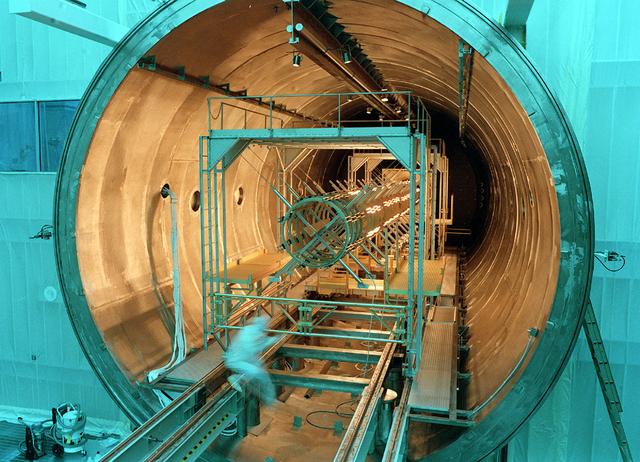

Marshall scientists testing a Lamp array at the X-Ray Calibration Facility (XRCF).
An array of miniature lamps will provide illumination to help scientists as they conduct experiments inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG). The European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA are developing the MSG for use aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Scientists will use the MSG to carry out multidisciplinary studies in combustion science, fluid physics and materials science. The MSG is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Photo Credit: NASA/MSFC
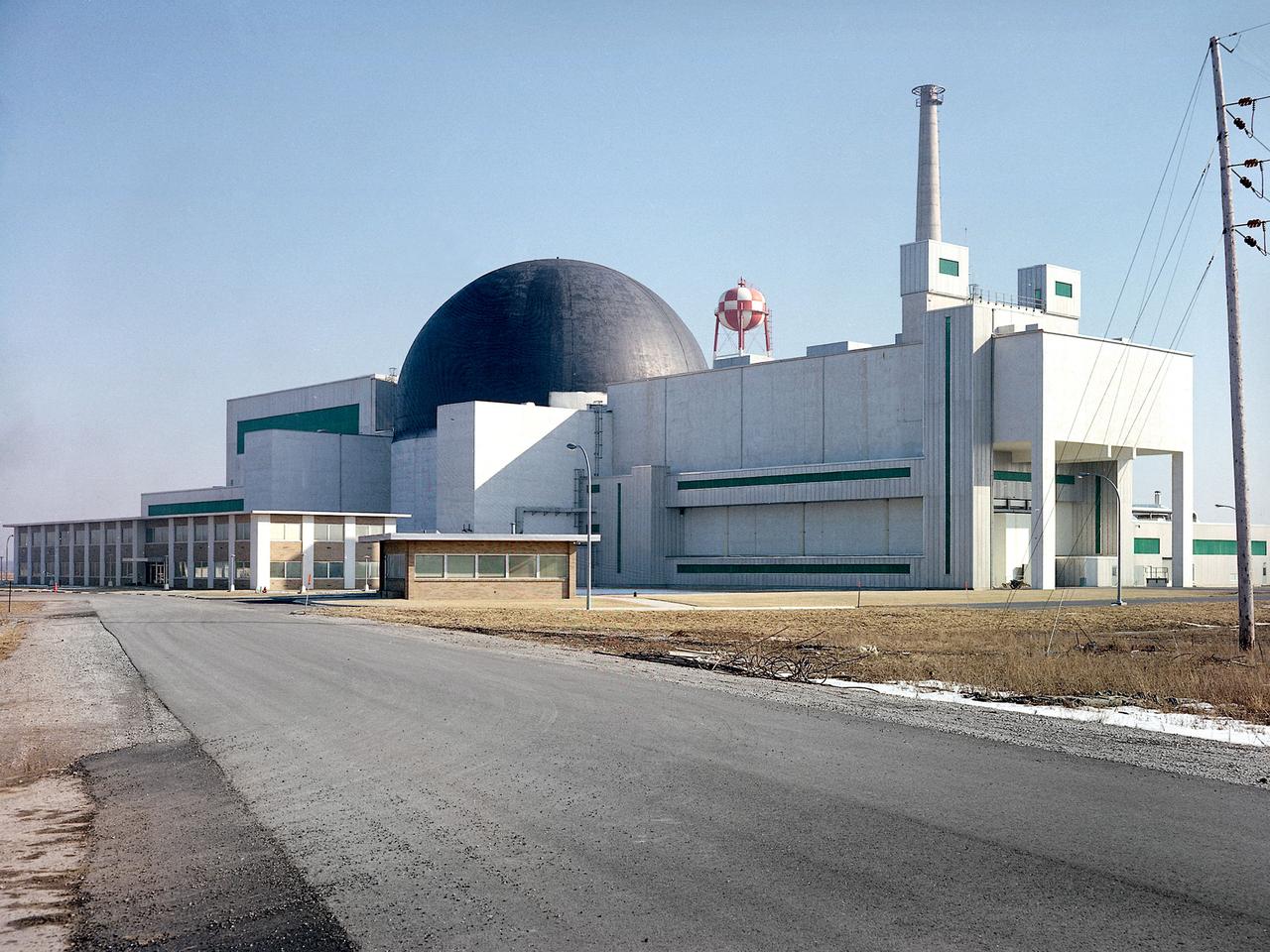

Exterior view of the Space Power Facility at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio. The $28.4-million facility, which began operations in 1969, is the largest high vacuum chamber ever built. The chamber is 100 feet in diameter and 120 feet high. It produces a vacuum deep enough to simulate the conditions at 300 miles altitude. The facility can sustain a high vacuum; simulate solar radiation via a 4-megawatt quartz heat lamp array, solar spectrum by a 400-kilowatt arc lamp, and cold environments. The Space Power Facility was originally designed to test nuclear power sources for spacecraft during long durations in a space atmosphere, but it was never used for that purpose. The facility’s first test in 1970 involved a 15 to 20-kilowatt Brayton Cycle Power System for space applications. Three different methods of simulating solar heat were employed during the Brayton tests. The facility was also used for jettison tests of the Centaur Standard Shroud. The shroud was designed for the new Titan-Centaur rocket that was scheduled to launch the Viking spacecraft to Mars. The new shroud was tested under conditions that simulated the time from launch to the separation of the stages. Test programs at the facility include high-energy experiments, shroud separation tests, Mars Lander system tests, deployable Solar Sail tests and International Space Station hardware tests.
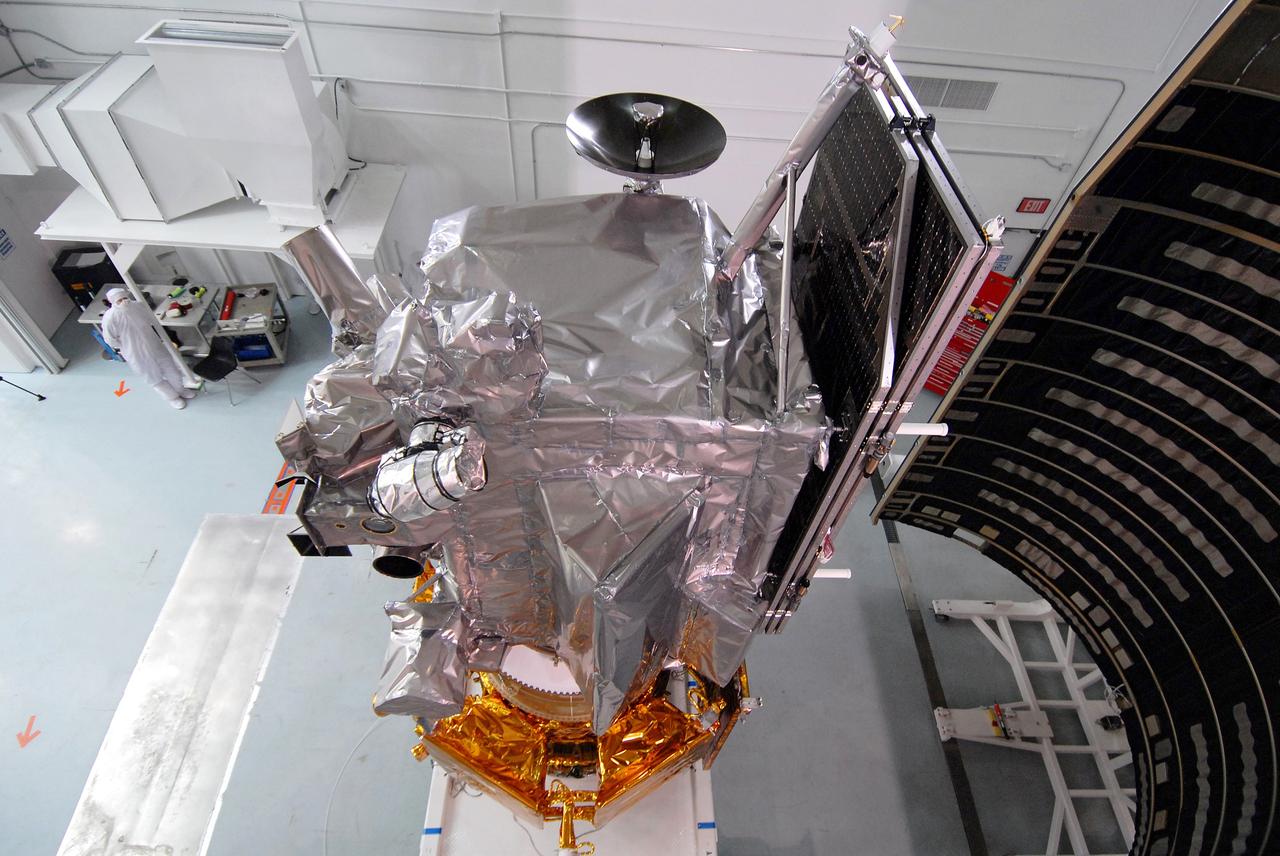

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS, are being prepared for fairing installation. On the right side of the LRO is part of the solar array. At far right is part of the fairing that will be installed around the spacecraft for launch. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the rocket and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. The LRO includes five instruments: DIVINER, LAMP, LEND, LOLA and LROC. They will be launched aboard an Atlas V/Centaur rocket no earlier than June 17 from Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
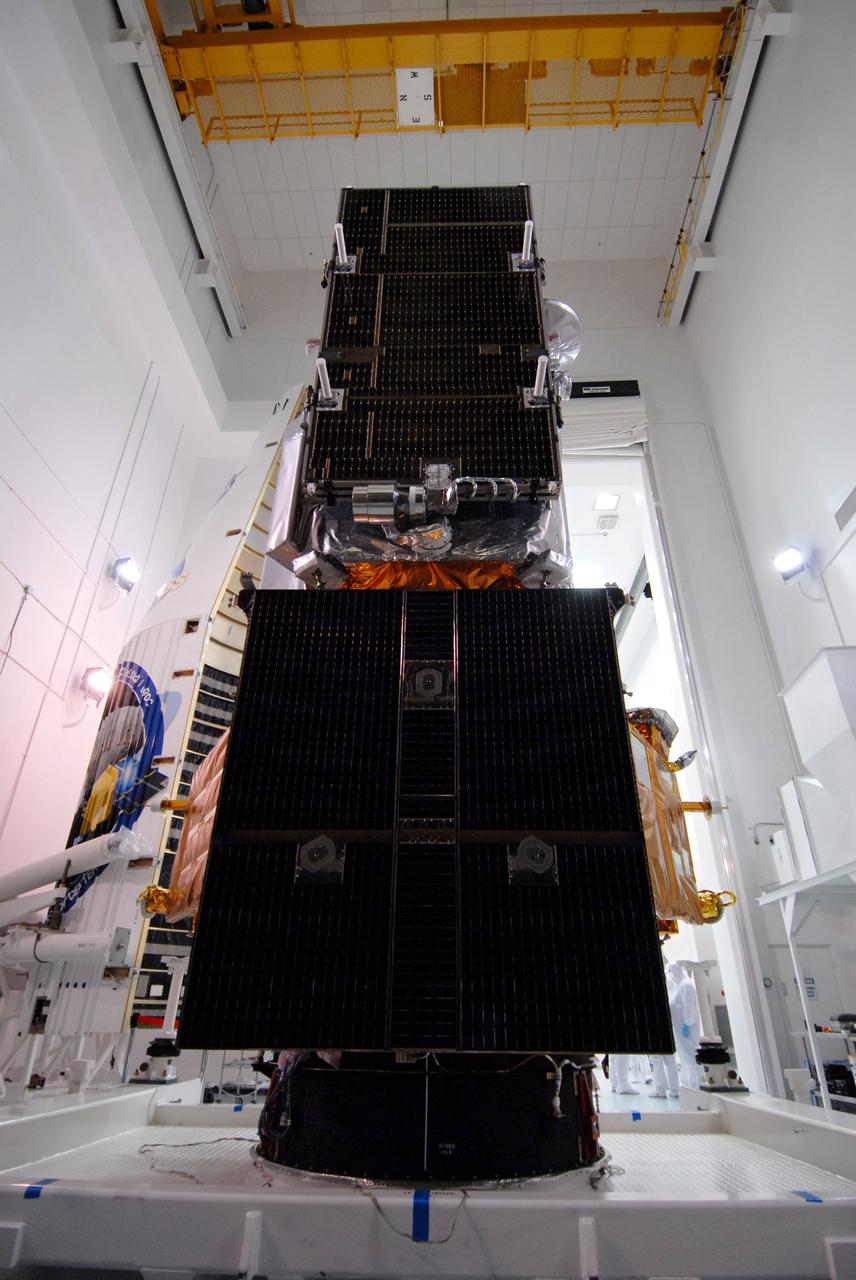

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS,are being prepared for fairing installation. Seen here are the solar arrays. In the background at left, with the decals, is part of the fairing that will be installed around the spacecraft for launch. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the rocket and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. The LRO includes five instruments: DIVINER, LAMP, LEND, LOLA and LROC. They will be launched aboard an Atlas V/Centaur rocket no earlier than June 17 from Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
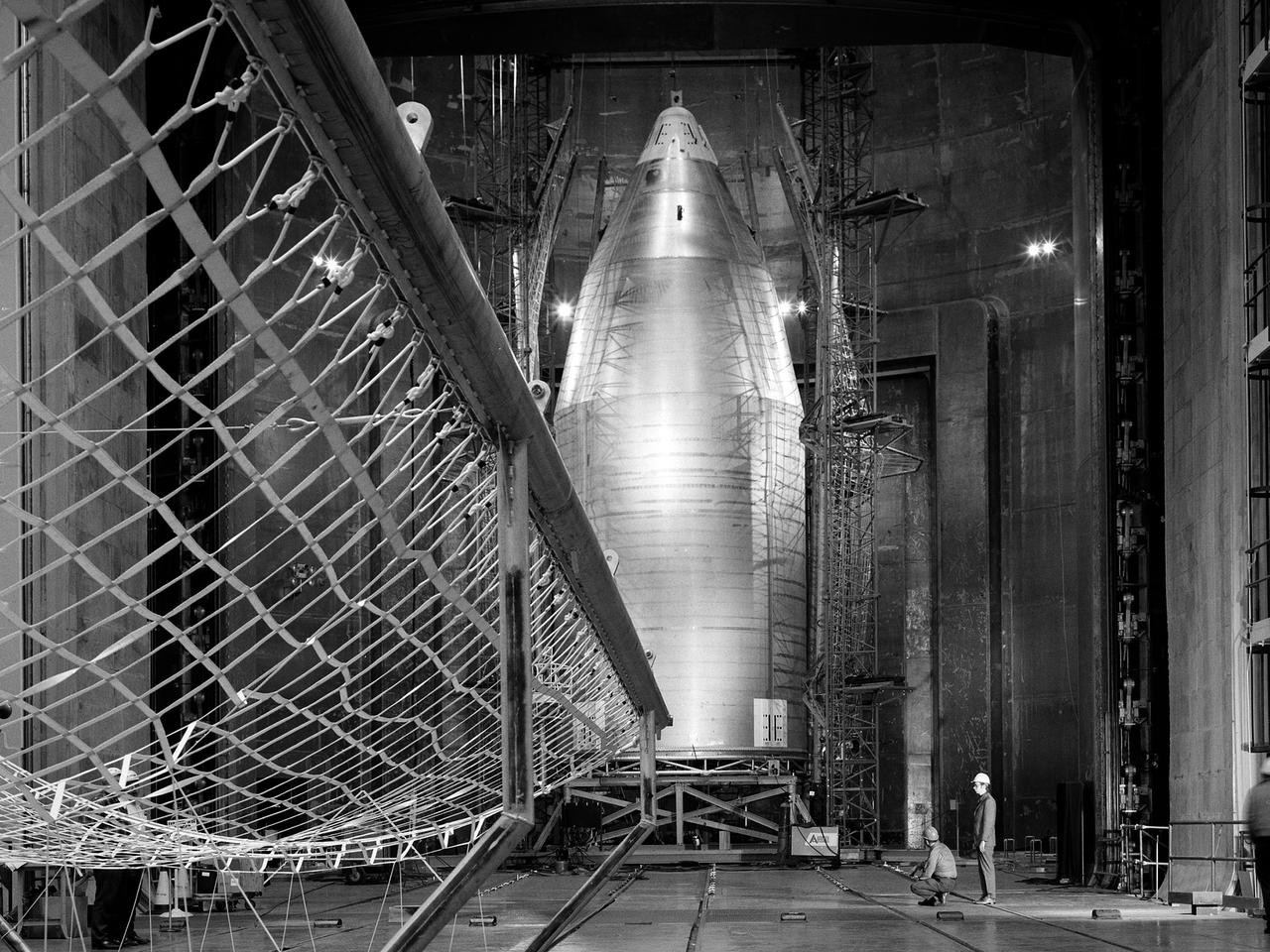

The 56-foot tall, 24,400-pound Skylab shroud installed in the Space Power Facility’s vacuum chamber at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station. The Space Power Facility, which began operations in 1969, is the largest high vacuum chamber ever built. The chamber is 100 feet in diameter and 120 feet high. It can produce a vacuum deep enough to simulate the conditions at 300 miles altitude. The Space Power Facility was originally designed to test nuclear-power sources for spacecraft during long durations in a space atmosphere, but it was never used for that purpose. Payload shrouds are aerodynamic fairings to protect the payload during launch and ascent to orbit. The Skylab mission utilized the largest shroud ever attempted. Unlike previous launches, the shroud would not be jettisoned until the spacecraft reached orbit. NASA engineers designed these tests to verify the dynamics of the jettison motion in a simulated space environment. Fifty-four runs and three full-scale jettison tests were conducted from mid-September 1970 to June 1971. The shroud behaved as its designers intended, the detonators all fired, and early design issues were remedied by the final test. The Space Power Facility continues to operate today. The facility can sustain a high vacuum; simulate solar radiation via a 4-megawatt quartz heat lamp array, solar spectrum by a 400-kilowatt arc lamp, and cold environments. Test programs at the facility include high-energy experiments, shroud separation tests, Mars Lander system tests, deployable Solar Sail tests and International Space Station hardware tests.