. During the winter months, the ice collects in Lake Erie and is prevented from flowing down the Niagara River (the international boundary between Ontario, Canada and New York State) by the Lake Erie-Niagara River Ice Boom. The 2,680-meter (8,800-foot) boom, administered by the 1909 Boundary Water Treaty's International Niagara Board of Control, is deployed each December. Operational since 1964, the boom serves several functions: it protects the water intakes for the Niagara River power plants, and minimizes ice runs and ice blockages that can create damage and flooding along the river. At the height of winter, the thickness of the ice at the Buffalo harbor can reach 3.5 meters (12 feet). The removal of the ice boom, usually in early April, is now marked by local celebrations. This year the boom was removed in mid-April, a bit later than usual.
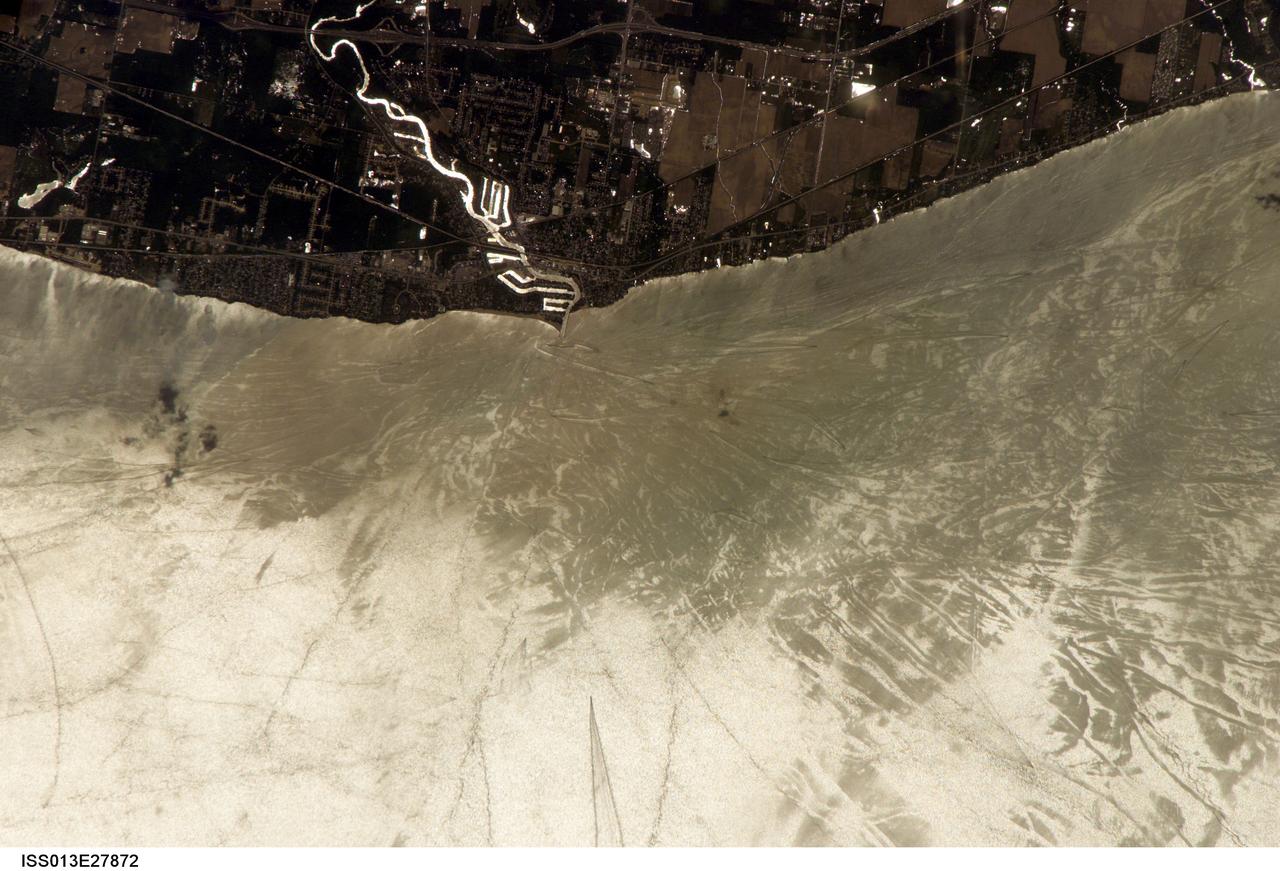

ISS013-E-27872 (28 May 2006) --- Considerable sunglint emphasizes features on Lake Erie in this image photographed by an Expedition 13 crewmember on the International Space Station. This detailed, south-looking image shows features on the surface of Lake Erie, about 30 miles west of Cleveland, Ohio. This view shows the Vermilion River in strong sunglint. The angular water bodies along the river are likely marinas. The main part of the image show numerous ship wakes in the zone of partial glint around the disk of the Sun's reflection point. The wakes radiate from the mouth of the Vermilion River, with many of them heading northwest in the direction of Detroit, Michigan.
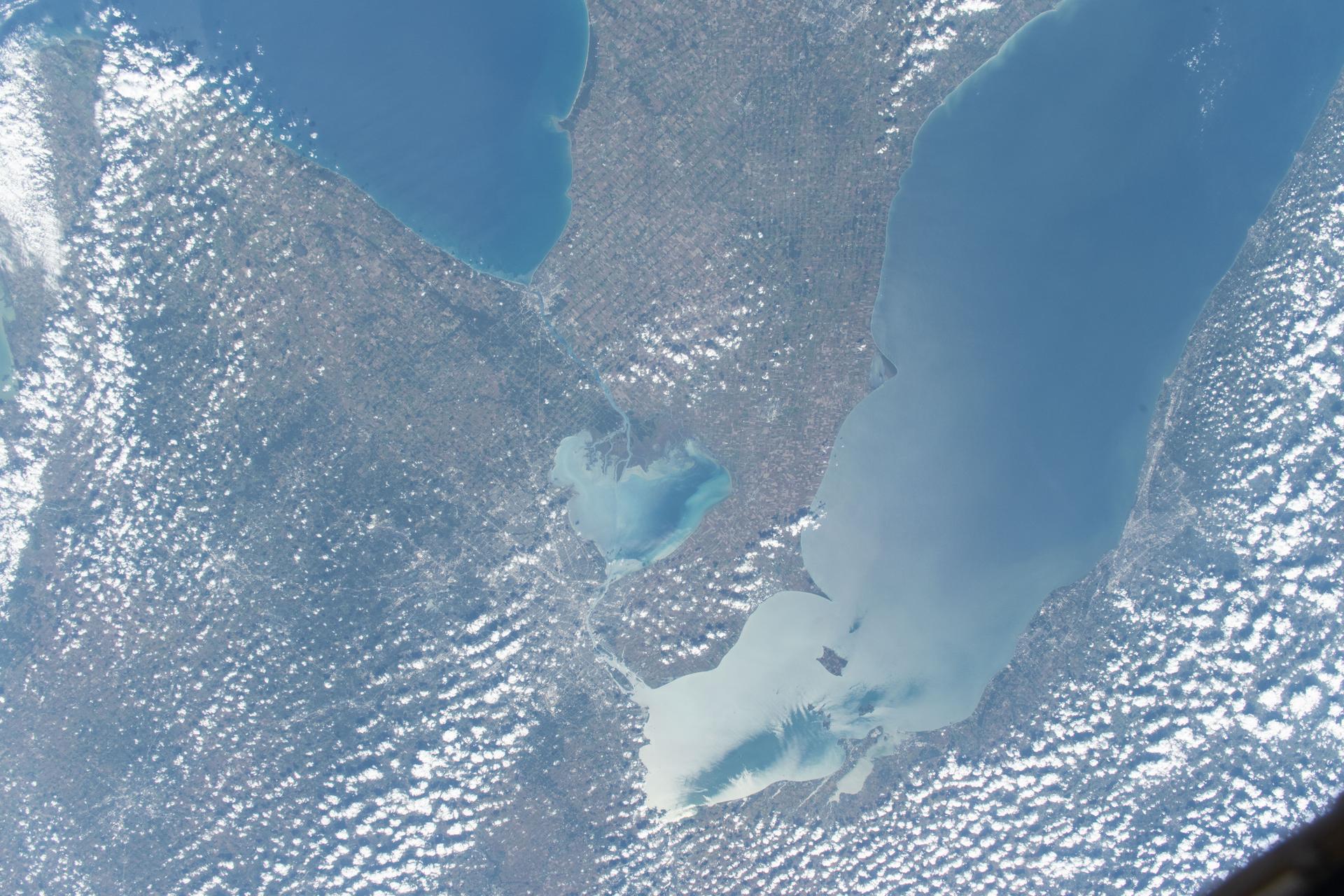

iss073e0814049 (Sept. 26, 2025) --- Detroit, Michigan, sits on the banks of the Detroit River, which connects Lake St. Clair (center) to Lake Erie to the south. To the north, the St. Clair River links Lake St. Clair with Lake Huron. Both rivers serve as natural borders between the United States and Canada. The International Space Station was orbiting 259 miles above Ontario, Canada, at the time of this photograph.
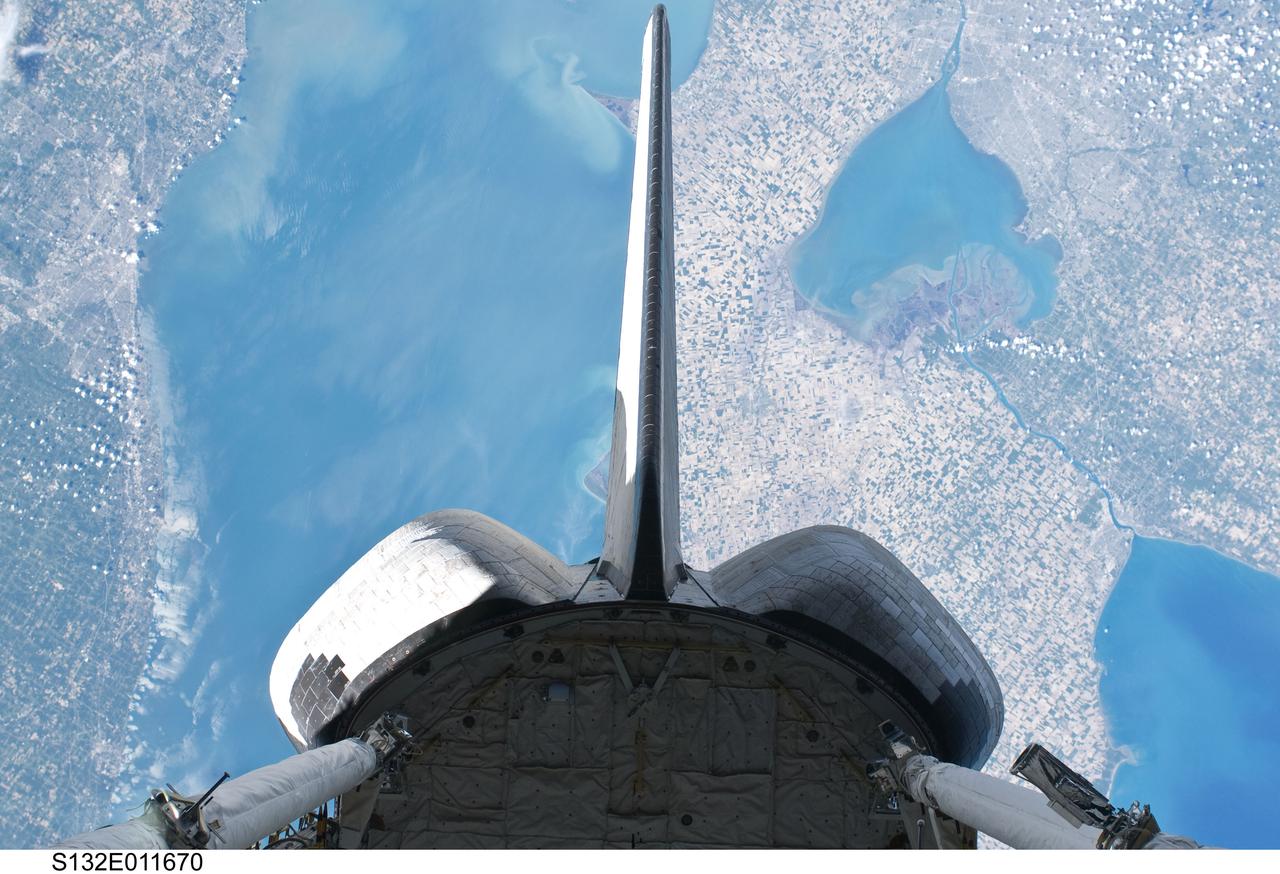

S132-E-011670 (25 May 2010) --- Backdropped over parts of Michigan and the Canadian province of Ontario, space shuttle Atlantis? vertical stabilizer, orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and aft payload bay are featured in this image photographed by an STS-132 on the shuttle during flight day 12 activities. Recognizable features in the photo include Lake St. Clair and parts of Lake Huron and Lake Erie.

ISS036-E-035635 (24 Aug. 2013) --- Plankton bloom and Lake Ontario are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 36 crew member on the International Space Station. This photograph highlights a late summer plankton bloom visible throughout much of Lake Ontario (one of the Great Lakes, together with Michigan, Superior, Erie, and Huron). Cyanobacteria, or blue-green algae, can reach such large concentrations that they color the water to such an extent that the change is visible from orbit. Harmful algal blooms, or HABs, have been observed in all of the Great Lakes – particularly Lake Erie - and are associated with a variety of causative factors including changes in precipitation; drought; invasive species (quagga, zebra mussels, Asian carp); nutrient loading from runoff and sewage (nitrogen and phosphorus); and warmer average temperatures. In addition to reduced water quality and human health concerns, algal blooms can also lead to hypoxia (reduction of oxygen in the bottom waters) that kills large numbers of fish and other aquatic life. Lake Ontario, like the other Great Lakes Erie, Huron, and Superior is roughly divided between the USA and Canada. The USA side of Lake Ontario has its shoreline along the state of New York, while its Canadian shoreline lies within the province of Ontario. The city of Kingston, Ontario, is visible near the Saint Lawrence River outflow from the lake. Several other landscape features of New York State are visible in the image, including the Finger Lakes region to the west of Syracuse, NY (upper left). To the northeast of Syracuse, the dark wooded slopes of the Adirondack Mountains are visible at lower right. Patchy white cloud cover obscures much of the land surface to the west of Lake Ontario.

NASA Glenn Research Pilot Jim Demers flies the T-34C Mentor aircraft. When NASA scientists study Great Lakes algal blooms, Demers is one of the pilots at the controls.
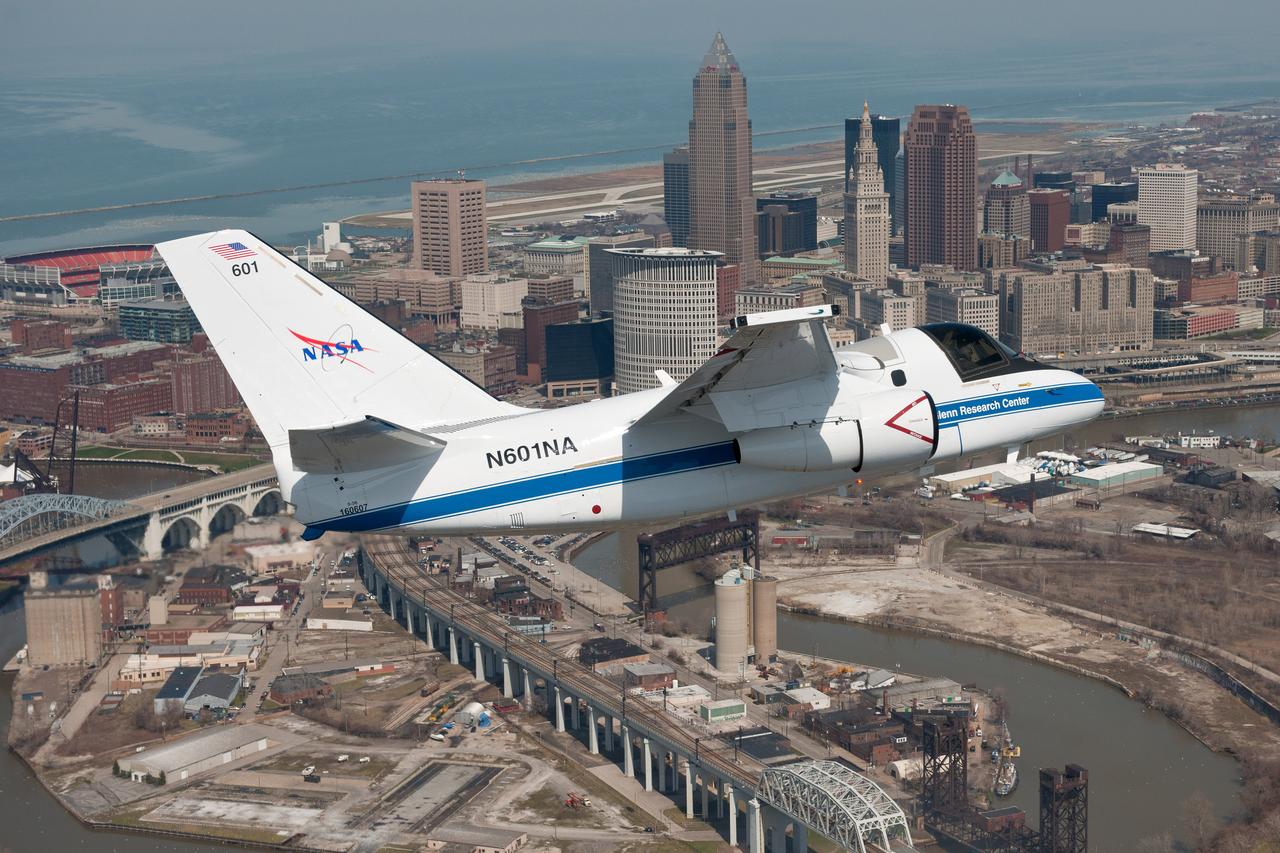

This photo shows NASA Glenn’s S-3 Viking Aircraft flying over downtown Cleveland, Ohio. The S-3 continues to conduct important research including regular flights over Lake Erie and other waterways to image algal blooms that have plagued the area’s waters.

iss065e000865 (April 19, 2021) --- Grand Island splits the Niagara River which runs past Buffalo, New York, and into Lake Erie. The International Space Station was orbiting 264 miles above southern Pennsylvania when this photograph was taken.
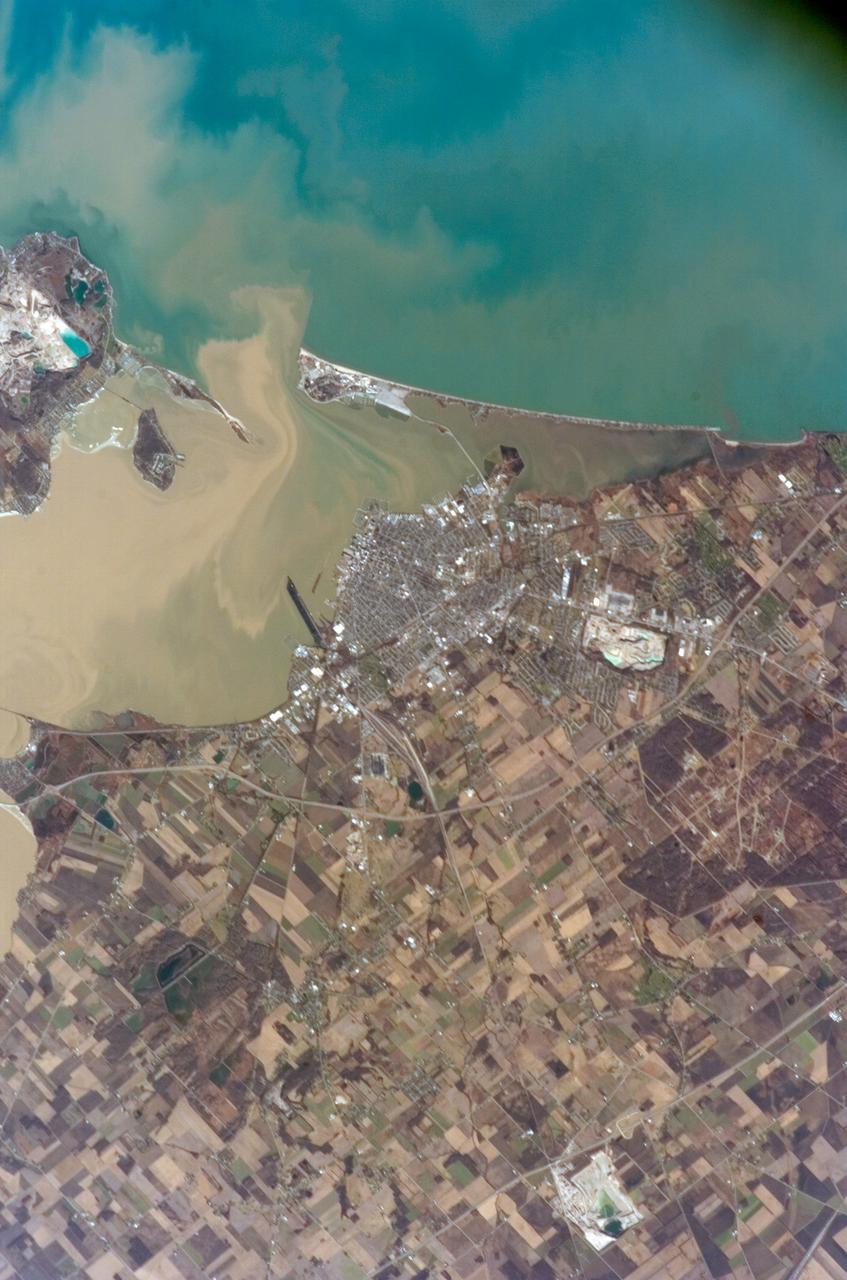

ISS012-E-15050 (12 Jan. 2006) --- Sandusky Bay is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 12 crew member on the International Space Station. Sandusky Bay appears with brown muddy water (left) in this view. The bay leads out into southern Lake Erie (top). The small city of Sandusky occupies the northeastern shore of the bay (center of the image). Highway 6 can be seen arcing around the south side of the city. Ferries connect Sandusky to Pelee Island (not visible) in the middle of the lake. In earlier days, Sandusky Bay was known as one of the best protected port sites in the Great Lakes. The most striking aspect of this image is the flow lines of the brown water in and out of the mouth of the bay. Slight movement of lake surface water, driven mainly by wind, causes a small ebb and flow of bay water. Sediment-charged water is derived from agricultural fields along the Sandusky River upstream. Mud plumes in Lake Erie originate from prior pulses of muddy water from the bay. According to scientists studying the station photos, it appears that water was flowing into the bay when this image was taken. Sandusky lies midway between Toledo and Cleveland, both about an hour’s drive away.
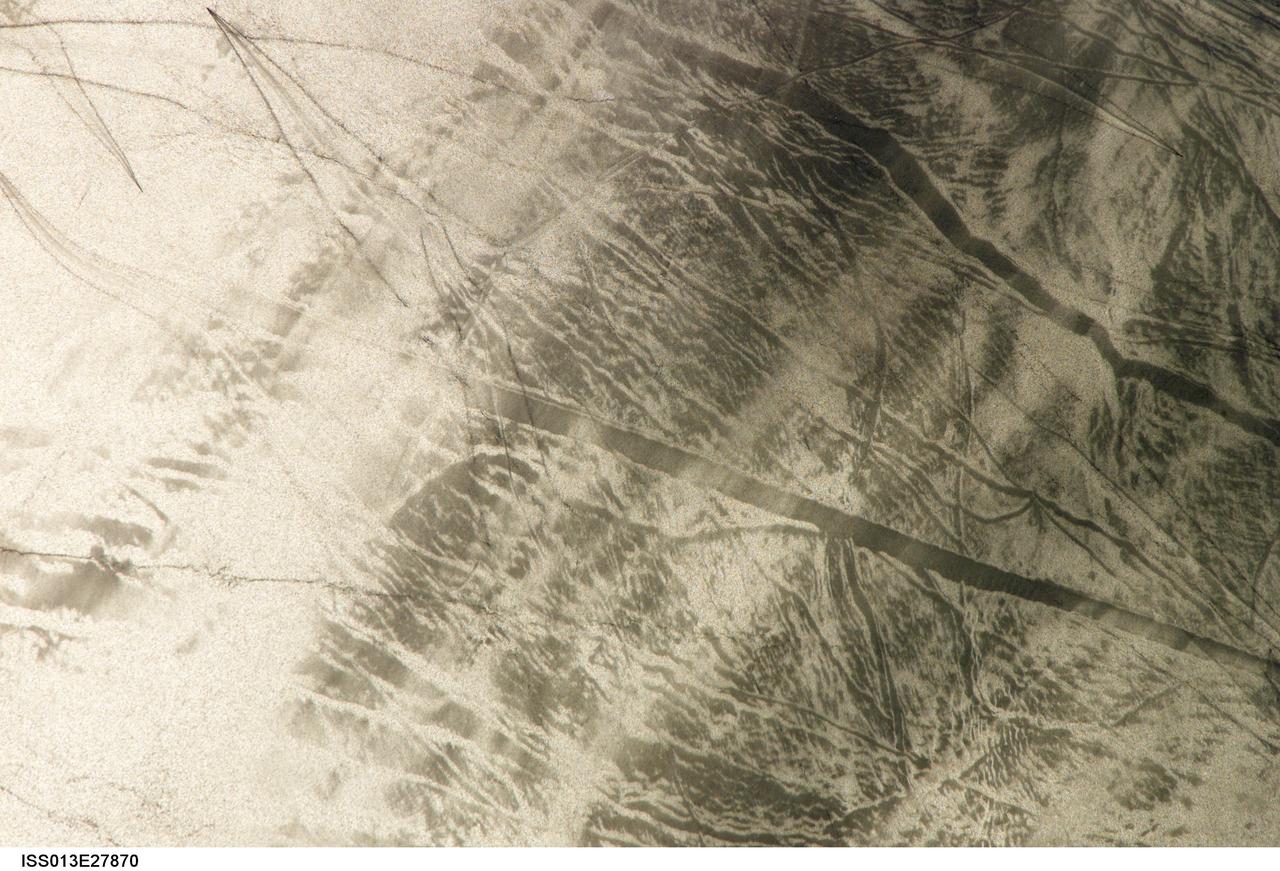
ISS013-E-27870 (28 May 2006) --- Considerable sunglint emphasizes features on Lake Erie in this image photographed by an Expedition 13 crewmember on the International Space Station. This detailed, south-looking image shows features on the surface of Lake Erie, about 30 miles west of Cleveland, Ohio. This view shows tight-V-shaped wakes of small craft. It also shows broad patterns of larger craft, probably large freighters carrying cargo that displace and disturb more water during passage. These larger wakes are aligned with the direct course between Detroit (out of frame) and Cleveland (out of frame). Some of the broad, ill-defined swaths of light and dark are streaks of wind-roughened water, which reflect the Sun differently.
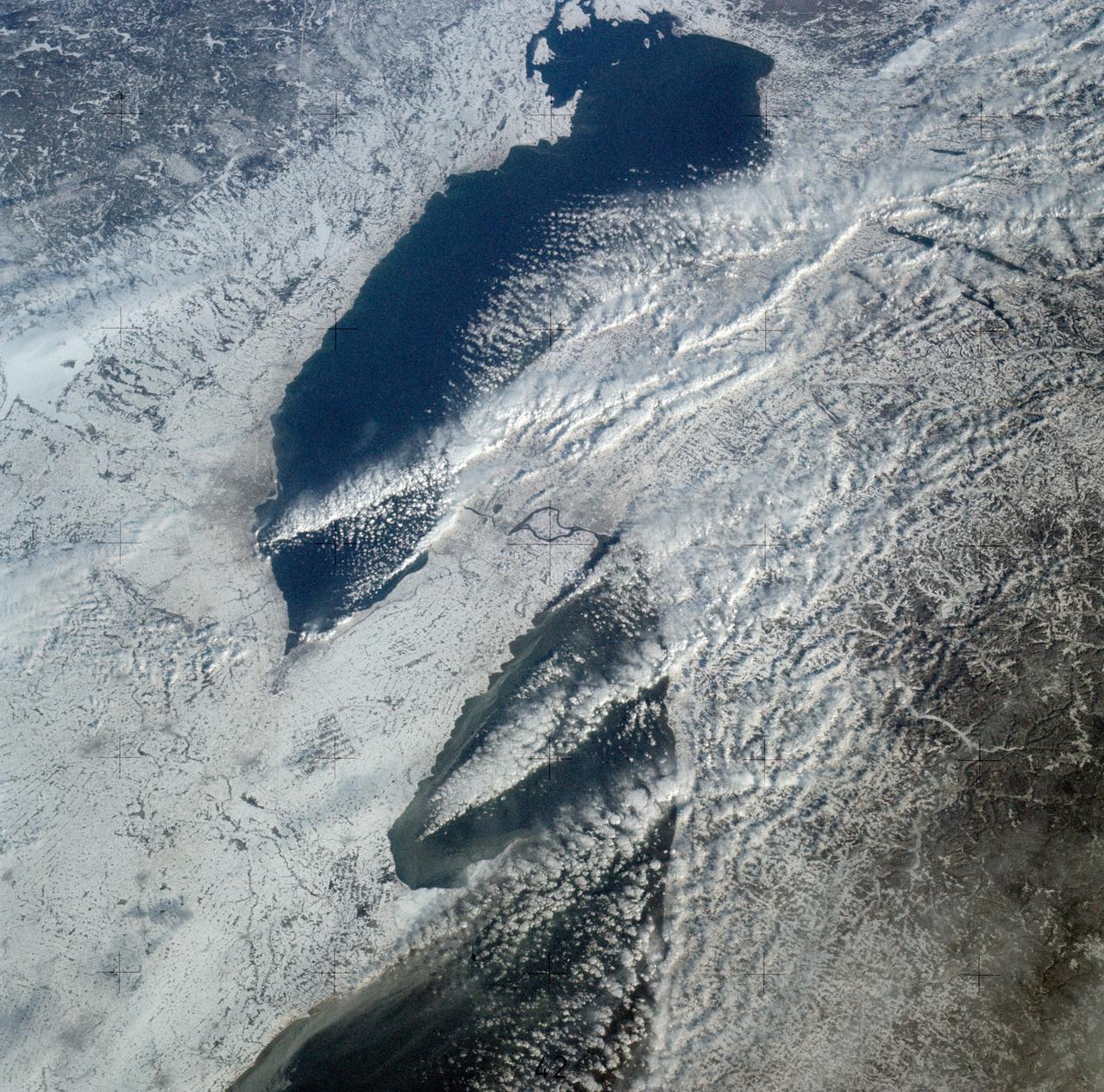

SL4-139-3989 (February 1974) --- An oblique view of a portion of the Great Lakes area as seen from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. This picture was taken with a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera. Lake Erie is in the foreground; and Lake Ontario is in the background. The Niagara Falls area is in the center of the photograph. Portions of Pennsylvania, New York, and Ontario, Canada are visible, but under nearly complete snow cover. Major structural features, drainage patterns, road systems and the cities of Buffalo and Toronto are easily distinguished and actually enhanced by the snow. At the time this picture was taken, these two Great Lakes had no observable ice, although cloud formations partially mask the southern shores of the two bodies of water. James Barnes, a snow-pattern expert, will analyze Skylab photographs like this one to gain further knowledge of snow cover over land masses. Photo credit: NASA
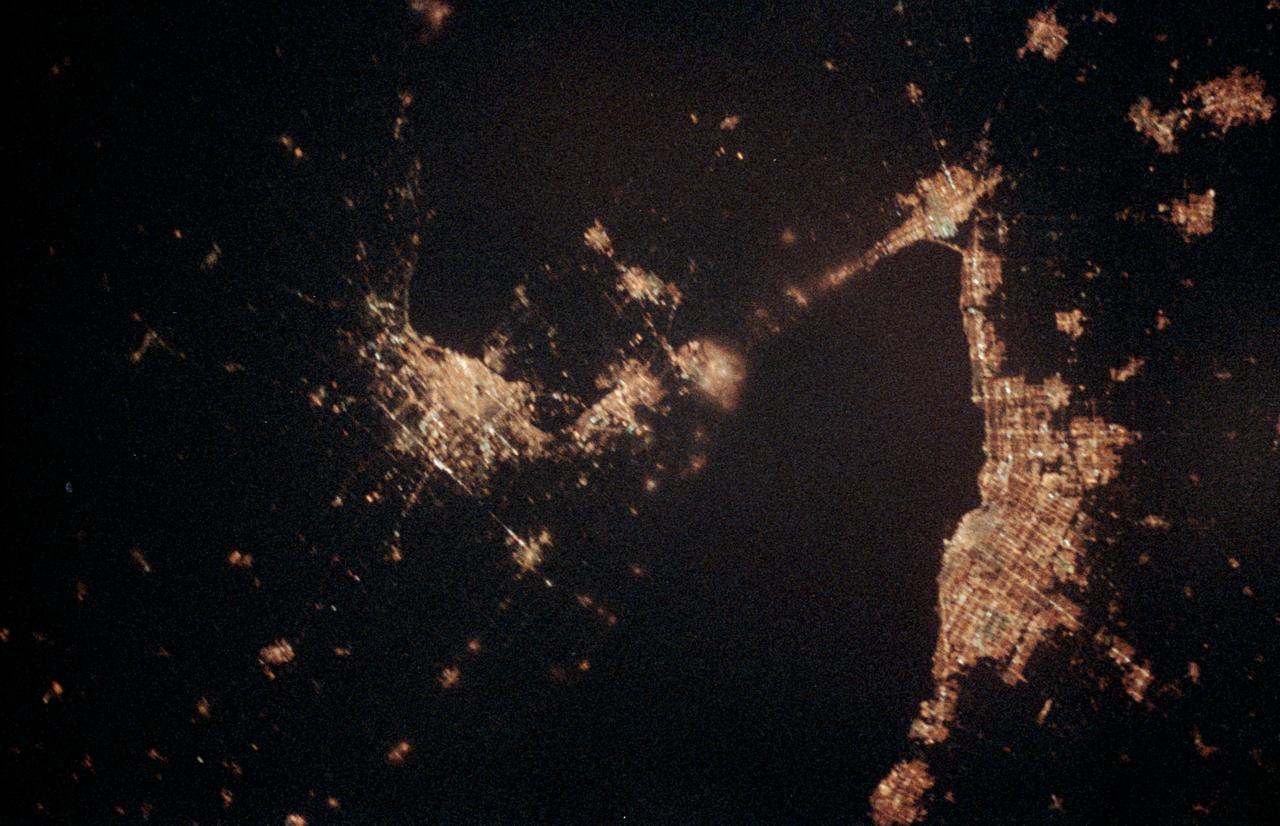

STS060-06-037 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- The city lights of Buffalo and Toronto outline the shores of the east end of Lake Erie and the west end of Lake Ontario in this night scene of western New York and southern Ontario. Between the two major cities are the cities of Niagara Falls, New York and Niagara Falls, Canada, which straddle the Niagara River just north of the actual falls. This photograph was taken with a special ASA-1600 film that is normally used for night-time photography of aurora, noctilucent clouds, biomass burning, and city lights.
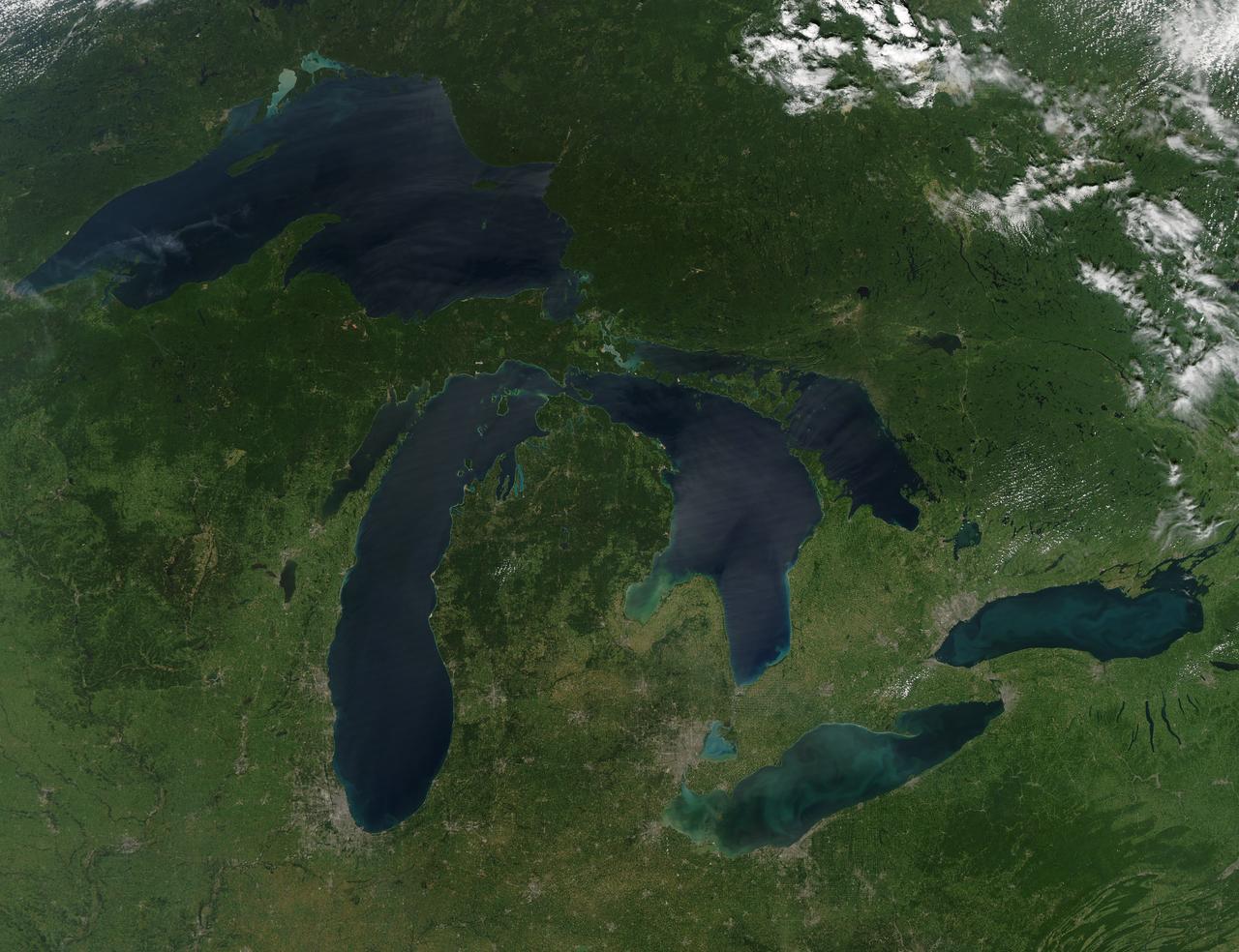
NASA image acquired August 28, 2010 Late August 2010 provided a rare satellite view of a cloudless summer day over the entire Great Lakes region. North Americans trying to sneak in a Labor Day weekend getaway on the lakes were hoping for more of the same. The Great Lakes comprise the largest collective body of fresh water on the planet, containing roughly 18 percent of Earth's supply. Only the polar ice caps contain more fresh water. The region around the Great Lakes basin is home to more than 10 percent of the population of the United States and 25 percent of the population of Canada. Many of those people have tried to escape record heat this summer by visiting the lakes. What they found, according to The Hamilton Spectator, was record-breaking water temperatures fueled by record-breaking air temperatures in the spring and summer. By mid-August, the waters of Lake Superior were 6 to 8°C (11 to 14°F) above normal. Lake Michigan set records at about 4°C (7°F) above normal. The other three Great Lakes – Huron, Erie, and Ontario -- were above normal temperatures, though no records were set. The image was gathered by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite at 1:30 p.m. Central Daylight Time (18:30 UTC) on August 28. Open water appears blue or nearly black. The pale blue and green swirls near the coasts are likely caused by algae or phytoplankton blooms, or by calcium carbonate (chalk) from the lake floor. The sweltering summer temperatures have produced an unprecedented bloom of toxic blue-green algae in western Lake Erie, according to the Cleveland Plain Dealer. NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team, Goddard Space Flight Center. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Instrument: Aqua - MODIS Click here to see more images from <b><a href="#//earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Goddard’s Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
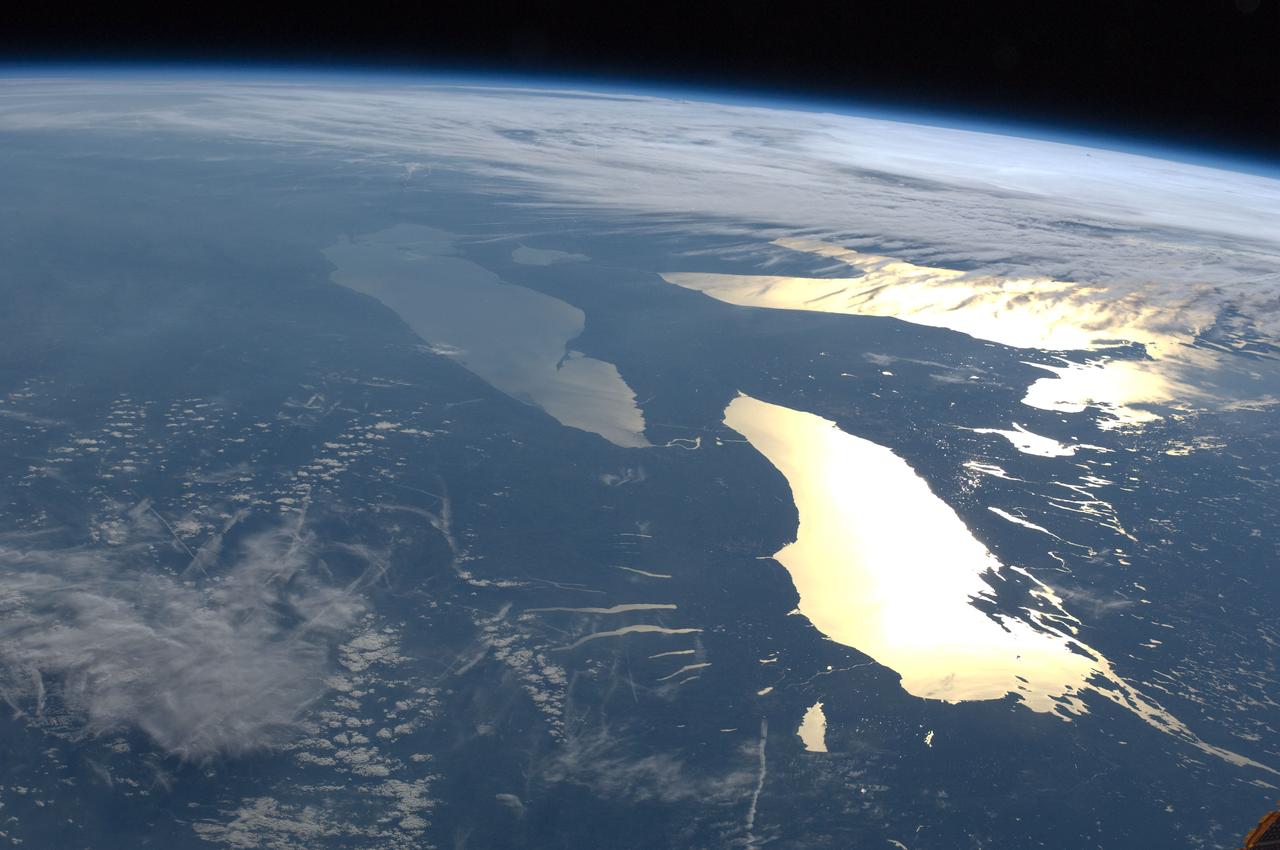

ISS031-E-123071 (14 June 2012) --- The Great Lakes in sunglint are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 31 crew member on the International Space Station. From the vantage point of the space station, crew members observe many spectacular phenomena including aurora, noctilucent clouds, airglow, and sunglint on Earth?s water bodies. Sunglint is light reflected off of a water surface towards the observer such that it creates the appearance of a mirror-like surface. If the viewing and lighting conditions are ideal, that mirror-like surface can extend over very large areas, such as the entire surface of Lake Ontario (approximately 18,960 square kilometers). This photograph was taken while the space station was located over a point to the southeast of Nova Scotia (approximately 1,200 kilometers ground distance from the center point of the image). Lake Ontario, Lake Huron, the Finger Lakes of upstate New York, and numerous other bodies of water appear brilliantly lit by sunglint. To the west, Lake Erie is also highlighted by sunglint, but less light is being reflected back towards the observer resulting in a duller appearance. Much of central Canada is obscured by extensive cloud cover in the image, whereas a smaller grouping of clouds obscures the Appalachian range and Pennsylvania (lower left). The blue envelope of Earth?s atmosphere is visible above the curved limb, or horizon line that extends across the upper third of the image. Such panoramic views of the planet are readily taken through space station viewing ports with handheld digital cameras which allow the crew to take advantage of the full range of viewing angles.

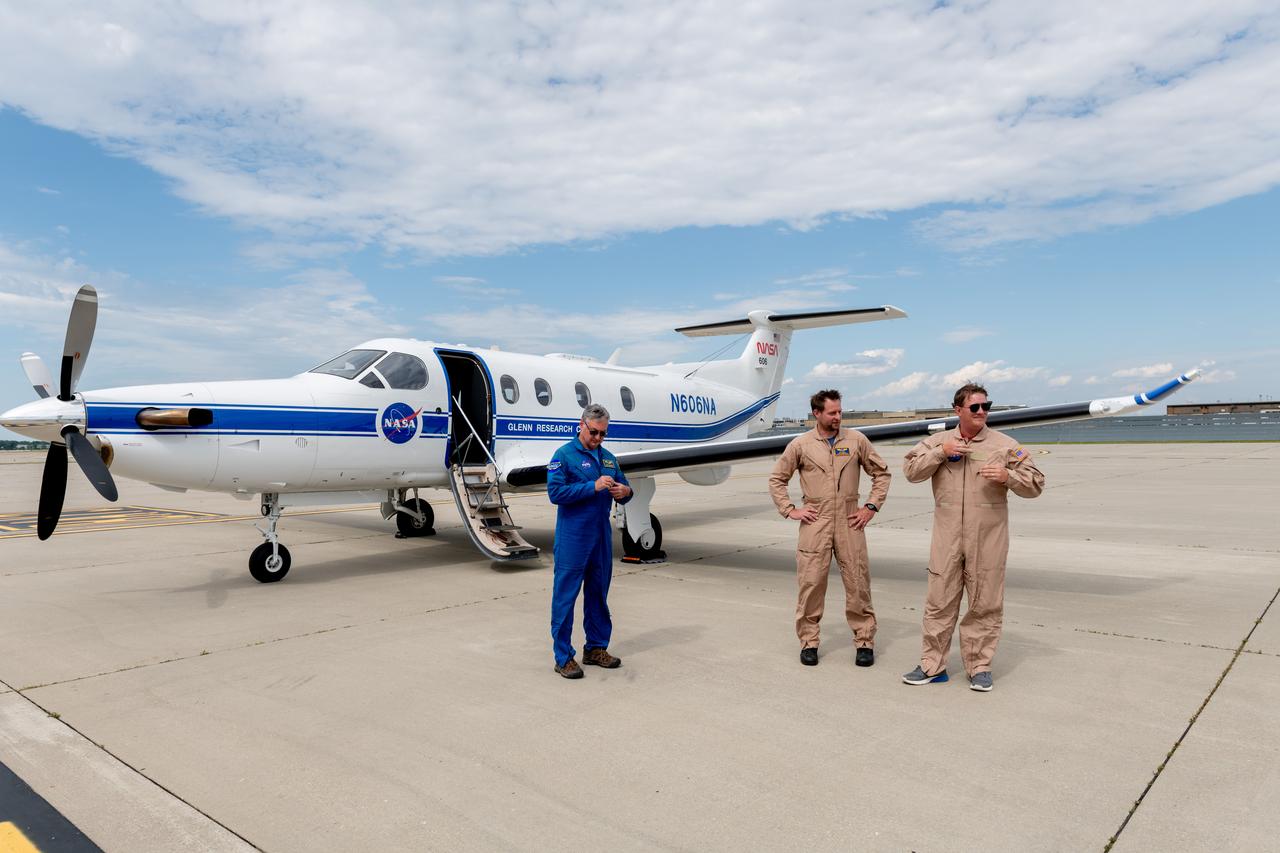
A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Pictured from Left to Right: James Demers, Adam Wroblewski, Shaun McKeehan, Kurt Blankenship. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data.

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data.

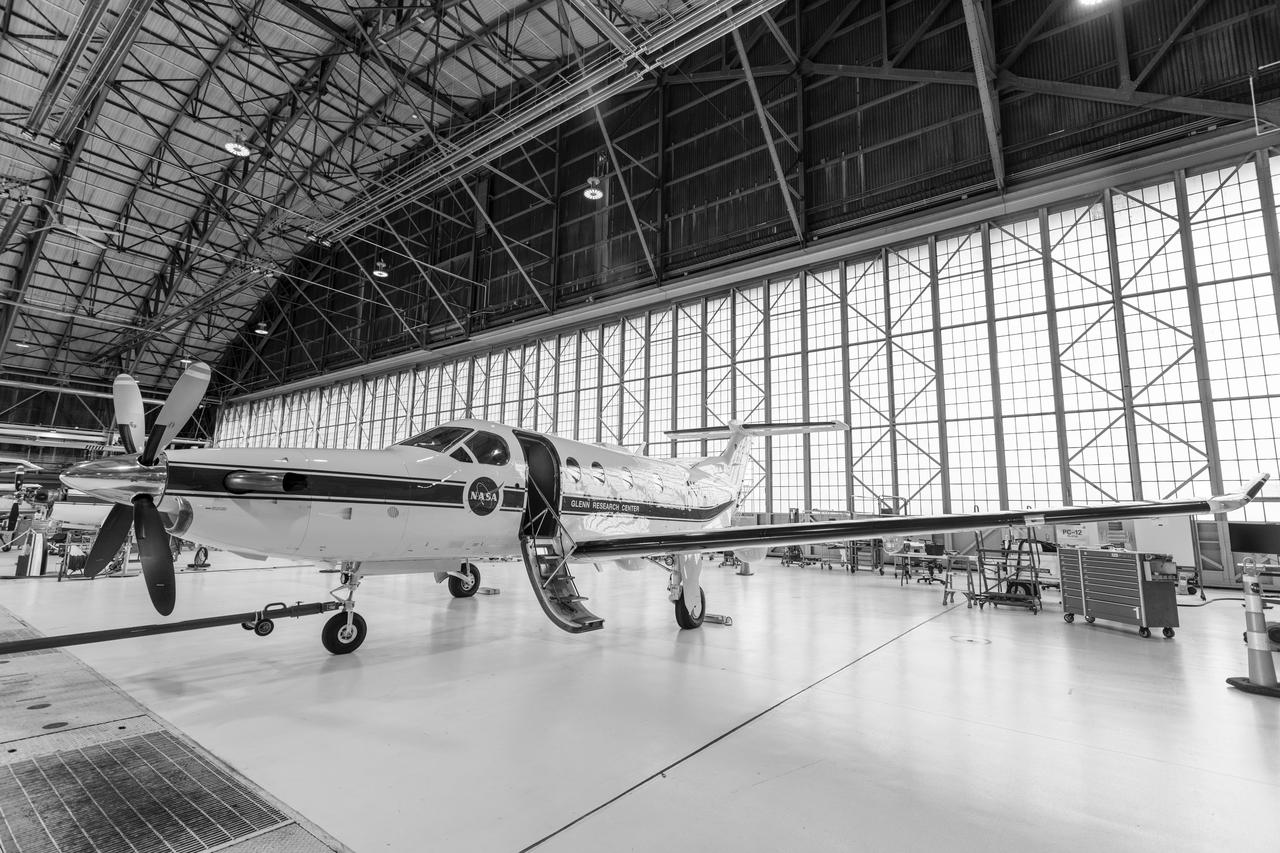
Pilatus PC-12 Aircraft Being Prepped for Takeoff on June 12, 2024. A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)

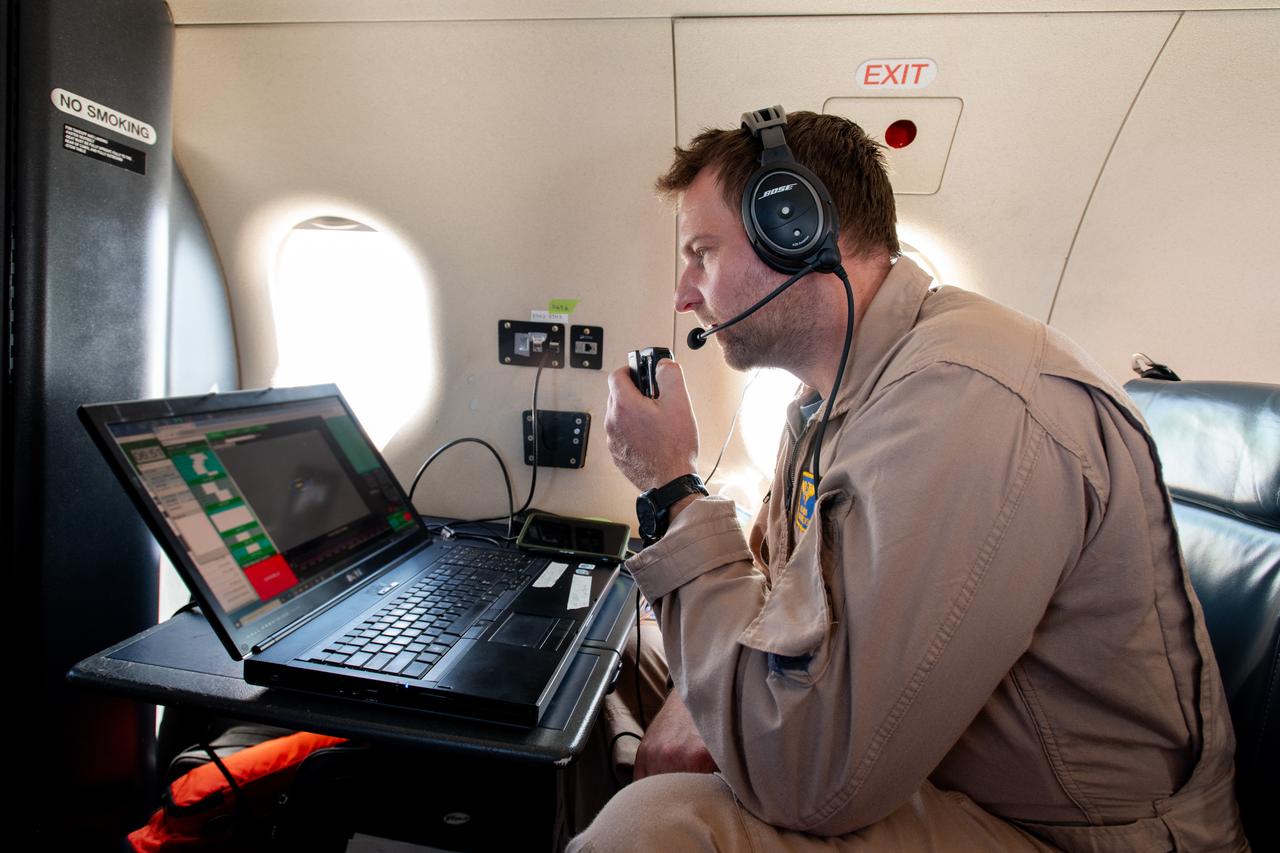
A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data.

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data.

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data.

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data.
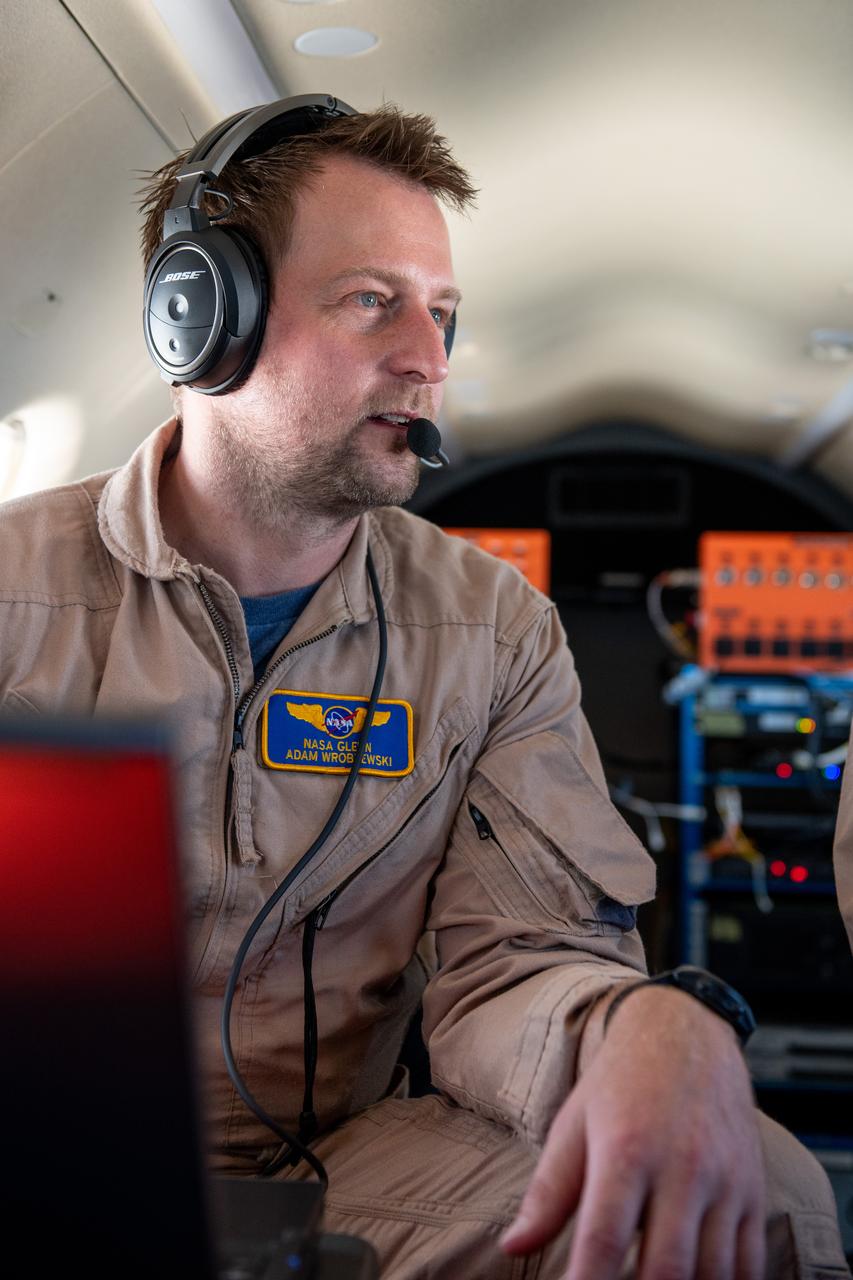

Adam Wroblewski p A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. Adam Wroblewski in the PC-12 over Lake Erie on June 13, 2024 sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
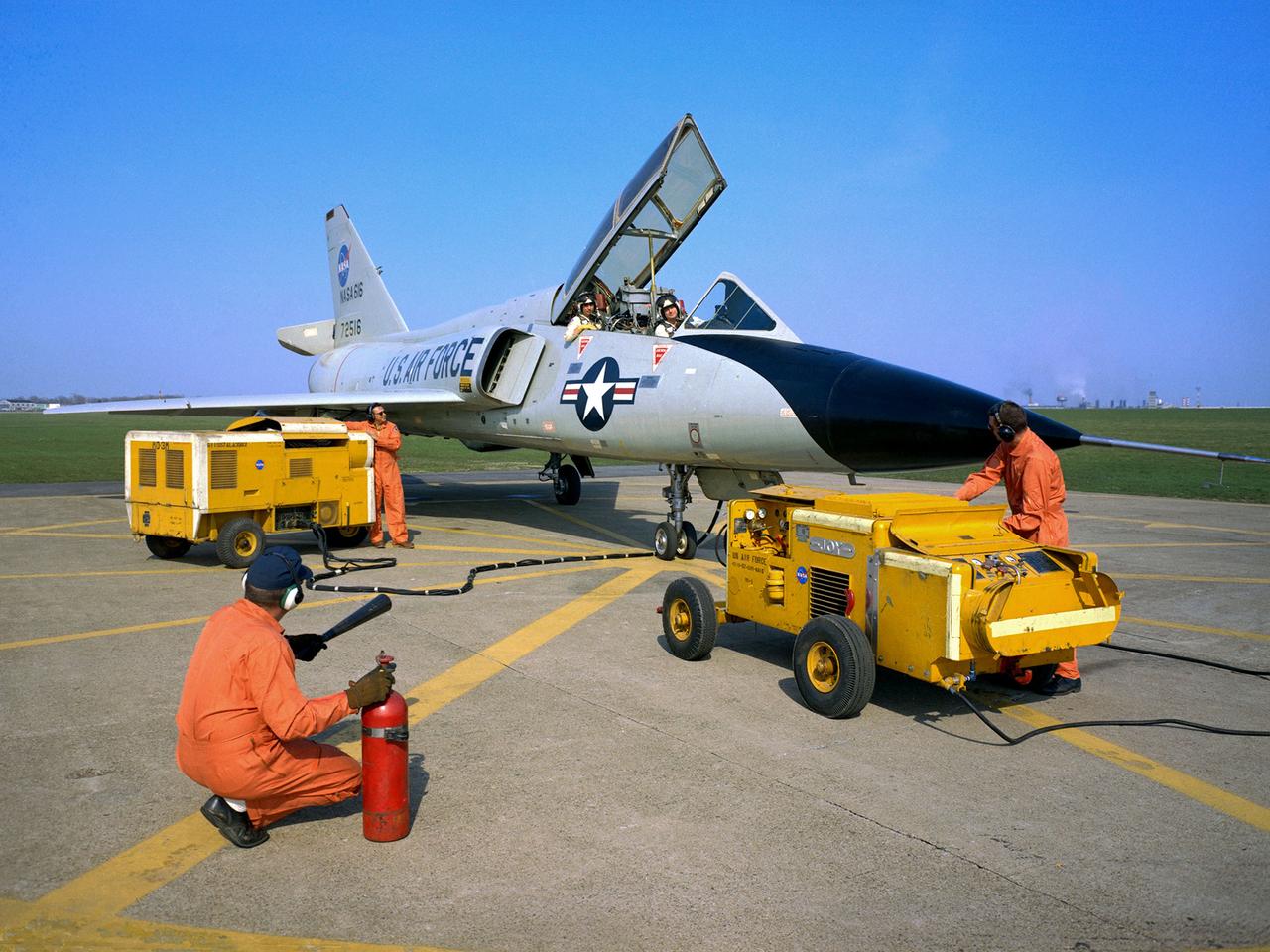

National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) pilot Cliff Crabbs and the flight operations crew prepare a Convair F-106B Delta Dart for a flight from the Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. NASA acquired the aircraft three years earlier to investigate noise-reducing inlet and nozzle designs for the supersonic transport engine program. Two General Electric J85 engines were installed underneath the aircraft’s delta wings to simulate the general shape of the supersonic transport’s engines. One of the engines was modified with experimental inlet or nozzle configurations. The unmodified engine was used for comparison. Most F-106B flights were flown in a 200-mile path over the lake between Buffalo and Sandusky, known as the Lake Erie Corridor. The 1100-miles per hour flight took only 11 minutes at an altitude of 30,000 feet. The aircraft almost always returned with a depleted fuel supply so a Visual Flight Rules operation was required. Following the crash of another jet fighter at Lewis in July 1969, the F-106s were stationed at Selfridge Air Force Base in Michigan. NASA pilots flew transport planes each morning to the base before commencing the F-106B missions.

STS078-726-000A (20 June - 7 July 1996) --- Though the Space Shuttle program has been ongoing since 1981, few pictures have been taken from Earth-orbit that show the Toledo area featured in this 70mm frame from the STS-78/LMS-1 mission. The muddy Maumee River flows through Toledo into the west end of Lake Erie. Toledo is the seat (1835) of Lucas county, northwestern Ohio, and is a principal Great Lakes port, being the hub of a metropolitan complex that includes Ottawa Hills, Maumee, Oregon, Sylvania, Perrysburg, and Rossford. Fort Industry (1803-05) was located at the mouth of Swan Creek (now downtown Toledo), where permanent settlement was made after the War of 1812. Two villages, Port Lawrence (1817) and Vistula (1832), were consolidated in 1833 and named for Toledo, Spain. The united community was incorporated as a city in 1837. Its population in 1990 was 332,943. There are many smaller Ohio cities in the photo including Bowling Green, Findlay, Tiffin, Fremont, Fostoria, and Sandusky (right edge).

Though North America is a full month into astronomical spring, the Great Lakes have been slow to give up on winter. As of April 22, 2014, the Great Lakes were 33.9 percent ice covered. The lake they call Superior dominated the pack. In the early afternoon on April 20, 2014, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite captured this natural-color image of Lake Superior, which straddles the United States–Canada border. At the time Aqua passed over, the lake was 63.5 percent ice covered, according to the NOAA Great Lakes Environmental Research Lab (GLERL). Averaged across Lake Superior, ice was 22.6 centimeters (8.9 inches) thick; it was as much as twice that thickness in some locations. GLERL researcher George Leshkevich affirmed that ice cover this spring is significantly above normal. For comparison, Lake Superior had 3.6 percent ice cover on April 20, 2013; in 2012, ice was completely gone by April 12. In the last winter that ice cover grew so thick on Lake Superior (2009), it reached 93.7 percent on March 2 but was down to 6.7 percent by April 21. Average water temperatures on all of the Great Lakes have been rising over the past 30 to 40 years and ice cover has generally been shrinking. (Lake Superior ice was down about 79 percent since the 1970s.) But chilled by persistent polar air masses throughout the 2013-14 winter, ice cover reached 88.4 percent on February 13 and 92.2 percent on March 6, 2014, the second highest level in four decades of record-keeping. Air temperatures in the Great Lakes region were well below normal for March, and the cool pattern is being reinforced along the coasts because the water is absorbing less sunlight and warming less than in typical spring conditions. The graph below, based on data from Environment Canada, shows the 2014 conditions for all of the Great Lakes in mid-April compared to the past 33 years. Lake Superior ice cover got as high as 95.3 percent on March 19. By April 22, it was reported at 59.9 percent; Lake Huron was nearly 30.4 percent. News outlets noted that as many as 70 ships have been backed up in Lakes Michigan, Huron, and Erie, waiting for passage into ports on Lake Superior. The U.S. Coast Guard has been grouping ships together into small convoys after they pass through locks at Sault Ste. Marie, in order to maximize ice-breaking efficiency and to protect ships from damage. Superior is the world’s largest freshwater lake by area (82,100 square kilometers or 31,700 square miles) and the third largest by volume. The waters average 147 meters (483 feet) in depth, and the basin is believed to hold about 10 percent of the world’s liquid fresh water. NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz LANCE/EOSDIS MODIS Rapid Response Team, GSFC. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Read more: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=83541&eocn=home&eoci=iotd_title" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=83541&eocn...</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

SL3-83-0152 (July-September 1973) --- A near vertical view of the metropolitan Detroit, Michigan area is seen in this Skylab 3 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch Earth terrain camera) photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The 25-mile long Detroit River drains the smaller body of water (Lake St. Clair) and flows southwestward separating Detroit from Windsor, Ontario, and empties into Lake Erie. The Detroit River handles a great deal of Great Lakes barge and ship traffic. Major streets and thoroughfares radiating from the city are clearly visible. Fighting Island is the highly reflective, white area located almost in the center of the picture. This high reflectivity is caused by the functional use of the island-disposal ponds for chemical salts. Sedimentation and/or pollution patterns in the area provide interesting visual phenomena for speculation and analysis. Distinct and rather unique cultivated field patterns can be observed south and east of Windsor, Ontario. This is a direct result of an English survey and land tenure system which was utilized when the area was settled. New areas of residential development are fairly easy to differentiate from older, established residential areas. Vegetation and extent of area coverage can be determined. The Oakland County Planning Commission and the Federal Bureau of Outdoor Recreation working closely with Irv Sattinger of the Environmental Research Institute of Michigan (University of Michigan) are presently processing and analyzing photographic and Multispectral scanner data to determine its usefulness for recreation and open space site studies for this area. Photo credit: NASA
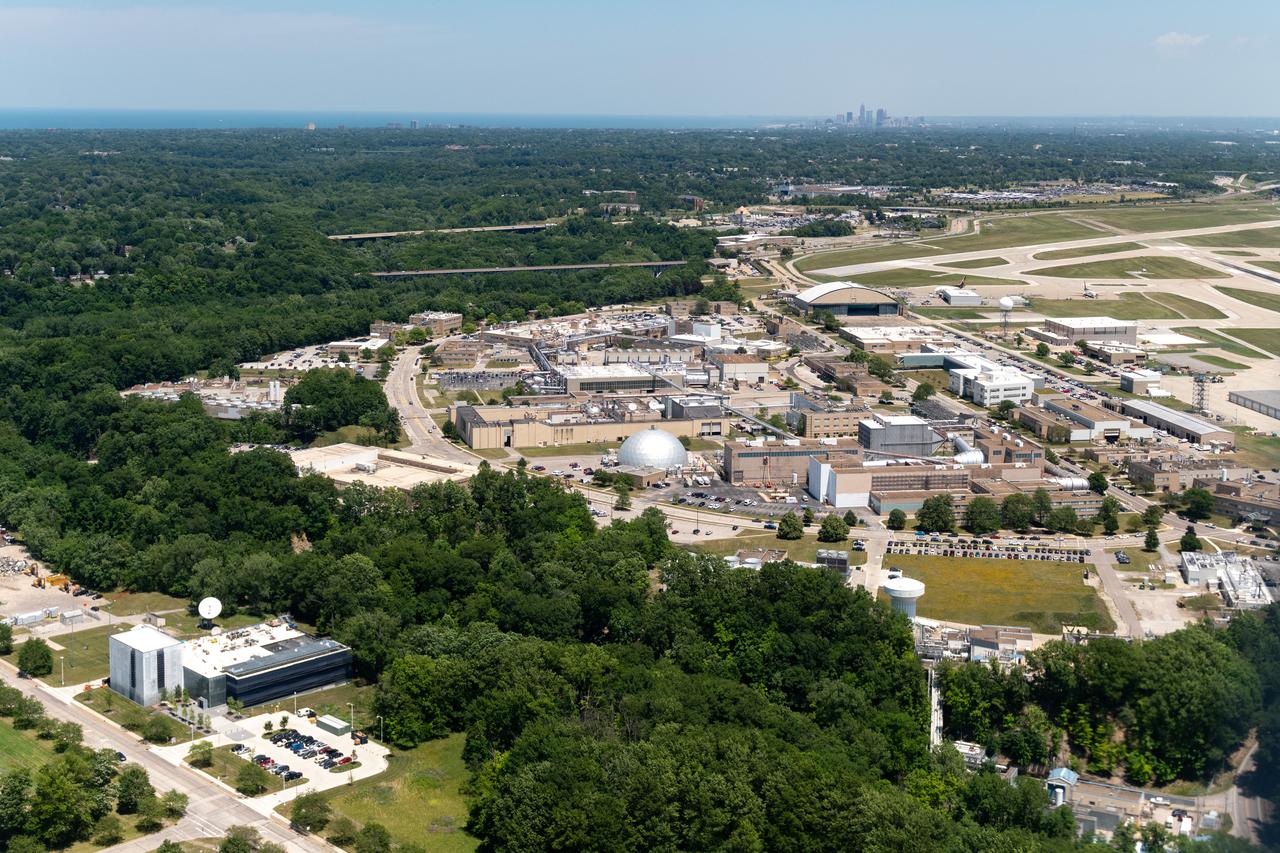

Aerial Photograph of Glenn Research Center With Downtown Cleveland in the Distance taken from the PC-12 on June 13, 2024. A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
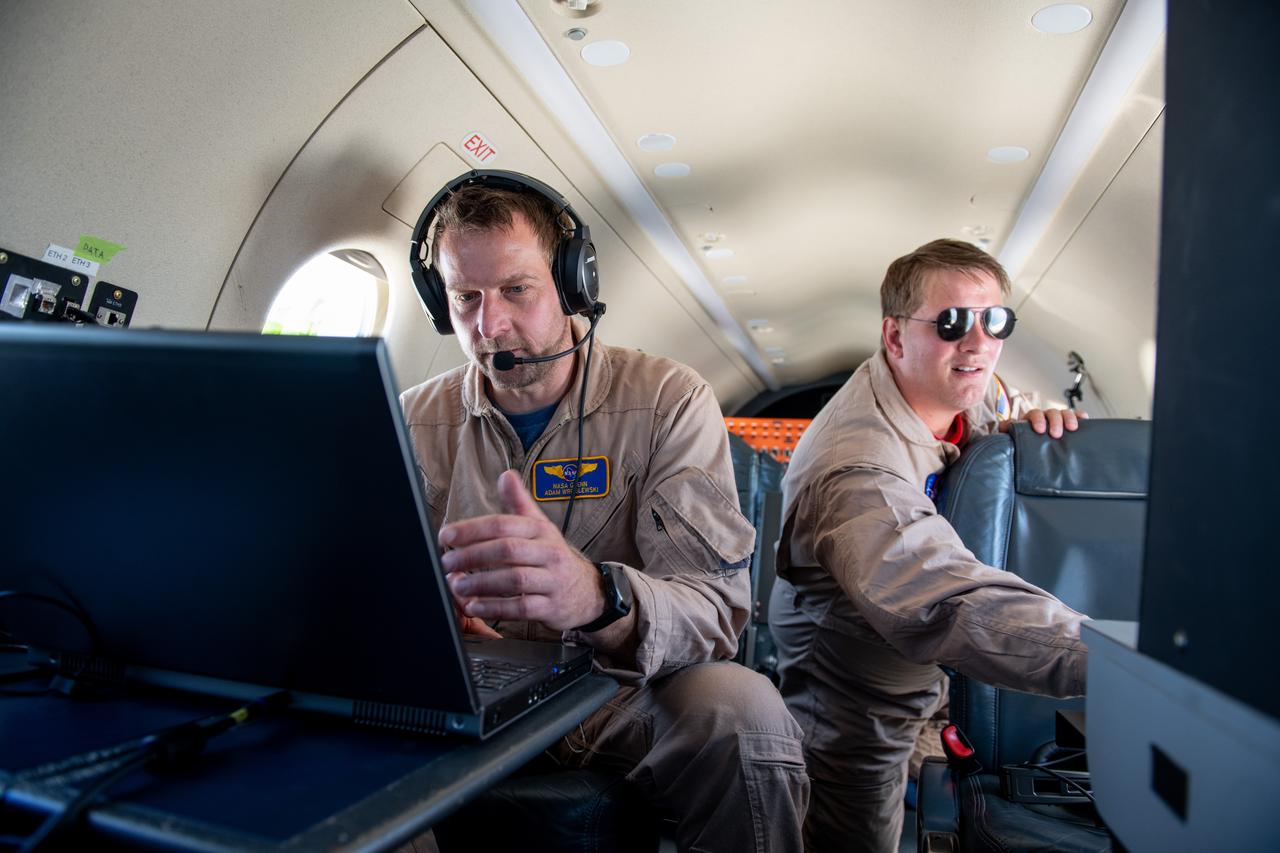

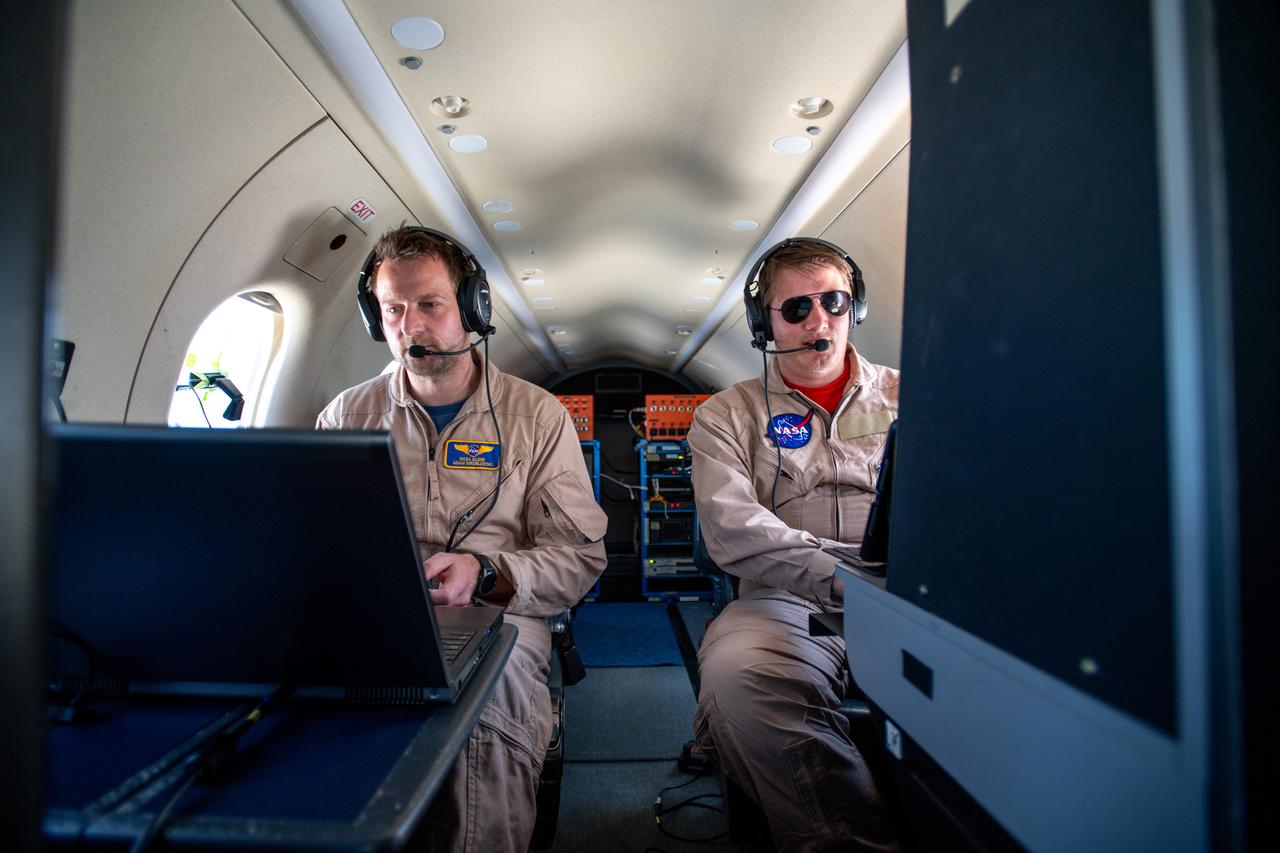
Adam Wroblewski and Shaun McKeehan Working In PC-12 Aircraft during in flight testing on June 13, 2024. A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)

A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Pictured here on June 13, 2024 from Left to Right: Kurt Blakenship, Adam Wroblewski, Shaun McKeehan. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
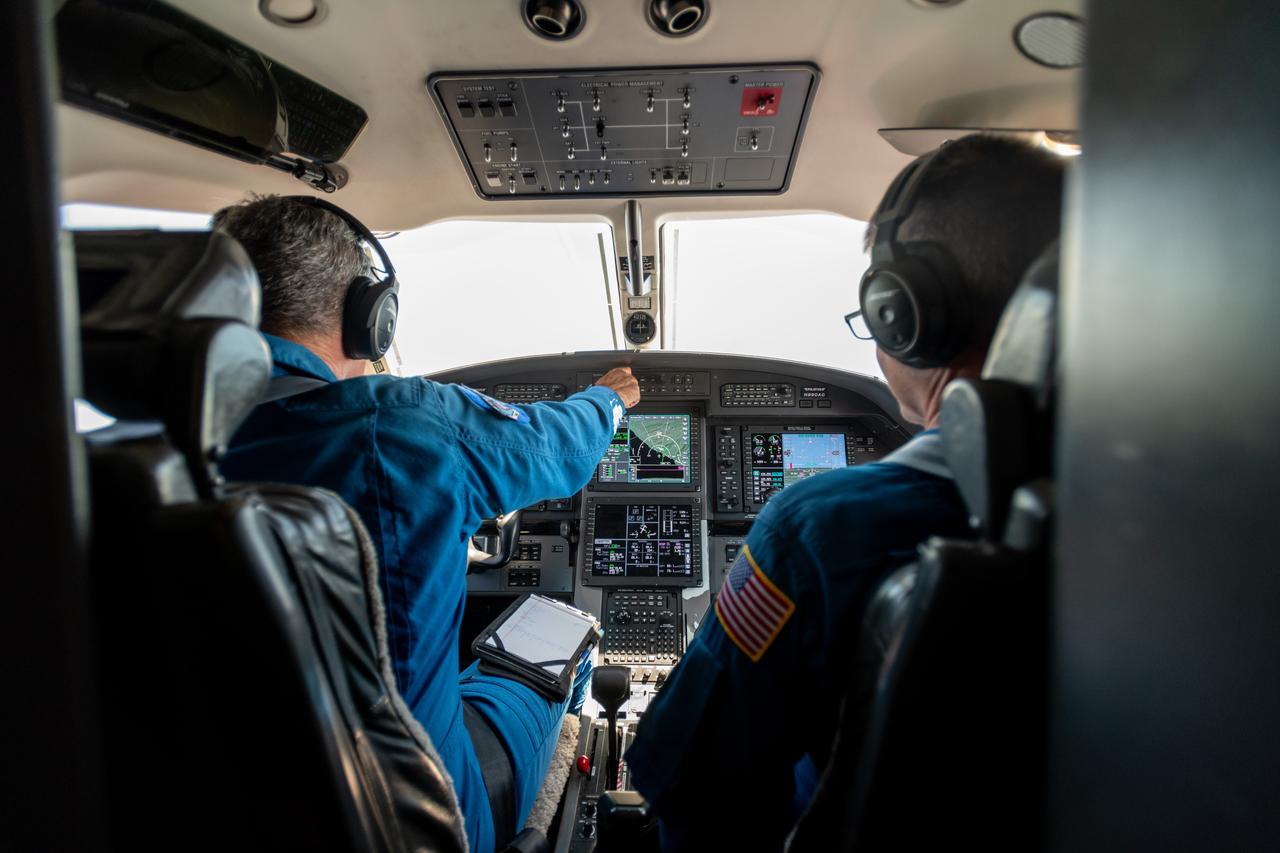

Kurt Blankenship and James Demers Fly PC-12 Aircraft During Testing on June 13, 2024. A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
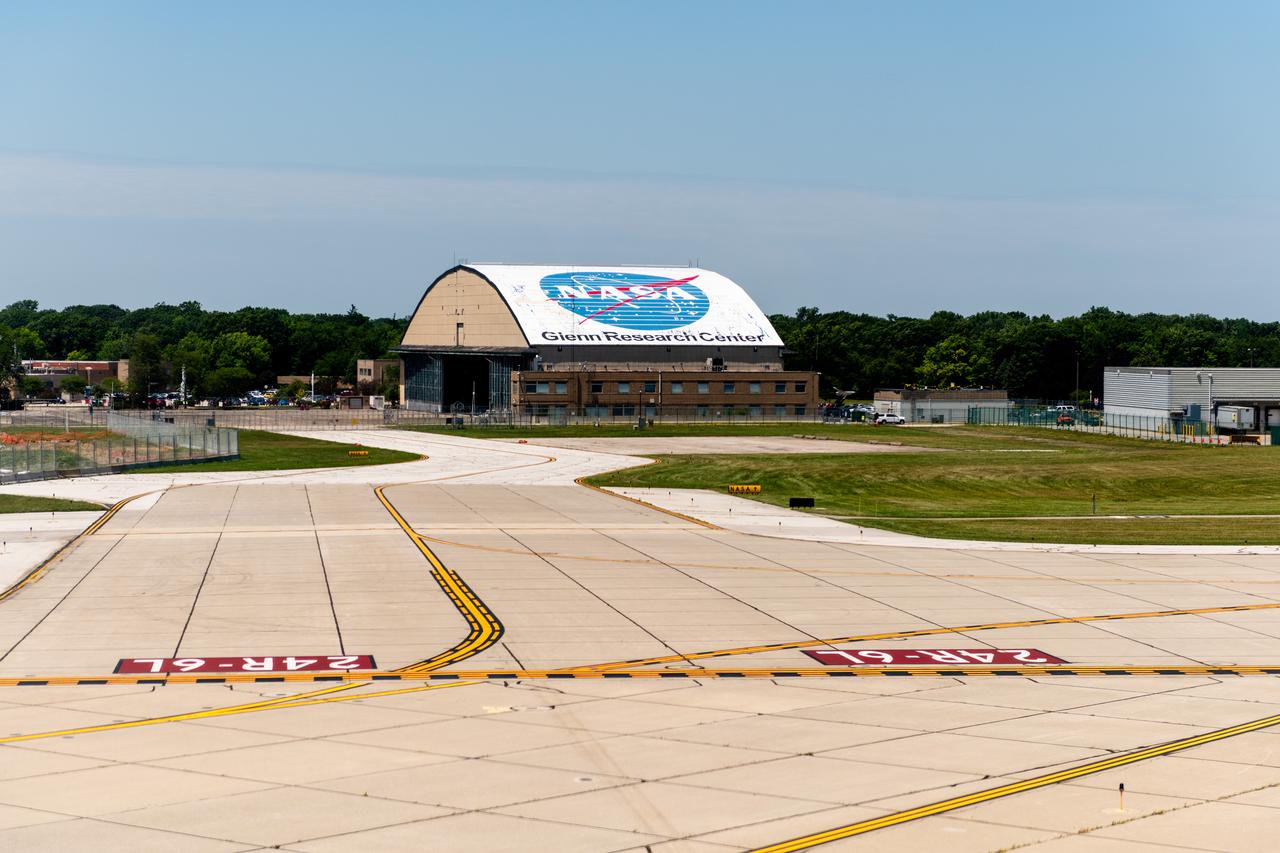

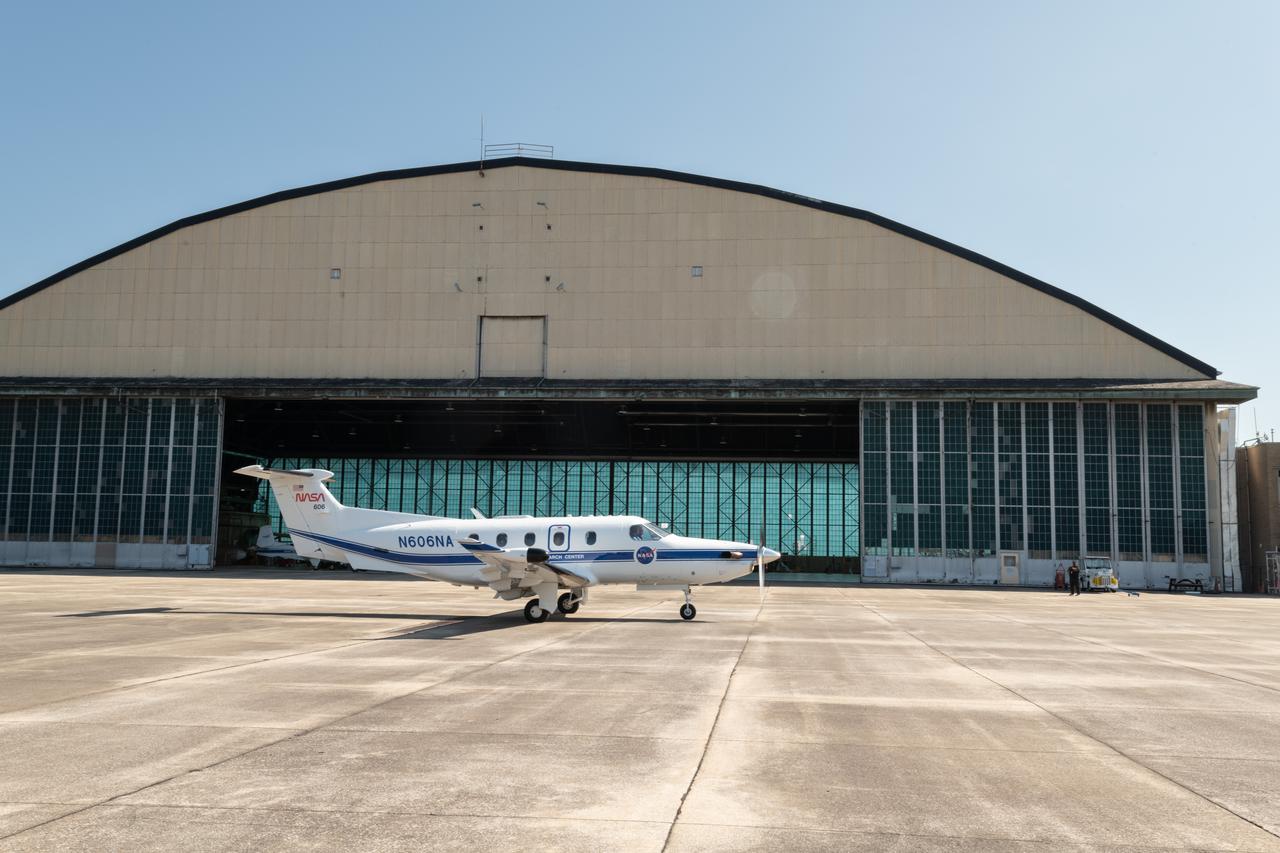
View of the Glenn Research Center Hangar from the Cleveland Hopkins Airport Runway during a testing flight on June 13, 2024. A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
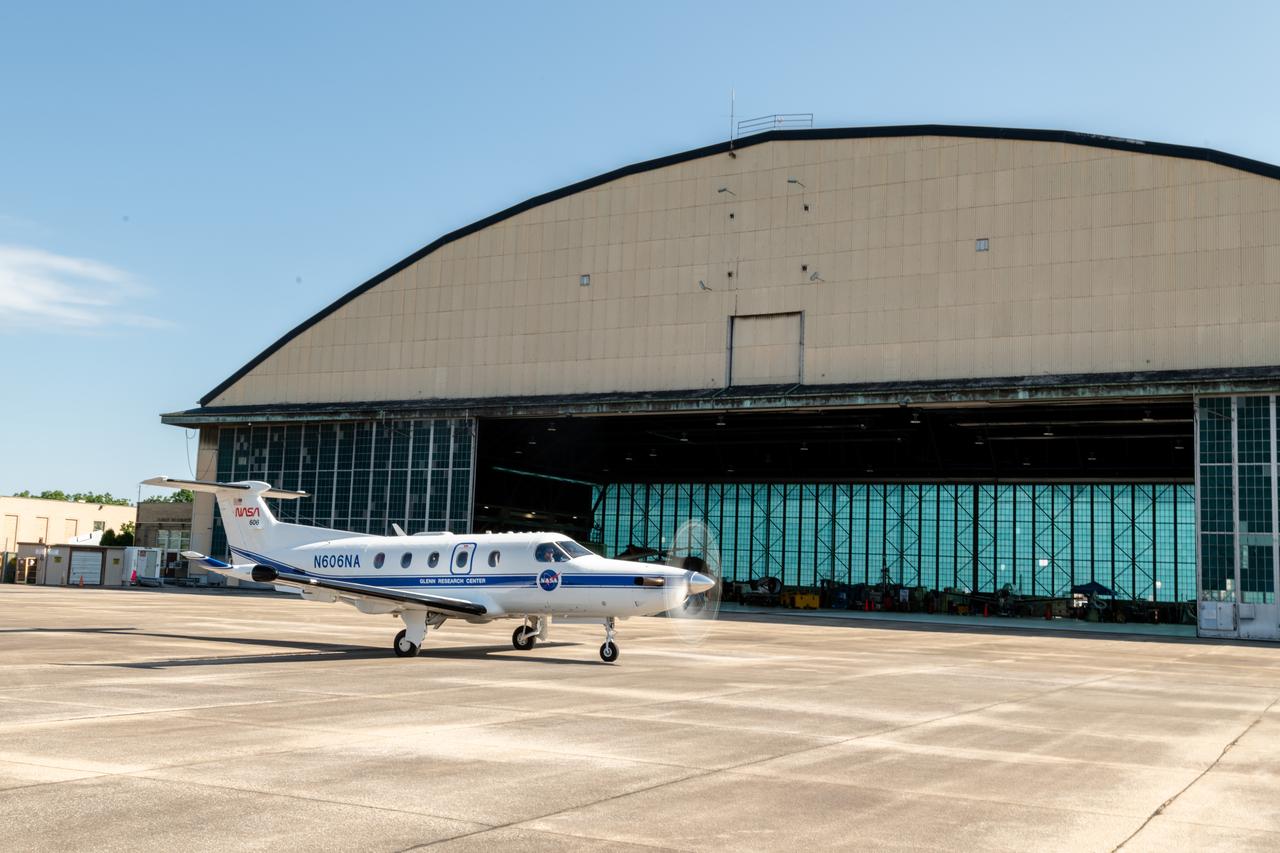

At Glenn Research Center, the PC-12 is Prepped for a flight and ready to takeoff on June 12, 2024. A team at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland streamed 4K video footage from an aircraft to the International Space Station and back for the first time using optical, or laser, communications. The feat was part of a series of tests on new technology that could provide live video coverage of astronauts on the Moon during the Artemis missions. Working with the Air Force Research Laboratory and NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research program, Glenn engineers temporarily installed a portable laser terminal on the belly of a Pilatus PC-12 aircraft. They then flew over Lake Erie sending data from the aircraft to an optical ground station in Cleveland. From there, it was sent over an Earth-based network to NASA’s White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, New Mexico, where scientists used infrared light signals to send the data. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
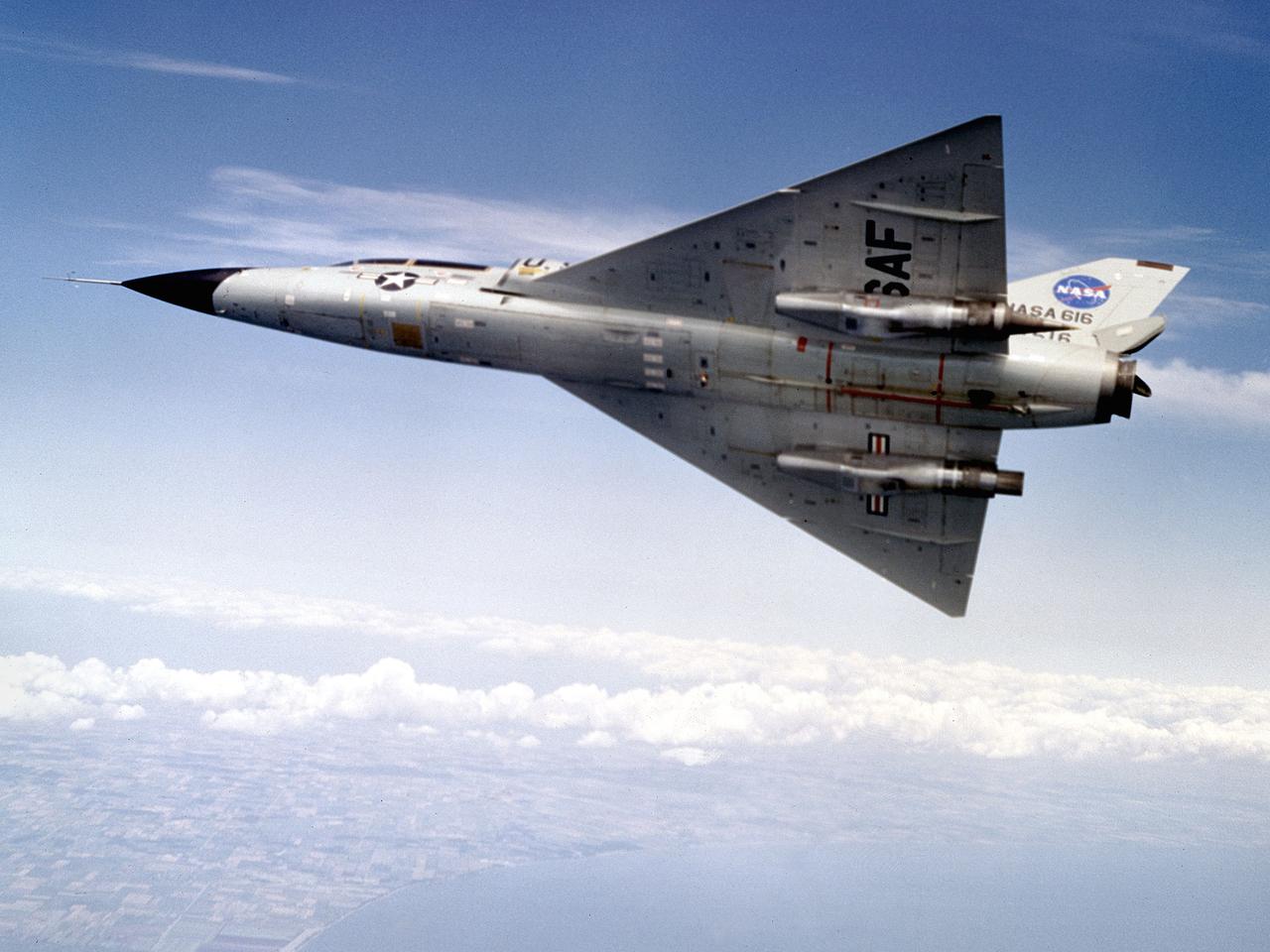

A Convair F-106B Delta Dart rolls to the right to reveal the two research engines installed under its wings by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Lewis acquired the aircraft in October of 1966 to study inlet and nozzle designs for the supersonic transport engine program. Two General Electric J85 engines were mounted beneath the F-106B’s wings and operated from Mach 1 to 1.5. The right wing always carried reference nozzle for which the performance was known. Six supersonic nozzle variations and two inlets were tested on the left engine. The designs had already been studied in the Lewis wind tunnels, but those tests were limited by shock waves in the tunnels. Most F-106B flights were flown in a 200-mile path over the lake between Buffalo and Sandusky, known as the Lake Erie Corridor. The 1100-mile-per-hour flight took only 11 minutes at an altitude of 30,000 feet. The aircraft almost always returned with a depleted fuel supply so a Visual Flight Rules operation was required. Following the crash of another jet fighter at Lewis in July 1969, the F-106s were stationed at Selfridge Air Force Base in Michigan. NASA pilots flew transport planes each morning to the base before commencing the F-106B missions. After the supersonic transport program was cancelled, the F-106B was used as a test bed for additional engine exhaust nozzle configurations. The F-106B was also used to test inlet configurations for the noise reduction program.
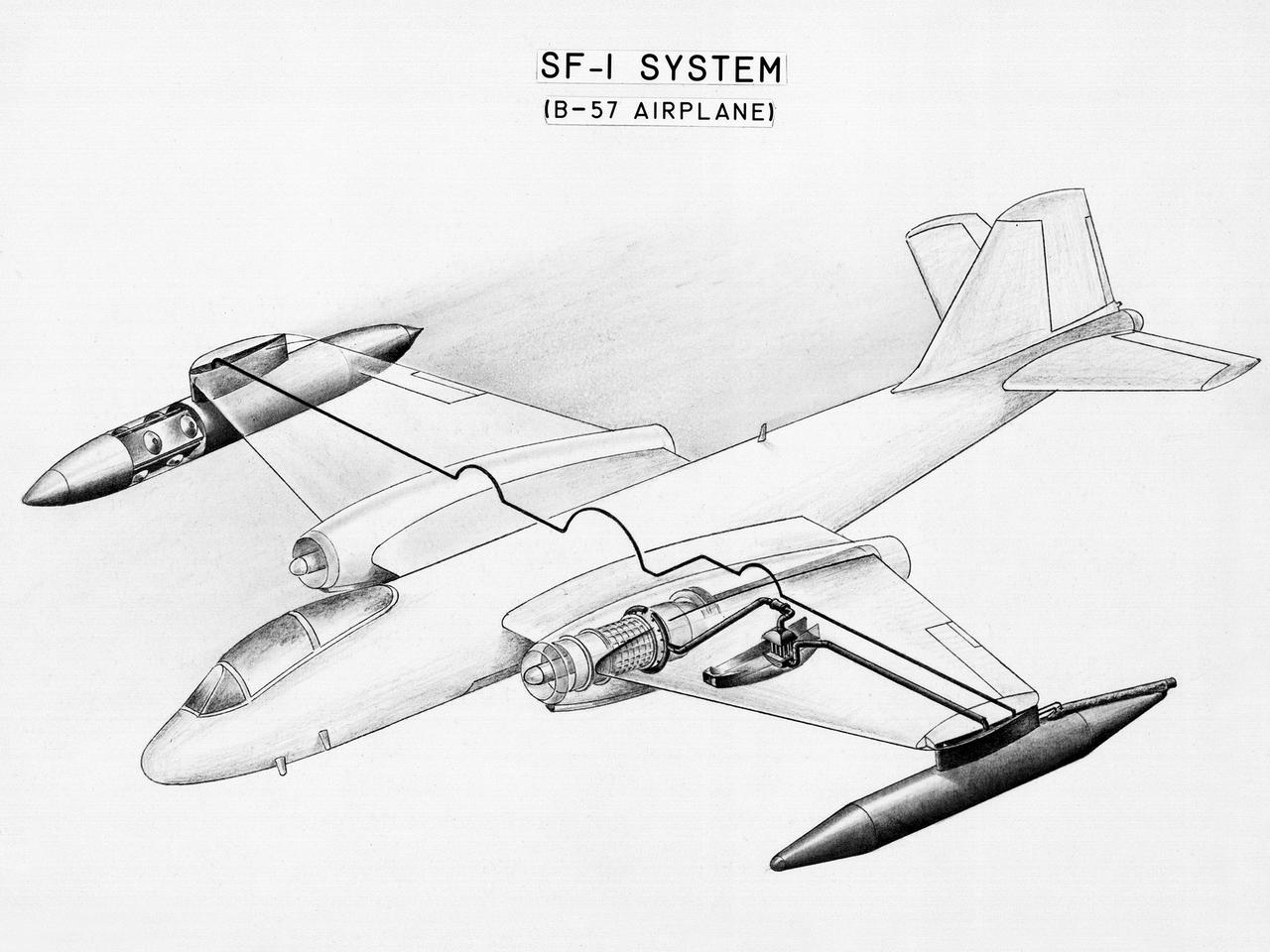
This diagram shows a hydrogen fuel system designed by researchers at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory and installed on a Martin B-57B Canberra aircraft. Lewis researchers accelerated their studies of high energy propellants in the early 1950s. In late 1954, Lewis researchers studied the combustion characteristics of gaseous hydrogen in a turbojet combustor. It was found that the hydrogen provided a very high efficiency. Almost immediately thereafter, Associate Director Abe Silverstein became focused on the possibilities of hydrogen for aircraft propulsion. That fall, Silverstein secured a contract to work with the air force to examine the practicality of liquid hydrogen aircraft. A B-57B Canberra was obtained by the air force especially for this project, referred to as Project Bee. The aircraft was powered by two Wright J65 engines, one of which was modified so that it could be operated using either traditional or liquid hydrogen propellants. The engine and its liquid hydrogen fuel system were tested extensively in the Altitude Wind Tunnel and the Four Burner Area test cells in 1955 and 1956. A B-57B flight program was planned to test the system on an actual aircraft. The aircraft would take off using jet fuel, switch to liquid hydrogen while over Lake Erie, then after burning the hydrogen supply switch back to jet fuel for the landing. The third test flight, in February 1957, was a success, and the ensuing B-57B flights remain the only demonstration of hydrogen-powered aircraft.

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center acquired two North American AJ-2 Savages in the early 1960s to fly microgravity-inducing parabola flight patterns. Lewis was in the midst of an extensive study to determine the behavior of liquid hydrogen in microgravity so that proper fuel systems could be designed. Jack Enders was the primary pilot for the program and future astronaut Fred Haise worked with the cameras and instrumentation in the rear of the aircraft. North American developed the AJ-2 for the Navy in the mid-1940s as a carrier-based bomber. By the 1960s the Savage was no longer considered a modern aircraft, but its performance capabilities made it appealing to the Lewis researchers. The AJ-2 ‘s power, speed, response time, structural robustness, and large interior space were applicable to the microgravity flights. The AJ-2 could also accommodate a pilot, flight engineer, and two observers. Lewis engineers installed a 100-litre liquid hydrogen dewar, cryogenic cooling system, and cameras in the bomb bay. The AJ-2 was flown on a level course over western Lake Erie then went into a 20-degree dip to generate 375 knot. At 13,000 feet the pilot pulled the nose up by 40 degrees. The speed decreased and both latitudinal and longitudinal accelerations were nullified. Upon reaching 17,000 feet, the pilot turned the aircraft into a 45-degree dive. As the speed reached 390 knots the pilot pulled the aircraft up again. Each maneuver produced approximately 27 seconds of microgravity.